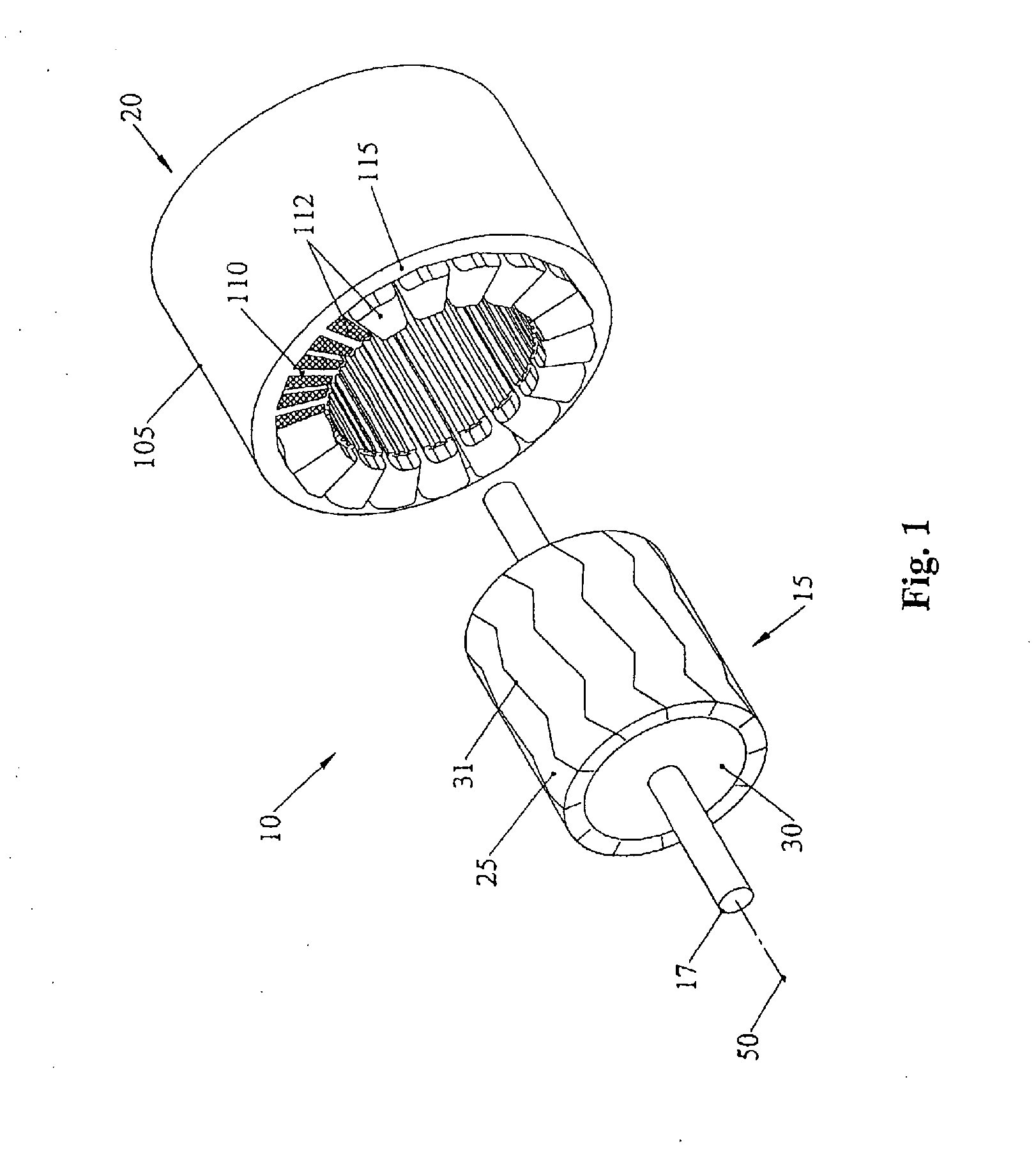
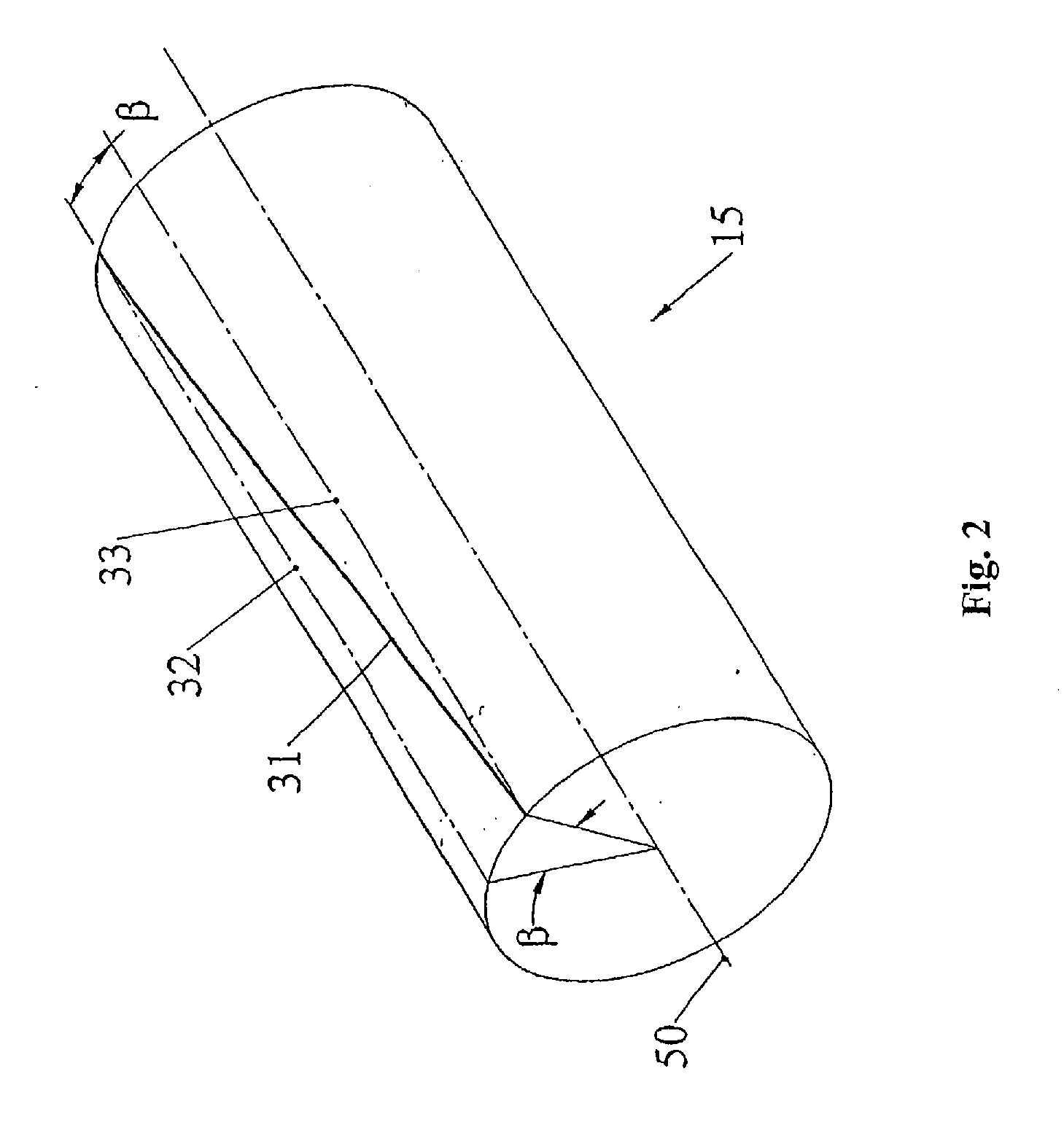
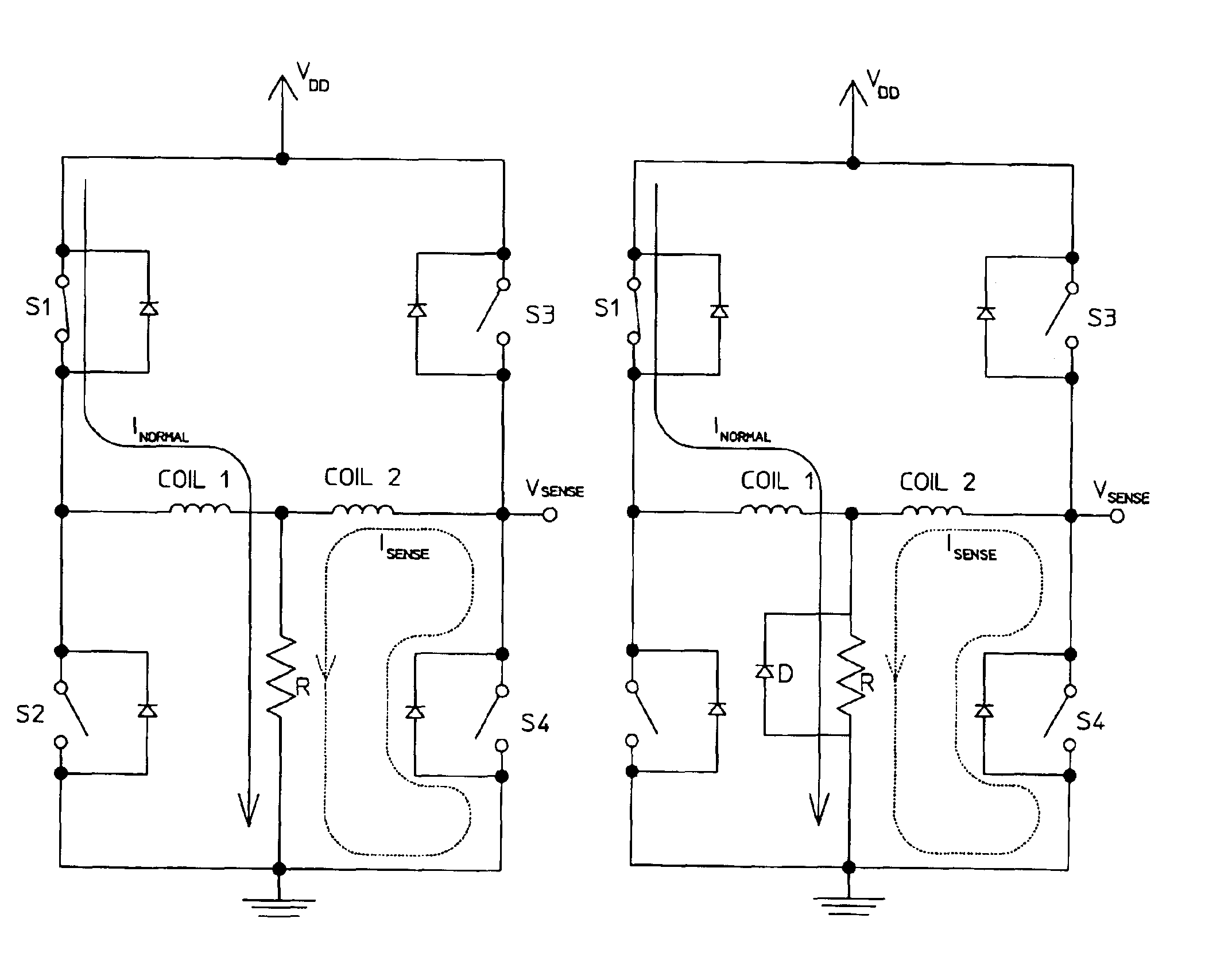
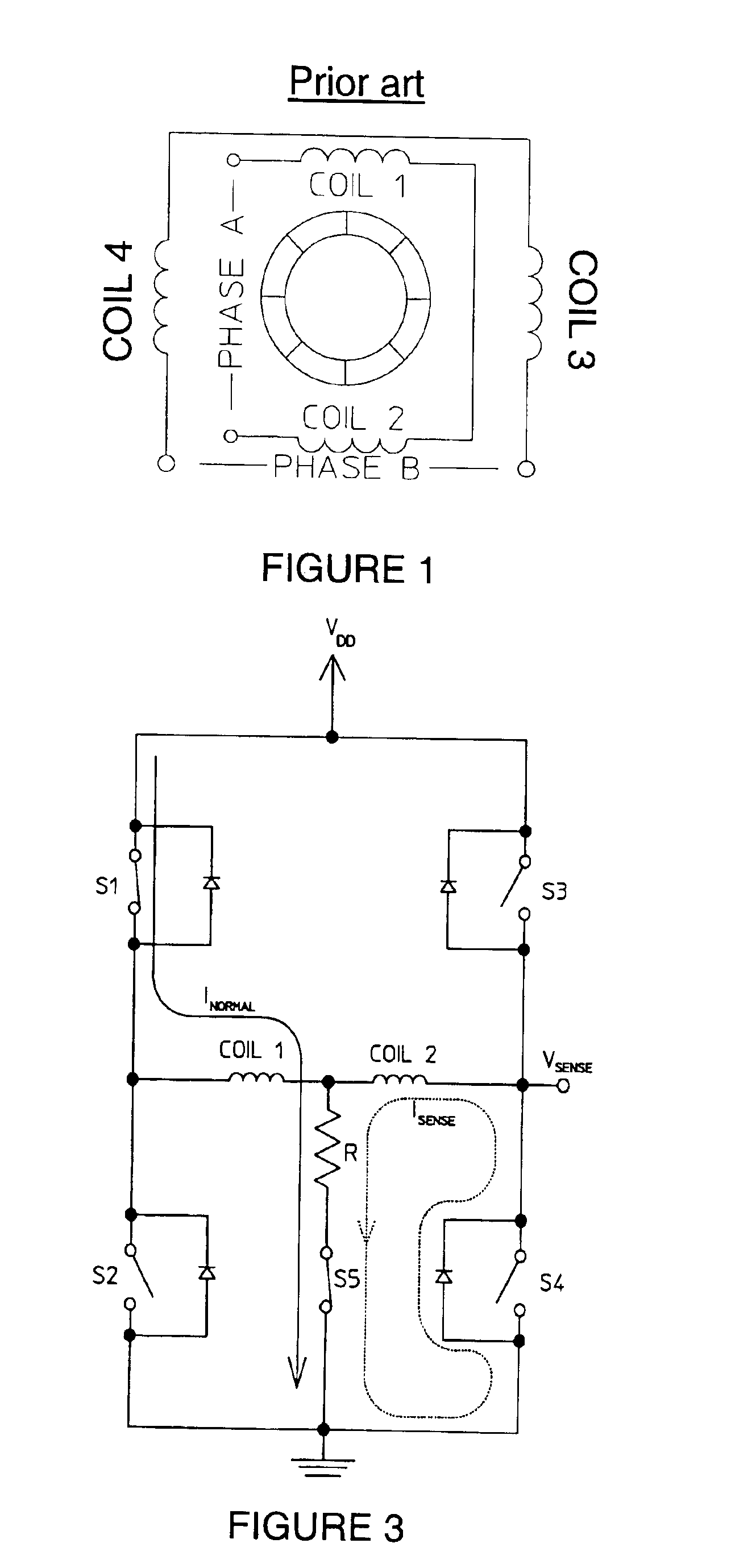
Patents
Literature
2549 results about "Counter-electromotive force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
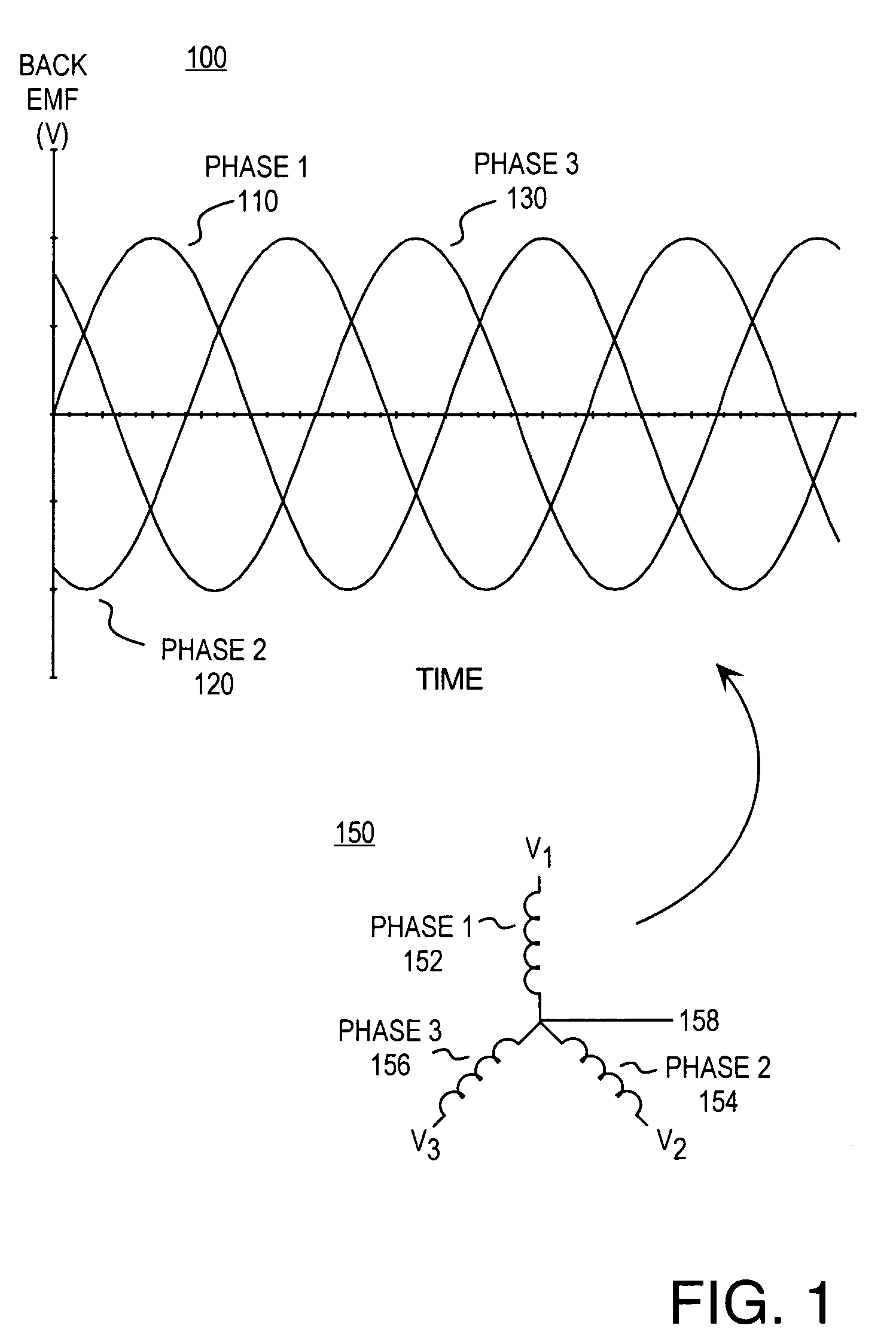
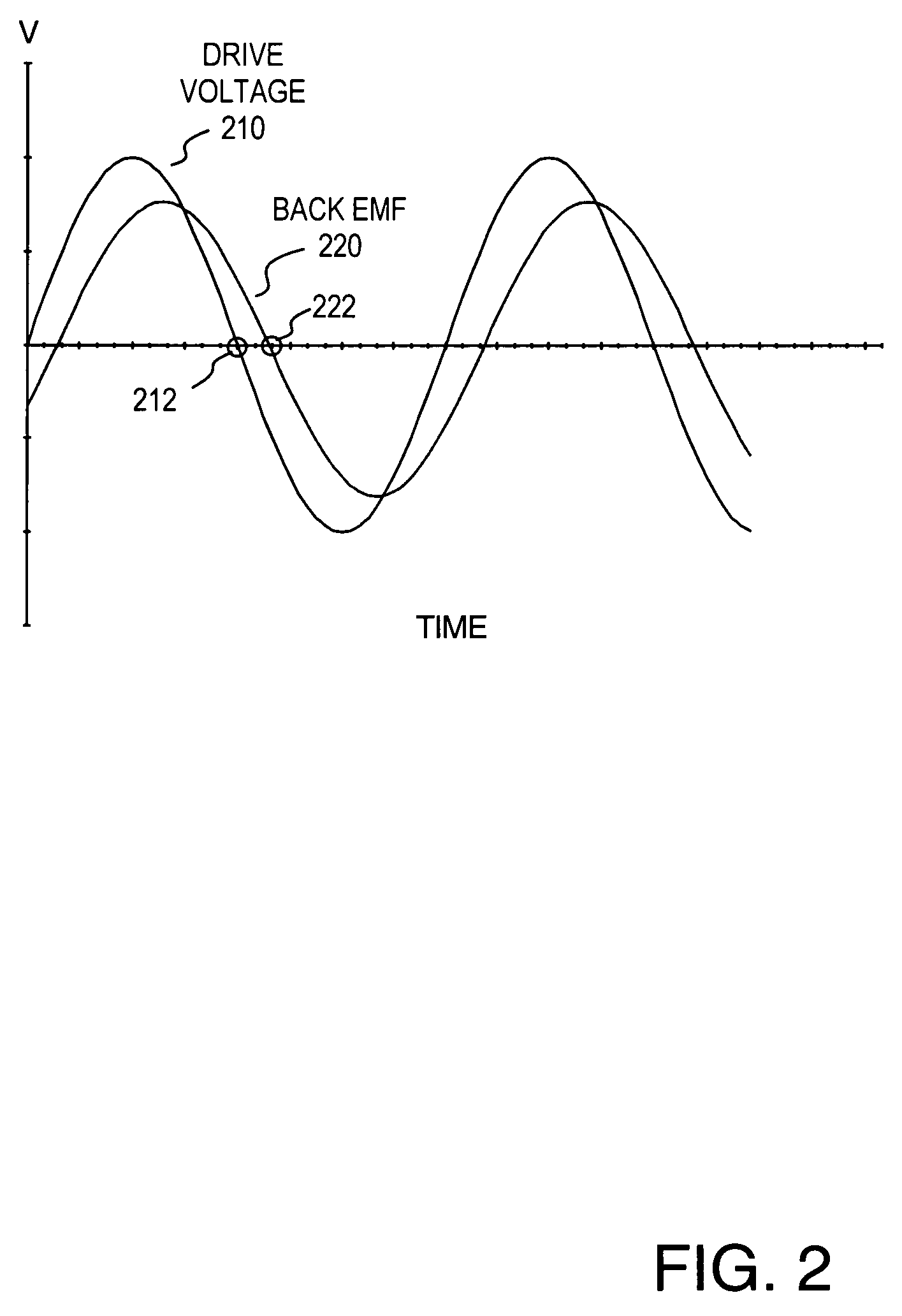
Counter-electromotive force (abbreviated counter EMF or simply CEMF), also known as back electromotive force (or back EMF), is the electromotive force or "voltage" that opposes the change in current which induced it. CEMF is the EMF caused by magnetic induction (see Faraday's law of induction, electromagnetic induction, Lenz's Law).
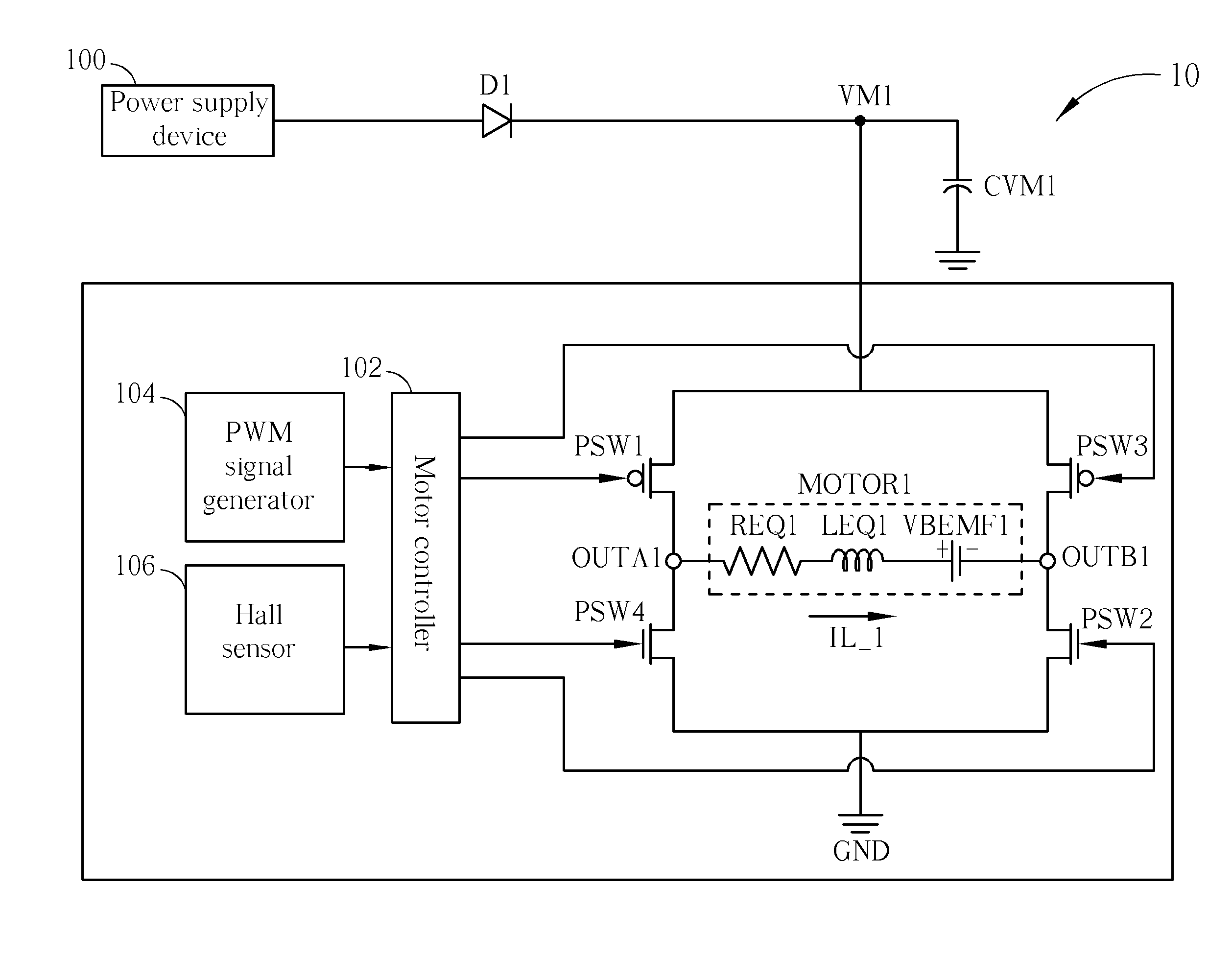
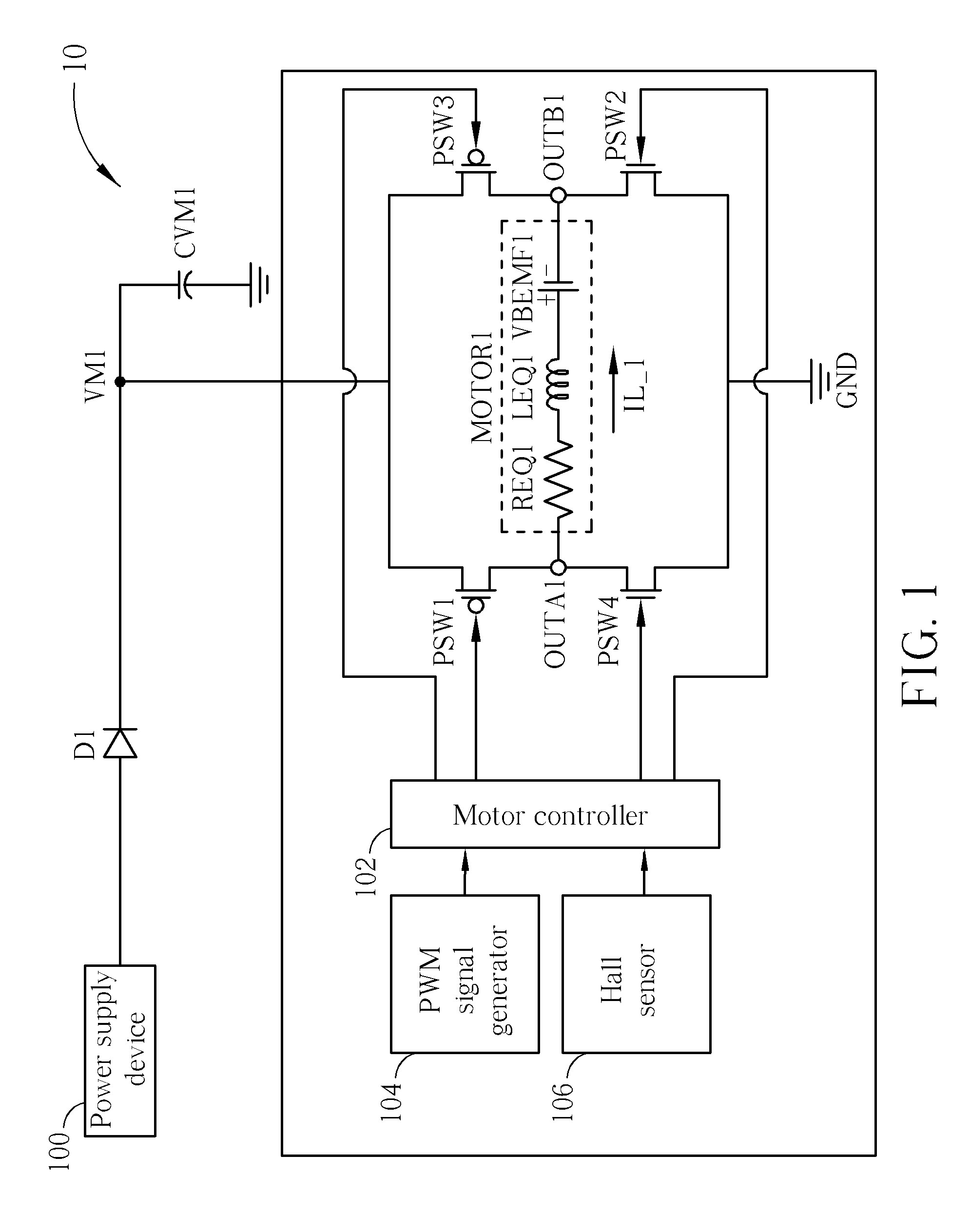
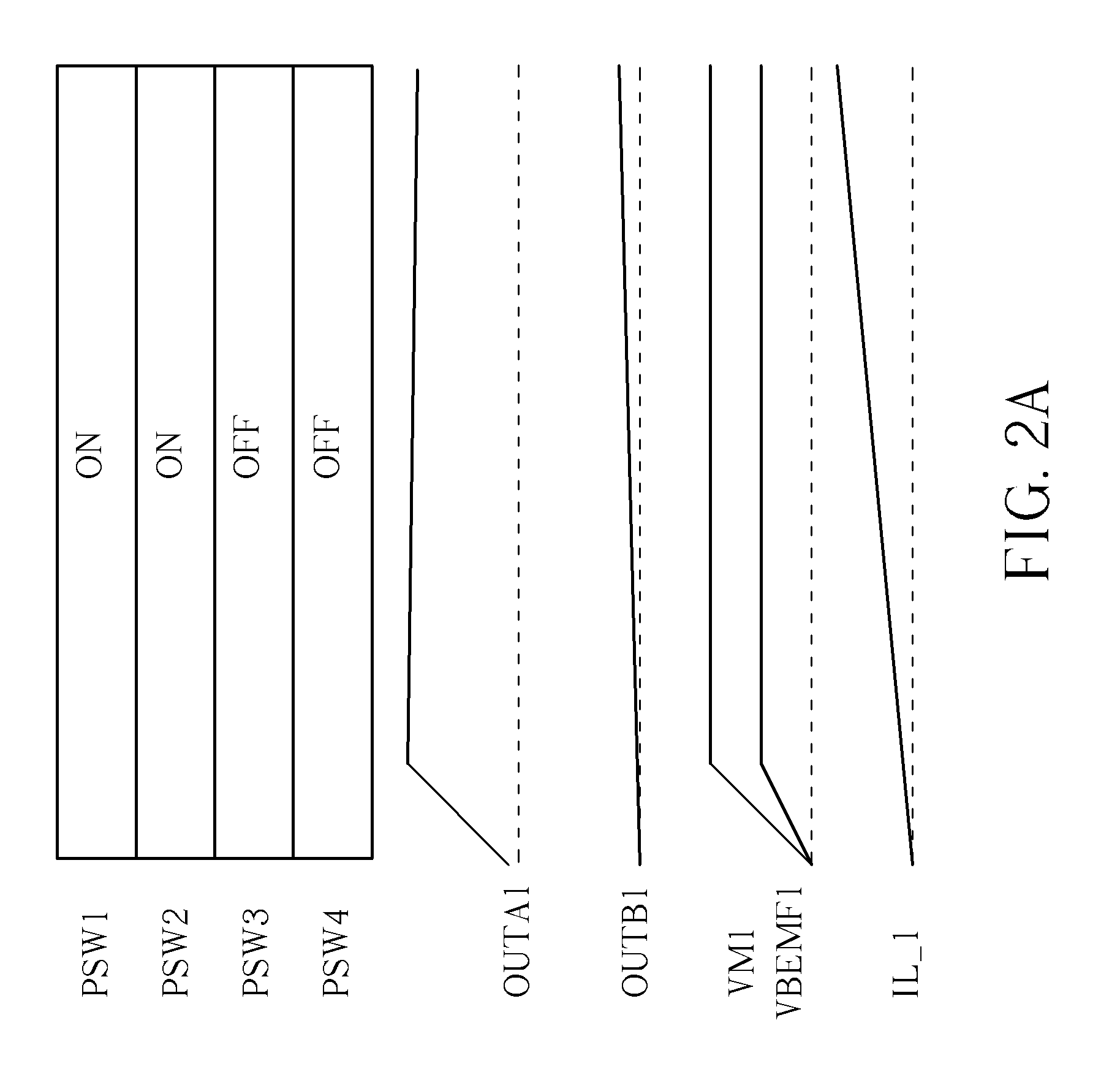
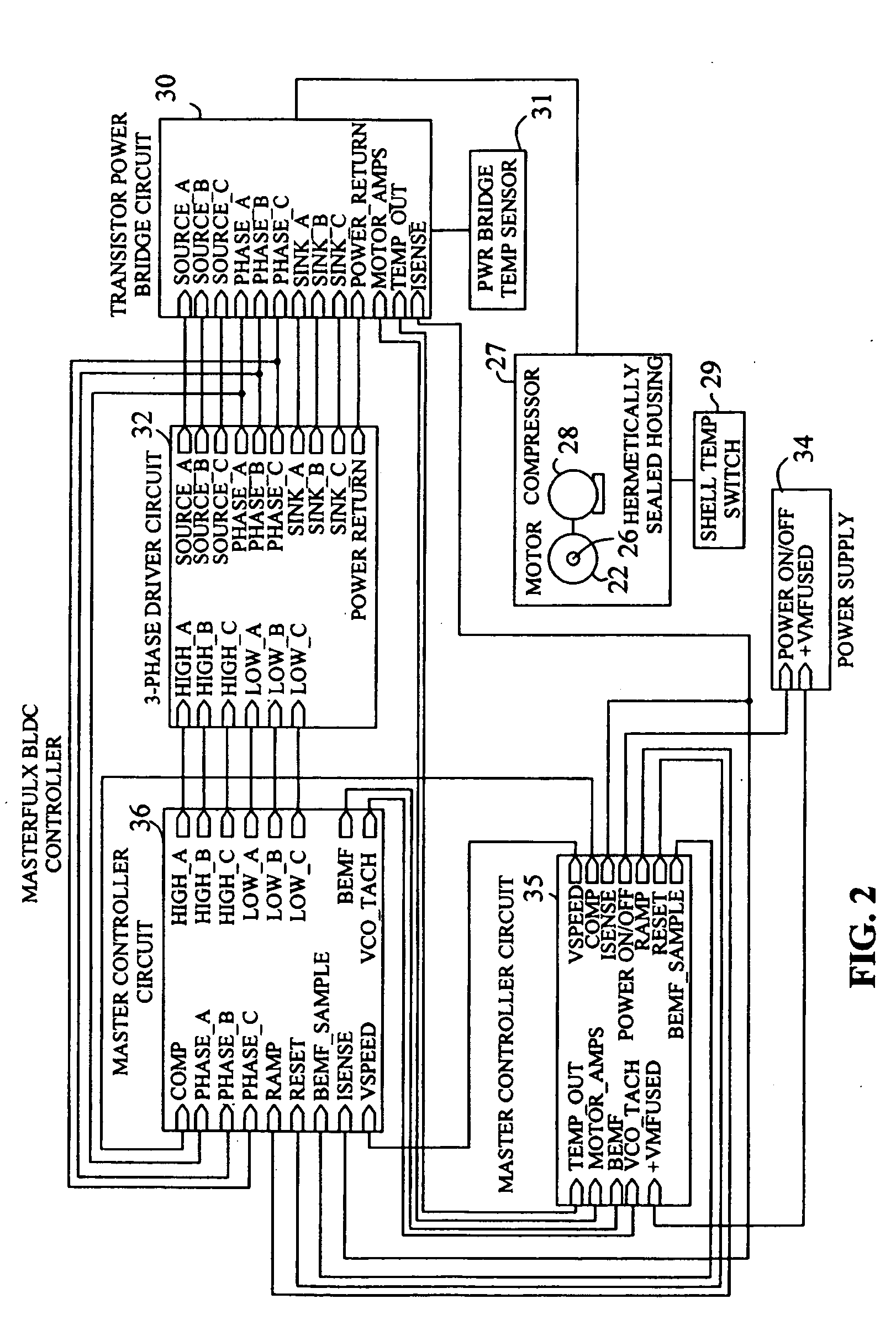
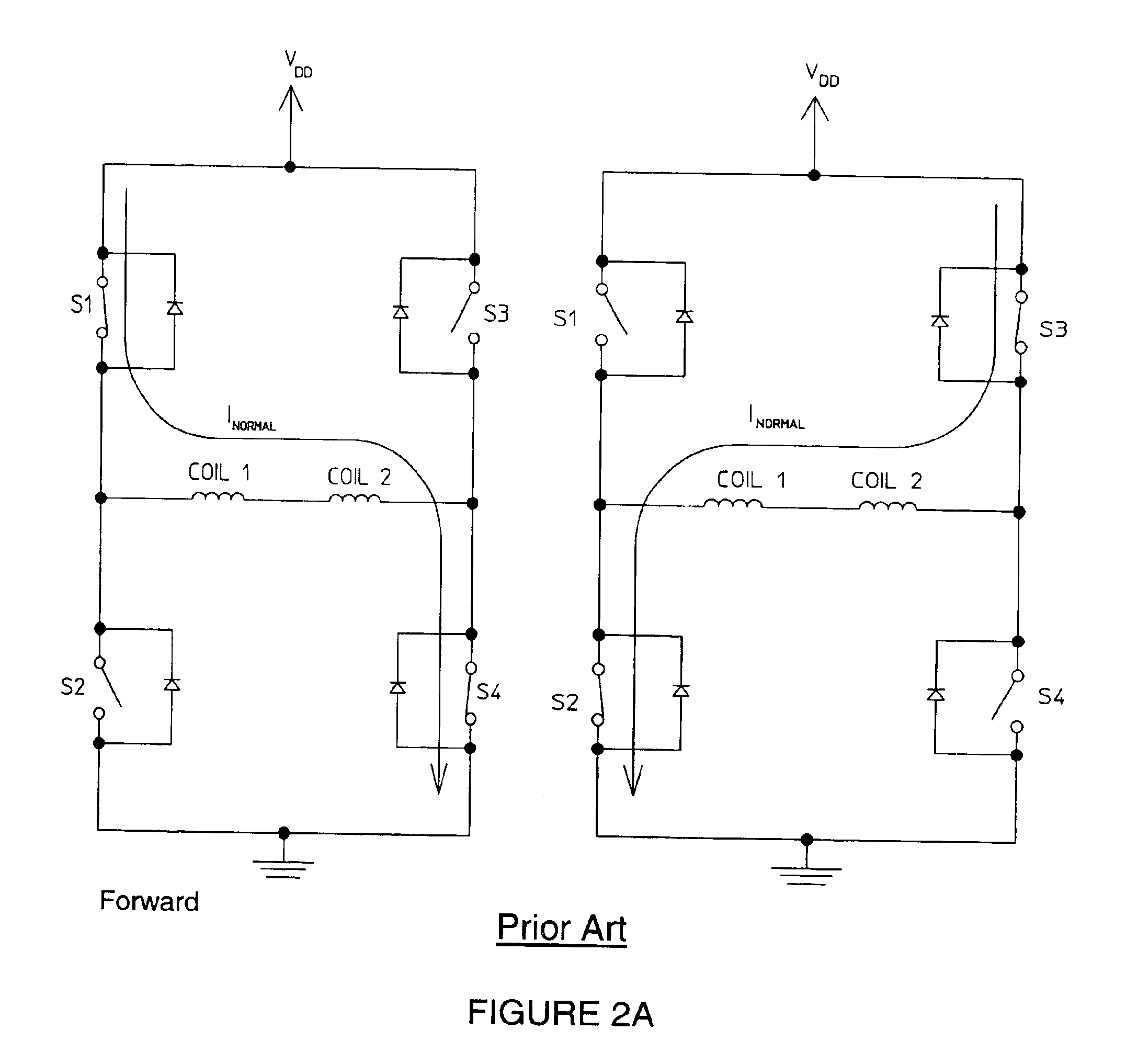
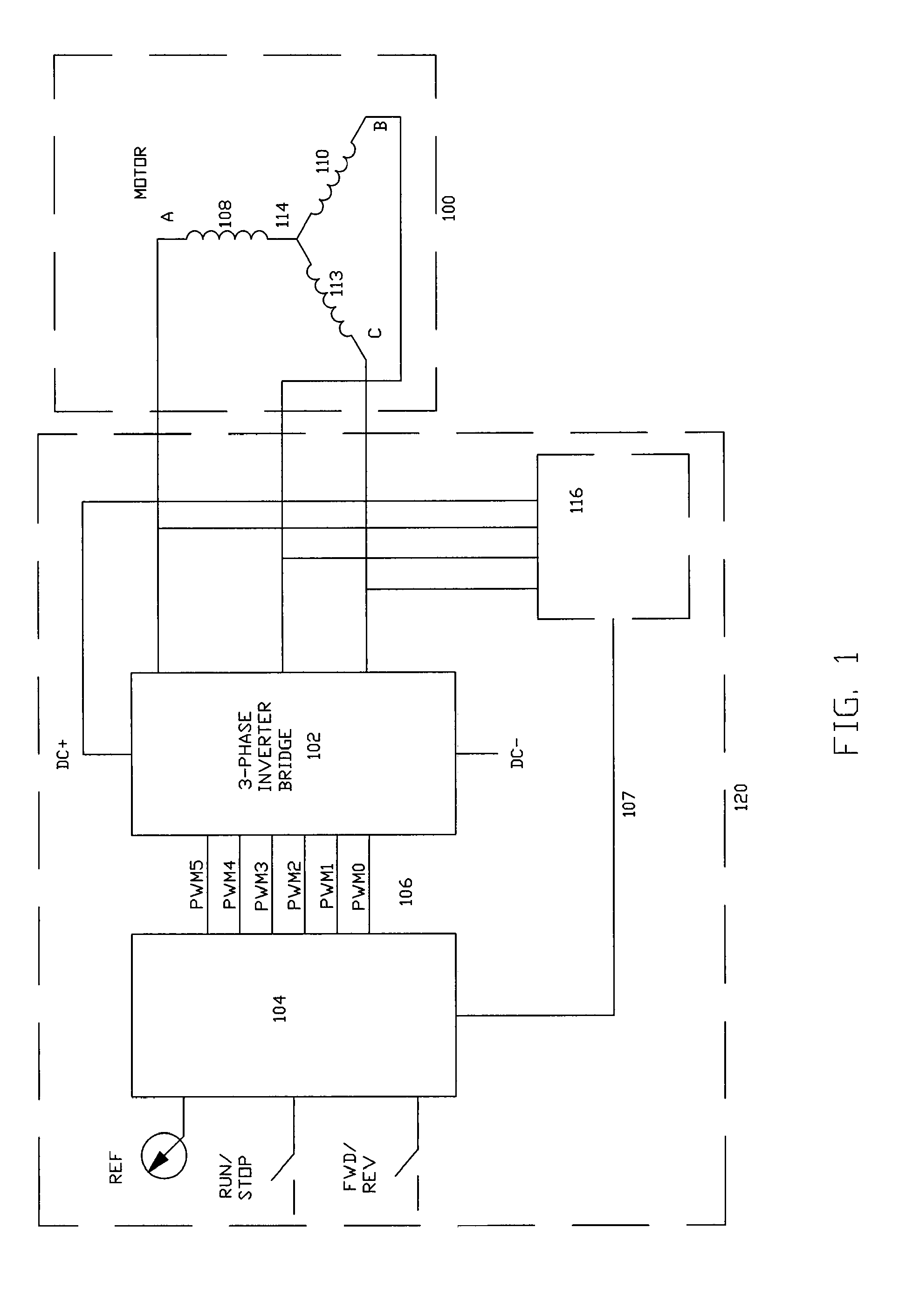
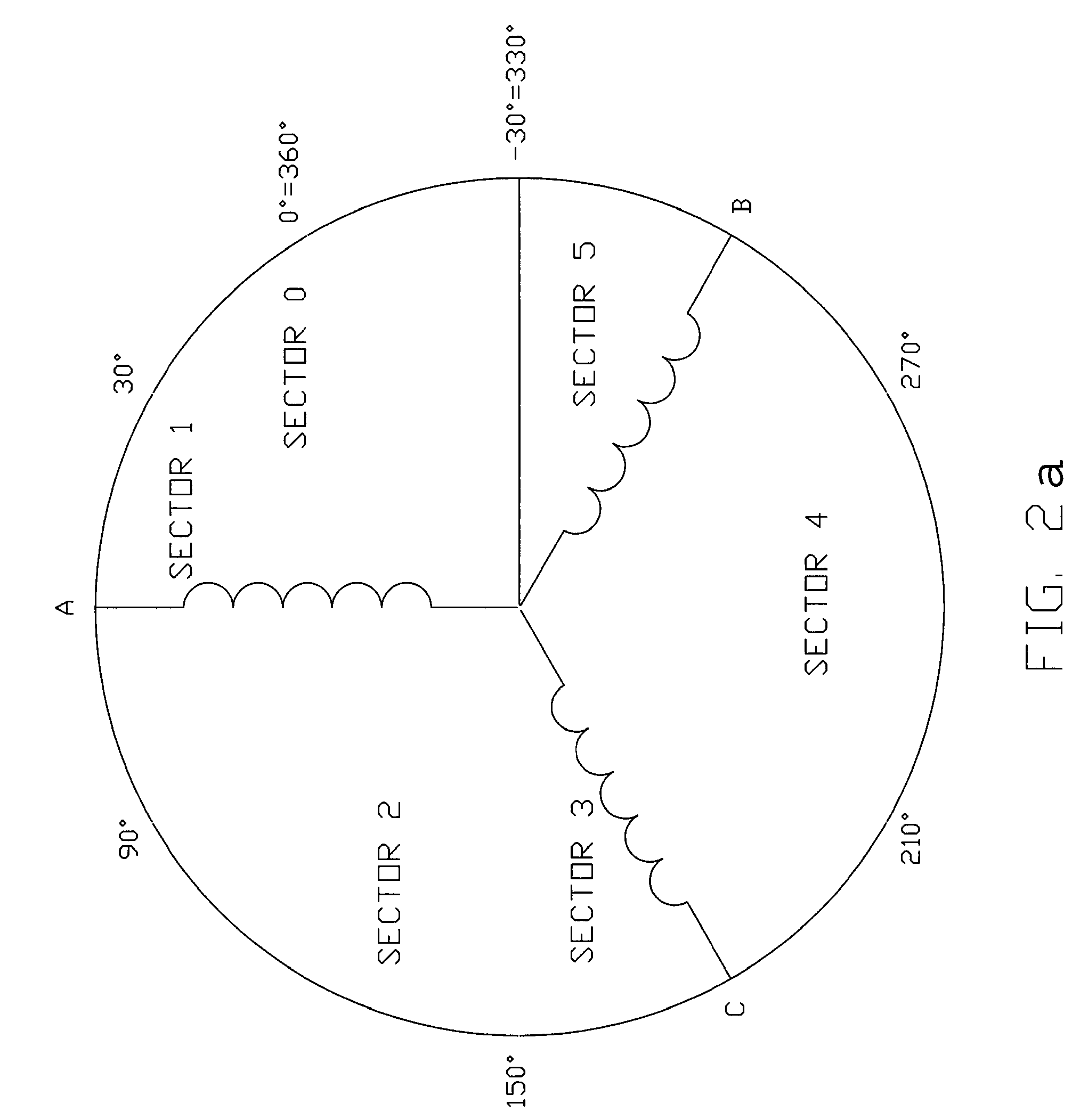
Method of driving DC motor and related circuit for avoiding reverse current
ActiveUS8183807B2Avoid it happening againMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlDriver circuitPower flow
Owner:ANPEC ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Position detection of an actuator using a capacitance measurement
InactiveUS20050031140A1Broadcast circuit arrangementsFrequency response correctionCapacitanceEngineering
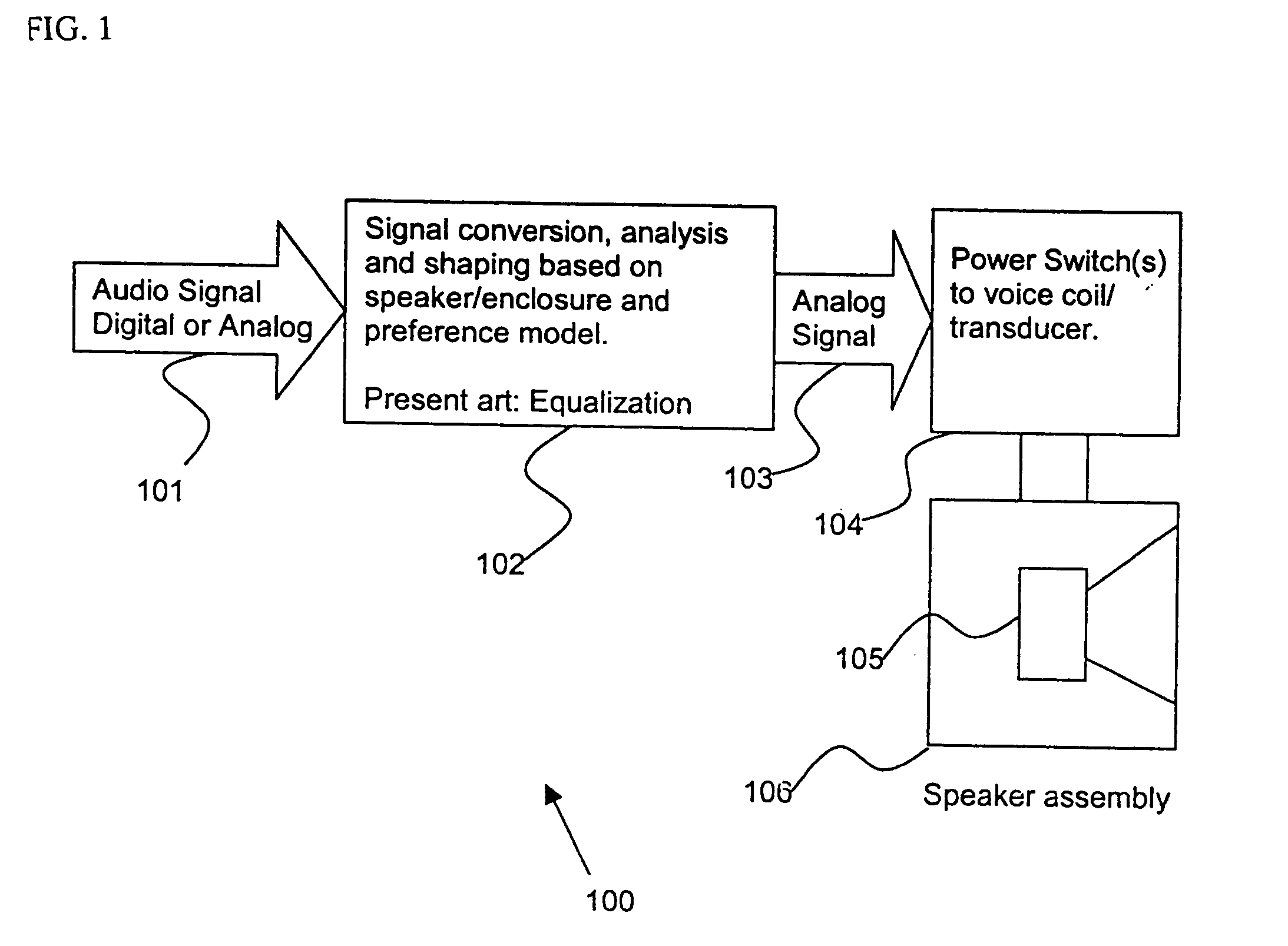
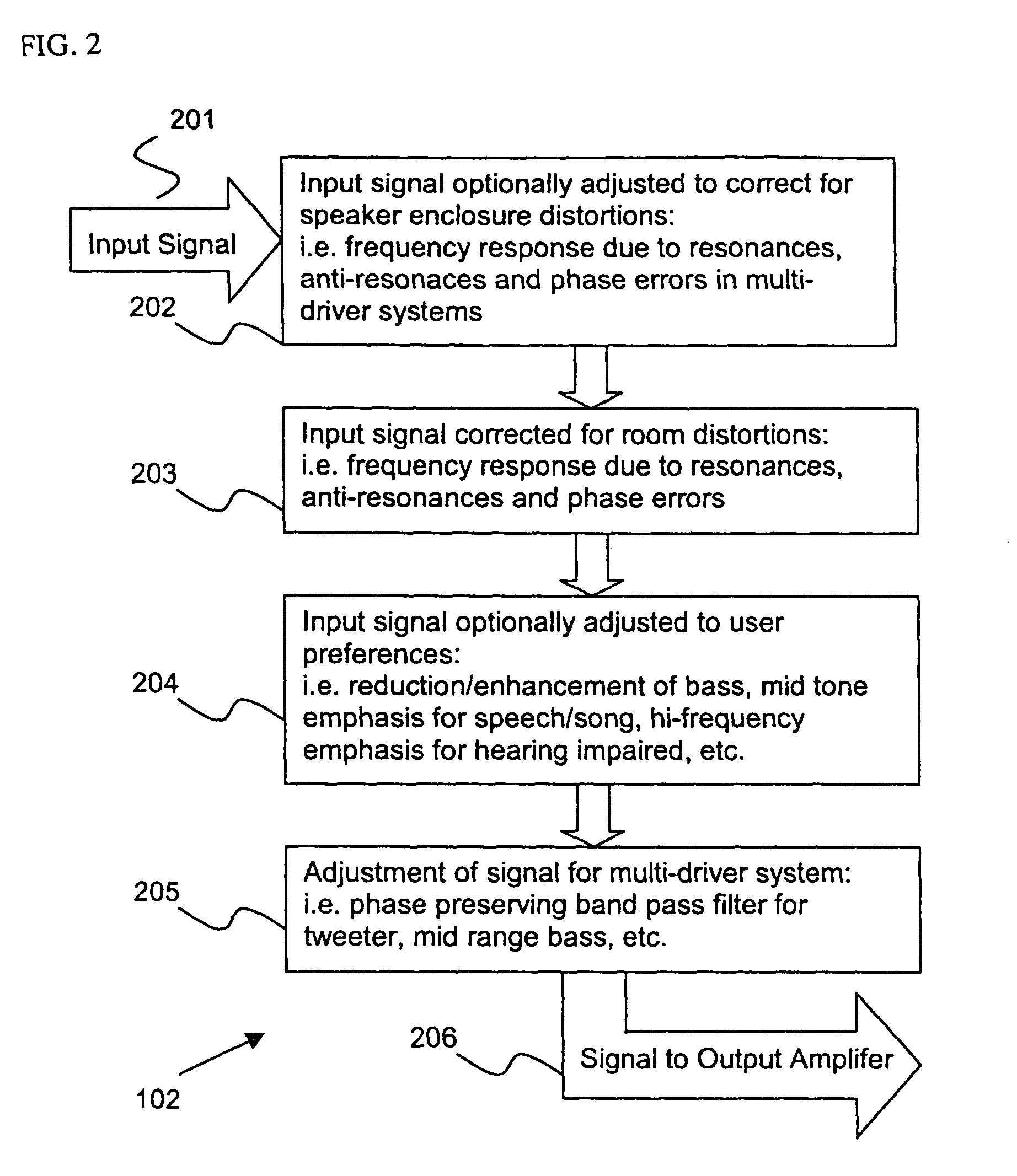
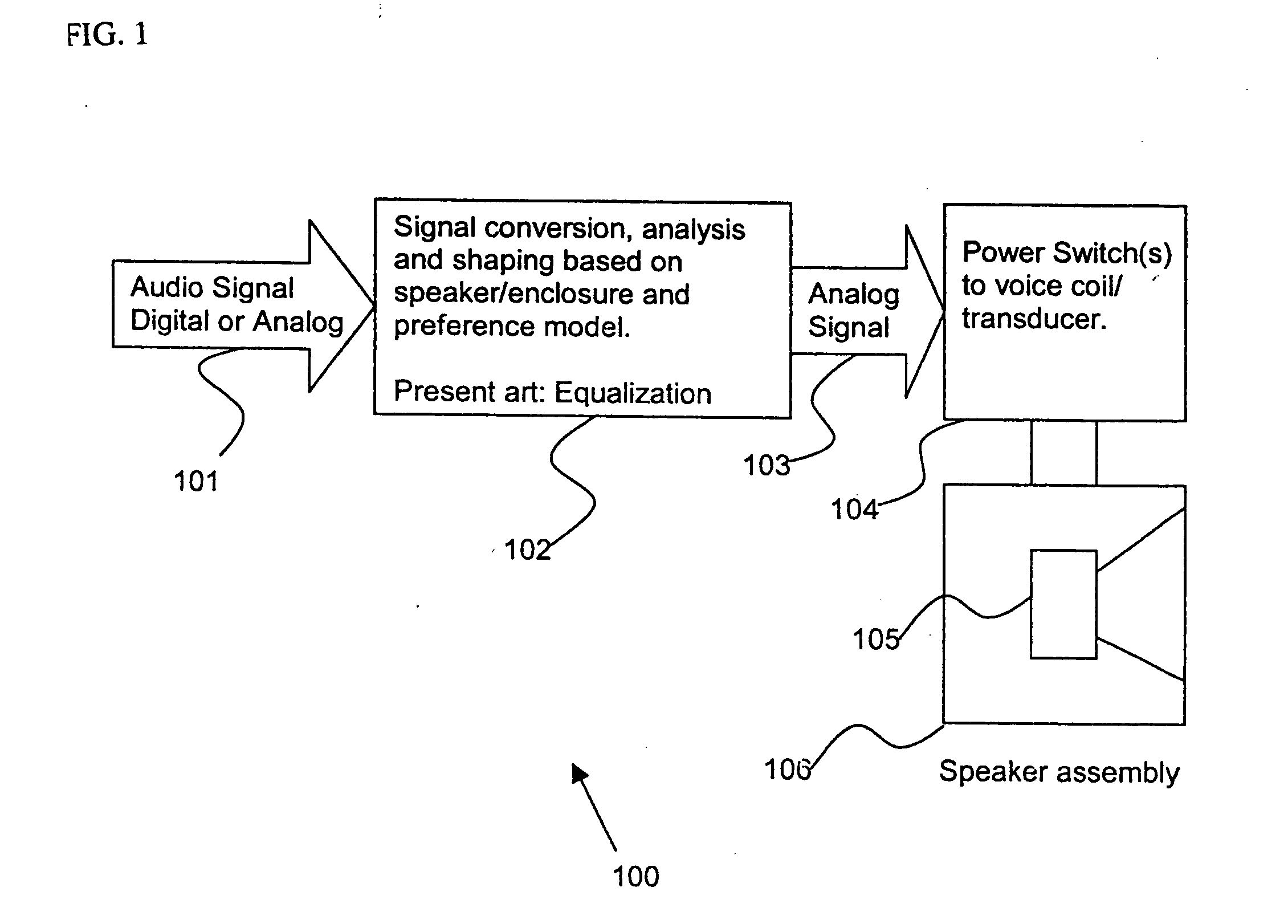
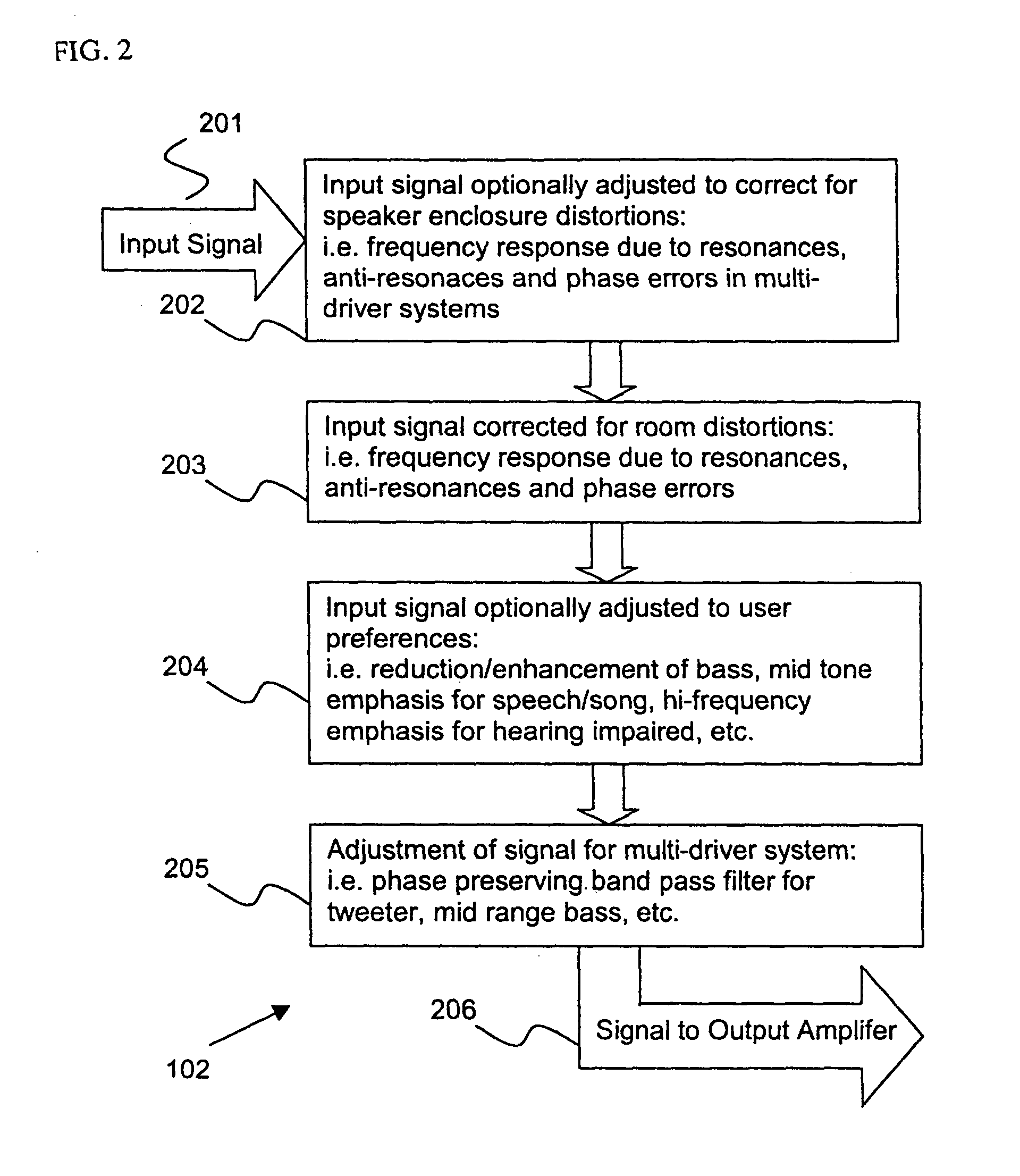
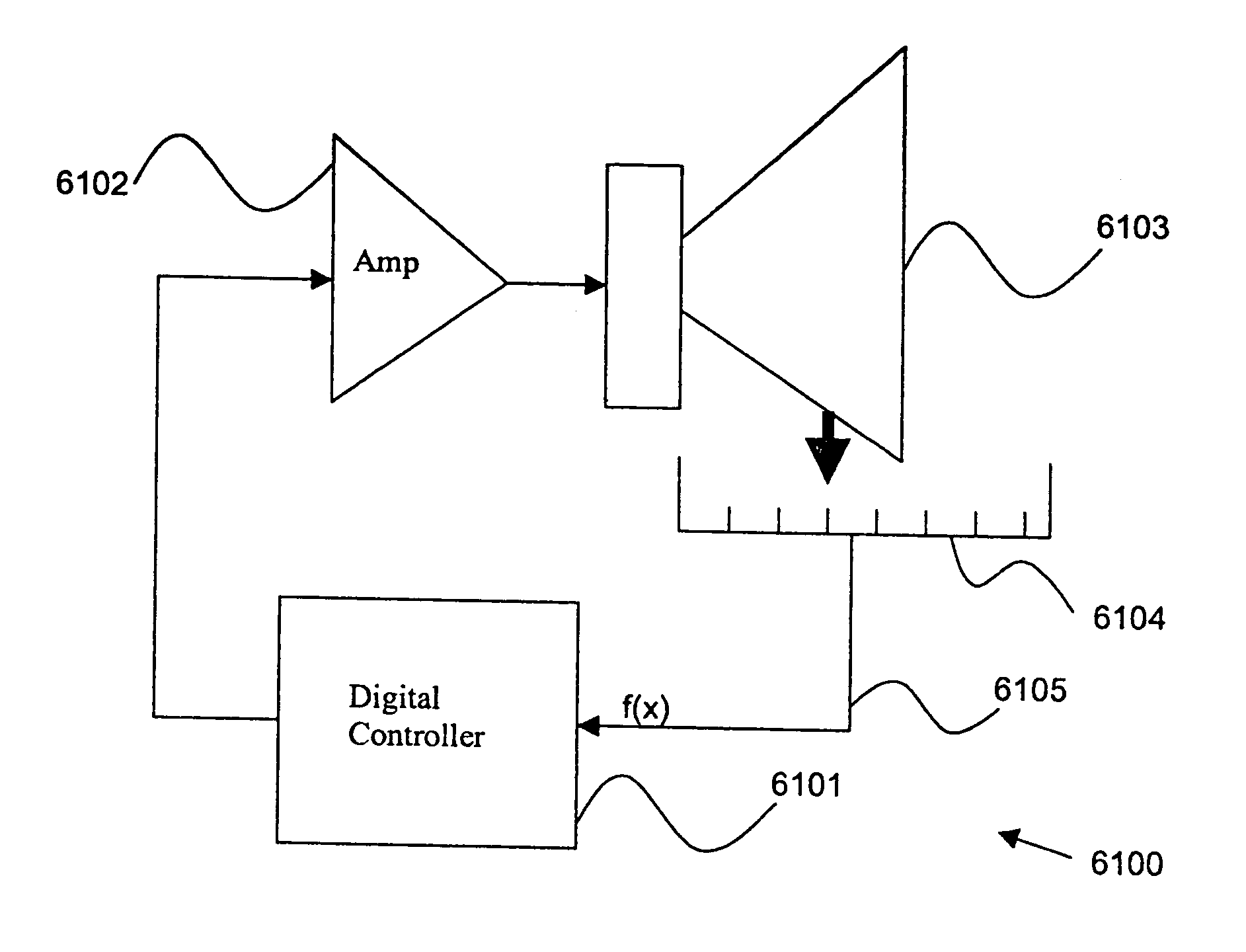
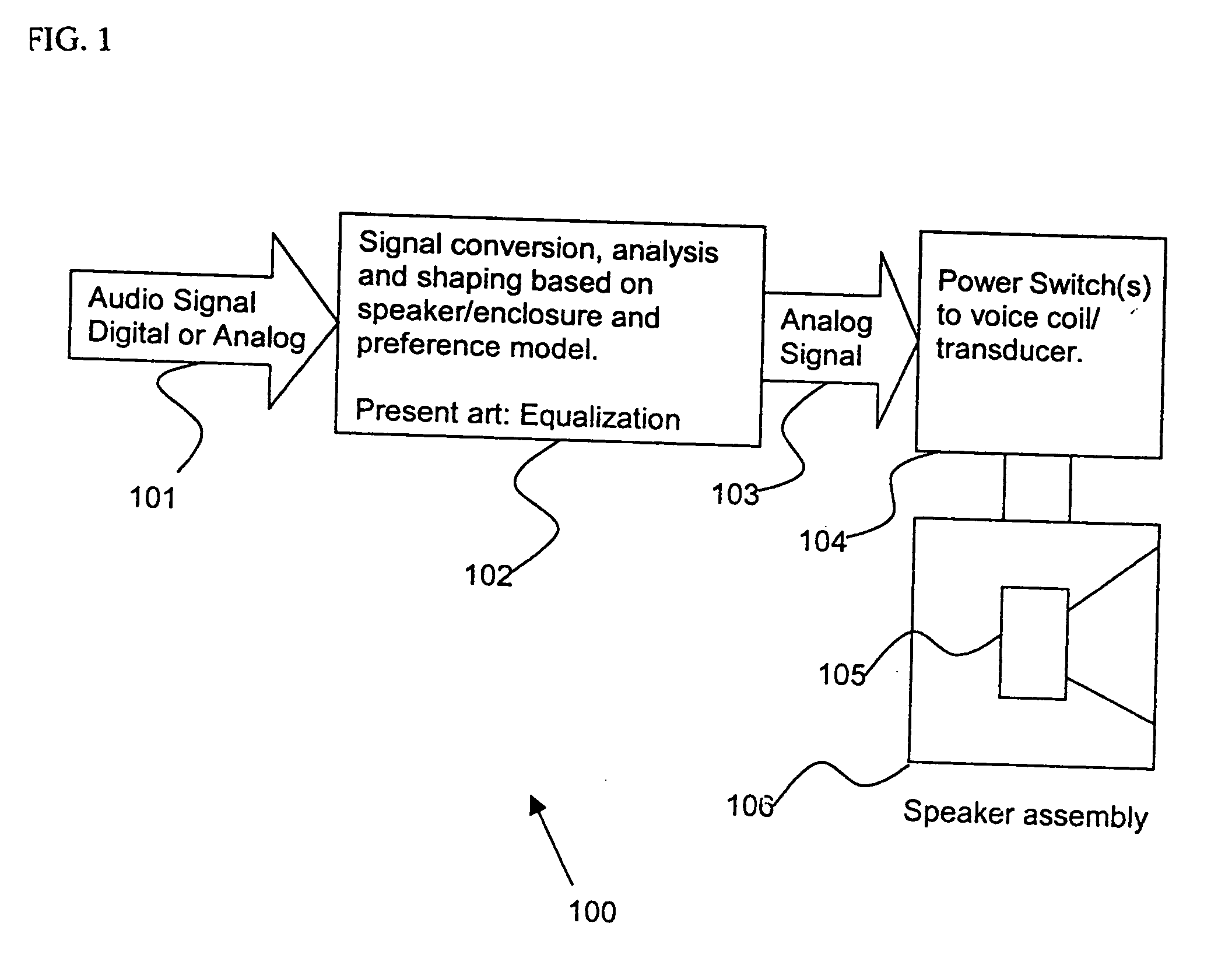
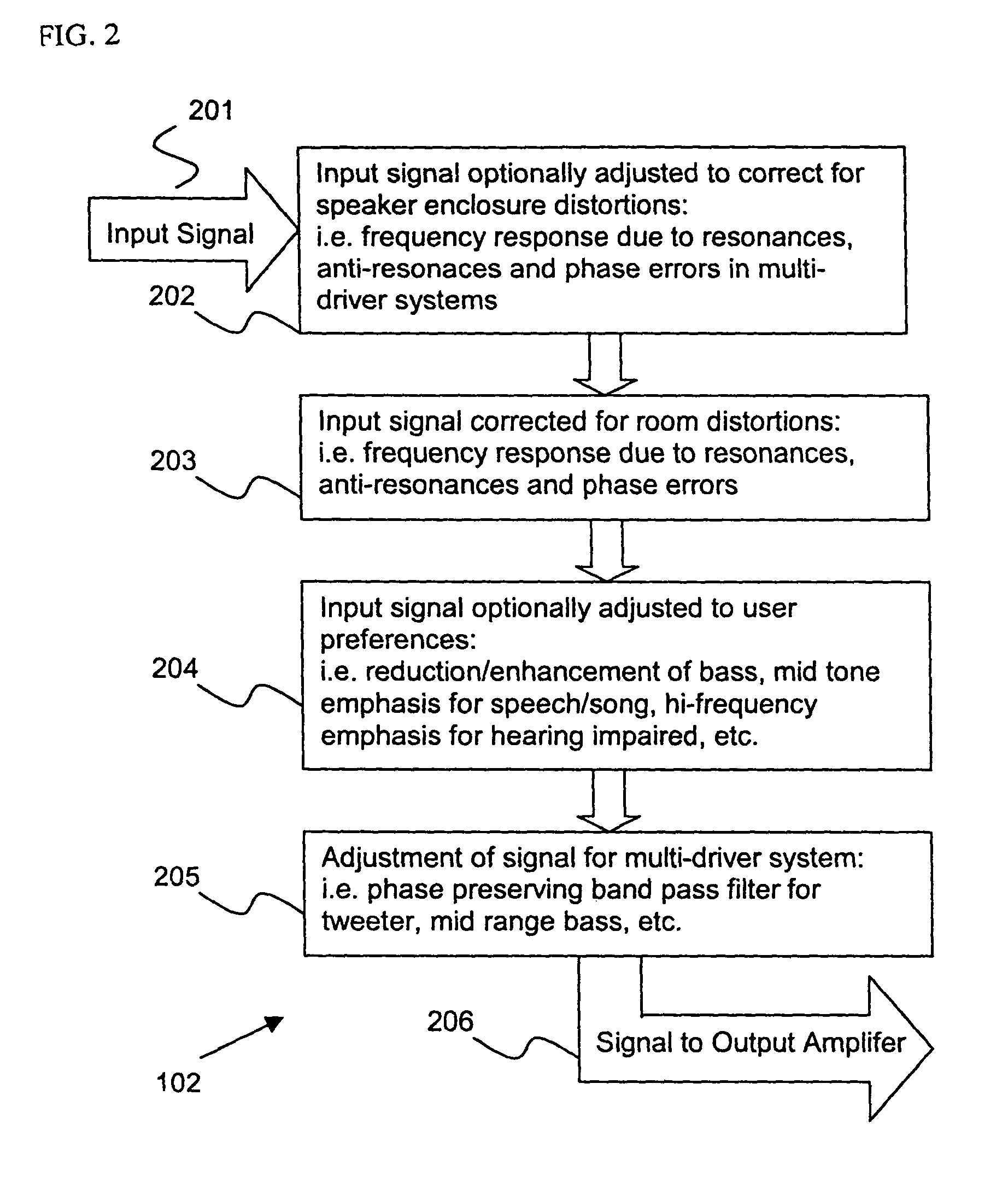
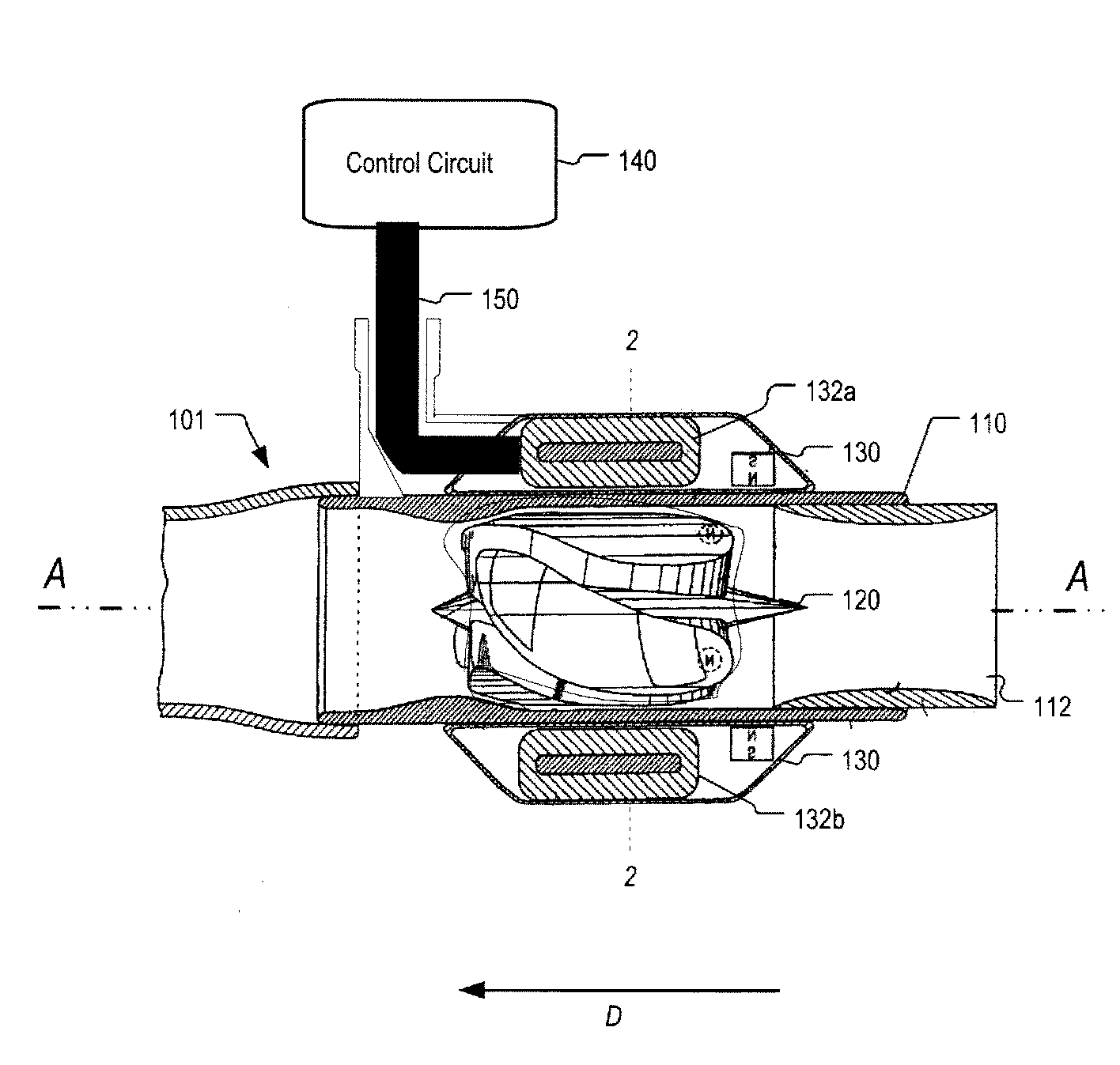
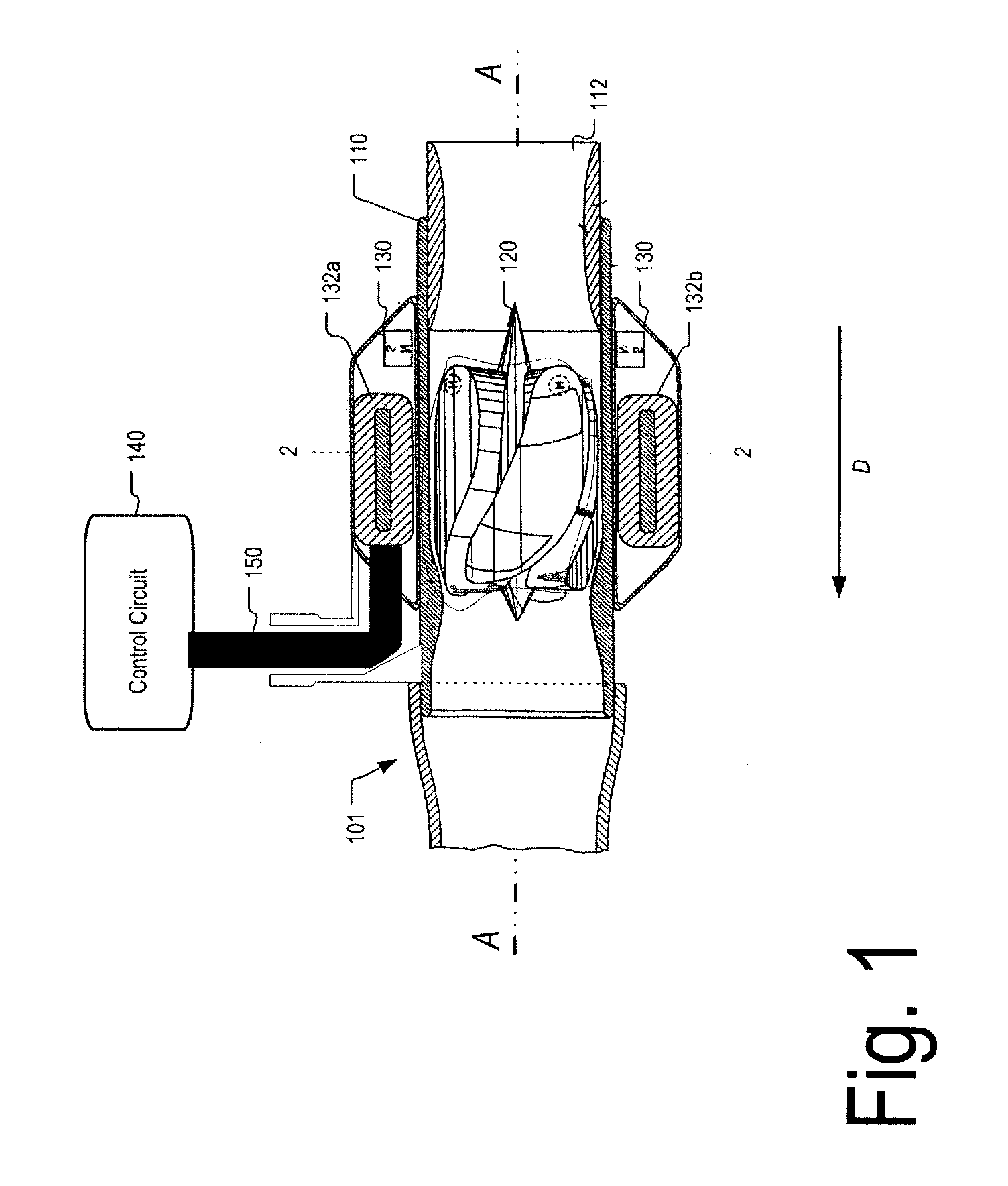
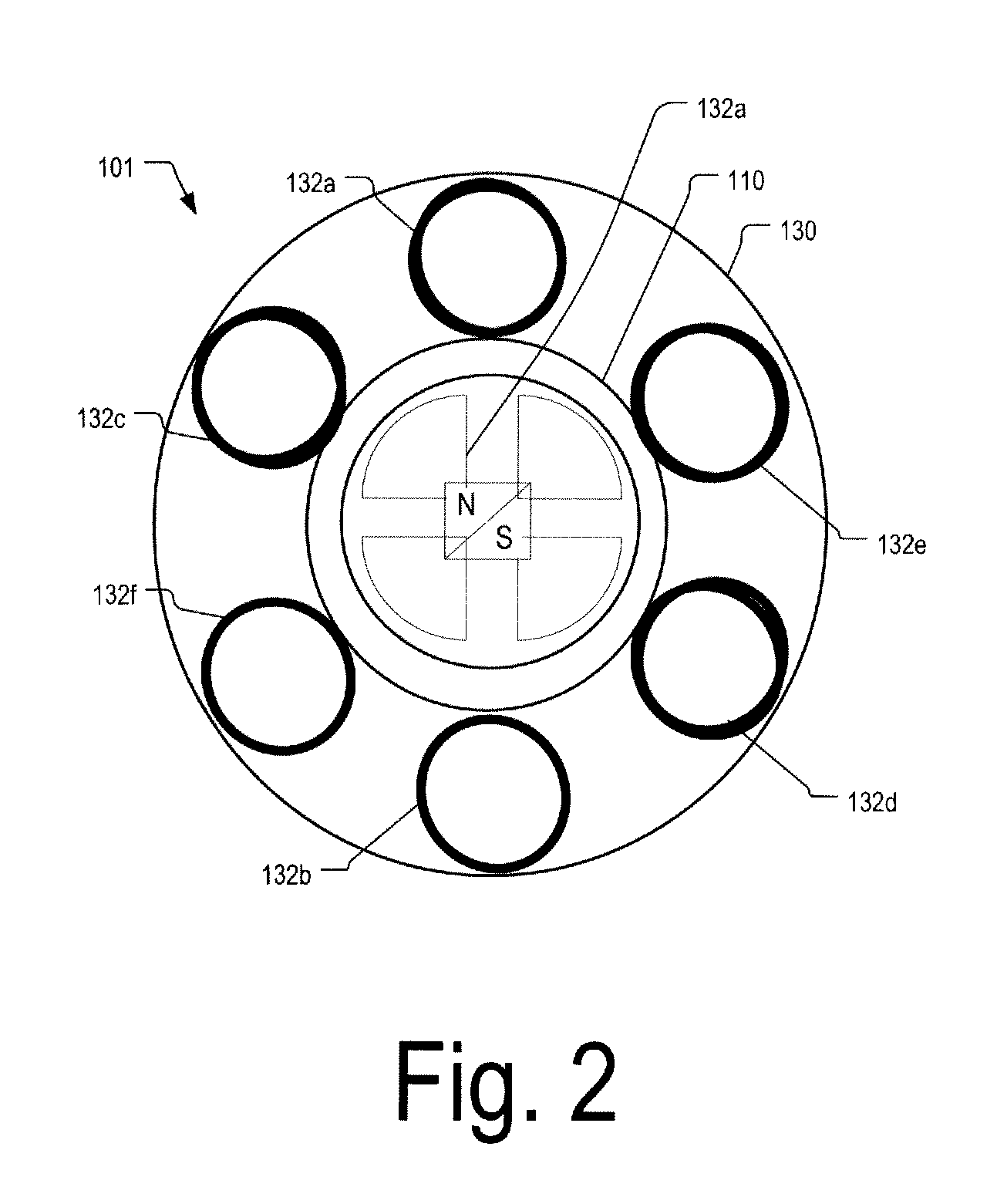
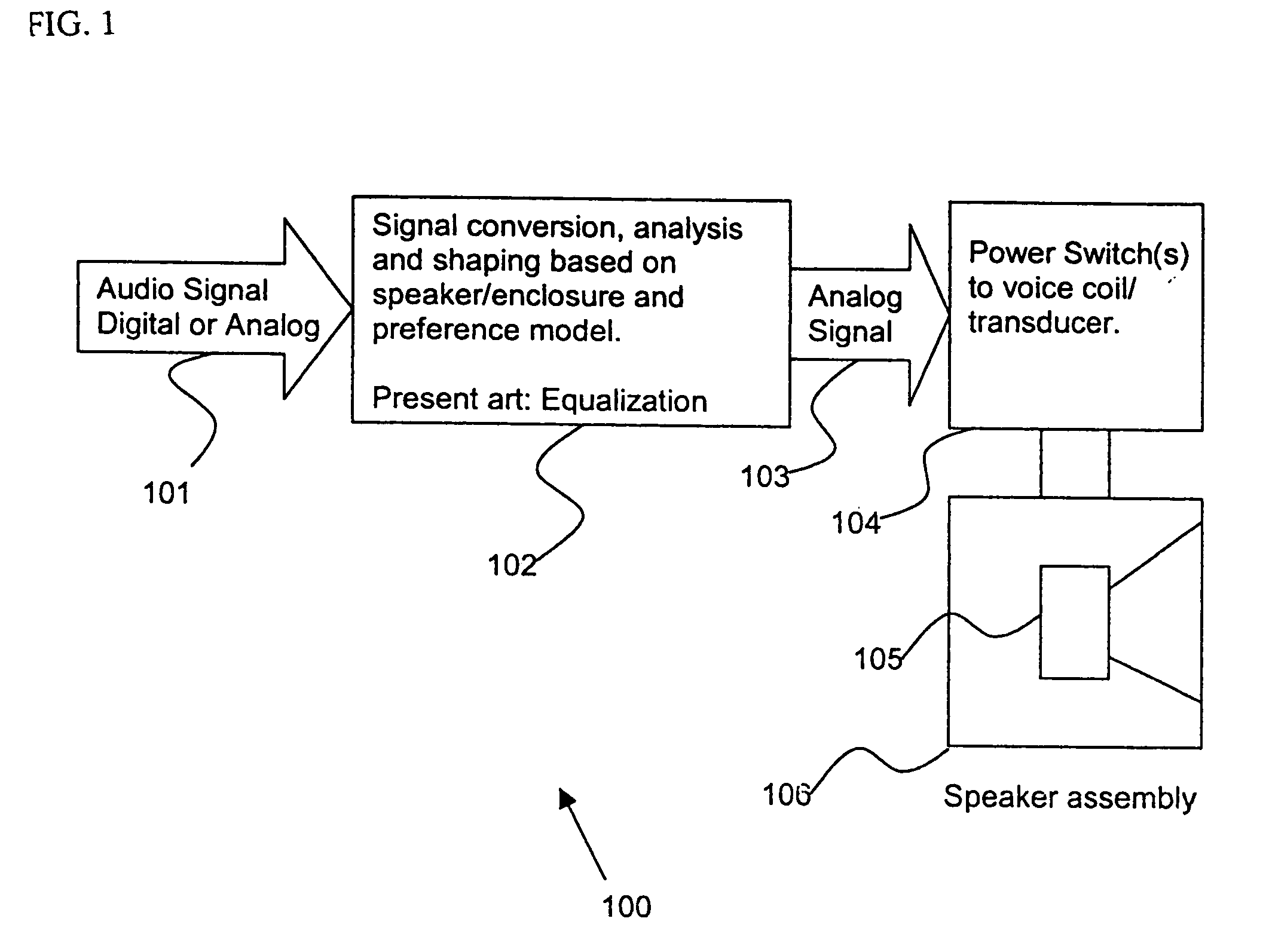
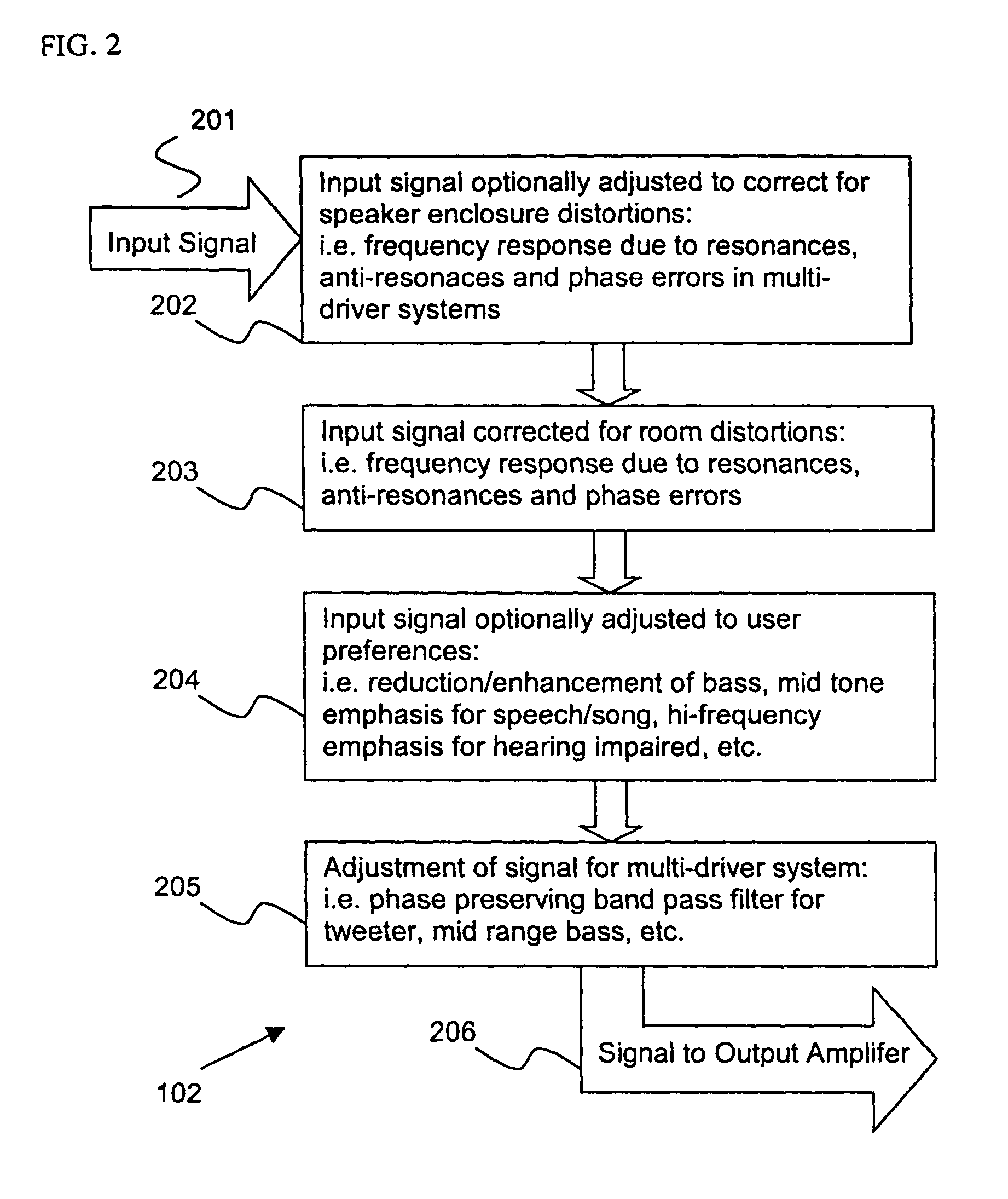
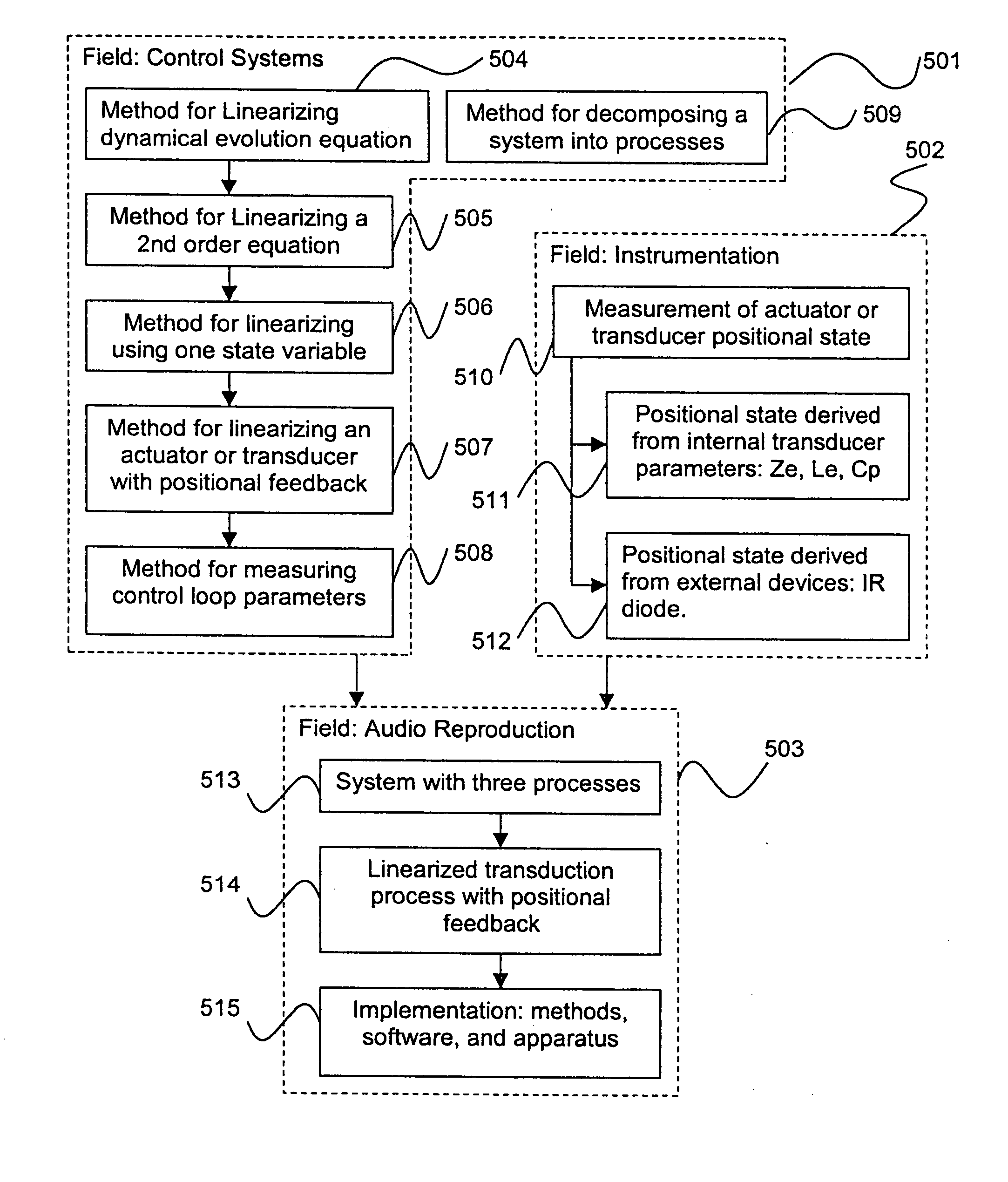
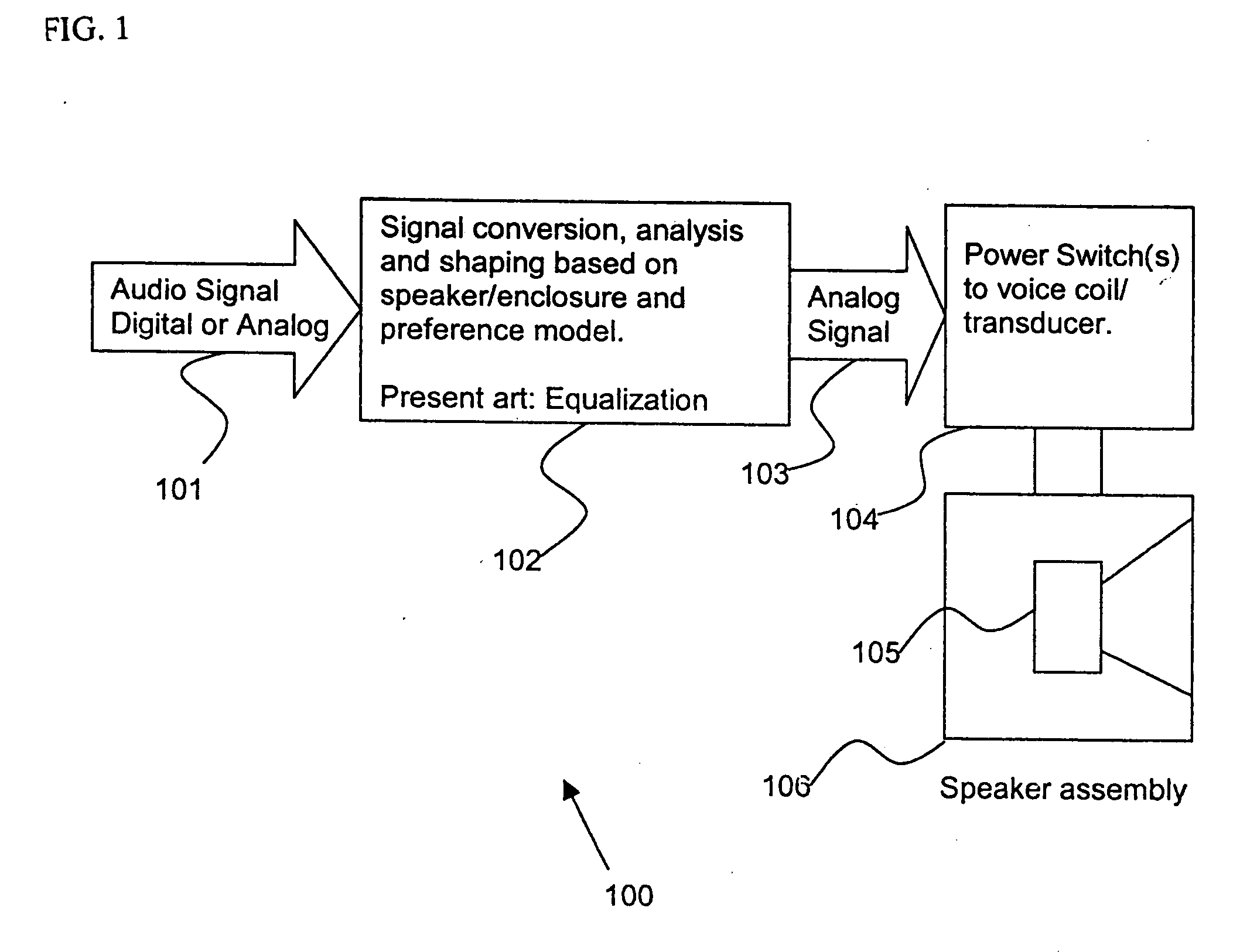
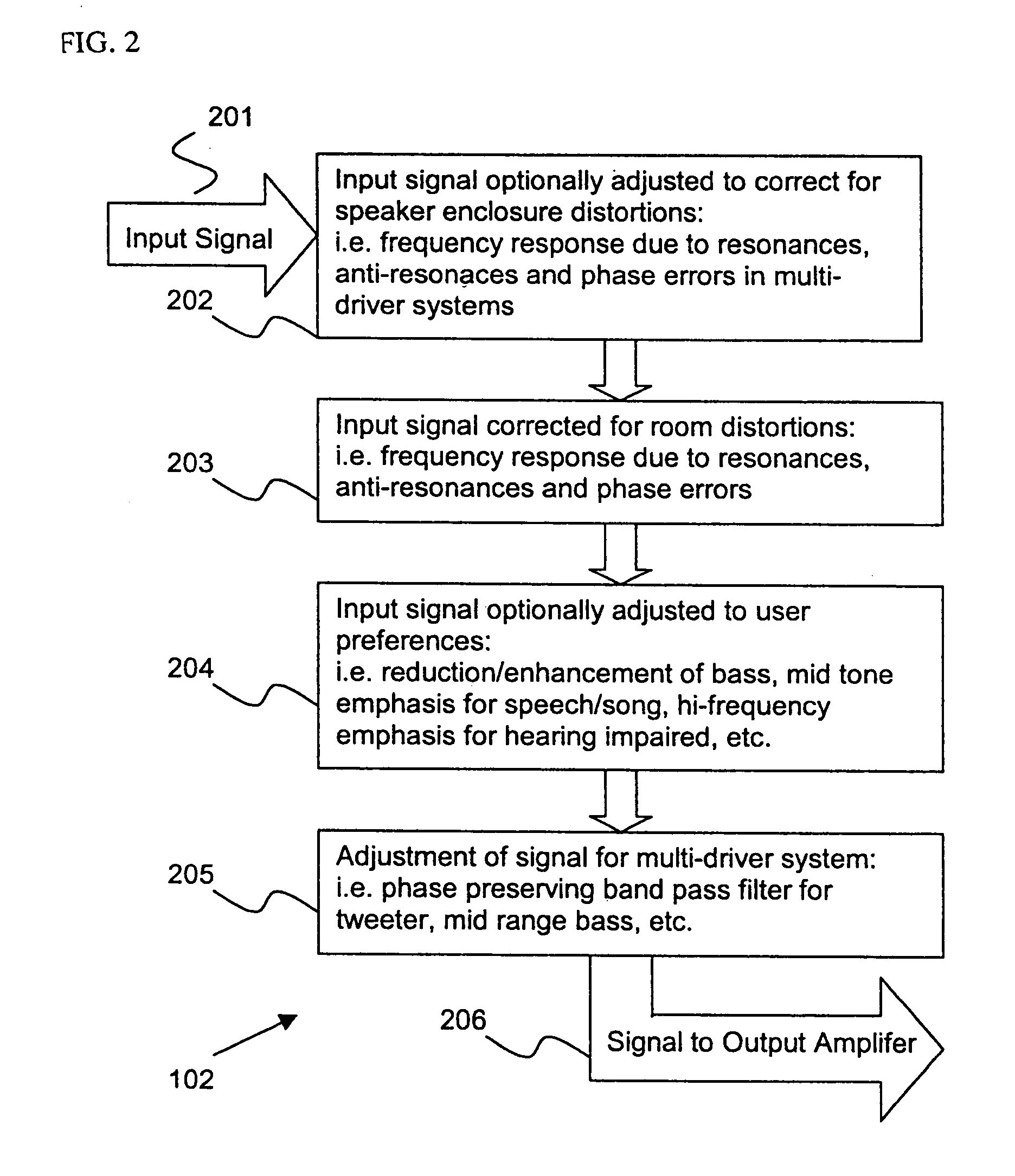
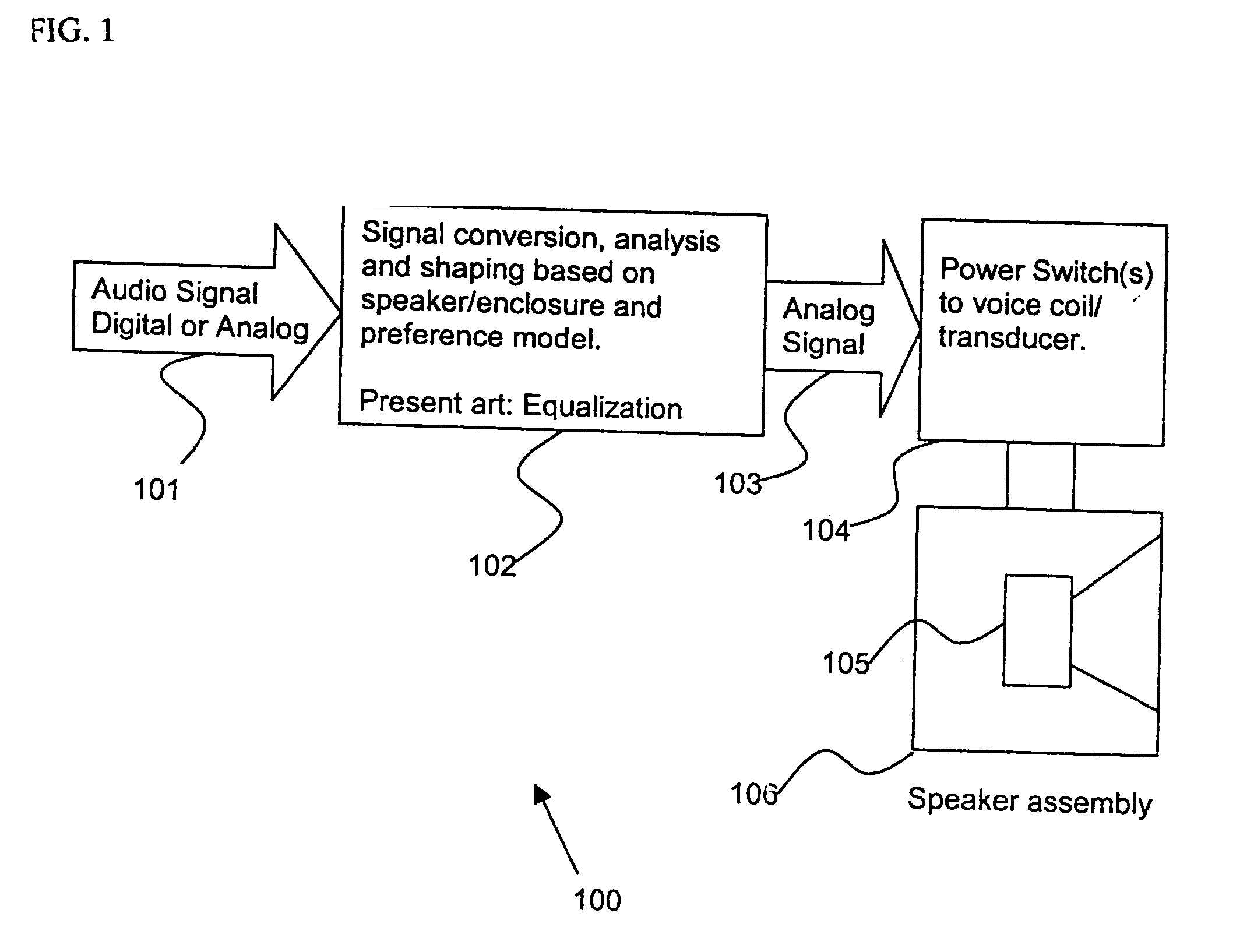
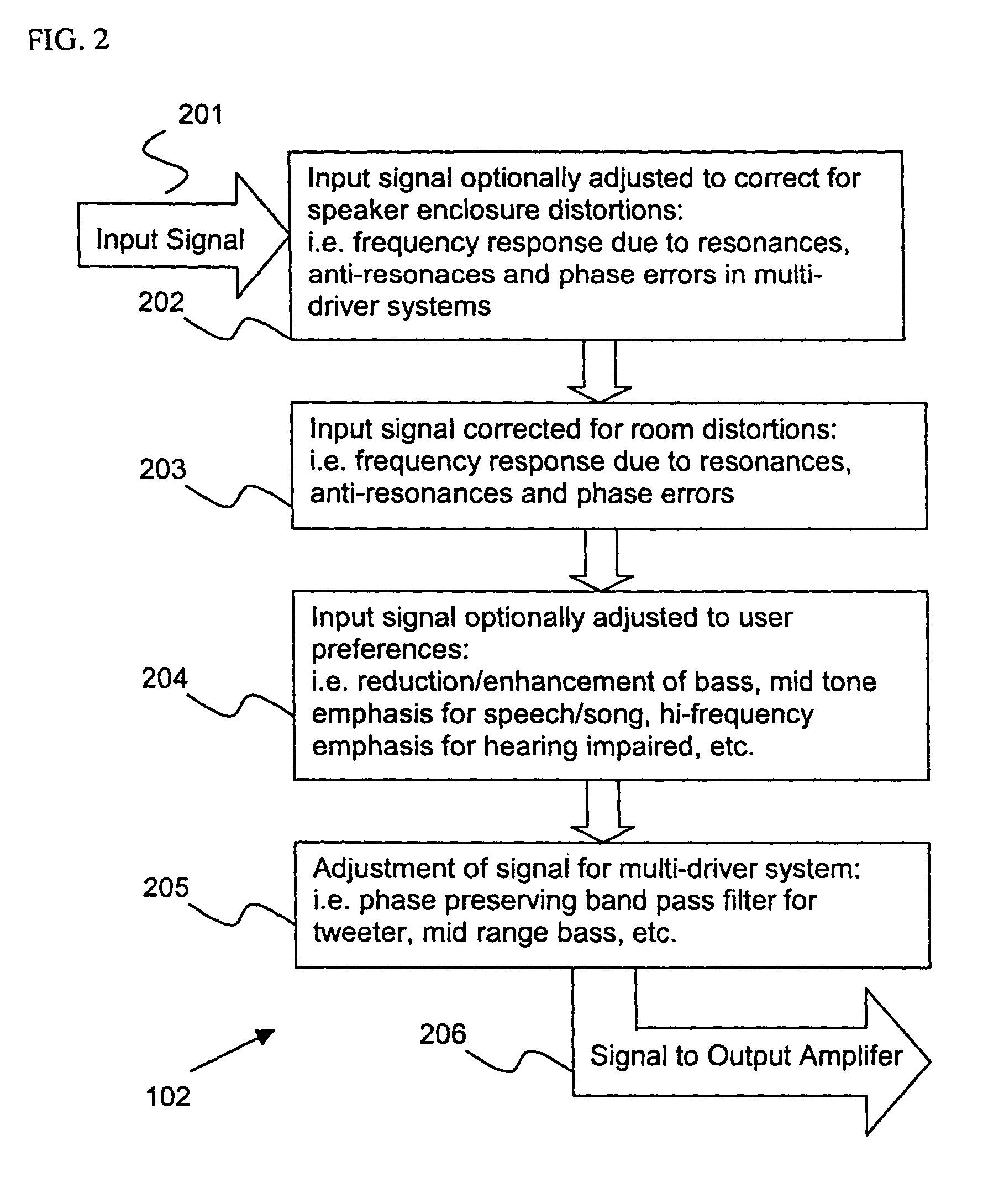
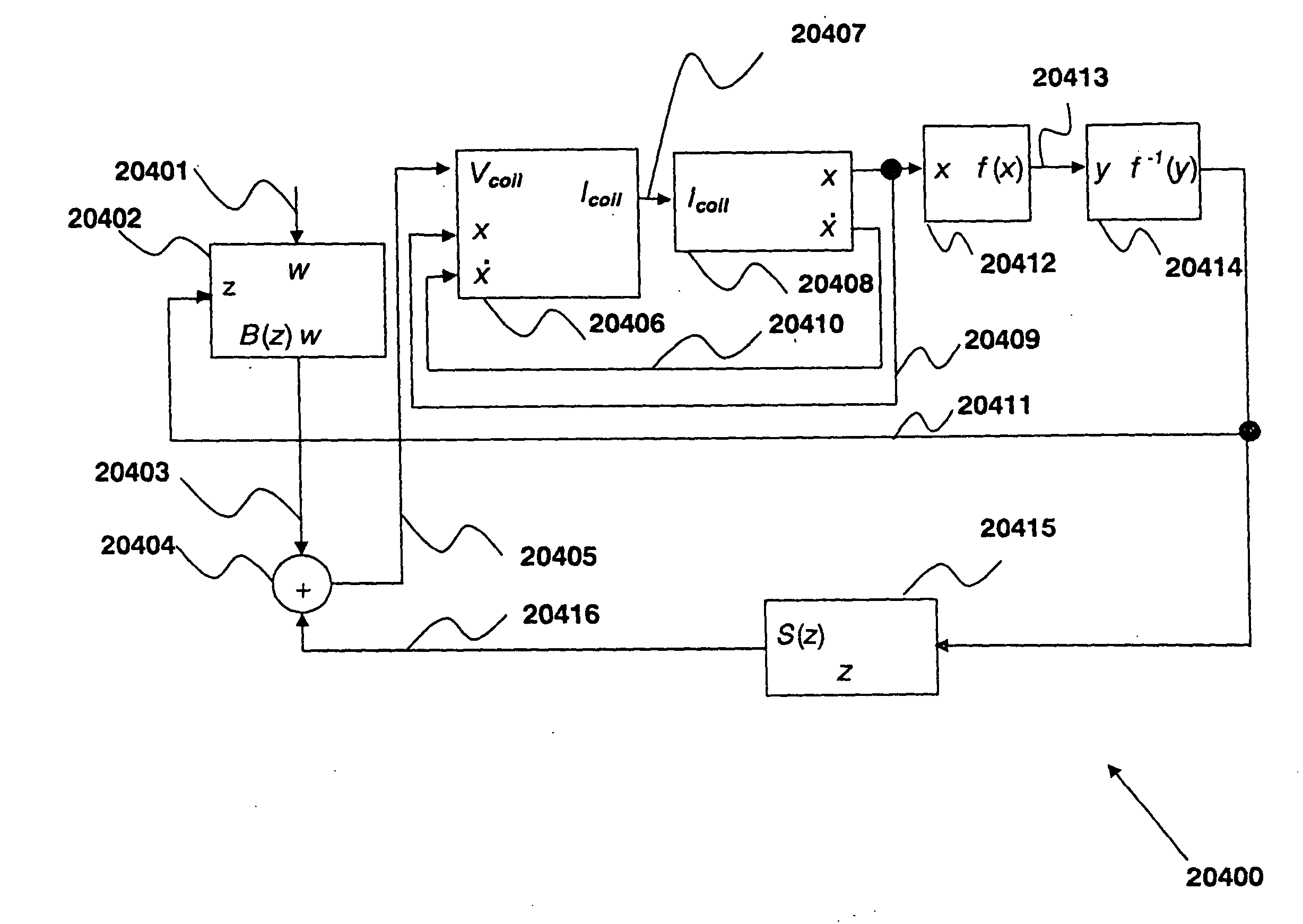
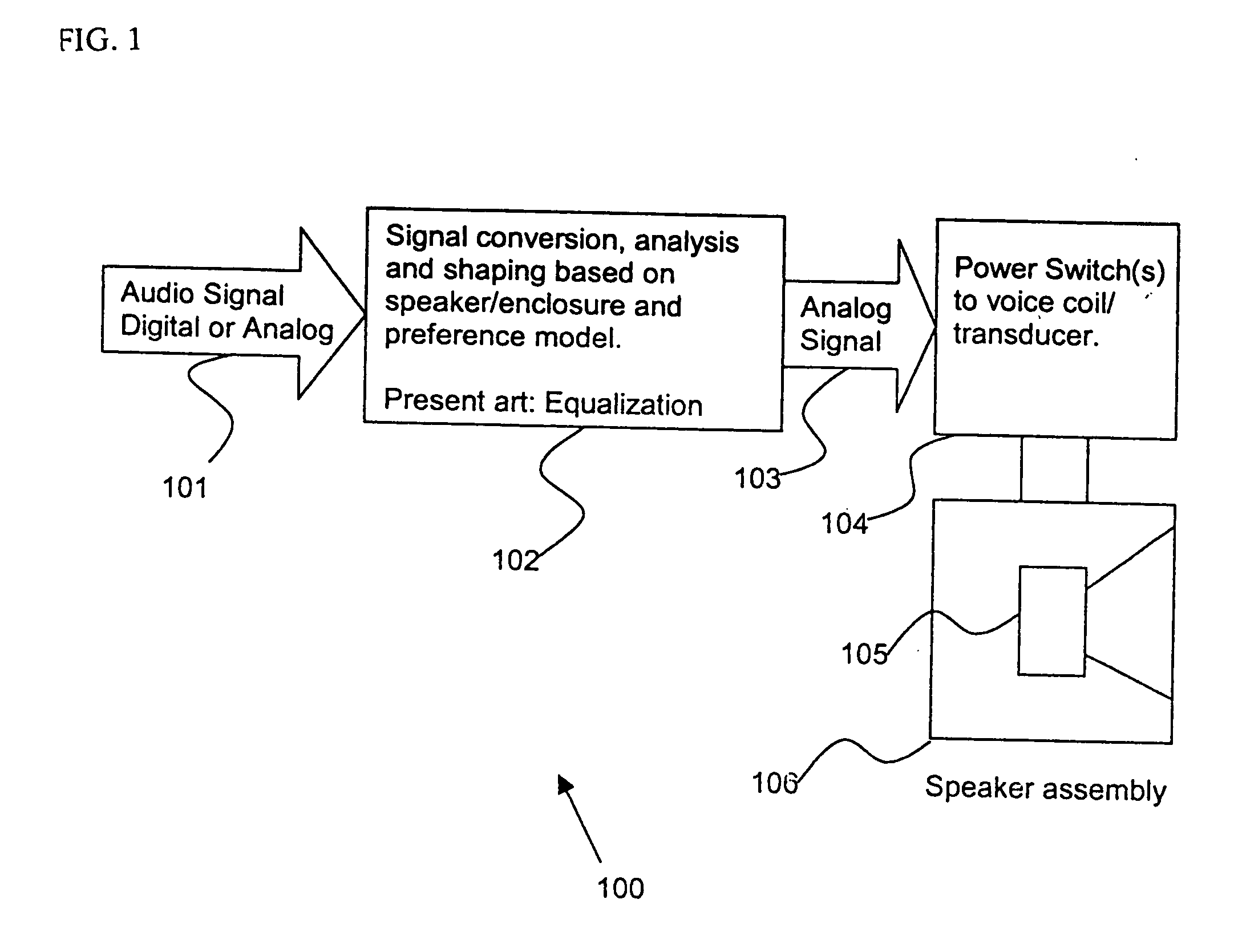
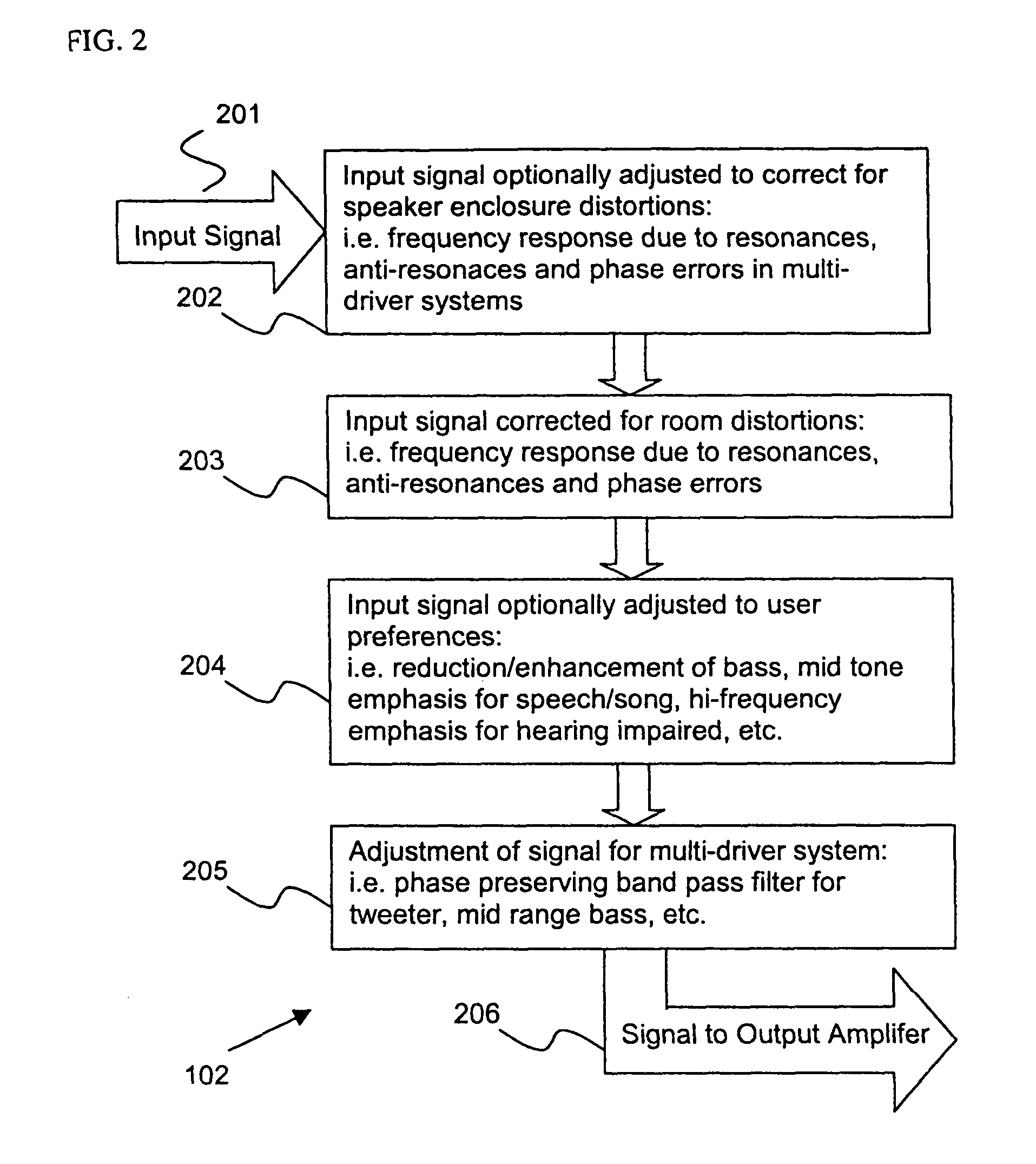
Control system for devices such as an audio reproduction system, an actuator device, an electromechanical device and a telephony device. The system includes control circuitry which receives an input signal and a signal indicative of a position of a portion of the controlled apparatus. The control circuit provides an output signal to the controlled apparatus to affect an operation of the controlled apparatus. The output signal provides control of the apparatus to compensate for one or more of: motor factor; spring factor; back electromotive force; and impedance of a coil in a driver of the controlled apparatus. The signal indicative of position is derived by one or more position indicator techniques such as an infrared LED and PIN diode combination, position dependent capacitance of one portion of the controlled apparatus with respect to another portion of the controlled apparatus, and impedance of a coil in the controlled apparatus. The control circuitry is configurable to control transconductance and / or transduction of the system being controlled. A technique is disclosed to detect and measure a cant of a voice coil transducer, the technique including measuring a capacitance between one portion of the voice coil transducer with respect to another portion of the voice coil transducer over a range of movement of the voice coil during operation.
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
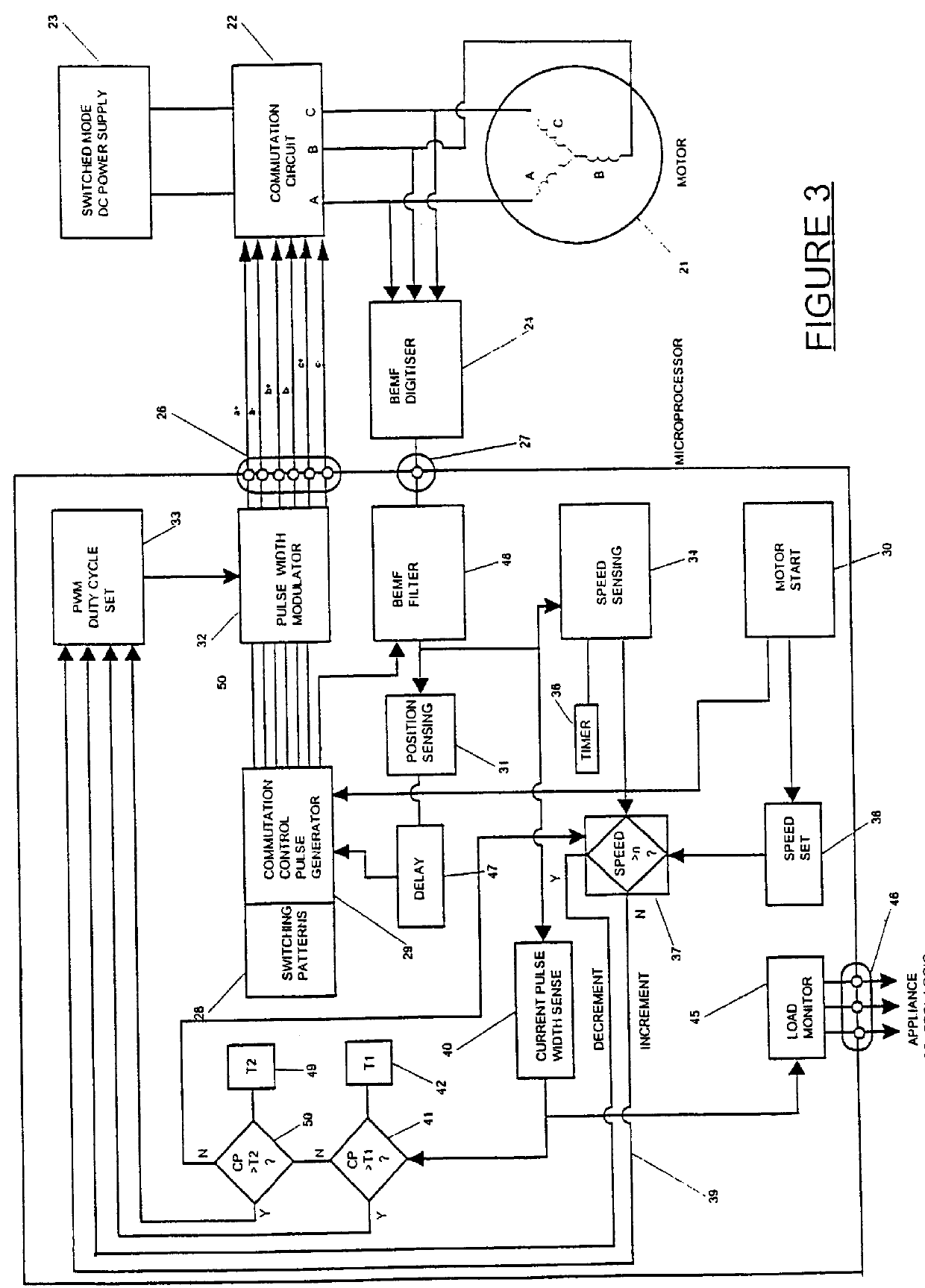
Brushless DC motor control
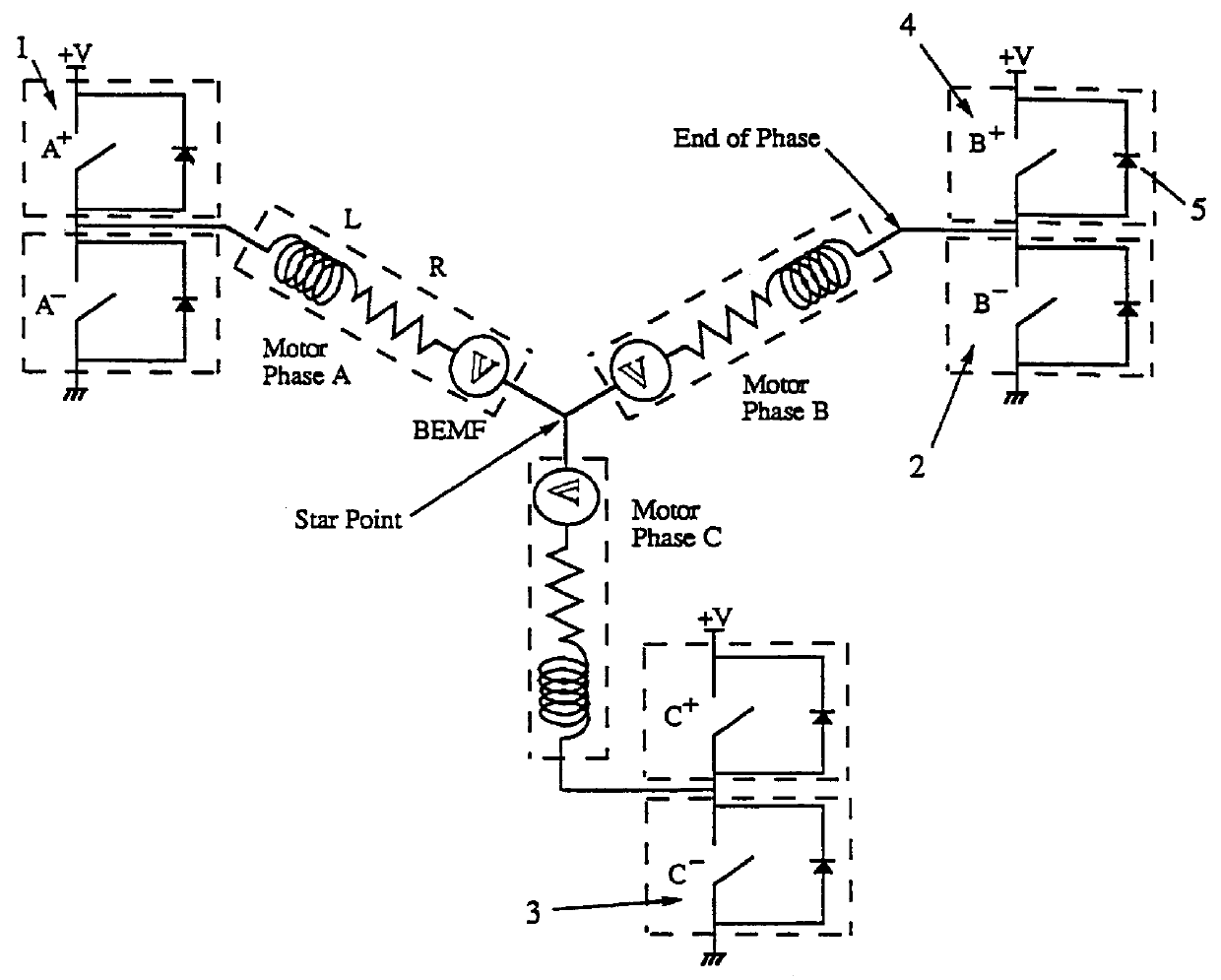
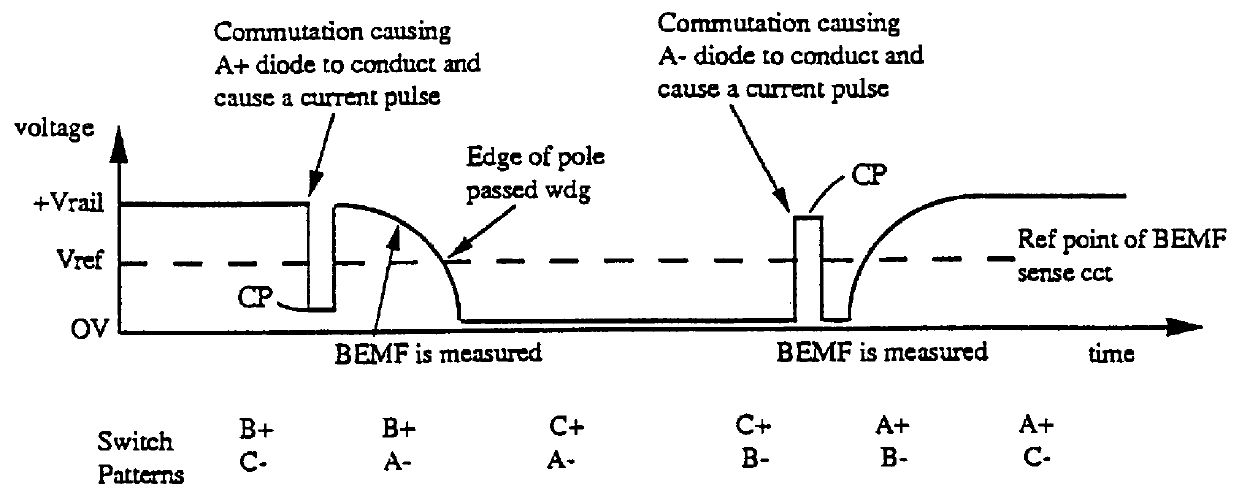
An electronically commutated brushless DC motor primarily for fractional horsepower applications of the type where at any instant one motor winding is unpowered and used to detect back EMF zero-crossings which information is used to initiate winding commutations. The duration of the pulse produced in this winding due to dissipation of stored energy by free-wheel diodes in parallel with the commutation devices after supply of current has been removed from this winding is used to provide a measure of motor current. This allows for simplified commutation device current limiting circuits and is available for control purposes which are a function of motor torque. There is also disclosed a method for maximizing useful power output by reducing the phase angle between the motor current and the back EMF. This is accomplished by introducing a delay in commutating the motor windings beyond the occurrence of each back EMF zero-crossing, with the delay being a function of the time between commutations.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
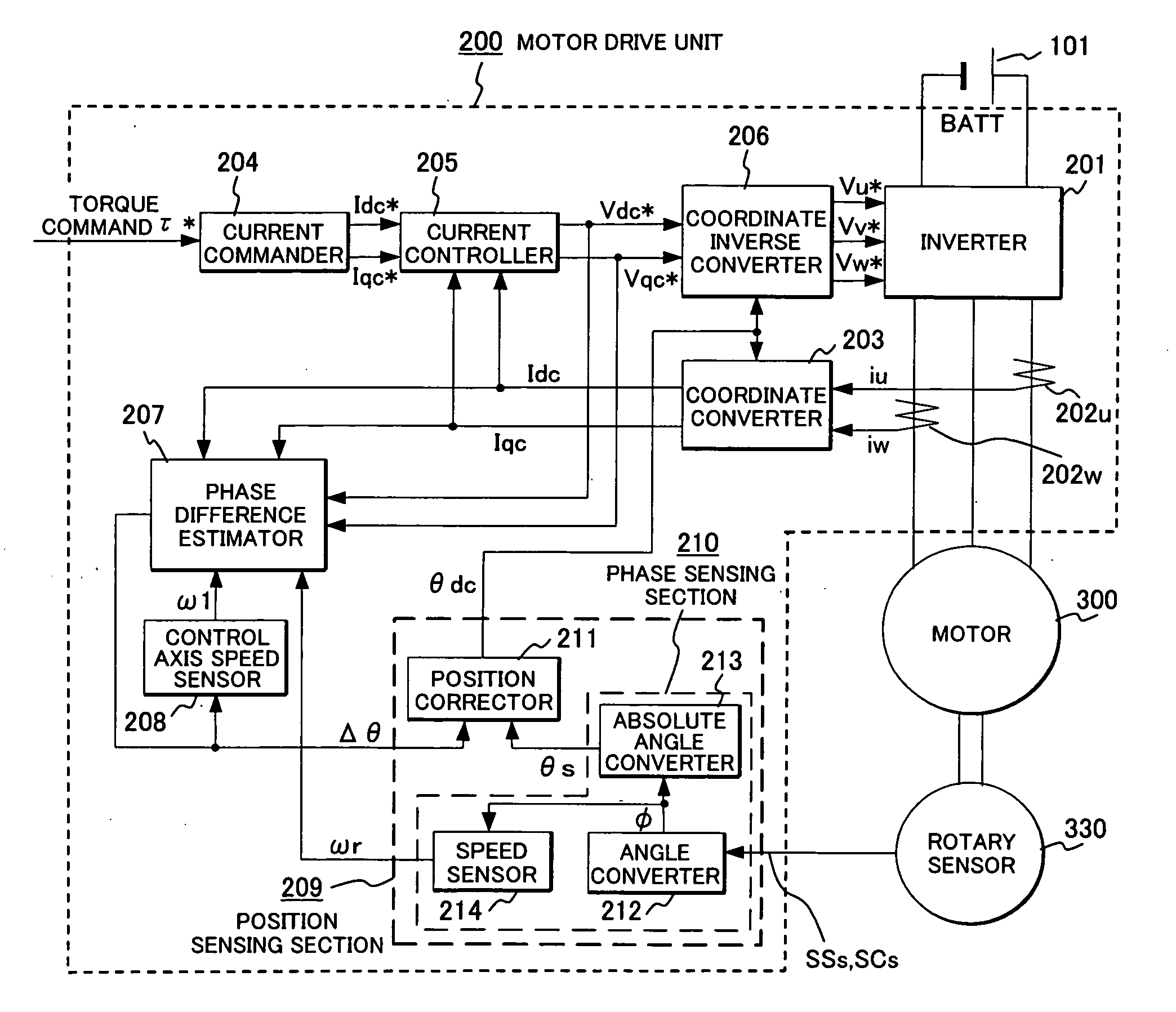
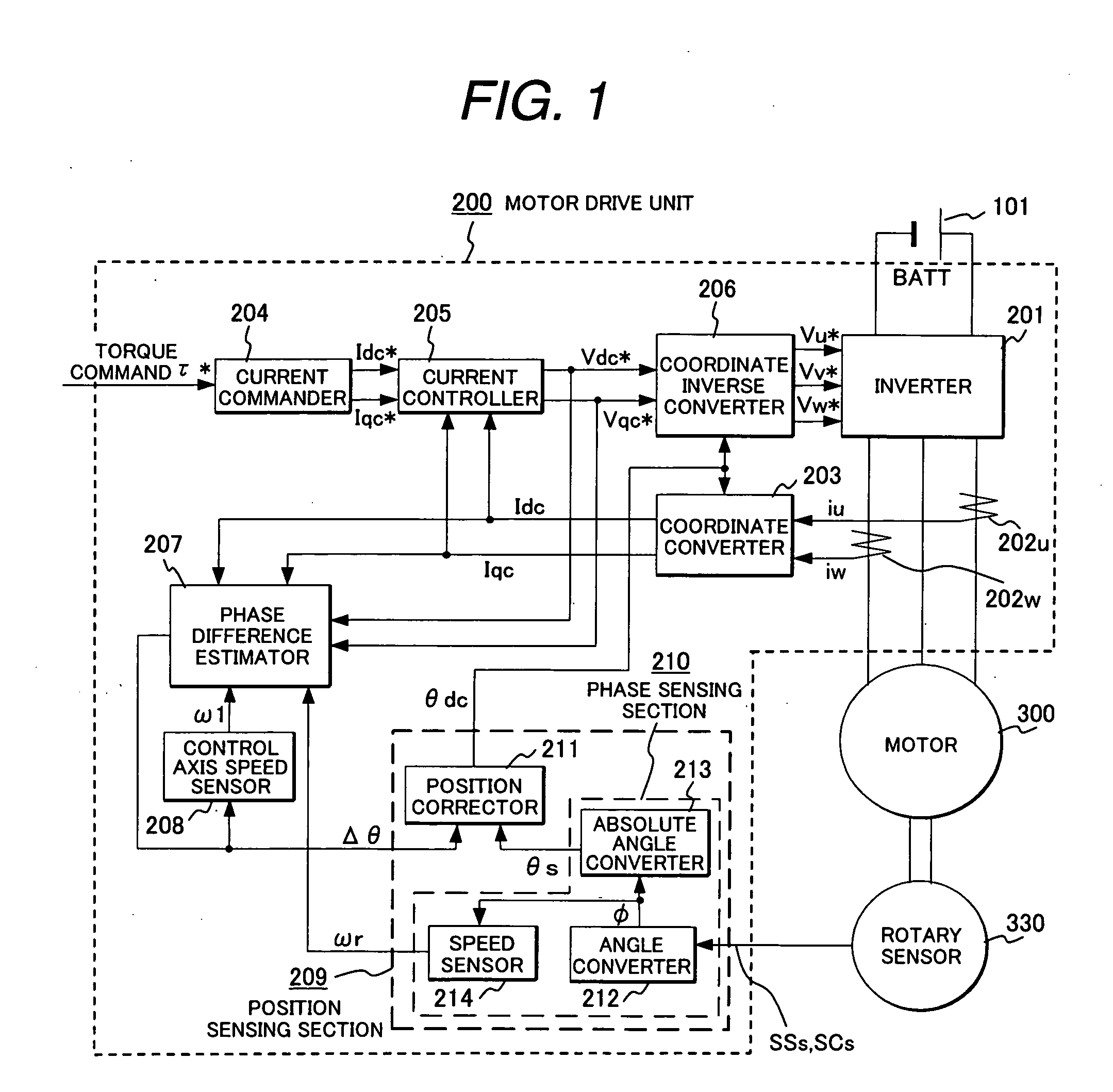
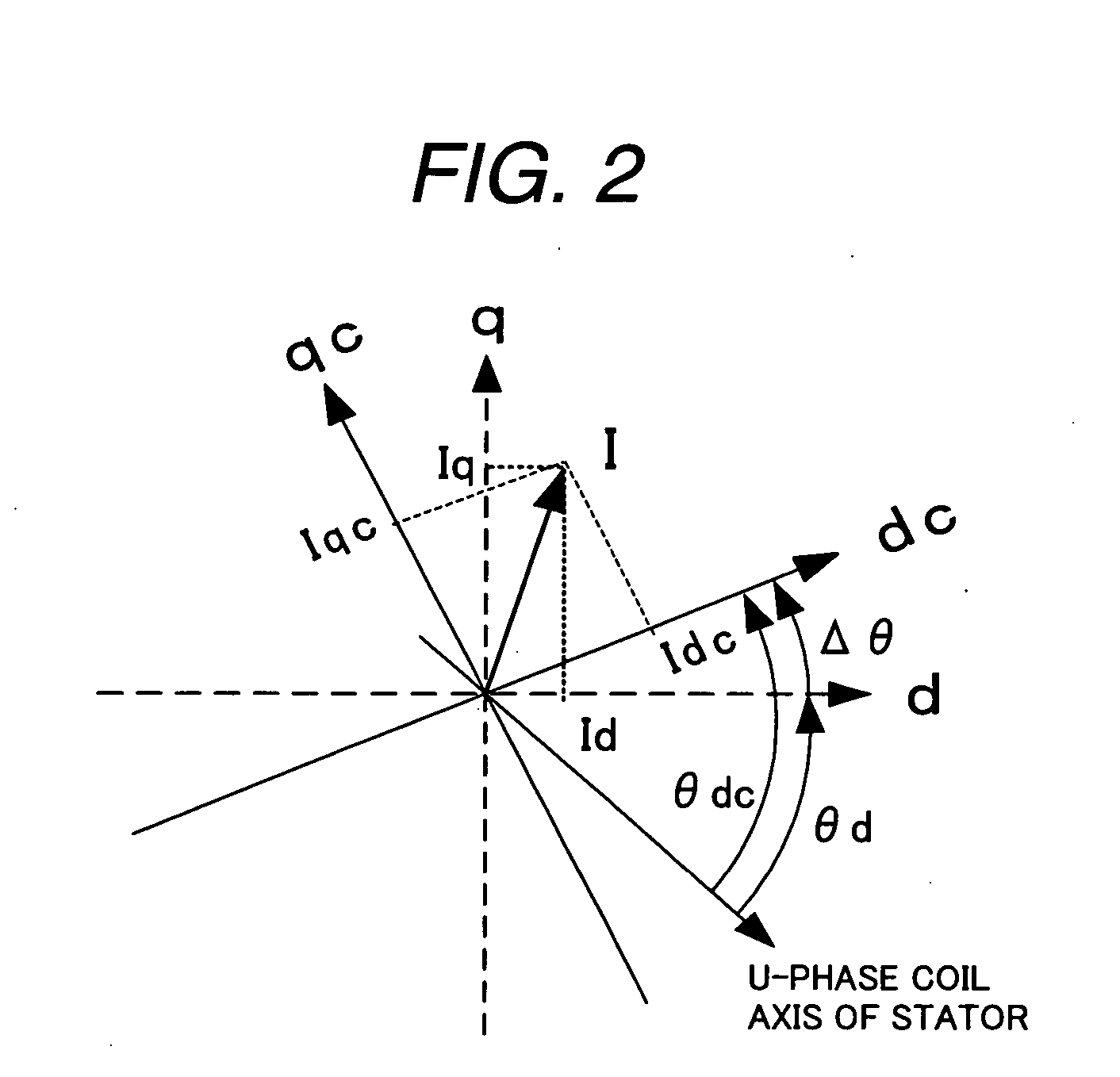
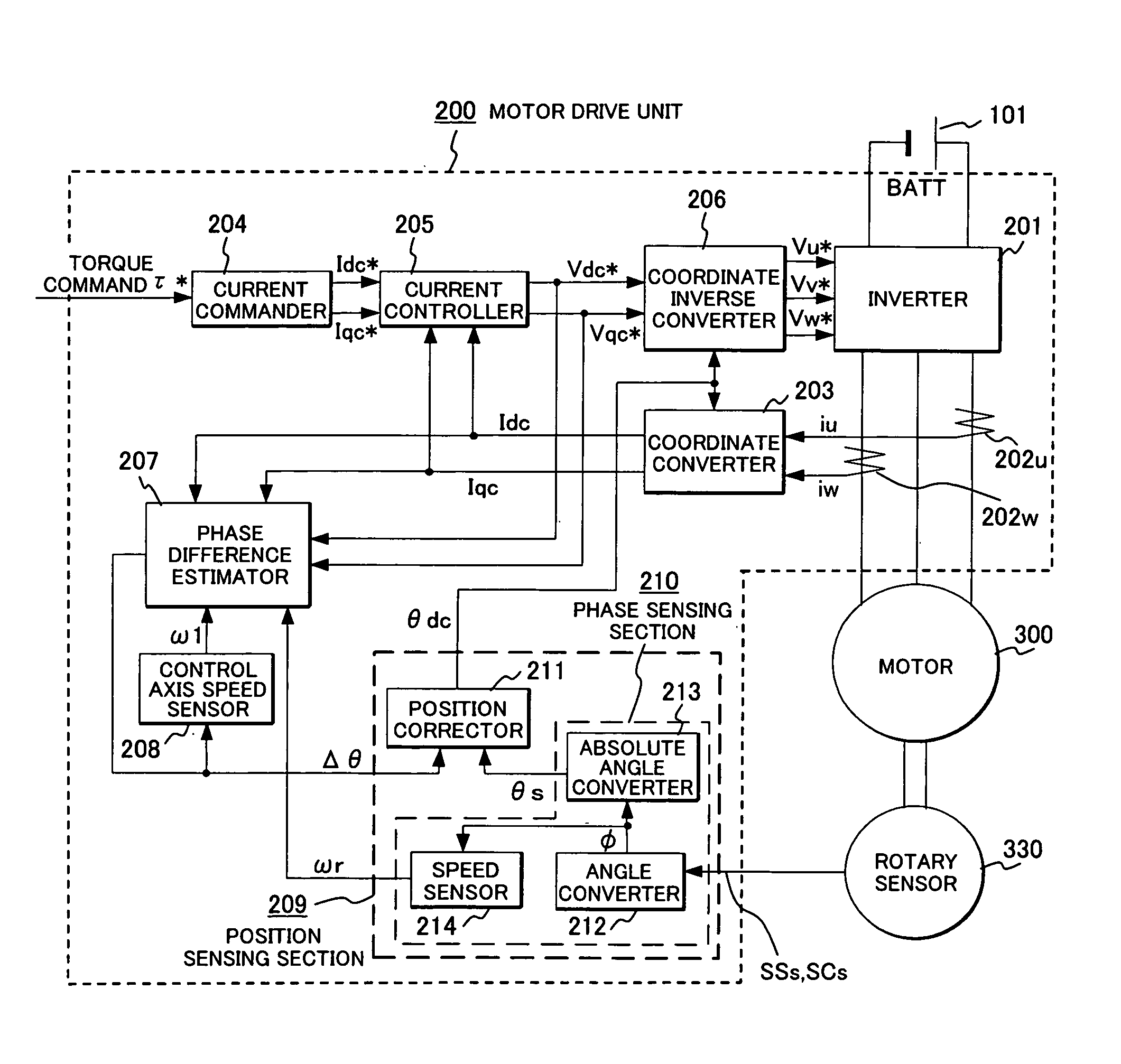
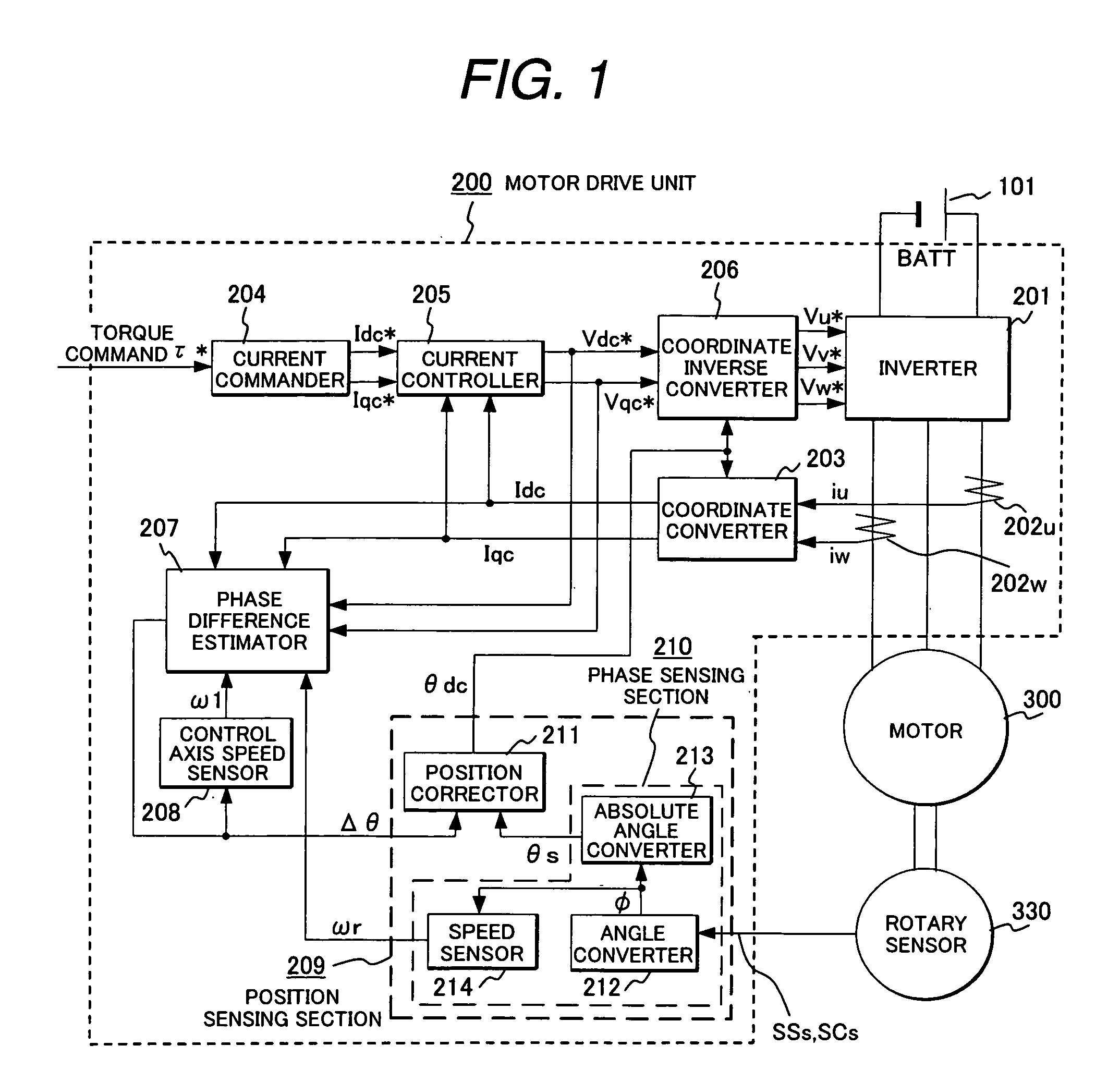
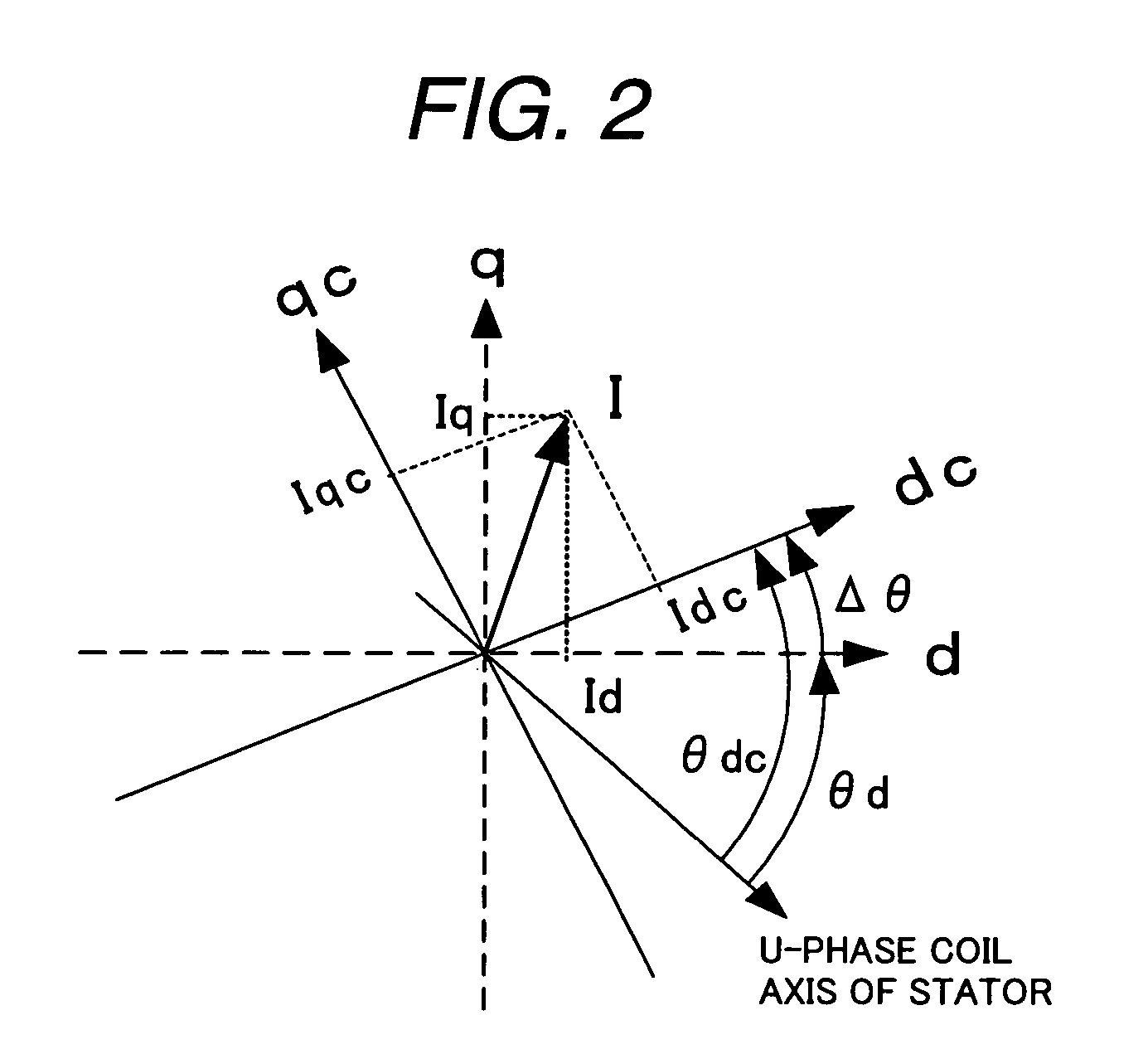
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS20060125439A1Efficient driveImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorPhase difference
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position. A high-efficiency motor drive unit with improved maintainability of rotary sensor and improved accuracy of sensing the magnet pole position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor that accelerates and decelerates very quickly in a wide range of speed is realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Hybrid magnetically suspended and rotated centrifugal pumping apparatus and method
InactiveUS6074180AAvoid displacementEfficient startSpecific fluid pumpsPump componentsMotor speedRotary pump
An apparatus and method for a centrifugal fluid pump for pumping sensitive biological fluids, which includes (i) an integral impeller and rotor which is entirely supported by an integral combination of permanent magnets and electromagnetic bearings and rotated by an integral motor, (ii) a pump housing and arcuate passages for fluid flow and containment, (iii) a brushless driving motor embedded and integral with the pump housing, (iv) a power supply, and (v) specific electronic sensing of impeller position, velocity or acceleration using a self-sensing method and physiological control algorithm for motor speed and pump performance based upon input from the electromagnetic bearing currents and motor back emf-all fitly joined together to provide efficient, durable and low maintenance pump operation. A specially designed impeller and pump housing provide the mechanism for transport and delivery of fluid through the pump to a pump output port with reduced fluid turbulence.
Owner:WORLD HEART +2
Calibration of an actuator
InactiveUS20050031137A1Broadcast circuit arrangementsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsCapacitanceEngineering
Control system for devices such as an audio reproduction system, an actuator device, an electromechanical device and a telephony device. The system includes control circuitry which receives an input signal and a signal indicative of a position of a portion of the controlled apparatus. The control circuit provides an output signal to the controlled apparatus to affect an operation of the controlled apparatus. The output signal provides control of the apparatus to compensate for one or more of: motor factor; spring factor; back electromotive force; and impedance of a coil in a driver of the controlled apparatus. The signal indicative of position is derived by one or more position indicator techniques such as an infrared LED and PIN diode combination, position dependent capacitance of one portion of the controlled apparatus with respect to another portion of the controlled apparatus, and impedance of a coil in the controlled apparatus. The control circuitry is configurable to control transconductance and / or transduction of the system being controlled. A technique is disclosed to detect and measure a cant of a voice coil transducer, the technique including measuring a capacitance between one portion of the voice coil transducer with respect to another portion of the voice coil transducer over a range of movement of the voice coil during operation.
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
Brushless and sensorless DC motor control system with locked and stopped rotor detection
ActiveUS20050029976A1Easy to modifyEasily interfaceCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlMotor speedDc motor control
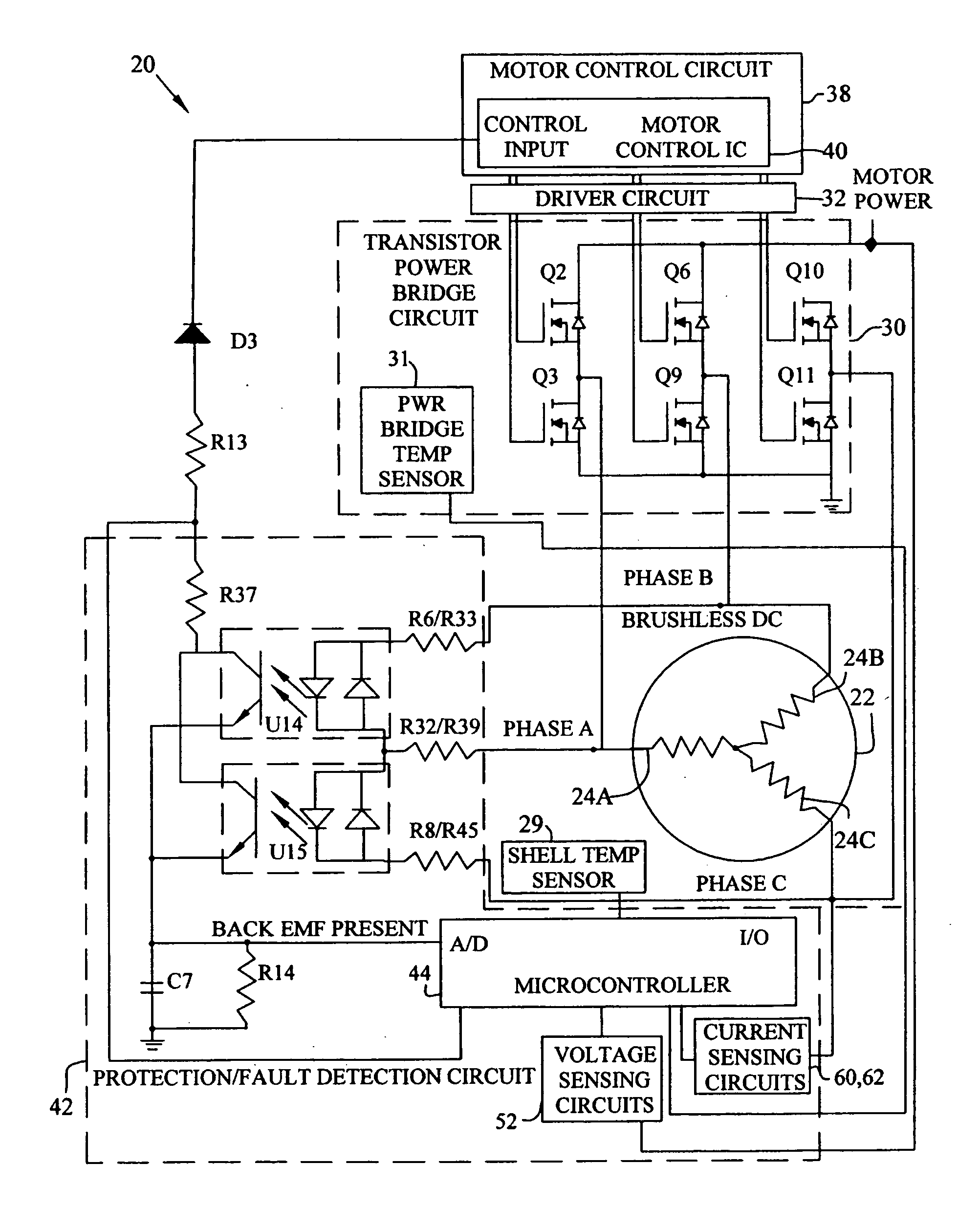
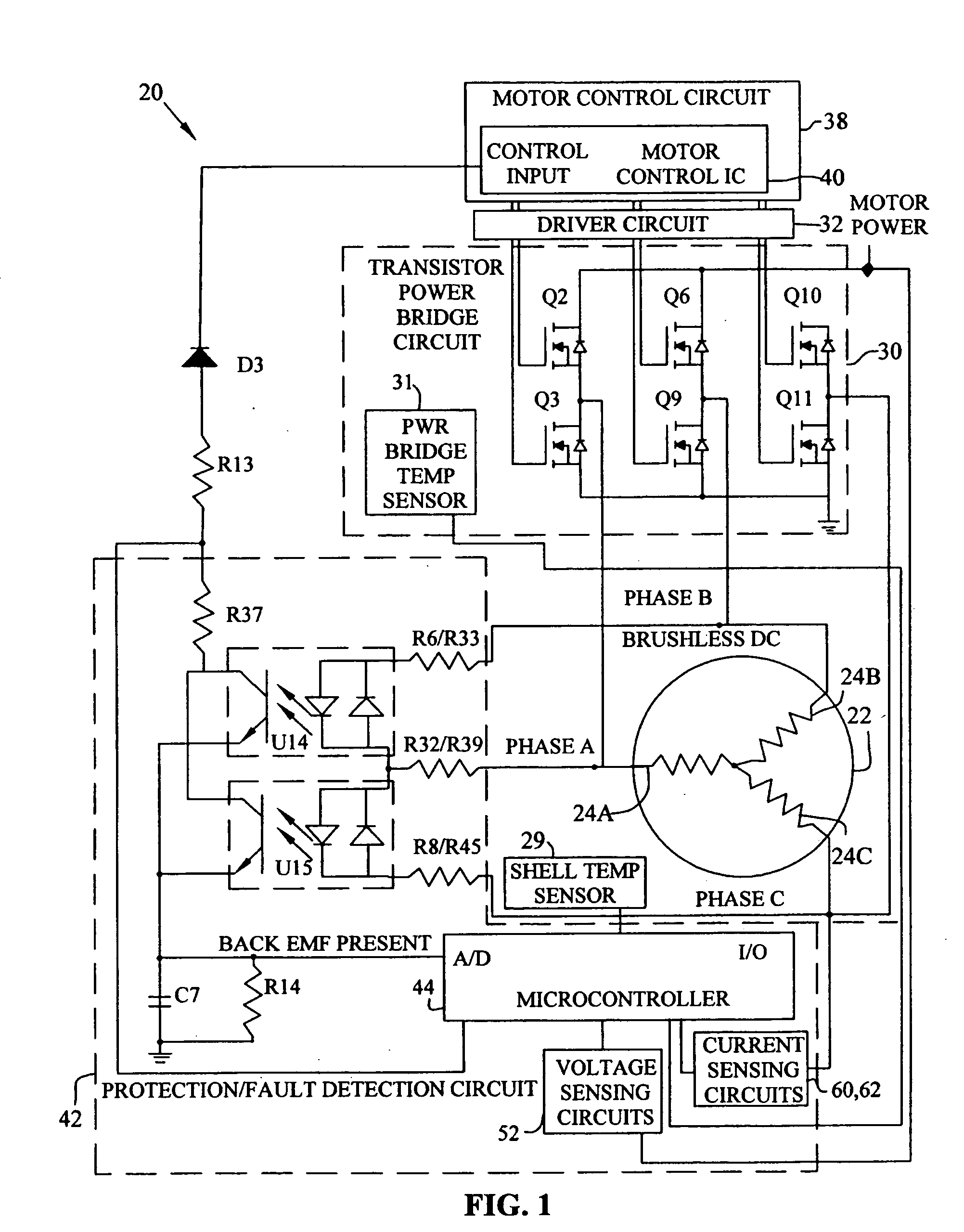
A motor control system for a brushless and sensorless DC motor for driving a compressor, pump or other application, includes a protection and fault detection circuit for detecting a locked rotor and a rotor which has stopped because of lost rotor phase lock. The motor control system also includes an off-the-shelf motor control integrated circuit having an input for disabling power outputs to the motor phase coils. The protection and fault detection circuit uses a back EMF sampling circuit coupled to the motor phase coils and momentarily disables power to the motor phase coils, via the motor control integrated circuit input, to determine if the motor rotor is rotating. The system also monitors supply voltage, supply current, temperature, and motor speed limits to detect faults and protect system components.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Control system
InactiveUS20050031132A1Frequency response correctionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsCapacitanceEngineering
Control system for devices such as an audio reproduction system, an actuator device, an electromechanical device and a telephony device. The system includes control circuitry which receives an input signal and a signal indicative of a position of a portion of the controlled apparatus. The control circuit provides an output signal to the controlled apparatus to affect an operation of the controlled apparatus. The output signal provides control of the apparatus to compensate for one or more of: motor factor; spring factor; back electromotive force; and impedance of a coil in a driver of the controlled apparatus. The signal indicative of position is derived by one or more position indicator techniques such as an infrared LED and PIN diode combination, position dependent capacitance of one portion of the controlled apparatus with respect to another portion of the controlled apparatus, and impedance of a coil in the controlled apparatus. The control circuitry is configurable to control transconductance and / or transduction of the system being controlled. A technique is disclosed to detect and measure a cant of a voice coil transducer, the technique including measuring a capacitance between one portion of the voice coil transducer with respect to another portion of the voice coil transducer over a range of movement of the voice coil during operation.
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
Flow estimation in a blood pump
The flow rate of blood in an implantable blood pump is determined at least in part based on a parameter related to thrust on the rotor of the pump. The parameter may be a parameter related to displacement of the rotor along its axis, such as a function of the back electromotive force generated in one or more coils of the stator. The back electromotive force may be measured during open-phase periods of a particular coil or set of coils, during which no power is applied to the coil or set of coils by the motor drive circuit. The parameter related to thrust may be used in conjunction with the speed of rotation of the rotor, the magnitude of current supplied to the rotor, or both to determine the flow rate. The pump may be controlled responsive to the determined flow rate.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Position detection of an actuator using infrared light
Control system for devices such as an audio reproduction system, an actuator device, an electromechanical device and a telephony device. The system includes control circuitry which receives an input signal and a signal indicative of a position of a portion of the controlled apparatus. The control circuit provides an output signal to the controlled apparatus to affect an operation of the controlled apparatus. The output signal provides control of the apparatus to compensate for one or more of: motor factor; spring factor; back electromotive force; and impedance of a coil in a driver of the controlled apparatus. The signal indicative of position is derived by one or more position indicator techniques such as an infrared LED and PIN diode combination, position dependent capacitance of one portion of the controlled apparatus with respect to another portion of the controlled apparatus, and impedance of a coil in the controlled apparatus. The control circuitry is configurable to control transconductance and / or transduction of the system being controlled. A technique is disclosed to detect and measure a cant of a voice coil transducer, the technique including measuring a capacitance between one portion of the voice coil transducer with respect to another portion of the voice coil transducer over a range of movement of the voice coil during operation.
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
Process for position indication
InactiveUS20050031133A1Transducer casings/cabinets/supportsTransducer circuitsCapacitanceEngineering
Control system for devices such as an audio reproduction system, an actuator device, an electromechanical device and a telephony device. The system includes control circuitry which receives an input signal and a signal indicative of a position of a portion of the controlled apparatus. The control circuit provides an output signal to the controlled apparatus to affect an operation of the controlled apparatus. The output signal provides control of the apparatus to compensate for one or more of: motor factor; spring factor; back electromotive force; and impedance of a coil in a driver of the controlled apparatus. The signal indicative of position is derived by one or more position indicator techniques such as an infrared LED and PIN diode combination, position dependent capacitance of one portion of the controlled apparatus with respect to another portion of the controlled apparatus, and impedance of a coil in the controlled apparatus. The control circuitry is configurable to control transconductance and / or transduction of the system being controlled. A technique is disclosed to detect and measure a cant of a voice coil transducer, the technique including measuring a capacitance between one portion of the voice coil transducer with respect to another portion of the voice coil transducer over a range of movement of the voice coil during operation.
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
Method of modifying dynamics of a system
InactiveUS20050031131A1Effective impedanceFrequency response correctionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsCapacitanceEngineering
Control system for devices such as an audio reproduction system, an actuator device, an electromechanical device and a telephony device. The system includes control circuitry which receives an input signal and a signal indicative of a position of a portion of the controlled apparatus. The control circuit provides an output signal to the controlled apparatus to affect an operation of the controlled apparatus. The output signal provides control of the apparatus to compensate for one or more of: motor factor; spring factor; back electromotive force; and impedance of a coil in a driver of the controlled apparatus. The signal indicative of position is derived by one or more position indicator techniques such as an infrared LED and PIN diode combination, position dependent capacitance of one portion of the controlled apparatus with respect to another portion of the controlled apparatus, and impedance of a coil in the controlled apparatus. The control circuitry is configurable to control transconductance and / or transduction of the system being controlled. A technique is disclosed to detect and measure a cant of a voice coil transducer, the technique including measuring a capacitance between one portion of the voice coil transducer with respect to another portion of the voice coil transducer over a range of movement of the voice coil during operation. COMPUTER PROGRAM LISTING APPENDIX
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
Electric motor and motor control
InactiveUS8575873B2Reduce noiseHigh complexitySingle-phase induction motor startersTorque ripple controlElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
Various embodiments of an electric motor and electronic control for an electric motor are disclosed. An exemplary electric motor comprises a single-phase brushless permanent magnet electric motor. In exemplary embodiments, the electronic motor control is configured to commutate an electric motor at a frequency other than line frequency, perform pulse width modulation, and drive the electric motor with a drive waveform that approximates the counter-electromotive force of the motor.
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling brushless DC motors in implantable medical devices
Methods and apparatus for controlling a polyphase motor in implantable medical device applications are provided. In one embodiment, the polyphase motor is a brushless DC motor. The back emf of a selected phase of the motor is sampled while a drive voltage of the selected phase is substantially zero. Various embodiments utilize sinusoidal or trapezoidal drive voltages. The sampled back emf provides an error signal indicative of the positional error of the rotor. In one embodiment, the sampled back emf is normalized with respect to a commanded angular velocity of the rotor to provide an error signal proportional only to the positional error of the motor rotor. The error signal is provided as feedback to control a frequency of the drive voltage. A speed control generates a speed control signal corresponding to a difference between a commanded angular velocity and an angular velocity inferred from the frequency of the drive voltage. The speed control signal is provided as feedback to control an amplitude of the drive voltage. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a brushless DC motor and a commutation control. The commutation control provides a commutation control signal for a selected phase of the motor in accordance with a sampled back electromotive force (emf) of that phase. The back emf of the phase is sampled only while the corresponding drive voltage for the selected phase is substantially zero, wherein a frequency of a drive voltage of the motor is varied in accordance with the commutation control signal.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Method of measuring a cant of an actuator
InactiveUS20050031138A1Broadcast circuit arrangementsFrequency response correctionCapacitanceEngineering
Control system for devices such as an audio reproduction system, an actuator device, an electromechanical device and a telephony device. The system includes control circuitry which receives an input signal and a signal indicative of a position of a portion of the controlled apparatus. The control circuit provides an output signal to the controlled apparatus to affect an operation of the controlled apparatus. The output signal provides control of the apparatus to compensate for one or more of: motor factor; spring factor; back electromotive force; and impedance of a coil in a driver of the controlled apparatus. The signal indicative of position is derived by one or more position indicator techniques such as an infrared LED and PIN diode combination, position dependent capacitance of one portion of the controlled apparatus with respect to another portion of the controlled apparatus, and impedance of a coil in the controlled apparatus. The control circuitry is configurable to control transconductance and / or transduction of the system being controlled. A technique is disclosed to detect and measure a cant of a voice coil transducer, the technique including measuring a capacitance between one portion of the voice coil transducer with respect to another portion of the voice coil transducer over a range of movement of the voice coil during operation.
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
Inspection apparatus and method
ActiveUS20100207620A1Current/voltage measurementMagnetic property measurementsCounter-electromotive forceEddy-current testing
An apparatus and method are disclosed for detecting flaws in electrically conductive materials by observing properties of the back-EMF of the eddy current field generated by driving magnetic flux through the object to be examined. The input signal may include sweeps at several frequencies, and may do so at one time under the principle of wave superposition. The sectorial observations of eddy currents summations may be compared to a known datum for a defect free material, the presence of anomalies in eddy field back EMF divergence tending to provide an indication of an irregularity in the underlying eddy field, and hence in the underlying material itself. The portable unit may have a number of different configurations depending on the nature of the object to be examined, be it a flat or large radius plate, a flange, a rail, or some other structural element.
Owner:ATHENA IND TECH
Disk drive controlling a voice coil motor during an emergency unload
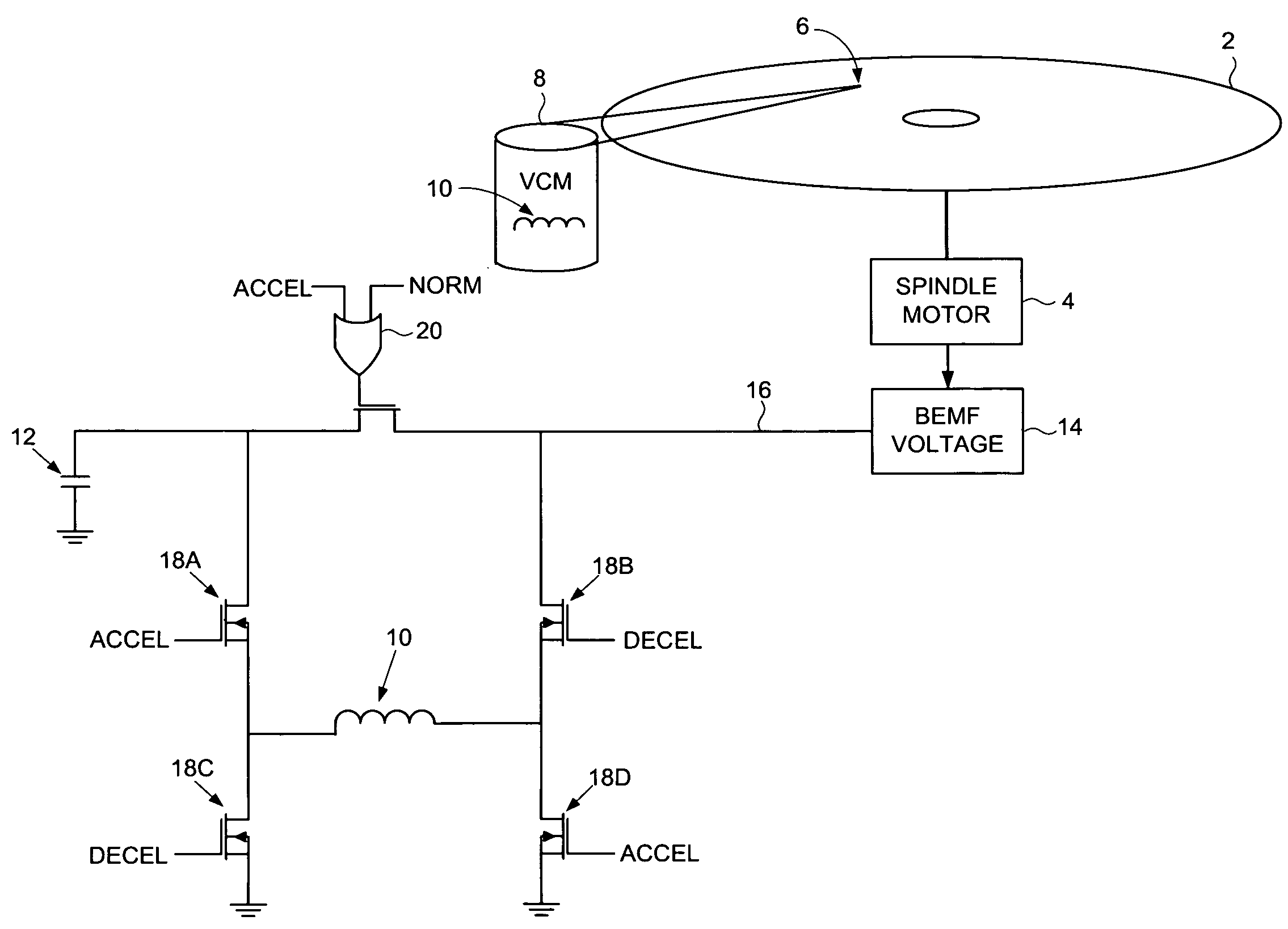
ActiveUS7548392B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageVoltage generatorElectric machine
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk, a spindle motor operable to rotate the disk, a head, and a voice coil motor (VCM) operable to actuate the head over the disk, wherein the VCM comprises a voice coil. The disk drive further comprises a capacitor, and a back electromotive force (BEMF) voltage generator operable to generate a BEMF voltage from the spindle motor. The disk drive further comprises switching circuitry operable to connect the voice coil to the capacitor while accelerating the VCM, and to disconnect the voice coil from the capacitor and connect the voice coil to the BEMF voltage while decelerating the VCM.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
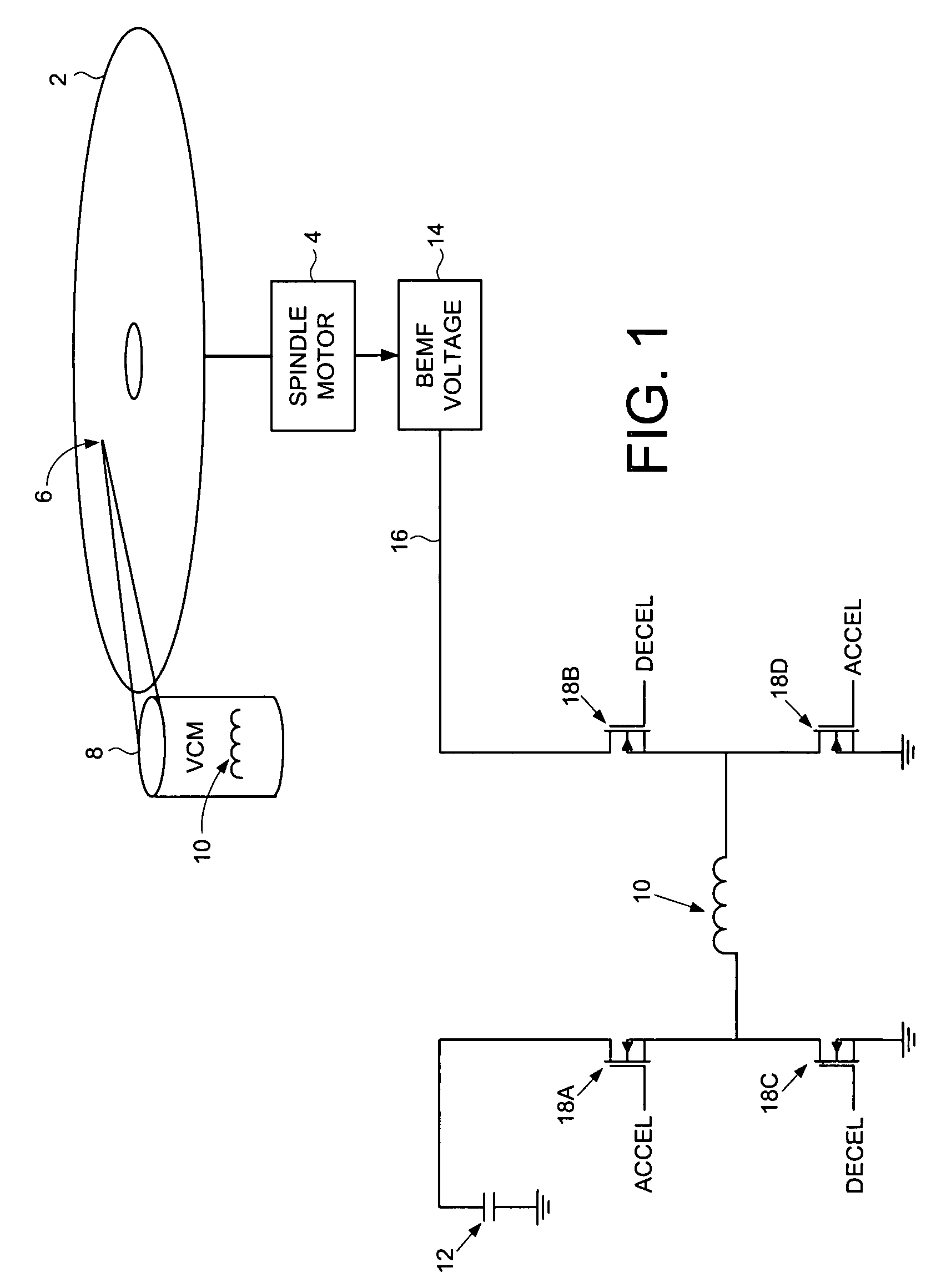
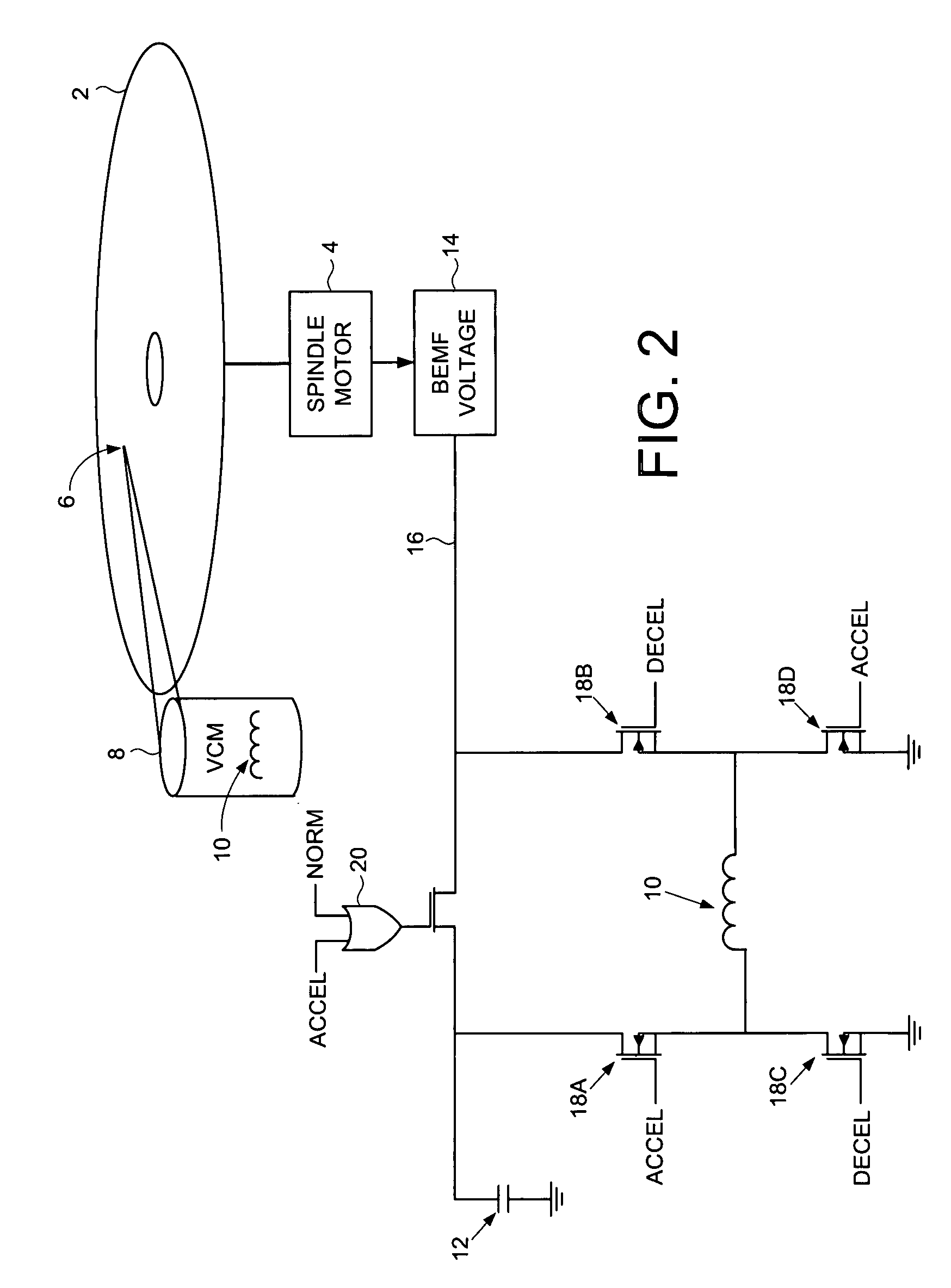
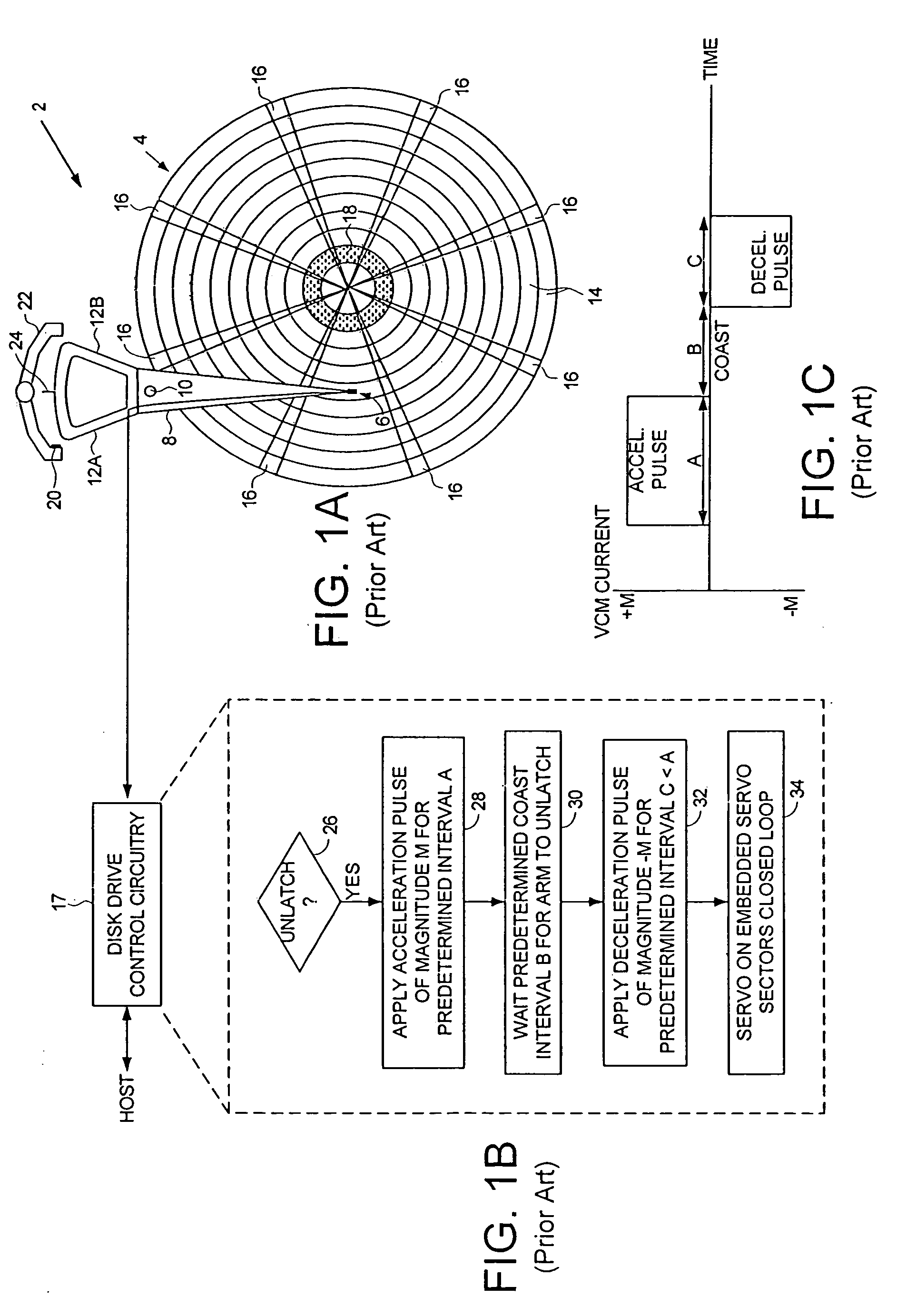
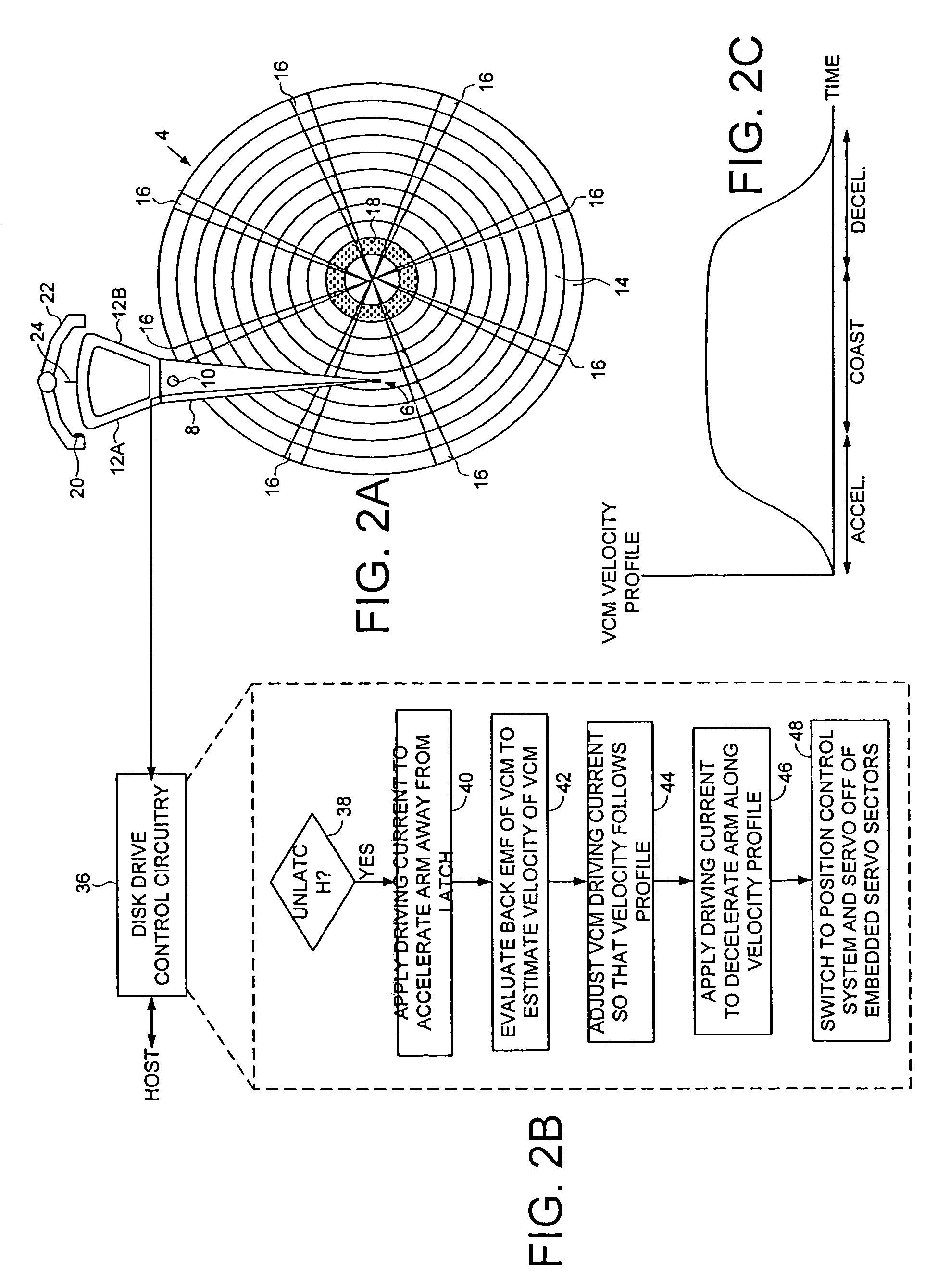
Disk drive employing a velocity profile and back EMF feedback to control a voice coil motor
InactiveUS7068463B1Reduce maximum latching force of magnetDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageDriving currentElectric machine
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk having a plurality of tracks, an actuator arm, a head connected to a distal end of the actuator arm, and a voice coil motor (VCM) for rotating the actuator arm about a pivot to actuate the head over the disk. A driving current is applied to the VCM to control the motion of the actuator arm. A back EMF voltage generated by the VCM is detected, and a velocity of the VCM is estimated in response to the back EMF voltage. The estimated VCM velocity is compared to a target velocity in a velocity profile, wherein the velocity profile comprises at least an acceleration component and a coast component. The driving current is adjusted in response to the comparison so that the velocity of the VCM substantially follows the velocity profile.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
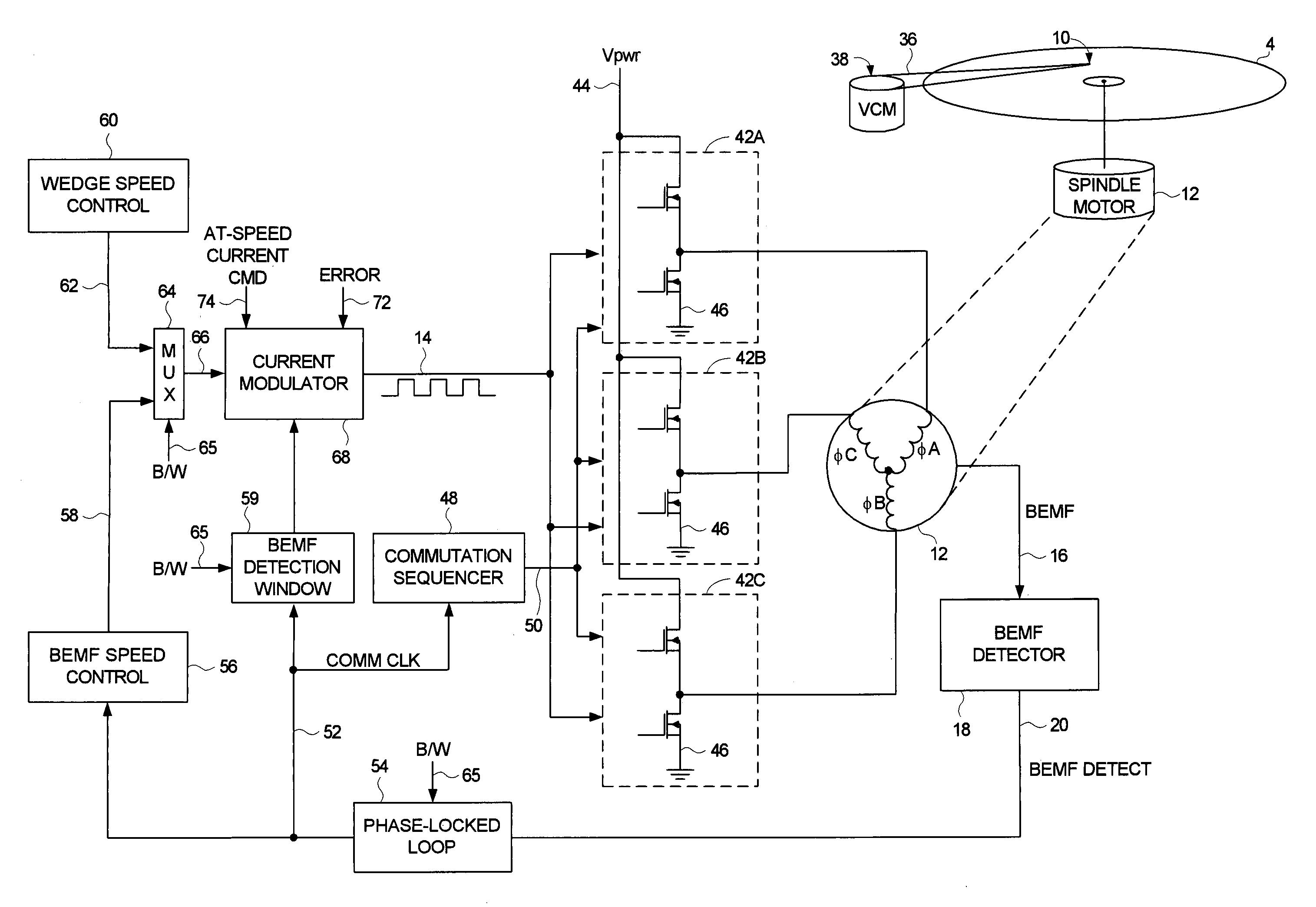
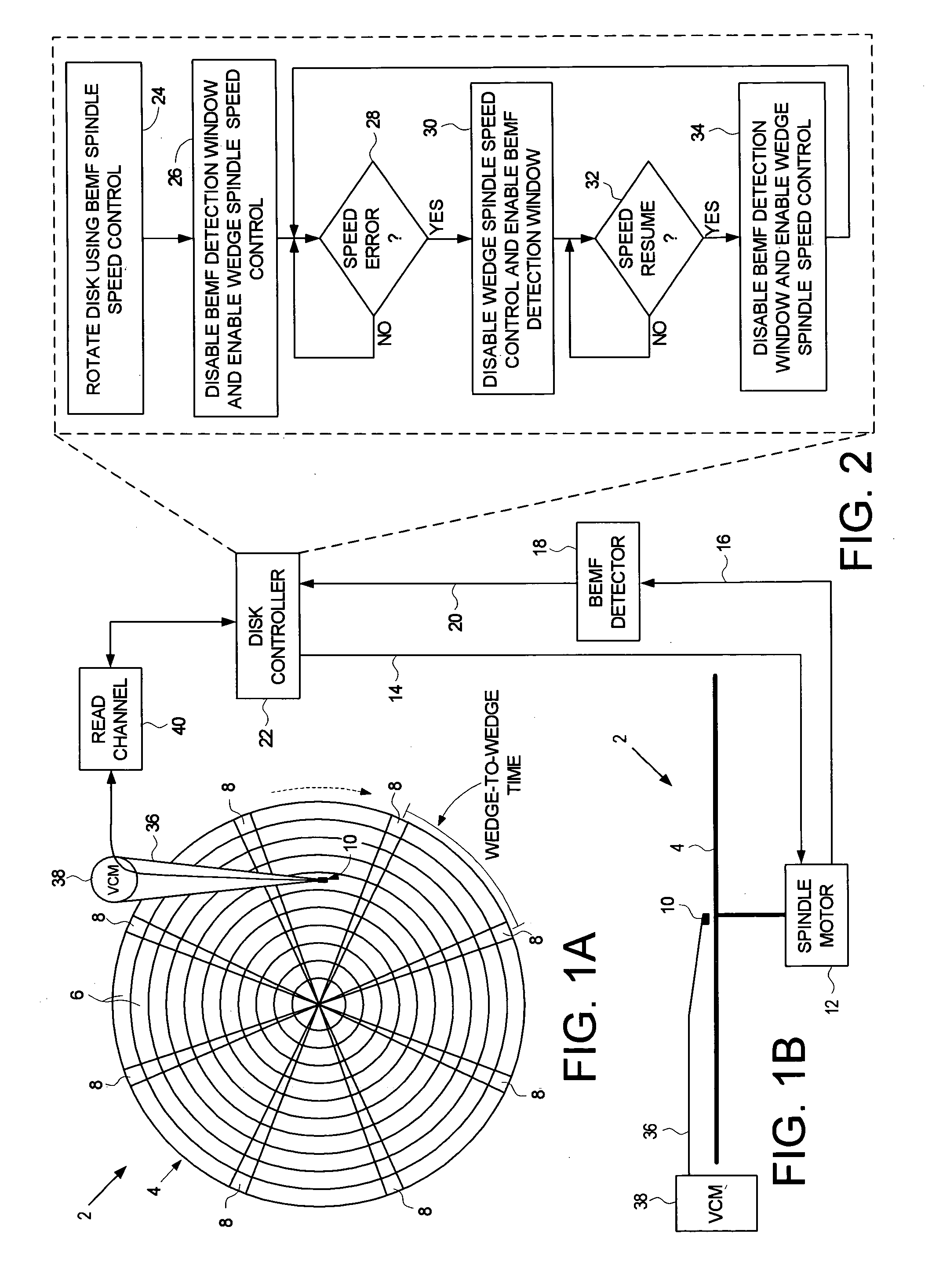
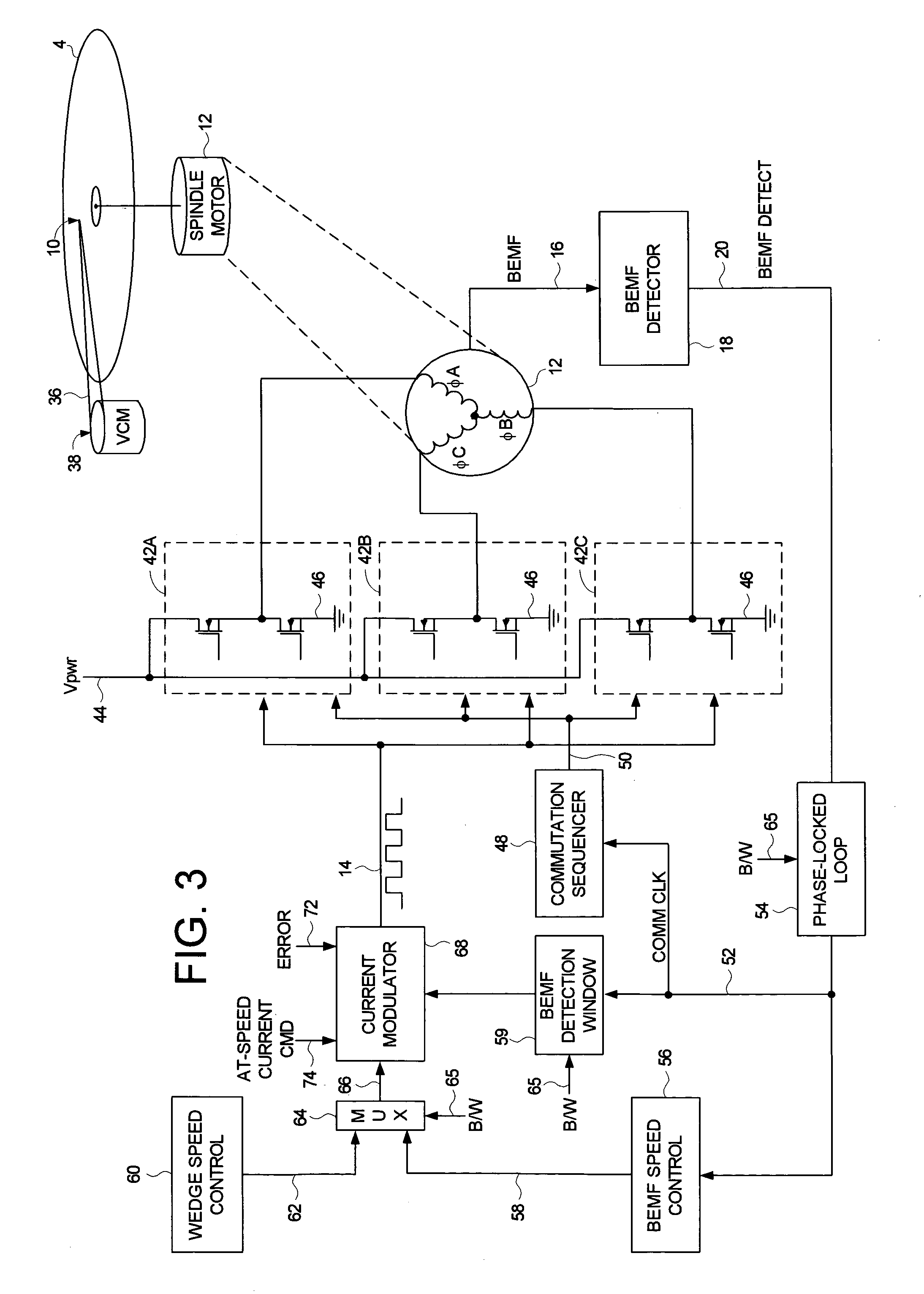
Disk drive disabling BEMF detection window to reduce acoustic noise while using wedge spindle speed control
InactiveUS6954324B1Reduce noiseRecord information storageCarrier speed control/regulation/indicationAcoustic noise reductionElectric machine
A disk drive is disclosed employing either back electromotive force (BEMF) spindle speed control mode or wedge spindle speed control mode. A BEMF detector monitors the BEMF voltage generated by the windings of the spindle motor to generate a BEMF speed error. The BEMF spindle speed control mode is used to spin up the disk to an operating speed, and the wedge spindle speed control to maintain the disk at the operating speed. While in the wedge spindle speed control mode, a BEMF detection window is disabled to reduce acoustic noise.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
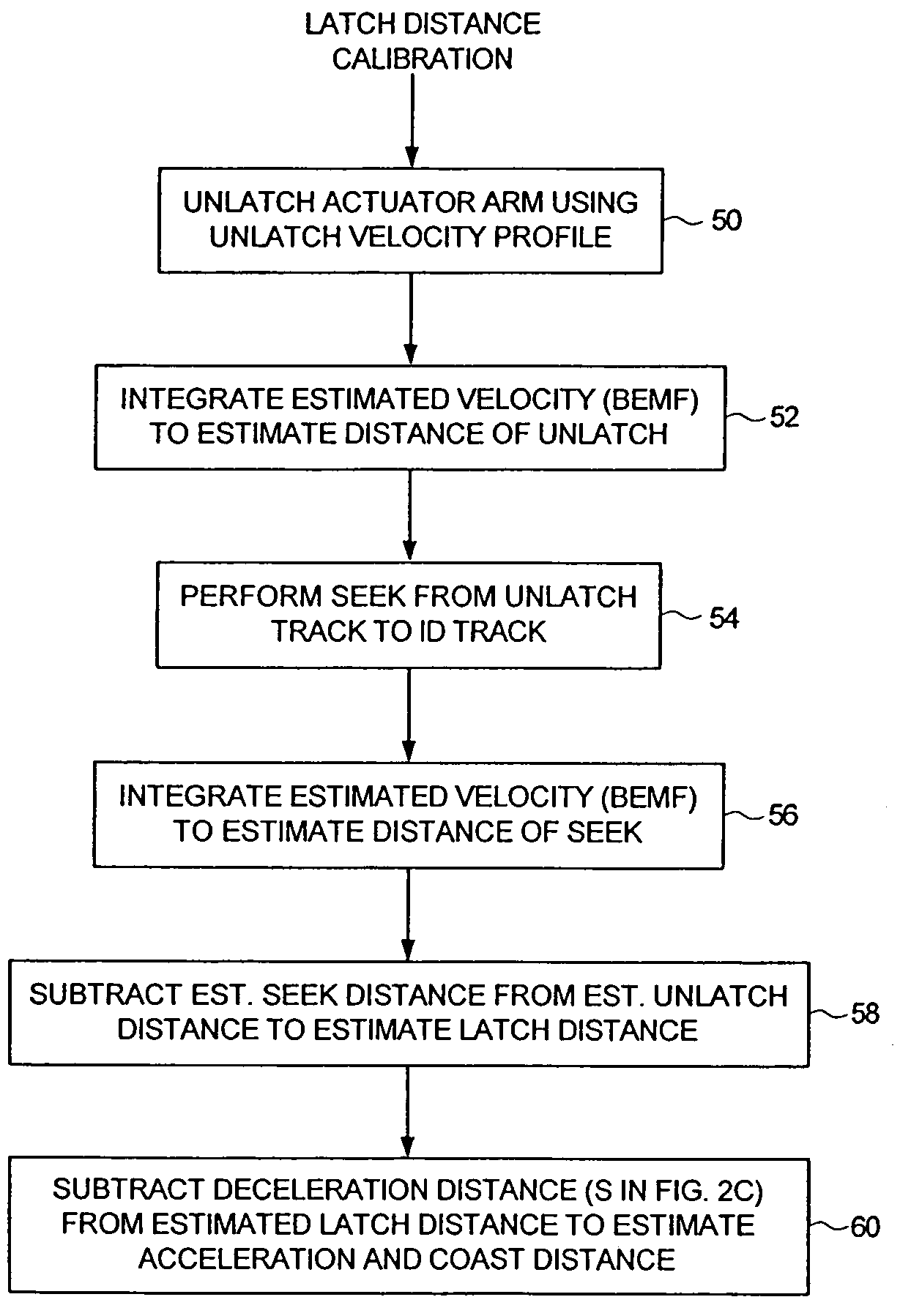
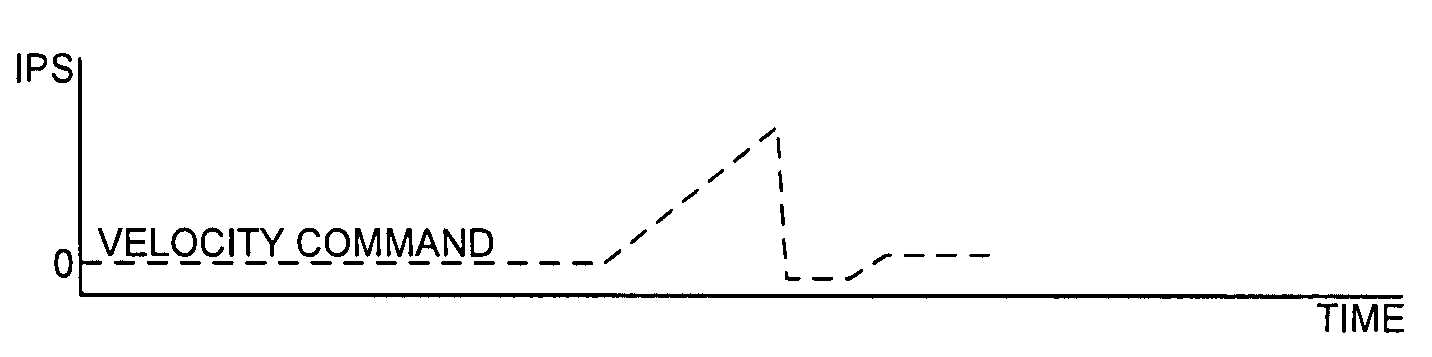
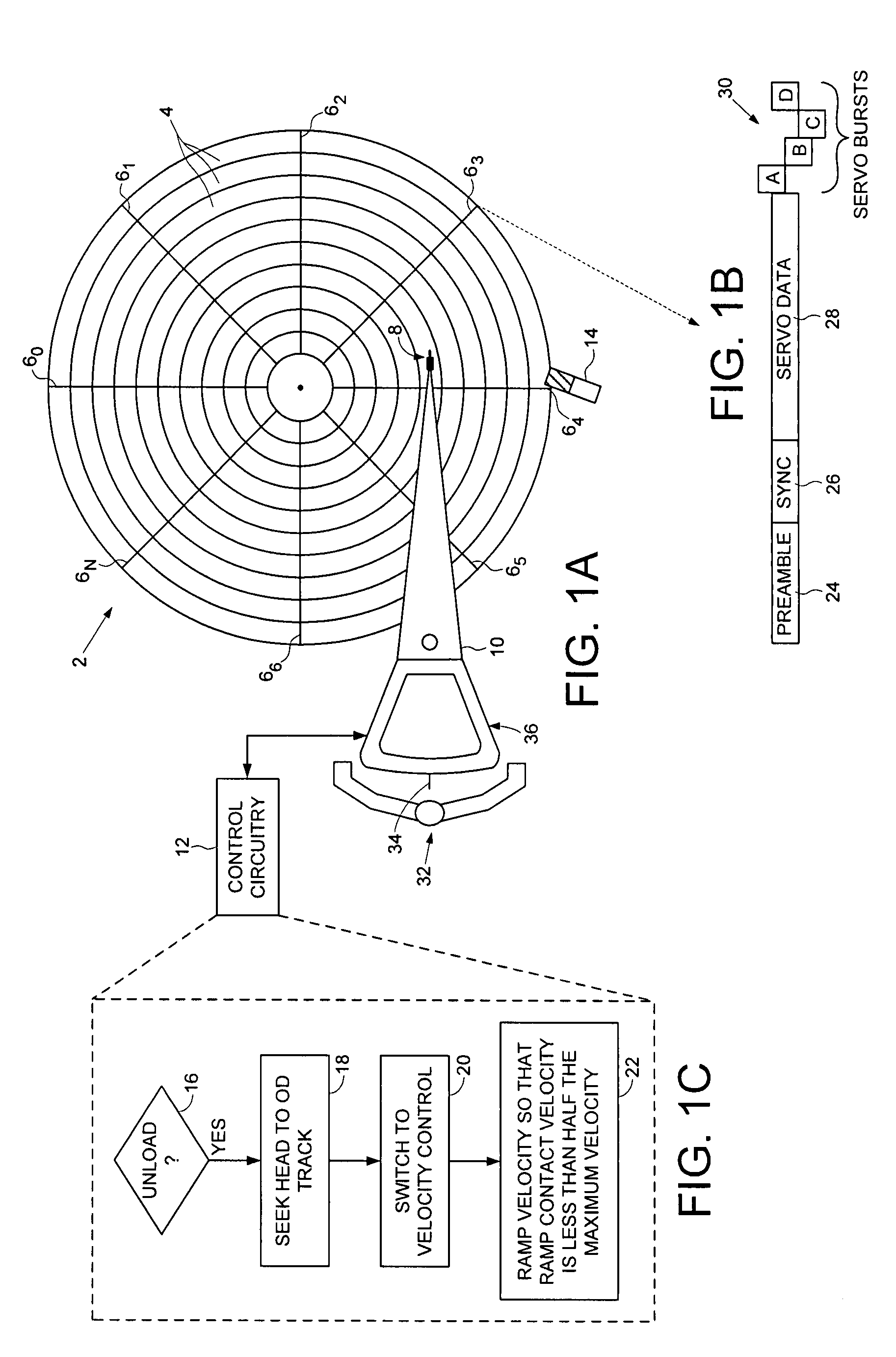
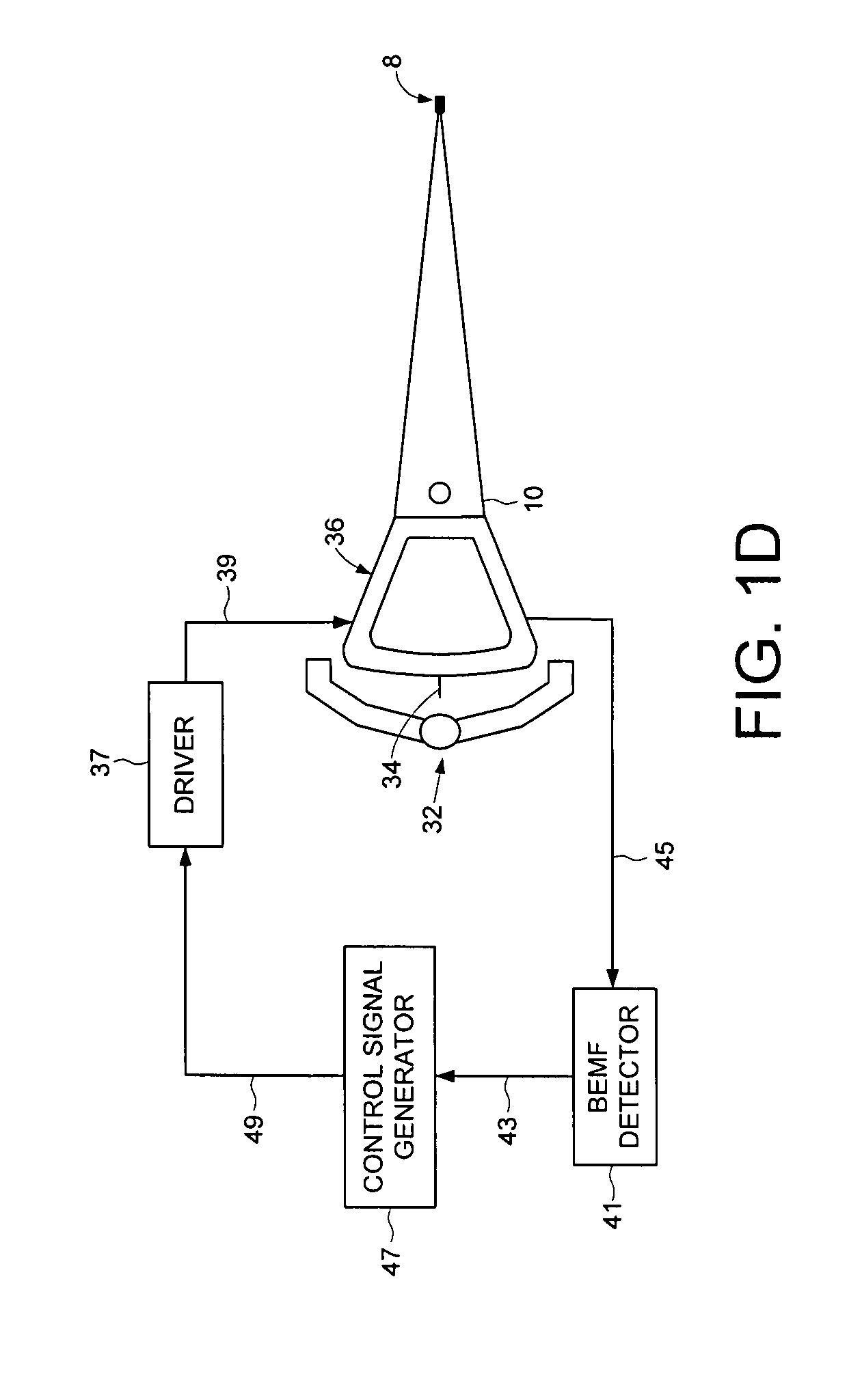
Disk drive seeking to OD track and then ramping velocity to implement fast unload
InactiveUS7573670B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageCounter-electromotive forceActuator
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk having a plurality of tracks, wherein each track comprises a plurality of embedded servo sectors. A head connected to a distal end of an actuator arm is rotated about a pivot by a voice coil motor (VCM) in order to actuate the head radially over the disk. The actuator arm is unloaded onto a ramp by seeking the head to a track near an outer diameter of the disk in response to the embedded servo sectors, switching to a velocity control mode to unload the actuator arm onto the ramp at a controlled unload velocity in response to a back electromotive force voltage generated by the VCM, and ramping a velocity command so that the velocity of the actuator arm when contacting the ramp is less than half the maximum unload velocity while traveling along the ramp.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
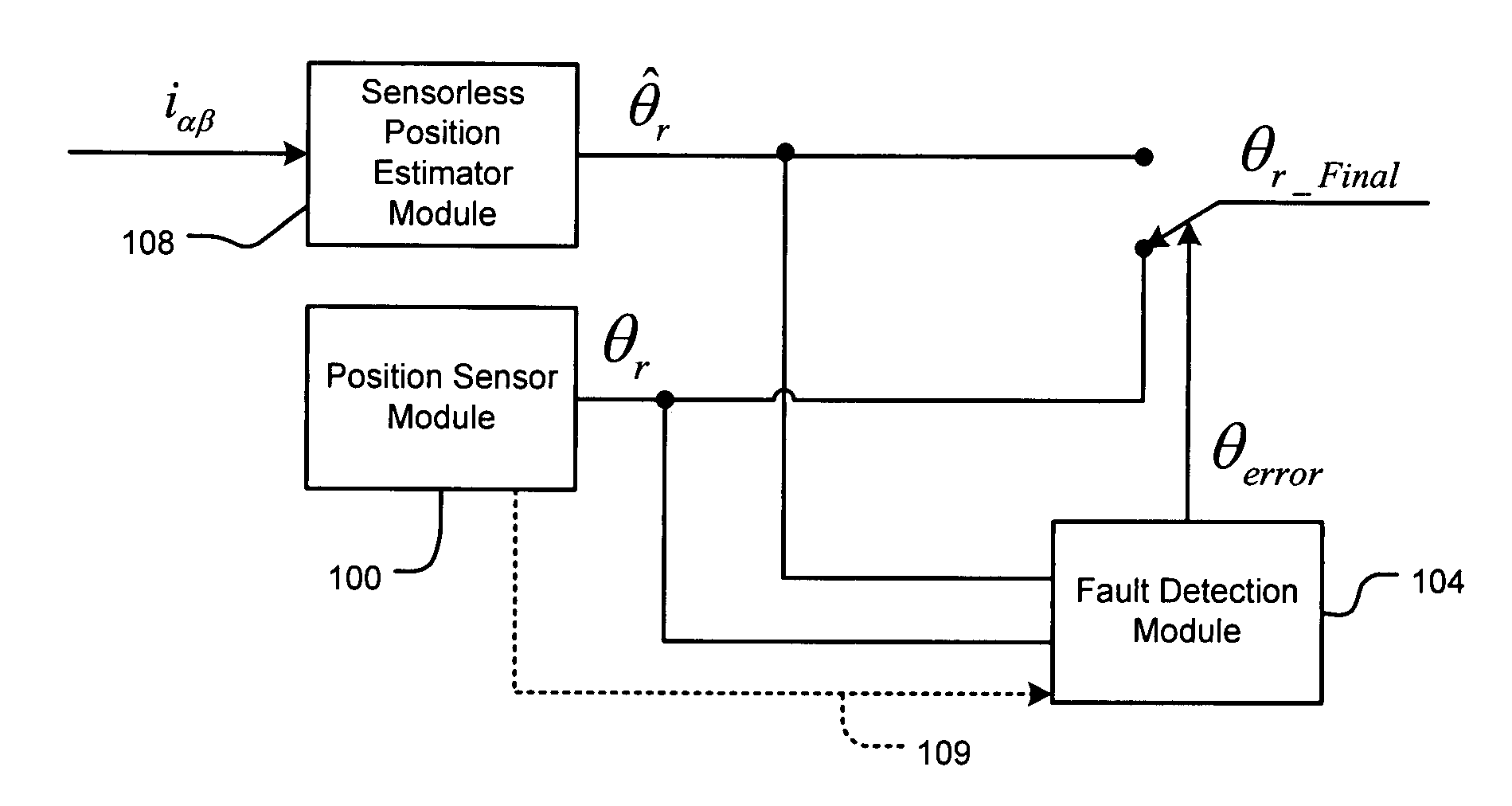
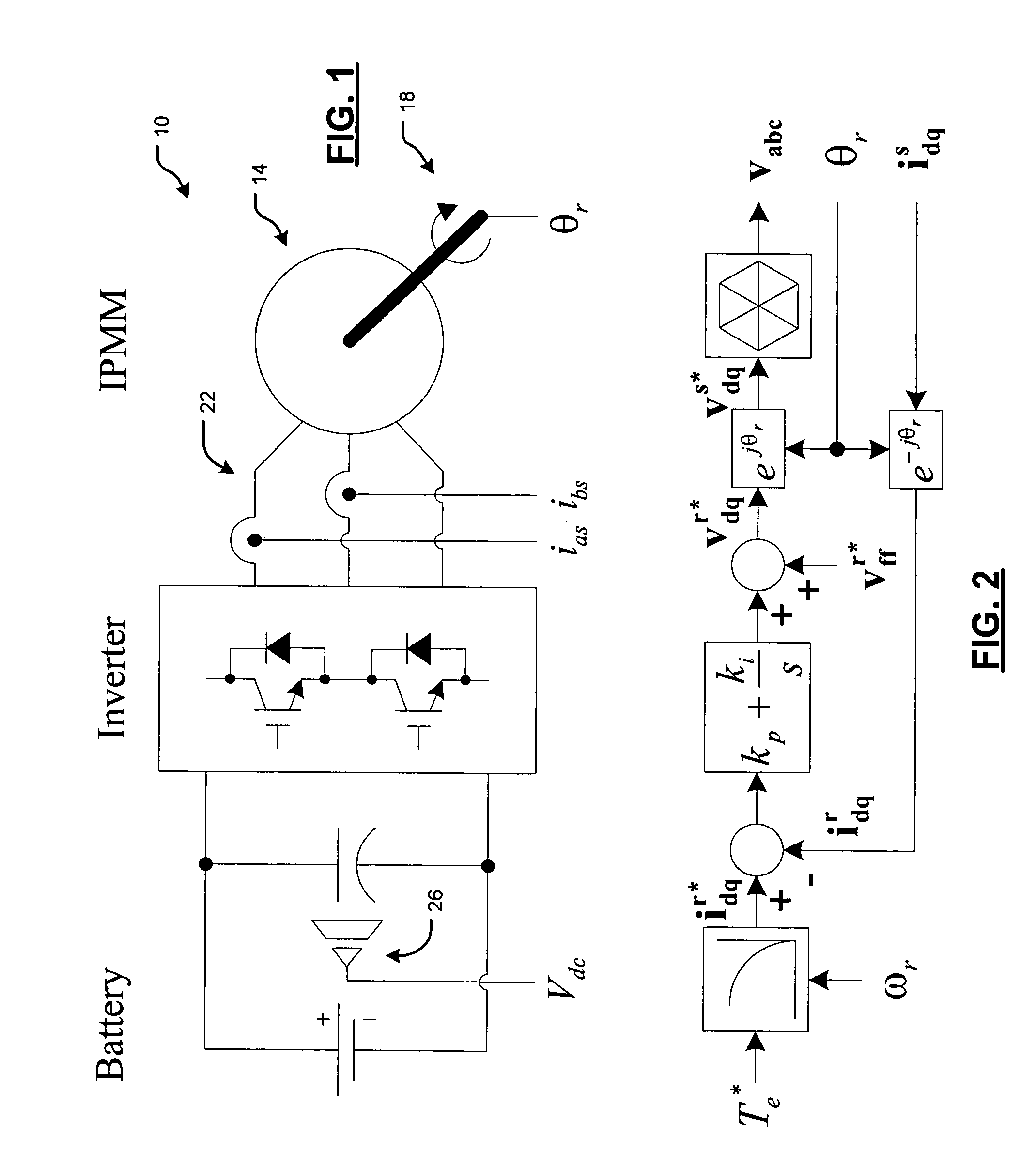
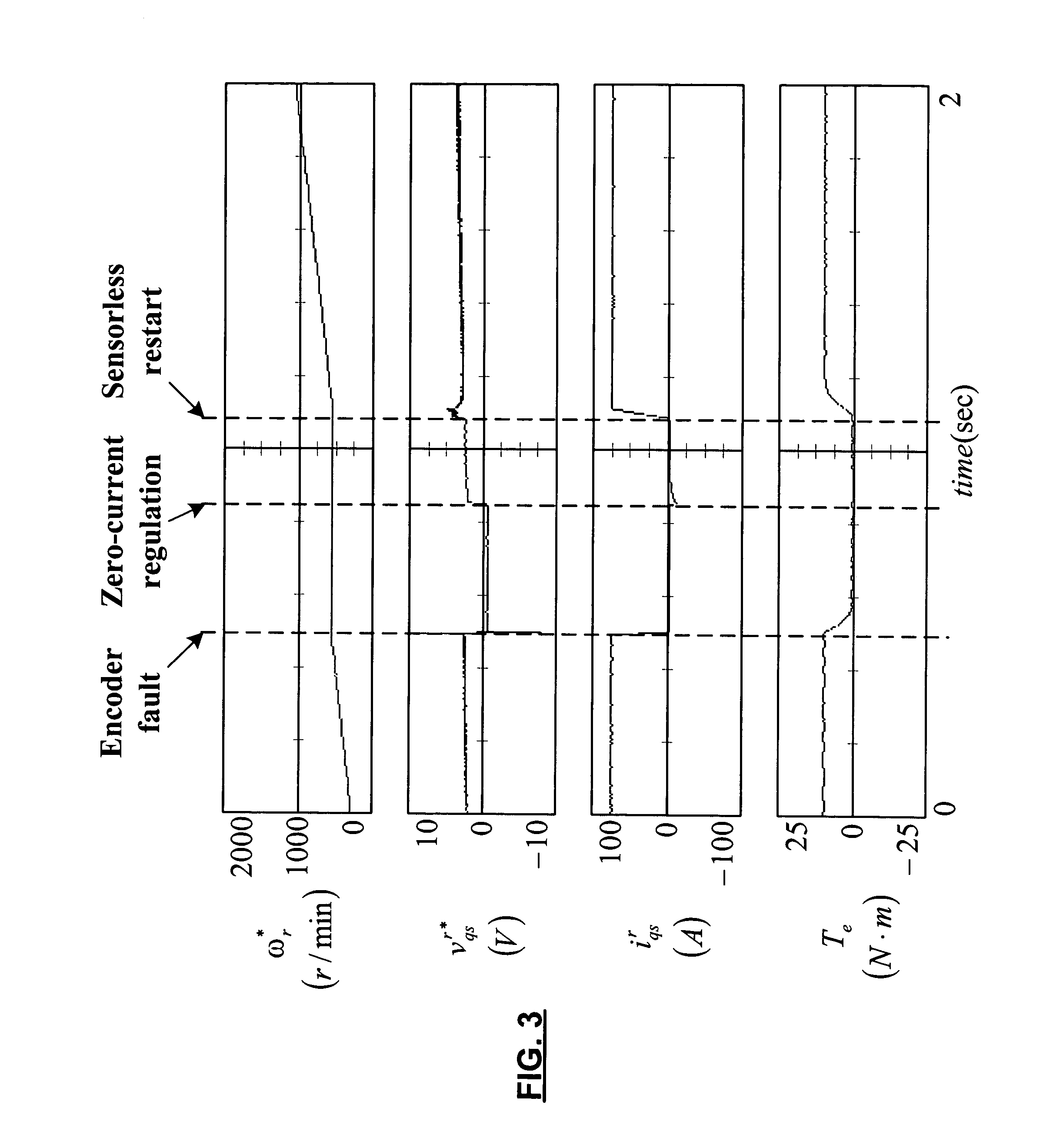
Position sensor fault tolerant control for automotive propulsion system
A control system for a motor including a rotor comprises a sensorless sensor module that includes a saliency-based estimator module that generates a first rotor position signal based on saliency and a back electromotive force (emf) estimator module that generates a second rotor position signal based on back emf. A selector selects the first rotor position signal for rotor speeds below a first rotor speed and the second rotor position signal for rotor speeds above the first rotor speed. A rotor position sensor senses a position of the rotor and generates a third rotor position signal. A fault detection module senses faults in the rotor position sensor and outputs the third rotor position signal when a fault is not detected and one of the first and second rotor position signals when the fault is detected. An indirect field oriented control (IFOC) system controls the motor based on a selected one of the first, second and third rotor position signals.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS7294988B2Improve sensing accuracyImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorEngineering
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
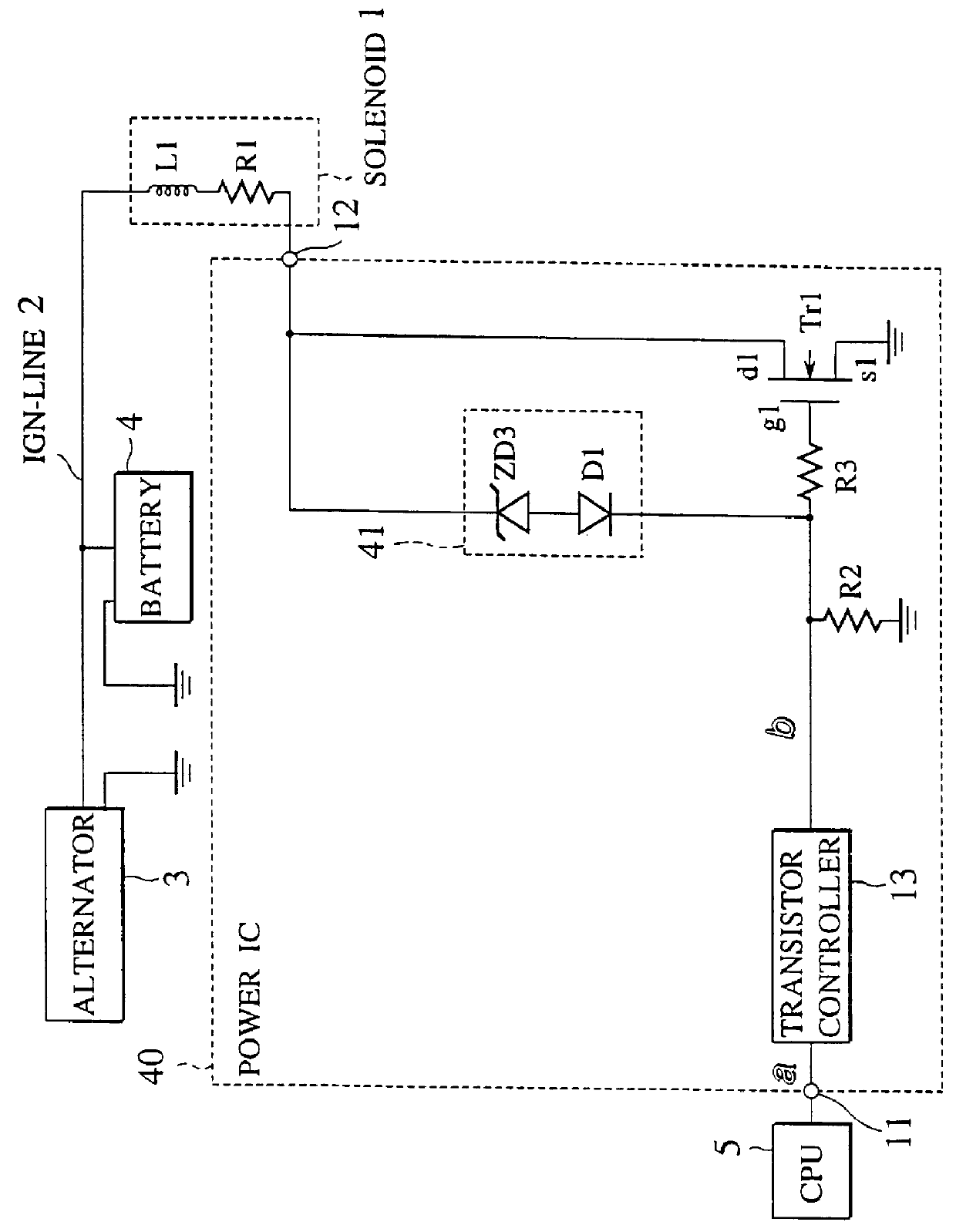
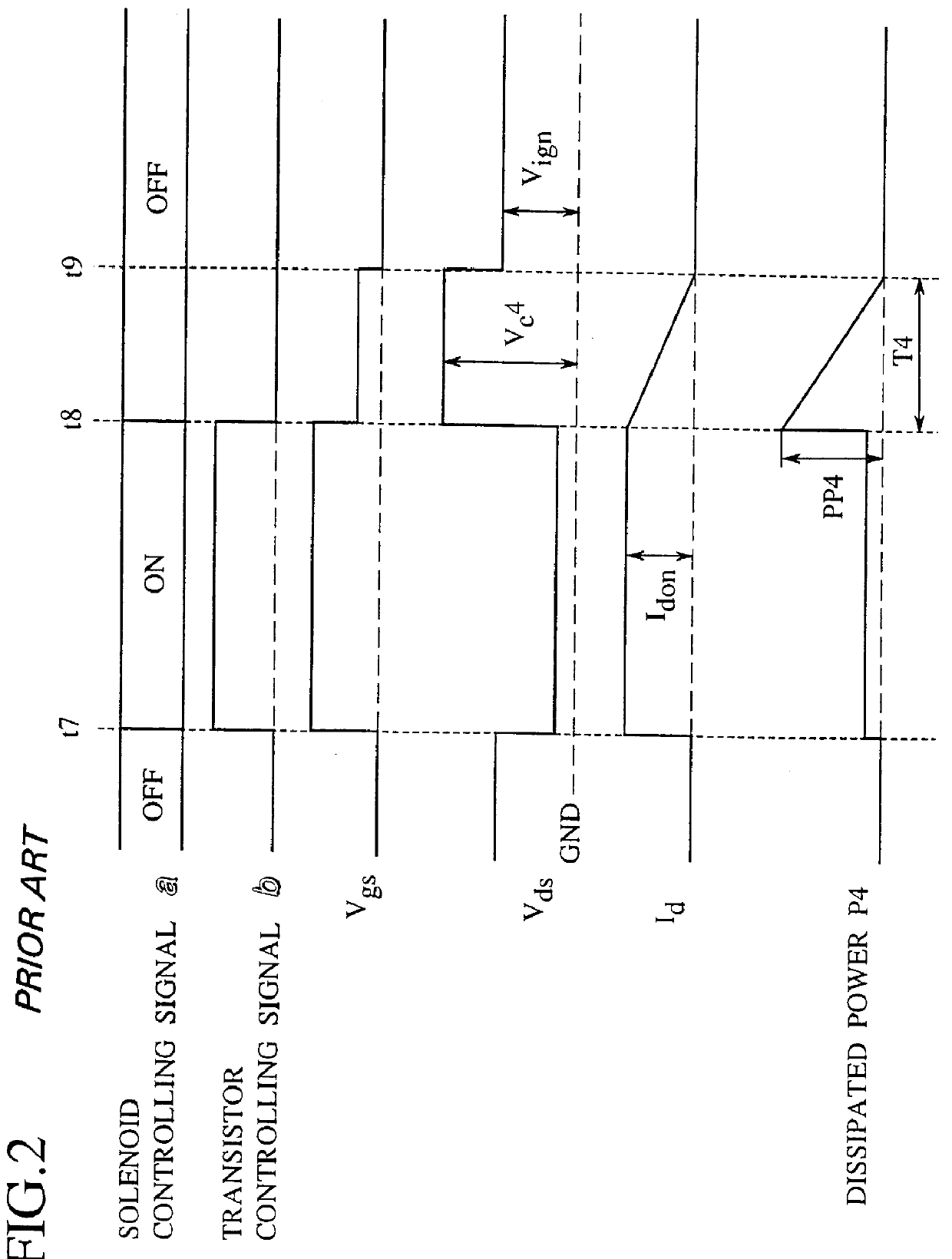
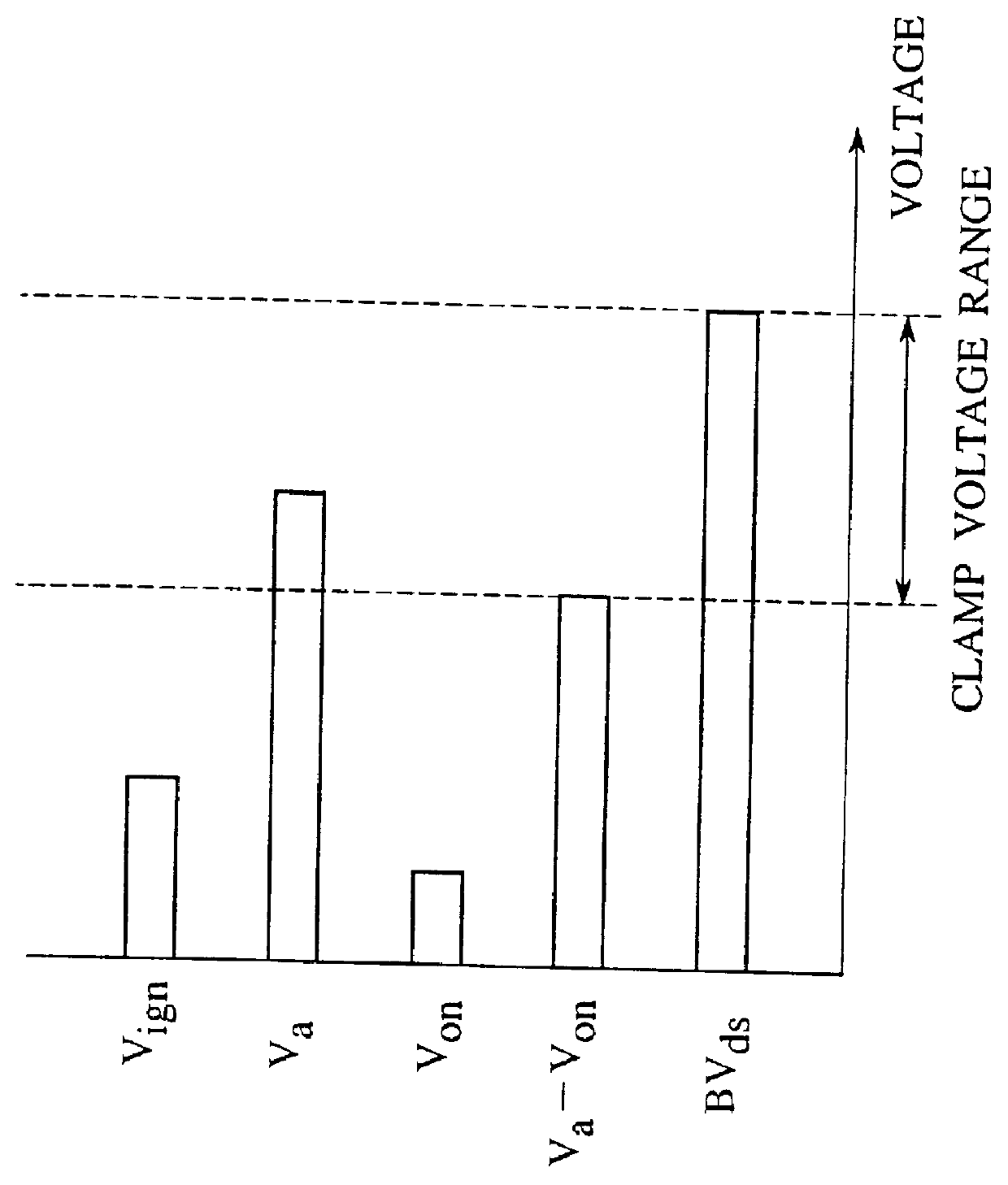
Integrated circuit having surge protection circuit
A trailing edge of a control signal of a transistor controller for controlling an output transistor is detected by an edge detector of a clamp controlling circuit. A surge voltage from a back electromotive voltage induced in an inductance L1 is absorbed from the output transistor, only for a given period immediately after the solenoid is turned off, by turning a switching transistor into an on-state by a timer to force a clamping circuit into conduction. At a normal operation, since the clamping circuit is cut off from an output terminal, the clamping voltage can be set in a manner to reduce to a normal voltage in an IGN-line. Therefore, a peak power value of a power loss caused by the surge voltage at the output transistor can be reduced, whereby generation of heat at the output transistor can be reduced. Therefore, the chip size of the power IC can be reduced.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
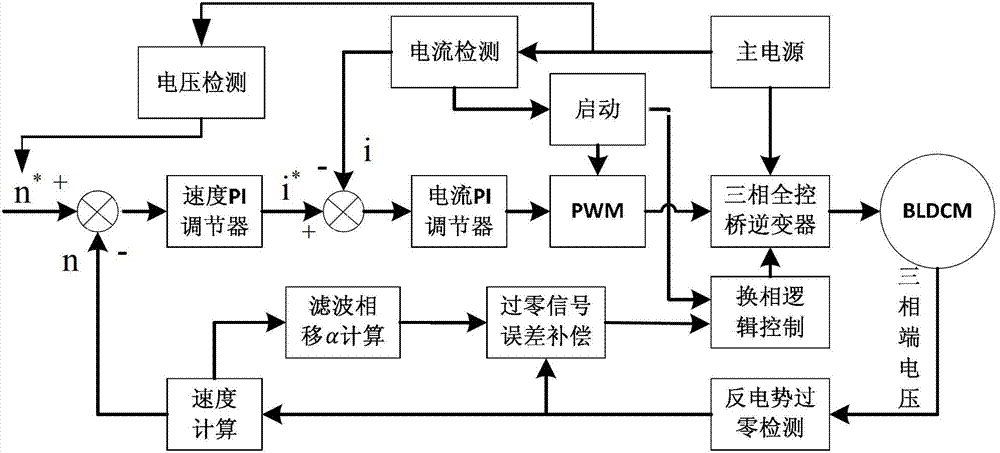
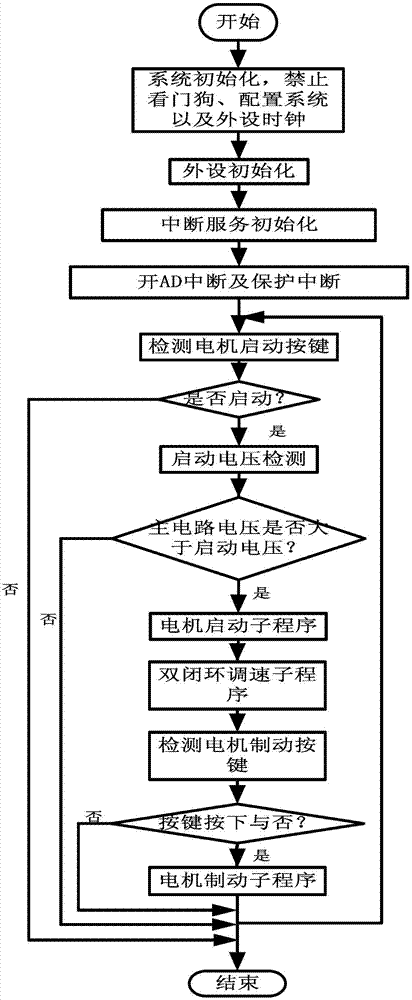
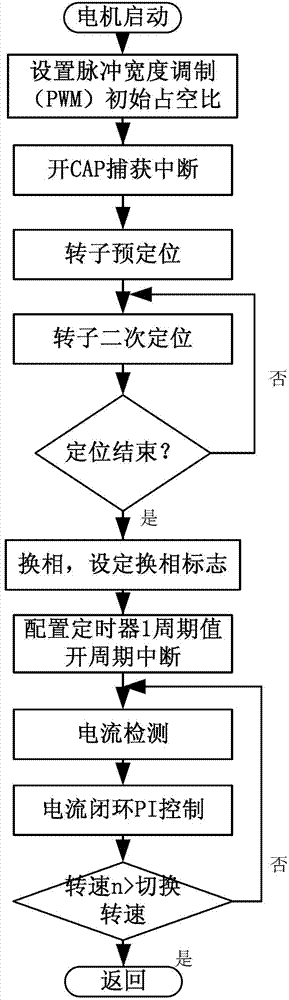
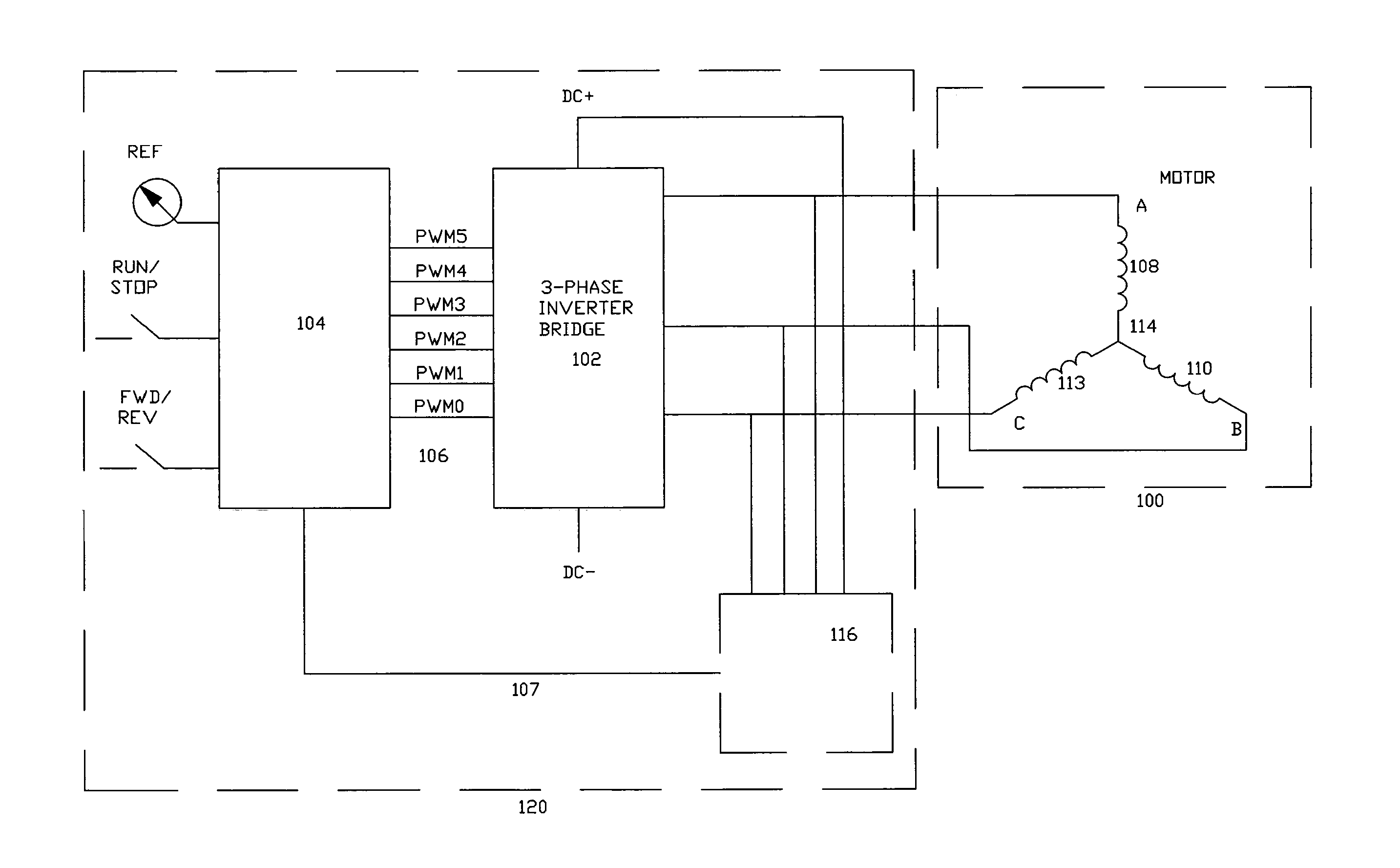
Position sensor-free double closed-loop speed regulation control method for brushless DC motor
InactiveCN103248294AAccurate control of different speedsSolve the problems of large volume and low speed accuracyTorque ripple controlSingle motor speed/torque controlClosed loopEngineering
A position sensor-free double closed-loop speed regulation control method for a brushless DC motor comprises the following steps: (1) initializing functional modules and peripherals; (2) opening AD (Analog-Digital) interruption and protection interruption; (3) detecting the start key of the motor, judging whether to start the motor, if yes, executing the next step, and if not, continuing to execute the step; (4) starting voltage detection, judging whether the voltage of a main circuit is larger than starting voltage, if yes, executing the next step, and if not, returning to the step (3); (5) entering a motor starting subprogram and beginning operating the motor; (6) entering a double closed-loop speed regulation subprogram, and regulating the rotational speed and the current of the motor according to voltage value; and (7) detecting a motor brake key, judging whether to press the key, if yes, entering a motor brake subprogram, and if not, returning to the step (3). The method provided by the invention overcomes the defects of larger size, low rotational speed accuracy and the like of the conventional motor controller, can accurately control different rotational speeds of the motor, and can simultaneously realize counter electromotive force zero-cross comparison position sensor-free reversing and Hall position signal reversing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Low noise back EMF sensing brushless DC motor
InactiveUS7141949B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersLow noiseEngineering
A low noise electronic three phase bridge controlled brushless DC motor suitable for whiteware appliance pumps and other appliance applications. Back EMF zero crossing sensing is used to determine rotor position and thus stator winding commutation times. Motor torque and speed are controlled by pulse width modulating the operation of that bridge switching device which has just been switched from an OFF state to an ON state on each new commutation. All three stator windings have current flowing in each winding commutation to improve motor current waveform and thereby reduce motor noise, but the current in one winding is always terminated before the end of the commutation period to allow the back EMF in that winding to be sensed to zero crossing.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
Electrical machine and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20060284581A1Synchronous motors startersAC motor controlElectric machineCounter-electromotive force
An electrical machine having a stator and a rotor. The stator includes a core and a plurality of windings disposed on the core in a multiple-phase arrangement. The rotor is disposed adjacent to the stator to interact with the stator. A method of operating the motor includes applying a pulsed voltage differential to first and second terminals of the windings resulting in movement of the rotor; monitoring the back electromotive force (BEMF) of the windings to sense rotor movement; after the applying and monitoring steps, monitoring the BEMF of the windings to determine whether the rotor is rotating in a desired direction, and electrically commutating the motor when the rotor is rotating in the desired direction and zero or more other conditions exist.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Stall detection circuit and method
InactiveUS6900657B2Avoid difficultyDetect changeDynamo-electric converter controlDynamo-electric machine testingCounter-electromotive forceConductor Coil
A stall detection circuit and method for a stepper motor. The circuit has an H-bridge configuration with an additional circuit pathway to ground being connected at a point between two center windings. During the transition between step sequences, the circuit employs a monitoring phase in which the previously active low side driver is turned off such that current passes through only the first winding and then is diverted to ground via the additional pathway. While the phase voltage is thus momentarily extinguished, the second coil is used to monitor the motor's back EMF, from which it can be determined whether the rotor is in a normal running mode, a stall, or a reverse condition.
Owner:SAIA BURGESS AUTOMOTIVE
Speed sensorless control algorithm for direct drive permanent magnet synchronous wind power system
InactiveCN102291079AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsDifferentiatorEngineering
The invention is a control algorithm that uses detected current and voltage to estimate the real-time value of the stator resistance and speed of the wind power generator, and uses the speed estimated by the algorithm as speed feedback to control the permanent magnet synchronous wind power generator. The speed value is estimated in the following way: According to the motor stator voltage and current value obtained by detection, the stator resistance value of the wind turbine is identified online based on the model reference adaptive system (MRAS), and the estimated electrical angle and the actual electrical angle of the rotor are obtained based on the back electromotive force. Error calculation formula, the fan speed is estimated by eliminating this error. The current and voltage values in the electrical angle error calculation formula are obtained by detection, the stator resistance value that changes during generator operation is obtained by MRAS identification, and the differential term of the stator current is realized by a tracking differentiator (TD), so that it can be estimated more accurately and quickly Rotating speed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
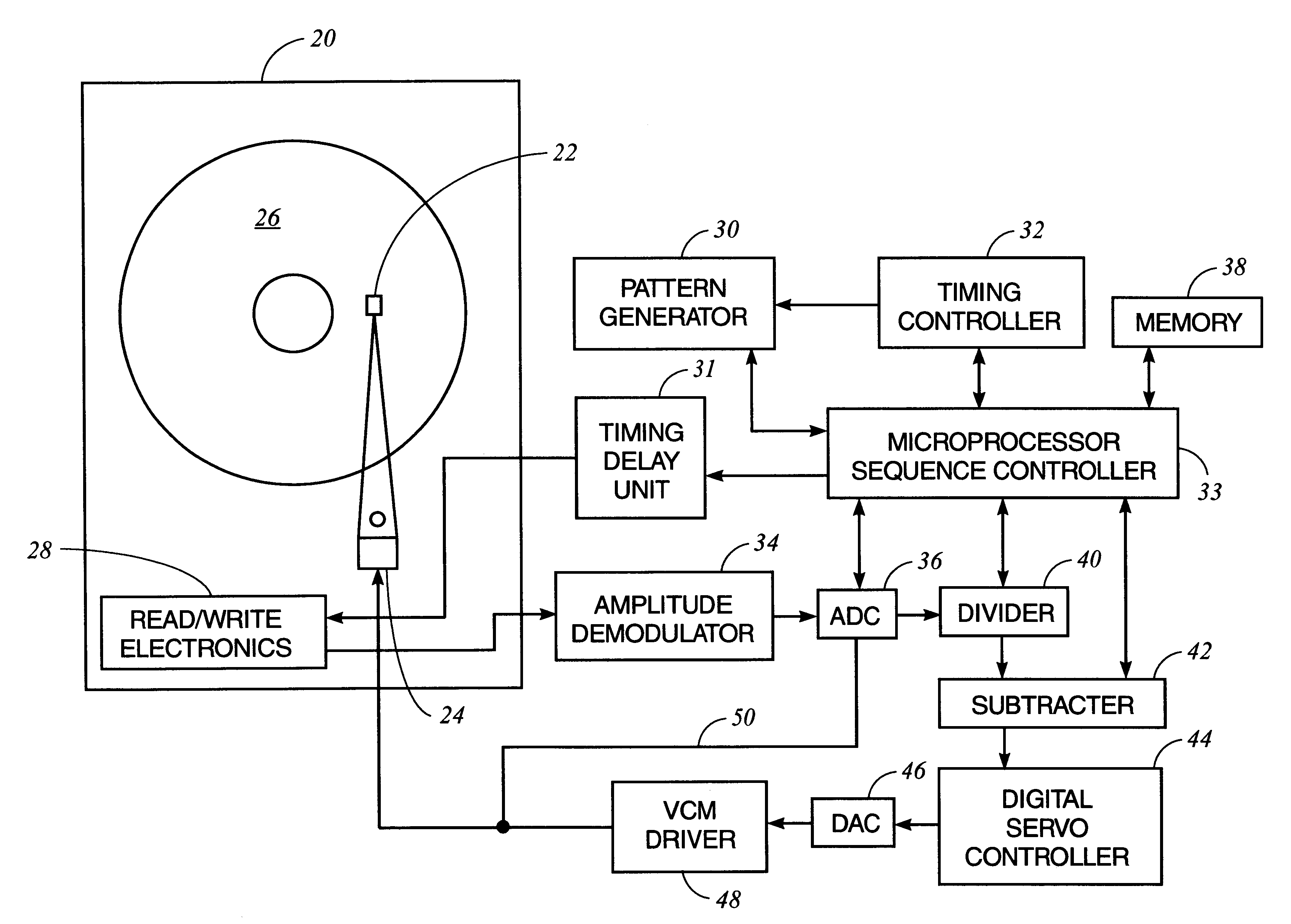
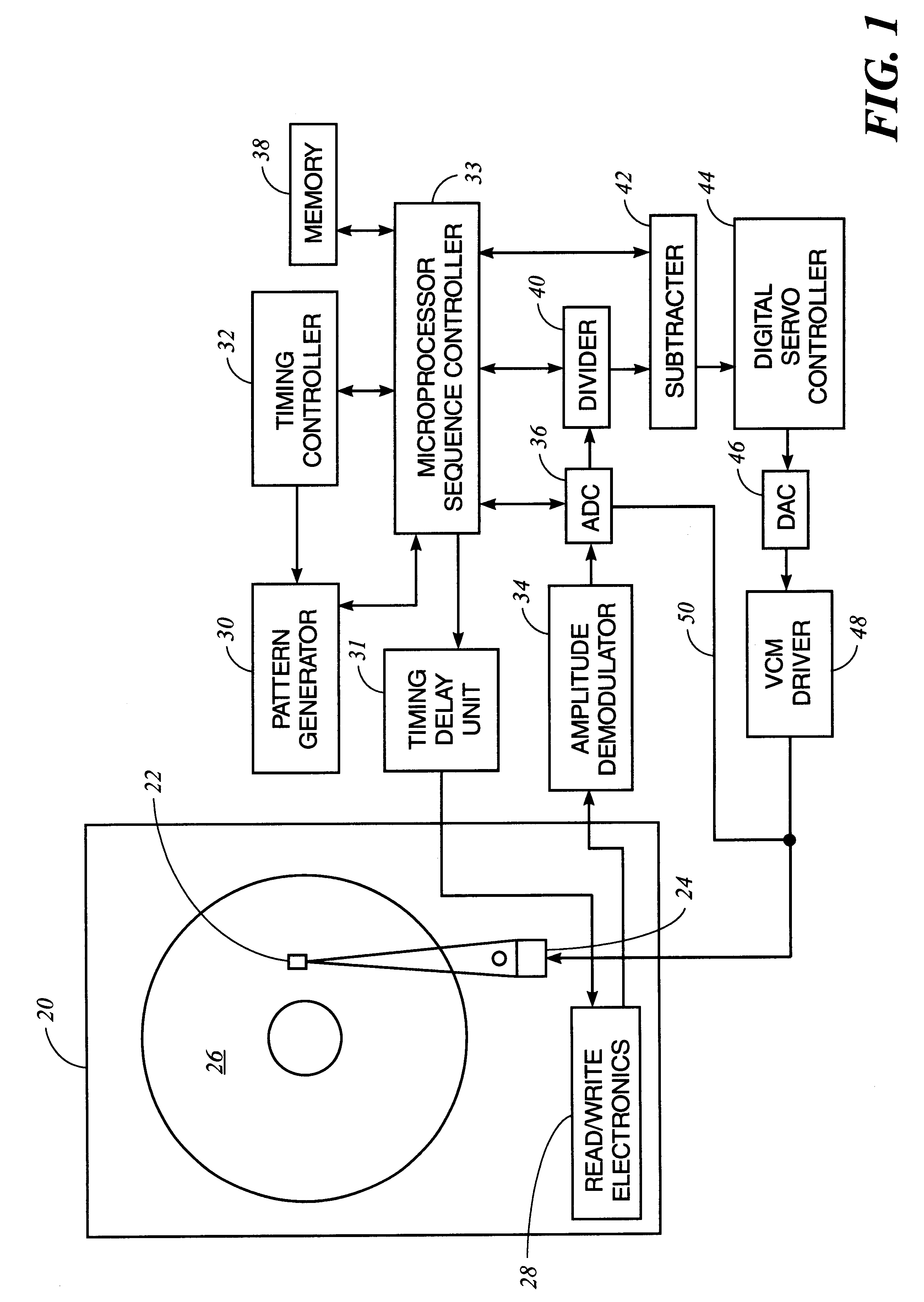
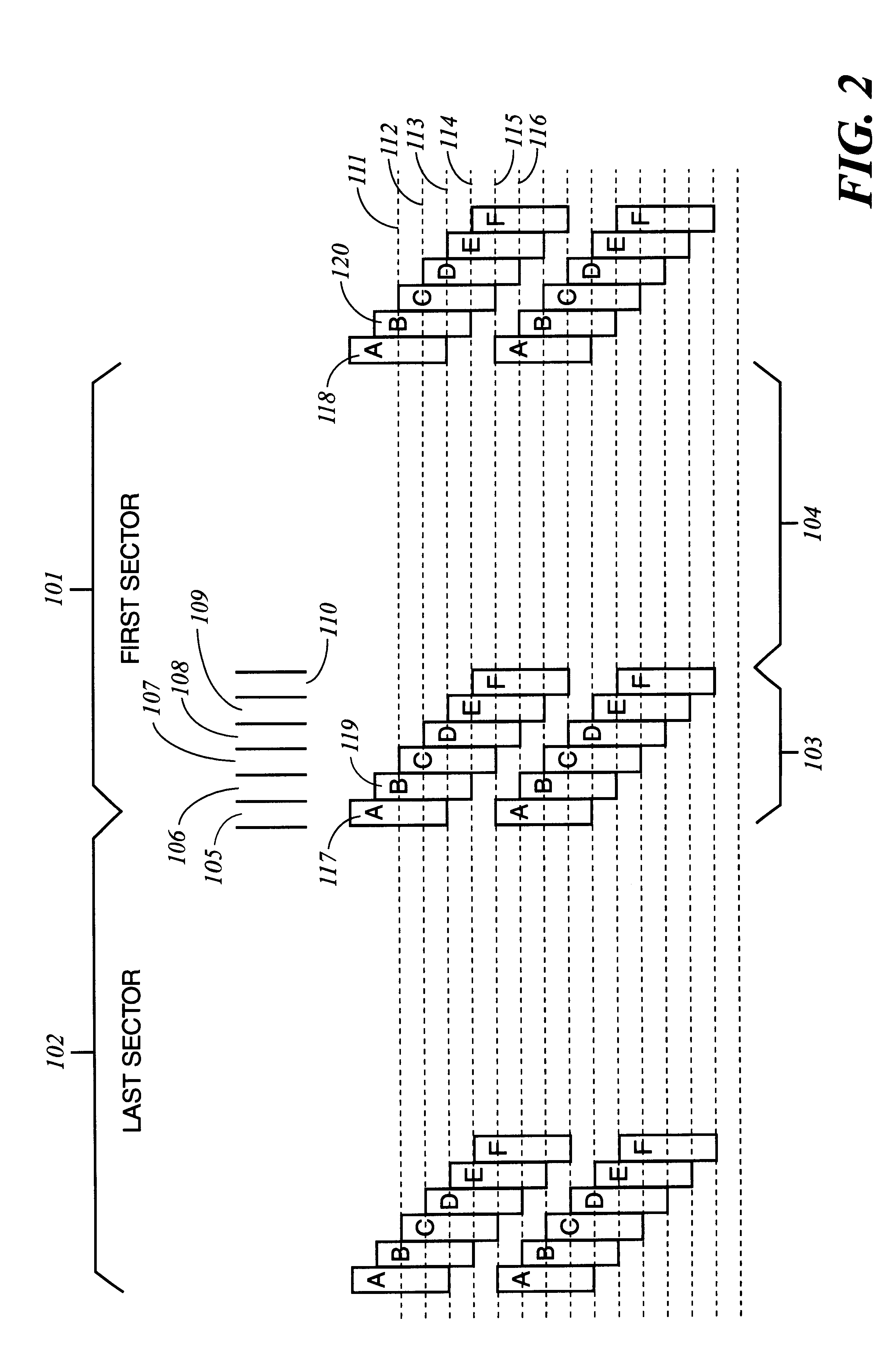
Method and apparatus for absolute track spacing determination for self-servowriting
A method and apparatus to determine and correct track spacing during self-servowriting on a rotating recording medium. The recording medium comprising a plurality of tracks, wherein each track comprises a plurality of sectors, and a transducer mounted on an actuator arm pivotally coupled to a voice coil motor (VCM). The actuator arm is positioned by a servo. The method comprising the steps of: servowriting the at least one of the plurality of sectors with a servo pattern consisting of recorded transitions. The servowriting is performed on one more tracks within the sectors where the number of tracks being servowritten is less than total number of tracks that fills the rotating medium. The transducer is positioned relative to the rotating recording medium to a preselected radial position over a previously servowritten area of the rotating recording medium that has one or more previously recorded transitions. Next, an angular acceleration is imposed on the actuator arm by applying a predetermined amount of current to the VCM. The measurement and correction of a spacing of the tracks in the previously servowritten area is performed by measuring the amplitudes of the previously recorded transitions at least one time during the passage of the sectors beneath the transducer, and if the calibratng of the spacing is outside a predetermined tolerance, then continuing servowriting new recorded transitions using said adjustment factor on tracks following said previously servowritten area. In one embodiment, the method includes measuring a VCM torque constant (K) by applying a current impulse for a predetermined time (t) and measuring the back Electromotive Force (EMF) generated from the VCM to determine the torque per unit for the current impulse for the predetermined time (t) and to determine the back Electronic Force (EMF) per unit of angular velocity of the actuator arm. After the torque constant is determined, an adjustment factor is computed based on the values of the torque constant (K), the current impulse for the period of time (t), and the back Electromotive Force (EMF)per unit of angular velocity of the actuator arm. This adjustment factor is used while servowriting now recorded transitions tacks following the previously servowritten area.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
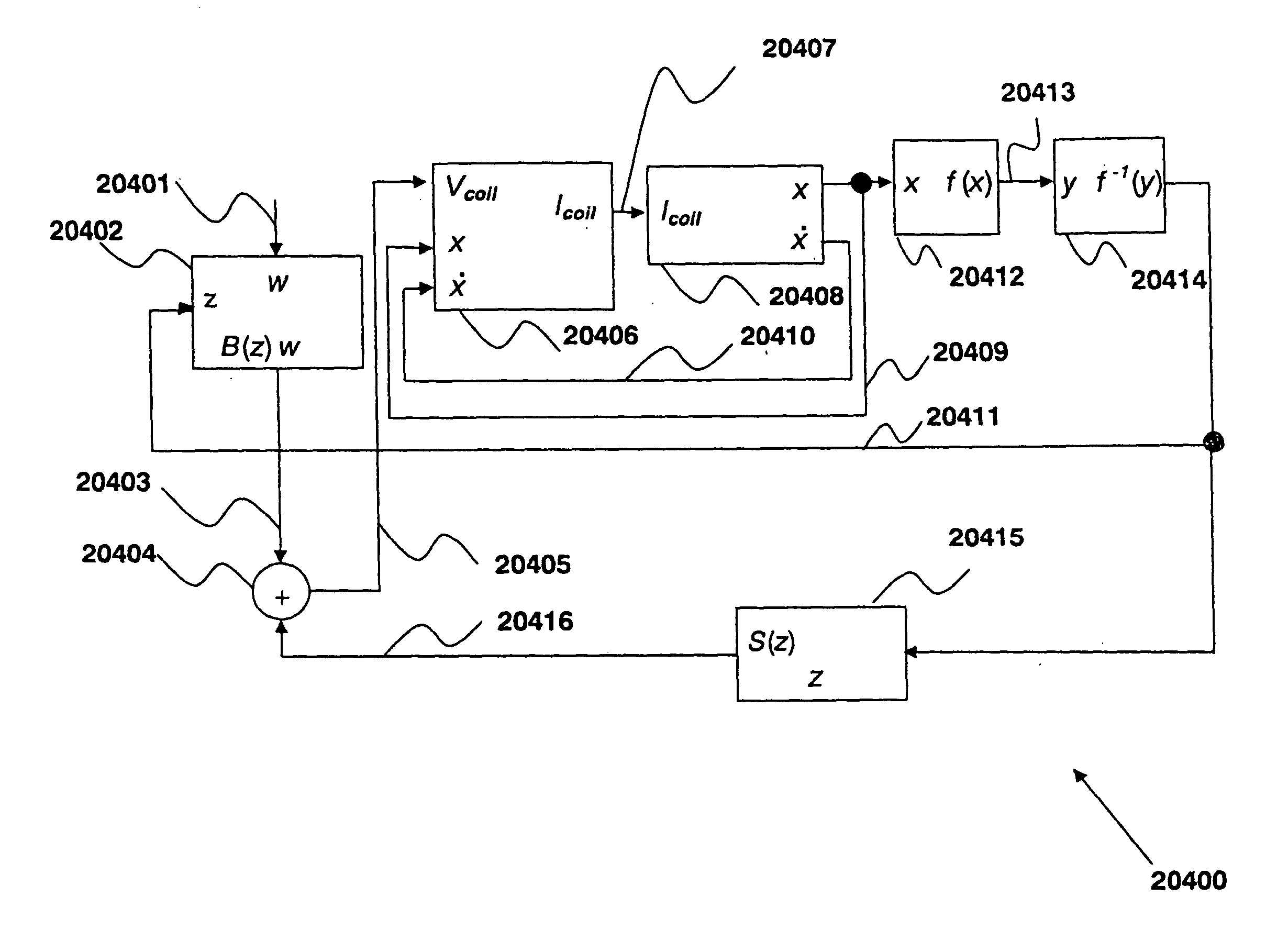
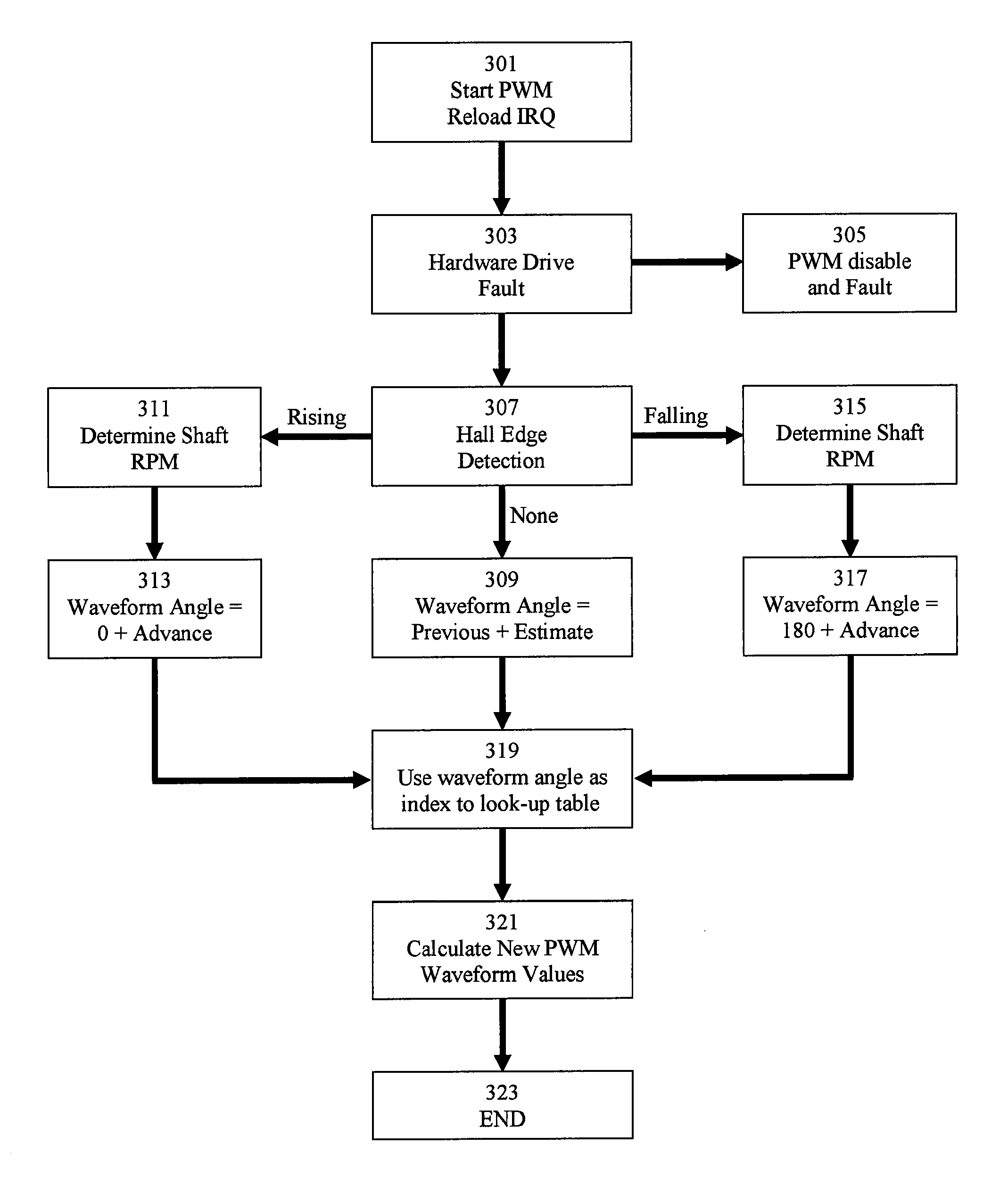
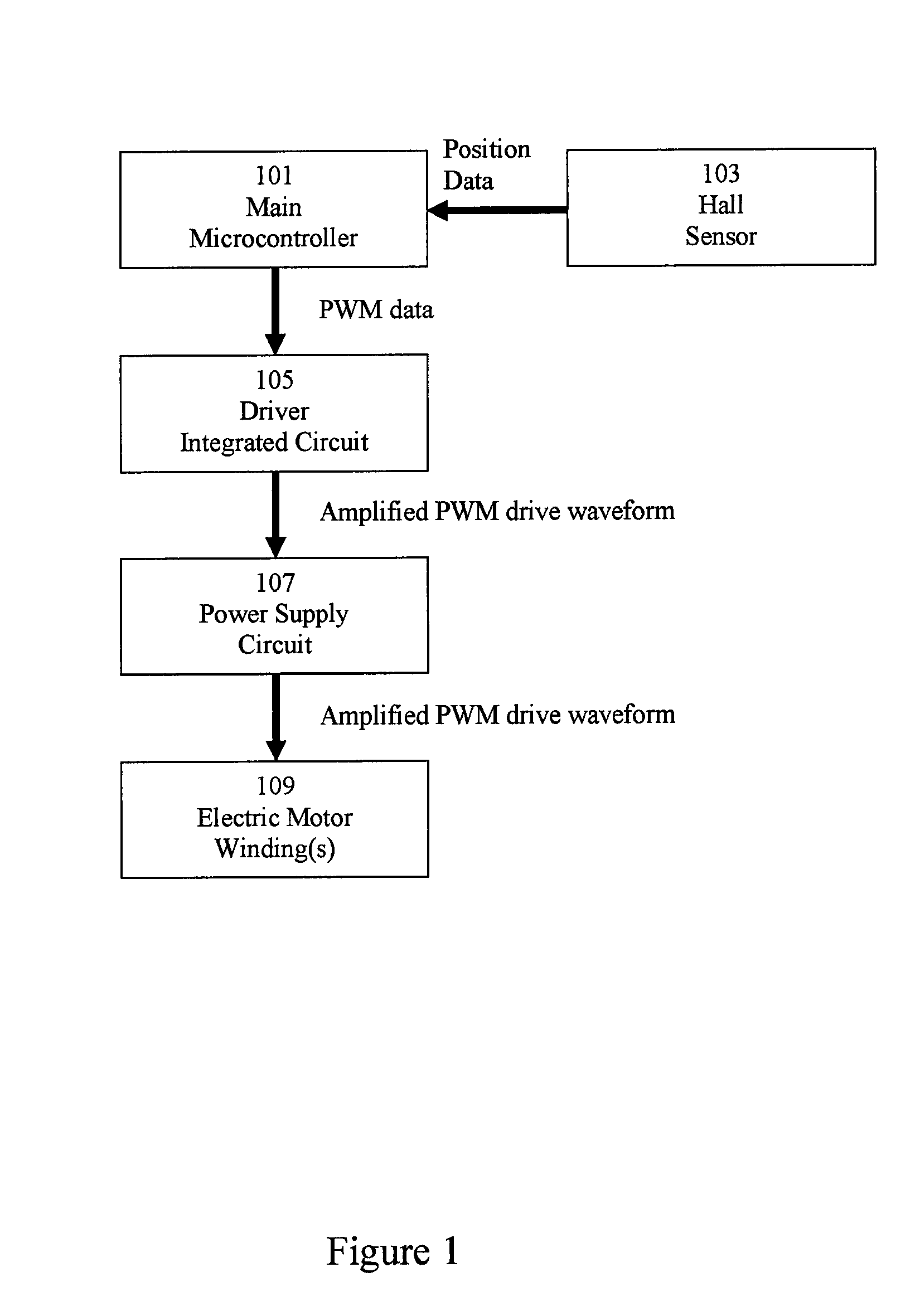
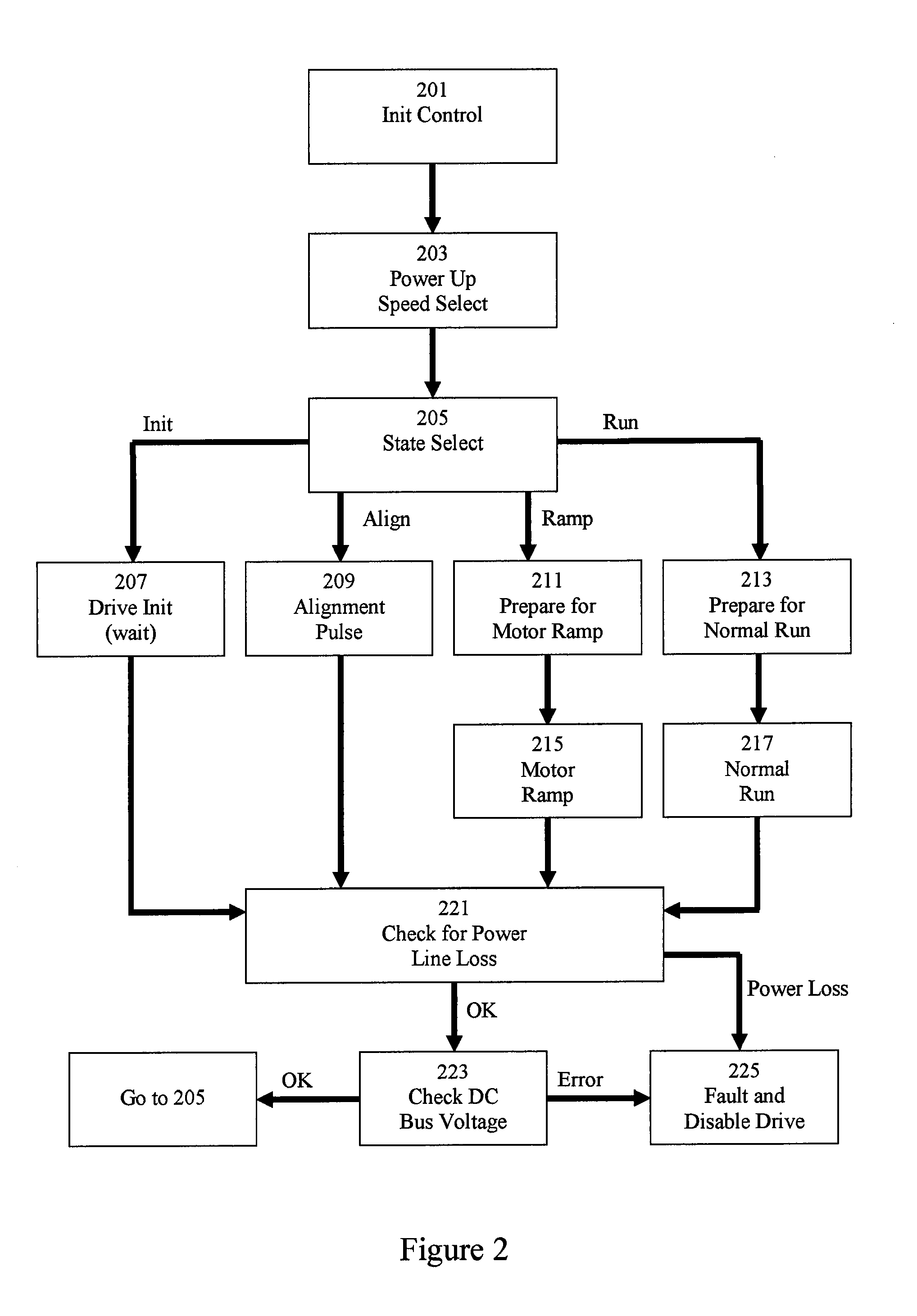
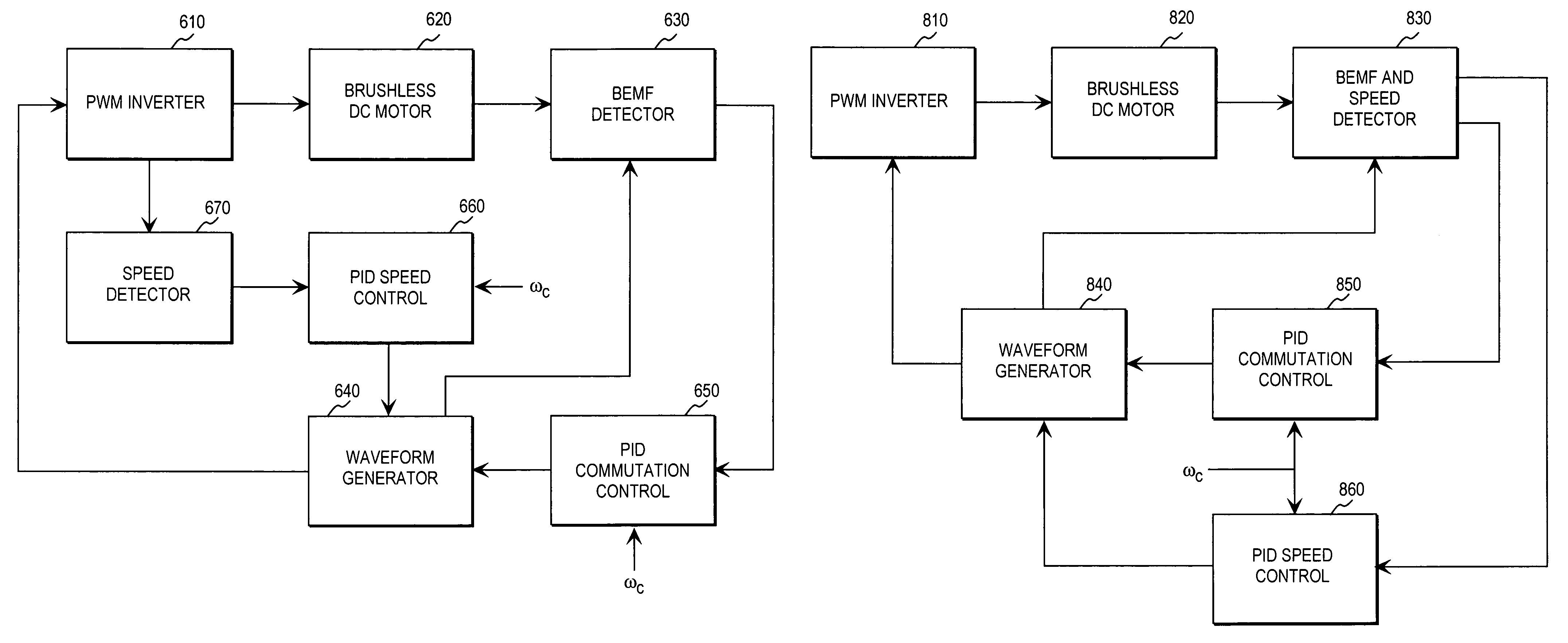
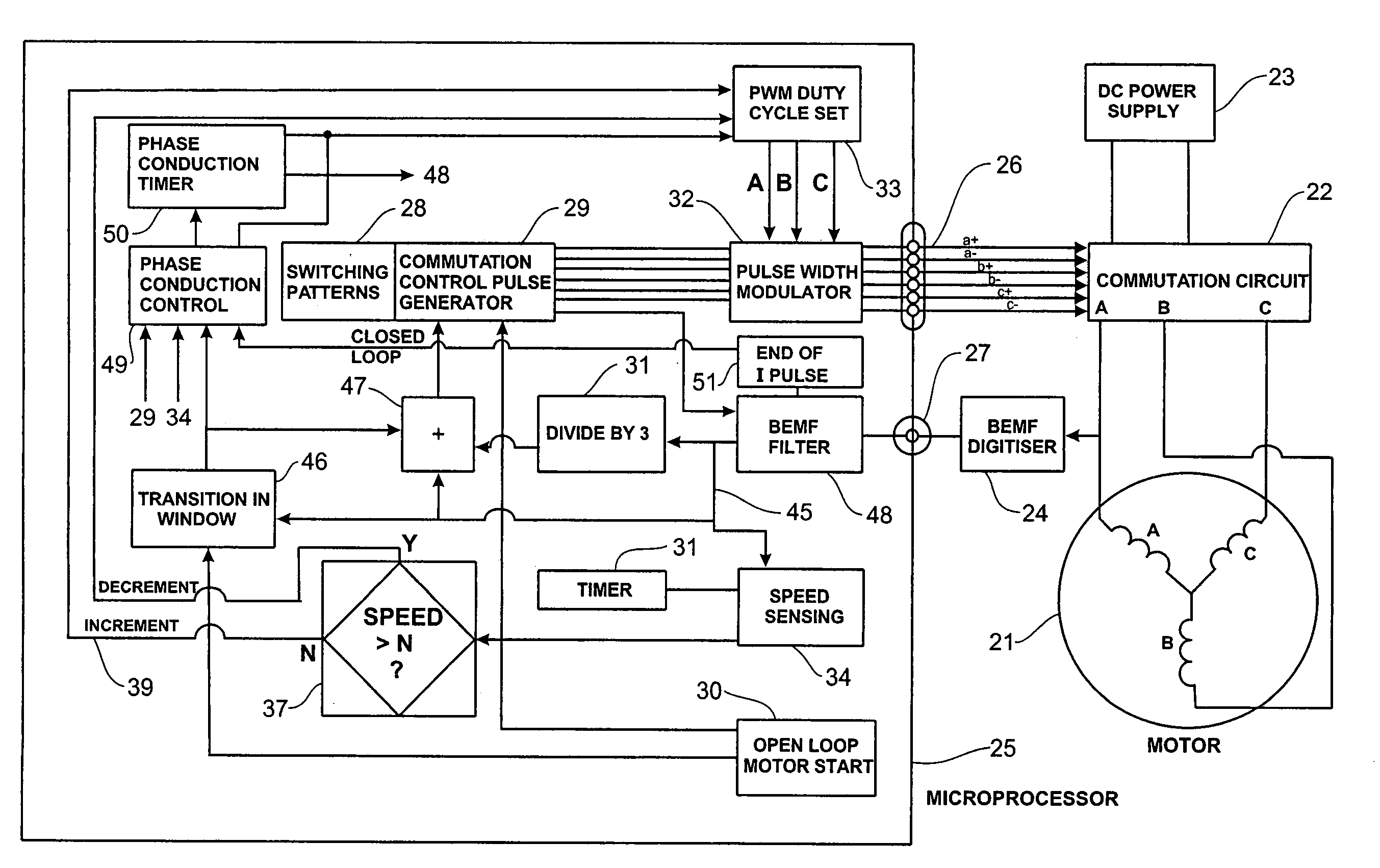
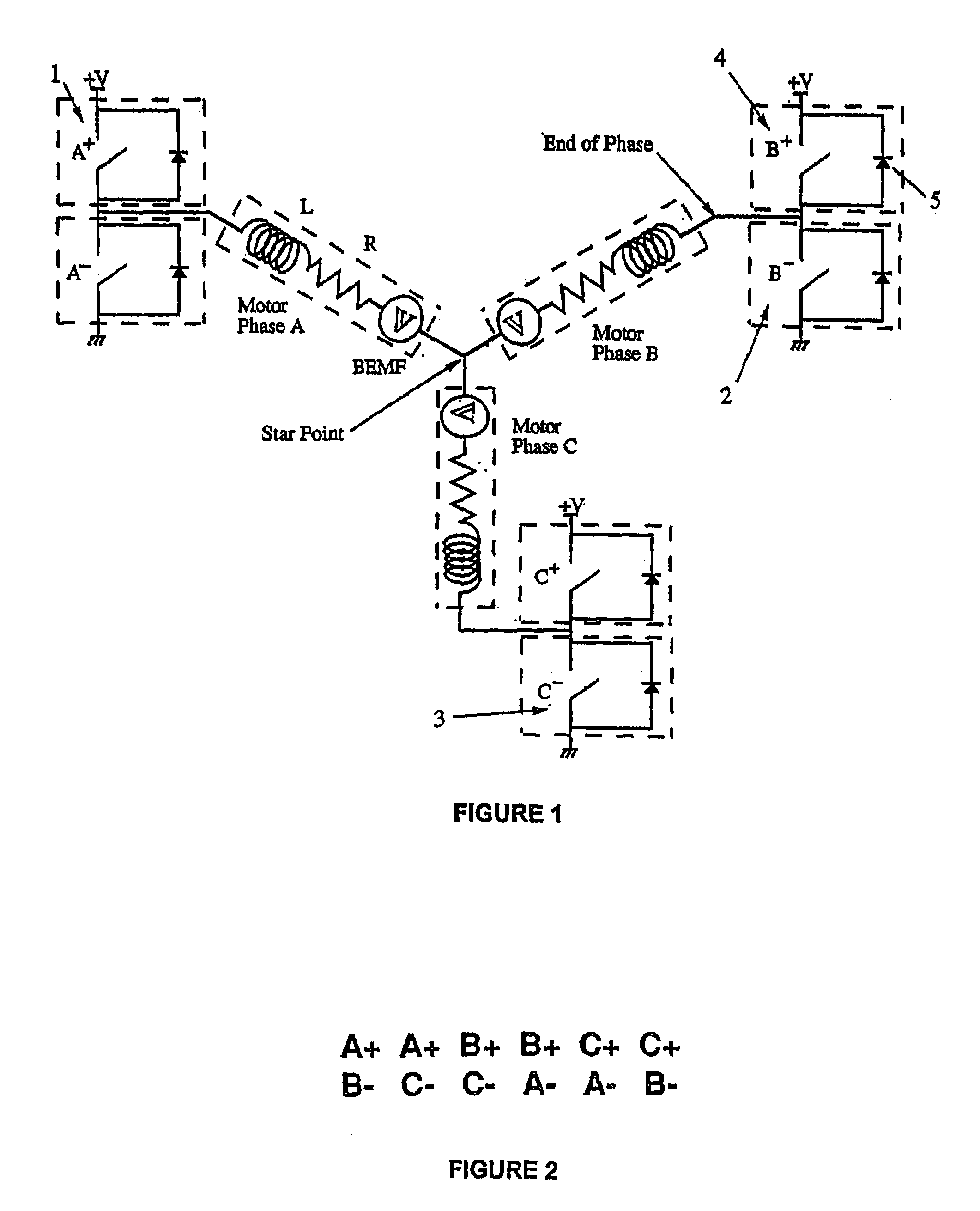
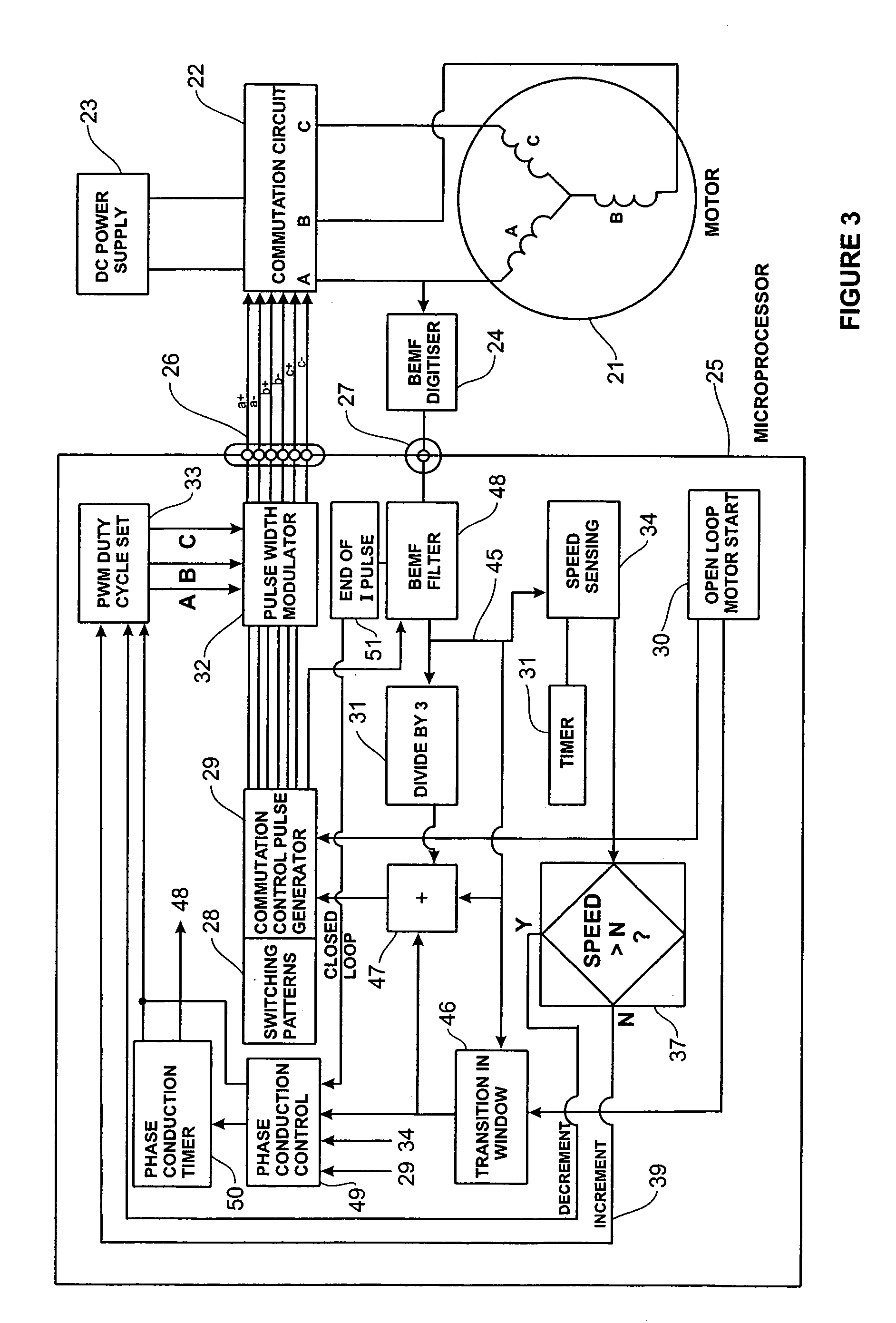
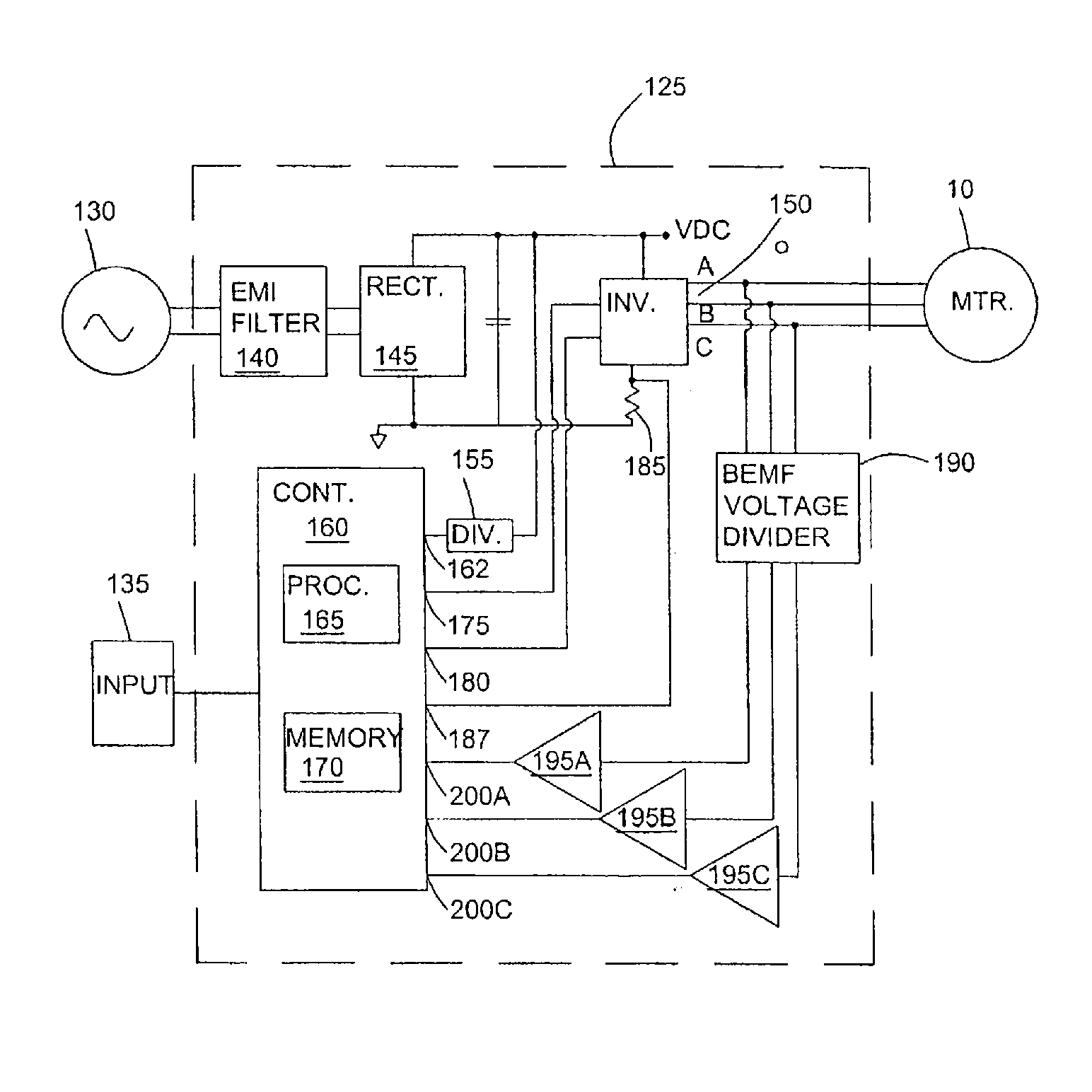
System and method for commutating a motor using back electromotive force signals
ActiveUS7477034B2Programme-controlled manipulatorDC motor speed/torque controlElectric machineEngineering
Owner:ALLIED MOTION CANADA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com