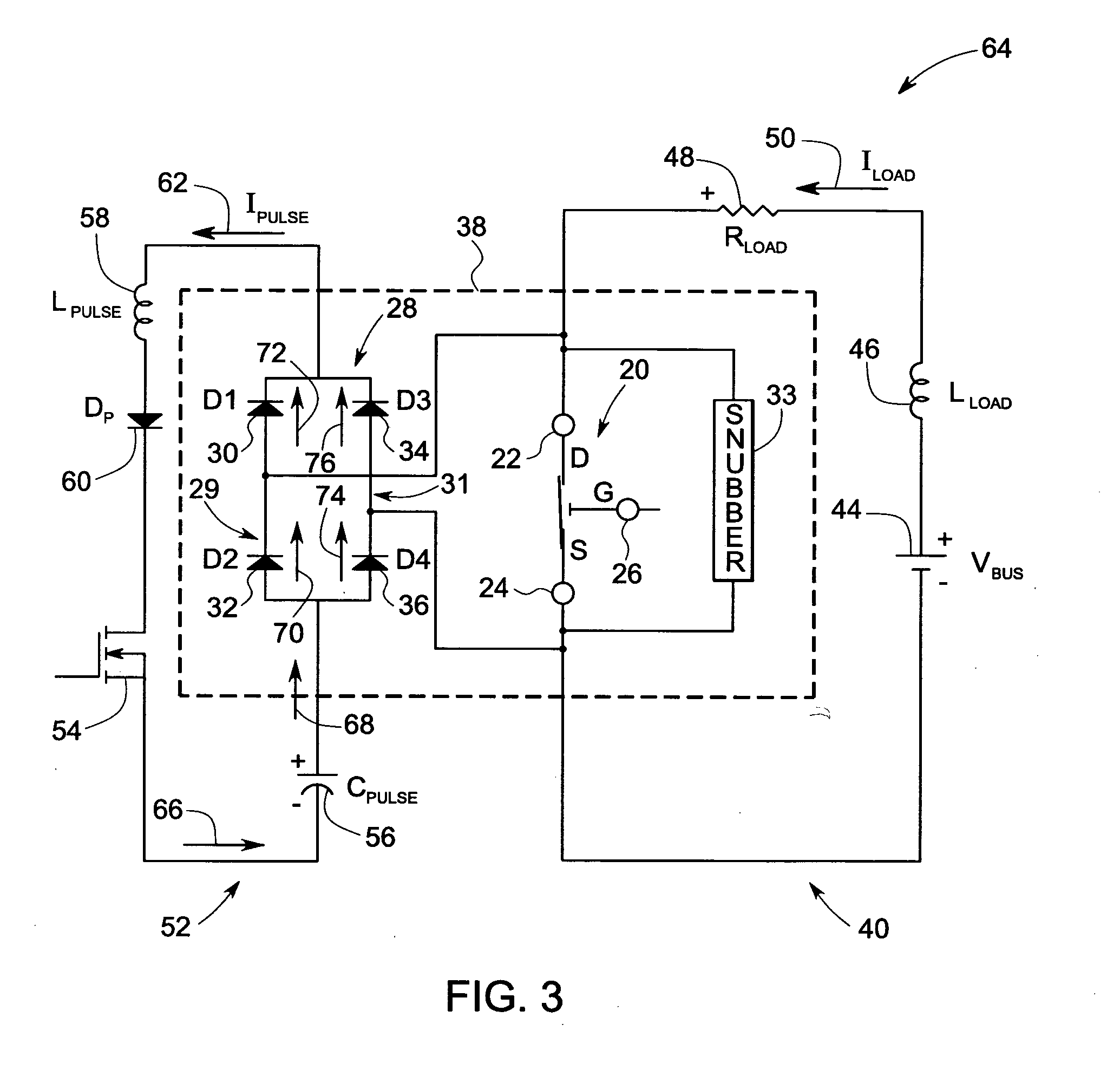
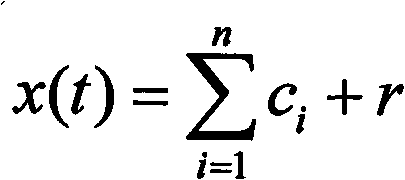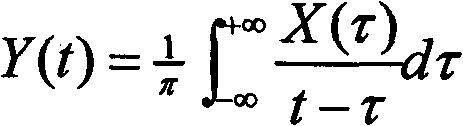Patents
Literature
1021 results about "Arc suppression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arc suppression is the reduction of sparks formed when current-carrying contacts are separated. The spark is a luminous discharge of highly energized electrons and ions, and is an electric arc.
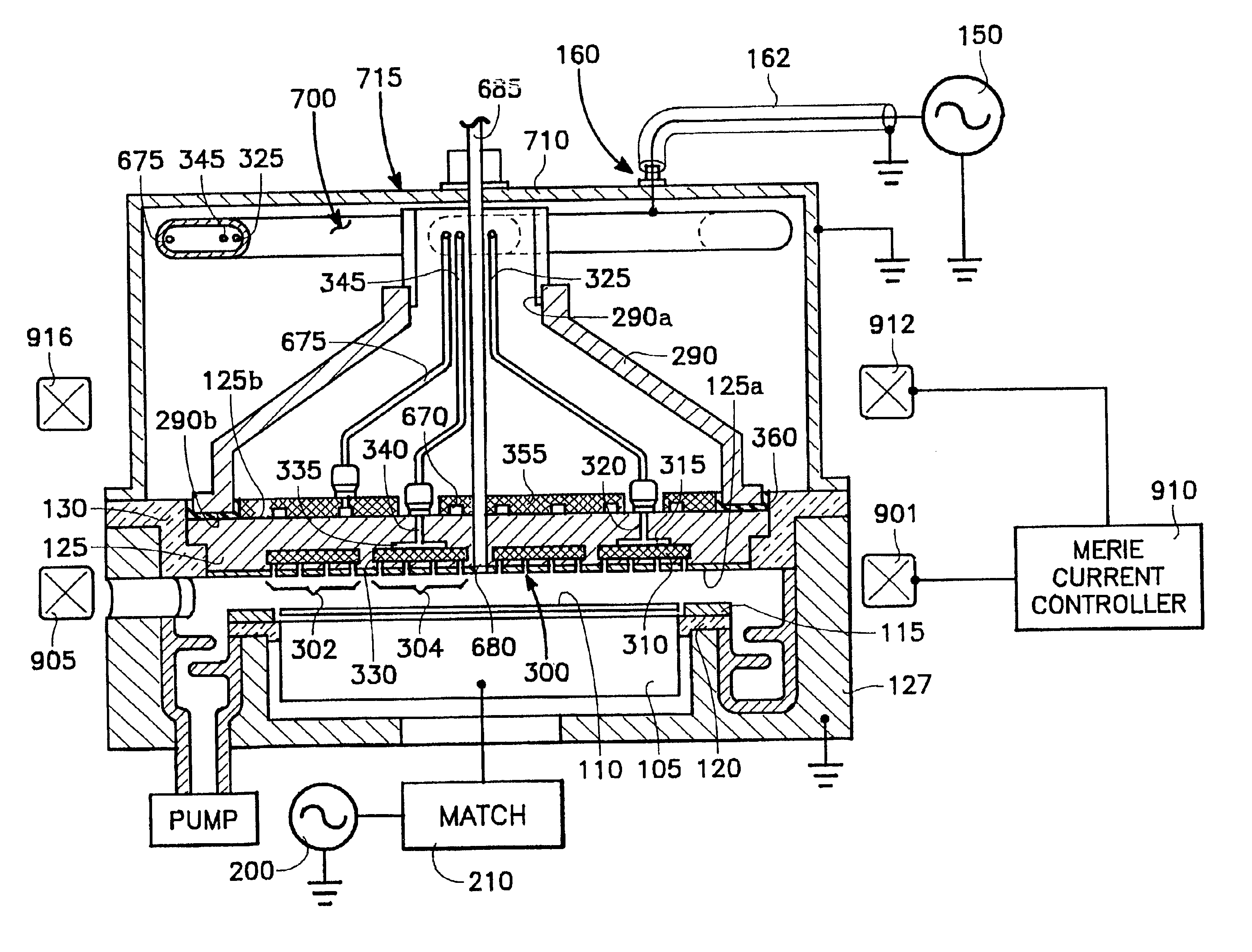
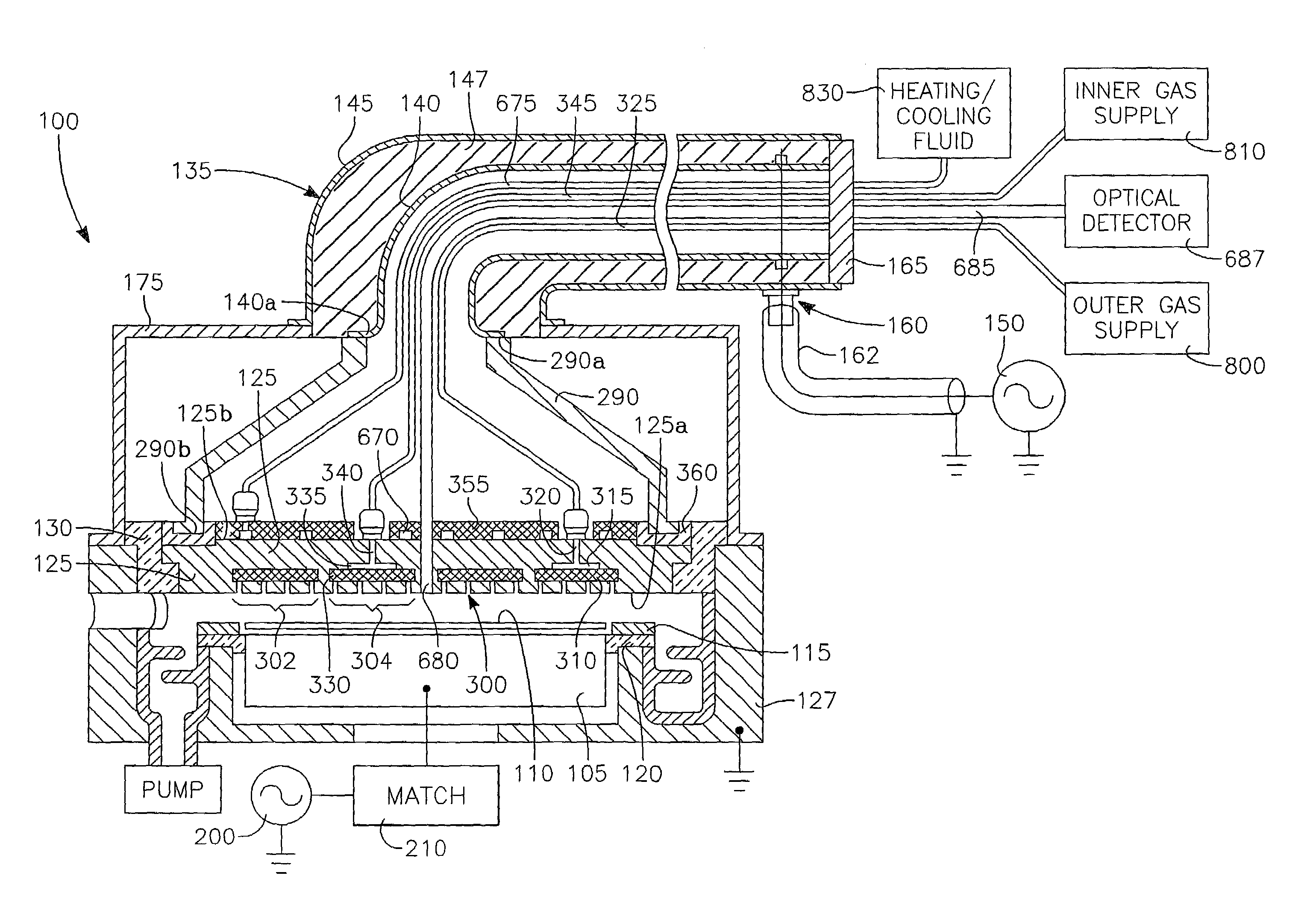
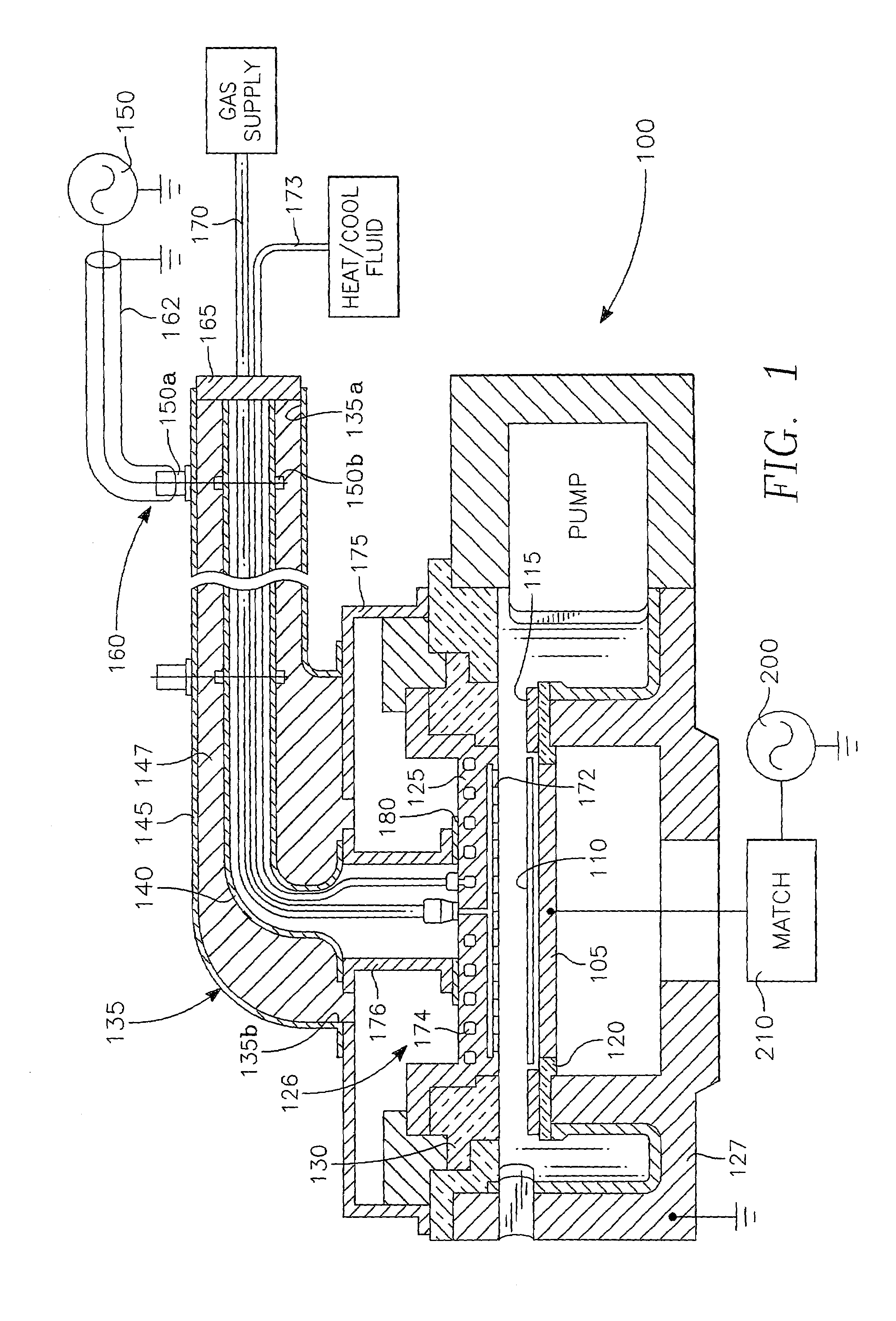
Merie plasma reactor with overhead RF electrode tuned to the plasma with arcing suppression
InactiveUS6894245B2Improve plasma ion density distribution uniformitySufficient capacitanceElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsCapacitanceIon density
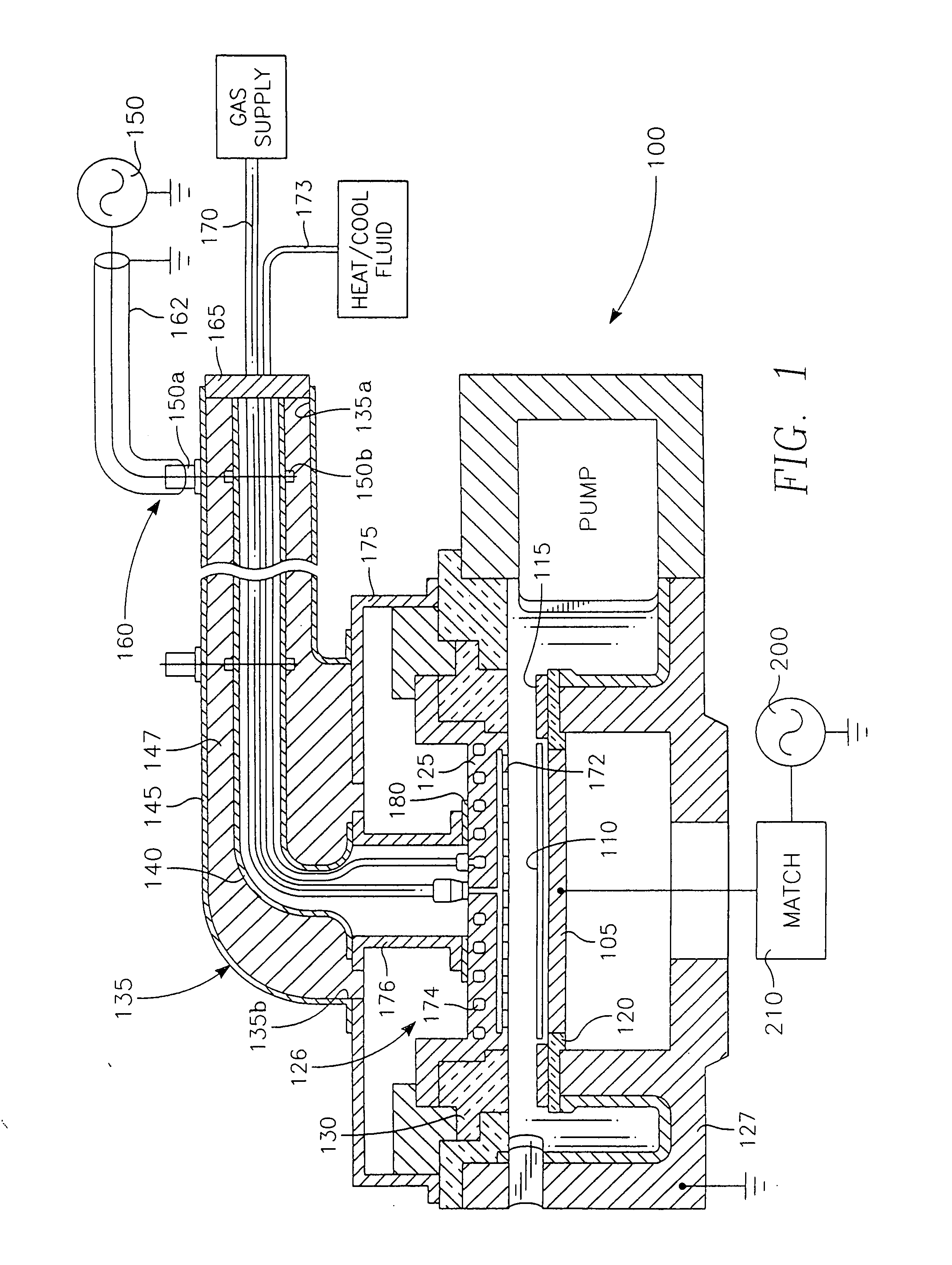
A plasma reactor for processing a semiconductor workpiece, includes a reactor chamber having a chamber wall and containing a workpiece support for holding the semiconductor support, the electrode comprising a portion of the chamber wall, an RF power generator for supplying power at a frequency of the generator to the overhead electrode and capable of maintaining a plasma within the chamber at a desired plasma ion density level. The overhead electrode has a capacitance such that the overhead electrode and the plasma formed in the chamber at the desired plasma ion density resonate together at an electrode-plasma resonant frequency, the frequency of the generator being at least near the electrode-plasma resonant frequency. The reactor further includes a set of MERIE magnets surrounding the plasma process area overlying the wafer surface that produce a slowly circulating magnetic field which stirs the plasma to improve plasma ion density distribution uniformity.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrical power distribution network single-phase earth fault type and phase distinguishing method
ActiveCN101452041ALess analogSimple calculationFault locationEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectric cablesElectric power
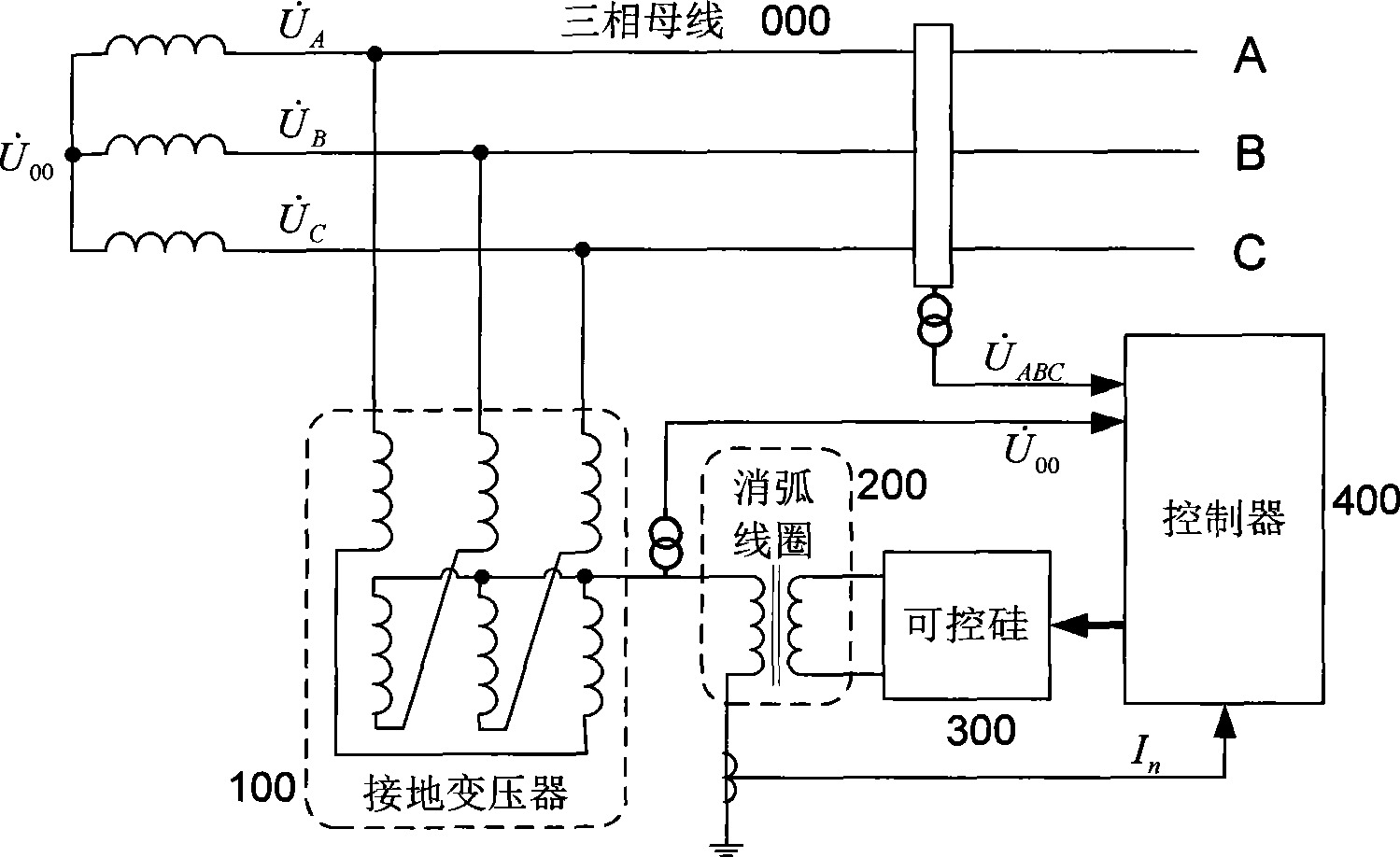
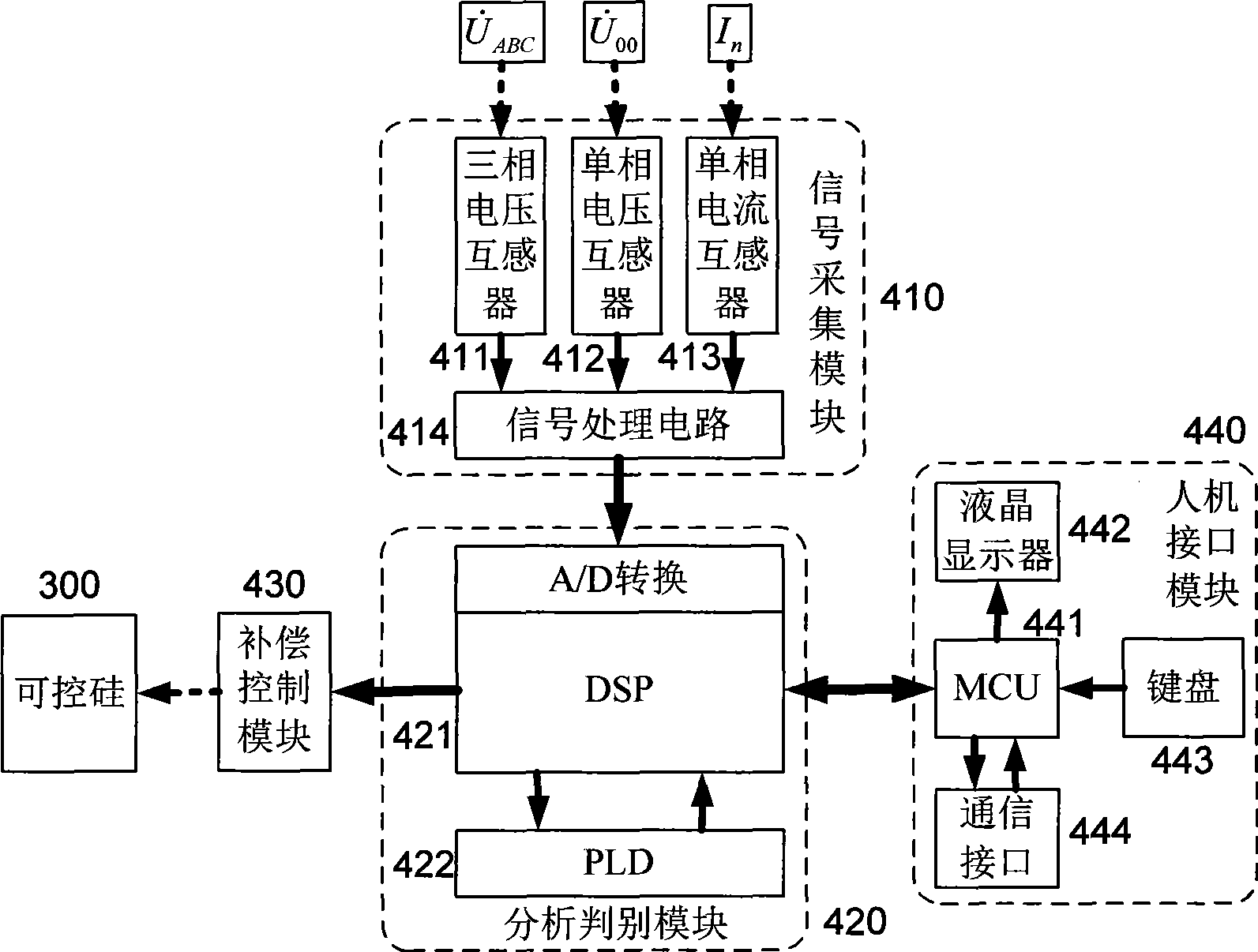
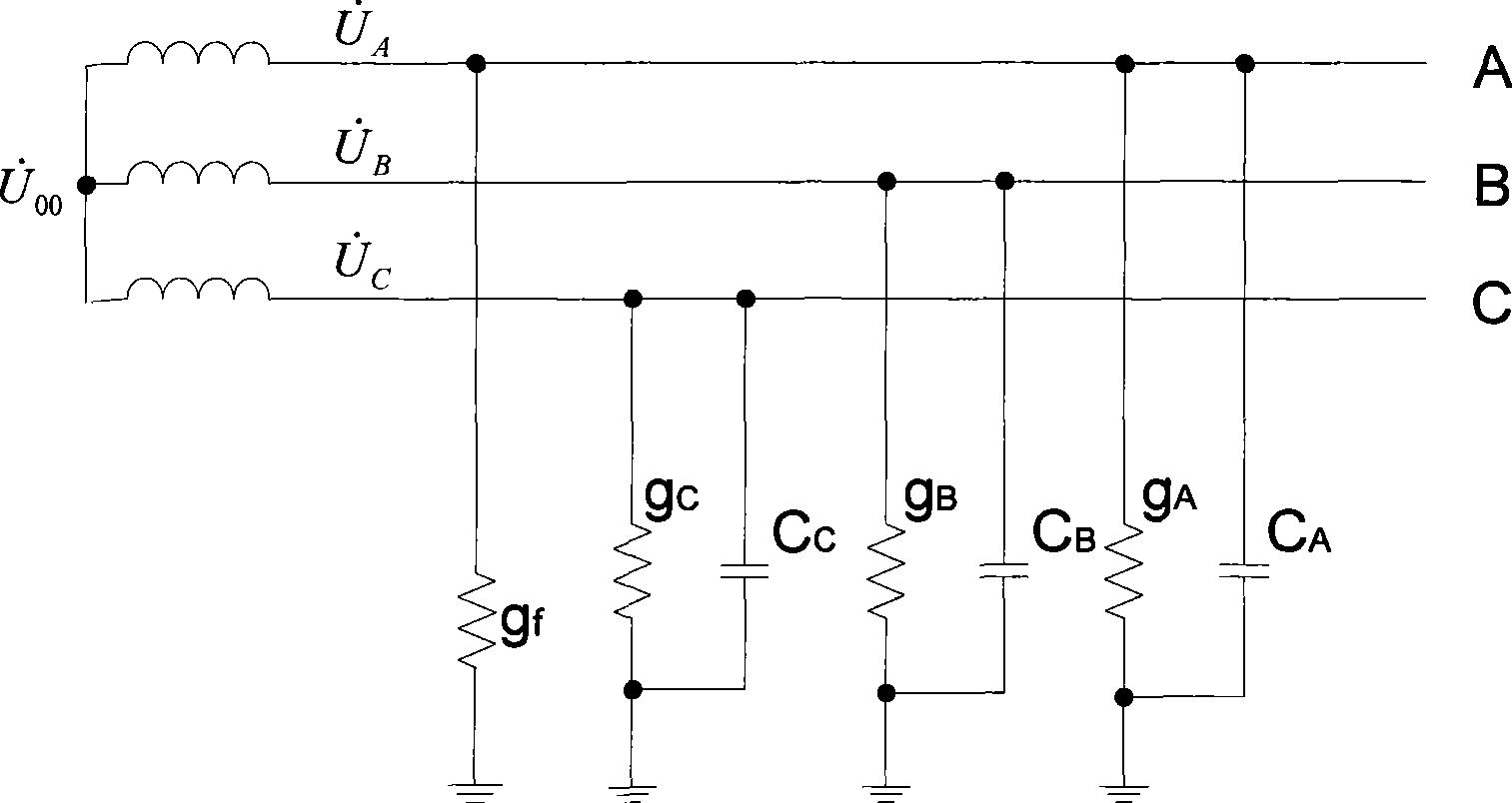
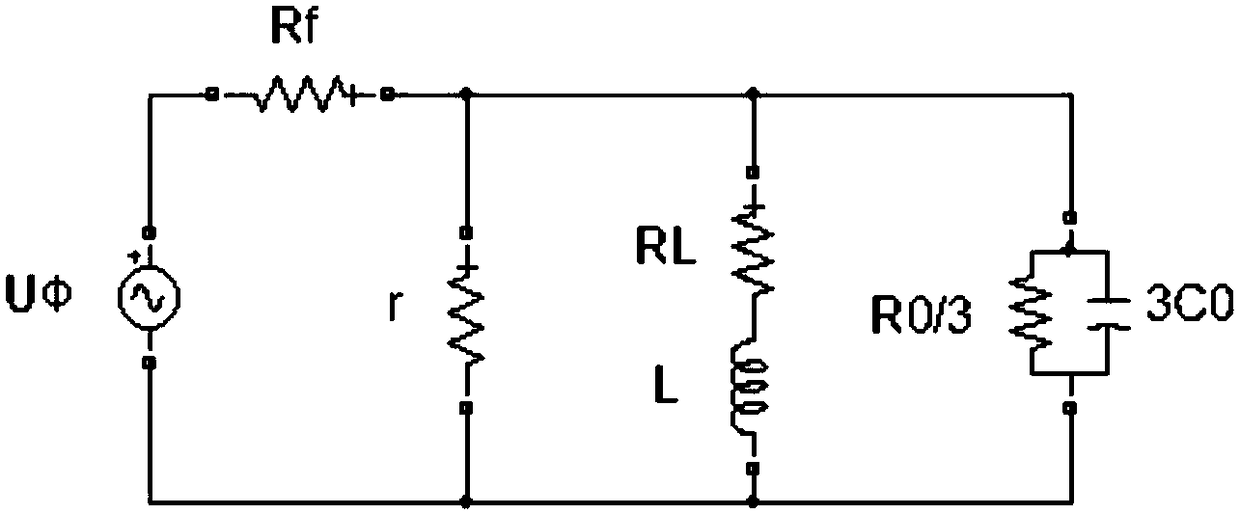
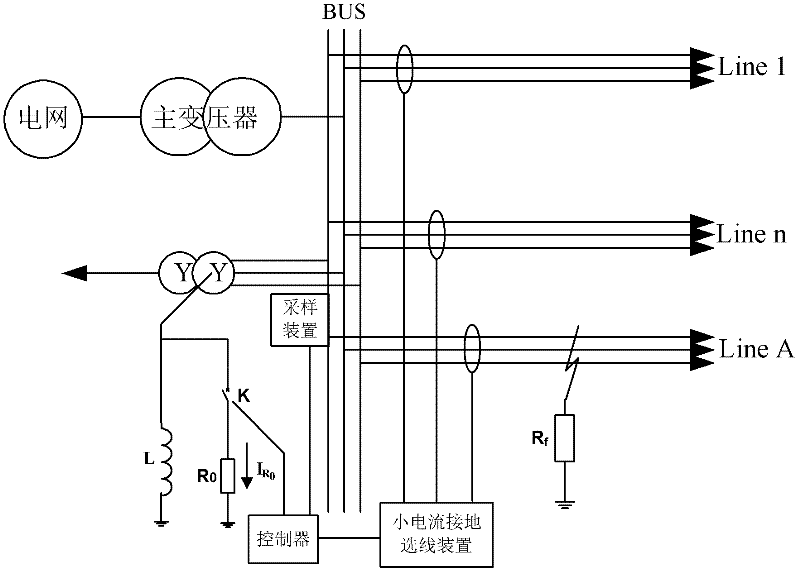
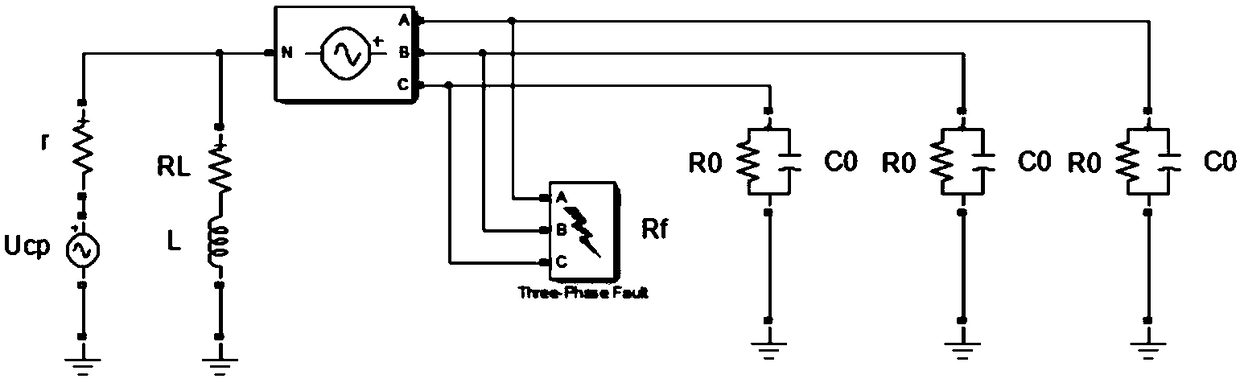
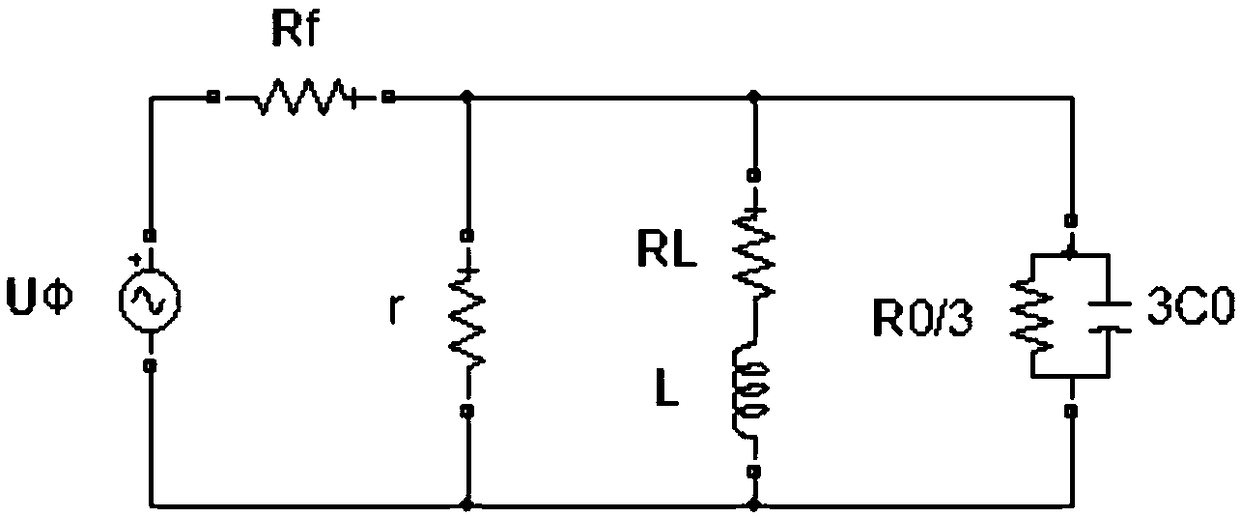
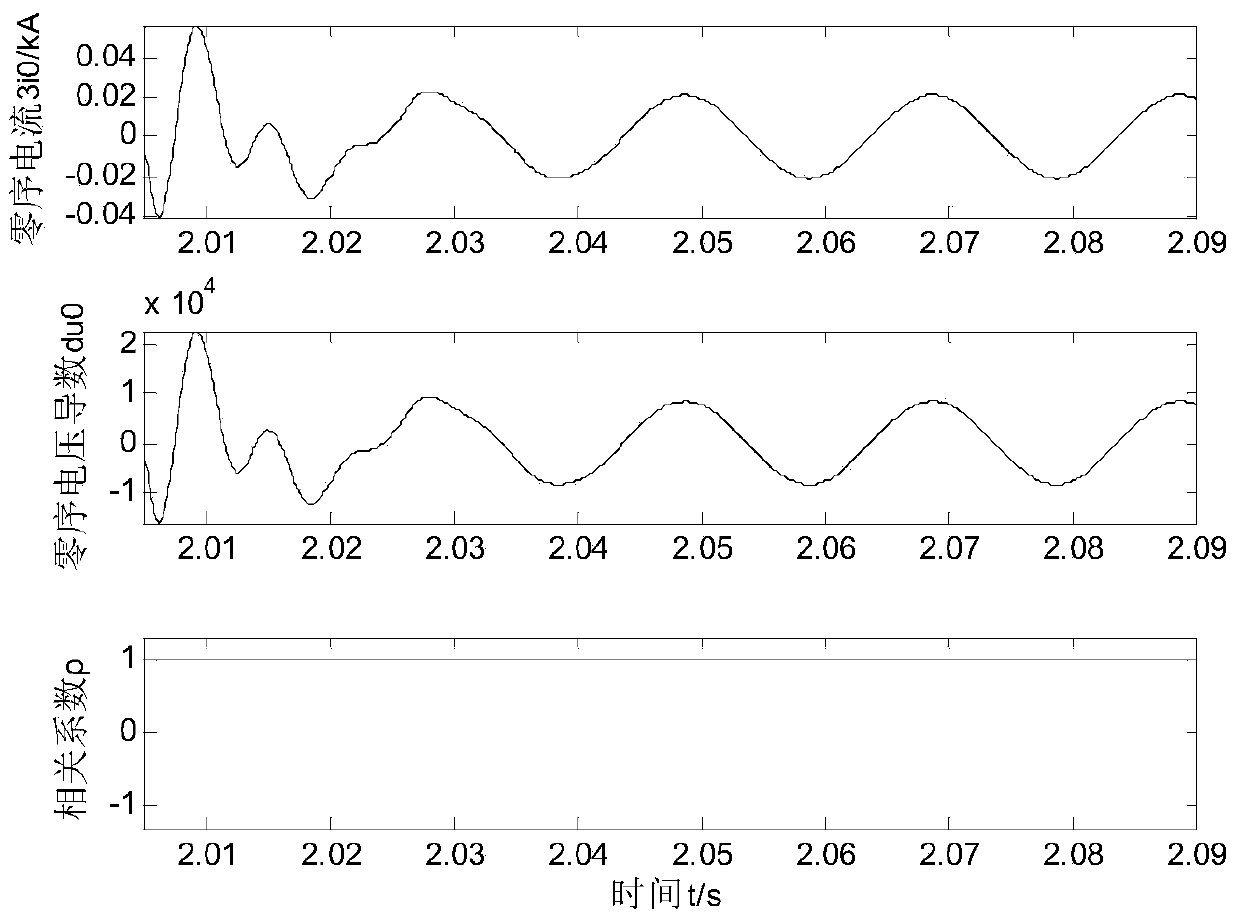
The invention discloses a distributing net single phase earth fault type and a distinguishing method of phase identification, relating to a distributing net single phase earth fault distinguishing method in the field of AC distributing net testing and relaying protection technology. According to the invention, through collecting three-phase voltage of the distributing net system and neutral point voltage of the distributing net system, phase angle of each eigenvector is computed through a special relation, the type of the fault and the phase identification can be fast distinguished through the phase angle distinguishing logic. The inventive working system is that a three-phase bus (000), a grounding transformer (100), a linear side of an arc suppression coil (200) are connected in turn with the earth; a controller (400), a thyristor (300) and a secondary side of an arc suppression coil (200) are connected in turn. The invention is simple in criterion, small in collection quantity, fast in distinguishing speed, high in accuracy, reliable in security, which is suitable for 3-66 KV distributing net based on an aerial line or a power cable.
Owner:STATE GRID HUBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Novel faulty line selection method in low current faulty grounding system
InactiveCN101701998ALine selection is accurateOvercome the problem of low accuracy of fault line selectionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationHarmonicSelection criterion
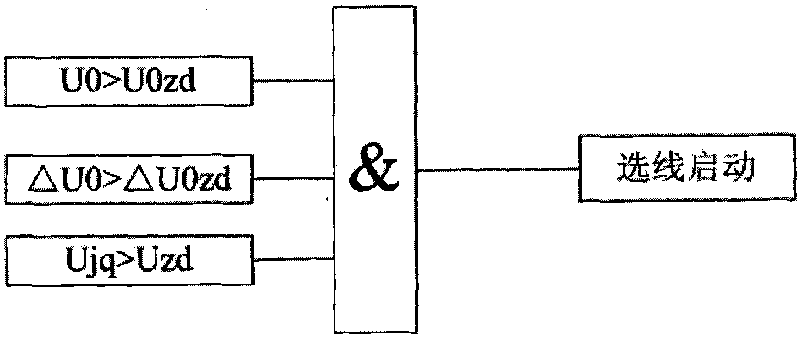
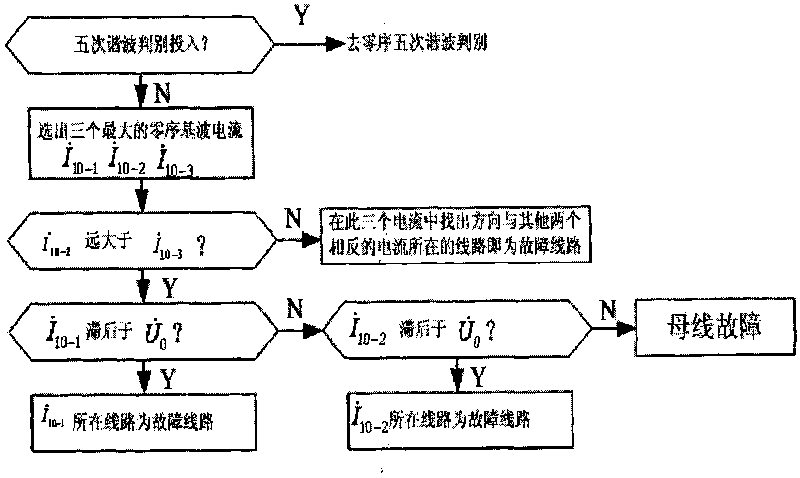
The invention discloses a novel faulty line selection method in a low current faulty grounding system, which judges whether a ground fault happens or not by detecting zero sequence voltage and phase voltage of a system bus, determines to judge grounded fault circuit adopting different faulty line selection methods according to the different characteristics of zero sequence fundamental wave and zero sequence quintuple harmonic current generated according to that arc suppression coil exists in a system when single-phase grounding fault happens on the premise that ground fault occurs, combines with some assistant line selection criteria to perform comprehensive judgment so as to select the circuit with a fault correctly, thus overcoming the problem of low accuracy of faulty line selection in a low current grounding system. The invention has the characteristics of reasonable method steps, high accuracy of faulty line selection and convenient operation and application.
Owner:山东泰开自动化有限公司
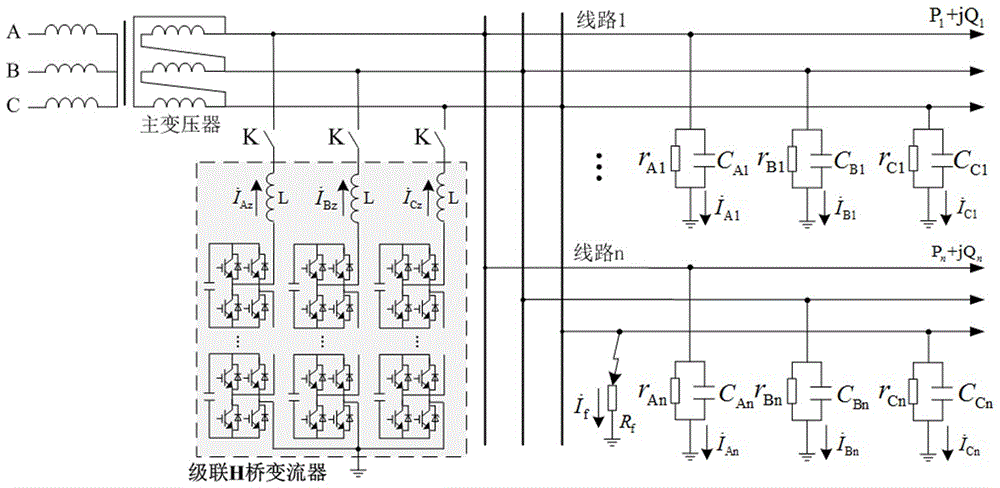
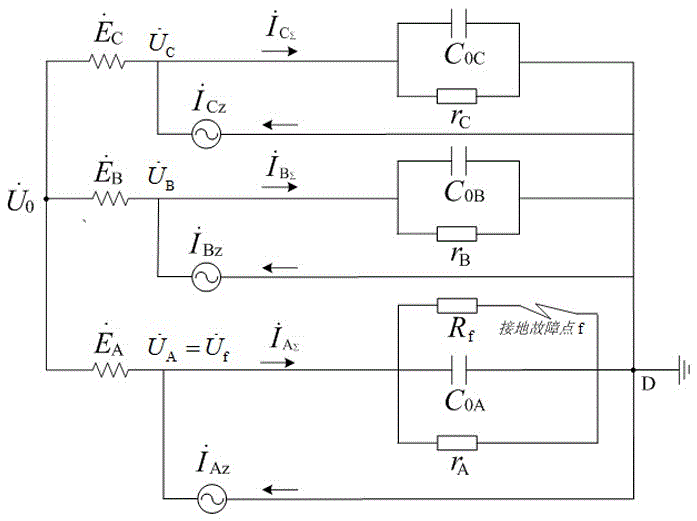
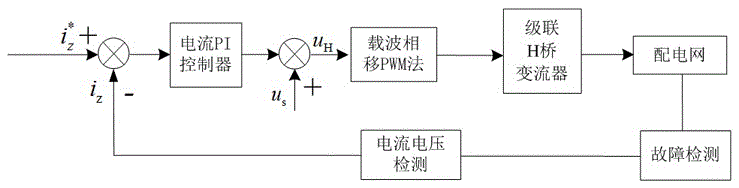
Distribution network ground fault arc suppression method based on three-phase cascade H bridge converters
ActiveCN105610147AEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitanceTransformer
The invention relates to a distribution network ground fault arc suppression method based on three-phase cascade H bridge converters. The three-phase cascade H bridge converters are adopted to replace arc suppression coils and mounted between phase lines and the ground, and power is supplied to capacitors on the direct current side of the converters by using phase voltages, so that boosting transformers and grounding transformers are saved, and the problem of source taking difficulty on the direct current side of the converters is solved. The converters inject current to a distribution network in a phase splitting mode to compensate the total current of a ground fault to be zero or to inhibit the phase voltage of the fault to be zero, so that the arc is automatically extinguished; and the reference compensation current is calculated by using real-time measured zero sequence voltage, so that the fault phase identification link is saved. The operation is simplified by using the voltage arc suppression method of controlling the zero sequence voltage to adjust the injected compensation current. In view of the influence of circuit parameters and load current on the arc suppression effect and the deduced relation between the ground fault residual current after the voltage arc suppression method is applied and the zero sequence voltage after the fault, an adaptive arc suppression method is put forward by using the zero sequence voltage as a voltage and current arc suppression method.
Owner:SHANGHAI HOLYSTAR INFORMATION TECH
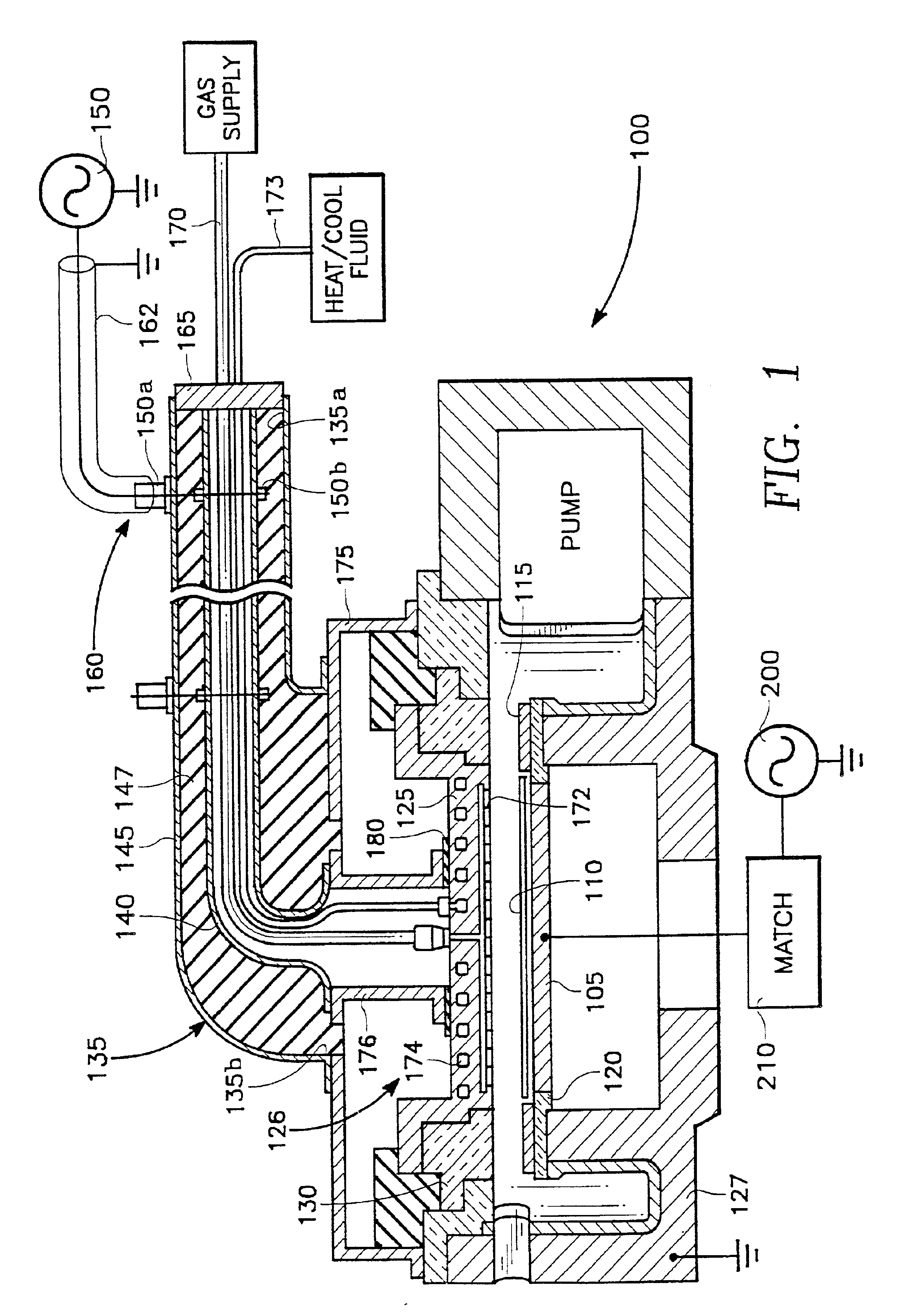
Plasma reactor with overhead RF electrode tuned to the plasma with arcing suppression
InactiveUS7030335B2Sufficient capacitanceAvoid insufficient thicknessCellsElectric discharge tubesCapacitanceIon density
A plasma reactor for processing a semiconductor workpiece, includes a reactor chamber having a chamber wall and containing a workpiece support for holding the semiconductor workpiece, an overhead electrode overlying said workpiece support, the electrode comprising a portion of said chamber wall, an RF power generator for supplying power at a frequency of said generator to said overhead electrode and capable of maintaining a plasma within said chamber at a desired plasma ion density level. The overhead electrode has a capacitance such that said overhead electrode and the plasma formed in said chamber at said desired plasma ion density resonate together at an electrode-plasma resonant frequency, said frequency of said generator being at least near said electrode-plasma resonant frequency. The reactor further includes an insulating layer formed on a surface of said overhead electrode facing said workpiece support, a capacitive insulating layer between said RF power generator and said overhead electrode, and a metal foam layer overlying and contacting a surface of said overhead electrode that faces away from said workpiece support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
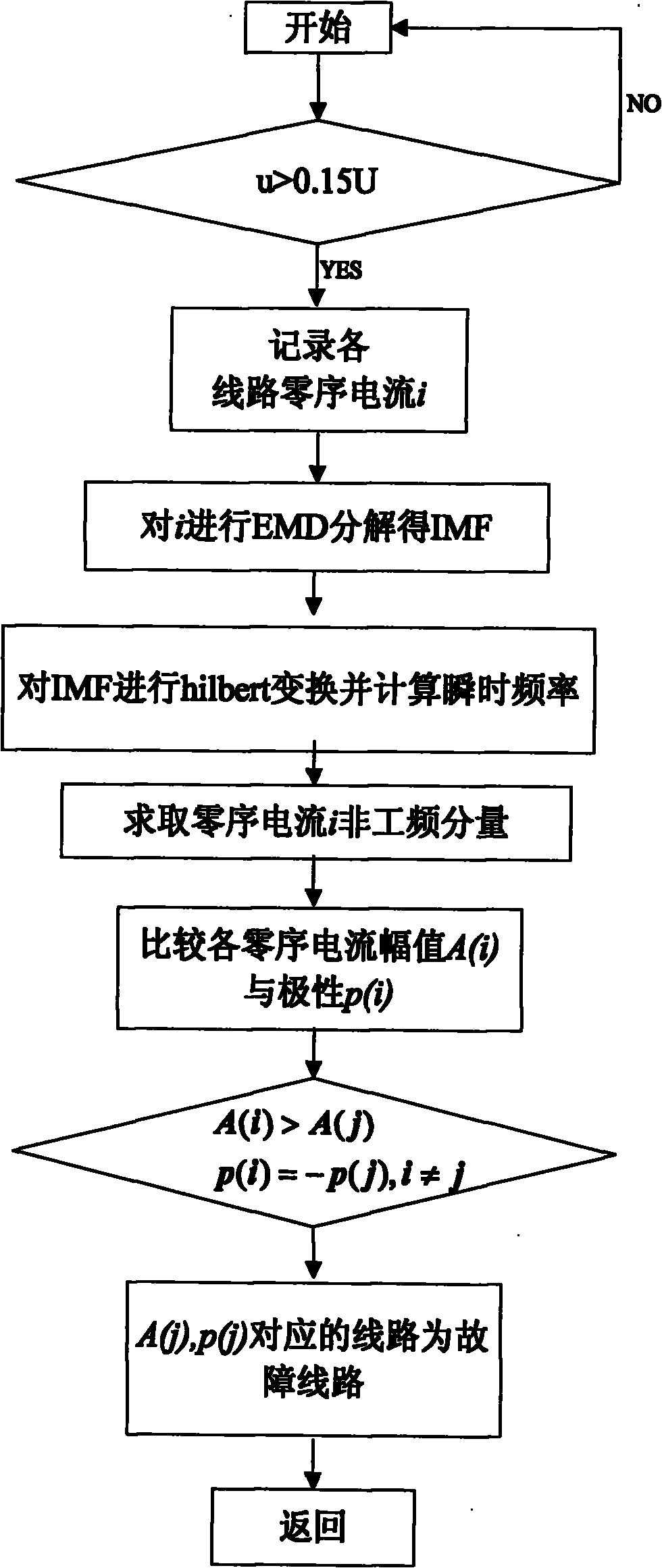
Distribution network fault line selection method using non-power frequency transient state component
InactiveCN101814731AIncrease amplitudeImprove anti-interference abilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDecompositionEngineering
The invention discloses a new method for performing fault line selection by using the characteristic of a non-power frequency transient state fault component for extracting single-phase fault zero-sequence current by using Hilbert-Huang transform (HHT). The method comprises the following steps: performing EMD decomposition on fault zero-sequence current of each feeder line by using the HHT to acquire an IMF component of the zero-sequence current of each feeder line; constructing a resolving signal according to Hilbert transform, solving instantaneous amplitude and frequency of the zero-sequence current of each feeder line, and eliminating a power frequency component in the instantaneous frequency of the zero-sequence current of each feeder line to acquire a non-power frequency fault component; and forming a line selection criterion according to the characteristics that the amplitude of the non-power frequency fault component of the fault line is greater than that of the non-fault line and the polarity of the fault line is opposite to that of the non-fault line. The line selection method is not affected by an arc suppression coil, and is applicable to non-grounded, arc suppression coil grounded and high-resistor grounded systems, overhead lines or cable lines and cable overhead mixed lines; and the line selection result shows that the method applied to low-current single-phase grounding fault line selection is accurate and reliable.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
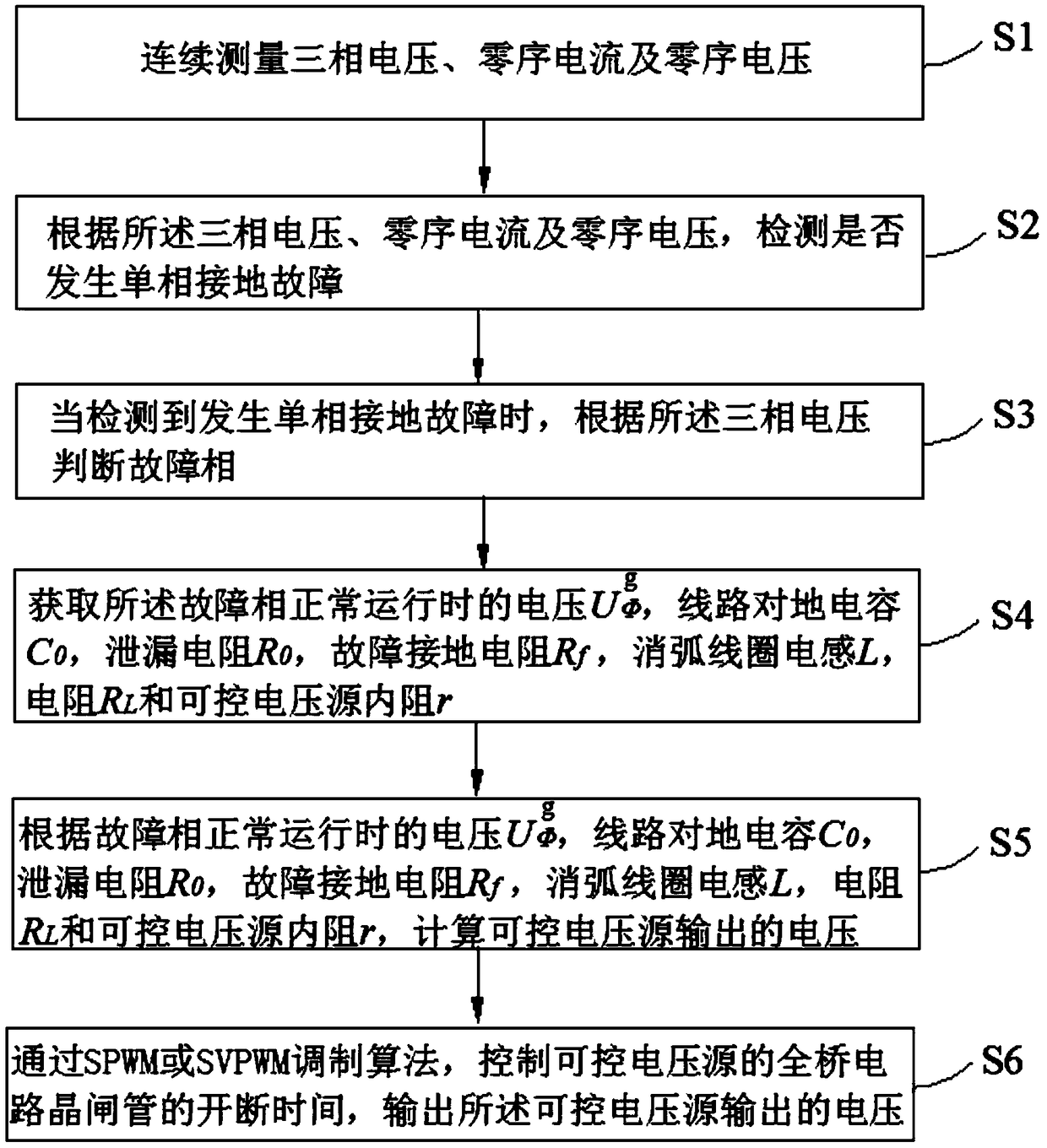
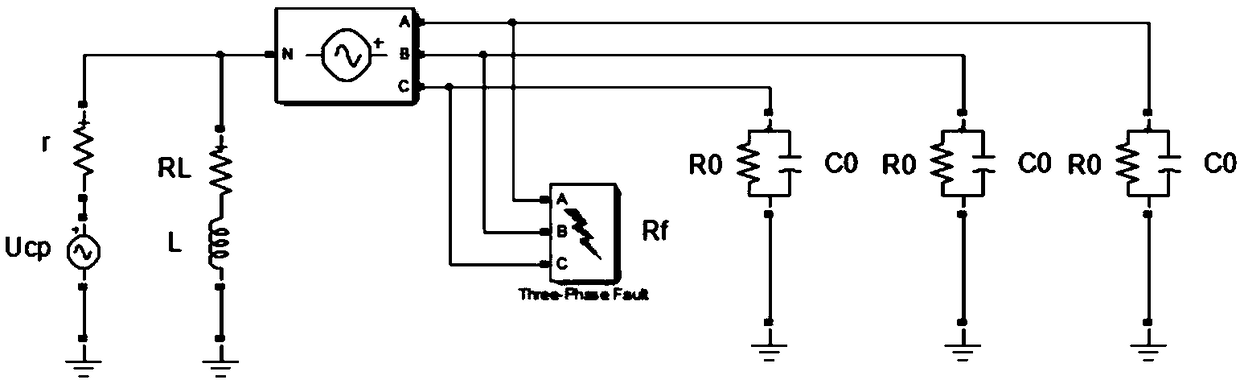
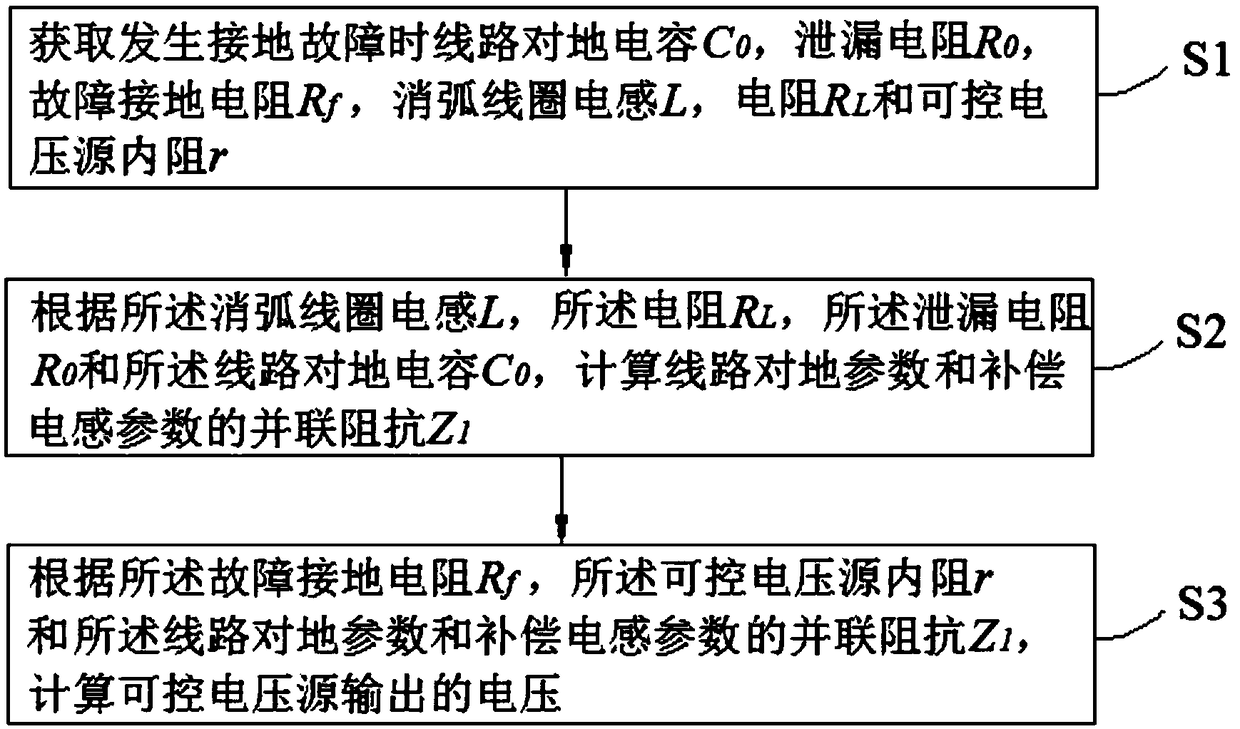
A grounding fault arc extinguishing method and a device based on a controllable voltage source
ActiveCN109167345AEnsure safe and stable operationSafe and stable operationEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a grounding fault arc extinguishing method and a device based on a controllable voltage source. The method comprises the following steps: continuously measuring three-phase voltage, zero-sequence current and zero-sequence voltage; When the fault is detected, the fault phase is judged according to the three-phase voltage. The voltage, line-to-ground capacitance, leakage resistance, fault grounding resistance, arc suppression coil inductance, resistance and internal resistance of controllable voltage source in normal operation of fault phase are obtained, and the output voltage of controllable voltage source is calculated. The output voltage of the controllable voltage source is output by SPWM or SVPWM modulation algorithm. By connecting the voltage source, the present application is easier to control and can effectively compensate the fault current and extinguish the arc at the fault point without considering the problem that the inductance parameter of the arc suppression coil and the capacitance of the line to ground are close to the power frequency resonance. The invention calculates the phase and amplitude of the output voltage, realizes the current extinction at the fault point by controlling the amplitude and phase of the controllable voltage source, and ensures the safe and stable operation of the power network and the failure point not to cause fire and other accidents.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
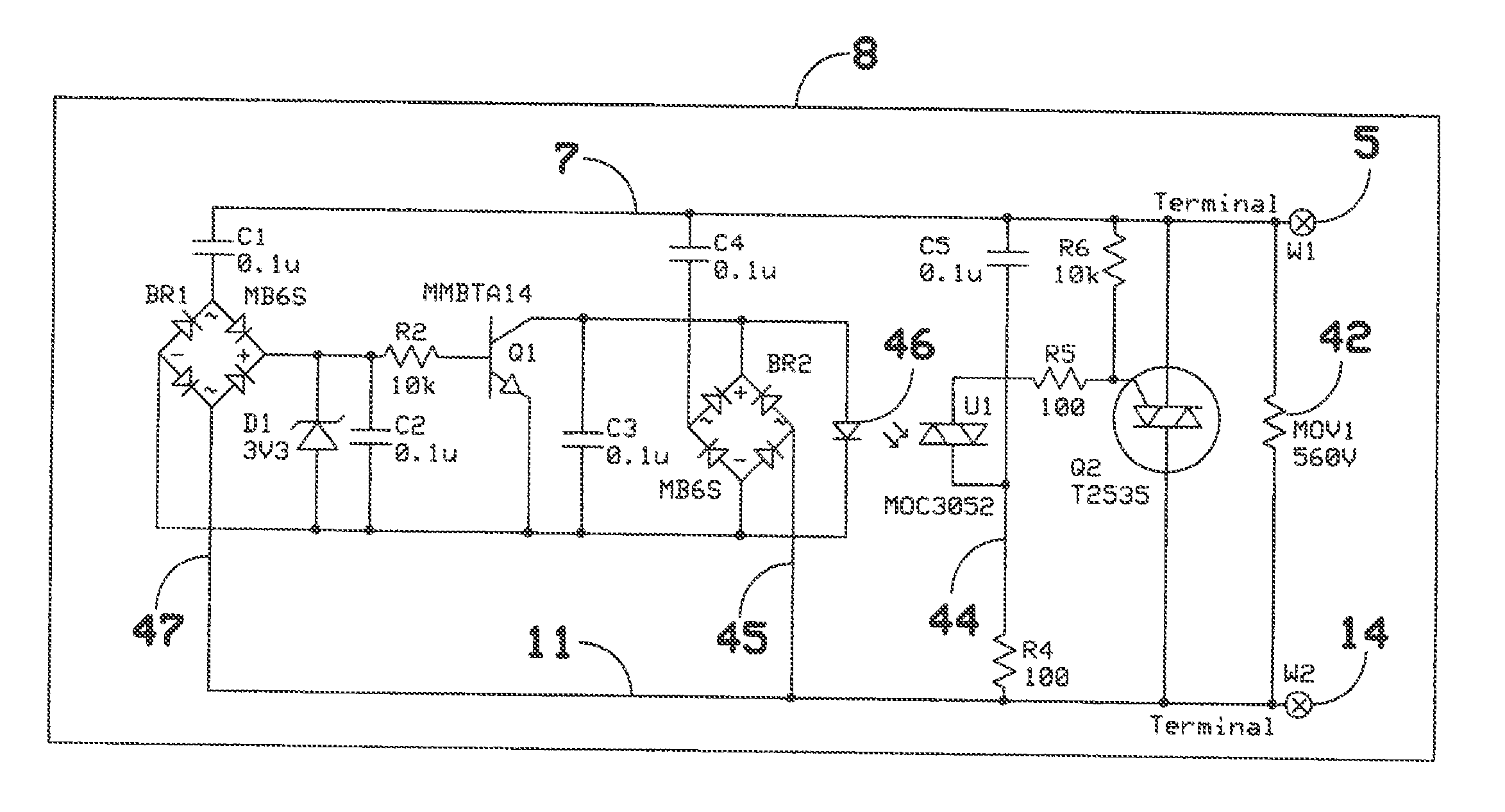
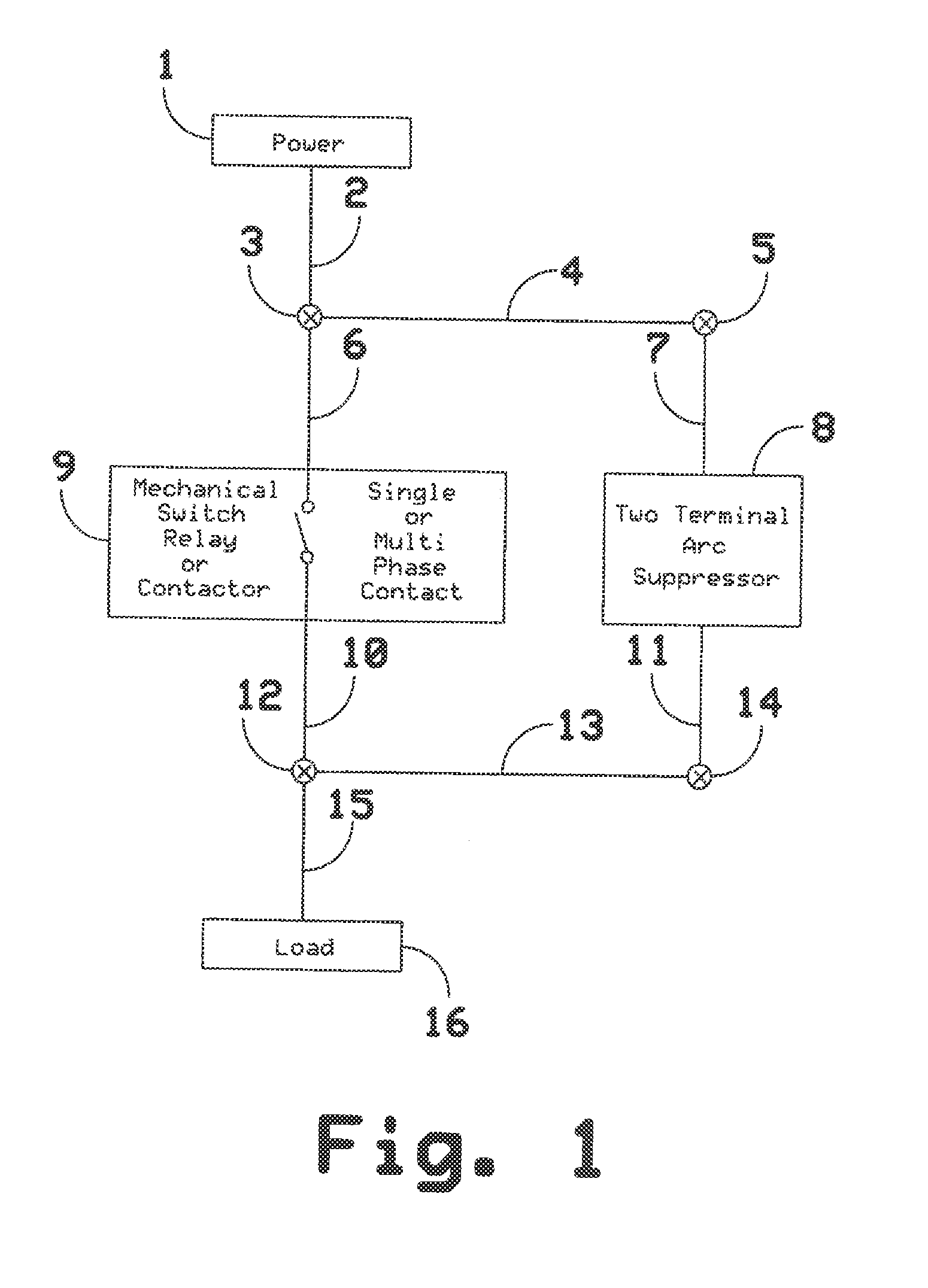
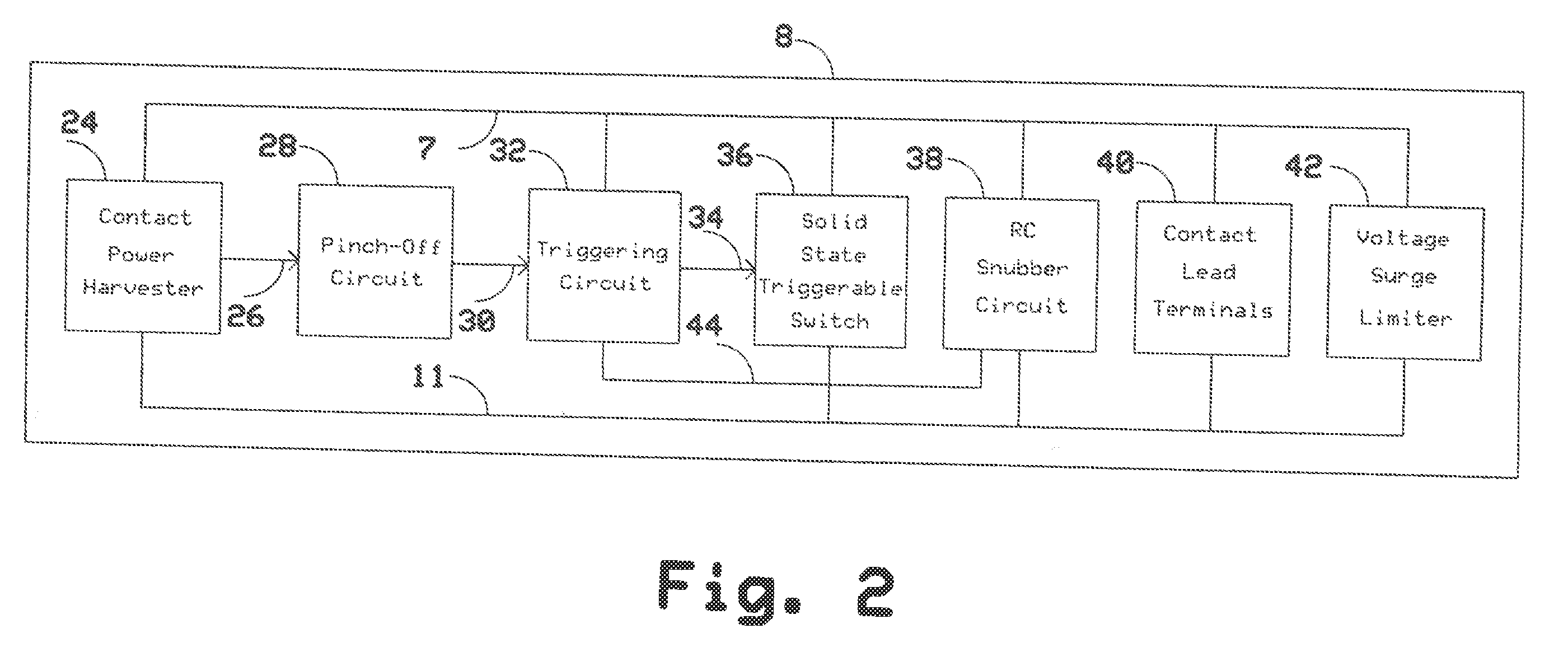
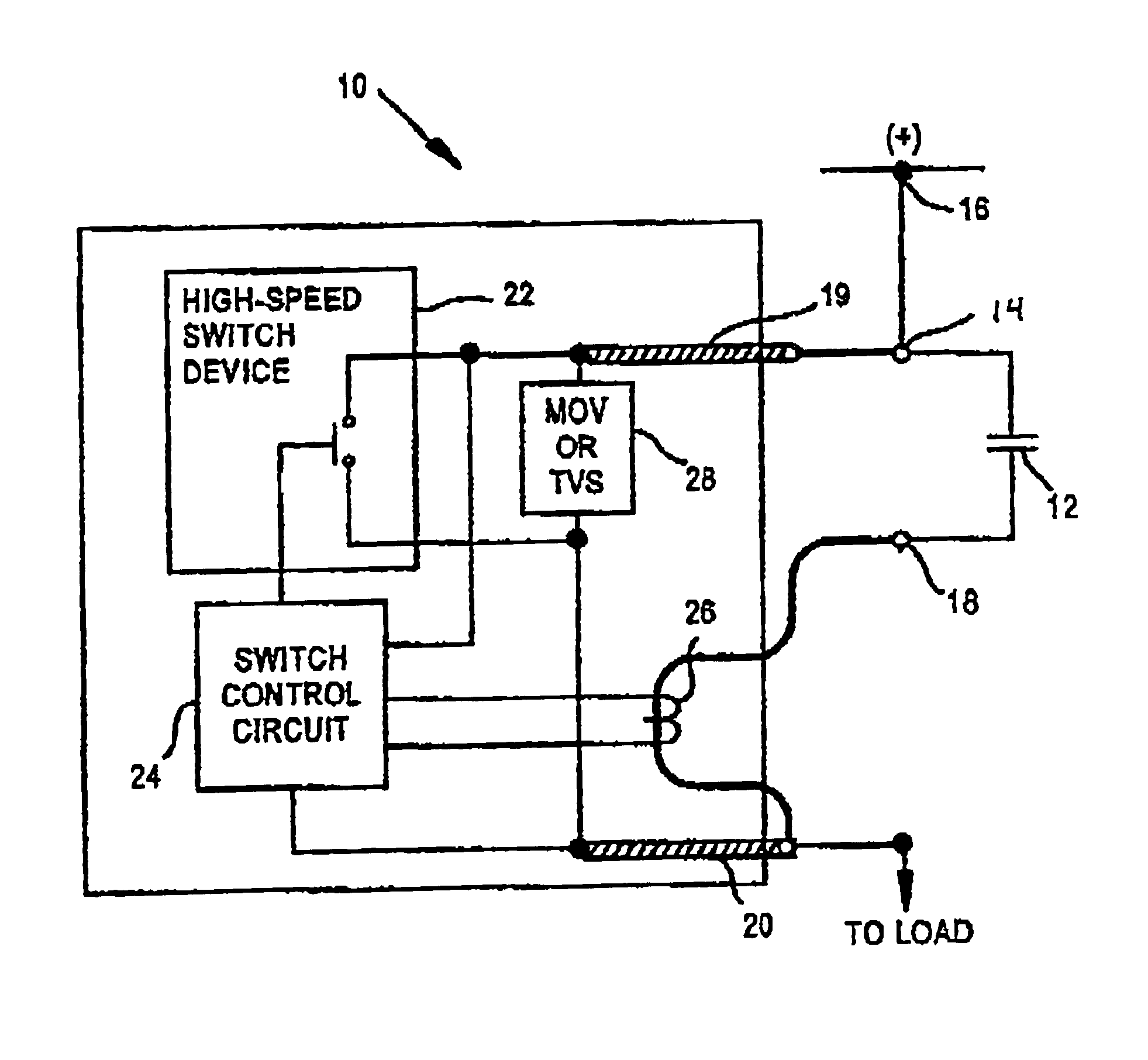
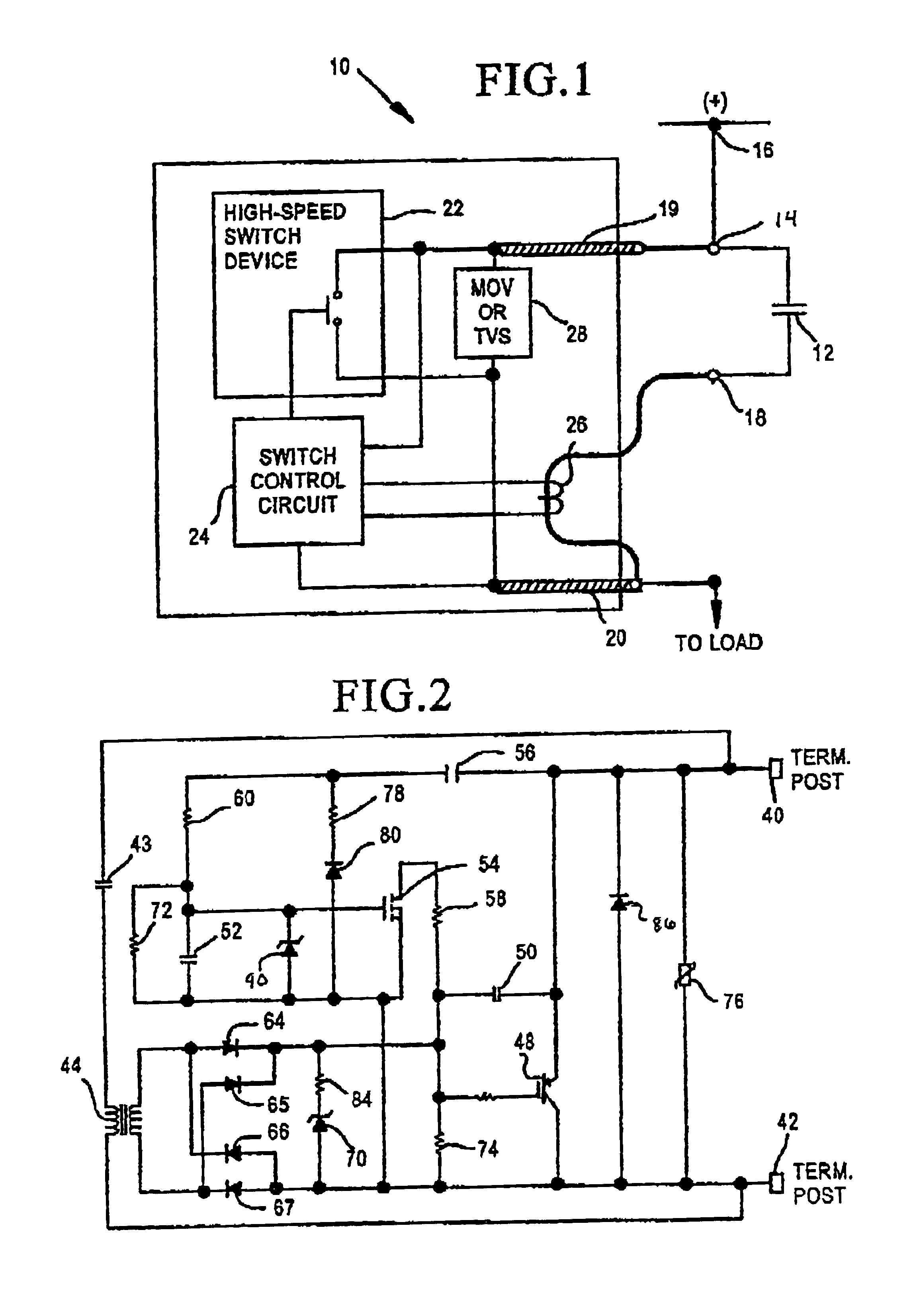
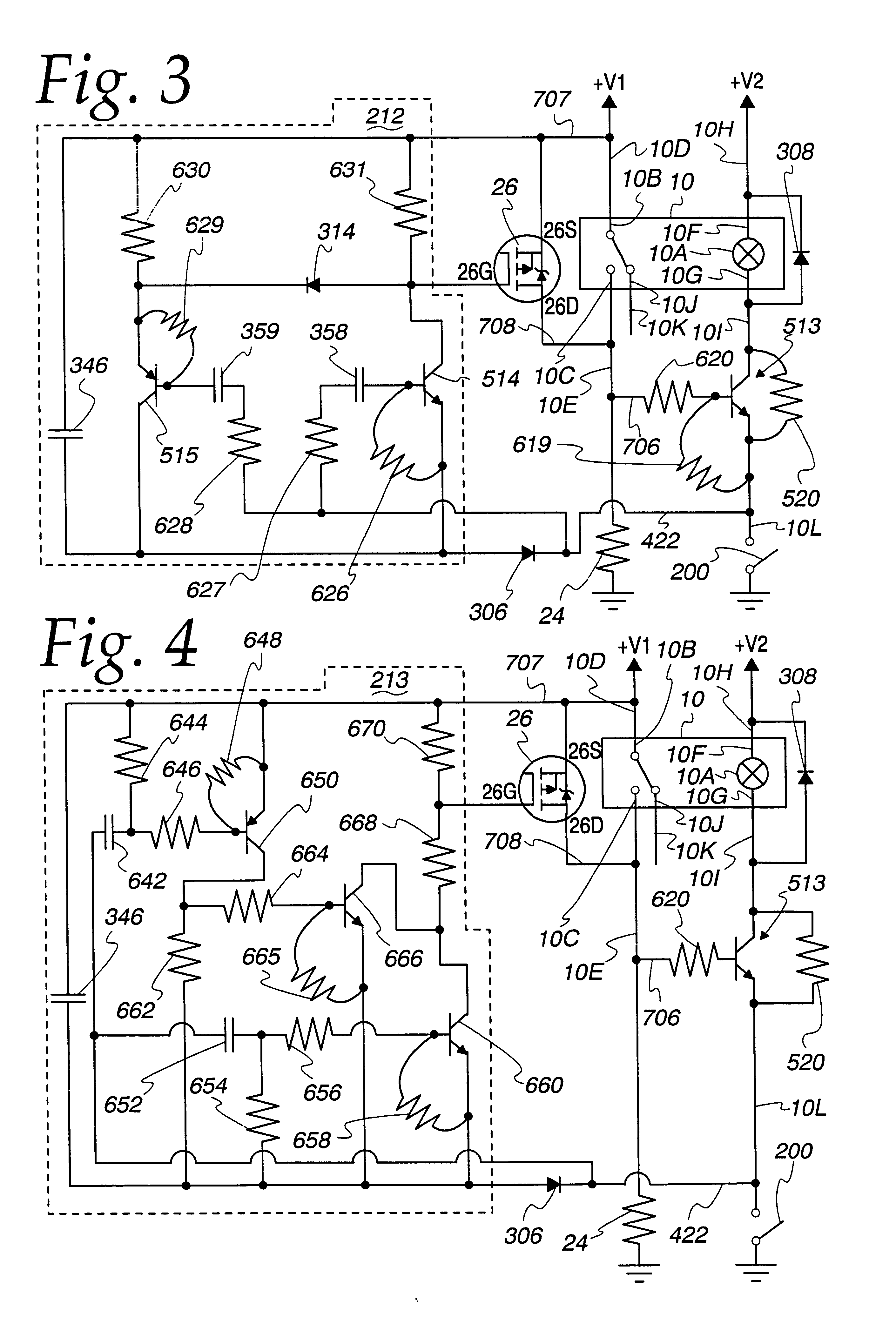
Two Terminal Arc Suppressor
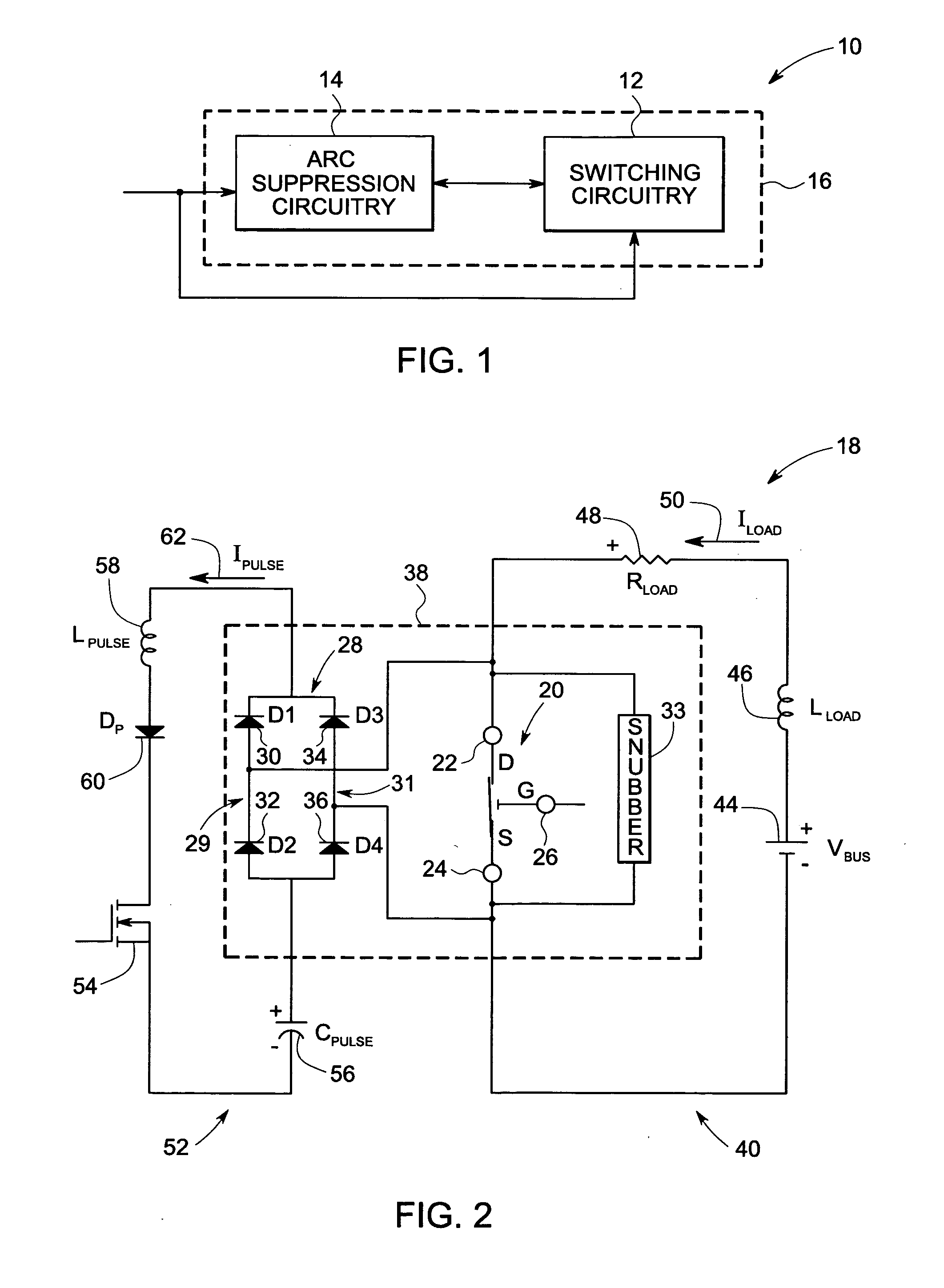
ActiveUS20110222191A1High strengthShorting outElectric switchesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDIACSuppressor
A two terminal arc suppressor for protecting switch, relay or contactor contacts and the like comprises a two terminal module adapted to be attached in parallel with the contacts to be protected and including a circuit for deriving an operating voltage upon the transitioning of the switch, relay or contactor contacts from a closed to an open disposition, the power being rectified and the resulting DC signal used to trigger a power triac switch via an optoisolator circuit whereby arc suppression pulses are generated for short predetermined intervals only at a transition of the mechanical switch, relay or contactor contacts from an closed to an open transition and, again, at an open to a close transition during contact bounce conditions.
Owner:ARC SUPPRESSION TECH LLC
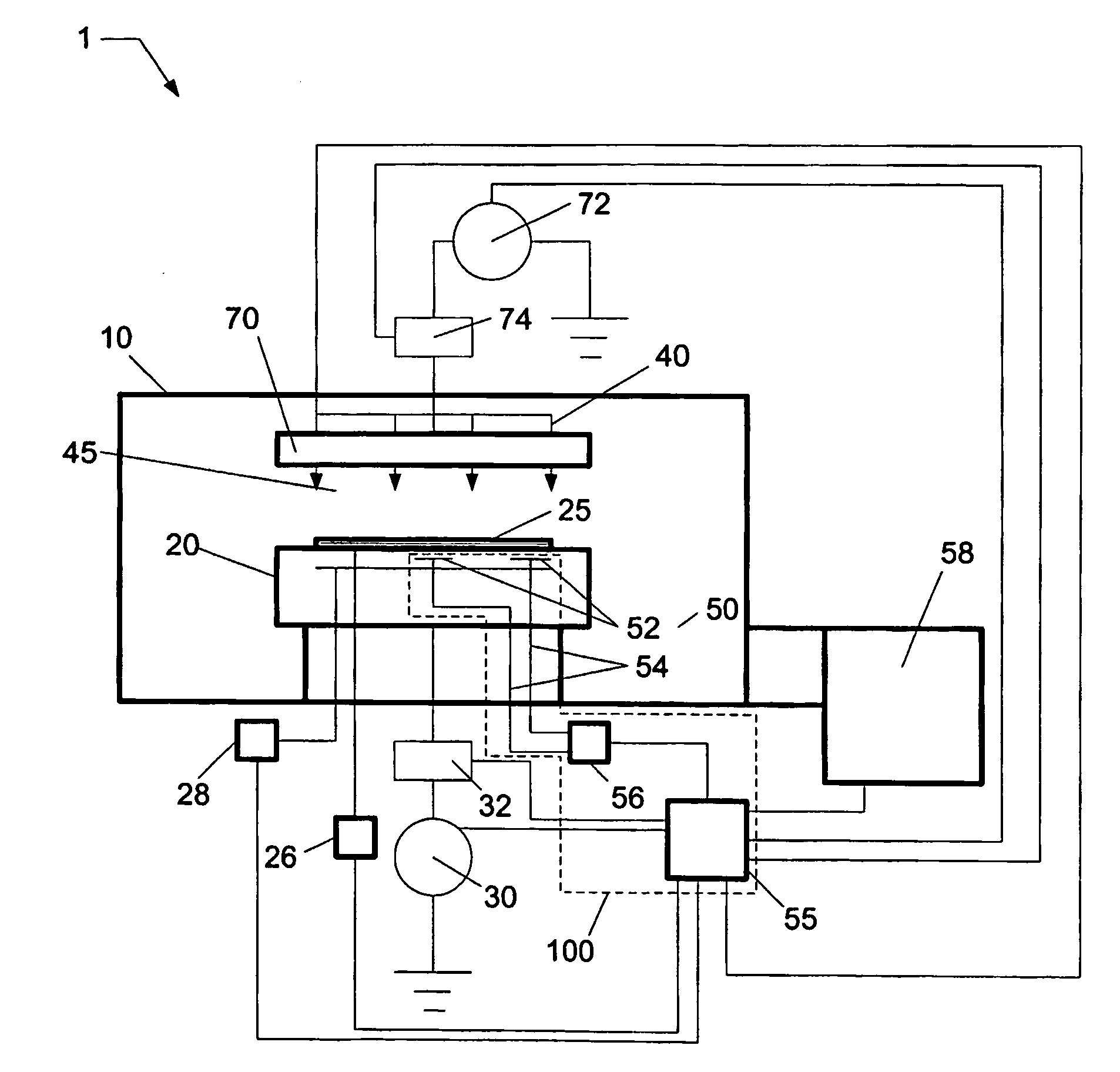
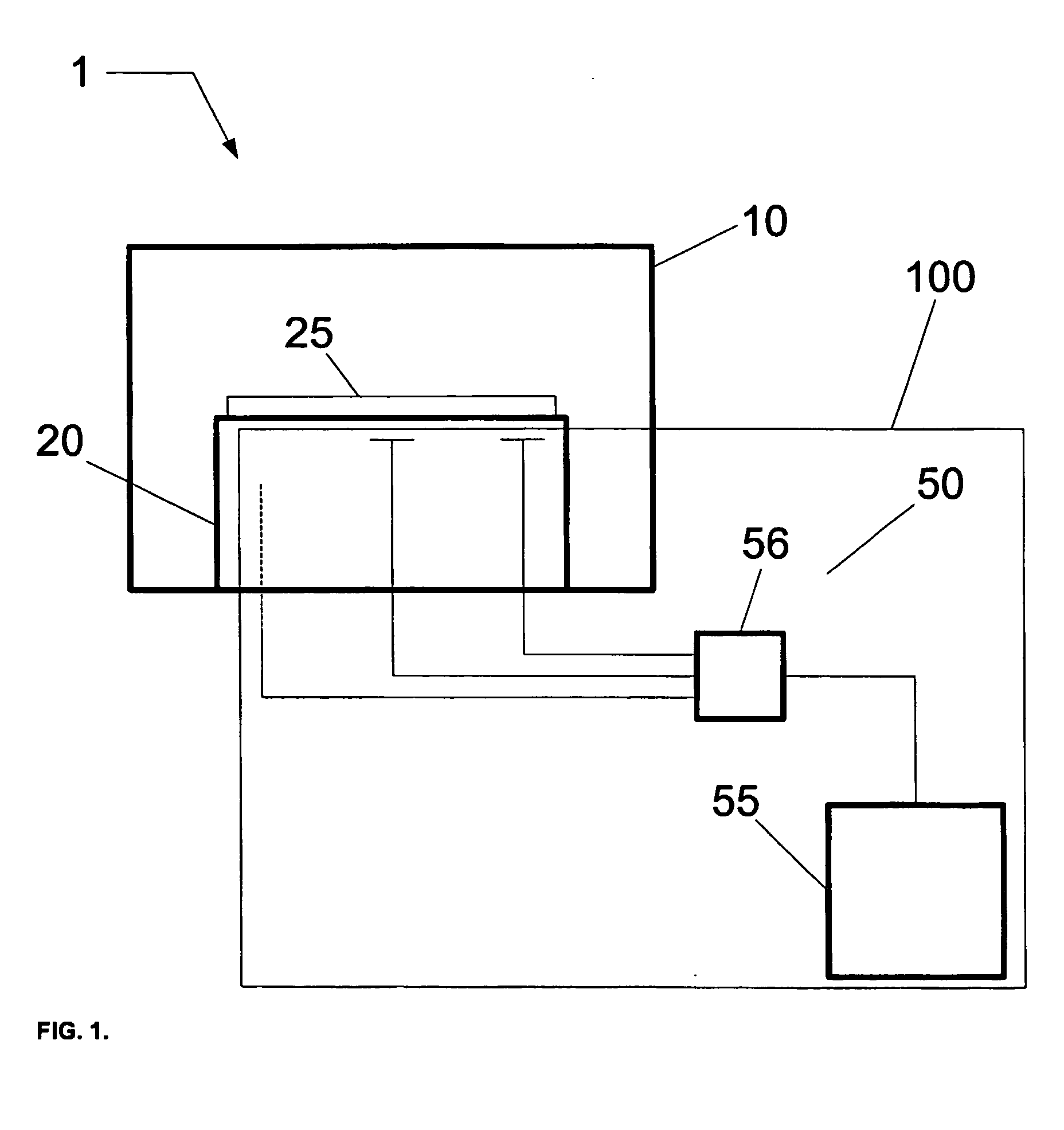
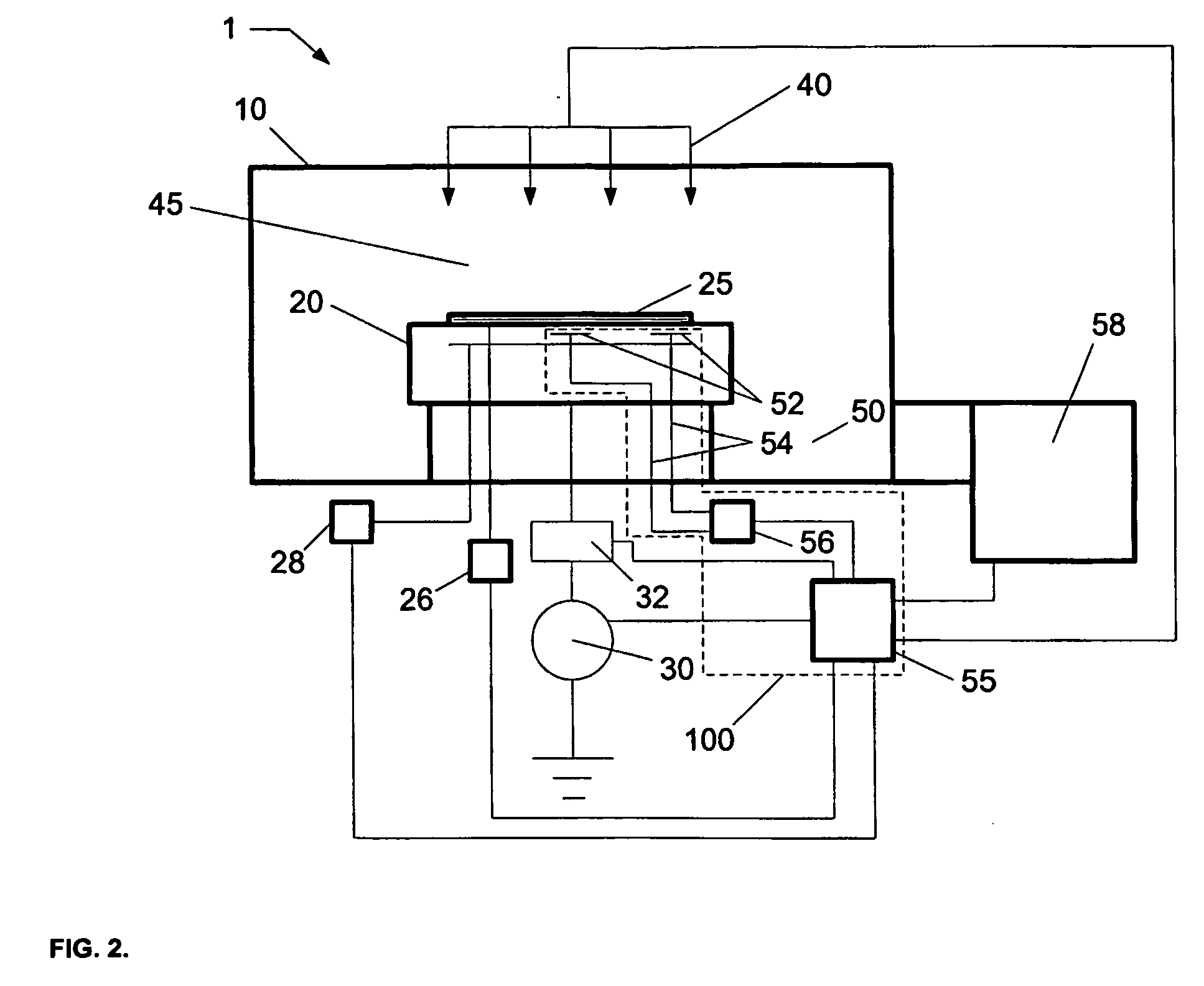
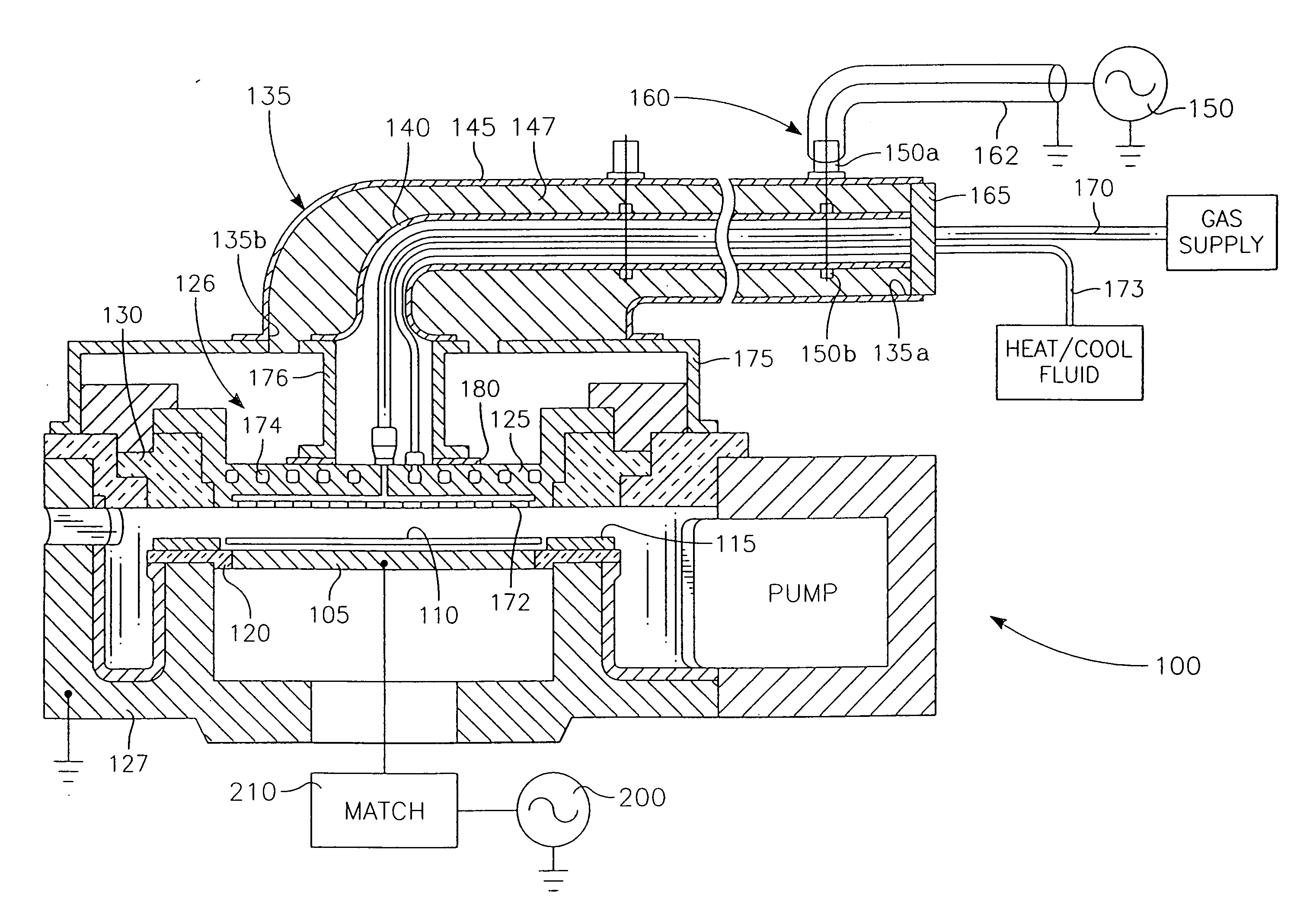
Method and system for arc suppression in a plasma processing system
ActiveUS20060081564A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPlasma processing
An arc suppression system for plasma processing comprising at least one sensor coupled to the plasma processing system, and a controller coupled to the at least one sensor. The controller provides at least one algorithm for determining a state of plasma in contact with a substrate using at least one signal generated from the at least one sensor and controlling a plasma processing system in order to suppress an arcing event. When voltage differences between sensors exceed a target difference, the plasma processing system is determined to be susceptible to arcing. During this condidtion, an operator is notified, and decision can be made to either continue processing, modify processing, or discontinue processing.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
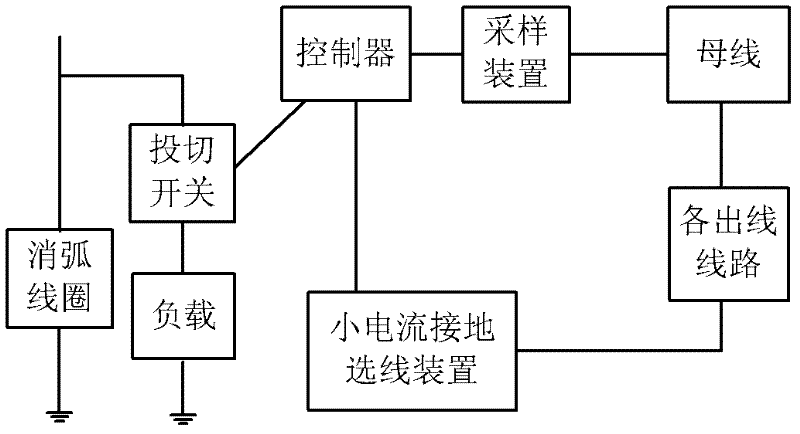
Detection system and detection method for single-phase grounding fault line selection in small current grounding system
InactiveCN102520314ASolve the problem of low line selection accuracySimple configurationFault locationGrounding lineSingle phase
The invention relates to a detection system and a detection method for single-phase grounding fault line selection in a small current grounding system. The system comprises a load switching device and a small current grounding line selection device, the load switching device comprises a load, a switching switch, a controller and a sampling device, the load is connected with the switching switch in series and further connected with an arc suppression coil in parallel, and the controller is respectively connected with the switching switch and the sampling device; the small current grounding line selection device is connected with each circuit in the small current grounding system, and the small current grounding line selection device is further connected with the controller in the load switching device. The system and the method can effectively solve the problem of difficulty in line selection of single-phase grounding fault in the small current grounding system, and improve the accuracy of line selection.
Owner:北京天能继保电力科技有限公司
Micro-electromechanical system based arc-less switching
InactiveUS20070139829A1Enhanced inhibitory effectElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysElectric switchesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A system is presented. The system includes a first micro-electromechanical system switch. Further, the system includes arc suppression circuitry coupled to the first micro-electromechanical system switch, wherein the arc suppression circuitry comprises a balanced diode bridge and is configured to facilitate suppression of an arc formation between contacts of the first micro-electromechanical system switch.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
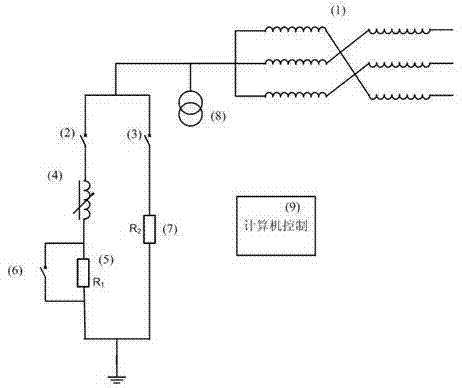
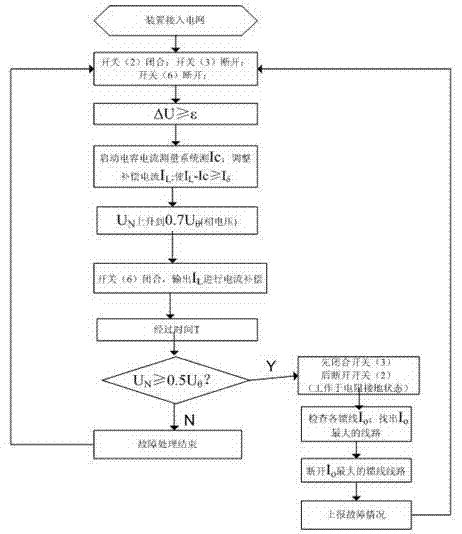
Intelligent dynamic power distribution network neutral-point grounding method and complete device
ActiveCN103208788AReduce lightning strike arc establishment rateReduce trip rateEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitanceTransformer
The invention discloses an intelligent dynamic power distribution network neutral-point grounding method and a complete device. The complete device comprises a grounding transformer (1), an arc suppression loop switch (2), a resistance loop switch (3), an adjustable reactor (4), a damping resistor (5), a damping resistor short-circuit switch (6), a resistor (7), a neutral-point voltage transformer (8) and a computer testing and control system (9). The intelligent dynamic power distribution network neutral-point grounding method and the complete device is technically characterized in that a power distribution network neutral-point grounding mode is dynamically converted from an arc suppression coil grounding mode into a small-resistance grounding mode. When the device is connected to a power grid or a power grid operation mode changes, the device firstly works in the arc suppression coil grounding mode. The device measures capacitive current, adjusts inductive current and enables IL-IC to be smaller than or equal to I delta, wherein the I delta is a preset residual current control value. When a single-phase grounding fault of the power grid occurs, the device outputs the inductive current to perform compensation and arc suppression to grounding fault current. If the fault is an instantaneous fault, the fault is eliminated through the compensation and the arc suppression. If the fault is a permanent fault and the grounding fault is still not eliminated after certain time T, the arc suppression coil grounding is converted into the resistance grounding mode, and a fault line is judged and disconnected by detecting zero-sequence current of feeder lines.
Owner:李景禄
Power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors
ActiveCN103245883AThe principle is simpleImprove timelinessFault locationElectric power systemTransient current
The invention relates to a power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. When a power distribution network runs into a single-phase earth fault via an arc suppression coil grounding system, a transient zero-sequence current component detected by a measuring end is a nonlinear non-stationary signal formed by different frequency components. By taking the fault component as a study object, time-frequency characteristics of a fault transient current of the fault component are analyzed by utilizing the wavelet packet theory, time-frequency distribution regularities among all feeder lines under different fault conditions are described according to similarity of the time-frequency characteristics, and consequently line selection criteria based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristics can be obtained. The method is simple in principle, only utilizes short-time window zero-sequence current data of 5ms after the fault, can identify faulty feeders under the conditions of small fault angle and high resistance ground fault, has excellent timeliness and robustness, is free from influence of an arc fault or a resistance ground fault, requires a low sampling rate for hardware, and is highly practical.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Arc suppression device, system and methods for liquid insulated electrical apparatus
InactiveUS20080192389A1Current/voltage measurementEmergency protective arrangement detailsElectrical devicesEngineering
Arc suppression systems, devices and methods for avoiding undesirable arcing conditions inside a liquid-filled tank of a high-voltage electrical apparatus.
Owner:COOPER TECH CO
Electric power system 1:1 voltage class distribution network single-phase ground fault simulation test platform
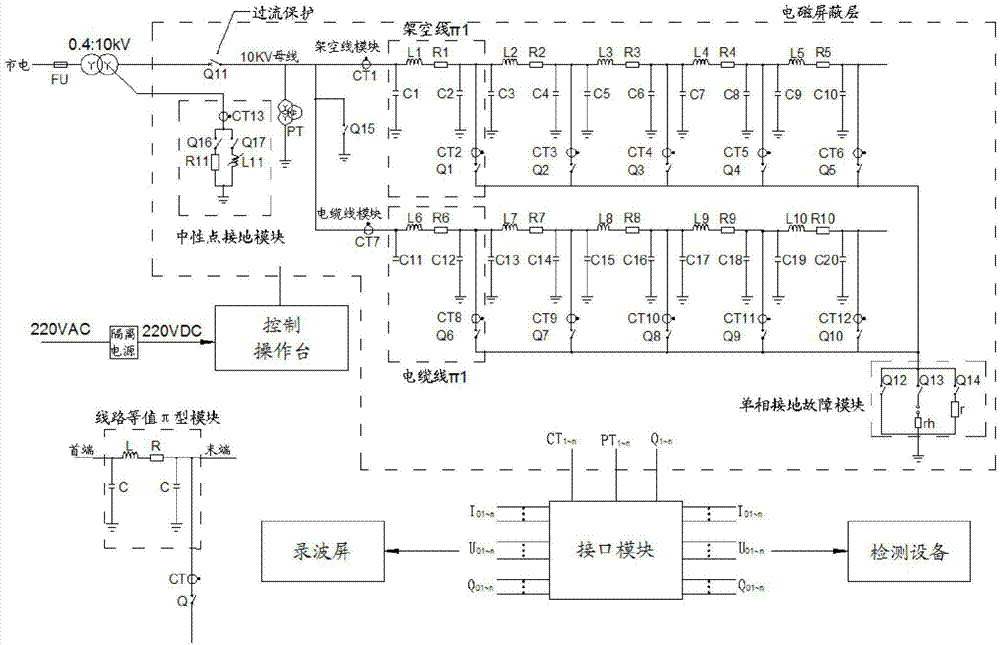
ActiveCN104732847AShield electromagnetic interferenceMake sure that there is a short circuit between the phasesEducational modelsFault indicatorHigh resistance
The invention discloses an electric power system 1:1 voltage class distribution network single-phase ground fault simulation test platform. The electric power system 1:1 voltage class distribution network single-phase ground fault simulation test platform comprises a neutral grounding module, a 10 kV bus, a 10 kV pi-type equivalent model electric transmission line module and a single-phase ground fault module. The electric power system 1:1 voltage class distribution network single-phase ground fault simulation test platform can dynamically simulate a single-phase ground fault of an overhead line of different lengths and a cable line of a distribution network in a 1:1 voltage class. The electric power system 1:1 voltage class distribution network single-phase ground fault simulation test platform can simulate different neutral grounding modes, such as neutral ungrounding, neutral low-resistance grounding and neutral grounding through an arc suppression coil; transmission lines of different lengths and different types can be simulated, such as the overhead line or the cable line; single-phase ground faults of various types can be simulated, such as metallic grounding, arc light grounding, high resistance grounding and the like; meanwhile, the electric power system 1:1 voltage class distribution network single-phase ground fault simulation test platform is provided with a distribution network fault indicator, a line selection and fault positioning device and ports of a DTU / FTU and other distribution network automation terminals, and the requirements for scientific researches, product development, product testing and related personnel operating training in directions of the distribution network single-phase ground fault line selection, traveling wave distance measurement accurate positioning and the like are met.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Method for achieving single-phase earth fault line selection of small current grounding system
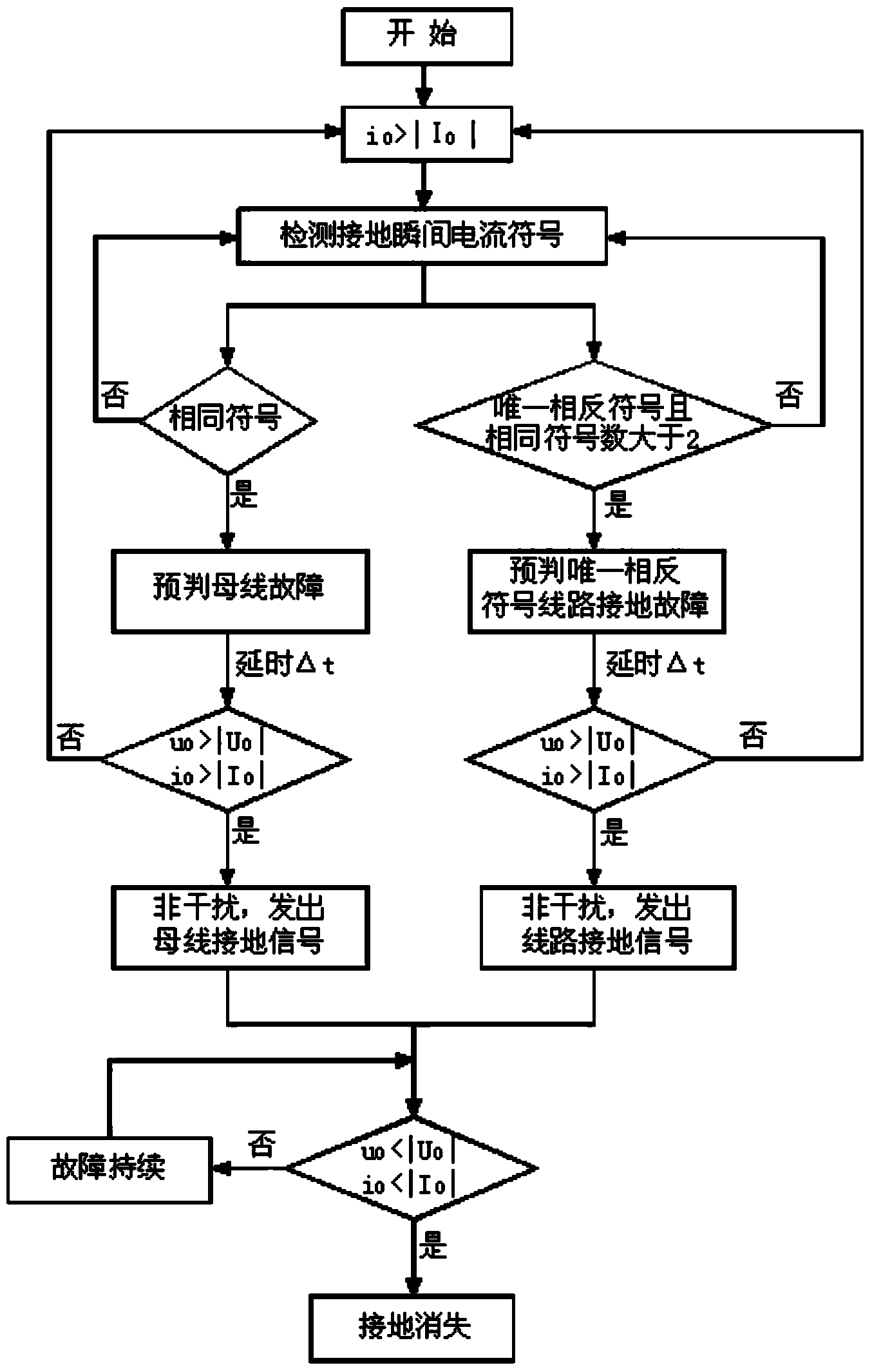
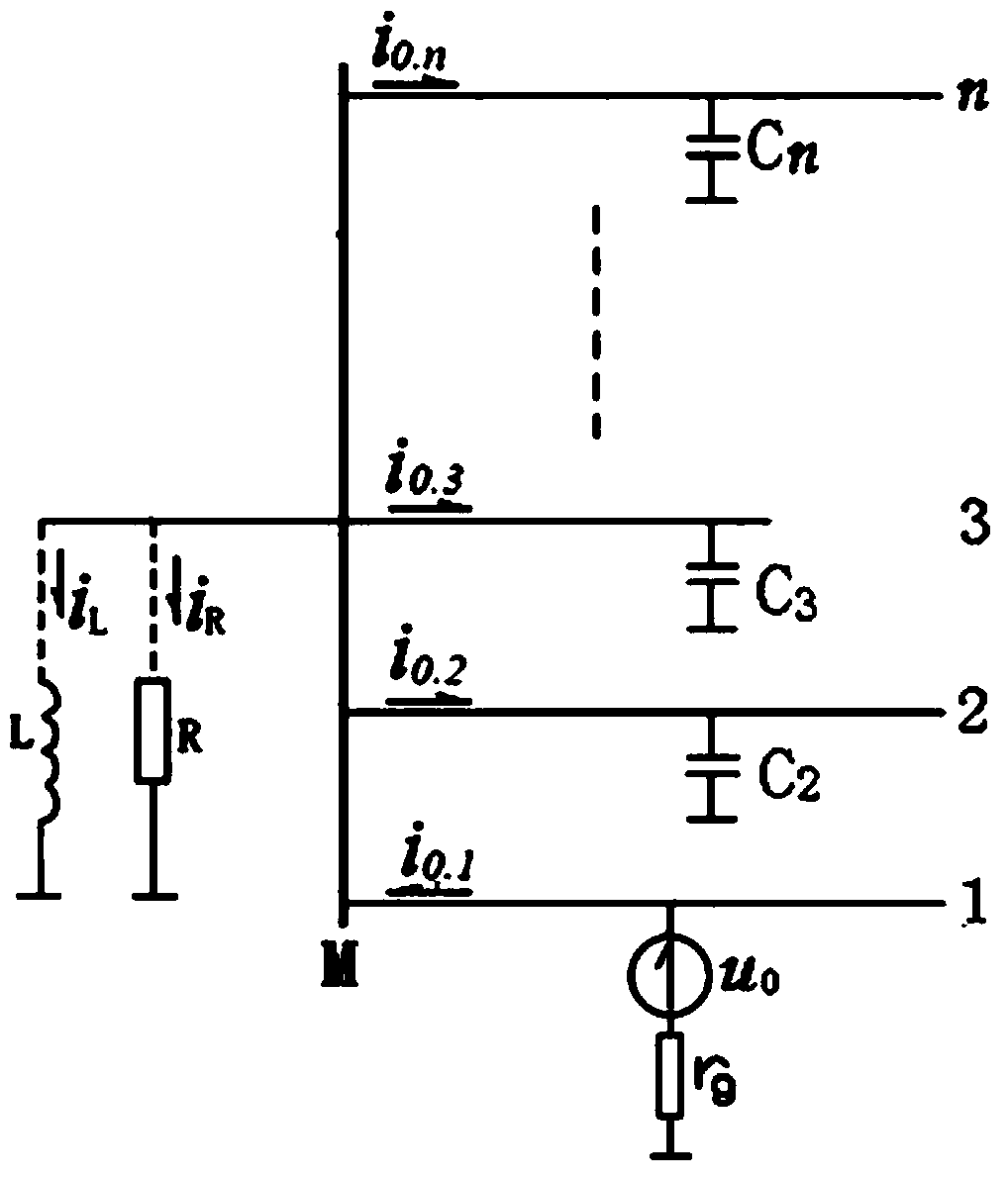
InactiveCN103592571AHigh sensitivityGuaranteed reliabilityFault locationHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A method for achieving single-phase earth fault line selection of a small current grounding system is characterized in that a high-precision zero-sequence current transformer is adopted by each feeder line; a single-phase earth fault of the system is confirmed when the instantaneous value of the zero-sequence current i0 of any one feeder line exceeds a set threshold / I0 / ; comparison is conducted on symbols of all loop circuits at the moment of threshold triggering, and data after the triggering do not participate in judgment; the symbol of a faulty line current is unique and opposite to the symbols of non-faulty line currents, and the number of non-faulty lines is larger than or equal to 2; when the symbols of all the currents are identical, a bus earth fault is confirmed. The method for achieving single-phase earth fault line selection of the small current grounding system is adaptable to three grounding modes, namely neutral non-grounding, arc suppression coil grounding and neutral point high resistance grounding, of the small current grounding system and is not affected by a grounding moment phase angle, system unreal grounding and TV disconnection, and correction operation can still be achieved when the zero-sequence voltage of a bus is reduced to be 10% of a phase voltage by a transition resistor.
Owner:珠海威瀚科技发展有限公司
Active arc-suppression circuit, system, and method of use
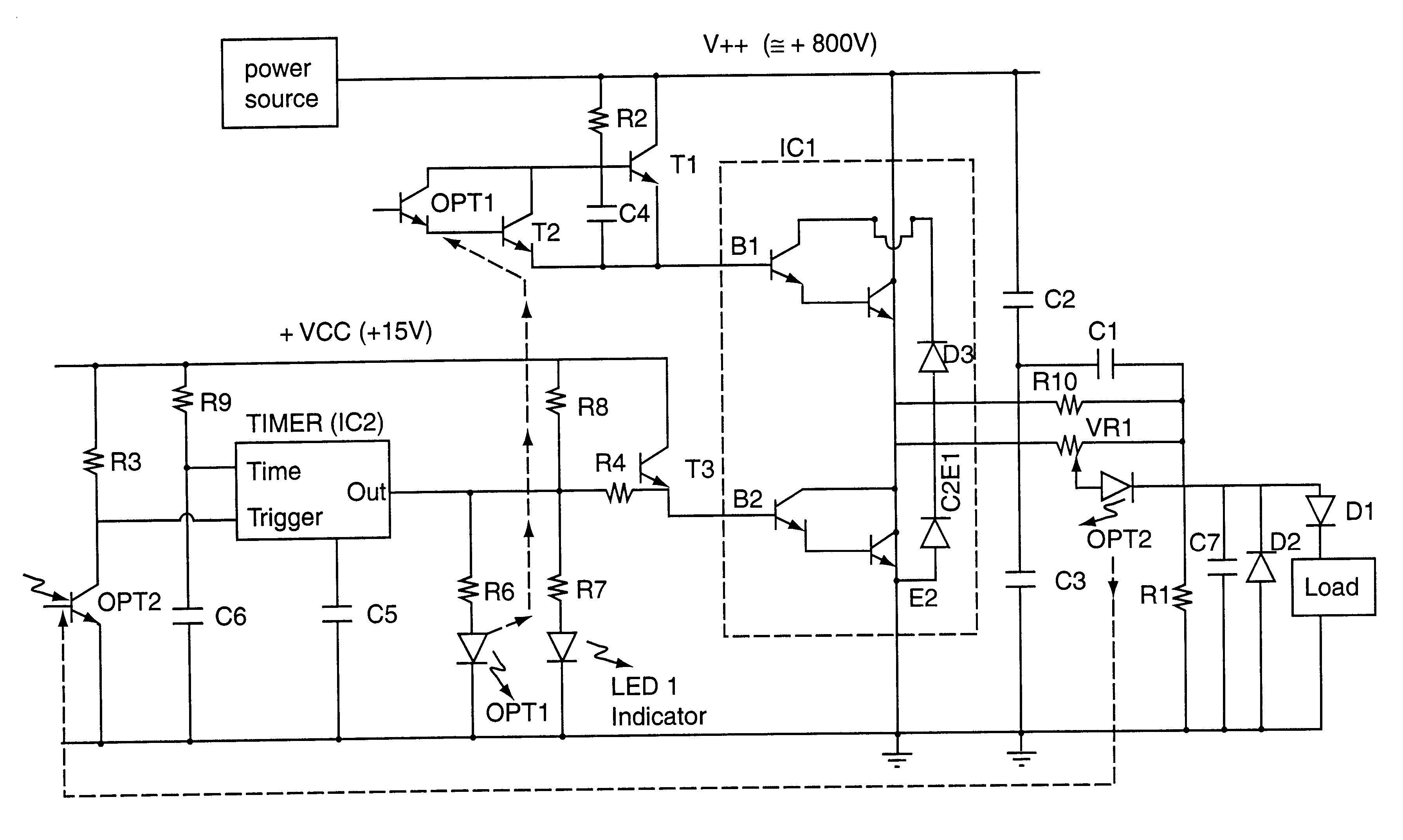
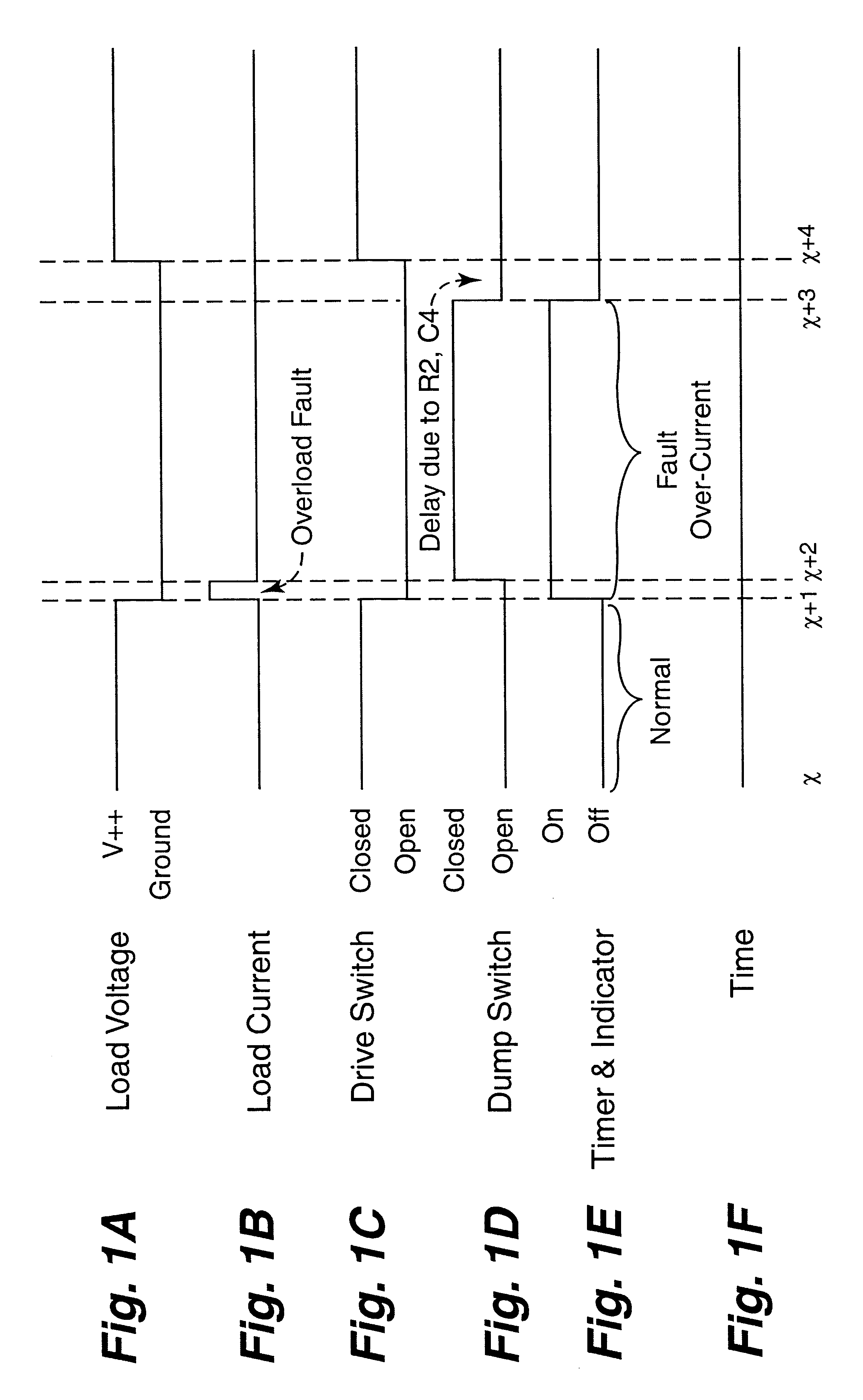
InactiveUS7259945B2Guaranteed uptimeEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesPower controllerControl theory
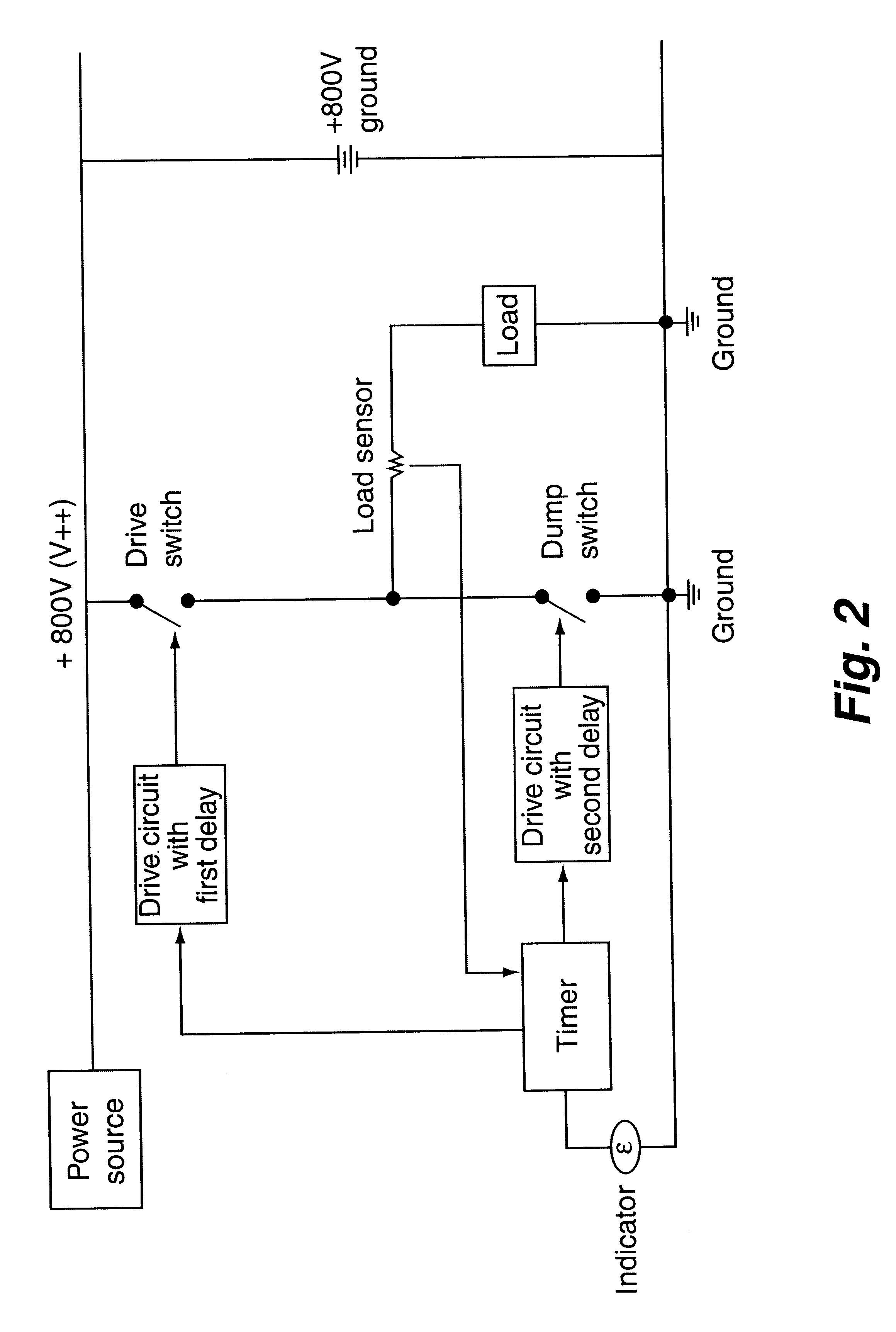
An active arc suppression circuit and systems and methods of use to suppress arcing in an electro-mechanical apparatus. The preferred circuit includes an electro-mechanical switch and a solid state shunt switch for temporarily shunting current around the electro-mechanical switch for a predetermined period of time. The preferred circuit also includes an electro-mechanical switch controller for delaying the activation of the electro-mechanical switch until after the predetermined period of time for shunting current through the solid state shunt switch has commenced. The preferred circuit may be used with power control equipment and systems, including in remotely controllable systems for telecommunications, computing, and other networks. In a particularly preferred embodiment, multiple such circuits may be disposed in a power controller housing to provide independent active arc suppression control of multiple power outputs also disposed in the power controller housing.
Owner:SERVER TECHNOLOGY
Apparatus and method for relay contact arc suppression
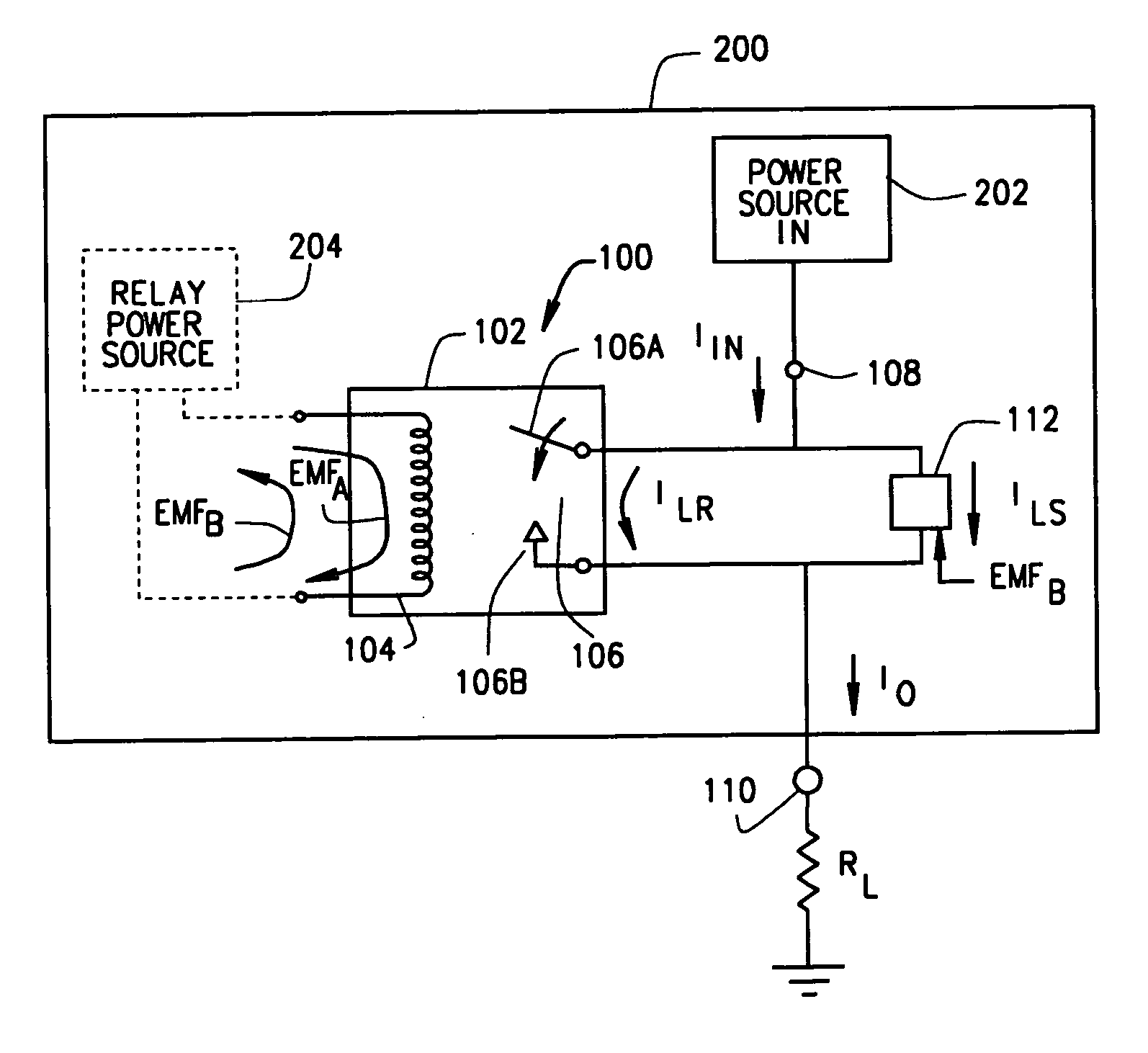
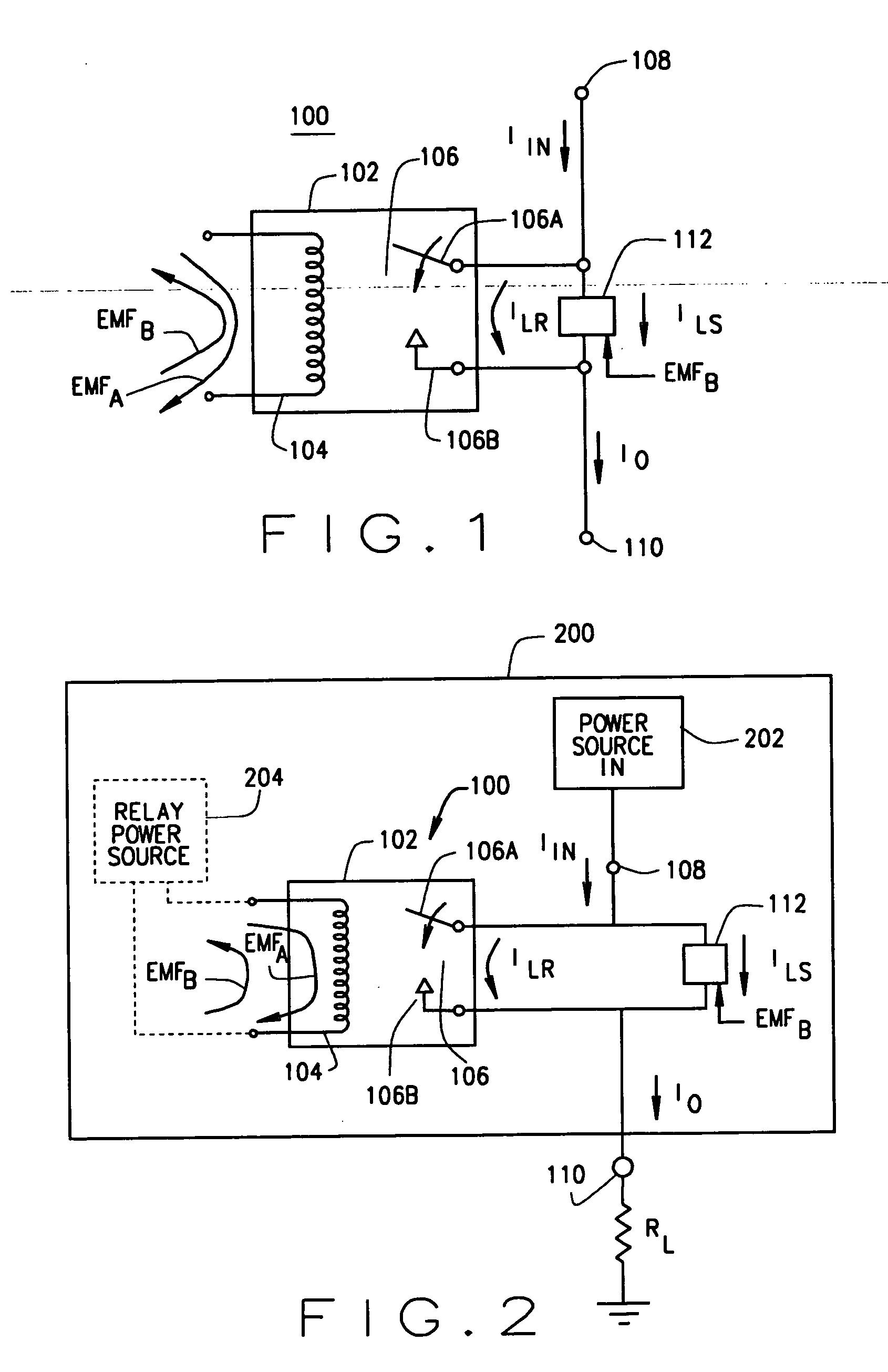
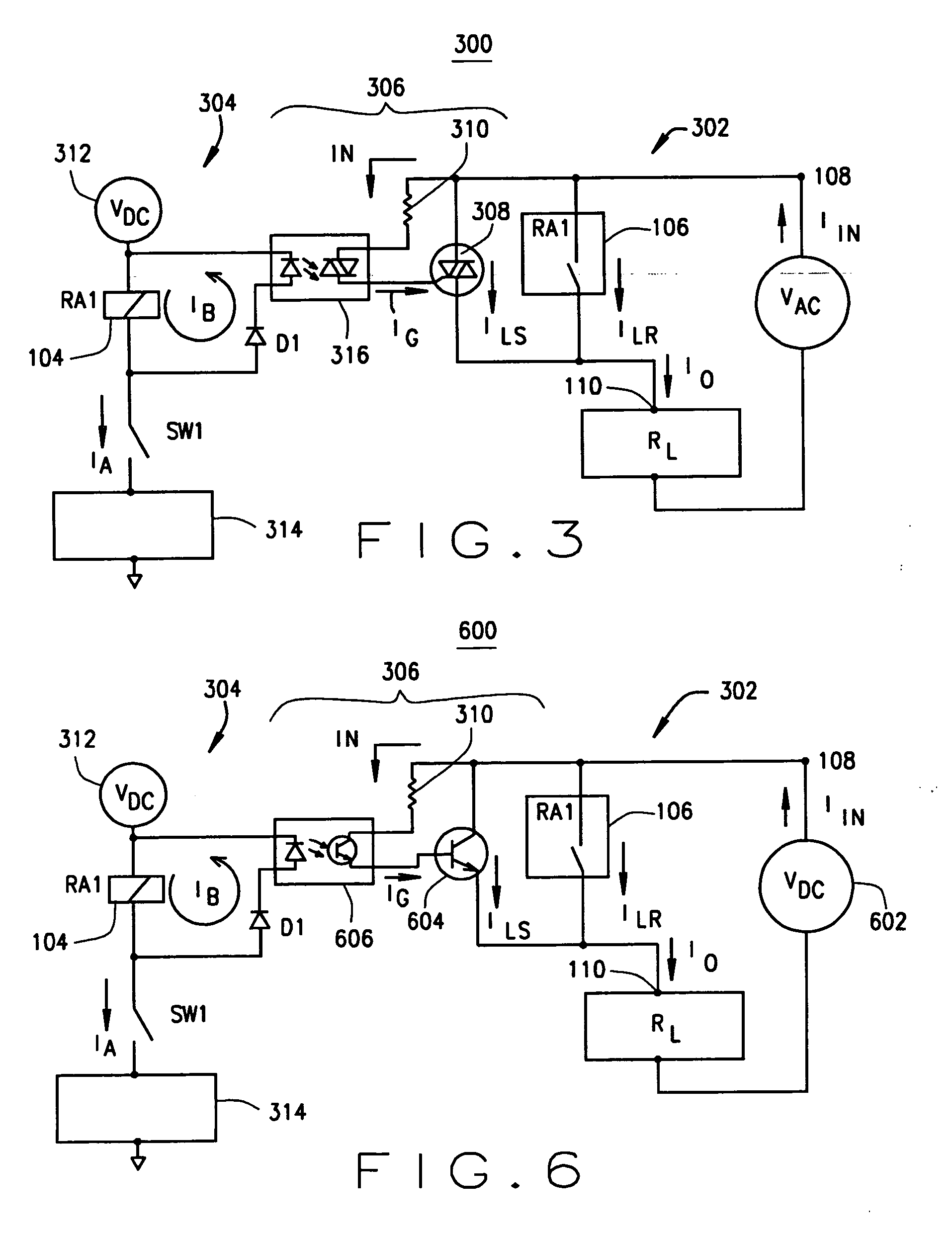
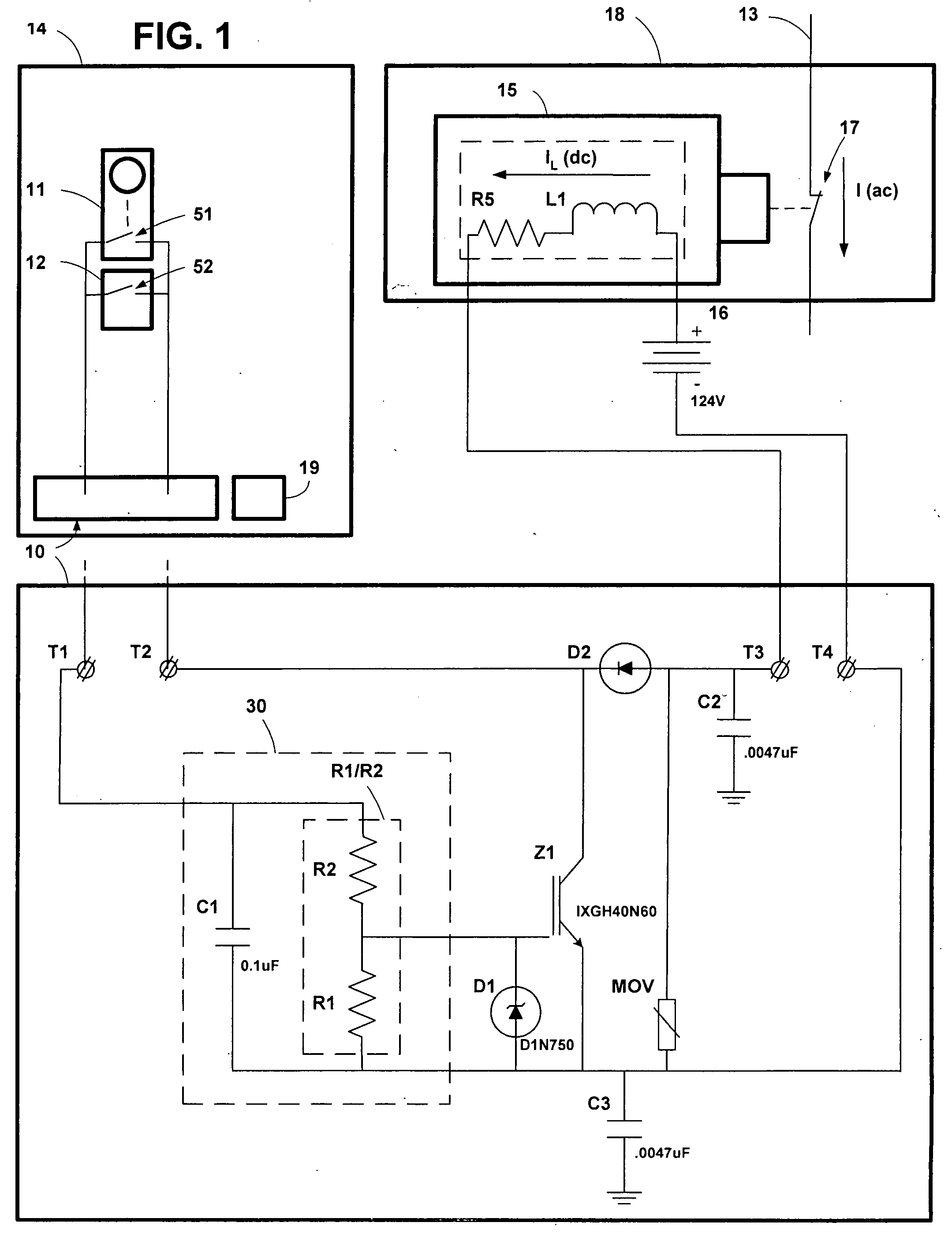
ActiveUS20070014055A1Low costAvoid damageElectric switchesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPower switchingCounter-electromotive force
An arc suppression circuit for a power switch or power supply with a relay having a coil and a set of contacts for providing a portion of an input power as load power to an output. The relay coil is configured for closing the relay contacts in response to receiving relay activating energy and for generating back EMF energy following termination of the receiving of the relay activating energy. A switch is connected in parallel to the relay contacts and is configured for providing a portion of the input power as supplemental load power to the output as a function of back EMF energy. Also, a method of suppressing damaging arcing across relay contacts in a power switch or power supply includes receiving back EMF energy generated by the relay coil following termination of the relay coil receiving activating energy and connecting supplemental load power to the output in parallel with the relay contacts in response to the receiving of the back EMF energy.
Owner:WATLOW ELECTRIC MFG
Ground fault fully compensated controllable voltage source output voltage computing method
InactiveCN109061372AEnsure safe and stable operationCompensation for fault currentFault location by conductor typesDesign optimisation/simulationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a ground fault fully compensated controllable voltage source output voltage computing method, comprising the steps of obtaining circuit ground capacitance, leakage resistance,fault ground resistance, arc suppression coil inductance, resistance and controllable voltage source internal resistance when a ground fault occurs; computing parallel impedance of a circuit ground parameter and a compensation inductance parameter according to the arc suppression coil inductance, the resistance, the leakage resistance and the circuit ground capacitance; and computing a controllable voltage source output voltage according to the fault ground resistance, the controllable voltage source internal resistance and the parallel impedance of the circuit ground parameter and the compensation inductance parameter. According to the method, in a voltage source access mode, the state problem that an arc suppression coil inductance parameter and the circuit ground capacitance approximateto power frequency resonance does not need to be taken into consideration; control is relatively easy; a fault current can be effectively compensated; and arc quenching is carried out on a fault point. According to the method, phase and amplitude of the output voltage are obtained through computing, the current at the fault point is quenched through control over the phase and amplitude of a controllable voltage source, and safe and stable operation of a power grid is ensured.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Arc suppression circuit
A circuit for suppressing electrical arcing in an ion beam source or other plasma devices is provided. The arc suppression circuit of this invention detects current rises on ion beam source grids which cause arcing, disconnects the current flowing to the grid, and grounds the ion beam source to allow excess charge and current to be drained from the ion beam source rather than letting the charge and current arc on the grids of the ion beam source. A novel timing sequence is used for activating and deactivating the arc suppression circuitry to prevent shorting out of the power source. The arc suppressor circuits of this invention can be used on devices other than ion beam sources or plasma devices.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
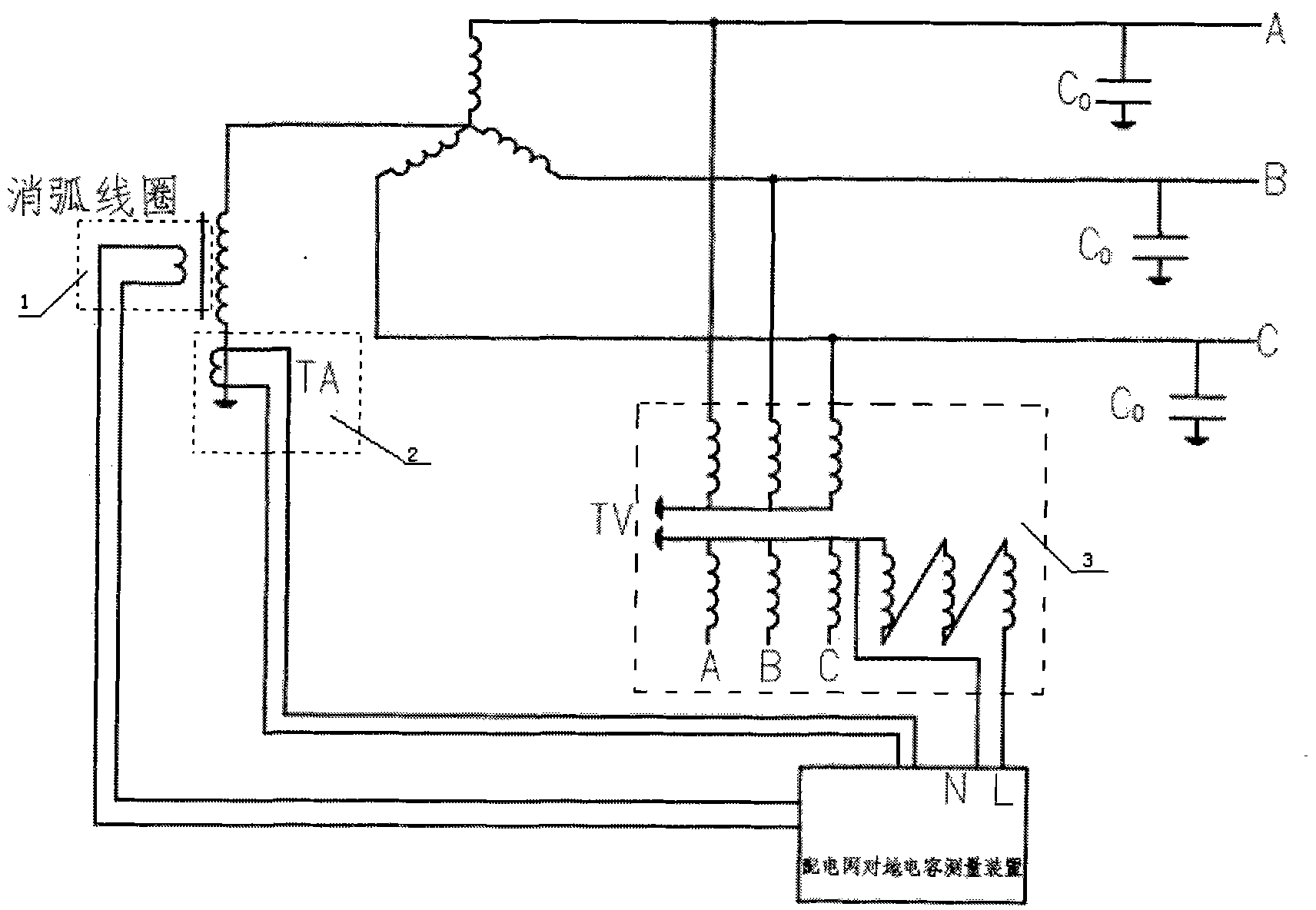
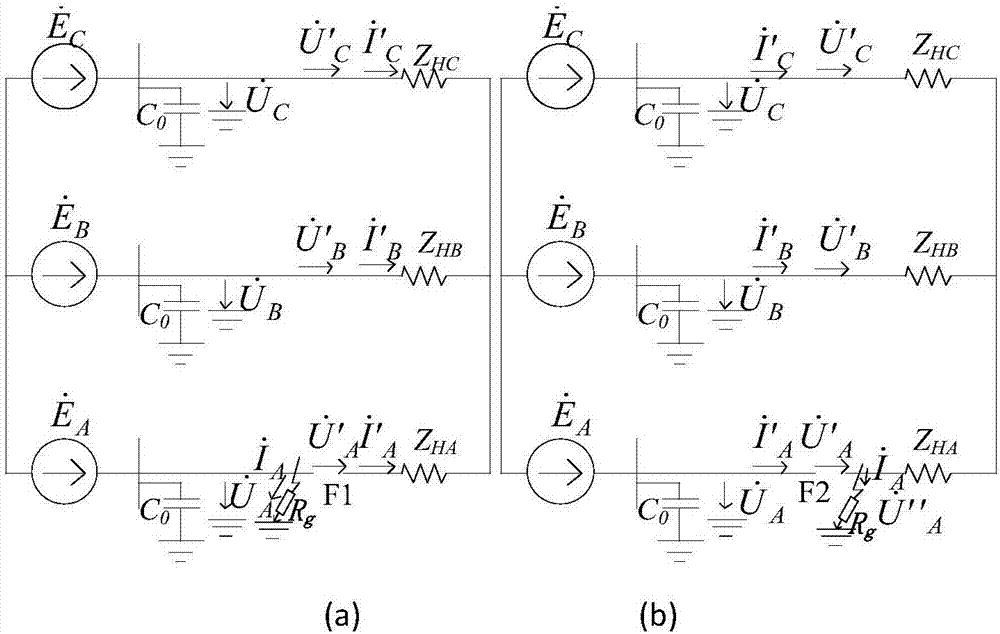
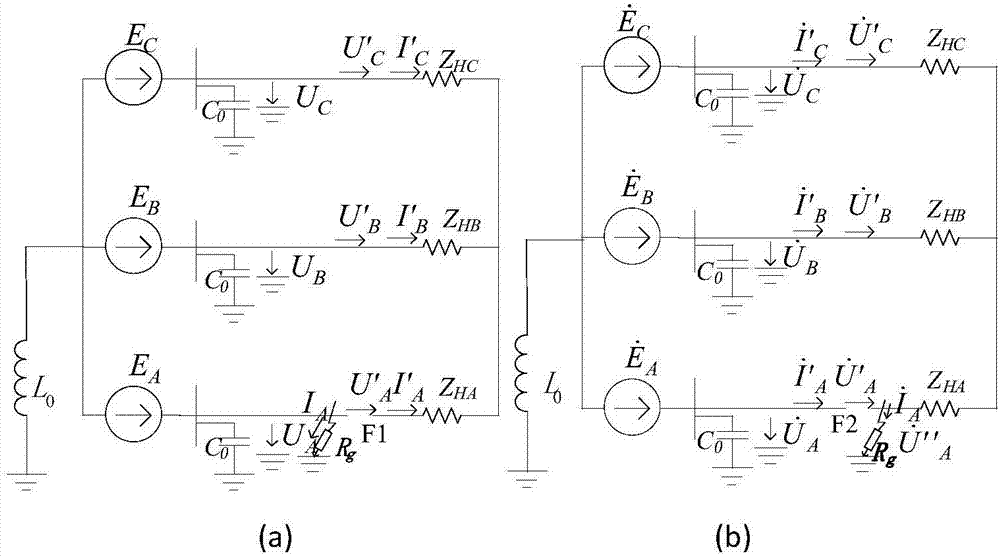
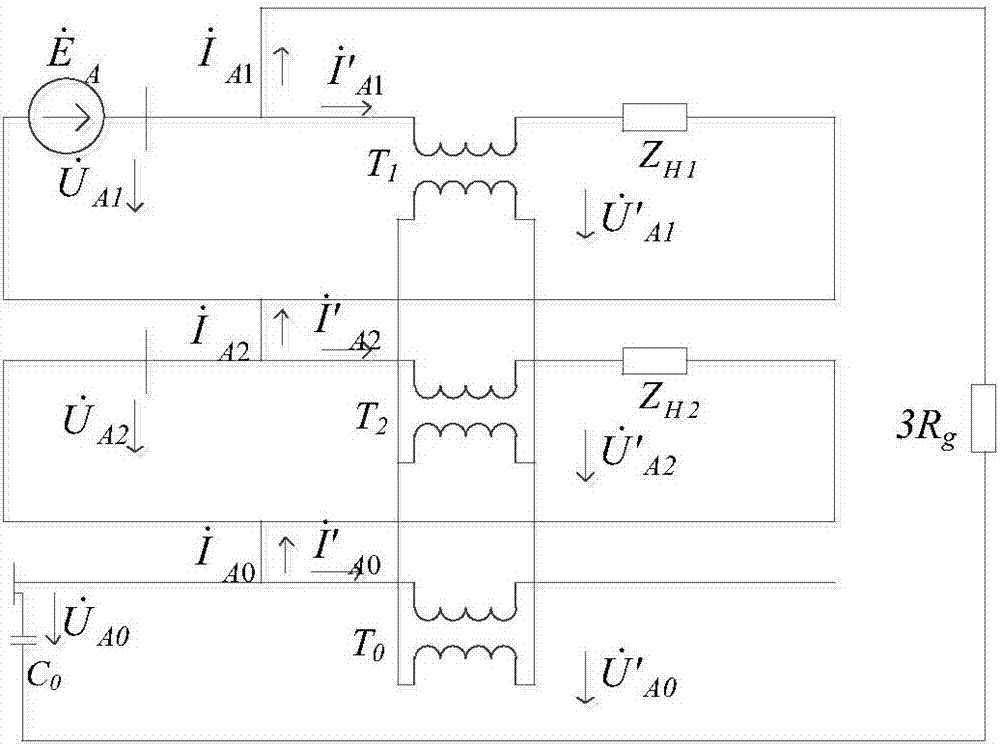
Capacitance measurement method and measurement device for power distribution network with neutral point grounded through arc suppression coil
InactiveCN101937024AEasy and accurate calculationEasy to measureResistance/reactance/impedenceMeasurement deviceElectrical bonding
The invention provides a capacitance measurement method for a power distribution network with a neutral point grounded through an arc suppression coil and a measurement device based on the method. The measurement method comprises the following steps of: (1) applying an excitation source, and injecting an excitation signal with the frequency between f0 and 2f0 (assuming the working frequency of the power distribution network as f0) into the power network through a secondary coil of the arc suppression coil, and assuming the frequency of the excitation signal as fc; (2) measuring the current, and measuring an output signal of a zero sequence current mutual inductor to obtain current magnitude; (3) measuring the voltage, and measuring voltage magnitude through a bus voltage transformer; and (4) calculating the capacitive reactance over the ground. The measuring device comprises a signal injecting module, and a bus voltage acquisition and processing module and a zero sequence current acquisition and processing module; the zero sequence current acquisition and processing module comprises a signal processing module electrically connected with an output end of the zero sequence current transformer. The measuring method can be used for conveniently and accurately measuring the capacitive reactance over the ground and the current, and the operations of an operator to the primary side of the power network are avoided.
Owner:JINAN AONUO CNC EQUIP
Power distribution network one-phase grounding fault location method based on zero sequence voltage
ActiveCN103792465AOvercome the problem of large errorsEasy to implementFault locationLow voltageDistributed parameter model
A power distribution network one-phase grounding fault location method based on a zero sequence voltage belongs to a power distribution network grounding fault location method. The fault location method starts from an overall zero sequence parameter of a single-end radial medium voltage power distribution network, analyzes a one-phase grounding fault while taking a distributed parameter model influence into consideration, measures a steady-state zero sequence voltage value and a zero sequence current of each feeder line at a bus position and at a tail end of each outlet line, and finds zero sequence voltage variation characteristics of a fault feeder line and non-fault feeder line. According to the invention, a large number of existing devices are used, the data sampling requirement is low in terms of being real-time, and the method of the invention is easy to realize; the simulation model analysis is established according to the actual parameters, so that the fault location can be realized in the system in which the neutral point is not grounded or the neutral point is grounded through an arc suppression coil; the precision is quite high; and the location method of the invention can be applied to the medium and low voltage power distribution network.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method capable of realizing low-current route selection and fault location
ActiveCN102798795AChange compensationChange ground capacitanceFault locationInformation technology support systemCapacitanceTransformer
The invention discloses a method capable of realizing low-current route selection and fault location and discloses a novel method capable of realizing single-phase grounding route selection and fault location. The method comprises the following steps: detecting the zero sequence voltage value of a system and the zero sequence current value of each branch line at the first time of the single-phase grounding fault; at the second time, changing the capacitance value or the inductance value of the whole power distribution network on the ground for a neutral point ungrounded system, changing the compensation degree of an arc suppression coil or changing the capacitance value or the inductance value of the whole power distribution network on the ground for an arc suppression coil grounding system, and detecting the zero sequence voltage value of the system and the zero sequence current value of each branch line at the second time after adjusting; and after determining the branch line of the single-phase grounding fault, uploading the detected zero sequence current value of the branch line, dividing the zero sequence voltage of the system by the detected zero sequence current value and judging to determine the position of the fault point. When the zero sequence current change of a voltage transformer on a bus influences the fault route selection and location, the zero sequence loop of the voltage transformer can be cut off, so that the detection precision is improved.
Owner:DALIAN ELECTRIC POWER SURVEY & DESIGN INST
Power distribution network single-phase earth fault section locating method based on correlation analysis
InactiveCN104181442ARapid positioningPrecise positioningFault locationSpecial data processing applicationsCapacitanceDistribution power system
The invention provides a power distribution network single-phase earth fault section locating method based on correlation analysis. The fault line selection problem in the single-phase earth fault process of a power distribution network is not solved well, and fault locating is more difficult to refer to. After a single-phase earth fault happens to a system, the first capacitive frequency band concept is utilized, each line is simplified into a capacitance model in a zero-sequence network under the selected frequency band, earth fault detection devices are arranged on line outlets and branches to measure zero-sequence voltages and zero-sequence currents, association coefficients of zero-sequence voltage differentials and the zero-sequence currents are obtained, whether fault points are in the section or not is judged according to plus and minus of the obtained association coefficients, finally the association coefficients are judged and calculated to be minus, and the section farthest away from a bus is the section where the fault points are located. The method is simple in principle and easy to implement, fault section locating can be carried out fast and reliably, and the method can be used for neutral ungrounding power distribution systems and can be used for power distribution systems with neutral points grounded through arc suppression coils.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +3
Current controlled contact arc suppressor
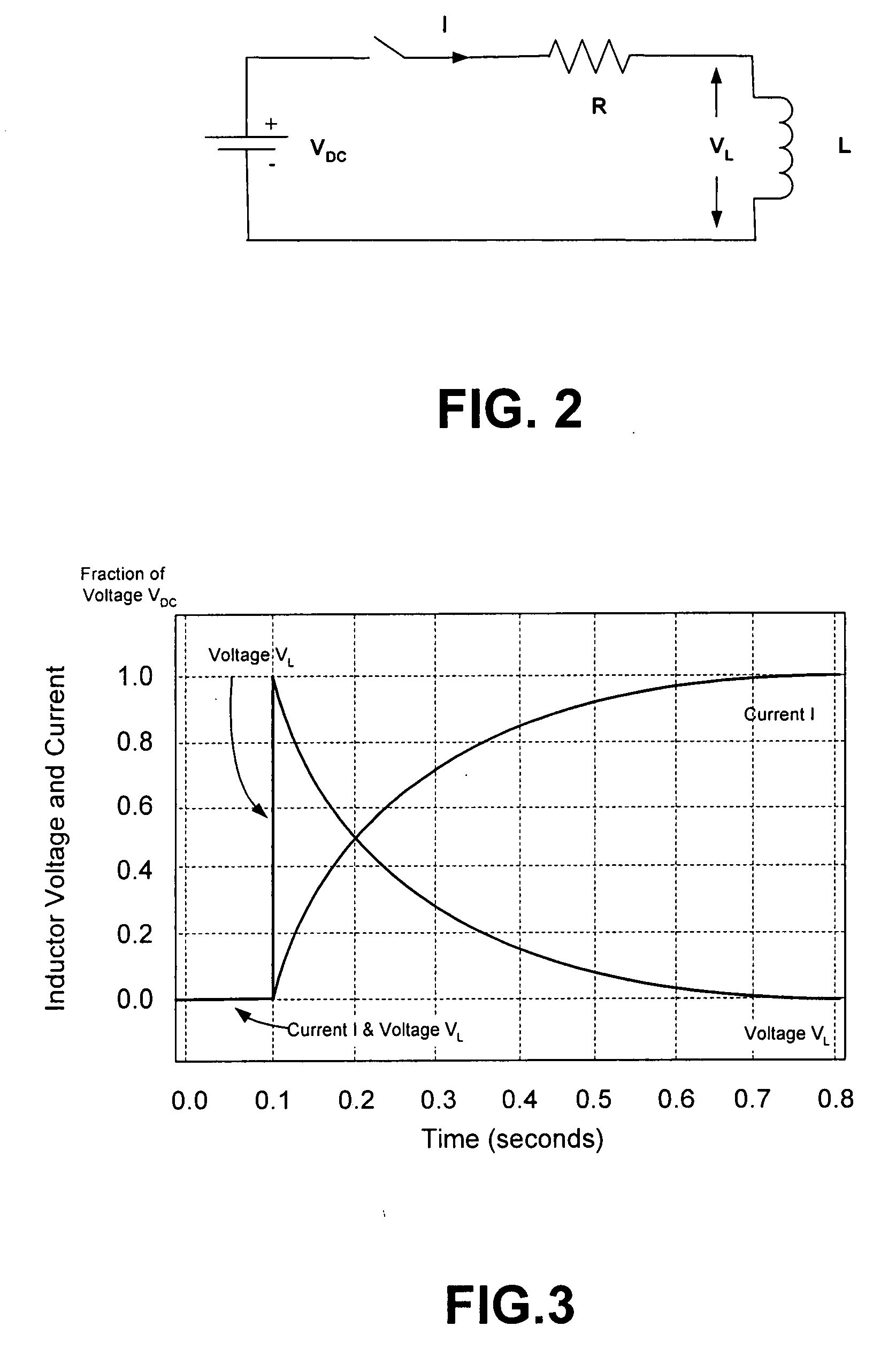
InactiveUS6956725B2Avoid arcingElectric switchesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSuppressorCurrent sensor
The arc suppression system for electrical contacts includes a transistor, such as an IGBT, which is connected across the contacts. A control circuit controls the operation of the transistor such that the turning on of the transistor results in a current path around the contacts, thereby tending to prevent arcing across the contacts. A current sensor, such as a flyback transformer, is positioned in series with the contacts, wherein when the contacts open, current is interrupted through the contacts and the transformer, a secondary voltage results which is applied to the transistor, which tends to maintain the transistor on for a time which is sufficient to allow the contacts to either open or close without an arc.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Merie plasma reactor with overhead RF electrode tuned to the plasma with arcing suppression
InactiveUS20050236377A1Increase ion densitySufficient capacitanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceIon density
A plasma reactor for processing a semiconductor workpiece, includes a reactor chamber having a chamber wall and containing a workpiece support for holding the semiconductor support, the electrode comprising a portion of the chamber wall, an RF power generator for supplying power at a frequency of the generator to the overhead electrode and capable of maintaining a plasma within the chamber at a desired plasma ion density level. The overhead electrode has a capacitance such that the overhead electrode and the plasma formed in the chamber at the desired plasma ion density resonate together at an electrode-plasma resonant frequency, the frequency of the generator being at least near the electrode-plasma resonant frequency. The reactor further includes a set of MERIE magnets surrounding the plasma process area overlying the wafer surface that produce a slowly circulating magnetic field which stirs the plasma to improve plasma ion density distribution uniformity.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Circuit for operating voltage range extension for a relay
InactiveUS6671142B2Shorting of contactSuppress contact opening arcingCoupling device detailsElectronic switchingMOSFETEngineering
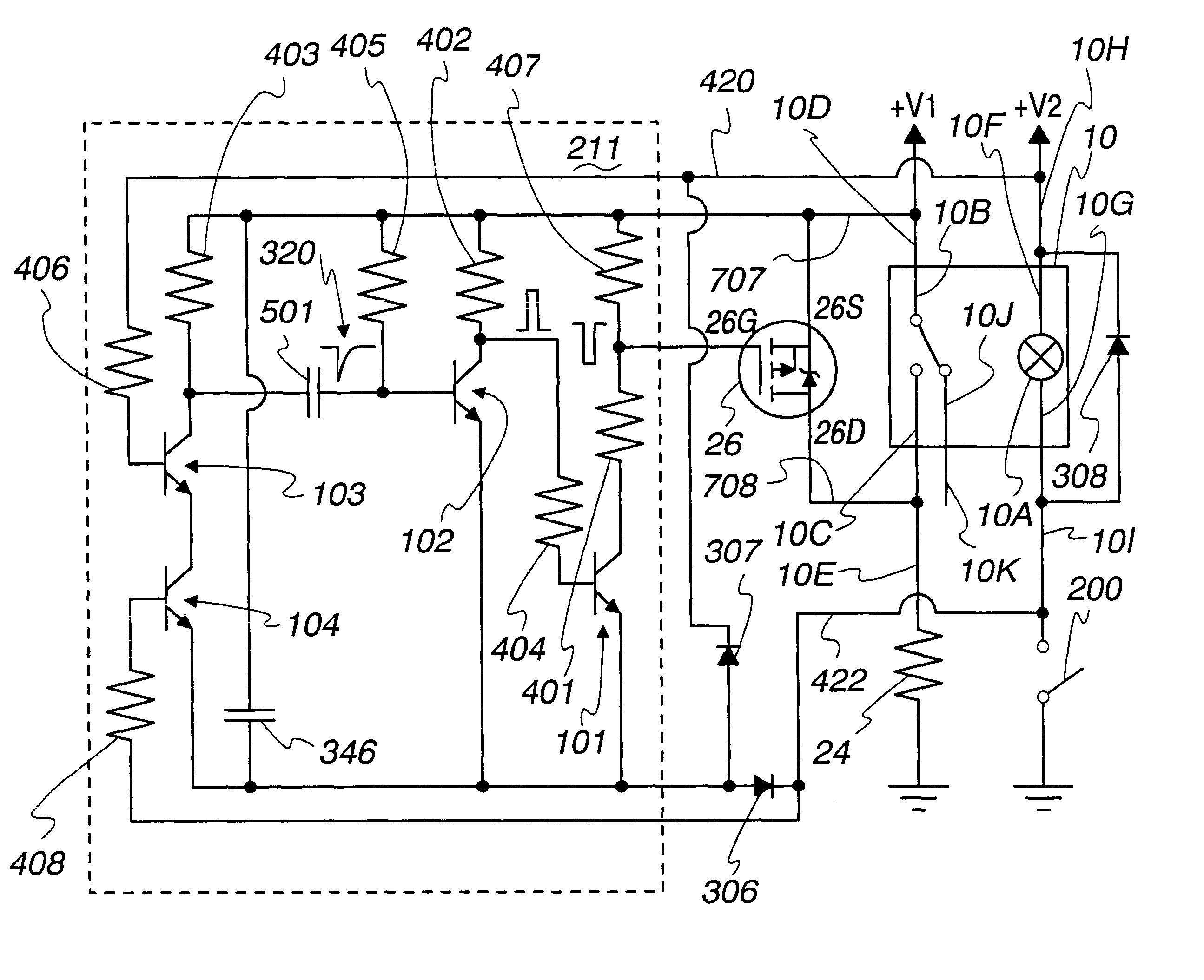
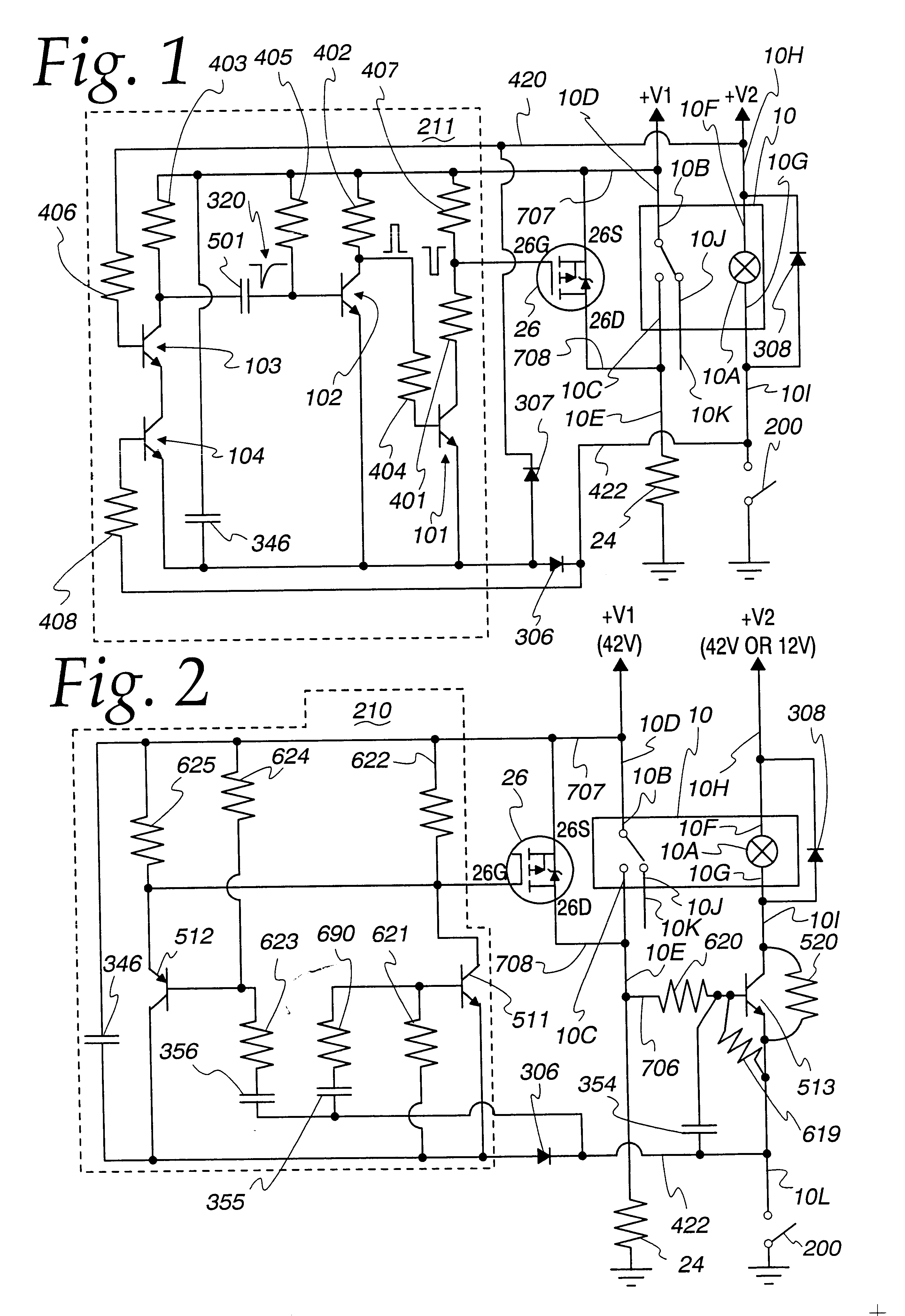
A relay is designed to be used in a circuit where the voltage levels are high in comparison to the spacing between the contacts when open. Contact closure arcing is suppressed by actuating a MOSFET that shorts the contacts together while they open. The same MOSFET can momentarily short the contacts together just before they first begin to close, allowing a test current to be passed through the MOSFET and through the terminals connecting to both relay contacts, to insure that arc suppression will be successful; and if this test fails, then the relay can be disabled by a switch in series with the relay coil to prevent arcing and a possible fire hazard. Relay deactuation can be sensed to trigger arc suppression, and relay actuation can be sensed to initiate fail-safe testing by a circuit that responds no matter which way the relay coil is connected into the external circuit that drives it.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Diagnosis method for single-phase line breakage grounding complex fault type of power distribution network based on zero sequence voltage
ActiveCN106872852AVersatileOffset angle characteristics are not affected by voltage levelFault location by conductor typesPhase differenceSymmetrical components
The invention discloses a diagnosis method for a single-phase line breakage grounding complex fault type of a power distribution network based on a zero sequence voltage, and the method comprises the steps: setting a start value of the zero sequence voltage through determining a small current grounding mode; extracting voltage sampling data of each phase of N cyclic waves before a line breakage moment and N cyclic waves after a fault moment, and calculating and obtaining the phase difference relation between the phase of the fault phase voltage before the fault and the phase of the steady-state zero sequence voltage after the fault and a reference function as the criterion through the FFT and a symmetrical component algorithm; judging whether the zero sequence voltage exceeds the start value or not: carrying out the extraction if the zero sequence voltage exceeds the start value and judging whether the phase difference between the phase of the zero sequence voltage and the phase of the fault phase voltage before the fault is corresponding to a load side grounding range of the criterion or not: determining that the fault is a single line breakage and load side grounding fault if the phase difference is corresponding to the load side grounding range of the criterion, or else determining that the fault is a single line breakage and power side grounding fault. The method is good in universality, and is suitable for power distribution networks at various voltage levels, wherein the neutral points of the power distribution networks are not grounded or the power distribution networks are grounded through arc suppression coils. Moreover, the deviation angle is not affected by the voltage level.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Arc suppression circuit for electrical contacts
ActiveUS7145758B2Slow chargingReduce probabilityElectric switchesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEngineeringCapacitor
A circuit to suppress arc across contacts of a relay is provided, in which the relay is electrically coupled to a power supply and a load. The circuit includes an arc suppression circuit electrically coupled between the first and second contacts of the relay, and the arc suppression circuit includes a capacitor and a switch, both of which are electrically coupled to the first and second contacts of the relay, in which the switch is configured to turn on when the first and second contacts of the relay change state, thereby providing an alternate path for a current flow through the load.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Arc suppression circuit using a semi-conductor switch
InactiveUS20080112097A1Avoid arcingElectric switchesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSufficient timeControl signal
An arc suppression circuit in a protection relay having trip contacts is used to turn off a battery-powered solenoid and trip an AC power circuit breaker. The arc suppression circuit uses a switch-control circuit to control the turning off of a semi-conductor switch so that the semi-conductor switch provides a current path around the trip contacts, and is carrying all, or substantially all, of the load current, before the trip contacts are opened. When the trip contacts begin to open, the switch-control circuit holds the semi-conductor switch on for a sufficient time to prevent an arc from becoming established before turning the semi-conductor switch off. In a second embodiment, the arc suppression circuit provides a second switch-control circuit. This second switch-control circuit is configured to accept control signals from a microprocessor within a protection relay. The microprocessor turns the semi-conductor switch on before the contacts begin to open, thereby providing a current path around the contacts before the contacts begin to open. The microprocessor turns the semi-conductor switch off after a time sufficient to prevent an arc from becoming established.
Owner:ABB TECH AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com