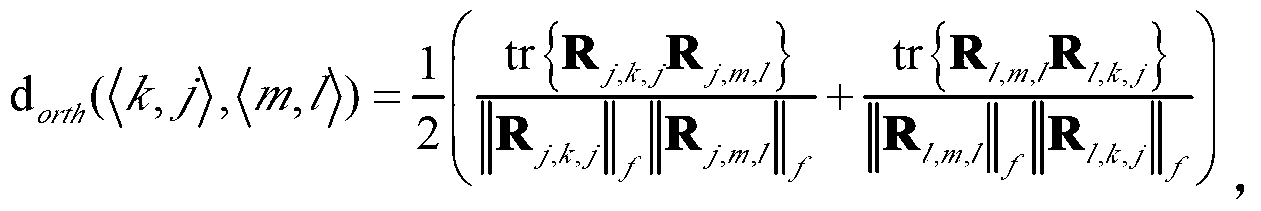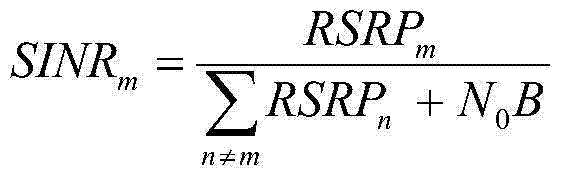Patents
Literature
305results about How to "Improve throughput performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
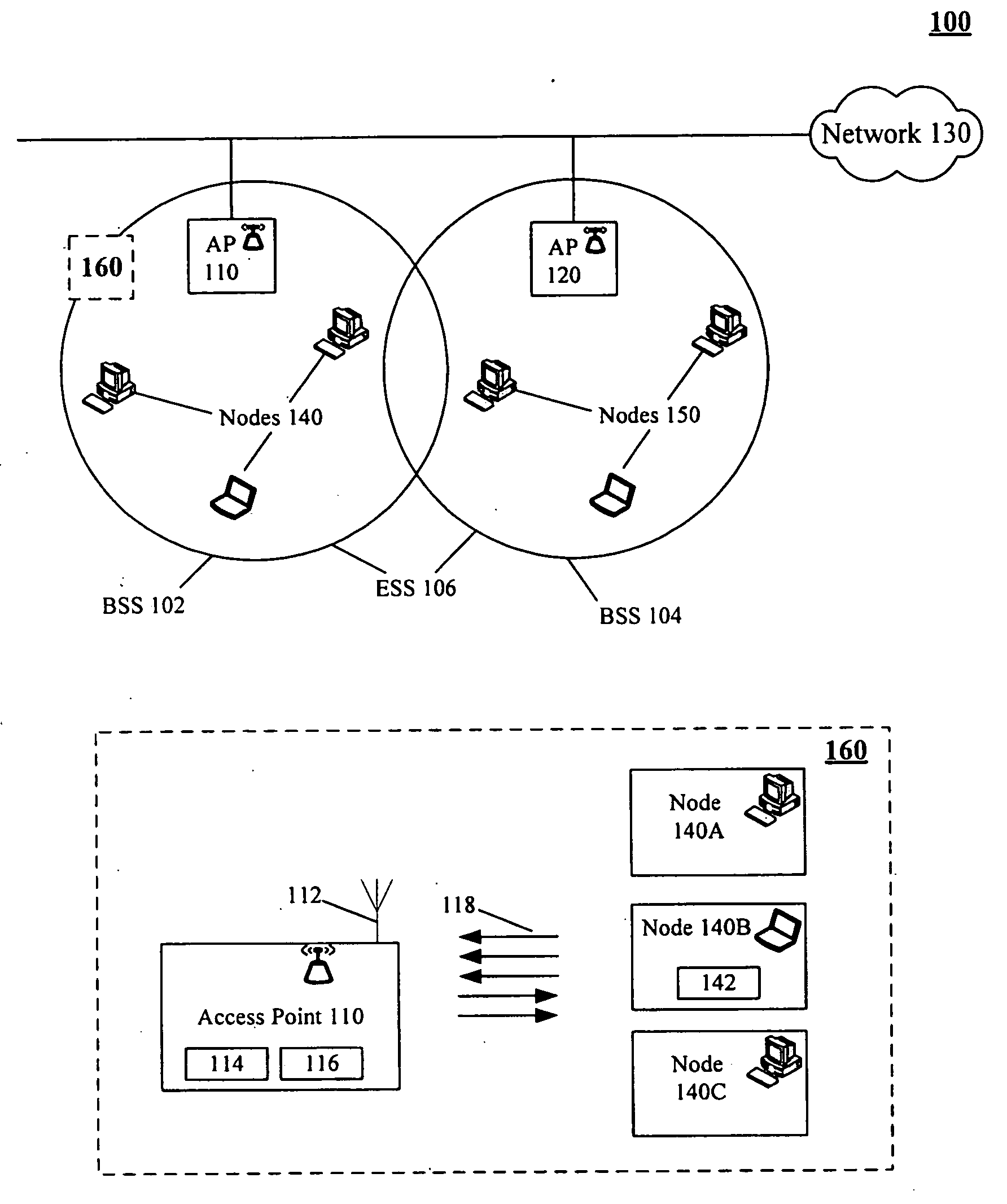
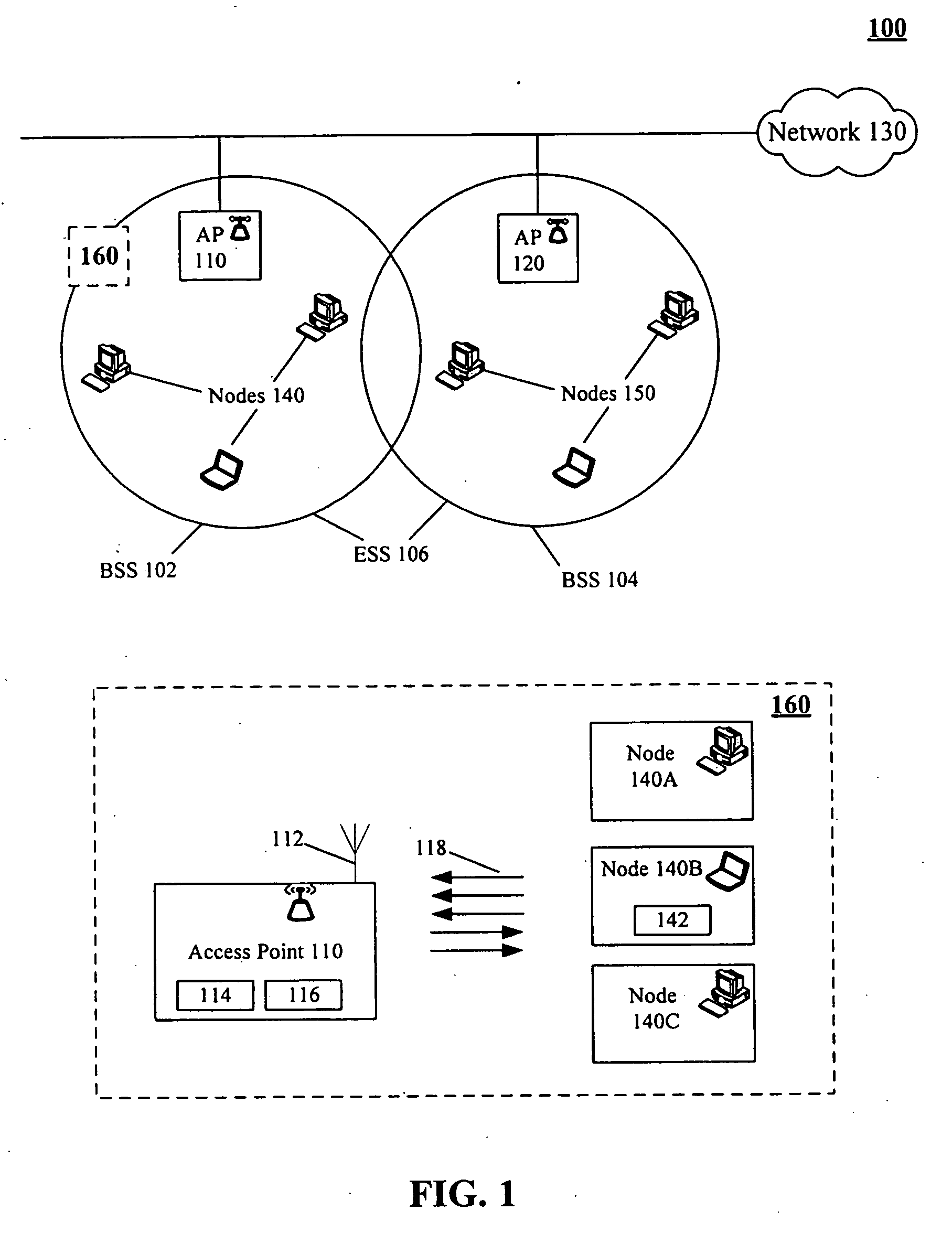
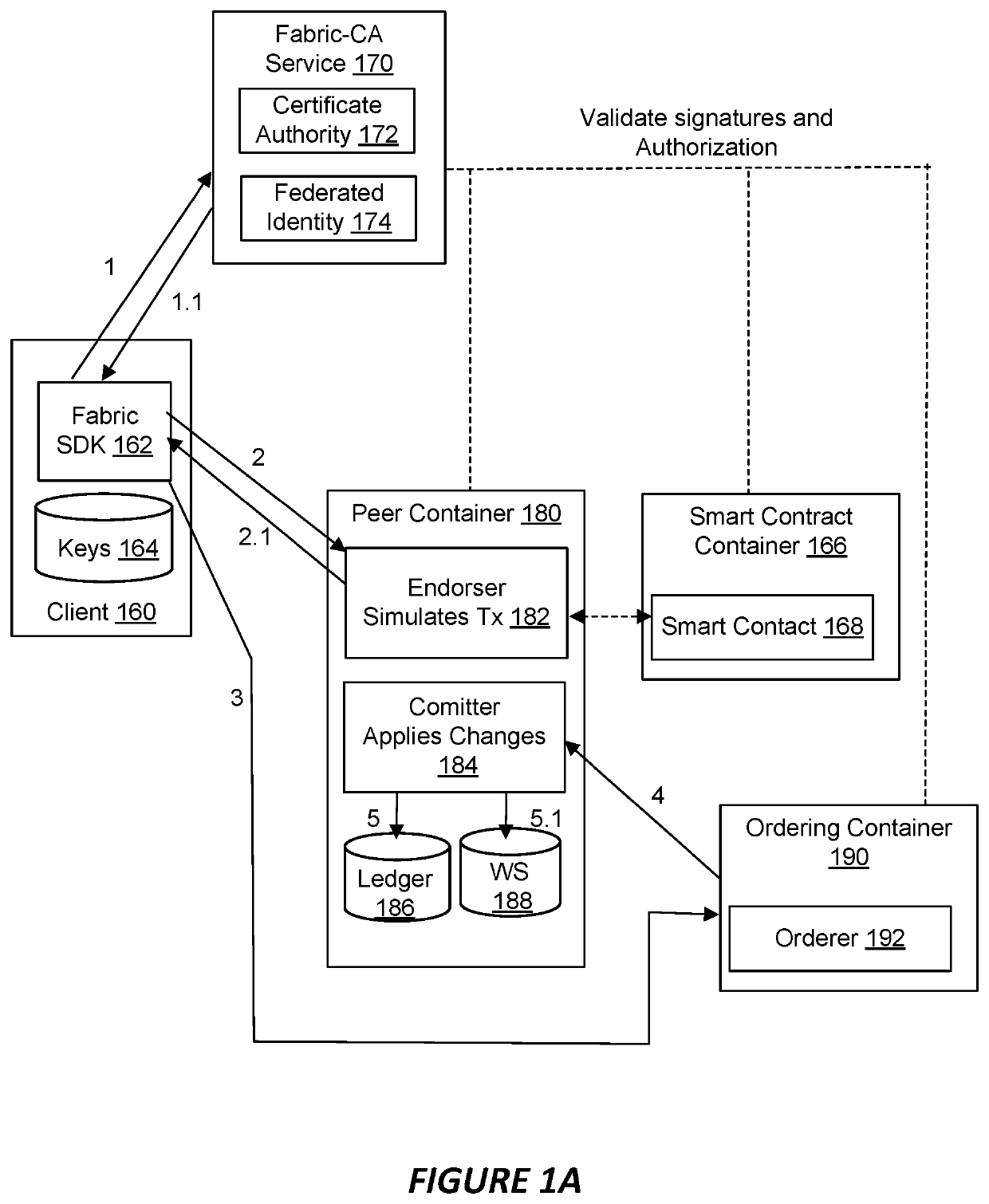
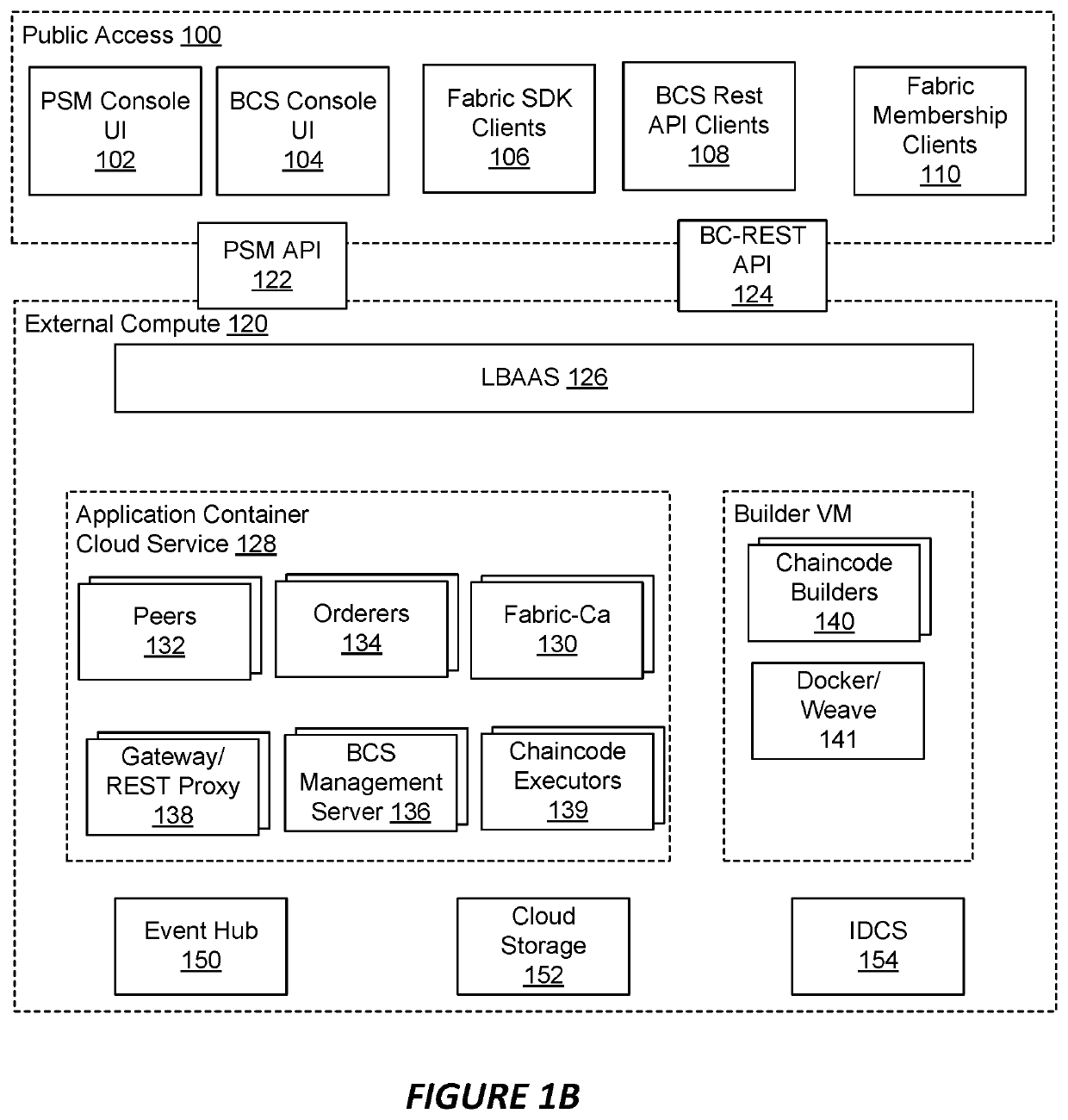
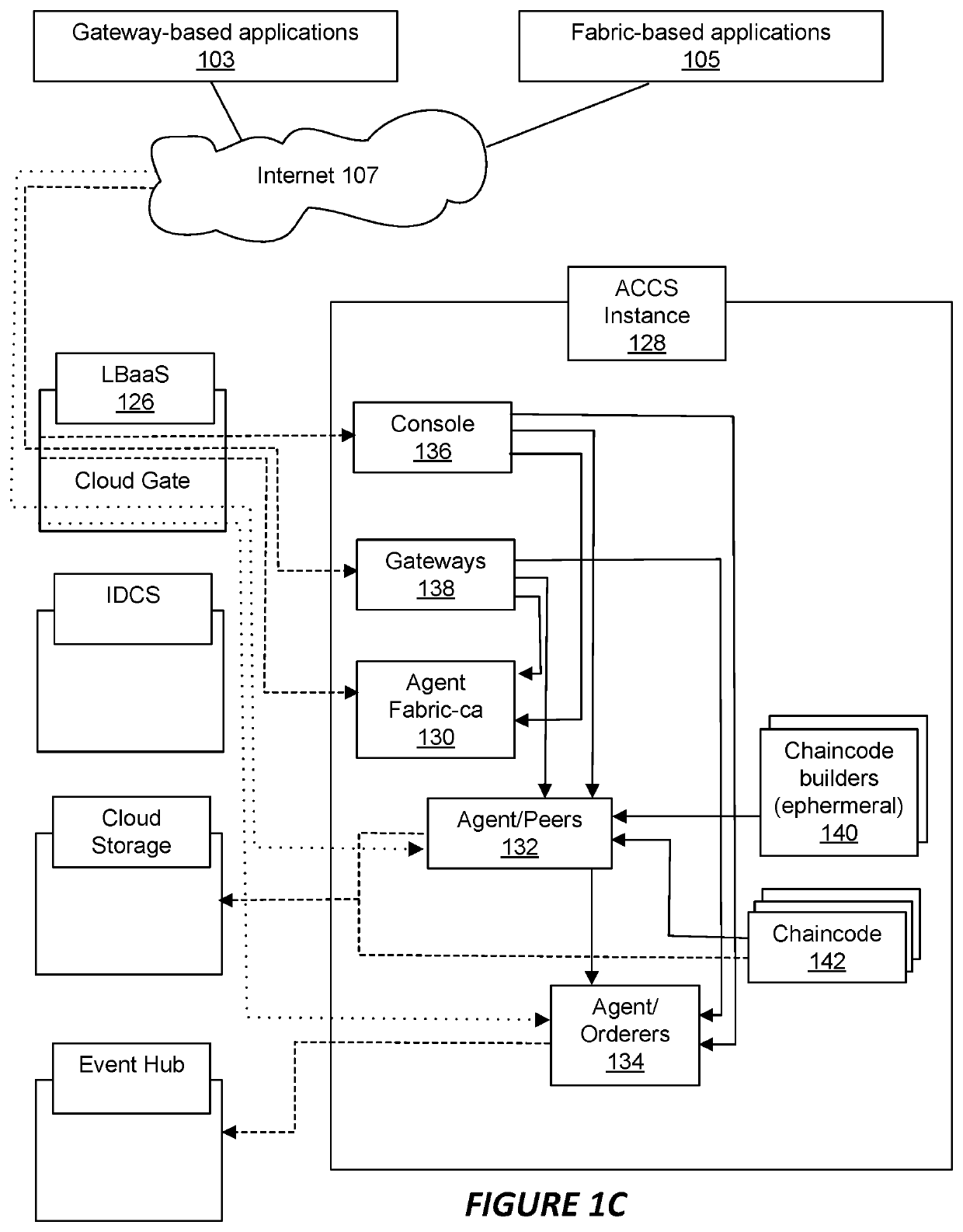
Medium access control in wireless local area networks with multi-beam access point
InactiveUS20060268760A1Improve throughput performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesWireless lanMedia access control
A method for conveying digitally encoded data within a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) using a contention based Media Access Control (MAC) protocol. In the method, a multi-beam access point can transmit a channel contention request and responsively receive channel contention responses. A set of nodes can be determined based upon the channel contention responses. Each node of the determined set can be assigned one beam of the multi-beam access point. The nodes can use the assigned beams to simultaneously communicate with said multi-beam access point in a collision-free fashion along an assigned beam.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
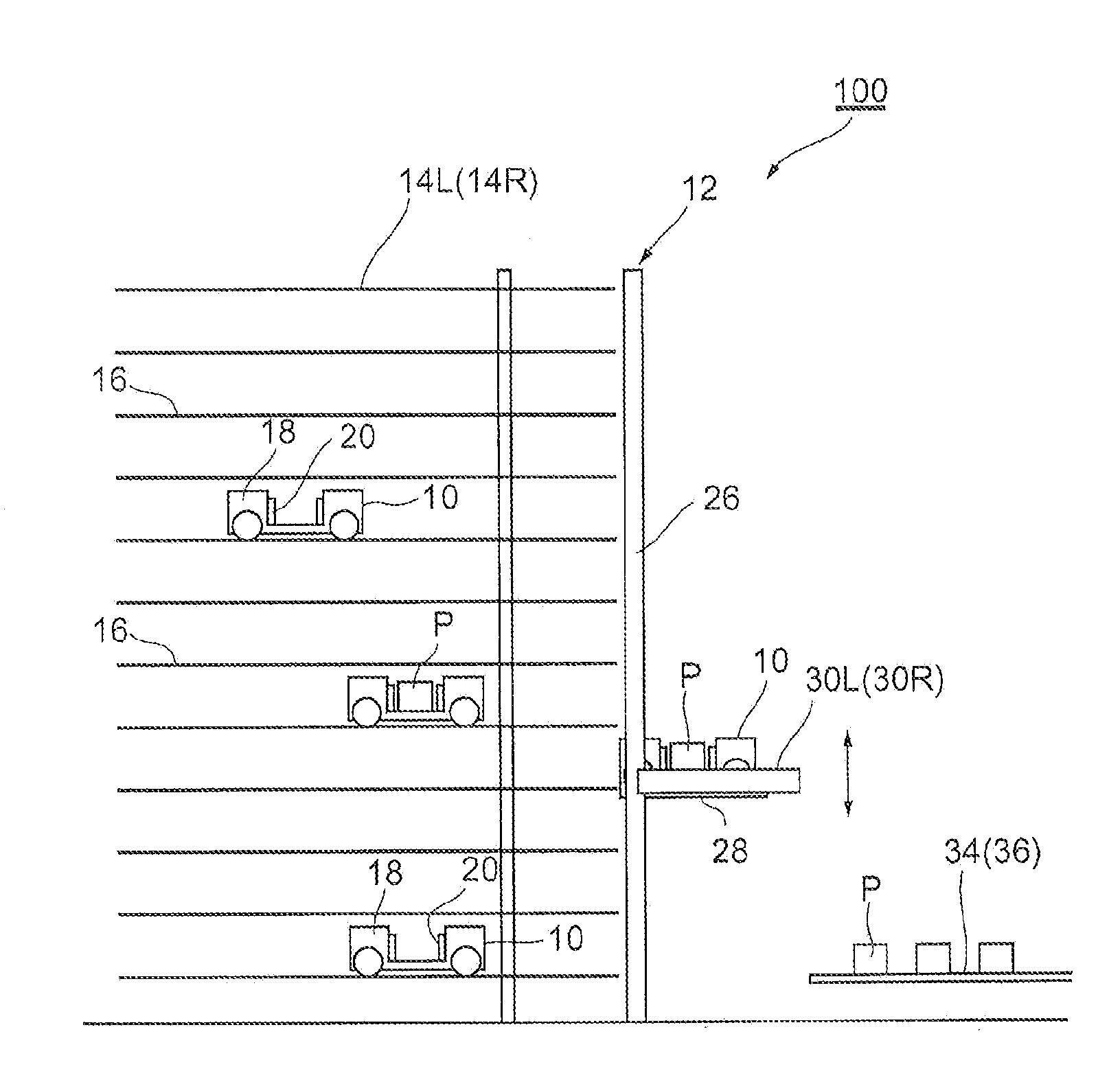
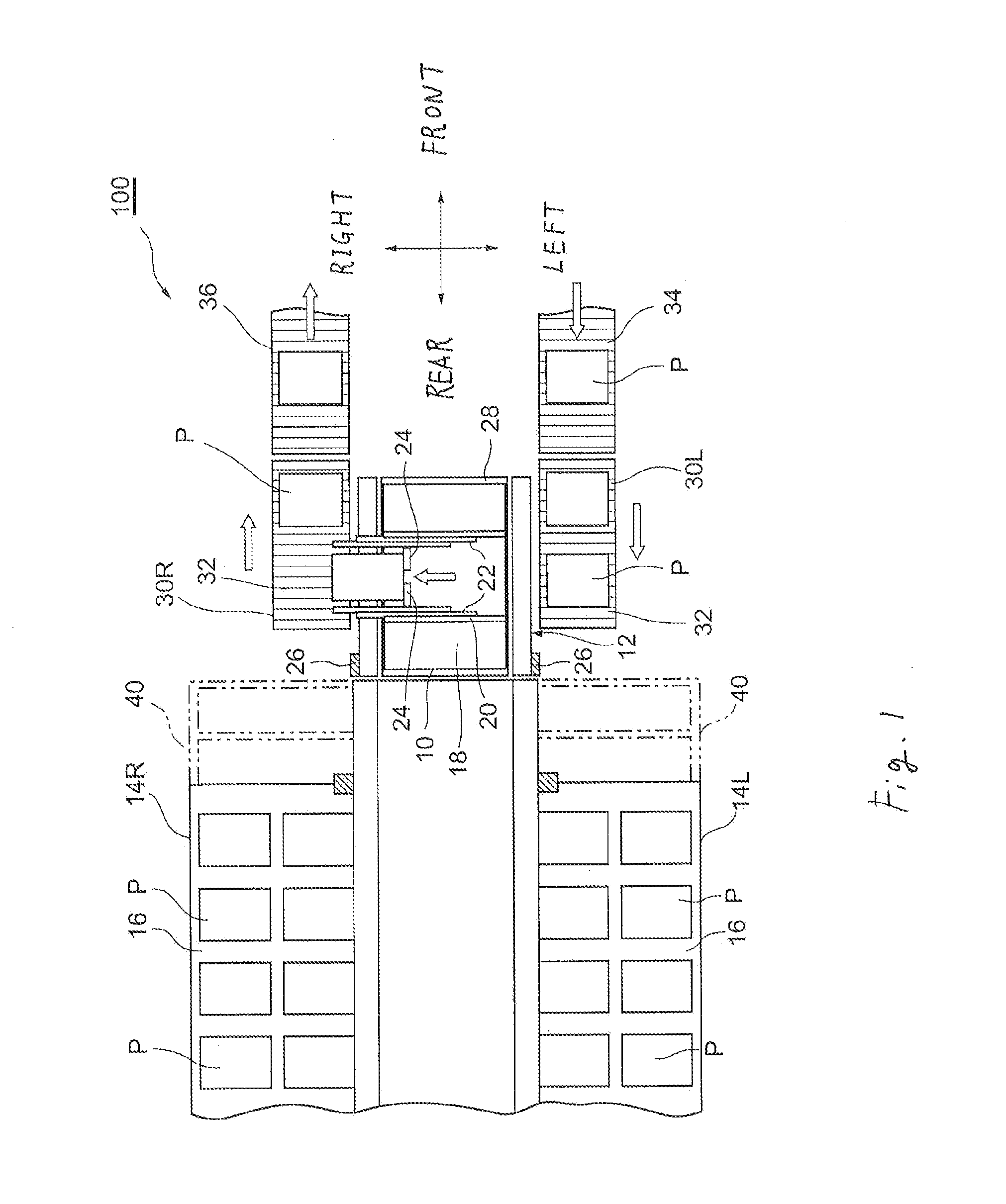
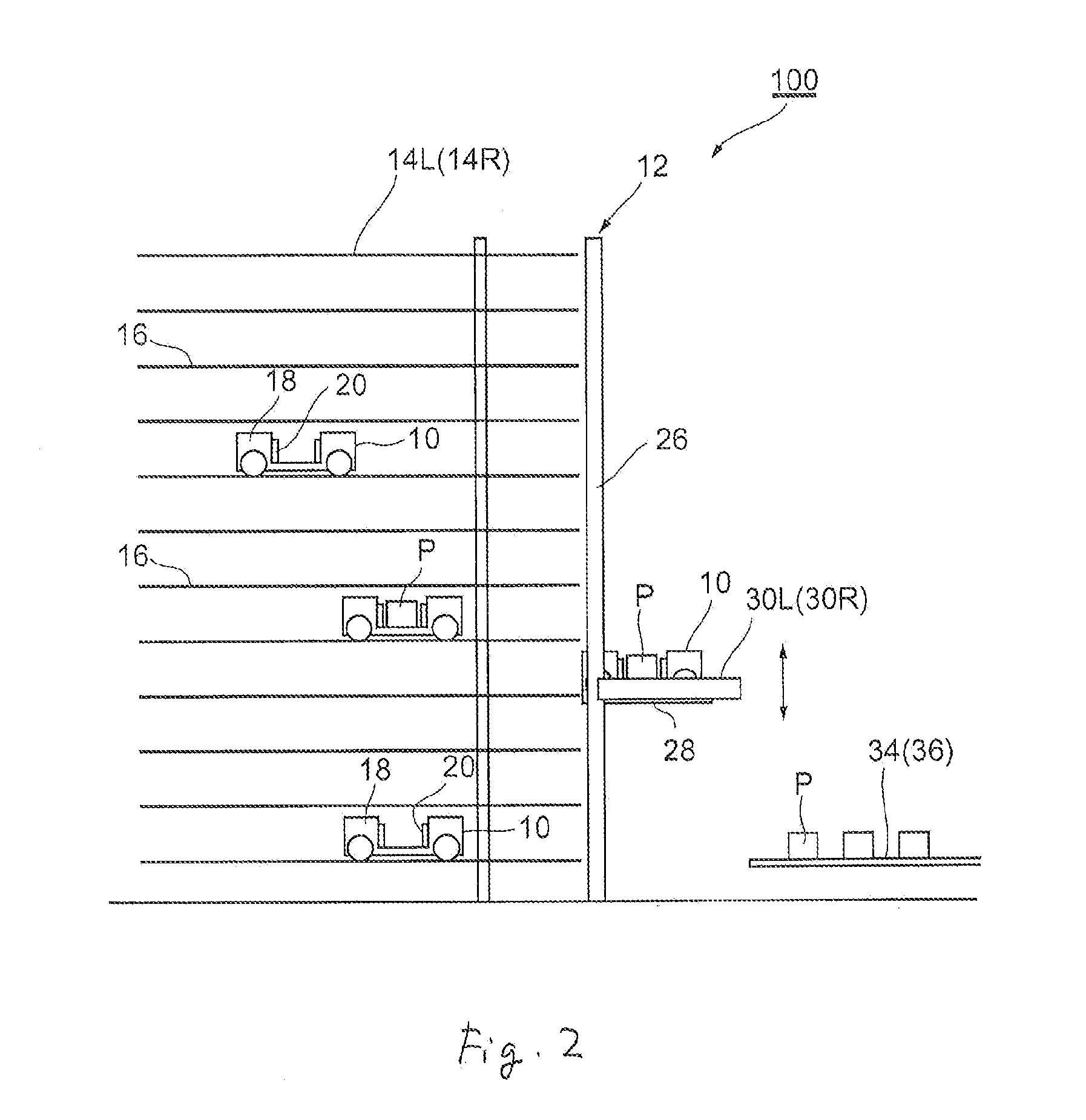
Multi-tier automated warehouse
ActiveUS20140124462A1Low costLimit throughput performanceShow cabinetsStorage devicesMechanical engineeringEngineering
A multi-tier automated warehouse includes first and second stacking racks having multiple tiers of shelves and being positioned facing one another in parallel; loading shuttles which are capable of horizontal travel between the stacking racks, and which carry out loading and unloading of cargo upon the shelves; and an elevator device for moving the loading shuttles to different tiers. The elevator device further includes masts which are positioned adjacent to the stacking racks; a shuttle elevator platform, which is positioned elevatably on the inner side of the masts, for elevating the loading shuttles; and cargo elevator platforms, which are positioned elevatably on the outer side of the masts, for elevating the cargo. In a state where the shuttle elevator platform is aligned with the cargo elevator platforms, it is possible for the loading shuttles on the shuttle elevator platforms to carry out cargo loading and unloading to the cargo elevator platforms, allowing handling cargo even while the loading shuttles are being elevated, obviating the need for wasteful waiting for cargo. As a result, it is possible to implement high performance.
Owner:DEMATIC
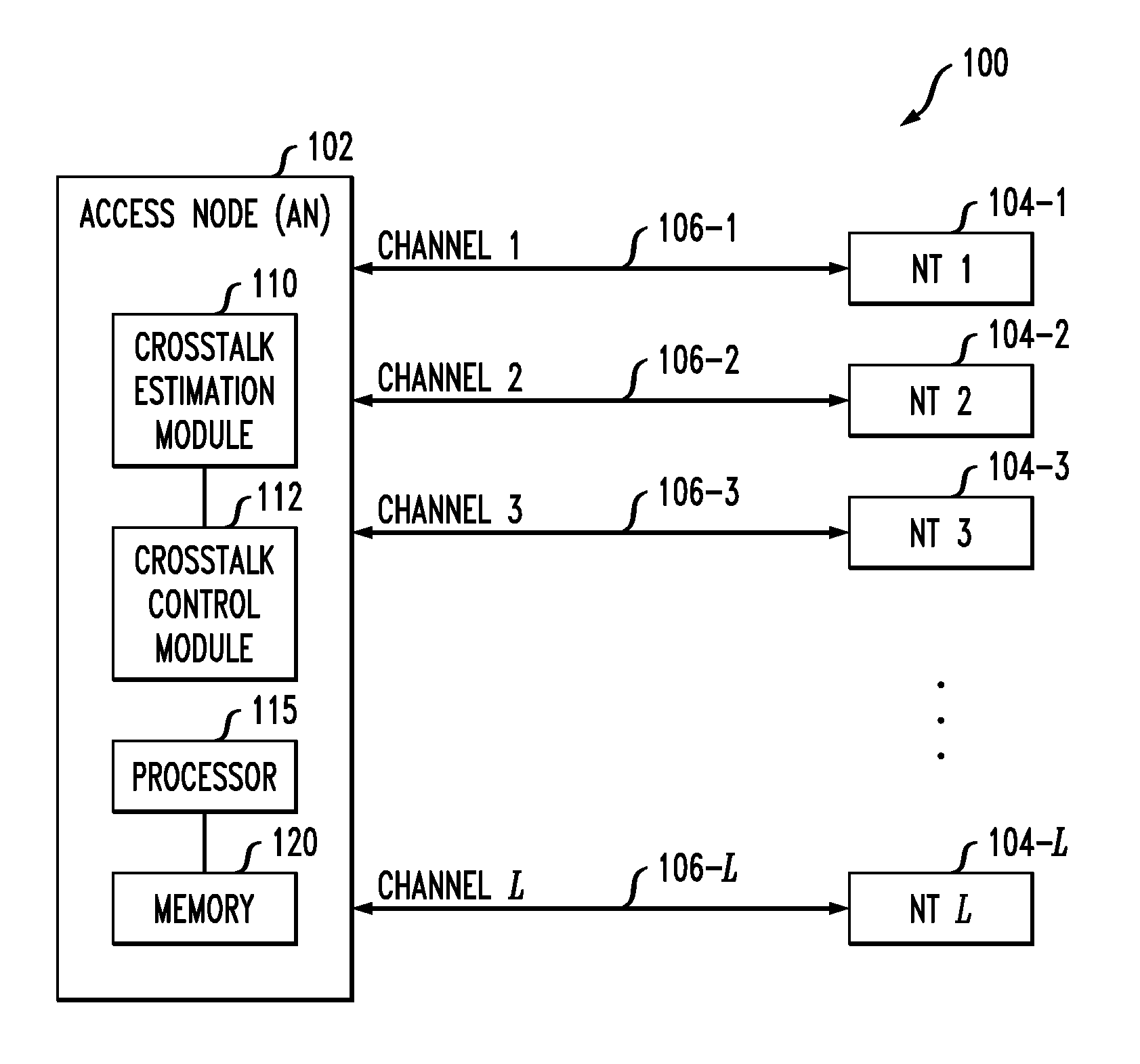
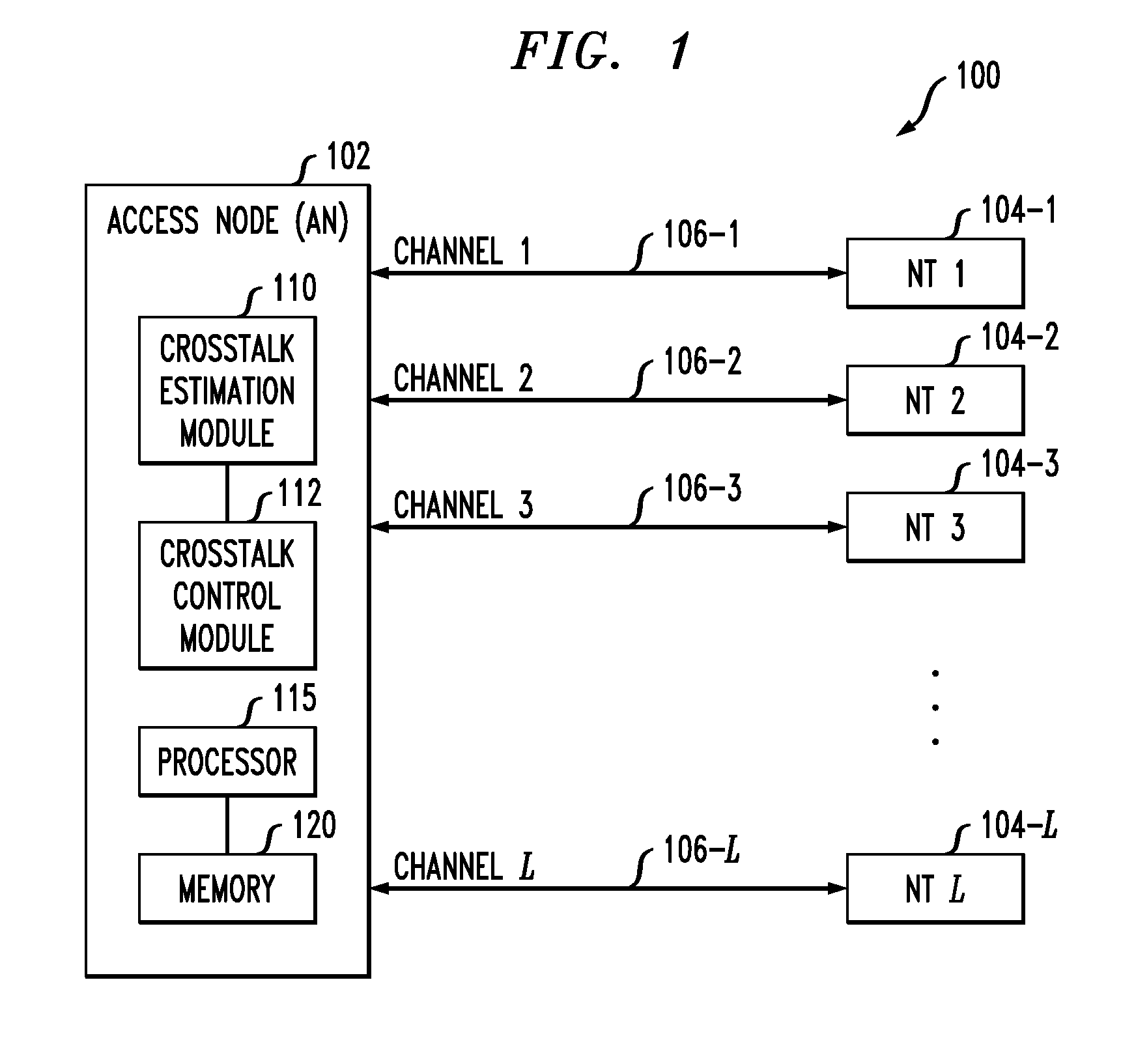
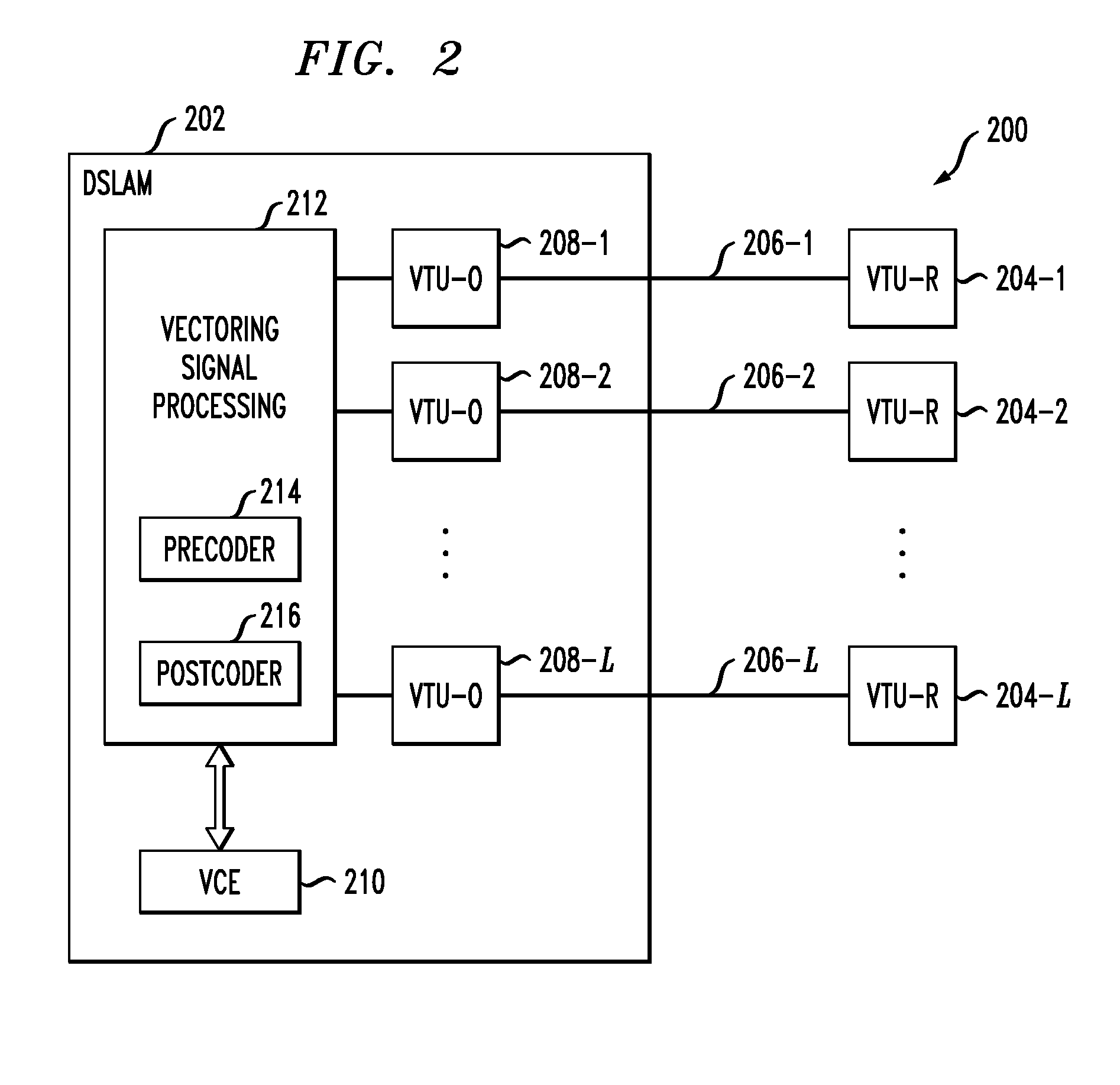
Multiplicative updating of precoder or postcoder matrices for crosstalk control in a communication system
ActiveUS20120195183A1Improve convergenceReduce amountSpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringCommunications system
An access node of a communication system is configured to control crosstalk between channels of the system. Vectoring circuitry in the access node estimates crosstalk between channels of the system, generates a compensation matrix based on the crosstalk estimates, and generates compensated signals based on the compensation matrix. The compensation matrix, which may be a precoder matrix or a postcoder matrix, is generated using a multiplicative update process in which a previous version of the compensation matrix comprising one or more non-zero off-diagonal elements is updated by at least one of pre-multiplying by a first auxiliary matrix and post-multiplying by a second auxiliary matrix, with a given one of the auxiliary matrices also comprising one or more non-zero off-diagonal elements. The compensated signals may be pre-compensated signals or post-compensated signals.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
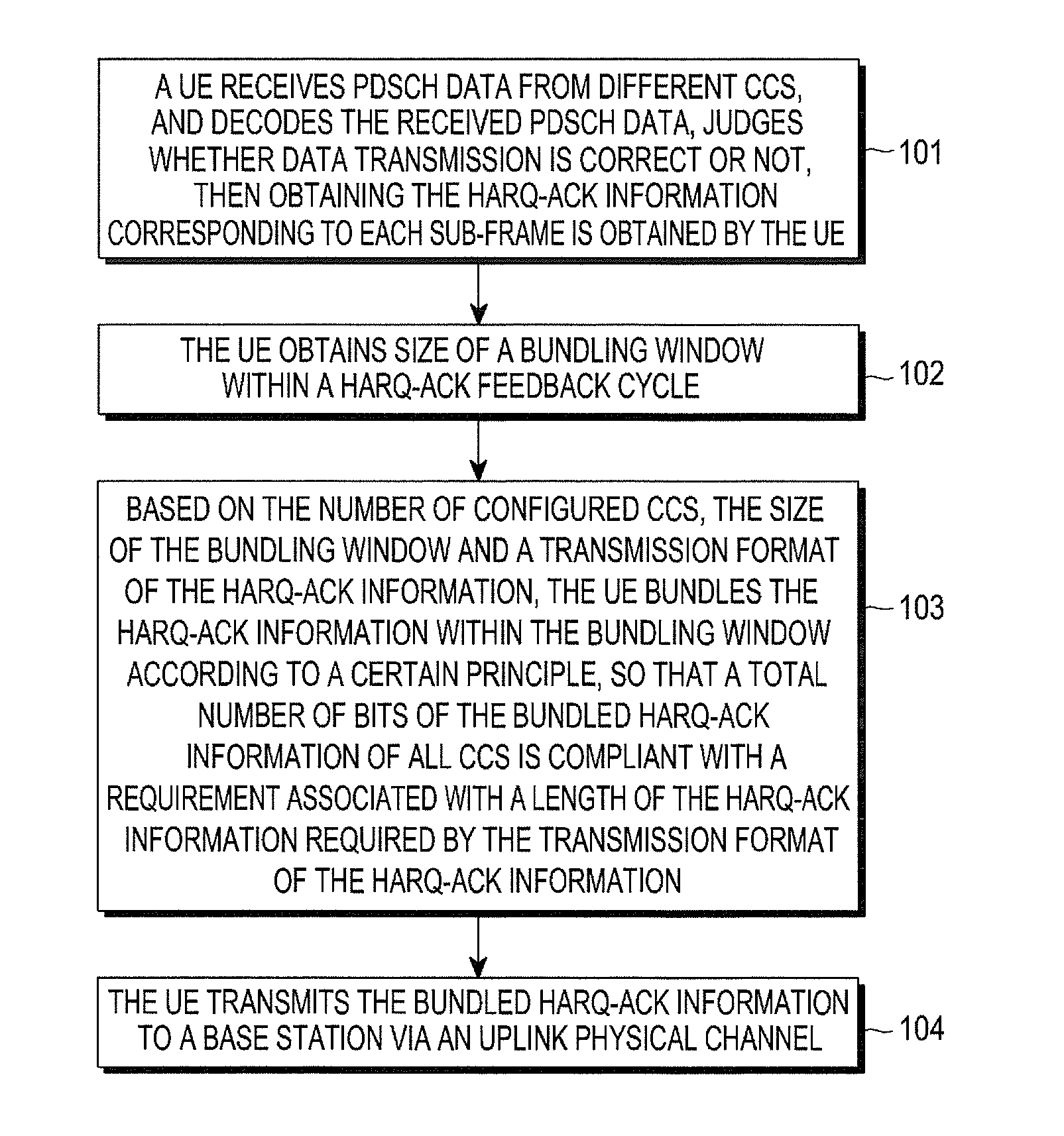
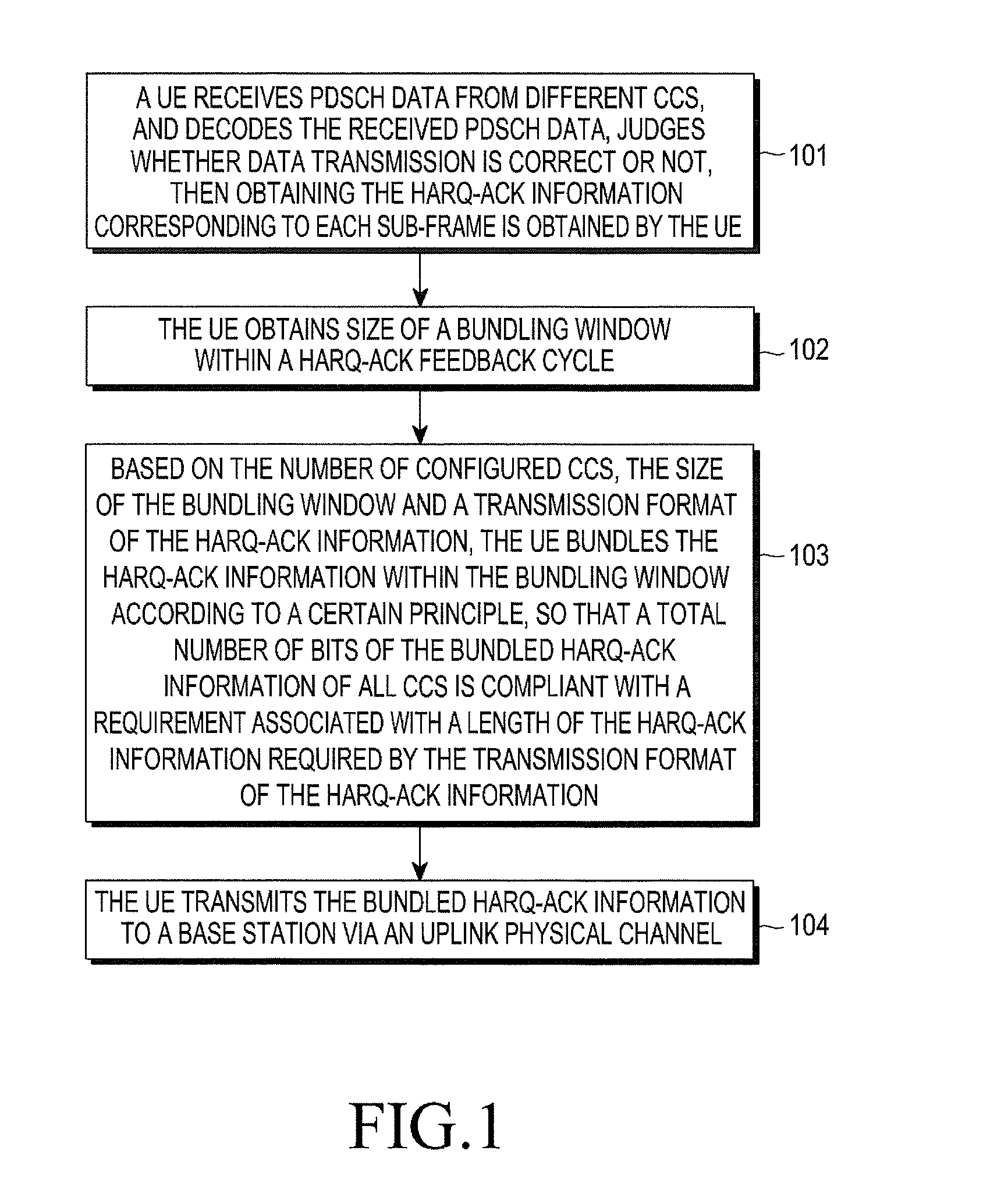
System and method for transmitting harq-ack information
InactiveUS20130114474A1Improve user throughputImprove throughputError preventionSignal allocationCarrier signalComputer science
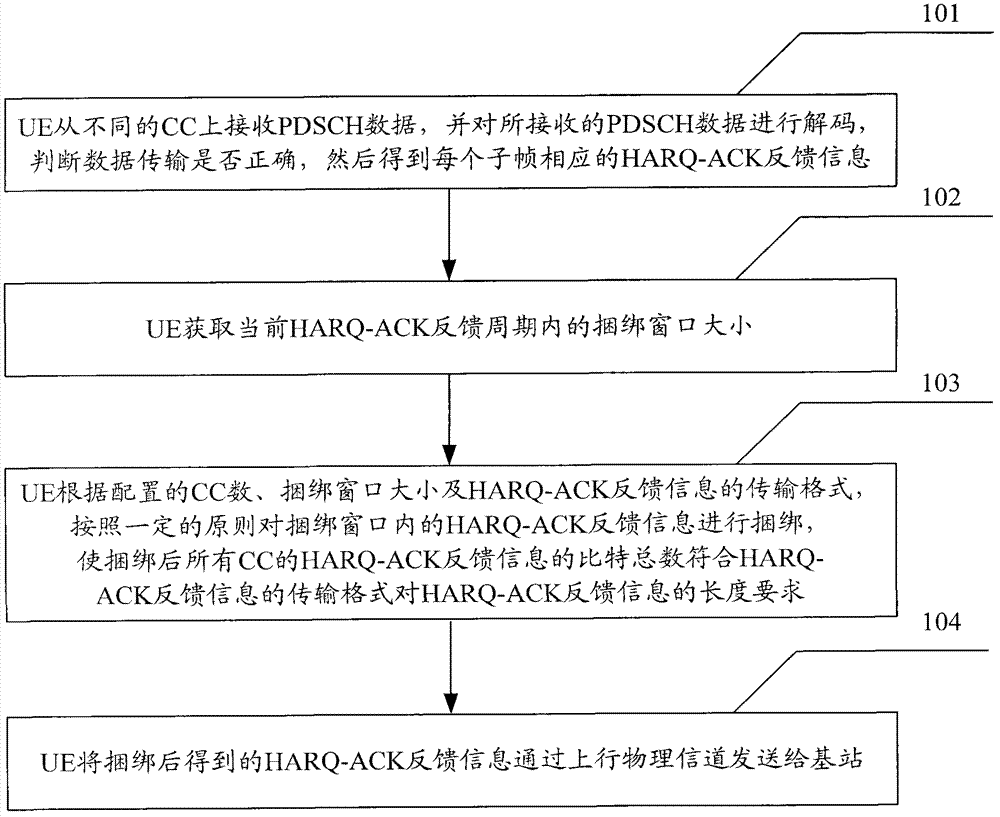
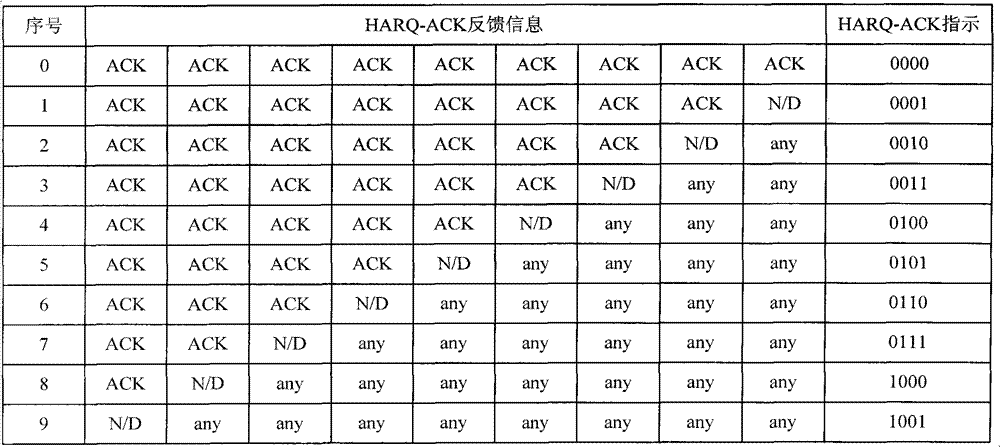
According to one embodiment, a method for transmitting HARQ-ACK information, in which the HARQ-ACK information within a current bundling window is bundled, so that a total number of bits of the bundled HARQ-ACK information is compliant with a requirement associated with a length of the HARQ-ACK information required by a transmission format of the HARQ-ACK information, which may support carrier aggregation with more CCs in TDD UL / DL configuration 5, such that a peak throughput of user downlink is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
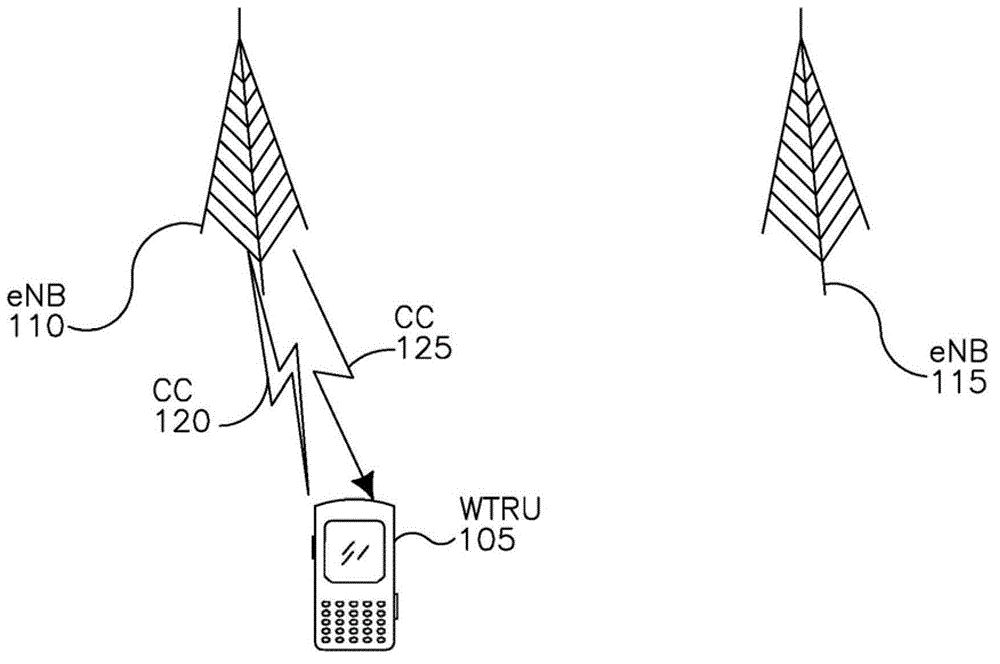
Method and apparatus for enhancing cell-edge user performance and signaling radio link failure conditions via downlink cooperative component carriers
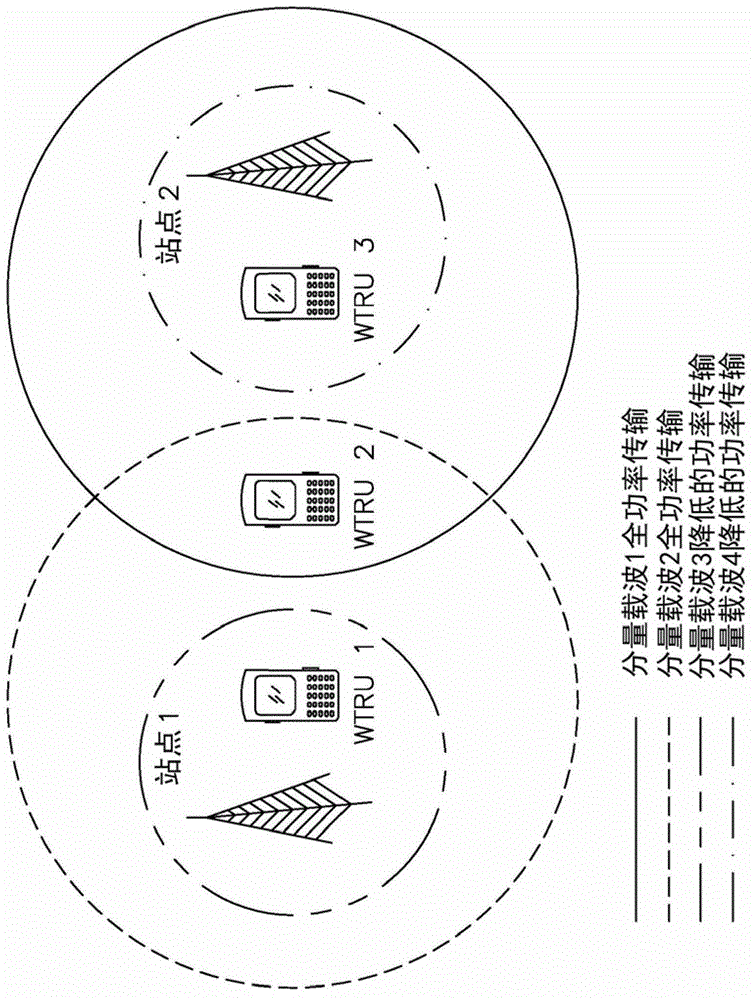
InactiveCN102754496AReduce transmit powerHigh transmission powerEnergy efficient ICTPower managementFrequency reuseTransmitted power
A wireless communication network and method are described for enhancing cell-edge performance of a wireless transmit / receive unit (WTRU). The WTRU may establish a connection with a plurality of sites via respective downlinks (DLs). Each DL may include at least one DL component carrier (CC) that operates on a frequency that is the same or different than one or more of the other CCs. The sites may manipulate their transmit power for a particular CC operating frequency such that the distance from a particular one of the sites to its cell boundary may become larger by increasing its transmit power on the particular frequency, and the distance from at least one of the other sites to its respective cell boundary may become smaller by decreasing its transmit power on the particular frequency. Thus, a coverage overlap between different CC frequencies may be created while maintaining a frequency reuse pattern of one.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Millimeter wave large-scale MIMO system multi-user transmission method based on space division multiple access and interference suppression
ActiveCN104052535AReduce computational complexitySolve the feedback problemSpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsPrecodingComputation complexity
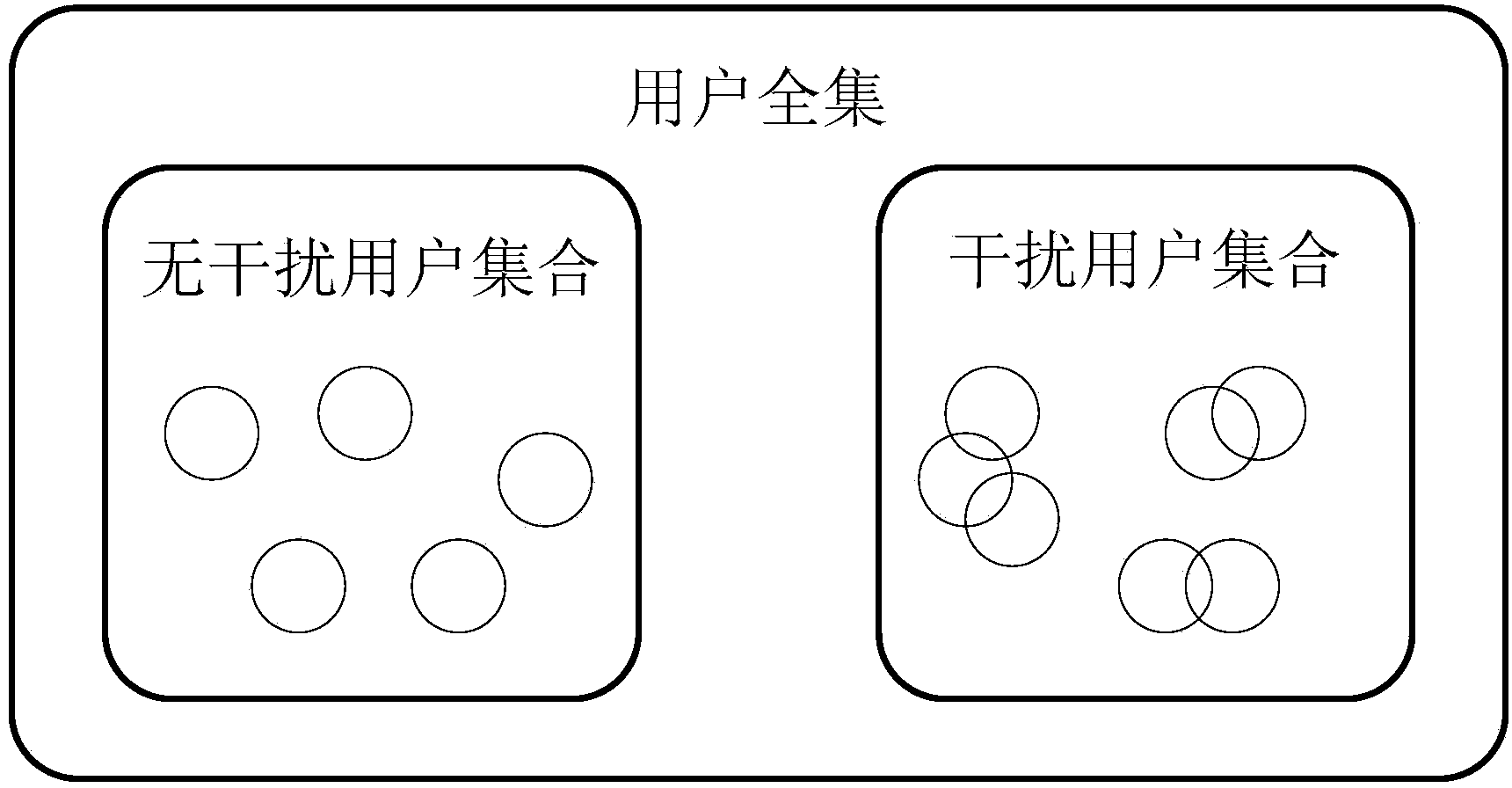
The invention discloses a millimeter wave large-scale MIMO system multi-user transmission method based on space division multiple access and interference suppression. A base station is provided with a millimeter wave large-scale uniform panel antenna array; a plurality of single-antenna users receive service from the base station on the same time-frequency resource; according to information of wave beam clusters selected by the users, a universal user set is divided into an interference-free user subset and an interference user subset; the space division multiple access transmission method based on double-layer pre-coded codes is adopted to the interference-free user subset, and the transmission method based on interference suppression is adopted to the interference user subset. According to the method, the advantages of two traditional multi-user transmission methods based on space division multiple access and interference suppression respectively are combined, and the bottleneck that in an FDD transmission mode, downlink channel information of a large-scale MIMO system is difficult to obtain is broken through; meanwhile, the computation complexity problem is solved, it is guaranteed that all the users can receive the service from the base station simultaneously, and considerable system performance and speed performance are achieved at limited feedback quantity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
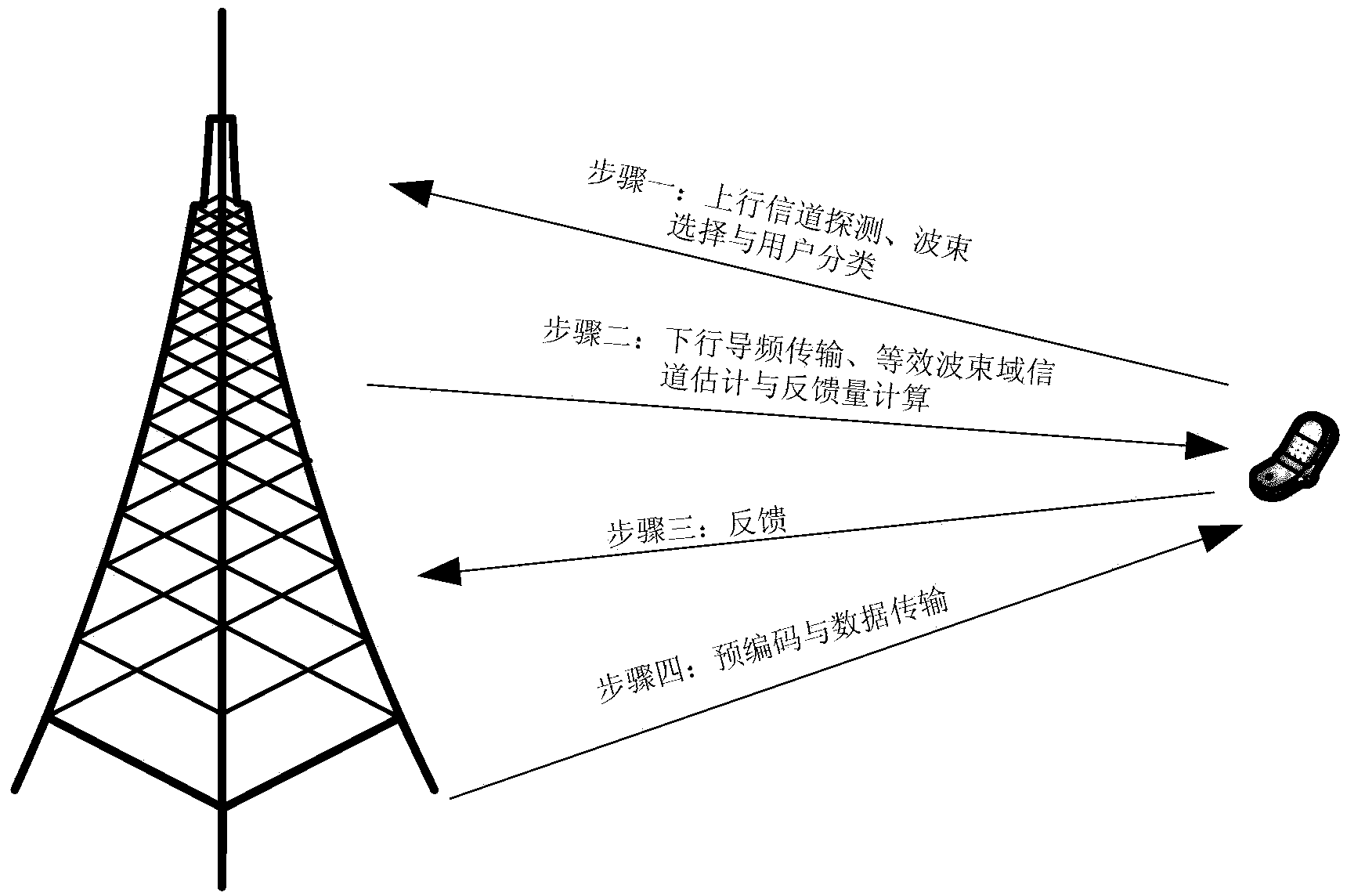
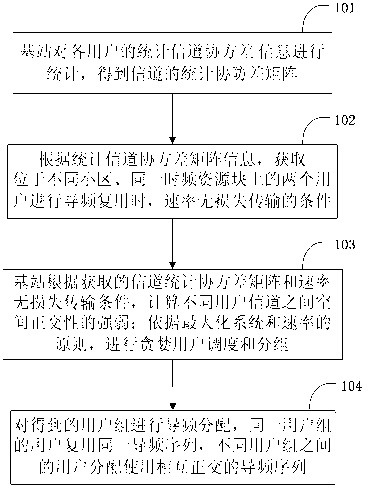
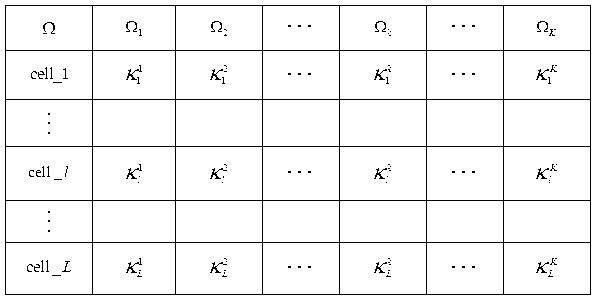
Spatial-orthogonality-based large-scale MIMO (multiple input multiple output) system pilot frequency distribution method
ActiveCN103298124ATake advantage ofReduce Feedback OverheadBaseband system detailsTransmission path multiple useChannel state informationMultiplexing
The invention relates to a spatial-orthogonality-based large-scale MIMO system pilot frequency distribution method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining the statistical covariance matrix information of every user terminal channel through a base station; 2) under the condition that the statistical covariance matrix information is known, obtaining the condition for achieving no-speed-loss transmission when two users located in different cells on the same time-frequency block perform pilot frequency multiplexing; 3) according to the information obtained in step 1), contrasting and calculating the spatial orthogonality degree among the channels of different users through the base station, and utilizing the condition of achieving the no-speed-loss transmission in step 2) to perform greedy packet scheduling on the users under the principle of maximizing the system sum speed; and 4) performing pilot frequency distribution on every user group. Under the condition that the user side does not know instantaneous channel state information, the spatial-orthogonality-based large-scale MIMO system pilot frequency distribution method can achieve the pilot frequency multiplexing and meanwhile effectively reduce the influence caused by the problem of pilot frequency pollution and improve the system throughput performance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
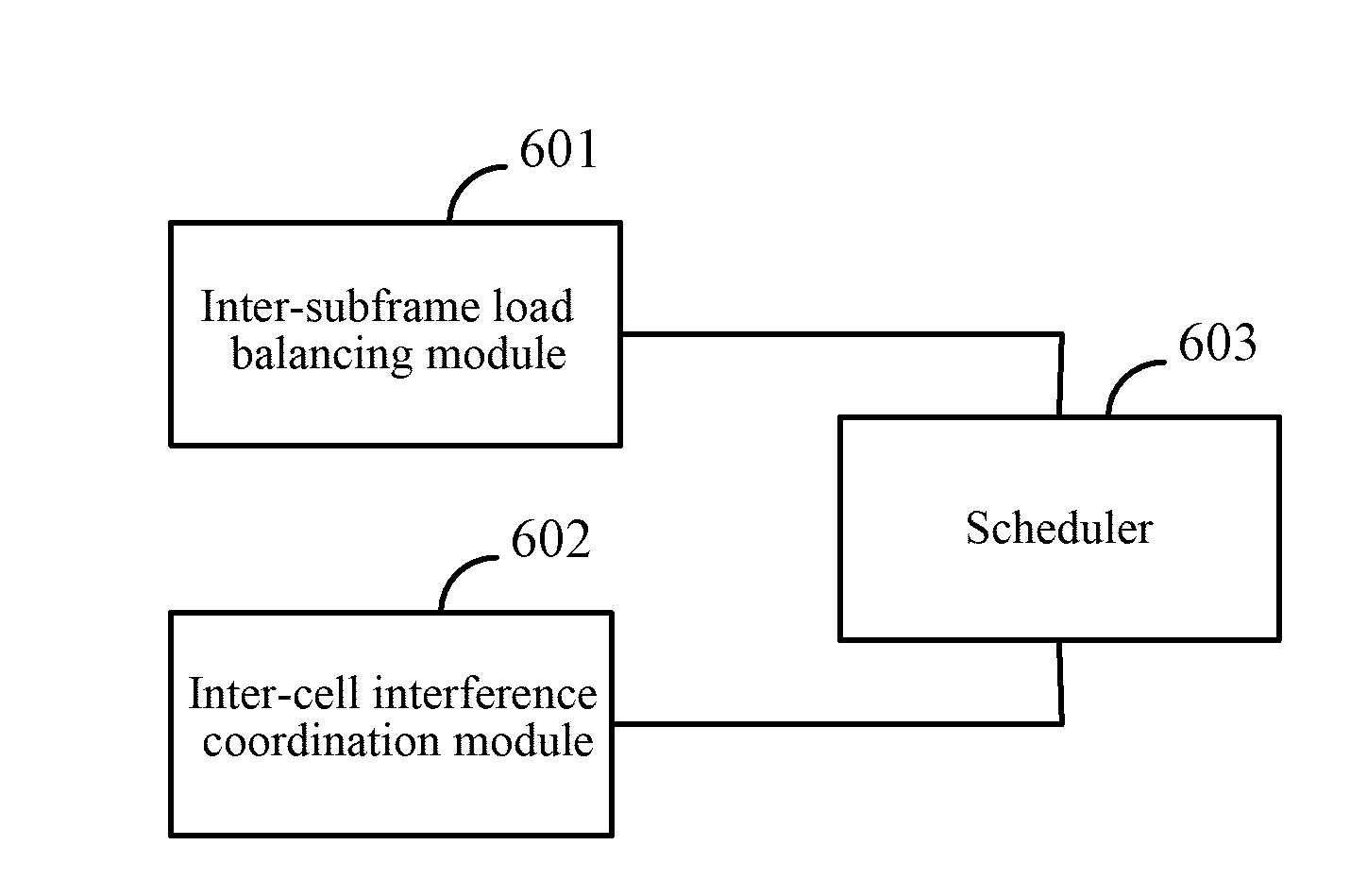
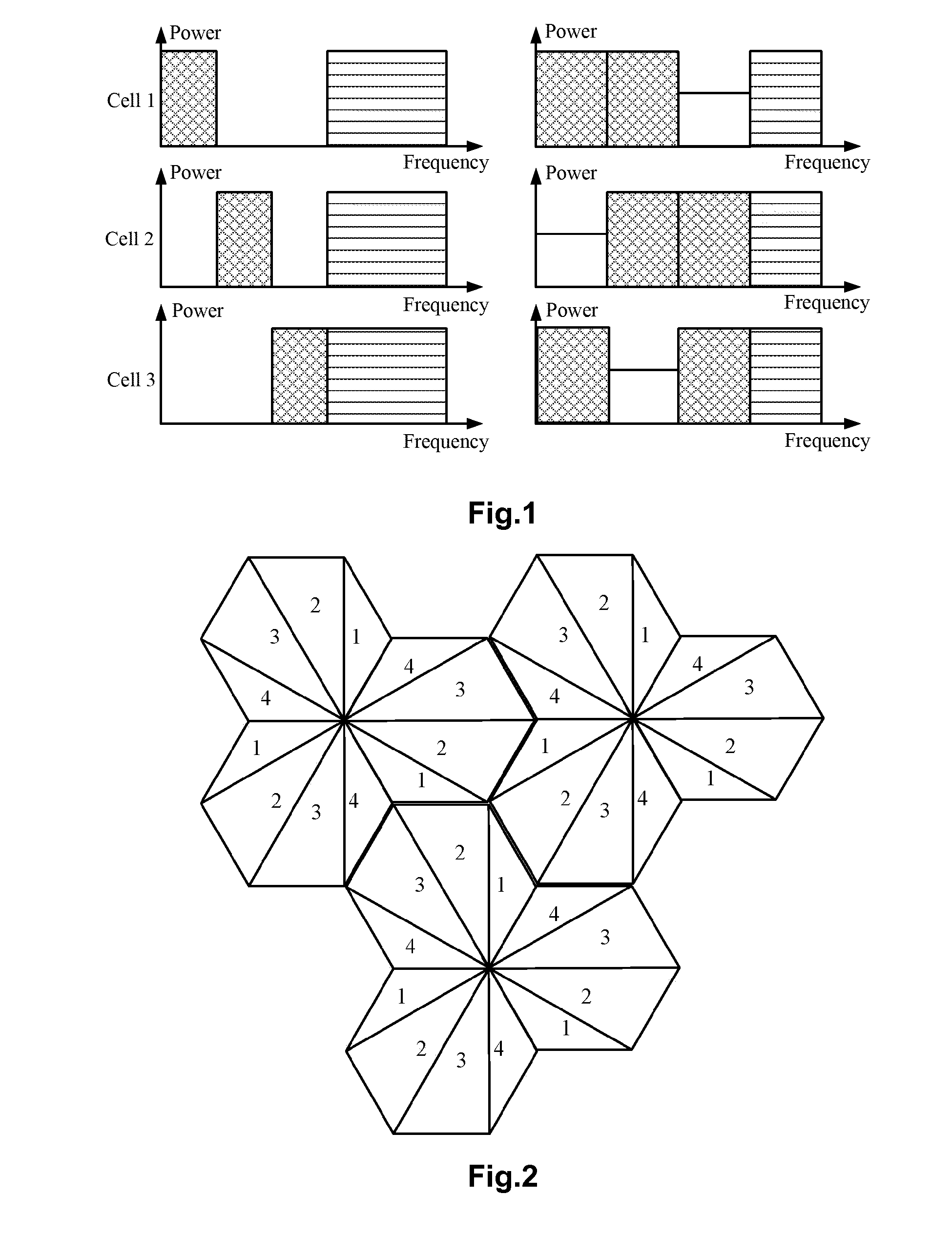
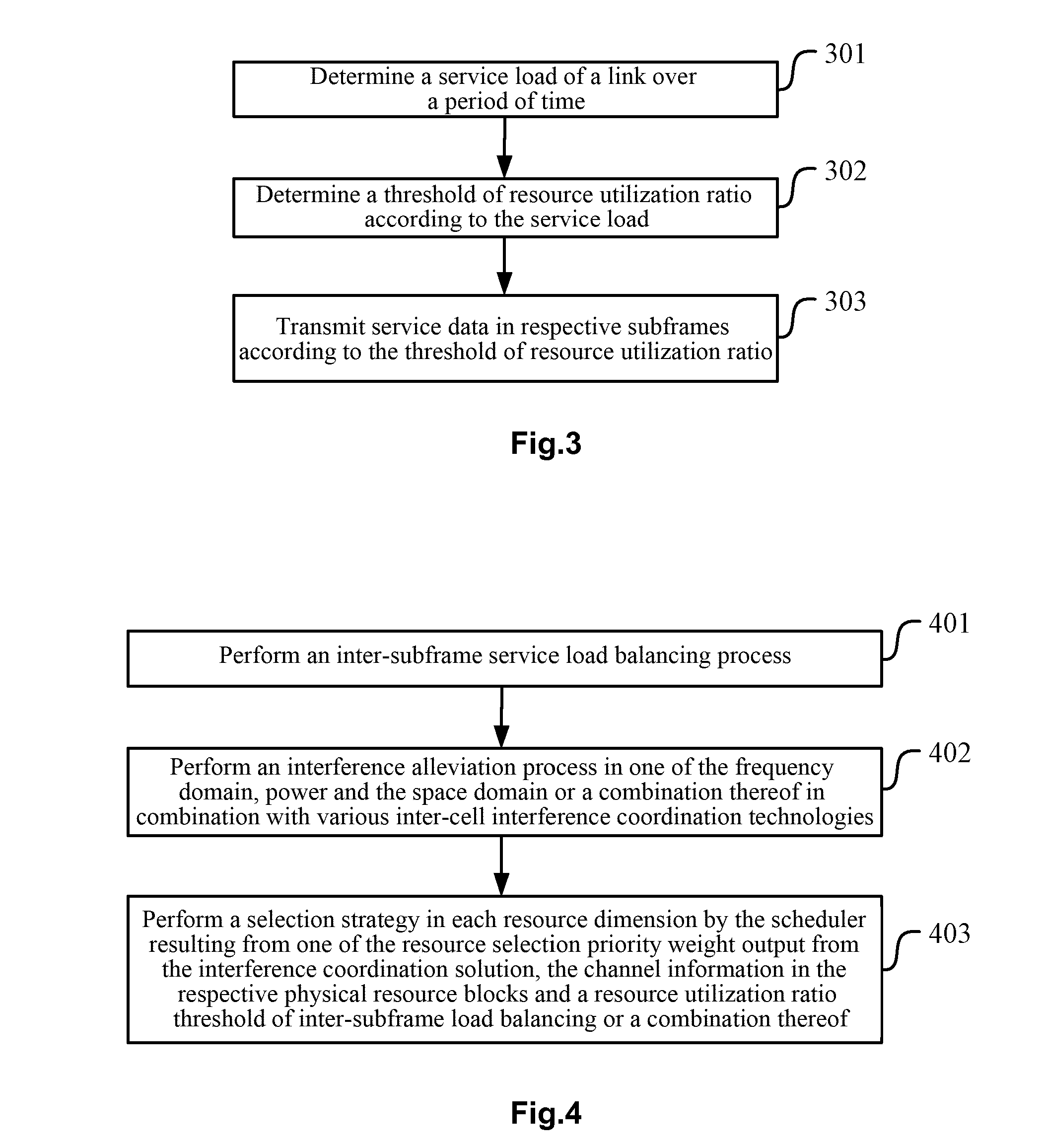
Method and device for processing inter-subframe service load balancing and processing inter-cell interference
ActiveUS20120331478A1Alleviate inter-cell interferenceImprove throughput performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementResource allocationDuplex systemFrequency domain
The present application provides a method and device for processing inter-subframe service load balancing and processing inter-cell interference, which includes: when processing the inter-subframe service load balancing, determining a service load of a link in a time period; determining a resource utilization ratio threshold according to the service load; and transmitting service data in each subframe according to the utilization ratio threshold. The inter-subframe service load balancing is processed when the inter-cell interference is processed, and in combination with various inter-cell interference coordination technologies, interference mitigation in one of a frequency domain, power and a space domain or the combination thereof is processed by the interference coordination technology. The present application can relieve the phenomenon that the interference mitigation effect is not good as the load information can not adapt well to the dynamic change of the inter-subframe service load in a time division duplex system, and can further mitigate the inter-cell interference in a long term evolution system, and improve the entire throughput performance of the system and the service quality of the subscriber in the system.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
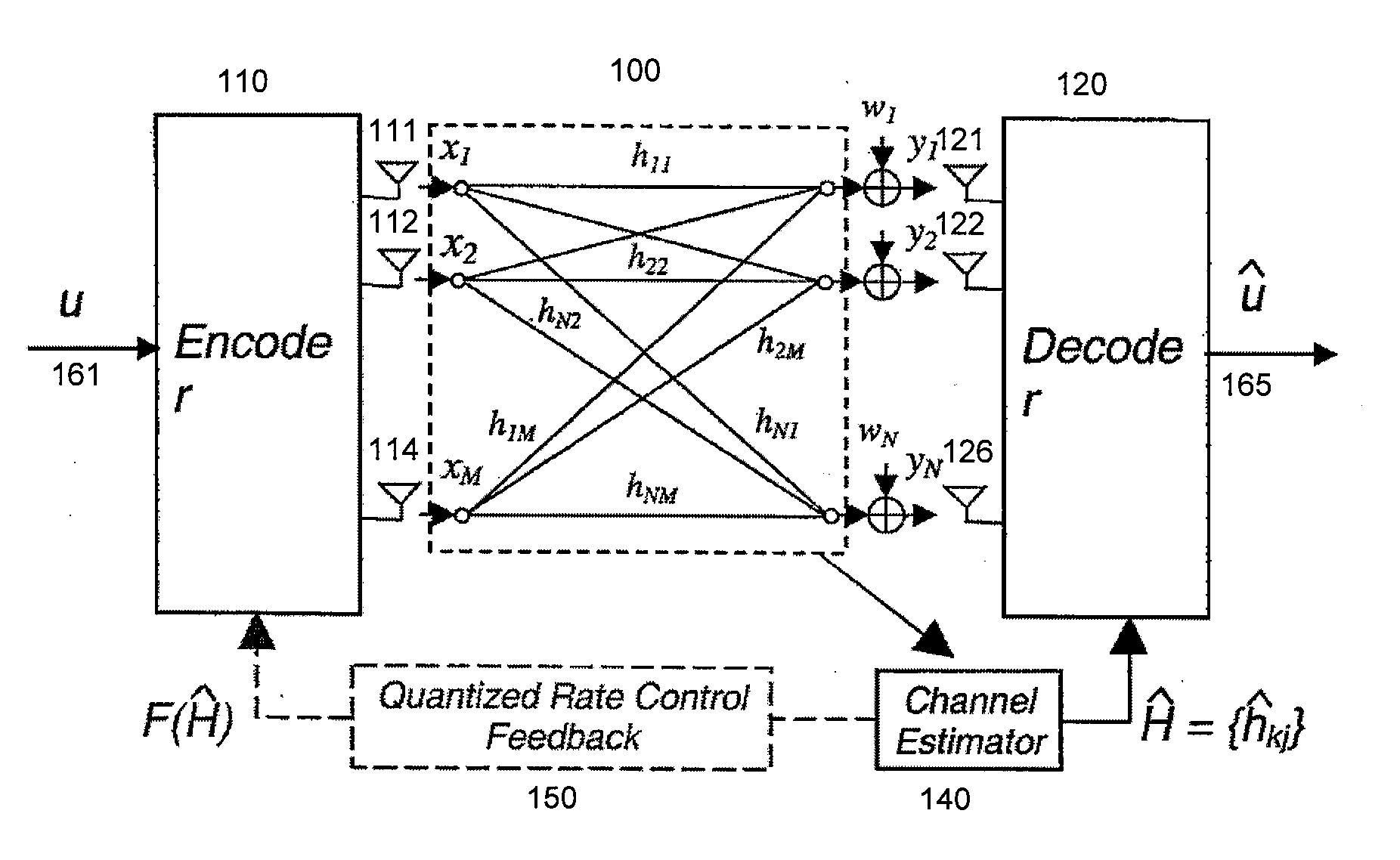
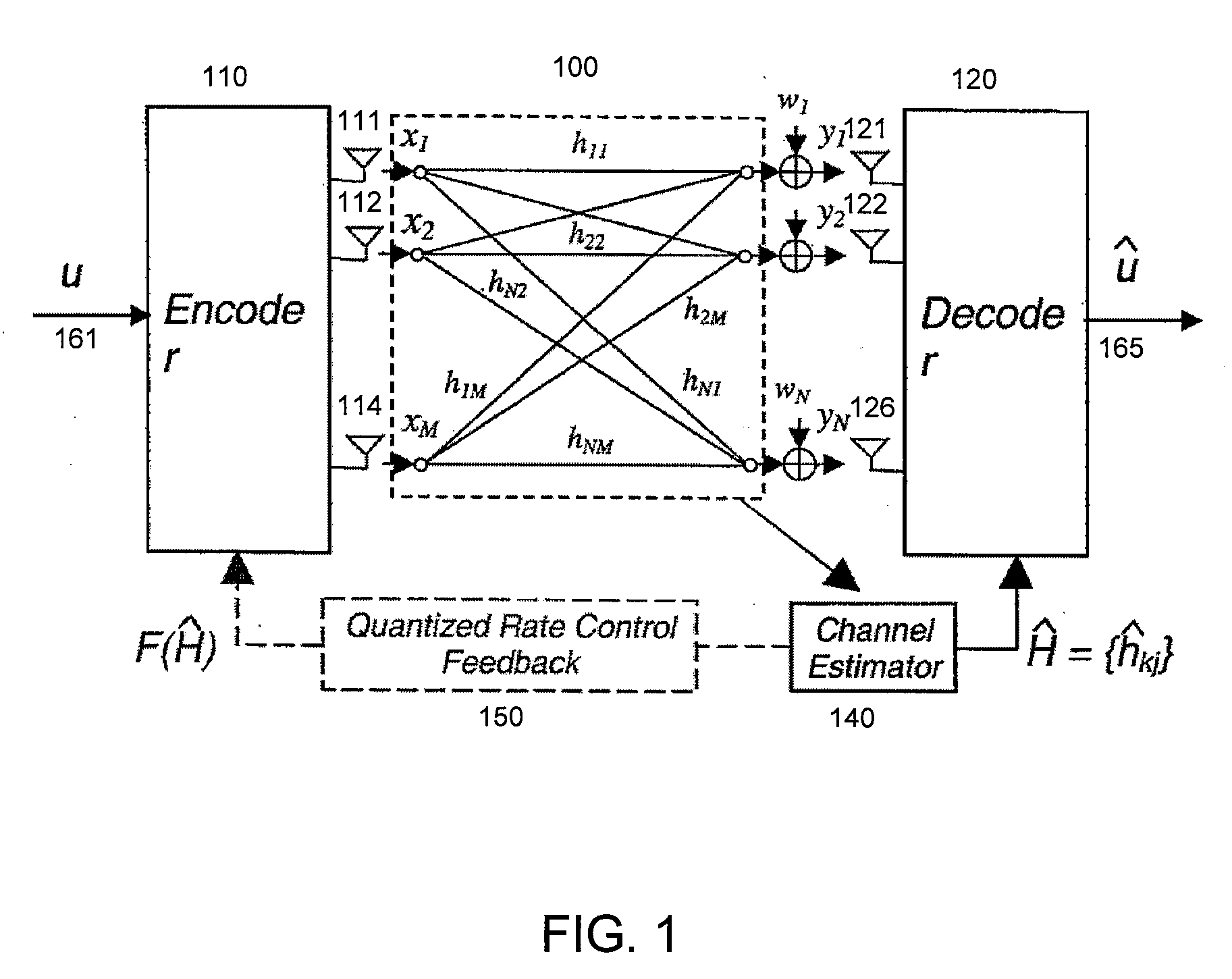
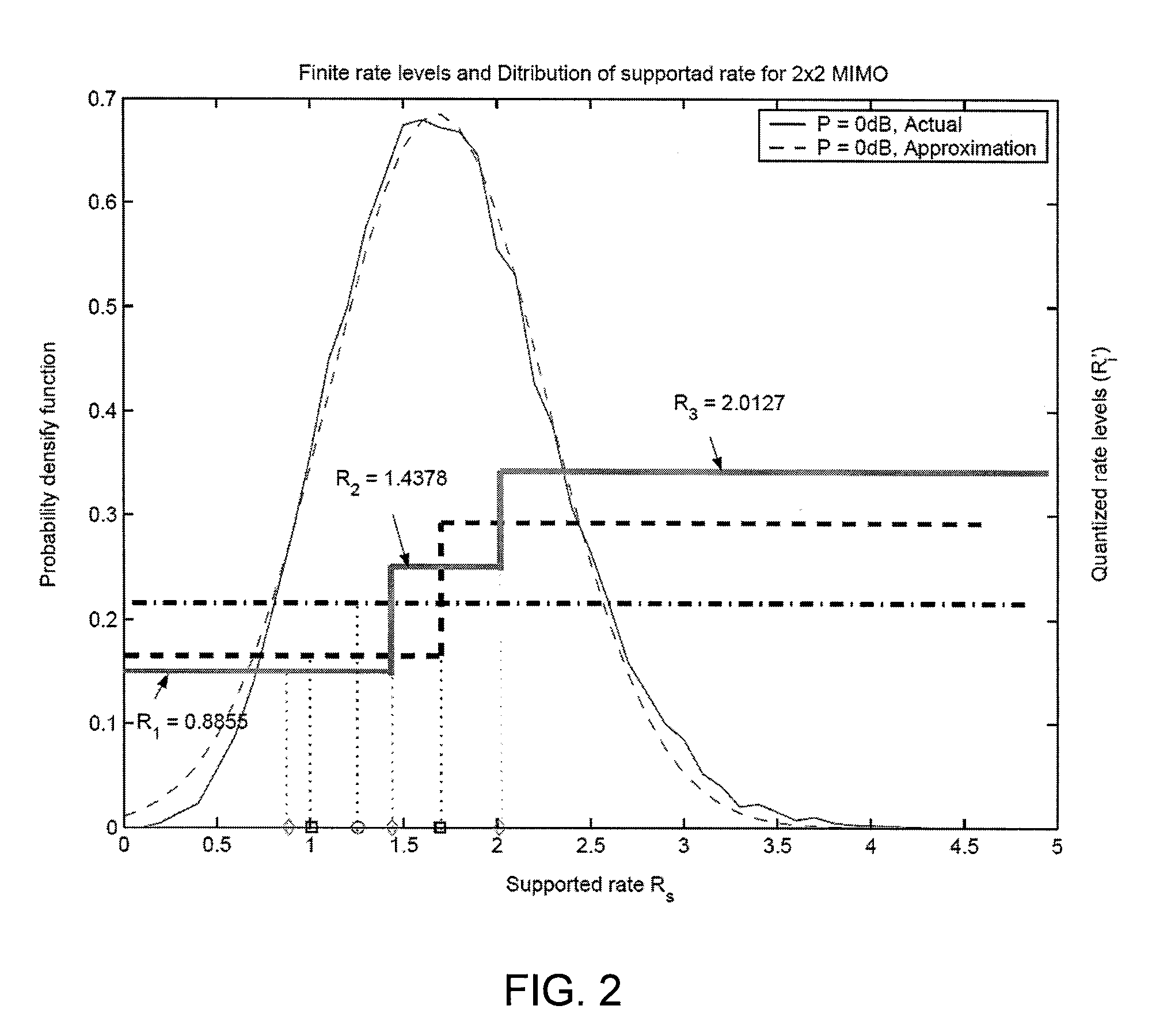
Throughput Maximization Using Quantized Rate Control in Multiple Antenna Communication
InactiveUS20060276217A1Improve system throughput performanceEfficiently findPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemEngineering
A feedback link between a receiver and a transmitter in a multiple antenna communication system is used to control the transmission rate and thereby improve system throughput performance.
Owner:NEC CORP
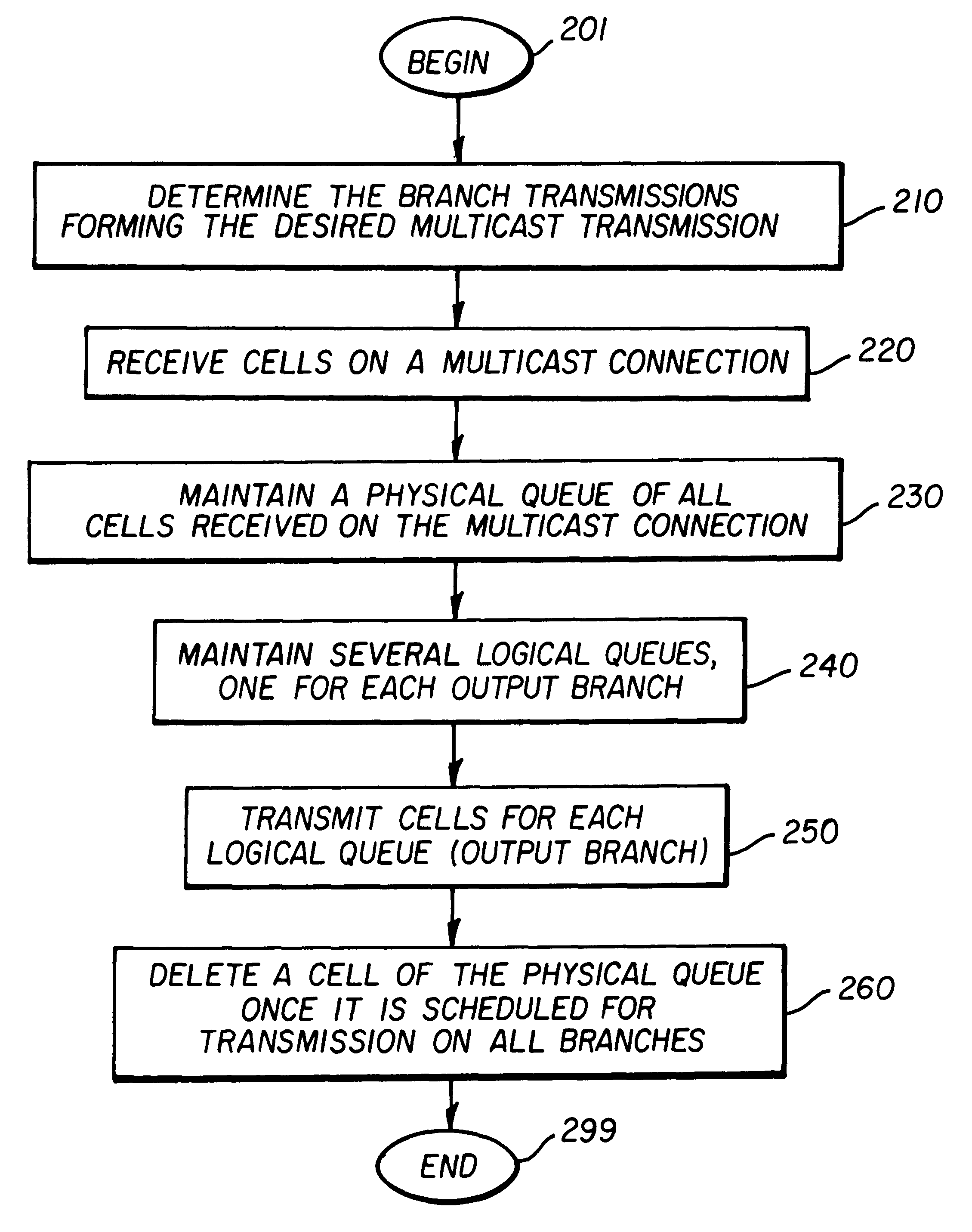
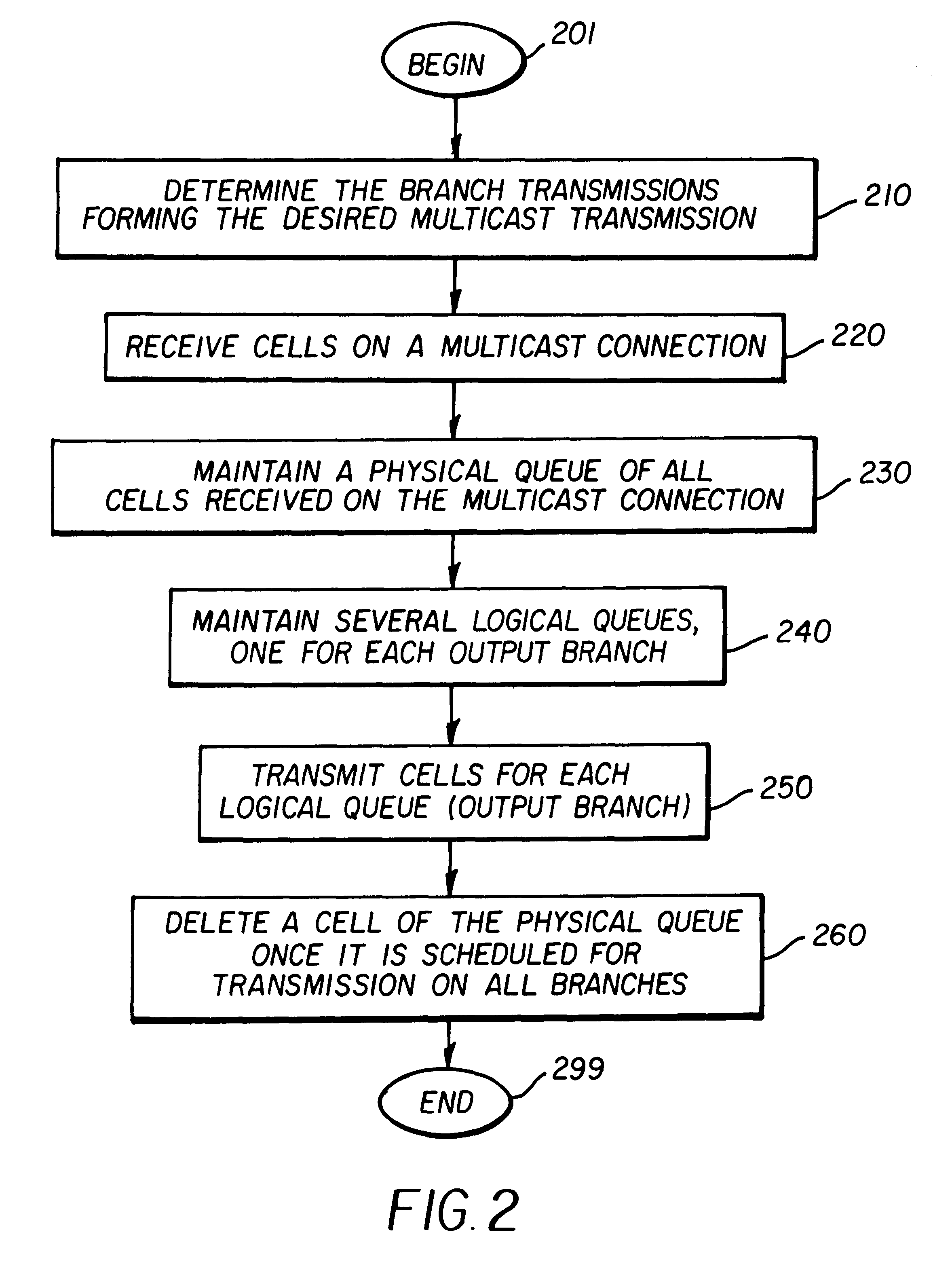
Queue management with support for multicasts in an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) switch
InactiveUS6219352B1Quantity minimizationImprove throughput performanceSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexQueue management systemAsynchronous Transfer Mode
An ATM switch supporting multicast transmissions and efficient transmission of frames. A cell is received on a multicast connection and transmitted on several branches / ports. Instead of copying a multicast cell several times for each output branch, only one copy of each multicast cell is maintained. The cell order and the stored cell data form a physical queue. Several logical queues are maintained, one for each output branch. In one embodiment, linked lists are used to maintain the queues. A cell in the physical queue is deleted after all logical queues traverse that cell. A shared tail pointer is used for all the logical queues to minimize additional processing and memory requirements due to the usage of logical queues. The queues enable cells forming a frame to be buffered until the end of frame cell is received, which provides for efficient handling of frames.
Owner:RIVERSTONE NETWORKS
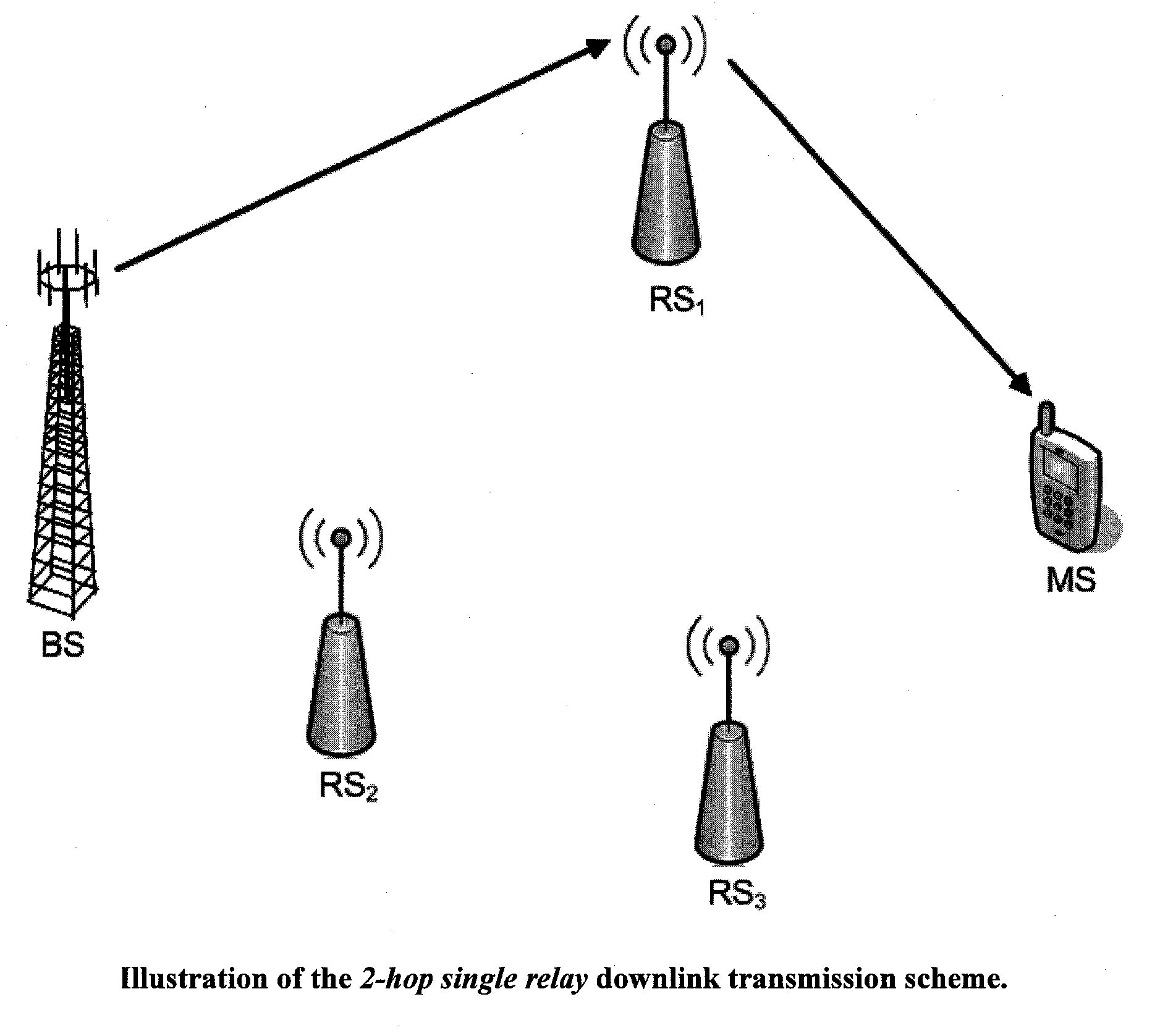
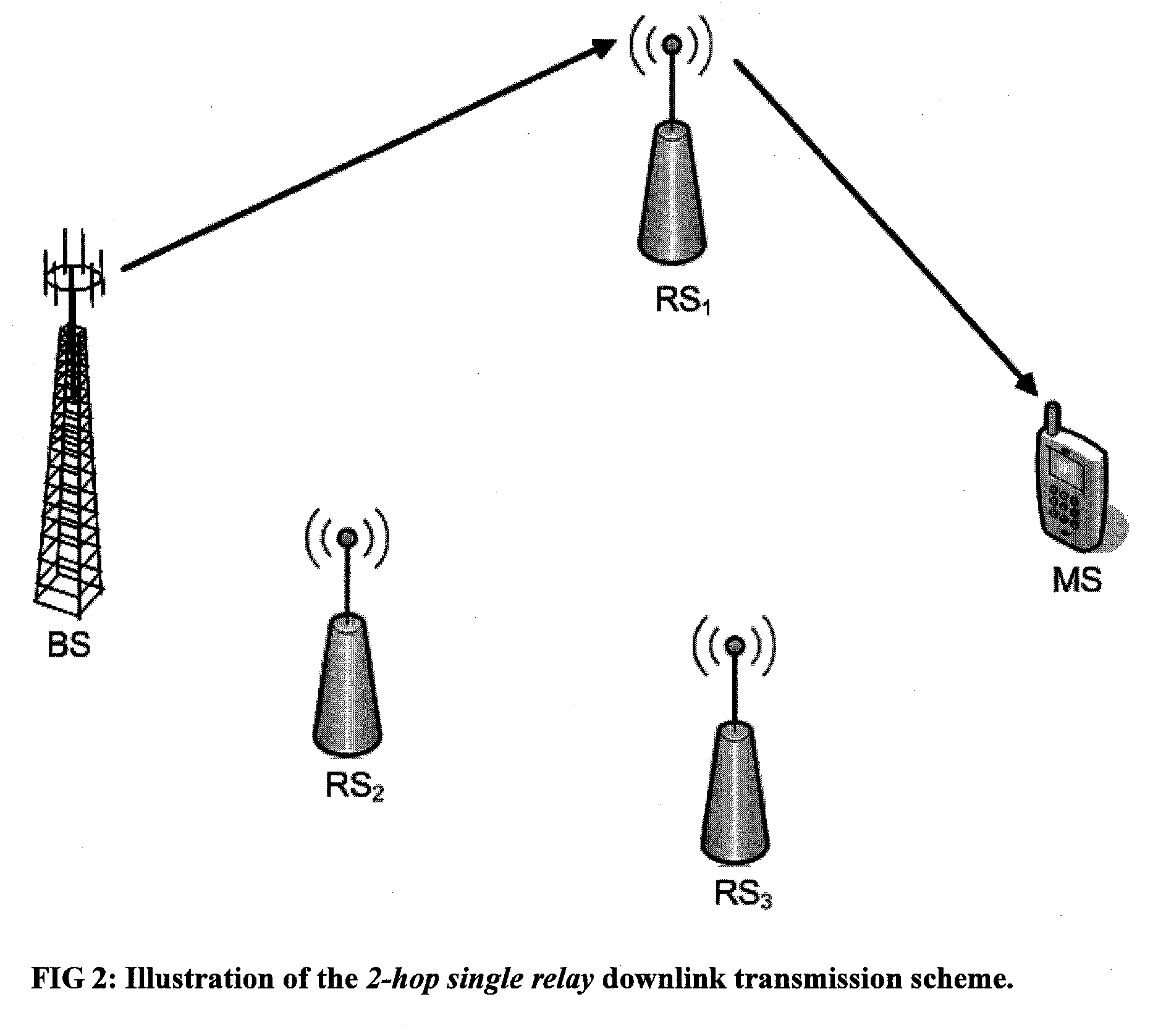
Method and system for opportunistic hybrid relay selection scheme for downlink transmission
InactiveUS20090116422A1Good outage probabilityImprove throughput performanceSite diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)RSS
An opportunistic hybrid-relay selection scheme for downlink transmission selects between cooperative relay and single relay schemes based on the channel conditions (e.g., signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR)) between the base station (BS) and RSs (i.e., BS-RSs link) and RSs and mobile station (MS) (i.e., RSs-MS link), respectively. In another selection scheme, a selection between the single relay (e.g., best-relay) transmission scheme or the cooperative-relay transmission scheme may be determined based on transmission paths (e.g., line-of-sight, obstructed-light-of-sight, non-light-of-sight) and channel conditions (e.g., SNR) between the BS-RSs link and the RSs-MS link, respectively.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
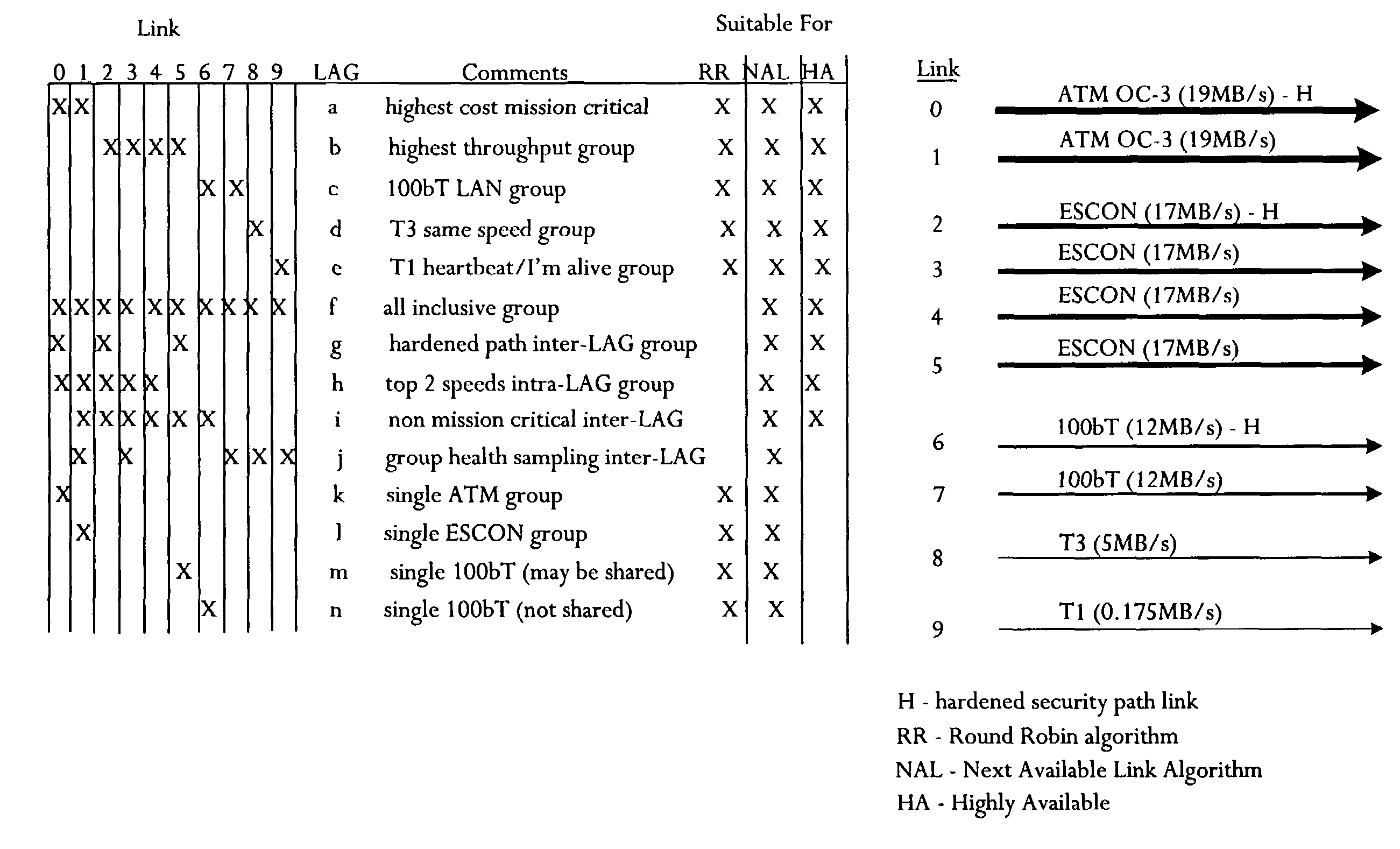
Storage system with link selection control
InactiveUS7478154B2Improve throughput performanceImprove throughputInput/output to record carriersError preventionCarrying capacityTelecommunications link
A storage system comprises an interface capable of interconnecting a network infrastructure via a plurality of communication links. The plurality of communication links has a diversity of data-carrying capacity and performance. The storage system further comprises a controller coupled to the interface that assigns the plurality of communication links into at least one link affinity group based on performance criteria and controls link selection based on link affinity group assignment.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
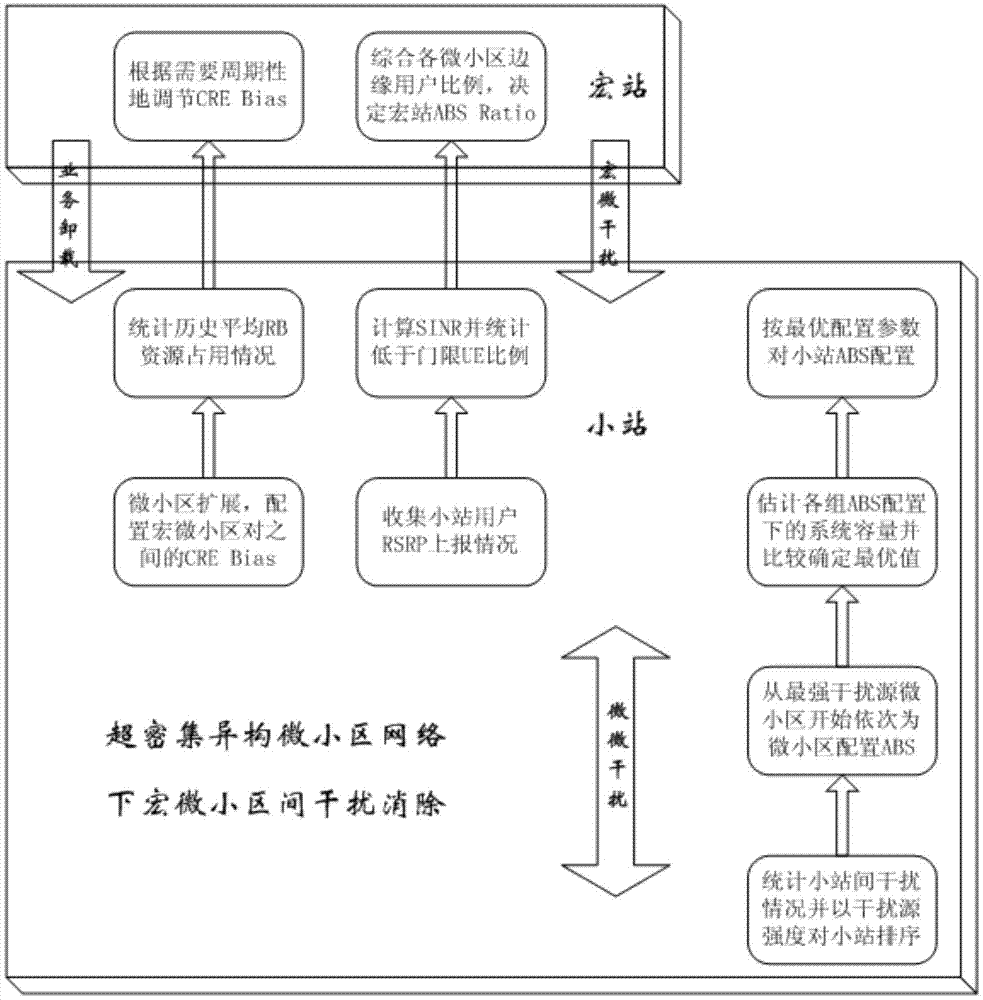
Cross-layer interference coordination optimization method in super dense heterogeneous network
ActiveCN103929781AGuaranteed Edge PerformanceImprove throughput performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementMicro cellHeterogeneous network
The invention discloses a cross-layer interference coordination optimization method in a super dense heterogeneous network. The method includes a cell range extension strategy, a micro station ABS allocation strategy and a small station ABS allocation strategy. According to the method, on the basis of the interference characteristics of scenes, cell range extension offset between macro cells and micro cells is reasonably planned for load balance, the same-layer manner and the cross-layer manner are combined to allocate nearly blank subframes for macro stations and micro stations so as to reduce interference between neighbor cells, and thus the total throughput capacity of a system can be maximized on the premise that the system edge user reliability is guaranteed.
Owner:白盒子(上海)微电子科技有限公司
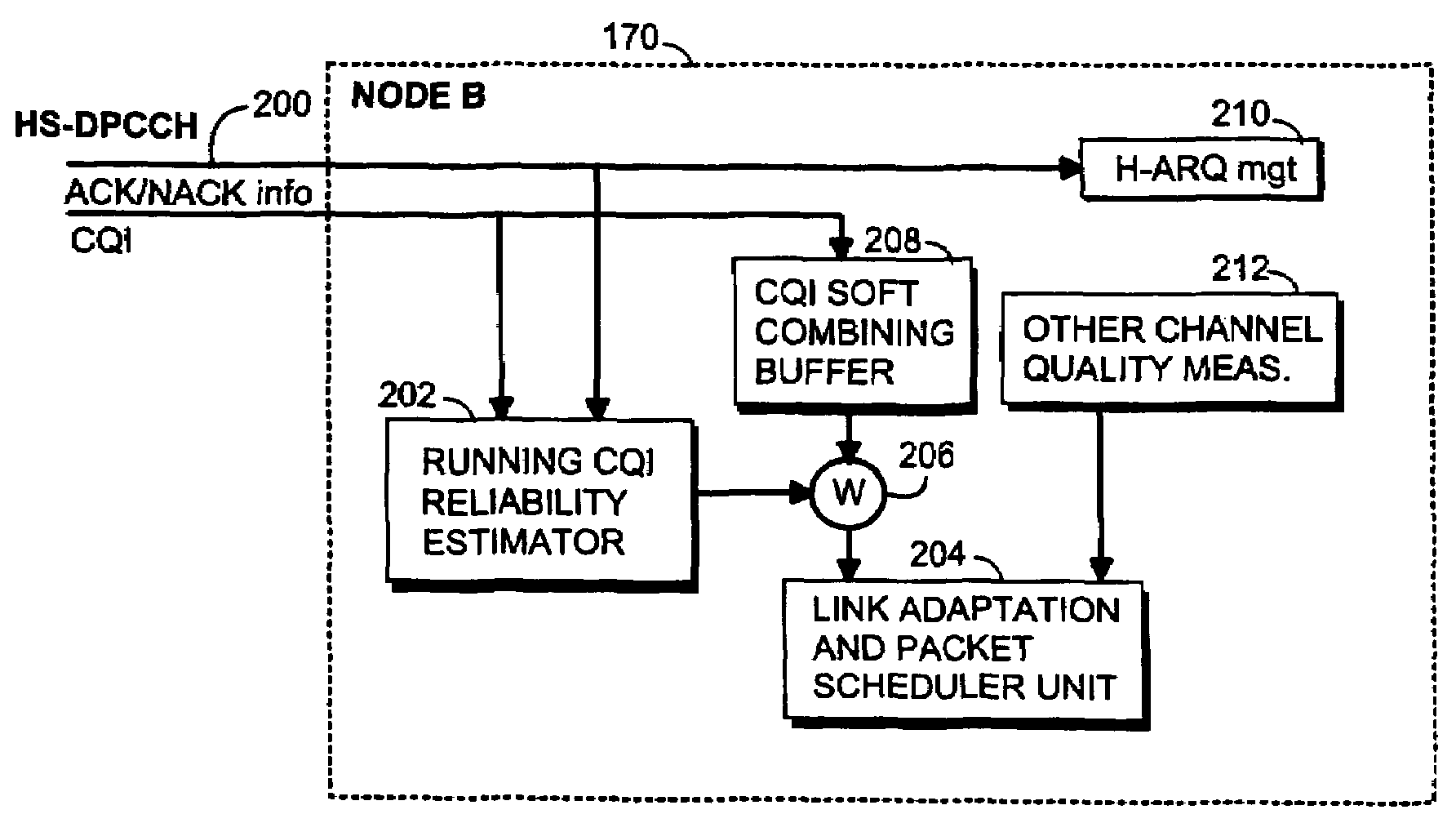
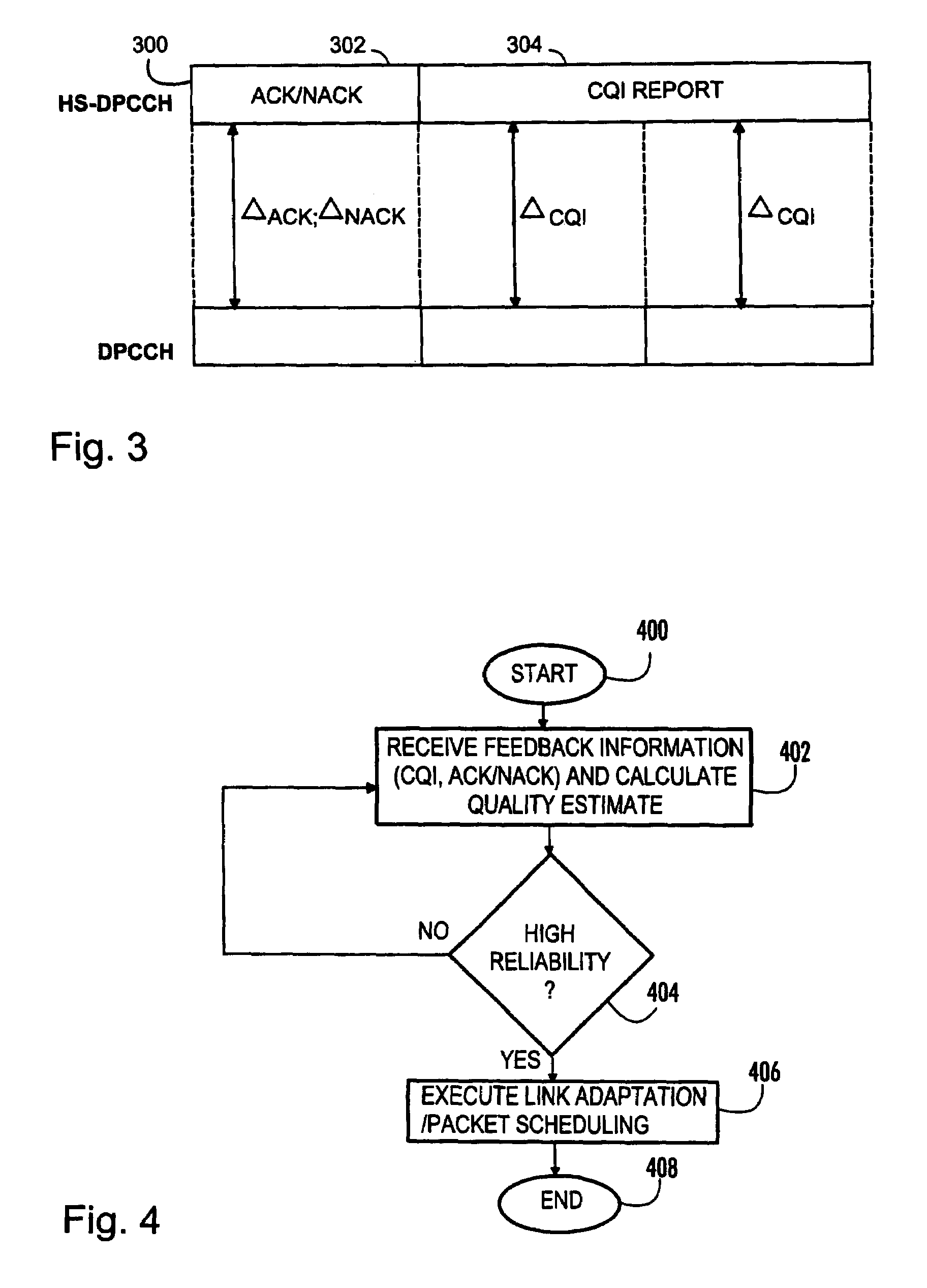
Method and base station for controlling link adaptation and packet scheduling in high speed downlink packet access (HSDPA) radio system
ActiveUS7539207B2Improve estimation accuracyReduce delaysError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl channelPacket scheduling
A method of controlling link adaptation and packet scheduling in an HSDPA (High Speed Downlink Packet Access) radio system and an HSDPA base station communicating over a control channel with one or more user equipment units is provided. According to one embodiment the base station includes a device for receiving feedback information from the user equipment. The base station further includes a device for calculating a quality estimate related to the feedback information and executing link adaptation and packet scheduling based on the calculated quality estimate.
Owner:RPX CORP
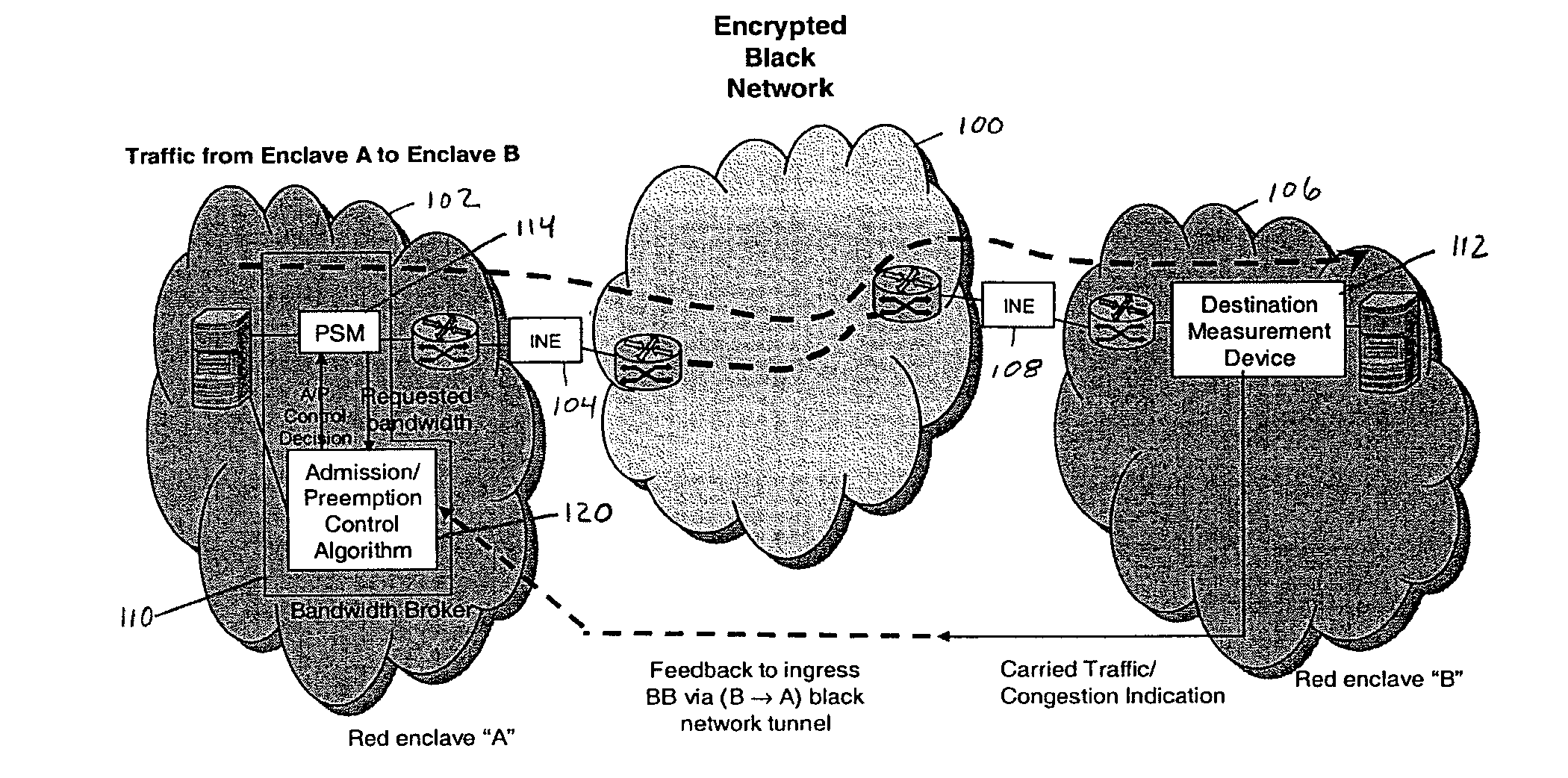
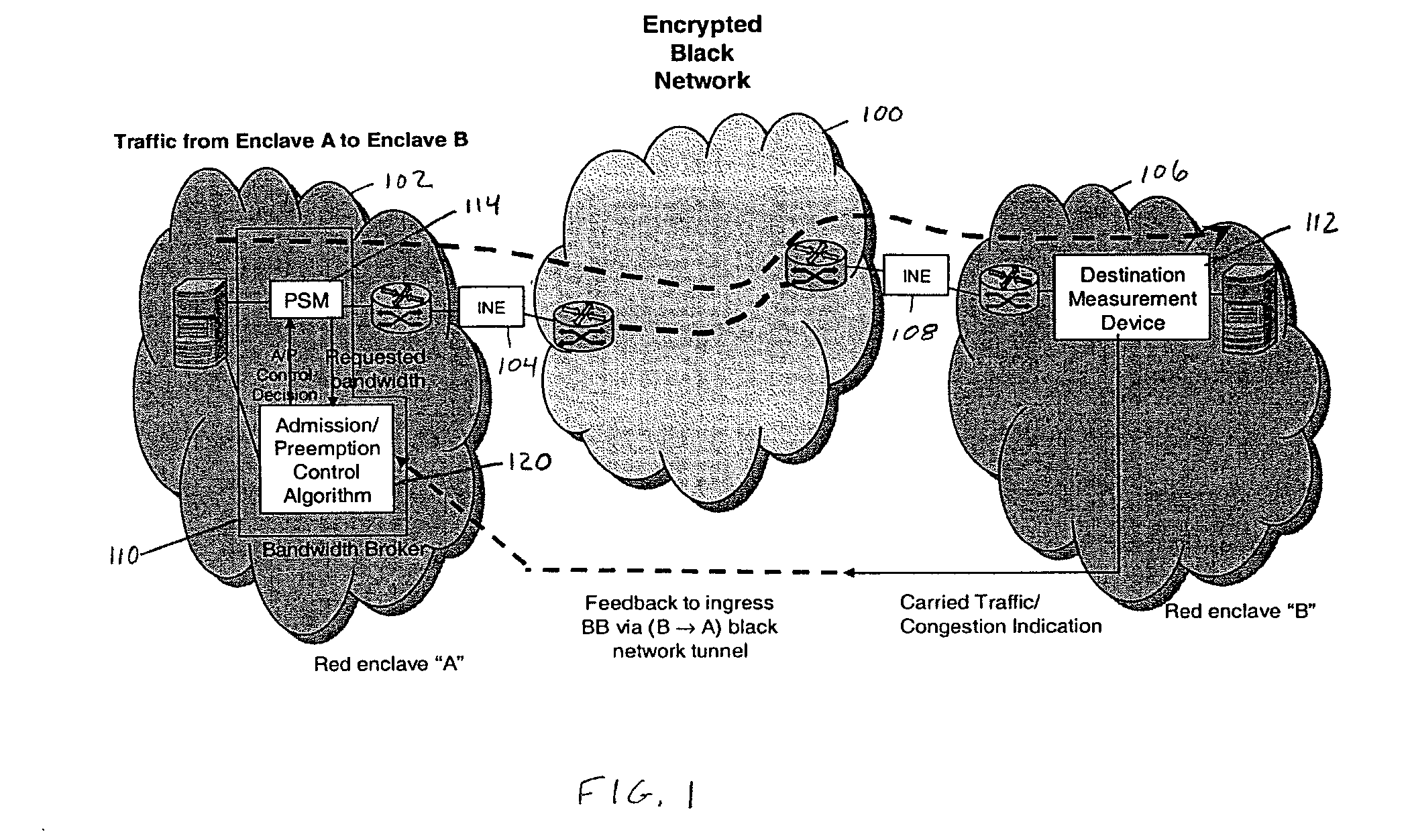
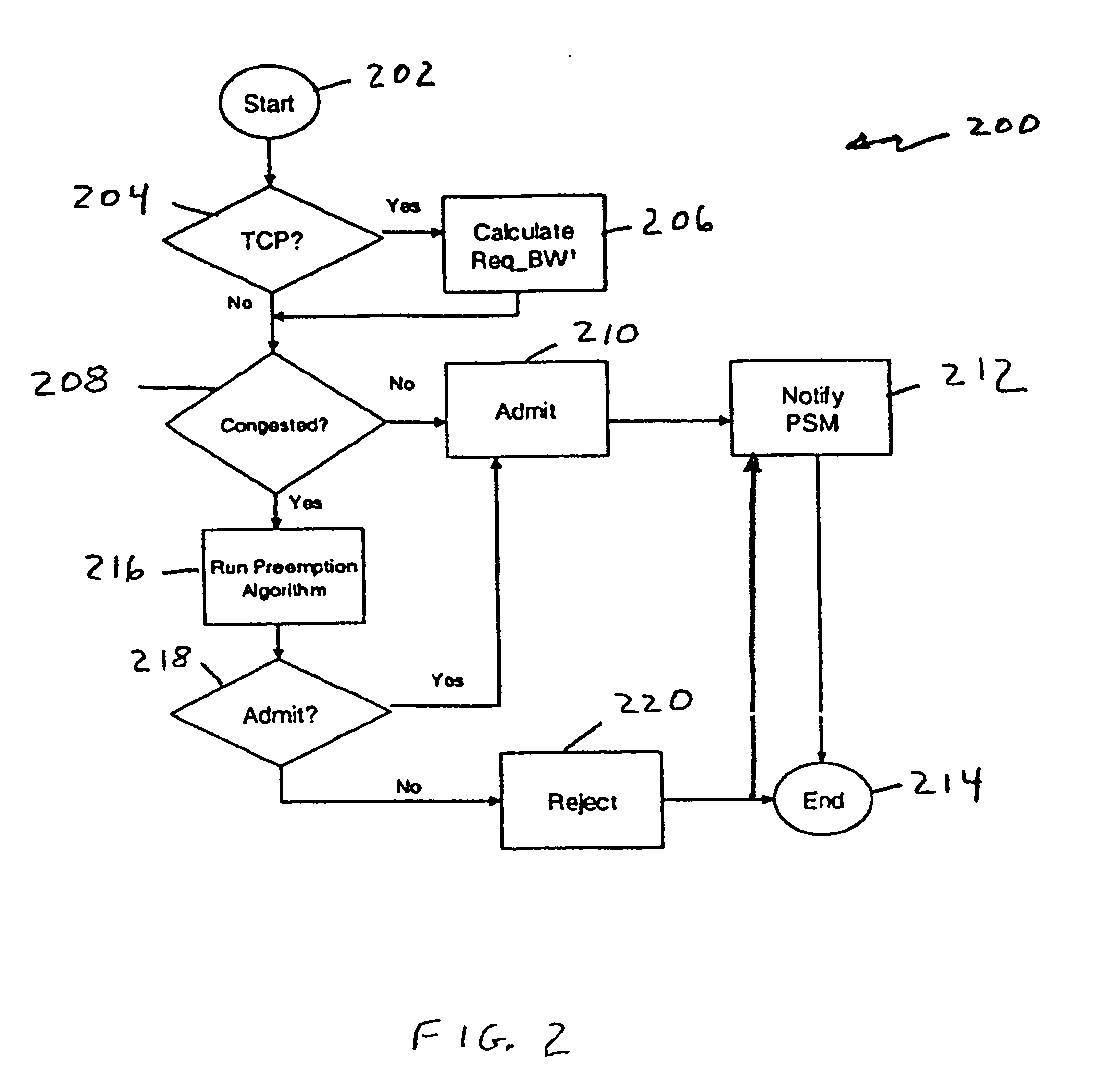
Call admission control and preemption control over a secure tactical network
ActiveUS20100011118A1Improve throughputImprove throughput performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTraffic capacityAdmission control algorithm
In a secure network where the network characteristics are not known, a call admission control algorithm and a preemption control algorithm based on a destination node informing the source node of the observed carried traffic are used to regulate the amount of traffic that needs to be preempted by the source. The amount of traffic that needs to be preempted is based on the carried traffic measured at the destination node. The traffic to be preempted is based on the priority of the traffic, where the lowest priority traffic is the first to be preempted until the amount of traffic preempted is sufficient to allow the remaining traffic to pass through the network without congestion.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
Radio communication system
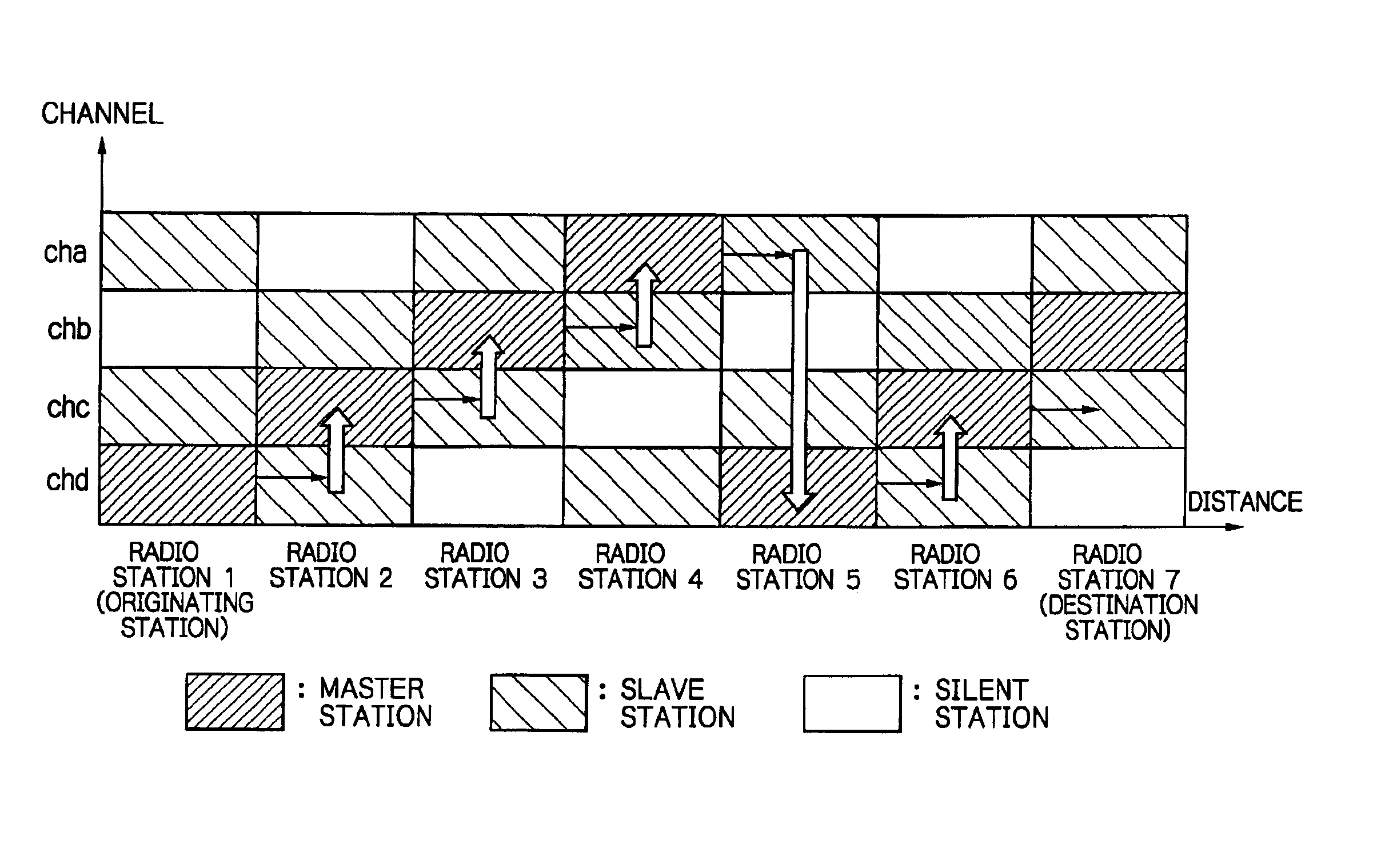
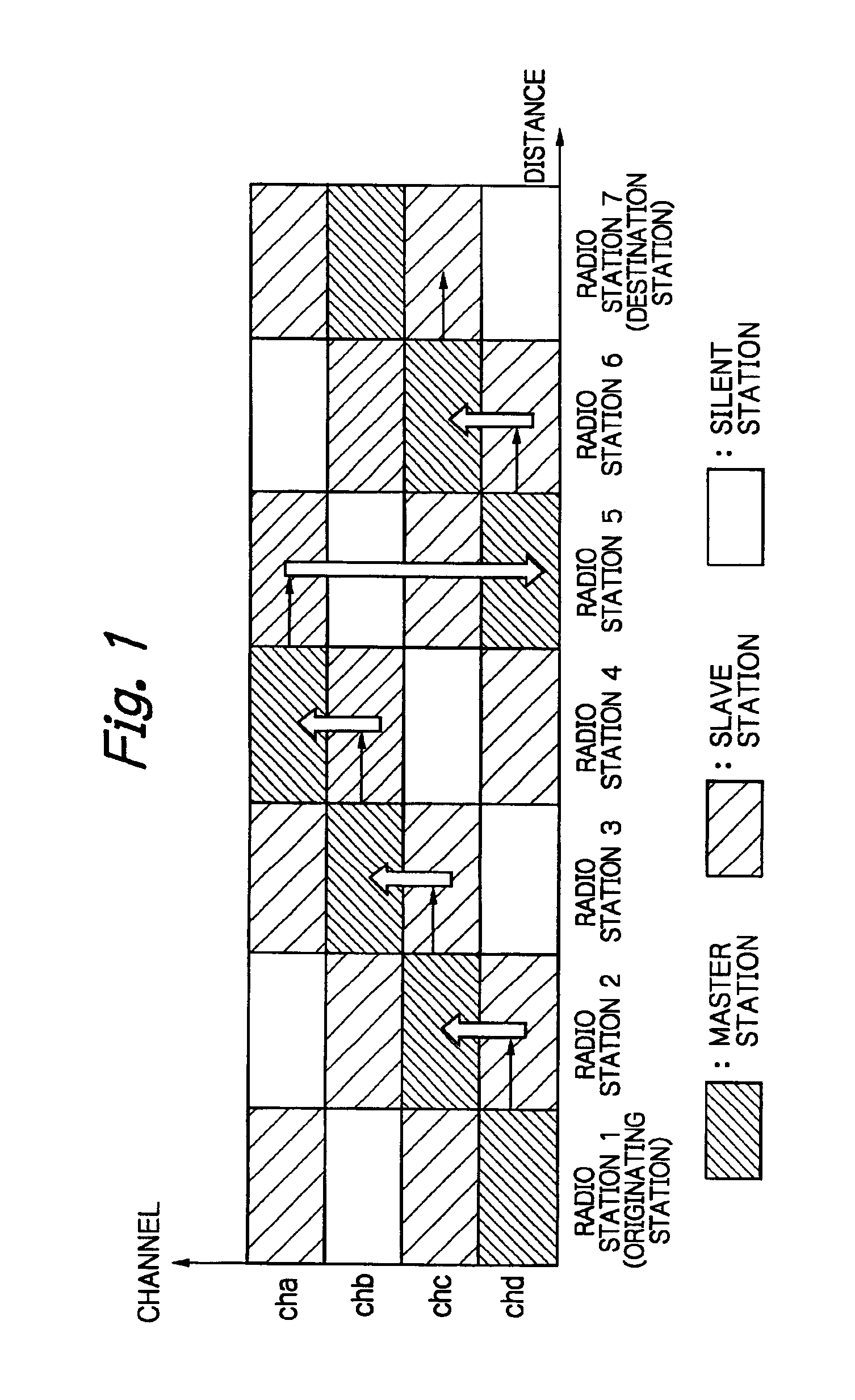
InactiveUS6934554B2Little delay timeImprove throughput performanceNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationCommunications systemMaster station
Each radio station can manage a plurality of channels, and functions both as a master station which controls transmission in each channel and a slave station which operates under control of a master station. In case of a master station, it transmits a signal under control of the own station, and in case of a slave station, it transmits a signal under control of the master station. Each radio station can communicate with any other radio station either directly or through another radio station. In each channel, communication is carried out in time division of centralized control access phase and distributed control access phase. A master station in case of centralized control access phase is determined in each channel and in each link.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Substrate processing apparatus, operation method thereof and program
InactiveUS6937917B2Suppress power consumptionImprove throughput performanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNormal modeProcess efficiency
Provided is a substrate processing apparatus that can reduce power consumption, while maintaining throughput. In addition to a normal mode in which all units are activated, the apparatus is provided with an energy saving mode that is selectable. When the energy saving mode is selected, only essential units that are requisites for a substrate processing are activated and used in the substrate processing. If it is necessary to increase process efficiency, any additional unit may be activated and used in the processing. During standby, only an essential unit can be activated and the rest is halted, or alternatively, all units may be halted. The transition to the energy saving mode can occur when the standby state continues for a predetermined period of time after the normal mode is selected.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Method for multi-user dispatching transmission based on 3D-MIMO codebook design
ActiveCN103780347AReasonable divisionImprove spectrum utilizationSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionFrequency spectrumComputer science
The invention discloses a method for multi-user dispatching transmission based on 3D-MIMO codebook design. The method comprises the steps that an even flat board array is adopted by a base station antenna, a direct product codebook for 3D-MIMO is adopted, a horizontal codebook in the direct product codebook is a DFT codebook, and a vertical codebook is obtained through space division; the codebooks are grouped according to basic beam directional diagrams corresponding to codons in the direct product codebook, and the limiting feedback quantity is calculated by users according to the codebook grouping condition and a channel estimation result and is fed back to a base station through a feedback channel; the users are paired and dispatched by the base station according to the limiting feedback quantity of the users and multi-user transmission is conducted. Compared with a two-dimension codebook, a traditional three-dimensional DFT direct product codebook and multi-user transmission methods of the two-dimension codebook and the traditional three-dimensional DFT direct product codebook, the use rate of a system frequency spectrum and the handling capacity performance are improved.
Owner:上海瀚芯实业发展合伙企业(有限合伙)
Full-duplex environment backscattering communication system, transmission method and resource allocation method
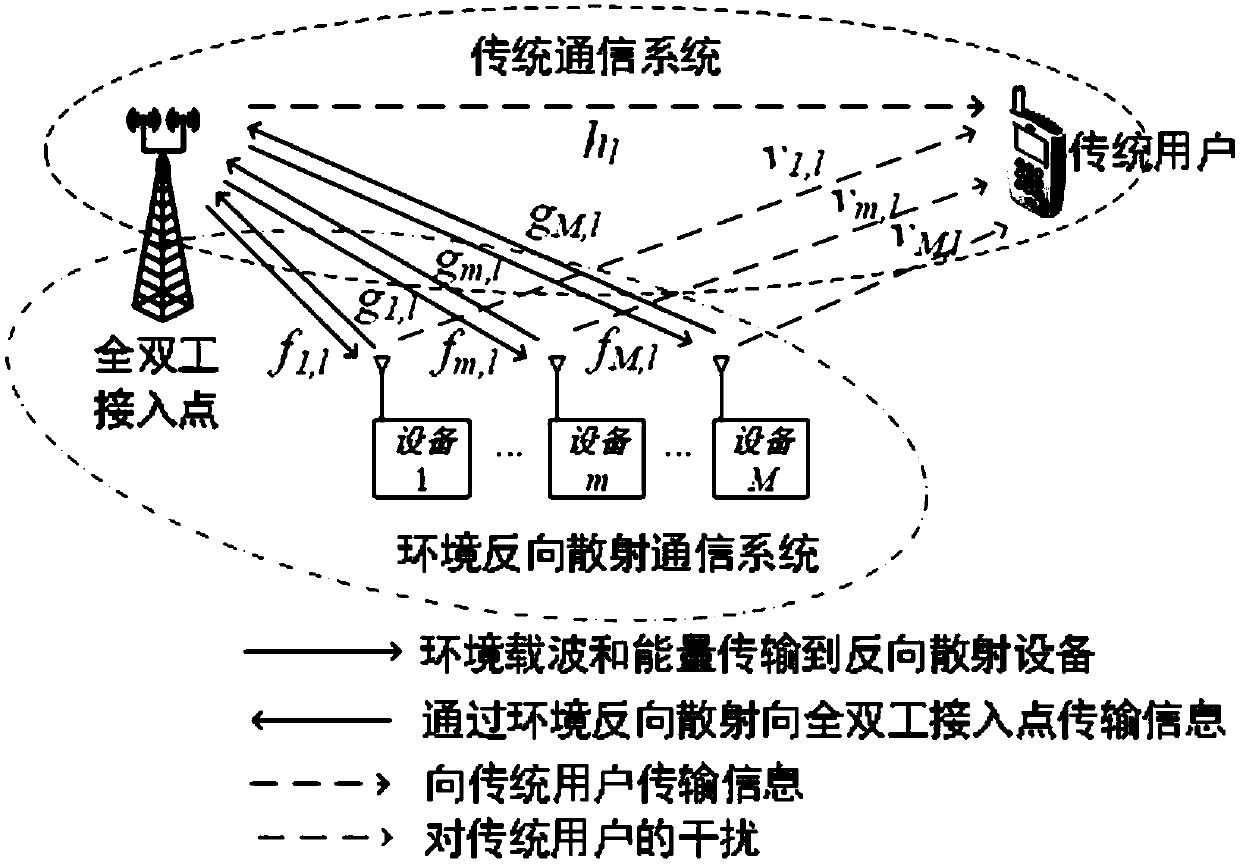
InactiveCN109547183AReduce complexityImprove throughput performanceBaseband system detailsDuplex signal operationCommunications systemData signal
The invention belongs to the field of communication technology, and relates to a full-duplex environment backscattering communication system, a transmission method and a resource allocation method. According to the system of the invention, a full-duplex-type access point is configured with one or more antennas, and two modes of channel estimation and full-duplex backscattering communication are included; in a channel estimation mode, the access point sends a downlink pilot signal, a plurality of backscattering devices carry out backscattering by respective fixed backscattering coefficients according to a manner of division multiplexing, the access point estimates channels of all the backscattering devices, and a traditional user utilizes the received pilot signal to estimate a downlink channel thereof; and in a full-duplex communication mode, the access point sends a downlink data signal, the traditional user uses the estimated downlink channel to carry out signal receiving detection,the backscattering devices select backscattering coefficients according to information bits for backscattering, and the access point detects signals of the backscattering devices. The system can be used in a variety of low-power-consumption Internet-of-things communication scenes, and has higher practicability.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Dag based methods and systems of transaction processing in a distributed ledger
ActiveUS20200065300A1Improve throughput performanceImprove performanceDatabase updatingDatabase distribution/replicationFinancial transactionTransaction processing system
Described herein are systems and methods for a DAG based transaction processing system and method in a distributed ledger. In accordance with an embodiment, a DAG based transaction processing system and method in a distributed ledger can be introduced. The model can help achieve improved throughput performance. With additional weight mechanism, the final performance can be adjusted based on various business requirements. This is different from existing work that uses linear structure and can achieve better performance.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
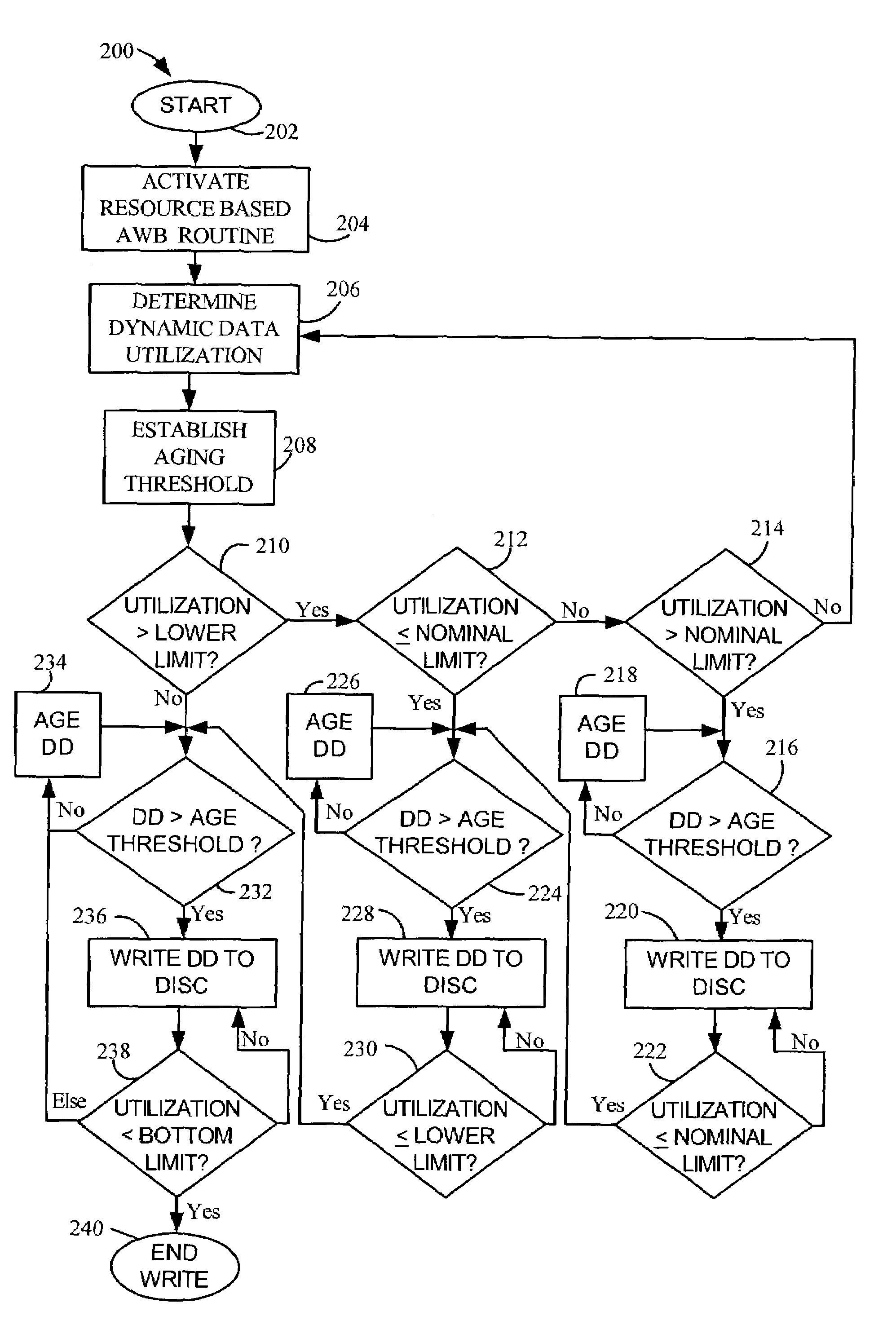
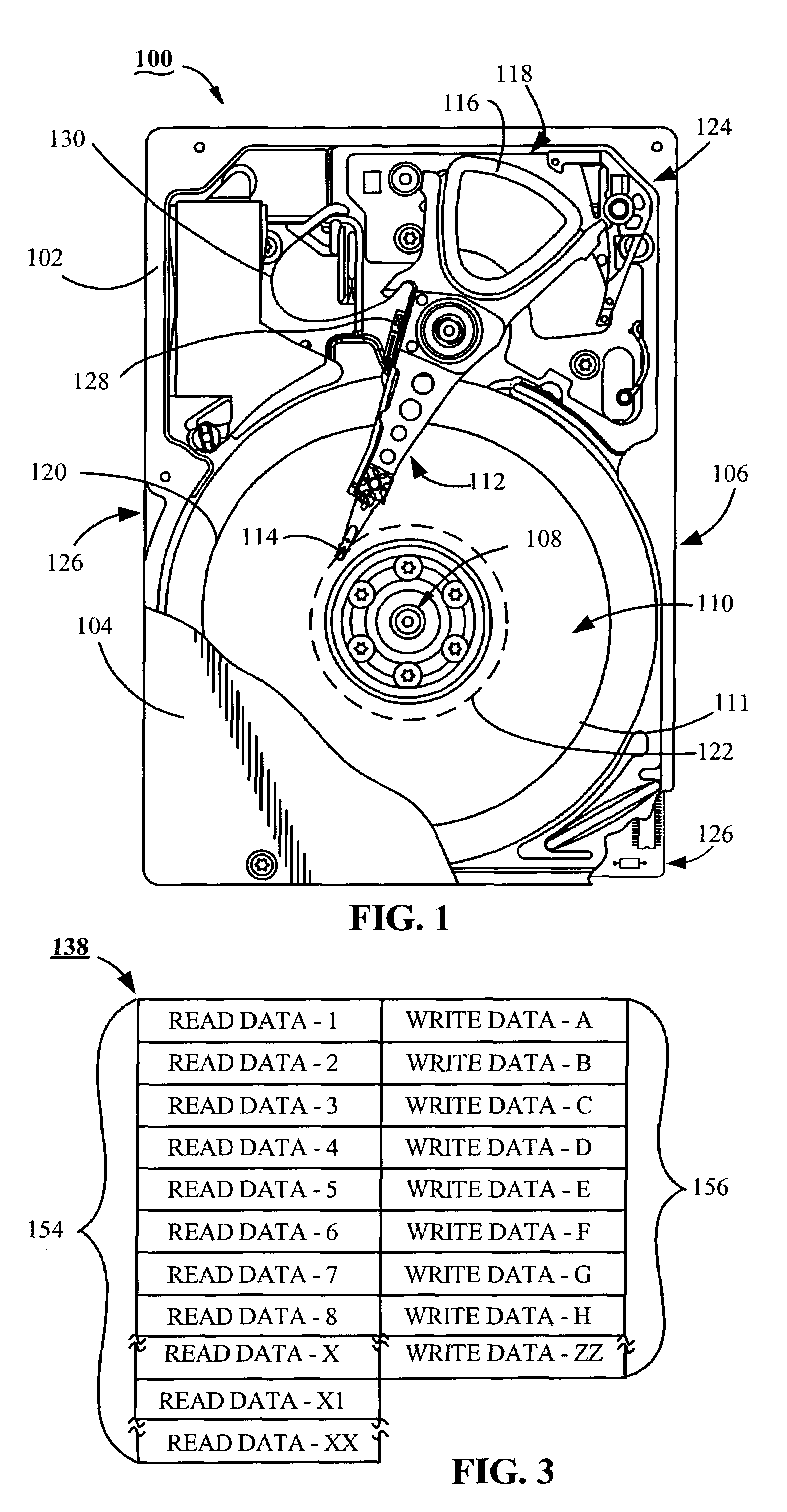
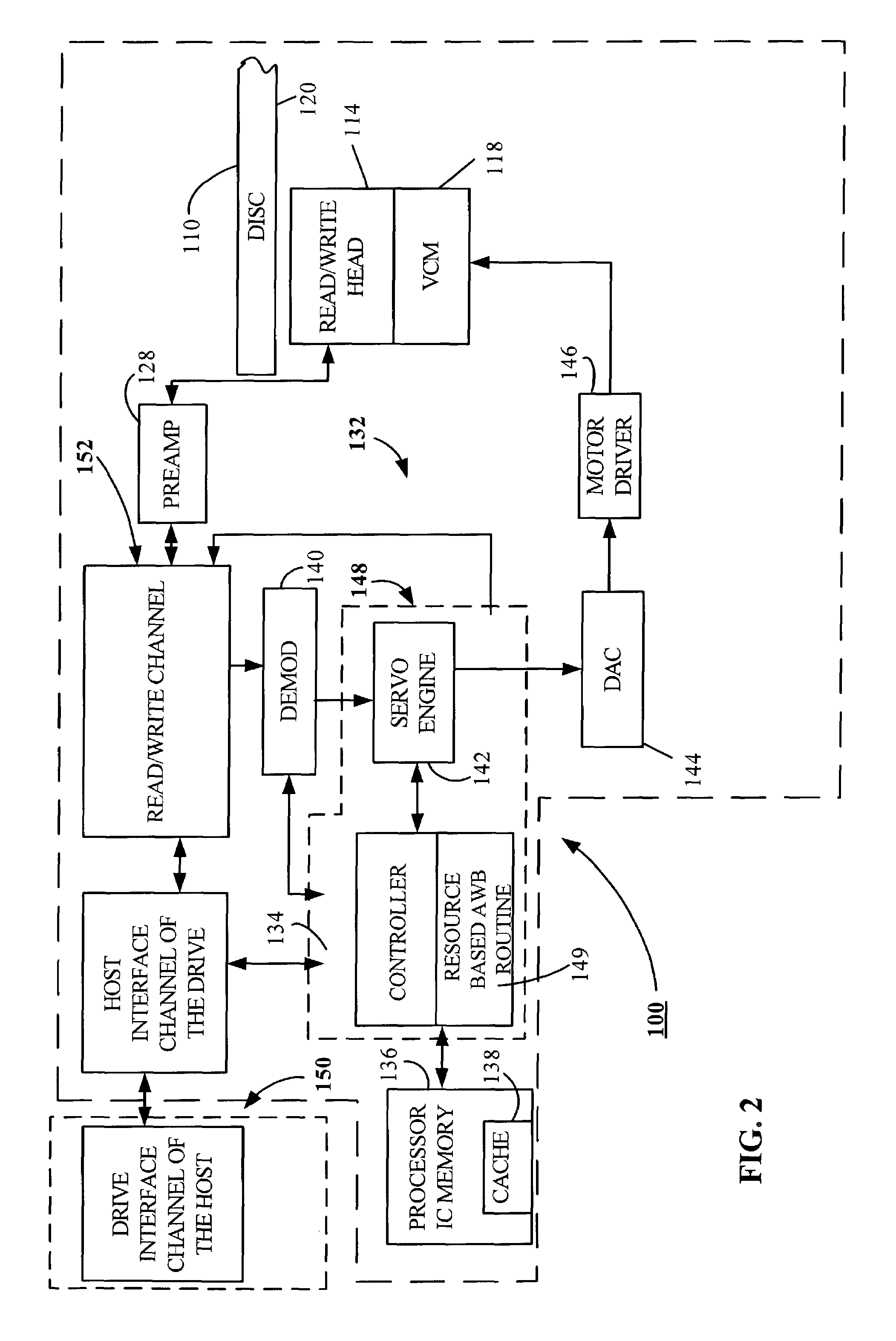
Adaptive resource controlled write-back aging for a data storage device
ActiveUS7310707B2Improve throughput performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRecord information storageSelf adaptiveData store
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
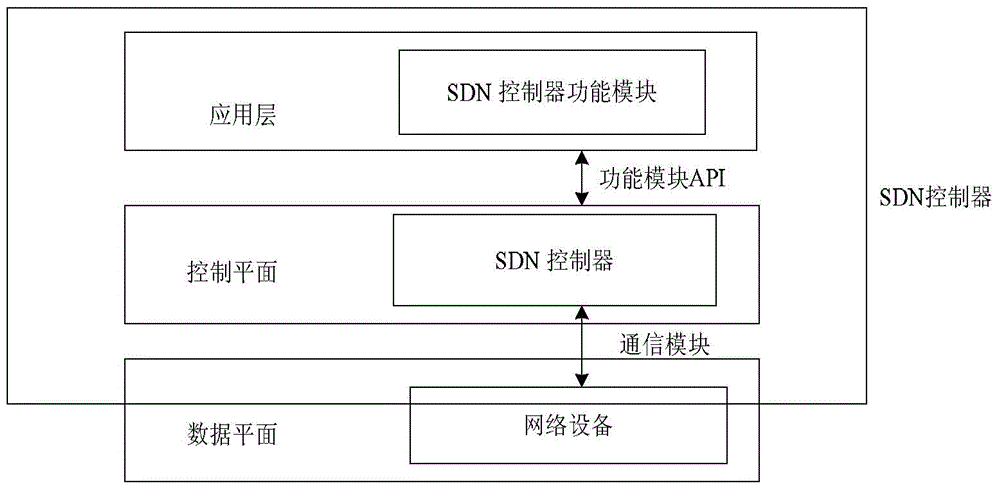
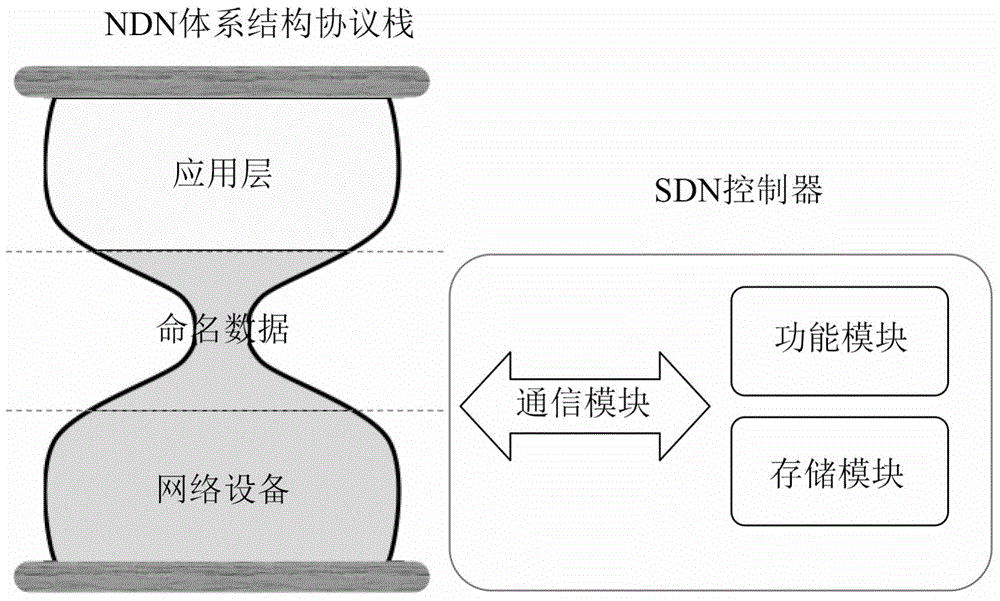
Software defined network controller system in named data networking and method thereof
ActiveCN104104614AImprove throughput performanceFlexible Control StrategyData switching networksSoftware-defined networkingRouting control plane
The invention discloses a software defined network controller system in named data networking and a method thereof. A control plane and a data plane of the named data networking are separated by the system. The software defined network controller system comprises a storage module which is used for storing the data plane and maintaining four data structures of the data plane including a topological structure, a rule table, a push table and a routing table, wherein the control plane utilizes the data structures to control forwarding of data flow in the named data networking; a communication module which utilizes a customized communication format to establish connection between a software defined network controller of the control plane and network equipment of the data plane, maintain connection and receive and process data flow transmitted by the named data networking; and a function module API which is used for packaging functions of the storage module and is utilized to operate the storage module by an application layer so that direction of data flow is controlled.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECHNOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Encapsulating packets into a frame for a network
ActiveUS20050063402A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedReduce in quantityData switching by path configurationReal-time computingNetwork packet
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method for determining transmission block size in high speed downlink grouping switch-in business
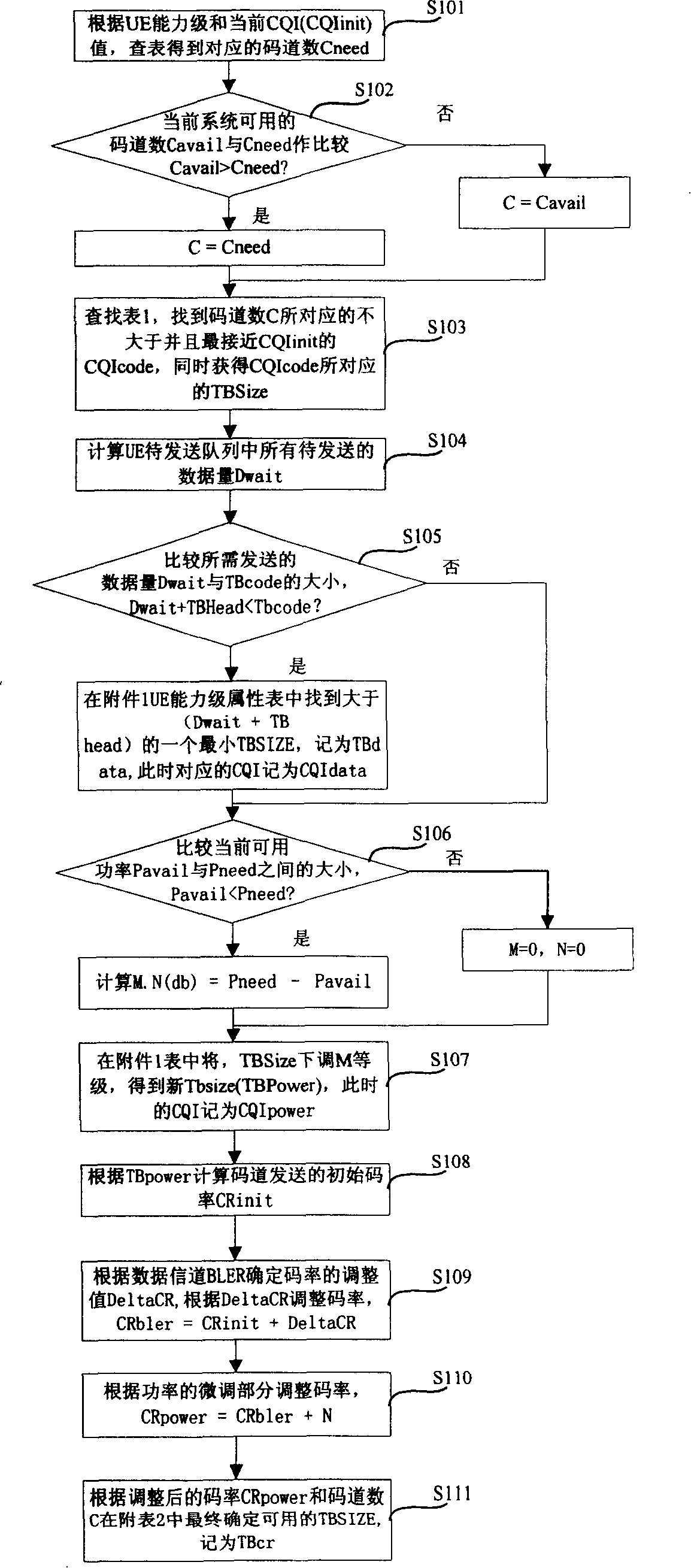
InactiveCN101207553AAchieve fine tuningImprove throughput performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationSize valueThroughput
The invention provides a method which can determine the size of a transmission block in the high speed downlink packet access service, wherein, the method comprises the following steps: the step one, the number of code channels required by the practicality is determined according to the corresponding relation of the wireless channel quality value reported by a user and the usable code channels of the high speed downlink packet access data channel, and the size of the transmission block which is corresponding to the number of the code channels required by the practicality is searched out in a UE capability set attribute table defined by the related protocols; the step two, all data quantities to be sent out in the queue which is to be sent out are calculated and whether the sum of the data quantities and the size value of the transmission block is smaller than the size value of the transmission block which is corresponding to the number of the code channels required by the practicality is judged, if the sum of the data quantities and the size value of the transmission block is smaller than the size value of the transmission block which is corresponding to the number of the code channels required by the practicality, the size of the transmission block is decreased; if the sum of the data quantities and the size value of the transmission block is not smaller than the size value of the transmission block which is corresponding to the number of the code channels required by the practicality, the size of the transmission block is not adjusted, thereby realizing the fine adjustment to the TBsize and achieving the effect to improve the throughput efficiency of the system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for sending hybridautomatic repeat-request acknowledgement (HARQ-ACK) feedback information
InactiveCN103095432AImprove peak throughputSave resourcesError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsComputer science
The invention provides a method for sending hybridautomatic repeat-request acknowledgement (HARQ-ACK) feedback information. According to the method for sending the HARQ-ACK feedback information, present HARQ-ACK feedback information in a binging window is bound, total number of bits is enabled to meet the length demand of an HARQ-ACK feedback information transport format for the HARQ-ACK feedback information, more component carriers (CC) are enabled to be supported to conduct carrier aggregation when 5 is configured by time division duplexing (TDD) uplink and downlink, so that peak throughput of user downlink is improved.
Owner:BEIJING SAMSUNG TELECOM R&D CENT +1
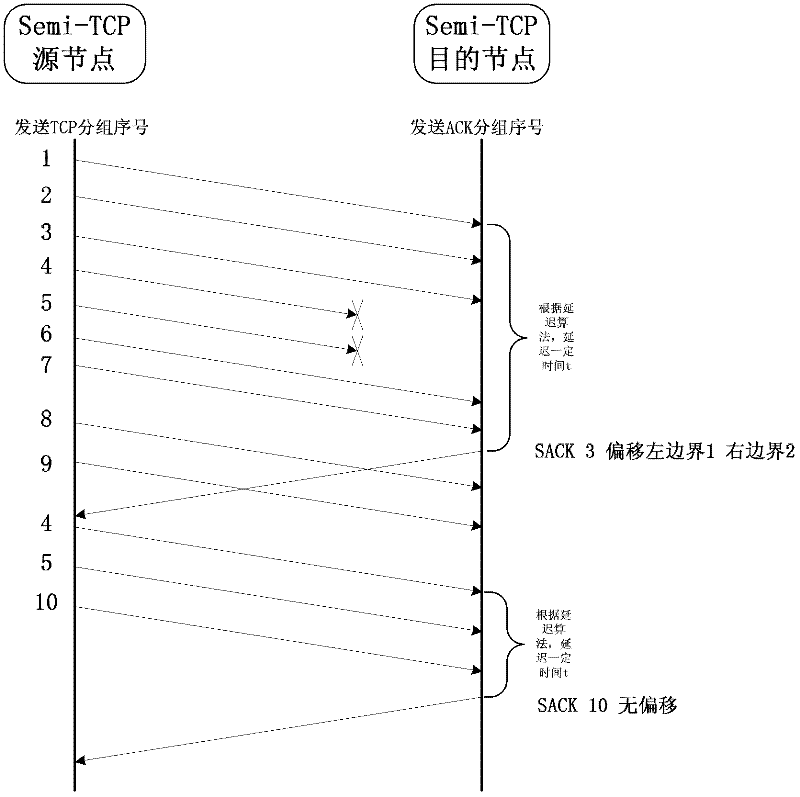
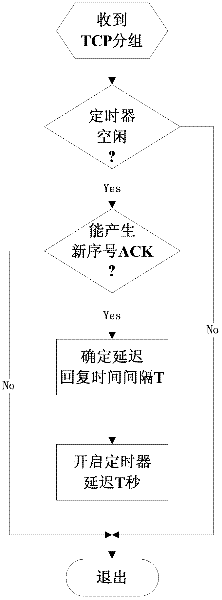
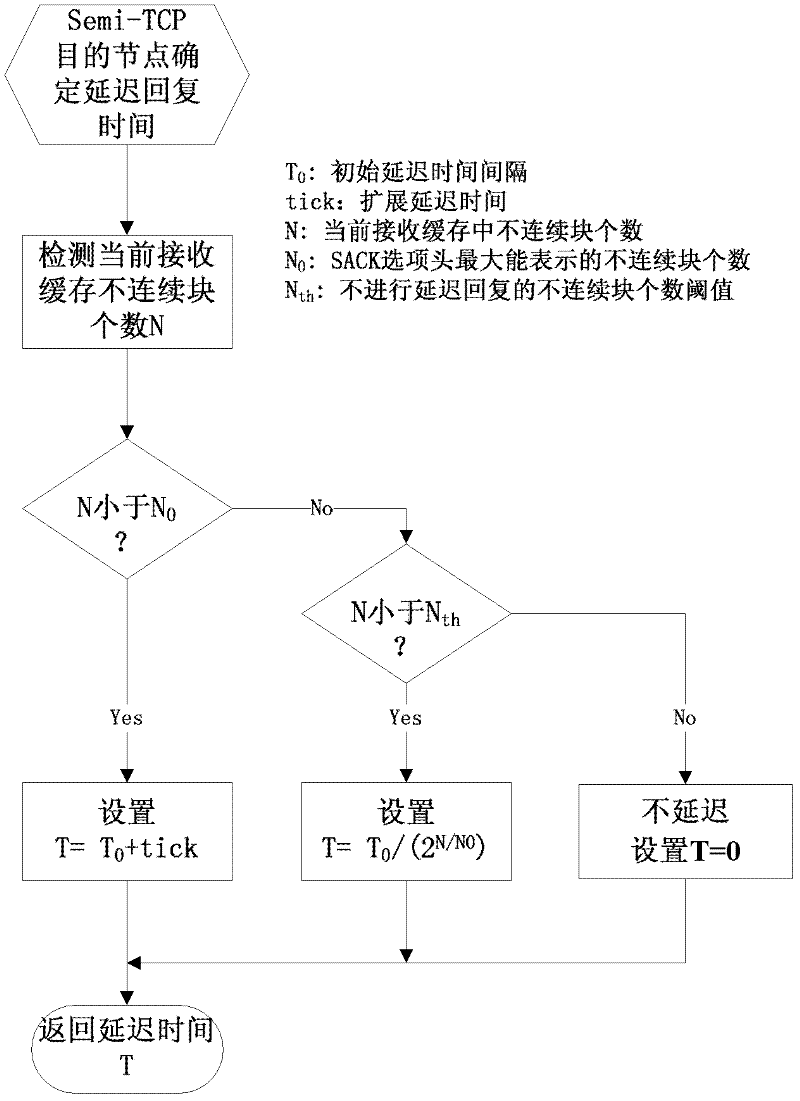
Method for adaptively determining packet delayed sending for Semi-TCP (transmission control protocol)
ActiveCN102413503APlay the role of reliability controlReduce in quantityNetwork traffic/resource managementSelf adaptivePositive data
The invention discloses a method for adaptively determining packet delayed sending for Semi-TCP (transmission control protocol). In the method, after receiving a TCP packet, a destination node using the Semi-TCP adaptively determines the time of sending an acknowledgement packet of a data packet, thus the sending quantity of the ACK (acknowledgement) packet is compressed, the sending of repeated ACK is canceled, and the competition for a wireless channel between a positive data flow and a negative data flow is reduced; and an acknowledgment state is a state described by the following parameters: continuity of packets in a receiving cache of the destination node, the maximum number of block boundaries which can be contained by a selective acknowledgement (SACK) packet head, a set time interval of sending ACK and the like. Meanwhile, in the method, the traditional SACK packet head is improved, and the sequence numbers of discontinuous TCP block boundaries are marked by a relative offset so as to improve the acknowledgment rate of the Semi-TCP source node packet and reduce the overhead resulting from the introduction of SACK.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
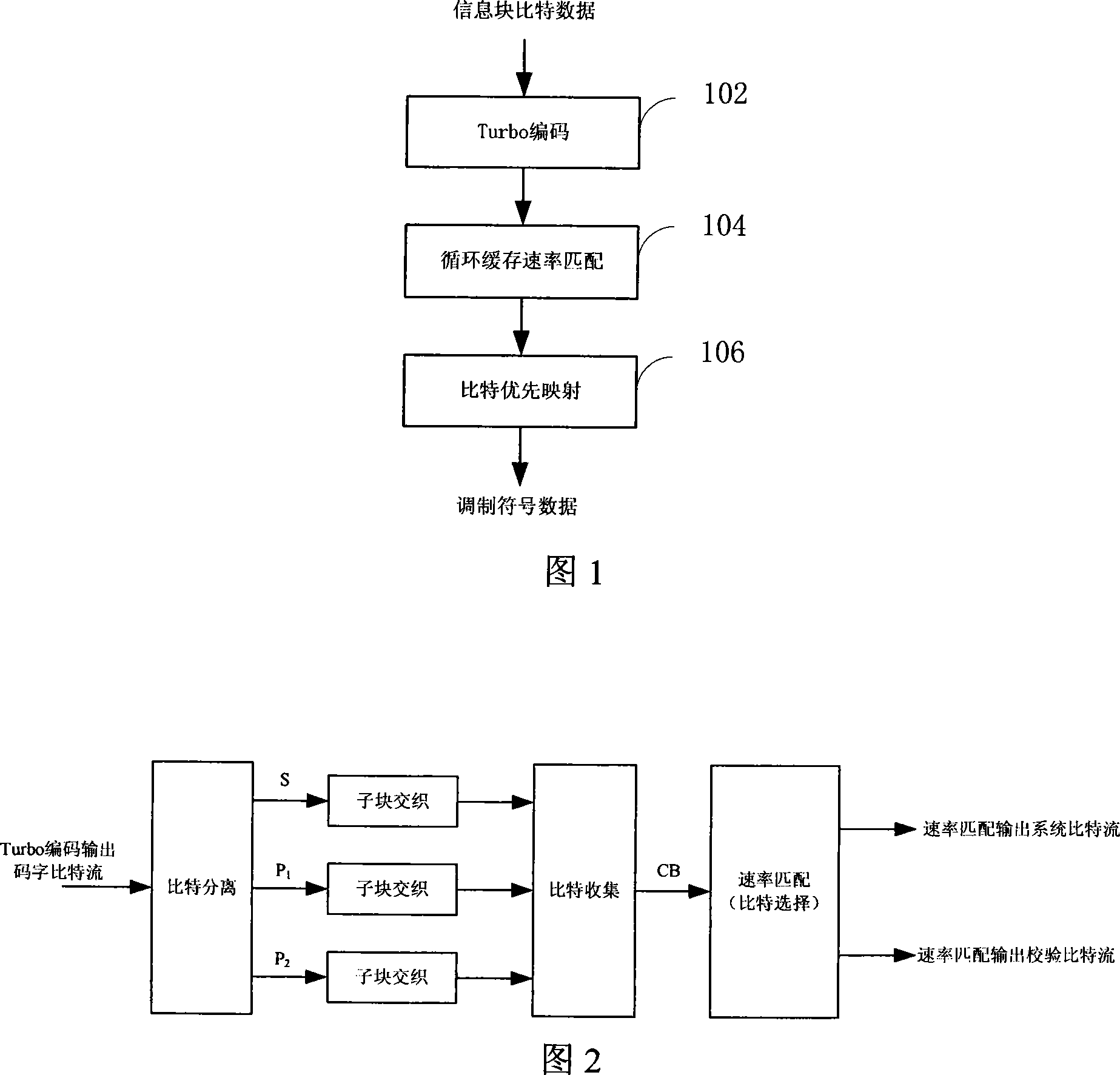
Radio physical layer channel code chain processing method
ActiveCN101090305AImprove throughput performanceImprove protectionError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionChannel codeComputer hardware
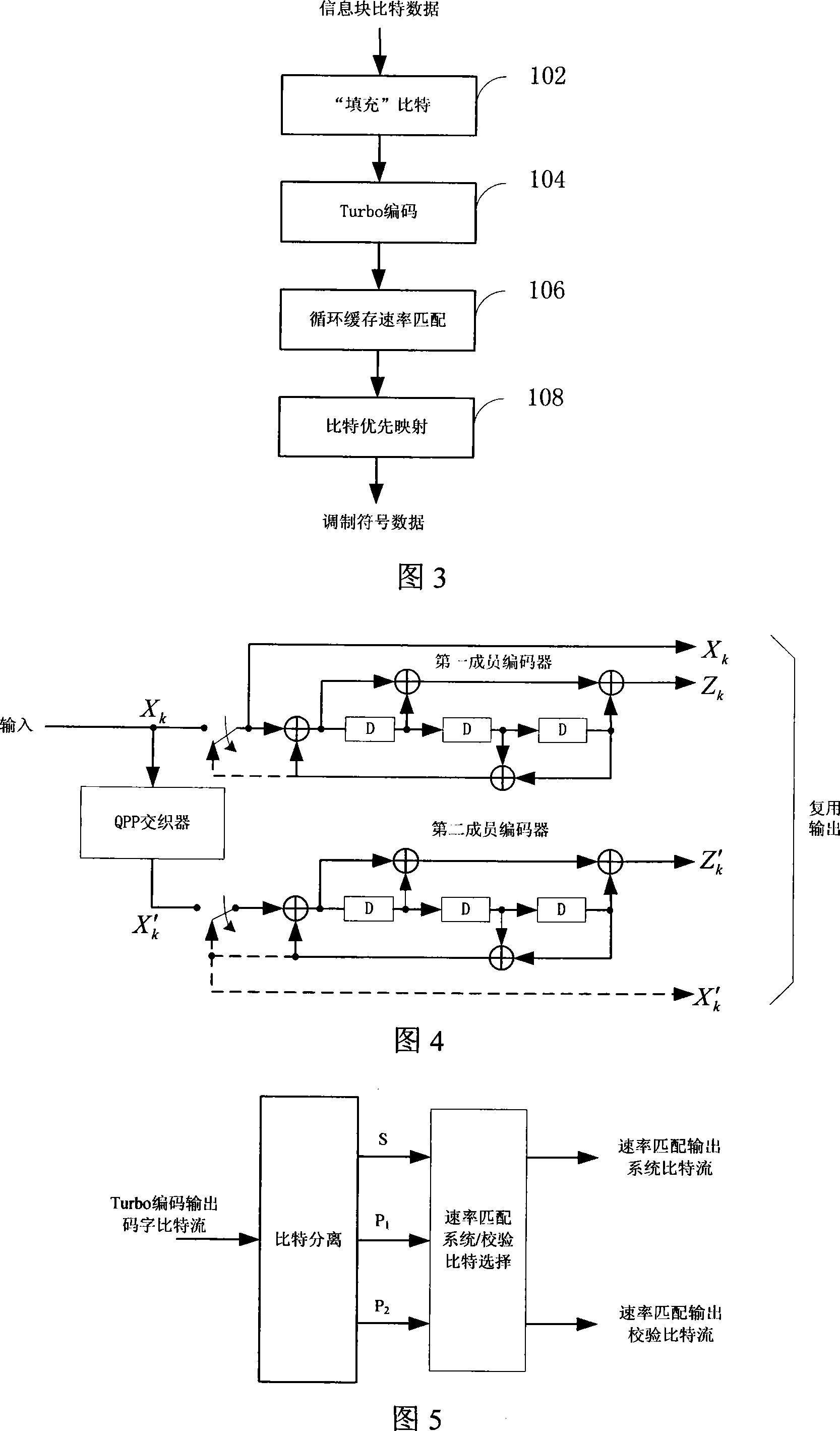
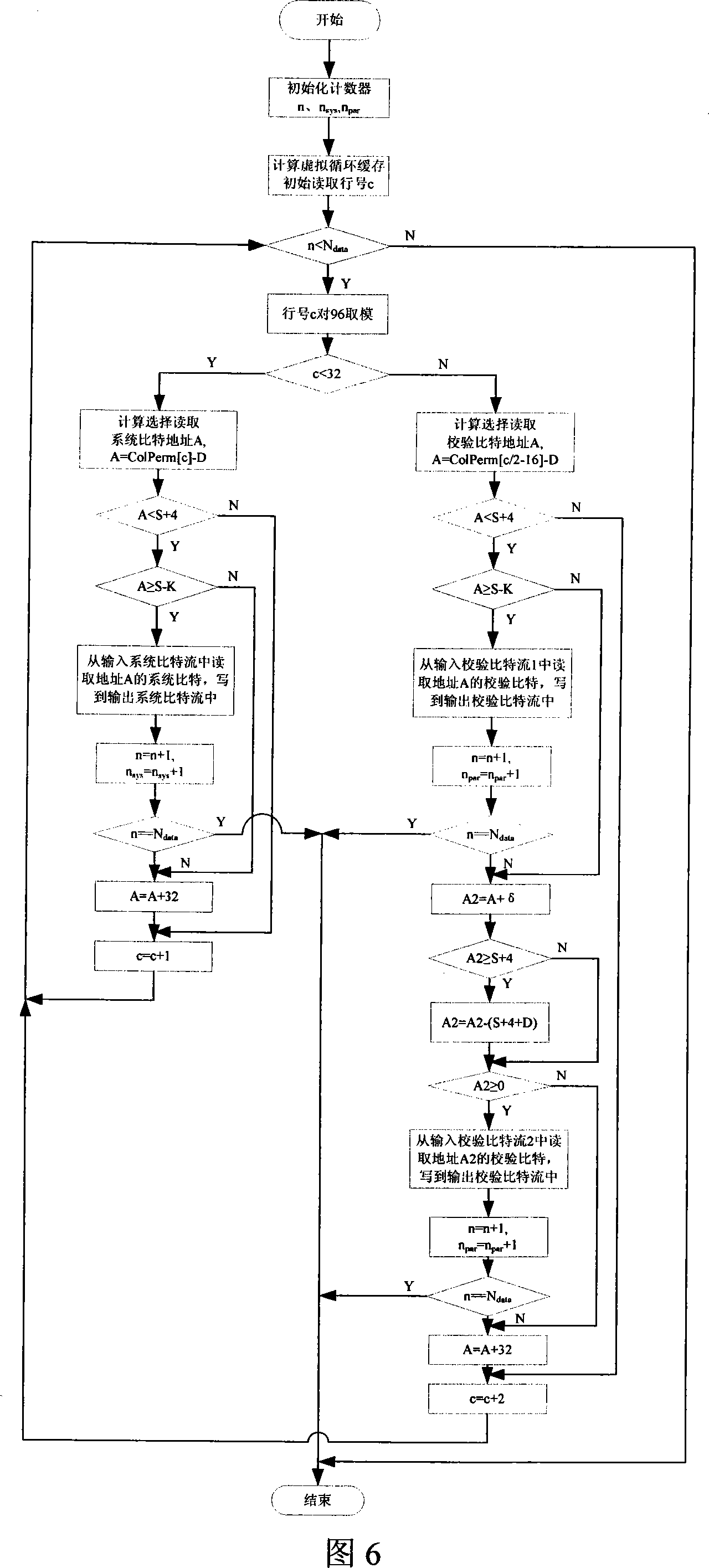
This invention relates to a channel coding link process method of wireless physical layer including: carrying out Turbo coding to information block bit data, carrying out rate match to the Turbo coded code bit based on circulation buffer storage, and bit priority mapping modulation to the system bit stream and verified bit stream.
Owner:ZTE CORP
High throughput WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) Mesh network rate selection method
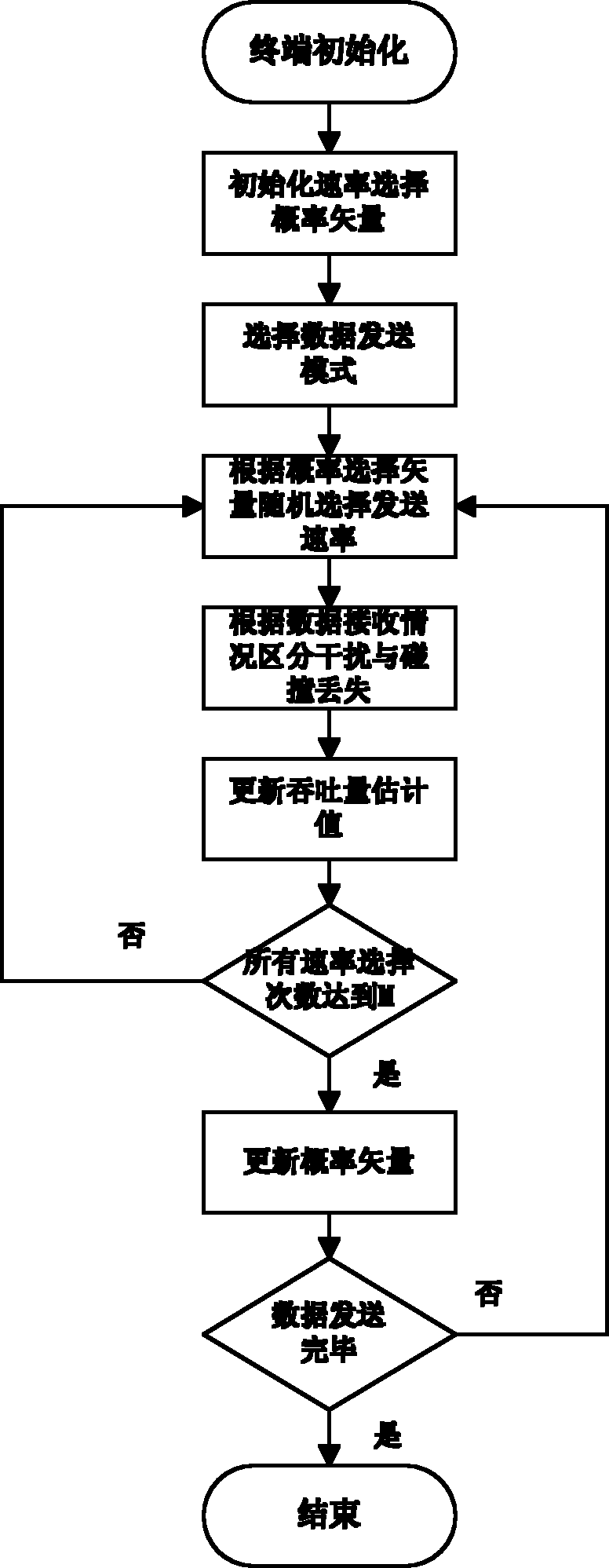
InactiveCN101925134AEfficiently Distinguishing Collision MissingEffectively distinguish interferenceNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesClear to sendPhysical layer
The invention relates to a high throughput WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) Mesh network rate selection method. A terminal firstly distinguishes impact loss from noise jamming loss according to a selected data sending mode; the loss is distinguished by adding negative frame NACK (Negative Acknowledgement) for a basic access mode, and the loss is distinguished by the sending and receiving conditions of an acknowledgement frame ACK and a clear-to-send frame CTS for an RTS / CTS (Request To Send / Clear To Send) mode. The accurate estimation of channel state is realized on the basis of self learning of local information of a local MAC (Media Access Control) layer acknowledgement frame to instruct the selection of the rate of a physical layer. The terminal utilizes the maximum system throughput as a target function by maintaining a rate selection probability vector. When each rate in the system is selected for certain times, the terminal starts to update the probability vector so as to ensure the astringency and the stability of the rate selection algorithm, and then, the terminal selects any one rate for data transmission with the probability in the probability vector.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Methods and Nodes in a Wireless Communication Network
InactiveUS20140348120A1Improve performanceMaximize throughputSpatial transmit diversityChannel estimationTelecommunicationsRadio networks
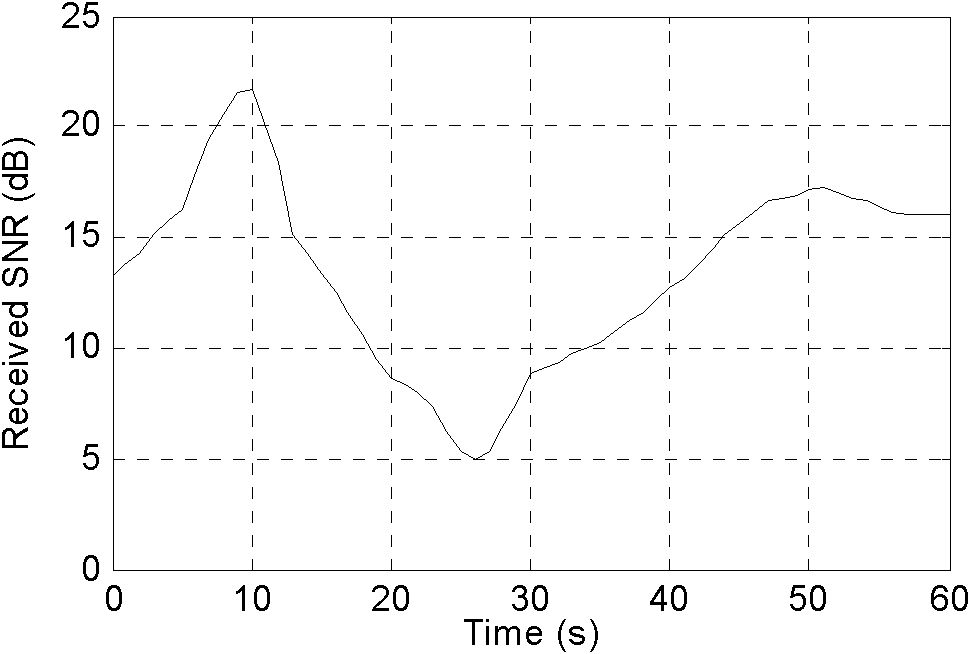
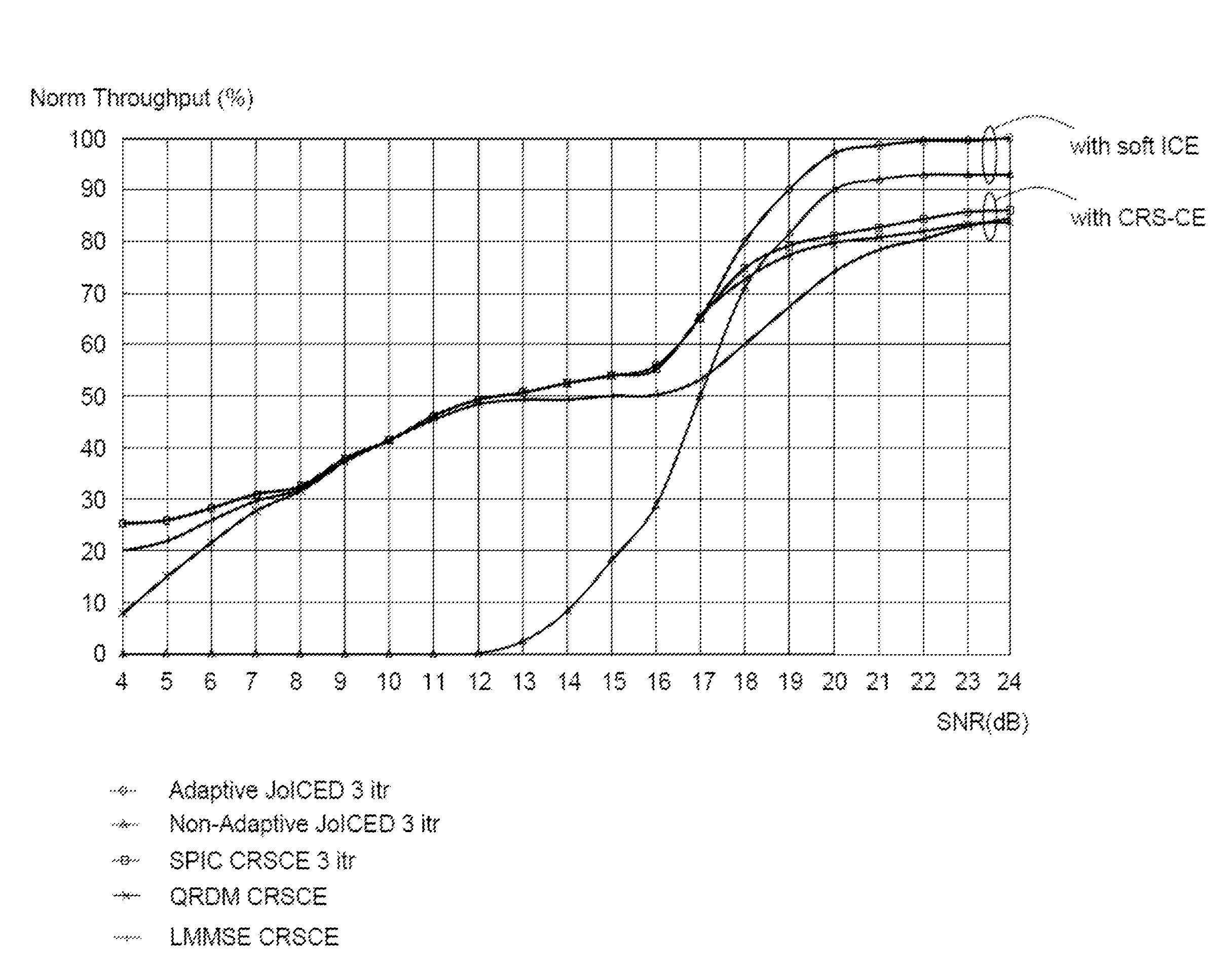
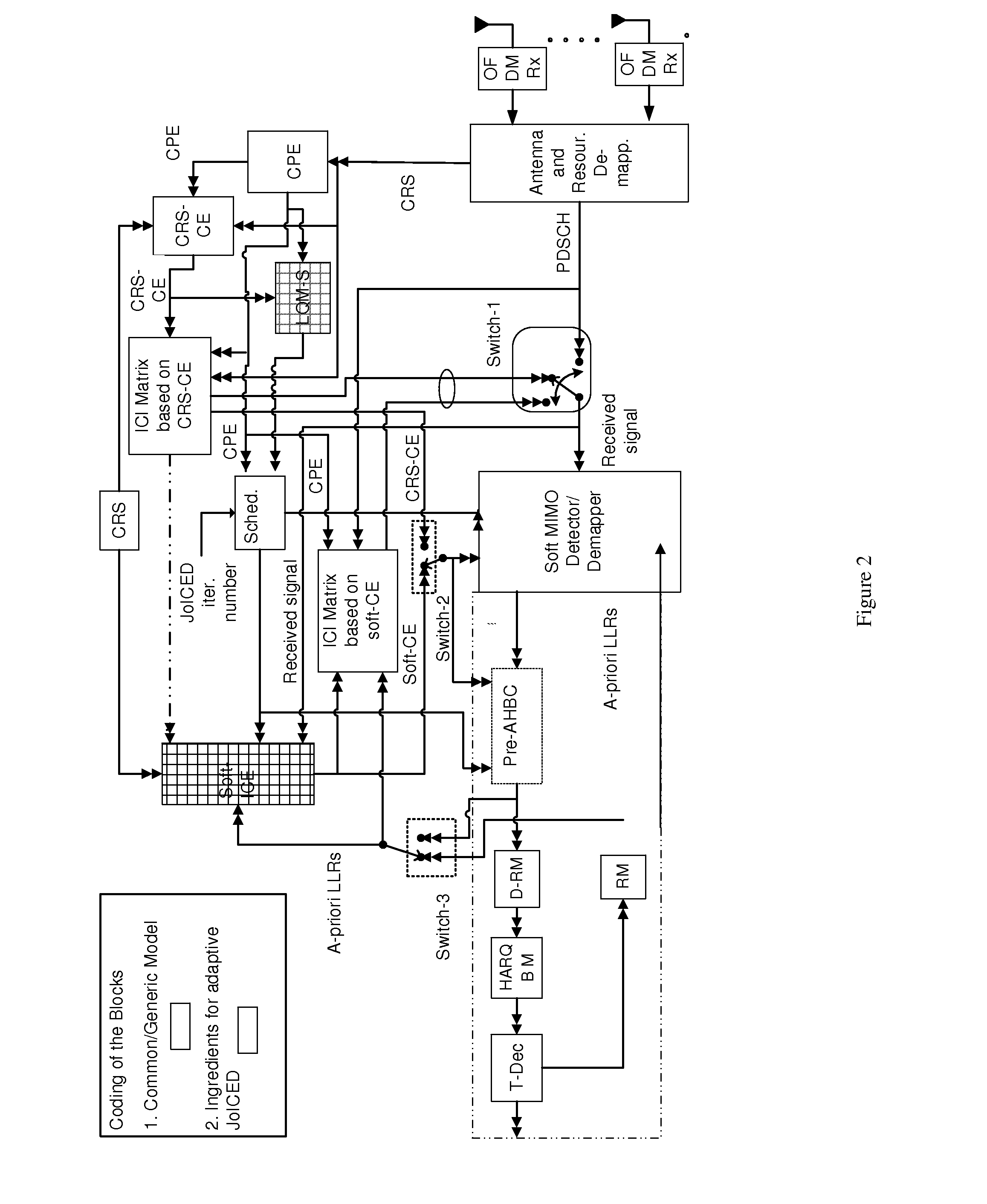
Receiver and method in a receiver, for iterative channel estimation and data decoding of signals received from a radio network node, located in a wireless communication network. The method comprises detecting a signal of the radio network node, performing channel estimation of the detected signal, based on iterative application of a Space Alternating Generalised Expectation and maximisation, SAGE, algorithm, determining a channel / link quality, based on the performed channel estimation and the estimated channel parameters, selecting Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output, MIMO, detector, based on the determined channel quality, determining to enable and / or disable, respectively, soft-Iterative Channel Estimation, soft-ICE, based on the determined channel quality, and iterating the performed channel estimation for a predetermined number of times.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Data processor and graphic data processing device
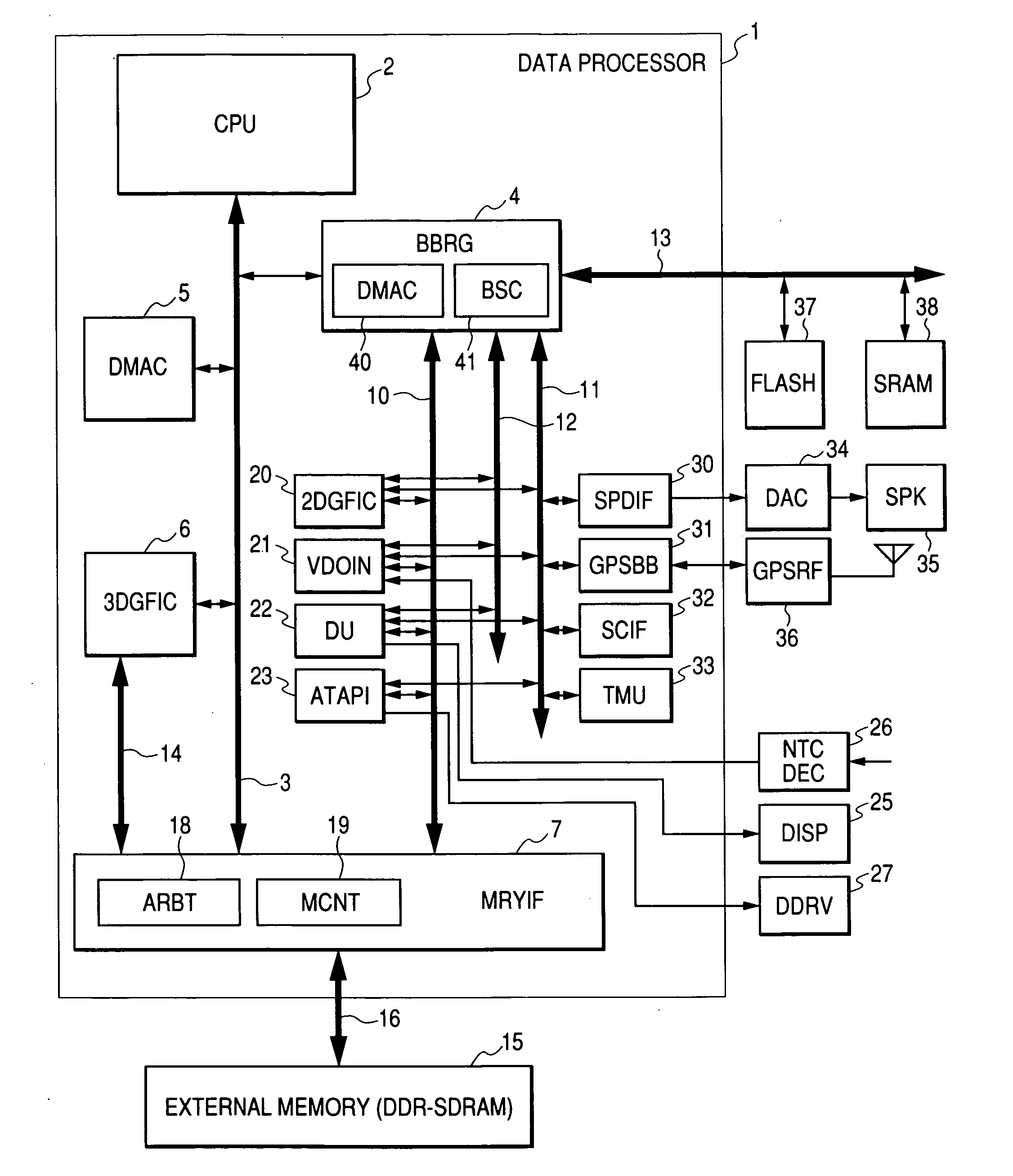
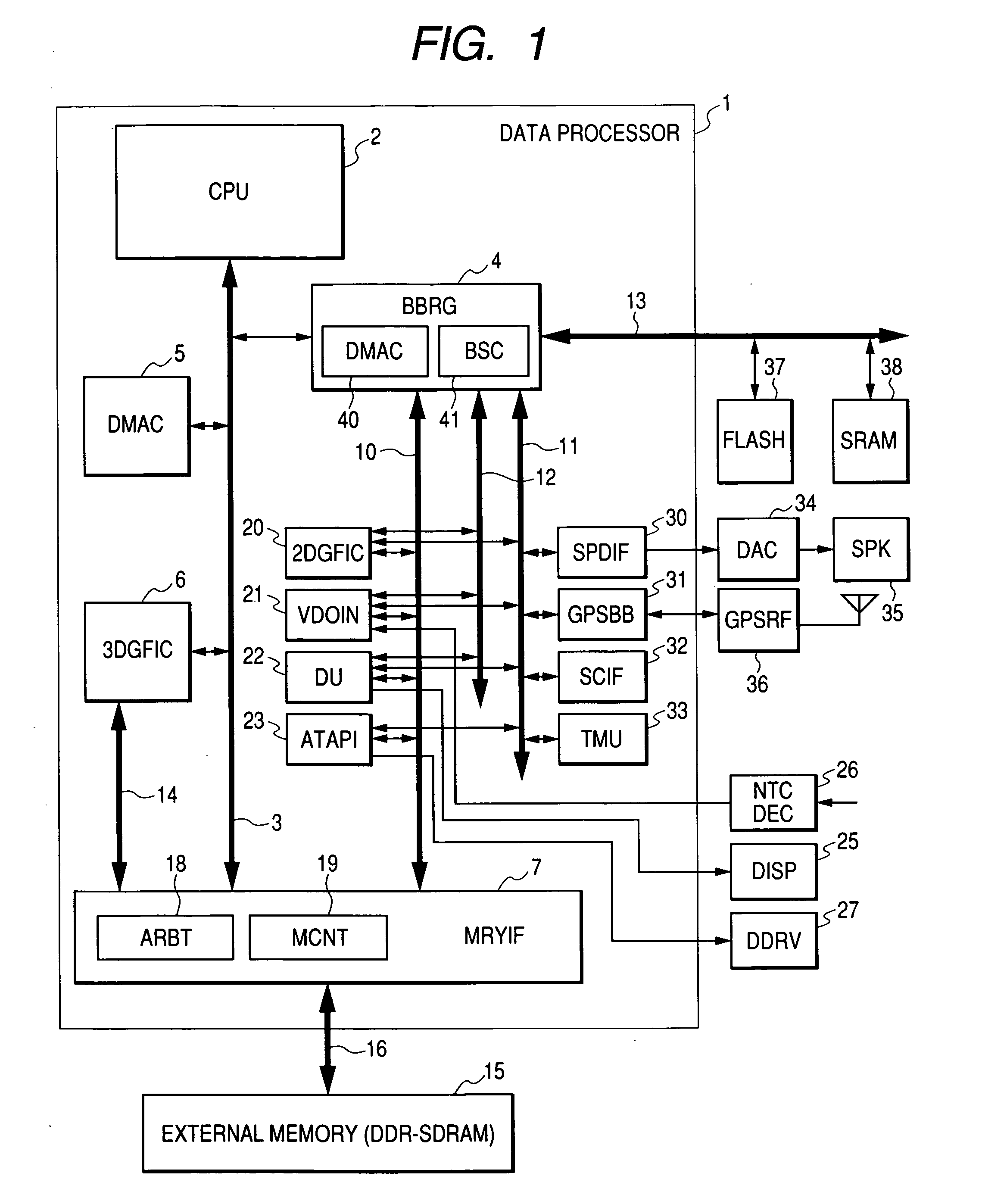
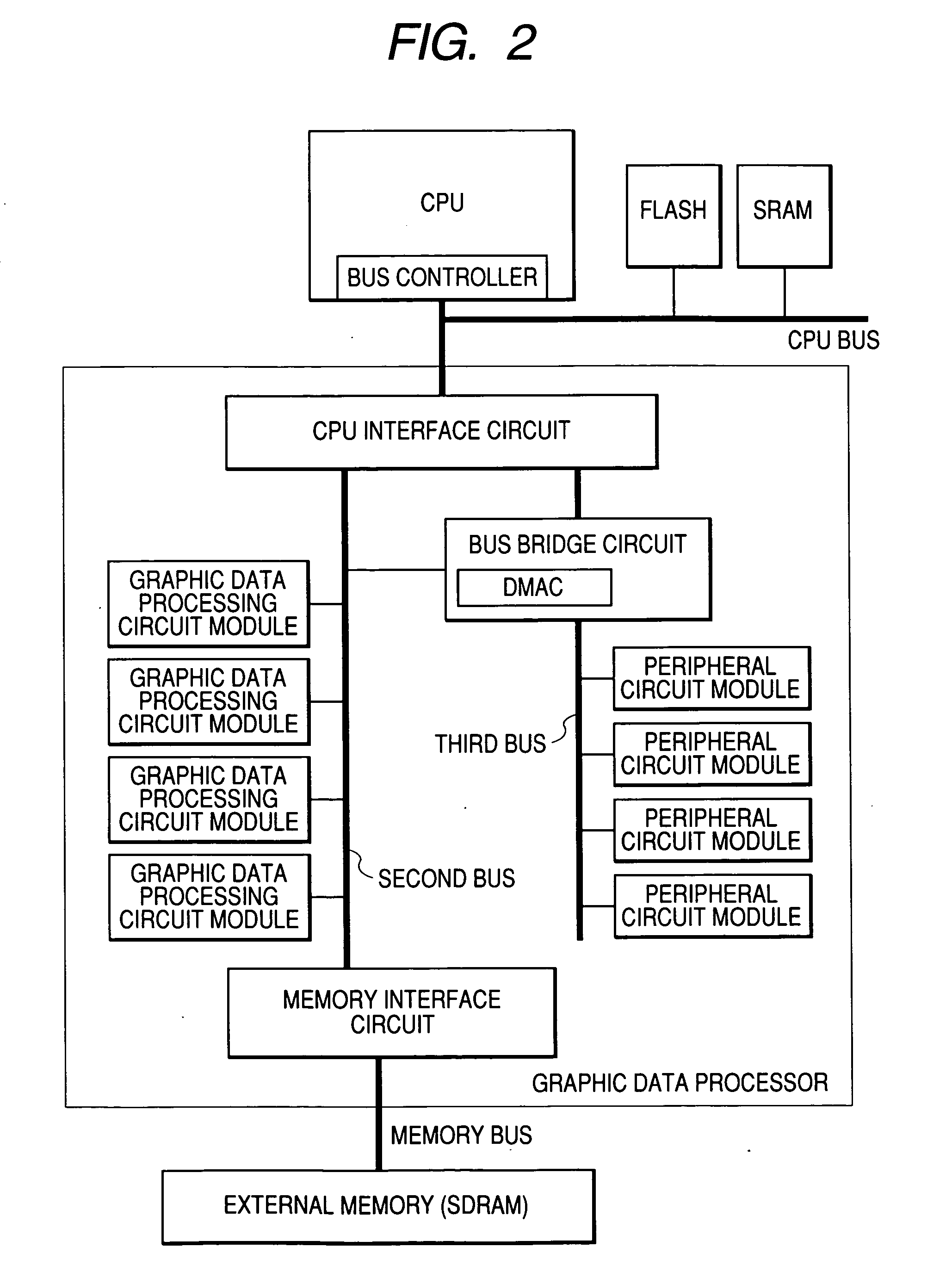
ActiveUS20050030311A1Improve data processing speedData transfer speed is fastDrawing from basic elementsProcessor architectures/configurationDirect memory accessExternal storage
An object of the present invention is to improve efficiency of transfer of control information, graphic data, and the like for drawing and display control in a graphic data processor. A graphic data processor includes: a CPU; a first bus coupled to the CPU; a DMAC for controlling a data transfer using the first bus; a bus bridge circuit for transmitting / receiving data to / from the first bus; a three-dimensional graphics module for receiving a command from the CPU via the first bus and performing a three-dimensional graphic process; a second bus coupled to the bus bridge circuit and a plurality of first circuit modules; a third bus coupled to the bus bridge circuit and second circuit modules; and a memory interface circuit coupled to the first and second buses and the three-dimensional graphic module and connectable to an external memory, wherein the bus bridge circuit can control a direct memory access transfer between an external circuit and the second bus.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com