Patents
Literature
463 results about "Enzymatic synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions for enhancing DNA synthesis, DNA polymerase-related factors and utilization thereof
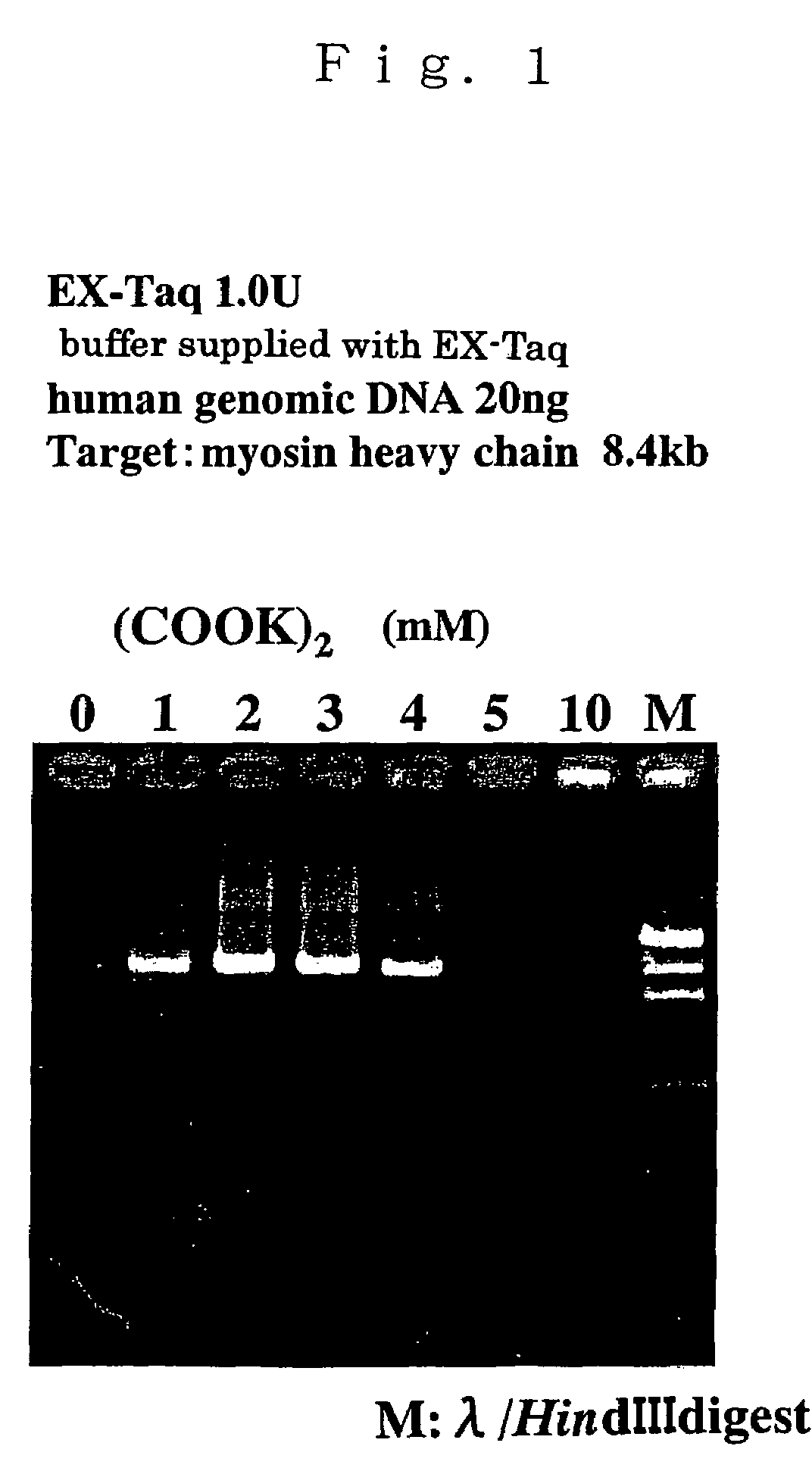
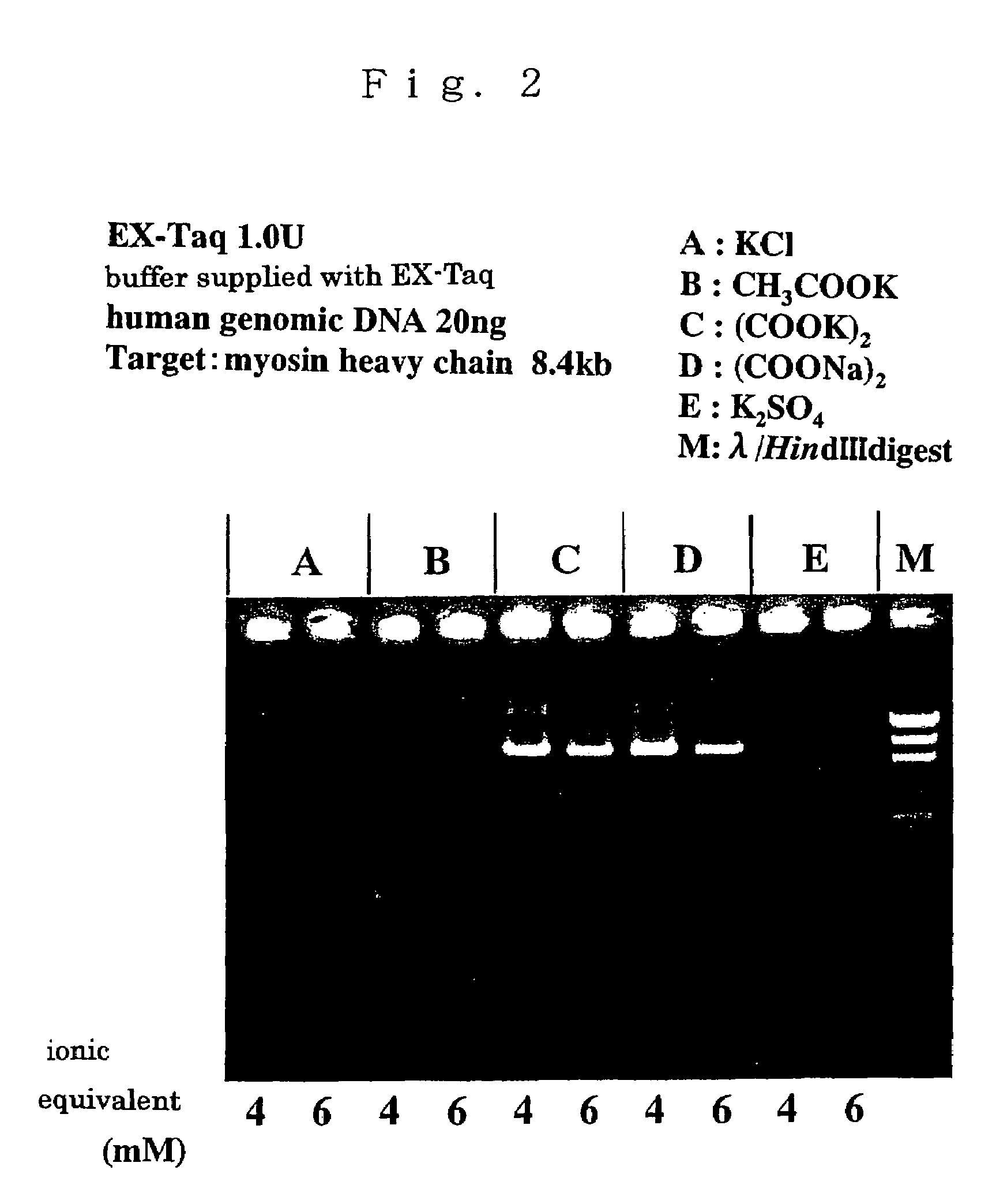
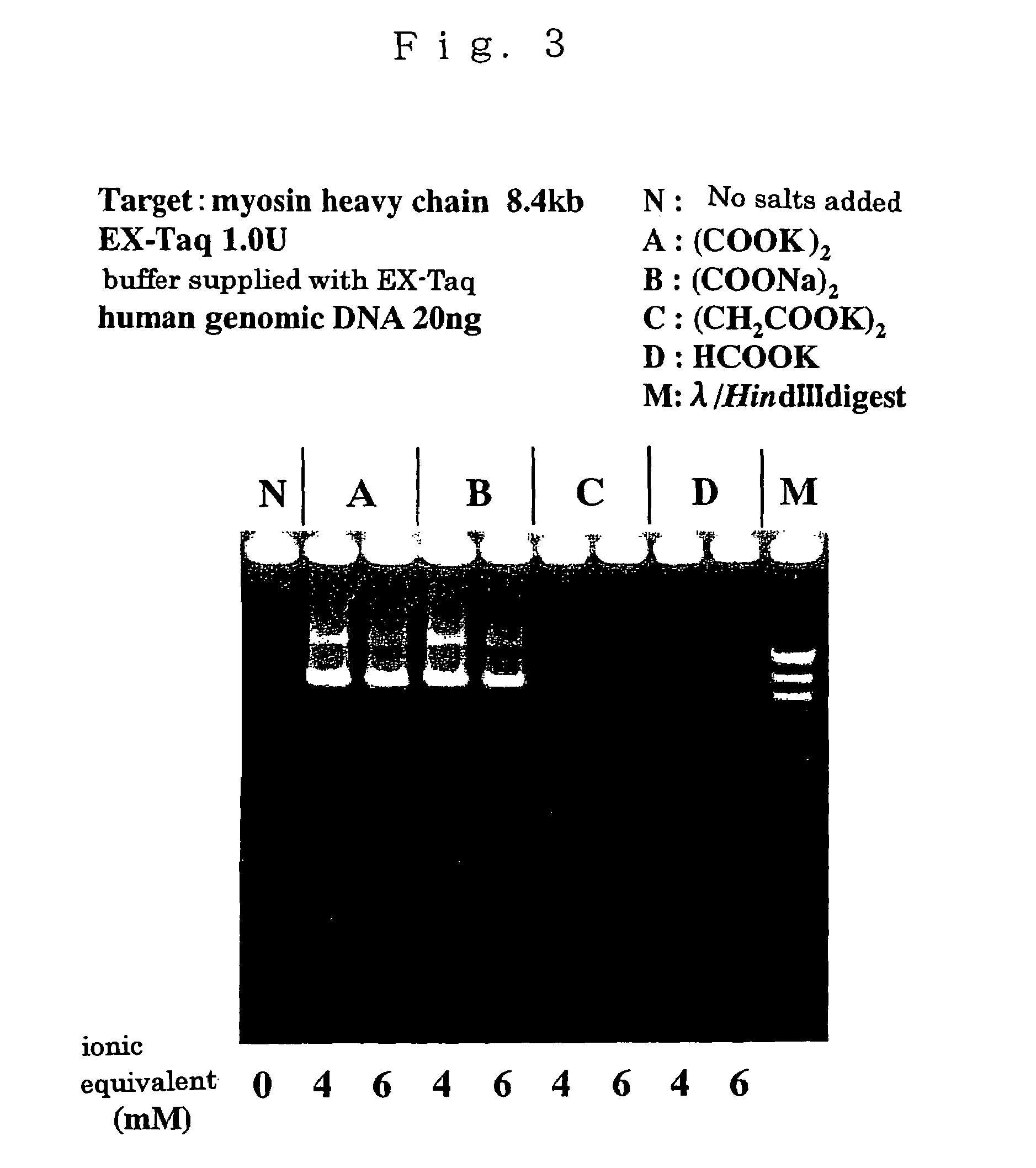
ActiveUS7384739B2High synthetic activityEnhancing PCR success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesEnzymatic synthesisPHA polymerase
The invention provides methods, kits, and compositions for enhancing synthesis of DNA involving a carboxylate ion-supplying substance that is effective in promoting DNA synthesis in enzymatic DNA synthesis reactions. The invention further provides a thermostable DNA polymerase-related factor derived from Thermococcus species, which has an activity to promote the DNA synthesis activity of DNA polymerase or which binds to DNA polymerase.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
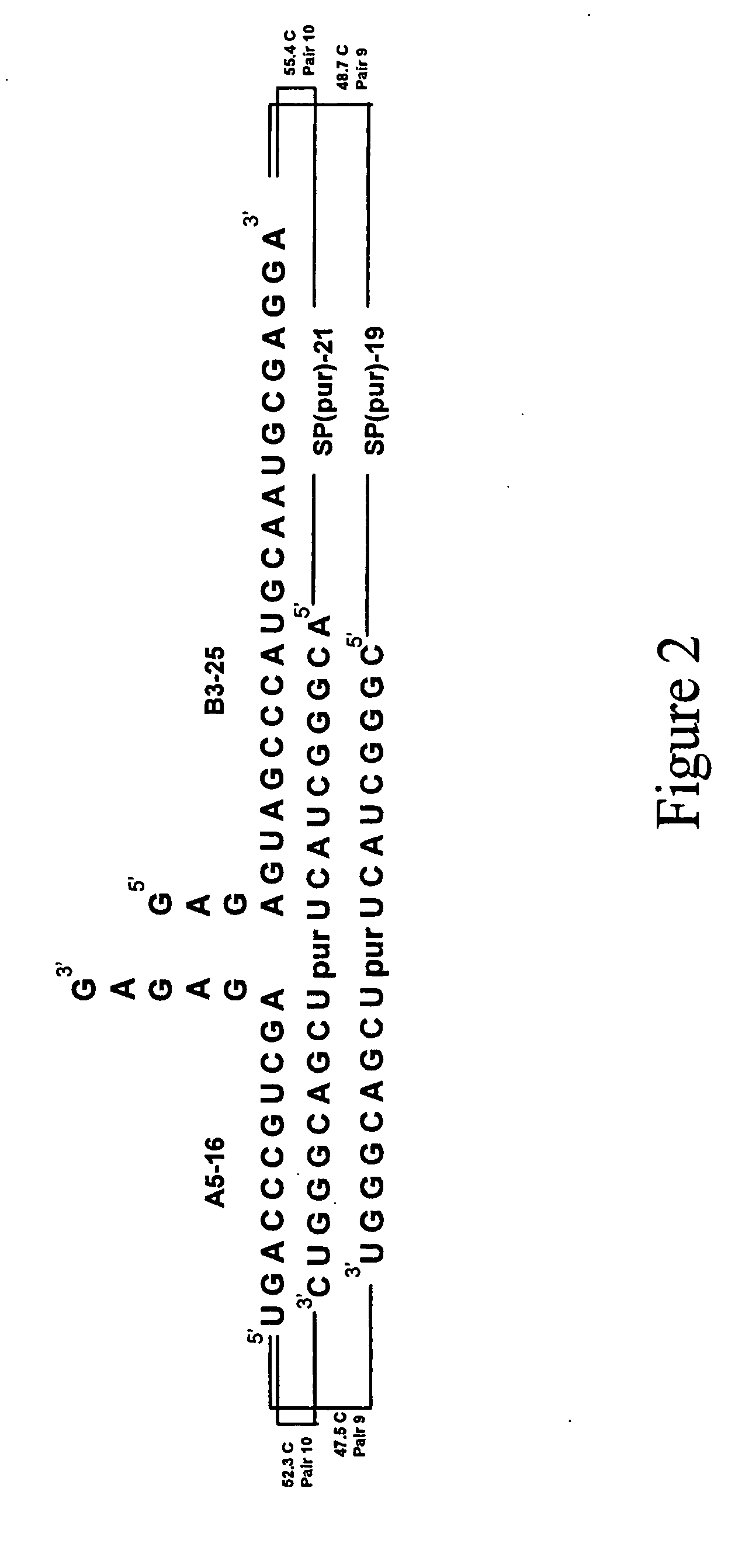
Splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis of polyribounucleotides
InactiveUS20050130201A1Ligate RNA moleculesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEnzymatic synthesisPolyribonucleotides
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis of polyribonucleotides using an RNA polymerizing enzyme. The invention provides ligating ribonucleotides comprising ligating a donor RNA molecule to an acceptor RNA molecule in the presence of RNA ligase and a splint, wherein the donor RNA molecule is comprised of at least one nucleotide and a ligation linker moiety, the acceptor RNA molecule is comprised of at least one nucleotide and a ligation linker moiety and the splint is comprised of a polyribonucleotide. The invention also provides splints for use in splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis using an RNA polymerizing enzyme.
Owner:DHARMACON INC
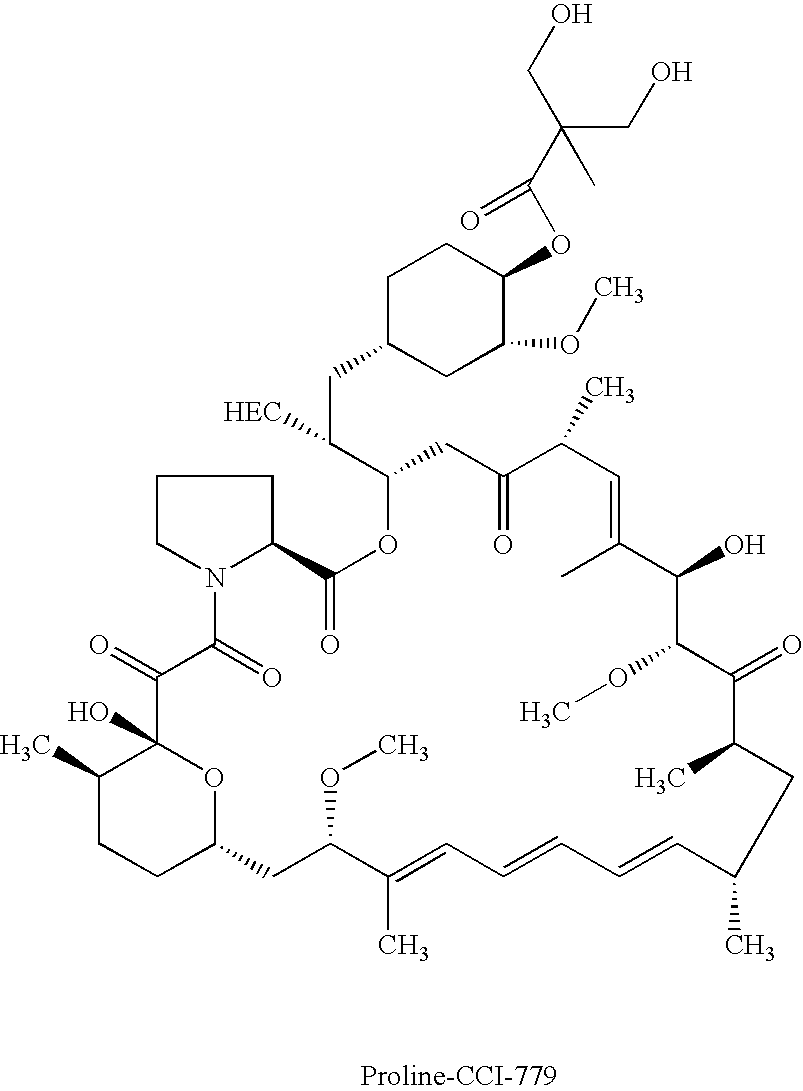
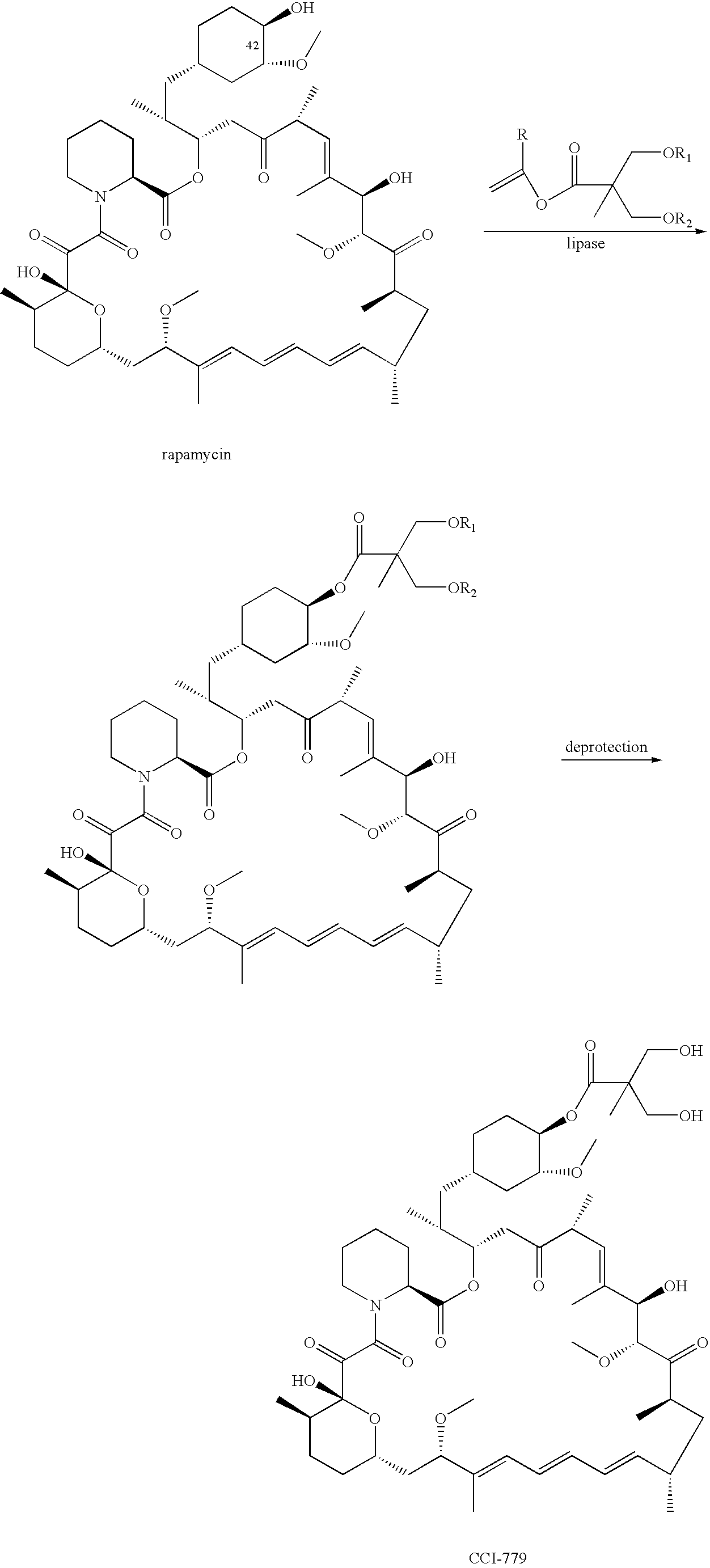
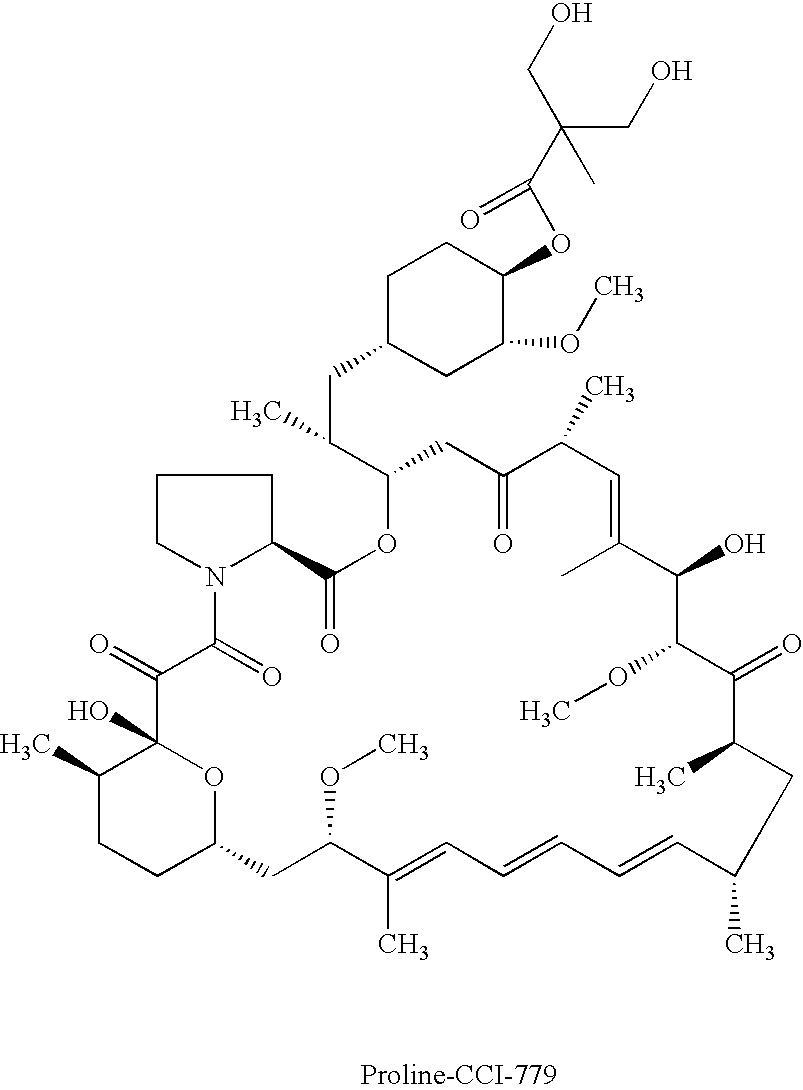
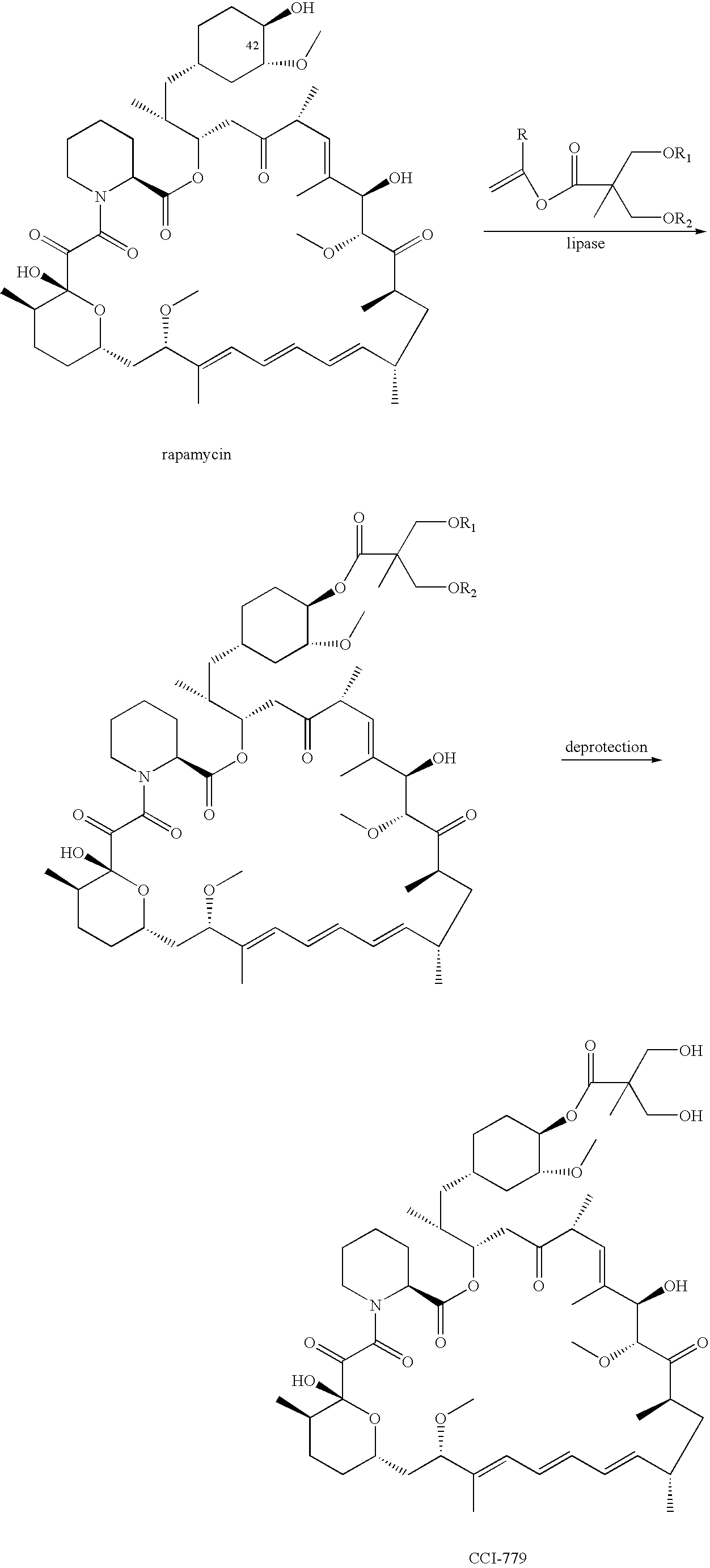
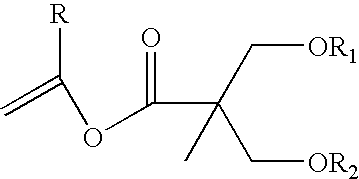
Proline CCI-779, production of and uses therefor, and two-step enzymatic synthesis of proline CCI-779 and CCI-779
Methods for the synthesis of CCI-779 and proline-CCI-779 are described, including a method involving lipase-catalyzed acetylation of 42-hydroxy of rapamycin with a vinyl ester of 2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl) propionic acid in an organic solvent followed by deprotection. Also provided are products containing proline-CCI-779 and uses thereof.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Production of Oligosaccharides By Microorganisms
InactiveUS20080145899A1Highly efficient and rapid and relatively low cost synthesisFermentationEnzymatic synthesisOligosaccharide
The present invention relates to the enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides, including sialylated product saccharides. In particular, it relates to the use of recombinant cells to take up low cost precursors such as glucose, pyruvate and N-actyl-glucosamine, and to synthesize activated sugar moieties that are used in oligosaccharide synthesis. The methods make possible the synthesis of many oligosaccharides using microorganisms and readily available, relatively inexpensive starting materials.
Owner:SENEB BIOSCI
Bacterial transglycosylases: assays for monitoring the activity using Lipid II substrate analogs and methods for discovering new antibiotics
InactiveUS6461829B1Easy to detectEasy to measureMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic synthesisSubstrate analog
This invention provides a direct method for monitoring bacterial transglycosylase activity using labeled substrates produced by chemo-enzymatic synthesis wherein the labels are selected to permit the detection of both polymeric and non-polymeric products simultaneously, either directly or following the separation of product from starting material. The invention promotes the discovery of new antibiotics with activity against bacterial transglycosylases by a) laying the groundwork for structural analysis of purified, active transglycosylase (which permits structure-based design); and b) providing an assay that can be used to screen for inhibitors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
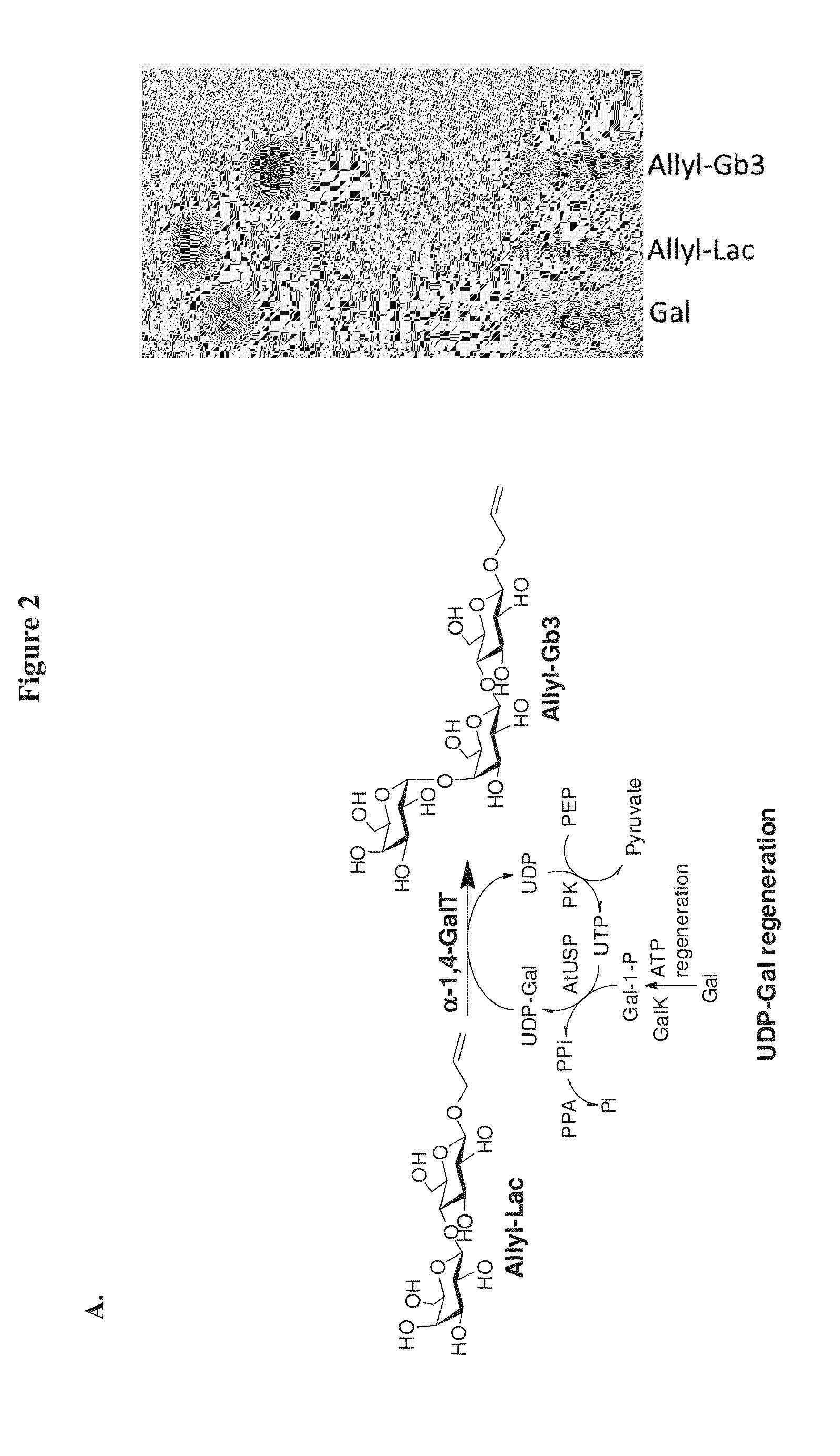
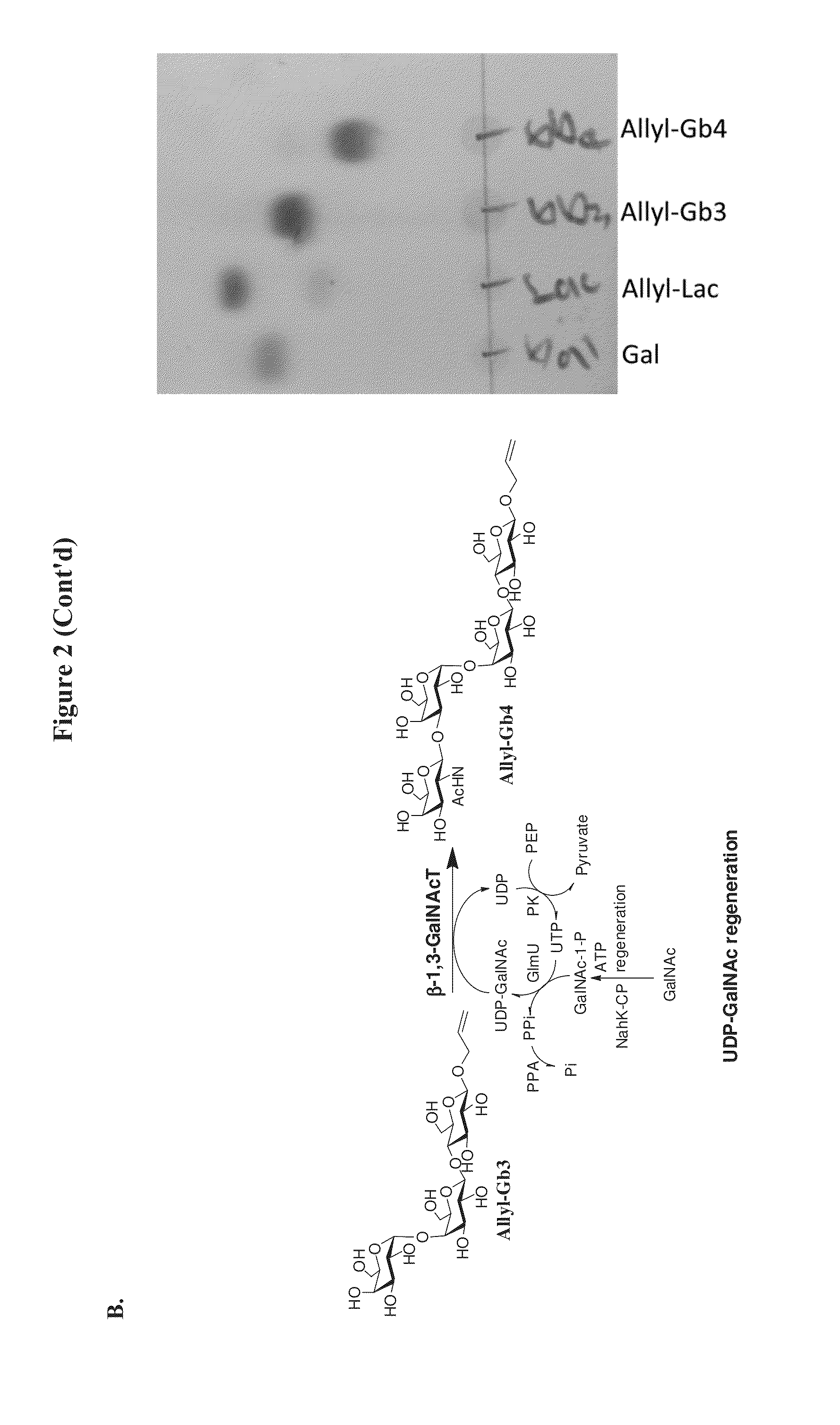
Large scale enzymatic synthesis of oligosaccharides
ActiveUS20140051127A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnzymatic synthesisNucleotide
A novel UDP-Gal regeneration process and its combined use with a galactosyltransferase to add galactose to a suitable acceptor substrate. Also described herein are synthetic methods for generating Globo-series oligosaccharides in large scale, wherein the methods may involve the combination of a glycosyltransferase reaction and a nucleotide sugar regeneration process.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
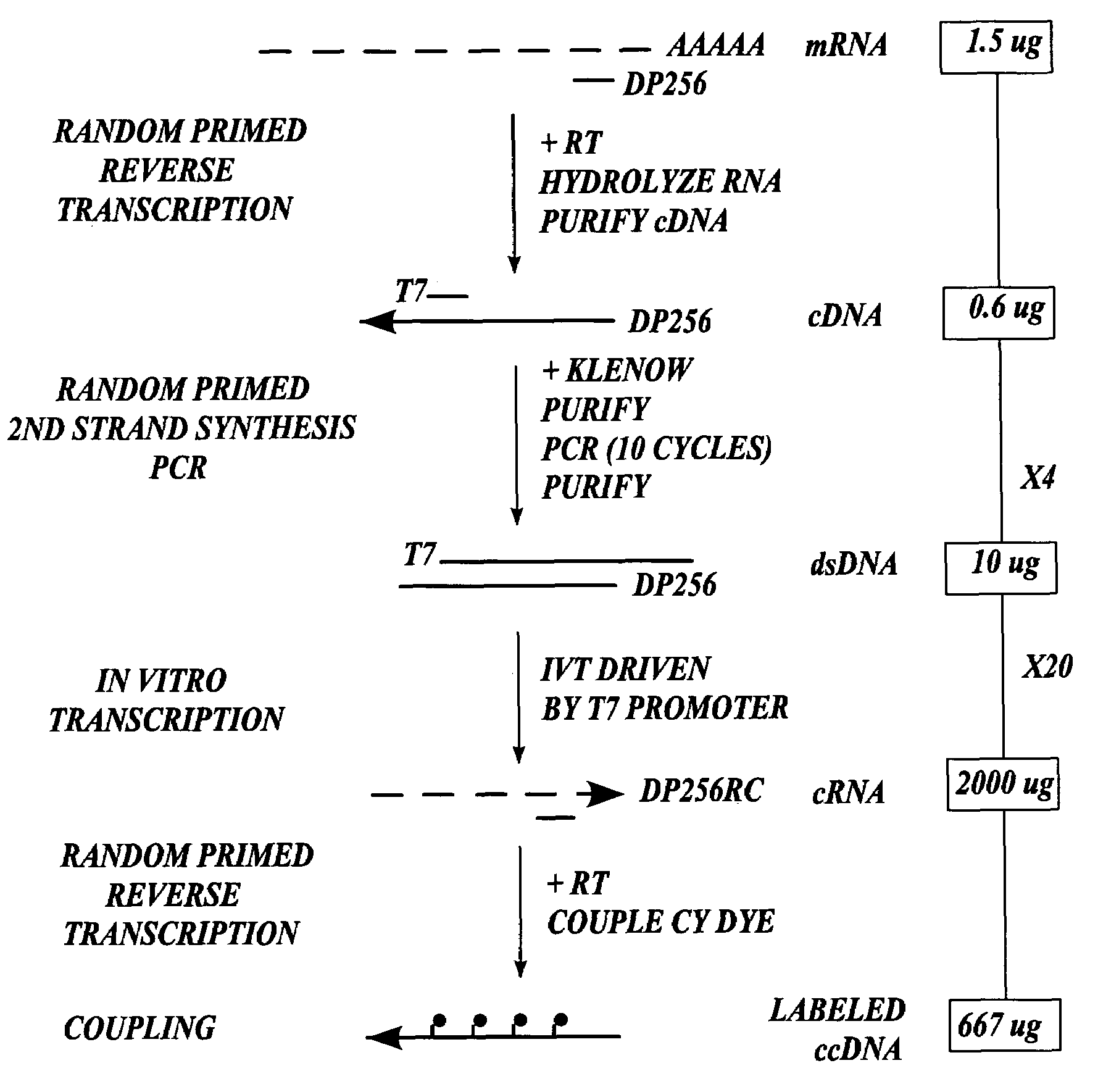
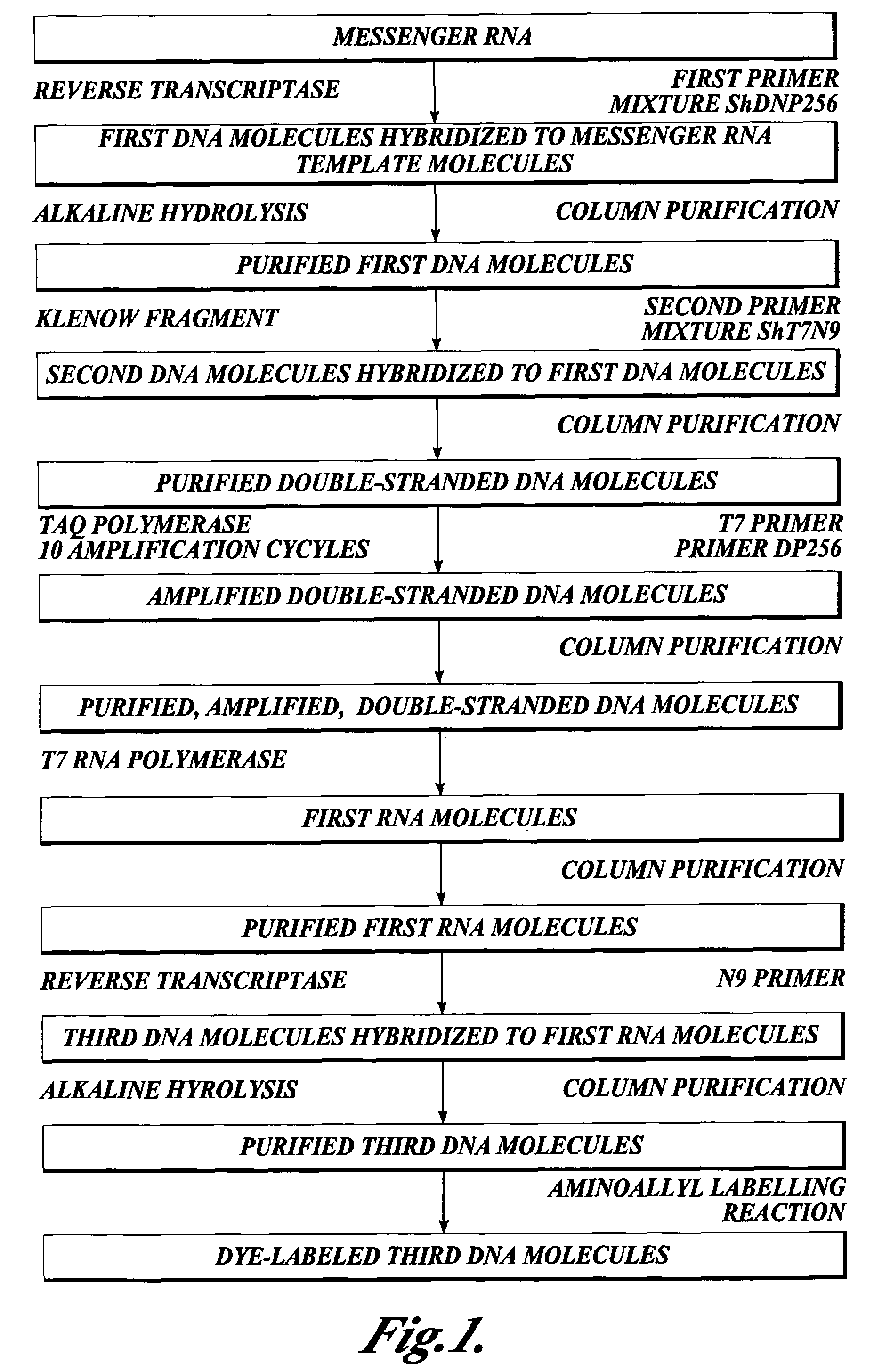
Methods for preparing nucleic acid samples useful for screening dna arrays
InactiveUS7432084B2High sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationEnzymatic synthesisImmobilized Nucleic Acids
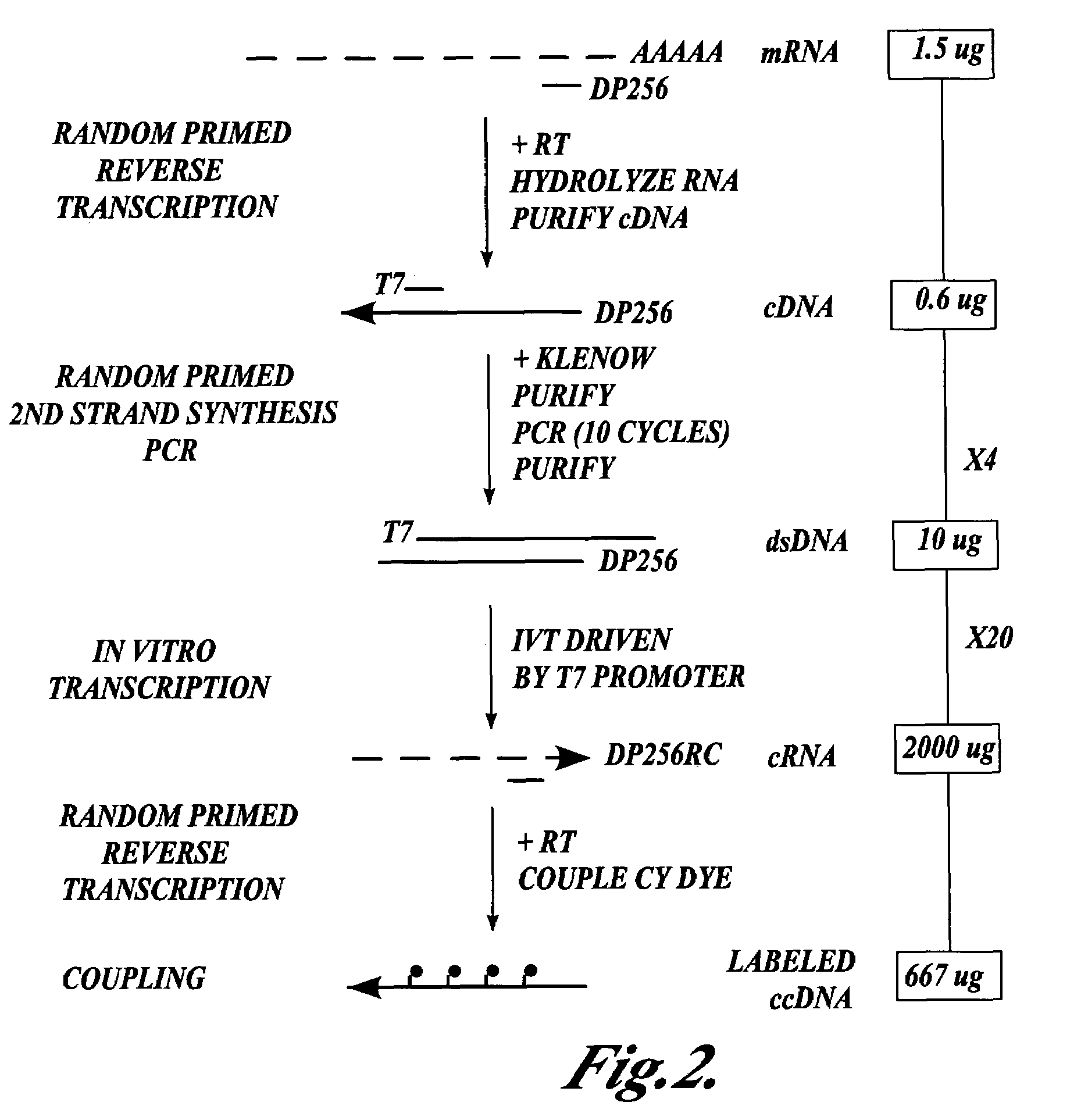
In one aspect the present invention provides methods of synthesizing a preparation of nucleic acid molecules, the methods comprising the steps of: (a) utilizing an RNA template to enzymatically synthesize a first DNA molecule that is complementary to at least 50 contiguous bases of the RNA template; (b) utilizing the first DNA molecule as a template to enzymatically synthesize a second DNA molecule, thereby forming a double-stranded DNA molecule wherein the first DNA molecule is hybridized to the second DNA molecule; (c) utilizing the first or second DNA molecule of the double-stranded DNA molecule as a template to enzymatically synthesize a first RNA molecule that is complementary to either the first DNA molecule or to the second DNA molecule; and (d) utilizing the first RNA molecule as a template to enzymatically synthesize a third DNA molecule that is complementary to the first RNA molecule. In another aspect, the present invention provides processed DNA samples prepared by a method of the invention for synthesizing a preparation of nucleic acid molecules. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods for hybridizing a processed DNA sample to a population of immobilized nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
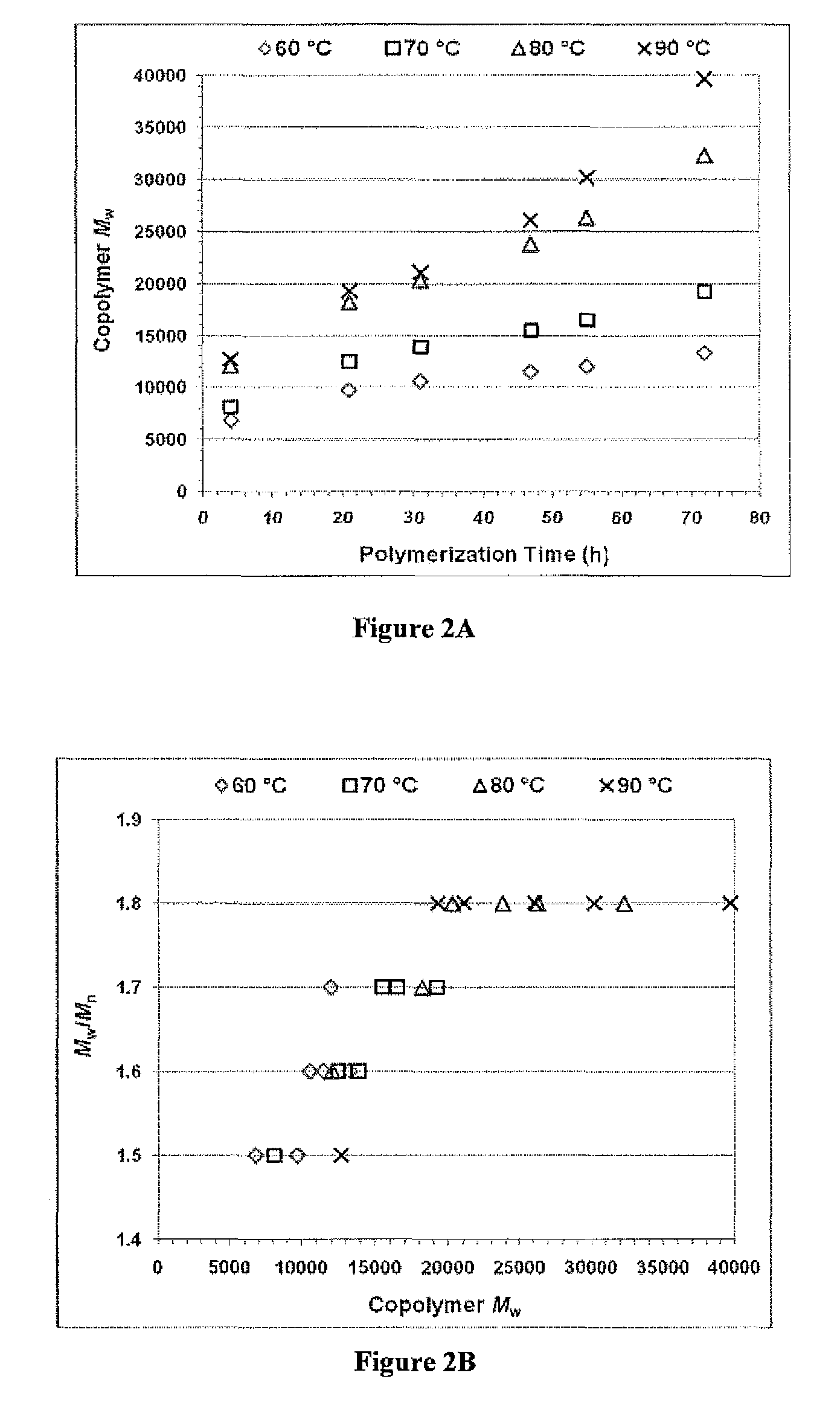
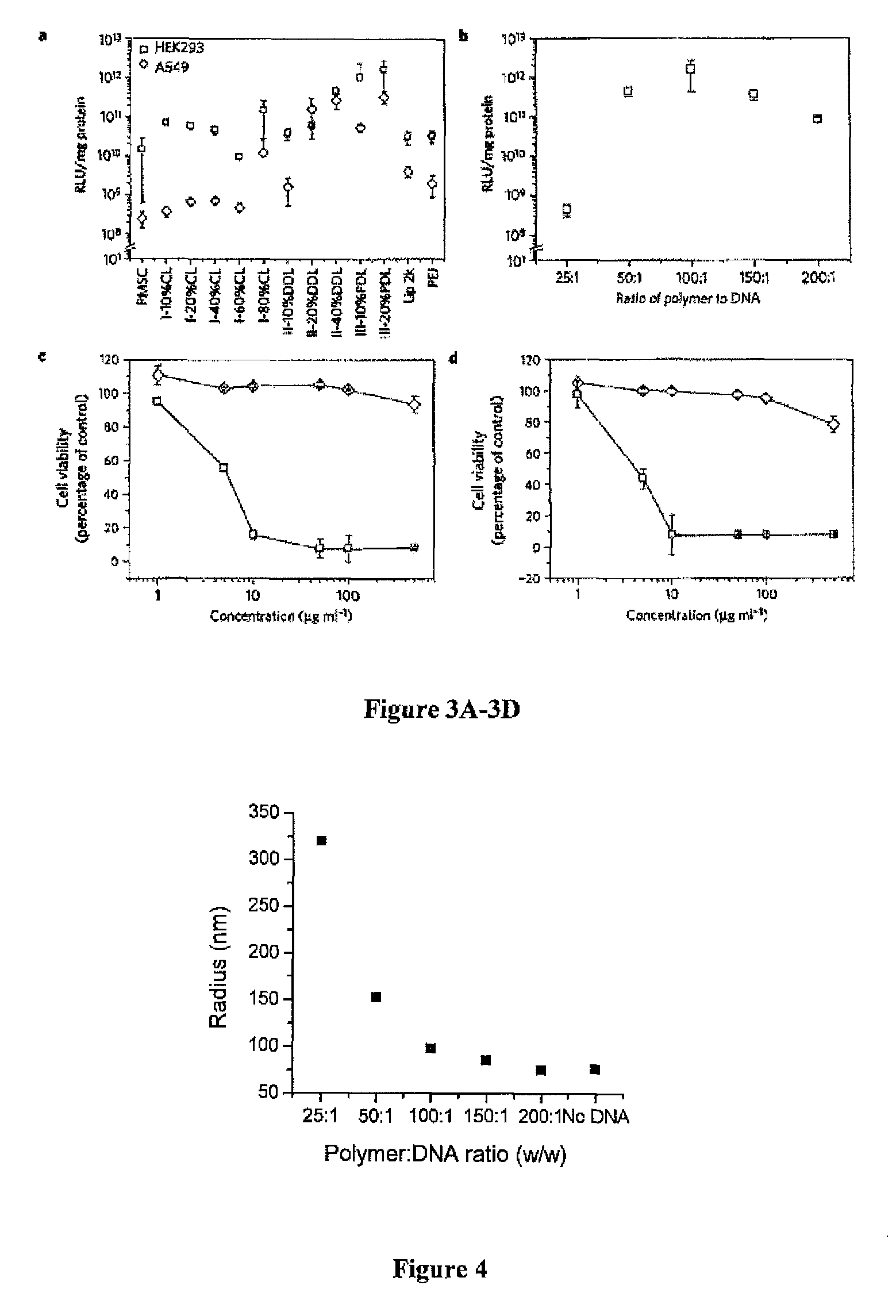
Enzymatic synthesis of poly(amine-co-esters) and methods of use thereof for gene delivery
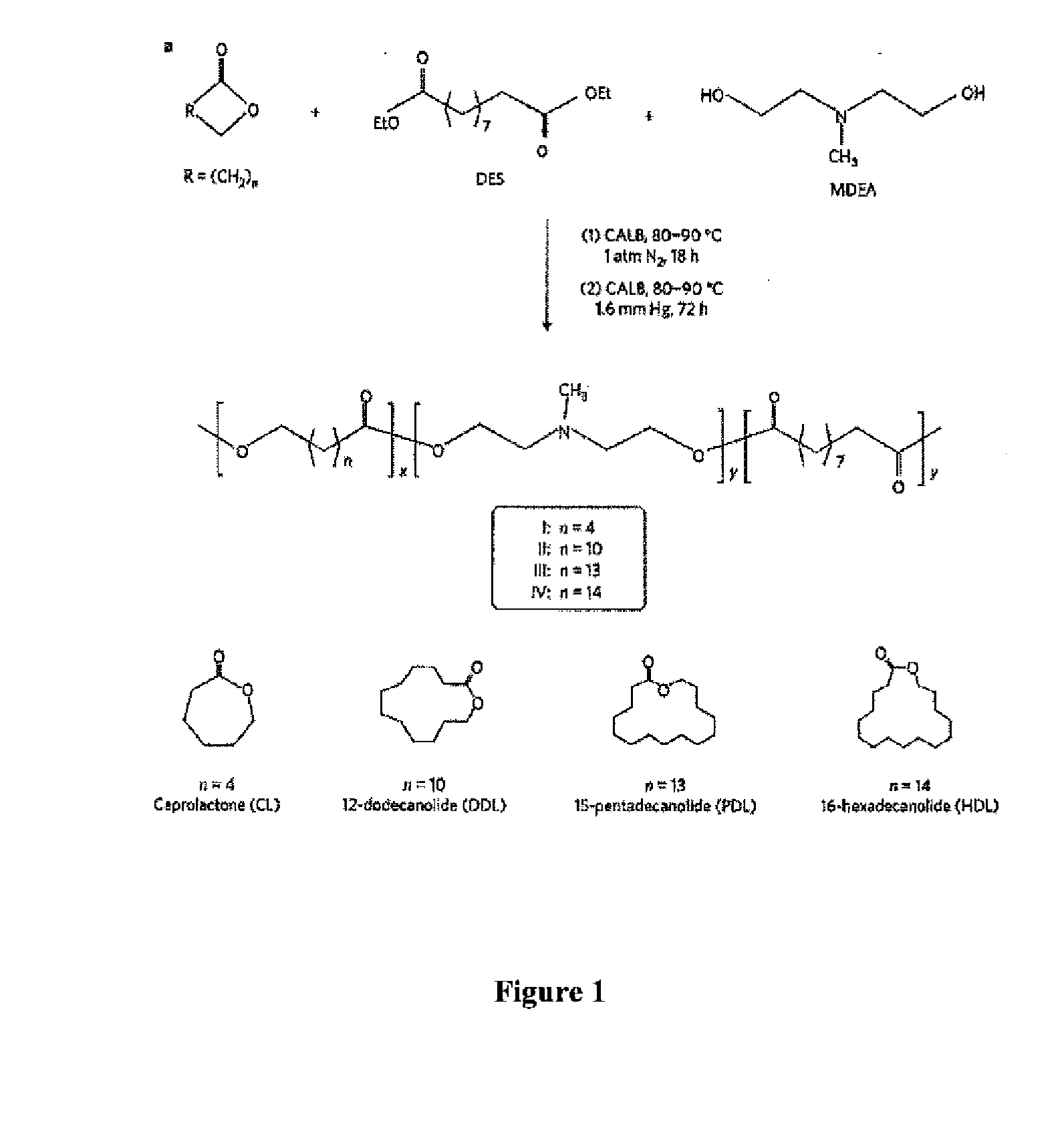
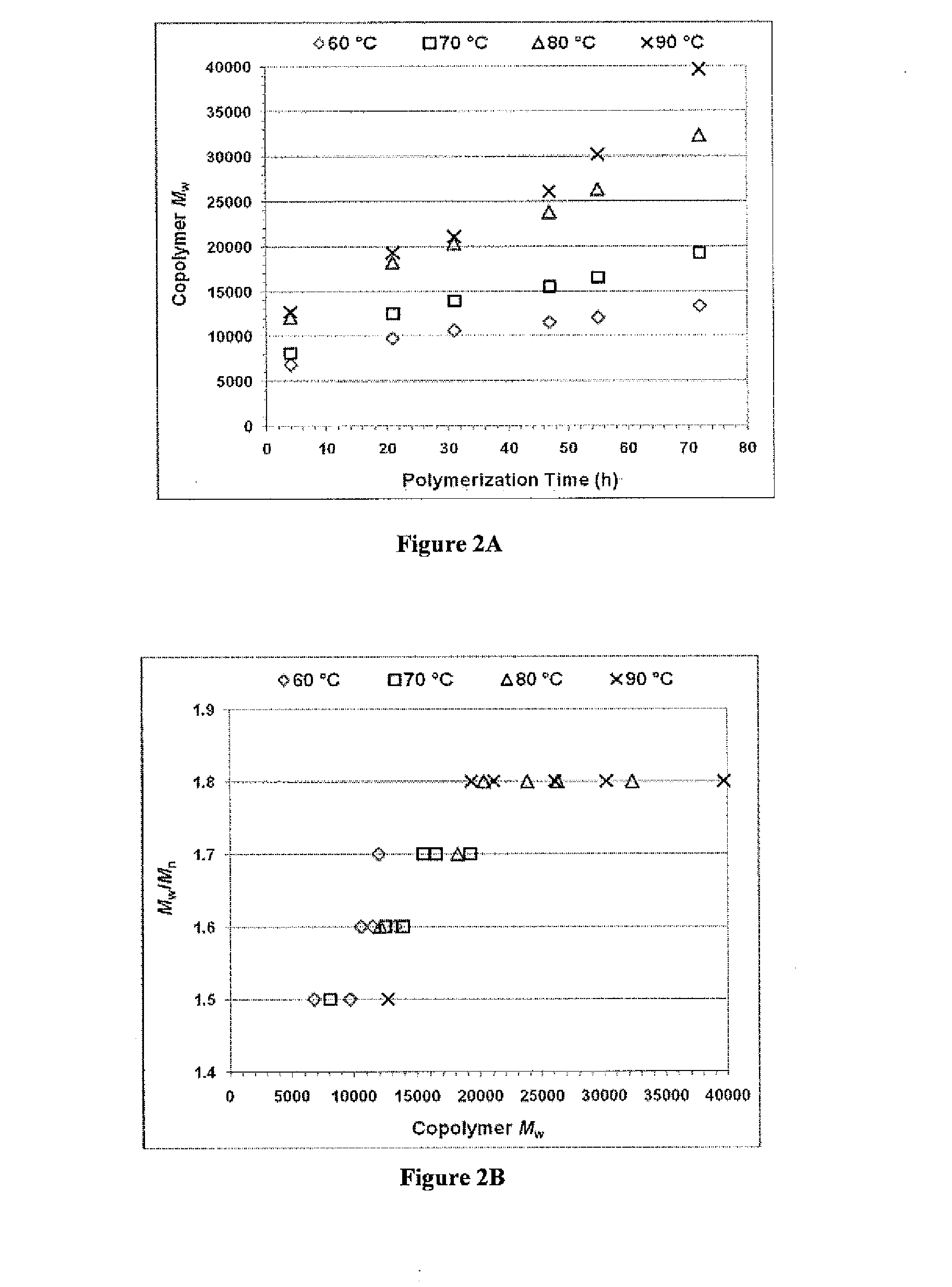
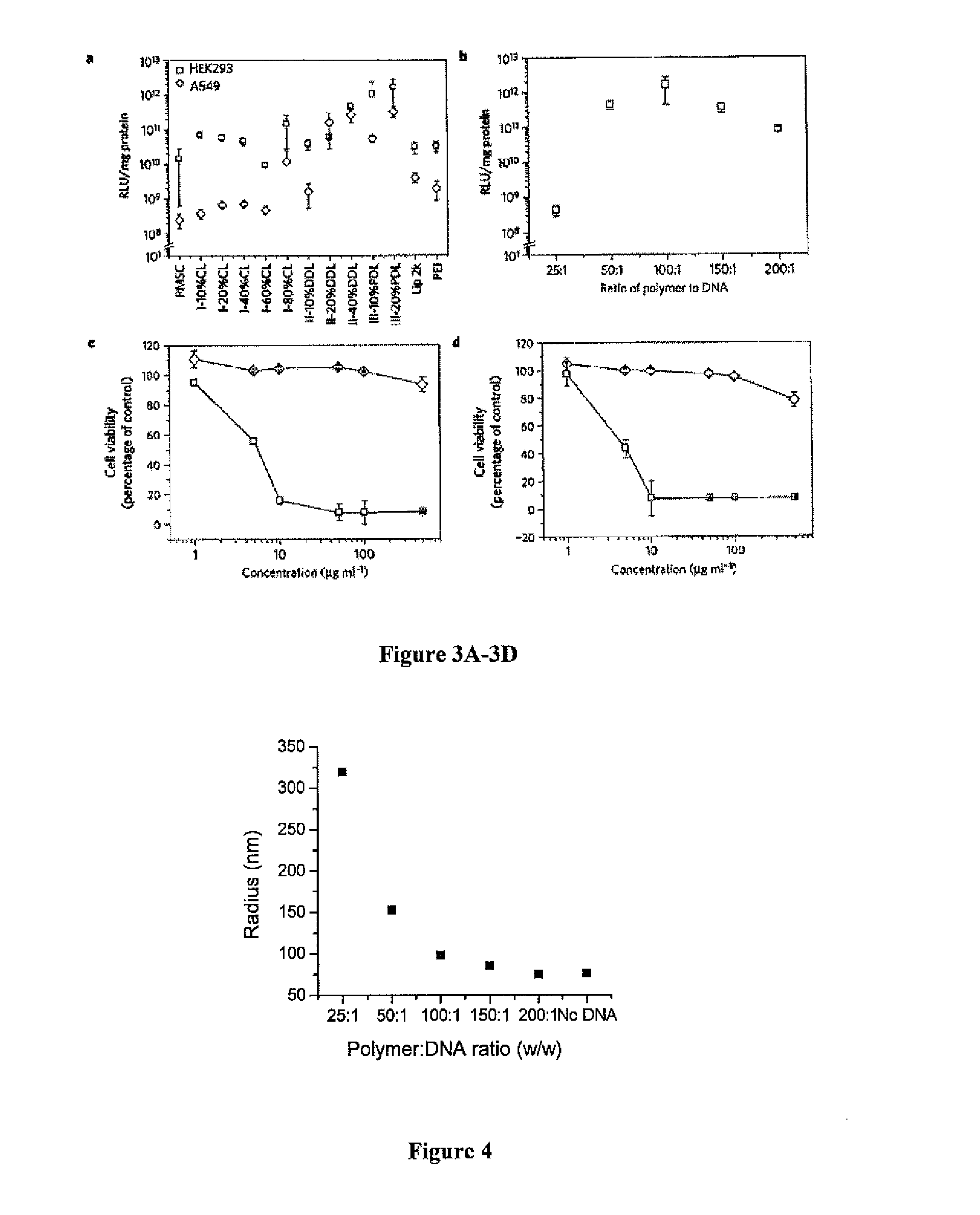
ActiveUS20140342003A1Improve efficiencyMaterial efficiencyPowder deliveryBiocideDiseaseEnzymatic synthesis
Poly(amine-co-ester) polymers, methods of forming active agent-load nanoparticles therefrom, and methods of using the nanoparticles for drug delivery are disclosed. The nanoparticles can be coated with an agent that reduces surface charge, an agent that increases cell-specific targeting, or a combination thereof. Typically, the loaded nanoparticles are less toxic, more efficient at drug delivery, or a combination thereof compared to a control other transfection reagents. In some embodiments, the nanoparticles are suitable for in vivo delivery, and can be administered systemically to a subject to treat a disease or condition.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Methods for producing sialyloligosaccharides in a dairy source
InactiveUS6323008B1High yieldBroaden the fieldVectorsSugar derivativesHigh concentrationEnzymatic synthesis
The present invention provides methods for producing sialyloligosaccharides in situ in dairy sources and cheese processing waste streams, prior to, during, or after processing of the dairy source during the cheese manufacturing process. The methods of the present invention use the catalytic activity of alpha(2-3) trans-sialidases to exploit the high concentrations of lactose and alpha(2-3) sialosides which naturally occur in dairy sources and cheese processing waste streams to drive the enzymatic synthesis of alpha(2-3) sialyllactose. alpha(2-3) sialyloligosaccharides produced according to these methods are additionally encompassed by the present invention. The invention also provides for recovery of the sialyloligosaccharides produced by these methods. The invention further provides a method for producing alpha(2-3) sialyllactose. The invention additionally provides a method of enriching for alpha(2-3) sialyllactose in milk using transgenic mammals that express an alpha(2-3) trans-sialidase transgene. The invention also provides for recovery of the sialyllactose contained in the milk produced by this transgenic mammal either before or after processing of the milk. Transgenic mammals containing an alpha(2-3) trans-sialidase encoding sequence operably linked to a regulatory sequence of a gene expressed in mammary tissue are also provided by the invention.
Owner:NEOSE TECH
Lipid Preparation for Enhancing Mineral Absorption
ActiveUS20080058415A1Promote absorptionEnhancement of formationBiocideSpread compositionsEnzymatic synthesisBone density
Disclosed is a dietary ingredient comprising at least one edible lipid which does not inhibit mineral absorption, enhances mineral absorption and intake, particularly a chemically or enzymatically synthesized synthetic oil, particularly glyceride-based lipid with high levels of mono- or polyunsaturated fatty acids at positions sn-1 and sn-3 of the glycerol backbone, vegetable- and plant-derived oil, such as flax and canola oils, short and medium chains lipid, preferably MCT and an oil mimicking the triglyceride composition of human mother's milk fat and its various uses.The dietary ingredient is particularly intended for use in enhancing calcium absorption and in the prevention and / or treatment of disorders associated with depletion of bone calcium and bone density, prevention and treatment of osteoporosis, for the enhancement of bone formation and bone mass maximization and for the enhancement of bone formation in infants and young children.
Owner:ENZYMOTEC
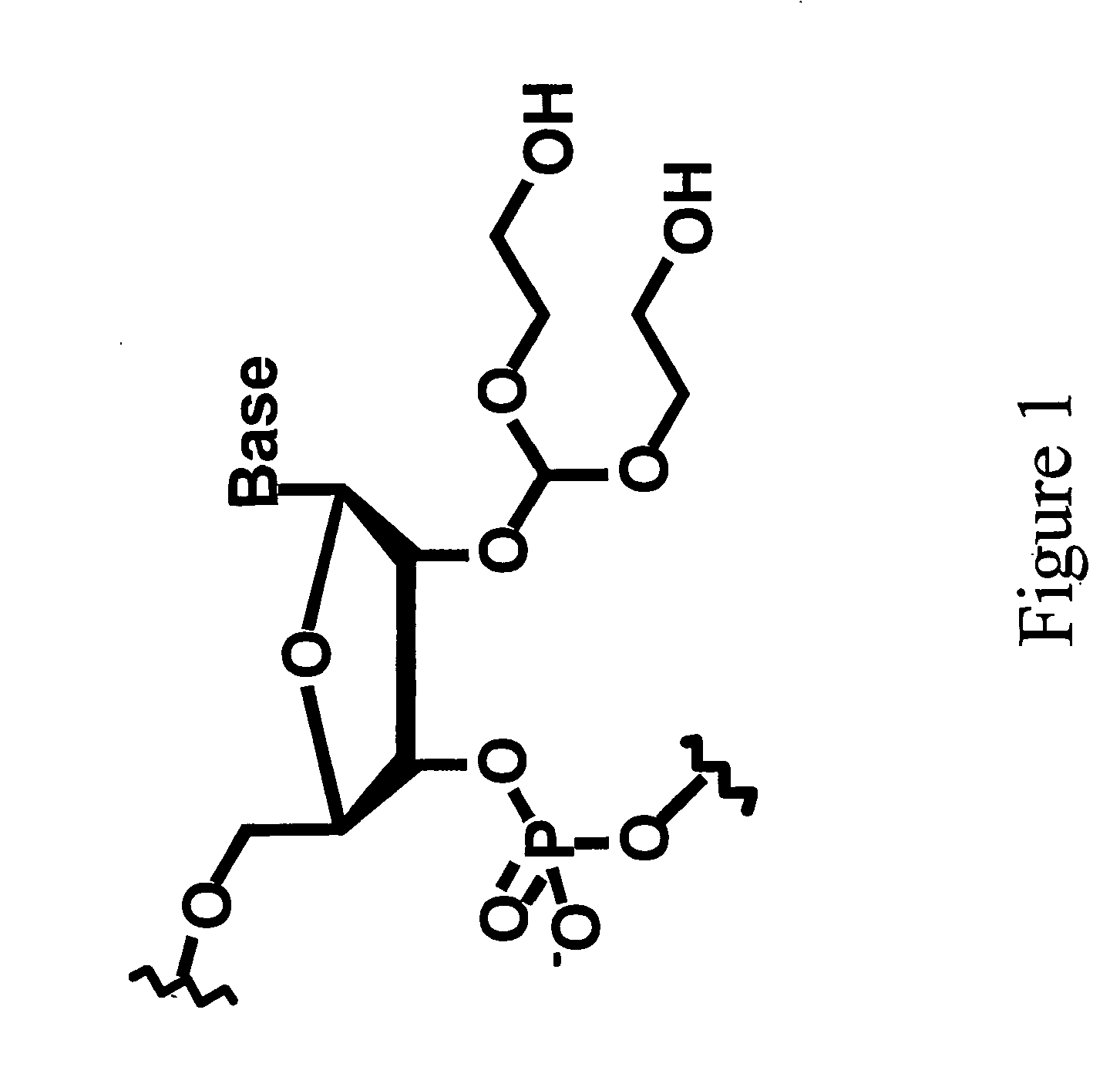
Triphosphate oligonucleotide modification reagents and uses thereof
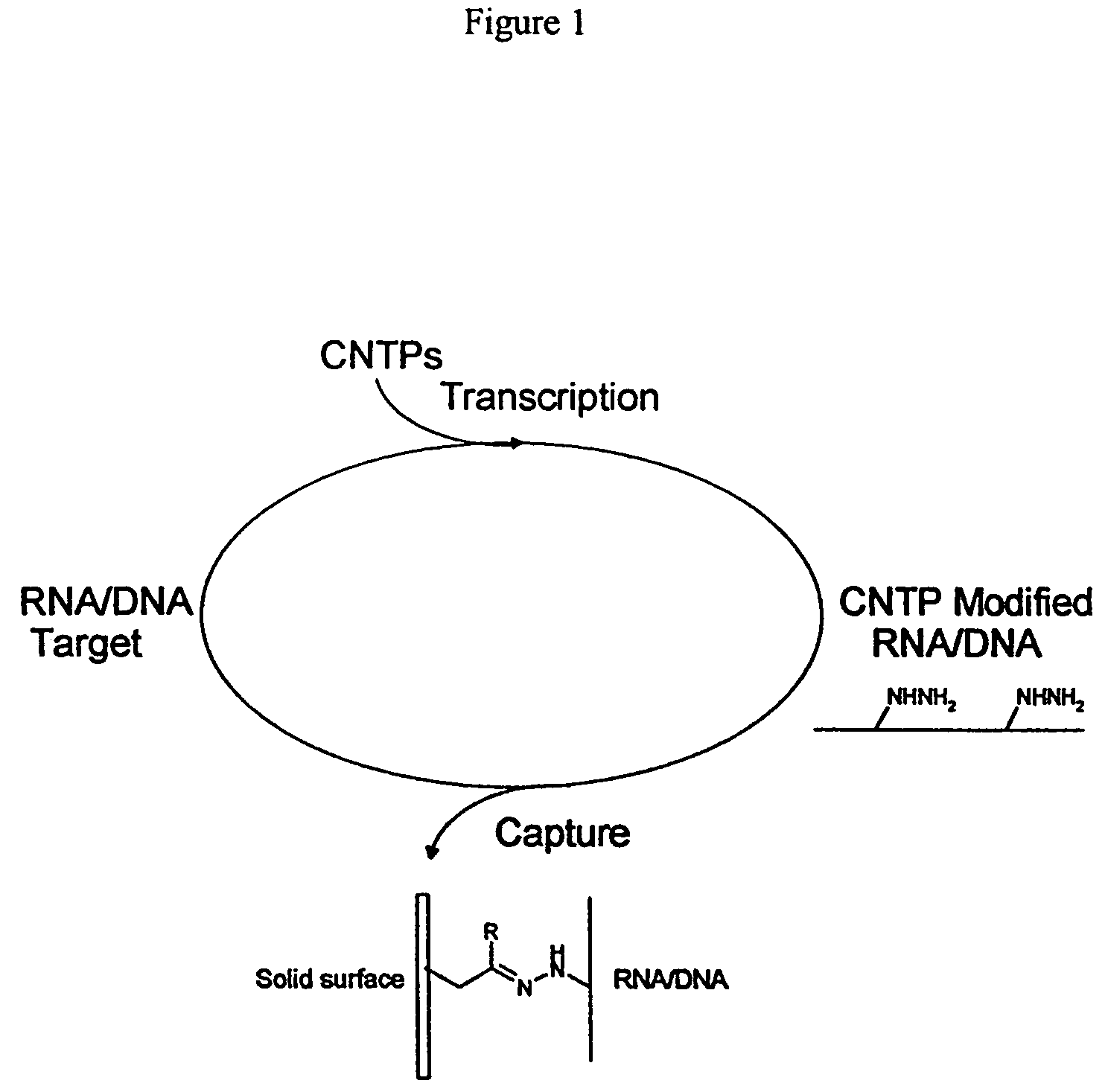
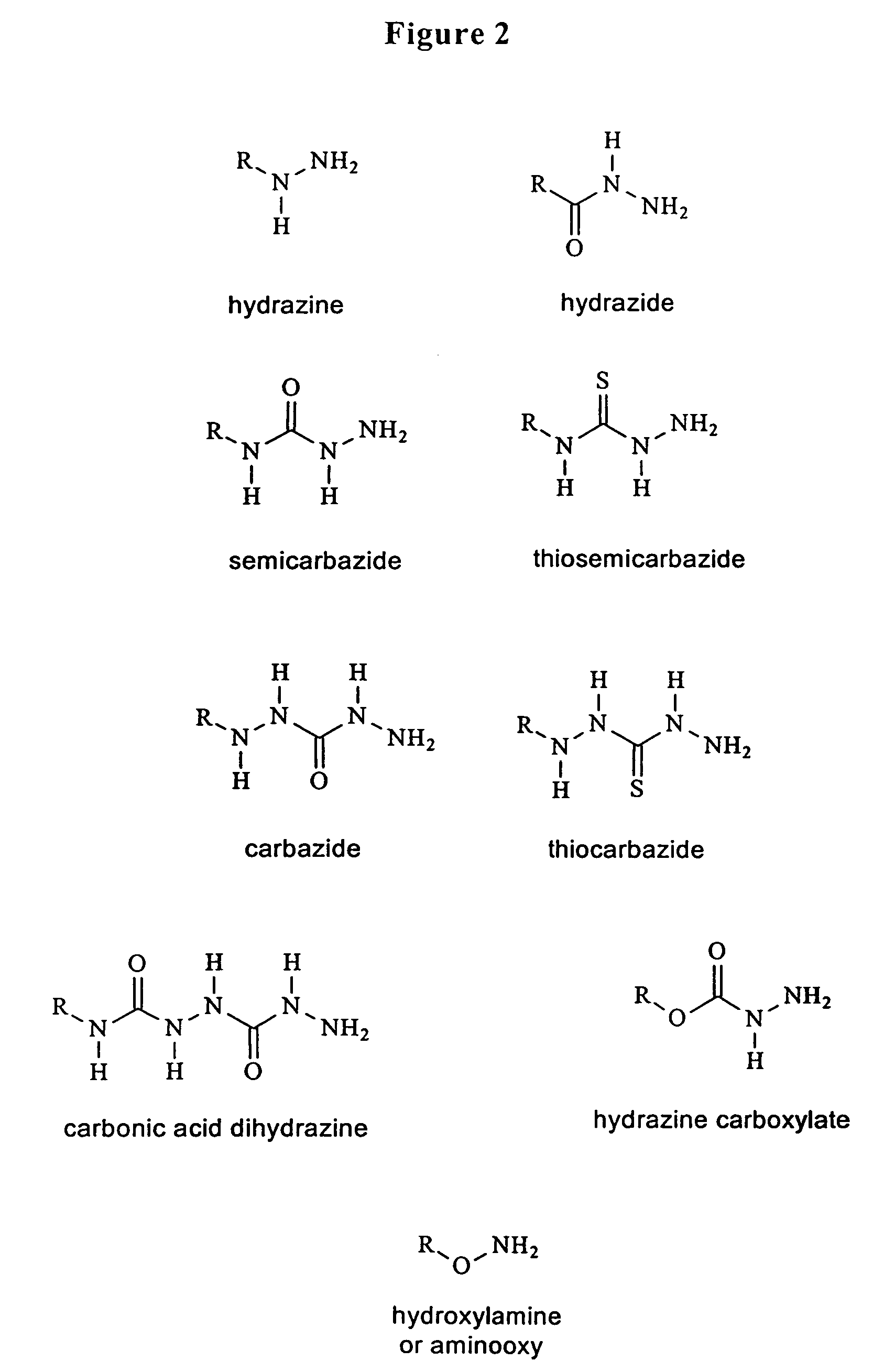
InactiveUS7173125B2Accurate measurementImprove the immunitySugar derivativesCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationEnzymatic synthesisHydrazone
Hydrazino, oxyamino and carbonyl-based monomers and methods for incorporation into oligonucleotides during enzymatic synthesis are provided. Modified oligonucleotides are provided that incorporate the monomers provided herein. Immobilized oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide conjugates that contain covalent hydrazone or oxime linkages are provided. Methods for preparation of surface bound oligonucleotides are provided. Methods for the preparation of oligonucleotide conjugates are also provided.
Owner:VECTOR LAB +1
Load-type ion liquid catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101664700AEasy to prepareHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationMolecular sieveEnzymatic synthesis
The invention discloses a load-type ion liquid catalyst and a preparation method and an application thereof. The load-type ion liquid catalyst is characterized in that a carrier is loaded with pyridine acidic ionic liquid [XPy]HSO4, wherein X is ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, normal-butyl, 3-methylbutyl or 3-amyl; the carrier is gamma-Al2O3, SiO2, mesoporous molecular sieve SBA-15 and carbon fiber; themass ratio of the carrier to the pyridine acidic ionic liquid is 0.5-1.5:1. The invention also discloses the preparation method of the load-type ion liquid catalyst and the application thereof in enzymatic synthesis of diglycol. The invention has the beneficial effects that the invention provides a novel load-type ion liquid catalyst, has simple catalyst preparing method, high catalyst activity and long service life, is applied to enzymatic synthesis of diglycol, has moderate reaction condition, simple production technology, higher diglycol percent conversion and selectivity and is suitable for industrialization.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Enzymatic synthesis of poly(amine-co-esters) and methods of use thereof for gene delivery
ActiveUS9272043B2Increase stability and half-lifeImprove targetingOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDiseaseEnzymatic synthesis
Poly(amine-co-ester) polymers, methods of forming active agent-load nanoparticles therefrom, and methods of using the nanoparticles for drug delivery are disclosed. The nanoparticles can be coated with an agent that reduces surface charge, an agent that increases cell-specific targeting, or a combination thereof. Typically, the loaded nanoparticles are less toxic, more efficient at drug delivery, or a combination thereof compared to a control other transfection reagents. In some embodiments, the nanoparticles are suitable for in vivo delivery, and can be administered systemically to a subject to treat a disease or condition.
Owner:YALE UNIV
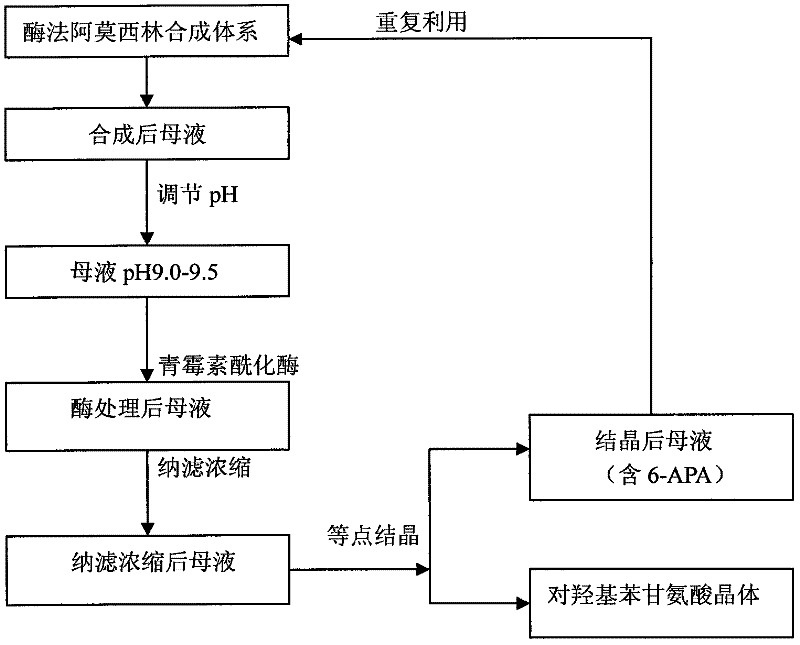
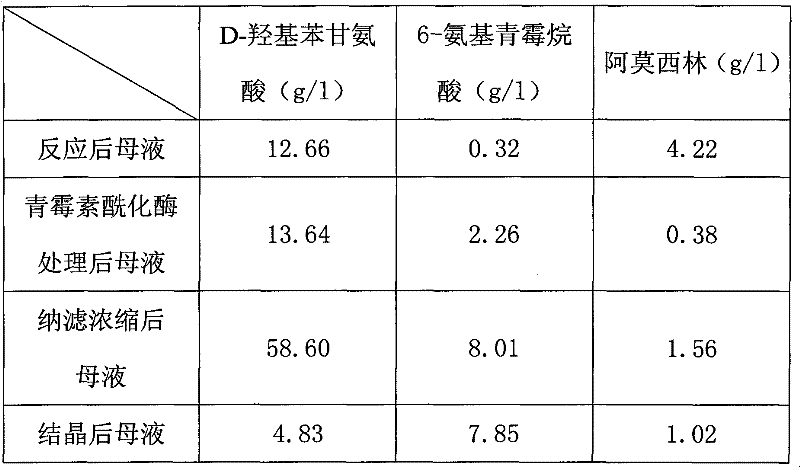
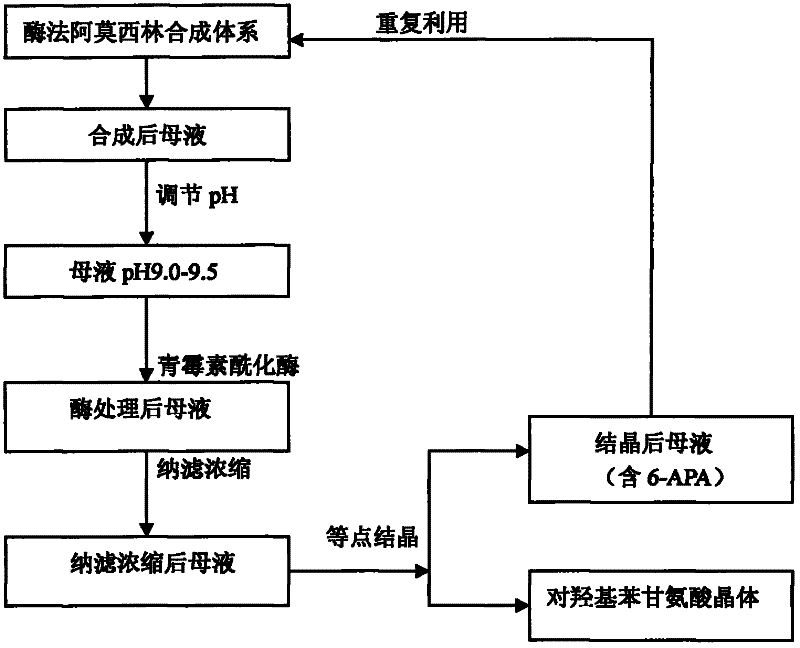
Recovering method of effective components in amoxicillin enzymatic synthesis mother liquor by utilizing nanofiltration
ActiveCN102392060AAvoid destructionImprove hydrolysis efficiencyOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationEnzymatic synthesisIsoelectric point
The invention discloses a recovering method of effective components in amoxicillin enzymatic synthesis mother liquor by utilizing nanofiltration. The method comprises the following steps: (1) regulating pH of the mother liquor; (2) hydrolyzing amoxicillin in the mother liquor by utilizing penicillin acylase, thus only D-hydroxyphenylglycine and 6-amino-penicillanic acid (6-amino-penicillanic acid) exist in the other liquor; (3) preparing concentrated mother liquor by nanofiltration; and (4) separating and recovering the D-hydroxyphenylglycine and the 6-amino-penicillanic acid (6-amino-penicillanic acid) by isoelectric point crystallization. The method has the advantages that: the recycling rate of an inactive lateral chain can be improved regarding certain amoxicillin synthetase with highhydrolysis activity, so that the enzymatic synthesis of amoxicillin is more economical.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA CHANGSHENG PHARMA
Method for continuous enzymatic synthesis of n-3PUFA glyceride
ActiveCN101736044ARealize continuous enrichment productionAchieve reuseFermentationEnzymatic synthesisMolecular sieve
The invention relates to a method for continuous enzymatic synthesis of n-3PUFA glyceride, comprising the following steps: preparing fish oil n-3PUFA (EPA, DHA) and glycerol into reaction liquid according to a certain proportion; then pumping reaction liquid into an enzyme reaction column provided with immobilized lipase through a constant current pump for carrying out reaction for enzymatic synthesis of n-3PUFA; finally realizing continuous enzymatic synthetic production of n-3PUFA by controlling circulation flow velocity of the reaction liquid in the reactor and setting a molecular sieve dehydrater in the reaction system. The n-3PUFA glyceride product prepared by the continuous syhthesis method features an ester yield of 30-50%, a monoester content of 20-30%, a diester content of 50-70%and a trig content of 10-20%. With the method of the invention adopted, recycle of enzyme can be realized, cost can be greatly reduced, production cycle can be shortened, production efficiency can beimproved and the operation is easy, so that the method is of great practical value to industrialized batch production.
Owner:舟山新诺佳生物工程有限责任公司
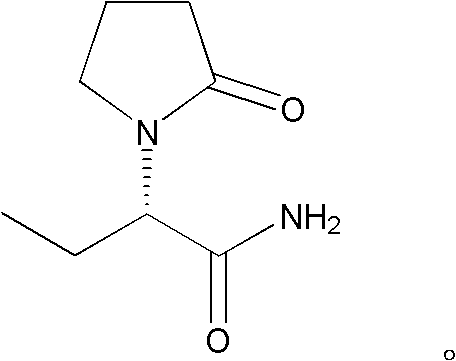
A method for preparing (s)-2-aminobutanamide by enzymatic method
InactiveCN102260721AReduce processing costsCost advantageFermentationEnzymatic synthesisOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a synthesis process for preparing (S)-2-aminobutyramide by enzymatic method. The current preparation method has problems such as high cost, low yield, and large environmental hazards. The technical scheme adopted in the invention is: using 2-aminobutyronitrile as a starting material to prepare (S)-2-aminobutyramide in one step in a buffer solution system through enzyme catalysis. In the present invention, water is used as a solvent in the main process, without using a large amount of organic solvents harmful to the environment, the whole process cost is low, and it is beneficial to large-scale industrial preparation.
Owner:SYNCOZYMES SHANGHAI
Process for enzymatic synthesis of cefprozil
InactiveCN104928340ASimple processEasy to operateOn/in organic carrierFermentationEnzymatic synthesisSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a medicine synthesis method, in particular to a process method for screening of immobilized cefprozil synthetase and enzymatic synthesis of cefprozil. In order to solve the problems that a conventional cefprozil enzymatic synthesis process has difficulties in screening and evaluating immobilized anzyme, tedious in production process step, poor in control point, long in reaction time, low in conversion ratio and the like, the invention provides an immobilized cefprozil synthetase and a novel process for cefprozil synthesis.
Owner:AMICOGEN CHINA BIOPHARM CO LTD
Proline CCI-779, production of and uses therefor, and two-step enzymatic synthesis of proline CCI-779 and CCI-779
Owner:WYETH LLC
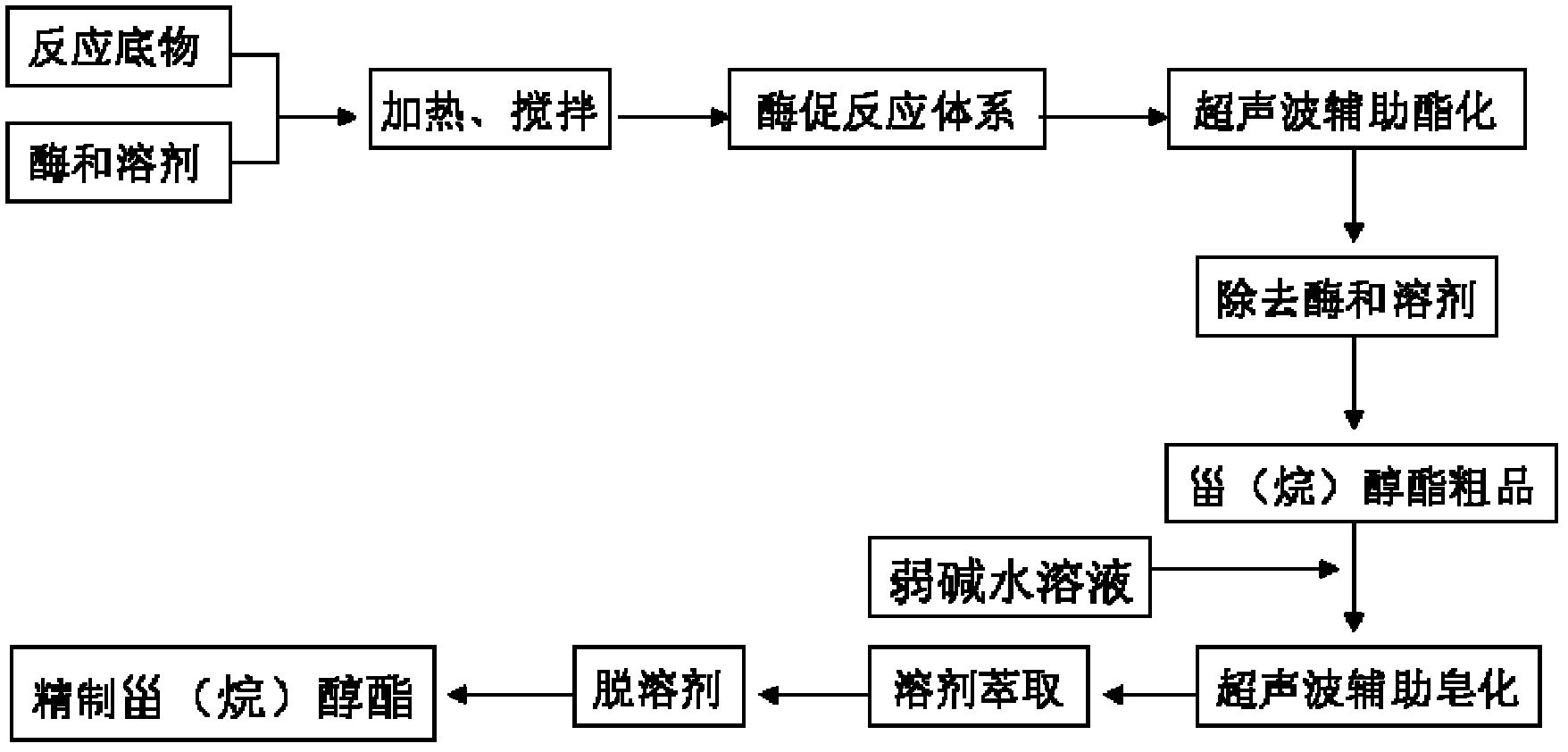
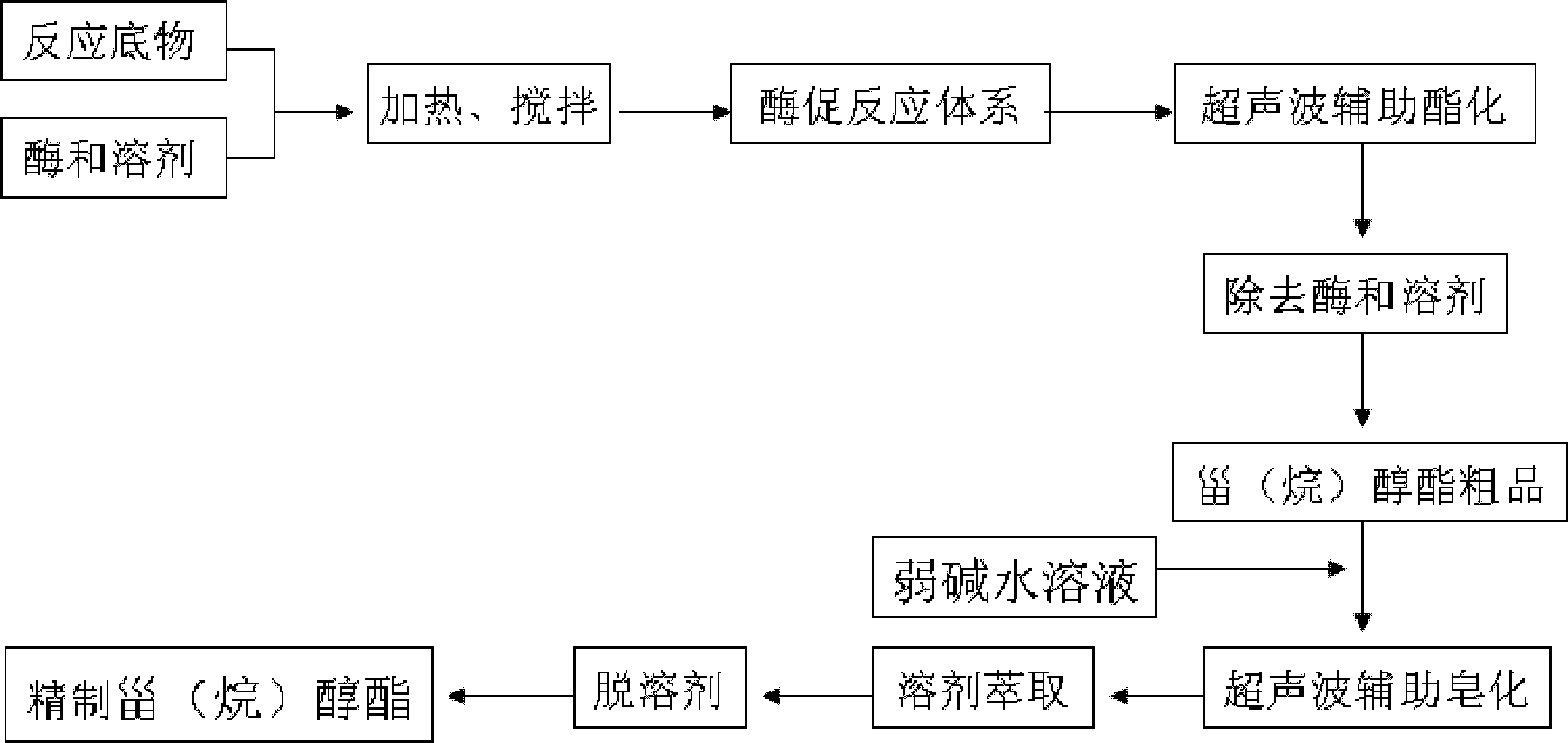
Enzymatic synthesis method of phytosterol ester/phytostanol ester by utilizing ultrasonic enhancement
ActiveCN102618615AWill not damage the structureHigh catalytic activityFermentationEnzymatic synthesisSterol ester
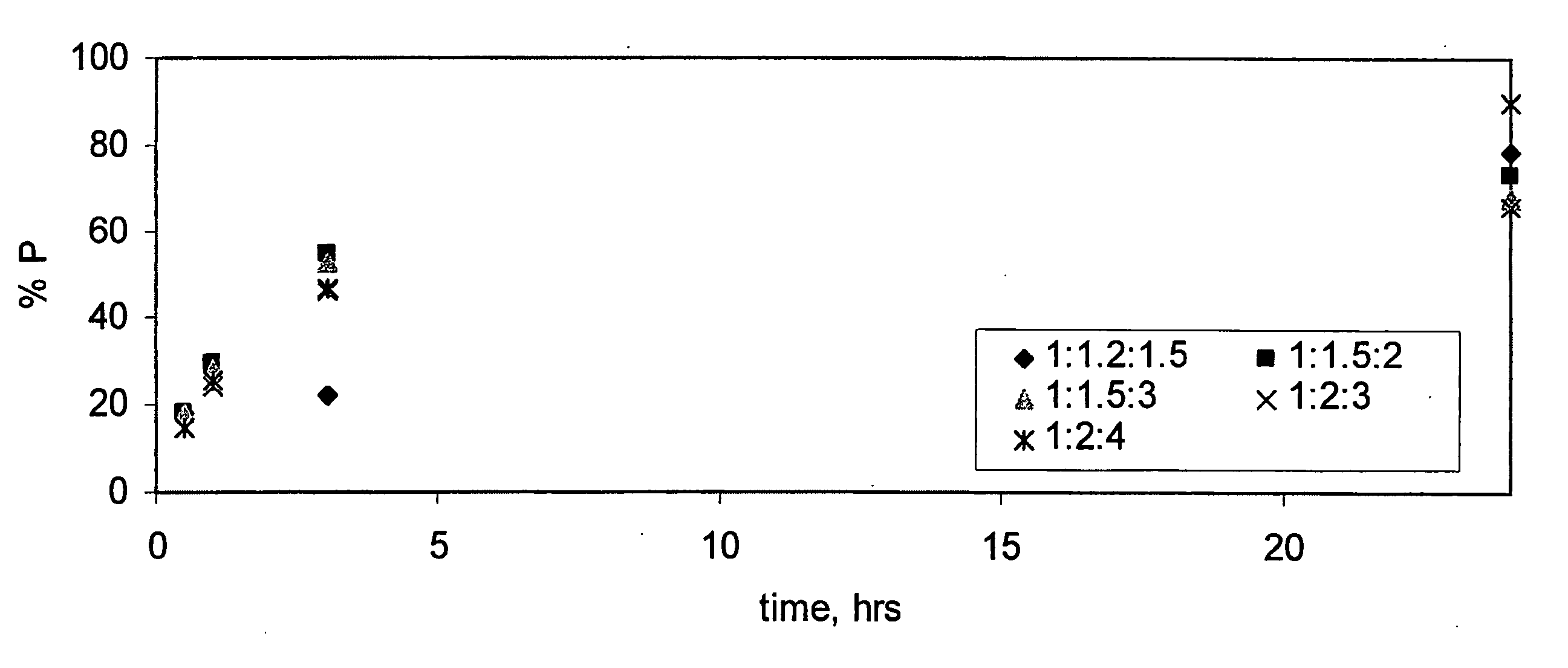
The invention relates to a preparation method of sterol ester and in particular relates to an enzymatic synthesis method of phytosterol ester / phytostanol ester by utilizing ultrasonic enhancement. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) preparing a heterogeneous enzyme reaction system: weighing the phytosterol ester / phytostanol ester and fatty acid at a molar ratio of 1:(1.2-2), adding a reaction solvent, and adding enzyme and a molecular sieve; 2) performing enzymatic esterification with ultrasonic assistance: immersing an ultrasonic probe in a reaction solution, opening an ultrasonic wave generator, constantly radiating with ultrasonic wave for 0.5 to 3 hours under mechanical stirring, and continuously reacting for 4 to 10 hours under mechanical stirring after the radiation is completed; and 3) removing the fatty acid with ultrasonic assisted saponification to obtain the product. According to the method, the enzymatic esterification reaction time can be remarkably shortened, the usage of enzyme can be reduced, and the saponification speed of excessive fatty acid can be accelerated, so that the efficiency of separation and purification can be improved, and the obtained phytosterol ester / phytostanol ester product has the characteristics of light color, high purity and safety without contamination.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
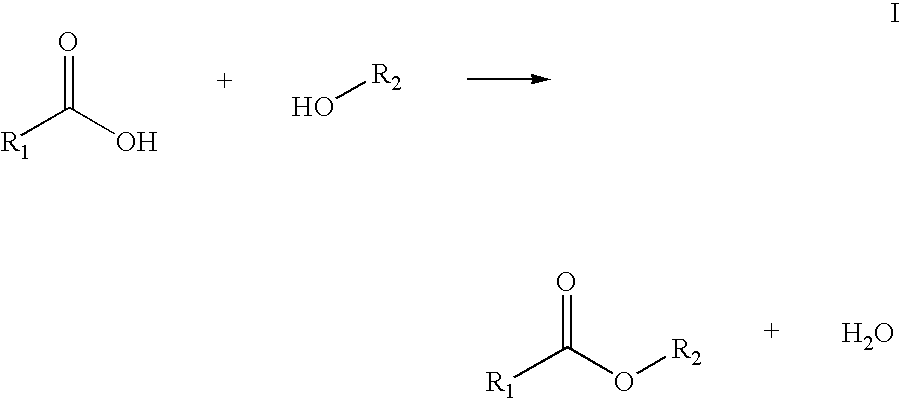
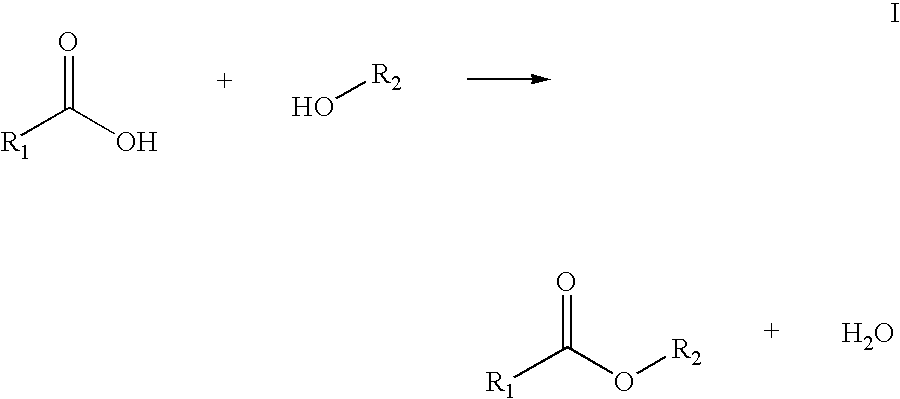
Process for enzymatically preparing carboxylic esters
ActiveUS8216813B2Speed up the conversion processShort reaction timeOrganic chemistryFermentationEnzymatic synthesisPolymer science
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Production method of rare ginsenoside Rh2
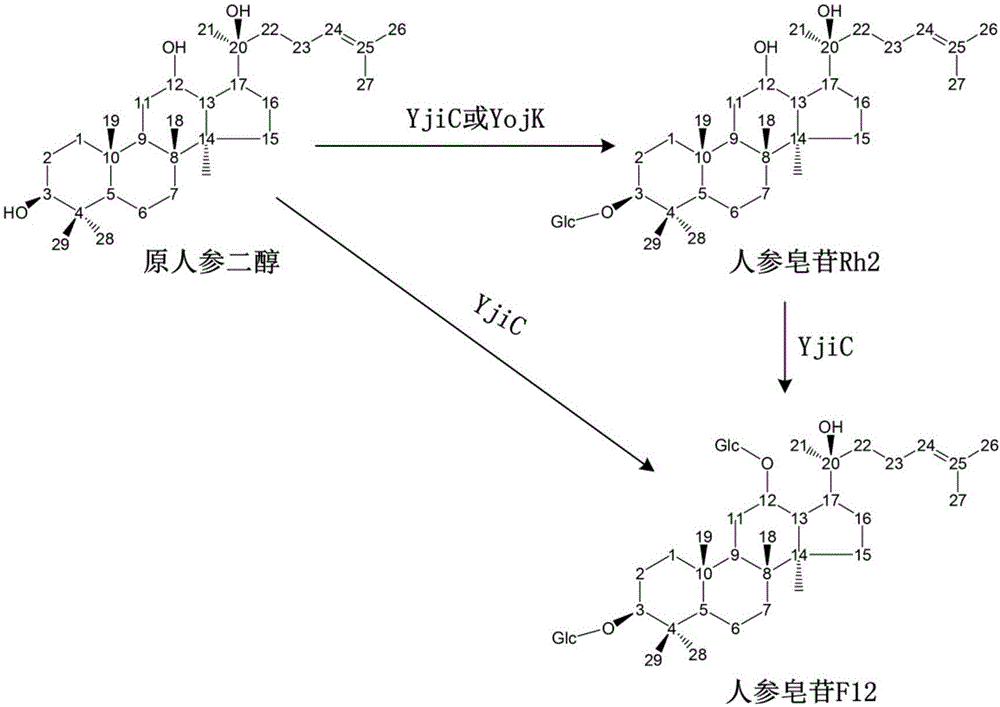
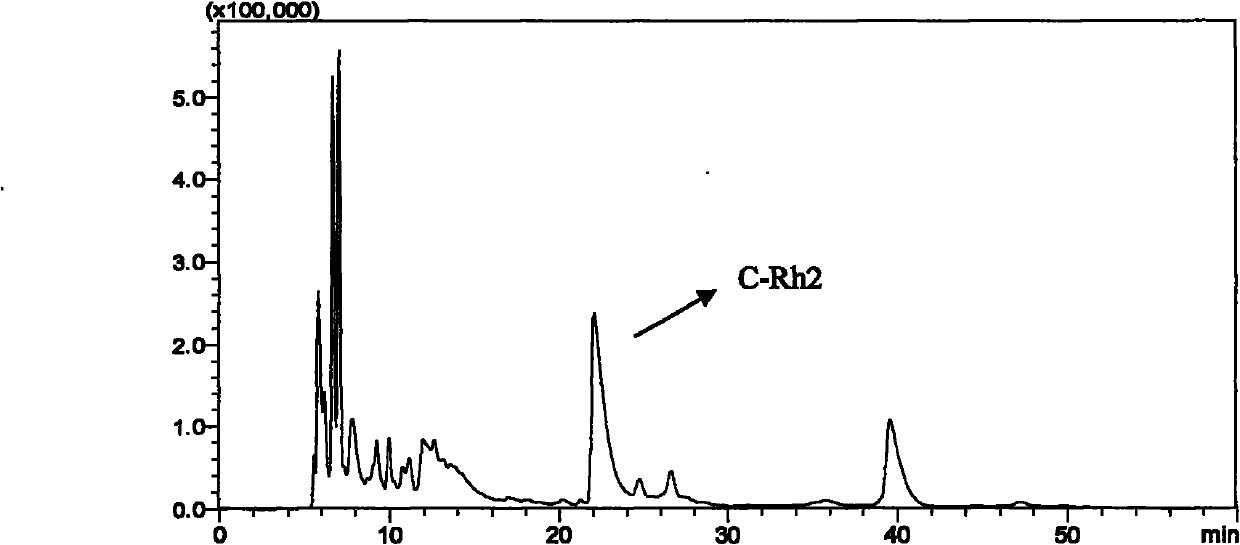
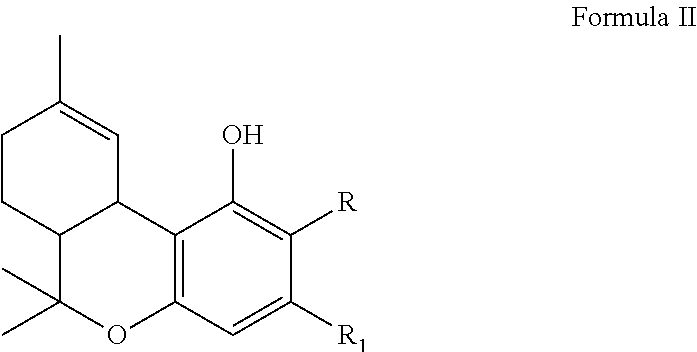
InactiveCN106350565AEfficient productionProduction economyTransferasesFermentationEnzymatic synthesisProtopanaxadiol
The invention discloses a production method of rare ginsenoside Rh2 and belongs to the field of enzymatic synthesis of ginsenoside. The production method includes that protopanoxadiol is used as a substrate, glycosyltransferase YjiC or YojK screened from bacillus subtilis is used as a catalyst, and the glycosylation of the C3 hydroxyl of the protopanoxadiol is efficiently catalyzed through in-vitro enzyme reaction to generate the ginsenoside Rh2. The production method is cheap in raw materials, high in ginsenoside Rh2 yield, low in production cost and capable of achieving large-scale production of the precious and rare ginsenoside Rh2.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Carbohybrate purification using ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis and nanofiltration
InactiveCN1242776APurification using adsorption agentsSugar derivativesEnzymatic synthesisUltrafiltration
The invention provides methods for purifying carbohydrates, including oligosaccharides, nucleotide sugars, and related compounds, by use of ultrafiltration, nanofiltration and / or reverse osmosis. The carbohydrates are purified away from undesired contaminants such as compounds present in reaction mixtures following enzymatic synthesis or degradation of oligosaccharides.
Owner:NEOSE TECH
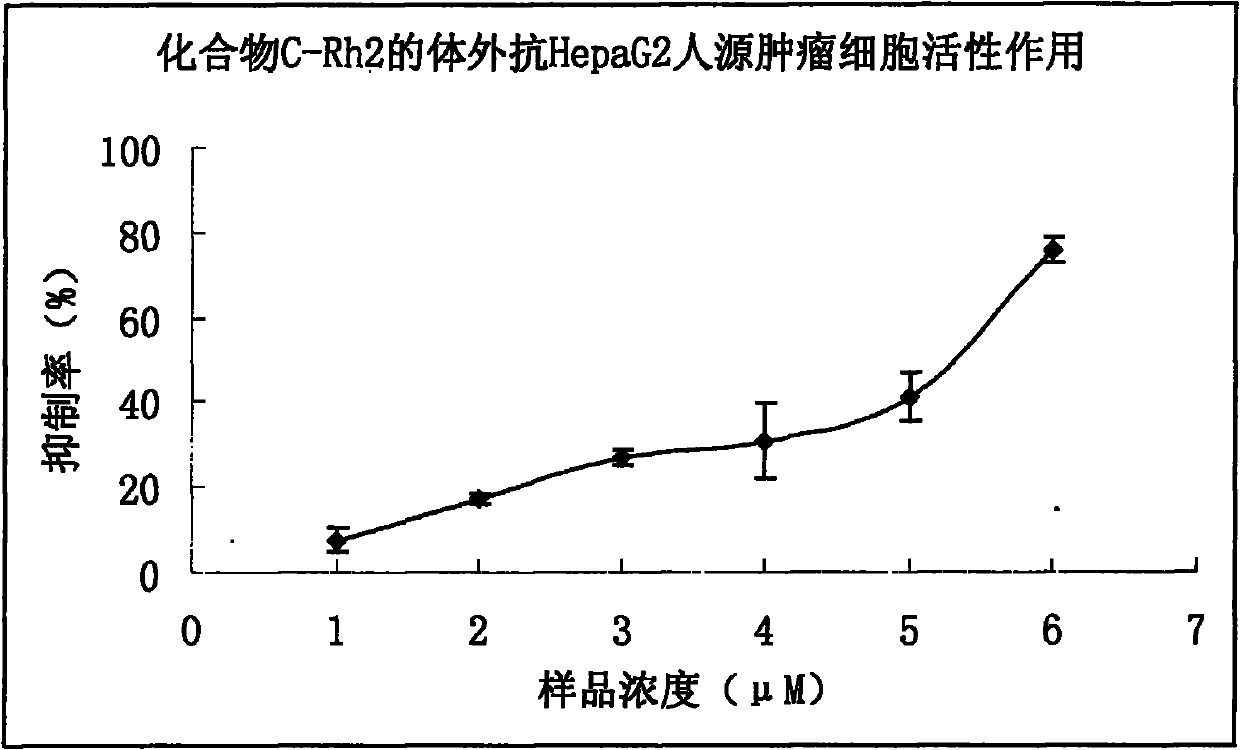
Preparation method and medicinal application of ginsenoside Rh2 aliphatic ester compound
The invention discloses two ginsenoside Rh2 aliphatic ester compounds. The compounds have the following structural formula described in the specification. In the formula, R is a C4-C22 fatty acid acyl. The invention also provides the chemical synthesis and enzymatic synthesis methods of the ginsenoside Rh2 aliphatic ester compounds, a pharmaceutical composition which takes the compounds as active ingredients and an application of the compounds and the pharmaceutical composition in preparation of an anticancer drug.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
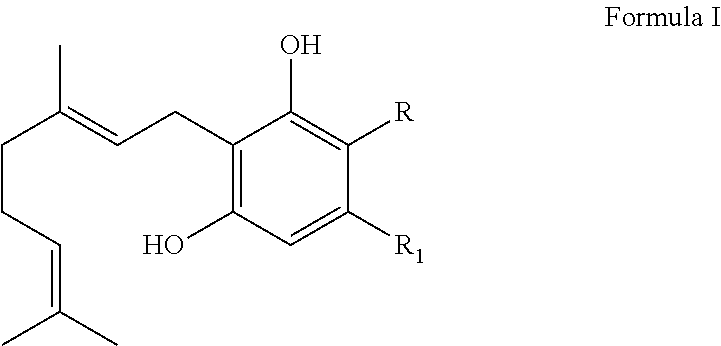
BIOENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF THC-v, CBV AND CBN AND THEIR USE AS THERAPEUTIC AGENTS
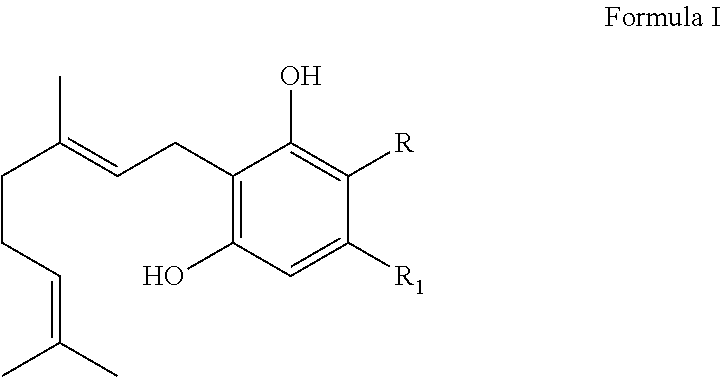
The present invention provides methods for producing cannabinoids. More specifically, the invention is directed to the bio-enzymatic synthesis of THC-v, CBV and CBN by contacting a compound according to Formula I with a cannabinoid synthase enzyme. Also described is a system for producing these pharmaceutically important cannabinoids and the use of such cannabinoids as therapeutic agents.
Owner:TEEWINOT TECH LTD
Process for enzymatically preparing carboxylic esters
ActiveUS20090181439A1Reduce the probability of reactionSpeed up the conversion processOrganic chemistryFermentationEnzymatic synthesisPolymer science
Process for enzymatically synthesizing carboxylic esters, characterized in that mixing and discharge of the water of reaction are effected by introducing a gas while achieving low effectiveness ratios EV.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
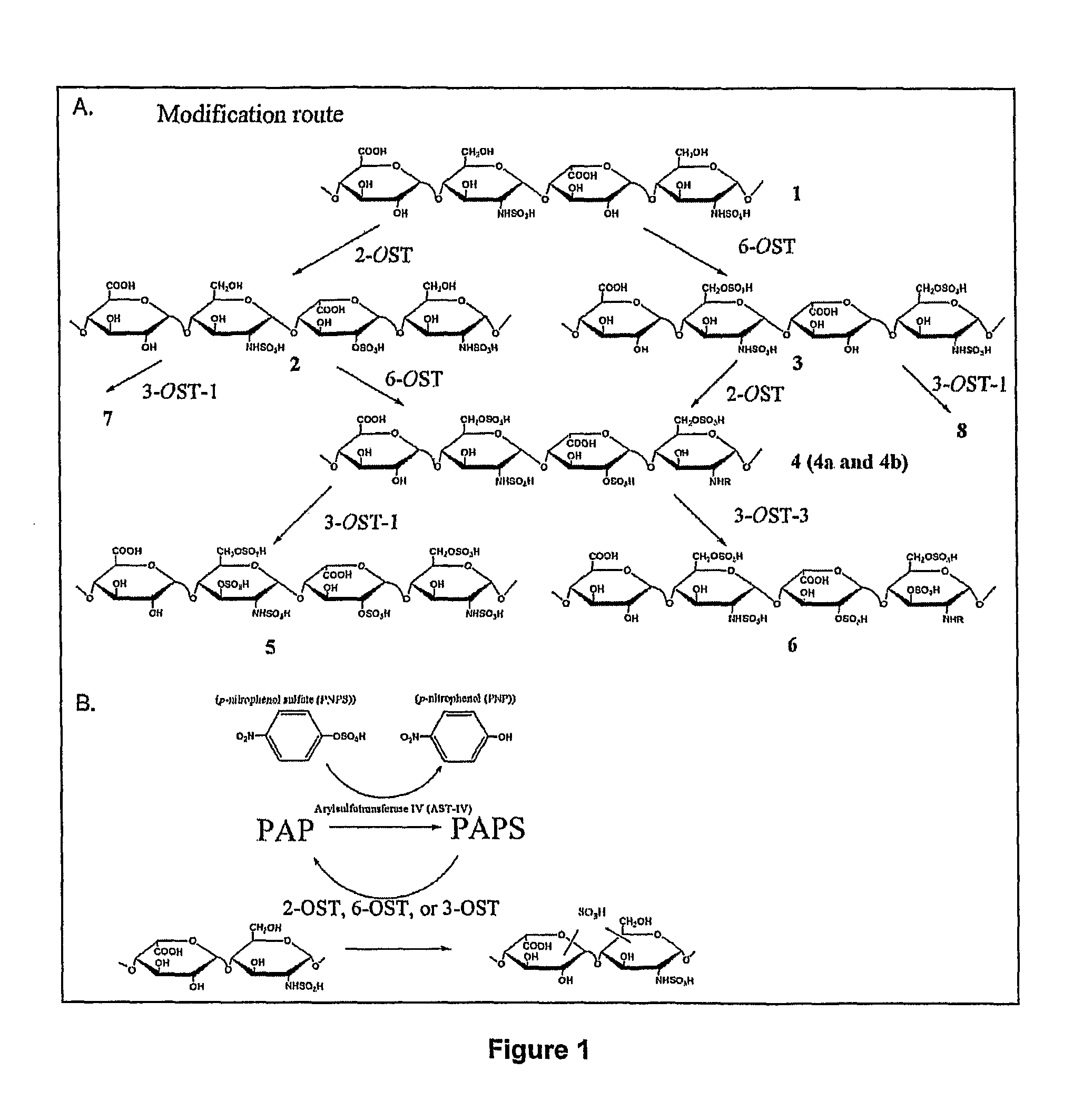
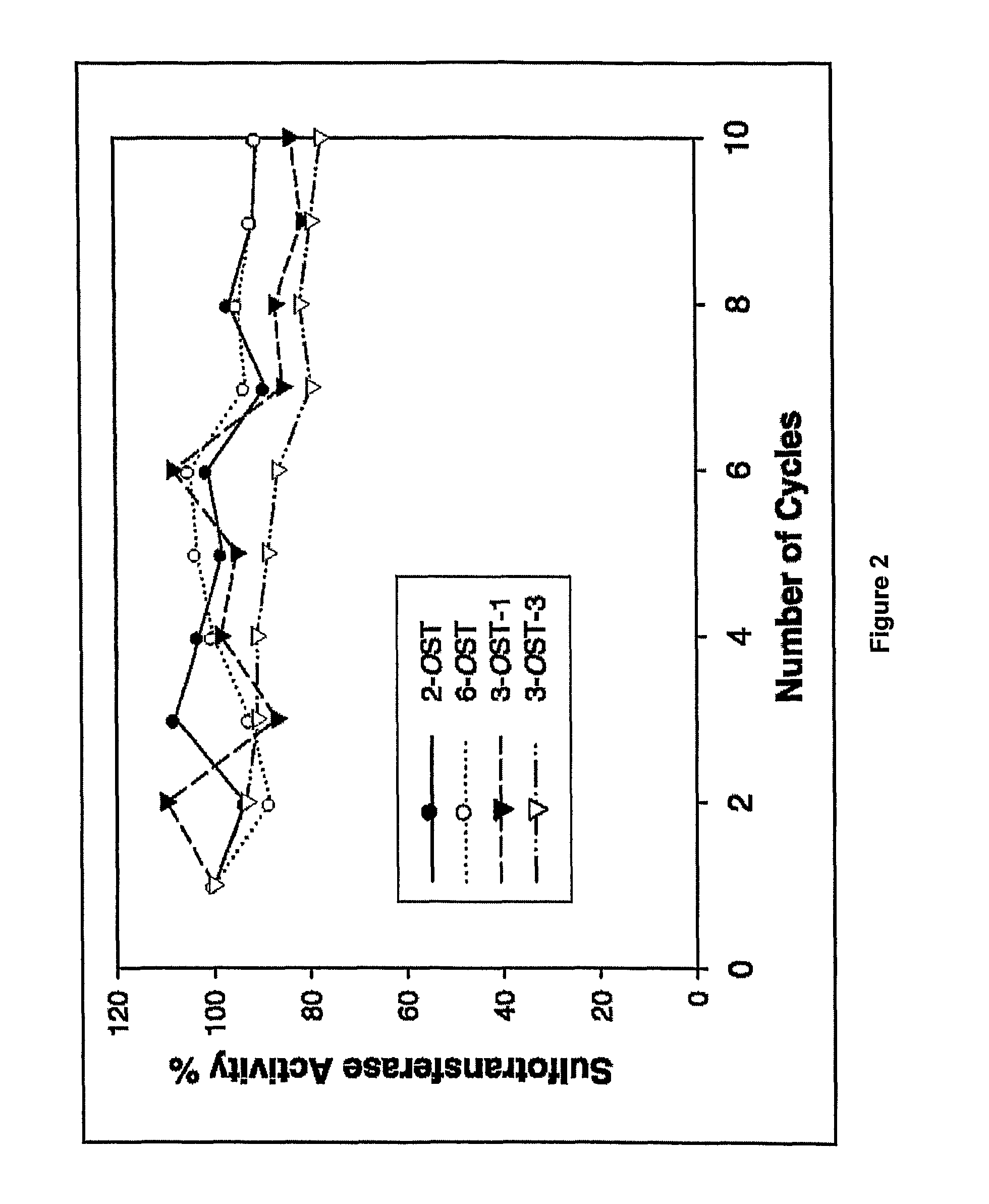
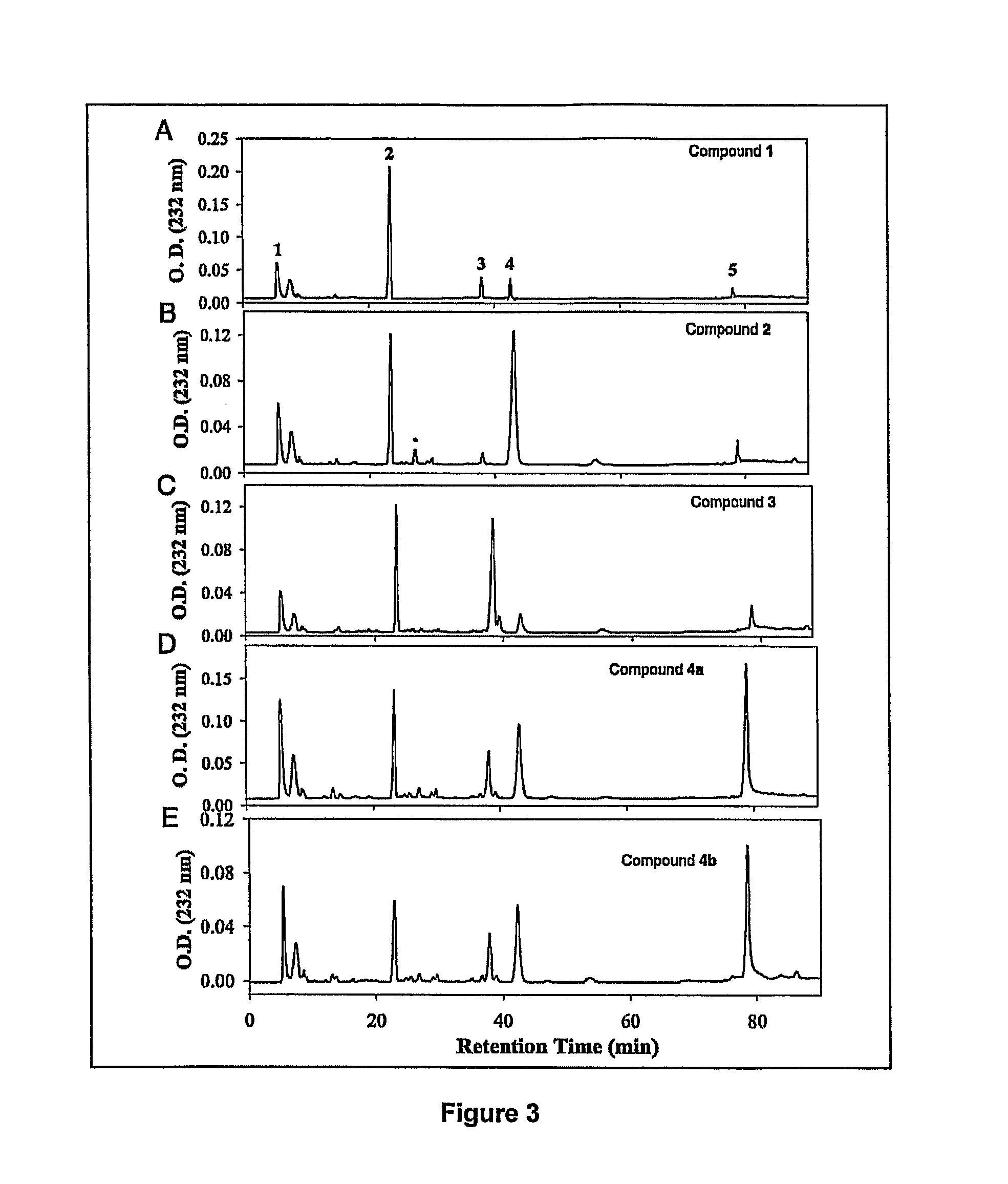
Enzymatic synthesis of sulfated polysaccharides
Heparin is synthesized from a polysaccharide comprised of a 1-4 glycosidically linked alternating polymer of uronic acid and glucosamine residues, wherein the uronic acid is selected from iduronic and glucuronic acid, wherein the glucosamine is partially N-sulfated; by a series of selective reactions catalyzed by recombinant enzymes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Method for producing L-ascorbyl palmitate through non-aqueous phase enzymatic synthesis
The invention discloses a method for producing L-ascorbyl palmitate through non-aqueous phase enzymatic synthesis. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing L-ascorbic acid with palmitic acid in a non-aqueous medium, adding immobilized lipase for catalytic reaction for 20-50 hours; (2) filtering the reaction liquid obtained in the step (1) to remove the immobilized lipase and undissolved L-ascorbic acid and evaporating the obtained filtrate under reduced pressure to remove a solvent; and (3) dissolving the residue obtained in the step (2) with ethyl acetate, washing with deionized water, separating an ethyl acetate phase out, evaporating under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, dissolving the residue with toluene, recrystallizing, centrifuging, washing the obtained substance with normal hexane and drying the obtained undissolved substance in vacuum to obtain an L-ascorbyl palmitate product. The method relates to non-aqueous enzymatic synthesis, has the advantages of high catalytic efficiency, mild reaction condition, low pollution, simple process, readily-available raw materials, high yield and convenience for large-scale production, and is accordant with the practical situation of the food additive production industry in China.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FOOD IND RES INST
Process for enzymatic synthesis of ethyl lactate in solvent phase
The invention discloses a ethyl lactate synthesis enzyme catalysis method in solvent phase and belongs to ethyl lactate preparation technology using lactic acid and ethanol, characterizing in the following steps: using chloroform, tert-butanol or tetrahydrofuran as sovent, or adding in the said solvent of lactic acid and ethanol in ratio of (1:5)-(1:10) and lipase according to 10-30 g enzyme catalysis per mol lactic acid, mixing sufficiently, constant temperature water bath in 60-70 DEG C while lactic acid concentration is 0.3-0.6mol / L, concussion table revolution being controlled 200-250revolution / min, reacting 24-48 hours, obtaining crude products containing ethyl lactate. Advantage of the invention compared with existing ethyl lactate preparation method lies in: temperate reaction condition, low energy consumption, easy operation of separating catalyst and products, apparatus not easy corroding, no pollution, high product quality and yield.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Enzymatically synthesized marine phospholipids
InactiveUS20060177486A1Increase ratingsReduce inhibitionFatty acid esterificationClimate change adaptationEnzymatic synthesisRed blood cell
This invention discloses an improved enzymatic process, under organic solvent free conditions, for the incorporation of fatty acids such as omega-3 fatty acids into phospholipids. The rate of transesterification is increased 4 times by adding a base to the reaction mixture, typically an amine. The invention also discloses novel phospholipid compositions as well as novel use of the phospholipid compositions as a food supplement, a fish feed, animal feed and human food. In addition to methods for enriching prey organisms used in aquaculture, methods of reducing arachidonic acid levels in mammalian plasma / red blood cells and methods for increasing DHA levels in the mammalian brain.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ASA
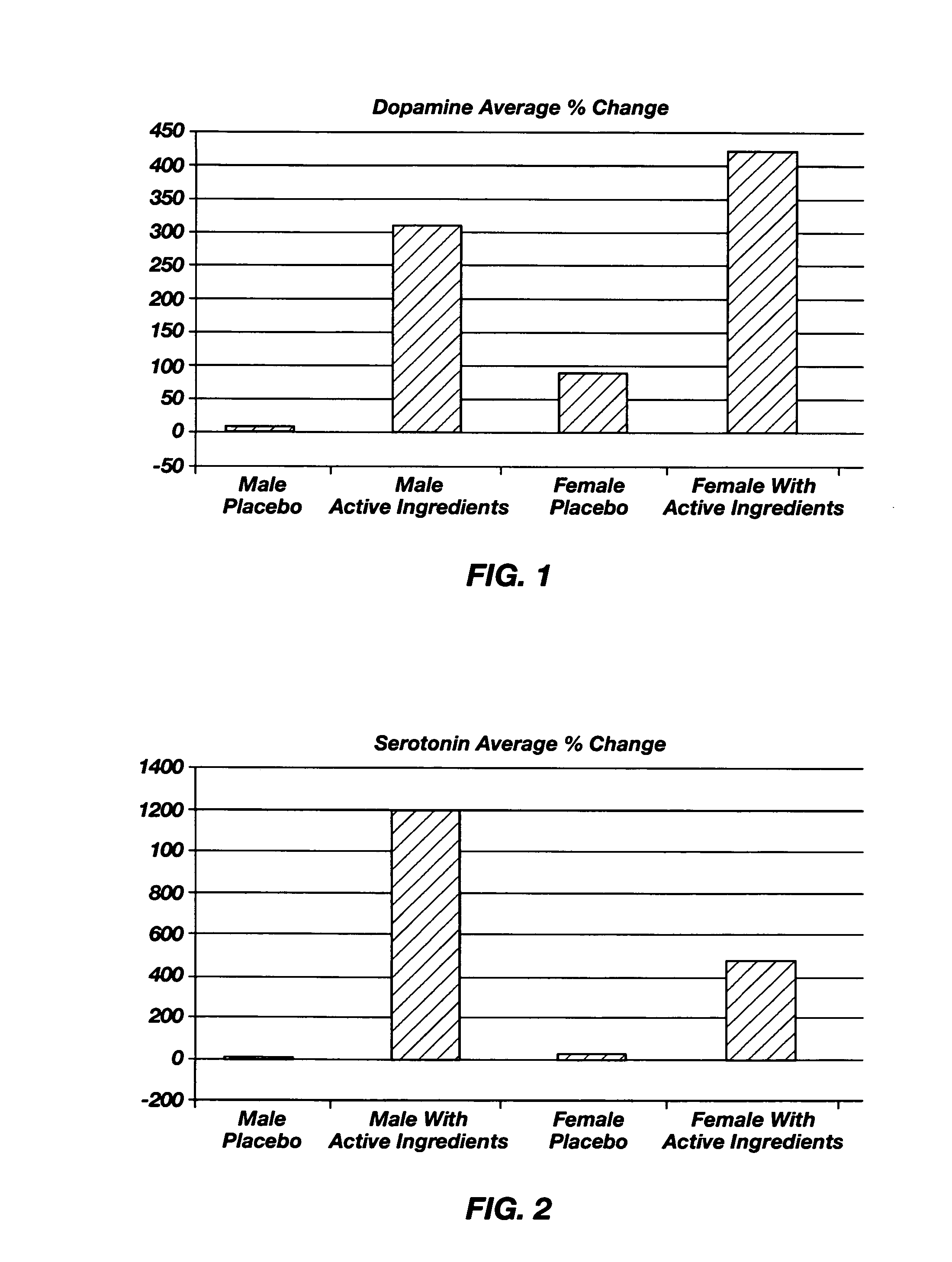
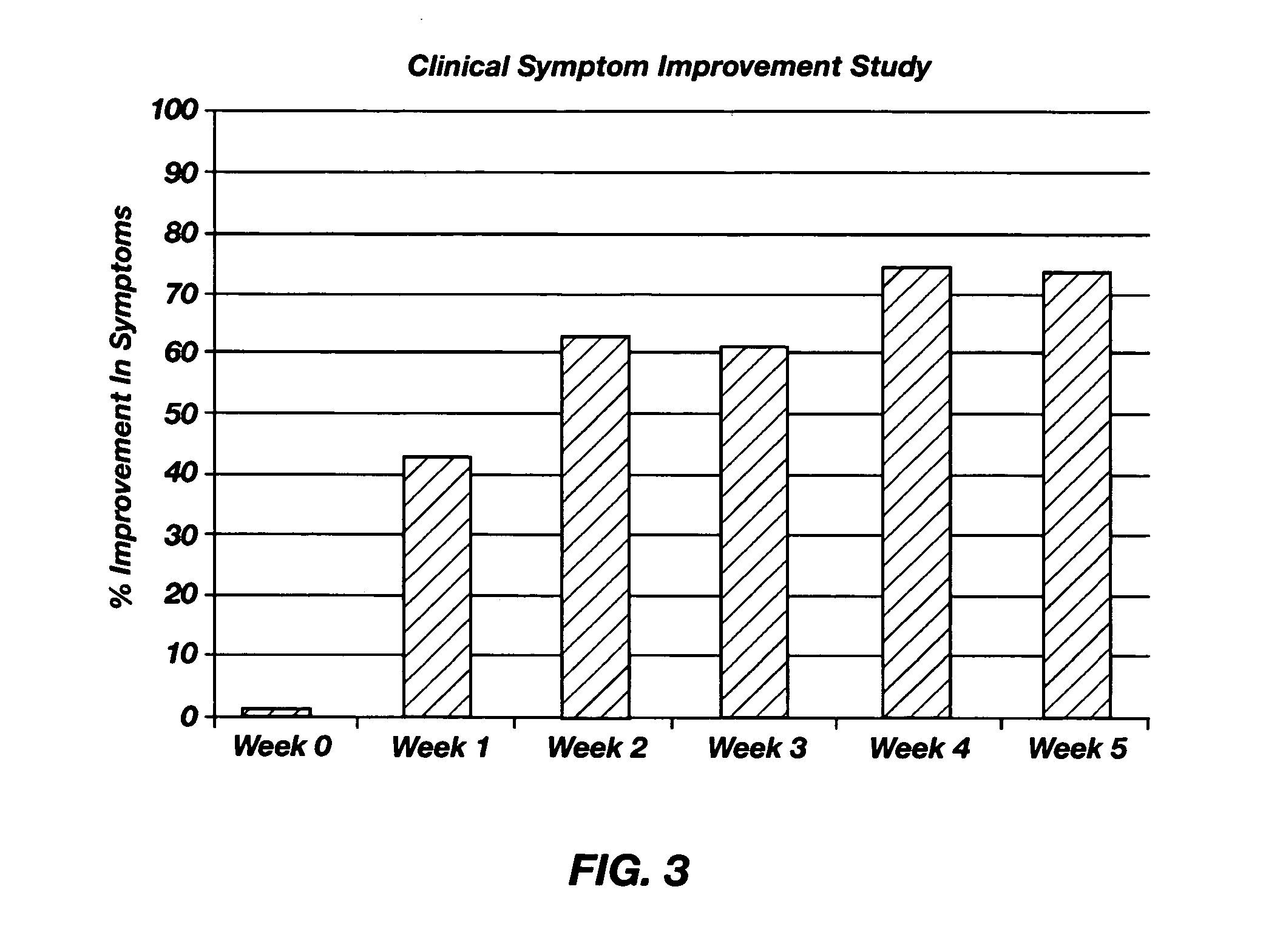
Dietary neurotransmitter precursors for balanced synthesis of neurotransmitters
Dietary supplements for treating a neurotransmitter deficiency include one or more precursors of the deficient neurotransmitter and a cofactor for activating in vivo enzymatic synthesis of the deficient neurotransmitter. The dietary supplements can also include an appropriate neurotransmitter, such as an amino acid. When administered through the oral mucosa, increases in levels of the deficient neurotransmitters and relief from deficiency symptoms are obtained.
Owner:HART CHERYLE RAM +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com