Patents
Literature
996results about "Motor control for motor oscillations damping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Motor control device
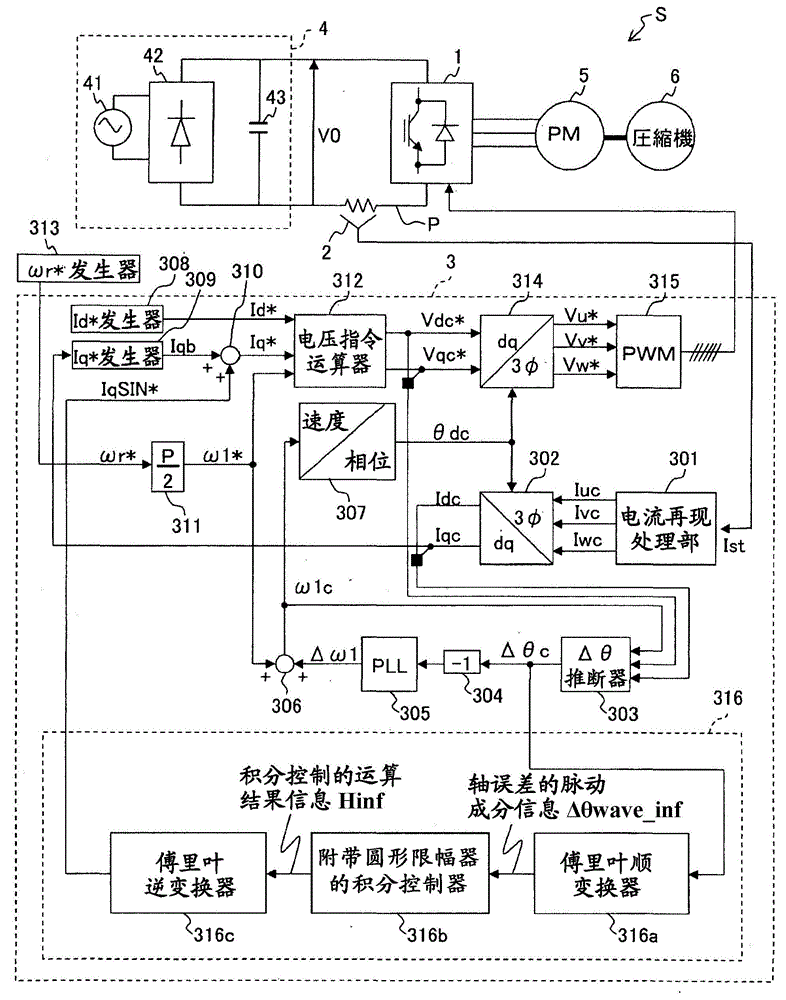
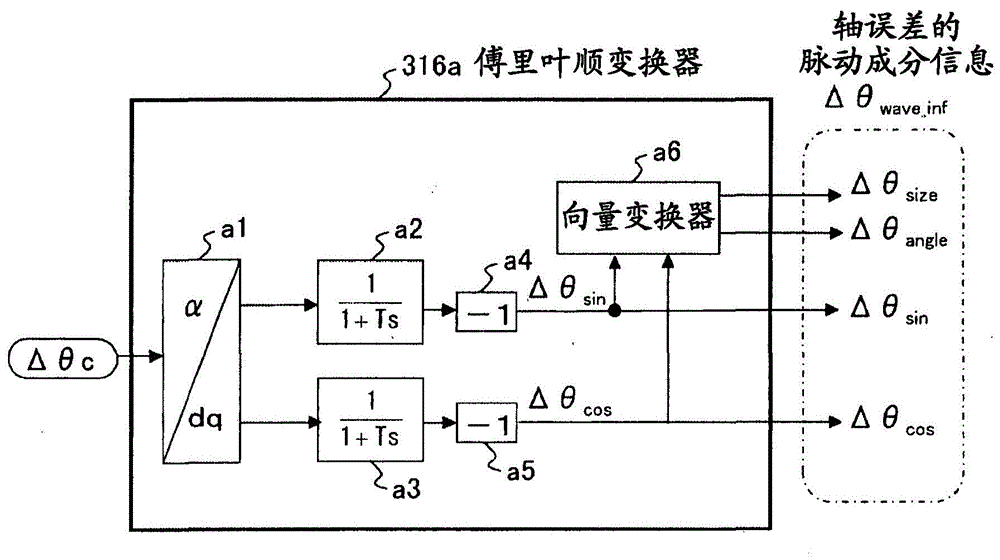
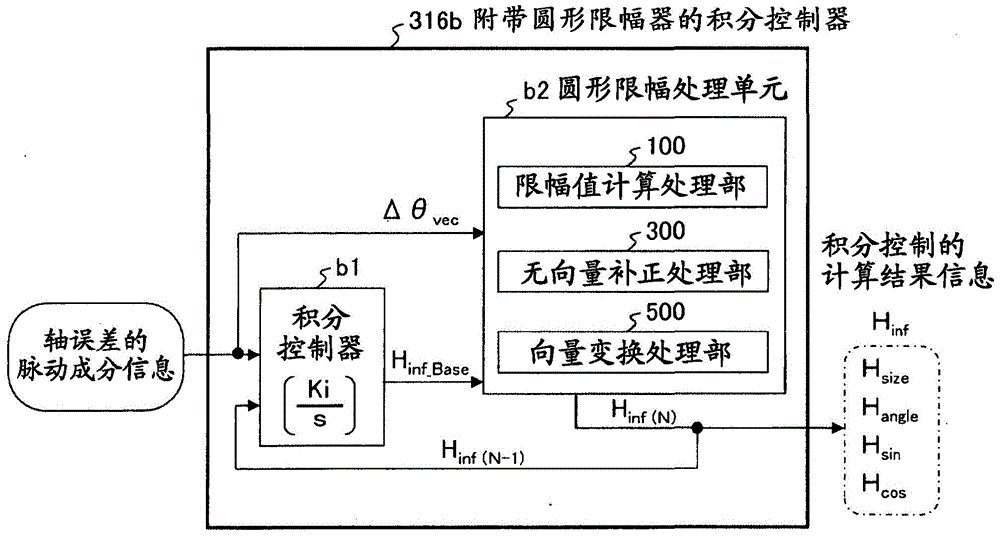
ActiveCN104038127ASuppression of pulsating torqueVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlCurrent sensorIntegral controller
A motor control device capable of suitably inhibiting the pulsating torque of an alternating-current motor is provided. The motor control device comprises an axis error inference machine (30) which infers an axis error based on a current value of an inverter, detected by a current sensor (2); a Fourier rectification machine (316a) which extracts an axis error vector from the time-base changes of the axis error; an integral control machine (316b) additionally provided with a circular amplitude limiter, which is used to calculate a correction current vector for offsetting the pulsating torque, wherein a circle with a set amplitude limiting value serving as the radius is used as the base for limiting the movement of the correction current vector, and the integral control machine (316b) additionally provided with the circular amplitude limiter performs the circular amplitude limiting for limiting the movement of the correction current vector so as to enable the deflection angle of the correction current vector to be close to the deflection angle of the axis error vector.
Owner:HITACHI JOHNSON CONTROLS AIR CONDITIONING INC
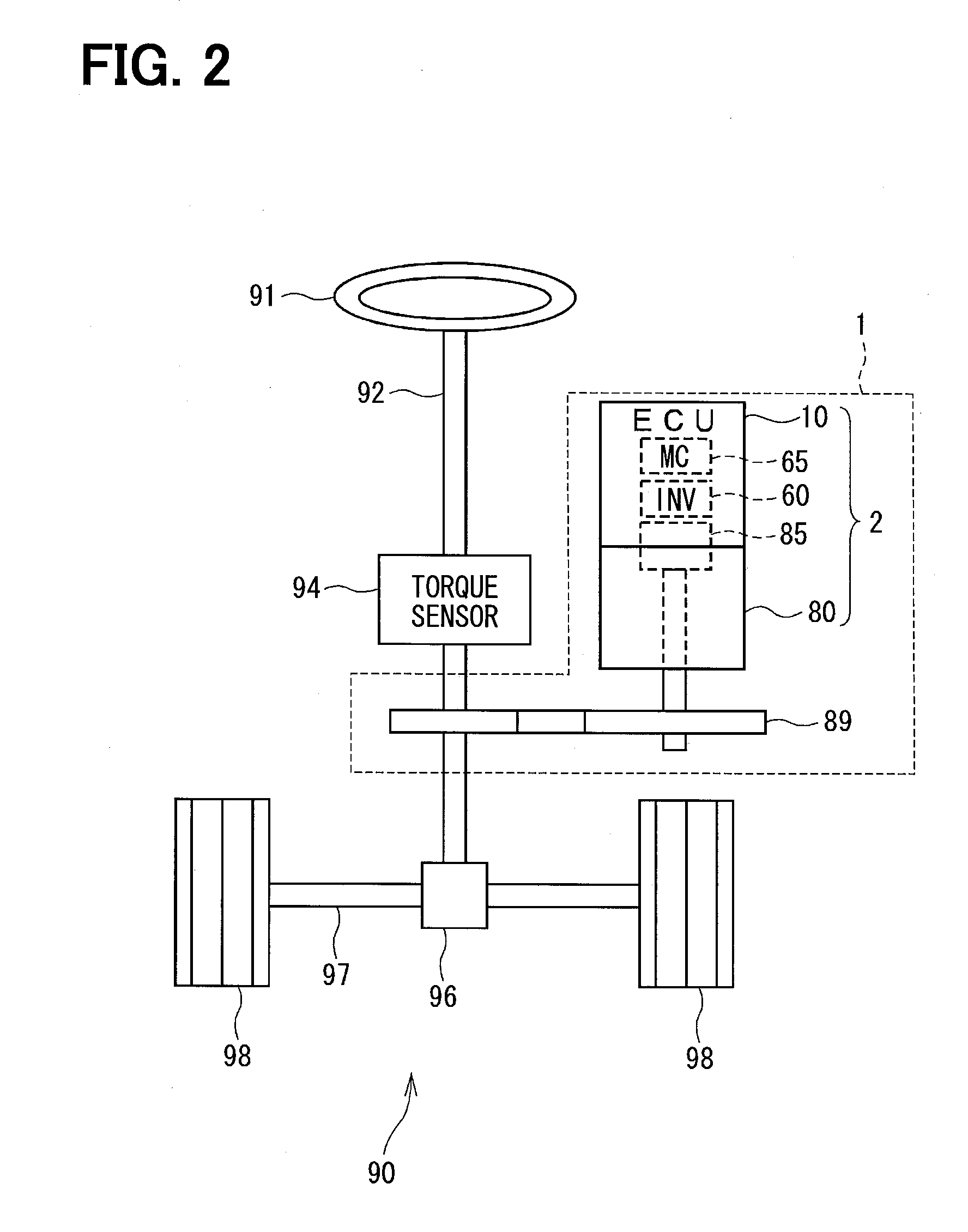
Motor drive apparatus, electric actuator and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20060001392A1Increase driving speedHigh areaTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringHigher order harmonics
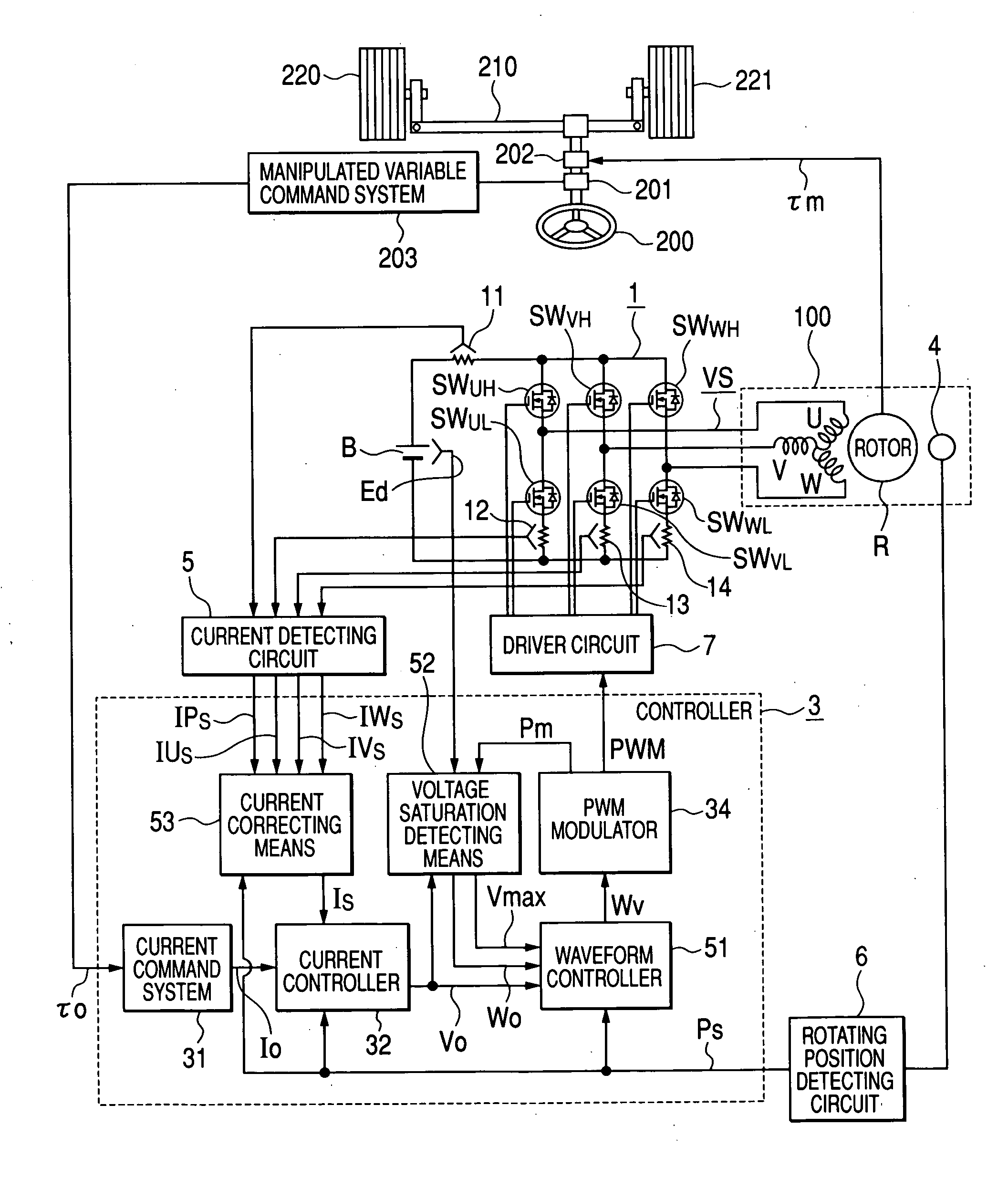
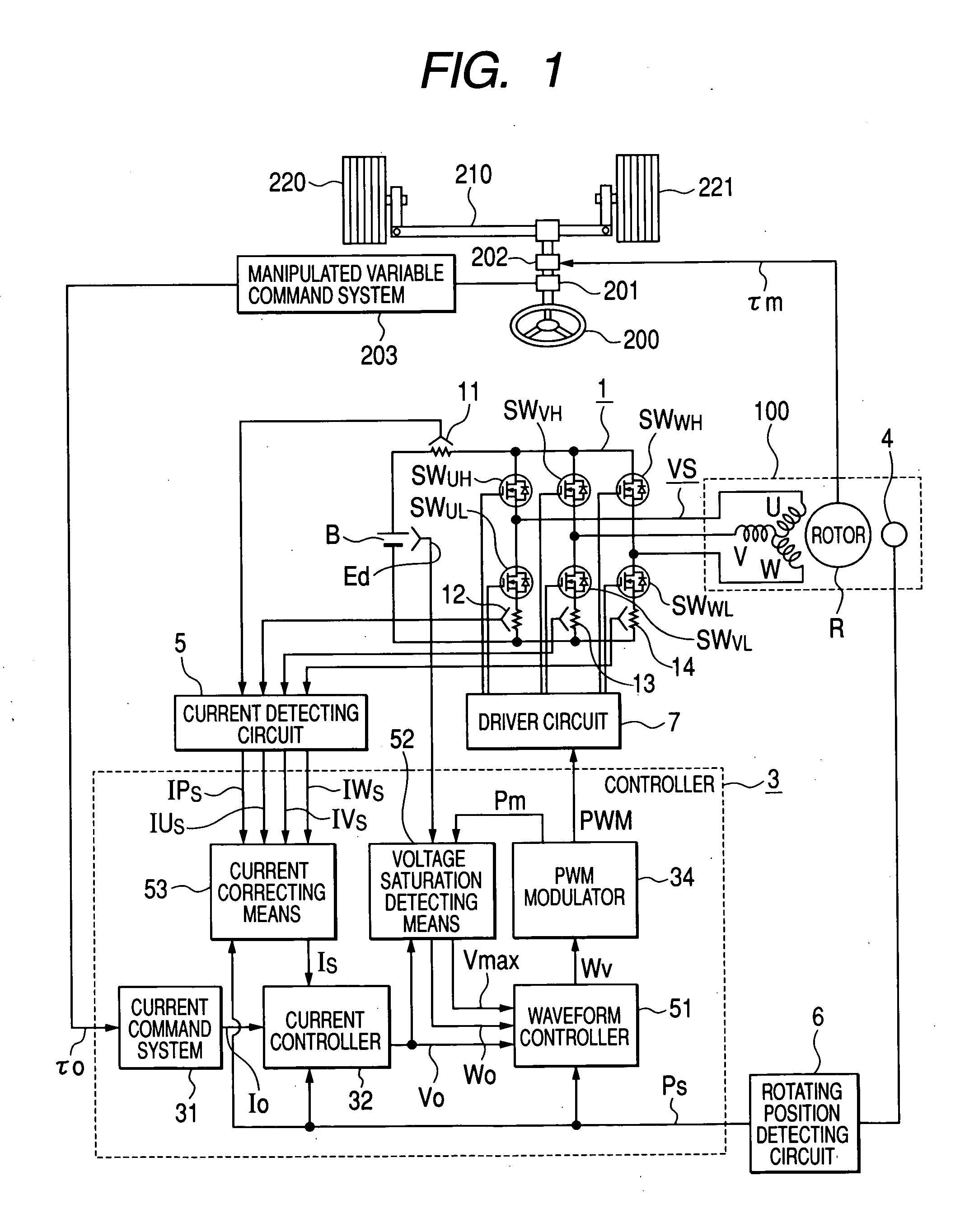
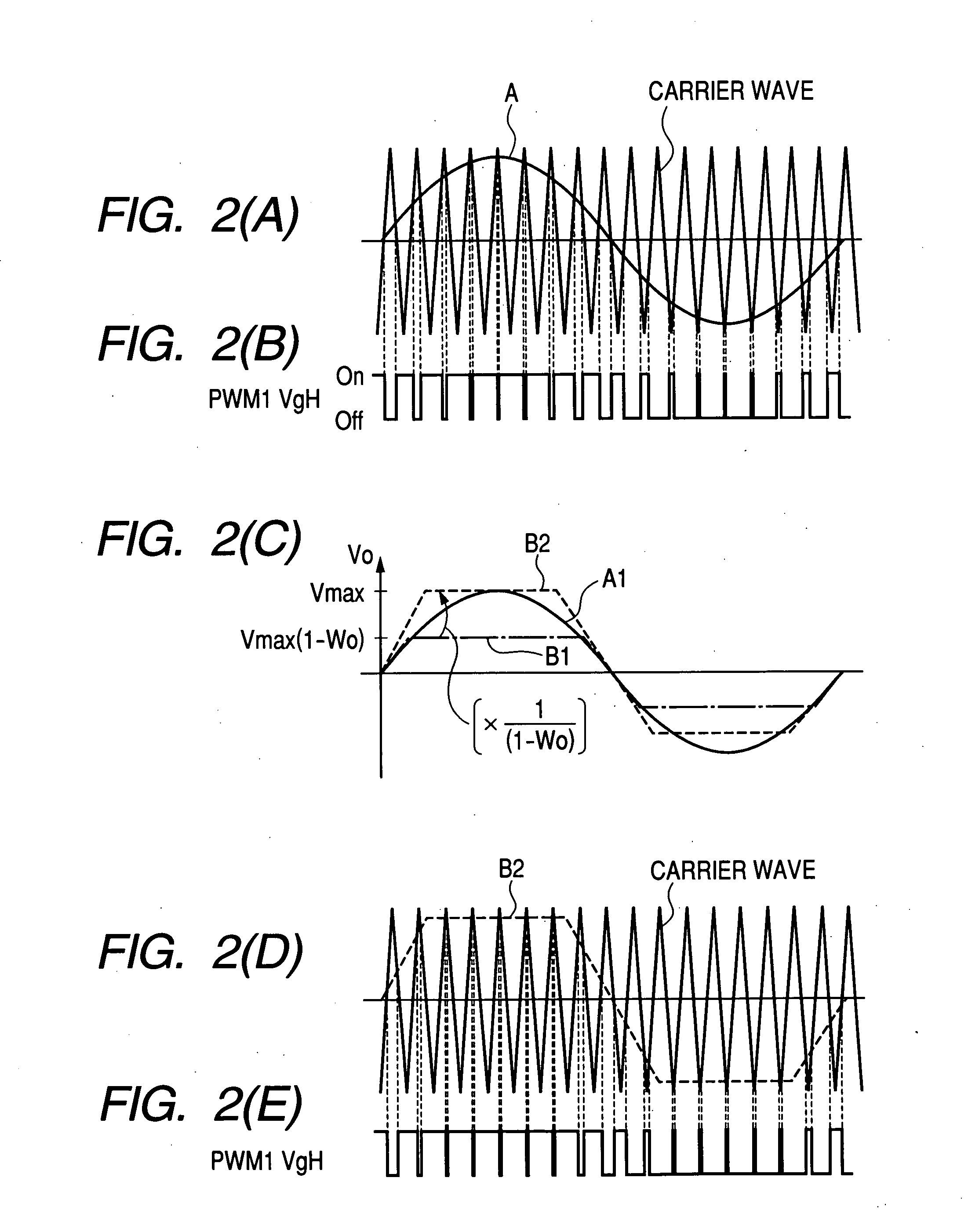
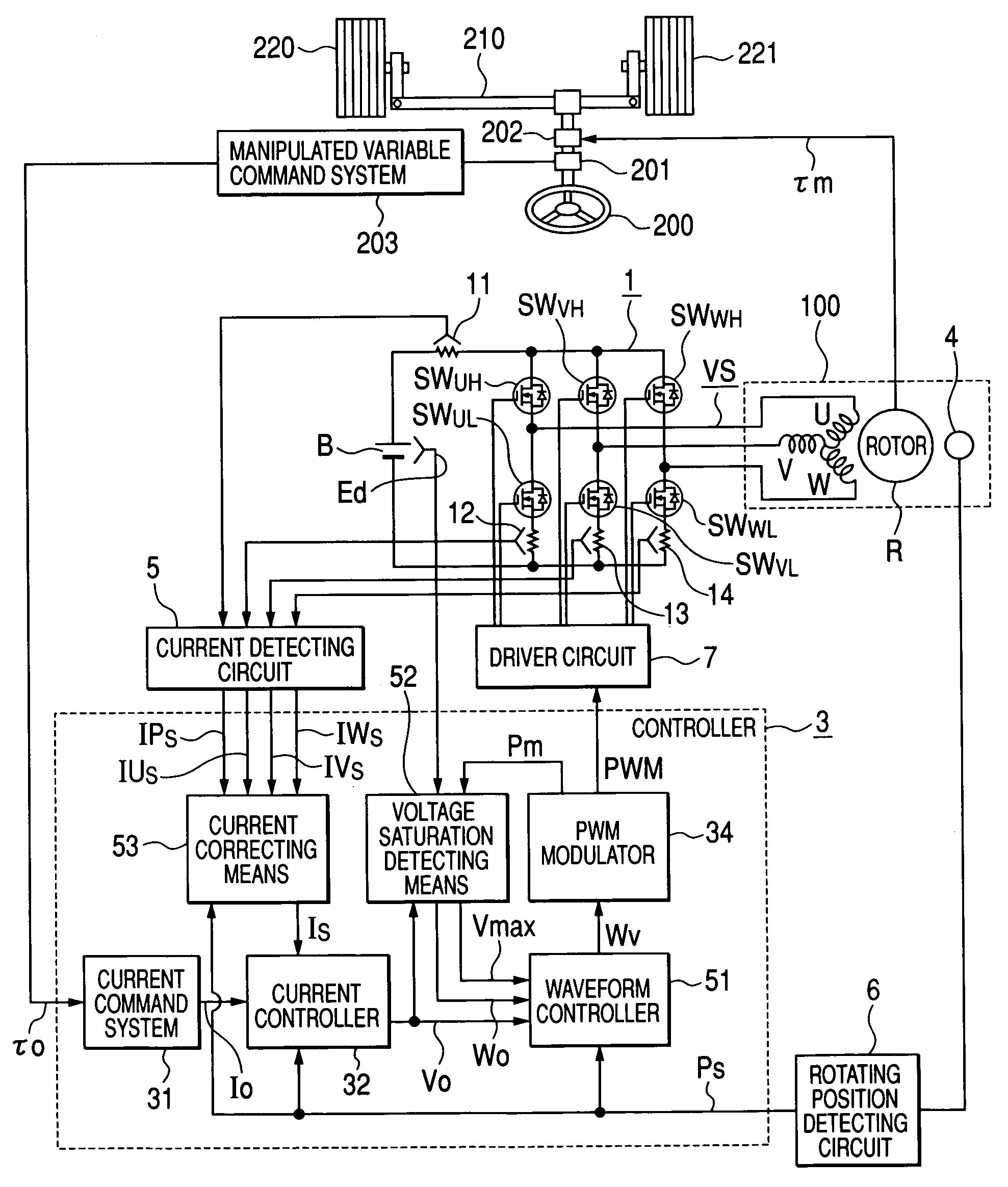
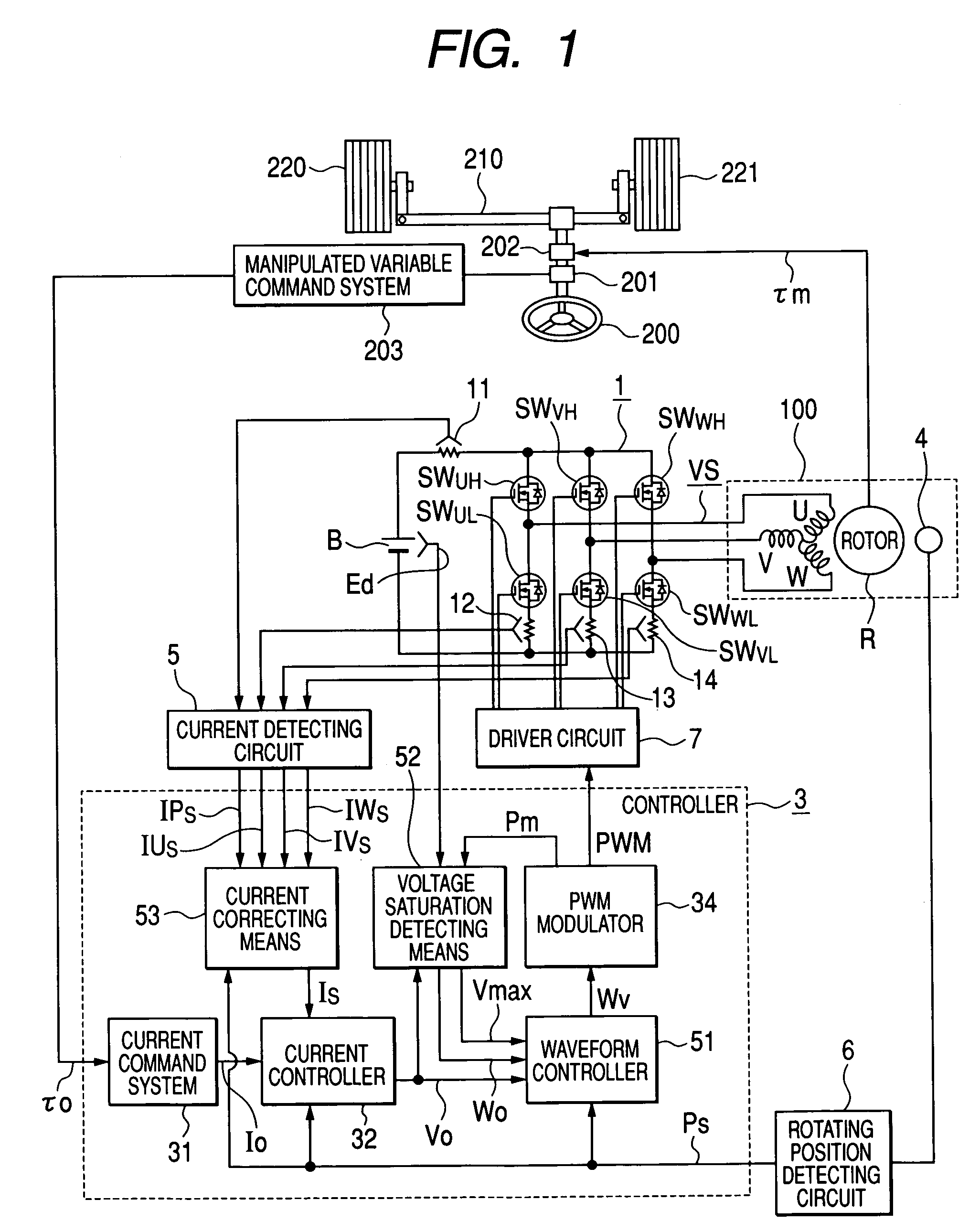
In an operation range of an actuator subjected to quick acceleration and deceleration, a motor drive apparatus, an electric actuator and an electric power steering apparatus capable of continuous torque control up to the high drive speed and high torque area. A controller comprises a voltage saturation detecting means for detecting the voltage saturation of the output voltage of an inverter circuit, based on the battery voltage, and a waveform controller that converts the drive waveform of the inverter circuit into the waveform created by superimposing harmonics of high odd-numbered order on a sinusoidal wave as a fundamental wave of the modulated wave modulated by a PWN carrier wave; and continuously changes the ratio of superimposing the high-order harmonics in response to the voltage saturation detected by a voltage saturation detecting means. This arrangement allows the controller to continuously change the drive waveform of the inverter circuit.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Motor drive apparatus, electric actuator and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS7161323B2Increase torqueTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringMotor drive
The disclosure concerns a a motor drive apparatus, an electric actuator and an electric power steering apparatus capable of continuous torque control up to the high drive speed and high torque area, in order to enable quick acceleration and deceleration. A controller comprises a voltage saturation detecting apparatus for detecting the voltage saturation of the output voltage of an inverter circuit, based on the battery voltage, and a waveform controller that converts the drive waveform of the inverter circuit into the waveform created by superimposing harmonics of high odd-numbered order on a sinusoidal wave as a fundamental wave of the modulated wave modulated by a PWN carrier wave; and continuously changes the ratio of superimposing the high-order harmonics in response to the voltage saturation detected by a voltage saturation detecting means. This arrangement allows the controller to continuously change the drive waveform of the inverter circuit.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Vehicle equipped with motor and inverter
ActiveUS20100052583A1Reduce noiseIncrease fuel consumptionSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsFrequency changerDrive wheel
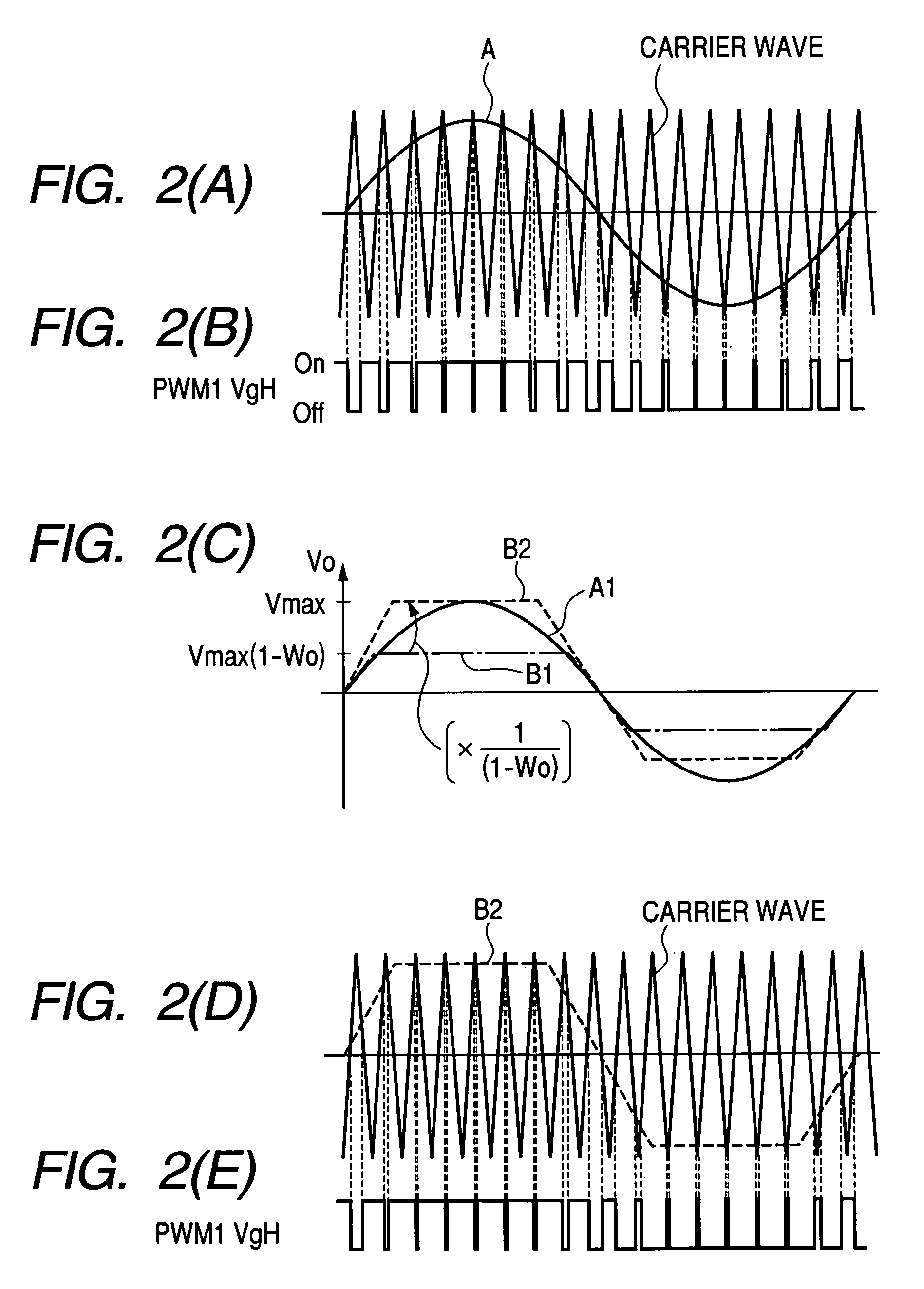
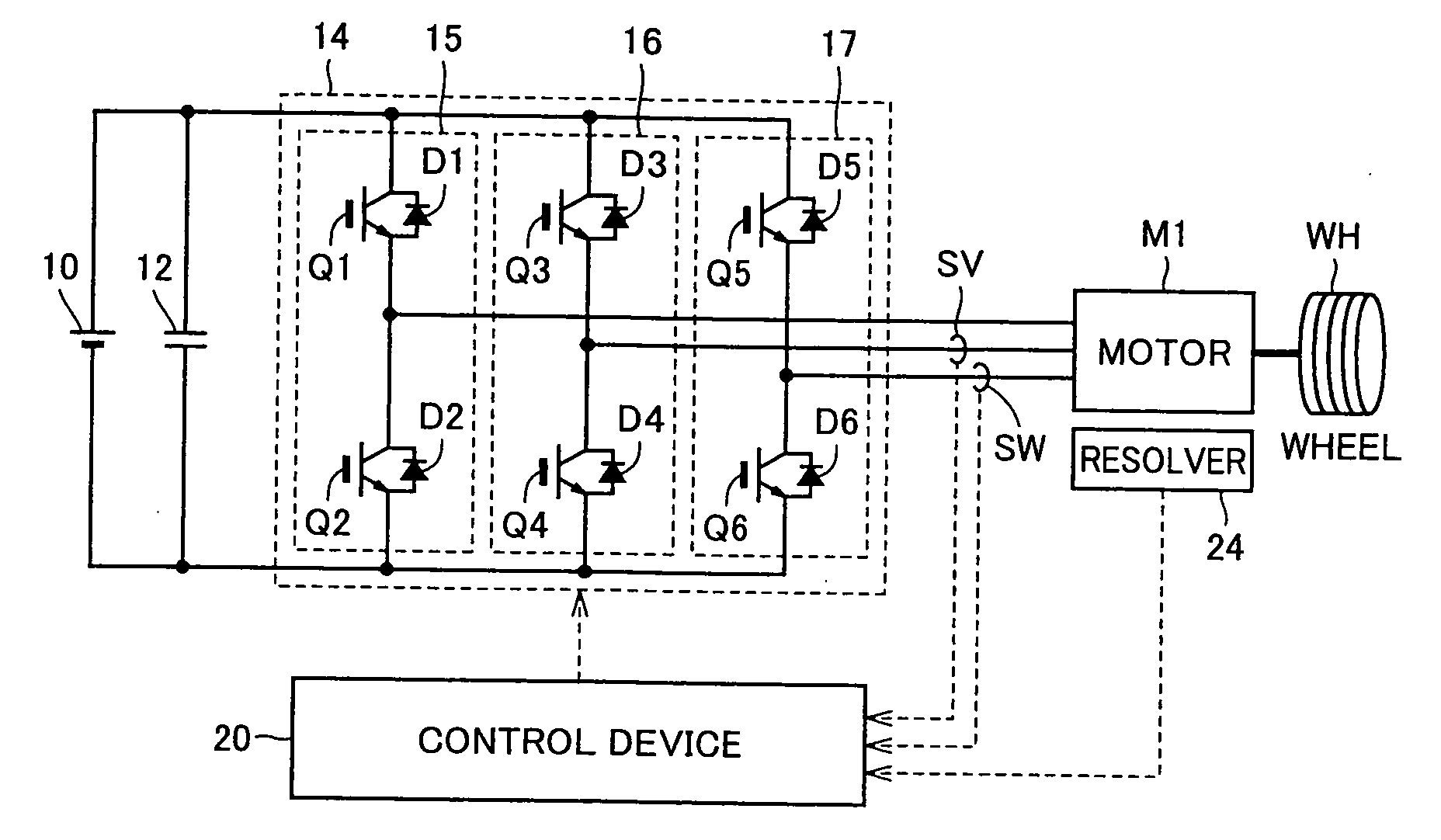
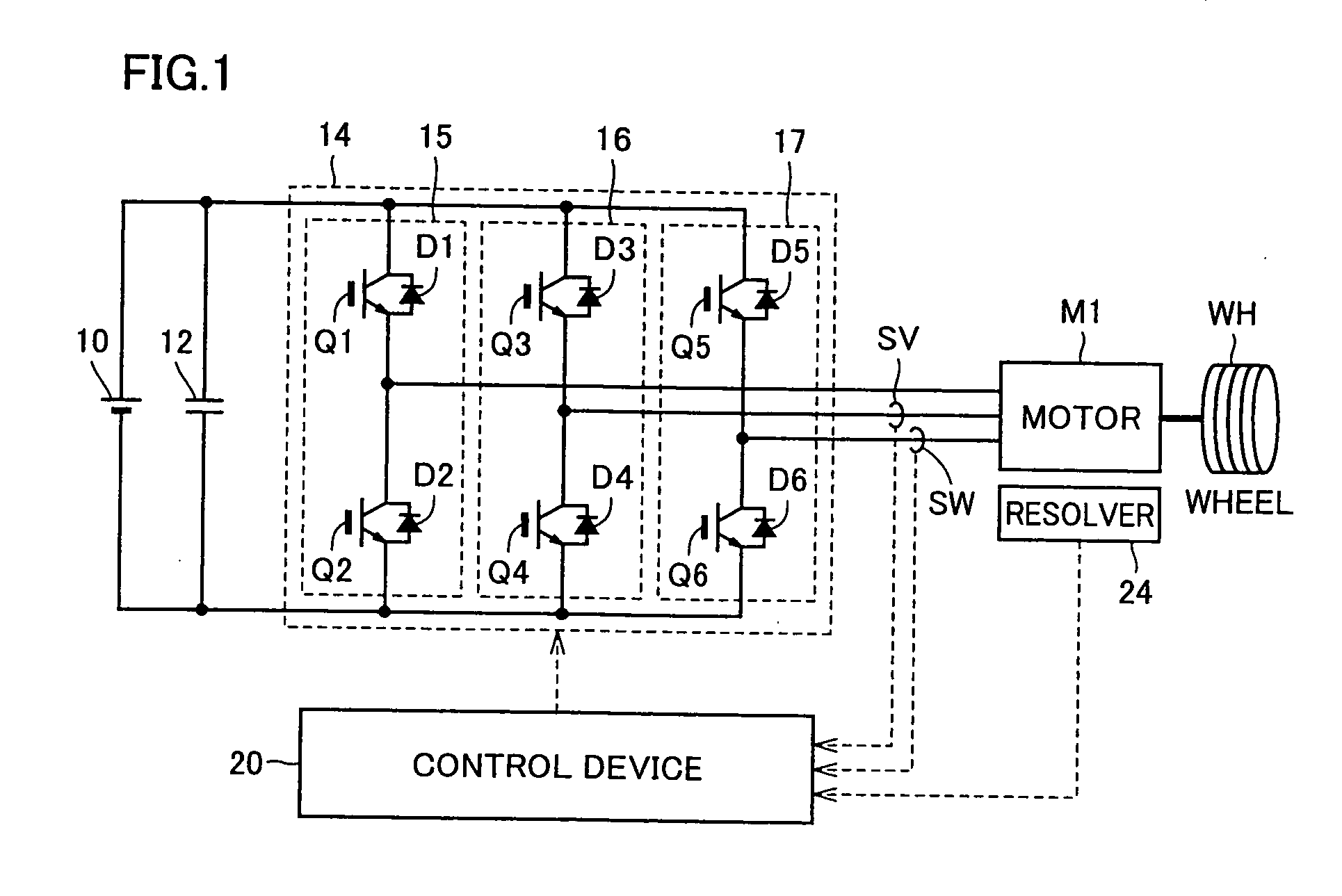
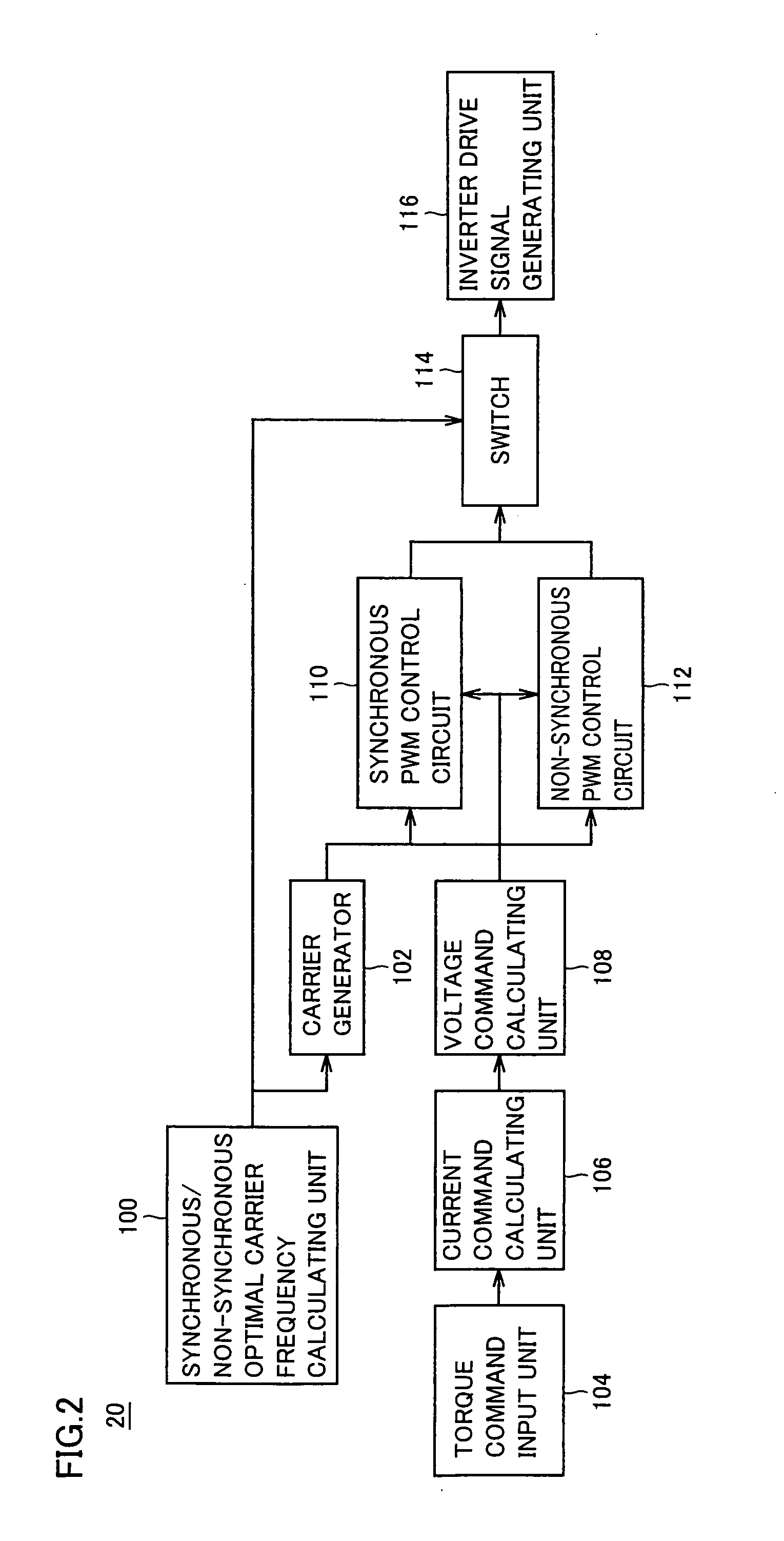
A vehicle includes a motor for driving wheels WH, an inverter to drive the motor, and a control device to perform PWM control of the inverter. The control device performs synchronous PWM control in a case where an electric current supplied to the motor by the inverter or torque generated in the motor is larger than a threshold value; and performs the synchronous PWM control or non-synchronous PWM control in a case where the electric current or the torque is smaller than the threshold value and sets carrier frequency or a pulse number of the PWM control to be higher than the case where the electric current or the torque is larger than the threshold value. Thereby, it is possible to provide a vehicle of achieving reduction of noise, reduction of cost and improvement of fuel consumption in a balanced manner.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Control device for electric power steering apparatus
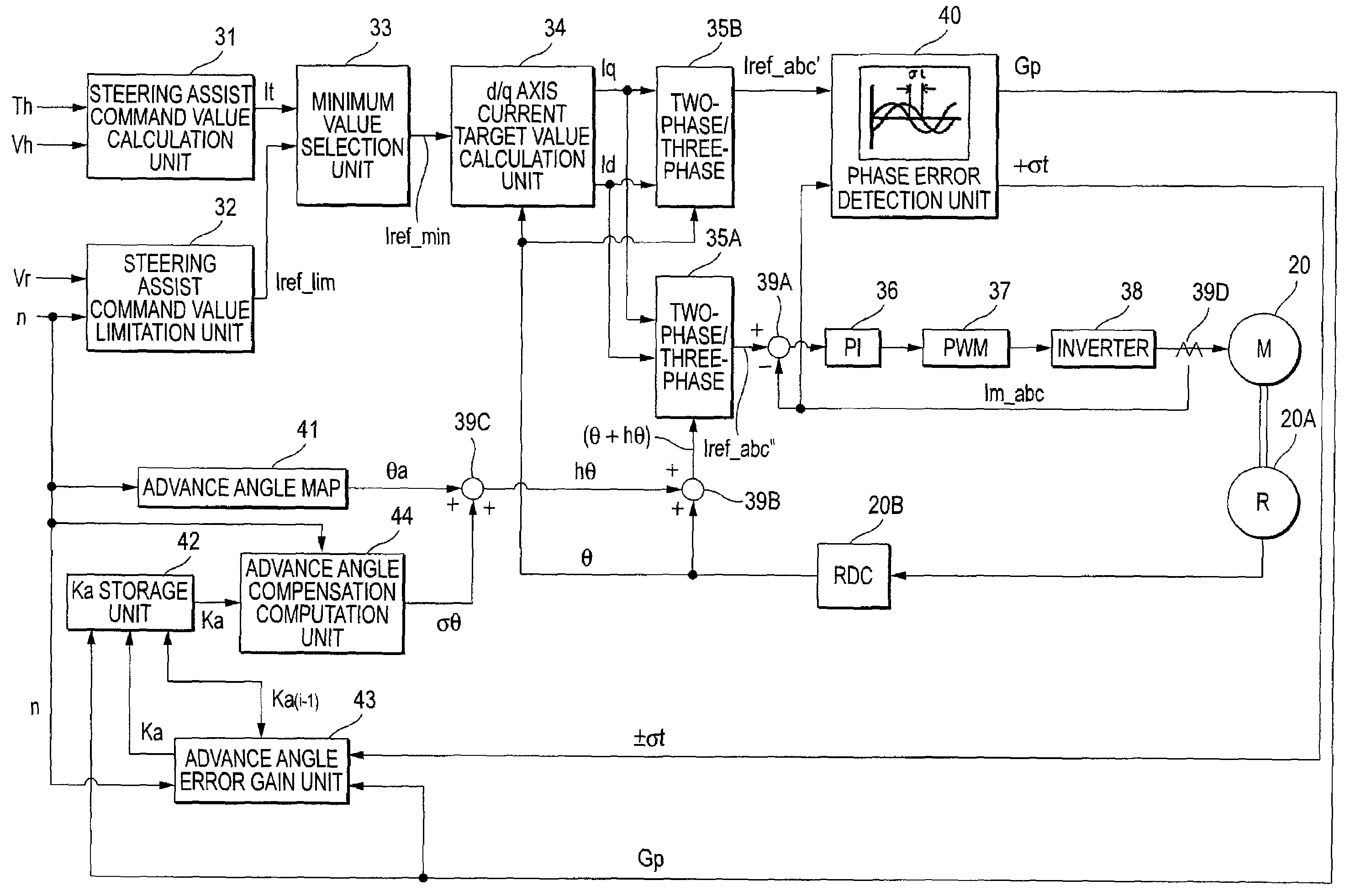
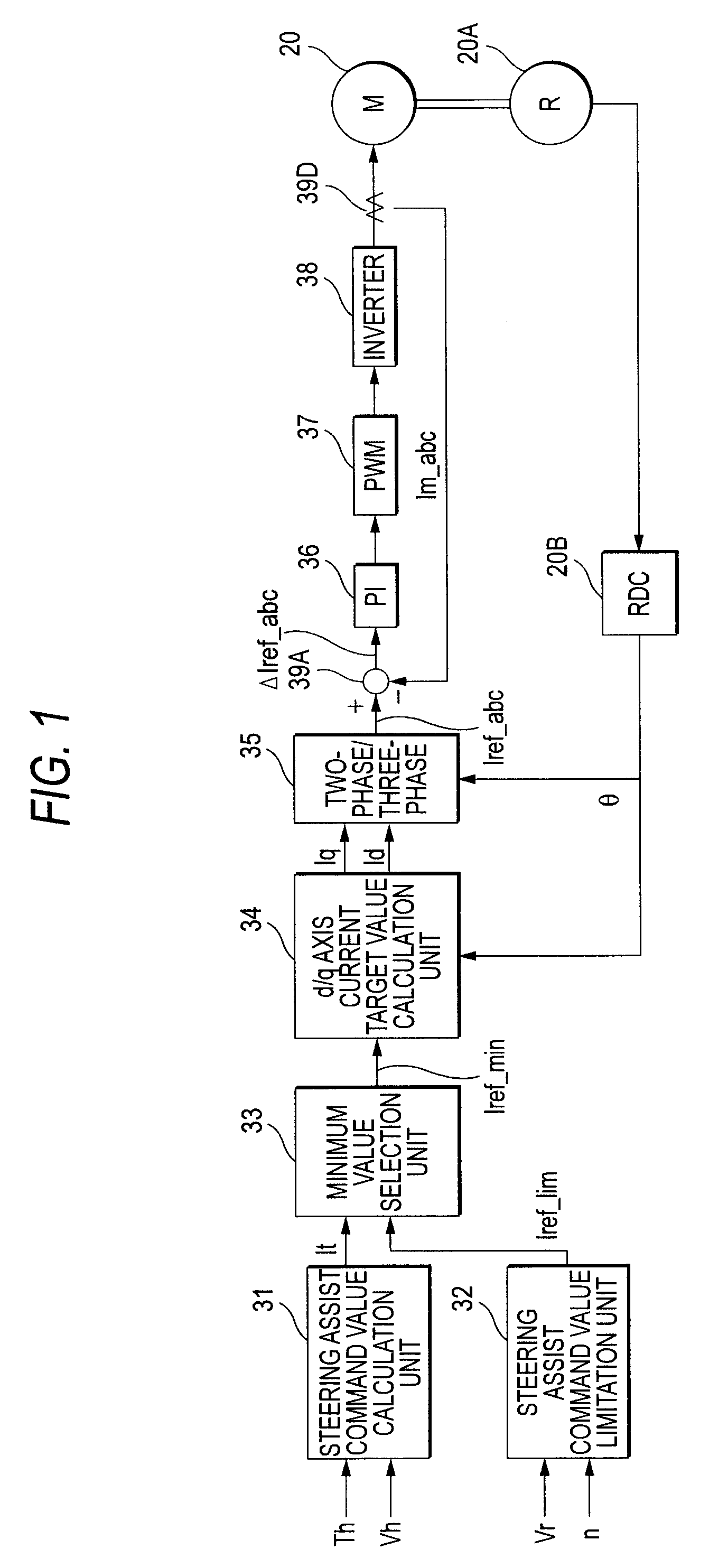
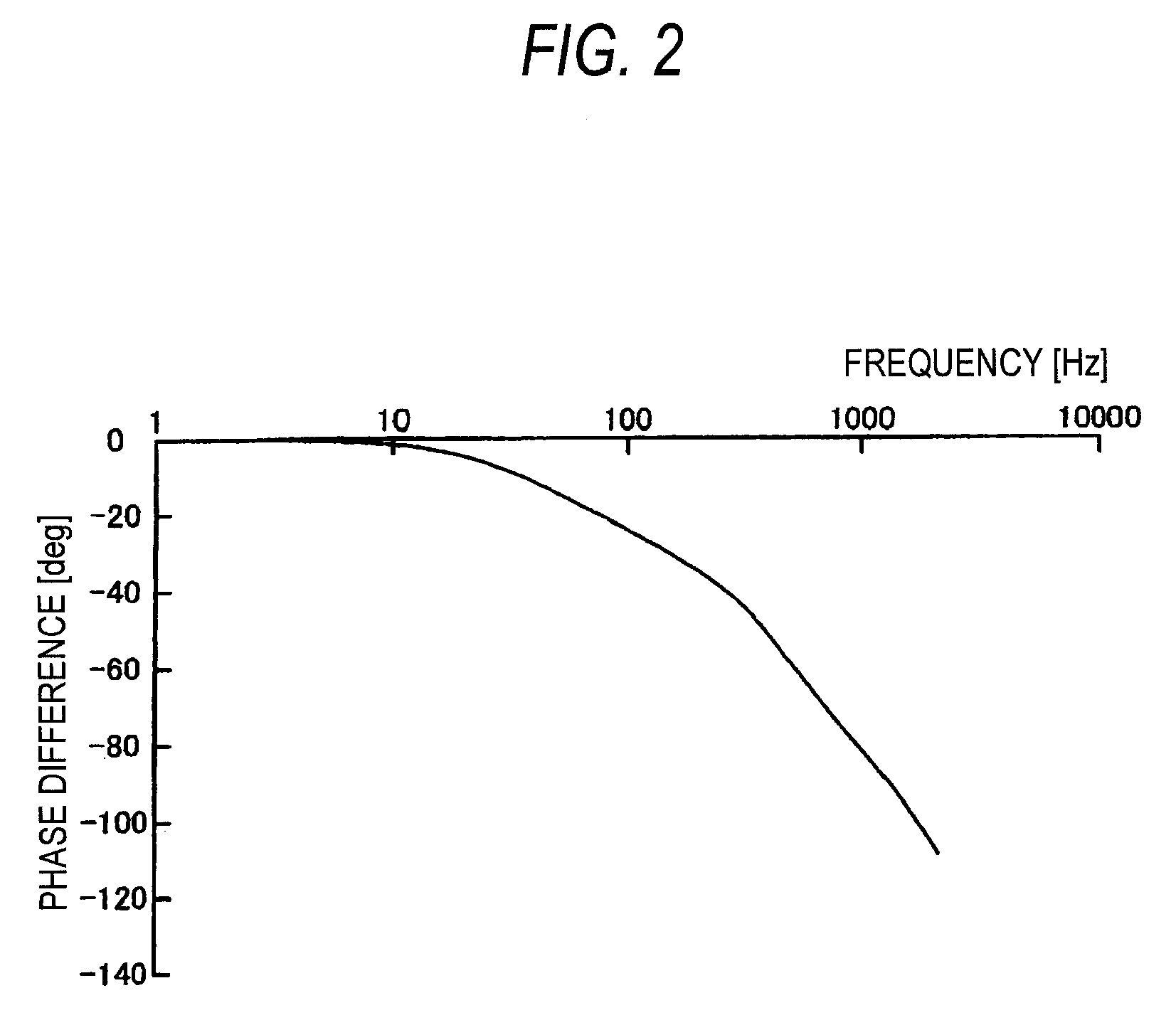
InactiveUS20080201041A1Reliable compensationPhase differenceTemperatue controlSingle motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringControl vector
A control device for an electric power steering apparatus includes a control unit which controls a motor giving steering assist force to a steering system according to a current command value computed based on steering toque and vehicle speed in a vector control manner and an advance angle map for compensating for a phase lag occurring in a motor current relative to the current command value. Advance angle compensation is made for the current command value based on the advance angle map.
Owner:NSK LTD
Motor driving device and automobile using the same
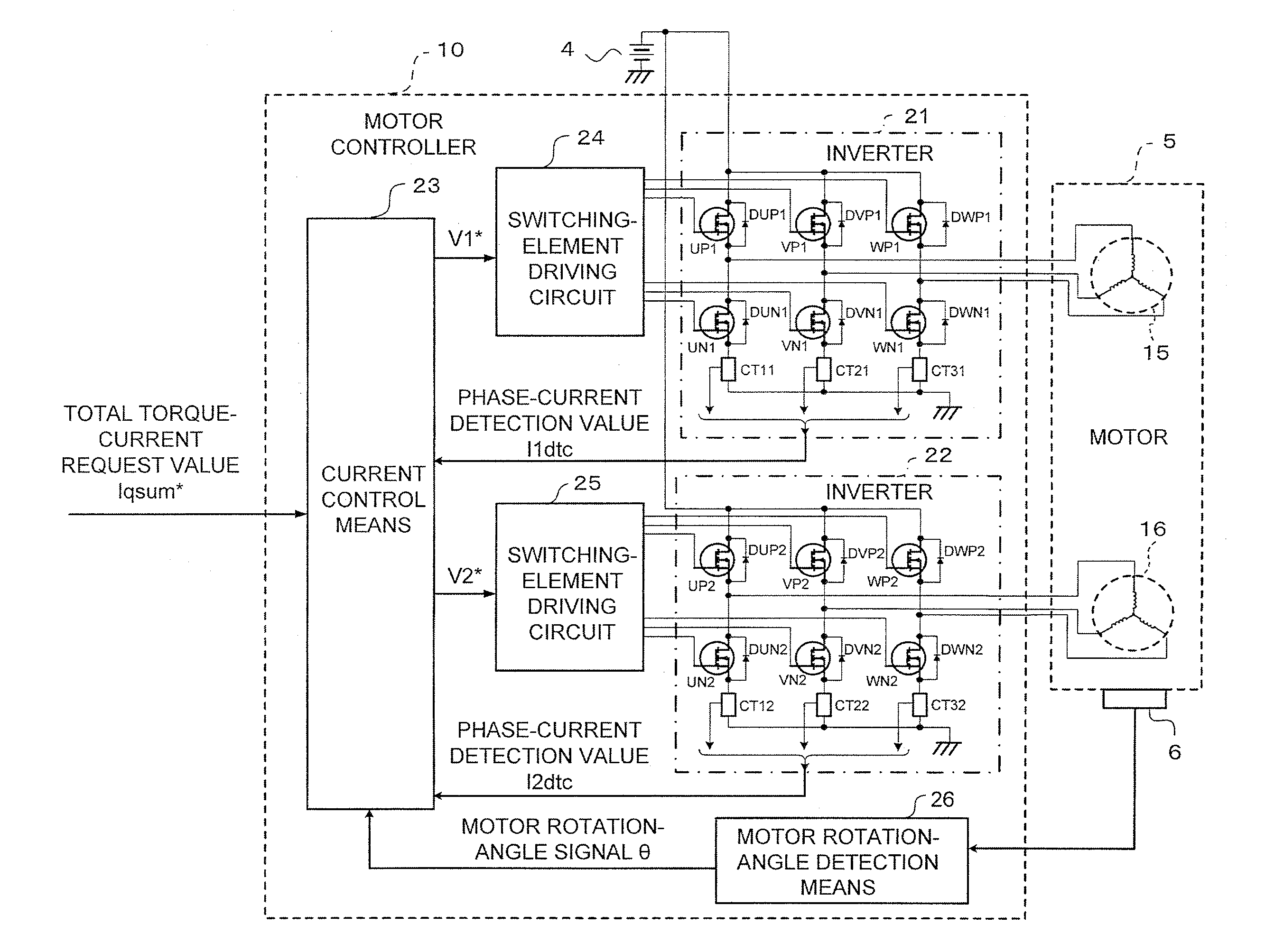
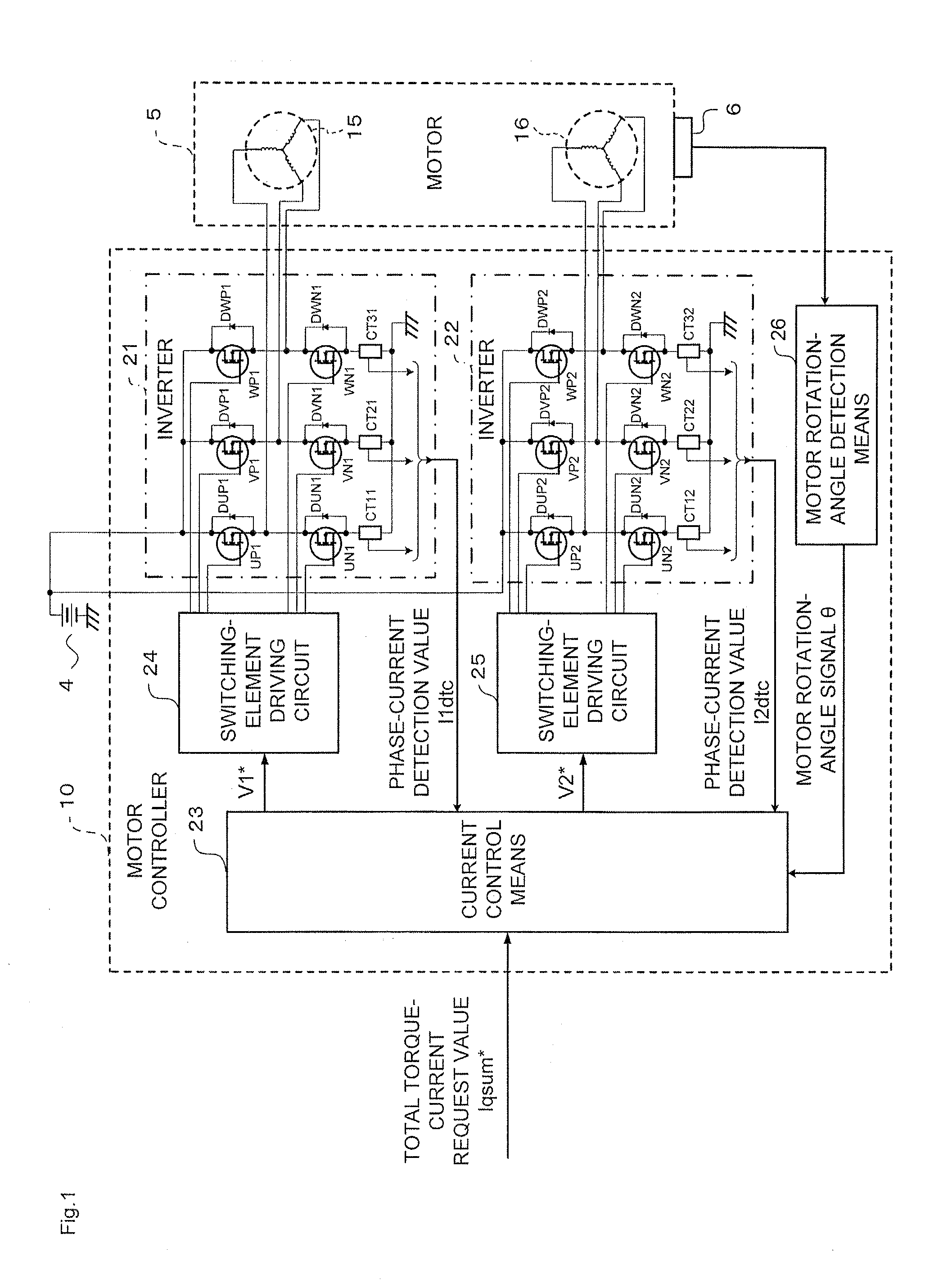
InactiveUS7439697B2Reduce lossesLoss generated in the first inverter can be reducedVehicular energy storageMechanical energy handlingMotor driveHigh voltage battery
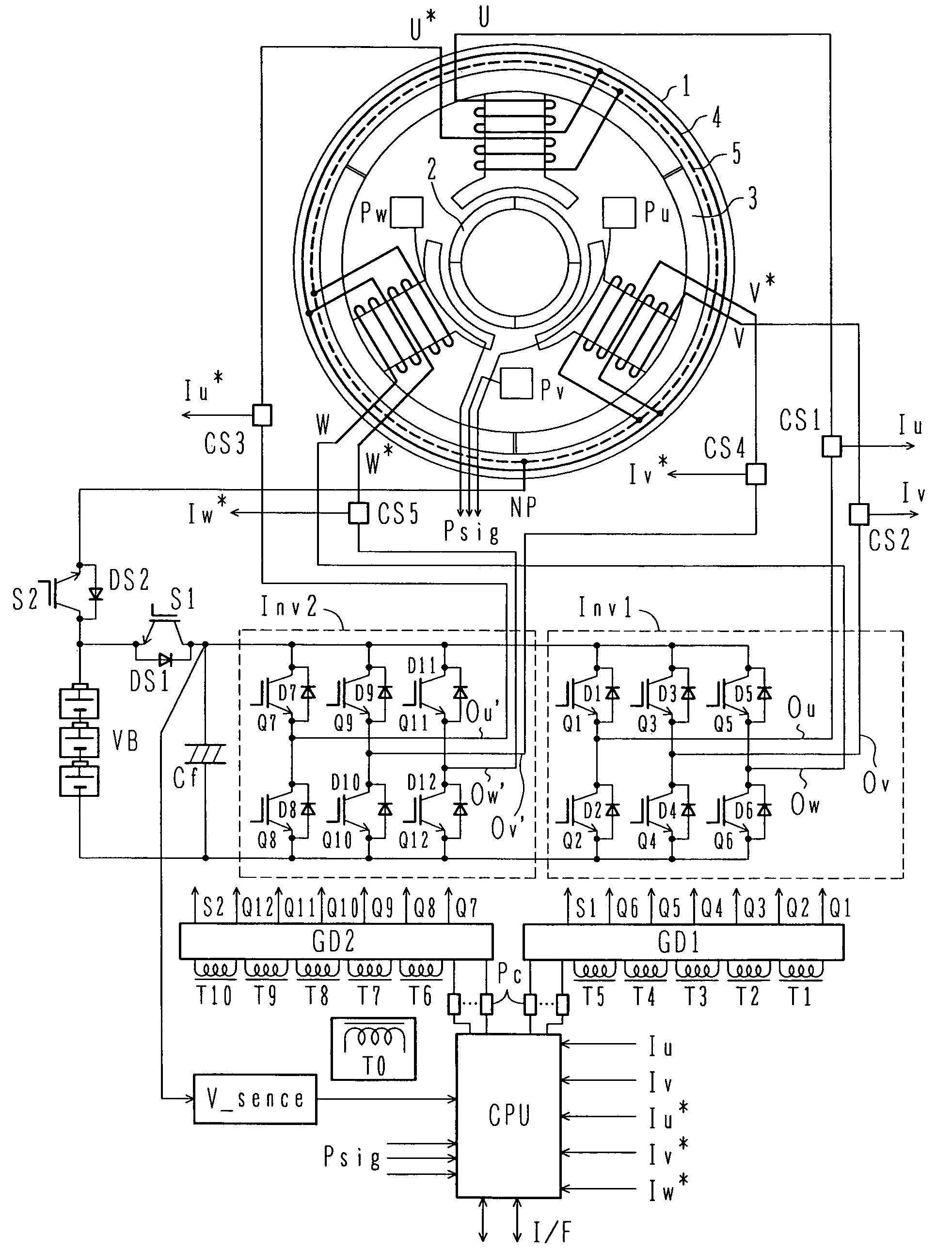
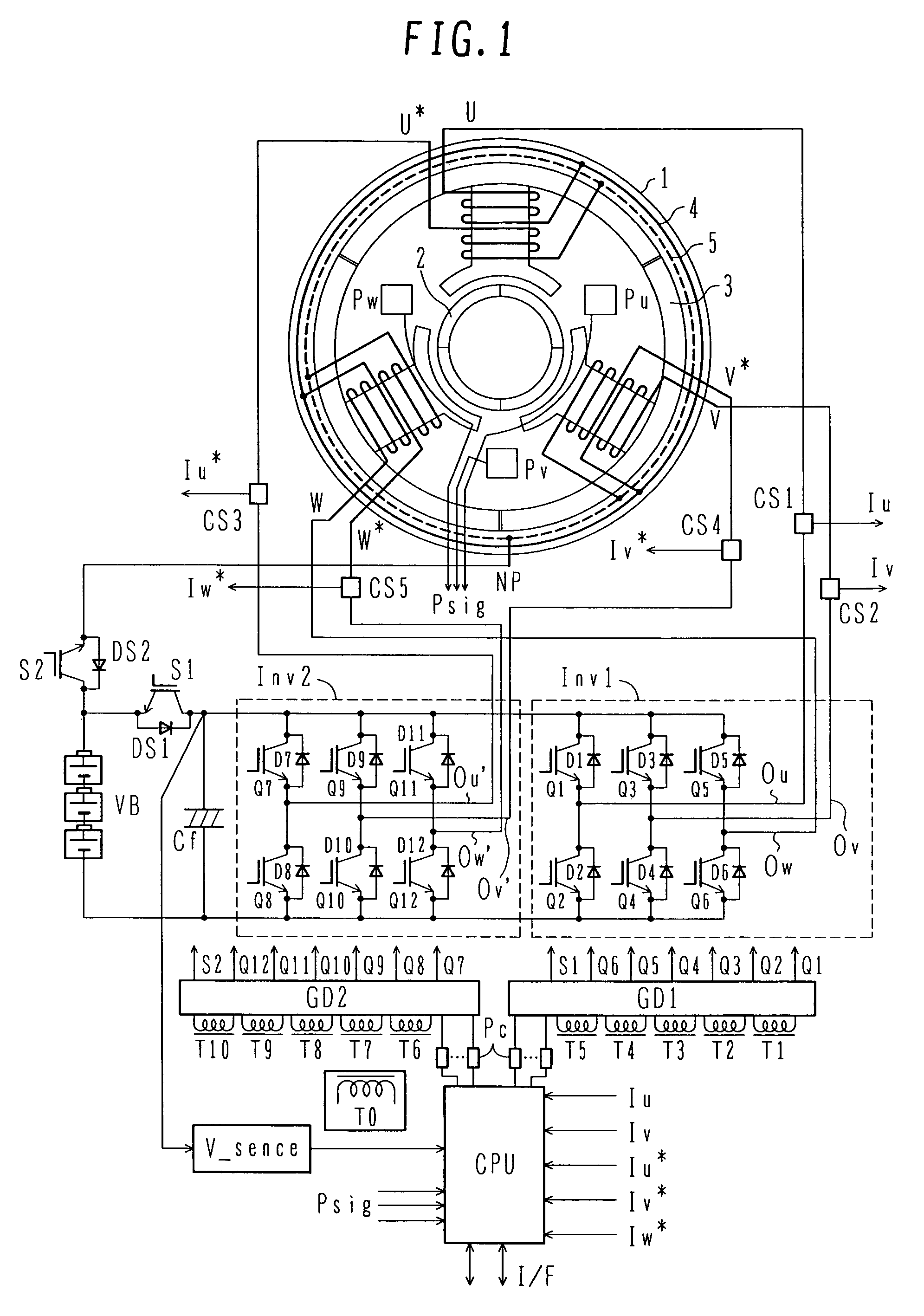
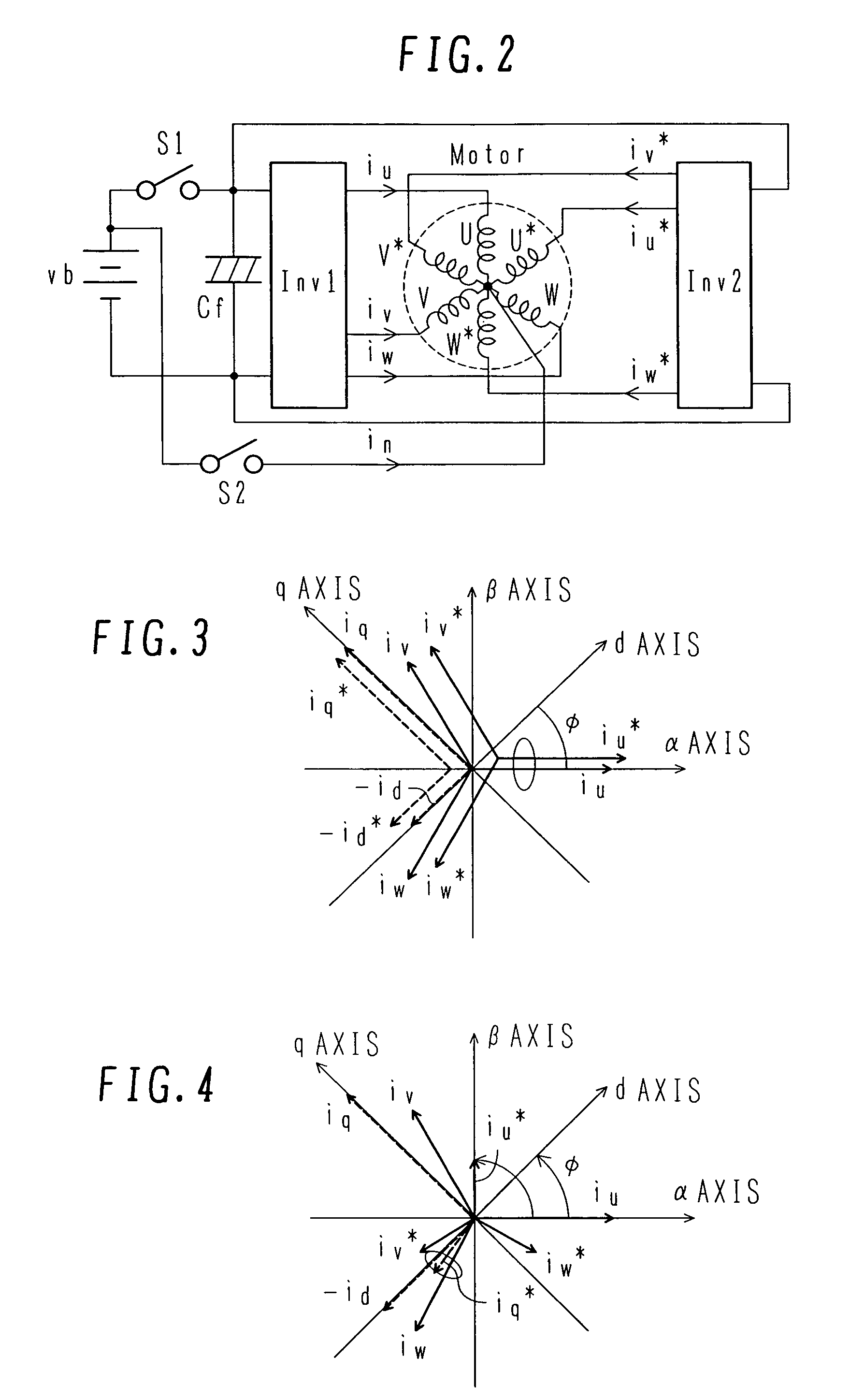
As a boosting-type motor driving device using no reactor, a motor driving device capable of controlling boosting operation and motor driving at the same time is provided, and an automobile using the motor driving device is also provided. The motor driving device is used for driving a motor with a double-winding structure having a first set of three-phase windings and a second set of three-phase winding which are wound over a stator, and includes first and second inverters, which are connected respectively to the first set of three-phase windings and the second set of three-phase windings, thereby controlling the first and second inverters to control a driving force of the motor with the double-winding structure. The first and second inverters have positive and negative terminals which are connected respectively in common to a high-voltage battery. The motor driving device further includes a first switch unit connected between the positive terminals of the first and second inverters connected in common and a positive pole of the high-voltage battery, and a second switch unit connected between a neutral point of the second set of three-phase windings and the positive pole of the high-voltage battery.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling electric power steering system
ActiveUS20090234538A1Efficient implementationSingle motor speed/torque controlDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringControl vector
Disclosed herein is a method for controlling an electric power steering system, wherein a motor is controlled by vector control and driven by a current command value calculated on the basis of a parameter such as a steering torque to provide a steering assist power to a vehicle steering system, and further wherein the current command value is limited on the basis of desired output characteristics and a desired angular speed during a field-weakening control and a non-field-weakening control of the vector control.
Owner:NSK LTD
Motor driving device and automobile using the same
InactiveUS20070120520A1Reduce lossesLoss generated in the first inverter can be reducedVehicular energy storageMechanical energy handlingMotor driveHigh voltage battery
As a boosting-type motor driving device using no reactor, a motor driving device capable of controlling boosting operation and motor driving at the same time is provided, and an automobile using the motor driving device is also provided. The motor driving device is used for driving a motor with a double-winding structure having a first set of three-phase windings and a second set of three-phase winding which are wound over a stator, and includes first and second inverters, which are connected respectively to the first set of three-phase windings and the second set of three-phase windings, thereby controlling the first and second inverters to control a driving force of the motor with the double-winding structure. The first and second inverters have positive and negative terminals which are connected respectively in common to a high-voltage battery. The motor driving device further includes a first switch unit connected between the positive terminals of the first and second inverters connected in common and a positive pole of the high-voltage battery, and a second switch unit connected between a neutral point of the second set of three-phase windings and the positive pole of the high-voltage battery.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for controlling an electric motor to reduce EMI
InactiveUS7202622B2Reduce the amount requiredLow costDC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motors startersPhase advanceDC-BUS
A method for reducing EMI emissions in the control of an electric motor supplied by a switching inverter fed by a DC bus comprising controlling a phase advance of a conduction angle period during which a phase of the motor is fed power by the inverter to control the conduction angle to control the speed of the motor, thereby to reduce the number of switching operations of the inverter and thereby reduce EMI.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Electric power converter, driving apparatus and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20120049782A1Total current dropExpand the adjustment rangeSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsElectric power steeringPhase shifted
A control unit of an electric power converter, which is used in a three-phase motor having two winding wire systems, performs for a first duty instruction signal regarding a voltage applied to a first winding wire group a flatbed two-phase modulation process, and performs for a second duty instruction signal regarding a voltage applied to a second winding wire group a flattop two-phase modulation process. By phase-shifting the second duty instruction signal by 30° from the first duty instruction signal, a timing of maximum value of the first duty instruction signal is shifted from a timing of minimum value of the second duty instruction signal. Even when the maximum value is greater than a center output value and the minimum value is smaller than the center output value, overlapping of capacitor discharge is avoided, thereby reducing a ripple electric current.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motor controller and electric power steering device using the same
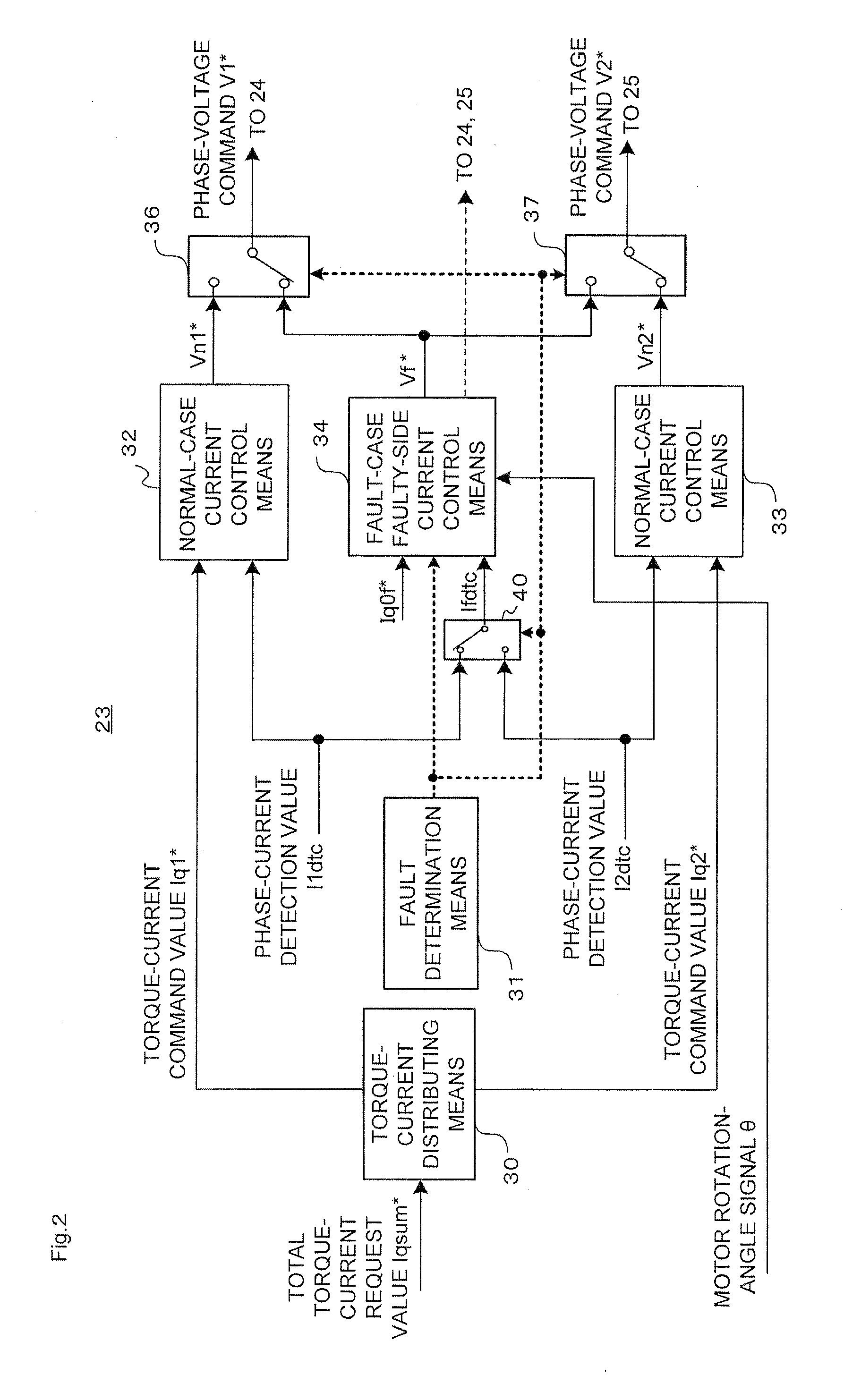
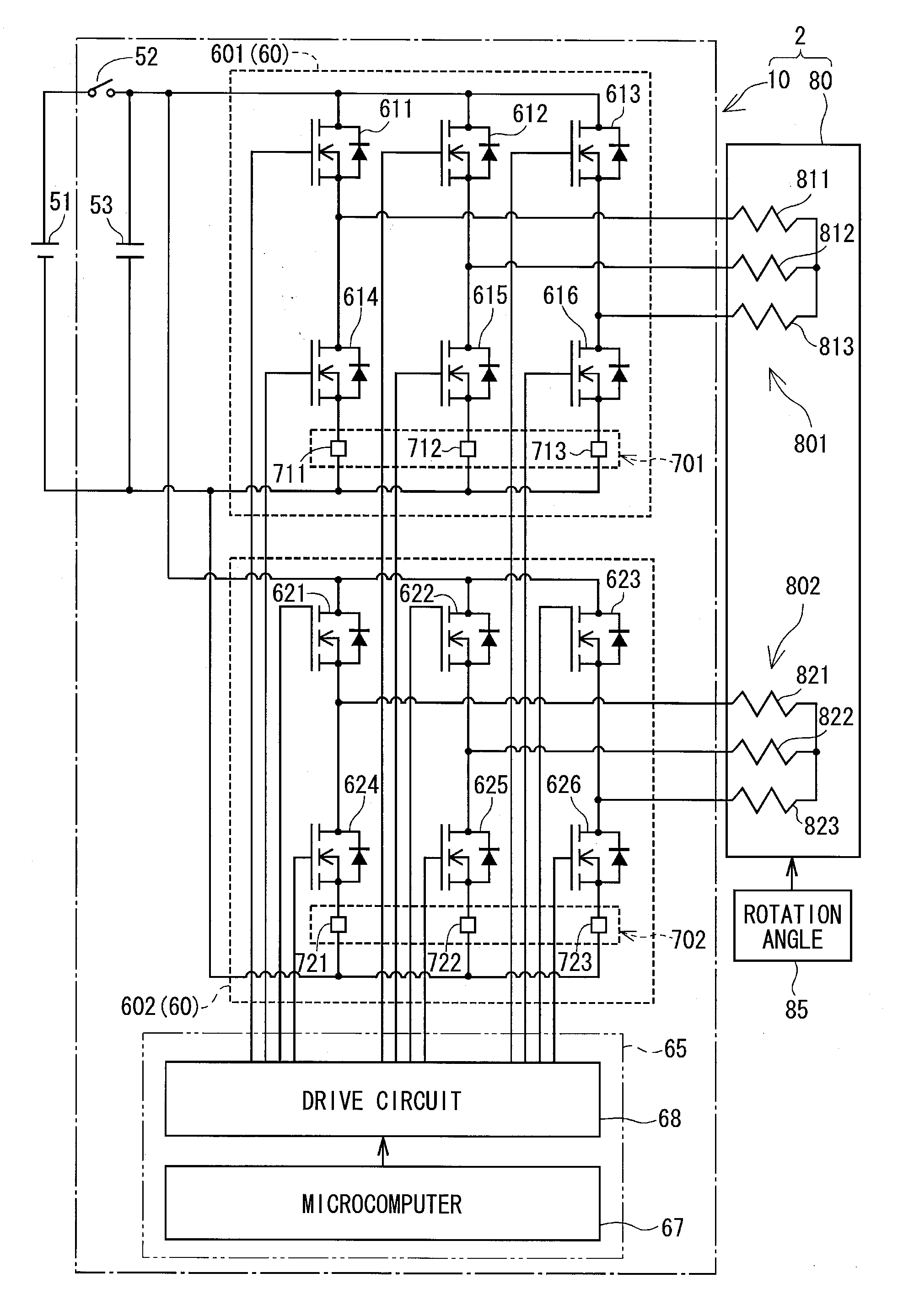
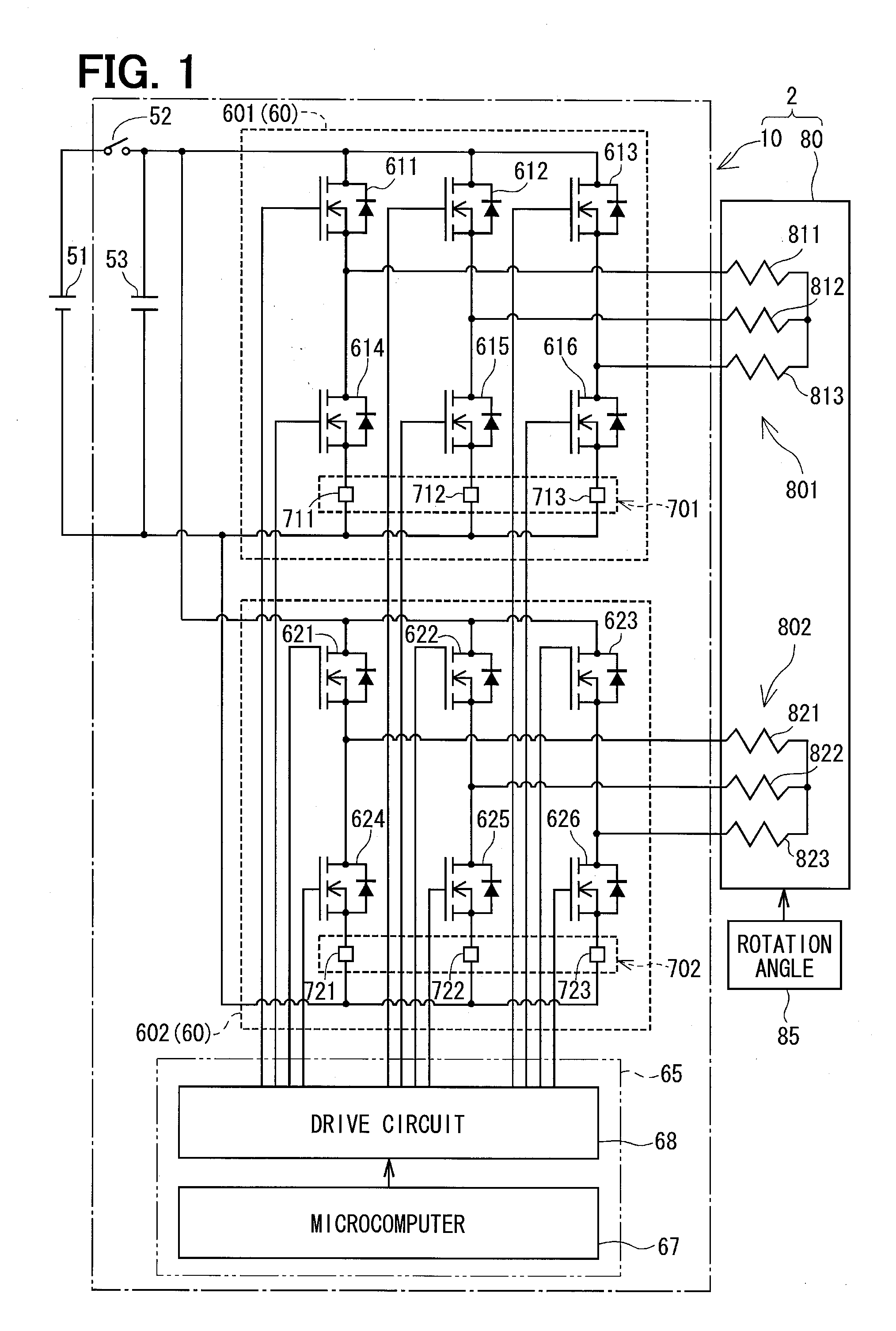
ActiveUS20130299271A1Low costSmall sizeCommutation monitoringMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectric power steeringMotor controller
Provided are a motor controller for suppressing a torque pulsation with a simple configuration and obtaining a sufficient output torque in the case of an open-type fault occurring in any one of windings of a motor and inverters, and an electric power steering device using the motor controller. In the motor controller for controlling a current supplied from and a voltage applied from a power source with respect to the motor including winding sets of a plurality of systems, when a fault determination unit (31) determines the occurrence of the open-type fault, the supply of the currents to the windings of one of the systems in which the fault has occurred is stopped by control performed on switching elements included in the inverter of the faulty system, whereas the supply of the currents to the windings of the normal system in which the fault has not occurred is continued.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Electric power steering apparatus
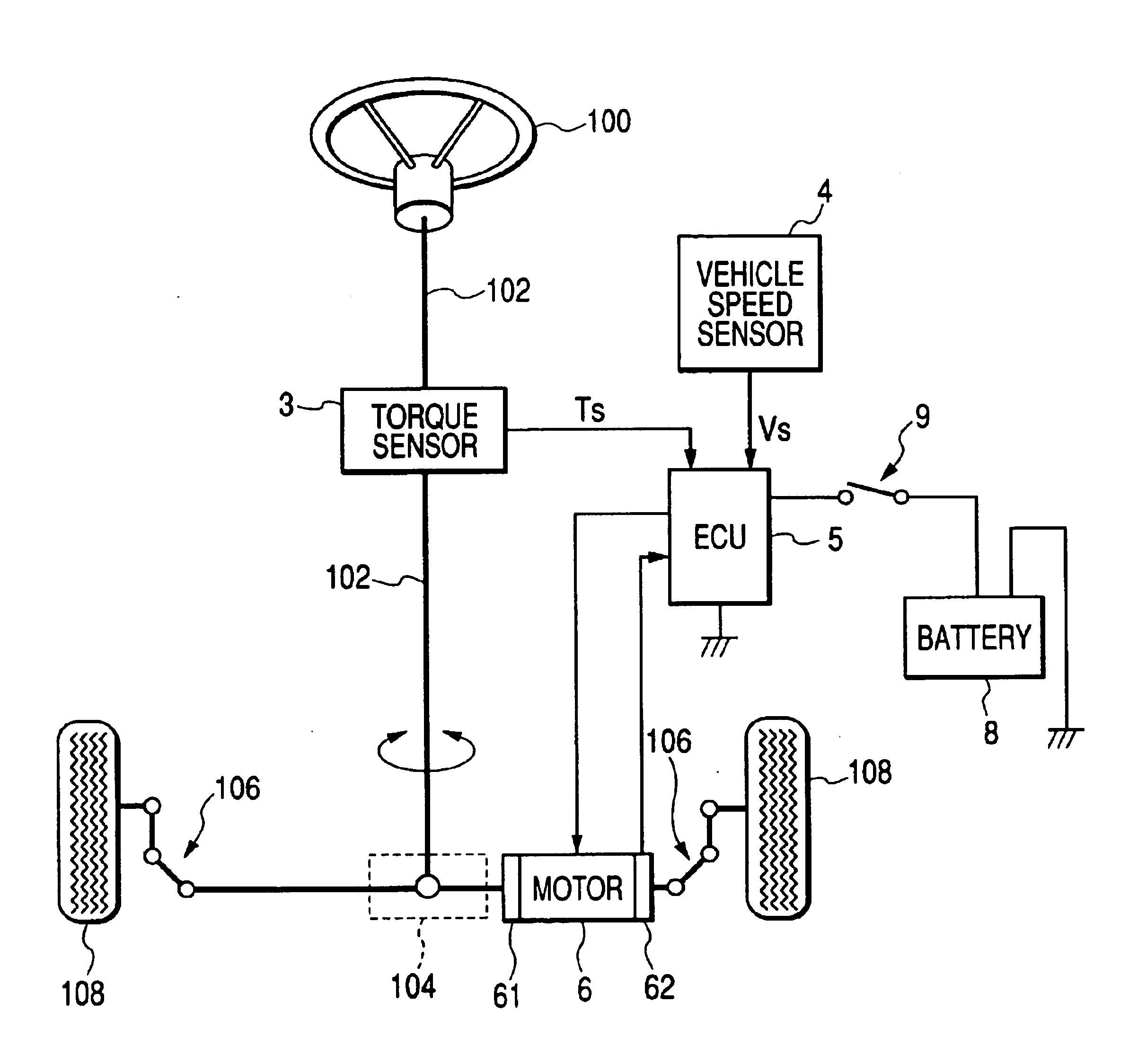
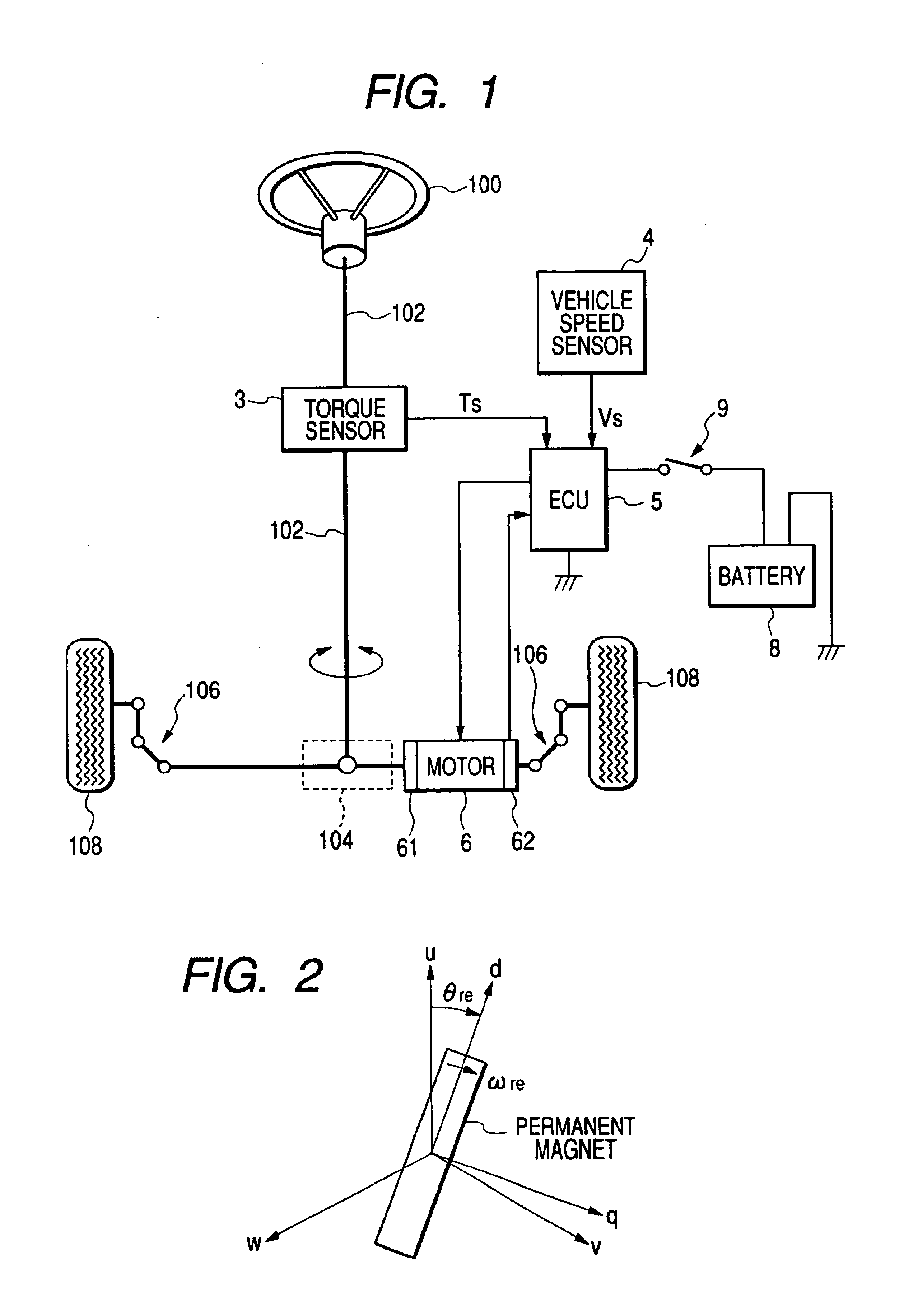
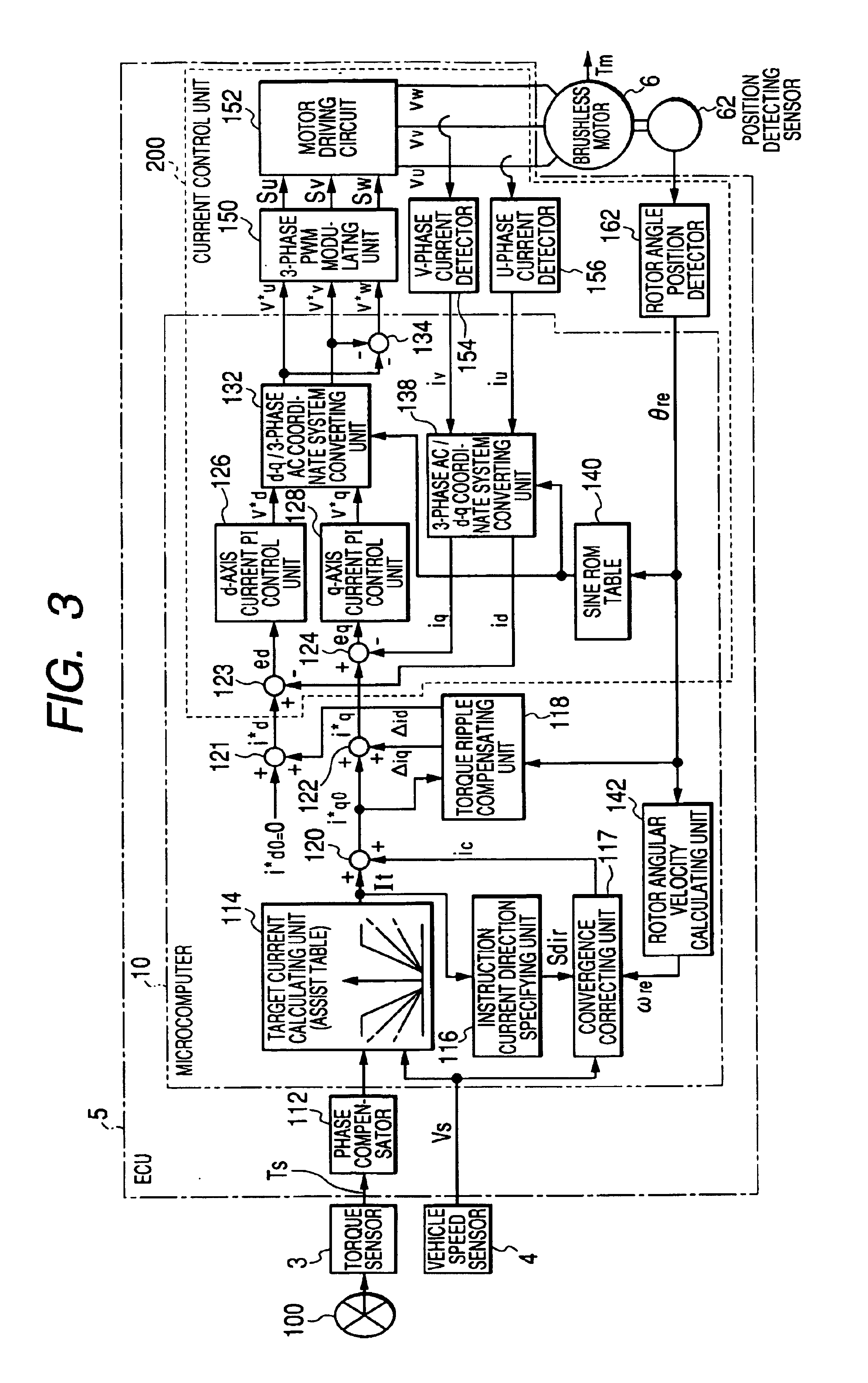
ActiveUS6927548B2Phase accurateReducing electric ripples sufficientlyTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringElectromotive force
An electric power steering apparatus includes: a rotation speed detecting unit which detects a rotation speed of the electric motor; a compensation current determining unit which determines an instruction value of a compensation current to flow through the electric motor to suppress torque ripples due to distortion of an induced electromotive force waveform of the electric motor in accordance with a load correspondence quantity as a physical quantity corresponding to a load of the electric motor and the rotation speed detected by the rotation speed detecting unit; a correcting unit which corrects the current target value on the basis of the compensation current instruction value; and a control unit which performs a feedback control on the electric motor so that a current having the current target value as corrected by the correcting unit flows through the electric motor.
Owner:KOYO SEIKO CO LTD
Resistive torsional mode damping system and method
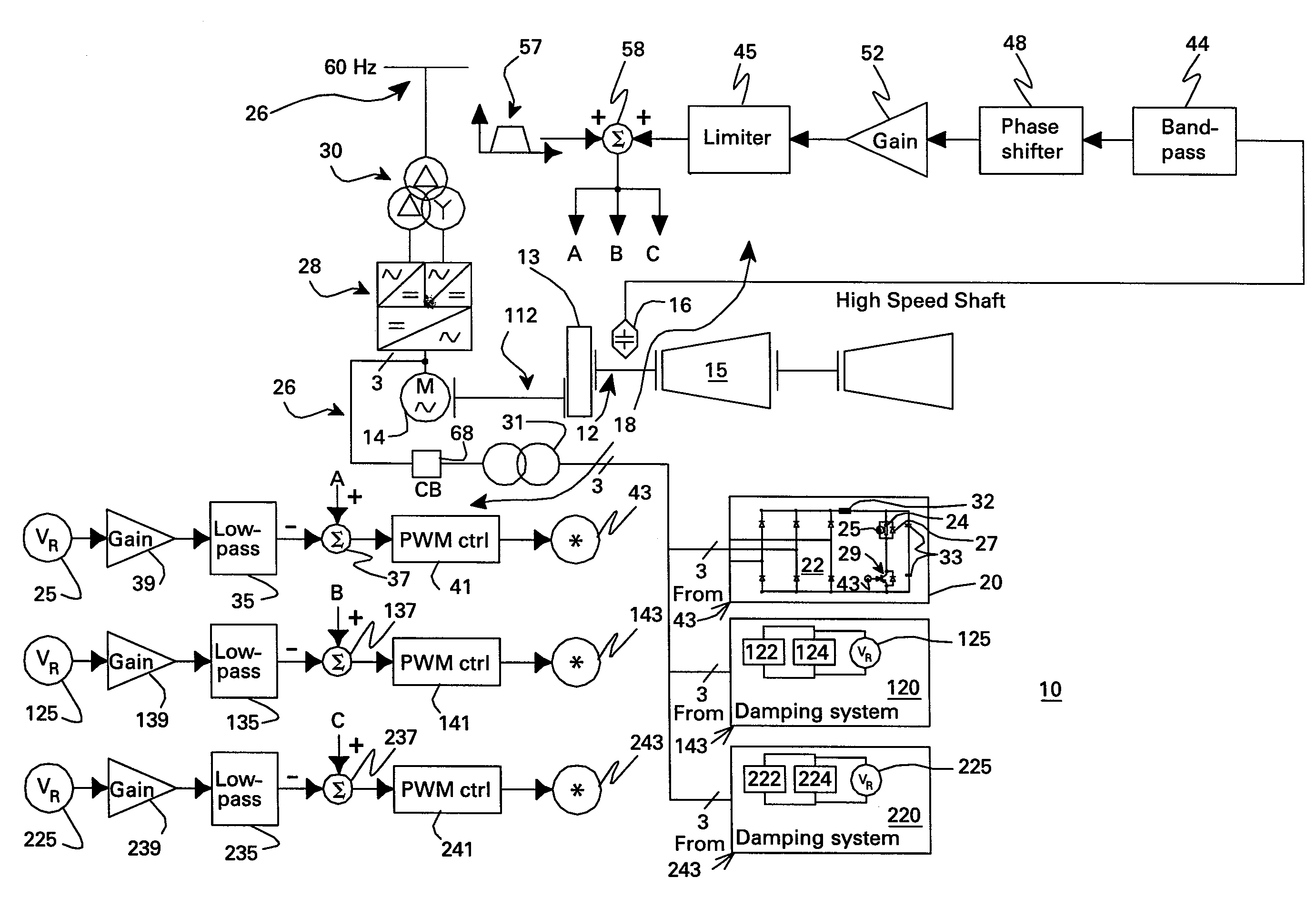
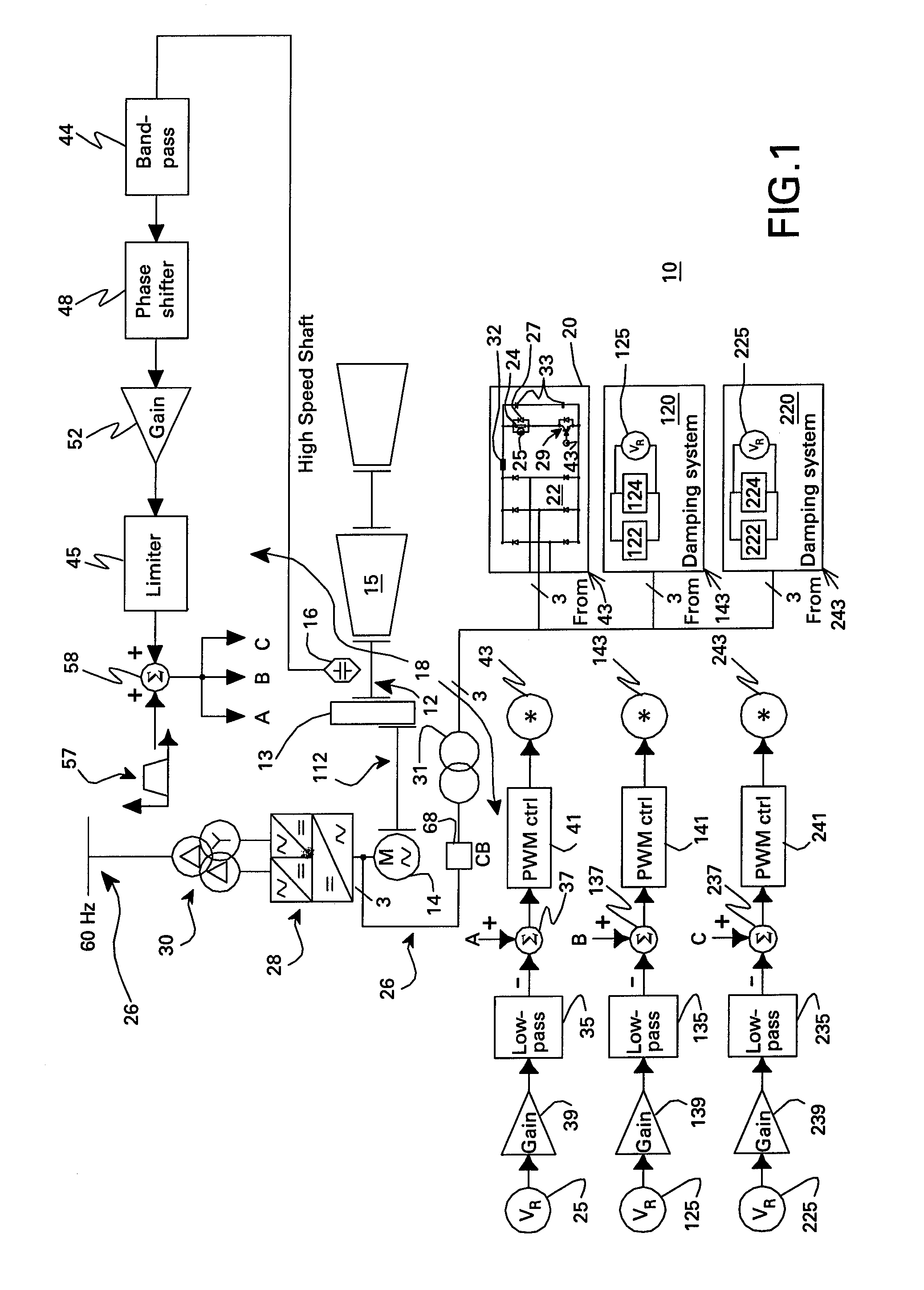
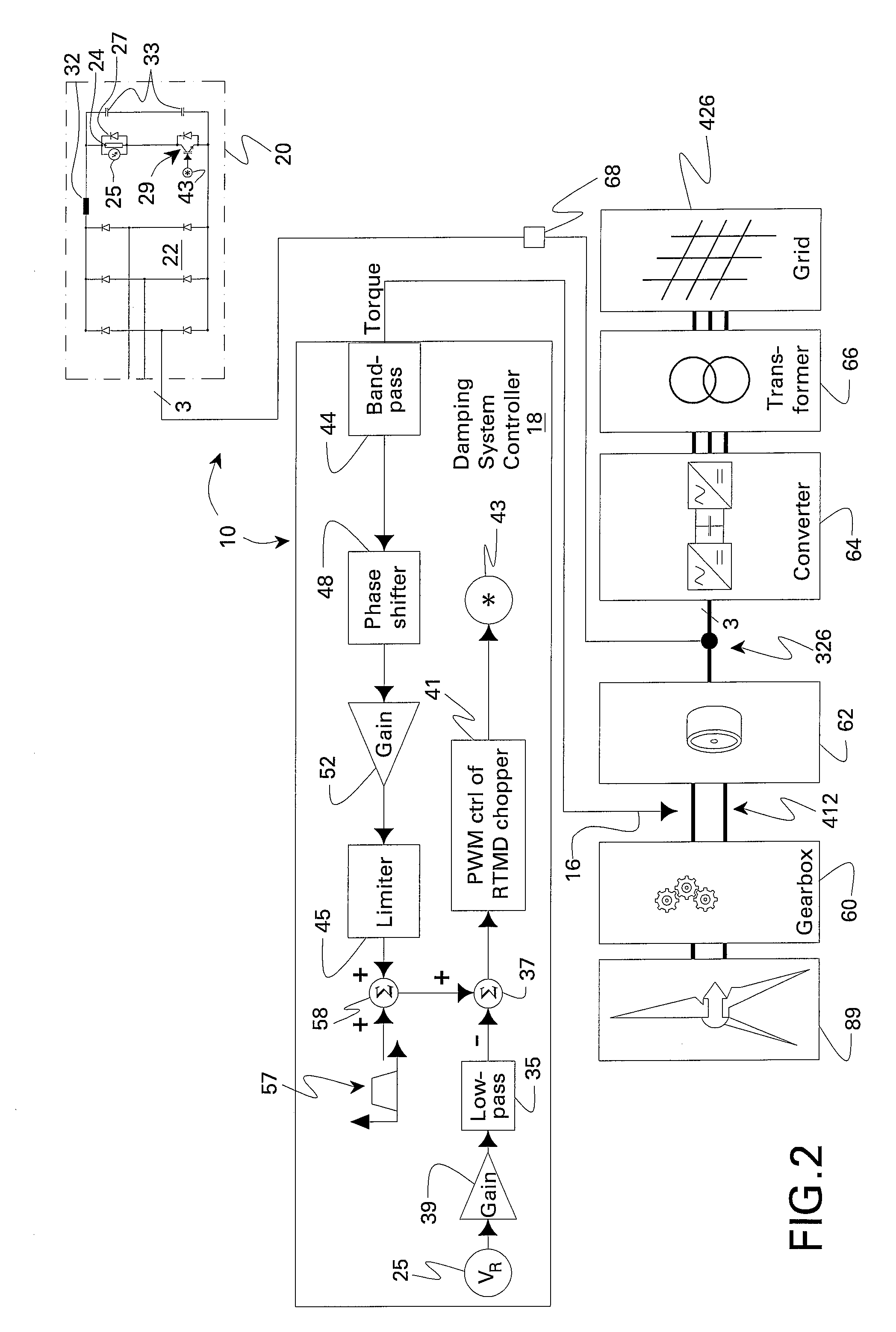
InactiveUS7423411B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlElectrical resistance and conductanceControl signal
A resistive torsional mode damping system for a shaft of a machine includes: a sensor configured for sensing a signal representative of torque on the shaft; a controller configured for using the sensed signal for detecting a presence of a torsional vibration on the shaft corresponding to a natural frequency of the shaft and for generating control signals for damping the torsional vibration; and a damper including a damping converter and resistor coupled to a DC output of the damping converter, the damping converter being coupled to the machine through a power bus and having a power rating on the order of less than or equal to about five percent of a nominal power of the machine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Synchronous motor driving system
InactiveUS20030052640A1DC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motors startersSynchronous motorMagnetic poles
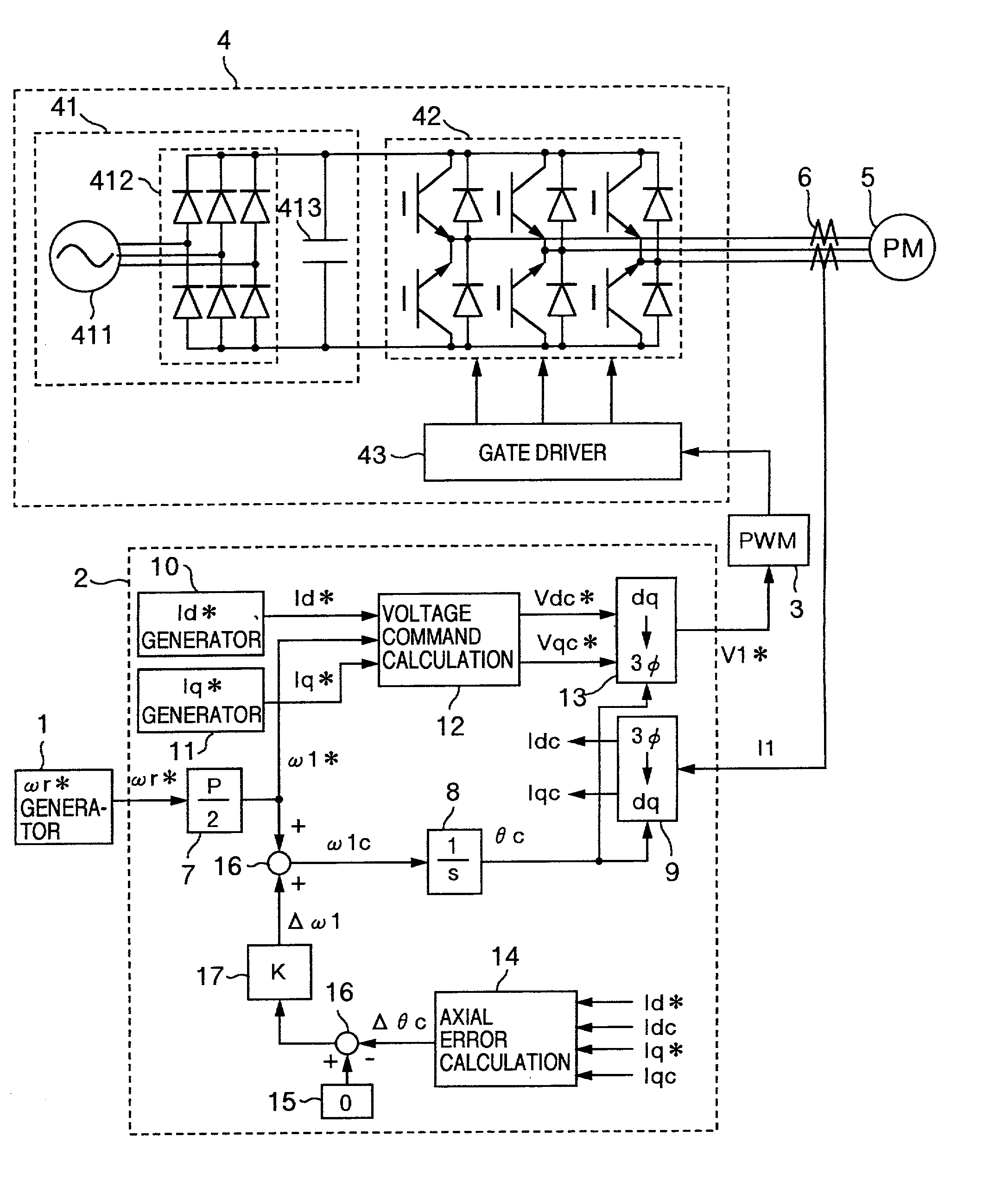
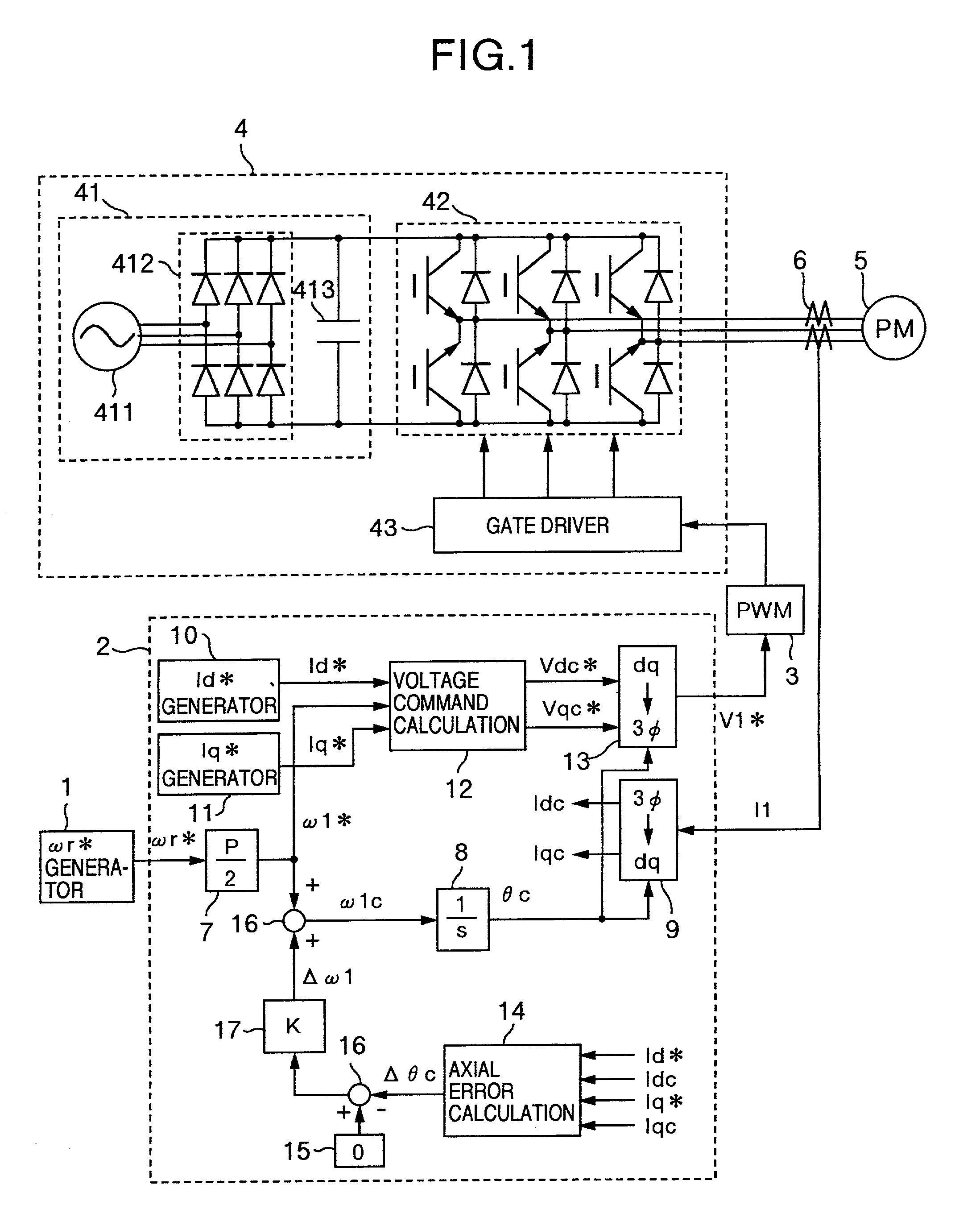
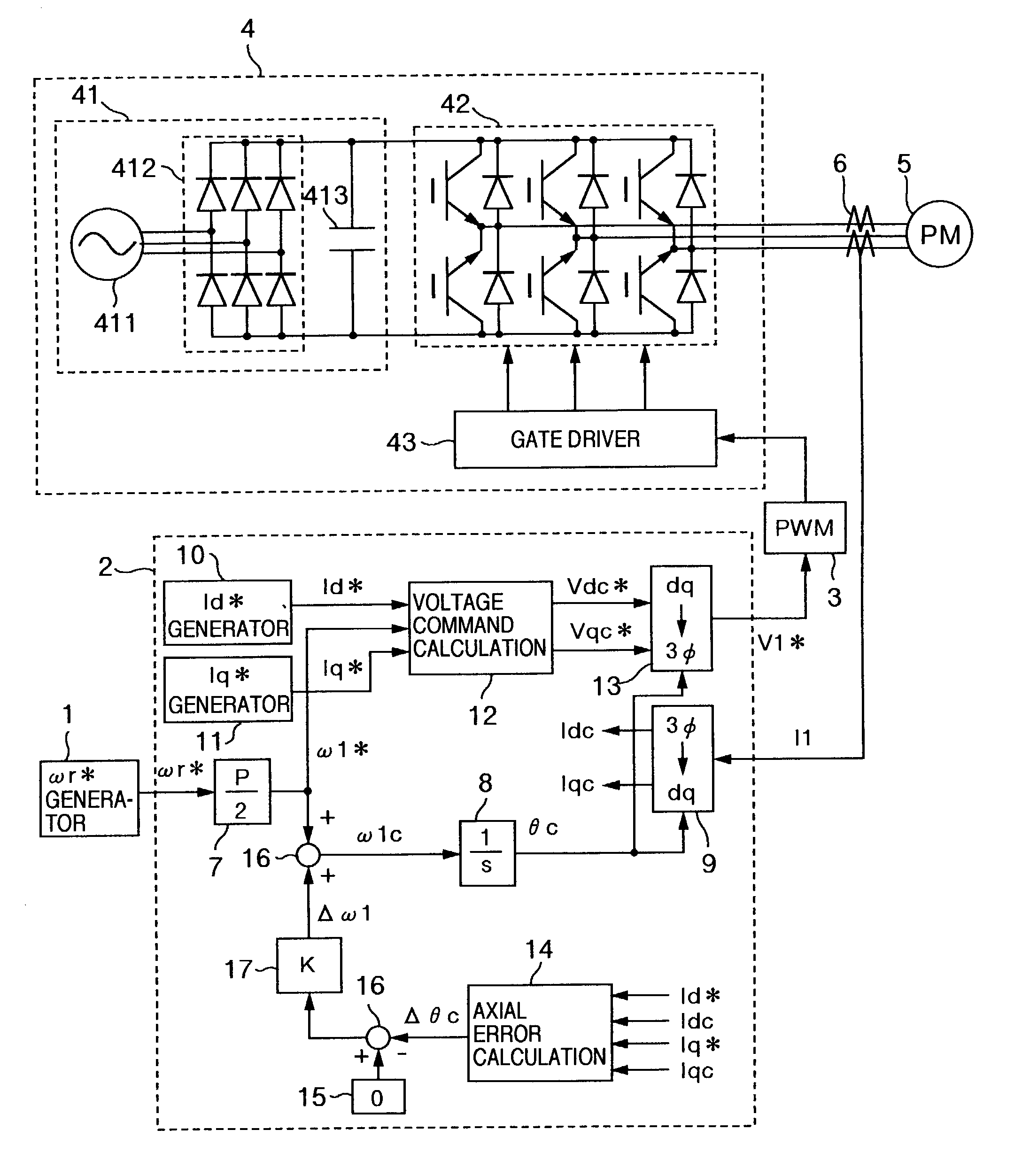
Axial error calculation unit is provided for estimating an axial error DELTAtheta between a d-q axis and a dc-qc axis by using Ld, Lq, Ke, Id*, Iq*, Idc and Iqc in a range of all rotational speeds except zero of a rotational speed command of a synchronous motor, Ld denoting an inductance on a magnetic pole axis d of the synchronous motor, Lq an inductance on a q axis orthogonal to the magnetic pole axis d, Ke a generated power constant of the motor, Id* a current command of the d axis, Iq* a current command on a q axis, Idc a detected current value on an assumed dc axis on control, and Iqc a detected current value on an assumed qc axis orthogonal to the assumed dc axis. Irrespective of presence of saliency, position sensorless control can be achieved in a wide range a low to high speed zone.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Skipping frequencies for variable speed controls
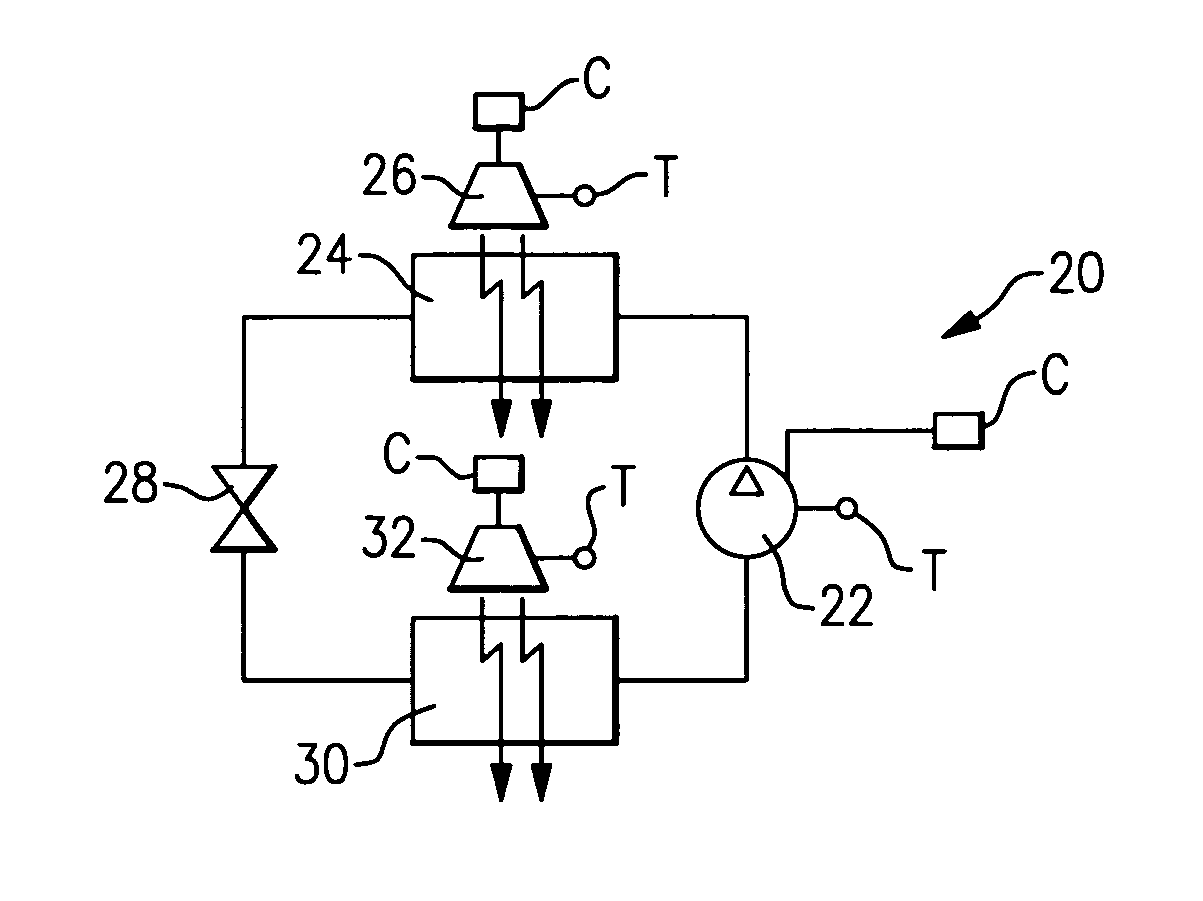
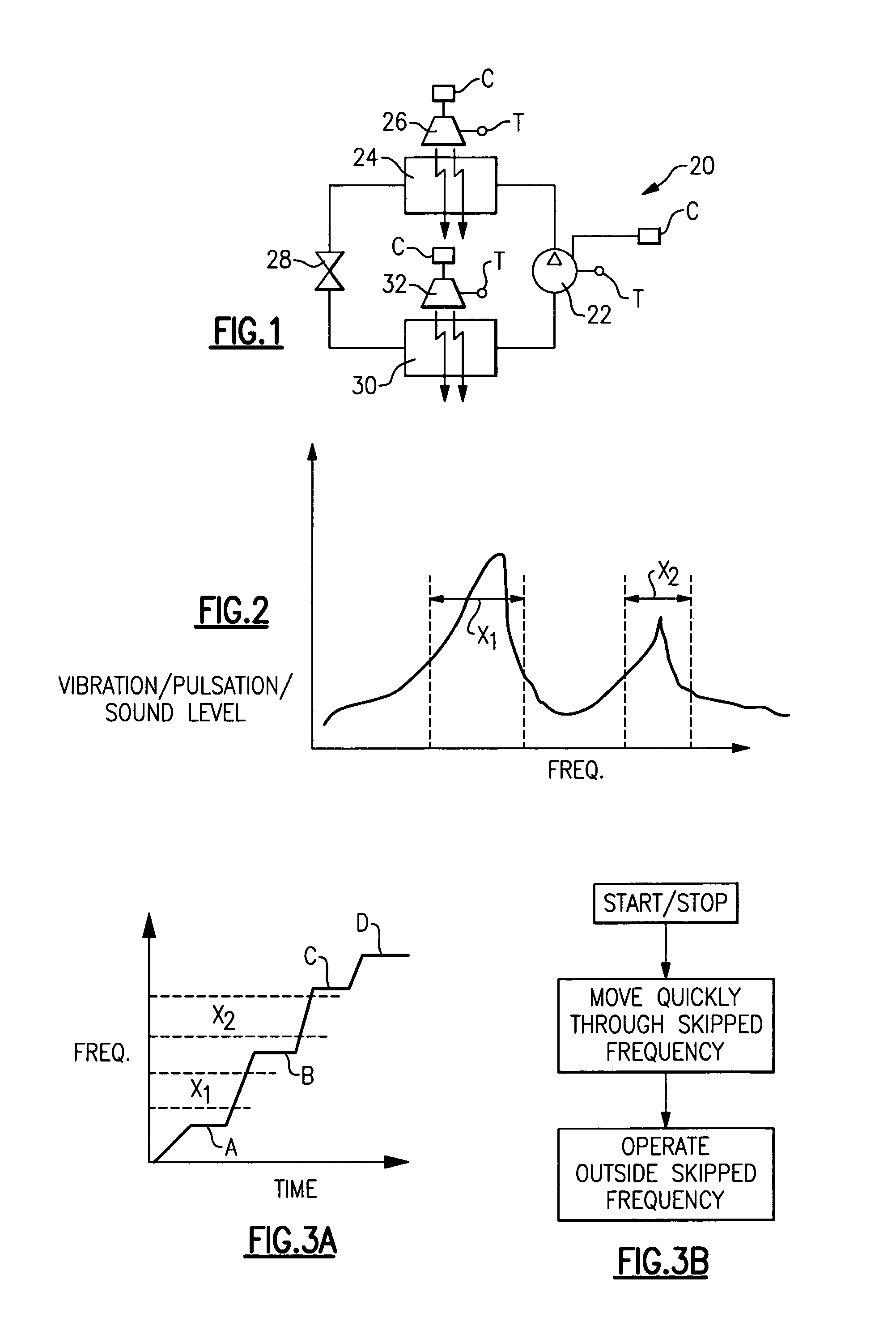
A control for an electric motor is utilized to avoid operation in or near the resonance frequencies for the electric motor and its associated system components. The resonance frequencies can be identified experimentally at the design stage, or during operation of a component and electric motor. During start-up, shutdown or frequency adjustment, the control drives the speed through the resonance frequency zones more rapidly, and also avoids operation in or near those resonance frequencies during steady state operation. In disclosed embodiments, the electric motors are associated with fans, pumps and compressors in a refrigerant system.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Synchronous motor driving system and sensorless control method for a synchronous motor
InactiveUS20030057912A1Synchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motorMagnetic poles
Axial error calculation unit is provided for estimating an axial error DELTAtheta between a d-q axis and a dc-qc axis by using Ld, Lq, Ke, Id*, Iq*, Idc and Iqc in a range of all rotational speeds except zero of a rotational speed command of a synchronous motor, Ld denoting an inductance on a magnetic pole axis d of the synchronous motor, Lq an inductance on a q axis orthogonal to the magnetic pole axis d, Ke a generated power constant of the motor, Id* a current command of the d axis, Iq* a current command on a q axis, Idc a detected current value on an assumed dc axis on control, and Iqc a detected current value on an assumed qc axis orthogonal to the assumed dc axis. Irrespective of presence of saliency, position sensorless control can be achieved in a wide range a low to high speed zone.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
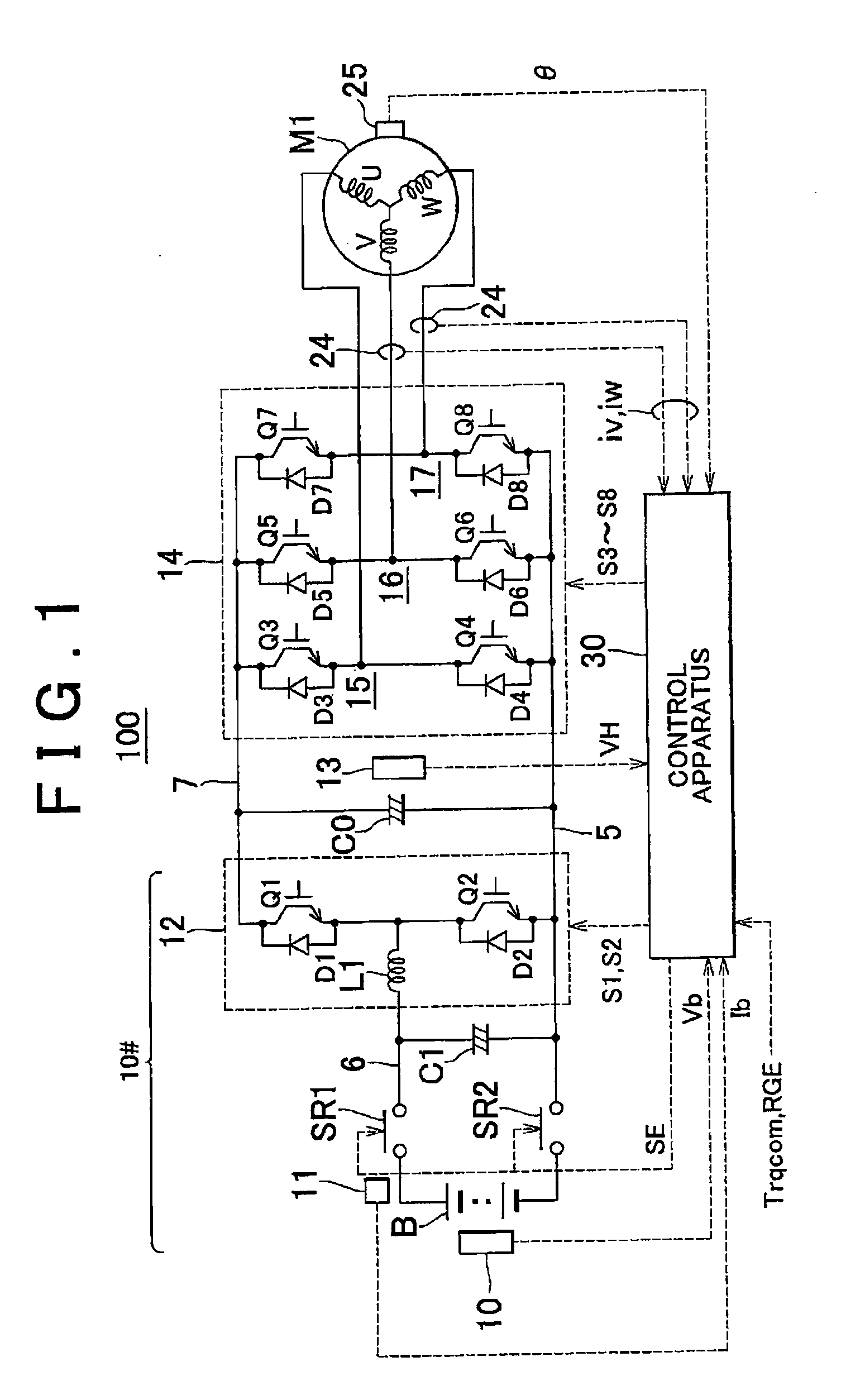
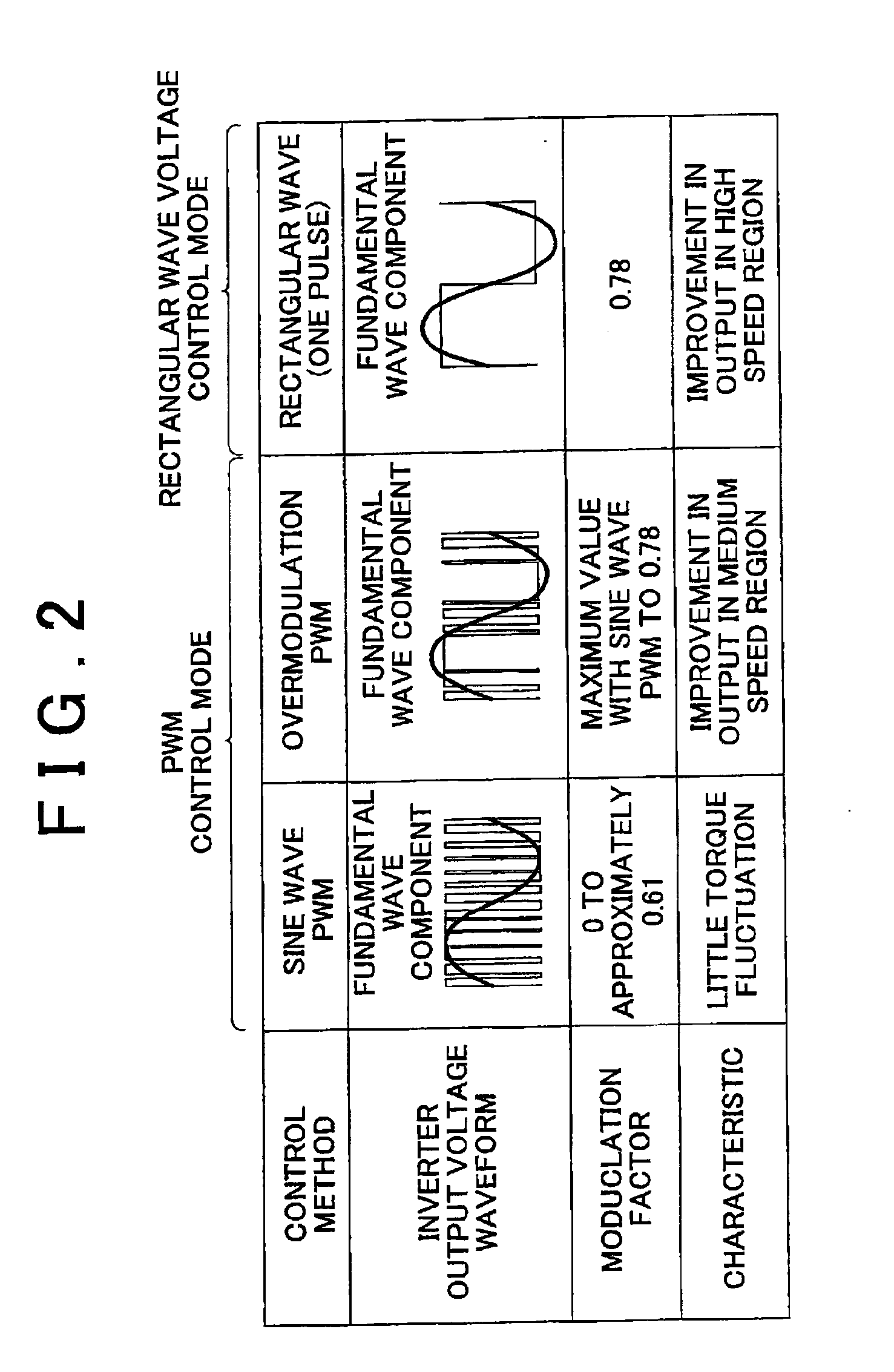
Alternating-current motor control apparatus
ActiveUS20100123418A1Simple structureImprove responsivenessVehicle testingTorque ripple controlPhase currentsCurrent meter
When a rectangular wave voltage control mode is selected, a control apparatus estimates the output torque of an alternating-current motor based on the outputs of a current sensor and a rotation angle sensor, and executes torque feedback control by adjusting the phase of rectangular wave voltage based on the difference between the torque estimated value and a torque command value. The control apparatus executes a switching interruption that outputs a control command to a switching element of an inverter every 60 degrees of electrical angle, and executes an angle interruption that samples the phase currents of the alternating-current motor based on the output of the current sensor and converts those phase currents into a d-axis current and a q-axis current every predetermined electrical angle that is set beforehand. The control apparatus for the alternating-current motor then sets the predetermined electrical angle such that the number of angle interruptions between switching interruptions varies according to the rotation speed of the alternating-current motor.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
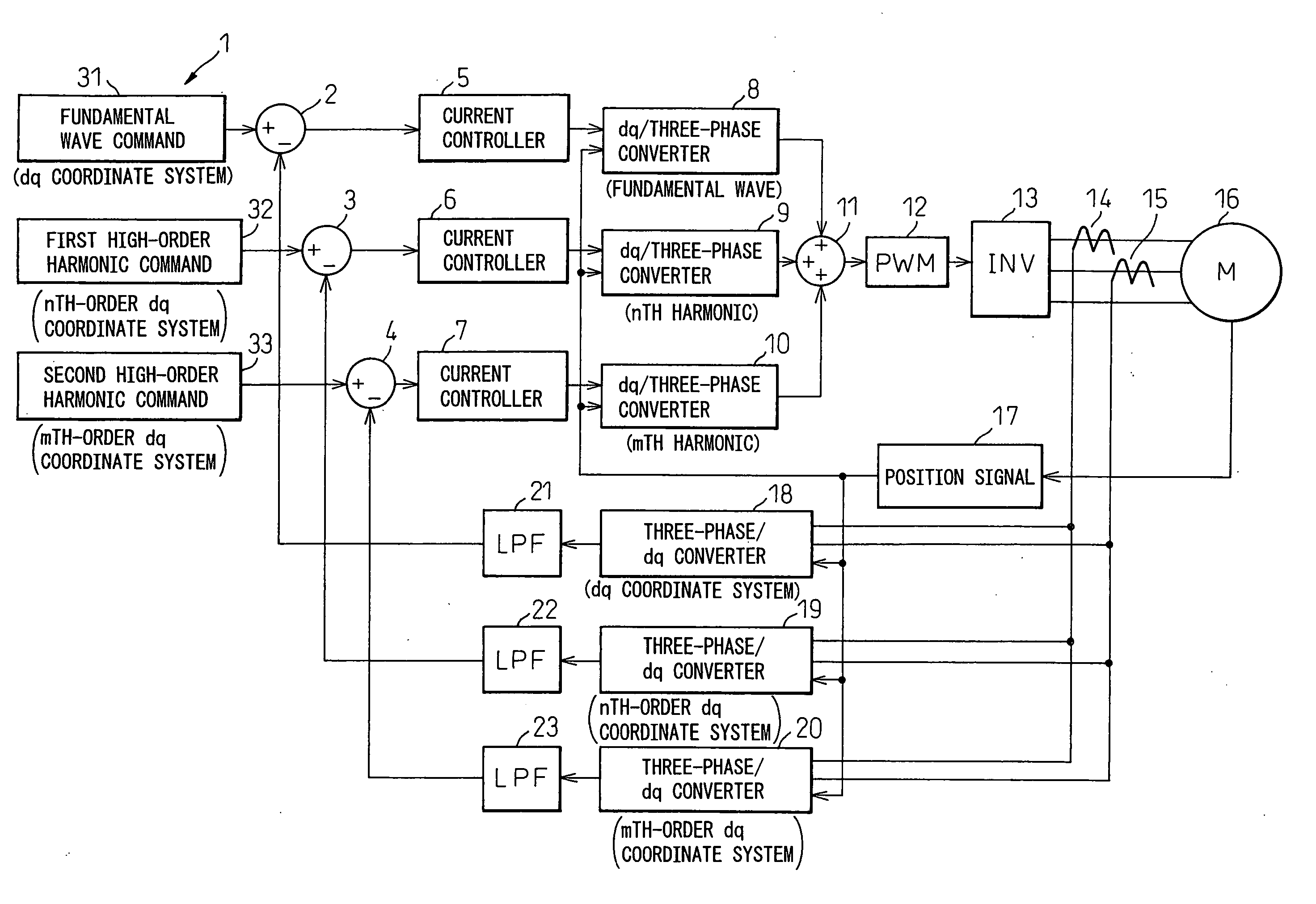
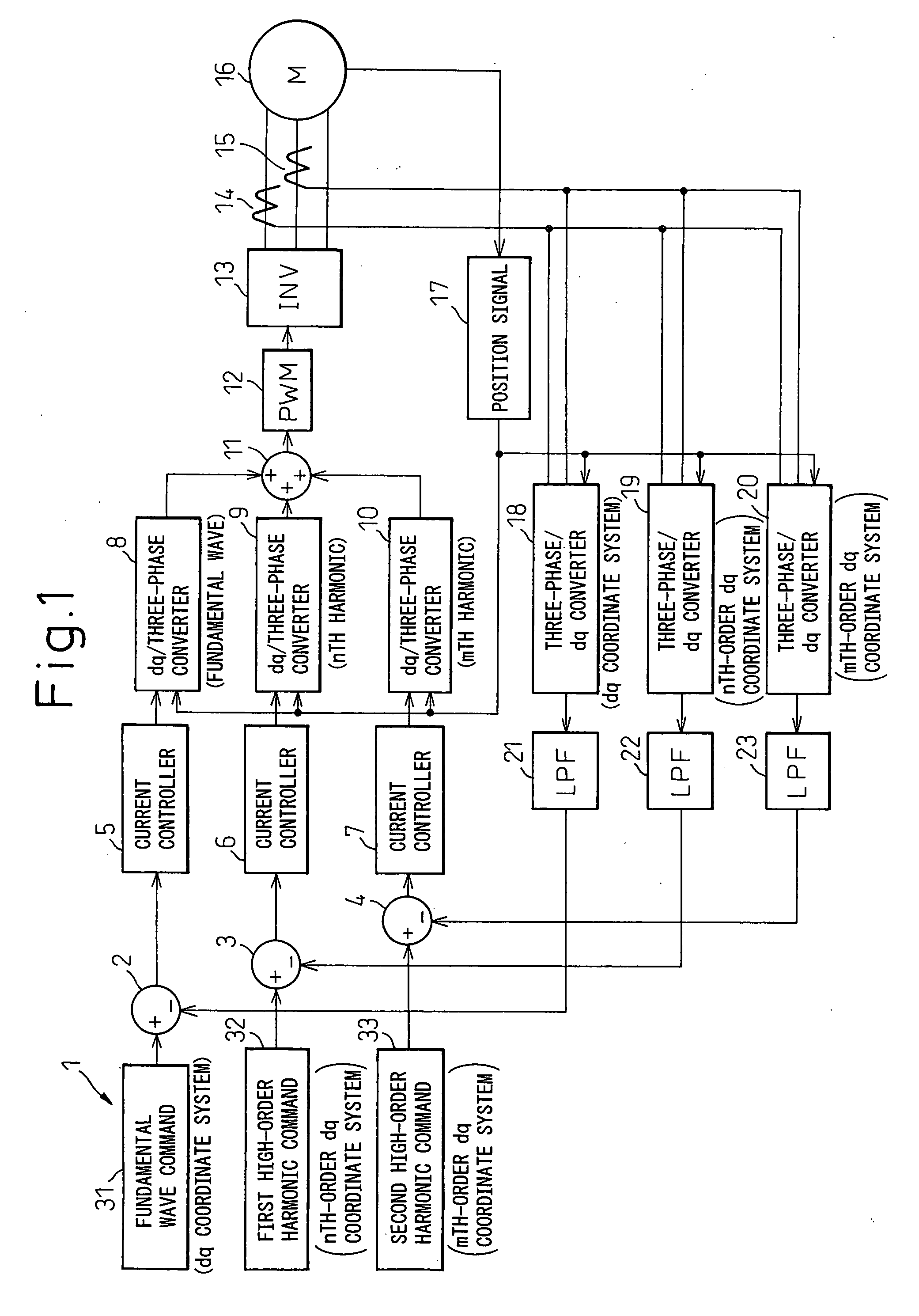
Motor control apparatus
InactiveUS20060038531A1Easy to controlSimple circuitTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersHarmonicLow-pass filter
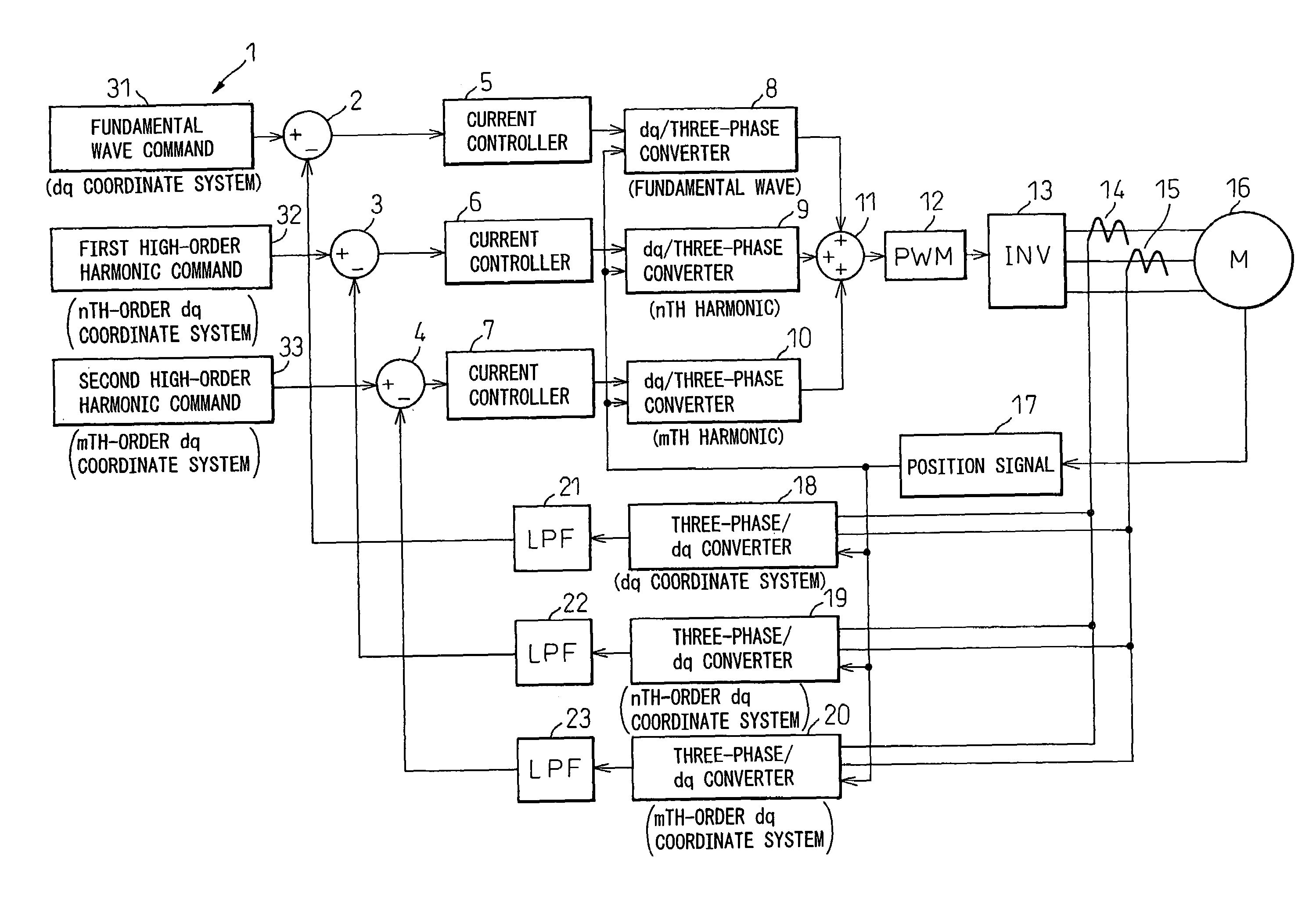
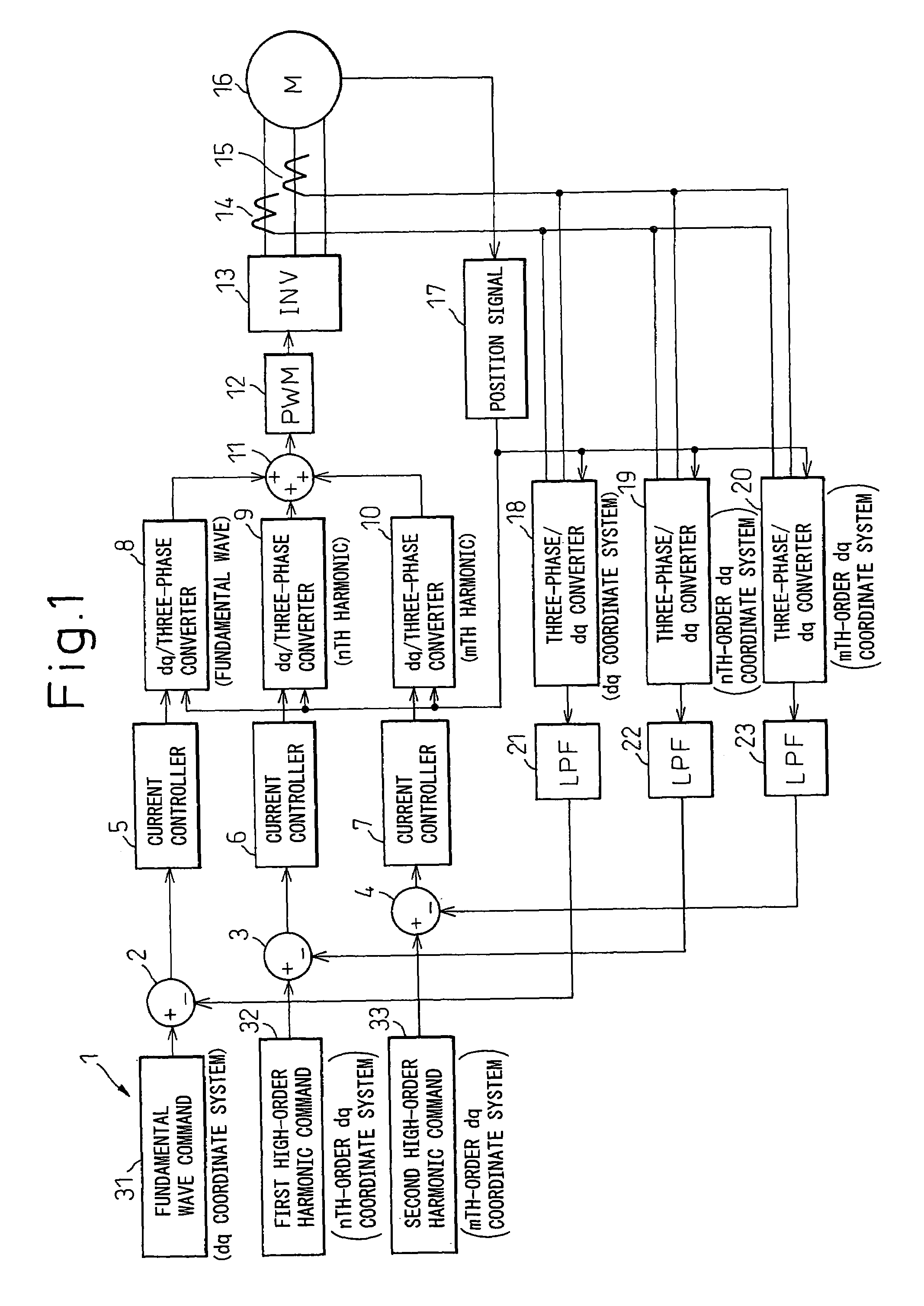
An object of the present invention is to provide a motor control apparatus having excellent harmonic current control performance, that can simplify circuit configuration and circuit processing while, at the same time, achieving improved control accuracy. To achieve this object, detected motor currents are converted by coordinate converters 19 and 20 into an nth-order dq-axis signal and an mth-order dq-axis signal, and their DC components are extracted by low-pass filters 22 and 23; then, the differences of the DC components relative to respective command values are converted back into three-phase AC signals to control the motor currents.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motor control apparatus
InactiveUS20030001536A1Torque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric machineControl system
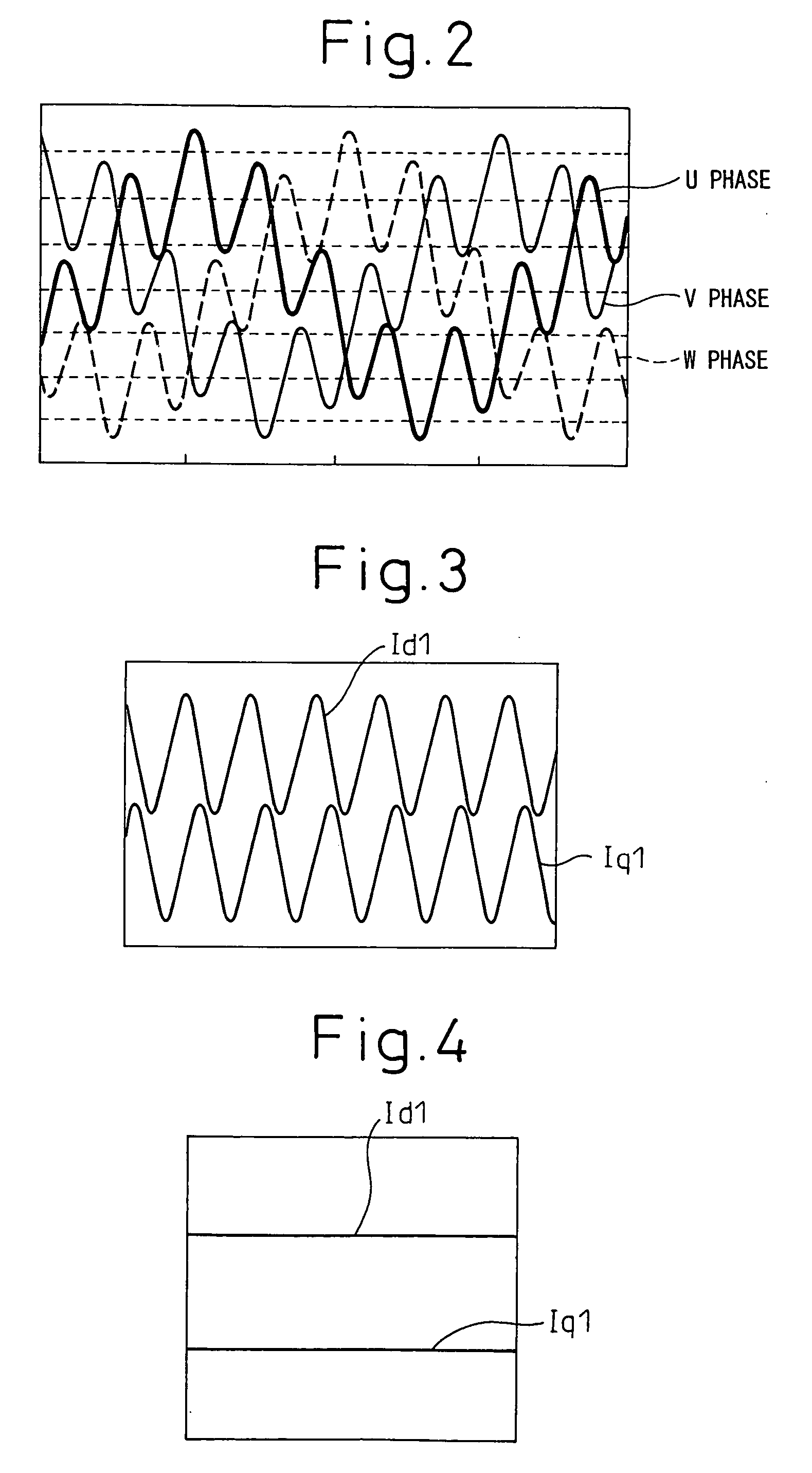
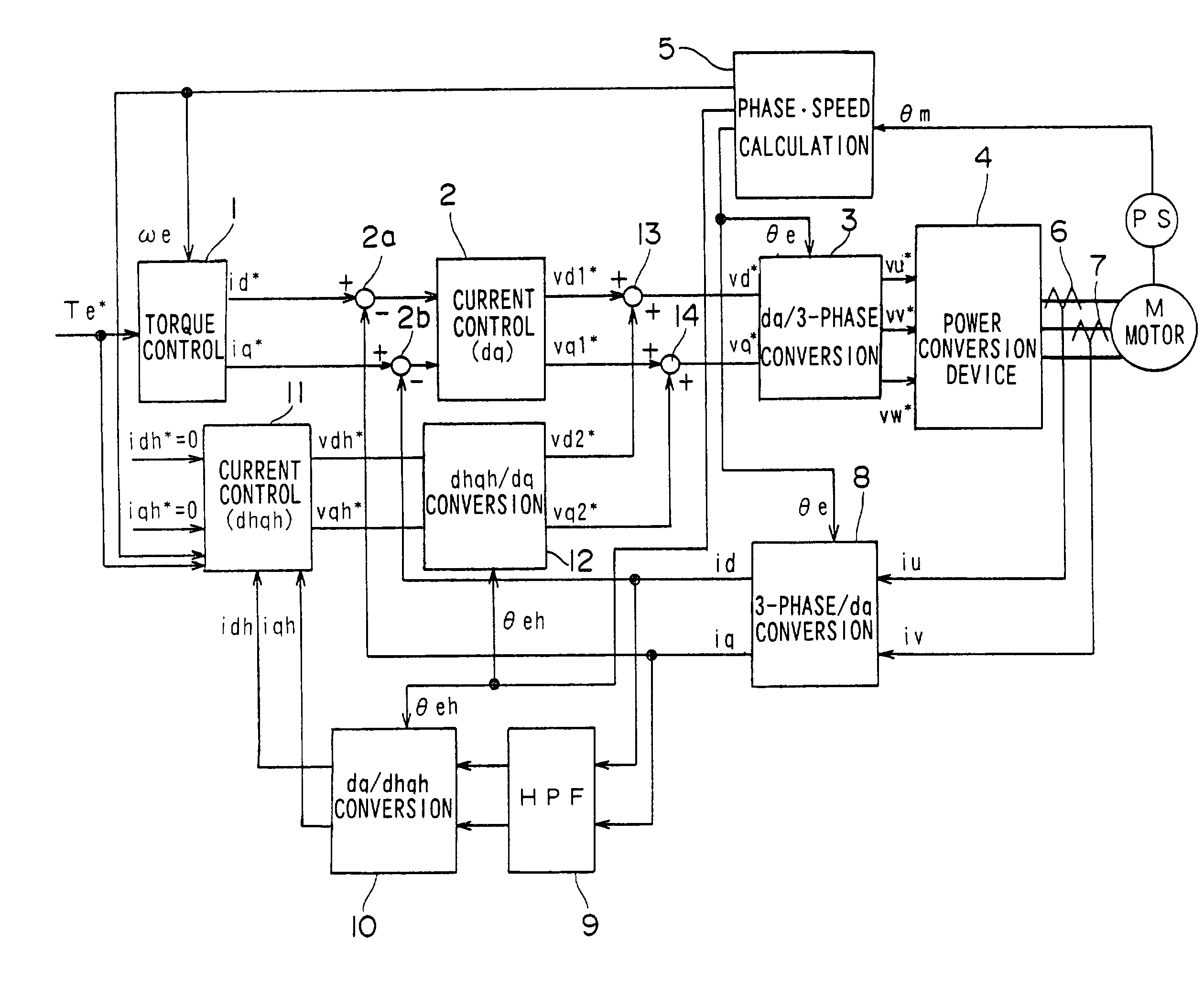
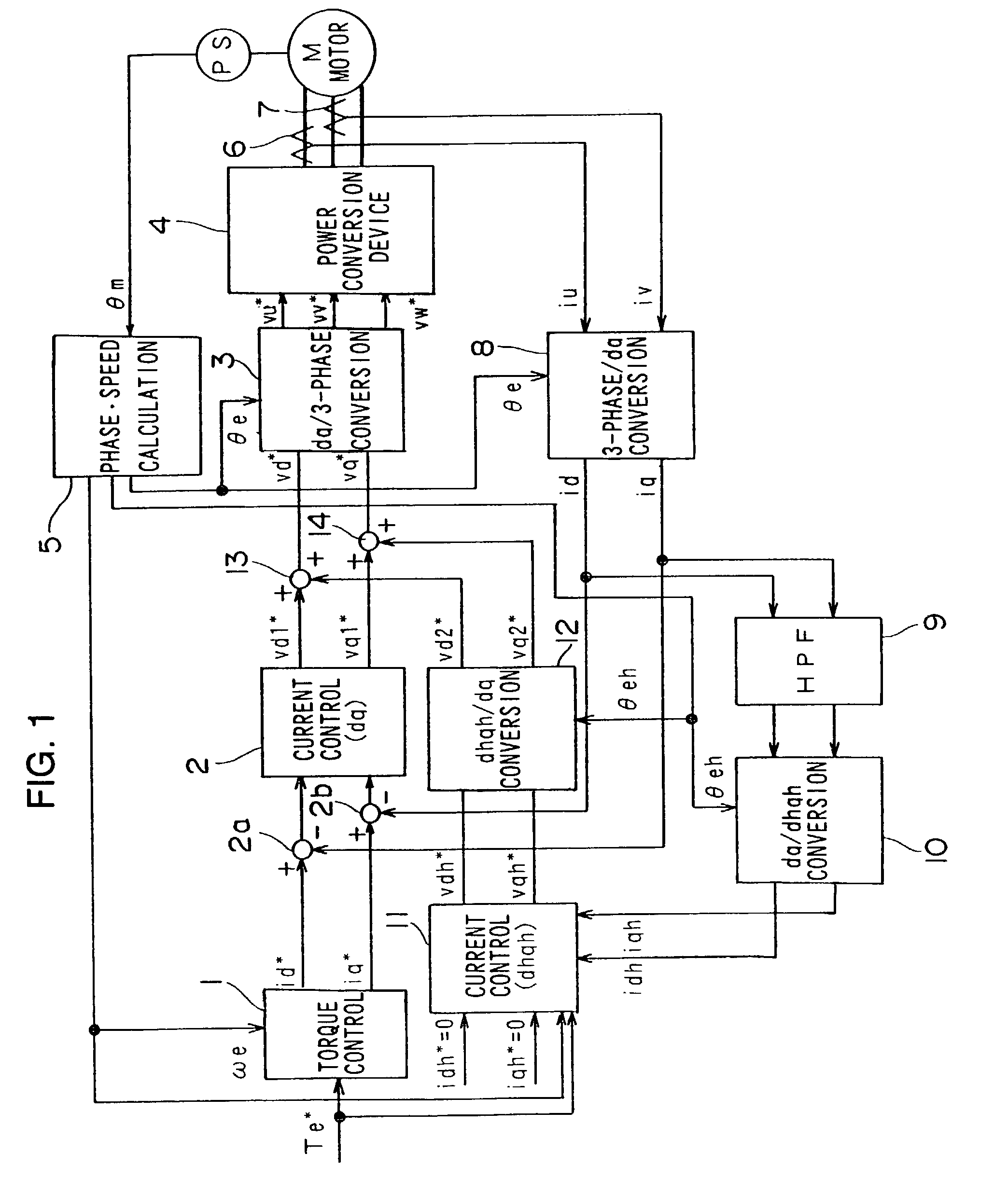
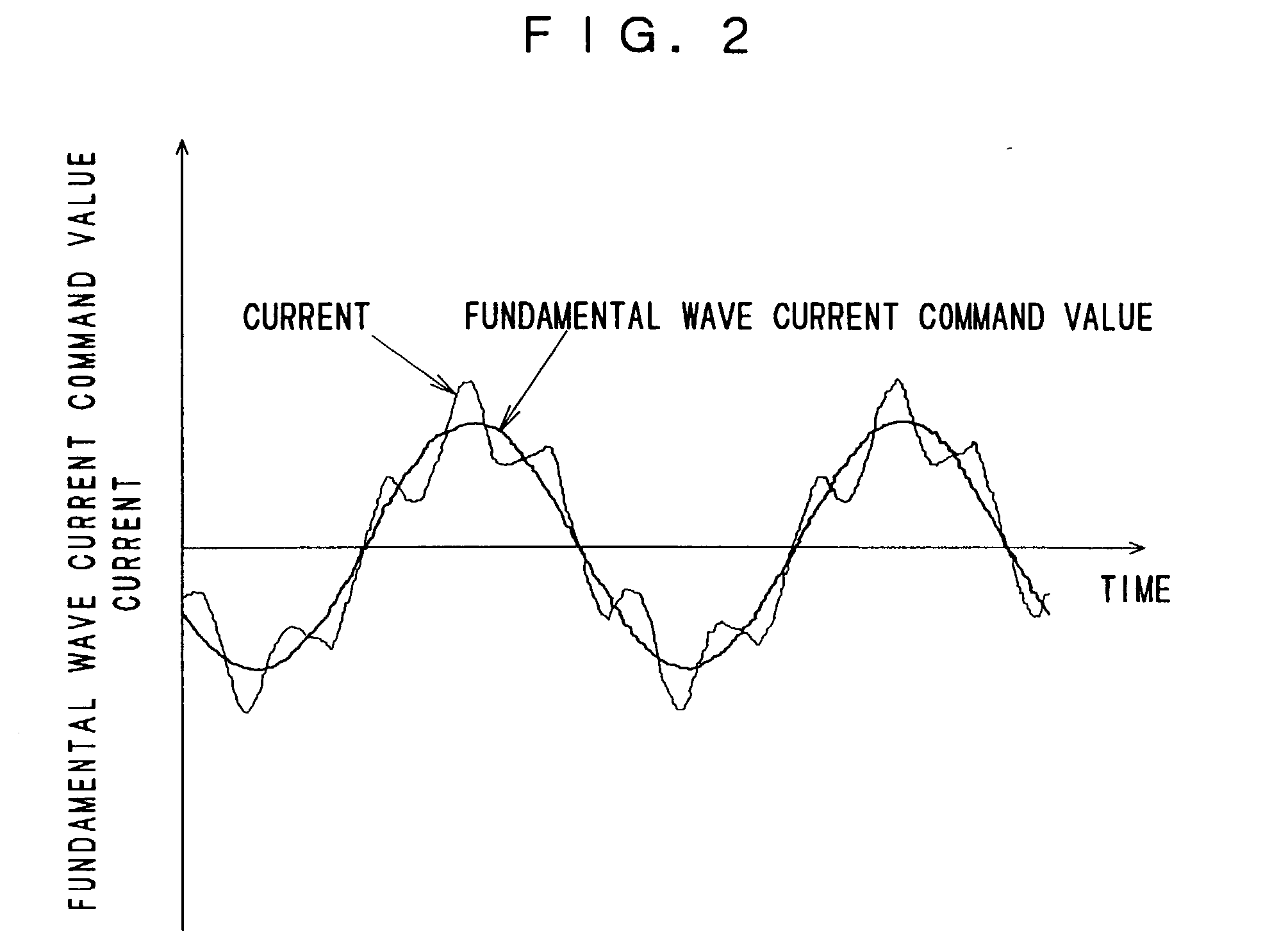
A motor control apparatus comprises a fundamental wave current control system that controls a fundamental wave component of a motor current in an orthogonal coordinate system which rotates in synchronization with a rotation of a 3-phase AC motor, a higher harmonic current control system that controls a higher harmonic component contained in the motor current in an orthogonal coordinate system rotating with a frequency which is an integral multiple of the frequency of the fundamental wave component of the motor current, a voltage command value generating device that generates 3-phase AC voltage command values by adding an output from the fundamental wave current control system and an output from the higher harmonic current control system, a power conversion device that converts a DC source voltage to a 3-phase AC voltage corresponding to the 3-phase AC voltage command values and outputs the 3-phase AC voltage to the 3-phase AC motor, a voltage saturation detection device which detects that an output voltage from the power conversion device is in a saturated state and a gain adjustment device that reduces a current control gain for the higher harmonic current control system if the voltage saturation detection device detects that an output voltage is in a saturated state.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Motor control apparatus and electric vehicle using same
InactiveUS20020117990A1Single-phase induction motor startersDC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motorMagnetic poles
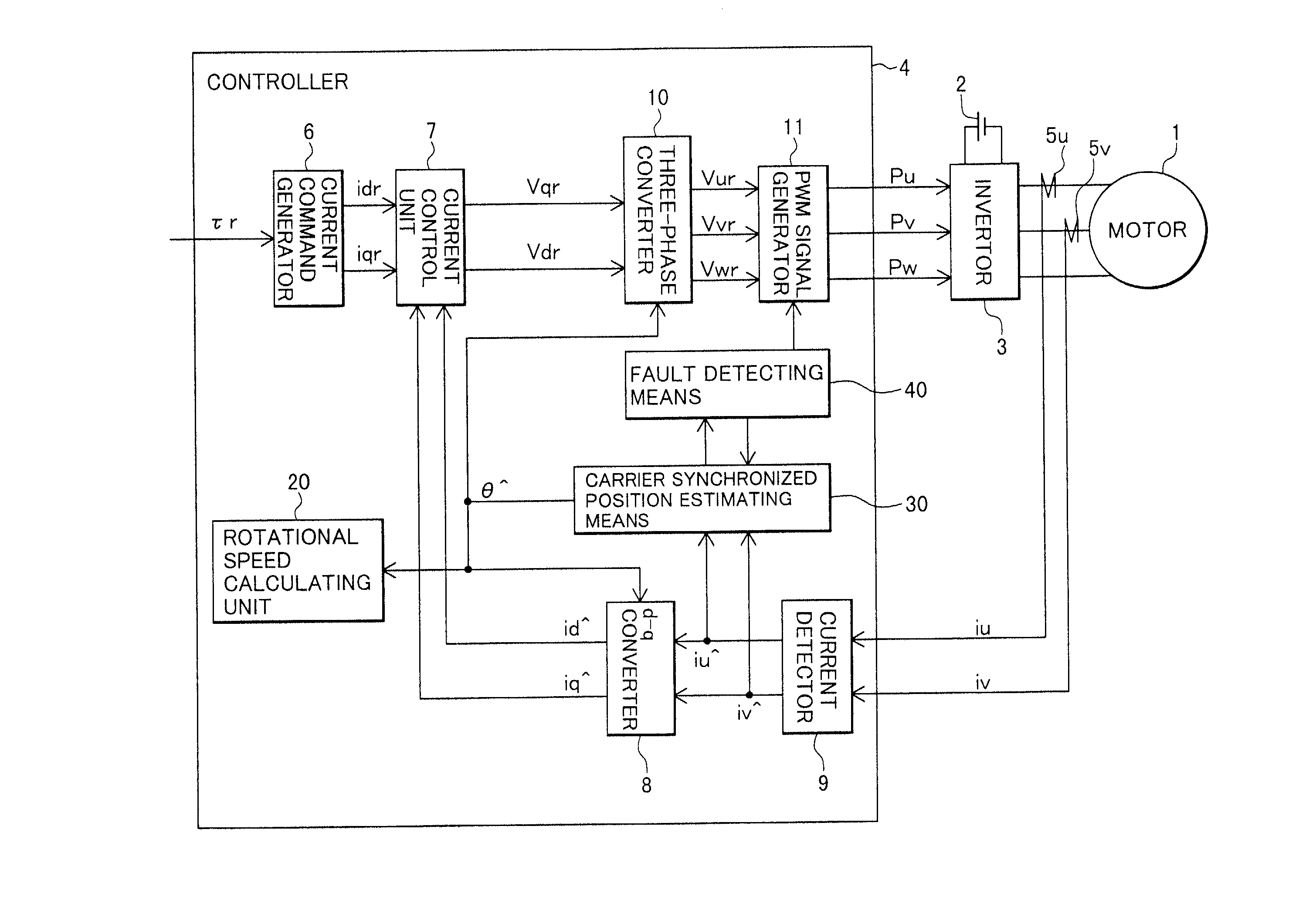
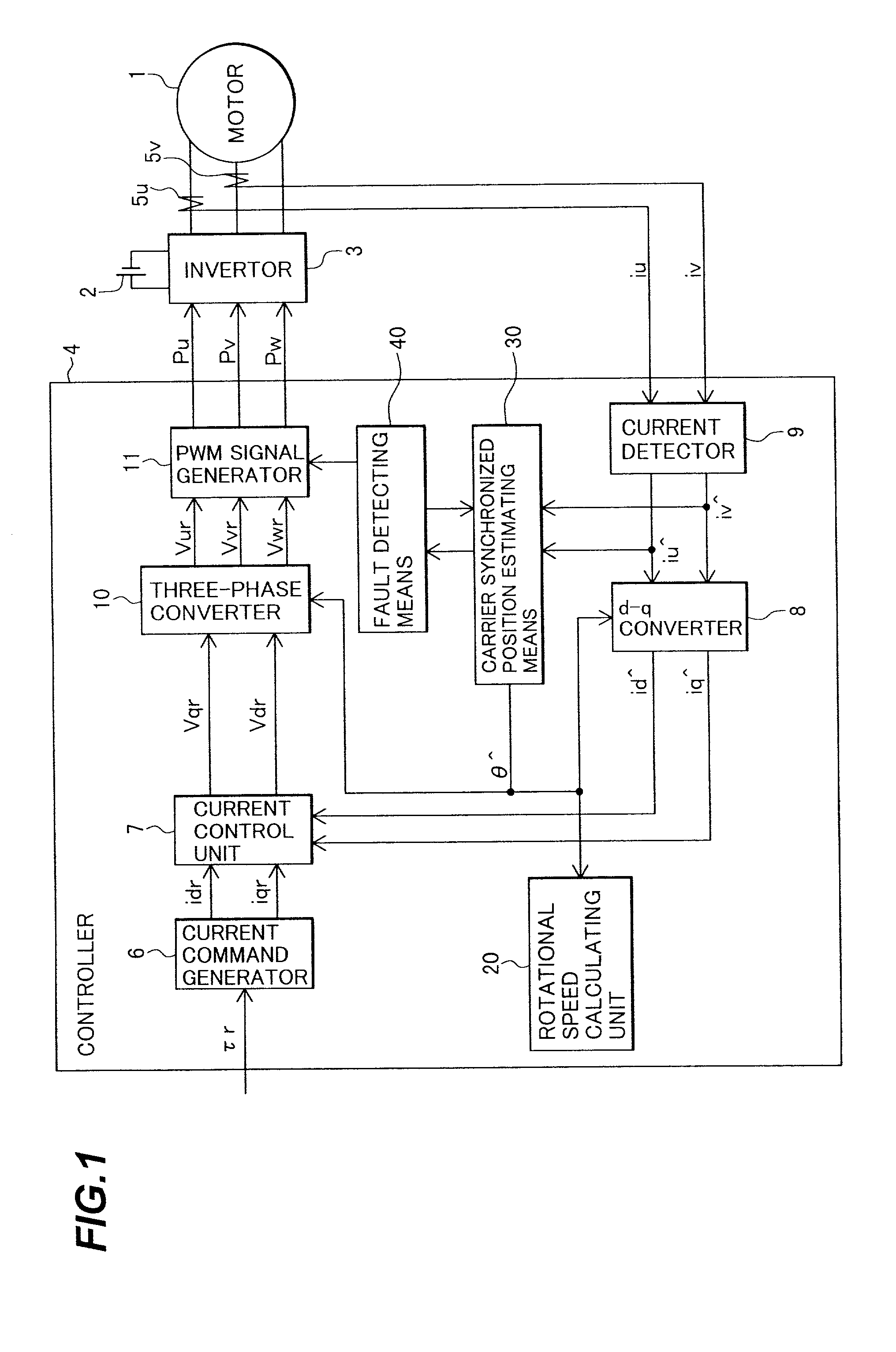
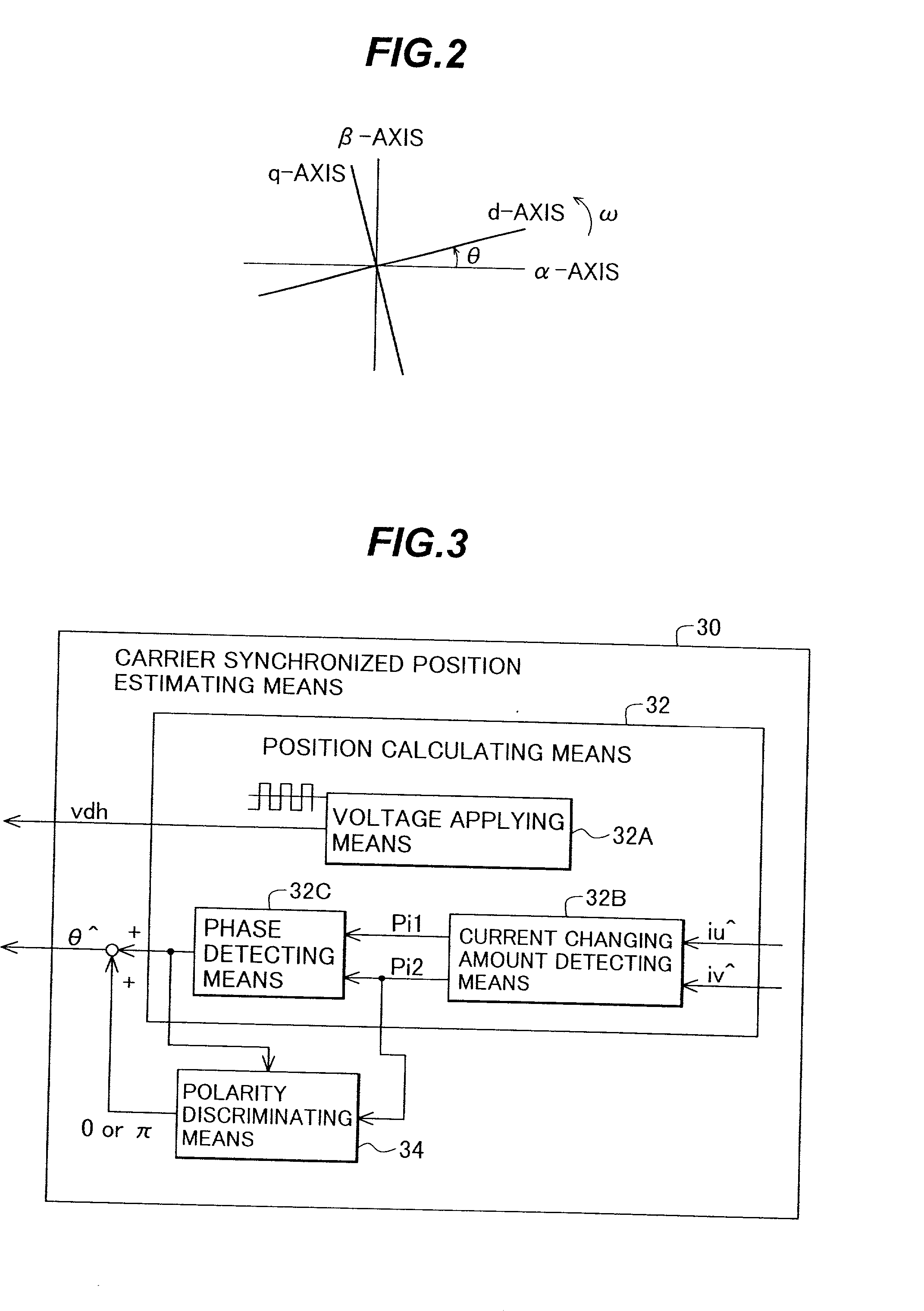
A synchronous motor controlling apparatus which can be applied to the carrier synchronized position estimating method as well and have protection-related functions such as detection of inverted magnetic pole position of a motor in a simple method, and an electric motor using the synchronous motor control apparatus. A controller controls a voltage applied to an AC motor with a PWM signal. A magnetic pole position detector of the controller detects a current of the AC motor to estimate a pole position of the AC motor. A fault detector detects a fault in the estimated magnetic position of the AC motor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Torque ripple suppression control apparatus and torque ripple suppression control method for rotating electrical machine
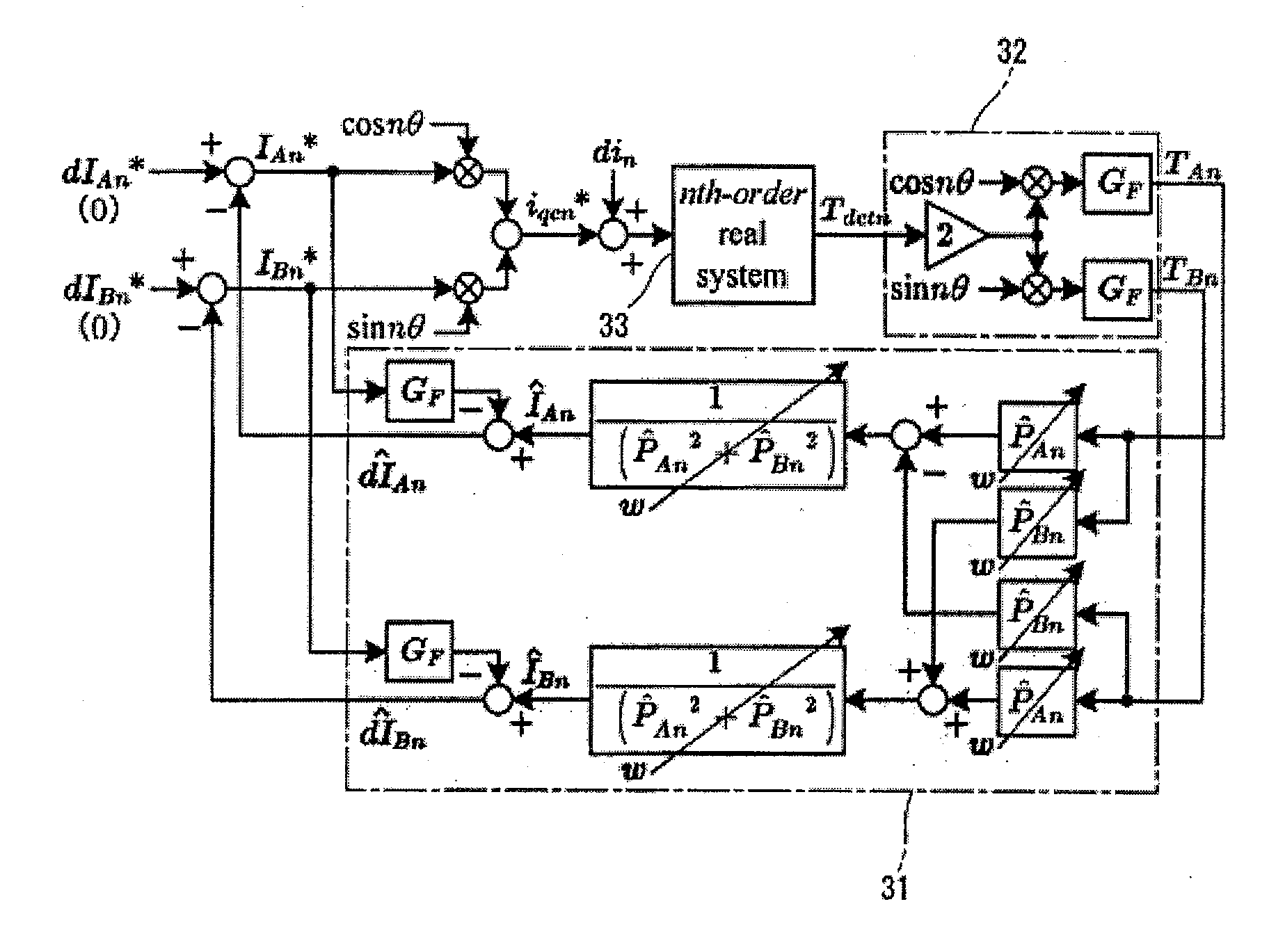
ActiveUS20120306411A1Current disturbanceSuppress torque ripple accuratelySynchronous motors startersVector control systemsEngineeringDisturbance observer
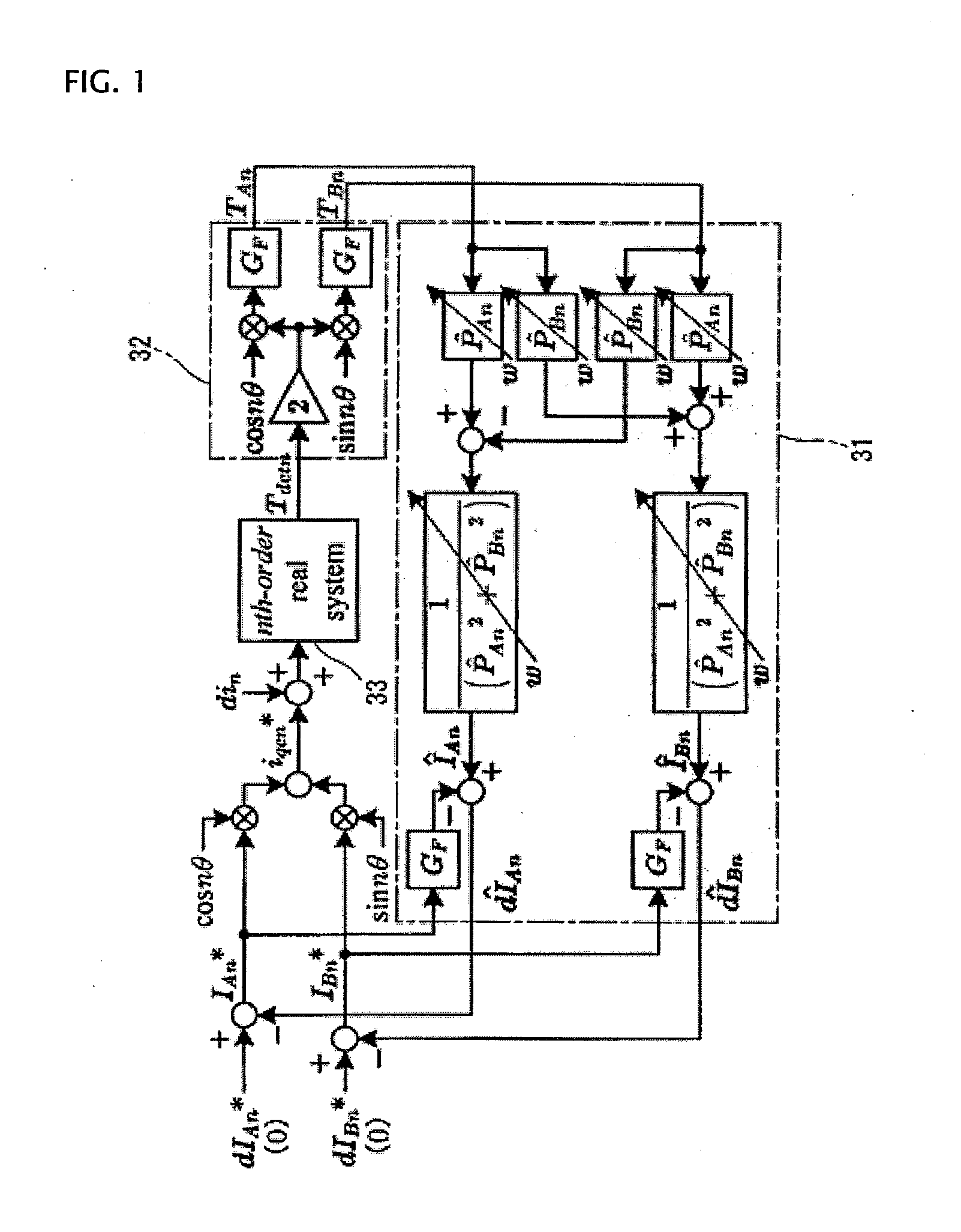
A periodic disturbance observer determines real part ÎAn and imaginary part ÎBn of an estimated current including a periodic disturbance, from value of identification identifying a system transfer function of an nth order torque ripple frequency component from a command torque to a detected torque value, with a one-dimensional complex vector having a real part P̂An and an imaginary part P̂Bn, a cosine coefficient TAn, a sine coefficient TBn, and the real part P̂An and imaginary part P̂Bn of the system transfer function; subtracts command compensating current IAn* and IBn* obtained through pulsation extracting filter GF, respectively, from the real part ÎAn and imaginary part ÎBn of the estimated current, and thereby determines estimated periodic disturbance current real part dÎAn and imaginary part dÎBn to cancel the periodic disturbance current.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
Motor control apparatus
InactiveUS7176652B2Excellent harmonic current control performanceSimple circuit configuration and circuit processingTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersLow-pass filterHarmonic
An object of the present invention is to provide a motor control apparatus having excellent harmonic current control performance, that can simplify circuit configuration and circuit processing while, at the same time, achieving improved control accuracy. To achieve this object, detected motor currents are converted by coordinate converters 19 and 20 into an nth-order dq-axis signal and an mth-order dq-axis signal, and their DC components are extracted by low-pass filters 22 and 23; then, the differences of the DC components relative to respective command values are converted back into three-phase AC signals to control the motor currents.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motor drive apparatus, vehicle having the same mounted therein, and computer readable storage medium having a program stored therein to cause computer to control voltage conversion
ActiveUS20060055349A1Reduce switching noiseReduce switching lossesSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsFrequency changerMotor drive
A control device receives a power supply current from a current sensor and a reactor current from a current sensor and detects a maximum value and a minimum value from the reactor current and from the detected maximum and minimum values and the power supply current determines whether the reactor current traverses the zero point, and if so the control device generates and outputs a signal to an up converter which responds to the signal by stopping switching to perform an up or down converting operation.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Synchronous motor control device and method for optimizing synchronous motor control
InactiveUS20090237014A1Torque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motorThree-phase
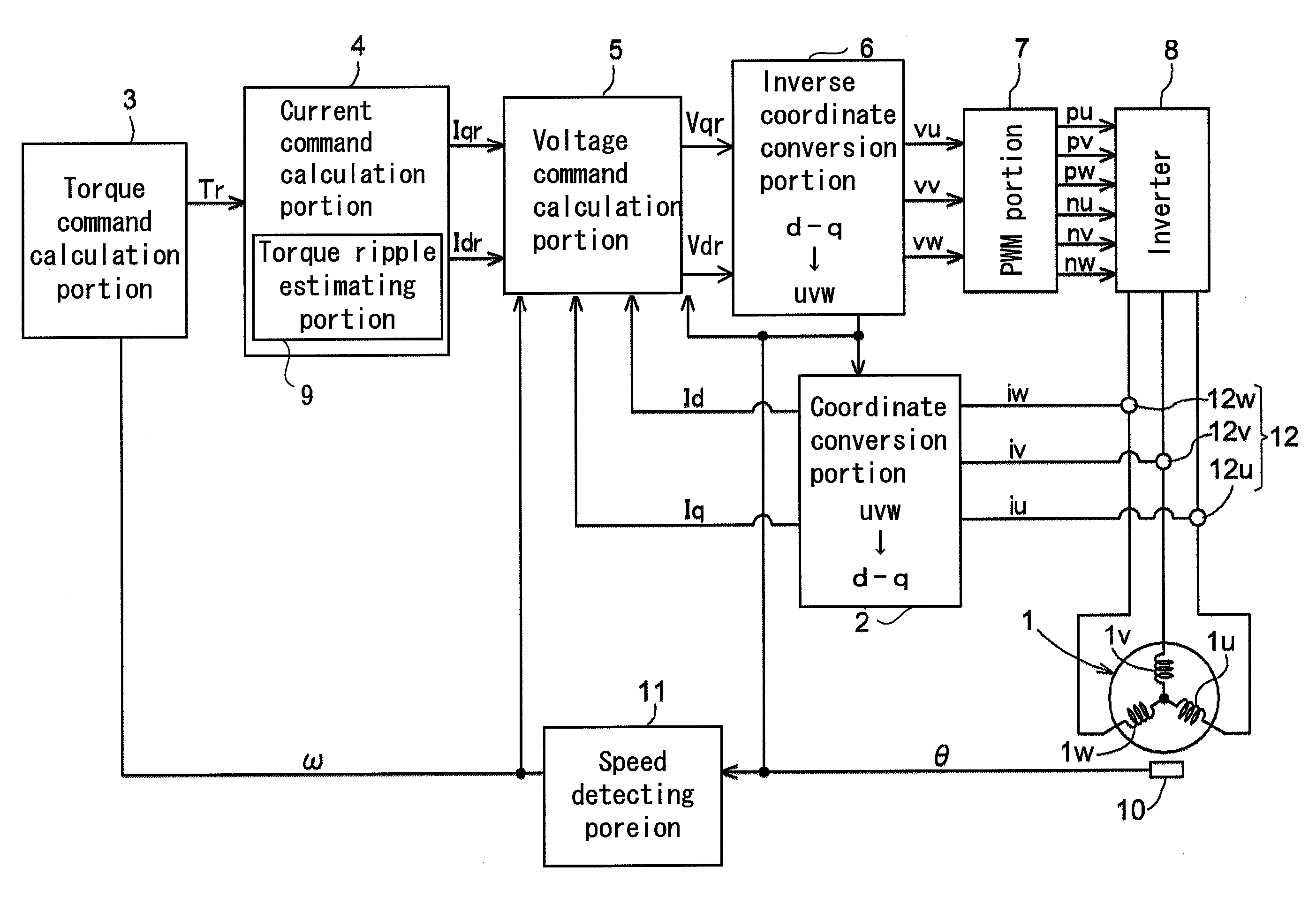
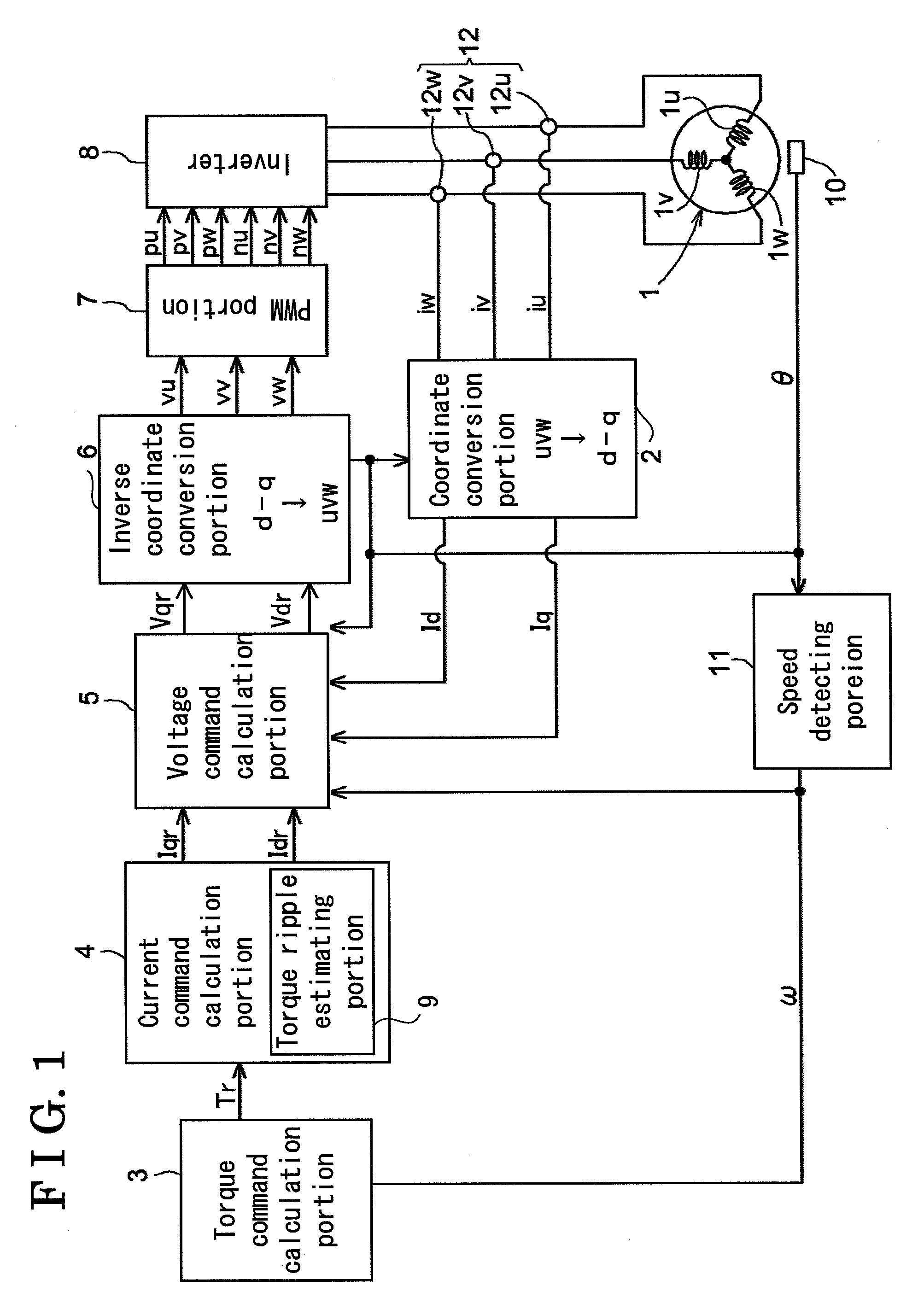
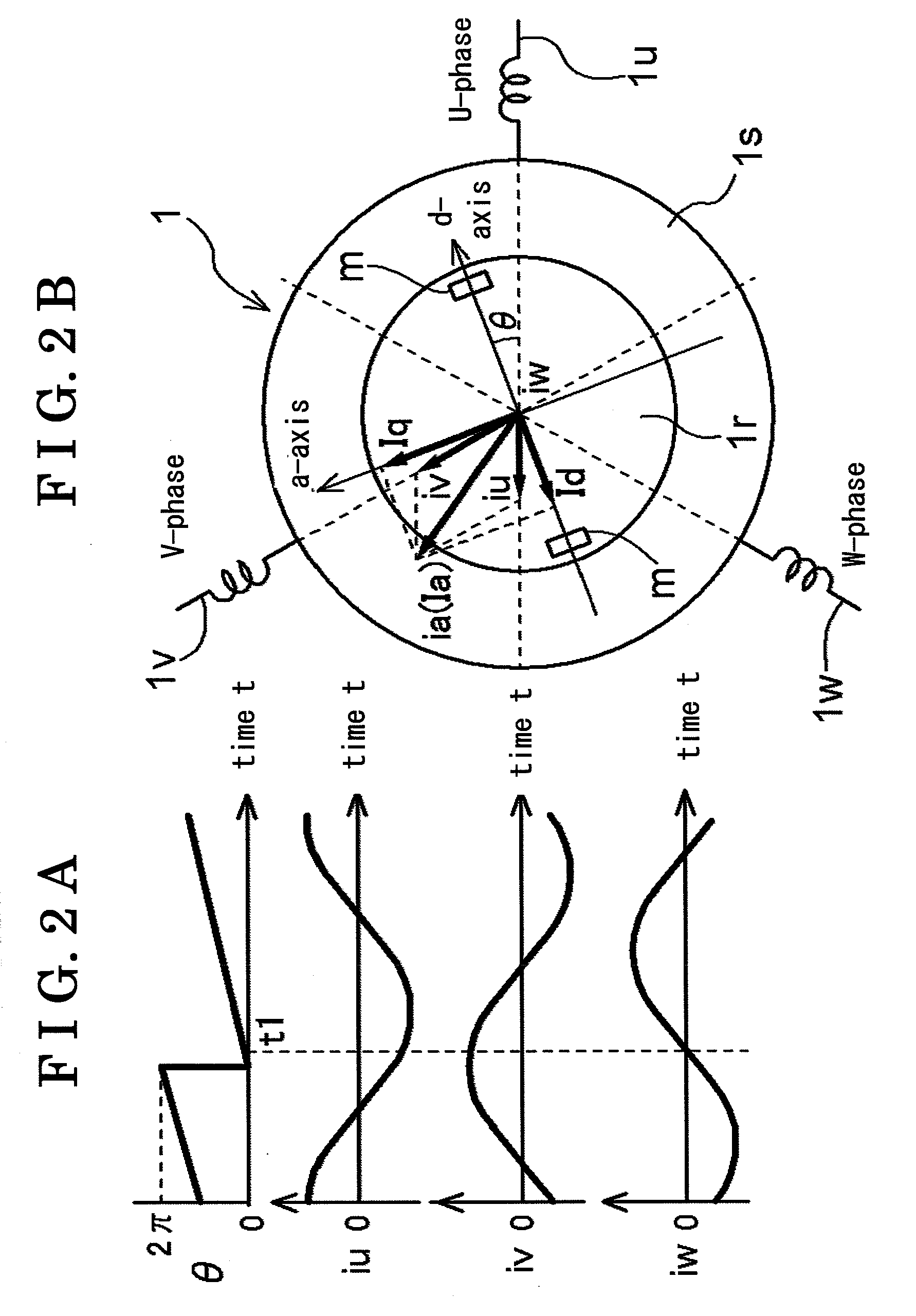
A synchronous motor control device, includes a coordinate transformation portion for coordinate transforming motor currents applied to respective three phases of a synchronous motor into a d-axis, corresponding to a direction of a magnetic field generated by a permanent magnet arranged at a rotor of the synchronous motor, and a q-axis orthogonal to the d-axis, a current command calculation portion for calculating a d-axis current command and a q-axis current command from a target torque, a voltage command calculation portion for calculating a d-axis voltage command and a q-axis voltage command, an inverse coordinate transformation portion for inversely coordinate transforming the d-axis voltage command and the q-axis voltage command into three-phase voltage commands, and a torque ripple estimating portion for estimating a torque ripple and feed-forwarding the estimation results to the current command calculation portion or the voltage command calculation portion.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
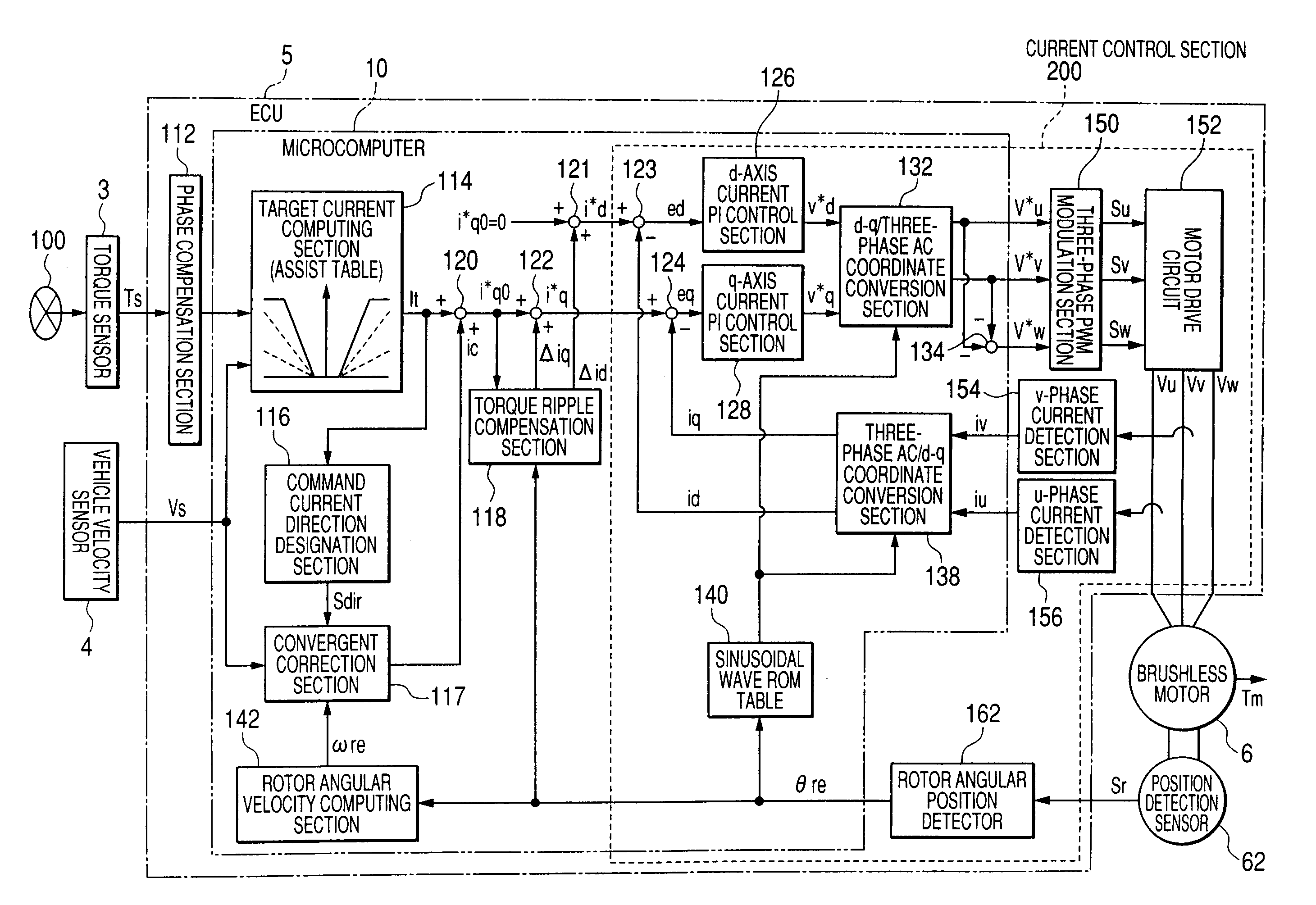
Motor controller and electric power steering system
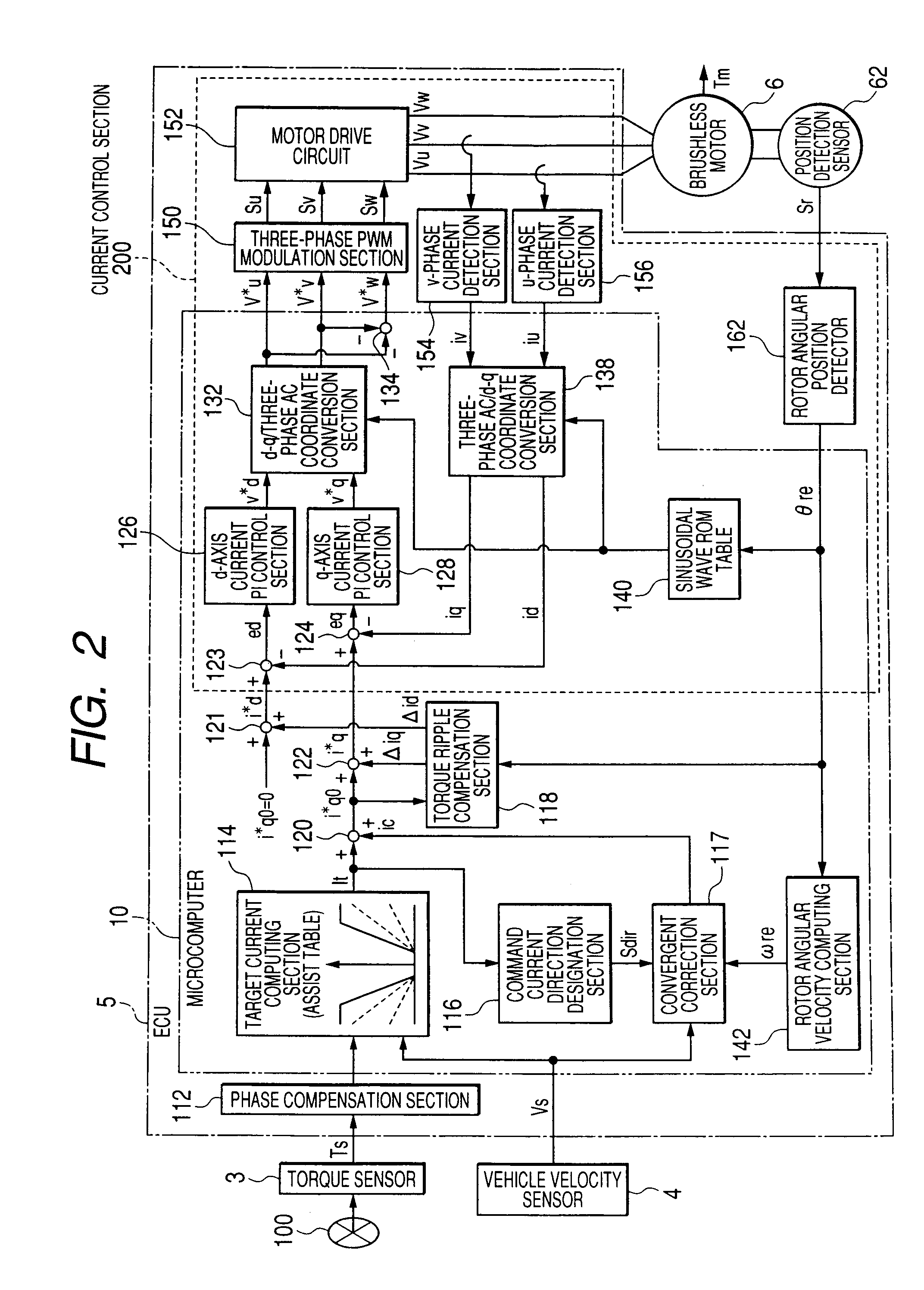
InactiveUS20080167779A1Reduce torque rippleReduce a torque rippleTorque ripple controlSingle motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringMicrocomputer
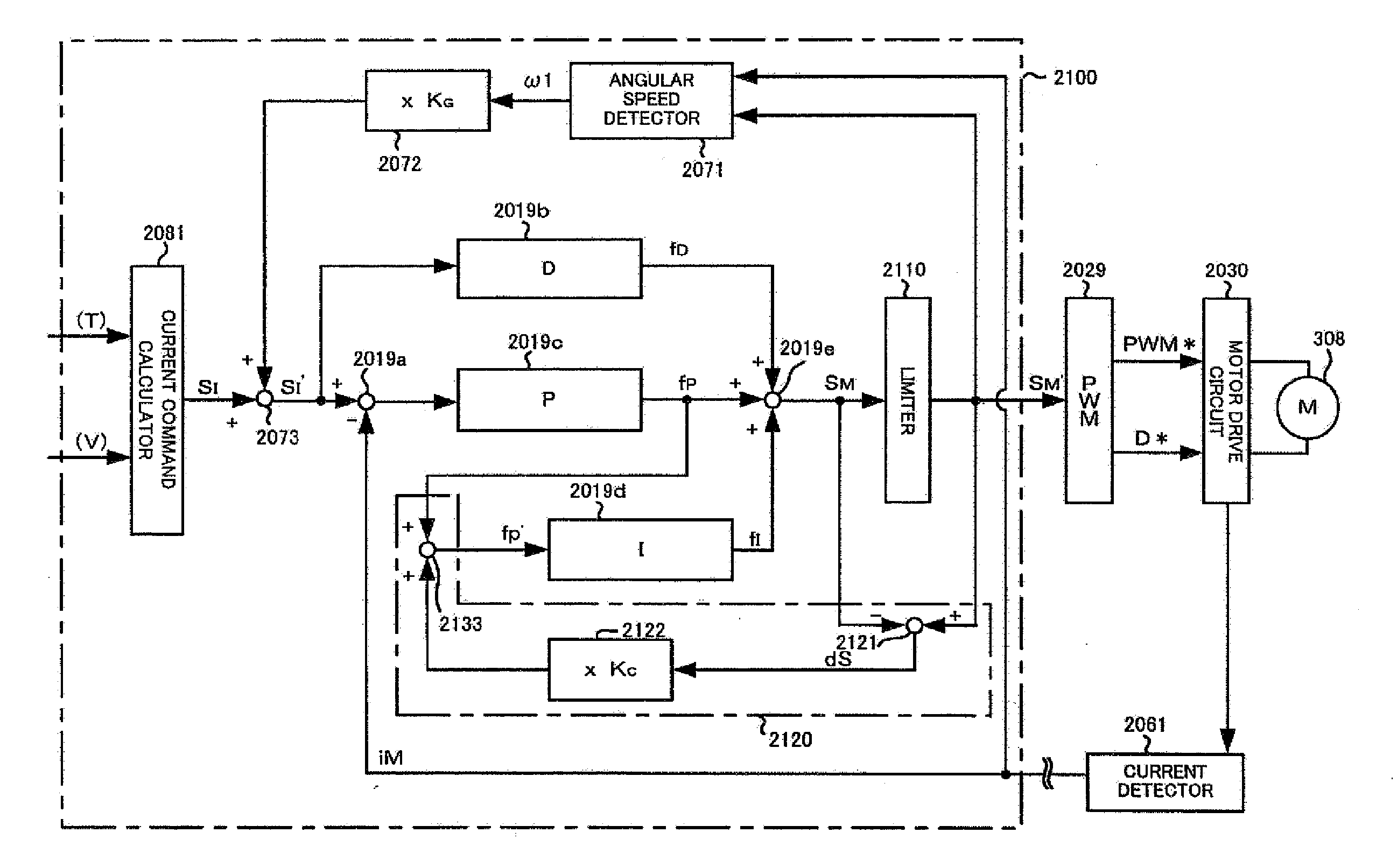
In a case where a computing period of a torque ripple compensation section which computes current compensation values Δid and Δiq to be caused to flow into a motor in order to prevent occurrence of a torque ripple in the motor differs from a control period of a current control section which controls a feedback to the motor in such a way that current command values i*d and i*q additionally provided with the current compensation values Δid and Δiq flow into the motor, the microcomputer sets the current compensation values Δid and Δiq to zero when a rotor angular velocity ωre of the motor is equal to or greater than a first threshold value ω1.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Three-phase rotary machine control apparatus
ActiveUS20130033210A1Suppress torque rippleSuppress overheatSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsPhase currentsThree-phase
A first inverter and a second inverter supply two coil sets forming a three-phase motor with AC voltages, which are the same in amplitude but shifted by 30° in phase. Current detectors detect phase currents supplied from the inverters to the coil sets. Temperature estimation sections estimate temperatures of the inverters or the coil sets based on an integration value of the phase current detection values. A current command value limitation section limits upper limits of current command values of both coil sets based on the estimated temperatures Tm1 and Tm2. Thus, the inverters and the coils sets are protected from overheating without increasing torque ripple.
Owner:DENSO CORP
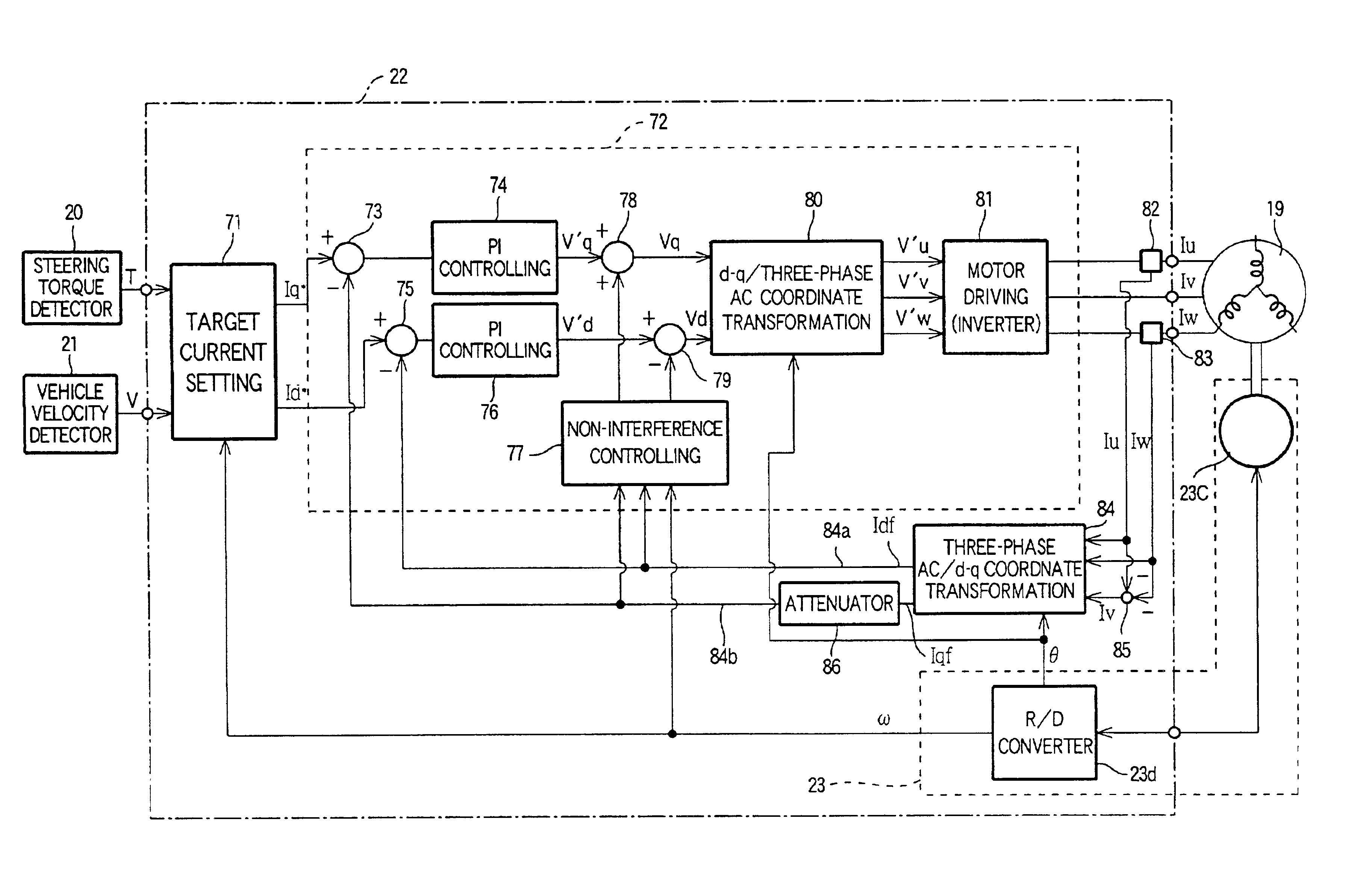
Electric power steering apparatus
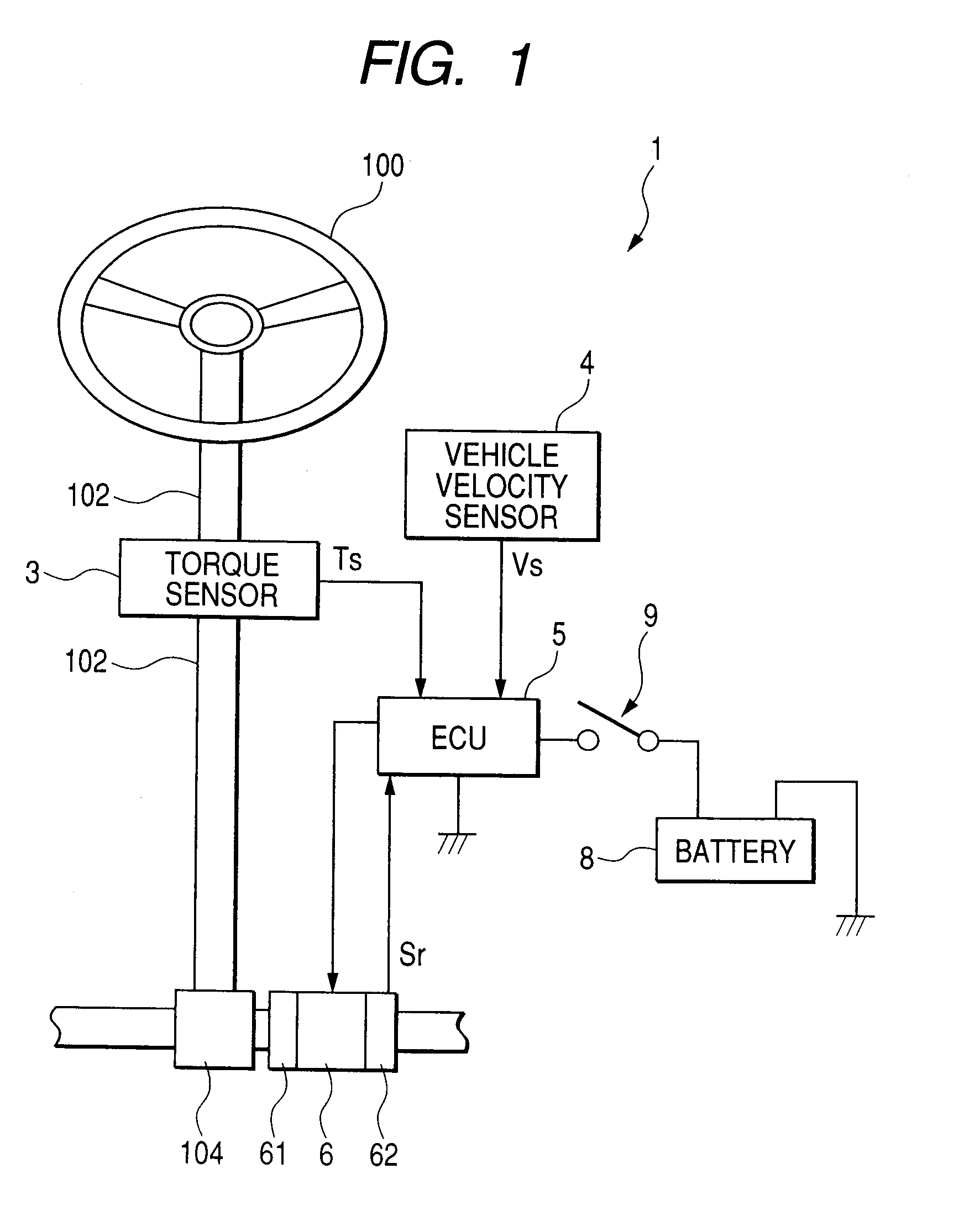
InactiveUS6838844B2Avoid volatilitySmooth feeling of steeringSingle motor speed/torque controlDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringBrushless motors
An electric power steering apparatus includes a steering torque detector, a brushless motor PWM-driven with a three-phase alternating motor current, a target current setting section for setting a d-axis target current value and a q-axis target current value, motor current detectors for detecting motor current values supplied to the brushless motor, a three-phase AC / d-q coordinate transformation circuit, a first deviation calculation circuit for calculating a deviation of a current value of a q-axis detection signal from the q-axis target current value, a second deviation calculation circuit for calculating a deviation of a direct current value a d-axis detection current signal from the d-axis target current, a motor control section for controlling driving of the brushless motor through a vector control process on the basis of deviation signals outputted from the first and second deviation calculation circuits, and an attenuation device provided in a feedback transmission path of the q-axis detection current signal for attenuating a high frequency noise mixed in the q-axis detection current signal.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
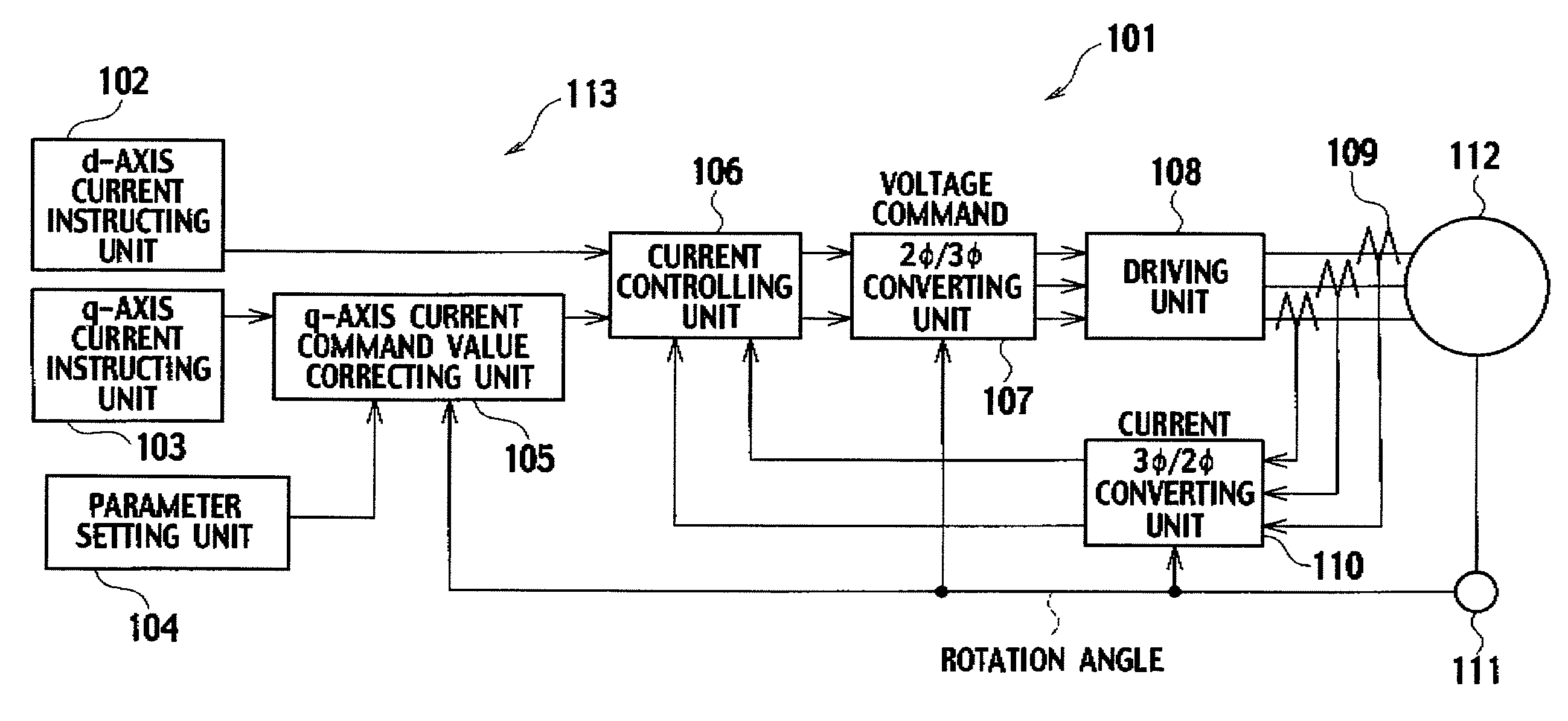
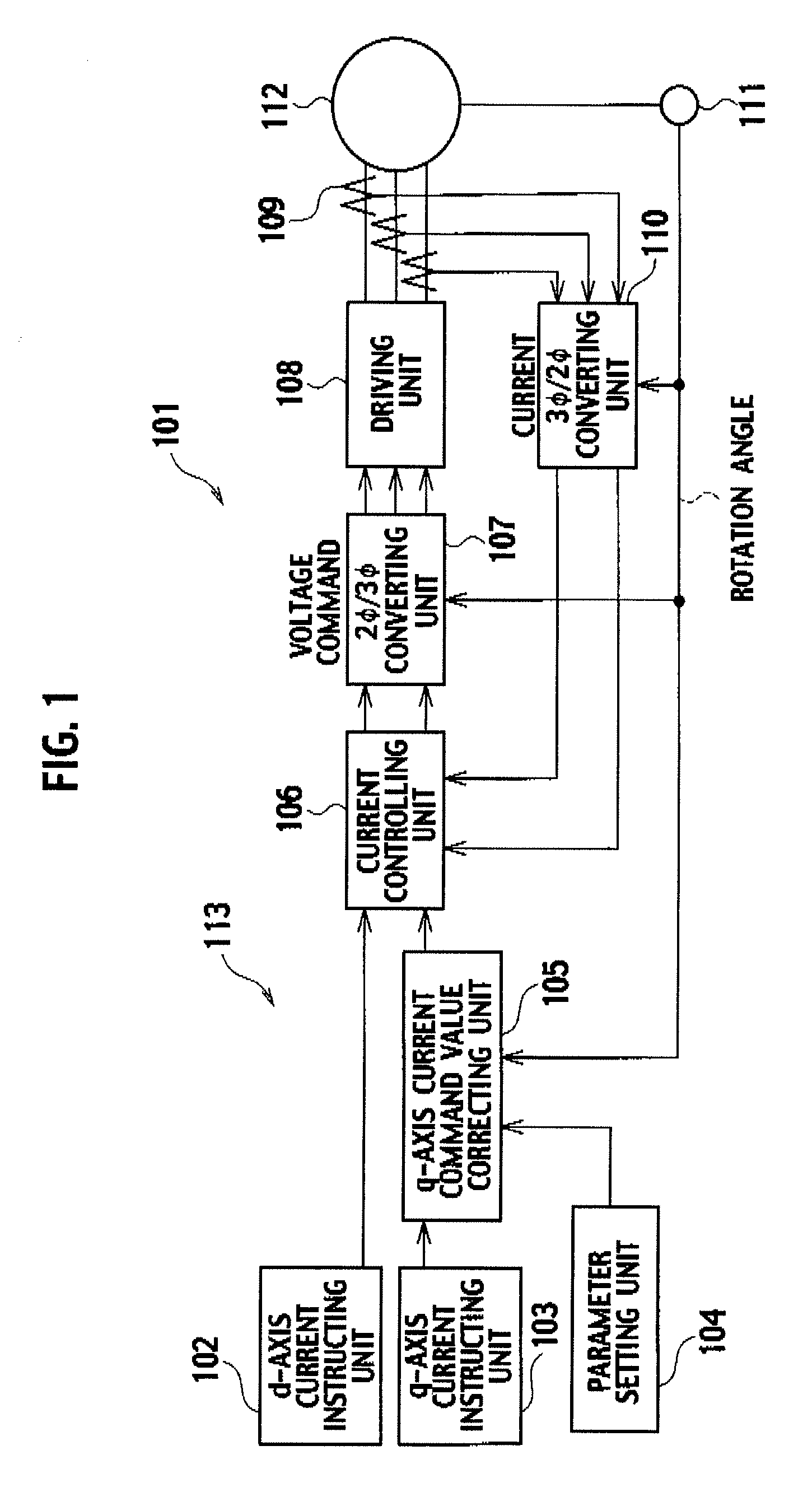
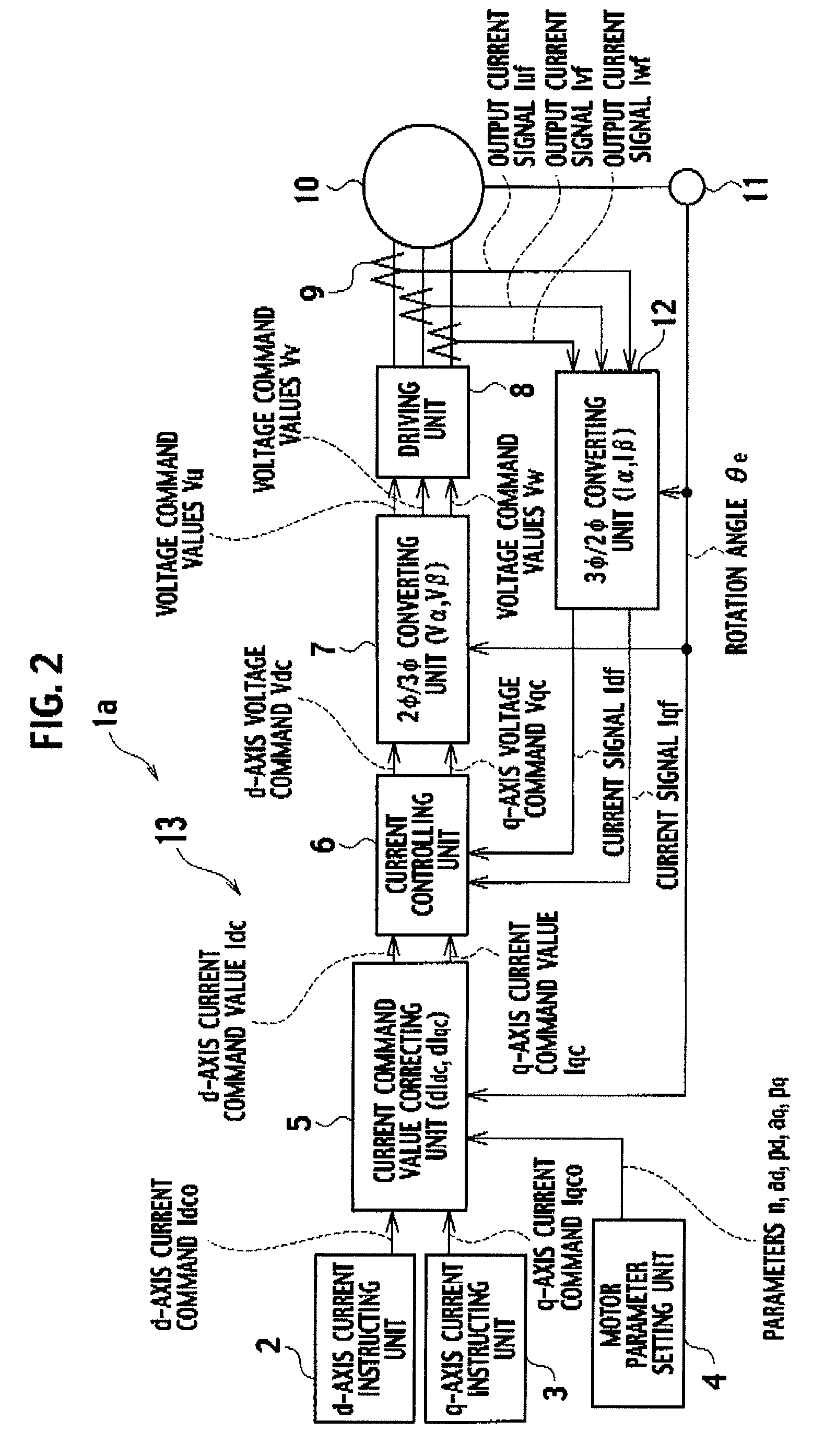
Control device
InactiveUS20090021194A1Reduce variationTorque ripple can be suppressedElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl theoryElectric current
Parameters “n”, “ad”, “pd”, “aq”, “pq” and the like of a motor parameter setting unit 4 are set so as to satisfy [Expression 23] and the like, a d-axis current command value “Idco” outputted from a d-axis current instructing unit 2 and a q-axis current command value “Iqco” outputted from q-axis current instructing unit 3 are corrected based on these parameters “n”, “ad”, “pd”, “aq” and “pq”, on a detection result of rotation angle detecting unit 11, and on the like, and a (6×n)f sine component, (6×n)f cosine component, (6×(n+1))f sine component and (6×(n+1))f cosine component of torque “T” shown in [Expression 22] are made zero. In such a way, 6×n and 6×(n+1) ripple components and the like, which are generated in a motor provided in elevator equipment or the like, are suppressed, and a torque ripple of the motor is reduced to a large extent.
Owner:TOSHIBA ELEVATOR KK
Method, device and system for suppressing shaking of electric automobile
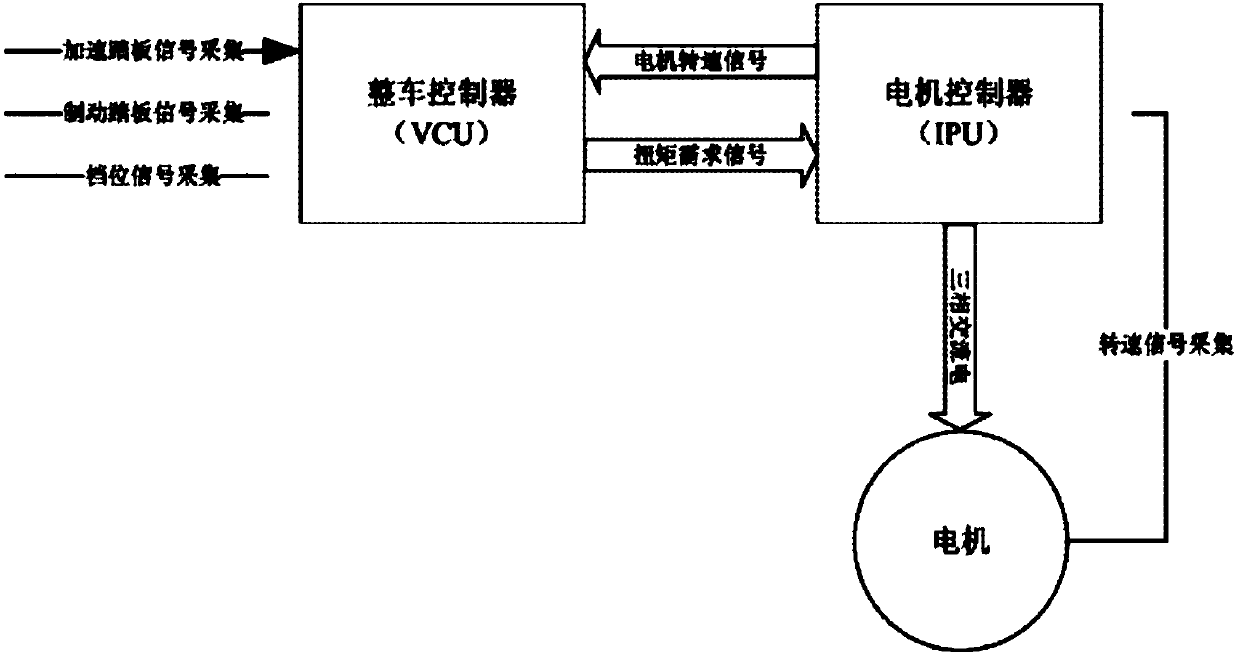
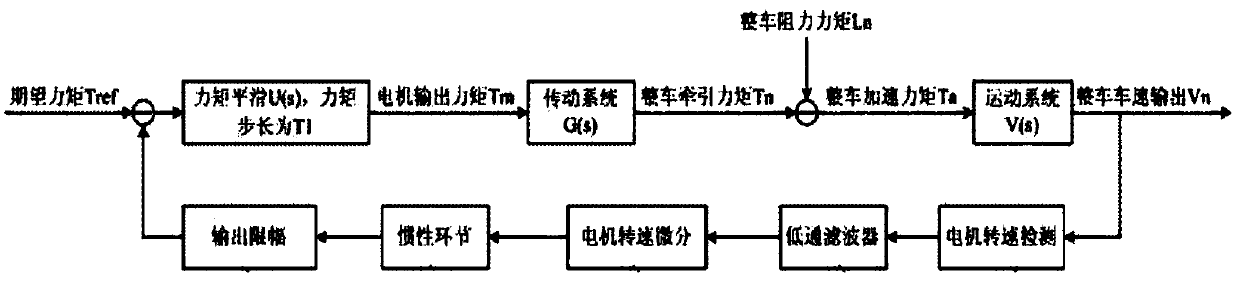
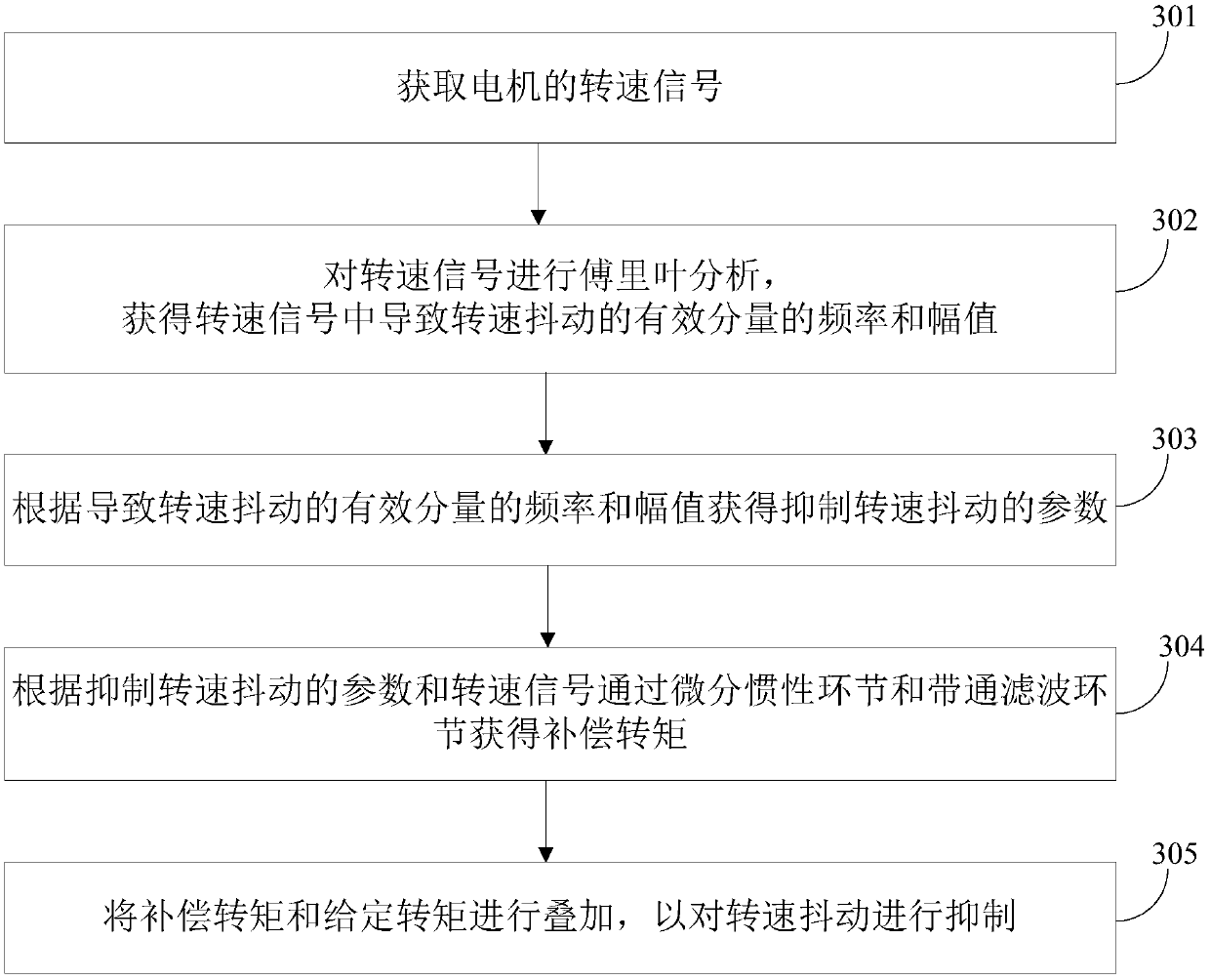
ActiveCN108068659ASuppress jitterSolve the problem of direct deviation in the extraction of rotational speed fluctuationsSpeed controllerElectric machinesBand-pass filterLinear relationship
The invention discloses a method, device and system for suppressing shaking of an electric automobile. The method, device and system are used for suppressing the shaking of the electric automobile andimproving the driving comfort level. The method includes the steps that a rotation speed signal of a motor is obtained; Fourier analysis is conducted on the rotation speed signal, and the frequency and the amplitude of an effective component, causing rotation speed shaking, in the rotation speed signal are obtained, wherein rotation speed shaking is shaking caused by the non-linear relationship between traction torque and the resistance moment of the electric automobile; according to the frequency and the amplitude of the effective component causing rotation speed shaking, a parameter for suppressing rotation speed shaking is obtained; according to the parameter for suppressing rotation speed shaking and the rotation speed signal, compensation torque is obtained through a differential inertial element and a band-pass filtering element; and the compensation torque and given torque are superposed so as to suppress the rotation speed shaking. Due to the fact that the shaking of the electric automobile is suppressed, mechanical resonance generated in the shaking process is reduced, and therefore hardware wear of the electric automobile is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Position detecting apparatus having electric motor and method for detecting position
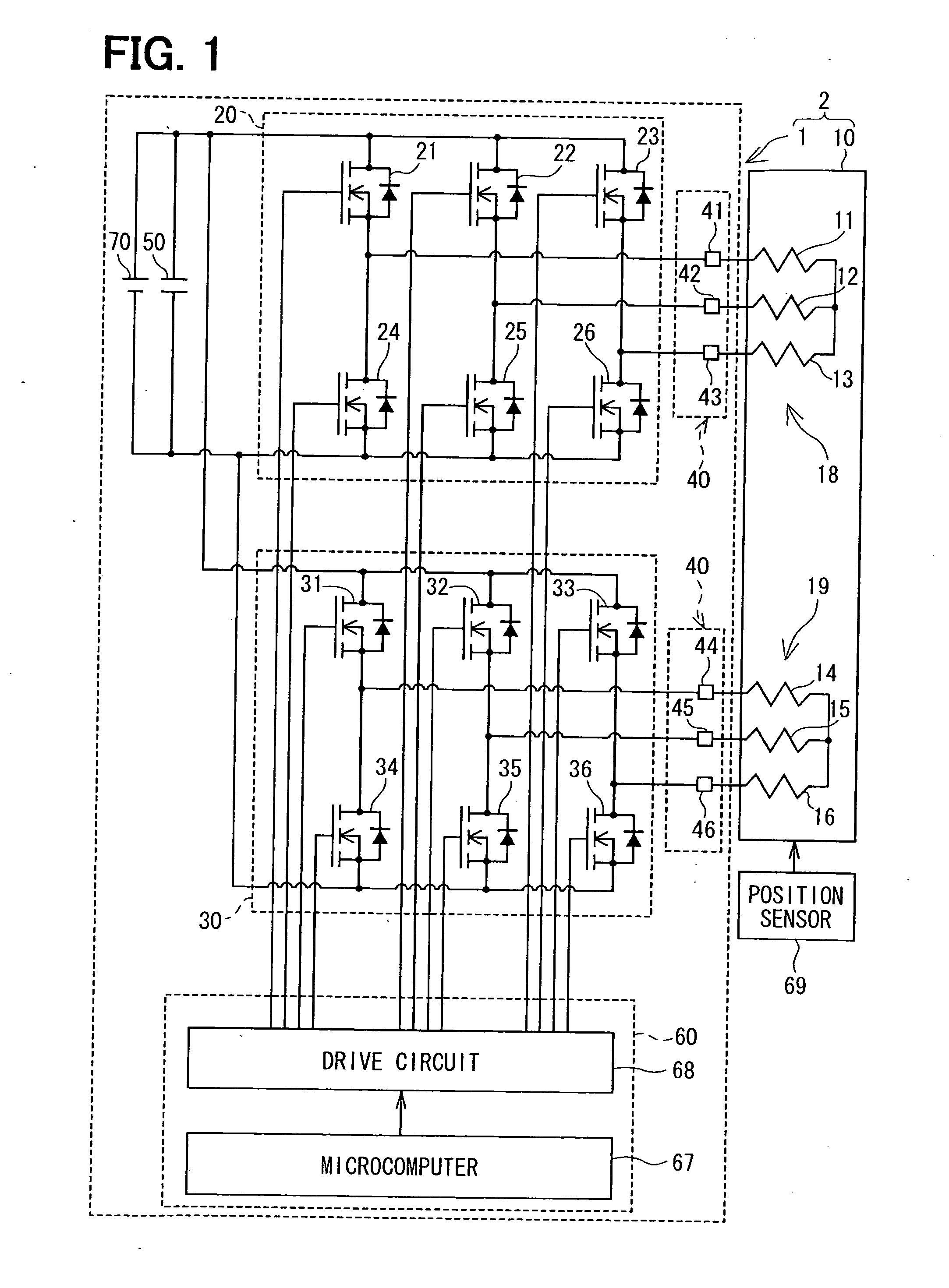
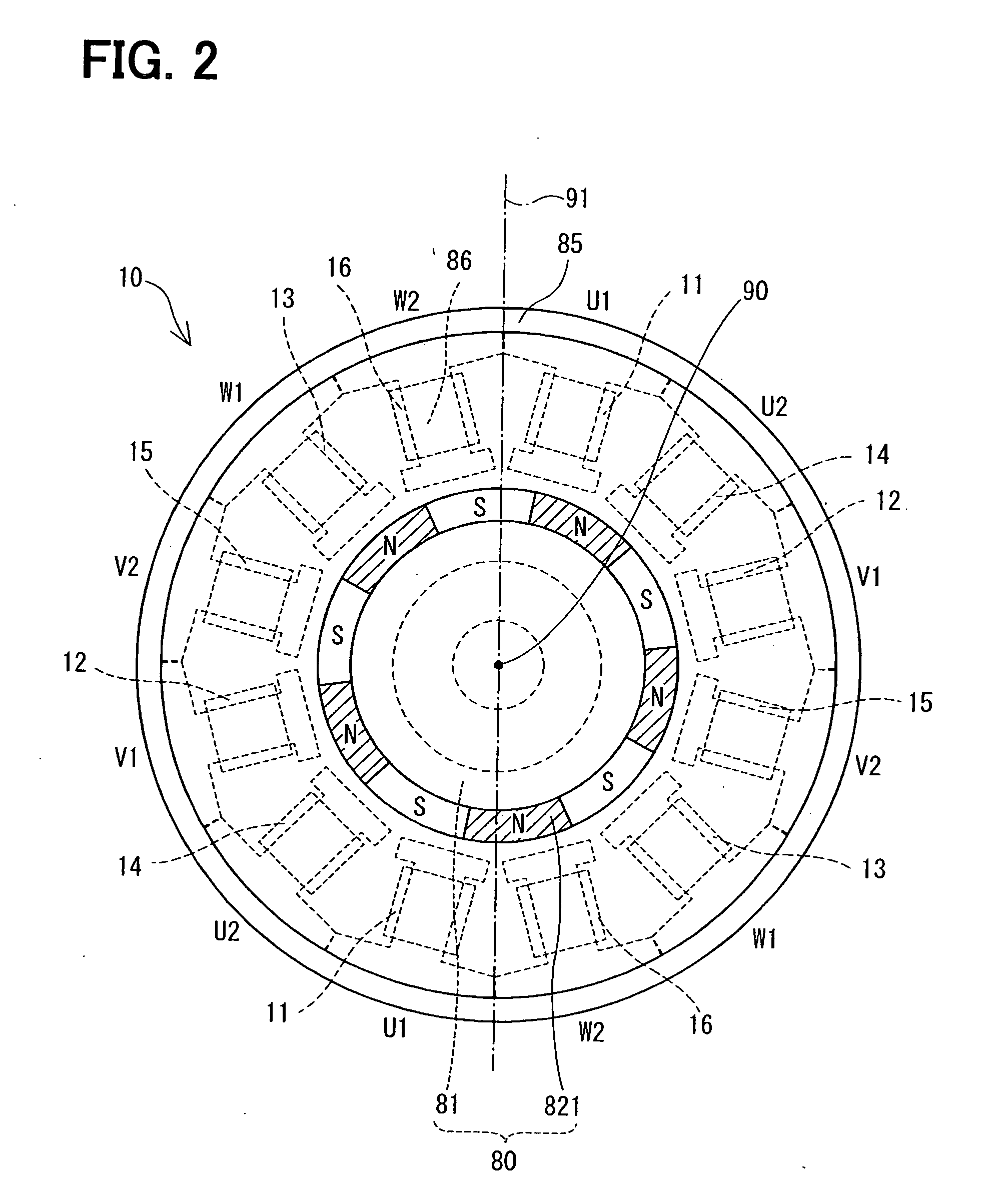
ActiveUS20060138880A1Reduce harmReduce loadWindingsMagnetic measurementsElectricityLocation detection
A reference position detecting apparatus includes an electric motor and a motor control unit. The electric motor includes a plurality of first coils and a plurality of second coils. The electric motor further includes a rotor that rotates when at least one of the plurality of first coils and the plurality of second coils is supplied with electricity. The motor control unit controls electricity supplied to either one of the plurality of first coils and the plurality of second coils to rotate the rotor to a limit position in a movable range of an object.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Popular searches
Electric generator control Dynamo-electric brake control Dynamo-electric gear control Motor control for motor oscillations damping Electronic commutators Dc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripples Electric/dynamo-electric converter starters Motor control in four quadrants Electric motor control Electric controllers
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com