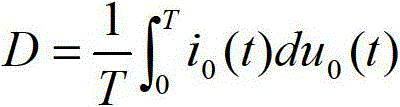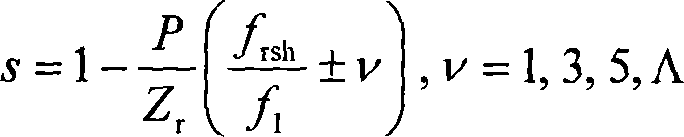Patents
Literature
946 results about "Transient current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
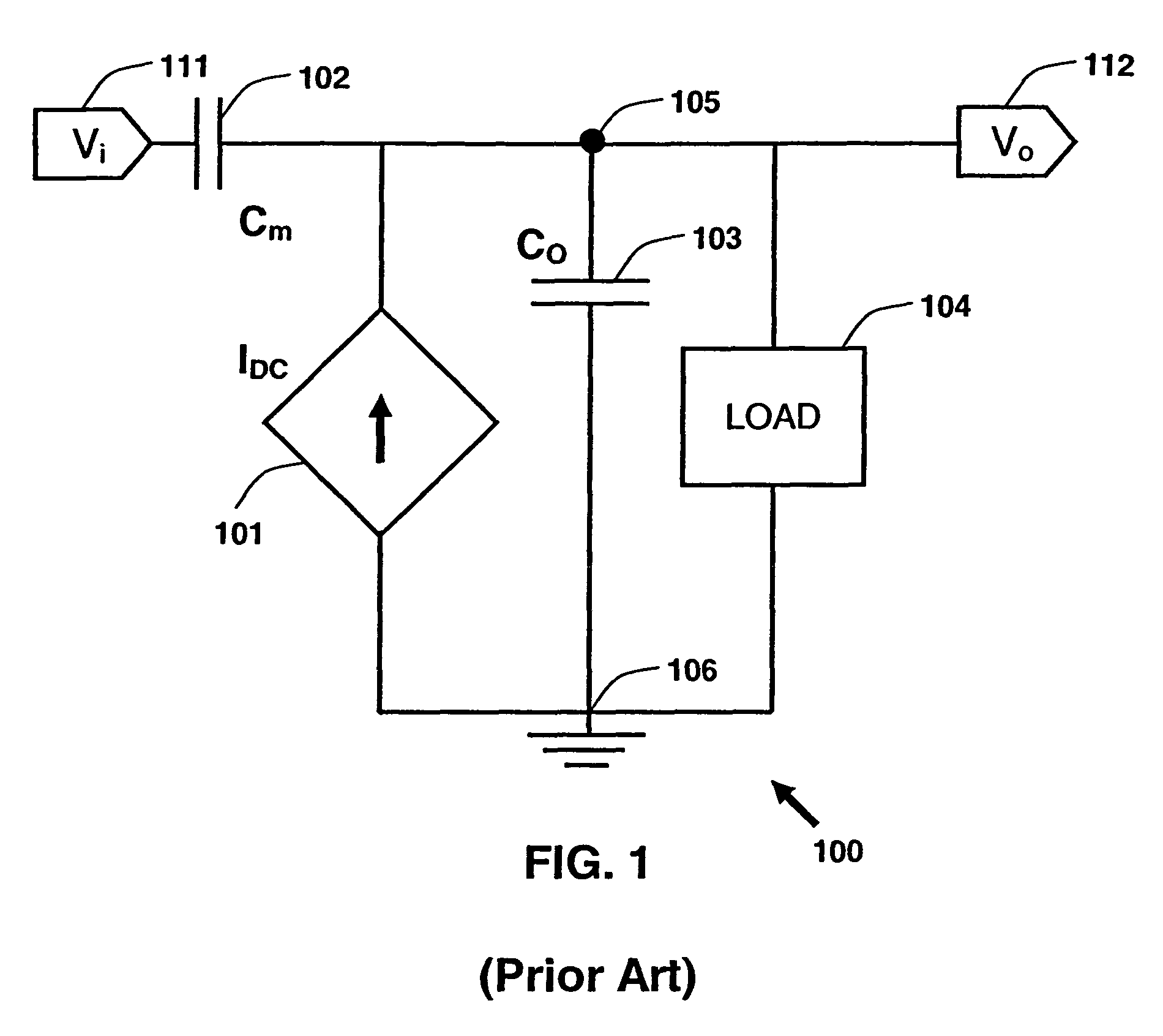
Transient current is an oscillatory or aperiodic current that flows in a circuit for a short time following an electromagnetic disturbance as a nearby stroke of lightning or switching.
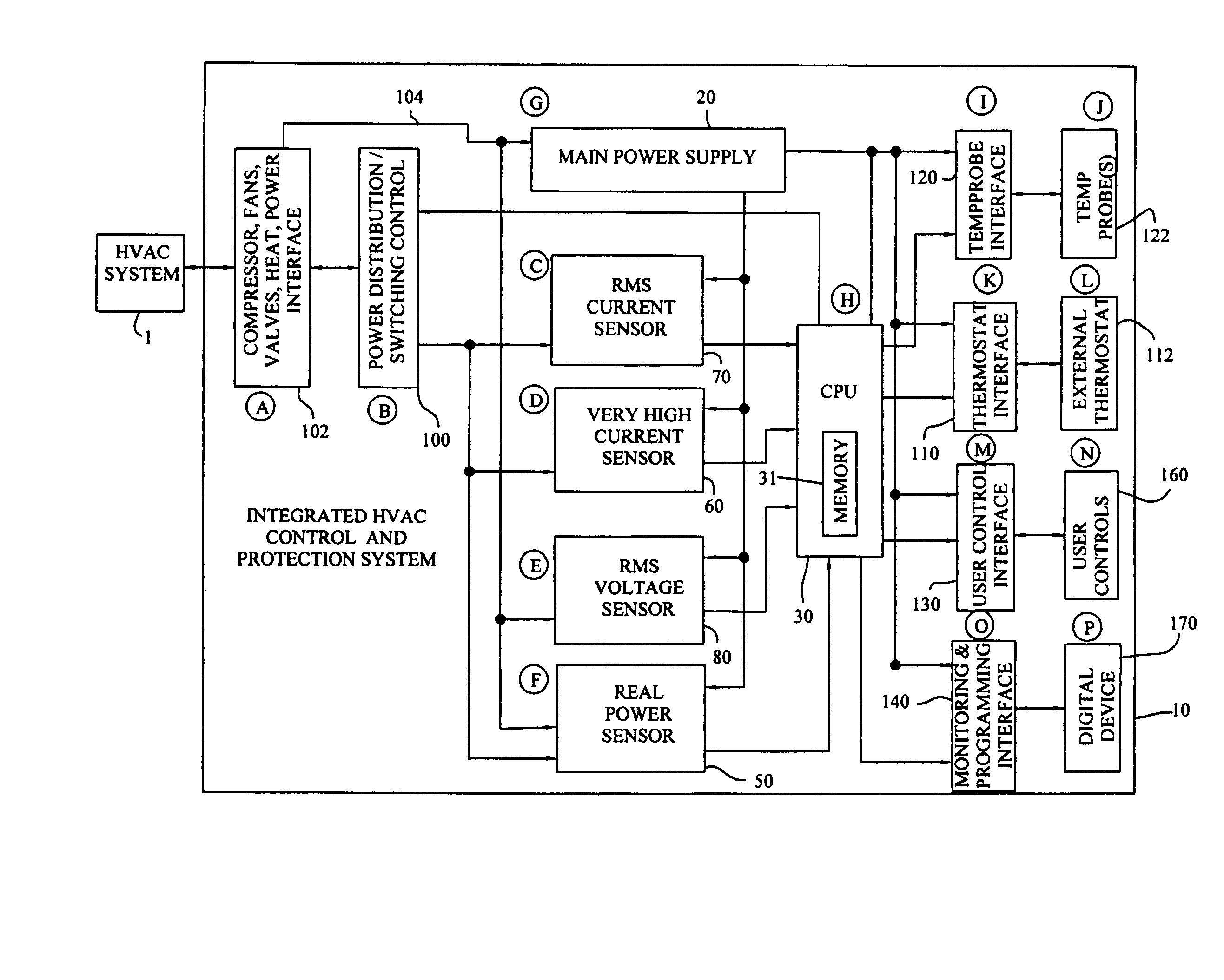
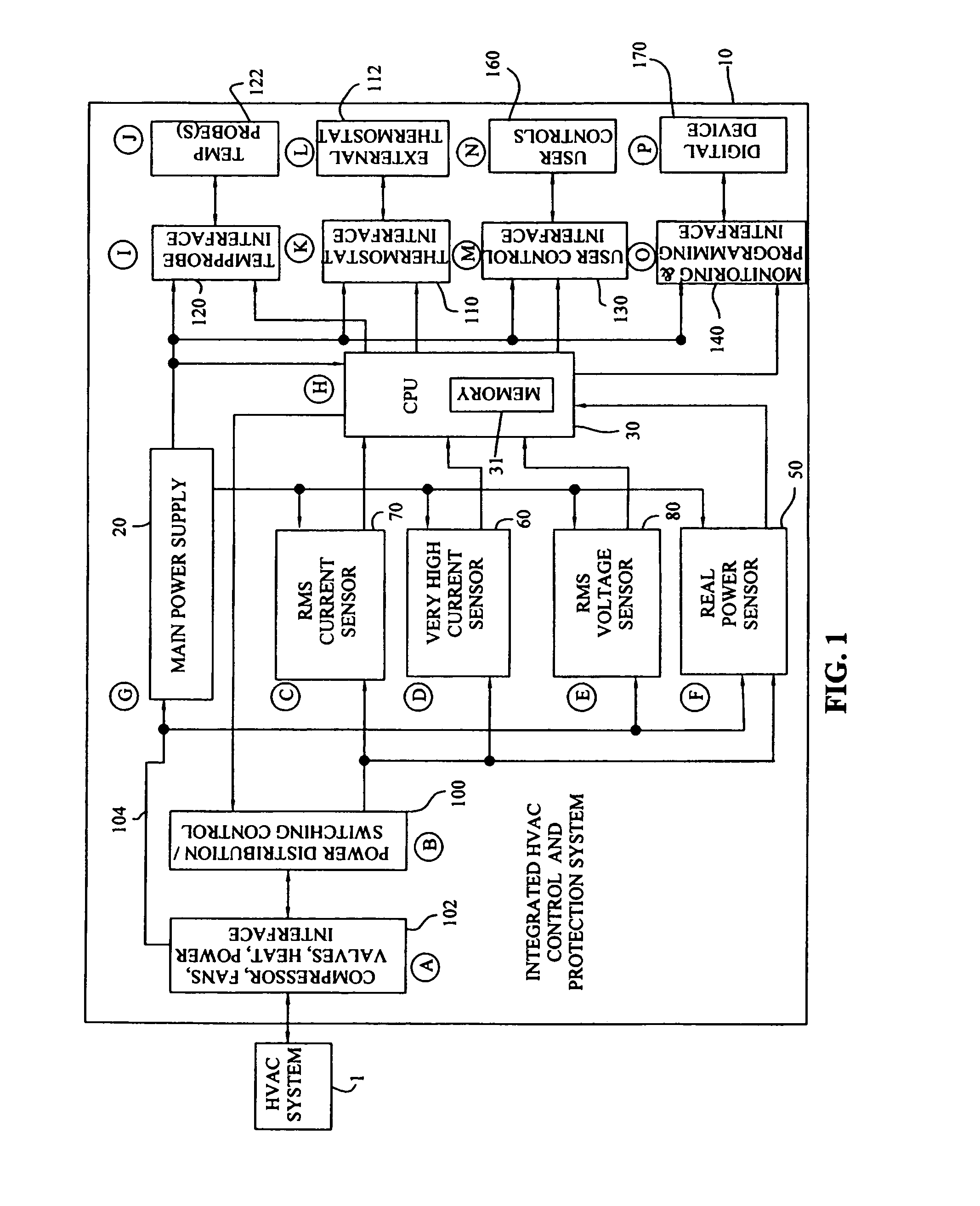
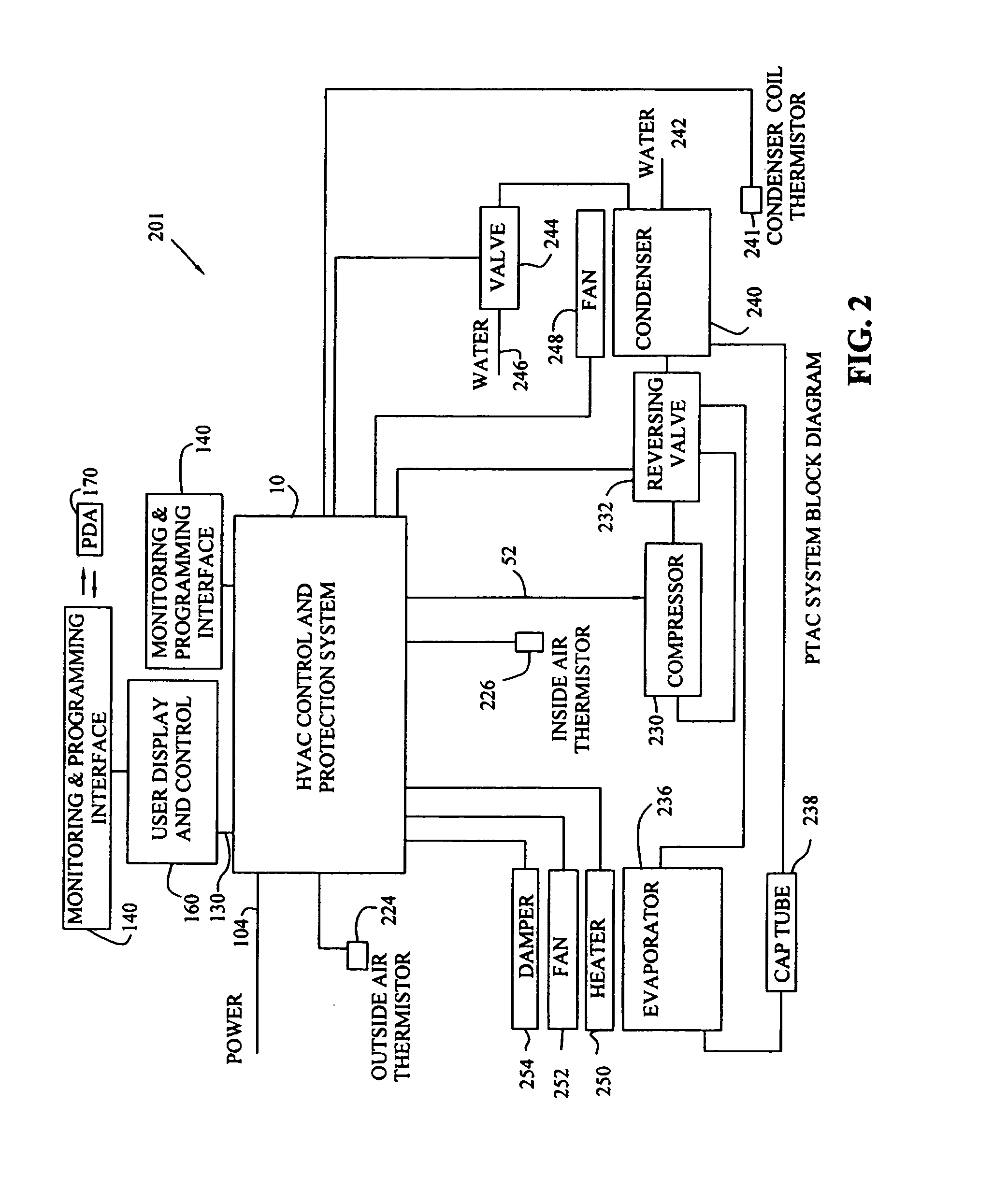
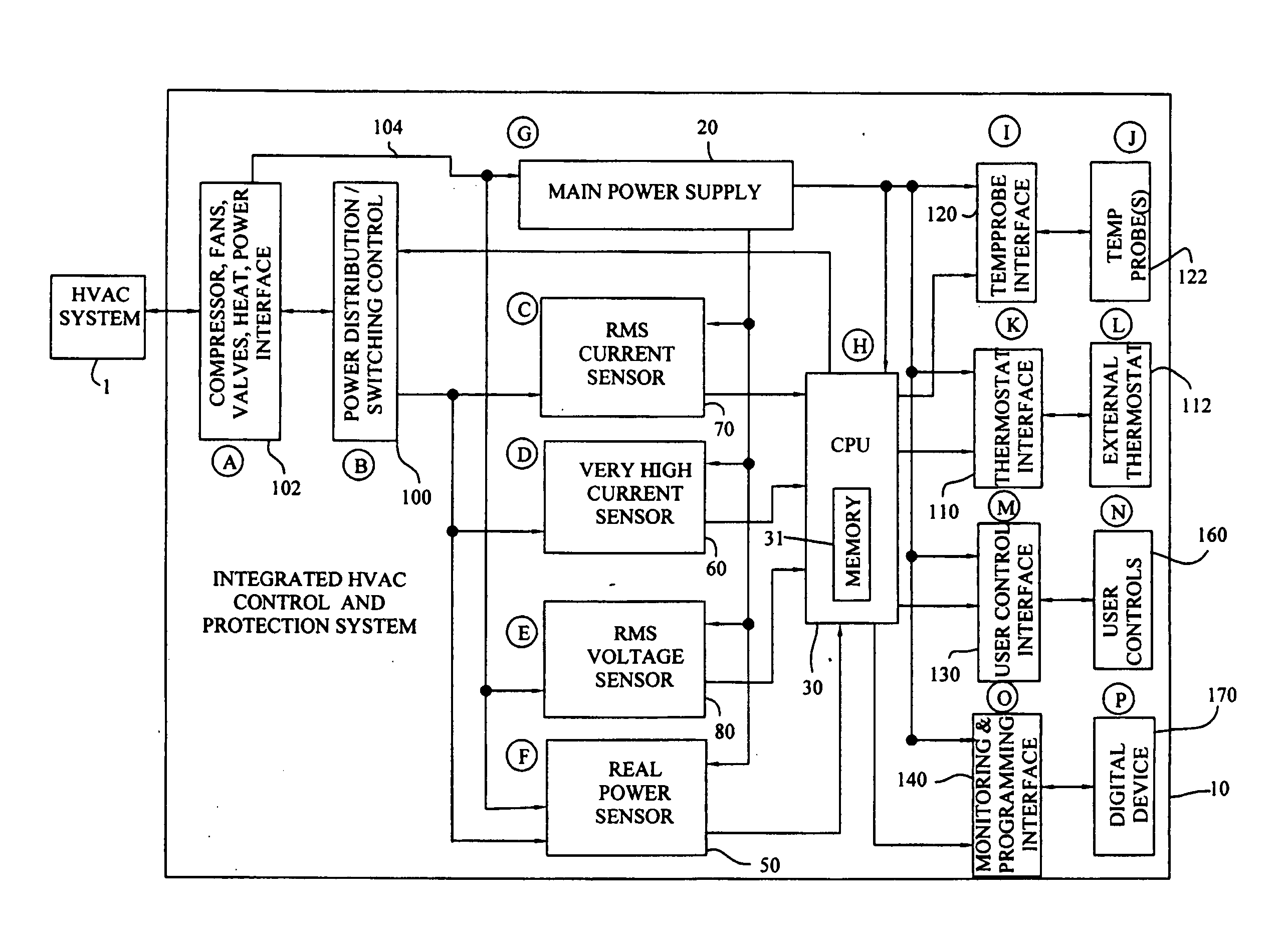
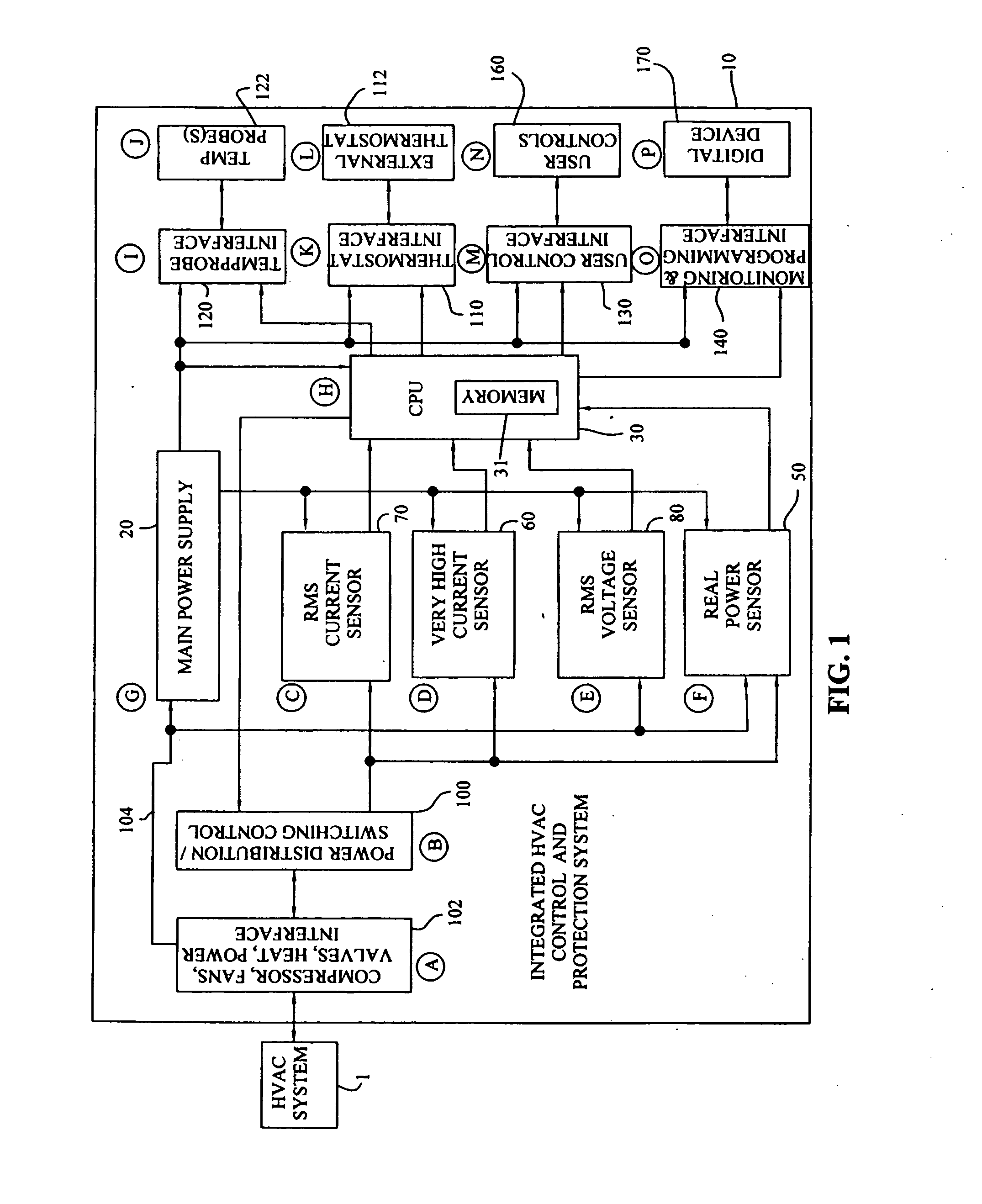
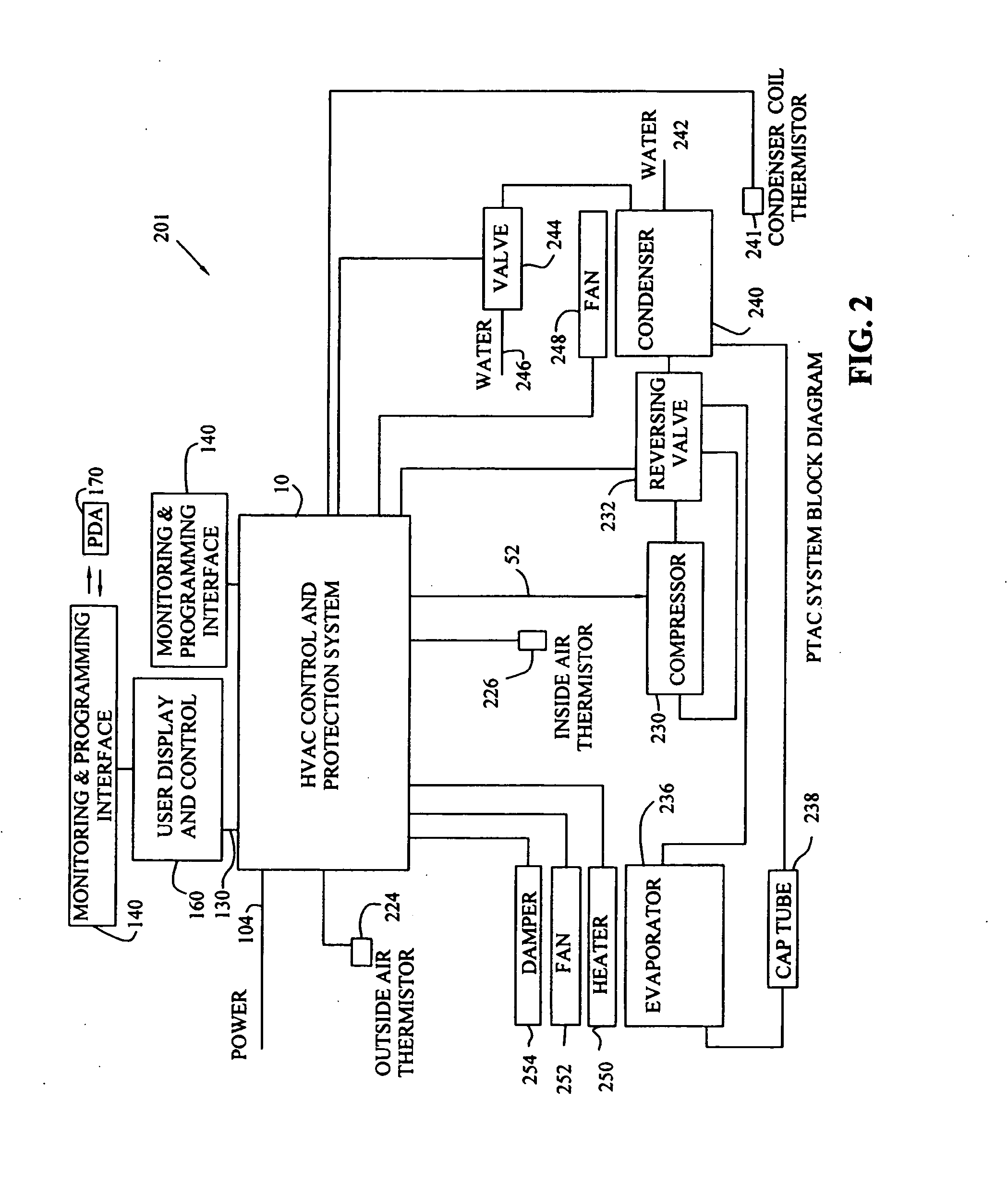
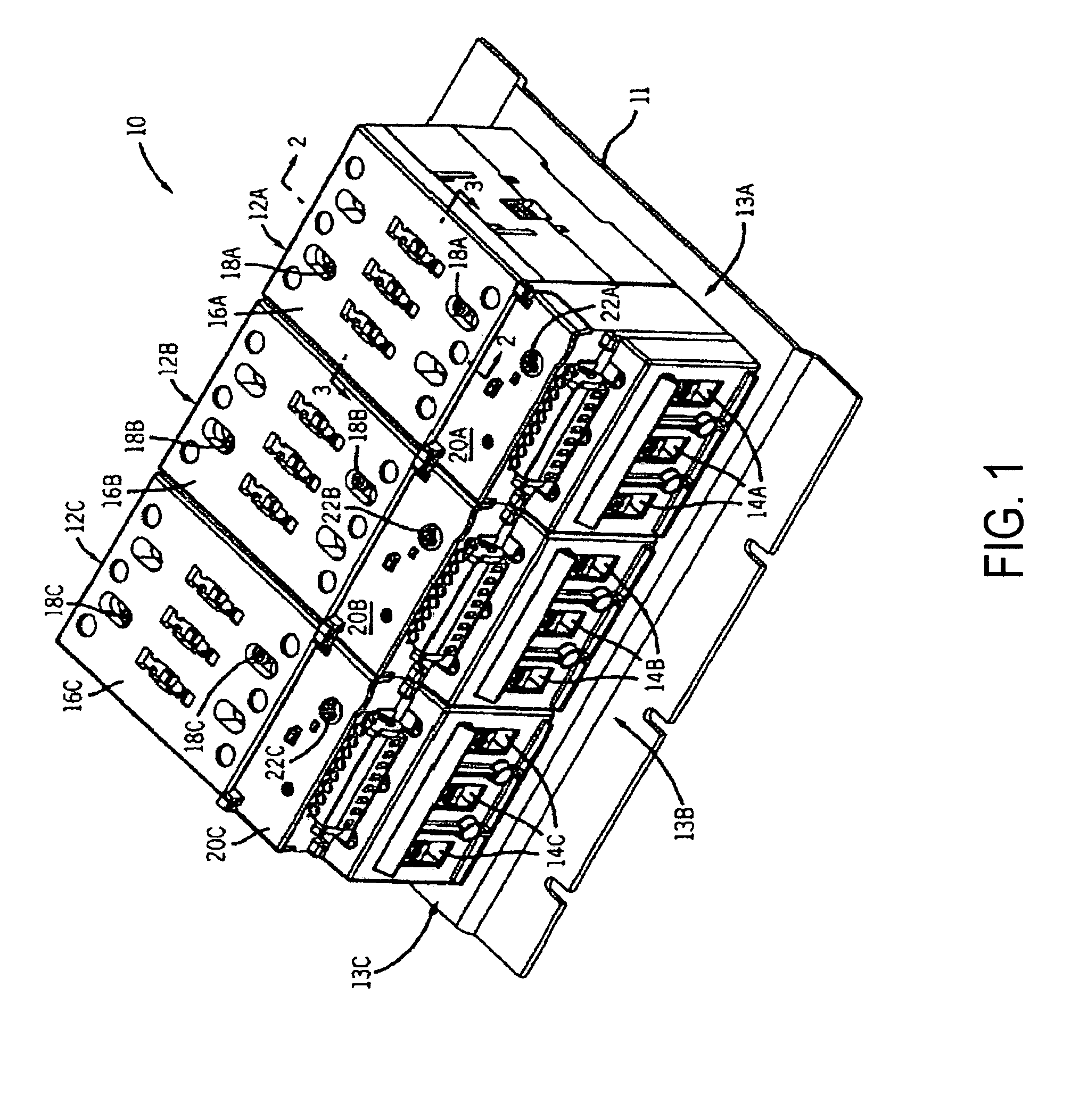
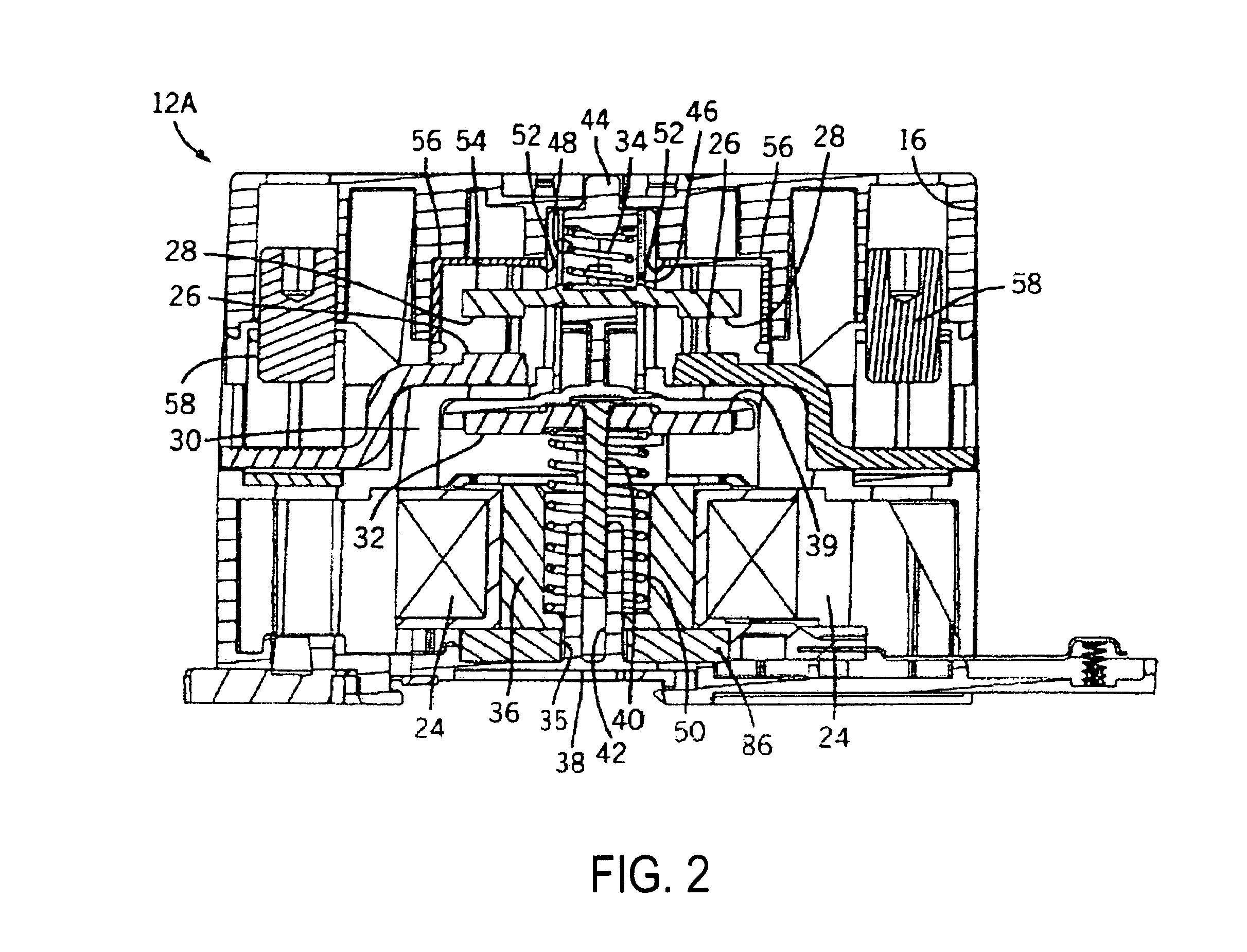
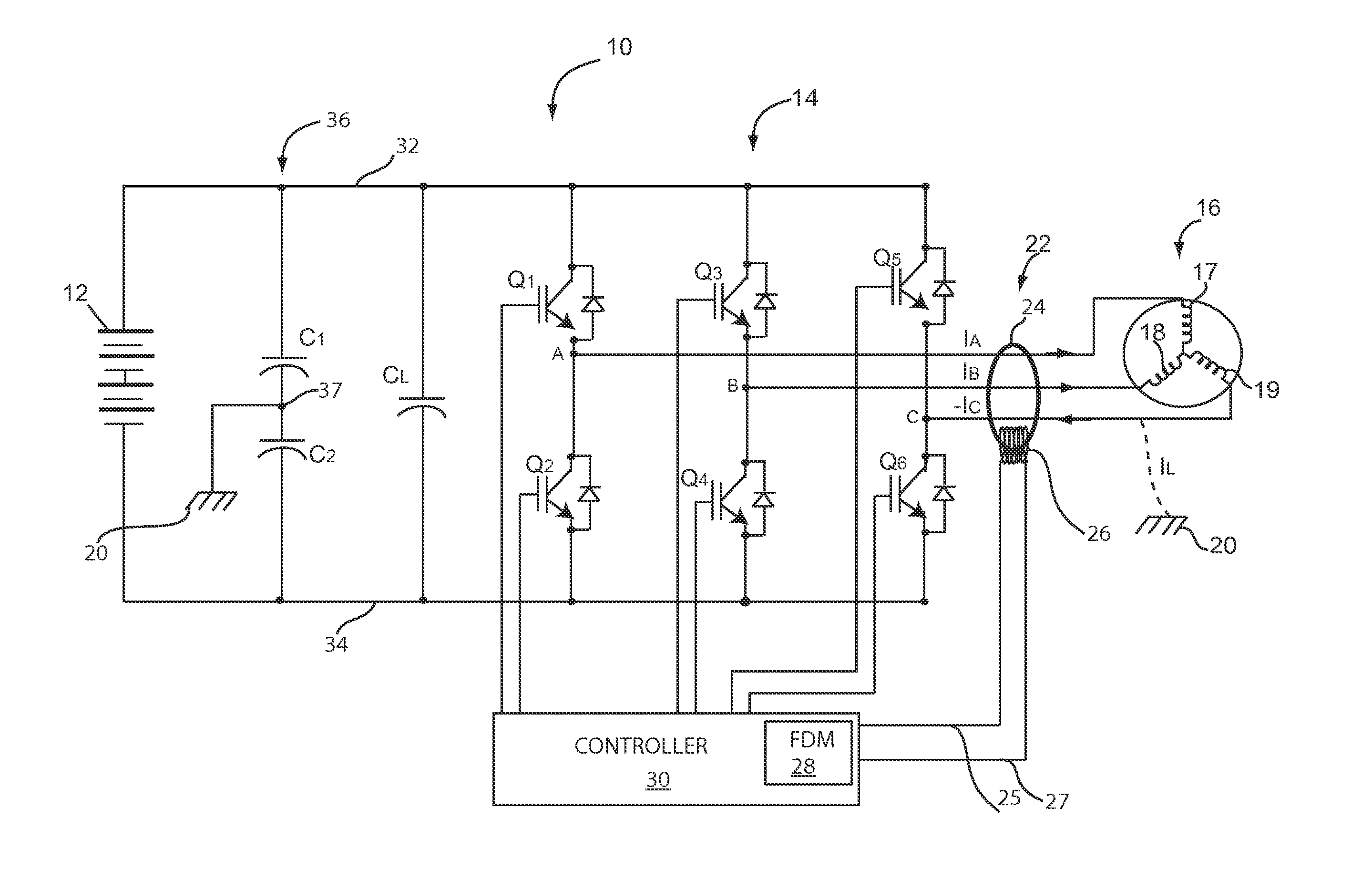
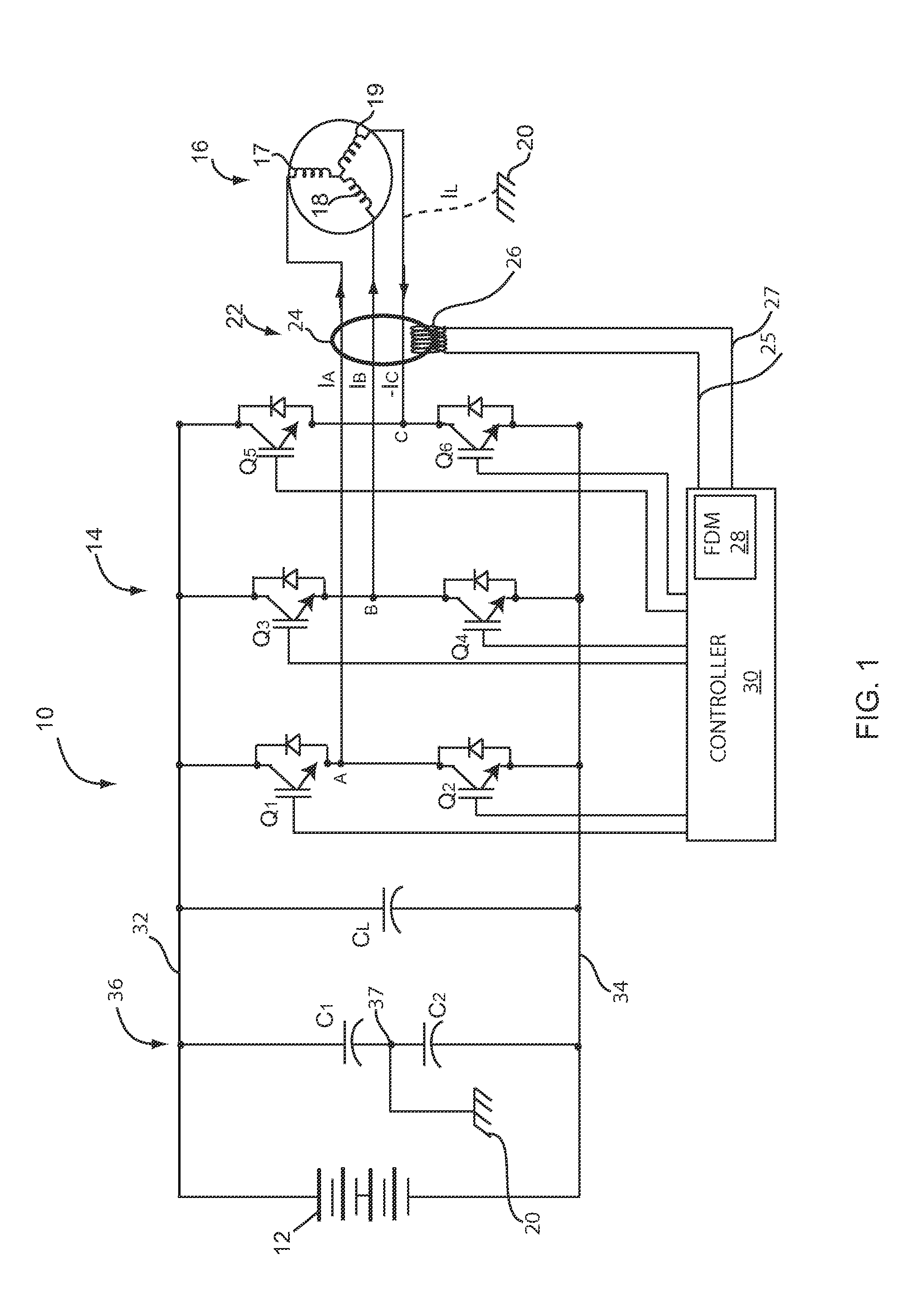
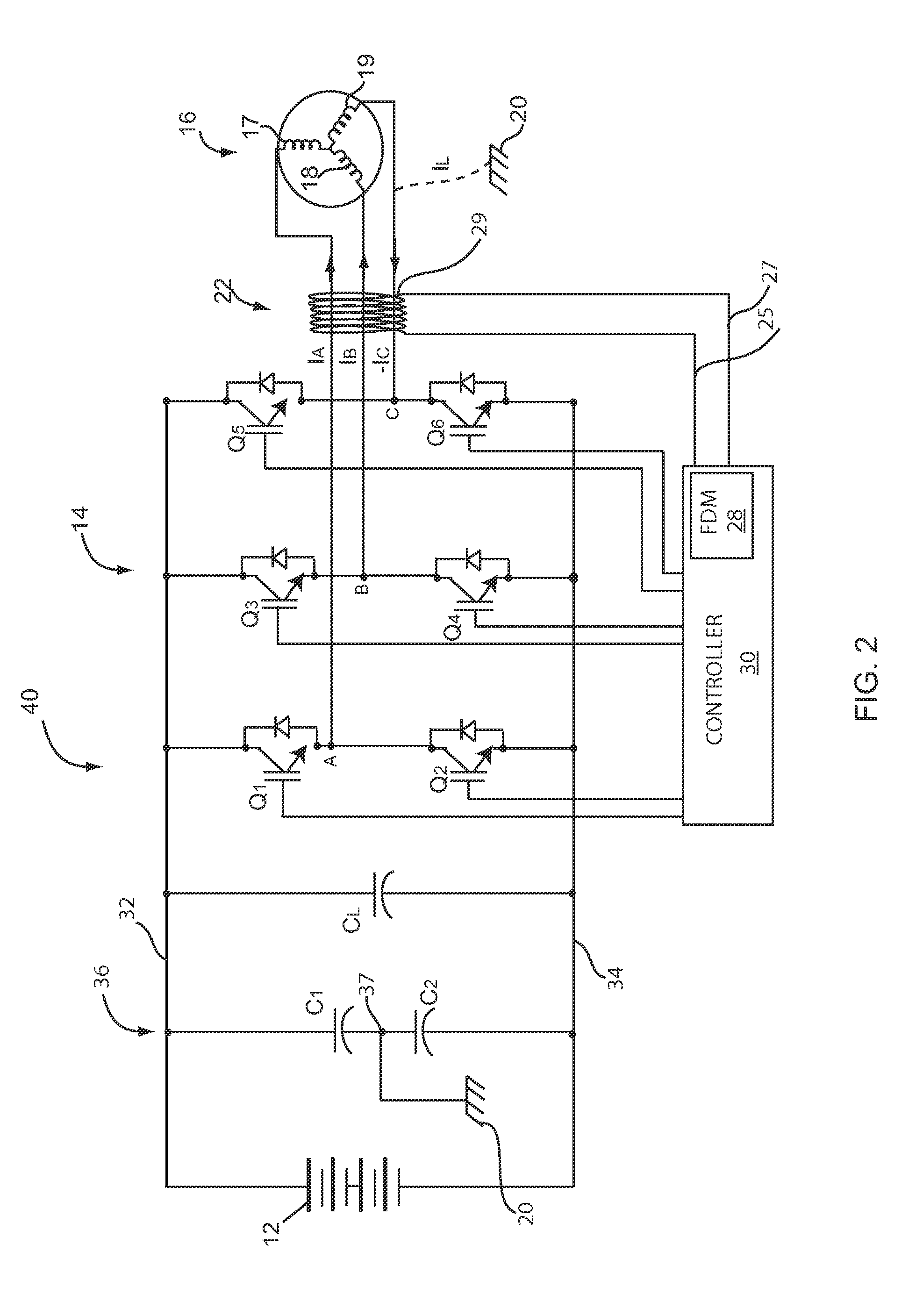
Integrated HVACR control and protection system
ActiveUS7089088B2Easy to reconfigureCost-effectiveProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsRemote controlControl system
An integrated HVACR control and protection system includes a modular and reprogrammable design providing a plurality of possible combinations of power detection, voltage detection, run current detection, transient current detection, temperature detection, universal thermostat interface, peripheral or remote control, and local display and control. The control and protection system is capable of evaluating the relationship between real power used by an HVACR system compressor and other system operating parameters to detect problems early in the failure cycle, i.e., before a failure has progressed to requiring a system shutdown or causing damage to other components. Additionally, a control system and method provide sensorless detection of various HVACR system faults, such as, for example, loss of refrigerant or a refrigerant flow restriction, that impact the relationship between real power and current, voltage, temperature, or other operating parameters. Peripheral or remote control includes wired or wireless system monitoring and parameter programming using a personal digital assistant (PDA), for example utilizing IR communication between the PDA and the control and protection system.
Owner:TECUMSEH PROD CO
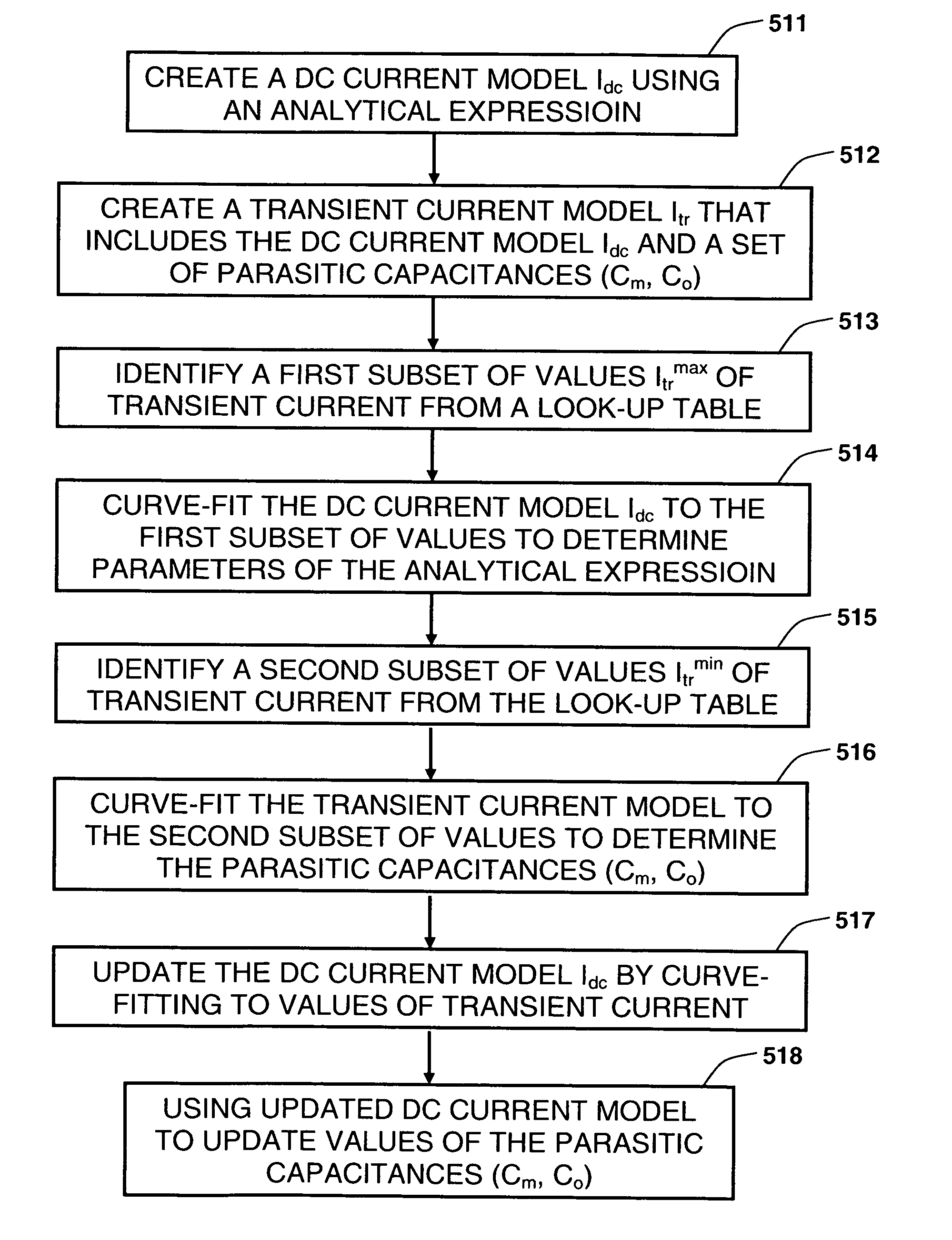
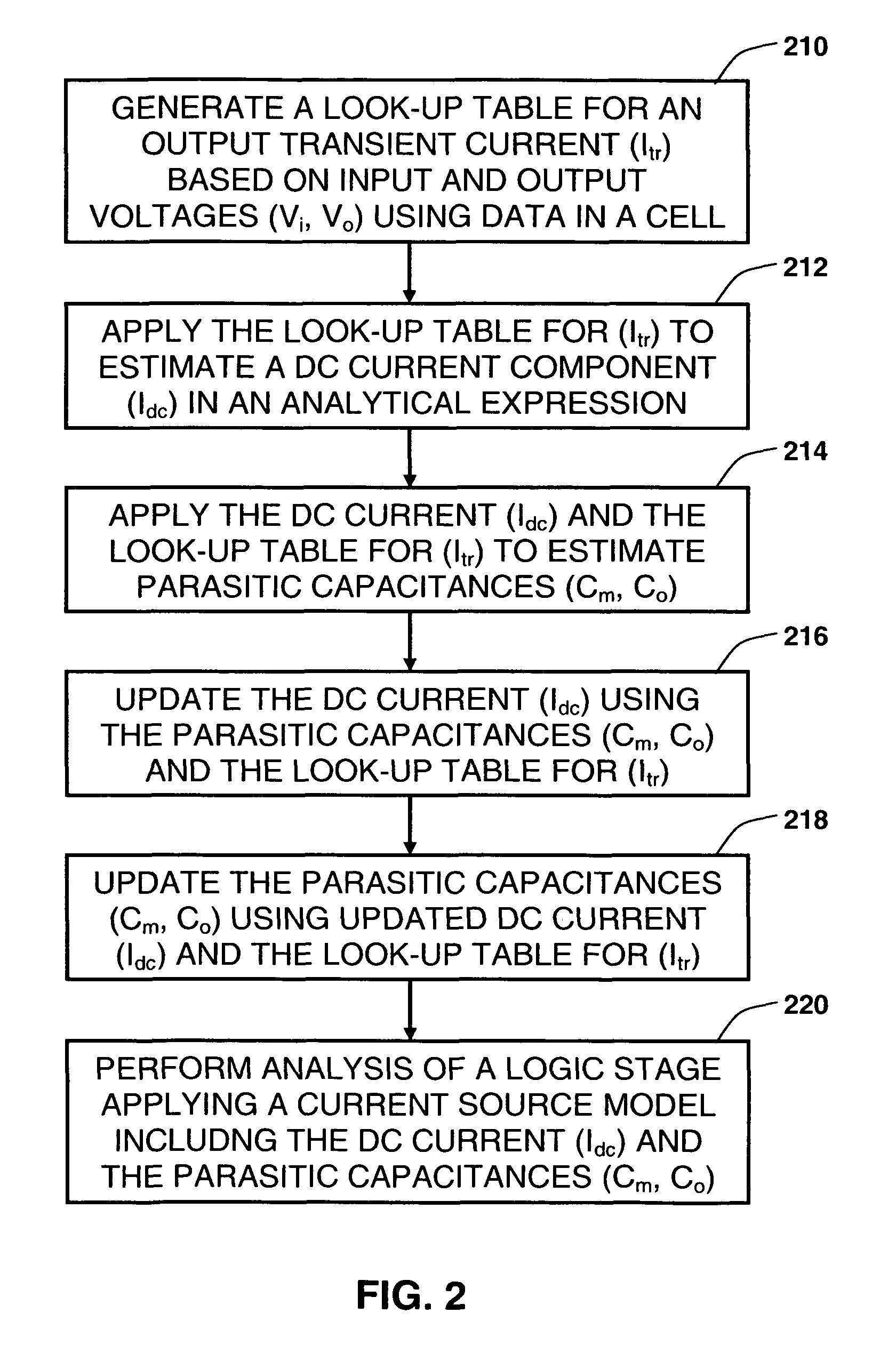
Synthesizing current source driver model for analysis of cell characteristics
InactiveUS7761275B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusCAD circuit designParasitic capacitanceEngineering
A method for performing an analysis of at least one logic stage in a netlist, which include one or more drivers, is provided. The method includes operations of generating at least one look-up table for an output transient current to be based on values of input and output voltages using data available from a cell library; synthesizing analytically at least one current source model, which includes a DC component and a plurality of parasitic capacitances, using the look-up table; simulating the logic stage using the current source model to model the drivers; and obtaining characteristics of the simulated logic stage. A system and a machine-readable medium for performing the method are also provided.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Step-up DC/DC voltage converter with improved transient current capability
InactiveUS20090102439A1High currentEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage regulation
A DC / DC voltage converter includes an inductive switching voltage regulator and a capacitive charge pump connected in series between the input and output terminals of the converter. The charge pump has a second input terminal connected to the input terminal of the converter. This reduces the series resistance in the current path by which charge is transferred from the capacitor in the charge pump to the output capacitor and thereby improves the ability of the converter to respond to rapid changes in current required by the load.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Charge perturbation detection system for DNA and other molecules
ActiveUS7785785B2Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapacitanceChemical reaction
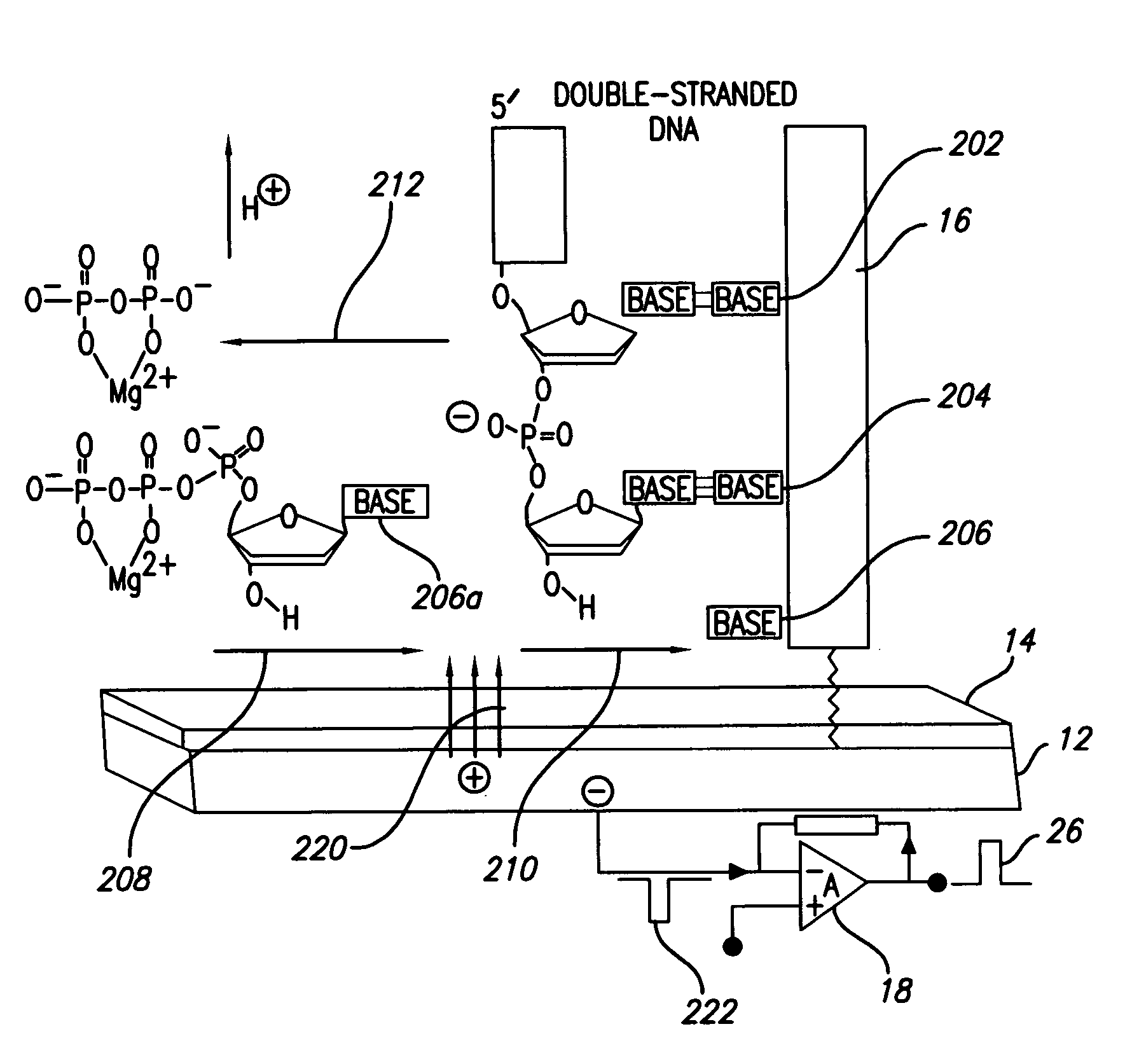
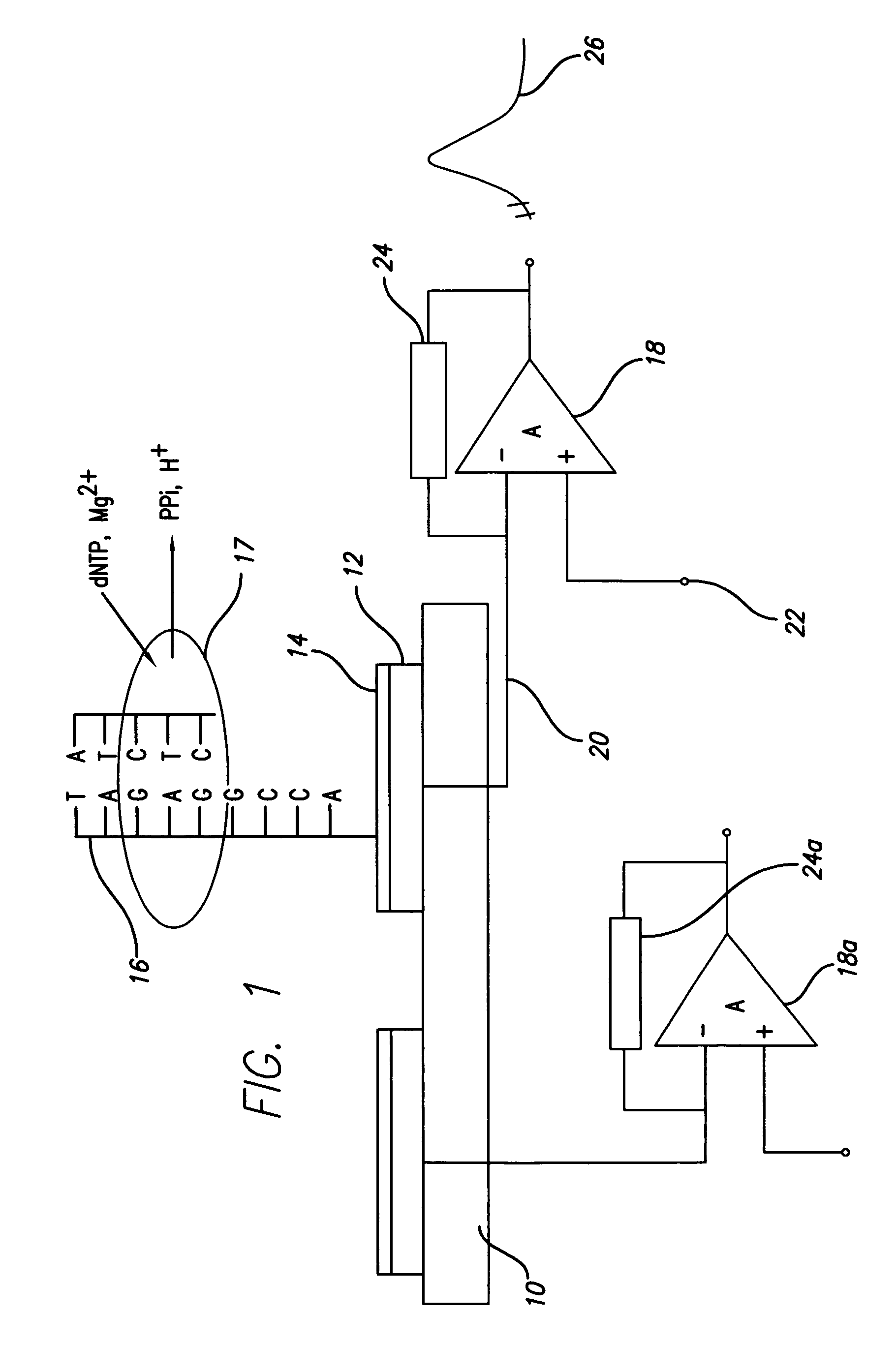
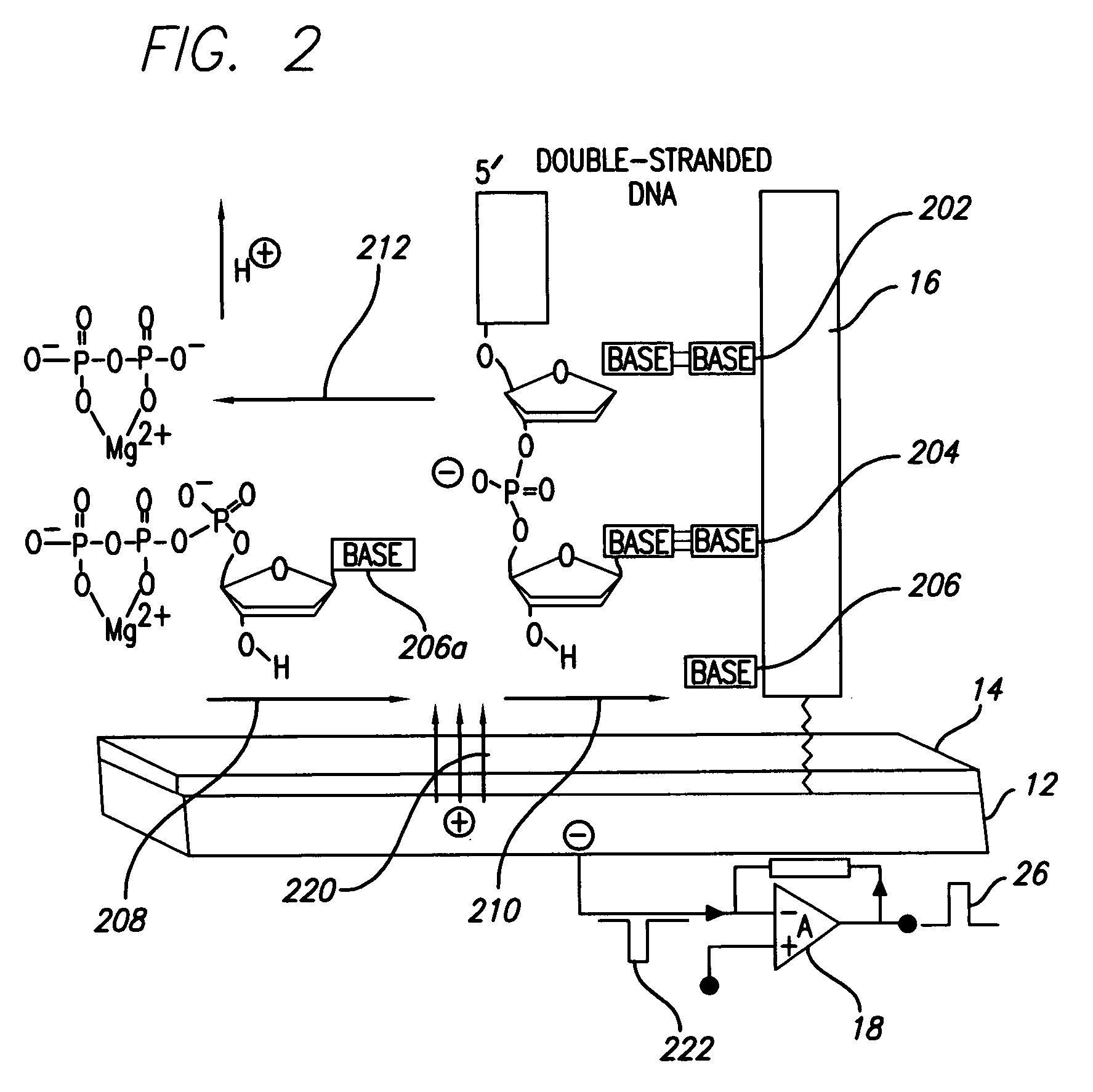
Methods and apparatus for direct detection of chemical reactions are provided. In a preferred embodiment, electric charge perturbations of the local environment during enzyme-catalyzed reactions are sensed by an electrode system with an immobilized target molecule. The target molecule is preferably DNA. The charge perturbation caused by the polymerase reaction can uniquely identify a DNA sequence. The polymerization process generates local perturbations of charge in the solution near the electrode surface and induces a charge in a polarazible gold electrode. This event is detected as a transient current by a voltage clamp amplifier. Detection of single nucleotides in a sequence can be determined by dispensing individual dNTPs to the electrode solution and detecting the charge perturbations. Alternatively, multiple bases can be determined at the same time using a mix of all dNTPs with subsequent analysis of the resulting signal. The initial enzyme attachment to the DNA molecule can be detected prior to polymerization, with electrode capacitance measurement using the same voltage-clamp amplifier. This technique and device may be adapted to other reaction determinations, such as enzymatic reactions, other electrode configurations, and other amplifying circuits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
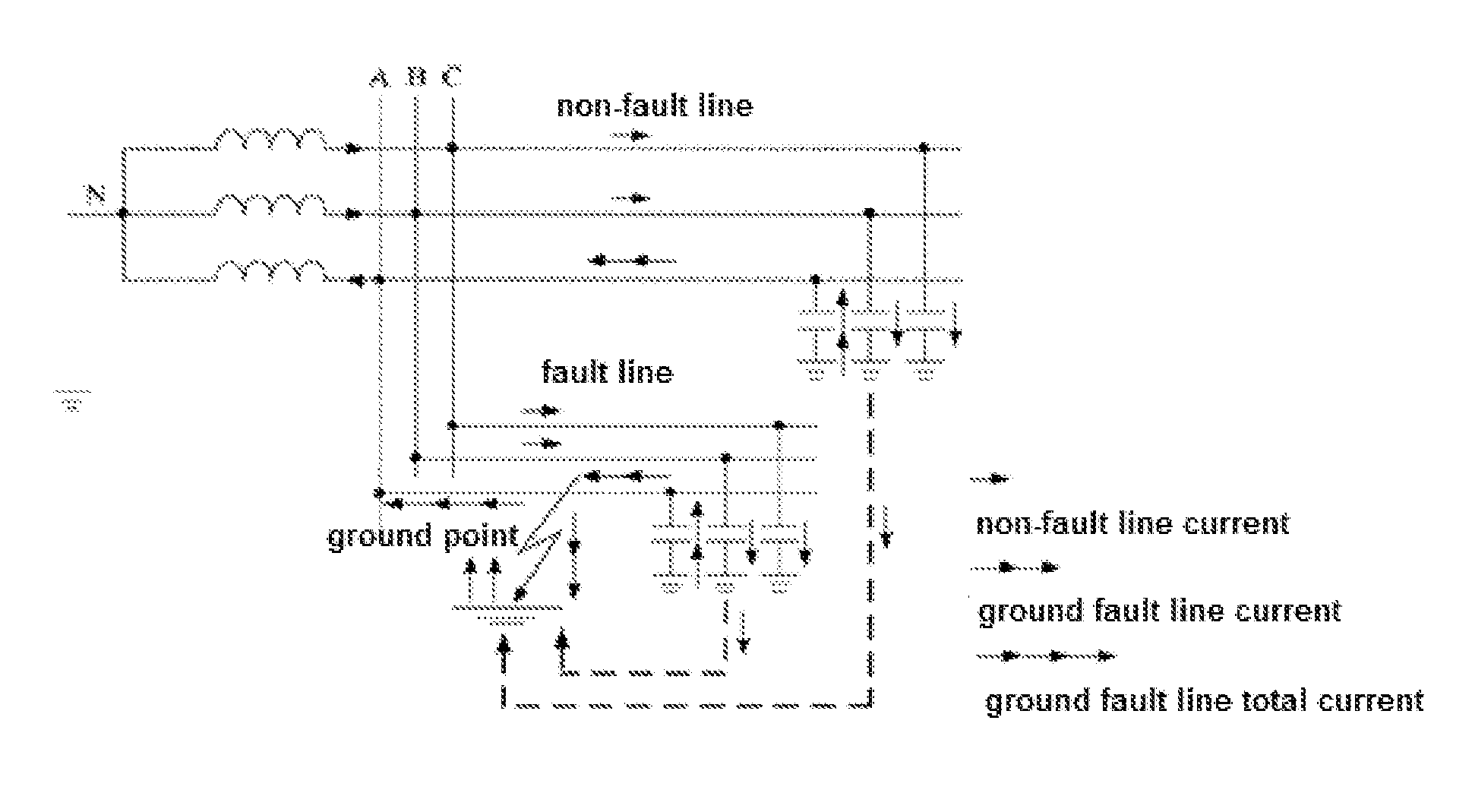
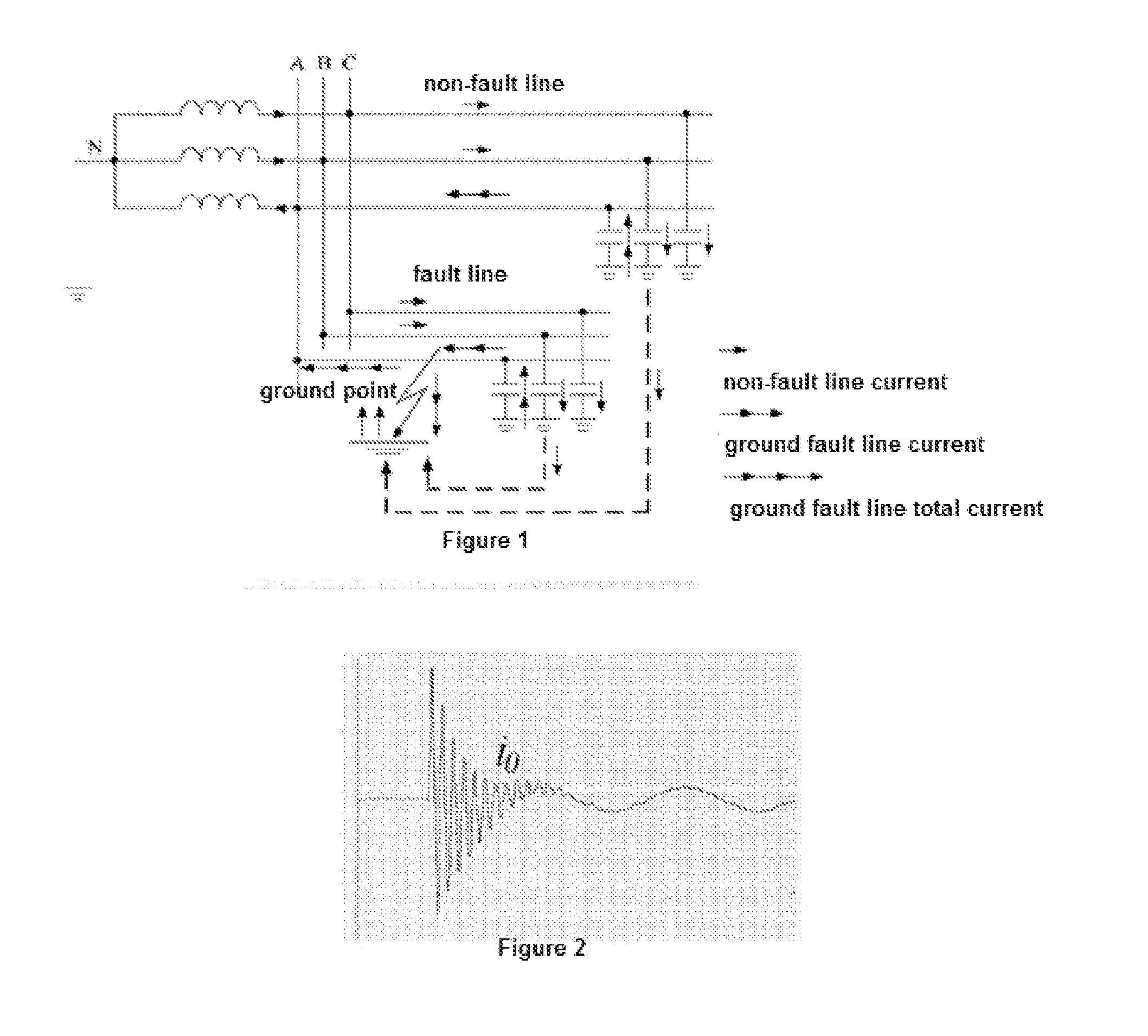
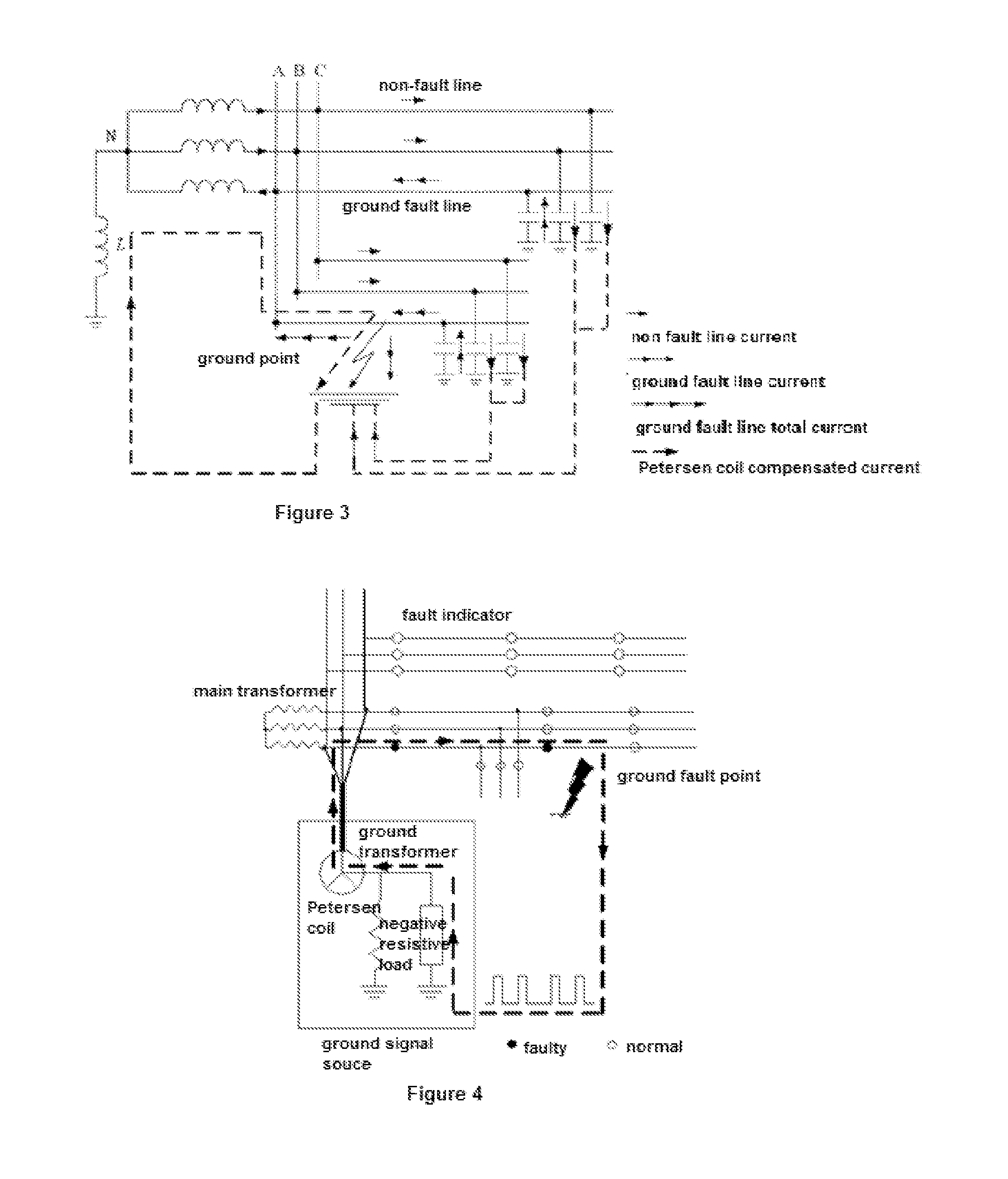
Method and system for detecting and locating single-phase ground fault on low current grounded power-distribution network
ActiveUS20160041216A1Accurate locationFault location by conductor typesShort-circuit testingThree-phaseElectric distribution network
A method and system for detecting and locating a single-phase ground fault on a low current grounded power-distribution network, comprising: respectively testing and picking up the voltage signals and current signals at multiple positions on each phase feeder (61), and determining the corresponding transient voltage signals and transient current signals according to the extraction of the voltage signals and the current signals (62); when the change in the transient voltage signals and the transient current signals exceeds a preset threshold (63), synchronously picking up the voltage signals and current signals at multiple positions on a three-phase feeder (64); calculating corresponding zero-sequence voltages and zero-sequence currents according to the voltage signals and current signals synchronously picked up at multiple positions on the three-phase feeder (65), and then extracting the steady-state signal and transient signal of the zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current at each position on the three-phase feeder (66); and determining a specific fault location on a faulty line according to the steady-state signal and the transient signal (67). The method effectively detects and displays a single-phase ground fault on a low current grounded power-distribution network.
Owner:BEIJING INHAND NETWORKS TECH
Integrated HVACR control and protection system
ActiveUS20050240312A1Protection from damageProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsControl systemRemote control
Owner:TECUMSEH PROD CO
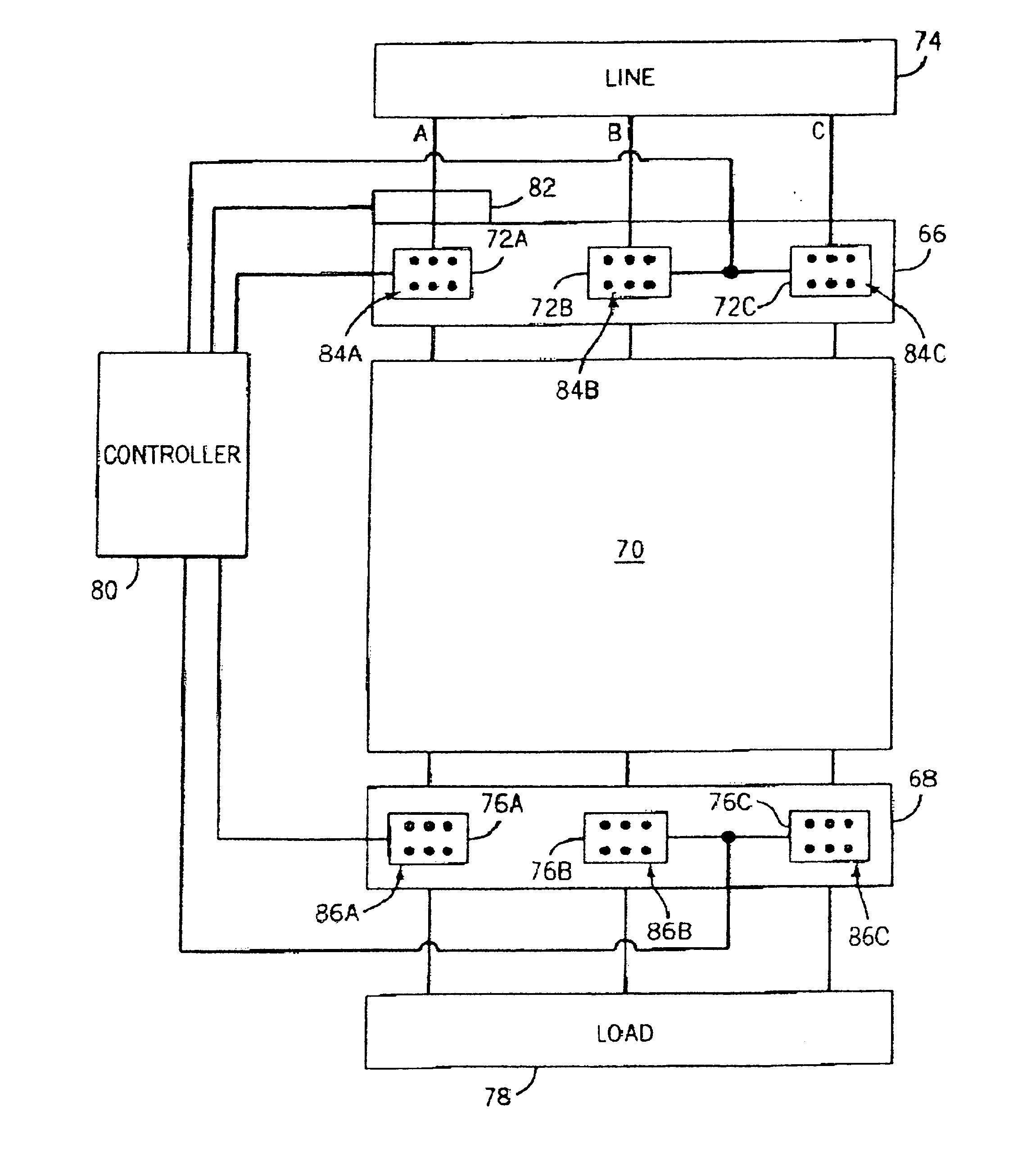
Method and system of controlling asynchronous contactors for a multi-phase electric load
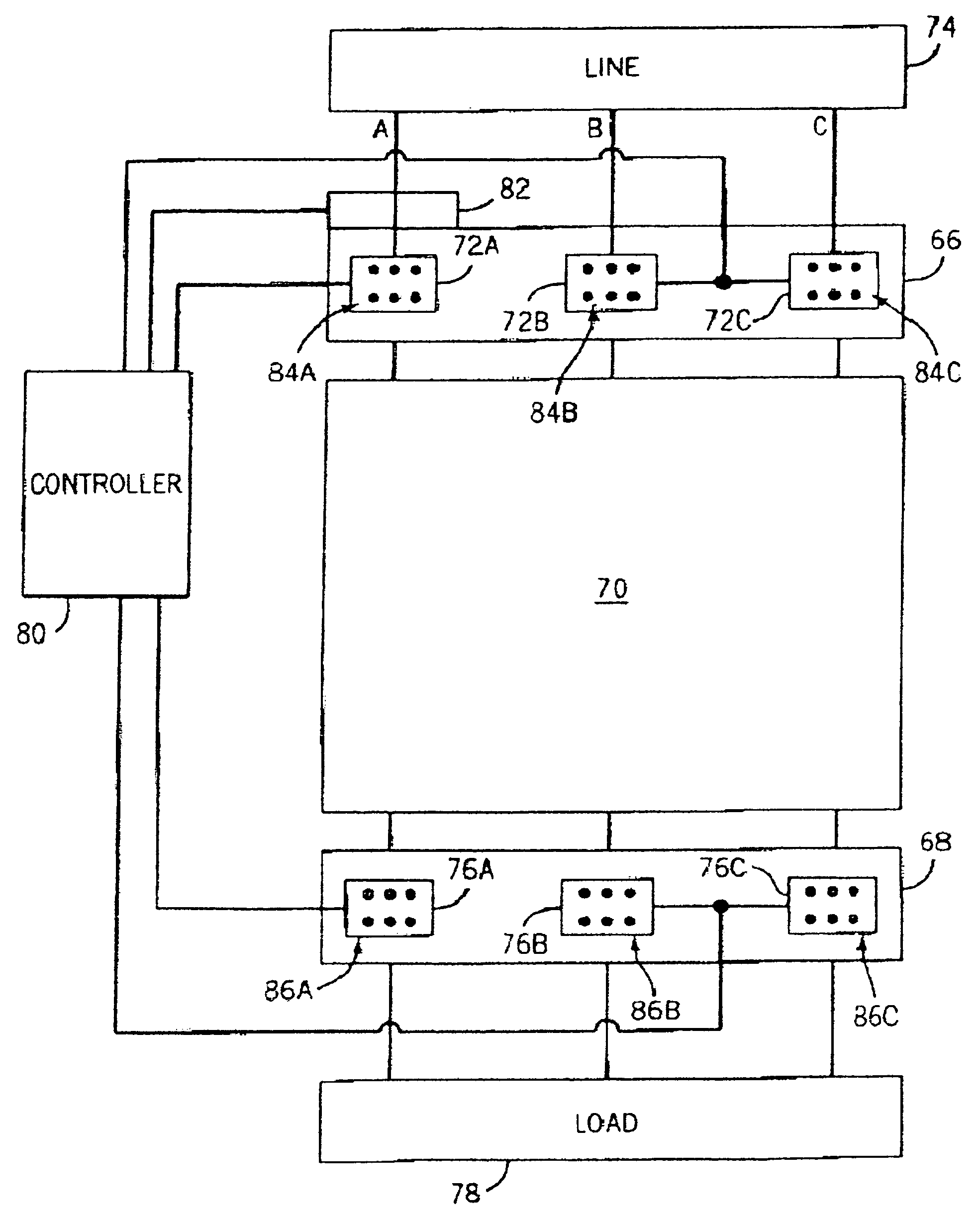
ActiveUS20050013085A1Reduce mechanical stressDamaging mechanical stresses placed on the induction motor can be reducedAC motor controlElectric switchesInduction motorModularity
Control of an induction motor is carried out to limit damaging arcing stress and mechanical stresses placed on the control contactor assembly and the induction motor resulting from the simultaneous or synchronous breaking and making of contactors employed to connect the windings of the motor to a power supply. Asynchronously connecting the windings to the power supply via the asynchronous or non-simultaneous closing of the contactors of a modular contactor assembly reduces the potentially damaging transient current, the associated torque oscillations, and mechanical stresses. The present invention is particularly applicable to delta motors that are started with its windings in a star or wye configuration followed by the reconnection of the windings in a delta configuration when the motor is at normal running speed.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Power control system for reducing power to lighting systems
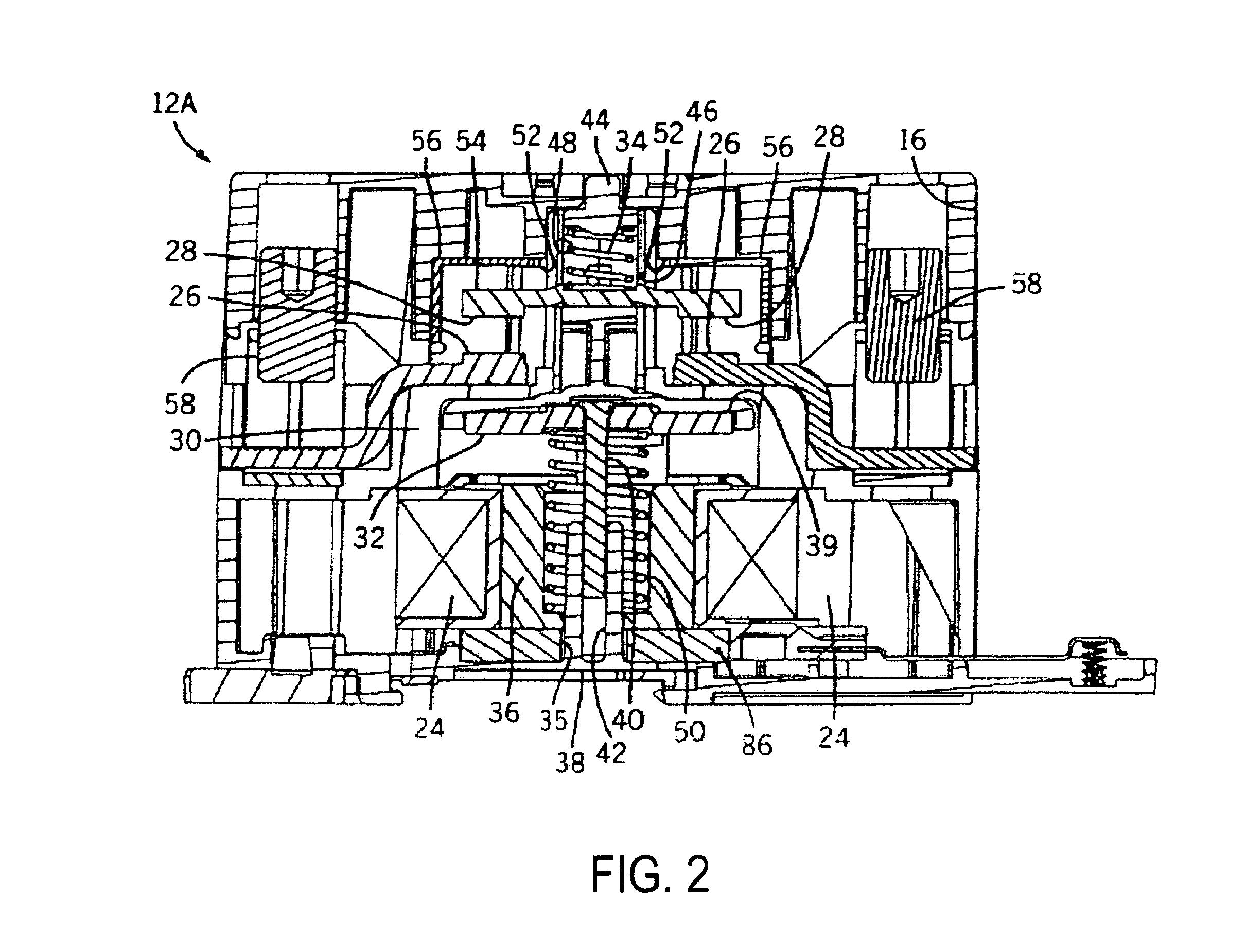
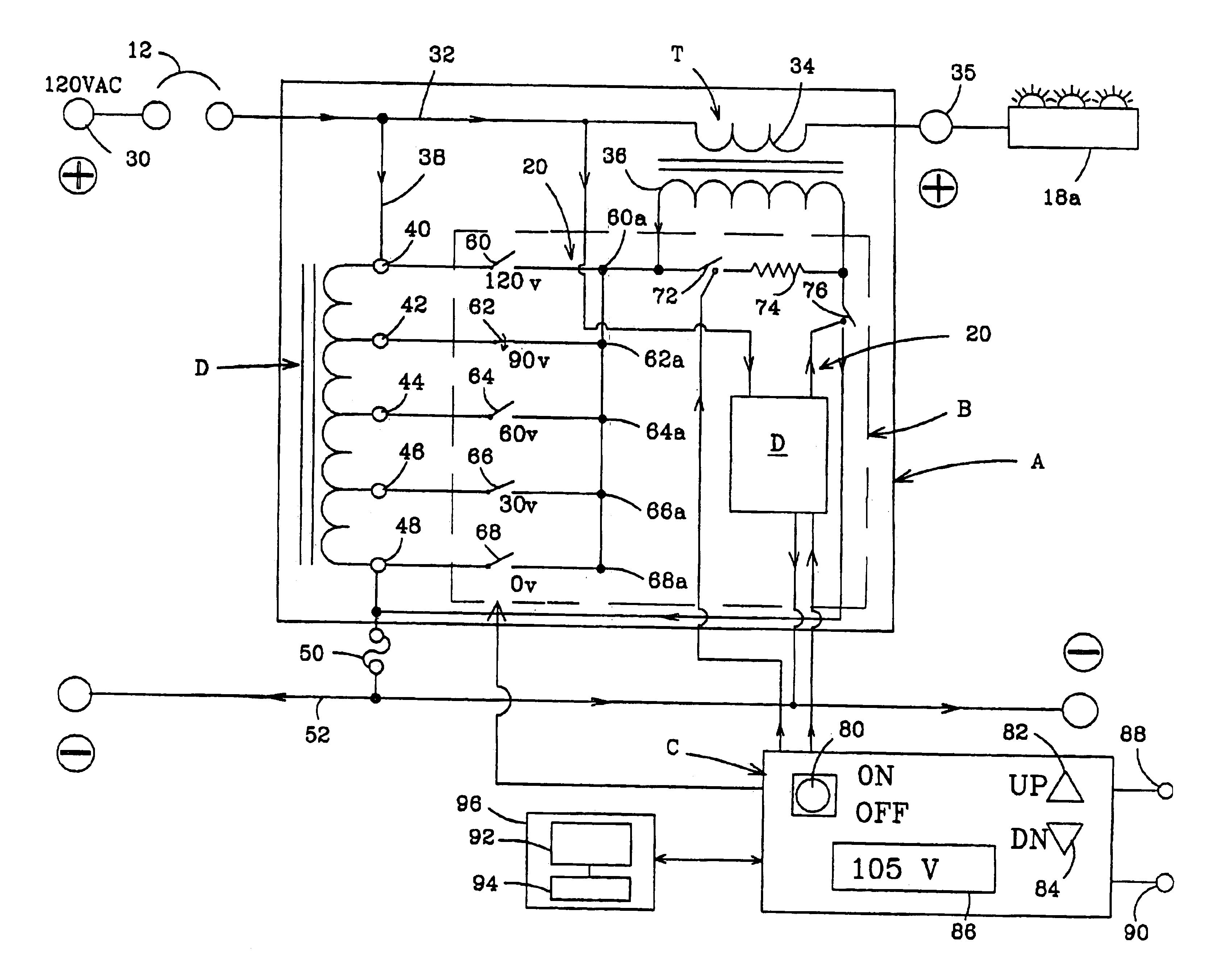
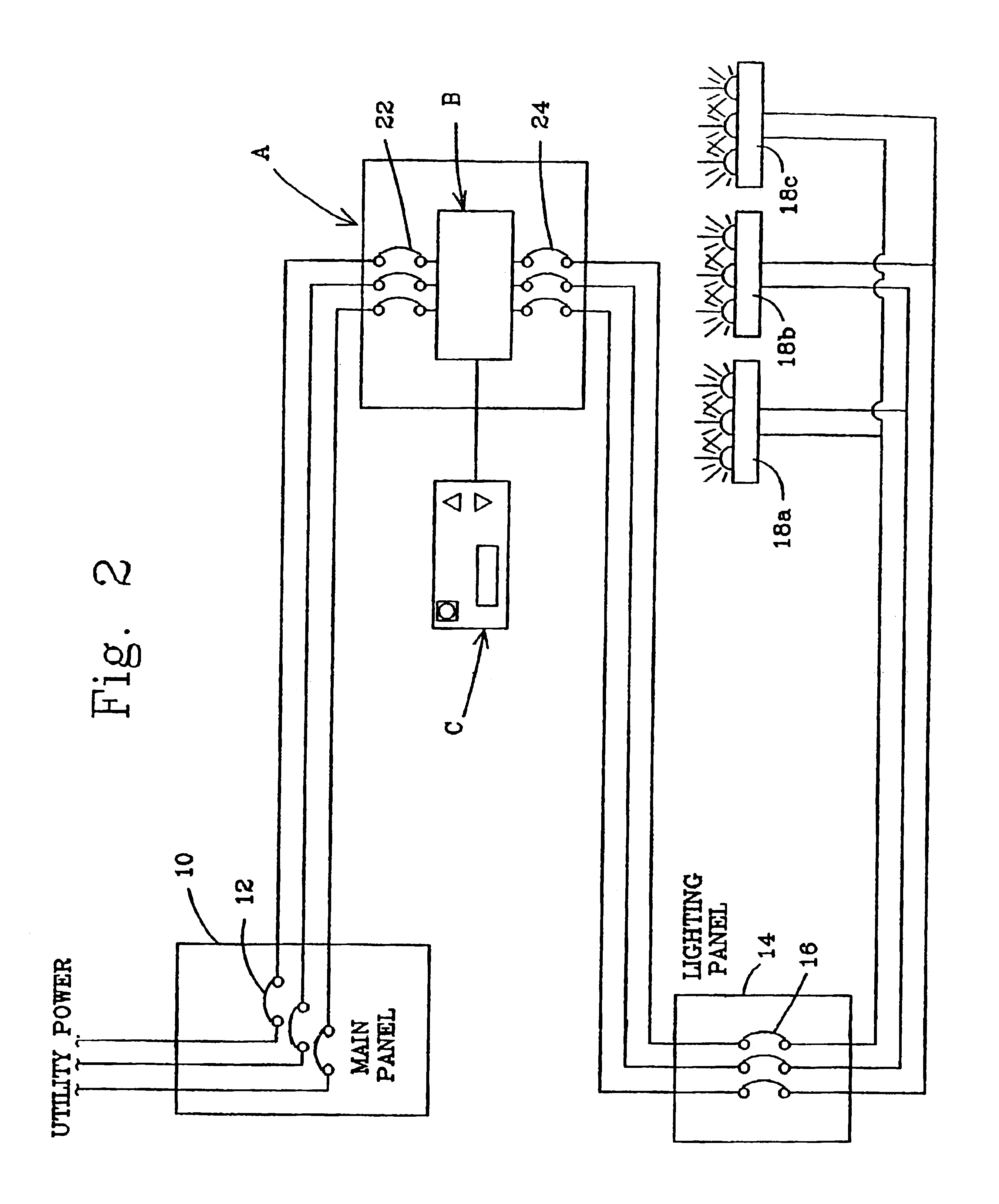
InactiveUS6906476B1Limited supplyLimited powerAc-dc conversion without reversalElectric light circuit arrangementPower control systemTransformer
A power control system is disclosed for controlling the power supplied to a lighting system and limiting power during time of peak demands and the like wherein the lighting system includes a power source and a lighting load connected to the power source. The control system comprises a main transformer having a first winding and a second winding, the first winding being connected between the power source and the lighting load. An autotransformer connected to the power source having a plurality of electrical transformer taps with prescribed voltage values. A plurality of solid-state tap switches is connected to the transformer taps and to the second winding of the main transformer to apply the prescribed voltage values across the second winding. A system controller has an input for receiving a voltage change signal representing a selected load voltage to be applied to the lighting load. The controller is connected to the tap switches for selectively closing one of the tap switches to produce said prescribed voltage value across the second winding of the main transformer whereby the selected load voltage is output across the first winding of the main transformer and applied to the lighting load without interruption of the lighting. A transient control circuit is connected across an output of the tap switches for dissipating transient currents during switching of tap switches.
Owner:ASP CORP
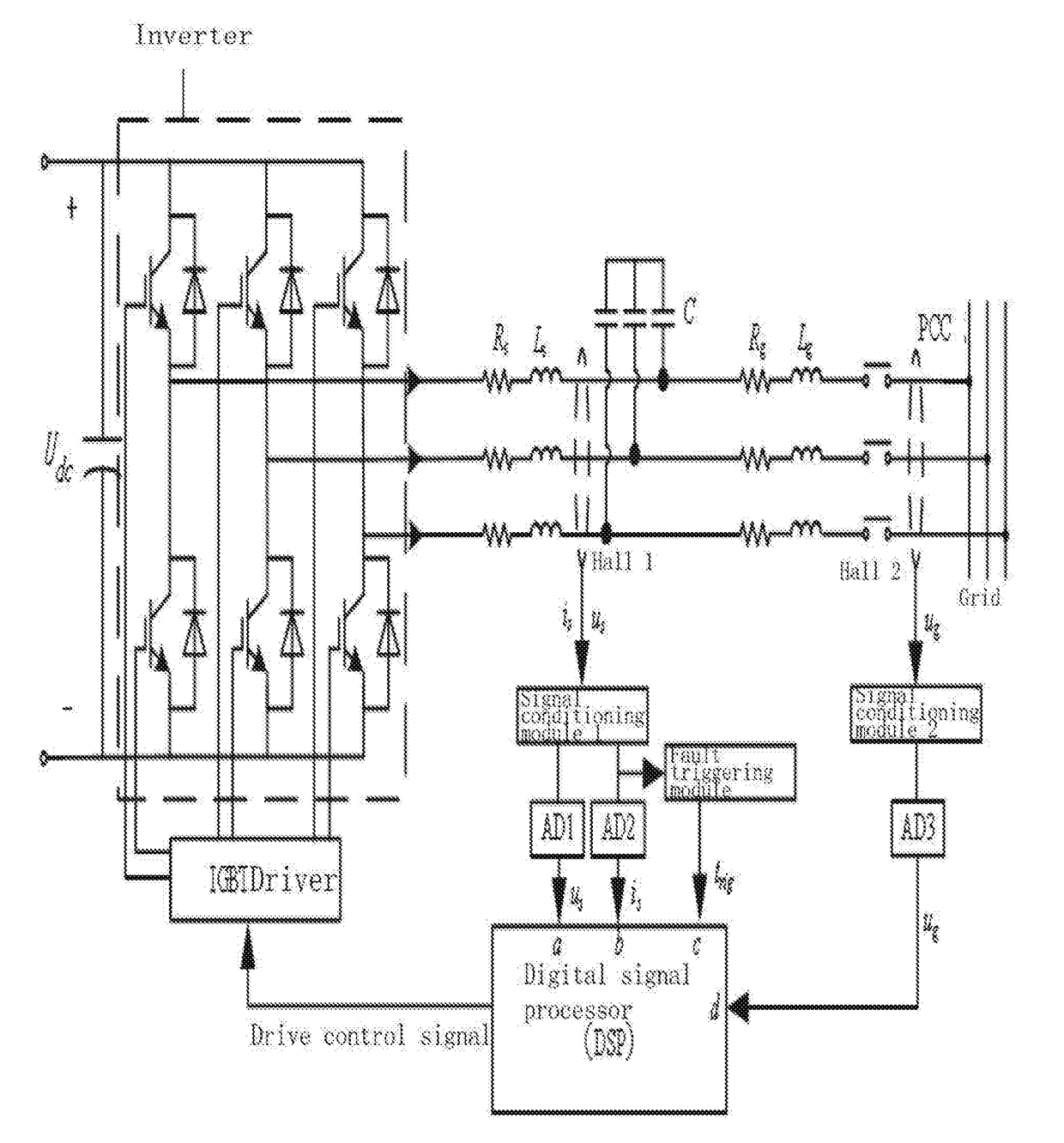
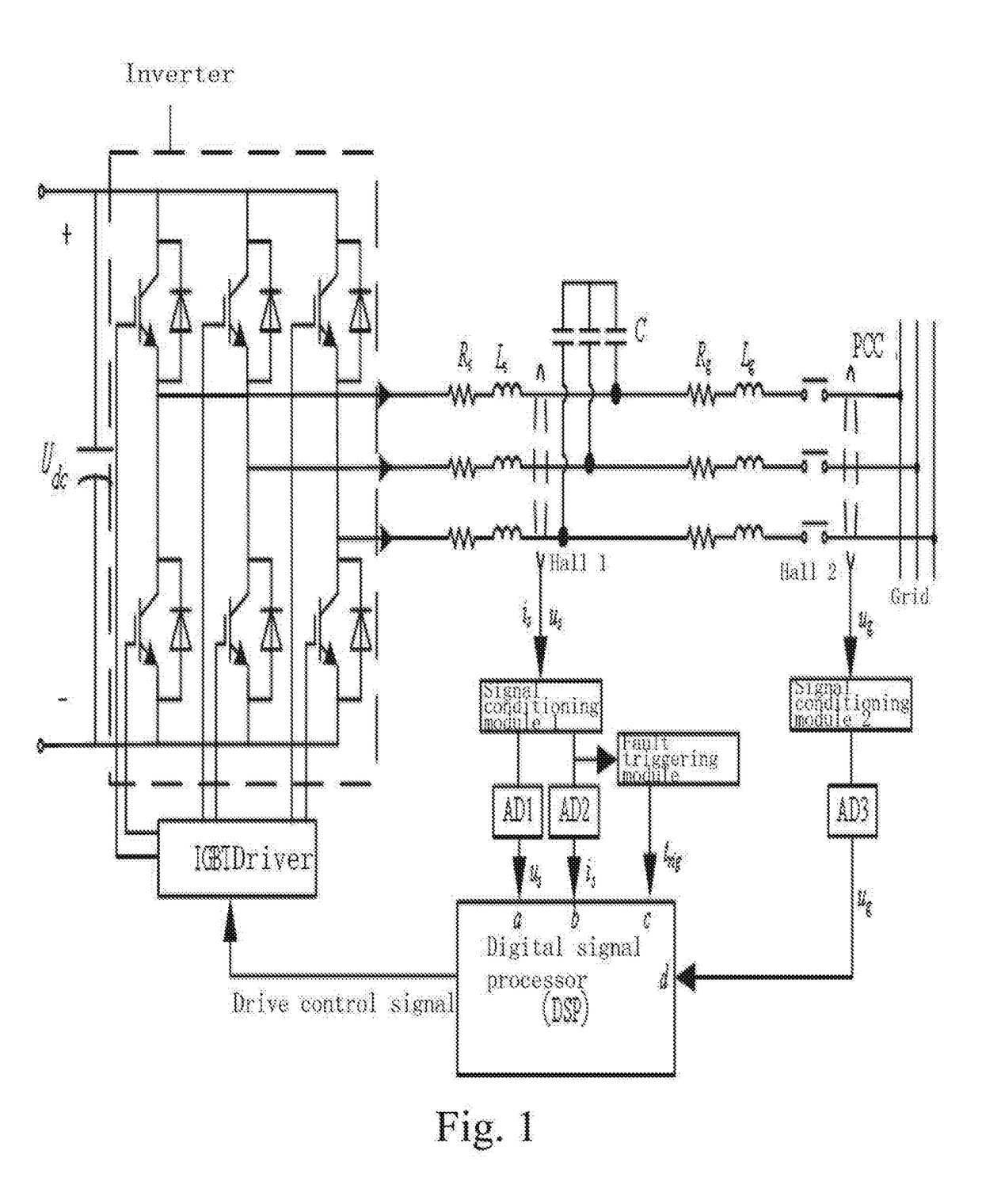
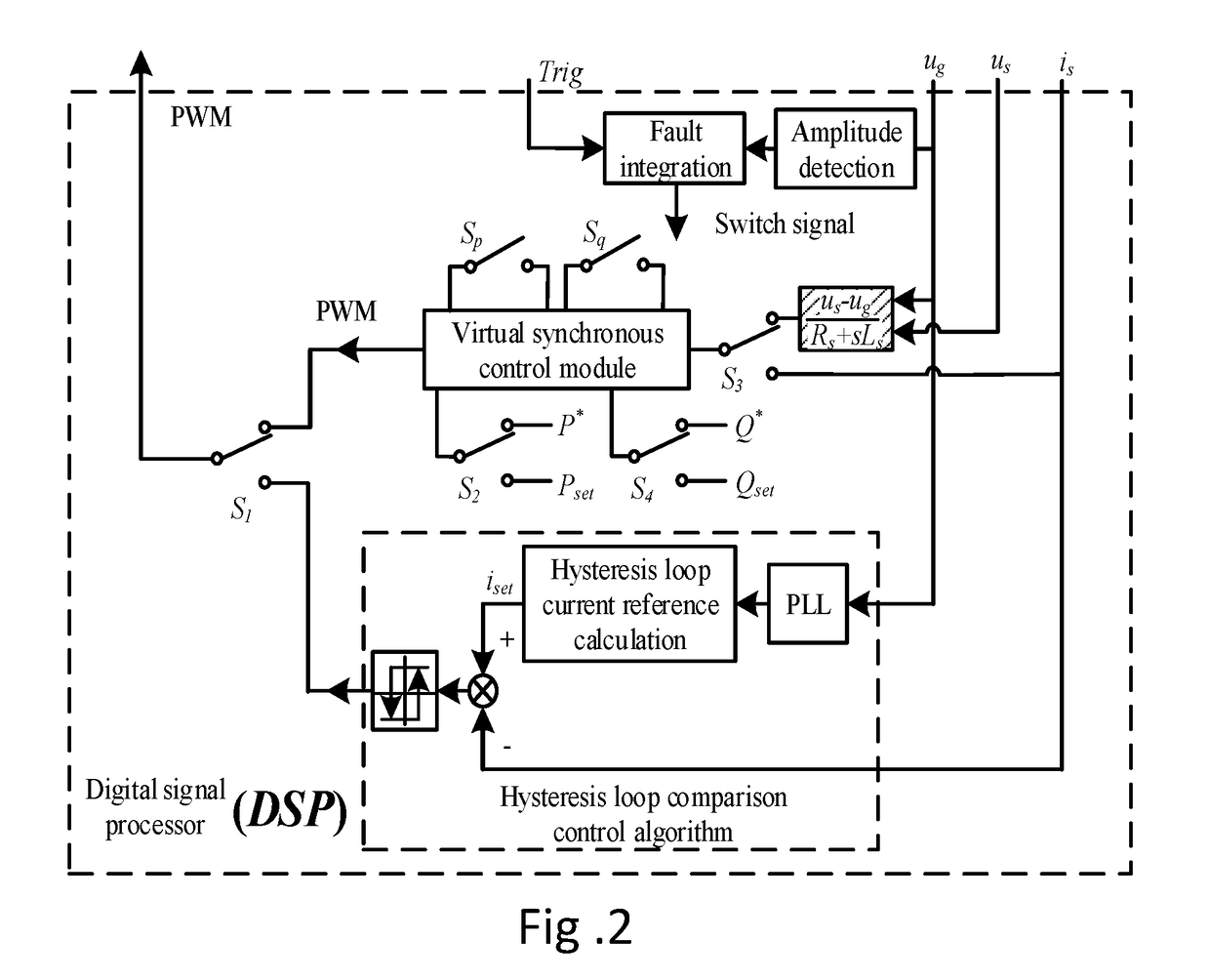
Virtual synchronous inverter with fast transient inrush fault currents restraining method thereof
ActiveUS20180145582A1Inhibit currentReduce voltageAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHysteresisVirtual synchrony
A fault inrush transient current restraining type virtual synchronous inverter and thereof is disclosed. The invention solves the problem that a virtual synchronous inverter will be burned due to inrush transient current in an extreme situation of a symmetrical fault occurring on the grid side by setting an information collection module for inverter output voltages and currents, a virtual synchronous inverting control module, a fault detection and synthesize module, a hysteresis comparison control module and a post fault clearing switch back grid-tie control module.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Transient voltage suppression device
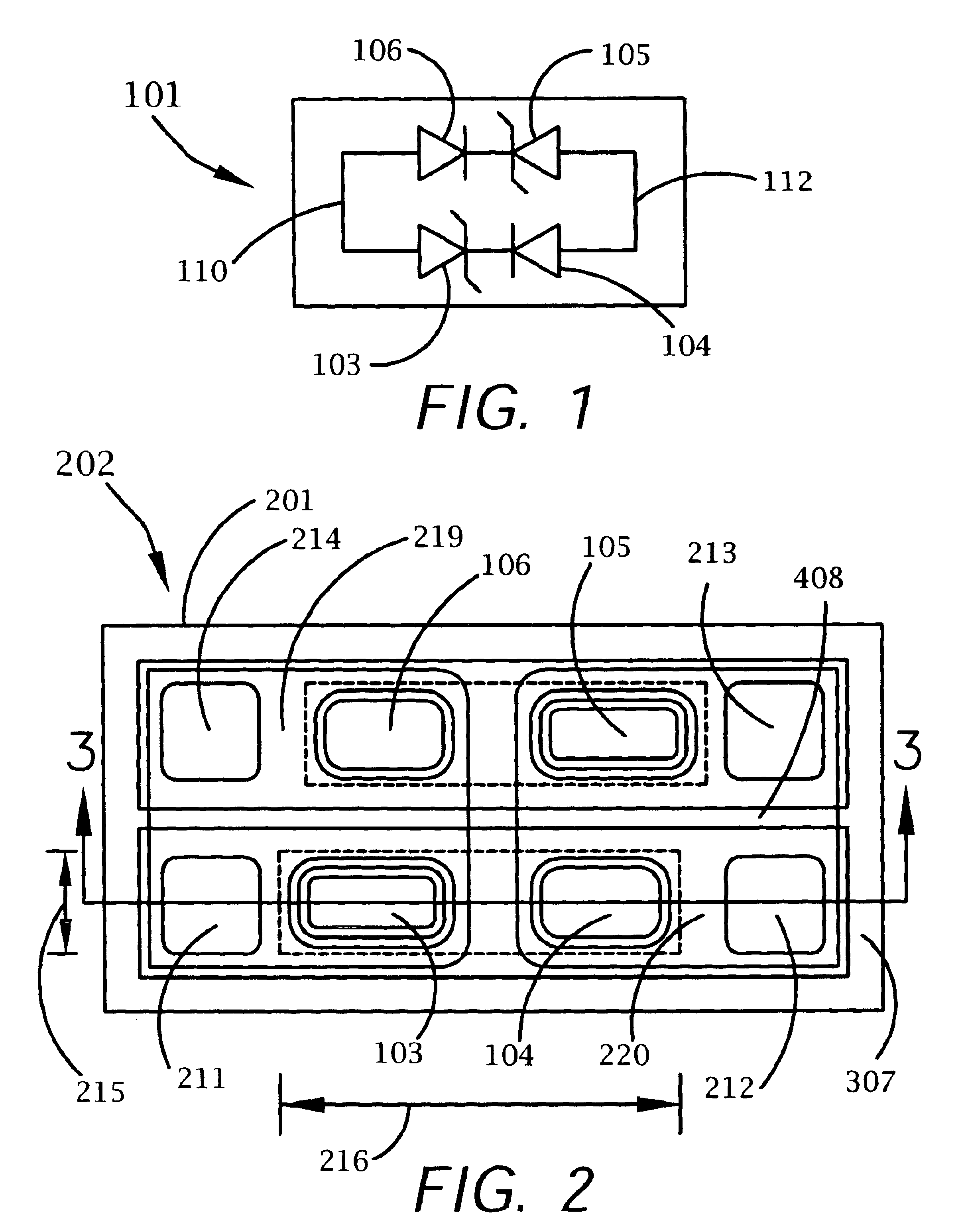
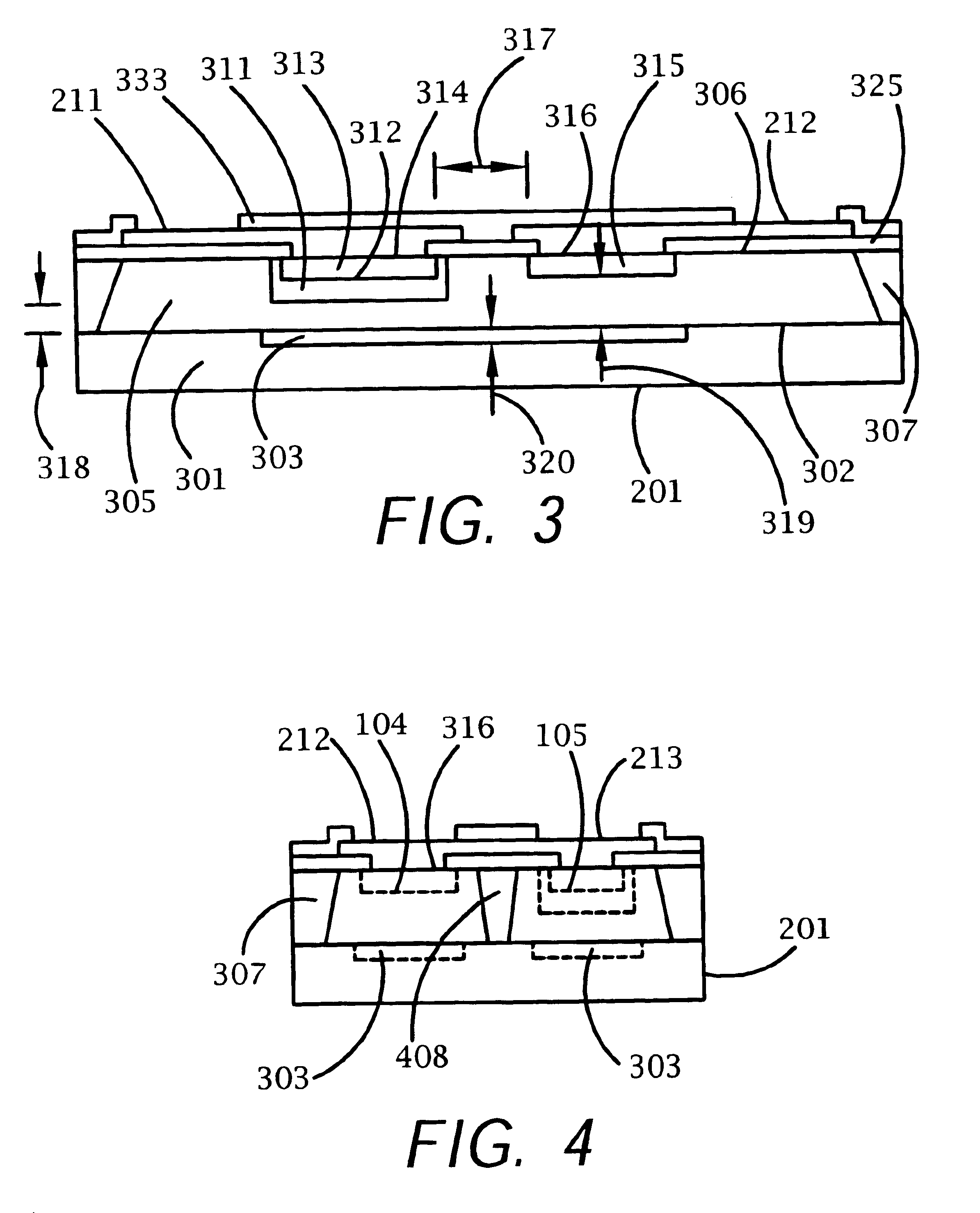
InactiveUS6867436B1Lower clamping voltageOvercome disadvantagesThyristorSolid-state devicesRectifier diodesHigh resistivity
A bi-directional transient voltage suppression (“TVS”) device (101) includes a semiconductor die (201) that has a first avalanche diode (103) in series with a first rectifier diode (104) connected cathode to cathode, electrically coupled in an anti-parallel configuration with a second avalanche diode (105) in series with a second rectifier diode (106) also connected cathode to cathode. All the diodes of the TVS device are on a single semiconductor substrate (301). The die has a low resistivity buried diffused layer (303) having a first conductivity type disposed between a semiconductor substrate (301) having the opposite conductivity type and a high resistivity epitaxial layer (305) having the first conductivity type. The buried diffused layer shunts most of a transient current away from a portion of the epitaxial layer between the first avalanche diode and the first rectifier diode, thereby reducing the clamping voltage relative to the breakdown voltage. The TVS device is packaged as a flip chip (202) that has four solder bump pads (211-214). The abstract is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims pursuant to 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b).
Owner:PROTEK DEVICES
Power distribution network single-phase earth fault locating method based on transient state
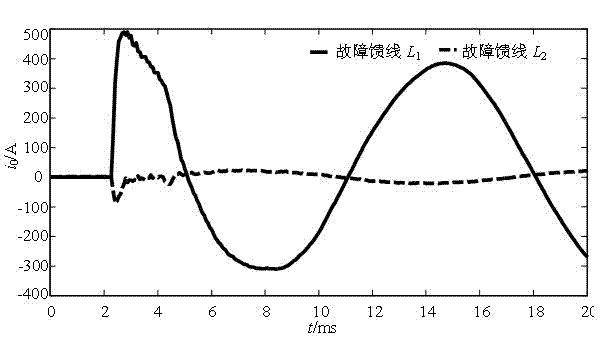
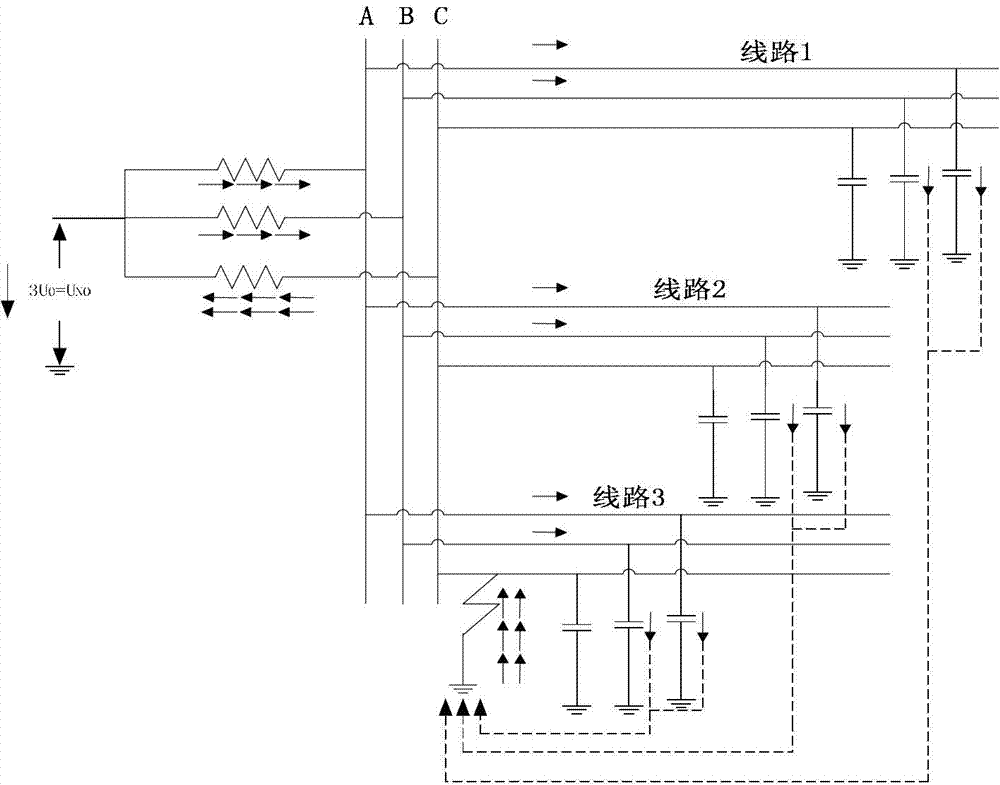
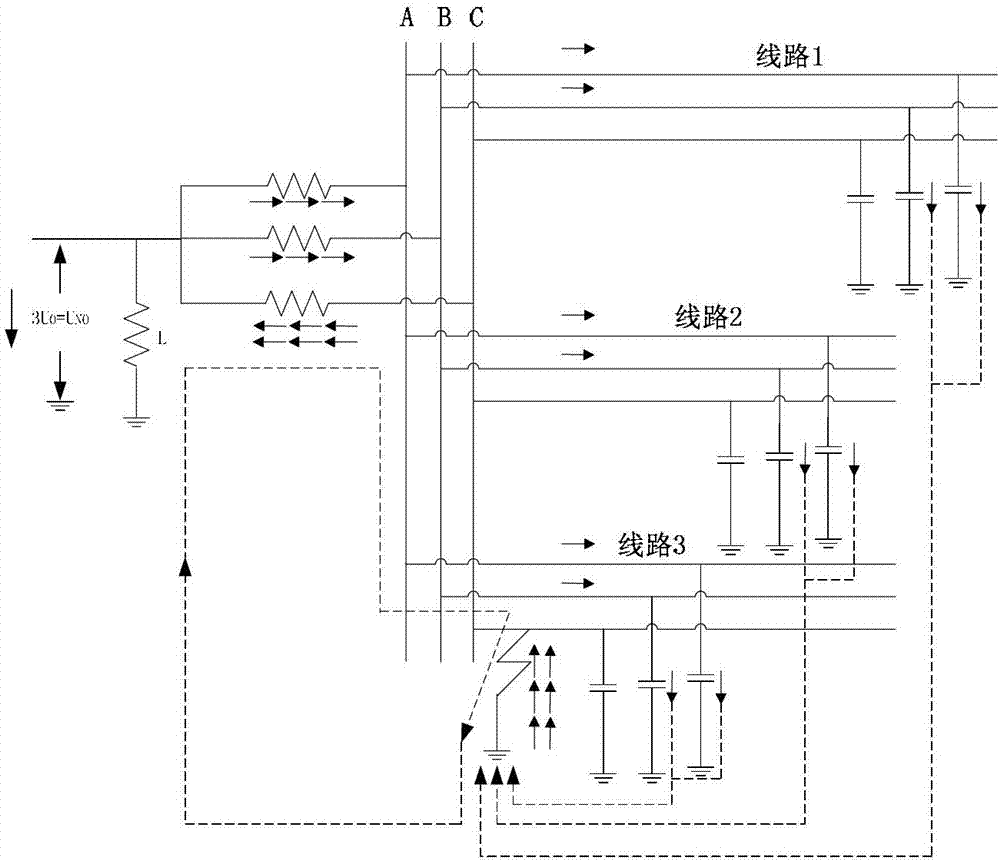
InactiveCN102944814AIncrease success rateImprove efficiencyFault locationInformation technology support systemHigh pressureTransient current
The invention relates to a method for detecting faults in cables, transmission lines or networks, in particular to a power distribution network single-phase earth fault locating method based on a transient state. The method includes: first, determining fault section in a large range according to a flow direction of detecting point transient current, and then determining a final fault section according to the similarity of zero-module current waveforms between two adjacent detecting points. The current waveform similarity calculating processing adopts a general correlation coefficient calculating method and a maximum correlation coefficient calculating method respectively. The technical scheme is that the method is a passive route selection method which is high in locating success rate and efficiency and not subject to effects of unstable arc and intermittent arc, an additional high-voltage primary device or movement coordination of other primary devices is not required, and high safety is achieved. Outage is not required for installing and detecting, and required installing space is small.
Owner:STATE GRID FUJIAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD +2
Voltage regulator with prevention from overvoltage at load transients
InactiveUS20070030054A1Stable output voltageElectric variable regulationOvervoltageVoltage regulation
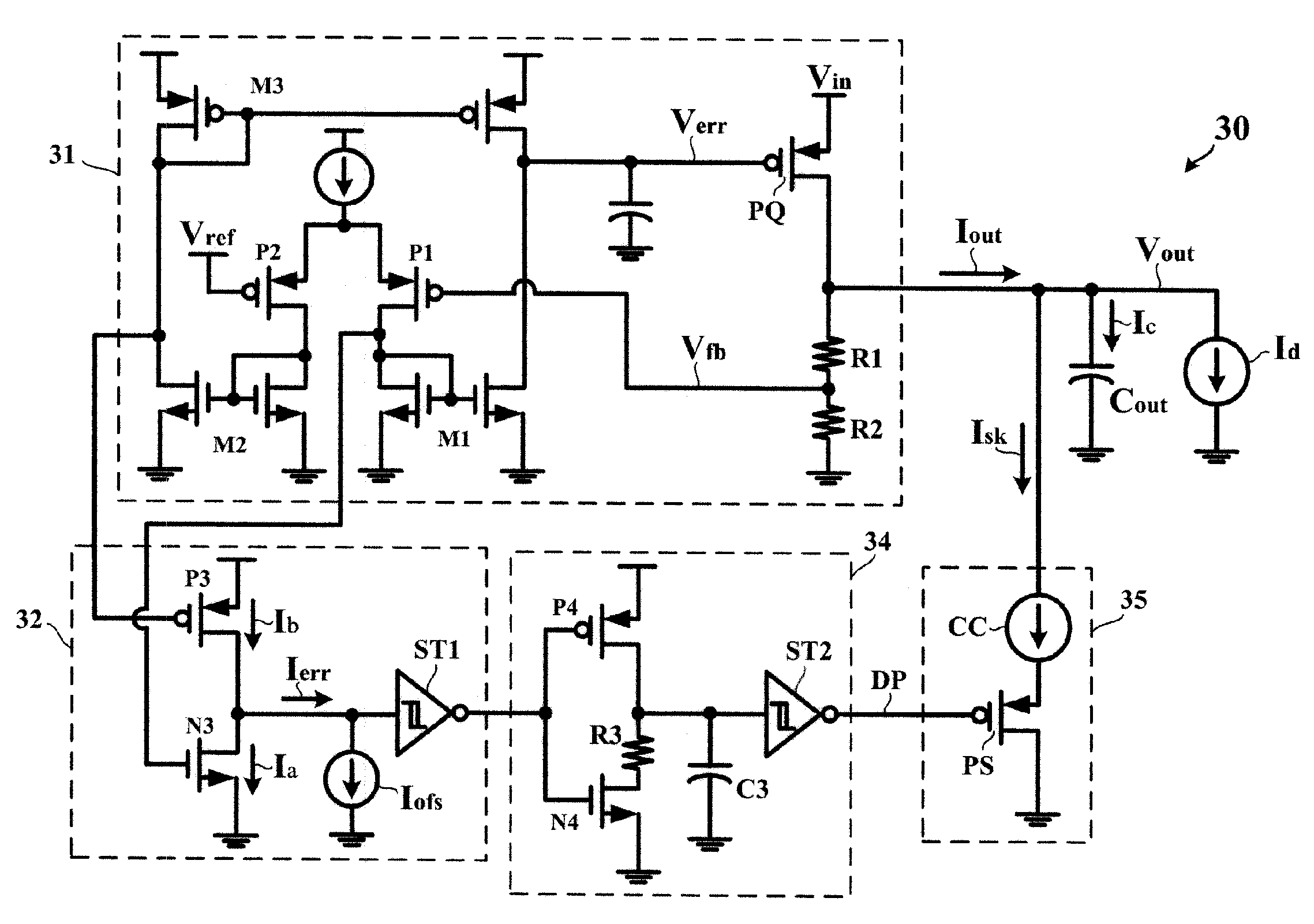
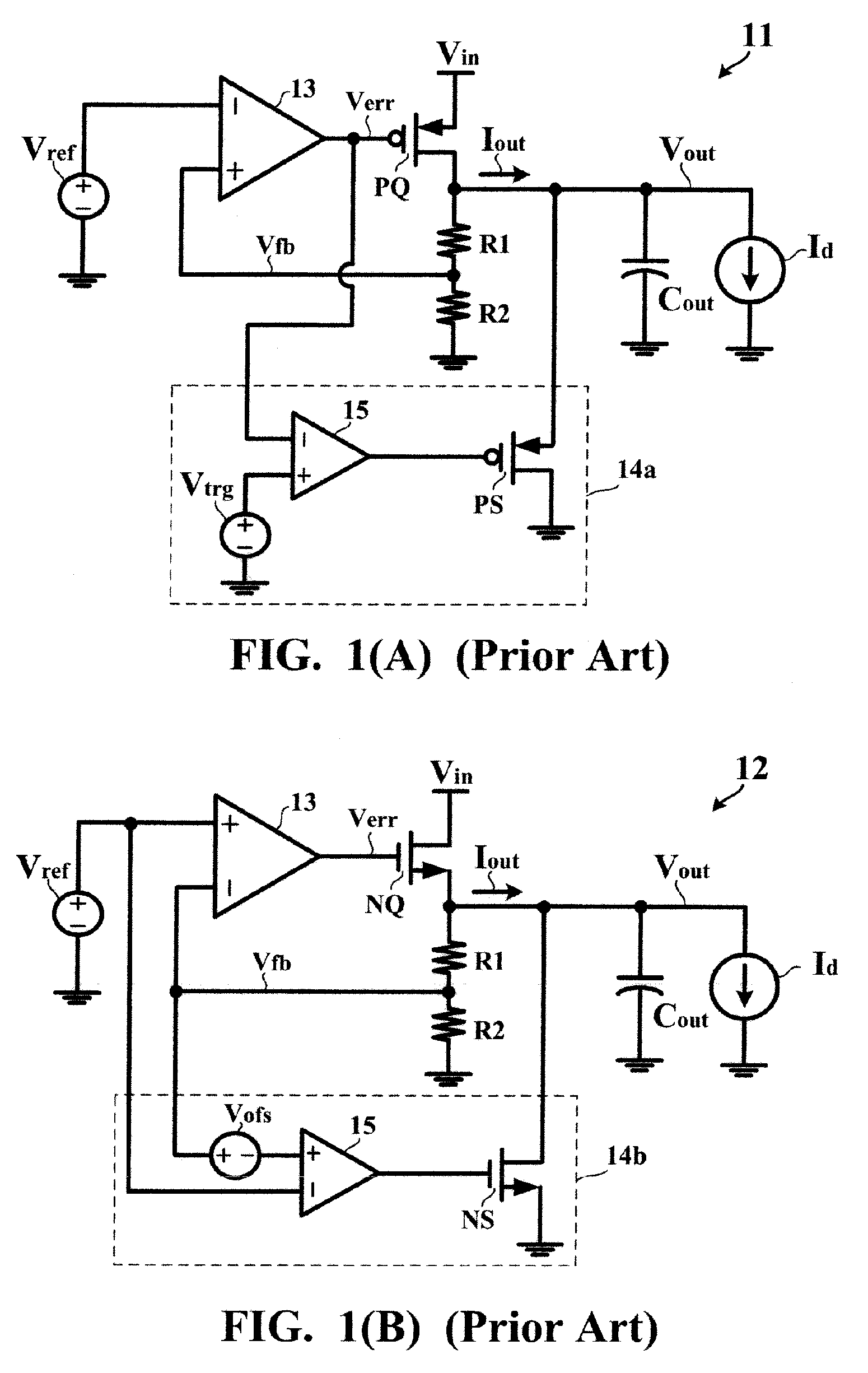
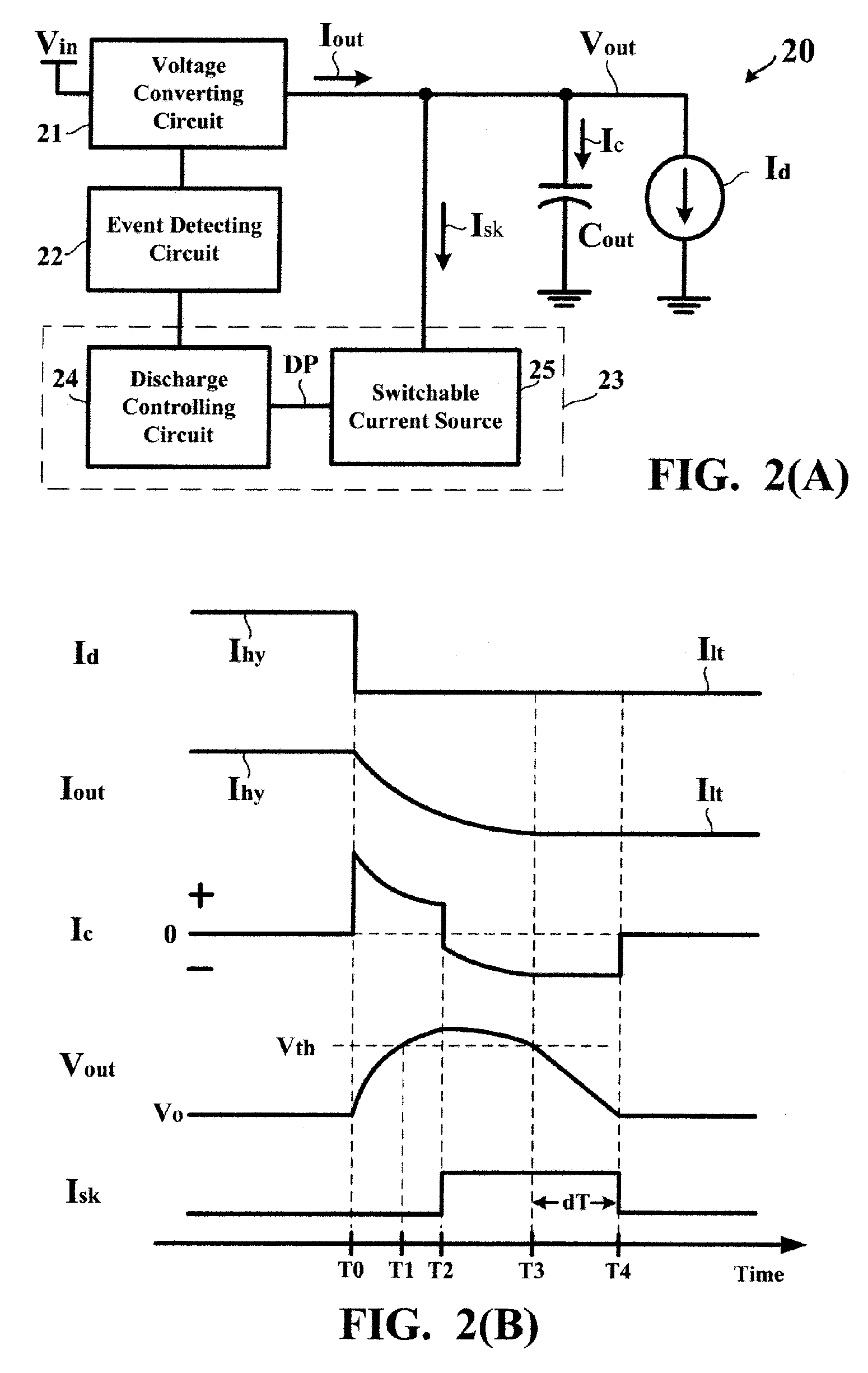
A voltage converting circuit has an output terminal for supplying an output current at an output voltage to a load. In response to a transient of the load, a current sinking circuit allows a current source to provide a sink current flowing from the output terminal of the voltage converting circuit into a ground potential. The sink current is finite and stable. When the output voltage decreases below a threshold voltage, the current sinking circuit allows the current source to keep providing the finite and stable sink current for an extension time, causing the output voltage to decrease from the threshold voltage to a regulated value.
Owner:GLOBAL MIXED MODE TECH
Cage type asynchronous motor rotor strip-broken failure detecting method
InactiveCN101025430AEliminate asymmetryEliminate air gap eccentricityDynamo-electric machine testingInduction motorDetection threshold
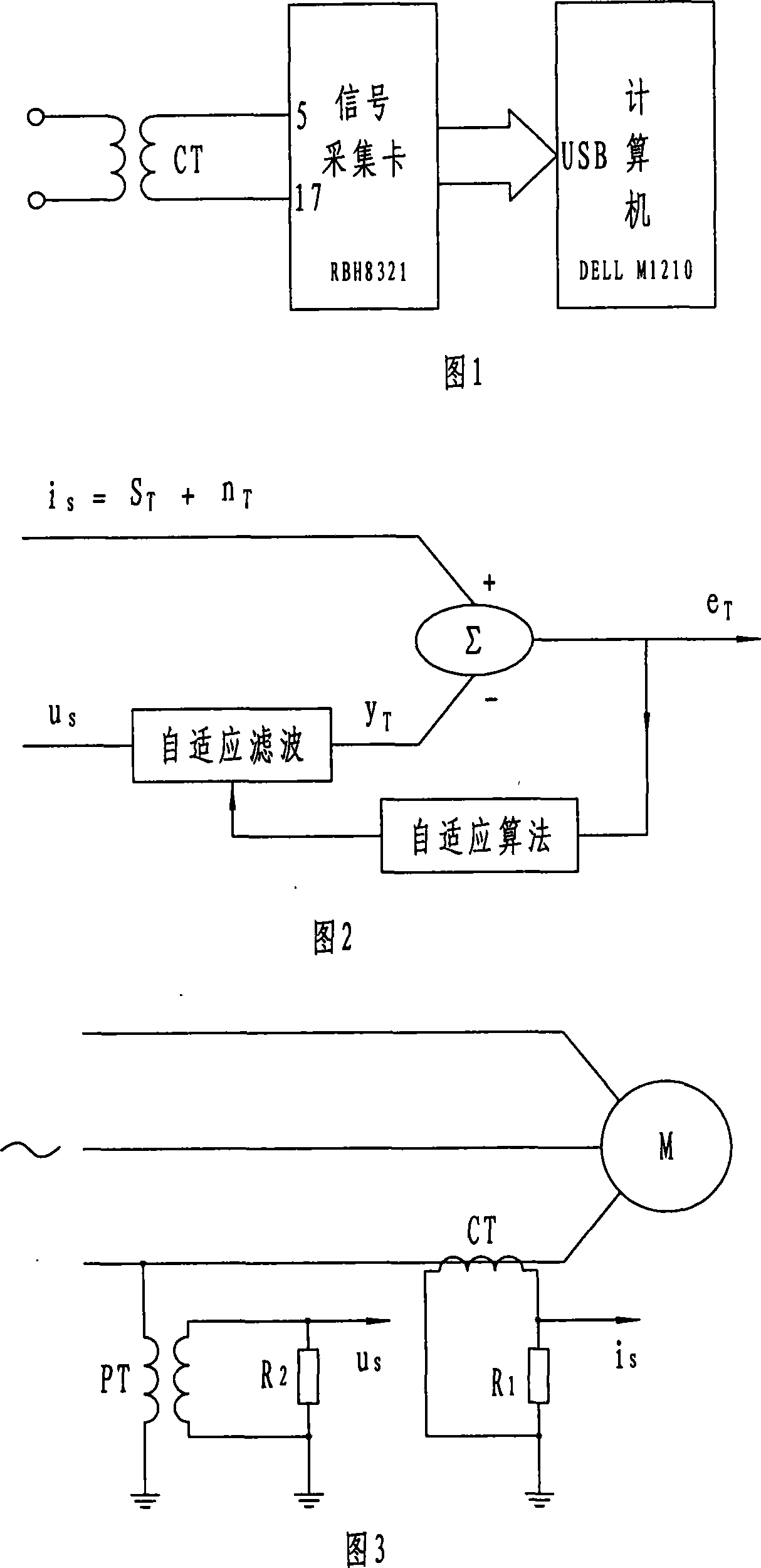
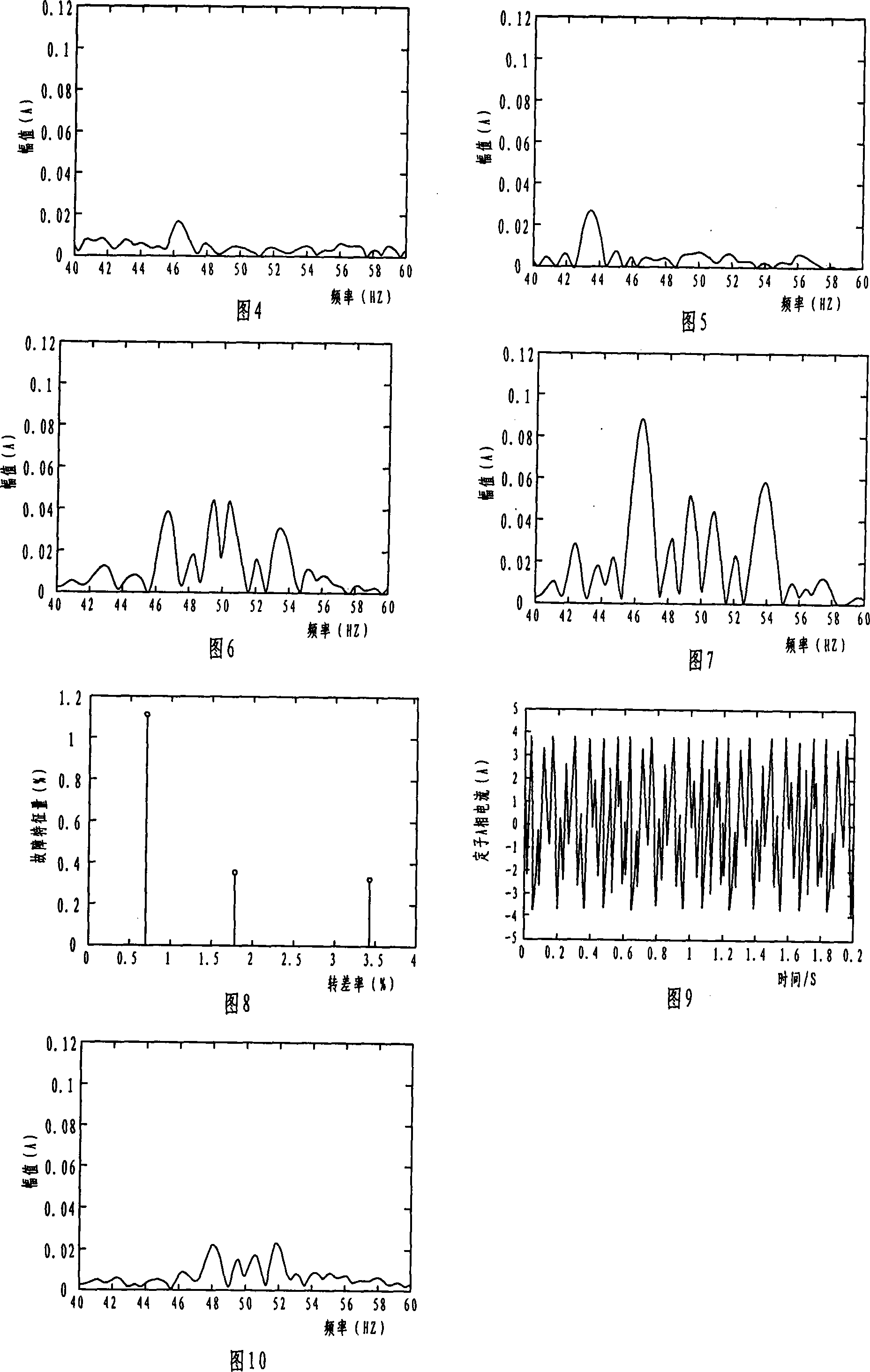
This invention is a methods and devices for detecting the fault of a cage rotor, which belongs to testing technology and for the settlement of broken rotor on the early detection of fault issue. Its technical program: through the acquisition of the stator transient current (is) continuously to do Fourier transform, receiving fundamental wave namely reference signal uS. Do adaptive filtering based the reference signal uS and the frequency f1 for the stator current transient signal. And then filter the output signal eT to do continuous the Fourier transform, identified (1 +- 2s) f1-frequency component and the amplitude of the fundamental components ratio as a failure features, the final determining fault index depending on fault detection threshold index and judge of Broken Bars, This invention can high sensitivity, high reliability and on-line detect the early induction motor of Broken Bars.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method and system of controlling asynchronous contactors for a multi-phase electric load
ActiveUS7224557B2Reduce mechanical stressDamaging mechanical stresses placed on the induction motor can be reducedAC motor controlElectric switchesInduction motorModularity
Control of an induction motor is carried out to limit damaging arcing stress and mechanical stresses placed on the control contactor assembly and the induction motor resulting from the simultaneous or synchronous breaking and making of contactors employed to connect the windings of the motor to a power supply. Asynchronously connecting the windings to the power supply via the asynchronous or non-simultaneous closing of the contactors of a modular contactor assembly reduces the potentially damaging transient current, the associated torque oscillations, and mechanical stresses. The present invention is particularly applicable to delta motors that are started with its windings in a star or wye configuration followed by the reconnection of the windings in a delta configuration when the motor is at normal running speed.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
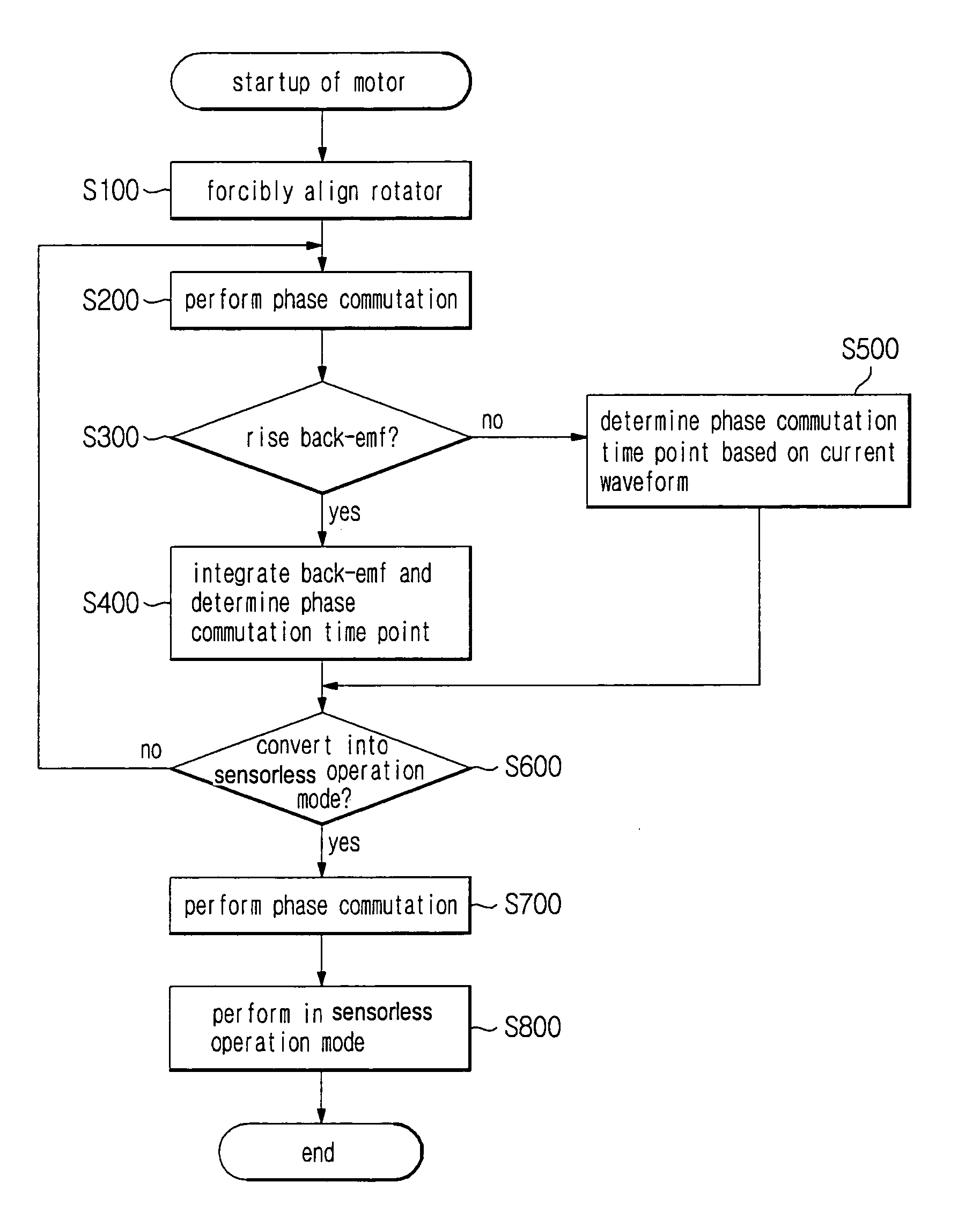
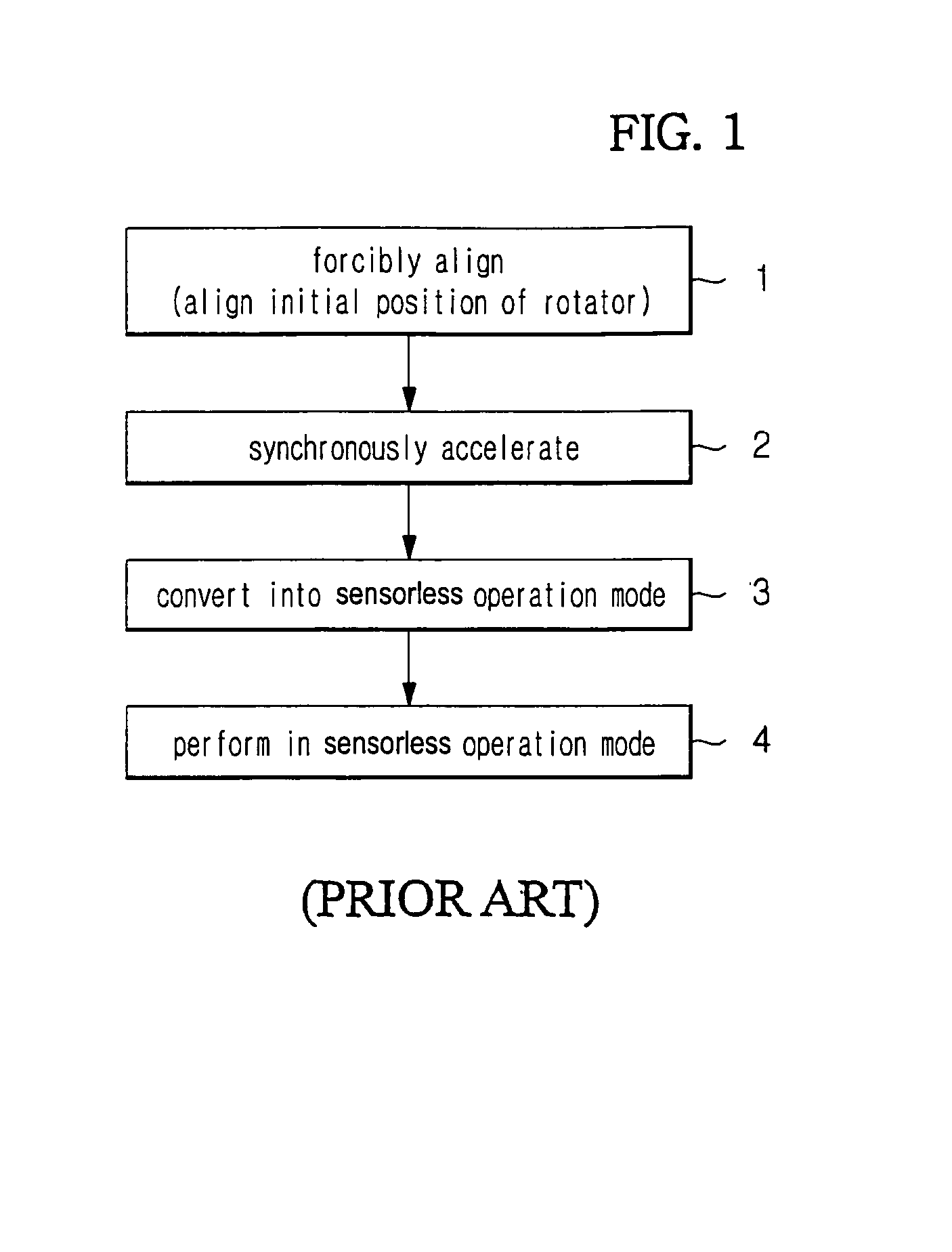
Startup control method of brushless DC motor
InactiveUS7095204B2Current is limitedReduce vibrationAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersFailure rateOperation mode
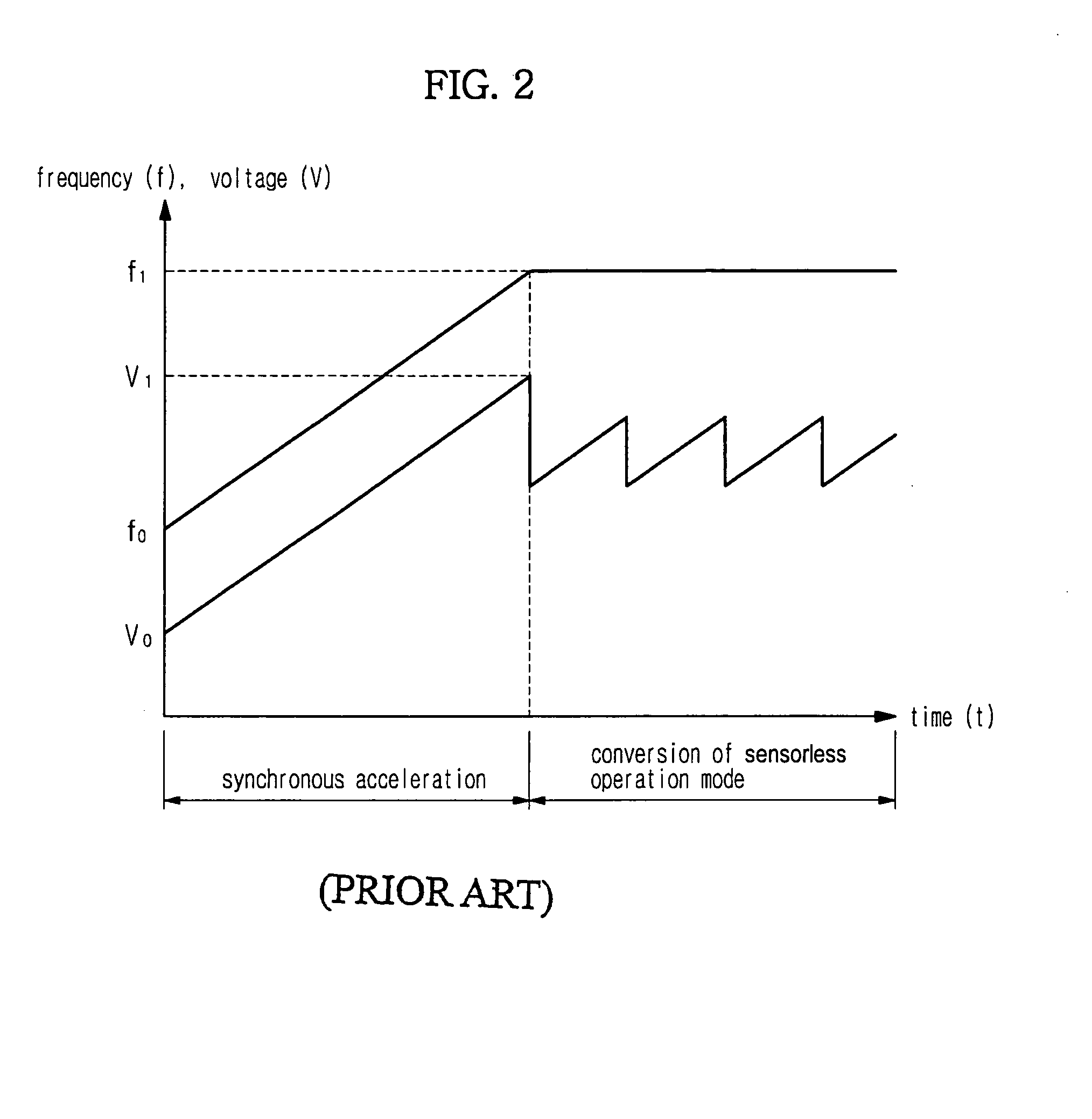
A startup control method of a BLDC motor is disclosed. The method can control the BLDC motor to prevent the generation of a transient current such that the vibration of the BLDC motor can be reduced at the startup stage and perform a stable conversion into a sensorless operation mode such that the startup failure rate of the BLDC motor can be reduced. The startup control method includes commutating a current applied to stator windings according to a rotor position. The method of operating the BLDC motor includes a rotor position that is forcibly aligned and so that phase commutation is performed, a back-electromotive force (back-emf) is detected from a lead voltage of a phase of a voltage which is not applied thereto after performing phase commutation and a determination is performed as to whether the detected back-emf is in a rising interval. The lead voltage of the phase of the voltage which is not applied thereto is integrated, such that if the back-emf is in a rising interval and if an instance that the integration result is greater than a predetermined value a phase commutation time point is set and conversion into a sensorless operation mode is performed if the back-emf detected from the lead voltage is in a stable interval, based on a frequency of the voltage applied to the stator winding.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
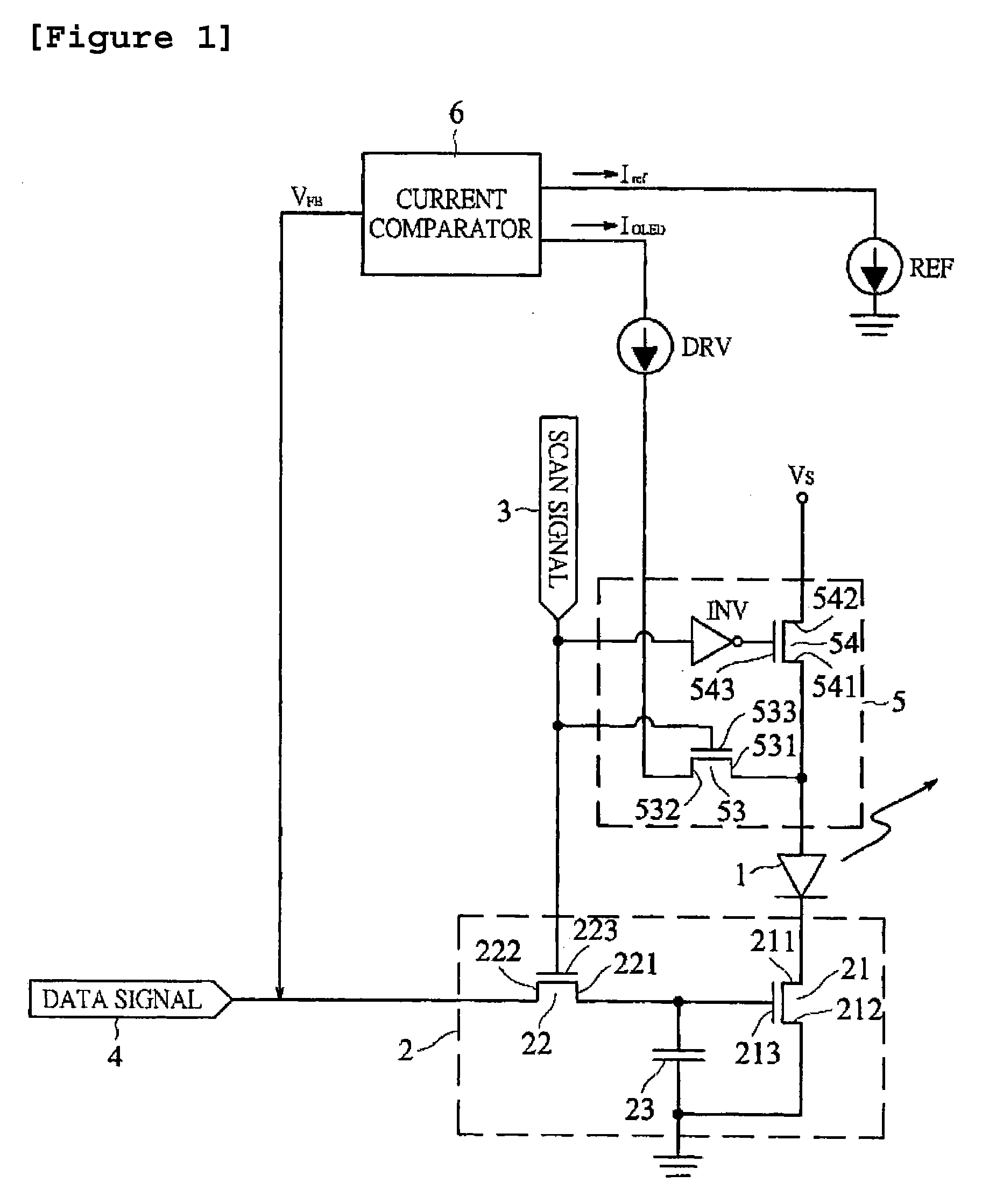
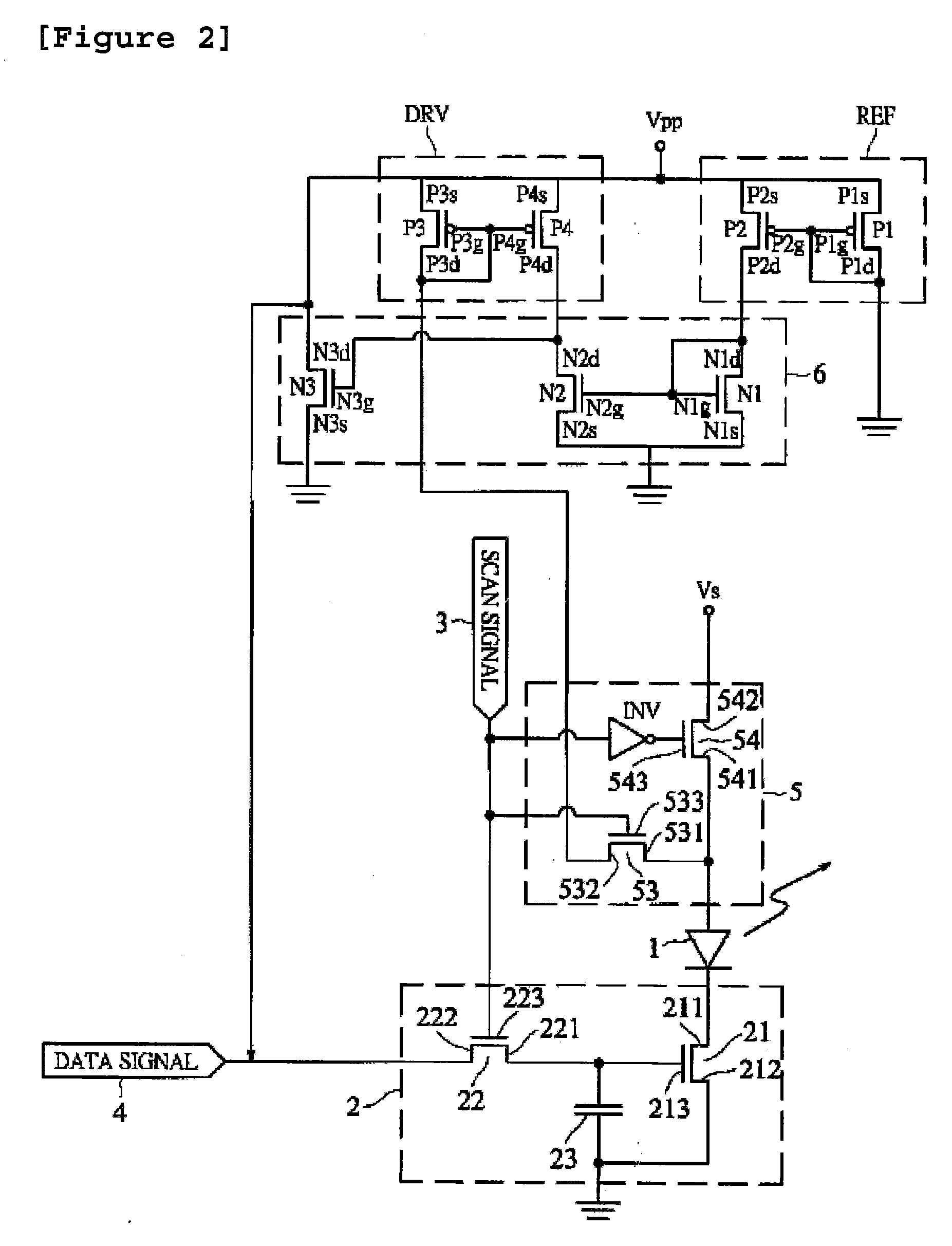
Amoled drive circuit using transient current feedback and active matrix driving method using the same
ActiveUS20080238327A1Drive fastReduce the numberCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital dataEngineering
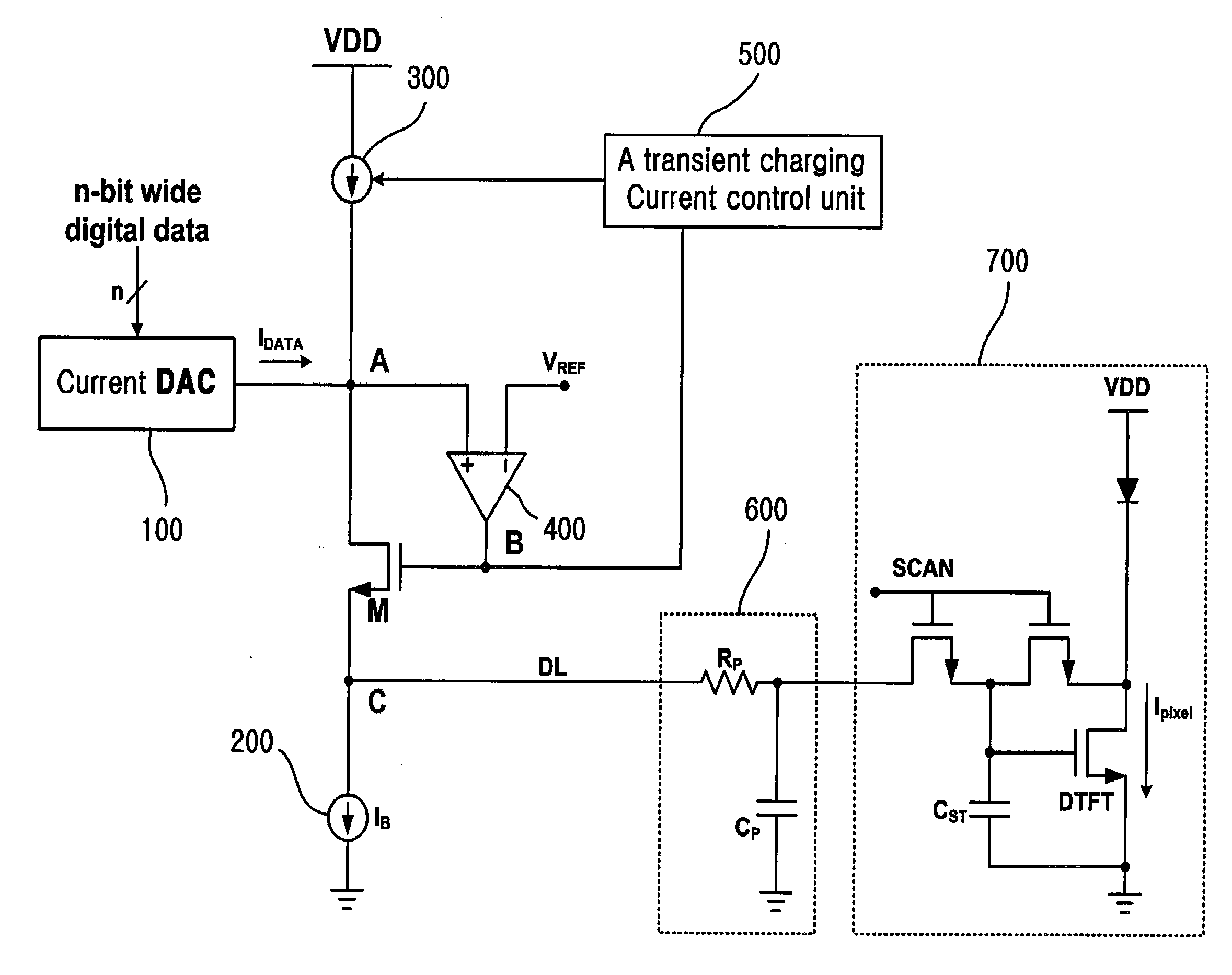
Disclosed herein is an Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting-Diode (AMOLED) drive circuit using transient current feedback. The AMOLED drive circuit includes a current Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC), a data line drive transistor, a constant current source, a variable current source, a differential amplifier, and a transient charging current control unit. The DAC generates current corresponding to input digital data. The data line drive transistor is configured such that the drain terminal thereof is connected to the output node of the current DAC. The constant current source is connected between the source terminal of the data line drive transistor and a ground. The variable current source is connected between both the output node of the current DAC and the drain terminal of the drive transistor, and a voltage source. The differential amplifier is configured to input the output voltage thereof to the gate terminal of the drive transistor. The transient charging current control unit is configured to increase or decrease the bias current of the variable current source depending on variation in the voltage of the output node of the current DAC.
Owner:HIDEEP INC
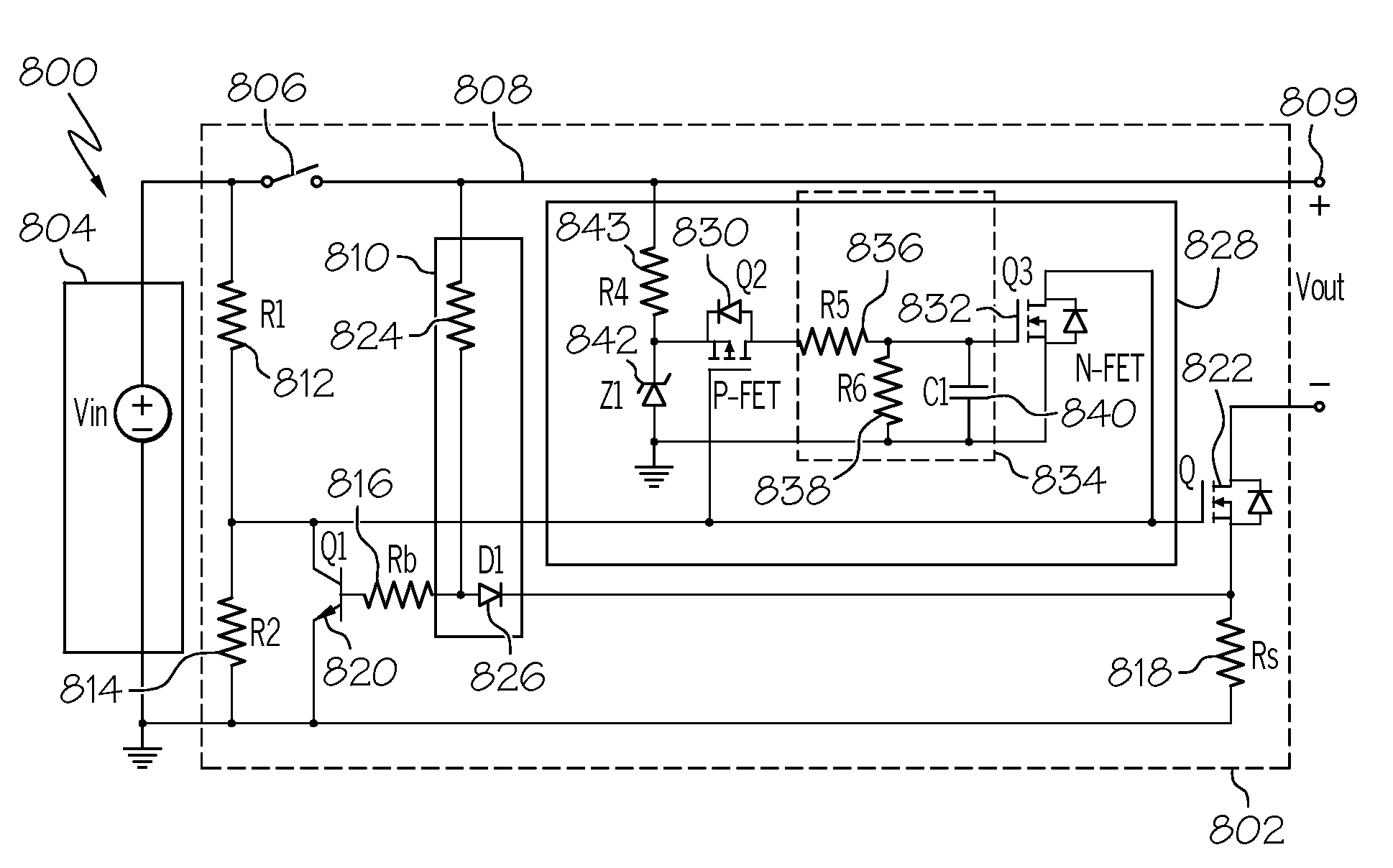
Advanced inrush/transient current limit and overload/short circuit protection method and apparatus for DC voltage power supply
InactiveUS7408755B1Arrangements responsive to excess currentEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCurrent limitingComputer module
The present invention provides a single circuit that may have multiple protection functions for a DC voltage power supply. The present invention may include separate circuit modules that are employed individually, or in various combinations. These separate circuit modules include: a temperature and input voltage variation compensated current limit circuit; an inrush and transient current limit combined with an overload and short circuit protection circuit; and a self adaptive short circuit turn-off timing circuit.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Liquid crystal display and driving method thereof
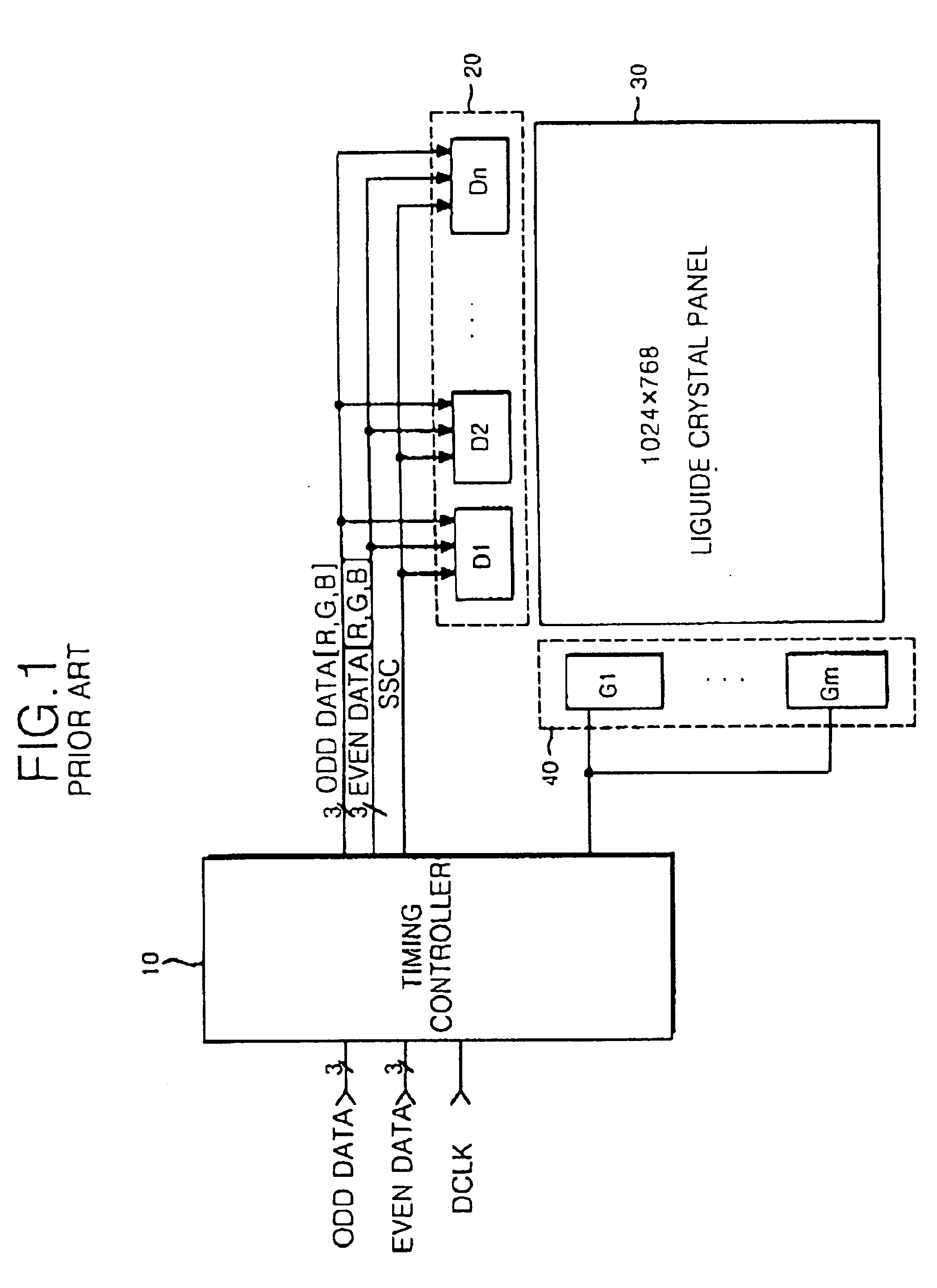
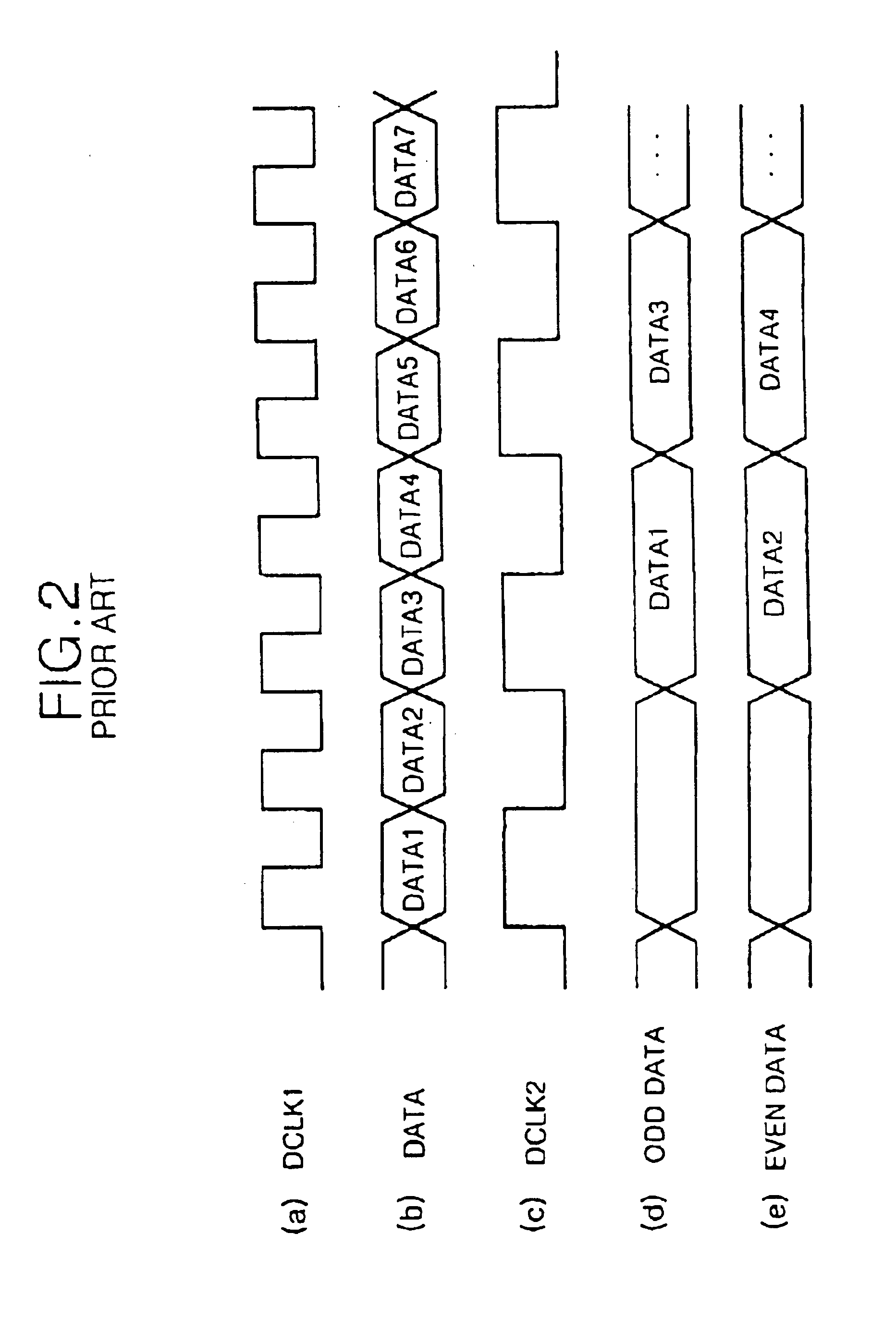
InactiveUS6867759B1Reduce generationAvoid generatingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayTransient current
A liquid crystal display device for restraining a generation of transient current is disclosed. In the device, a line memory divides a data for at least one line inputted from the exterior thereof into a plurality of groups to store the divided data therein and outputs the data at a desired unit from each of the groups. A driving circuit includes n driver integrated circuits (wherein n is an integer) that are connected to the line memory and a liquid crystal display panel to drive the liquid crystal display panel in response to the data outputted from the line memory. A timing controller is connected to the line memory and the driving circuit to receive a data clock inputted from the exterior thereof for outputting the data from the plurality of groups of said line memory to the driving circuit every period of the data clock in response to a time corresponding to the number of said groups.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors
ActiveCN103245883AThe principle is simpleImprove timelinessFault locationElectric power systemTransient current
The invention relates to a power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. When a power distribution network runs into a single-phase earth fault via an arc suppression coil grounding system, a transient zero-sequence current component detected by a measuring end is a nonlinear non-stationary signal formed by different frequency components. By taking the fault component as a study object, time-frequency characteristics of a fault transient current of the fault component are analyzed by utilizing the wavelet packet theory, time-frequency distribution regularities among all feeder lines under different fault conditions are described according to similarity of the time-frequency characteristics, and consequently line selection criteria based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristics can be obtained. The method is simple in principle, only utilizes short-time window zero-sequence current data of 5ms after the fault, can identify faulty feeders under the conditions of small fault angle and high resistance ground fault, has excellent timeliness and robustness, is free from influence of an arc fault or a resistance ground fault, requires a low sampling rate for hardware, and is highly practical.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Shift register, drive device and displayer
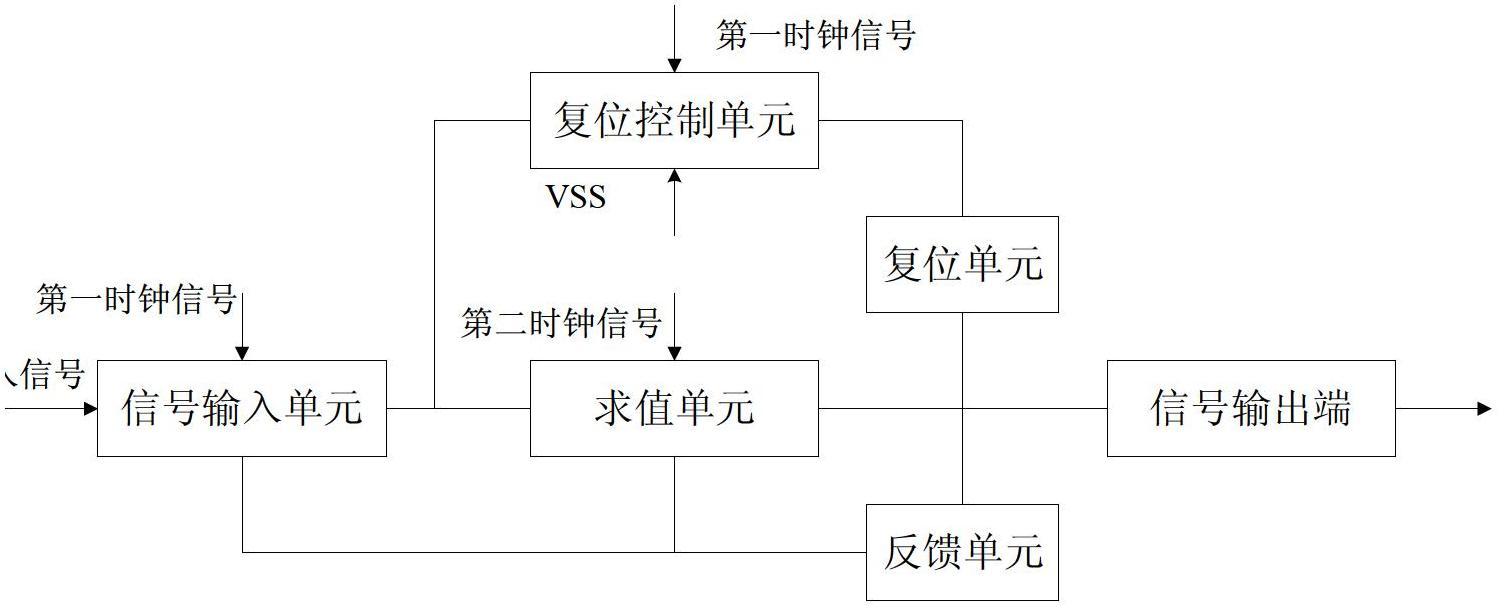
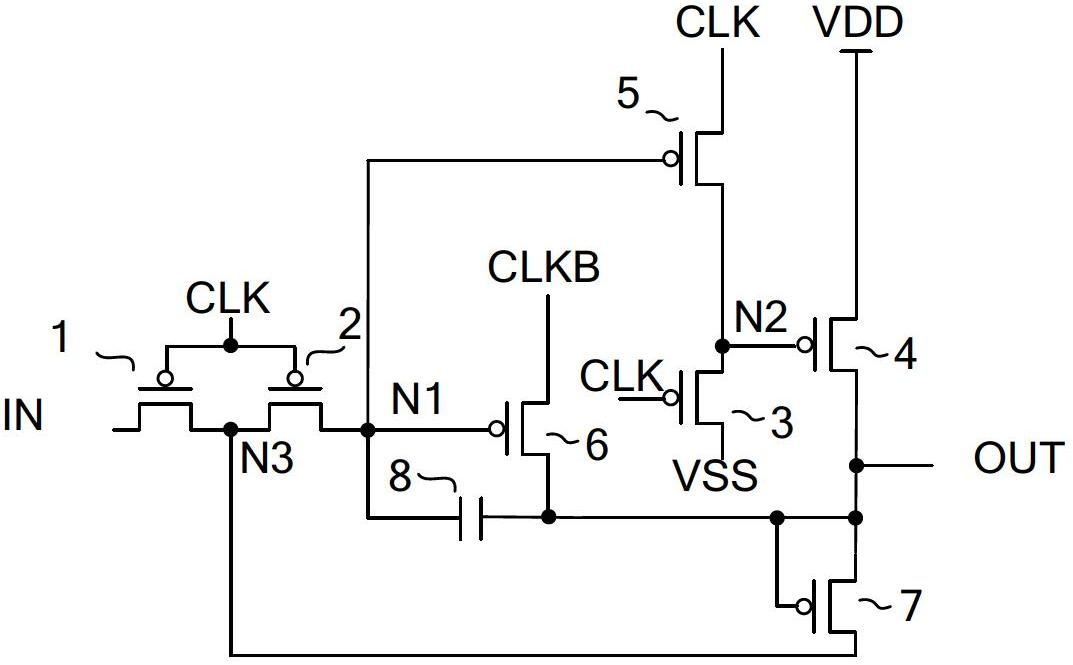
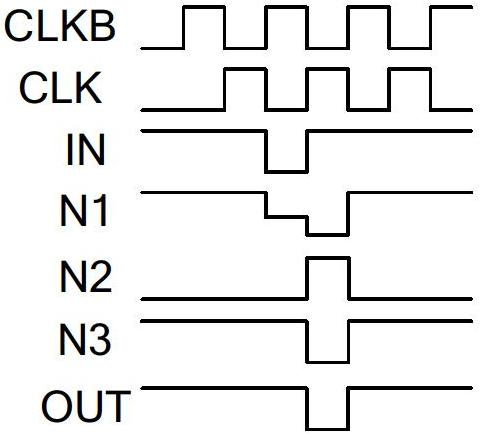
ActiveCN102682692ATimely shutdownAvoid large transient currentsStatic indicating devicesElectric analogue storesShift registerControl signal
The invention relates to the technical field of display devices, and provides a shift register, a drive device and a displayer. The shift register provided by the invention comprises a valuation unit, a reset control unit and a reset unit. The valuation unit is used for outputting a signal to a signal output end under the control of an input signal and a second clock signal; the reset control unit of which one end is connected with the valuation unit is used for inputting a control signal to the reset unit under the control of a first clock signal and a low-level signal; and the reset unit is used for resetting the signal output end under the control of the control signal and a high-level signal input by the reset control unit. The shift register provided by the invention can quickly charge the grid of a reset transistor grid while valuating the output end, so that the transistor can be turned off in time, a larger transient current generated when the reset transistor and a valuation transistor are switched on at the same time is avoided, the power consumption is reduced and circuit elements are protected. The shift register also can reduce the influence of leakage current from an input tube, reduce the power consumption and enhance the stability based on the output voltage feedback and input tube double-grid technology.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Fault line selection method of low current grounding system using time-frequency atom decomposition theory
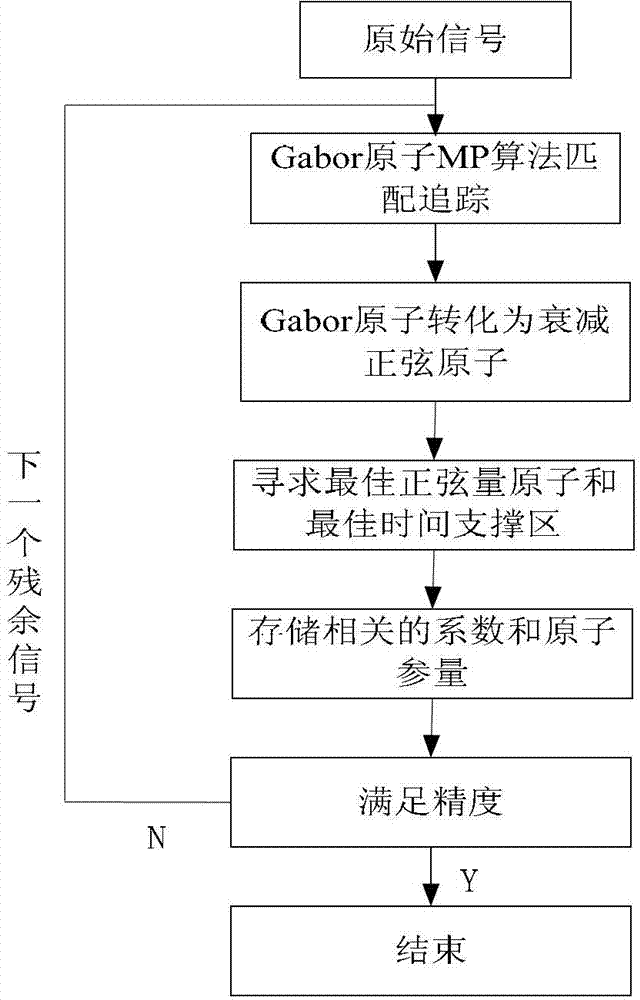
ActiveCN102854437AGood localization propertiesAccurate quantitative starting and ending timeFault locationUltrasound attenuationDecomposition
The invention provides a fault line selection method of a low current grounding system using a time-frequency atom decomposition theory. The method comprises the following steps of: based on the time-frequency atom decomposition theory, performing sparse decomposition on zero-sequence current data in a Gabor over-complete dictionary, and then obtaining matched attenuation sinusoidal quantity atoms through optimizing and solving relevant parameters. By the time-frequency atom decomposition method, the disturbance characteristics such as start / stop moments, amplitudes, frequencies and change rules of fundamental wave and each subharmonic can be exactly obtained, and interference signals can be effectively filtered. Energy entropies of the atoms decomposed by time-frequency atoms are arranged from large to small; except from the zero-sequence transient current fundamental wave atom, atom phase angles (polarity) similar with zero-sequence current frequency of each line are compared; if the atom phase angle (polarity) similar with the zero-sequence transient frequency of the line is opposite to that of other lines, the line is the fault line; and if the atom phase angle (polarity) of each line is the same, the fault is bus fault, and the fault line is determined by the comparison result of each frequency phase angle.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
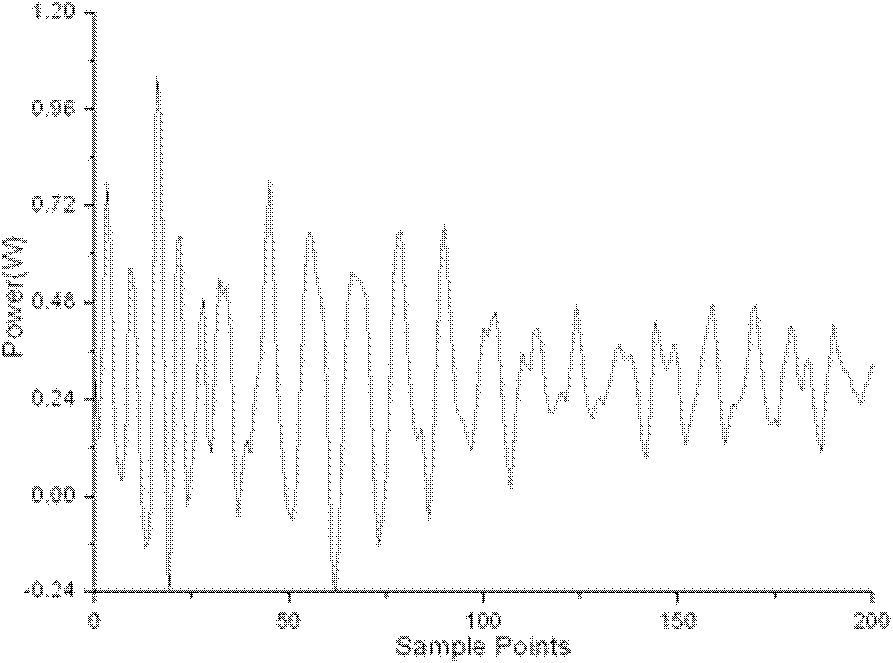
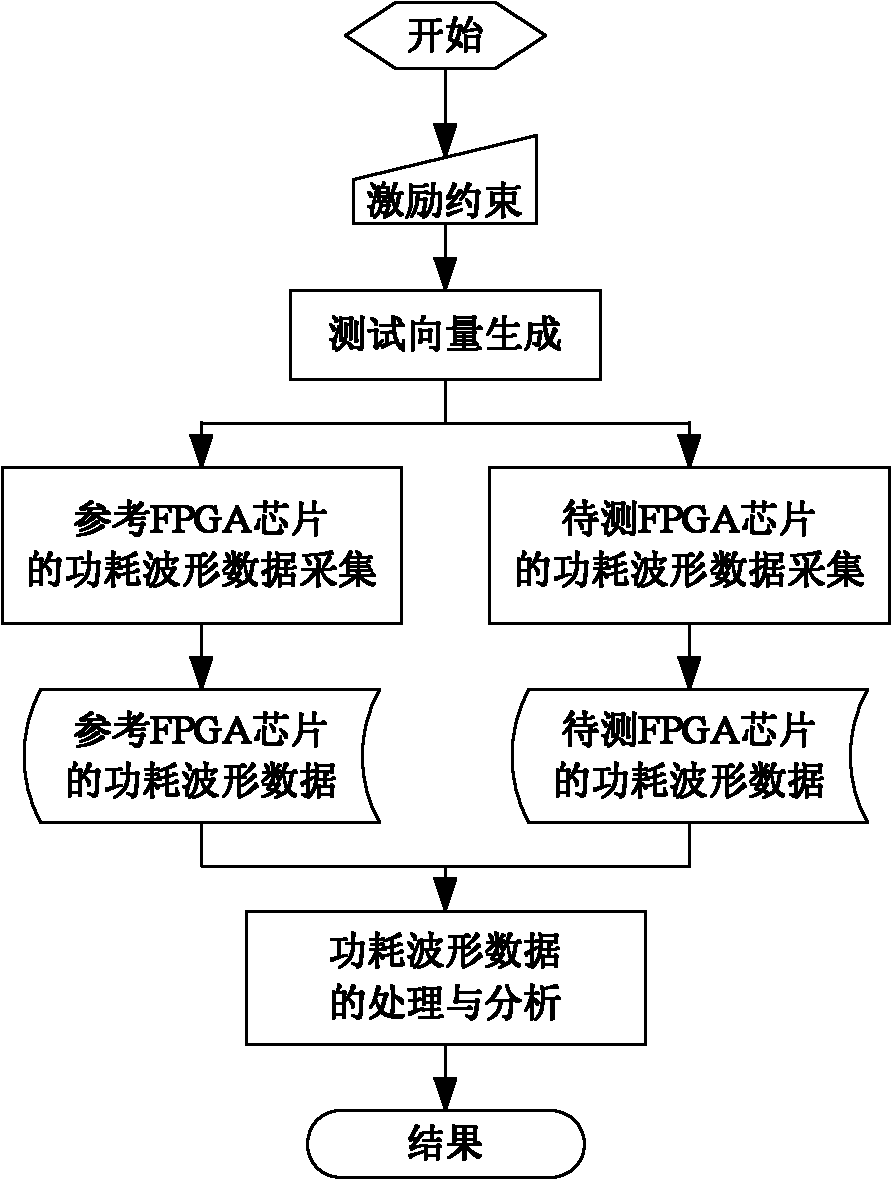
Method for detecting malicious circuit in FPGA (field programmable gate array) chip by power consumption analysis and system thereof
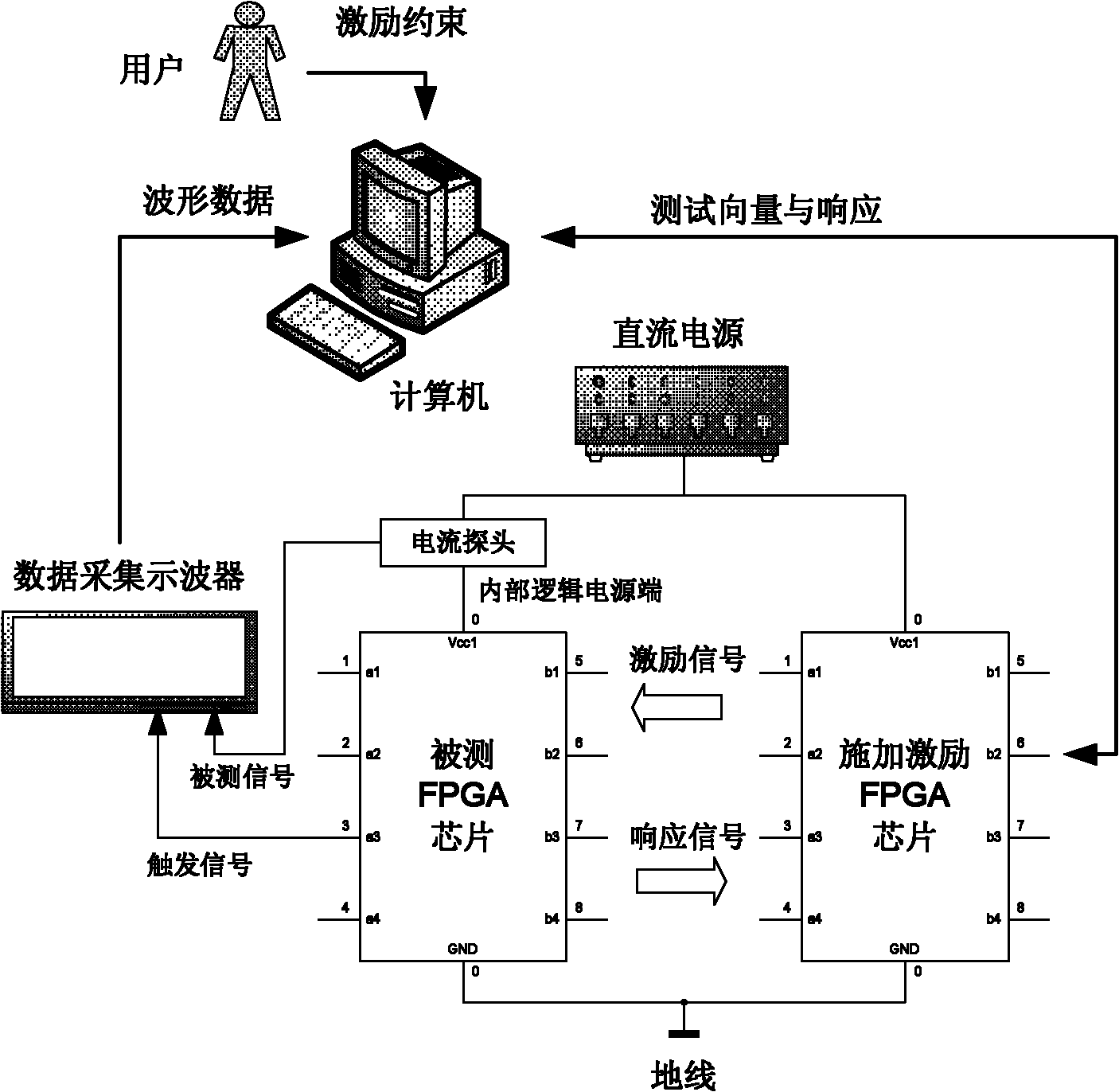
ActiveCN102592068AHigh measurement accuracyAchieve installationInternal/peripheral component protectionVoltage sourceFpga chip
The invention discloses a system for detecting malicious circuits in an FPGA (field programmable gate array) chip by power consumption analysis. The system comprises a DC (direct current) stabilized voltage source for supplying DC power to a to-be-detected FPGA chip and an excitation applying FPGA chip; a current probe for measuring a transient current at the power end of the to-be-detected FPGA chip; an oscilloscope triggered by a trigger signal generated by the to-be-detected FPGA chip to collect the current signal measured by the current probe; the excitation applying FPGA chip for applying an excitation signal to the to-be-detected FPGA chip, and transmitting the response signal of the to-be-detected FPGA chip to a computer for further verification and comparison with an expected response value; and the computer for receiving excitation restraint compiled by a user, generating a test vector, and completing response verification, oscilloscope setting, waveform data collection, data analysis and treatment. The invention also discloses a method for detecting malicious circuits in the FPGA chip by using the above system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS PROD RELIABILITY & ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING RES INST
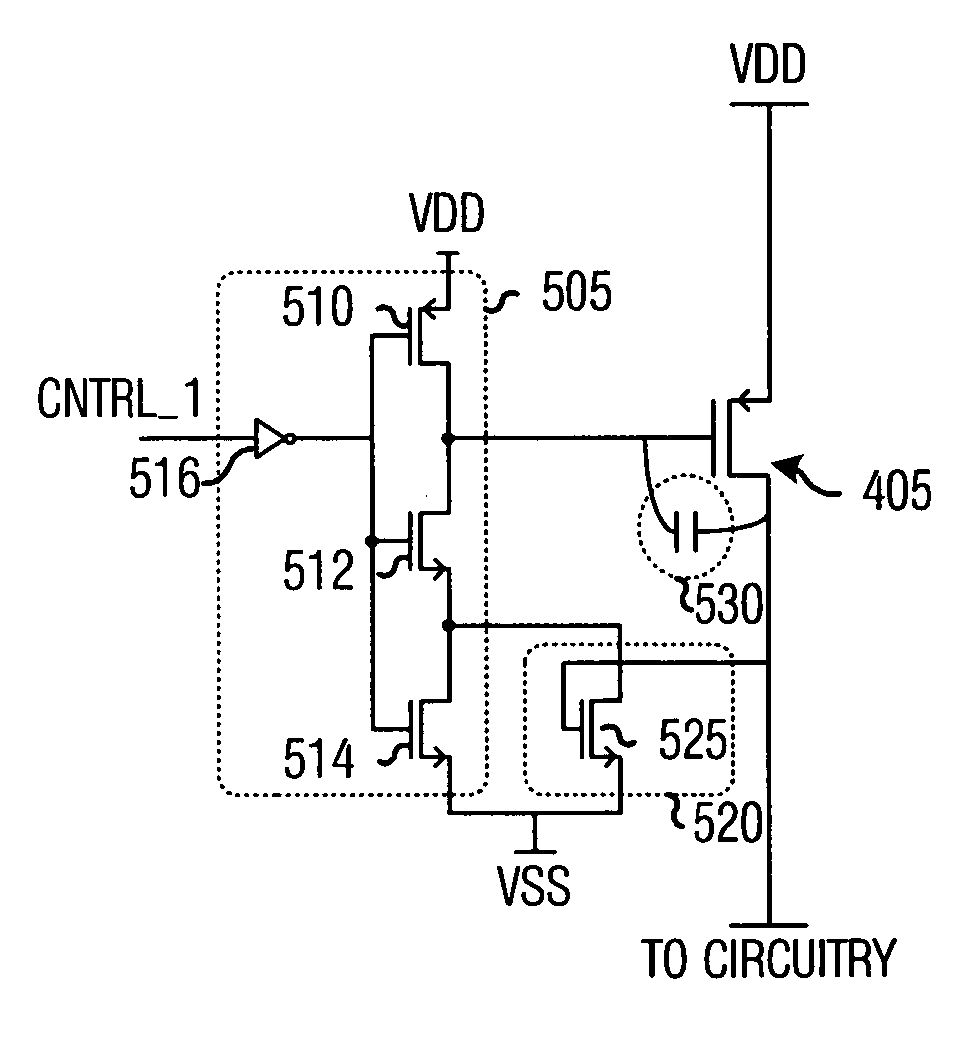
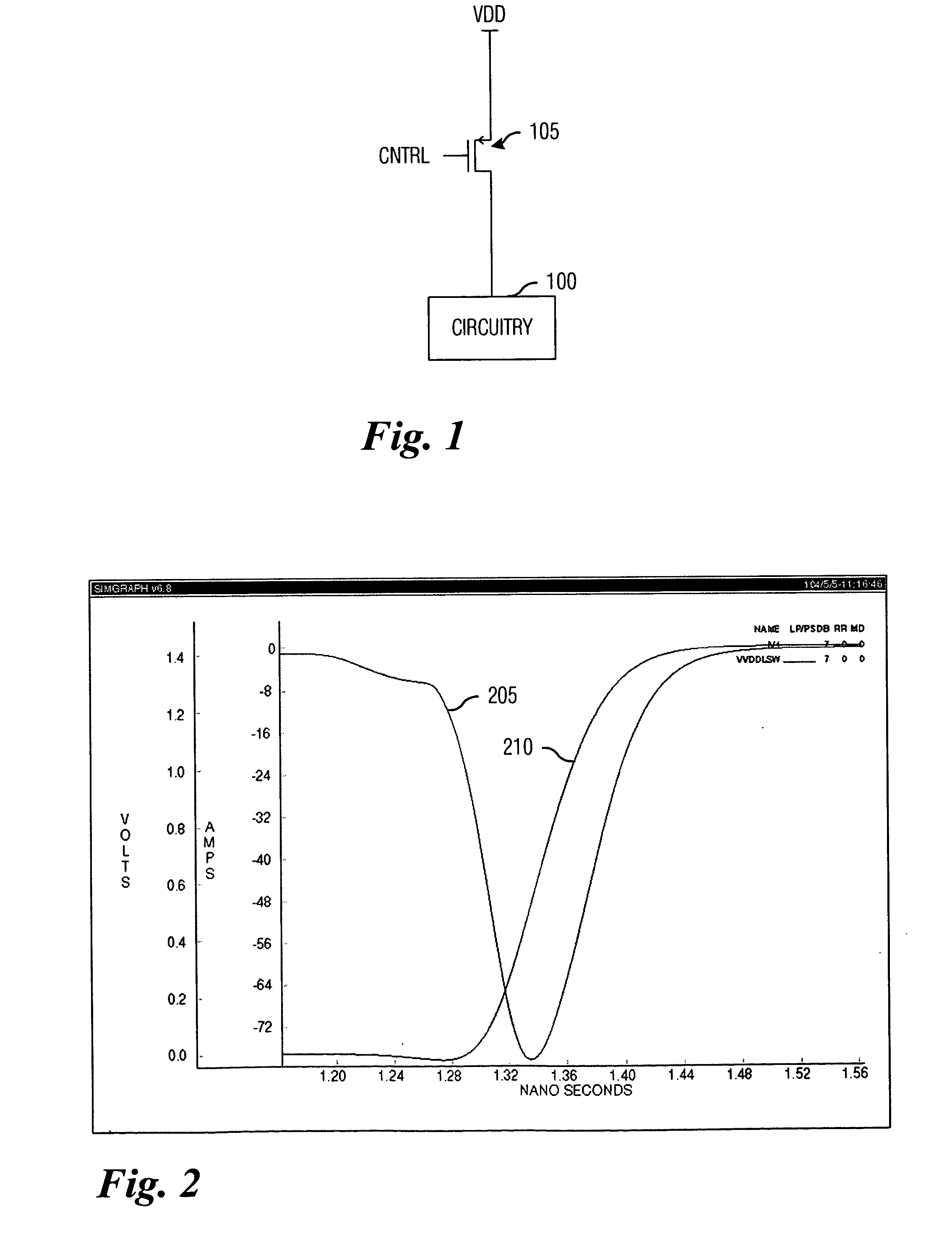
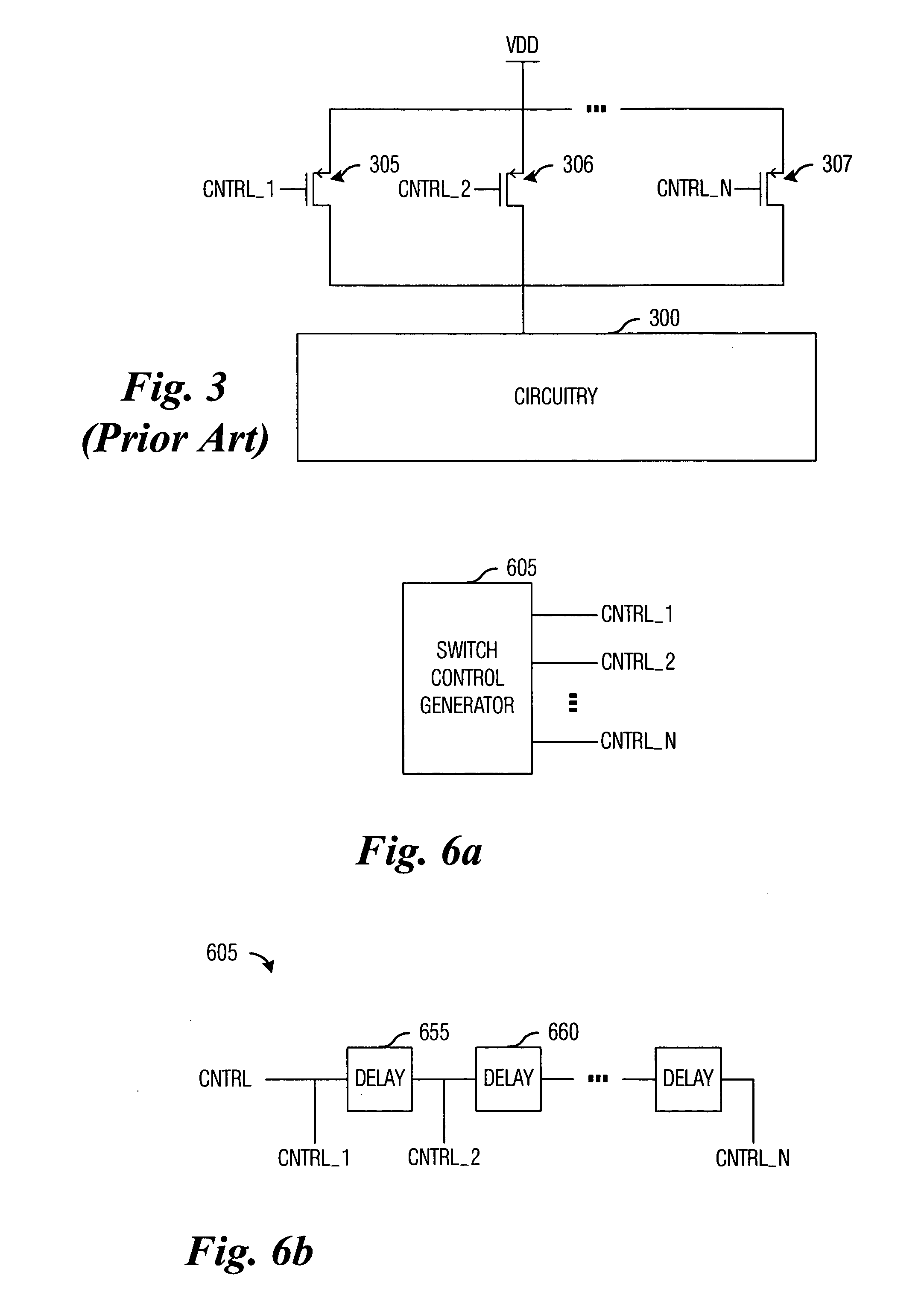
Switch driver with slew rate control
ActiveUS20060033551A1Total current dropReduced magnitudePower reduction by control/clock signalElectronic switchingDriver circuitCapacitance
System and method for providing power to circuitry while avoiding a large transient current. A preferred embodiment comprises a distributed switch (such as switch arrangement 400) with a plurality of switches (such as switch 405) coupling a power supply to the circuitry. Each switch is individually controlled by a control signal and is turned on sequentially. Also coupled to each switch is a pre-driver circuit (such as pre-driver circuit 410). The pre-driver circuit comprises a potential adjust circuit (such as potential adjust circuit 505) that rapidly adjusts a voltage potential at the switch and a rate adjust circuit (such as the rate adjust circuit 520) that accelerates the power ramp-up across the switch once transient currents are no longer a concern. Adjusting the voltage potential so that the switch operates in a saturation mode increases an effective capacitance across the switch and thereby retarding the power ramp-up across the switch.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
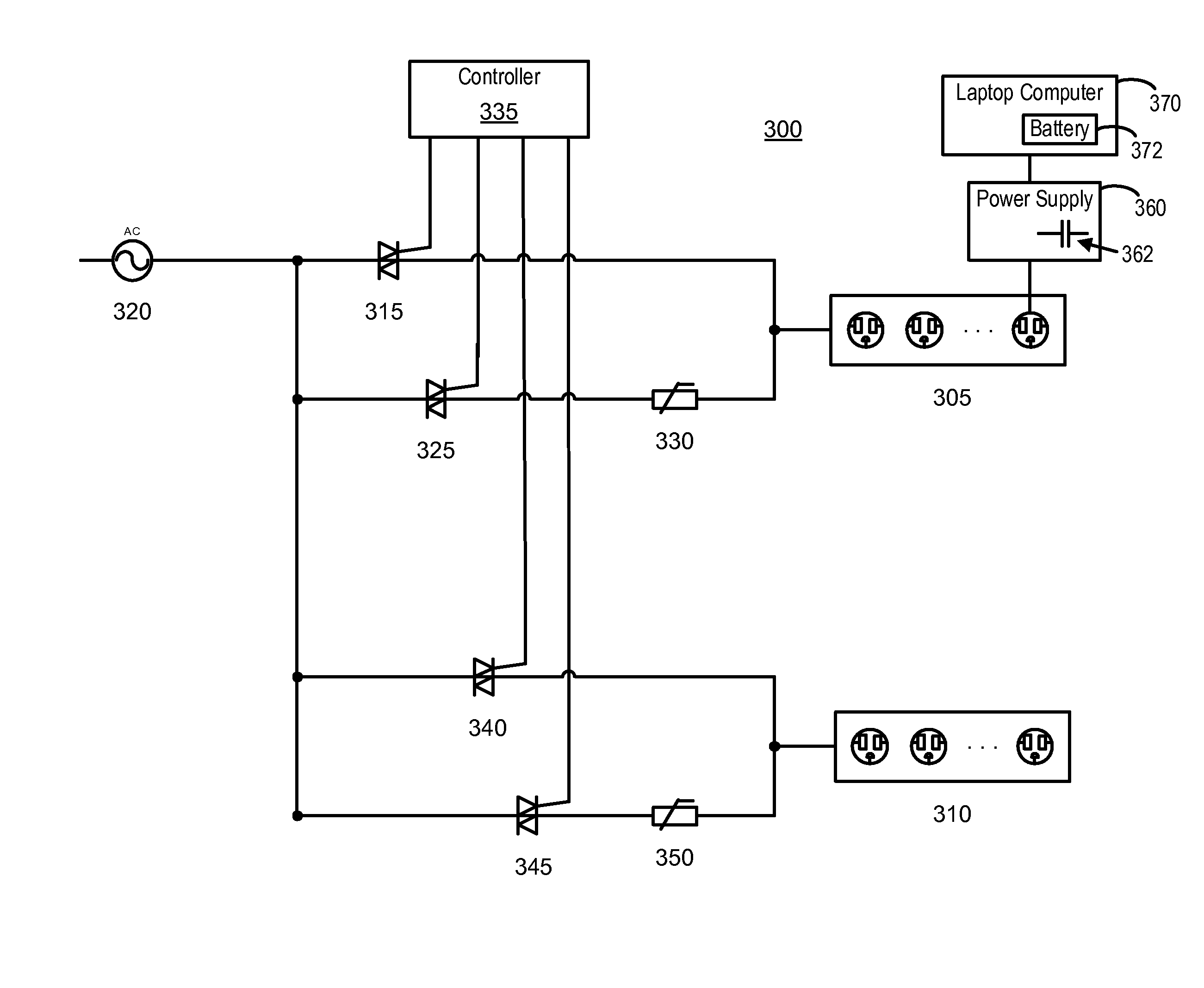
Laptop computer storage and battery charging systems and methods including transient current inrush limiter
A control system of a laptop computer storage system comprises a plurality of receptacles for charging one or more laptop computer batteries. A first switch may be provided for coupling the receptacles to a power source via a current limiter having an impedance that initially limits a current inrush and then decreases with temperature. A second switch may be provided for coupling the receptacles to the power source via a low impedance path. A controller may be provided and configured to activate the first switch to limit an initial current inrush while charging energy storing components associated with the laptop computer's power supply and then activate the second switch to allow each laptop coupled to the receptacles to at least partially charge its battery.
Owner:ERGOTRON
Using output drop detection pulses to achieve fast transient response from a low-power mode
ActiveUS20110157924A1Low costImprove transient responseEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDetector circuitsSmall peak
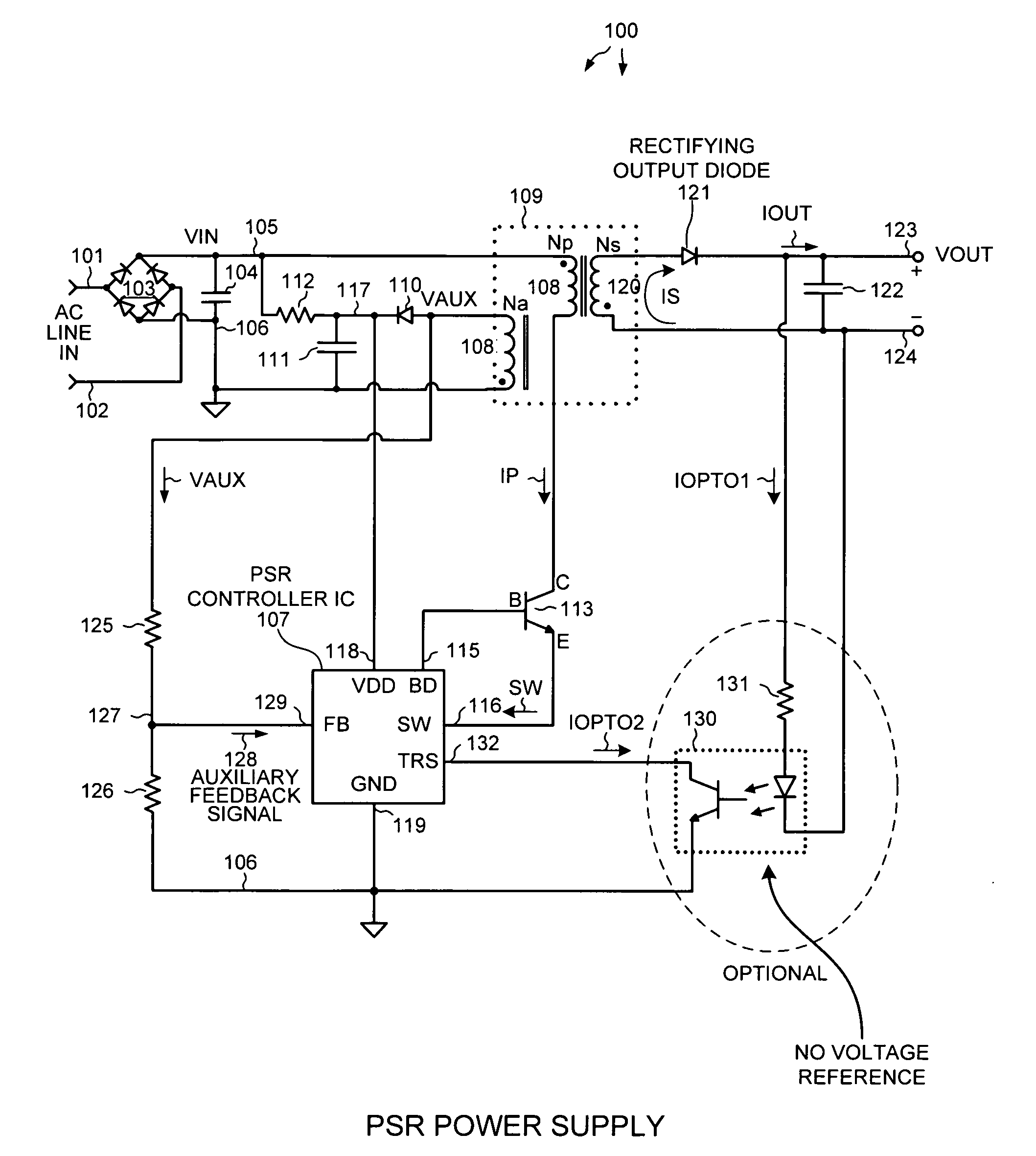
In a first aspect, in a Primary Side Regulation (PSR) power supply, some primary current pulses are used to forward bias an output diode such that an auxiliary winding voltage can be properly sampled after each pulse. The samples are used to regulate the power supply output voltage (VOUT). Other primary current pulses, however, are of a smaller peak amplitude. These pulses are not used for VOUT regulation, but rather are used to determine whether the VOUT has dropped. In a second aspect, a transient current detector circuit within the PSR controller integrated circuit detects whether an optocoupler current has dropped in a predetermined way. If the TRS current detector detects that the optocoupler current has dropped, then the power supply stops operating in a sleep mode and is made to operate in another higher power operating mode in which the power supply switches.
Owner:ACTIVE SEMI
Pixel circuit, display and driving method thereof
ActiveUS7535442B2Reduce impactExclude influenceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitancePotential difference
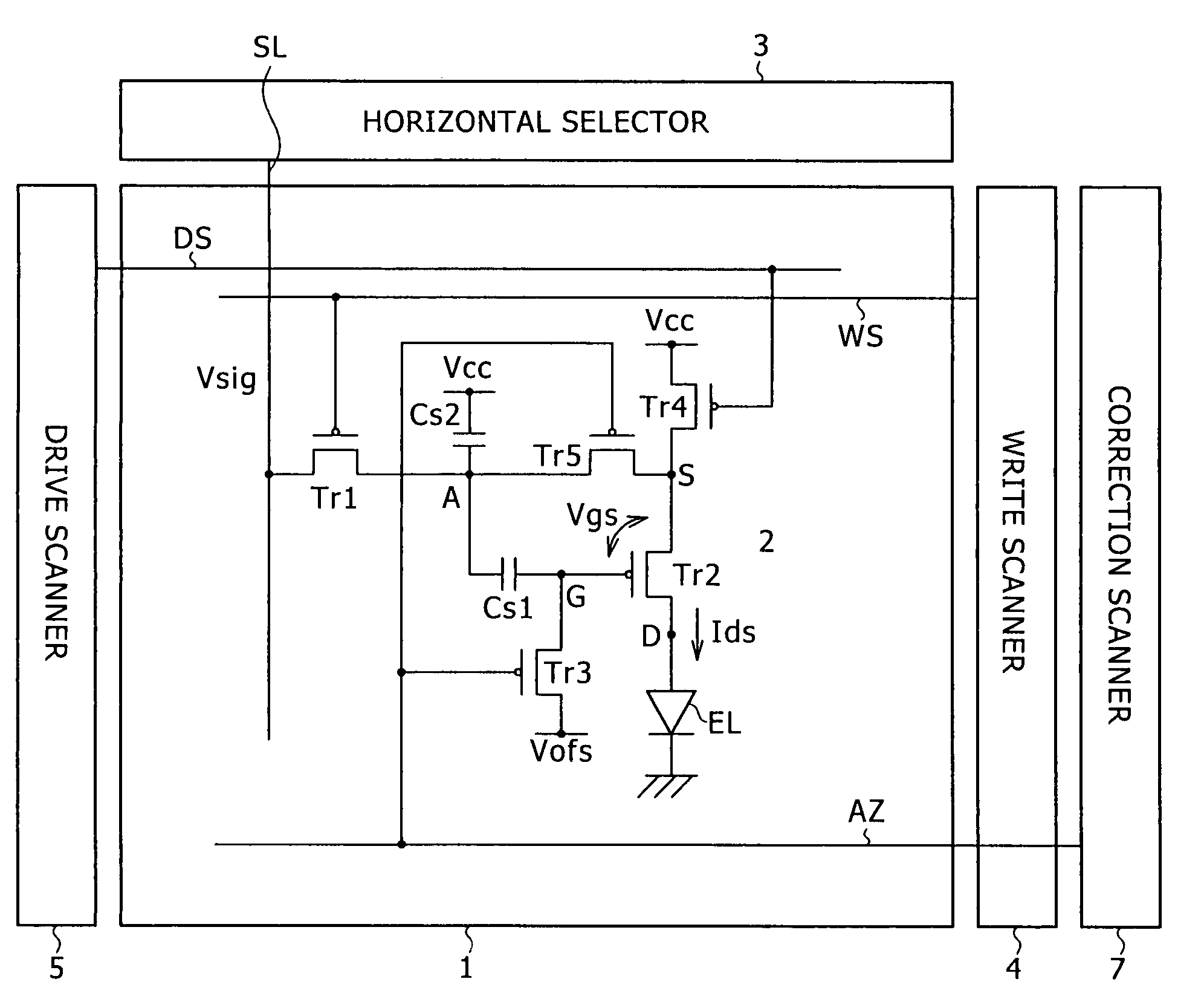
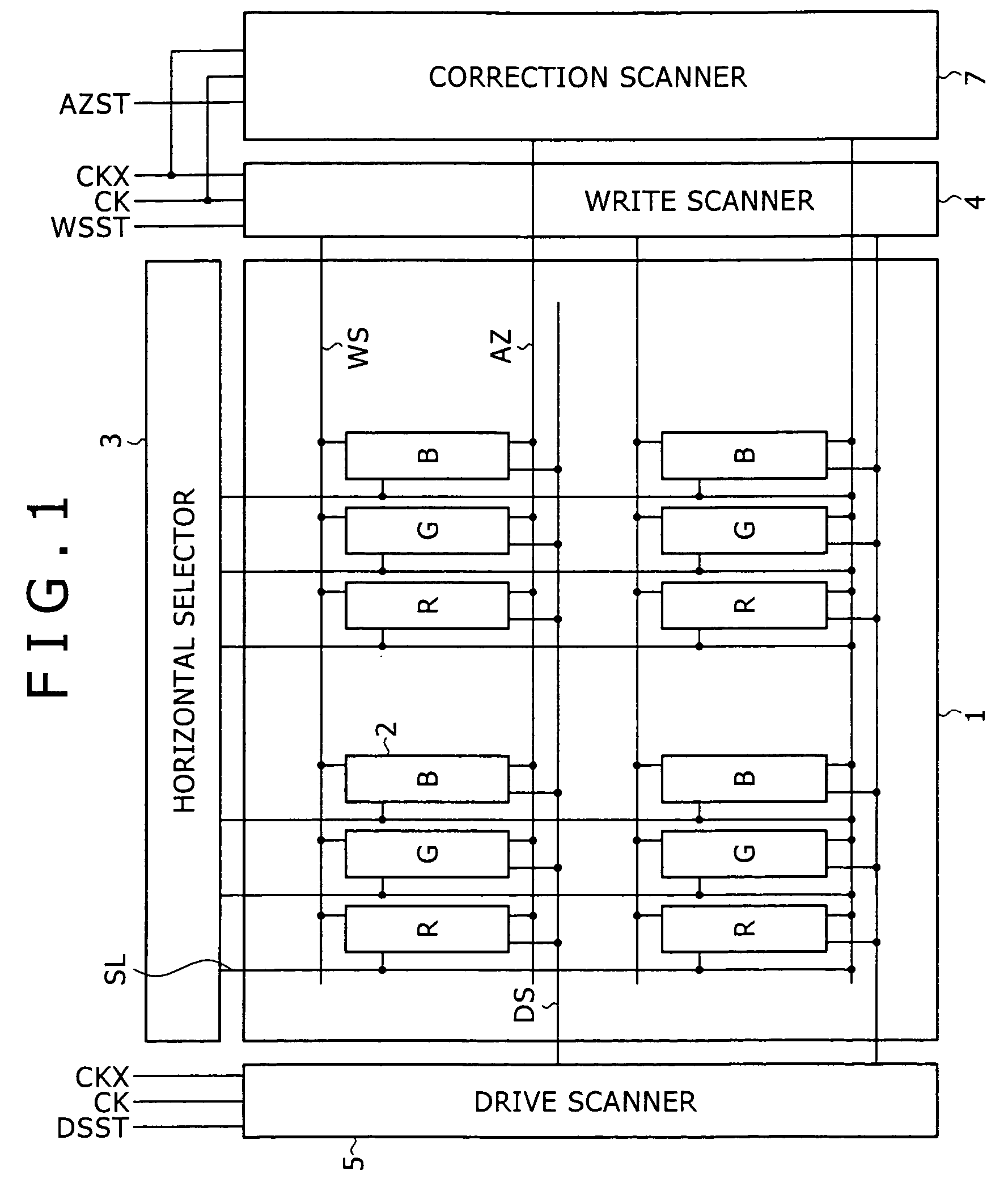
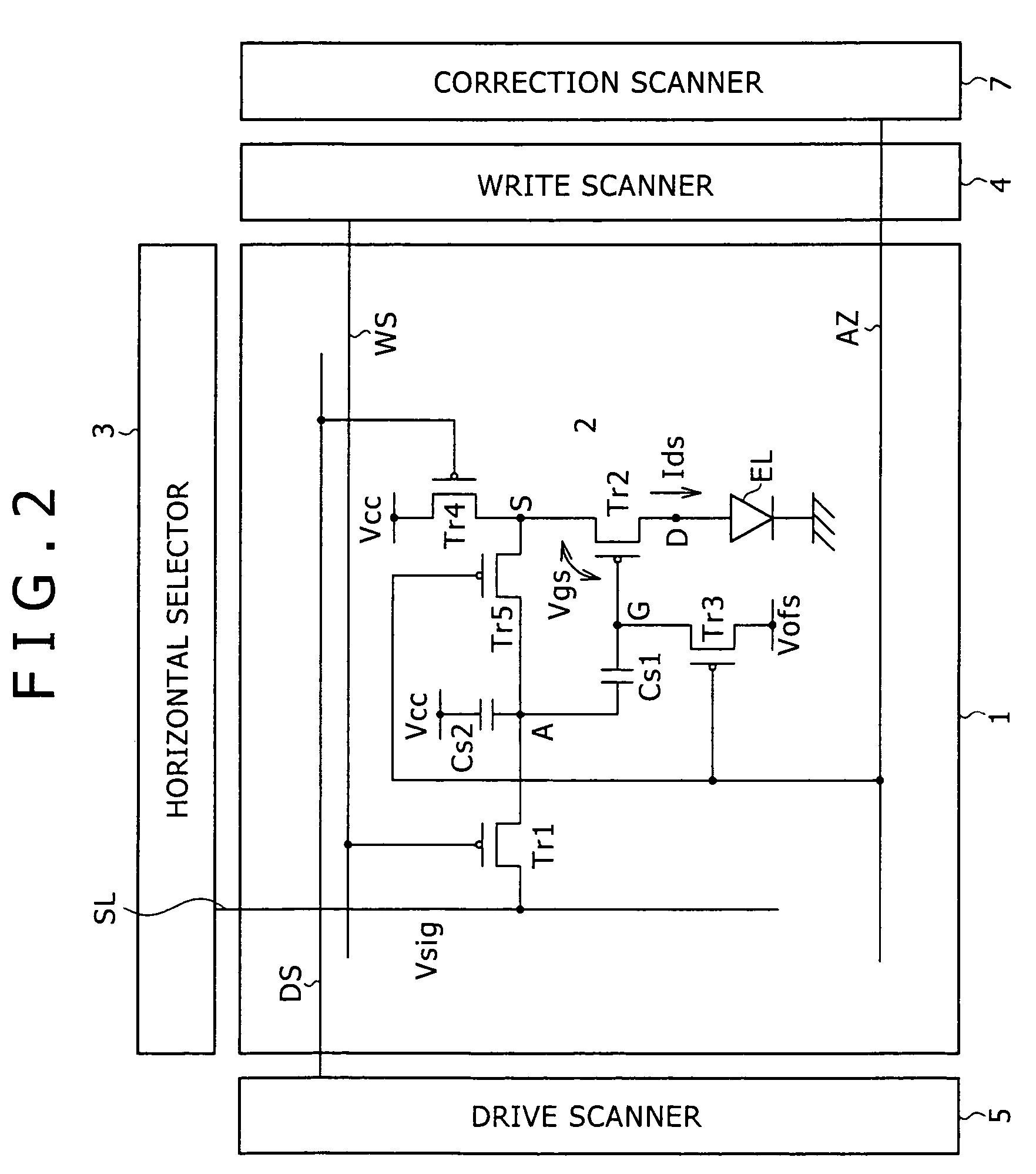
The invention provides a pixel circuit that allows simultaneous correction of both influence of the threshold voltage of a drive transistor and influence of the mobility of the drive transistor. Correction means is connected to a drive transistor and a capacitance part, and operates during a correction period preceding to a sampling period. The correction period is separated into a reset period and a detection period. During the reset period, the correction means energizes the capacitance part to reset the potential of the capacitance part. During the detection period, the correction means stops the energization and detects the potential difference arising between the source and gate of the drive transistor during the period when a transient current flows through the drive transistor. The capacitance part holds the potential corresponding to the detected potential difference. The held potential includes both a potential component for reducing the influence of the threshold voltage on the output current of the drive transistor, and a potential component for reducing the influence of the carrier mobility thereon.
Owner:SONY CORP
Non-intrusive load identification method and Non-intrusive load identification device
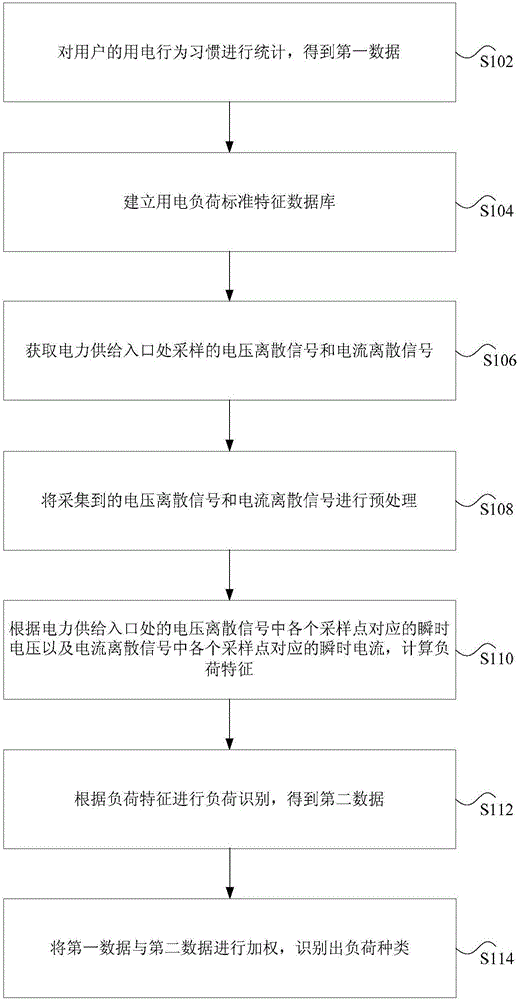
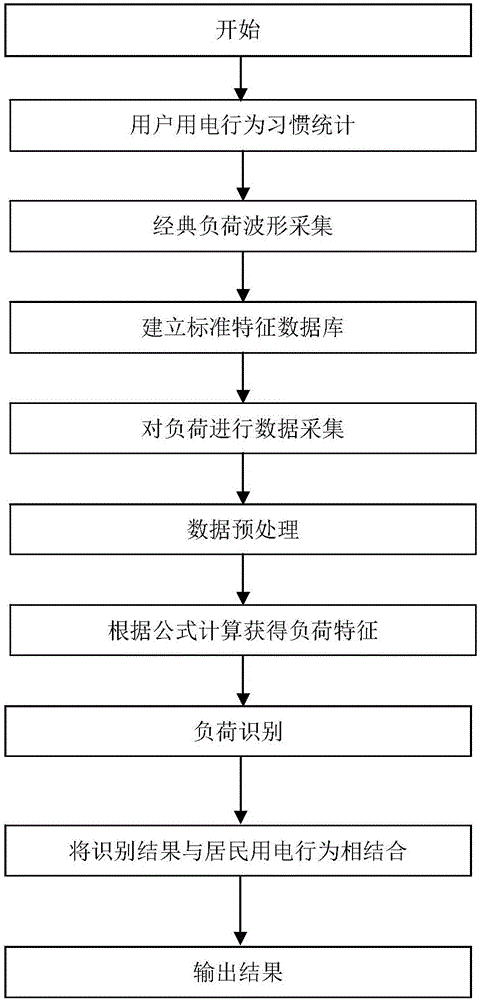
InactiveCN106815677AIn line with electricity habitsSolve technical problems with low accuracyResourcesElectricityUtilization behavior
The invention discloses a non-intrusive load identification method and a non-intrusive load identification device. The non-intrusive load identification method comprises steps that electricity utilization behavior habits of users are counted to acquire first data; an electricity utilization load standard characteristic database is established; a voltage discrete signal and a current discrete signal sampled on a power supply entrance are acquired; the acquired voltage discrete signal and the acquired current discrete signal are preprocessed; load characteristics are calculated according to the transient voltages corresponding to various sampling points in the voltage discrete signal of the power supply entrance and the transient currents corresponding to the various sampling points in the current discrete signal of the power supply entrance; the load identification is carried out according to the load characteristics, and second data is acquired; the weighting of the first data and the second data is carried out, and the type of the load is identified. The technical problem of the prior art of the low accuracy of the load identification during non-intrusive load monitoring is solved.
Owner:STATE GRID BEIJING ELECTRIC POWER +1
Controllable discharge switch of high-energy impulse in three electrodes under vacuum environment
InactiveCN1697107AReduce ablation rateDiffusion fastSpark gaps with auxillary triggeringHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesElectricityHigh energy
The disclosed discharge switch includes upper and lower electrodes setup inside insulated case. Pressure inside the air locked shell body formed by the insulated case and flanges at two ends of the case is 10 -3 - 10 -4 Pa. At least one of the upper and lower electrodes is a movable electrode. Trigger electrode is inlaid inside the fixed electrode or setup between the upper and lower electrodes. Since being air locked in vacuum environment, the upper and lower electrodes possess tremendous ability of ducting transient current in high energy. Moreover, operation reliability of pulse switch is raised because vacuum environment is not interfered from outside. Features are: raised reliability, very low ablation rate of electrode, and wide range of stable operation voltage.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
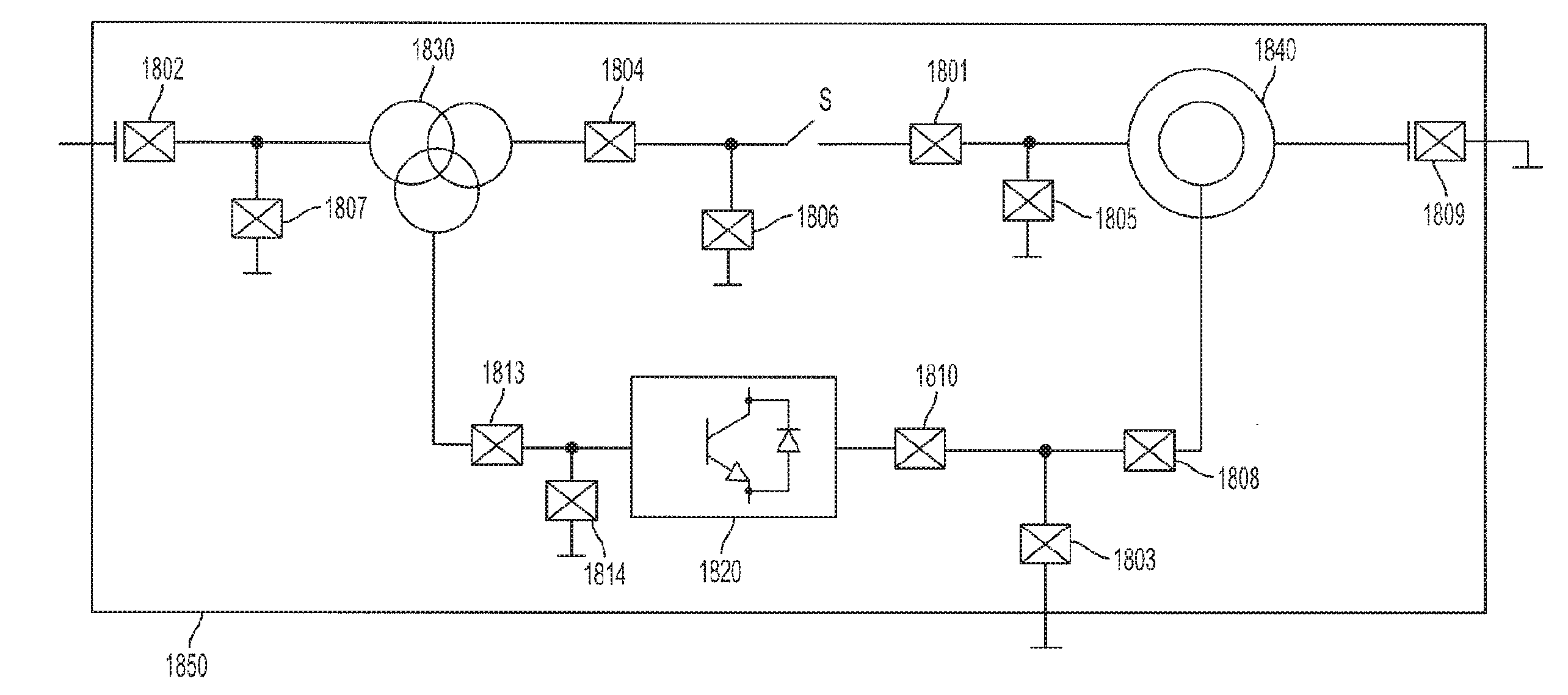
Hybrid/Electrical Vehicle HV AC System Leakage and Ground Fault Detection
ActiveUS20140132278A1Testing electric installations on transportShort-circuit testingReverse currentHigh pressure
Apparatus and methods for detection of a ground fault on a DC side as well as on an AC side of an inverter are presented. A detection means can receive forward and reverse current and provide an induced current based on the difference between them. A parameter associated with the induced current, or a parameter associated with a voltage generated by conduction of the induced current through a device, can be used to detect a ground fault. In addition, a detection means can be configured to receive transient current, and a resulting voltage at the detection means can be used for fault detection. A detection means can be disposed at the DC side of an inverter or at the AC side of the inverter. Apparatus and methods can be configured to detect AC leakage current caused by a ground fault.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Variable impedance device for a wind turbine
ActiveUS20160333856A1Generator control circuitsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityPower flow
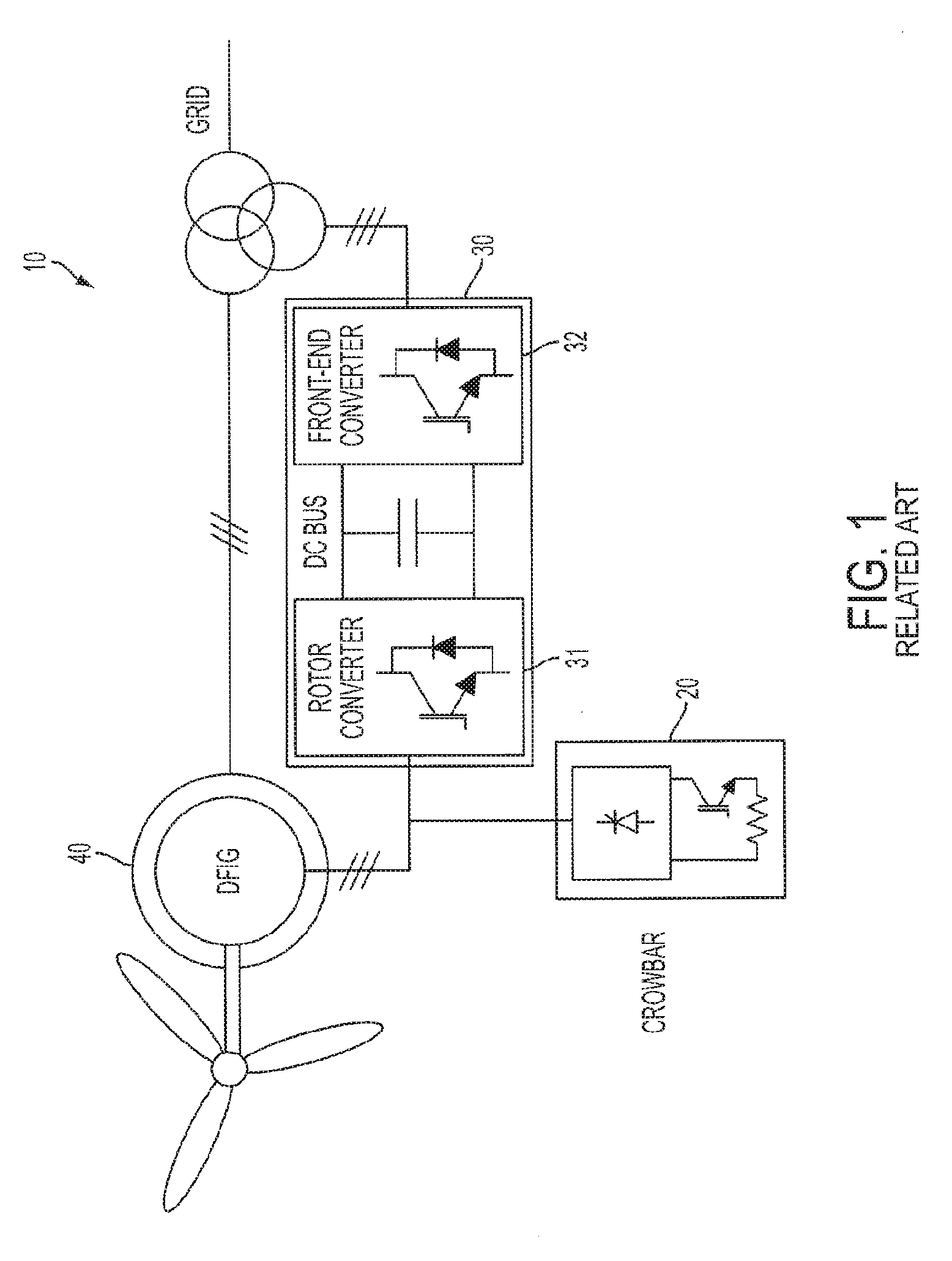
A wind turbine that includes a housing, an asynchronous generator disposed in the housing and configured to be electrically connected to a power grid connection; a power converter circuit disposed in the housing and configured to be electrically connected to the asynchronous generator; and a variable impedance device disposed in the housing, connected to the generator and configured to limit current by varying impedance in response to a transient current. The wind turbine delivers reactive power to the power grid when the variable impedance device varies impedance in response to the transient current. The variable impedance device can be arranged in series between the asynchronous generator and the power grid connection, or can be in a shunt arrangement between the asynchronous generator and a neural point.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com