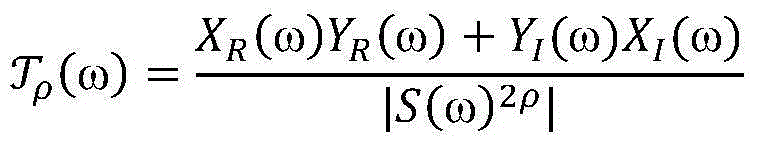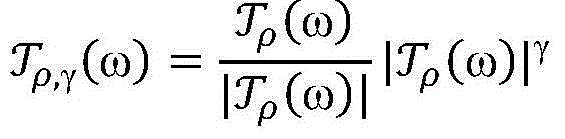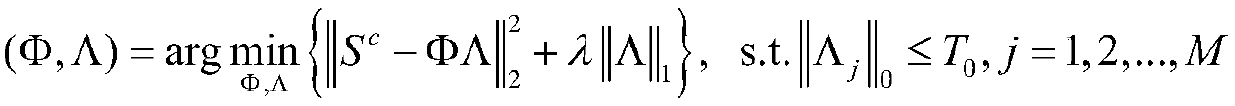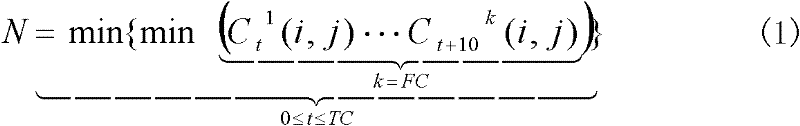Patents
Literature
371 results about "A posteriori probability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A posteriori probability. The conditional probability of an event taking place under certain conditions, to be contrasted with its unconditional or a priori probability. There is no difference between the meaning of the terms "conditional" and "a posteriori".
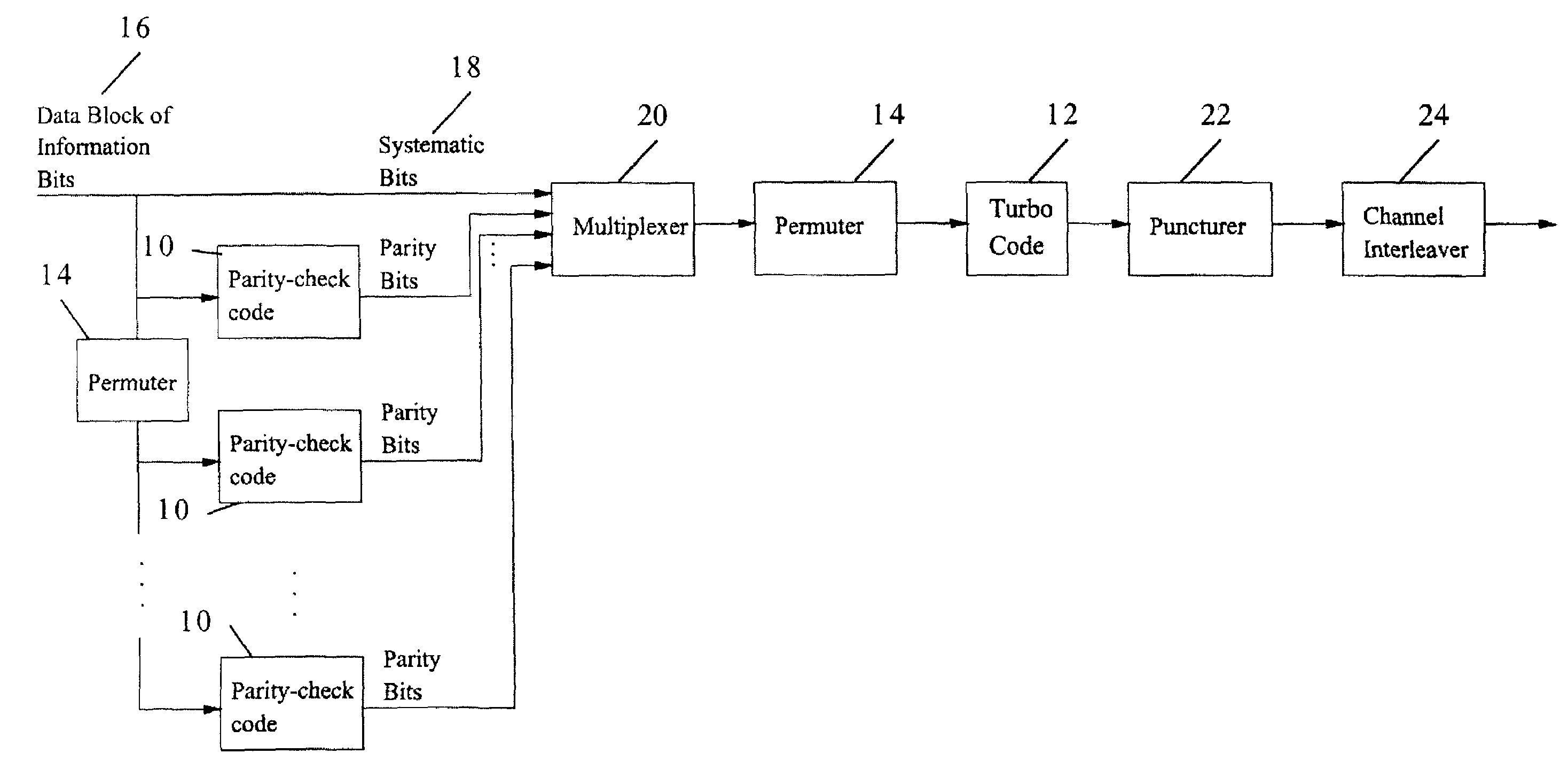
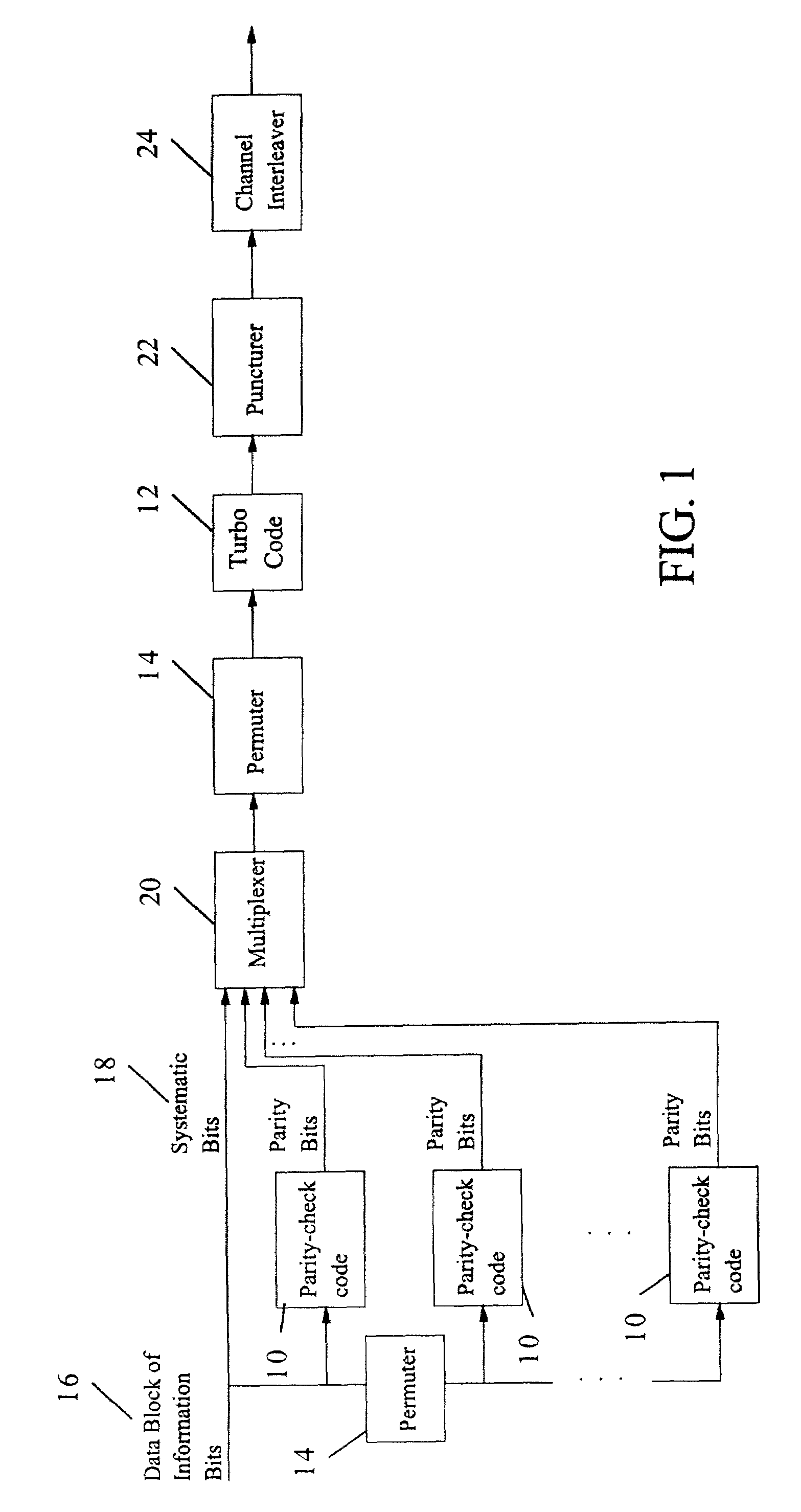
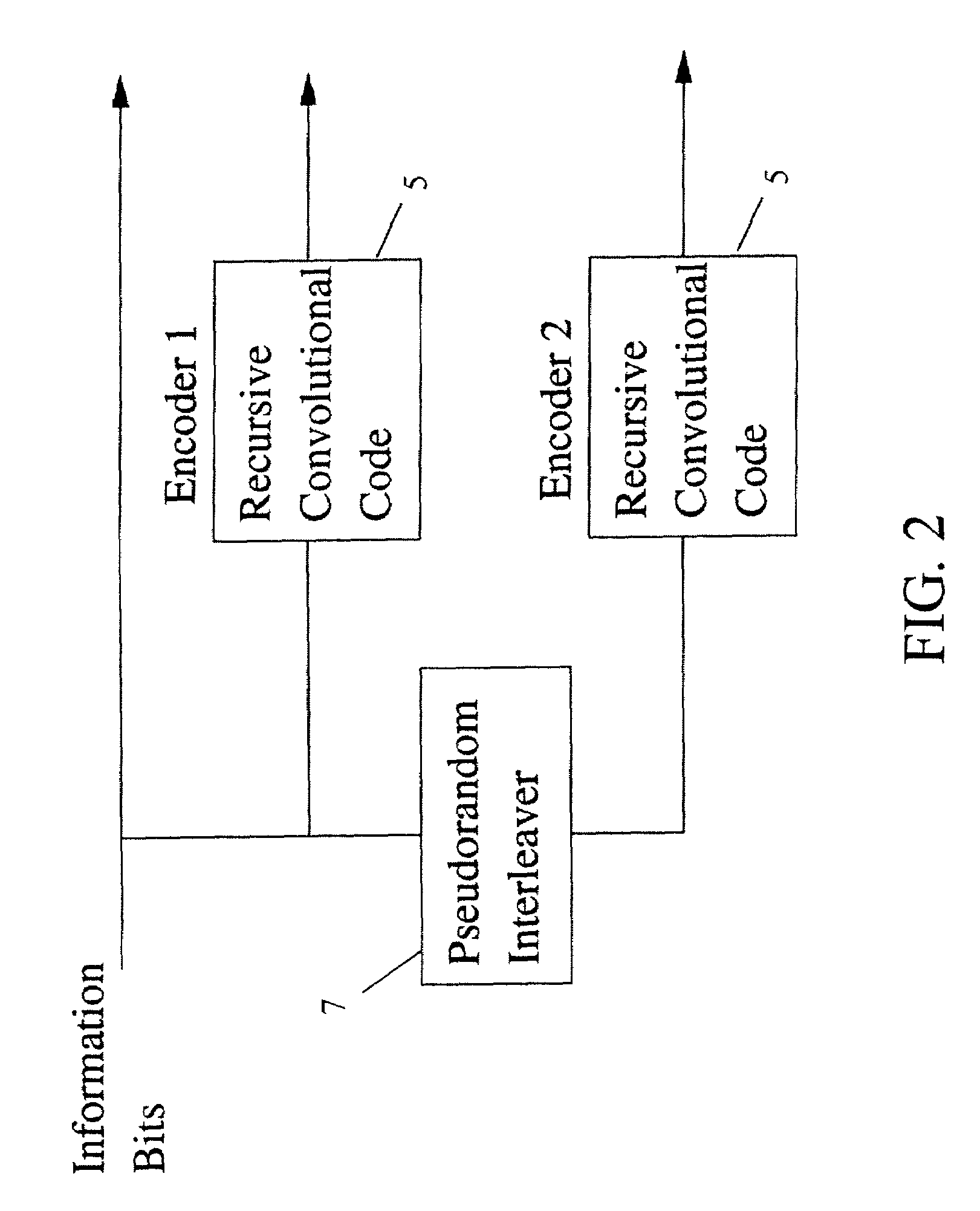
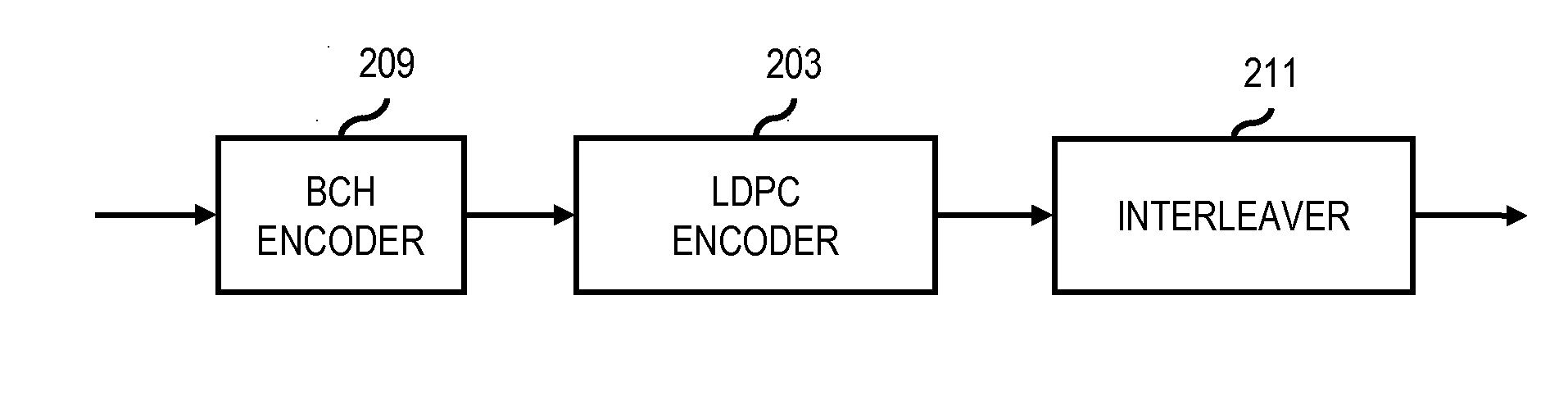
Method and coding means for error-correction utilizing concatenated parity and turbo codes
InactiveUS7093179B2Reduction in rateImprove overall utilizationError preventionError detection/correctionParallel computingTurbo coded
A method and apparatus for encoding and decoding data using an overall code comprising an outer parity-check and an inner parallel concatenated convolutional, or turbo code. The overall code provides error probabilities that are significantly lower than can be achieved by using turbo codes alone. The output of the inner code can be punctured to maintain the same turbo code rate as the turbo code encoding without the outer code. Multiple parity-check codes can be concatanated either serially or in parallel as outer codes. Decoding can be performed with iterative a posteriori probability (APP) decoders or with other decoders, depending on the requirements of the system. The parity-check code can be applied to a subset of the bits to achieve unequal error protection. Moreover, the techniques presented can be mapped to higher order modulation schemes to achieve improved power and bandwidth efficiency.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
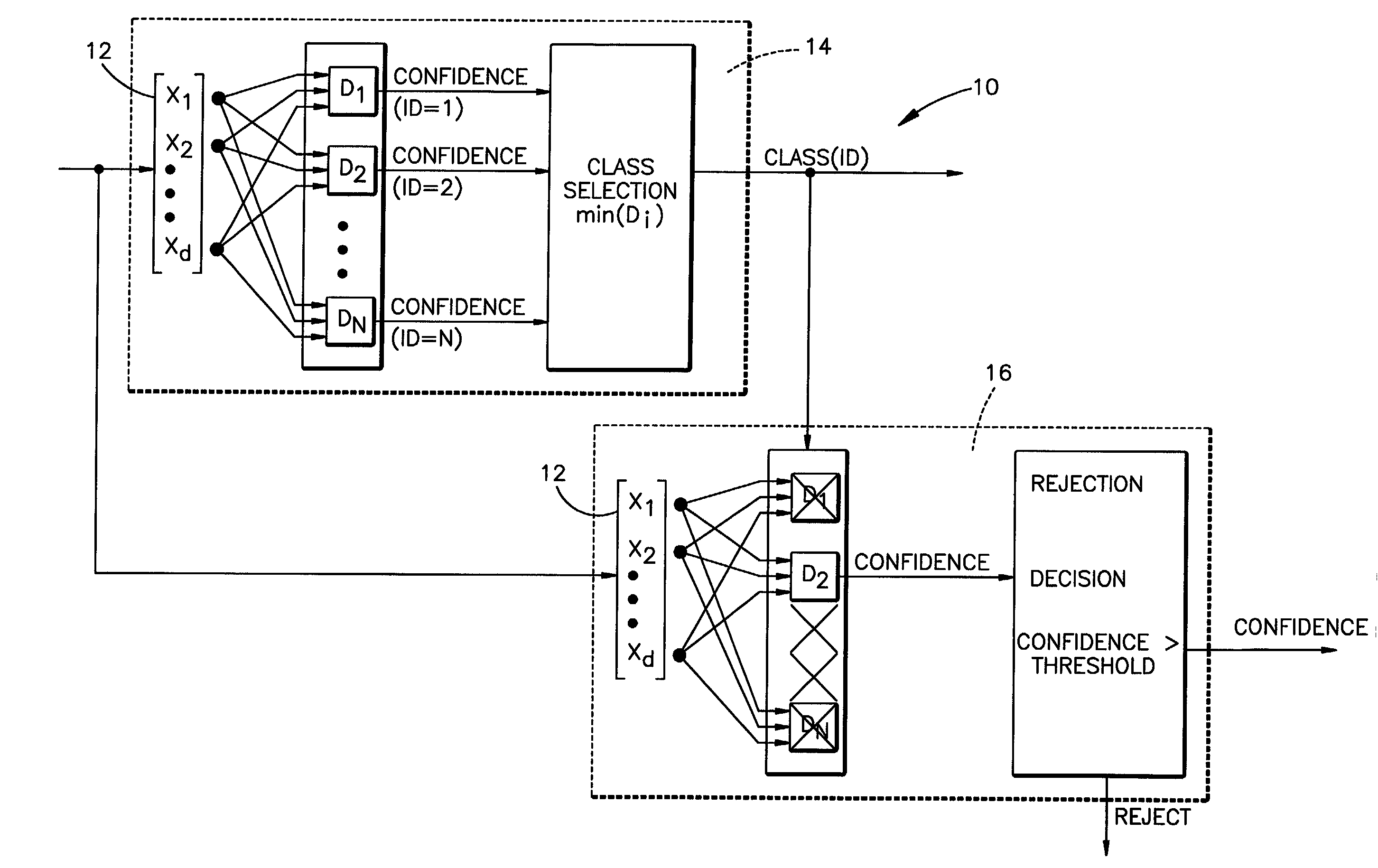
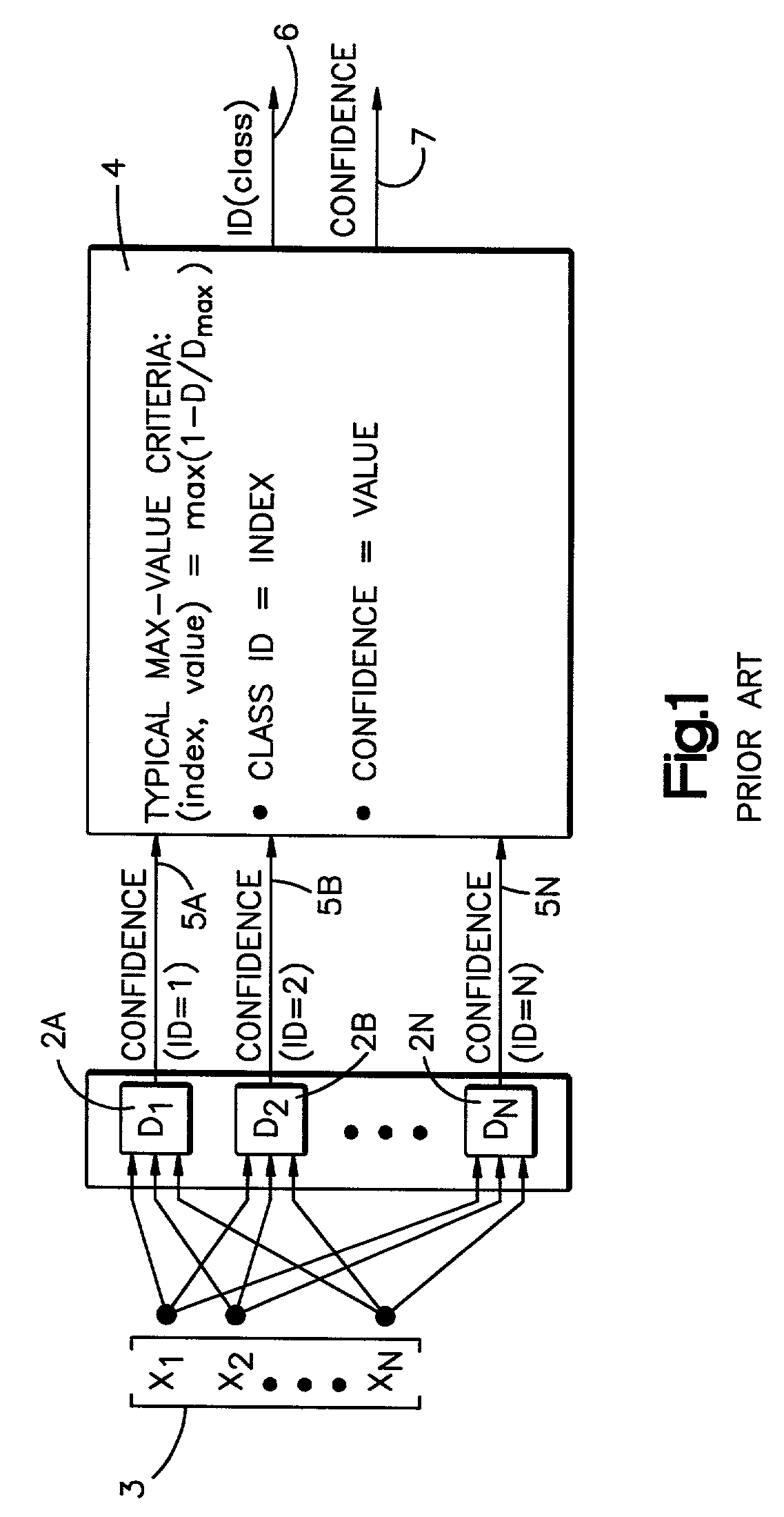
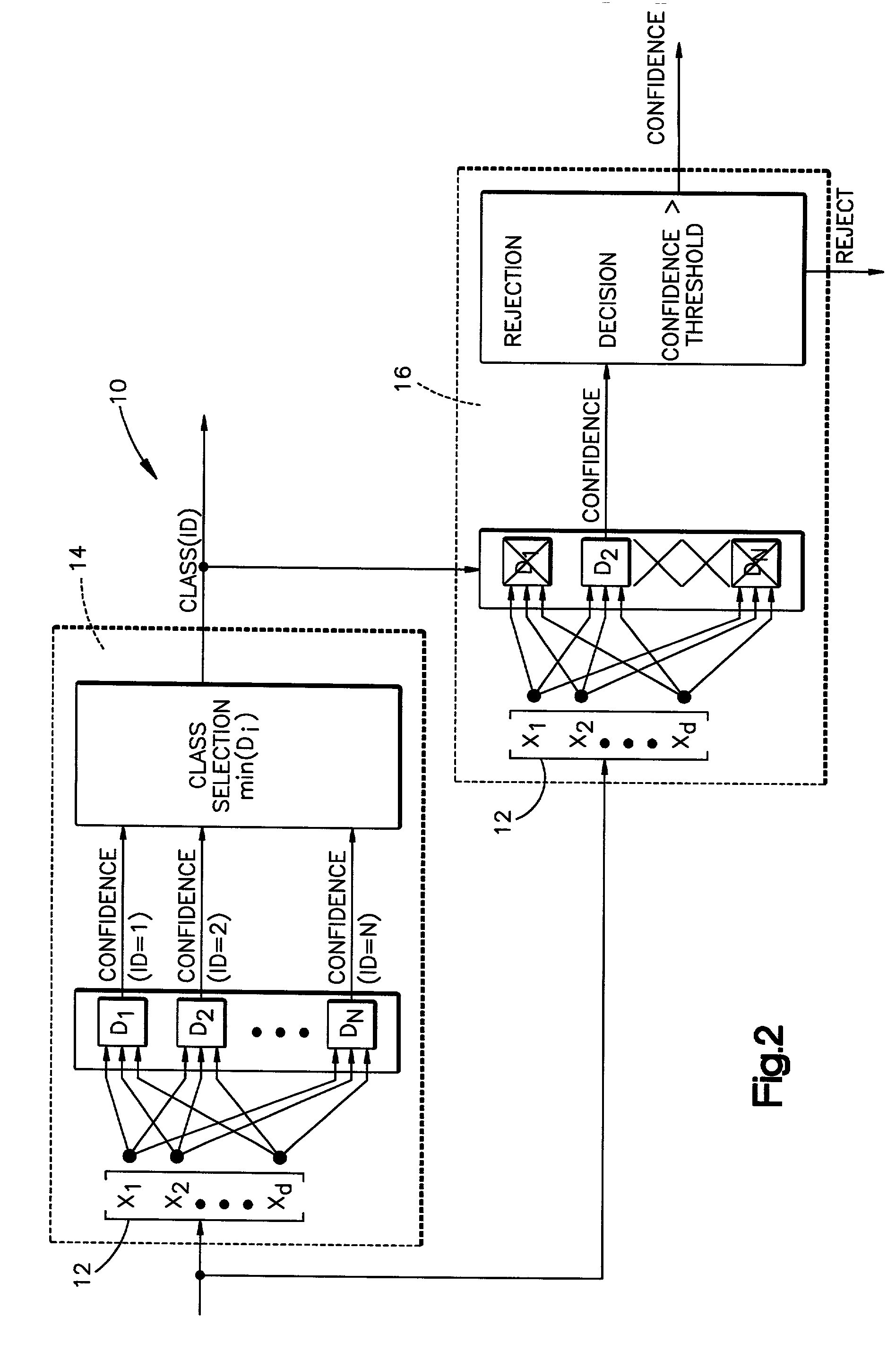
Compound classifier for pattern recognition applications
A method is disclosed for classifying an input pattern into an associated class through use of a compound classifier. Data pertaining to preselected features present within the input pattern are extracted. A discriminant value for each of a plurality of classes is then determined via a first classification technique. This value reflects the relative likelihood that a class is the associated class. The class with the highest relative likelihood is selected. A confidence value is generated via a second classification technique. This confidence value is reflective of the a posteriori probability that the selected class is the associated class. The selected class is rejected if the determined confidence value is below a predetermined threshold value.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
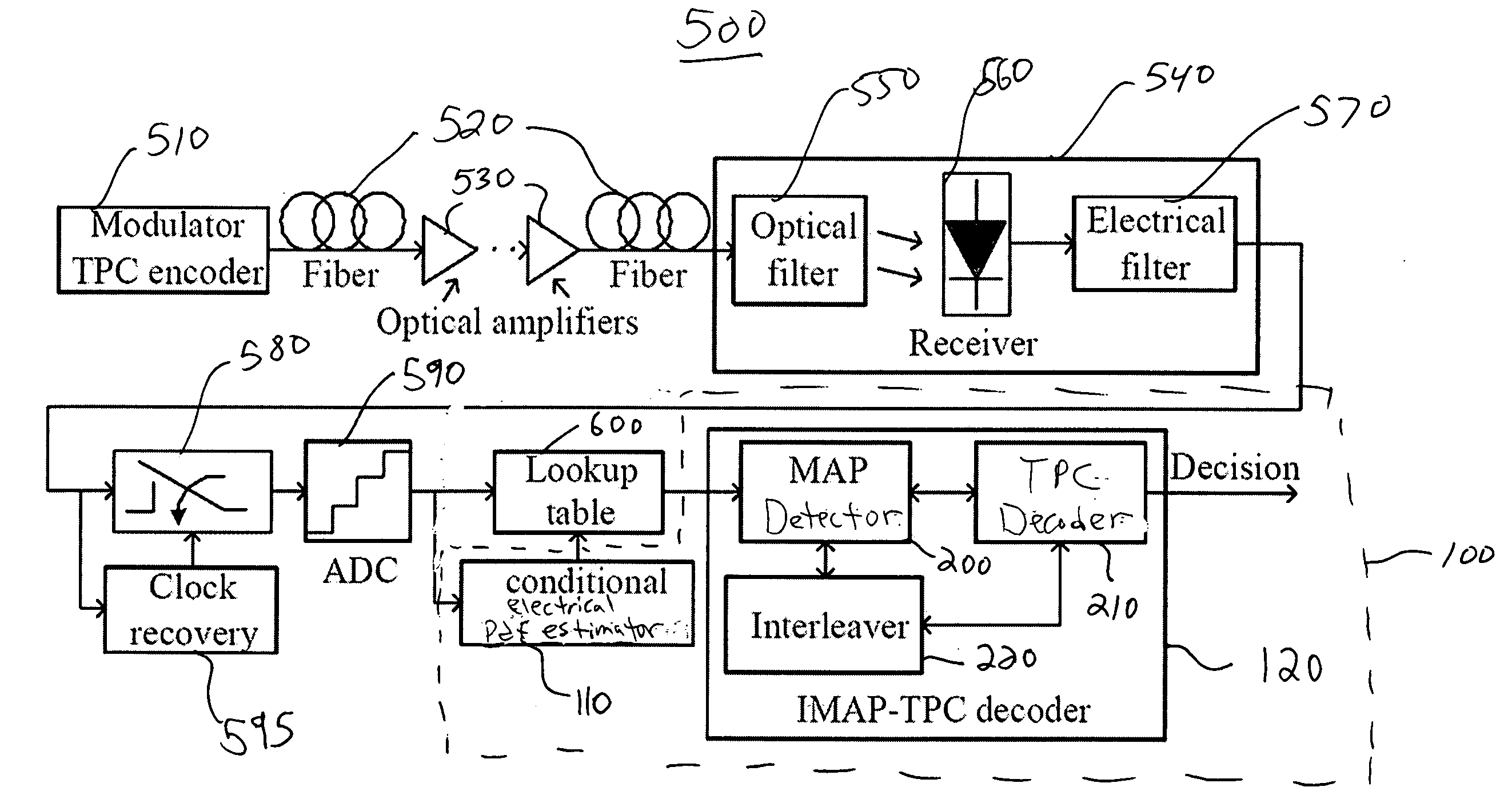
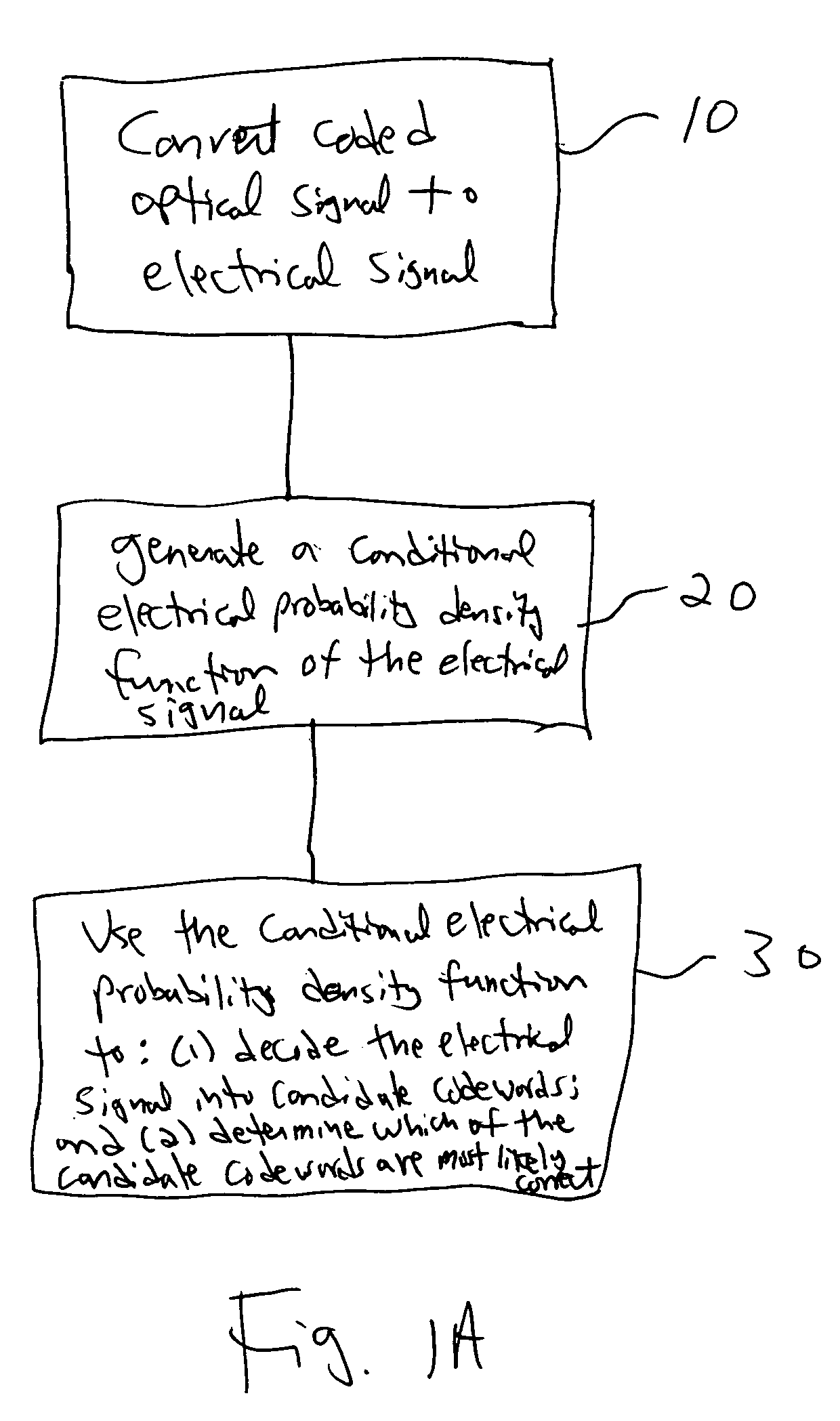
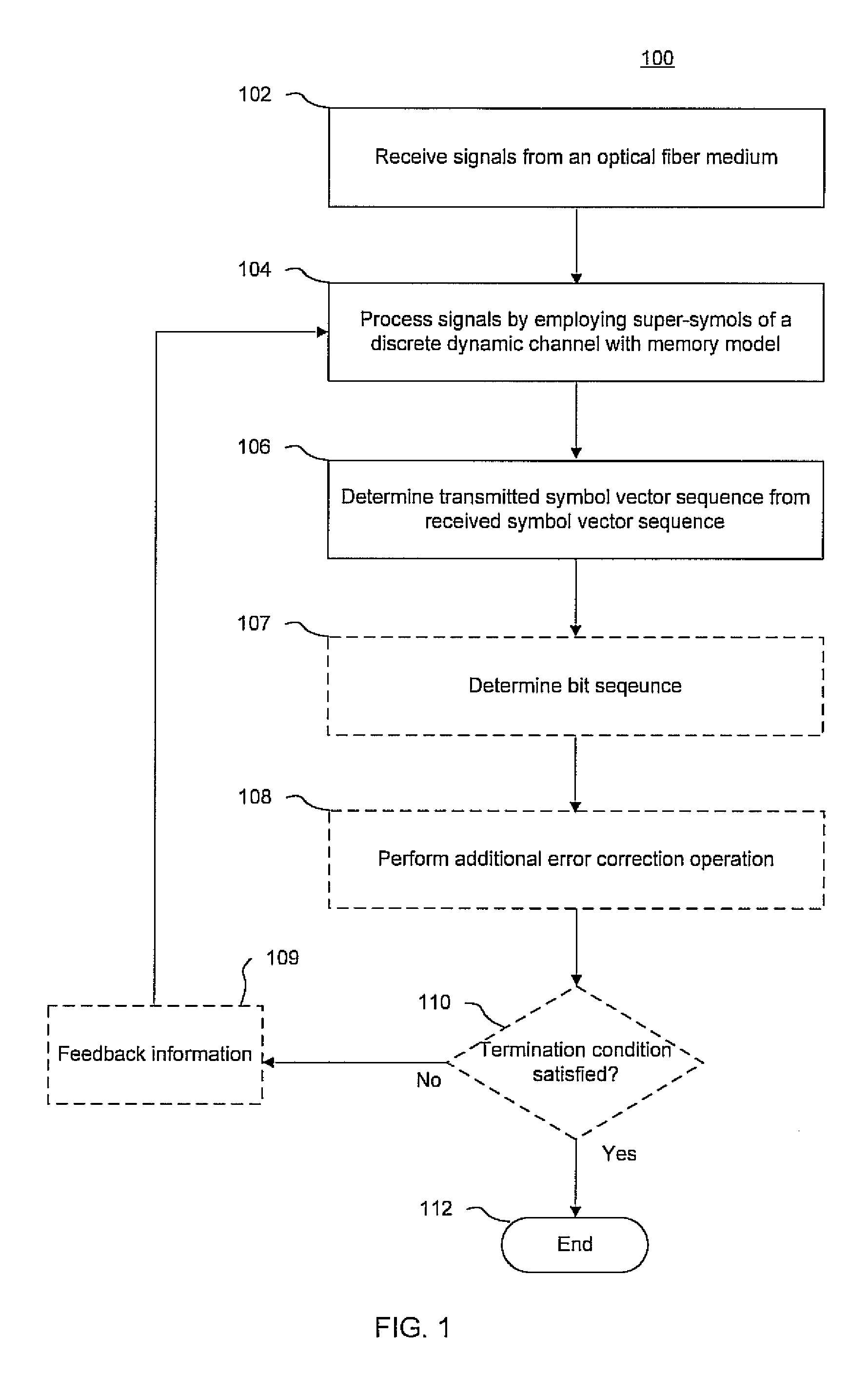
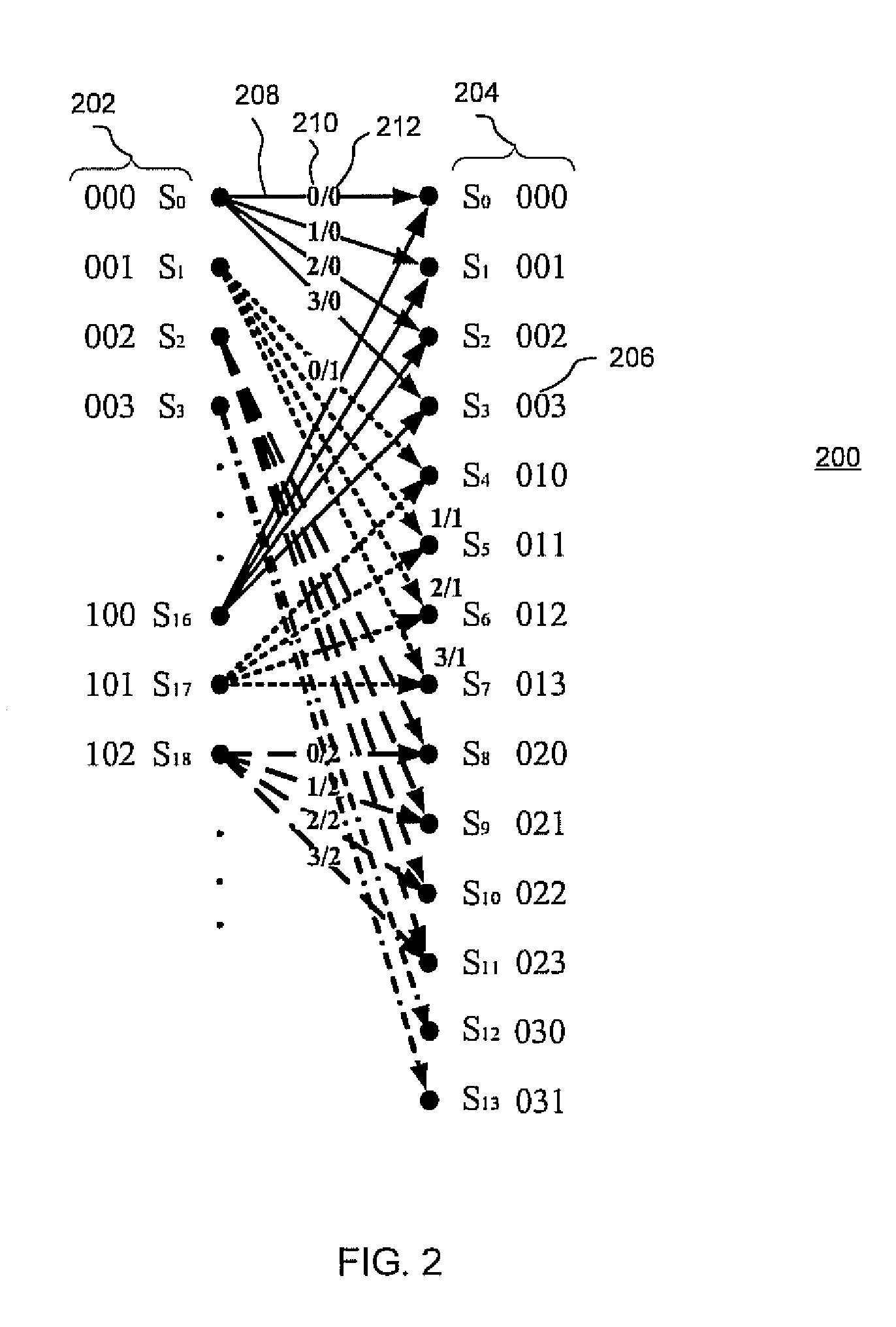
Integrated maximum a posteriori (MAP) and turbo product coding for optical communications systems
InactiveUS20060285852A1Improve fiber performanceImprove bit error rateElectromagnetic transmissionBaseband systemsLogitEqualization
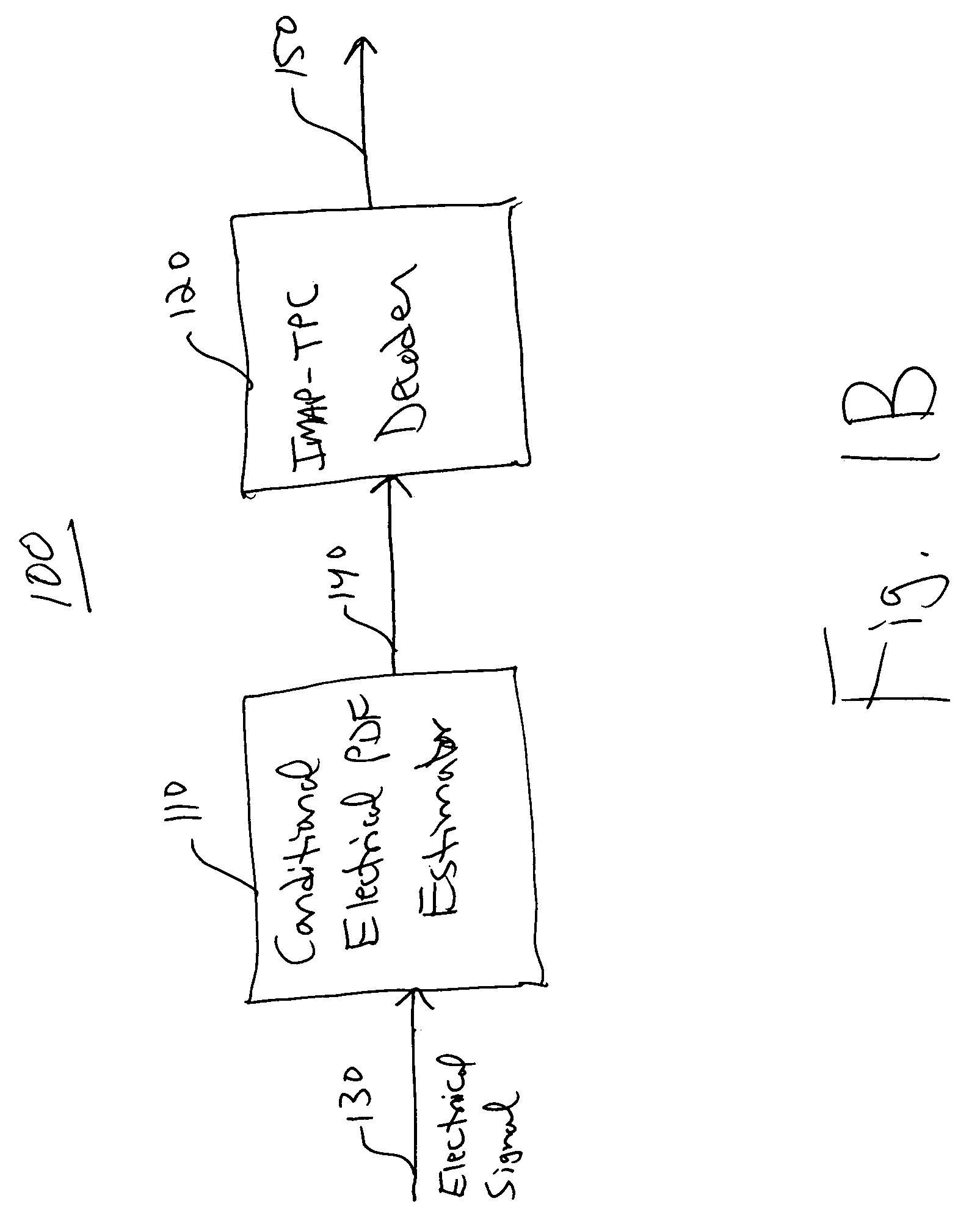
An integrated maximum a posteriori equalization and turbo product coding (IMAP-TPC) system for optical fiber communications systems (OFCS) is provided that uses probabilistic characterization of the electrical current in the presence of inter-symbol interference (ISI) and noise to compensate their effects and improve the bit error rate. In the IMAP-TPC system, turbo product code (TPC) decoding is integrated with a symbol-by-symbol maximum a posteriori (MAP) detector. The MAP detector calculates the log-likelihood ratio of a received symbol using the conditional electrical probability density information, and hence obtains a much more accurate reliability measure than the traditional measure used in the TPC decoder.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Method for splitting news video program, and method and system for cataloging news videos
InactiveCN102547139APromote expansionAccurate segmentationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCatalogingEngineering
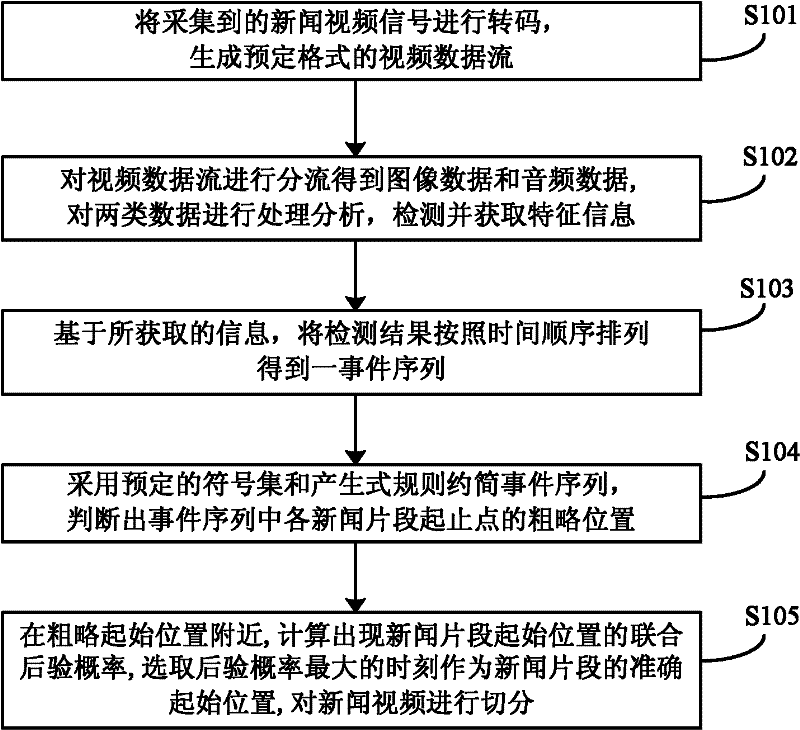
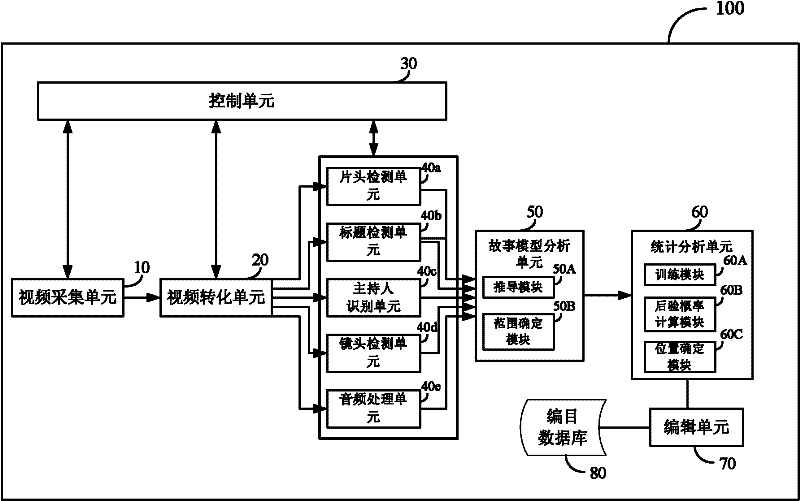
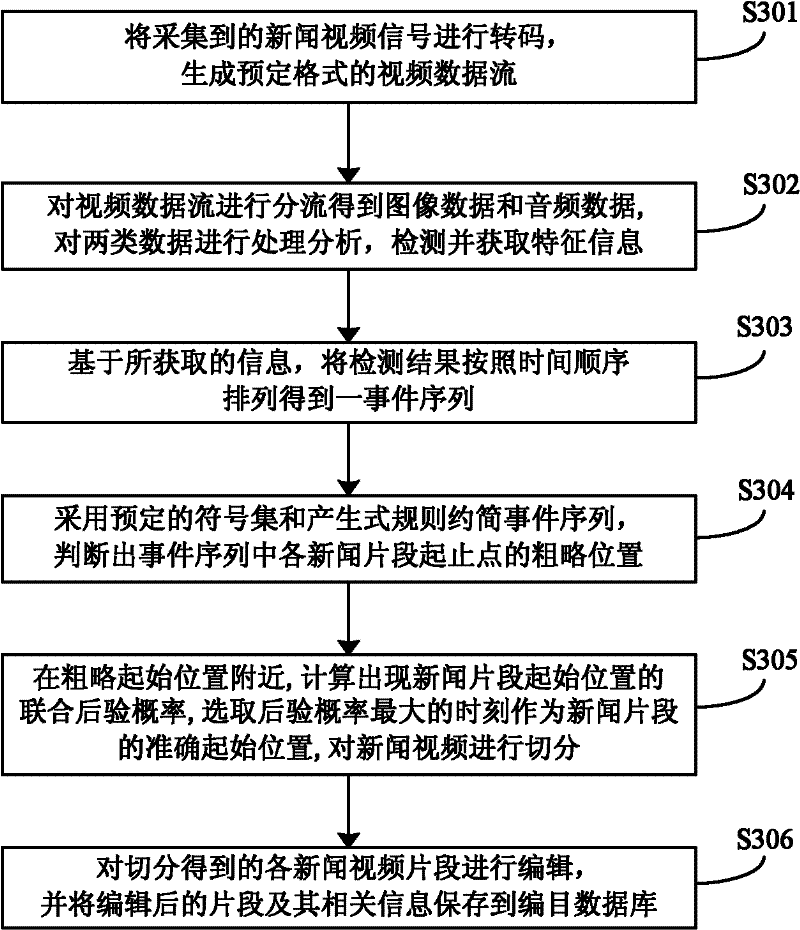
The invention discloses a method for splitting a news video program and a method and a system for cataloging news videos. The method for splitting the news video program comprises the following steps of: sequencing detection results according to a time sequence to obtain an event sequence by detecting characteristic information of titles of the news video, a headline, characteristic information of comperes, lens transformation, a mute point of an audio, a switching point, a keynote period sudden change point and the like; briefing the event sequence by adopting a preset symbol set and a production rule, and judging rough positions of start points and end points of news sections in the event sequence; calculating a union posterior probability of a start position of each news section near the rough start position according to the event sequence, selecting the moment with the maximum posterior probability as the accurate start position of each news section, splitting the news video, and thus obtaining the news video sections. According to the method, the adopted algorithm is stable and effective; the structural information in the news video can be summarized effectively; the accurate positions of splitting points of the news sections can be determined; and the news video can be split stably and accurately.
Owner:北京新岸线网络技术有限公司
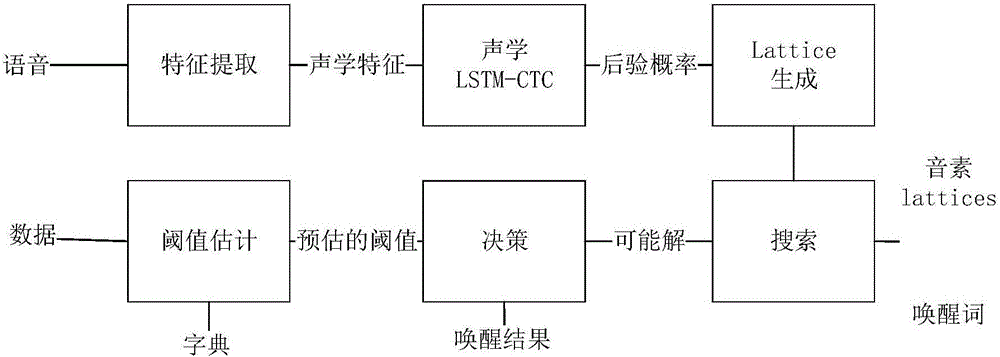
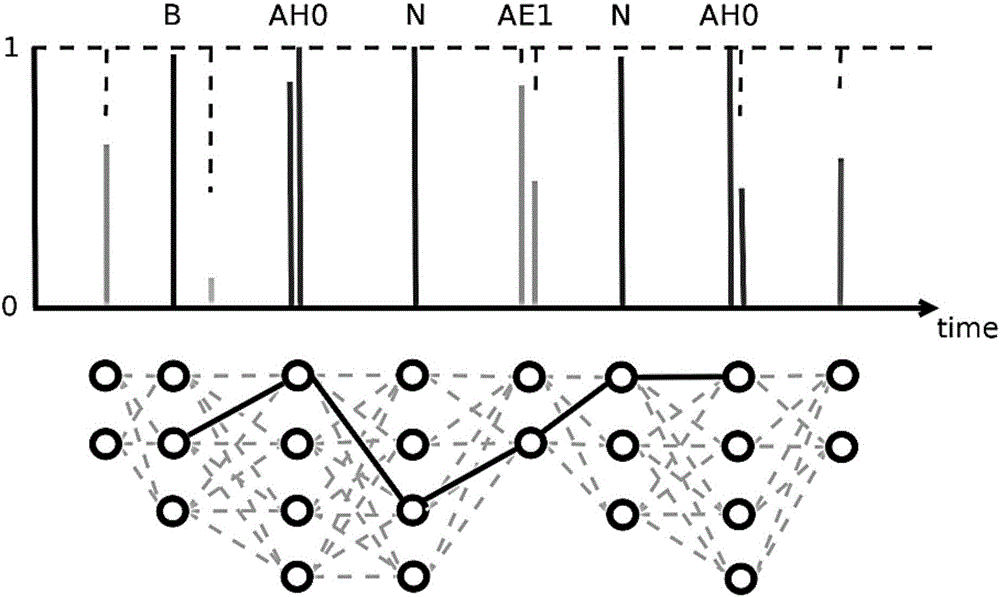
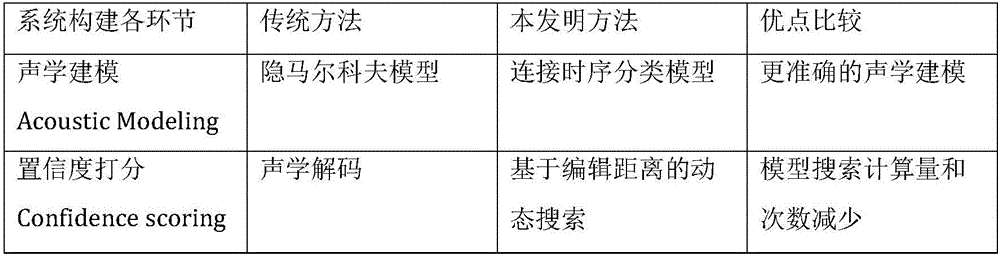
Customizable voice wake-up method and system
ActiveCN106098059AReduce consumptionImprove wake-up effectSpeech recognitionCategorical modelsSpeech sound
The invention discloses a customizable voice wake-up method and a system. Through using a long and short memory network and a connection time sequence classification model, phoneme information of the voice information is modeled, the model is trained, the model after training is adopted for testing, and a possible phoneme sequence most similar to a customized wake-up word is searched in a generated Lattice network structure and serves as a judgment basis. The feature of CTC model output posteriori probability sparsity is used for high-efficiency searching, and the technique of calculating the confidence of the wake-up word is completed. On one hand, high wake-up performance can be obtained, that is, high accuracy and low error wake-up can be obtained; and on the other hand, the calculation resources of the application system are relatively little consumed.
Owner:AISPEECH CO LTD
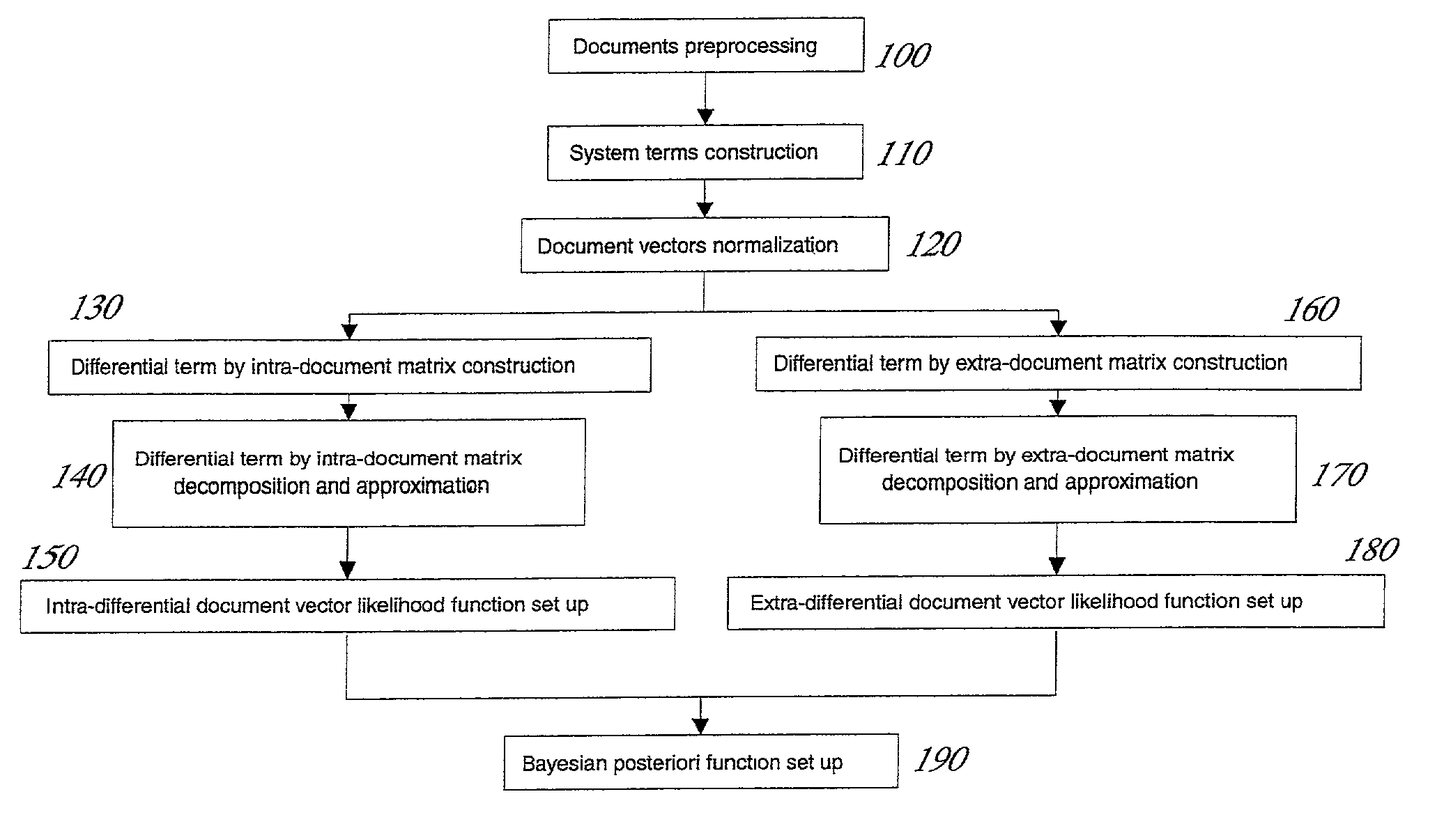
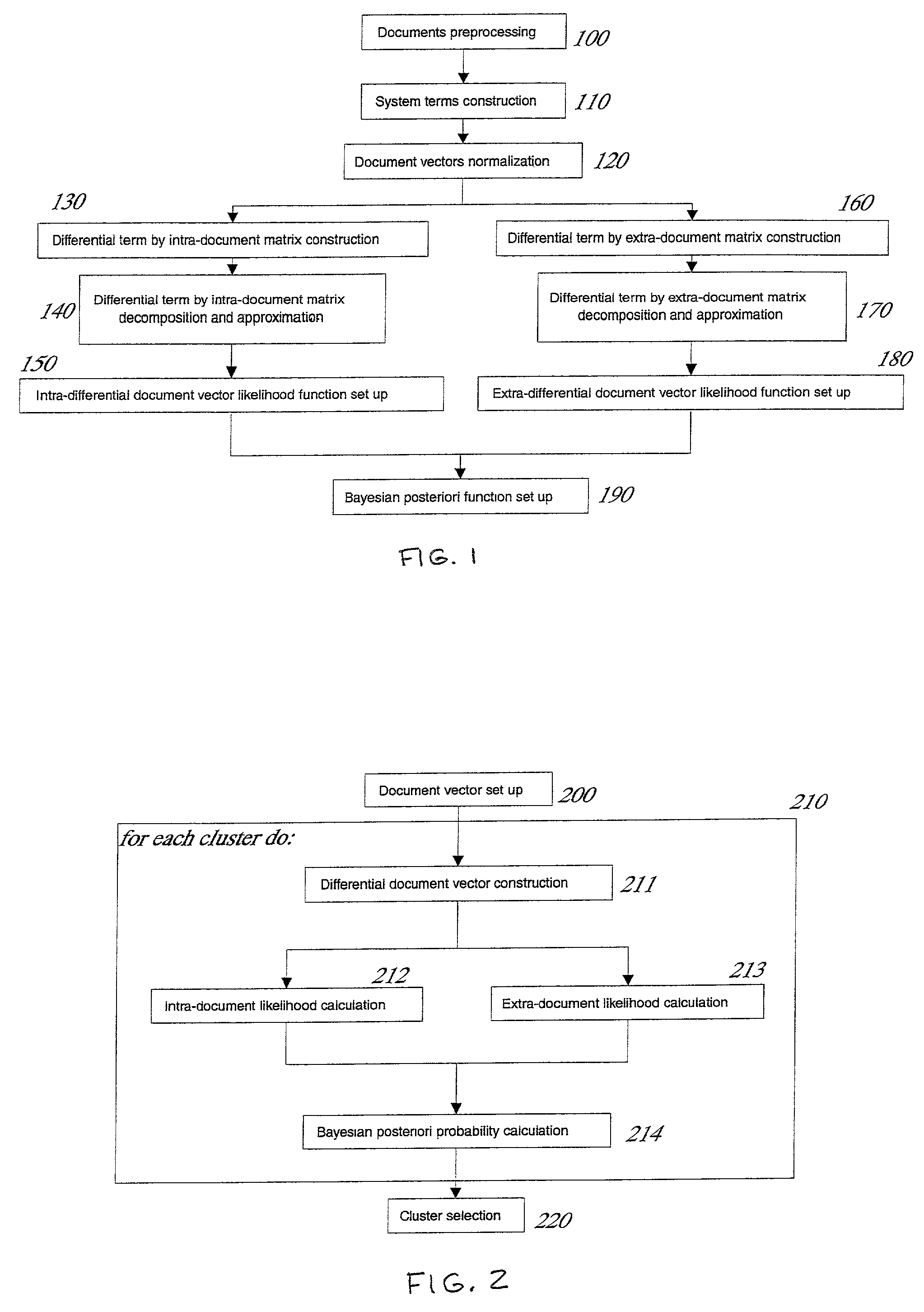
Differential LSI space-based probabilistic document classifier
InactiveUS7024400B2Retention characteristicImprove adaptabilityDigital computer detailsChaos modelsSemanticsCombined use
A computerized method for automatic document classification based on a combined use of the projection and the distance of the differential document vectors to the differential latent semantics index (DLSI) spaces. The method includes the setting up of a DLSI space-based classifier to be stored in computer storage and the use of such classifier by a computer to evaluate the possibility of a document belonging to a given cluster using a posteriori probability function and to classify the document in the cluster. The classifier is effective in operating on very large numbers of documents such as with document retrieval systems over a distributed computer network.
Owner:SUNFLARE CO LTD
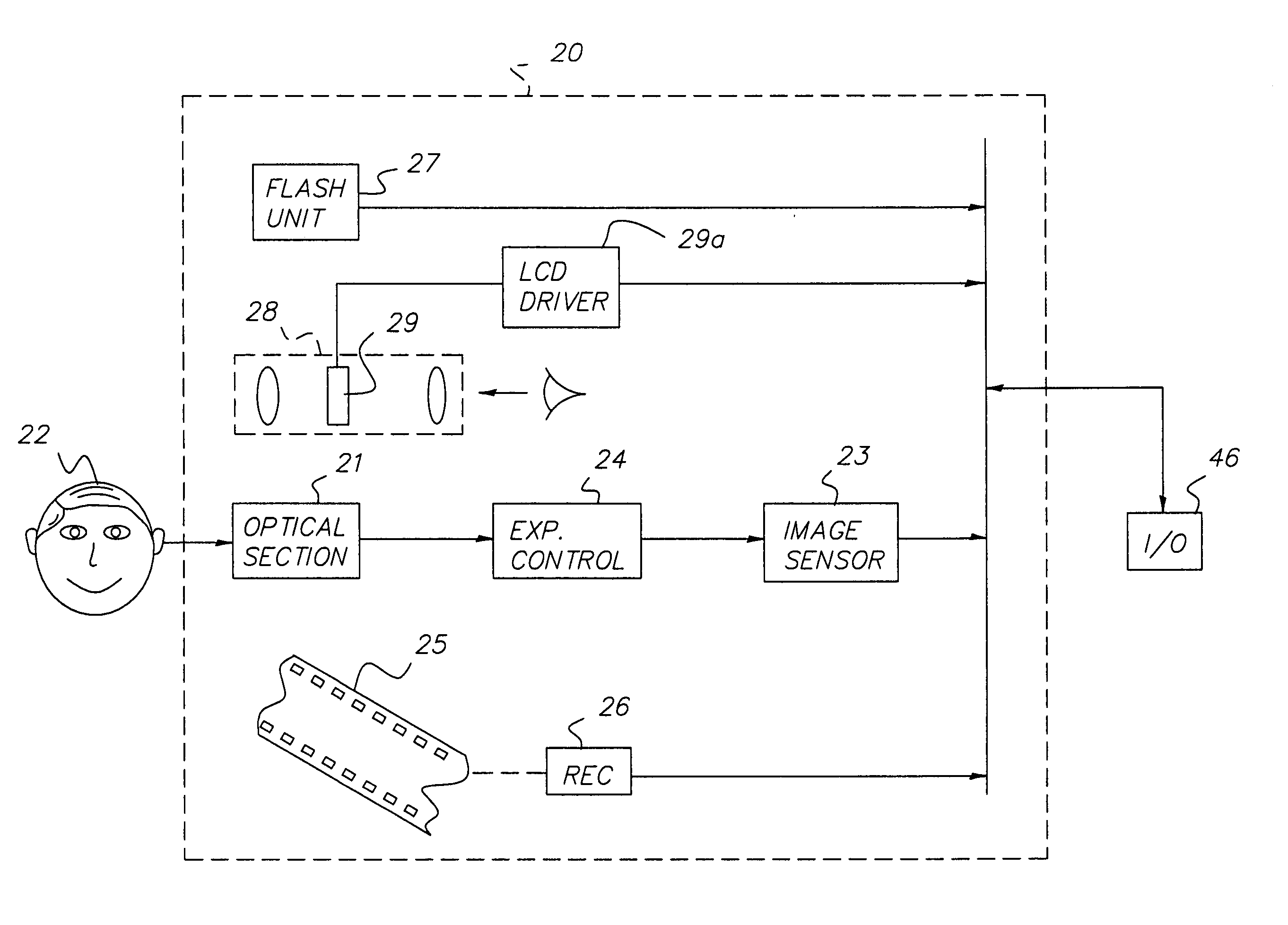
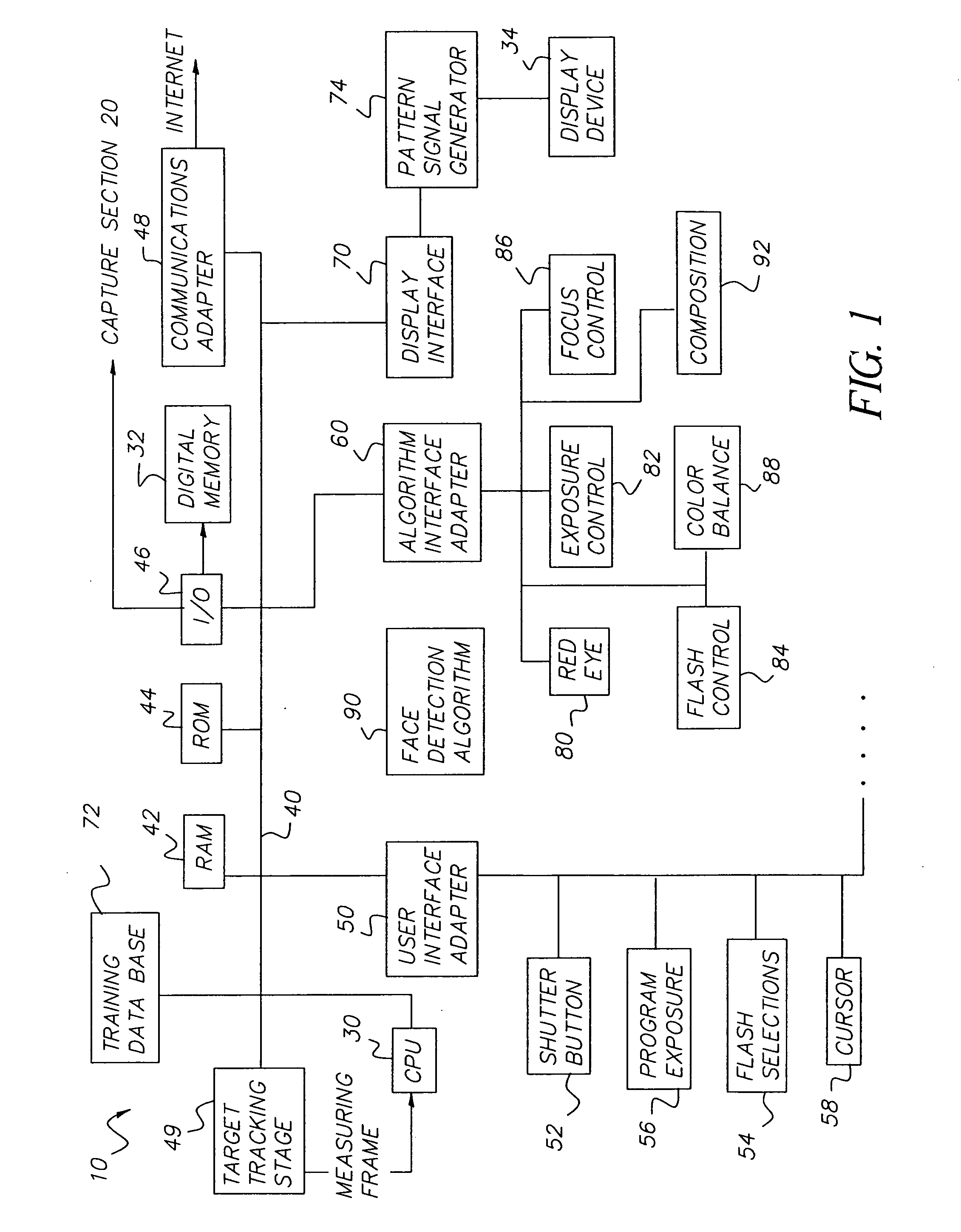
Face detecting camera and method
InactiveUS20050264658A1Quality improvementIncrease valueTelevision system detailsImage analysisFace detectionPattern matching
A method for determining the presence of a face from image data utilizes at least first and second algorithms. The first algorithm prescreens the image data, by determining a plurality of face candidates utilizing a pattern matching technique that identifies image windows likely to contain faces based on color and shape information. The second algorithm processes the face candidates determined by the first algorithm, and uses a posterior probability function classifier to determine the presence of the face.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Apparatus and method using reduced memory for channel decoding in a software-defined radio system
InactiveUS20080123781A1Data representation error detection/correctionFault responseSoftware define radioMaximum a posteriori estimation
A maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) block decoder for decoding a received data block of input samples. The MAP block decoder segments the received data block into at least a first segment and a second segment and calculates and stores alpha values during forward processing of the first segment. The MAP block decoder uses a first selected alpha value calculated during forward processing of the first segment as initial state information during forward processing of the second segment. The first and second segments may overlap each other, such that the last M samples of the first segment are the same as the first M samples of the second segment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for providing low density parity check (LDPC) encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20110202820A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
An approach is provided for processing structure Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes. Memory storing edge information and a posteriori probability information associated with a structured parity check matrix used to generate Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) coded signal are accessed. The edge information represent relationship between bit nodes and check nodes, and are stored according to a predetermined scheme that permits concurrent retrieval of a set of the edge information.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
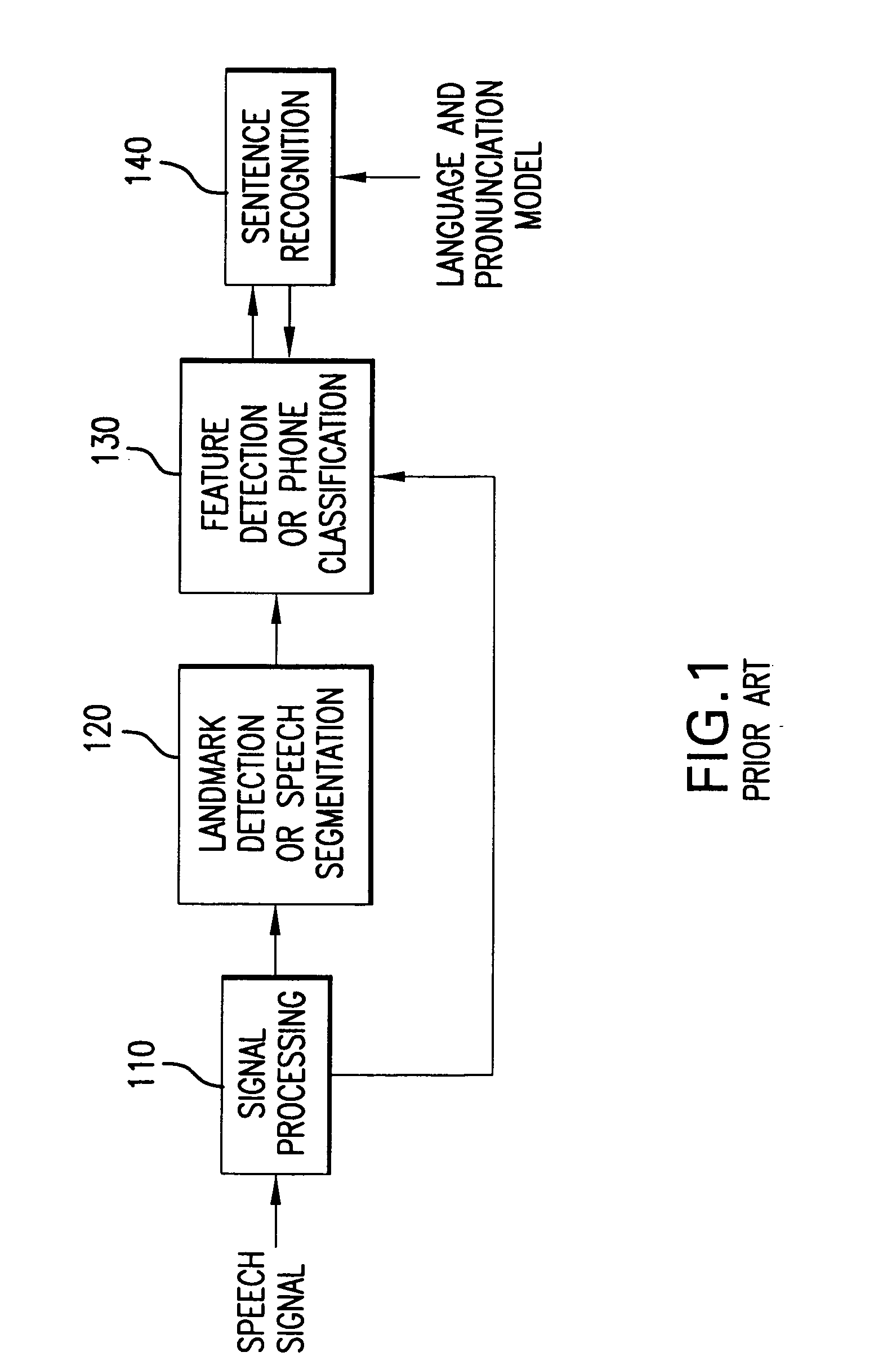
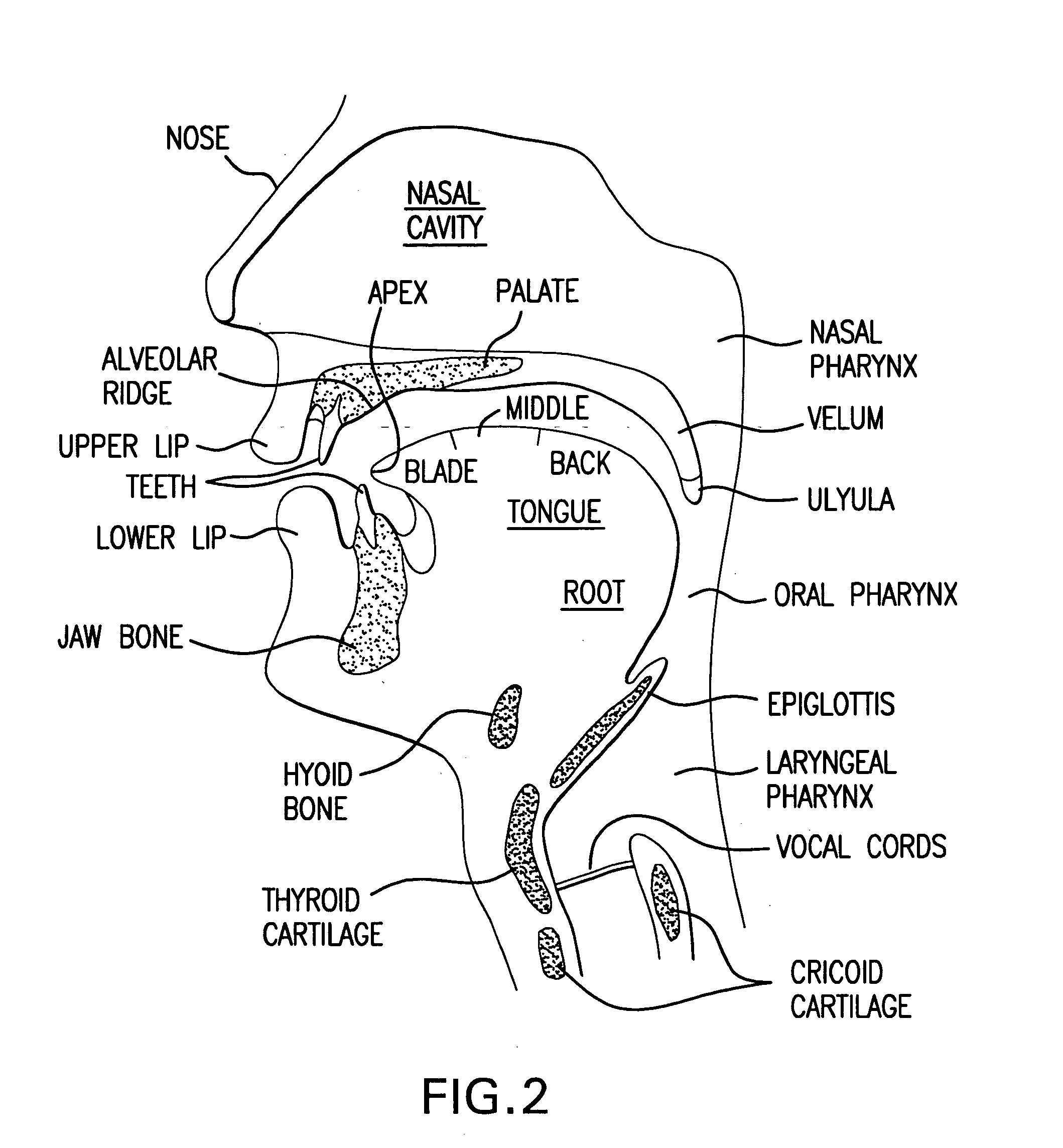
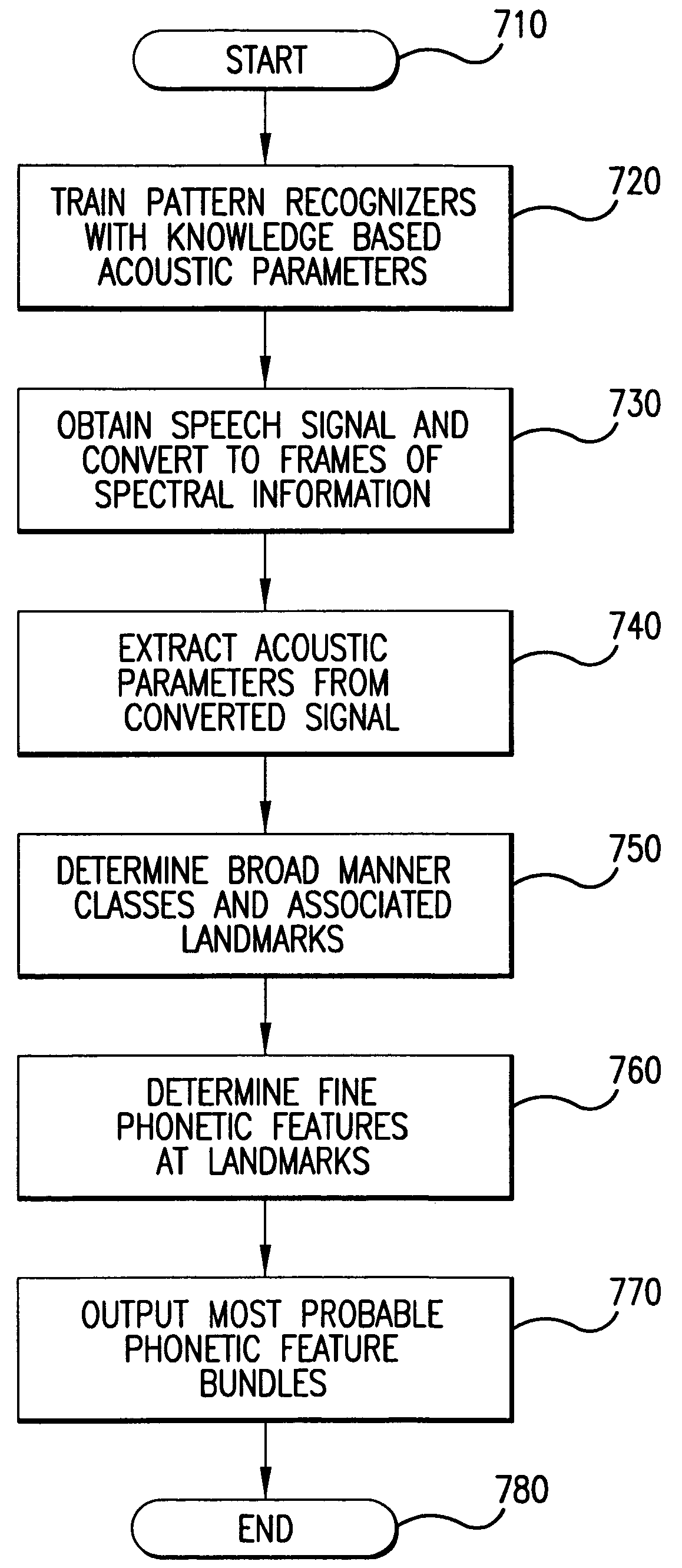
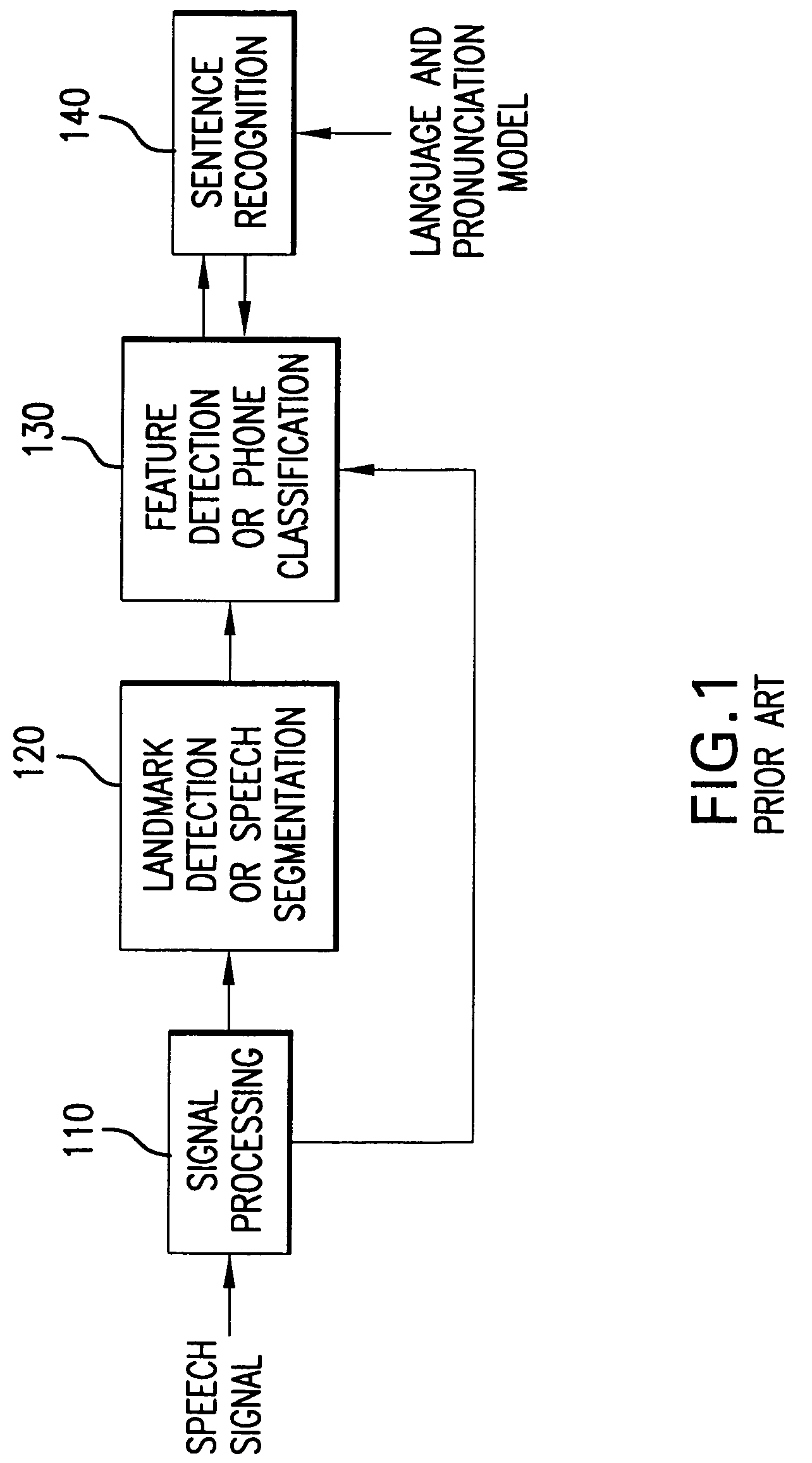
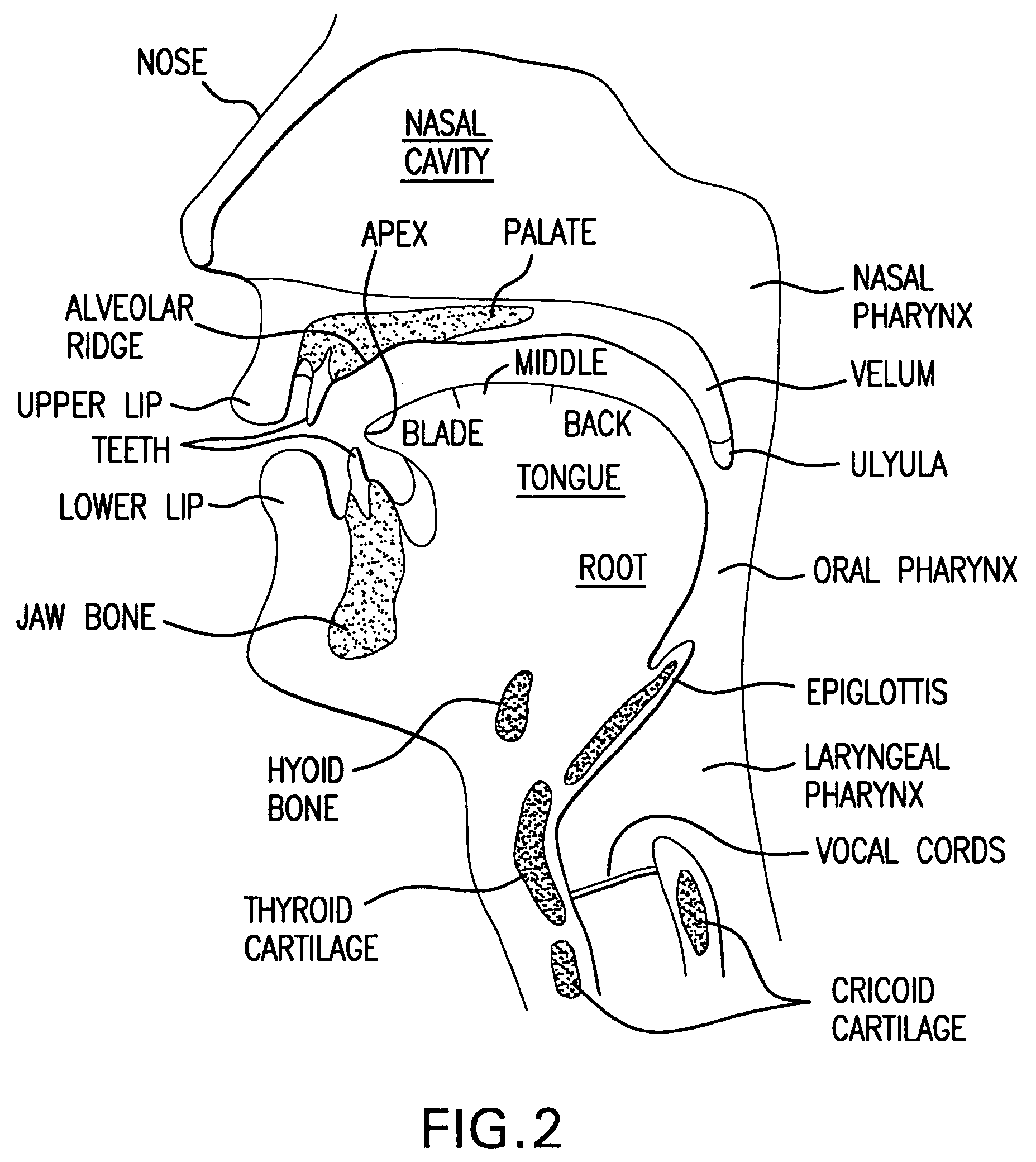
System and method for automatic speech recognition from phonetic features and acoustic landmarks
A probabilistic framework for acoustic-phonetic automatic speech recognition organizes a set of phonetic features into a hierarchy consisting of a broad manner feature sub-hierarchy and a fine phonetic feature sub-hierarchy. Each phonetic feature of said hierarchy corresponds to a set of acoustic correlates and each broad manner feature of said broad manner feature sub-hierarchy is further associated with a corresponding set of acoustic landmarks. A pattern recognizer is trained from a knowledge base of phonetic features and corresponding acoustic correlates. Acoustic correlates are extracted from a speech signal and are presented to the pattern recognizer. Acoustic landmarks are identified and located from broad manner classes classified by the pattern recognizer. Fine phonetic features are determined by the pattern recognizer at and around the acoustic landmarks. The determination of fine phonetic features may be constrained by a pronunciation model. The most probable feature bundles corresponding to words and sentences are those that maximize the joint a posteriori probability of the fine phonetic features and corresponding acoustic landmarks. When the hierarchy is organized as a binary tree, binary classifiers such as Support Vector Machines can be used in the pattern classifier and the outputs thereof can be converted probability measures which, in turn may be used in the computation of the aforementioned joint probability of fine phonetic features and corresponding landmarks.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Information recording and reproducing apparatus and method and signal decoding circuit having improved noise processing characteristics
InactiveUS7031090B2Effective applicationImprove decoding performanceModification of read/write signalsOther decoding techniquesMaximum a posteriori estimationComputer science
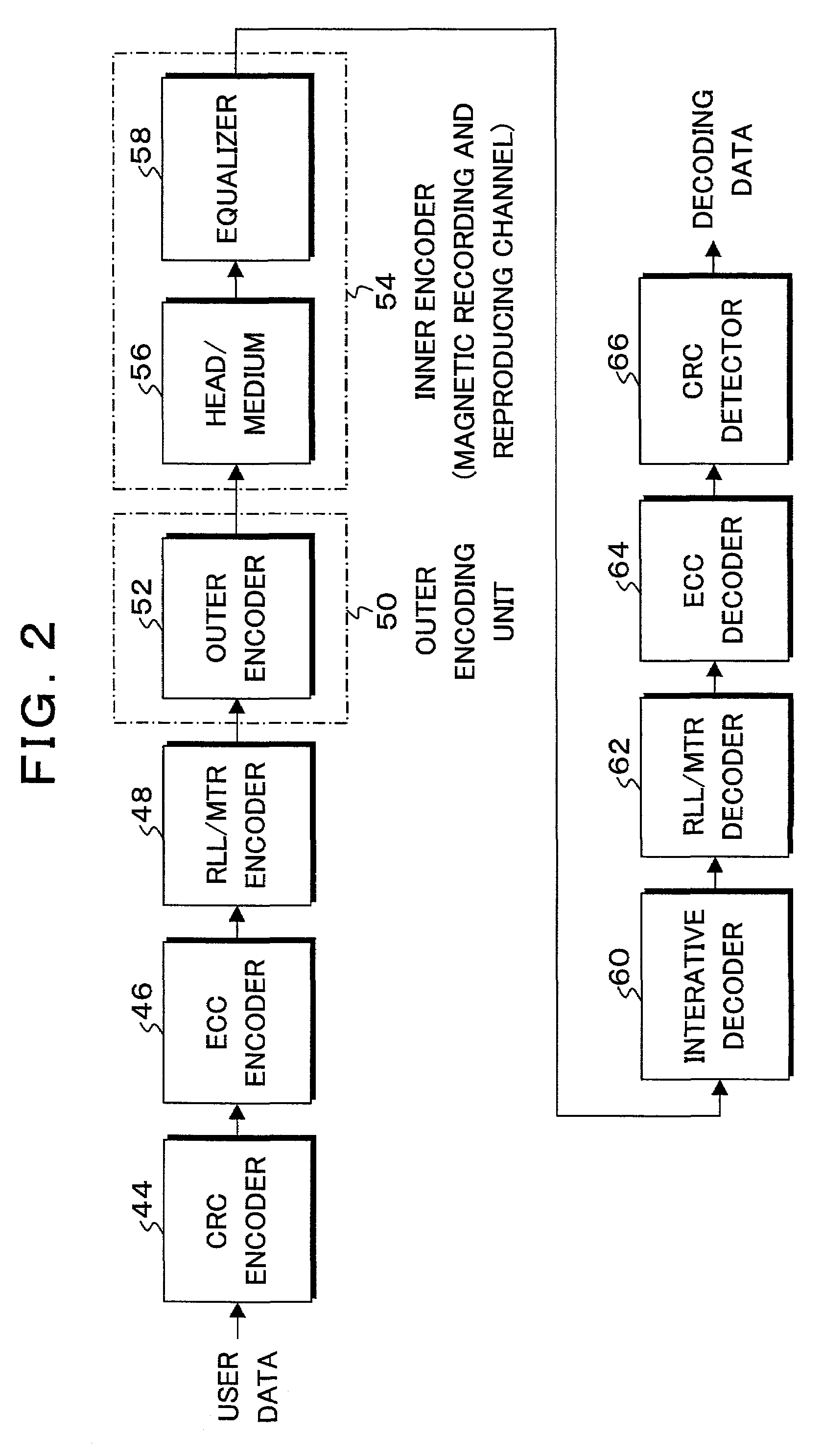
In a Maximum A posteriori Probability decoding (MAP decoding), a correlation and a deviation of noises for past and future states which depend on input signal patterns in past N bits and future Q bits are calculated by training by a noise correlation arithmetic operating unit 84 and they are stored. Upon reproduction, in a white noise arithmetic operating unit 91, white noise values for the past and future states in which colored noises are converted into white noises are obtained by using the stored correlation and deviation of the noises. In an input signal arithmetic operating unit 92, an input signal (channel information) Λc(yk|Smk) of the MAP decoding is calculated from the white noise values and the deviation for the past and future states. A likelihood in the MAP decoding is obtained from the input signal.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
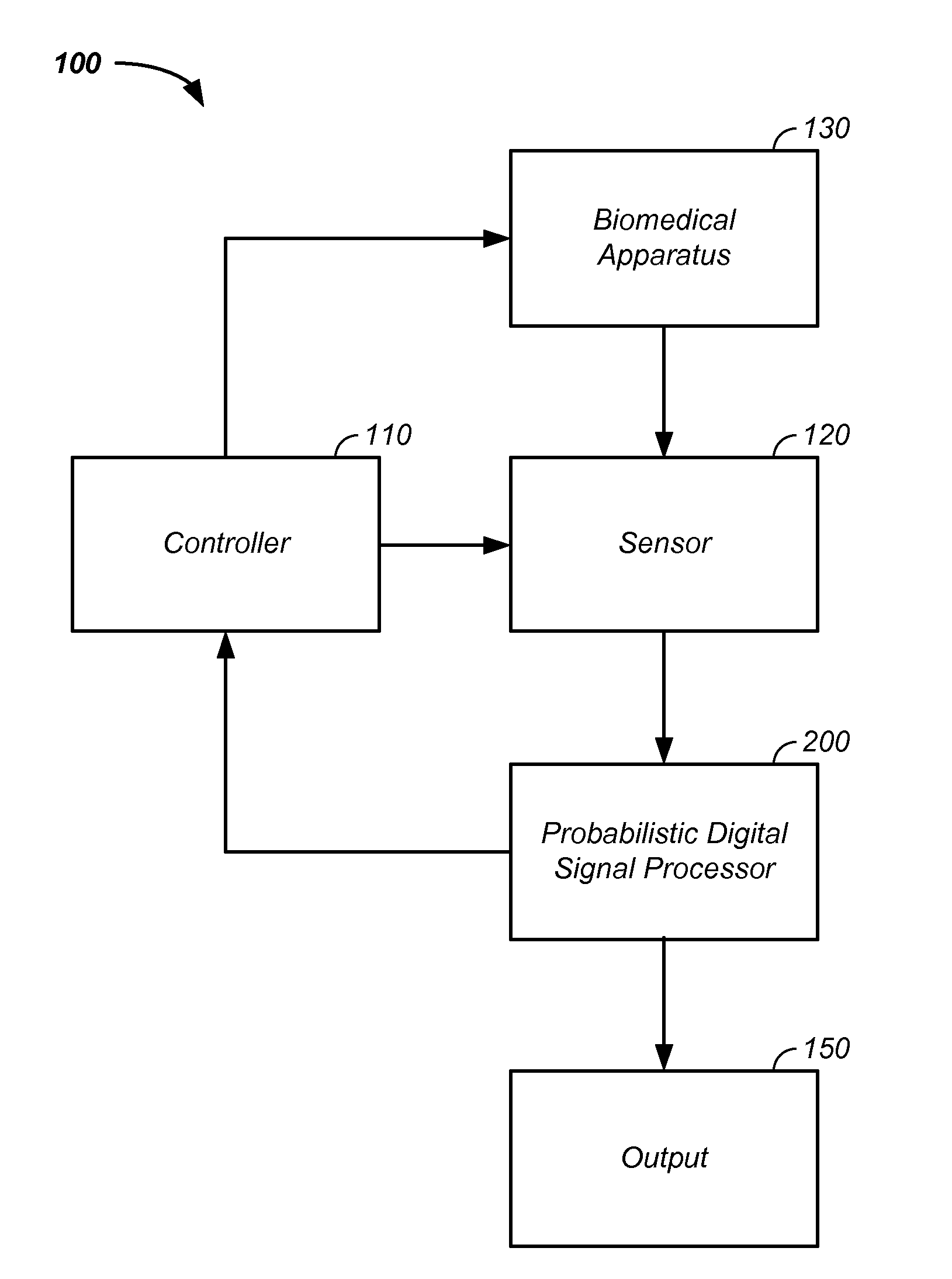
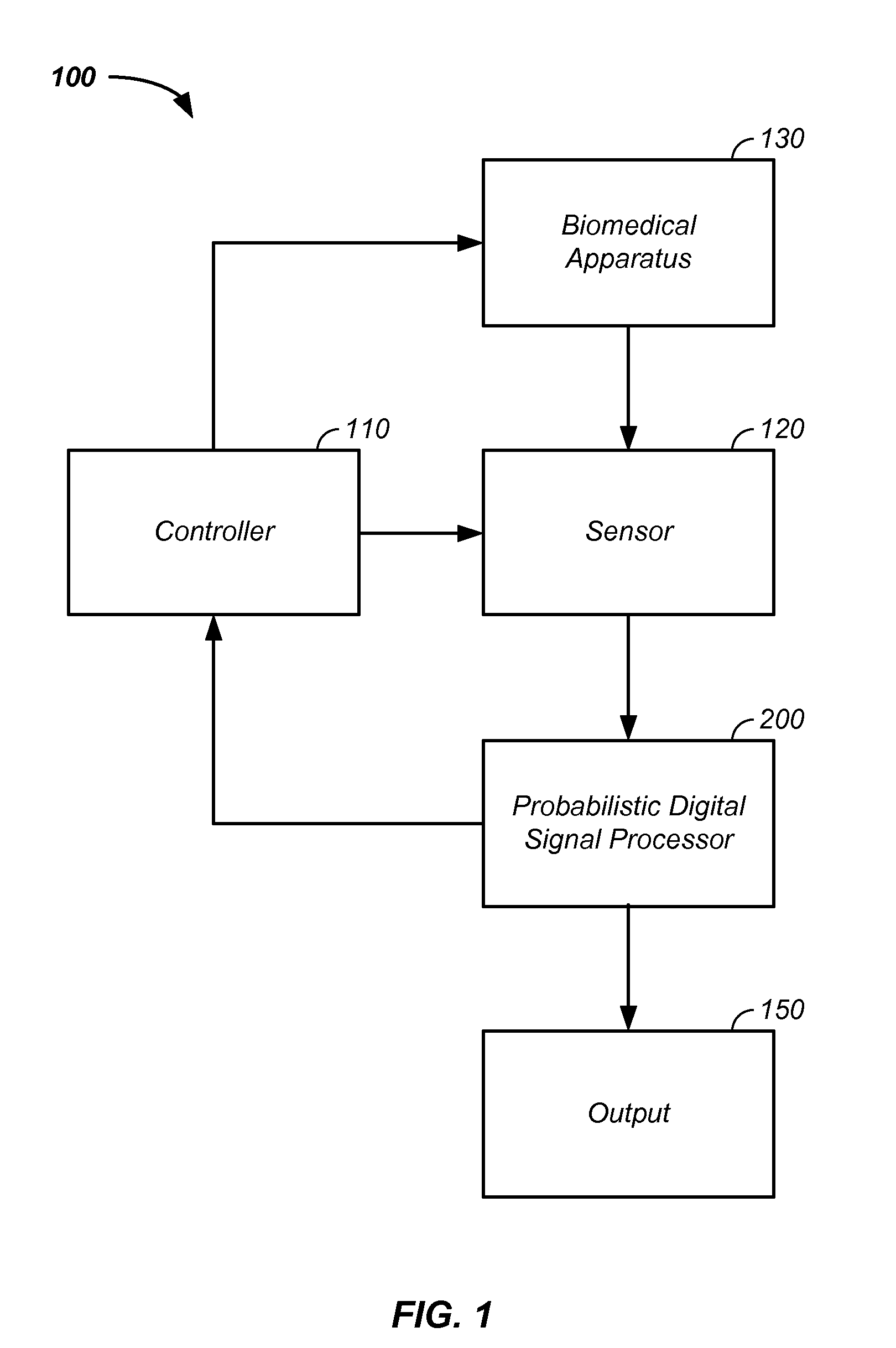
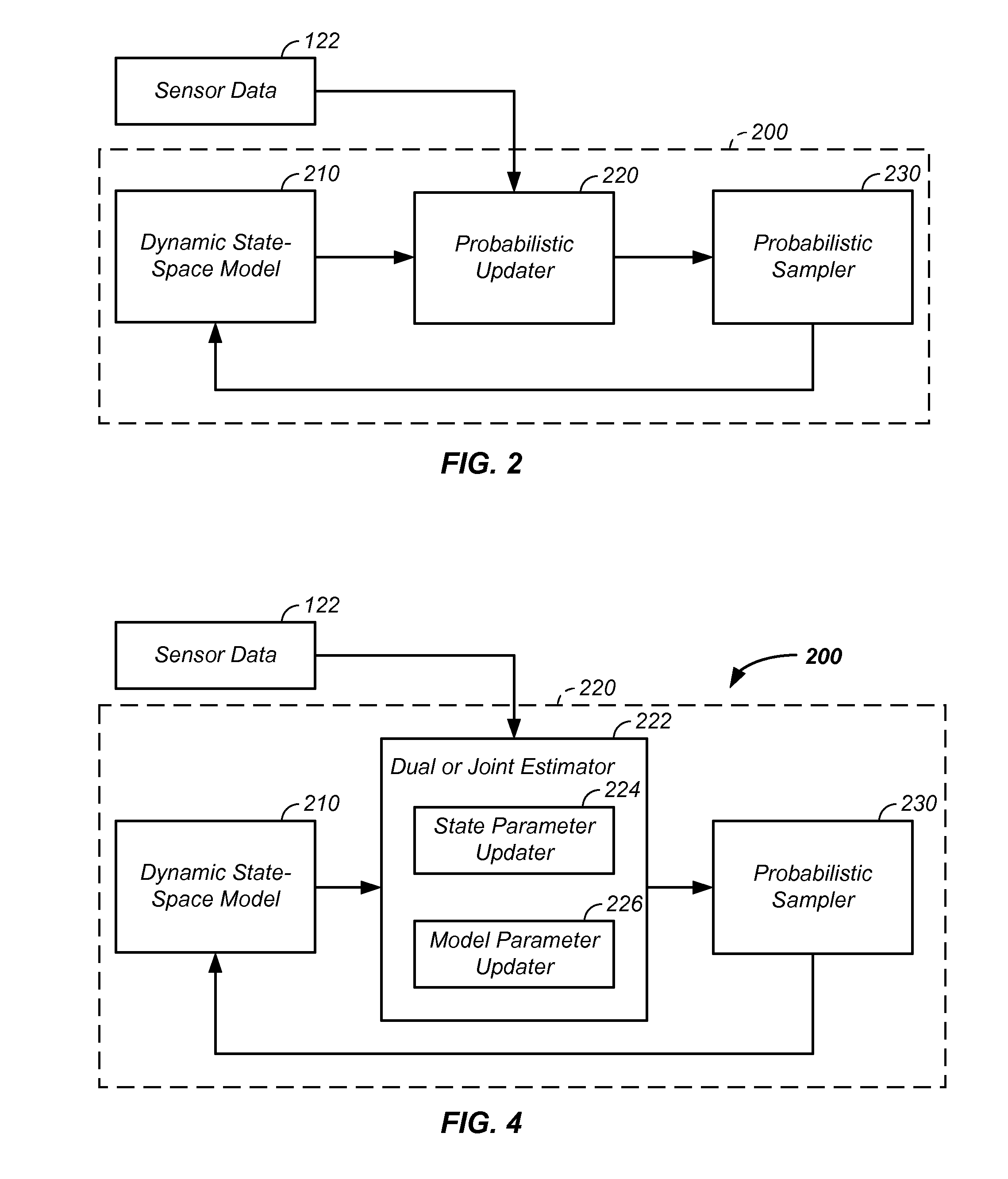
Probabilistic biomedical parameter estimation apparatus and method of operation therefor
A probabilistic digital signal processor for medical function is described. Initial probability distribution functions are input to a dynamic state-space model, which operates on state and / or model probability distribution functions to generate a prior probability distribution function, which is input to a probabilistic updater. The probabilistic updater integrates sensor data with the prior to generate a posterior probability distribution function passed to a probabilistic sampler, which estimates one or more parameters using the posterior, which is output or re-sampled in an iterative algorithm. For example, the probabilistic processor operates using a physical model on data from a medical meter, where the medical meter uses a first physical parameter, such as blood oxygen saturation levels from a pulse oximeter, to generate a second physical parameter not output by the medical meter, such as a heart stroke volume, a cardiac output flow rate, and / or a blood pressure.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
Countercheck method for automatically identifying speaker aiming to voice deception
ActiveCN105139857ACountermeasures work wellEnhanced confrontation abilitySpeech analysisCosine similaritySupport vector machine
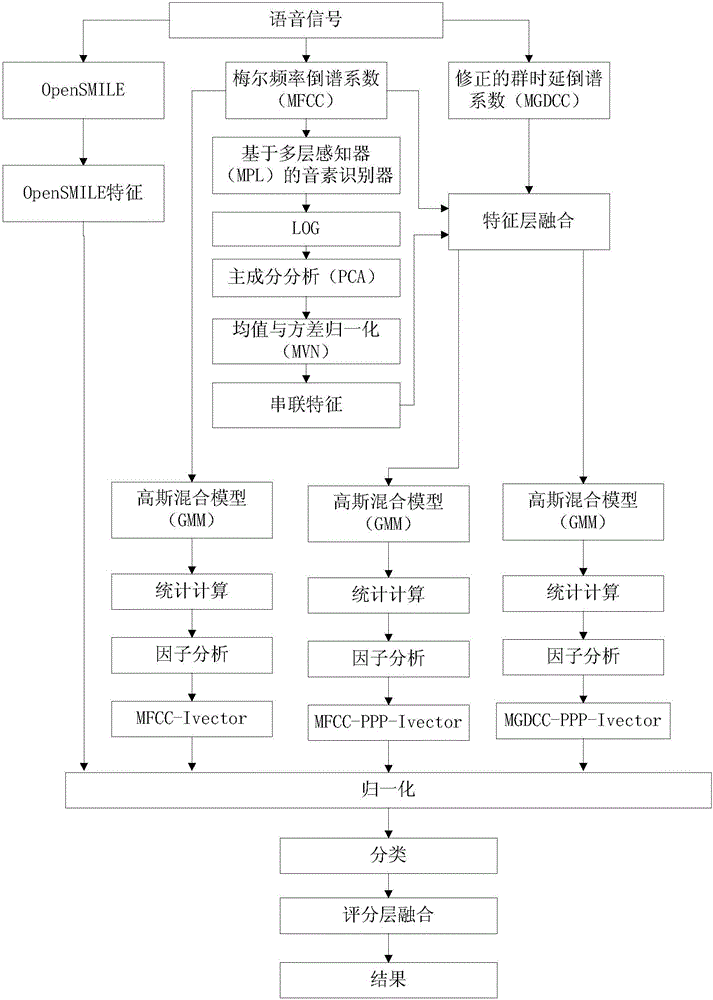
The invention provides a countercheck method for automatically identifying a speaker aiming to voice deception, which is a voice anti-spoofing technology based on a method combining various features and a plurality of sub-systems. According to the invention, the serial features of the posterior probability of a phoneme in the phonological level and the MFCC features of voice level or MFDCC features of phase level are combined, thus the performance of the system is significantly enhanced. By combining the provided i-vector sub-system and OpenSMILE (open Speech and Music Interpretation by Large Space Extraction criterion containing voice and rhythmic information, the final presentation of the system is further enhanced. To a back-end model, the development datum are used; and under the situation of knowing deceptive attacks, a two-level support vector machine has better performance compared with one-level cosine similarity or PLDA evaluations, while the one-level evaluation approach has better robustness under the situation without seeing the test datum and knowing the deceptive conditions.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
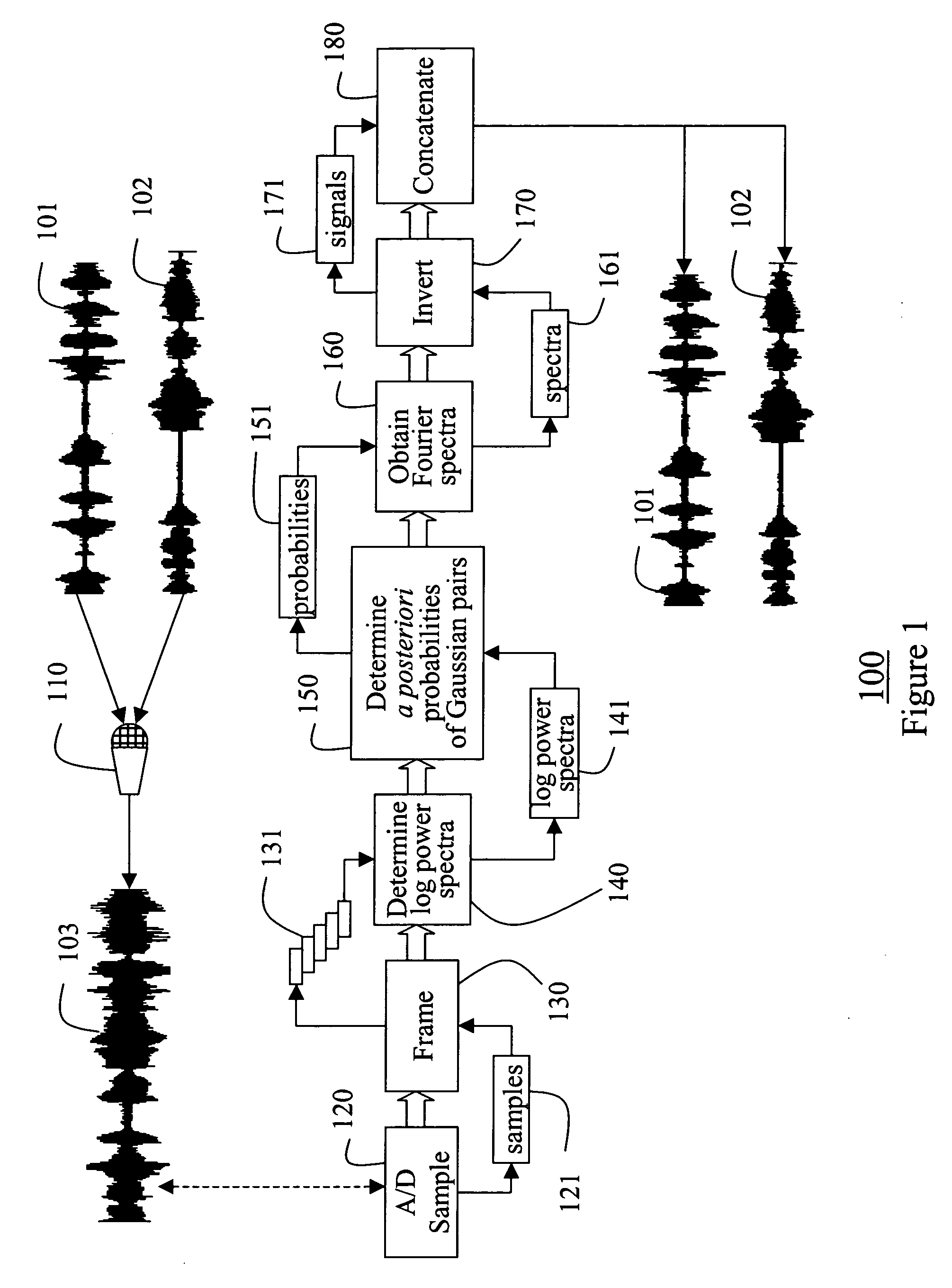
Separating multiple audio signals recorded as a single mixed signal
InactiveUS20060056647A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpeech analysisSlide windowLogit
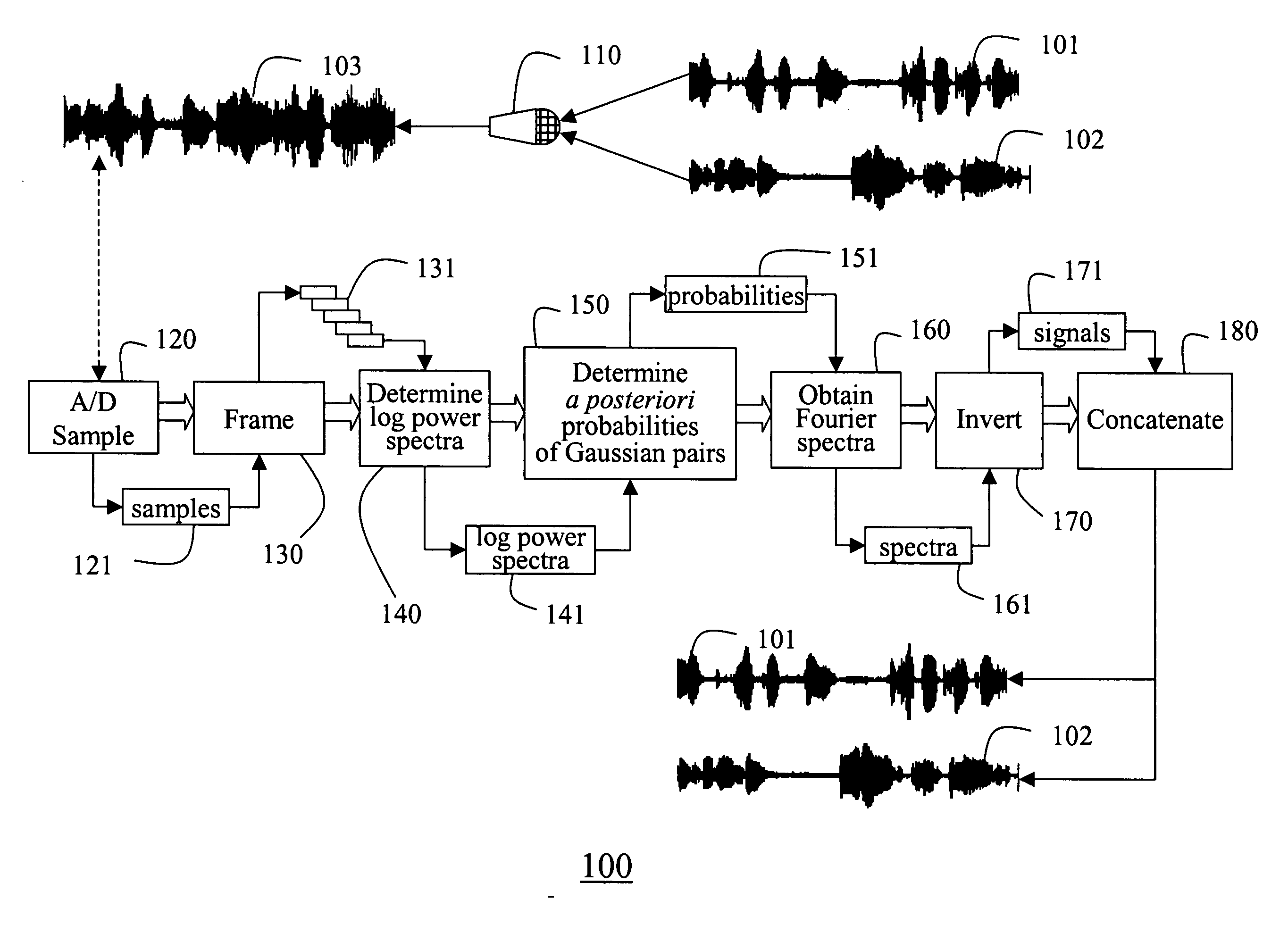
A method according to the invention separates multiple audio signals recorded as a mixed signal via a single channel. The mixed signal is A / D converted and sampled. A sliding window is applied to the samples to obtain frames. The logarithms of the power spectra of the frames are determined. From the spectra, the a posteriori probabilities of pairs of spectra are determined. The probabilities are used to obtain Fourier spectra for each individual signal in each frame. The invention provides a minimum-mean-squared error metho or a soft mask method for making this determination. The Fourier spectra are inverted to obtain corresponding signals, which are concatenated to recover the individual signals.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
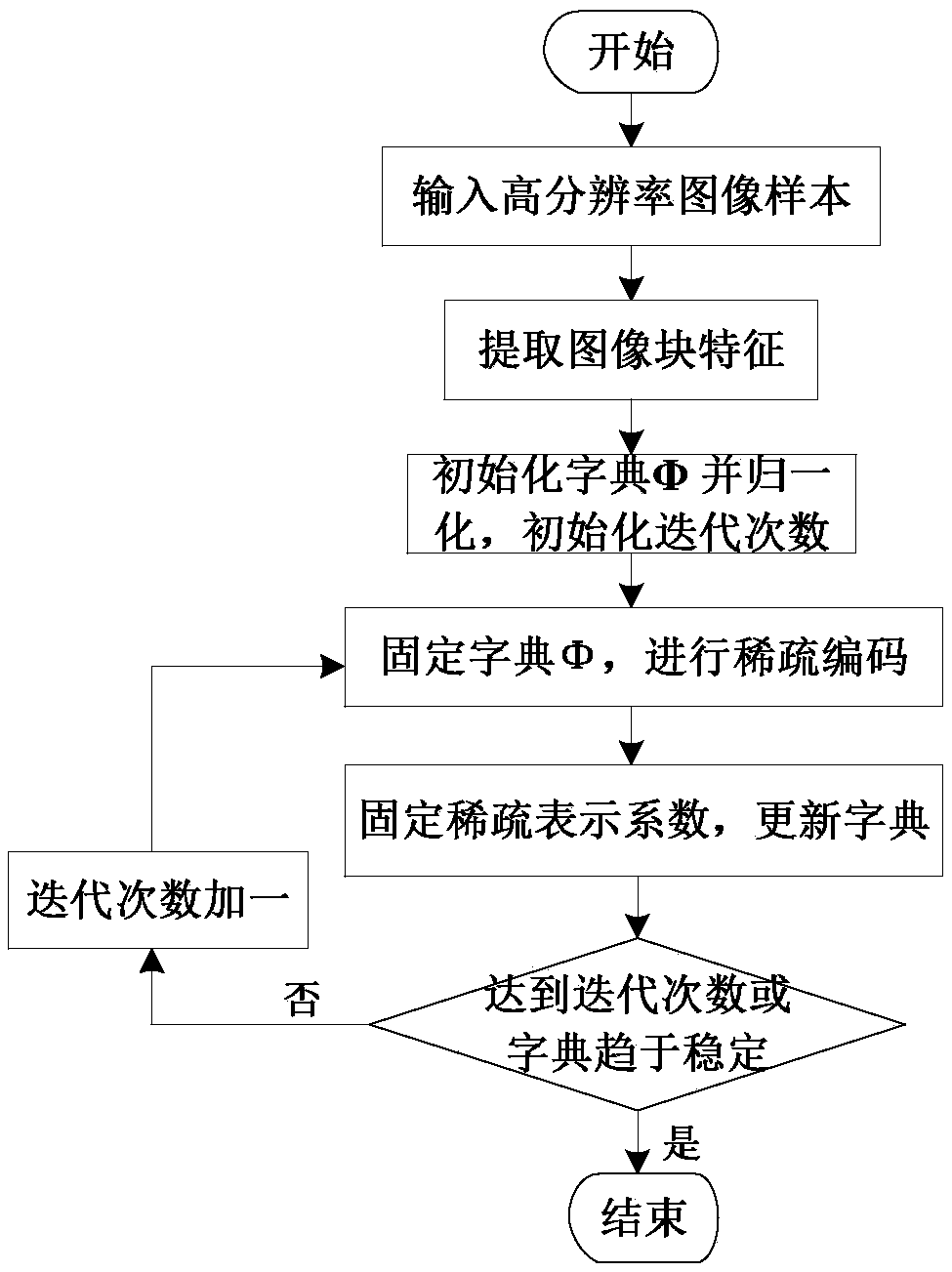
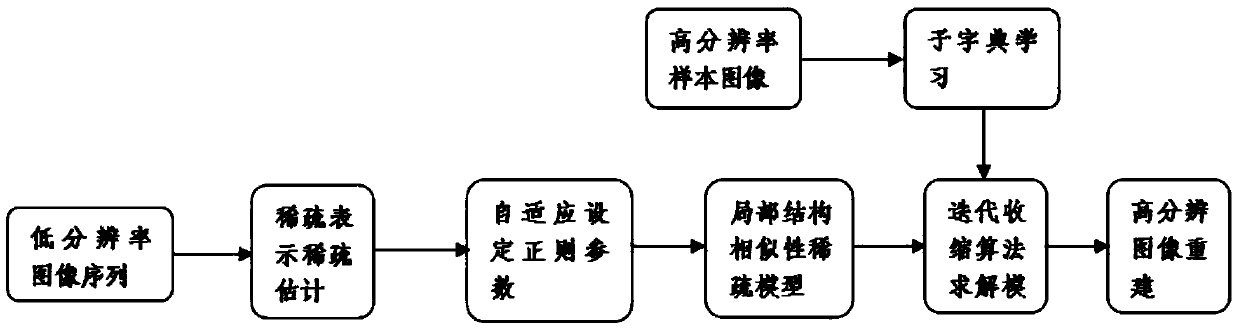
Regularized parameter adaptive sparse representation image reconstruction method
PendingCN109064406AImprove effectivenessMaintain structureGeometric image transformationDictionary learningMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention provides a regularized parameter adaptive sparse representation image reconstruction method, comprising the following steps: adopting a sparse dictionary learning algorithm, extracting image edge features to train a compact sparse dictionary, and adaptively allocating sub-dictionaries to each image block for sparse coding; Learning the Sparse Estimation of Sparse Coding from an Overcomplete Dictionary; Making full use of the local structure similarity of images, the regularization parameters are adaptively solved by using the method based on the maximum a posteriori probability.Adaptive sparse representation model of regularized parameters is established. The invention improves the effectiveness of sparse representation by utilizing the local structure similarity, and the edge and the structure of the image are well maintained. Adaptively adjusting the regularization parameters based on the maximum a posteriori probability, updating the regularization parameters in eachiteration process, better adapting to the current situation, greatly reducing the workload of manual selection of the regularization parameters; It has good image reconstruction effect and strong robustness to noise and motion blur.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Parameter Estimation method, Parameter Estimation Device and Collation Method
InactiveUS20070230773A1Short processing timeReduce processing costsImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionEstimation methodsA posteriori probability
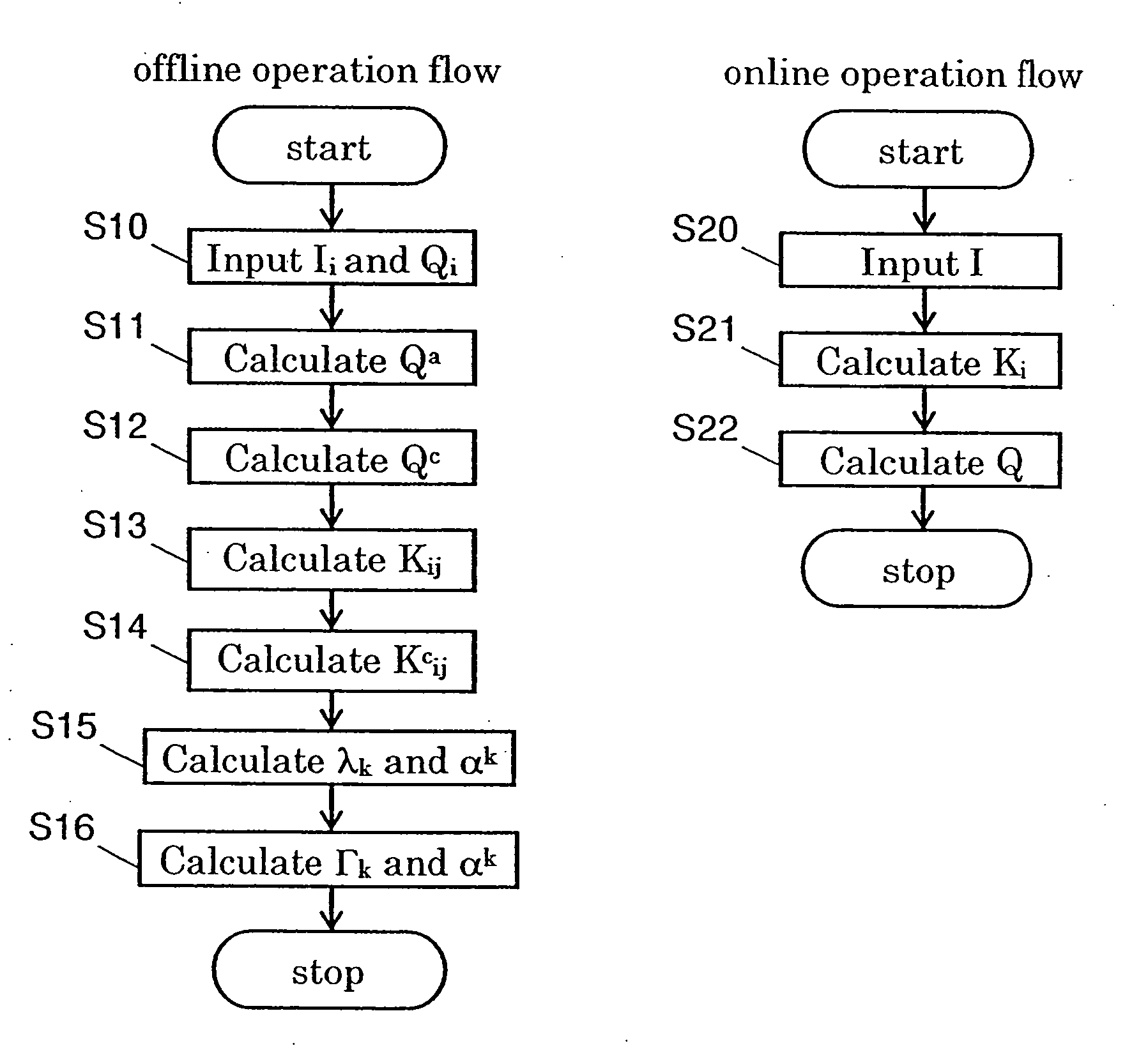
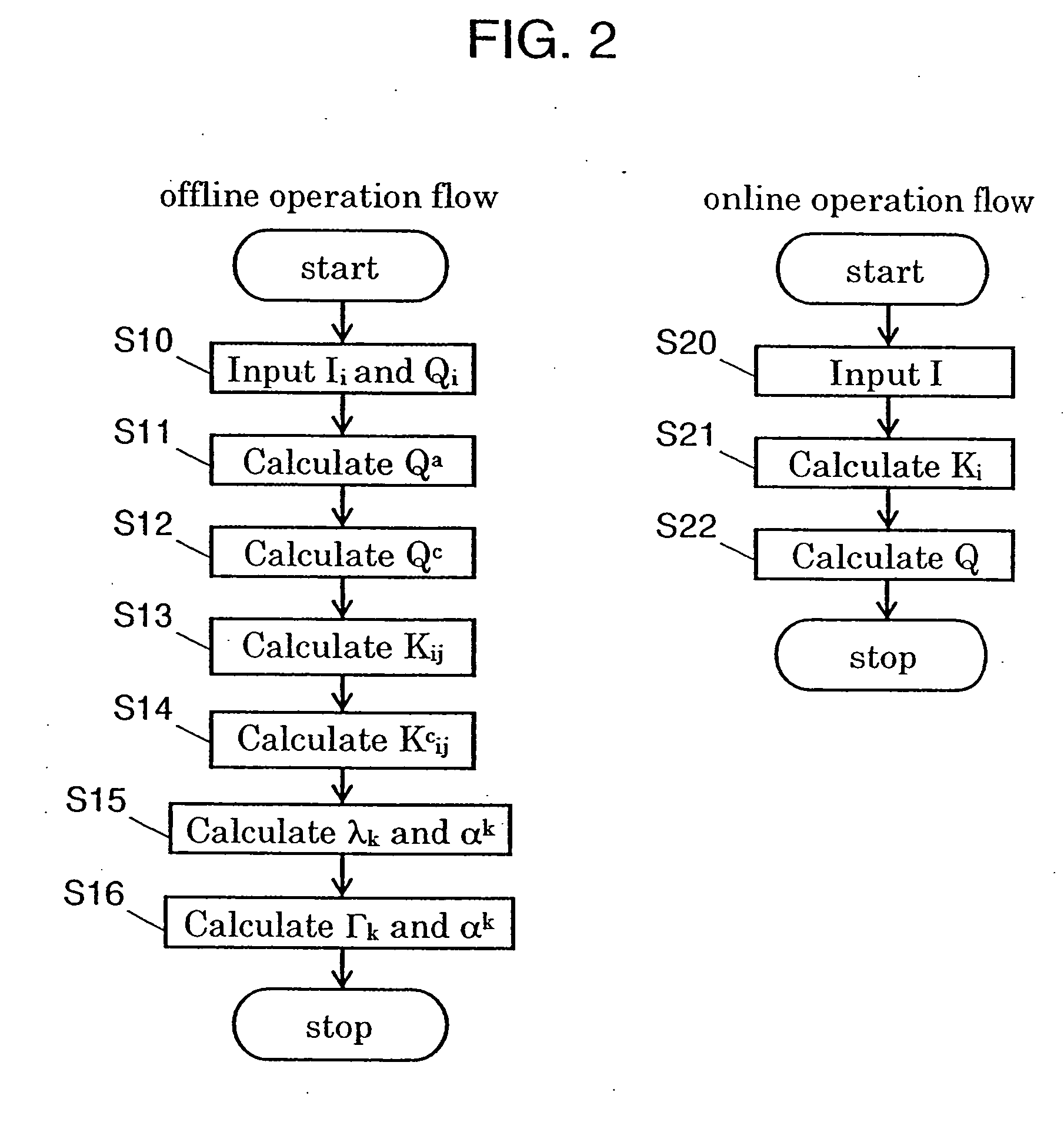
A parameter estimation method for estimating a parameter by estimating maximum a posteriori probability for input data. Operation for the input data is expressed by an inner product for the input data and the inner product is replaced by a Kernel function. By using the calculation result of the kernel function, a parameter is estimated. The method includes a step (offline operation) for learning a correlation between a plurality of learning input data in which a parameter to be estimated is known and the parameter corresponding to each of the learning input data; and a step (online operation) for estimating the parameter for the estimating input data in which a parameter to be estimated is unknown, by using the learned correlation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Self-adaptive semi-supervised network traffic classification method, system and equipment
ActiveCN107846326AGuaranteed uniformityImplement extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionData switching networksInternet trafficEngineering
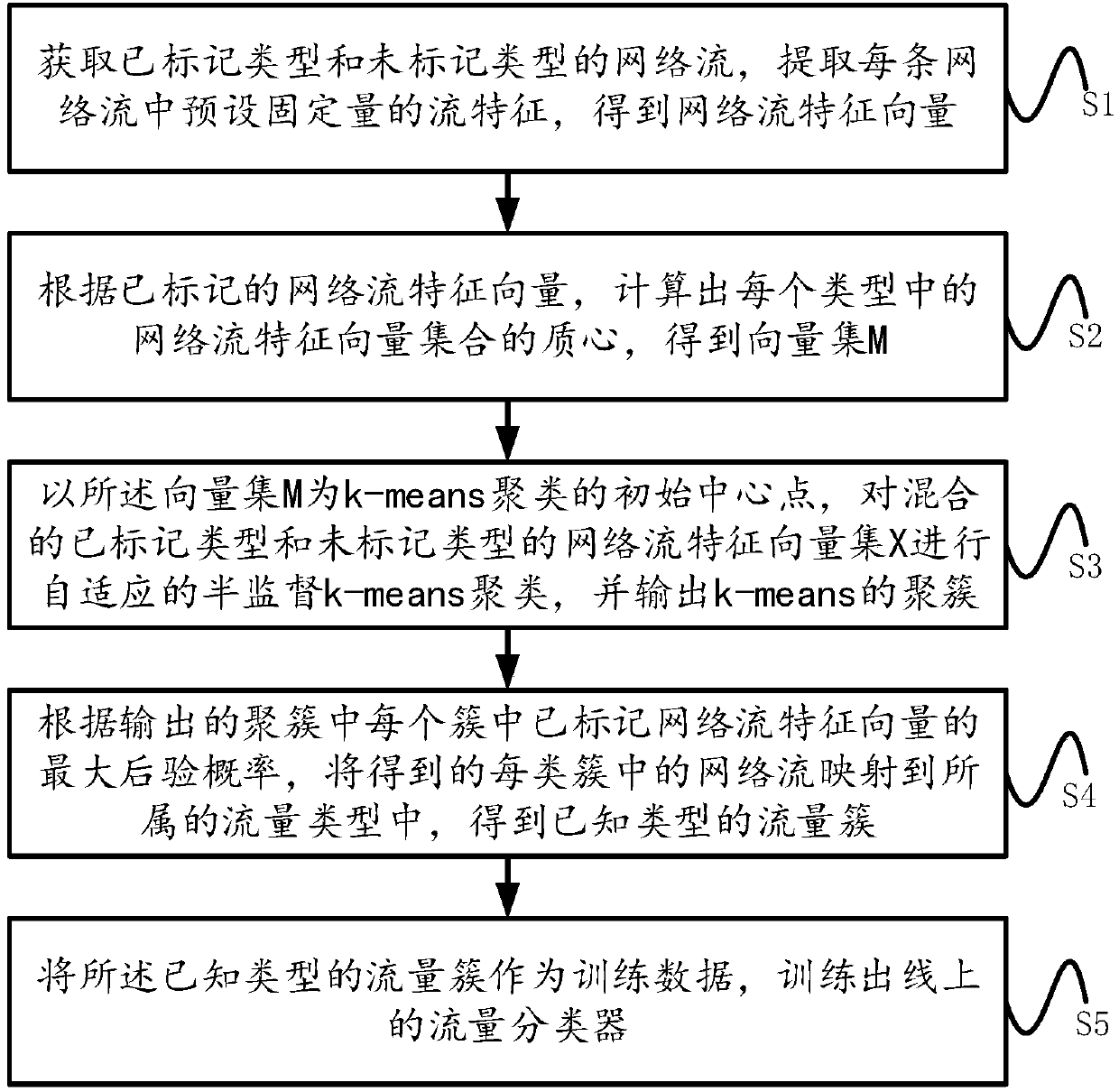
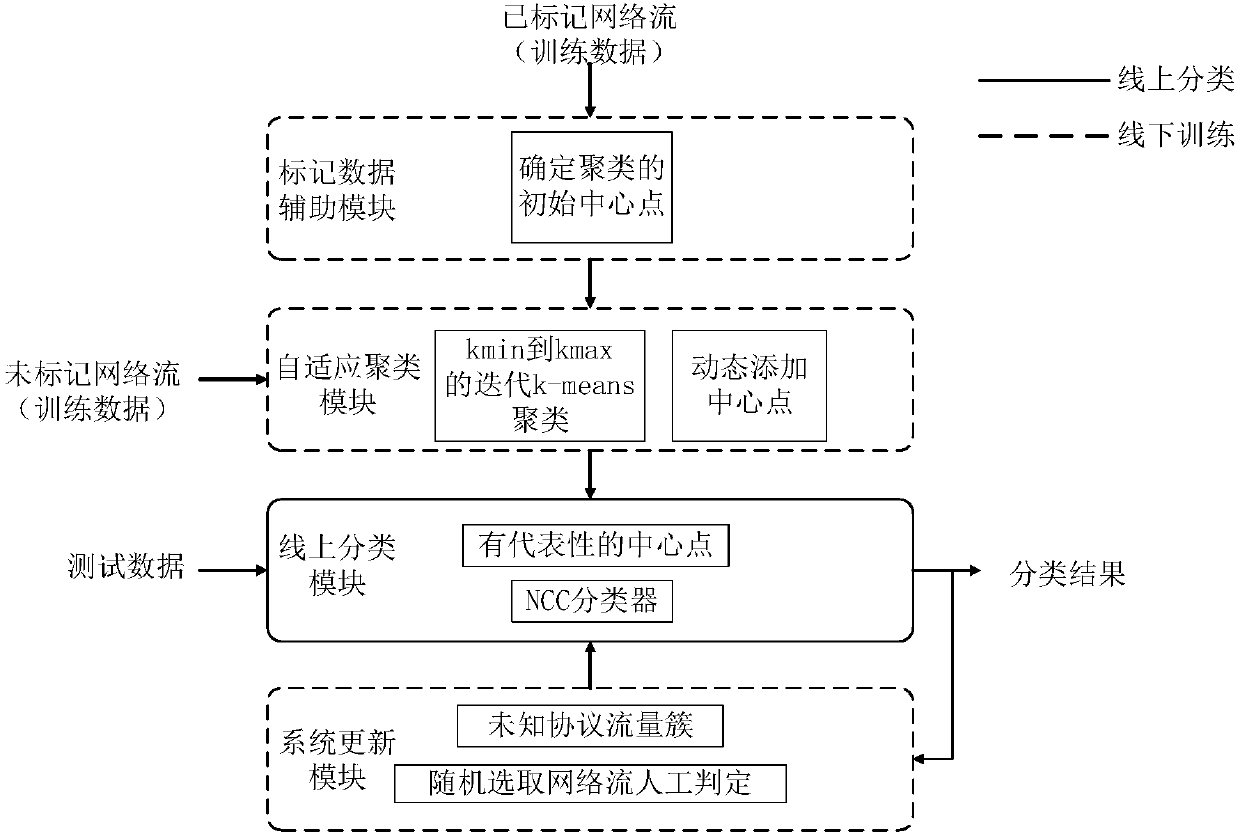
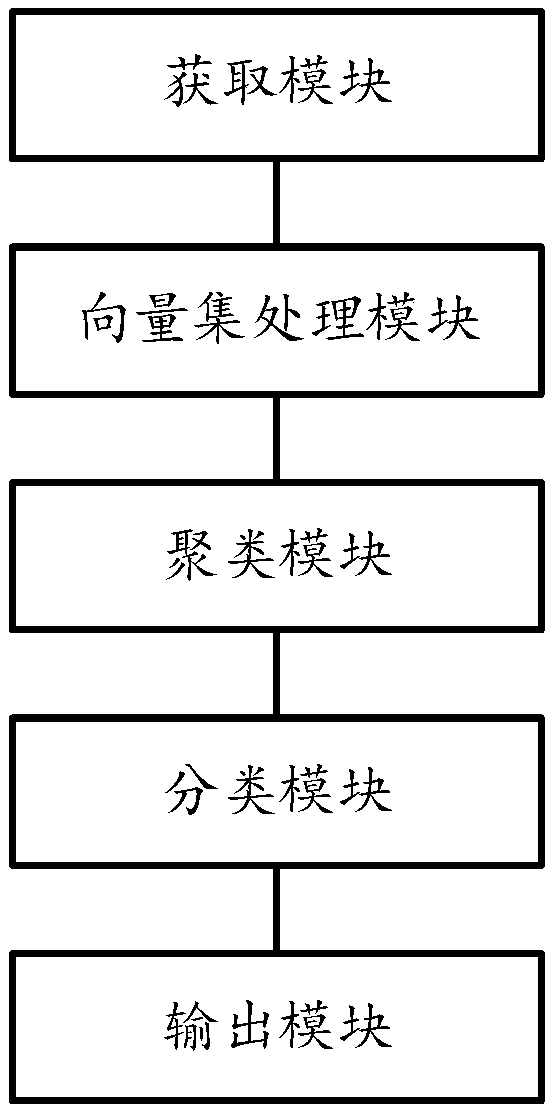
The invention relates a self-adaptive semi-supervised network traffic classification method, system and equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a network stream, extracting thestream feature with the preset fixed quantity in each network stream to obtain a network stream feature vector; computing the centroid of the network stream feature vector in each type according to the marked network stream feature vector, thereby obtaining a vector set M; performing self-adaptive semi-supervised k-means clustering by taking the vector set M as an initial center point; mapping theobtained network stream in each type of cluster to the belonged traffic type according to the maximum posterior probability; taking the traffic cluster of the known type as the training data to trainan online traffic classifier. The invention further relates to a system, the system comprises an acquisition module, a vector set processing module, a clustering module, a classification module, andan output module. The invention relates to the equipment. The equipment comprises a processor, a memorizer, and a computer program stored on the memorizer and capable of being run on the memorizer.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
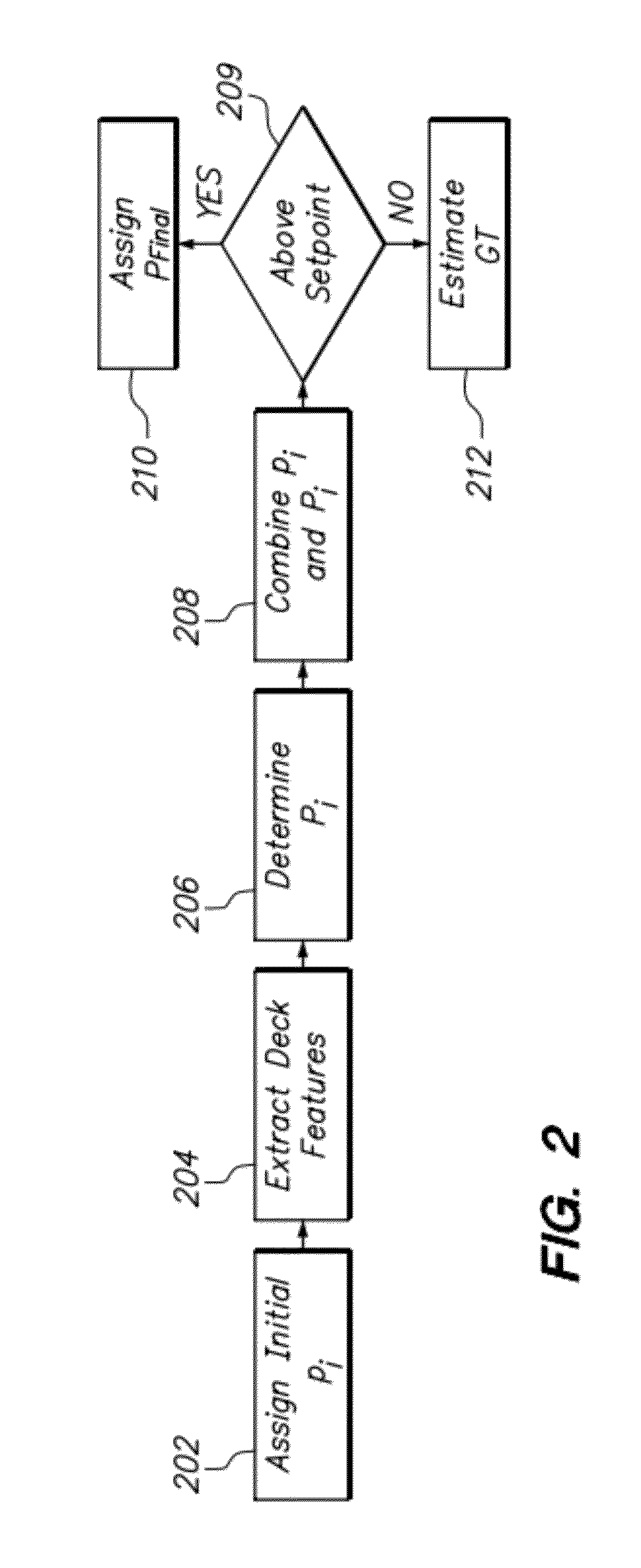
Method for classifying vessels using features extracted from overhead imagery
ActiveUS8170272B1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsFeature extractionBlood vessel
Methods for processing overhead imagery of a vessel include the step of determining an initial classification and classification probability based on the vessel length and length-to-width ratio. Next, mutually exclusive deck features can be extracted from the image. For several embodiments, the extracted deck features that can be spherical tanks, hatches and containers that are stored on deck. The initial classification probability is then weighted using the results of the deck feature extraction step to yield a posterior classification probability for the ship image. If the posterior classification probability is above a predetermined value, the image is assigned a posterior classification. If the posterior probability is below the predetermined value, the vessel image is classified as unknown, and the gross tonnage of the vessel is calculated using the length and width of the vessel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Iterative rake receiver and corresponding reception process
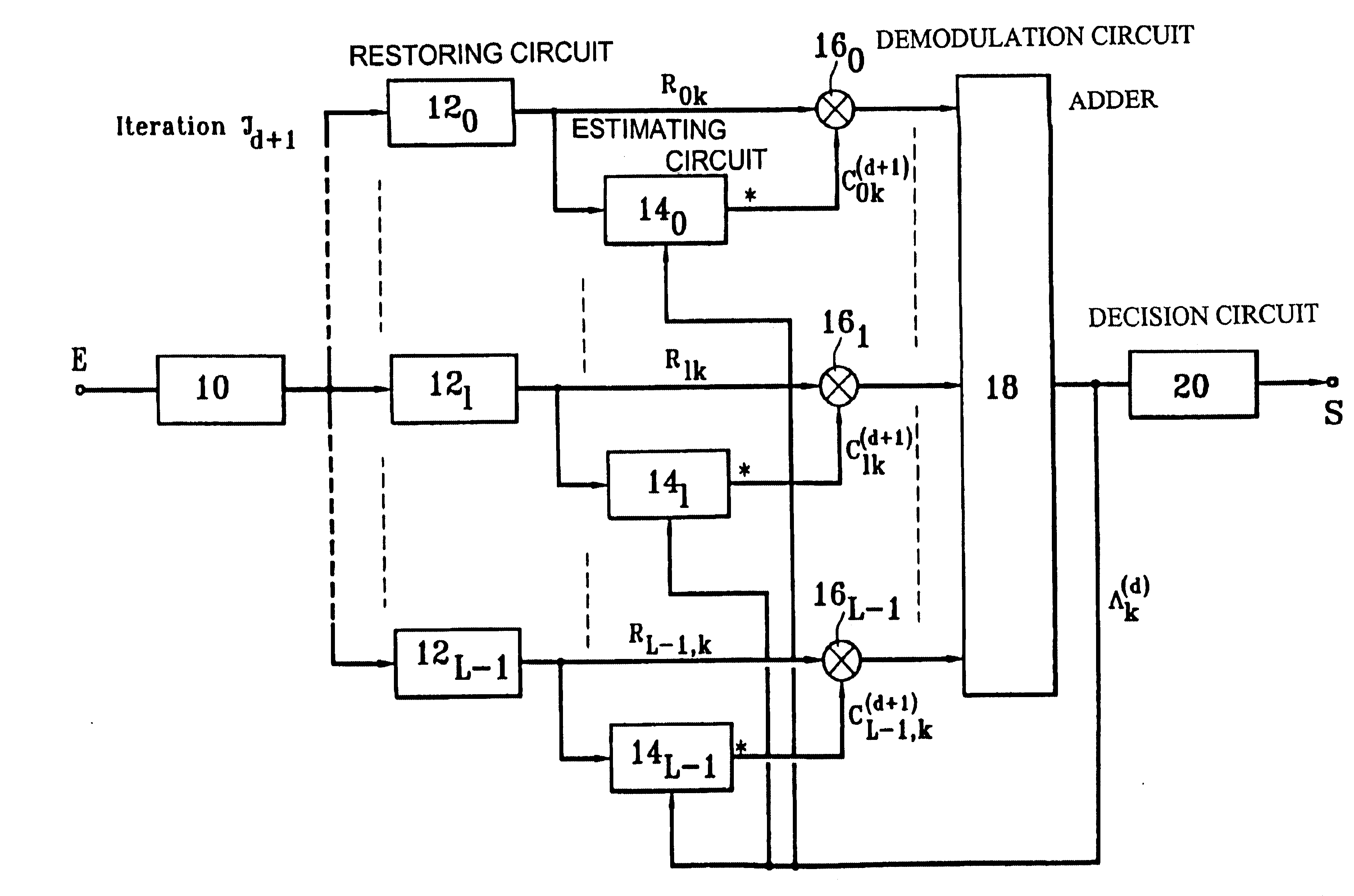
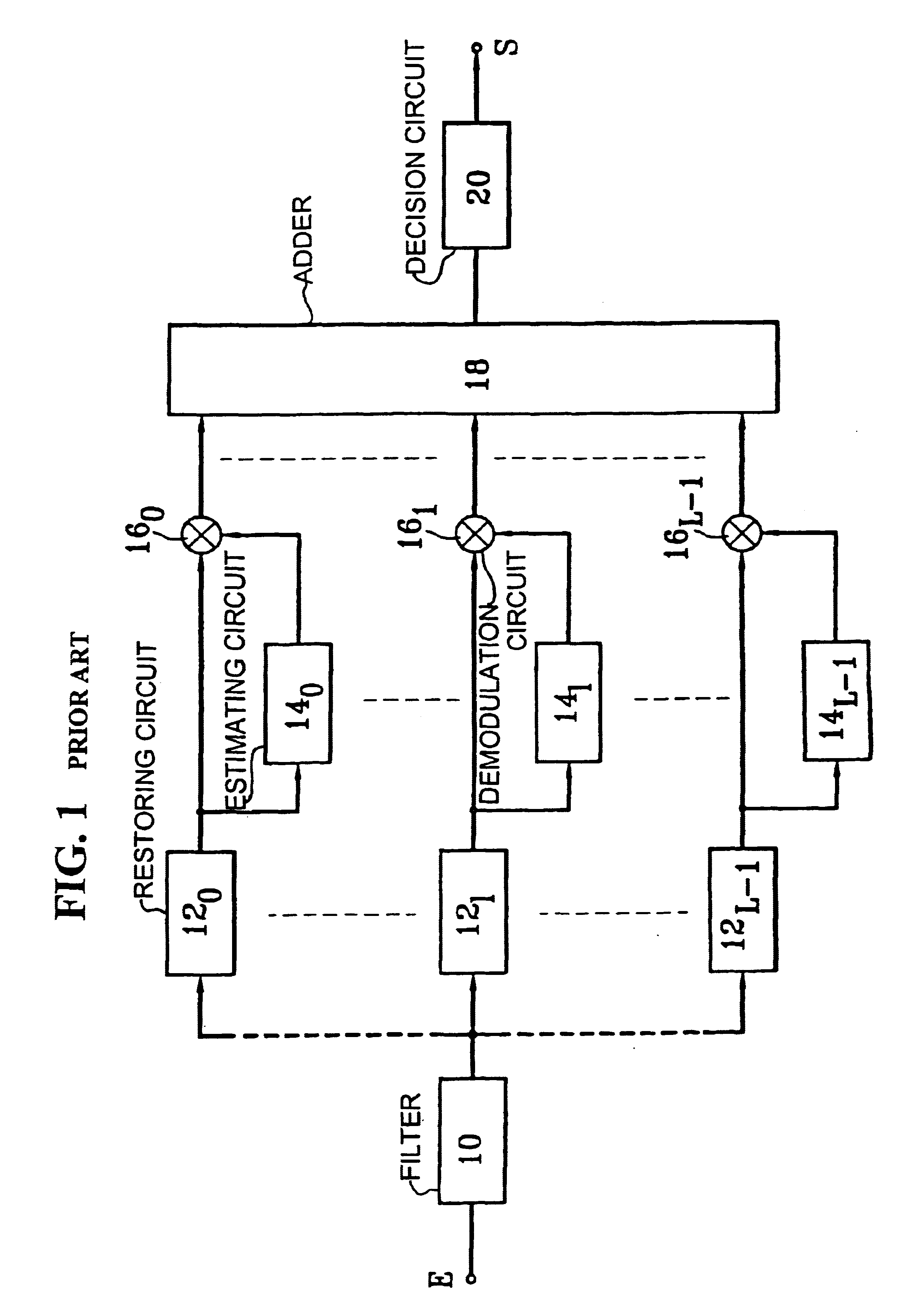
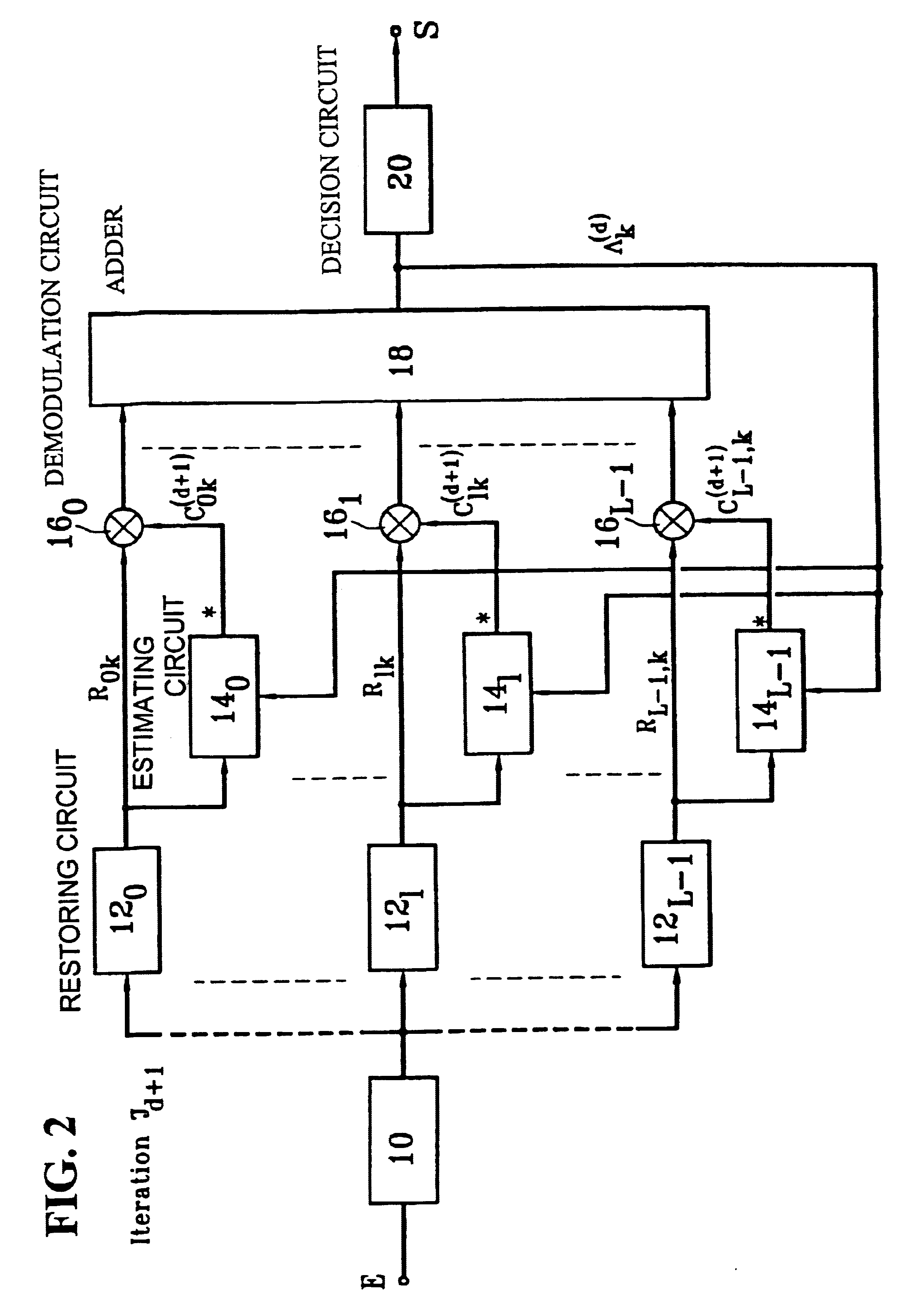
InactiveUS6674740B1Code division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDecision circuitFrequency spectrum
A CDMA radiocommunication signals receiver for receiving signals obtained from spectrum symbols spread using pseudo-random sequences and having been propagated along a number of paths. The receiver includes a filter configured to restore L unspread signals for each symbol, corresponding to L different paths, a calculating circuit configured to calculate L estimates of the L different paths, and a demodulator configured to process each of the L unspread signals using the corresponding L estimates to obtain L path contributions. Also included is an adder configured to form a sum of the L path contributions and for outputting an estimate of a received symbol, and a decision circuit configured to make a decision about a value of the received symbol based on a value of the estimate of the received symbol output by the adder. Further, the receiver processes blocks of N symbols, each block having data symbols and control symbols, each symbol being identified by a rank k that it occupies in the block, where k varies from 0 to N-1. Also, for each path identified by an index l, where l varies from 0 to L-1, and for each block, the receiver considers a vector Cl with N components that characterizes the path during the block, and the receiver defines a vector base BK, vectors of the vector base BK being N eigenvectors of the matrix E [ClCl<.T>], each vector Cl being decomposed in the vector base, where decomposition coefficients denoted GlK form independent random Gaussian variables. In addition, coefficients GlK, define a vector Gl with N components for each path l, and the calculating circuit estimates each vector Gl, using an iterative process based on EM estimation-maximization algorithm based on a maximum a posteriori probability criterion.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
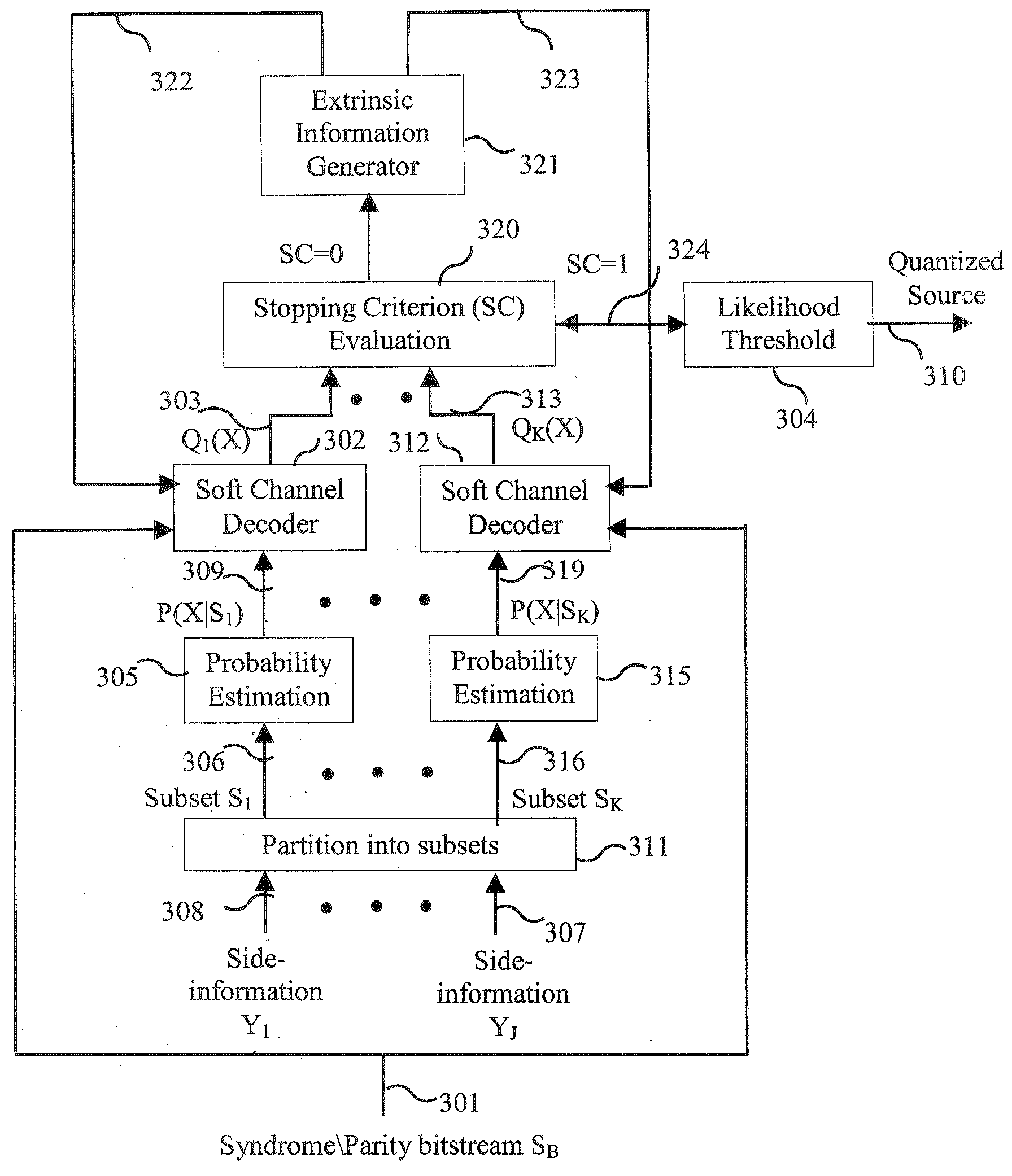
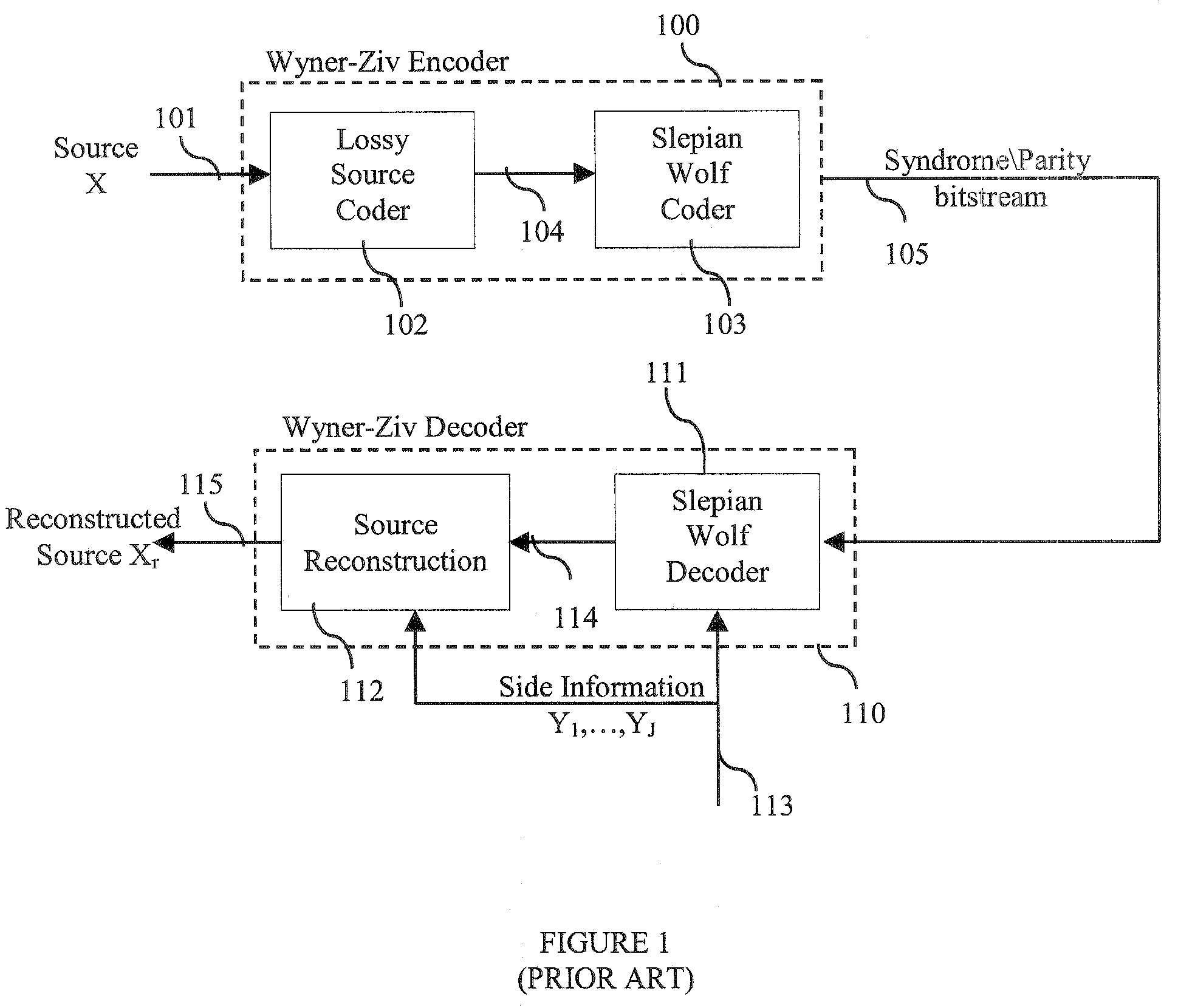
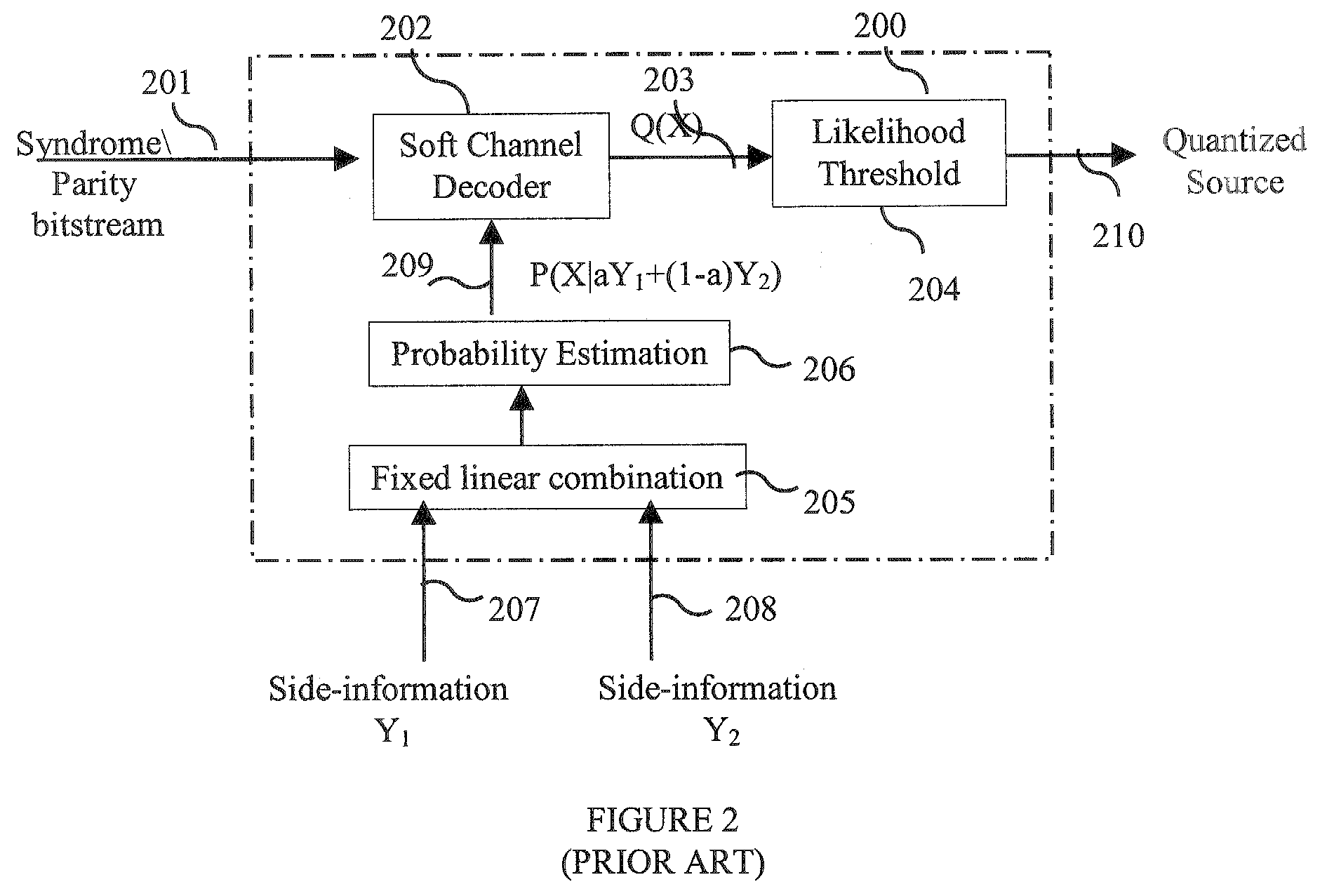
Method and Apparatus for Multi-Hypothesis Decoder Side-Information Coding
InactiveUS20080189073A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionData compressionHypothesis
A computer-implemented method for decompression in data compression systems with decpder side-information including a plurality of signals each of which is correlated to a source, includes determining a conditional probability function of the source conditioned upon a subset of decoder side-information signals, wherein the decoder side-information signals include pre-stored and received statistical information, estimating an a-posteriori probability function based on the conditional probability function and extrinsic information, evaluating a stopping criterion for decompresiion, generating the extrinsic information based on the a-posteriori probability function, and determining a likelihood threshold for determining a most probable value of a quantized source signal based on the a-posteriori probability function and outputting the quantized source upon determining to stop decompression.
Owner:IBM CORP
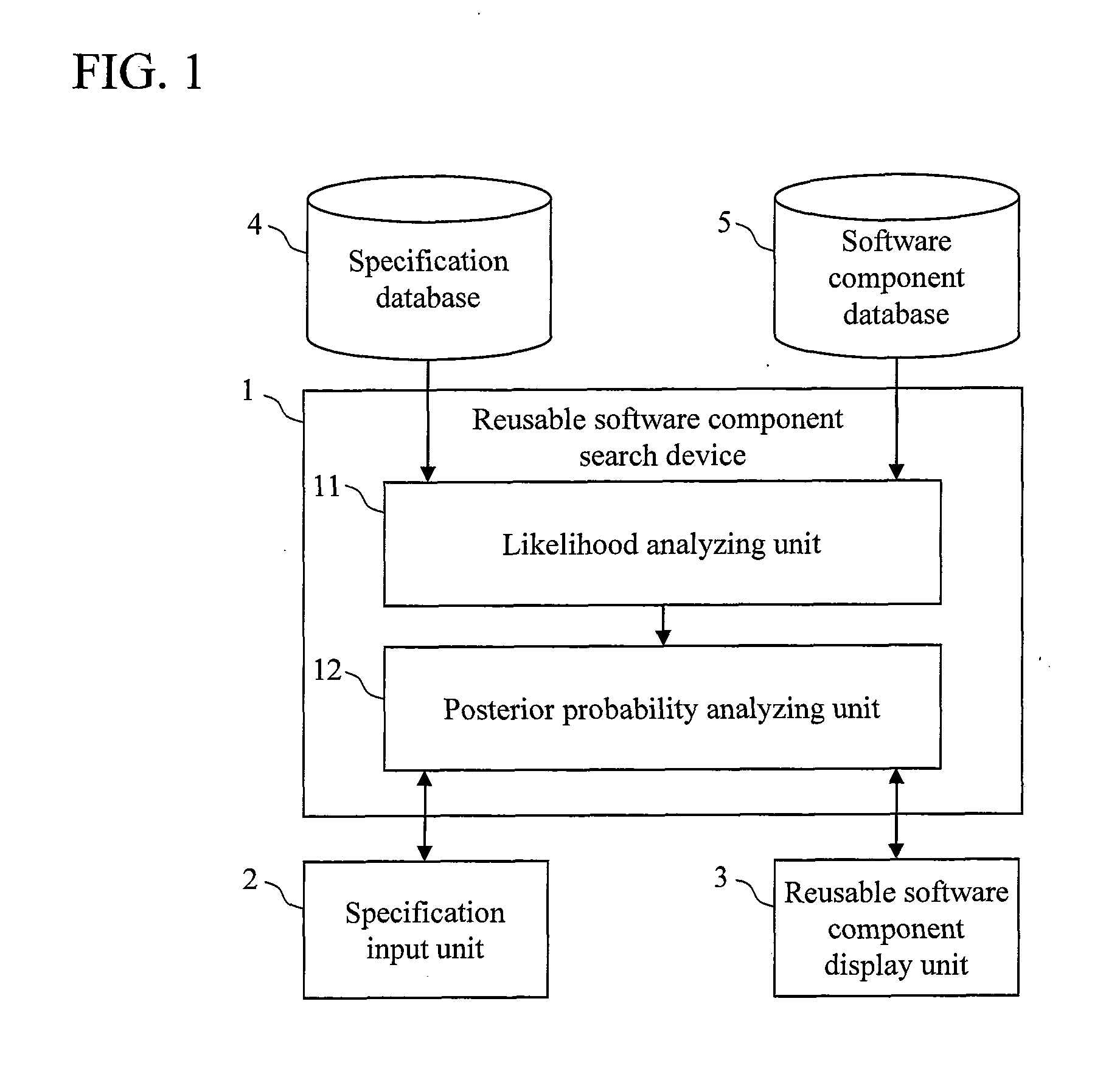
Software Reuse Support Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20100269099A1Software reuseSpecific program execution arrangementsReusabilityControl software
A likelihood indicating the distribution of the frequency of use of each specification of the existing device is calculated for each version of a software component used in the control software of the existing device, and a prior probability indicating the distribution of the frequency of use of each version is calculated for each software component used in the control software of the existing device. A posterior probability indicating the reusability of each version of the existing software component is calculated for each specification of a device to be developed, on the basis of the likelihood and the prior probability.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
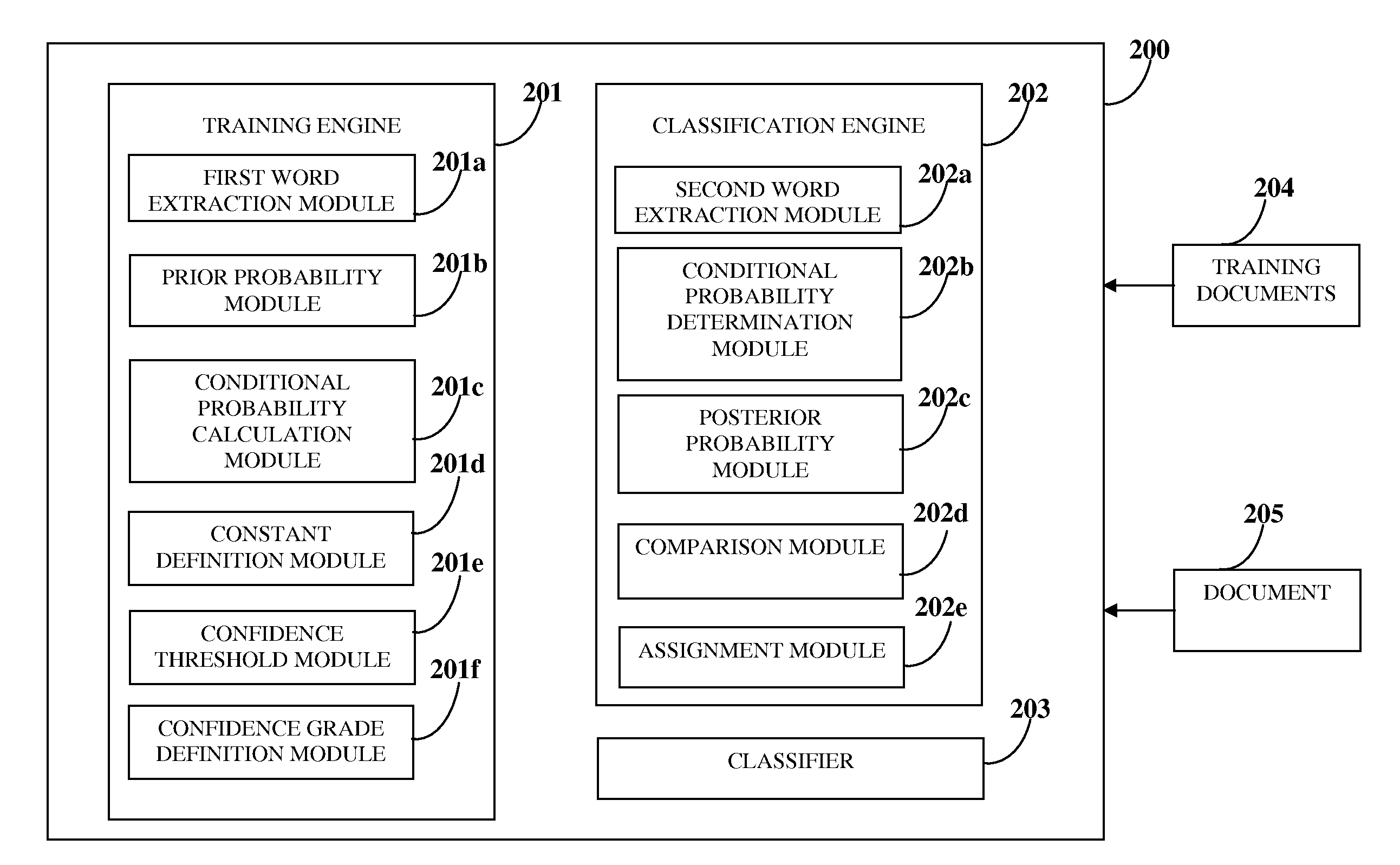
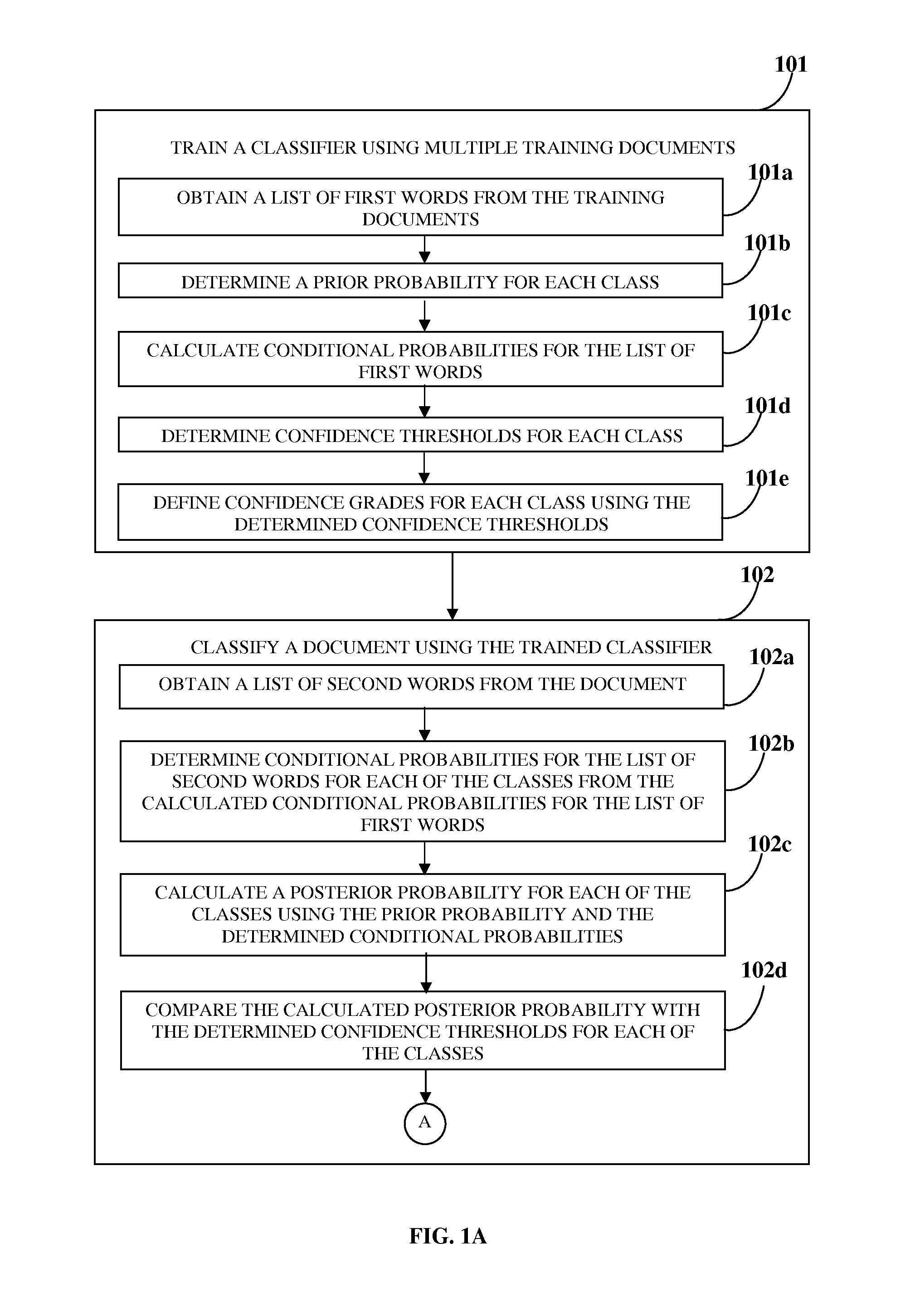
Text Classification With Confidence Grading
InactiveUS20120221496A1Digital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsConditional probabilityMachine learning
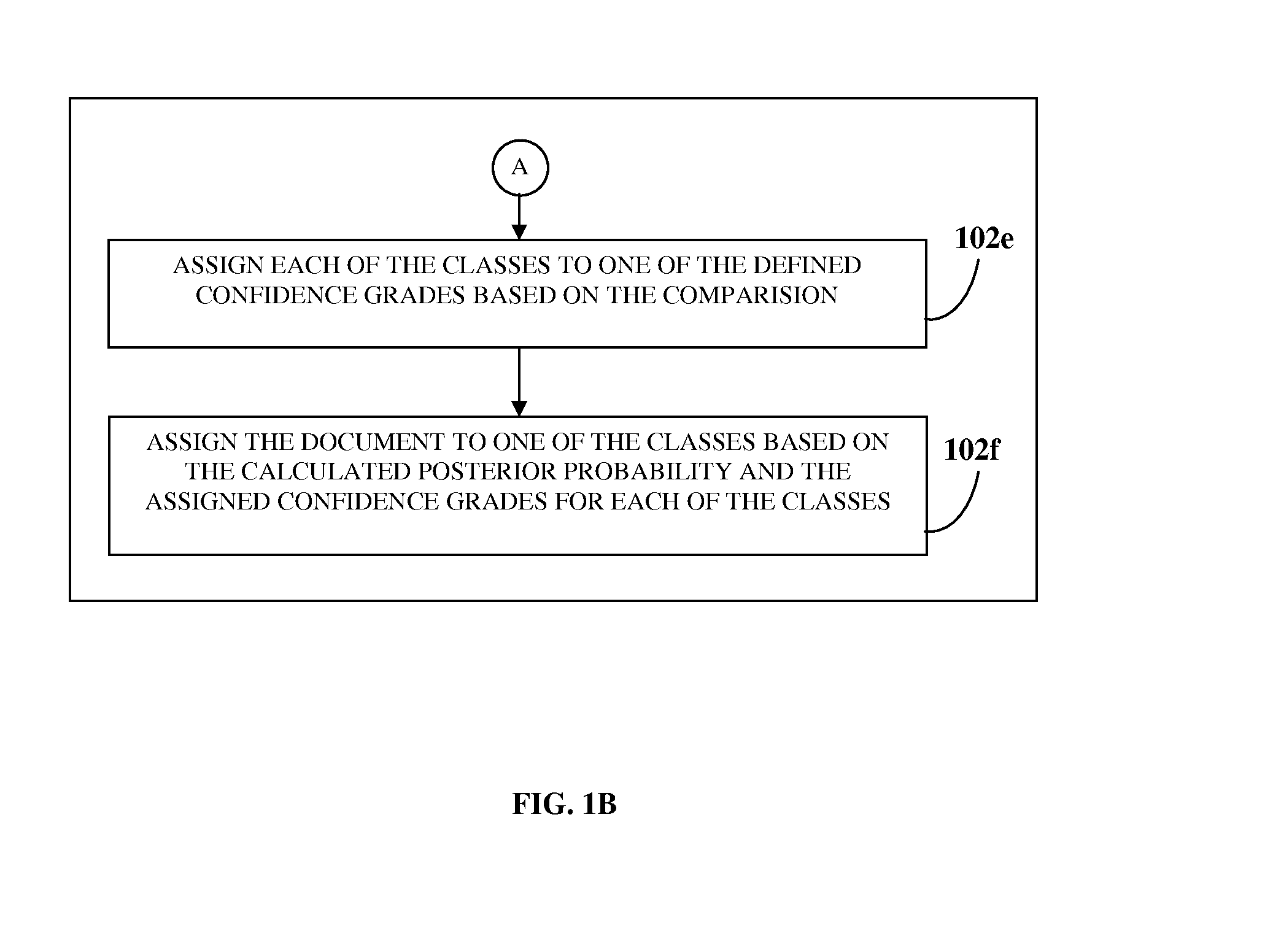
A computer implemented method and system is provided for classifying a document. A classifier is trained using training documents. A list of first words is obtained from the training documents. A prior probability is determined for each class of multiple classes. Conditional probabilities are calculated for the first words for each class. Confidence thresholds are determined. Confidence grades are defined for the classes using the confidence thresholds. A list of second words is obtained from the document. Conditional probabilities for the list of second words are determined from the calculated conditional probabilities for the list of first words. A posterior probability is calculated for each of the classes and compared with the determined confidence thresholds. Each class is assigned to one of the defined confidence grades based on the comparison. The document is assigned to one of the classes based on the posterior probability and the assigned confidence grades.
Owner:KETERA TECH INC
Hierarchical Block Irregular Low Density Check Code Decoder and Decoding Method
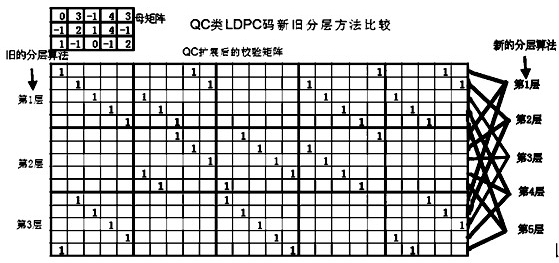
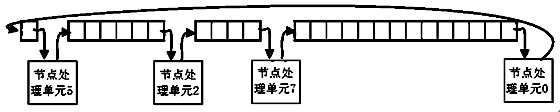
ActiveCN102281125ANo pipelining contentionPipeline contention conflict eliminationError preventionCheck digitDegree of parallelism
The invention discloses a laminated and partitioned irregular low density parity check (LDPC) code decoder and a decoding method in the technical field of communication. An external information storage unit outputs a soft value transmitted to an information node by a last iterated check node to a decoding processing module. A cyclic shift register transmits a posterior probability likelihood ratio update value of the information node to the decoding processing module. The decoding processing module transmits the check update value in the iteration to the external information storage unit, andsimultaneously transmits the posterior probability likelihood ratio update value of the information node to the cyclic shift register through a decoding processing module interweaving network. The decoder is suitable for decoding all quality control (QC) LDPC codes, and all the partitioned LDPC code words support decoding; the decoder has no stream competition conflict, and has better throughput performance and relatively simple working time sequence; and the consumption of the interweaving network of huge resources is not needed, many hardware resources are saved, and the resource consumption of the whole decoder is relatively low. The decoding supporting parallelism degree can be flexibly changed.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT OF DIGITAL TELEVISION
Communication system
InactiveUS20110142181A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationDigital dataCommunications system
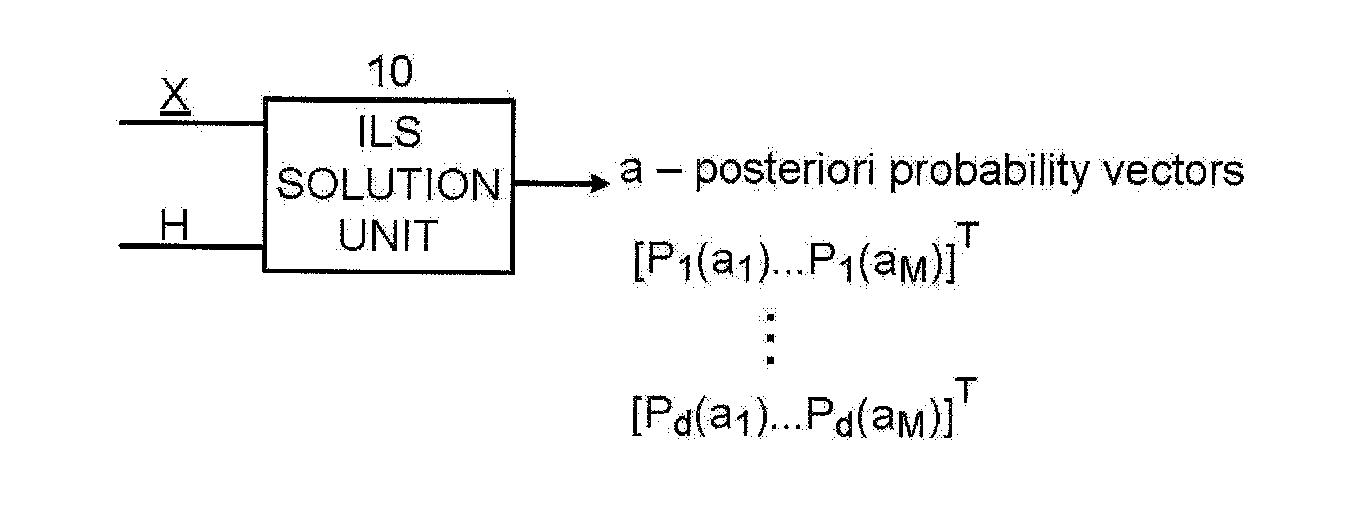
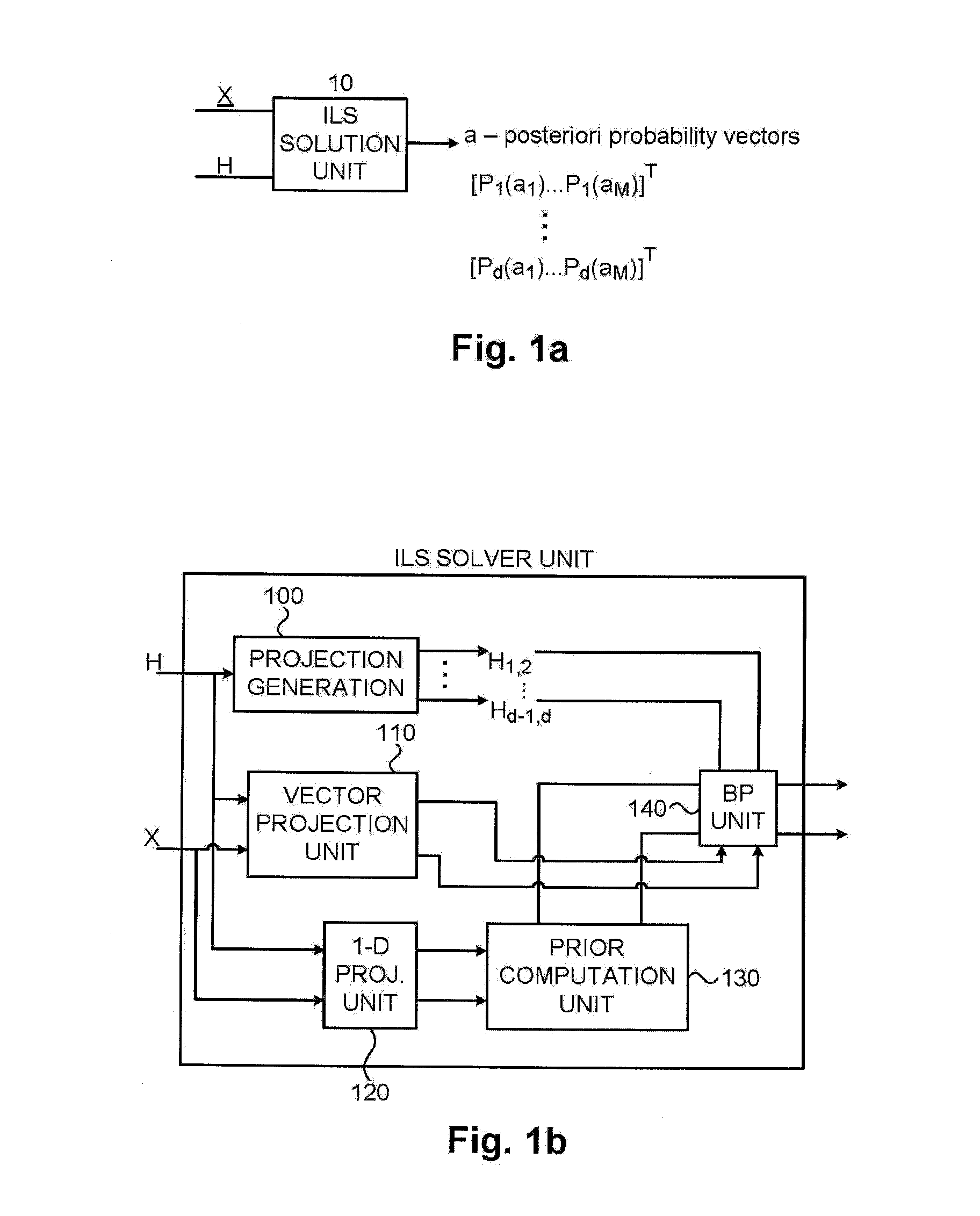
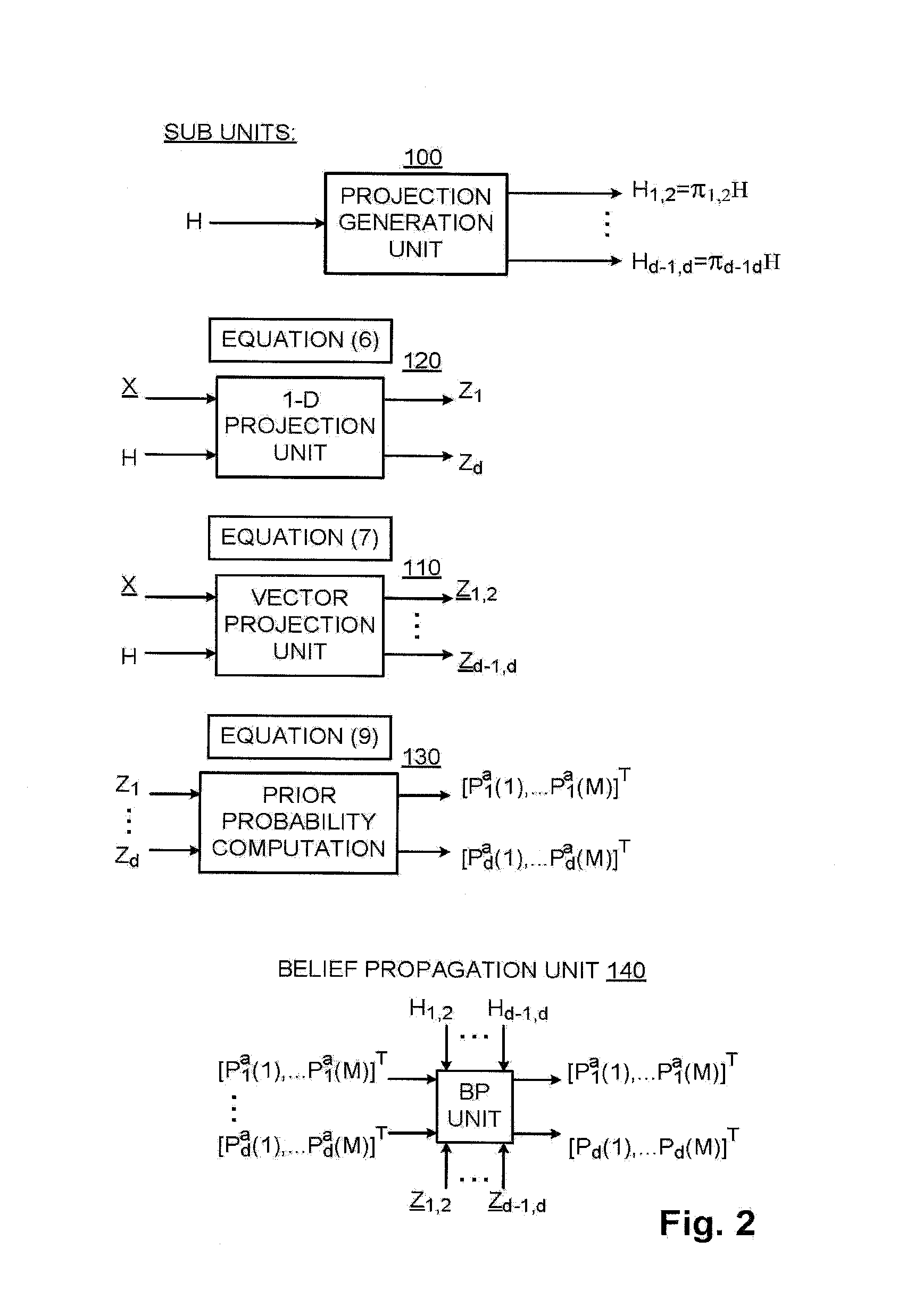
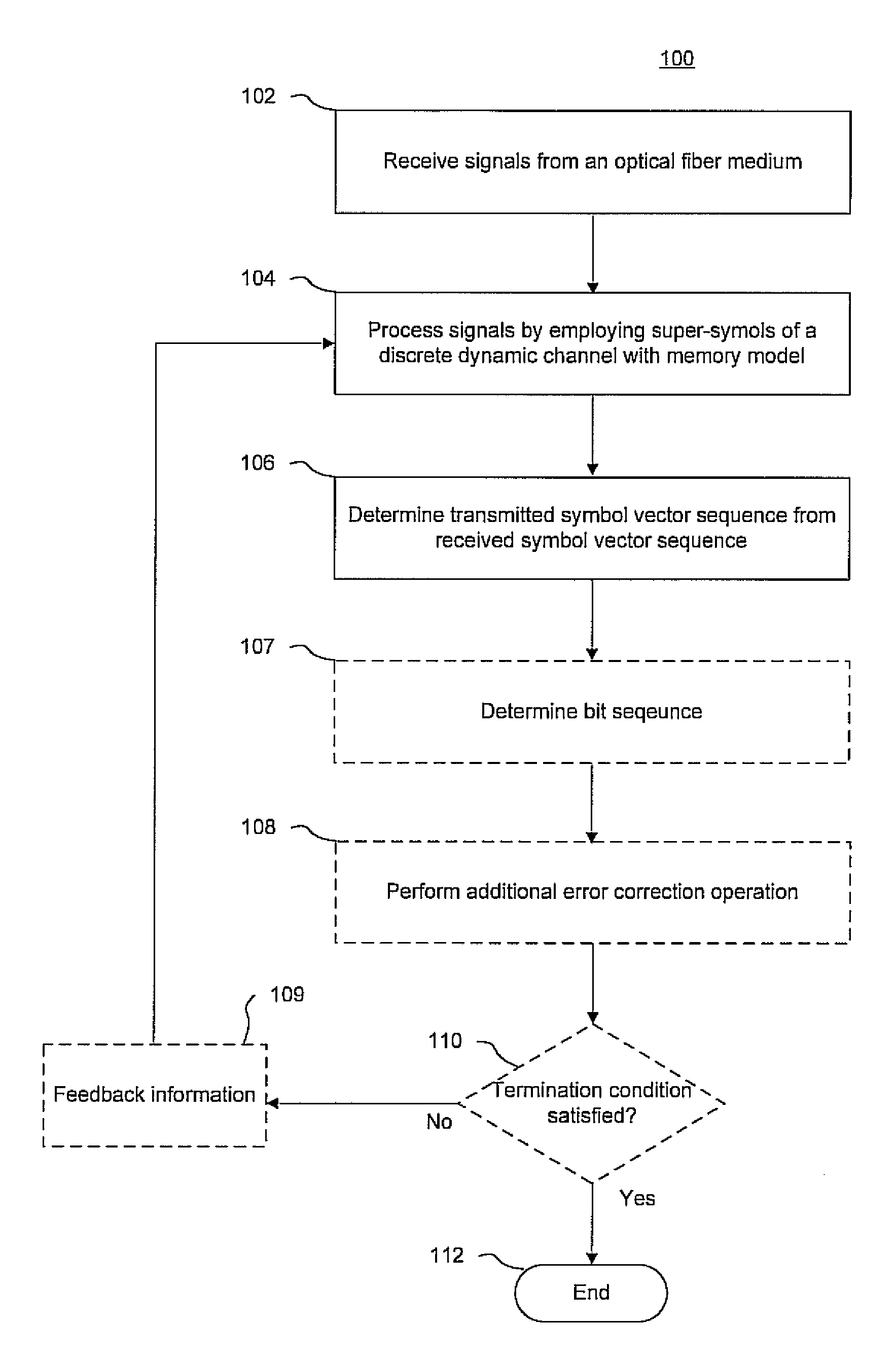
A communication system having a program of machine-readable instructions for solving an ILS problem, tangibly embodied on a computer readable memory and executable by a digital data processor, to perform actions directed toward outputting a set of a-posteriori probability vectors.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV
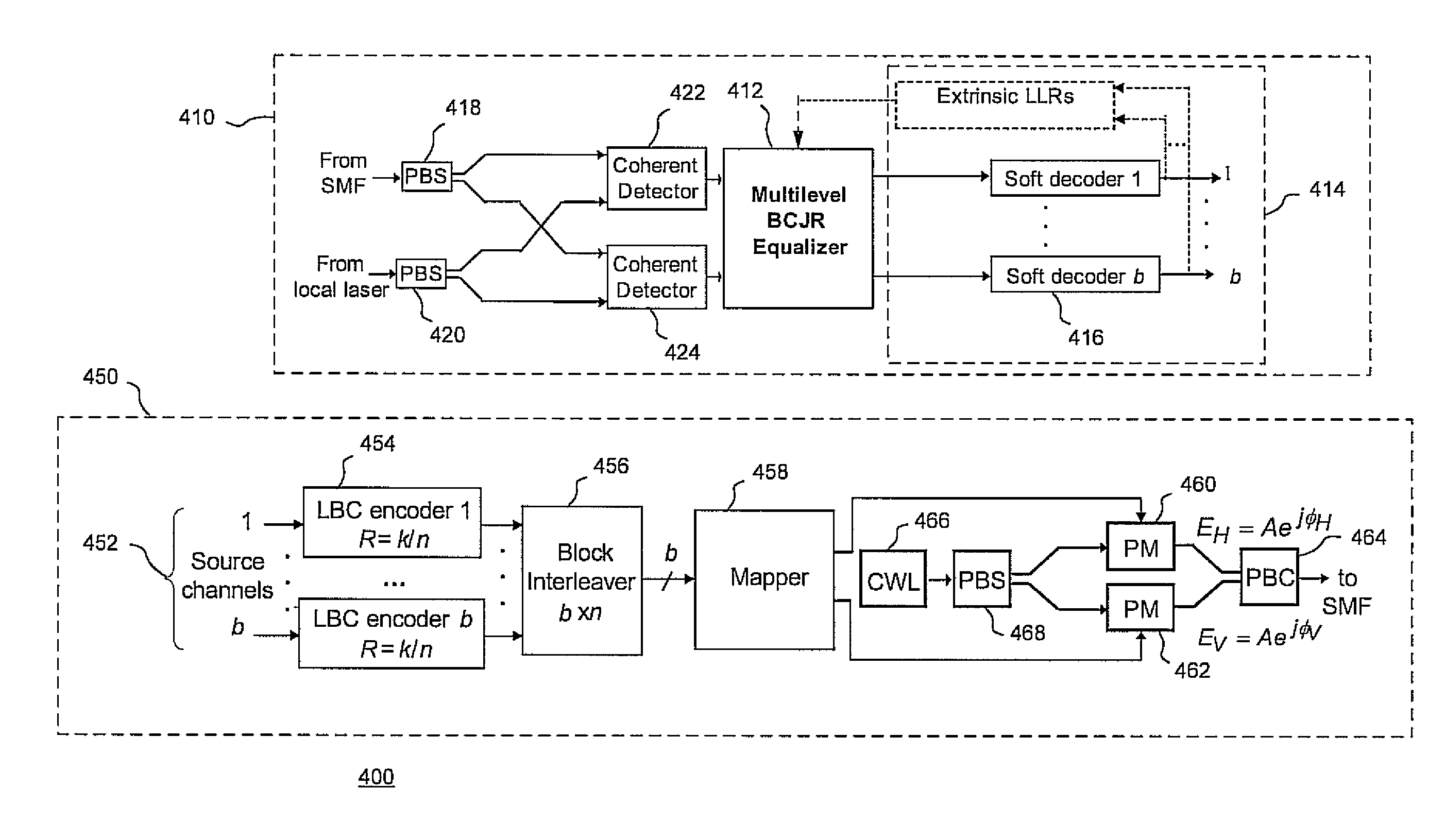
Methods and systems for polarization multiplexed multilevel modulation for optical communication
ActiveUS20100232804A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMultiple-port networksPolarisation multiplex systemsMaximum a posteriori estimationPolarization multiplexed
Multilevel soft-equalizer detectors, such as a maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) detector, suitable for use in polarization multiplexed optical communications using multilevel modulations and coherent detection are disclosed. Detection systems and methods may consider two symbols transmitted over two orthogonal polarization states as a two-component symbol, which is effective in eliminating the bit error ratio (BER) floor phenomenon introduced by conventional soft equalizers.
Owner:NEC CORP
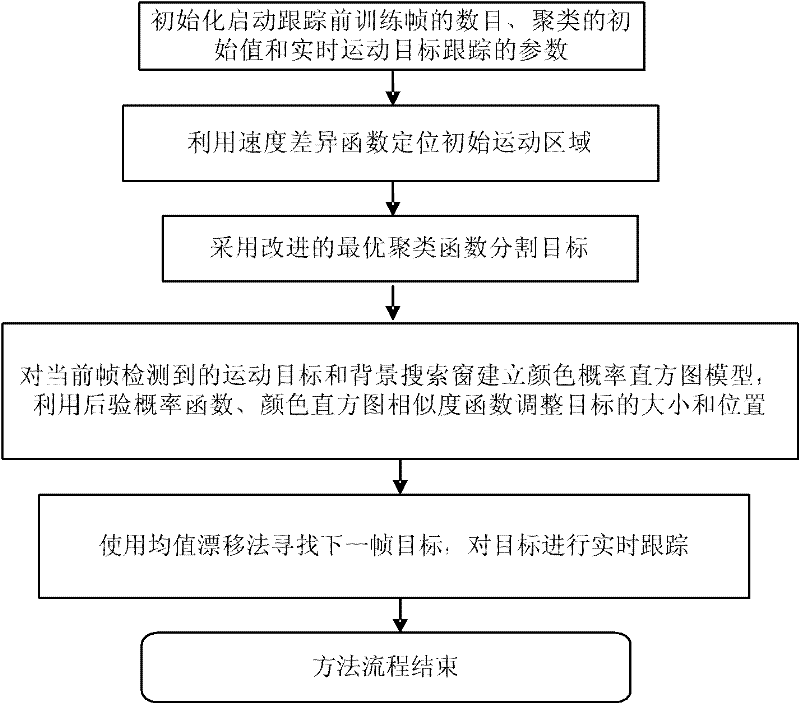
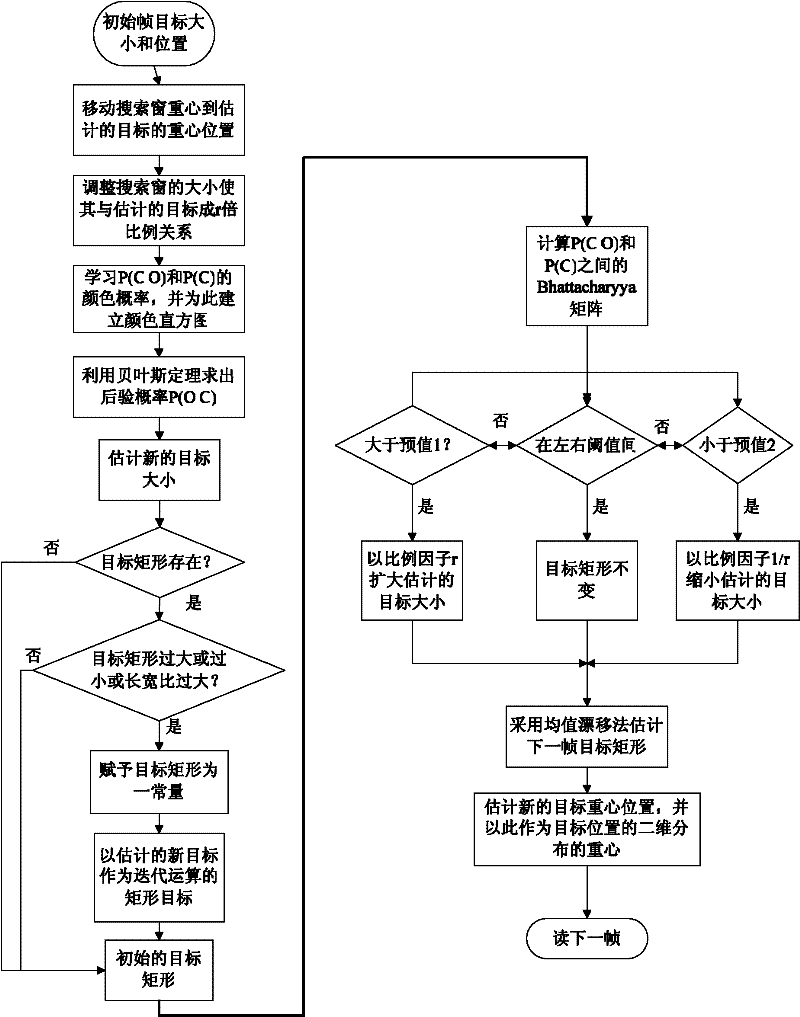
Probabilistic model based automatic target tracking method for moving camera
ActiveCN102332166AAddresses issues with inaccurate tracking of targetsImage analysisProbit modelMean-shift
The invention provides a probabilistic model based automatic target tracking method for a moving camera, which comprises the following specific steps of: firstly, initializing start tracking parameters and real-time moving target tracking parameters; secondly, utilizing a speed difference function to position an initial moving area, and adopting an improved optimal clustering function to segment a moving target; thirdly, establishing a color probability histogram model for the moving target detected by the current frame and a background search window, and utilizing a posteriori probability function and a color histogram similarity function to adjust the size and position of the target; and finally, using a continuously adaptive mean shift method to find the next-frame moving target to achieve the real-time tracking of the moving target in the dynamic background. In the invention, the reliability of moving target tracking is improved, and the problems of selection of initial targets and multi-target tracking, and the problems that the target and background have the same color and the target color changes can be effectively solved under the moving camera.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Methods and systems for polarization multiplexed multilevel modulation for optical communication
ActiveUS8175466B2Reduce impactBit error ratio floor phenomenon can be eliminatedMultiple-port networksPolarisation multiplex systemsMultilevel modelMaximum a posteriori estimation
Multilevel soft-equalizer detectors, such as a maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) detector, suitable for use in polarization multiplexed optical communications using multilevel modulations and coherent detection are disclosed. Detection systems and methods may consider two symbols transmitted over two orthogonal polarization states as a two-component symbol, which is effective in eliminating the bit error ratio (BER) floor phenomenon introduced by conventional soft equalizers.
Owner:NEC CORP
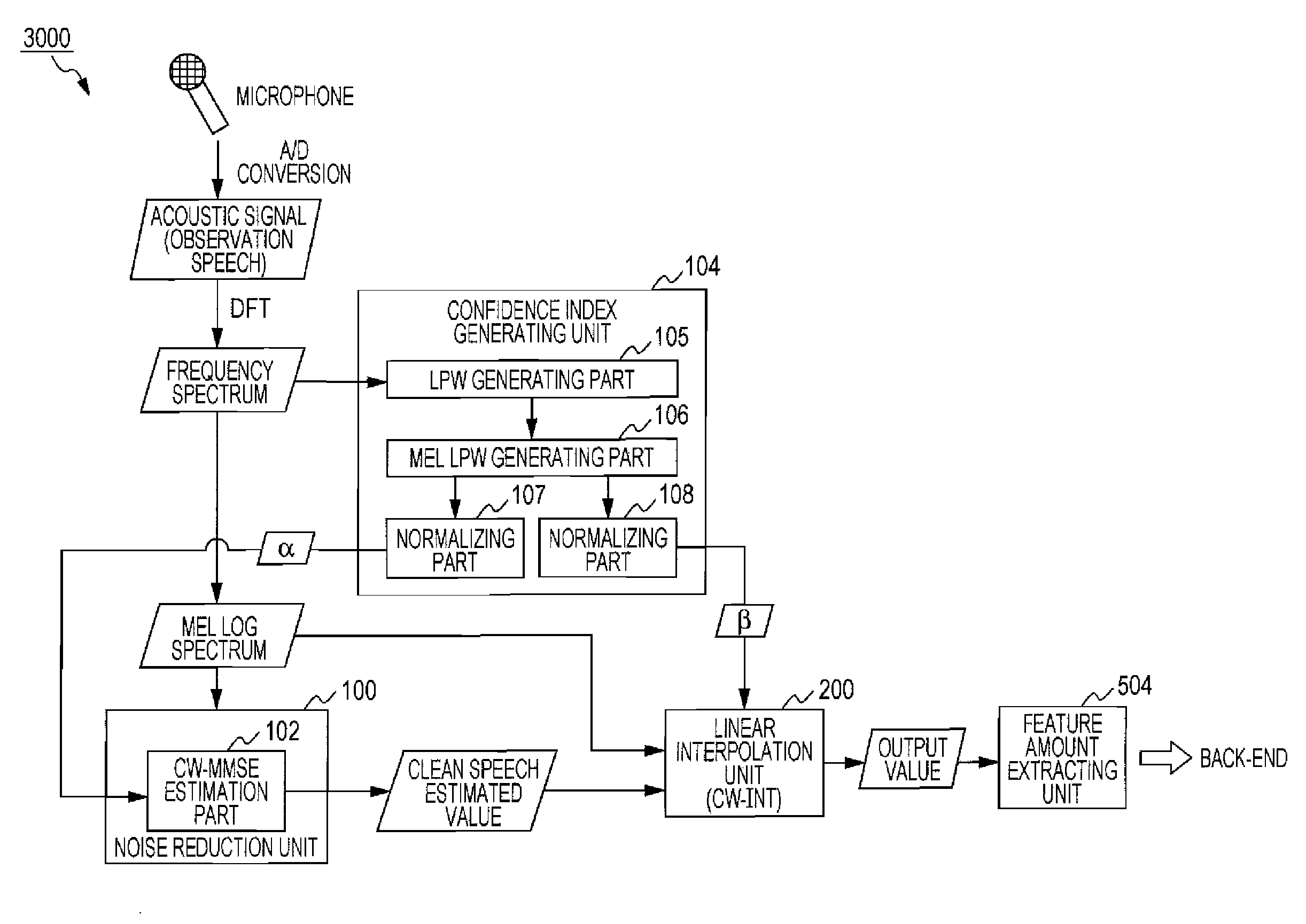
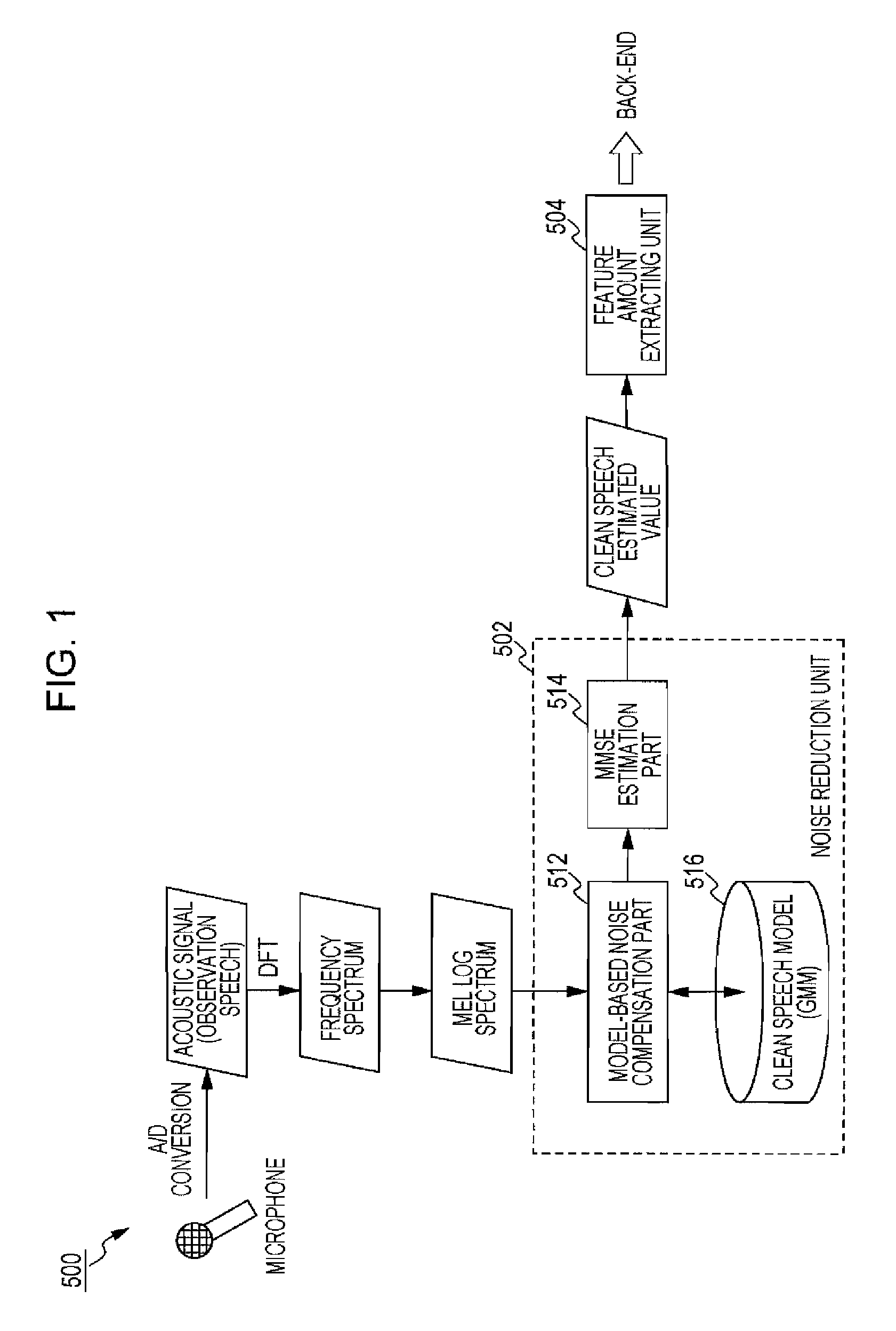
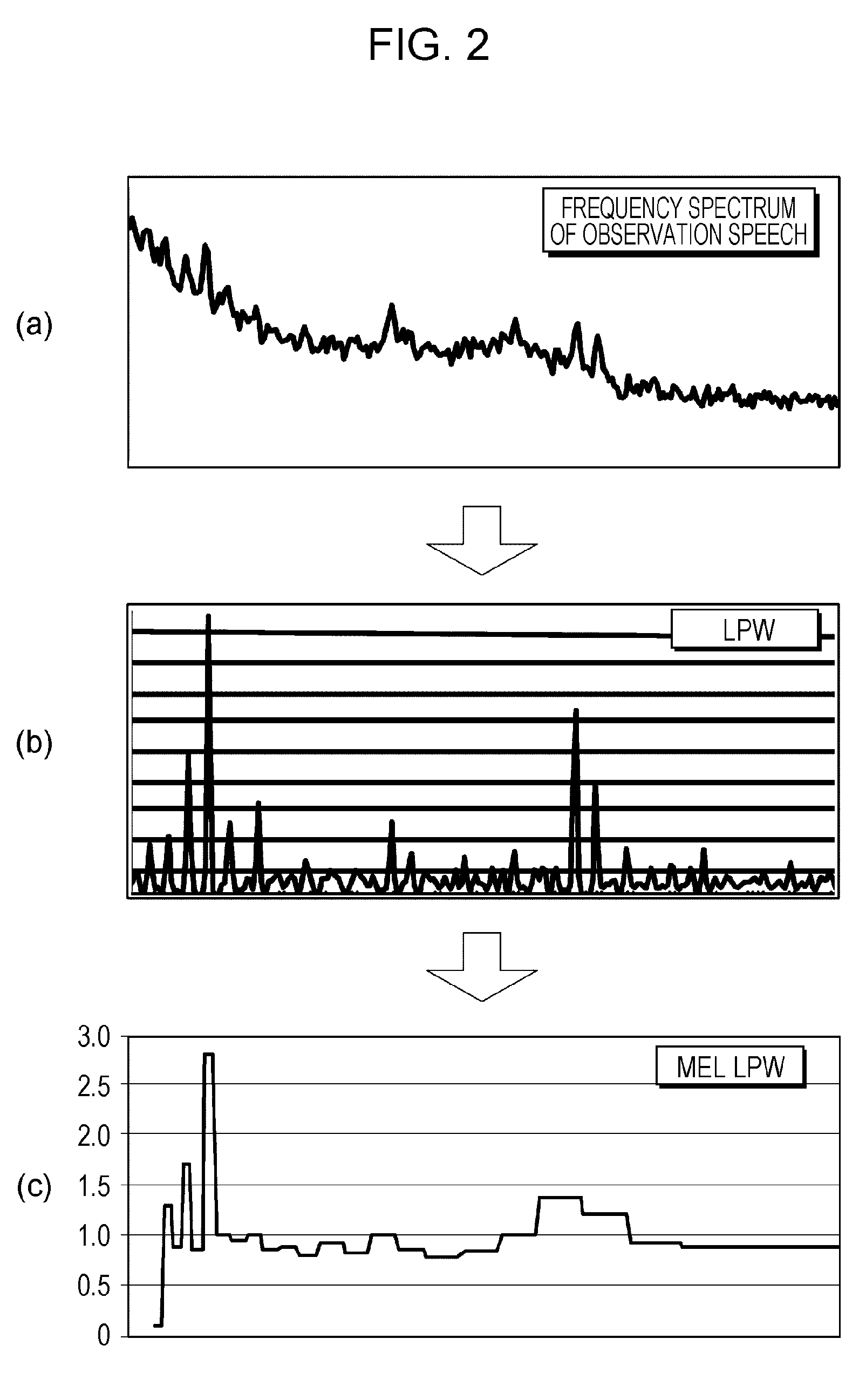
Local peak weighted-minimum mean square error (lpw-mmse) estimation for robust speech
A system and method for noise reduction applied to a speech recognition front-end. An output of a front-end is optimized by giving, as a weight to the output for each band, a confidence index representing the remarkableness of the harmonic structure of observation speech. In a first method, when clean speech is estimated by executing MMSE estimation on a model that gives a probability distribution of noise-removed speech generated from observation speech, the posterior probability of the MMSE estimation is weighted using the confidence index as a weight. In a second method, linear interpolation is executed, for each band, between an observed value of observation speech and an estimated value of clean speech, with the confidence index serving as a weight. The first method and the second method can be combined.
Owner:IBM CORP
SAR image change detection method based on priori, fusion gray level and textural feature
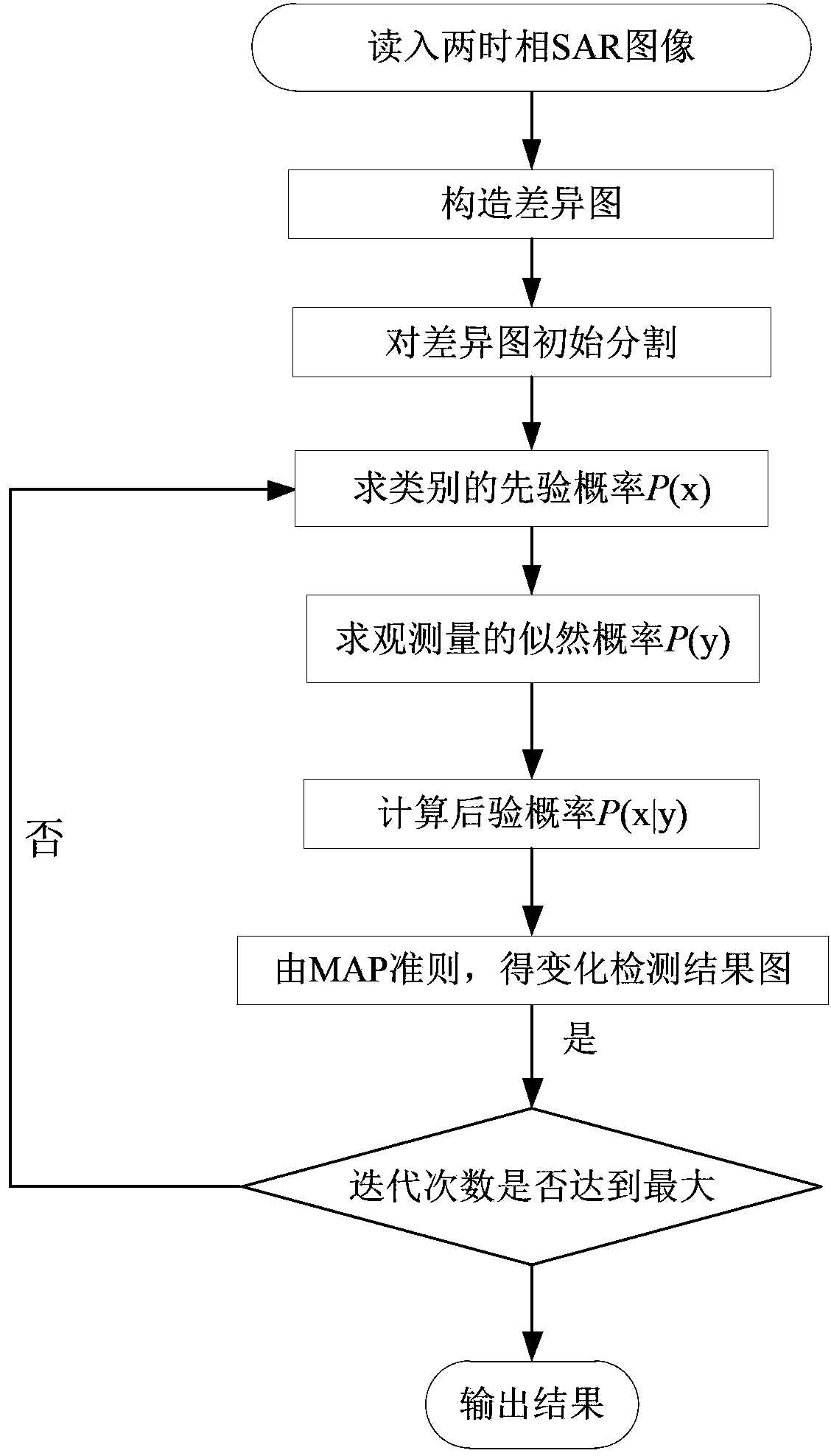
InactiveCN103353989AAvoid estimationSimple processImage analysisScene recognitionMaximum a posteriori estimationDifference-map algorithm
The invention discloses a SAR image change detection method based on a priori, a fusion gray level and a textural feature. By using the method of the invention, problems that a Gaussian model can not completely fit distribution of a difference graph and change detection accuracy is low because only pixel gray level information of the SAR image is used are mainly solved. The method comprises the following realization steps that (1) two time phase SAR images which are registered and corrected are read in; (2) a wavelet fusion strategy is performed on the two images so as to construct the difference graph; (3) a classified priori probability of the difference graph is calculated; (4) the gray level of the difference graph and the texture information are fused so as to acquire an observed quantity likelihood probability; (5) the classified priori probability and the observed quantity likelihood probability are used to calculate a posteriori probability; (6) a maximum posteriori probability criterion is used to divide the difference graph into a change type and a non-change type; (7) a step (3) to a step (6) are repeated till a terminal condition is satisfied and a final change detection result is output. The method of the invention has the advantage that change detection precision to the SAR image is high. The method can be used to extract and acquire change detail information of the SAR image.
Owner:陕西国博政通信息科技有限公司
System and method for automatic speech recognition from phonetic features and acoustic landmarks
A probabilistic framework for acoustic-phonetic automatic speech recognition organizes a set of phonetic features into a hierarchy consisting of a broad manner feature sub-hierarchy and a fine phonetic feature sub-hierarchy. Each phonetic feature of said hierarchy corresponds to a set of acoustic correlates and each broad manner feature of said broad manner feature sub-hierarchy is further associated with a corresponding set of acoustic landmarks. A pattern recognizer is trained from a knowledge base of phonetic features and corresponding acoustic correlates. Acoustic correlates are extracted from a speech signal and are presented to the pattern recognizer. Acoustic landmarks are identified and located from broad manner classes classified by the pattern recognizer. Fine phonetic features are determined by the pattern recognizer at and around the acoustic landmarks. The determination of fine phonetic features may be constrained by a pronunciation model. The most probable feature bundles corresponding to words and sentences are those that maximize the joint a posteriori probability of the fine phonetic features and corresponding acoustic landmarks. When the hierarchy is organized as a binary tree, binary classifiers such as Support Vector Machines can be used in the pattern classifier and the outputs thereof can be converted probability measures which, in turn may be used in the computation of the aforementioned joint probability of fine phonetic features and corresponding landmarks.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com