Patents
Literature
145results about How to "Improve maximization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
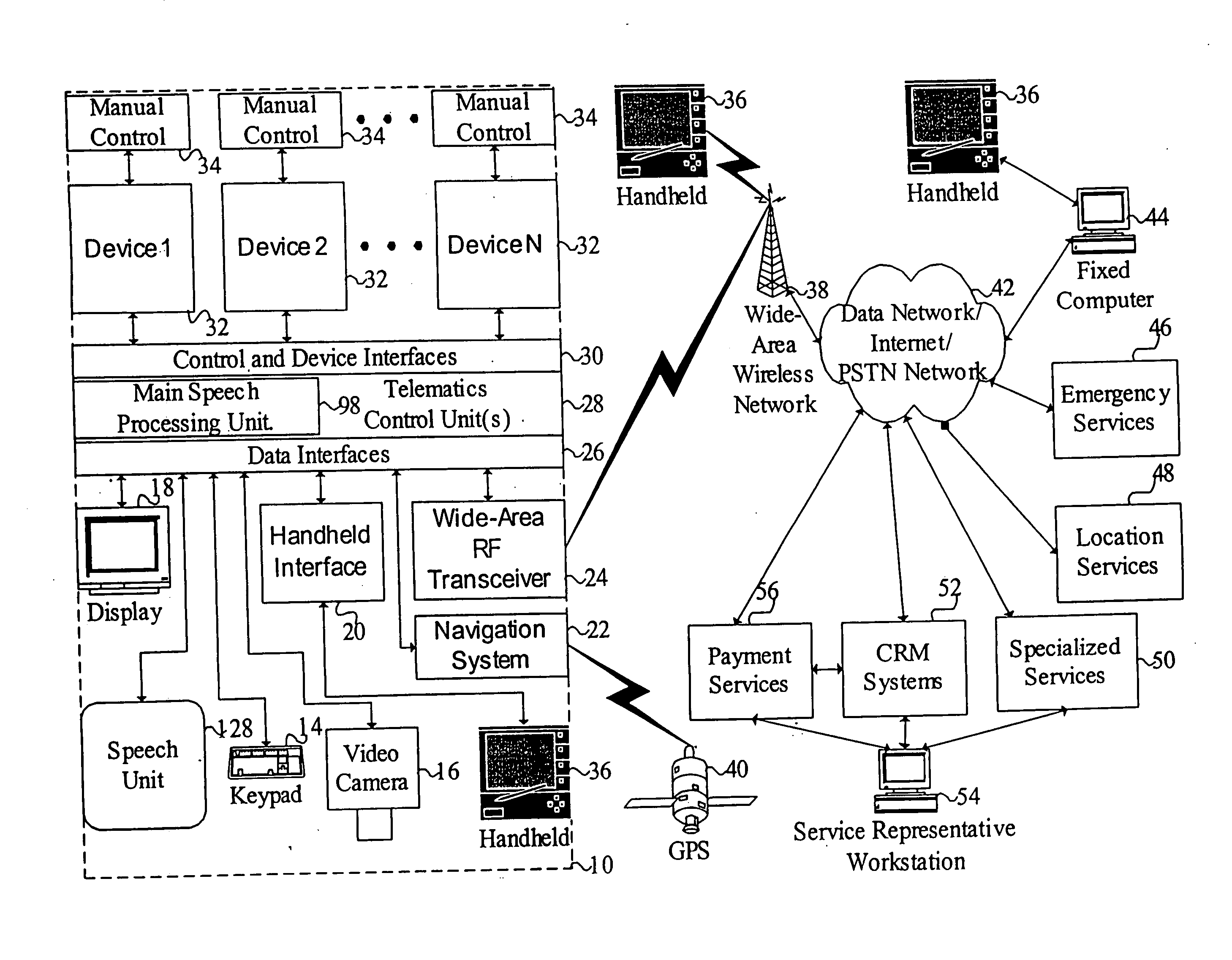
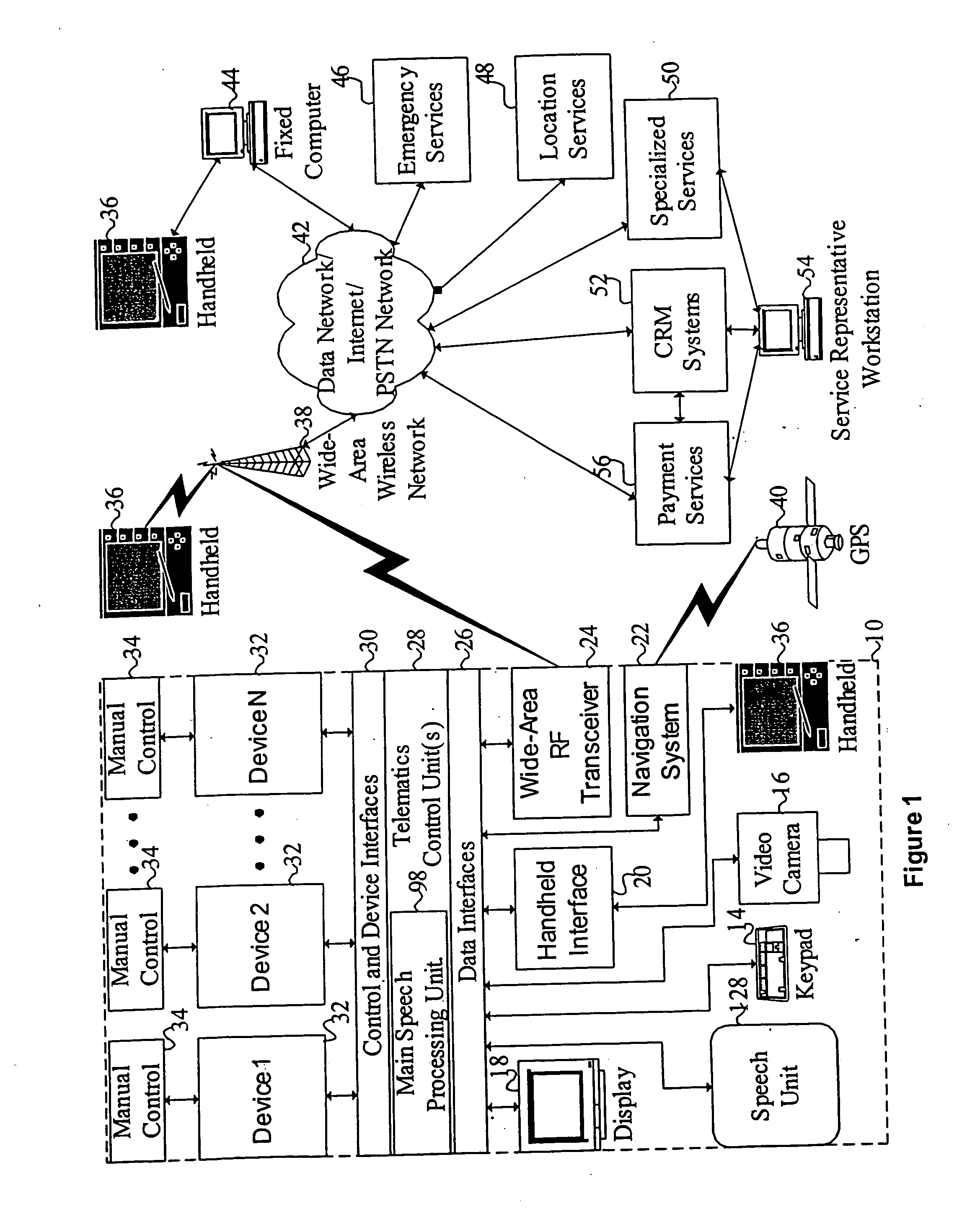
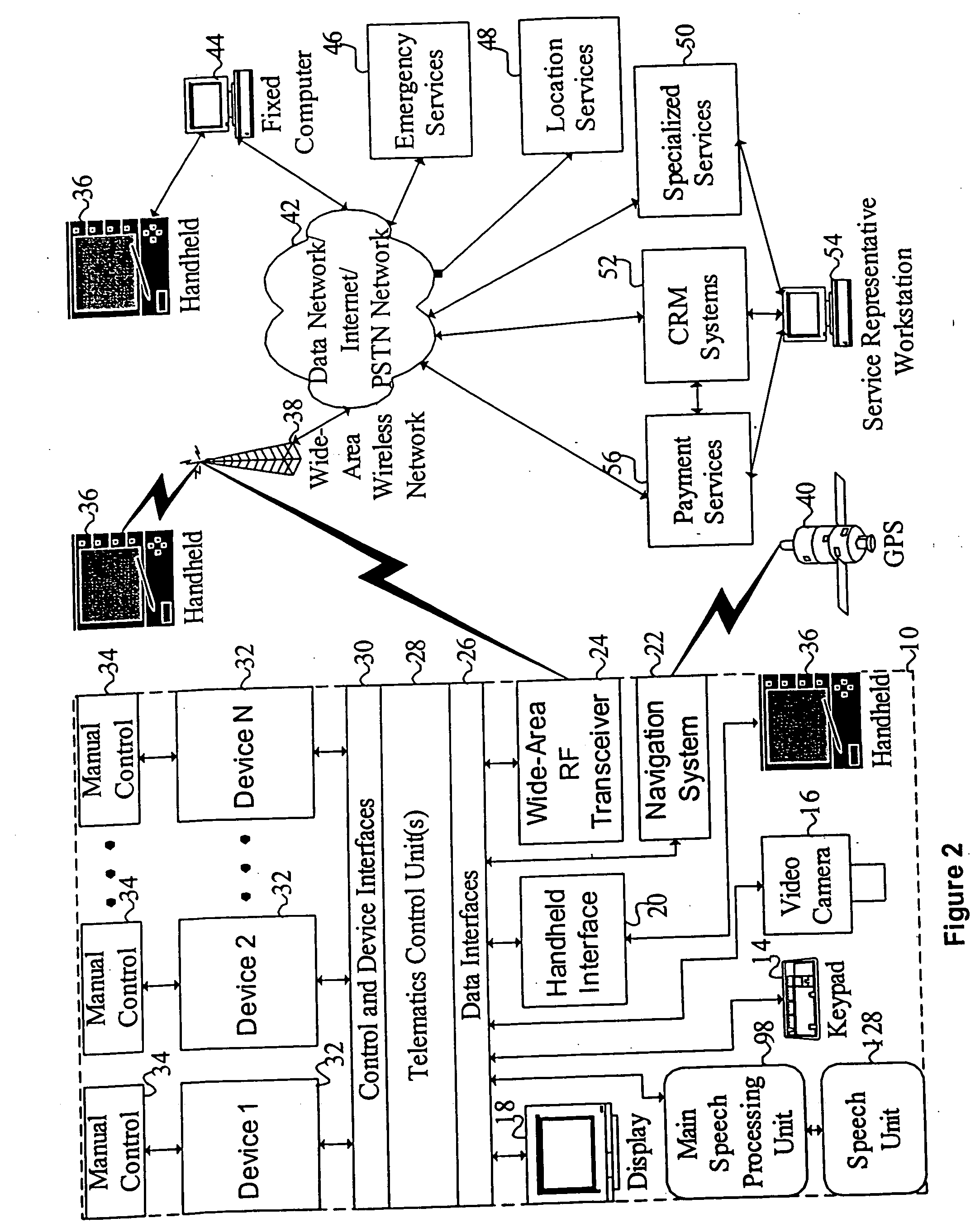
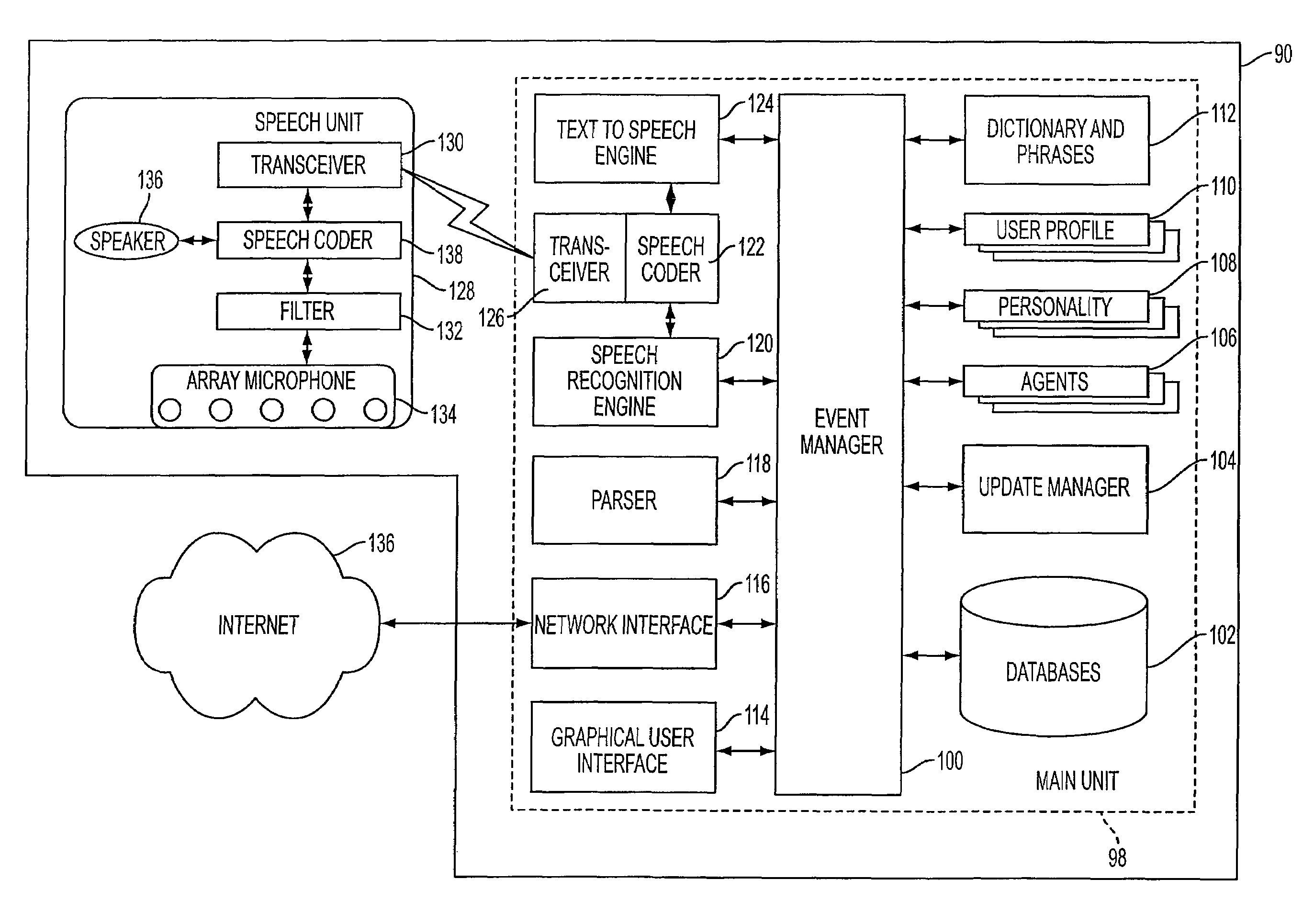
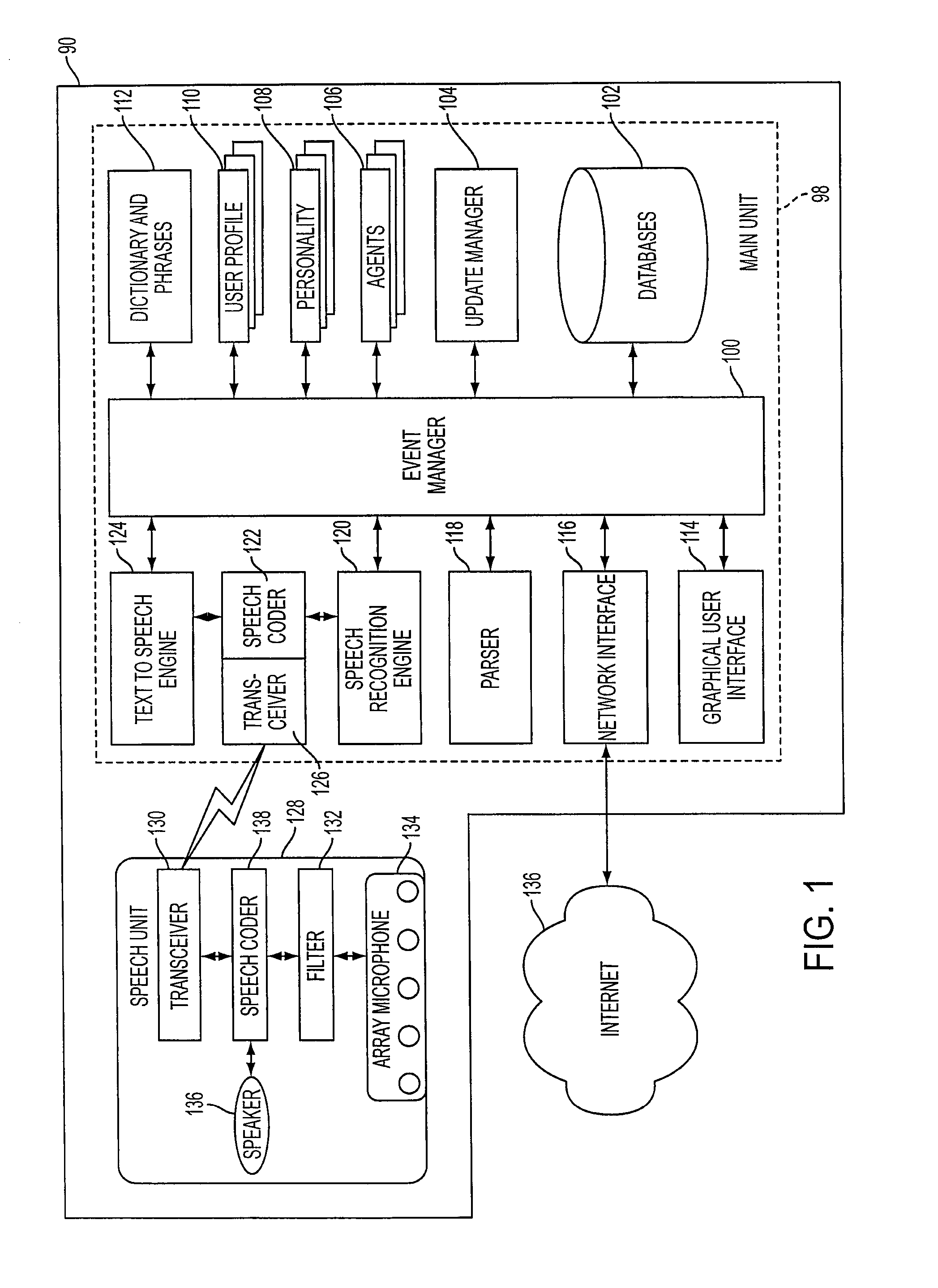
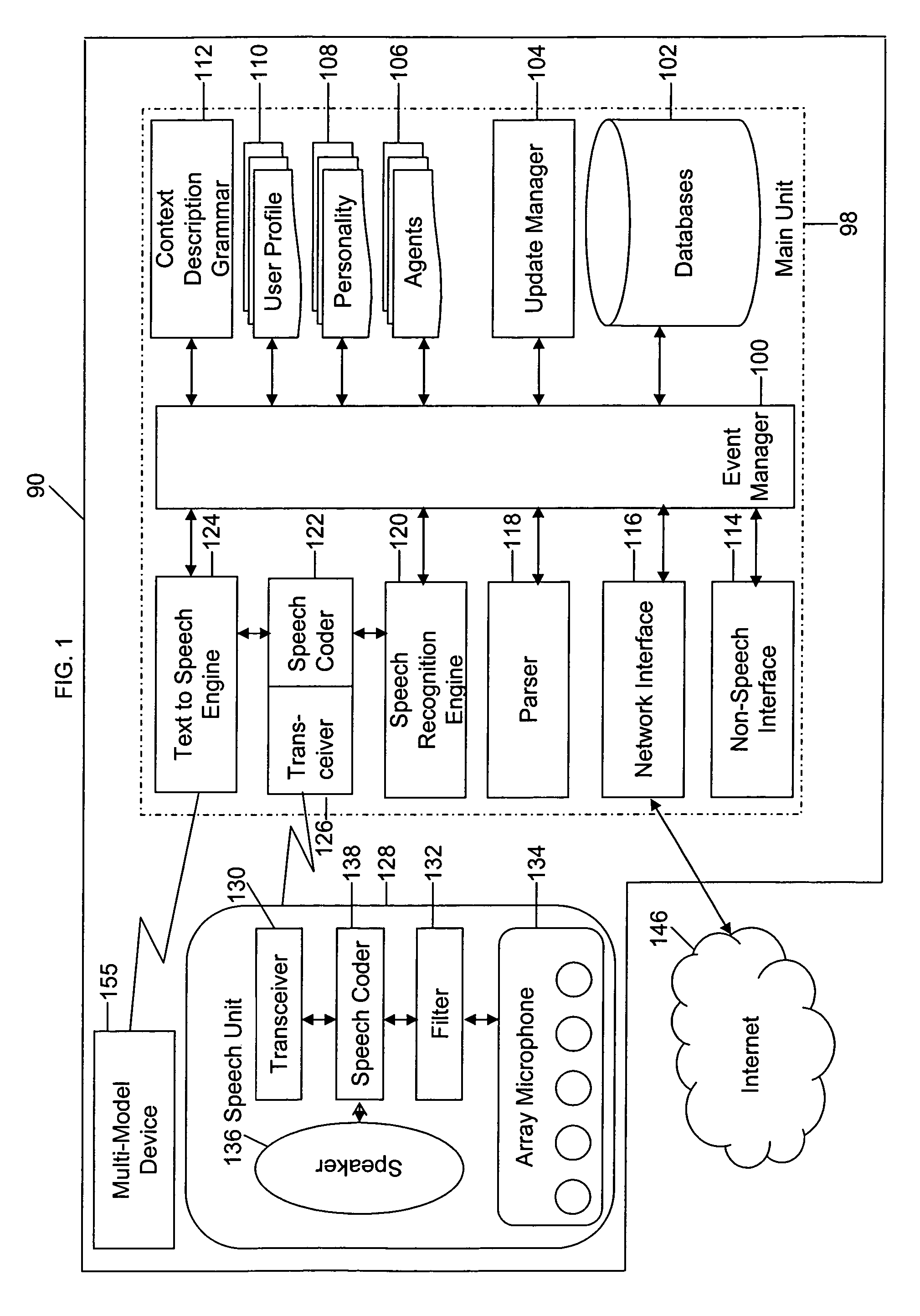
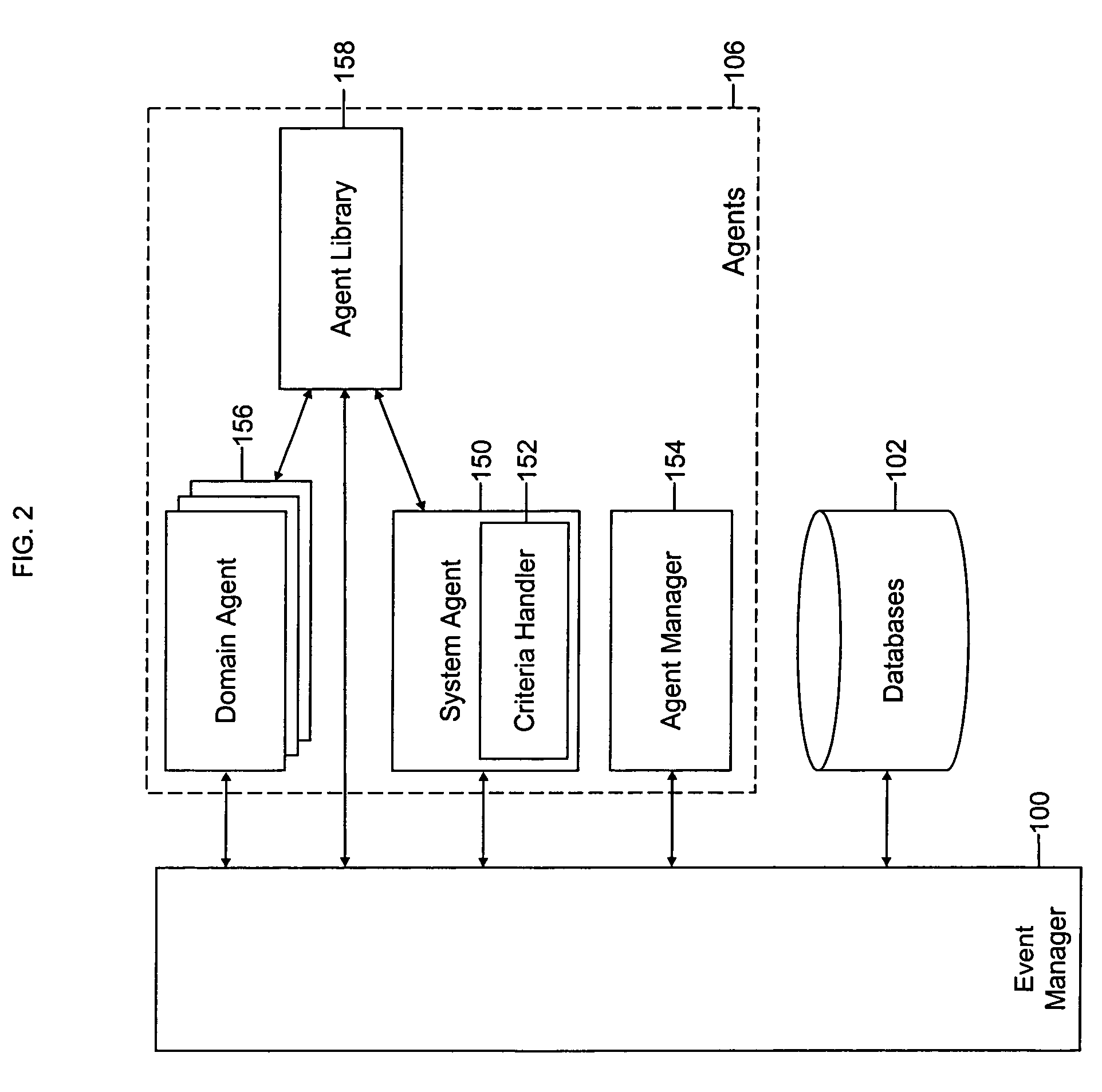
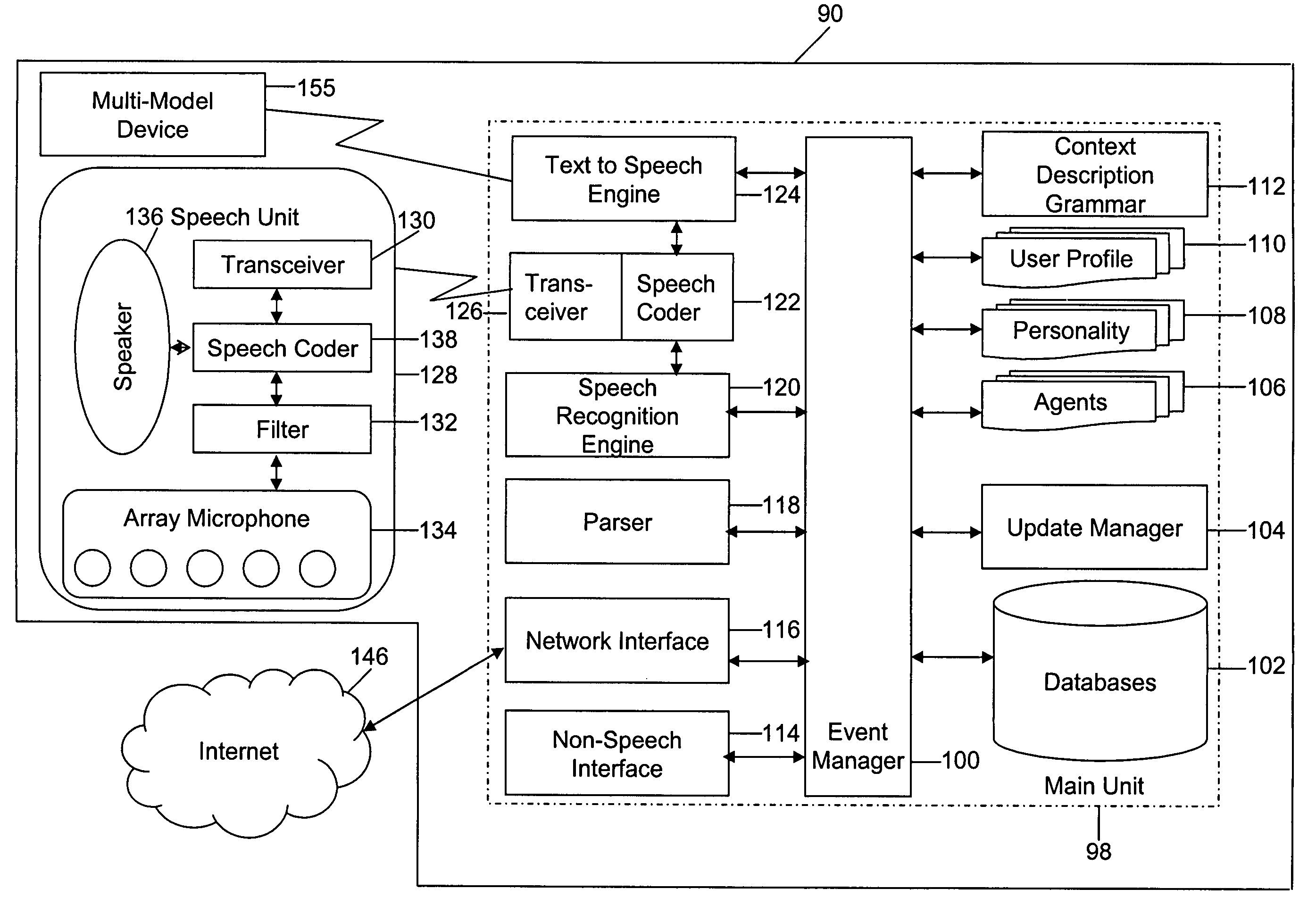
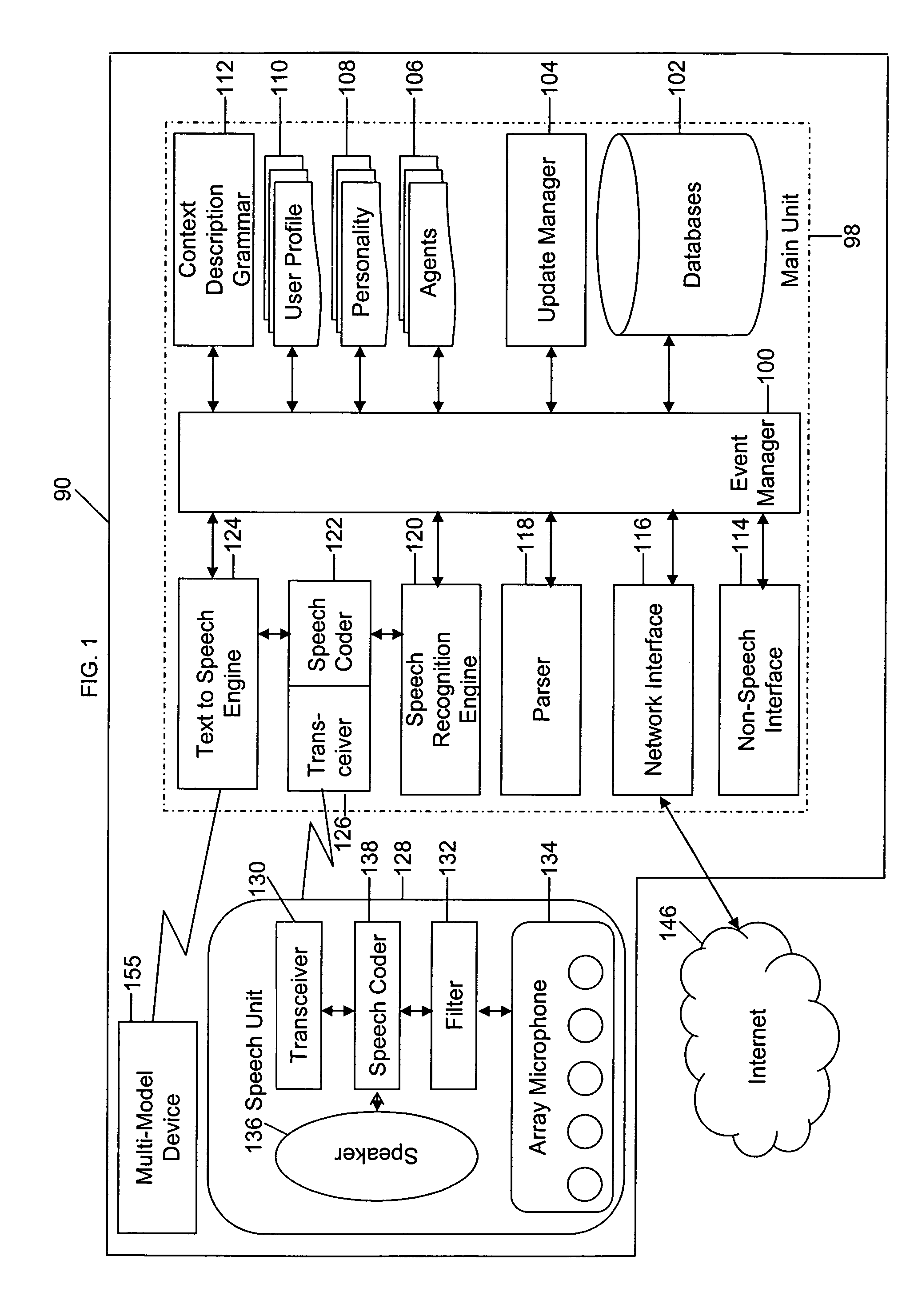
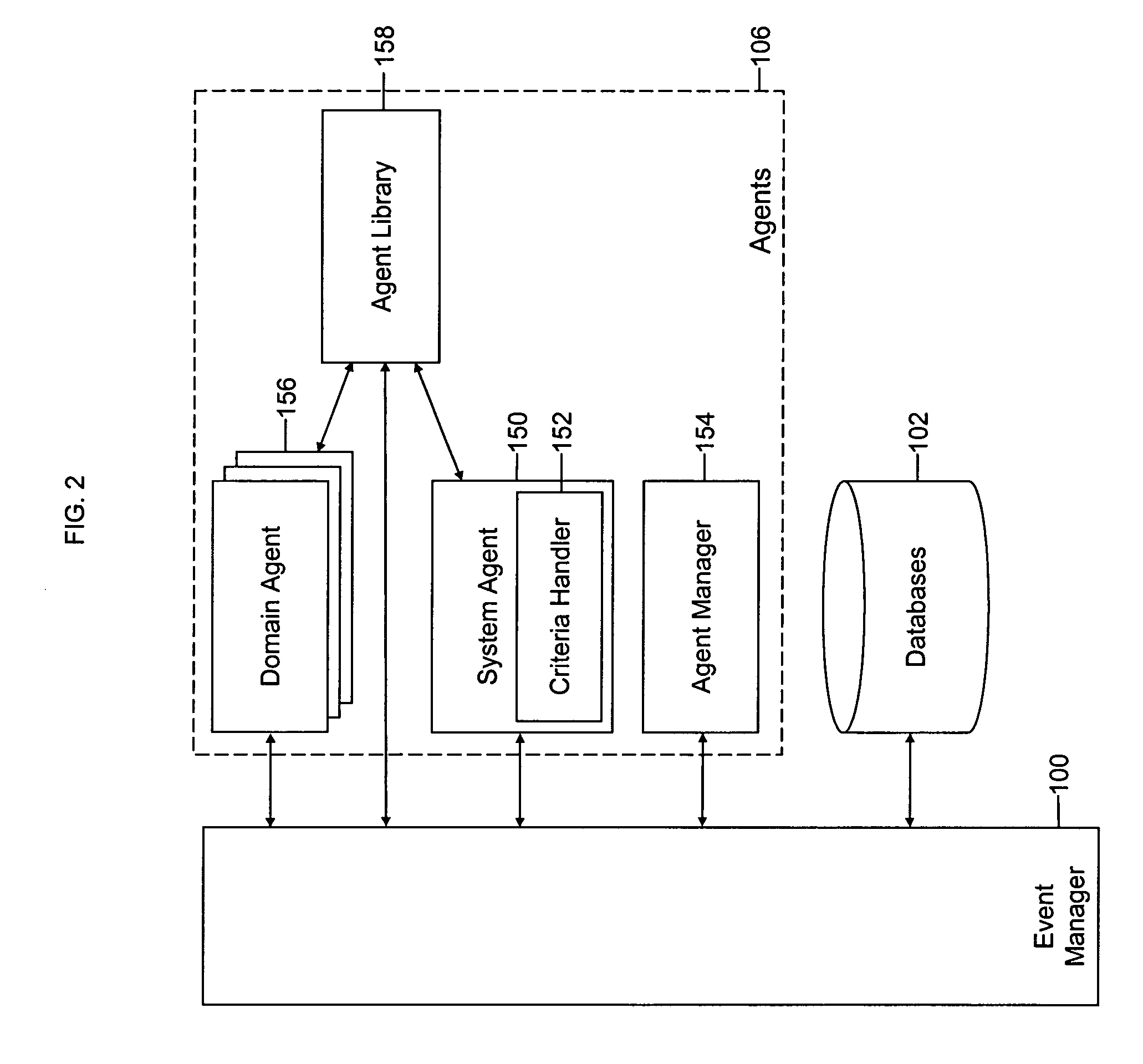
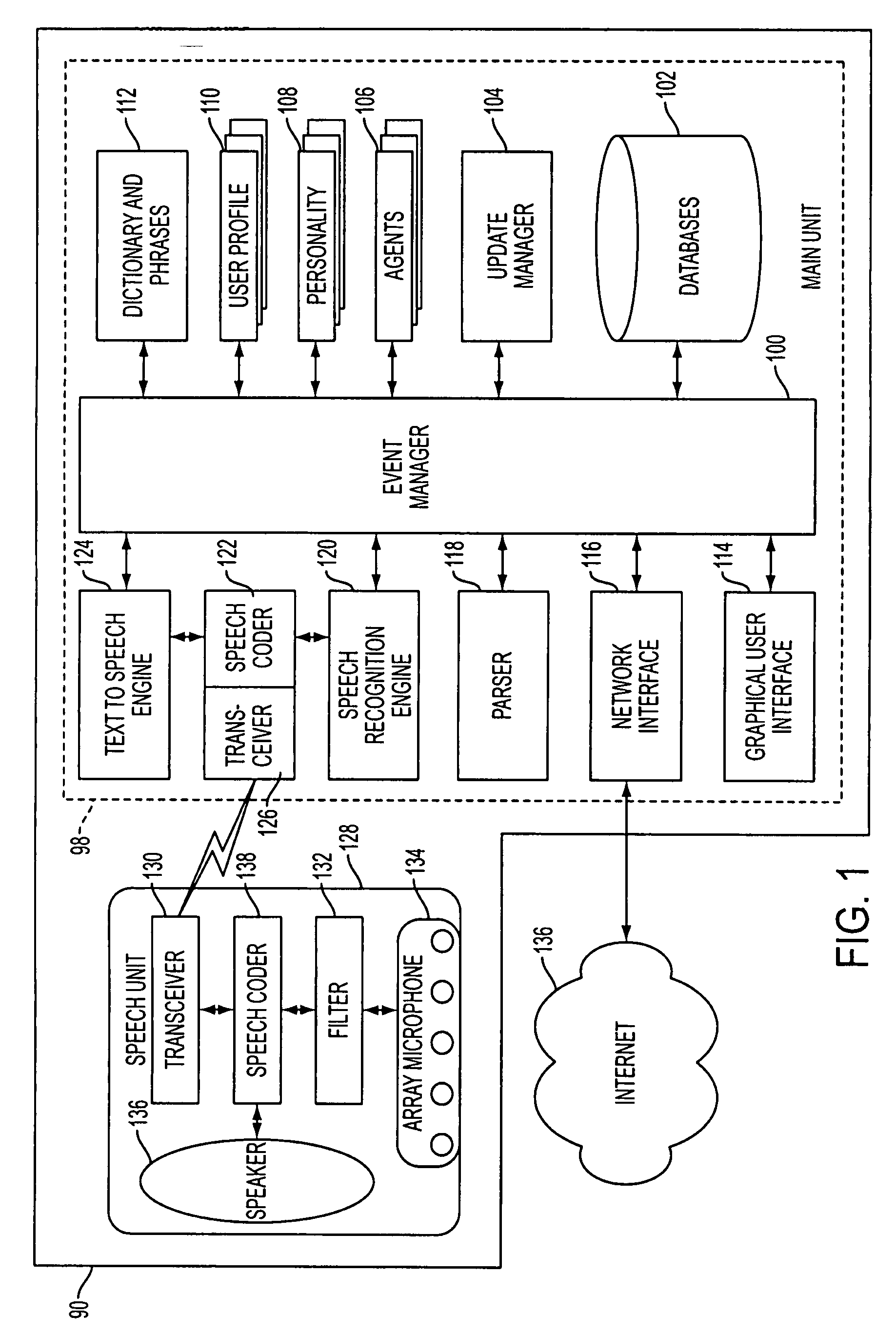
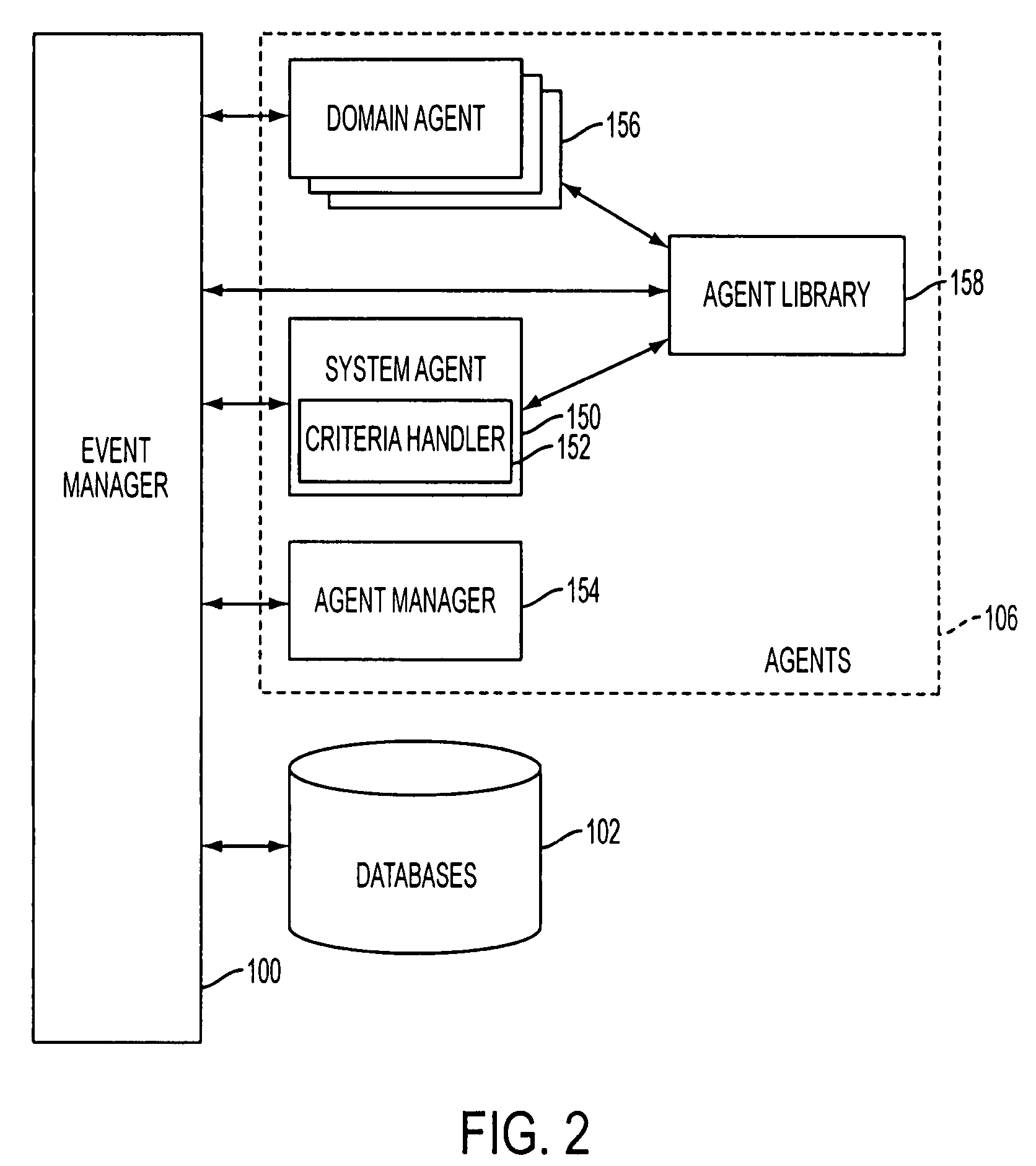
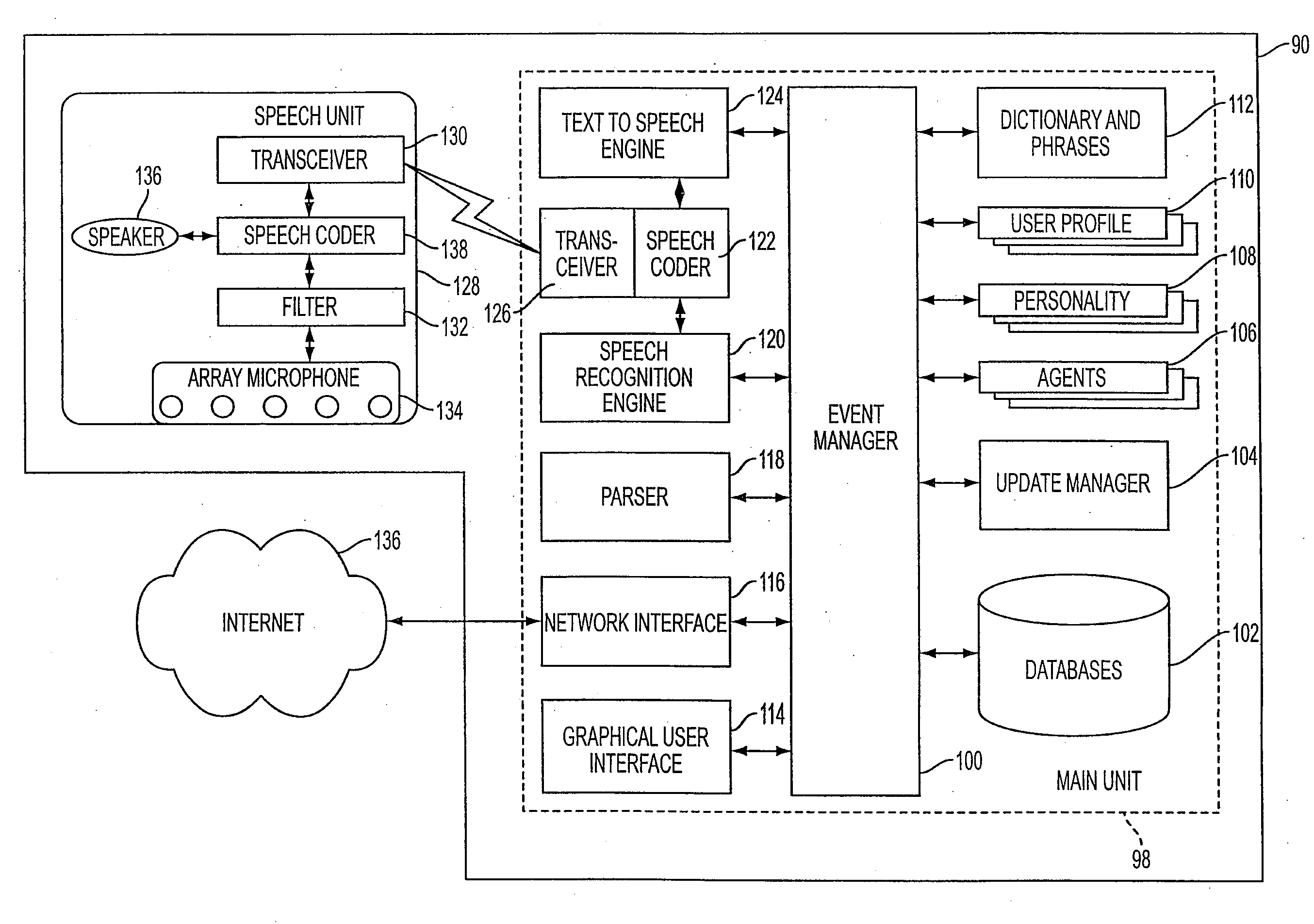
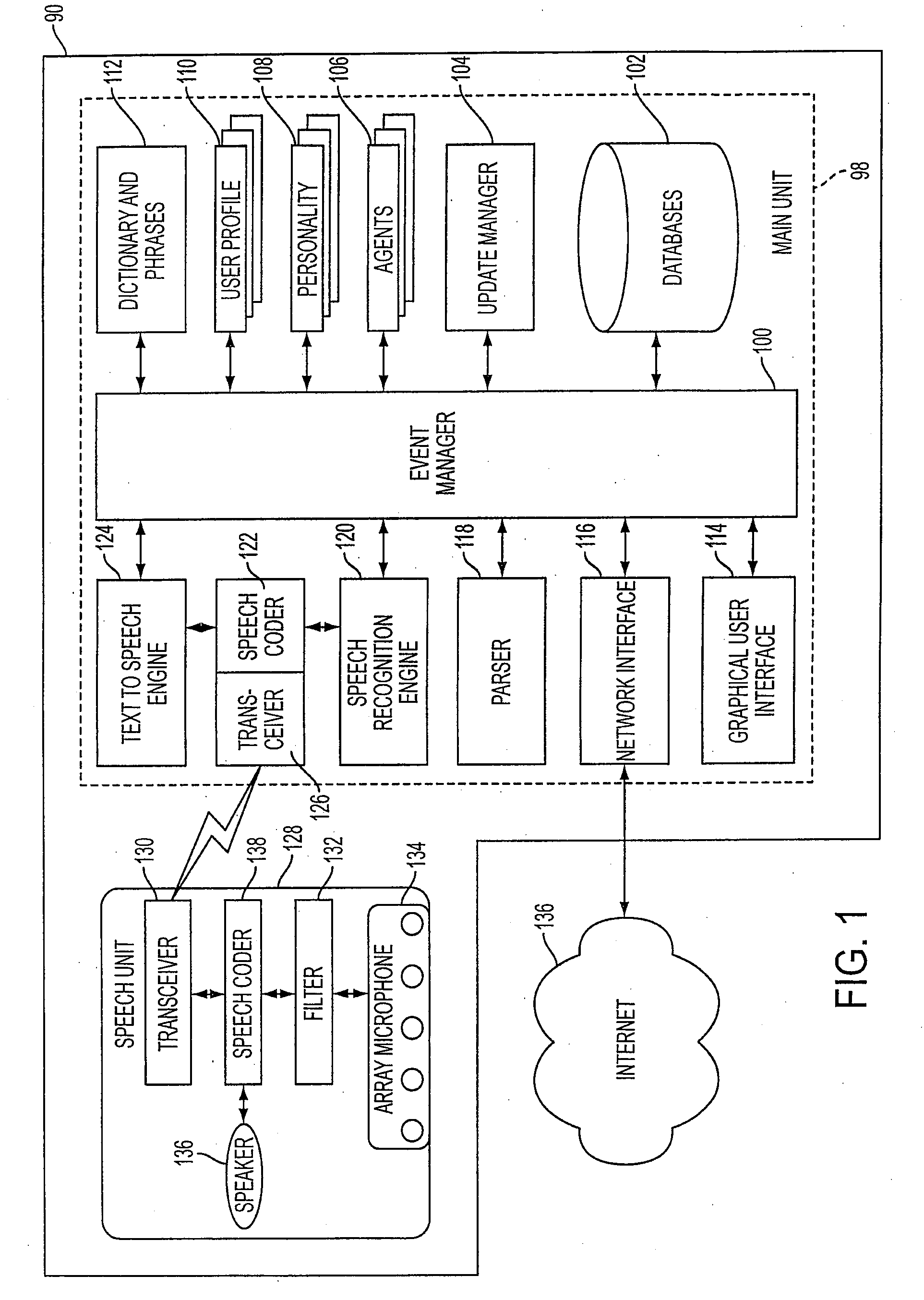
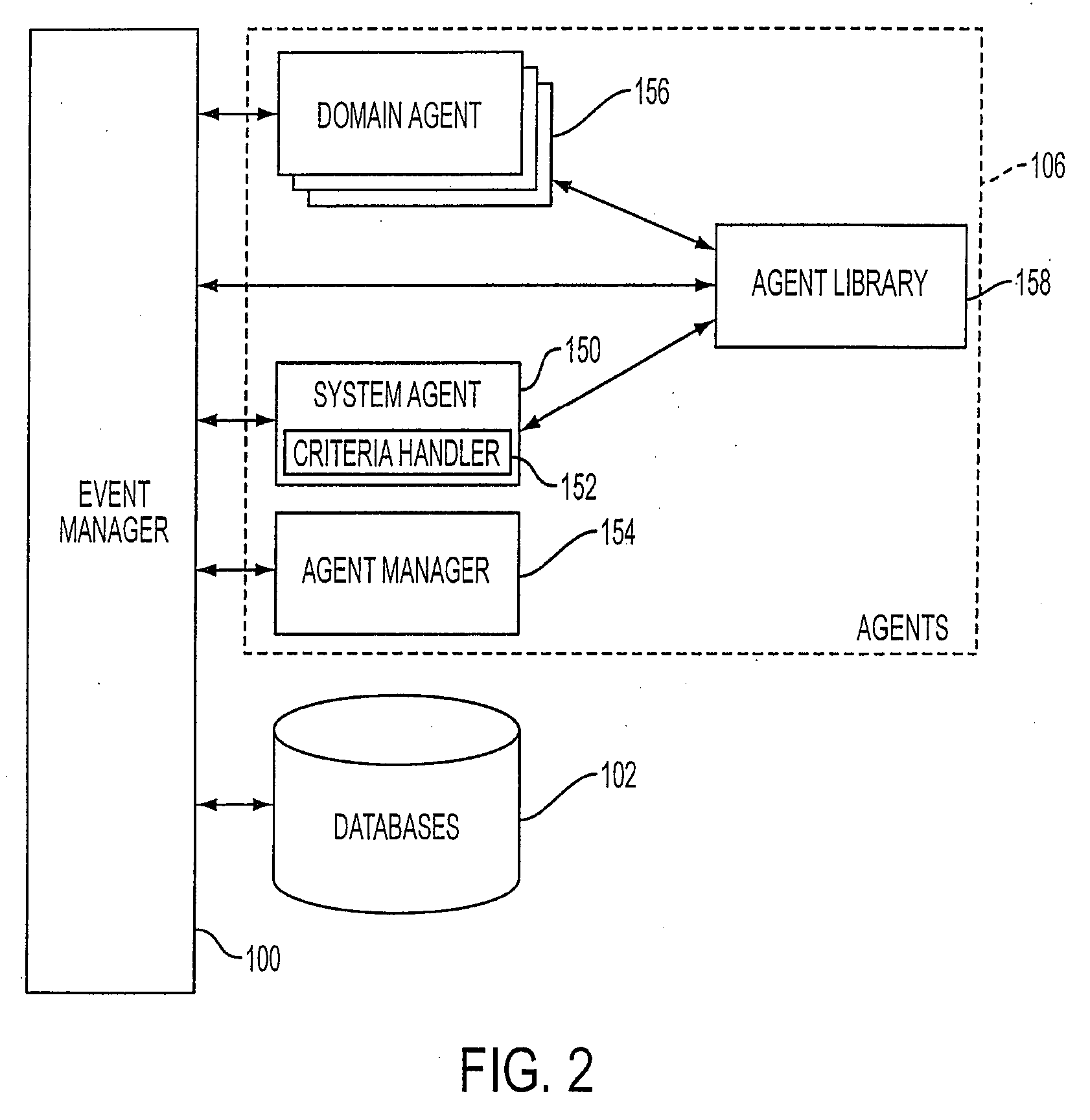
Mobile systems and methods of supporting natural language human-machine interactions
ActiveUS20070050191A1Improve maximizationHigh bandwidthWeb data indexingDevices with voice recognitionNatural languageDependability
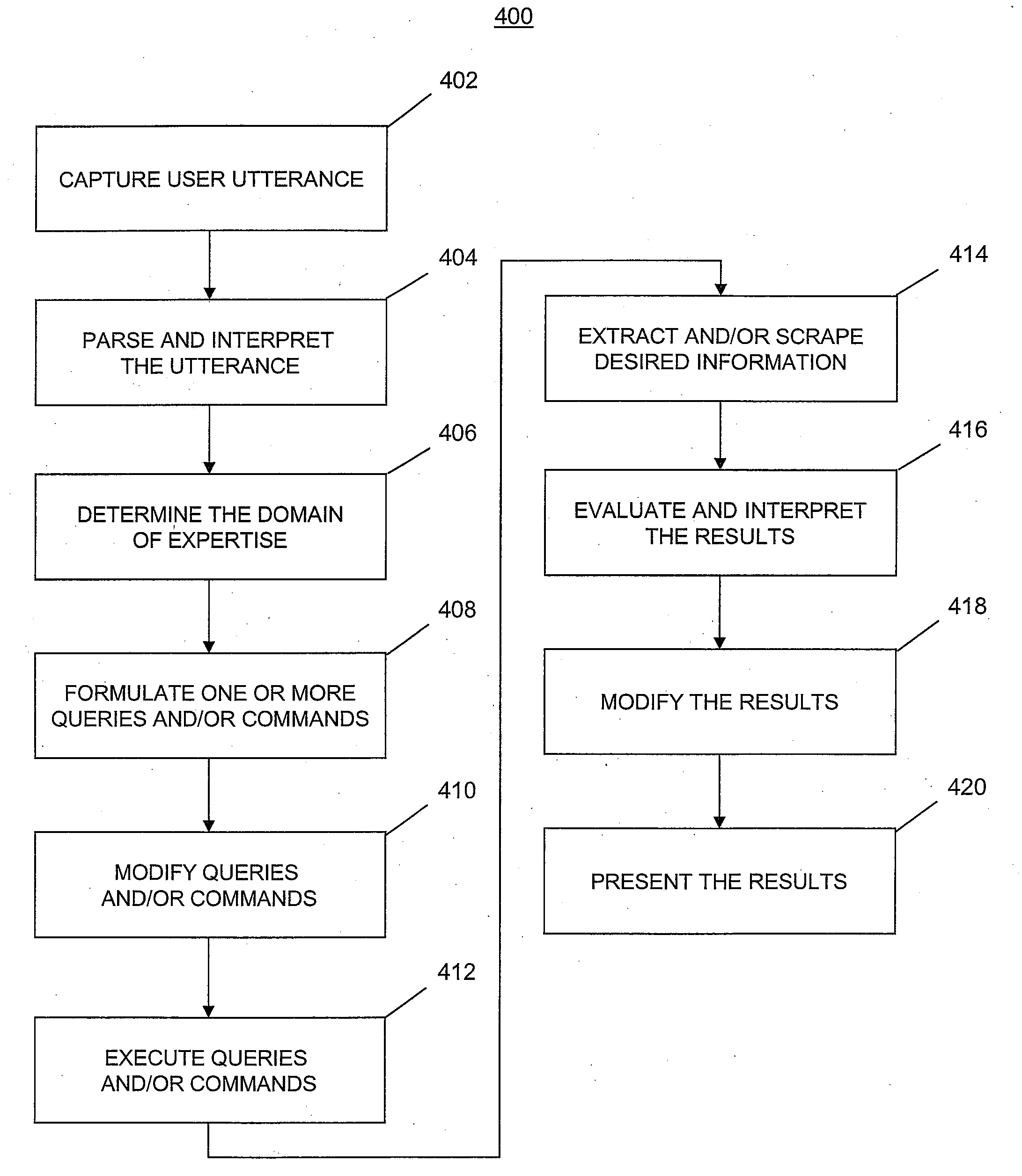
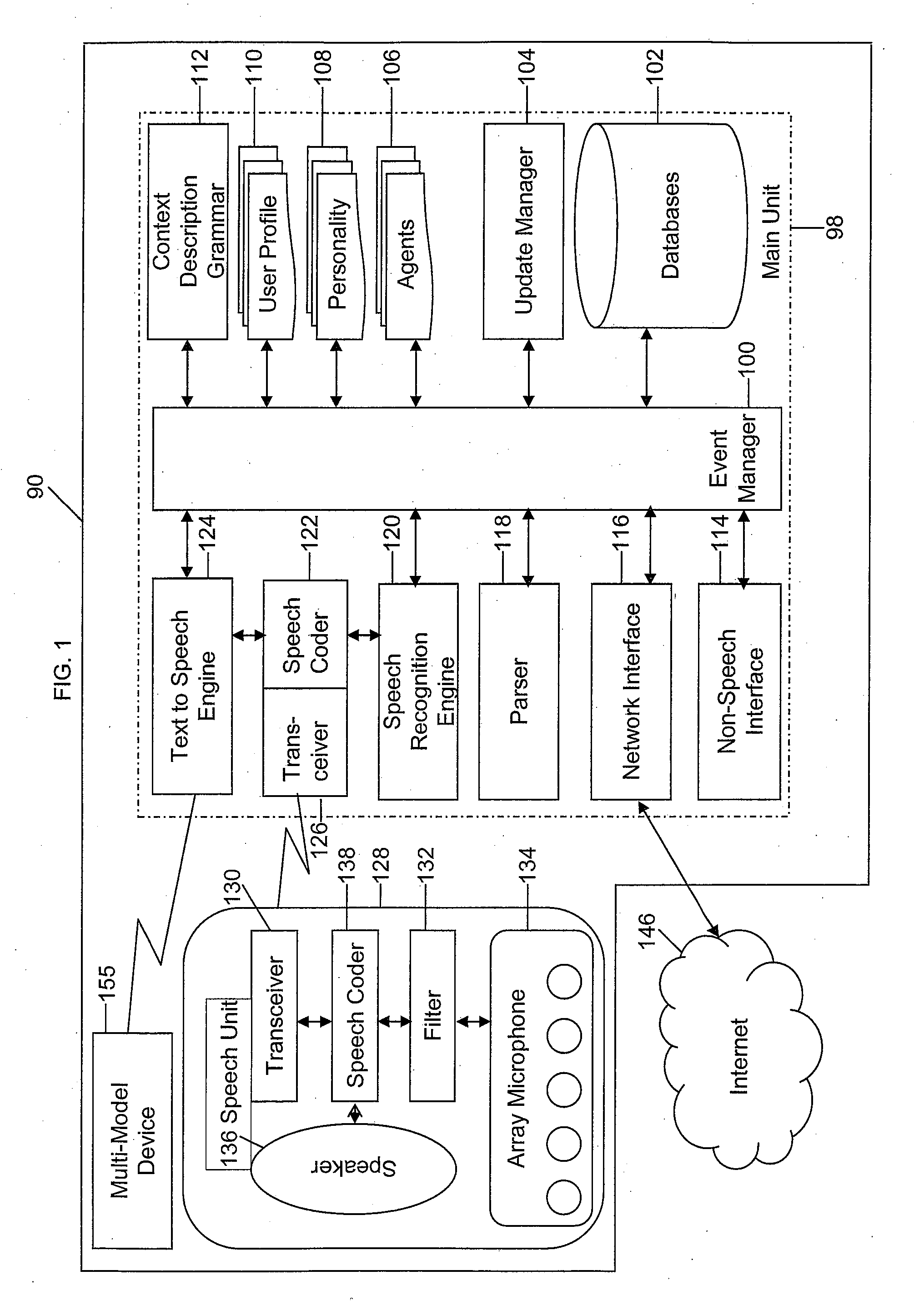
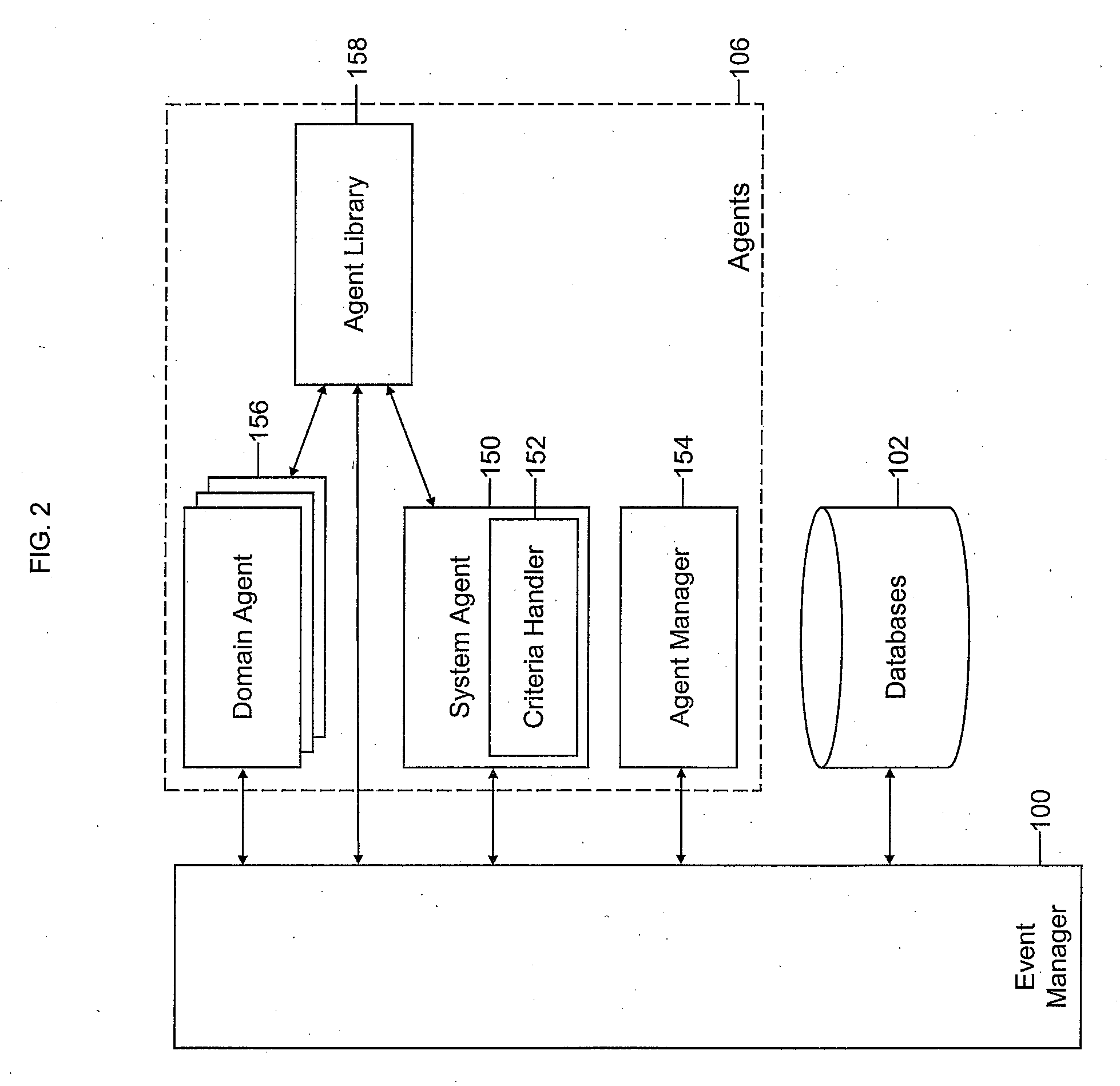
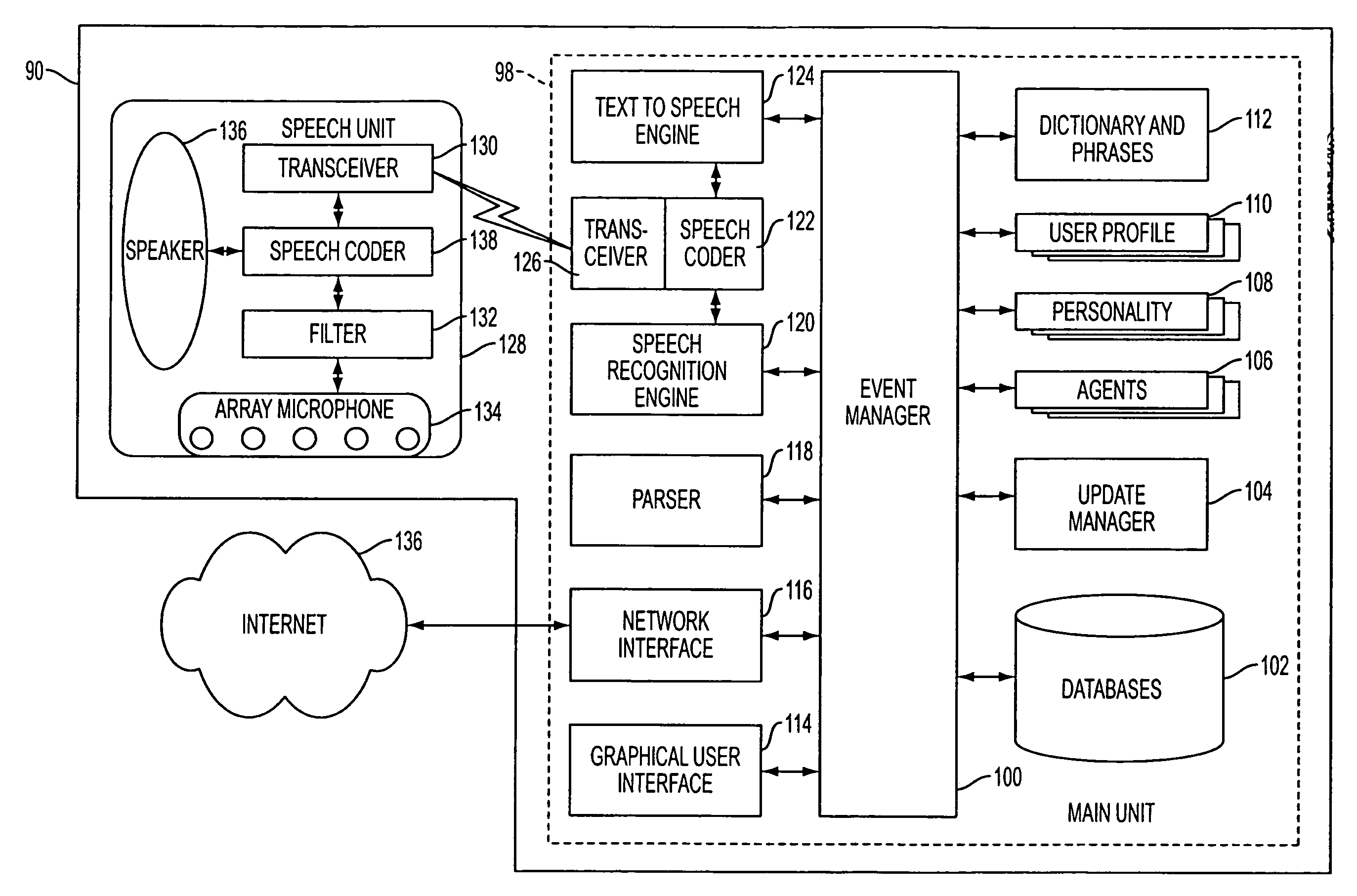
A mobile system is provided that includes speech-based and non-speech-based interfaces for telematics applications. The mobile system identifies and uses context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for users that submit requests and / or commands in multiple domains. The invention creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command. The invention may organize domain specific behavior and information into agents, that are distributable or updateable over a wide area network.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
Systems and methods for responding to natural language speech utterance
ActiveUS7398209B2Promotes feeling of naturalOvercome deficienciesData processing applicationsNatural language data processingPrior informationDependability
Systems and methods for receiving natural language queries and / or commands and execute the queries and / or commands. The systems and methods overcomes the deficiencies of prior art speech query and response systems through the application of a complete speech-based information query, retrieval, presentation and command environment. This environment makes significant use of context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for one or more users making queries or commands in multiple domains. Through this integrated approach, a complete speech-based natural language query and response environment can be created. The systems and methods creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
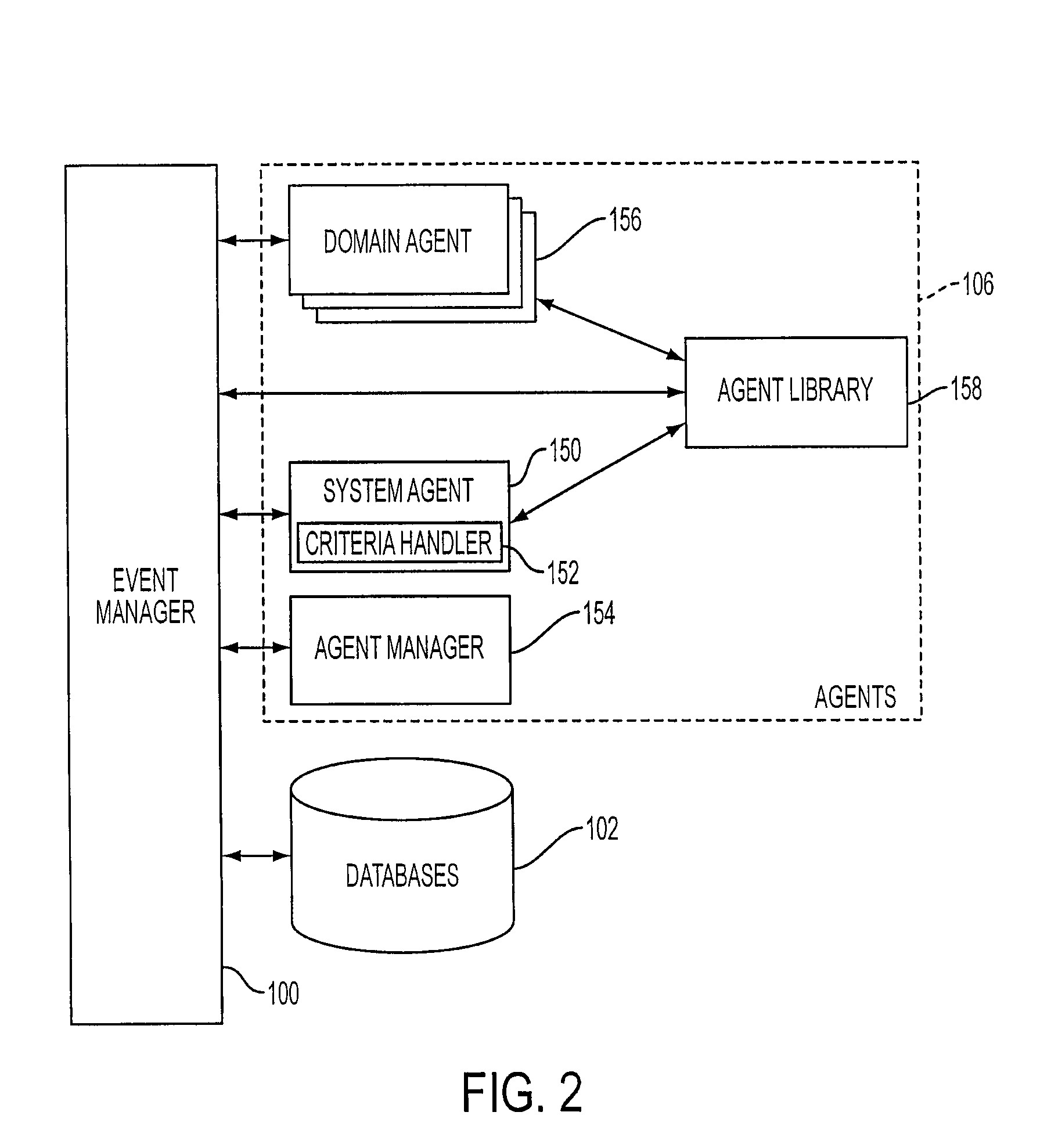
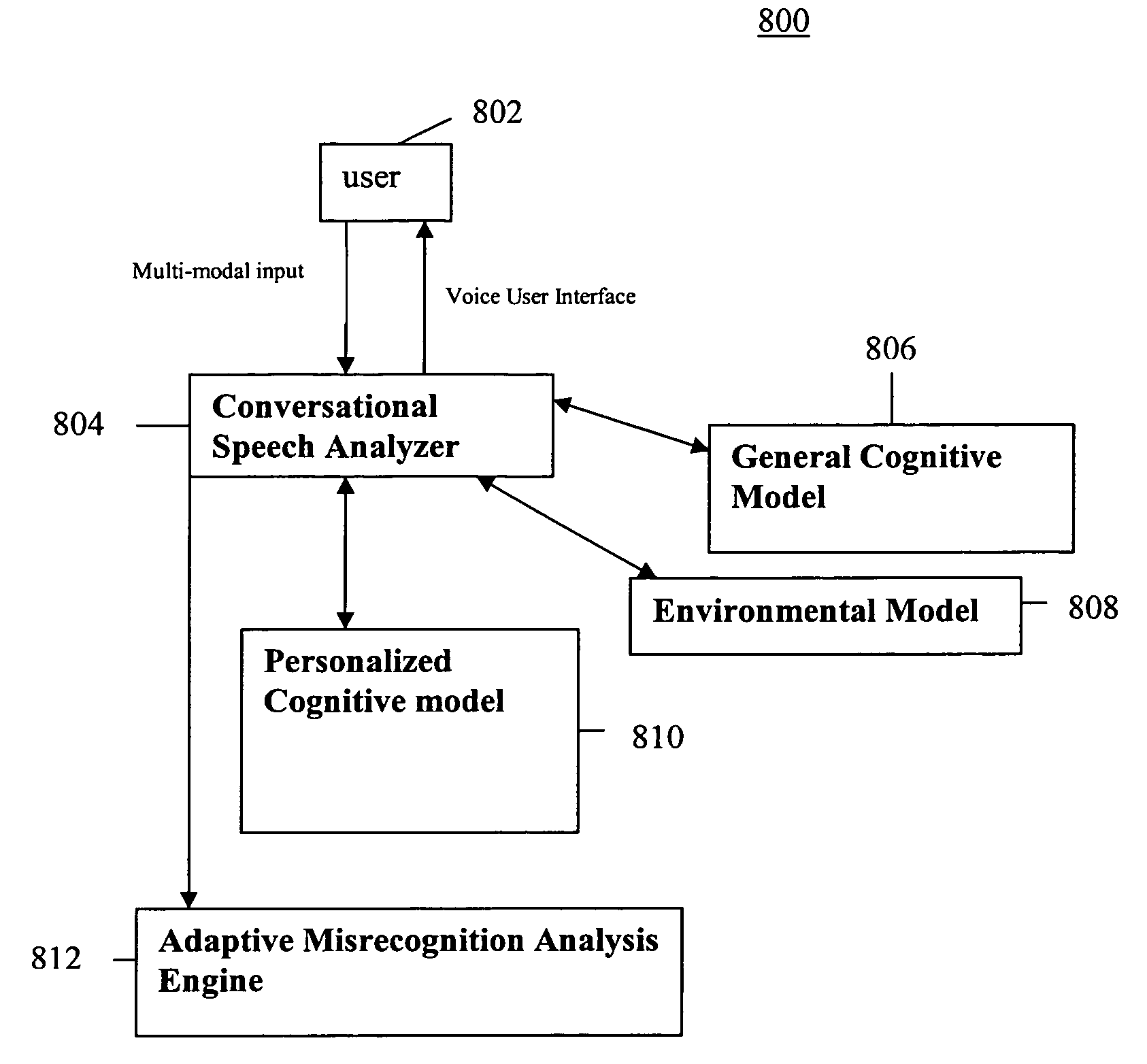
System and method of supporting adaptive misrecognition in conversational speech
ActiveUS7620549B2Promotes feeling of naturalSignificant to useNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionPersonalizationHuman–machine interface
A system and method are provided for receiving speech and / or non-speech communications of natural language questions and / or commands and executing the questions and / or commands. The invention provides a conversational human-machine interface that includes a conversational speech analyzer, a general cognitive model, an environmental model, and a personalized cognitive model to determine context, domain knowledge, and invoke prior information to interpret a spoken utterance or a received non-spoken message. The system and method creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context of the speech or non-speech communication and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
Systems and methods for responding to natural language speech utterance
ActiveUS7640160B2Promotes feeling of naturalSignificant to useDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisPrior informationSpeech sound
Systems and methods are provided for receiving speech and non-speech communications of natural language questions and / or commands, transcribing the speech and non-speech communications to textual messages, and executing the questions and / or commands. The invention applies context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for one or more users presenting questions or commands across multiple domains. The systems and methods creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context of the speech and non-speech communications and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
Systems and methods for responding to natural language speech utterance
ActiveUS20100057443A1Promotes feeling of naturalSignificant to useDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisPrior informationSpeech sound
Systems and methods are provided for receiving speech and non-speech communications of natural language questions and / or commands, transcribing the speech and non-speech communications to textual messages, and executing the questions and / or commands. The invention applies context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for one or more users presenting questions or commands across multiple domains. The systems and methods creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context of the speech and non-speech communications and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
Systems and methods for responding to natural language speech utterance
InactiveUS20070265850A1Disseminate their knowledgeImprove system performanceData processing applicationsNatural language data processingPrior informationConfigfs
Systems and methods for receiving natural language queries and / or commands and execute the queries and / or commands. The systems and methods overcomes the deficiencies of prior art speech query and response systems through the application of a complete speech-based information query, retrieval, presentation and command environment. This environment makes significant use of context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for one or more users making queries or commands in multiple domains. Through this integrated approach, a complete speech-based natural language query and response environment can be created. The systems and methods creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
Systems and methods for responding to natural language speech utterance
ActiveUS20080235023A1Promotes feeling of naturalOvercome deficienciesData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsWorld Wide WebHuman language
Systems and methods for receiving natural language queries and / or commands and execute the queries and / or commands. The systems and methods overcomes the deficiencies of prior art speech query and response systems through the application of a complete speech-based information query, retrieval, presentation and command environment. This environment makes significant use of context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for one or more users making queries or commands in multiple domains. Through this integrated approach, a complete speech-based natural language query and response environment can be created. The systems and methods creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
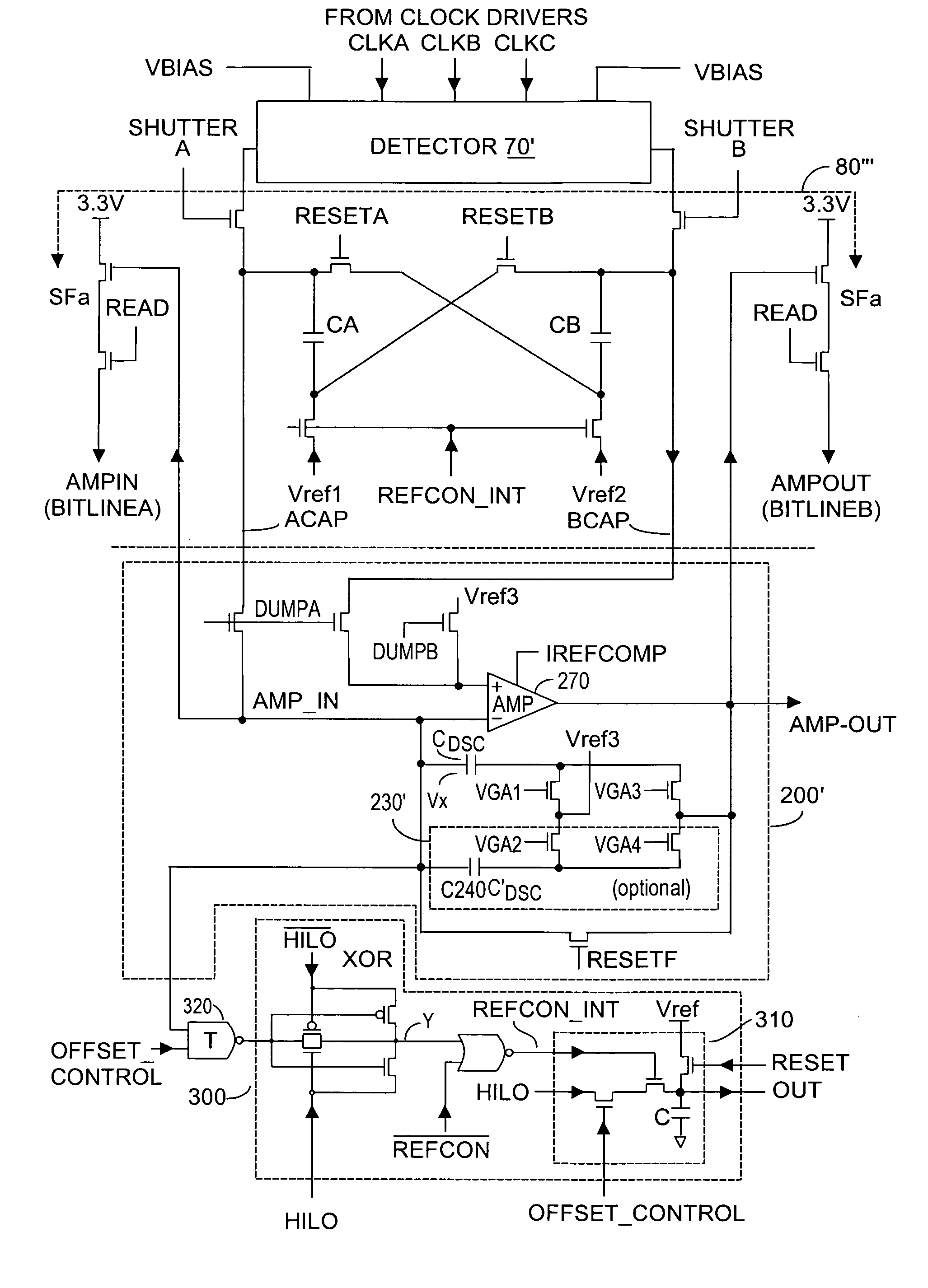
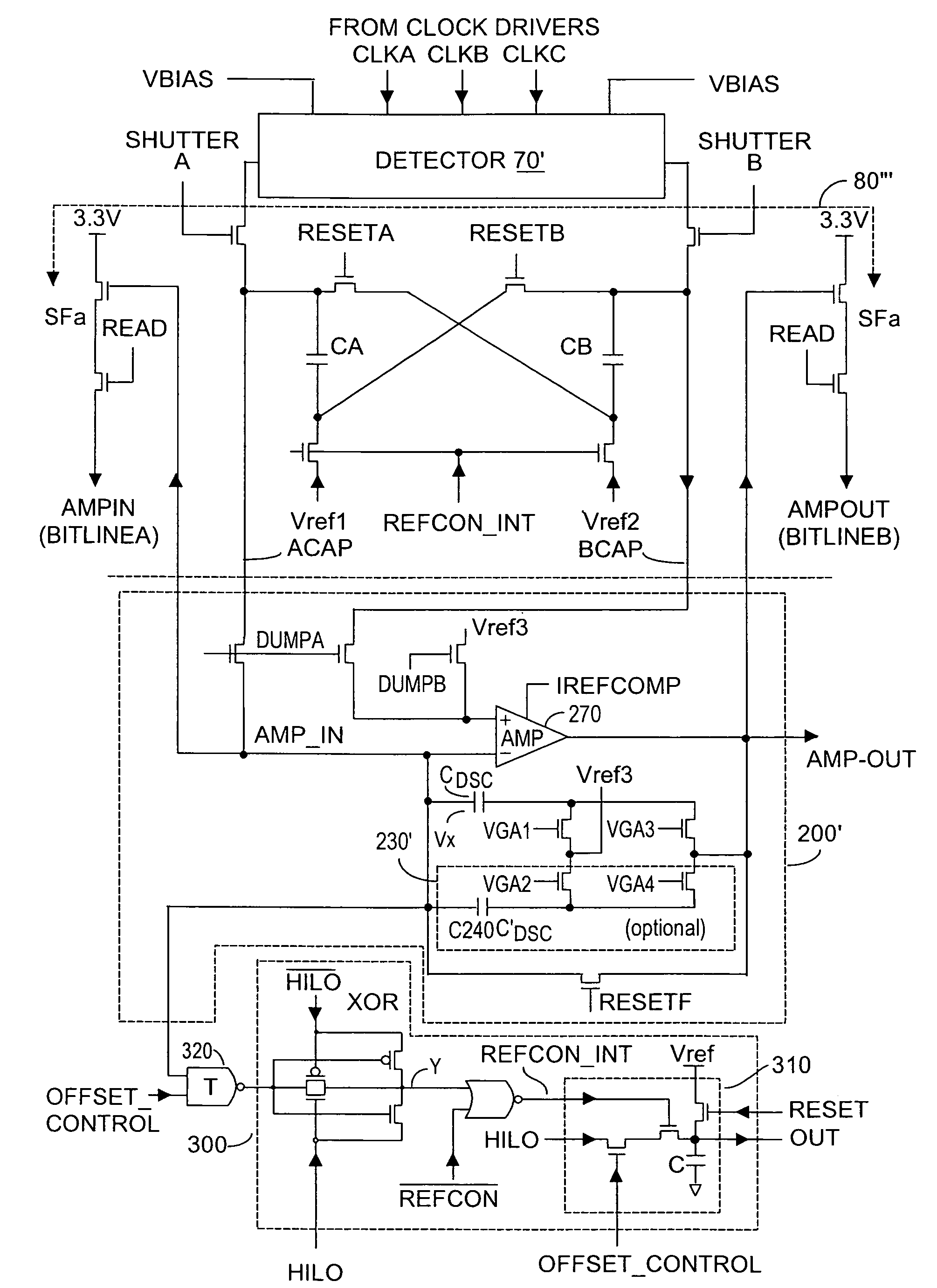
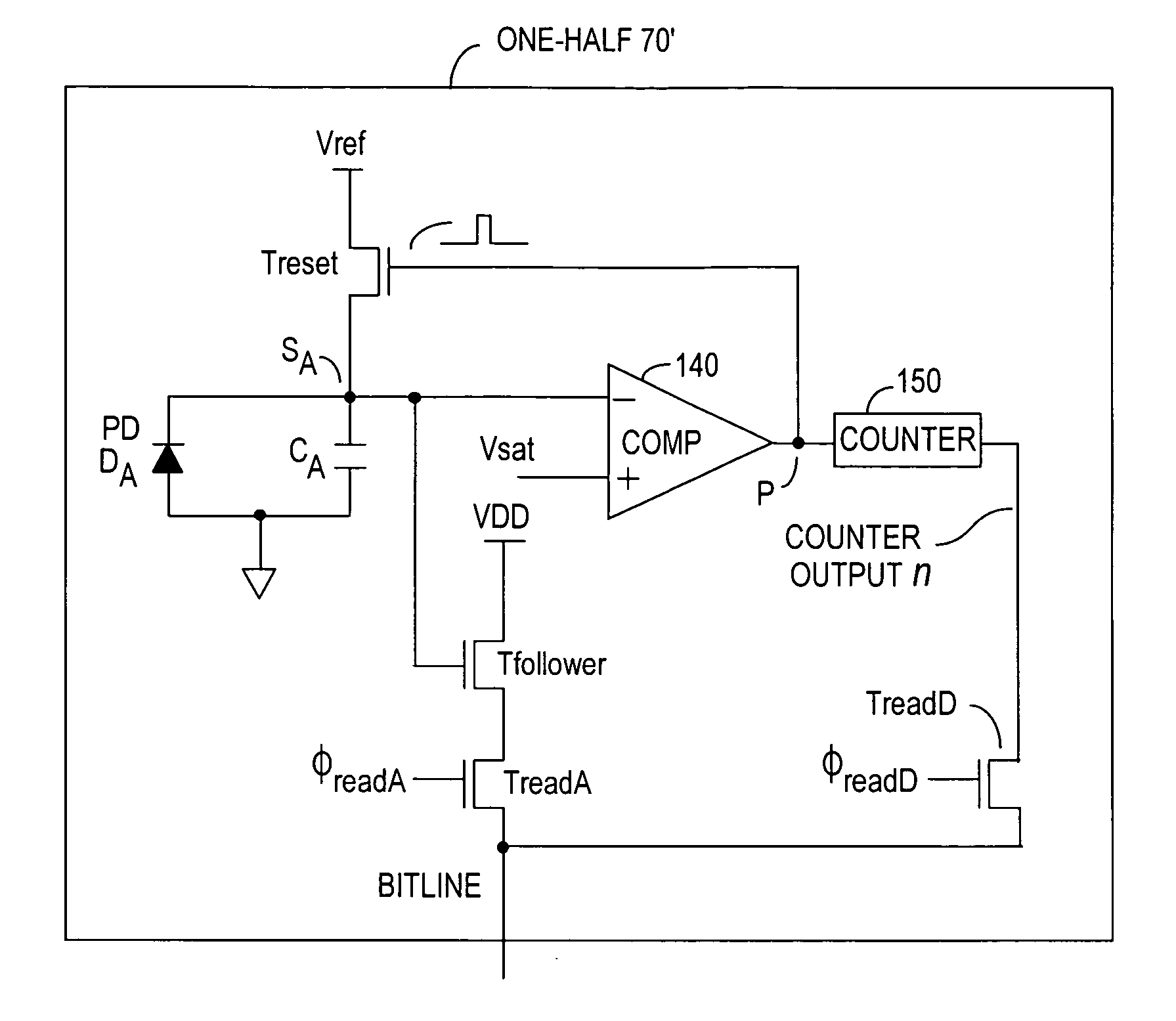
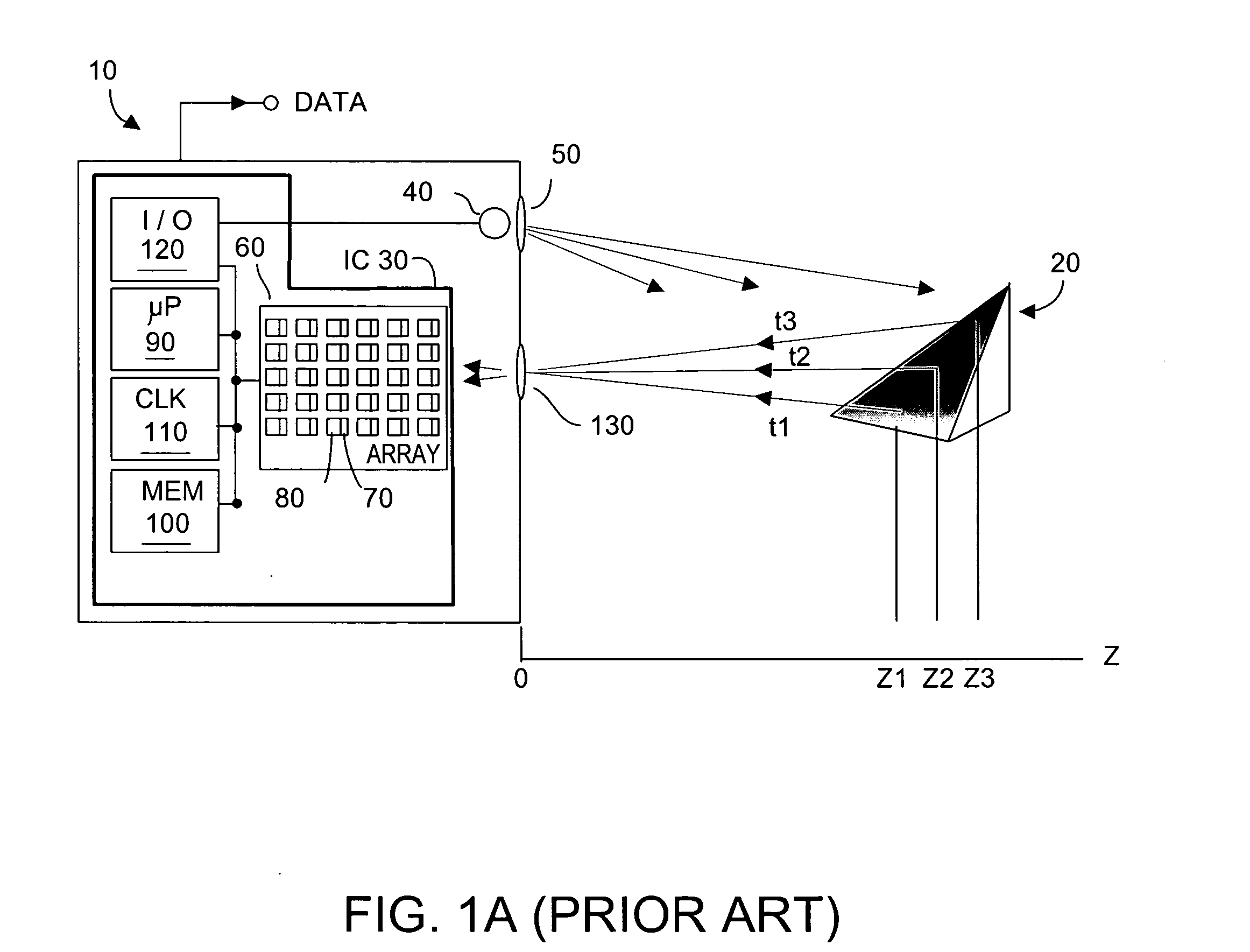
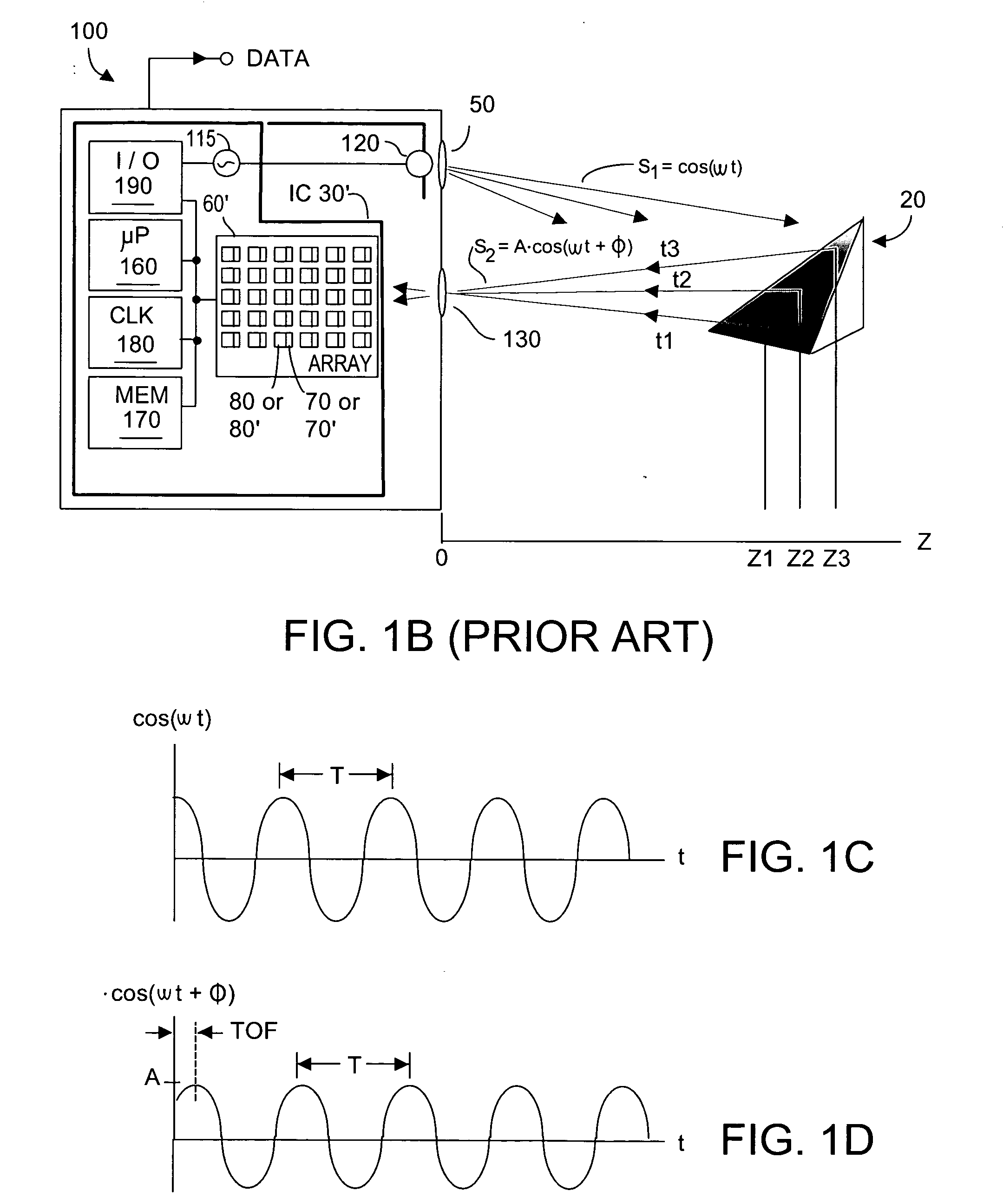
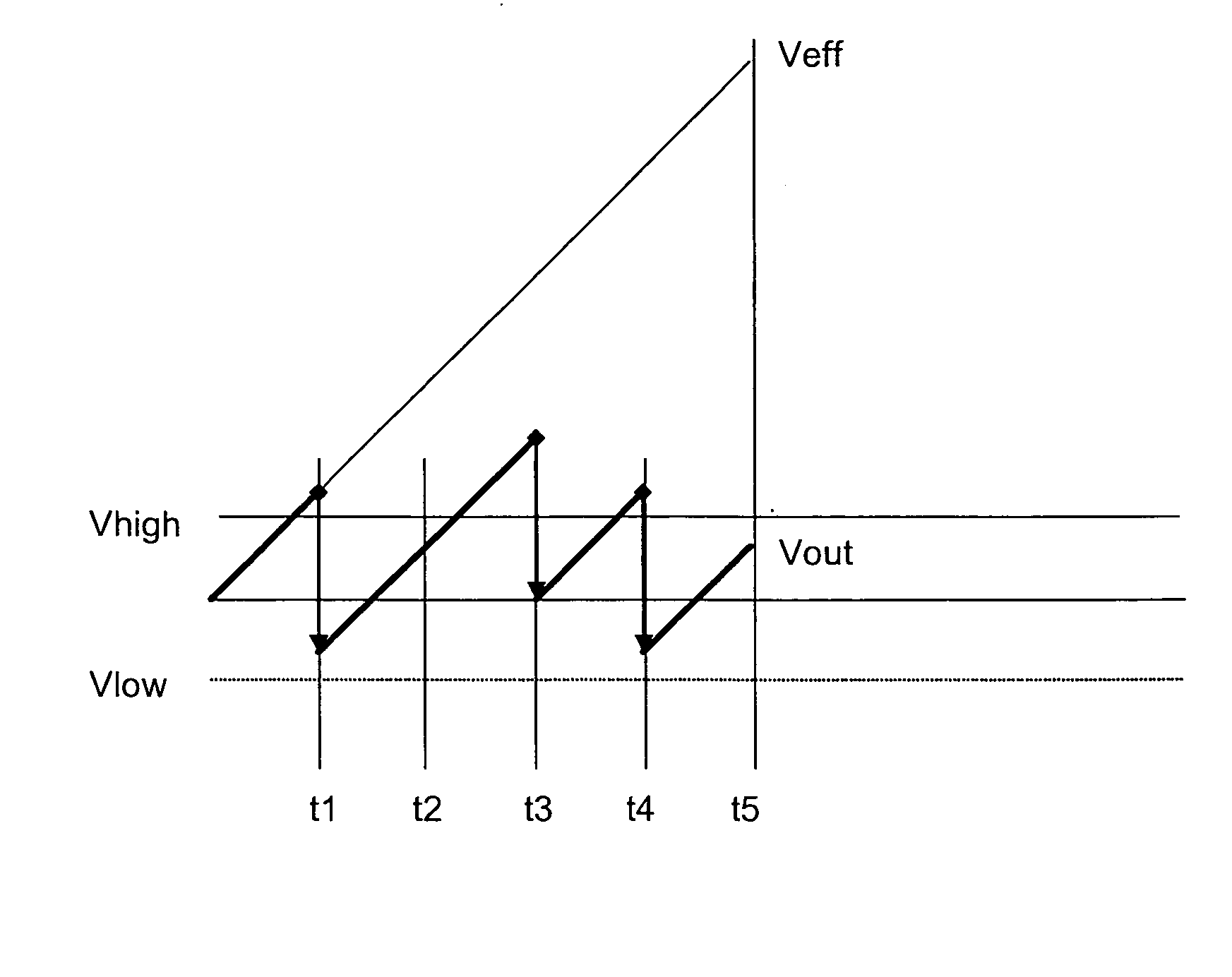
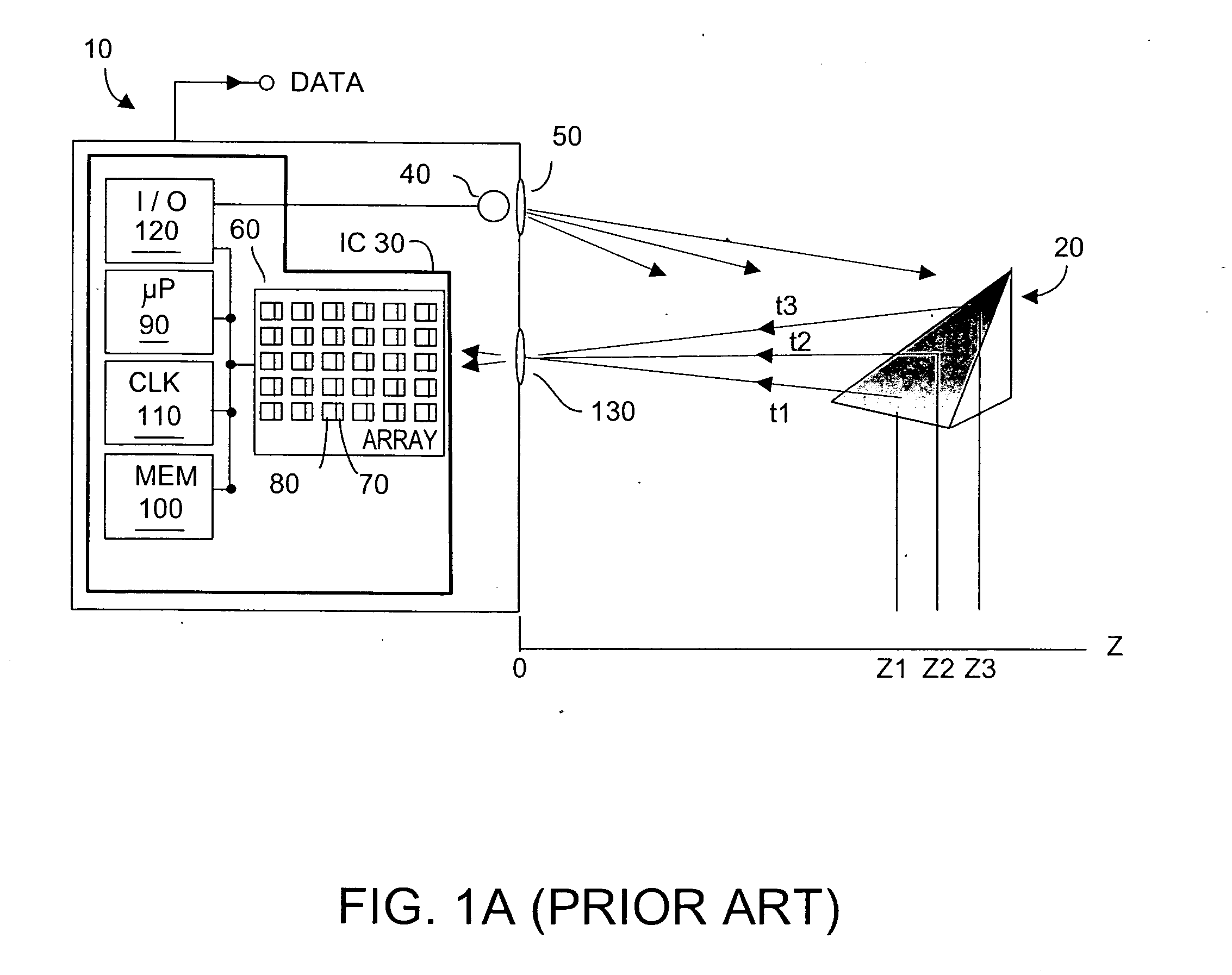
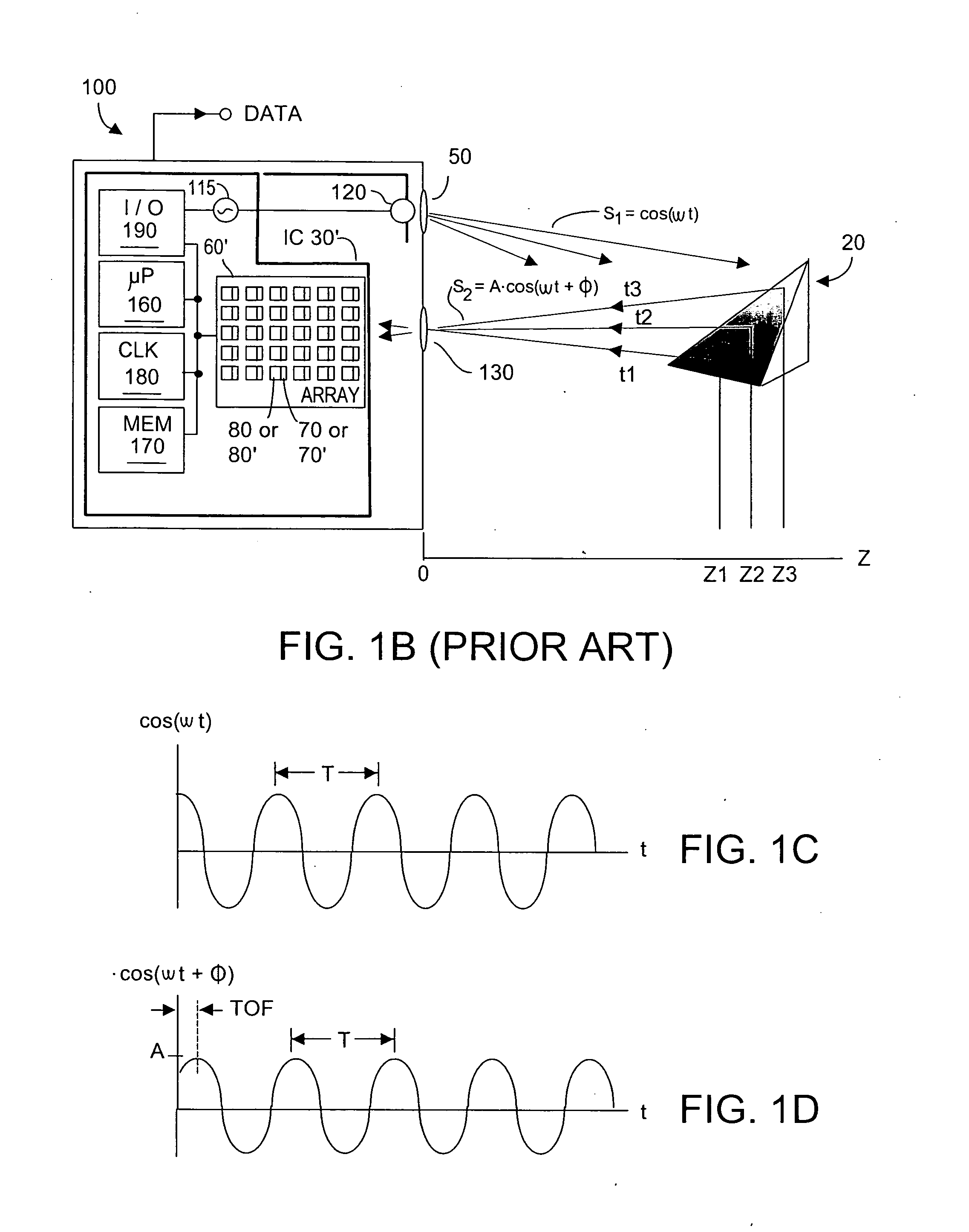
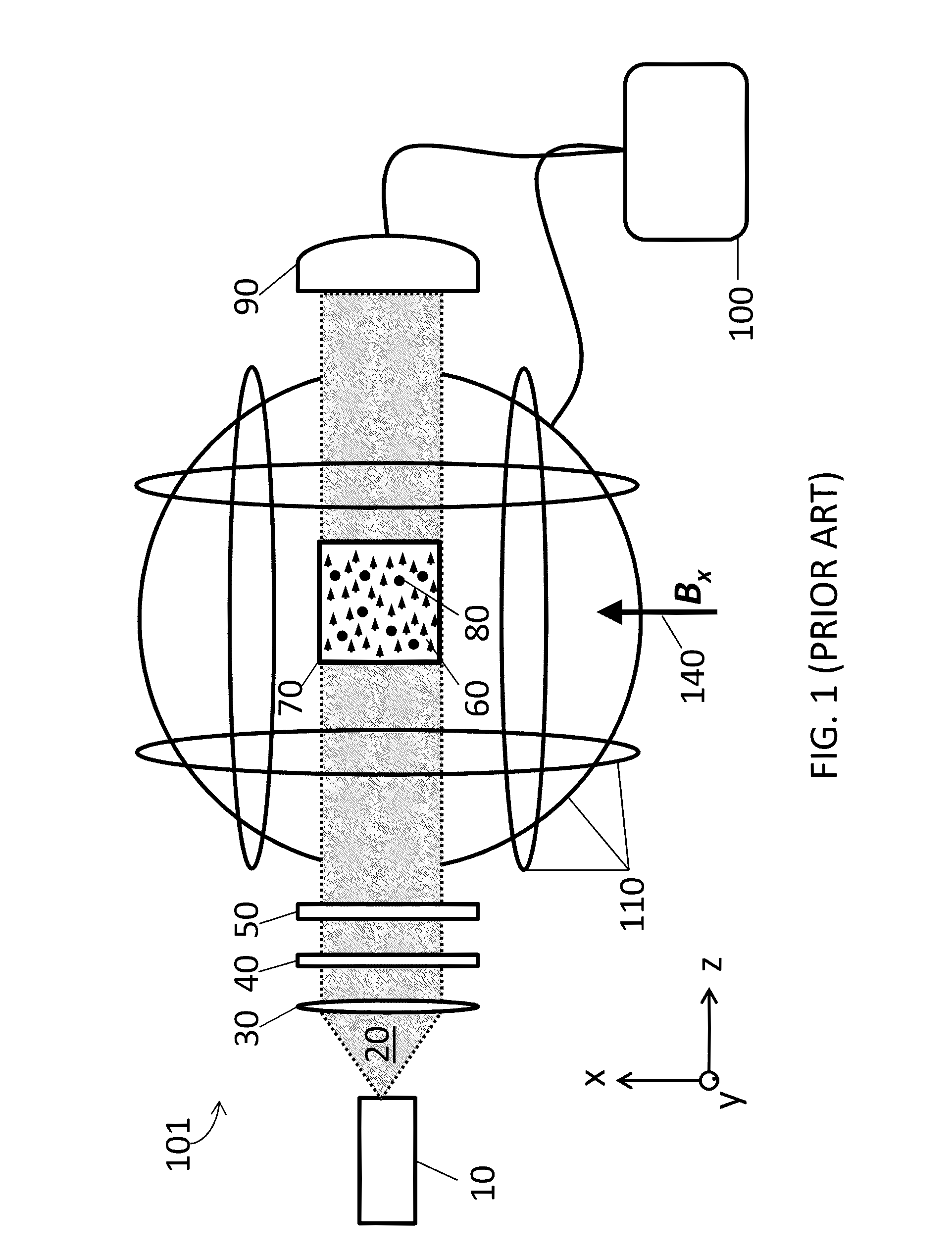
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
ActiveUS7157685B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSCapacitor voltage
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
InactiveUS7321111B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSAudio power amplifier
Dynamic range of a differential pixel is enhanced by injecting, synchronously or asynchronously, a compensating offset (ΔCOMP) into a differential signal capacitor whenever magnitude of the differential signal across the capacitor exceeds a predetermined value. Positive and negative magnitudes of ΔCOMP need not be equal. The number (N) of ΔCOMP offsets made is counted. Effective differential signal capacitor voltage V(t)=Vo±N·ΔCOMP, where Vo is capacitor voltage. In other embodiments magnitude of ΔCOMP in a sequence of compensations can differ, and the sum total of compensations in recorded. Differential pixel signal / noise ratio is increased by dynamically maximizing operational amplifier gain AG for each differential pixel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
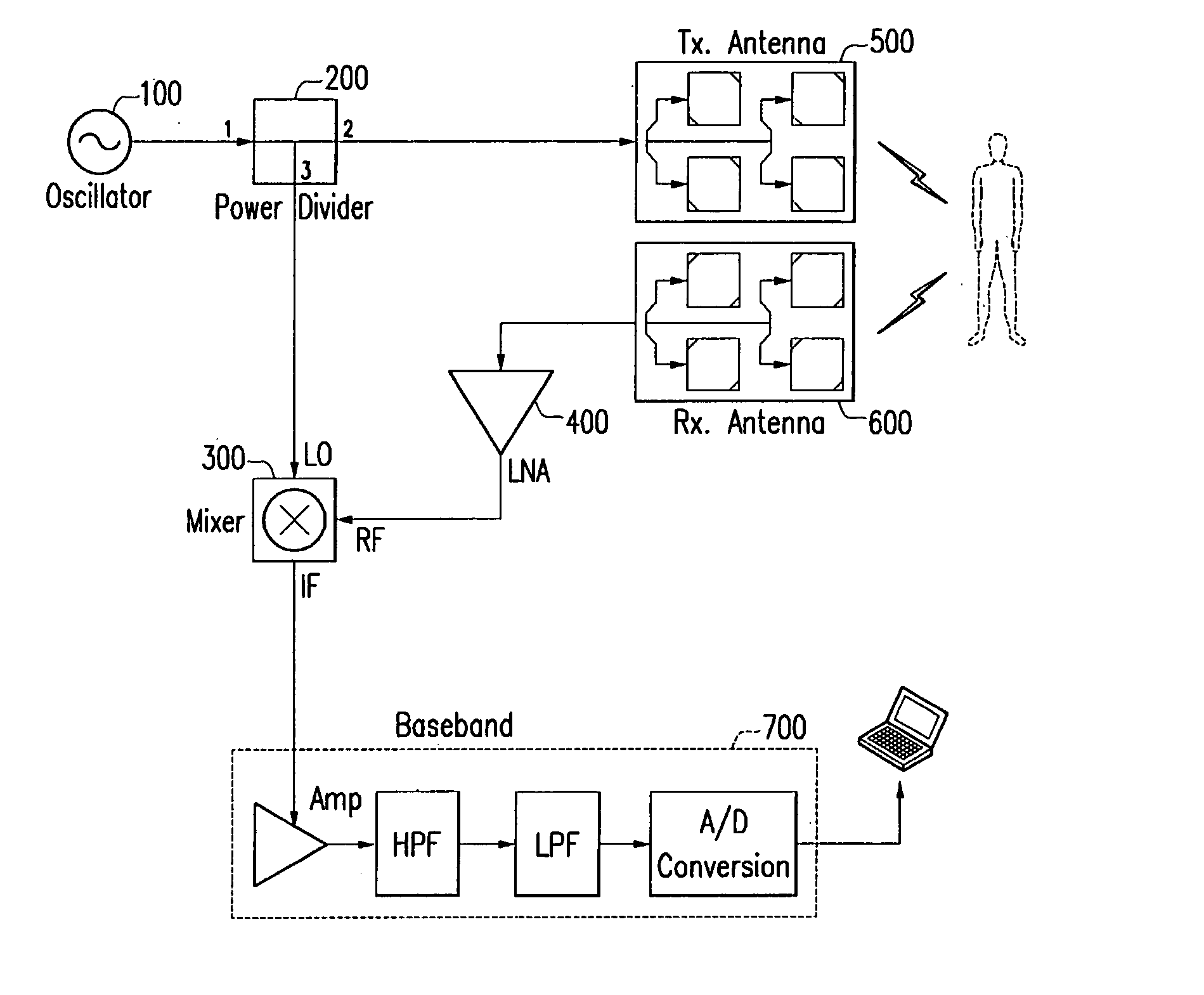
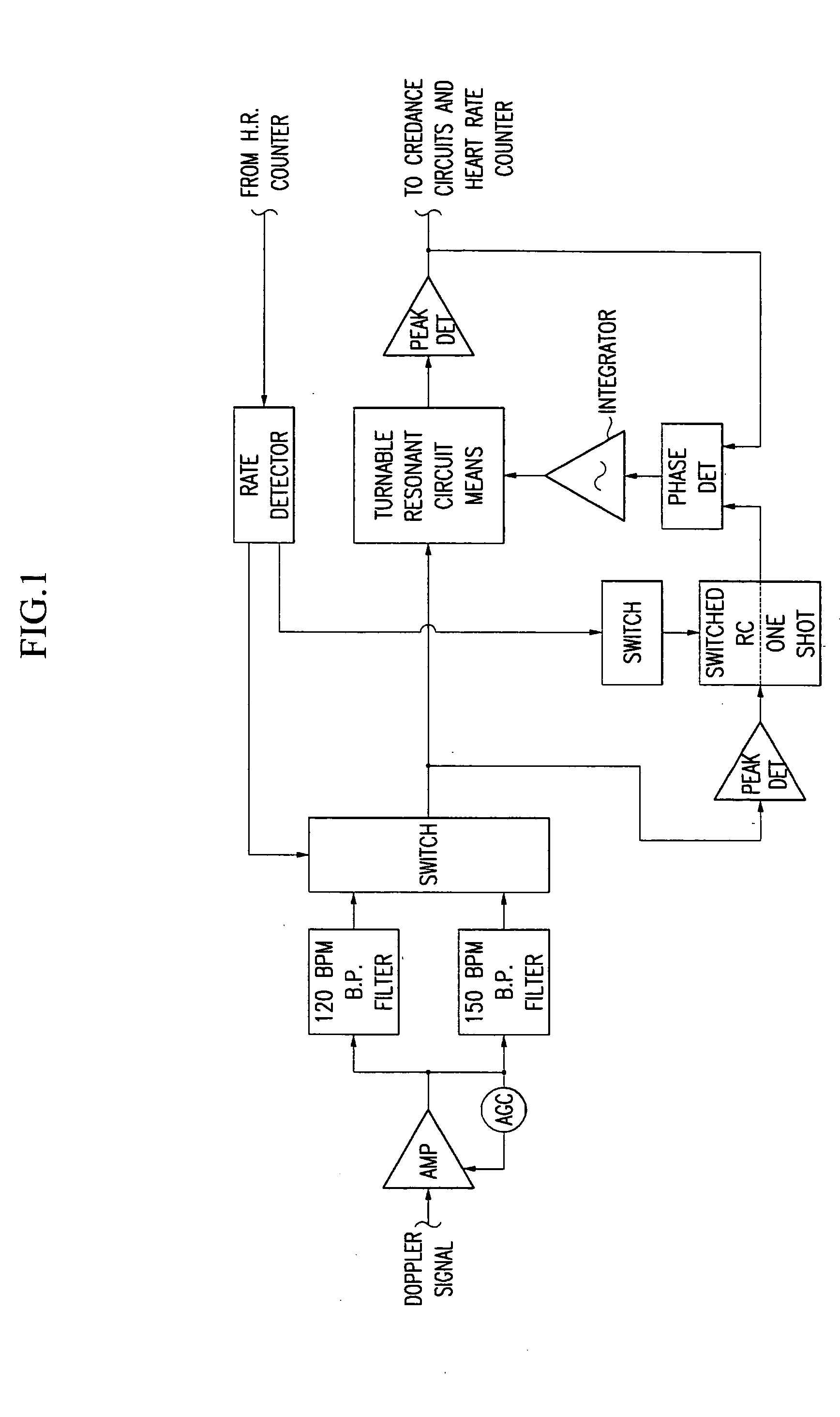
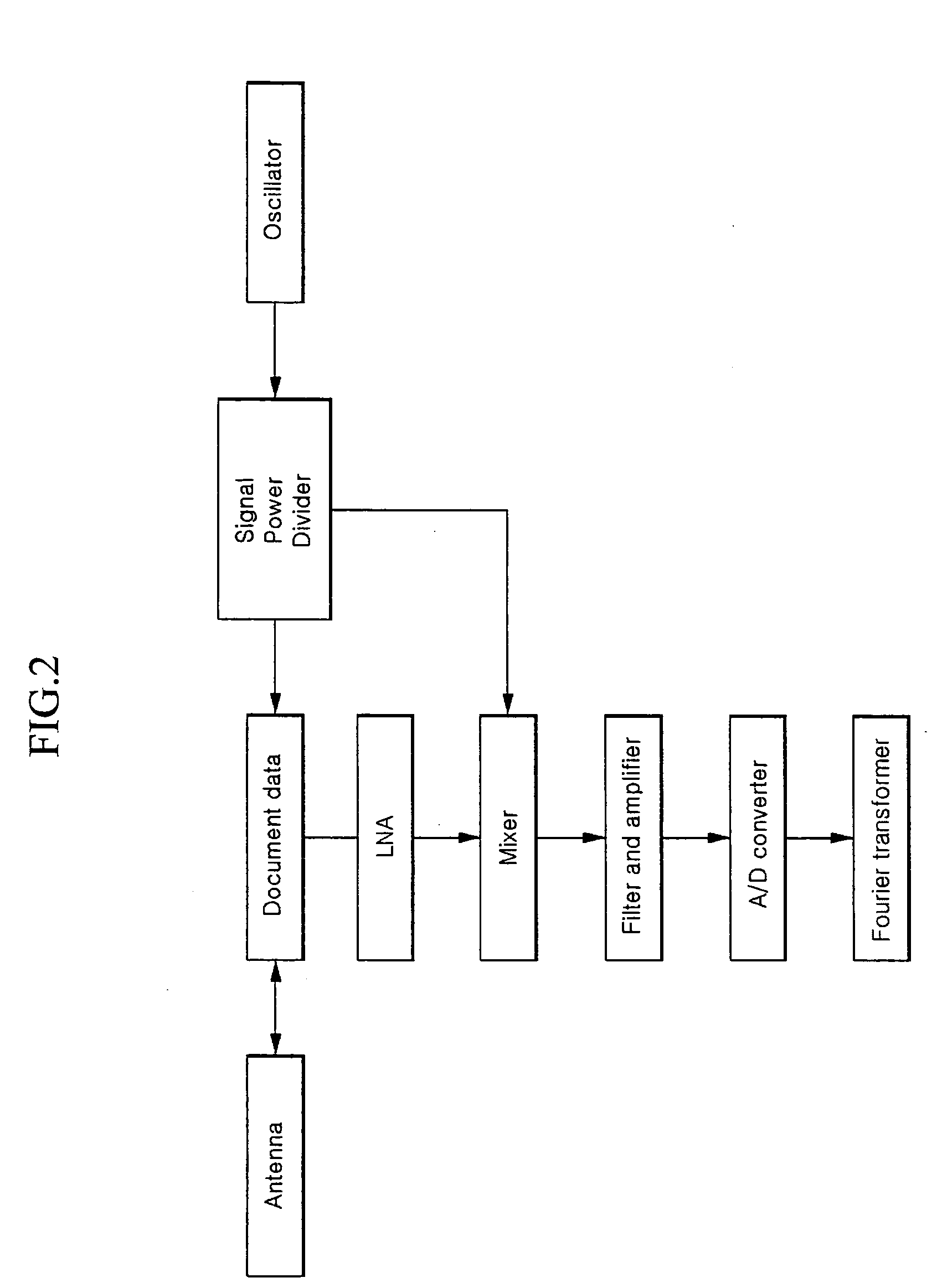
Wireless heart rate sensing system and method
InactiveUS20050143667A1Small sizeCancel noiseSensorsTelemetric patient monitoringFrequency mixerEngineering
Disclosed is a wireless heart rate sensing system which comprises: an oscillator for generating signals of a specific frequency; a power divider for dividing power of the signals generated by the oscillator; a transmit antenna for radiating a first signal output by the power divider to a patient's chest; a receive antenna for receiving a signal, the frequency of which is transited by a motion of the patient's chest and which is reflected and returned; a mixer for combining frequency components of an RF signal received through the receive antenna and a second signal output by the power divider; and a baseband unit for filtering the signal combined by the mixer, converting it into a digital signal, and outputting the digital signal.
Owner:INFORMATION & COMM UNIV EDUCATIONAL FOUND
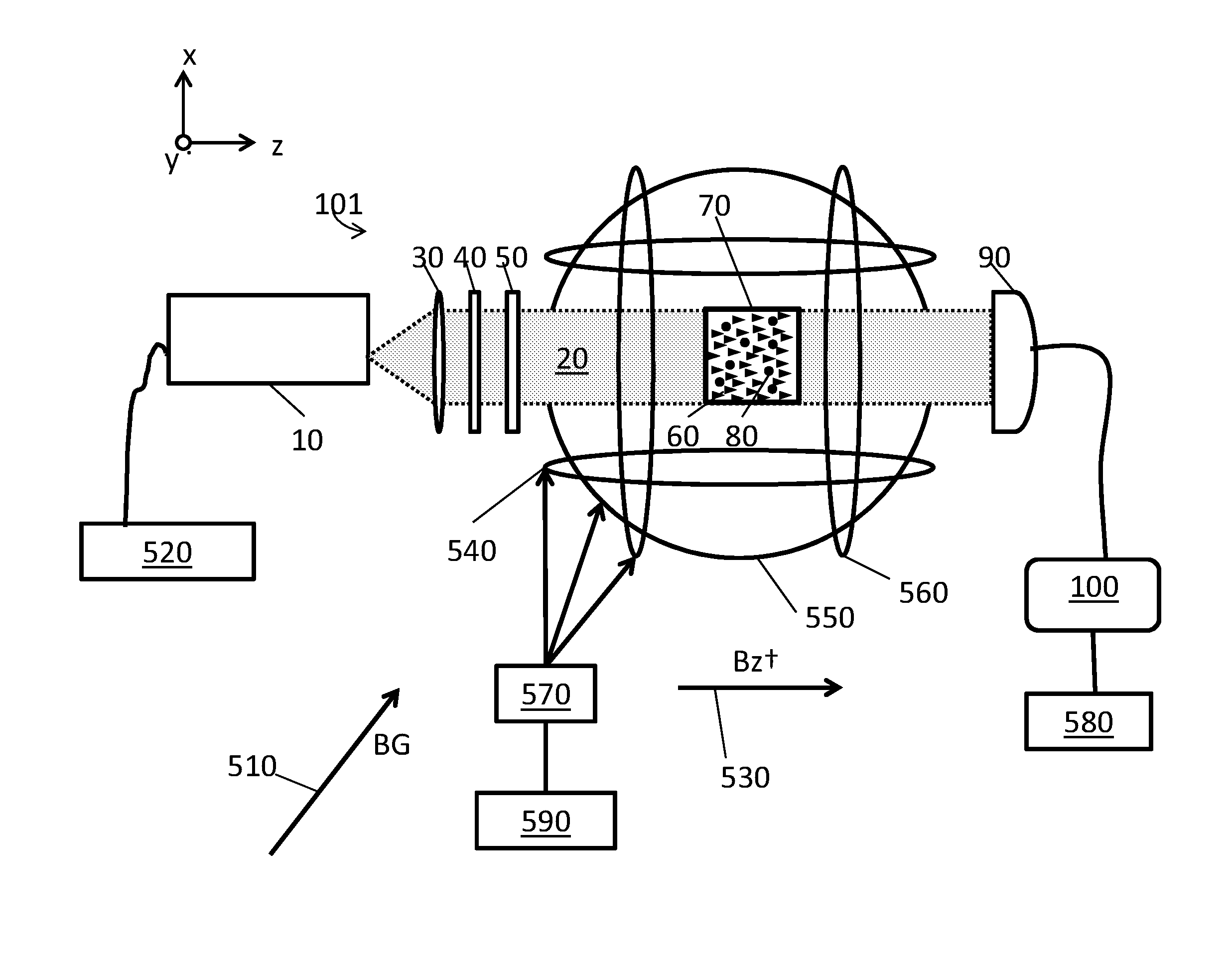
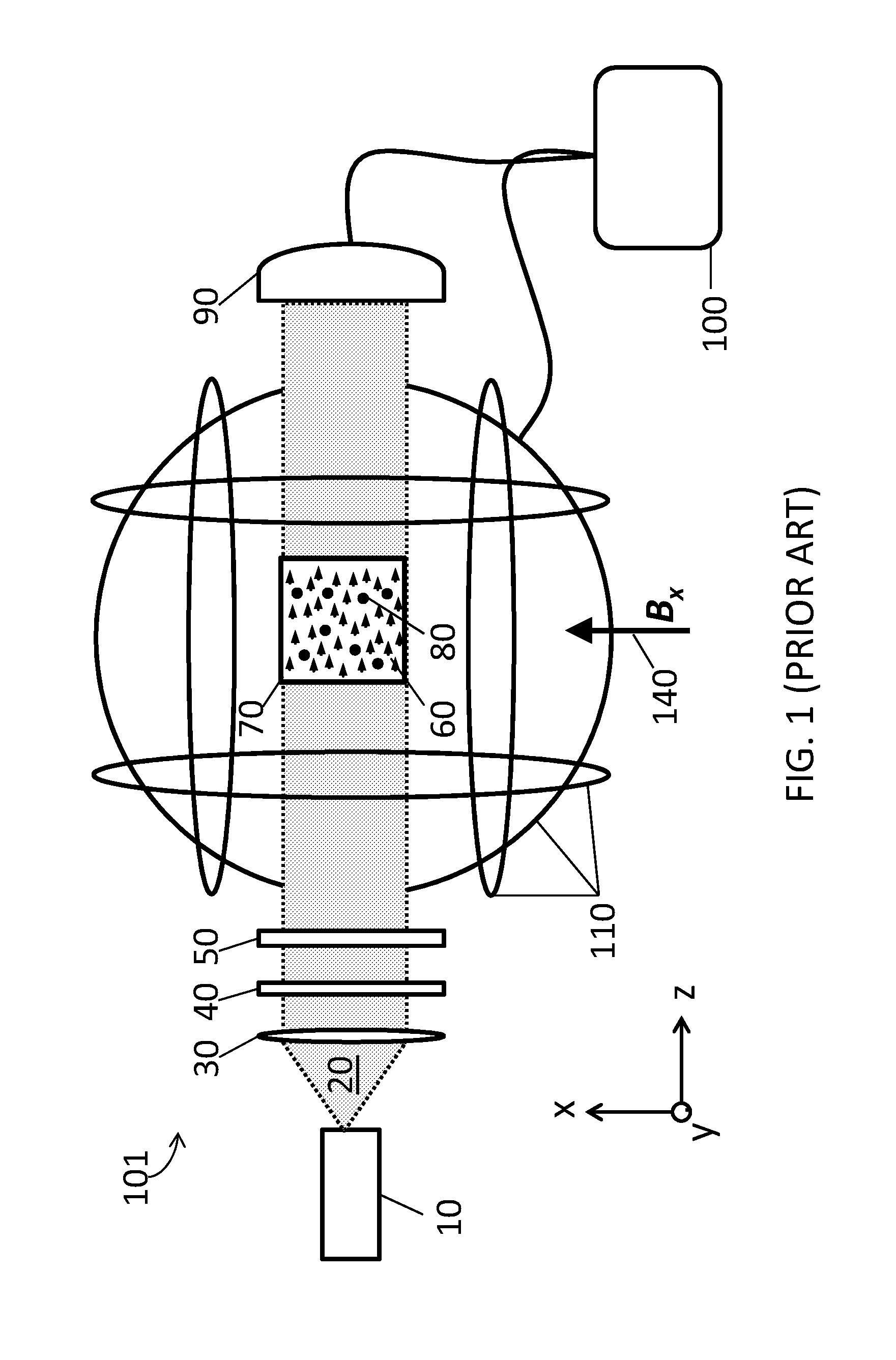
System for detecting zero-field resonance
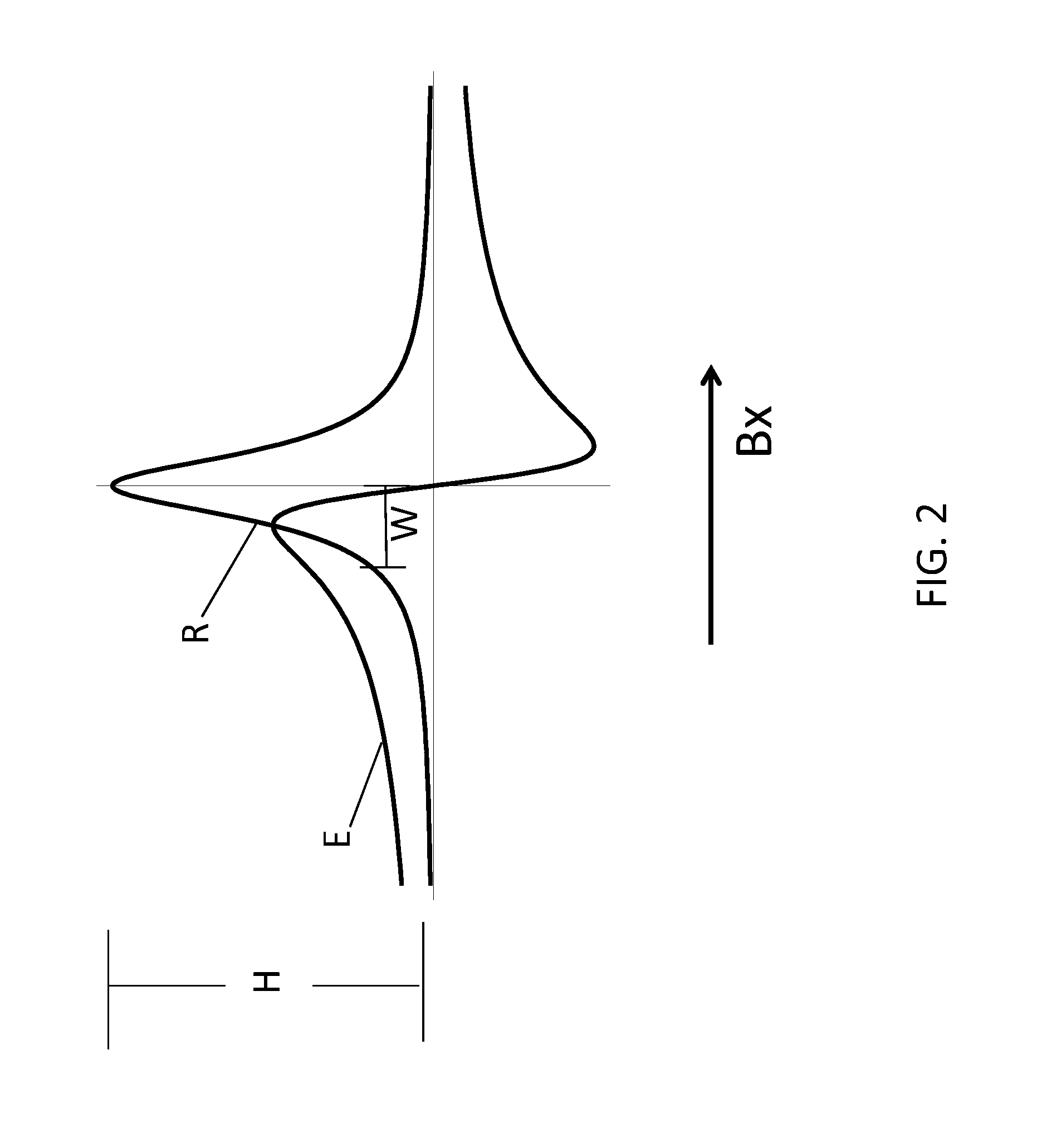
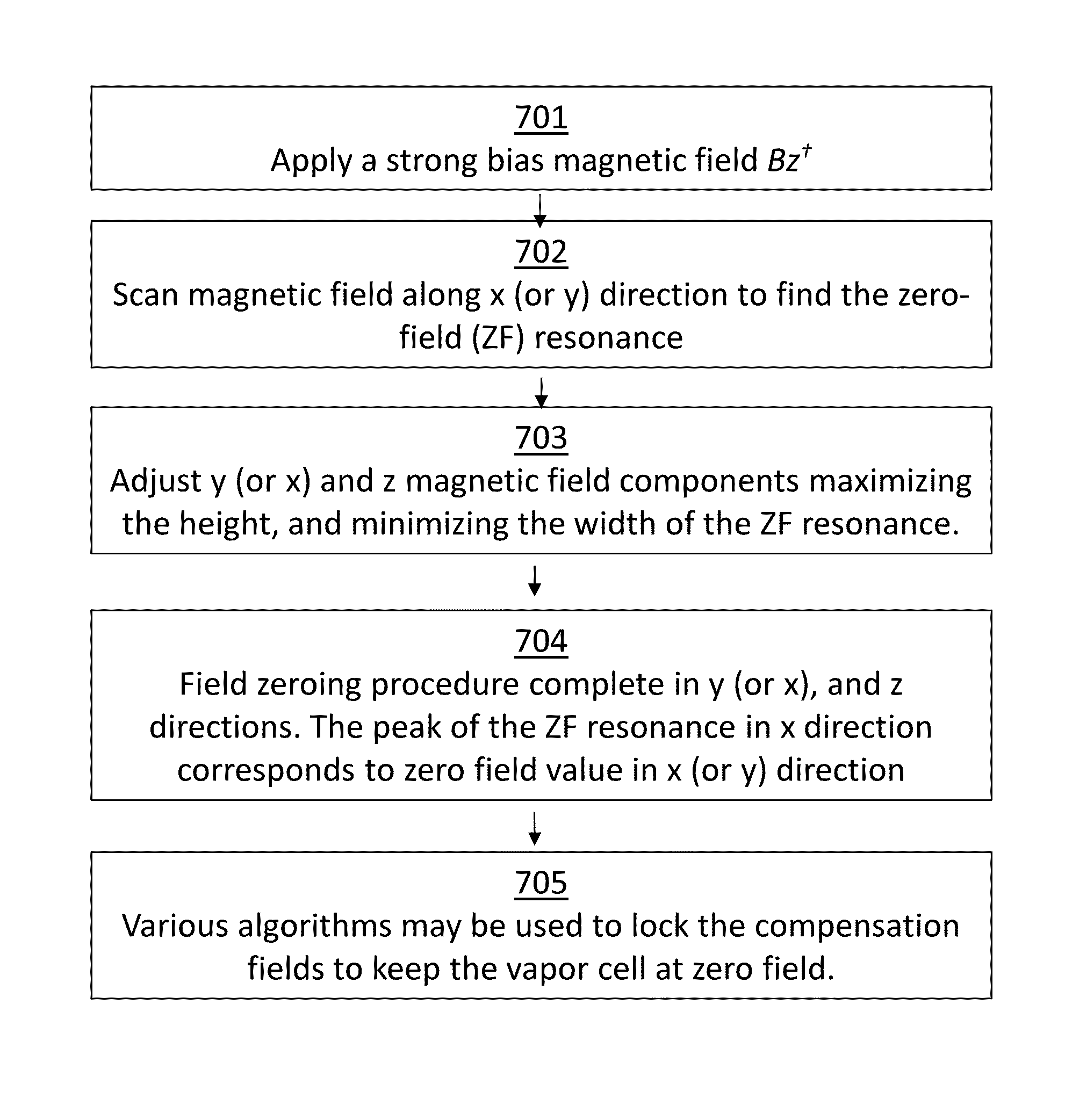
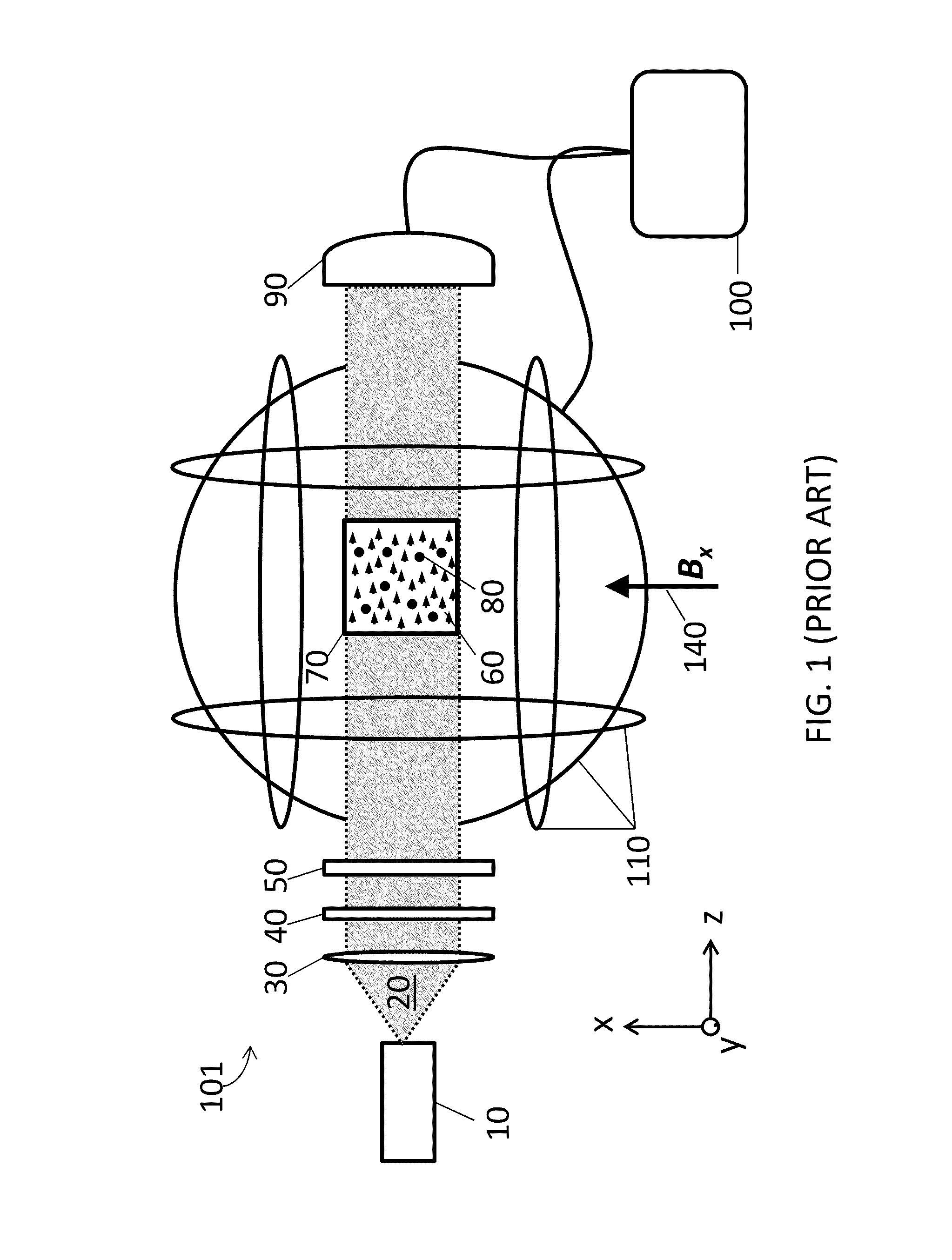
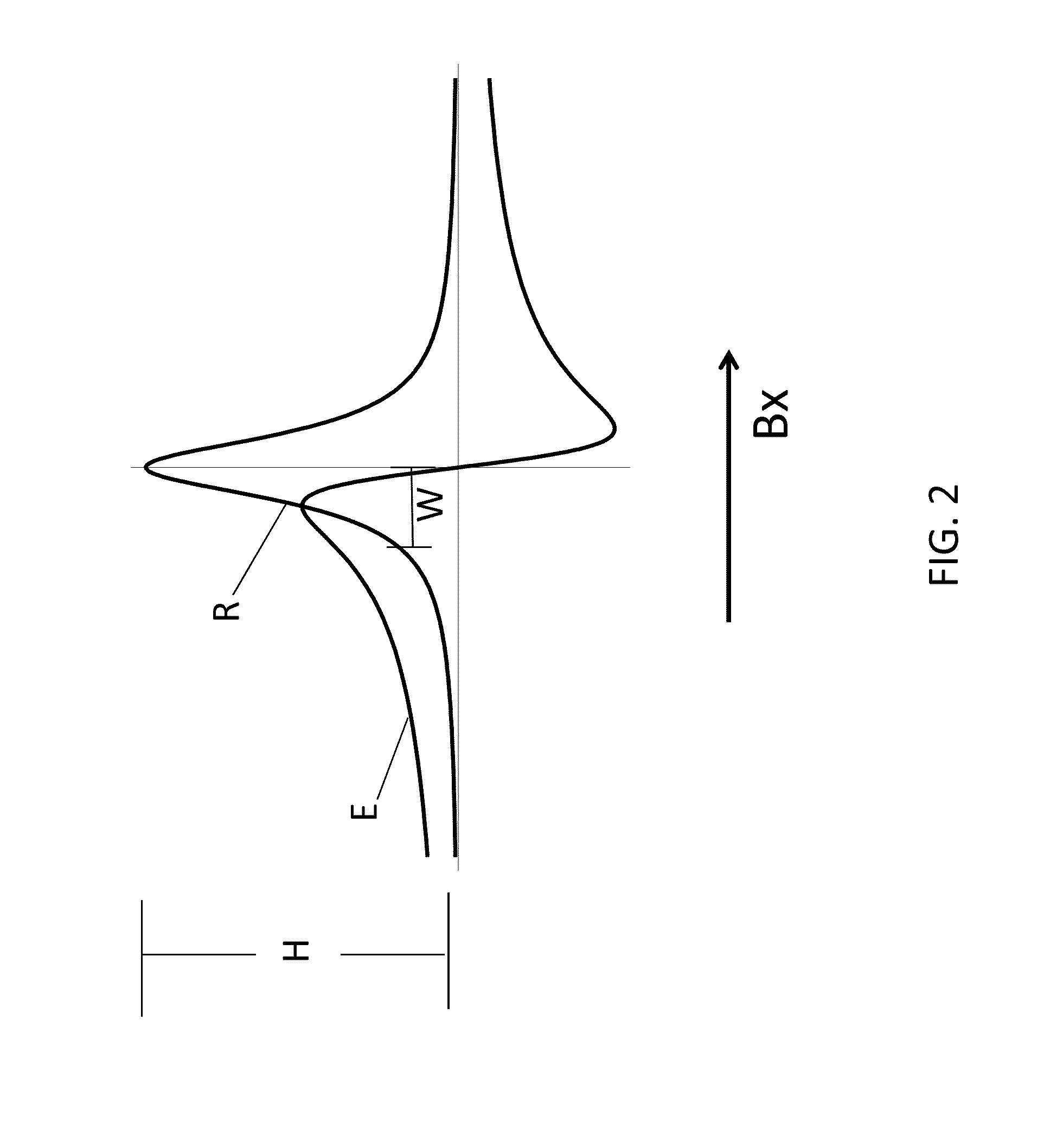
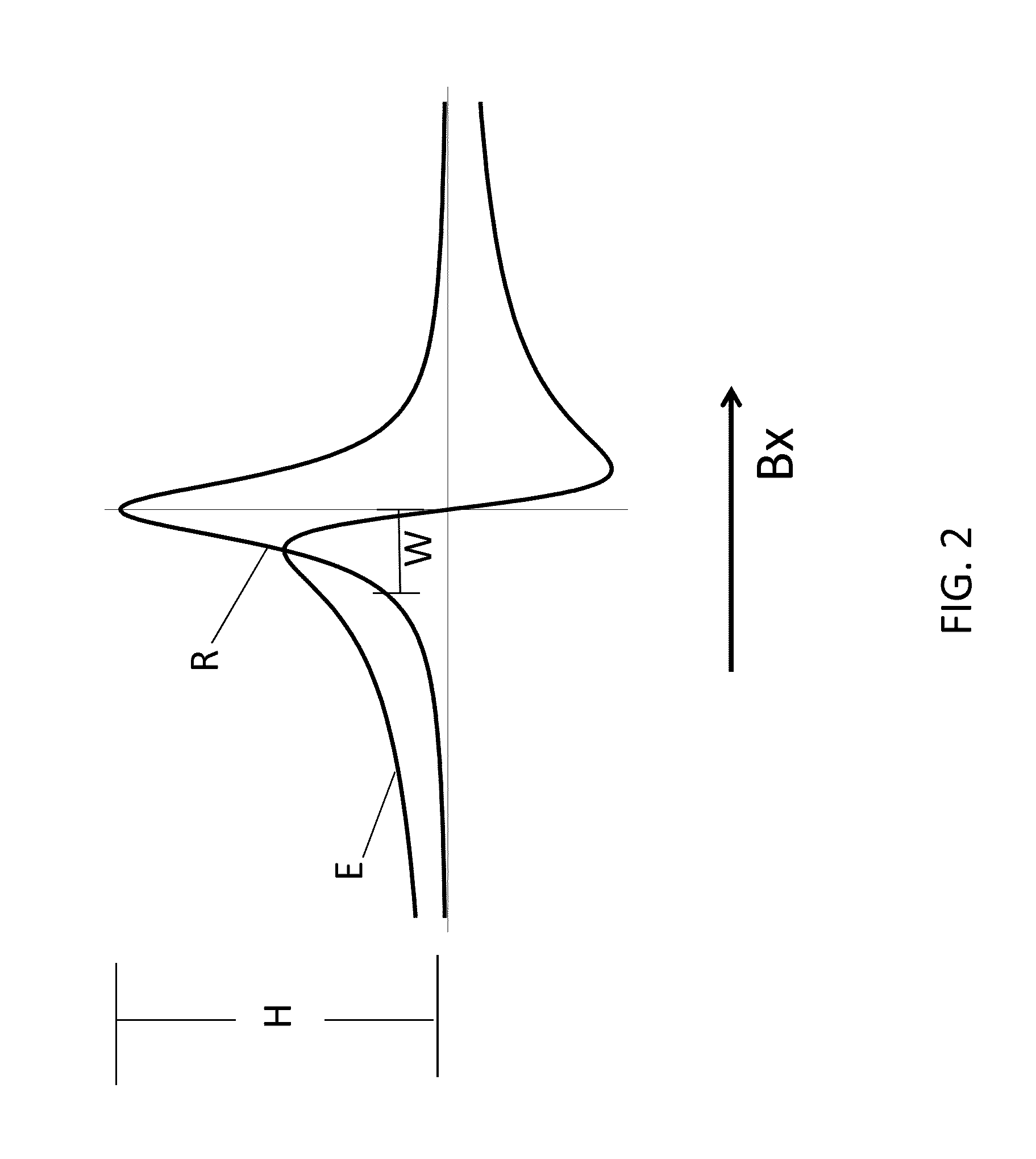
ActiveUS20160223627A1Width minimizedImprove maximizationAnalysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceResonanceBias field
A zero-field paramagnetic resonance magnetometer (ZF-PRM) system and method for quickly and efficiently finding and optimizing the zero-field (ZF) resonance is described. In this system and method a magnetic coil is used to apply a magnetic bias field in the direction of the pump beam to artificially broaden the width and maximize the strength of the ZF resonance. By making the ZF resonance easy to detect, the ZF resonance may be found quickly found without the use of additional components and complex algorithms. Once the ZF resonance is found, a compensating magnetic field can be applied to null the magnetic field in the vicinity of the vapor cell in the ZF-PRM, thereby initializing it for operation.
Owner:QUSPIN
Low Profile Lighting Fixture With Movable Heat Sink And Lighting Element Assembly
ActiveUS20170059135A1Low profileEffective maintenanceLighting support devicesElectric circuit arrangementsVertical alignmentEffect light
A low-profile, recessed light fixture with a housing, a lighting element enclosure with a heat sink, and a junction box containing a lighting driver. The base of the housing has an illumination aperture disposed therein. The heat sink acts as the top of the lighting element enclosure and is movable between an operation position and a service position. In the operation position, the heat sink is vertically aligned with the illumination aperture. In the service position, the heat sink is horizontally displaced from vertical alignment with the illumination aperture. When the heat sink is in the service position, the interior of the junction box is accessible through the illumination aperture, allowing the user to remove the lighting driver and other electrical components from the junction box for maintenance.
Owner:USAI LLC
Method for detecting zero-field resonance
ActiveUS9116201B2Width minimizedImprove maximizationAnalysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceResonanceBias field
A zero-field paramagnetic resonance magnetometer (ZF-PRM) system and method for quickly and efficiently finding and optimizing the zero-field (ZF) resonance is described. In this system and method a magnetic coil is used to apply a magnetic bias field in the direction of the pump beam to artificially broaden the width and maximize the strength of the ZF resonance. By making the ZF resonance easy to detect, the ZF resonance may be found quickly found without the use of additional components and complex algorithms. Once the ZF resonance is found, a compensating magnetic field can be applied to null the magnetic field in the vicinity of the vapor cell in the ZF-PRM, thereby initializing it for operation.
Owner:QUSPIN
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
ActiveUS20060157643A1Increase elasticityFunction providedTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSAudio power amplifier
Dynamic range of a differential pixel is enhanced by injecting, synchronously or asynchronously, a fixed compensating offset (ΔV) into a differential signal capacitor whenever magnitude of the differential signal across the capacitor exceeds a predetermined value. The number (N) of ΔV offsets made is counted. Effective differential signal capacitor voltage V(t)=Vo+N·ΔV, where Vo is capacitor voltage. Differential pixel signal / noise ratio is increased by dynamically maximizing operational amplifier gain AG for each differential pixel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
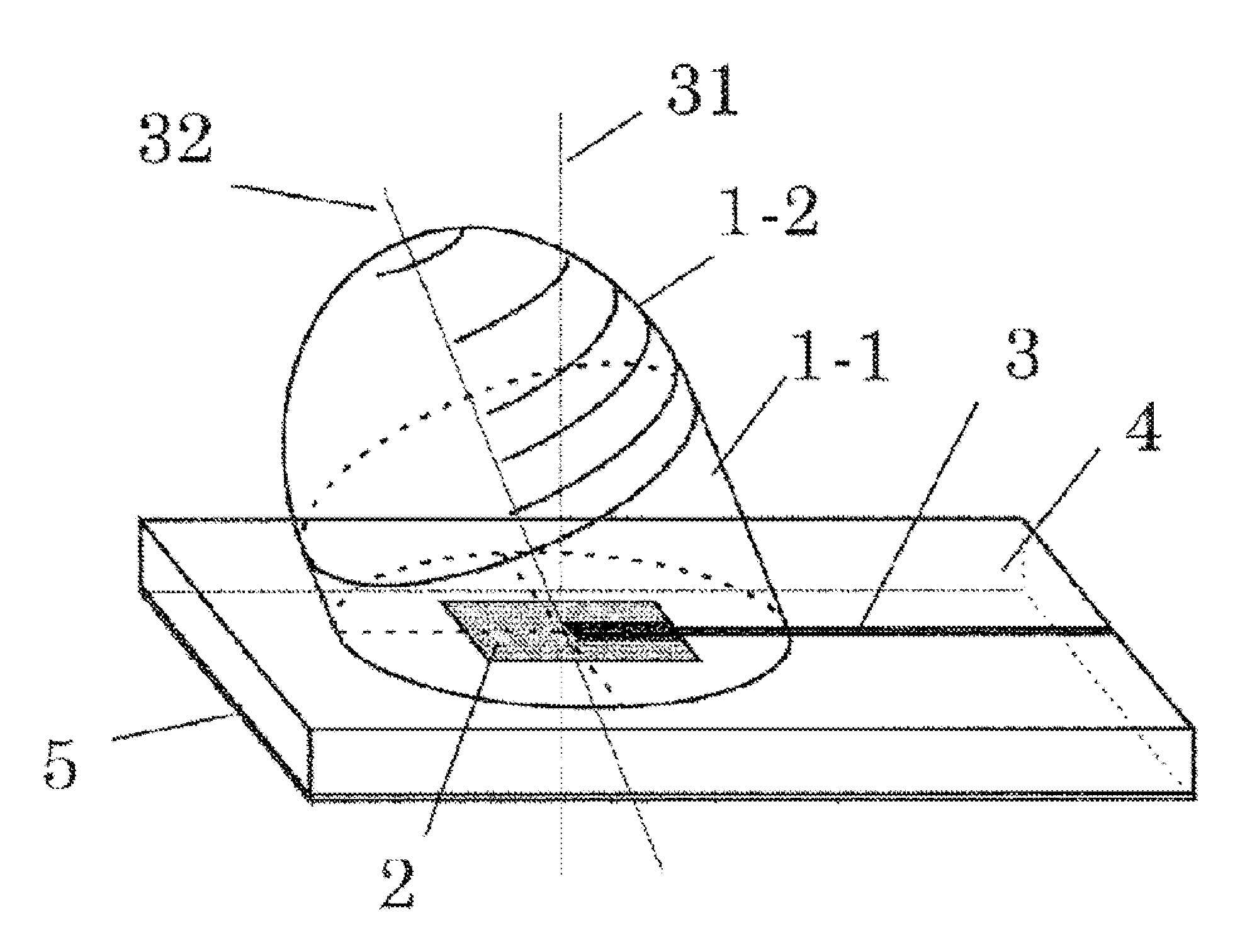
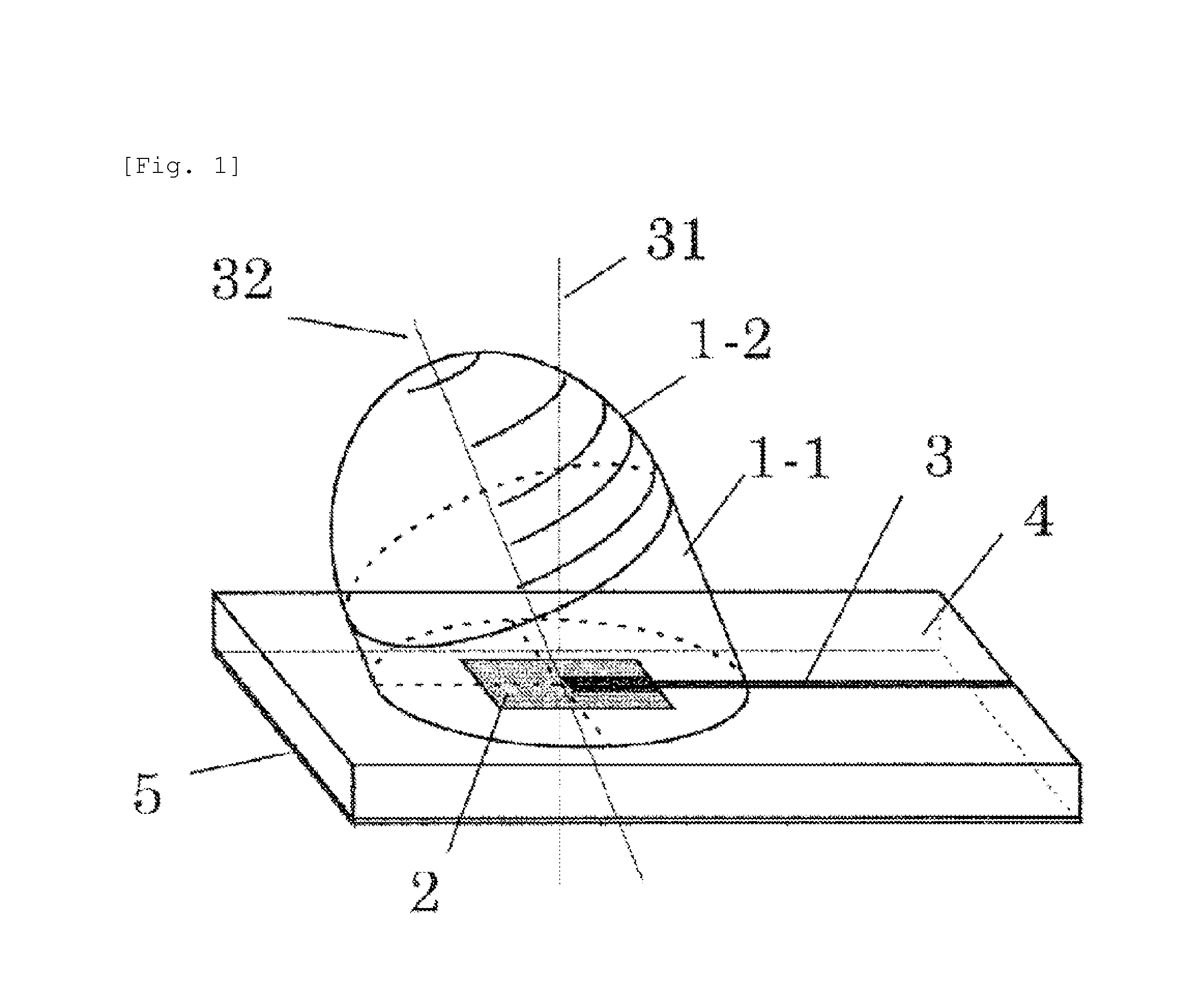
Millimeter-Wave Dielectric Lens Antenna and Speed Sensor Using Same
ActiveUS20150346334A1Improve maximizationImprove productivityRadiating elements structural formsRadiating element housingsElectricityOptical axis
A speed sensor which aligns a normal direction of one patch antenna which is disposed on a mounted board, and an optical axis of a dielectric lens uses a frame for inclining a sensor module, in order to obtain a component cos θ in a traveling direction when the speed sensor is installed on a horizontally vertical surface of an automobile or a railway car. When beams are condensed by using the one patch antenna and the cannonball-shaped dielectric lens, the dielectric lens is inclined and a bottom surface portion of the lens is cut with a plane parallel with a surface of the antenna-mounted board. The one patch antenna is configured by one patch and a GND electrode and the gain center of radiation characteristics is a normal direction of the antenna board. However, the radiation characteristics have a substantially hemisphere surface wave shape.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Deviation based antenna control algorithm for an access point
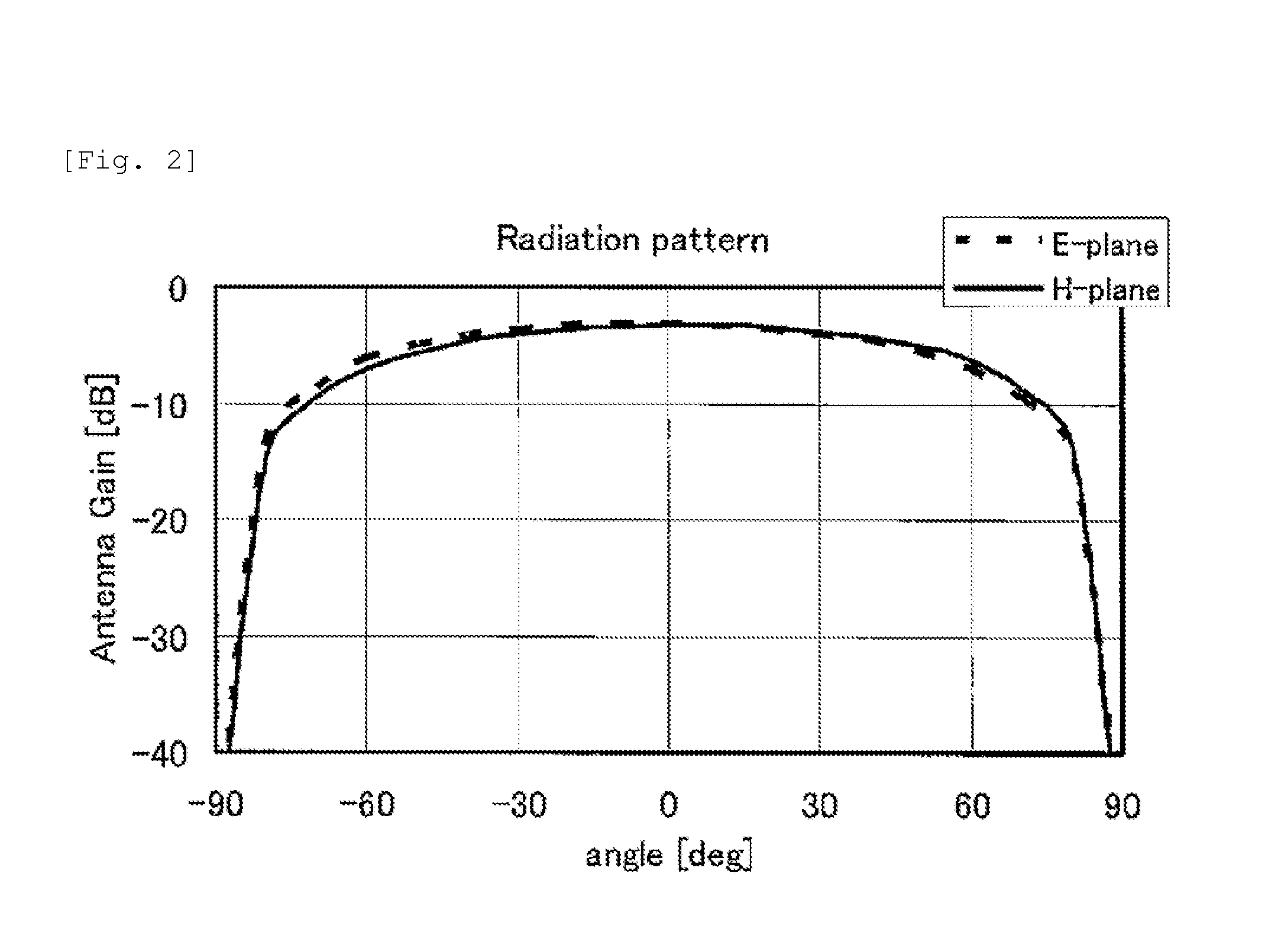
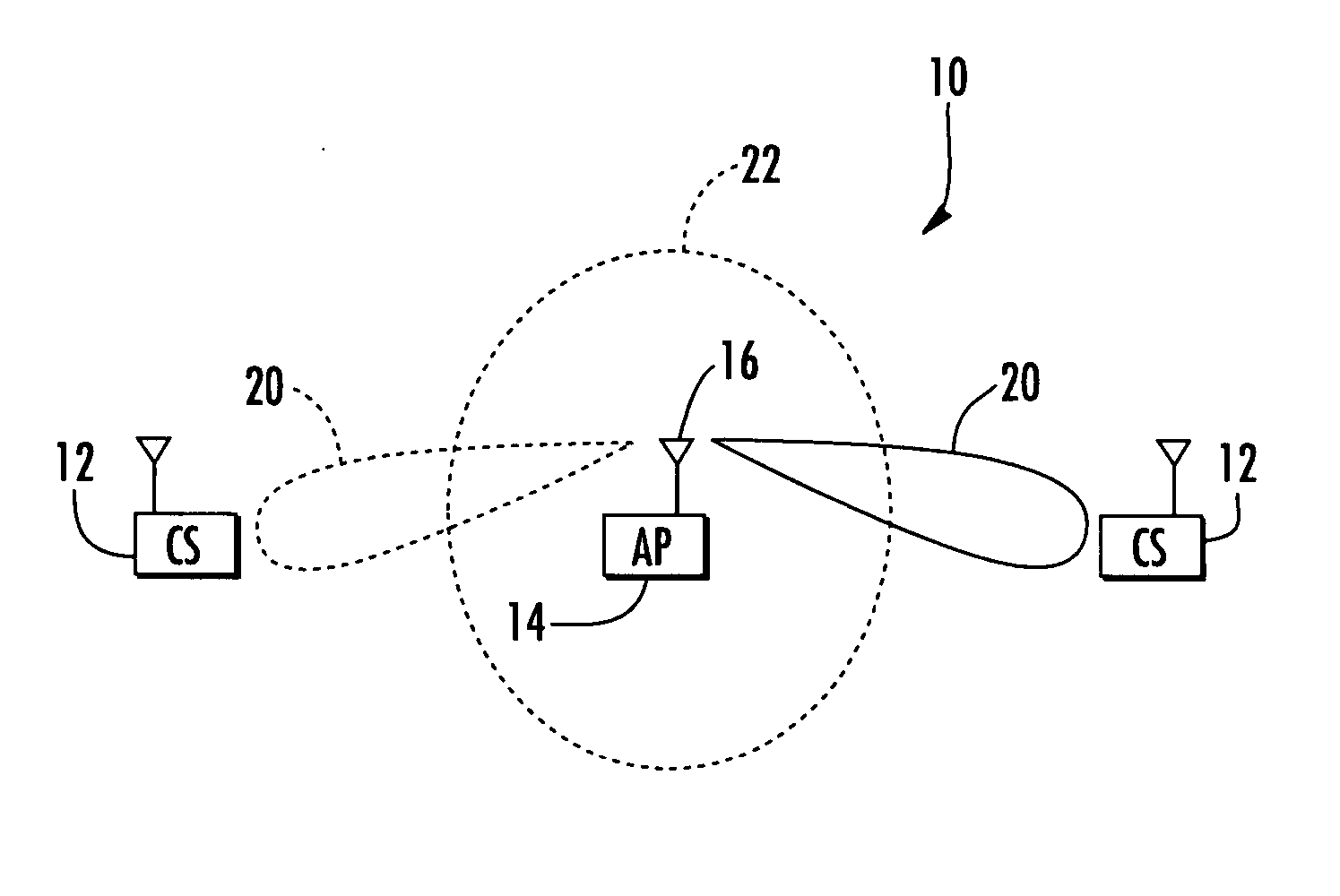
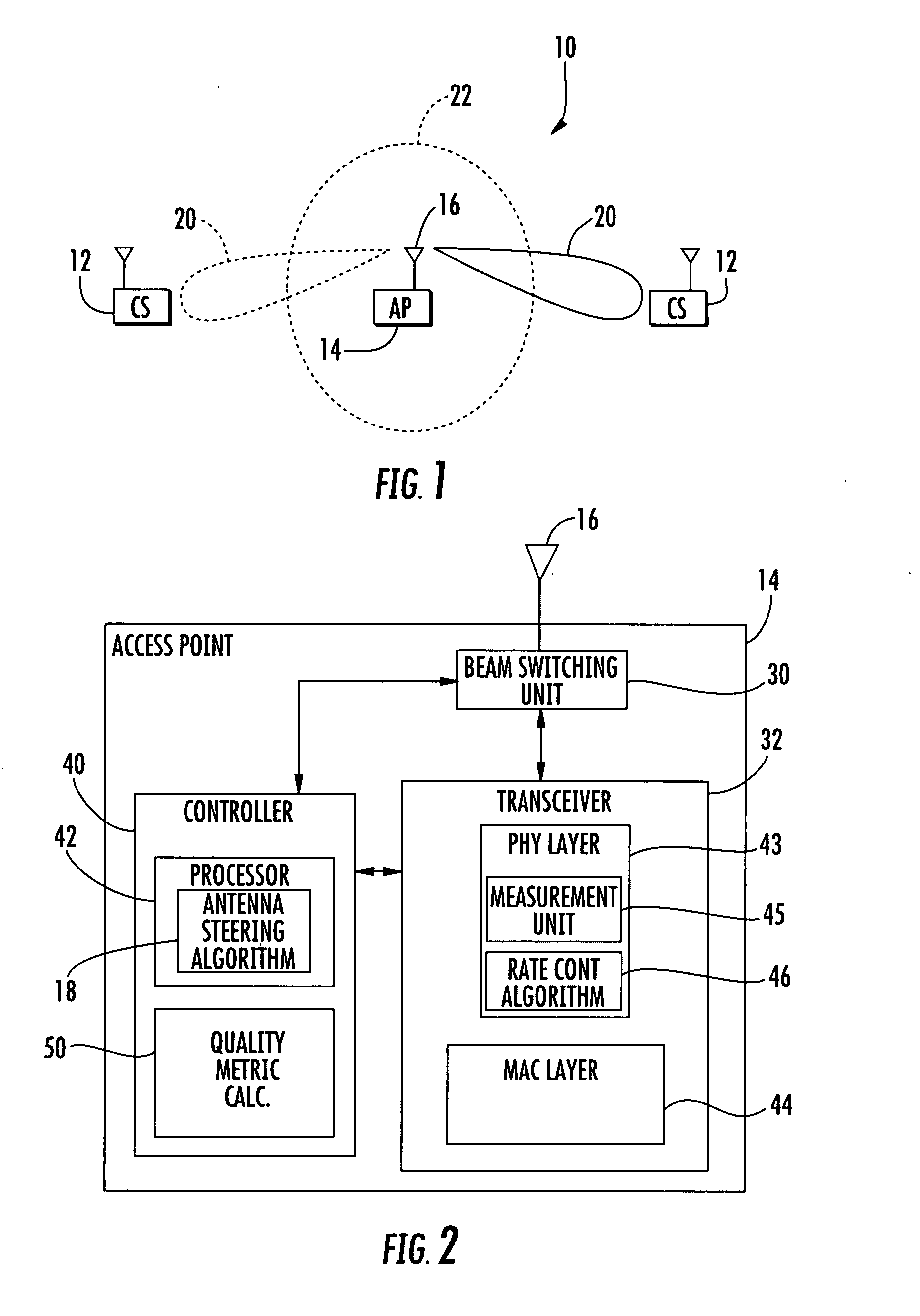
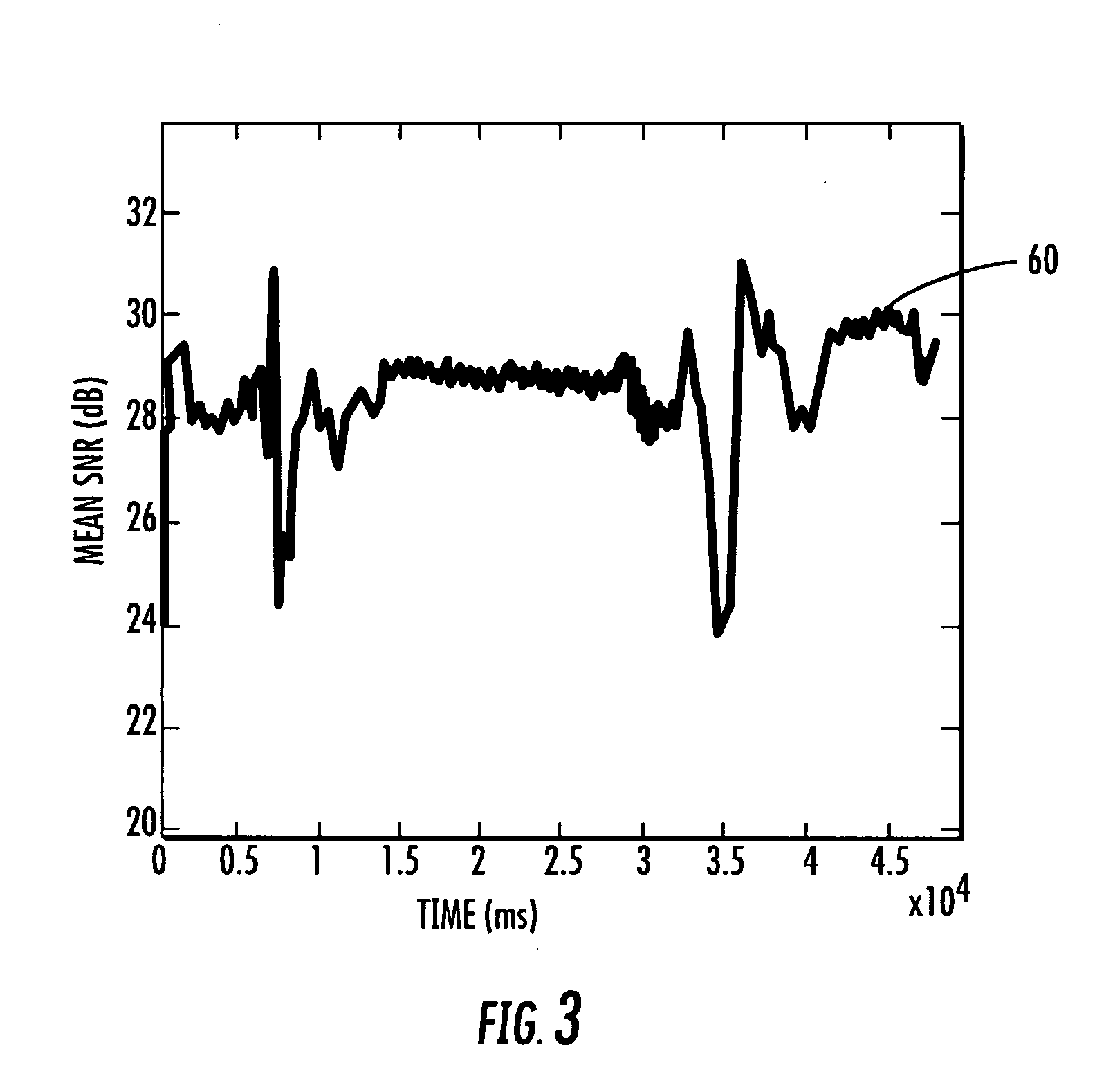
InactiveUS20070232359A1Minimal overheadQuickly to environmental changeSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Directional antenna
An access point operating in a wireless communication network includes a smart antenna for generating directional antenna beams. A method for operating the access point includes communicating with a client station using a selected directional antenna beam, with the client station initially being in a stationary position. Signal to noise ratios of signals received from the client station within a time interval are measured. At least one variation metric of a mean of the measured signal to noise ratios within the time interval is determined. This at least one determined variation metric is compared to a threshold for determining if the client station is moving.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
InactiveUS20070158533A1Increase elasticityFunction providedTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSCapacitance
Dynamic range of a differential pixel is enhanced by injecting, synchronously or asynchronously, a compensating offset (ΔCOMP) into a differential signal capacitor whenever magnitude of the differential signal across the capacitor exceeds a predetermined value. Positive and negative magnitudes of ΔCOMP need not be equal. The number (N) of ΔCOMP offsets made is counted. Effective differential signal capacitor voltage V(t)=Vo±N·ΔCOMP, where Vo is capacitor voltage. In other embodiments magnitude of ΔCOMP in a sequence of compensations can differ, and the sum total of compensations in recorded. Differential pixel signal / noise ratio is increased by dynamically maximizing operational amplifier gain AG for each differential pixel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
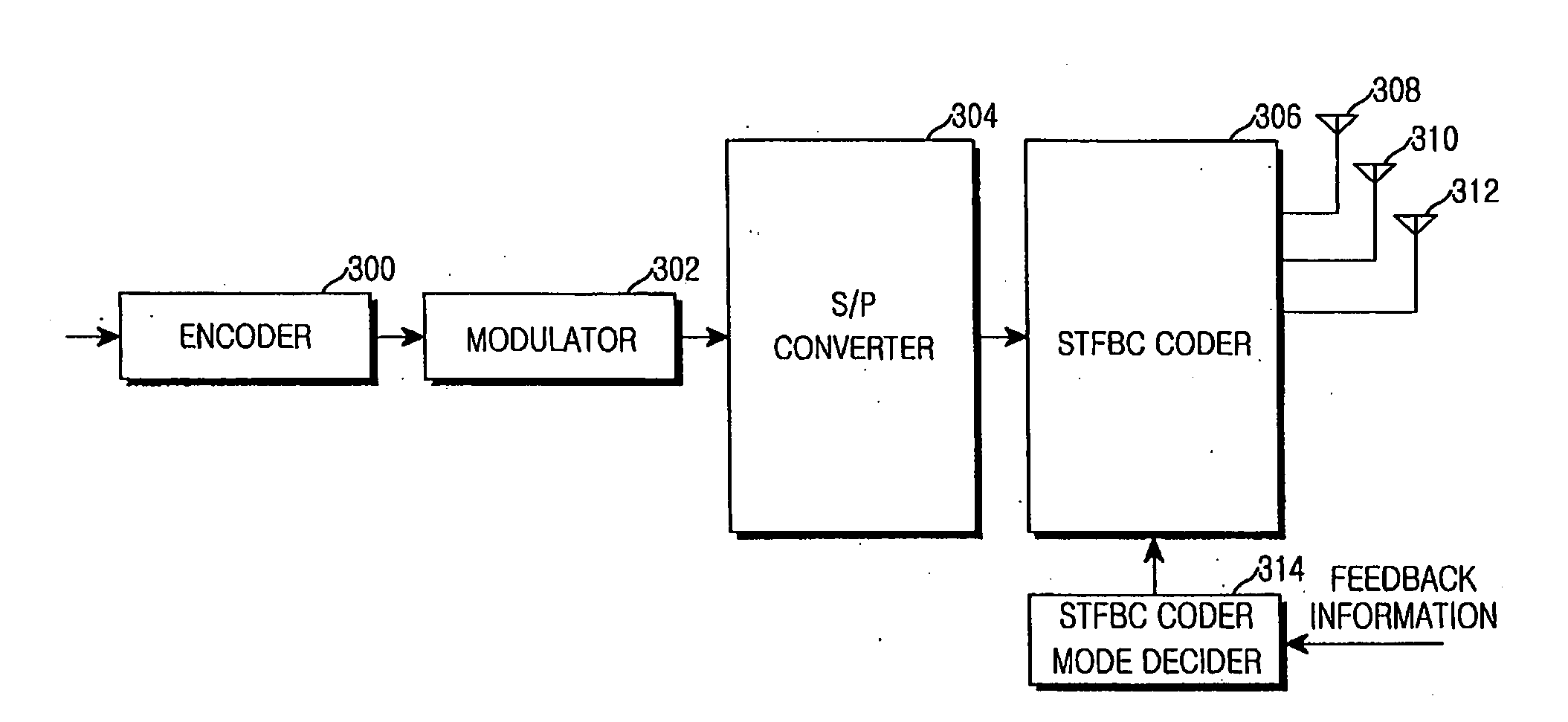
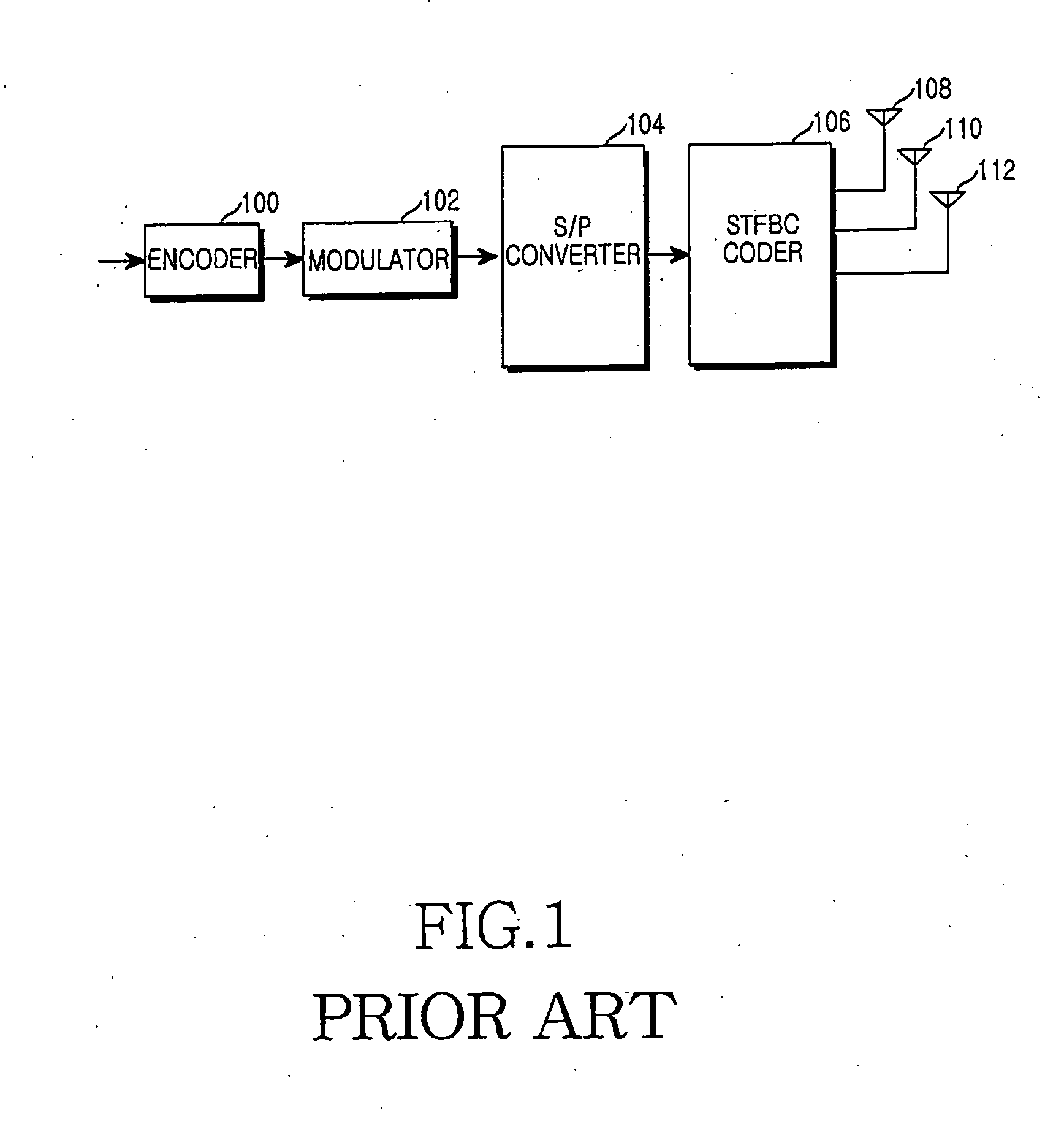
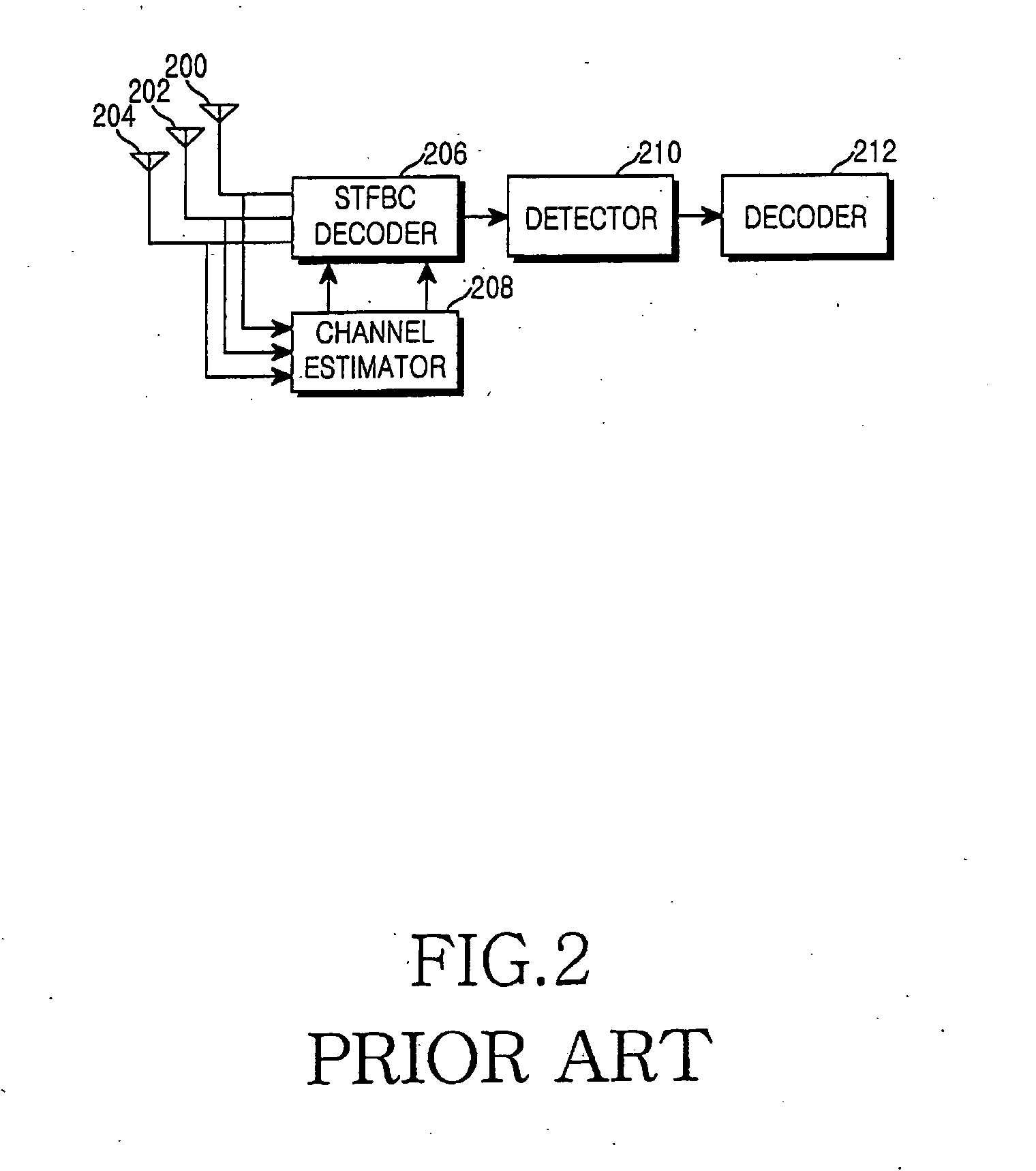
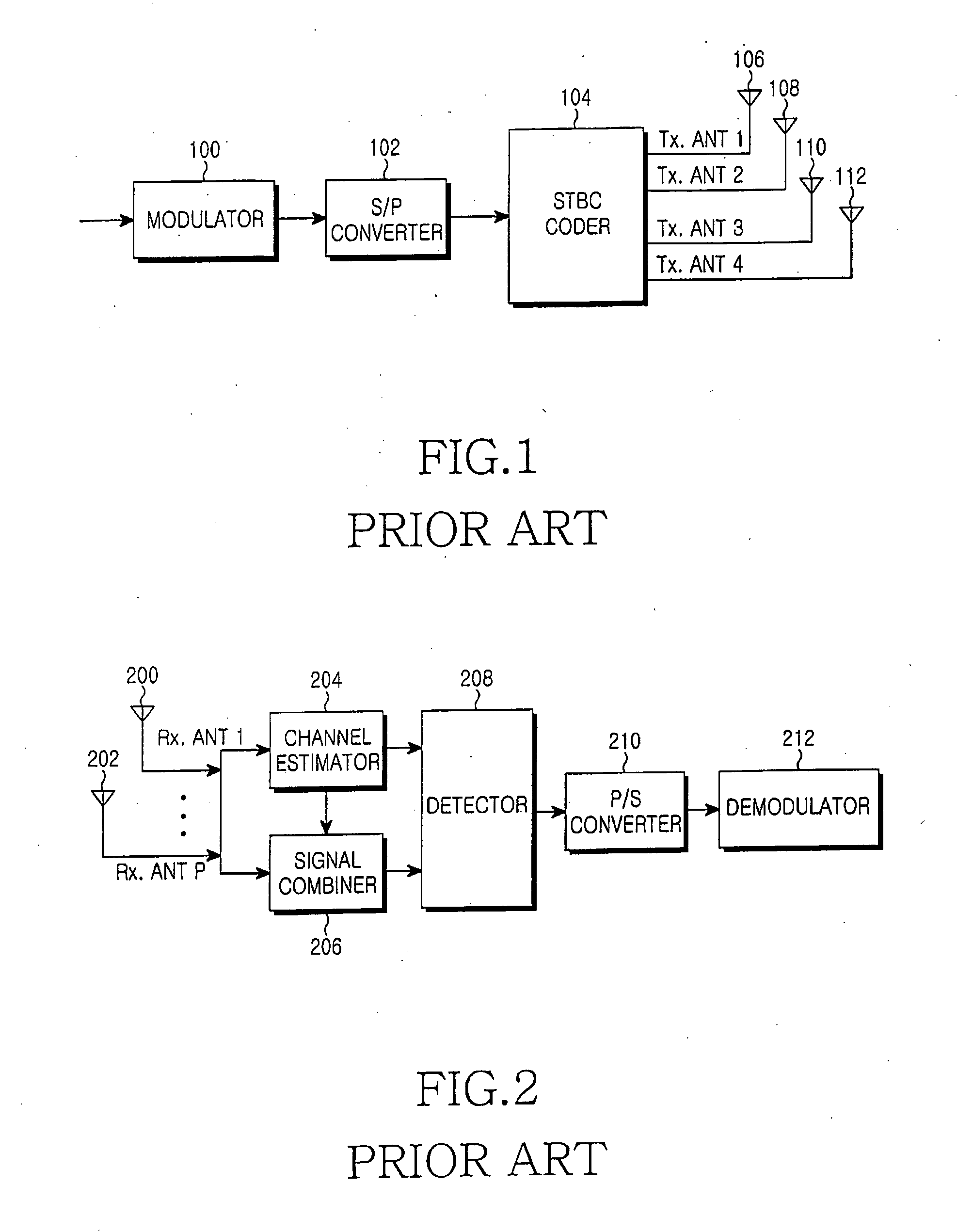
Apparatus and method for space-time-frequency block coding
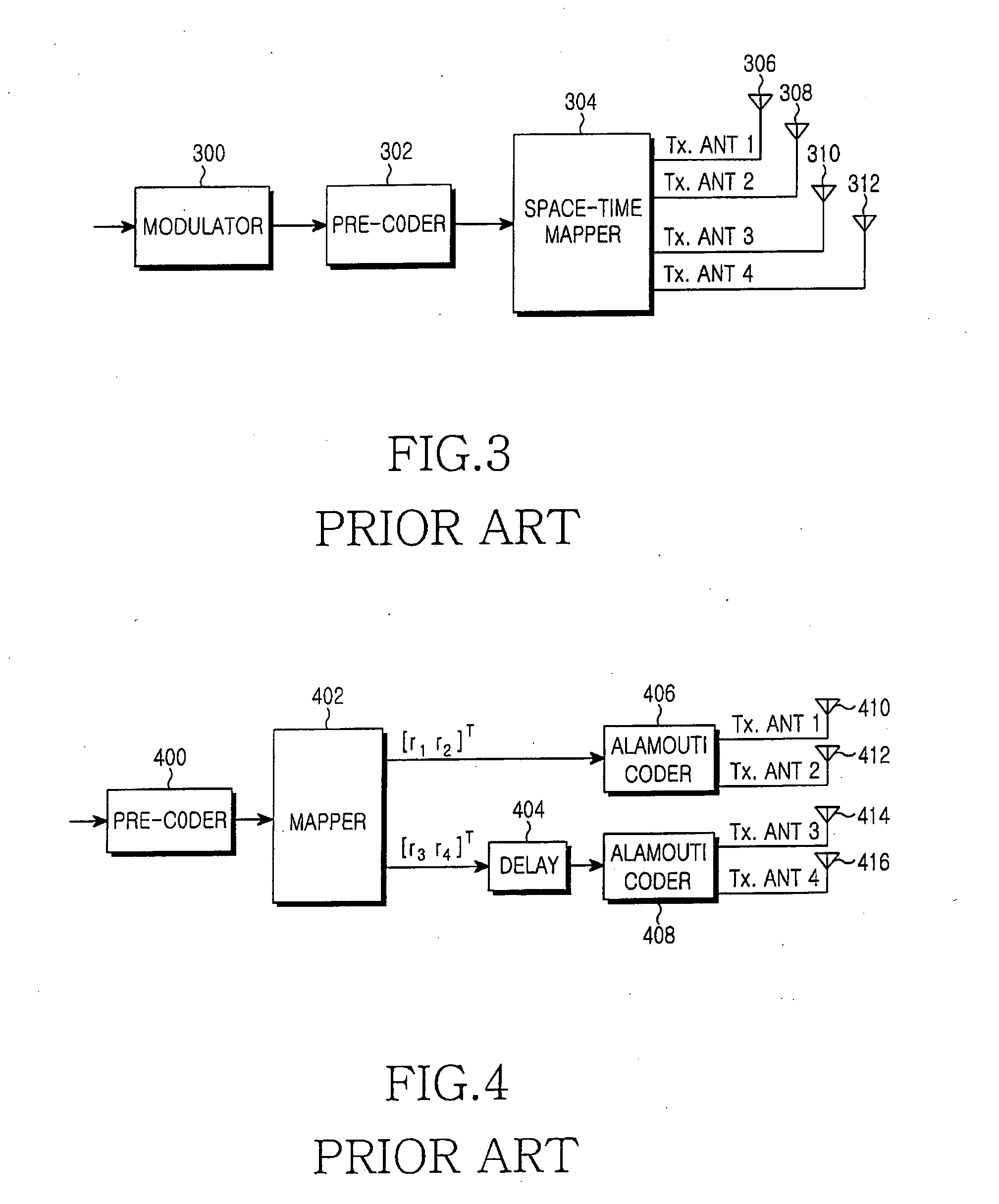
InactiveUS20060093066A1Improve performanceImprove maximizationSpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationSpace time frequencyTransfer mode
A transmitter for maximizing coding gain by transmitting an input symbol sequence through a plurality of transmit antennas method according to feedback CQIs from a receiver in a 3 Tx-rate 2 communication system. In the transmitter, an S / P converter converts serial modulated data to parallel modulated data. A coder mode decider determines a transmission mode based on the channel quality indicator of each transmit antenna fed back from a receiver. A coder transmits the parallel modulated data through the three transmit antennas according to the determined transmission mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
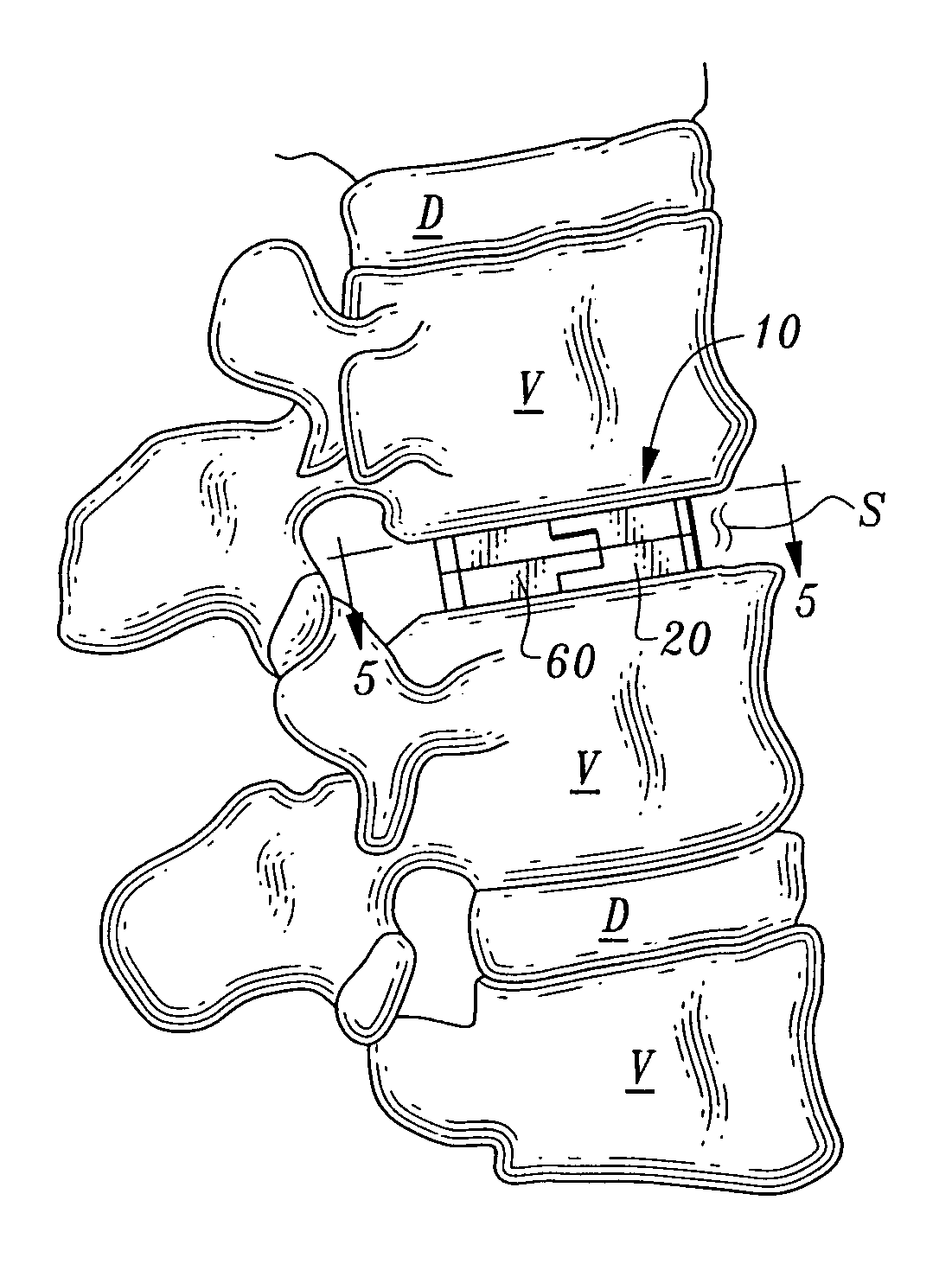
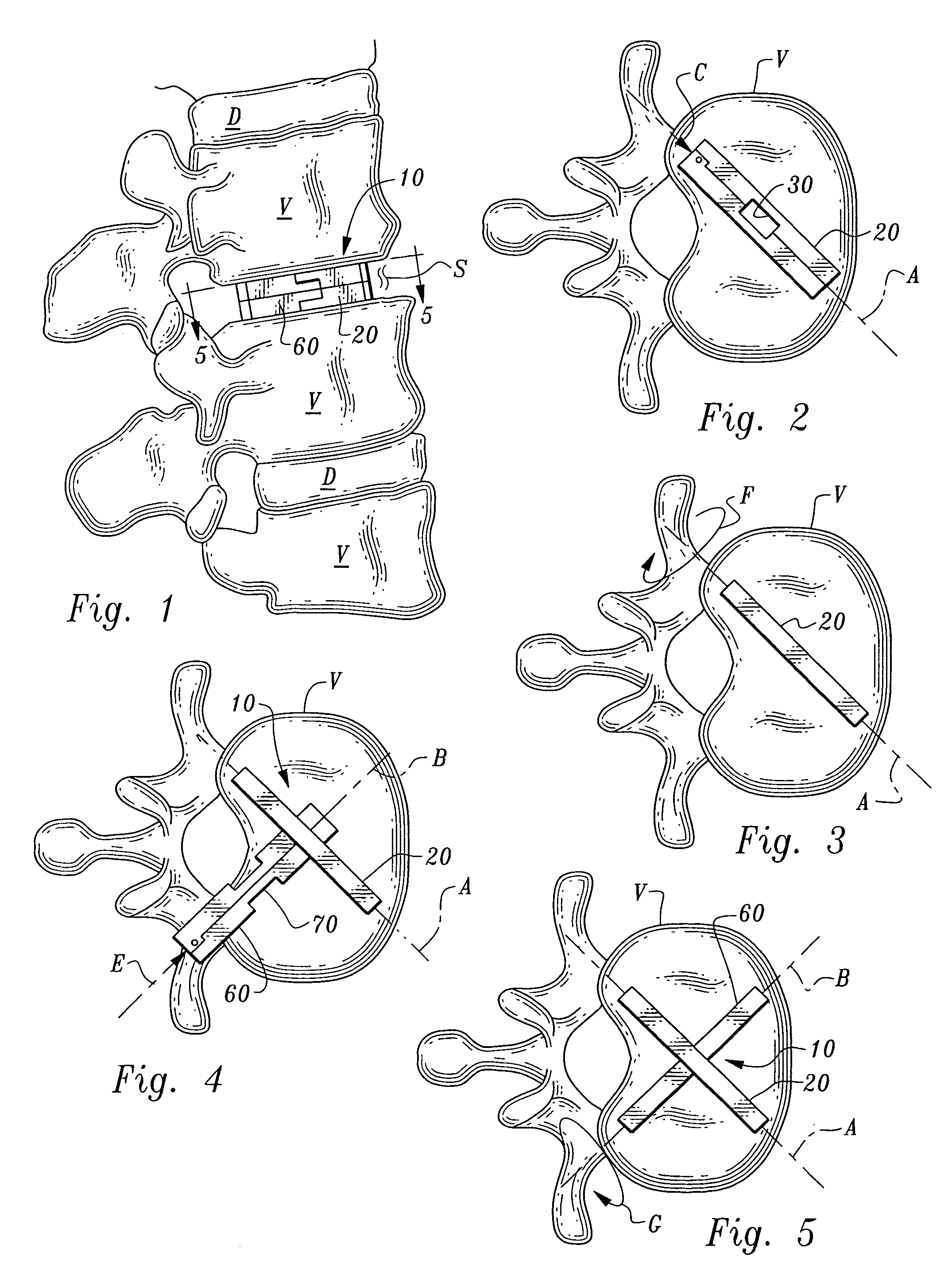
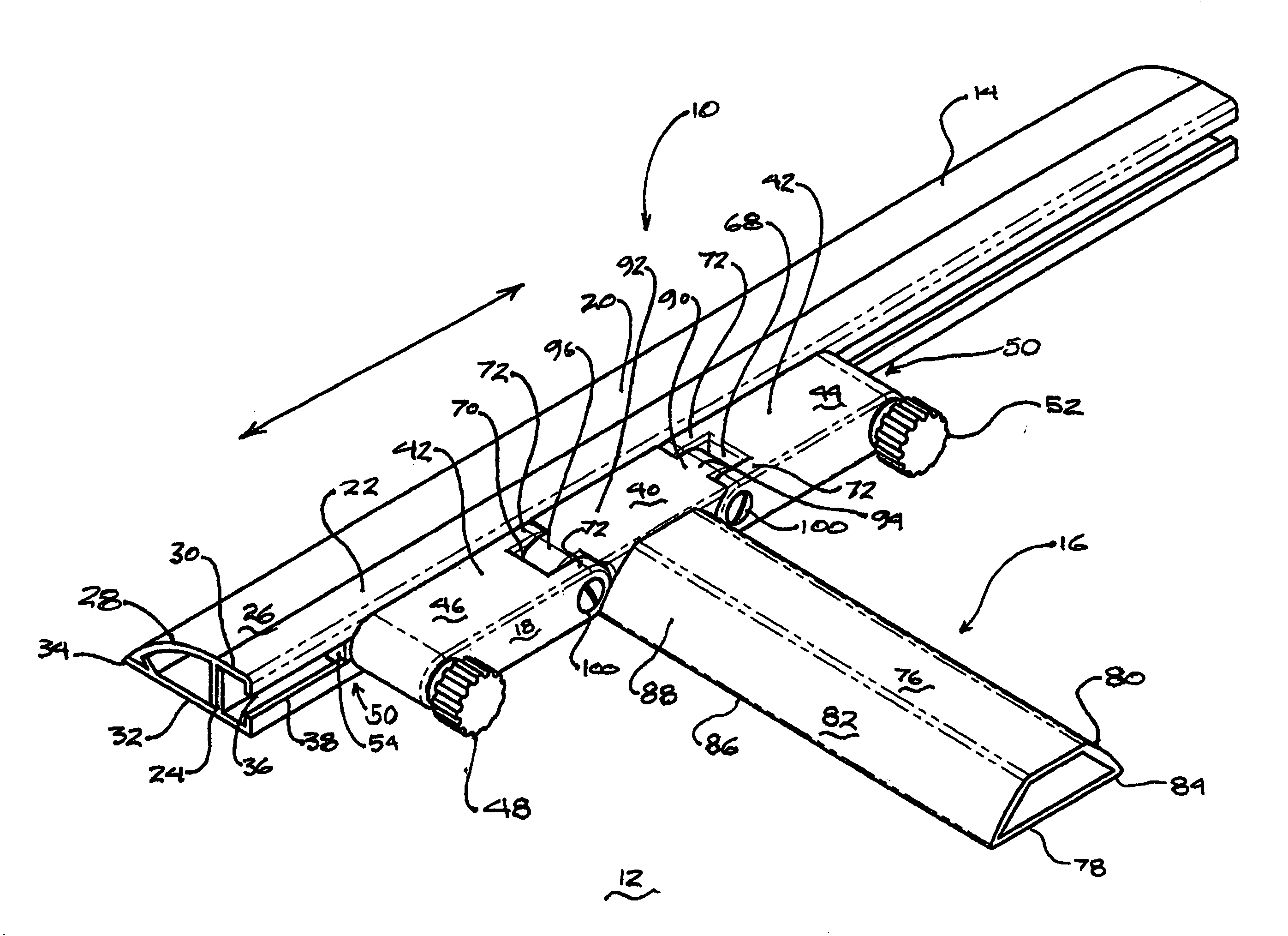
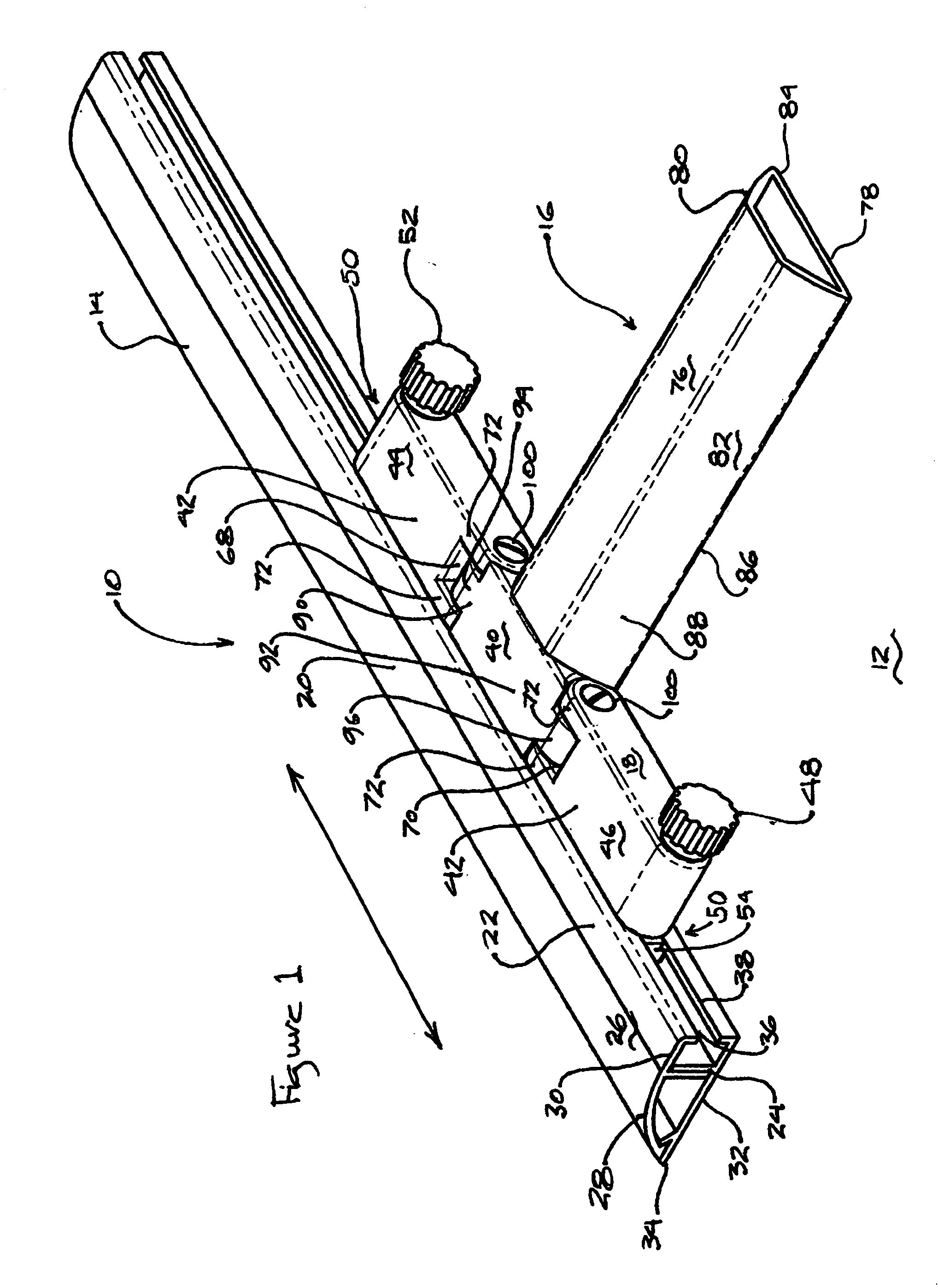
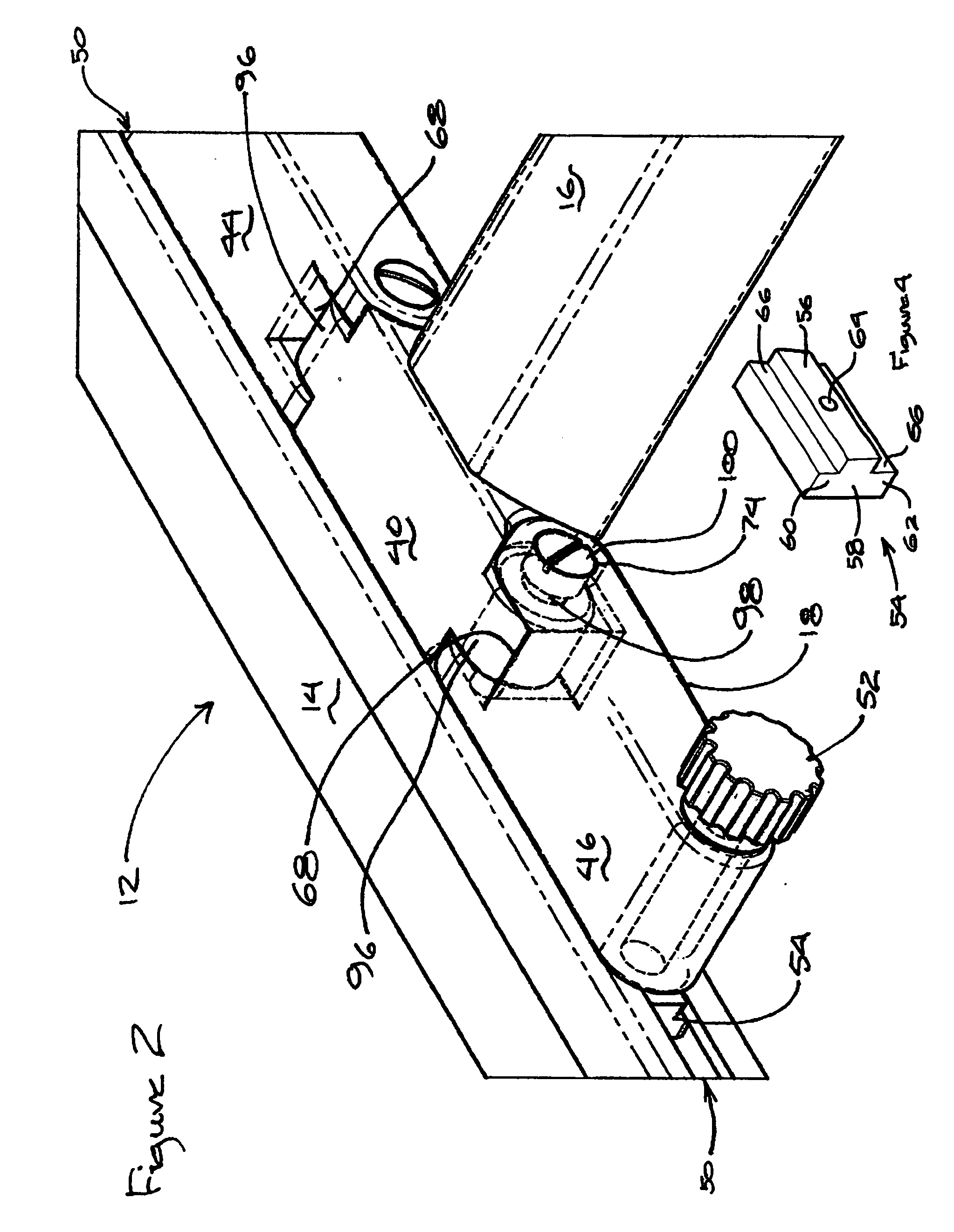
Intervertebral space implant for use in spinal fusion procedures
InactiveUS7621951B2Maximize sizeMaximum amount of flexibilitySurgeryJoint implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral space
An implant assembly is provided for surgical implantation into an intervertebral space, such as for stabilization of vertebrae adjacent the intervertebral space during a spinal fusion procedure. The implant assembly includes a primary segment separate from a secondary segment. These segments are elongate and of sufficiently small cross-section that they can be implanted posteriorly in a minimally invasive manner. The primary segment preferably includes a tunnel and the secondary segment preferably includes a neck with the tunnel and neck sized complementally so that the segments stabilize each other where they intersect with the neck within the tunnel. The entire implant assembly is thus provided which both widens and supports the intervertebral space and is sufficiently rigid to provide adequate support for the intervertebral space as the vertebrae are fusing together.
Owner:DEPUY ACROMED INC +1
Variable vane arm/unison ring attachment system
InactiveUS6984104B2Increase the carrying areaWear minimizationEngine manufactureWind motor controlMechanical engineeringEngineering
An attachment system for use with a variable incidence vane is disclosed. The attachment system includes a vane arm for joining a unison ring to a vane spindle. The vane arm has an arm portion and a bushing connected to the arm portion. The attachment system further has a pin for joining the vane arm to the unison ring. The pin fits within an interior bore in the bushing and is joined to the unison ring by a dual swage.
Owner:RTX CORP
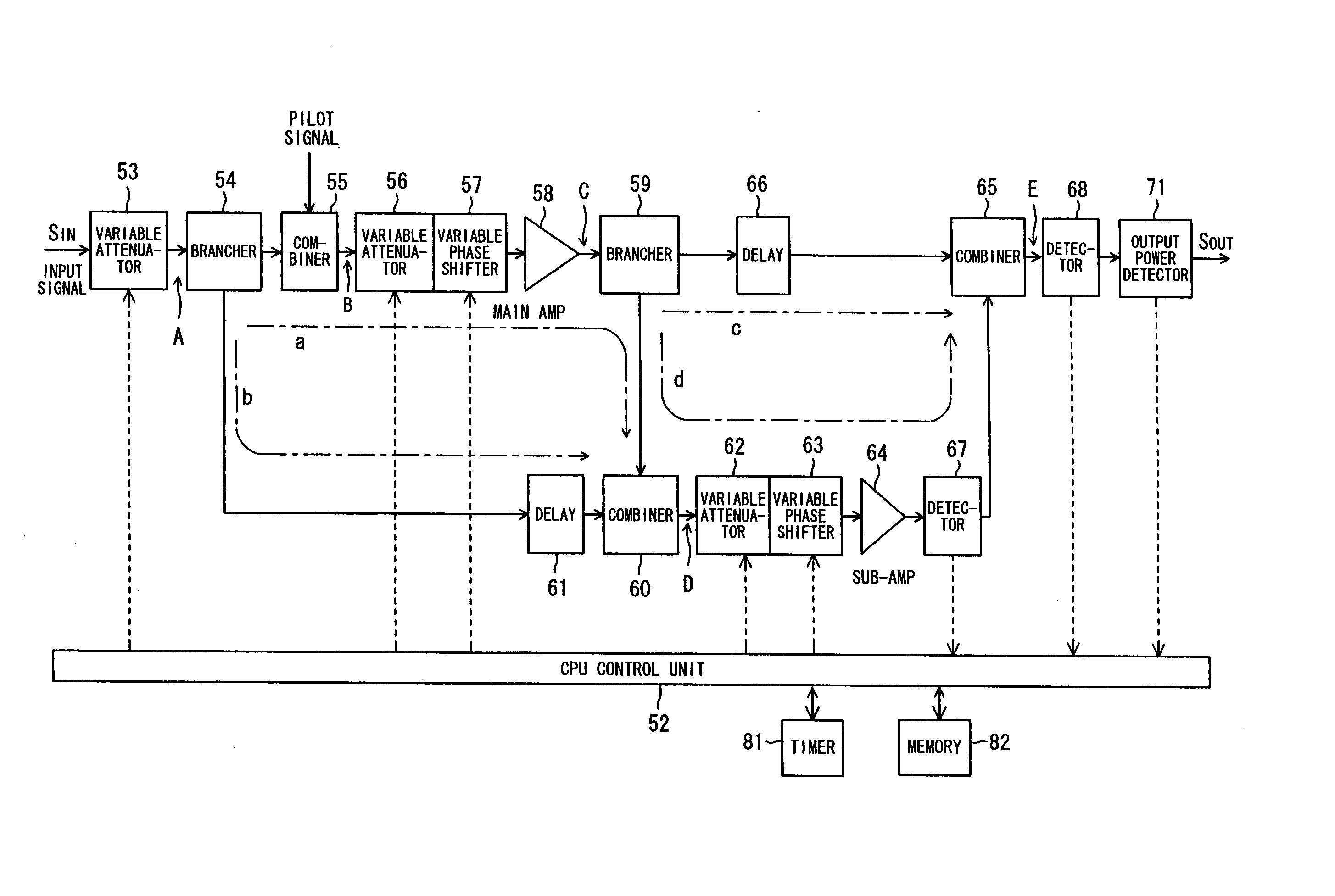
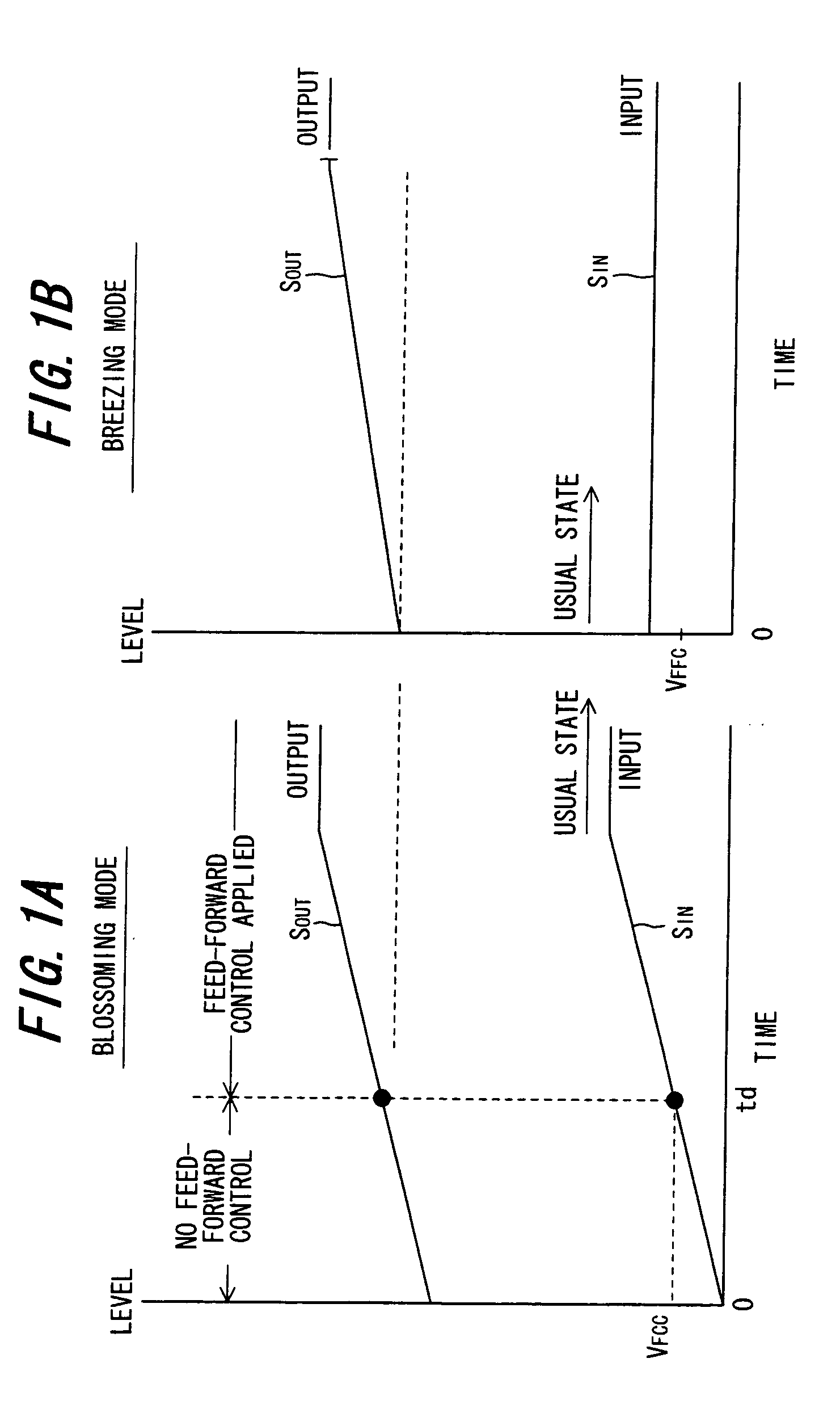
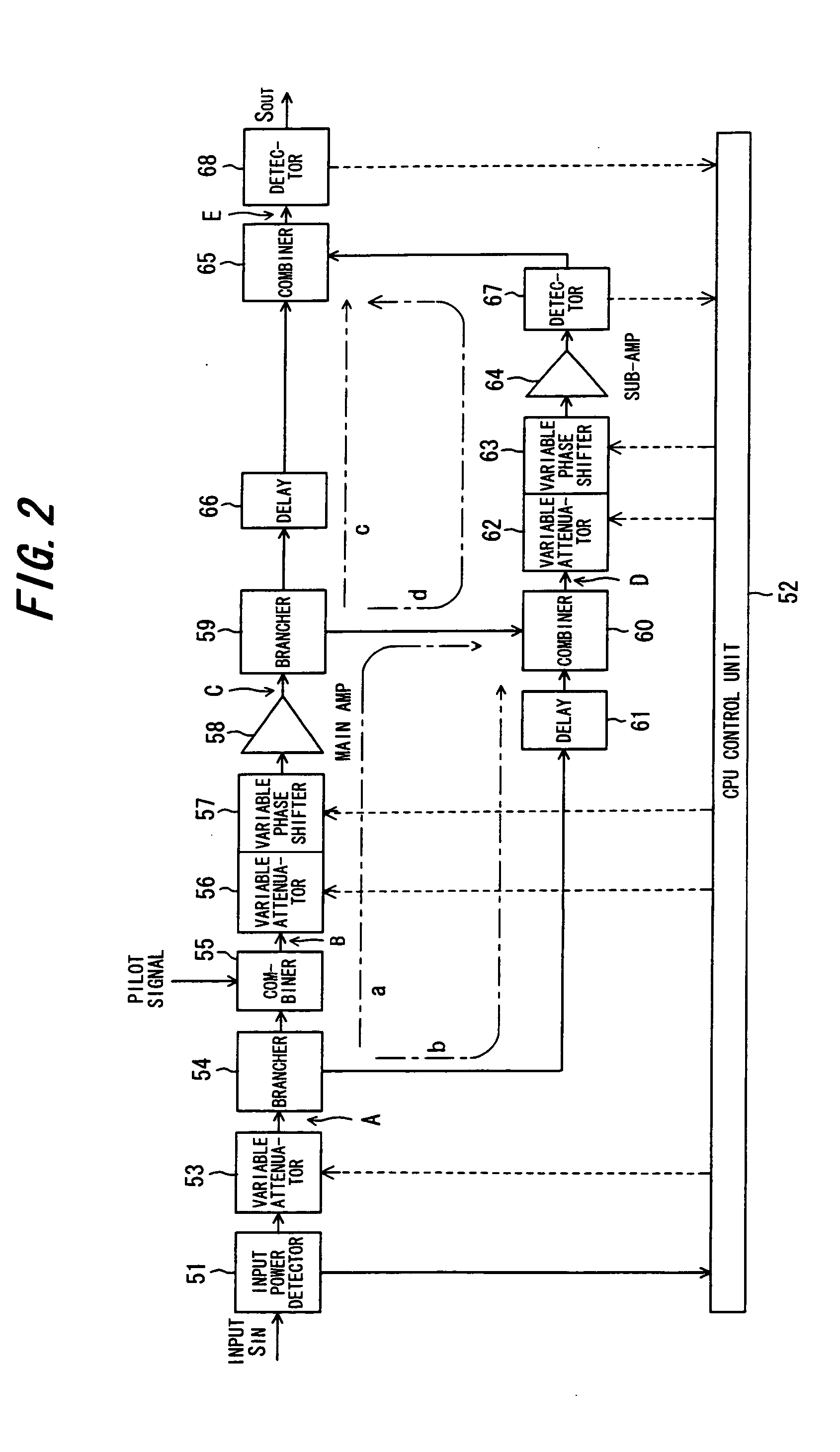
Transmission power amplifier unit
InactiveUS20060040625A1Increase transmit powerDistortion can be for quicklyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower managementNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
A transmission power amplifier unit of a base-station apparatus for compensating for non-linear distortion of a transmission power amplifier by feed-forward control is provided with a gain varying unit for varying gain of the transmission power amplifier unit. At start-up of the transmission power amplifier unit, a controller determines whether the base-station apparatus is in a blossoming mode or breathing mode, maximizes gain of the transmission power amplifier unit by controlling the gain varying unit if the mode is the blossoming mode and increases the gain gradually in proportion to the passage of time if the mode is the breathing mode.
Owner:SAITO YUTAKA +1
Lipid Preparation for Enhancing Mineral Absorption
ActiveUS20080058415A1Promote absorptionEnhancement of formationBiocideSpread compositionsEnzymatic synthesisBone density
Disclosed is a dietary ingredient comprising at least one edible lipid which does not inhibit mineral absorption, enhances mineral absorption and intake, particularly a chemically or enzymatically synthesized synthetic oil, particularly glyceride-based lipid with high levels of mono- or polyunsaturated fatty acids at positions sn-1 and sn-3 of the glycerol backbone, vegetable- and plant-derived oil, such as flax and canola oils, short and medium chains lipid, preferably MCT and an oil mimicking the triglyceride composition of human mother's milk fat and its various uses.The dietary ingredient is particularly intended for use in enhancing calcium absorption and in the prevention and / or treatment of disorders associated with depletion of bone calcium and bone density, prevention and treatment of osteoporosis, for the enhancement of bone formation and bone mass maximization and for the enhancement of bone formation in infants and young children.
Owner:ENZYMOTEC
Method for detecting zero-field resonance
ActiveUS20150212168A1Minimize widthHeight be maximizeAnalysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceZero fieldBias field
A zero-field paramagnetic resonance magnetometer (ZF-PRM) system and method for quickly and efficiently finding and optimizing the zero-field (ZF) resonance is described. In this system and method a magnetic coil is used to apply a magnetic bias field in the direction of the pump beam to artificially broaden the width and maximize the strength of the ZF resonance. By making the ZF resonance easy to detect, the ZF resonance may be found quickly found without the use of additional components and complex algorithms. Once the ZF resonance is found, a compensating magnetic field can be applied to null the magnetic field in the vicinity of the vapor cell in the ZF-PRM, thereby initializing it for operation.
Owner:QUSPIN
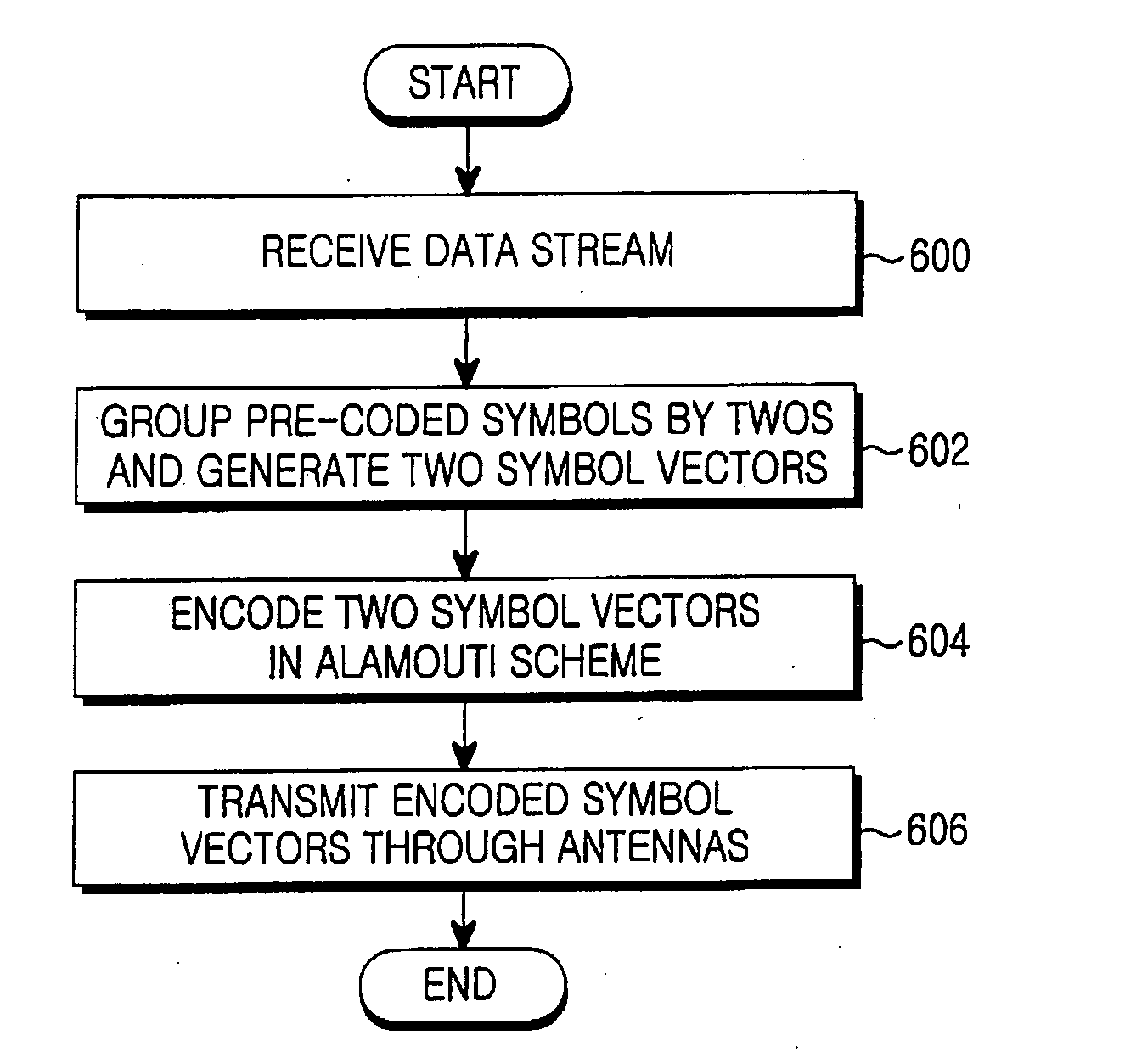
Apparatus and method for space-time block coding for increasing coding gain
InactiveUS20060039495A1High gainImprove maximizationSpatial transmit diversitySecret communicationPrecodingComputer science
A space-time block coding apparatus and method in a transmitter with four transmit antennas in a system using a space-time block coding scheme, a pre-coder pre-codes an input symbol sequence by multiplying the input symbol sequence by ejθ, θ being a phase rotation angle, in case of QPSK in range of 0≦θ≦90, 23.5≦θ≦24.5, or 65.5≦θ≦66.5, in case of 16QAM in range of 0≦θ≦90, 15.5≦θ≦17.5 or 72.5≦θ≦74.5, the pre-coded symbol sequence being reconstructed to have real and imaginary parts. A mapper generates symbol vectors by recombining the real and imaginary parts of the pre-coded symbol sequence in an interleaving scheme. A plurality of Alamouti coders encodes the symbol vectors in an Alamouti scheme and transmits the encoded symbol vectors through corresponding transmit antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
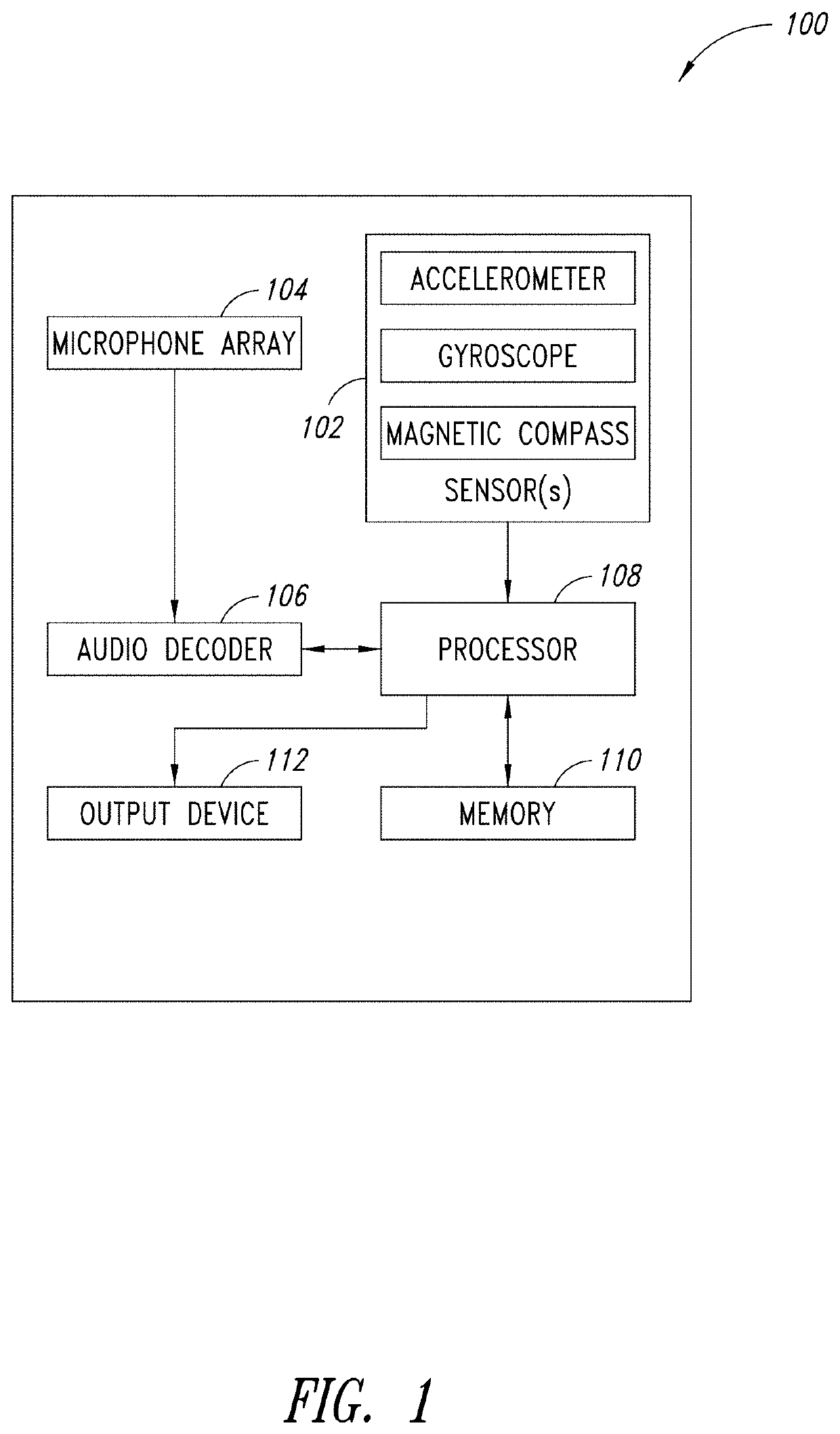
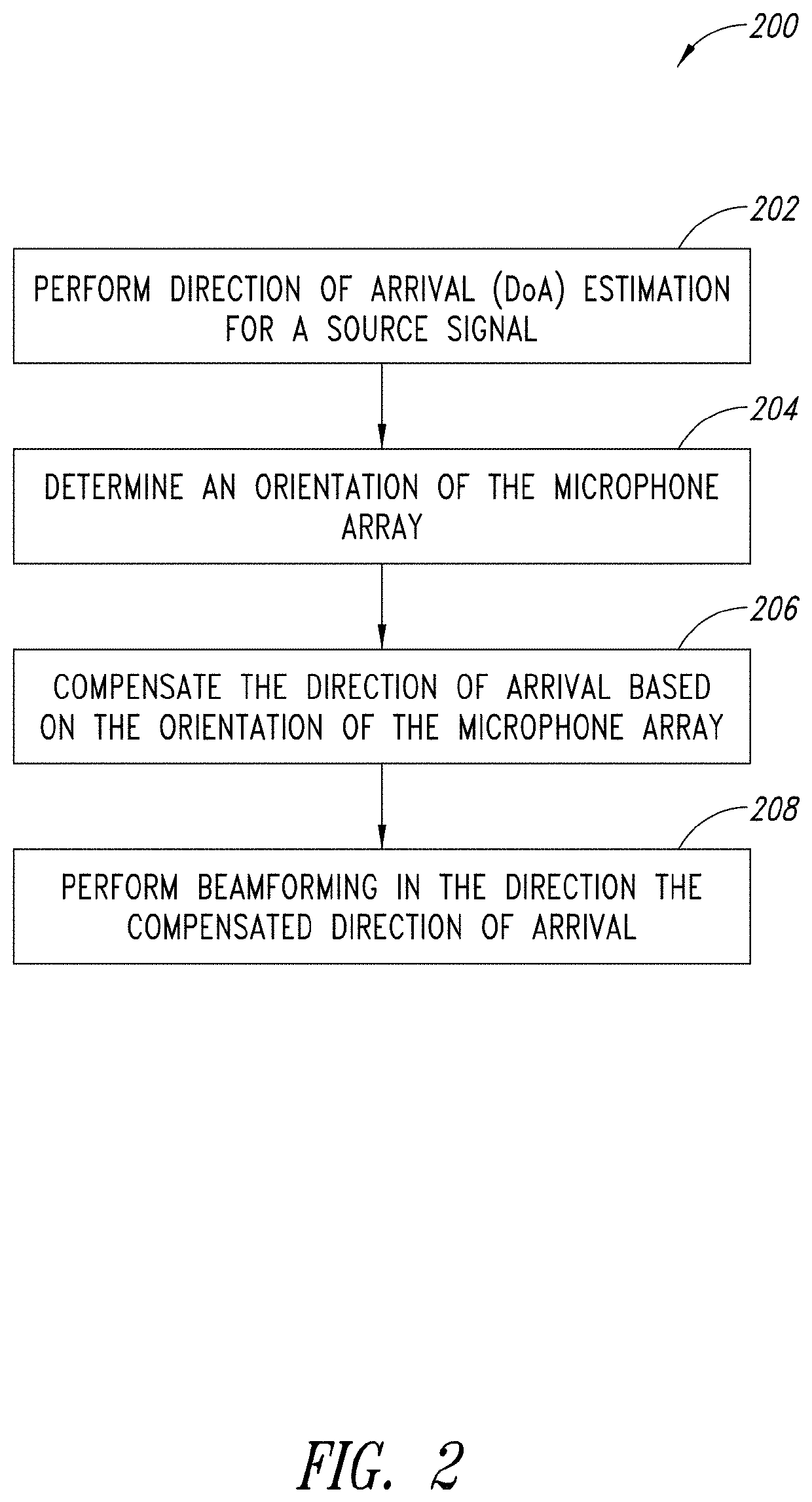
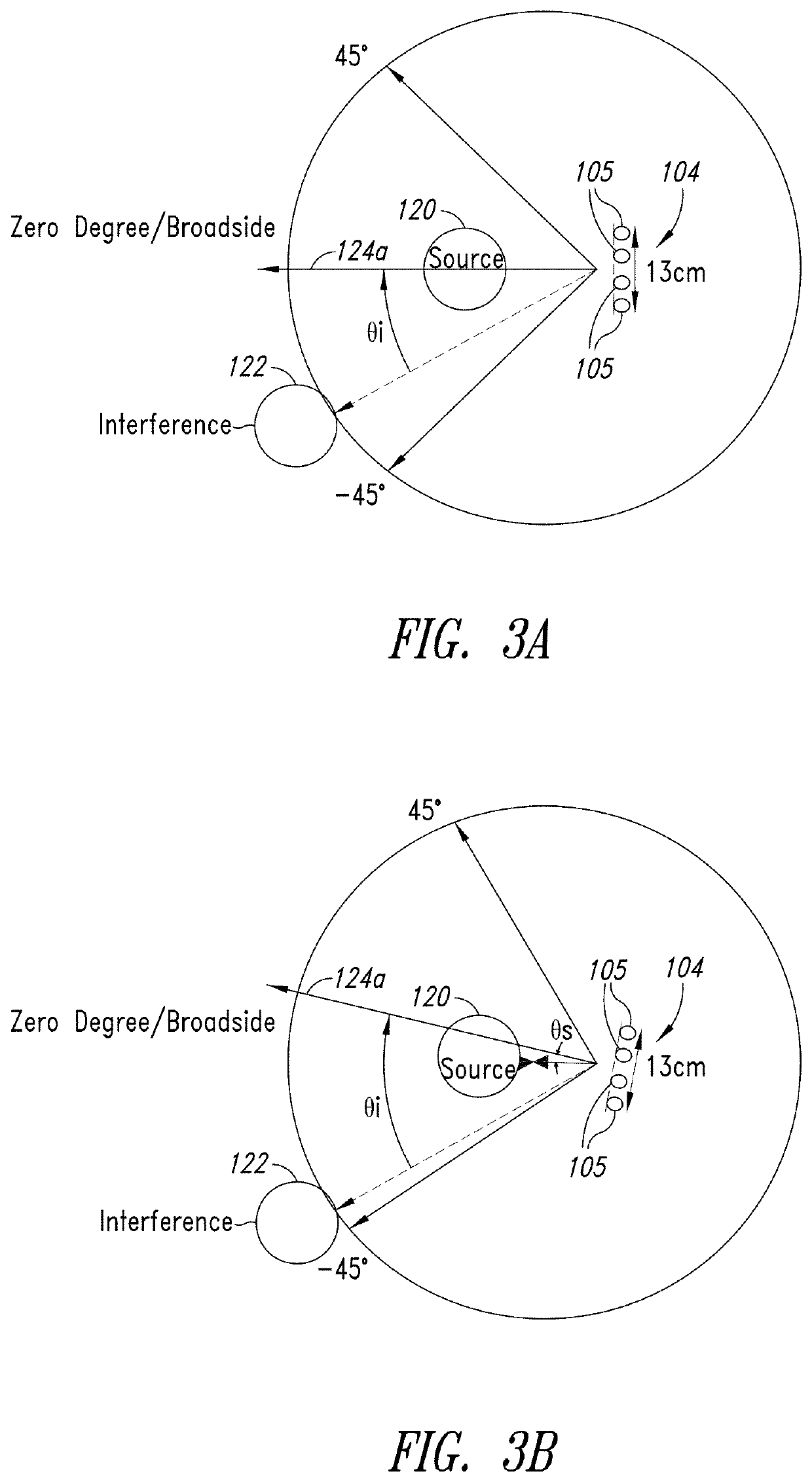
Microphone array auto-directive adaptive wideband beamforming using orientation information from MEMS sensors
ActiveUS10979805B2Improve maximizationGain is minimizedMicrophonesSolid-state devicesBeam patternMems sensors
A method and apparatus for auto-directive adaptive beamforming for a microphone array using microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) sensor orientation information are provided. The microphone array captures audio and the MEMS sensor detects an orientation of the microphone array. A direction of arrival of a source signal is estimated based on the data representative of the audio. A change in an orientation of the microphone array is detected based on the orientation and the direction of arrival is compensates based on the change in the orientation of the microphone array. The apparatus pre-steers a beam of a beam pattern of the microphone array based on the compensated direction of arrival to retain the source signal in a broadside of the microphone array and performs adaptive wideband beamforming to null one or more interfering sources in the beam pattern while retaining the source signal in the broadside of the microphone array.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
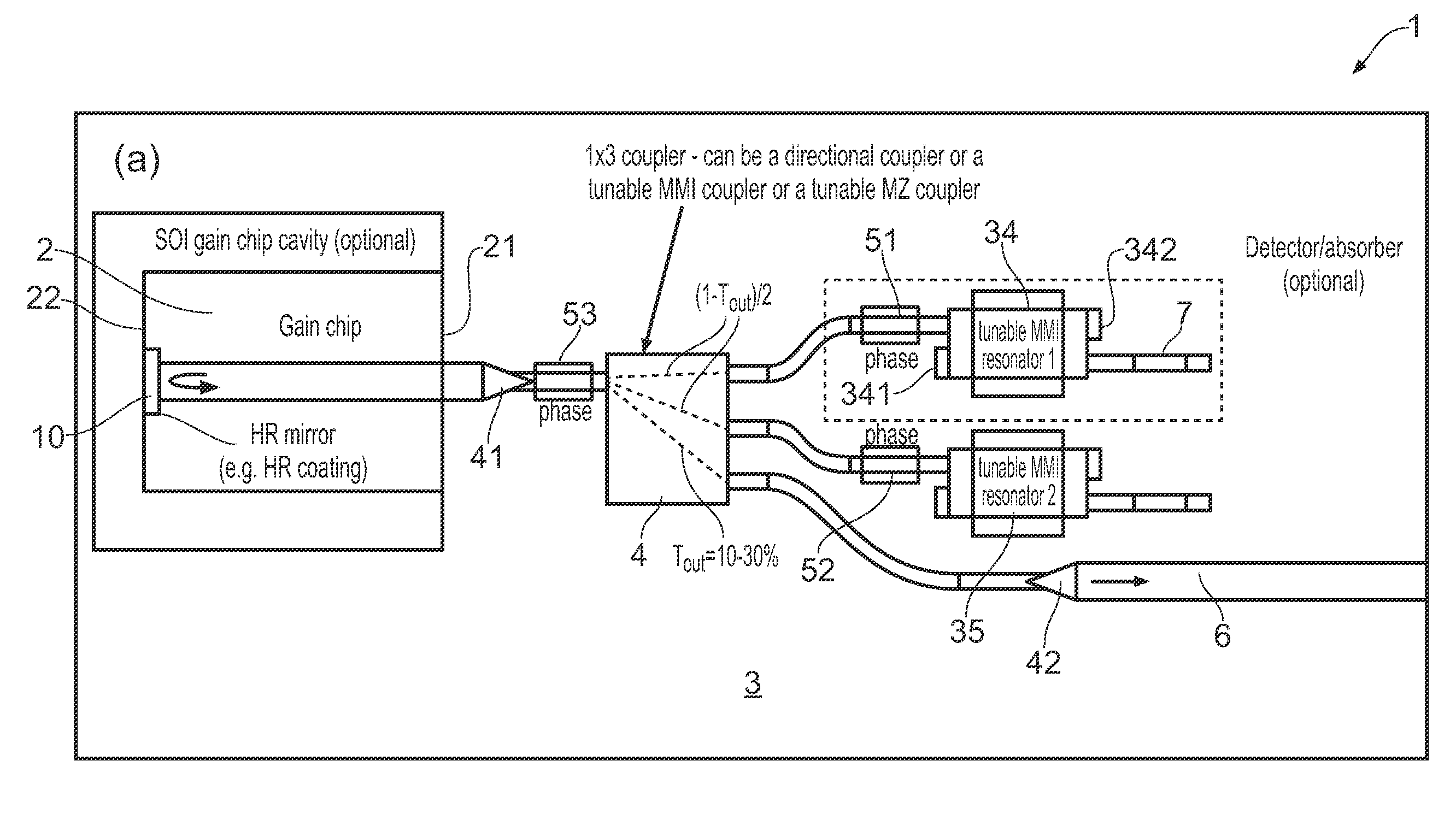
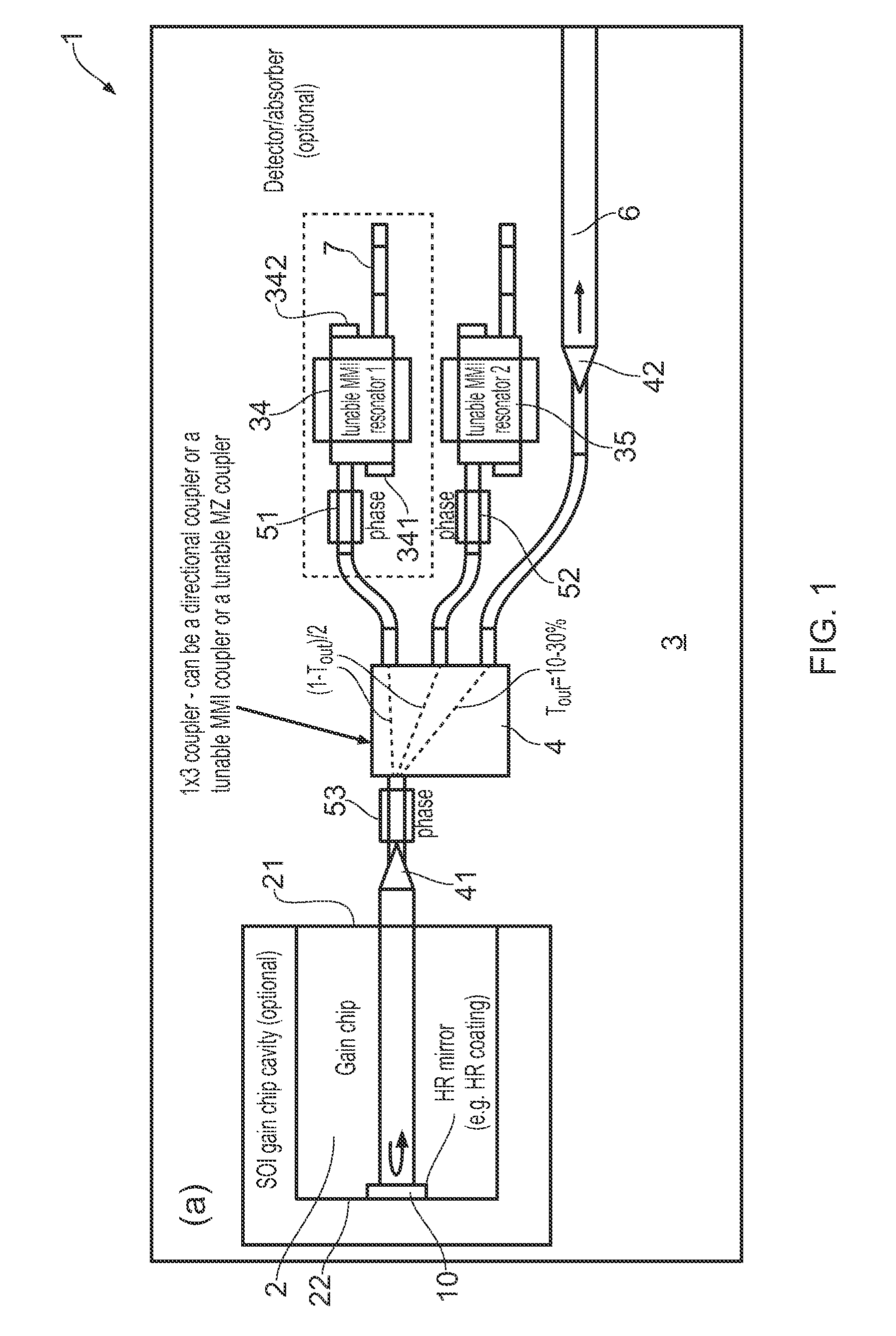
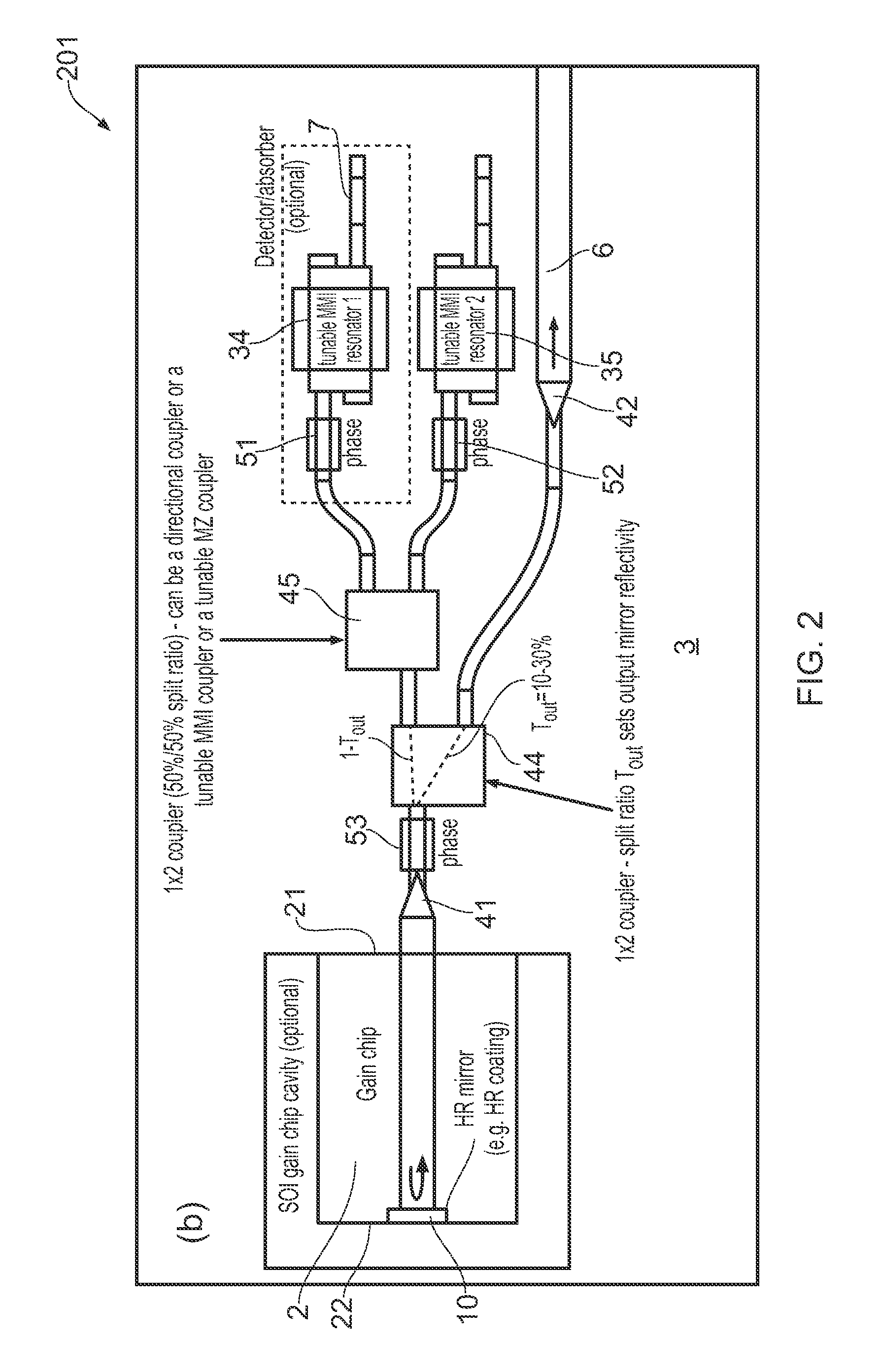
Tunable soi laser
ActiveUS20150207291A1Strong index changeMinimal absorption increaseLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsLength waveFront and back ends
A wavelength tunable silicon-on-insulator (SOI) laser comprising: a laser cavity including: a semiconductor gain medium having a front end and a back end, wherein a mirror of the laser cavity is located at the back end of the semiconductor gain medium; and a phase-tunable waveguide platform coupled to the front end of the semiconductor gain medium, the phase-tunable waveguide platform comprising: a first resonator and a second resonator; at least one resonator being a phase-tunable resonator; wherein the first resonator is any one of: an MMI device including a pair of reflective surfaces defining a resonator cavity therebetween such that the device is configured to act as a Fabry-Perot filter; a ring resonator; or a waveguide Fabry-Perot filter; and wherein the second resonator is any one of: an MMI device including a pair of reflective surfaces defining a resonator cavity therebetween such that the device is configured to act as a Fabry-Perot filter; a ring resonator; or a waveguide Fabry-Perot filter.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS LTD
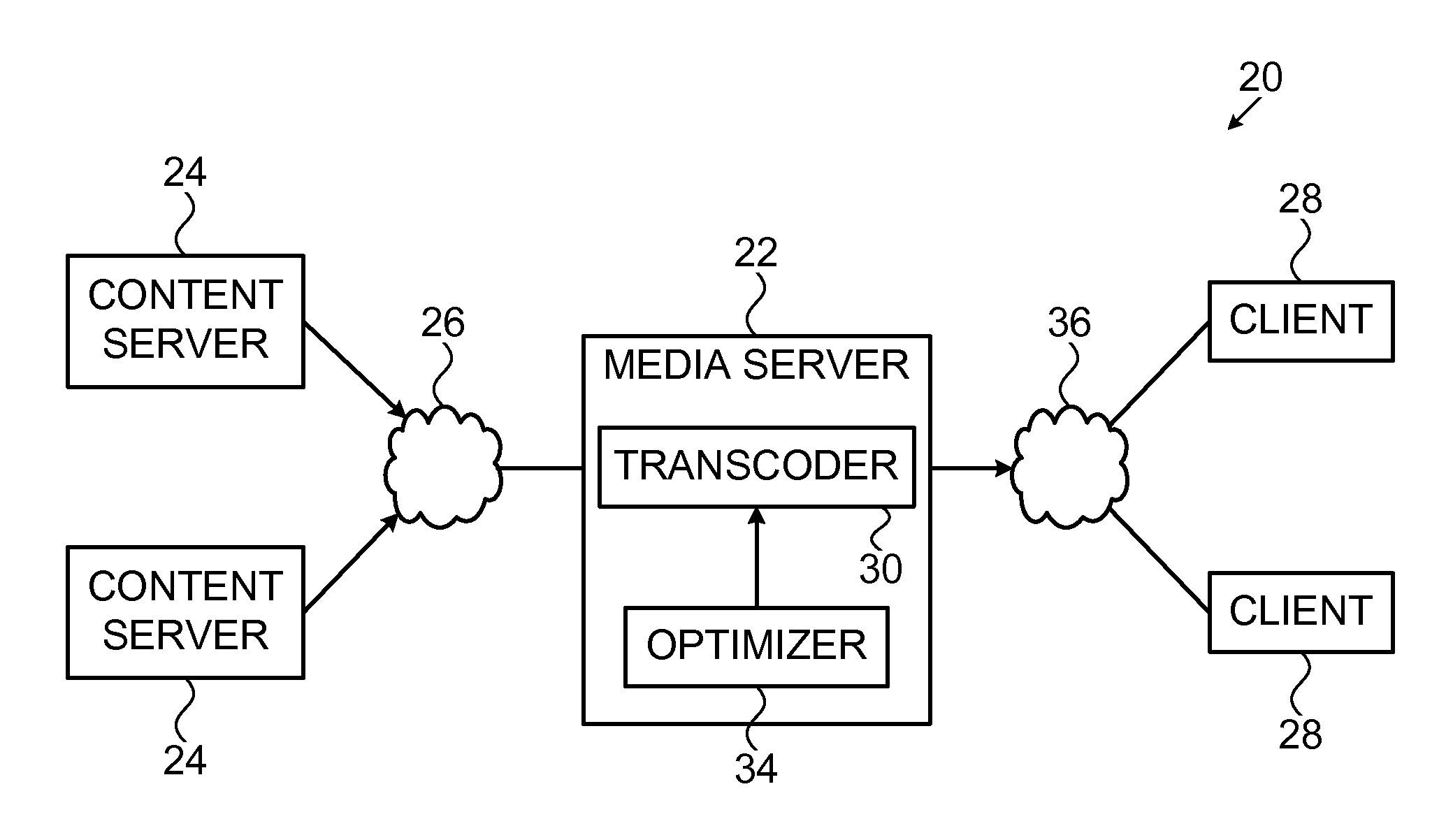
Network optimization
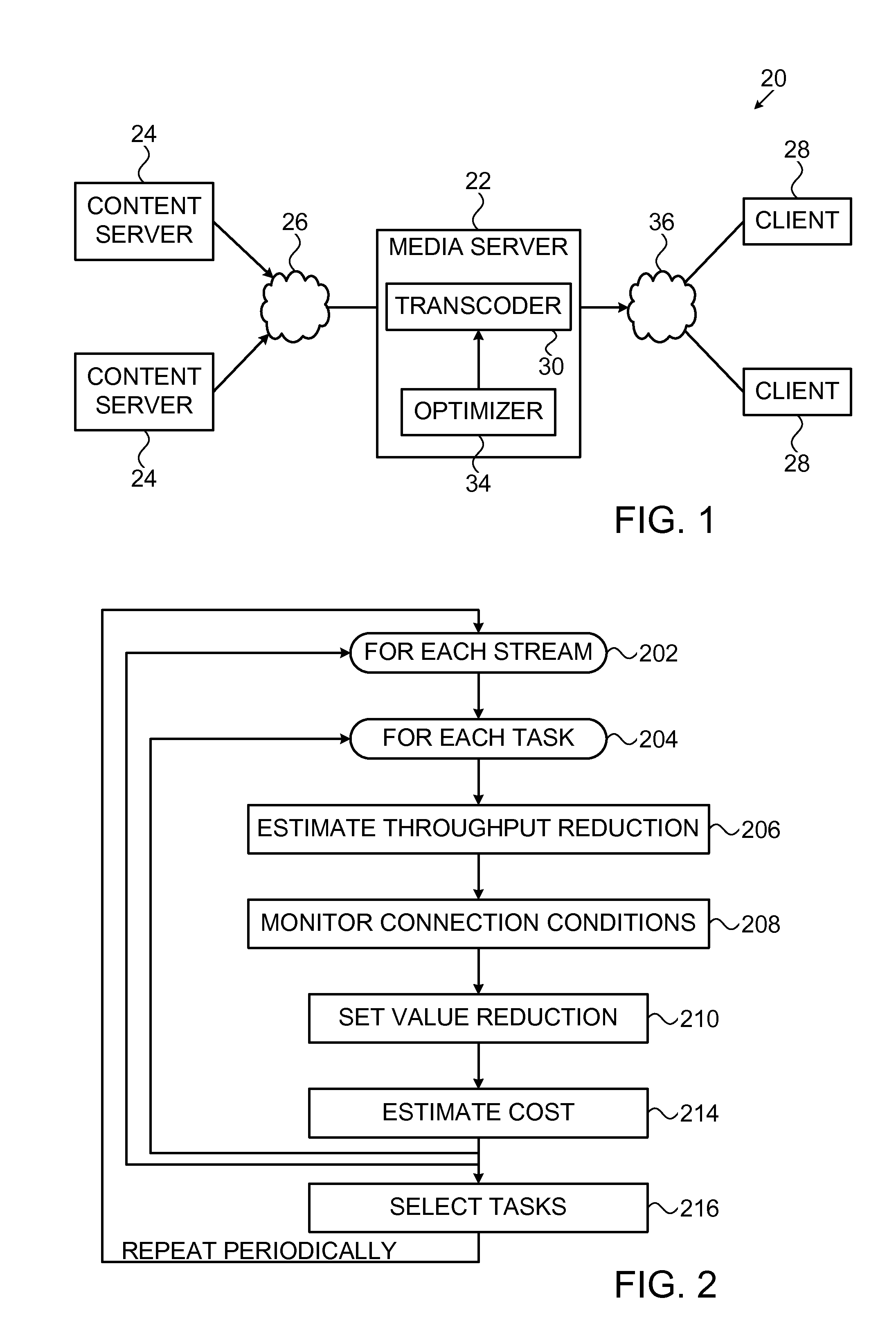
ActiveUS20120023504A1Enhanced server-side controlEasy to controlMultiprogramming arrangementsDigital video signal modificationAlgorithmVector optimization
A method for handling communication data involving identifying available resources for applying compression tasks and estimating a throughput reduction value to be achieved by applying each of a plurality of different compression tasks to a plurality of media items. A cost of applying the plurality of different compression tasks to the plurality of media items is estimated. The method further includes finding an optimization solution that maximizes the throughput reduction value over possible pairs of the compression tasks and the media items, while keeping the cost of the tasks of the solution within the identified available resources and providing instructions to apply compression tasks according to the optimization solution.
Owner:MOBIXELL NETWORKS
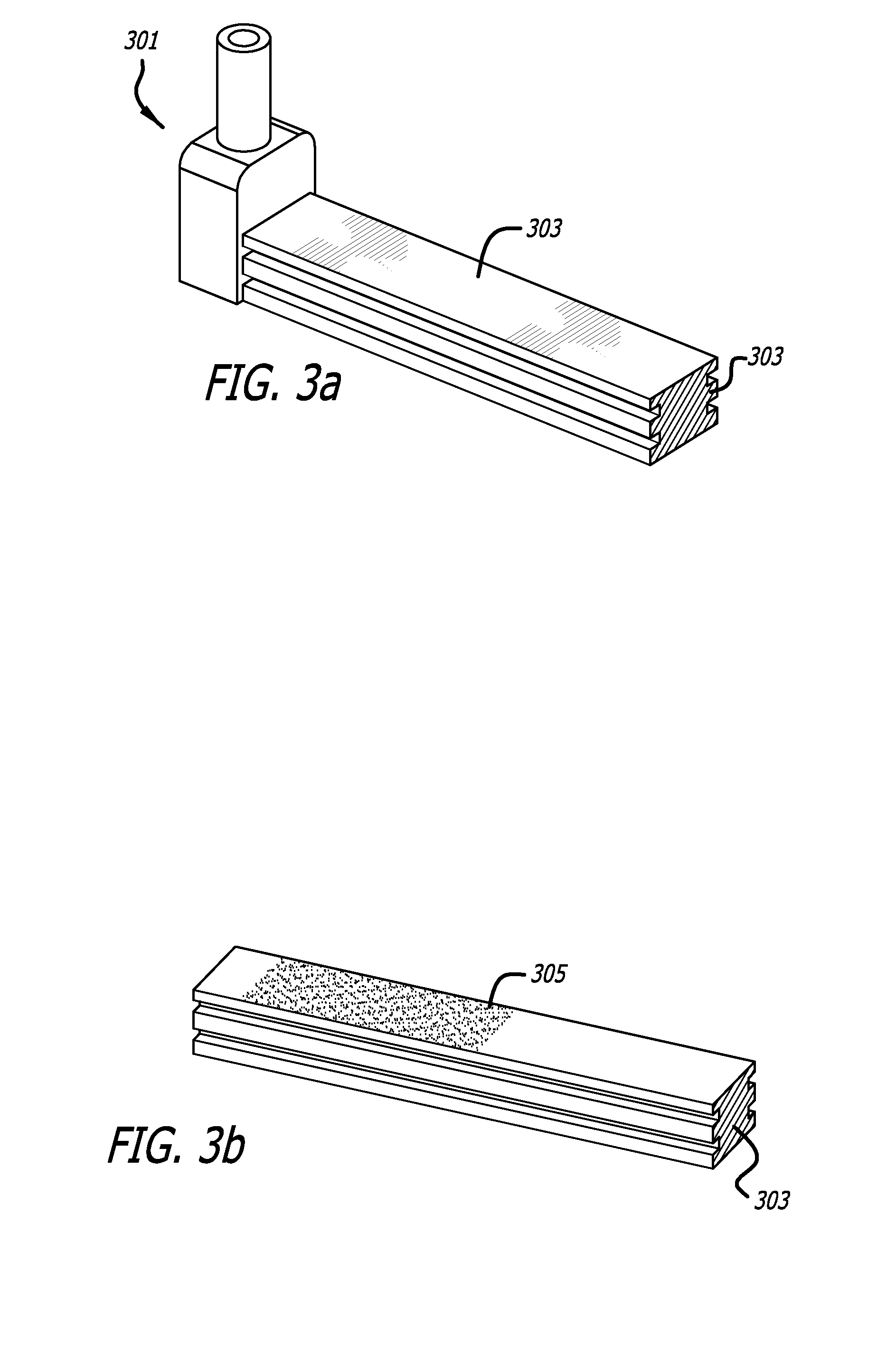
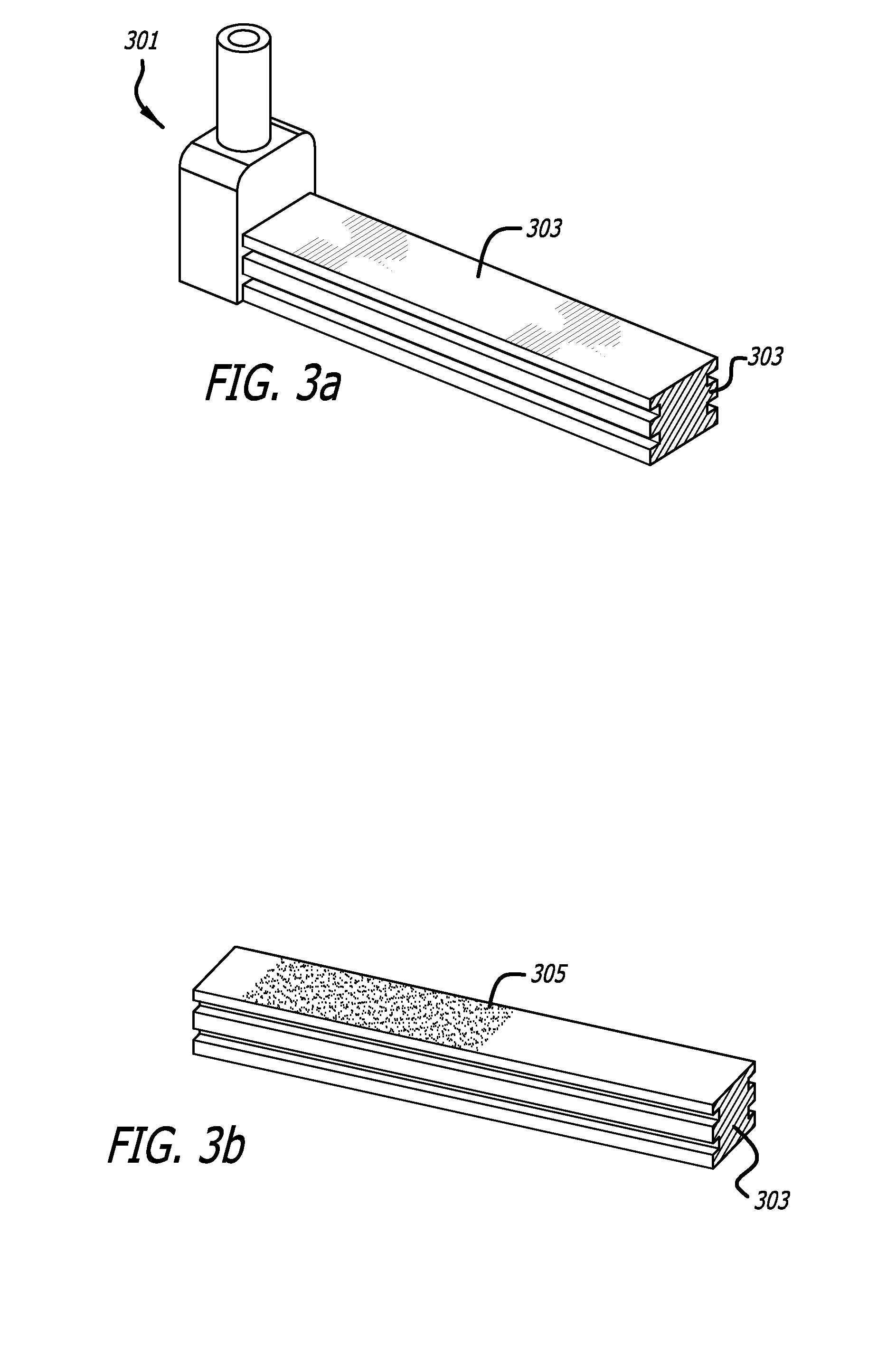
Contour crafting extrusion nozzles
An automated extrusion construction system may include an extrusion nozzle configured to extrude construction material in a substantially horizontal direction against an elongated and substantially vertical surface. An extrusion nozzle may have a height adjustment mechanism configured to adjust the height of an outlet in response to level deviations in the surface on which the construction material is extruded by the extrusion nozzle. An automated extrusion construction system may include a slicing mechanism configured to controllably slice through the extruded layer.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Contour crafting extrusion nozzles
ActiveUS20100257792A1Improve maximizationWallsLayered productsArchitectural engineeringBuilding material
An automated extrusion construction system may include an extrusion nozzle configured to extrude construction material in a substantially horizontal direction against an elongated and substantially vertical surface. An extrusion nozzle may have a height adjustment mechanism configured to adjust the height of an outlet in response to level deviations in the surface on which the construction material is extruded by the extrusion nozzle. An automated extrusion construction system may include a slicing mechanism configured to controllably slice through the extruded layer.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Vehicle roof rack having a height adjustable cross-member
A vehicle article carrier apparatus includes a pair of side-rails adapted to be secured in fixed position to the outer top surface of the vehicle in a spaced apart relation to one another and generally parallel to the longitudinal centerline of the vehicle; at least one cross-member spanning generally transversely between the side-rails, the at least one cross-member having opposing ends; and a bracket assembly at the end of each cross member and being slidably connected to the side rails and including a plurality of pivotally connected components configured so that the cross-member has a first lowered position, and the cross-member is moved to a second position that is elevated from outer top surface of the vehicle above the first position, by pivoting about greater than four generally transversely oriented pivotal axes. Methods of use of the article carrier are also disclosed.
Owner:MERLYN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com