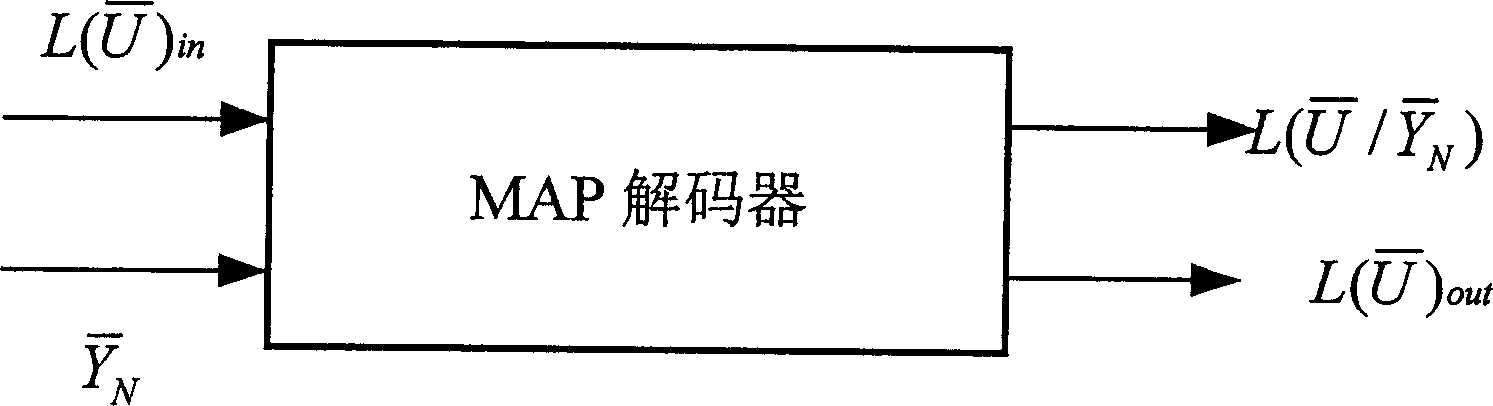
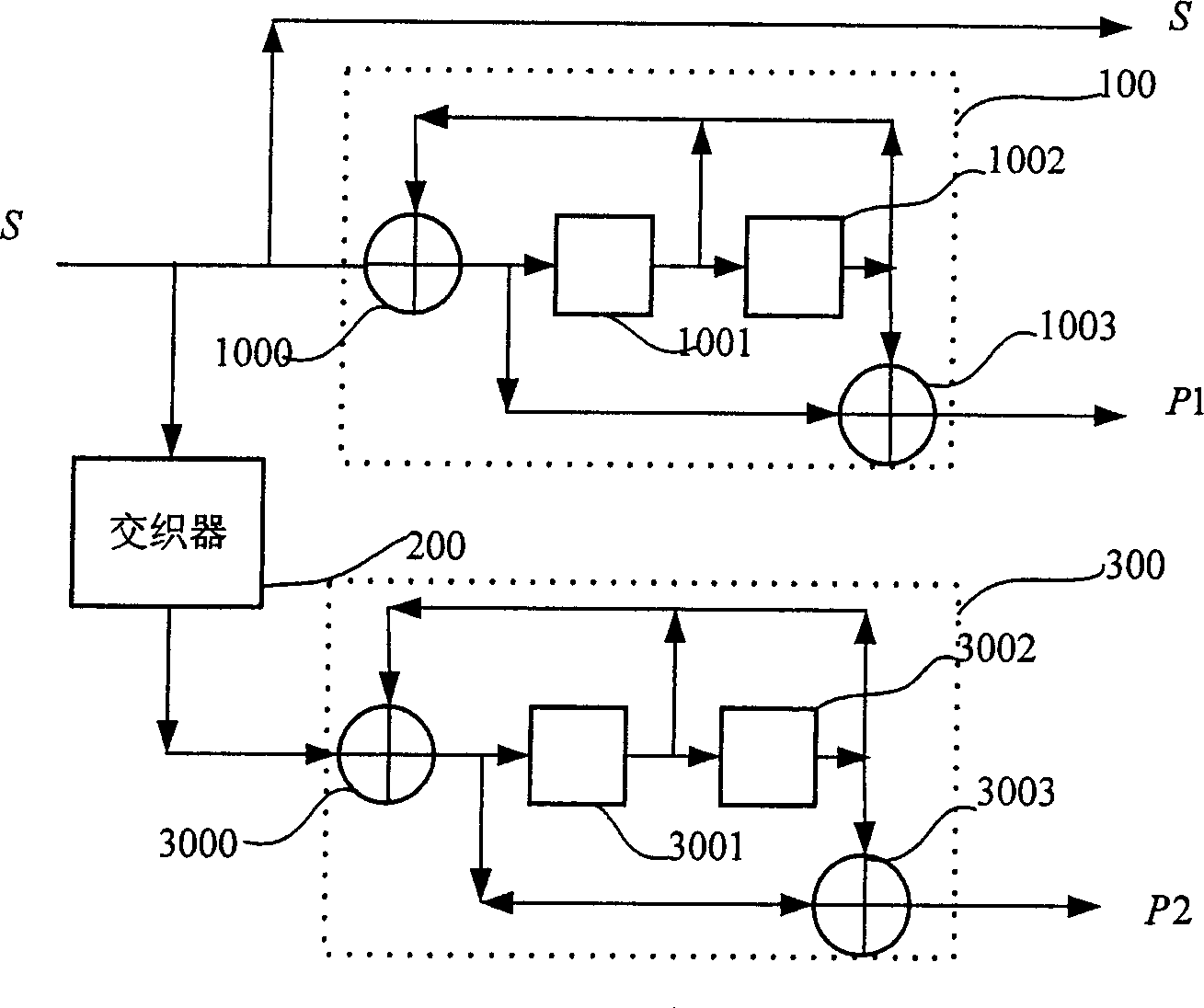
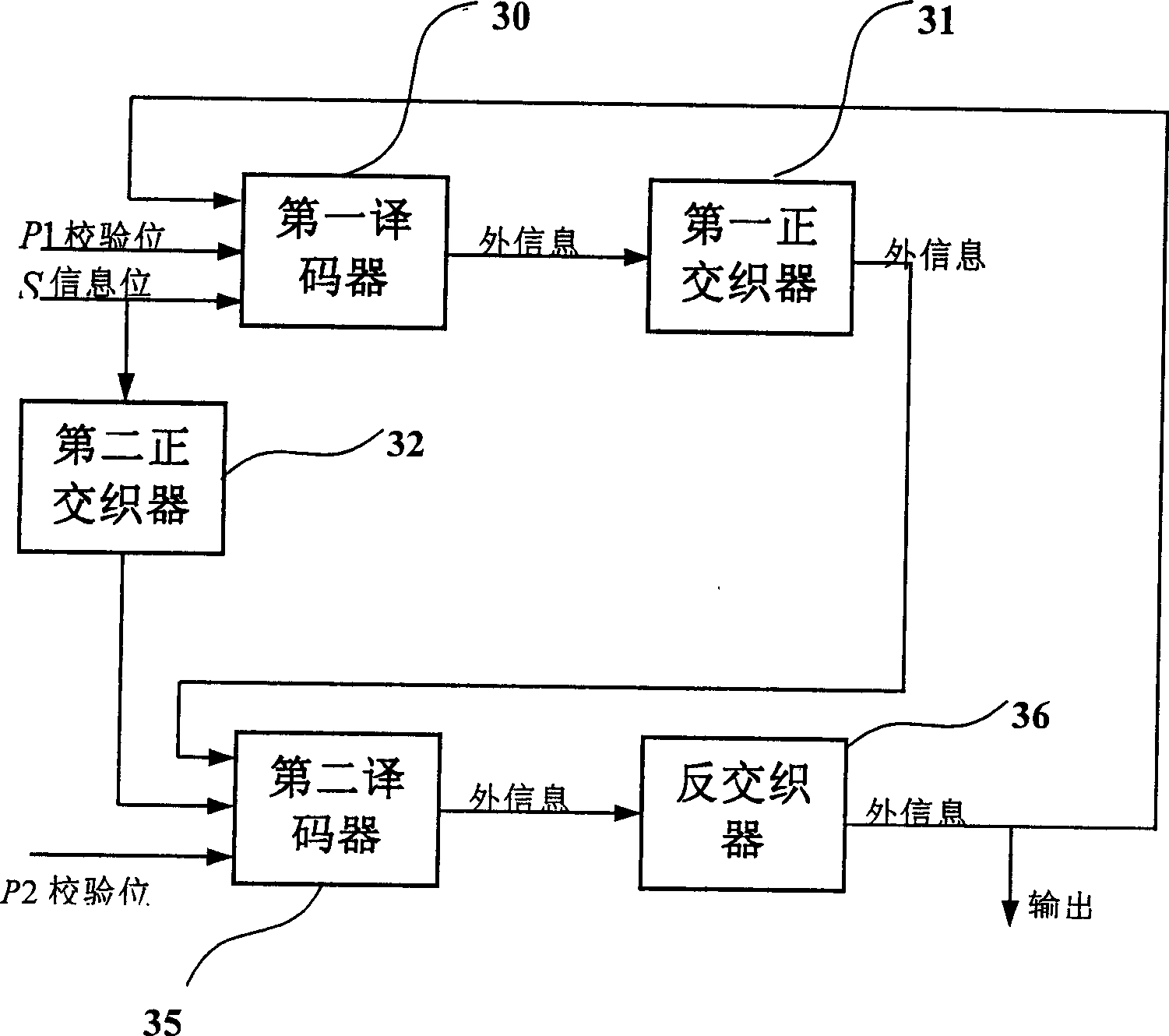
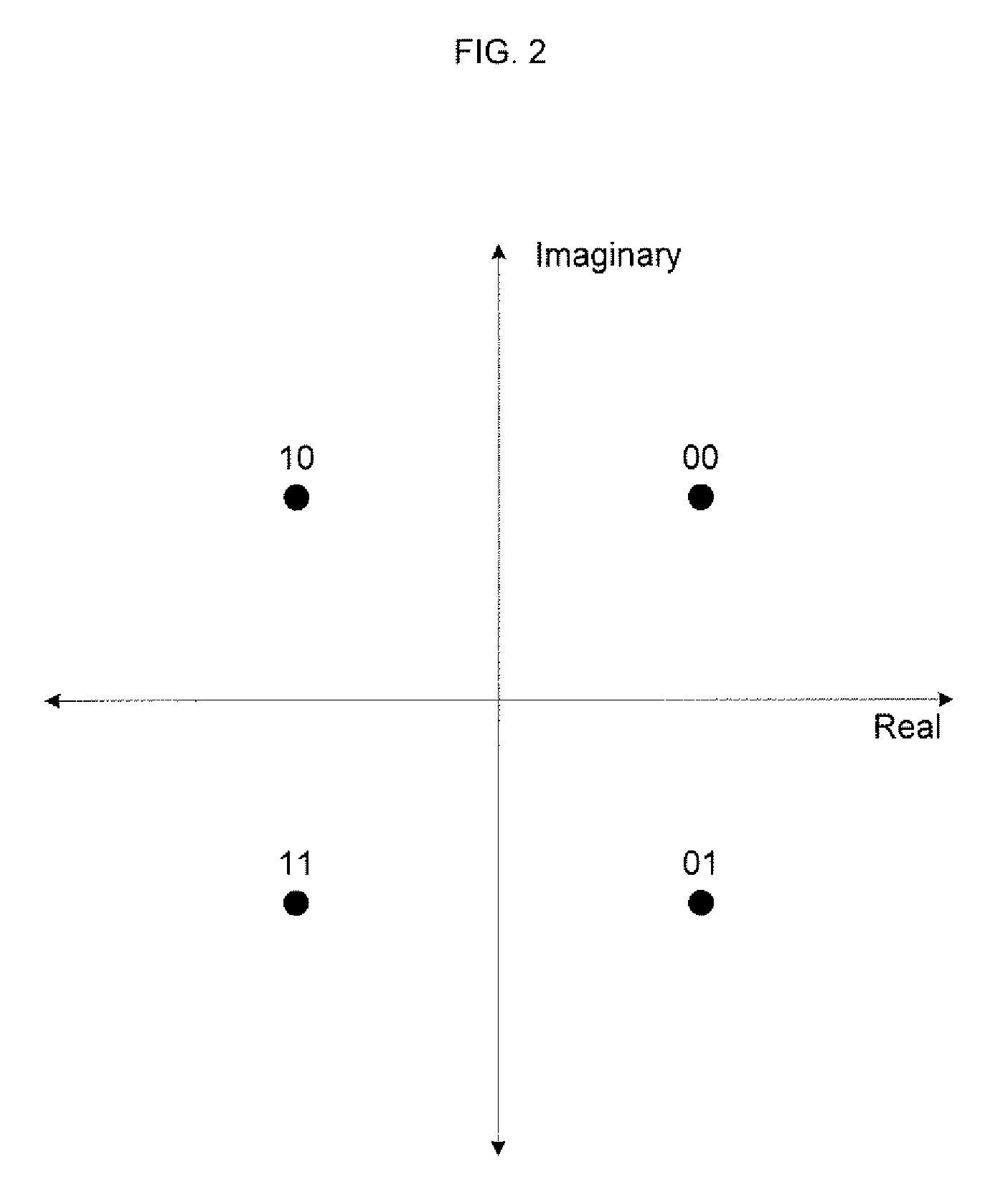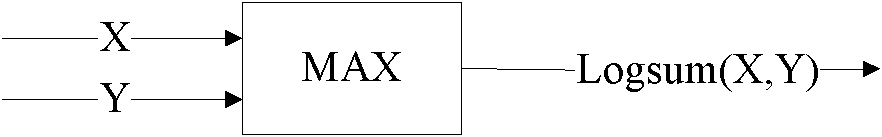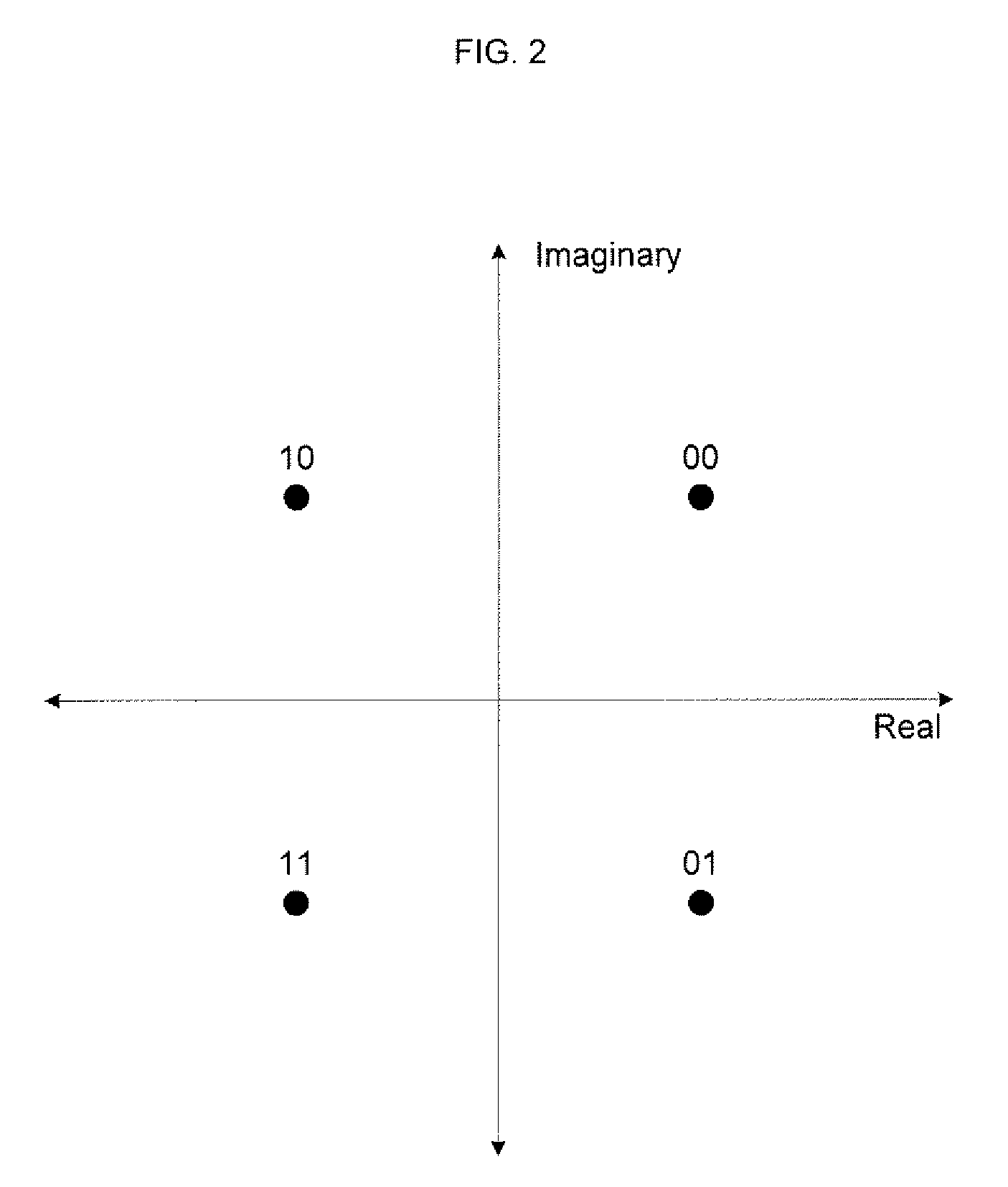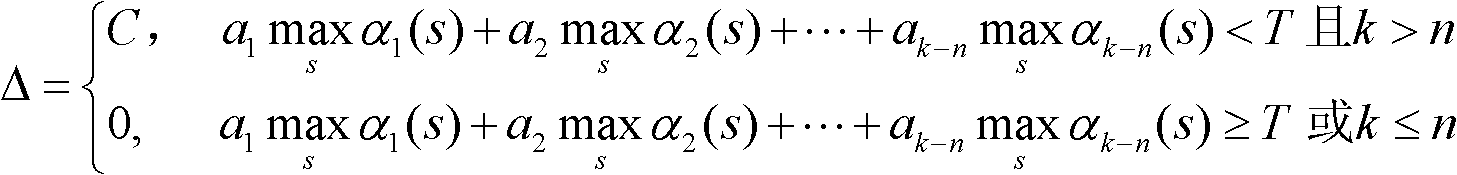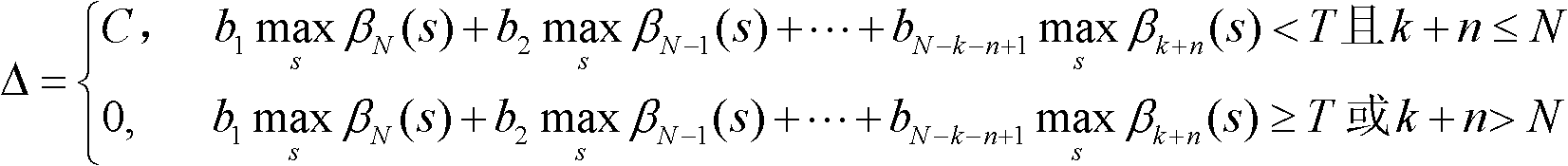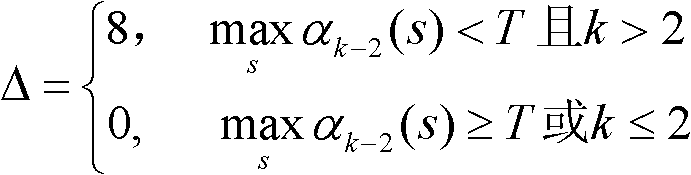Patents
Literature
80 results about "Map decoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
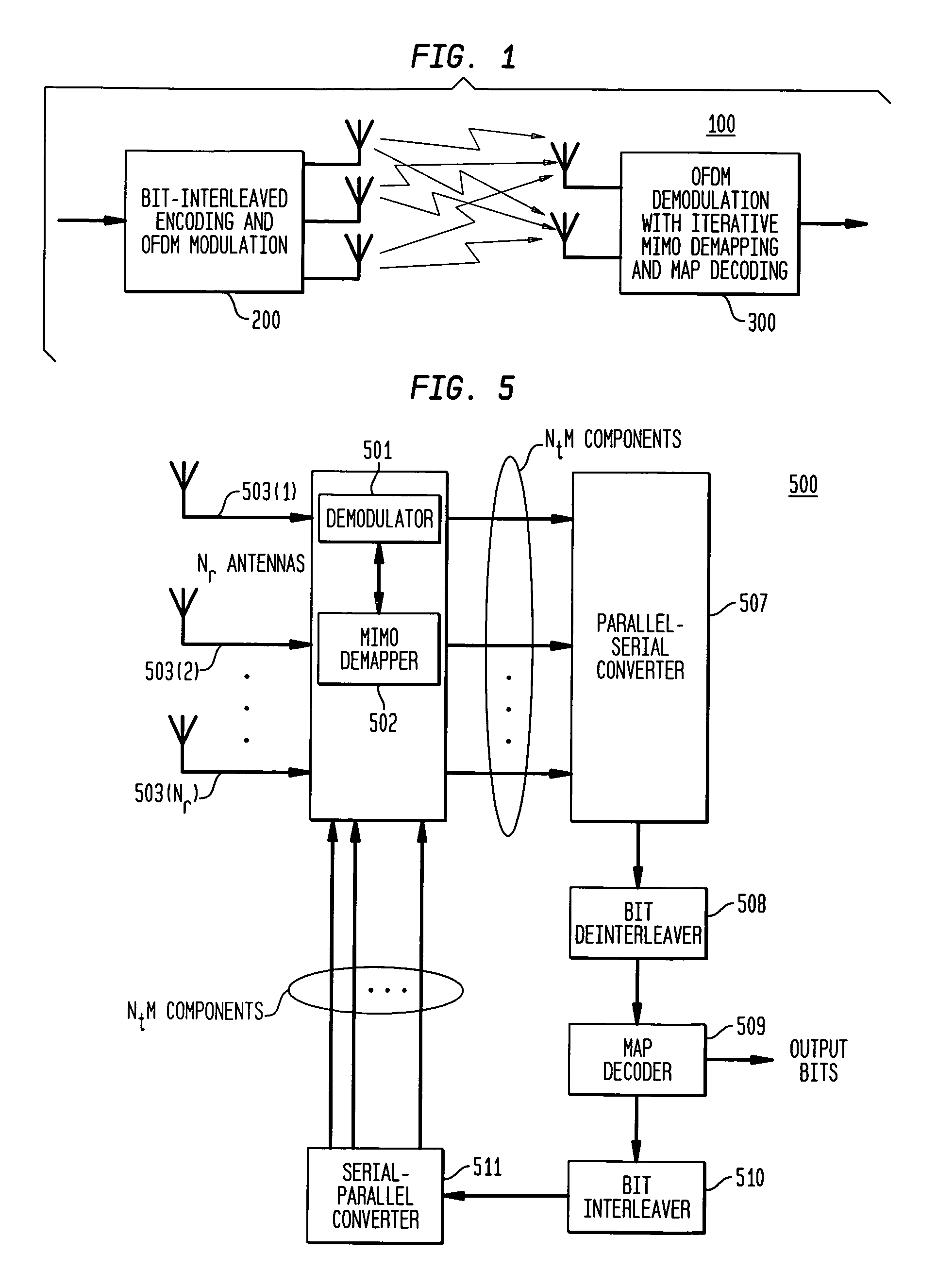
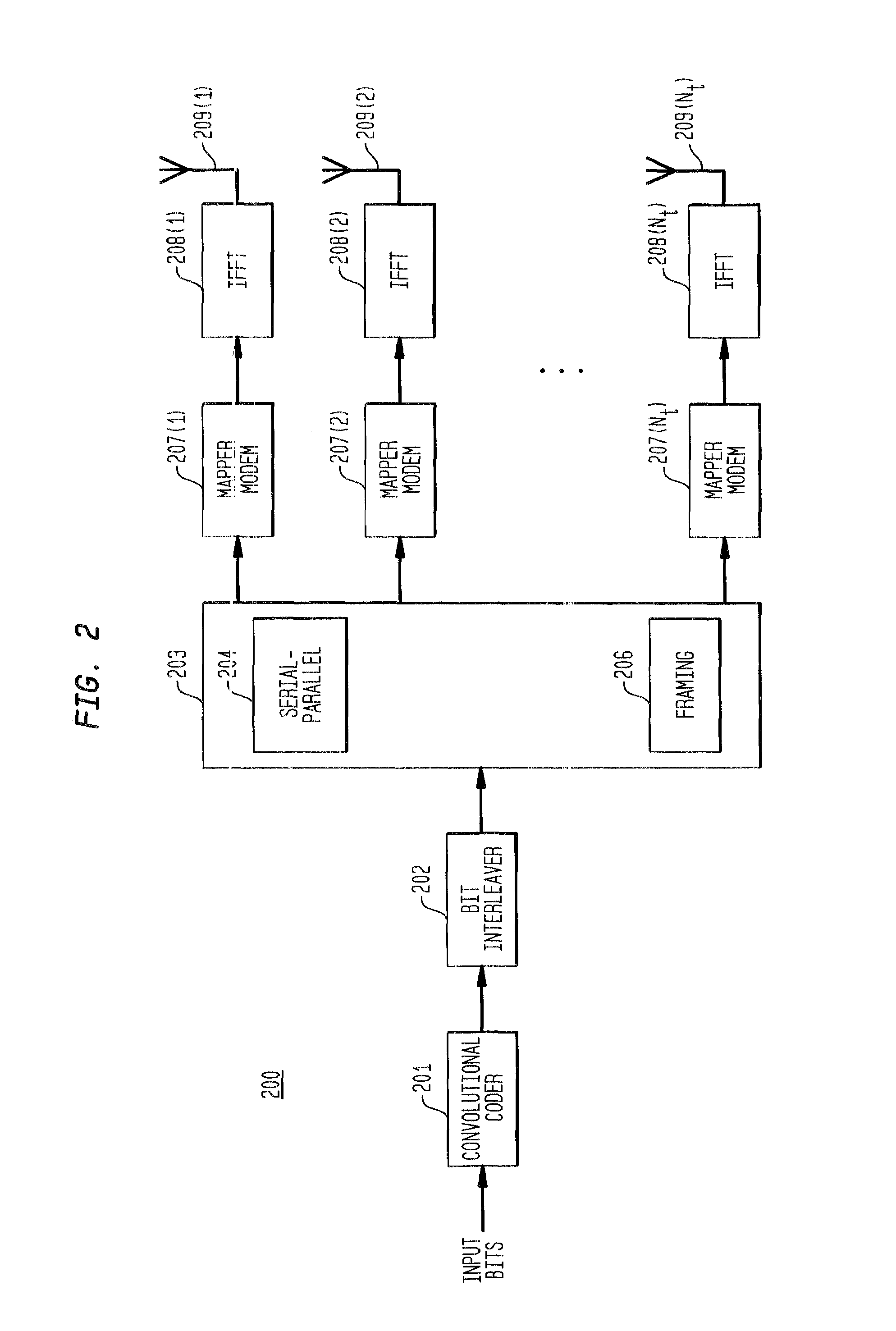
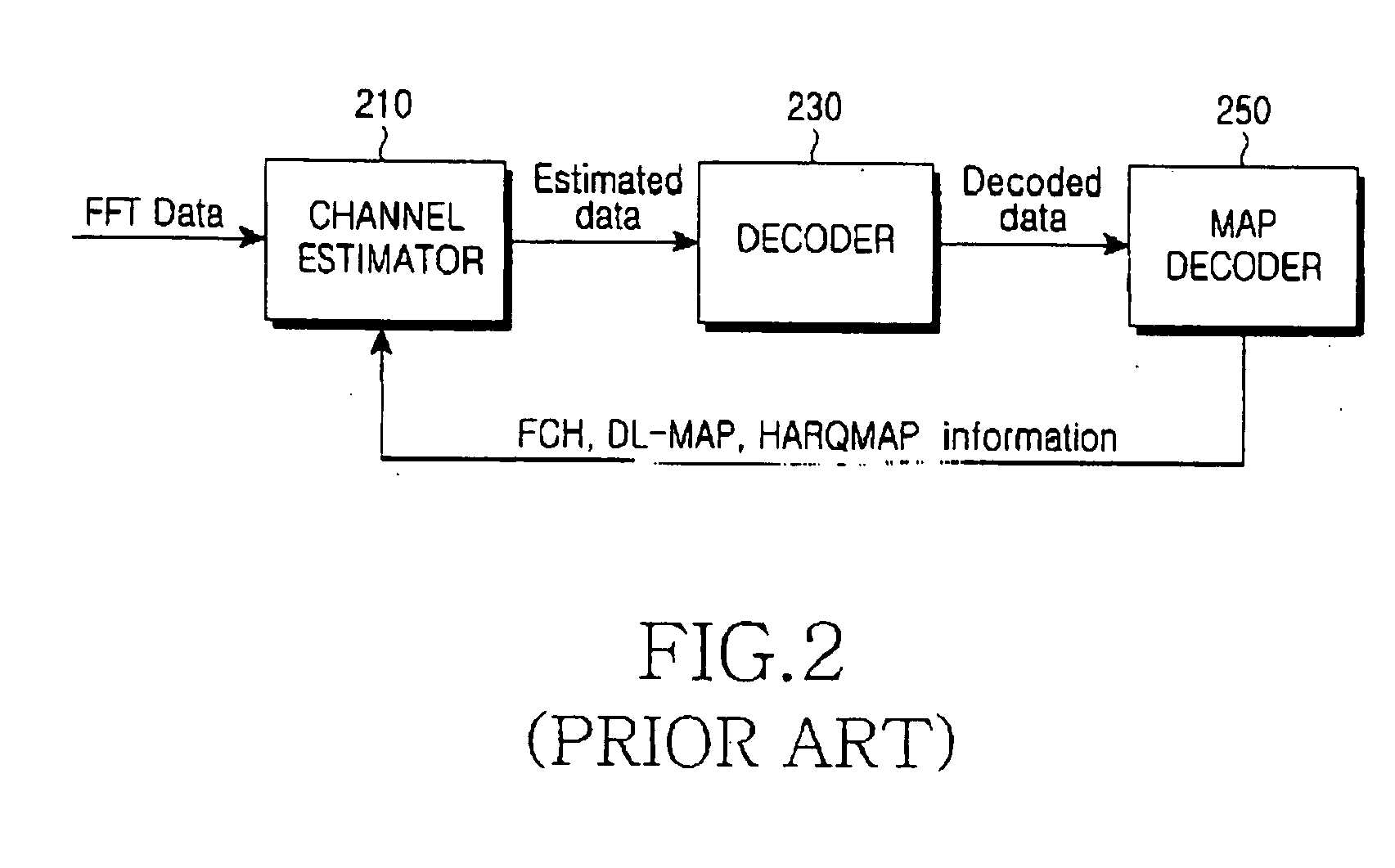
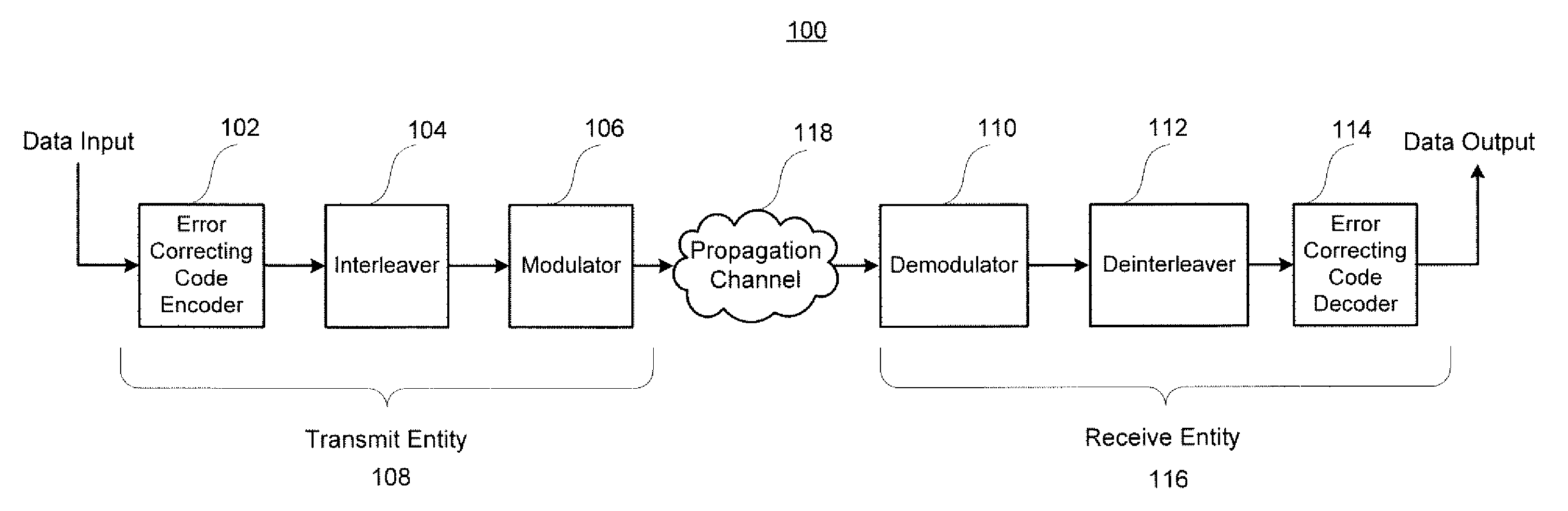
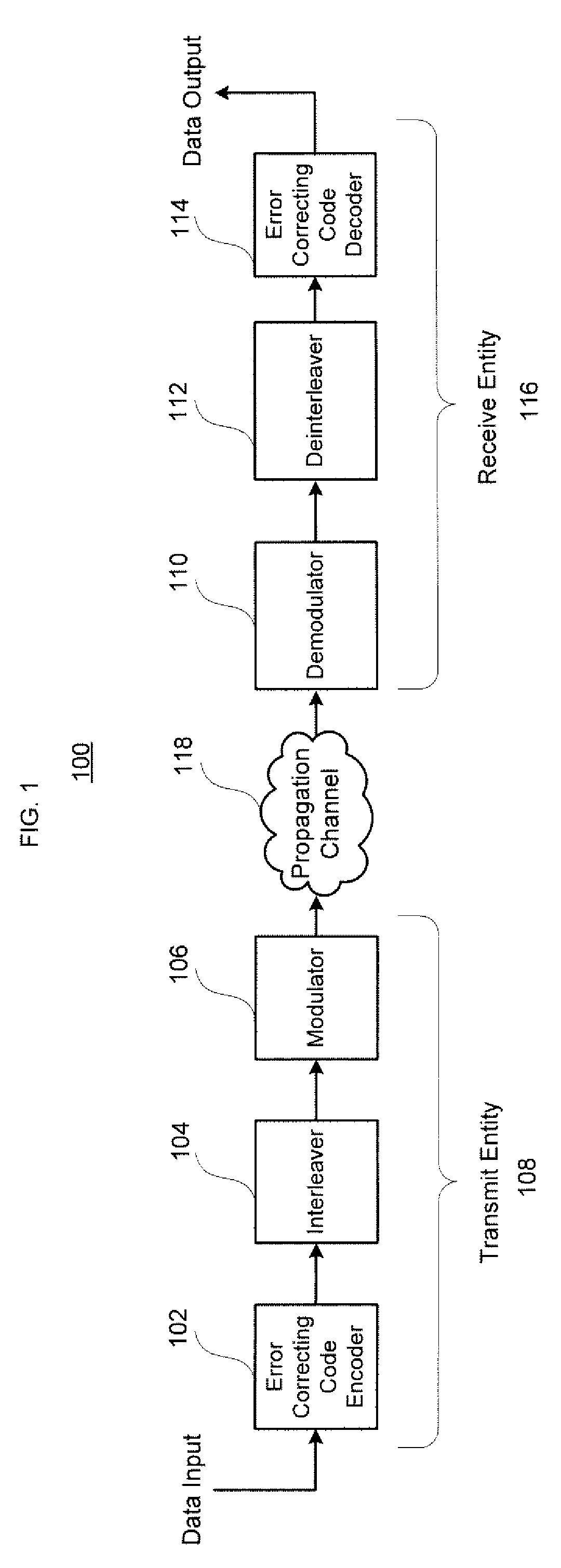
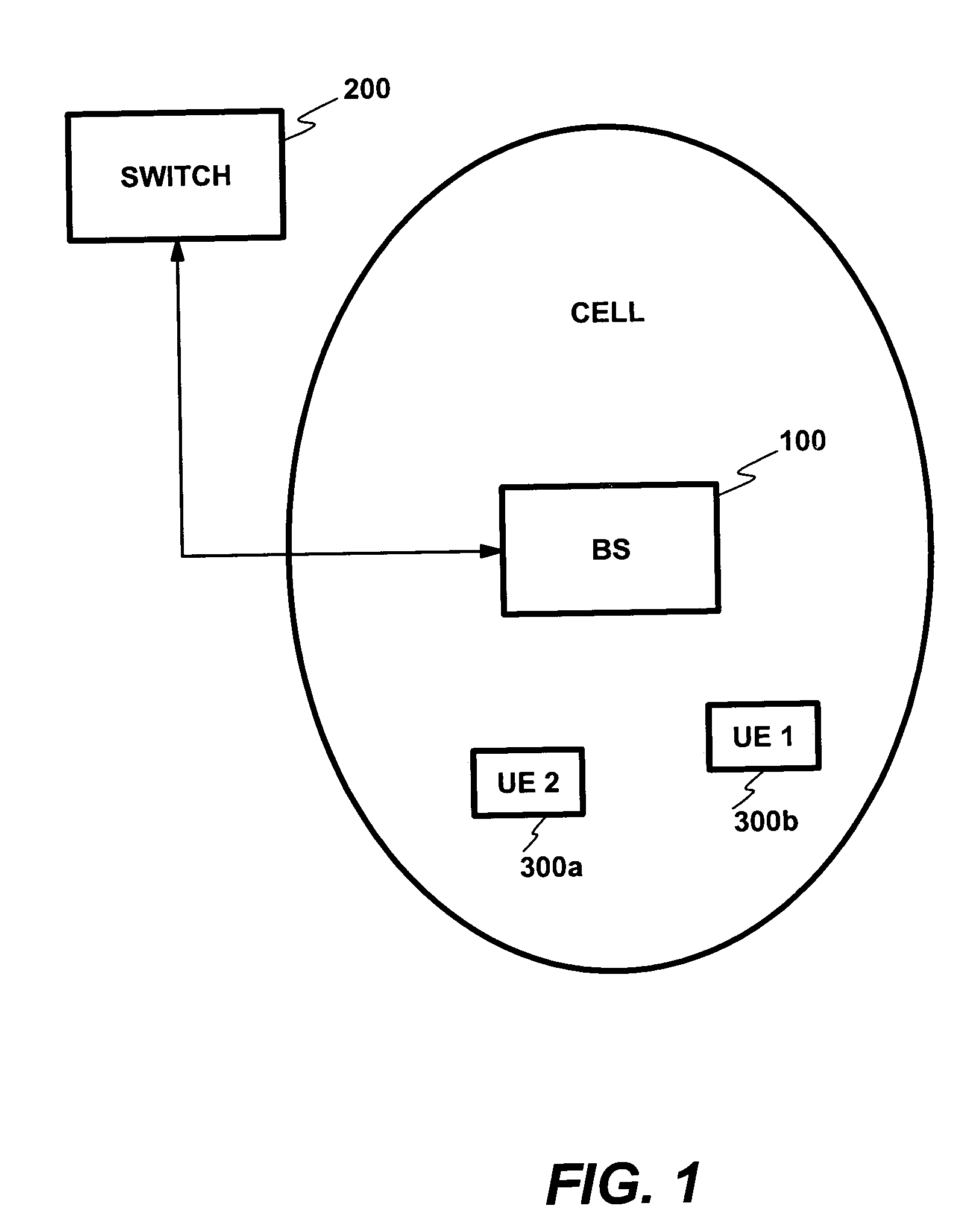
Decoding method and system for real-time wireless channel estimation
InactiveUS7974368B2Avoid performanceAvoid problemsCode conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDecoding methodsComputer science
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
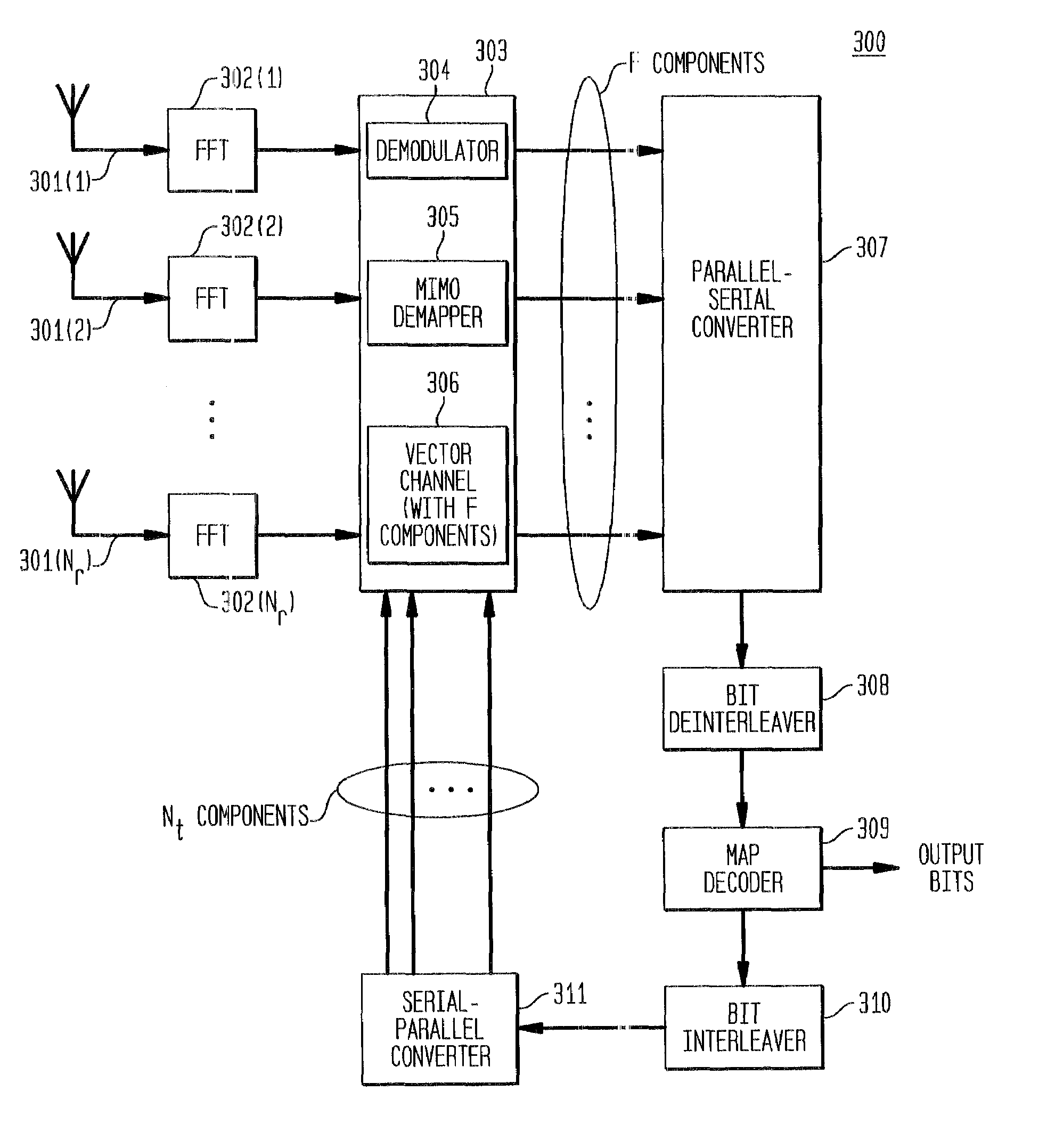
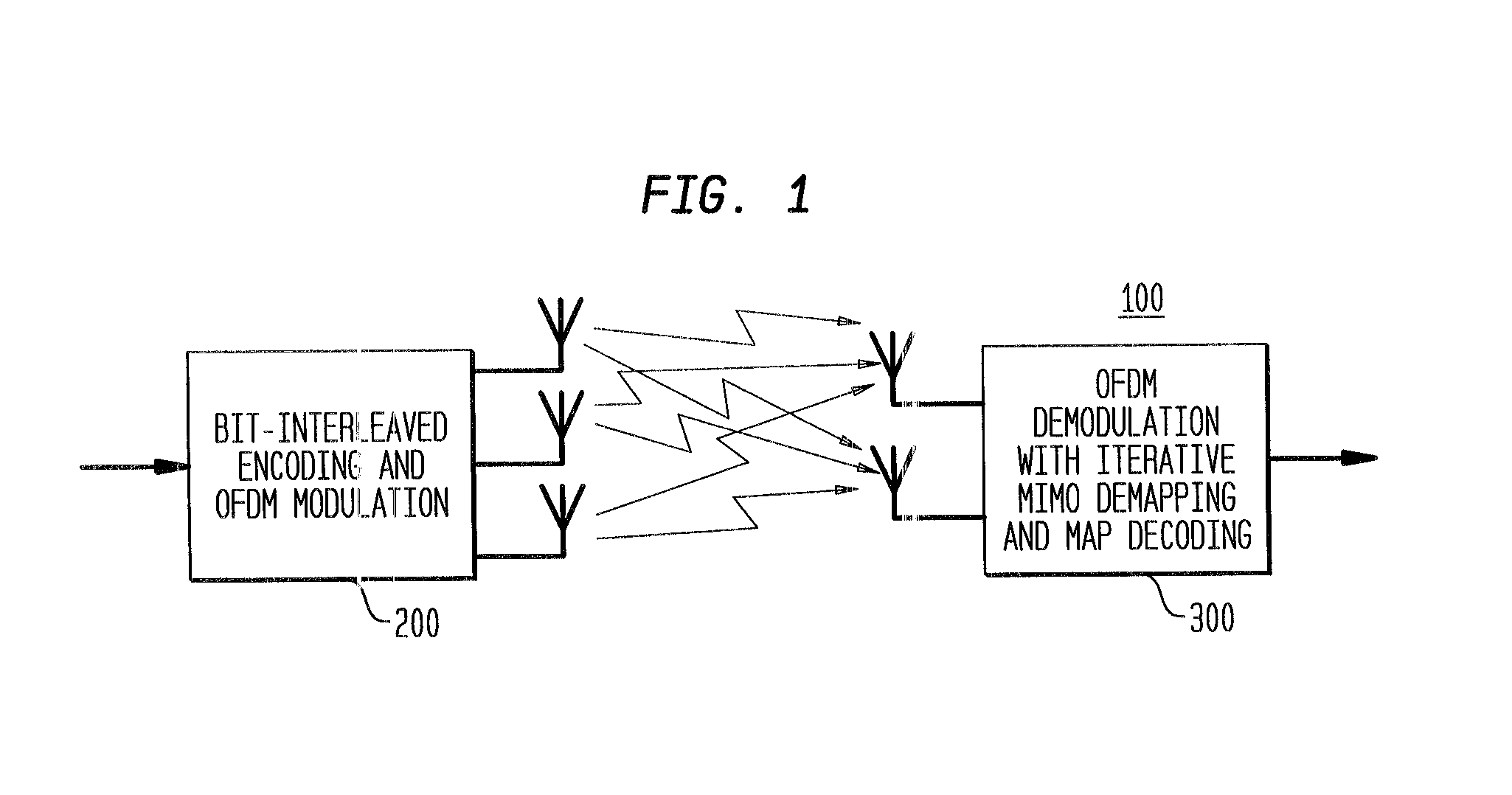
Reduced complexity receiver for space-time- bit-interleaved coded modulation
InactiveUS7095812B2Improve bit error rate performanceReduce in quantityData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionMulti inputRadio channel
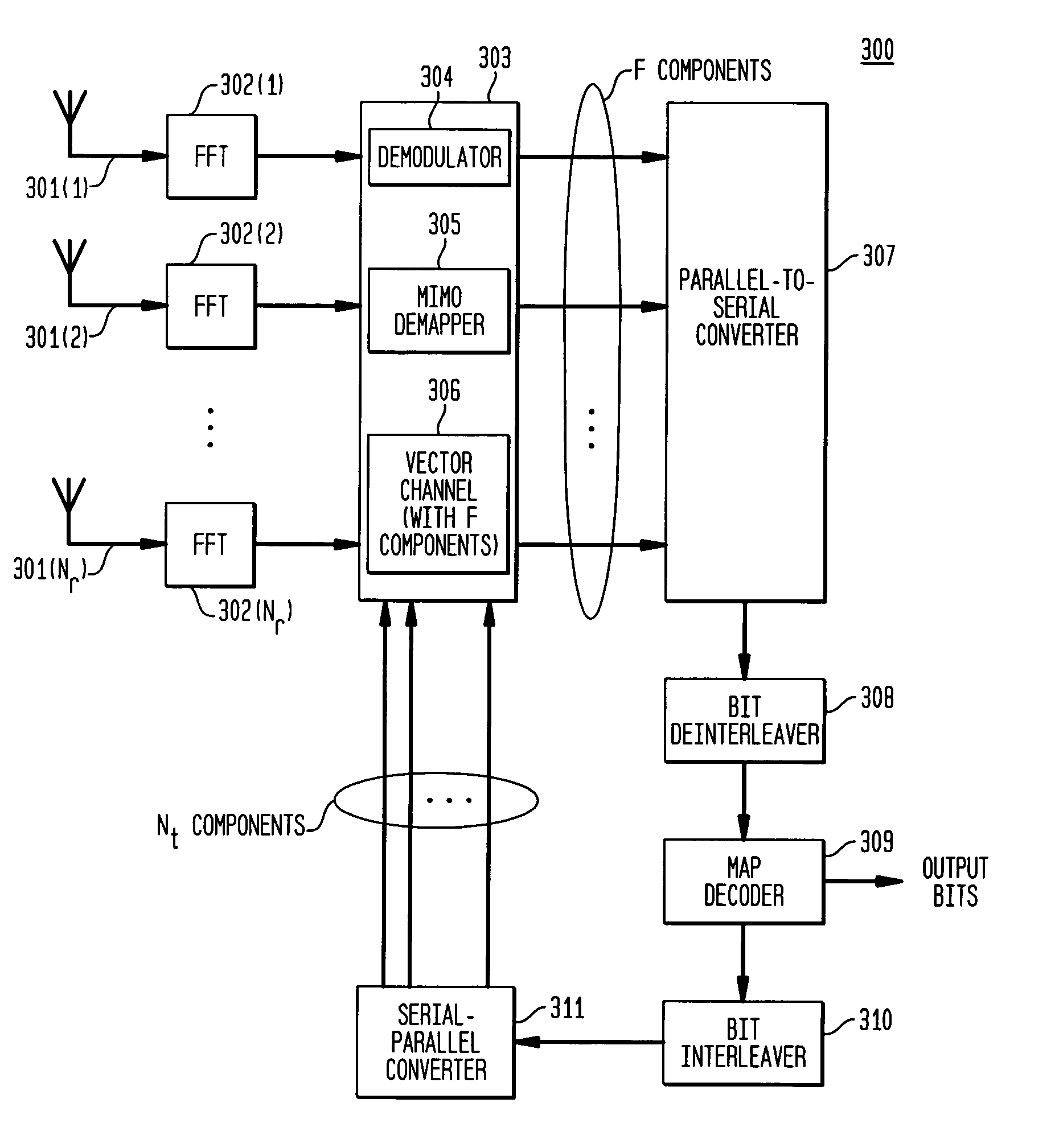
A system employs space-time coding characterized at the transmitter by bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) combined with modulating several streams of the BICM encoded data for transmission over two or more antennas. Space-time coding techniques improve transmission efficiency in radio channels by using multiple transmit and / or receive antennas and coordination of the signaling over these antennas. Bit-interleaved coded modulation provides good diversity gain with higher-order modulation schemes that employ binary convolutional codes. A receiver demodulates the received signals and applies multi-input, multi-output (MIMO) demapping to estimate the BICM encoded bitstream. After deinterleaving of the BICM encoded bitstream, maximum a posteriori (MAP) decoding is applied to the resulting bit stream to generate soft output values. By applying well-known turbo-decoding principles to iteratively demap and decode, the overall receiver performance is significantly improved. The MIMO demapping and MAP decoding processes exchange likelihood information to improve the bit error rate performance over several iterations of demapping / decoding. By generating tentative decisions for transmitted bits, the overall number of evaluations used for demapping may be reduced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
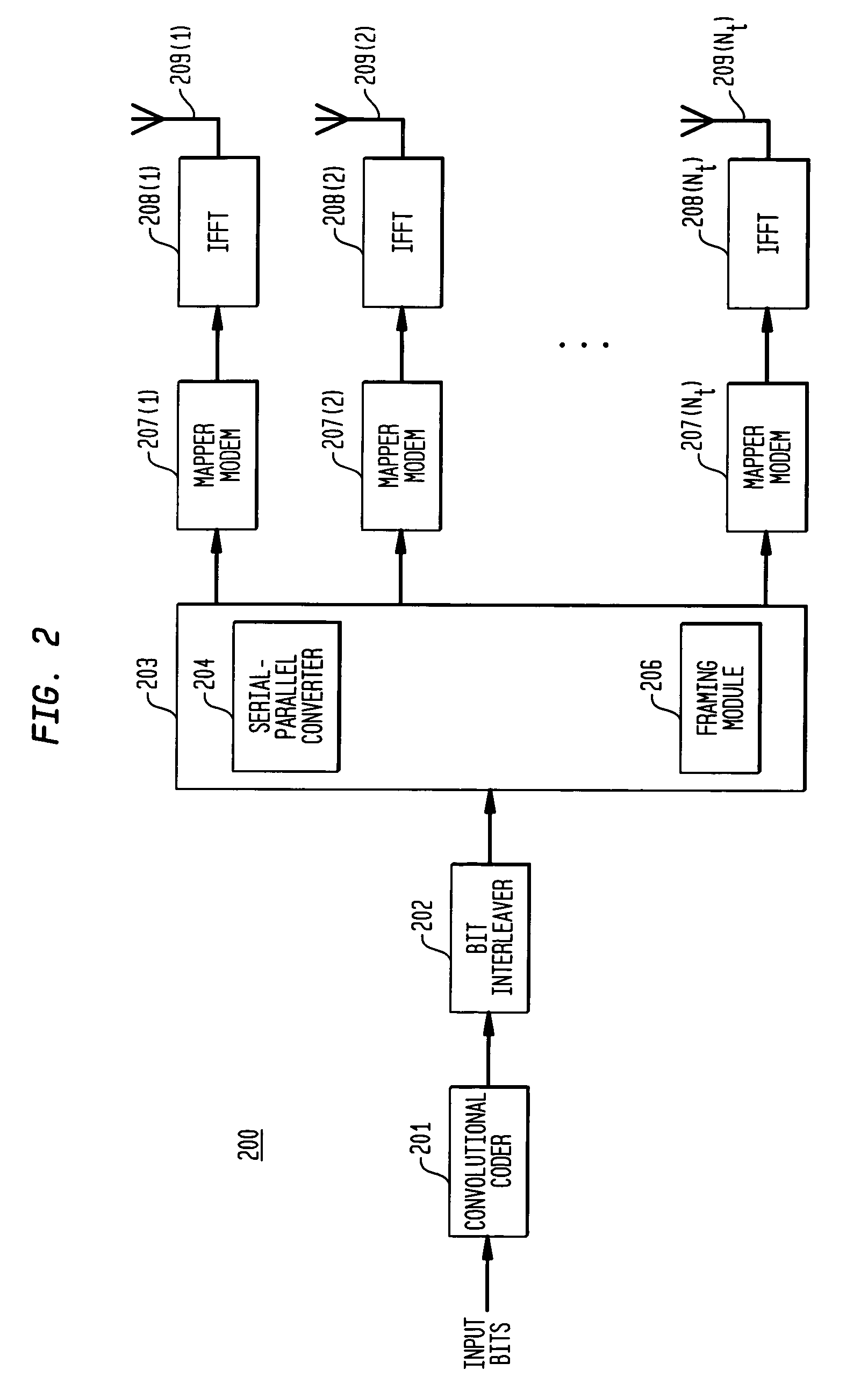
Space-time bit-interleaved coded modulation for wideband transmission
ActiveUS7359313B2Improve bit error rate performancePhase-modulated carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexMulti inputBroadband transmission
A system employs space-time coding characterized at the transmitter by bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) combined with multi-carrier Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) modulation. Space-Time coding techniques improve transmission efficiency in radio channels by using multiple transmit and / or receive antennas and coordination of the signaling over these antennas. Bit-interleaved coded modulation provides good diversity gain with higher-order modulation schemes that employ binary convolutional codes. OFDM modulation allows for wideband transmission over frequency selective radio channels. A receiver demodulates the OFDM signal and applies multi-input, multi-output (MIMO) demapping to estimate the BICM encoded bitstream. After deinterleaving of the BICM encoded bitstream, maximum a posteriori (MAP) decoding is applied to the resulting bit stream to generate soft output values. The MIMO demapping and MAP decoding processes exchange likelihood information to improve the bit error rate performance over several iterations of demapping / decoding. By applying well-known turbo-decoding principles to iteratively demap and decode, the overall receiver performance is significantly improved.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
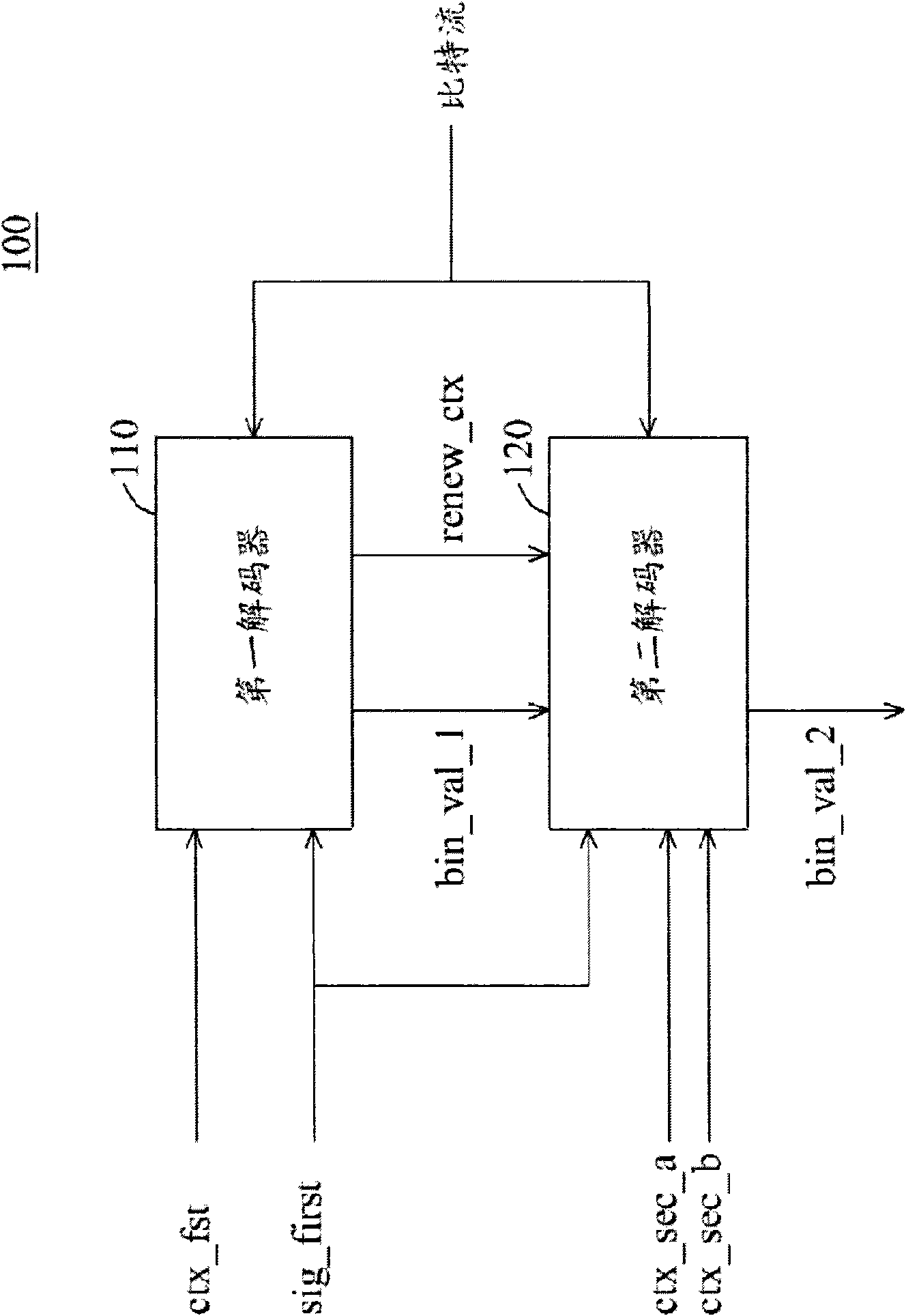
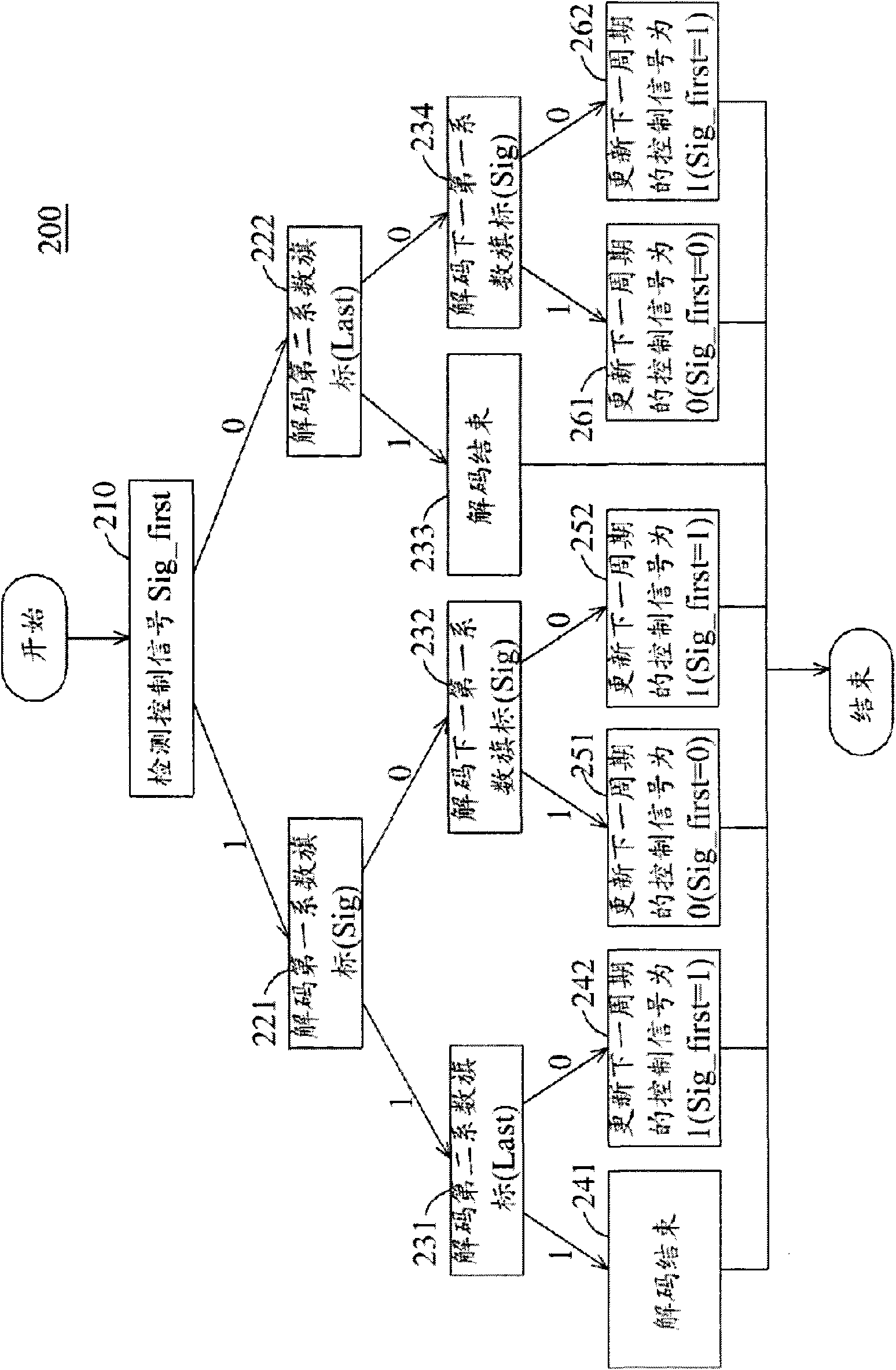
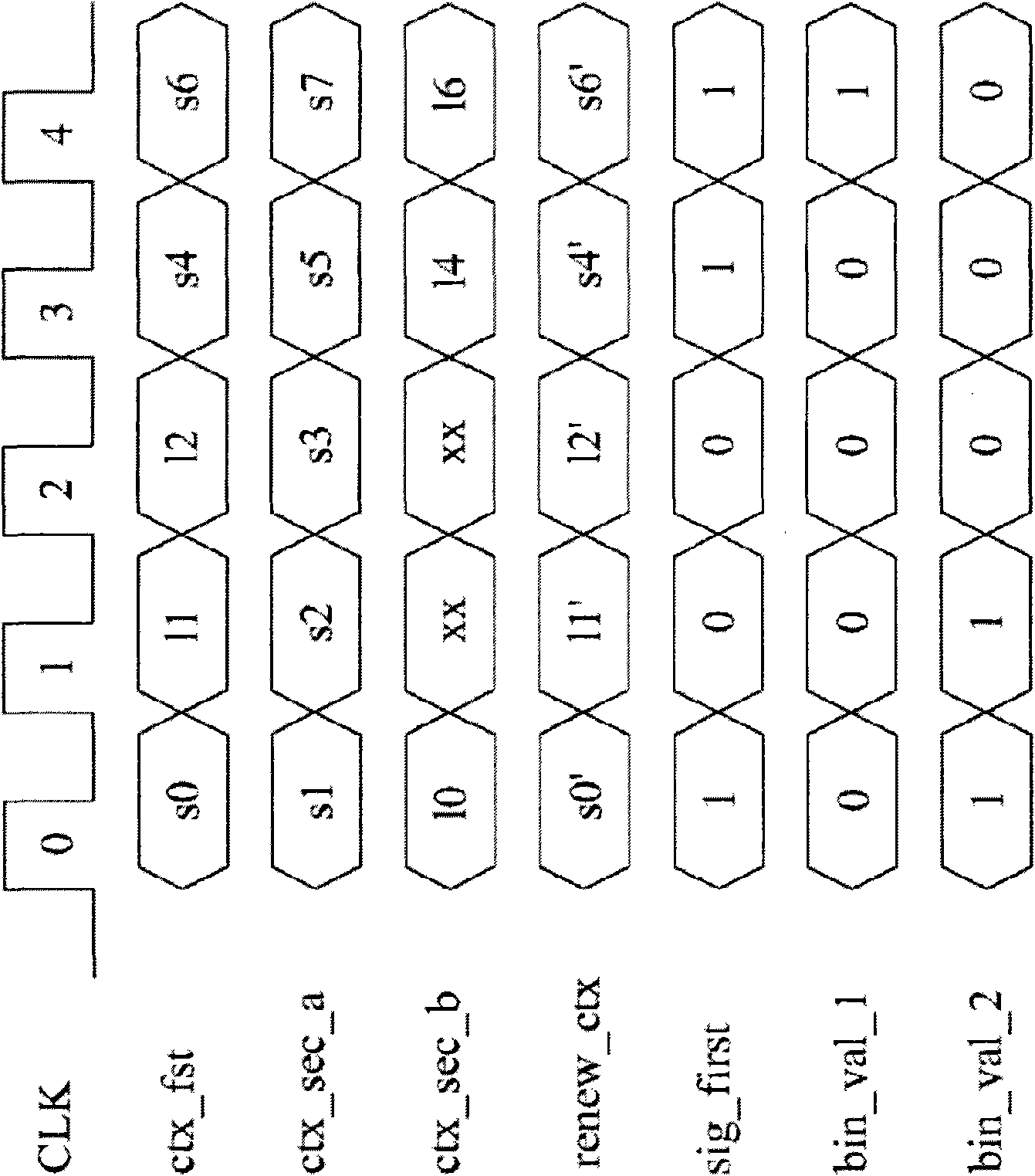
Cabac decoding unit and method
ActiveCN101600104AImprove decoding efficiencyImprove decoding speedCode conversionTelevision systemsComputer architectureControl signal
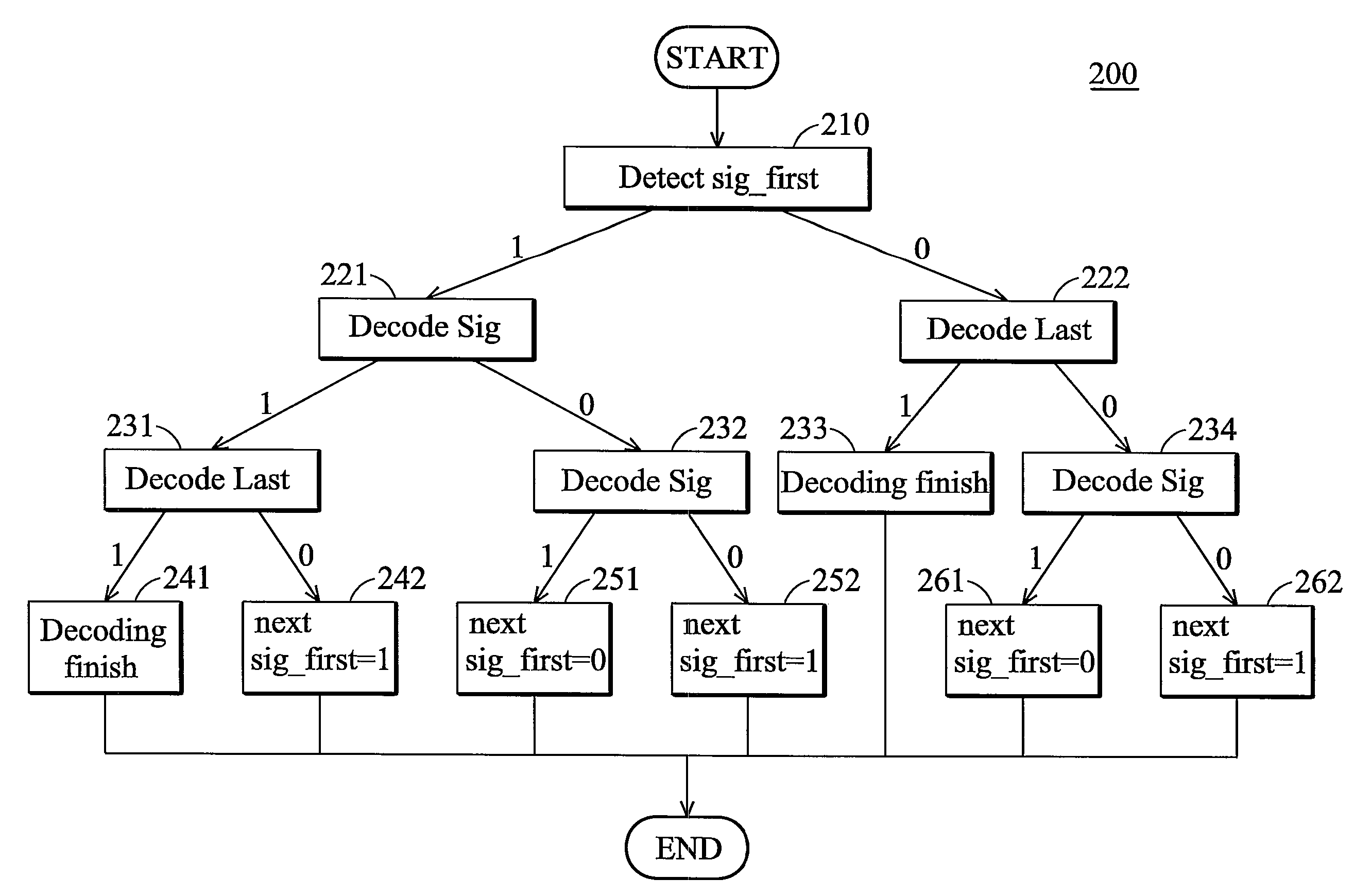
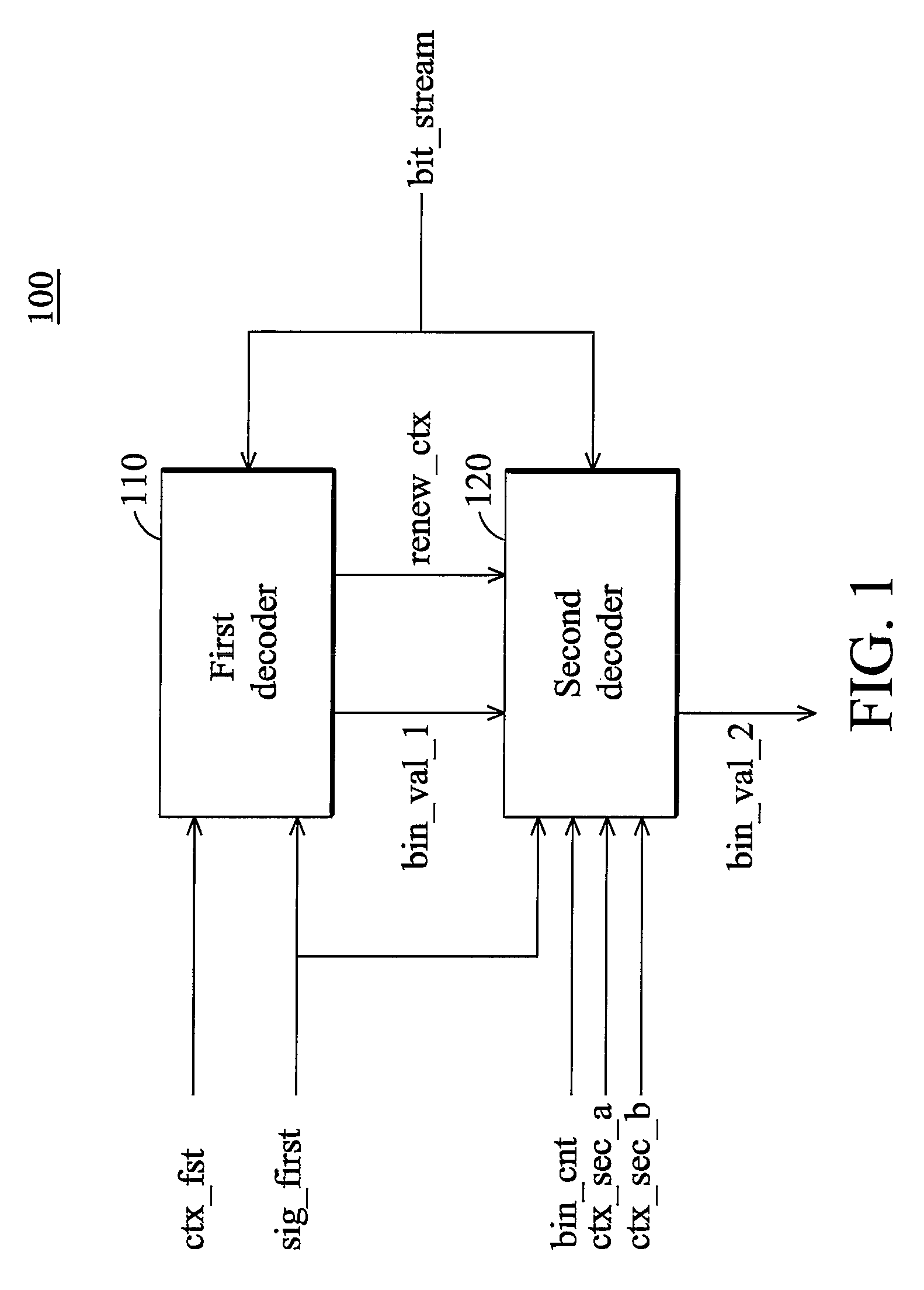
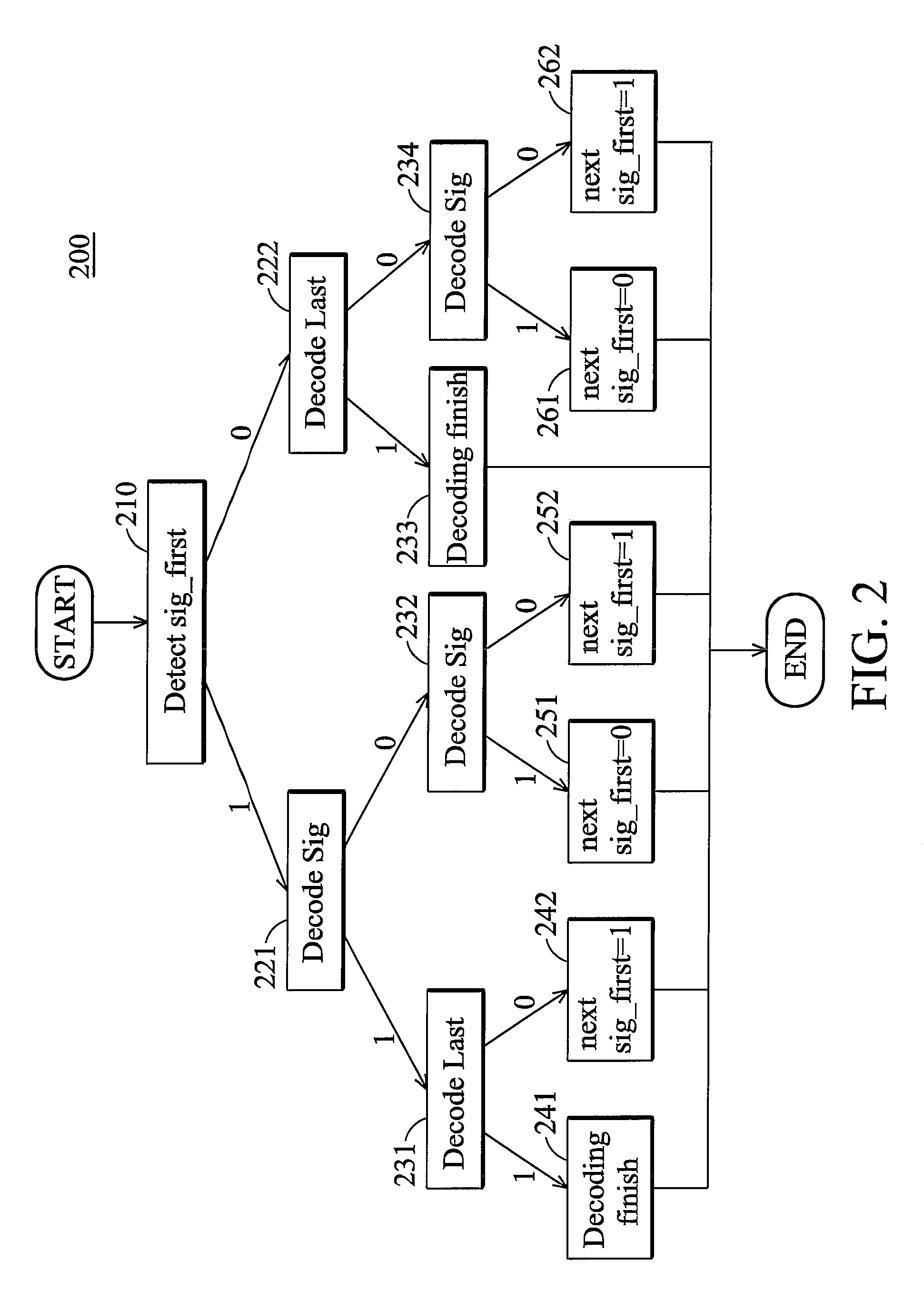
A context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding (CABAC) method. The CABAC method for a bitstream comprises: detecting a control signal (Sig_first); decoding a first bin representing one of a first coefficient flag (Sig) and a second coefficient flag (Last) from the bitstream according to the control signal (Sig_first); decoding a second bin representing one of the second coefficient flag (Last) and a next first coefficient flag (Sig) from the bitstream according to the decoded first bin and the control signal (Sig_first); and updating the control signal (Sig_first) according to the decoded first and second bins. The first and second bins are decoded in one clock cycle, the first coefficient flag (Sig) indicates whether a corresponding coefficient value is zero, and the second coefficient flag (Last) indicates whether a coefficient map decoding process is finished.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
CABAC decoding unit and method
ActiveUS7592937B1Multiplex communicationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer architectureControl signal
A context-based adaptive binary arithmetic coding (CABAC) method. The CABAC method for a bitstream comprises: detecting a control signal (Sig_first); decoding a first bin representing one of a first coefficient flag (Sig) and a second coefficient flag (Last) from the bitstream according to the control signal (Sig_first); decoding a second bin representing one of the second coefficient flag (Last) and a next first coefficient flag (Sig) from the bitstream according to the decoded first bin and the control signal (Sig_first); and updating the control signal (Sig_first) according to the decoded first and second bins. The first and second bins are decoded in one clock cycle, the first coefficient flag (Sig) indicates whether a corresponding coefficient value is zero, and the second coefficient flag (Last) indicates whether a coefficient map decoding process is finished.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
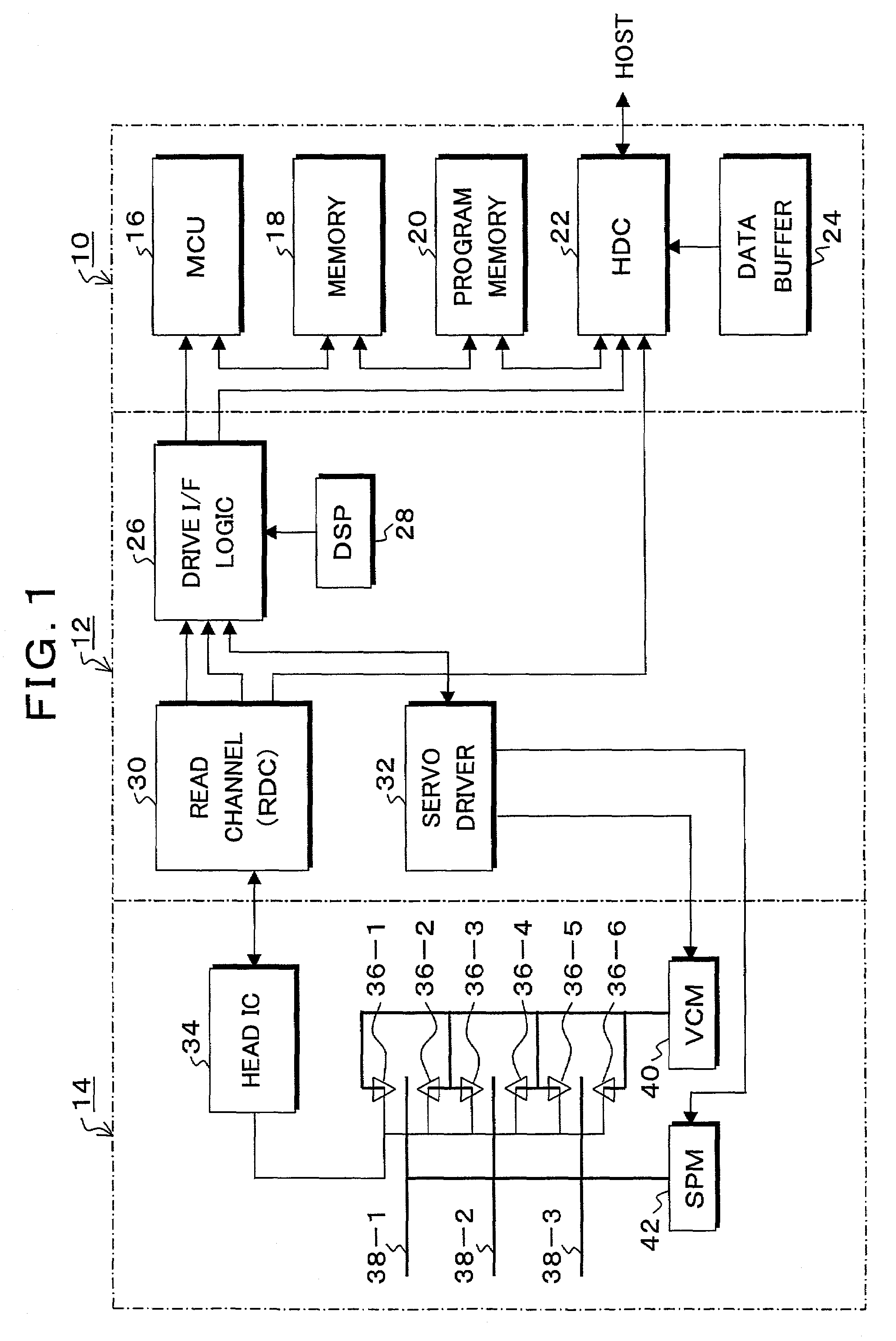
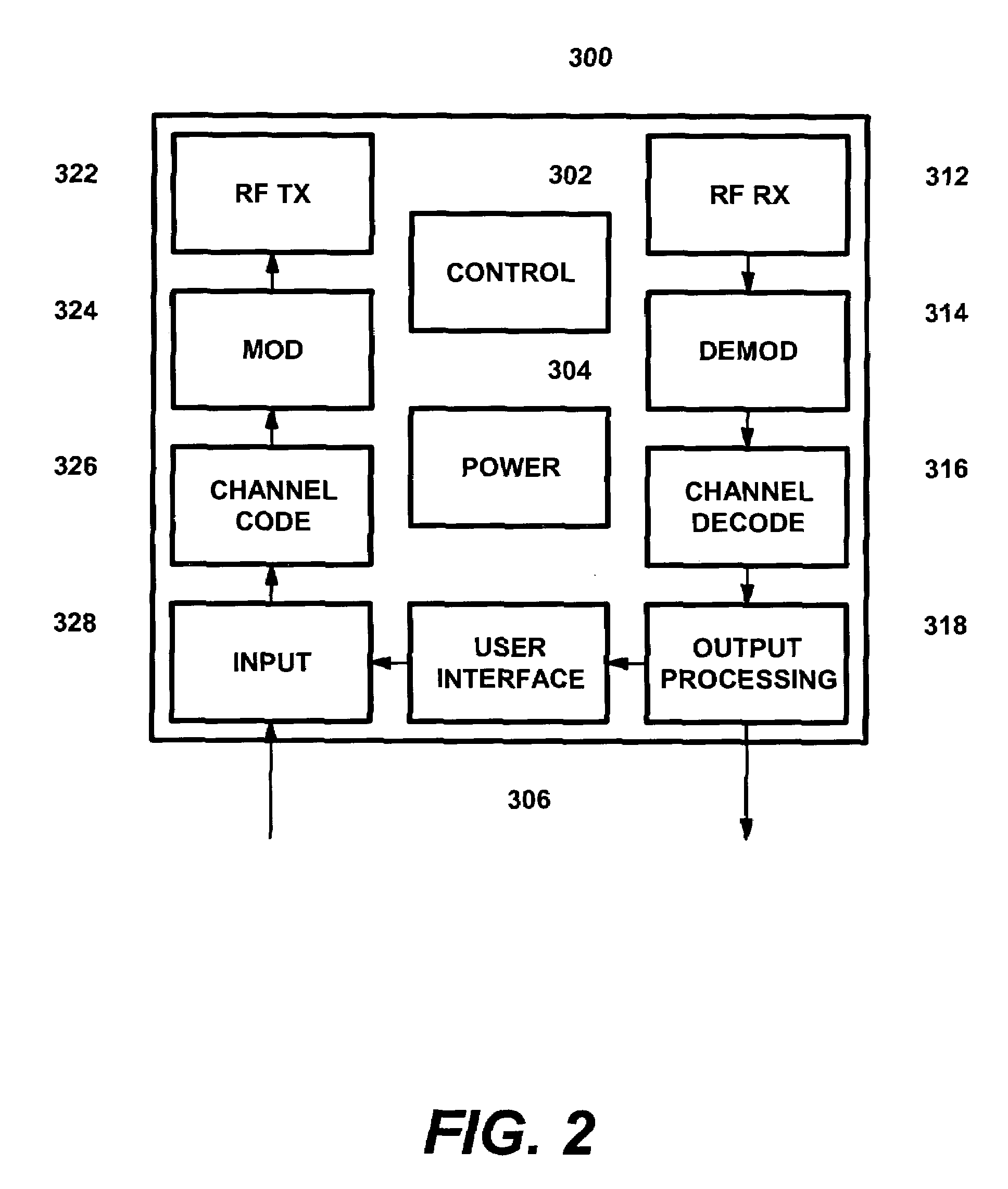
Information recording and reproducing apparatus and method and signal decoding circuit having improved noise processing characteristics
InactiveUS7031090B2Effective applicationImprove decoding performanceModification of read/write signalsOther decoding techniquesMaximum a posteriori estimationComputer science
In a Maximum A posteriori Probability decoding (MAP decoding), a correlation and a deviation of noises for past and future states which depend on input signal patterns in past N bits and future Q bits are calculated by training by a noise correlation arithmetic operating unit 84 and they are stored. Upon reproduction, in a white noise arithmetic operating unit 91, white noise values for the past and future states in which colored noises are converted into white noises are obtained by using the stored correlation and deviation of the noises. In an input signal arithmetic operating unit 92, an input signal (channel information) Λc(yk|Smk) of the MAP decoding is calculated from the white noise values and the deviation for the past and future states. A likelihood in the MAP decoding is obtained from the input signal.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
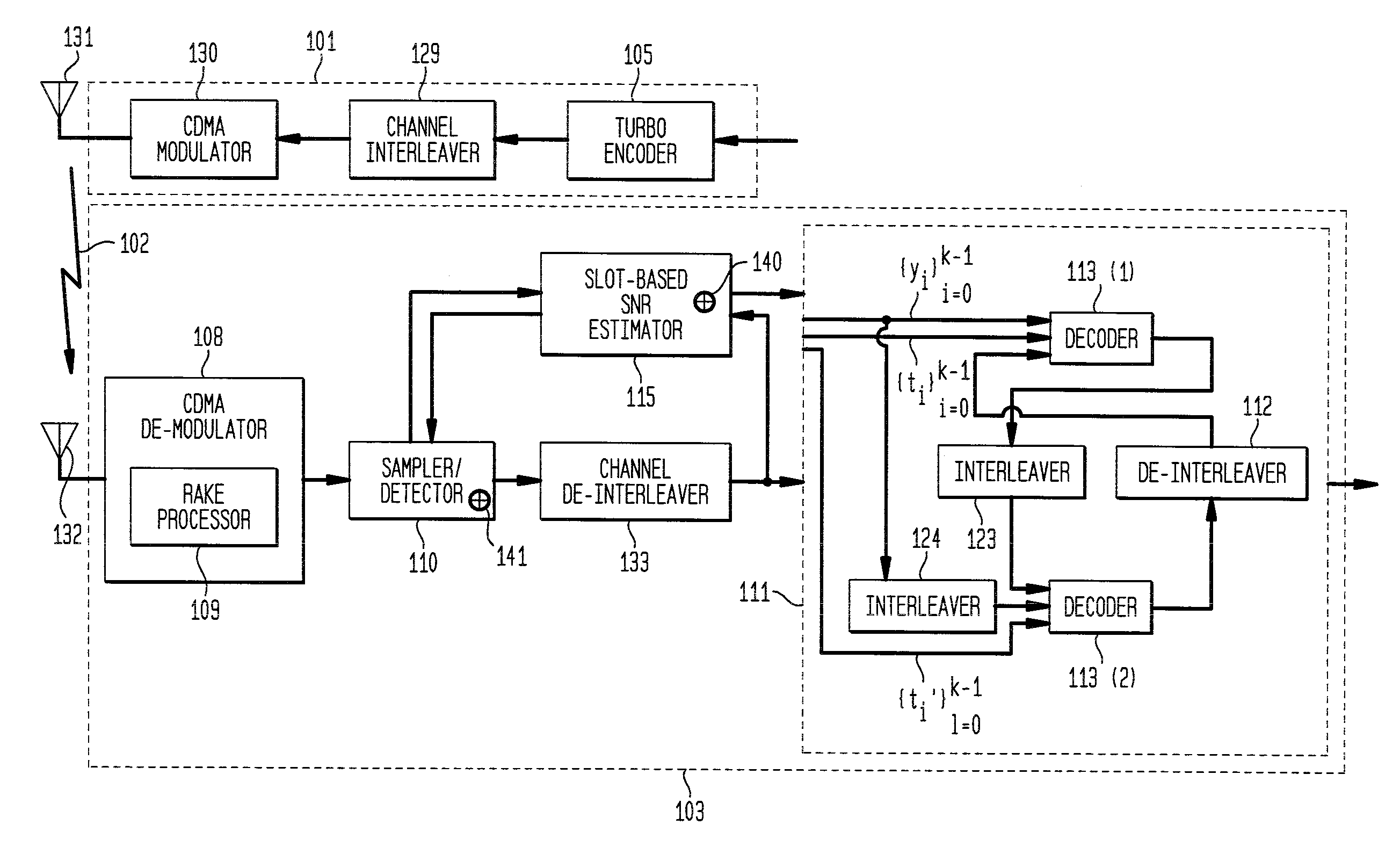
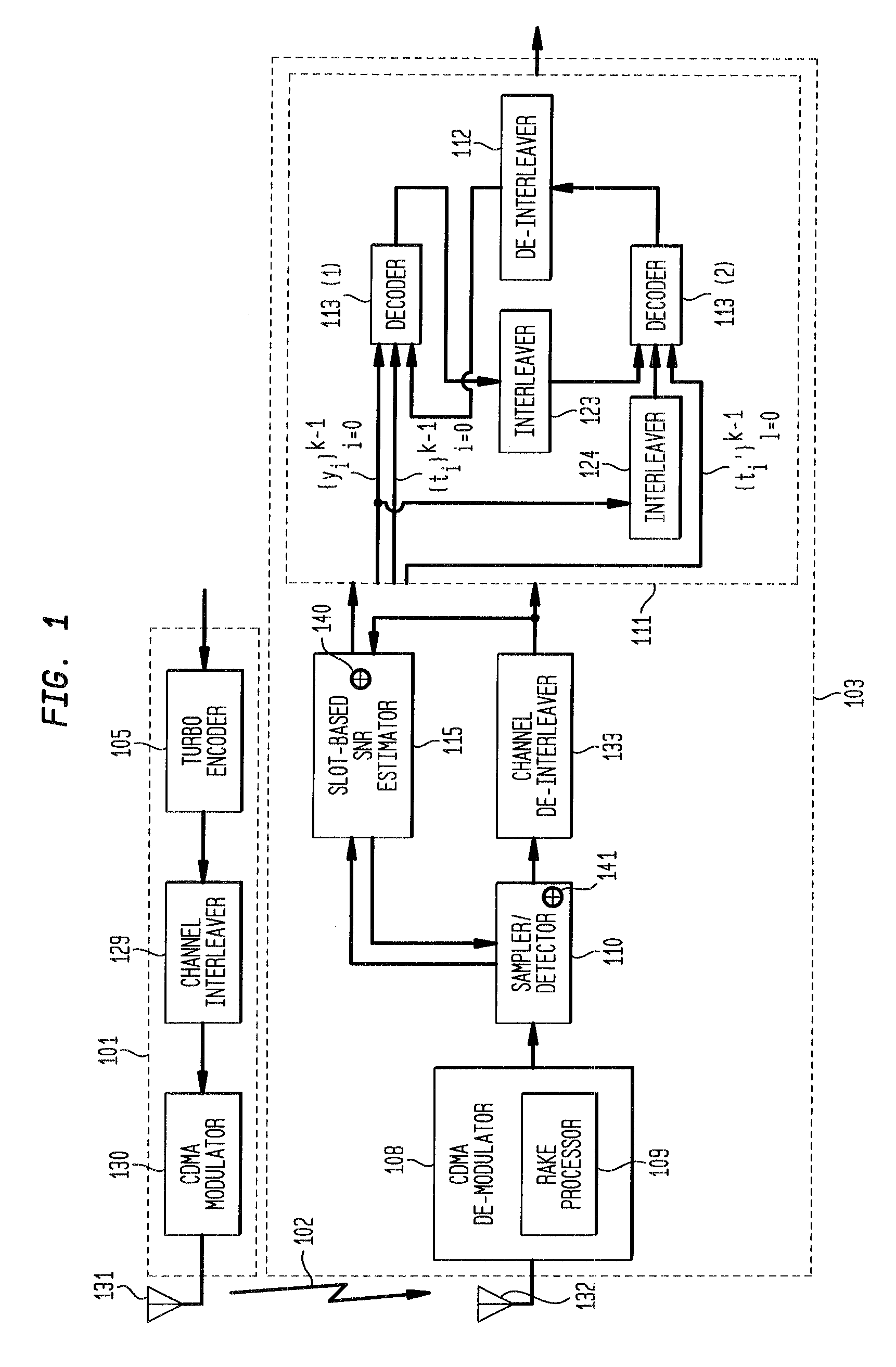
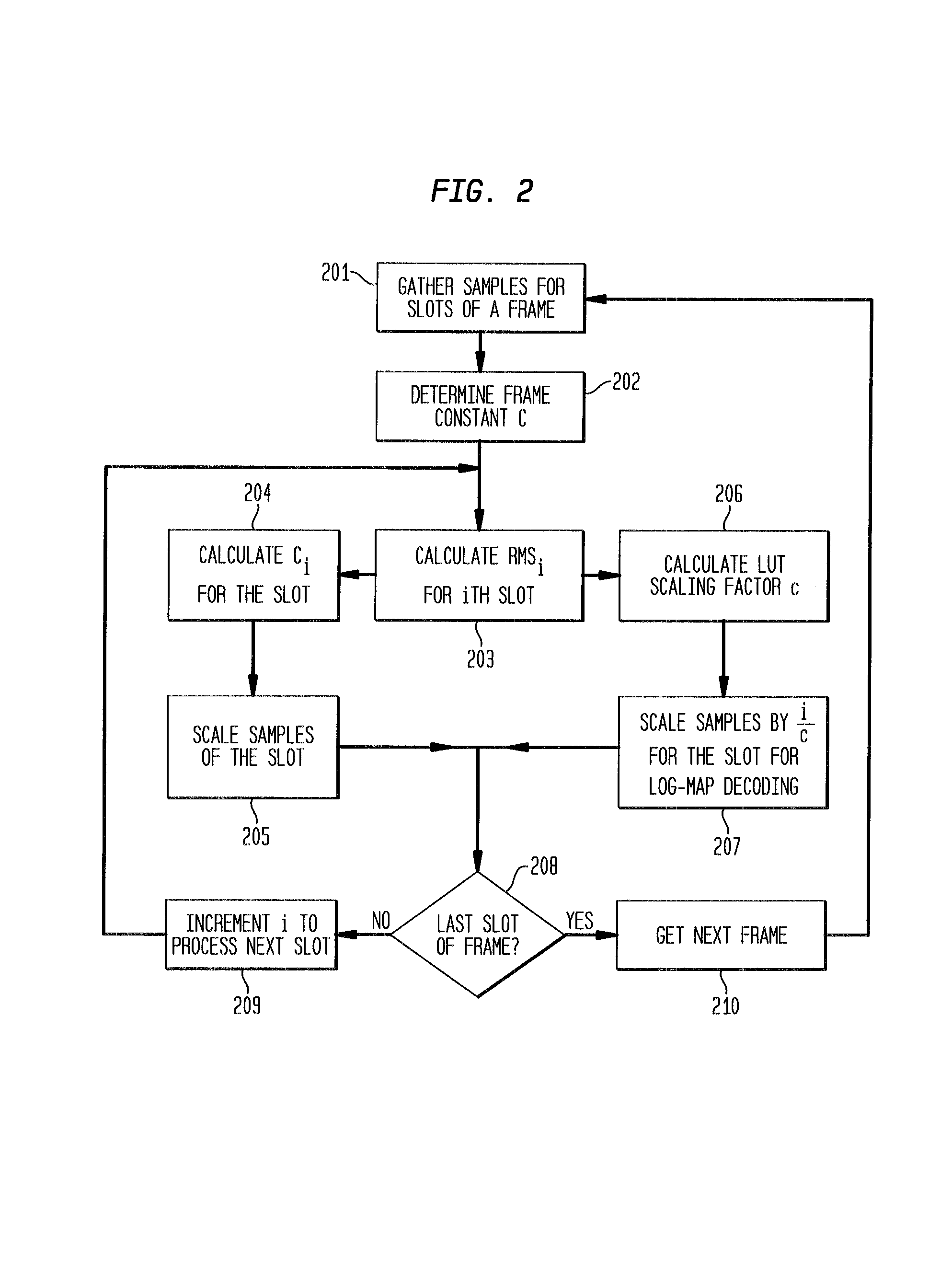
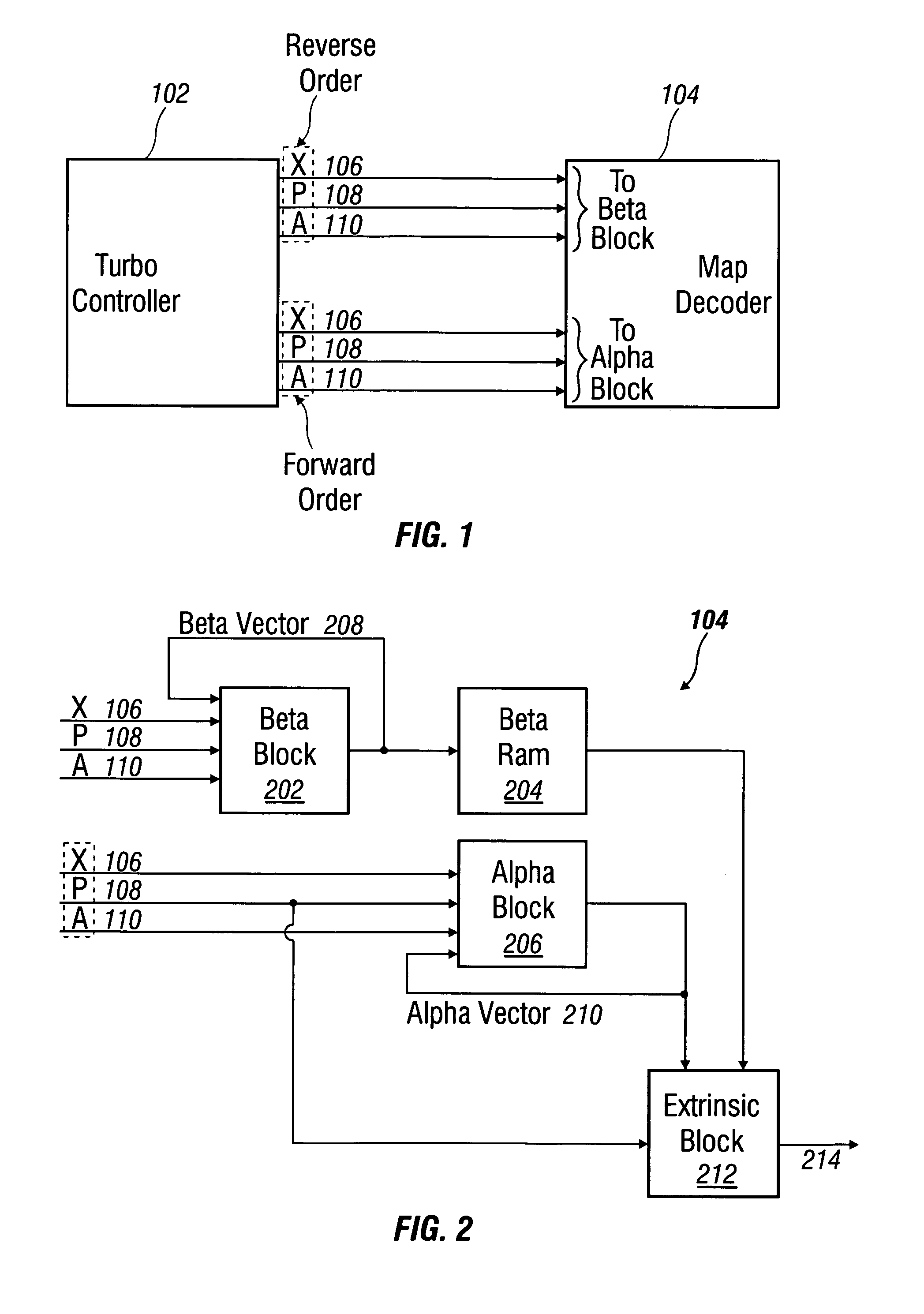
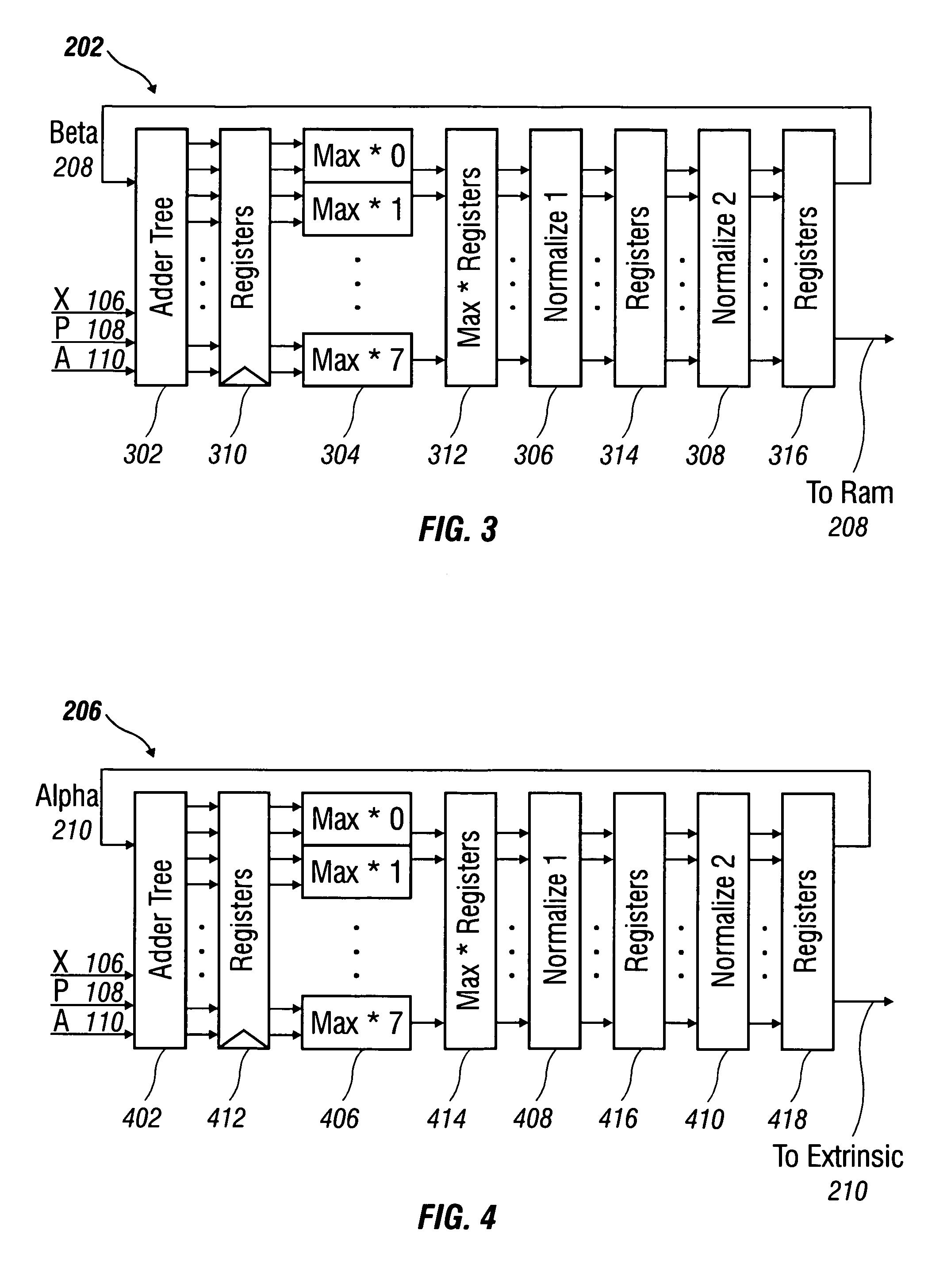
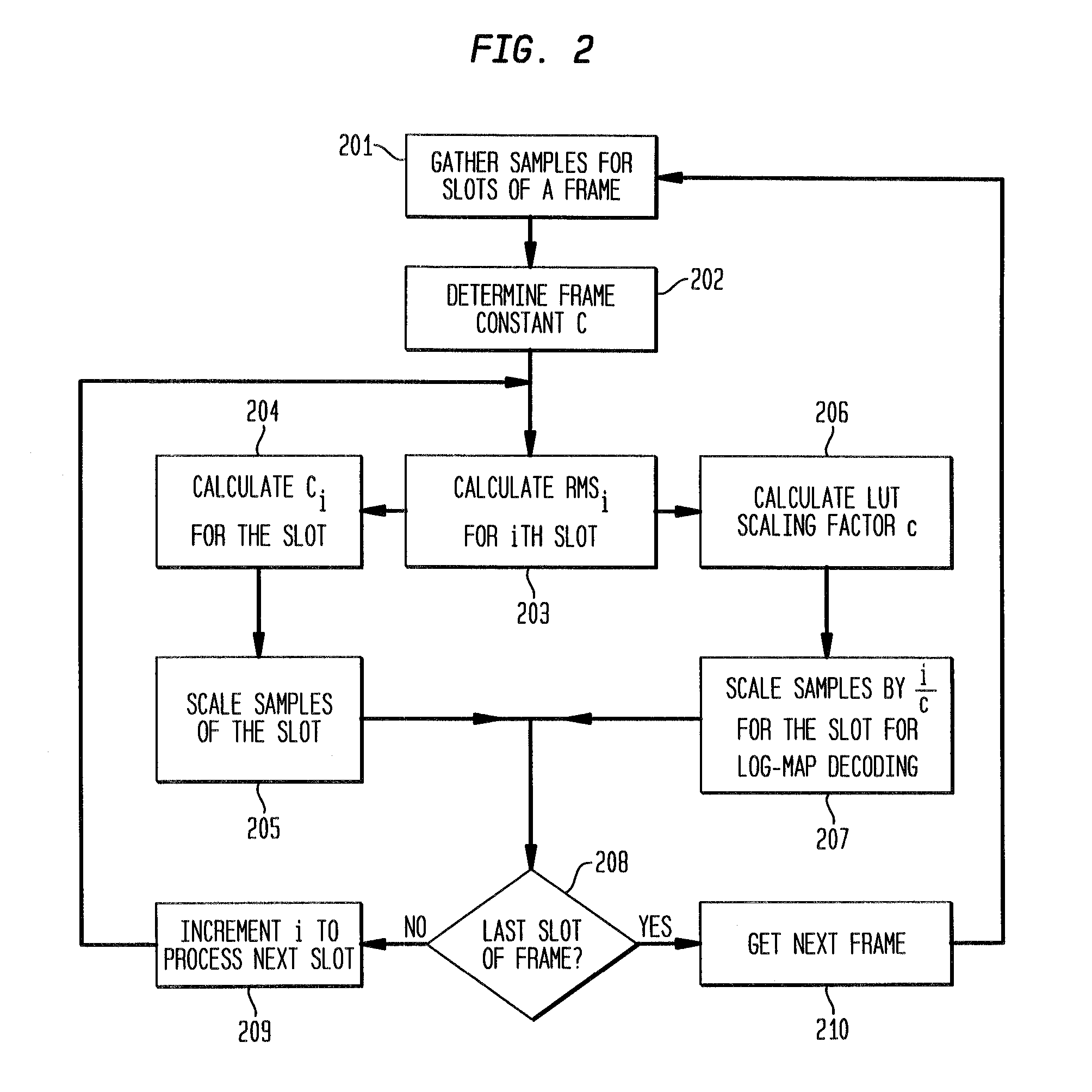
Soft sample scaling in a turbo decoder
ActiveUS7340013B2Other decoding techniquesComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsAlgorithmRoot mean square
A receiver for iterative decoding of a received, encoded signal employs slot-based scaling of soft samples. Iterative decoding employs a constituent maximum a priori (MAP) decoder for each constituent encoding of information of the encoded signal. Root mean square (RMS) values for soft samples over a slot are selected for dynamic range scaling. Squared RMS values are combined and equal the squared RMS value for a frame multiplied by a control constant, and this relationship may be employed to derive scaling constants for each slot. Alternatively, the square root of the RMS value multiplied by a constant serves as an SNR estimator that may be employed to scale samples to reduce dynamic range and modify logarithmic correction values for max* term calculation during log-MAP decoding.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
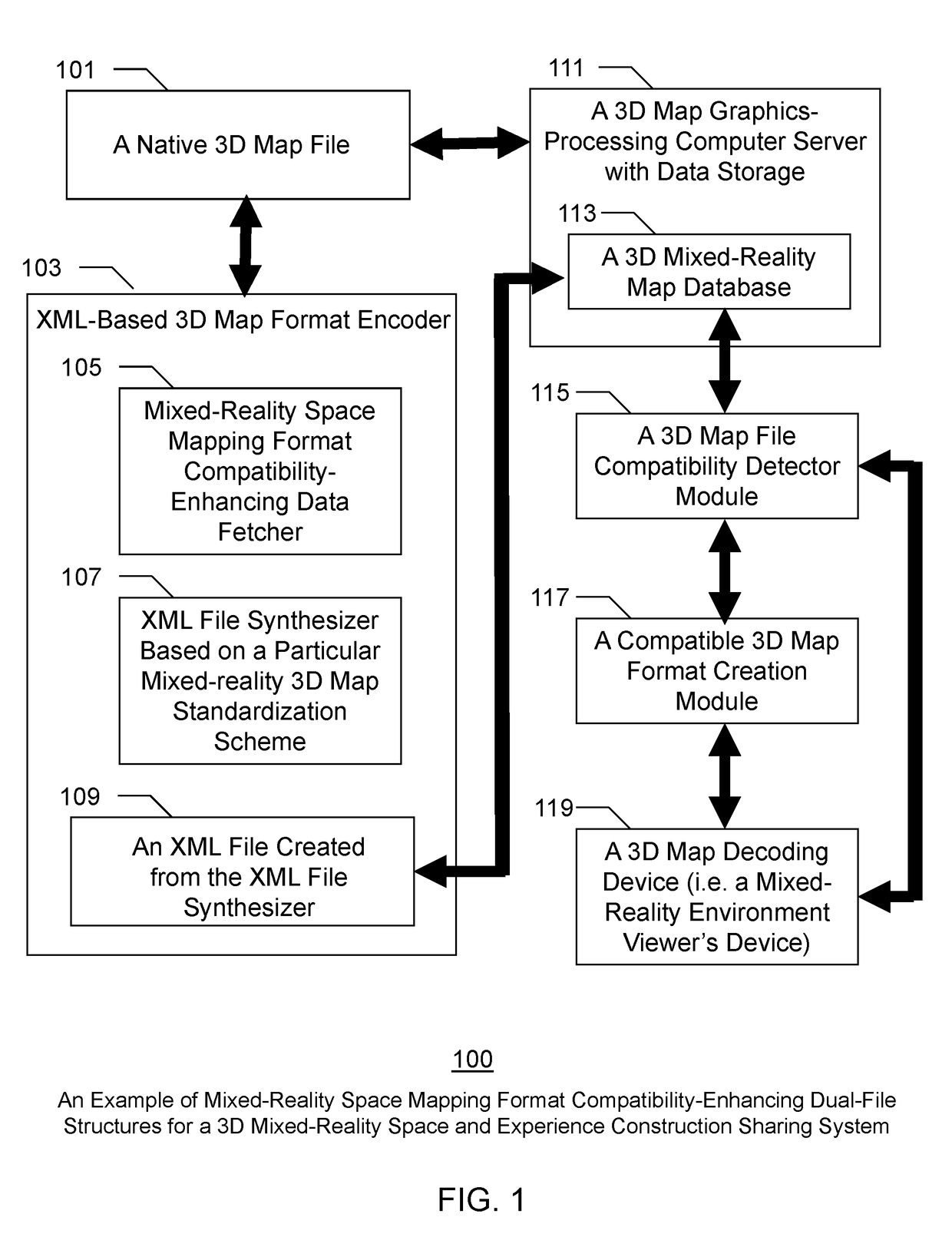
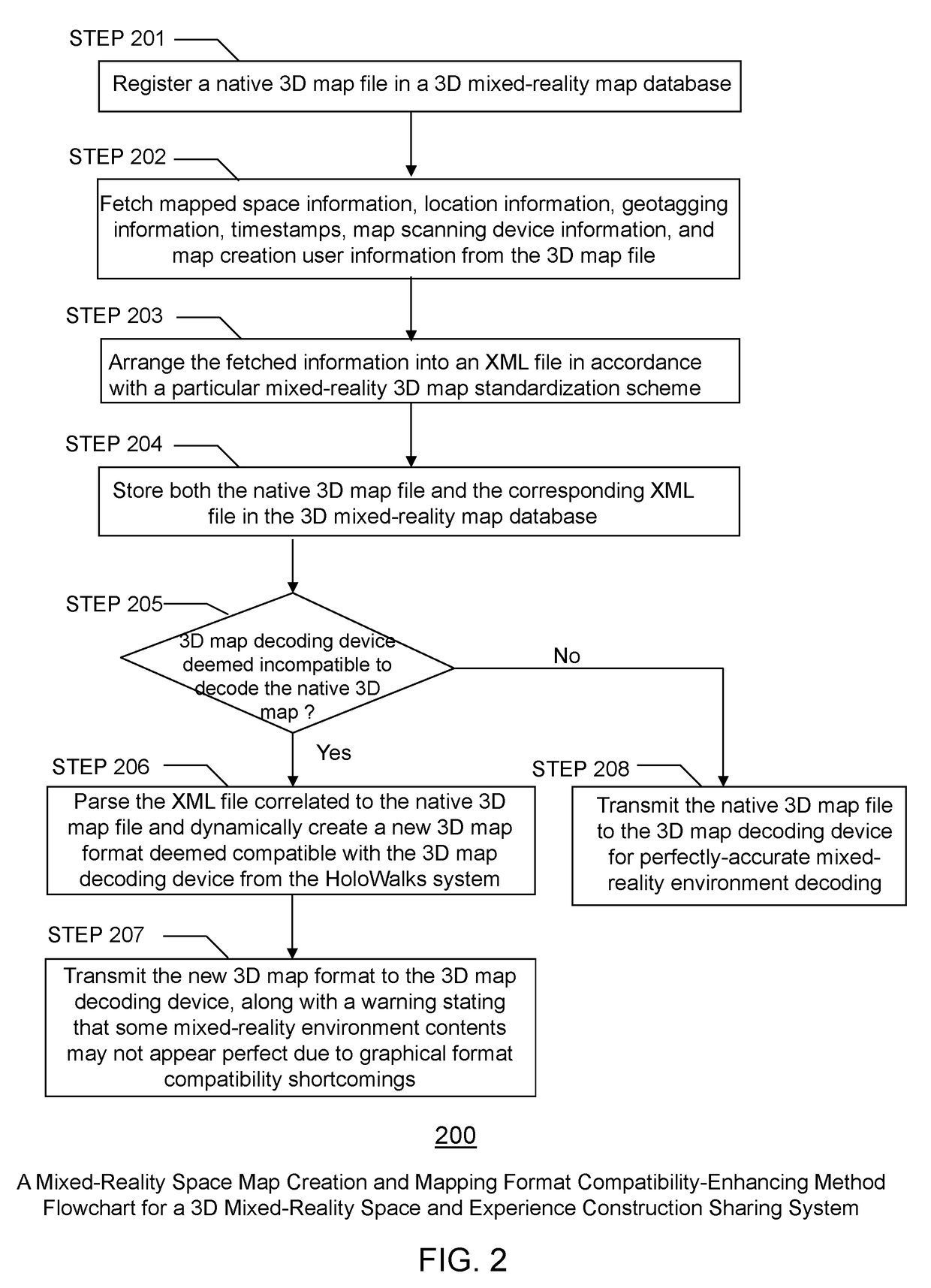
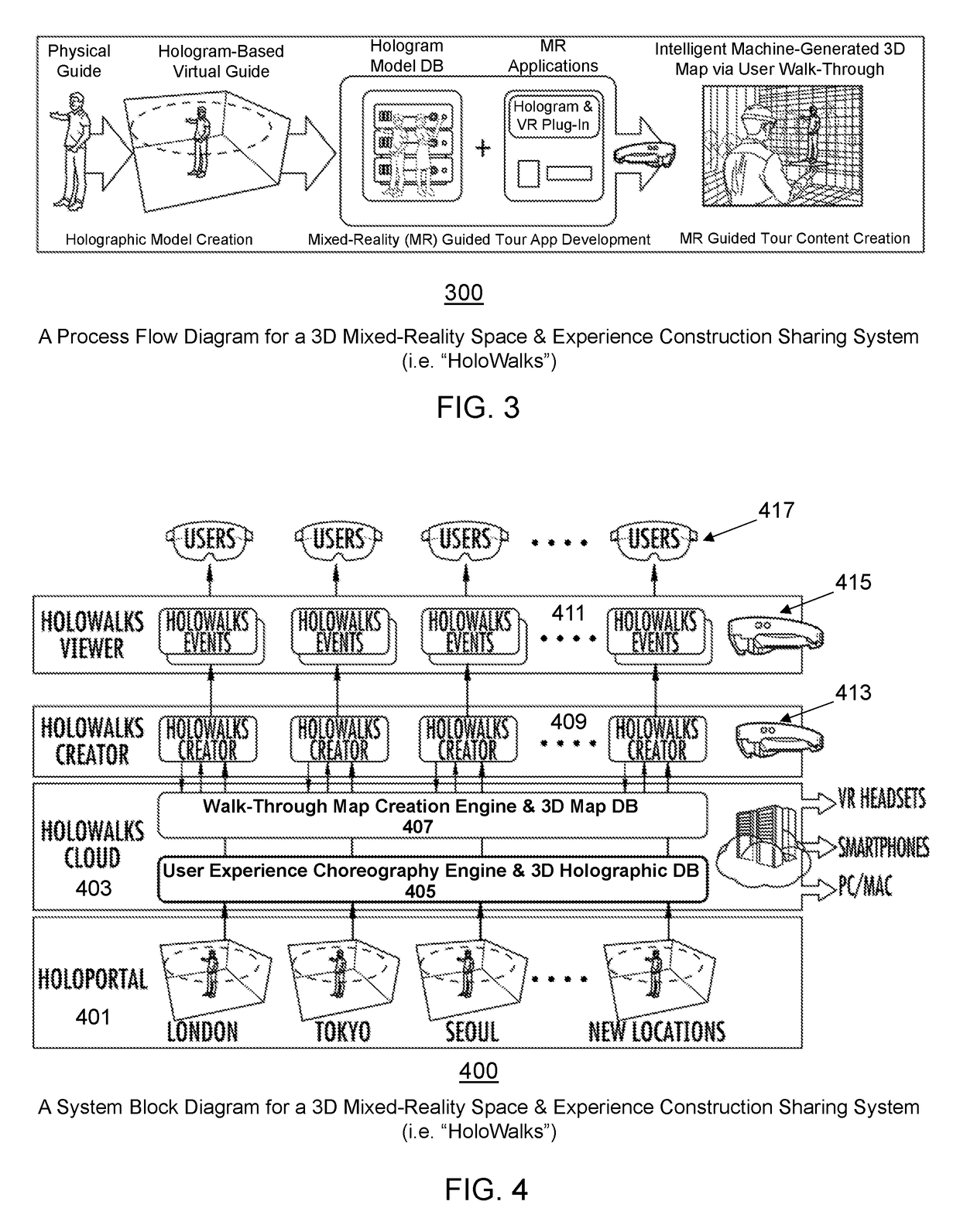
Mixed-Reality Space Map Creation and Mapping Format Compatibility-Enhancing Method for a Three-Dimensional Mixed-Reality Space and Experience Construction Sharing System
ActiveUS20190073832A1Enhancing format compatibilityAccurate graphical renderingNatural language data processingImage data processingMixed realityData set
A novel method for enhancing mixed-reality space map creation and mapping format compatibilities among various three-dimensional mixed-reality space and experience construction platforms is disclosed. In one example, mapped space information, current location information, geotagging information, timestamps, map scanning device information, and map creation user information are fetched from a native 3D map dataset, and are saved separately along with the native 3D map dataset. Based on a specific 3D map standardization scheme, the fetched information and at least some portions of the native 3D map dataset can then be saved as an XML metadata file. If a 3D map decoding device requesting the 3D map is deemed incompatible to the native 3D map dataset format, then the mixed-reality space map creation and mapping format compatibility-enhancing method converts the XML file on the fly into a 3D map format determined to be most compatible with the 3D map decoding device.
Owner:DOUBLEME INC (OF KOREA)
CT image segmentation system based on attention convolutional neural network
ActiveCN111325751AImprove segmentation execution efficiencyReduce lossesImage enhancementImage analysisFeature codingImage segmentation
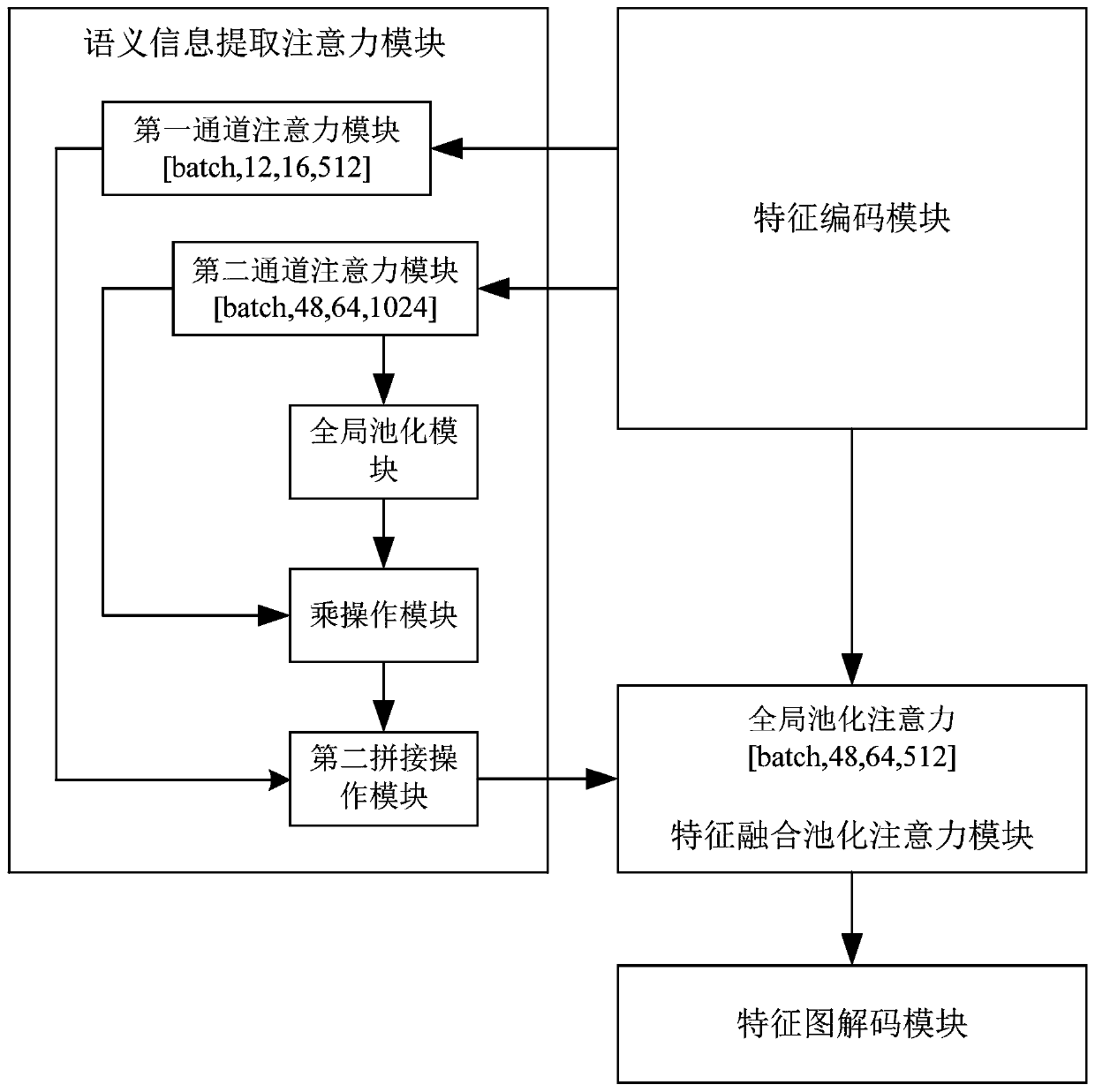
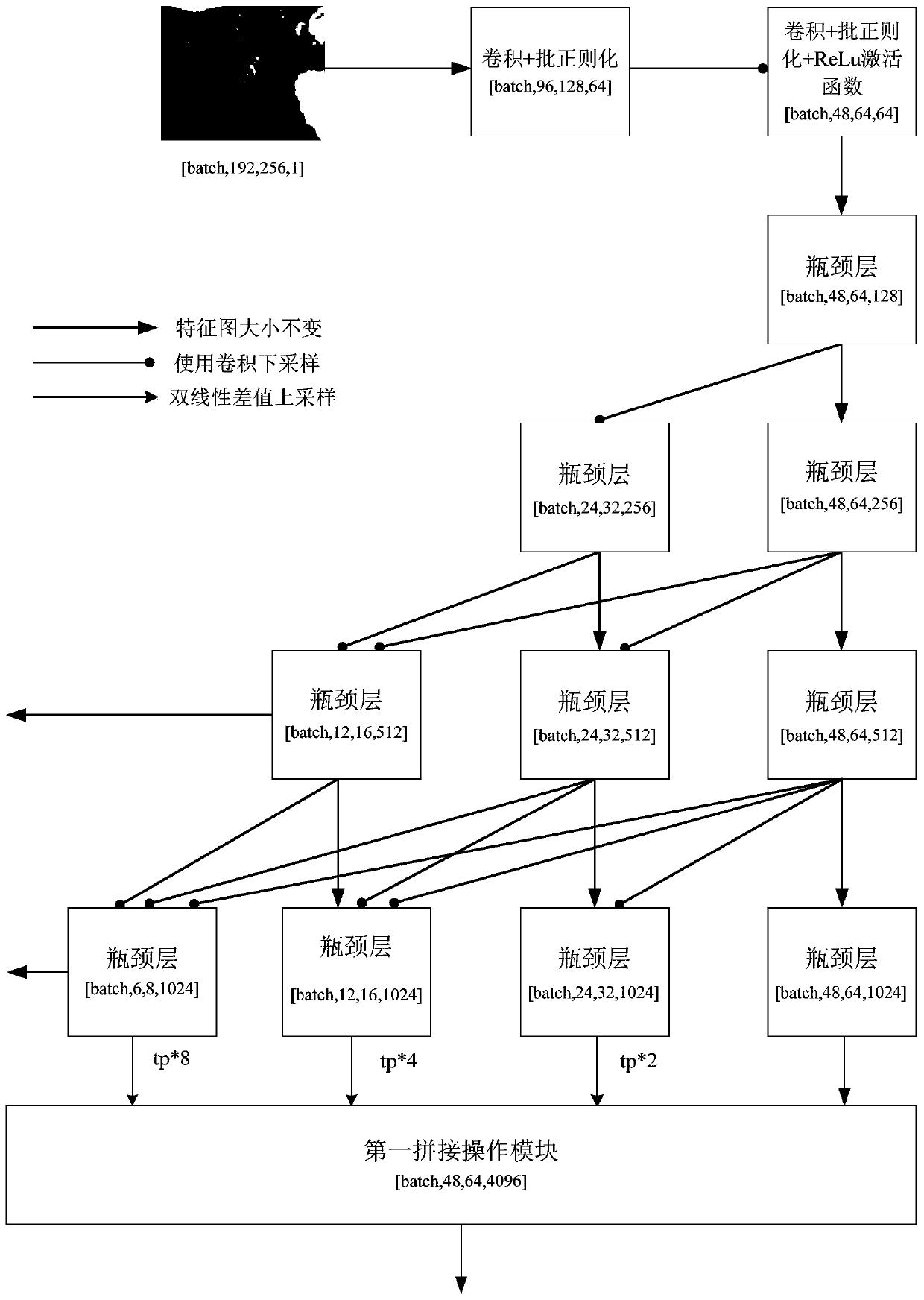
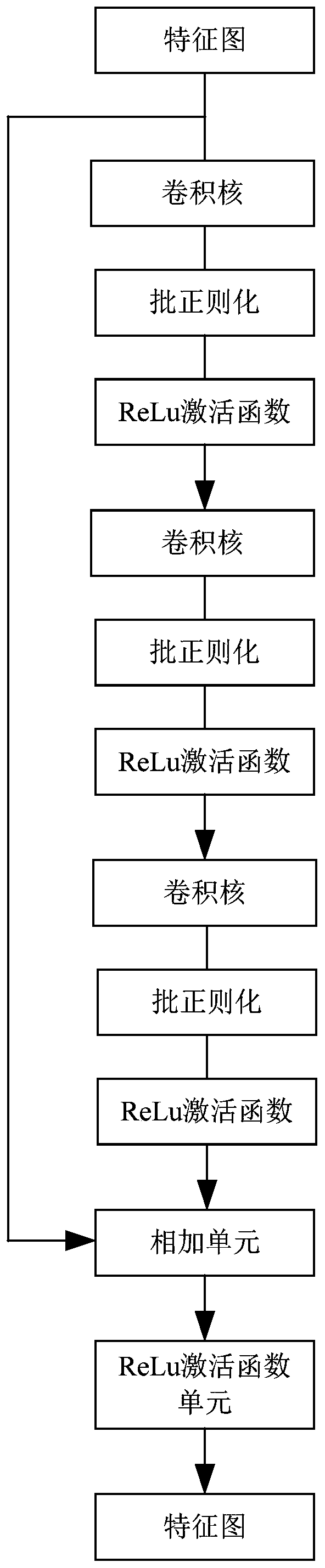
The invention provides a CT image segmentation system based on an attention convolutional neural network, and the system comprises a feature coding module which uses a parallel convolutional neural network to gradually reduce the size of a feature map of an input image, and achieves the simultaneous extraction of image semantic information and spatial information through the multiplexing of a network layer and the interception and fusion of features of all layers; the semantic information extraction attention module which is used for generating attention features by pooling and further refining the semantic information features extracted by the feature coding module; the feature fusion pooling attention module which is used for fusing the refined semantic information features with the semantic information and spatial information features spliced by the feature coding module to form an attention feature map by using parallel connection of maximum pooling and average pooling; and the feature map decoding module which is used for gradually and finely restoring the attention feature map into the size of the input image by using a convolution module and an up-sampling module. Accordingto the invention, by fusing the attention module, efficient and accurate image segmentation is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
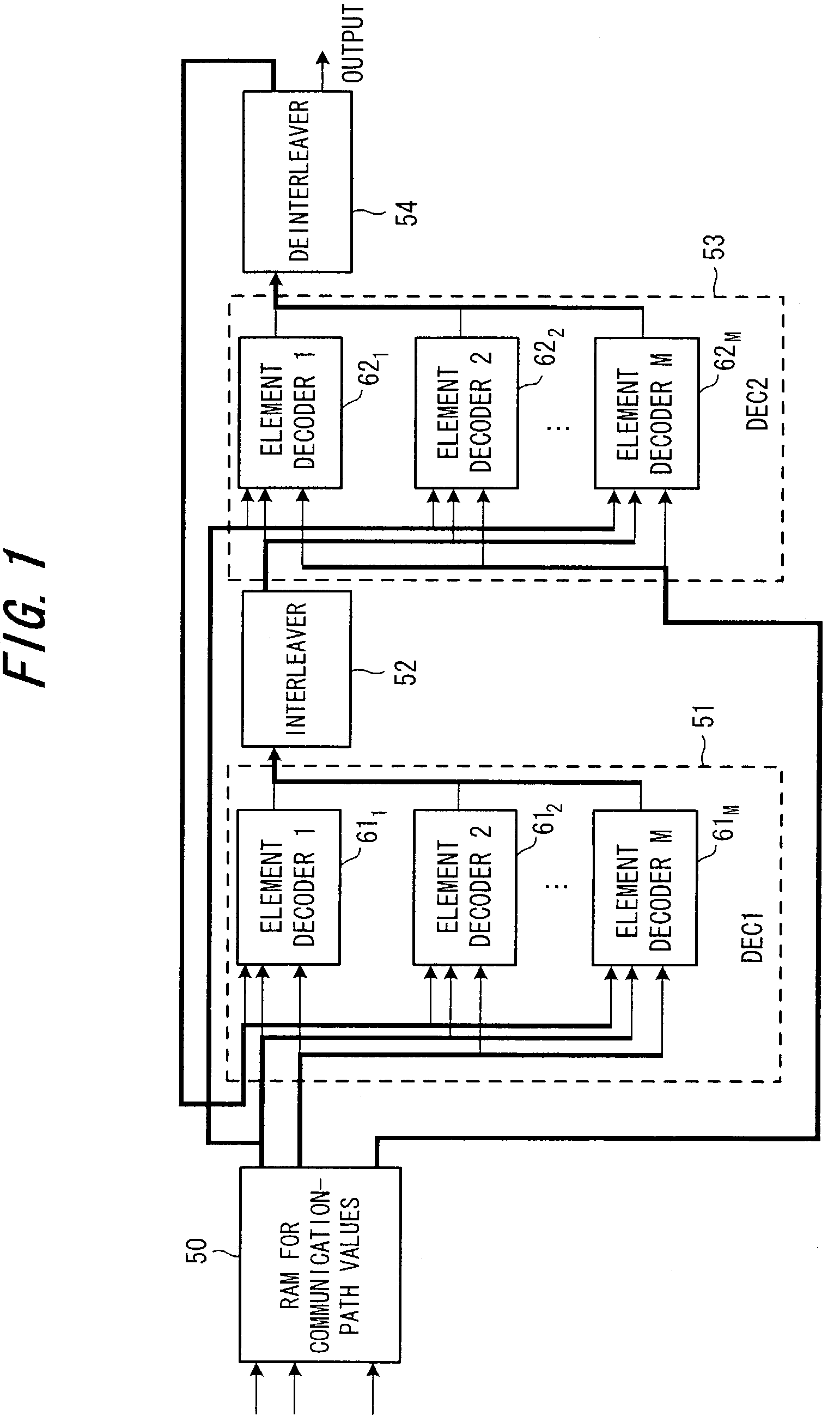
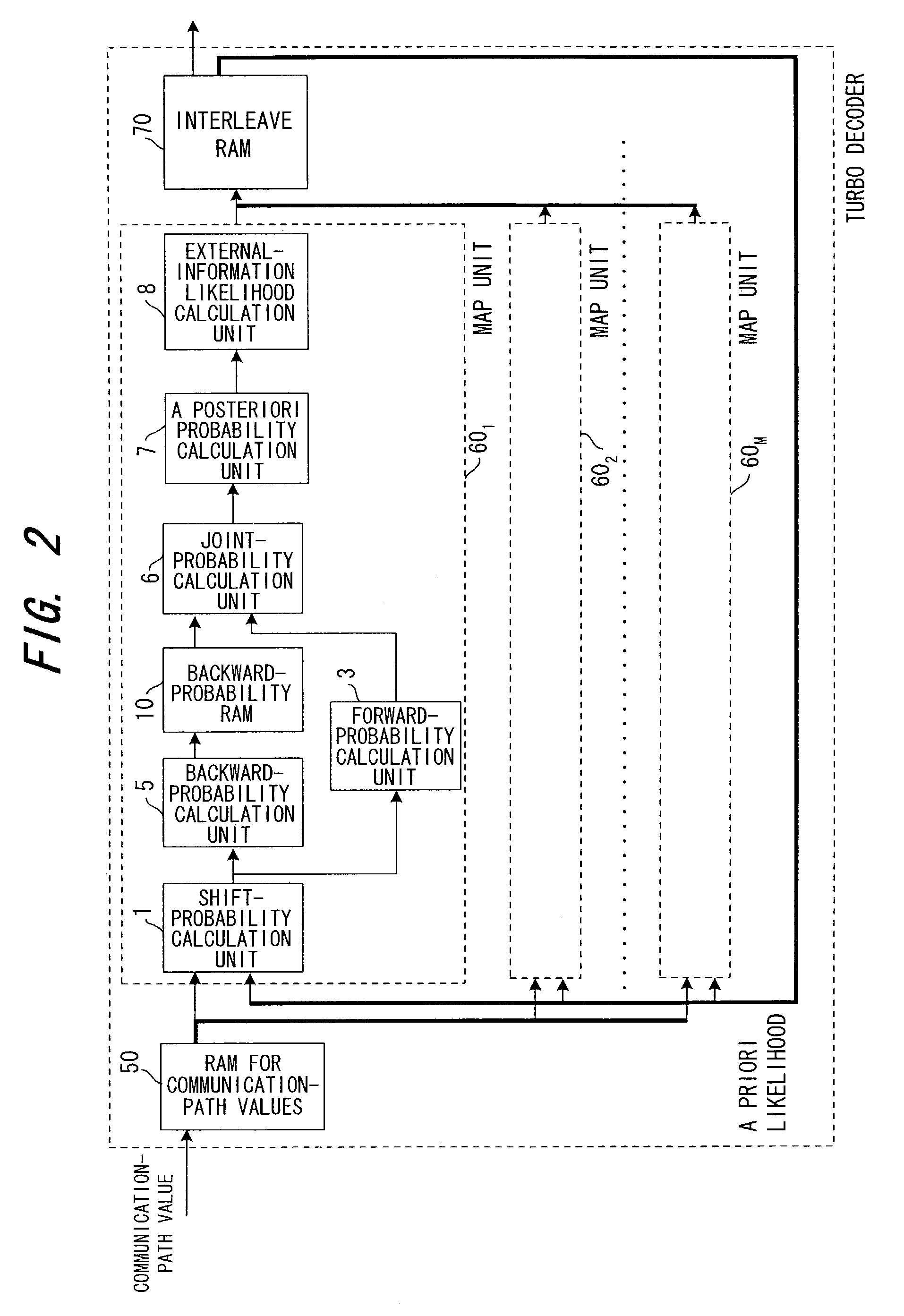
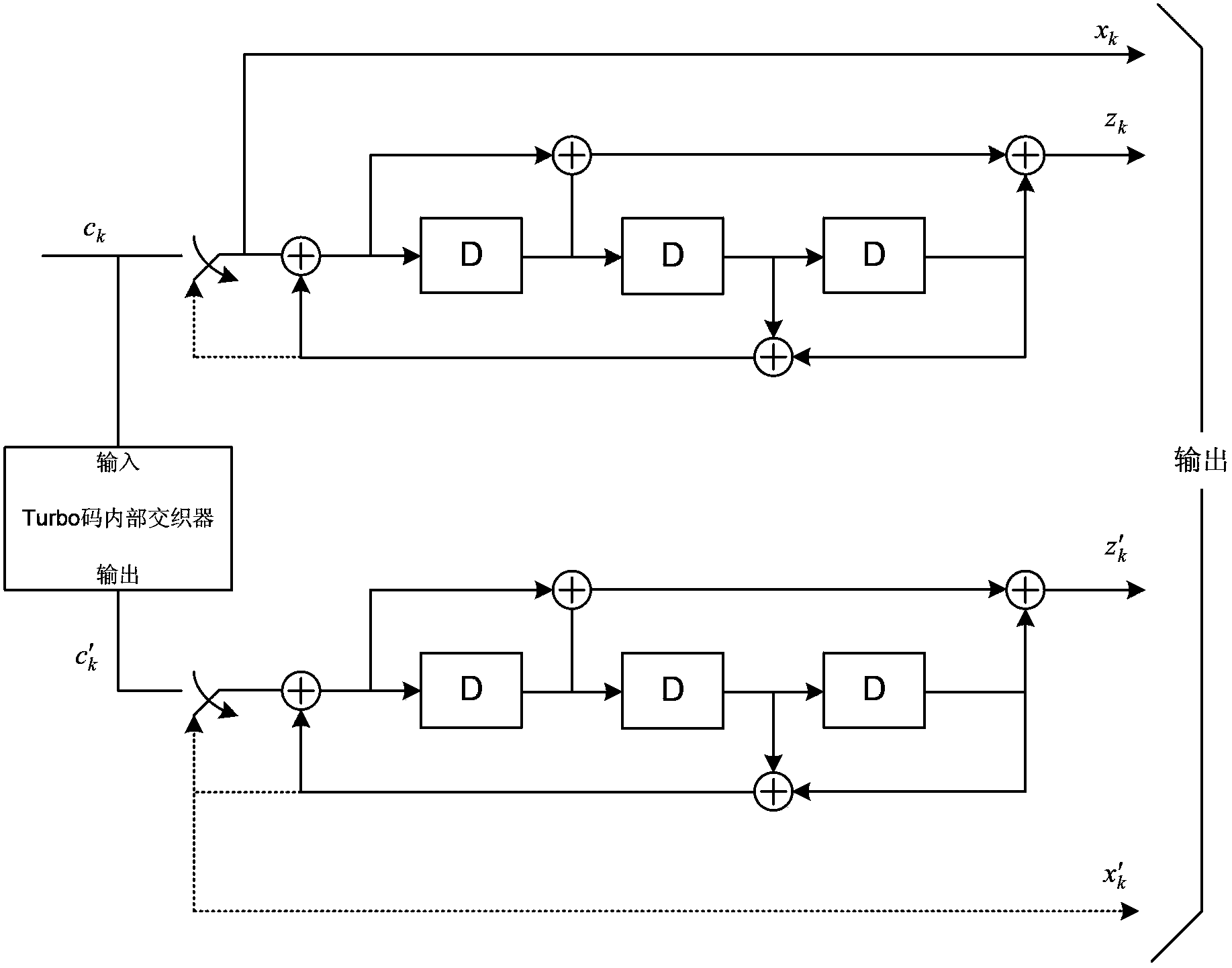
Turbo decoding method and turbo decoding apparatus
InactiveUS7530011B2Reduce latencyReduce the necessary timeData representation error detection/correctionError preventionComputer scienceTurbo decoding
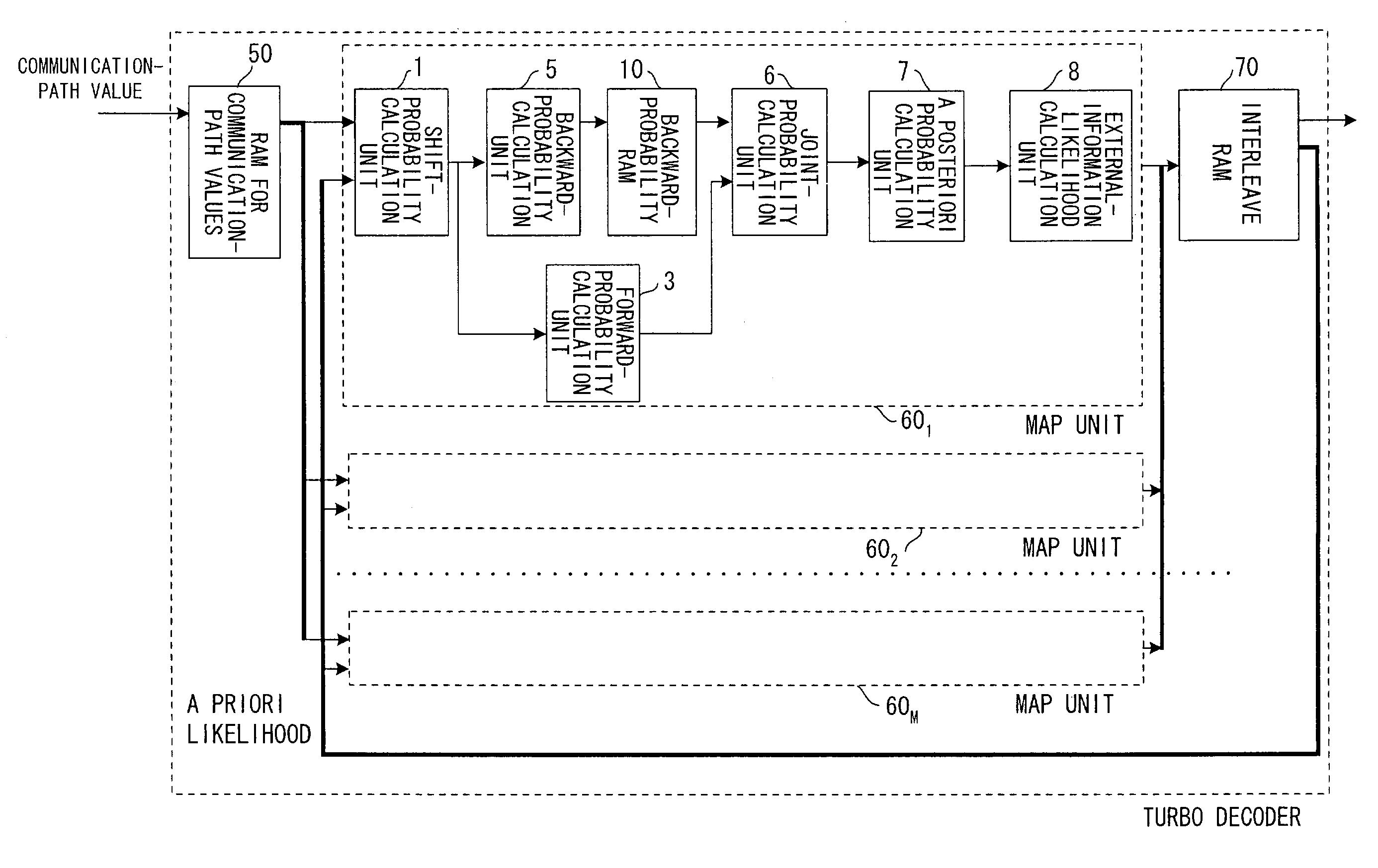
Disclosed are a turbo decoding apparatus and method for decoding a turbo-encoded signal by repeating element decoding. The apparatus includes a plurality of element decoders for applying element decoding, e.g., MAP decoding, in parallel to respective ones of a plurality of divided signals to be decoded, and an interleaver / deinterleaver for interleaving or deinterleaving a plurality of results of element decoding collectively. Each element decoder applies element decoding to a respective one of the divided signals, and the interleaver / deinterleaver alternately interleaves and deinterleaves a plurality of results of element decoding collectively. Turbo decoding is carried out by repeating these operations a prescribed number of times.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
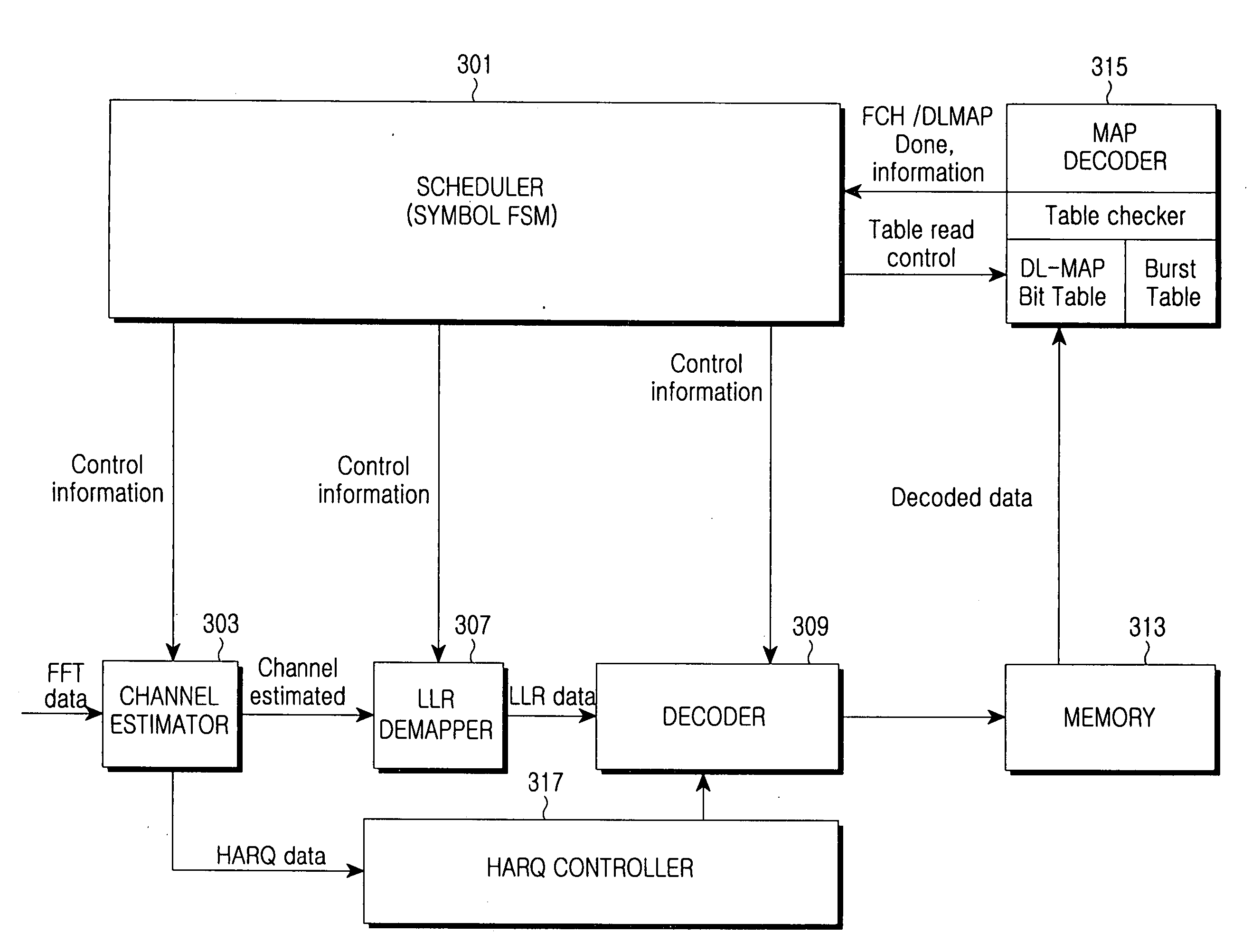
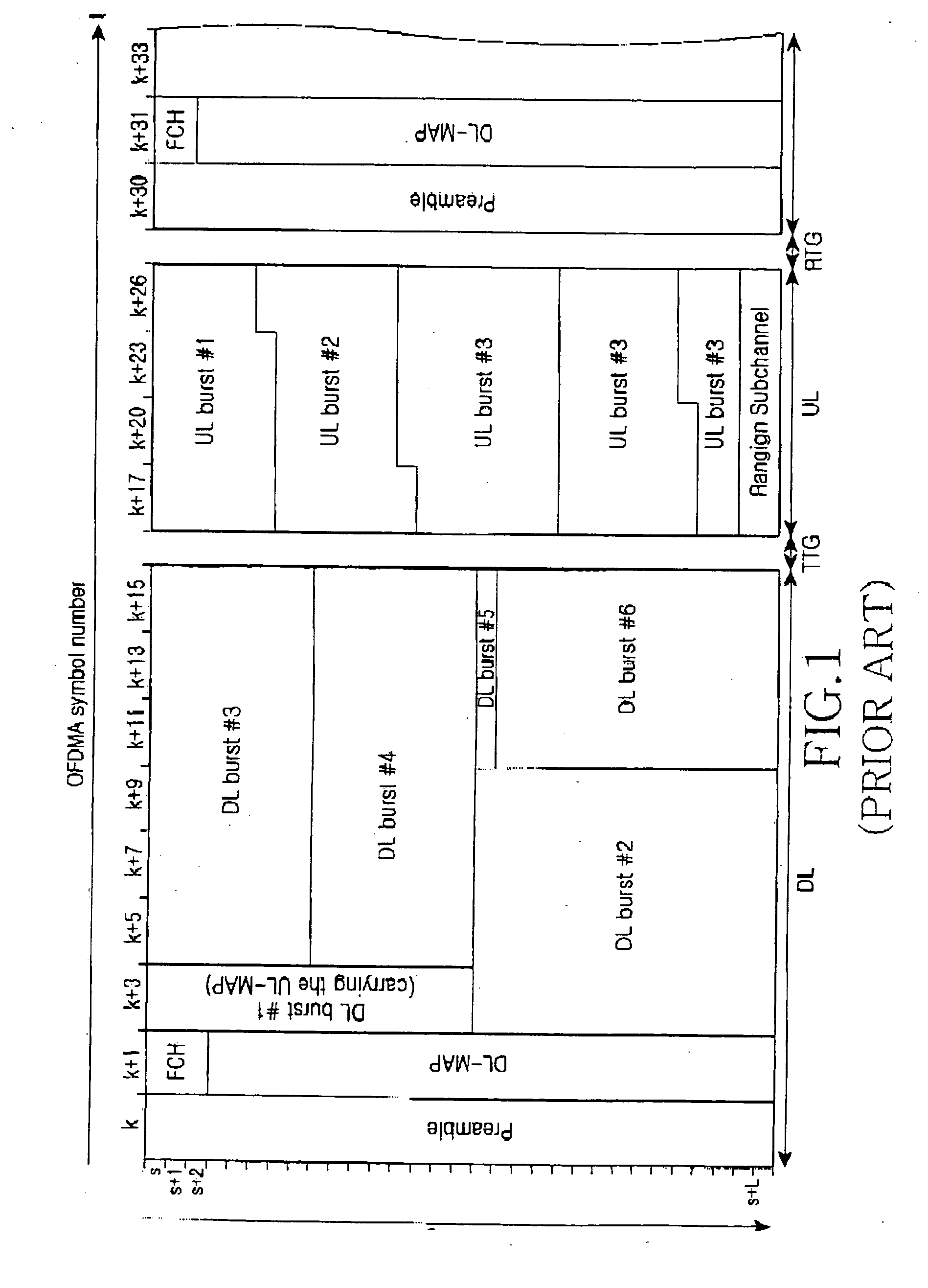
Apparatus and method for scheduling data in a modem
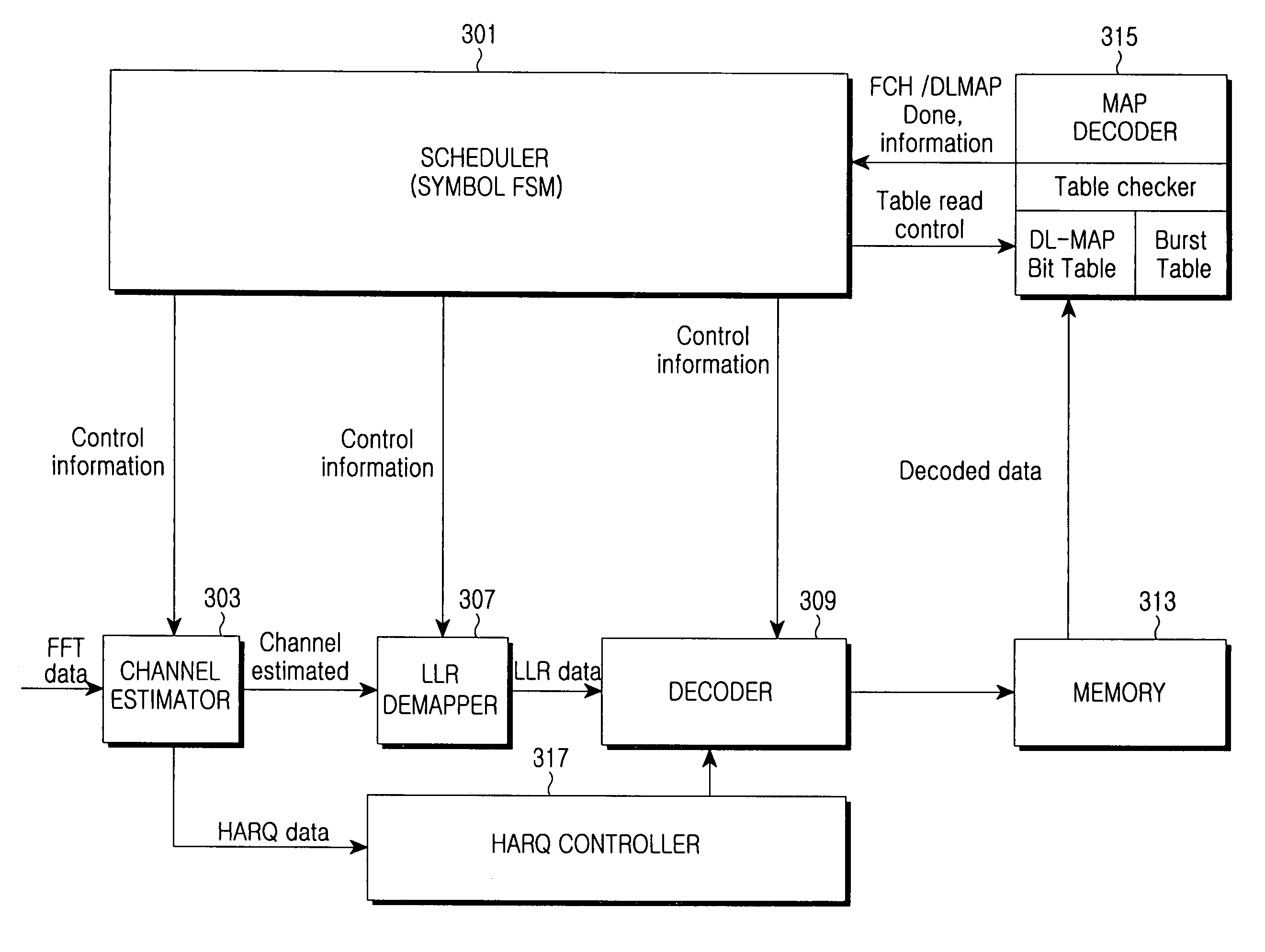
InactiveUS20070002977A1Fast data processingHigh data rateTime-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemModem device
A scheduling method is provided for processing data in a communication system. The method includes performing downlink MAP (DL-MAP) decoding; generating a configuration table through the DL-MAP decoding; and processing data in a predetermined unit according to the generated configuration table.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
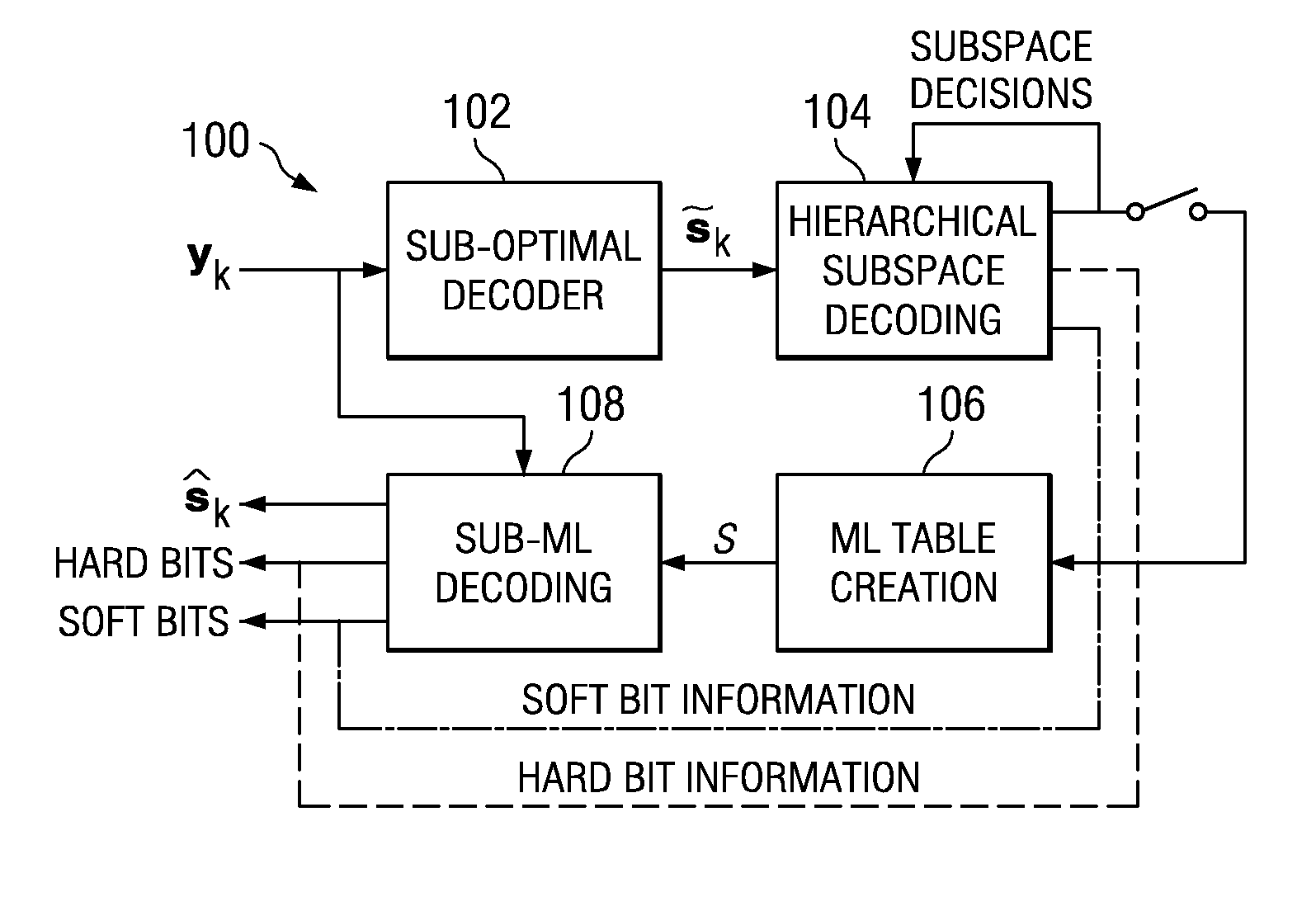
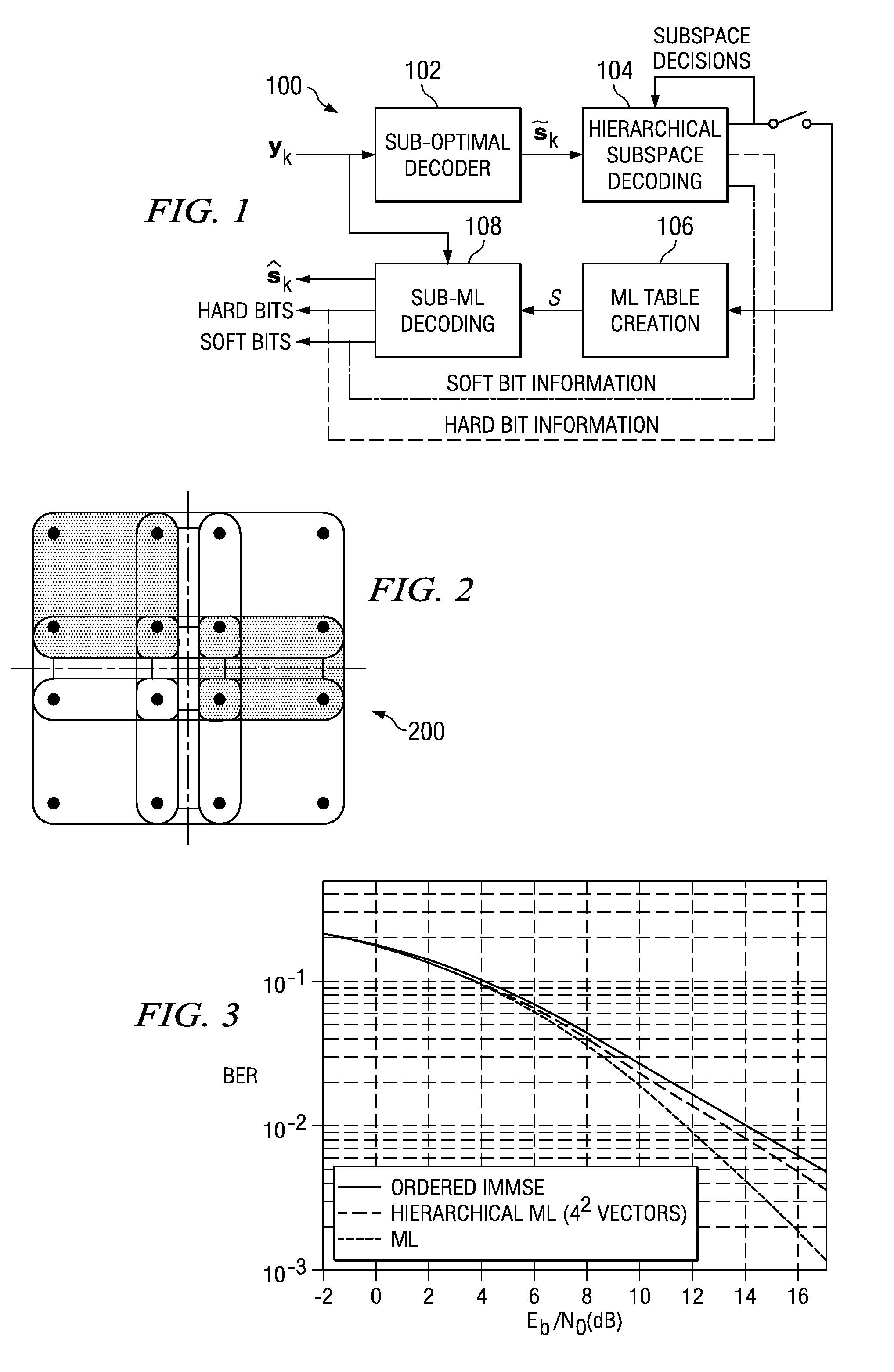
Low-complexity hierarchical decoding for communications systems using multidimensional QAM signaling
ActiveUS7280622B2Reduced search space decoding methodDramatic complexityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationDecoding methodsCommunications system
A reduced search space minimum distance decoding method provides average probability of error performance close to optimal MAP decoding. The decoding algorithm provides dramatic complexity reductions compared with MAP decoding. A a sub-optimal decoder receives a collection of signal vectors y1 . . . yk, with k denoting a positive integer and generates an estimated transmitted multidimensional symbol {tilde over (S)}. The estimated transmitted multidimensional symbol {tilde over (S)} is decoded using hierarchical subset decoding a subset is determined therefrom. A reduced search space V is generated and minimum distance decoding is used to decode the received symbol vectors y1 . . . yk in the reduced search space V. one or more of the following: an estimated multidimensional symbol {tilde over (S)}, soft bit information, or hard bit information are cienerated therefrom.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
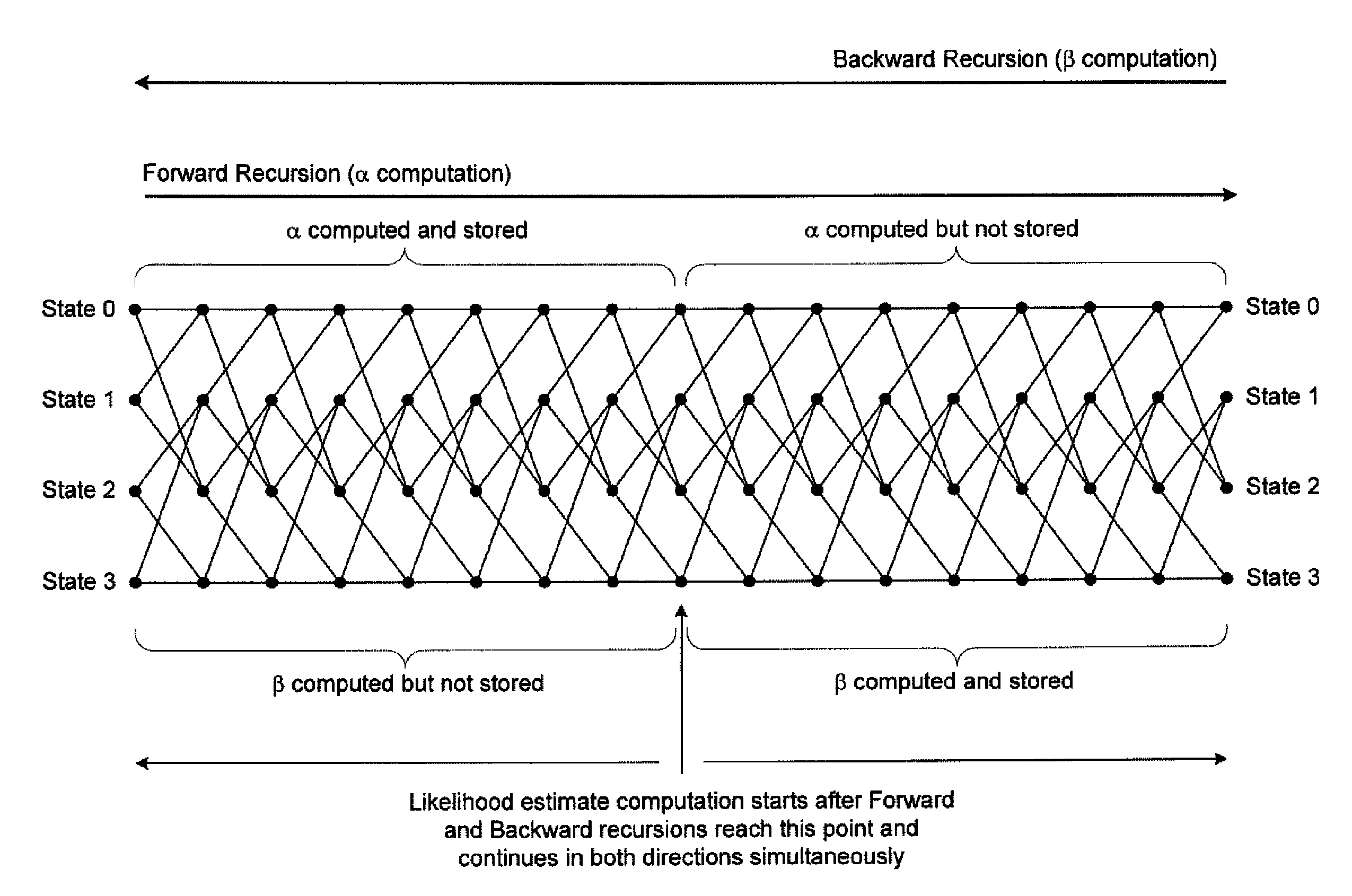
MAP decoding with parallelized sliding window processing
InactiveUS6980605B2High data reliabilityReduce memory requirementsData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesSlide windowComputer science
A turbo decoder in which a sliding-block MAP decoder pipelines the forward-propagating and backward-propagating computations.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Soft sample scaling in a turbo decoder
InactiveUS20080019468A1Reduced dynamic rangeAccurate valueOther decoding techniquesDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAlgorithmLogit
A receiver for iterative decoding of a received, encoded signal employs slot-based scaling of soft samples. Iterative decoding employs a constituent maximum a priori (MAP) decoder for each constituent encoding of information of the encoded signal. Root mean square (RMS) values for soft samples over a slot are selected for dynamic range scaling. Squared RMS values are combined and equal the squared RMS value for a frame multiplied by a control constant, and this relationship may be employed to derive scaling constants for each slot. Alternatively, the square root of the RMS value multiplied by a constant serves as an SNR estimator that may be employed to scale samples to reduce dynamic range and modify logarithmic correction values for max* term calculation during log-MAP decoding.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
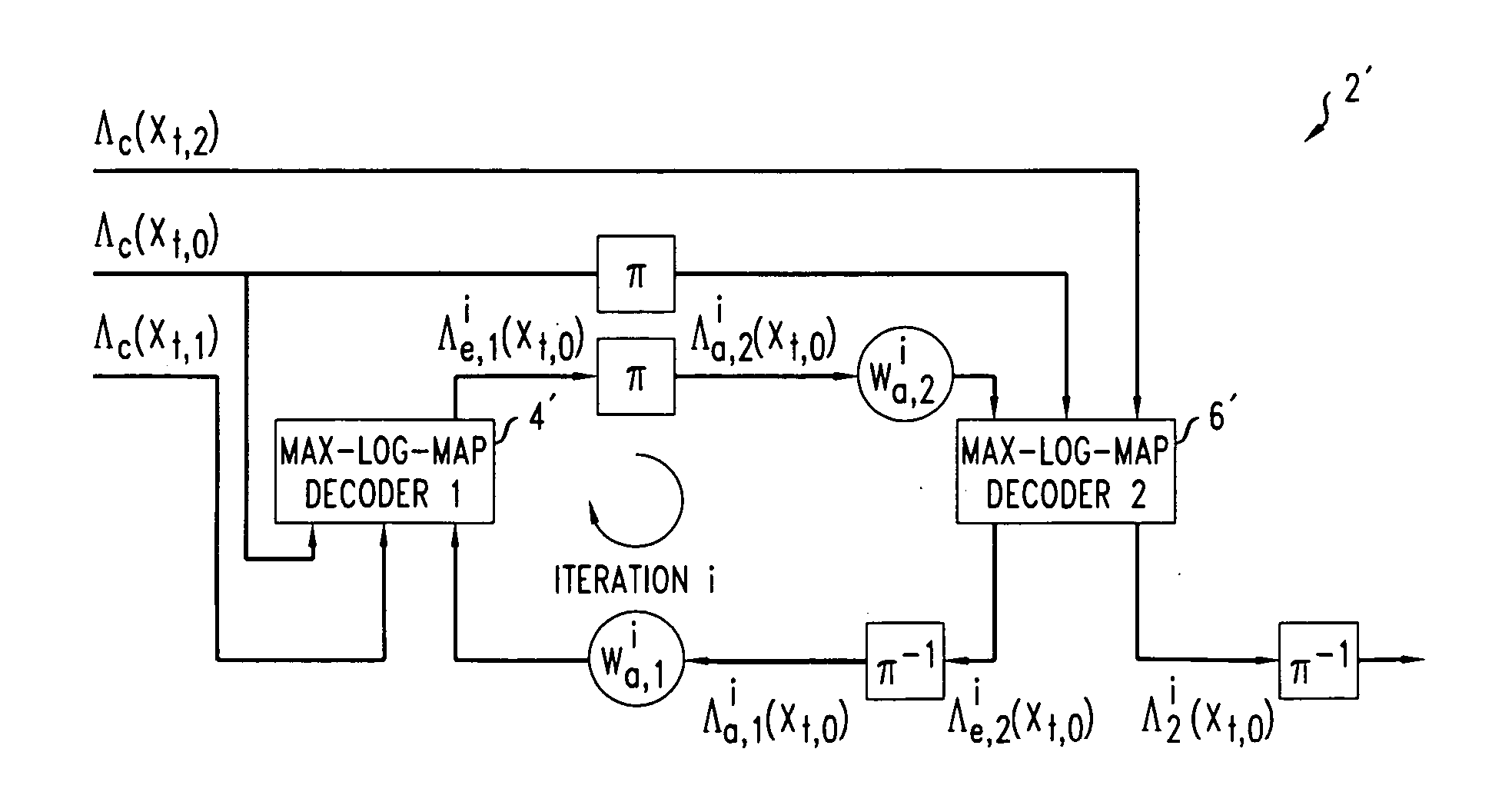
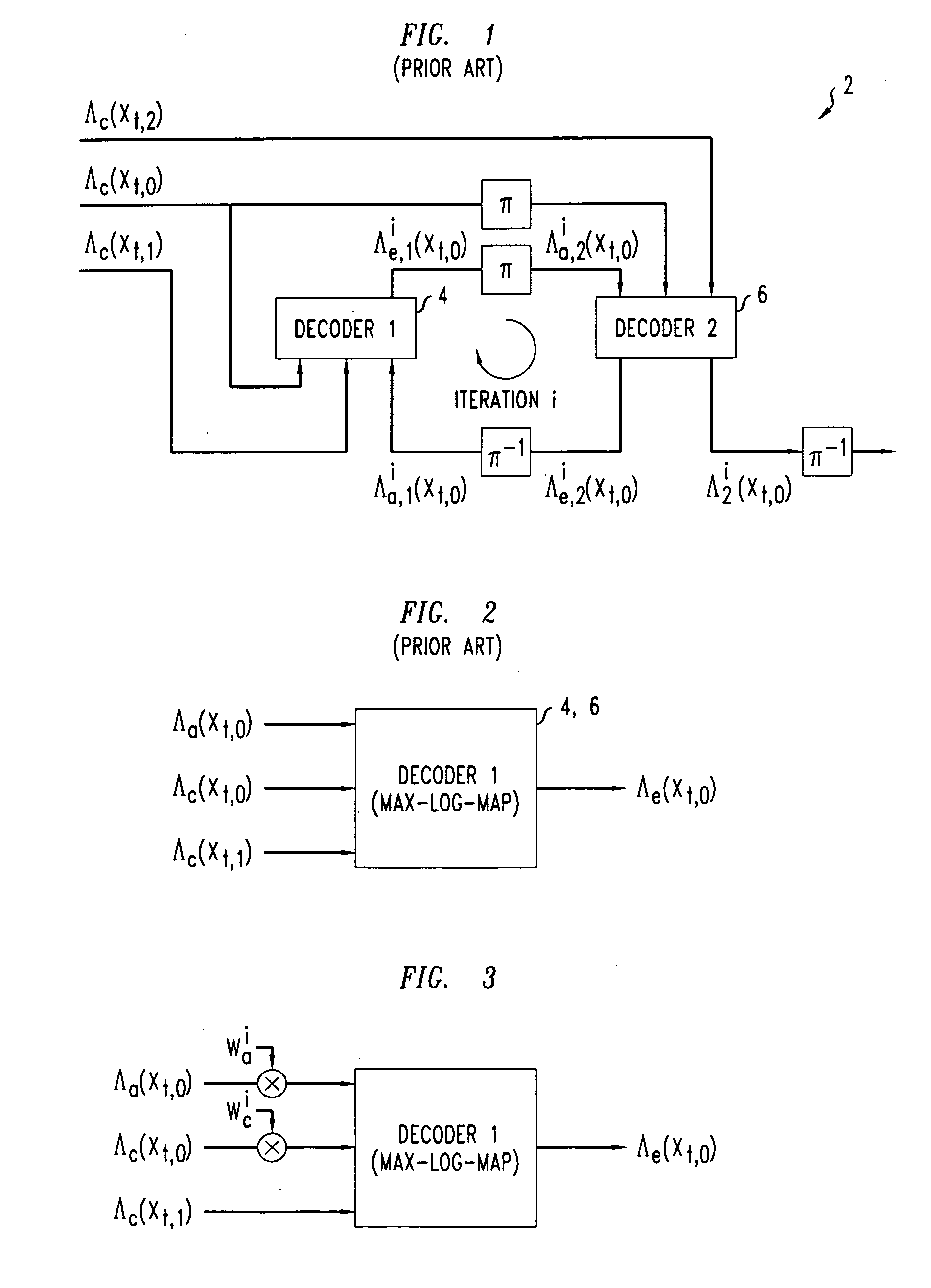
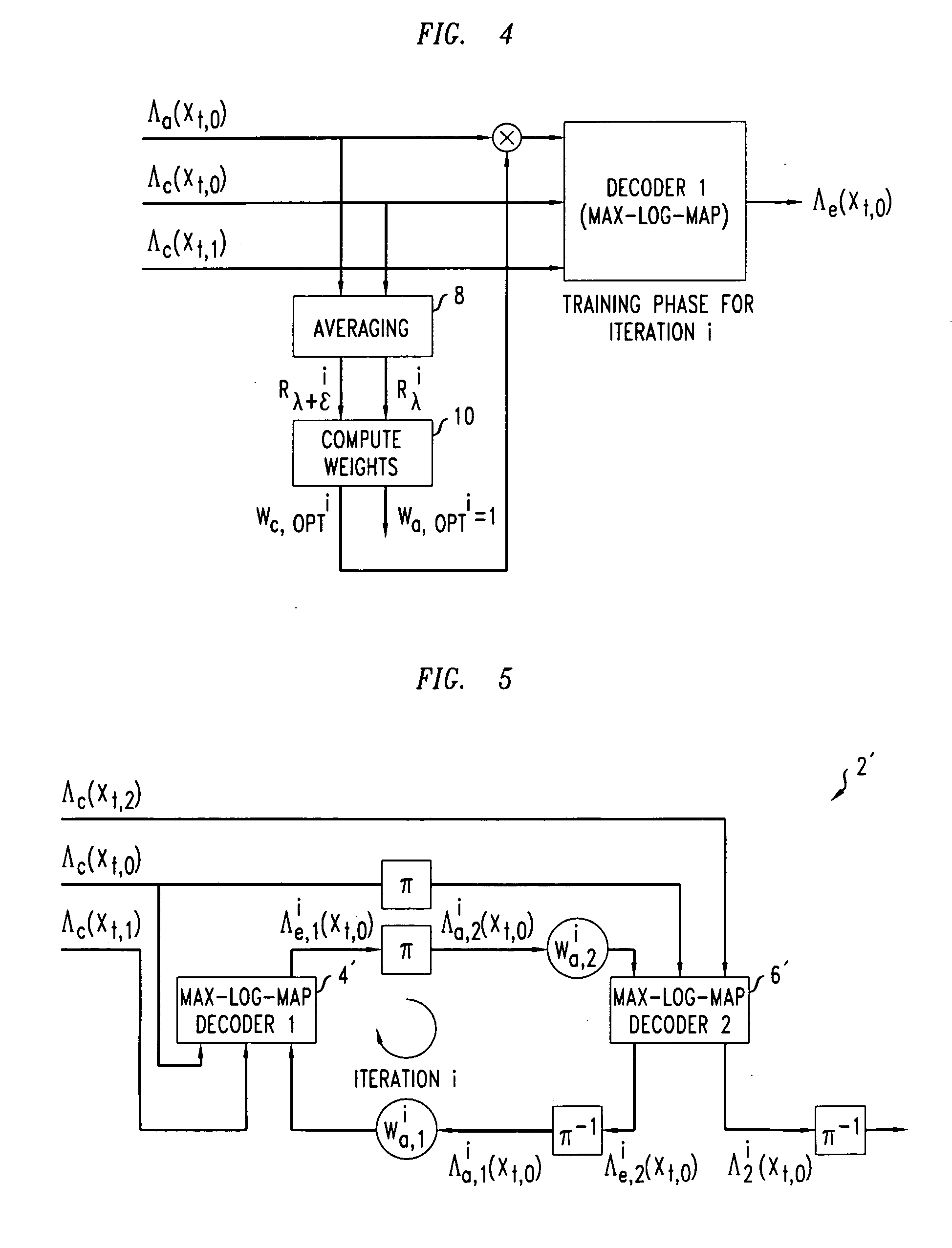
Decoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050031053A1Improve performanceReduce complexityData representation error detection/correctionError preventionComputer hardwareDecoding methods
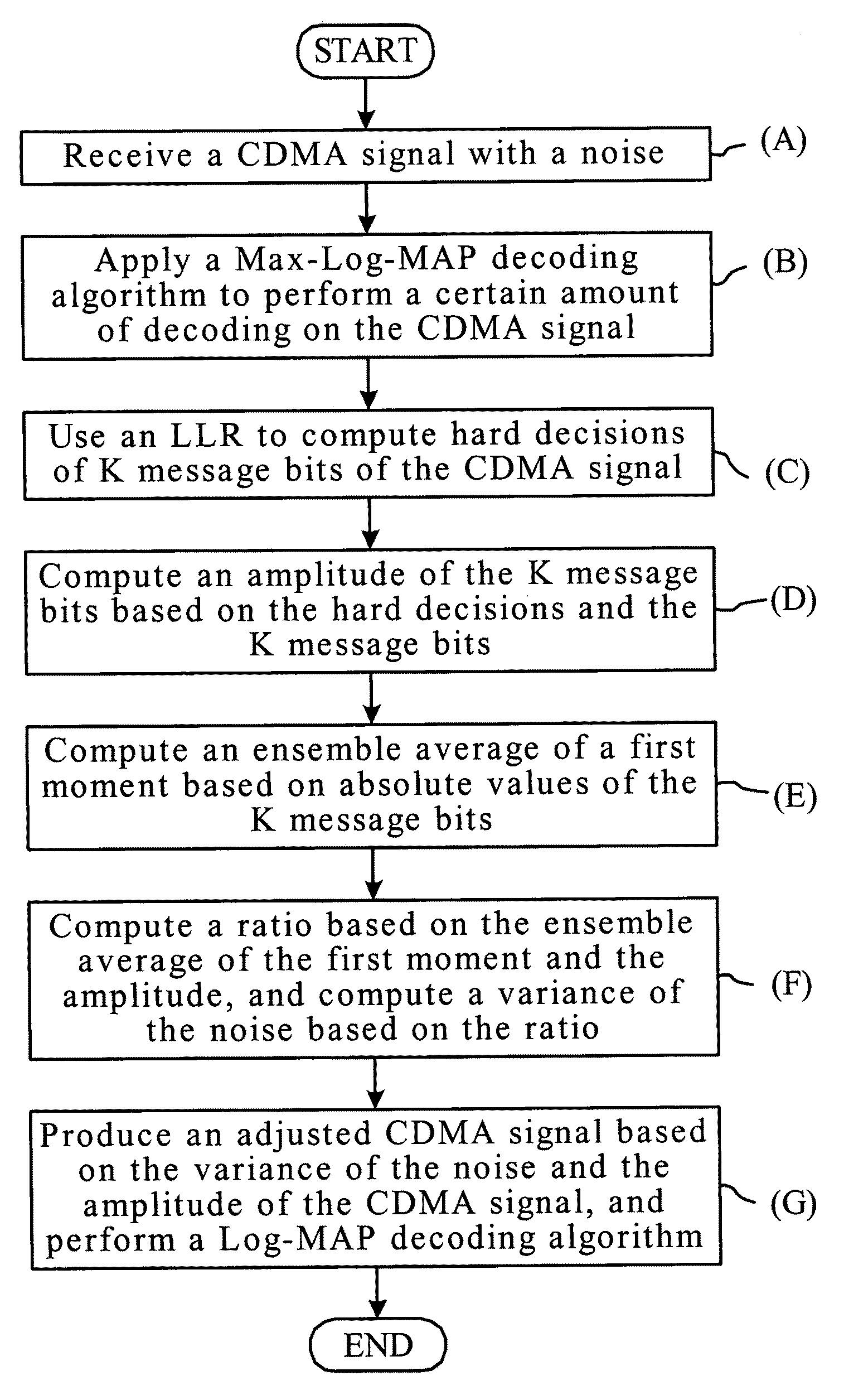
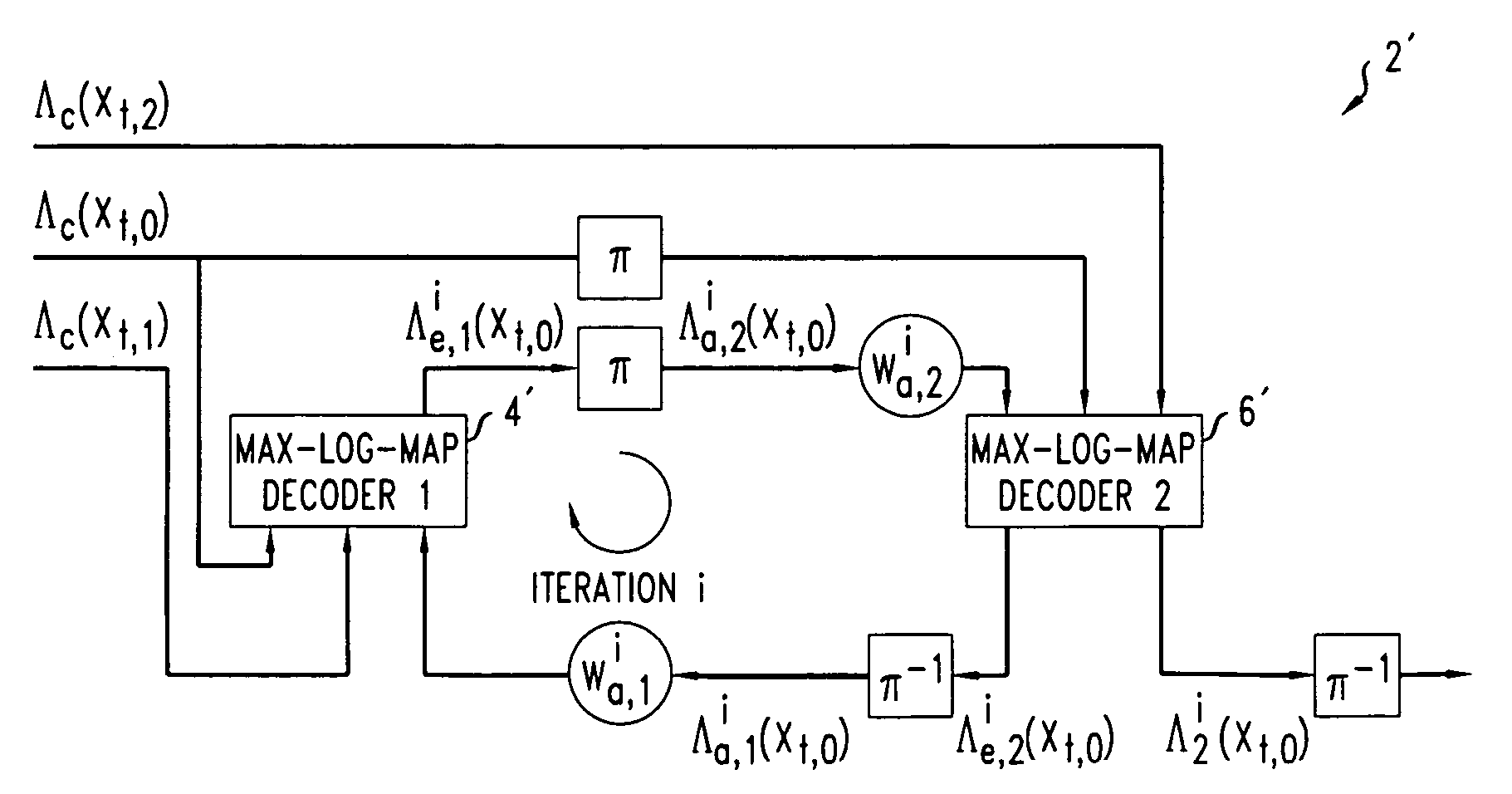
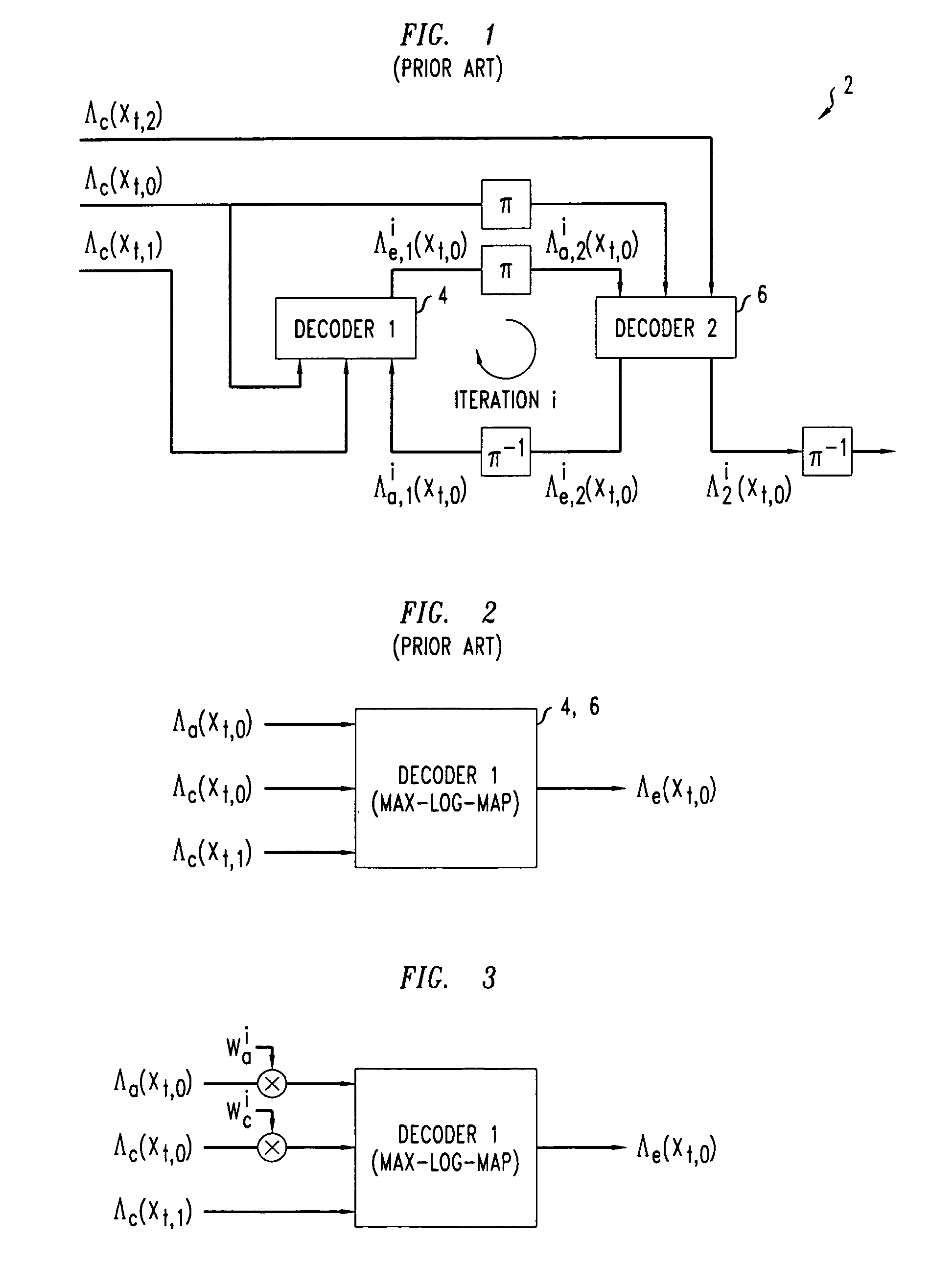
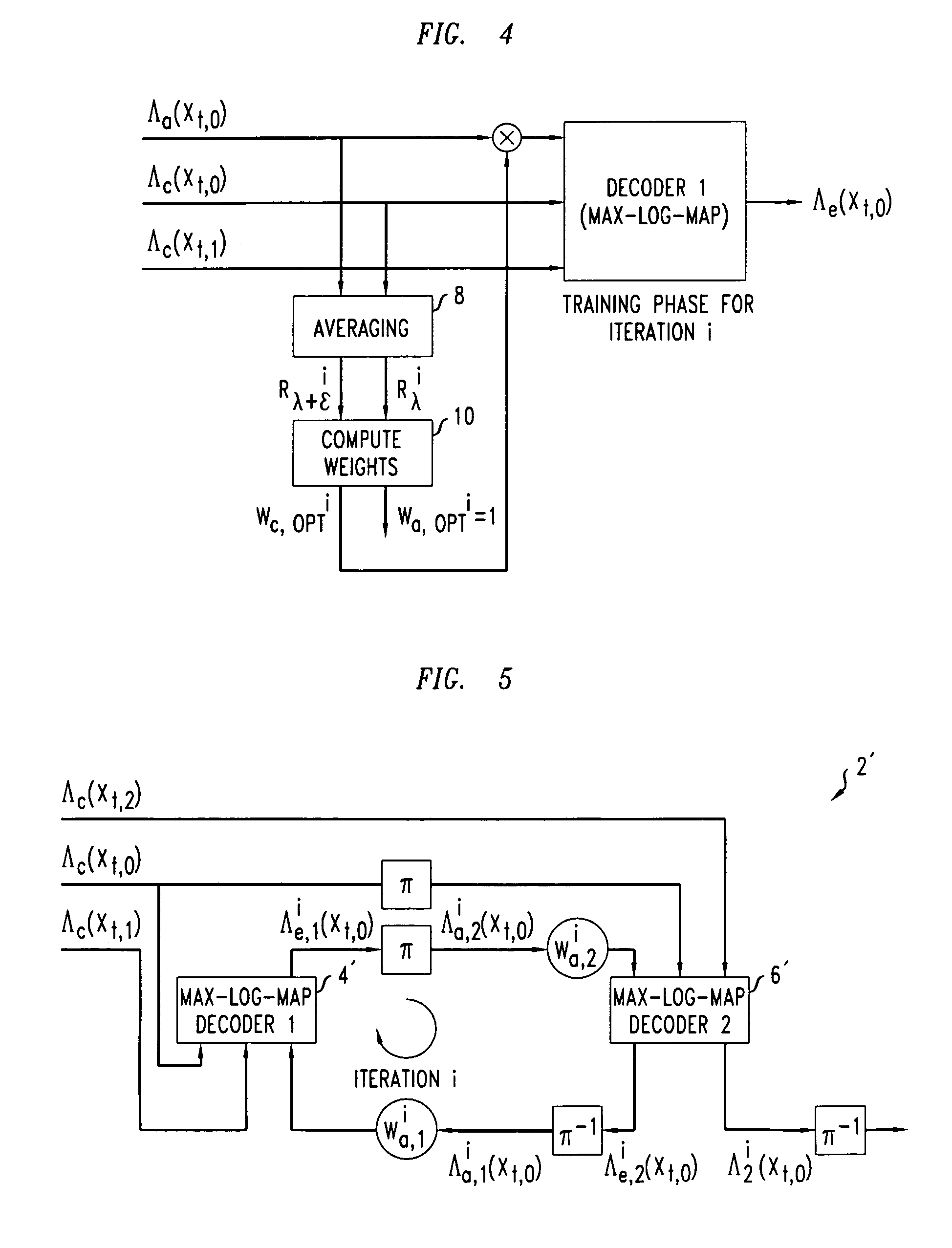
A method of decoding is provided comprising processing iterations. In each processing iteration, there is a first Max-Log-MAP decoding operation giving rise to a systematic error due to the Max-Log approximation, and a first weighting operation to weight extrinsic information from the first decoding operation to be applied as a priori information to the second Max-Log-MAP decoding operation. This is followed by a second Max-Log-MAP decoding operation, also giving rise to a systematic error due to the Max-Log approximation, and a second weighting operation to weight extrinsic information from the second decoding to be applied as a priori information to the first Max-Log-MAP decoding of the next iteration. The weights are applied to compensate for the systematic error due to the Max-Log approximation made in the last Max-Log-MAP decoding operation.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Apparatus and method for scheduling data in a modem
InactiveUS7873026B2Fast data processingHigh data rateTime-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemModem device
A scheduling method is provided for processing data in a communication system. The method includes performing downlink MAP (DL-MAP) decoding; generating a configuration table through the DL-MAP decoding; and processing data in a predetermined unit according to the generated configuration table.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
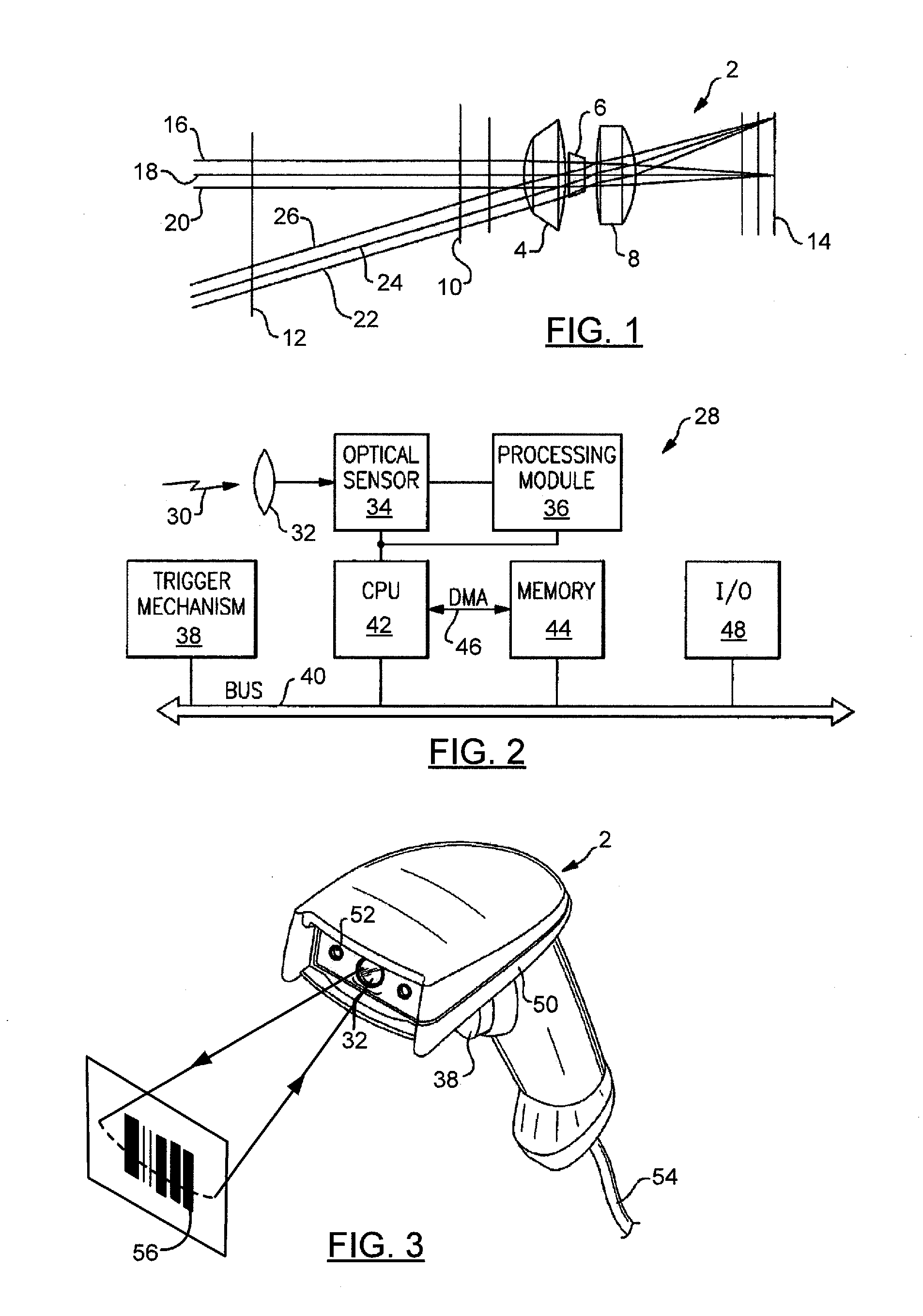
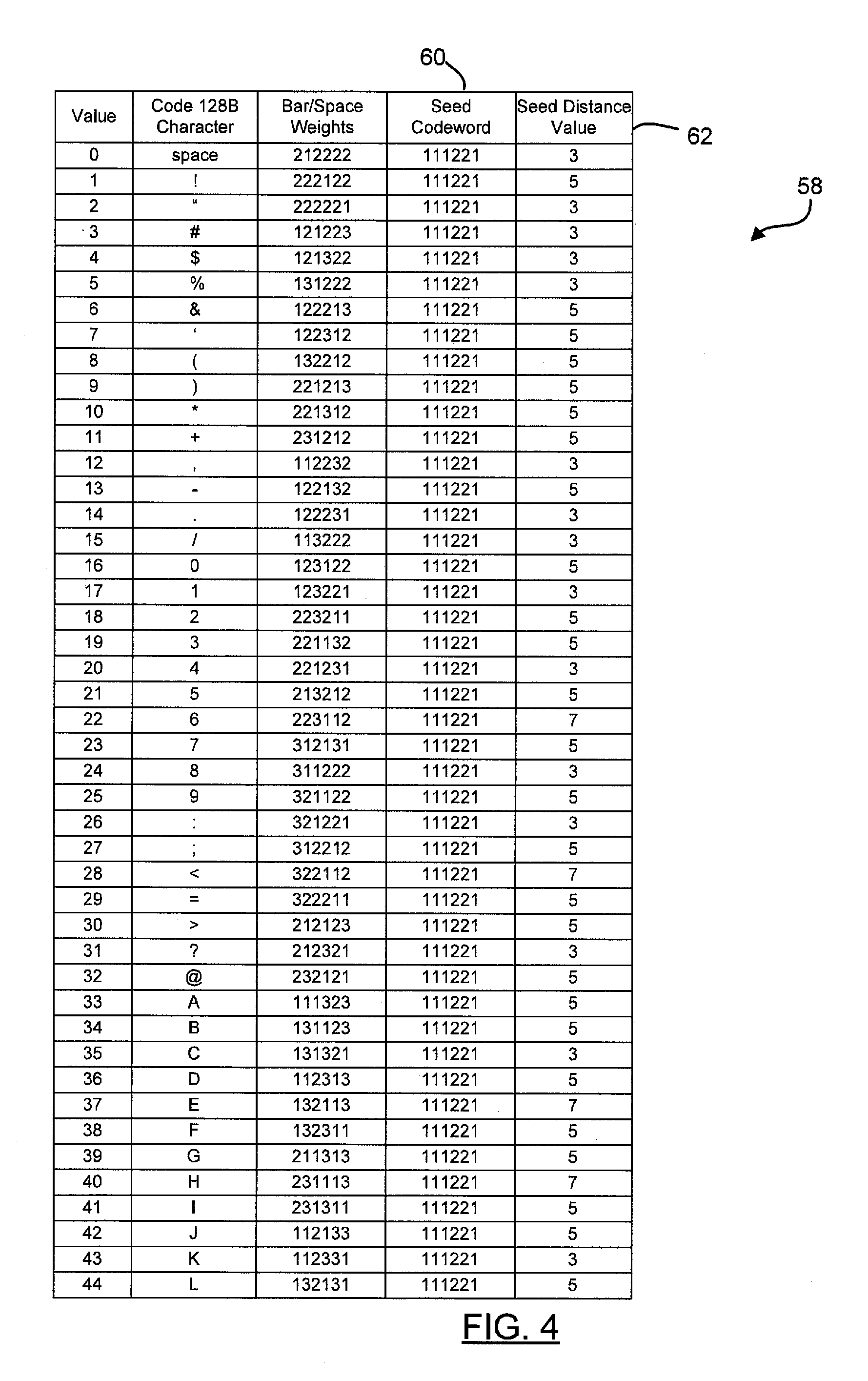
Optical reader using distance map decoding
ActiveUS20120048941A1Special data processing applicationsSensing by electromagnetic radiationSymbolic SystemsAlgorithm
A method for decoding an encoded candidate character of a symbology is provided that includes the steps of providing a plurality of valid barcode characters of a symbology having n elements, generating a seed codeword comprising n elements, computing a seed distance value from the seed codeword to each character in the symbology, generating a distance map comprising each character in the symbology and the associated computed seed distance value, and arranging the plurality of seed distance values into a plurality of bins. Each bin contains a subset of the characters in the symbology. The method includes the steps of selecting a candidate barcode character for decoding, computing a candidate distance value from the candidate barcode character to the seed codeword, identifying the bin containing the candidate distance value, and comparing the candidate barcode character with the valid barcode characters in the bin having the candidate distance value.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
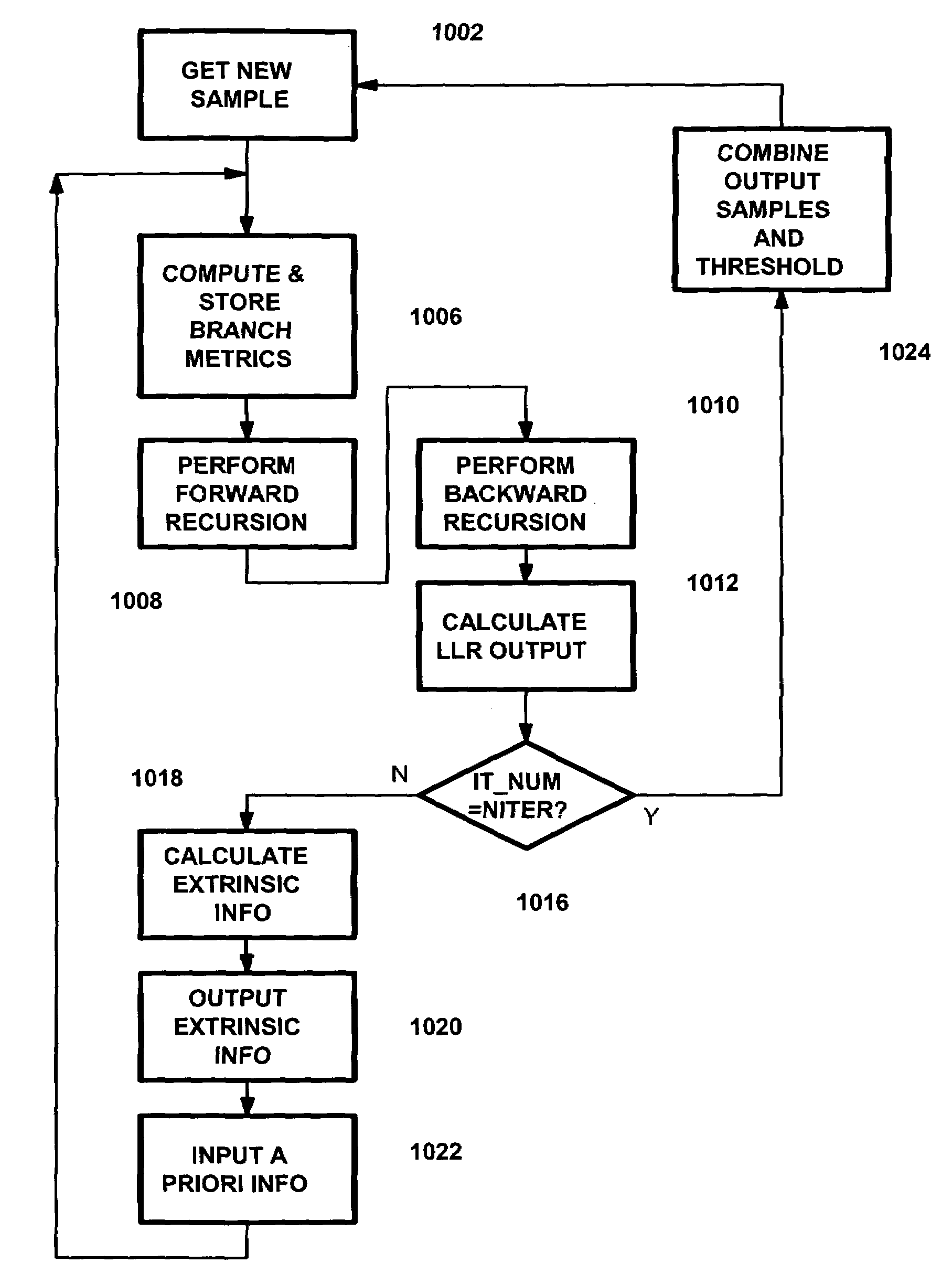
High throughput and low latency map decoder
ActiveUS20090067554A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionComputer hardwareCommunications system
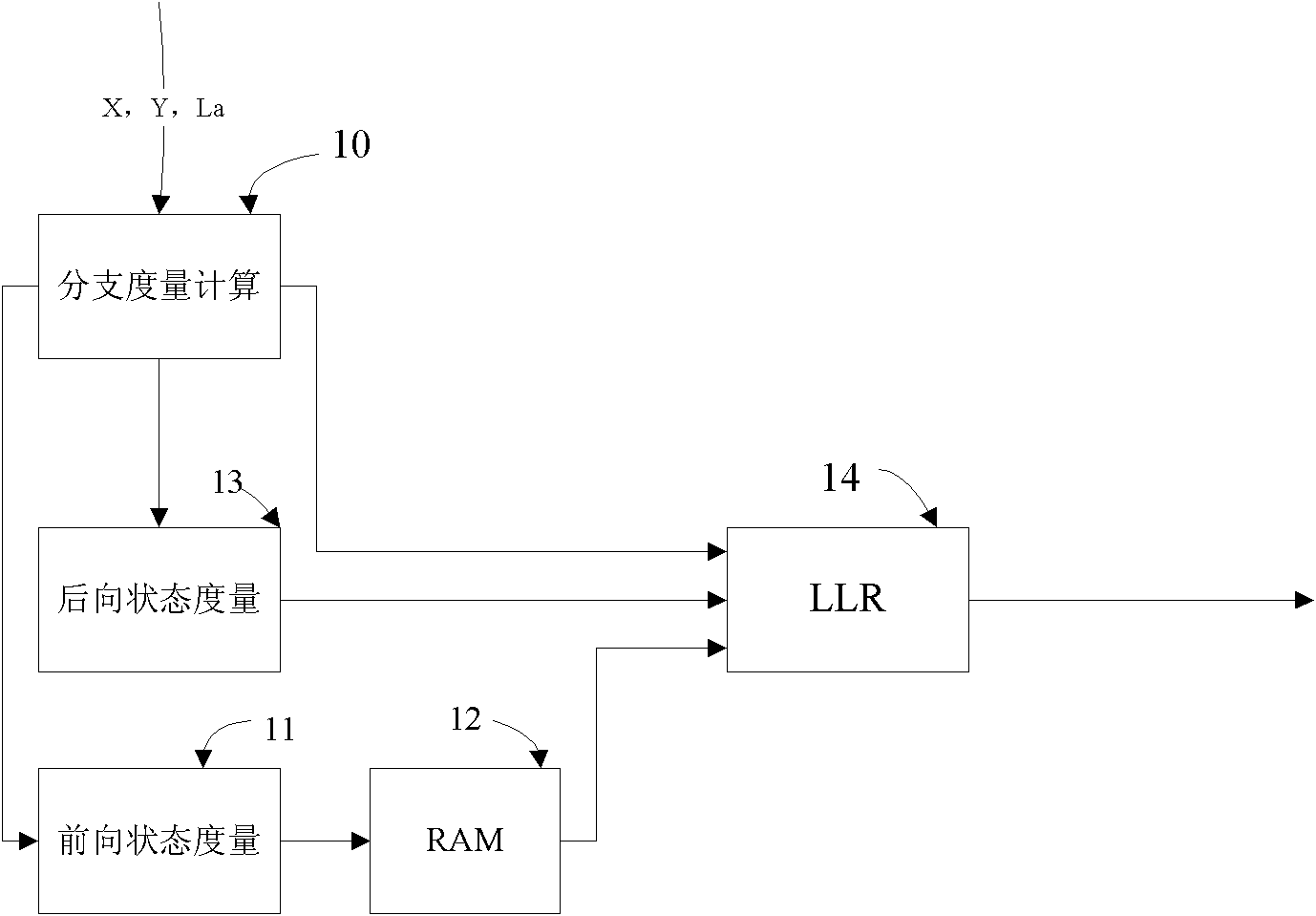
In digital communication systems forward error correction coding techniques are typically used to improve the bit error rate performance. The receiver of the digital communication systems employs a decoding apparatus which may use Maximum A posteriori Probability (MAP) algorithm and its variations such as Logarithmic-MAP (Log-MAP), Maximum-Logarithmic-MAP (Max-Log-MAP). MAP decoding apparatus is commonly used as a key component in of decoder for error correcting codes such as convolutional codes and turbo codes. The MAP decoding apparatus computes likelihood estimates as the output. The present invention performs faster MAP decoding by computing likelihood estimates in parallel.
Owner:MBIT WIRELESS
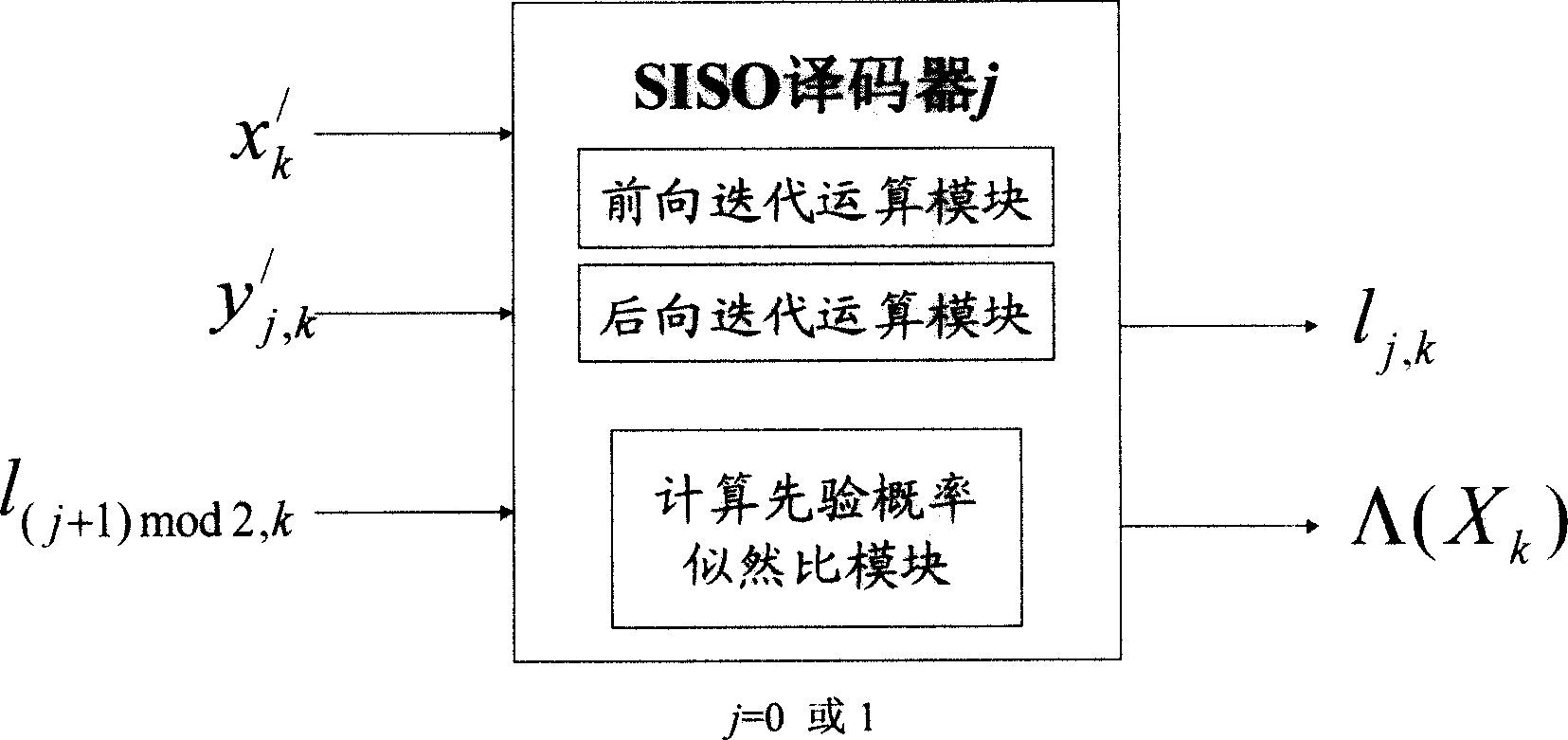
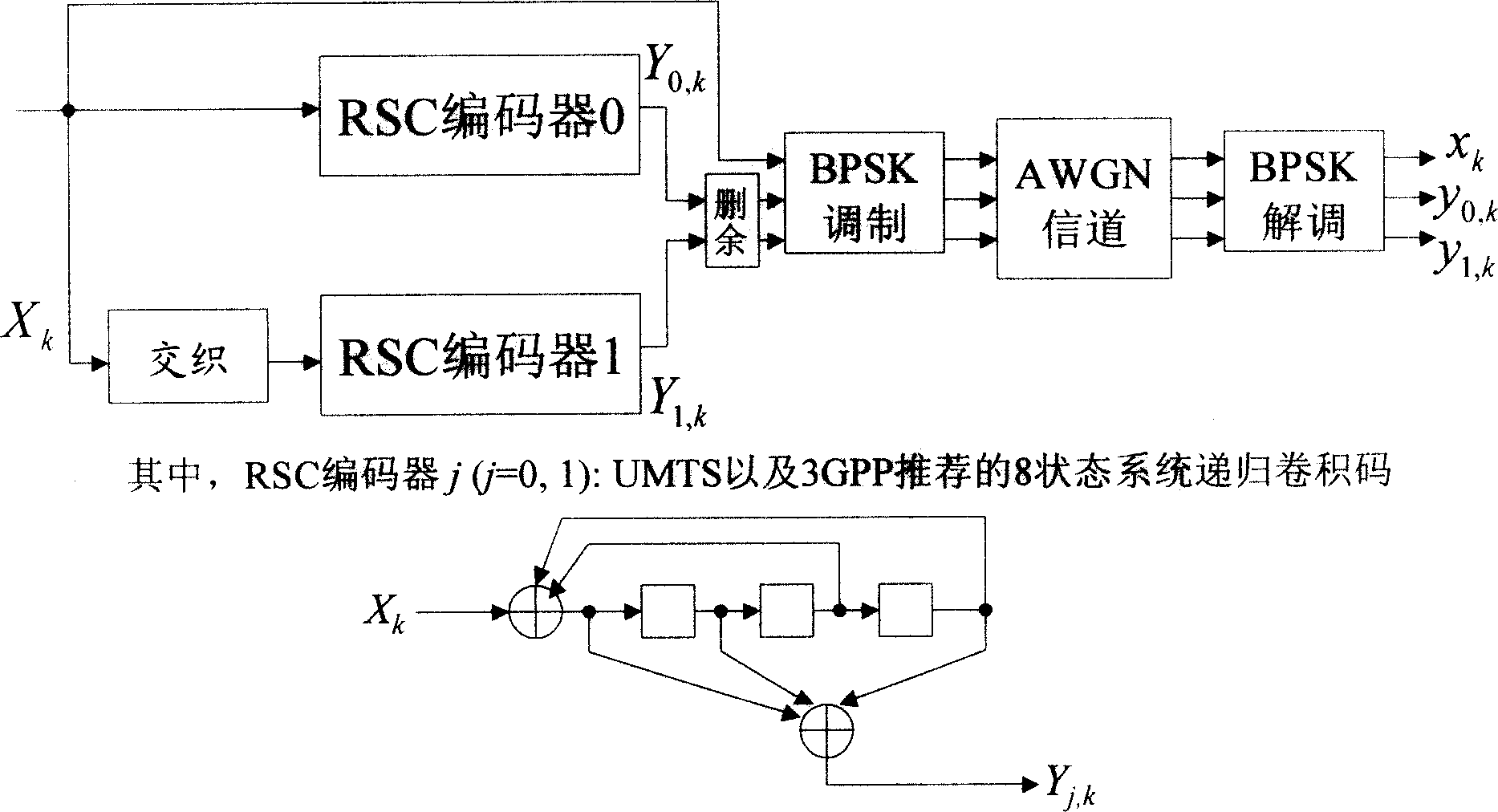
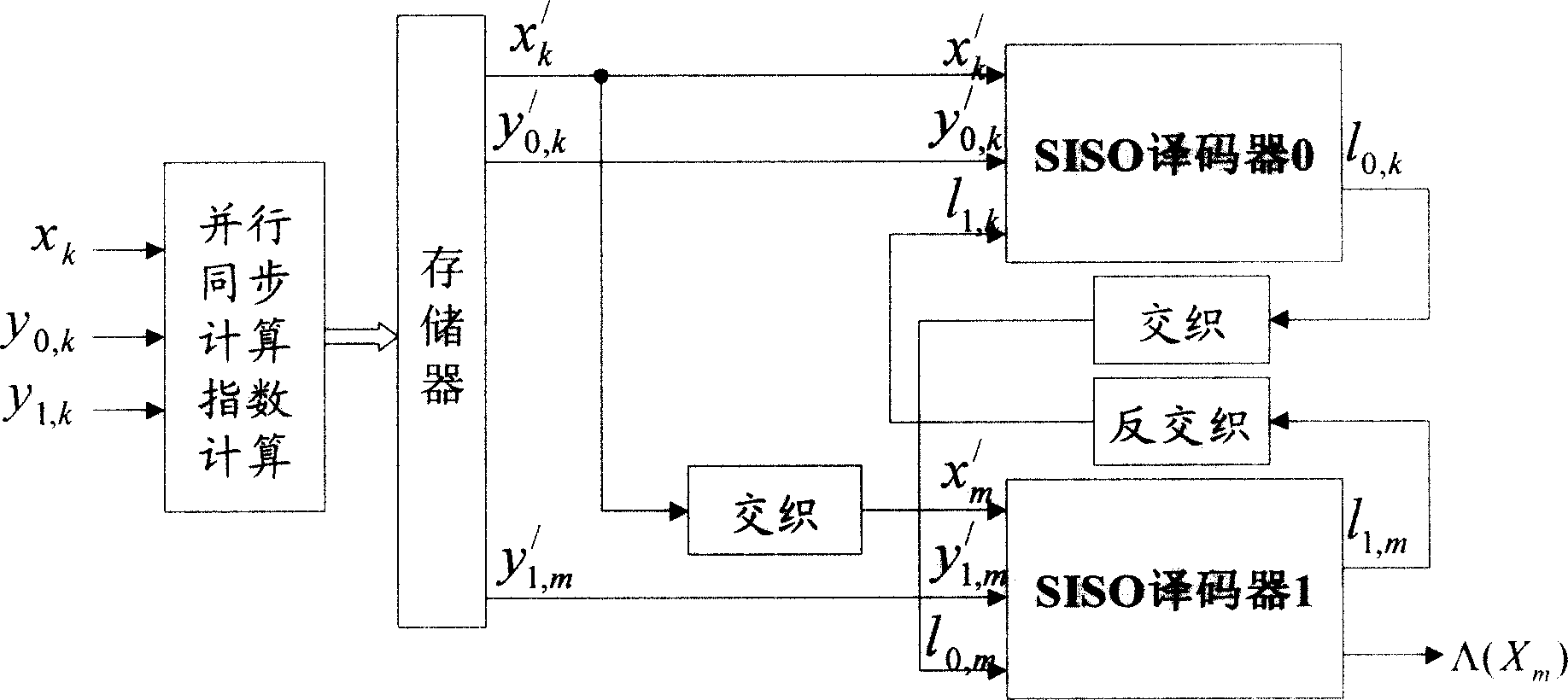
Non-logarithm-domain high-speed maximum posteroir probability Turbo decoding method
InactiveCN1710815AImprove computing efficiencyReduce decoding delayError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresDecoding methodsStandard map
Unipolar binary signal (0,1) instead of traditional bipolar binary signal (+1, -1) is adopted in the disclosed decoding method to realize calculation of probability measure of state transition so as to obtain high speed decoding algorithm of iteration in software in and software out (SISO) in non-logarithm field. The SISO decoding algorithm of iteration eliminates a great lot exponential operation and logarithm operation, which is must be carried out in standard MAP decoding procedure of iteration. Comparing with standard MAP decoding method, the invention possesses same performance of optimal error correction. Comparing with LOG-MAP decoding method based on logarithm field, the invention possesses quicker decoding speed. Decoding delay of the invention is very close to approximate method MAX - LOG - MAP of LOG - MAP logarithm.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Iteration de-mapping decoding device
ActiveCN104333435AReduce overheadEasy to implementError correction/detection using LDPC codesCode conversionProcessor registerLow density
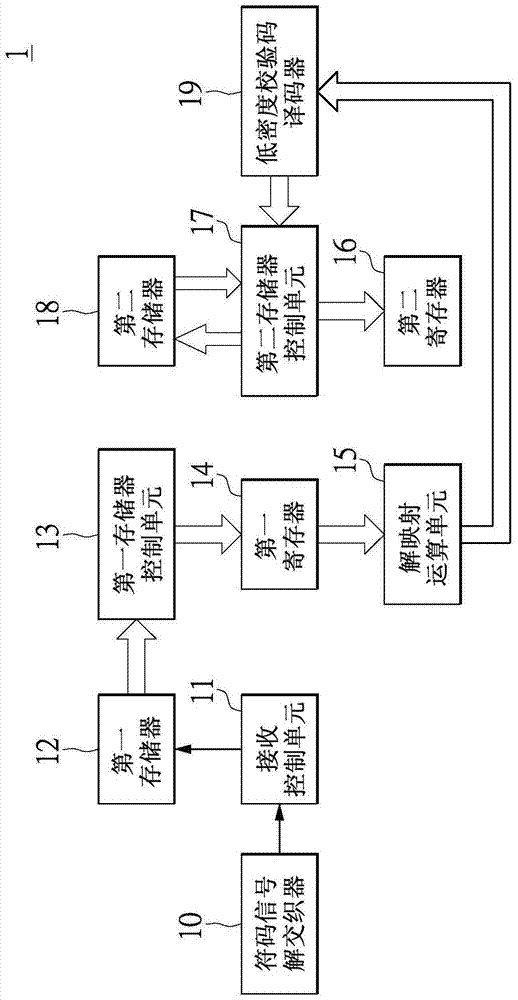
Provided is an iteration de-mapping decoding device. A storage device control unit is applied to store M first feedback logarithmic likelihood ratio generated by a low-density check code decoder each time to a storage device in a parallel way, and the M*(N-1) first feedback logarithmic likelihood ratio stored in the storage device is extracted from the storage device to be temporarily stored to a register. A de-mapping operation unit is used for extracting the temporarily stored M*(N-1) first feedback logarithmic likelihood ratio from the register, and calculating M specific bits of each logarithmic likelihood ratio according to the extracted M*(N-1) first feedback logarithmic likelihood ratio.
Owner:ALICORP
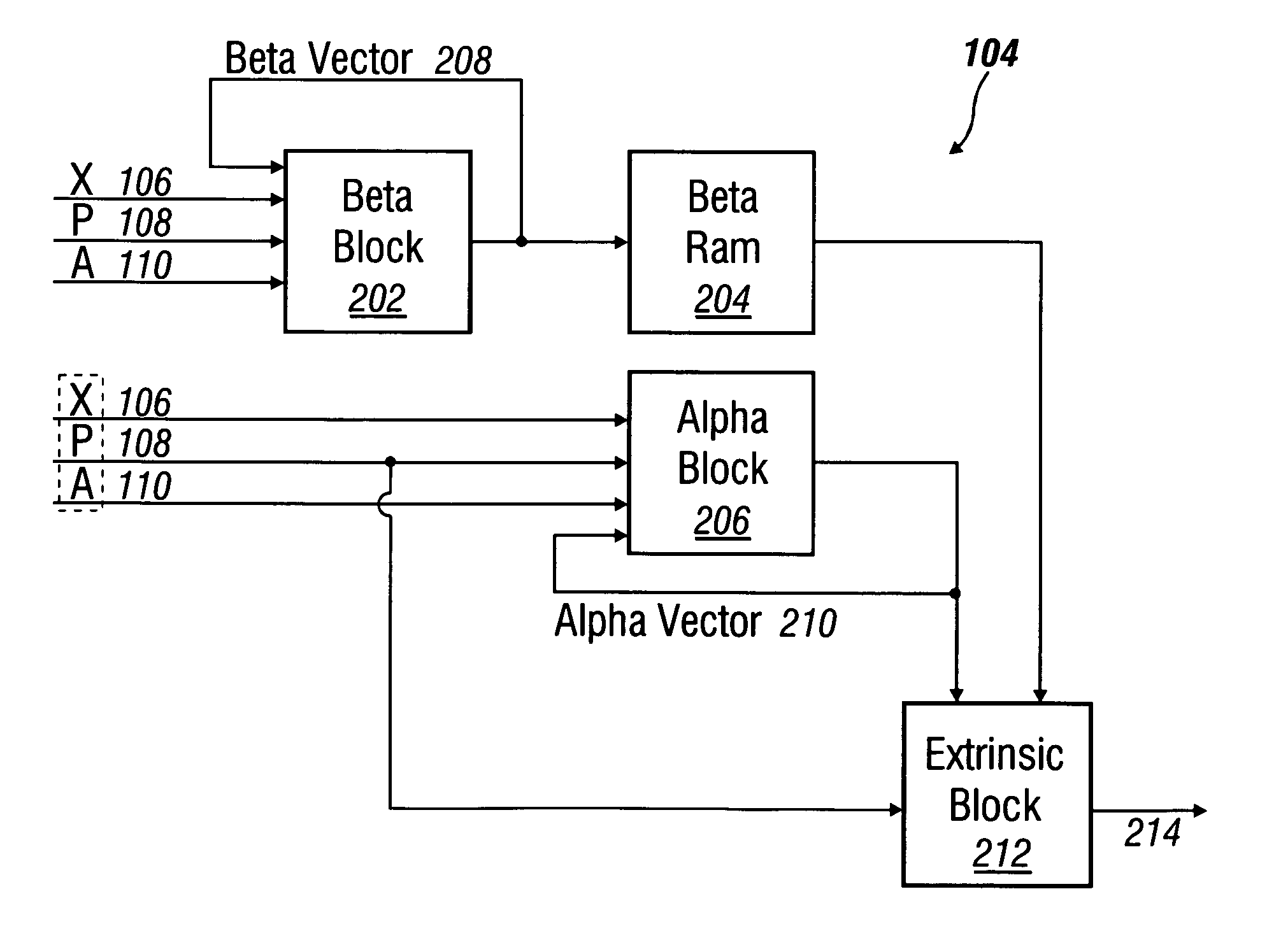
Log-MAP based decoding method and decoding device thereof in turbo decoding
InactiveCN101964665AImprove decoding performanceReduce complexityError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresDecoding methodsComputer science
The invention relates to a method and a device thereof in the technical field of mobile communication technologies, in particular to a Log-MAP based decoding method and a decoding device thereof in turbo decoding. In the invention, in a Log-MAP decoding structure, the realizations of a forward state measurement and recursion structure and a backward state measurement and recursion structure are separated from the realization of an LLR computation structure; in LLR computation, an eight-input Logsum structure is not realized by adopting a two-input Logsum structure any more; the recursion of forward state measurement and the backward state measurement is realized by adopting a Max-Log-Map structure, so that the two-input Logsum structure still maintains a lowest realization complexity, meanwhile, the realization complexity of the eight-input Logsum structure is also reduced; and most importantly, the decoding properties and good properties close to an optimal Log-Map method are also maintained. The invention obtains good balance between the realization complexity and the properties of a decoder.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
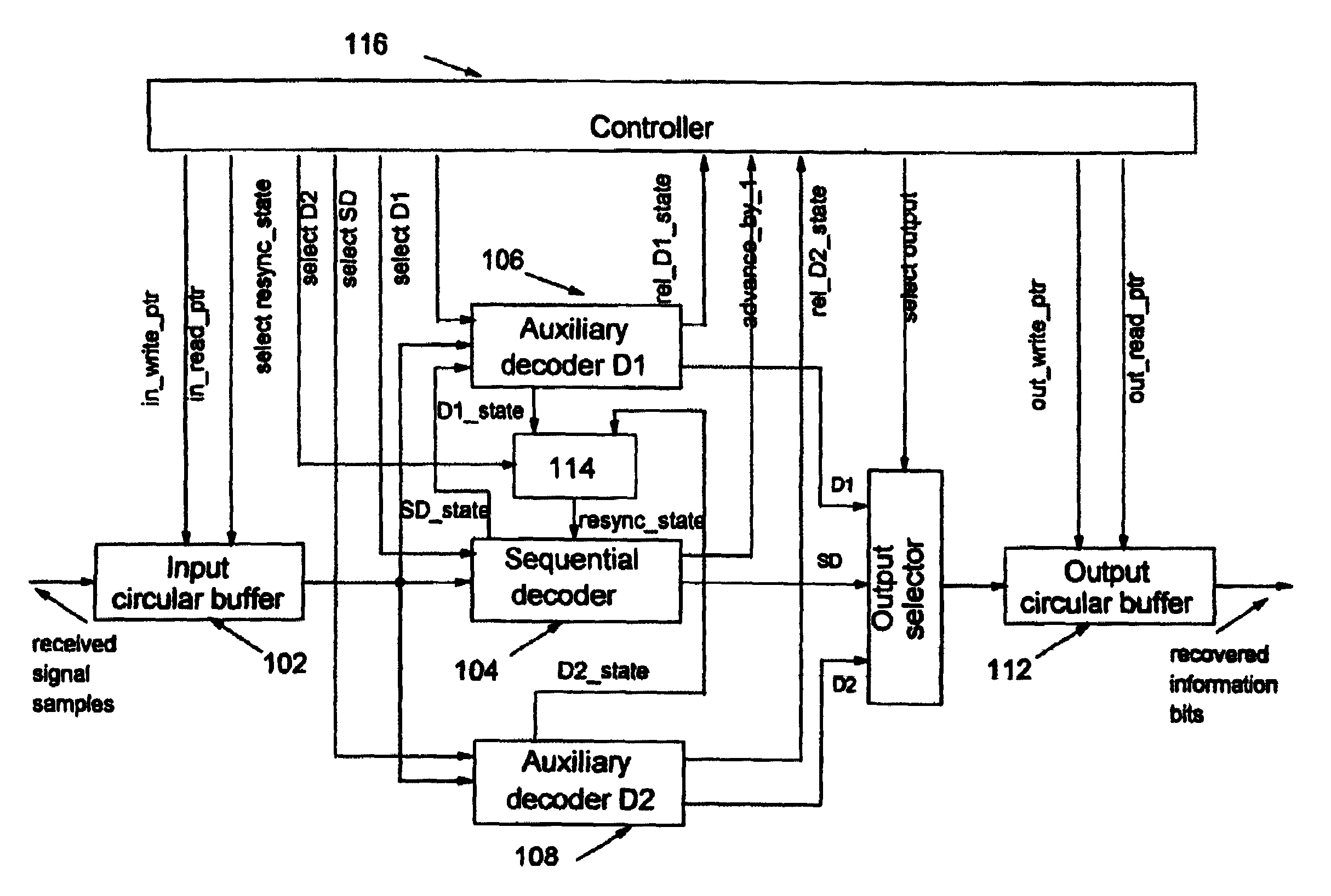
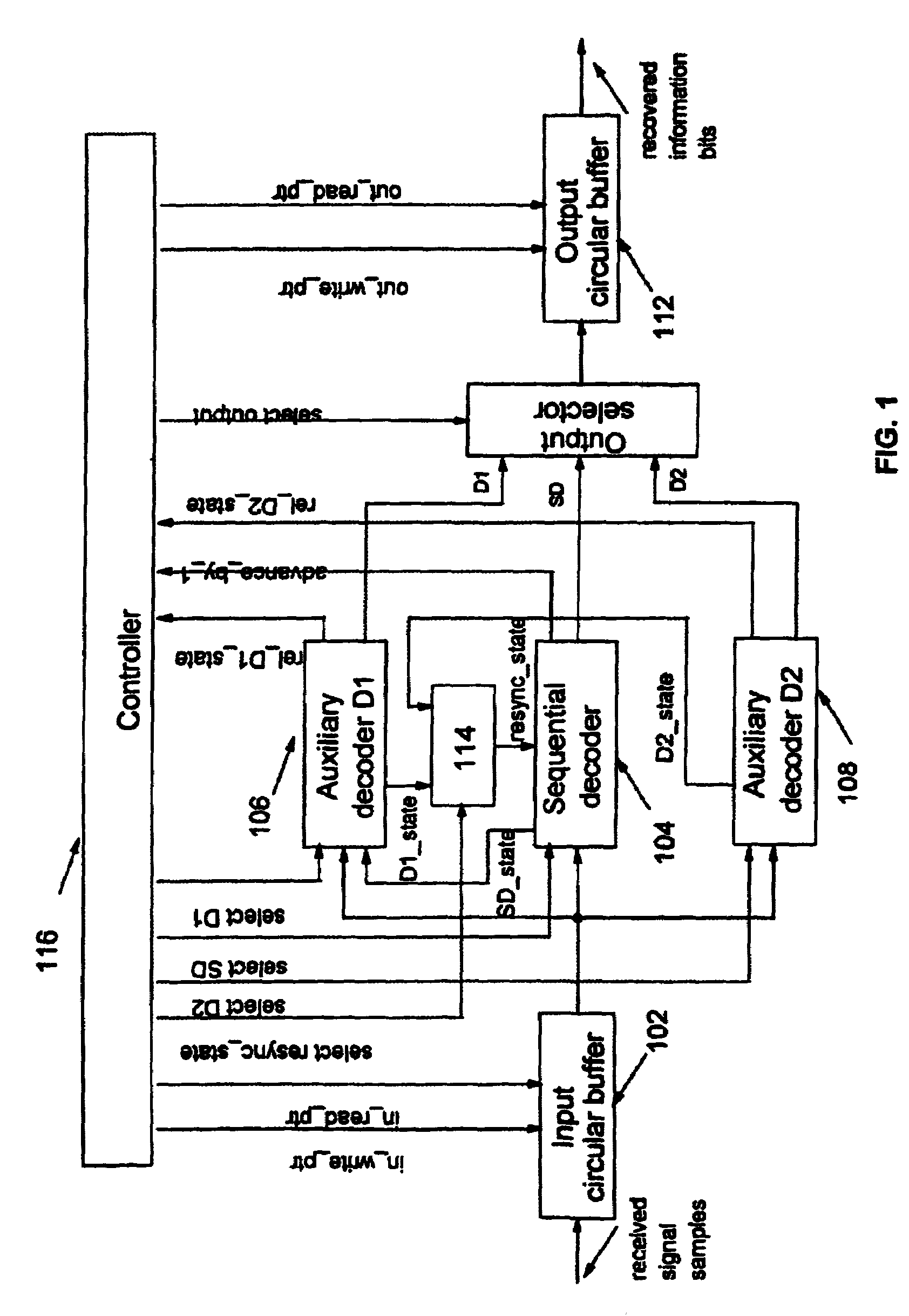
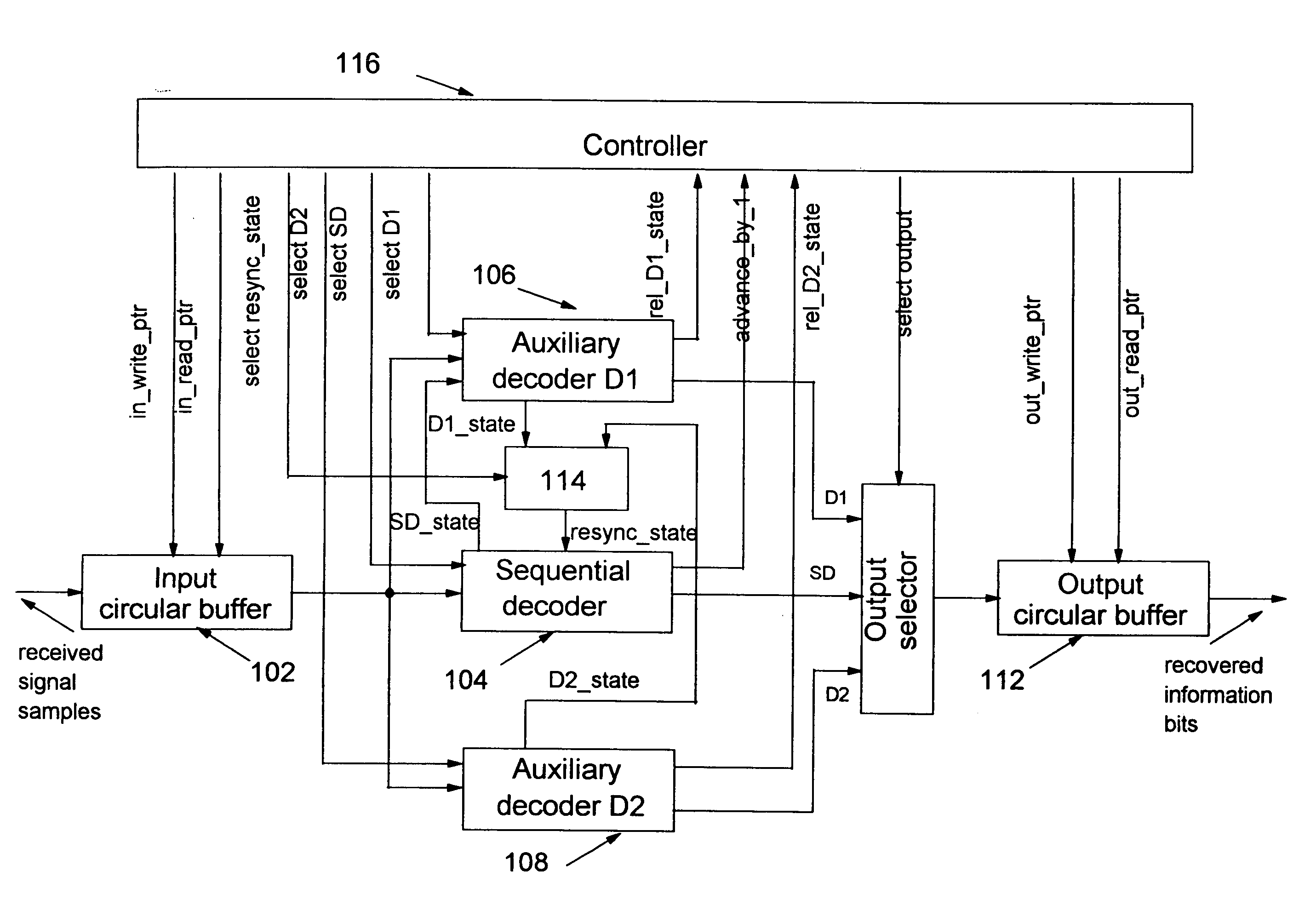
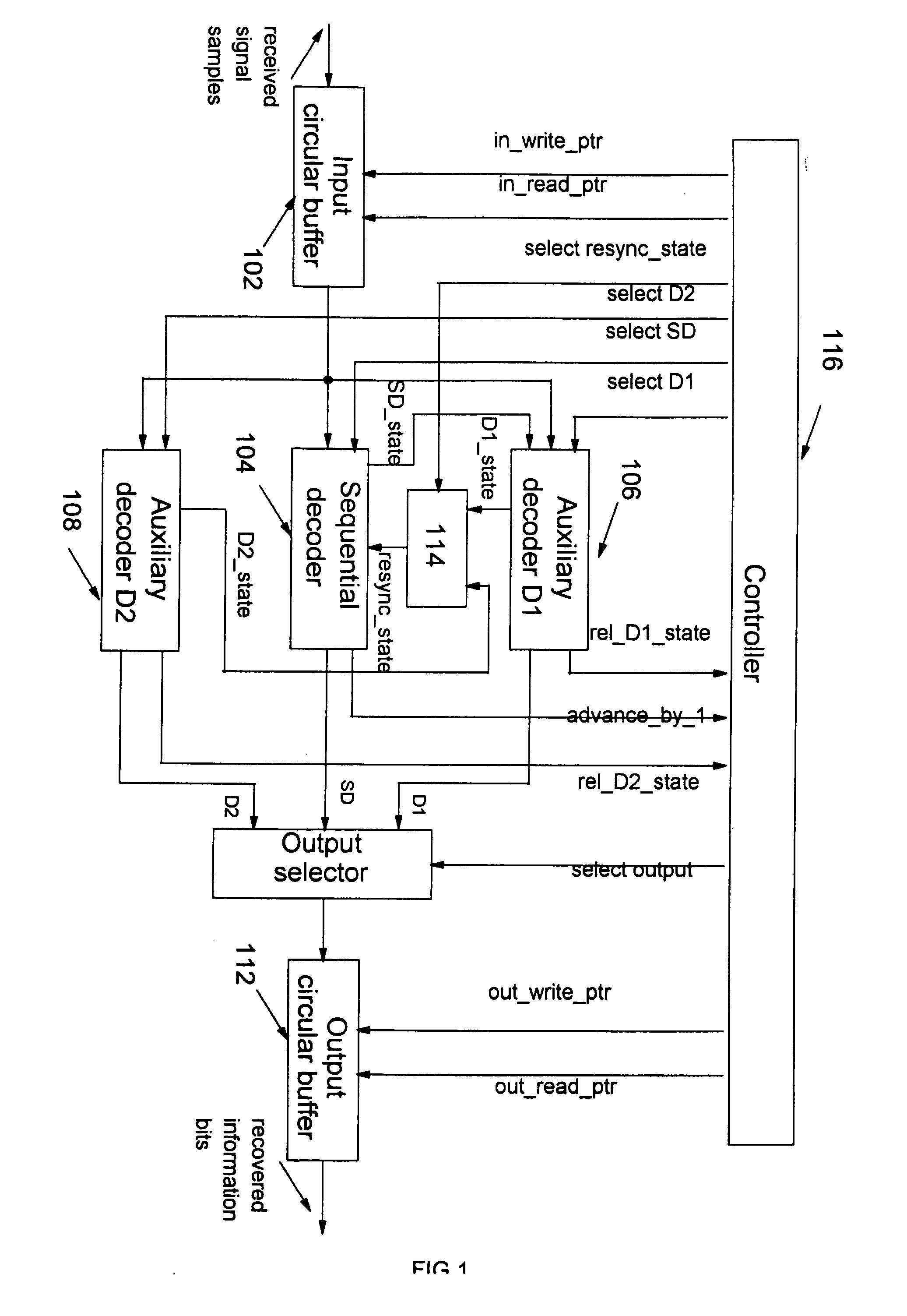
Method and apparatus for reliable resynchronization of sequential decoders
InactiveUS7096411B2Reduce complexityReliable estimateData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer hardwareWrite pointer
A system and method for the resynchronization of a sequential decoder that decodes received signal samples stored within an input buffer is disclosed. The system comprises two auxiliary decoders coupled to the sequential decoder for running a simplified MAP decoding process when the input buffer reaches a threshold saturation level. Control of the respective increments of a read pointer and a write pointer allows one to detect the saturation of the input buffer and to derive a sequence of signal samples to the appropriate auxiliary decoder. The selected auxiliary decoder estimates a resynchronization state for the sequential decoder based on the sequence of signal samples. According to the read and the write pointers value, normal sequential decoding is resumed, otherwise, the second auxiliary decoder is selected. The selected auxiliary decoder estimates a resynchronization state for the sequential decoder based on a new sequence of signal samples.
Owner:IBM CORP
Decoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS7391826B2Reduce complexityImprove performanceData representation error detection/correctionError preventionDecoding methodsSystematic error
A method of decoding is provided comprising processing iterations. In each processing iteration, there is a first Max-Log-MAP decoding operation giving rise to a systematic error due to the Max-Log approximation, and a first weighting operation to weight extrinsic information from the first decoding operation to be applied as a priori information to the second Max-Log-MAP decoding operation. This is followed by a second Max-Log-MAP decoding operation, also giving rise to a systematic error due to the Max-Log approximation, and a second weighting operation to weight extrinsic information from the second decoding to be applied as a priori information to the first Max-Log-MAP decoding of the next iteration. The weights are applied to compensate for the systematic error due to the Max-Log approximation made in the last Max-Log-MAP decoding operation.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method for duobinary Turbo code to stop iterative decoding
InactiveCN101257315AError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresLimited resourcesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to a stopping method of iterative decoding based on dual-binary turbo code of symbol in communication, which makes use of max-log-map decoding algorithm based on symbolic information of dual-binary turbo code, considers the information exclusive the symbol transferred between component decoder as the conditional judge values to step the iterative decoding method, and compares the values with a threshold value. If at least one absolute value of the information exclusive the symbol is larger than the threshold value, iterative decoding is stopped, on the contrary, the next iterative decoding is performed. The invention combines the symbol decoding algorithm with the symbol stop method, gives attention to the three indexes of decoding performance, decoding complexity and resource occupation, improves the signal-noise ratio of the algorithm under the condition of low complexity, limited resource occupation and ideal decoding complexity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Log-MAP decoding method and decoder
InactiveCN103532571AReduce operational complexityImprove decoding performanceOther decoding techniquesError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresRound complexityCorrelation function
The invention relates to a Log-MAP decoding method and decoder. According to the Log-MAP decoding method and decoder, a simplified Log-MAP algorithm is used so that under a condition that an algorithm complexity is reduced, decoding performance close to the Log-MAP algorithm is still maintained. In the Log-MAP decoding method, max*() is used to calculate a forward metric, a backward metric and a log-likelihood ratio, wherein with respect to an operation expression: Max * (x, y) = ln (e<x>+e<y>) = max (x, y) +ln (1+e<-|x-y|>), a piecewise-approximation fitting function is used to approximately substitute a correlation function ln (1+e<-|x-y|>).
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
Method and apparatus for reliable resynchronization of sequential decoders
InactiveUS20060026493A1Reduce complexityAvoid erasureData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer scienceWrite pointer
A system and method for the resynchronization of a sequential decoder that decodes received signal samples stored within an input buffer is disclosed. The system comprises two auxiliary decoders coupled to the sequential decoder for running a simplified MAP decoding process when the input buffer reaches a threshold saturation level. Control of the respective increments of a read pointer and a write pointer allows one to detect the saturation of the input buffer and to derive a sequence of signal samples to the appropriate auxiliary decoder. The selected auxiliary decoder estimates a resynchronization state for the sequential decoder based on the sequence of signal samples. According to the read and the write pointers value, normal sequential decoding is resumed, otherwise, the second auxiliary decoder is selected. The selected auxiliary decoder estimates a resynchronization state for the sequential decoder based on a new sequence of signal samples.
Owner:IBM CORP
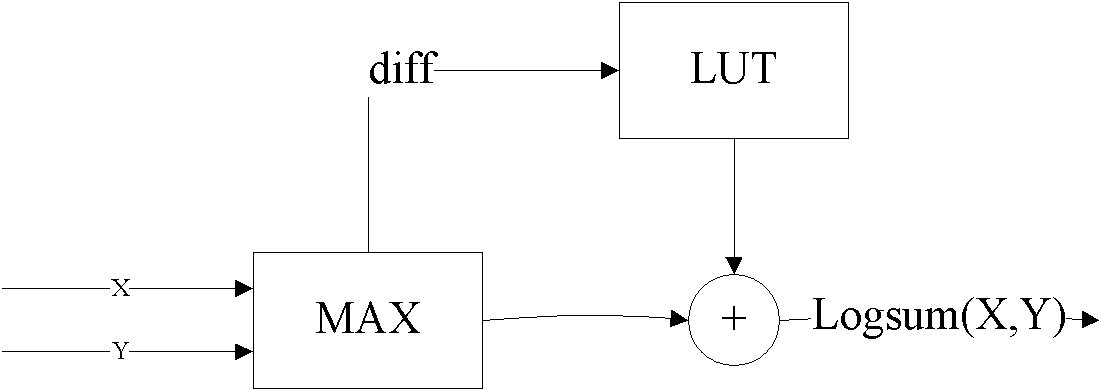
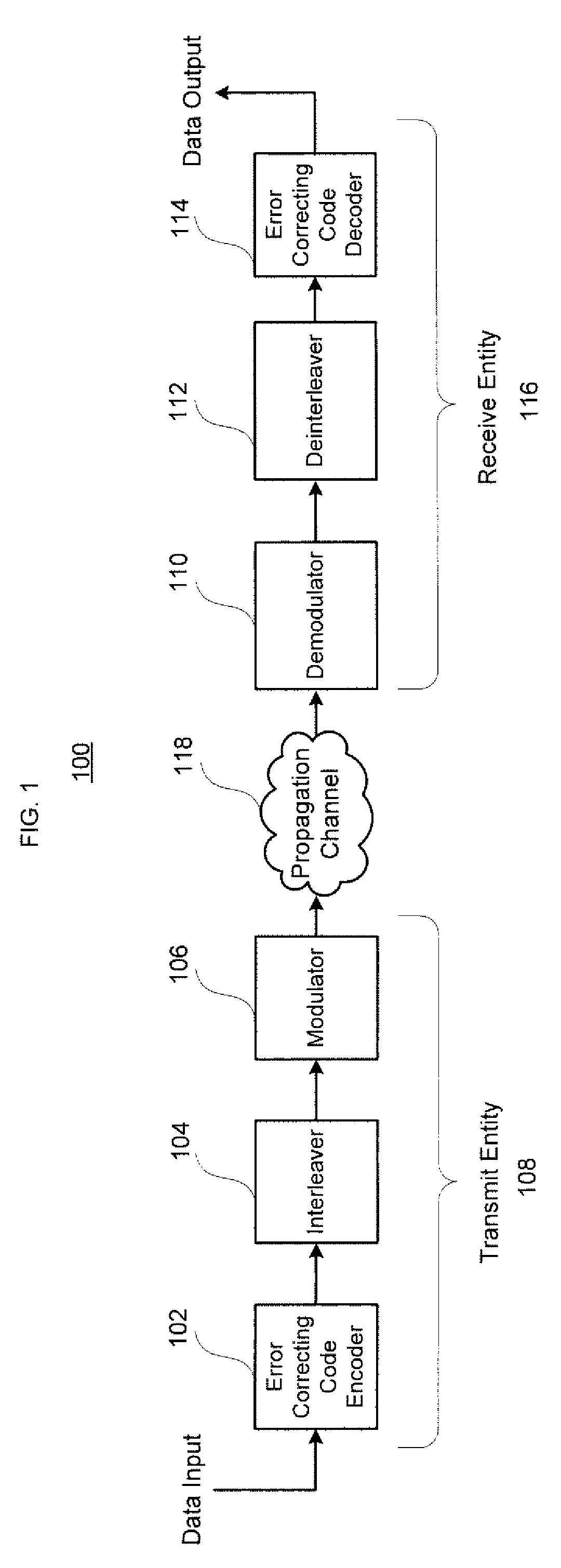
Map decoding
InactiveUS7594161B2Improve accuracyEasy to operateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingData representation error detection/correctionComputer scienceMap decoding
A method of approximating the generation of a logarithm of a sum of exponents, for use in a log-MAP decoding operation, by performing a first operation on the data, calculating a correction term in a second operation, and adding the correction term to the results of the first operation, in which the second operation comprises calculating an approximate correction term by an operation including at least one division stage in which a first result obtained based on said data and at least a first coefficient is divided by a second result obtained based on said data and at least a second coefficient.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High throughput and low latency map decoder
ActiveUS8358713B2Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionConcurrent computationConvolutional code
In digital communication systems forward error correction coding techniques are typically used to improve the bit error rate performance. The receiver of the digital communication systems employs a decoding apparatus which may use Maximum A posteriori Probability (MAP) algorithm and its variations such as Logarithmic-MAP (Log-MAP), Maximum-Logarithmic-MAP (Max-Log-MAP). MAP decoding apparatus is commonly used as a key component in of decoder for error correcting codes such as convolutional codes and turbo codes. The MAP decoding apparatus computes likelihood estimates as the output. The present invention performs faster MAP decoding by computing likelihood estimates in parallel.
Owner:MBIT WIRELESS
MAP decoding method and device
InactiveCN1841941ASave storage spaceConducive to high speedCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresDecoding methodsMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses a mix posterior probability decoding method and device. It chooses the current time betasubmaxima value and mix value and stores the rate and the corresponding two conditions during the back course, except for the plurality of code bits. It stores the difference value of the betasubmaxima value and mix value. It chooses the corresponding front time alpha and gamma by the stored betavalue and the corresponding two conditions during the course of computing and outputting the likelihood ratio, except for the plurality of code bits.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
A Control Method of State Metric Overflow in Turbo Code Decoder
InactiveCN102270994AReduce computationFast operationError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresTurbo codedDecoding throughput
The invention relates to an overflow control method for a state metric of a Turbo code decoder. A correction value delta of a branch metric of a current beat is determined according to logarithm metric sizes of all states before n times that are obtained by recursions from a current time k; a branch metric of the current time k is calculated and is corrected; and finally, a state metric of the current time k is calculated according to the corrected branch metric and amplitude limiting is carried out; when the calculated result is larger than a maximum max, the value of the state metric is max; when the calculated result is less than a minimum min, the value of the state metric is min; and the state metric that has been processed by the amplitude limiting is used for a next recursion. According to the invention, it can be ensured that state metrics of forward and backward recursions during a MAP decoding algorithm process of a Turbo code will not overflow; determination operations can be completed in advance; it is allowed to realize anti-overflow control by a pipelining method. Therefore, an influence of an anti-overflow operation on a recursion speed of a state metric can be reduced, so that a recursion speed during hardware realization can be improved and a decoding throughput capacity can be enhanced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com