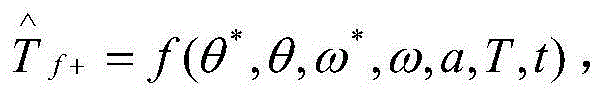Patents
Literature
111 results about "Torque constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
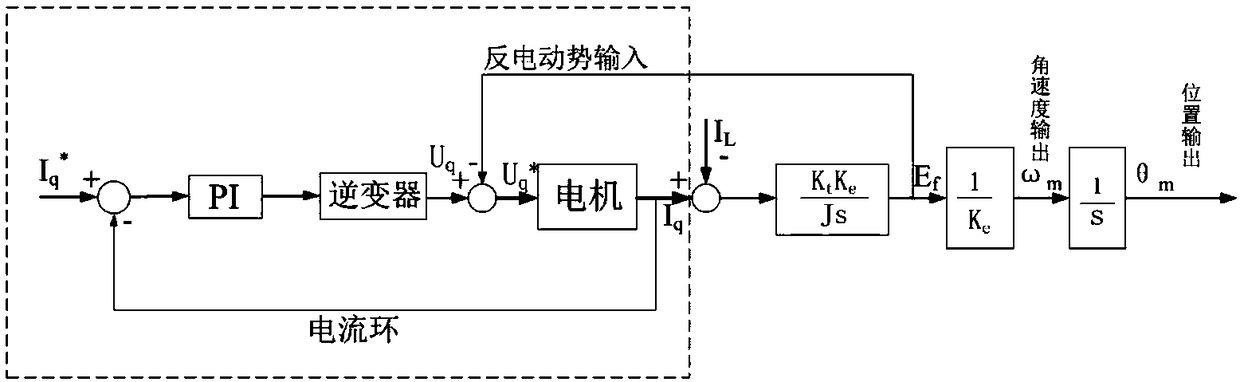
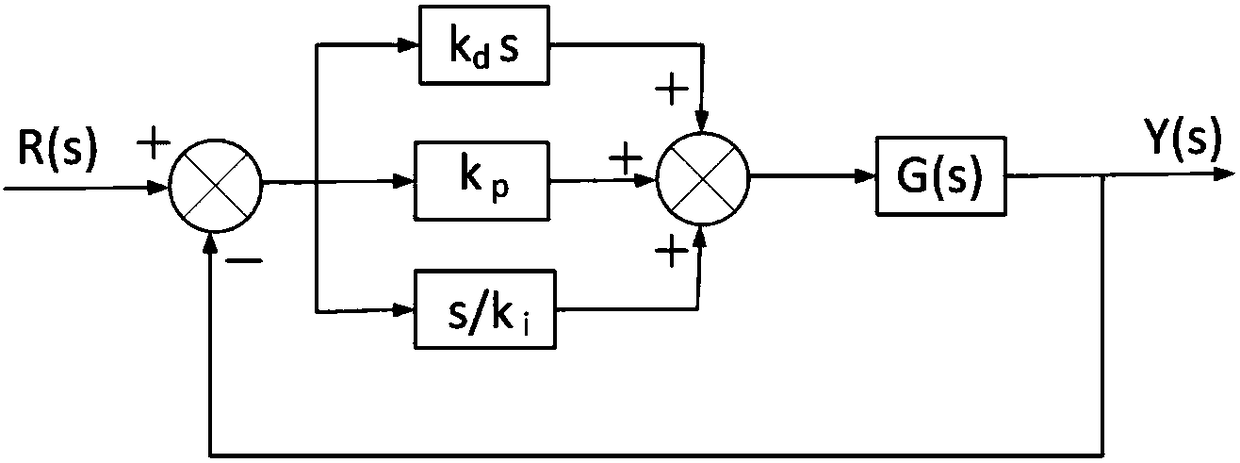
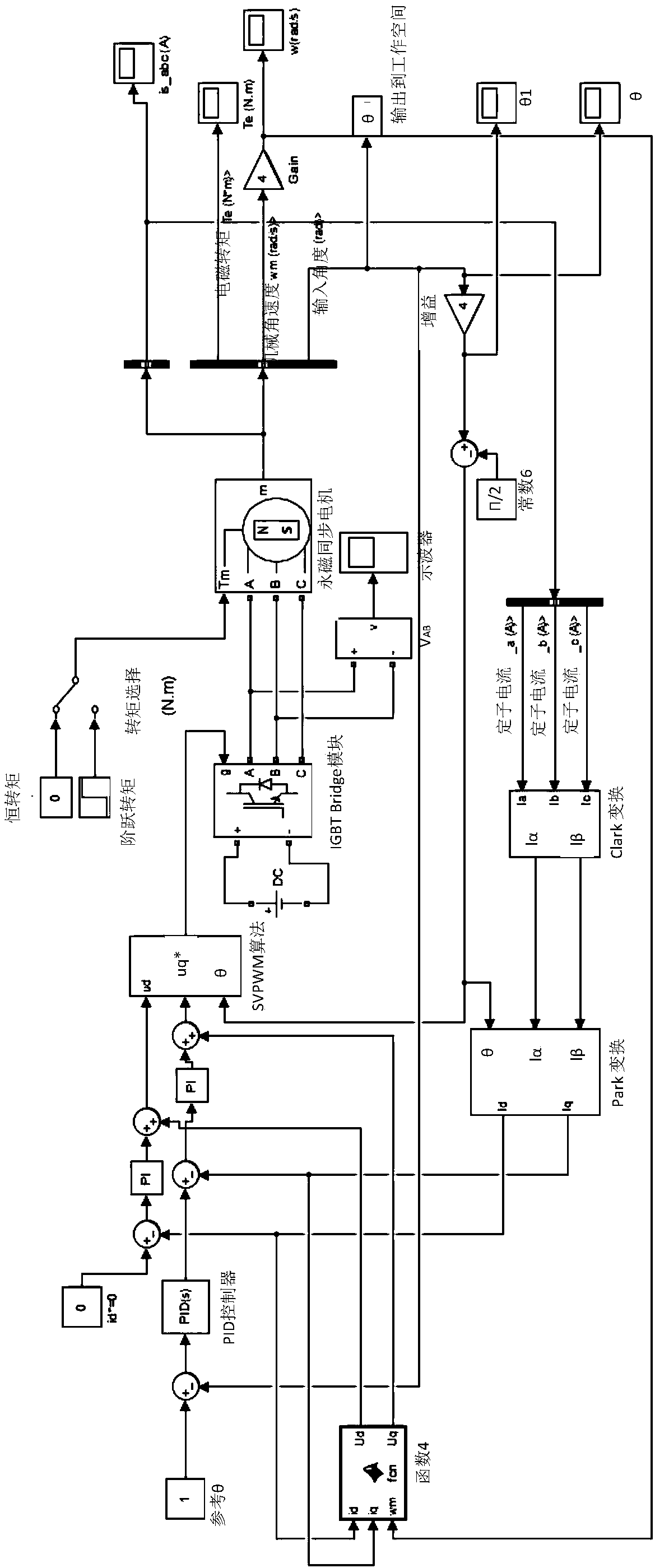
Motor torque constant is just the motor torque divided by the armature current. This figure is usually used to determine the armature current of a motor at a particular torque. This can be obtained from the slope of a torque-current curve of a motor.
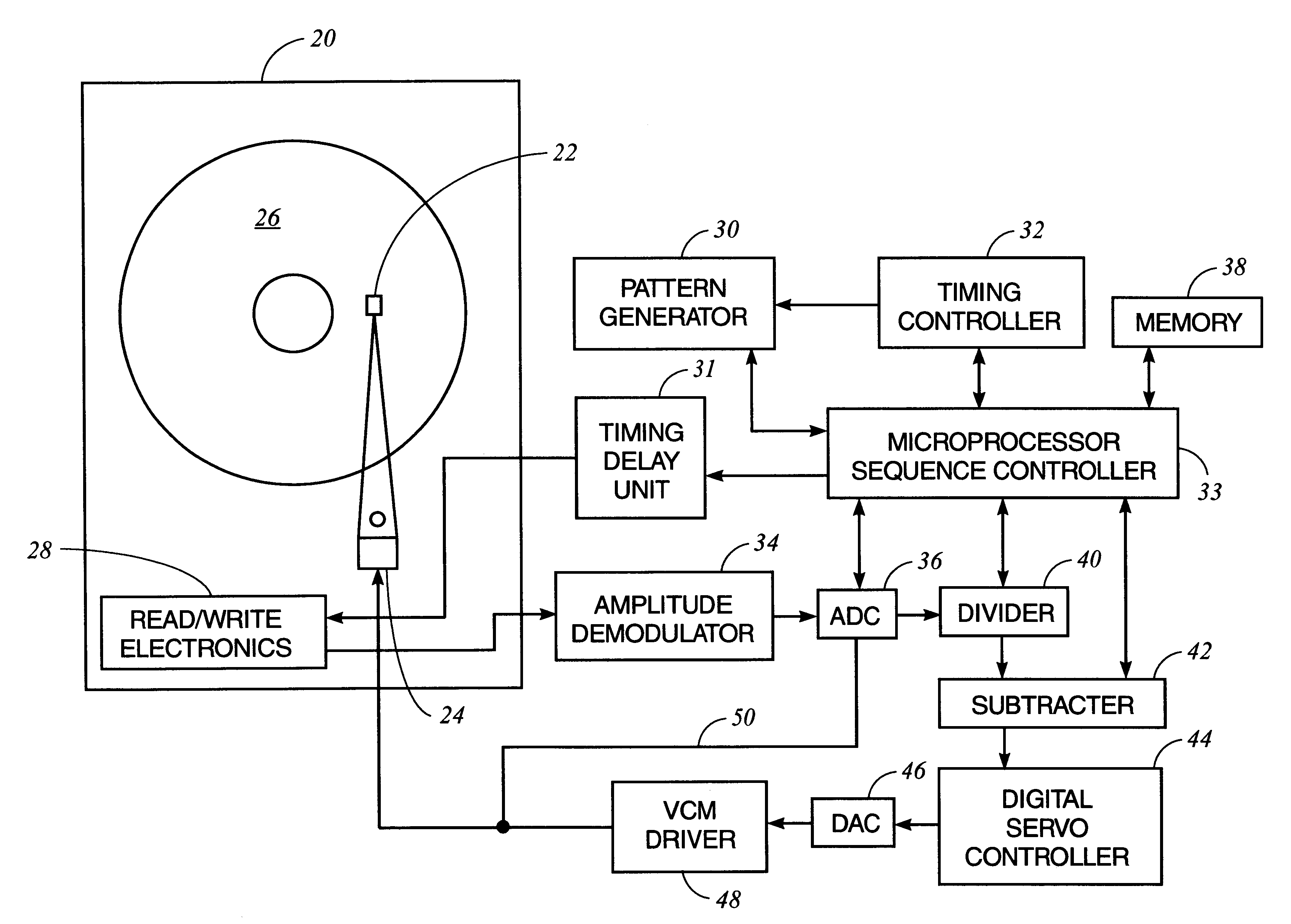
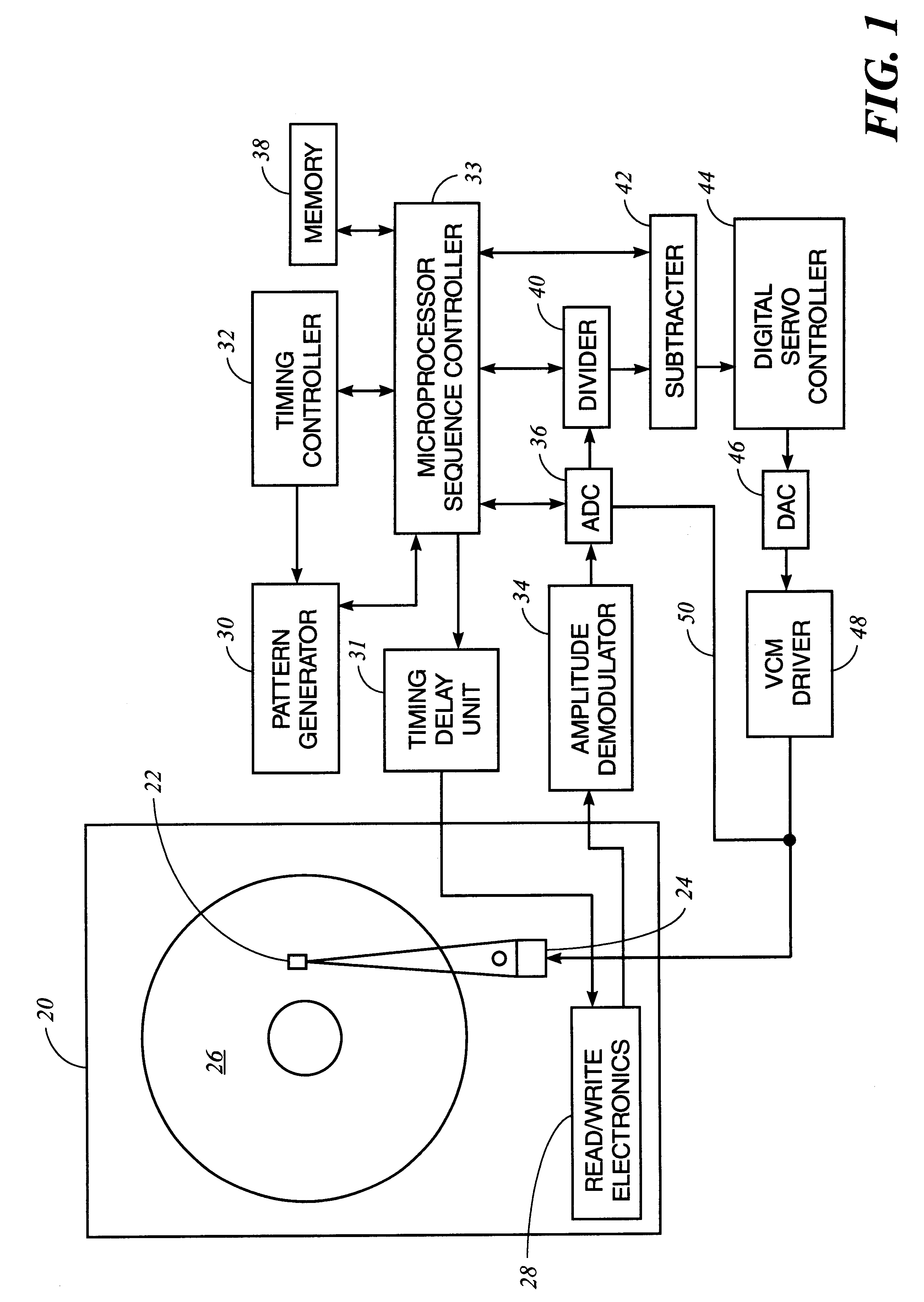
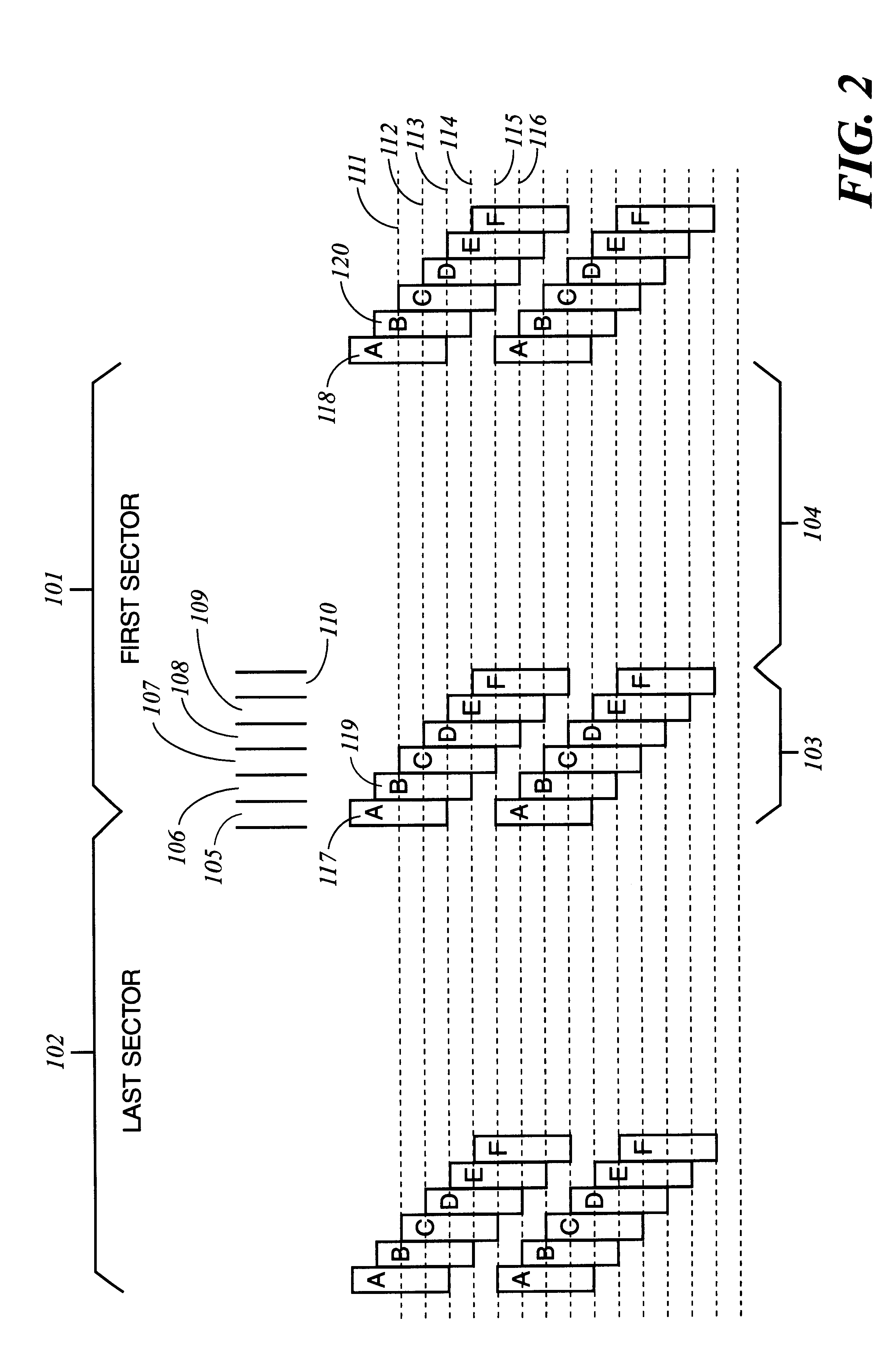
Method and apparatus for absolute track spacing determination for self-servowriting
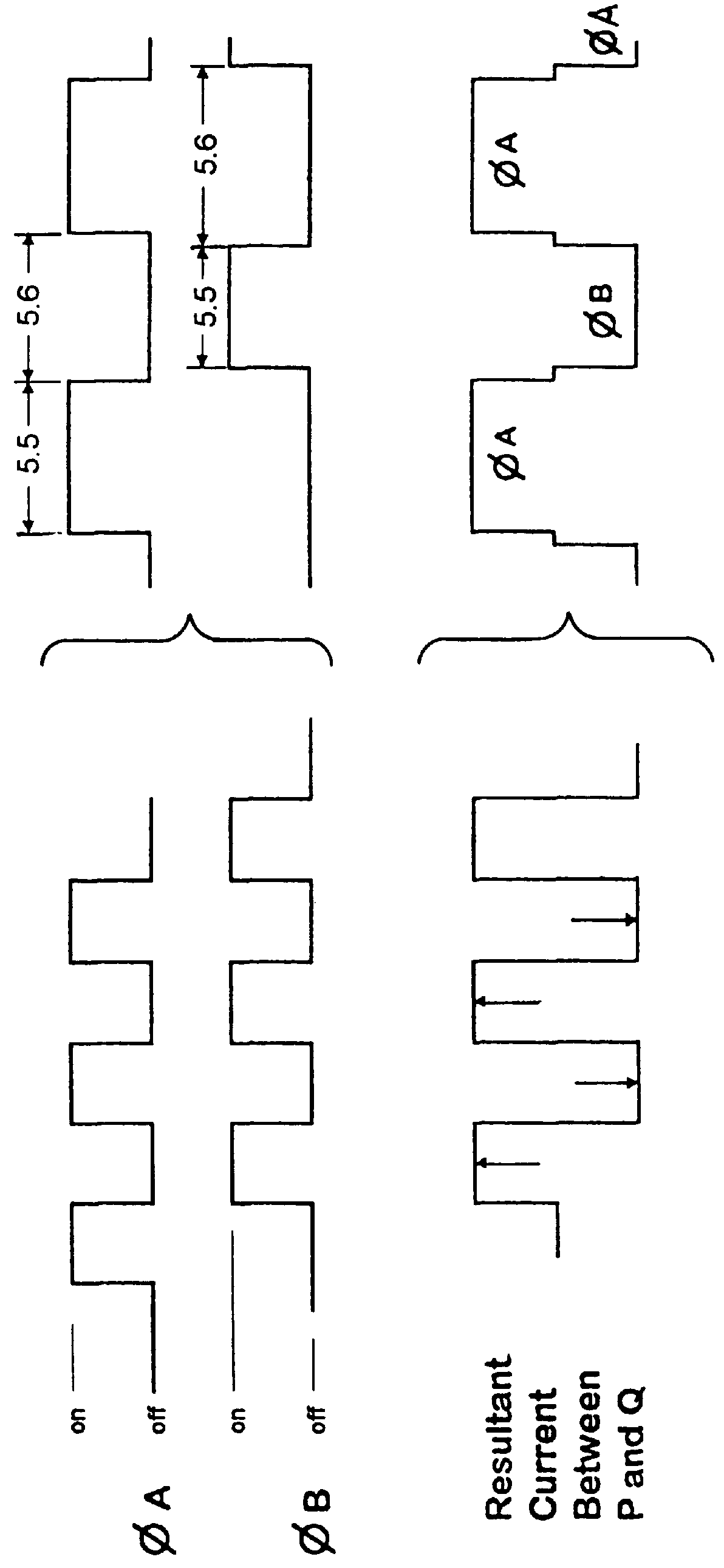
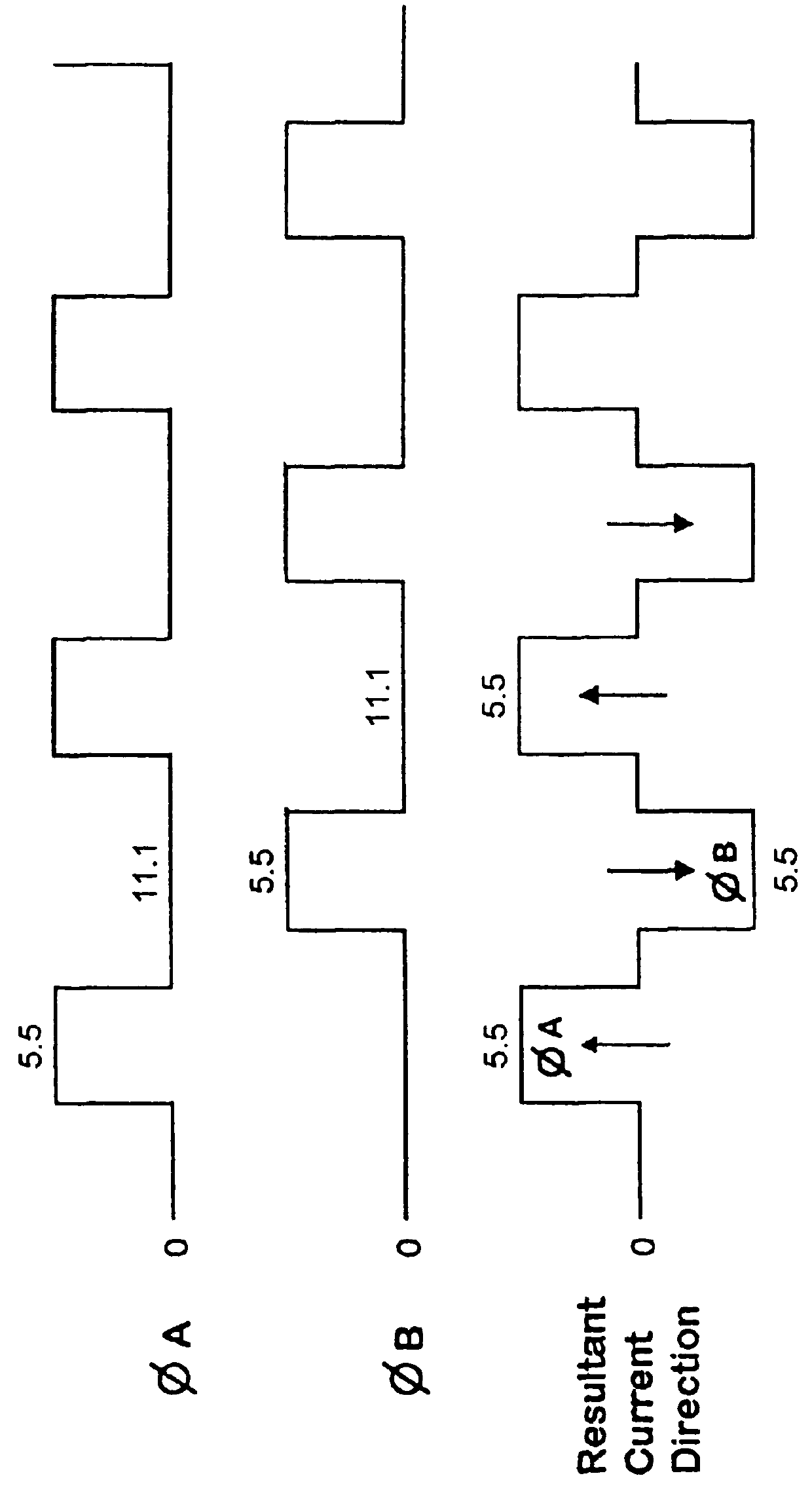
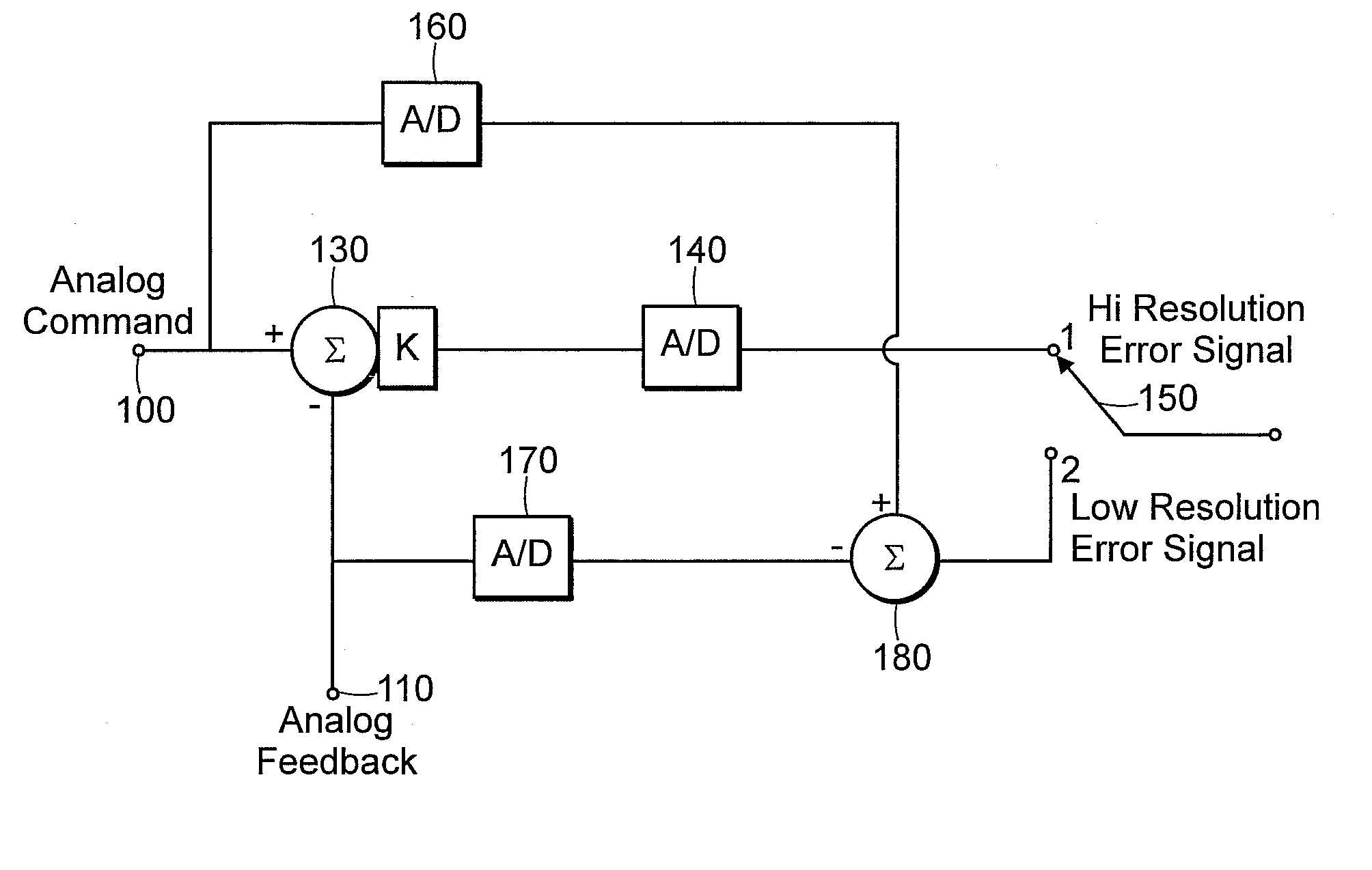
A method and apparatus to determine and correct track spacing during self-servowriting on a rotating recording medium. The recording medium comprising a plurality of tracks, wherein each track comprises a plurality of sectors, and a transducer mounted on an actuator arm pivotally coupled to a voice coil motor (VCM). The actuator arm is positioned by a servo. The method comprising the steps of: servowriting the at least one of the plurality of sectors with a servo pattern consisting of recorded transitions. The servowriting is performed on one more tracks within the sectors where the number of tracks being servowritten is less than total number of tracks that fills the rotating medium. The transducer is positioned relative to the rotating recording medium to a preselected radial position over a previously servowritten area of the rotating recording medium that has one or more previously recorded transitions. Next, an angular acceleration is imposed on the actuator arm by applying a predetermined amount of current to the VCM. The measurement and correction of a spacing of the tracks in the previously servowritten area is performed by measuring the amplitudes of the previously recorded transitions at least one time during the passage of the sectors beneath the transducer, and if the calibratng of the spacing is outside a predetermined tolerance, then continuing servowriting new recorded transitions using said adjustment factor on tracks following said previously servowritten area. In one embodiment, the method includes measuring a VCM torque constant (K) by applying a current impulse for a predetermined time (t) and measuring the back Electromotive Force (EMF) generated from the VCM to determine the torque per unit for the current impulse for the predetermined time (t) and to determine the back Electronic Force (EMF) per unit of angular velocity of the actuator arm. After the torque constant is determined, an adjustment factor is computed based on the values of the torque constant (K), the current impulse for the period of time (t), and the back Electromotive Force (EMF)per unit of angular velocity of the actuator arm. This adjustment factor is used while servowriting now recorded transitions tacks following the previously servowritten area.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
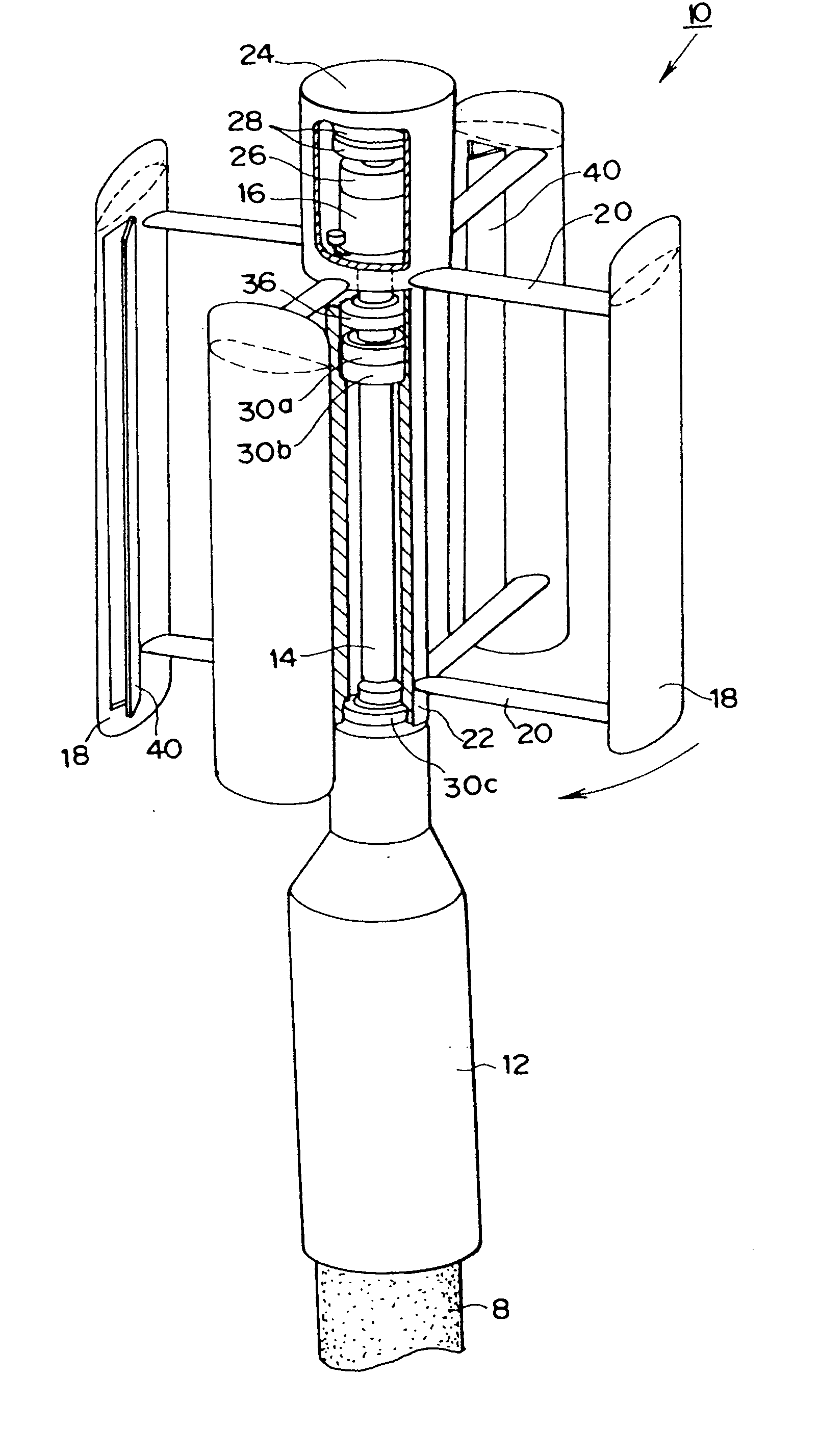
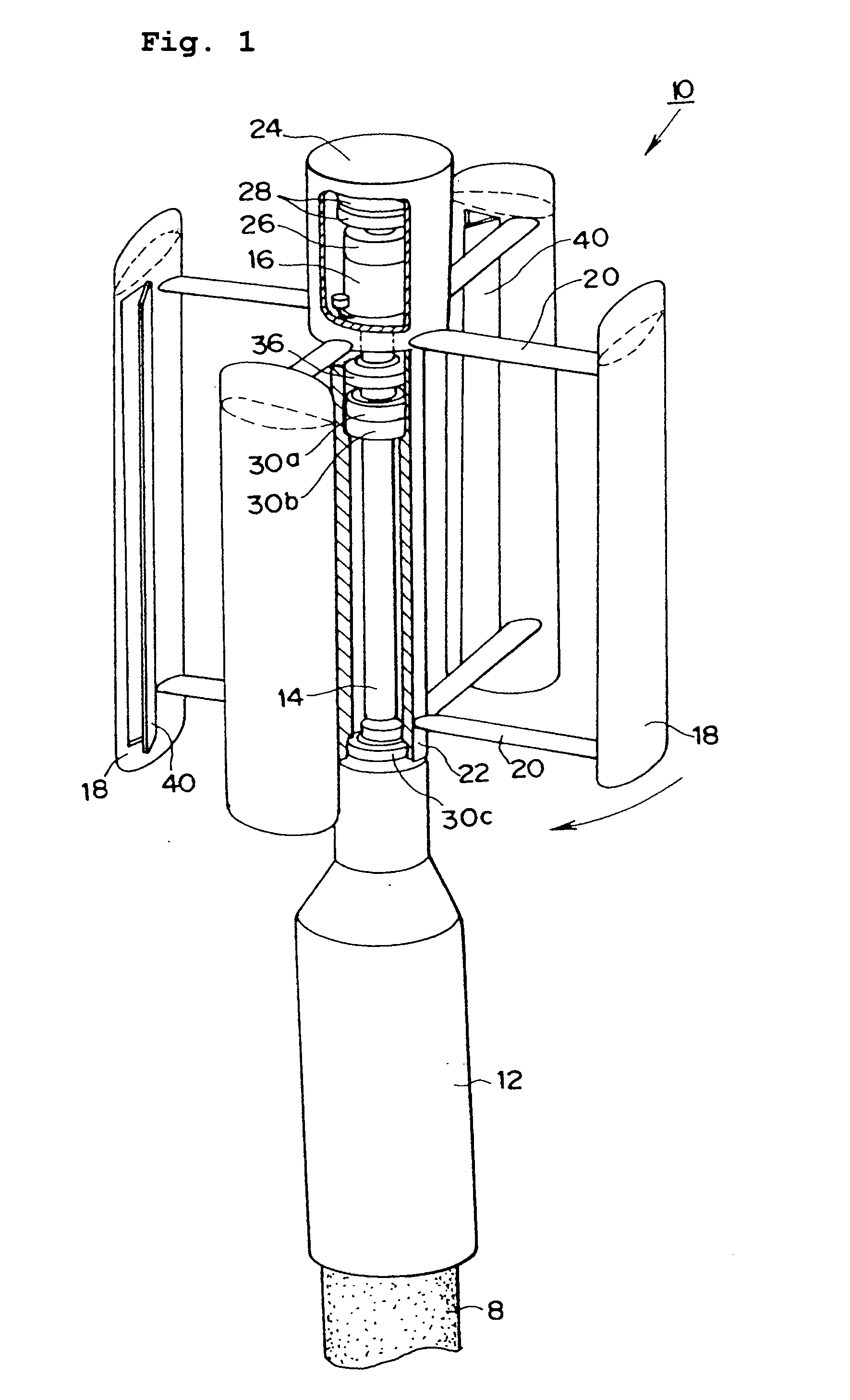
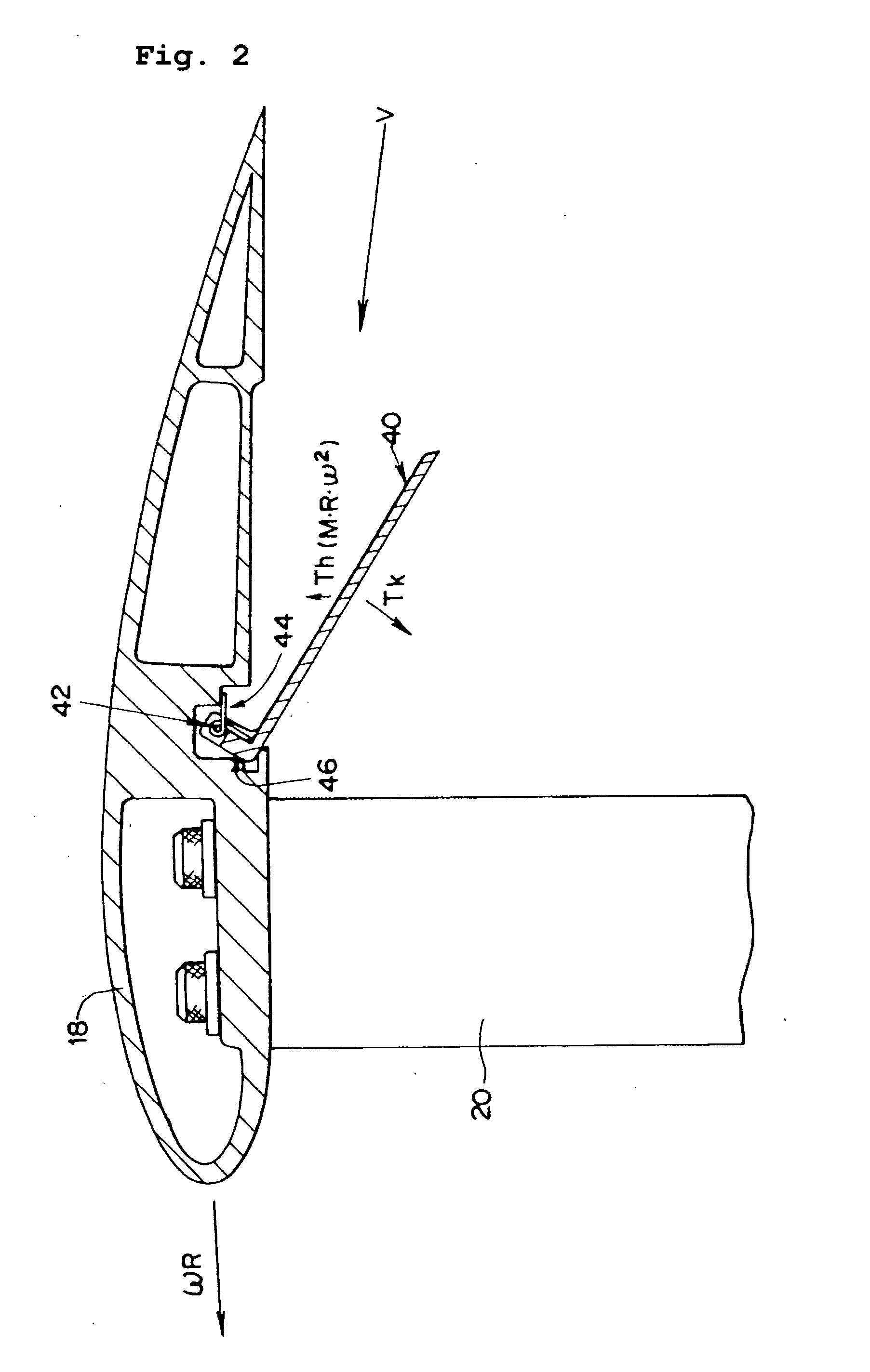
Vertical axis wind turbine and wind turbine blade
InactiveUS20070177970A1Improve lifting performanceImprove startup performanceWind motor controlMachines/enginesTurbine bladeVertical axis wind turbine
It is an object of the invention is to provide a vertical axis wind turbine and a wind turbine blade, which are excellent in self-starting performance and have a high torque constant. Since the present invention comprises a wind receiving plate 40 having a wind receiving surface and an openable and closable pivot 42, which wind receiving plate 40 is operated to close in the direction in which the centrifugal force is produced in proportion to the revolution of a blade 18 generating a lifting power, and an energizing means (such as spring 44) for energizing an opening force to open the wind receiving plate to the wind receiving side, the starting performance of the lift type wind turbine can be improved by means of the wind receiving plate 40, which opens at a low revolution of the blade 18 so as to function as a drag type wind turbine, and automatically closes at a high revolution of the blade 18 so as to function as a lift type wind turbine.
Owner:INTPROP BANK CORP (JP)
Mixed field excitation type flux switch motor
InactiveCN101277053AImprove robustnessSuitable for high speed operationSynchronous machinesElectric machineExcitation current
The present invention provides a hybrid field excitation flux switching electric motor. On one hand, a stator part adopts a centralized armature winding, an exciting winding, a straight channel rotor, and a permanent magnet arranged in the stator. On the other hand, the rotor part is a salient pole and is not provided with a permanent magnet or a winding. The structure is extraordinary simple and durable. The electromagnetic capability of four centralized armature coils which are designed to form a single-phase armature winding is controlled by the corresponding exciting winding coil through the exciting current. On structure, the advantages of compactness, simpleness, good robustness and suitability for operation with high speed of the permanent magnet flux switching electric motor are kept. The function of hybrid field excitation can be realized without additionally adding the volume of the electric motor. The electric motor is guaranteed to have stronger torque output capability and higher power density. The electric motor is especially suitable for the application occasion with high volume and large output. The functions of large torque in torque-constant area and broad velocity modulation in power-constant area can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
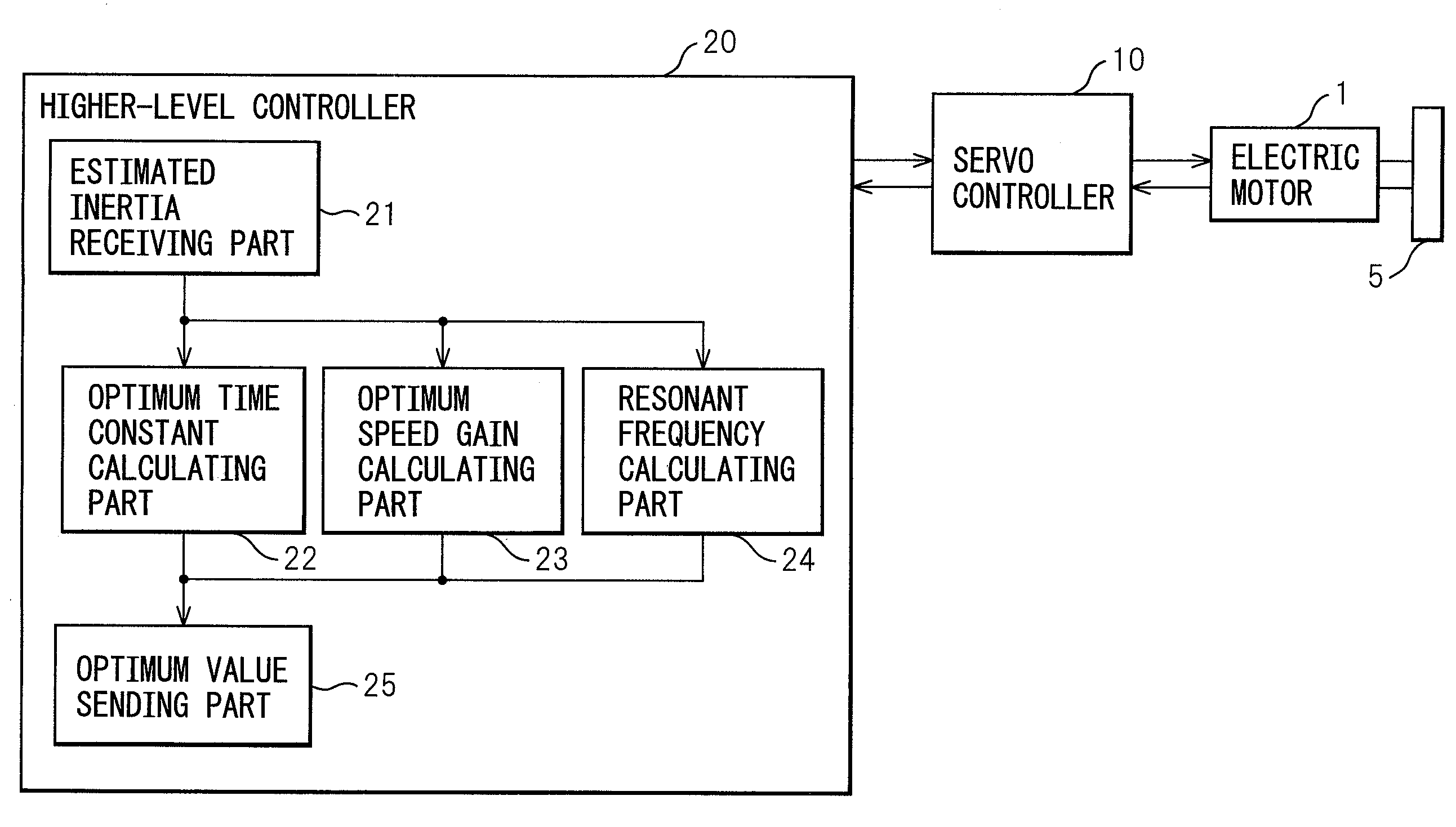
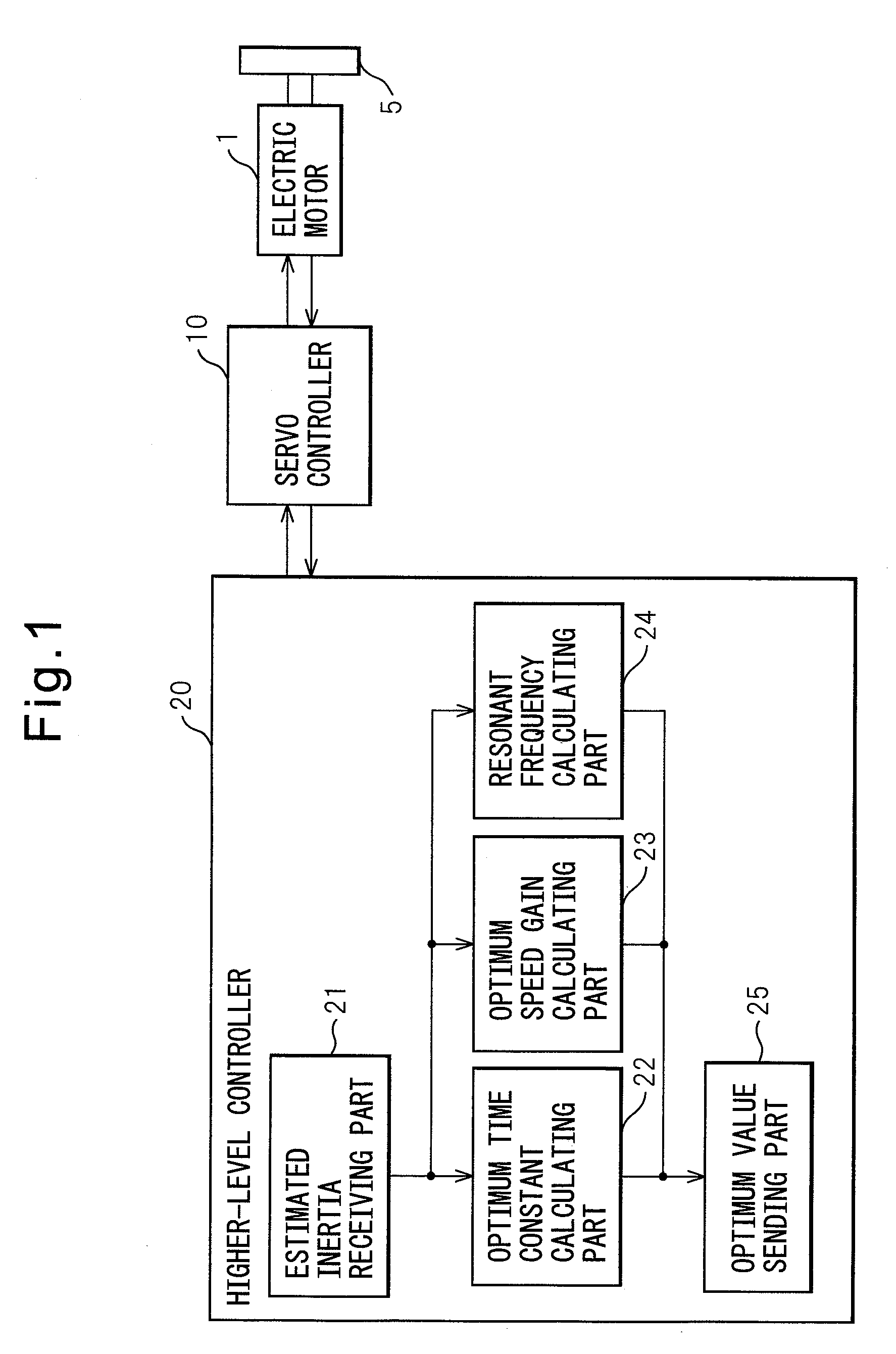
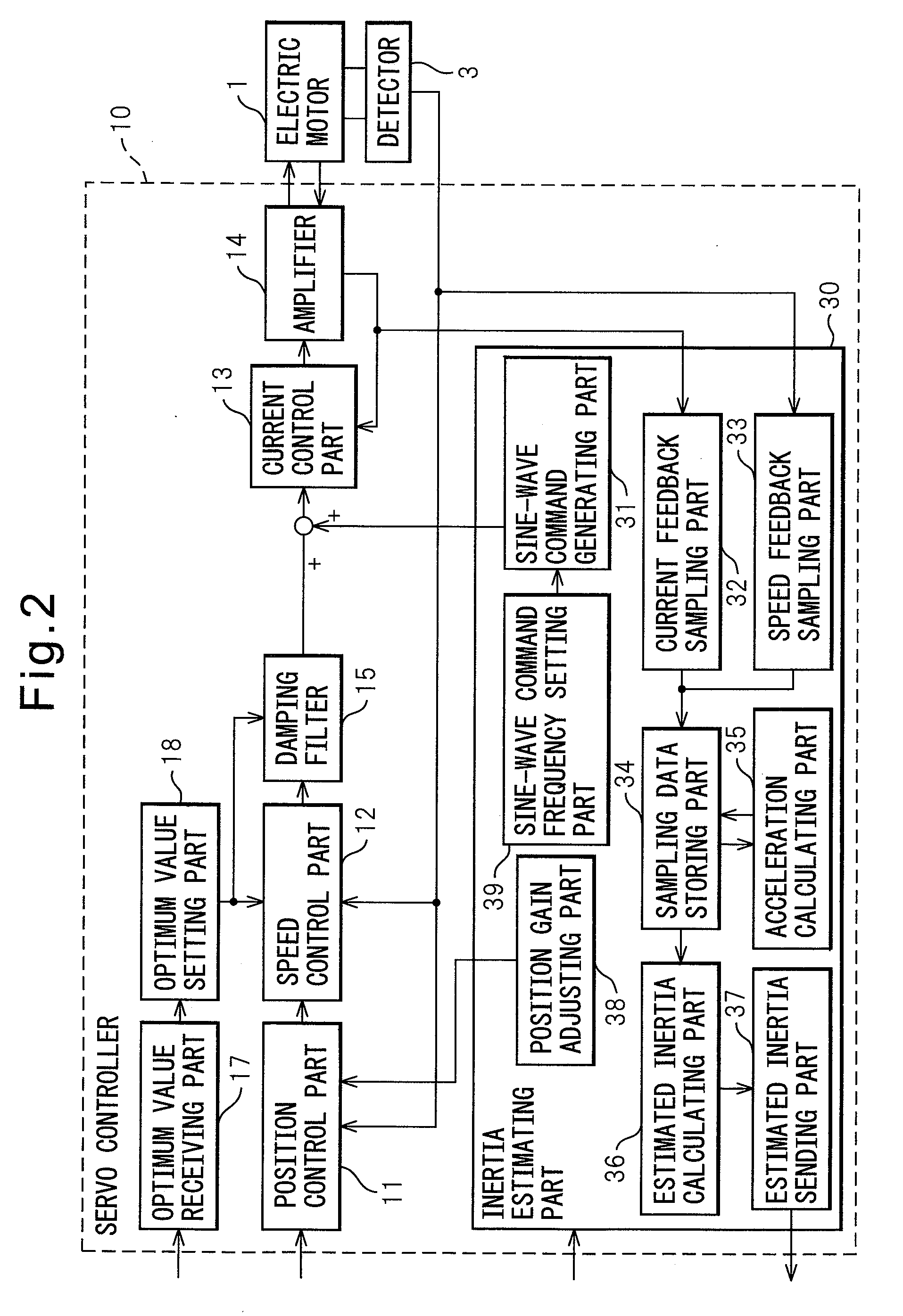
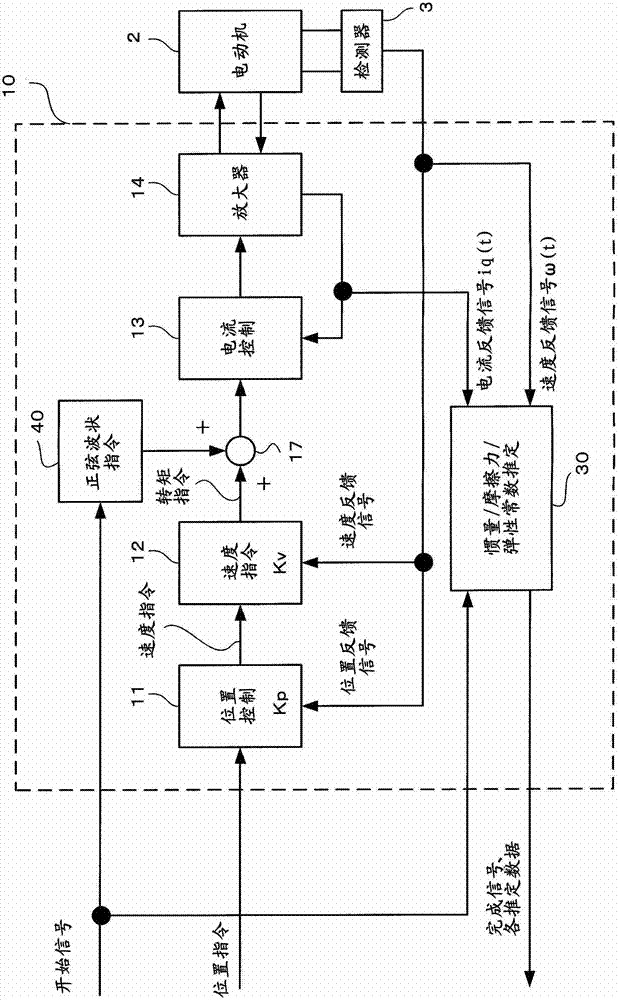
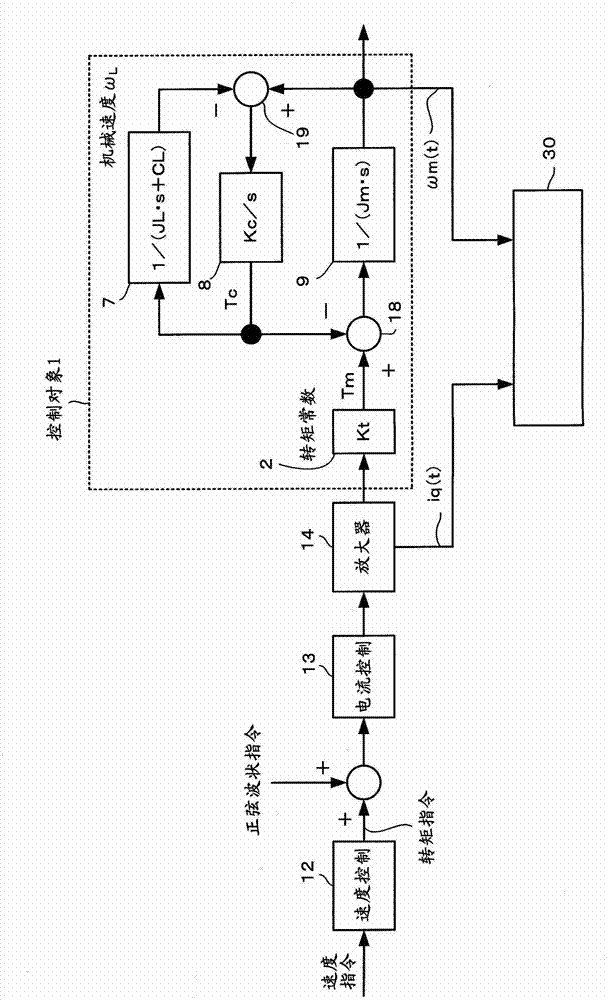
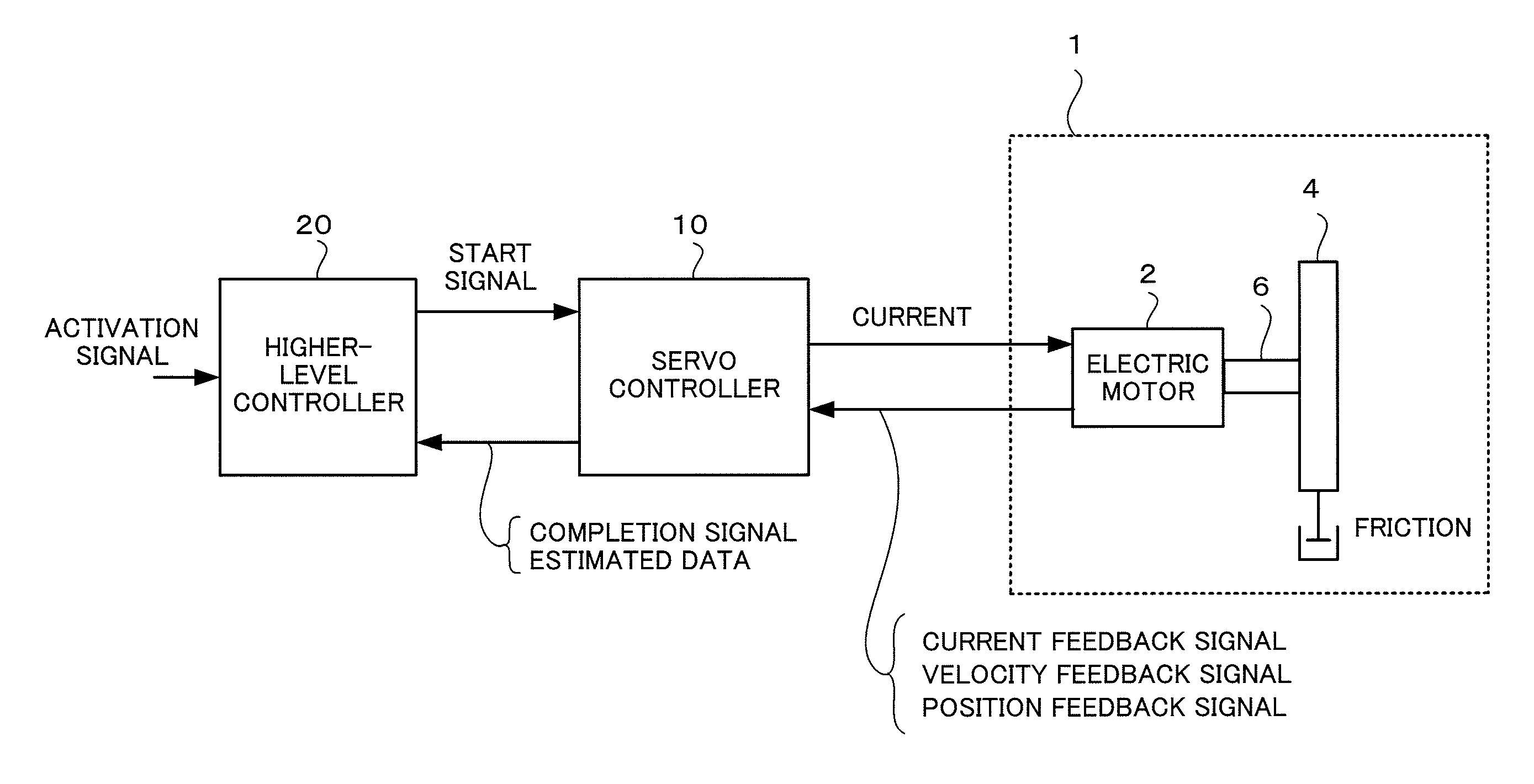
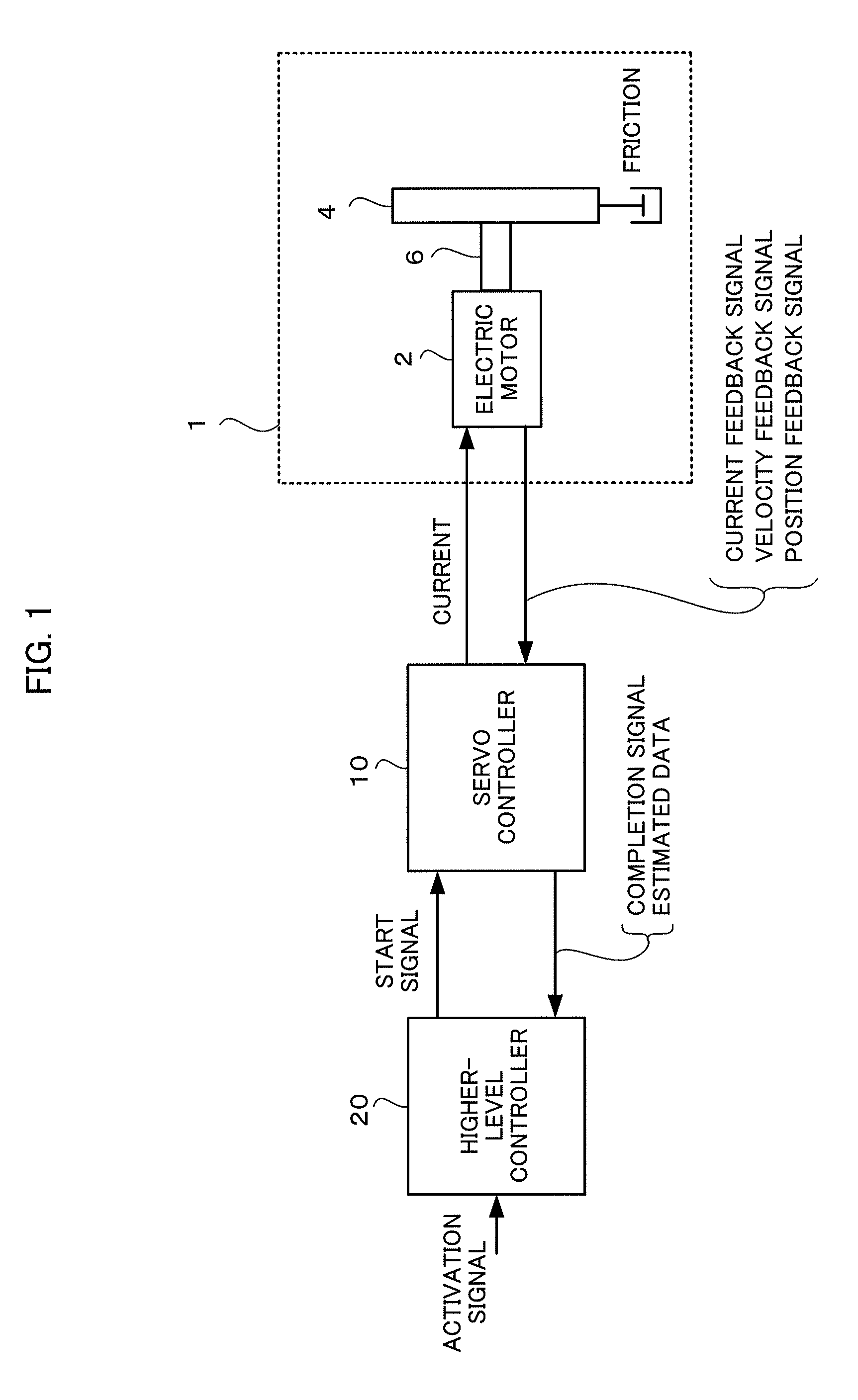
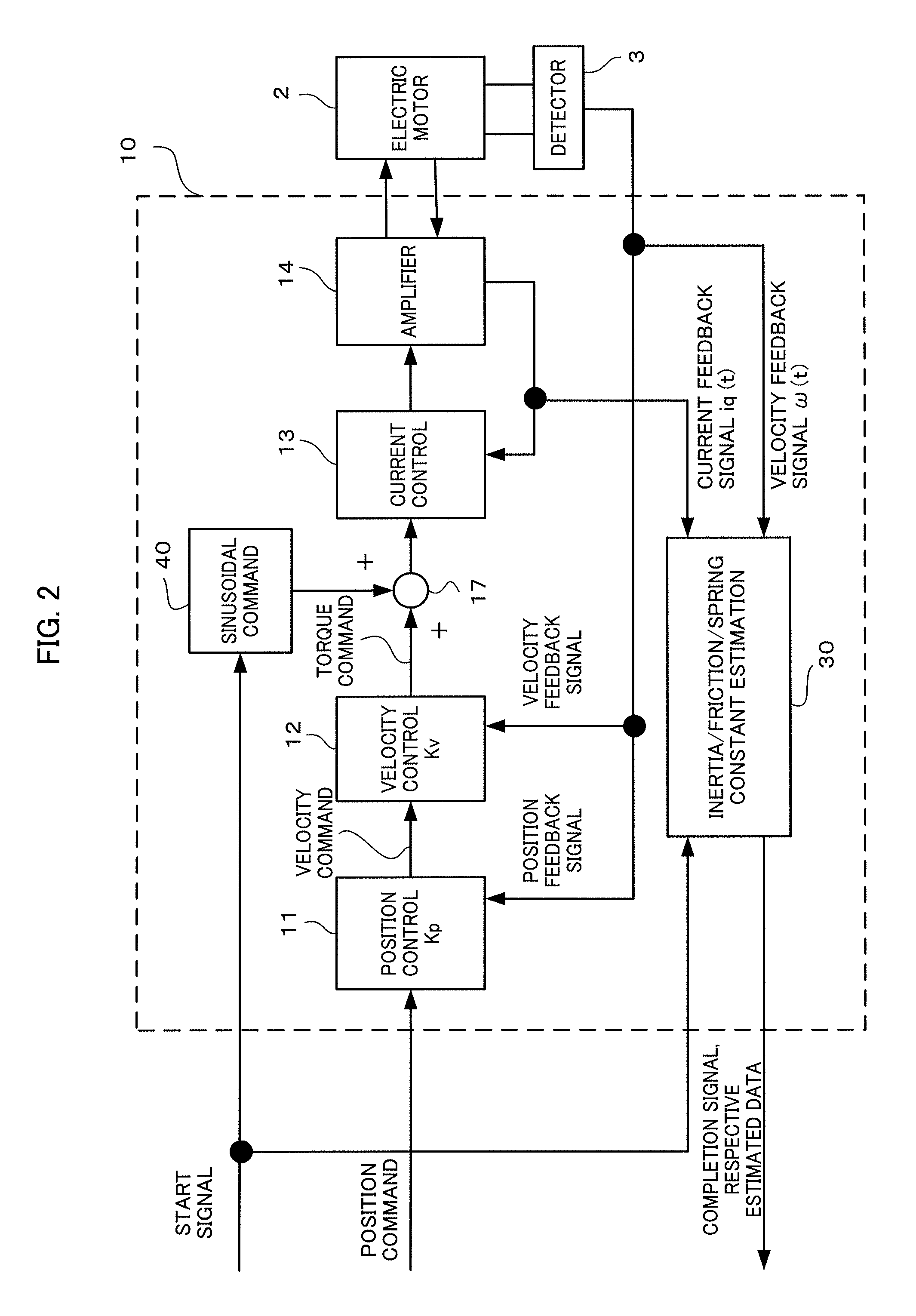
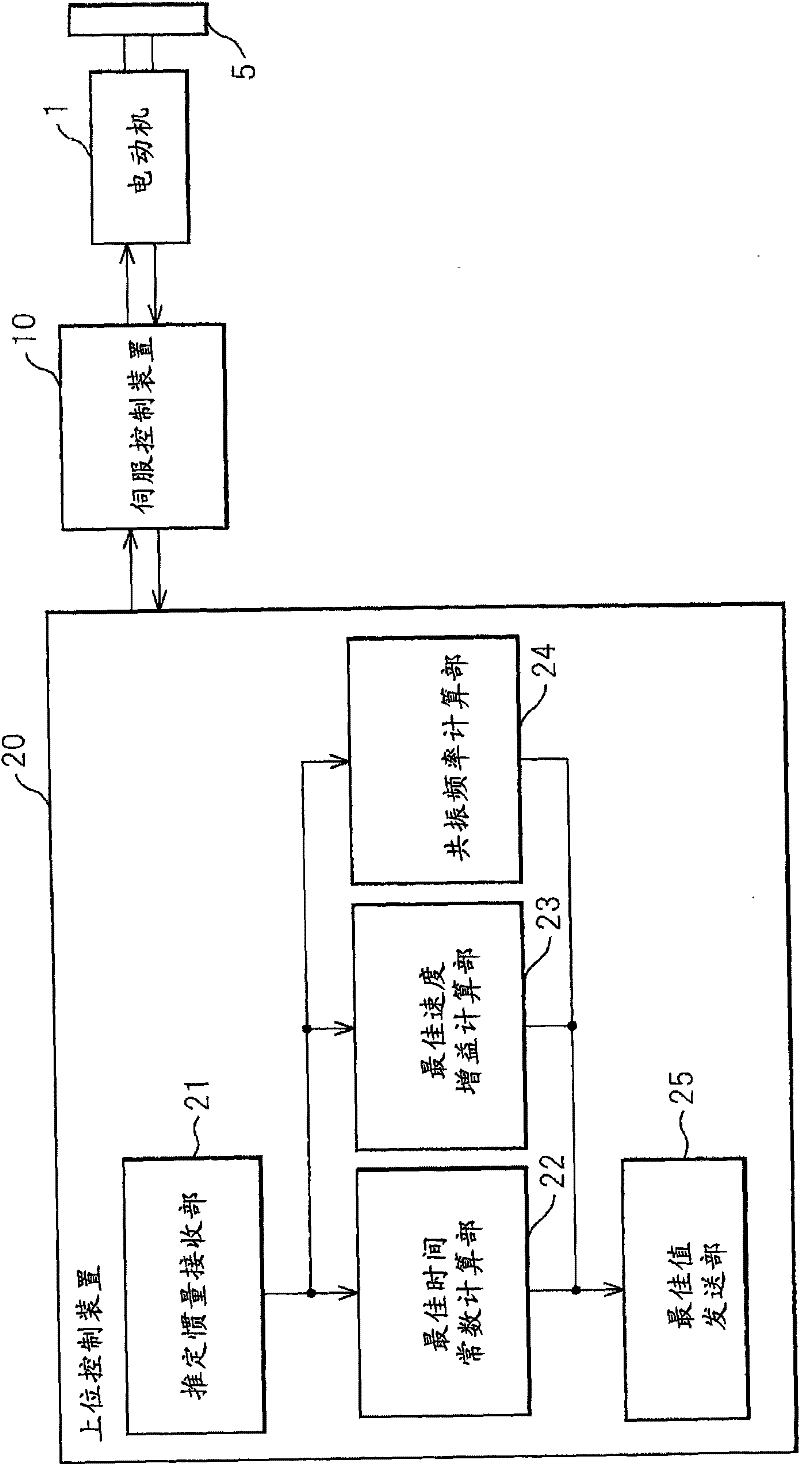
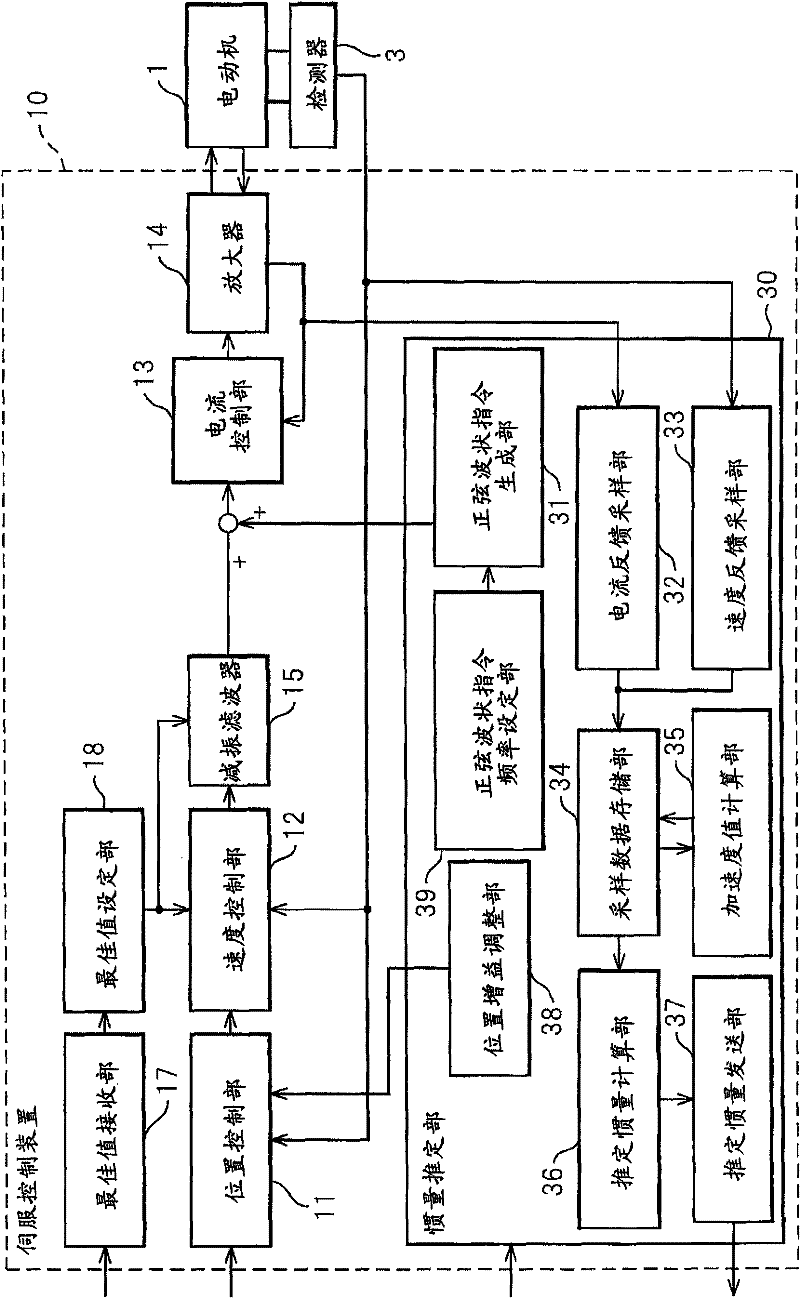
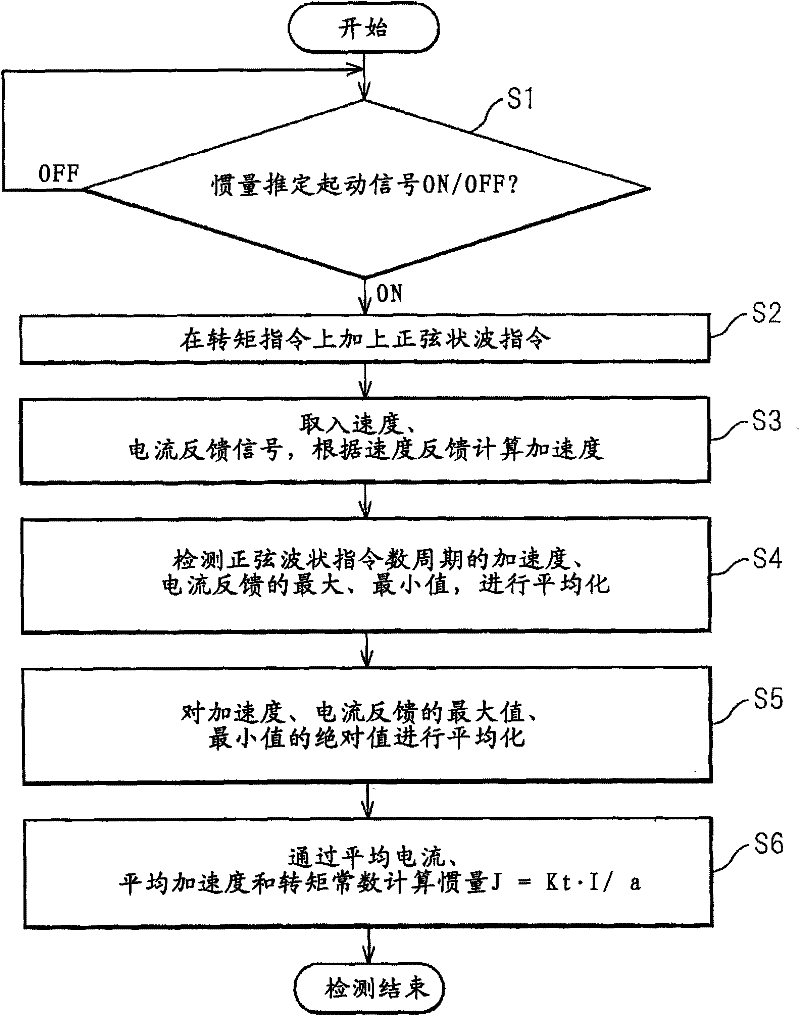
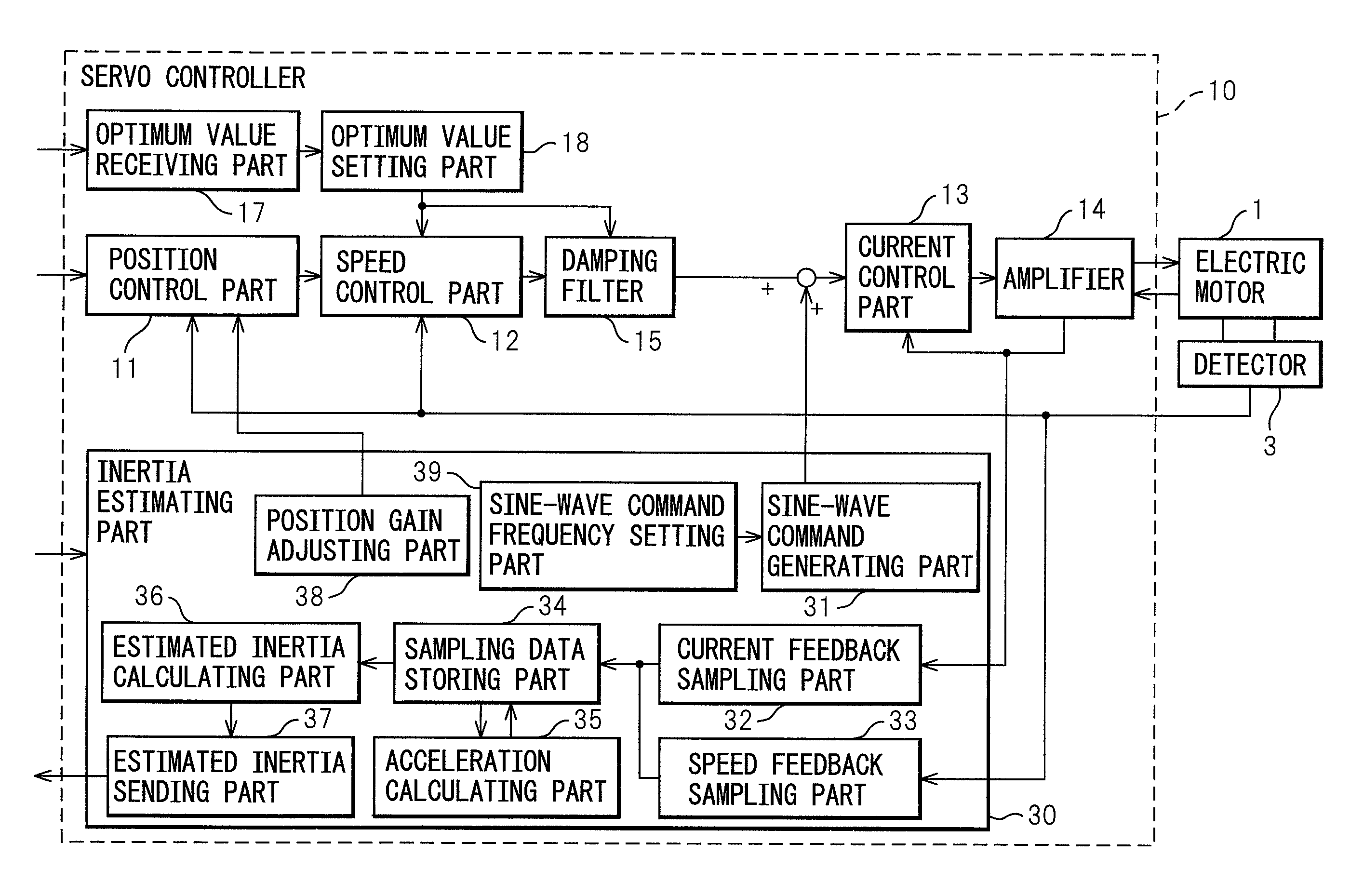
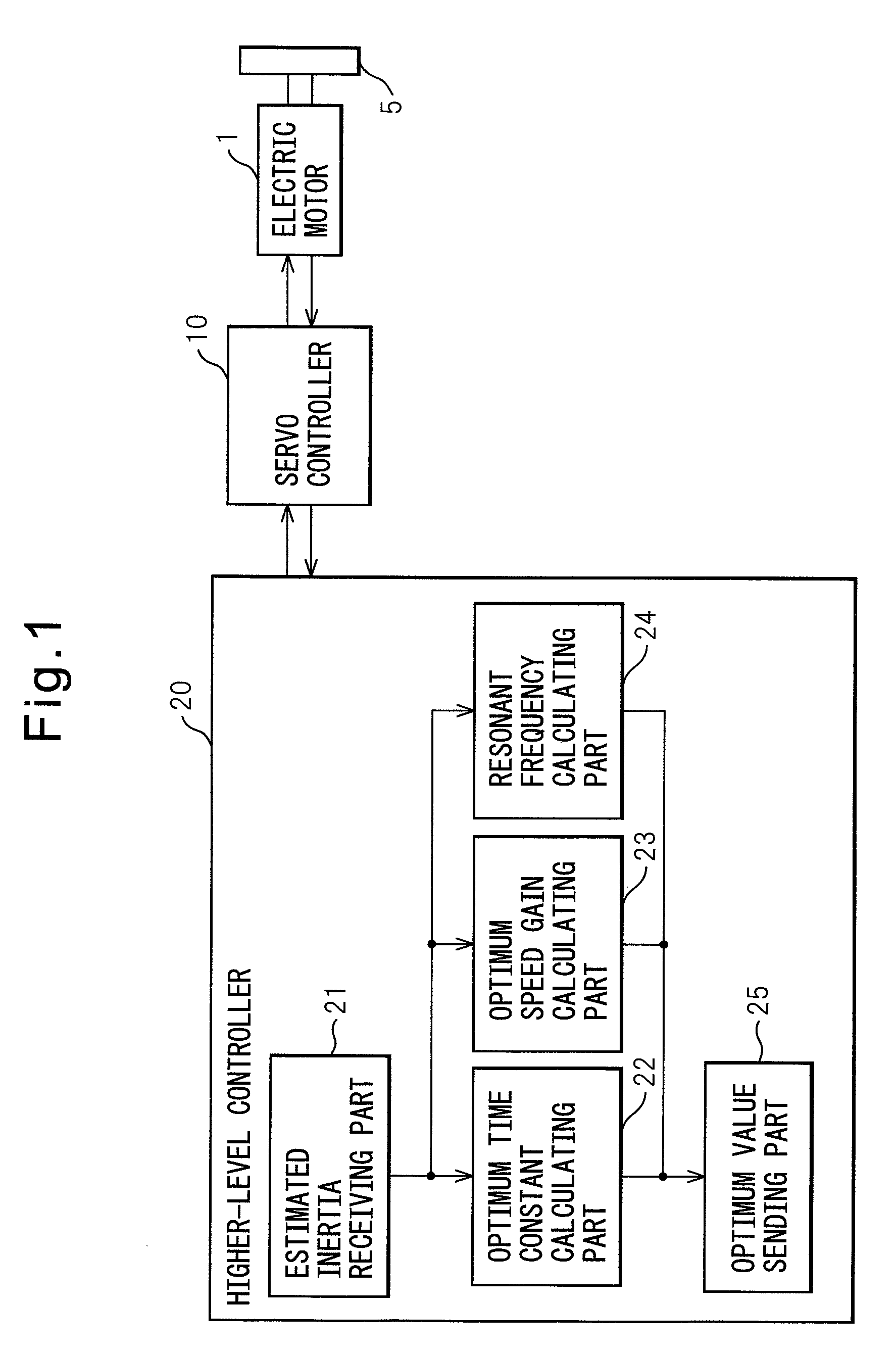
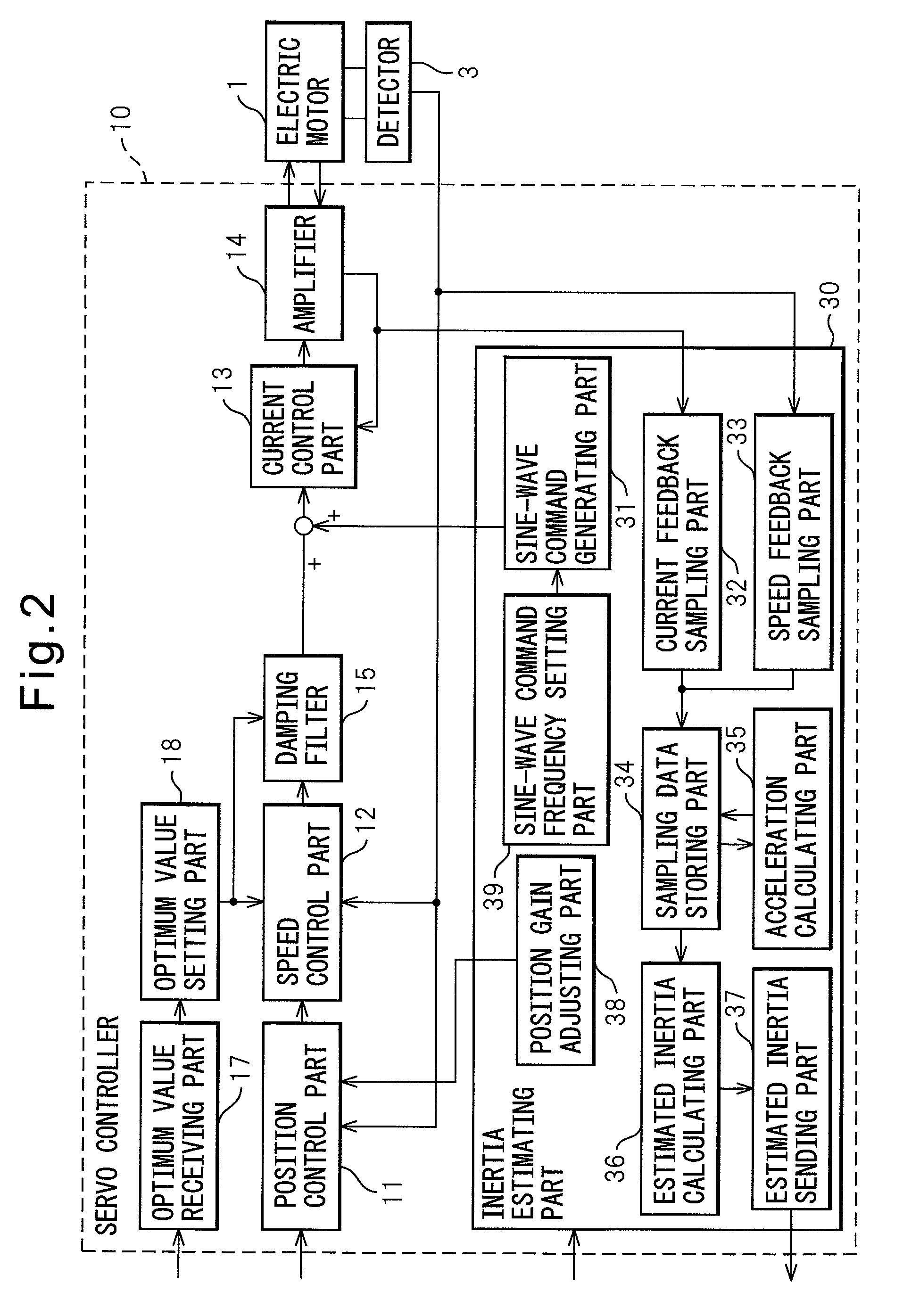
Inertia estimating controller and control system
ActiveUS20100148714A1Increase pointsProgramme controlDC motor speed/torque controlControl systemData storing
A controller and a control system capable of estimating inertia of an article to be driven in a short period of time, with a small operation range of an electric motor. The controller for the motor has an inertia estimating part which includes a sine-wave command generating part which adds a sine-wave command to a torque command for the motor; a current feedback sampling part which obtains a current value of the motor; a speed feedback sampling part which obtains a speed feedback of the motor; an acceleration calculating part which calculates an acceleration value based on the speed feedback; and an estimated inertia calculating part which estimates the inertia of the article, based on a representative current value, a representative acceleration value and a torque constant of the motor, which are calculated from current and acceleration values in a plurality of cycles of the sine-wave command and stored in a sampling data storing part.
Owner:FANUC LTD
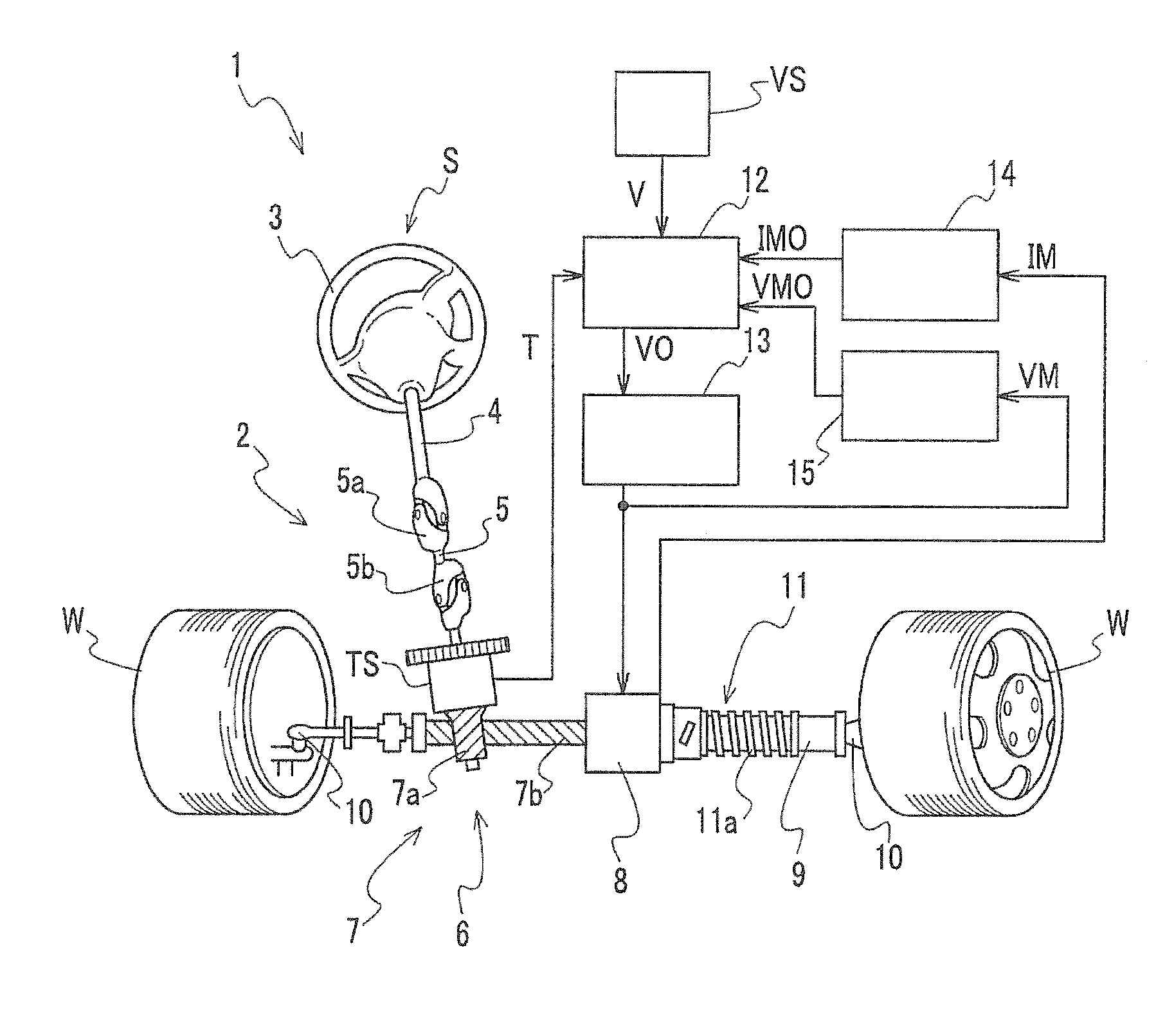
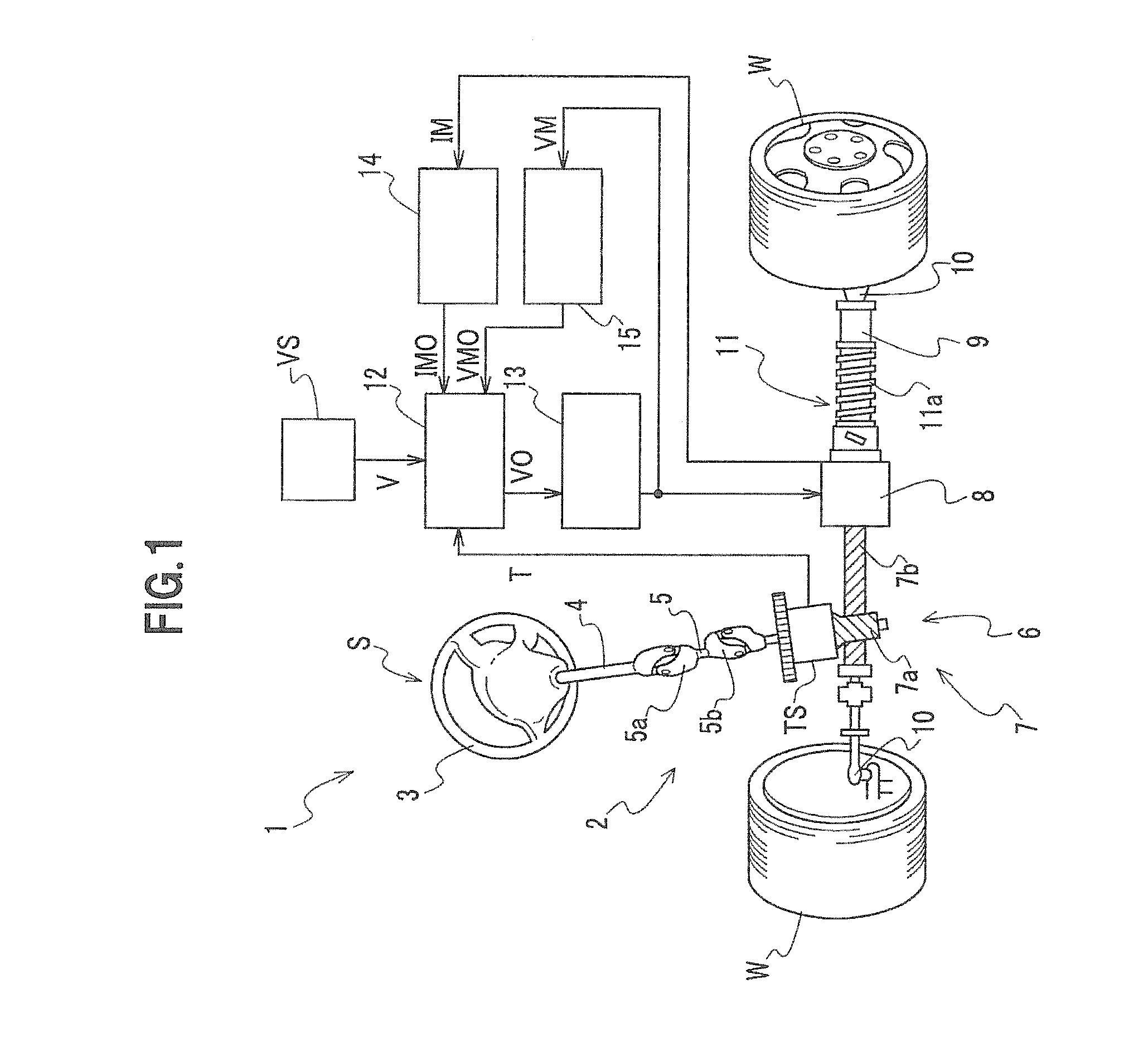
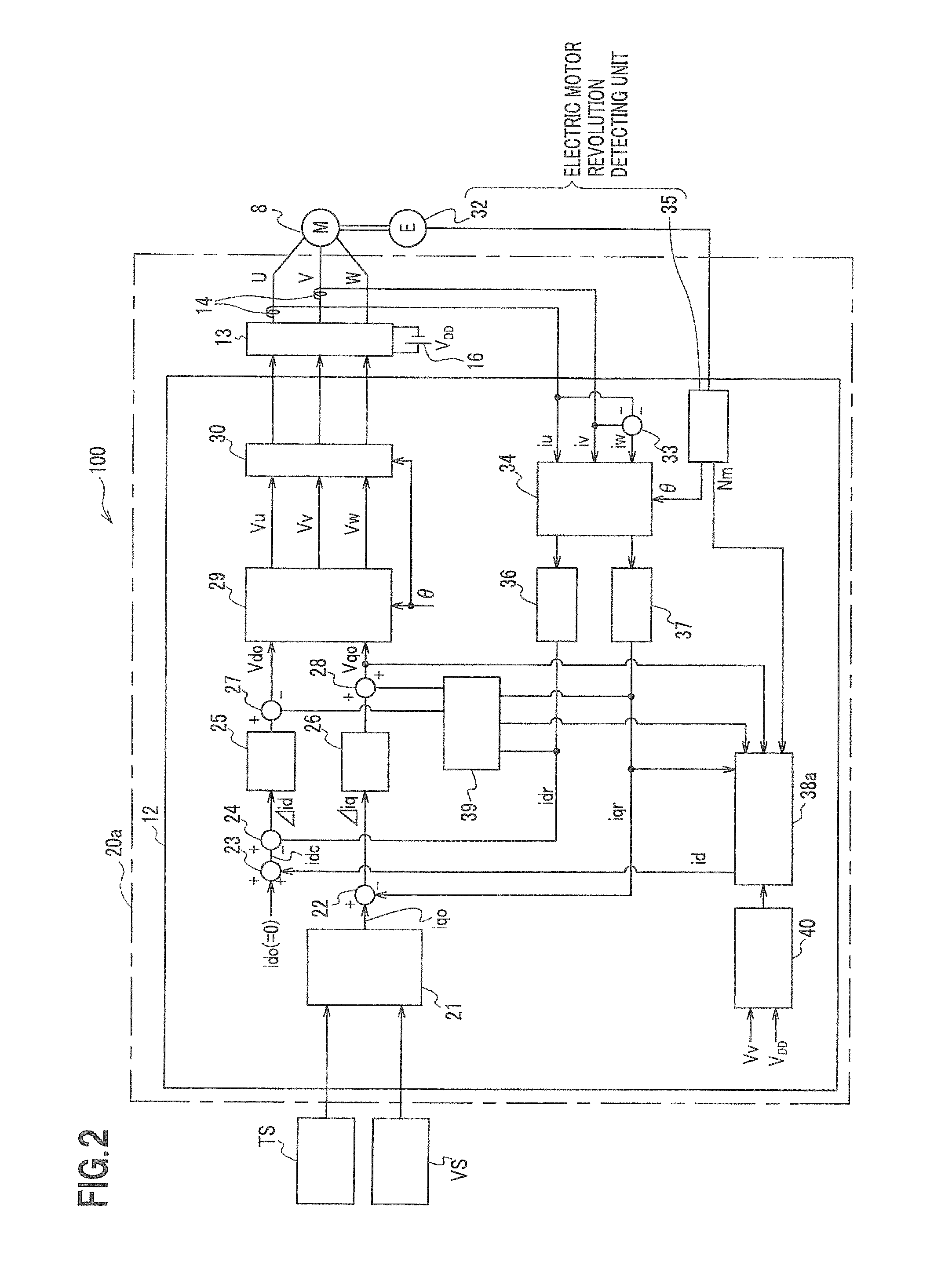
Electric power steering apparatus and electric motor driving controller used for the apparatus
InactiveUS20110231066A1Suppressing torque rippleIncrease rotation speedDigital data processing detailsSingle motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringPower flow
A q-axis target current setting unit generates a q-axis current command value based on a steering input signal from a steering torque sensor and a vehicle speed signal from a vehicle speed sensor. An electric motor generates a predetermined torque based on the q-axis current command value and a q-axis current (a torque current) to which a fed back q-axis real current is added. On the other hand, a d-axis correction current setting unit sets a field weakening current (a d-axis current) in response to a voltage saturation (duty ratio=driving voltage of electric motor / power supply voltage) output from a voltage saturation calculating unit. For this reason, when the voltage saturation becomes high, distortion (harmonics component) in current can be decreased by decreasing the voltage saturation while keeping the torque constant using a predetermined torque current, and a torque ripple can be suppressed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method of damping vibration on coil supports in high performance disk drives with rotary actuators
InactiveUS6947260B2Improve performanceImprove throughput performanceApparatus modification to store record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionMulti materialElectric machine
A damping assembly for the actuator of high performance disk drive assembly is formed from multiple materials. The damping assembly is added to the actuator to dampen vibration that occurs during operation of the drive. The damping assembly is connected to an exterior portion of a coil region of the actuator. The damping assembly helps dampen vibration modes for coil torsion and coil bending, thereby improving dynamics settling performance to improve overall file input / output throughput performance. This also allows for a higher voice coil motor torque constant by increasing the magnet radius, thereby also improving move time, which further improves file input / output throughput performance. The overall file performance is improved by reducing settling times associated with coil torsion and coil bending modes, and allowing a higher torque constant to also improve move time. Both of these effects contribute to improving file performance.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Virtual signal injection-based maximum torque current ratio control method of synchronous motor
ActiveCN107800344AGuaranteed steady state accuracyQuick responseElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMaximum torqueIntegrator
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
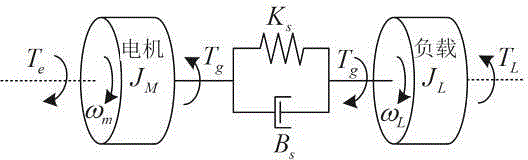
Electric motor controller comprising function for simultaneously estimating inertia, friction, and spring
ActiveCN102904521APresumed elasticityEstimated nonlinear frictionElectric motor controlVector control systemsCouplingControl theory
The invention provides an electric motor controller comprising functions for simultaneously estimating inertia, friction, and spring. A sinusoidal command is added to a torque command of a controller to acquire a velocity and a current value of an electric motor. An estimated coupling torque value is calculated by calculating an input torque value from the current value and a torque constant of the electric motor and further calculating a coupling torque value from a velocity difference, motor inertia, and the input torque. An estimated torque error is then calculated from the estimated coupling torque value and the coupling torque value, and inertia, friction, and a spring constant are estimated from the estimated torque error, the velocity, and the coupling torque value.
Owner:FANUC LTD
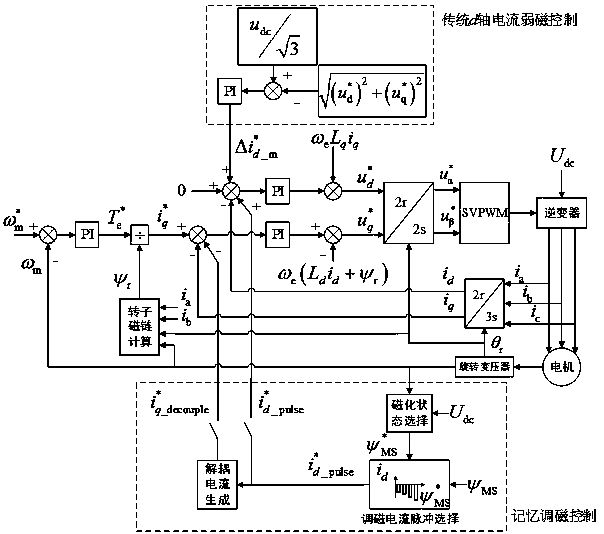
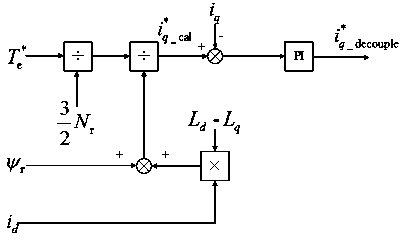
A method for restraining the flux-adjusting torque ripple of a memory motor based on current decoupling
InactiveCN109150022AImprove efficiencyReduce magnetic lossTorque ripple controlMemory motorControl theory
The invention discloses a method for restraining the flux-adjusting torque ripple of a memory motor based on current decoupling, including setting given values of d, q-axis current, Both and d, The deviation from the q-axis current setpoint is input to the PI regulator, the output of the d-axis current PI regulator is subtracted from omega eLqiq to obtain the d-axis voltage given value, To the output of q-axis current PI regulator, [omega]e(Ldid + [psi]r) is added to get the given value of q-axis voltage. D, q-axis voltage is controlled by coordinate transformation and SVPWM modulation to drive the inverter motor. When the rotational speed of the motor is higher than the base speed, the magnetization state of the permanent magnet is adjusted discretely by using the memory magnetization method, and the d-axis current weakening method is used to continuously adjust the magnetization state in each magnetization state, and the q-axis decoupling current is applied at the same time as the d-axis current is applied, so as to keep the torque constant during the magnetization adjustment period and suppress the torque ripple during the magnetization adjustment period.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Brushless motor control method
InactiveUS6838848B2Reduce torque rippleTorque ripple can be reducedTorque ripple controlCommutation monitoringBrushless motorsDriver/operator
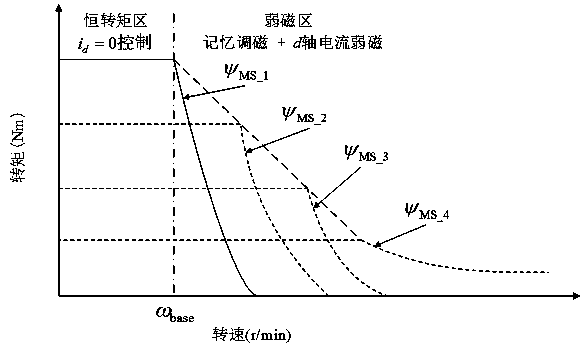
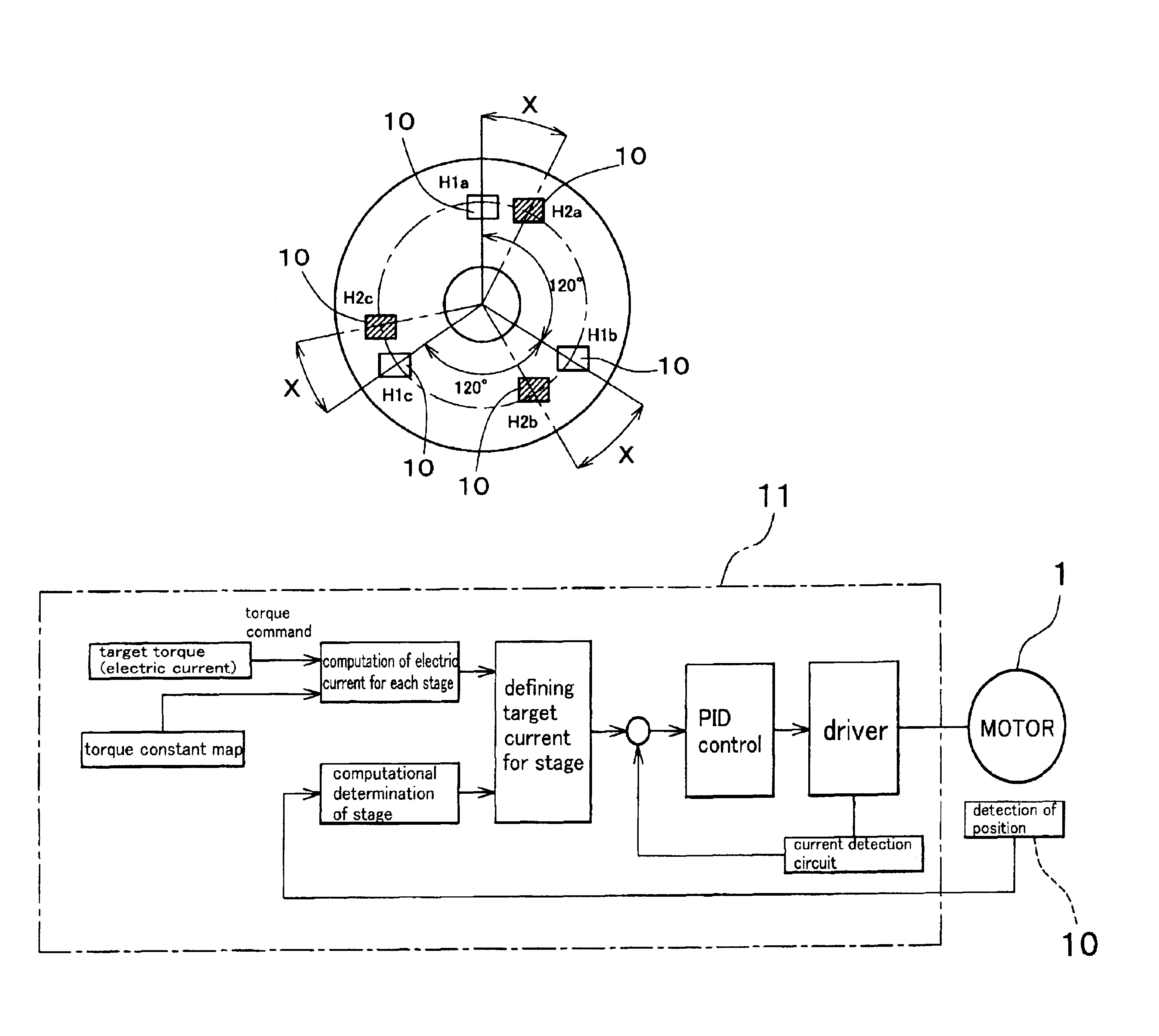
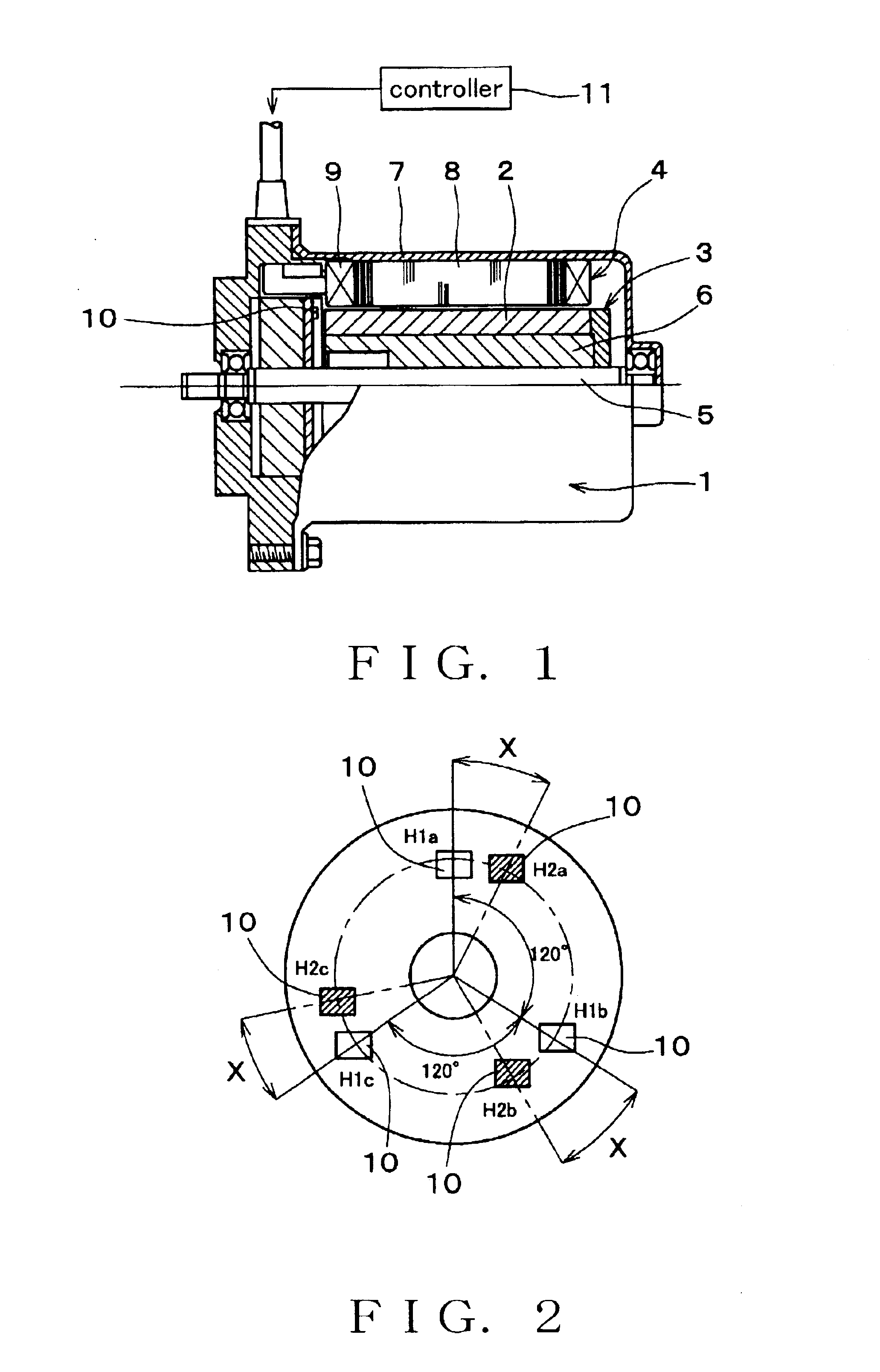
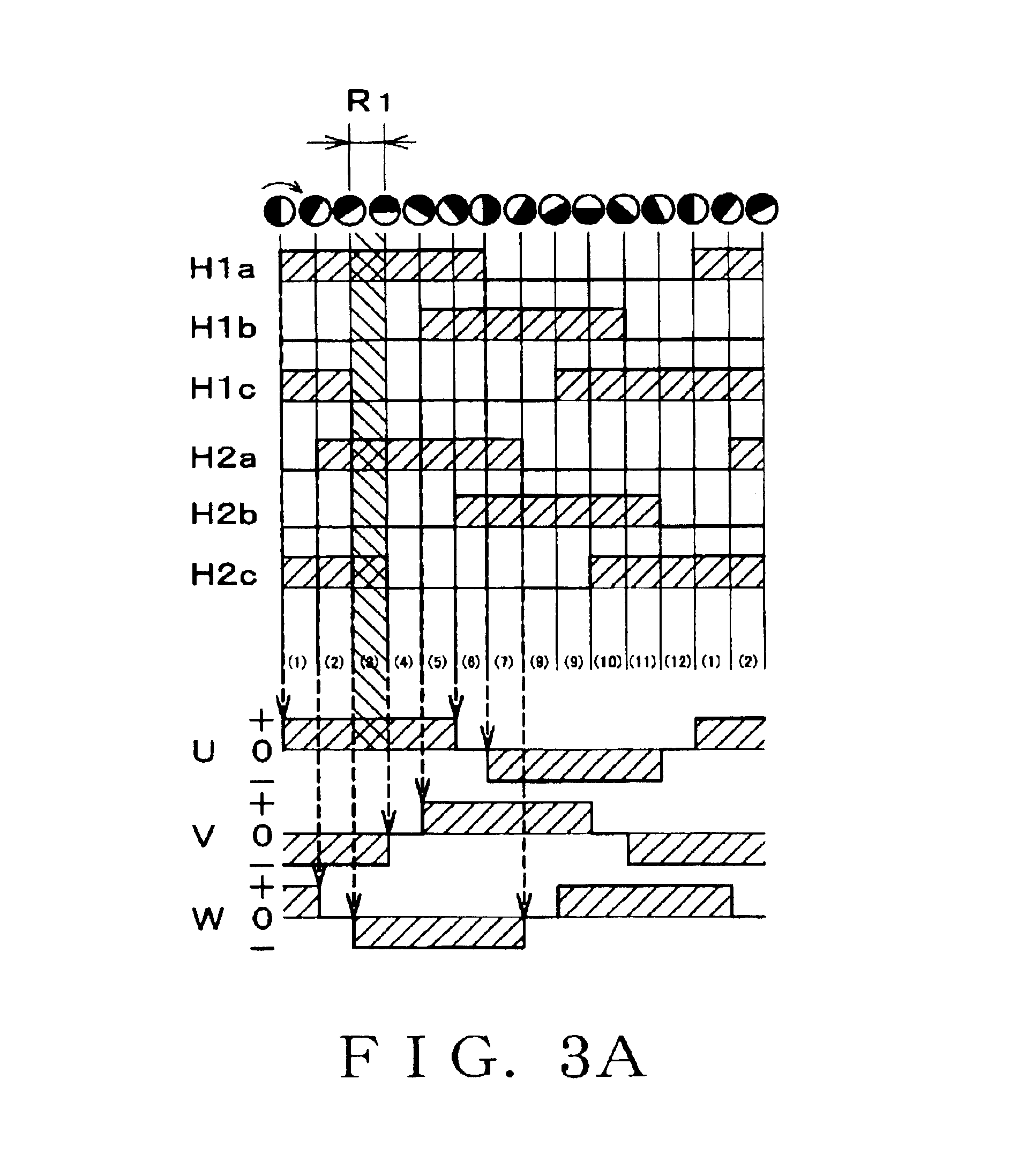
Energization stages are formed by first and second sensor groups and a torque constant is defined for each of the stages. A target current value is computationally determined so as to drive a motor under control. As a torque command showing a target torque of the motor is input to the controller, the target current value is computationally determined for each stage according to a torque constant map, which provides a table of torque constants for different phases and different stages. The rotor angle of the motor is detected by Hall sensors and the current stage is computationally determined on the basis of the detected rotor angle. Then, a target current value is defined as a function of the target torque for each stage on the basis of the current stage and the motor is driven by the driver under PID control based on the target current value.
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Electric motor controller comprising function for simultaneously estimating inertia, friction, and spring
A sinusoidal command is added to a torque command of a controller to acquire a velocity and a current value of an electric motor. An estimated coupling torque value is calculated by calculating an input torque value from the current value and a torque constant of the electric motor and further calculating a coupling torque value from a velocity difference, motor inertia, and the input torque. An estimated torque error is then calculated from the estimated coupling torque value and the coupling torque value, and inertia, friction, and a spring constant are estimated from the estimated torque error, the velocity, and the coupling torque value.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Two-mass system resonance suppression method
ActiveCN104993766ASuppress mechanical vibrationNo additional costMotor control for motor oscillations dampingViscous dampingAuto regulation
The invention discloses a two-mass system resonance suppression method. Two-mass system resonance is suppressed by adopting a method of increasing a motor shaft end equivalent viscous damping force. The method comprises the steps of firstly multiplying a difference value between the motor rotating speed and the load end rotating speed by an equivalent damping compensation coefficient so as to generate a motor shaft end equivalent viscous damping force; then dividing the equivalent damping force by a torque constant so as to be converted into equivalent damping compensation current, and applying the equivalent damping compensation current to subtraction of current instructions. Meanwhile, the equivalent viscous damping force, which needs to be added to the motor shaft end, is enabled to be associated with the resonant amplitude of the system, thereby establishing a corresponding adaption law, automatically adjusting the equivalent damping compensation coefficient, and achieving an effect of adaptive resonance suppression. The two-mass system resonance suppression method is easy for engineering implementation, parameters are easy to adjust, and a purpose of adaptive resonance suppression can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING ESTUN AUTOMATION CO LTD
High Torque Low Inductance Rotary Actuator
ActiveUS20130181549A1Synchronous machinesMagnetic circuit stationary partsRotor magnetsCoil inductance
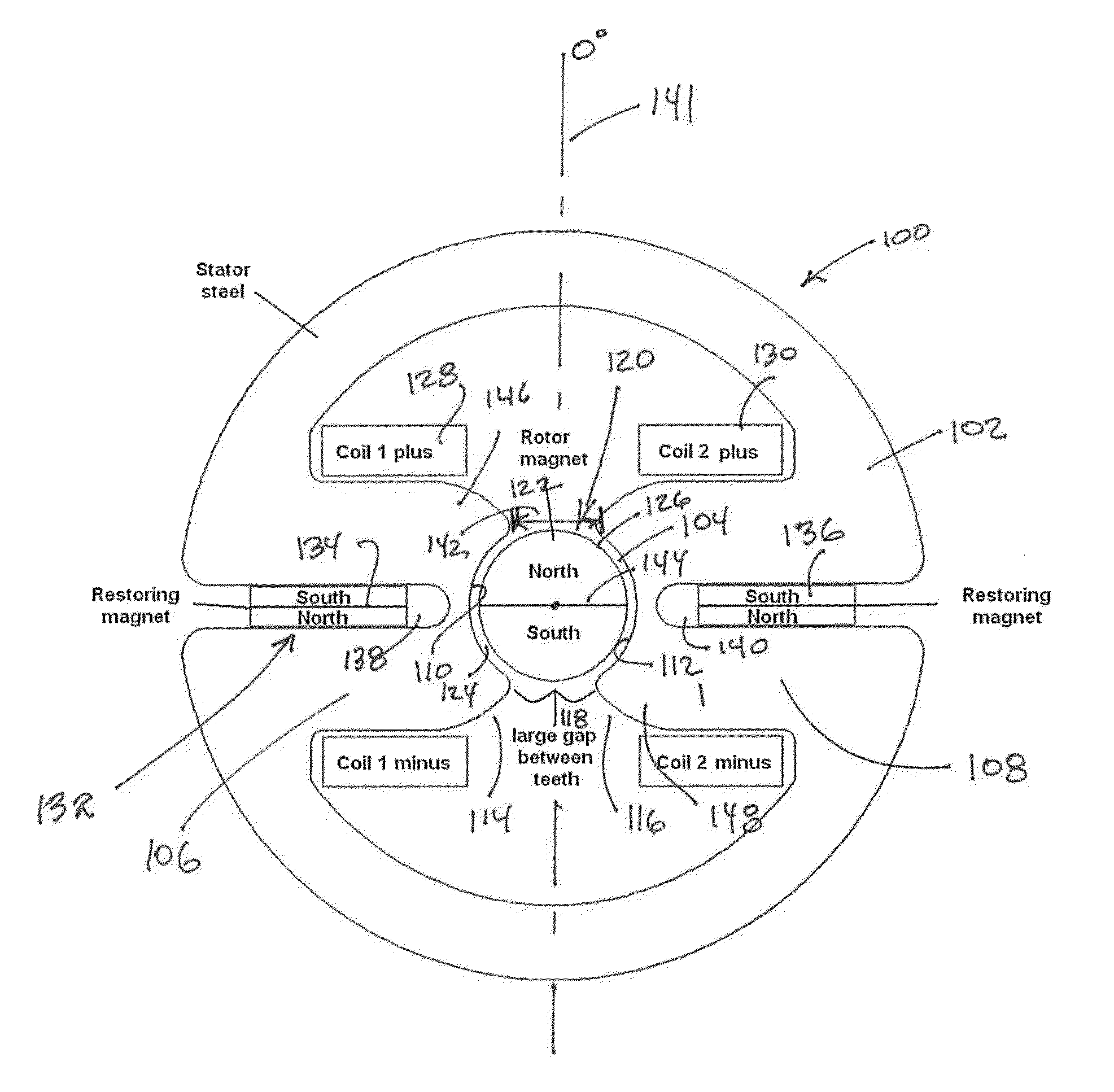
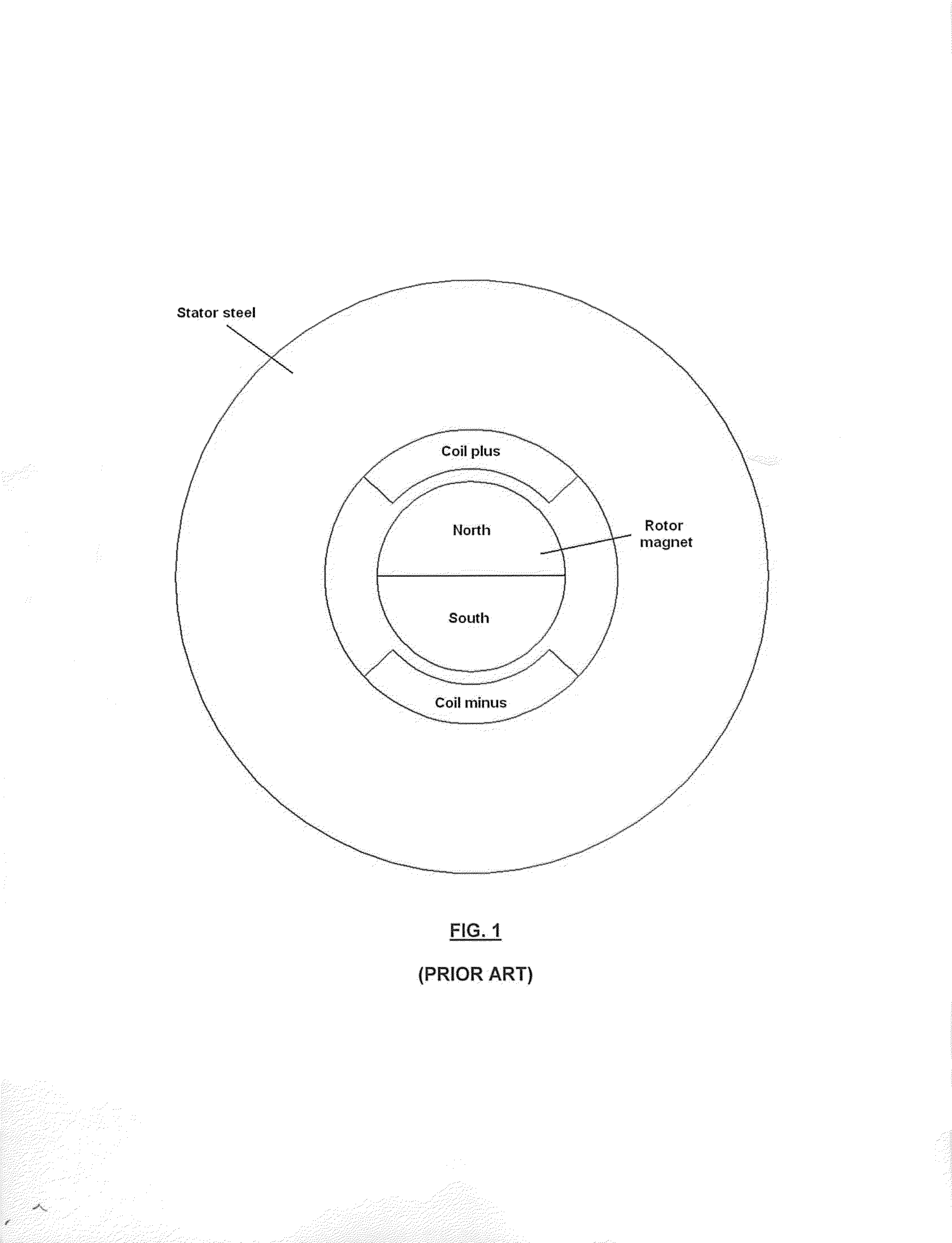
An electromechanical rotary actuator includes a rotor and a stator having one or more slots into which one or more coils are placed. The stator includes a rotor position restoring means which overcomes cogging outside a desired rotation range. The rotor position restoration means may include one or more restoring magnets or optionally include a contoured cavity within the stator proximate the rotor. One stator includes teeth having contoured ends forming a portion of the aperture within which the rotor operates. Distal ends of the teeth form a relatively large gap compared to typical actuators, wherein the gap is sized to the rotor magnet. An actuator desirably having a high torque constant, low coil resistance and a low coil inductance is provided.
Owner:BENNER JR WILLIAM R
PMSM position servo system high-order object controller design and parameter determination method
InactiveCN108599649AIncrease reflectionReflect the impactElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsClosed loopPwm inverter
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Inertia estimating controller and control system
A controller and a control system capable of estimating inertia of an article to be driven in a short period of time, with a small operation range of an electric motor. The controller for the motor has an inertia estimating part which includes a sine-wave command generating part which adds a sine-wave command to a torque command for the motor; a current feedback sampling part which obtains a current value of the motor; a speed feedback sampling part which obtains a speed feedback of the motor; an acceleration calculating part which calculates an acceleration value based on the speed feedback; and an estimated inertia calculating part which estimates the inertia of the article, based on a representative current value, a representative acceleration value and a torque constant of the motor, which are calculated from current and acceleration values in a plurality of cycles of the sine-wave command and stored in a sampling data storing part.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Variable speed control for AC induction motors
InactiveUS6140795AConstant torque outputCheap manufacturingMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlElectric machineControl theory
A speed control apparatus for varying the speed of an AC motor while maintaining the torque and power constant over a range of angular speeds The AC motor is driven by a D.C. source. A universal conmutator capable of providing two symmetrical non-contending signals with a frequency that can be selectively varied. A microprocessor unit for monitoring the frequency of the signals and control proportionally varying the duty cycle of the signals calculates the necessary duty cycle to maintain the torque constant over a range of angular speeds.
Owner:CUMMINS MICHAEL D
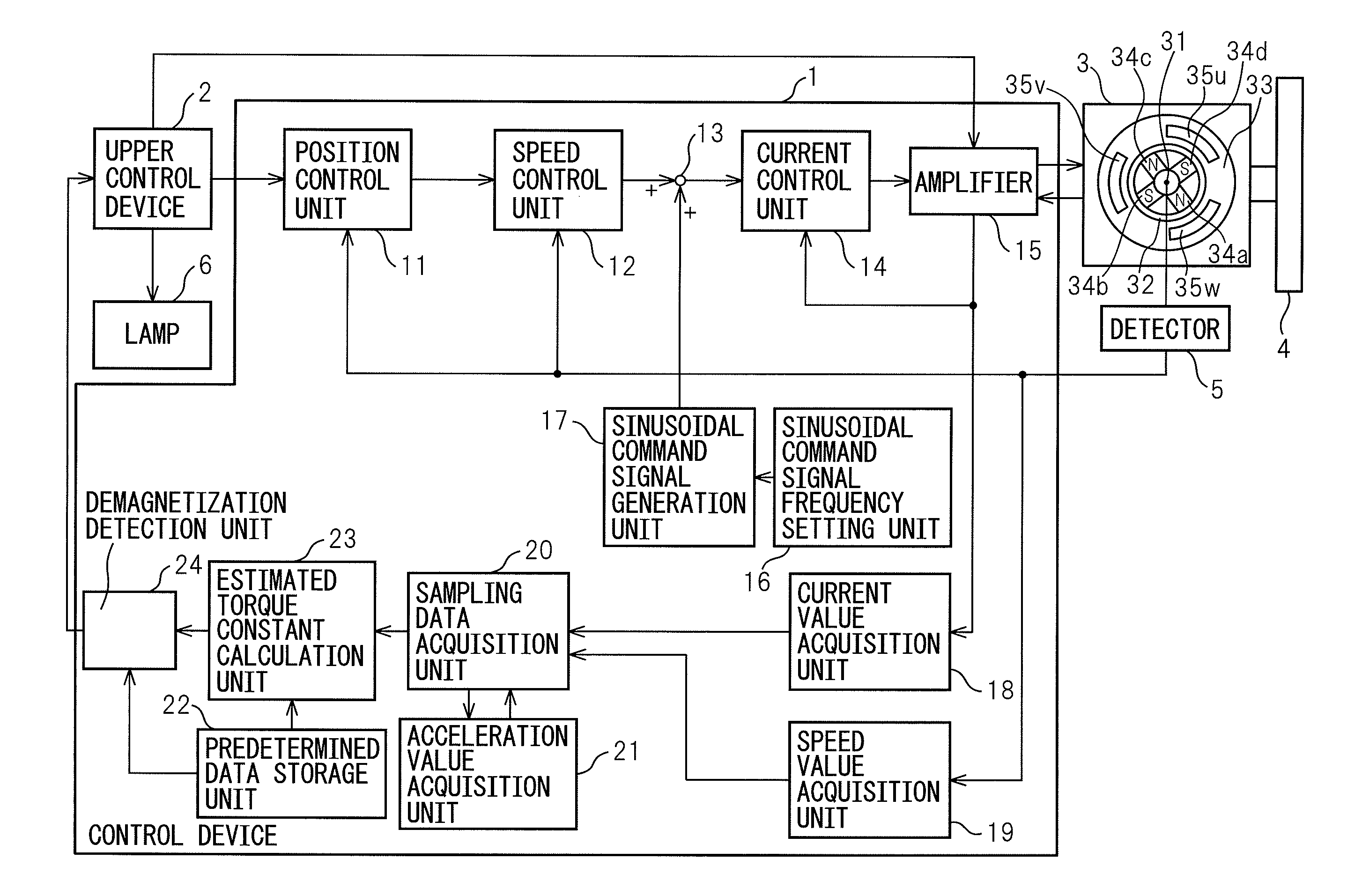
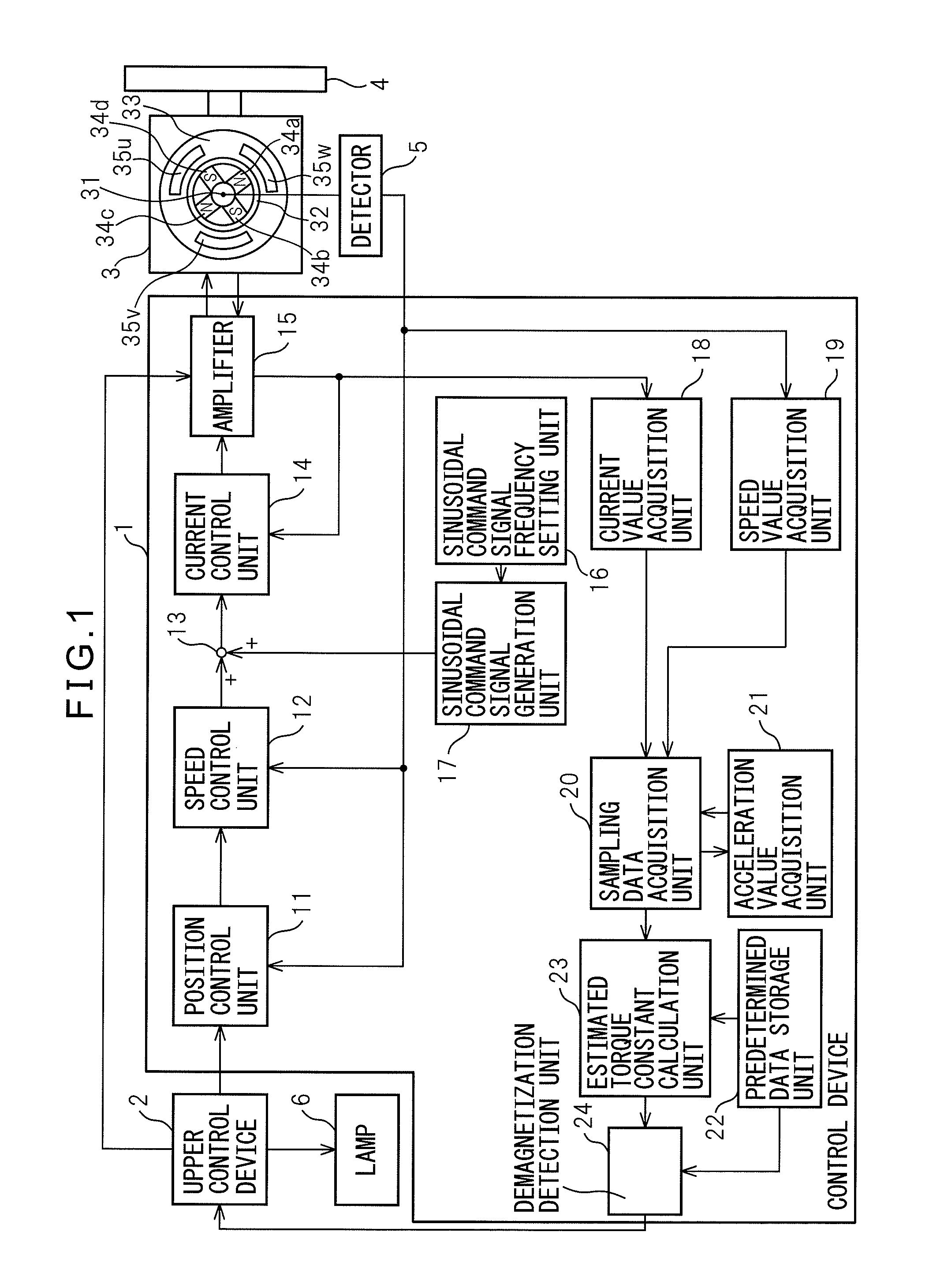
Control device that detects whether or not irreversible demagnetization has occurred in permanent magnet of permanent magnet synchronous motor
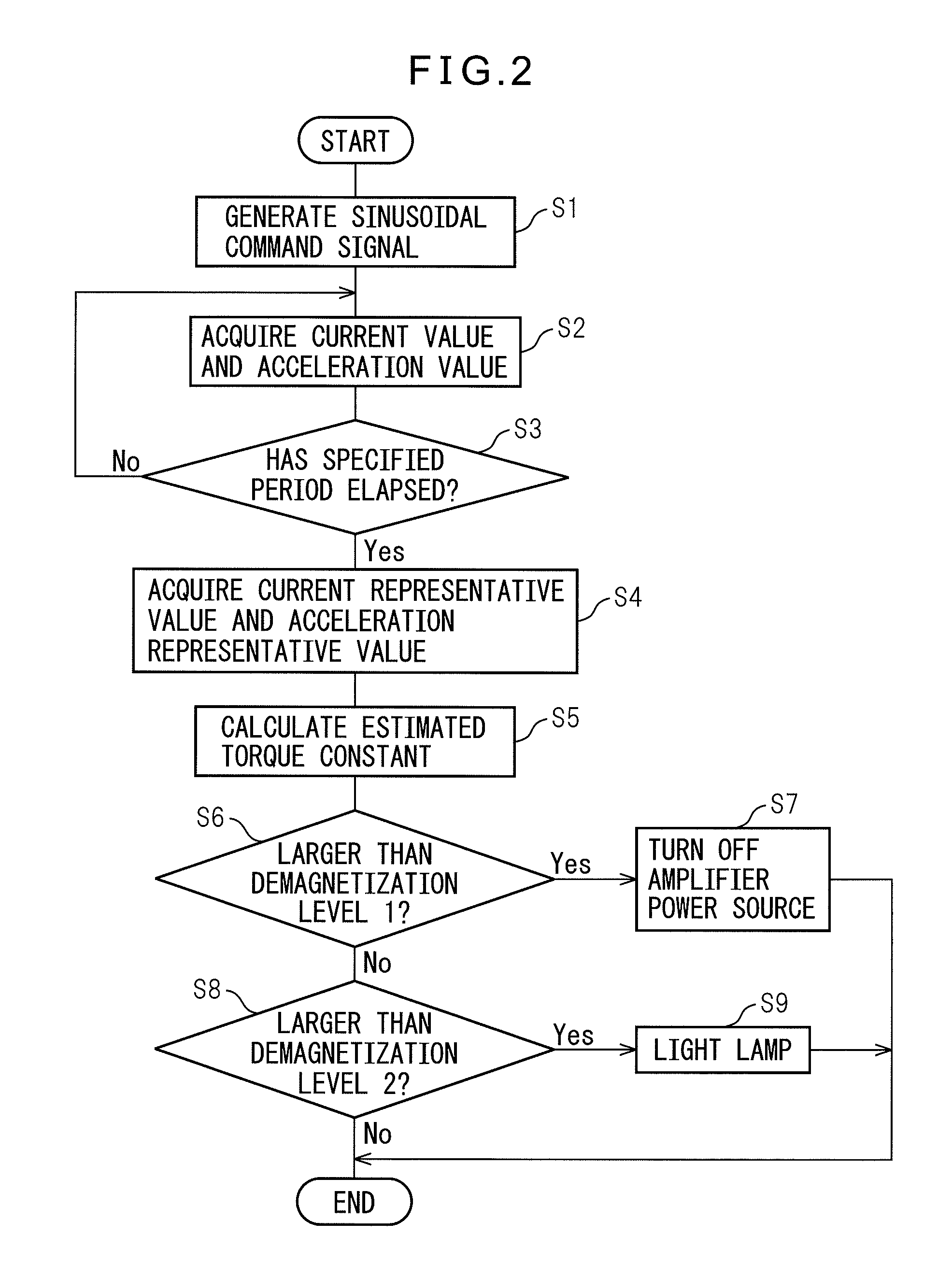
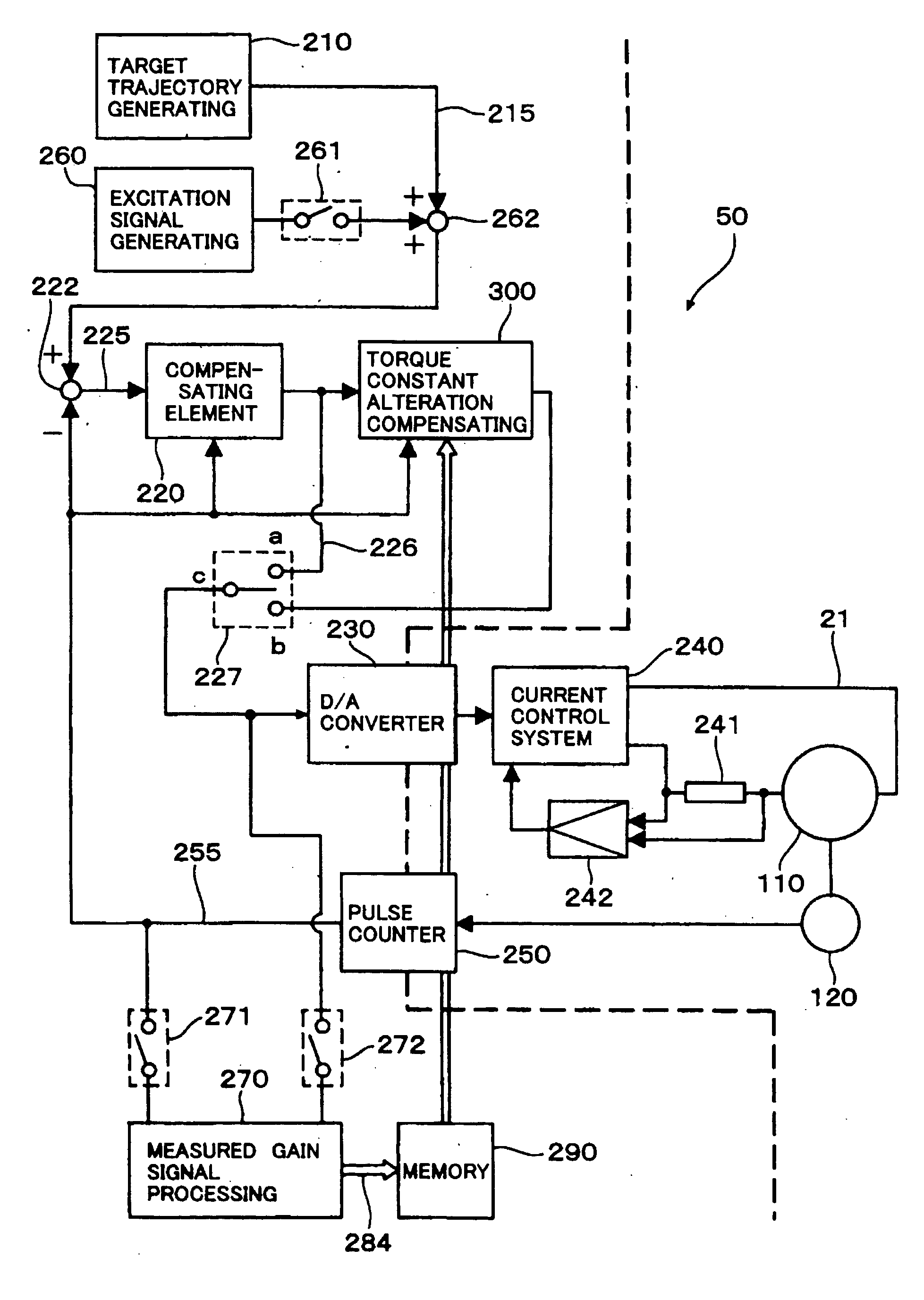
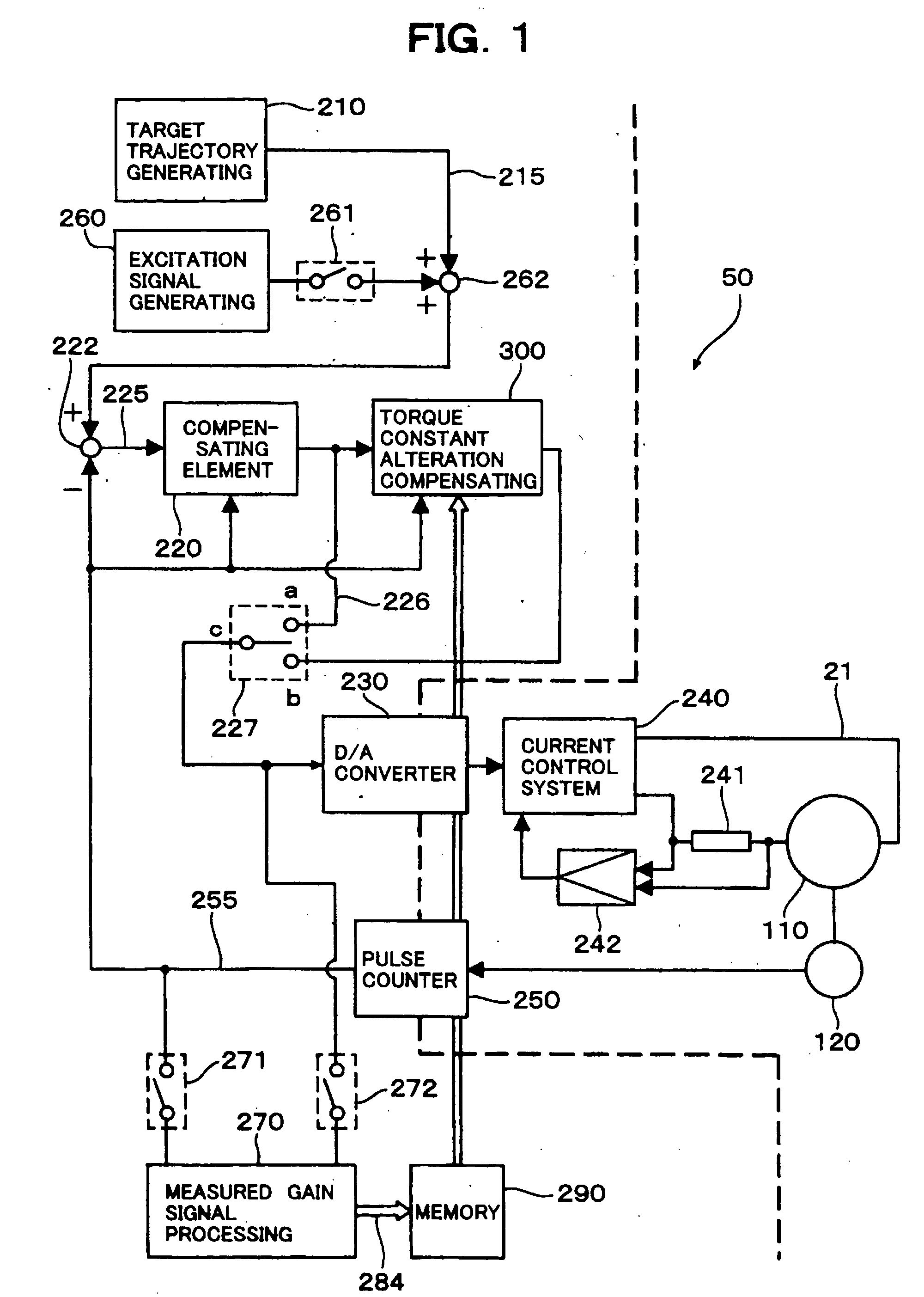
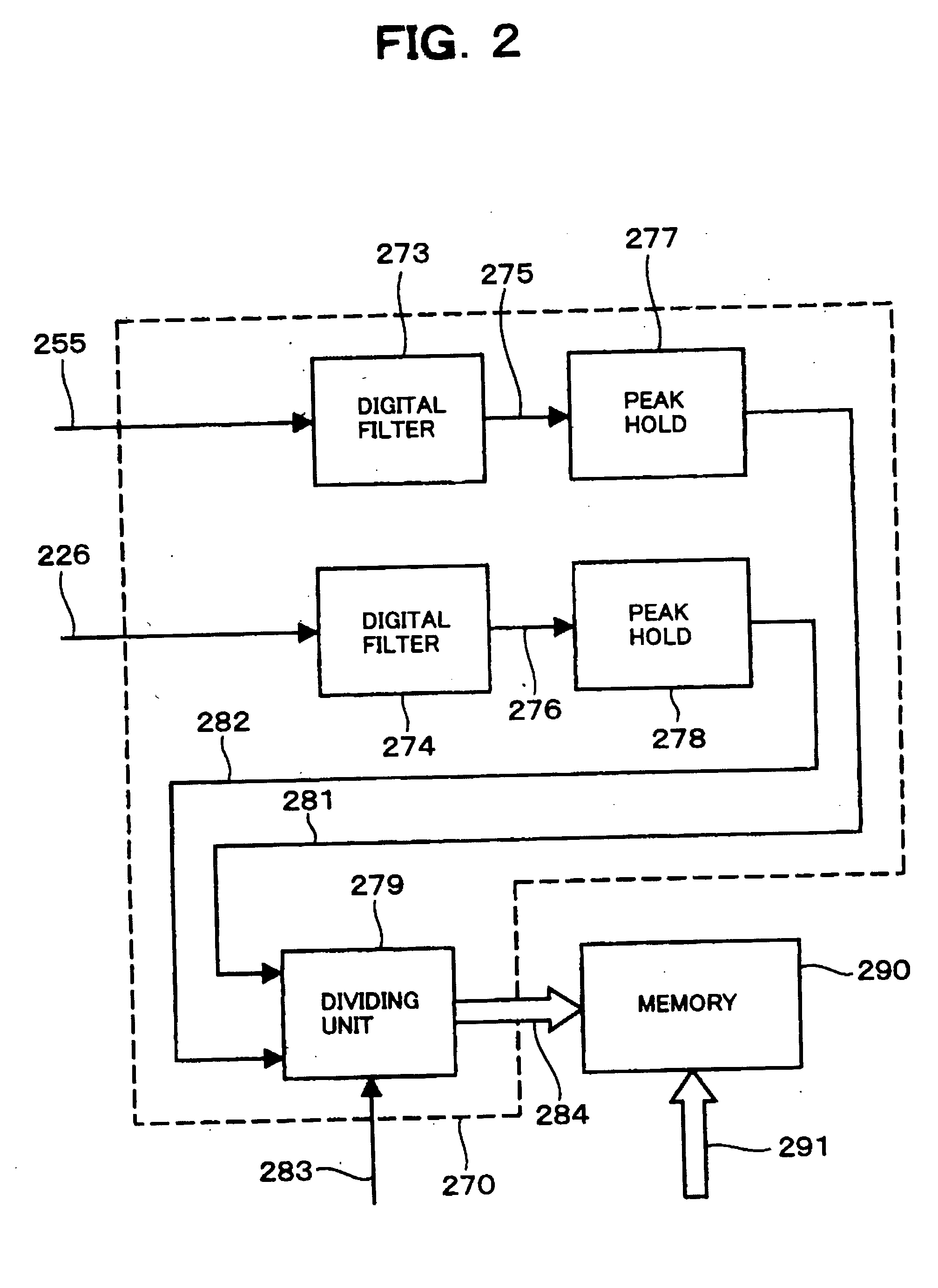
ActiveUS20130026959A1Operating range is reducedAppropriately detect irreversible demagnetizationMotor/generator/converter stoppersCommutation monitoringPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
An estimated torque constant calculation unit calculates an estimated torque constant relating to the permanent magnet synchronous motor from a current representative value and an acceleration representative value acquired from a plurality of current values and a plurality of acceleration values in the same operation state over a plurality of periods of a sinusoidal command signal and a predetermined inertia relating to the permanent magnet synchronous motor. A demagnetization detection unit detects whether or not irreversible demagnetization has occurred in the permanent magnet of the permanent magnet synchronous motor based on a difference between the estimated torque constant and a predetermined torque constant relating to the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Optical scanner control method, optical scanner and laser machining apparatus
ActiveUS20050184156A1Increase machine speedMirrorsPrinted circuit manufactureOptical scannersActuator
A optical scanner control method and a optical scanner capable of positioning a mirror at a high speed independently of a rocking angle, and a laser machining apparatus for irradiating a printed circuit board with a laser beam by use of the optical scanner to thereby perforate the printed circuit board. In order to operate an actuator for rocking the mirror based on a deviation of a current position from an commanded value, a change in gain of the actuator is measured in accordance with each rocking angle in advance, and the manipulated variable of the actuator is corrected to cancel the change in gain. Thus, the influence of the alteration of a torque constant in accordance with the rocking angle can be suppressed so that the response characteristic becomes uniform all over a scanning region, and the positioning speed can be improved.
Owner:HITACHI SEIKO LTD
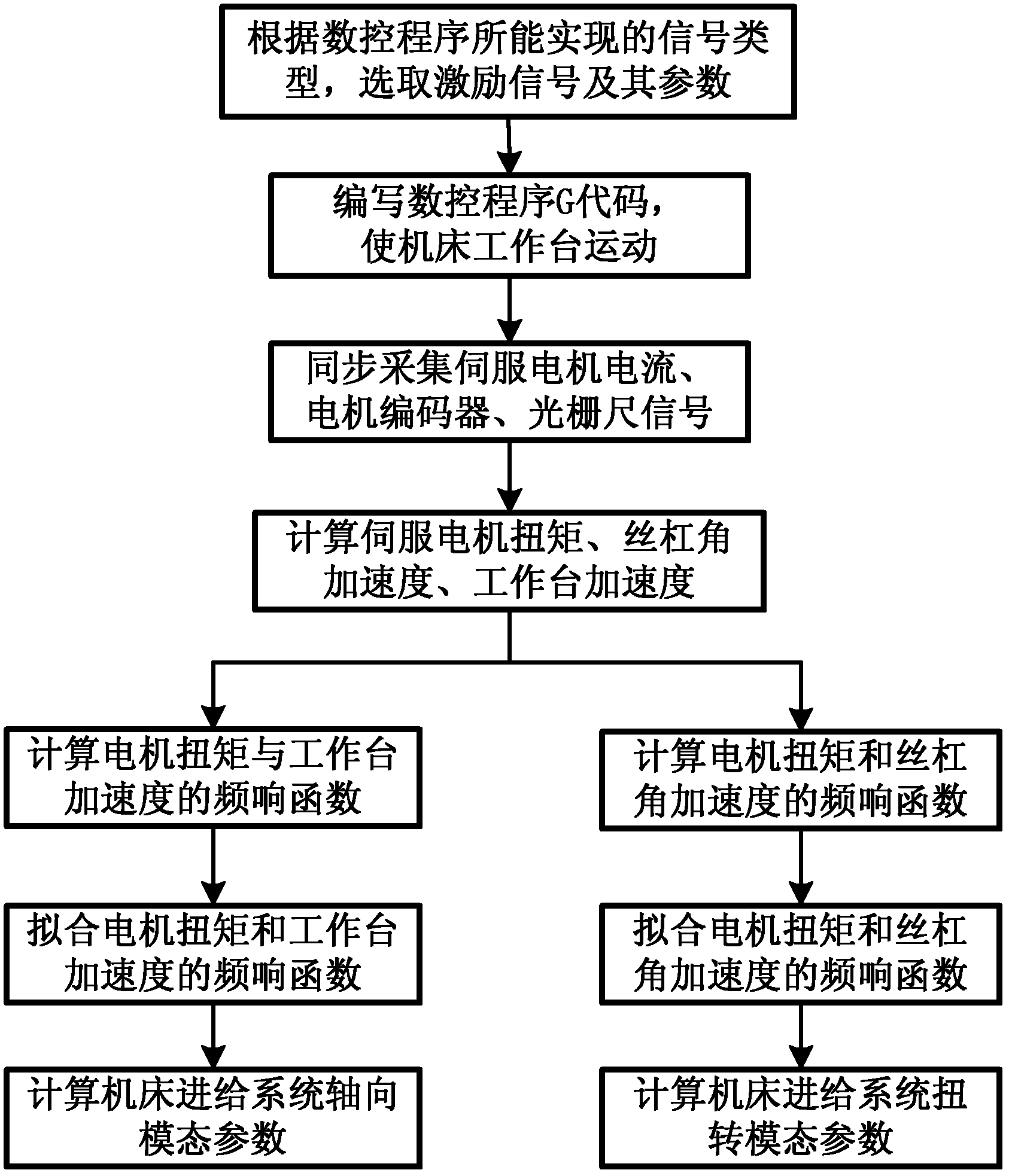
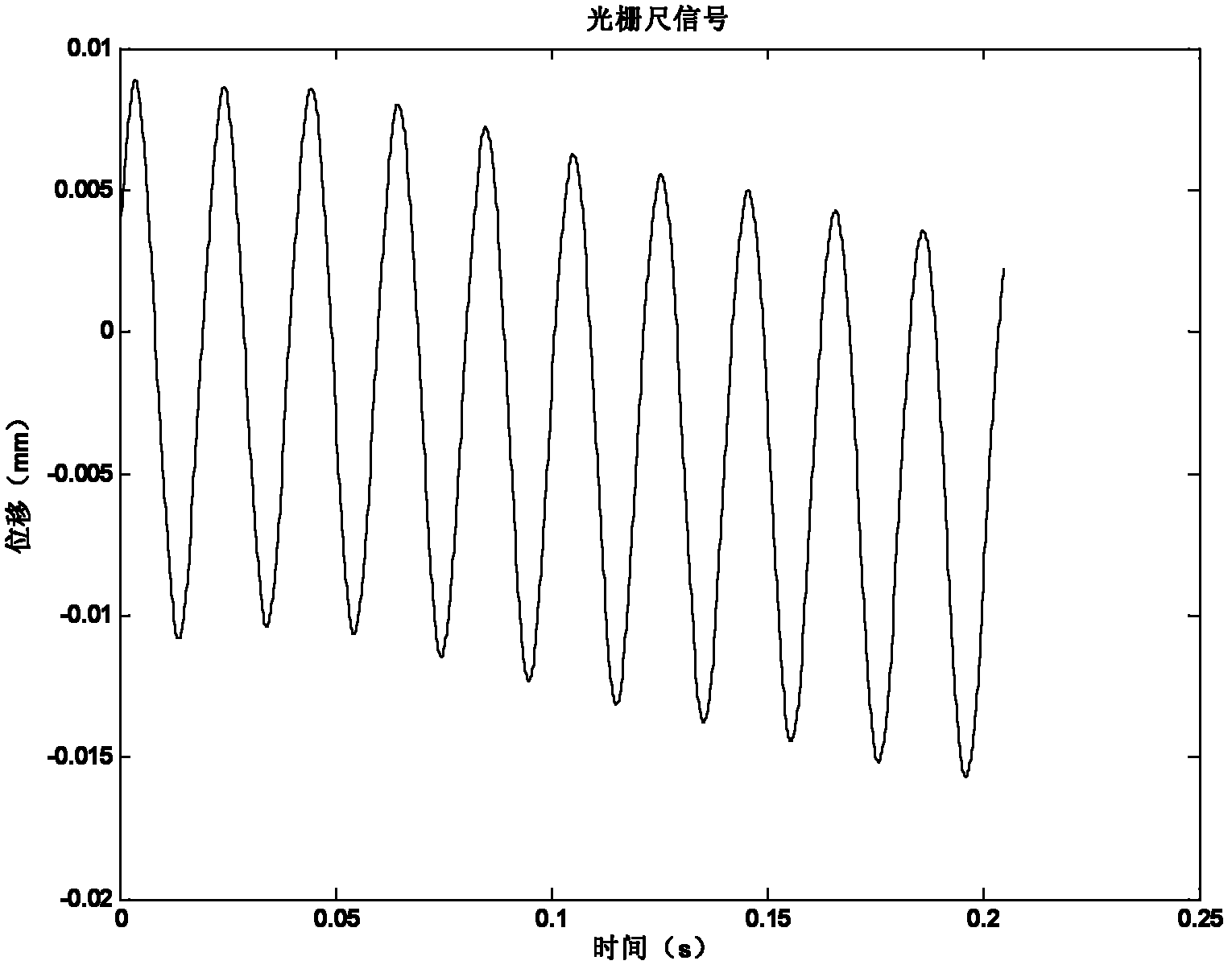
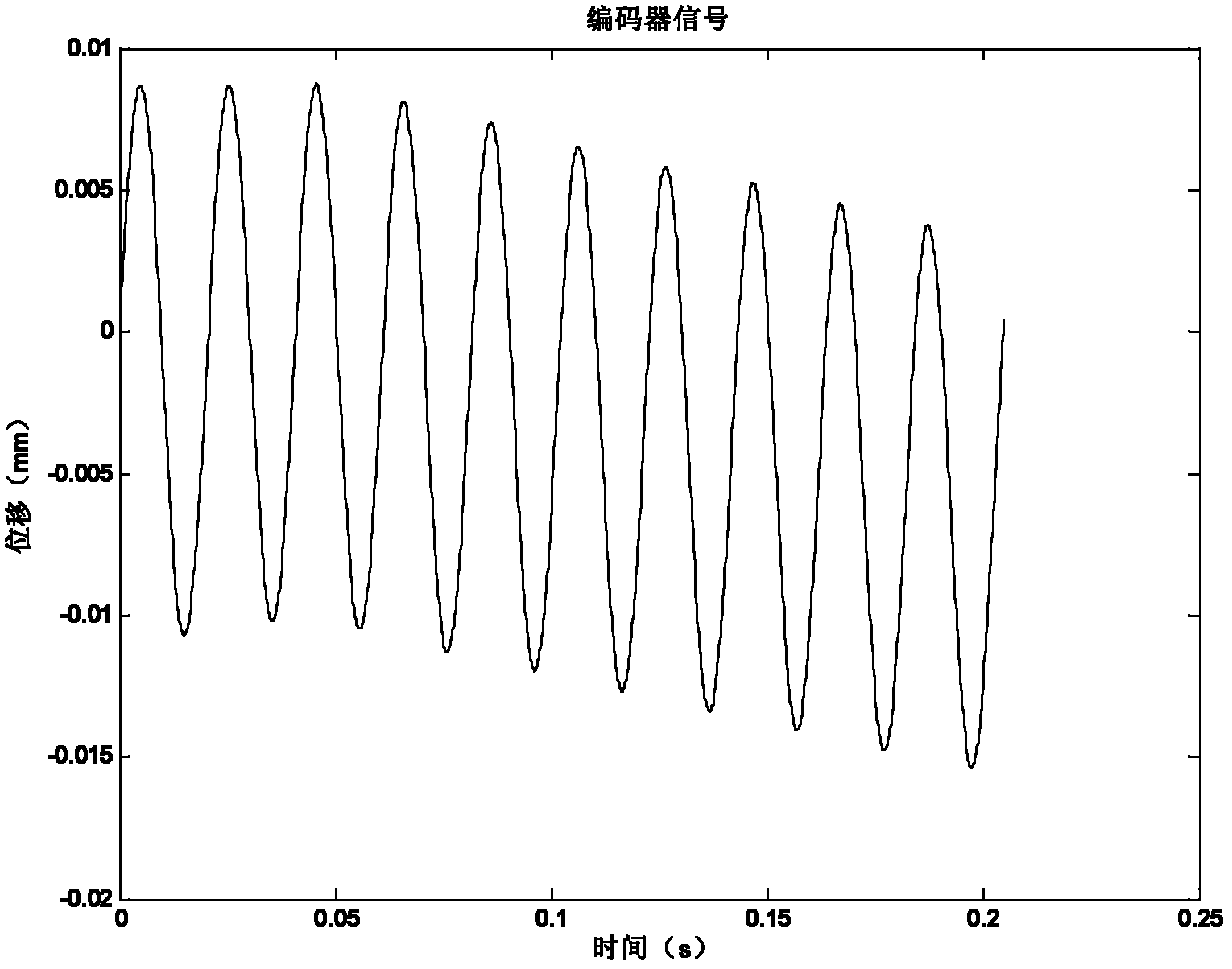
Modal testing method of numerical control machine tool feed system based on built-in sensors
ActiveCN102658503AReduce testing costsRealize online testMeasurement/indication equipmentsNumerical controlModal testing
The invention discloses a modal testing method of a numerical control machine tool feed system based on built-in sensors. The method comprises the following steps: a numerical control machine tool worktable is moved in accordance with given excitation signals, and at the same time servo motor current signals, motor coder signals and grating scale signals are acquired synchronously by using a signal acquisition device; the motor current signals are multiplied by the torque constant of a motor to produce the torque of the motor; second order difference is performed on the coder signals and the grating scale signals to produce acceleration signals of the worktable and angular acceleration of a screw rod; a frequency response function of the torque of the motor and an acceleration of the worktable and a frequency response function of the torque of the motor and an angular acceleration of the screw rod are calculated; fitting is performed on the two frequency response functions to obtain a fitted frequency response function; and axial modal parameters and torsional modal parameters are calculated finally. Compared with conventional modal testing methods, the novel method provided in the invention reduces cost of tests, and can realizes on-line testing of feed system modal parameters.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
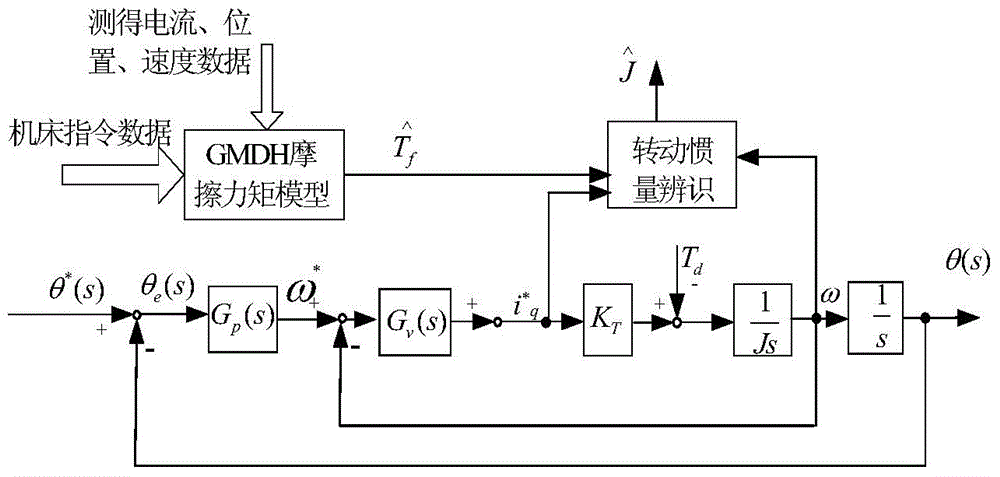
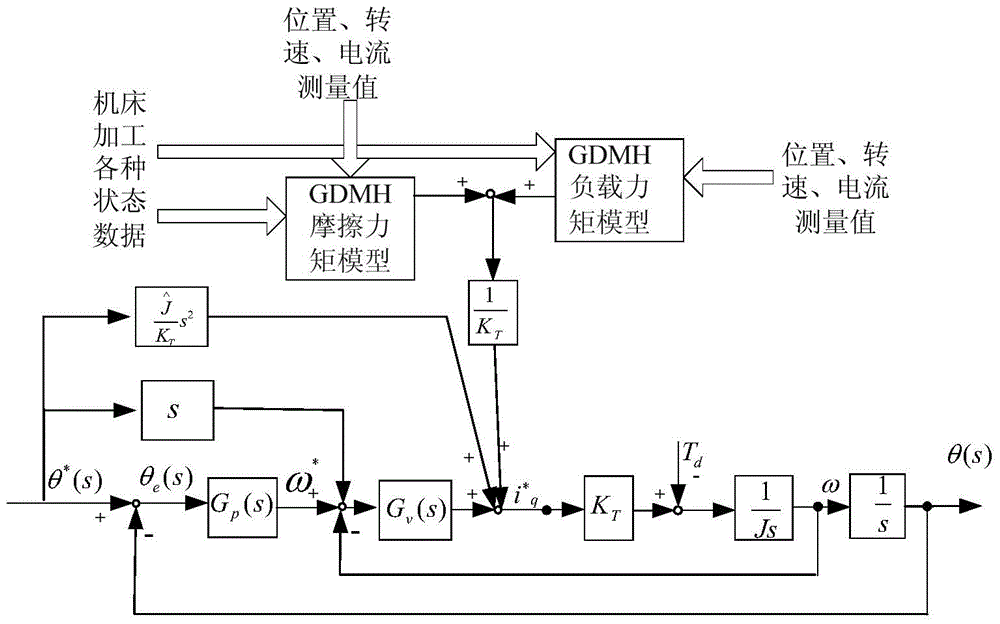
Machine tool feed system feedforward control method based on GMDH (Group Method of Data Handling) data mining algorithm
ActiveCN104950806AImprove fast trackingImprove tracking accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlControl theoryMachine tool
The invention discloses a machine tool feed system feedforward control method based on a GMDH (Group Method of Data Handling) data mining algorithm. The machine tool feed system feedforward control method is characterized by firstly, building a friction moment model and a load moment model of a machine tool by utilizing a GMDH algorithm; secondly, compensating feedforward to an input end of a current loop after dividing the obtained friction moment model and the obtained load moment model by a torque constant of a motor, directly applying the speed of a command signal to an input position of a speed loop at the same time to complete the input of speed feedforward, multiplying the acceleration of the command signal by a coefficient, enabling a result to be acted on an input position of the current loop to complete the input of acceleration feedforward. According to the machine tool feed system feedforward control method disclosed by the invention, the tracking accuracy and high-speed response performance on position are increased, and the machining quality of a workpiece can be increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Inertia estimating controller and control system
ActiveUS7902780B2Increase pointsProgramme controlDC motor speed/torque controlControl systemData storing
Owner:FANUC LTD
Variable magnetic flux-type rotary electric machine
ActiveUS20150340915A1Inhibit amount of magnetic fluxGenerates bulkMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineStator coil
A variable magnetic flux-type rotary electric machine includes a stator and a rotor. The stator includes a stator coil wound on teeth. The rotor defines an air gap between the rotor and the stator. The rotor has at least one permanent magnet arranged in the d-axis magnetic path. The stator and the rotor are arranged relative to the permanent magnet to set a characteristic of d(Kt(I)) / dI≧0 in a range of at or below magnetic saturation of a core material of at least one of the stator and the rotor, where KT represents a torque constant, and I represents an applied current, and a function of KT with respect to I is represented by KT=Kt(I) for a torque Tr acting on the rotor that is represented by Tr=KT×I.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Digital control servo system
InactiveUS20070239290A1Great effective rangeGreat effective resolutionBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsComputer controlDigital controlField of view
A limited rotation motor optical scanning system is disclosed that includes a limited rotation motor scanner, a digital controller servo system, a position feedback unit, a wide angle compensation unit, a digital processor, and an adjustment unit. The limited rotation motor scanner element is adapted for directing an energy beam to at least one location within a field of view. The digital controlled servo system is adapted for controlling motion of the limited rotation motor scanner element in accordance with a servo command waveform. The position feedback unit is for providing a position feedback signal indicative of a rotational position of the limited rotation motor scanner element. The wide angle compensation unit is for receiving the position feedback signal and for providing a boost signal that is representative of a boost factor that compensates for torque constant variation with the rotational position of said limited rotation motor scanner element. The digital processor is for providing a set of control parameters for use during the command waveform in conformance with which the command waveform will be employed to control motion of the limited rotation motor scanner element. The adjustment unit is for providing an adjusted output signal responsive to the control parameters and responsive to the boost signal to control the motion of the limited rotation motor scanner element while compensating for torque constant variation with the rotational position of the limited rotation motor scanner element during the command waveform.
Owner:THE GSI GRP LLC
Combined stator structure with flat winding
InactiveCN1469526AAccurately control the number of turnsAdjust the back EMF voltageMagnetic circuit stationary partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionStator coilCounter-electromotive force
The present invention is one combined stator structure with flat winding. When great work current is needed, the combined stator structure has high duty ratio, correct winding turn number, and precisely controlled torque constant or counter electromotive force, and this makes the motor or generator in fixed volume obtain accurately designed maximum rotation speed or counter electromotive force.The flat winding has low copper wire impedance, and this makes the motor or generator possess high operation efficiency.
Owner:GRIZZLY TECH CORP
System and method of damping vibration on coil supports in high performance disk drives with rotary actuators
InactiveUS20040095682A1Improve performanceImprove throughput performanceApparatus modification to store record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionMulti materialElectric machine
A damping assembly for the actuator of high performance disk drive assembly is formed from multiple materials. The damping assembly is added to the actuator to dampen vibration that occurs during operation of the drive. The damping assembly is connected to an exterior portion of a coil region of the actuator. The damping assembly helps dampen vibration modes for coil torsion and coil bending, thereby improving dynamics settling performance to improve overall file input / output throughput performance. This also allows for a higher voice coil motor torque constant by increasing the magnet radius, thereby also improving move time, which further improves file input / output throughput performance. The overall file performance is improved by reducing settling times associated with coil torsion and coil bending modes, and allowing a higher torque constant to also improve move time. Both of these effects contribute to improving file performance.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Air conditioning valve actuator for a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6853160B1Improve efficiencySmall size and weightAir-treating devicesSafety arrangmentsMobile vehicleValve actuator
An air conditioning valve actuator for a motor vehicle operating on an electric step motor with a permanent magnet capable of delivering mechanical power at least equal to 50 mW, and a reduction unit for decreasing the amplitude of the angular pitch and increase the output torque. The motor is defined by the following relationship: 10−6<γ2 / R0<, wherein: γ is the torque constant, proportional to the magnet volume and, R0 is the characteristic coefficient of the volume of copper and the length of the average turn of the coils, in which R0=ρ.Lsp / (Scu.σ), ρ being the resistivity of copper, Lsp being the length of the average turn of a coil, Scu being the copper section of a coil and σ the filling coefficient of a coil. A controller is cooperative with the motor power supply enabling to accelerate gradually the frequency of the supply of the windings.
Owner:SOC IND DE SONCEBOZ
Method for controlling a motor
ActiveUS20120119686A1Improve efficiencyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersTorque constantDc current
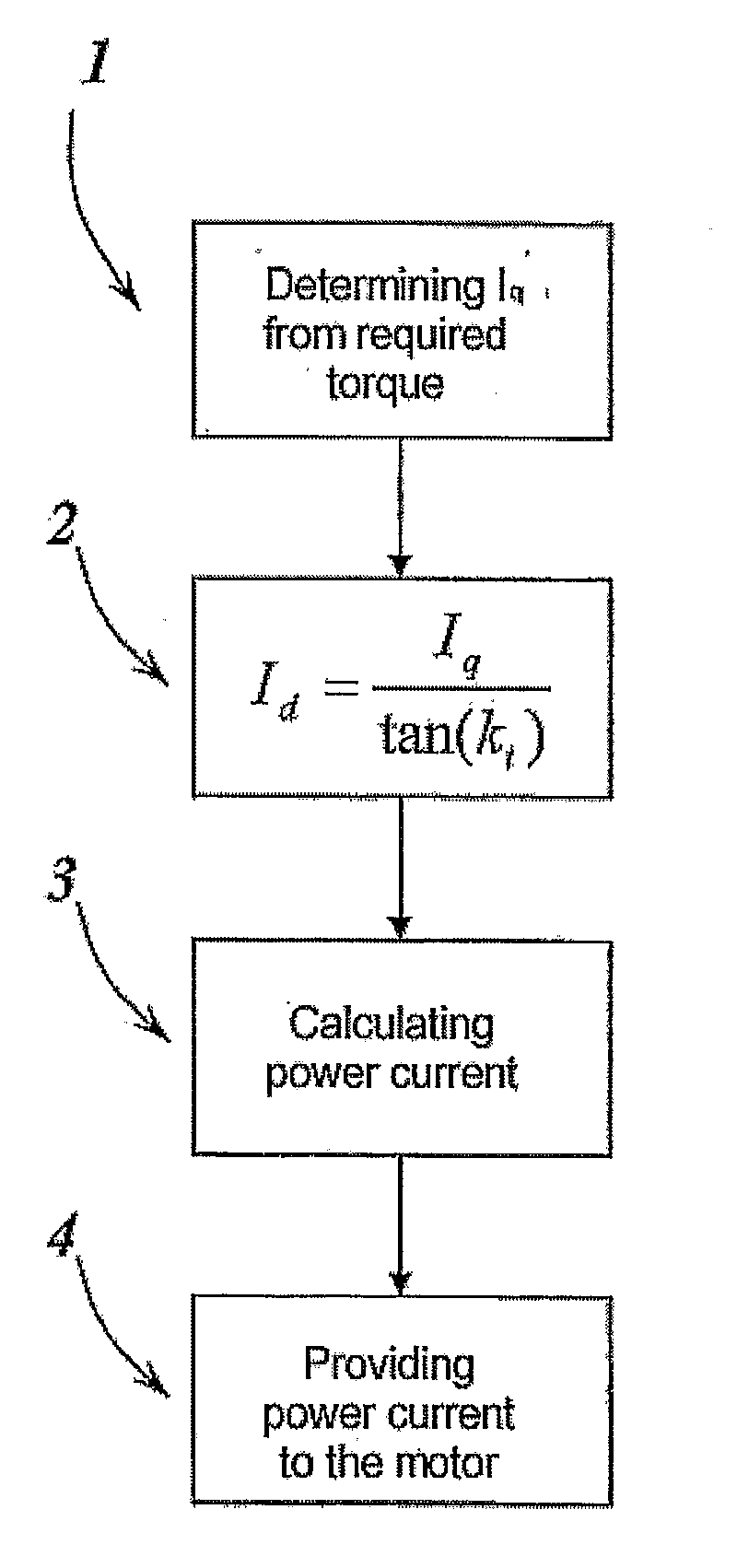
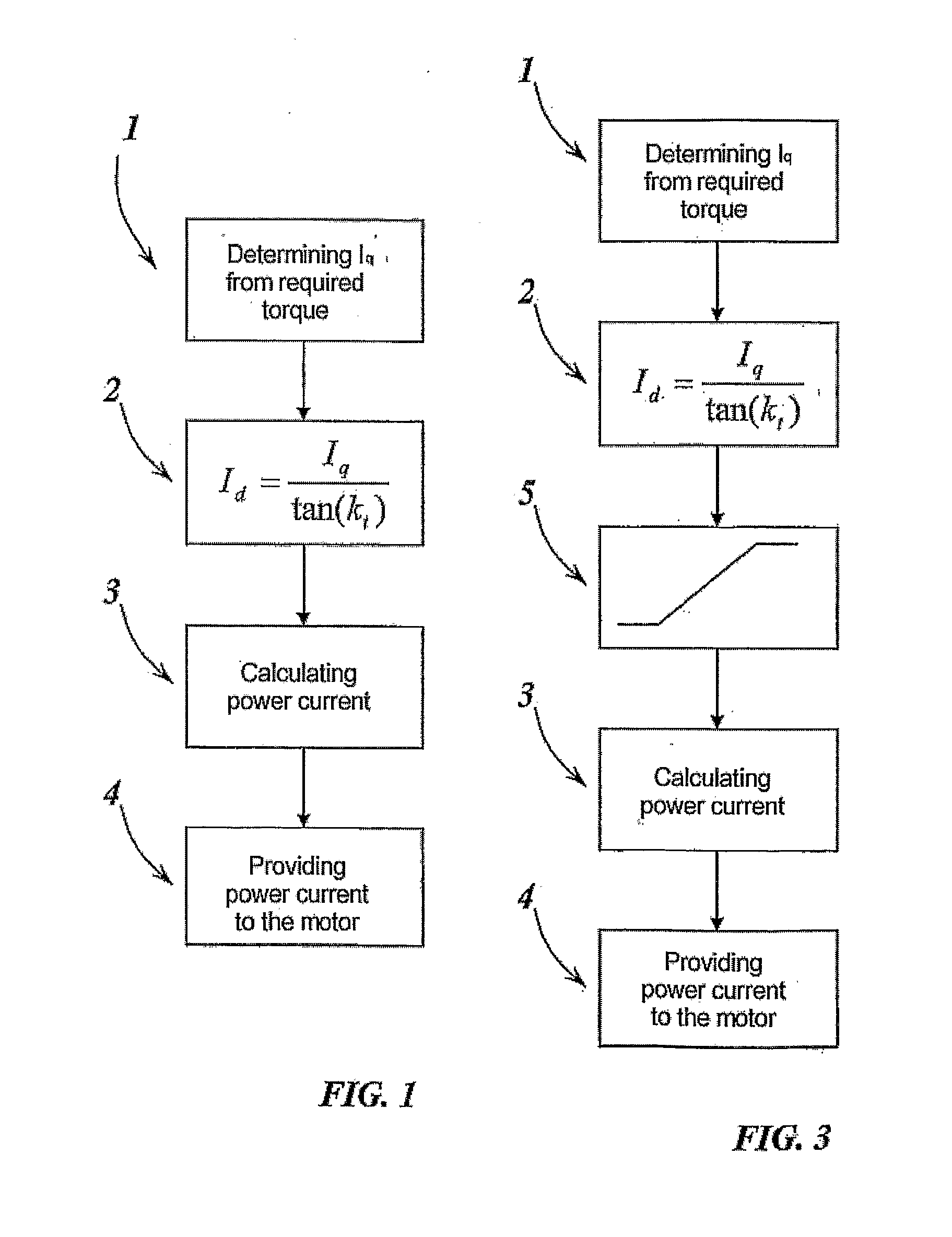
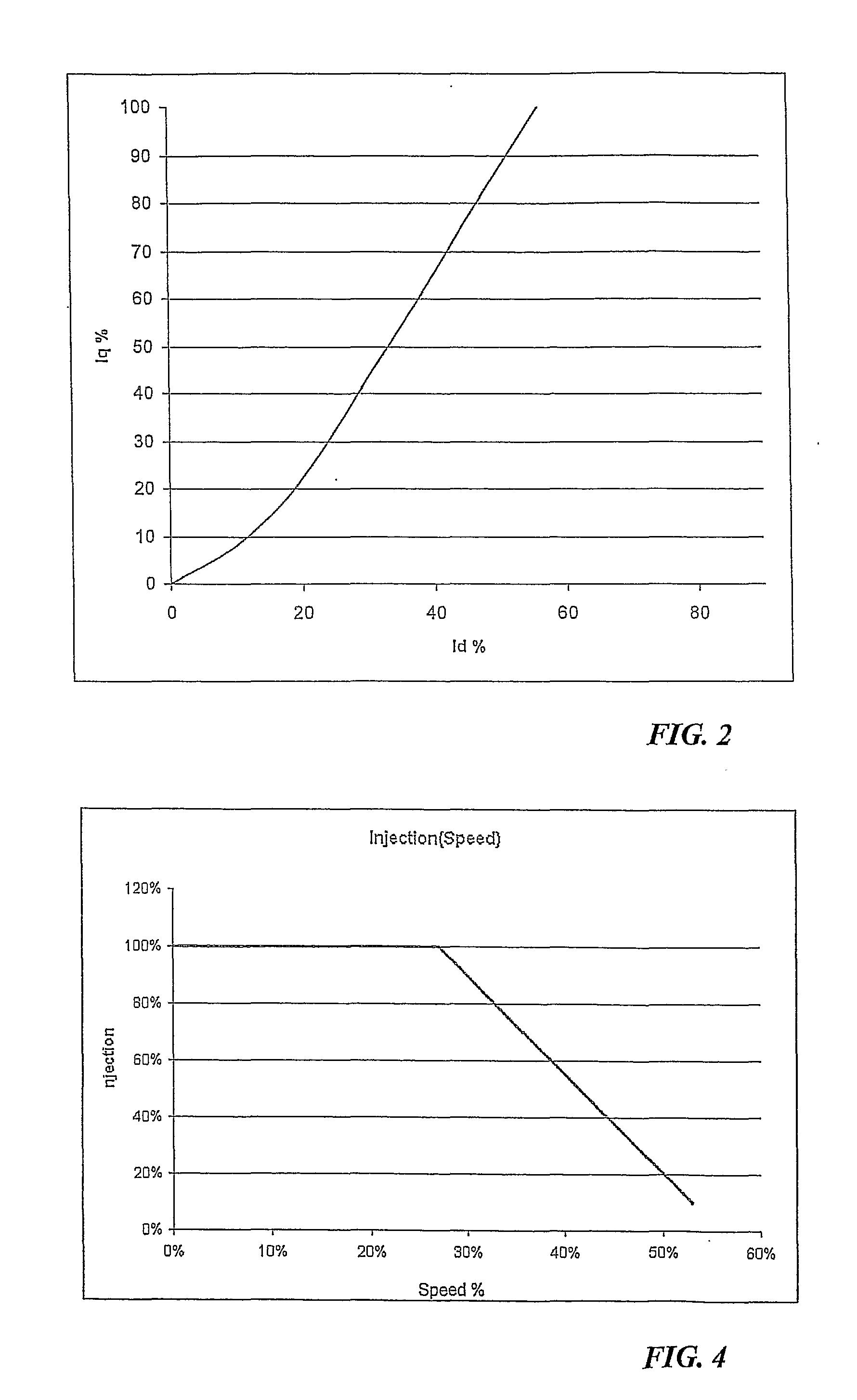
A method for controlling a motor by an inverter and by a vectorial technique, comprising the following steps: determining the value of a quadrature current Iq necessary for said motor to generate the desired torque; calculating the value of a direct current to be supplied to the motor by an equation as a function of the phase of the current vector on which the torque constant of the motor depends; calculating the power current of said motor from the direct current and the quadrature current; supplying the power current to the motor through the inverter.
Owner:KSB AG
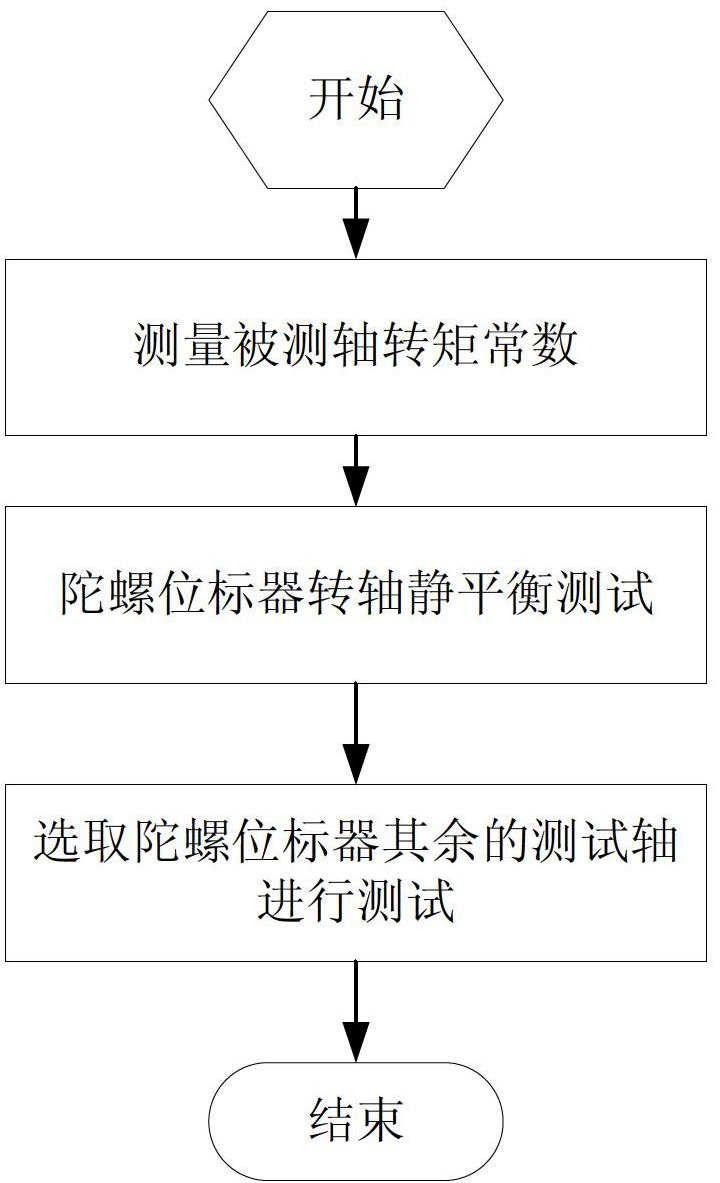
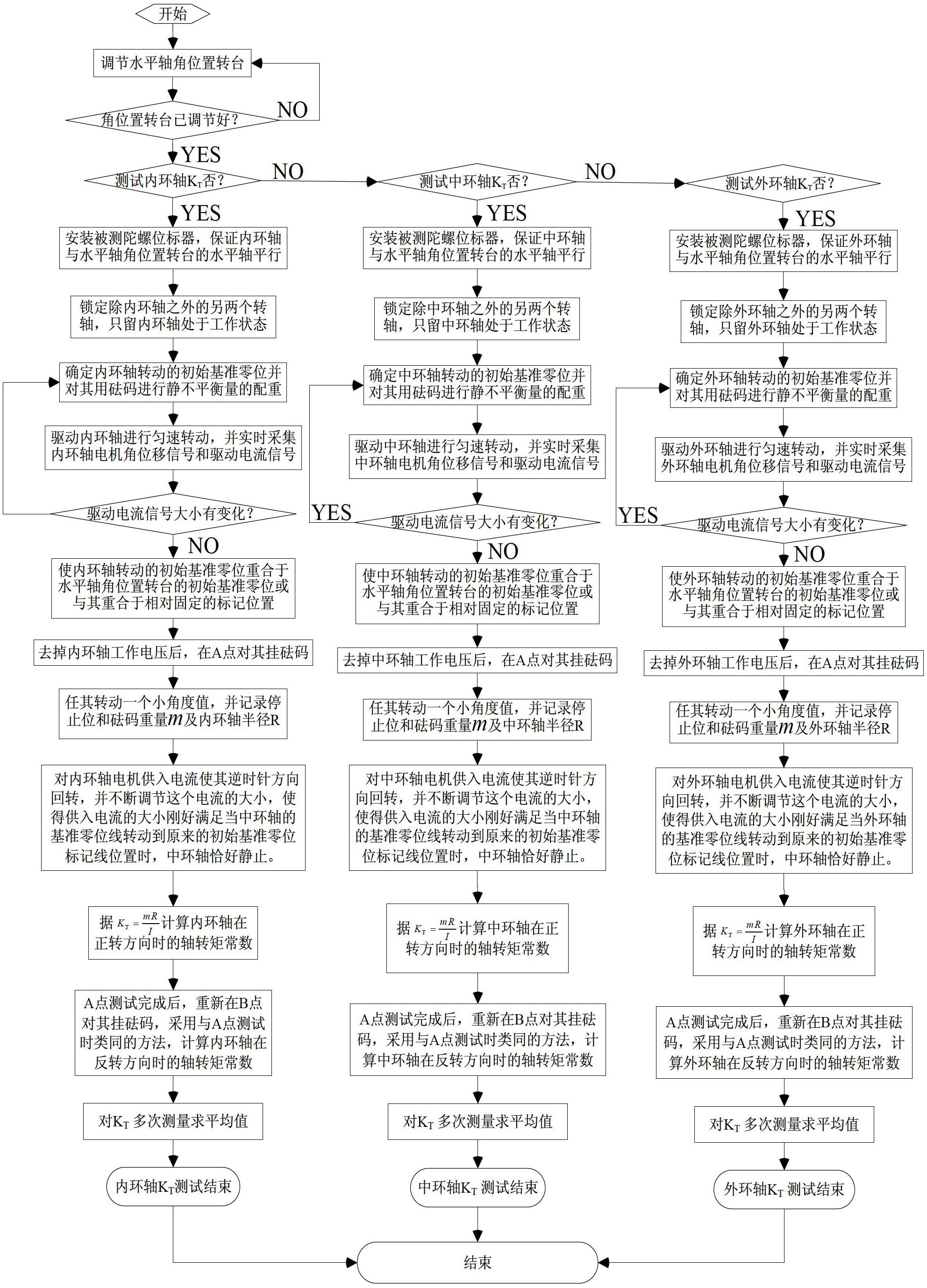
Static balance test method applied to gyroscope position marker spindle
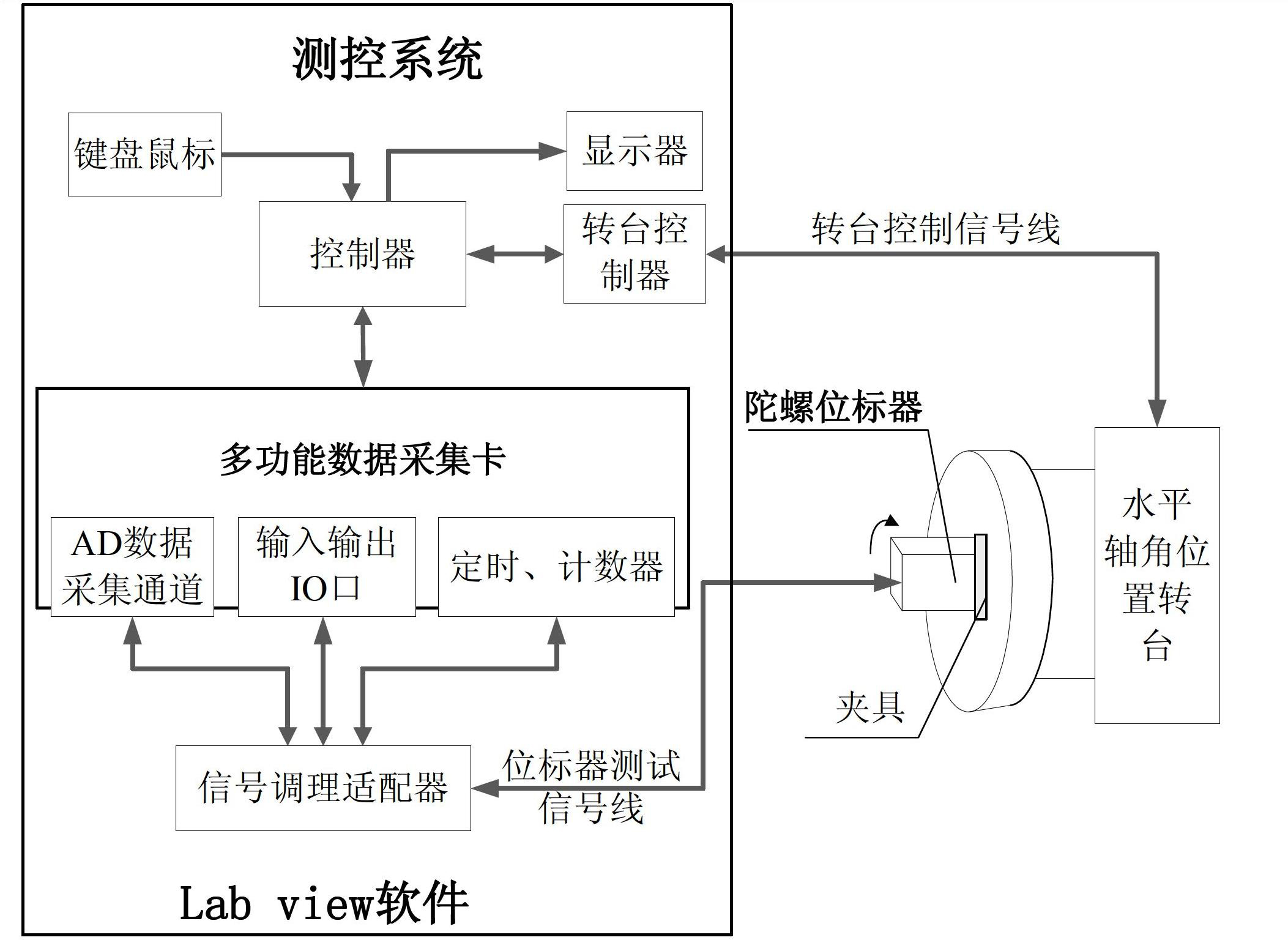
InactiveCN102679970AHigh control precisionQuick noteSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesAxis–angle representationSpecific test
The invention discloses a static balance test method applied to a gyroscope position marker spindle. A horizontal axis angular position rotary table is used for mounting and clamping a gyroscope position marker to be tested, any one axis to be tested of the gyroscope position marker is parallel to the horizontal axis of the rotary table by adjusting direction of a mounting fixture, a measurement and control system drives the tested axis to complete sine small angle vibration at each locking angular position of the rotary table, value of a static unbalance can be solved by virtue of integration on measured quantities in a driving current period of the tested axis, and position of the static unbalance can be obtained by observing the driving current and an angular position signal and combining a corner of the horizontal rotary table. The concrete test process comprises the following steps of: step one, measuring torque constant of the tested axis; step two, carrying out static balance test on the gyroscope position marker spindle; and step three, selecting the rest test axes of the gyroscope position marker and carrying out test, after the tested axis is determined, repeating the step one and the step two, and finally completing test on three tested axes, namely an outer annular axis, a middle annular axis and an inner annular axis, thus the test method disclosed by the invention is finished.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
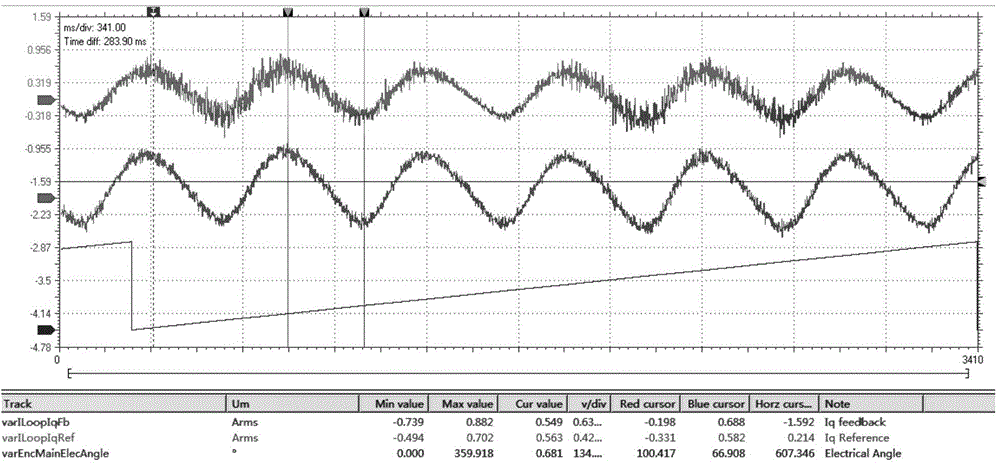
Cogging-torque test method for alternating-current permanent-magnet synchronous servo motor
InactiveCN104655339AGuaranteed uptimeEasy to useWork measurementTorque measurementElectric machineEngineering
The invention relates to a cogging-torque test method for an alternating-current permanent-magnet synchronous servo motor. According to the cogging-torque test method, a servo driver is utilized to drive a tested motor to stably rotate at a lower rotating speed, an encoder is utilized to detect the speed and the position information of the motor, and the cogging torque of the motor can be tested through the combination of recorded feedback currents at different positions with the torque constant of the electric current. According to the cogging-torque test method disclosed by the invention, no special tool or work equipment needs to be prepared, all that is needed is to connect the motor with the driver and regulate the control parameters to proper values, so that the motor can stably run at a lower rotating speed, then data can be acquired, and the cogging torque can be calculated; the cogging-torque test method is simple and convenient in usage.
Owner:PHASE MOTION CONTROL NINGBO
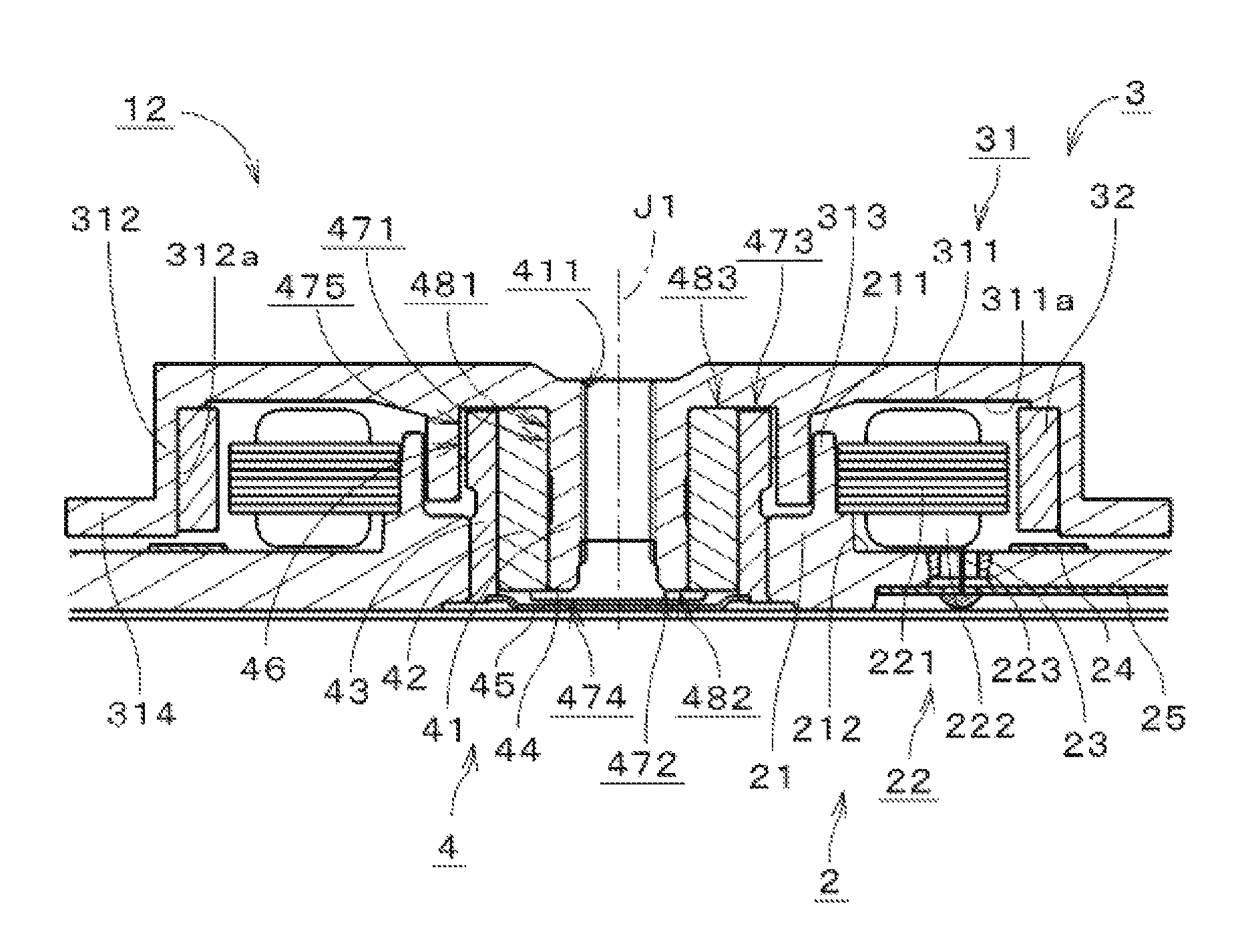
Spindle motor and disk drive apparatus
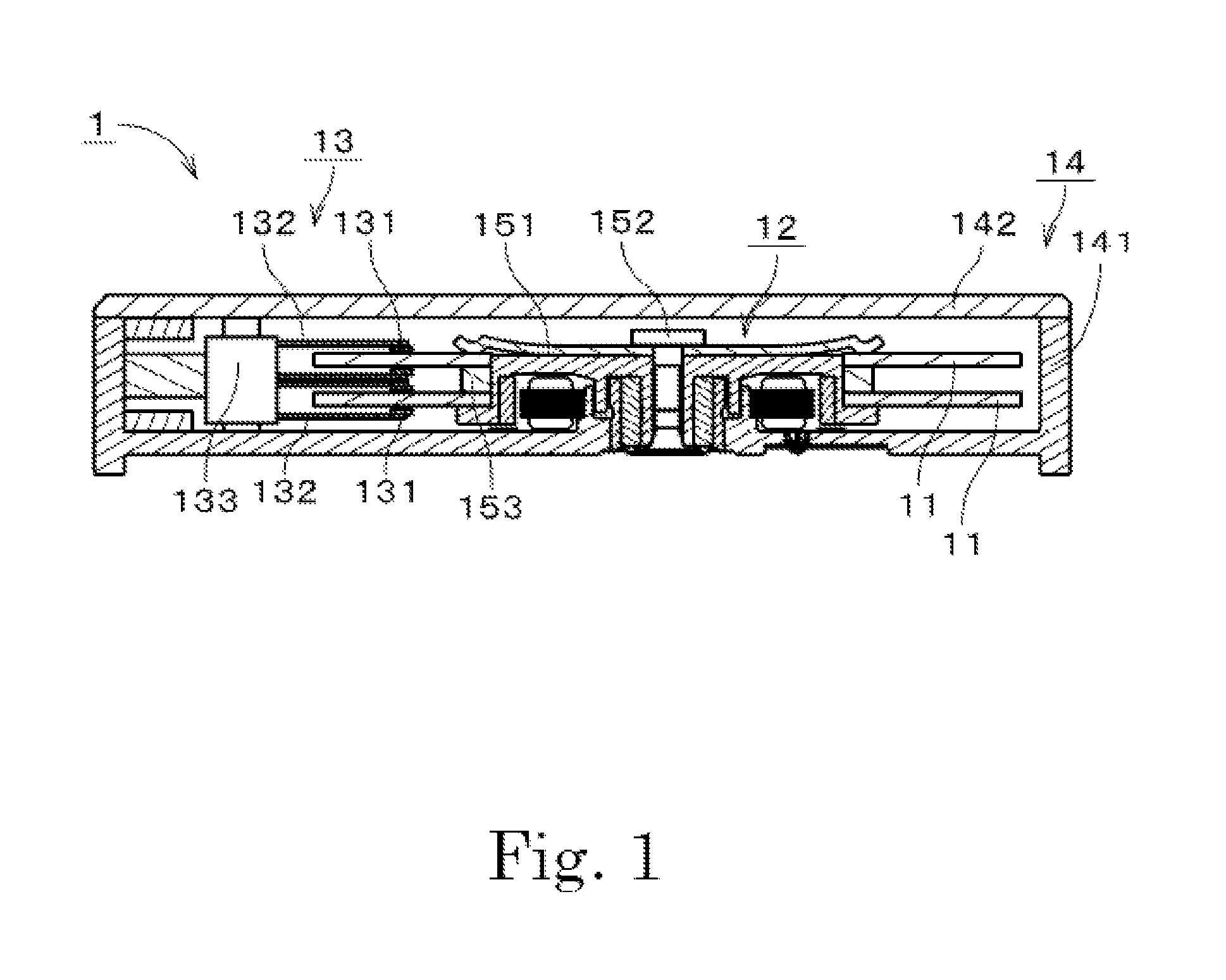
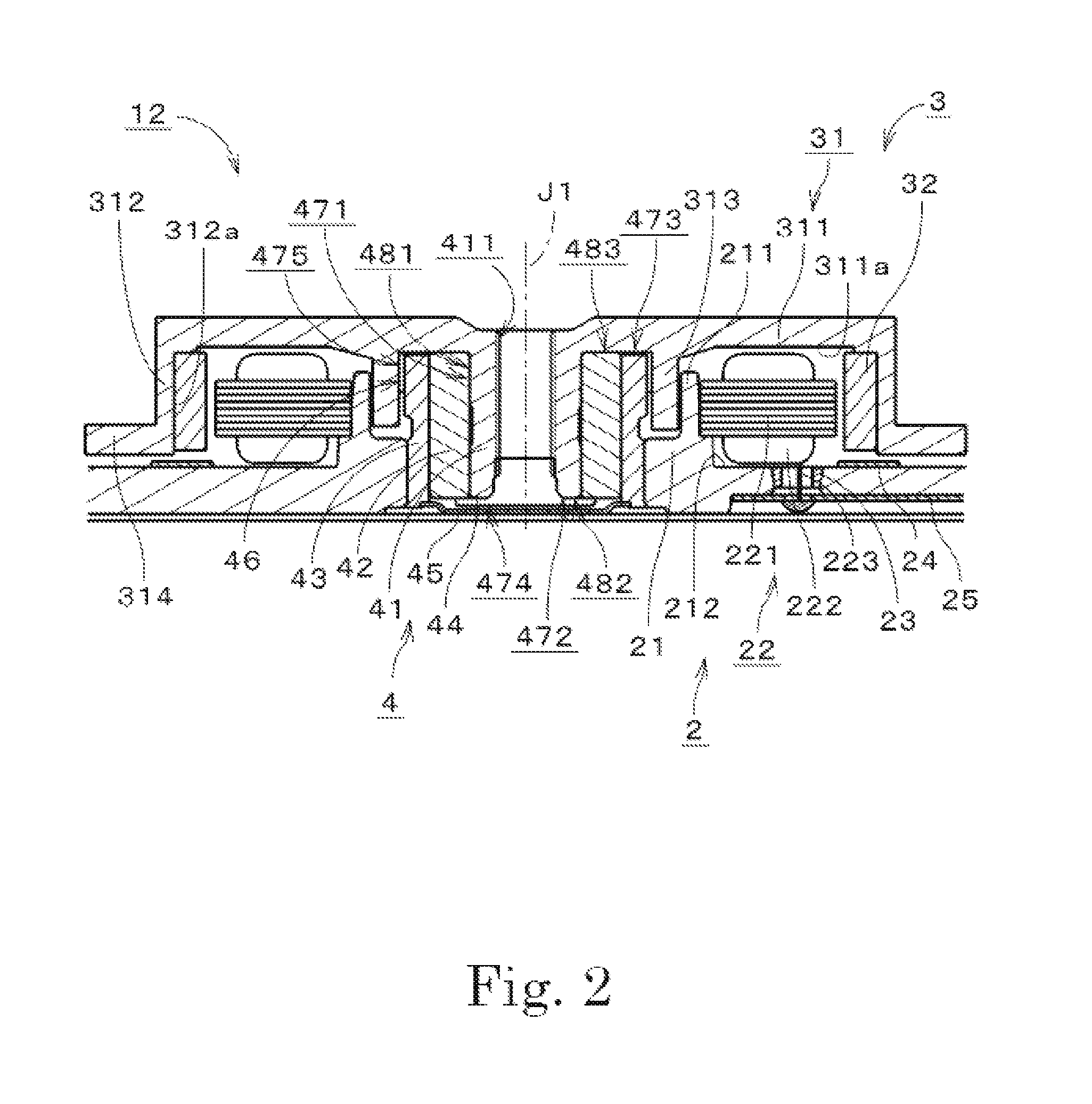
ActiveUS8599517B1Sufficient torqueReduce startup timeRecord information storageRecording on magnetic disksRotor magnetsElectric machine
A spindle motor of a disk drive apparatus includes a base unit, a stator, a covered cylindrical rotor hub, a rotor magnet, and a bearing mechanism. The rotor magnet is an Nd—Fe—B bond magnet. The thickness of the rotor magnet in the radial direction is about 0.7 mm or more and about 1.0 mm or less. The distance between the rotor magnet and the stator core in the radial direction is about 0.15 mm or more and about 0.20 mm or less. A torque constant Kt of torque generated between the stator and the rotor magnet is about 4 mN·m / A or more and about 6 mN·m / A or less. A motor constant Km is about 2 mN·m / (A·√Ω) or more and about 4 mN·m / (A·√Ω) or less.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com