Patents
Literature
672 results about "Turbo coded" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
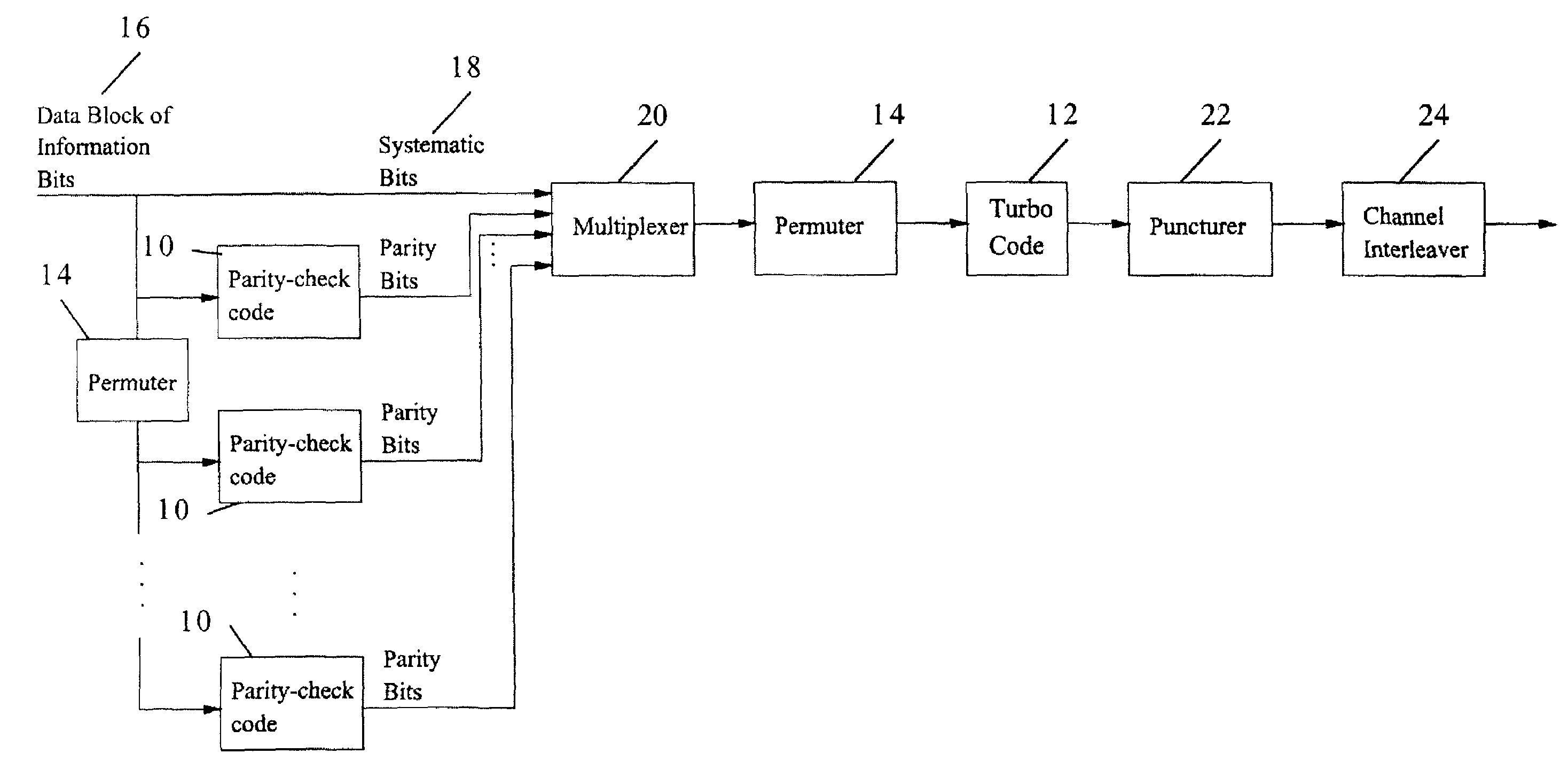
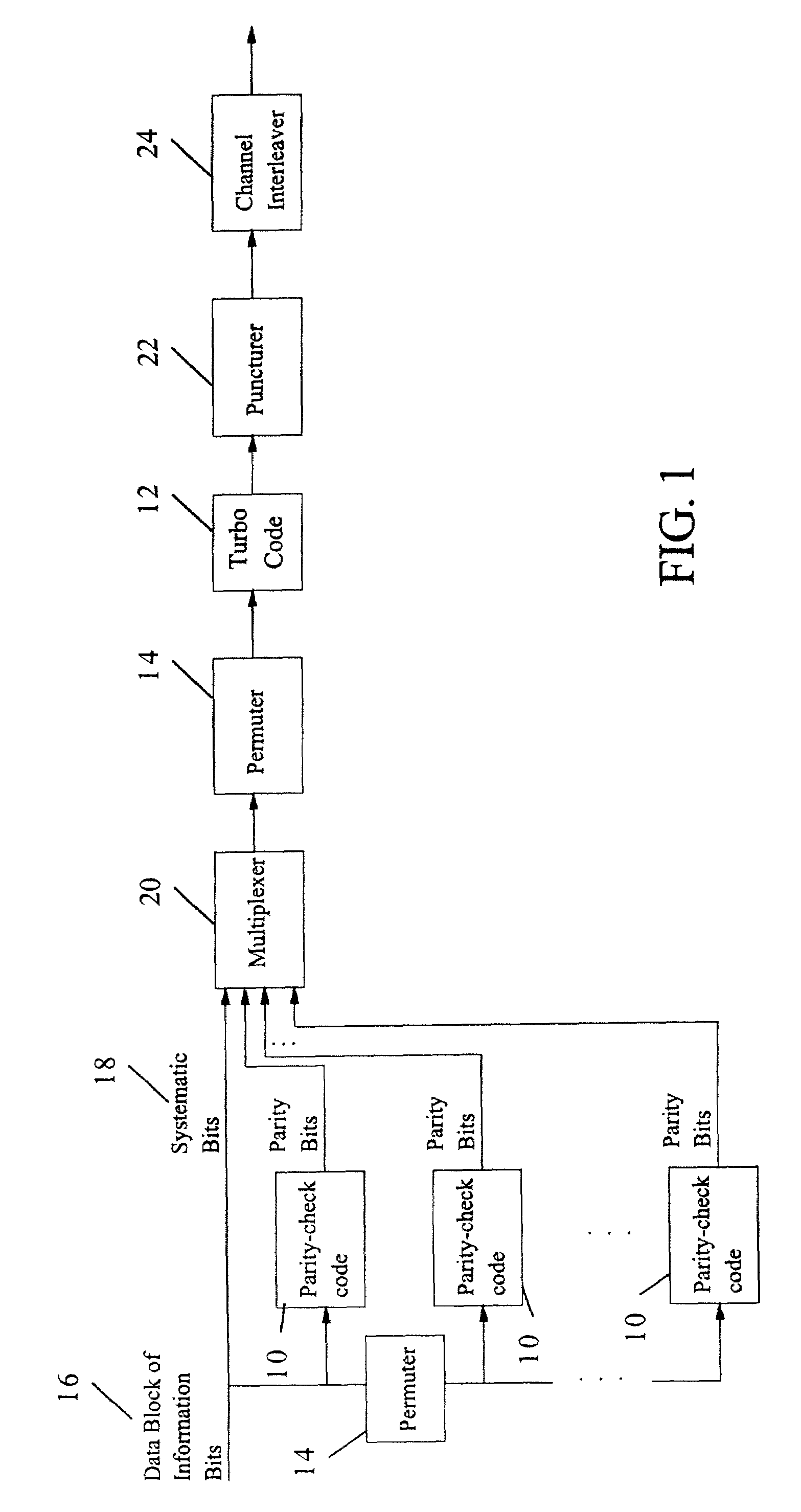
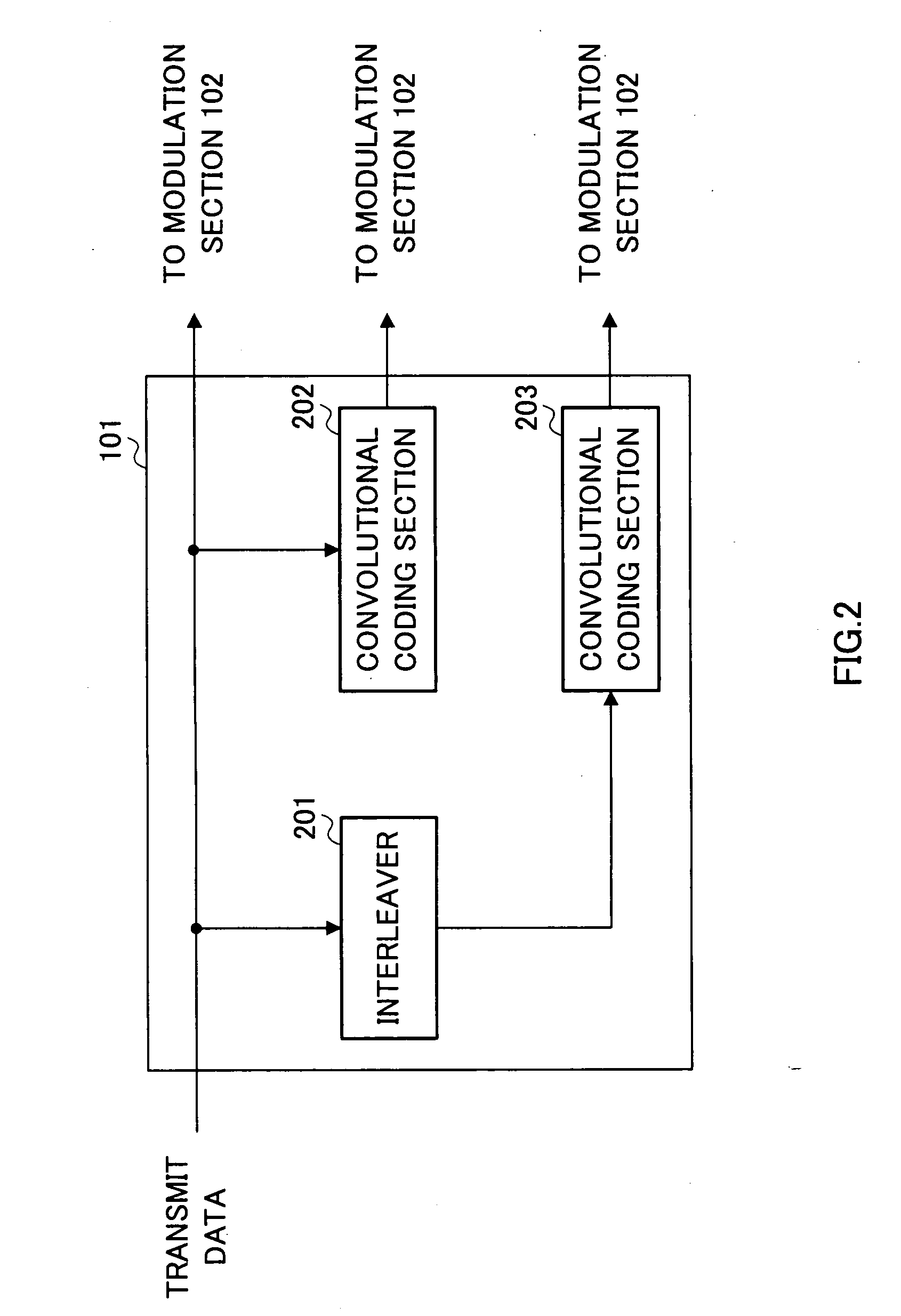
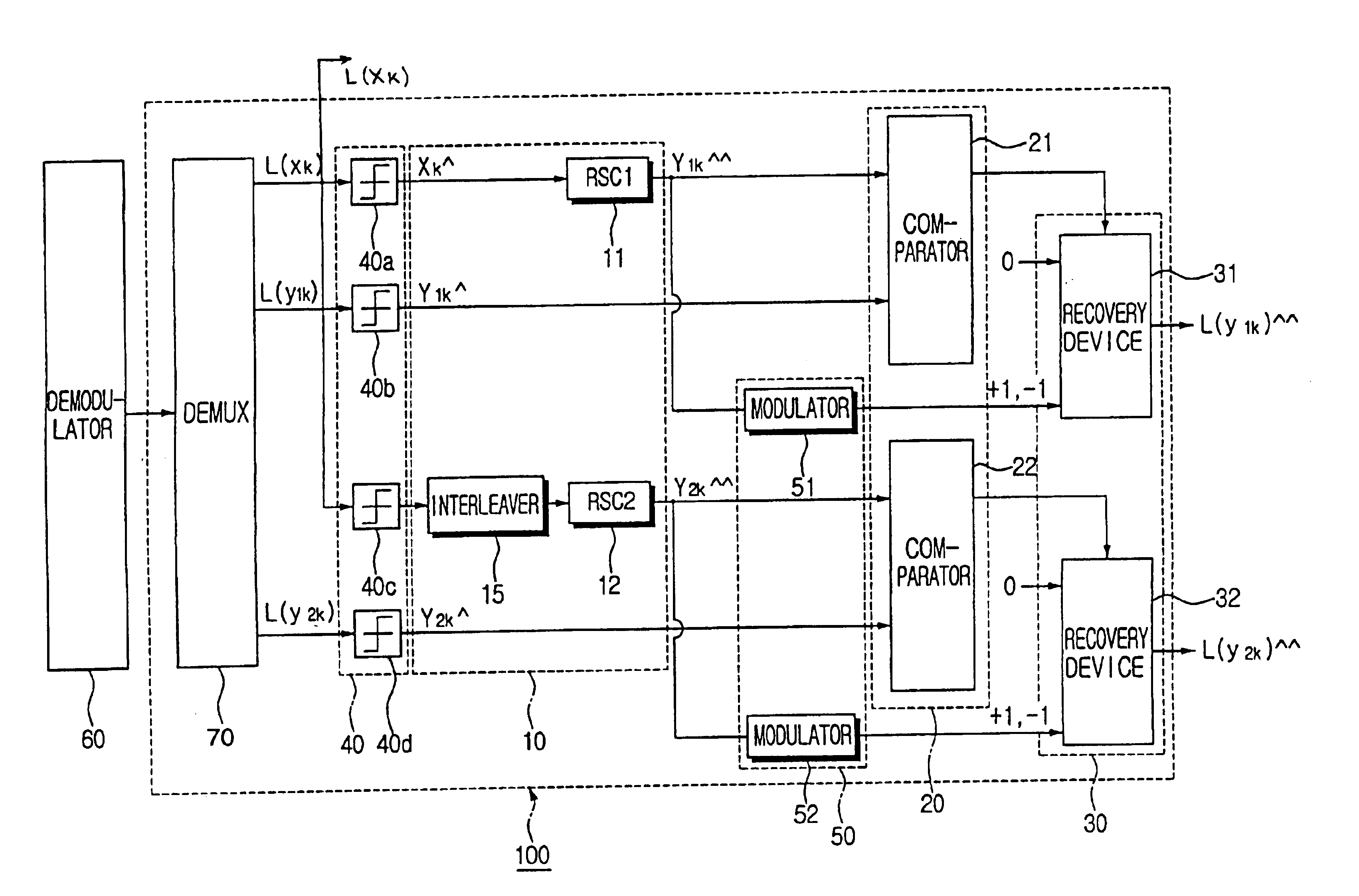
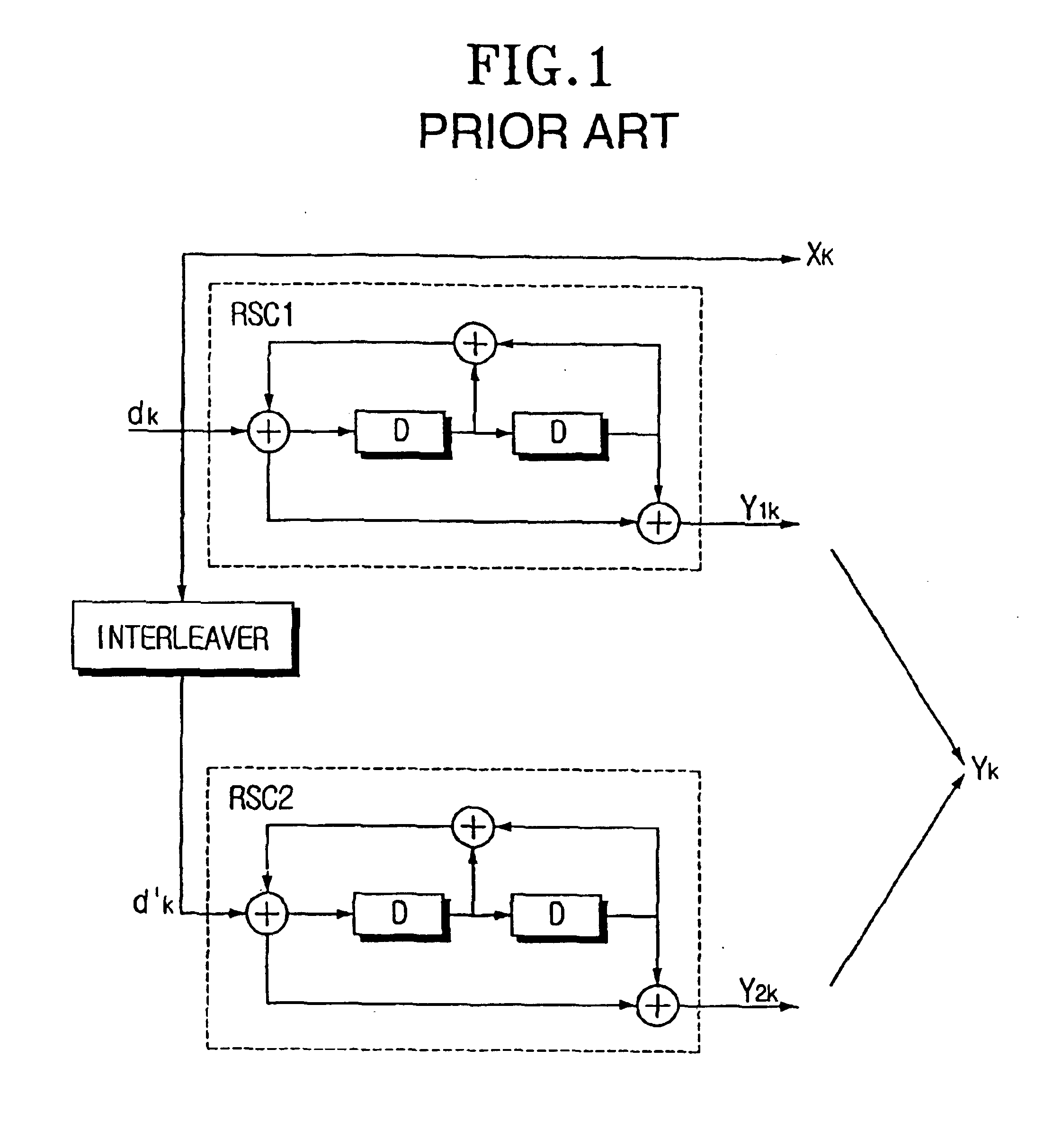
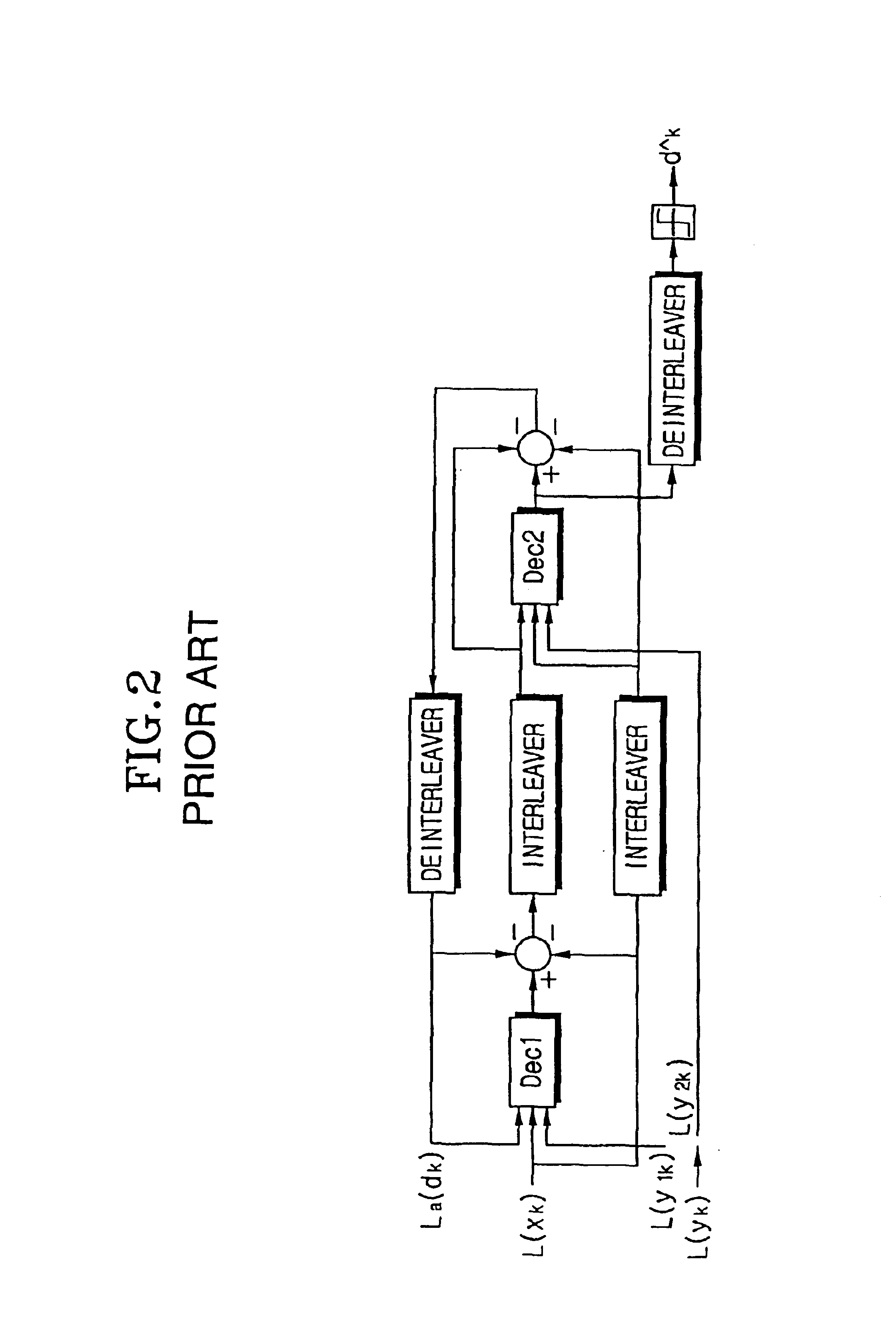
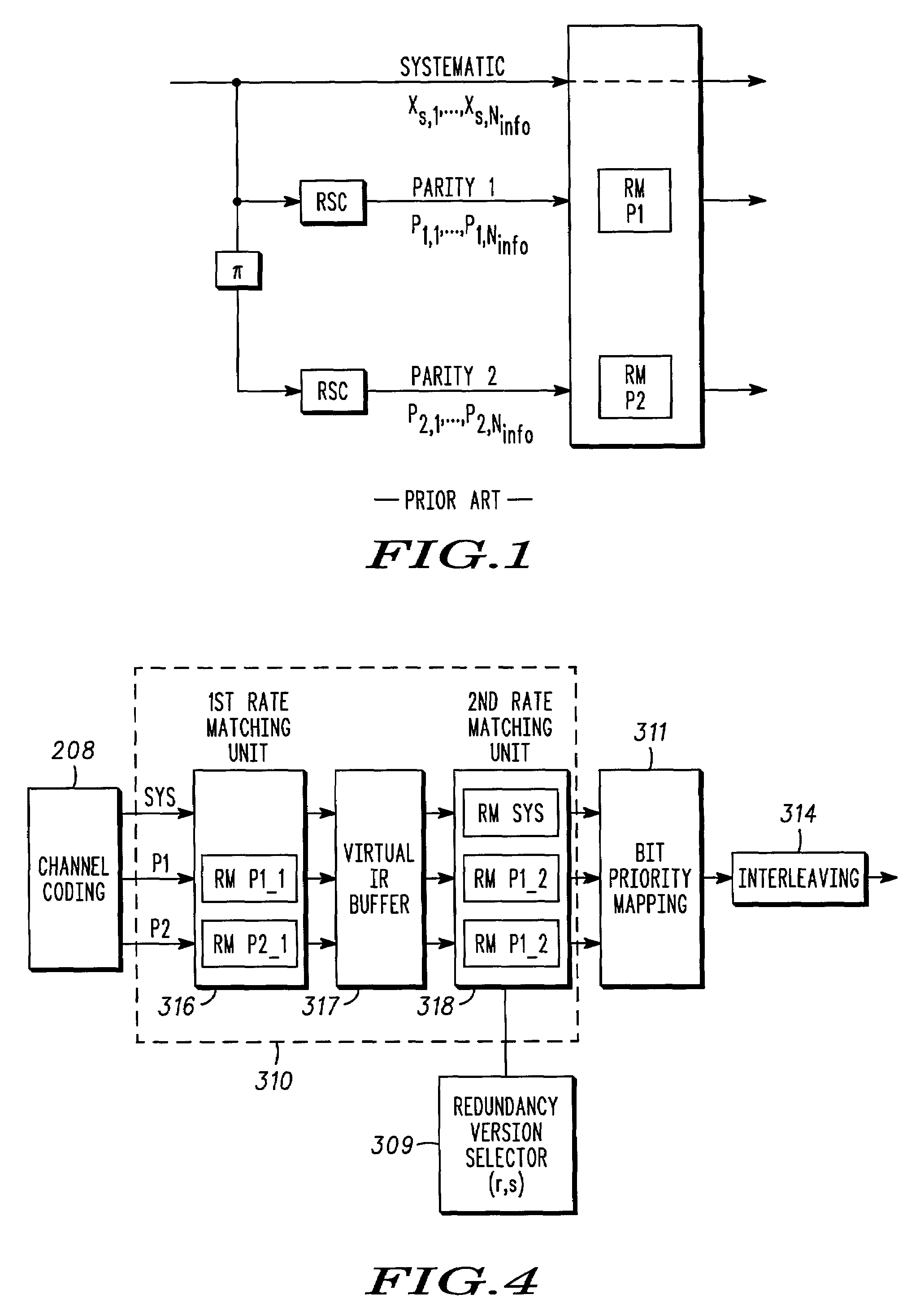
Method and coding means for error-correction utilizing concatenated parity and turbo codes
InactiveUS7093179B2Reduction in rateImprove overall utilizationError preventionError detection/correctionParallel computingTurbo coded
A method and apparatus for encoding and decoding data using an overall code comprising an outer parity-check and an inner parallel concatenated convolutional, or turbo code. The overall code provides error probabilities that are significantly lower than can be achieved by using turbo codes alone. The output of the inner code can be punctured to maintain the same turbo code rate as the turbo code encoding without the outer code. Multiple parity-check codes can be concatanated either serially or in parallel as outer codes. Decoding can be performed with iterative a posteriori probability (APP) decoders or with other decoders, depending on the requirements of the system. The parity-check code can be applied to a subset of the bits to achieve unequal error protection. Moreover, the techniques presented can be mapped to higher order modulation schemes to achieve improved power and bandwidth efficiency.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
Polarization code decoding method for cyclic redundancy check assistance
InactiveCN102694625AStrong error correction abilityReduce operational complexityError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesCommunications systemCode division multiple access
The invention relates to a polarization code decoding method for cyclic redundancy check assistance. When a polarization code is decoded, in all the routes with cyclic redundancy check values of corresponding bit estimation sequences of being zero from a root node to leaf nodes on a code tree corresponding to the polarization code, one route with maximum reliability metric value is searched by taking a list or stack as assistance for route search, and the bit estimation sequence corresponding to the route is output as a decoding result. The method comprises the following operation steps of: determining parameters according to a search assistance method, constructing an auxiliary structure of the decoding method, searching a candidate bit estimation sequence and executing cyclic redundancy check. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, error correcting capability of a communication system which adopts the polarization code as channel coding is greatly improved, operation steps are simpler, and operation complexity is equivalent to or even lower than that of a Turbo code coding and decoding method used in a WCDMA (wideband code division multiple access) system, thus the method disclosed by the invention has a good practical prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
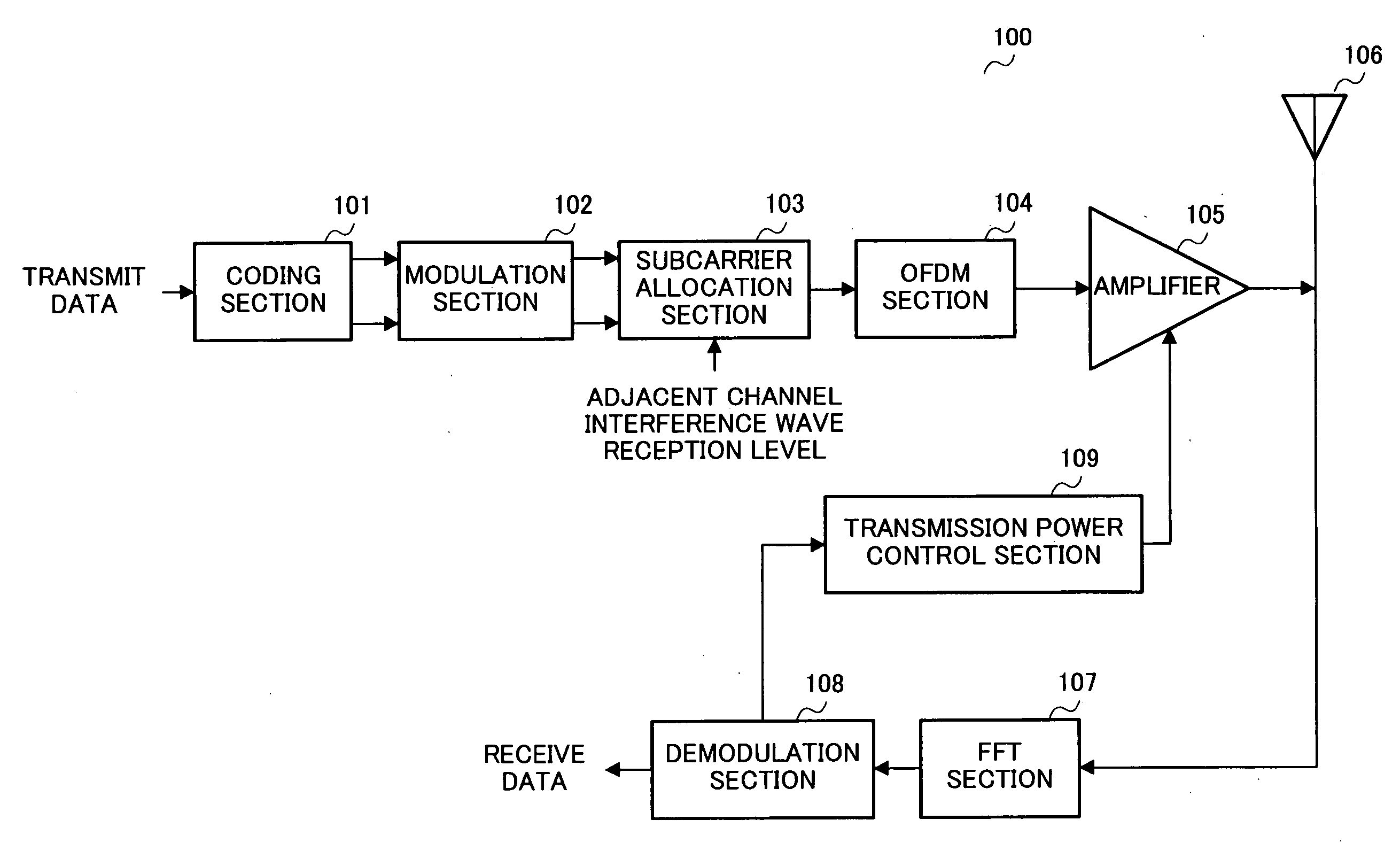
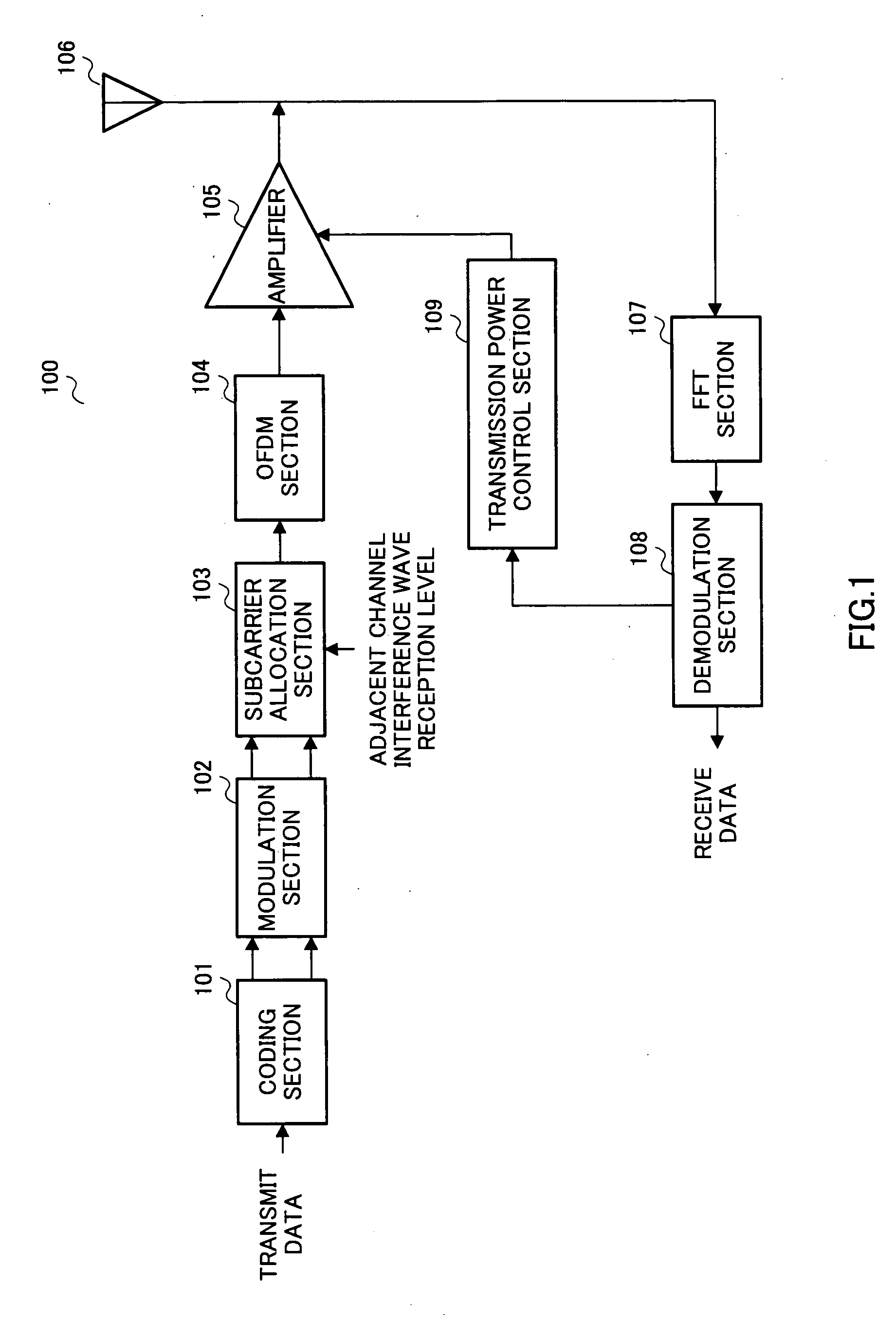
Multi-carrier transmitting apparatus and multi-carrier transmitting method
ActiveUS20060160498A1Prevent degradationImprove significantly the error rate characteristics of transmit dataOther decoding techniquesTransmission path divisionCarrier signalTurbo coded
A coding section 101 turbo-codes transmit data and outputs parity bit data, and systematic bit data for which good quality is required. A modulation section 102 modulates the parity bit data and systematic bit data. A subcarrier allocation section 103 rearranges the transmit data so that systematic bit data is allocated to subcarriers in the vicinity of the center frequency and parity bit data is allocated to subcarriers in the vicinity of both ends. An OFDM section 104 performs orthogonal frequency division multiplexing of the transmit data, and allocates parity bit data and systematic bit data to respective subcarriers. By this means, it is possible to improve significantly the error rate characteristics of transmit data for which good quality is required, and prevent degradation of the quality of transmit data for which good quality is required.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Random-access multi-directional CDMA2000 turbo code interleaver
InactiveUS6871303B2Fuselage framesData representation error detection/correctionControl signalParallel computing
An interleaver that implements the LCS turbo interleaver algorithm utilized by the CDMA2000 standard is described. The interleaver includes a first computation unit for receiving an input address and computing a first sequential interleaved address during a first clock cycle in response thereto. A second computation unit is included for receiving an input address and computing a second sequential interleaved address during the first clock cycle in response thereto. The interleaver further includes a comparator for determining whether the first or the second sequential interleaved address is invalid and generating a signal in response thereto. The output of the comparator provides a control signal to a switch which selects the first or the second sequential interleaved address as an output interleaved address for the first clock cycle. The interleaver is further designed to move in a forward direction or a reverse direction.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Apparatus and method for generating and decoding forward error correction codes having variable rate in a high-rate wireless data communication system
ActiveUS20050160347A1Data representation error detection/correctionError preventionComputer hardwareCommunications system
An apparatus for generating Quasi-Complementary Duo-Binary Turbo Codes (QC-DBTC). The apparatus includes a QC-DBTC encoder which receives an information symbol stream and generates a plurality of systematic symbol streams and a plurality of parity symbol streams according to a given code rate. The apparatus further includes a quad-symbol mapper which quad-maps the systematic symbol streams to one symbol stream, a channel interleaver which independently interleaves the quad-mapped systematic symbol stream and the parity symbol streams, quad-demaps the quad-mapped systematic symbol stream, interlaces symbols in parity symbol streams, and serial-concatenates the quad-demapped systematic symbol stream to the interlaced parity symbol streams. A duo-binary turbo code generator is further provided to repeat the serial-concatenated symbol stream, and select a predetermined number of symbols from the repeated symbol stream according to a code rate and selection information, thereby generating QC-DBTC codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
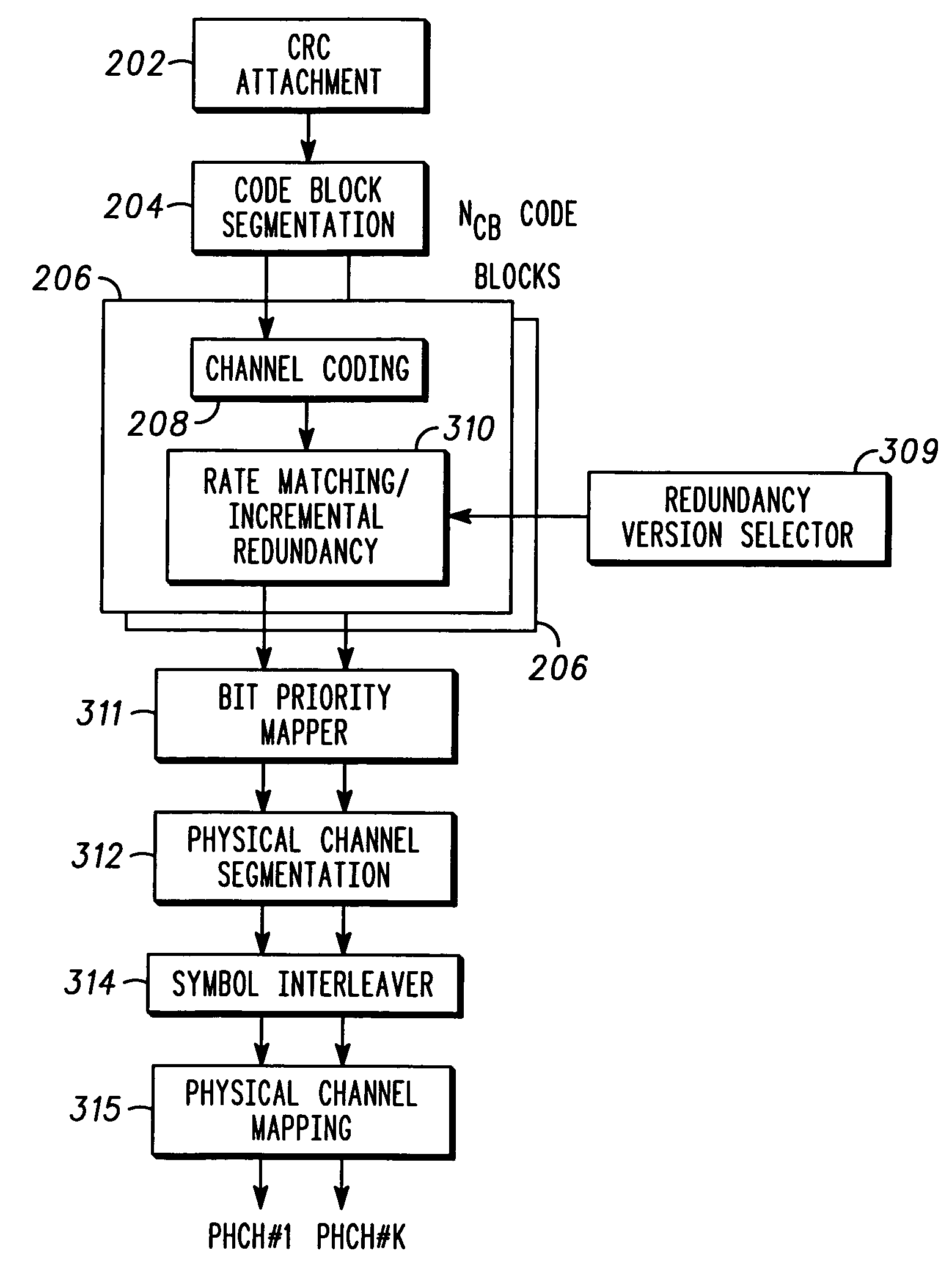
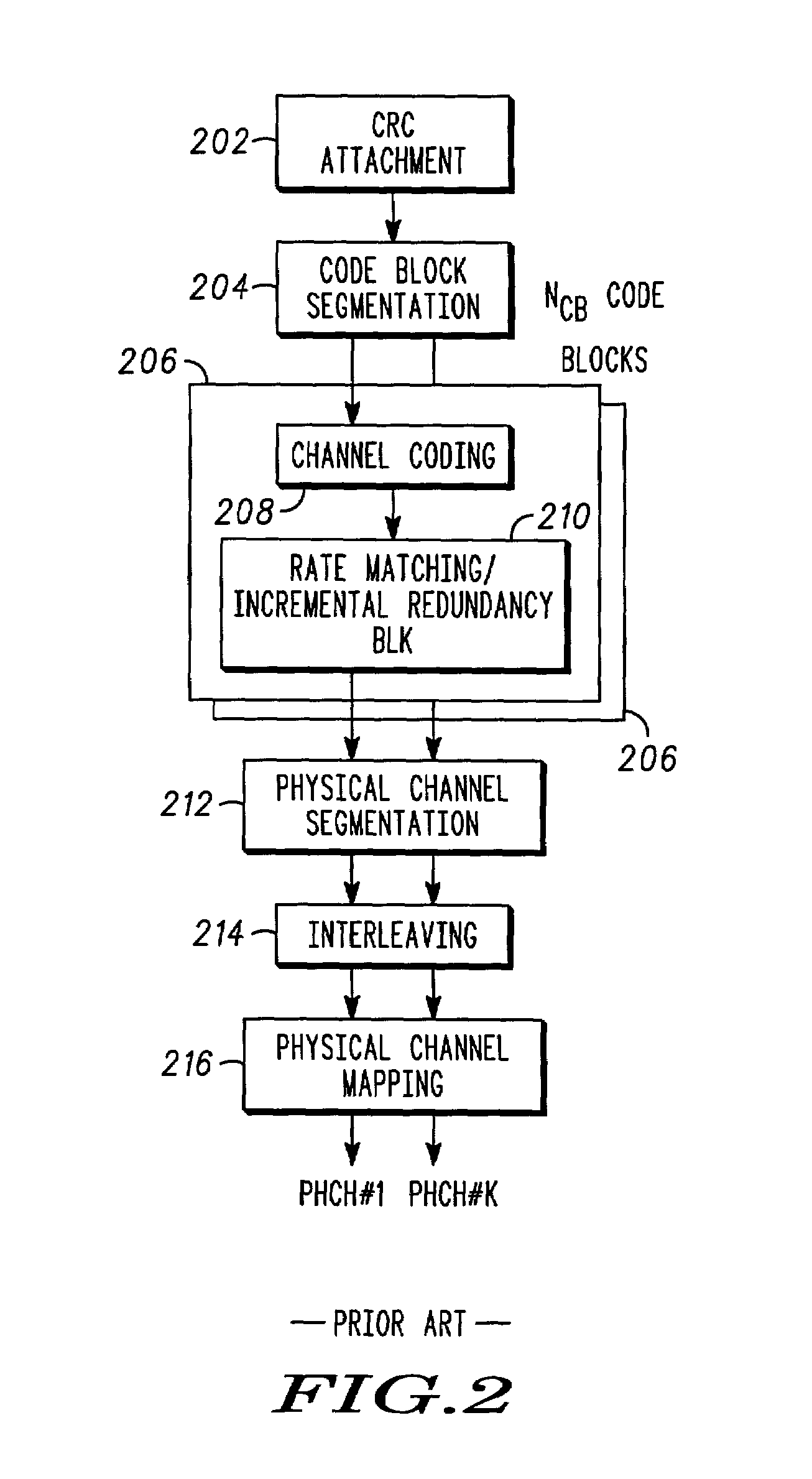
Method and apparatus for encoding transport block
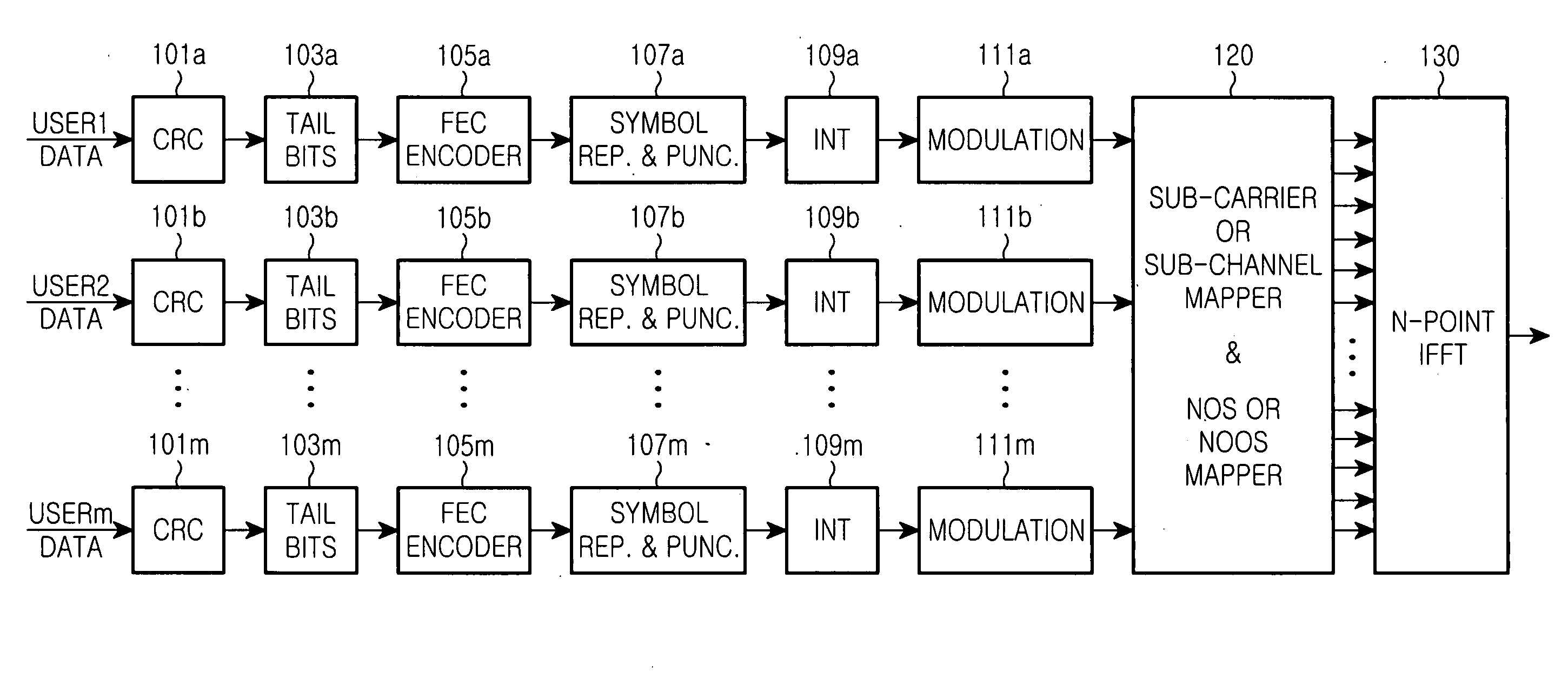
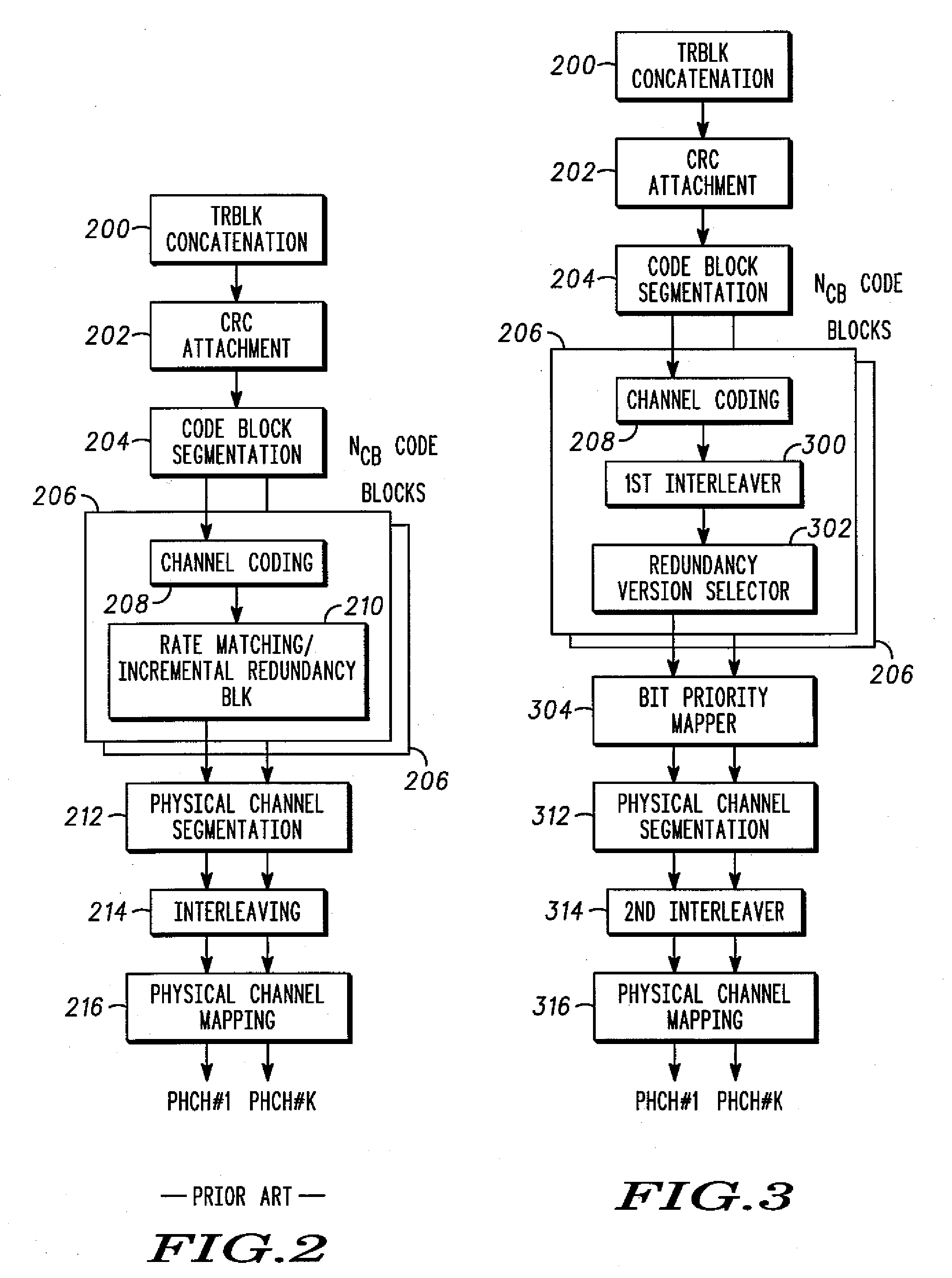
ActiveUS20140153484A1Easy to receiveFacilitate transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionCoding blockComputer science
A method and apparatus for encoding a transport block are provided. The method for encoding the transport block includes: determining, by a transmitter, a size of transport block; dividing, by the transmitter, the transport block into at least one code block based on the size of transport block; interleaving, by the transmitter, the at least one code block by an interleaver; and performing, by the transmitter, a turbo coding for the interleaved at least one code block, wherein the size of transport block is determined based on the number of the divided code blocks.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
IPHD (iterative parallel hybrid decoding) of various MLC (multi-level code) signals
InactiveUS20050166132A1Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using LDPC codesLow densityComputer science
IPHD (Iterative Parallel Hybrid Decoding) of various MLC (Multi-Level Code) signals. Various embodiments are provided by which IPHD may be performed on MLC LDPC (Multi-Level Code Low Density Parity Check) coded modulation signals mapped using a plurality of mappings. This IPHD may also be performed on MLC LDPC coded modulation signals mapped using only a singe mapping as well. In addition, various embodiments are provided by which IPHD may be performed on ML TC (Multi-Level Turbo Code) signals. These principles of IPHD, shown with respect to various embodiments IPHD of MLC LDPC coded modulation signals as well as the IPHD of ML TC signals, may be extended to performing IPHD of other signal types as well. Generally speaking, based on the degree of the MLC signal, a corresponding number of parallel paths operate in cooperation to decode the various levels of the MLC signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Pre-decoder for a turbo decoder, for recovering punctured parity symbols, and a method for recovering a turbo code
InactiveUS6910170B2Improve decoding performanceReduce the number of iterationsError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesTurbo encoderTurbo coded
A pre-decoder applied to a turbo decoder for decoding a punctured turbo code. The turbo code consists of a data bit stream and a plurality of parity bit streams, parts of which are punctured. The pre-decoder has an arithmetic unit for calculating estimated parity bit streams by carrying out, with respect to the data bit stream, the same algorithm used by a turbo encoder to produce the parity bit streams, a comparison unit for comparing the plurality of parity bit streams with the estimated parity bit streams, and a recovery unit for substituting estimated parity symbols for corresponding punctured parts of the parity symbol streams when related non-punctured bits of the parity bit streams are identical with corresponding estimated non-punctured parity bits. The punctured parity symbols are recovered by the pre-decoder completely, or at least partially, and provided to the turbo decoder. Accordingly, the decoding performance of the turbo decoder is enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Turbo code based incremental redundancy
InactiveUS7000173B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using convolutional codesData streamComputer science
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
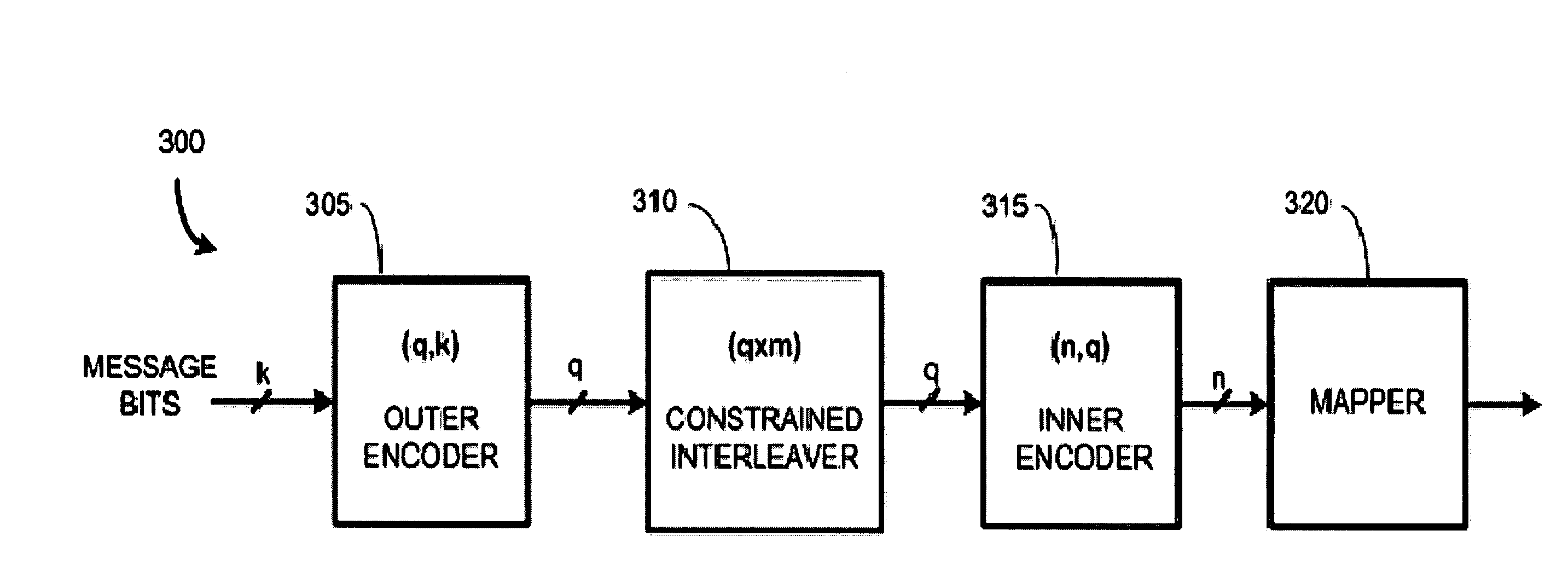
Encoding and decoding using constrained interleaving
InactiveUS20120063533A1Reduce measurementEfficient implementationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationSimple componentNoise margin
Serially-concatenated codes are formed in accordance with the present invention using a constrained interleaver. The constrained interleaver cause the minimum distance of the serial concatenated code to increase above the minimum distance of the inner code alone by adding a constraint that forces some or all of the distance of the outer code onto the serially-concatenated code. This allows the serially-concatenated code to be jointly optimized in terms of both minimum distance and error coefficient to provide significant performance advantages. These performance advantages allow a noise margin target to be achieved using simpler component codes and a much shorter interleaver than was needed when using prior art codes such as Turbo codes. Decoders are also provided. Both encoding and decoding complexity can be lowered, and interleavers can be made much shorter, thereby shortening the block lengths needed in receiver elements such as equalizers and other decision-directed loops. Also, other advantages are provided such as the elimination of a error floor present in prior art serially-concatenated codes. That allows the present invention to achieve much higher performance at lower error rates such as are needed in optical communication systems.
Owner:TRELLIS PHASE COMM LP
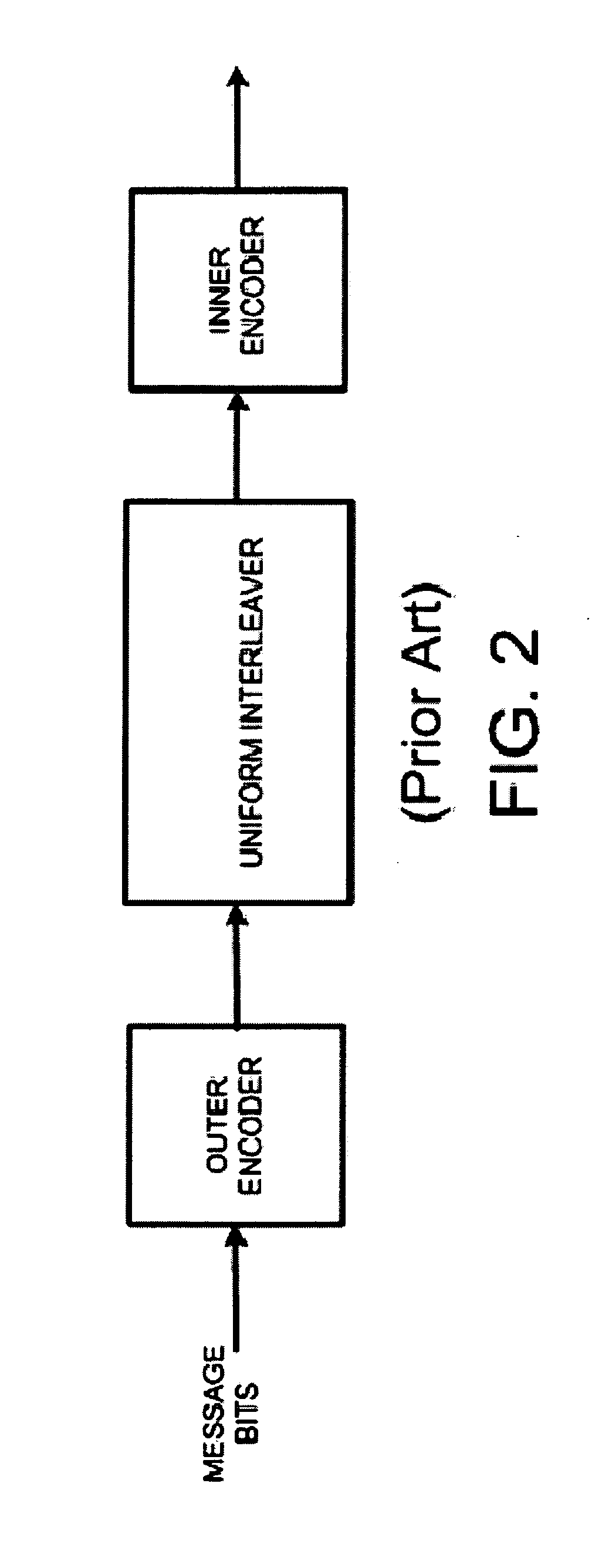
Combining spectral shaping with turbo coding in a channel coding system
InactiveUS20060156171A1Code conversionRecord information storageTelecommunicationsFrequency spectrum
A method of combining spectral shaping with turbo coding in a channel coding system. The method comprises encoding user data with spectrally shaped encoding to provide a suppressed DC user data sector output. The method also comprises generating turbo coded redundant bits for the suppressed DC user data sector. The turbo coded redundant bits are interleaved with additive coding to provide a suppressed DC parity sector.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
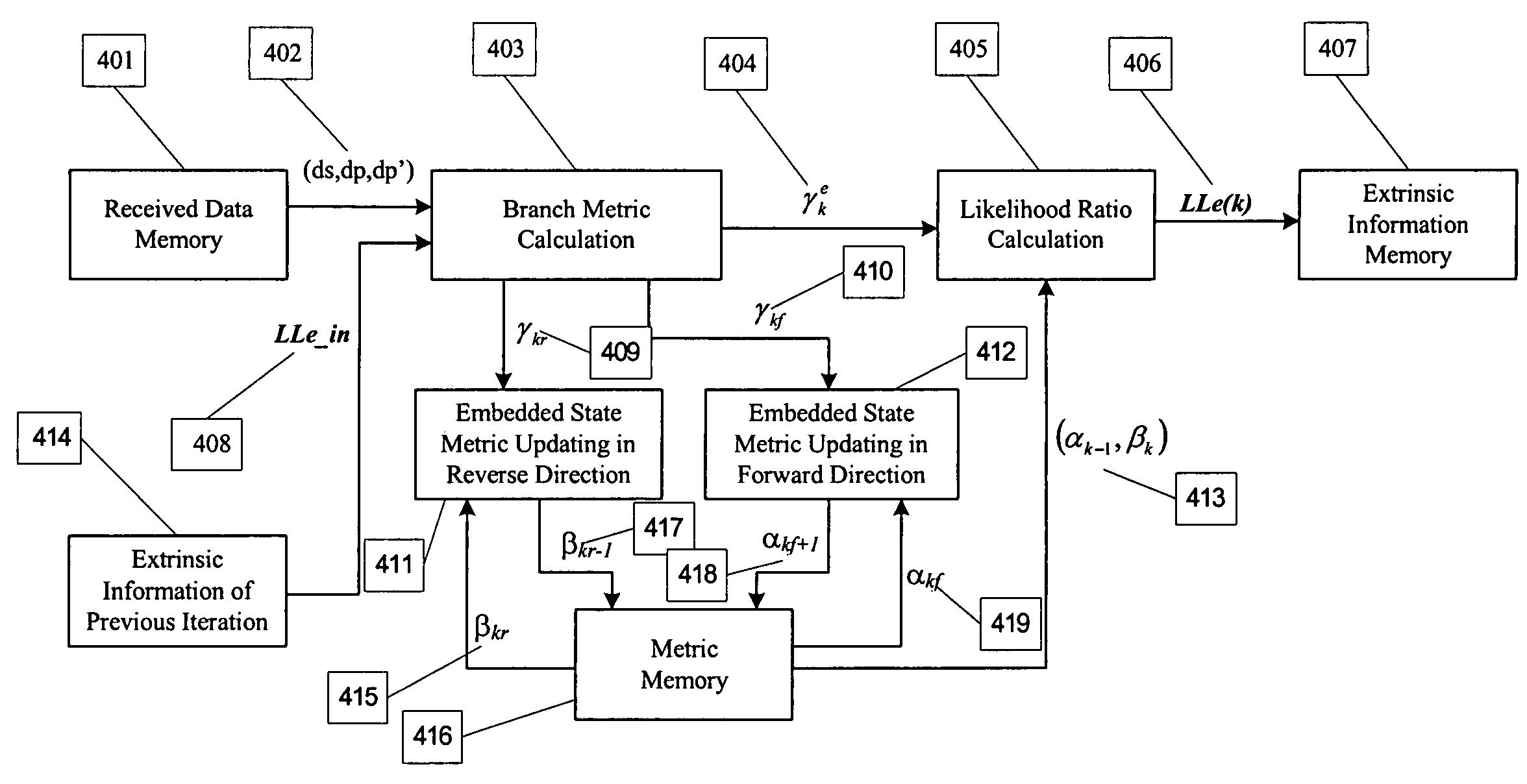
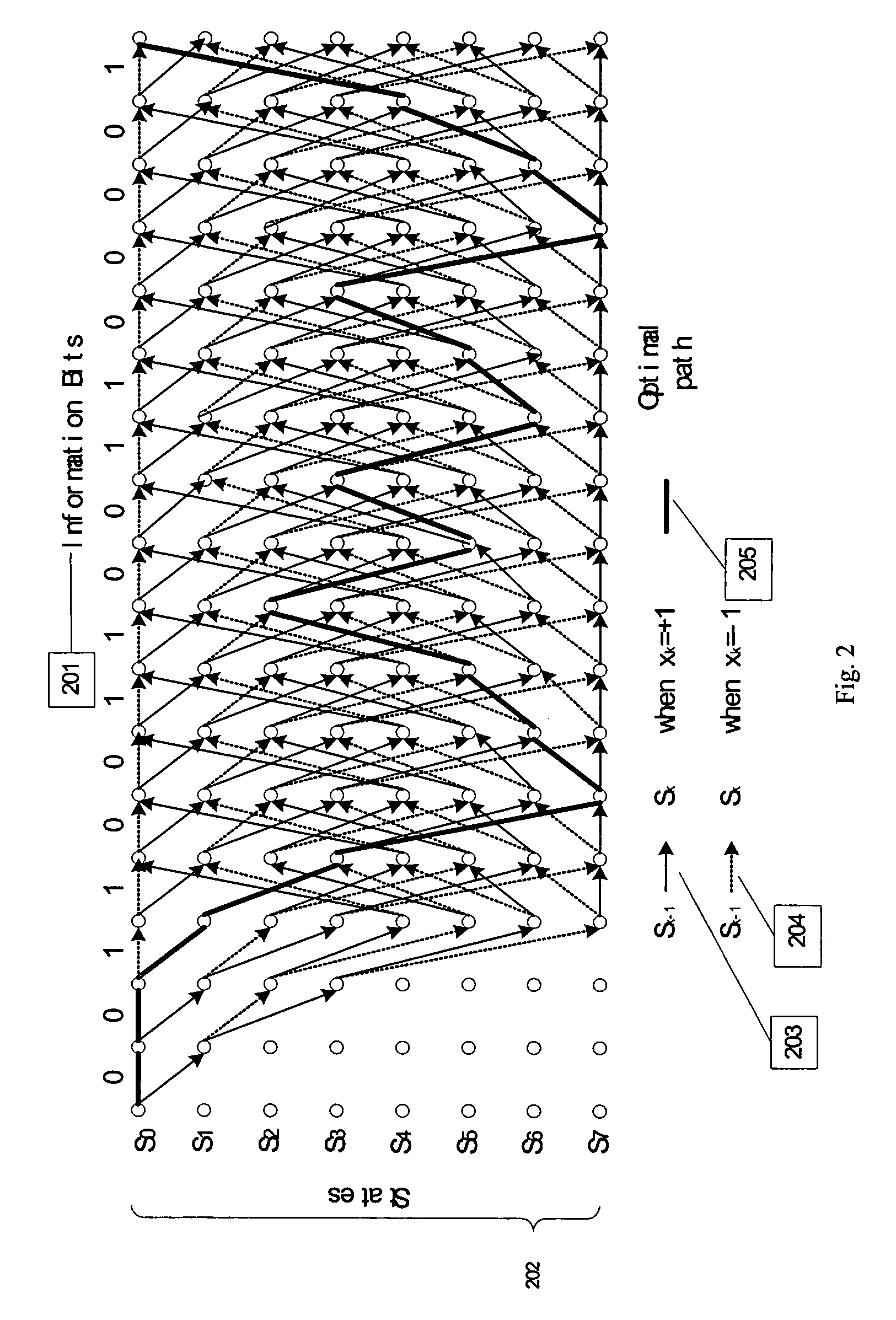
Embedded state metric storage for MAP decoder of turbo codes
ActiveUS7441174B2Reduce memory requirementsSimplification a Max log-MAP decoderData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionTurbo codedOperating system
Owner:HONG KONG THE UNIV OF +1
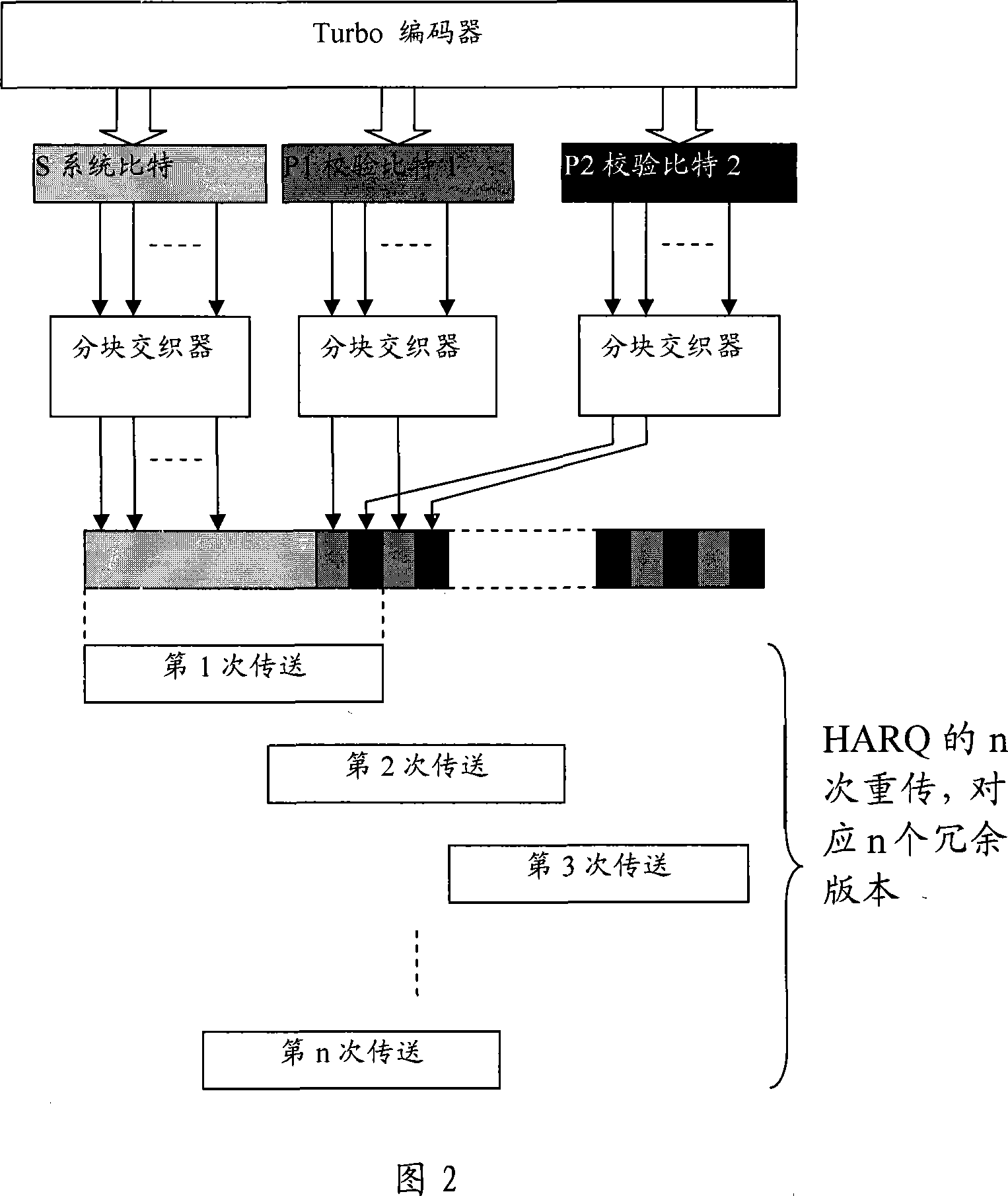
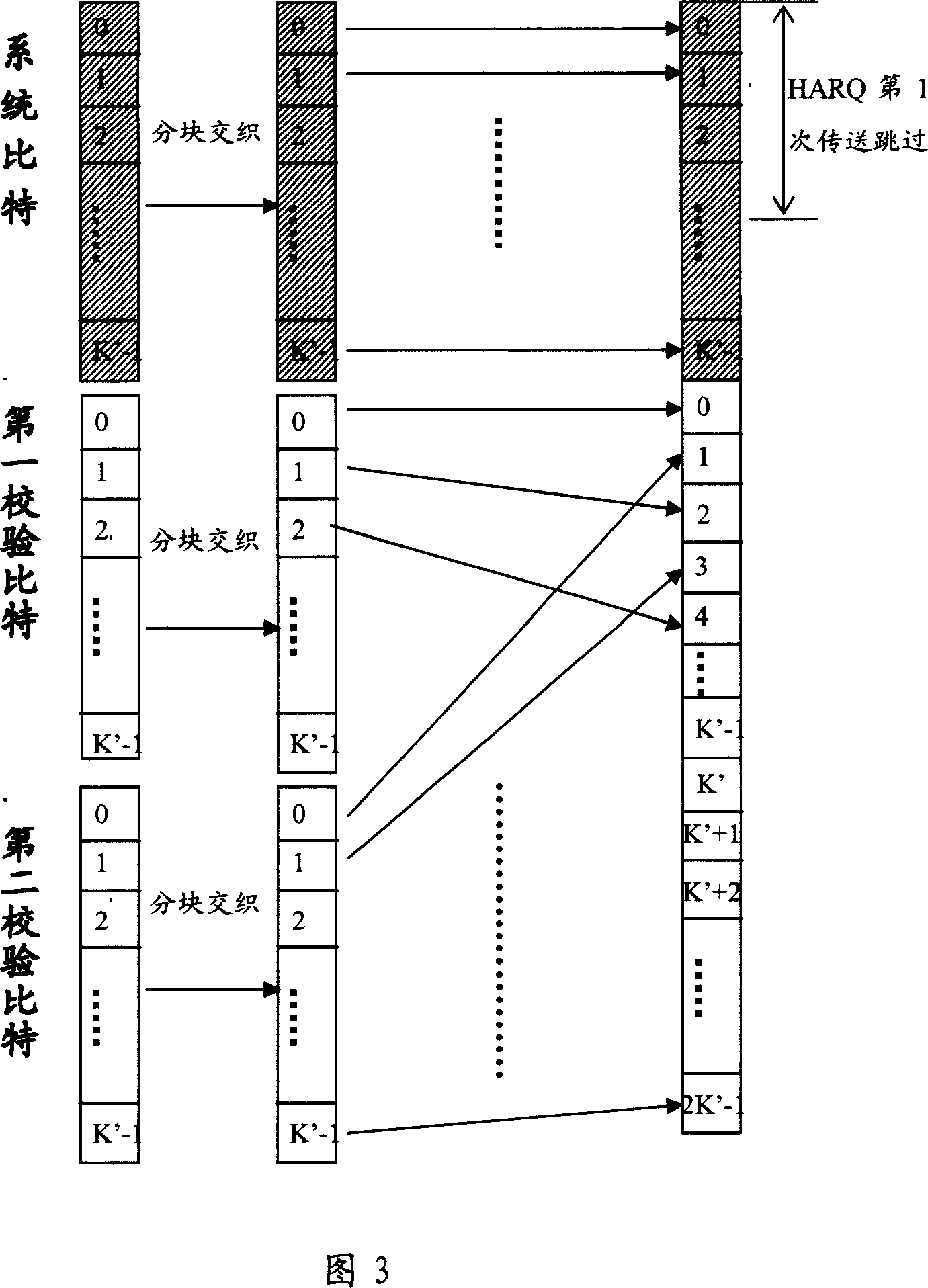
Method for generating turbo-code block intersection and HARQ packet
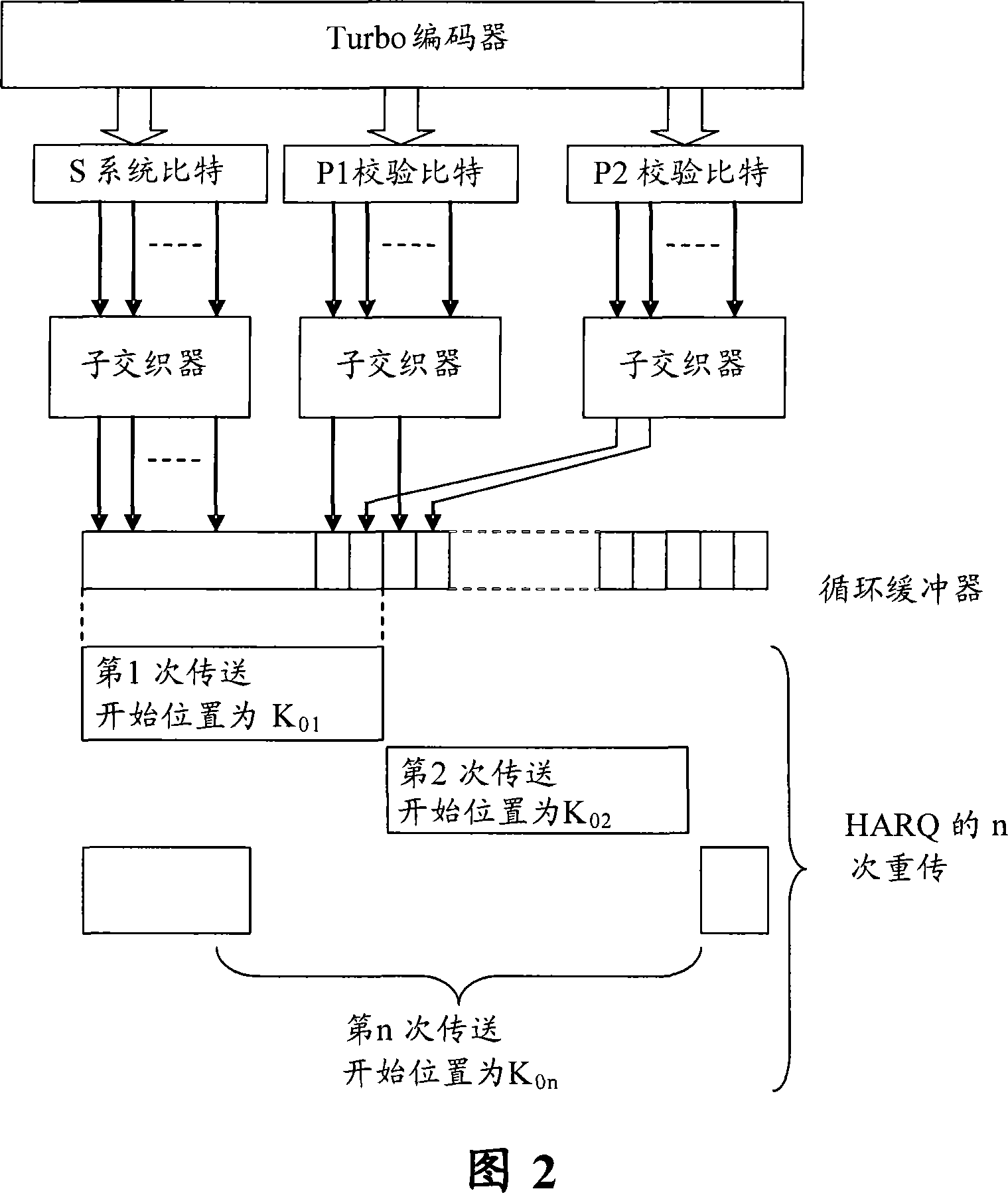
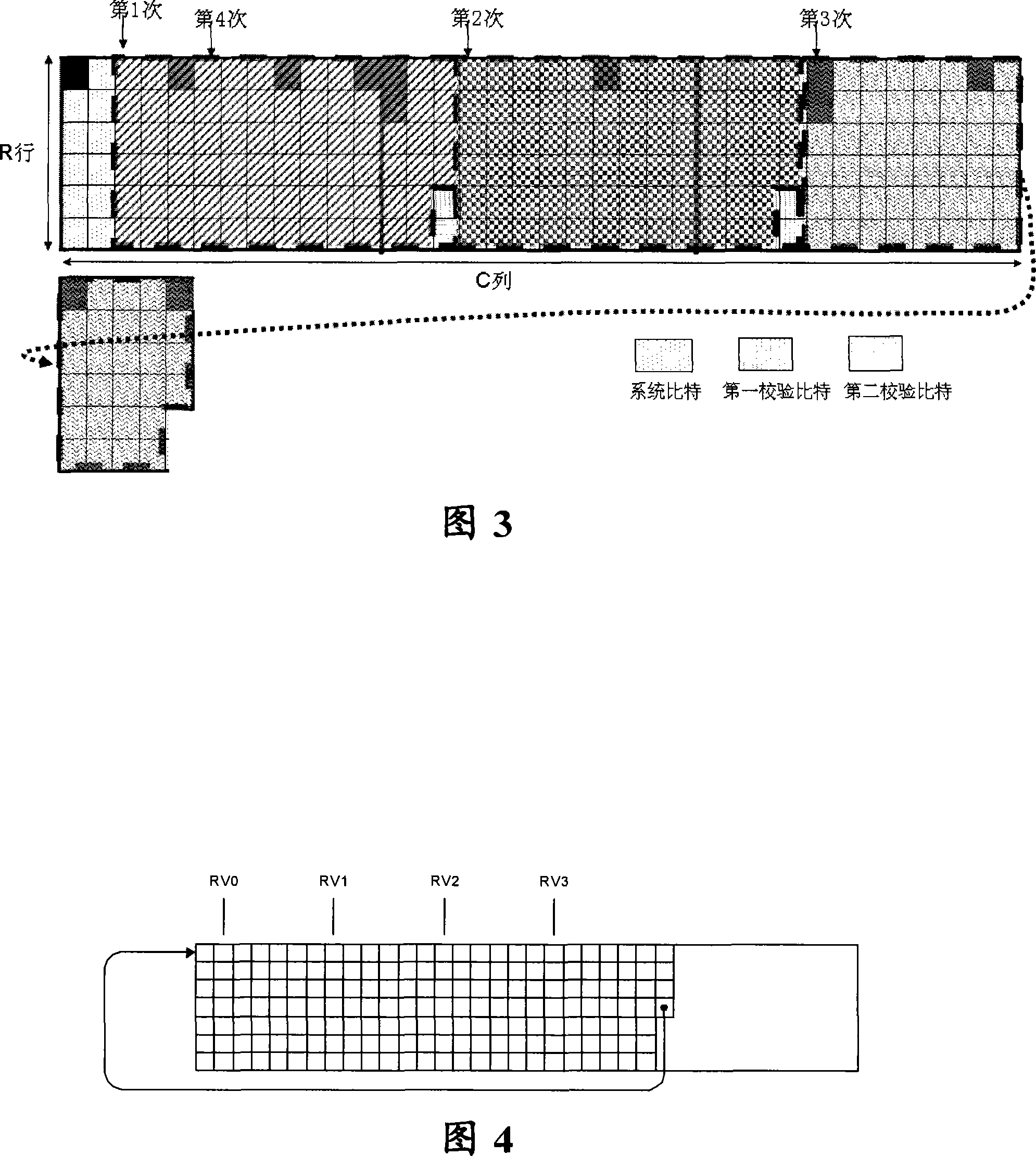
InactiveCN101075857AImprove performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksParallel computingTurbo coded
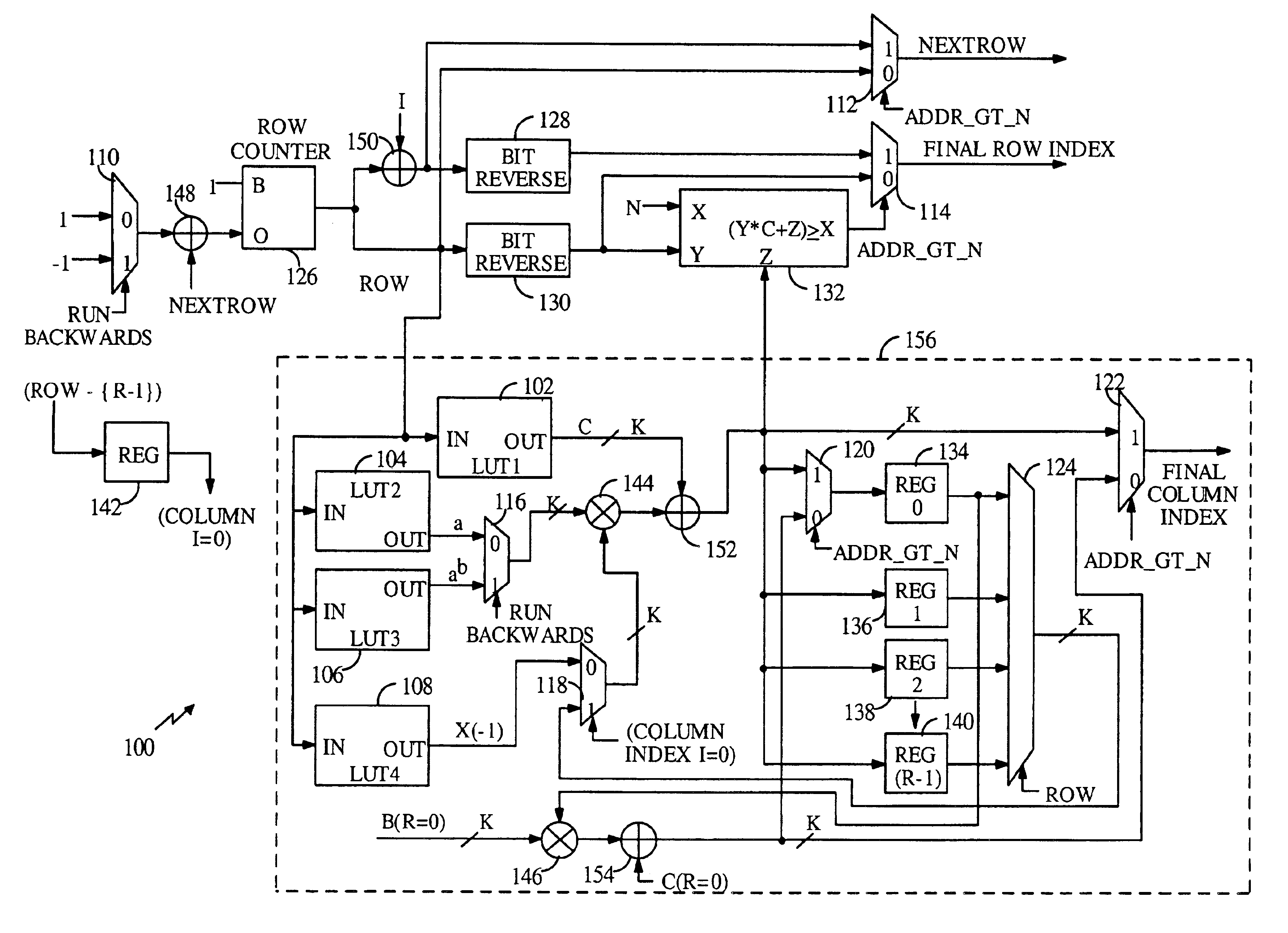
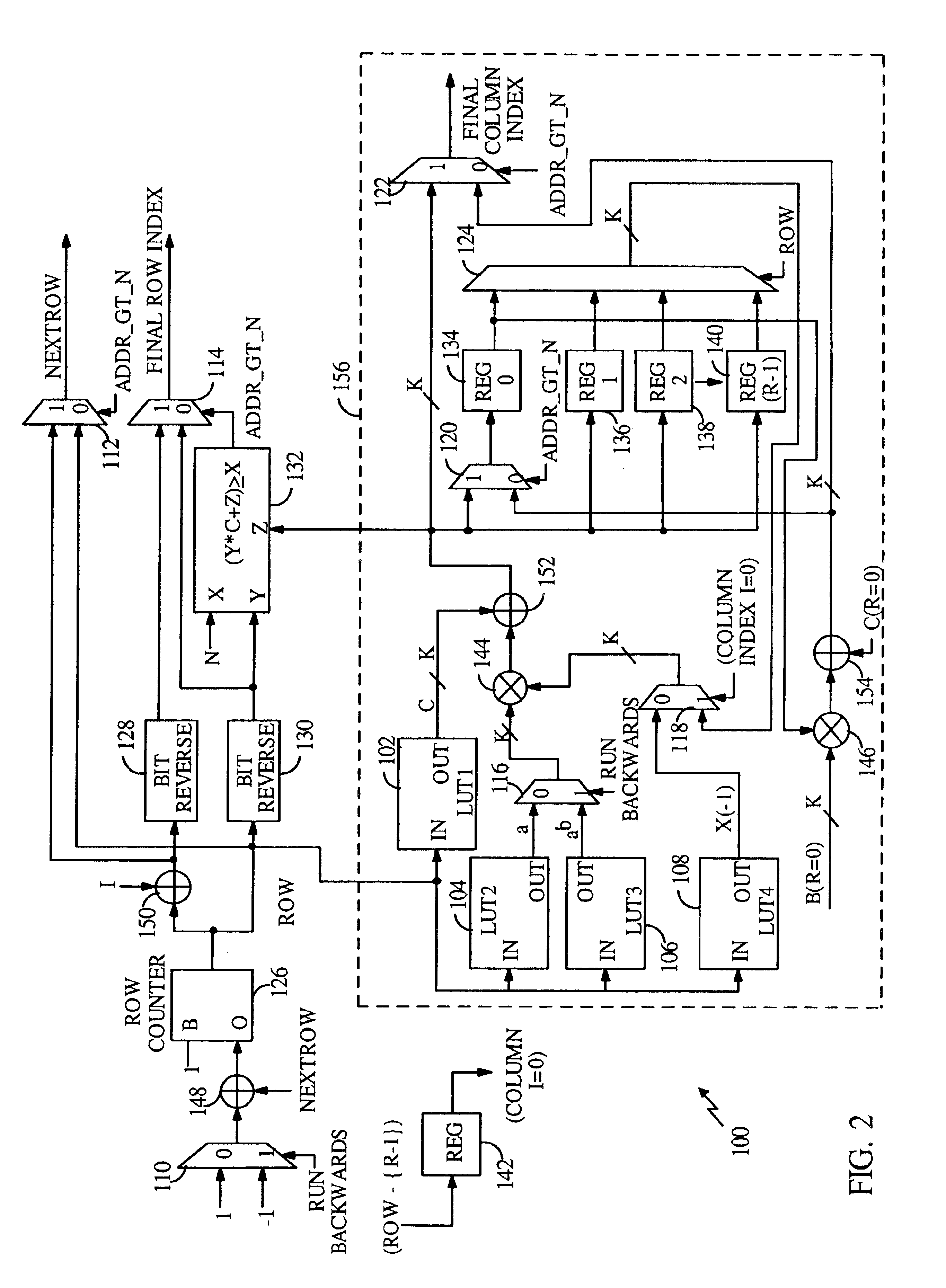
The method comprises: the message packet is sent to a turbo code encoder with 1 / 3 code rate to generate a system bit-stream, a first even-odd check bit-stream and a second event-odd check bit-stream; wherein, the system bit-stream and the first even-odd check bit-stream uses the block interleavers which use 2M equaling lengths, based on bit-reversed order (BRO), and taken as column displacement function; bias delta of both block interleavers are zero; bias delta of the block interleaver of the second even-odd check bit-stream is not always zero. The invention also provides a cyclic buffer based turbo code HAQQ packet generation method.
Owner:ZTE CORP
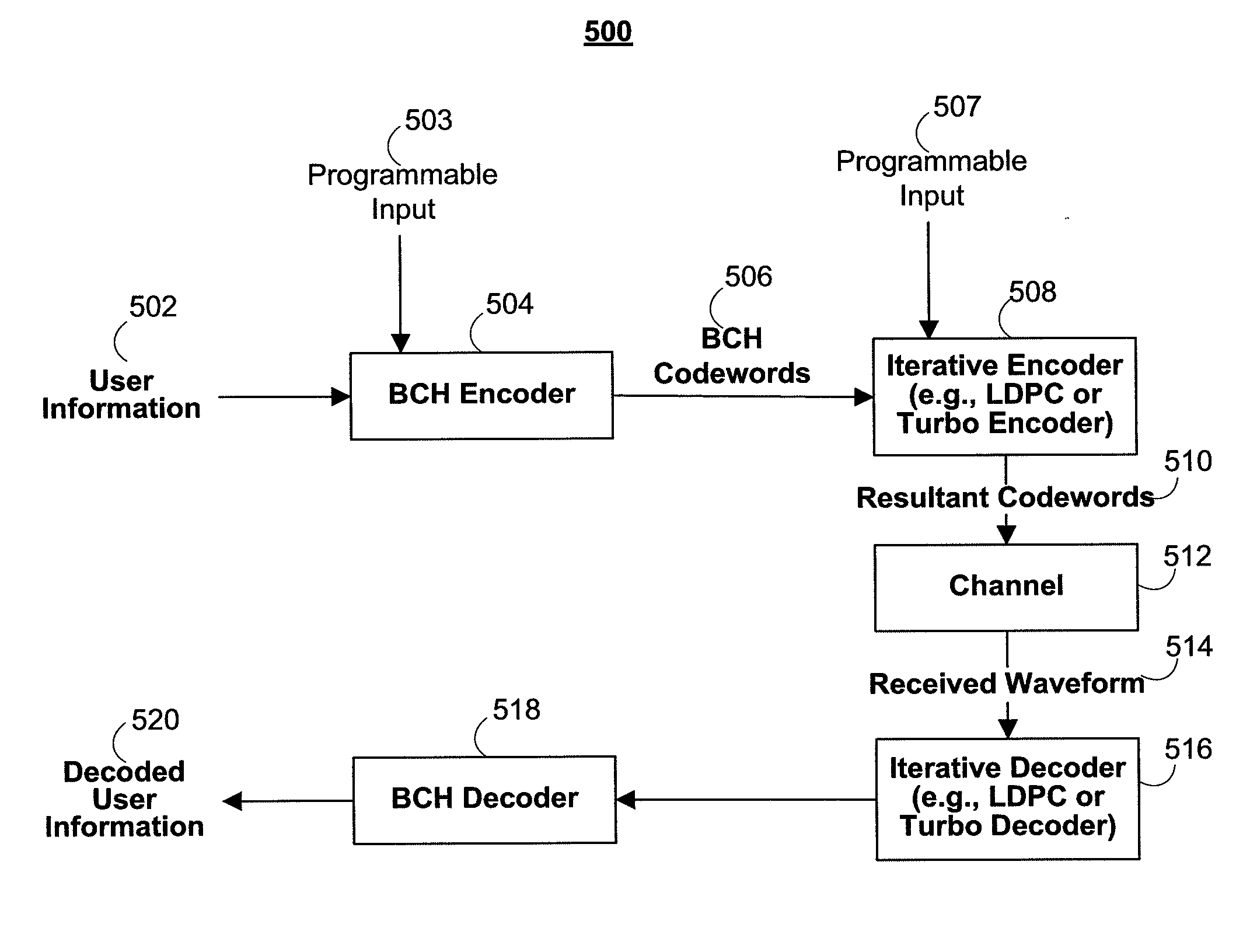
Concatenated codes for holographic storage
ActiveUS20080163026A1Robust implementationGood flexibilityError preventionTransmission systemsComputer hardwareHolographic storage
Systems and methods for constructing concatenated codes for data storage channels, such as holographic storage channels, are provided. The concatenated codes include an outer BCH code and an inner iteratively decodable code, such as an LDPC code or turbo code. The correction power and coding rate of one or both of the codes may be programmable based on the channel characteristics and the desired SNR coding gain. The correction power and / or coding rate of the inner and / or outer code may also be dynamically adjusted in real-time to compensate for time-varying error conditions on the channel.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
High-performance low-memory interleaver banks for turbo-codes
InactiveUS6857087B2Data representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceTurbo coded
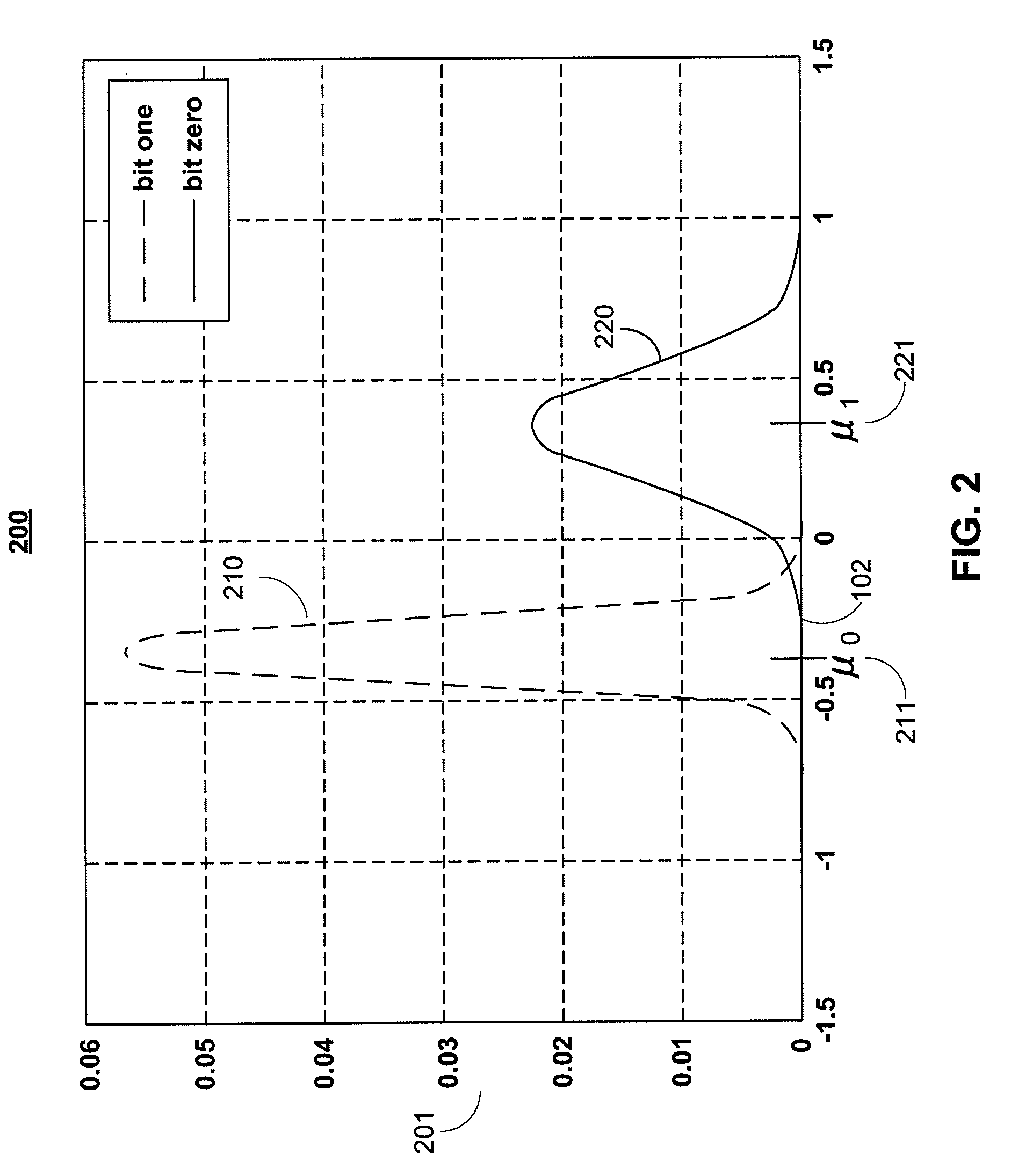
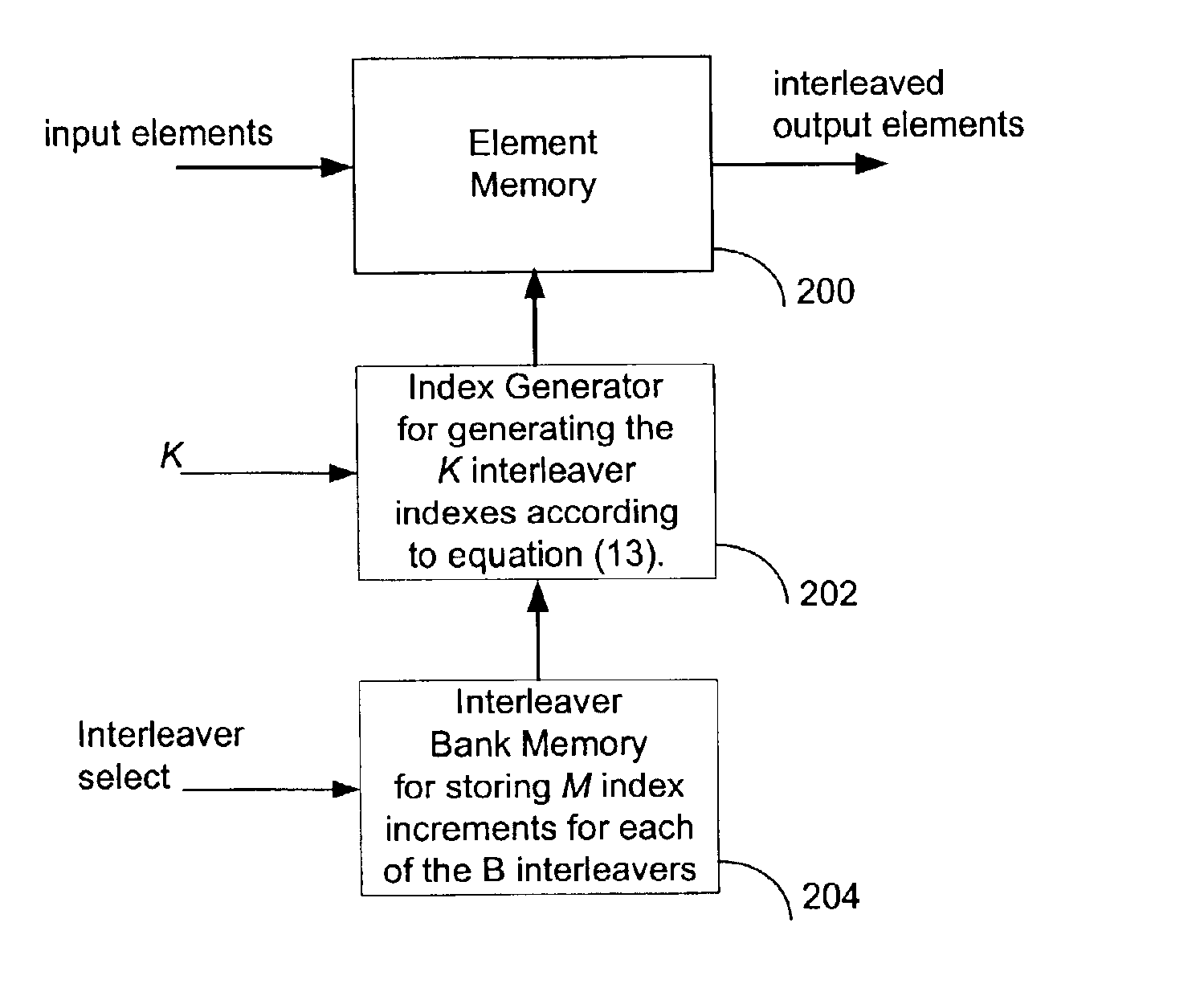
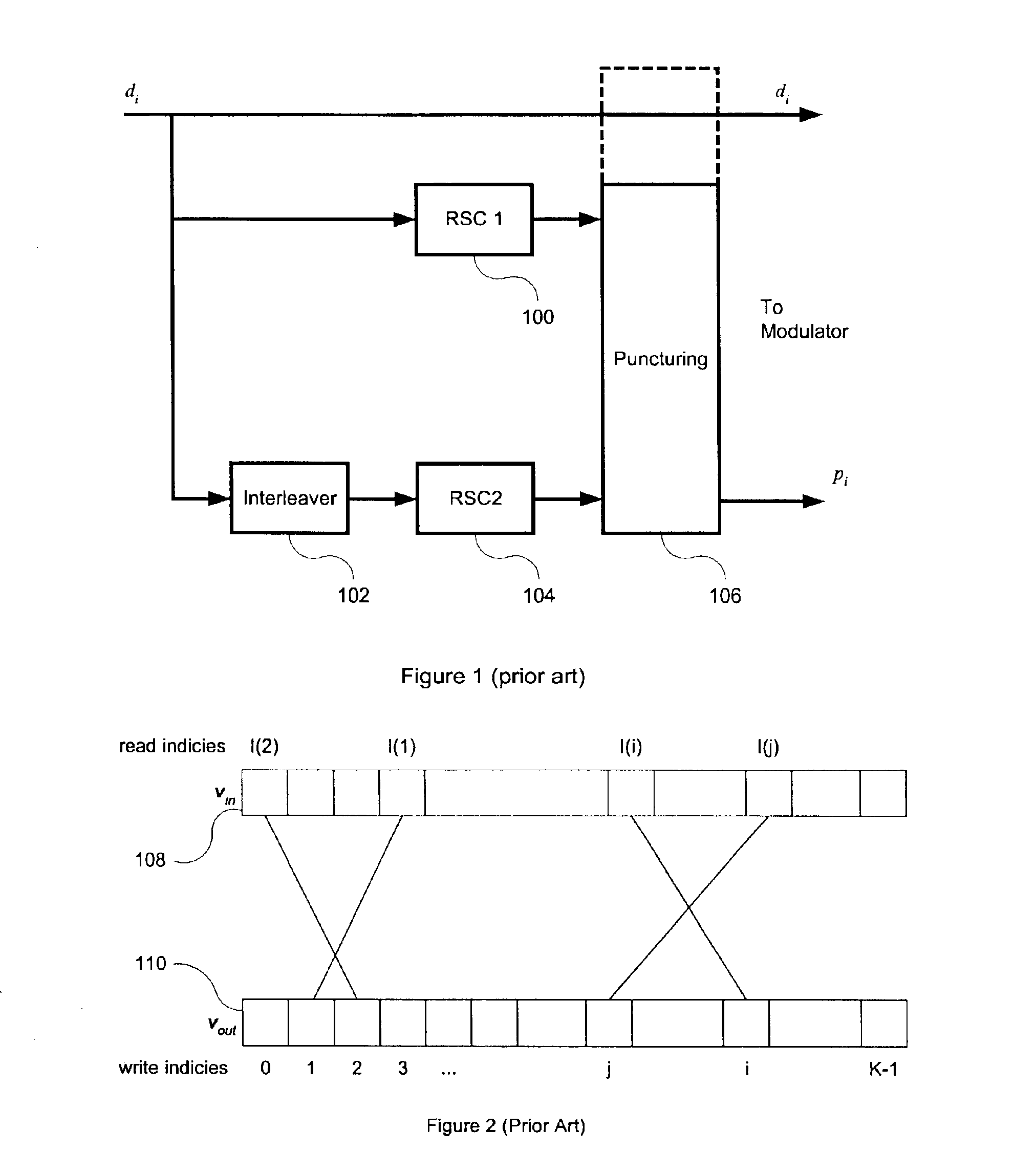
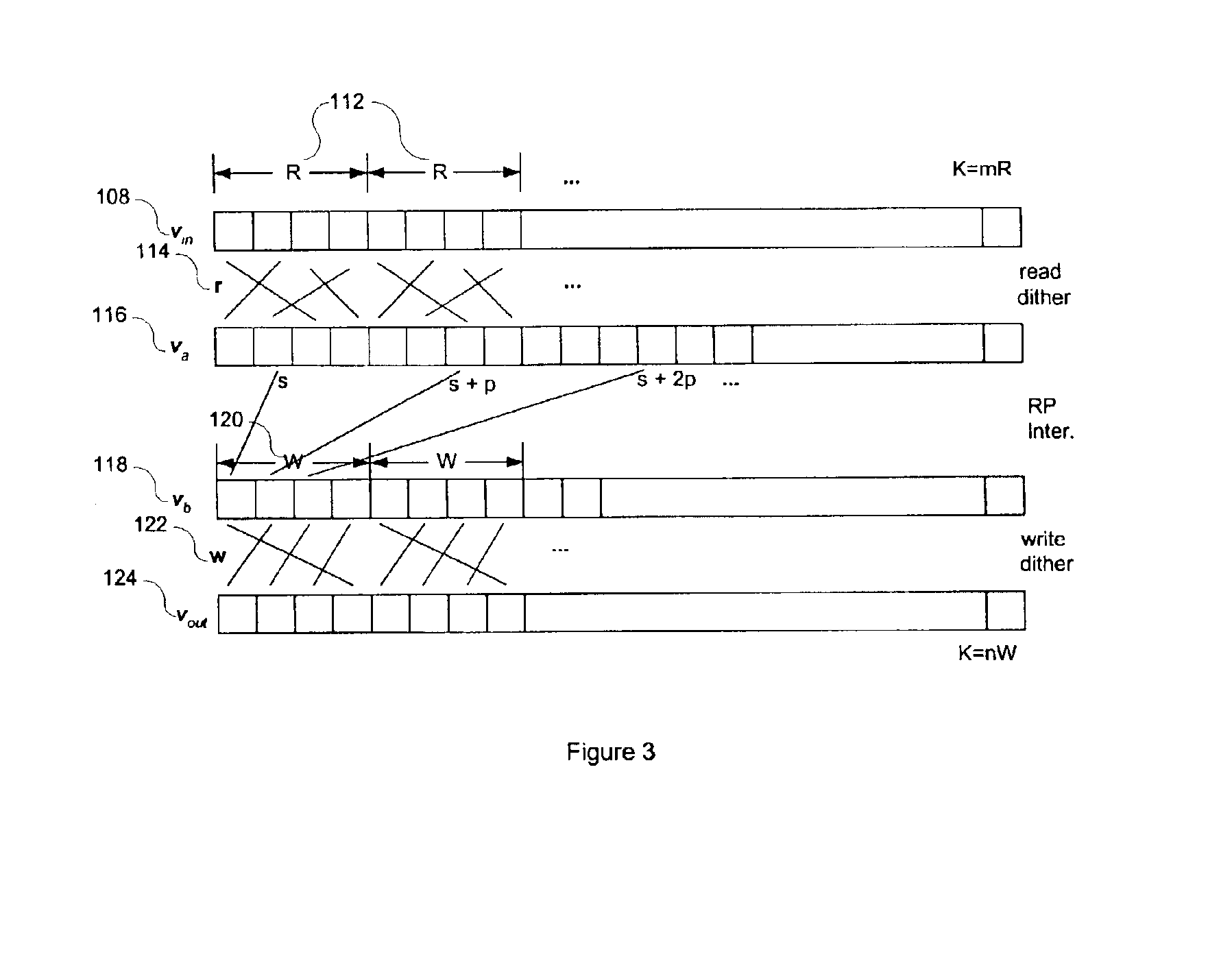
An interleaver for interleaving a set of K ordered elements is disclosed herein. The disclosed interleaver can be expressed as a single permutation that corresponds to two local dithering operations and a global permutation operation. The single permutation can be represented as a small collection of short vectors, and can be calculated recursively, allowing the interleaver to be both stored and implemented using a smaller amount of memory than conventionally possible.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
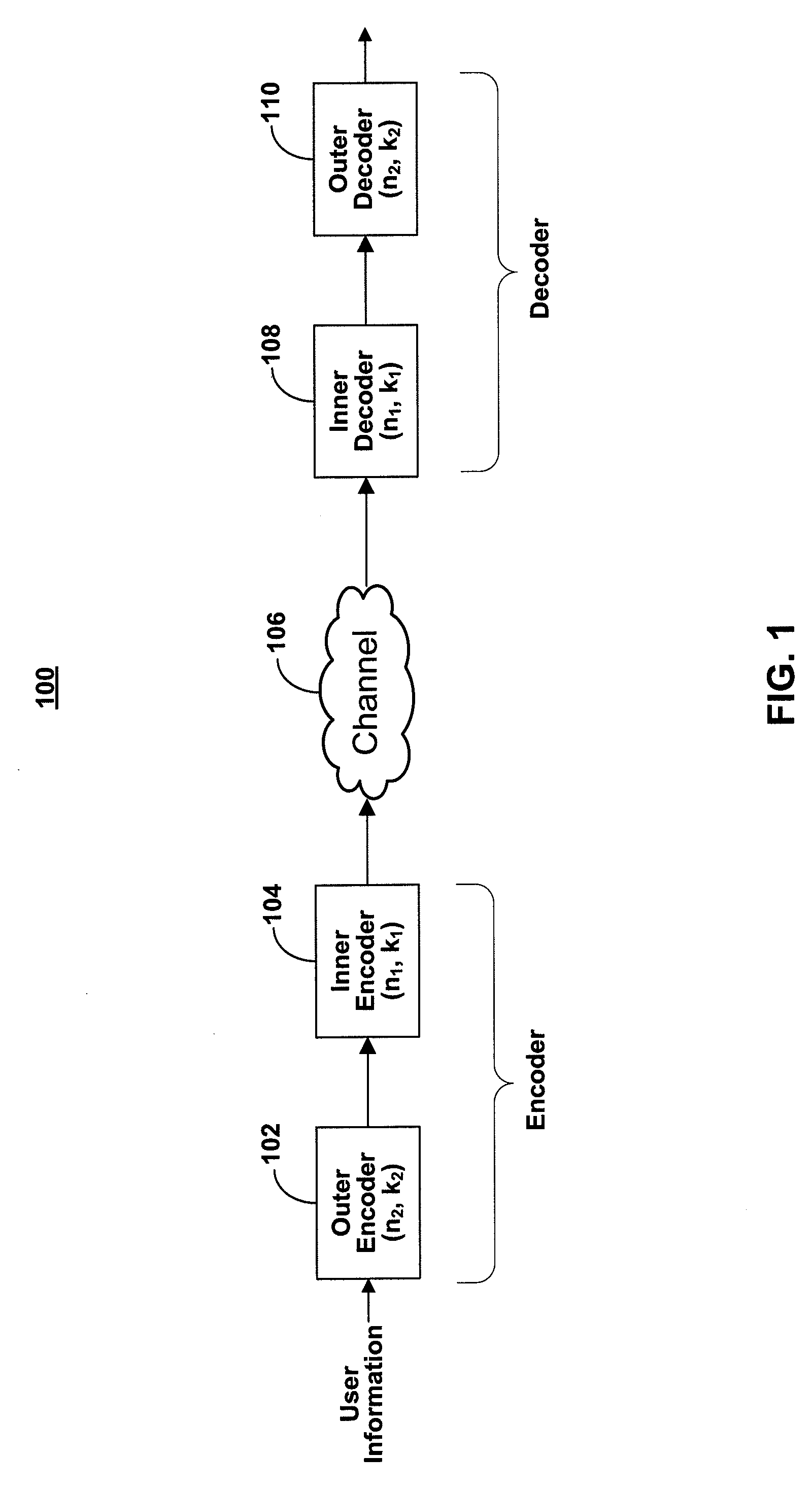
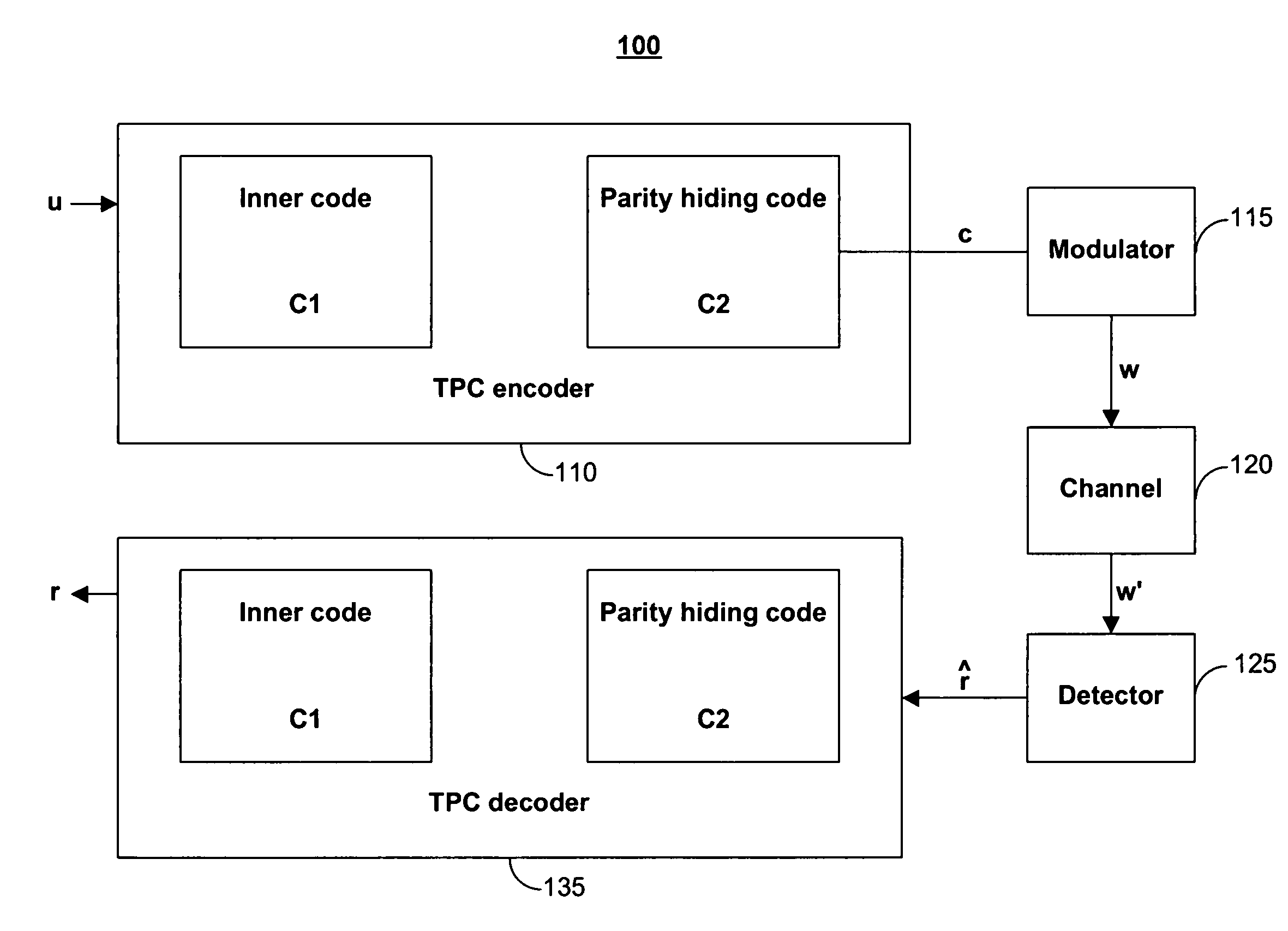
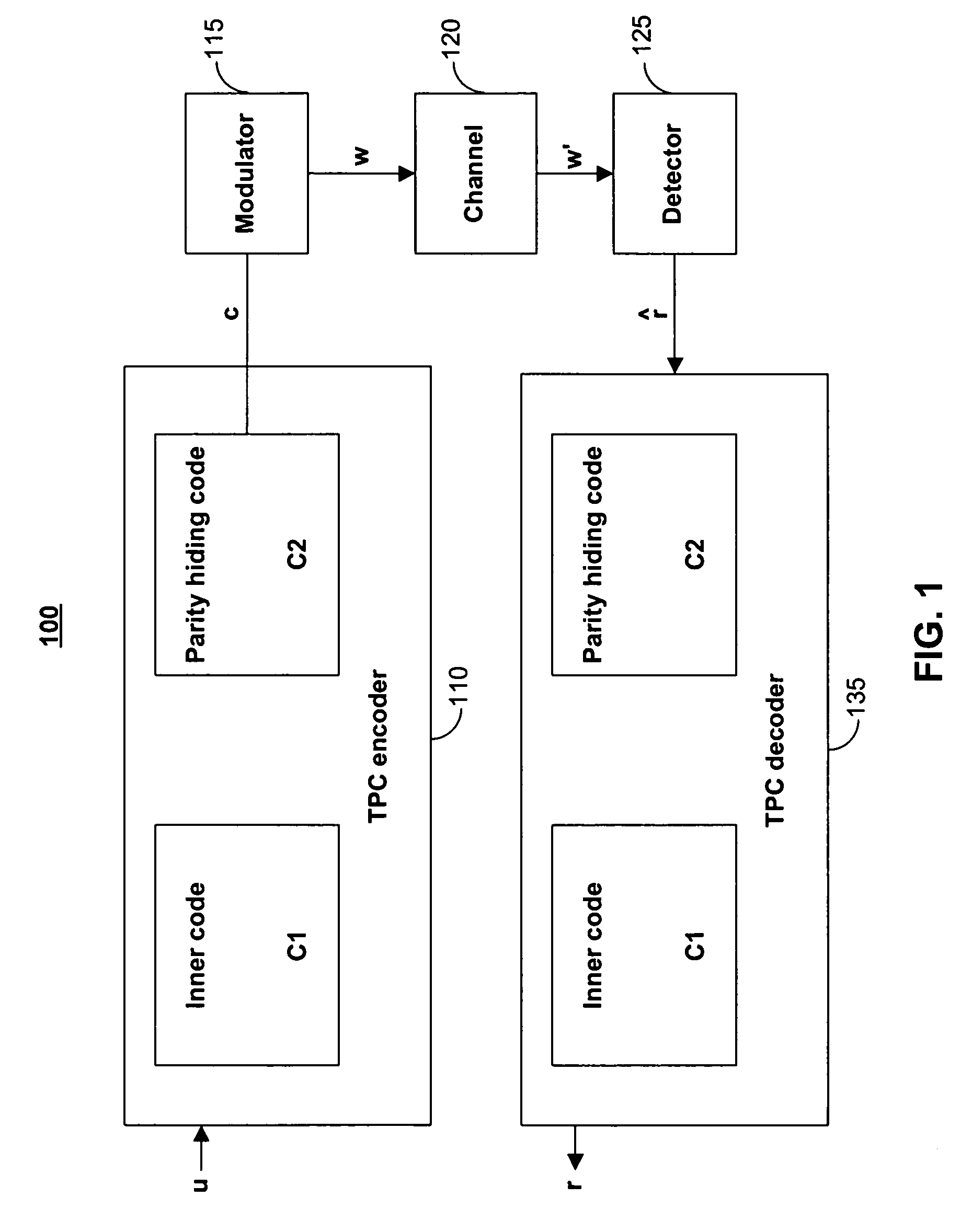
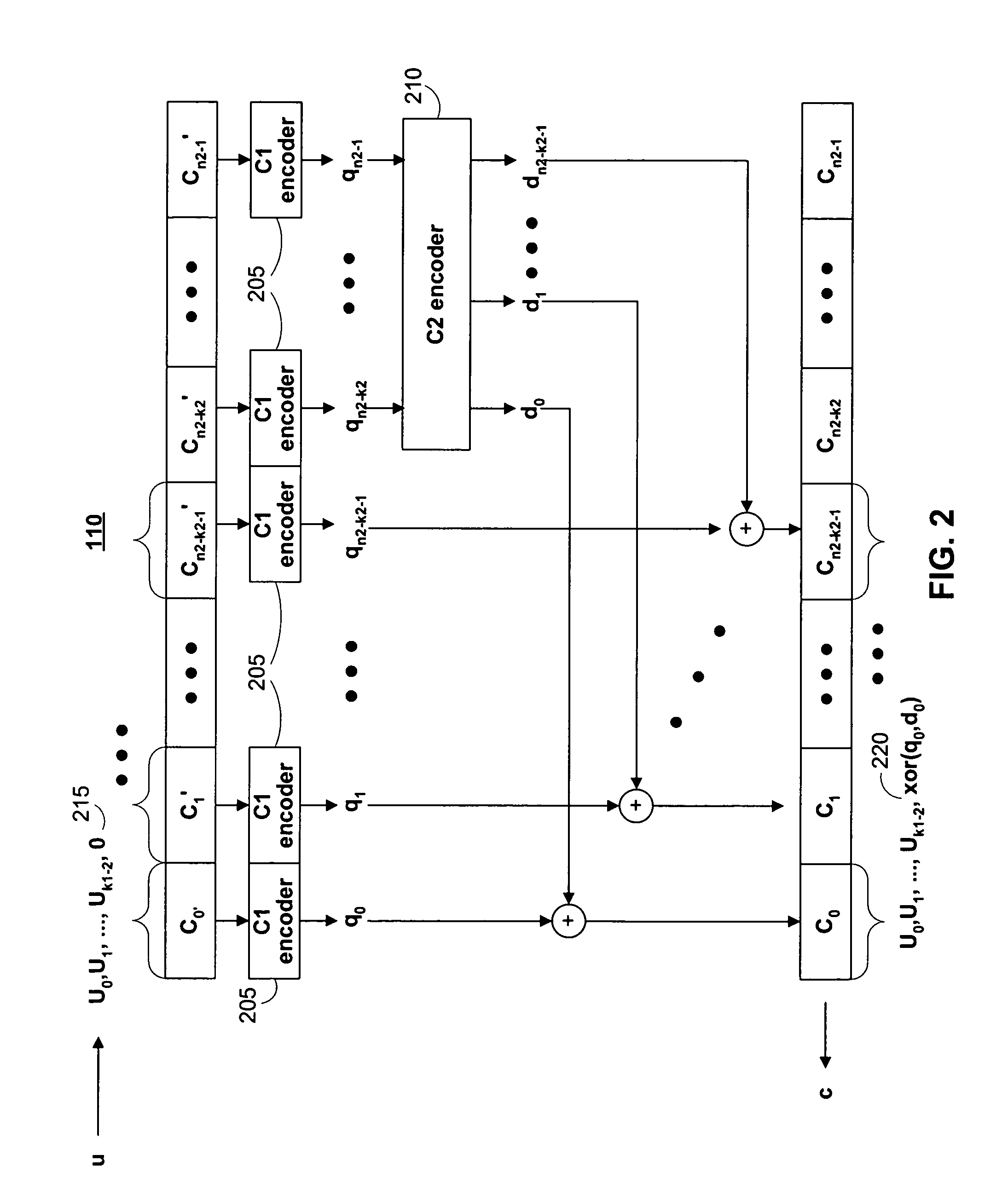
Tensor product codes containing an iterative code
Systems and methods are provided for encoding a stream of datawords based on a tensor product code to provide a stream of codewords, and detecting and decoding a stream of received data based on a tensor product code to provide a decoded stream of data. In one aspect, the tensor product code is based on two codes including an inner code and an outer parity hiding code, where the outer parity hiding code is an iterative code. In certain embodiments, the outer parity hiding code is a Turbo code or a low density parity check (LDPC) code.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Velocity matching method for limited longness circulation caching of Turbo code
ActiveCN101183875AImprove retransmission performanceReduce sizeError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresNetwork packetTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a rate matching method for finite length loop buffer of a turbo code, comprising the steps: turbo coding is carried out to data bits of an input data block, upon which the size of a one-dimensional finite length loop buffer is decided; the initial positions of hybrid automatic repeat request data packets appointed by a plurality of predefined redundancy version values are evenly or approximately distributed in the one-dimensional finite length loop buffer; a redundancy version value is selected from the predefined redundancy version values in line with times of the hybrid automatic repeat requests; then data bits with specific length are read in turn from the initial position of hybrid automatic repeat request data packets appointed by the selected redundancy version values, thus a hybrid automatic repeat request data packet is formed and then sent out. The invention has the advantages of reduced size of circular buffer and improved repeat performance of hybrid automatic repeat request data packet.
Owner:ZTE CORP
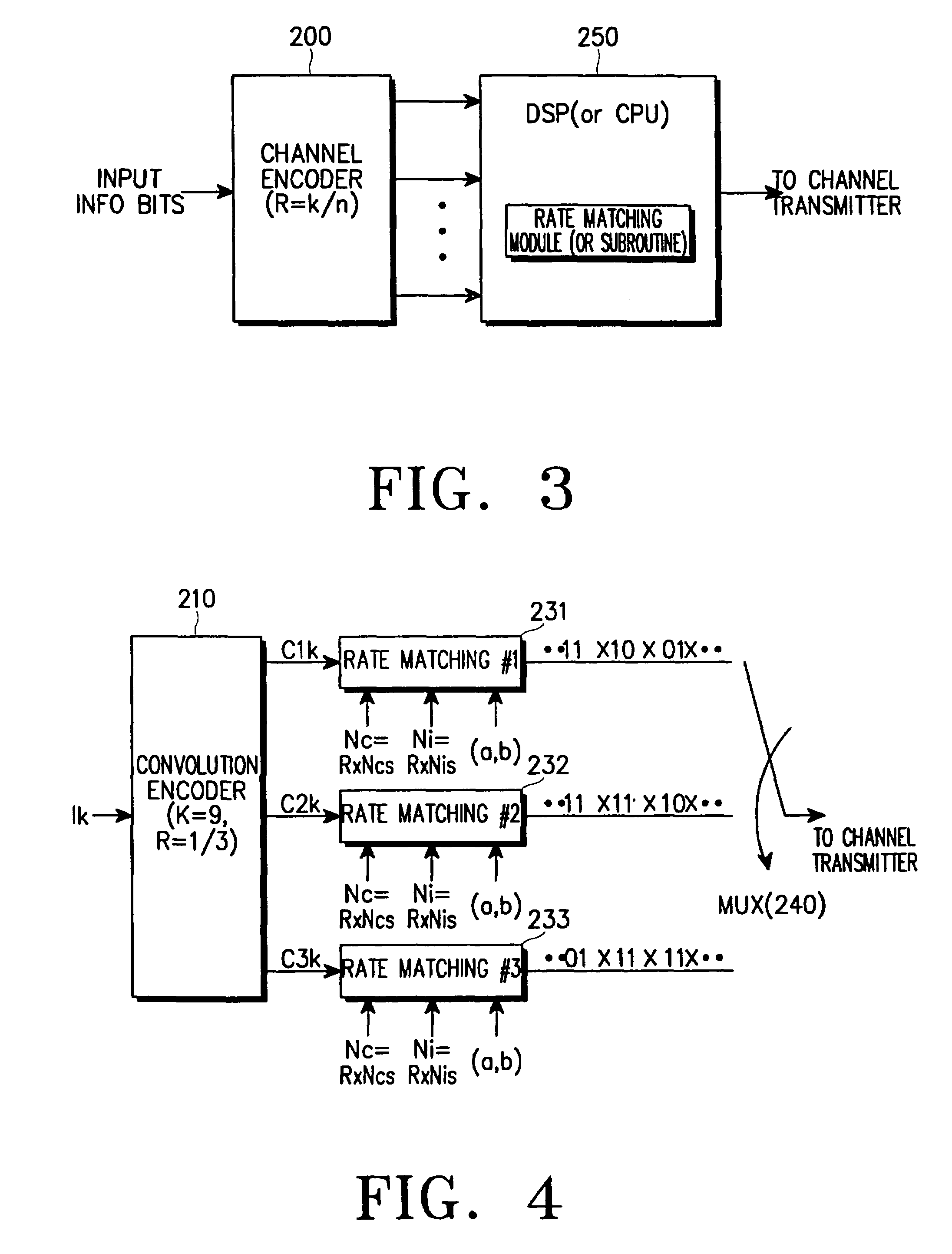
Rate matching device and method for a data communication system
InactiveUS7451383B2Improve data transfer efficiencyImprove system performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionCommunications systemBlock code
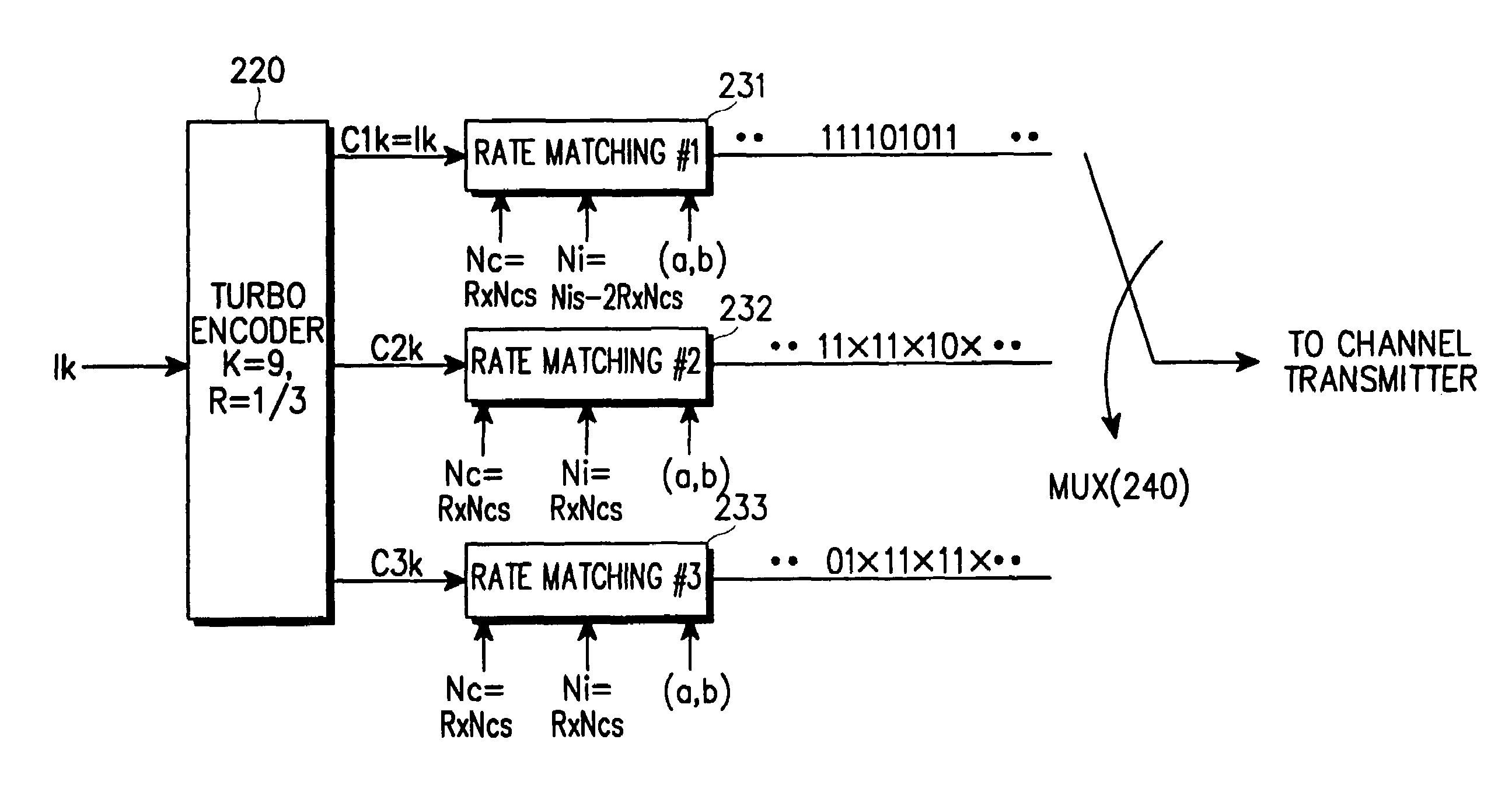
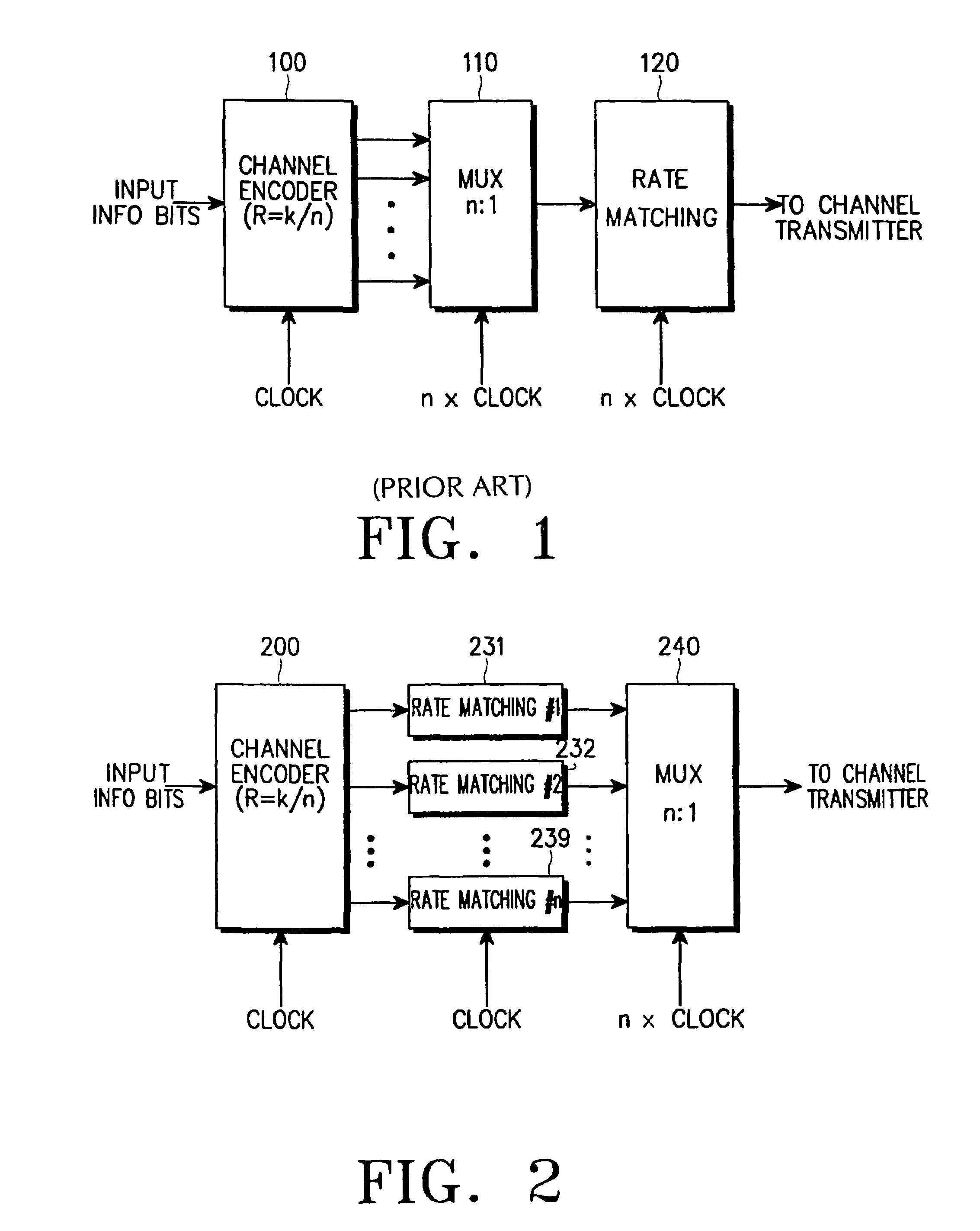
A device and method for rate matching channel-encoded symbols in a data communication system. The rate matching device and method can be applied to a data communication system which uses one or both of a non-systematic code (such as a convolutional code or a linear block code) and a systematic code (such as a turbo code). In one aspect, the rate matching device includes a plurality of rate matching blocks, the number of the rate matching blocks being equal to a reciprocal of a coding rate of a channel encoder. The rate matching device can rate match the symbols encoded with a non-systematic code or the symbols encoded with a systematic code, by changing initial parameters including the number of input symbols, the number of output symbols, and the puncturing or repetition pattern determining parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
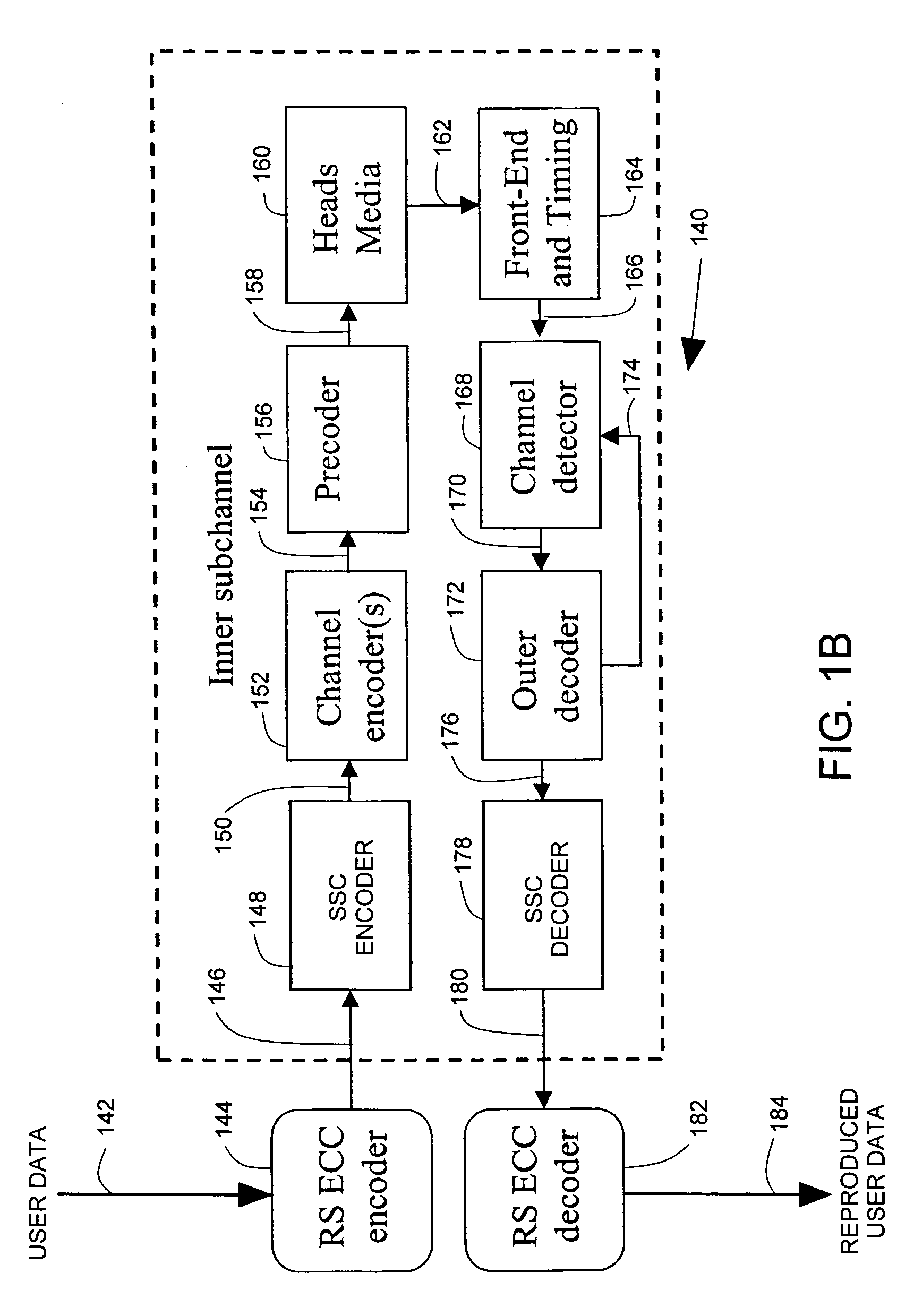
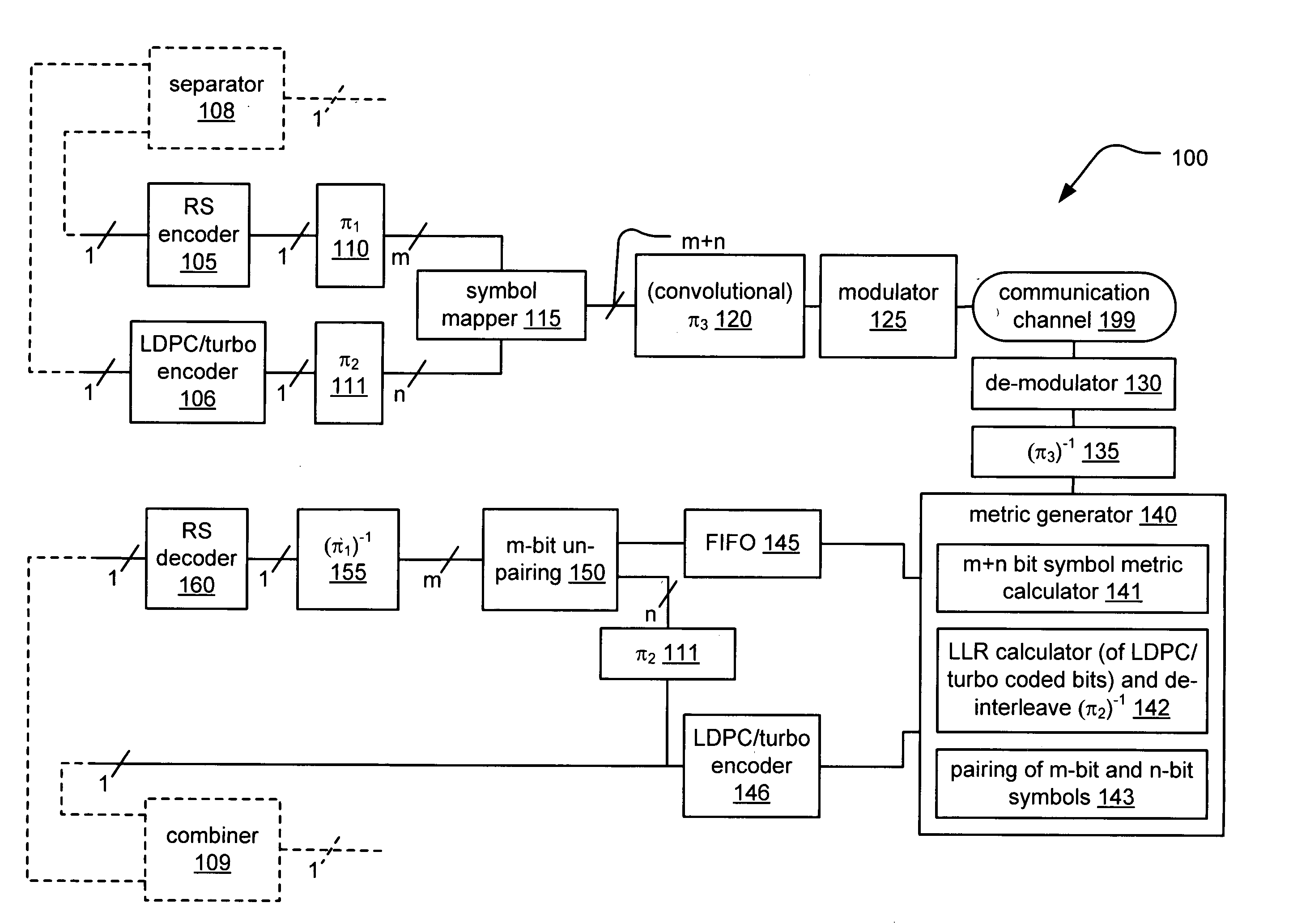
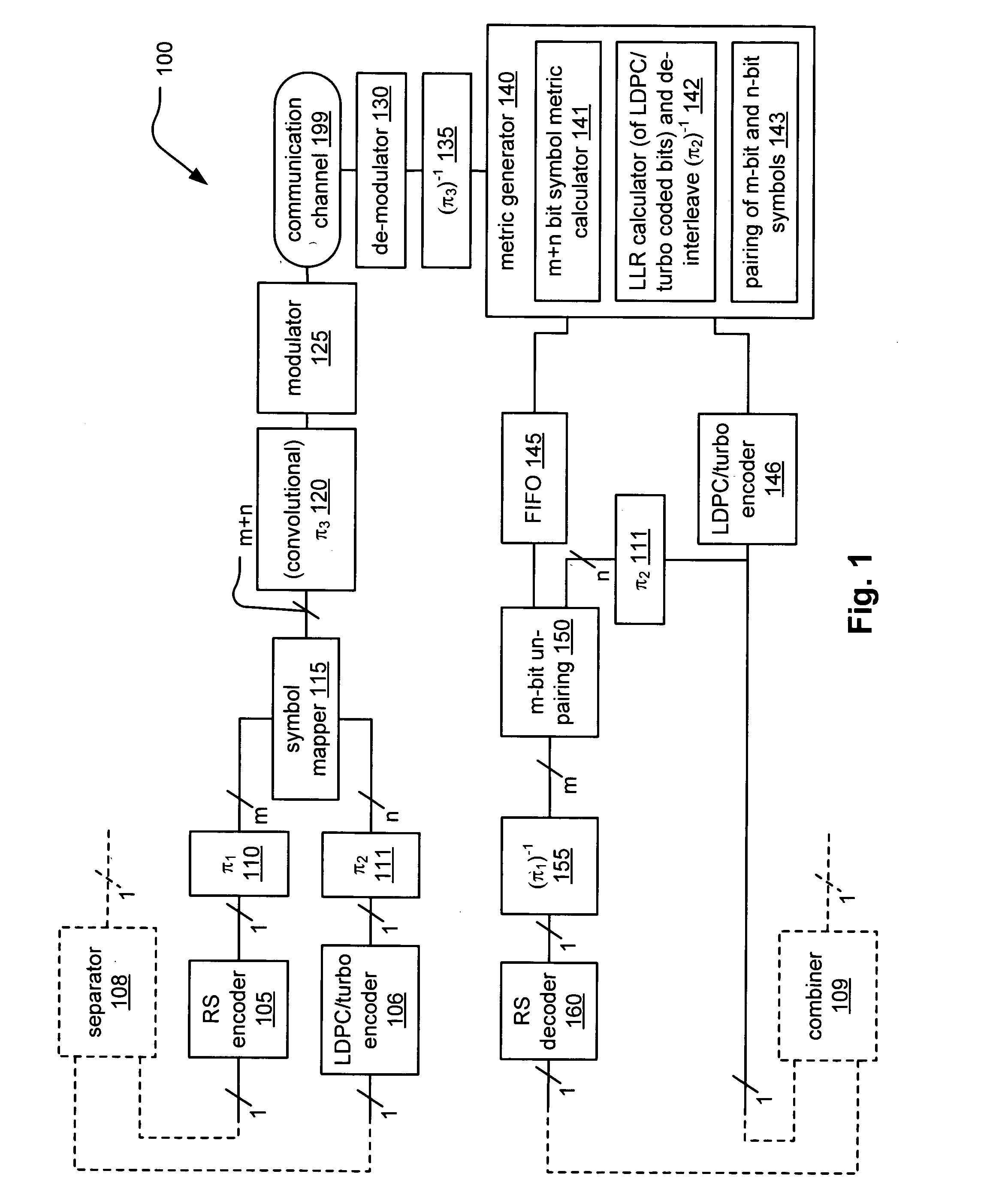
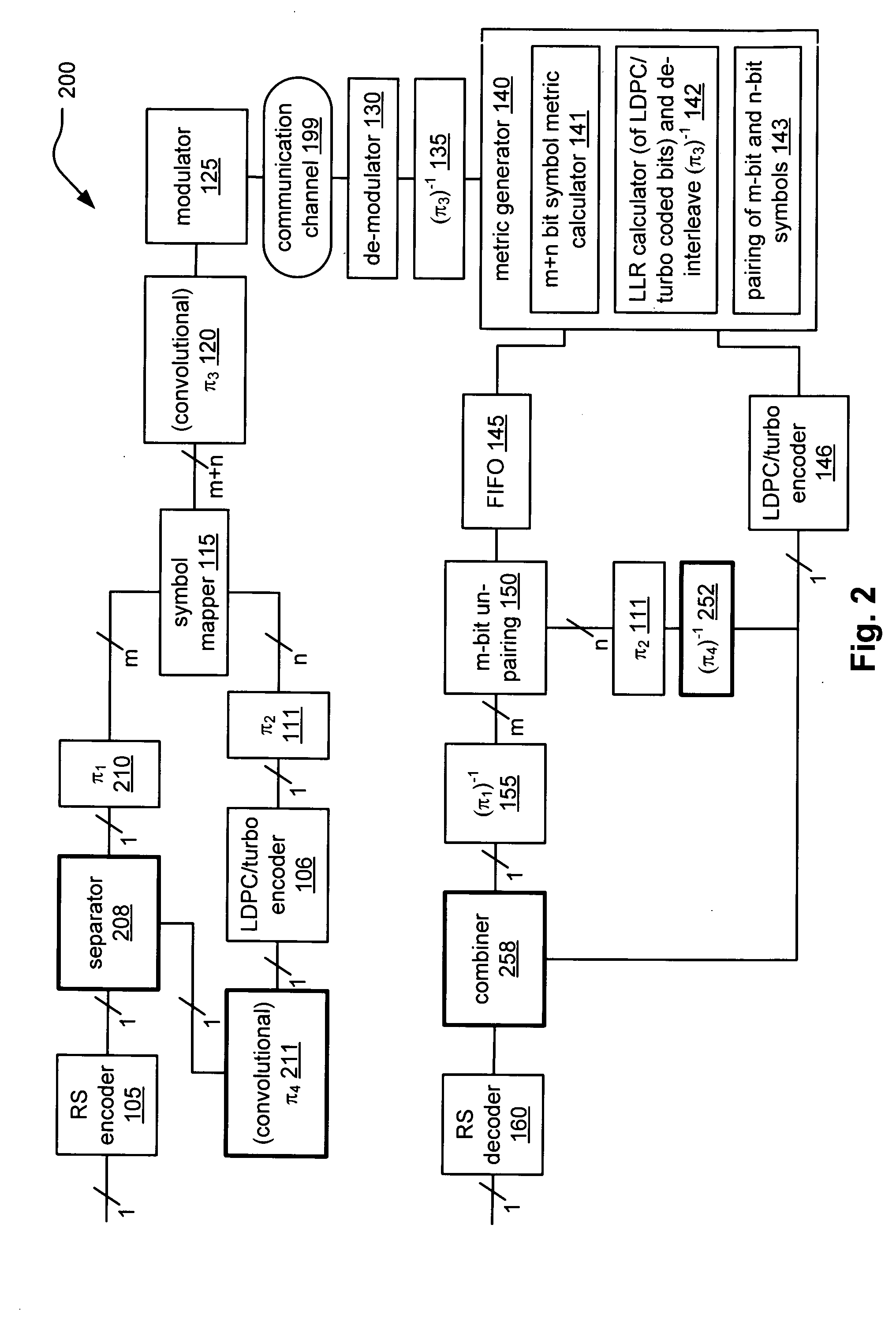
System correcting random and/or burst errors using RS (Reed-Solomon) code, turbo/LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code and convolutional interleave
InactiveUS20060224935A1Error correction/detection using concatenated codesError detection/correctionComputer hardwareBurst error
System correcting random and / or burst errors using RS (Reed-Solomon) code, turbo / LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code and convolutional interleave. A novel approach is presented that combines different coding types within a communication system to perform various types of error correction. This combination of accommodating different coding types may be employed at either end of a communication channel (e.g., at a transmitter end when performing encoding and / or at a receiver end when performing decoding). By combining different coding types within a communication system, the error correcting capabilities of the overall system is significantly improved. The appropriate combination of turbo code and / or LDPC code along with RS code allows for error correction or various error types including random error and burst error (or impulse noise).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Dual-binary system tailbaiting Turbo code coding method and apparatus
InactiveCN101083512AImprove throughputEliminate the phenomenon of "error flat bottom"Error preventionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresTurbo codedCode rate
The invention publishes the equipment and a method of double binary system for Turbo code encoding, which solve the problem that could not support any even number information block length and the random code rate in existing technology. The invention includes: The first component code encoder, the second component code encoder, the mark interweave and the speed matching device. The invention method includes the following step: the system sent the bit sequence to the first component code encoder, the mark interweave and the speed matching device; create check bit in the first component code encoder; carry on data interior exchange in the code interweaves for every other a pair of data; structure the matrix, carry on replace between each line; create two check bit in the second component code encoder; output bit sequence by the speed matching device to the system, the first component encoder and a second component encoder carries on the number rate match, so can obtain the code rate needed. Thus, it can support any even number information block length and the random code rate.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Multicarrier DS/CDMA system using a turbo code with nonuniform repetition coding
ActiveUS20040202138A1Increase the number ofReduce fadingError correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionProgramming languageConvolutional code
The present invention relates to a multicarrier direct sequence code division multiple access (DS / CDMA) system using a turbo code with nonuniform repetition coding. In particular, it relates to a multicarrier DS / CDMA system using a turbo code with unequal diversity order in its code symbols instead of using a convolutional code.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
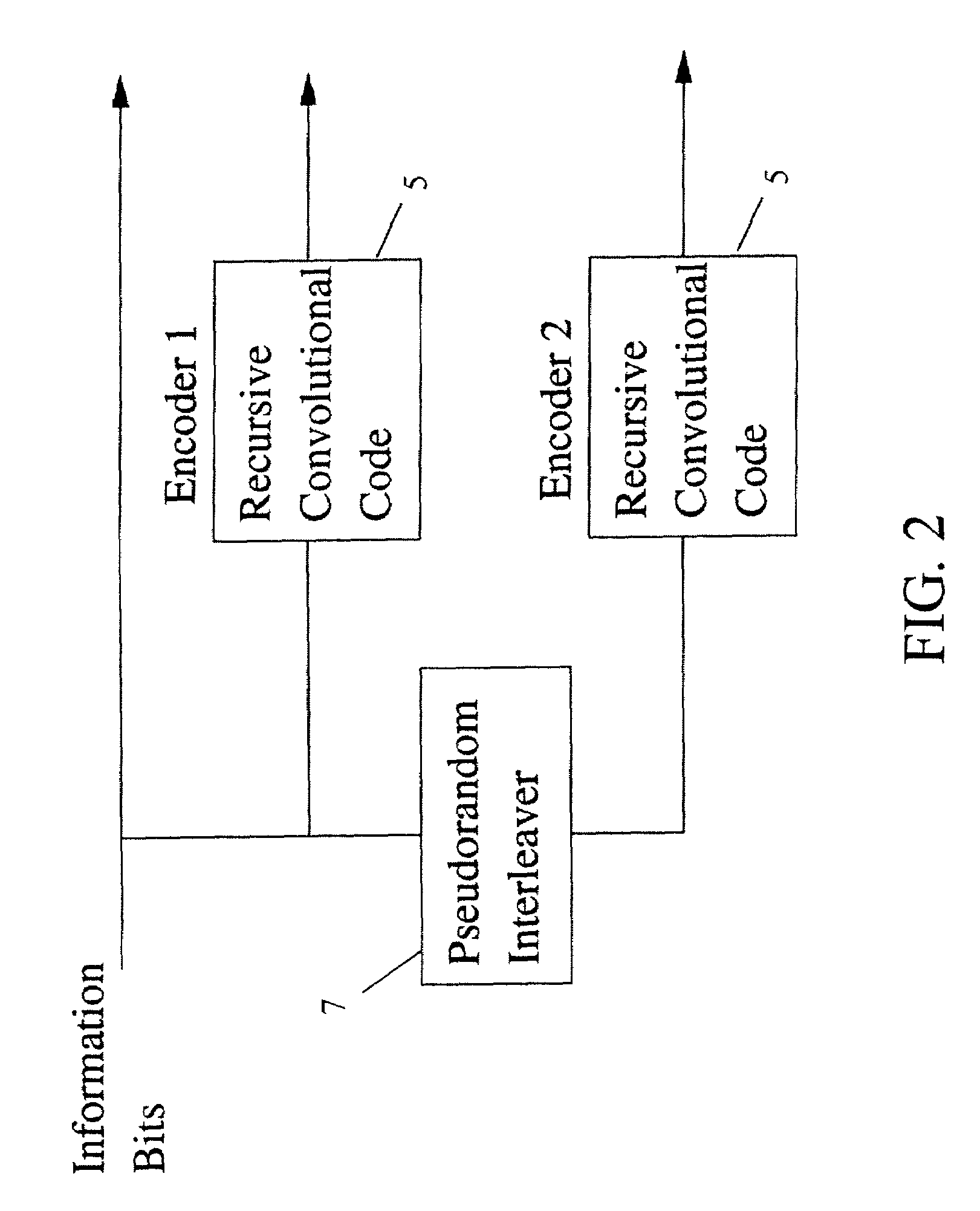
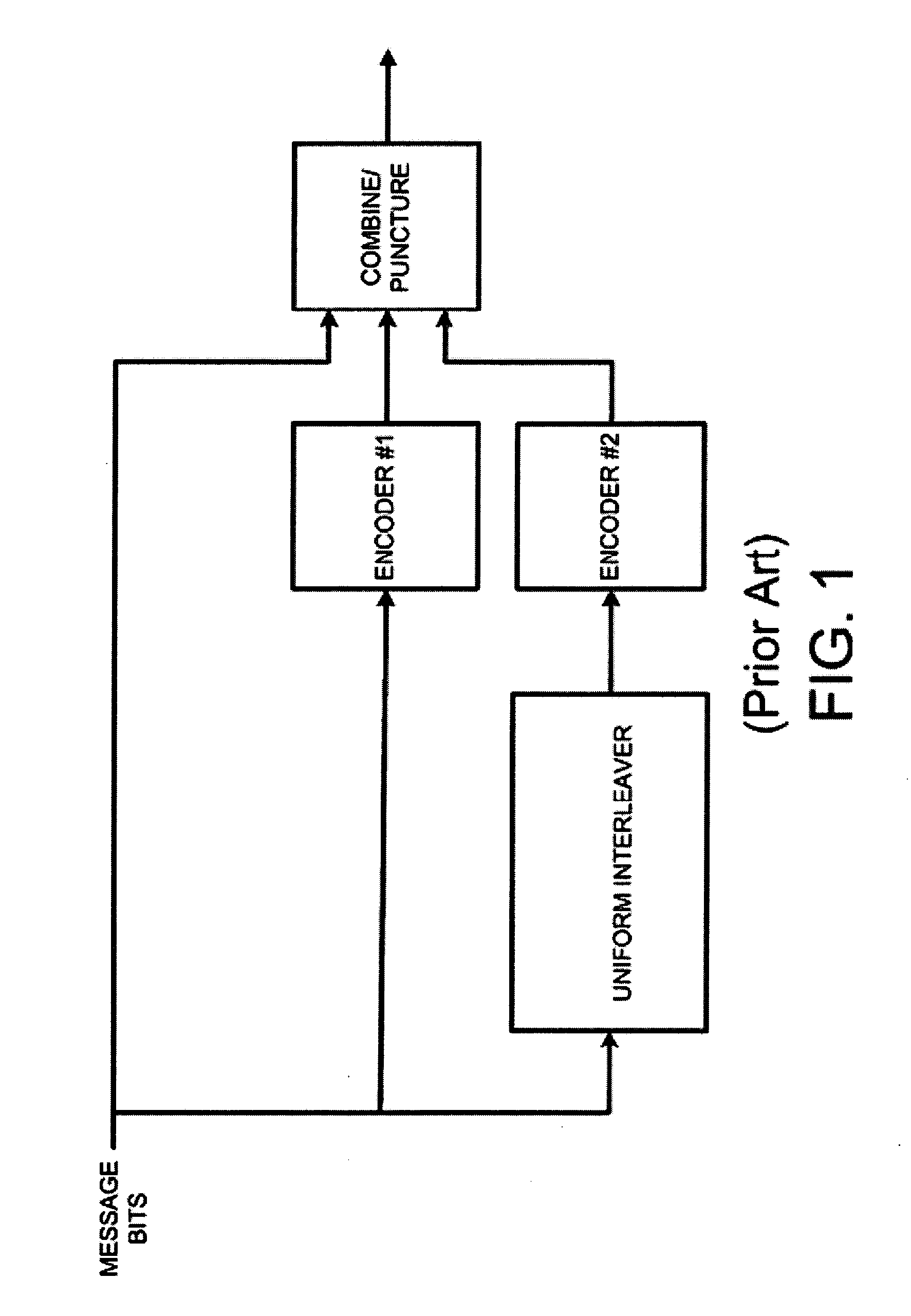
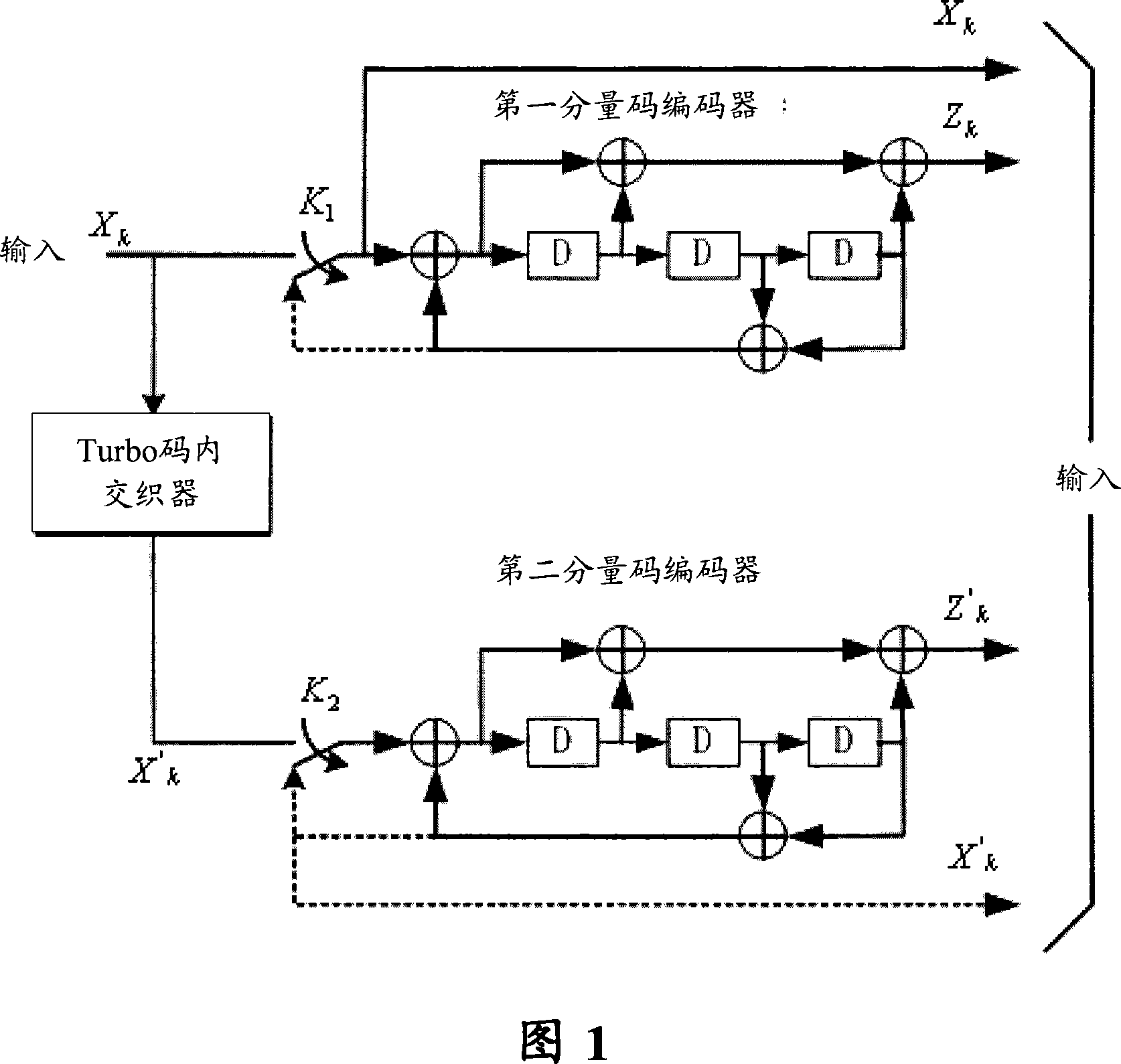
Turbo code encoder having an improved interleaver
InactiveUS6862707B2Improve performanceReduce overheadData representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareProcessor register
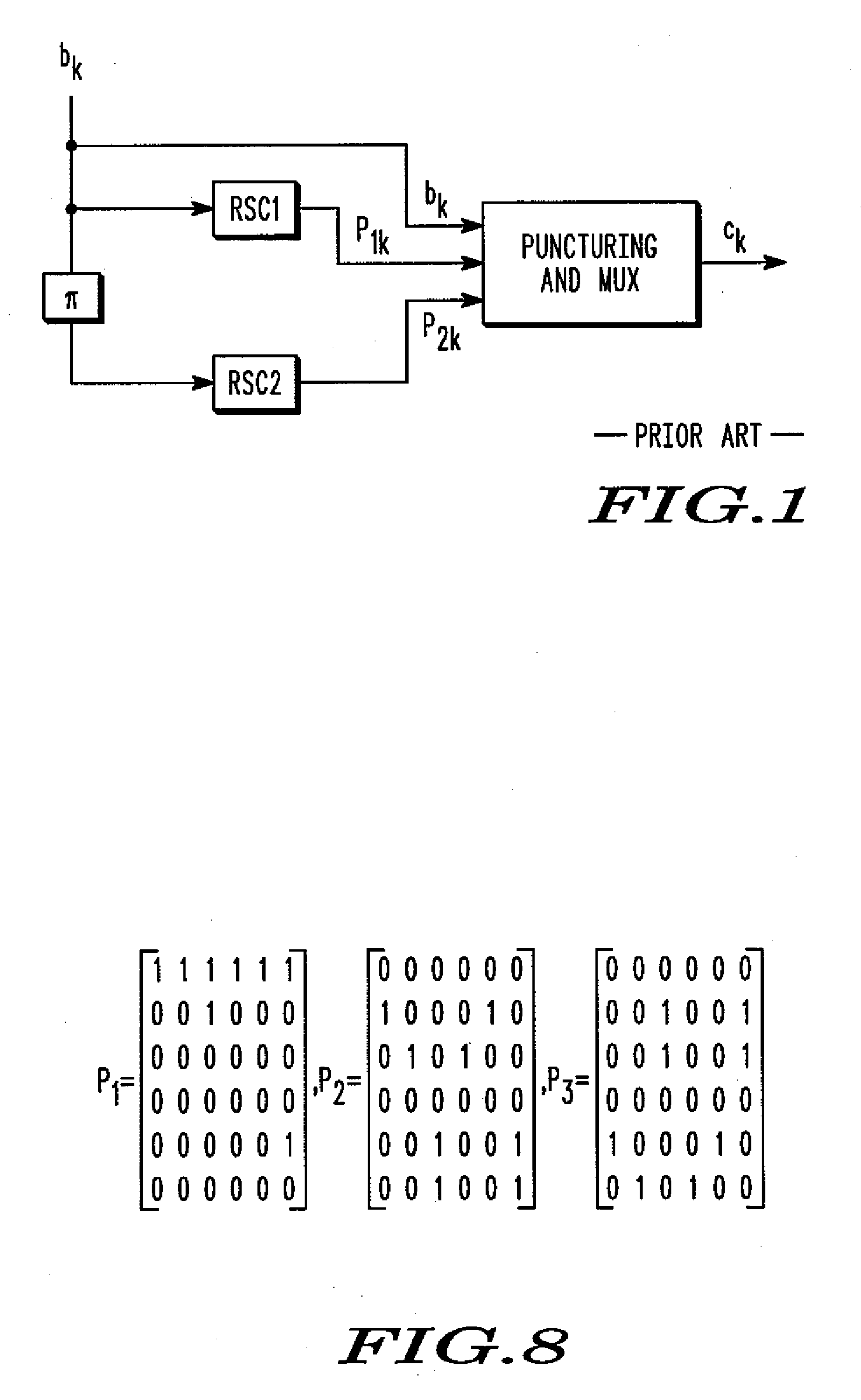
A turbo code encoder with an interleaver having two recursive systematic constituent code (RSC) encoders. The encoder encodes a finite sequence of informative bits without requiring a plurality of tail bits to flush the registers of each encoder to an all-zero state. The interleaver reduces the turbo code overhead by using only a single tail bit sequence. The interleaver also selectively reorders integers in accordance with a predefined set of rules.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
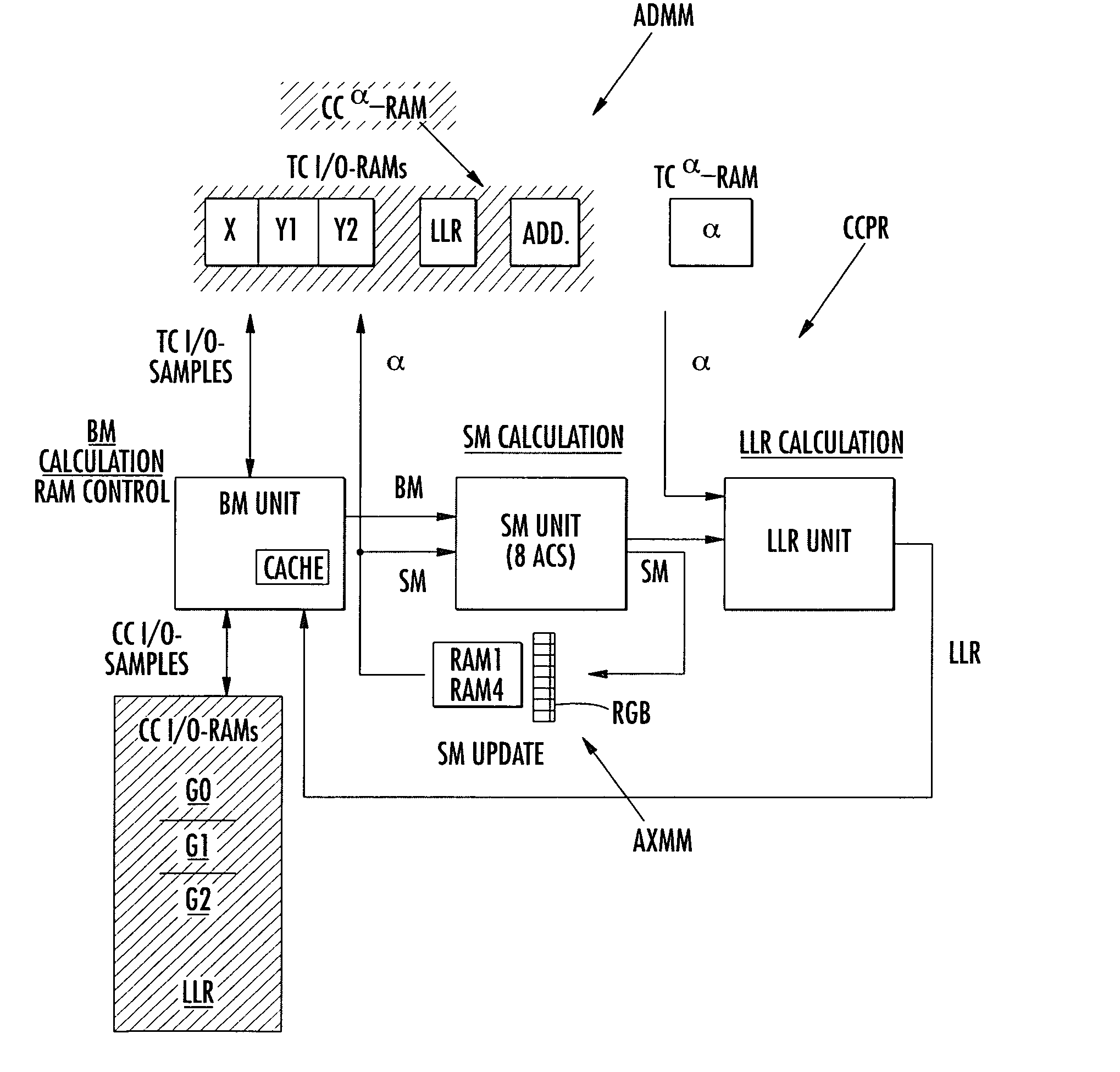
Combined turbo-code/convolutional code decoder, in particular for mobile radio systems
A combined decoder reuses input / output RAM of a turbo-code decoding circuit as alpha-RAM or beta-RAM for a convolutional code decoding circuit. Additional operational units are used for both turbo-coding and convolutional coding. An effective harware folding scheme permits calculation of 256 states serially on 8 ACS units.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Method and apparatus for generating low rate turbo codes
ActiveUS20080238730A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionComputer hardwareTurbo coded
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Block puncturing for turbo code based incremental redundancy
InactiveUS20070061690A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/correctionData streamTheoretical computer science
A method of block puncturing for turbo code based incremental redundancy includes a first step (1200) of coding an input data stream into systematic bits and parity bits. A next step (1202) includes loading the systematic bits and parity bits into respective systematic and parity block interleavers in a column-wise manner. A next step (1204) includes selecting a predefined redundancy. A next step (1206) includes outputting bits from the block interleavers in a row-wise manner in accordance with the selected predefined redundancy.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Method for Generating Candidates used in Turbo Coded Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing System with Selective Mapping Technique
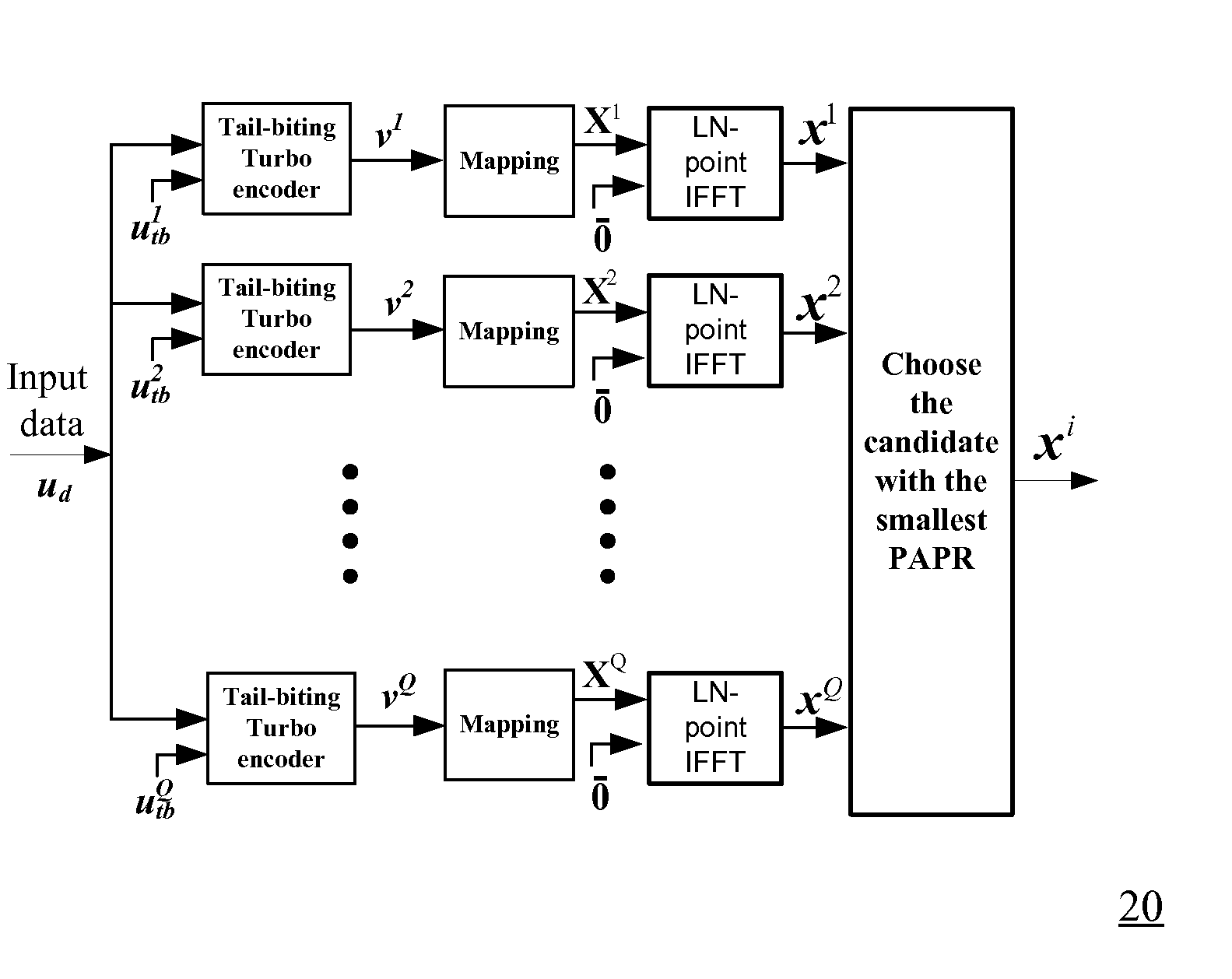
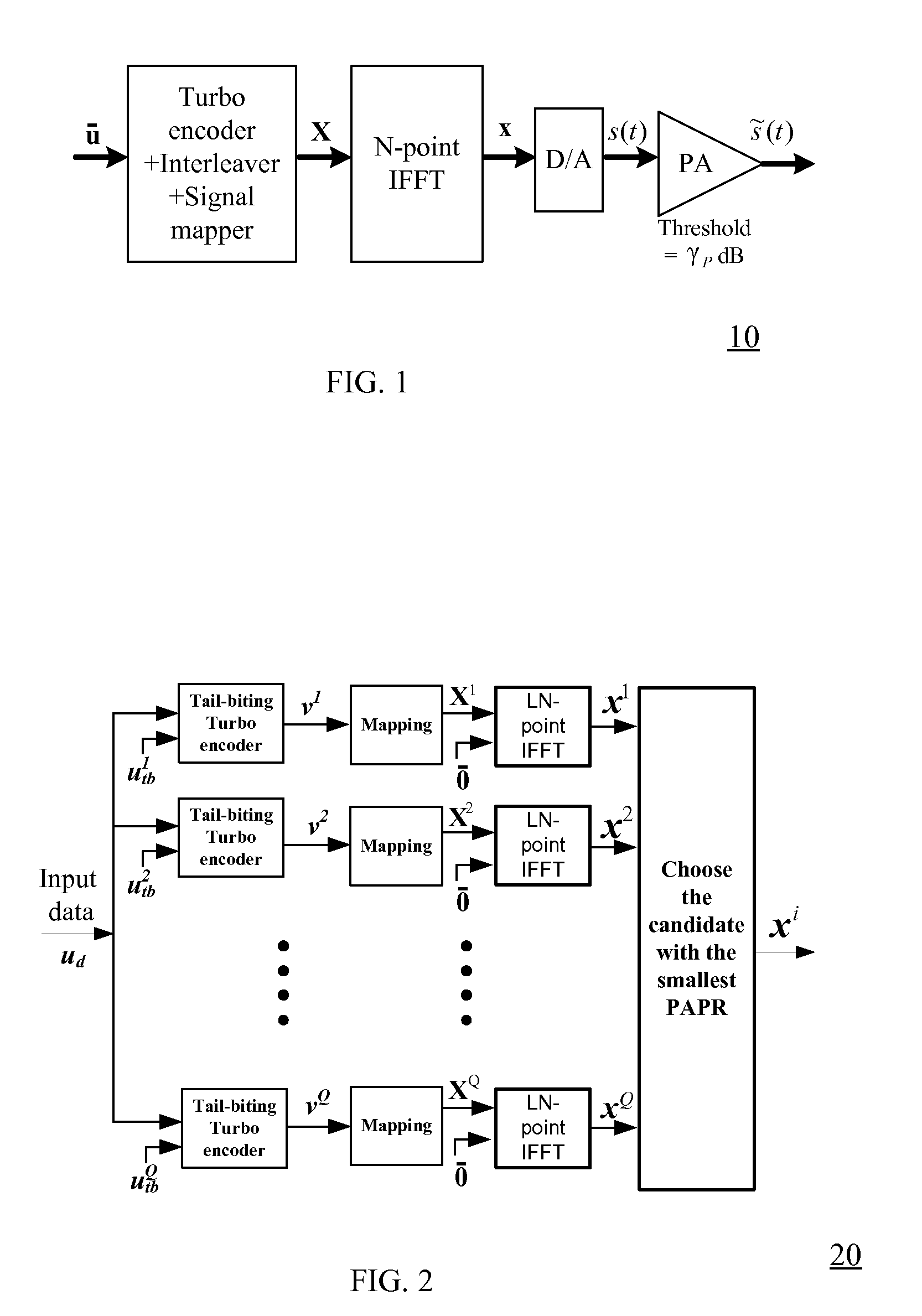
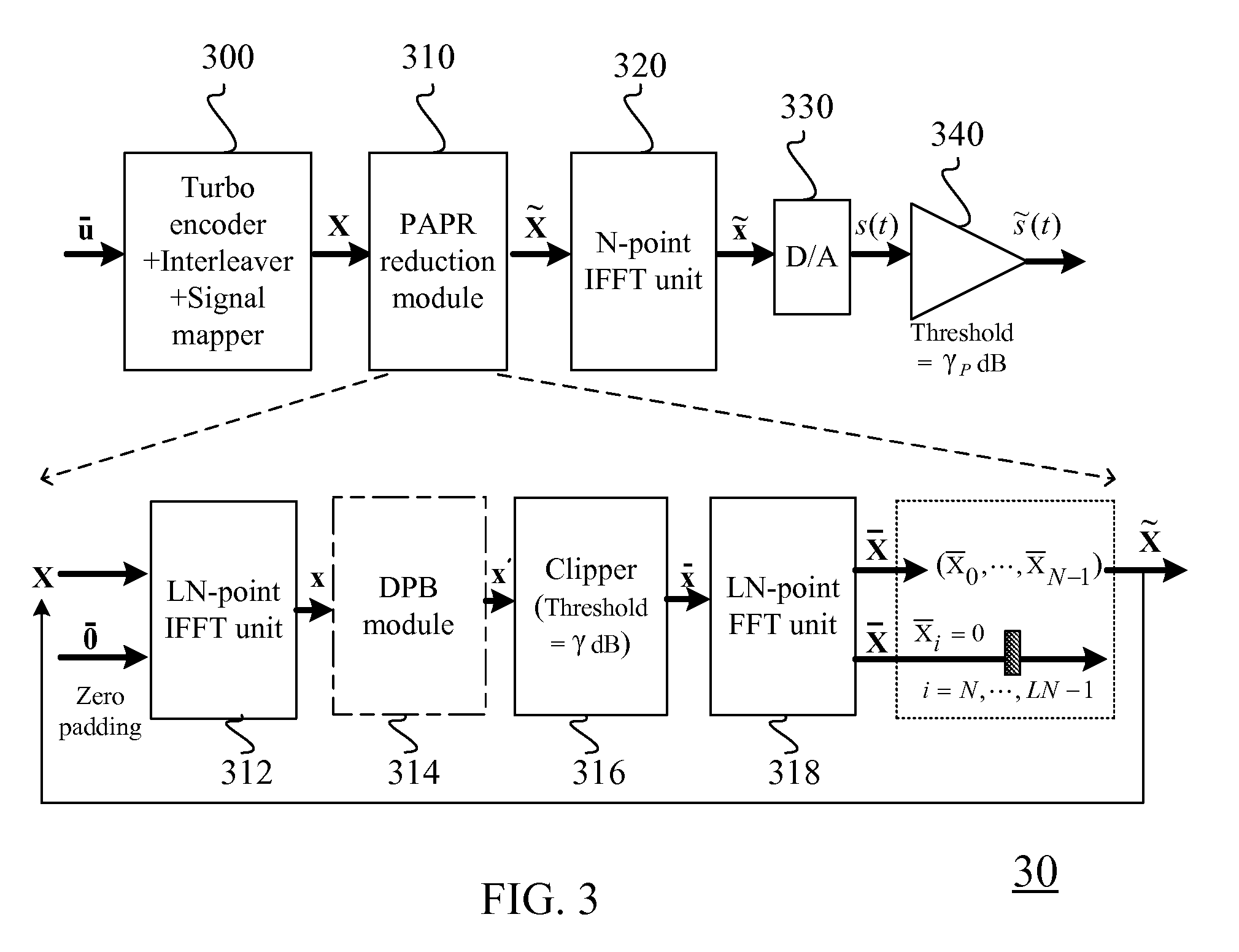
InactiveUS20080285432A1Reduce PAPRImprove performanceError preventionModulated-carrier systemsMapping techniquesTail-biting
A method for generating candidate used in TCOFDM (turbo coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing) with SLM (selective mapping) technique, a user data is combined with a plurality of seeds to generate corresponding a plurality of message vectors. The method is characterized in performing tail-biting turbo encoding on the message vectors to generate corresponding turbo codewords used for generating candidates, and the seed of each message vector is different from the seeds of other message vectors.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Full CMOS min-sum analog iterative decoders
InactiveUS20050240647A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple designDigital data processing detailsError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsMOSFETCMOS
Analog iterative decoders are provided that are based on the so-called min-sum algorithm (also referred to as max-sum or max-product, Max-Log-MAP or BP-based decoding) and can be used to decode powerful coding schemes such as low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes and turbo codes. The circuits can be implemented by standard CMOS technology, which means lower fabrication cost and / or simpler design compared to previously reported analog iterative decoders that are based on BiCMOS or sub-threshold CMOS technology. Soft information is passed among variable nodes and parity-check nodes. A low-voltage high-swing Max WTA circuit is also provided. The circuit can be implemented by short channel MOSFET transistors and yet provide a reasonably high degree of accuracy. Applications include soft computing, and analog signal processing, in general. A Min WTA circuit can also be built based on this circuit by subtracting the input currents from a large reference current.
Owner:BANIHASHEMI AMIR +1
Method and apparatus for encoding blocks of data with a blocks oriented code and for decoding such blocks with a controllable latency decoding, in particular for a wireless communication system of the WLAN or wpan type
ActiveUS20070139229A1Lower latencyImprove communication performanceCode conversionError detection onlyComputer hardwareCommunications system
To control a decoding latency, larger blocks are nonequally segmented into smaller ones. The decoding process starts directly after reception of the first small block. The latency is defined by the latency of the last small block decoding. Changing the number of iterations during the turbo-code decoding also permits control of the decoding latency.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Stopping Criteria for Turbo Decoder
ActiveUS20170005674A1Reduce power consumptionAvoid excessive power consumptionError preventionOther decoding techniquesCoding blockComputer hardware
This disclosure relates to providing negative stopping criteria for turbo decoding for a wireless device. A device may wirelessly receive turbo coded data. Turbo decoding may be performed on the turbo coded data. Performing turbo decoding may use one or more negative stopping criteria for early termination of the turbo decoding for each code block of the turbo coded data. The negative stopping criteria may be selected to terminate the turbo decoding of a code block early under poor wireless medium conditions. Turbo decoding of a code block may be terminated early if the one or more negative stopping criteria for the code block are met.
Owner:APPLE INC
Rate de-matching method
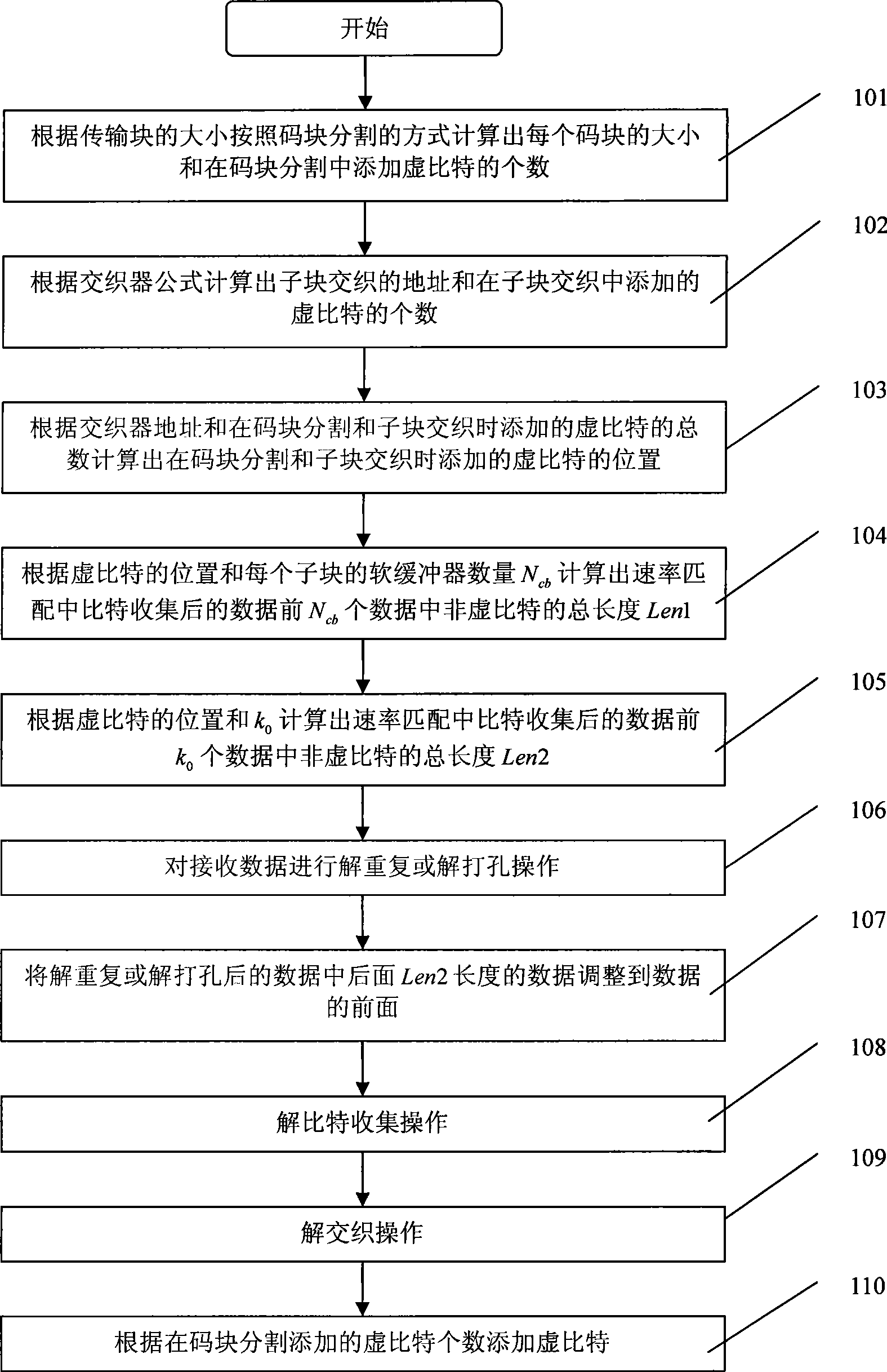
ActiveCN101388751AReduce handlingEasy to implementError preventionData switching networksCoding blockComputer science
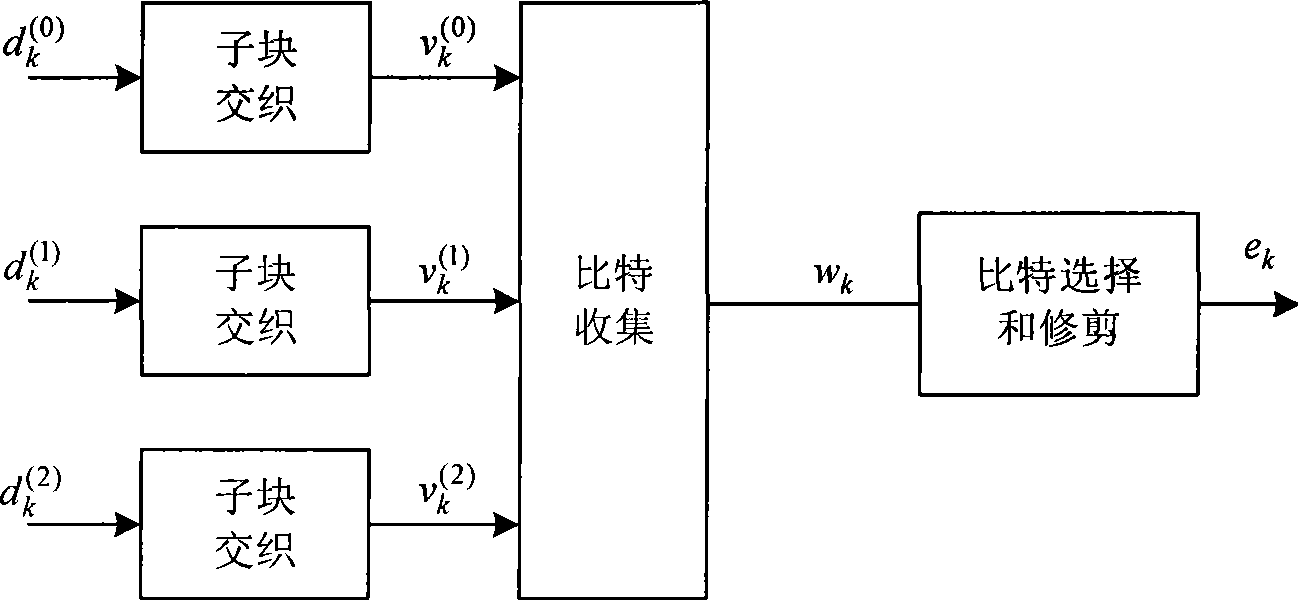
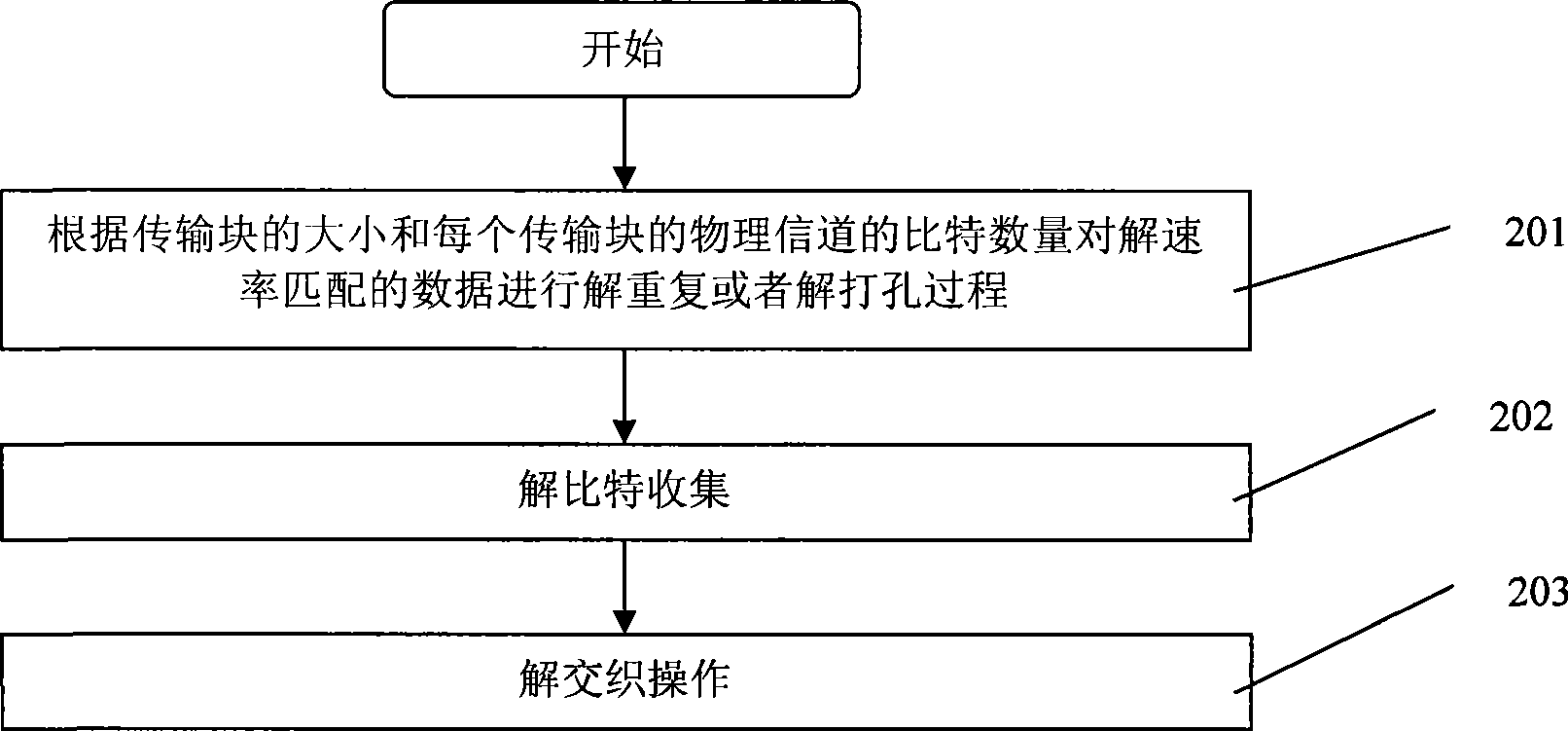
The invention provides a method for solving rate matching, which comprises the following steps: without inserting dummy bits into receiving data, which are added during the dividing of code blocks and the interweaving of sub-blocks before the de-repeating operation or the de-drilling operation, directly carrying out the de-repeating operation or the de-drilling operation to the receiving data, then carrying out the de-bit-collecting and the de-interweaving, wherein for the rate de-matching of Turbo codes, the process of inserting the dummy bits into the receiving data, which are added during the dividing of the code blocks and the interweaving of the sub-blocks, is concealed, and the de-repeating operation or the de-drilling operation can be carried out only through calculating the length of non-dummy bits in the former Ncb of data and the former k0 of data in the data after the collection of bits in the rate matching, and for the rate de-matching of convolution codes, the method is more simplified, namely the de-repeating operation or the de-drilling operation can be directly carried out to the receiving date according to the size of transmission blocks. Compared with the prior art, the method simplifies the de-rate matching process, reduces the data transmitting process, greatly reduces the processing time, reduces the data quantity which needs to be processed and improves the processing efficiency.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com