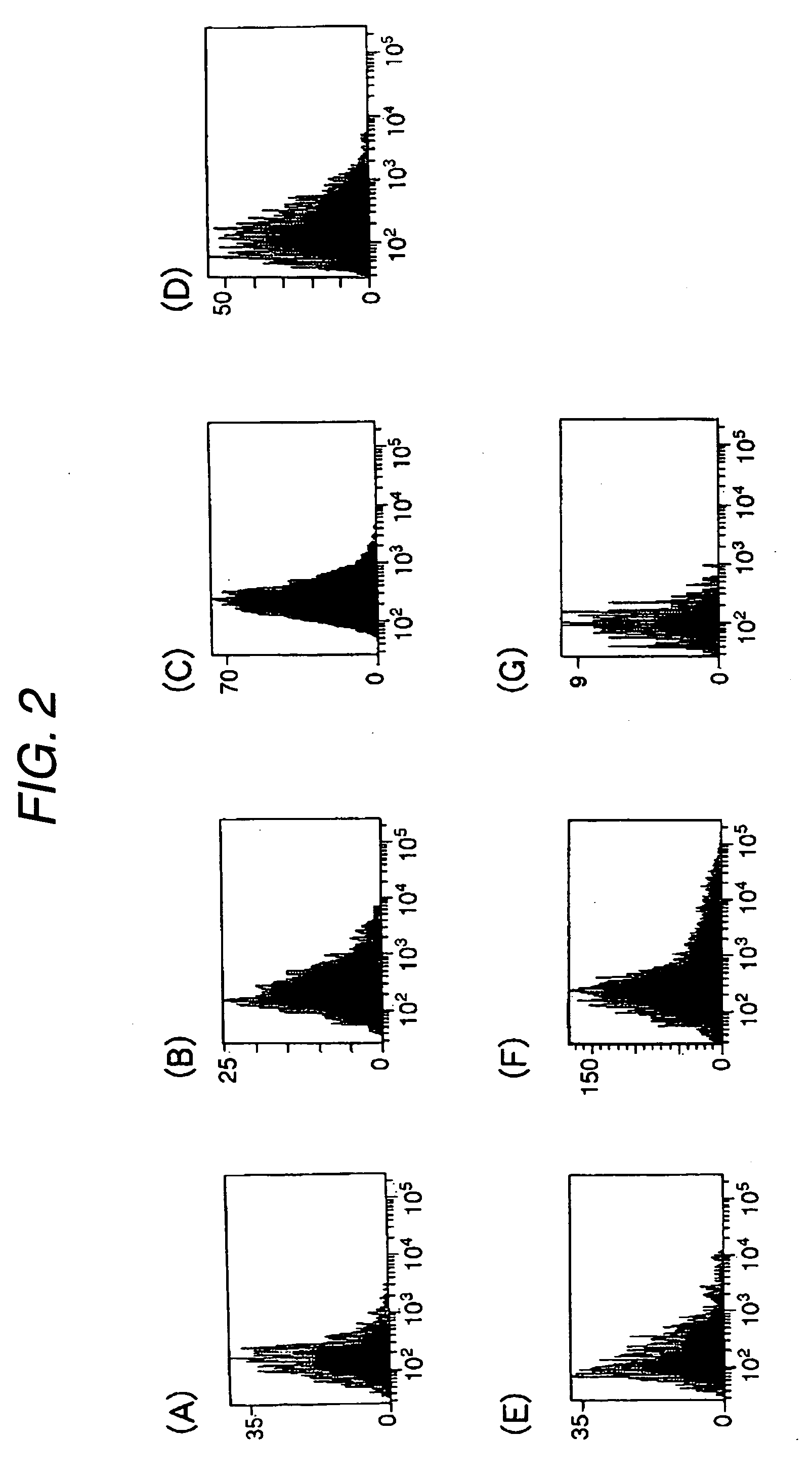
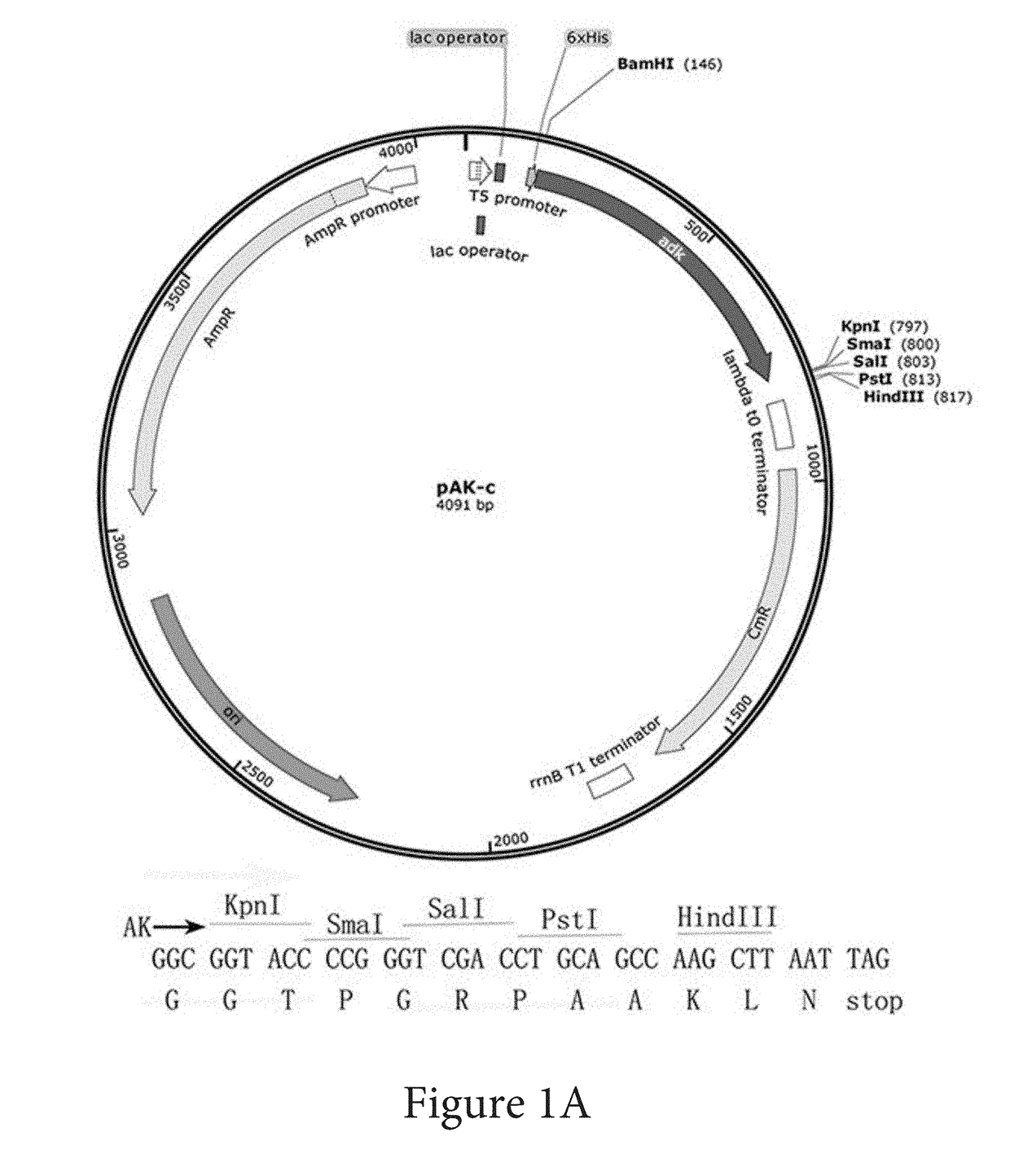
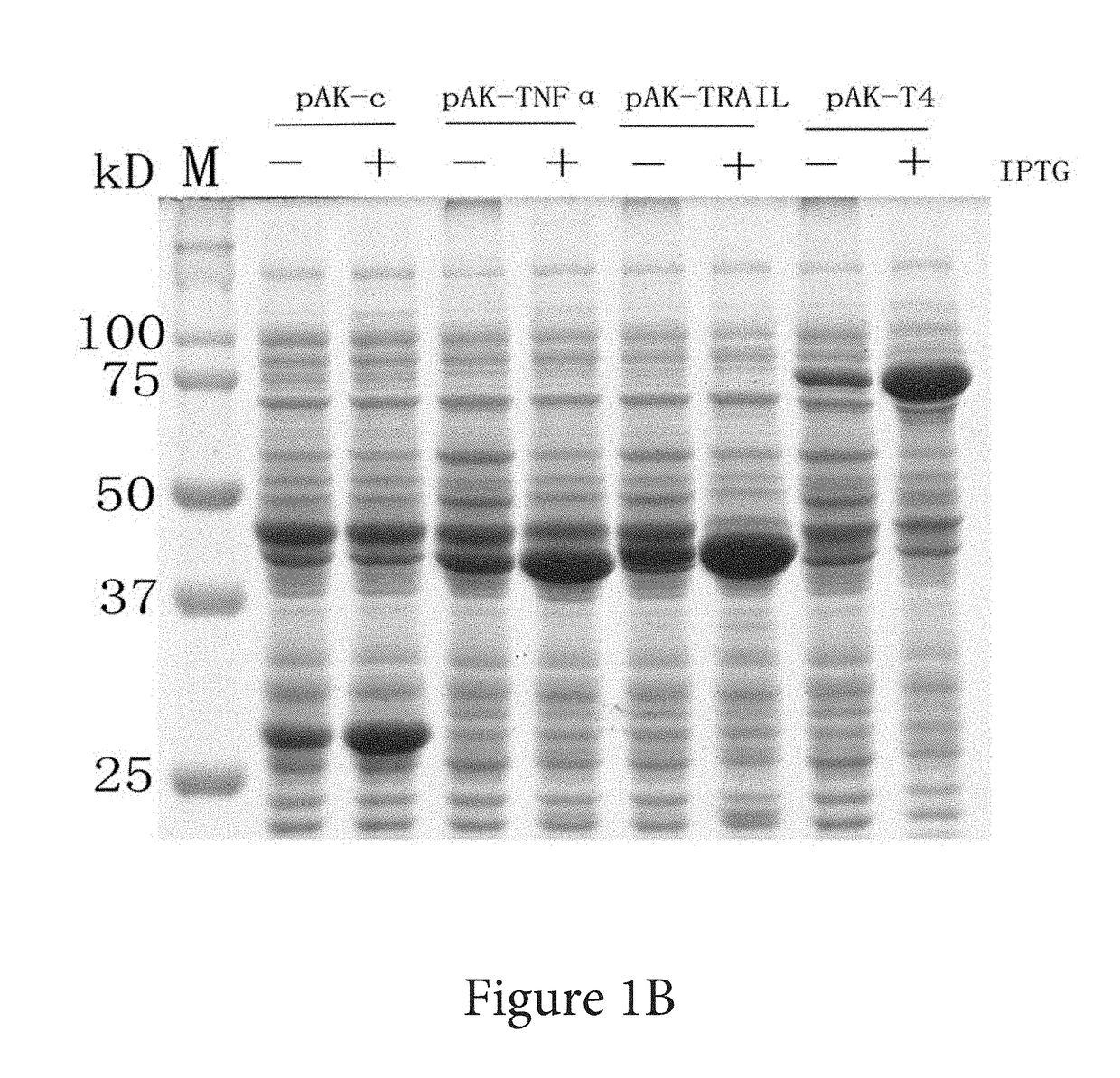
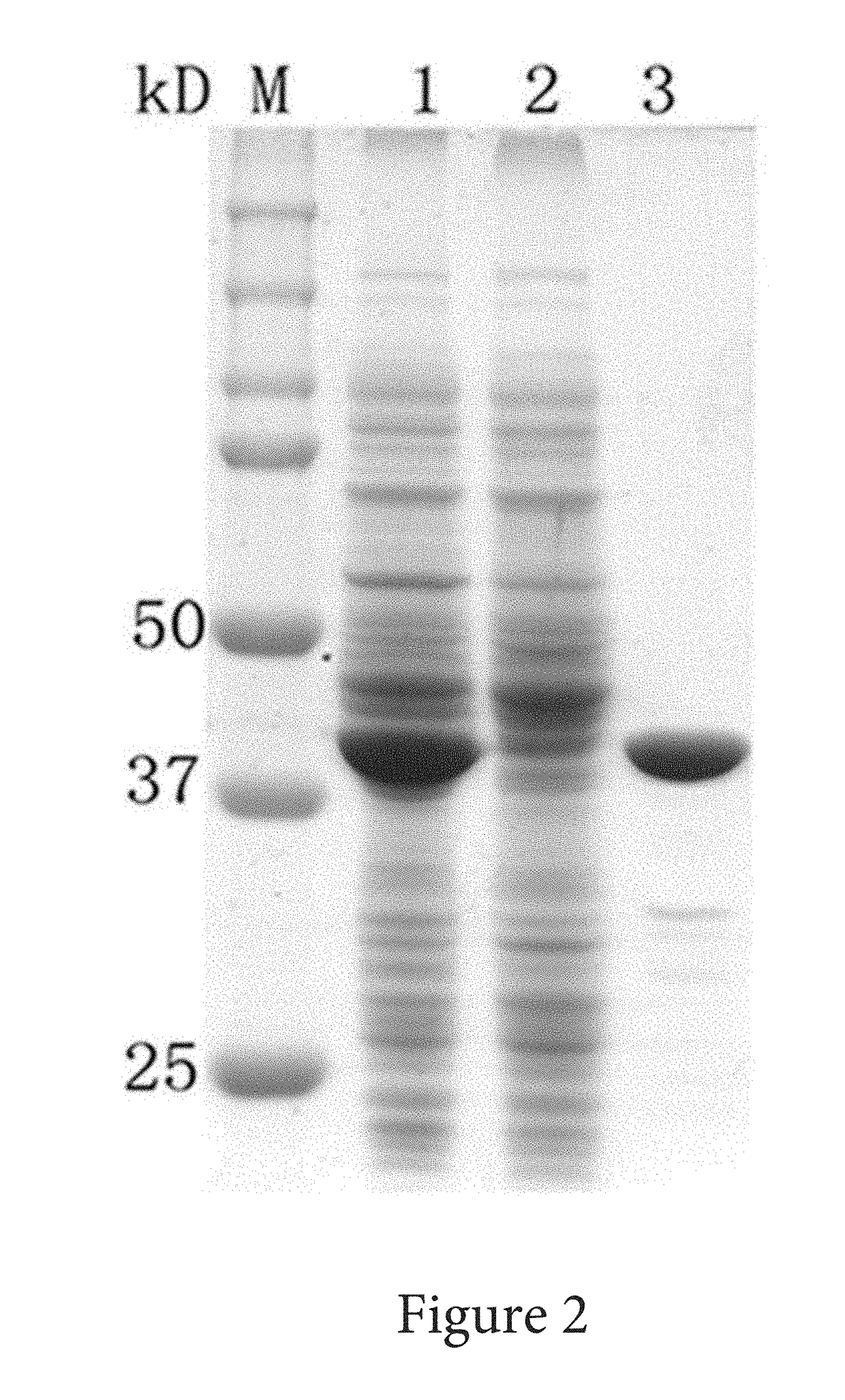
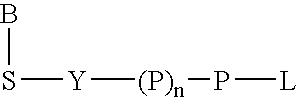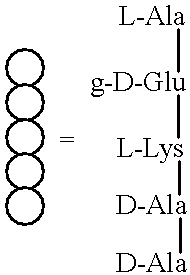Patents
Literature
34 results about "Substrate analog" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Substrate analogs (substrate state analogues), are chemical compounds with a chemical structure that resemble the substrate molecule in an enzyme-catalyzed chemical reaction. Substrate analogs can act as competitive inhibitors of an enzymatic reaction.
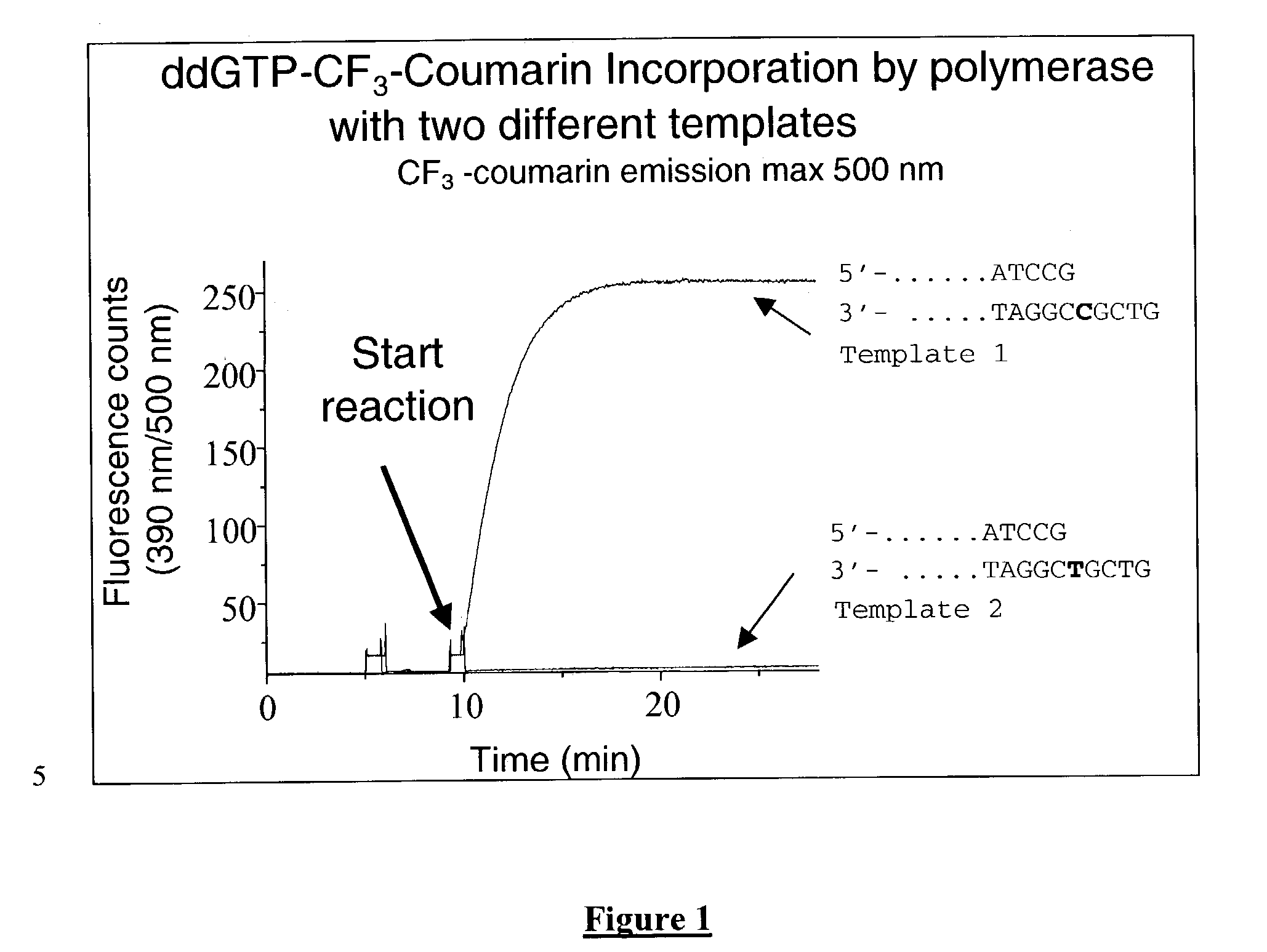
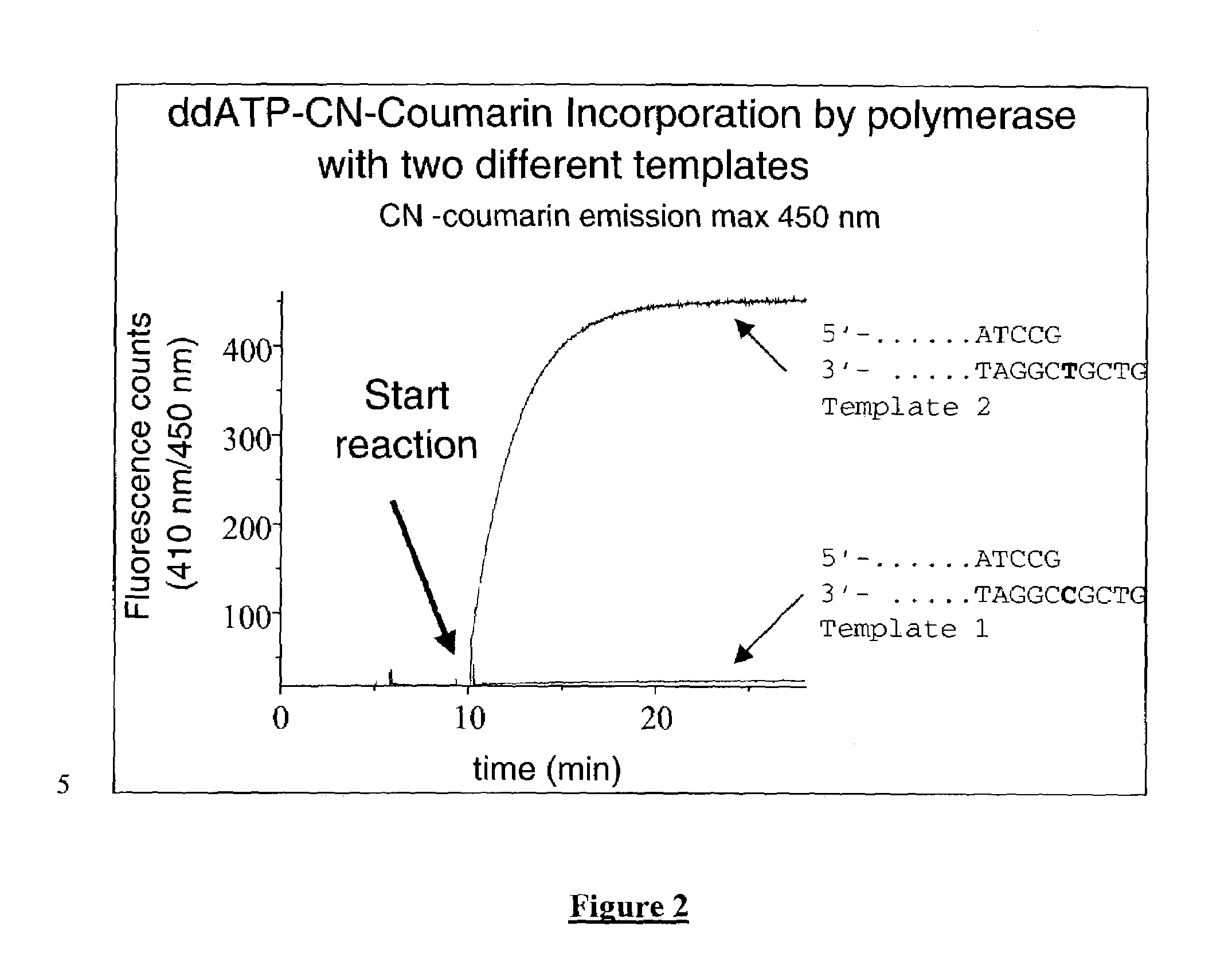
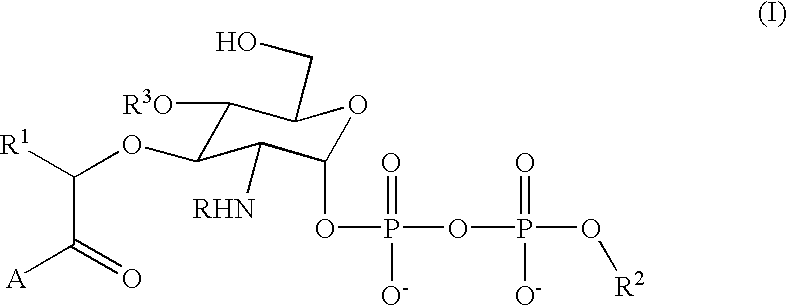
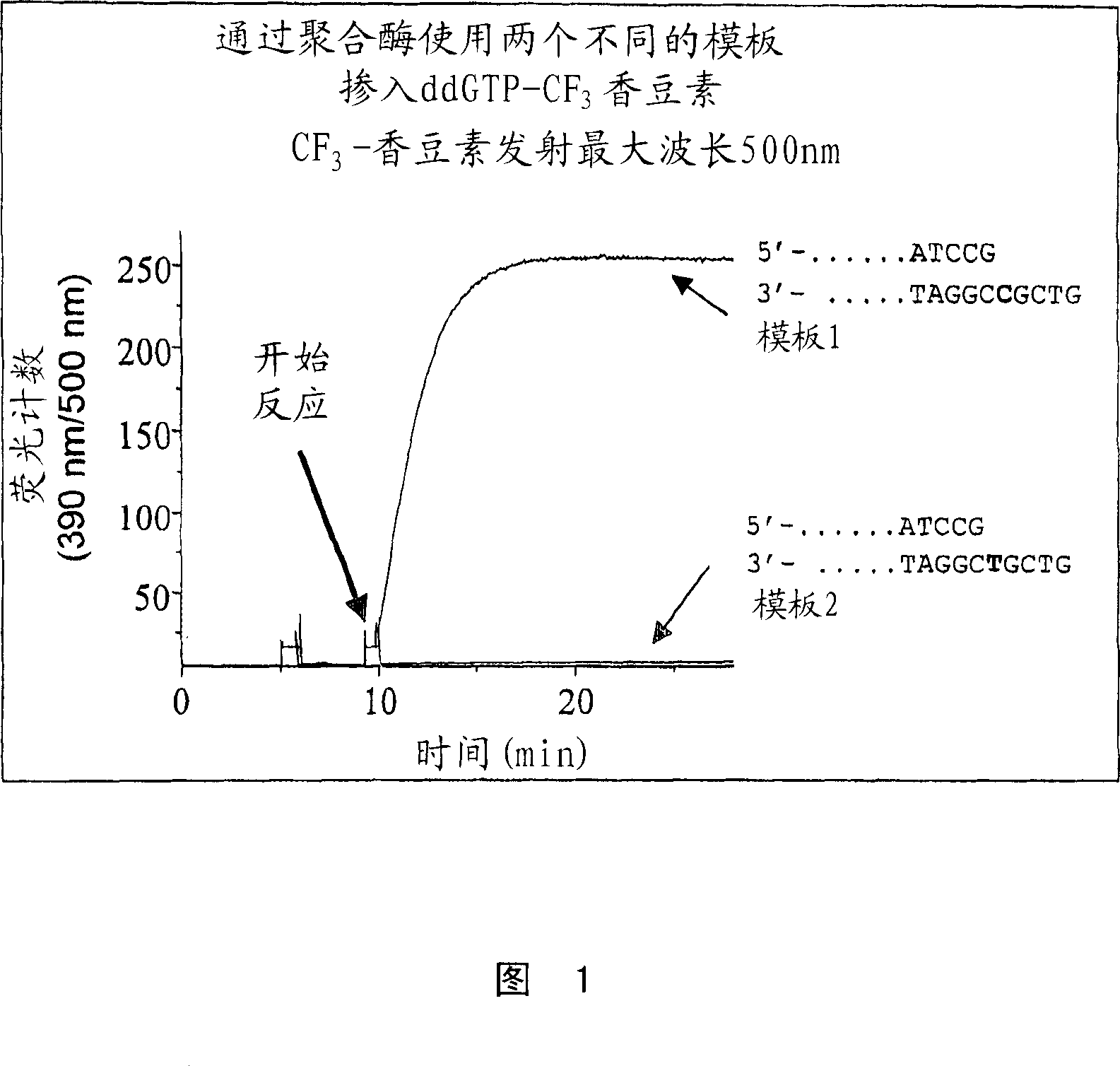
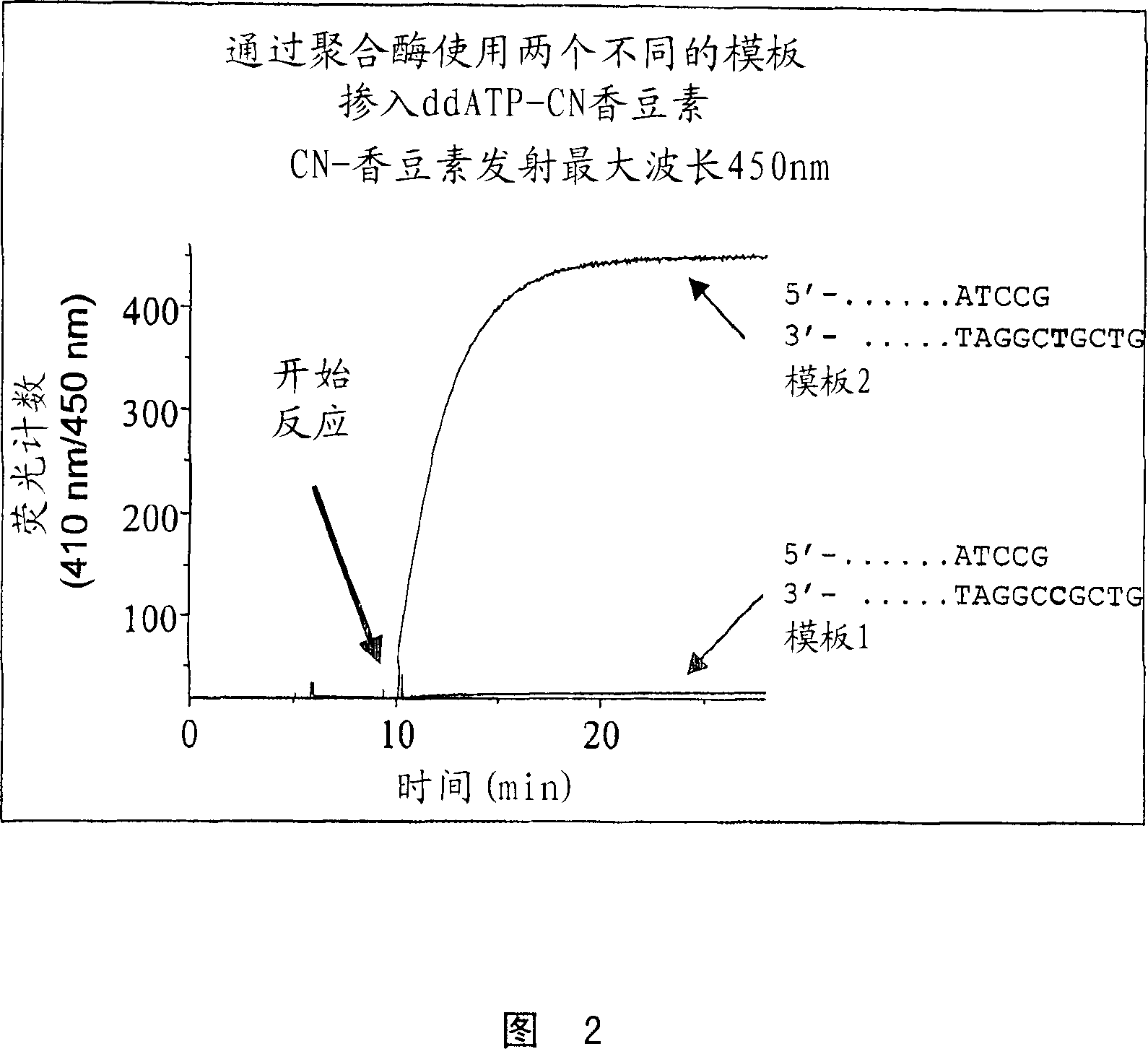
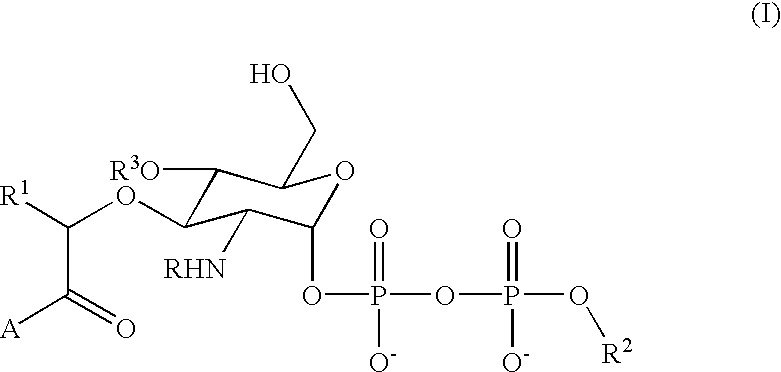
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention relates to improved methods of detecting a target using a labeled substrate or substrate analog. The methods comprise reacting the substrate or substrate analog in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which produces a labeled moiety with independently detectable signal only when such substrate or substrate analog reacts. The present invention, in particular, describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
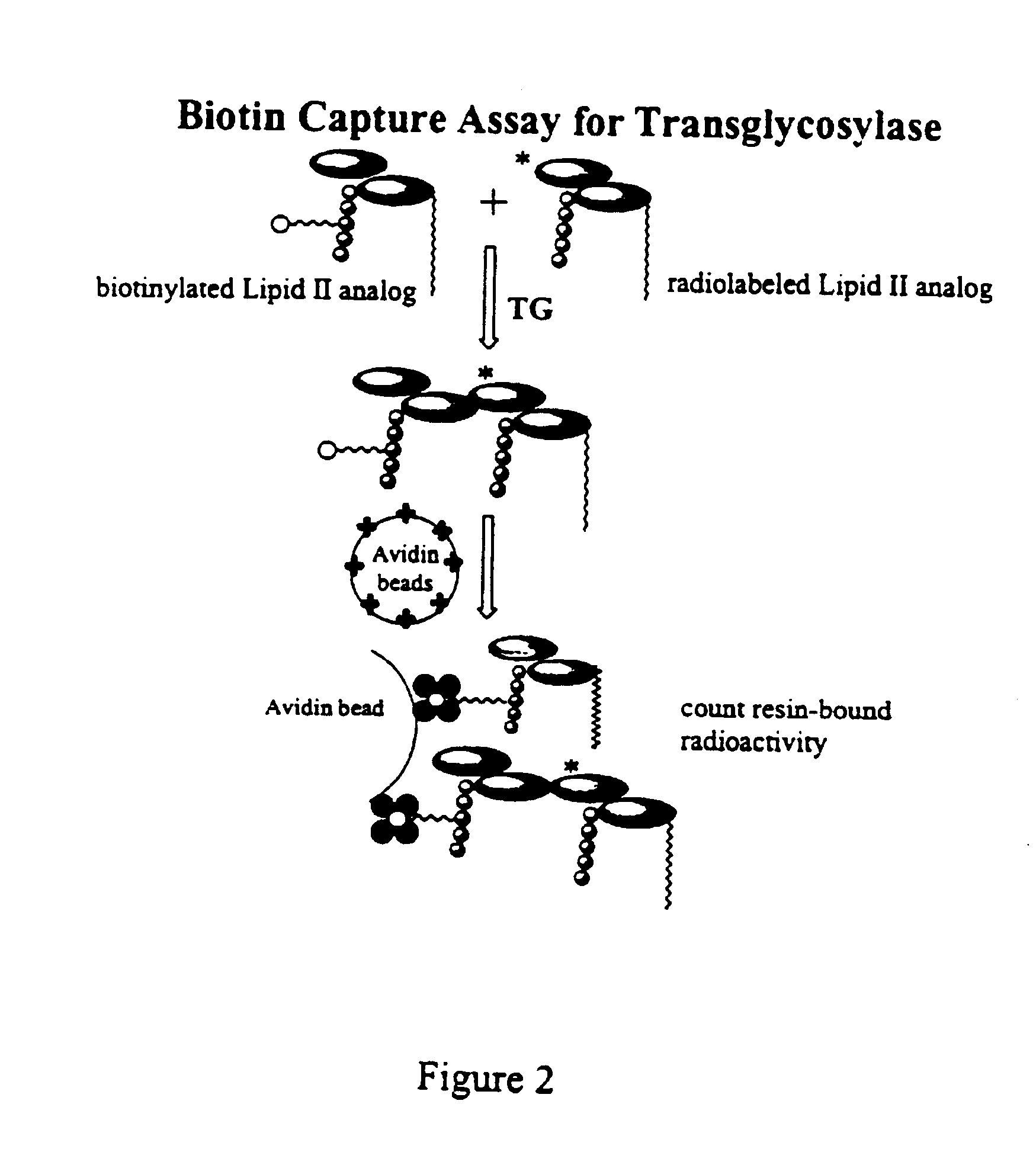
Bacterial transglycosylases: assays for monitoring the activity using Lipid II substrate analogs and methods for discovering new antibiotics
InactiveUS6461829B1Easy to detectEasy to measureMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic synthesisSubstrate analog
This invention provides a direct method for monitoring bacterial transglycosylase activity using labeled substrates produced by chemo-enzymatic synthesis wherein the labels are selected to permit the detection of both polymeric and non-polymeric products simultaneously, either directly or following the separation of product from starting material. The invention promotes the discovery of new antibiotics with activity against bacterial transglycosylases by a) laying the groundwork for structural analysis of purified, active transglycosylase (which permits structure-based design); and b) providing an assay that can be used to screen for inhibitors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
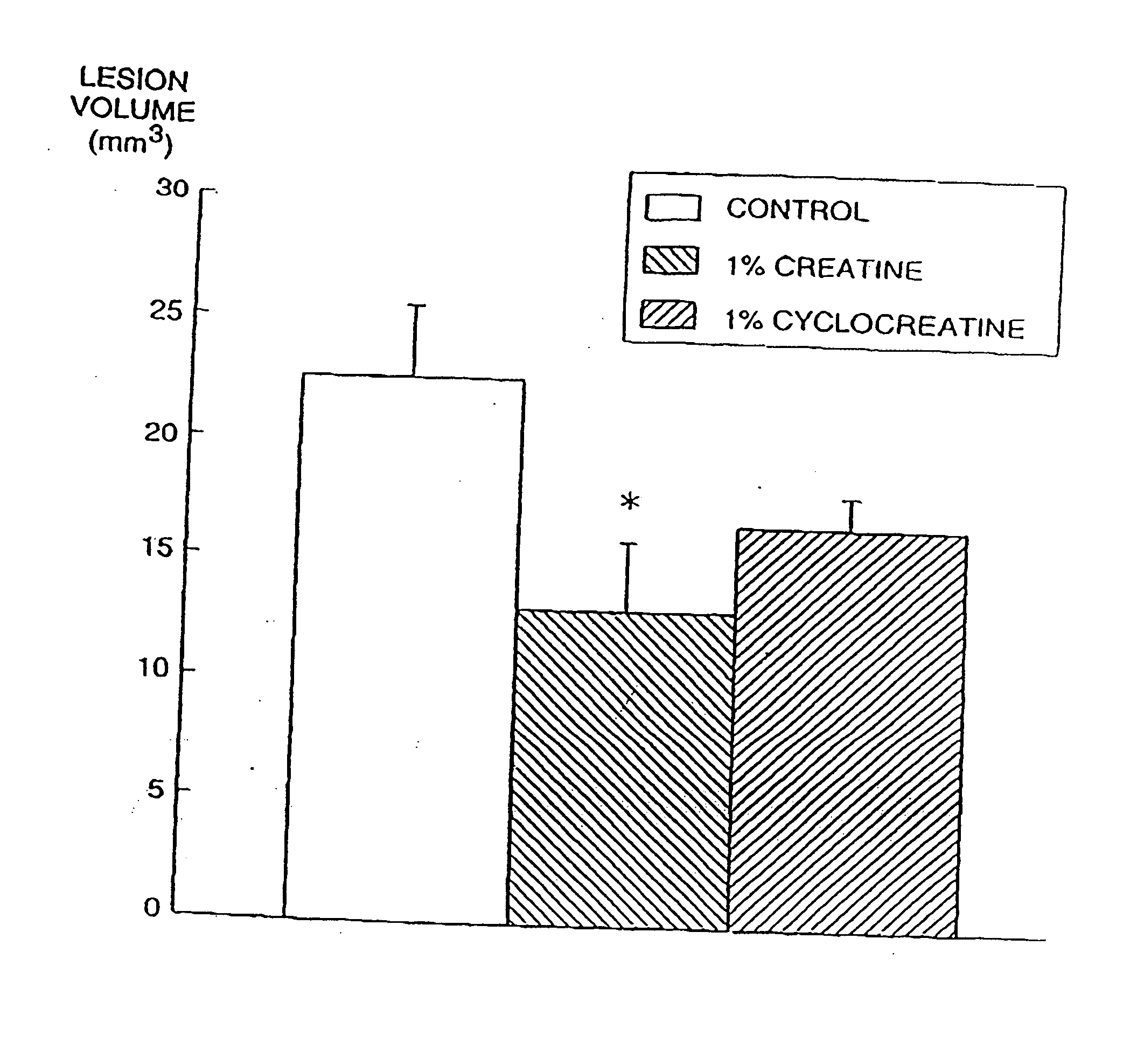
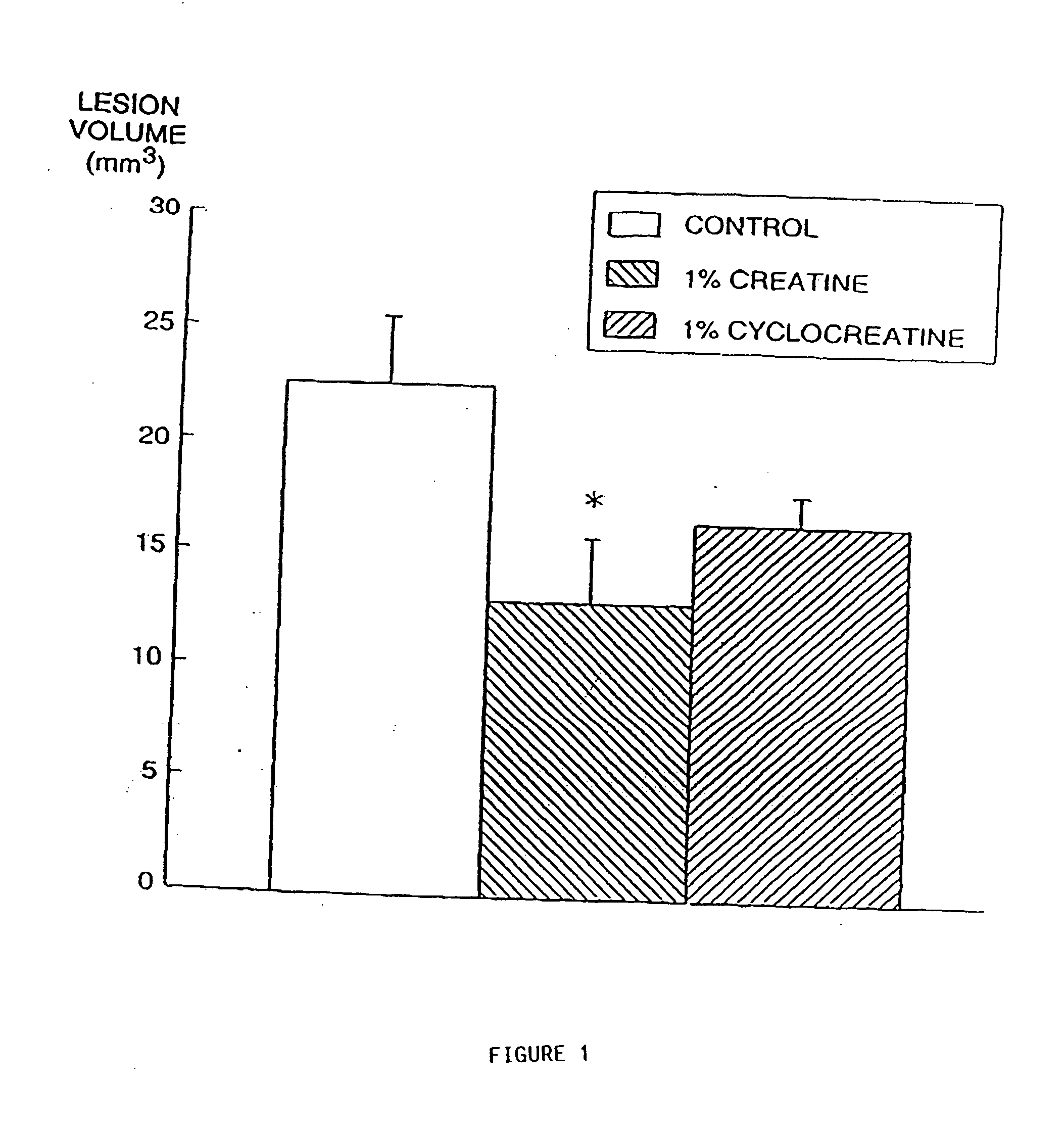
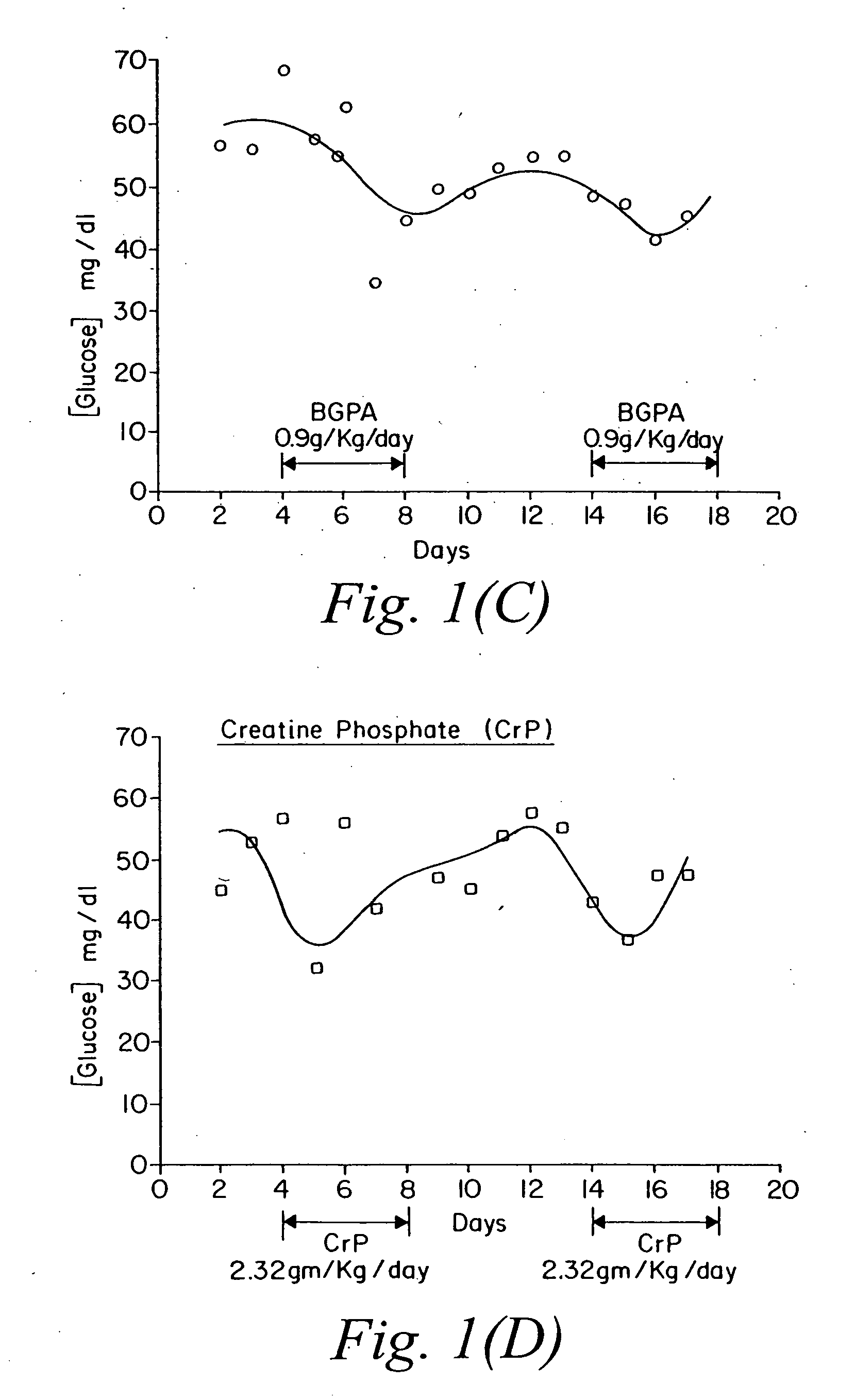
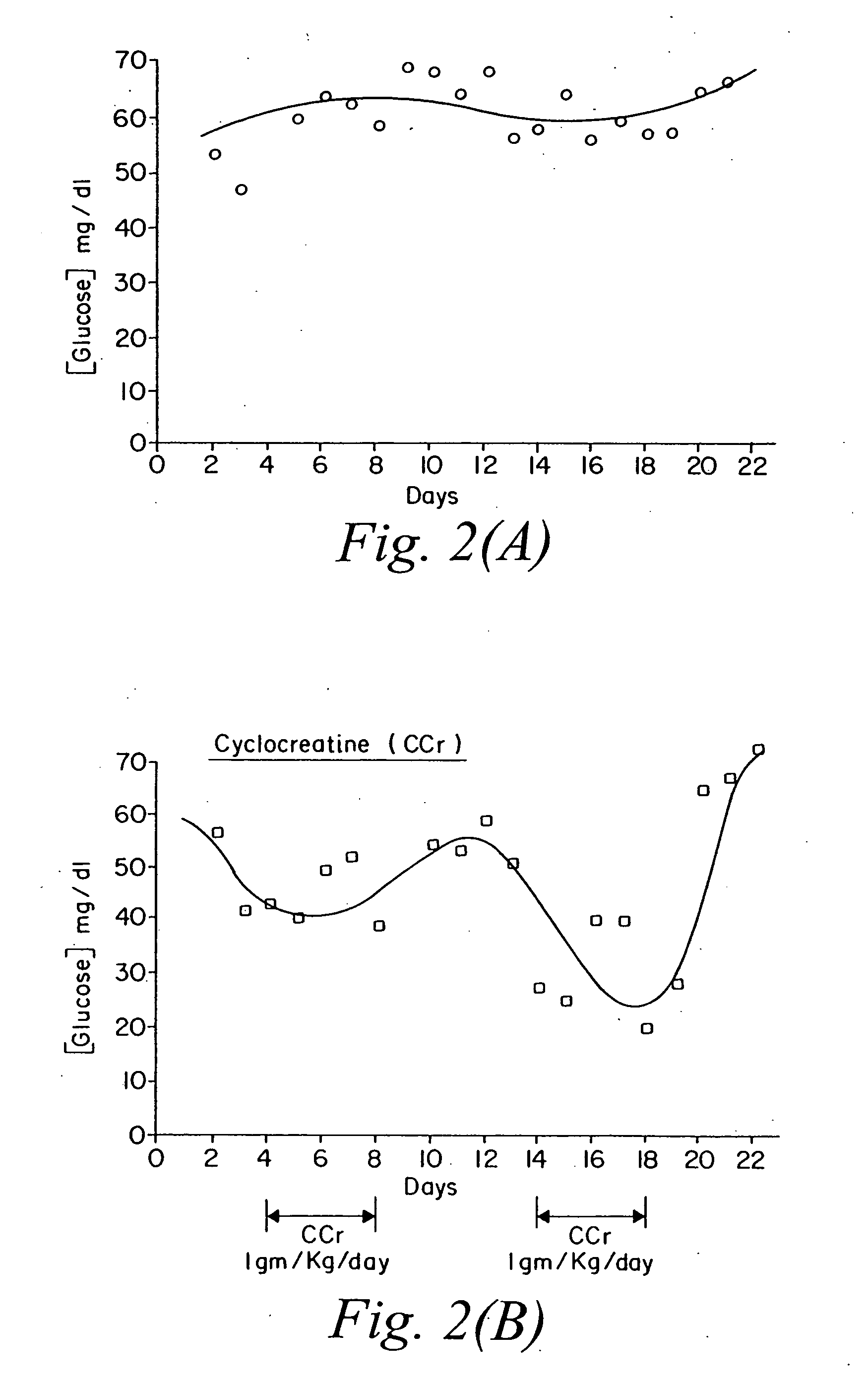
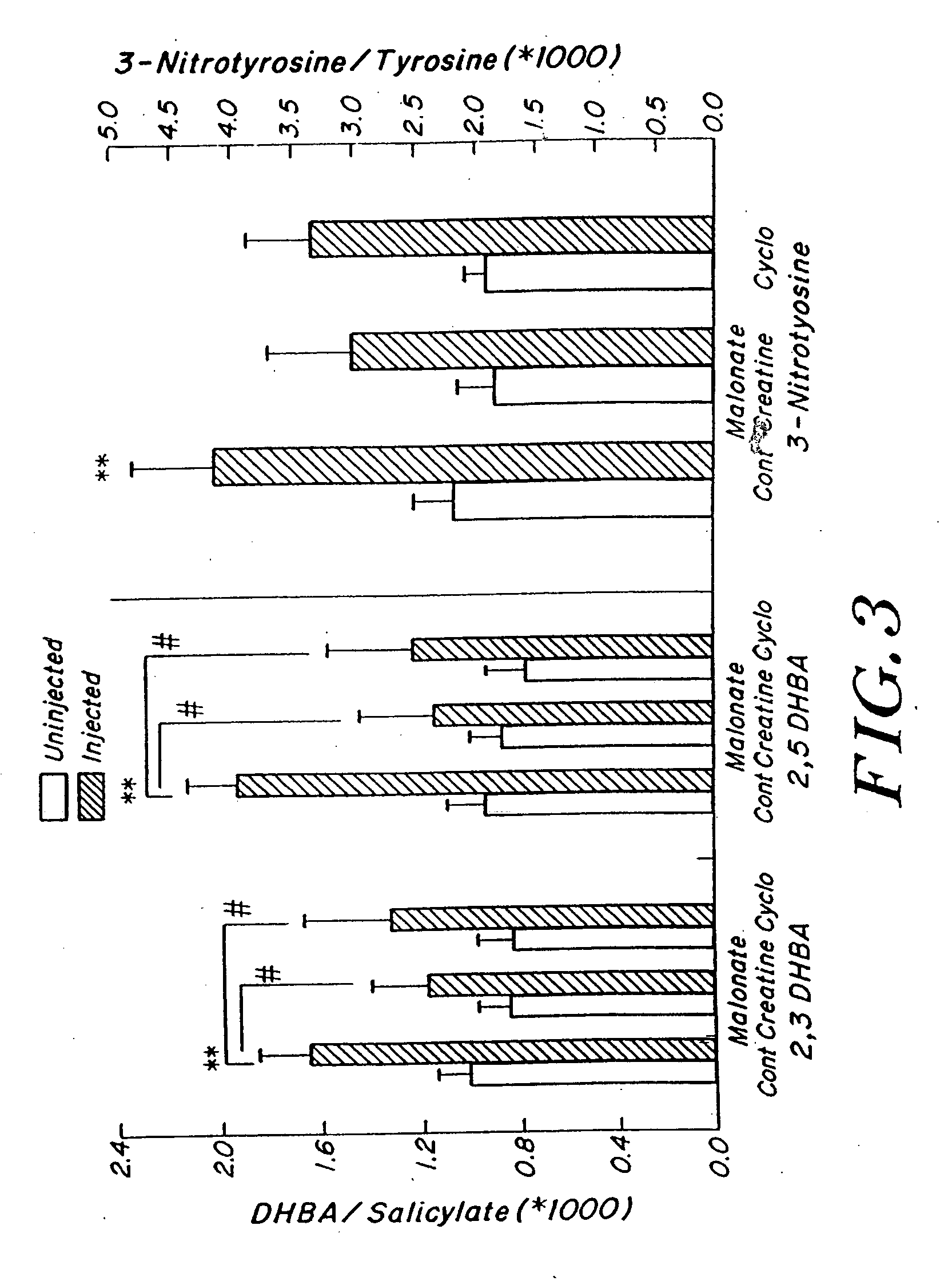
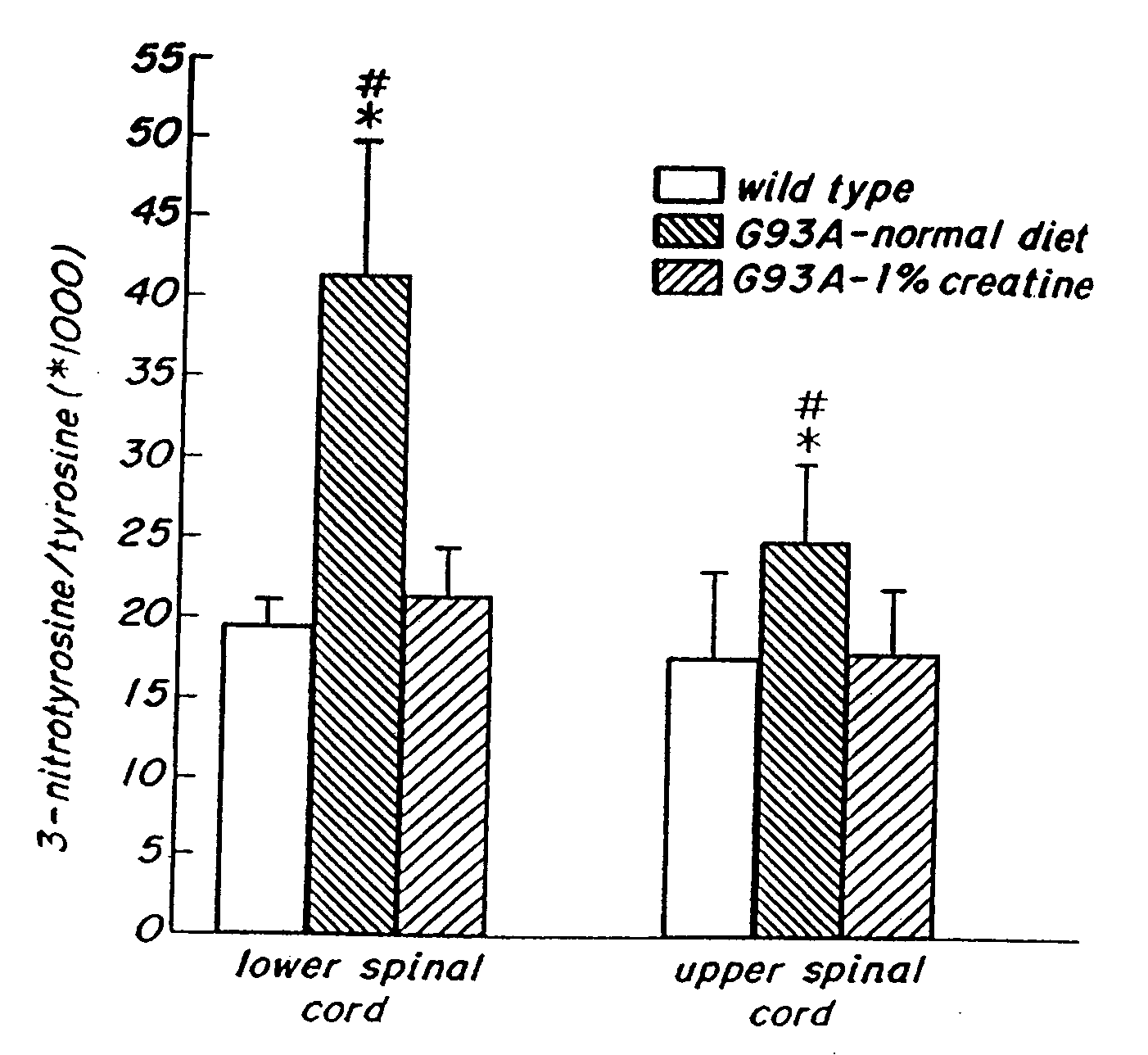
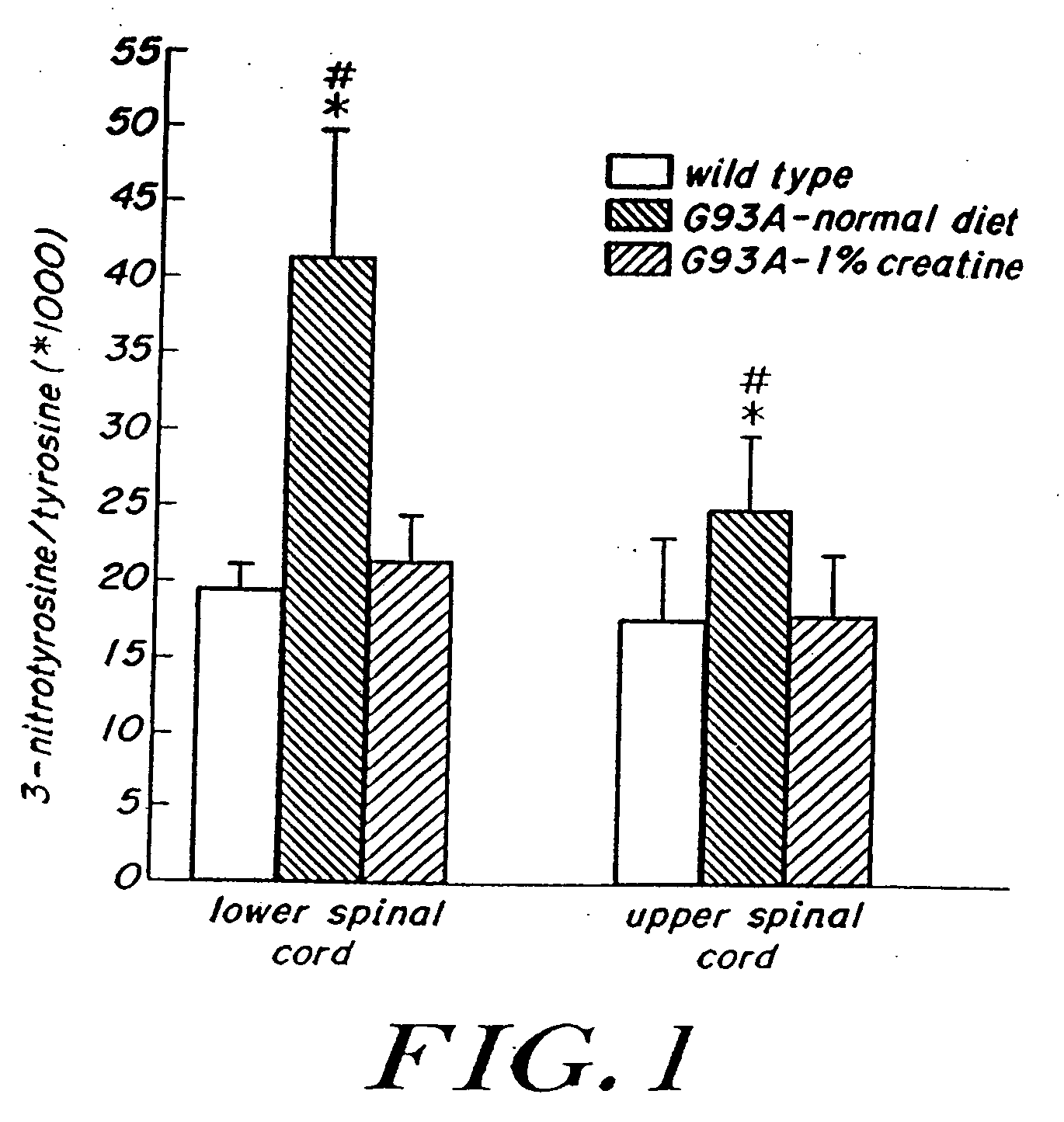
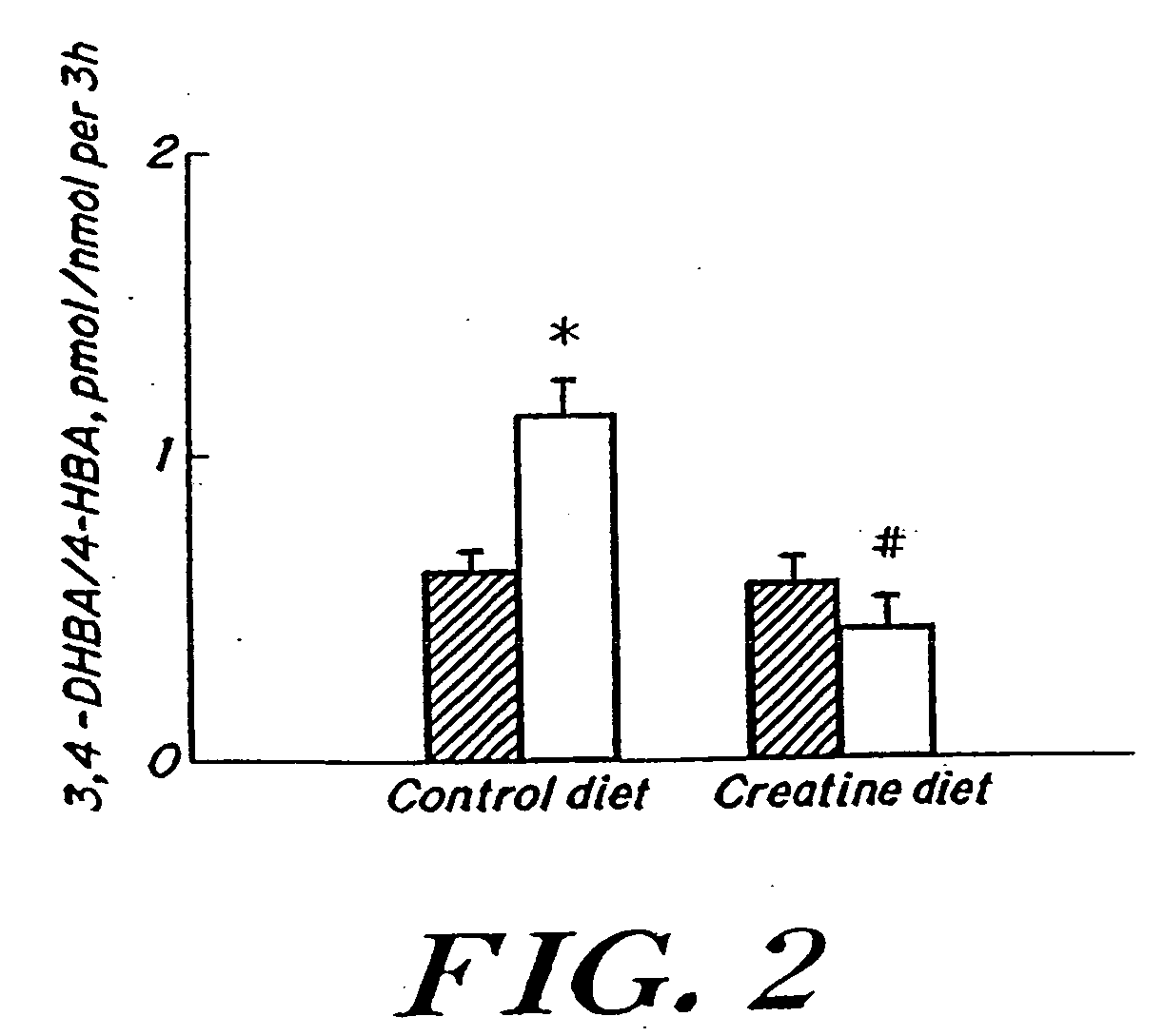
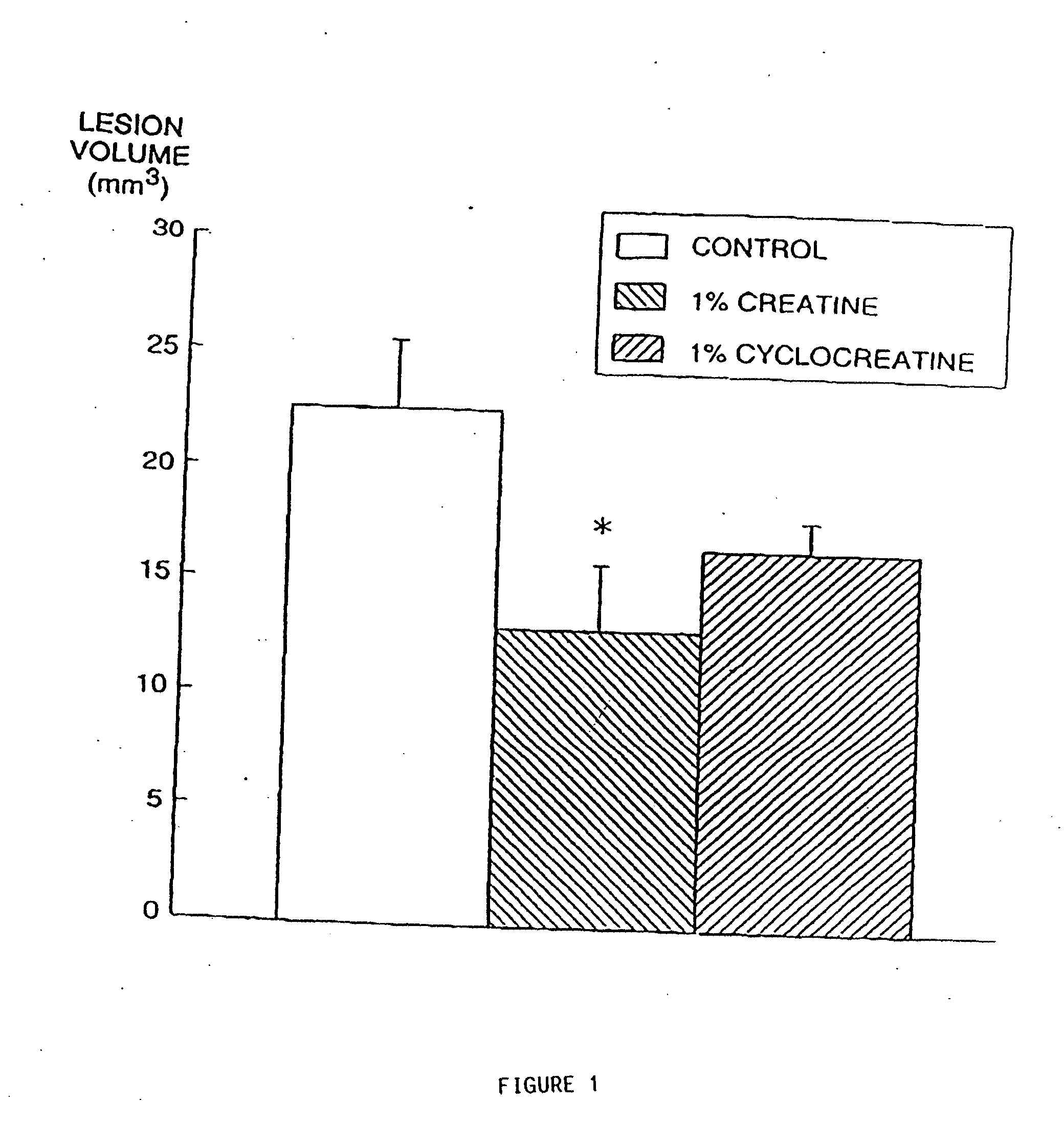
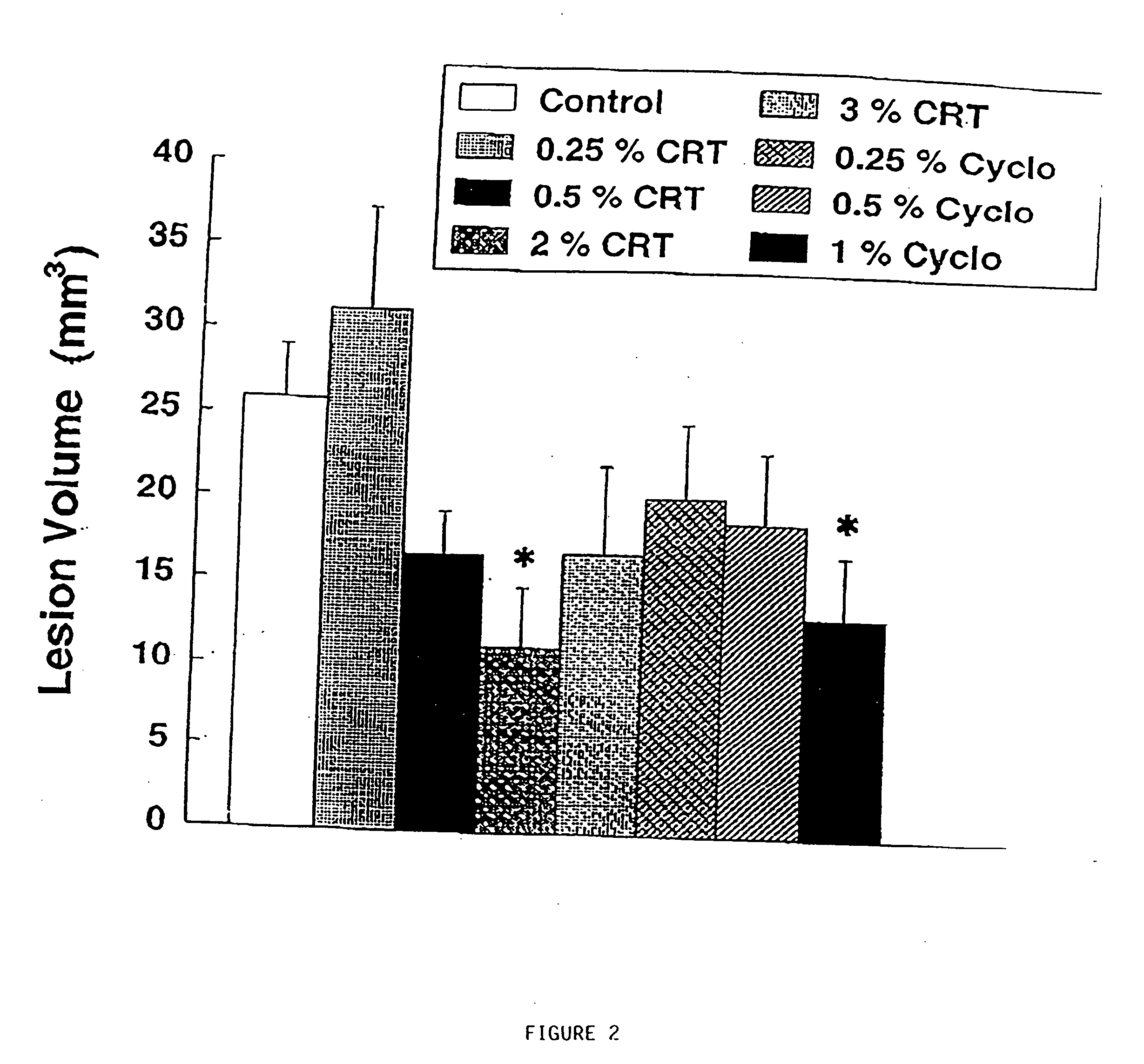
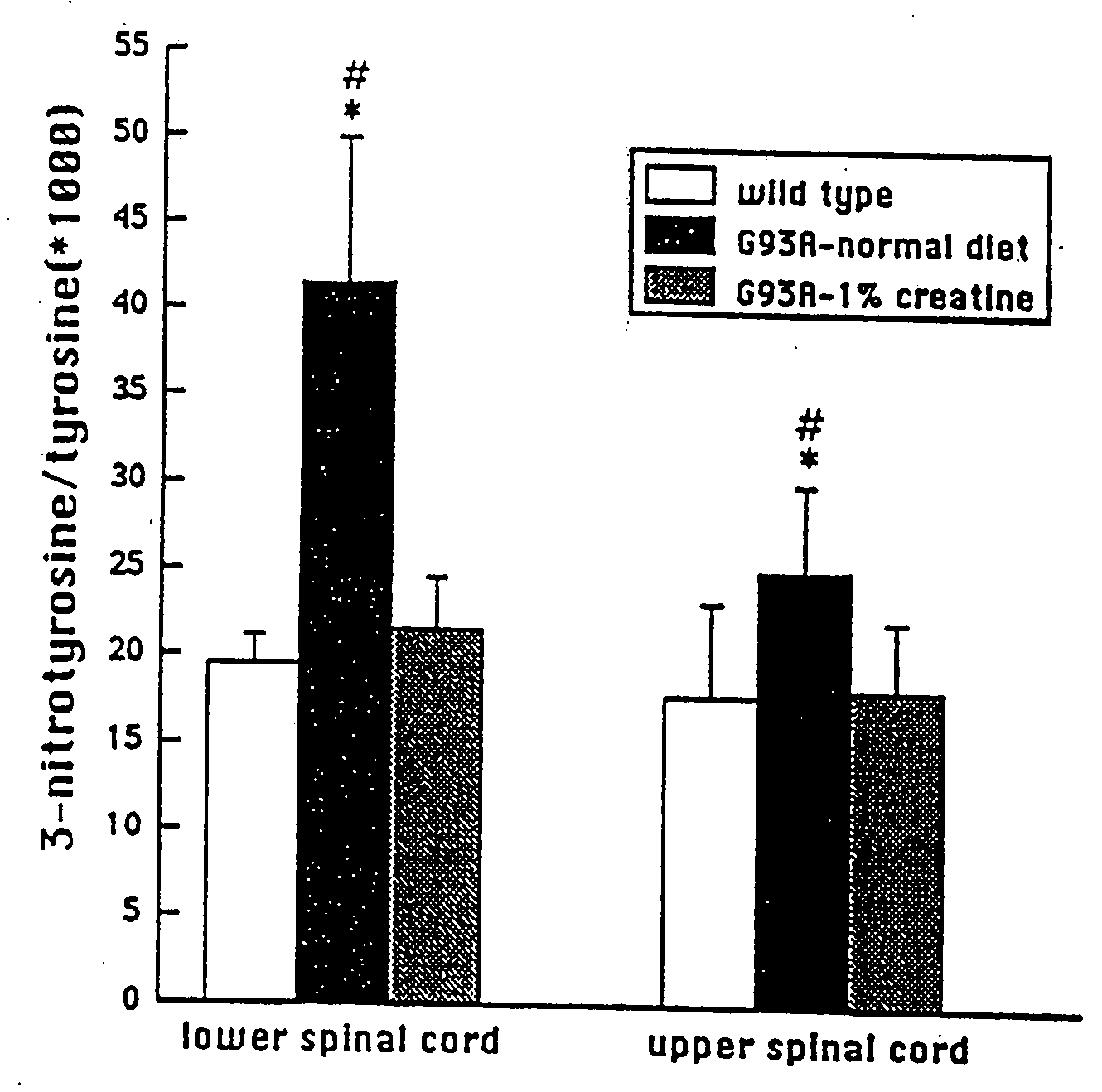
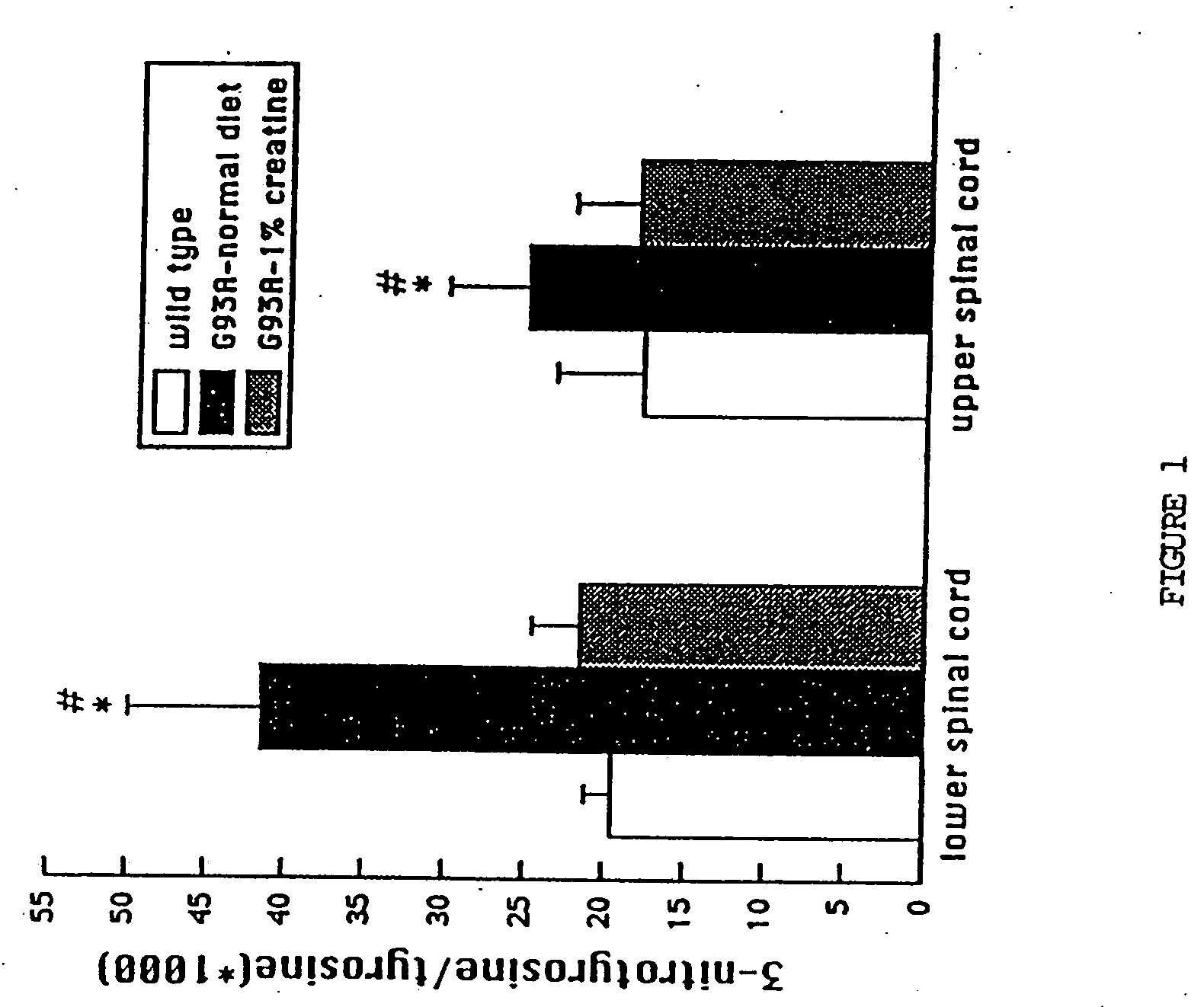
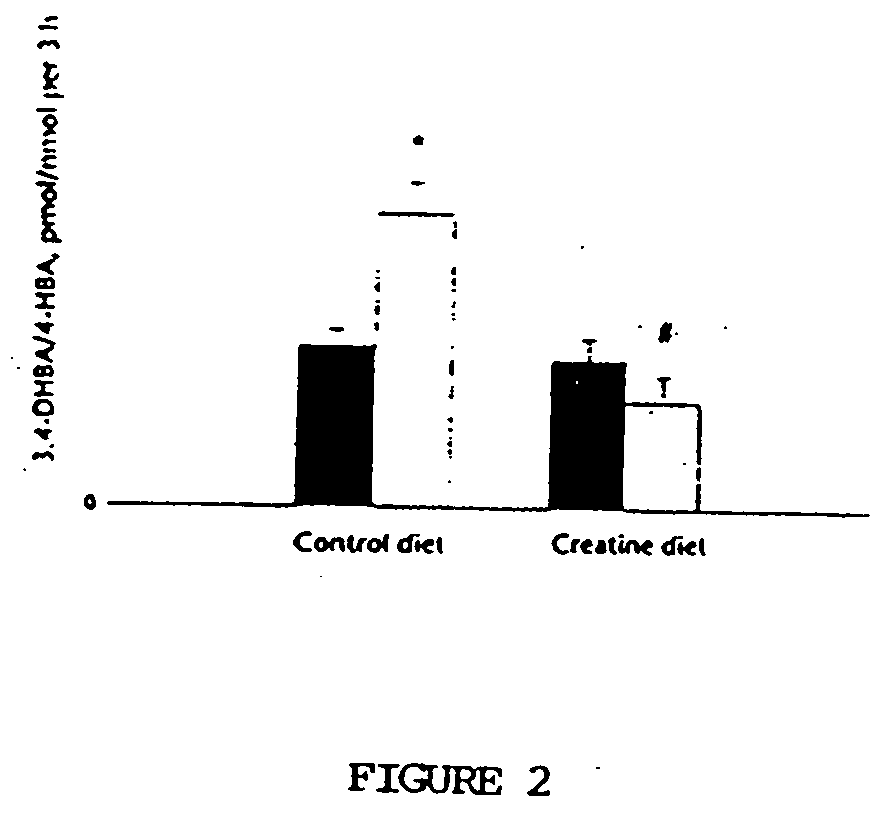
Compositions containing a combination of a creatine compound and a second agent
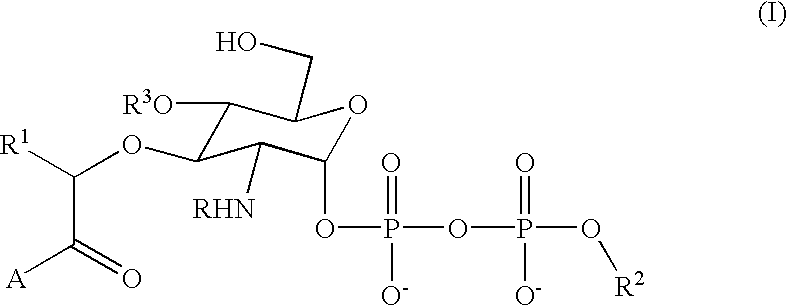
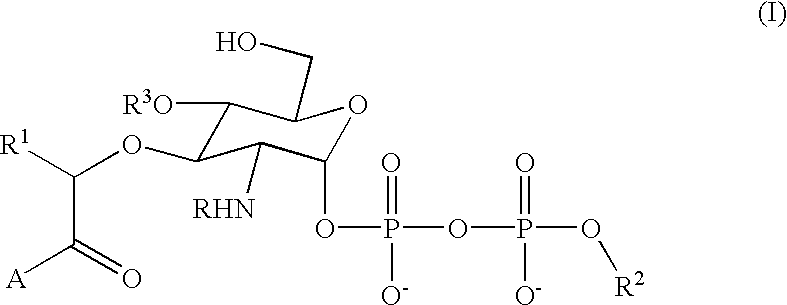
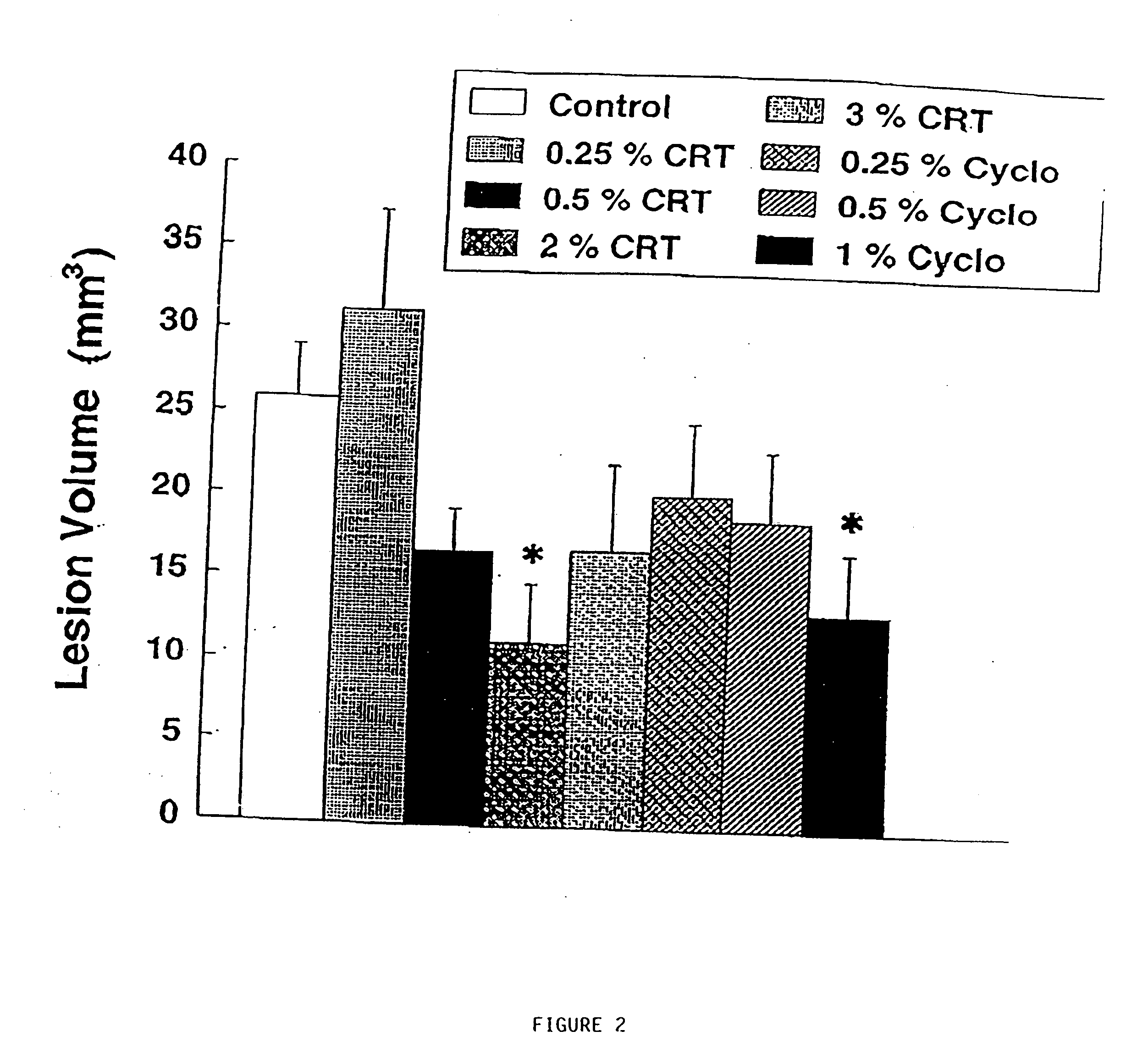
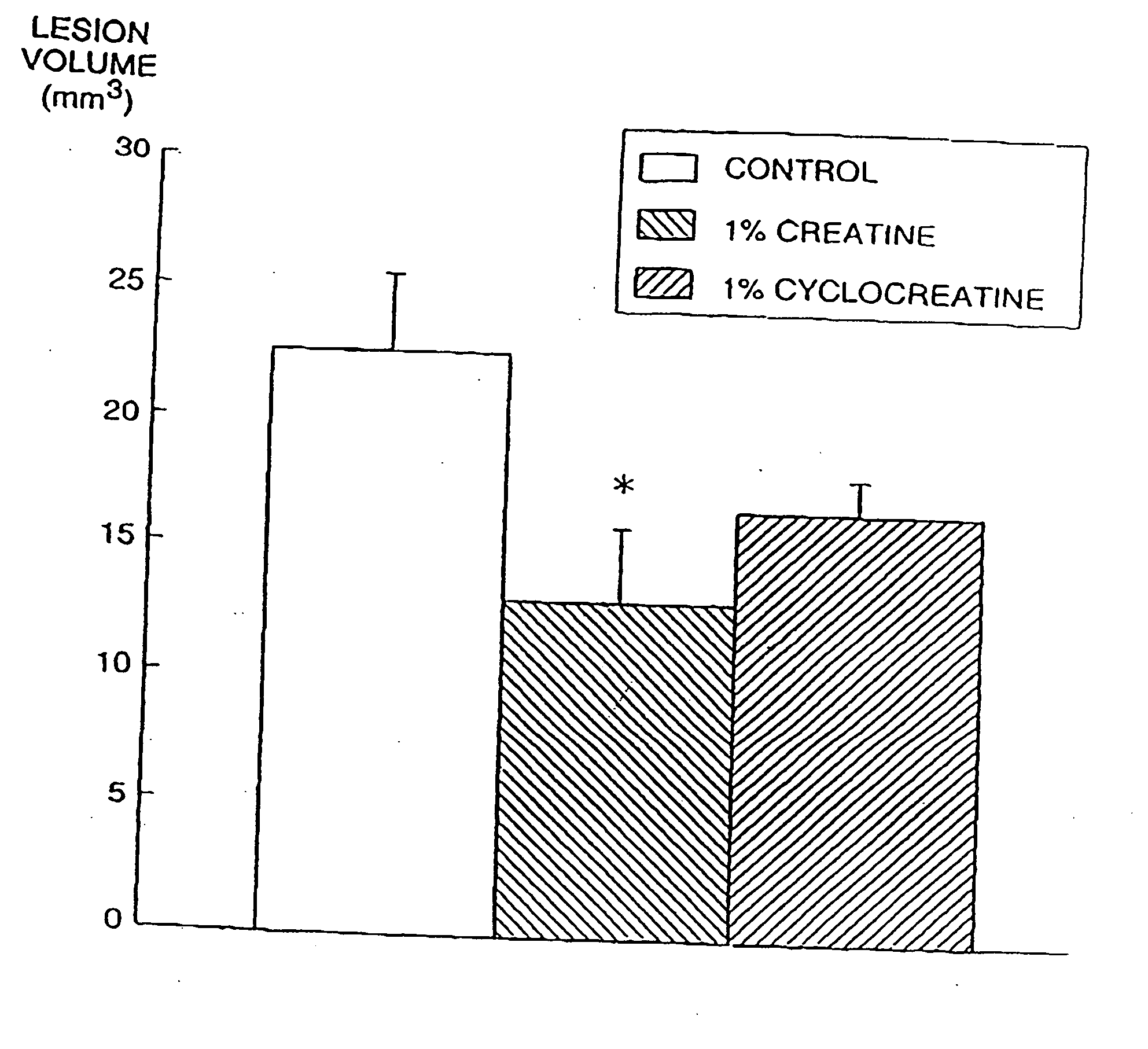
The present invention relates to the use of creatine compound and neuroprotective combinations including creatine, creatine phosphate or analogs of creatine, such as cyclocreatine, for treating diseases of the nervous system. Creatine compounds in combination with neuroprotective agents can be used as therapeutically effective compositions against a variety of diseases of the nervous system such as diabetic and toxic neuropathies, peripheral nervous system diseases, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson's disease, stroke, Huntington's disease, amyotropic lateral sclerosis, motor neuron disease, traumatic nerve injury, multiple sclerosis, dysmyelination and demyelination disorders, and mitochondrial diseases. The creatine compounds which can be used in the present method include (1) creatine, creatine phosphate and analogs of these compounds which can act as substrates or substrate analogs for creatine kinase; (2) bisubstrate inhibitors of creatine kinase comprising covalently linked structural analogs of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and creatine; (3) creatine analogs which can act as reversible or irreversible inhibitors of creatine kinase; and (4) N-phosphorocreatine analogs bearing non-transferable moieties which mimic the N-phosphoryl group.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
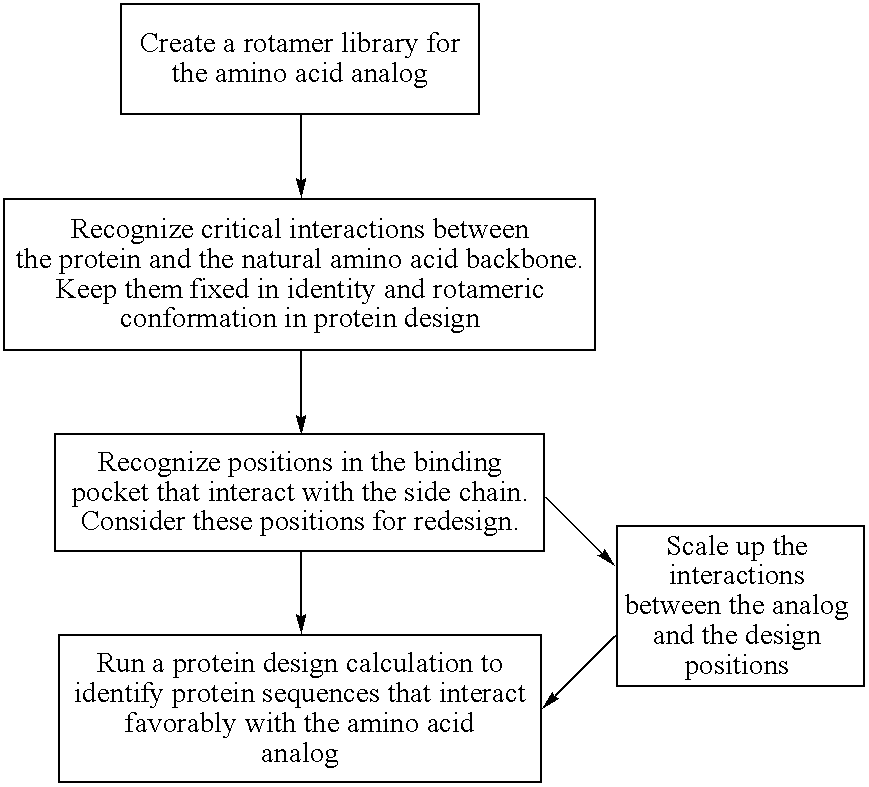
Computational method for designing enzymes for incorporation of non natural amino acids into proteins
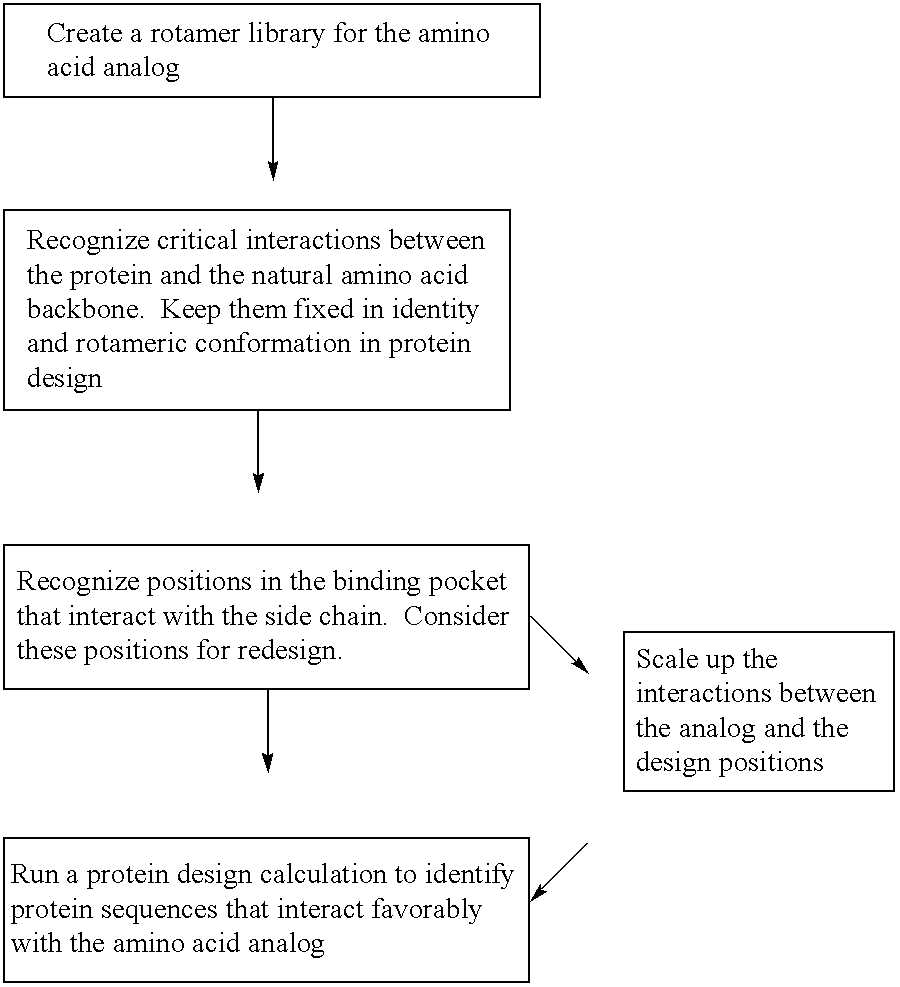
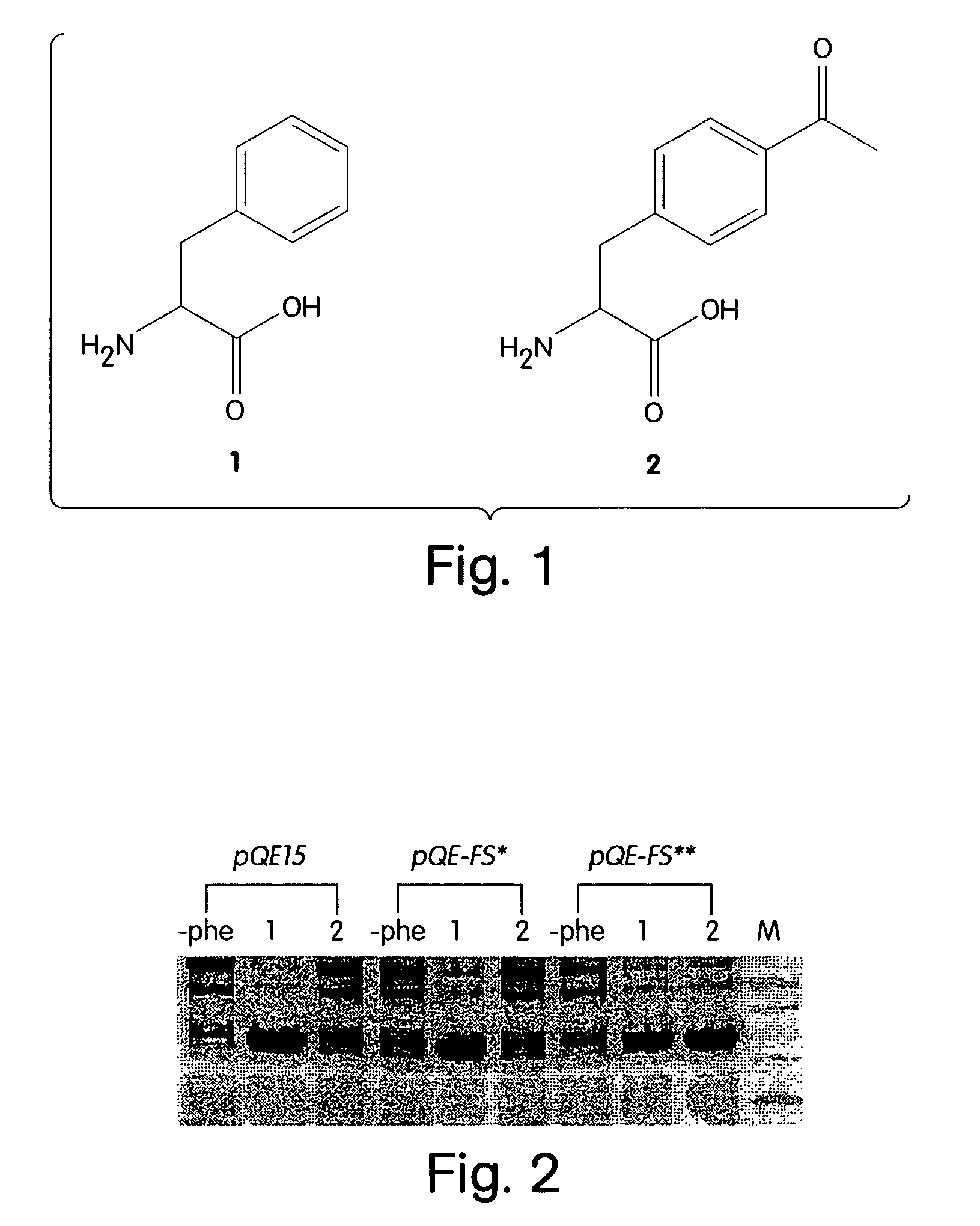
The instant invention provides methods, reagents, and computational tools for designing non-natural substrate analogs for enzymes, especially for designing unnatural amino acid analogs for aminoacyl tRNA Synthetases (AARSs), such as the Phe tRNA Synthetase. The instant invention also provides methods to incorporate unnatural amino acid analogs, especially those with interesting functional groups, into protein products to generate proteins of modified or novel functions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods of treating fatty liver disease
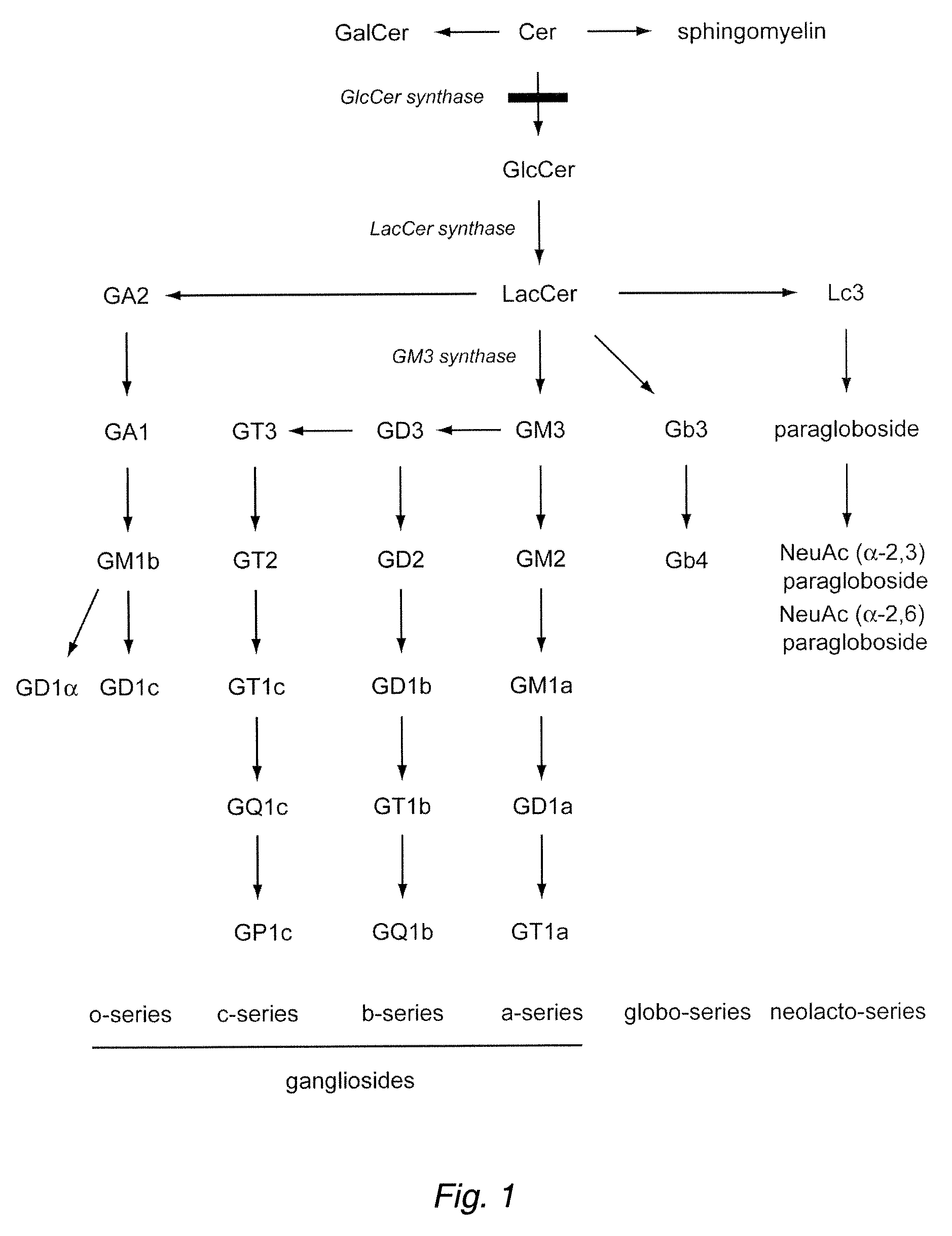
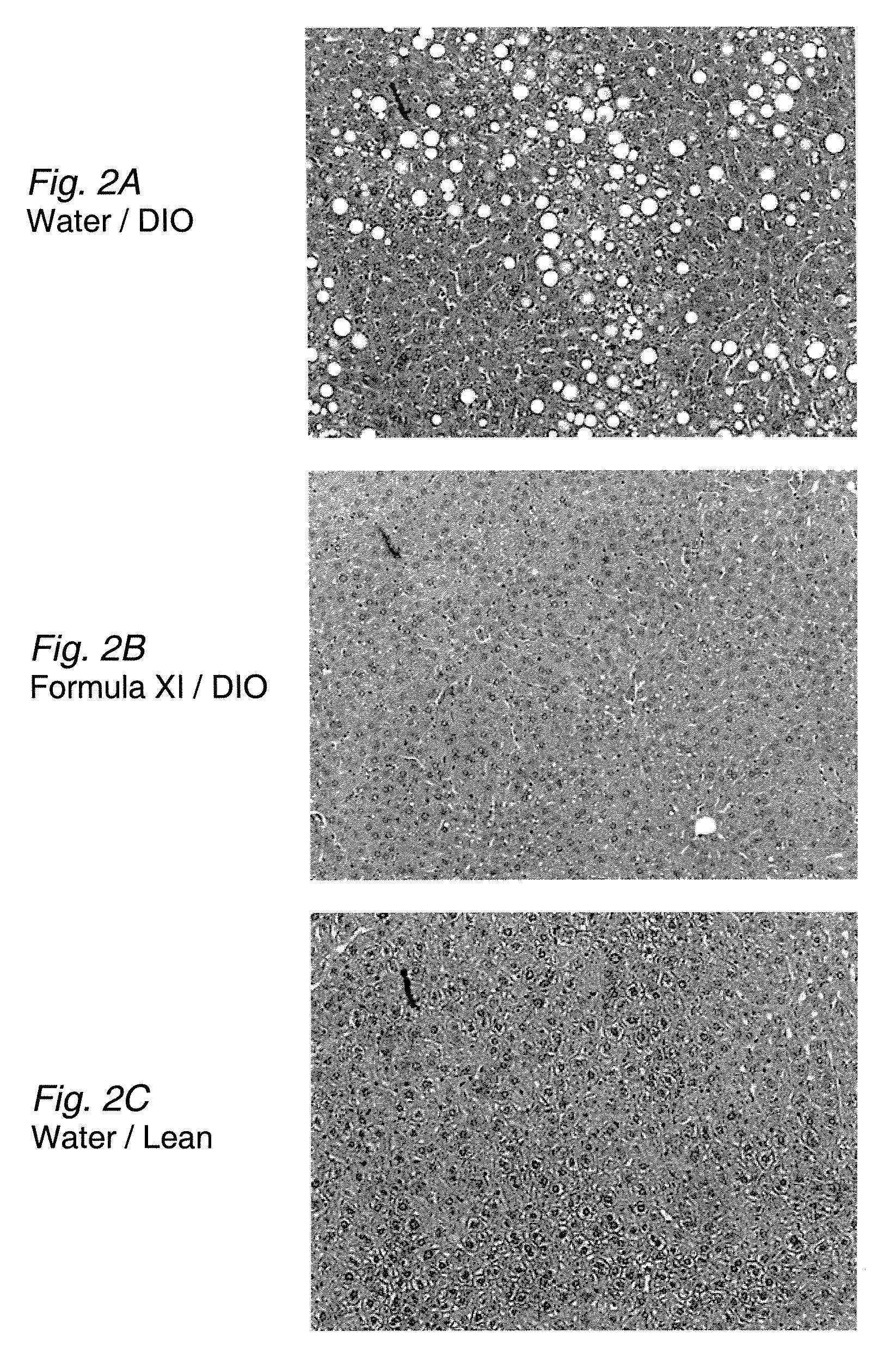
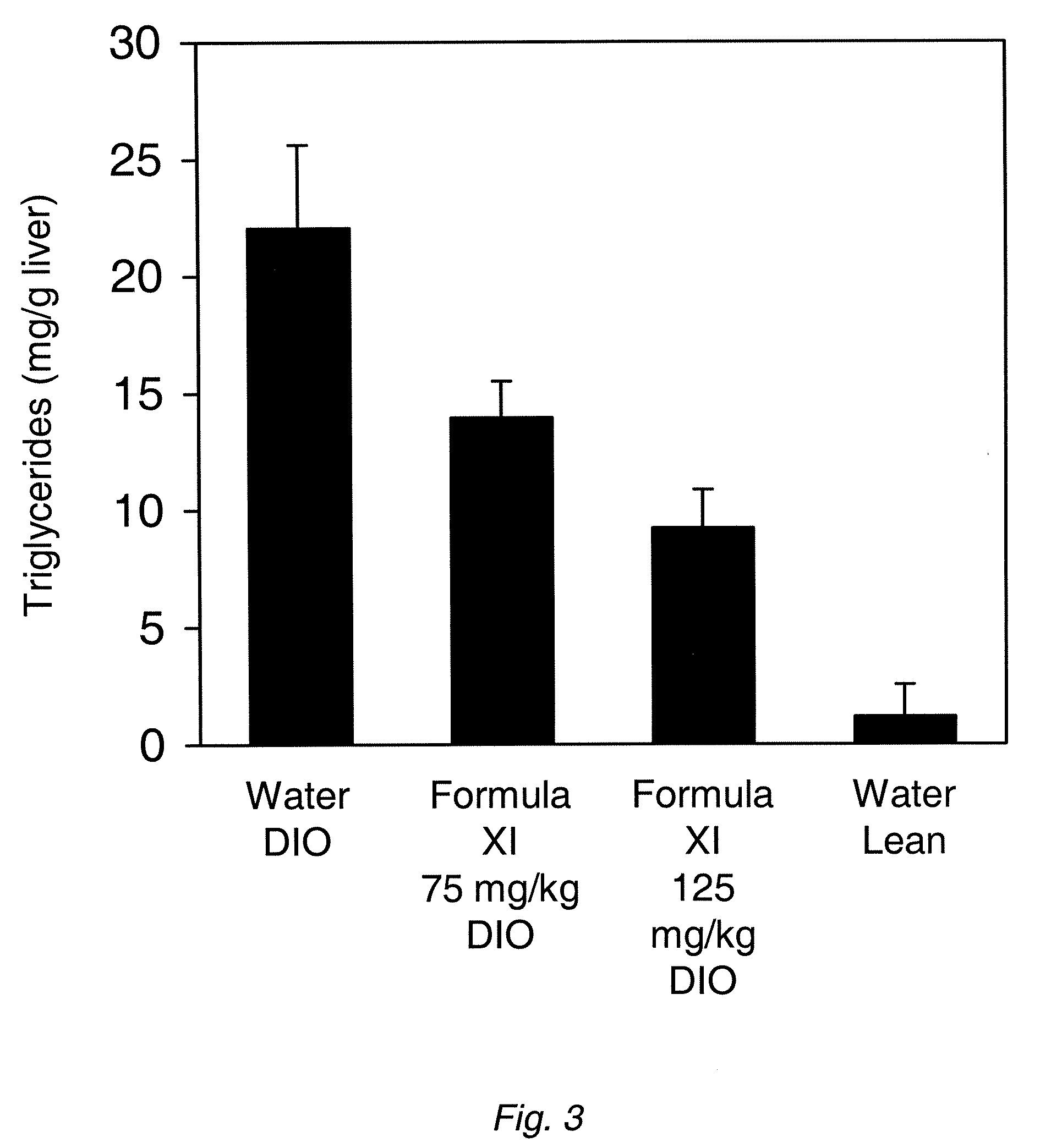
The disclosure provides methods for treating fatty liver disease and associated conditions by inhibiting the synthesis of glucosphingolipids, as exemplified by the use of glucosylceramide synthase substrate analogs.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
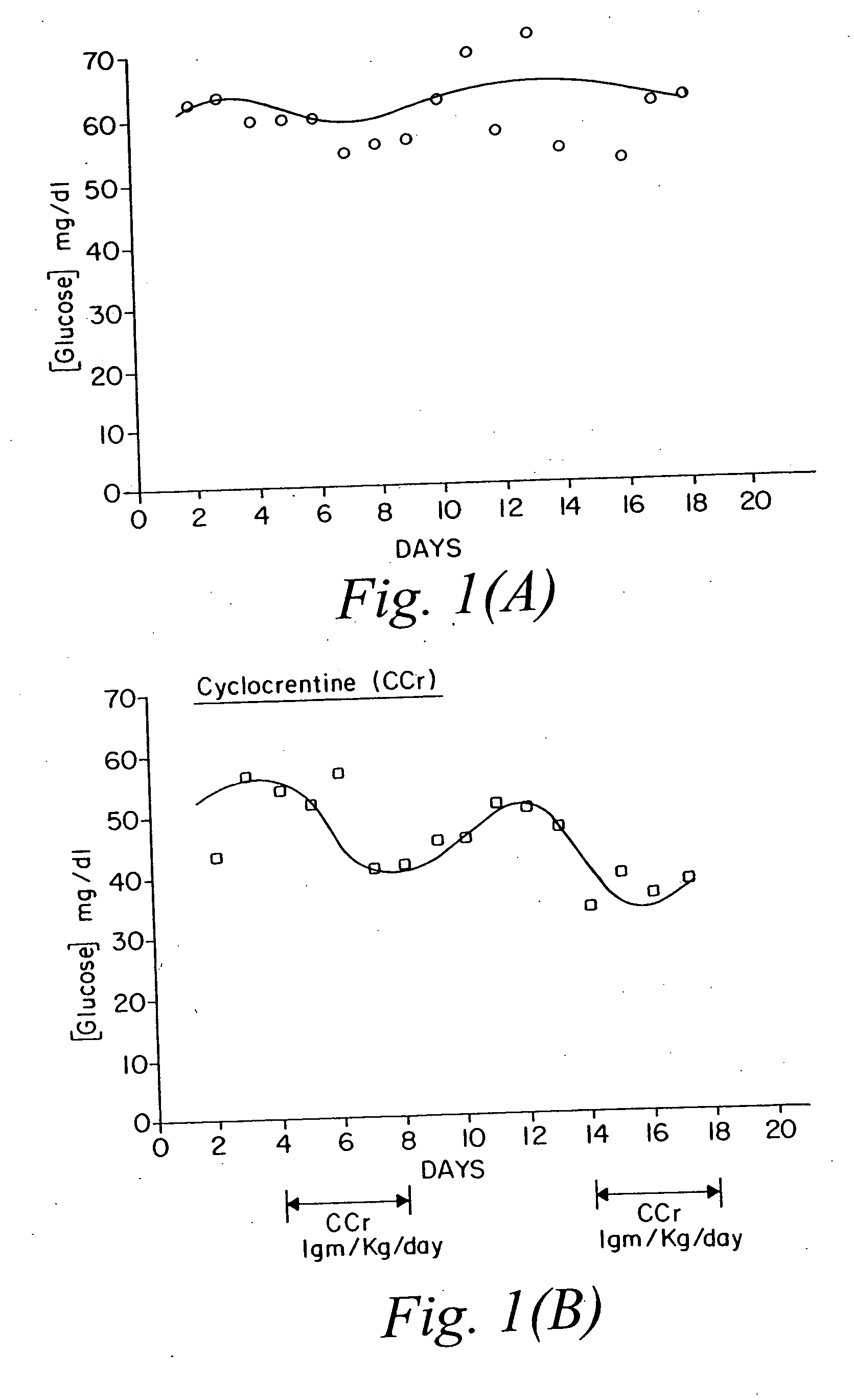
Use of creatine analogues and creatine kinase modulators for the prevention and treatment of glucose metabolic disorders
InactiveUS20050256134A1Affect glucose levelAlleviate and prevent symptomBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAcute hyperglycaemia
The present invention relates to the use of creatine compounds including cyclocreatine and creatine phosphate for treating or preventing a metabolic disorder consisting of hyperglycemia, insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance, hyperinsulinemia, insulin insensitivity, diabetes related diseases in a patient experiencing said disorder. The creatine compounds which can be used in the present method include (1) analogues of creatine which can act as substrates or substrate analogues for the enzyme creatine kinase; (2) compounds which can act as activators or inhibitors of creatine kinase; (3) compounds which can modulate the creatine transporter (4) N-phosphocreatine analogues bearing transferable or non-transferable moieties which mimic the N-phosphoryl group. (5) compounds which modify the association of creatine kinase with other cellular components.
Owner:AVICENA GROUP +1
Use of creatine or creatine compounds for skin preservation
InactiveUS20050226840A1Easy to spreadEasy to processCosmetic preparationsBiocidePresent methodPhosphate
The present invention relates to the use of creatine compounds such as, for example, creatine, creatine phosphate or analogs of creatine, such as creatine-pyruvate, creatine-ascorbate, cyclocreatine, 3 guanidinopropionic acid, guanidinoacetate, homocyclocreatine, guanidino benzoates as energy generating systems and antioxidants for preservation of skin against adverse aging effects and damage secondary to insults such as harmful sun radiations, stress and fatigue. The creatine compounds which can be used in the present method include (1) creatine, creatine phosphate and analogs of these compounds which can act as substrates or substrate analogs for creatine kinase; (2) molecules that mimic the biological activity of creatine (3) molecules that modulate the creatine kinase system.
Owner:AVICENA GROUP
Use of creatine or creatine compounds for skin preservation
InactiveUS20050227996A1Easy to spreadEasy to processCosmetic preparationsBiocidePresent methodPhosphate
The present invention relates to the use of creatine compounds such as, for example, creatine, creatine phosphate or analogs of creatine, such as creatine-pyruvate, creatine-ascorbate, cyclocreatine, 3 guanidinopropionic acid, guanidinoacetate, homocyclocreatine, guanidino benzoates as energy generating systems and antioxidants for preservation of skin against adverse aging effects and damage secondary to insults such as harmful sun radiations, stress and fatigue. The creatine compounds which can be used in the present method include (1) creatine, creatine phosphate and analogs of these compounds which can act as substrates or substrate analogs for creatine kinase; (2) molecules that mimic the biological activity of creatine (3) molecules that modulate the creatine kinase system.
Owner:LIBRARY PHARMA
Inhibitors of memapsin 2 and use thereof
InactiveUS7244708B2Reduce molecular weightGrowth inhibitionNervous disorderHydrolasesDiseaseSubstrate analog
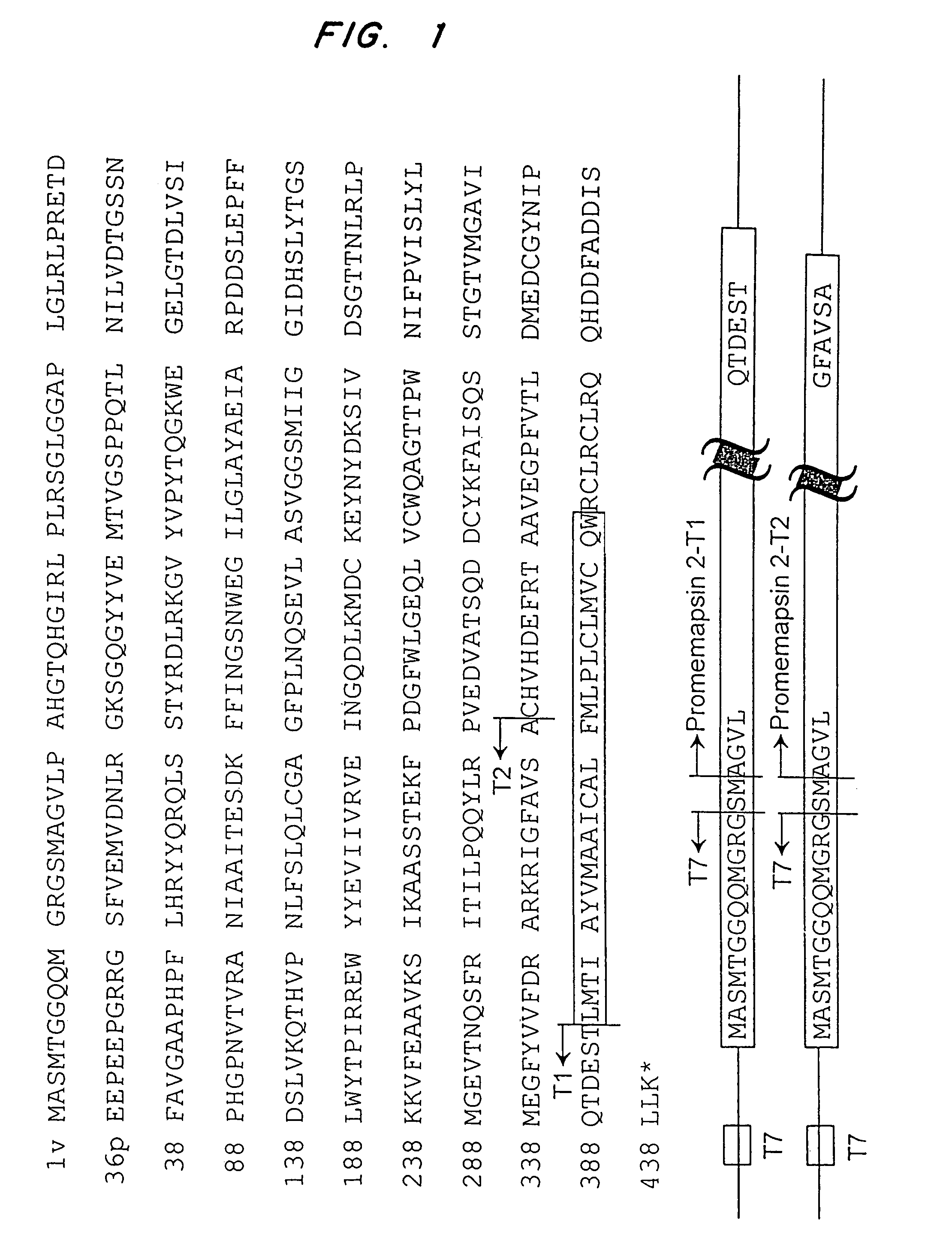
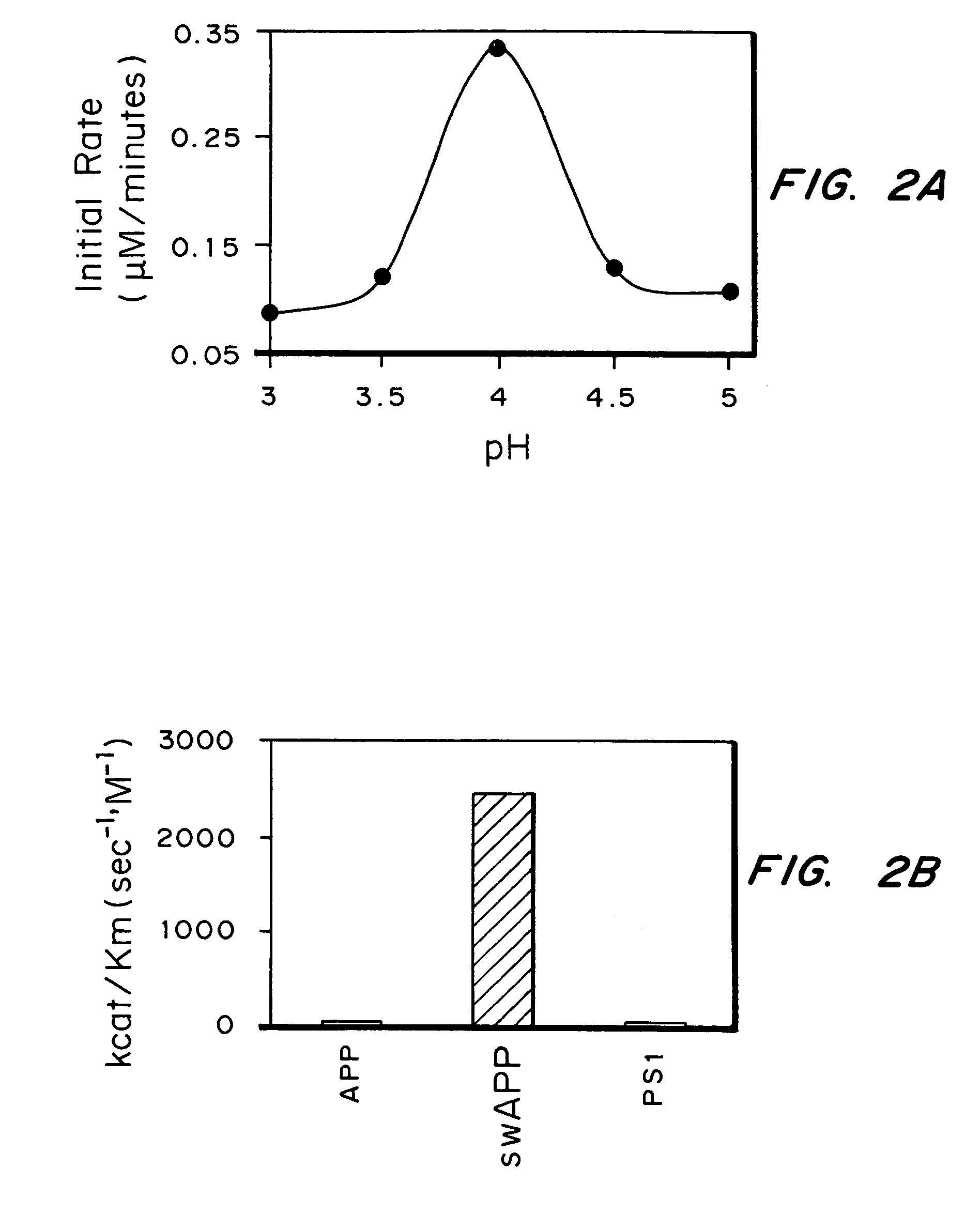
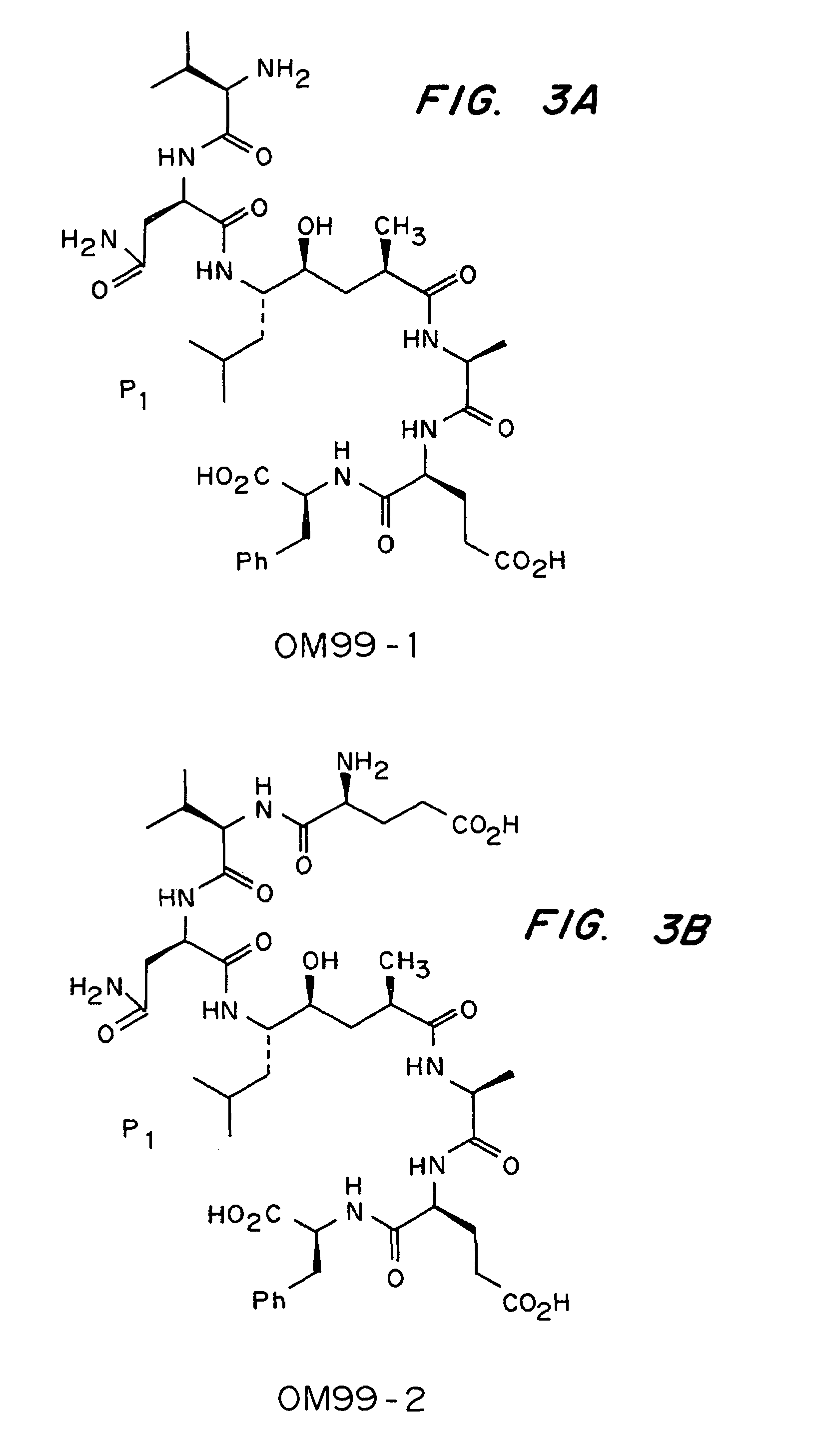
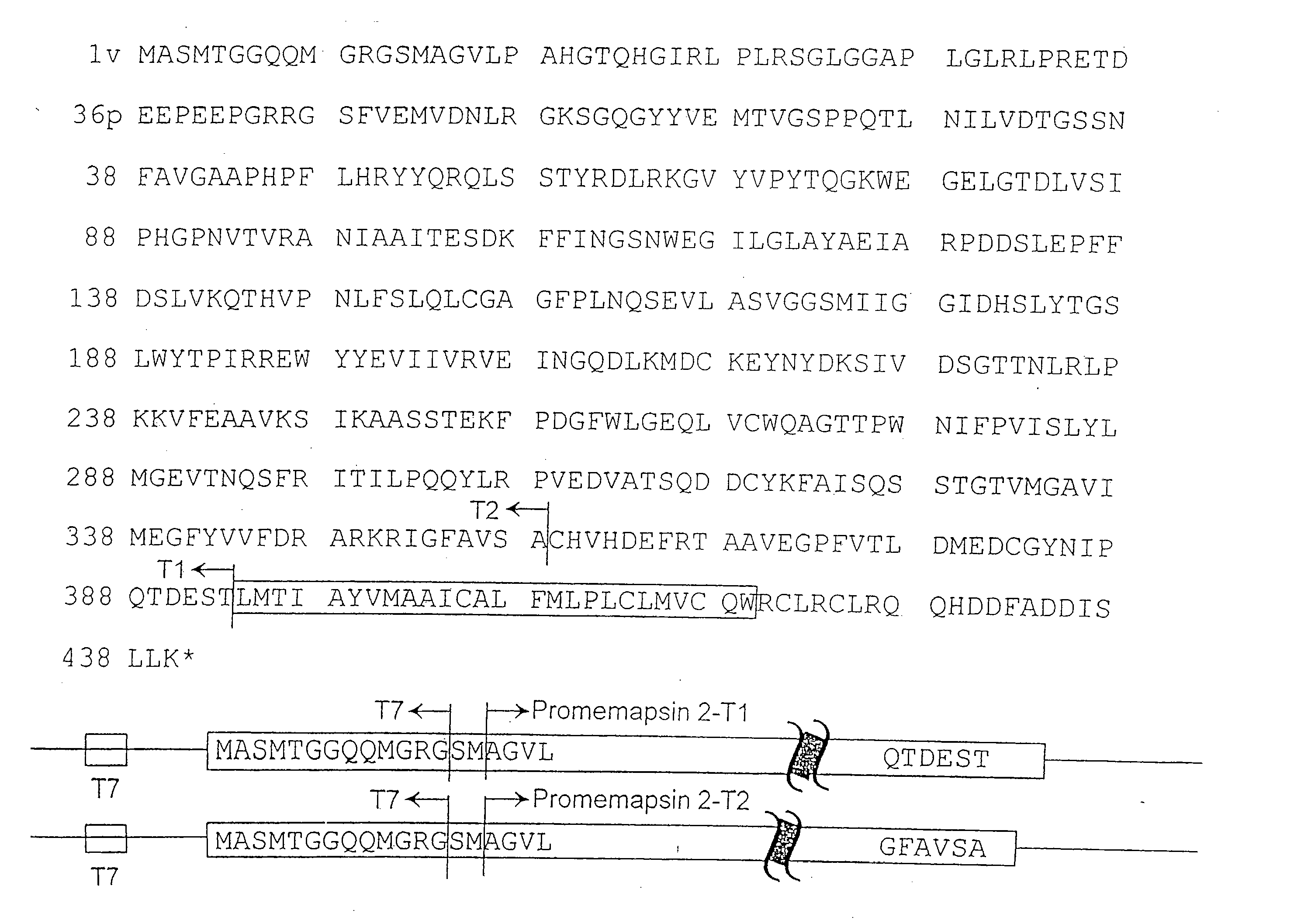
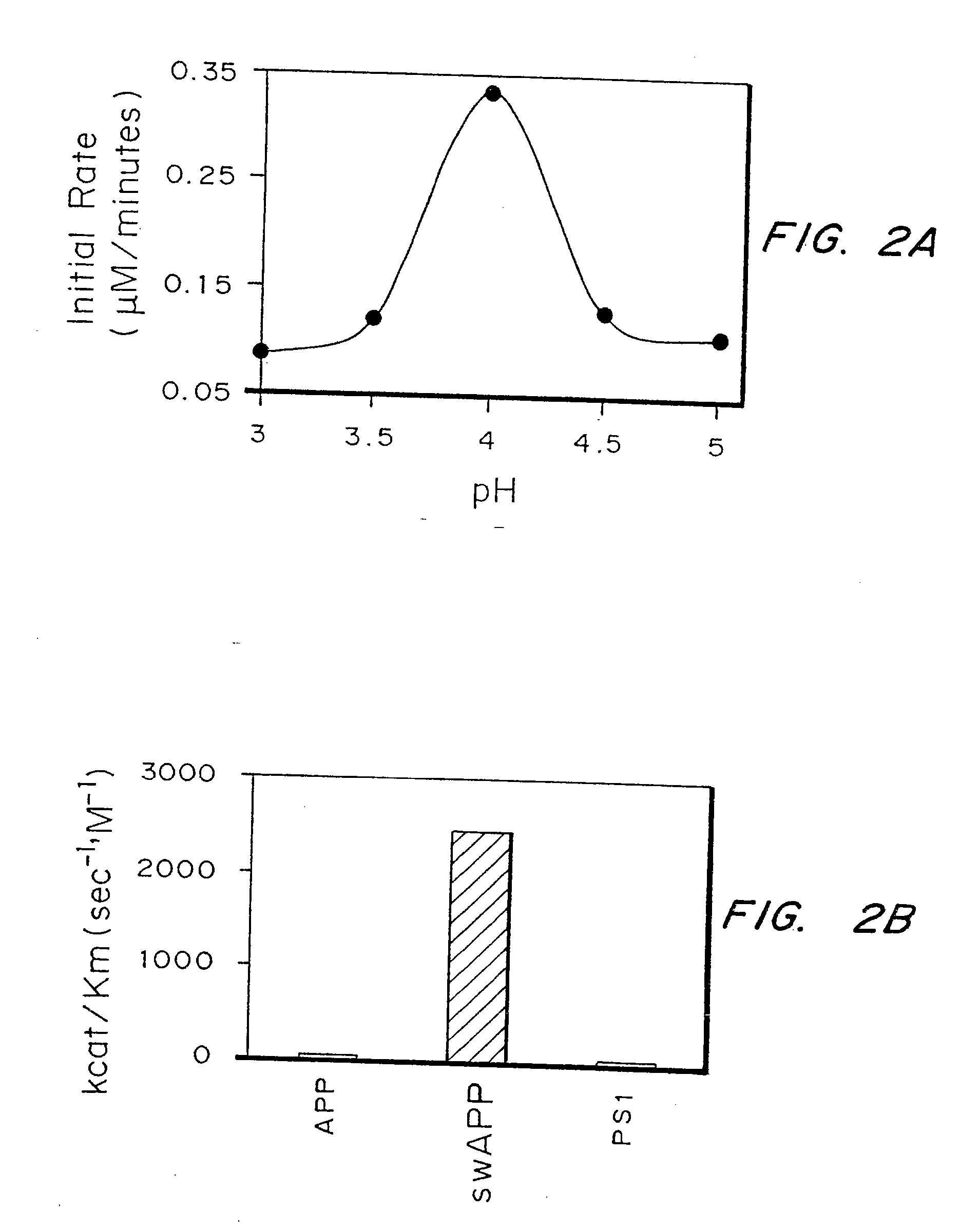
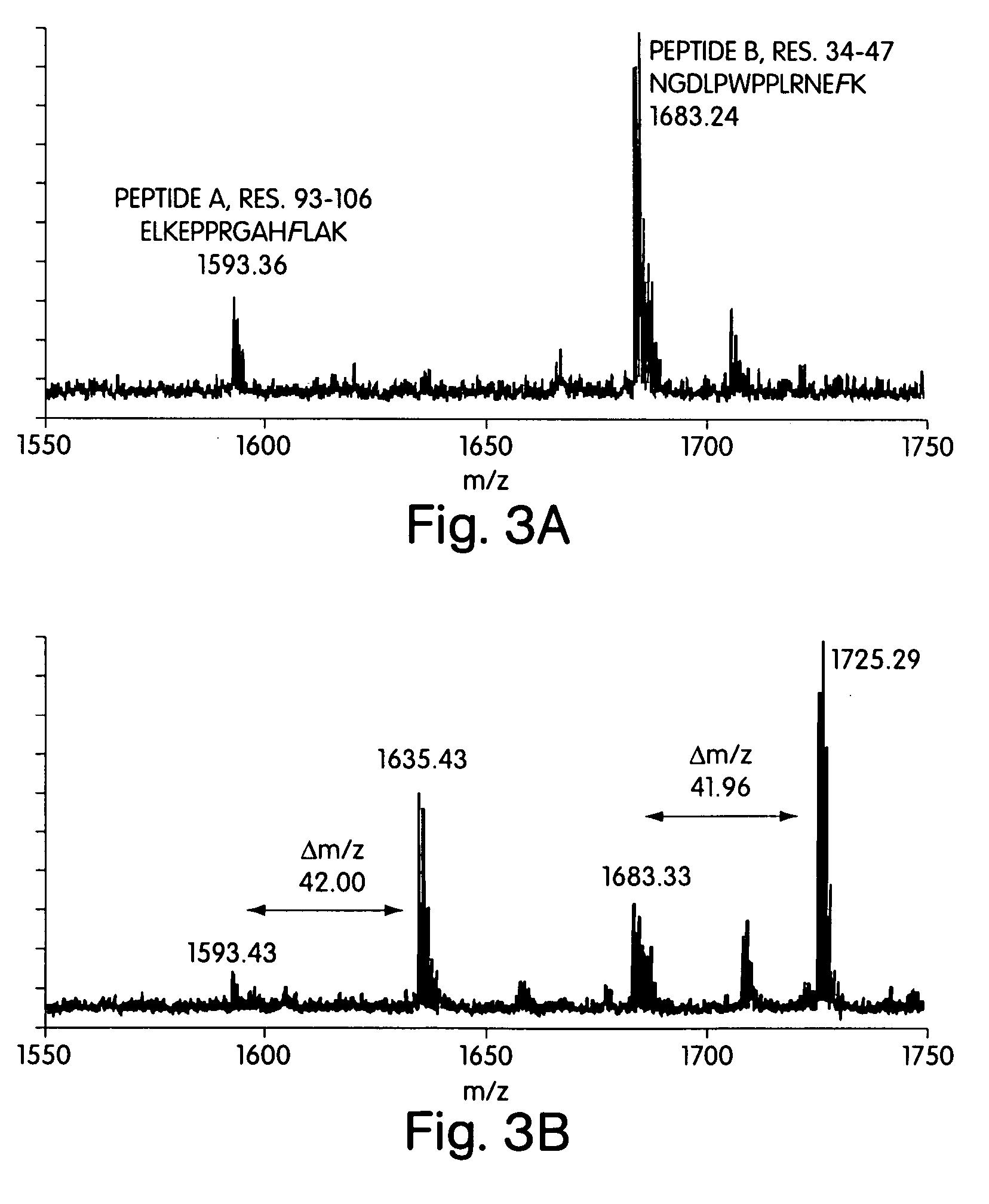
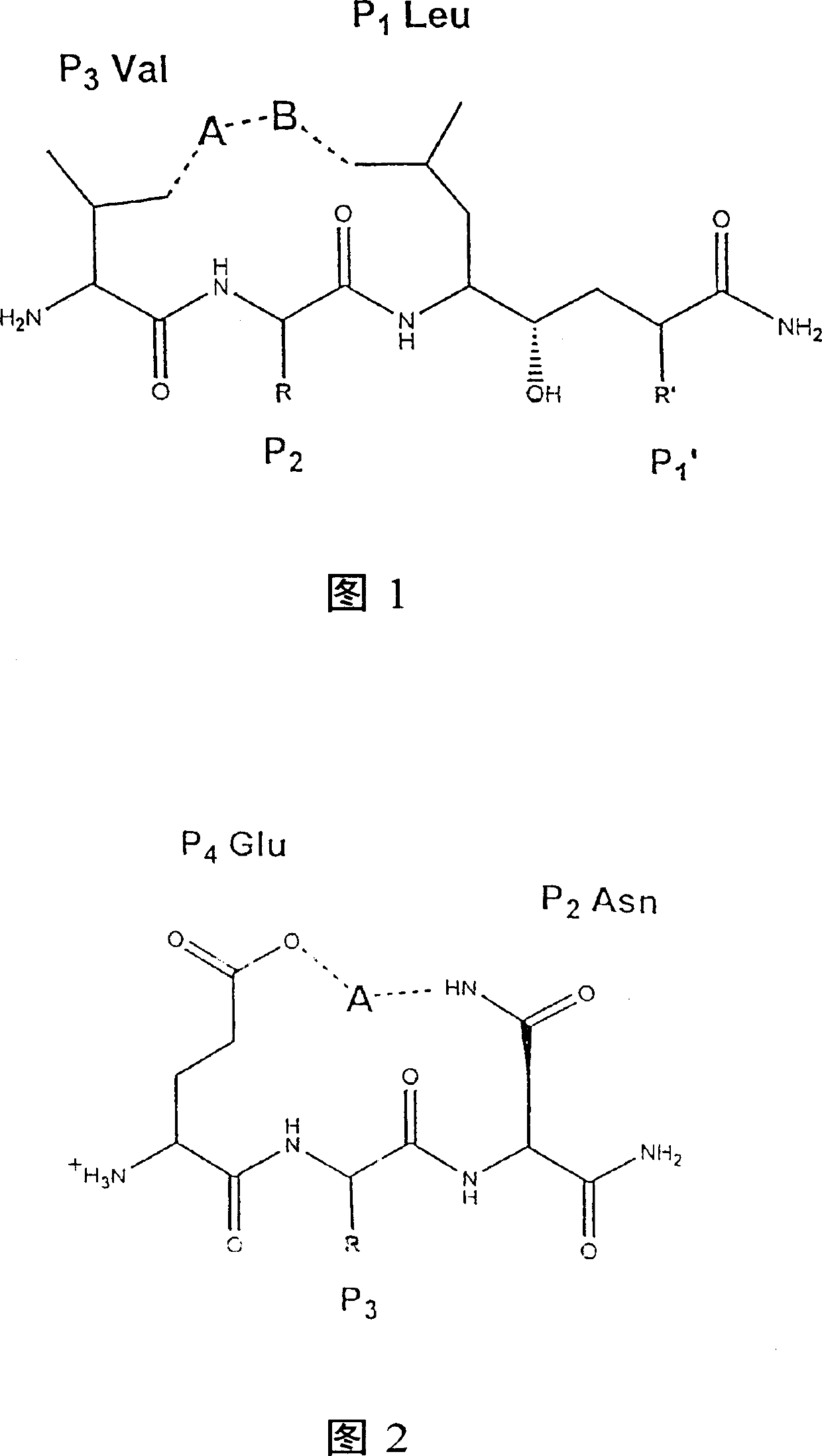
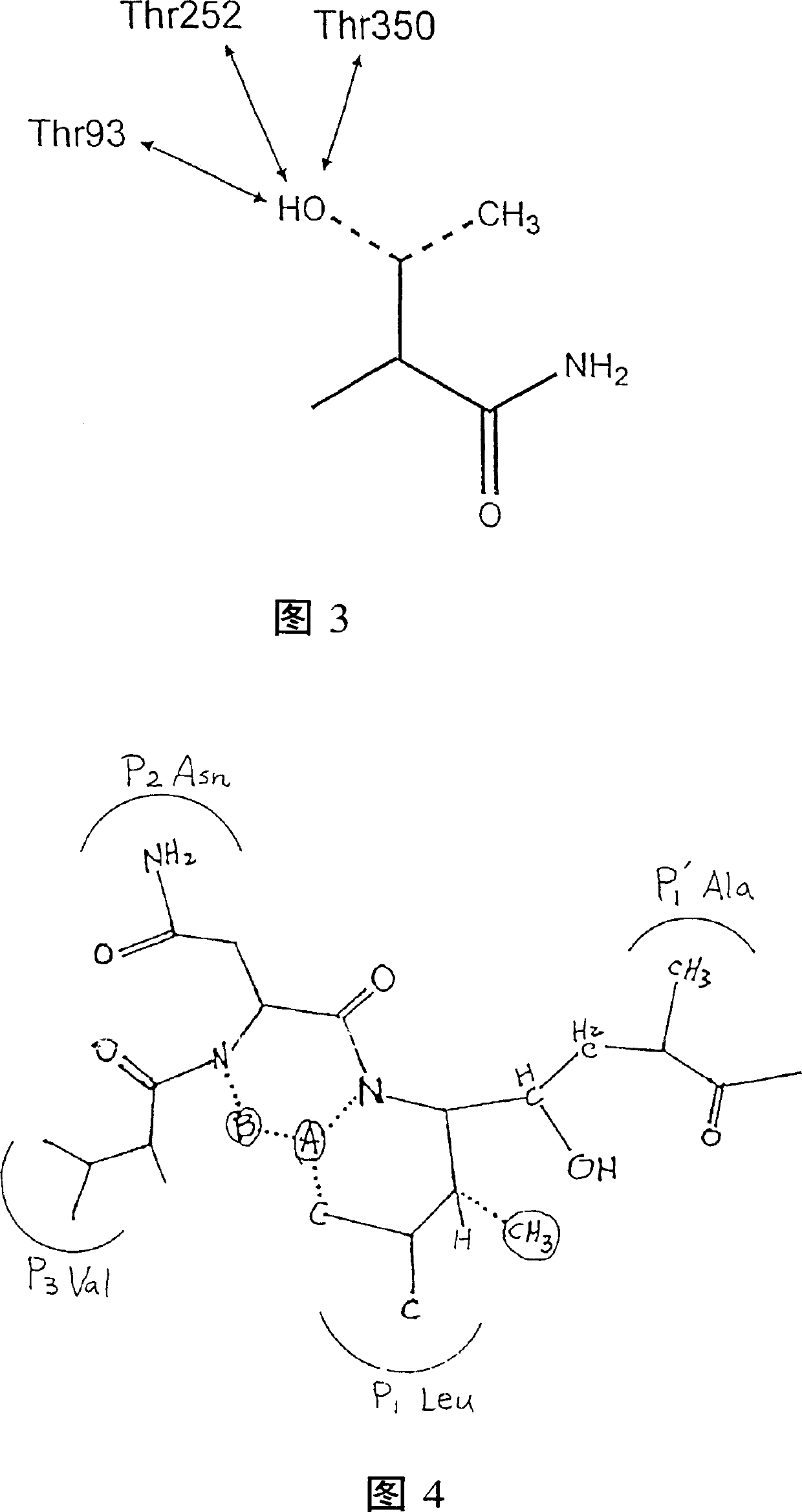
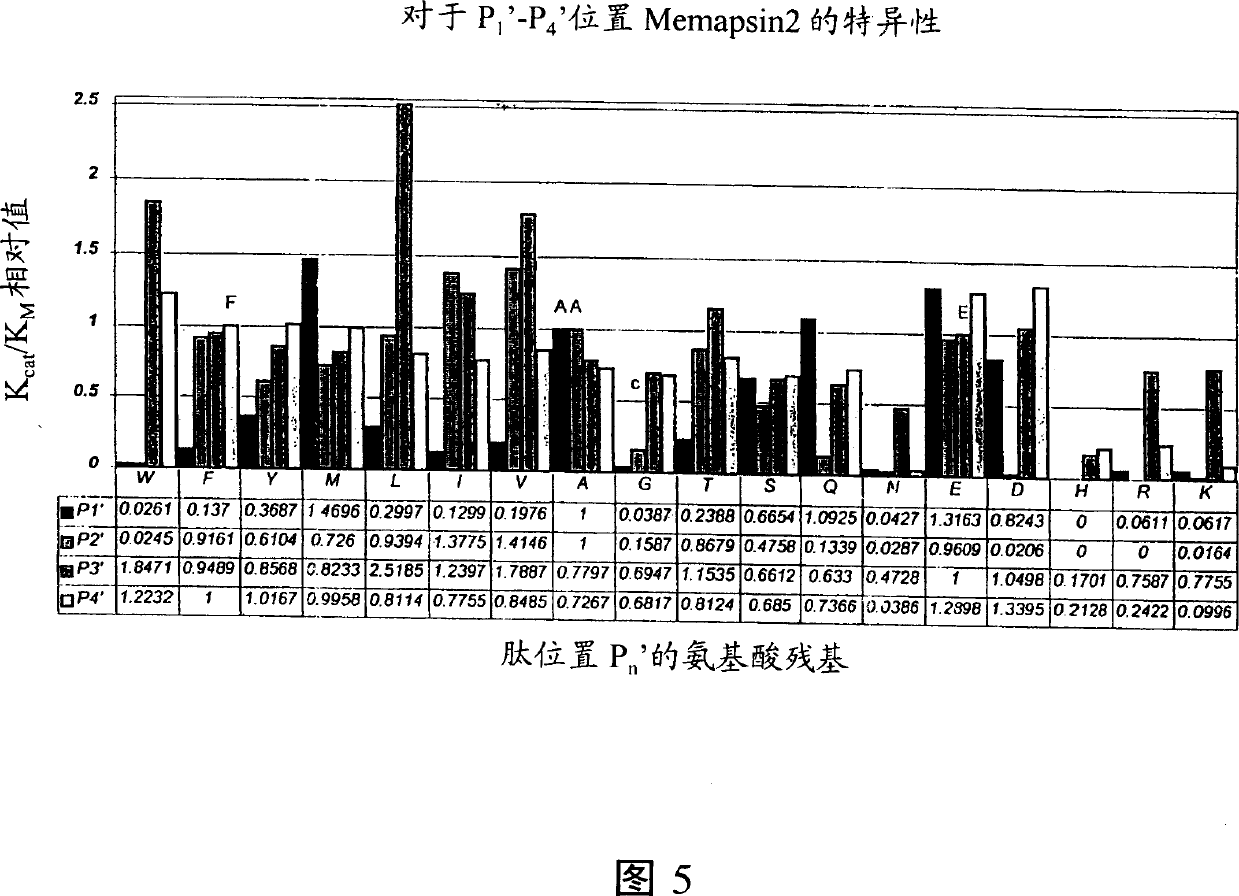
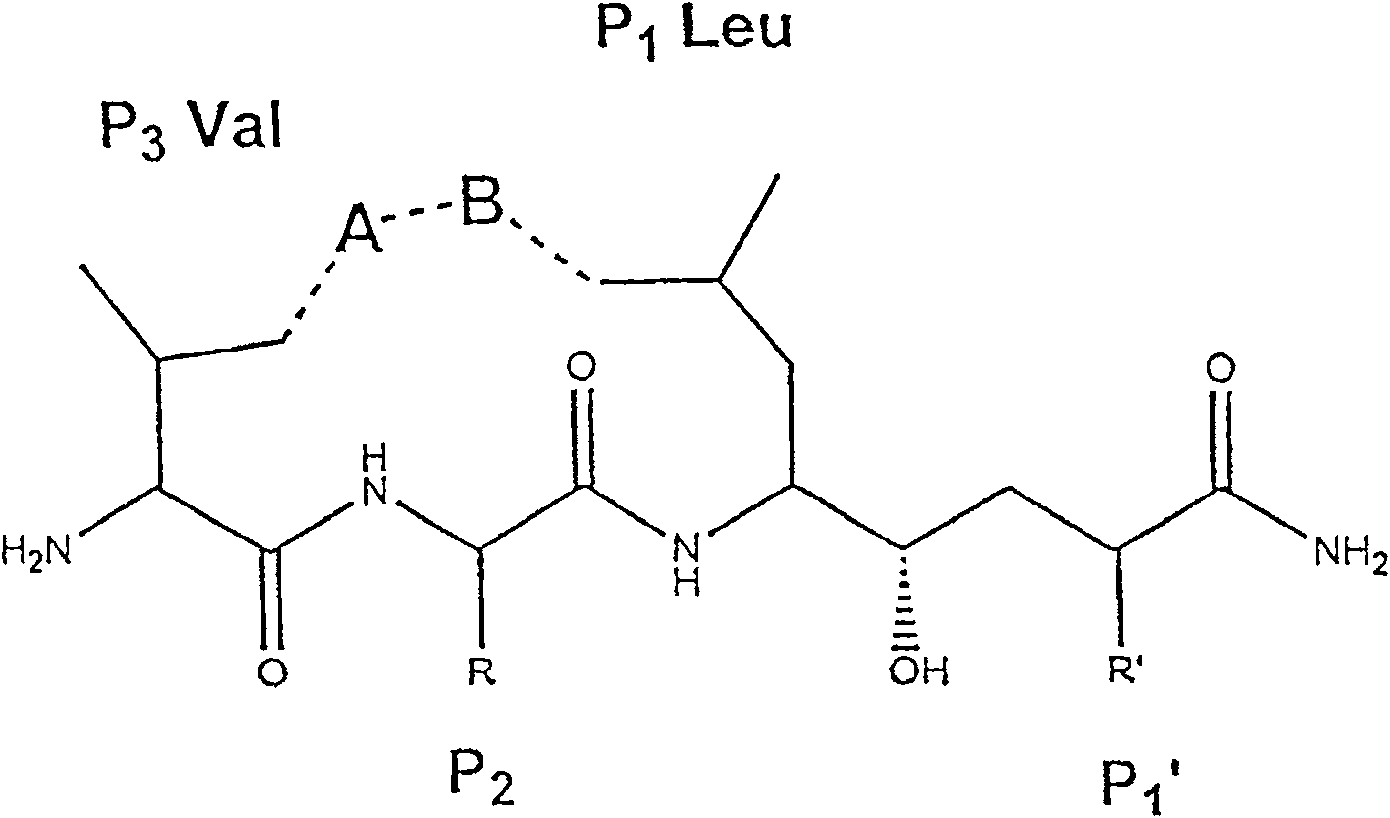
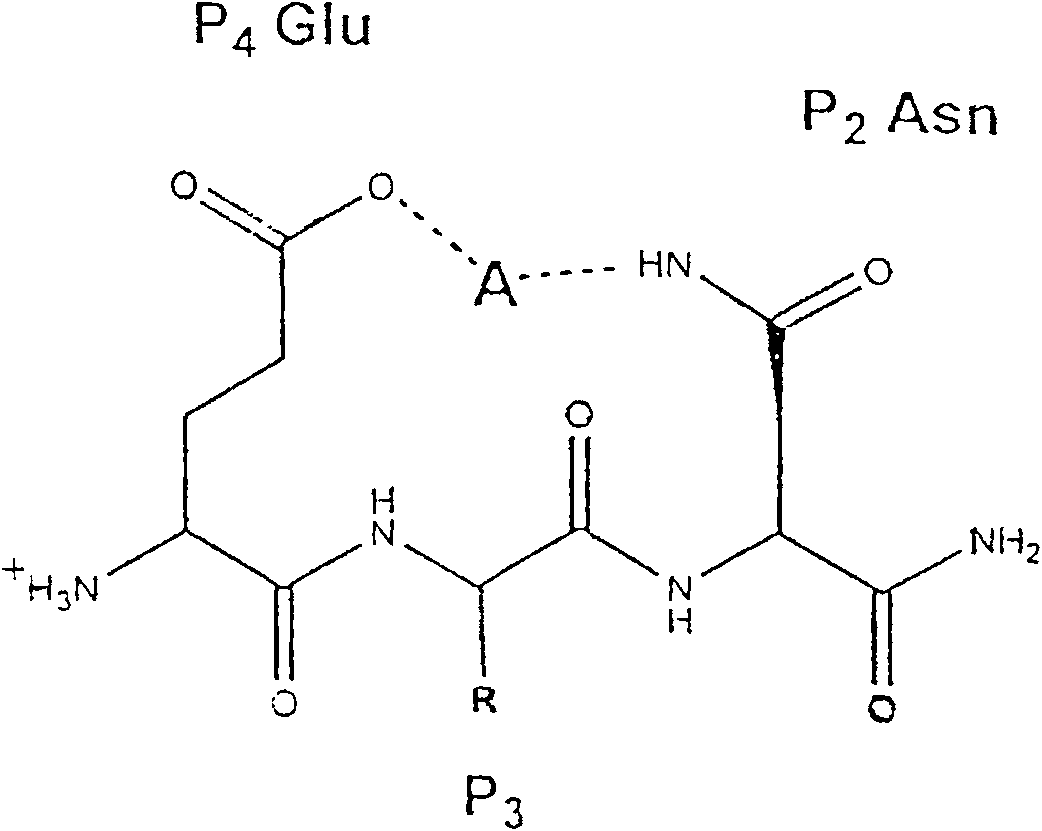
Methods for the production of purified, catalytically active, recombinant memapsin 2 have been developed. The substrate and subsite specificity of the catalytically active enzyme have been determined and were used to design substrate analogs of the natural -2 substrate that can inhibit the function of memapsin 2. Processes for the synthesis of two substrate analogues including isosteres at the sites of the critical amino acid residues were developed and the substrate analogues, OMR99-1 and OM99-2, were synthesized. The inhibition constant of OM99-2 is 1.6×10−9 M against recombinant pro-memapsin 2. Crystallography of memapsin 2 bound to this inhibitor was used to determine the three dimensional structure of the protein, and the importance of the various residues in binding. This information is useful for designing new inhibitors to memapsin 2, for diagnosing and treating and / or preventing Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Compositions containing a combination of a creatine compound and a second agent
The present invention relates to the use of creatine compound and neuroprotective combinations including creatine, creatine phosphate or analogs of creatine, such as cyclocreatine, for treating diseases of the nervous system. Creatine compounds in combination with neuroprotective agents can be used as therapeutically effective compositions against a variety of diseases of the nervous system such as diabetic and toxic neuropathies, peripheral nervous system diseases, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson's disease, stroke, Huntington's disease, amyotropic lateral sclerosis, motor neuron disease, traumatic nerve injury, multiple sclerosis, dysmyelination and demyelination disorders, and mitochondrial diseases. The creatine compounds which can be used in the present method include (1) creatine, creatine phosphate and analogs of these compounds which can act as substrates or substrate analogs for creatine kinase; (2) bisubstrate inhibitors of creatine kinase comprising covalently linked structural analogs of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and creatine; (3) creatine analogs which can act as reversible or irreversible inhibitors of creatine kinase; and (4) N-phosphorocreatine analogs bearing non-transferable moieties which mimic the N-phosphoryl group.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Use of creatine or creatine compounds for skin preservation
InactiveUS20050186195A1Easy to spreadPreserve energyCosmetic preparationsBiocidePresent methodPhosphate
The present invention relates to the use of creatine compounds such as, for example, creatine, creatine phosphate or analogs of creatine, such as creatine-pyruvate, creatine-ascorbate, cyclocreatine, 3 guanidinopropionic acid, guanidinoacetate, homocyclocreatine, guanidino benzoates as energy generating systems and antioxidants for preservation of skin against adverse aging effects and damage secondary to insults such as harmful sun radiations, stress and fatigue. The creatine compounds which can be used in the present method include (1) creatine, creatine phosphate and analogs of these compounds which can act as substrates or substrate analogs for creatine kinase; (2) molecules that mimic the biological activity of creatine (3) molecules that modulate the creatine kinase system.
Owner:AVICENA GROUP
Inhibitors of memapsin 2 and use thereof
InactiveUS20080021196A1Reduce molecular weightGrowth inhibitionNervous disorderHydrolasesDiseaseActive enzyme
Methods for the production of purified, catalytically active, recombinant memapsin 2 have been developed. The substrate and subsite specificity of the catalytically active enzyme have been determined. The substrate and subsite specificity information was used to design substrate analogs of the natural memapsin 2 substrate that can inhibit the function of memapsin 2. The substrate analogs are based on peptide sequences, shown to be related to the natural peptide substrates for memapsin 2. The substrate analogs contain at least one analog of an amide bond which is not capable of being cleaved by memapsin 2. Processes for the synthesis of two substrate analogues including isosteres at the sites of the critical amino acid residues were developed and the substrate analogues, OMR99-1 and OM99-2, were synthesized. OM99-2 is based on an octapeptide Glu-Val-Asn-Leu-Ala-Ala-Glu-Phe (SEQ ID NO:28) with the Leu-Ala peptide bond substituted by a transition-state isostere hydroxyethylene group (FIG. 1). The inhibition constant of OM99-2 is 1.6×10−9 M against recombinant pro-memapsin 2. Crystallography of memapsin 2 bound to this inhibitor was used to determine the three dimensional structure of the protein, as well as the importance of the various residues in binding. This information can be used by those skilled in the art to design new inhibitors, using commercially available software programs and techniques familiar to those in organic chemistry and enzymology, to design new inhibitors to memapsin 2, useful in diagnostics and for the treatment and / or prevention of Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention relates to improved methods of detecting a target using a labeled substrate or substrate analog. The methods comprise reacting the substrate or substrate analog in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which produces a labeled moiety with independently detectable signal only when such substrate or substrate analog reacts. The present invention, in particular, describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrate for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Bacterial transglycosylases: assays for monitoring the activity using Lipid II substrate analogs and methods for discovering new antibiotics
InactiveUS20030129683A1Easy to detectEasy to measureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymatic synthesisSubstrate analog
This invention provides a direct method for monitoring bacterial transglycosylase activity using labeled substrates produced by chemo-enzymatic synthesis wherein the labels are selected to permit the detection of both polymeric and non-polymeric products simultaneously, either directly or following the separation of product from starting material. The invention promotes the discovery of new antibiotics with activity against bacterial transglycosylases by a) laying the groundwork for structural analysis of purified, active transglycosylase (which permits structure-based design); and b) providing an assay that can be used to screen for inhibitors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
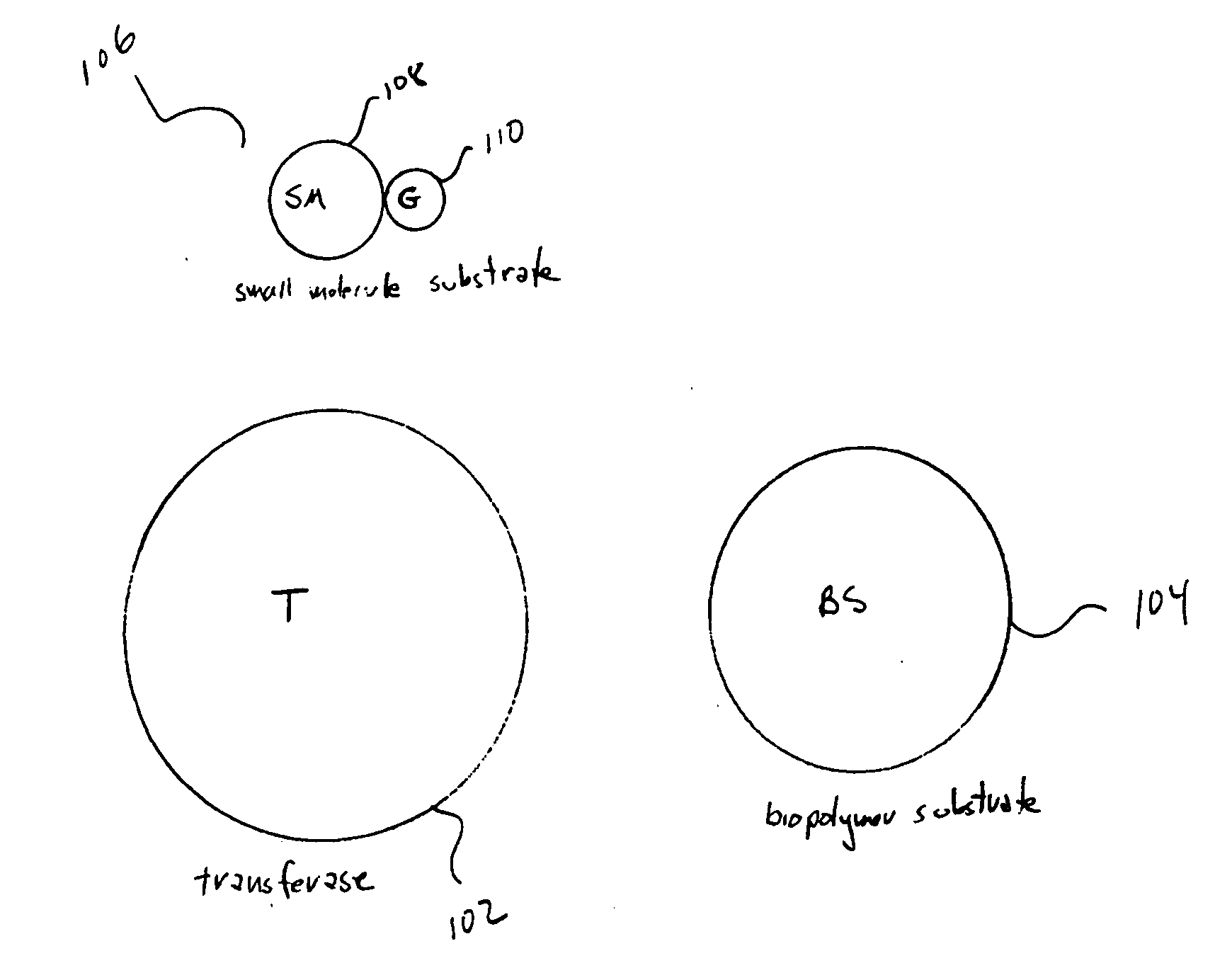
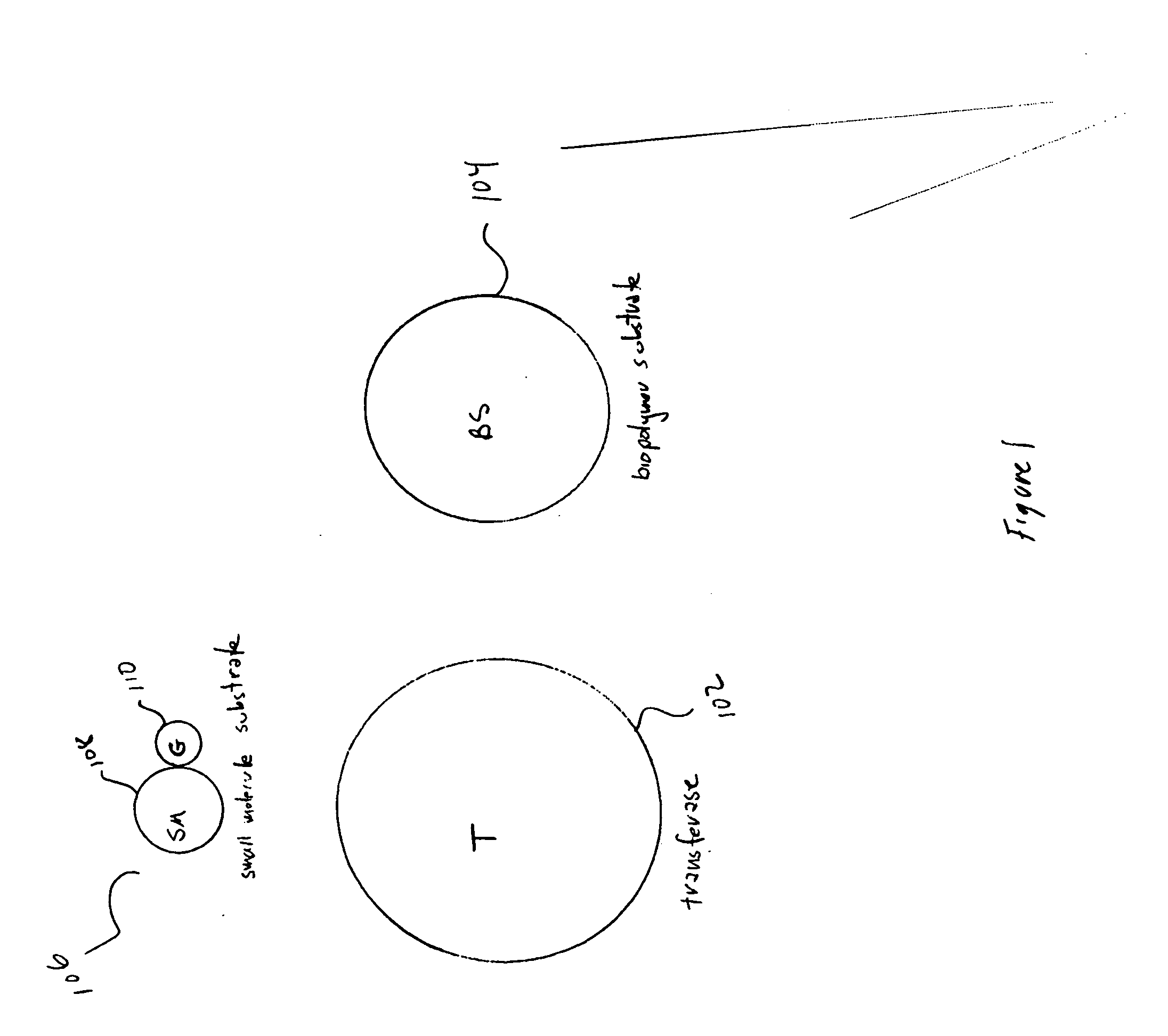
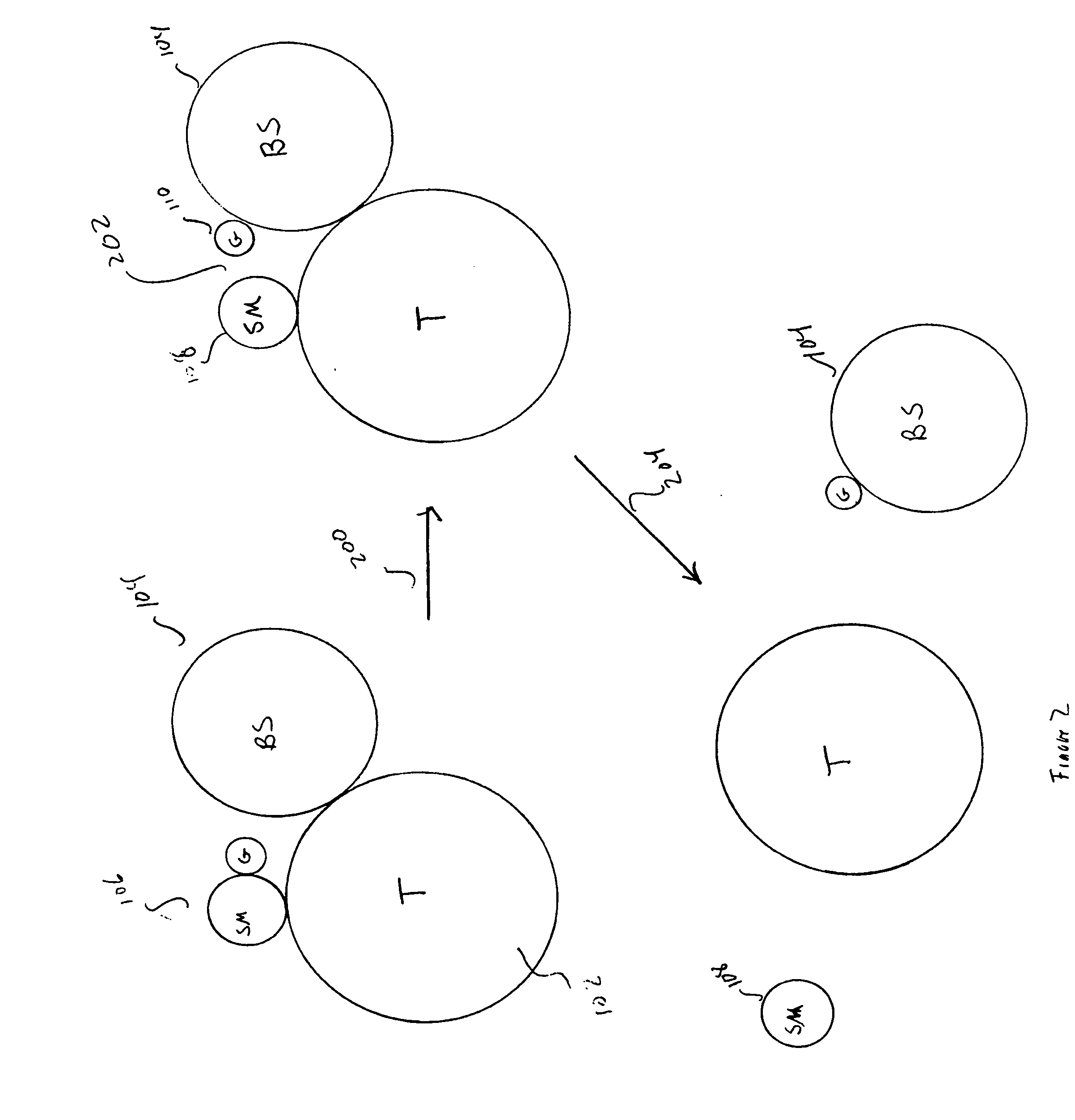
Method and system for assaying transferase activity
InactiveUS20070264667A1Easy to detectPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSubstrate analogBiopolymer
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to sensitive, specific, and commercially feasible assays for transferase activity. Various embodiments of the present invention include artificial, multifunctional substrates specific for particular transferases that are chemically altered by the transferases to produce easily detectable, modified, multifunctional substrates. In one class of embodiments, the artificial, multifunctional substrate comprises a small-molecule-substrate component, or small-molecule-substrate-analog component, linked by a linking component to a biopolymer-substrate-mimetic or biopolymer-substrate-analog component. At least two, generally well-separated reporter moieties are included in the artificial, multifunctional substrate. The transferase, for which the artificial, multifunctional substrate is designed to serve as an assay reagent, catalyzes a generally covalent modification of the artificial, multifunctional substrate to produce a modified, artificial, multifunctional substrate reaction product in which the two reporter moieties are closely positioned to one another. When closely positioned to one another, the reporter moieties are detectable by one of various instrumental techniques.
Owner:GELLIBOLIAN ROBERT +1
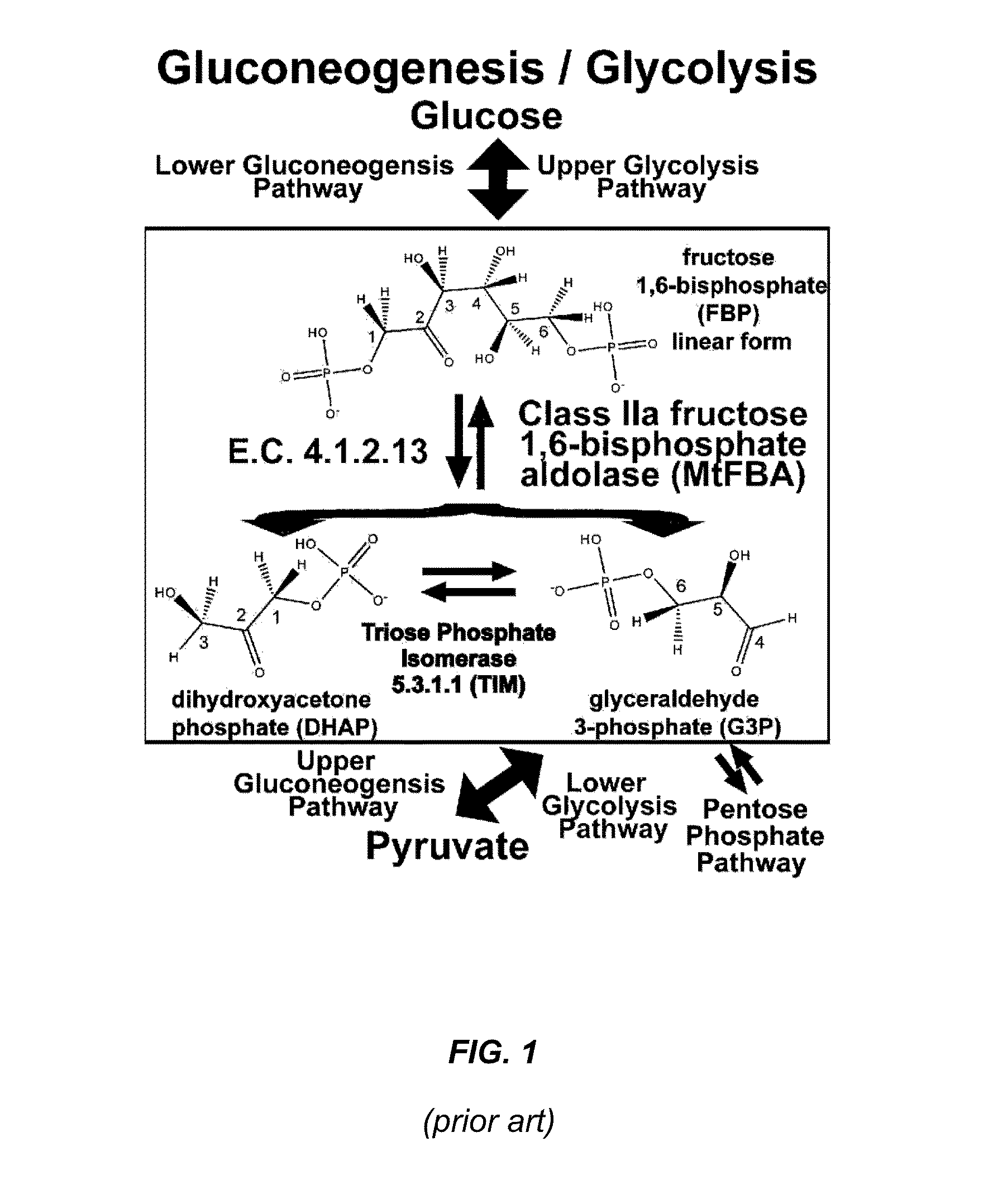
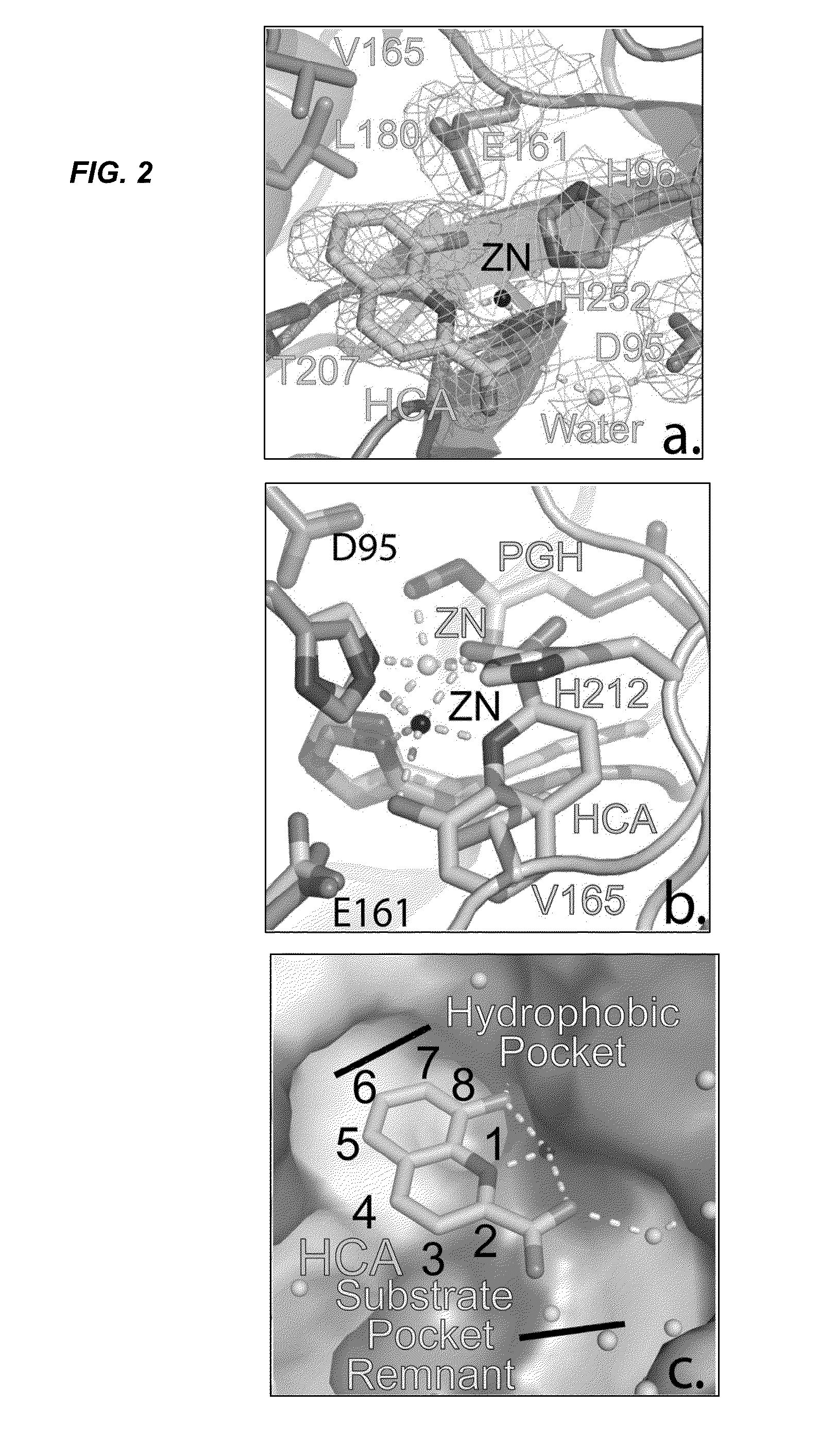
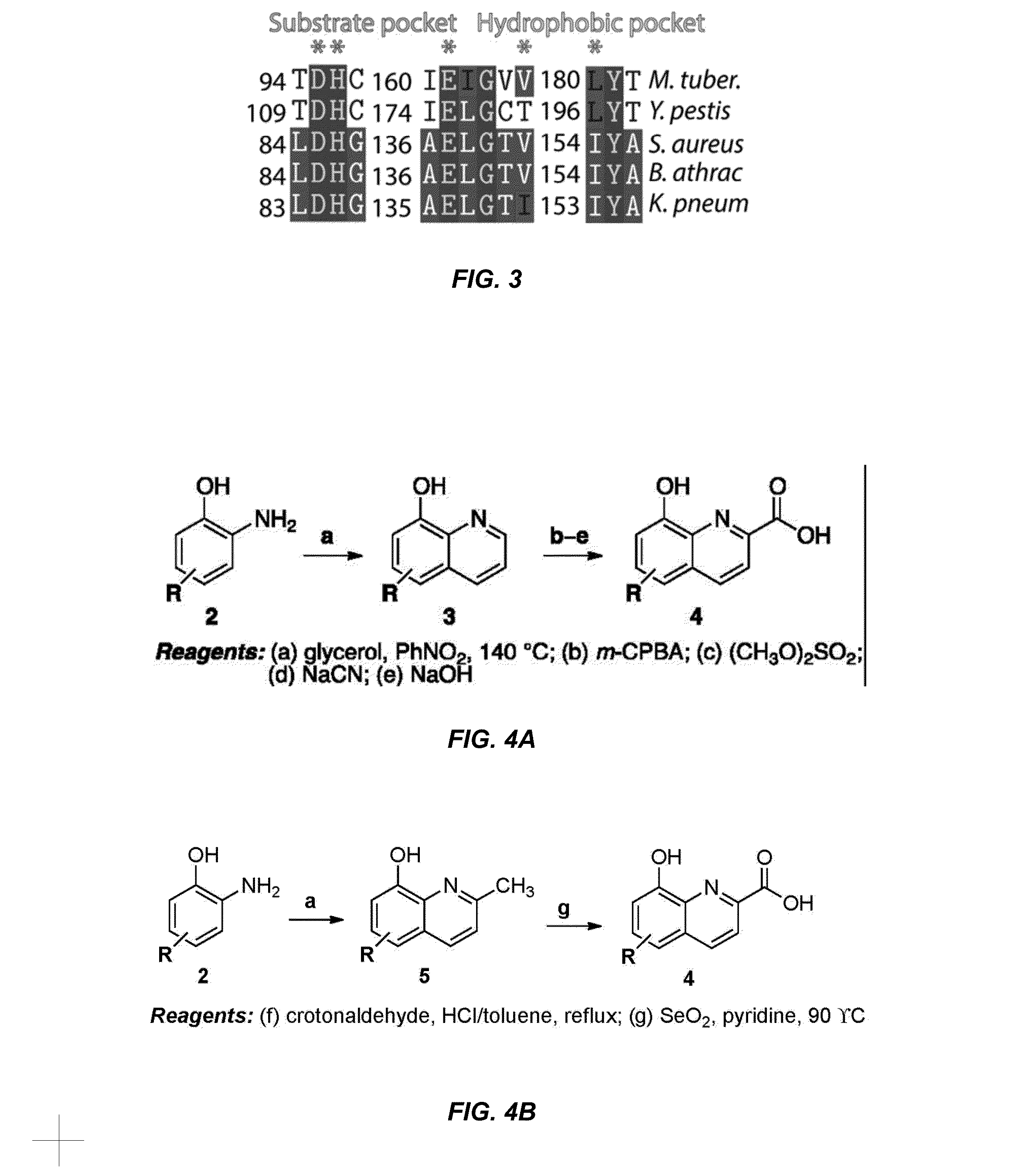
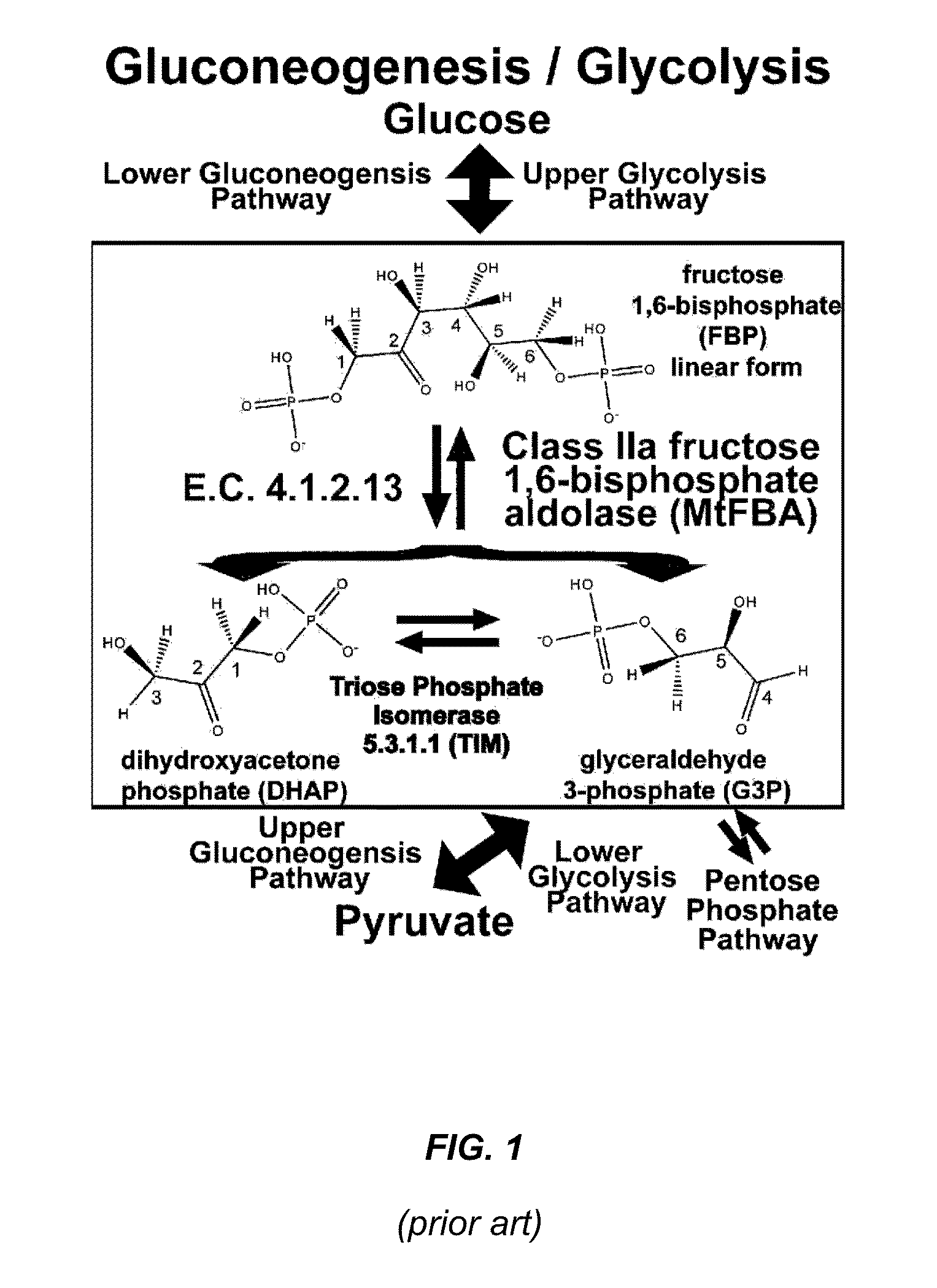
Antibiotic and Anti-Parasitic Agents that Modulate Class II Fructose 1, 6-Bisphosphate Aldolase
ActiveUS20140336221A1Inhibit growthInhibition of replicationBiocideCompound screeningSubstrate analogAntiparasite agent
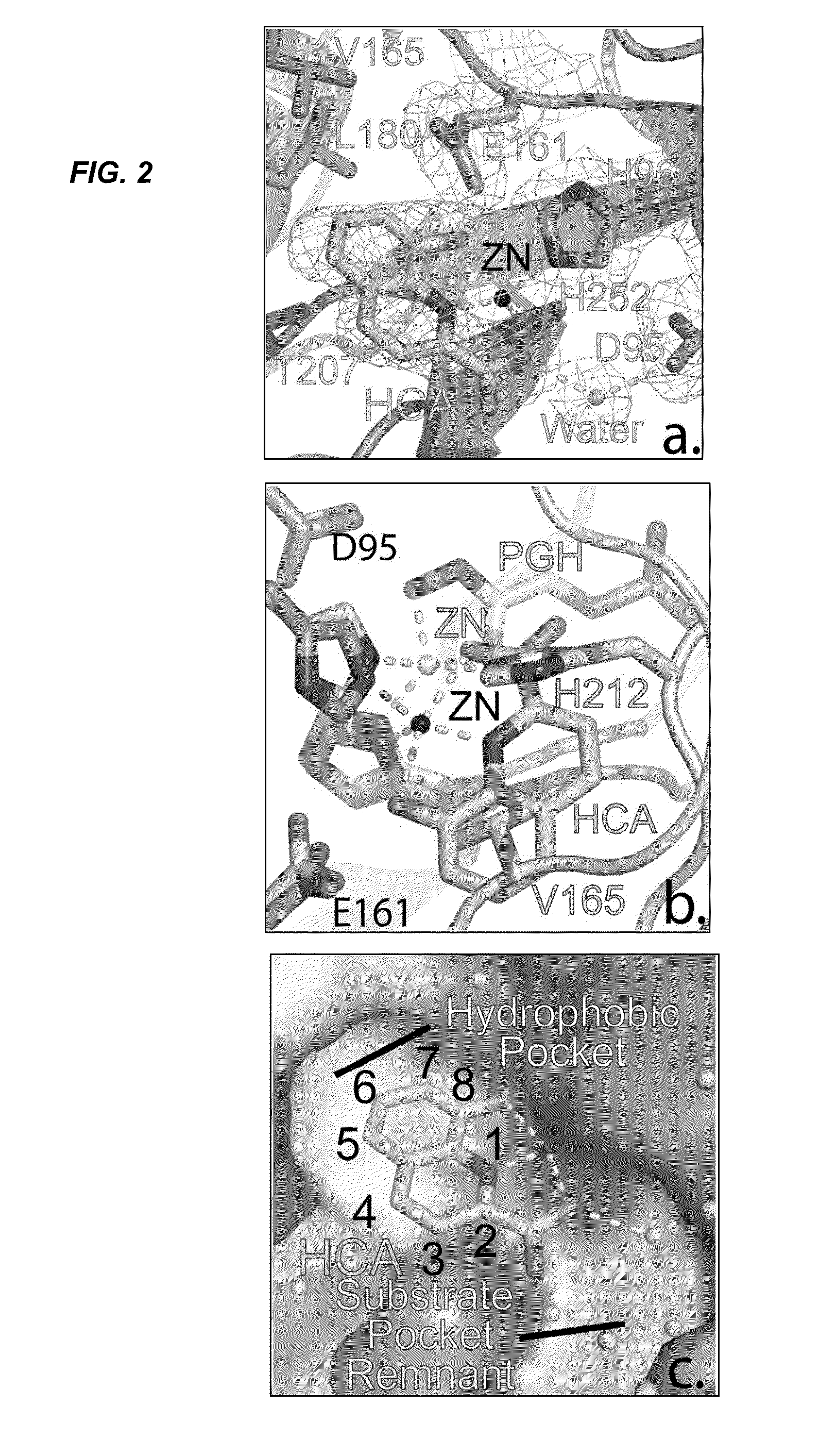
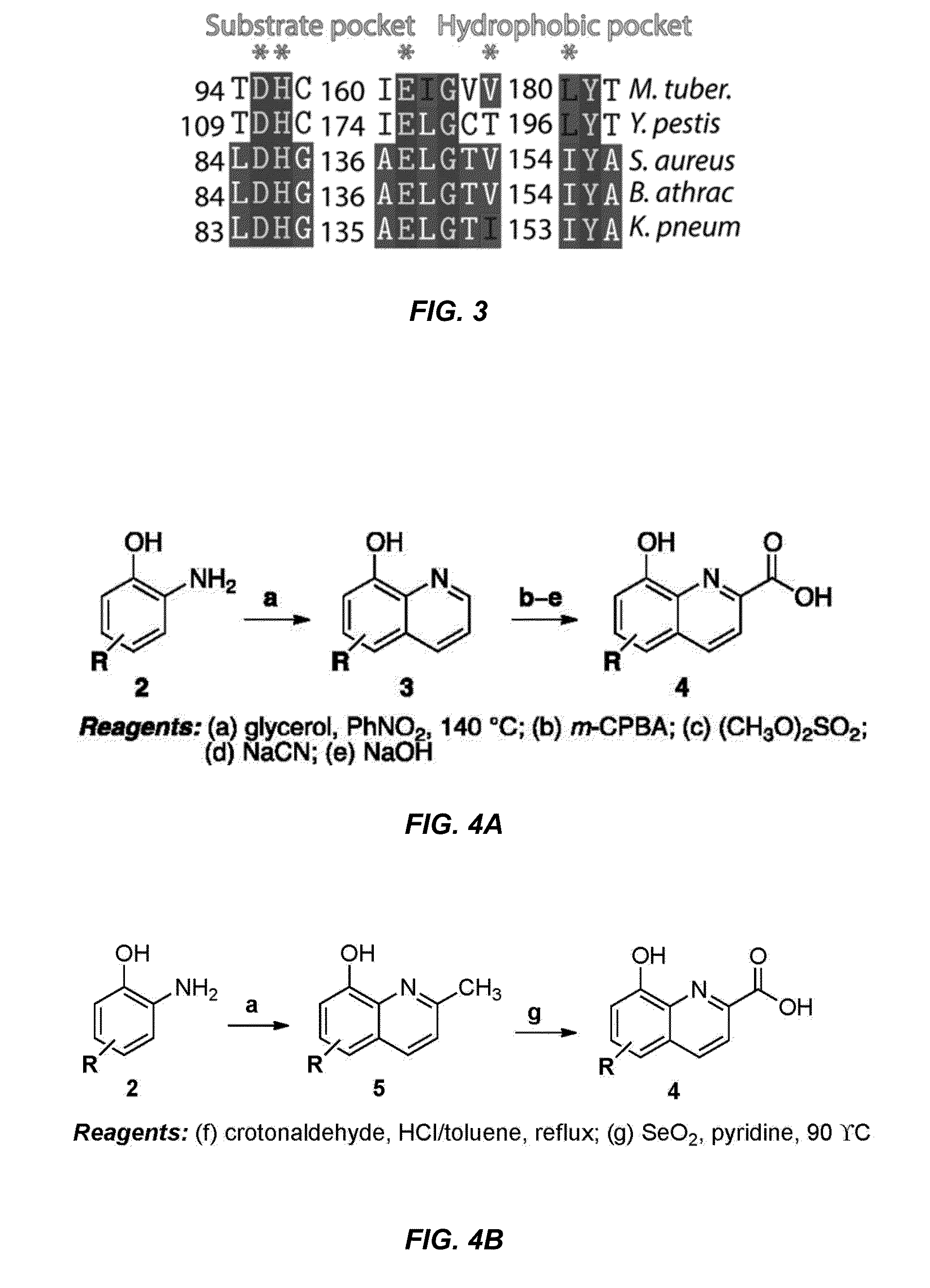
This invention provides a family of compounds that inhibit Class II fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA), which is implicated in the pathogenic activity of a broad range of bacterial and parasitic agents. The compounds were identified by empirical testing, and provide a basis for further derivatization and optimization of 8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxylic acid and related compounds. Crystal structure shows that the compounds don't bind directly to the catalytic site of the enzyme, and so are not defined simply as substrate analogs. Instead, they create a pocket by induced fit, resulting a powerful and specific inhibitory effect on FBA activity.
Owner:THE UNIV OF DENVER +1
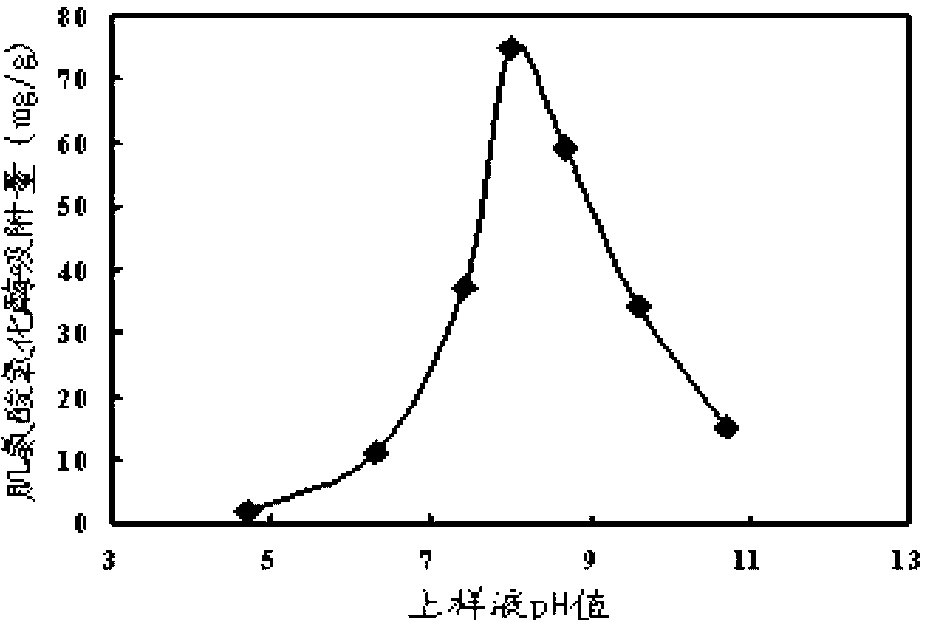
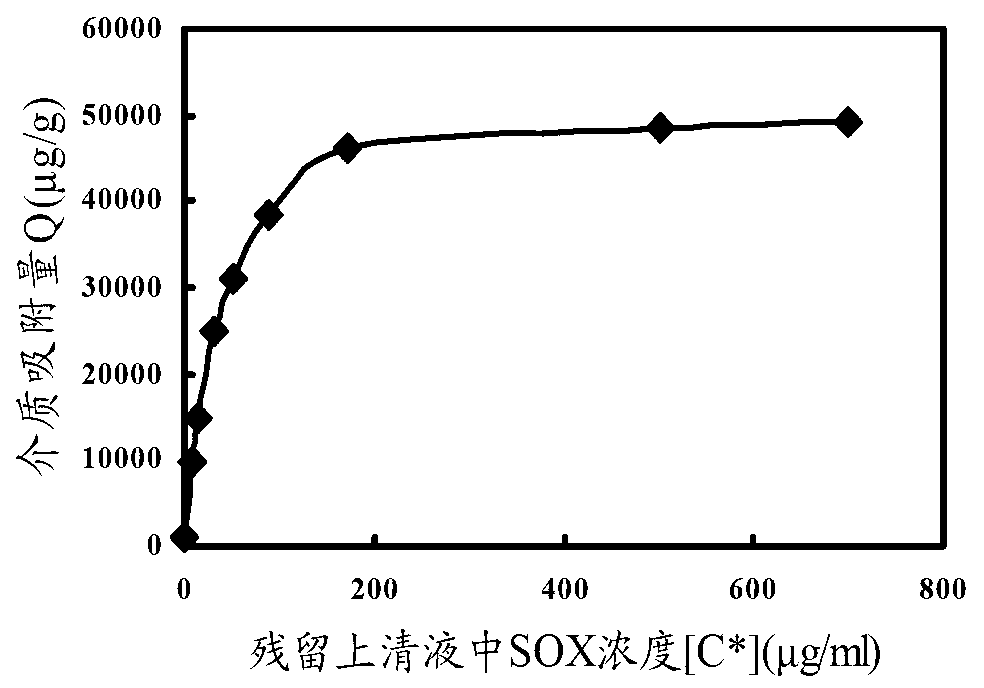
Sarcosine oxidase affinity medium and method for synthesizing and purifying sarcosine oxidase
ActiveCN103055825AEfficient purificationImprove purification efficiencyOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationSarcosine oxidaseSubstrate analog
The invention discloses a sarcosine oxidase affinity medium and a method for synthesizing and purifying sarcosine oxidase, which belong to the technical field of biologic engineering. The sarcosine oxidase affinity medium disclosed by the invention is prepared by connecting a sarcosine oxidase affinity ligand with a chromatography medium; preferably, the sarcosine oxidase affinity ligand is a substrate analog 4-amino pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid, and the chromatography medium is Sepharose or poly-chitosan; the invention further provides a synthesis method of the sarcosine oxidase affinity medium, and a method for purifying the sarcosine oxidase in a large scale by using the sarcosine oxidase affinity medium. By utilizing the sarcosine oxidase affinity medium disclosed by the invention, the sarcosine oxidase can be rapidly separated and purified in a large scale, and a sarcosine oxidase pure product can be obtained under the condition of one step affinity chromatography; and the whole purification step is short in time, the protein and activity recovering rate is high, and thus being applicable to large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bacterial transglycosylases: assays for monitoring the activity using Lipid II substrate analogs and methods for discovering new antibiotics
InactiveUS6911318B2Easy to detectEasy to measureMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic synthesisSubstrate analog
This invention provides a direct method for monitoring bacterial transglycosylase activity using labeled substrates produced by chemo-enzymatic synthesis wherein the labels are selected to permit the detection of both polymeric and non-polymeric products simultaneously, either directly or following the separation of product from starting material. The invention promotes the discovery of new antibiotics with activity against bacterial transglycosylases by a) laying the groundwork for structural analysis of purified, active transglycosylase (which permits structure-based design); and b) providing an assay that can be used to screen for inhibitors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF PRINCETON UNIV
Use of creatine or creatine compounds for skin preservation
InactiveUS20070253944A1Easy to spreadEasy to processCosmetic preparationsBiocidePresent methodPhosphate
Owner:AVICENA GROUP
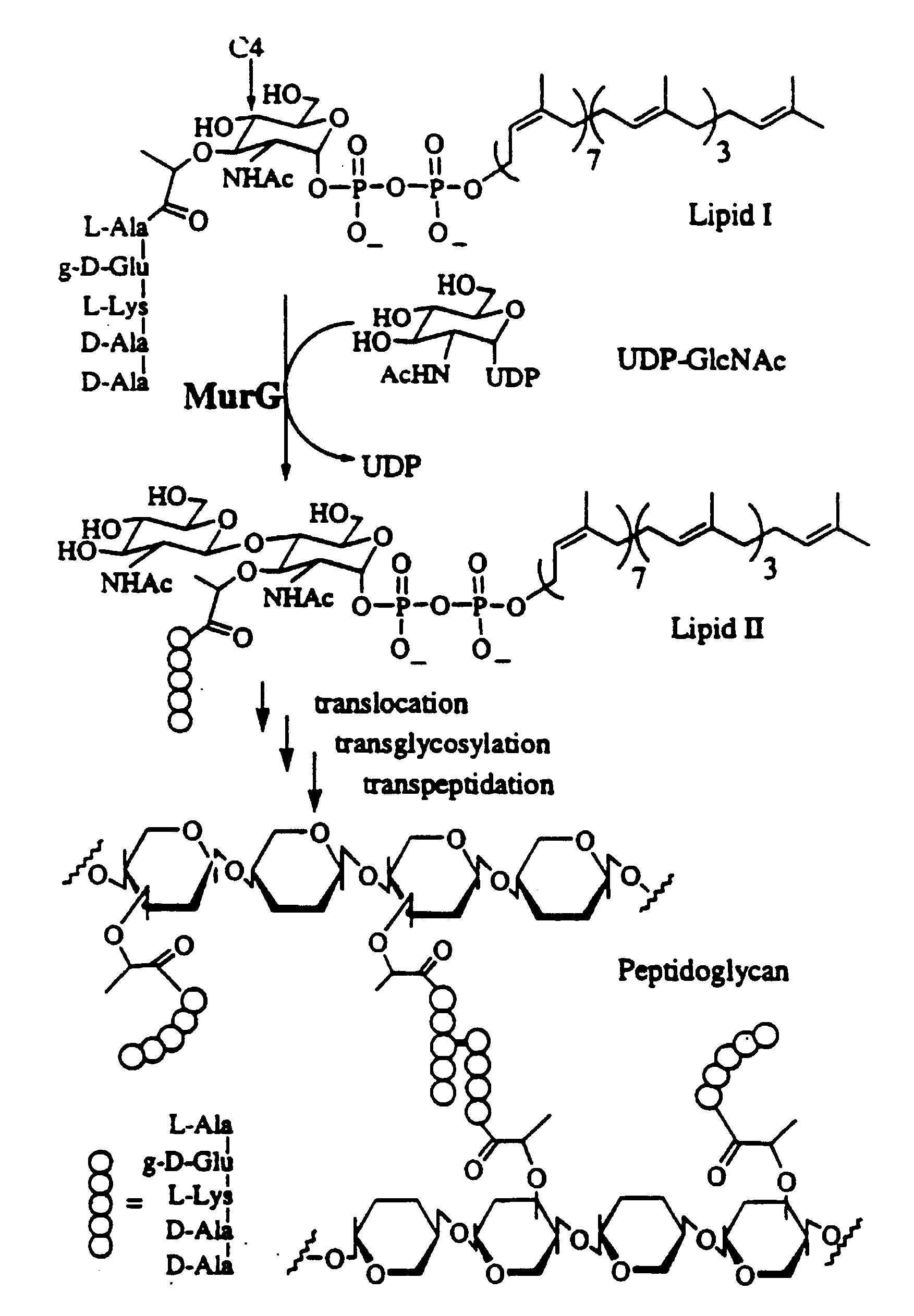
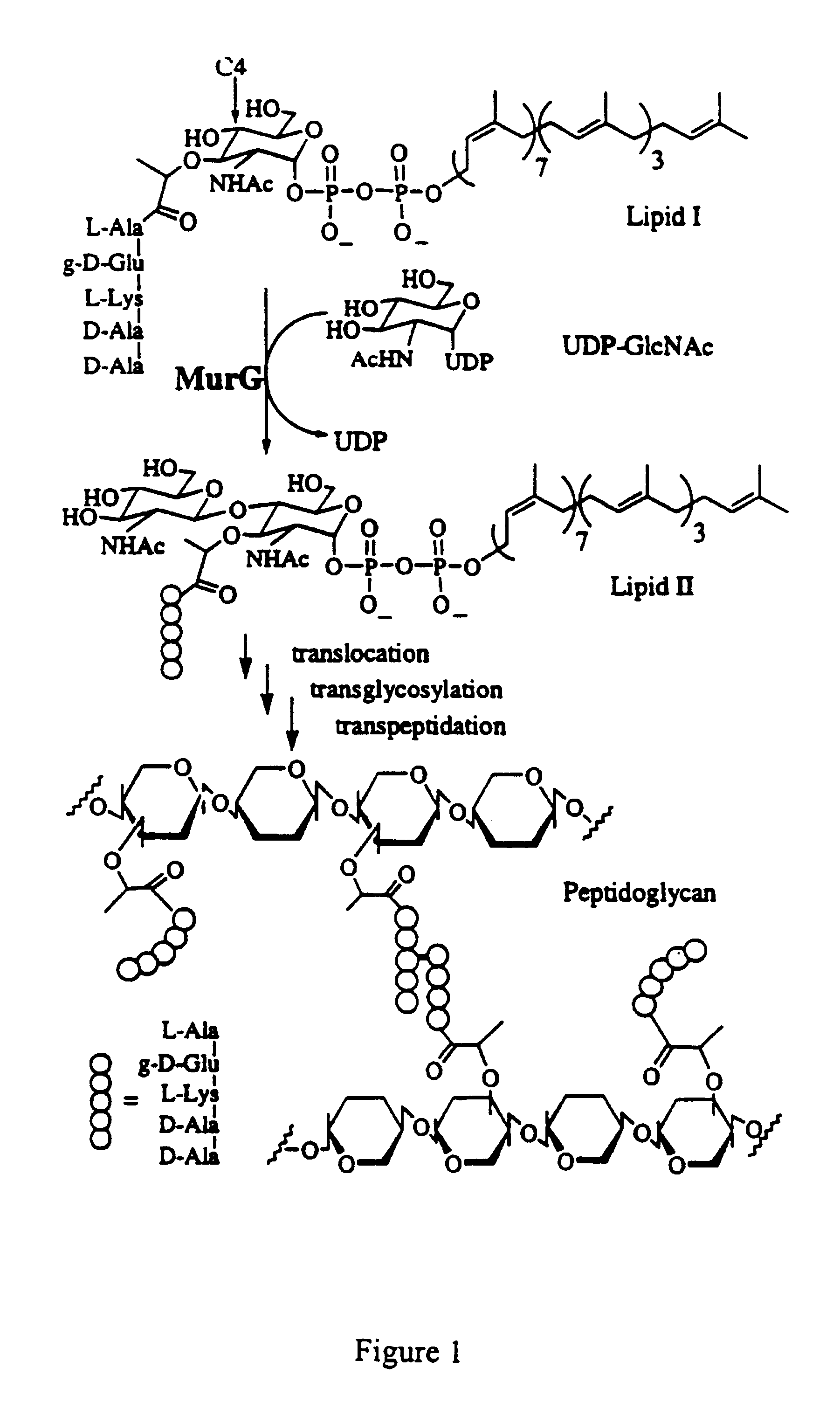
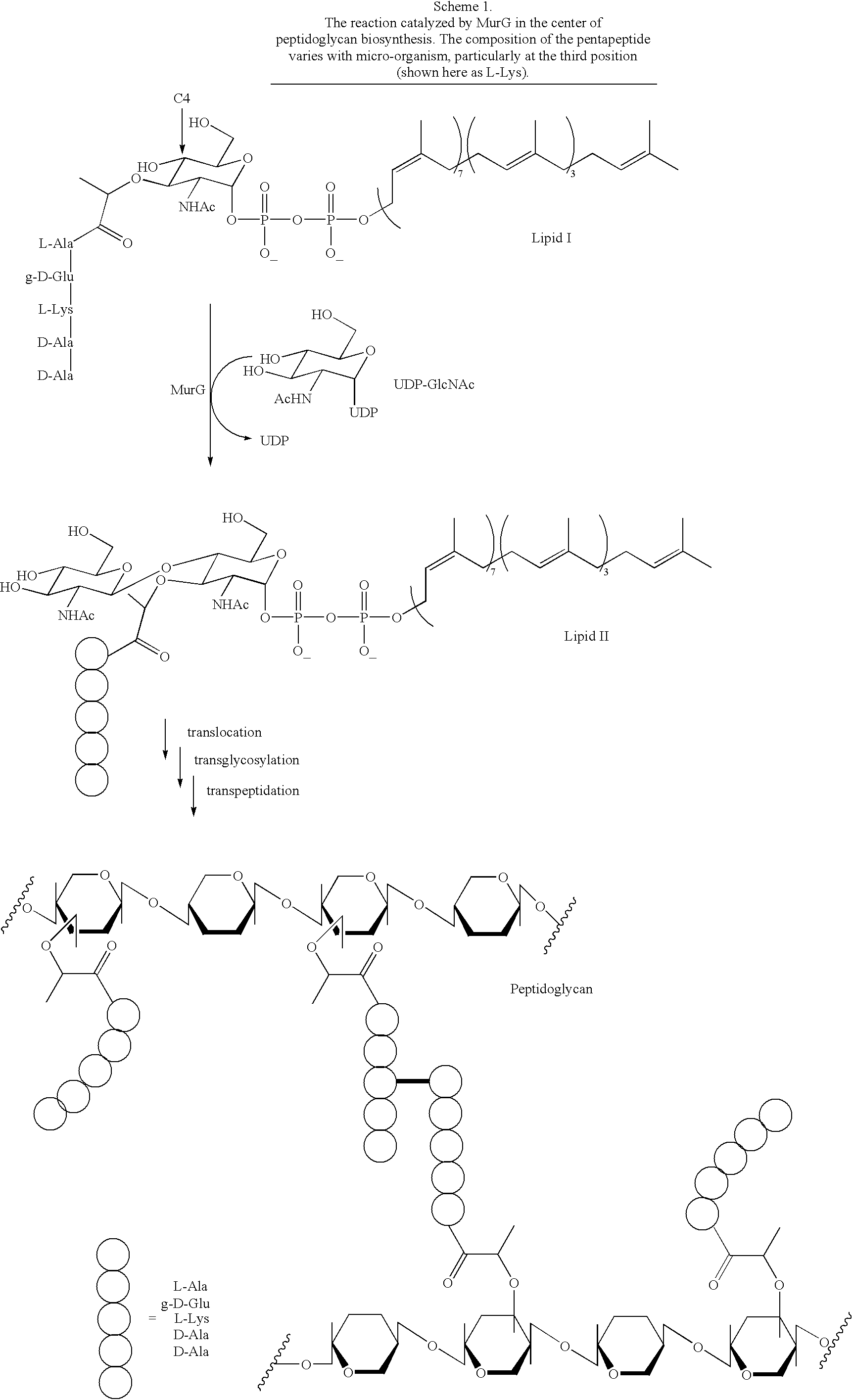
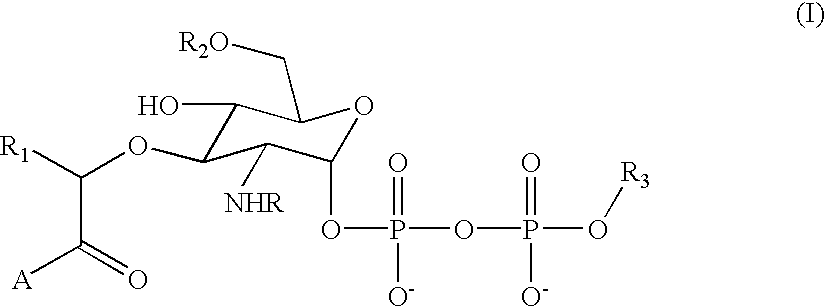
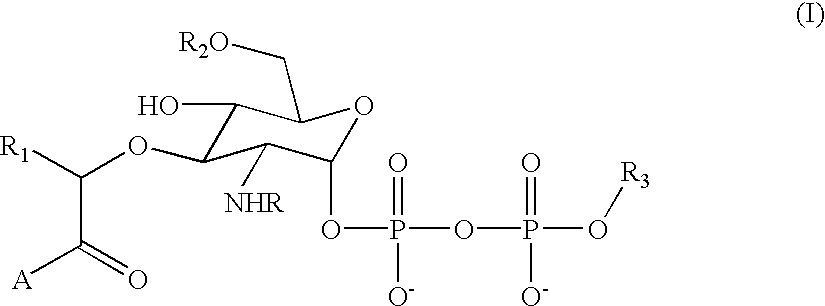
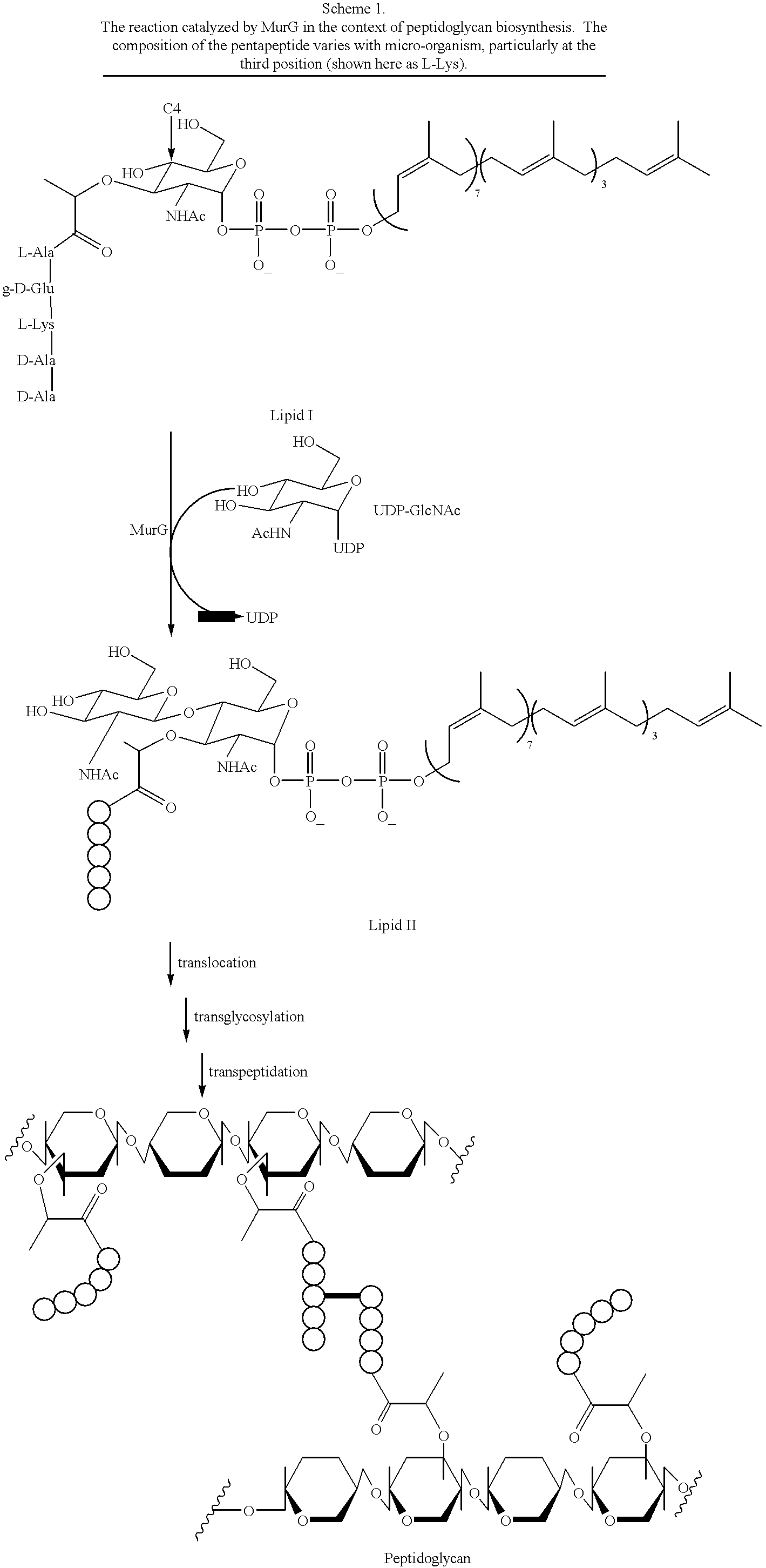
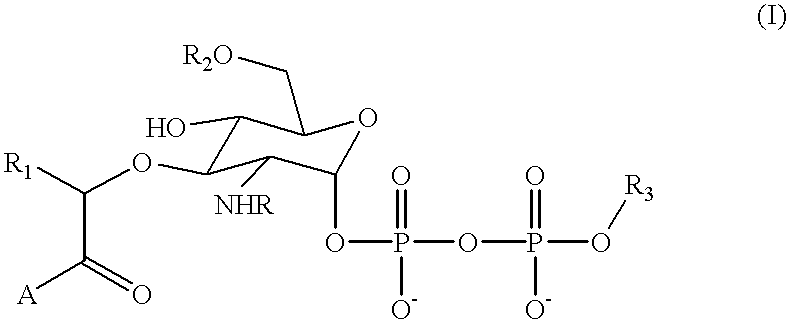
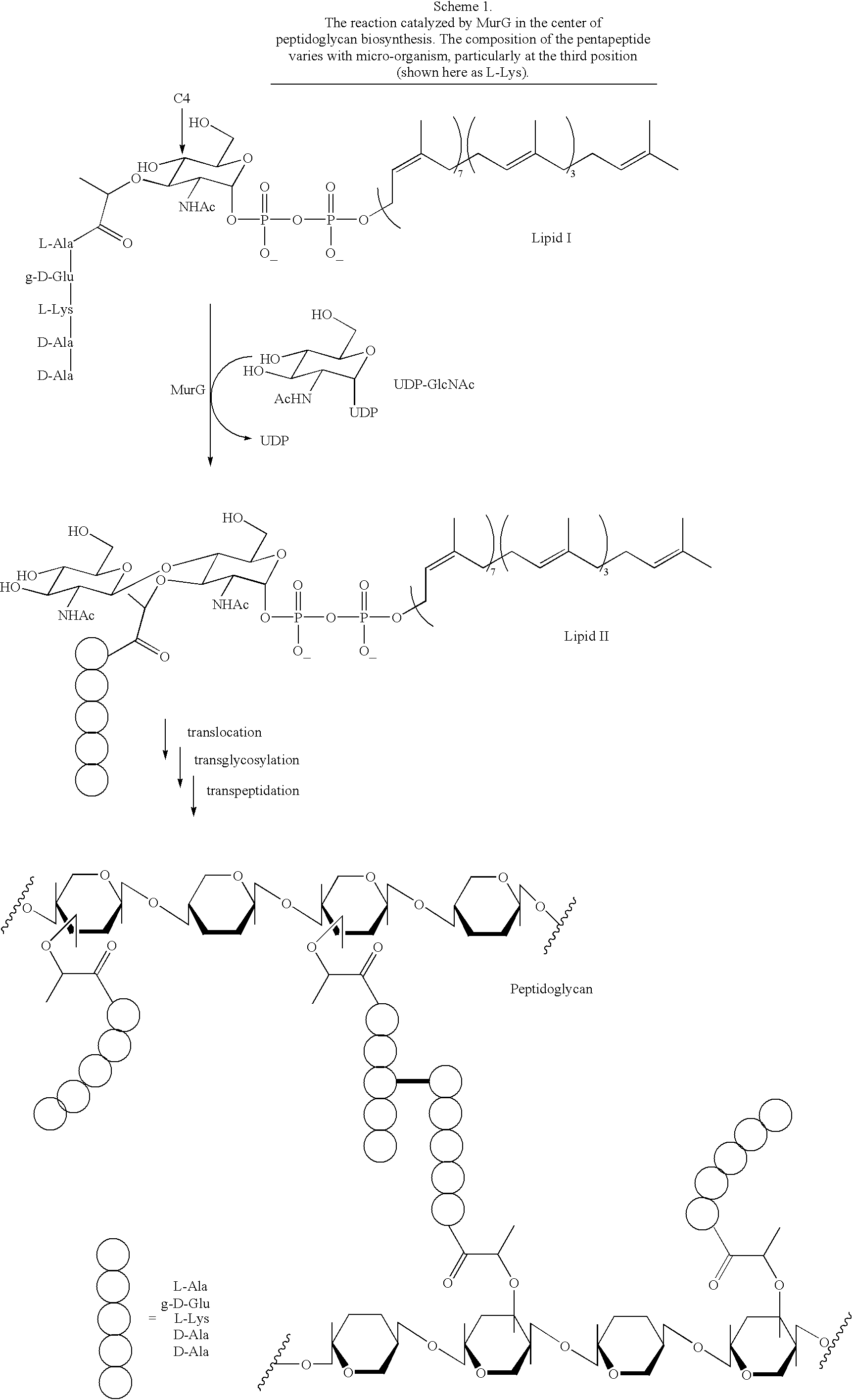
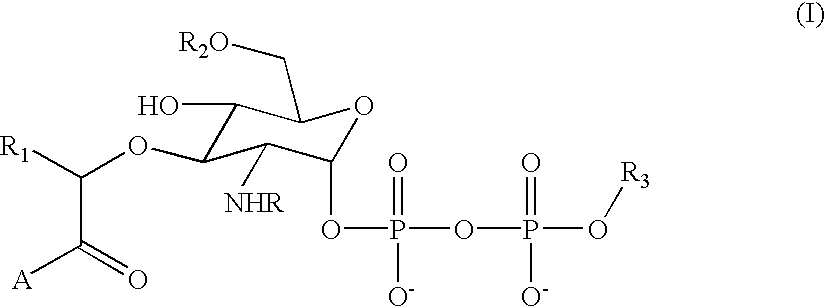
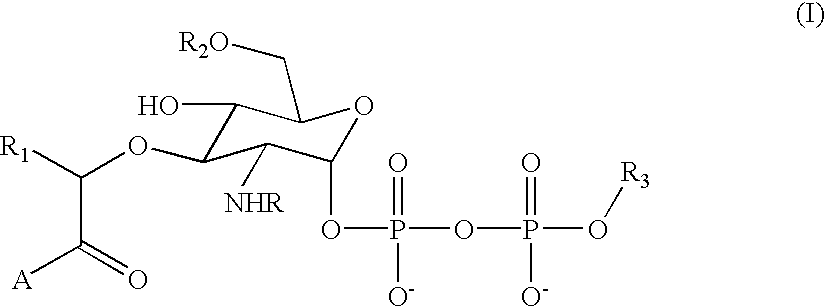
Substrate analogs for MurG, methods of making same and assays using same
InactiveUS20020182661A1Easy to separateEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideSubstrate analogLipid formation
General methods for monitoring the activity of MurG, a GlcNAc transferase involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, is disclosed. More particularly, the synthesis of simplified substrate analogs of Lipid I (the natural substrate for MurG), which function as acceptors for UDP-GlcNAc in an enzymatic reaction catalyzed by MurG, is described. Assays using the substrate analogs of the invention are further disclosed, which are useful for identifing a variety of other substrates, including inhibitors of MurG activity, for facilitating mechanistic and / or structural studies of the enzyme and for other uses. High throughput assays are also described.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Substrate analogs that substitute for lipid I as a substrate for MurG
InactiveUS6413732B1Easy to separateEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideSubstrate analogLipid formation
General methods for monitoring the activity of MurG, a GlcNAc transferase involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, is disclosed. More particularly, the synthesis of simplified substrate analogs of Lipid I (the natural substrate for MurG), which function as acceptors for UDP-GlcNAc in an enzymatic reaction catalyzed by MurG, is described. Assays using the substrate analogs of the invention are further disclosed, which are useful for identifying a variety of other substrates, including inhibitors of MurG activity, for facilitating mechanistic and / or structural studies of the enzyme and for other uses. High throughput assays are also described.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Substrate analogs for MurG, methods of making same and assays using same
InactiveUS6703213B2Easy to separateEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideLipid formationSubstrate analog
General methods for monitoring the activity of MurG, a GlcNAc transferase involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, is disclosed. More particularly, the synthesis of simplified substrate analogs of Lipid I (the natural substrate for MurG), which function as acceptors for UDP-GlcNAc in an enzymatic reaction catalyzed by MurG, is described. Assays using the substrate analogs of the invention are further disclosed, which are useful for identifying a variety of other substrates, including inhibitors of MurG activity, for facilitating mechanistic and / or structural studies of the enzyme and for other uses. High throughput assays are also described.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF PRINCETON UNIV
Computational method for designing enzymes for incorporation of amino acid analogs into proteins
InactiveUS20060177865A1Facilitate accommodationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementSubstrate analogComputational chemistry
The instant invention provides methods, reagents, and computational tools for designing non-natural substrate analogs for enzymes, especially for designing unnatural amino acid analogs for aminoacyl tRNA Synthetases (AARSs), such as the Phe tRNA Synthetase. The instant invention also provides methods to incorporate unnatural amino acid analogs, especially those with interesting functional groups, into protein products to generate proteins of modified or novel functions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Inhibitors of MEMAPSIN2 and use thereof
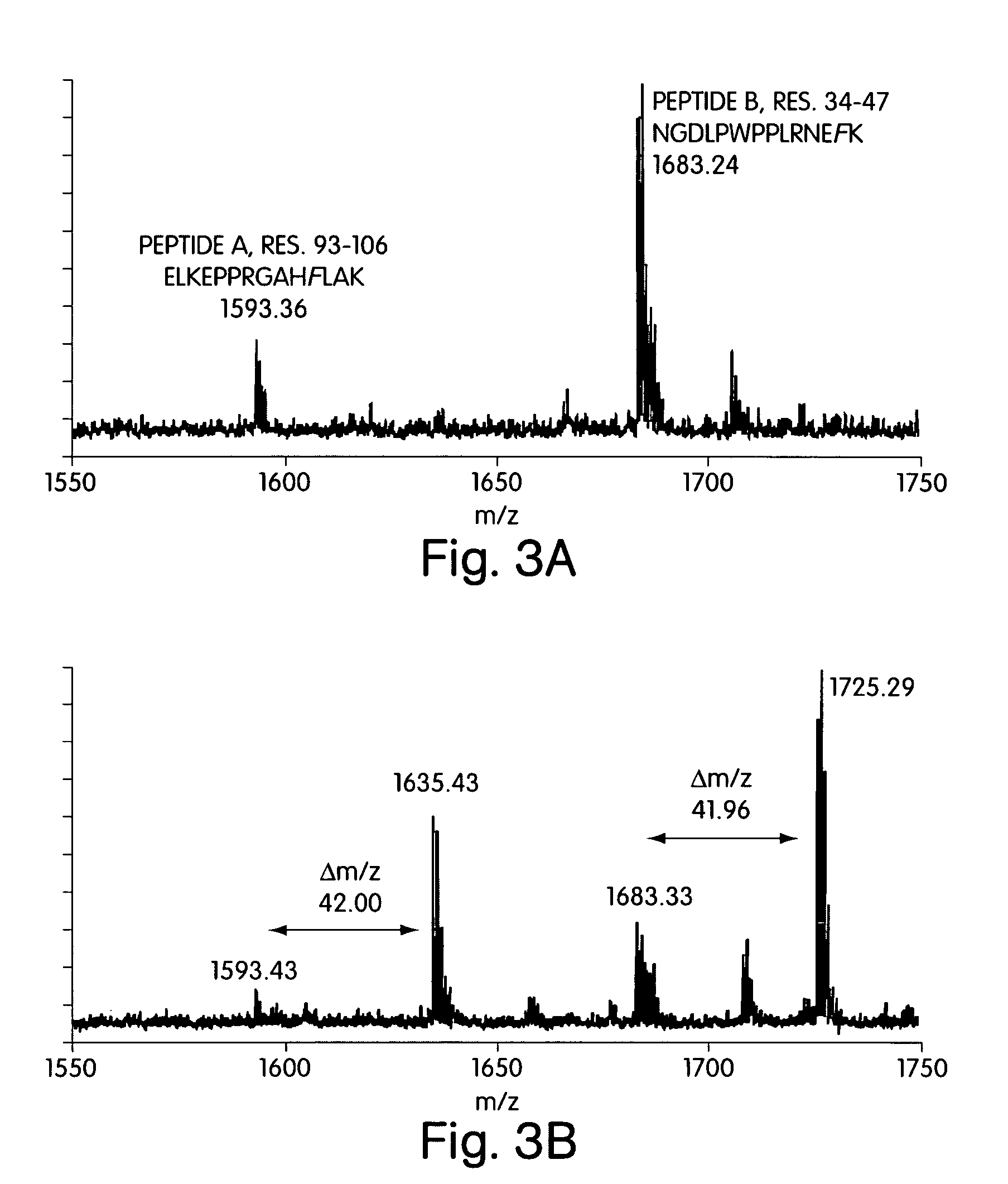
The substrate and subsite specificity of the catalytically active enzyme was determined by measuring the initial hydrolysis rate of the substrate using MALDI-TOF / MS. In addition, memapsin subsite specificity was determined by probing the inhibitor library with memapsin2 and detecting bound memapsin2 with a memapsin2 antibody and alkaline phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibody. Substrate and subsite specificity information can be used to design analogs of natural memapsin2 substrates capable of inhibiting memapsin2 function. Substrate analogs are based on peptide sequences related to the native peptide substrate of memapsin2. Substrate analogs contain at least one analog whose amide bond cannot be broken by memapsin2. A synthetic method for analogues containing isosteric substrates at key amino acid residue positions has been developed, and more than 70 substrate analogues have been synthesized, including MM1-005, MM1-012, MM1-017, MM1- 018, MM1-025, MM1-026, MM1-037, MM1-039, MM1-040, MM1-066, MM1-070 and MM1-071 correspond to recombinant pro-memapsin2 with inhibition constants in the range of 1.4-61.4×109M . These inhibitors are useful in the diagnosis, treatment and / or prevention of Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND +1
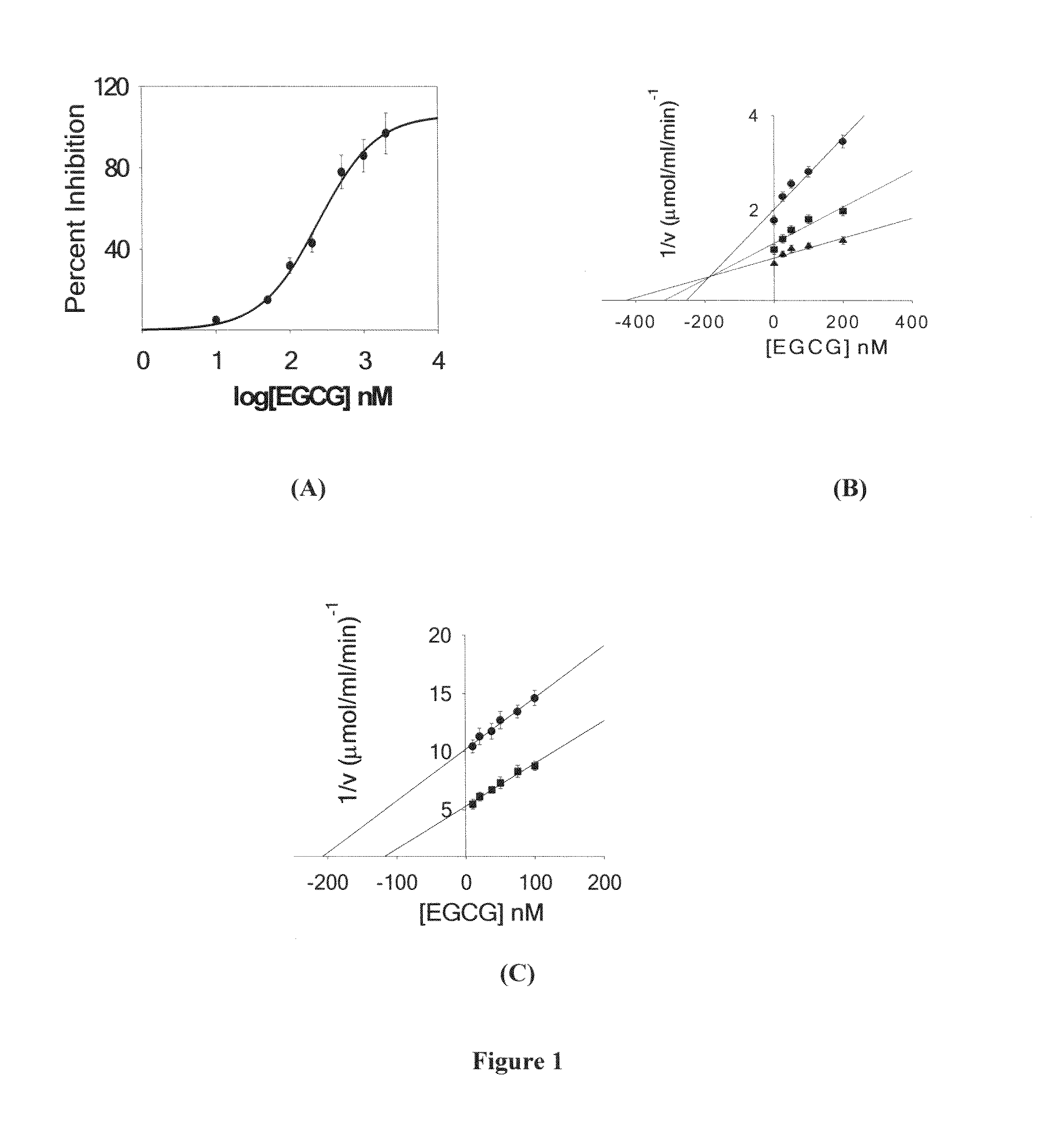
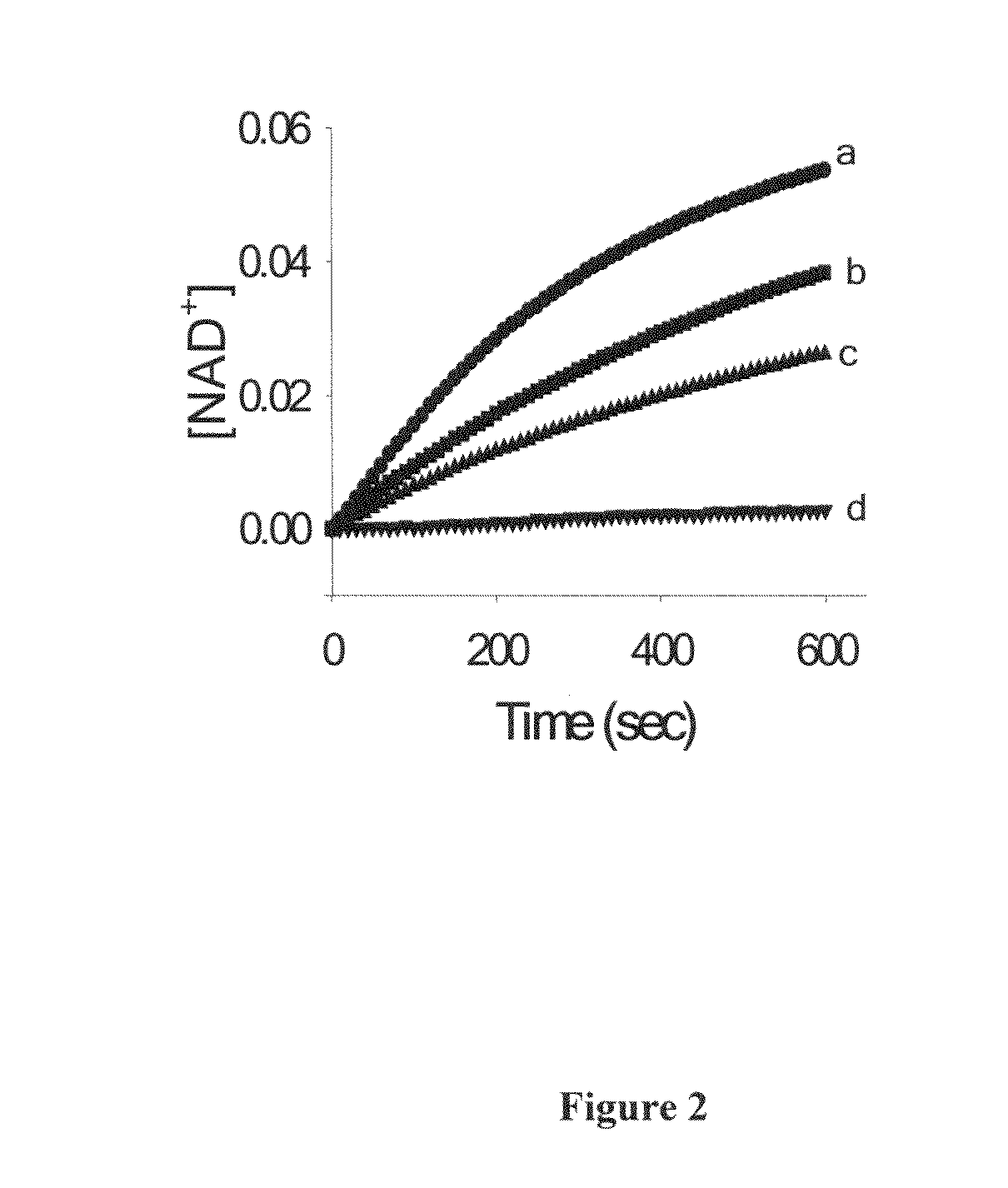
Synergistic composition for modulating activity of substrate analogs for NAD+, NADP+, NADH or NADPH dependent enzymes and process thereof
The present disclosure provides a composition for enhancing effect of an inhibitor in inhibiting NAD+ / NADP+ or NADH / NADPH dependent enzymes. The inhibition of the NAD+ / NADP+ or NADH / NADPH dependent enzymes such as Enoyl-ACP reductase (ENR) by the composition of the present disclosure serves as a target for treating malaria and other infectious diseases. The present disclosure provides composition comprising inhibitor and polyphenol, wherein the polyphenol was found to enhance the inhibitory activity of the inhibitor. The present disclosure provides method for treating an infectious disease comprising administering an effective amount of the composition of the present disclosure to patients in need thereof. The present disclosure further provides a method for identifying a compound that enhances the effect of the inhibitor, a method of determining the antimalarial activity of a compound and use of polyphenol as a bioenhancer that enhances effect of an inhibitor for inhibiting NAD+ / NADP+ or NADH / NADPH dependent enzymes. The present disclosure provides a composition comprising inhibitor and a polyphenol wherein the polyphenol enhances effect of the inhibitor for inhibiting aldose reductase for treating complications of diabetes that include diabetic retinopathy, cataract neuropathy and neural complication.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTUTUTE OF IMMUNOLOGY +1
Inhibition of Infiltration, and Cell Killing Agent
InactiveUS20080318297A1Effectively suppressing intercell adhesionOrganic active ingredientsHybrid immunoglobulinsAntigenCell Surface Antigens
As suppressor of binding between selectin binding sugar chain and selectin or cell killing agent, (1) siRNA suppressing expression of genes which relates to cell surface antigen CD43 and selectin ligand sugar chain by RNA interference; (2) an inhibitor of sugar chain synthesis such as analogue of substrates in sugar chain synthesis; (3) an enzyme severing cell surface antigen CD43 and selectin ligand sugar chain; and (4) antibodies of cell surface antigen CD43 and selectin ligand sugar chain are used to selectin ligand sugar chain expressed in cell surface antigen CD43 to provide a suppressor of infiltration which is able to suppression of infiltration to tissues by leukocytes and a method of suppression thereof, and a cell killing agent of CD43 expressing cell and a cell killing method thereof.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Solubility and Affinity Tag for Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification
InactiveUS20170226489A1Convenient verificationHigh purityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTumor necrosis factorSolubilityAdenylate kinase
Systems and methods of coding for and isolating a fusion protein are provided. The fusion protein may be expressed by a DNA sequence and comprise an adenylate kinase linked by its carboxy-terminus to a biologically active polypeptide or protein. Later processing steps include isolating the biologically active polypeptide or protein via affinity elution of the fusion proteins with substrate analog of adenylate kinase.
Owner:GENHUNTER
Method of Improving Resistance to Substrate Analog of Nitric Acid in Microalga
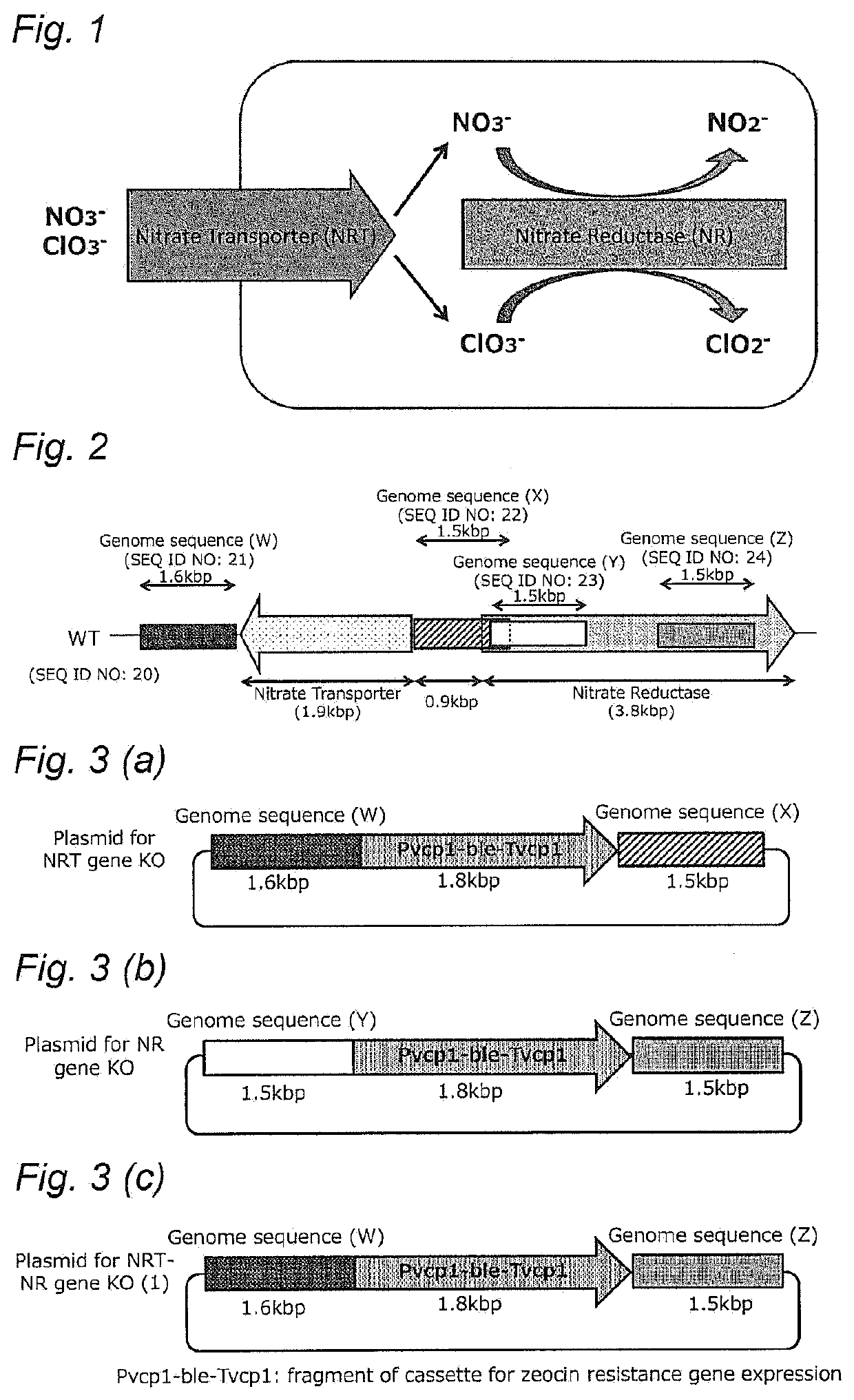
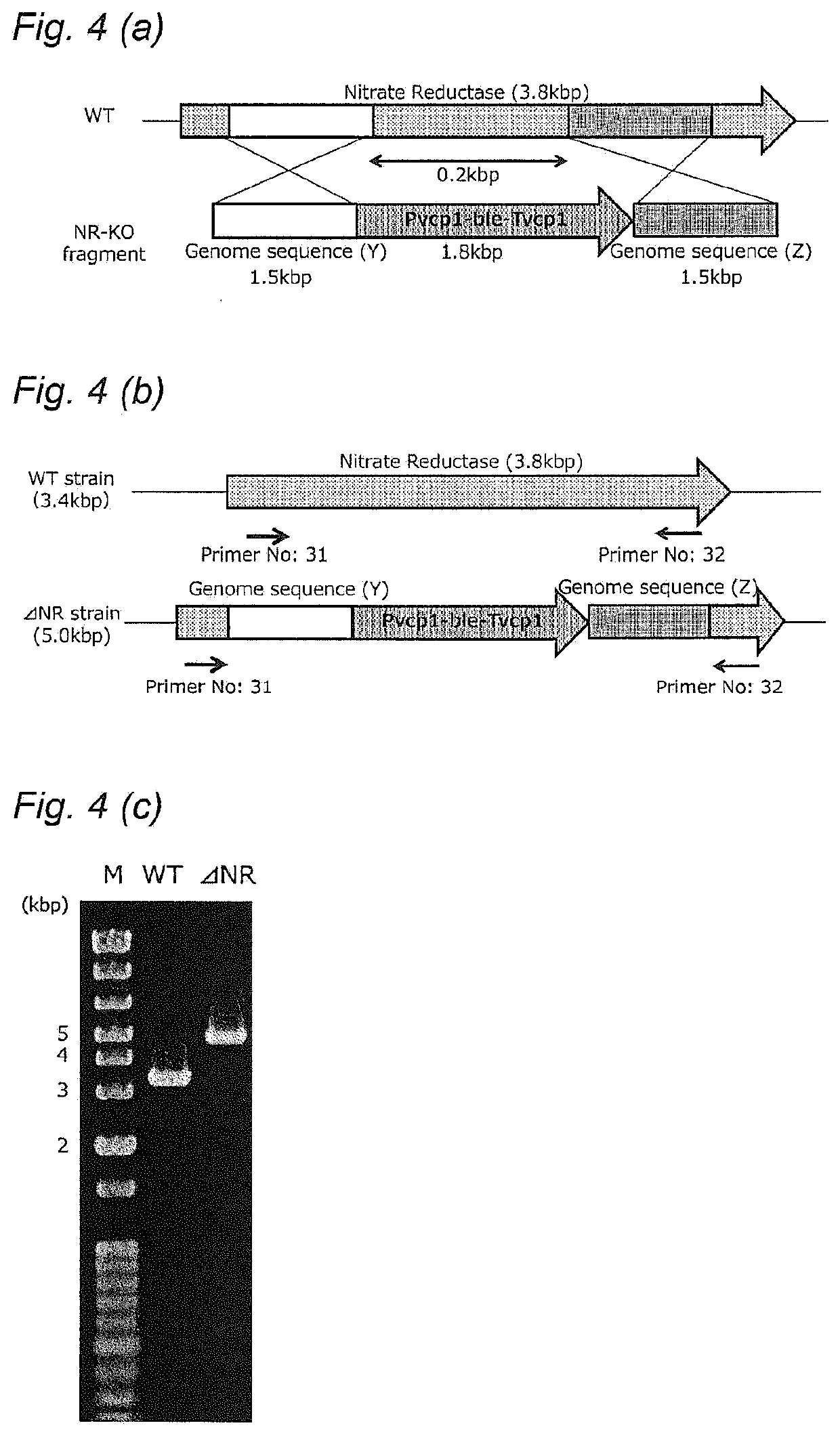
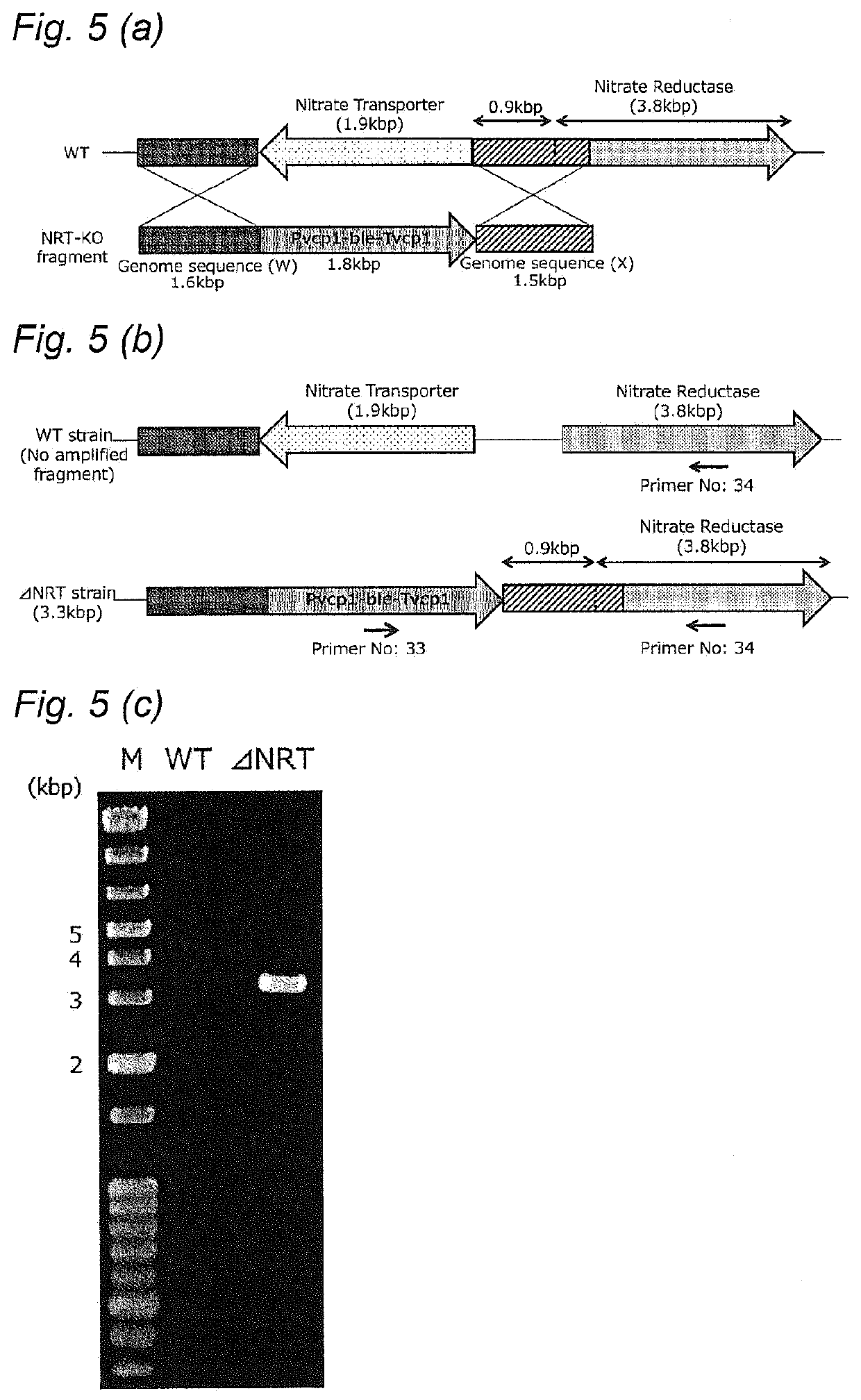
PendingUS20210102161A1Down-regulated expressionUnicellular algaeBacteria peptidesSubstrate analogGenome
A method of improving resistance to a substrate analog of nitric acid in a microalga, containingdeleting a gene encoding the following protein (A) or (B) present in the genome of the microalga, or downregulating expression of a gene encoding the following protein (A) or (B):(A) a protein consisting of the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 41; and(B) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence having 70% or more identity with the amino acid sequence of the protein (A), and having nitrate transporter activity.
Owner:KAO CORP
Antibiotic and anti-parasitic agents that modulate class II fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase
This invention provides a family of compounds that inhibit Class II fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA), which is implicated in the pathogenic activity of a broad range of bacterial and parasitic agents. The compounds were identified by empirical testing, and provide a basis for further derivatization and optimization of 8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxylic acid and related compounds. Crystal structure shows that the compounds don't bind directly to the catalytic site of the enzyme, and so are not defined simply as substrate analogs. Instead, they create a pocket by induced fit, resulting a powerful and specific inhibitory effect on FBA activity.
Owner:THE UNIV OF DENVER +1
Inhibitors of MEMAPSIN2 and use thereof
Methods for the production of purified, catalytically active, recombinant memapsin 2 have been developed. The substrate and subsite specificity of the catalytically active enzyme have been determinedby a method which determines the initial hydrolysis rate of the substrate by using MALDI-TOF / MS. Alternatively, the subsite specificity of mepapsin can be determined by probing a library of inhibitorswith memapsin 2 and subsequently detecting the bound memapsin 2 with an antibody raised to memapsin 2 and an alkaline phosphatase conjugated secondary antibody. The substrate and subsite specificityinformation was used to design substrate analogs of the natural memapsin 2 substrate that can inhibit the function of memapsin2. The substrate analogs are based on peptide sequences, shown to be related to the natural peptide substrates for memapsin 2. The substrate analogs contain at least one analog of an amide bond which is not capable of being cleaved by memapsin 2. Processes for the synthesisof substrate analogues including isoteres at the sites of the critical amino acid residues were developed and the more than seventy substrate analogues were synthetized, among which MMI-005, MMI-012,MMI-017, MMI-018, MMI-025, MMI-026, MMI-037, MMI-039, MMI-040, MMI-066, MMI-070, and MMI-071 have inhibition constants in the range of 1.4-61.4 x 10<9> M against recombinant pro-memapsin 2. These inhibitors are useful in diagnostics and for the treatment and / or prevention of Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com