Patents
Literature
994 results about "Time codes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
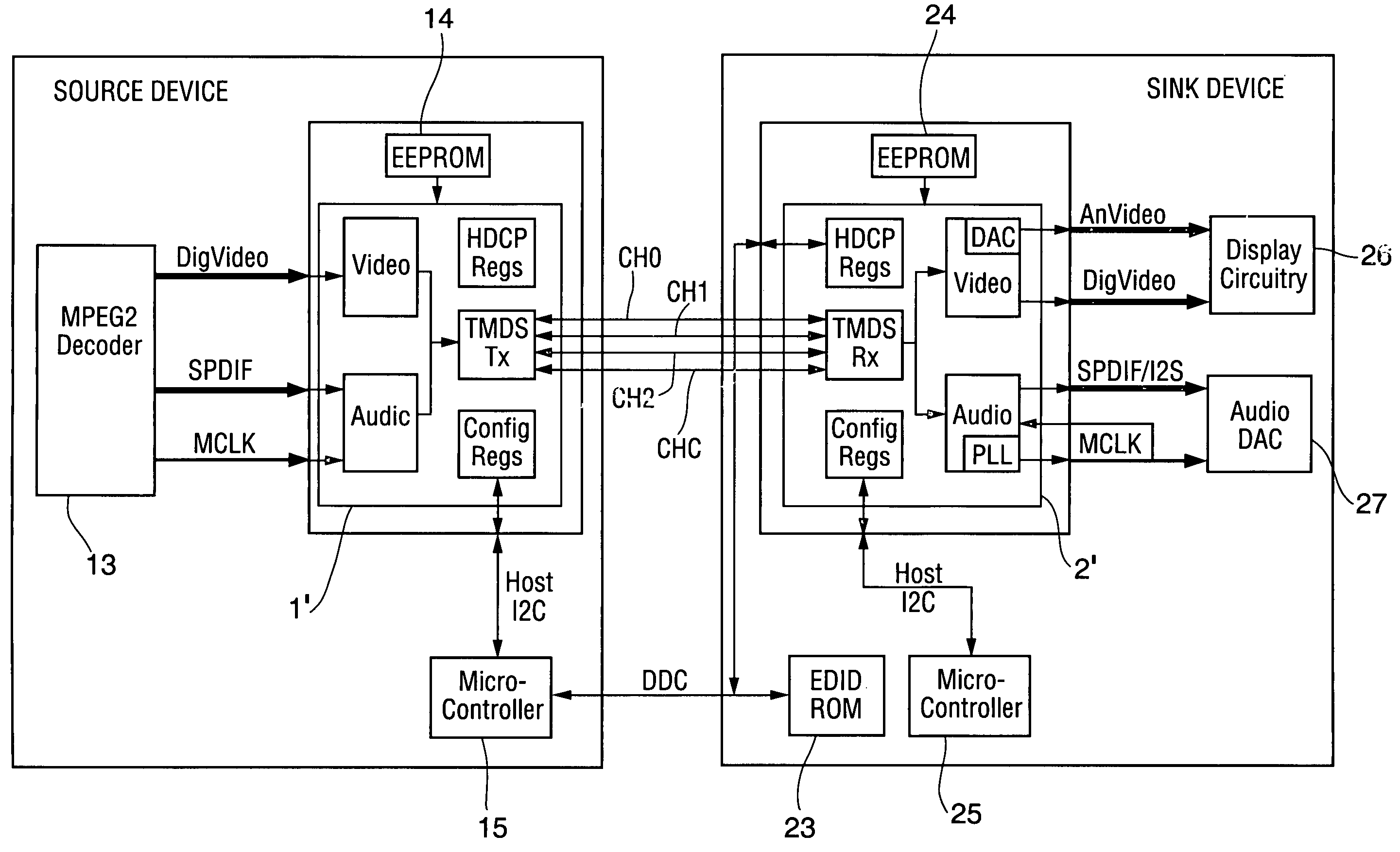
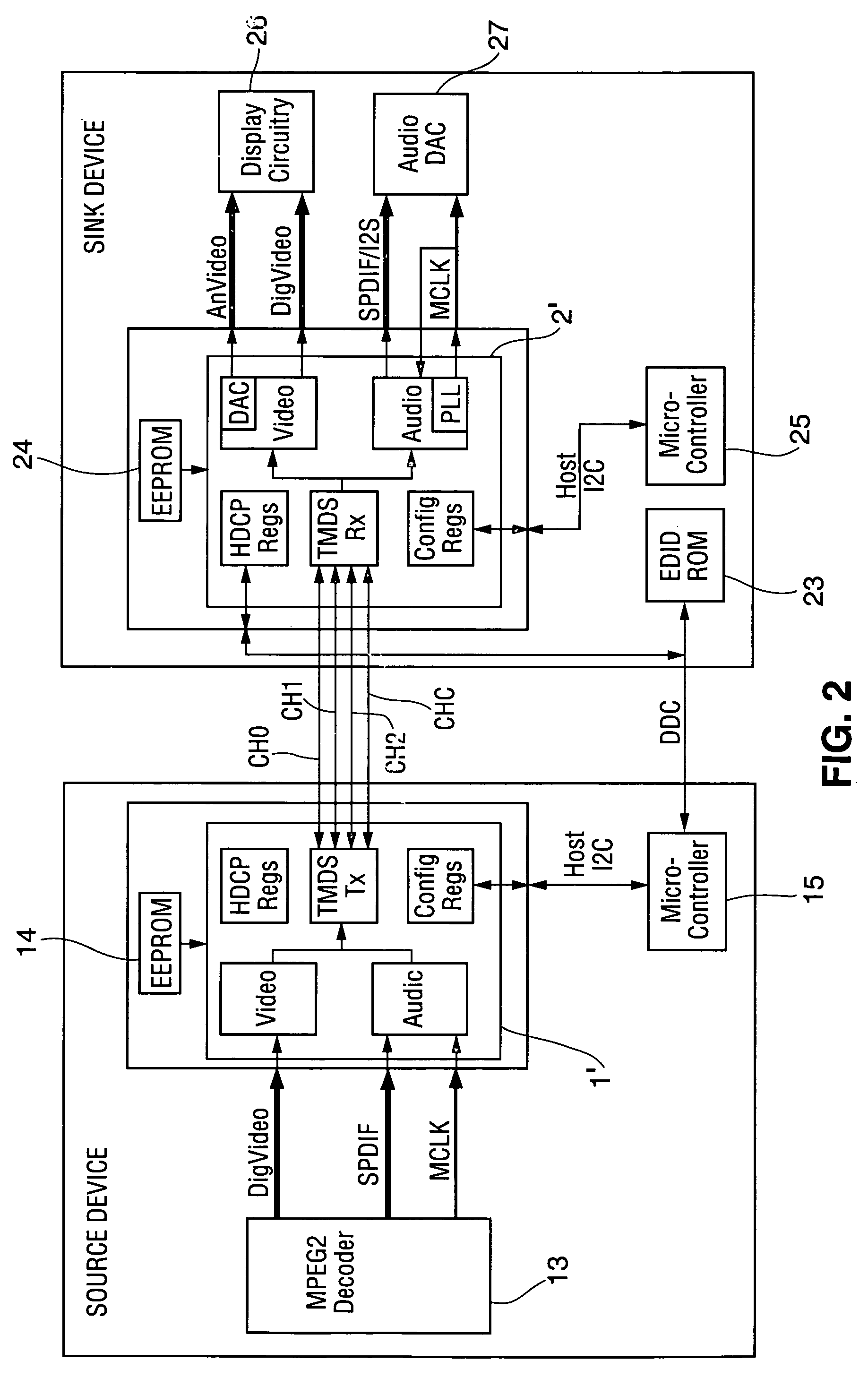
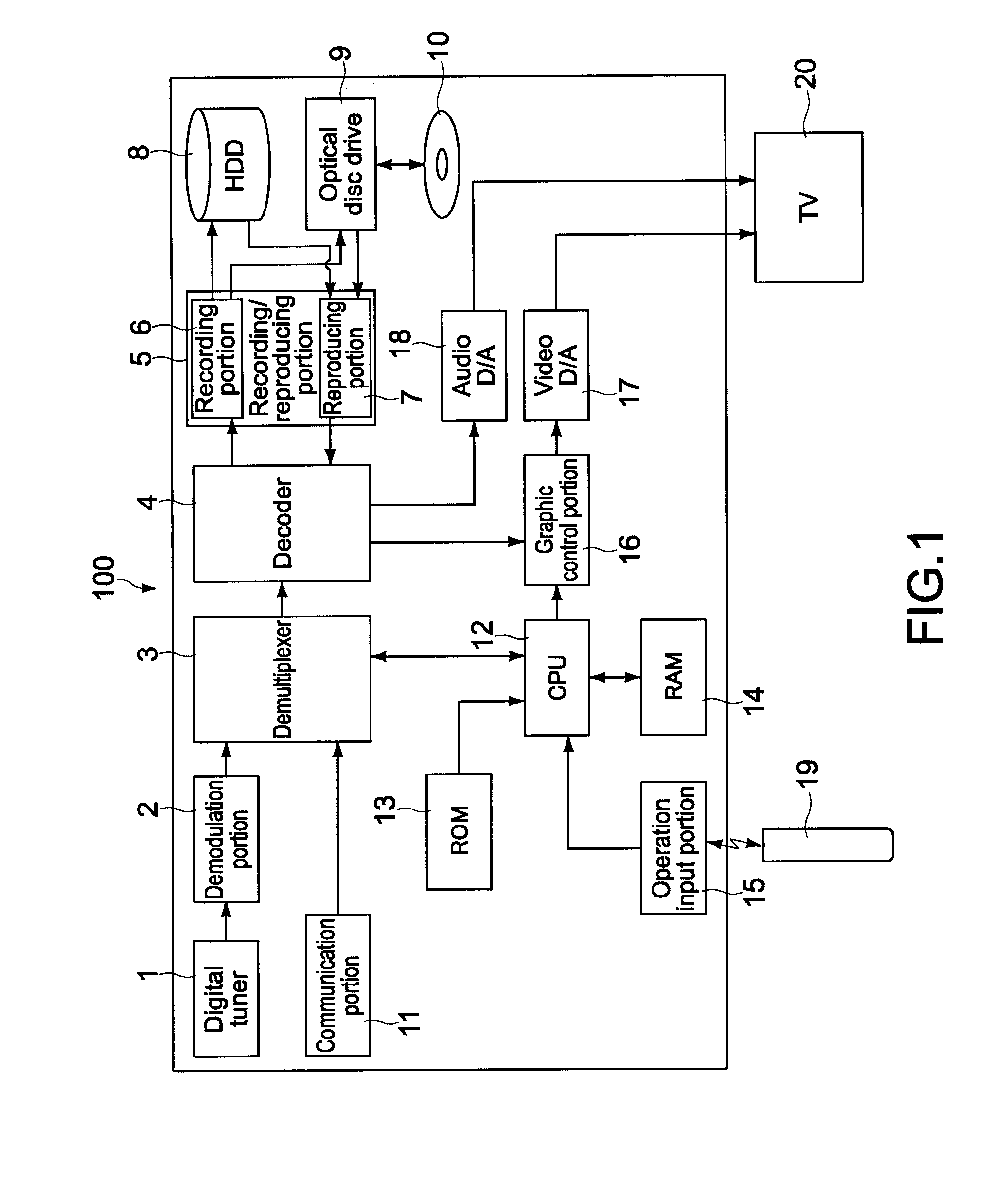
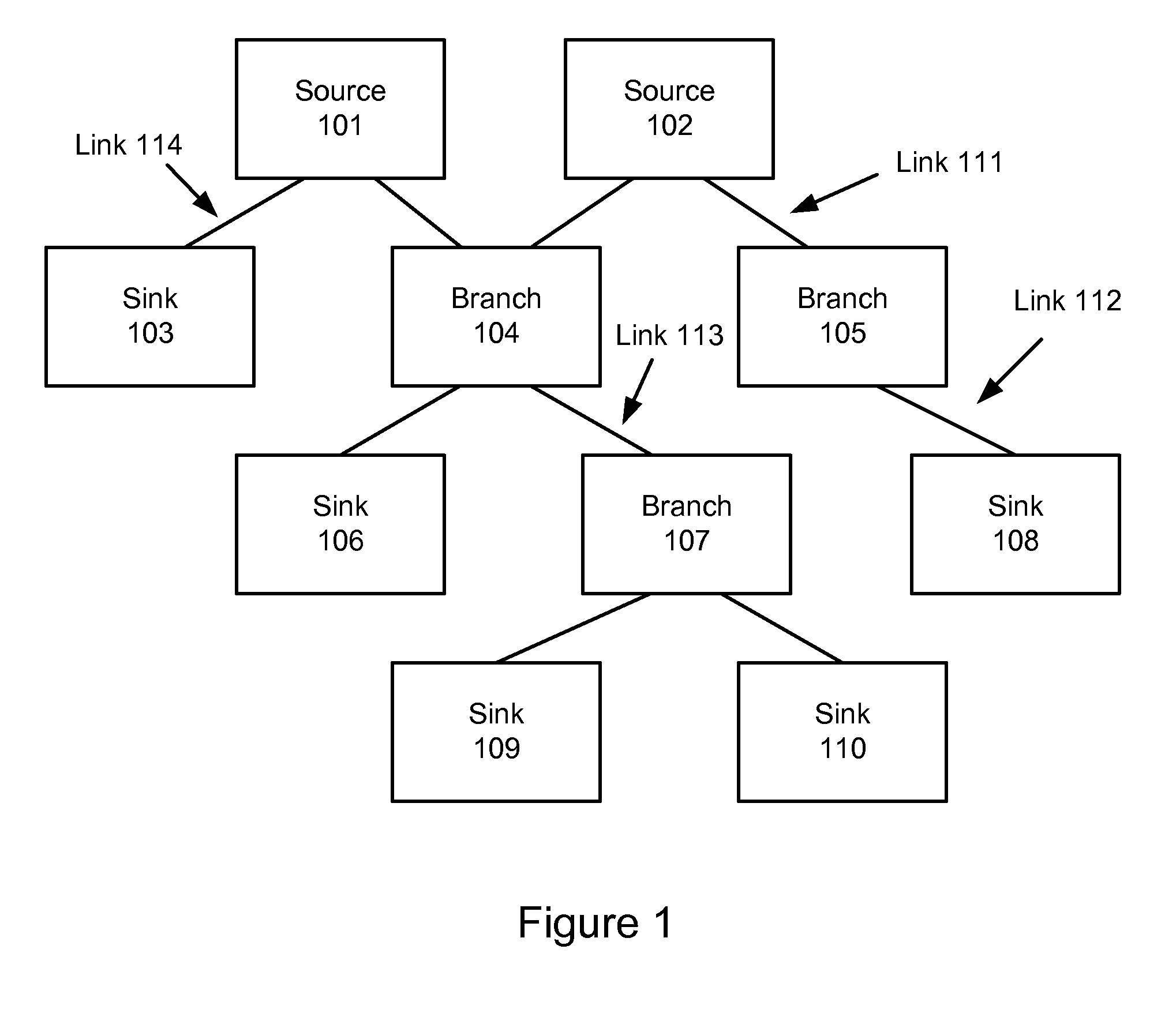
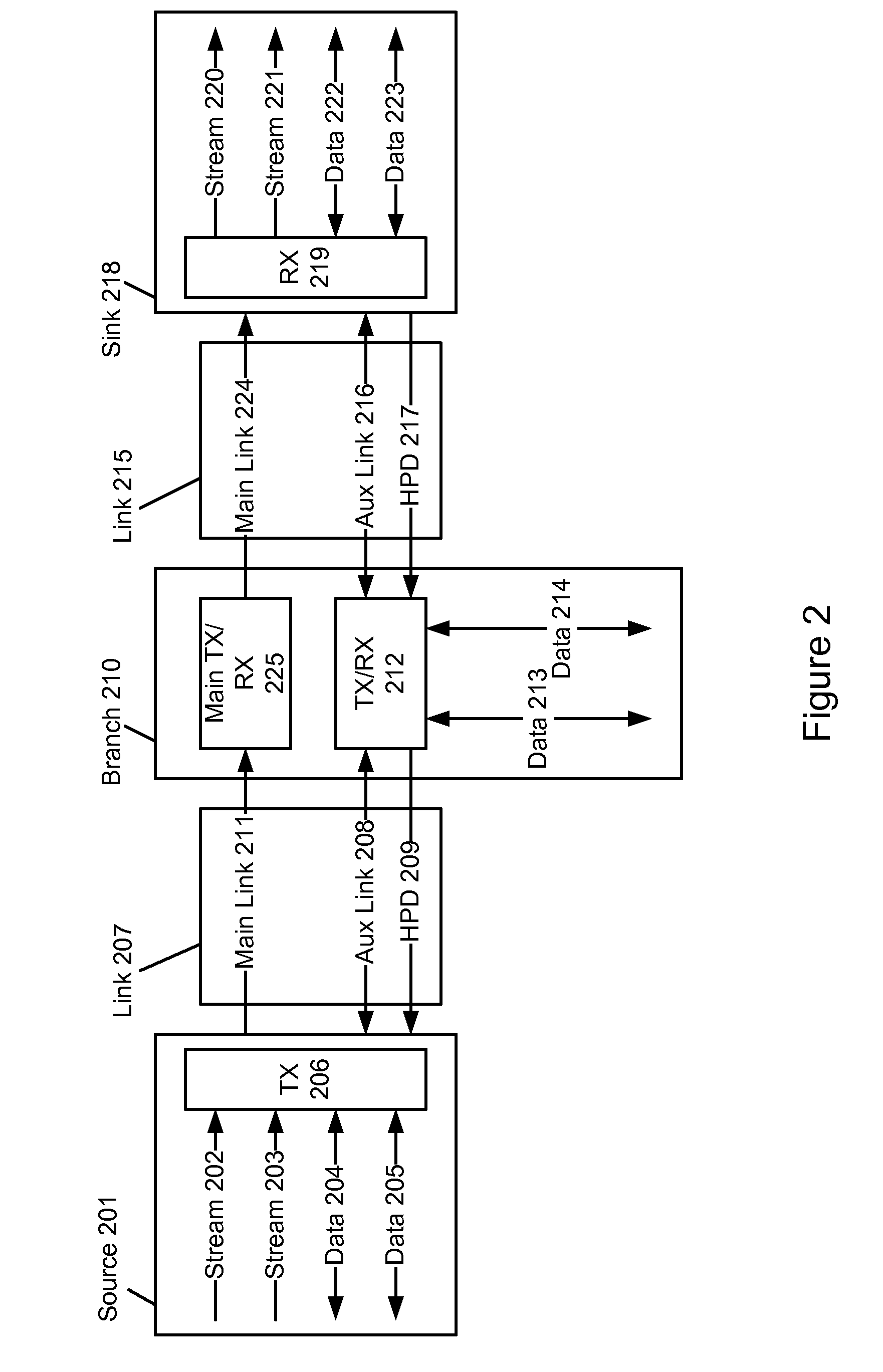
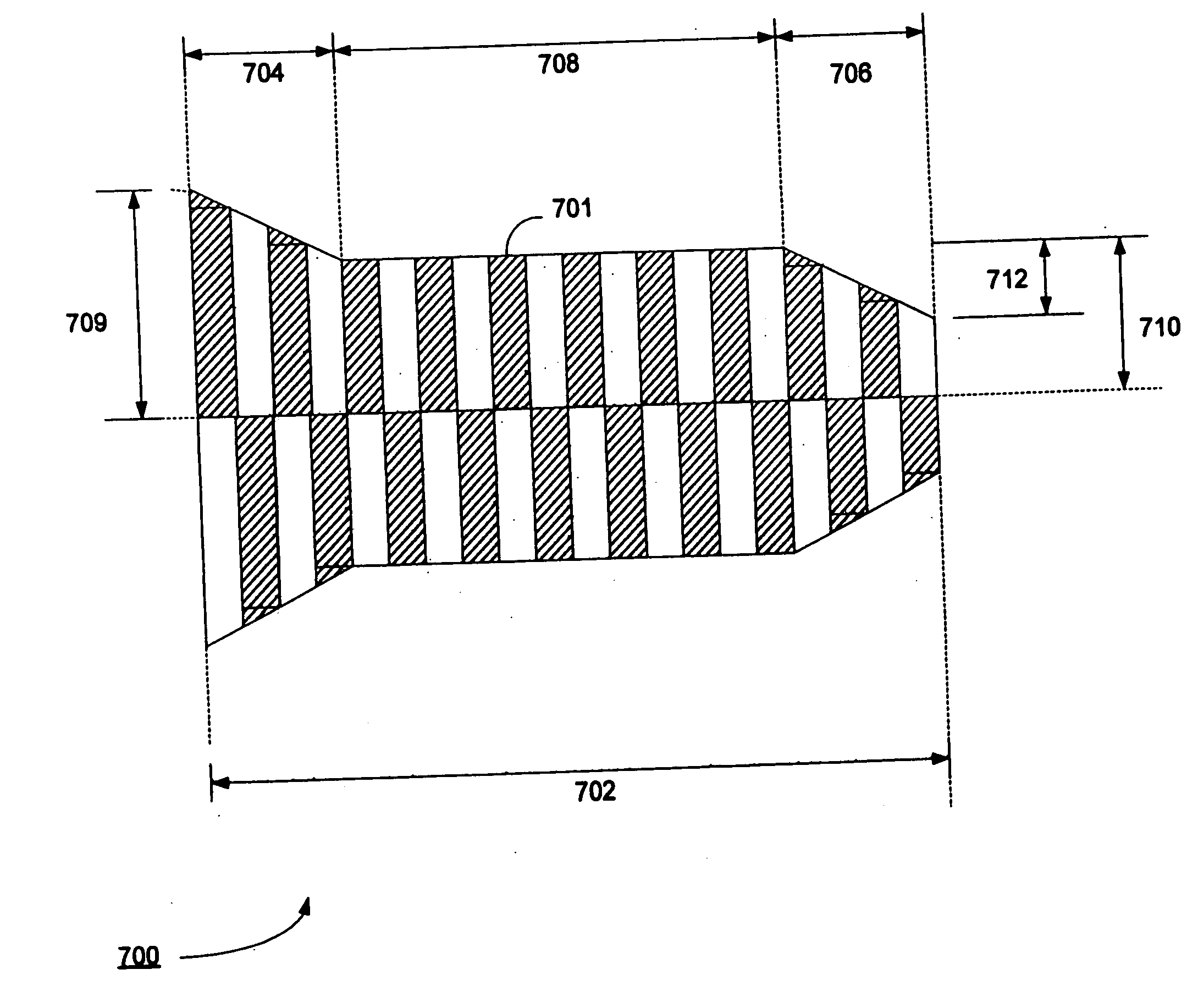
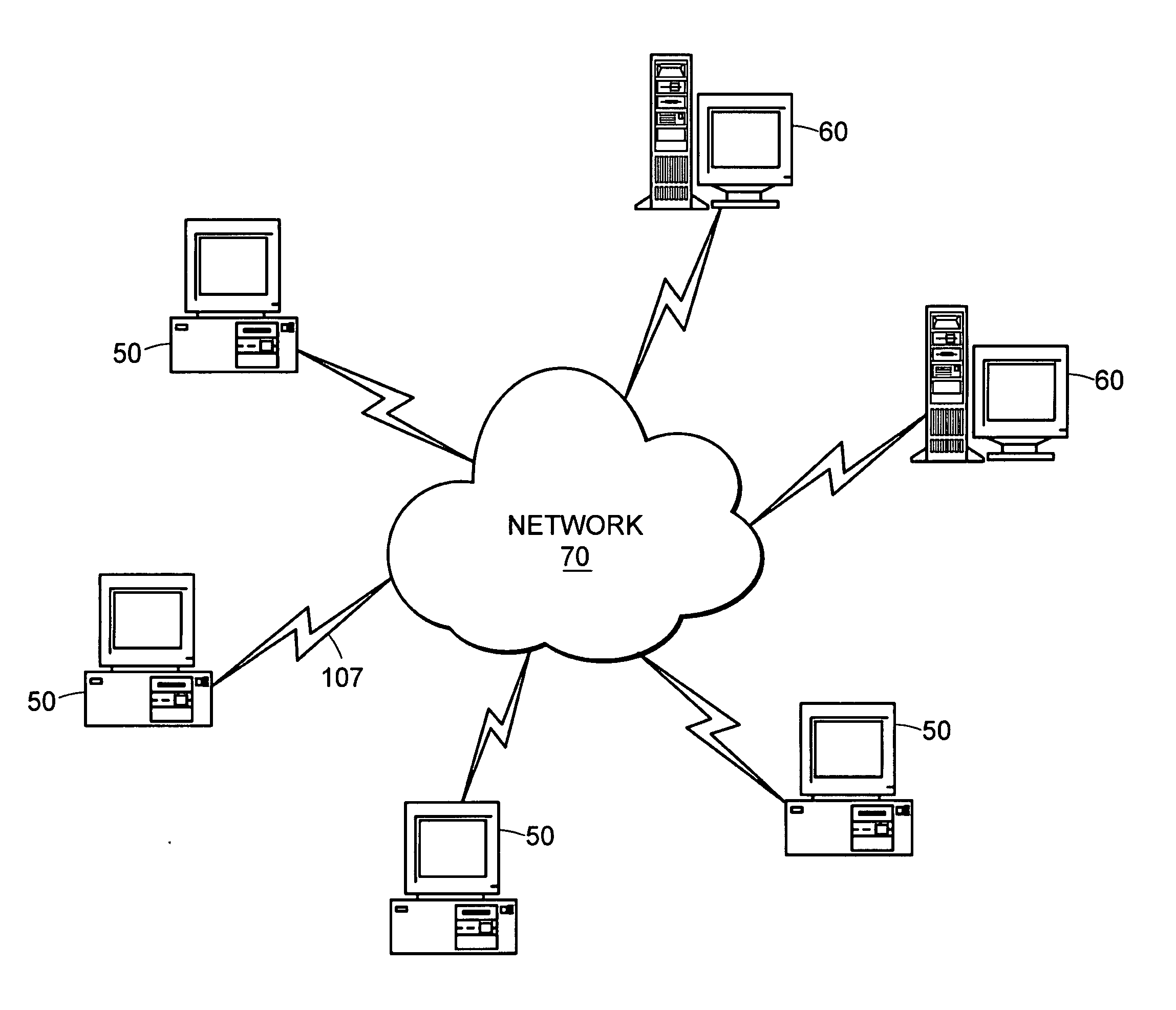
Method and apparatus for regenerating a clock for auxiliary data transmitted over a serial link with video data
ActiveUS7088398B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareCommunications system
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
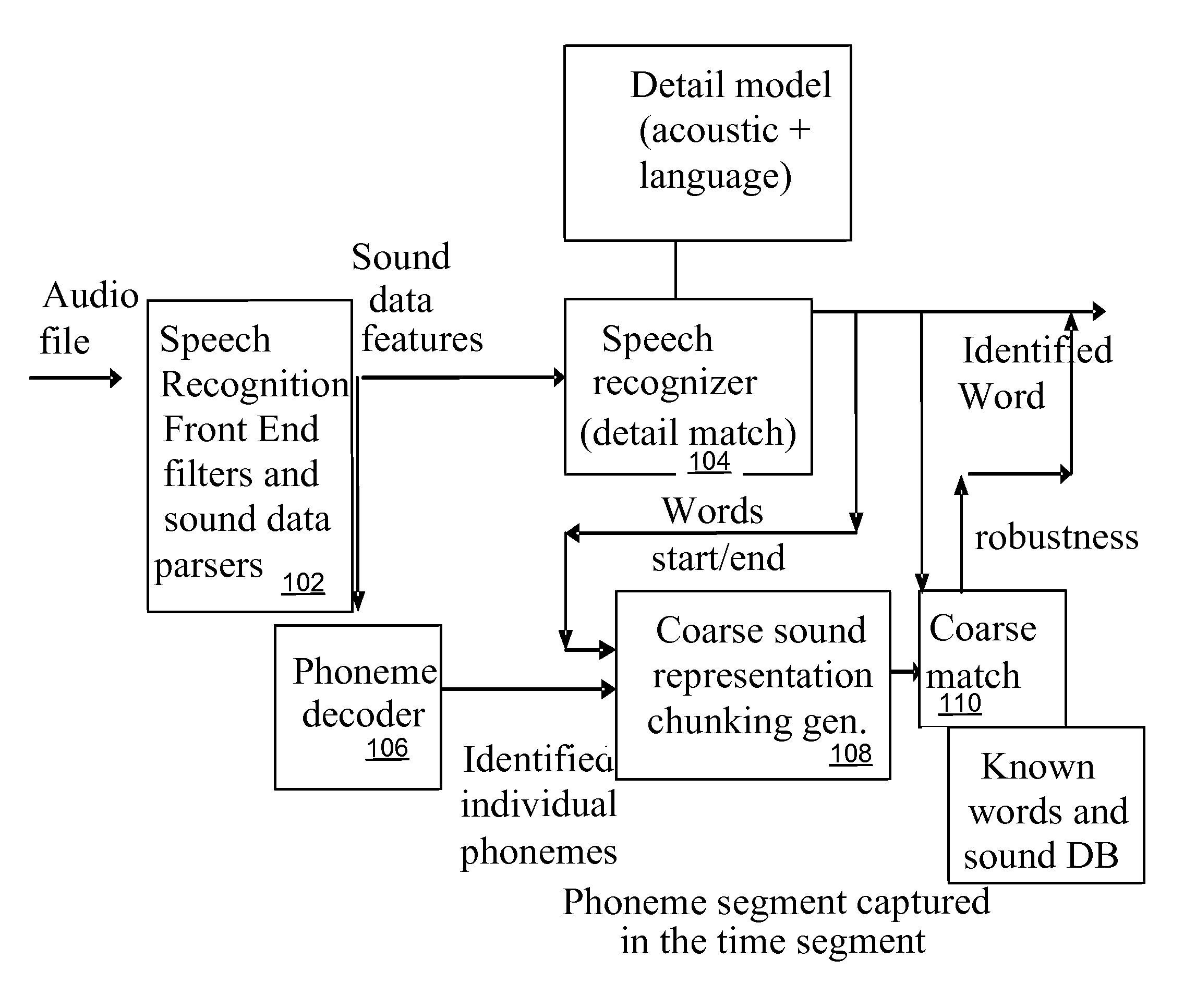
Various apparatus and methods for a speech recognition system
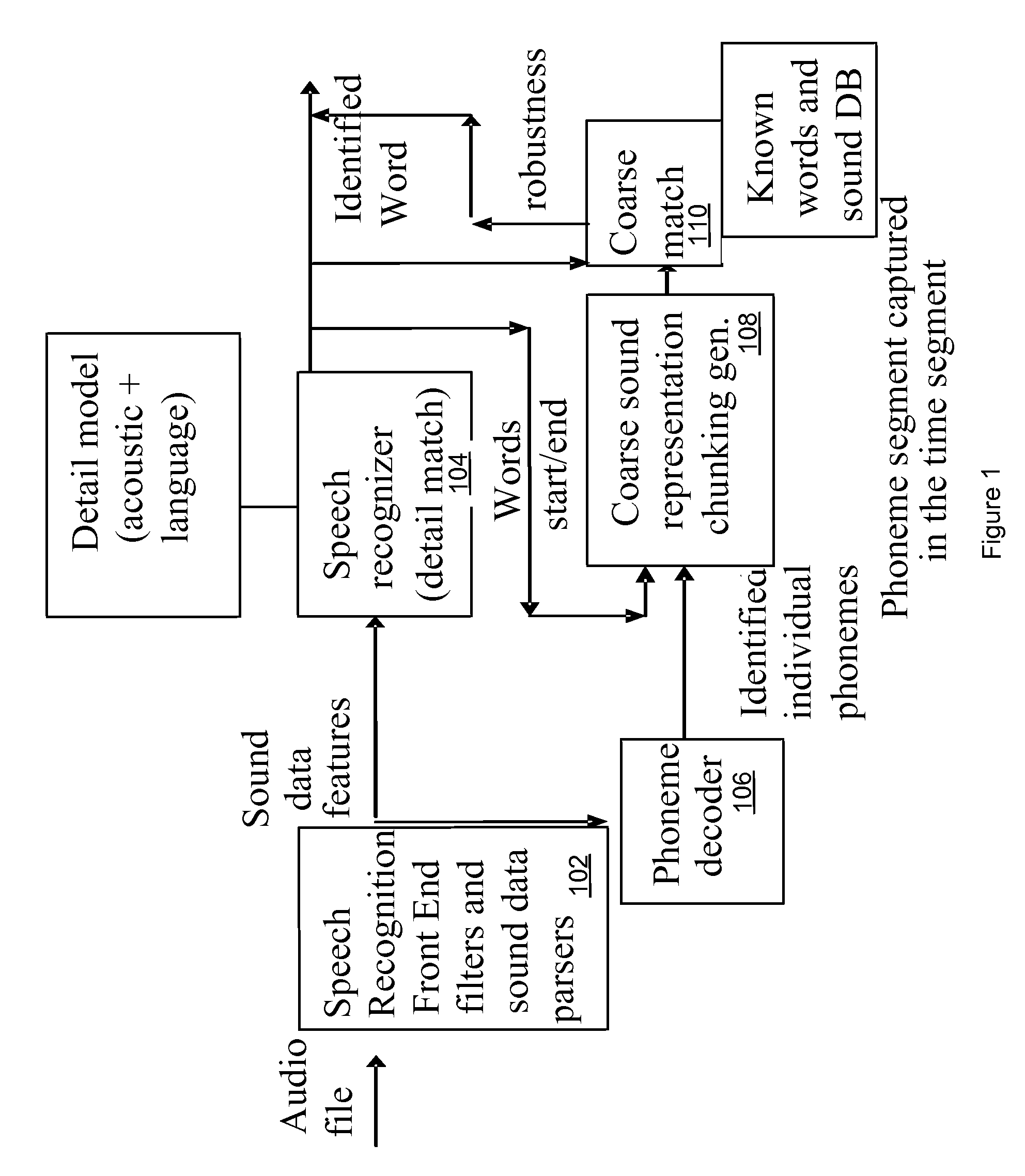
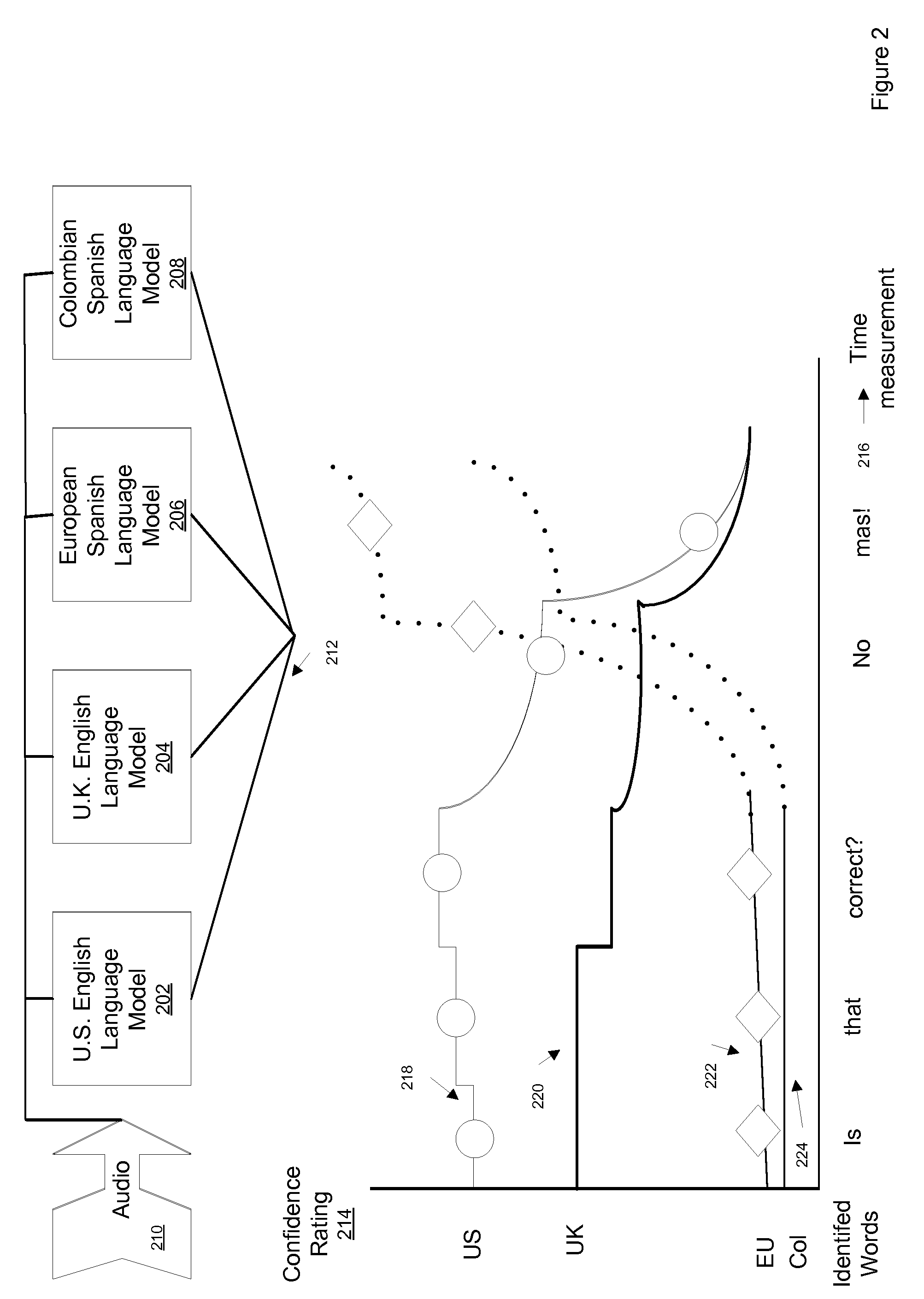
A method, apparatus, and system are described for a continuous speech recognition engine that includes a fine speech recognizer model, a coarse sound representation generator, and a coarse match generator. The fine speech recognizer model receives a time coded sequence of sound feature frames, applies a speech recognition process to the sound feature frames and determines at least a best guess at each recognizable word that corresponds to the sound feature frames. The coarse sound representation generator generates a coarse sound representation of the recognized word. The coarse match generator determines a likelihood of the coarse sound representation actually being the recognized word based on comparing the coarse sound representation of the recognized word to a database containing the known sound of that recognized word and assigns the likelihood as a robust confidence level parameter to that recognized word.
Owner:LONGSAND
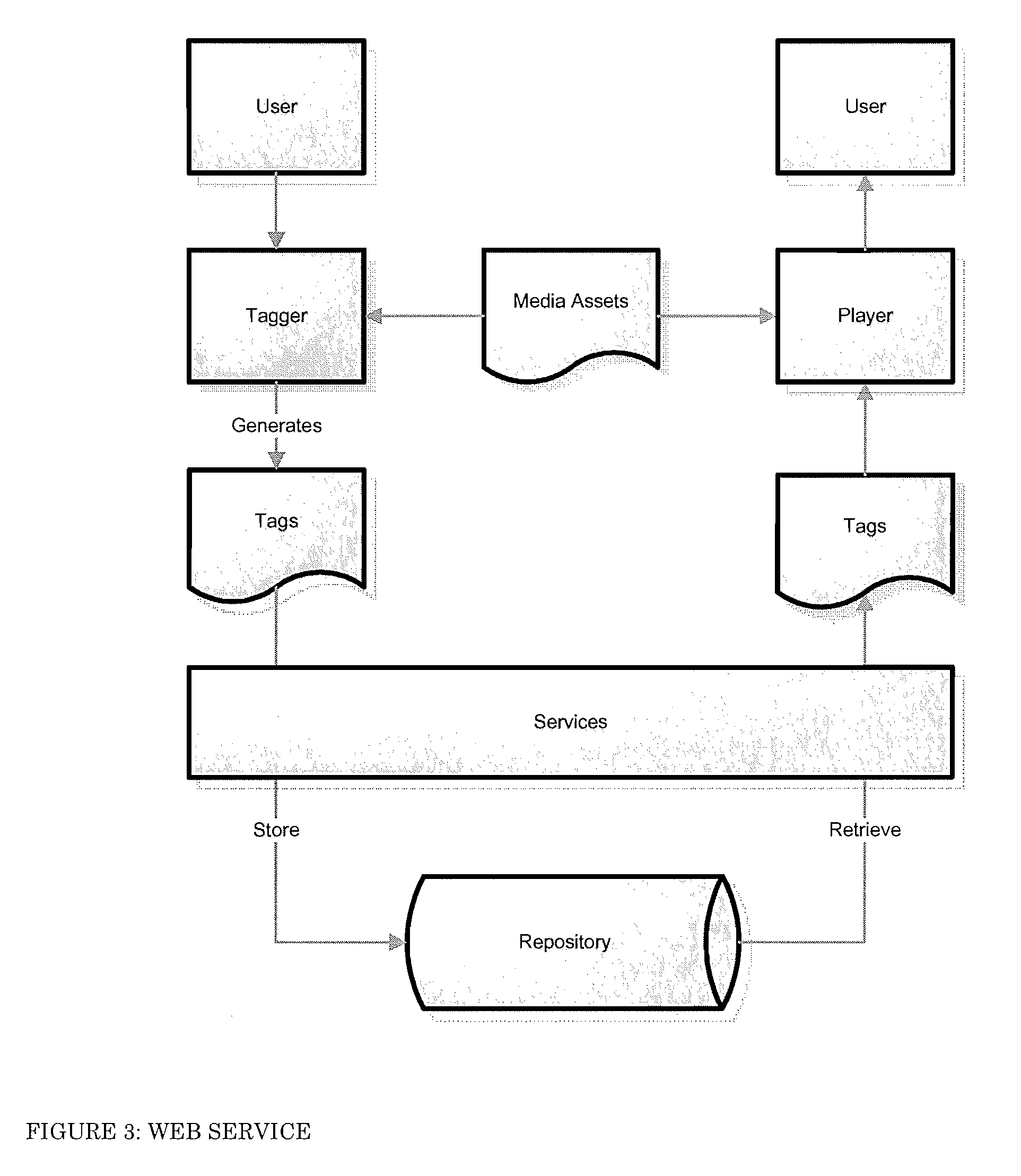
System and method for tagging, searching for, and presenting items contained within video media assets
InactiveUS20080126191A1Simple keyword searchingSpeed transmissionMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsThumbnailResult list
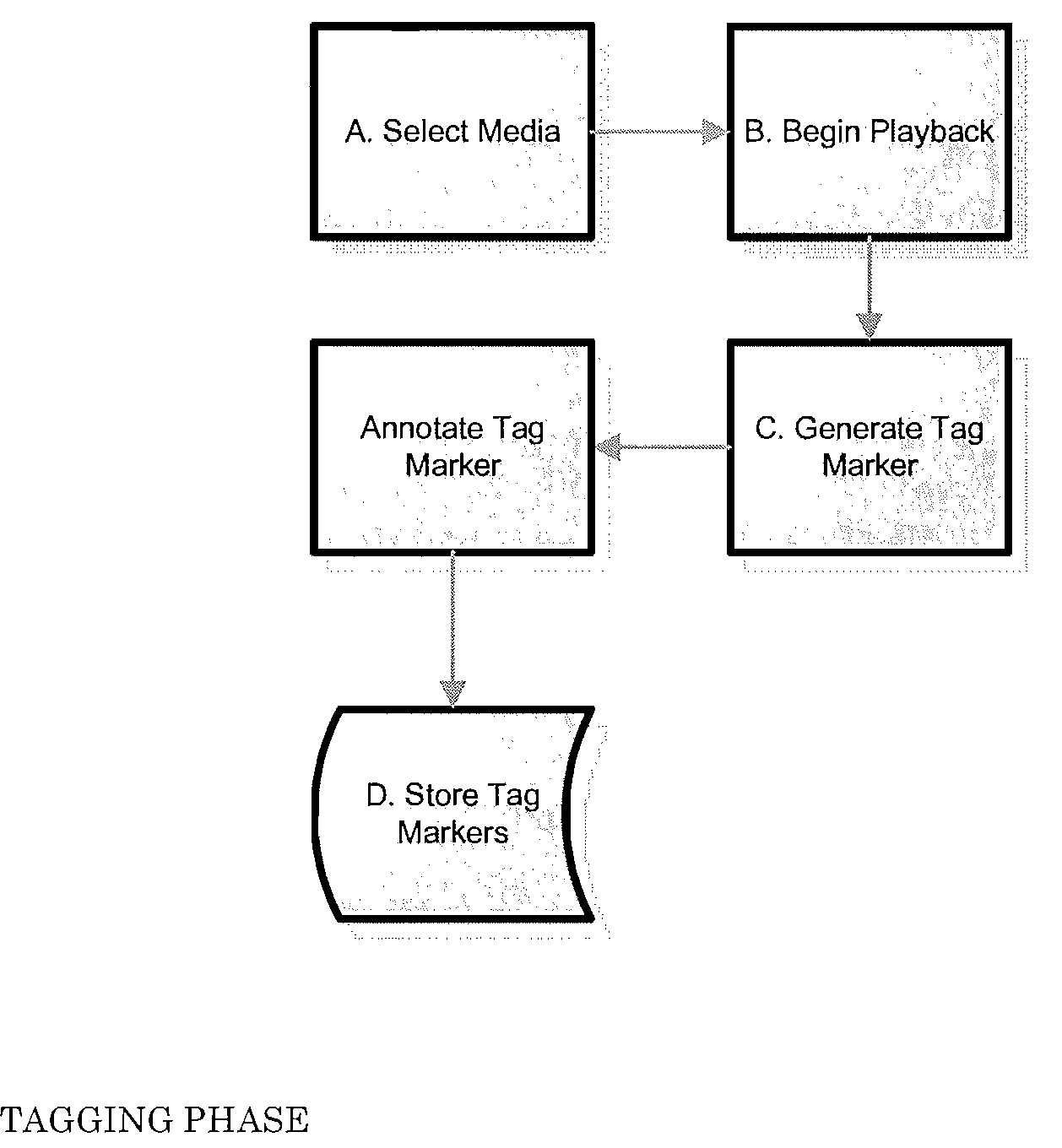
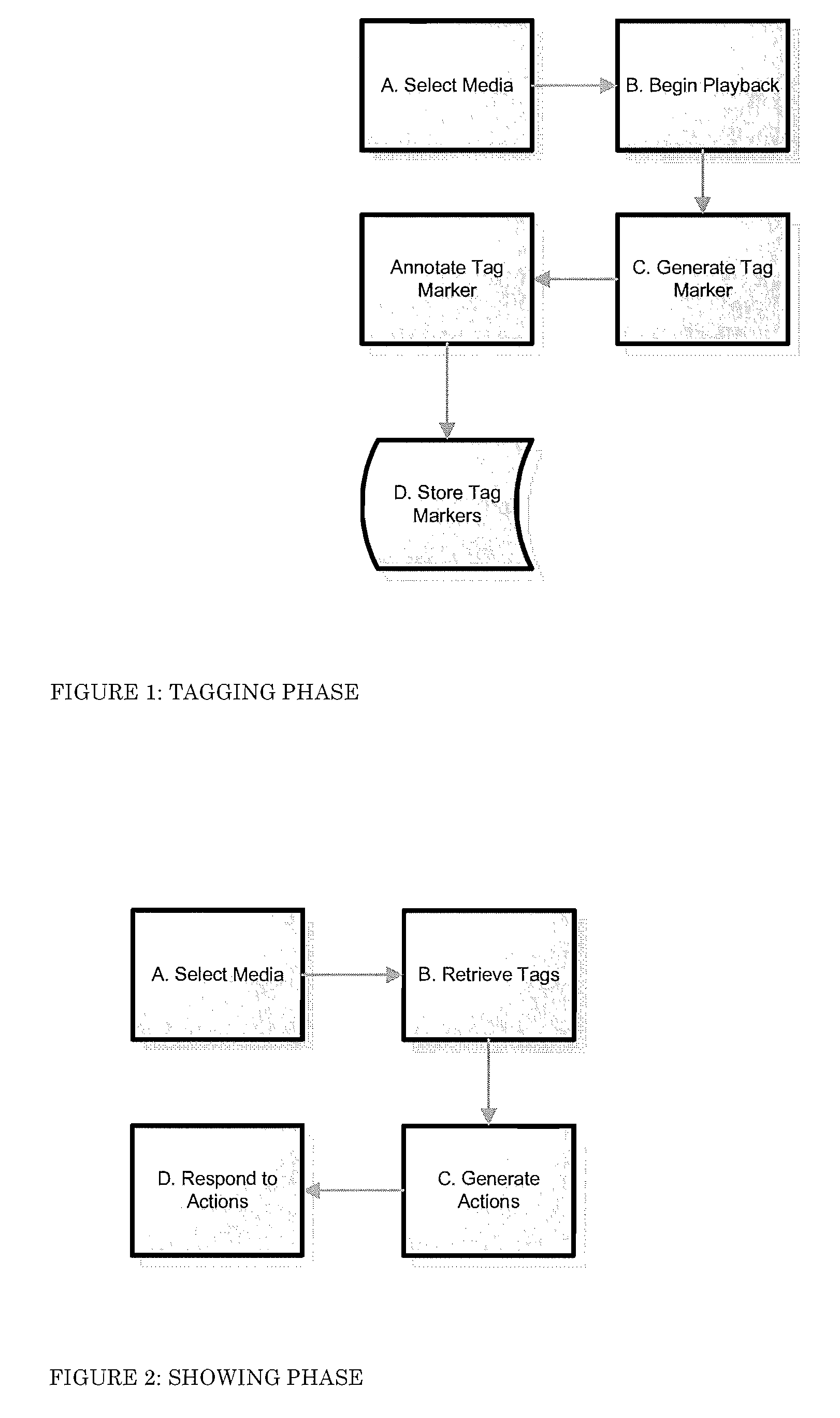
A system and method for computerized searching for items of interest contained in visual media assets, such as a movie or video, stores digital tag information for tagged visual media assets which includes for each tag a time code for a representative image frame, an address code for the storage location of a captured image-still of the frame, and one or more keywords representing the item(s) of interest or their characteristics. When a search request is entered with keywords for items of interest, the search result lists entries from tags containing those keywords, and can also display the captured image-stills (or thumbnail photos thereof) as a visual depiction of the search results. The search service enables advertisers and vendors to bid on rights to link their advertising and other information displays to the search results. The search service can also be used for playback of clips from media assets to viewers on a video viewing website or on a networked playback device.
Owner:SCHIAVI RICHARD
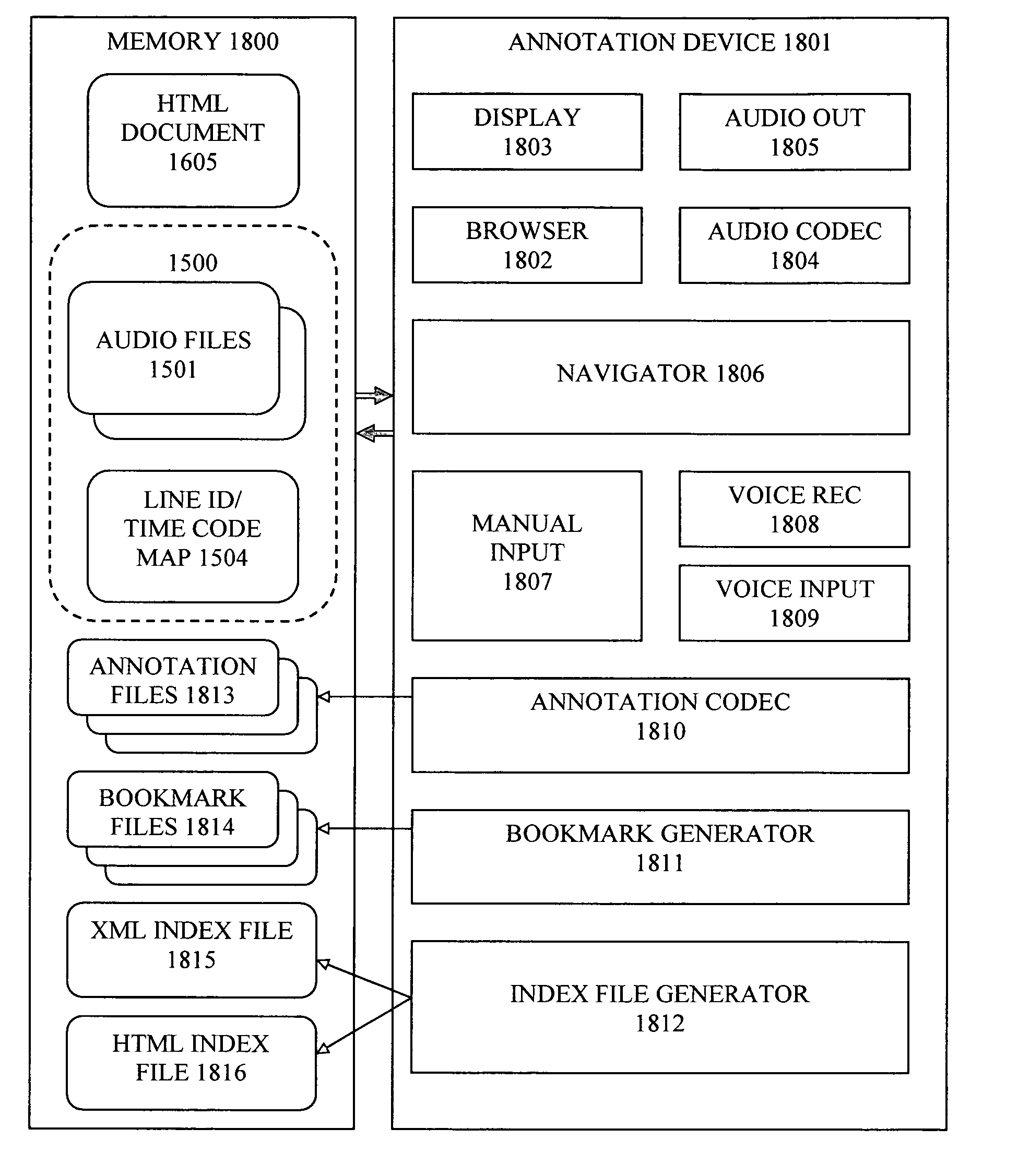
Method and apparatus for annotating a line-based document
InactiveUS20060143559A1Way of increaseSimple methodNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionNumber timesText annotation
To facilitate the use of audio files for annotation purposes, an audio file format, which includes audio data for playback purposes, is augmented with a parallel data channel of line identifiers, or with a map associating time codes for the audio data with line numbers on the original document. The line number-time code information in the audio file is used to navigate within the audio file, and also to associate bookmark links and captured audio annotation files with line numbers of the original text document. An annotation device may provide an output document wherein links to audio and / or text annotation files are embedded at corresponding line numbers. Also, a navigation index may be generated, having links to annotation files and associated document line numbers, as well as bookmark links to selected document line numbers.
Owner:COPERNICUS INVESTMENTS
Electronic Apparatus, Reproduction Method, and Program
InactiveUS20100278509A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComputer graphics (images)Time line
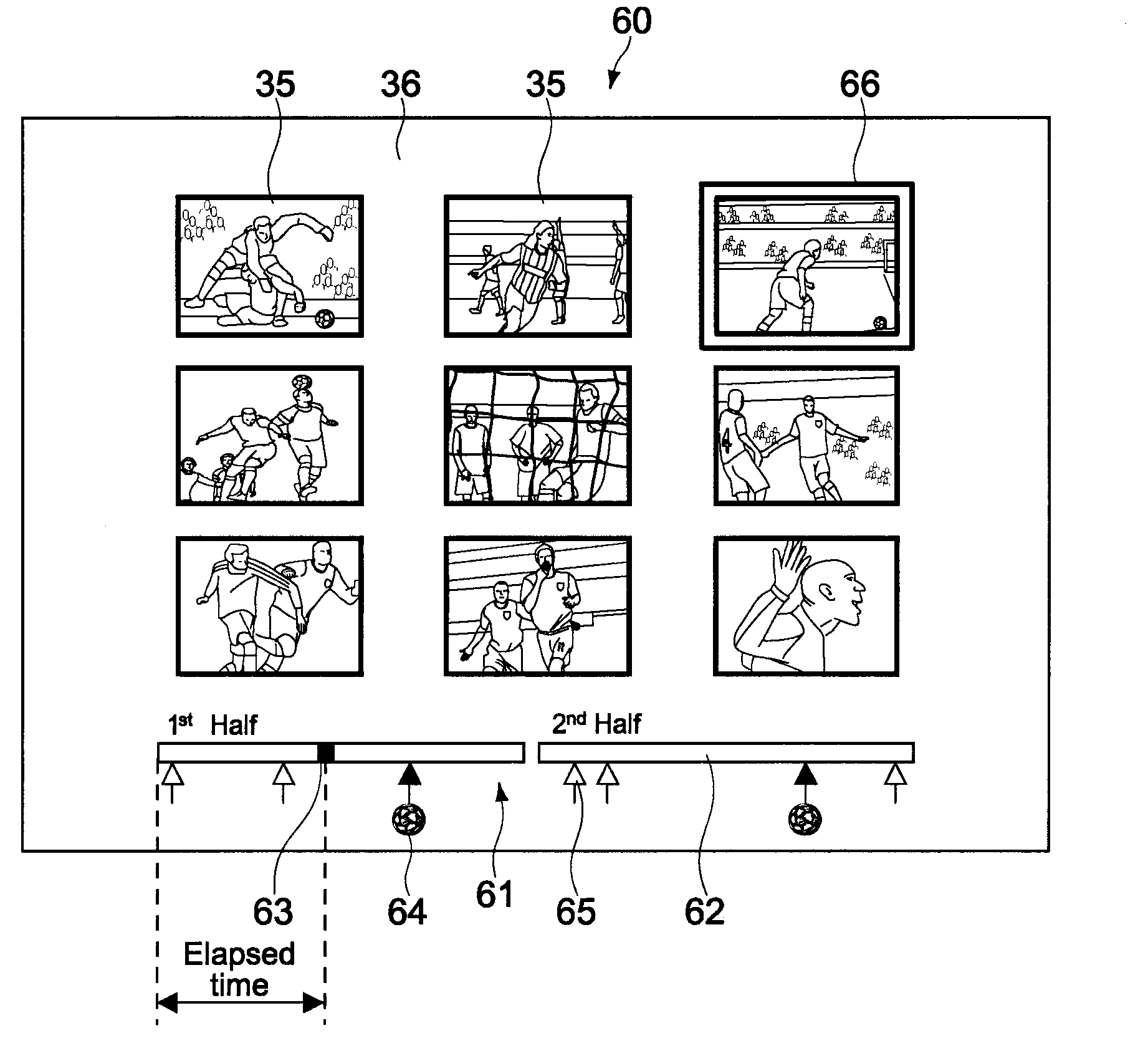
[Object] To reproduce a plurality of video contents recorded on a recording medium on one screen and select and reproduce any of the video contents without using a plurality of dedicated decoders.[Solving Means] A recording / reproducing apparatus (100) reads single angle videos (21) that are shot from a plurality of angles and a multi-angle video (22) obtained by performing authoring on those single angle videos (21) so as to be reproducible on one screen from a BD-ROM (10), combines a time-line operation bar (61) and a cursor (66) with the multi-angle video (22), and displays a multi-angle screen (60). When an operation of selecting a single angle video (21) on which the cursor (66) is positioned is performed on the multi-angle screen (60), the single angle video (21) is reproduced in full screen based on a time code at a time when the selection operation is made. When an operation of pressing a multi-angle key (23) is performed during the full-screen reproduction, the multi-angle screen (60) is reproduced again based on a time code at a time when the press operation is made.
Owner:SONY CORP
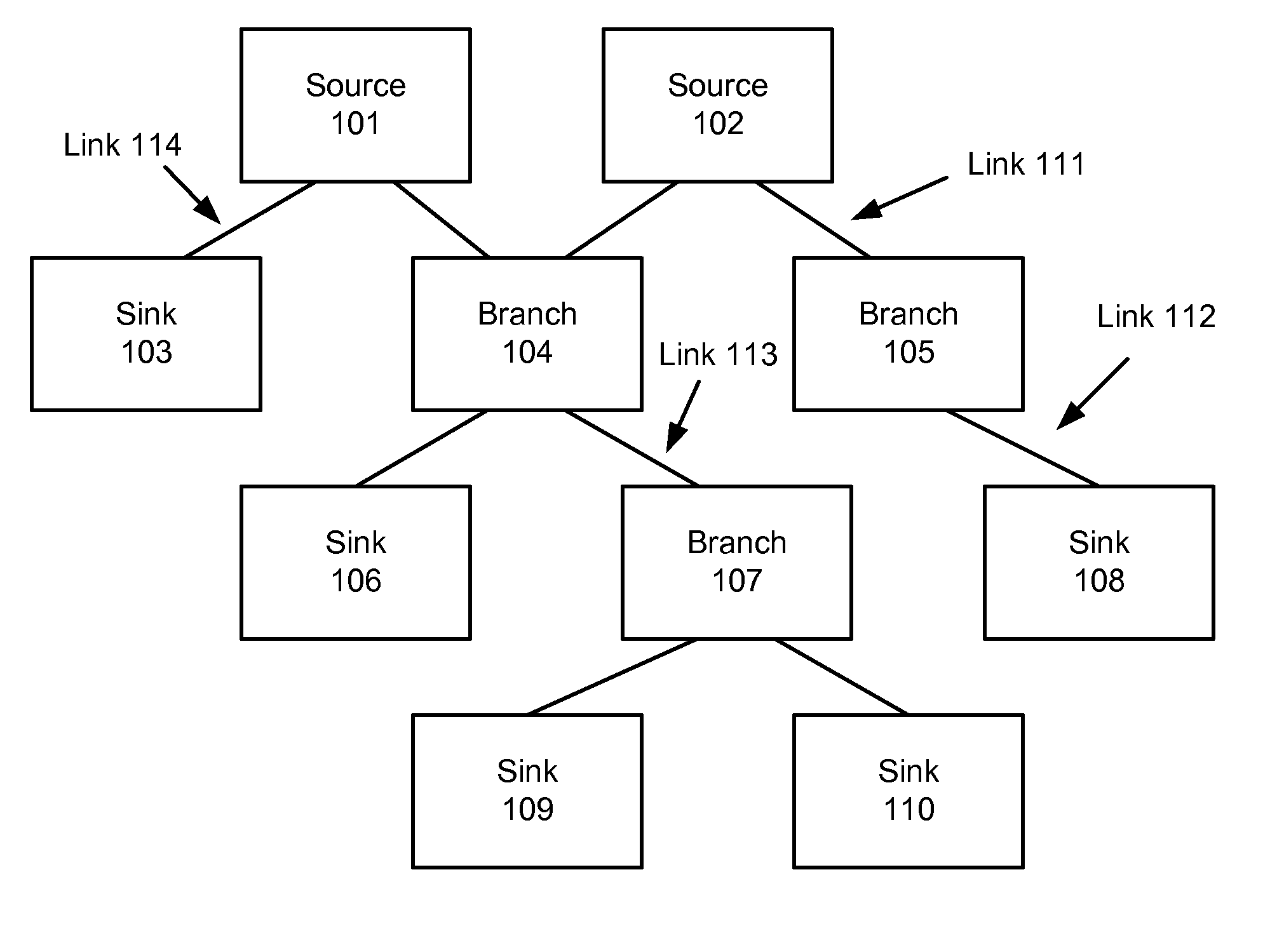
System and method for packet messaging and synchronization
InactiveUS20100272102A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMessage passingData transmission
System and method for packet messaging and synchronization through a packet based display interface includes using a multiple packet transport protocols, translating packet messages between protocols and achieving time code synchronization with a packet protocol between multiple devices in a multimedia network. A packet based display interface includes a dual data transport module to communicate packet messages using first and second packet transport protocols across a bidirectional link and a media transport module to communicate video packets across a unidirectional link. A method for communicating packet messages between source and slave devices in a multimedia network includes translating messages between different packet transport protocols. An apparatus for synchronizing a sink device to a source device includes a counter module configured to be adjusted based on a received source global time code value and a transport module to transmit a sink global time code value to the source device.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
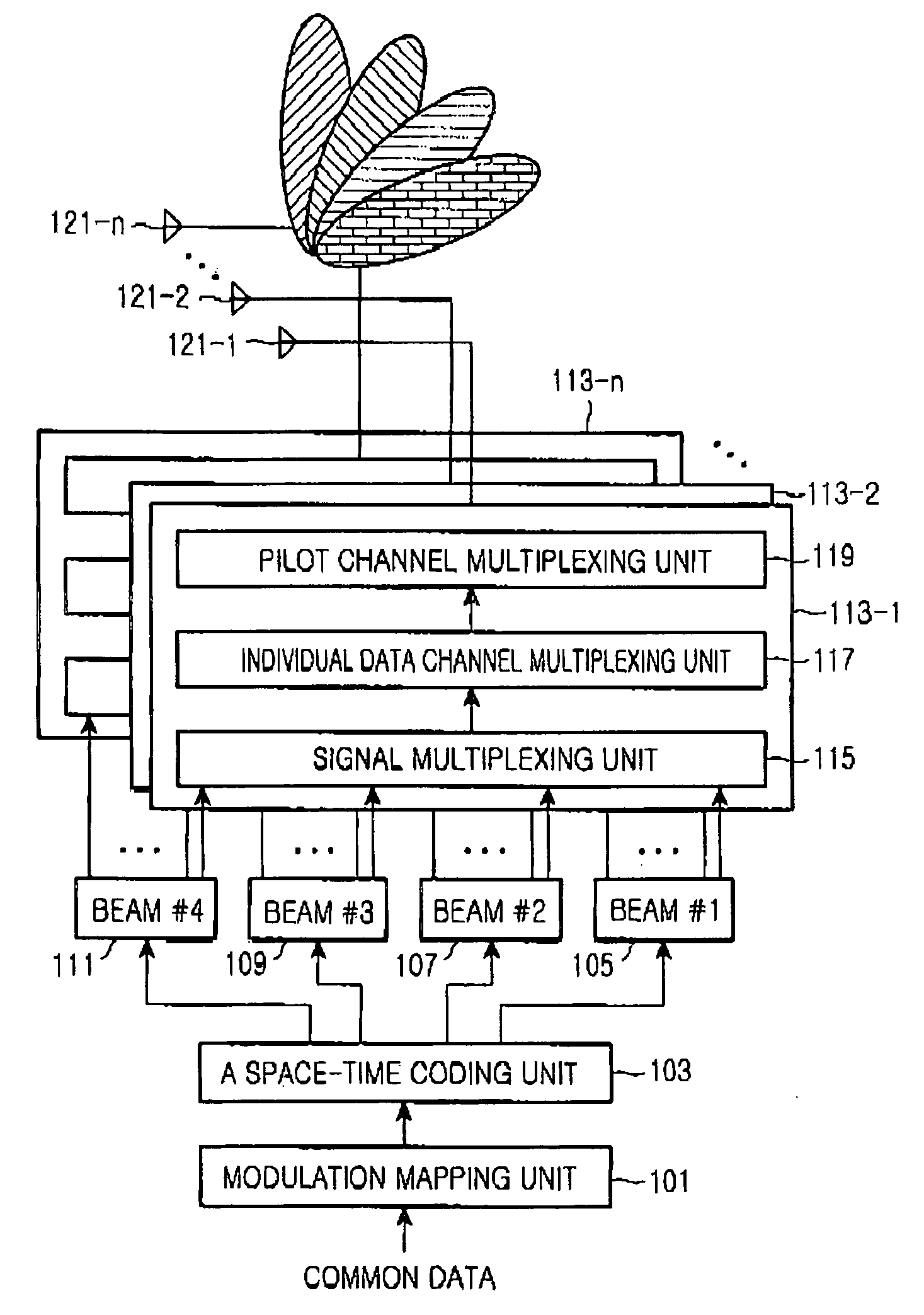
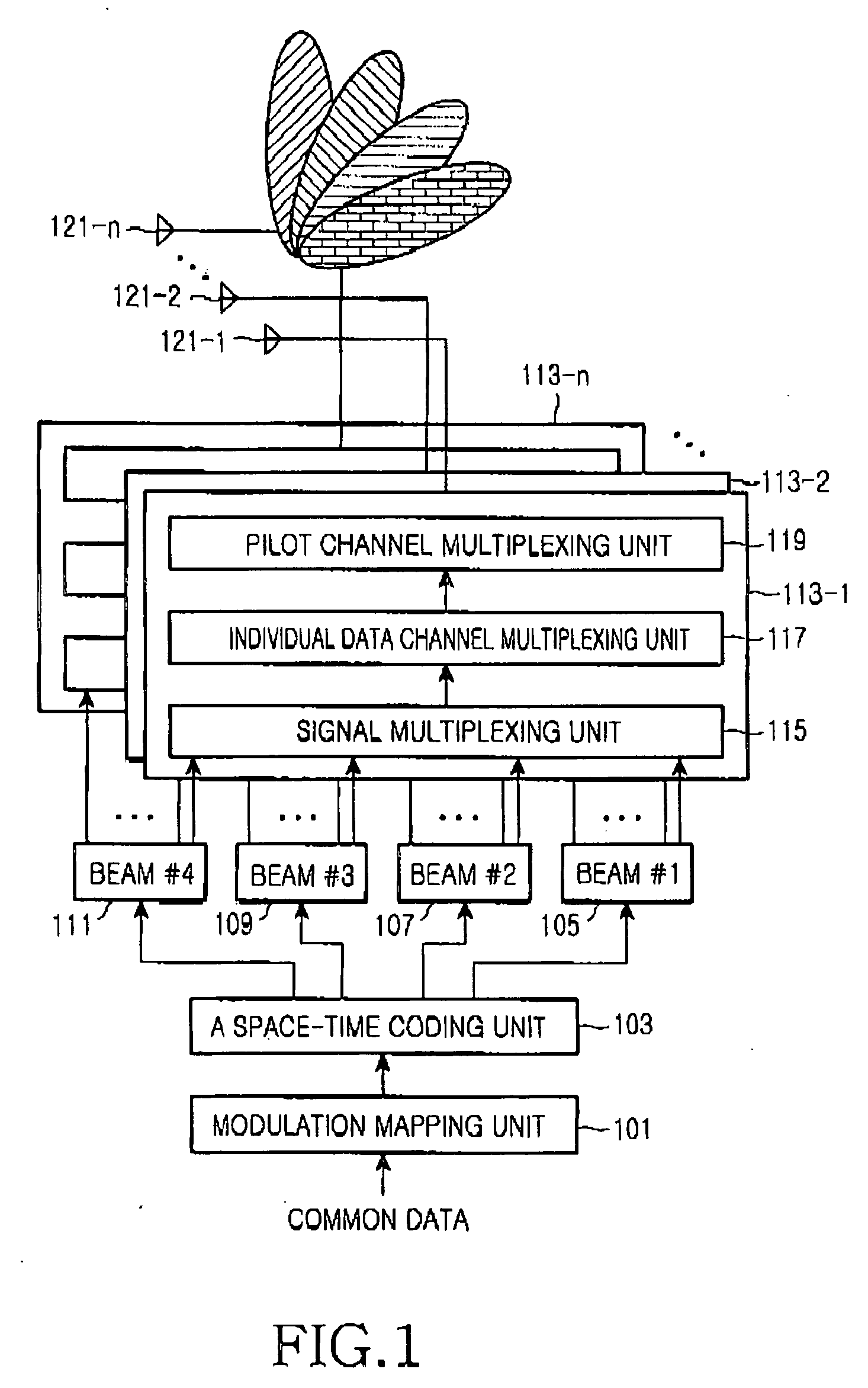
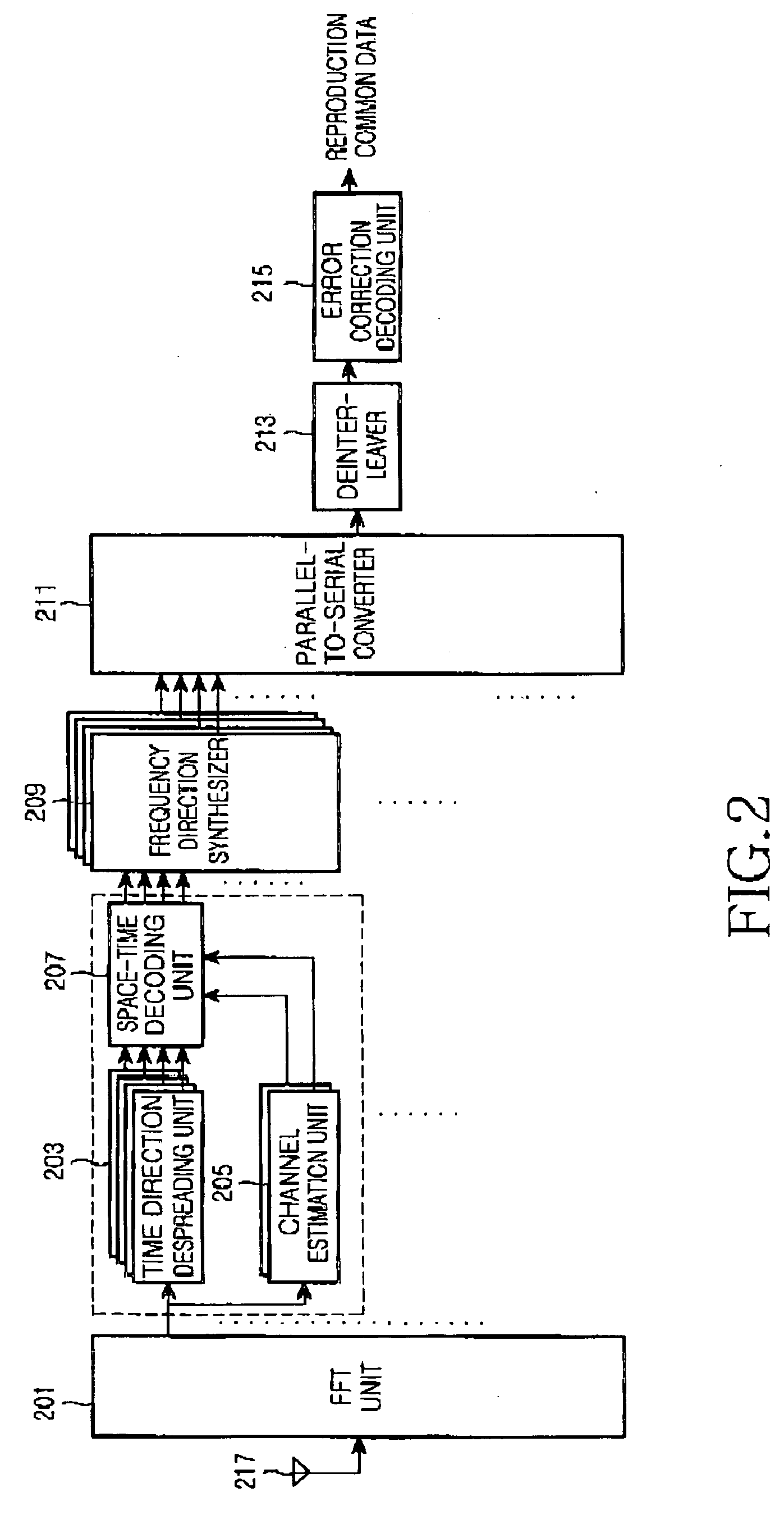
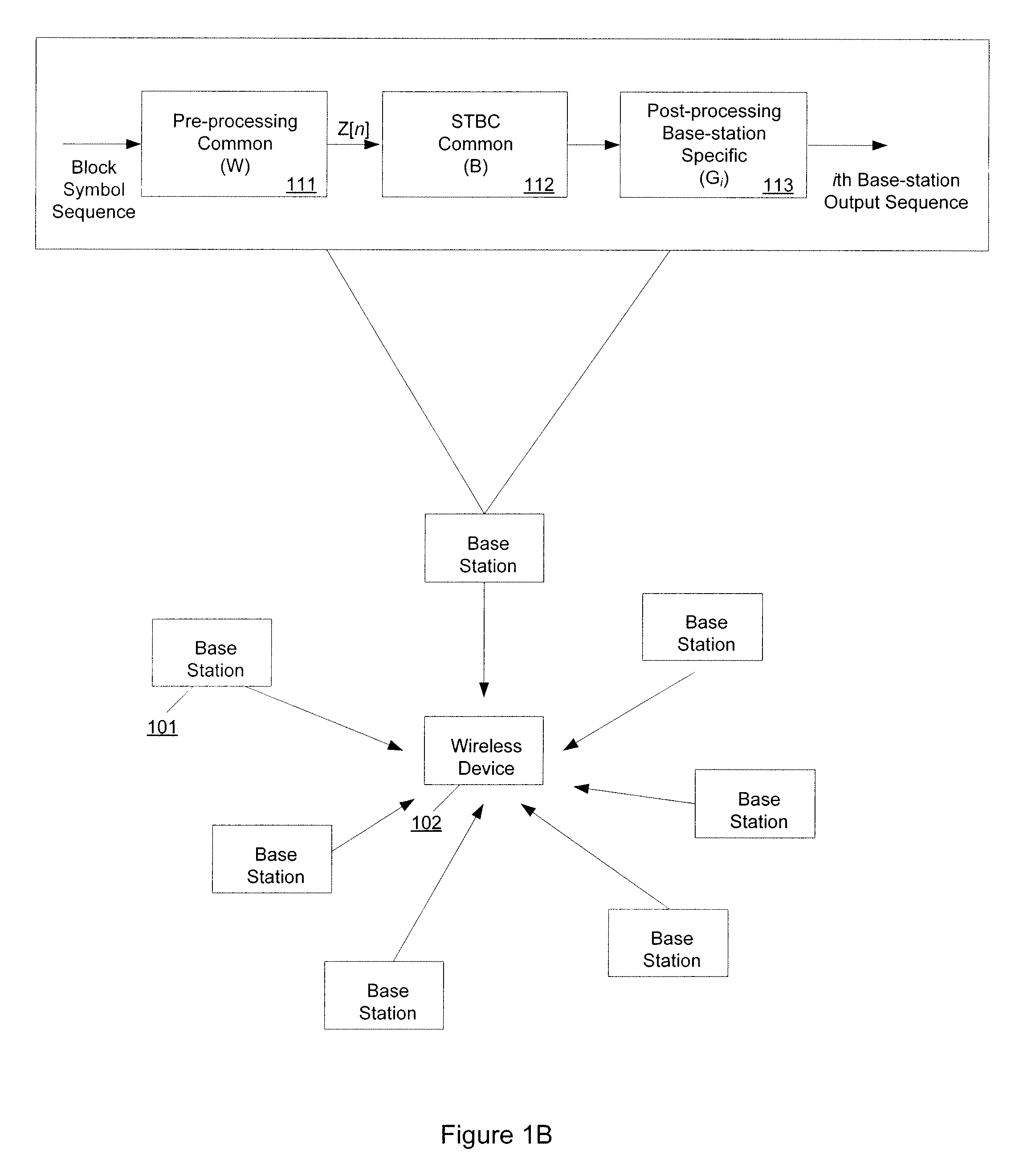
System and method for transmitting common data in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050073976A1Spatial transmit diversityBroadcast service distributionTelecommunicationsTransfer system
A common channel transmission system and method for transmitting common data to multiple users by means of a multibeam. A common data coding means space-time codes the common data throughout all beams included in the multibeam. A data transmission means assigns the common data space-time coded by the common data coding means to all beams included in the multibeam and transmits the common data to the multiple users.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
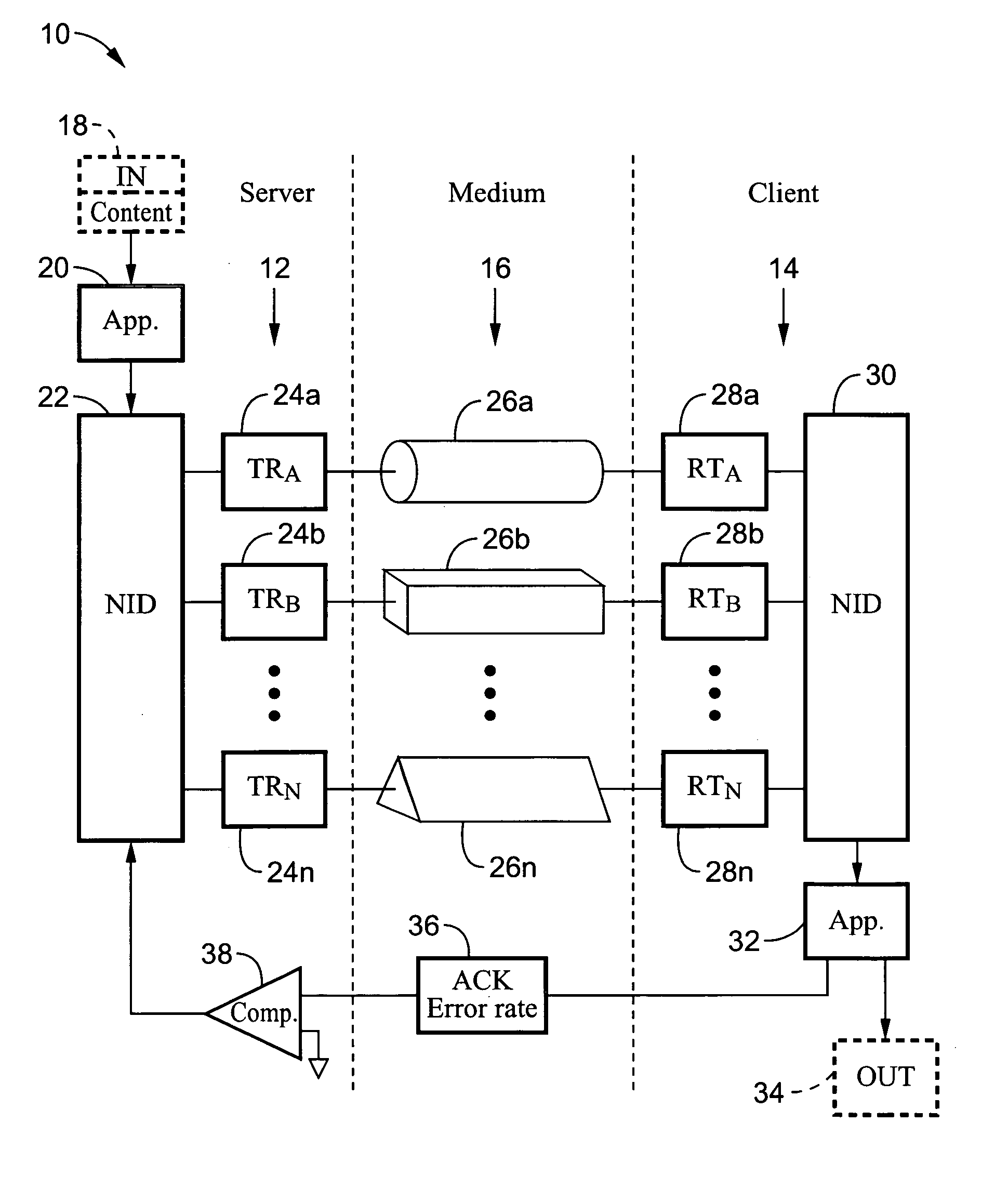
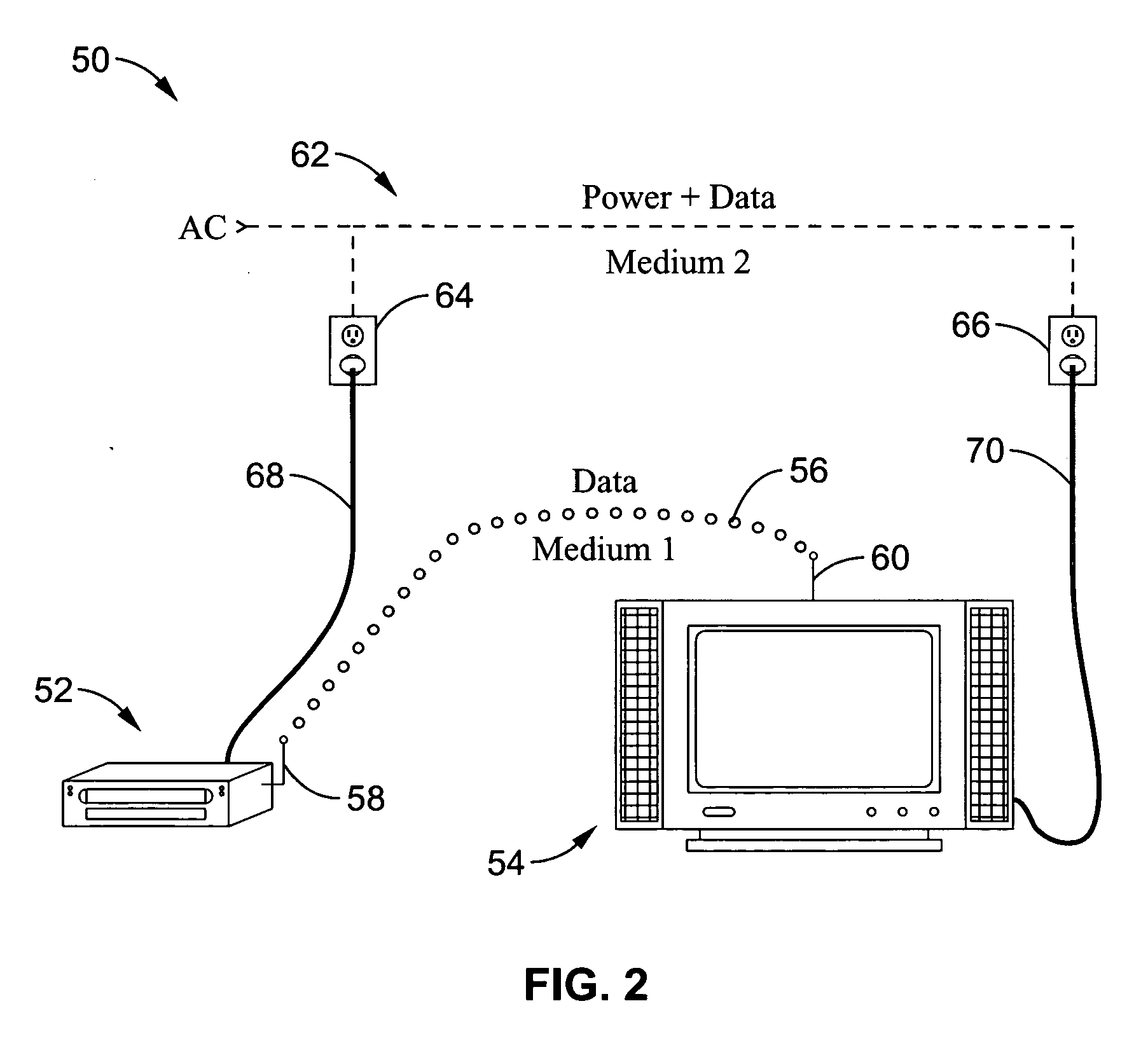
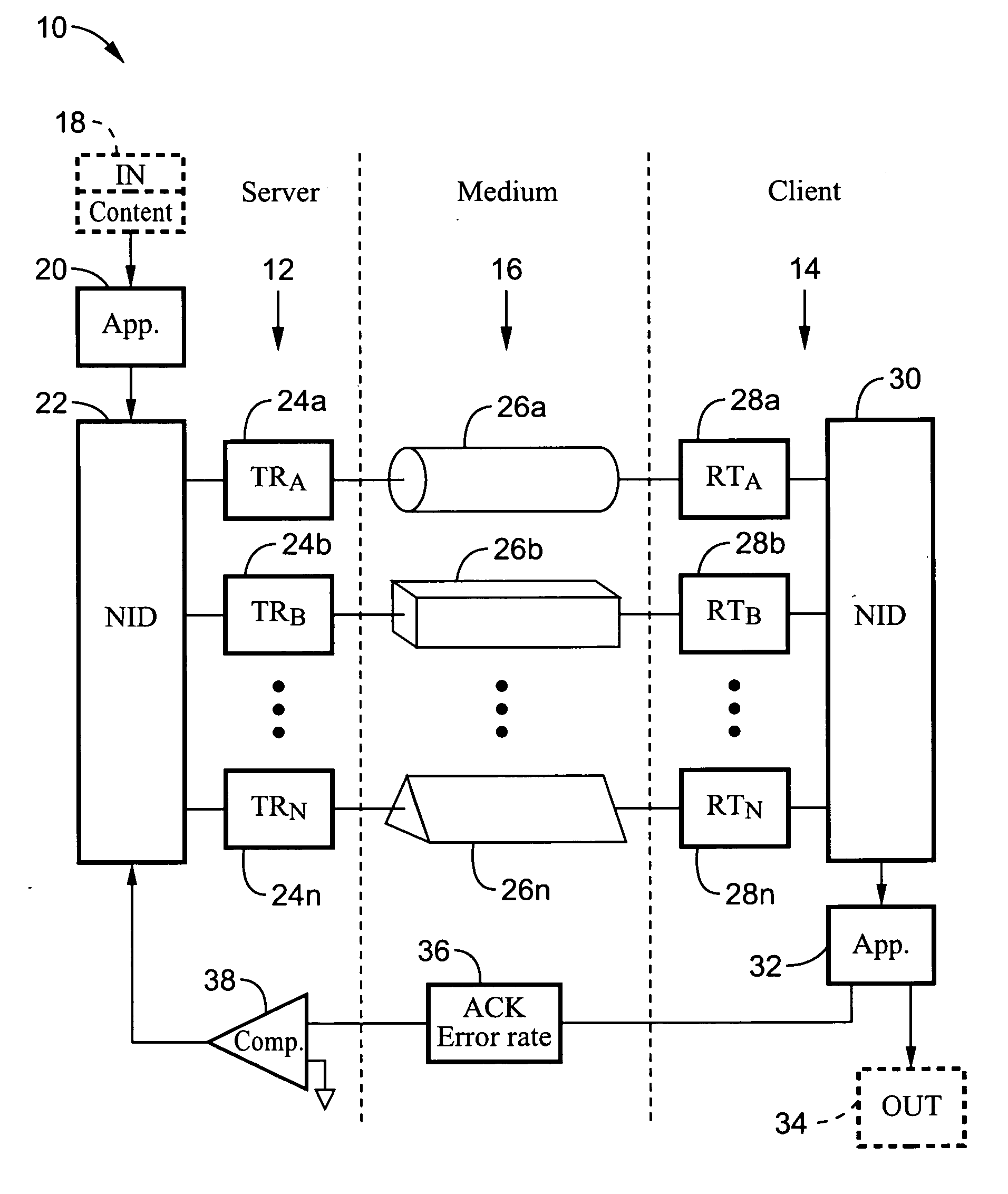
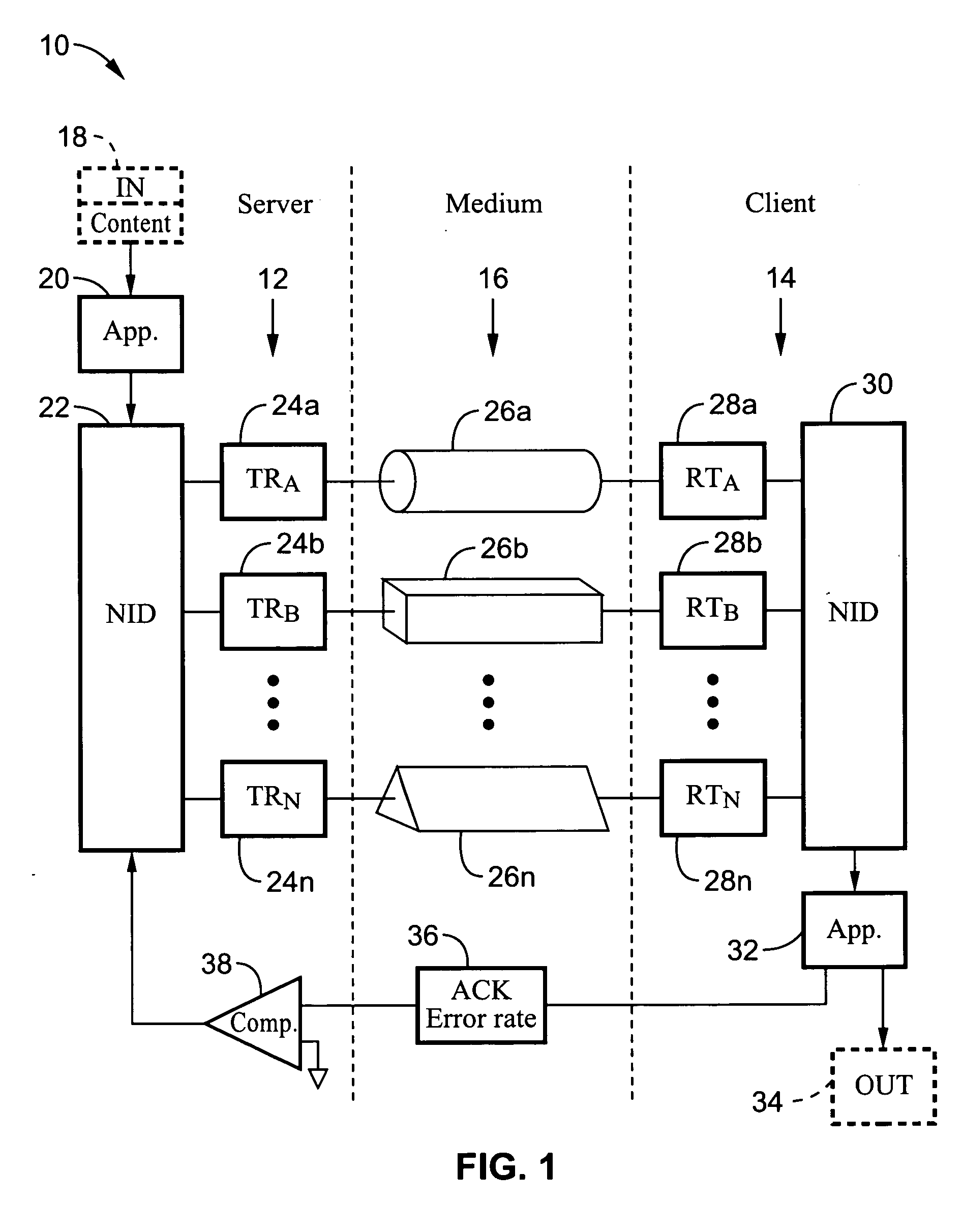
Reliable audio-video transmission system using multi-media diversity
InactiveUS20060062242A1Maintaining service qualityMaintain qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexQuality of servicePower line network
A system and method for switching data packet traffic distribution across diverse transmission medium according to detected quality of service characteristics for a given data packet rate from server to client. It should be recognized that diverse medium are not interdependent with regard to fading or signal strength considerations. One mode of switching comprises switching all the data packets from transmission on a first medium to transmission over a second diverse medium. In a second mode of switching the distribution is changed according to a media-time coding mechanism in which typically data is being transmitted simultaneously across more than one of the multiple diverse medium. The data packet transmissions preferably comprise audio-video data packet streams, such as MPEG-2 streams. By way of example, the diverse transmission medium may comprise a wireless connection (i.e. WiFi) used in combination with a power-line network connection, such as within a home network.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Iterative video teaching aid with recordable commentary and indexing
InactiveUS6599130B2Improve appreciationIncrease valueEducational modelsTeaching apparatusVision basedApplication software
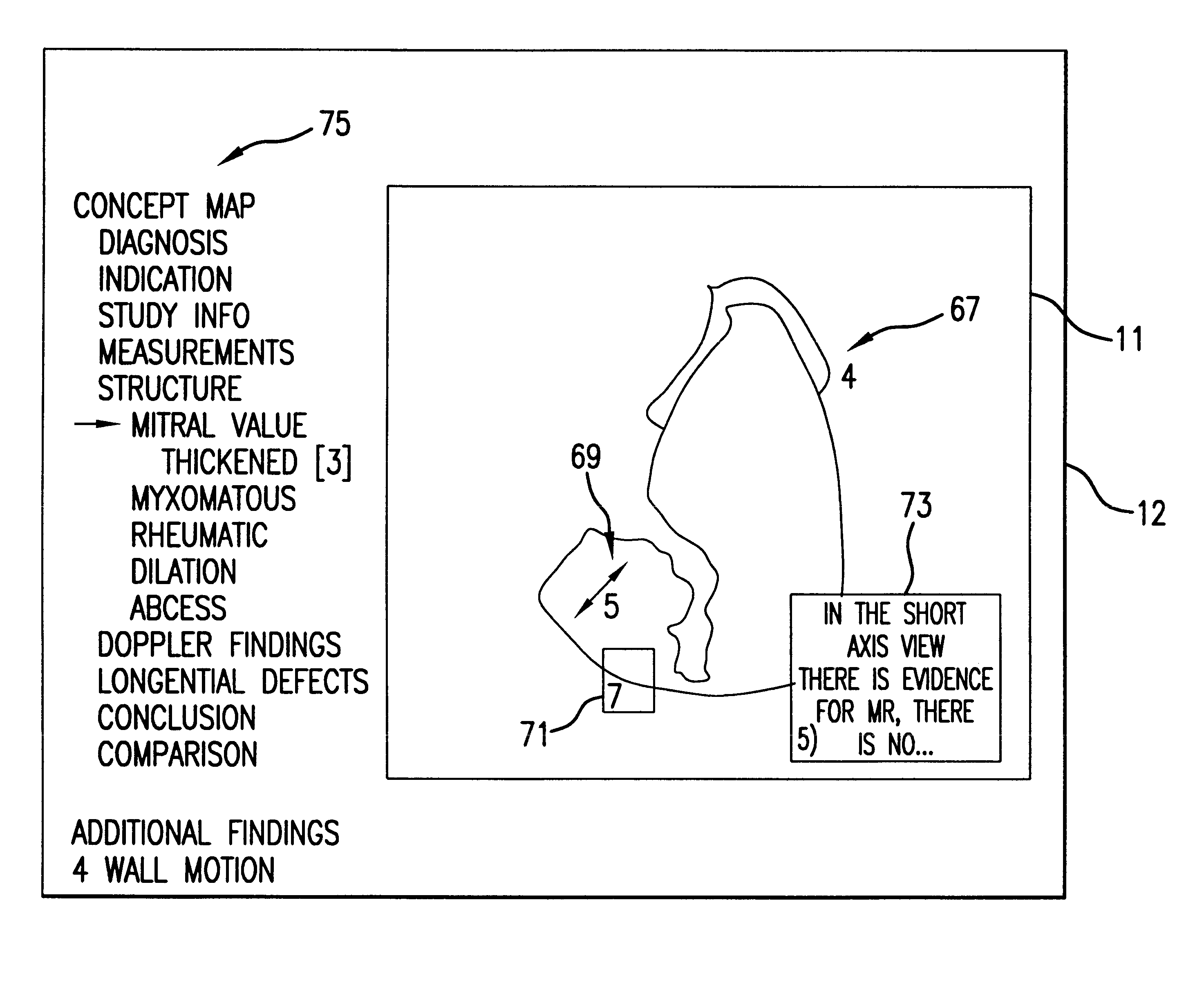
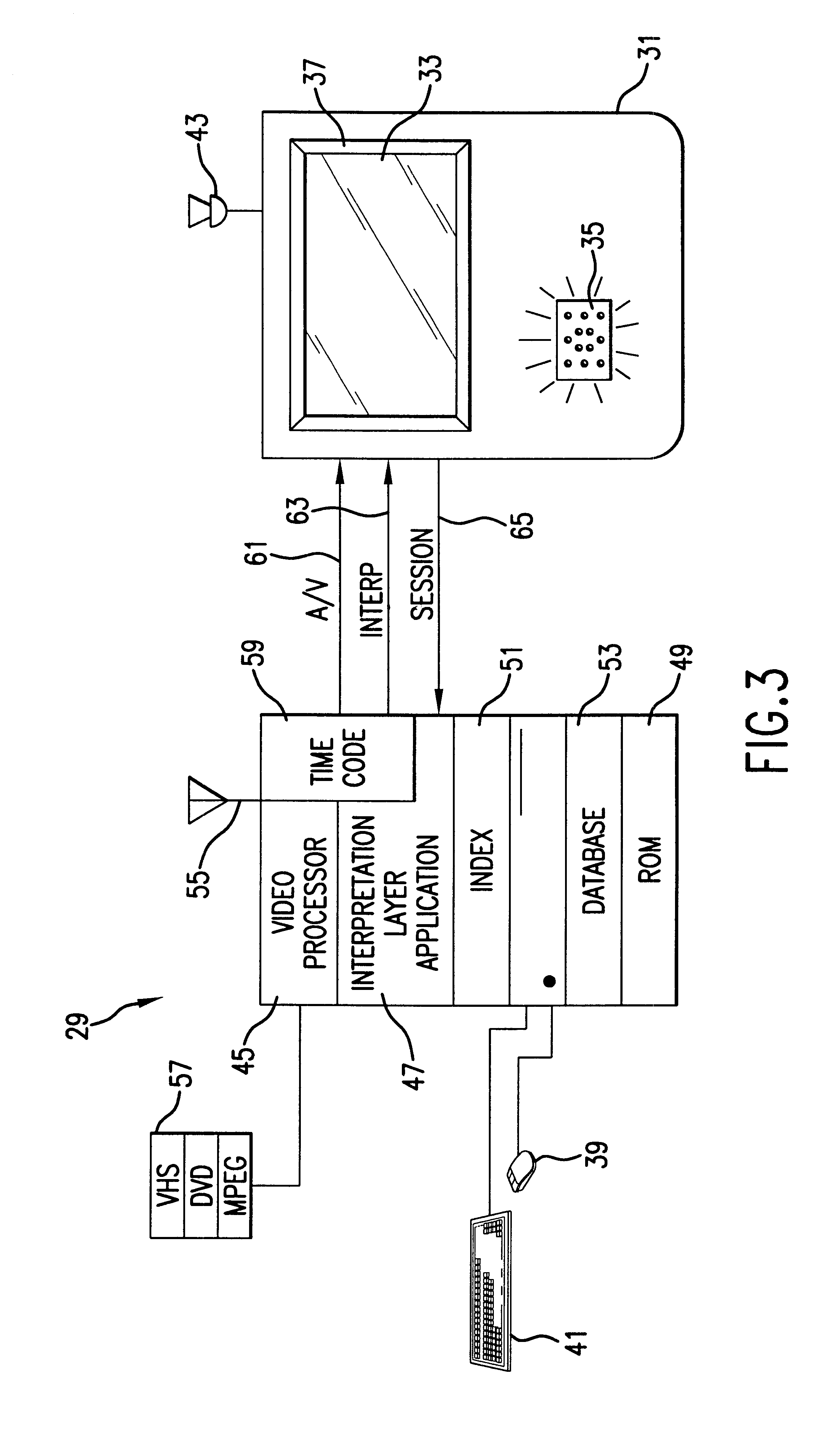
A tutorial or diagnostic aid based on the representation and iterative interpretation of visual images is taught. A teaching or diagnostic session is created by overlaying an interpretation layer via a software application onto the visual image layer and synchronizing the two with the time code of the visual image. The interpretation layer allows the reviewer to identify image areas of interest by gesture and append comments thereto in real time; i.e. images or portions of images within the visual representation playback may be identified and labeled and have the concurrent commentary associated therewith. The comments are indexed and linked to a database of similar topics. The flow of the session is recorded to show the images, deictic gestures associated therewith, and commentary associated with the gestures, to enable subsequent users to playback a session and follow the flow of thought (i.e. image identification and commentary within the original session). Iterative sessions allow additional image identification and commentary to be accomplished. Additional database access through the index may further enhance a teaching session, or provide for research sessions and report generation.
Owner:TAMABO INC
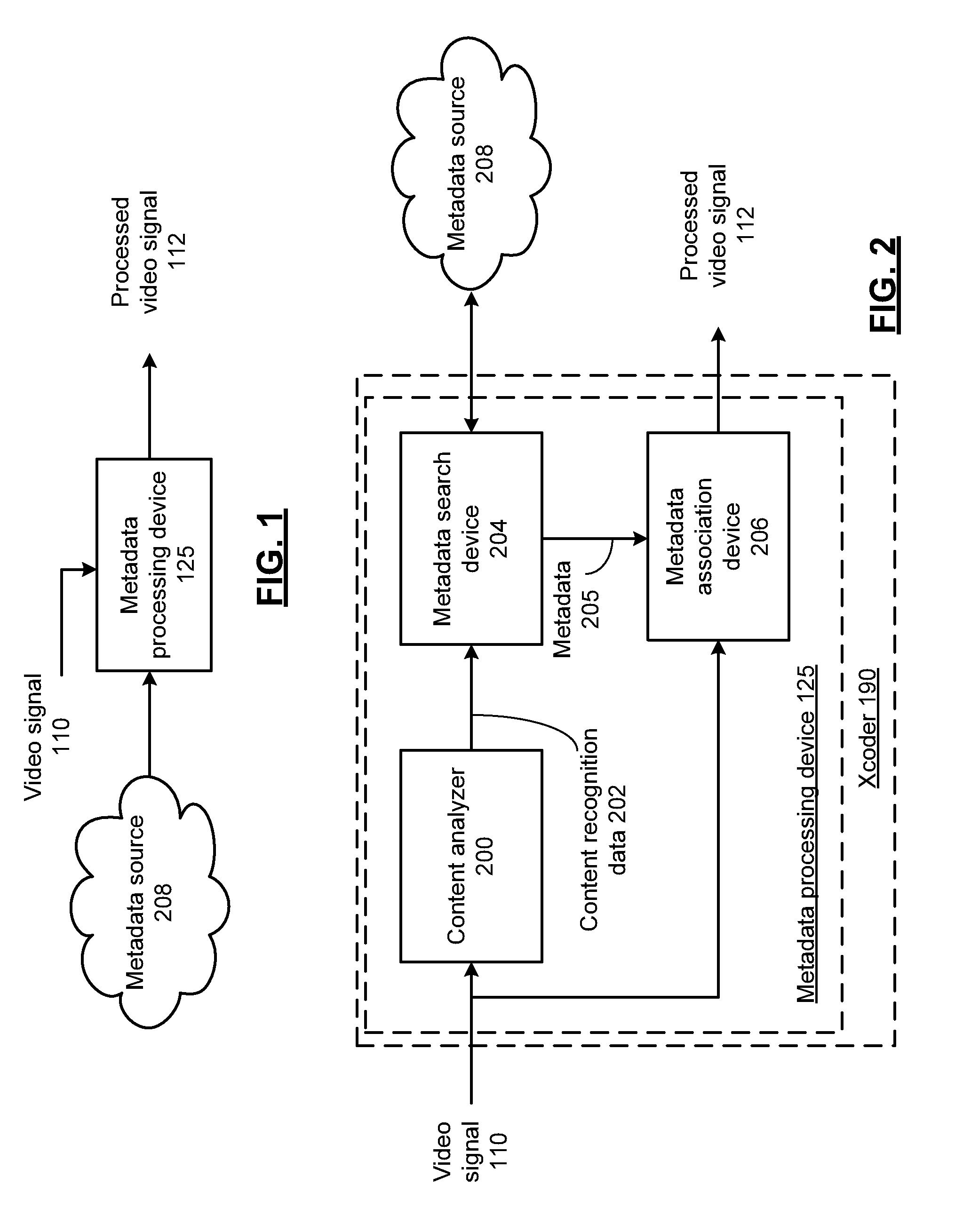
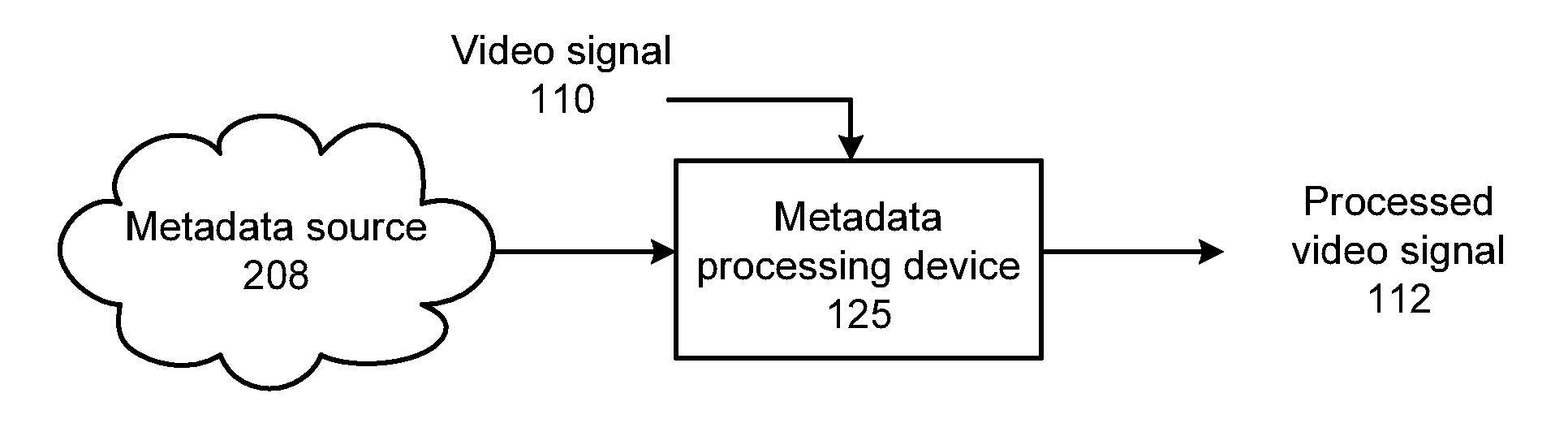
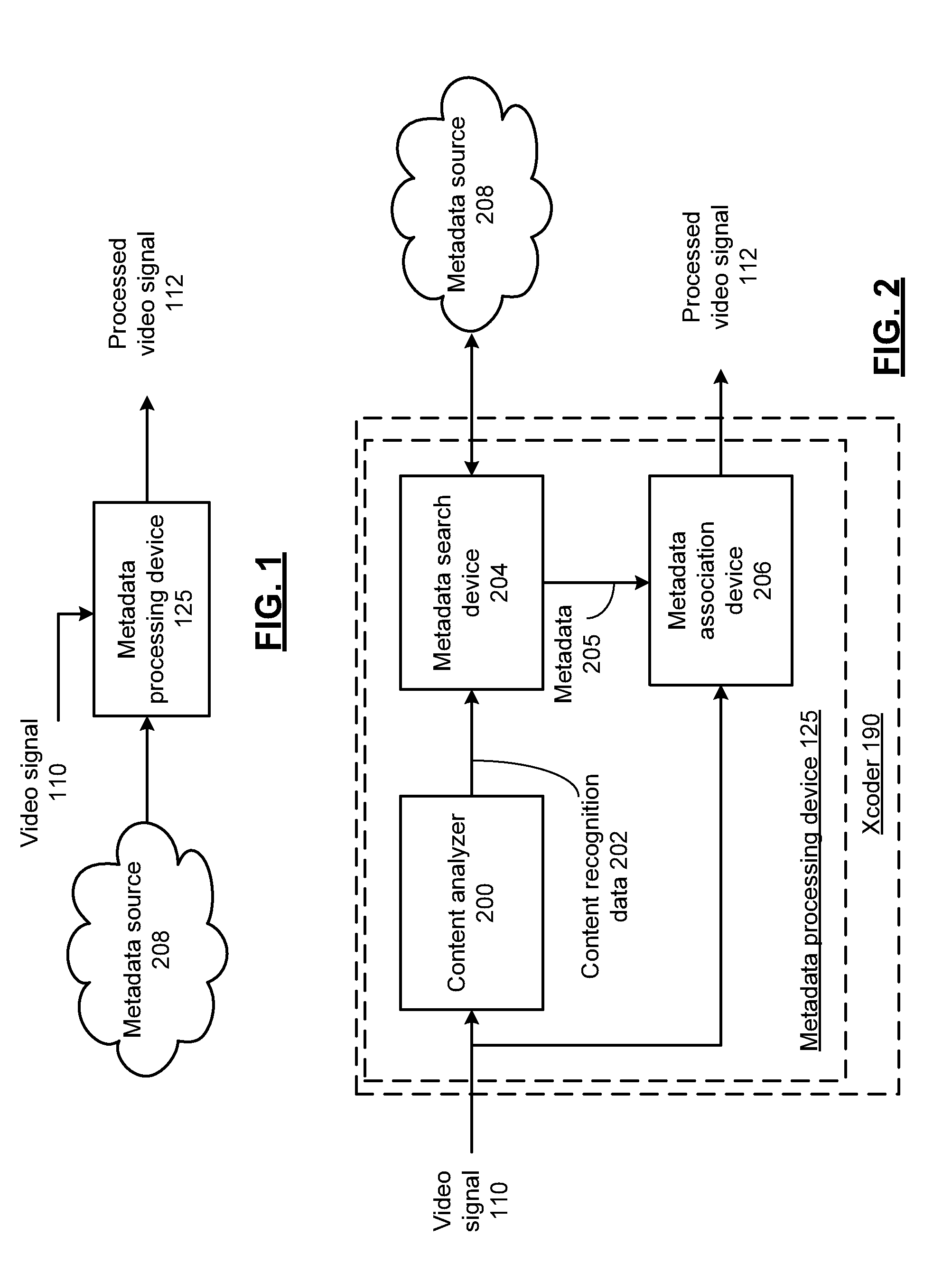
Video processing device for embedding time-coded metadata and methods for use therewith
ActiveUS8842879B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationVideo processingMetadata
A video processing device includes a content analyzer that receives a video signal and generates content recognition data based on the video signal, wherein the content recognition data is associated with at least one timestamp included in the video signal. A metadata search device generates time-coded metadata in response to content recognition data and in accordance with the at least one time stamp. A metadata association device generates a processed video signal from the video signal, wherein the processed video signal includes the time-coded metadata.
Owner:PIXELWORKS
Real-time code preview for a model based development process
InactiveUS7849440B1Visual/graphical programmingSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsGraphical user interface
In a graphical modeling environment, a preview of code generated in response to a selected component in a graphical model is presented using a graphical user interface. The code preview provides feedback to a user regarding the impact of the settings for the selected component, allowing the user to observe the effect of certain settings before generating code for the entire graphical model. The code preview may be presented through the same graphical user interface used to select the settings for the component, or a separate graphical user interface.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Reduced complexity receiver for space-time- bit-interleaved coded modulation
InactiveUS7095812B2Improve bit error rate performanceReduce in quantityData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionMulti inputRadio channel
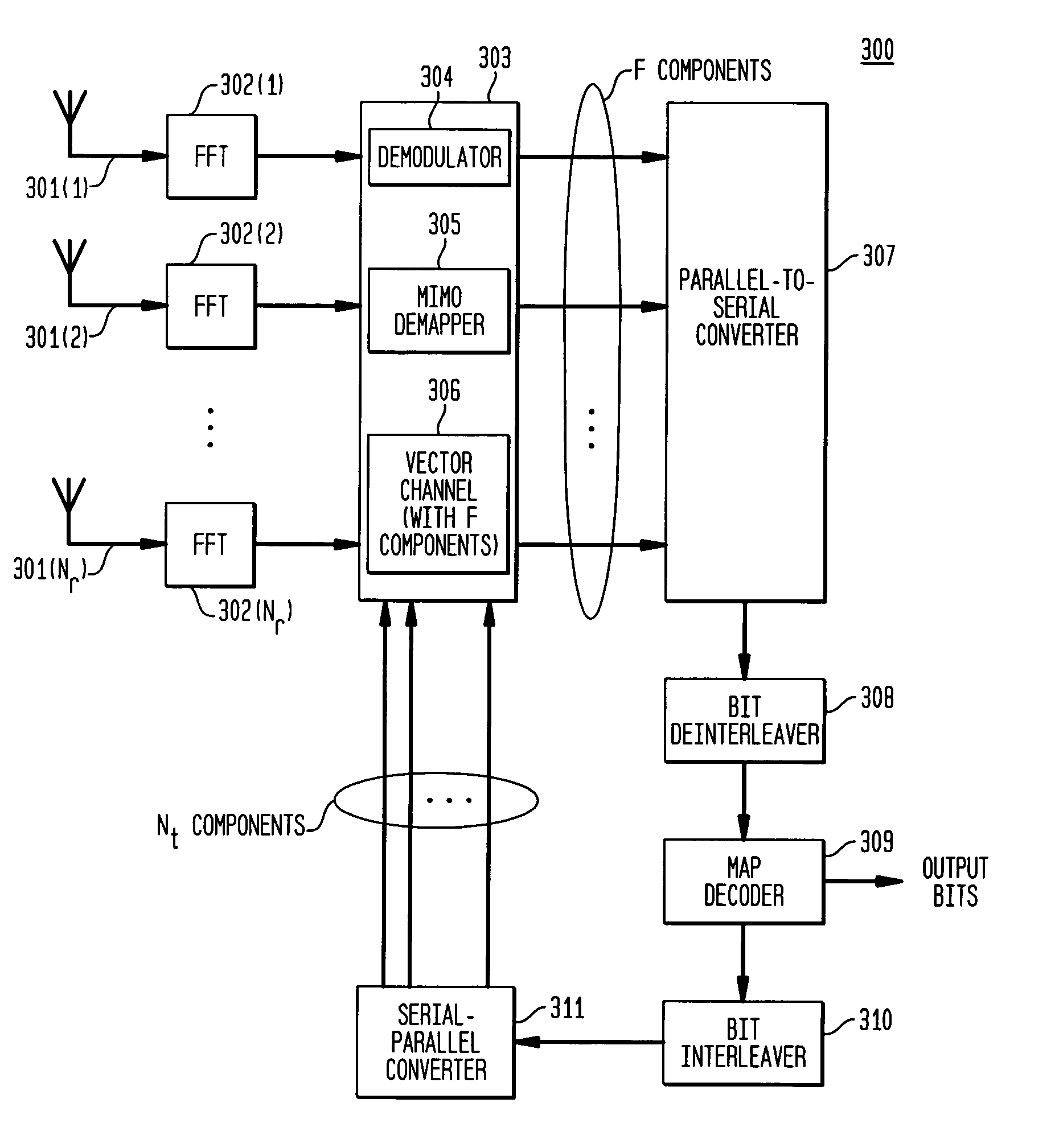
A system employs space-time coding characterized at the transmitter by bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) combined with modulating several streams of the BICM encoded data for transmission over two or more antennas. Space-time coding techniques improve transmission efficiency in radio channels by using multiple transmit and / or receive antennas and coordination of the signaling over these antennas. Bit-interleaved coded modulation provides good diversity gain with higher-order modulation schemes that employ binary convolutional codes. A receiver demodulates the received signals and applies multi-input, multi-output (MIMO) demapping to estimate the BICM encoded bitstream. After deinterleaving of the BICM encoded bitstream, maximum a posteriori (MAP) decoding is applied to the resulting bit stream to generate soft output values. By applying well-known turbo-decoding principles to iteratively demap and decode, the overall receiver performance is significantly improved. The MIMO demapping and MAP decoding processes exchange likelihood information to improve the bit error rate performance over several iterations of demapping / decoding. By generating tentative decisions for transmitted bits, the overall number of evaluations used for demapping may be reduced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
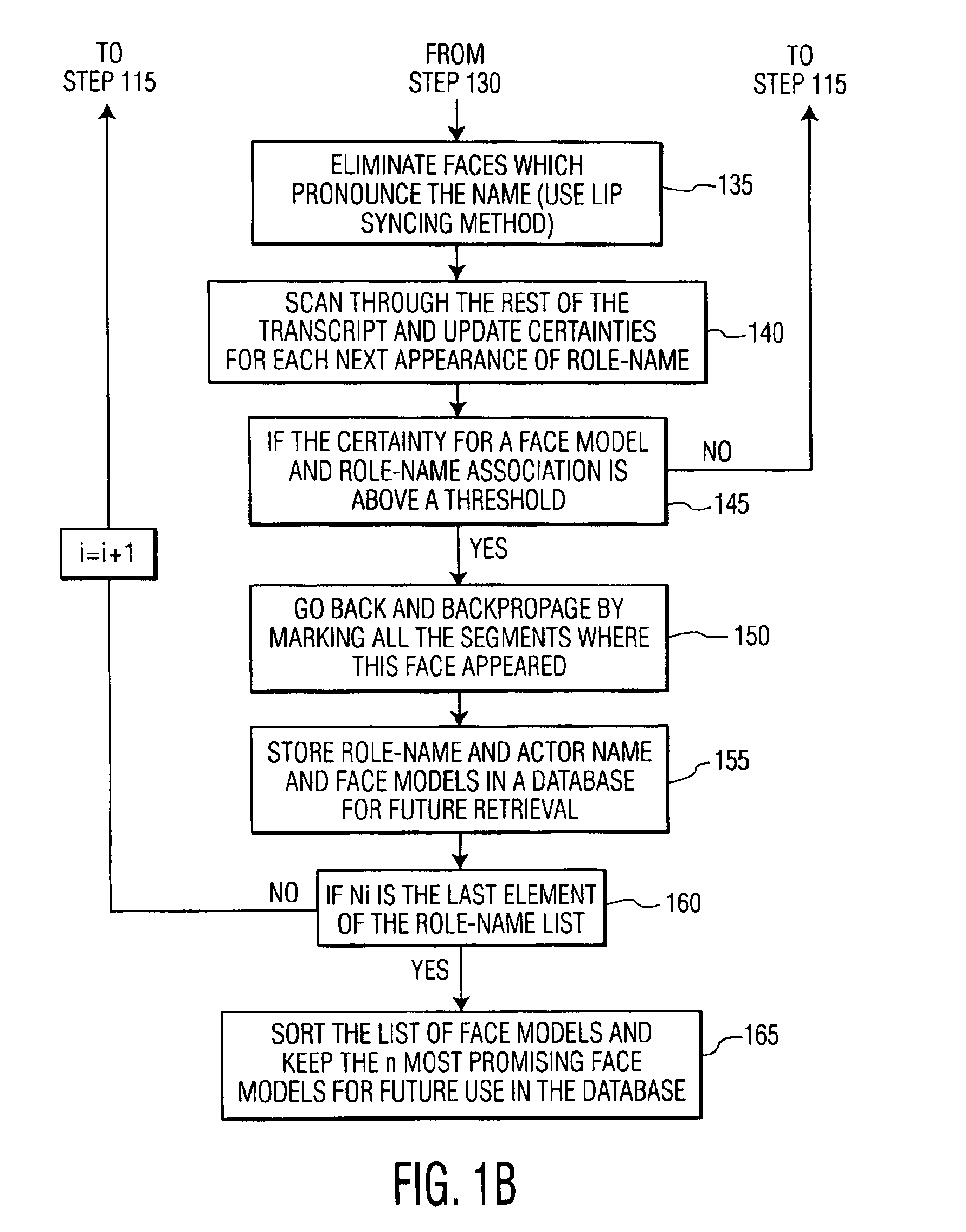
Method and system for name-face/voice-role association
InactiveUS6925197B2Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsText recognitionVideo sequence
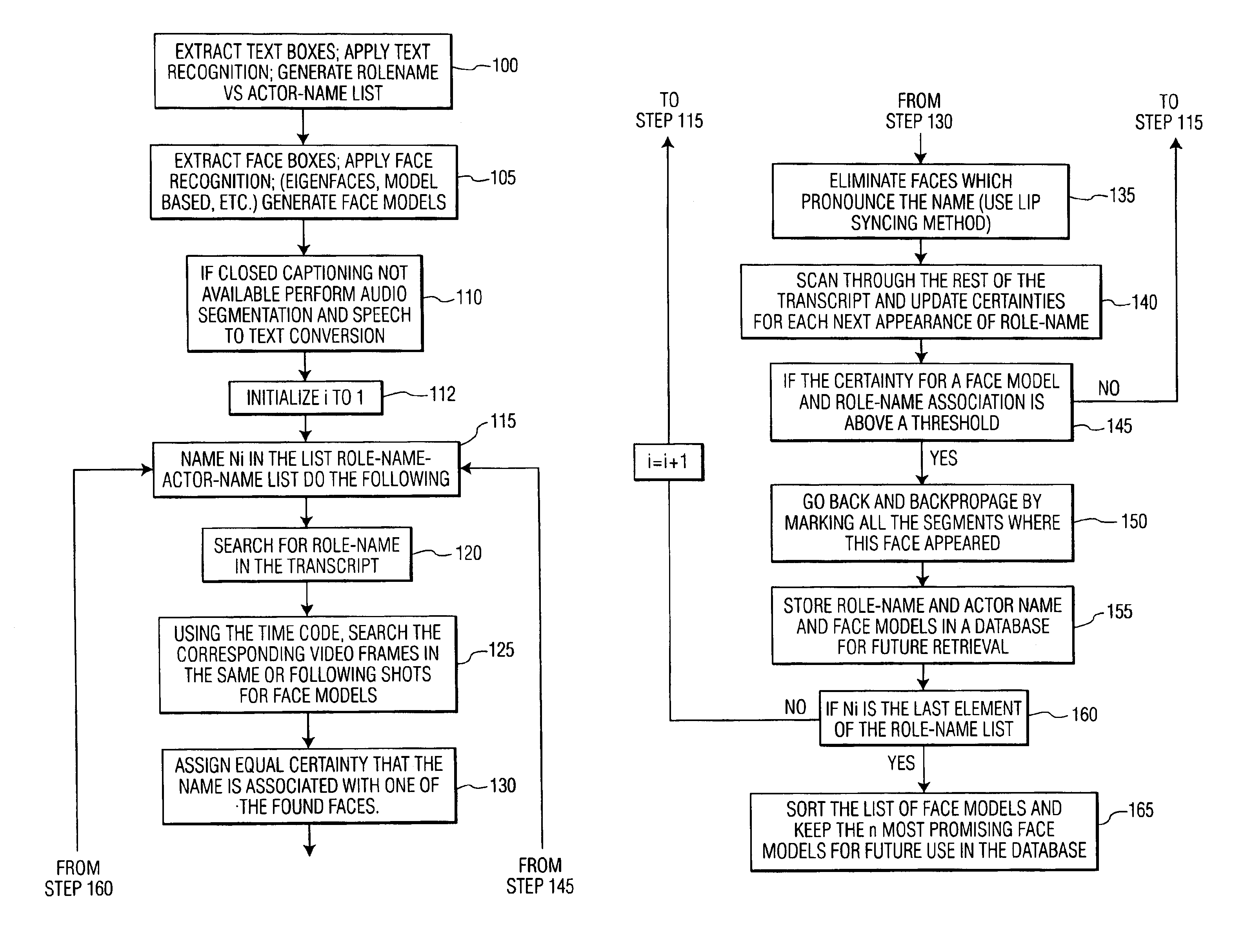
A method for providing name-face / voice-role association includes determining whether a closed captioned text accompanies a video sequence, providing one of text recognition and speech to text conversion to the video sequence to generate a role-name versus actor-name list from the video sequence, extracting face boxes from the video sequence and generating face models, searching a predetermined portion of text for an entry on the role-name versus actor-name list, searching video frames for face models / voice models that correspond to the text searched by using a time code so that the video frames correspond to portions of the text where role-names are detected, assigning an equal level of certainty for each of the face models found, using lip reading to eliminate face models found that pronounce a role-name corresponding to said entry on the role-name versus actor-name list, scanning a remaining portion of text provided and updating a level of certainty for said each of the face models previously found. Once a particular face model / voice model and role-name association has reached a threshold the role-name, actor name, and particular face model / voice model is stored in a database and can be displayed by a user when the threshold for the particular face model has been reached. Thus the user can query information by entry of role-name, actor name, face model, or even words spoken by the role-name as a basis for the association. A system provides hardware and software to perform these functions.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Card with illuminated codes for use in secure transactions
Owner:X CARD HLDG
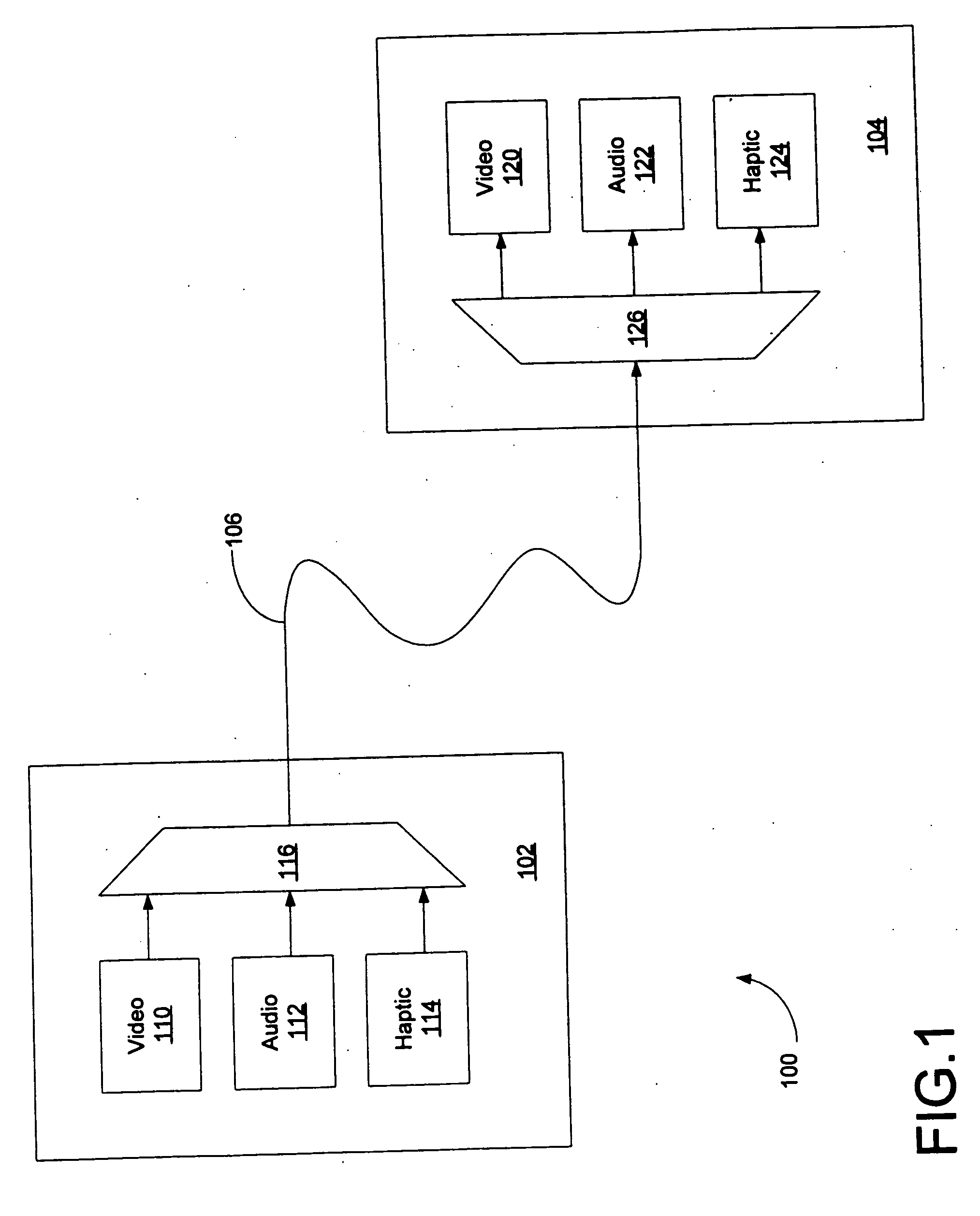
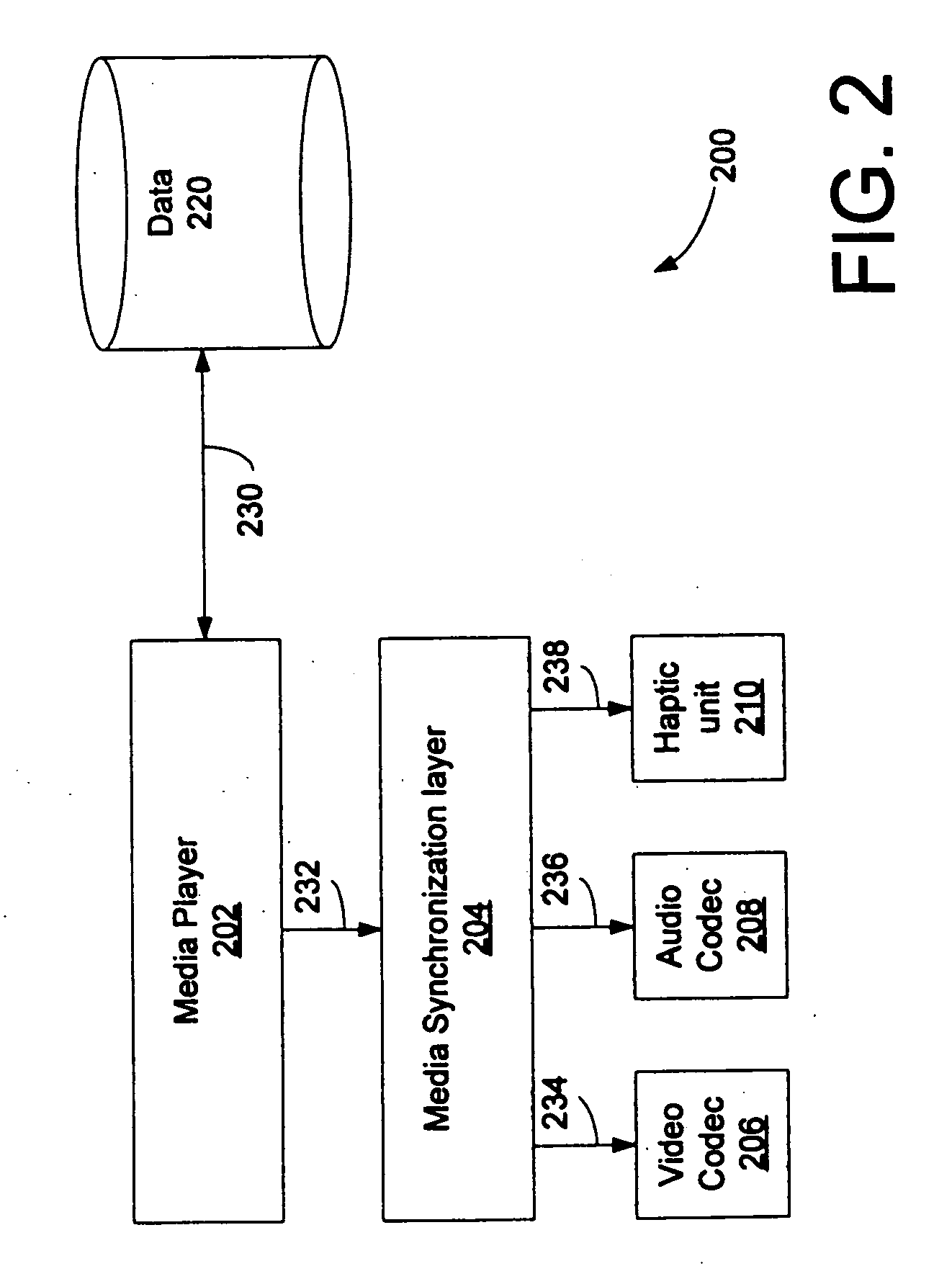
Synchronization of haptic effect data in a media transport stream
Haptic information in a series of frames of a media transport stream is identified and time stamps corresponding thereto are determined in accordance with a master time code signal embedded in the media transport stream. Each media transport stream frame containing haptic information is subsequently assigned a time stamp so that it will be used to activate an actuator at a proper time responsive to the time stamp to generate a haptic effect in accordance with the haptic information.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
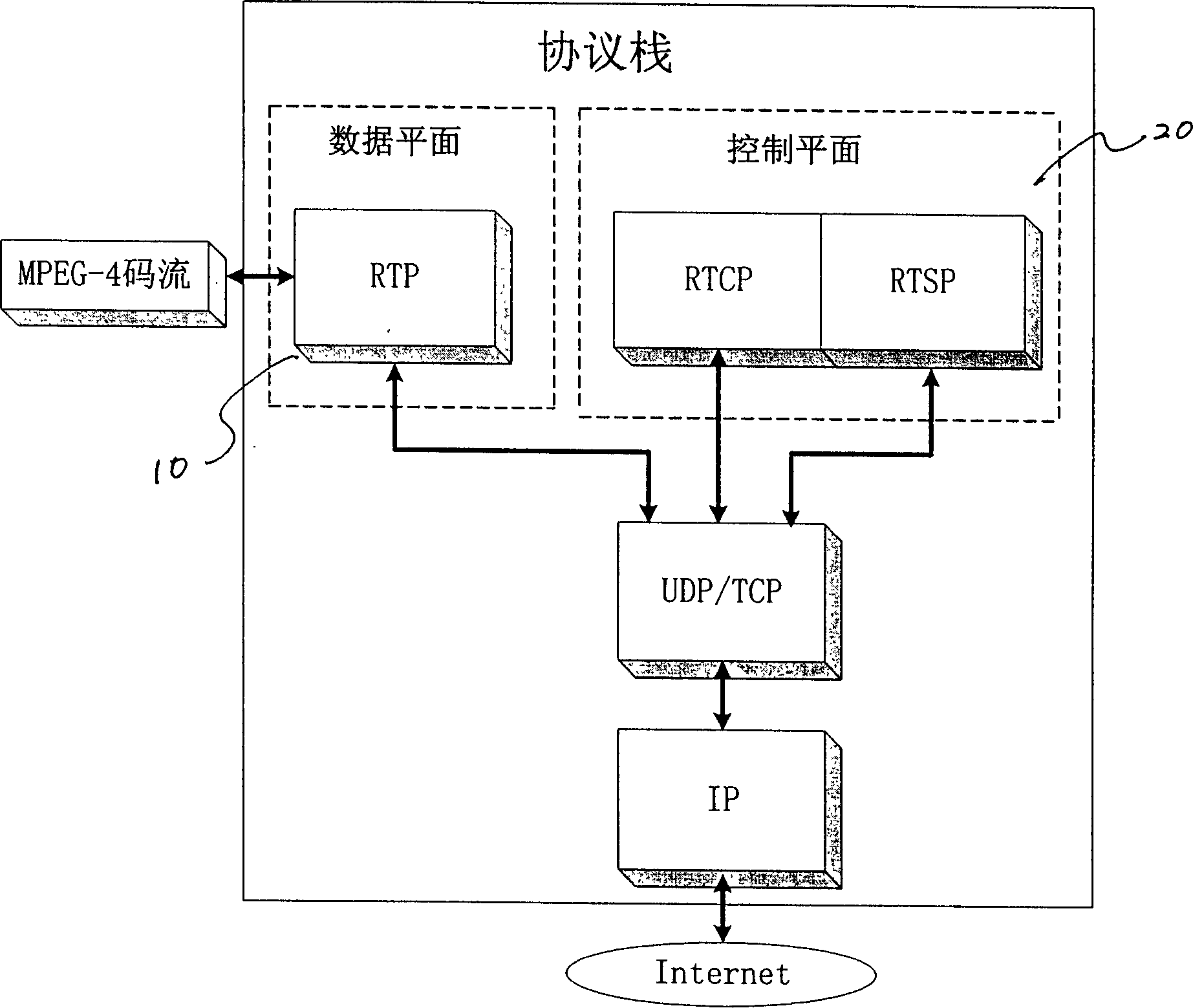
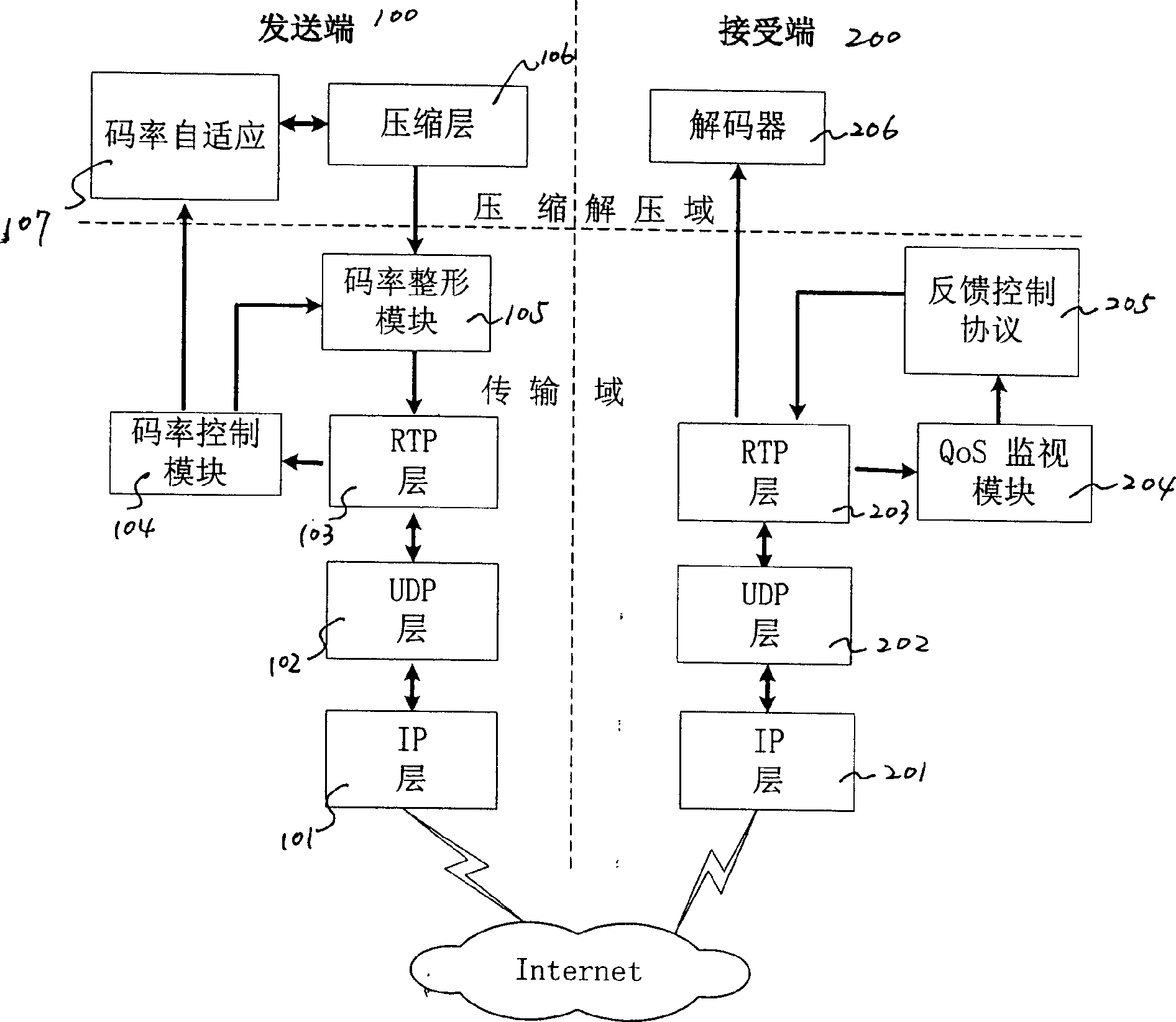
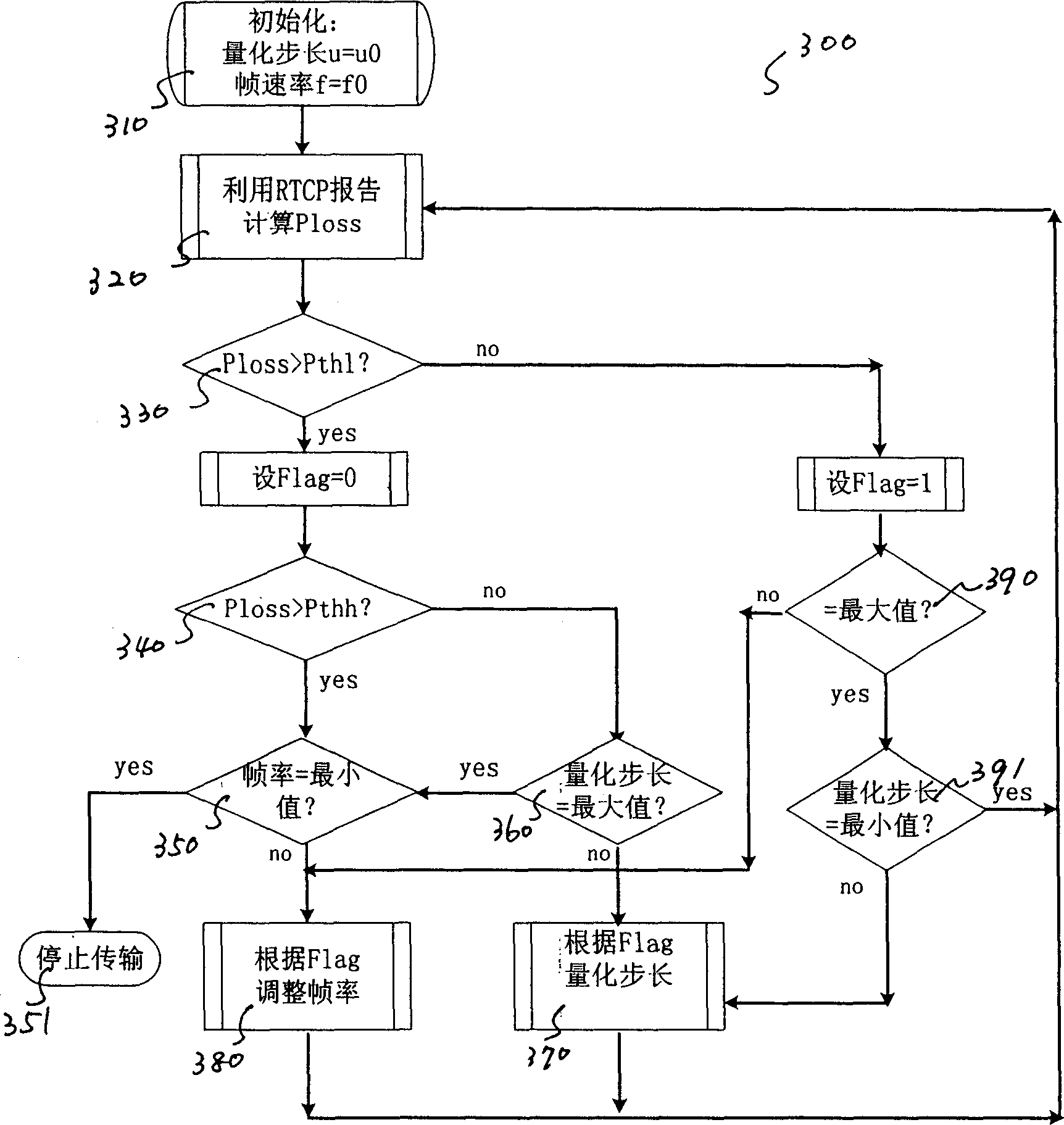
Media flow self-adapting transmission method based on internet
The invention discloses a media stream self-adapting transporting method based on the internet comprising, a. establishing RTP / UDP / IP protocol structure, wherein the data plane of the protocol structure is in charge of using the media video stream and audio stream packaged by RTP, while the control plane of the protocol structure transmits the control instructions simultaneously using the RTCP feed back network information and RTSP, establishing a congestion control structure based on the transmitting end that can be applied both in the real time coding and in the video frequency transfer storage. The invention can realize the best playback quality possible on the user end under the changes of the network operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUNTEK TECH
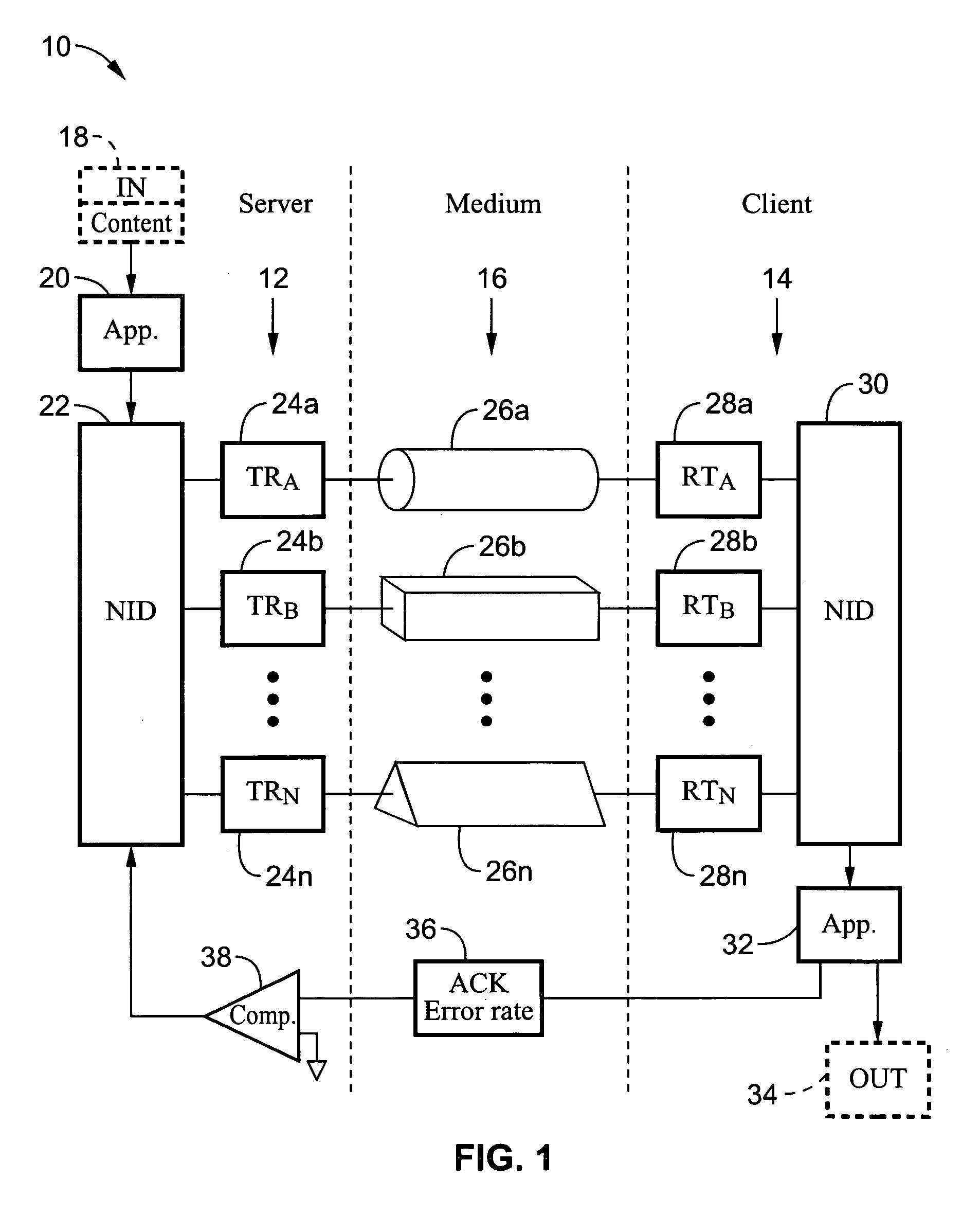
Reliable audio-video transmission system using multi-media diversity
ActiveUS20060062243A1Improve service qualityCharacteristic is differentNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexQuality of servicePower line network
A system and method for switching data packet traffic distribution across diverse transmission medium according to detected quality of service characteristics for a given data packet rate from server to client. It should be recognized that diverse medium are not interdependent with regard to fading or signal strength considerations. Two general modes of switching are described, switching all the data packets, and switching according to a media-time coding mechanism. In one embodiment the data is encoded using Fountain encoding prior to transmission. The data packet transmissions preferably comprise audio-video data packet streams, such as MPEG-2 streams. By way of example, the diverse transmission medium may comprise a wireless connection (i.e., WiFi) used in combination with a power-line network connection, such as within a home network.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Dual mode adaptive threshold architecture for 3-D ladar FPA
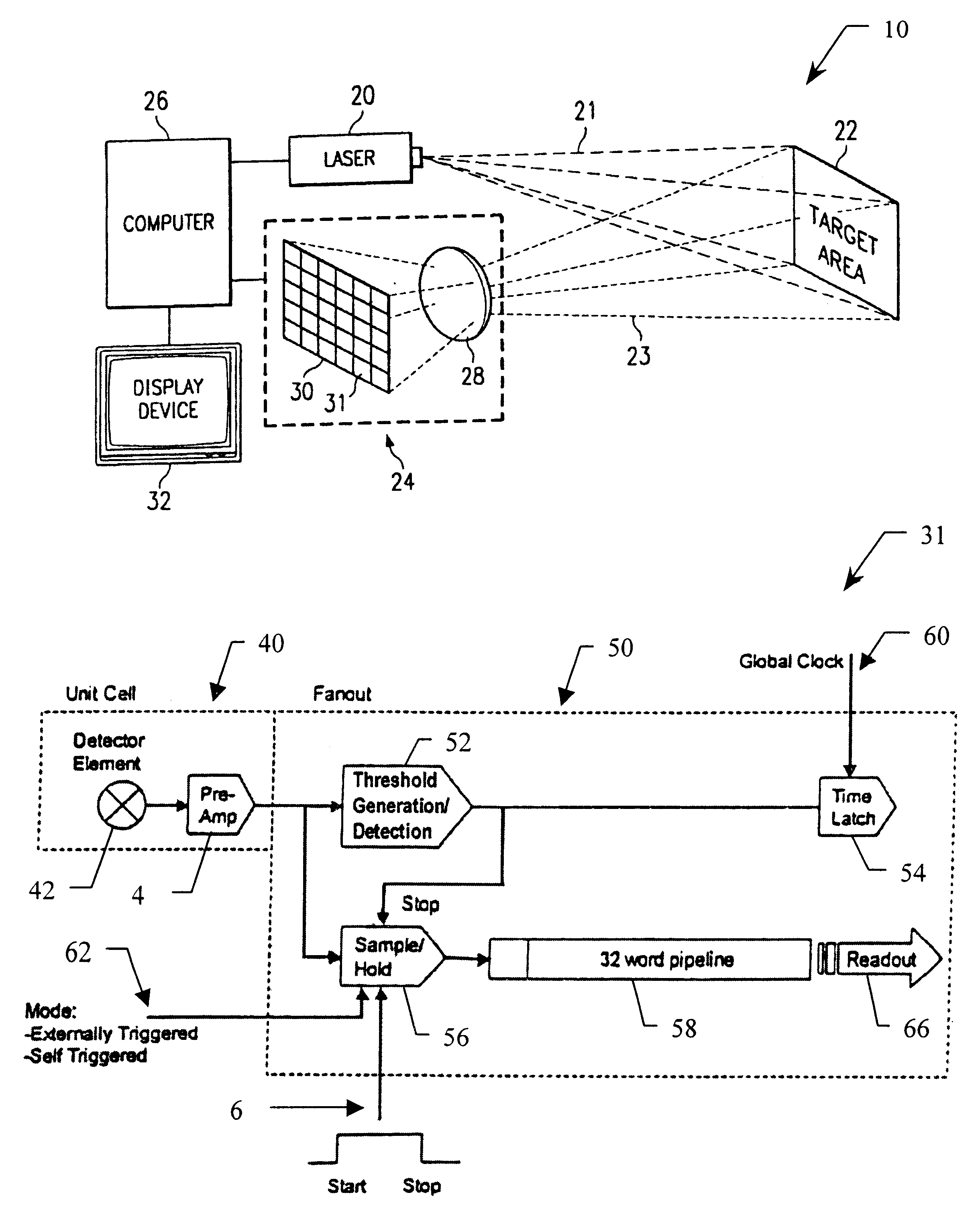
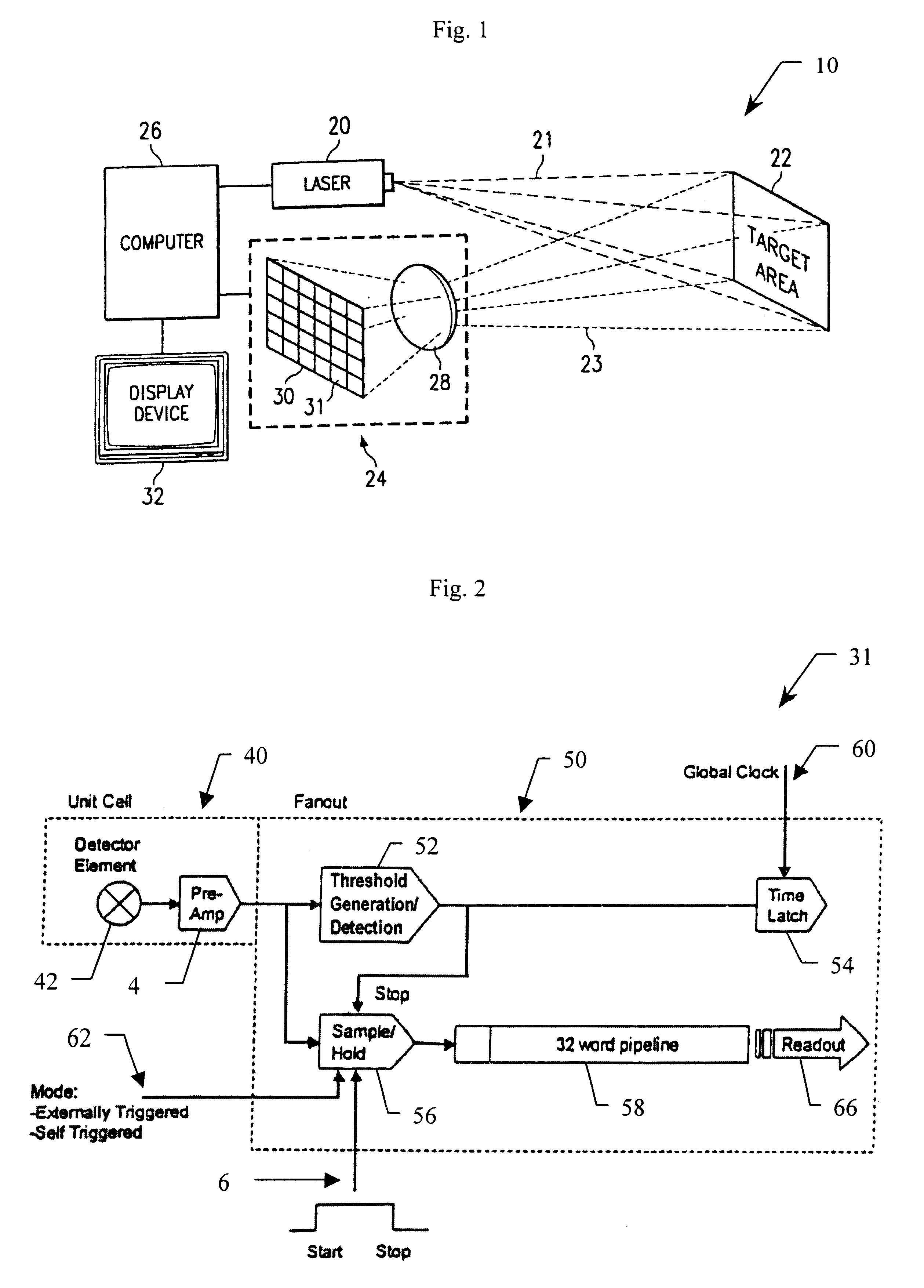
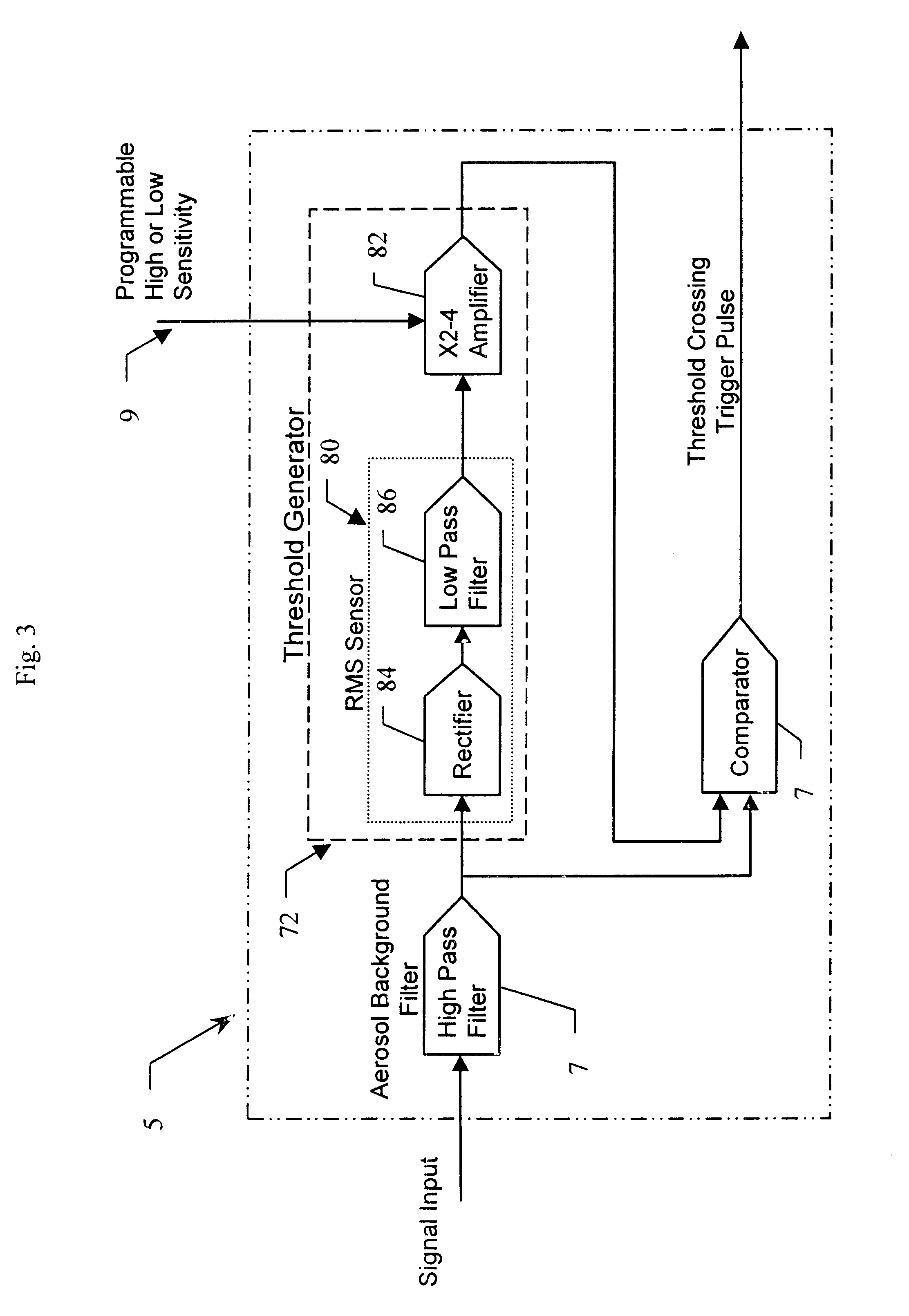
An integrated detector and signal processor (31) for ladar focal plane arrays (30) which internally compensates for variations in detector gain, noise, and aerosol backscatter. The invention (31) is comprised of a detector element (42) for receiving an input signal, a circuit (72) for generating a threshold based on the RMS noise level of the input signal, and a circuit (74) determining when the input signal is above that threshold. The detector element (42) is physically located in the interior of the detector array (30), while the signal processing circuitry (50) is located on the periphery of the array (30). In the preferred embodiment, the signal processor (31) also includes a circuit (56) for sampling the input signal and a circuit (58) storing multiple samples, allowing for multiple returns to be detected. In the preferred embodiment, the signal processor (31) can be operated in two modes: self triggered and externally triggered (range-gate mode). In the self triggered mode, the detector continually monitors and samples the incoming signal until a return is detected (by the thresholding circuit). In the range-gate mode, the detector stops sampling when it receives a signal from an external source. Once the data has been acquired, readout electronics (66) output the stored samples along with the stored "stopped" time code to an external computer (26).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Video editing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060206526A1Improve user interactionElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsUsing non-detectable carrier informationComputer configurationData store
A computer video editing system and method in a network of computers is disclosed. The system and method include a datastore or other source of subject video data, a transcription module and an assembly member. The transcription module generates a working transcript of the corresponding audio data of subject source video data. The working transcript includes original source video time coding for the passages (statements) forming the transcript. The assembly member enables user selection and ordering of transcript portions. For each user selected transcript portion, the assembly member, in real-time, (i) obtains the respective corresponding source video data portion and (ii) combines the obtained video data portions to form a resulting video work. The resulting video work is displayed to users and may be displayed simultaneously with display of the whole original working transcript to enable further editing and / or user comment. A text script of the resulting video work is also displayed. The video editing system and method may be implemented in a local area network of computers, as a browser based application on a host in a global computer network, as well as on stand alone computer configurations with a remote or integrated transcription service. The subject video data may be from a video blog, email, a user discussion thread or other user forum based on a computer network.
Owner:PORTALVIDEO
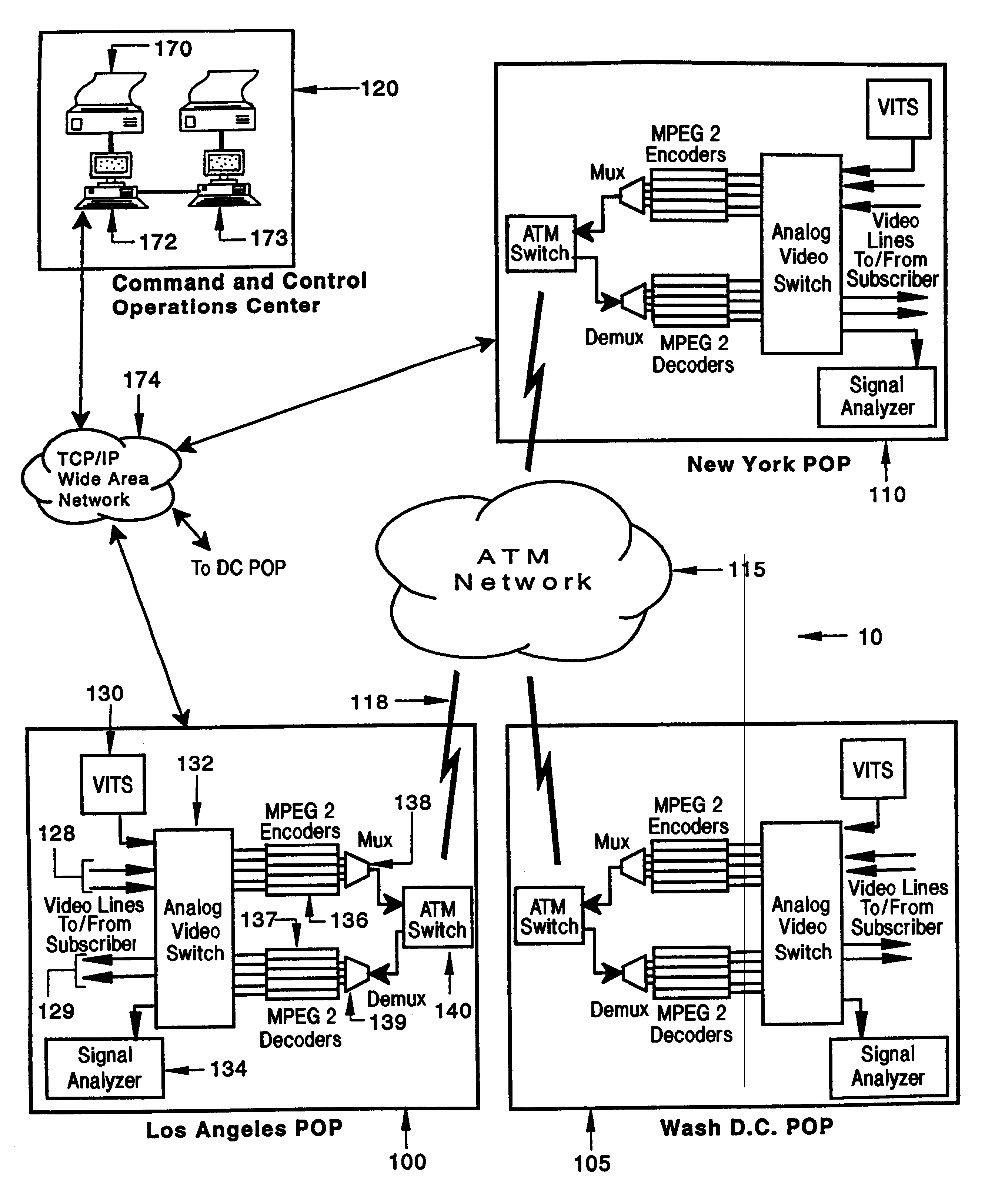
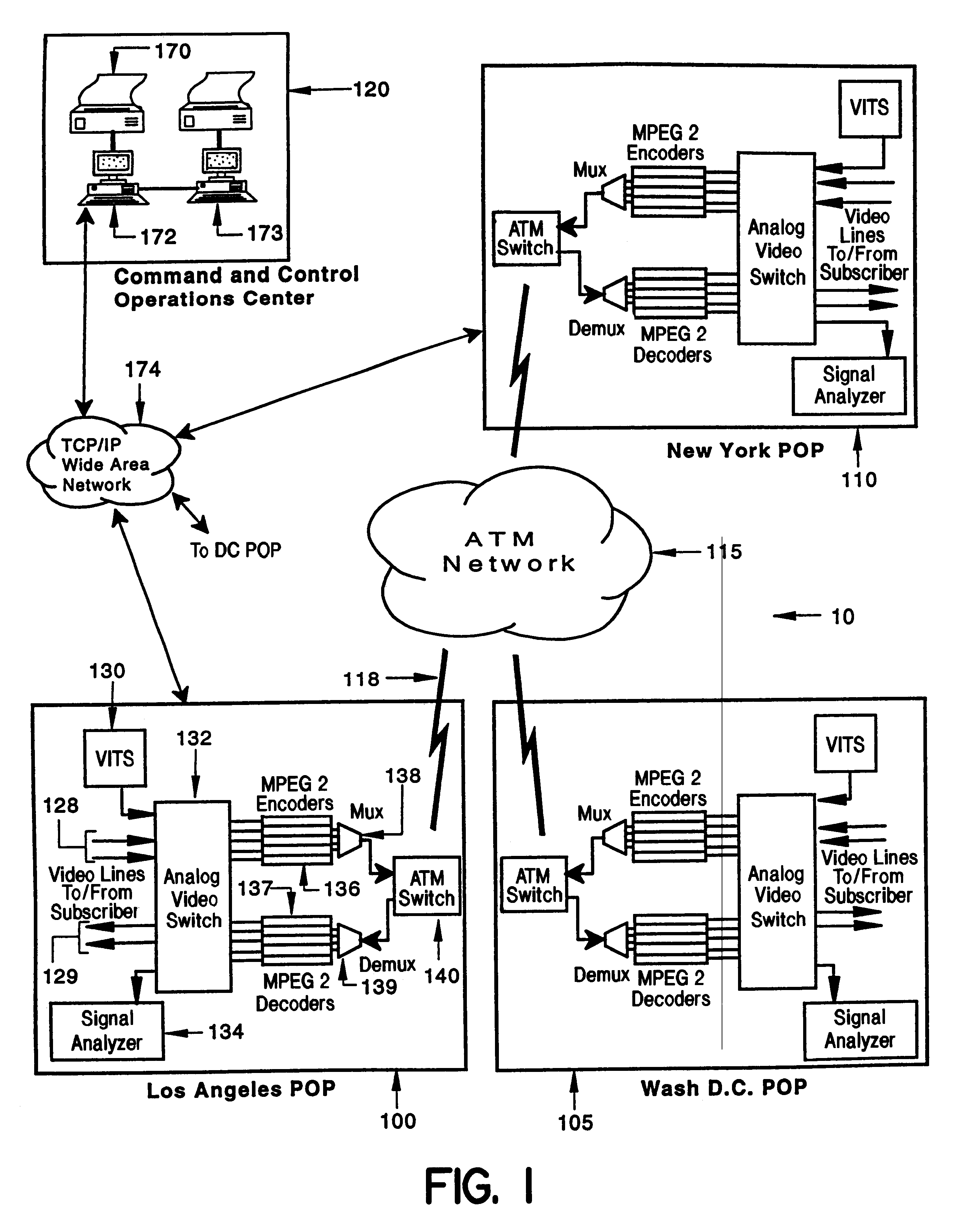
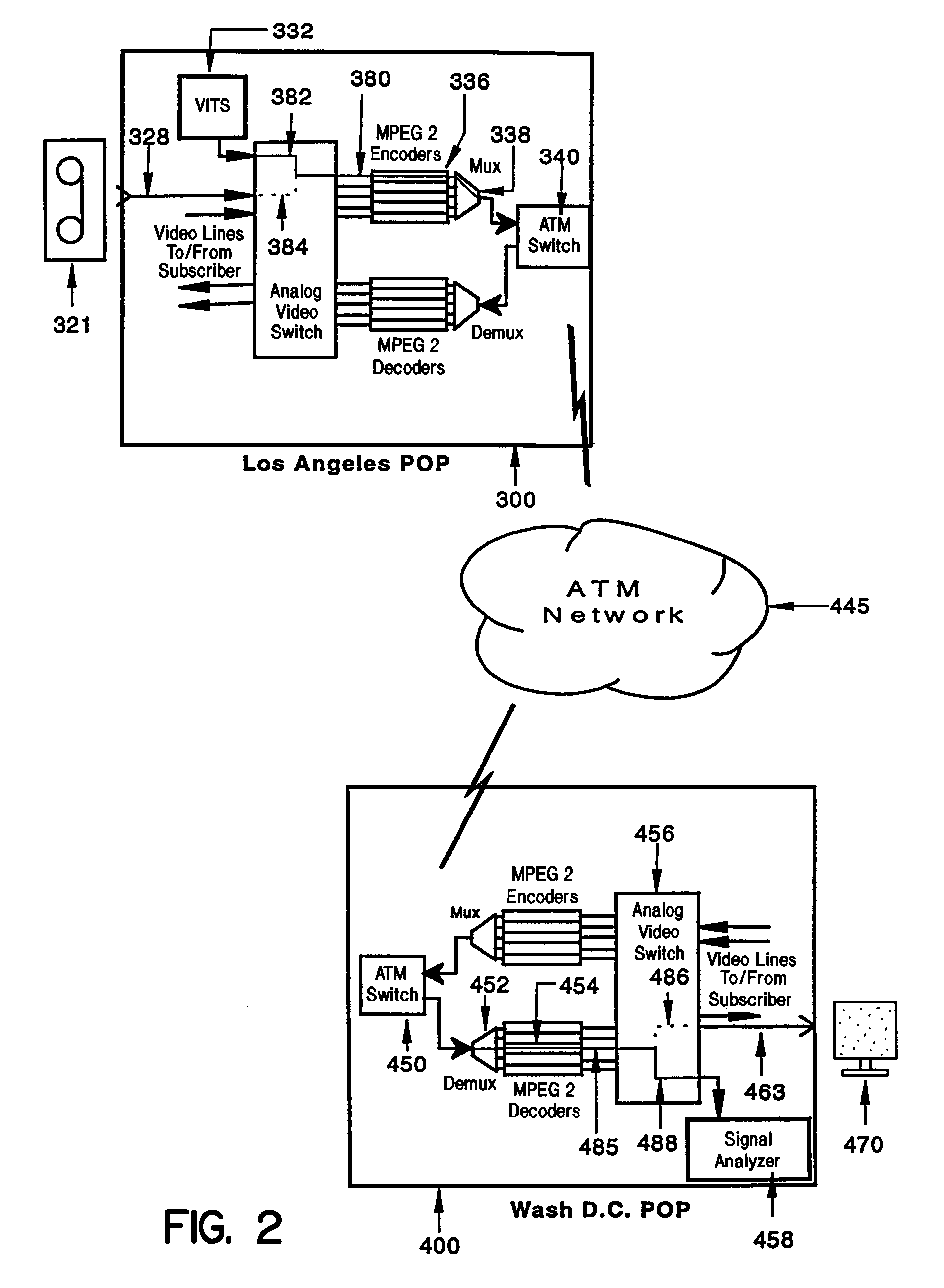
System and method of in-service testing of compressed digital broadcast video
A switched digital video broadcast network provides in-service testing of digitized broadcast video signals subject to analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion. The network includes a plurality of gateways, each gateway coupled to video signal sources and sink. Video frames transmitted on the network are subject to analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion and compression in an MPEG 2 encoder / decoder. Each gateway and includes a test pattern generator and test measurement analyzer for in-service testing of the video signals. The test pattern generator inserts a test signal on pre-selected lines (22, 23 or 261,262) in a Video Blanking Interval (VBI) and time periods of a video frame. The test signal may be dynamically placed at any location in the frame using concealment techniques The video lines are not seen by television viewers. The test pattern generator and test measurement analyzer are synchronized using vertical integral time code and a trigger packet sent by the transmitting station. The test signals enable both in-service and out-of-service testing to be performed for the entire suite of EIA / TIA 250C standard video tests.
Owner:IBM CORP
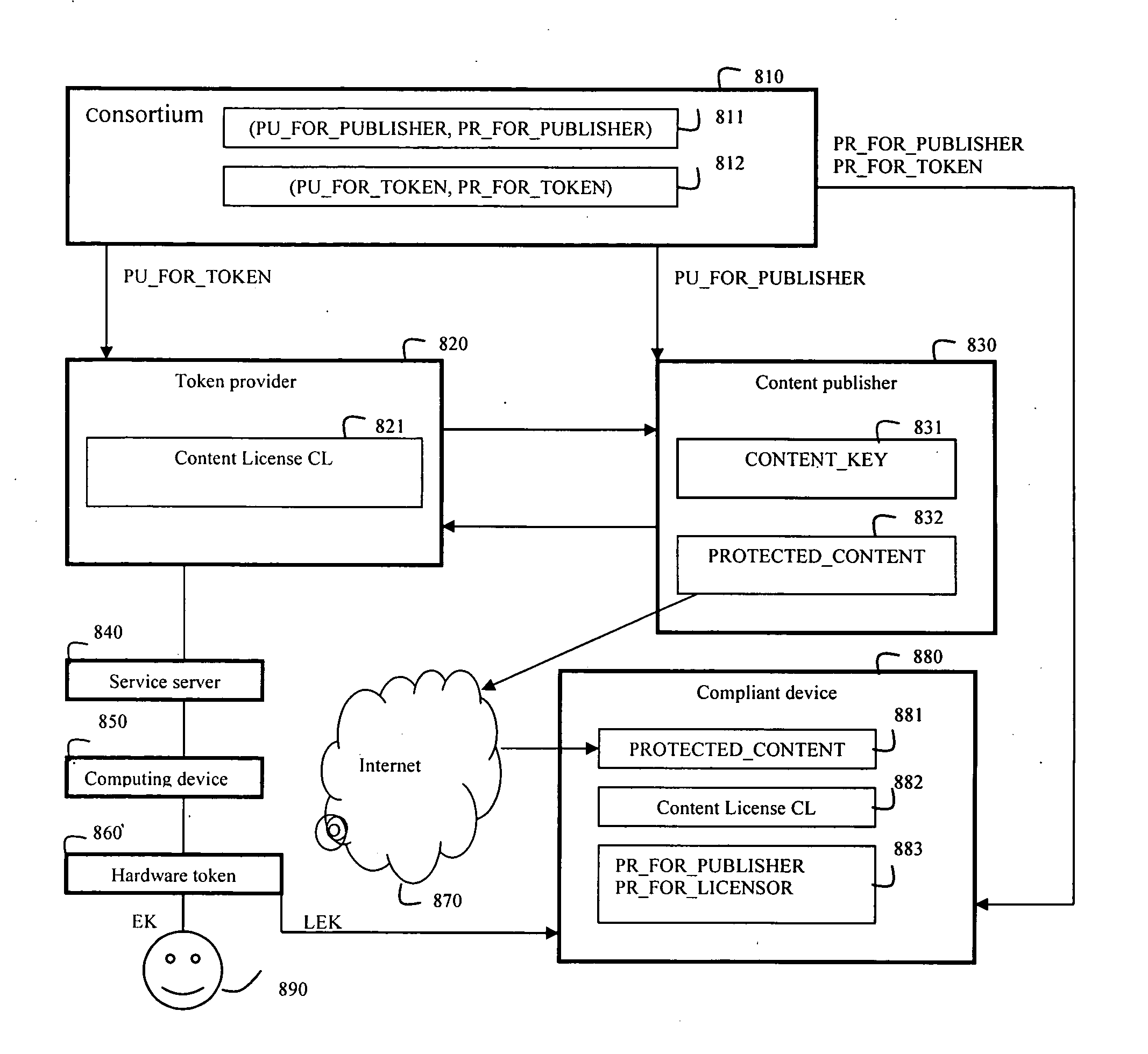
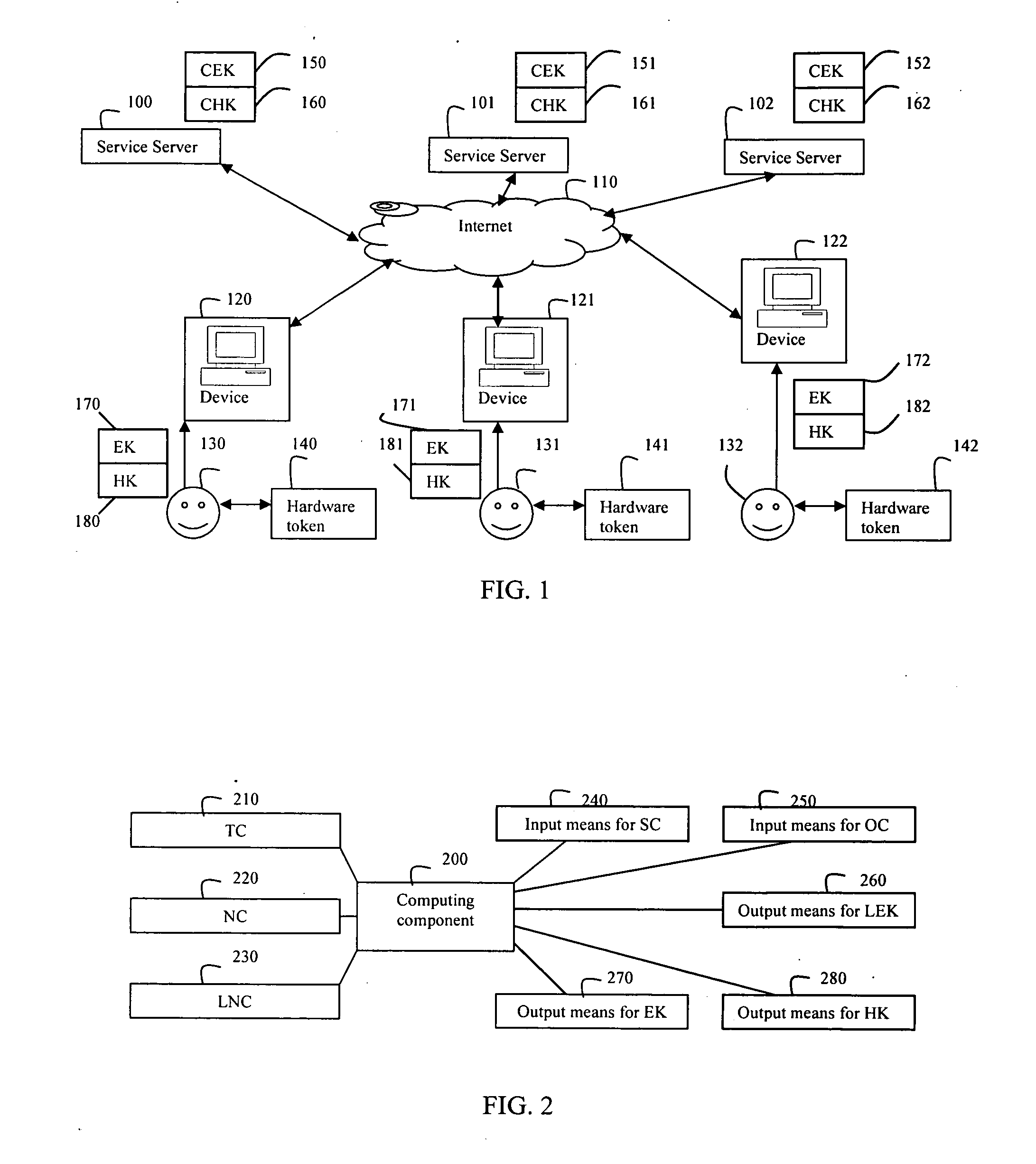
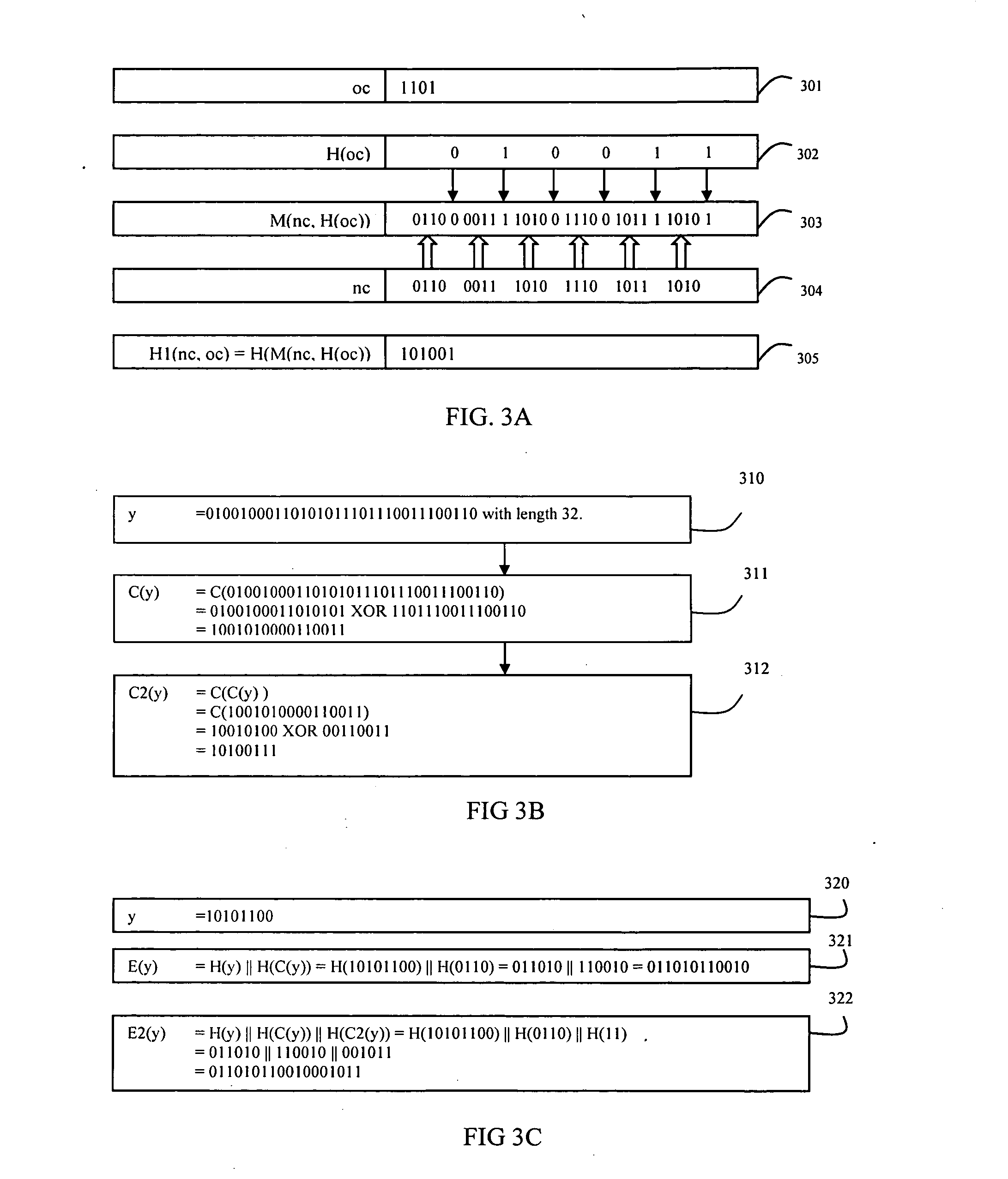
System and method for user authentication with exposed and hidden keys
InactiveUS20080240447A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageDigital contentOnline and offline
The present invention relates to a system and method for digitally authenticating users both online and offline. In one embodiment, a hardware token assigned by a trusted token provider to the user is employed to ensure the identity of the user. In the online authentication, the token is adapted for generating an exposed key EK and a hidden key HK based on a noise code NC and a time code TC of the token, a space code SC of a service server, and an owner code OC of the user. A login session is initialized by entering a user identifier at the service server and the generated EK from a computing device. The service server computes an expose key CEK and a hidden key CHK based one an authentication license generated by the token provider. The service server authenticates the user if the CEK is same as the EK, and sends a response message encrypted the CHK to the computing device. Then, the user provides the HK to the computing device to decrypt the encrypted response message so as to access his / her account. In the offline authentication, the token is adapted for generating a license exposed key LEK used to render the encrypted digital content on an offline compliant device. The compliant device authenticates the user if a license exposed key computed by the compliant device based on a content license of which the user bought is same as LEK, so as to render the protected digital content after authentication.
Owner:ZHU YUNZHOU +1
Digital presentation apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20090129753A1Desired performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoAudio power amplifier
An apparatus and method is provided for displaying components of a performance. The apparatus includes a computer and a time code generator in communication with the computer and selectively controlled by the computer to generate a time code signal. The system further comprises a digital video recorder with at least one output channel that each have respective video and audio outputs. The digital video recorder is in operable communication with the time code generator and responsive to the time code signal to output at least a portion of a first video component and a corresponding first audio component of the performance synchronized to the time code signal to a respective first video display and first audio amplifier.
Owner:WAGENLANDER CLAYTON
Method and apparatus for digital media management, retrieval, and collaboration
InactiveUS6922691B2Facilitating later searchingEasy to customizeData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData streamComputer graphics (images)
A system has first and second metadata streams with respect to a video stream, the first metadata stream time-coded with respect to the video stream and the second metadata stream not time-coded with respect to the video stream. The the second metadata stream is aligned with the first metadata stream. Time ccodes are added to the second metadata stream, based on the alignment. Proper names are searched for within the second metadata stream. Faces are found within the video stream, faces are matched with proper names, and the matched faces and proper names are placed into a reference library.
Owner:BEN GRP INC
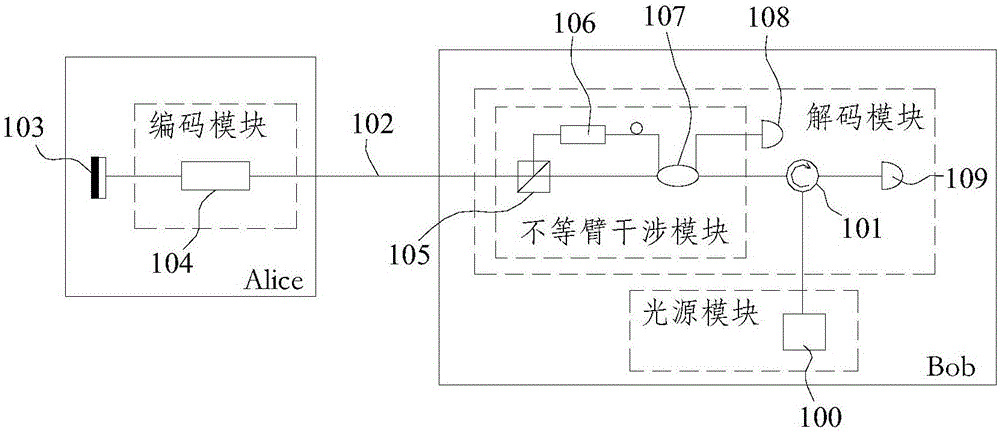
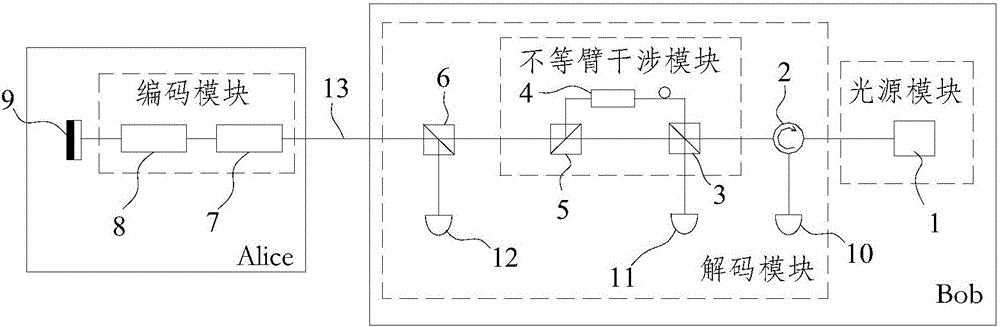
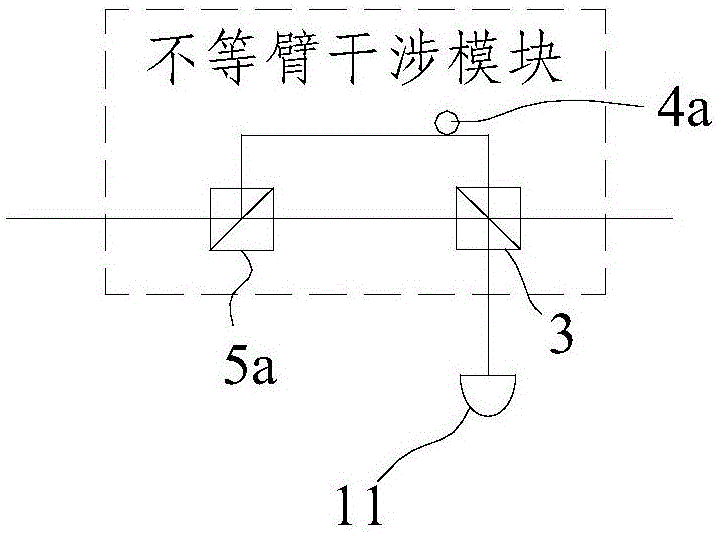
Plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system and method based on time-phase encoding, transmitting end and receiving end
ActiveCN106161011AImprove bit rateKey distribution for secure communicationCode moduleComputer architecture
The invention discloses a plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system and method based on time-phase encoding, a transmitting end and a receiving end. The plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system comprises the transmitting end and the receiving end which are in mutually optical connection, a coding module in the transmitting end comprises a Z basis vector time coding module coding optical signals according to any sequence and a phase coding module which is an X basis vector phase coding module, and a decoding module in the receiving end is matched with the coding module. The plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution method includes: after an Alice end receives and reflects optical signals from a Bob end, performing Z basis vector time coding and phase coding; sending the optical signals after going through Z basis vector time coding and phase coding to the Bob end for decoding and detecting, wherein phase coding refers to X basis vector phase coding. Improved time-phase coding is used, so that ultrahigh-contrast coding and decoding can be realized, and code generating rate can be increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENZHOU QUANTUM NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Delivery and transmission of dolby digital AC-3 over television broadcast
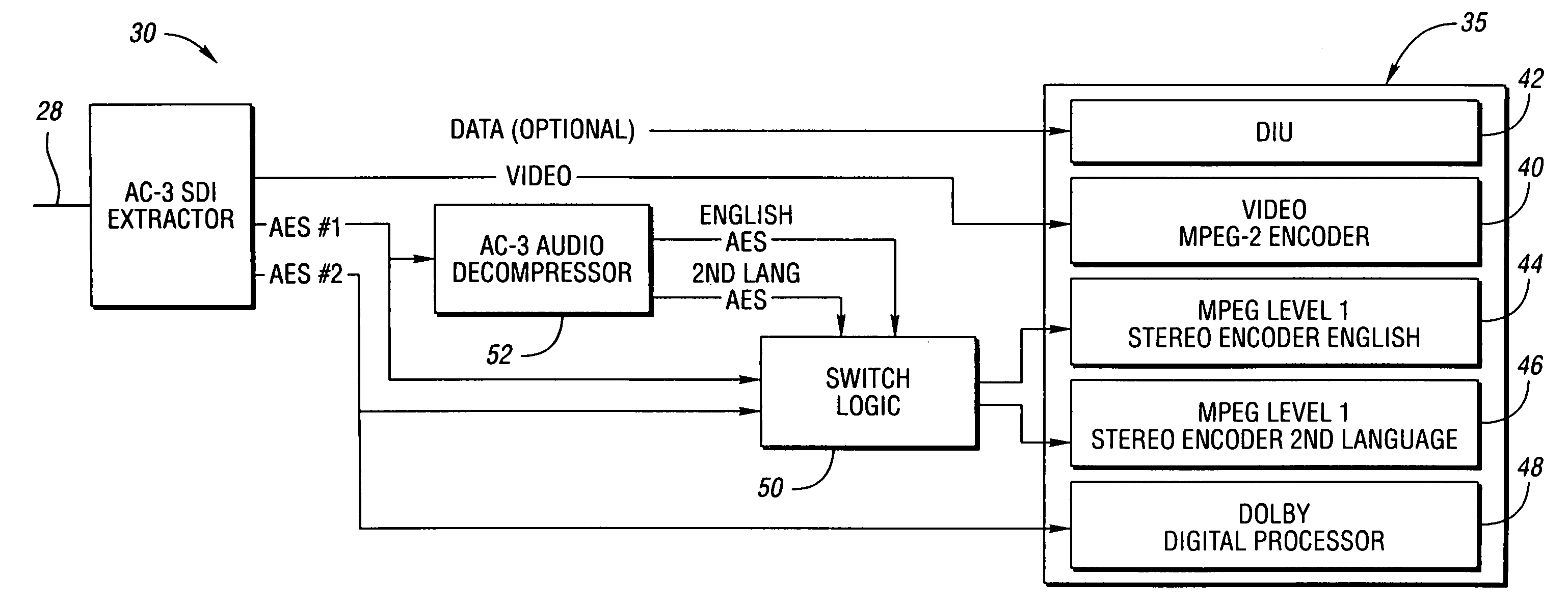
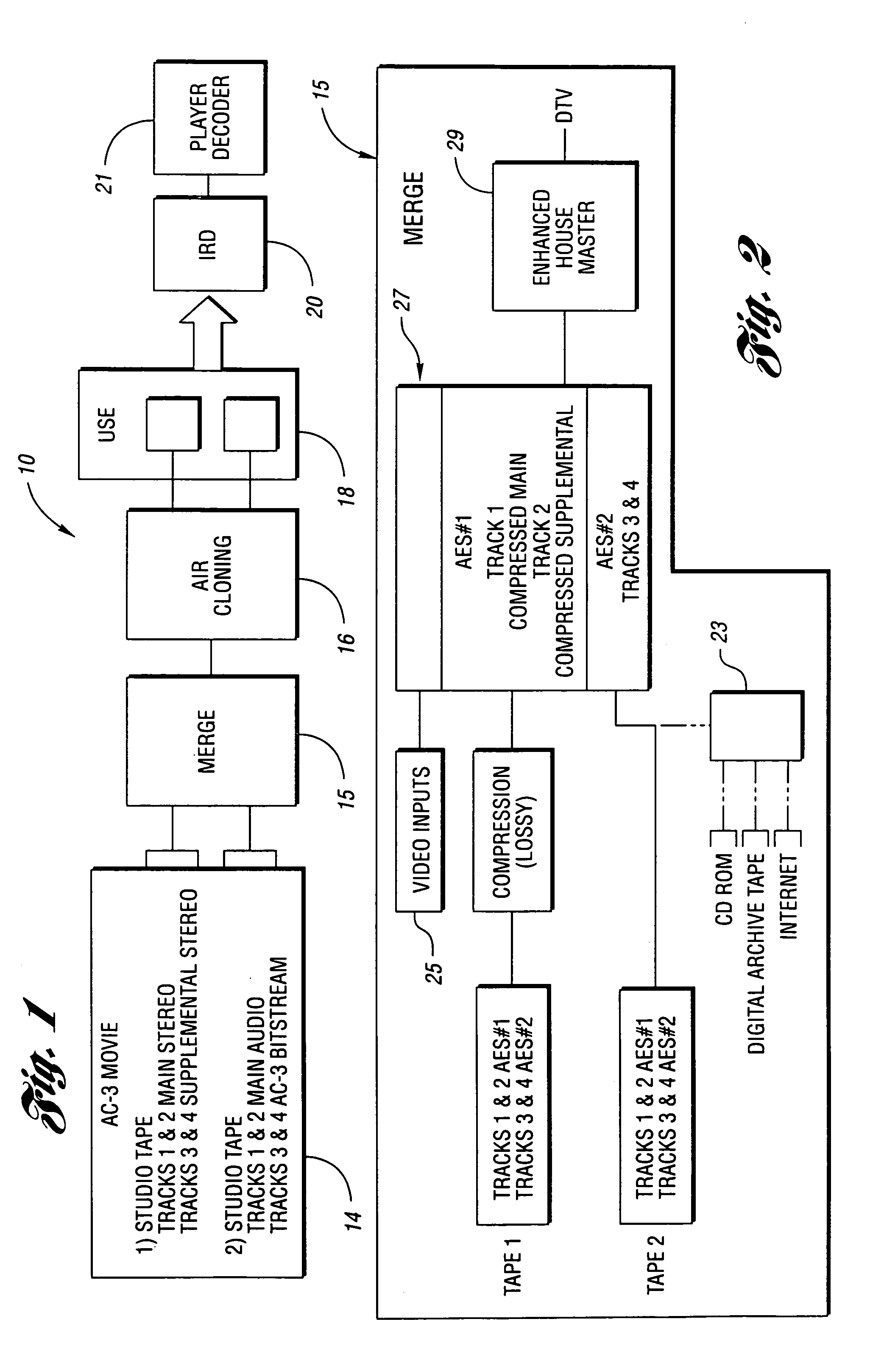
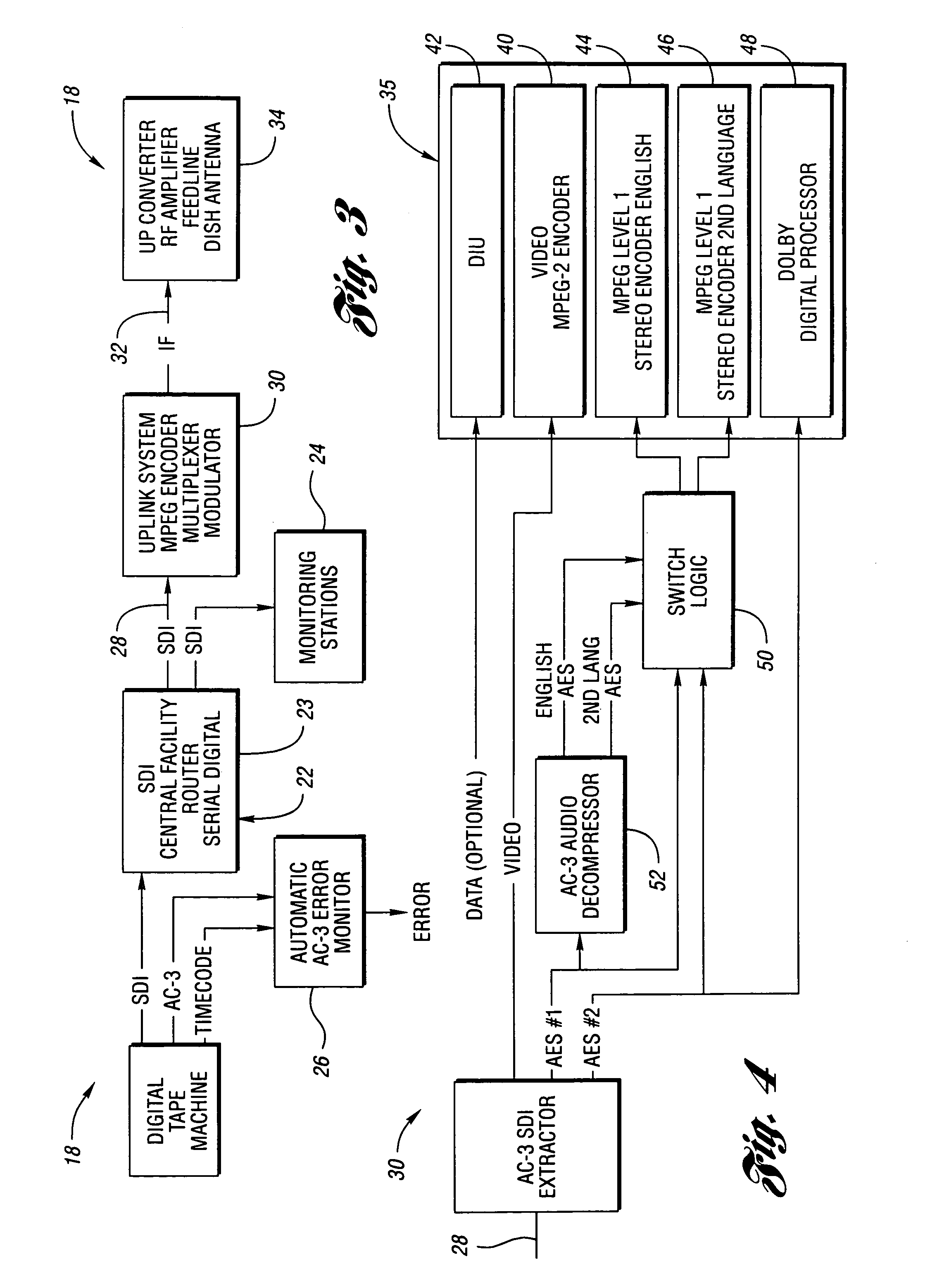
InactiveUS7283965B1Quality assuranceBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisData compressionIntegrated receiver/decoder
Methods and apparatus for broadcasting high quality audio “studio direct” with the same digital information employed in the studio by the video producer with AC-3 digital audio signals for broadcast to integrated receiver decoders (IRD). The methods and apparatus permit proper handling of AC-3 data by switching signals to encoders in response to detection of the encoded signals representing compression of the data. Control over individual data bits such as copyright bits is maintained by determining the bit status, comparing it to a preferred status, changing the status if it does not comply with the preferred status, and reevaluating cyclical redundancy check value in each data packet to avoid disruption in the data transmission. In addition, the system includes an uplink device which automatically checks, logs and reports errors in Dolby Digital AC-3 signals by a monitor which employs a processor, a digital audio card and an SMPTE timecode reader. As an option, an ethernet interface may be provided to permit AC-3 transmission to expedite storage and transmission of the audio data by media such as compact disks. The monitor employs a state machine that finds AC-3 packets, locks into the packets and detects discontinuities or loss of signal. The monitor then computes and checks the cyclical redundancy check value of the AC-3 packet found. In addition, the system enables the device to play AC-3 signals such as Dolby Digital out in sync with video signals, regardless of the storage media for the files. A sound card having an input for receiving house reference AES clock pulses enables the AES clock of the playback signal to be locked to the frequency of a production house master as a time code reader or an editor's contact closure match video and audio signals playback.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
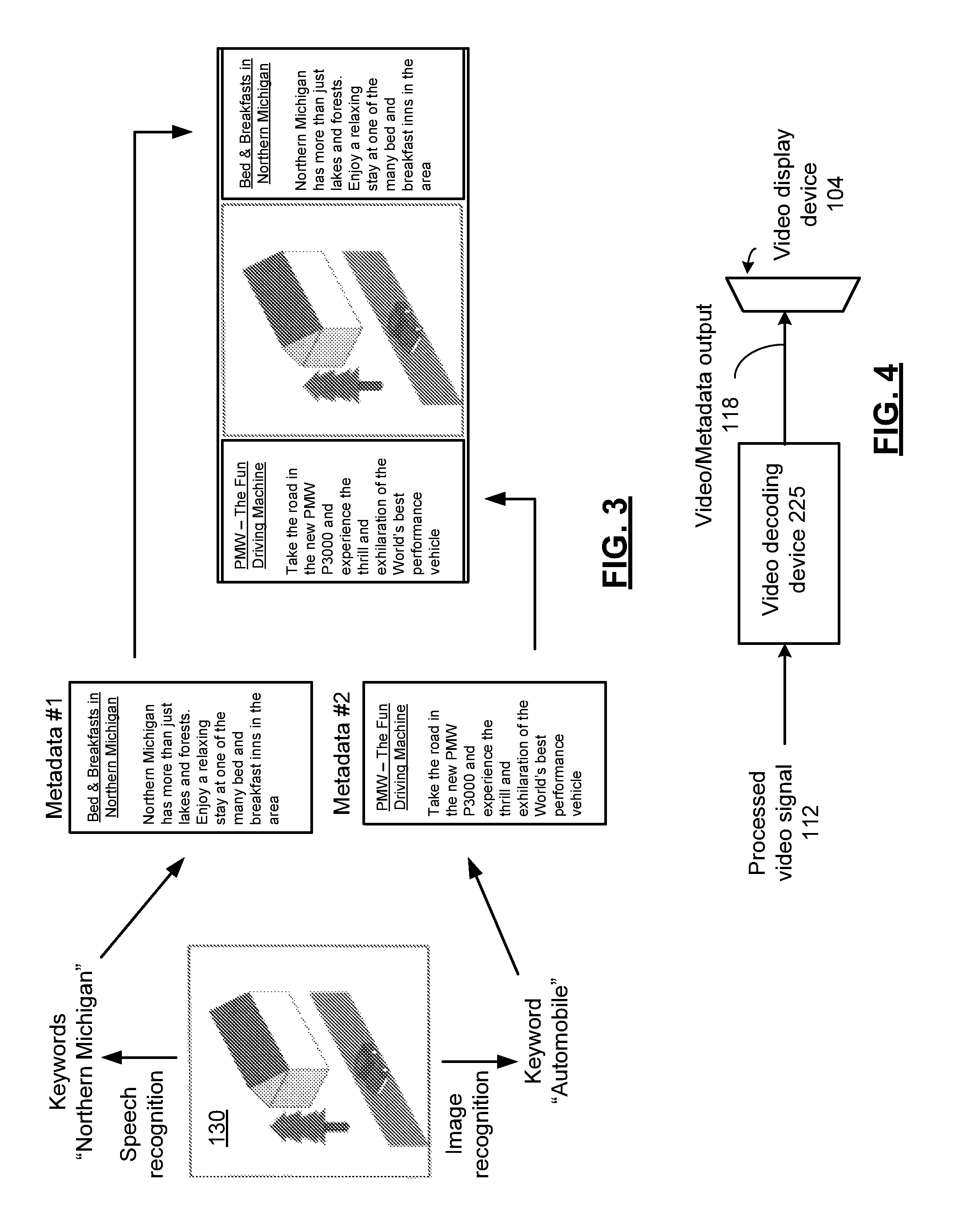
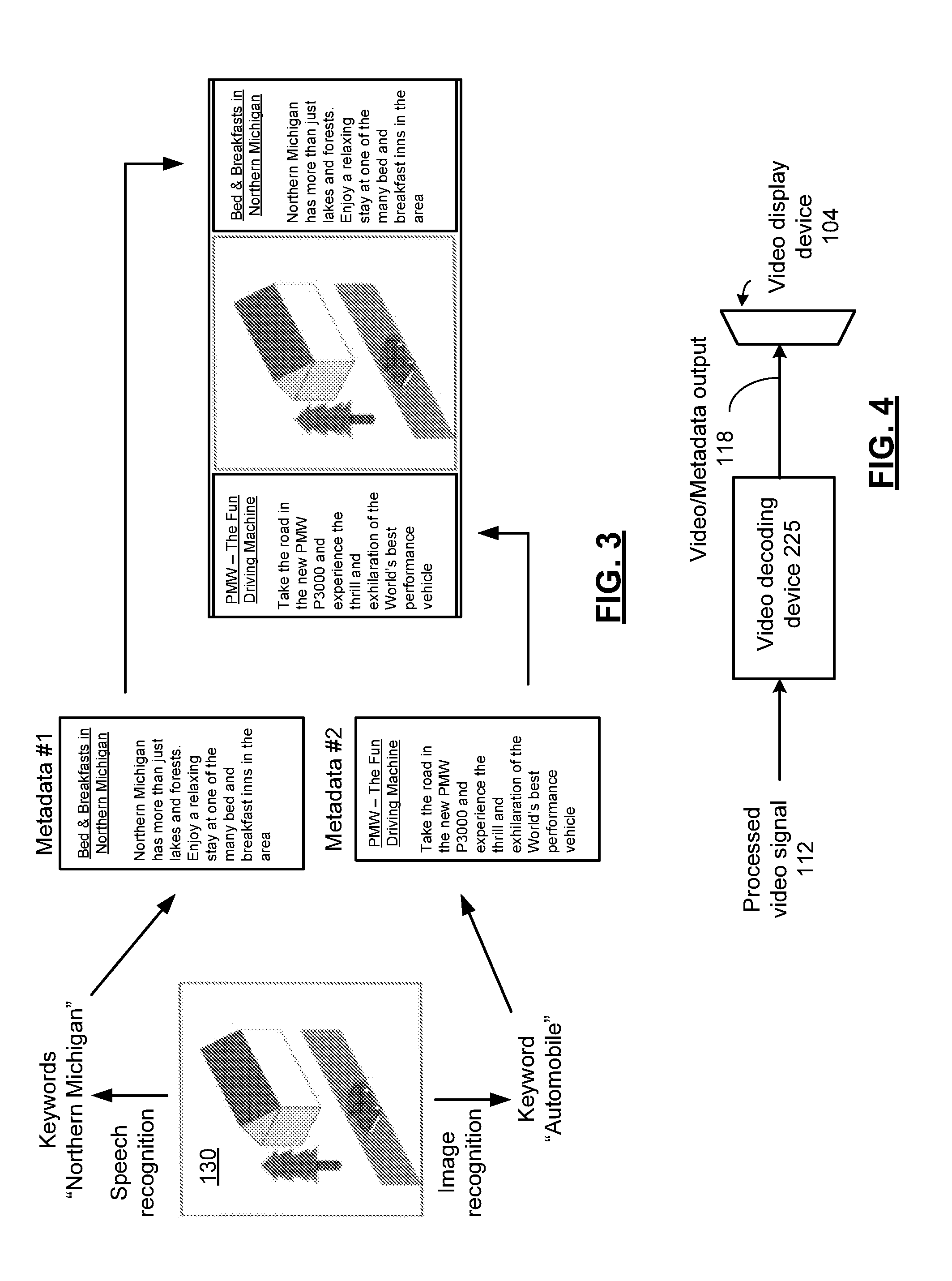
Video decoding device for extracting embedded metadata and methods for use therewith
InactiveUS20130094590A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningData synchronizationComputer graphics (images)
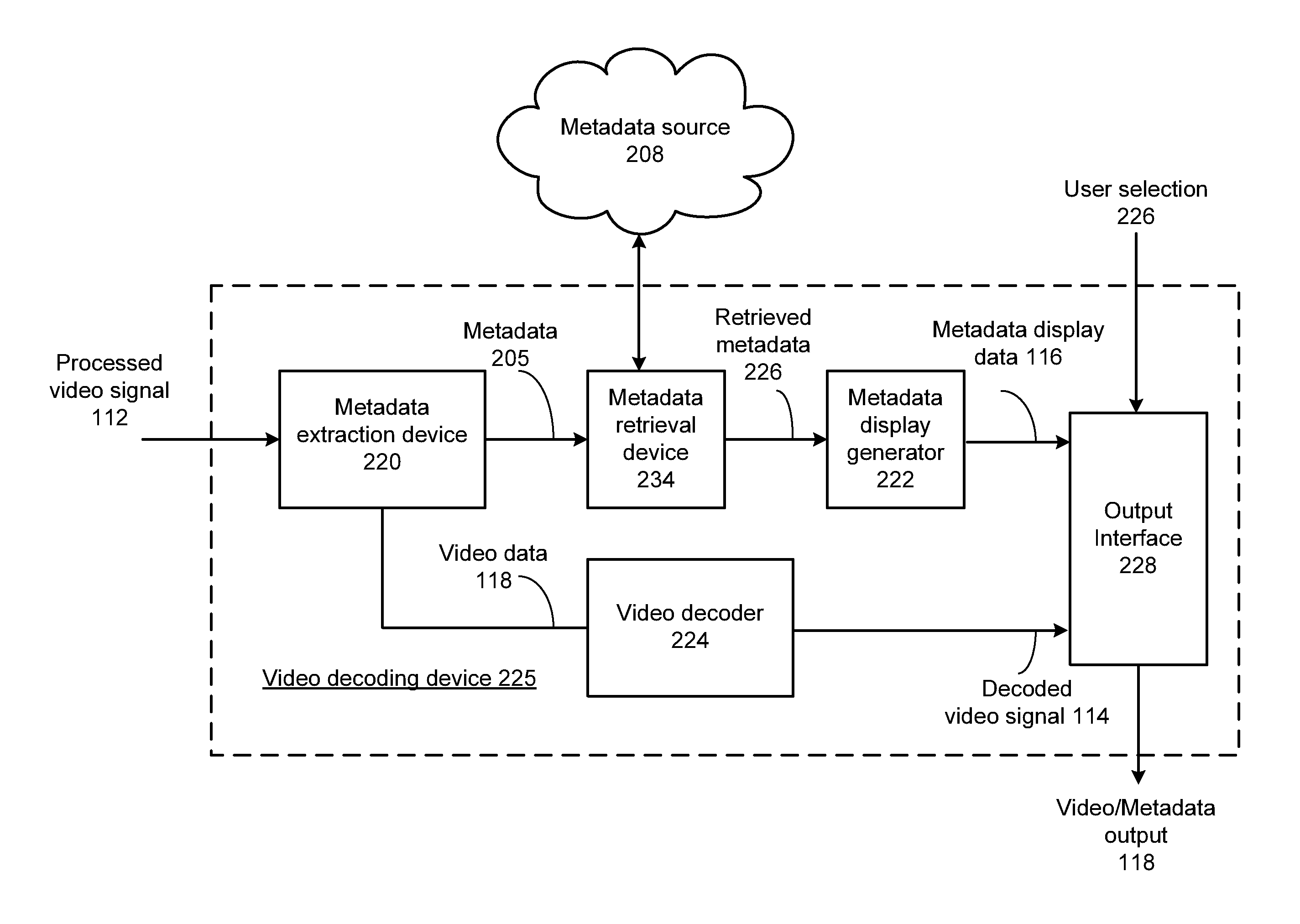
A video decoding device includes a metadata extraction device that extracts metadata and a video signal from a processed video signal, wherein the metadata is time-coded in accordance with at least one time stamp of the video signal. A metadata display generator generates metadata display data in response to the metadata. A video decoder decodes the video signal to generate a decoded video signal. An output interface generates a video / metadata output by synchronizing the metadata display data to the decoded video signal in accordance with the at least one time stamp.
Owner:VIXS SYSTEMS INC
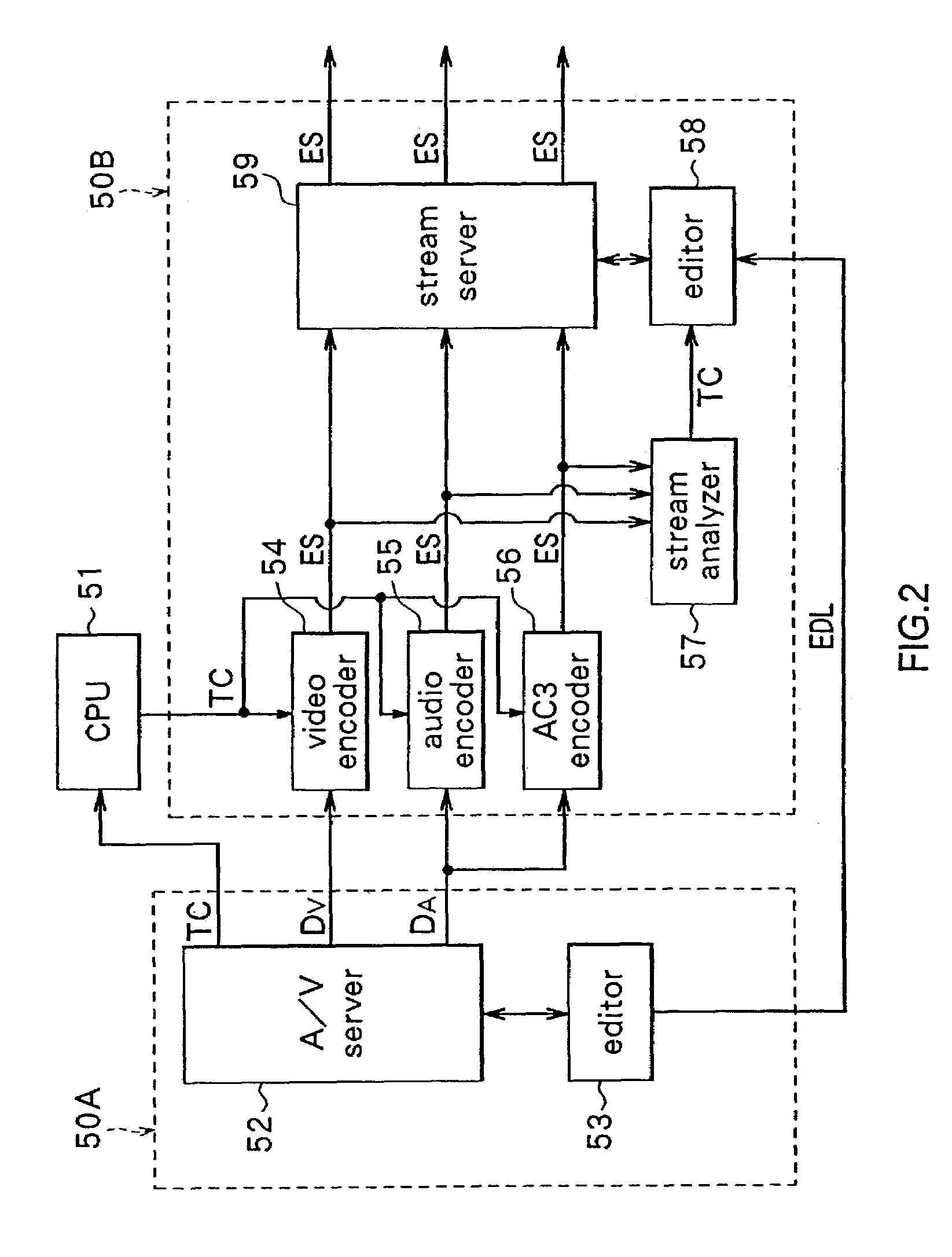
Encoded stream generating apparatus and method, data transmission system and method, and editing system and method
InactiveUS7209636B2Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareData stream
Owner:SONY CORP
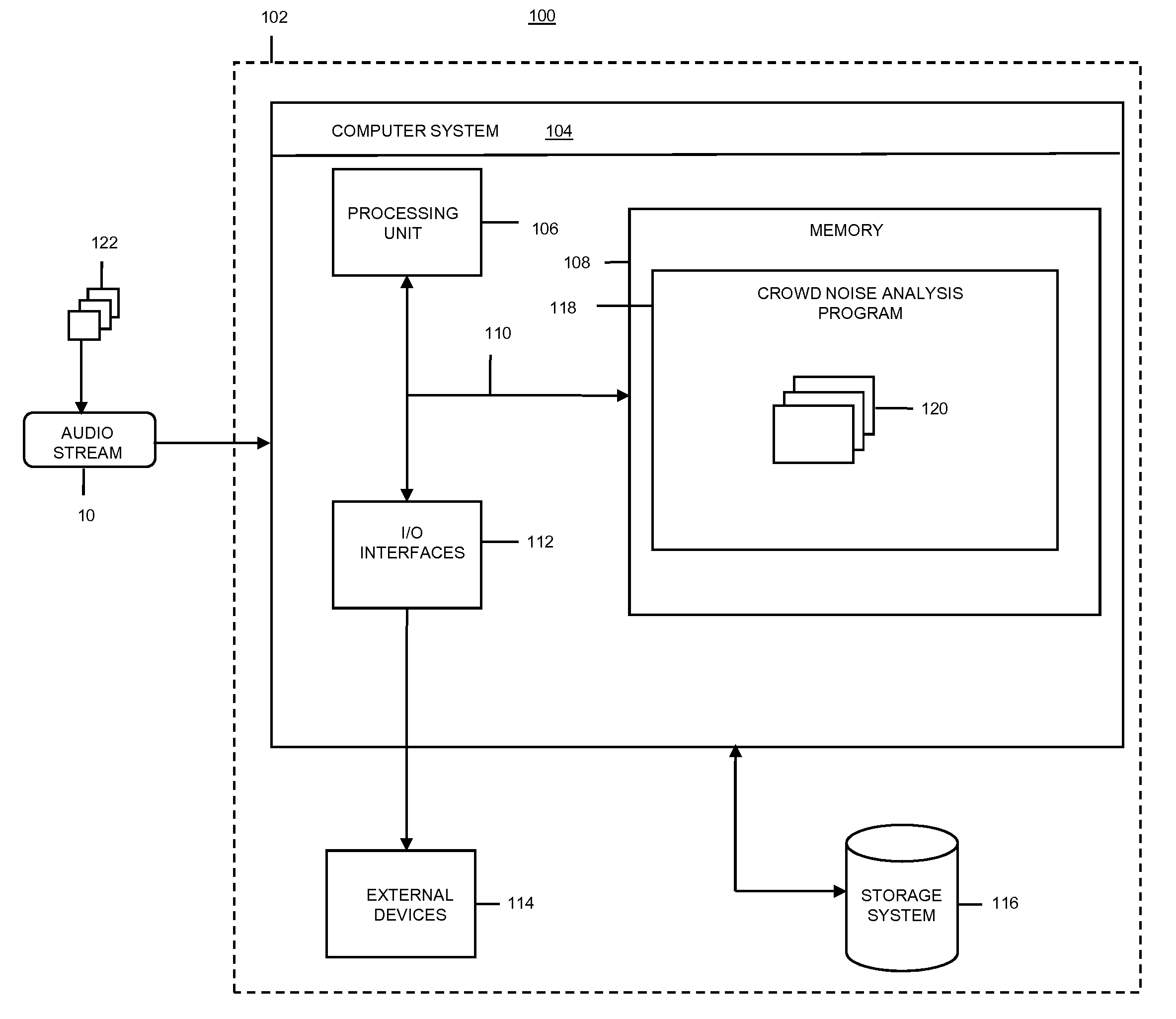
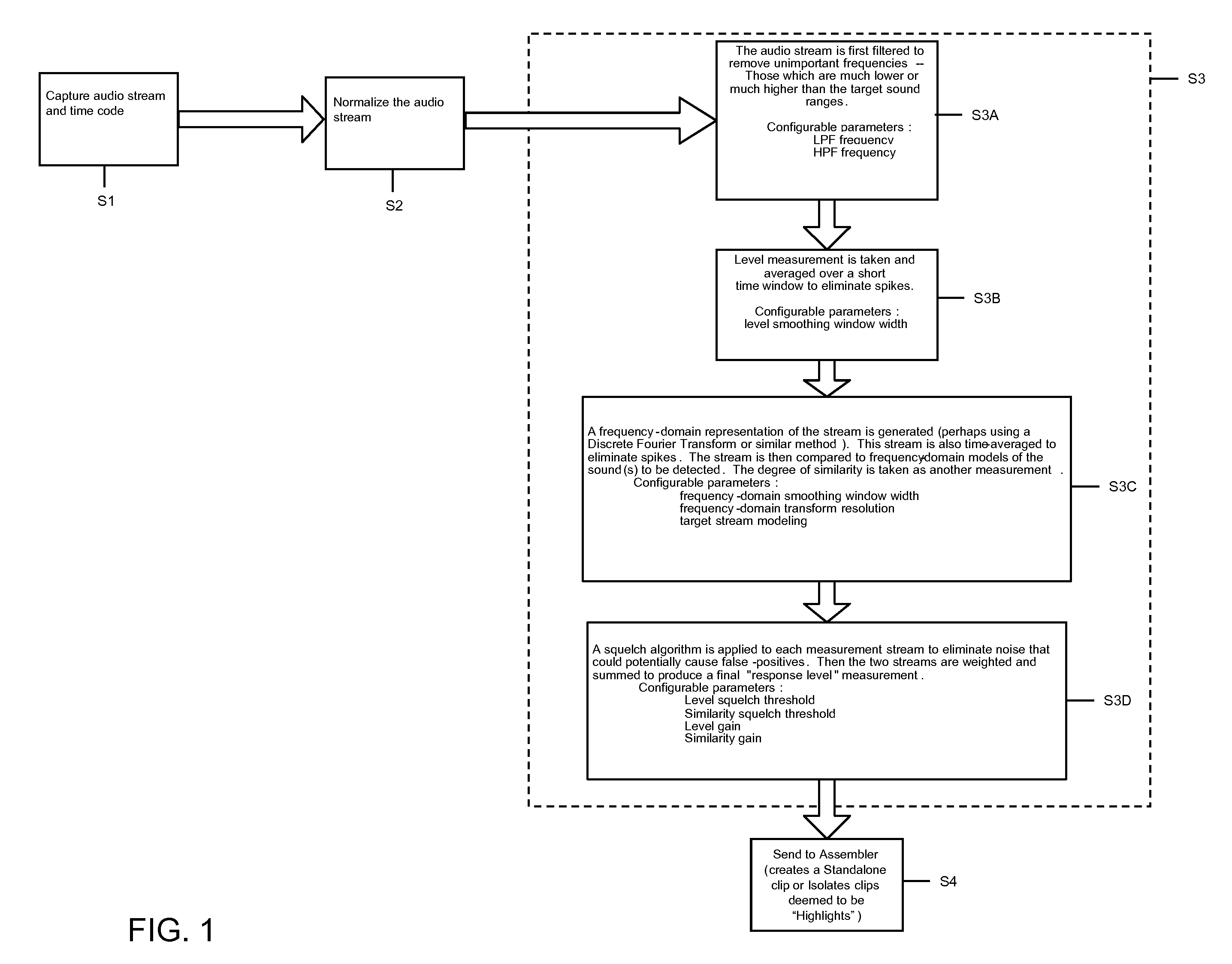
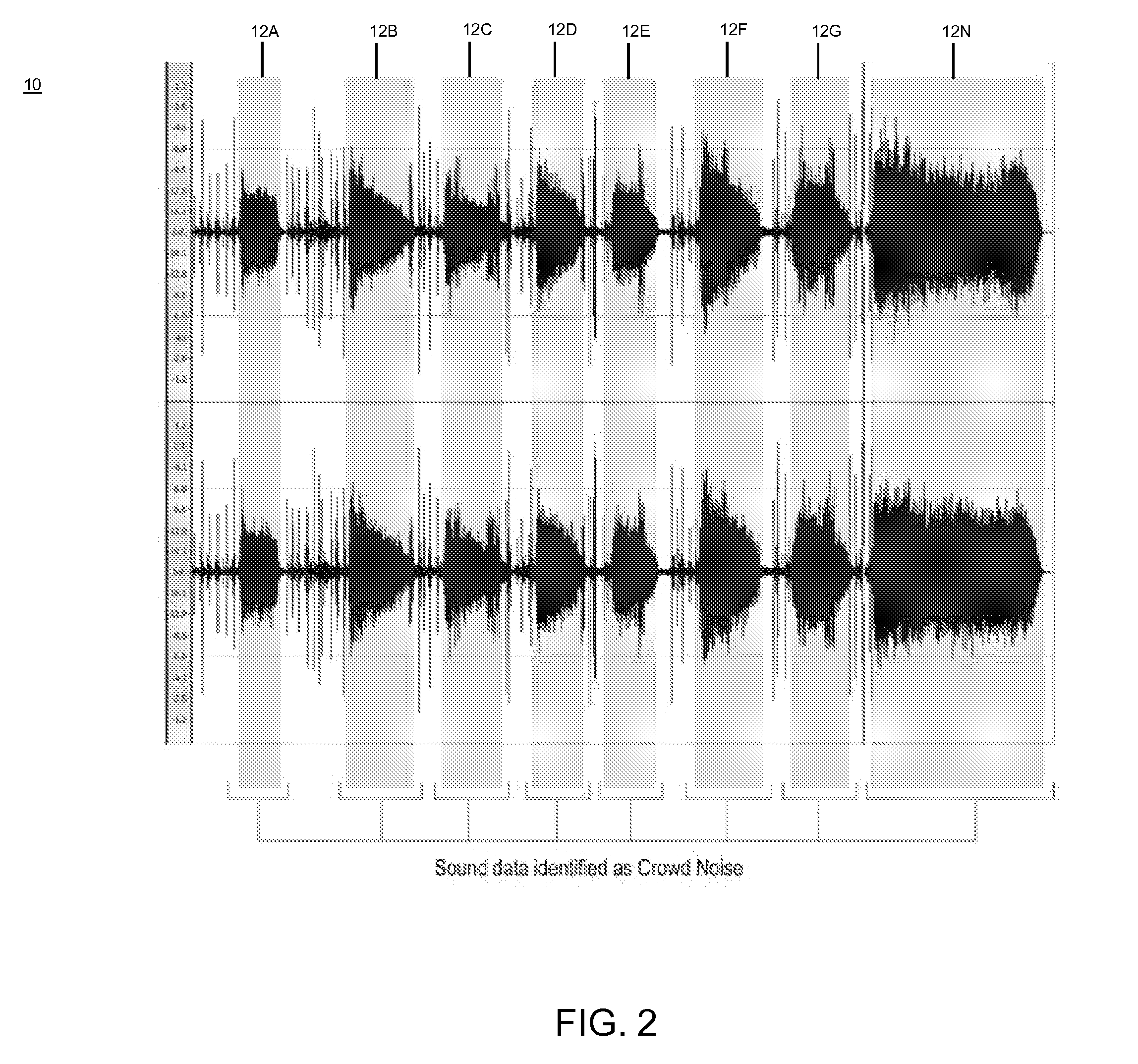
Crowd noise analysis
ActiveUS20080300700A1Eliminate undesired artifactEliminate spikesElectrical apparatusSpeech analysisPattern recognitionCrowds
The present invention generally provides a way to analyze crowd noise to identify “highlights” or the like. Specifically, an audio stream containing crowd noise from an event (e.g., sporting event, political rally, religious gathering, etc) is captured (e.g., using microphones) and time coded. The audio stream is normalized based on geography and processed to remove undesired artifacts and to identify a set (at least one) of highlights. Based on at least one threshold, at least one highlight is selected from the set of highlights.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
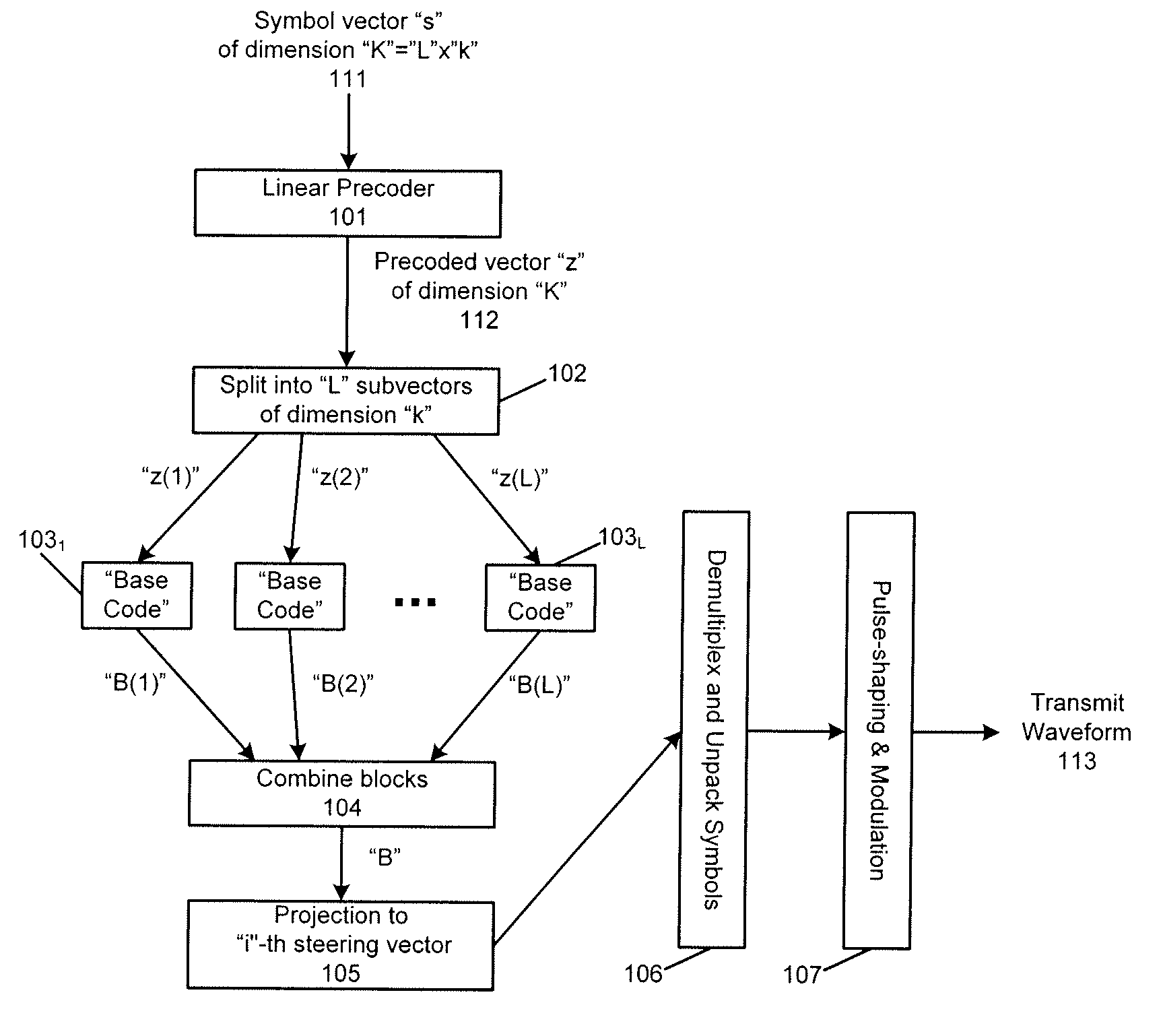
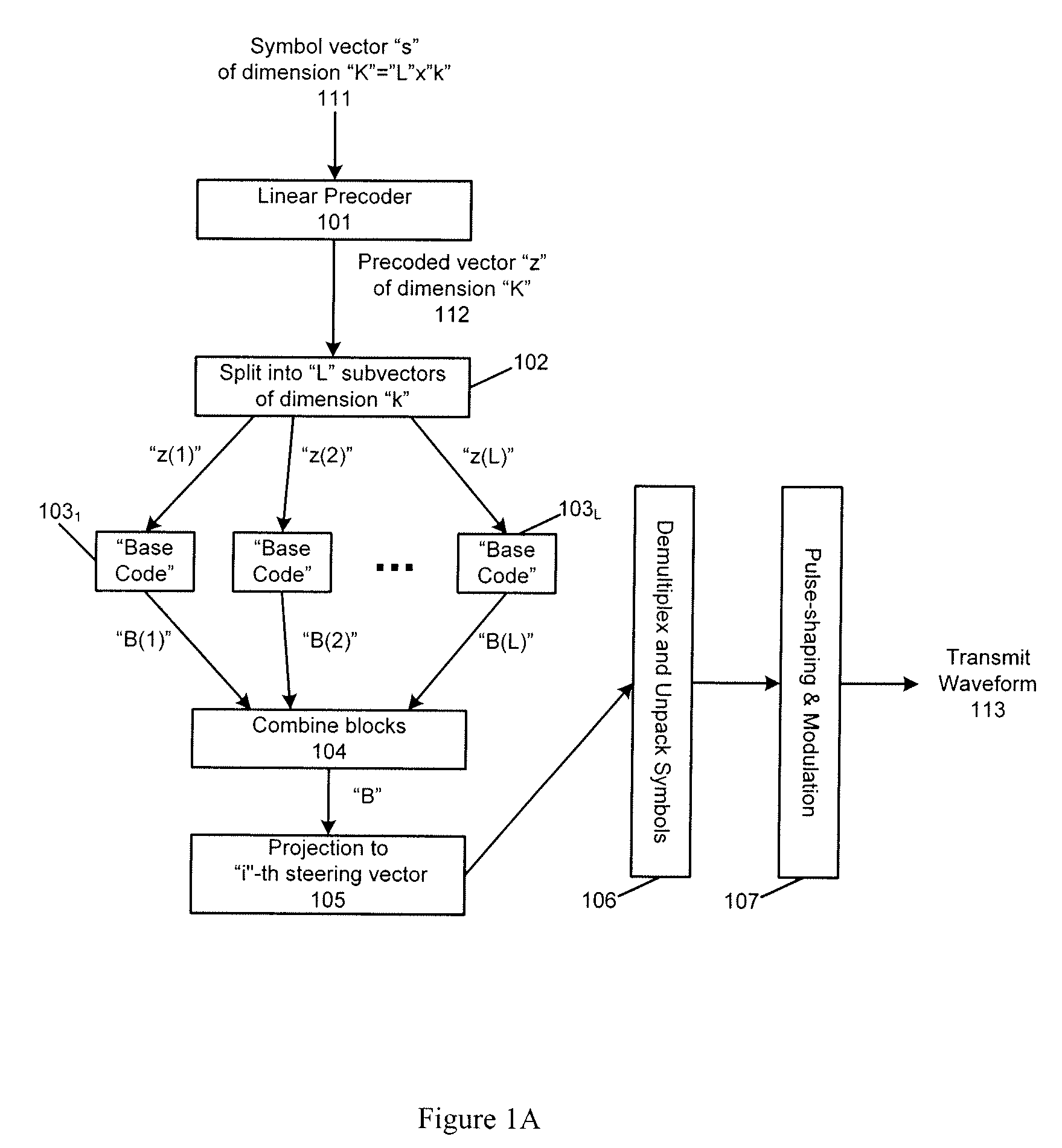
Method and apparatus for distributed space-time coding in wireless radio networks
ActiveUS20070281633A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationSite diversityRadio networksWireless sensor network
A method and apparatus is diclosed herein for performing distributed space-time coding. In one embodiment, the distributed space-time coding is used for downlink communications in wireless radio networks. In one embodiment, the method comprises storing information-bearing sequence at two or more base stations in a group of base stations; and transmitting data coprresponding to the information-bearing sequence from a number of base stations for receipt by a reciever of a user, where the number of base stations is not globally known a priori and indicates a diversity of order, such that the diversity of order M is obtained if a total of M number of antennas spread over multiple base stations transmit the information-bearing sequence, where M is an integer.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
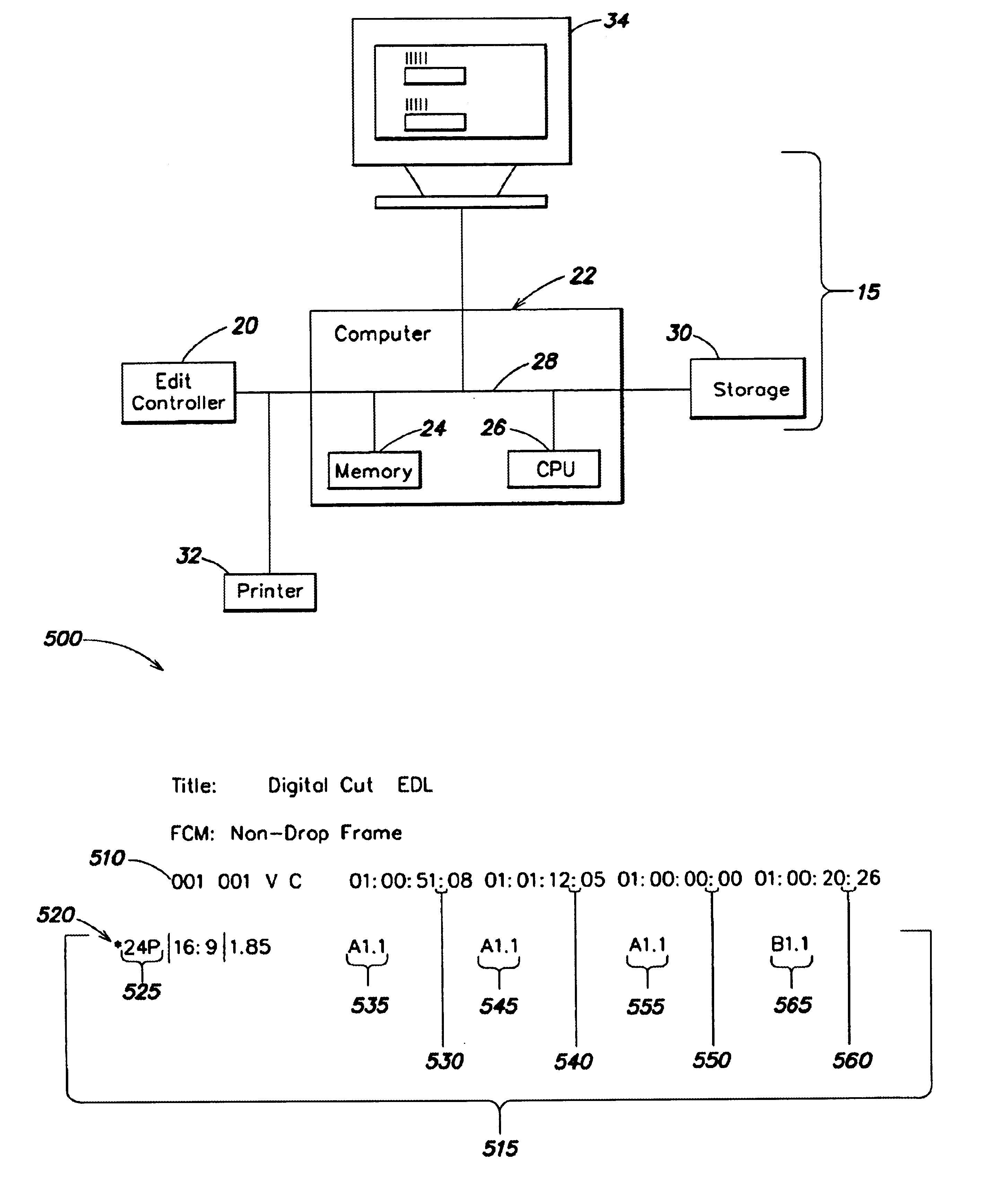
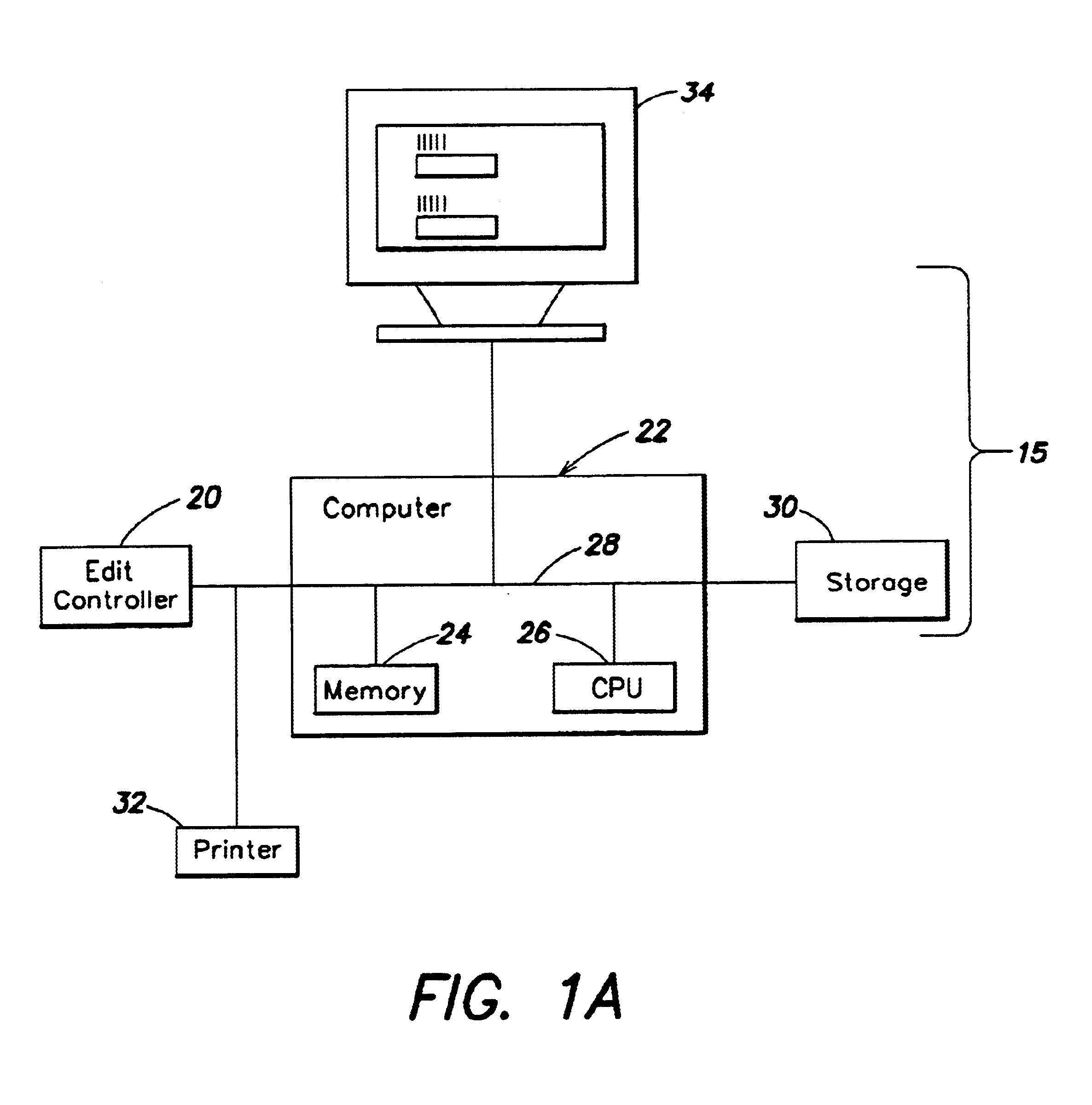
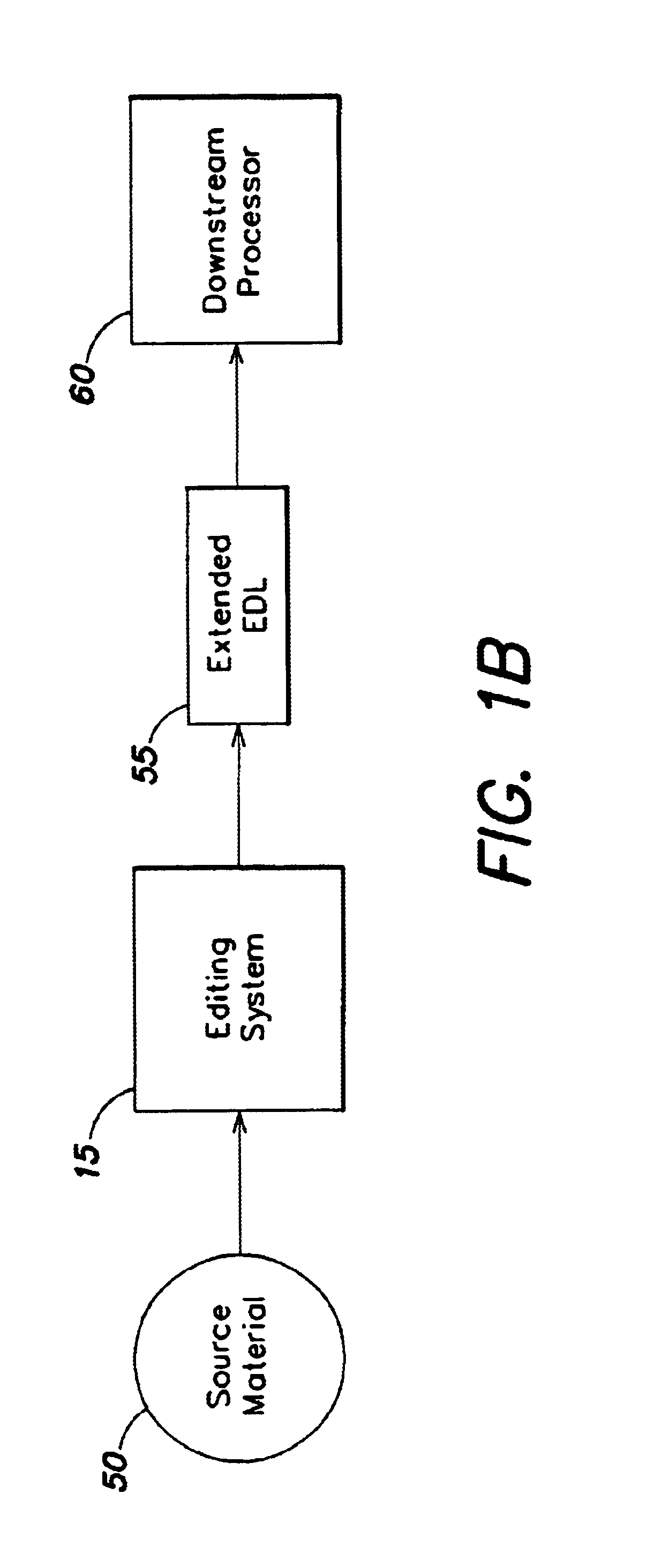
Edit decision list for identifying the pull down phase of a video signal
InactiveUS6871003B1Easy to optimizeFacilitate the processTelevision system detailsElectronic editing analogue information signalsRecording durationDownstream processing
The invention provides an editing system for editing and combining media material into a resulting media composition. The media may be film or video based material, and also may include audio material. The video may adhere to either NTSC or PAL timing. In response to editing instructions, an Edit Decision List (EDL) is produced that specifies the material that makes up the edited composition, and the order of presentation of this material in the output composition. The EDL specifies the input clips that are taken from the source material using source timecode and similarly defines the output order again according to a new time code, the record time code. The editing system produces an extended EDL that facilitates the downstream processing (after the editing has been completed) for post production tasks requiring the need to know accurately where edit points occur.
Owner:AVID TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com