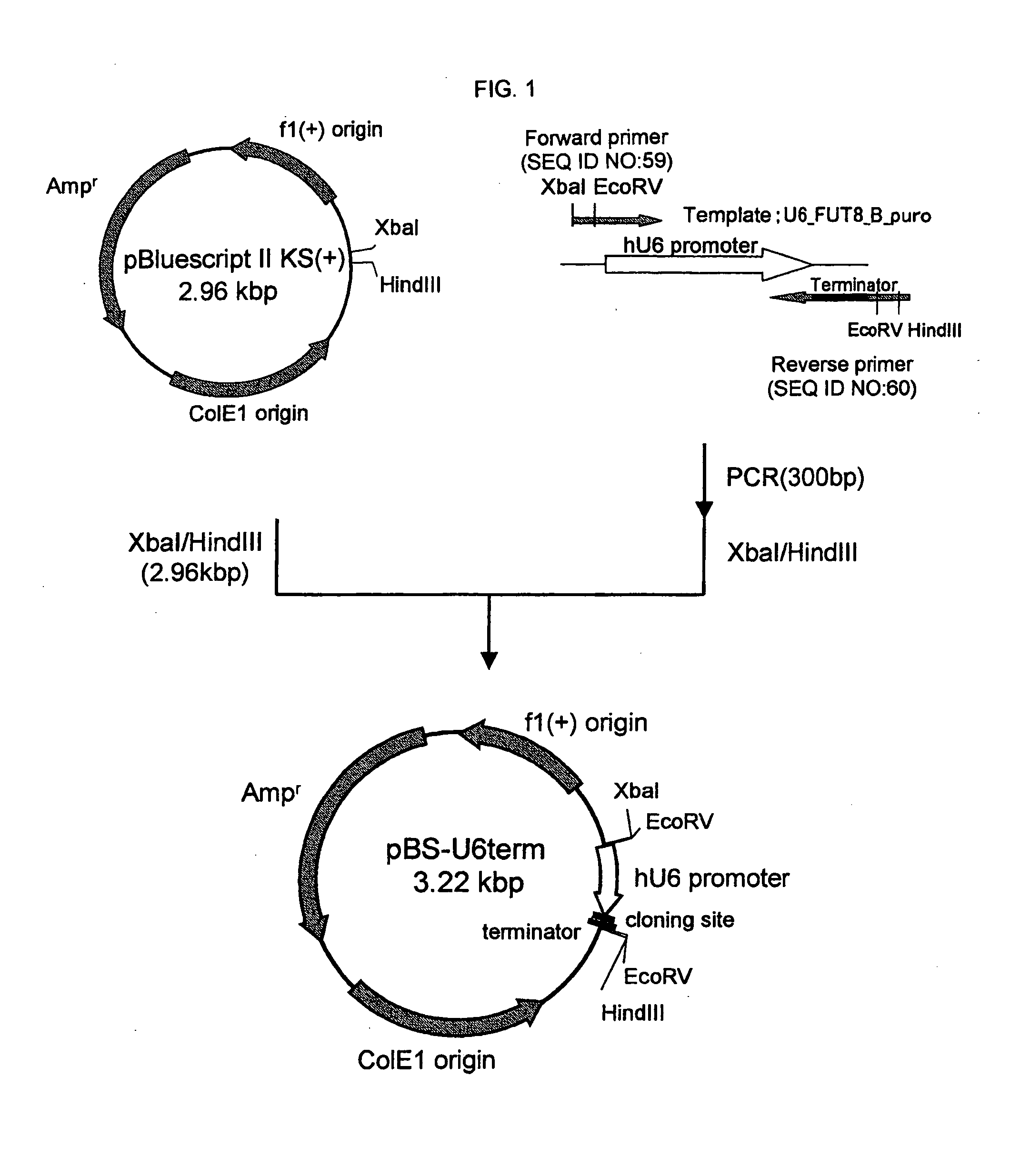
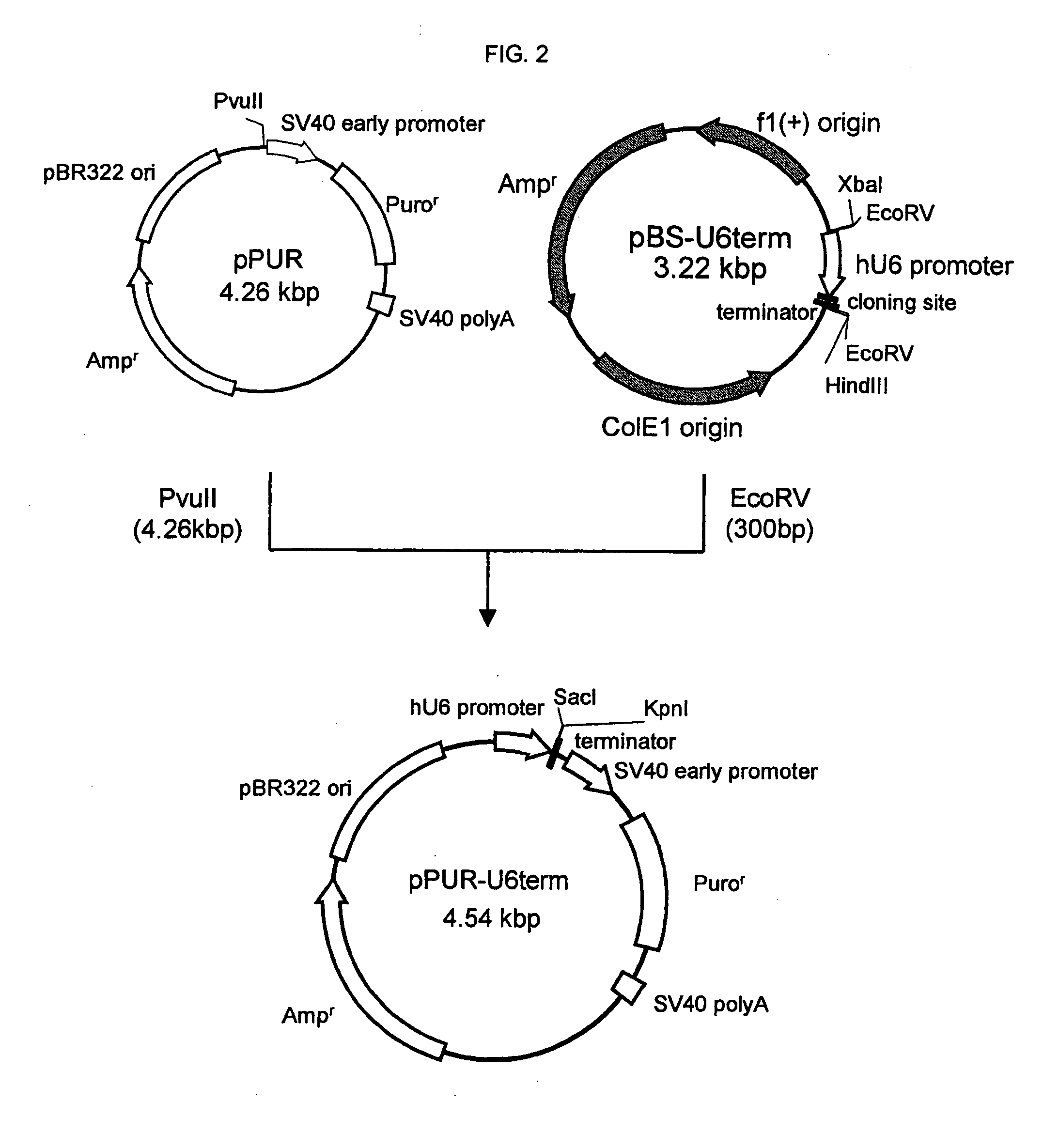
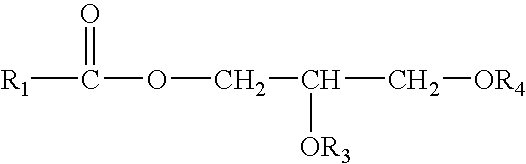
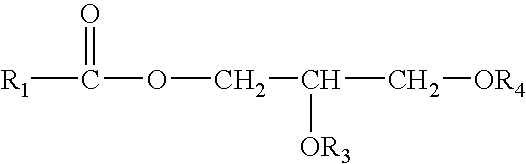
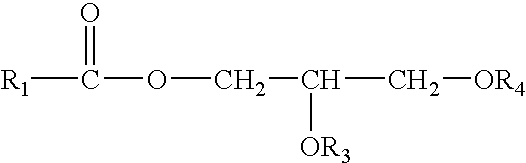
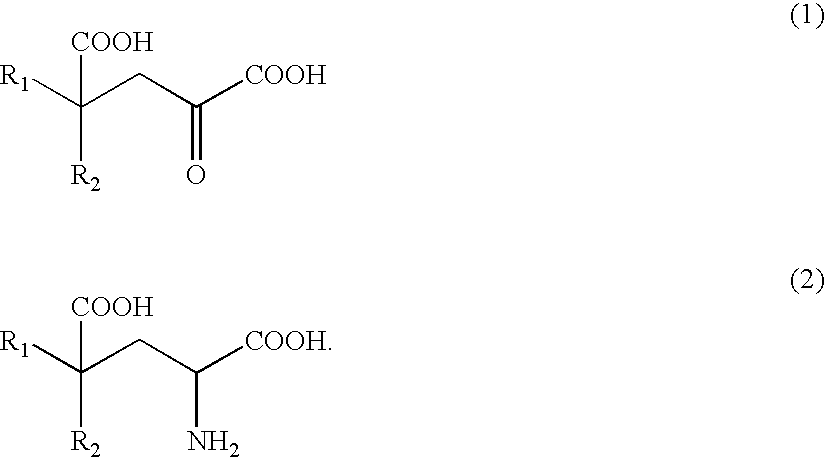
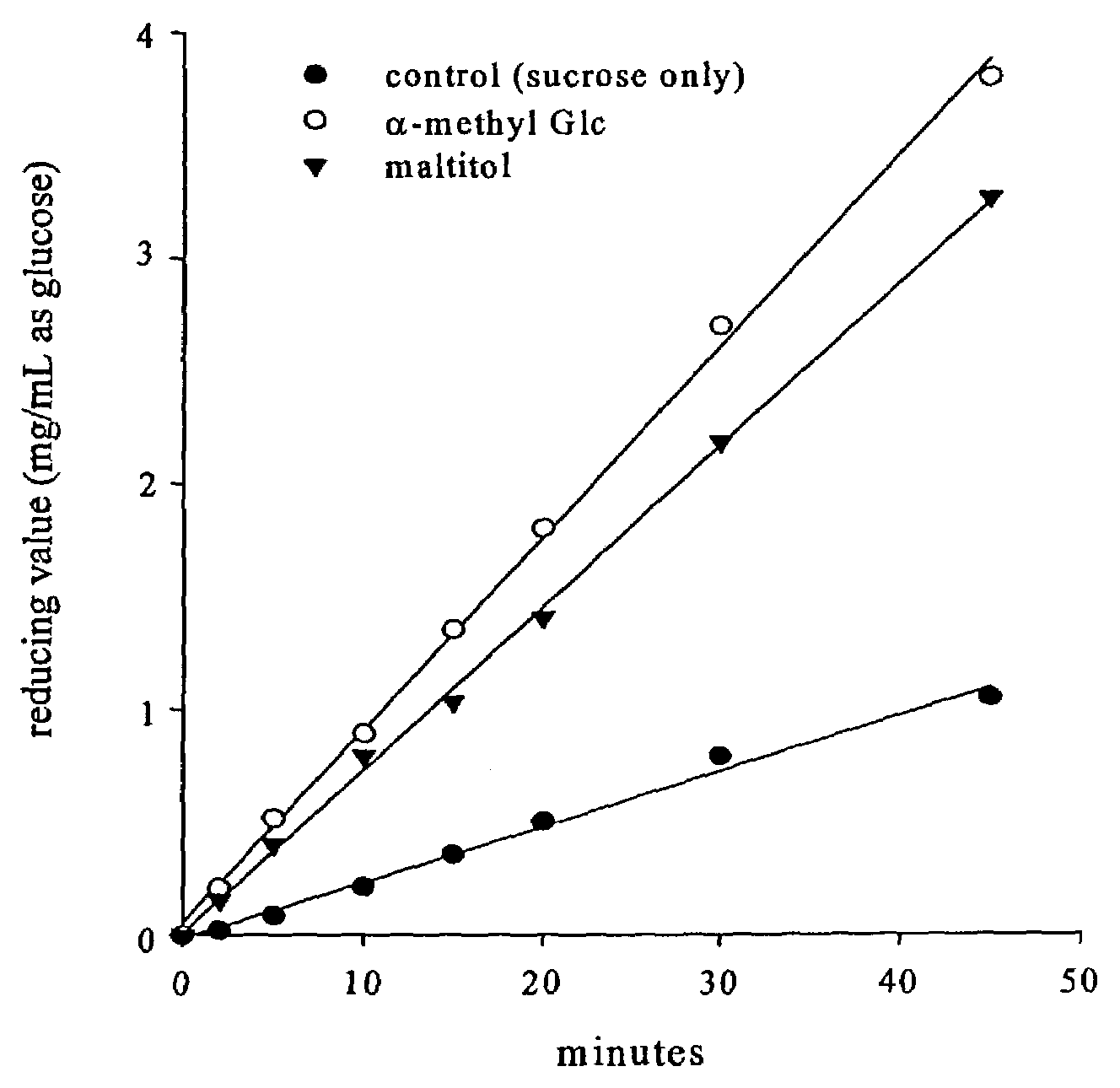
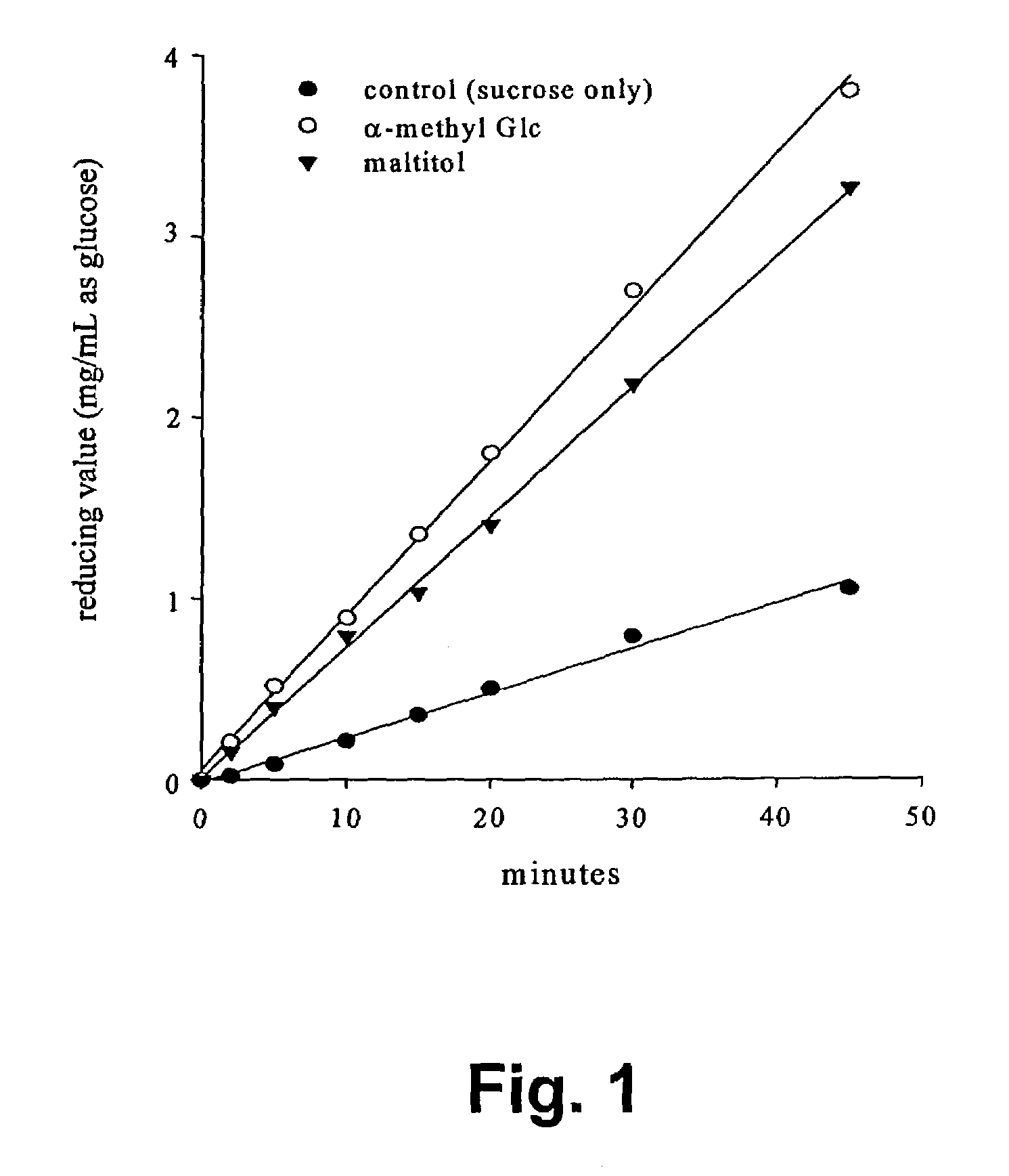
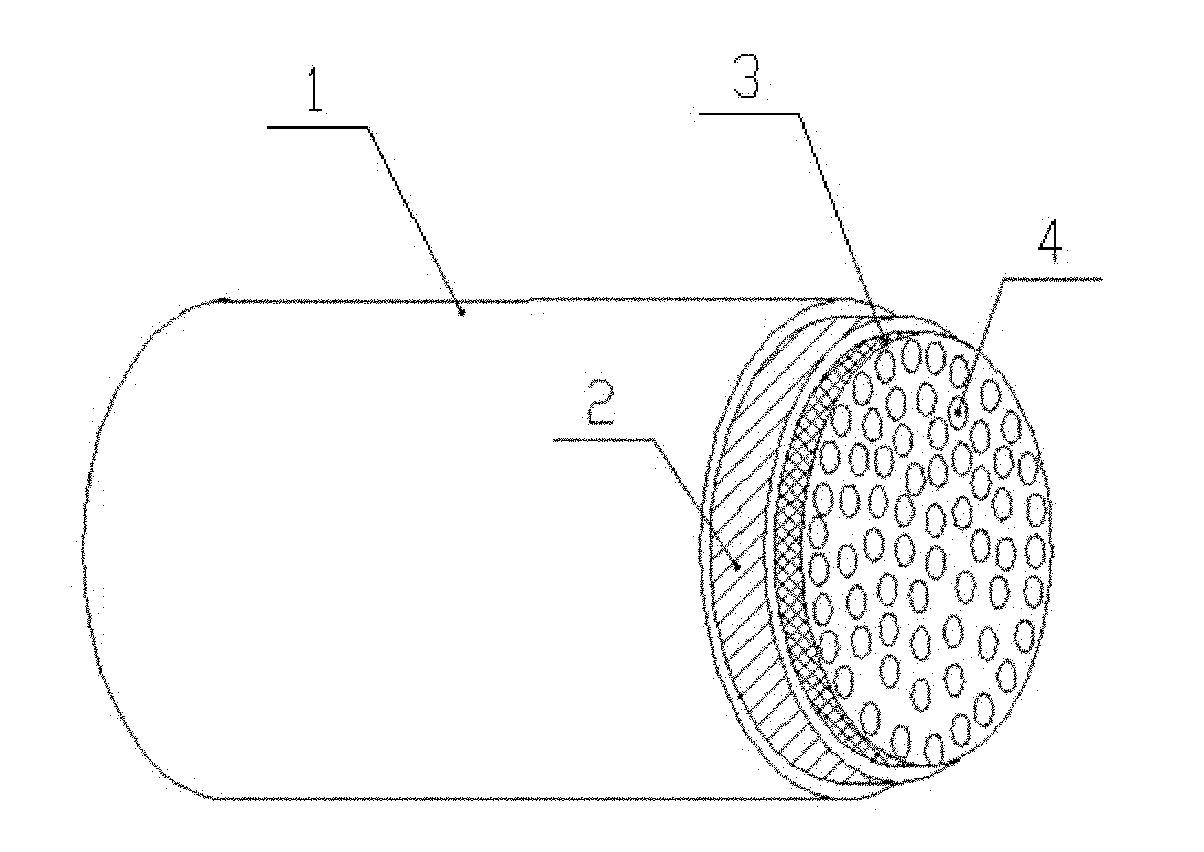
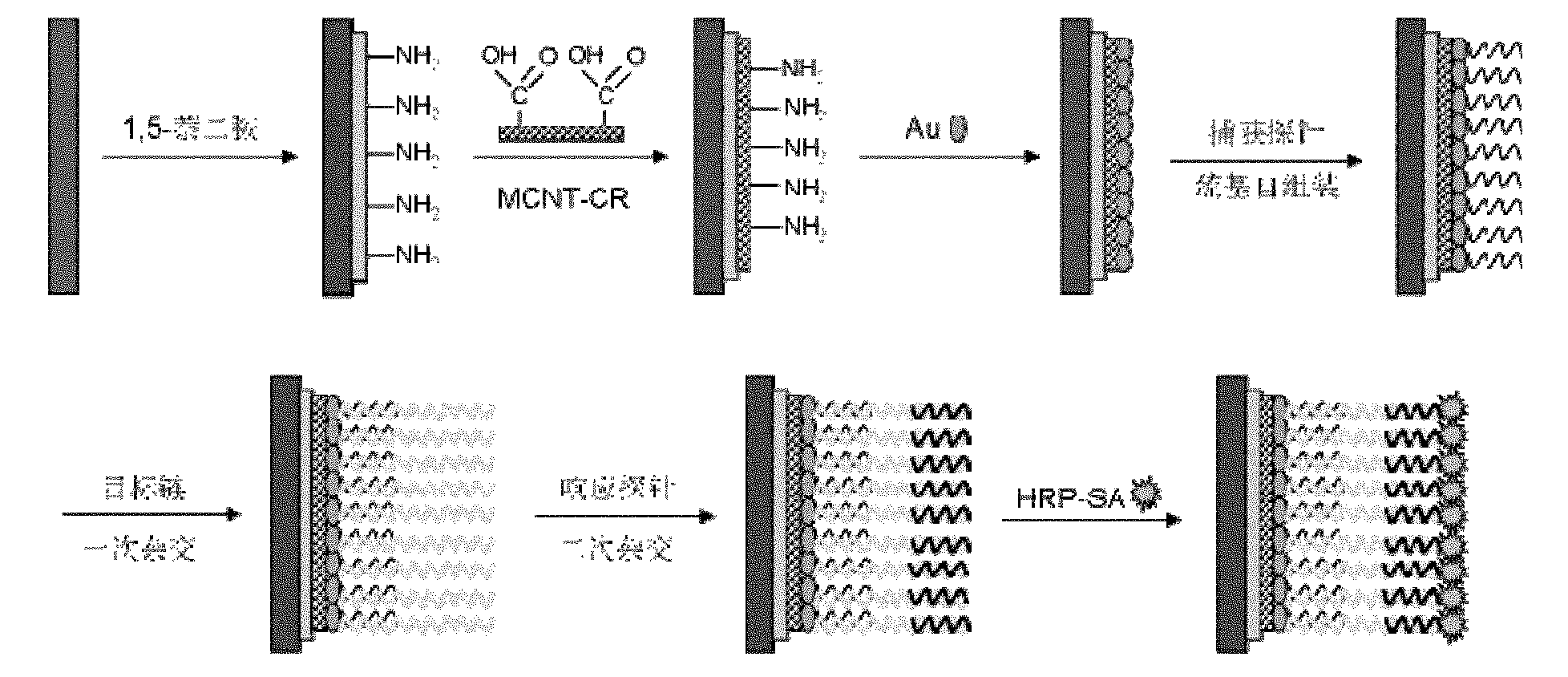
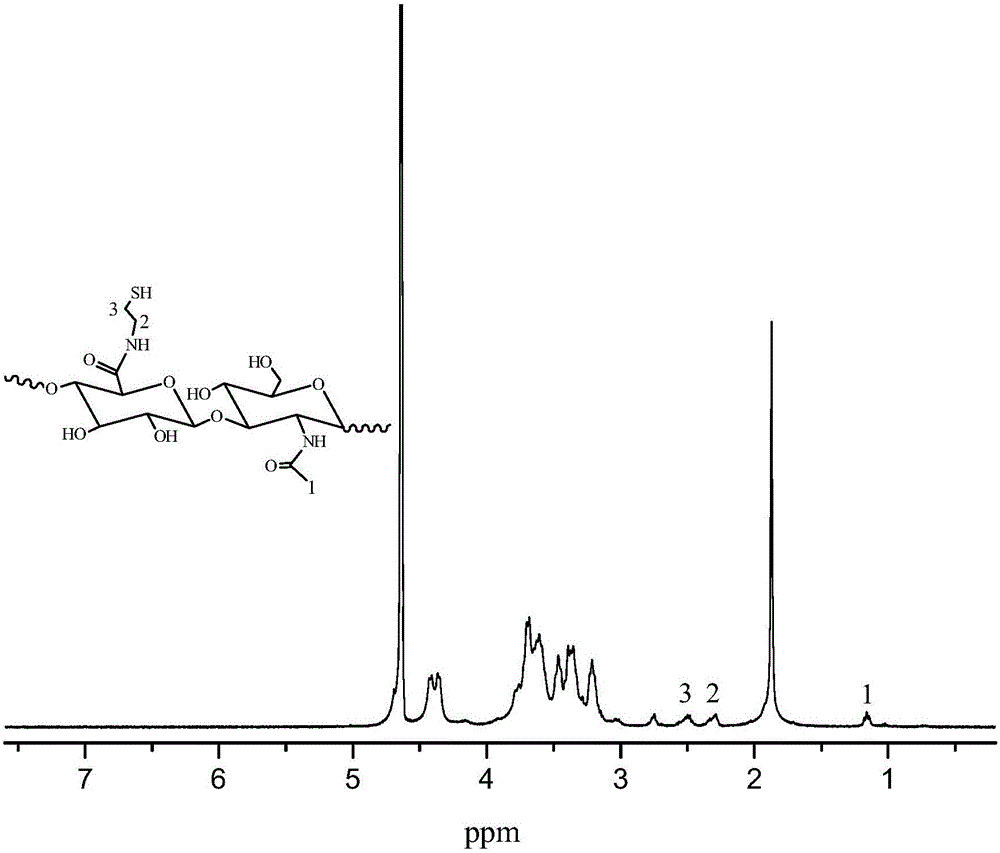
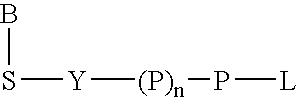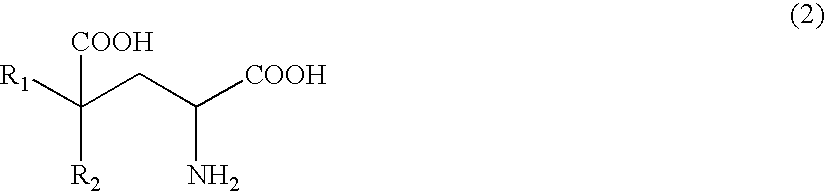Patents
Literature
602 results about "Enzyme catalyzed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enzymes Are Catalysts. A catalyst is a chemical that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being changed by the reaction. The fact that they aren't changed by participating in a reaction distinguishes catalysts from substrates, which are the reactants on which catalysts work. Enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions.
Production of Peracids Using An Enzyme Having Perhydrolysis Activity
ActiveUS20080176783A1Efficient implementationReduce concentrationBiocideHydrolasesMedicinal chemistryPeroxide
A process is provided for producing peroxycarboxylic acids from carboxylic acid esters. More specifically, carboxylic acid esters are reacted with an inorganic peroxide, such as hydrogen peroxide, in the presence of an enzyme catalyst having perhydrolysis activity. The present perhydrolase catalysts are classified as members of the carbohydrate esterase family 7 (CE-7) based on the conserved structural features. Further, disinfectant formulations comprising the peracids produced by the processes described herein are provided.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Enzyme-catalyzed metal deposition for the enhanced detection of analytes of interest
ActiveUS20050100976A1Rapidly and accurately determinedHigh detection sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTarget analysisAnalyte
The invention is directed to enhanced methods for detecting an analyte of interest in situ, by immunoassay, or by hybridization comprising binding an enzyme-labeled conjugate molecule to an analyte of interest in the presence of a redox-inactive reductive species and a soluble metal ion. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of the inactive reductive species to an active reducing agent, which in turn reduces the metal ion to a metal atom thereby providing an enhanced means of detecting the analyte via metal deposition.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
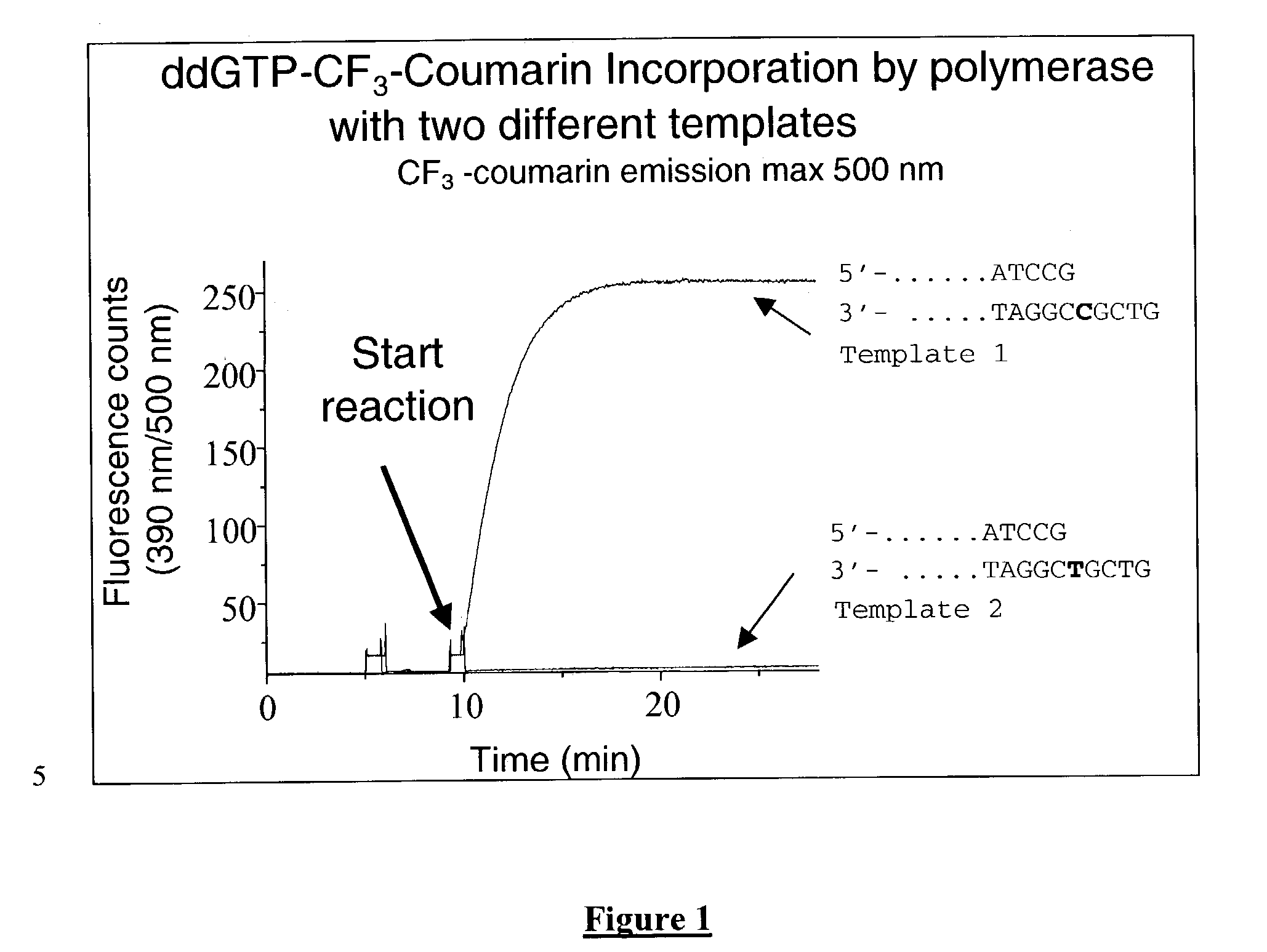
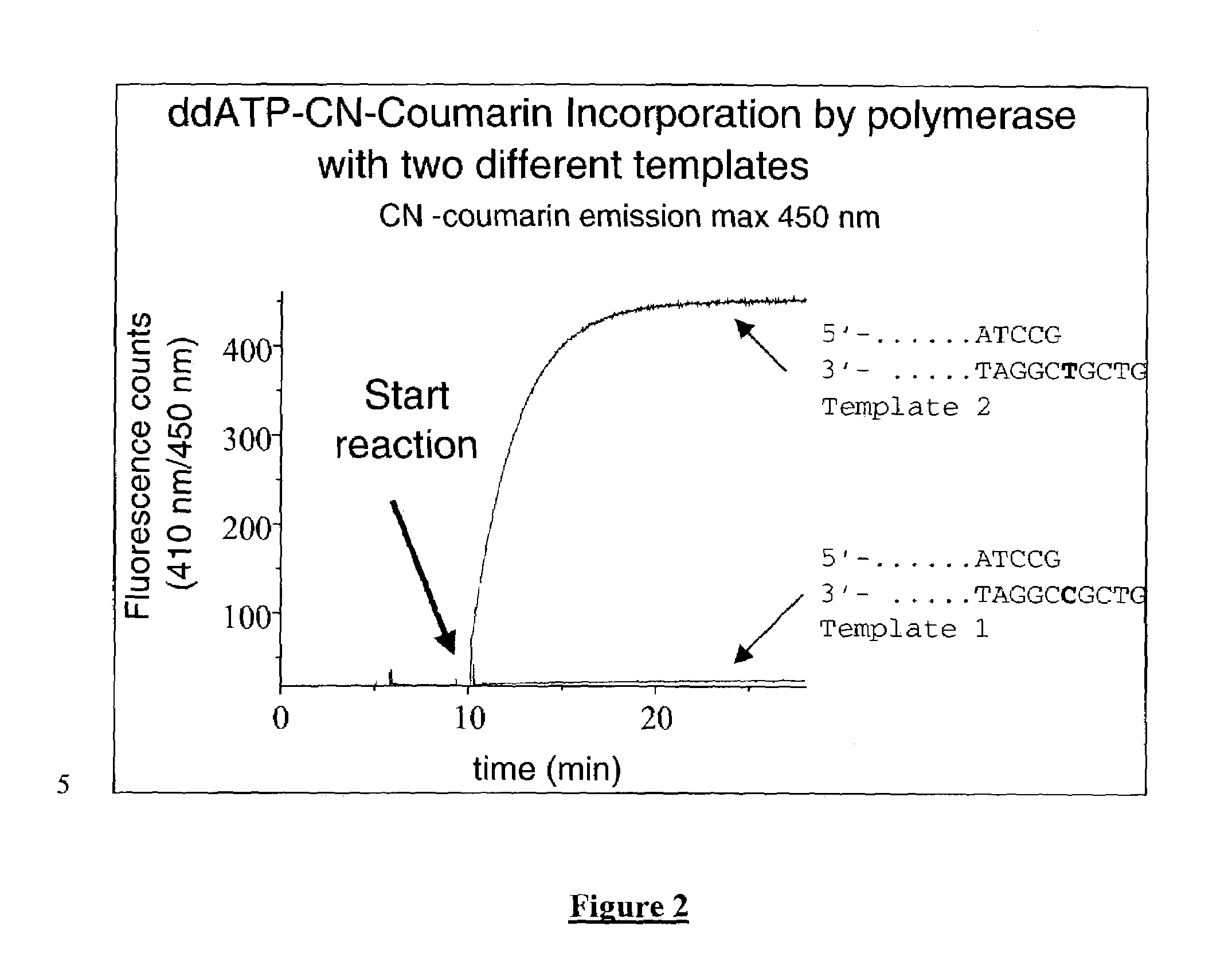
The present invention relates to improved methods of detecting a target using a labeled substrate or substrate analog. The methods comprise reacting the substrate or substrate analog in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which produces a labeled moiety with independently detectable signal only when such substrate or substrate analog reacts. The present invention, in particular, describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Charge perturbation detection system for DNA and other molecules
ActiveUS7785785B2Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapacitanceChemical reaction
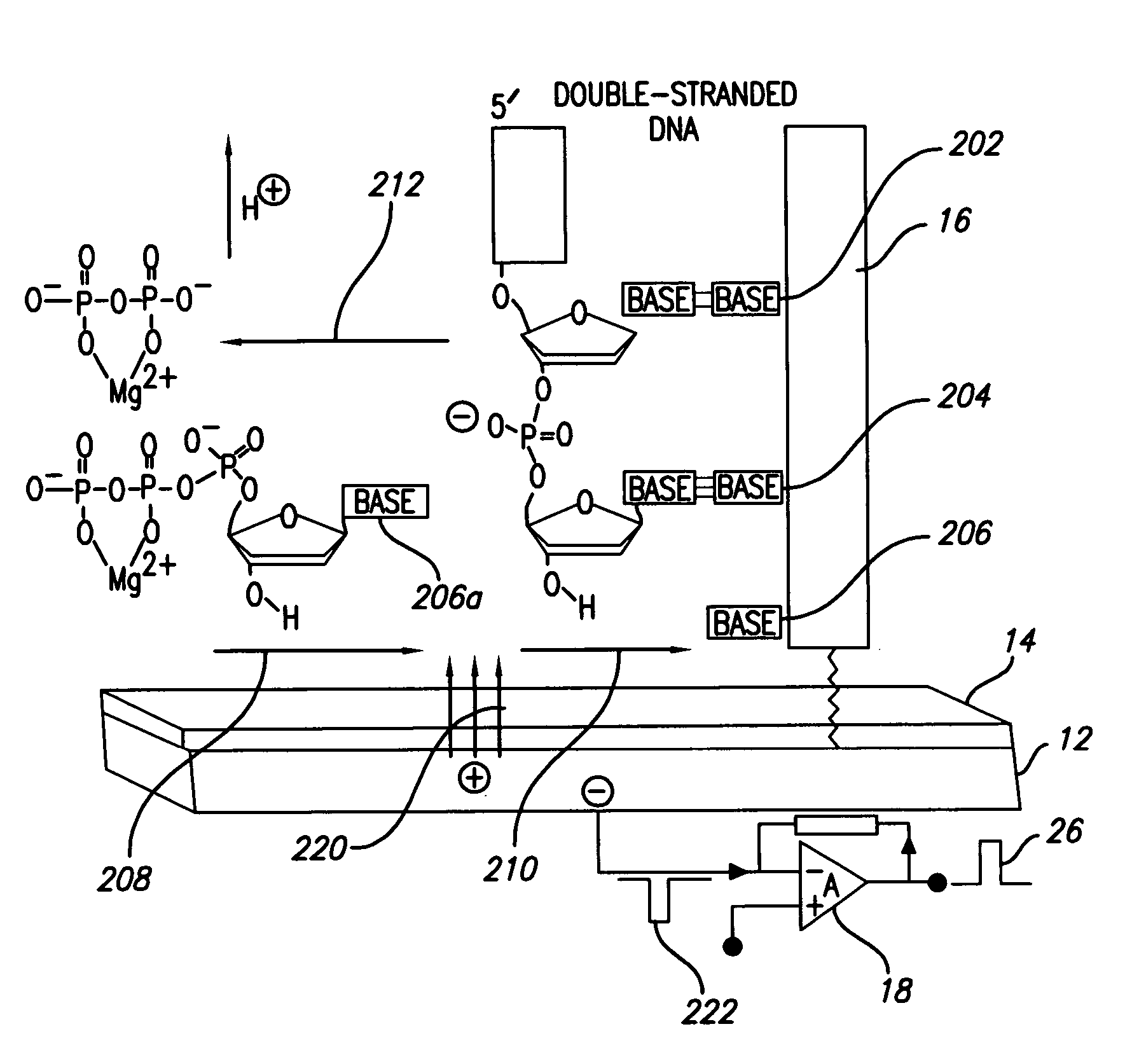
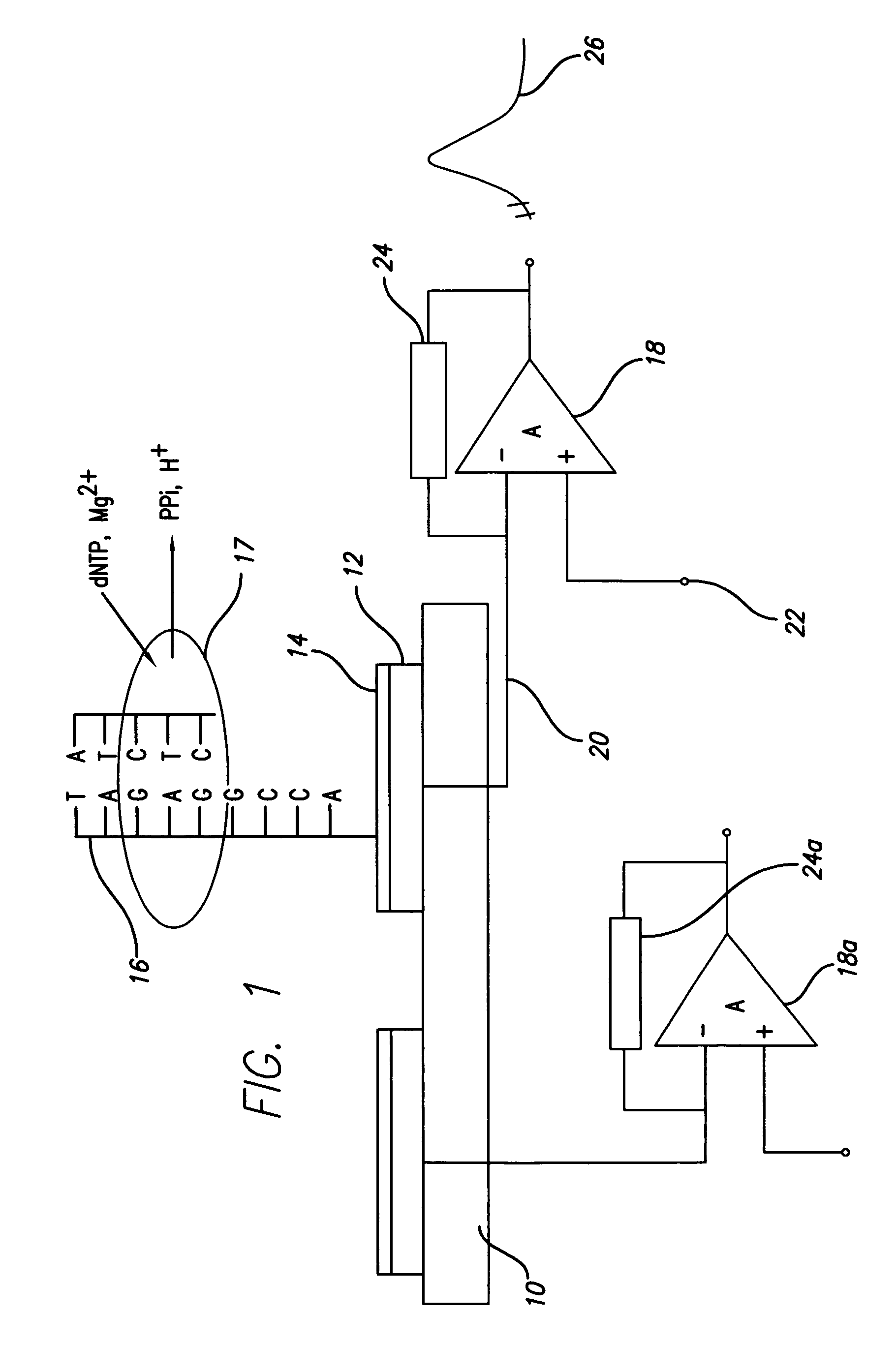
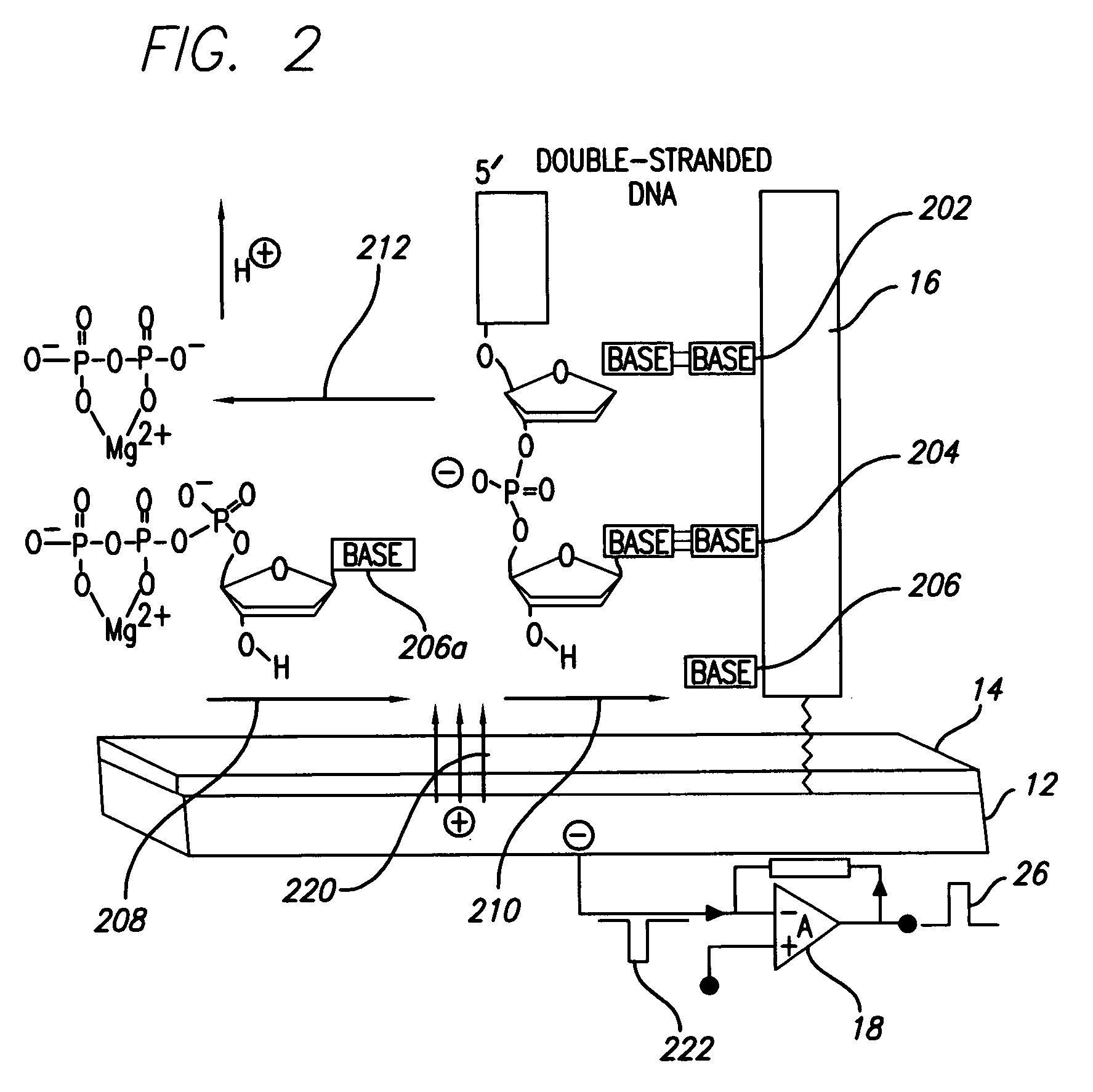
Methods and apparatus for direct detection of chemical reactions are provided. In a preferred embodiment, electric charge perturbations of the local environment during enzyme-catalyzed reactions are sensed by an electrode system with an immobilized target molecule. The target molecule is preferably DNA. The charge perturbation caused by the polymerase reaction can uniquely identify a DNA sequence. The polymerization process generates local perturbations of charge in the solution near the electrode surface and induces a charge in a polarazible gold electrode. This event is detected as a transient current by a voltage clamp amplifier. Detection of single nucleotides in a sequence can be determined by dispensing individual dNTPs to the electrode solution and detecting the charge perturbations. Alternatively, multiple bases can be determined at the same time using a mix of all dNTPs with subsequent analysis of the resulting signal. The initial enzyme attachment to the DNA molecule can be detected prior to polymerization, with electrode capacitance measurement using the same voltage-clamp amplifier. This technique and device may be adapted to other reaction determinations, such as enzymatic reactions, other electrode configurations, and other amplifying circuits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Strip electrode with conductive nano tube printing
InactiveUS20050186333A1Accurate electronic readoutMinimizing strip to strip variationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSilver inkCarbon nanotube
A sensor system that detects a current representative of a compound in a liquid mixture features a multi or three electrode strip adapted for releasable attachment to signal readout circuitry. The strip comprises an elongated support which is preferably flat adapted for releasable attachment to the readout circuitry; a first conductor and a second and a third conductor each extend along the support and comprise means for connection to the circuitry. The circuit is formed with single-walled or multi walled nanotubes conductive traces and may be formed from multiple layers or dispersions containing, carbon nanotubes, carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-cloride. An active electrode formed from a separate conductive carbon nanotubes layer or suitable dispersion, positioned to contact the liquid mixture and the first conductor, comprises a deposit of an enzyme capable of catalyzing a reaction involving the compound and preferably an electron mediator, capable of transferring electrons between the enzyme-catalyzed reaction and the first conductor. A reference electrode also formed from a conductive carbon nanotube layer or suitable dispersion is positioned to contact the mixture and the second conductor. The system includes circuitry adapted to provide an electrical signal representative of the current which is formed from printing conductive inks made with nano size particles such as conductive carbon or carbon / platinum or carbon / silver, or carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide to form a conductive carbon nanotube layers. The multiple-electrode strip is manufactured, by then applying the enzyme and preferably the mediator onto the electrode. Alternatively the electrode can have a carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-cloride surface and or a conductive carbon or silver ink surface connecting leg. The carbon nanotube solution is first coated and patterned into electro shapes and the conductive carbon nanotubes, carbon or silver ink can be attached by printing the ink to interface with the carbon nanotube electro surface. A platinum electrode test strip is also disclosed that is formed from either nano platinum distributed in the carbon nanotube layer or by application or incorporation of platinum to the carbon nanotube conductive ink.
Owner:DOUGLAS JOEL S MR
Process for producing glycoprotein composition
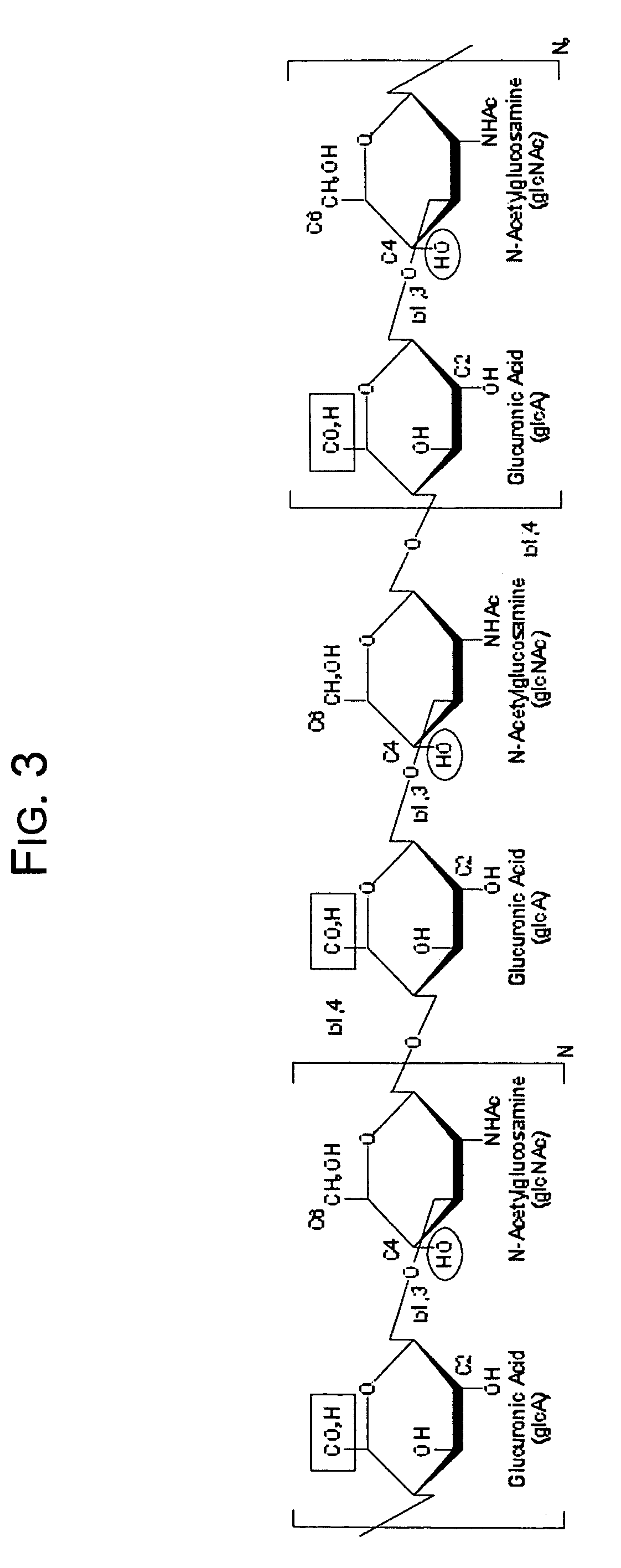
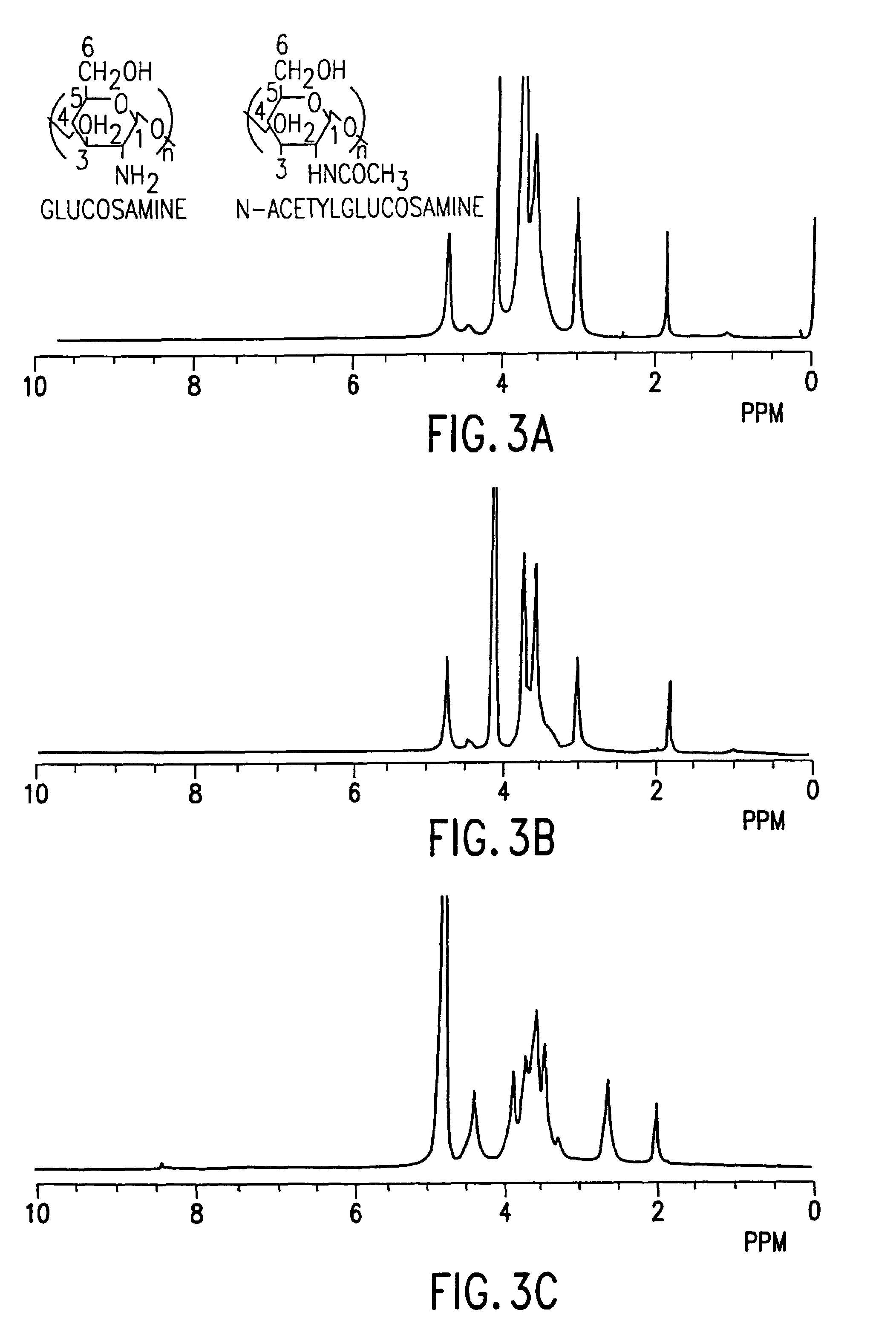
InactiveUS20060223147A1Raise the ratioAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticComplex typeN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention relates to a cell into which an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme catalyzing a reaction which converts GDP-mannose into GDP-4-keto,6-deoxy-GDP-mannose is introduced; a process for producing a glycoprotein using the cell; a cell into which an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme relating to modification of a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in the complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chain, and an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme relating to synthesis of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, or an RNA capable of suppressing the function of a protein relating to transport of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, to the Golgi body are introduced; a process for producing a glycoprotein composition using the cell; and the like.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
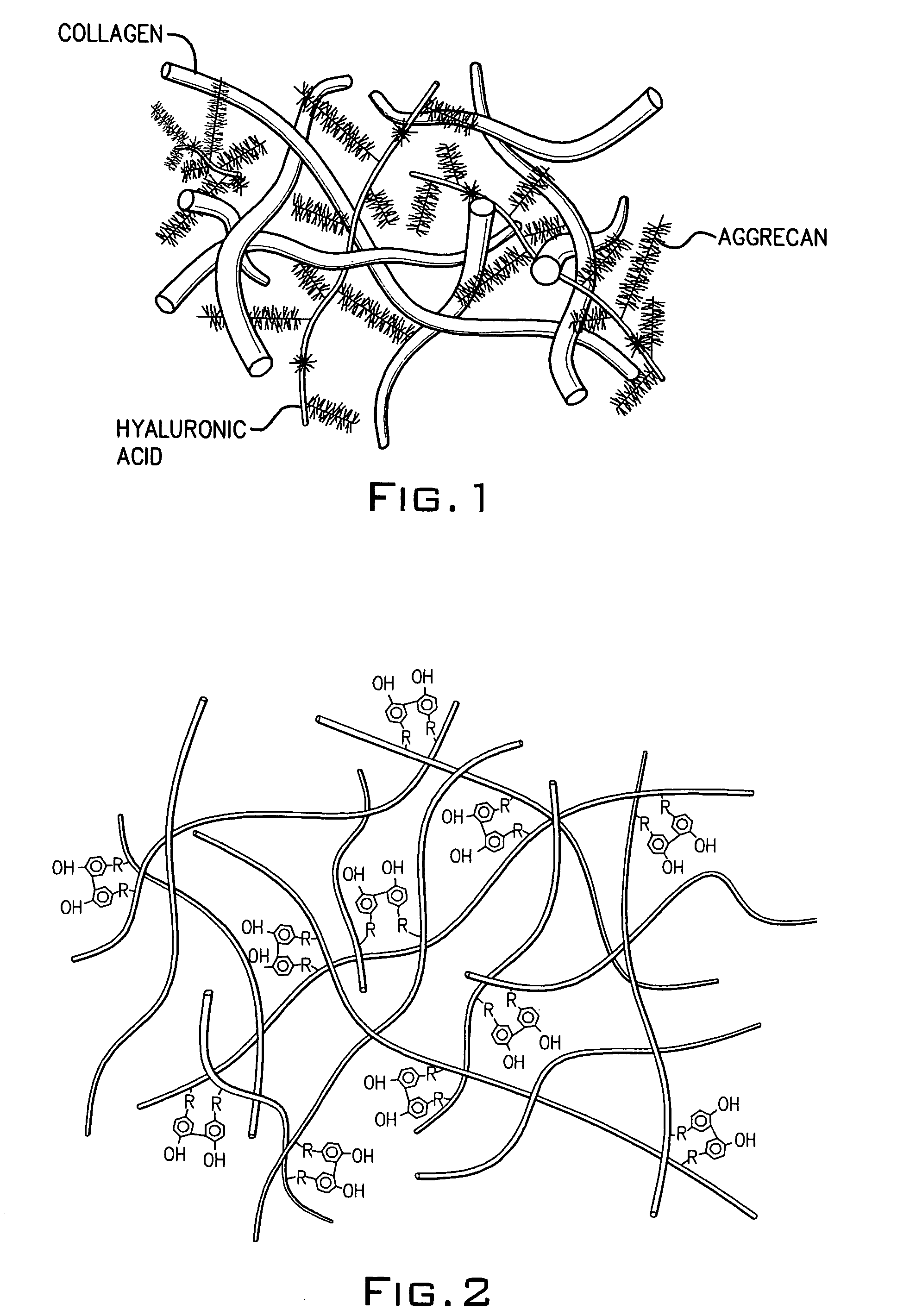
Hydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network and applications thereof
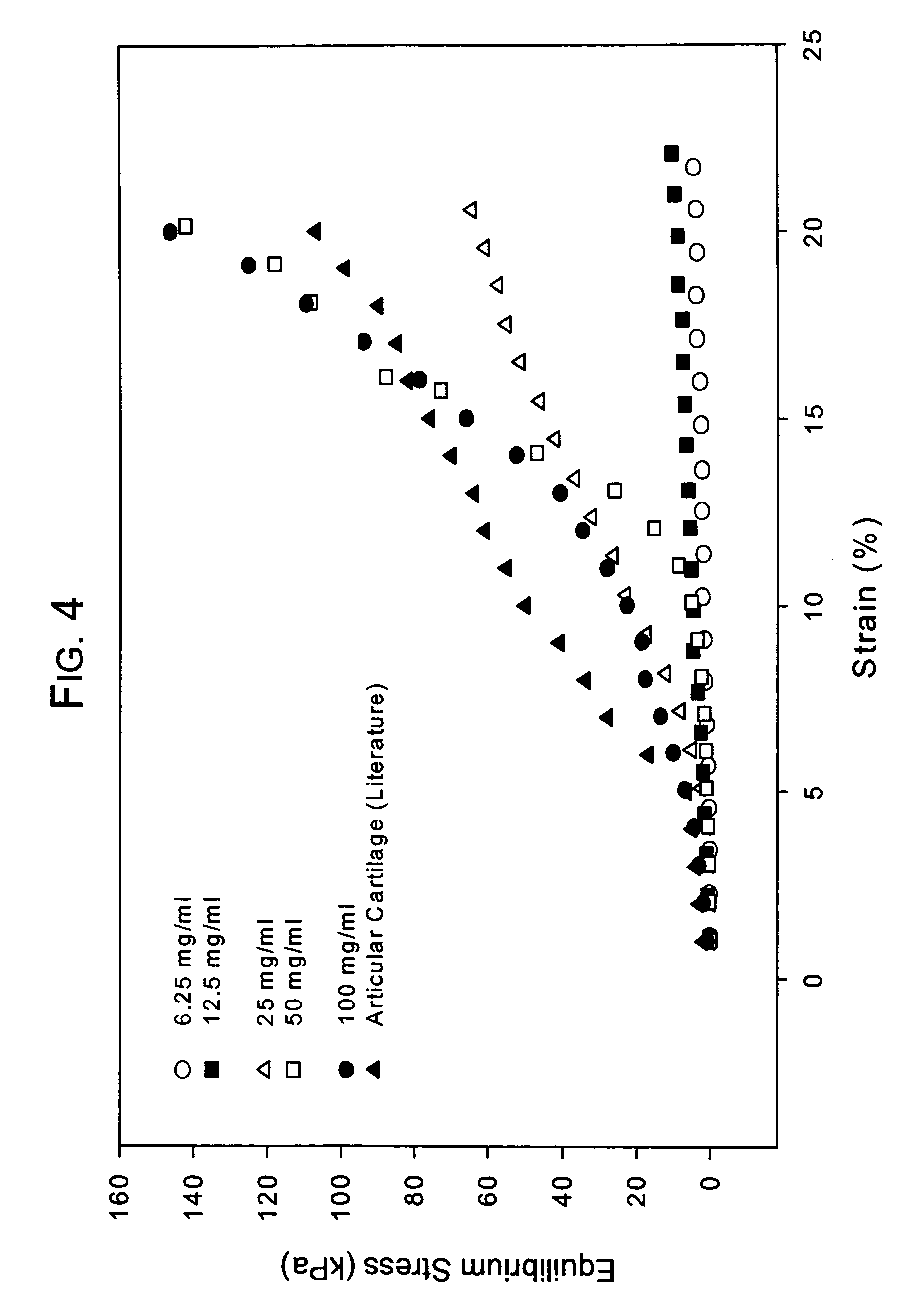
A dihydroxyphenyl cross-linked macromolecular network is provided that is useful in artificial tissue and tissue engineering applications, such as artificial or synthetic cartilage. The network is made by first providing a polyamine or polycarboxylate macromolecule (having a plurality of amine or carboxylic acid groups respectively attached along the length of the molecule), reacting this macromolecule with a hydroxyphenyl compound having a free carboxylic acid group in the case of a polyamine or a free primary amine group in the case of a polycarboxylate, and substituting the hydroxyphenyl compound onto the macromolecule via a carbodiimide-mediated reaction pathway to provide a hydroxyphenyl-substituted macromolecule. This macromolecule is then linked to other such macromolecules via an enzyme catalyzed dimerization reaction between two hydroxyphenyl groups attached respectively to different macromolecules under metabolic conditions of temperature and pH. In a preferred embodiment, the macromolecular network is made up of tyramine-substituted hyaluronan molecules that are linked by dityramine bonds to provide a stable, coherent hydrogel with desired physical properties. A method of preparing such a network is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Enzyme electrode
InactiveUS20070131546A1Small distanceLarge current valueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical responseElectron transfer mediator
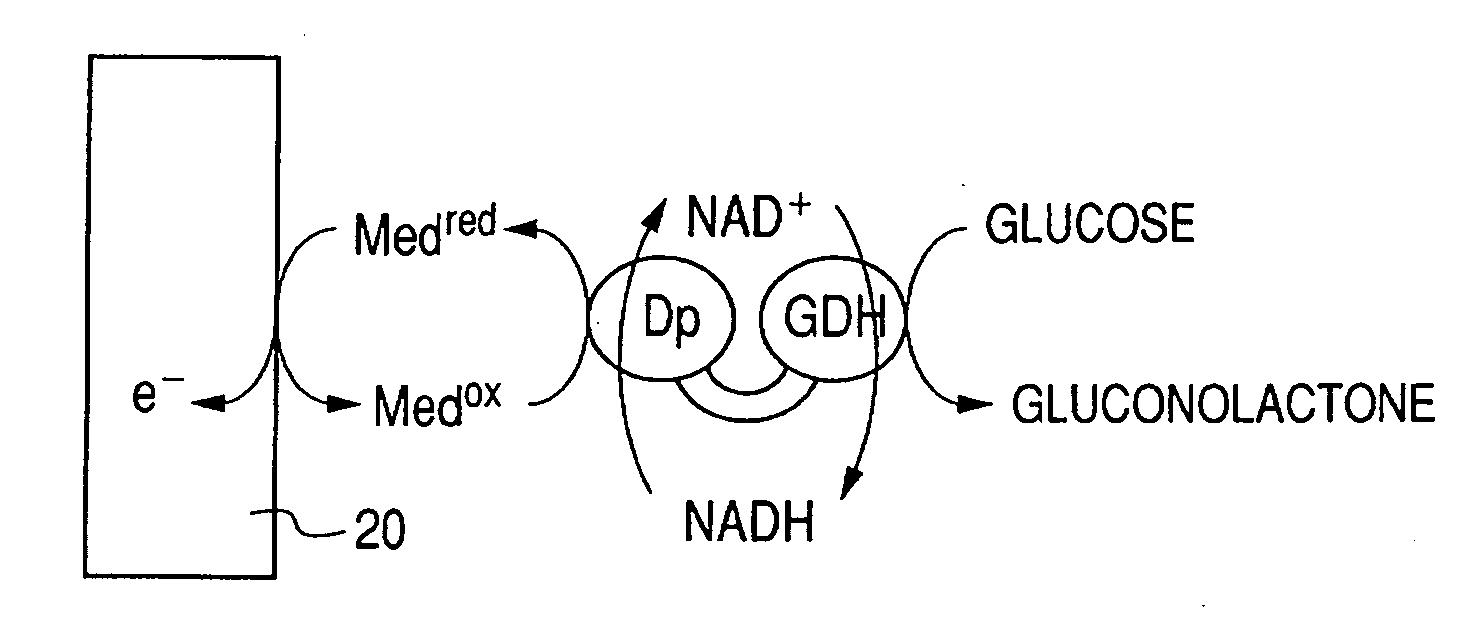
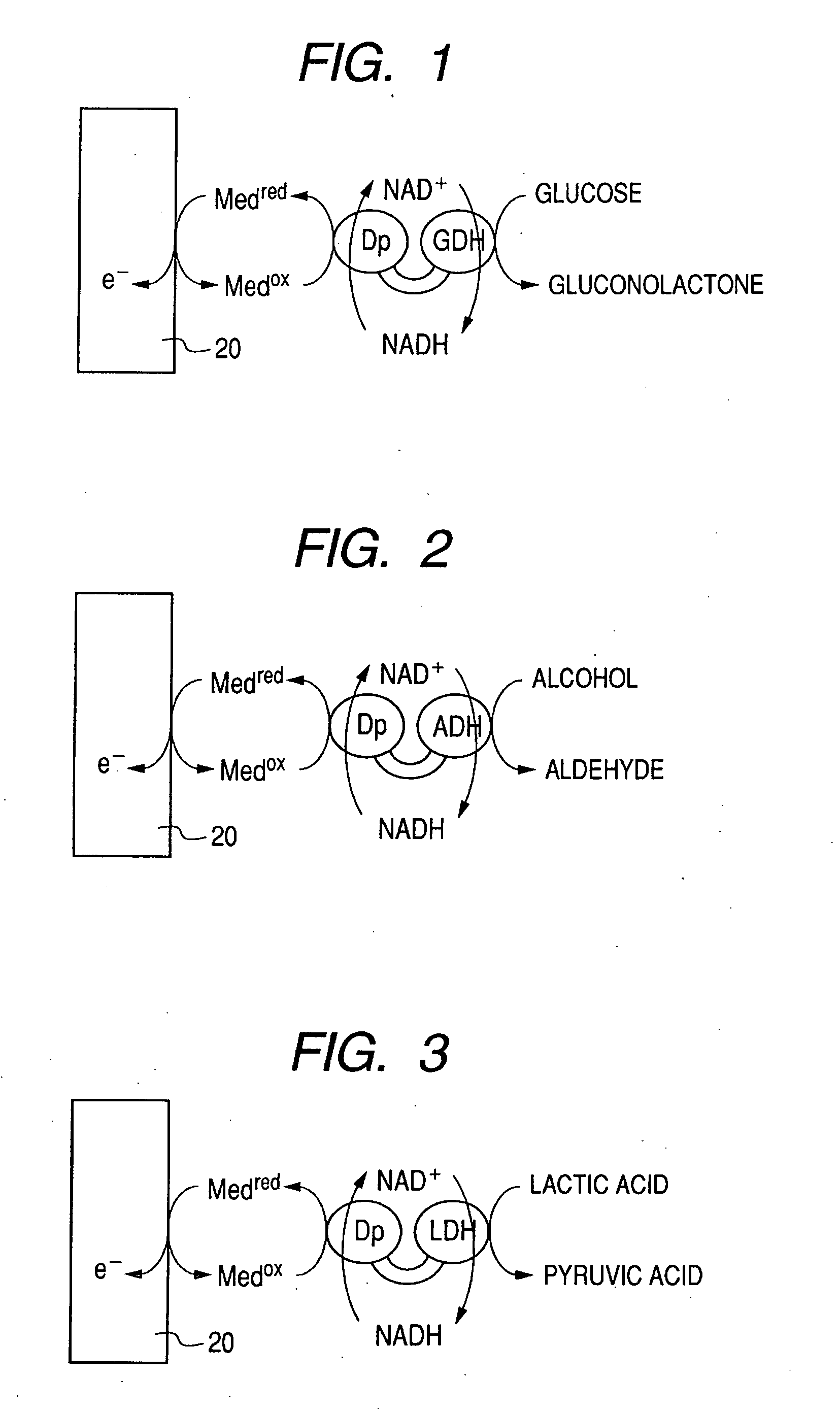
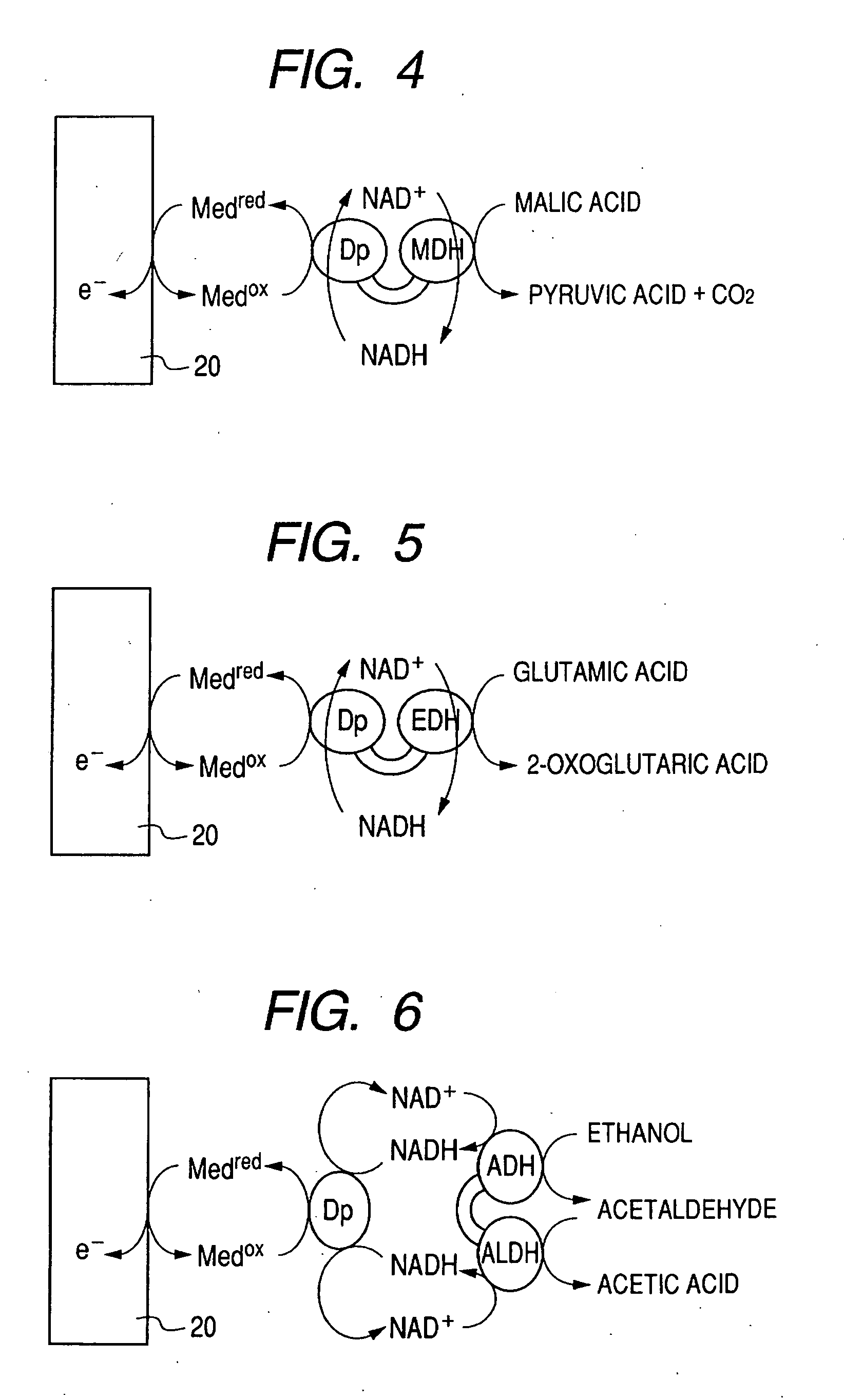
There is provided with an enzyme electrode which can be used as a sensor with high sensitivity, a biofuel cell with high output, and an electrochemical reaction device with high reaction efficiency. The enzyme electrode has a conductive base plate, a fusion protein immobilized to the conductive base plate and an electron transfer mediator, wherein the fusion protein is a fusion protein of a enzyme 1 to catalyze a chemical reaction for producing a reaction product 1 from a reaction substrate 1 and a enzyme 2 to catalyze a chemical reaction for producing a reaction product 2 from a reaction substrate 2, and at least one chemical substance of the reaction product 1 is identical to at least one chemical substance of the reaction substrate 2.
Owner:CANON KK
Removal of Water and Methanol from Fluids
ActiveUS20080099400A1Efficient separationPowerfulMembranesUltrafiltrationChemical reactionInternal combustion engine
A method of removing water and / or methanol from fluid mixtures of the water or methanol with other compounds uses vapor permeation or pervaporation of the water or methanol, as the case may be, from the mixture through a membrane having an amorphous perfluoropolymer selectively permeable layer. The novel process can be applied in such exemplary embodiments as (a) removing water or methanol from mixtures of compounds that have relative volatility of about 1-1.1 or that form azeotropic mixtures with water or methanol, (b) the dehydration of hydrocarbon oil such as hydraulic fluid to concentrations of water less than about 50 ppm, (c) removing water and methanol byproducts of reversible chemical reactions thereby shifting equilibrium to favor high conversion of reactants to desirable products, (d) drying ethanol to less than 0.5 wt. % water as can be used in fuel for internal combustion engines, and (e) controlling the water content to optimum concentration in enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions carried out in organic media.
Owner:COMPACT MEMBRANE SYST INC
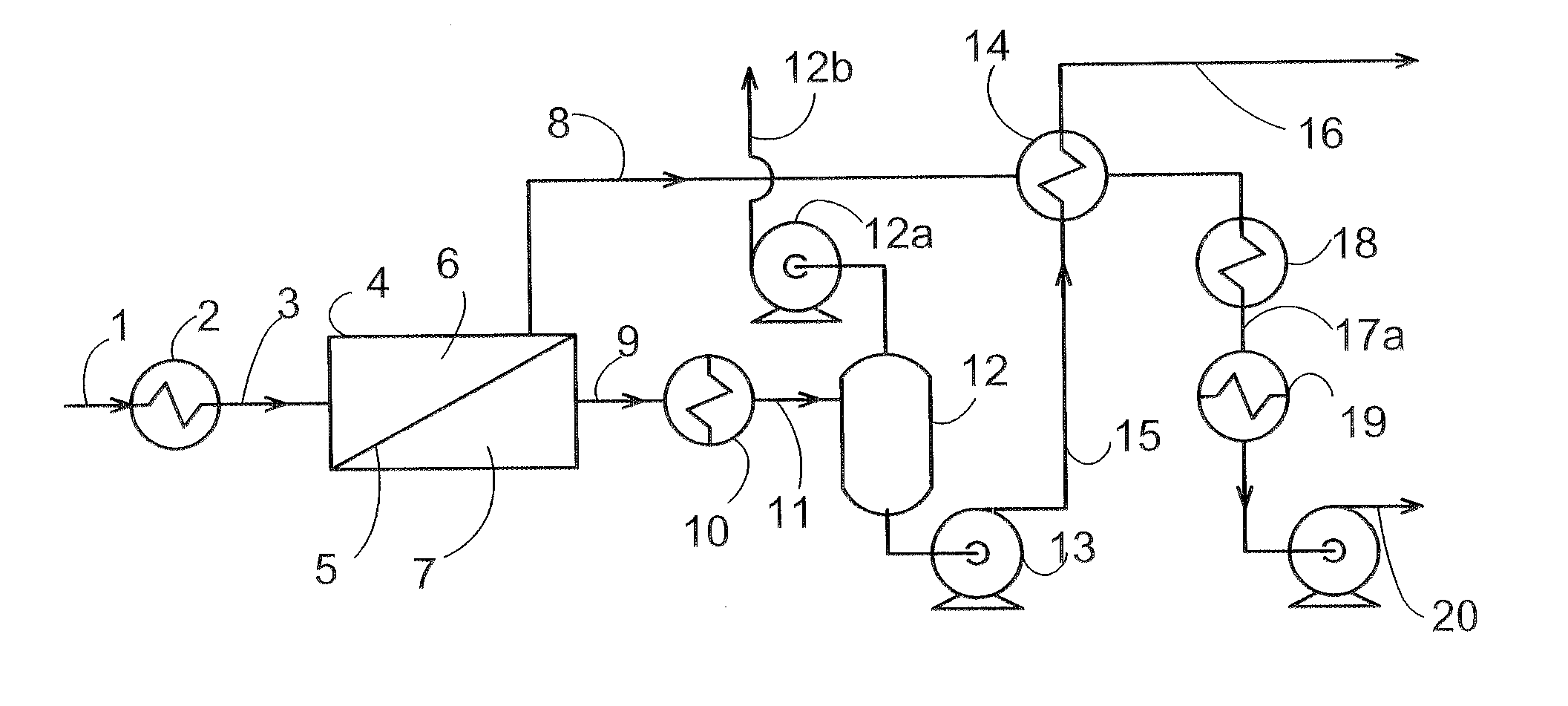
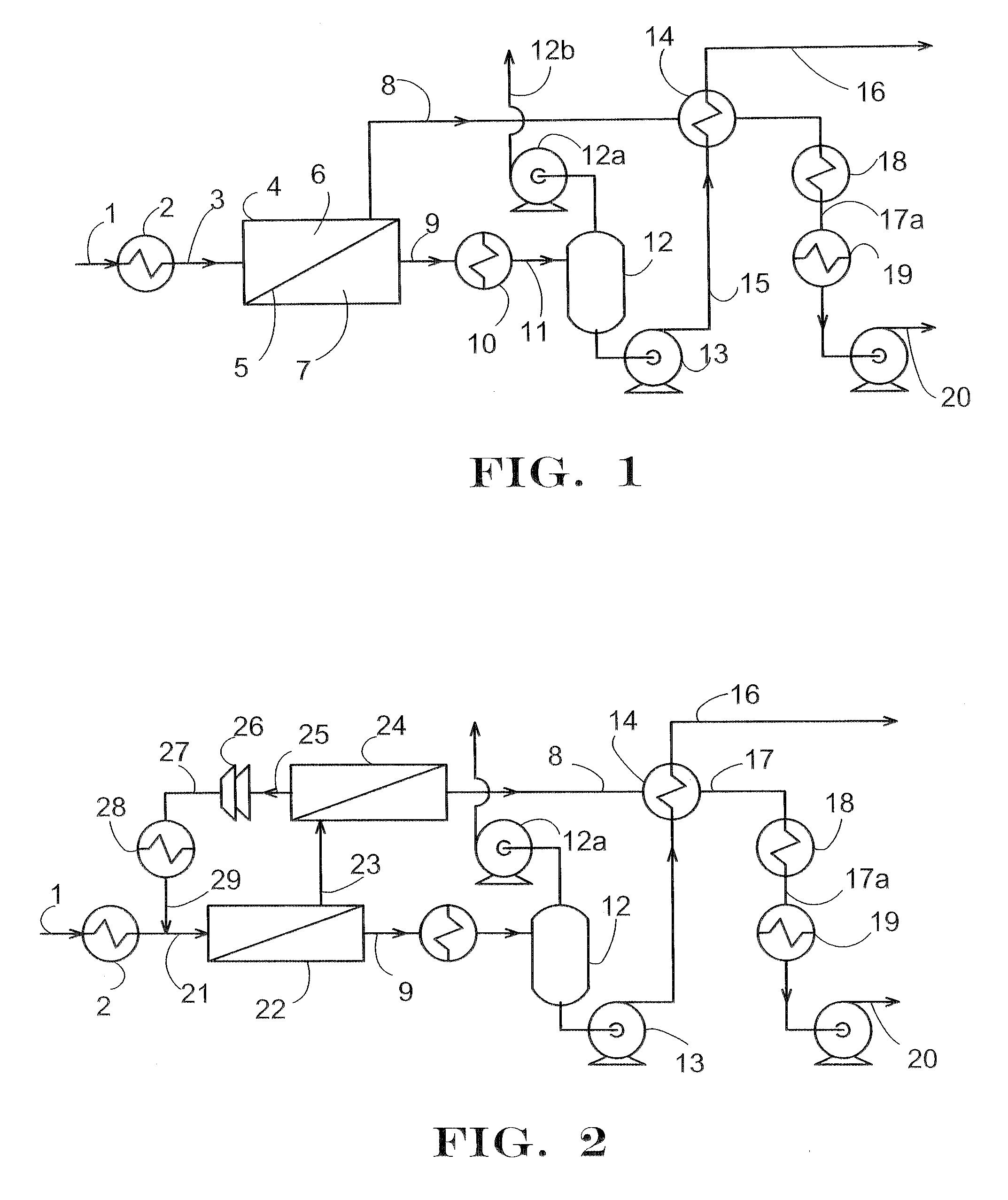
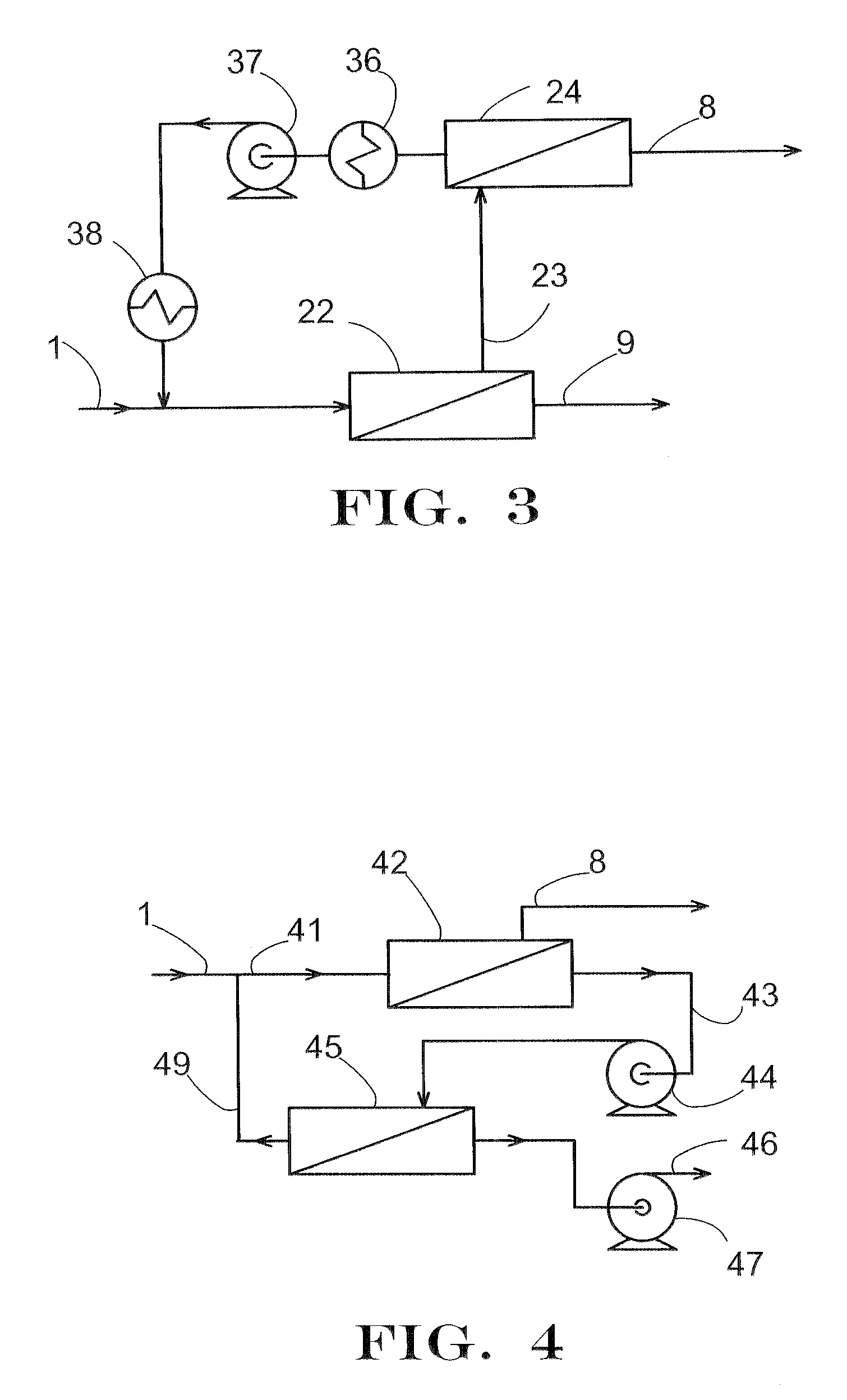
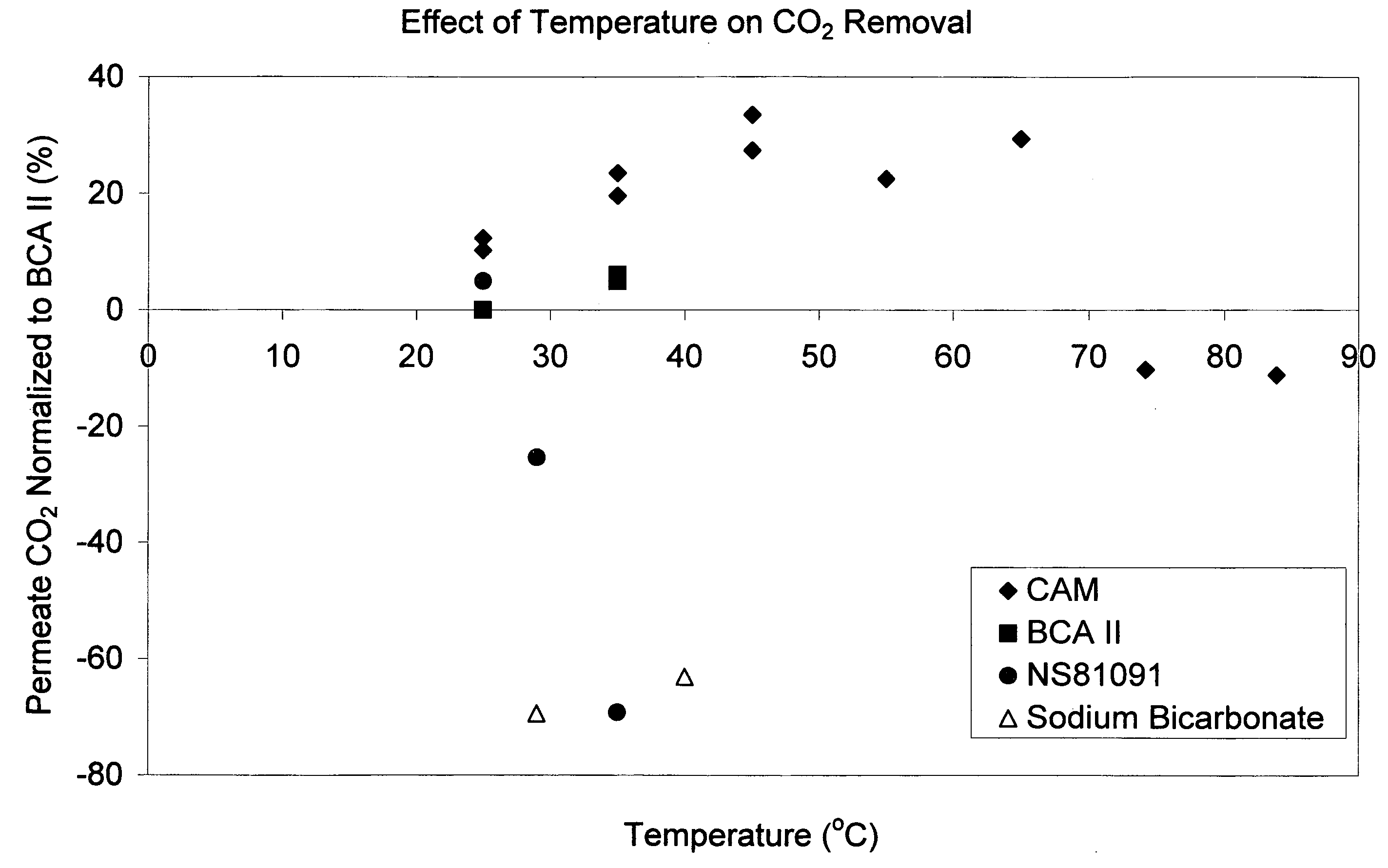
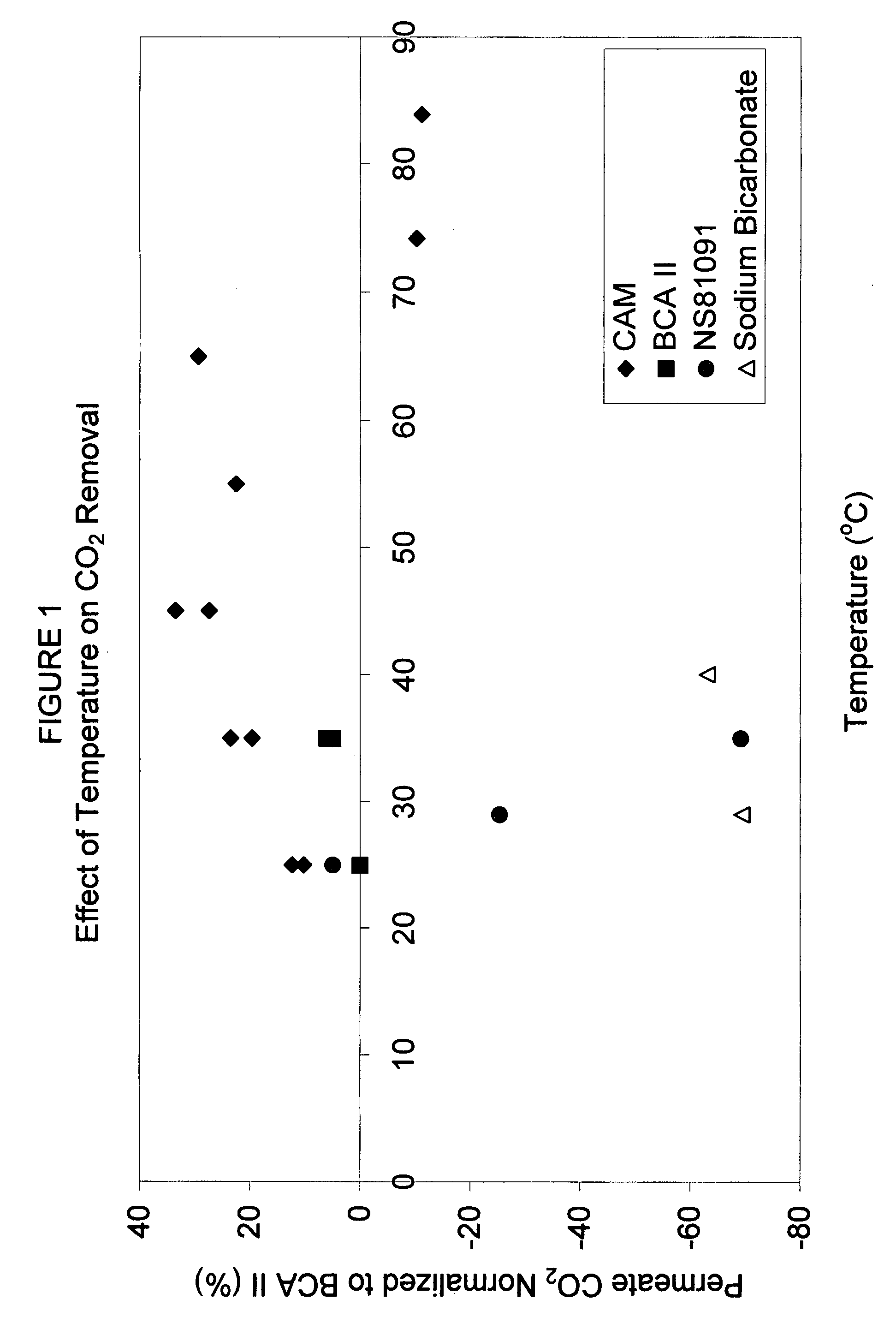
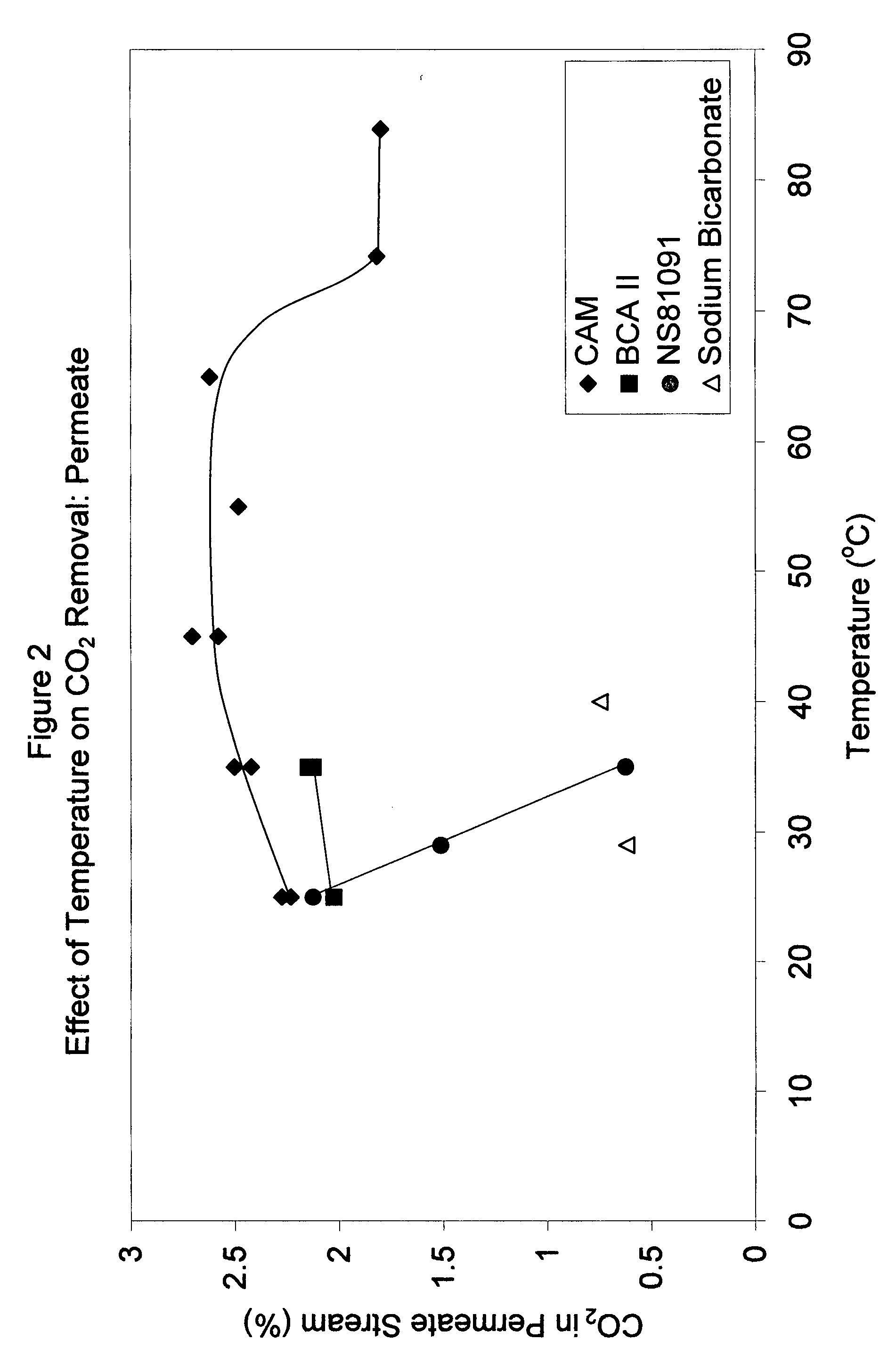
Novel enzyme compositions for removing carbon dioxide from a mixed gas
A process is disclosed for gas separation wherein carbon dioxide in a mixed gas stream is converted to bicarbonate by contacting a gamma carbonic anhydrase enzyme designated as CAM in the temperature range of 40 degrees to 85 degrees C. in an enzyme catalyzed carbon dioxide capture system.
Owner:TRACHTENBERG MICHAEL C
Modified chitosan polymers and enzymatic methods for the production thereof
The present invention is directed to homogeneous phase enzyme-catalyzed processes for producing modified chitosan polymers or oligomers. An enzyme is reacted with a phenolic substrate in the presence of a chitosan polymer or oligomer to produce a modified chitosan polymer or oligomer. The invention also includes modified chitosan polymers or oligomers produced by the novel processes, in particular modified chitosan polymers or oligomers having useful functional properties, such as base solubility and / or high viscosity.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BIOTECH INST +2
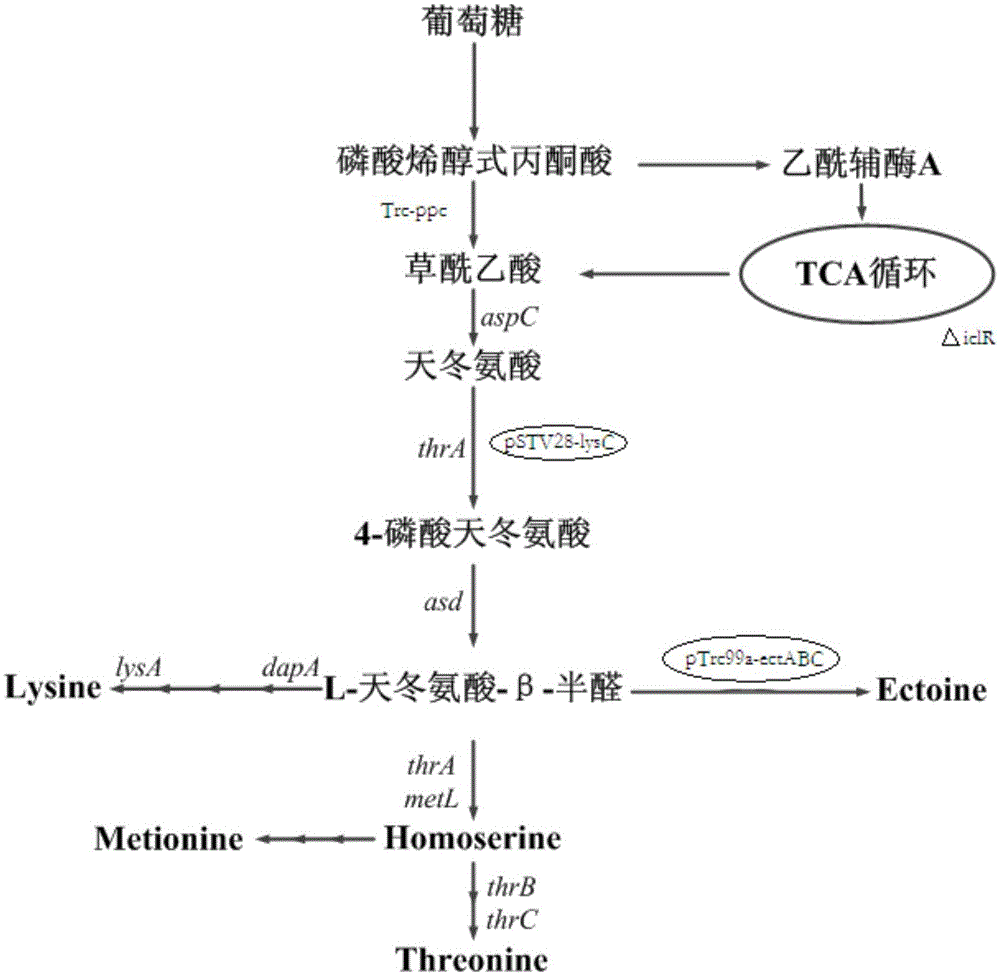
Genetically engineered bacterium producing tetrahydropyrimidine and structuring method and application thereof
ActiveCN105018403AIncrease productivityLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisBiotechnology
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium producing tetrahydropyrimidine and a structuring method and application thereof. The genetically engineered bacterium is Escherichia coli with a specific genotype, comprises Halomonas-elogata-derived ectABC gene, has three gene deficiency variants including lysA, thrA and iclR and has corynebacterium glutamicum lysC gene controlled by a lac promoter and ppc gene controlled by a trc promoter. The defect that chemical synthesis methods have harsh reaction conditions and high energy consumption can be overcome by using the genetically engineered bacterium and utilizing glucose fermentation to produce tetrahydropyrimidine. The defect that Halomonas-elogata fermentation or enzyme-catalyzed methods are complex in process and high in production cost can be overcome. After fermentation for 20-28h, yield of tetrahydropyrimidine reaches 12-18g / L, and the genetically engineered bacterium has high industrial application value.
Owner:合肥和晨生物科技有限公司
Control Of Enzymatic Peracid Generation
InactiveUS20100048448A1Reduce and prevent corrosive effectDisinfect or remove stains from textilesBacteriaHydrolasesCarboxylic acidTarget concentration
A process is provided for producing target concentrations of peroxycarboxylic acids from carboxylic acid esters. More specifically, carboxylic acid esters are reacted with an inorganic peroxide, such as hydrogen peroxide, in the presence of an enzyme catalyst having perhydrolysis activity under conditions where control of reaction pH by selection of buffer concentration and concentration of perhydrolase and reactants produces a targeted concentration of peroxycarboxylic acids. The present perhydrolase catalysts are classified as members of the carbohydrate esterase family 7 (CE-7) based on the conserved structural features. Further, disinfectant formulations comprising the peracids produced by the processes described herein are provided, as are corresponding methods of use.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
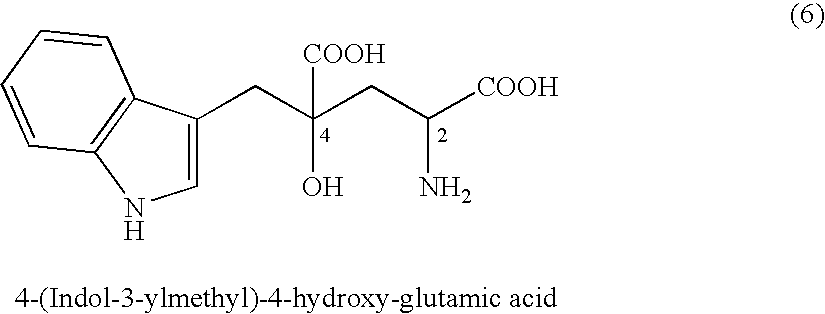
Process of producing glutamate derivatives
InactiveUS7297800B2Efficient productionOrganic chemistryFermentationGlutamic Acid DerivativesMedicinal chemistry
The present invention relates to a process for producing efficiently glutamic acid derivatives (including salts thereof) such as monatin by converting a substituted α-keto acid of formula (1) into a glutamic acid derivative of formula (2) in the presence of an enzyme catalyzing conversion of the same
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Enzyme-catalyzed metal deposition for the enhanced detection of analytes of interest
ActiveUS7642064B2Rapidly and accurately determinedHigh detection sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteRedox
The invention is directed to enhanced methods for detecting an analyte of interest in situ, by immunoassay, or by hybridization comprising binding an enzyme-labeled conjugate molecule to an analyte of interest in the presence of a redox-inactive reductive species and a soluble metal ion. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of the inactive reductive species to an active reducing agent, which in turn reduces the metal ion to a metal atom thereby providing an enhanced means of detecting the analyte via metal deposition.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Prebiotic oligosaccharides via alternansucrase acceptor reactions
InactiveUS7182954B1Promote growthEffective controlBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesEscherichia coli
Oligosaccharides produced by an alternansucrase enzyme catalyzed reaction of sucrose with an acceptor oligosaccharide are effective as prebiotics for controlling enteric bacterial pathogens. Populations of enteropathogenic bacteria may be substantially reduced or inhibited by treatment of an animal with a composition comprising one or more of these oligosaccharides in an amount effective to promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. The method is particularly effective for the control of Salmonella species, enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, and Clostridia perfringens.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY +1
Composite membrane modified biosensor and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101982764AImprove conductivityGood biocompatibilityDecorative surface effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementElectricityCongo red
The invention discloses a composite membrane modified biosensor and preparation and application thereof. The biosensor comprises a matrix electrode, the induction end of the matrix electrode is wrapped with an aromatic diamine polymer membrane, a carbon nano tube-Congo red combination layer is modified on the membrane, and a nano gold particle layer is adsorbed on the combination layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: forming the polymer membrane at the induction end of the matrix electrode by electric polymerization reaction; and modifying the carbon nano tube-Congo red combination layer on the membrane, and finally electrically depositing nano gold on the combination layer. The biosensor can be applied in detecting target genes; and during detecting, a probe is first designed, then a capture probe is modified, and whether the target genes are contained in hybridization solution to be detected and the concentration of the target genes can be judged by first and second hybridization and enzyme catalytic reaction. The biosensor has the advantages of good electric conductivity, good biocompatibility, high sensitivity, storing anti-interference performance, good selectivity, low manufacturing cost and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
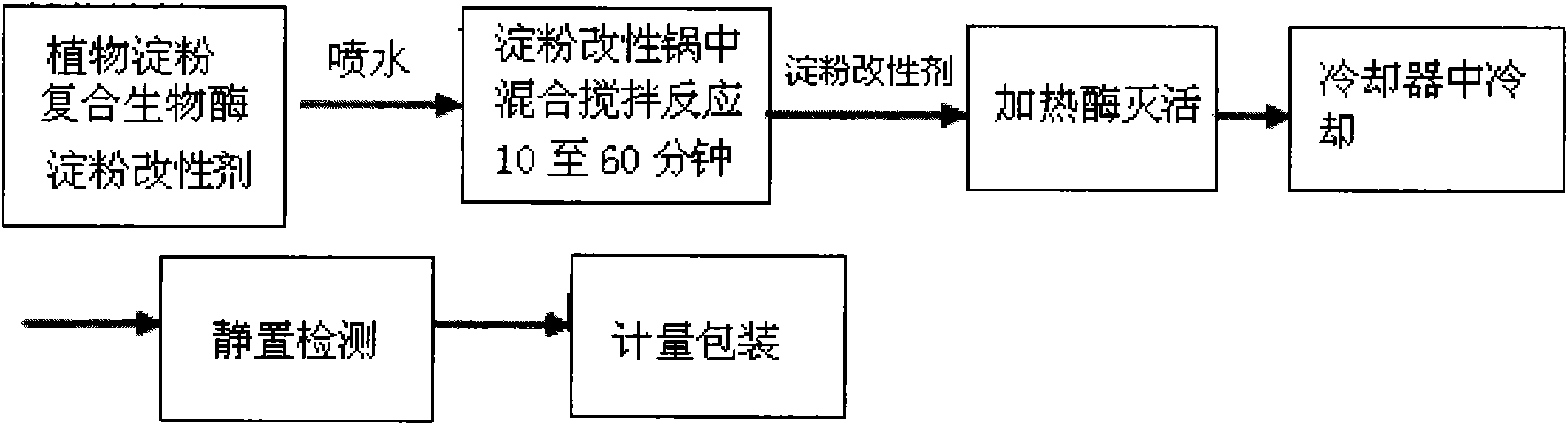
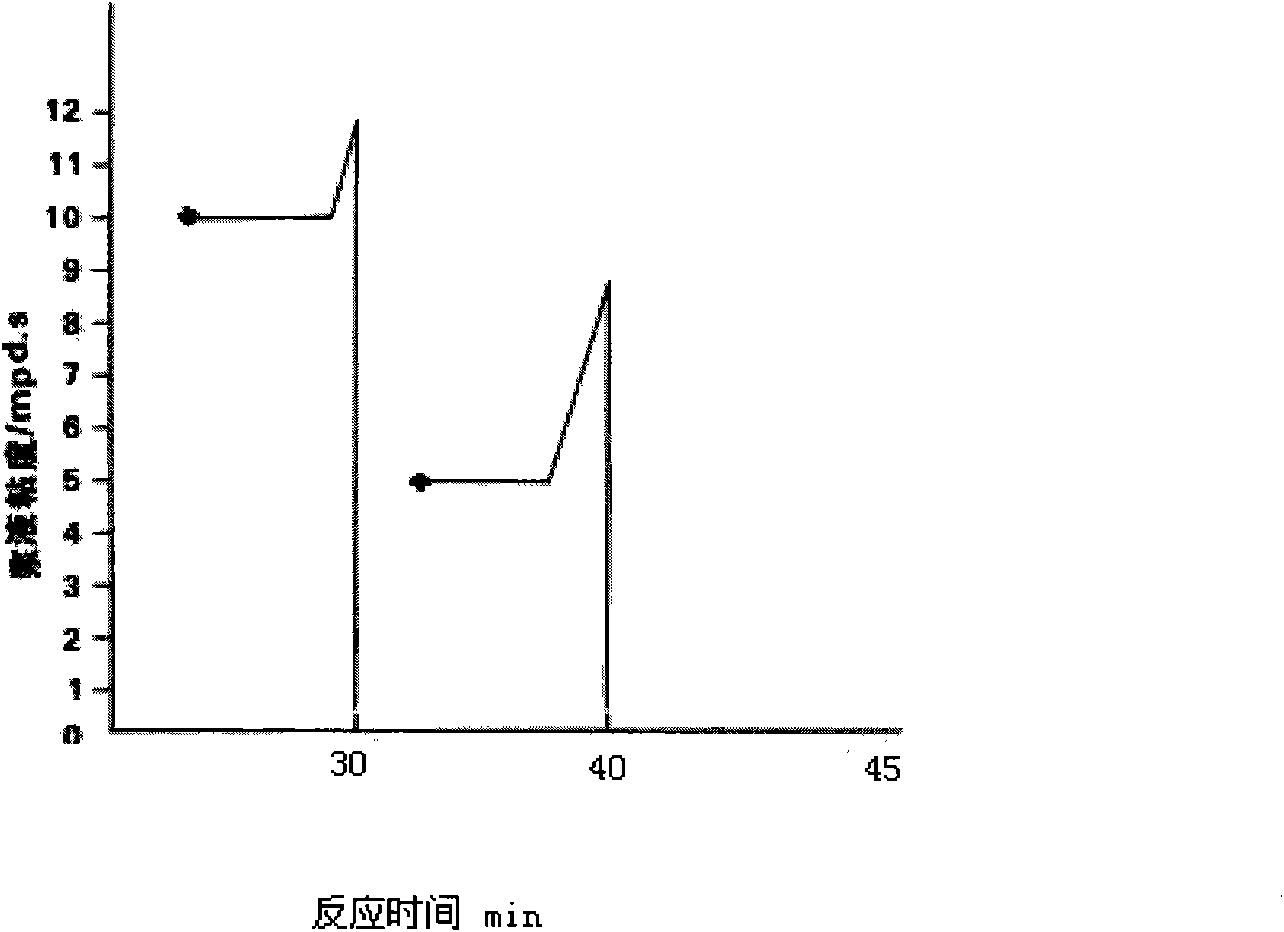
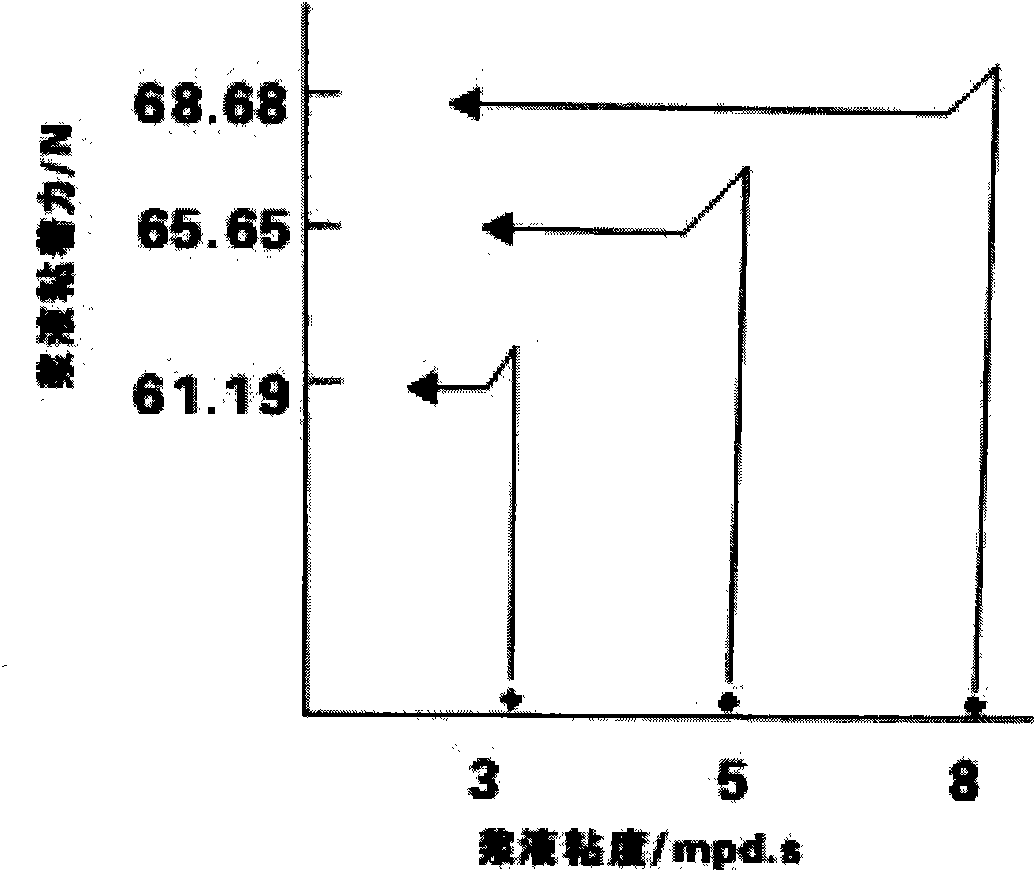
Modified starch catalyzed by compound bio-enzymes and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101942119AIncrease reaction rateShort reaction timeNon-fibrous pulp additionFibre treatmentChemistryToxic environment
The invention provides a preparation method and application of modified starch catalyzed by compound bio-enzymes. The modified starch is a non-toxic environment-friendly new material prepared by modifying raw plant starch by starch modifying assistants and compound bio-enzyme catalysts through special processes. The invention adopts the following technical scheme: the compound bio-enzyme catalysts are adopted to improve the reaction rate, shorten the reaction time and simplify the production process; and molecular recombination, namely grafting, is simultaneously carried out when the required viscosity is achieved, thus improving the use performance of the starch, reducing the use quantity of the assistants and reducing COD emission. The modified starch is widely applied to such fields as disposable environment-friendly tableware, wrappers, non-woven fabrics, pulp for paper-making, industrial and agricultural membranes, fabrics warp sizing, especially to fabrics warp sizing, and can replace PVA and other size.
Owner:WUHAN GREEN BOAT ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION TECH
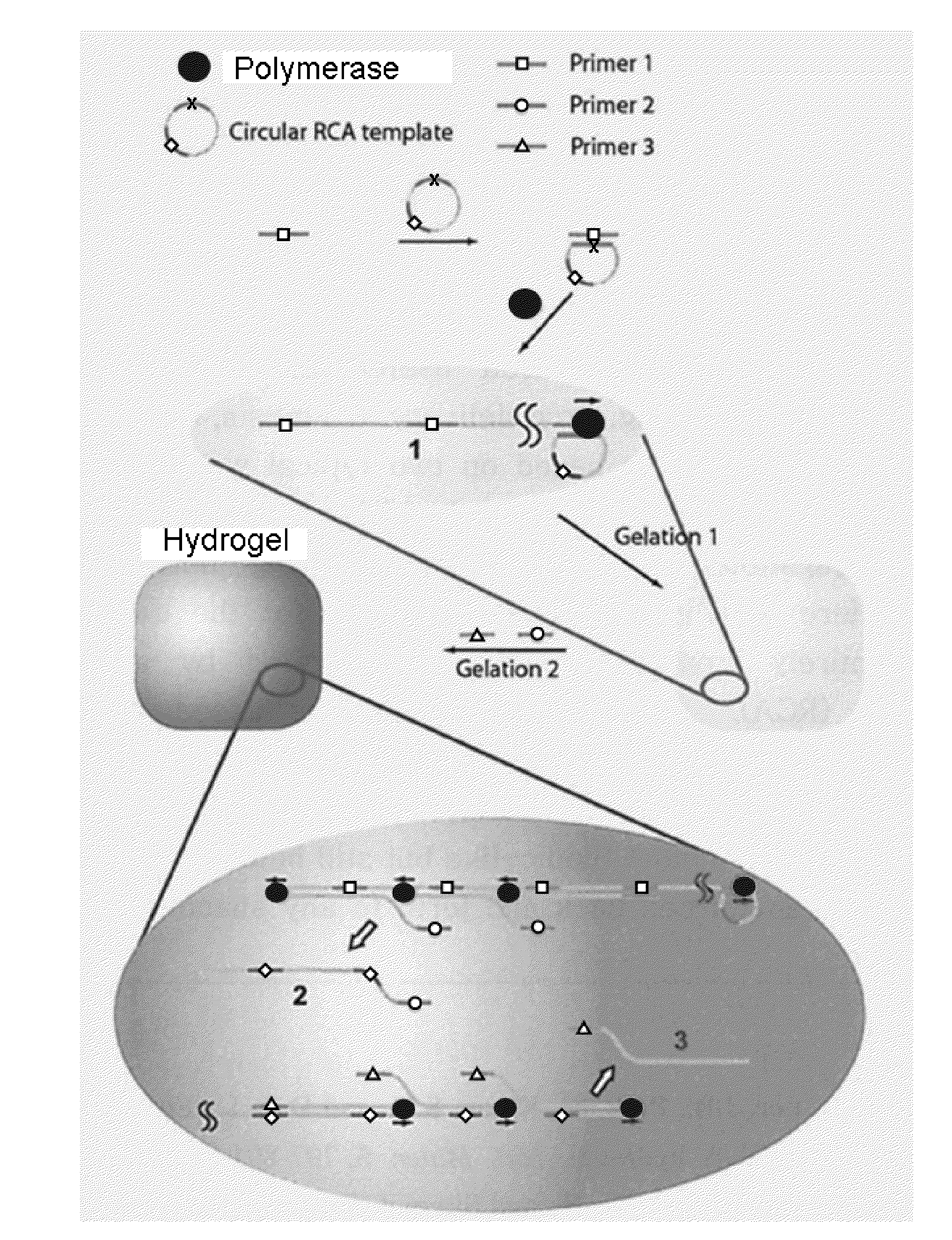
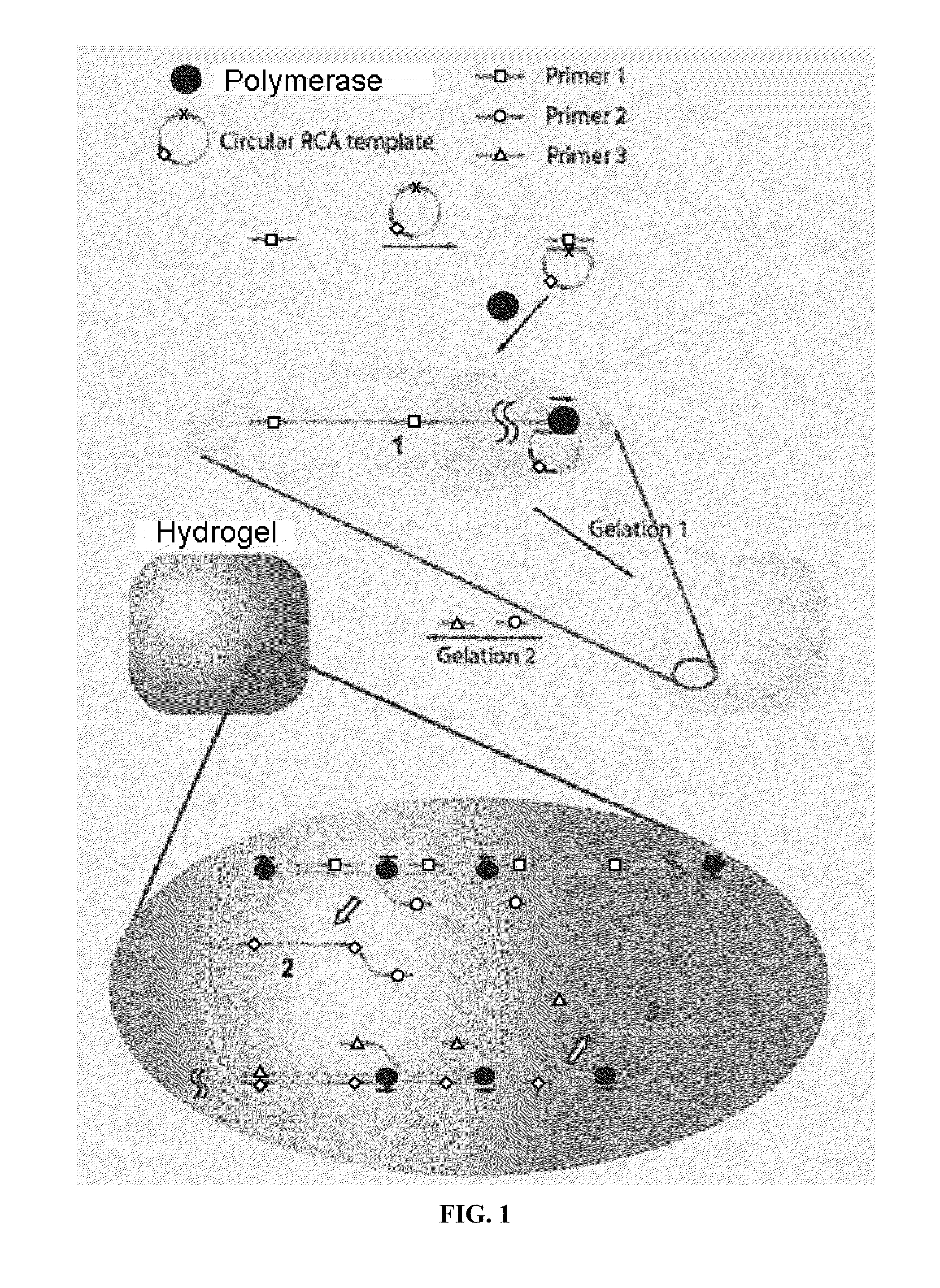
Nucleic acid hydrogel via rolling circle amplification
Methods and compositions are provided for producing nucleic acid-based compositions. Methods include enzyme catalyzed or nucleic acid polymer conjugation. Compositions include nucleic acid-containing hydrogels which can be elongated via rolling circle amplification. The hydrogels can encapsulate bioactive agents for drug delivery.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
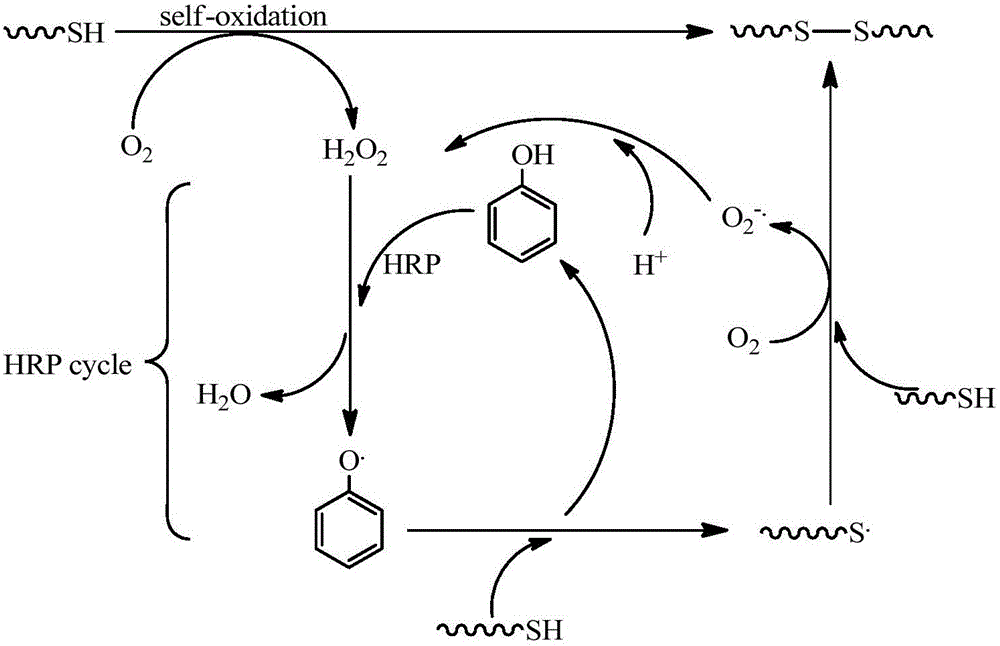
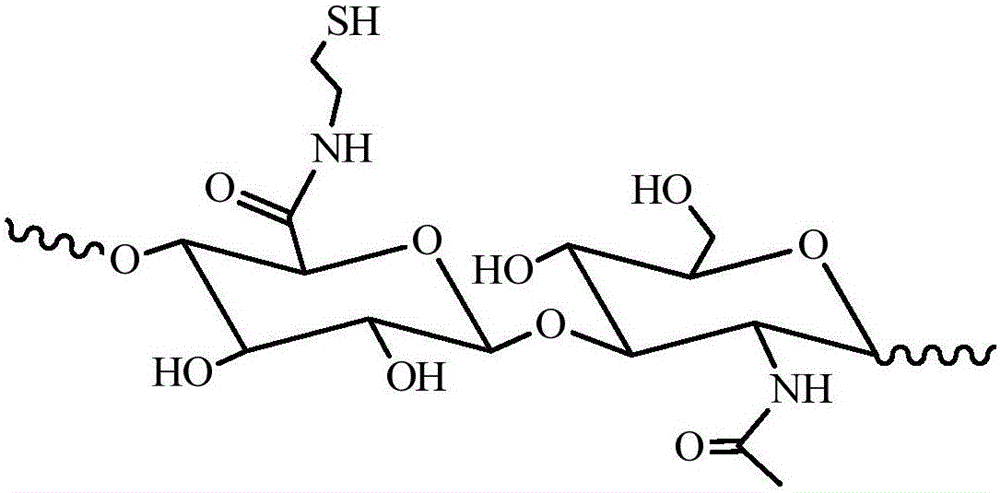
Enzyme-catalyzed disulfide bond-crosslinked natural polymer hydrogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105039465AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateFermentationBiocompatibility TestingDisulfide bond
The invention provides enzyme-catalyzed disulfide bond-crosslinked natural polymer hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The hydrogel comprises a three-dimensional net structure composed of crosslink bonds of cystamine or N,N-diacetyl-L-cystine; under the conditions that horseradish peroxidase is used as a catalyst and a phenol compound is used as an enzyme substrate, sulfydryl-grafted natural polymers are rapidly oxidized to form disulfide bonds, so that the hydrogel is obtained. According to the invention, raw materials are safe in source and environment-friendly, the product has excellent biocompatibility; reaction conditions are mild, and the operation is simple; the system is not required to be additionally added with hydrogen peroxide, and physiological activity of a loaded drug or cells is completely guaranteed.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Synthetic biomaterials having incorporated therein bioactive factors through enzymatically degradable linkages
Synthetic biomaterials containing bioactive factors or modified bioactive factors that are covalently bound to the synthetic precursor components and / or biomaterials by an enzymatically degradable linkage are described herein. Further described are methods to covalently bind bioactive factors to synthetic biomaterials by means of enzymatic catalysis, the biomaterials produced therewith and the bioactive factors necessary for practicing these methods. The bioactive factors contain an amino acid sequence which can serve as a substrate domain for cross-linkable enzymes. The enzyme catalyzes the cross-linking reaction between the substrate domain of the bioactive factor and functional groups of the synthetic precursor components capable of forming the biomaterial and / or synthetic biomaterial susceptible to an enzymatically catalyzed cross-linking reaction. The biomaterials described herein may be used for localized delivery of the bioactive factors, for tissue repair and regeneration and in particular for regeneration of soft and hard tissue, such as skin, bone, tendons and cartilage.
Owner:KUROS BIOSURGERY AG
Chemical luminescence immune assay determination reagent kit for detecting human growth hormone
InactiveCN101368973AImprove performanceEasy to operateChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingLuminescencePollution
The invention relates to the immunoassay field, in particular discloses a chemiluminescence immunoassay test kit and a preparing method thereof for detecting human growth hormone. The test kit uses principle of enzyme-catalyzed chemiluminescence, and adopts the micro hole plate as the solid-phase carrier so as to achieve batch detection. The monoclonal antibody can be labeled by alkaline phosphatase and horseradish peroxidase. Without radioactive pollution, the test kit has stable performance, simple operation, accurate and sensitive result and swift reaction speed.
Owner:北京科美东雅生物技术有限公司
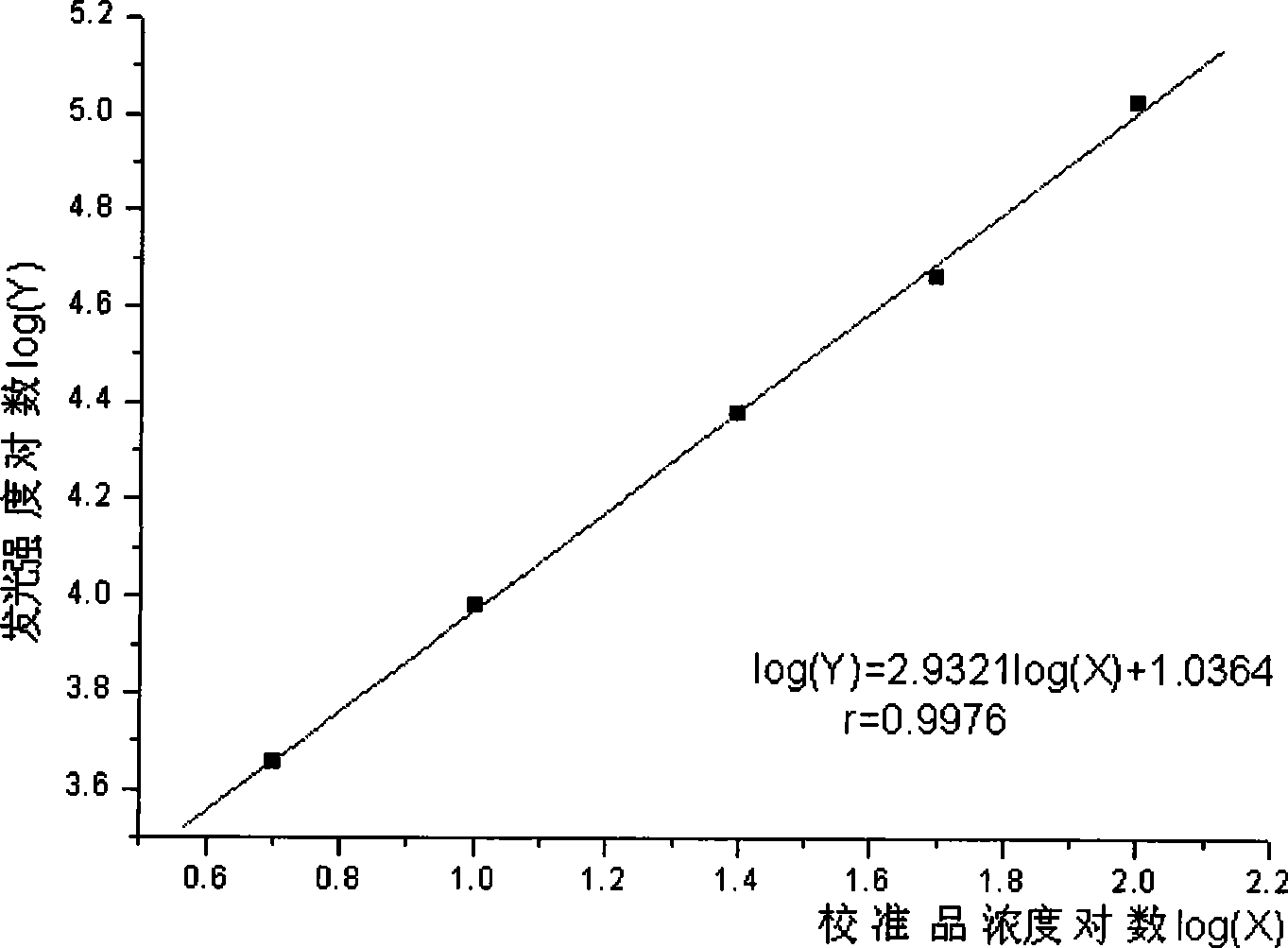
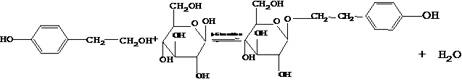
Method for synthesizing salidroside by utilizing enzyme catalyzed direct glucosylation
InactiveCN102174620AGuaranteed stabilityLower water activityChemical recyclingFermentationSolubilitySalidroside
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing salidroside by utilizing enzyme catalyzed direct glucosylation, comprising the following steps: carrying out a reaction on glucose, tyrosol and enzyme in a solvent containing a buffer solution; and collecting the salidroside by adopting the conventional method, wherein, the solvent comprises an icon-containing liquid and an organic solvent. Compared with the existing method, in the method, a reaction medium composed of the ionic liquid is adopted as a reaction system for synthesizing the salidroside by utilizing the enzyme catalyzed direct glucosylation; the enzyme activity and the enzyme stability are ensured; the dissolubility of the substrate in the reaction system is improved; the water activity in the reaction system is reduced; the expensive glucoside donor needs not to be used, and the salidroside can be further synthesized; the separation and purification processes of the product are simple, the unreacted tyrosol can be recovered and recycled, thus lowering the production cost, and satisfying the requirements of rapidly developing the medical industries.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Microcapsule preparation technology beneficial for quality control
InactiveCN105613792AQuality assurancePrevent oxidationFood shapingEdible oils/fatsProtein solutionVegetable oil
The invention discloses a microcapsule preparation technology beneficial for quality control. The technology comprises the following steps that 1, a protein solution is prepared, wherein isolated soybean protein and an emulsifying agent are mixed and then stirred by adding water; 2, a predissolving colloid is prepared, wherein glucose and konjac glucomannan powder are added into water and stirred; 3, emulsifying is performed, wherein vegetable oil and the colloidal solution prepared in the step 2 are sequentially added into the protein solution prepared in the step 1 at the temperature of 50 DEG C-60 DEG C, stirring is performed at low speed, homogenizing is performed at high speed, and then the pH is adjusted; 4, enzyme-catalyzed gelling is performed, wherein a solidified enzyme is added for a gelling reaction; 5, vacuum freeze drying is performed, wherein microcapsule dispersion liquid obtained in the step 4 is centrifuged at low temperature at high speed and then subjected to vacuum drying for 35-50 h at the temperature of minus 30 DEG C-minus 50 DEG C under the pressure of 1.5 Pa-2.5 Pa. According to the microcapsule preparation technology beneficial for the quality control, microcapsules are dried through a low-temperature vacuum freeze drying technology, therefore, the phenomenon that the vegetable oil in the microcapsules are oxidized due to the high temperature is avoided, the nutritional value of the vegetable oil is guaranteed, and the quality of the microcapsules is guaranteed.
Owner:CHENGDU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
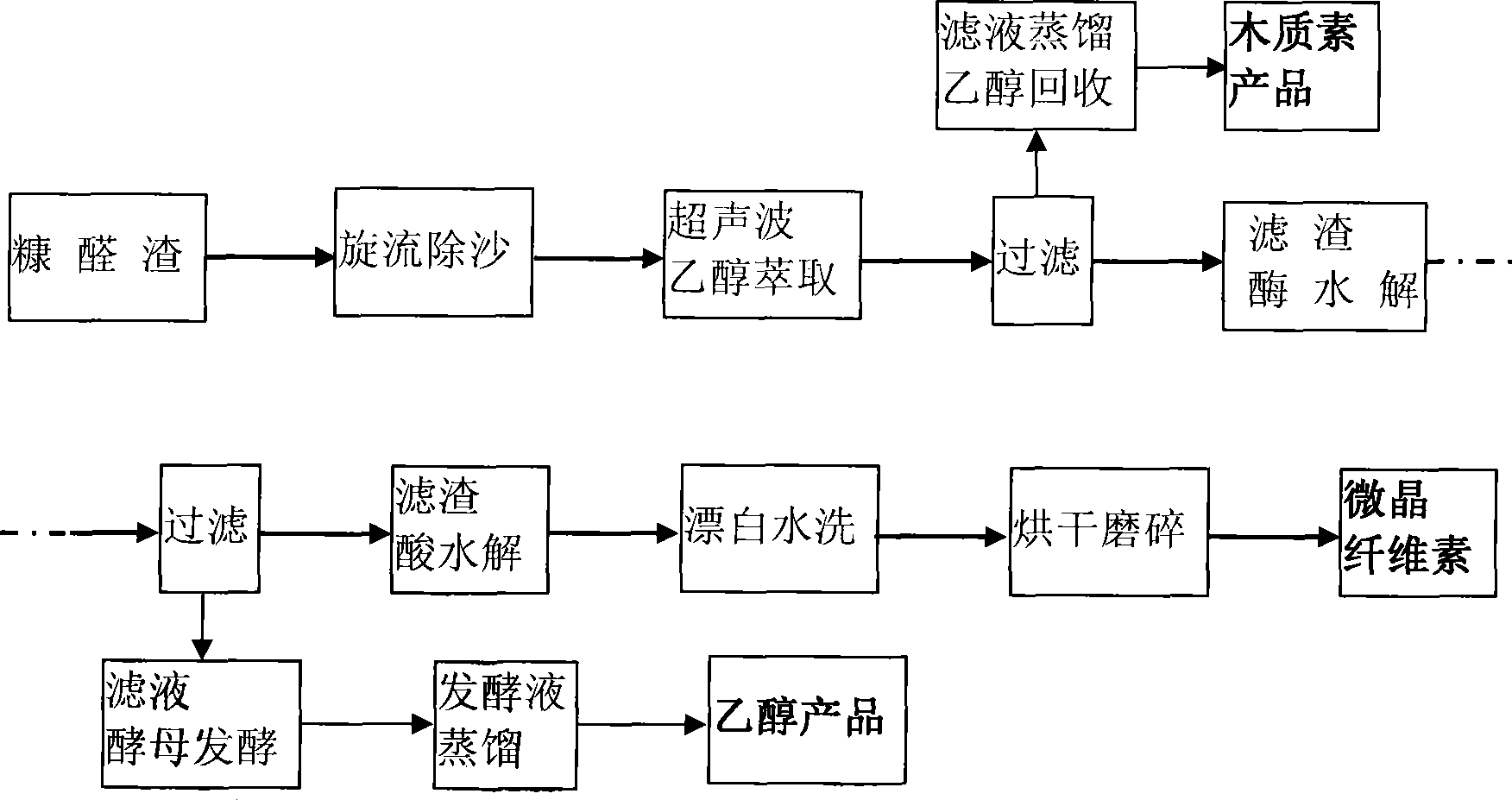
Method for preparing microcrystalline cellulose and cellulose fuel ethanol by separating furfural residue
InactiveCN101413016ATake advantage ofSpecial structureMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberHydrolysate
The invention relates to a method for preparing microcrystalline cellulose and fiber ethanol by separating furfural residues, which comprises the following steps: (1) ethanol is taken as a solvent, a circulating ultrasonic extraction method is adopted to extract, and lignin is separated from an extraction liquid; (2) extraction residues adopt complex enzyme of endoglucanase and beta-glucosaccharase for enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis, and a hydrolysate is fermented to prepare the ethanol; and (3) hydrolysis residues are subjected to acid-catalyzed hydrolysis to separate the microcrystalline cellulose. The extraction method has the advantages that the extraction method is green and environment-friendly, the enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis has mild conditions, the side effect is small, the acid concentration needed by acid hydrolysis is low, the action time is short, and the yield of each step is high; and the method has smart process combination, can greatly reduce the production cost for the microcrystalline cellulose and the fiber ethanol by utilizing a special structure of furfural waste residues, and has double benefits of economization and environmental protection.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method of zyme catalyzing cyclo-olefin oxidation
InactiveCN101109016AAvoid Potential ContaminationReduced mass productionFermentationEpoxyCyclohexene
The invention relates to a method of enzyme catalyzing olefin expoxidation. In the aqueous solution, the bromine peroxidase is applied for biological catalyst and hydrogen peroxide or oxygen is taken as oxygen source to oxidate the olefin into expoxidation. Take the cyclohexen as example. The hydrogen peroxide is applied as the source. They react under the 20 DEG C. to 70 DEG C. for two to ten hours. The yield of epoxy cyclohexane to the hydrogen peroxide is more than 50 per cent and the selectivity of the epoxy cyclohexane is more than 85 per cent. After the reaction, the water phase is separated from the organic phase automatically, and the enzymes left in the water phase can be recycled. Boasting easy technical process, recycled enzymes and easy yield separation, the method is an environment-friendly green chemical process.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing l-phenylephrine using an alcohol dehydrogenase of aromatoleum aromaticum ebn1 (azoarcus sp. ebn1)
ActiveUS20110171700A1High stereoselectivityMoreOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationAlcoholAzoarcus sp.
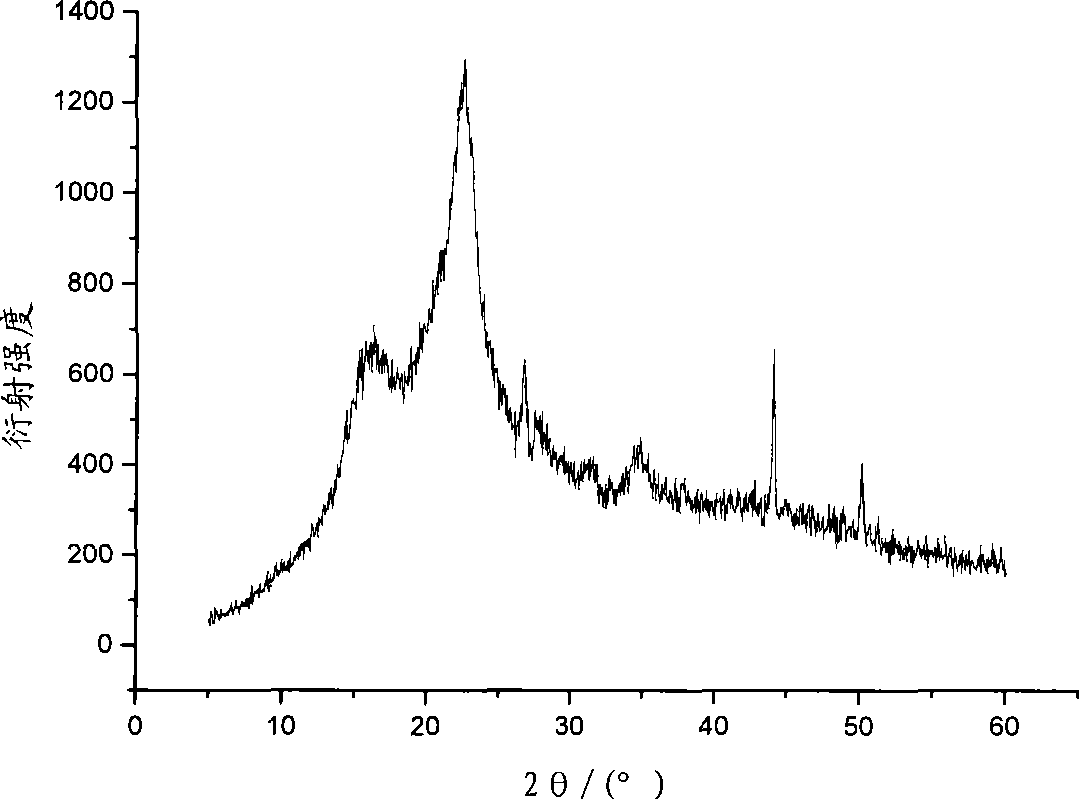
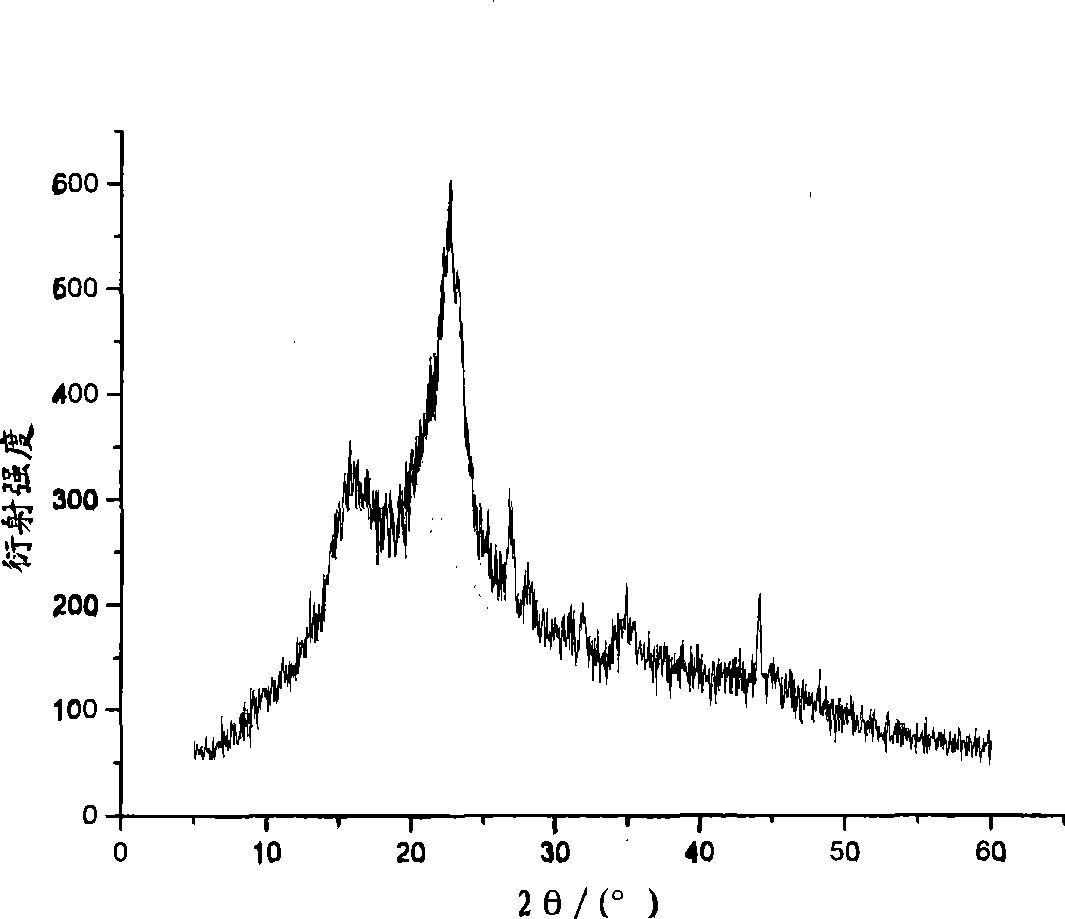
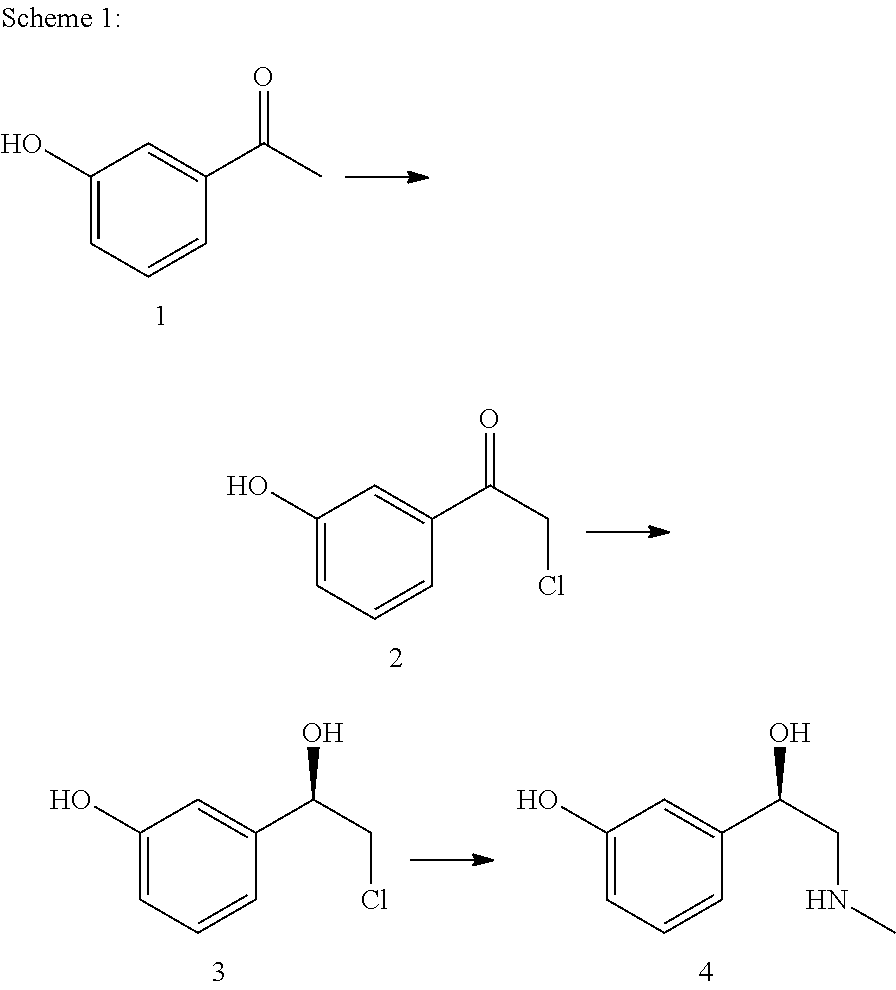
The present invention relates to a multi-stage process for producing substituted, optically active alcohols, comprising an enzyme-catalyzed synthesis step, in particular a synthesis step which is catalyzed by an alcohol dehydrogenase. The inventive method is particularly suitable for producing phenylephrine, i.e. 3-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-methylamino-ethyl]-phenol.
Owner:BASF AG
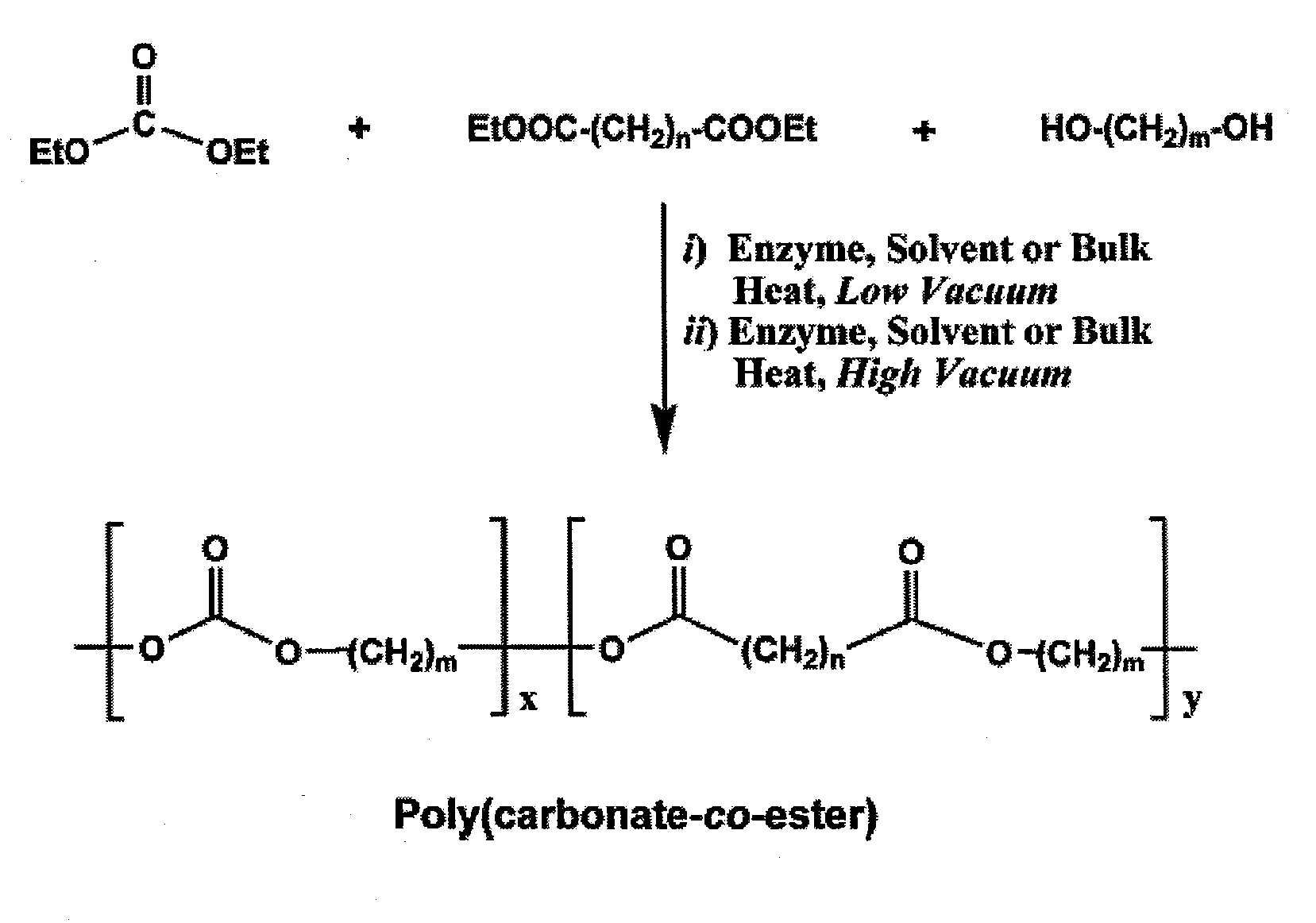
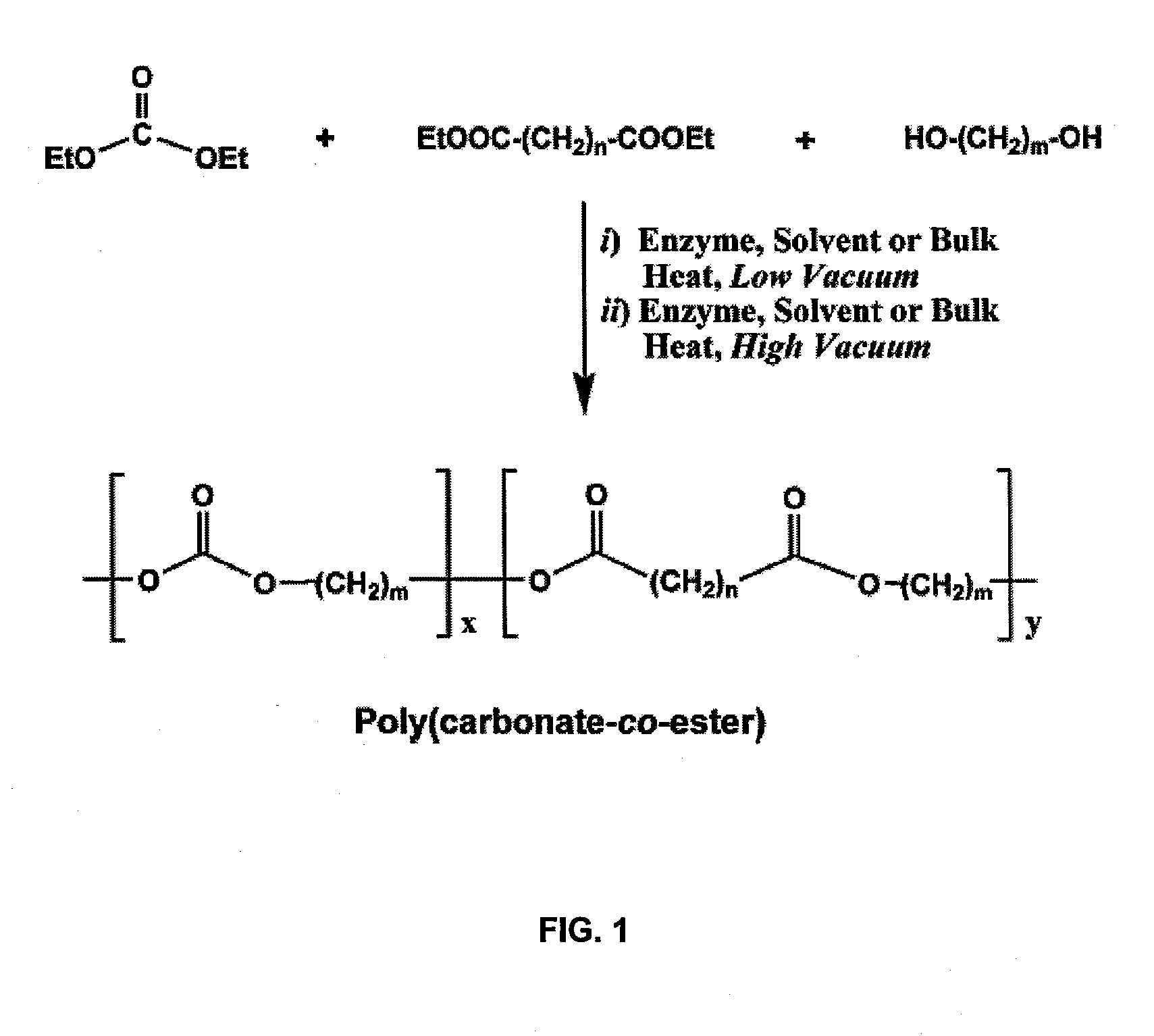
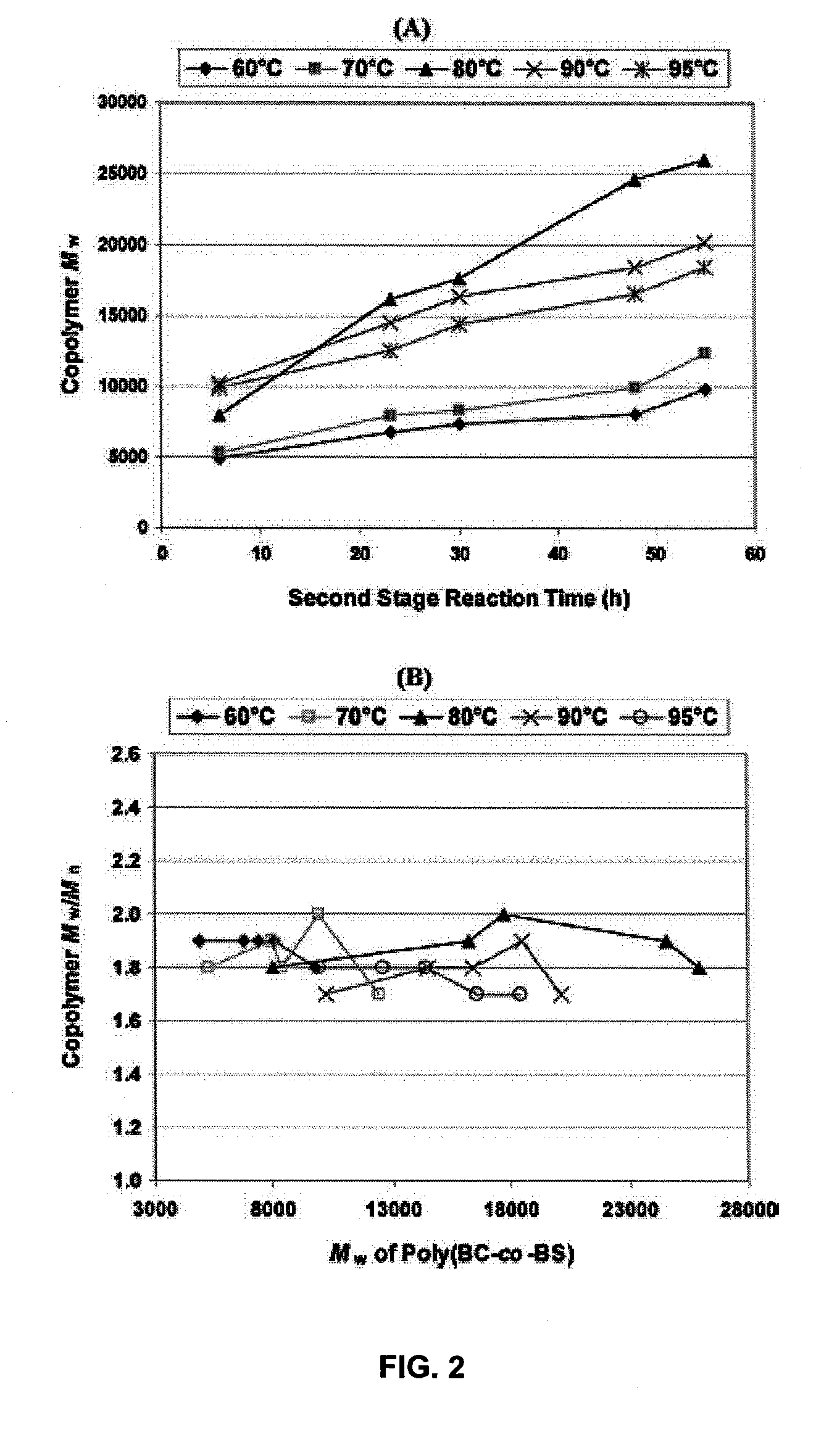
Enzyme-catalyzed polycarbonate and polycarbonate ester synthesis
InactiveUS20100041856A1Strong specificityEasy to controlFermentationTransesterificationPolycarbonate
An enzymatic process for preparing aliphatic polycarbonates via terpolymerization or transesterification using a dialkyl carbonate, an aliphatic diester, and an aliphatic diol or triol reactant. A catalyst having an enzyme capable of catalyzing an ester hydrolysis reaction in an aqueous environment is subsequently added to the reaction mixture. Next, polymerization of the reaction proceeds for an allotted time at a temperature≦100° C. Finally, the copolymer is isolated from an the catalyst via filtration.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
Processes for the production of triglycerides of unsaturated fatty acids in the presence of enzymes
InactiveUS20050233426A1Delayed reaction timeReduce the probability of reactionFatty acid esterificationFermentationDistillationFiltration
Processes for the enzyme-catalyzed production of triglycerides using polyunsaturated fatty acids, in which (a) the reaction of polyunsaturated fatty acids and / or C1-4 alkyl esters thereof with glycerol in vacuo in the presence of an immobilized enzyme to form their triglycerides is accelerated by addition of an additive from the group of weakly basic salts, complexing agents and ion exchangers and / or addition of a weakly basic salt and / or addition of an entraining agent in the form of a solvent or a gas and / or addition of glycerol-binding adsorbers and / or heat treatment of the partial glyceride intermediate product, (b) the immobilized enzymes are removed from the triglyceride by separation or filtration and (c) the remaining fatty acids and / or C1-4 alkyl esters thereof are removed from the triglyceride by distillation, refining or extraction.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Strip electrode with conductive nano tube printing
InactiveUS20080023327A1Improve consistencyFlat surfaceImmobilised enzymesMaterial nanotechnologySilver inkCarbon nanotube
A sensor system that detects a current representative of a compound in a liquid mixture features a multi or three electrode strip adapted for releasable attachment to signal readout circuitry. The strip comprises an elongated support which is preferably flat adapted for releasable attachment to the readout circuitry; a first conductor and a second and a third conductor each extend along the support and comprise means for connection to the circuitry. The circuit is formed with single-walled or multi walled nanotubes conductive traces and may be formed from multiple layers or dispersions containing, carbon nanotubes, carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-chloride. An active electrode formed from a separate conductive carbon nanotubes layer or suitable dispersion, positioned to contact the liquid mixture and the first conductor, comprises a deposit of an enzyme capable of catalyzing a reaction involving the compound and preferably an electron mediator, capable of transferring electrons between the enzyme-catalyzed reaction and the first conductor. A reference electrode also formed from a conductive carbon nanotube layer or suitable dispersion is positioned to contact the mixture and the second conductor. The system includes circuitry adapted to provide an electrical signal representative of the current which is formed from printing conductive inks made with nano size particles such as conductive carbon or carbon / platinum or carbon / silver, or carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide to form a conductive carbon nanotube layers. The multiple-electrode strip is manufactured, by then applying the enzyme and preferably the mediator onto the electrode. Alternatively the electrode can have a carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-chloride surface and or a conductive carbon or silver ink surface connecting leg. The carbon nanotube solution is first coated and patterned into electro shapes and the conductive carbon nanotubes, carbon or silver ink can be attached by printing the ink to interface with the carbon nanotube electro surface. A platinum electrode test strip is also disclosed that is formed from either nano platinum distributed in the carbon nanotube layer or by application or incorporation of platinum to the carbon nanotube conductive ink.
Owner:MYSTICMD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com