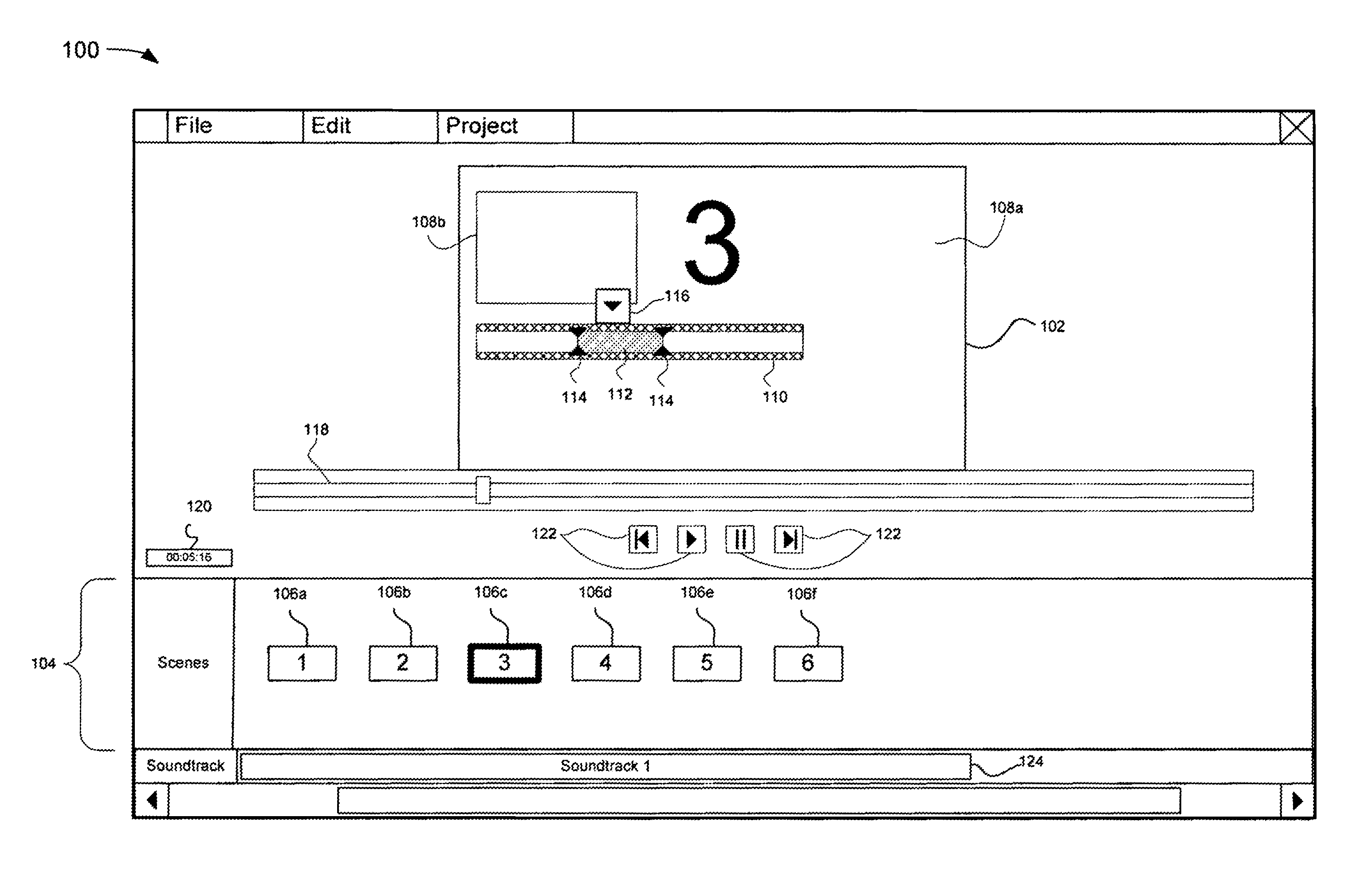
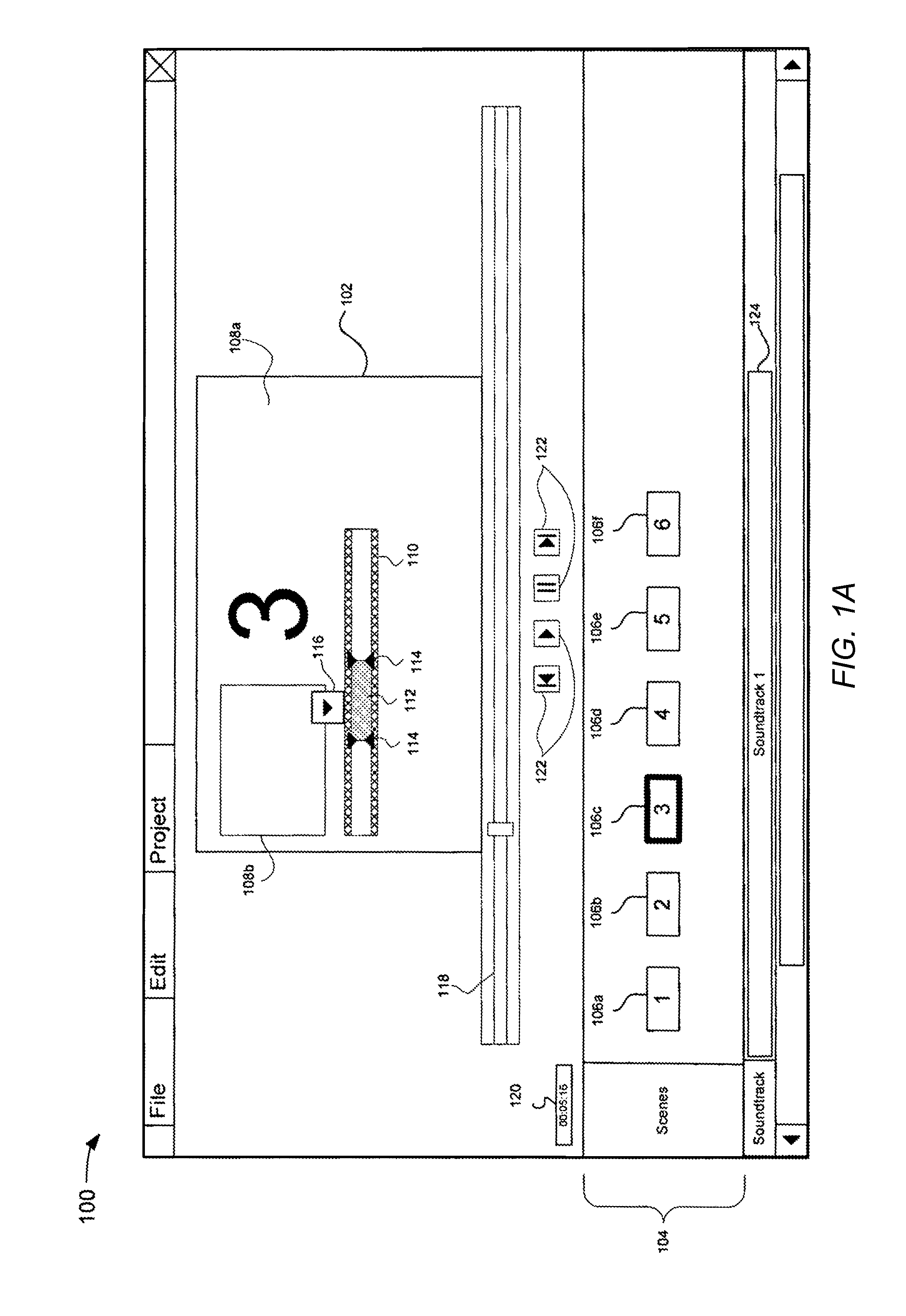
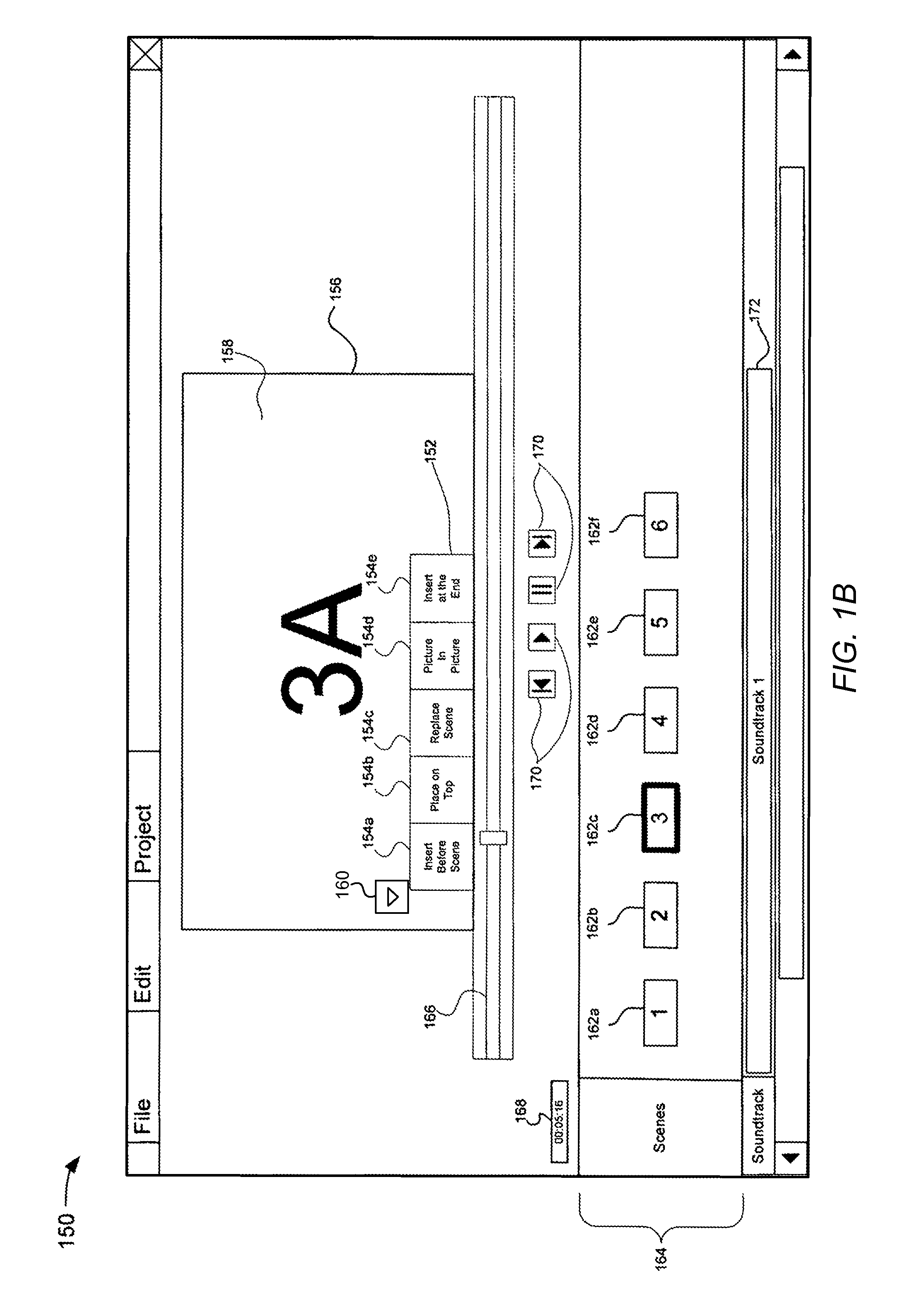
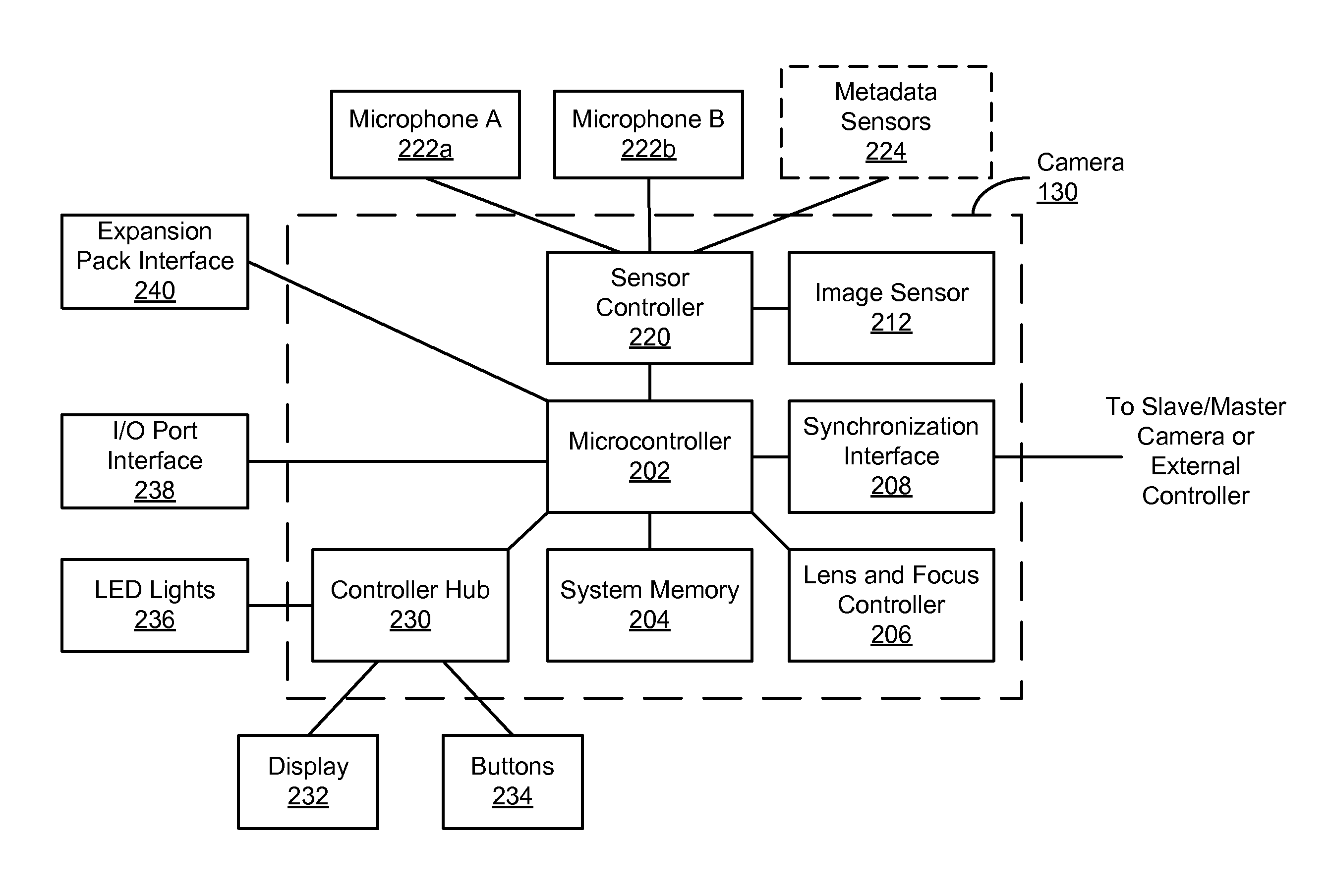
Patents
Literature
1074 results about "Video editing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
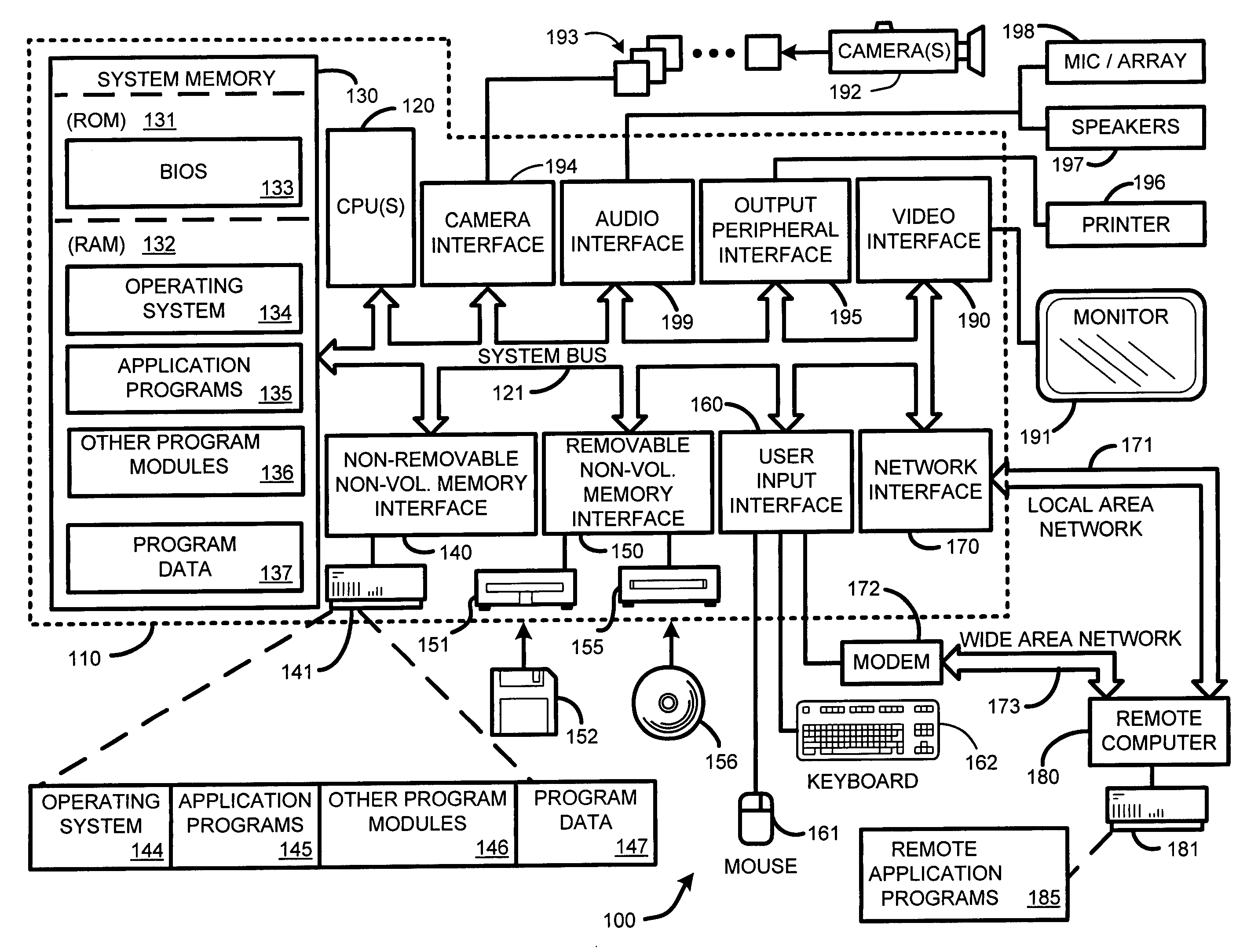
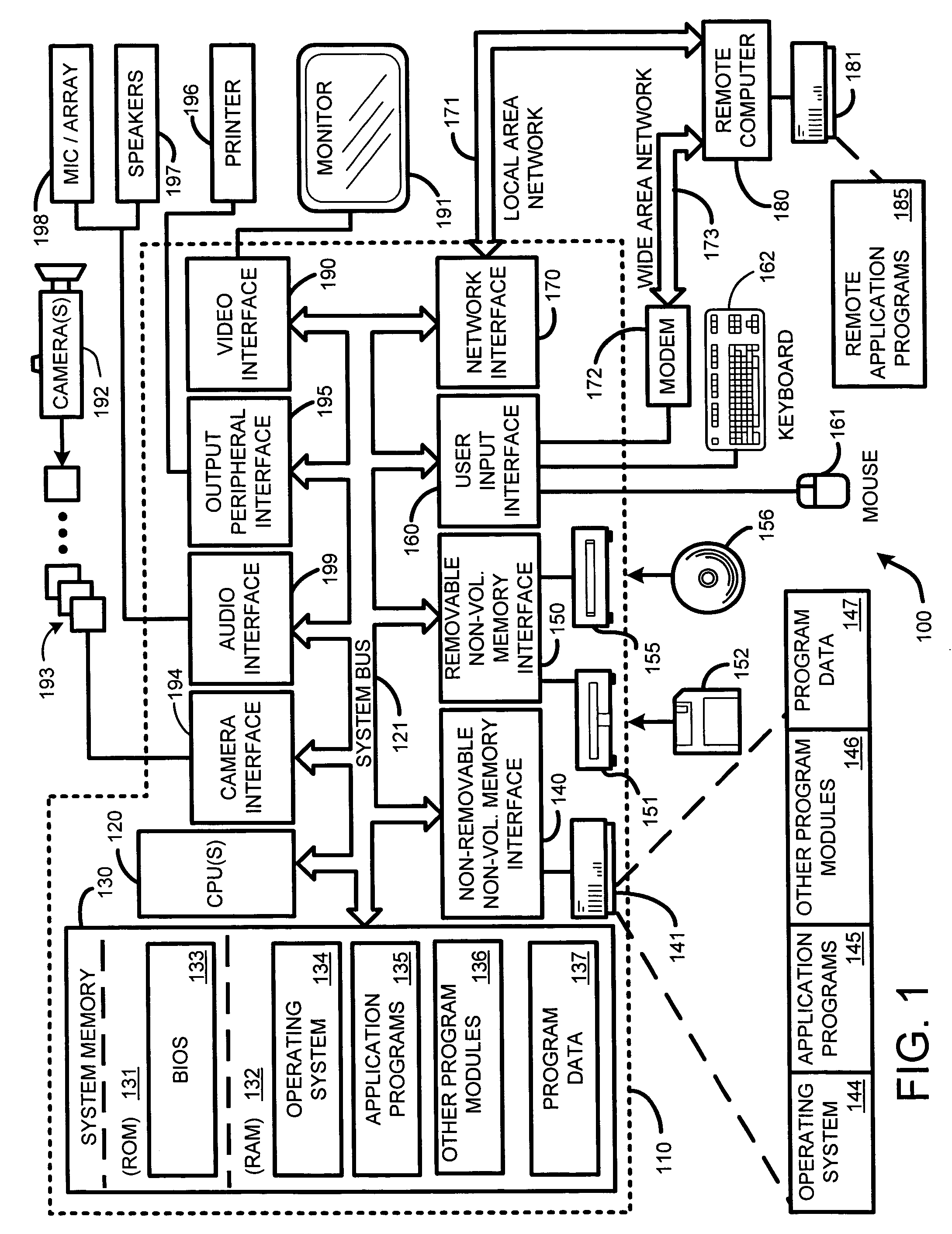
Video editing is the manipulation and arrangement of video shots. Video editing is used to structure and present all video information, including films and television shows, video advertisements and video essays. Video editing has been dramatically democratized in recent years by editing software available for personal computers. Editing video can be difficult and tedious, so several technologies have been produced to aid people in this task. Pen based video editing software was developed in order to give people a more intuitive and fast way to edit video.
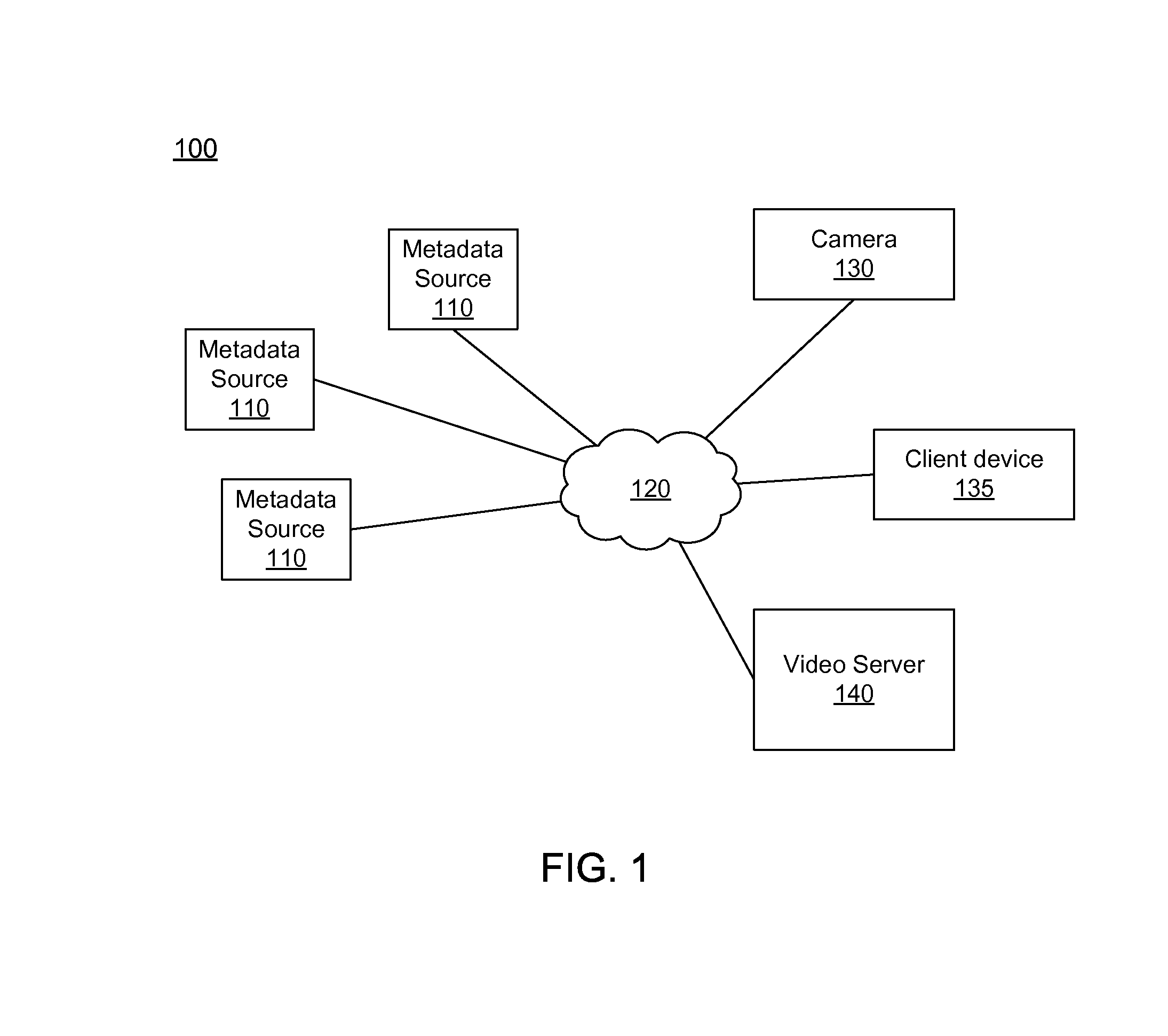
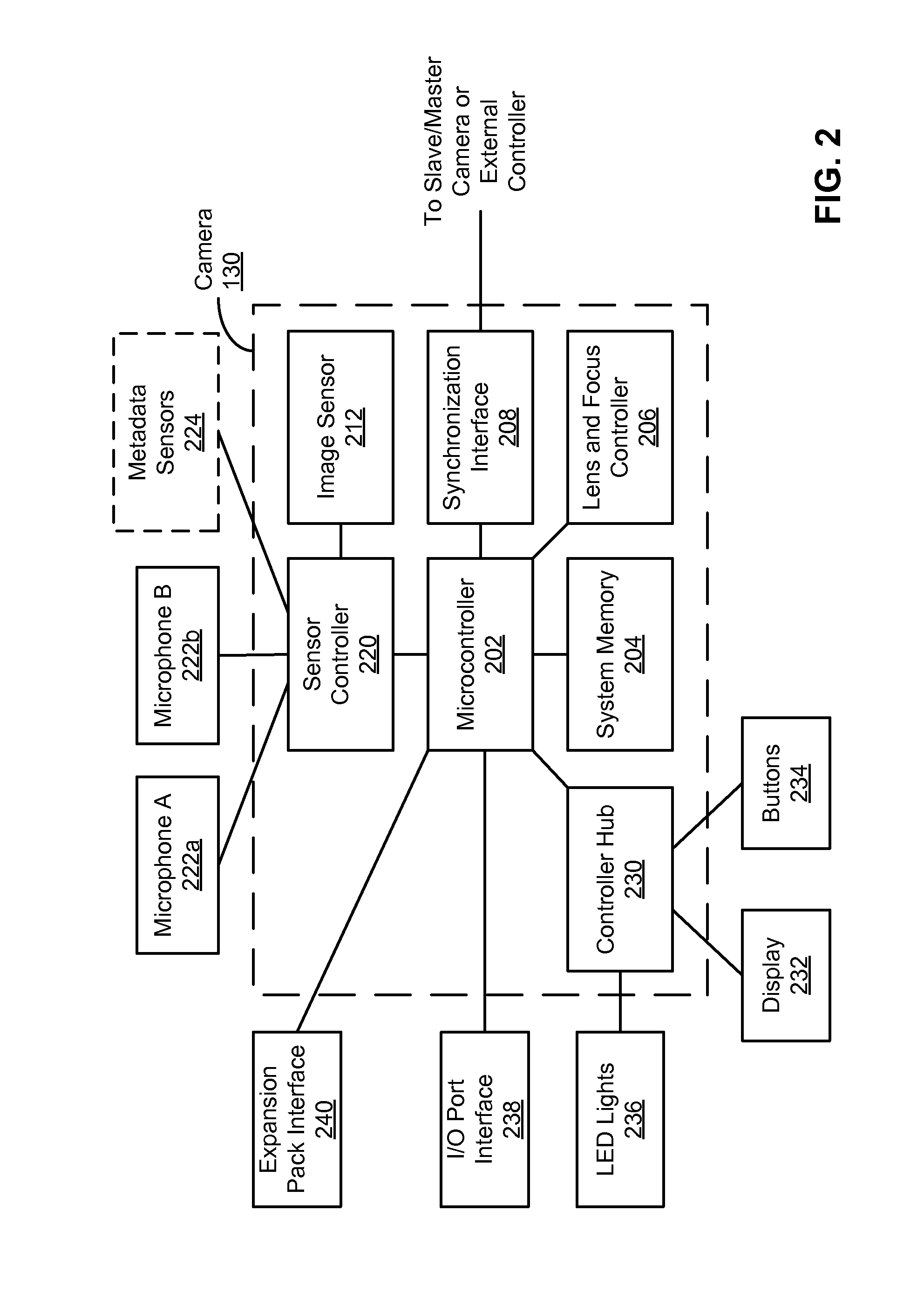
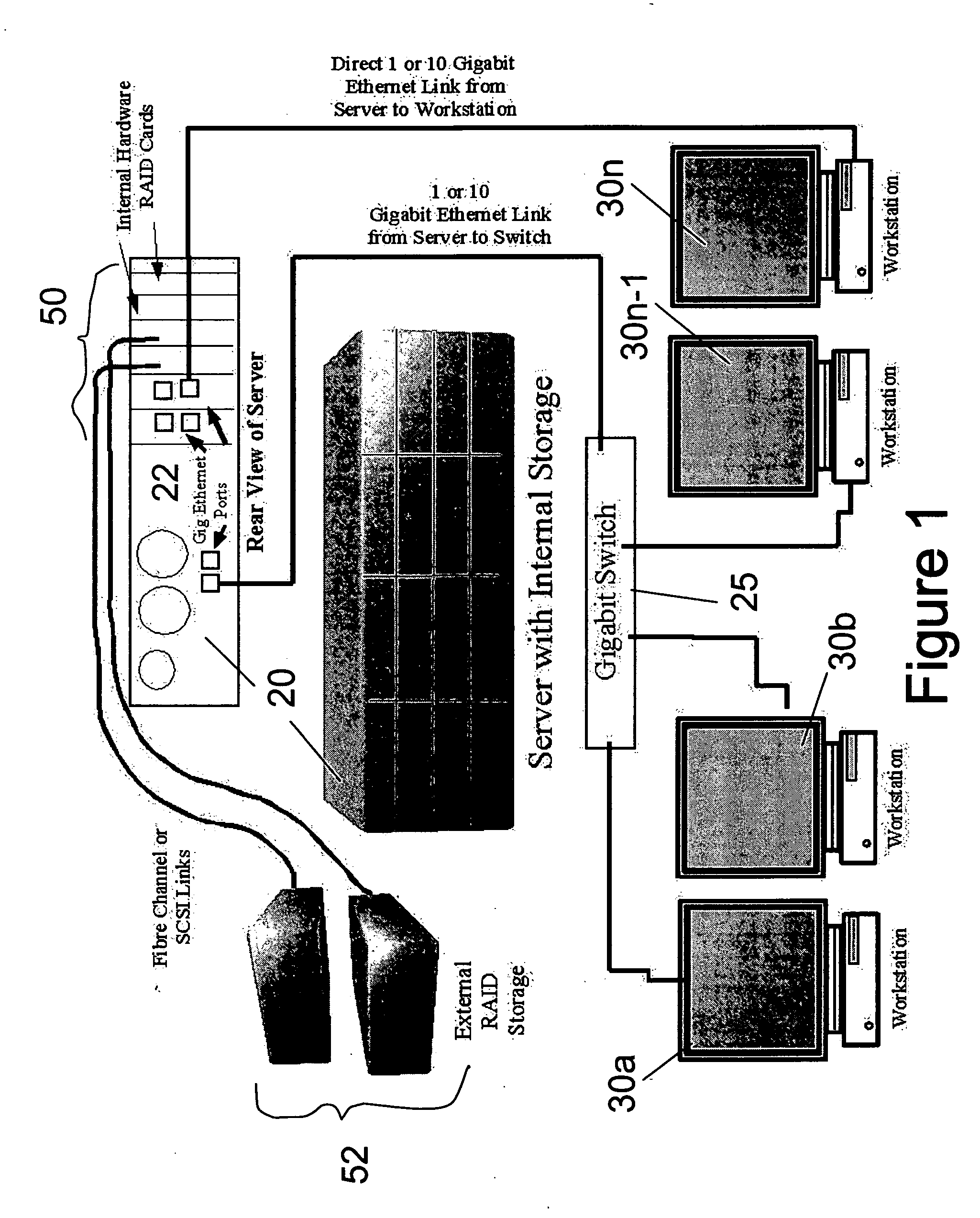
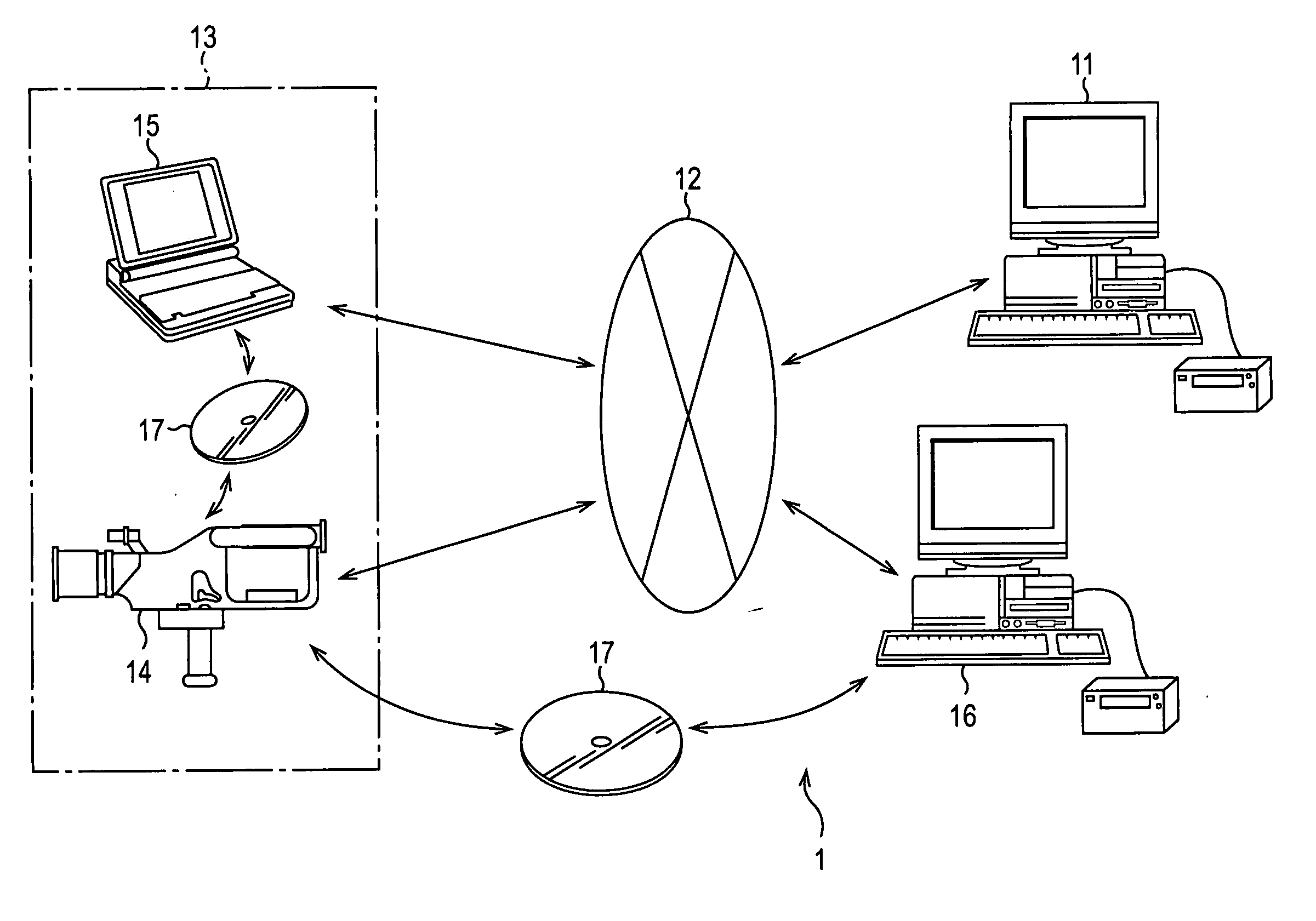
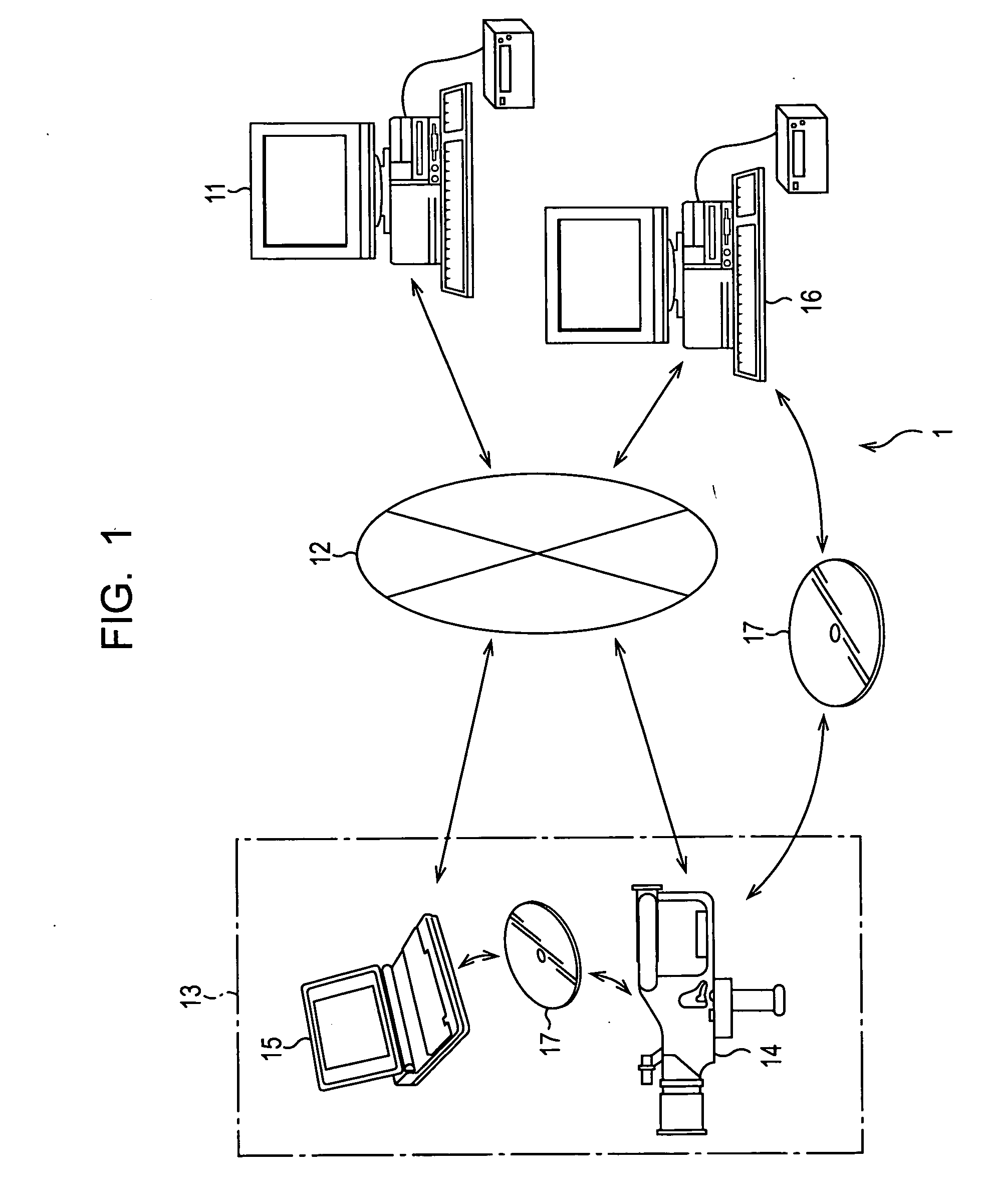
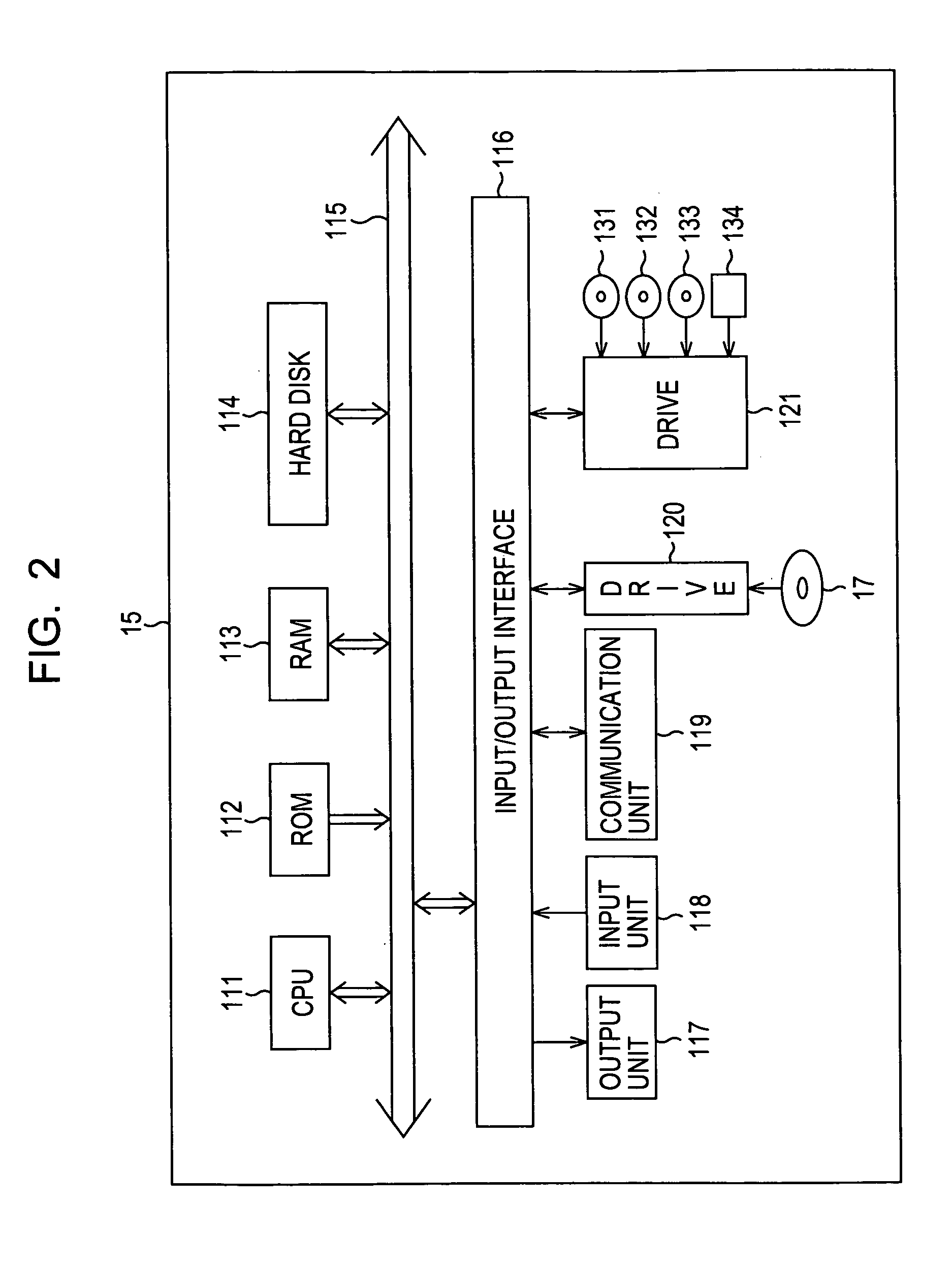
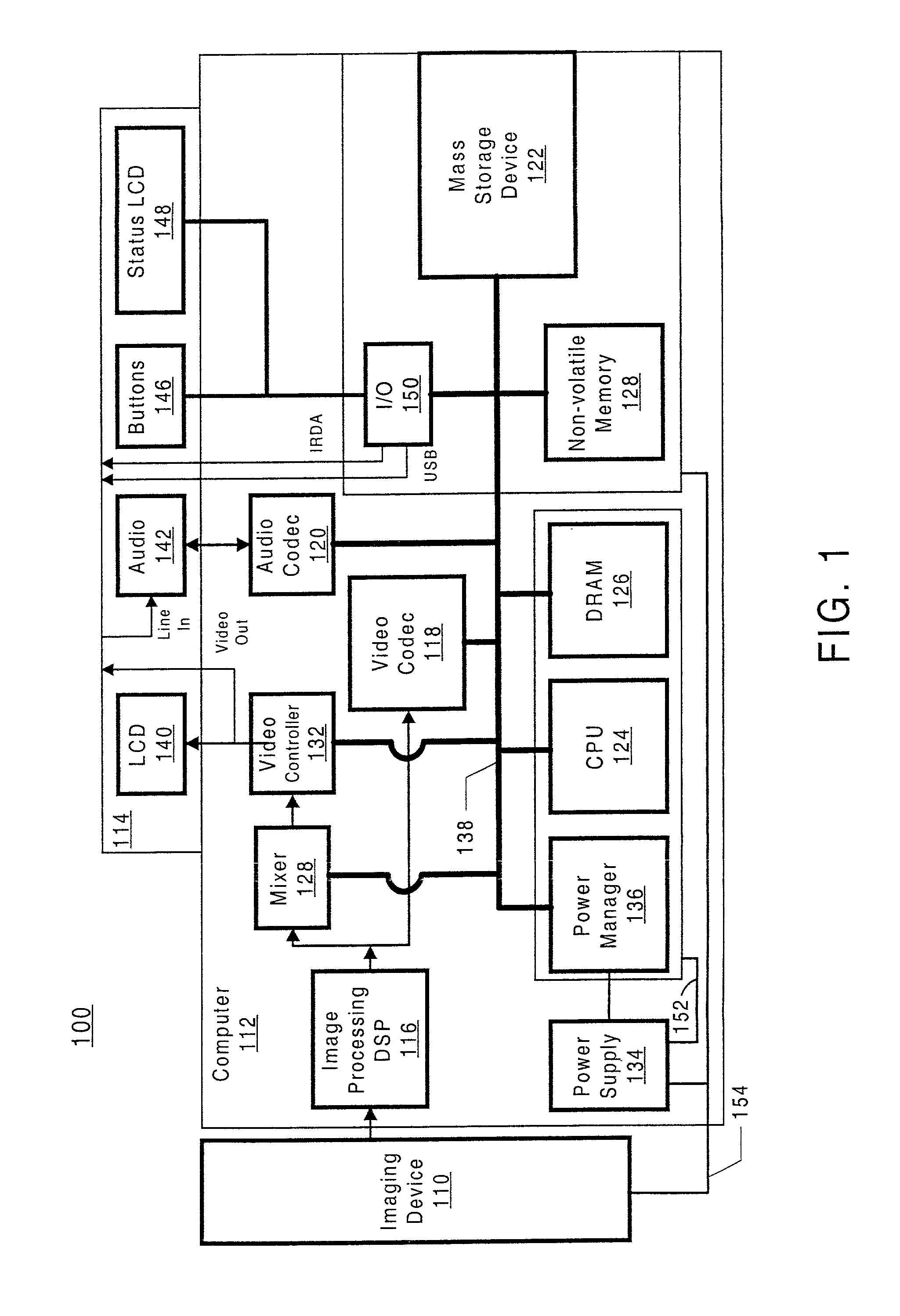
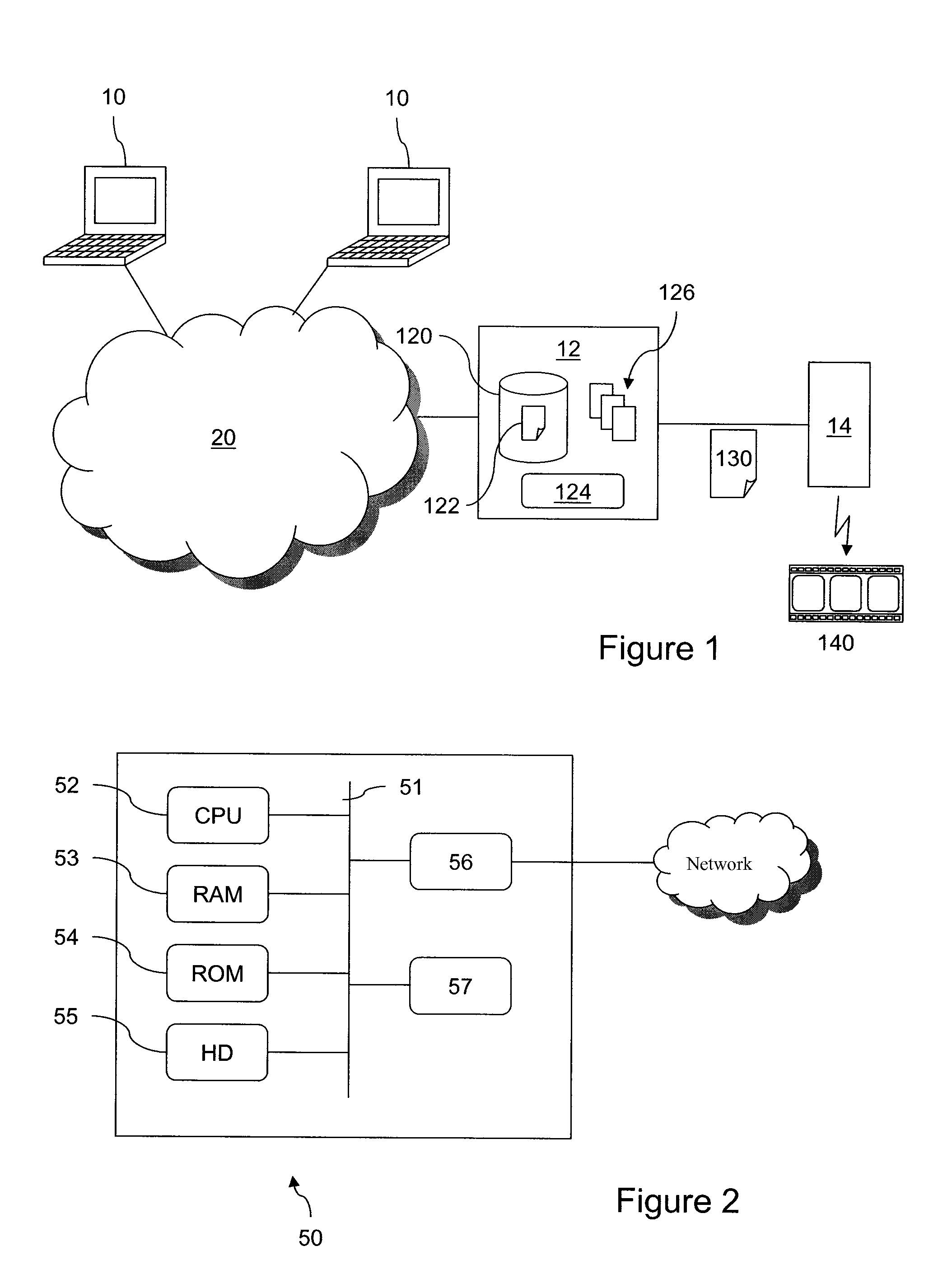
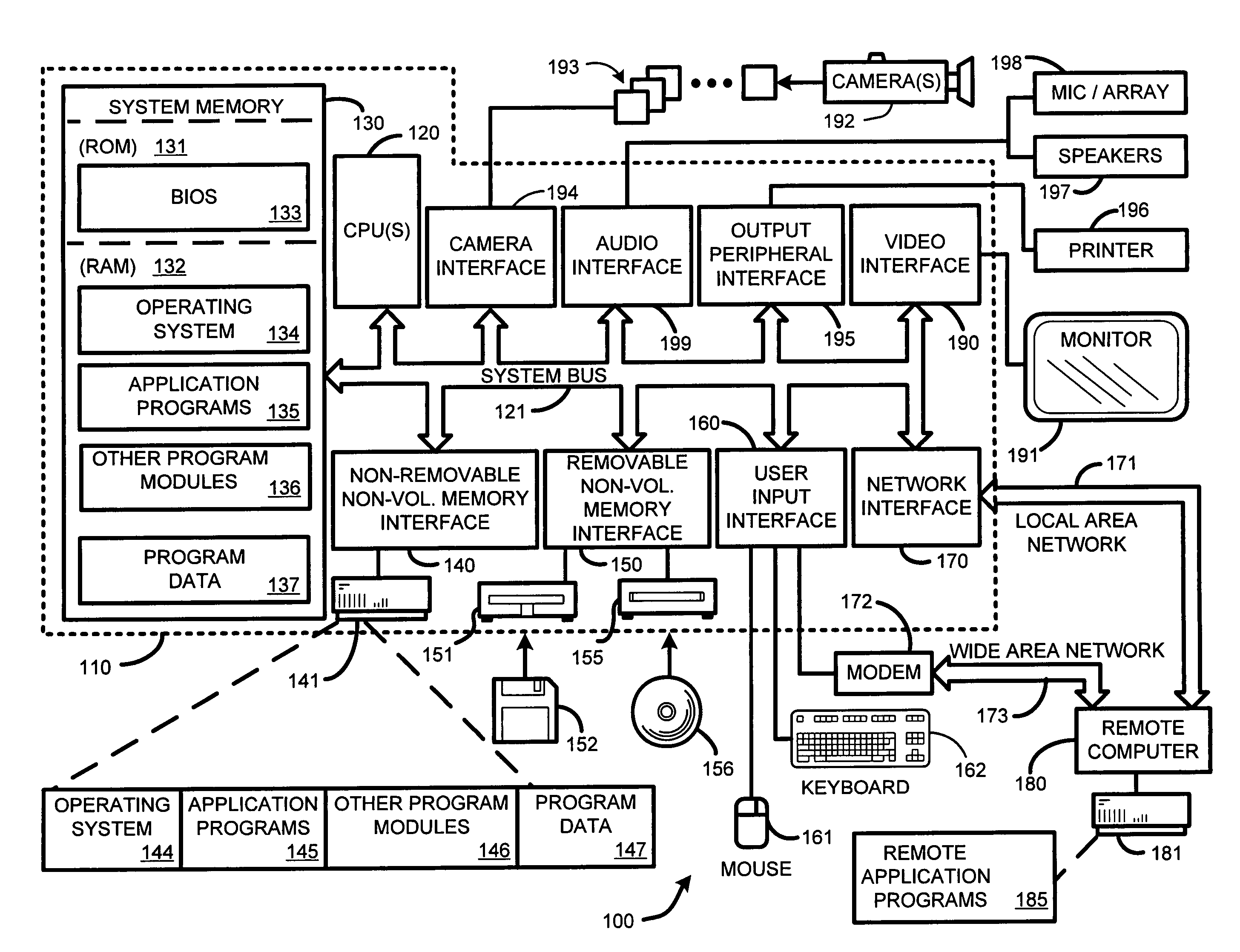
Integrated system and method for processing video
InactiveUS6476826B1Improve productivityShorten the timeElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsDigital computer detailsVideo processingEngineering
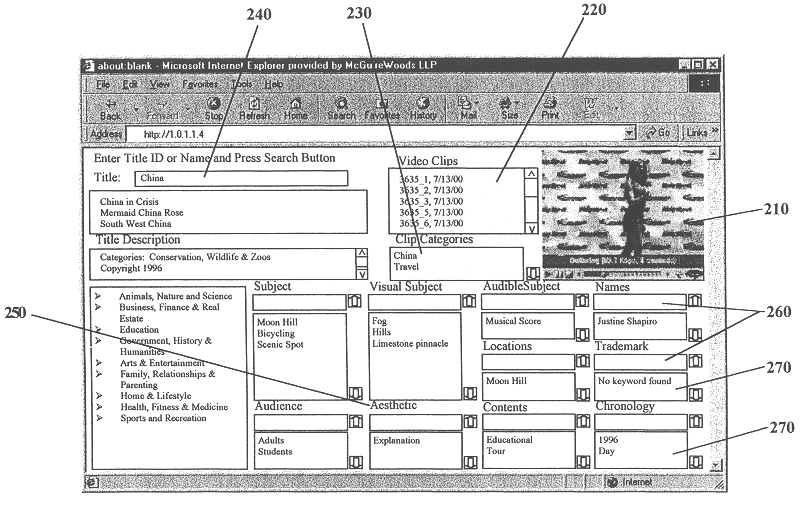
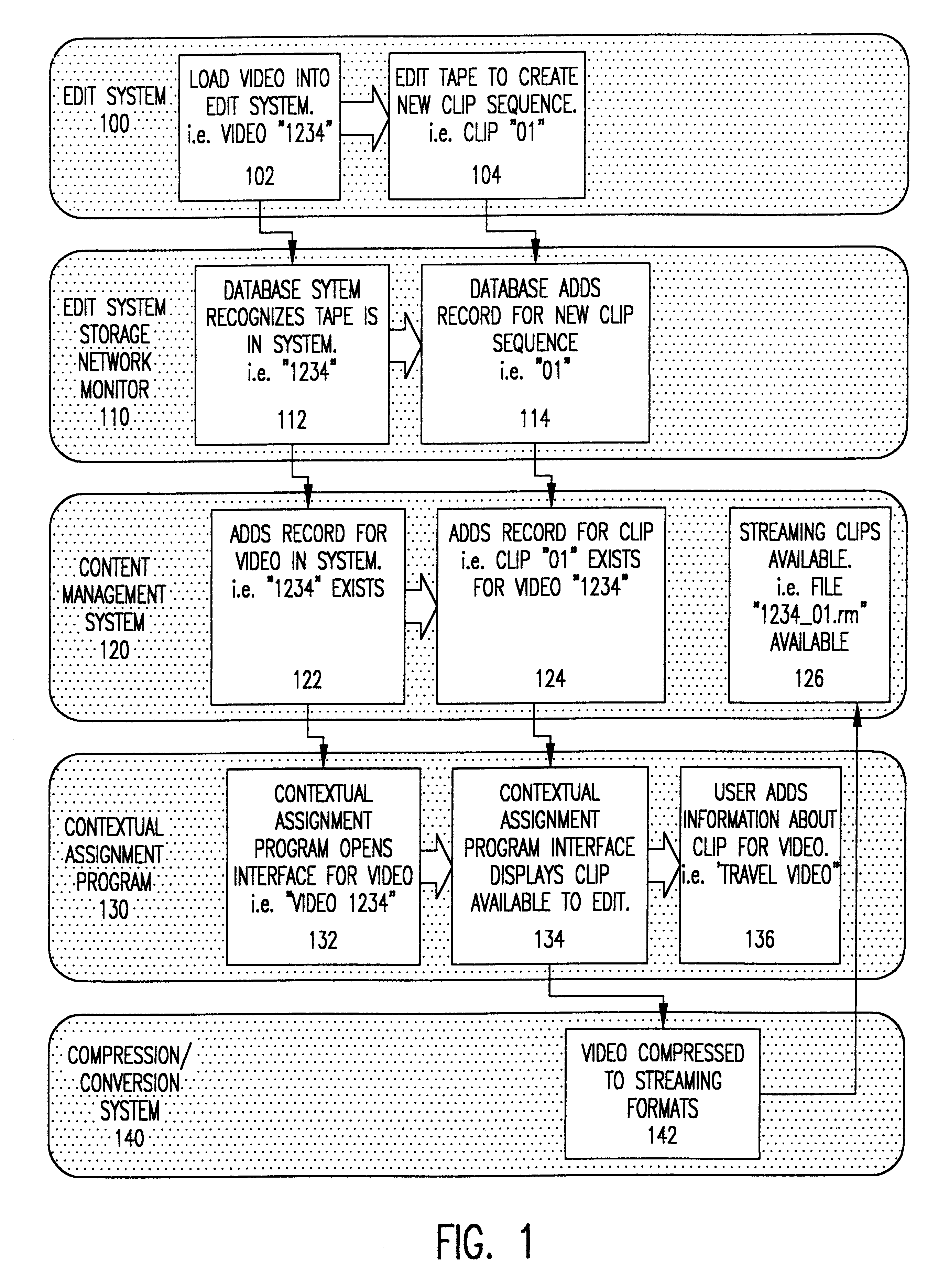
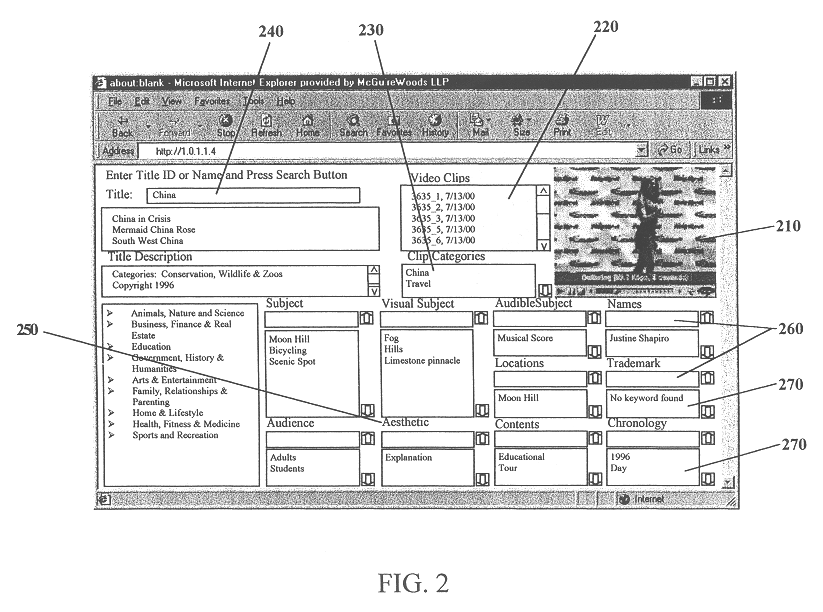
A system and method is provided that can integrate a set of video processing systems for the purpose of increasing productivity and throughput. The integrated system edits video into clips, automatically adds records corresponding to these clips in a centralized database system, adds information about the content of these clips into these records, and controls the compression or conversion of these clips for distribution. The database system is used for managing the clips as well as for the searching of the clips based primarily on the content information added in the above process. Using this process, a digital production line may be built that allows video editors to edit sections from a video tape, have these sections (or clips) be dynamically added to a database system, and provide a mechanism for the editors to apply meta-information to the newly created clips at the same time the clips have been authored. Also, this system provides for the automatic processing of the edited material into alternate formats for such purposes as Internet streaming. The combination of these processes provides significant improvement productivity in the generation of clips, such as video highlights, from complete video.
Owner:VAST
Graphical user interface for a motion video planning and editing system for a computer
InactiveUS7124366B2Simplified user interfaceSimple interfaceFlat record carrier combinationsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsGraphicsGraphical user interface
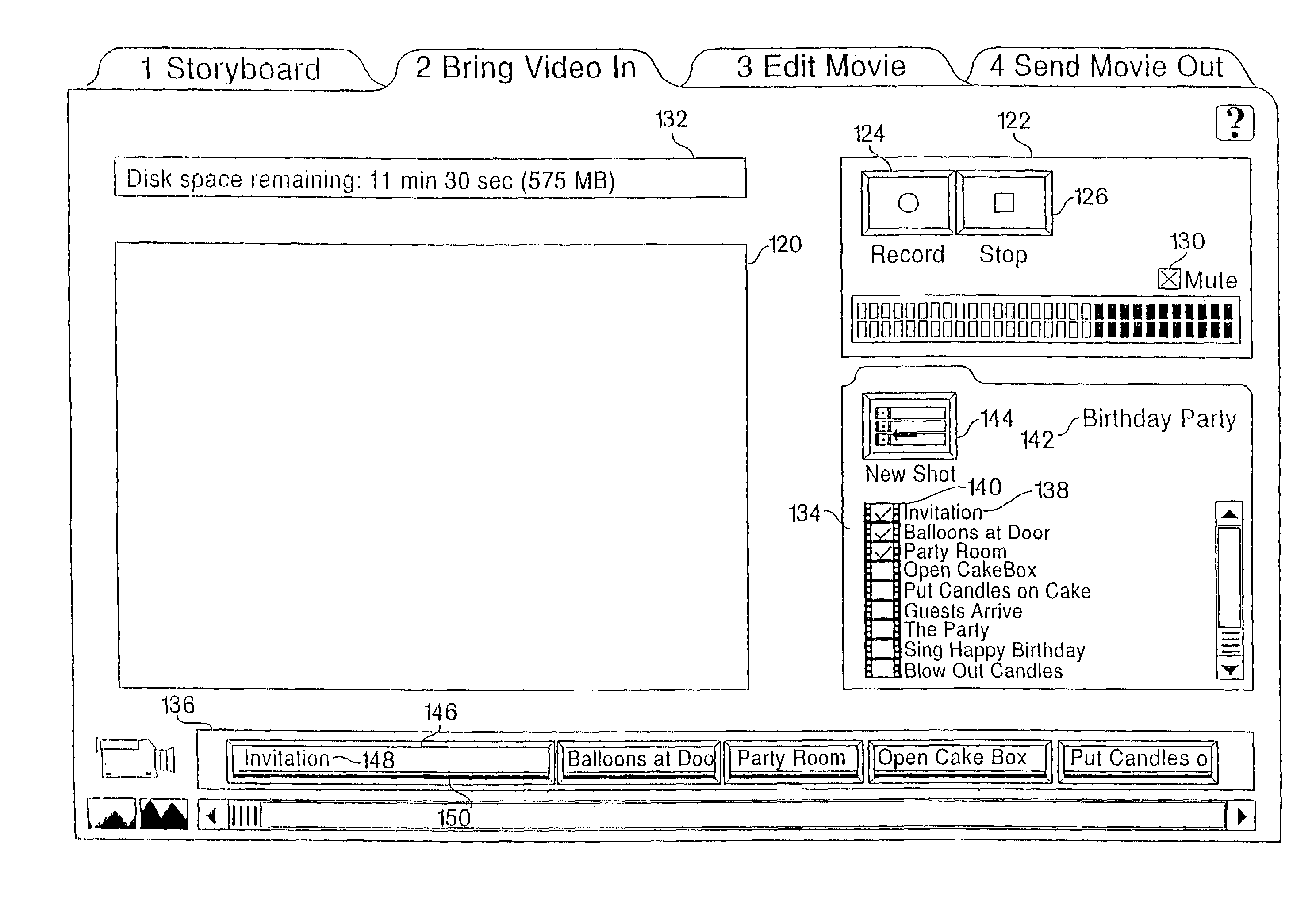
A graphical user interface for a computer-assisted motion video editing system directs a user through the process of editing a video program. The graphical user interface may also enables a user to plan a video program. Alternatively selectable interfaces within a single window interface, each of which provide a group of planning, capturing, editing, and recording functions can provide such an interface for producing a video program. Other simplifications to the user interface can be provided to assist in editing, such as by maintaining a video display window for displaying the edited video program at a fixed position for all available editing operations. Additionally, video information can be captured directly into a timeline representation of a video program, rather than a bin. Using a storyboard tied to the capturing process, a user is directed through the process of collecting and capturing the video clips to be used in the video program.
Owner:AVID TECHNOLOGY
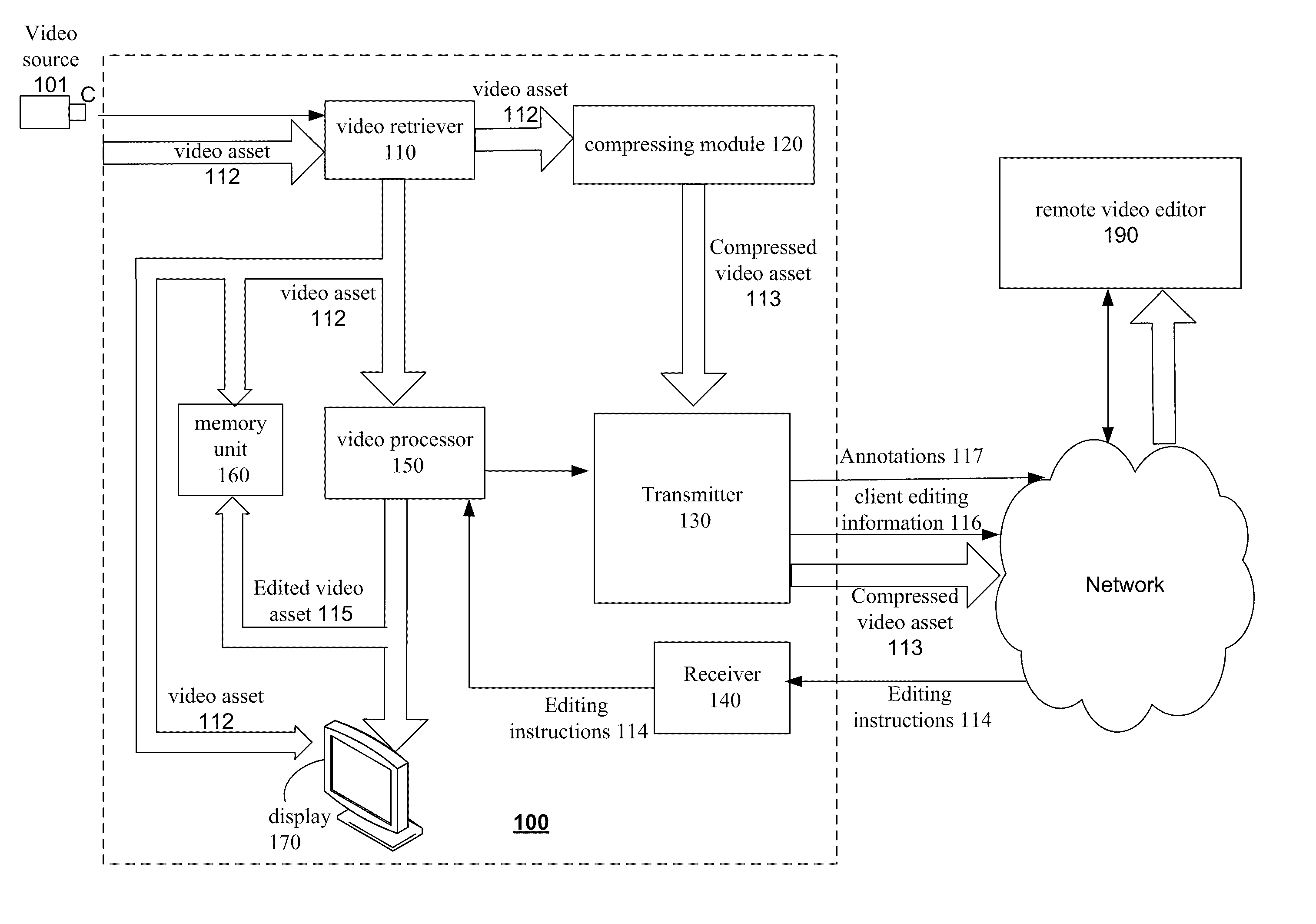
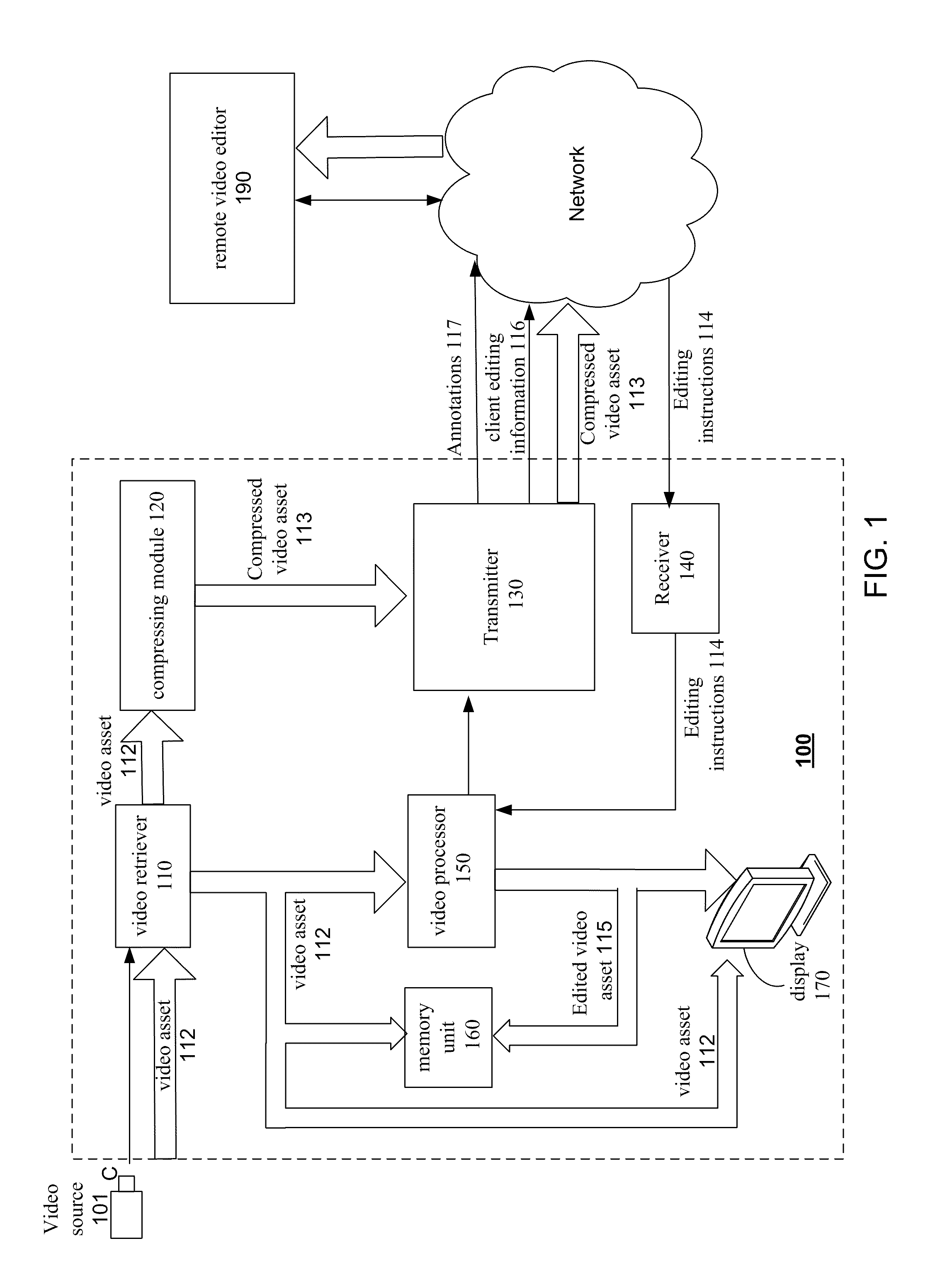
Video processing system and a method for editing a video asset
InactiveUS20110206351A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsImage resolutionVideo processing
A video processing system and a method for editing a video asset, the method includes: obtaining a video asset of a first resolution; compressing, by compressing module, a video asset to provide a compressed video asset of a second resolution that is lower than the first resolution; transmitting, by a transmitter that is a hardware component, the compressed video asset to a remote video editor; requesting the remote video editor to edit the compressed video asset; receiving editing instructions from the remote video editor, the editing instructions are generated by the remote editor when editing the compressed video asset; processing, by a video processor, the video asset based on the editing instructions to provide an edited video asset; and performing at least one of storing, displaying or publishing the edited video asset.
Owner:GIVOLI TAL
Video editing functions displayed on or near video sequences
ActiveUS7890867B1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsVideo sequenceVideo editing
Video editing functions displayed in or near video sequences are described, including displaying a video window including a video sequence of a video presentation, receiving an input to enable an editing panel for performing an editing function for the video sequence, and displaying the editing panel using the video window in response to the receiving.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Variable playback speed template for video editing application
ActiveUS20160225405A1Shorten the length of timeAmount of timeTelevision system detailsElectronic editing analogue information signalsStart timeTime duration
A playback speed effect is applied to a video using a playback speed template. The playback speed template specifies playback speed ratios (i.e., ratios between playback duration and capture duration) at the highlight moment, at a template start time, and at a template end time. A video associated with a highlight tag indicating a highlight capture time of a highlight moment within the video is accessed. An input portion of the video including the highlight moment is identified. The duration of the input portion has a duration depending on the template start time and the template end time. A playback speed template is applied to the input portion. A modified video including a modified video portion is generated from the input portion of the video according to the applied playback speed template and is provided for subsequent playback.
Owner:GOPRO
Method of enabling an application program running on an electronic device to provide media manipulation capabilities
InactiveUS20060184980A1Minimal effortComplexity of easyTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersApplication procedureApplication sharing
Conventionally, media manipulation tools, such as tools for editing video, are an integral part of a video editing application. But with the present invention, these tools can be shared by any application that can generate a video window in which video can be played back Hence, a conventional media player can now include video editing etc. functionality. Even more power-fully, any other application that can generate a video window, such as a presentation program, can now also be extended to include media manipulation tools.
Owner:INTERNET PRO VIDEO
Template-based edit decision list management system
InactiveUS6016380ARapid responseEasy maintenanceTelevision system detailsElectronic editing analogue information signalsDigital videoTemplate based
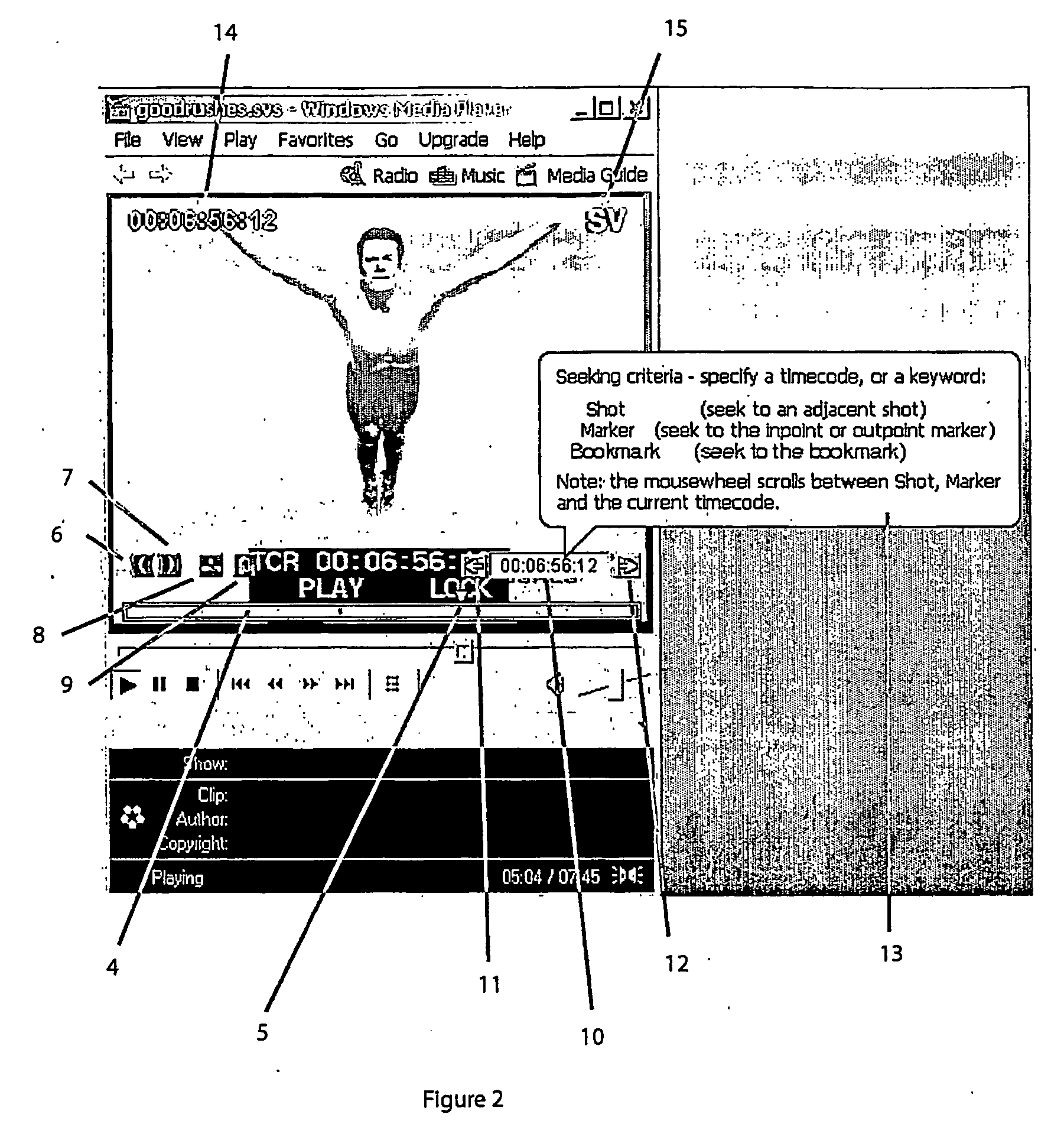
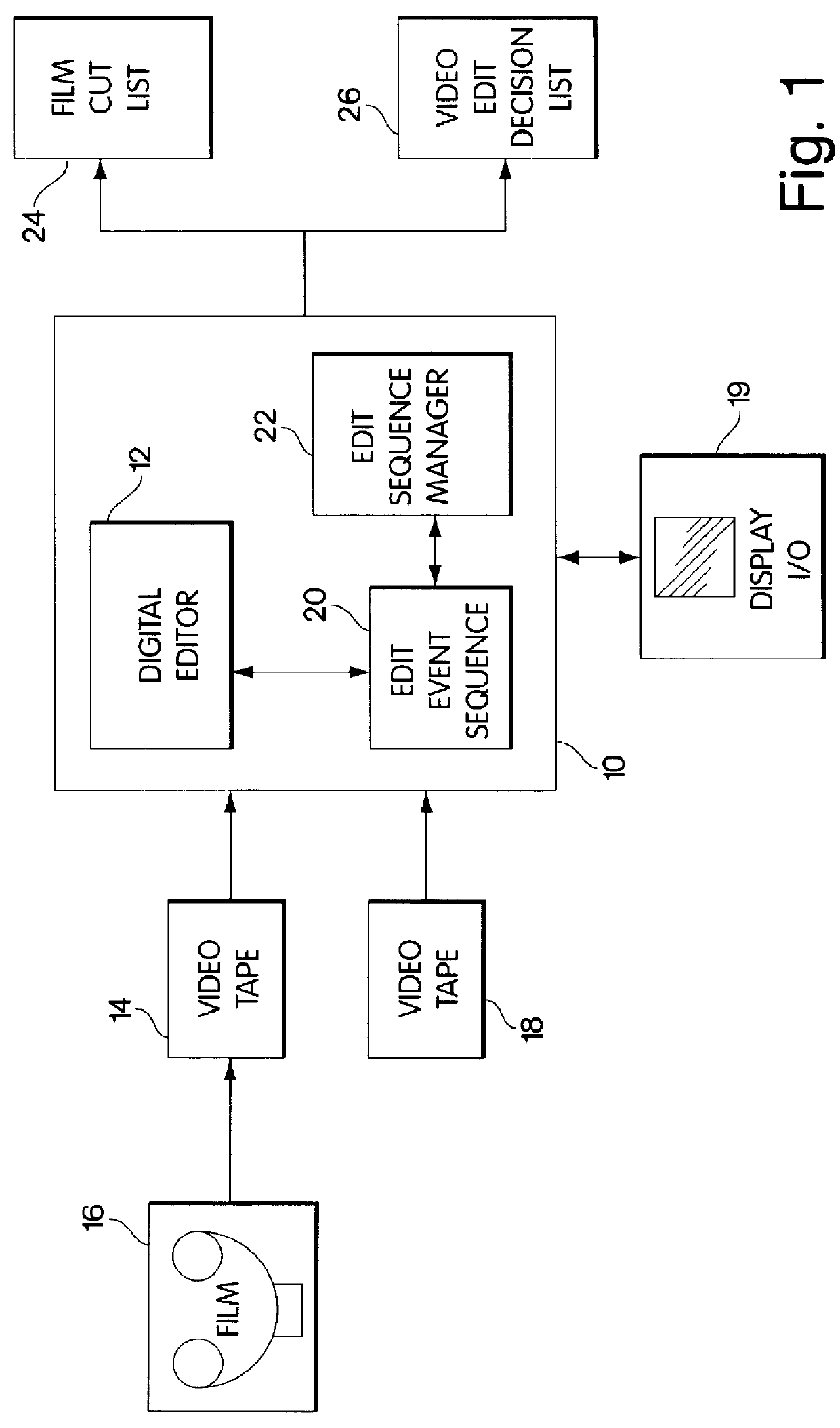
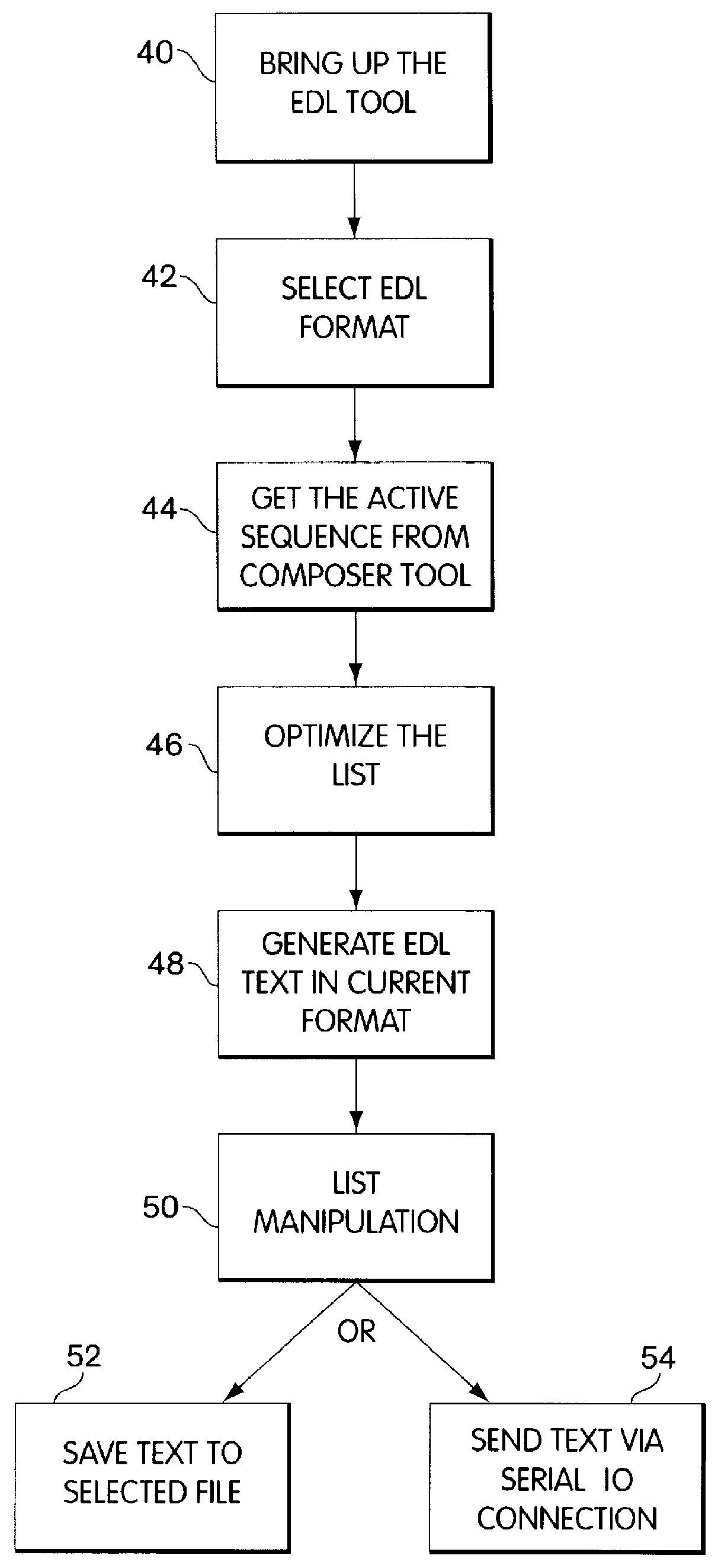
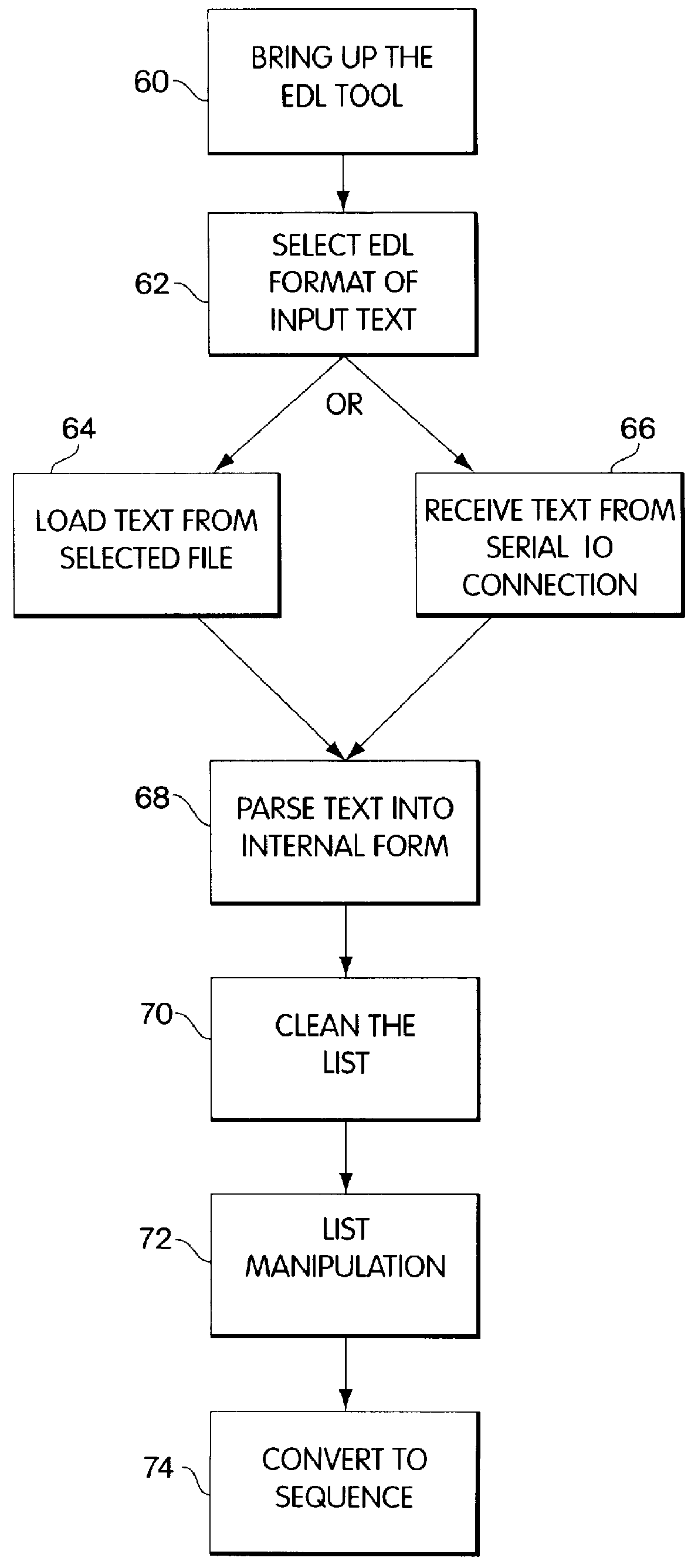
A computer-based system for generating a video edit decision list, which tabulates video editing events and video synchronization points corresponding to the video editing events. The invention accepts a sequence of video and audio manipulations produced by a digital video editing system, each manipulation effecting a particular video editing event, and generates, based on the manipulation sequence, a list of video editing events and corresponding synchronization points. The invention then conforms the list to a user-specified format selected from a plurality of video edit decision list format templates, provided by the system, which each specify a model for defining video editing events distinctly in that format, and then the video edit decision list is output in the user-specified format. The invention is adapted to also convert a video edit decision list from a first format to a second, user-specified format; and further is adapted to generate a sequence of video and audio manipulations to be used by a digital video editor for editing a video, based on a video edit decision list.
Owner:AVID TECHNOLOGY
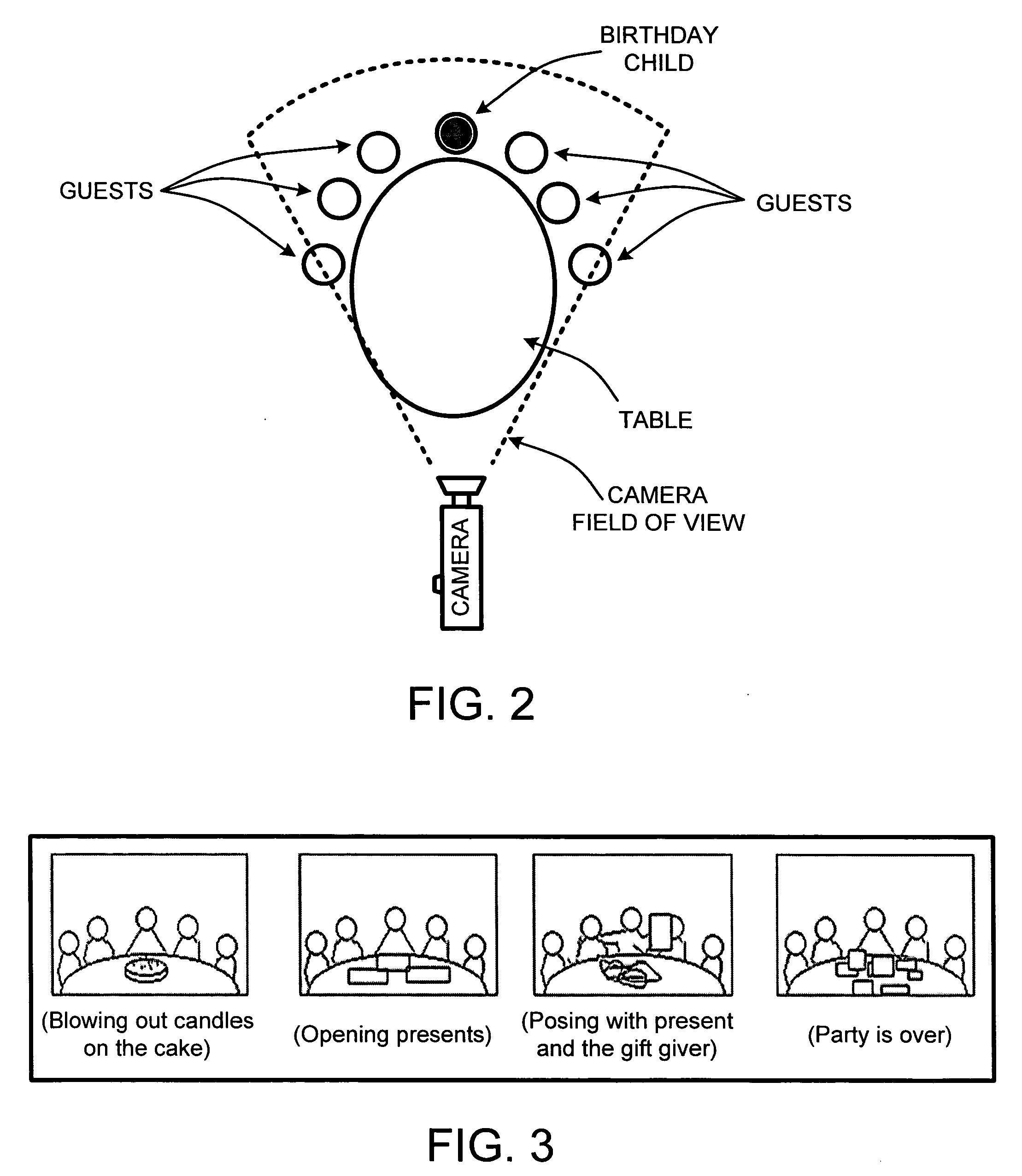
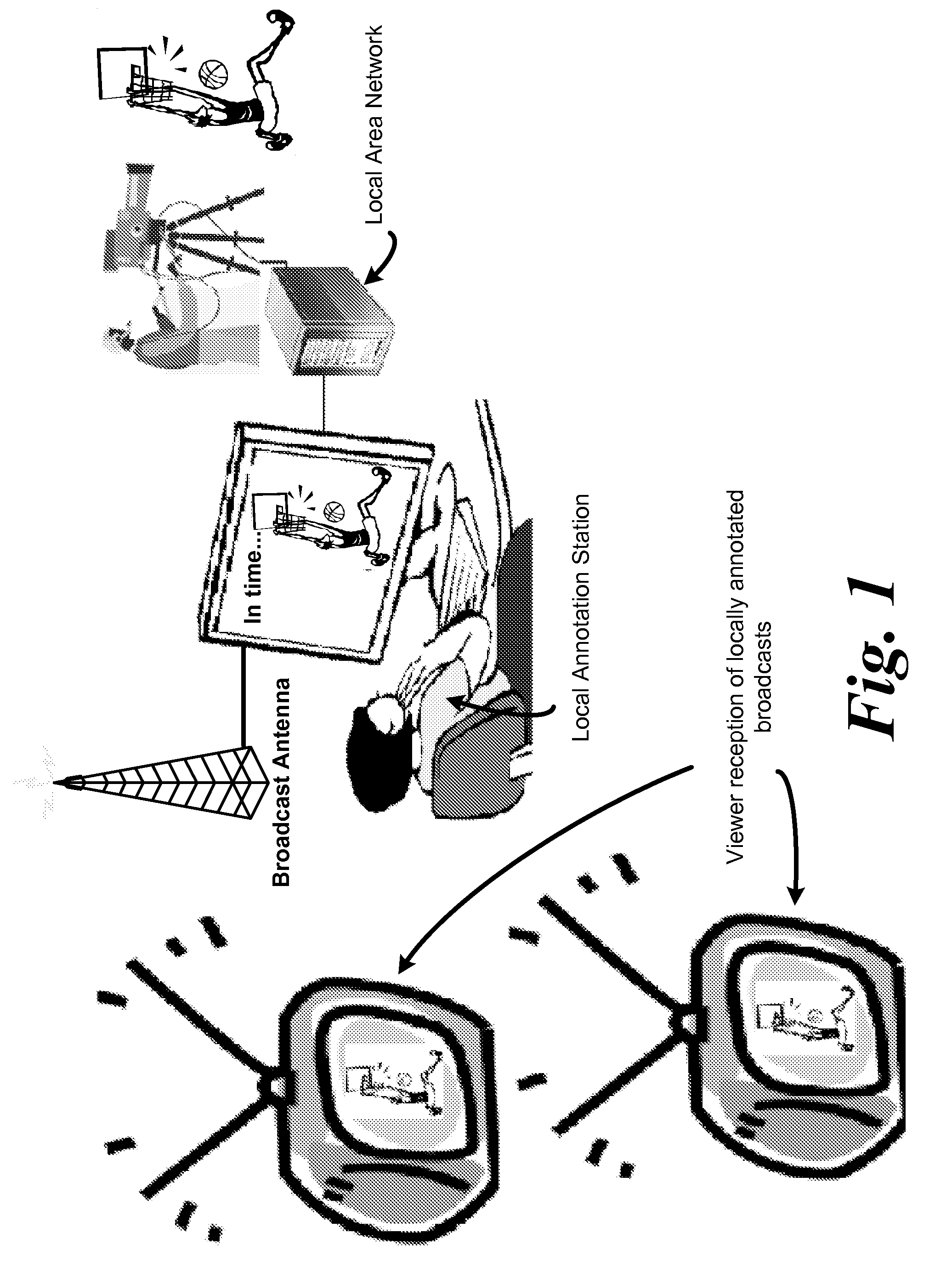
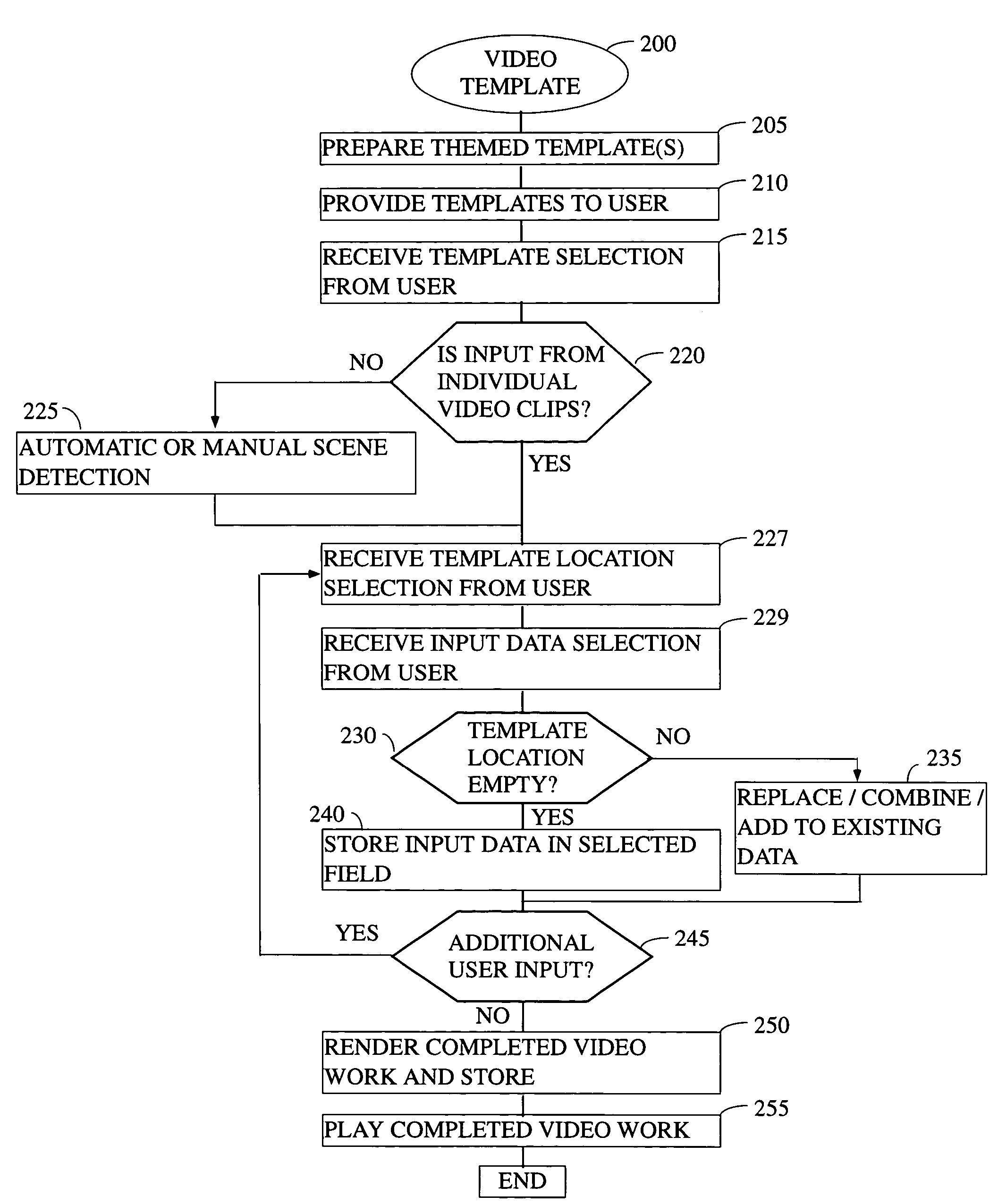
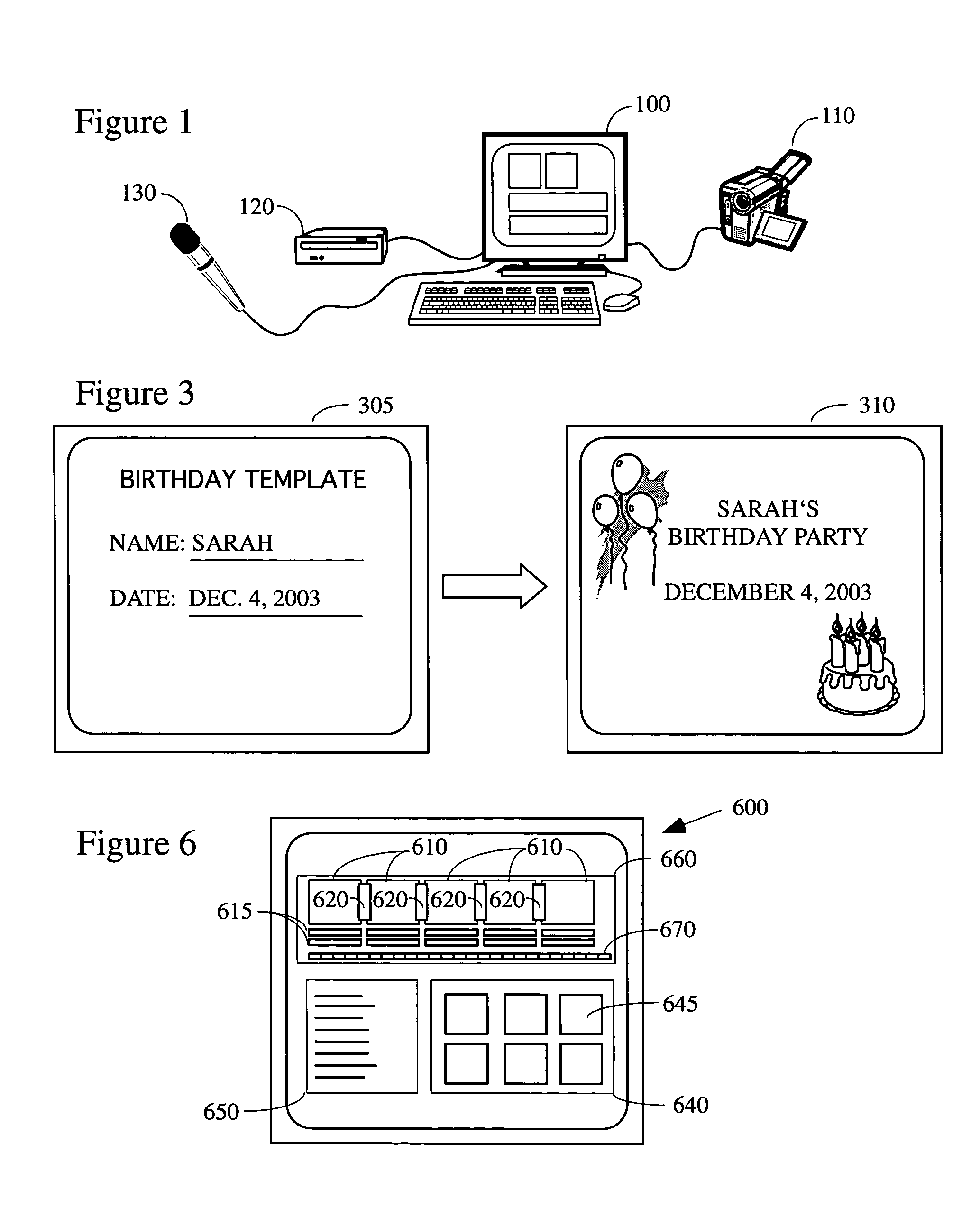
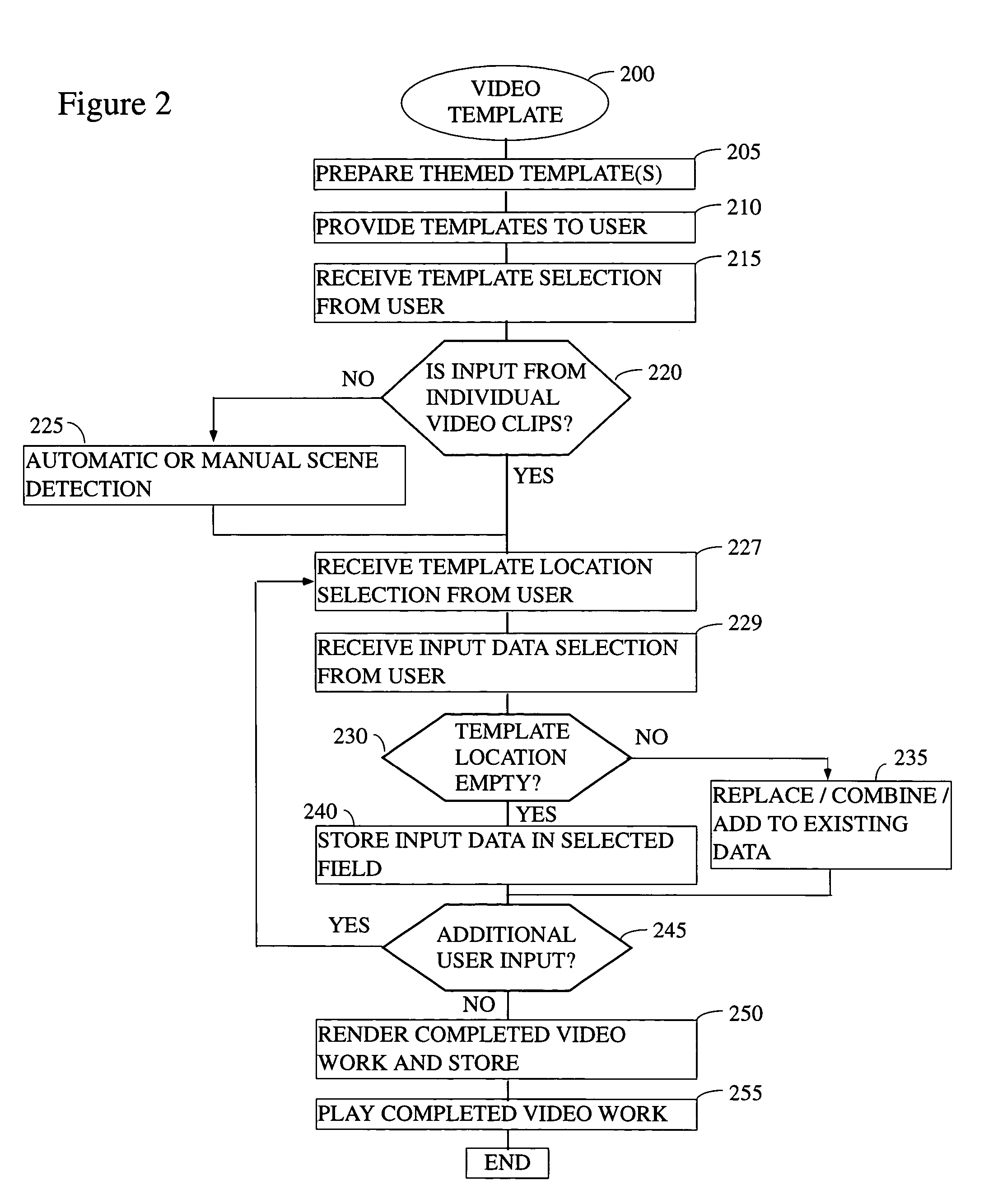
System and method for improved video editing
ActiveUS20050084232A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsTheme parkAudio frequency
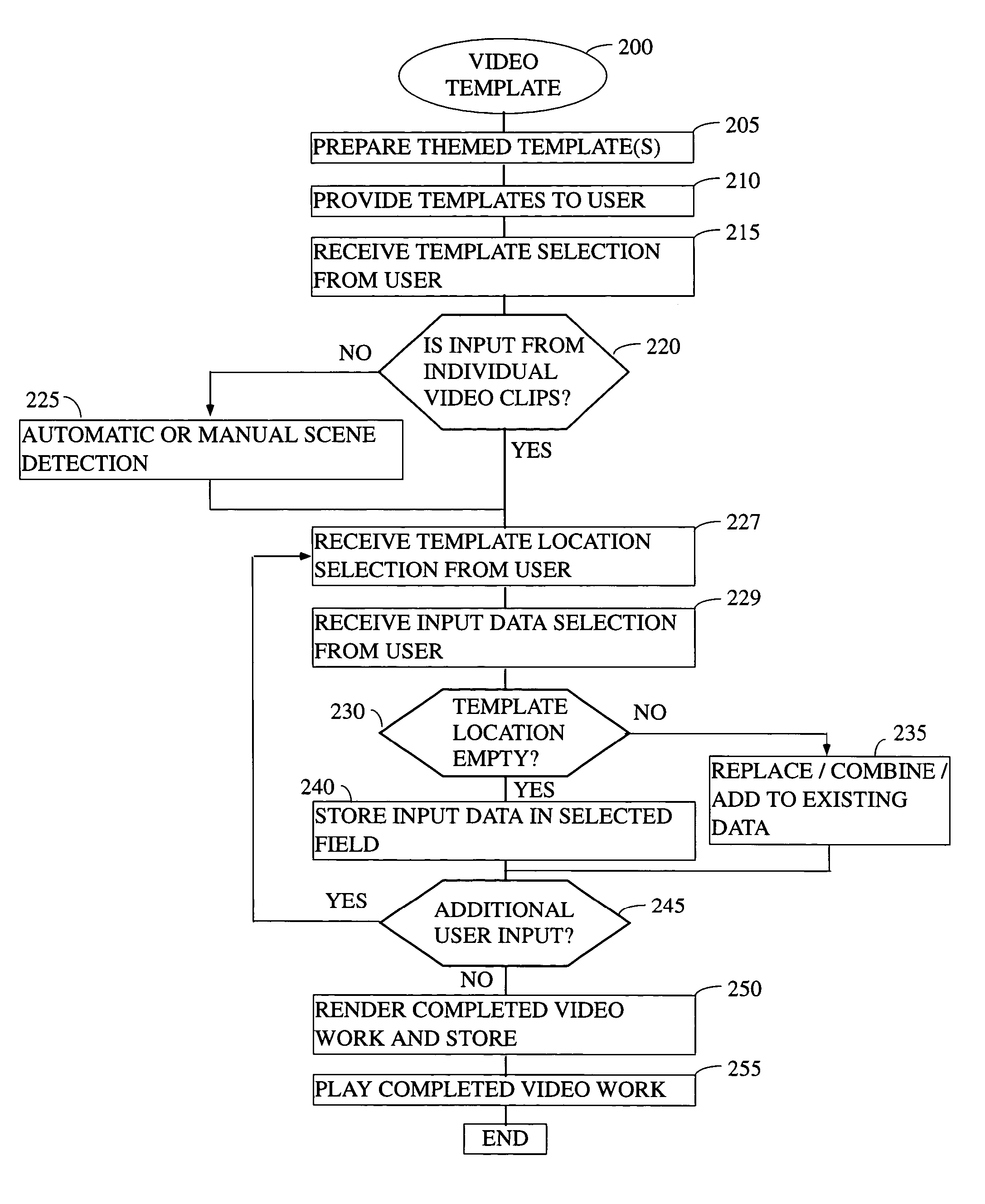
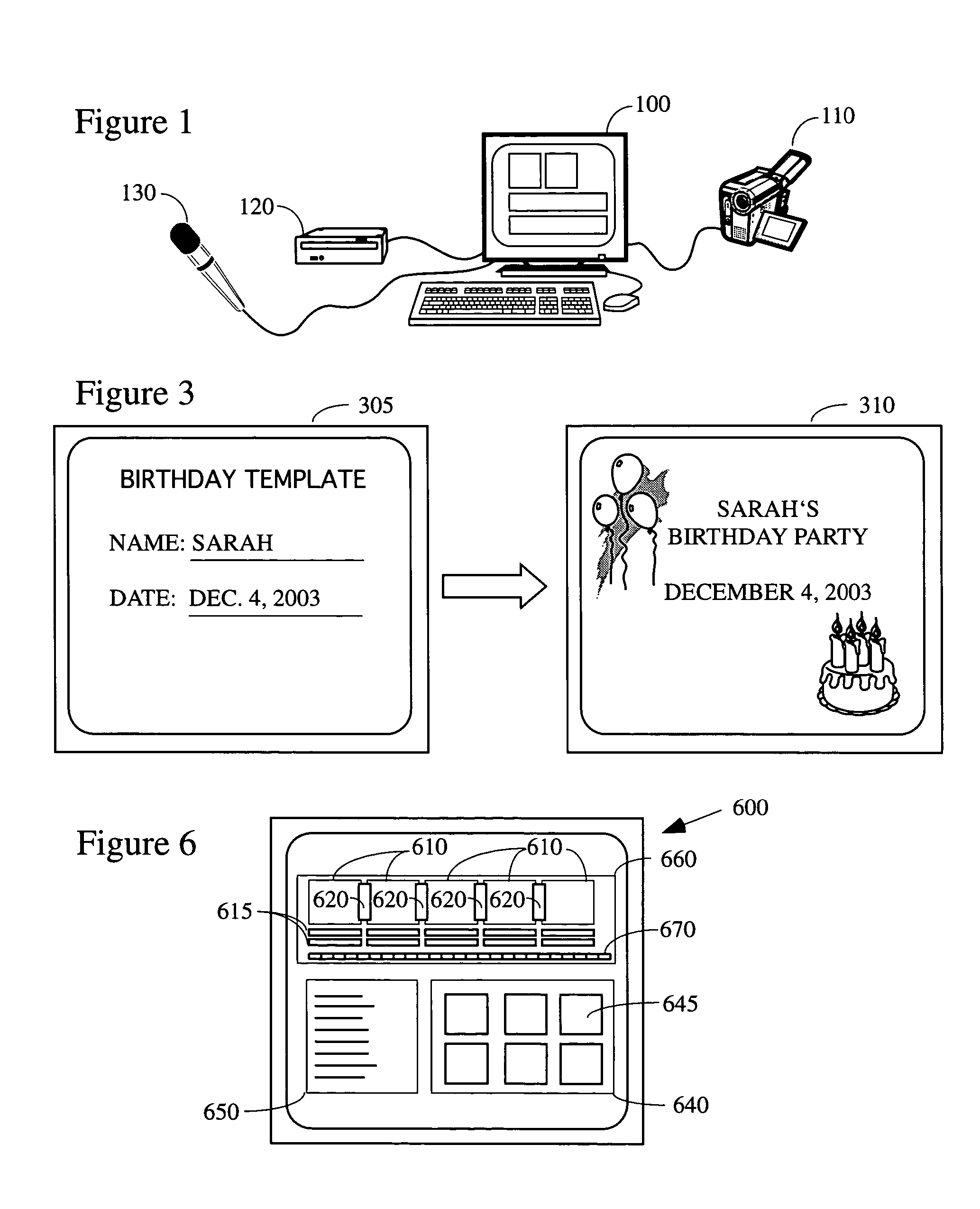
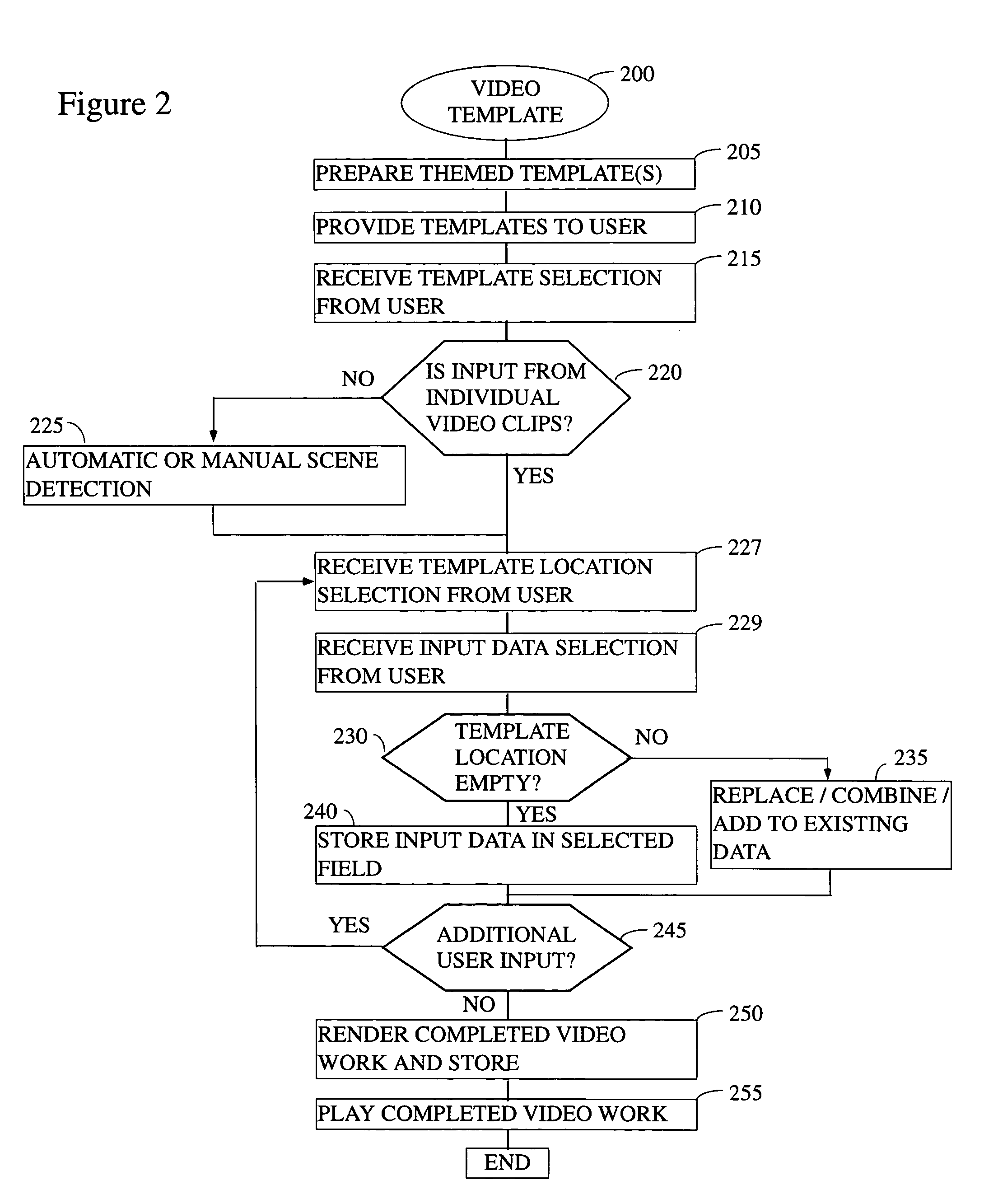
There is provided herein an invention that utilizes a themed template which is designed to assist novice video editors quickly compose a complete video work which memorializes a particular familiar occasion such as, for example, a birthday, a wedding, a trips to a theme park, etc. The template for each such occasion will be customized with predefined cells that are annotated with descriptions of events that might occur during said occasions. A user will be able to drop his or her own video and / or audio clips taken at the occasion into the cells and, if this is done according to the annotations, thereby create a complete video work that memorializes the selected occasion.
Owner:MAGIX
Novel media file access and storage solution for multi-workstation/multi-platform non-linear video editing systems
ActiveUS20060184673A1Digital data processing detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsSymbolic linkMulti platform
Owner:EDITSHARE LLC
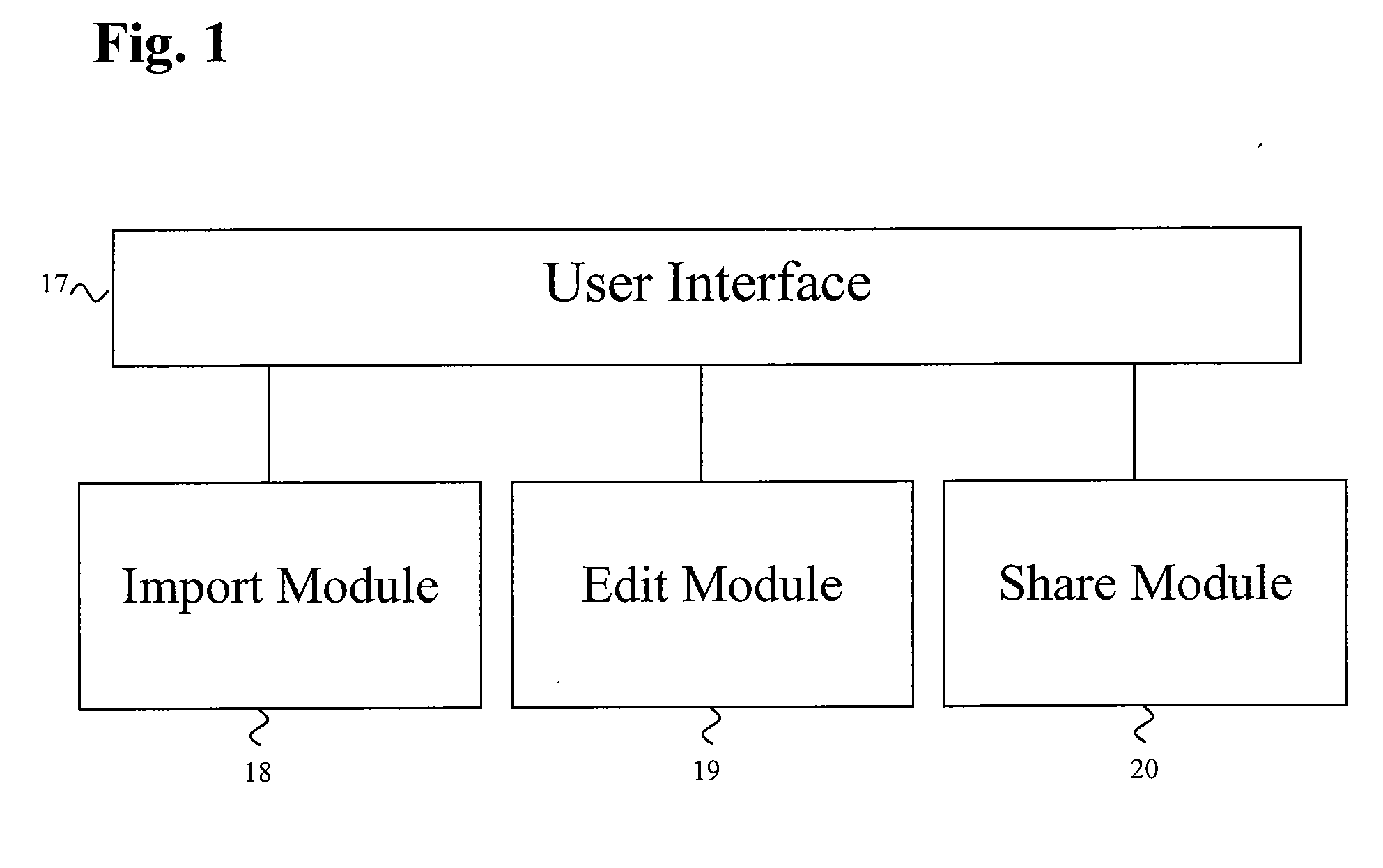
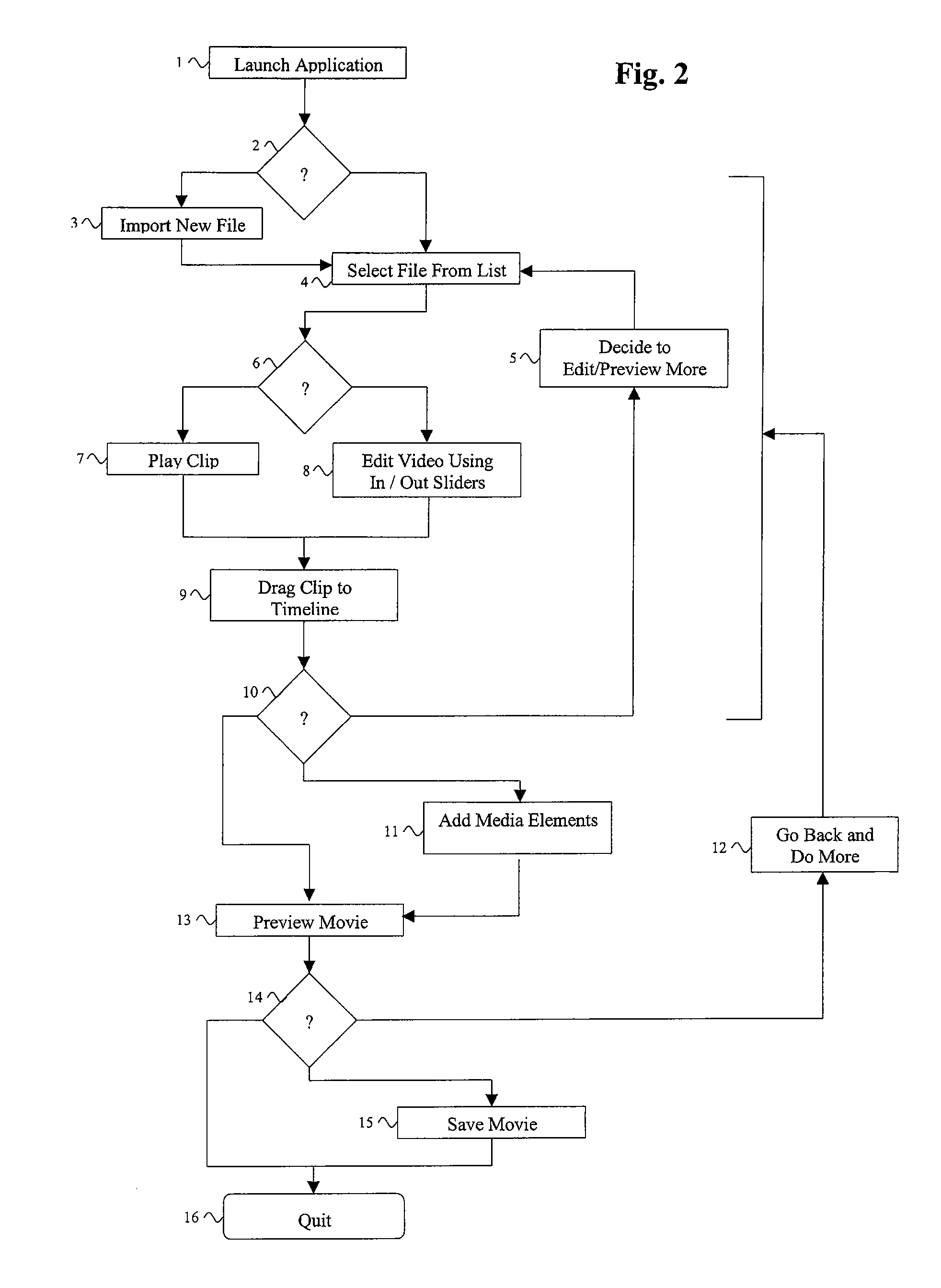
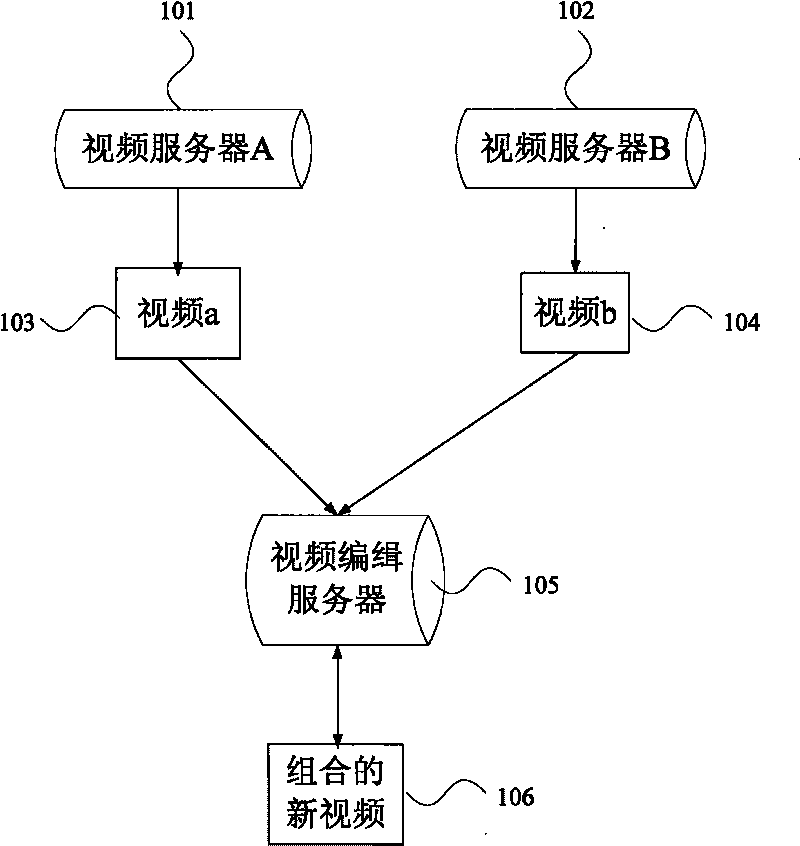
Systems and methods for encoding, editing and sharing multimedia files
InactiveUS20080013916A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsVideo editingComputer based
The present invention is directed to computer based editing systems, methods for editing videos, methods for communicating from server to the desktop and computer readable storage media that are capable of executing certain methods and applying certain video editing systems. Through the use of the present invention one can efficiently combine a plurality of media elements that are in a plurality of different forms into one video. In certain embodiment, the invention couples an editing tool with a channel that communicates to a server in a format that is downloaded from a server that may or may not be the server with which it continues to communicate. That channel can deliver live updatable multi-media formats e.g. text, flash, gifs. to the editing tool whenever the user is online.
Owner:VIDEOTHANG
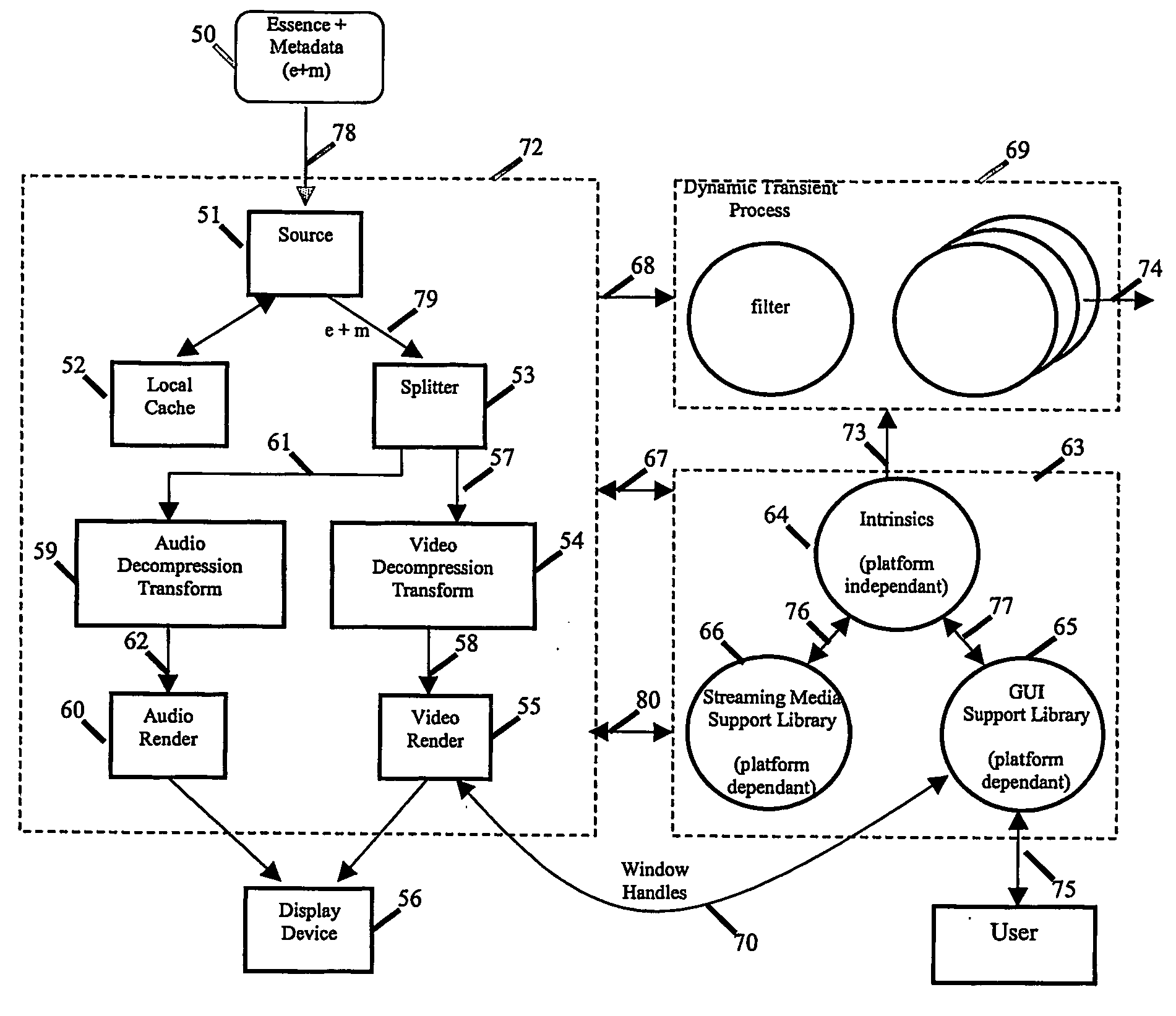
Video editor and editing method, recording medium, and program
InactiveUS20060098941A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsTerminal equipmentVideo image
An object of the present invention is to perform speedy editing to produce images including desired features. A disc video monitor program 161 sets an essence mark, which is digital mark data indicating a feature of an image, in metadata related to video content data for displaying images. A video display program 172 controls the display of images based on the video content data. An essence-mark display program 171 controls the display of the temporal position of the image having the feature indicated by the digital mark data based on the metadata in which the essence mark, which is digital mark data, is set. The video-image editing apparatus of the present invention is applicable to a filming terminal device.
Owner:SONY CORP
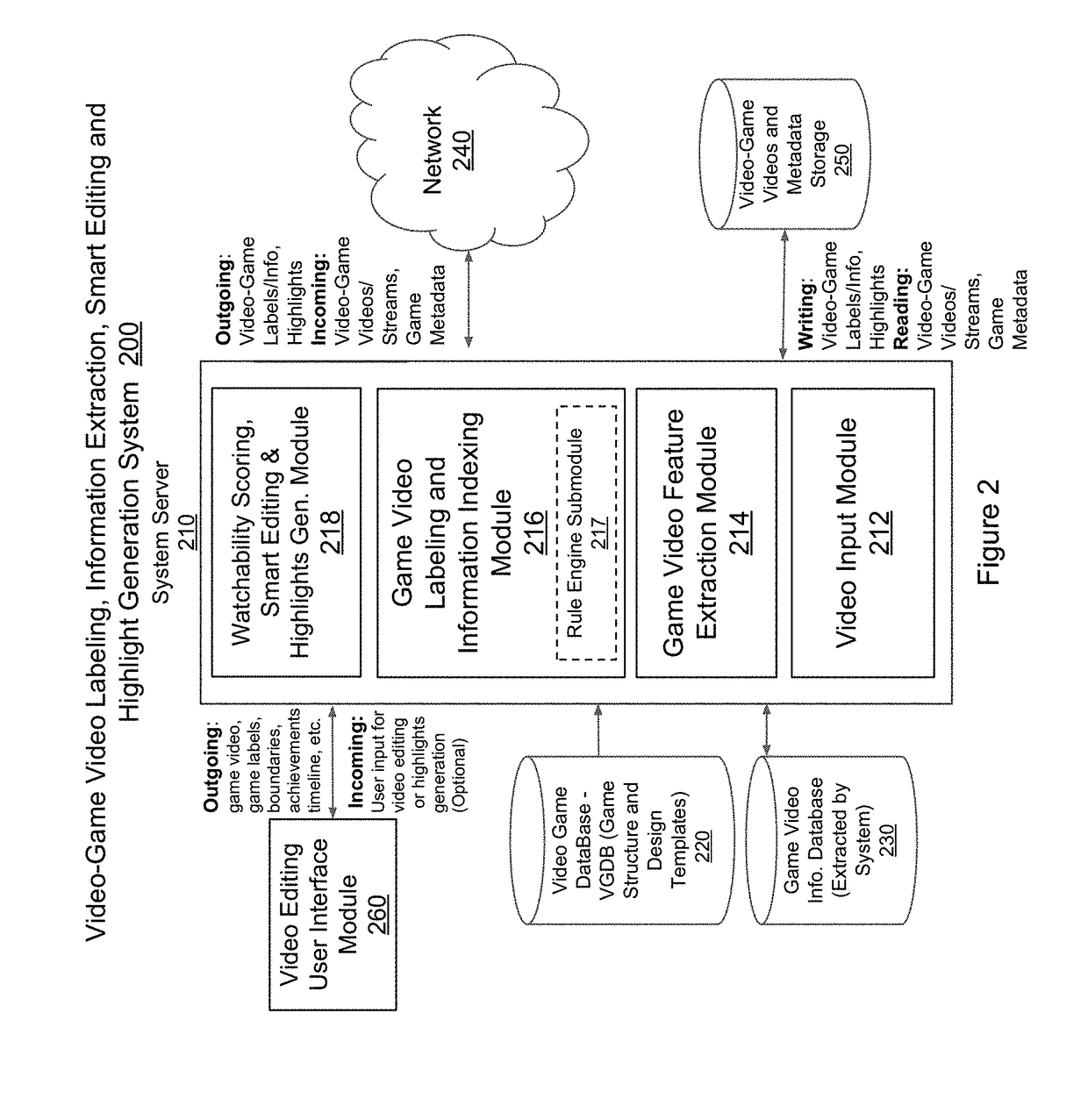
Analysis of video game videos for information extraction, content labeling, smart video editing/creation and highlights generation
InactiveUS20170228600A1Promote generationElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsUsing detectable carrier informationGaming videoFilm editing
Methods and systems for analyzing video-game videos in connection with facilitating video editing and creation and performing automated extraction of information of interest to facilitate labeling of and / or highlight generation for such videos is provided. According to one embodiment, a video, containing content pertaining to a video game, is received by a video-game video analysis system. Information regarding the status of the video game over time is received by retrieving game metadata through an API of the video game or by analyzing audio or visual features within the content. Multiple clips are automatically identified within the video for proposed inclusion within an edited version of the video based on the status of the video game over time. The edited version of the video is then generated by (i) joining the automatically identified clips or (ii) joining multiple user-selected clips, including at least one clip selected from the automatically identified clips.
Owner:CLIPMINE
System and method for automatic video editing using object recognition
InactiveUS20060251382A1Automatically simulateTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsStationary objectUnique object
An “automated video editor” (AVE) automatically processes one or more input videos to create an edited video stream with little or no user interaction. The AVE produces cinematic effects such as cross-cuts, zooms, pans, insets, 3-D effects, etc., by applying a combination of cinematic rules, object recognition techniques, and digital editing of the input video. Consequently, the AVE is capable of using a simple video taken with a fixed camera to automatically simulate cinematic editing effects that would normally require multiple cameras and / or professional editing. The AVE first defines a list of scenes in the video and generates a rank-ordered list of candidate shots for each scene. Each frame of each scene is then analyzed or “parsed” using object detection techniques (“detectors”) for isolating unique objects (faces, moving / stationary objects, etc.) in the scene. Shots are then automatically selected for each scene and used to construct the edited video stream.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for clipping video based on browser
InactiveCN101740082AEasy onlineConstruct logical relationshipElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsTransmissionWeb siteVideo encoding
The invention discloses a method and a system for clipping a video based on a browser. The method mainly comprises the following steps: creating a video editor on line through Active X technology embedded in the browser, such as flash technology; loading videos in different video websites in the video editor, or uploading the local video, and easily editing the currently loaded video; softly clipping a required video segment; and gathering the videos from different network addresses through an XML structural mode to generate a multi-source video customized by a user. The user can clip the videos in the different video websites on line, so that a plurality of video segments from the different network addresses or the same network address can be combined into a new video; and no damage is caused to the structure of the original video code. Particularly, the method and the system of the invention support various video formats, including video stream of streaming media form.
Owner:孟智平
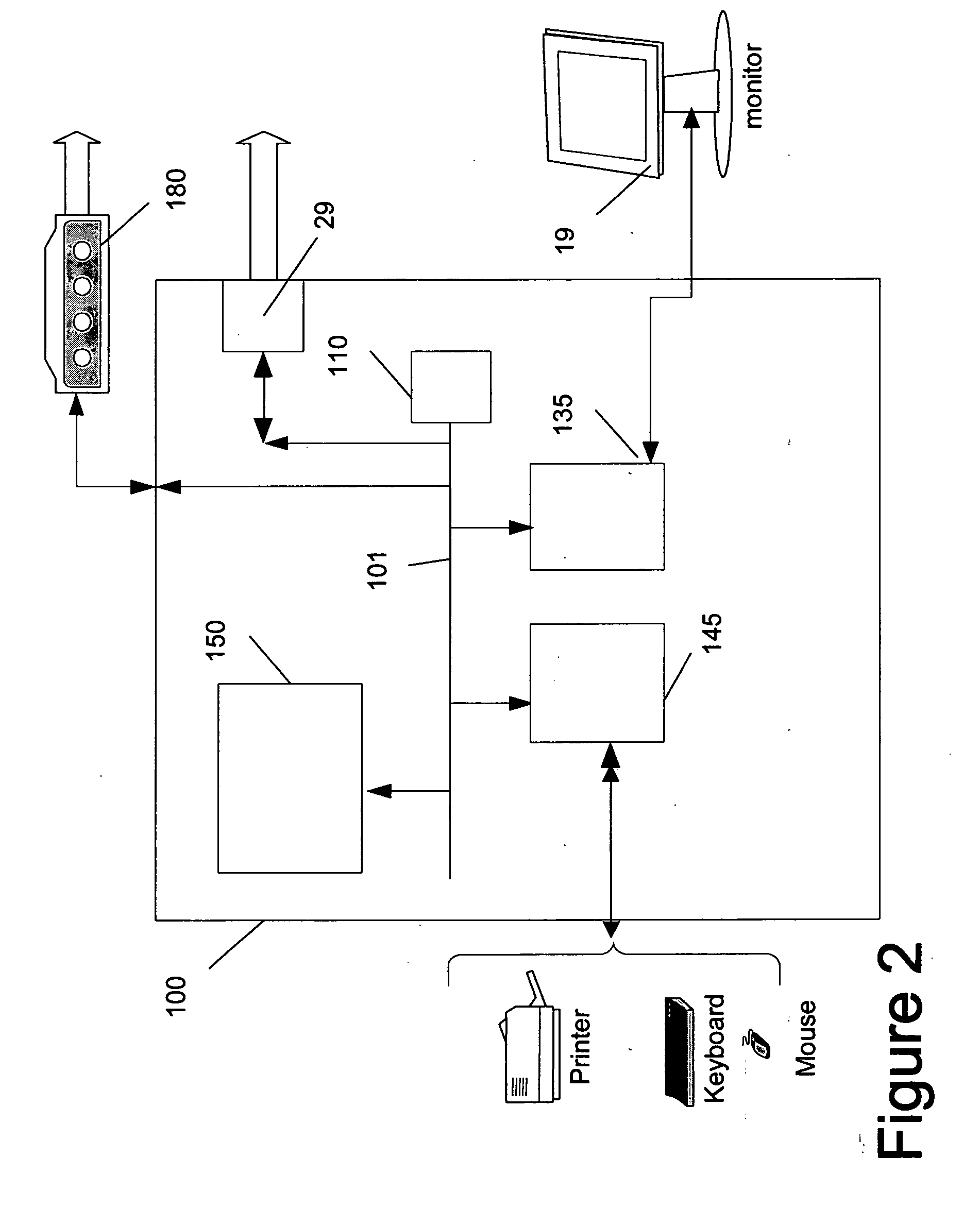
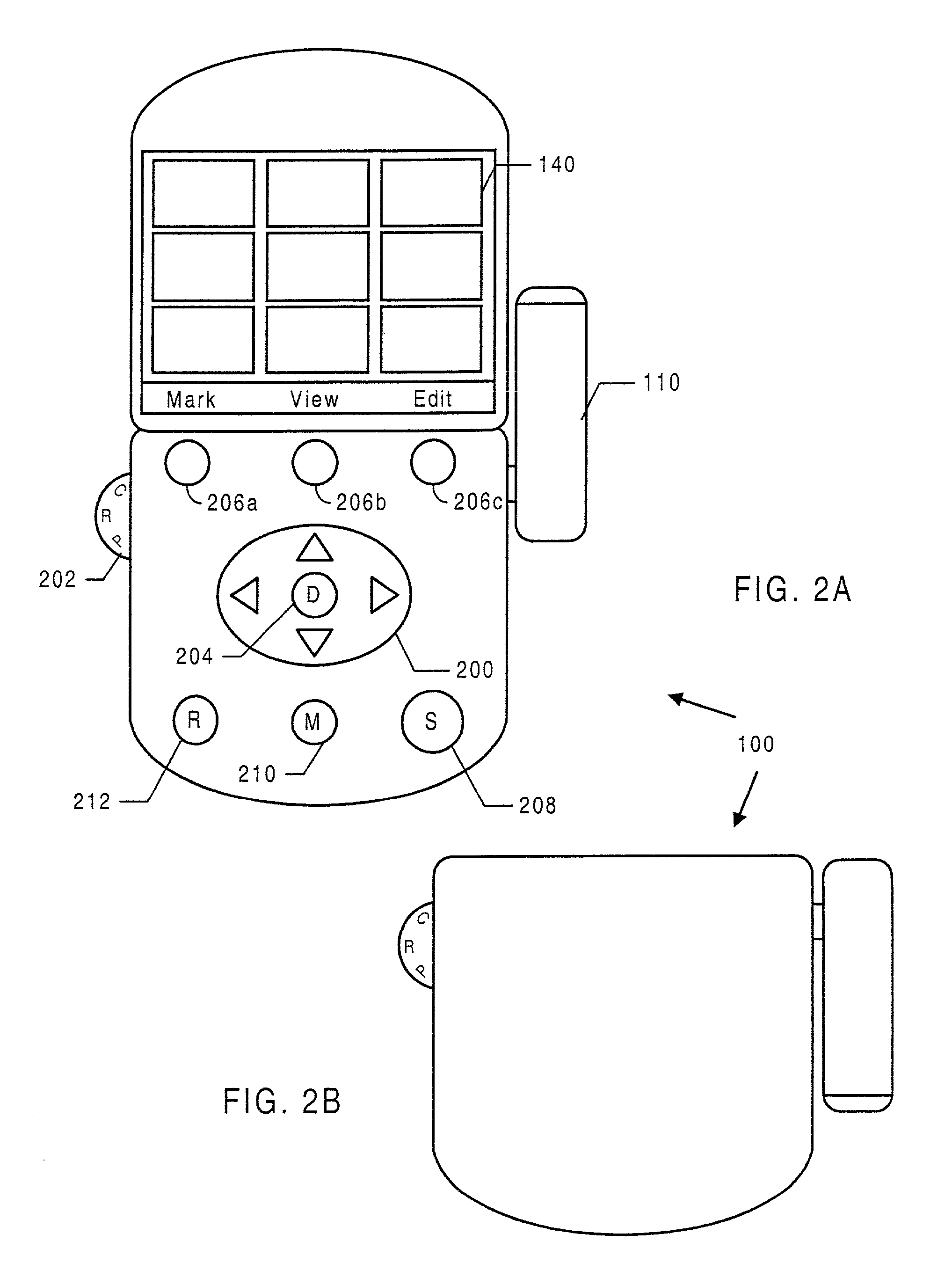
Method and apparatus for editing heterogeneous media objects in a digital imaging device
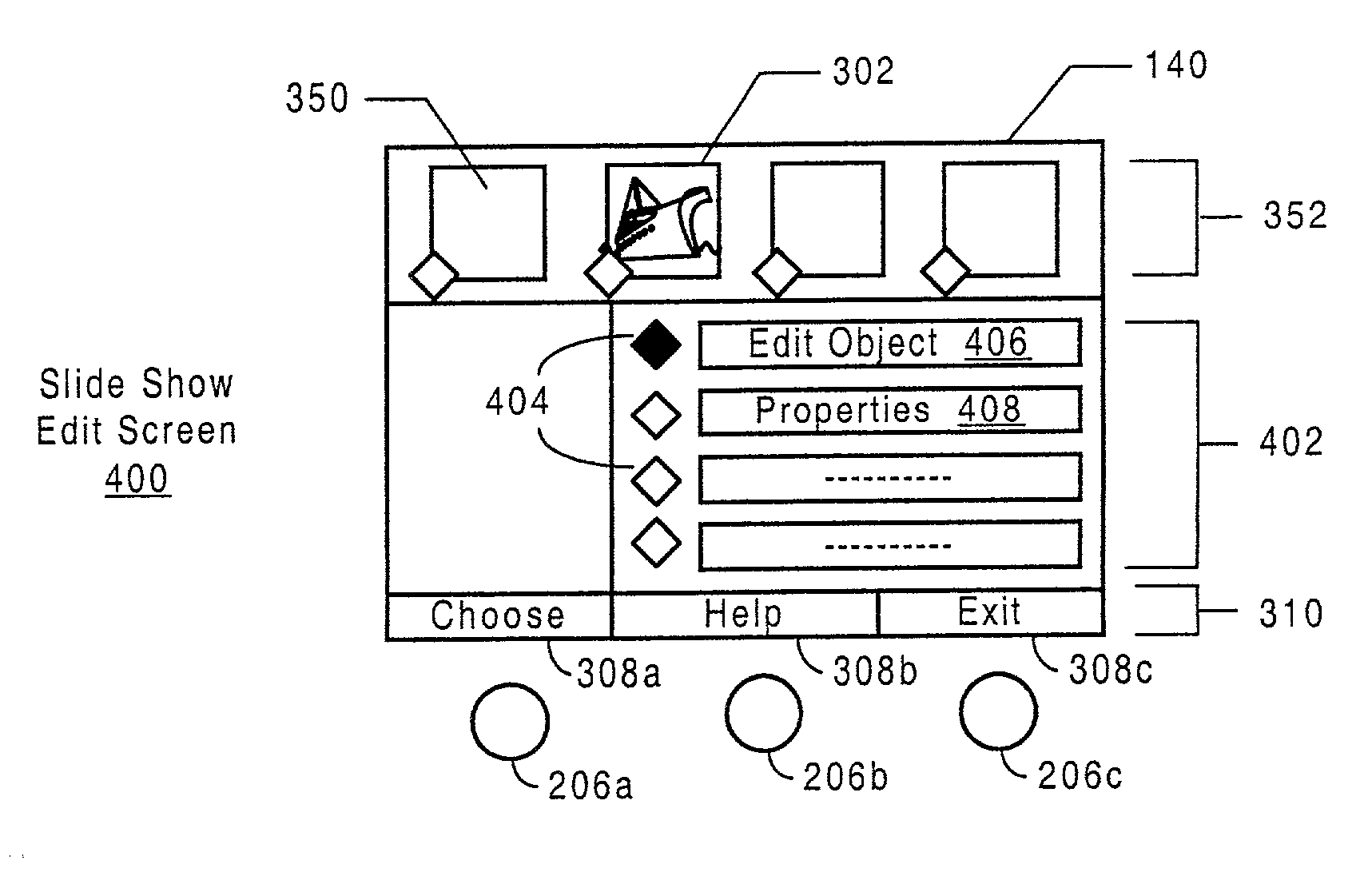
InactiveUS20080115066A1Ease use and operationEasy to createElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsRecord information storageDigital imagingMedia type
A method and apparatus for editing heterogeneous media objects in a digital imaging device having a display screen, where each one of the media objects has one or more media types associated therewith, such as a still image, a sequential image, video, audio, and text. The method aspect of the present invention begins by displaying a representation of each one of the media objects on the display screen to allow a user to randomly select a particular media object to edit. In response to a user pressing a key to edit a selected media object, one or more specialized edit screens is invoked for editing the media types associated with the selected media object. If the media object includes a still or a sequential image, then an image editing screen is invoked. If the media object includes a video clip, then a video editing screen is invoked. If the media object includes an audio clip, then an audio editing screen is invoked. And if the media object includes a text clip, then a text editing screen is invoked.
Owner:FLASHPOINT TECH
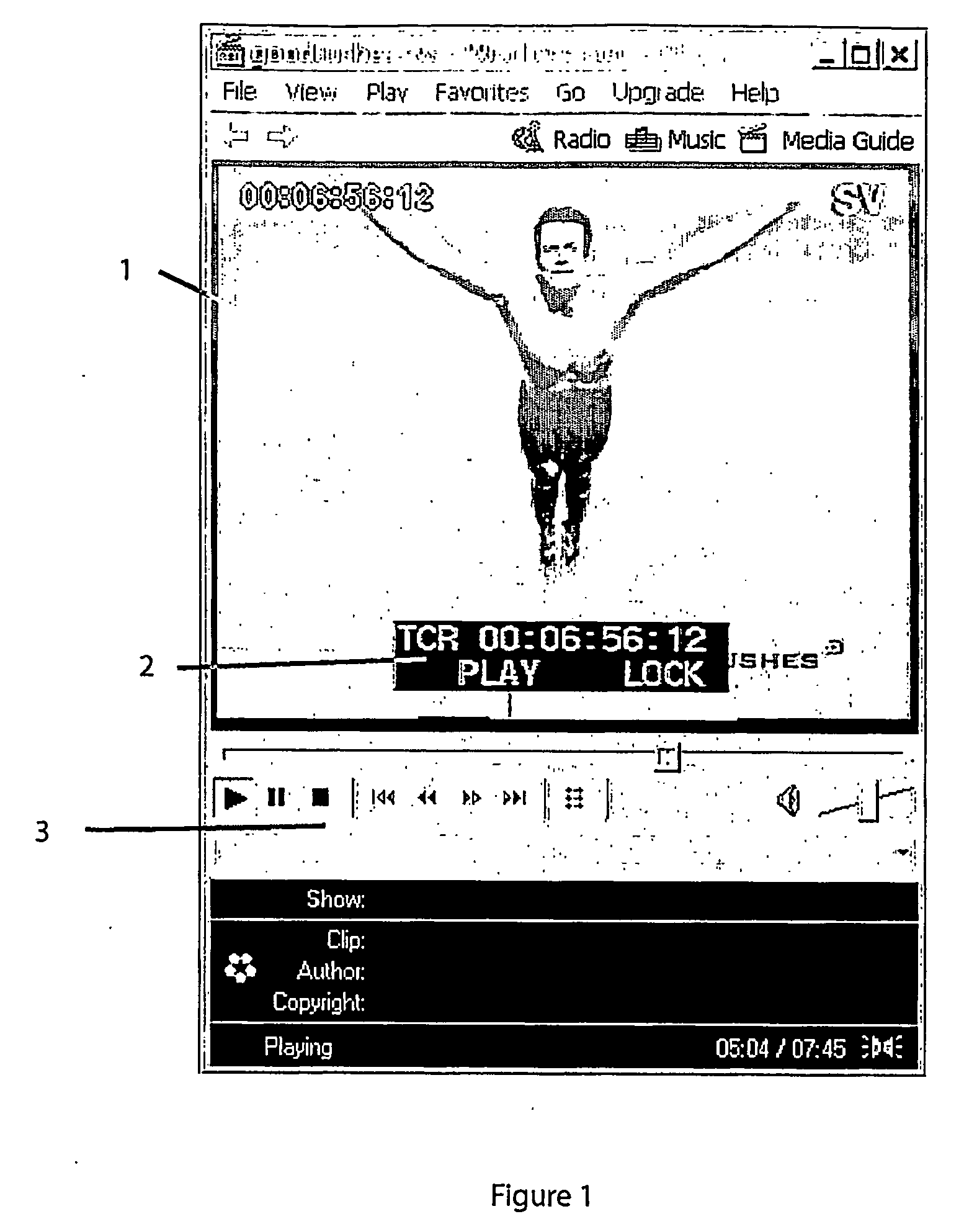
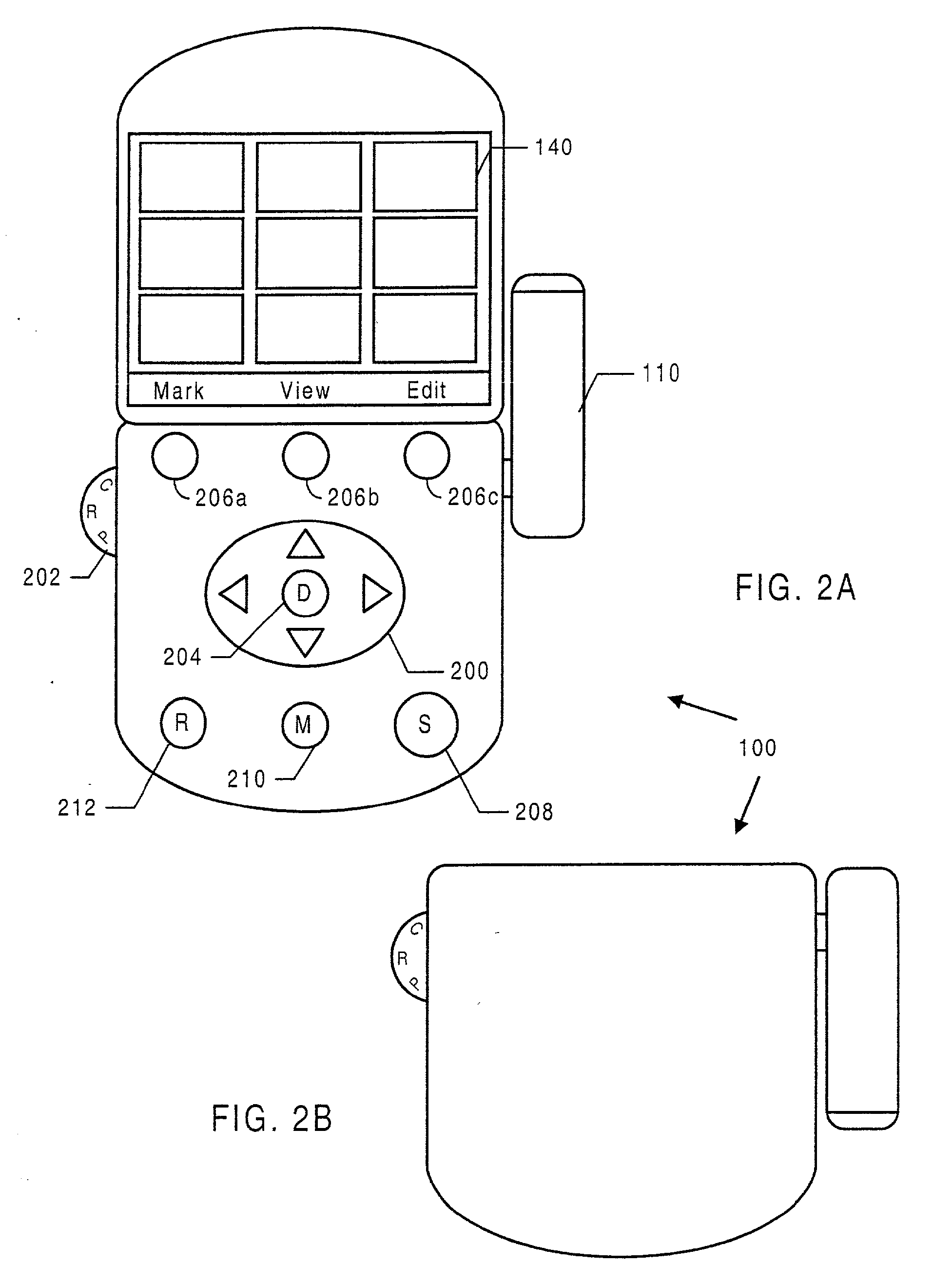
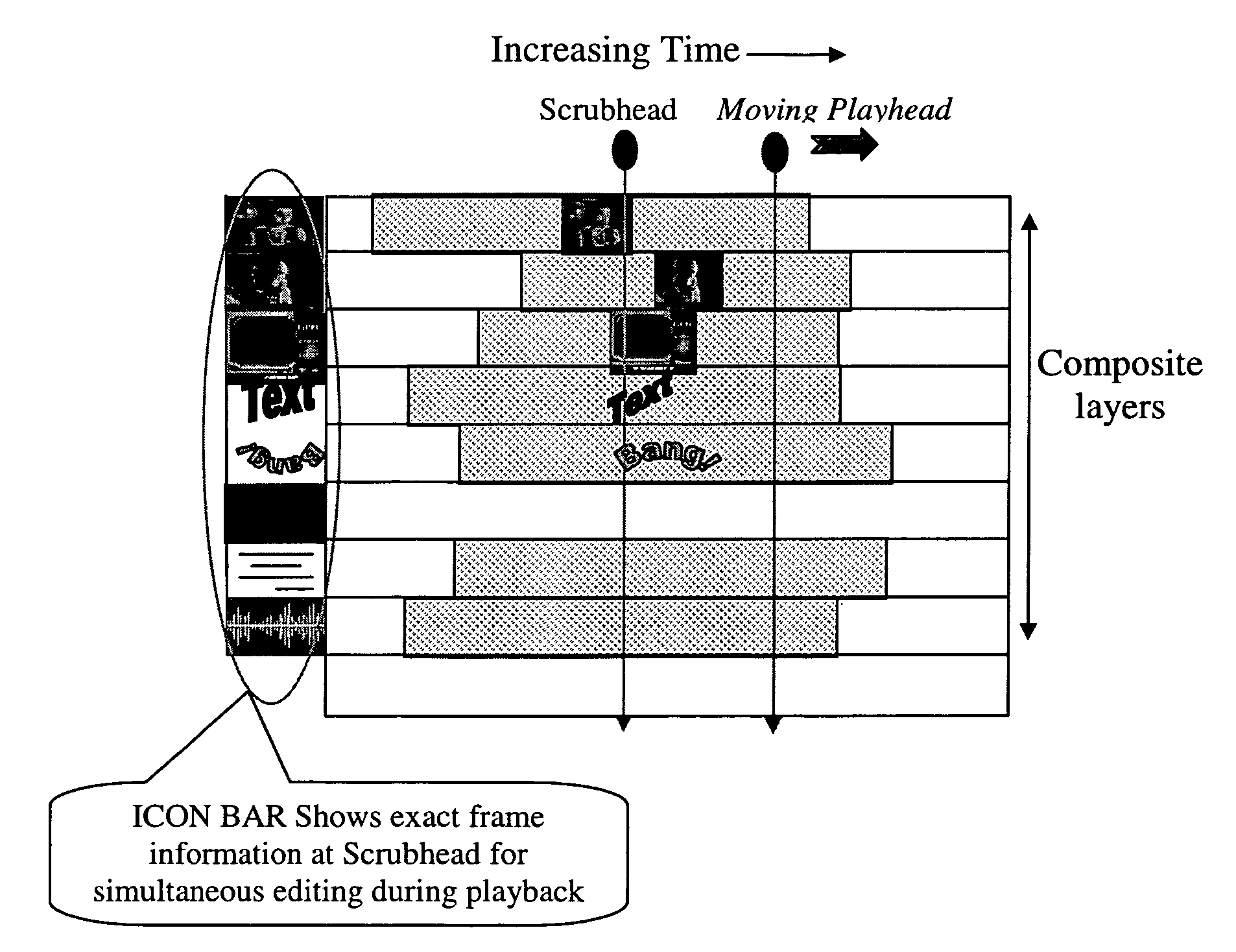
Icon bar display for video editing system
ActiveUS7434155B2Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDisplay deviceVideo sequence
Owner:HBC SOLUTIONS
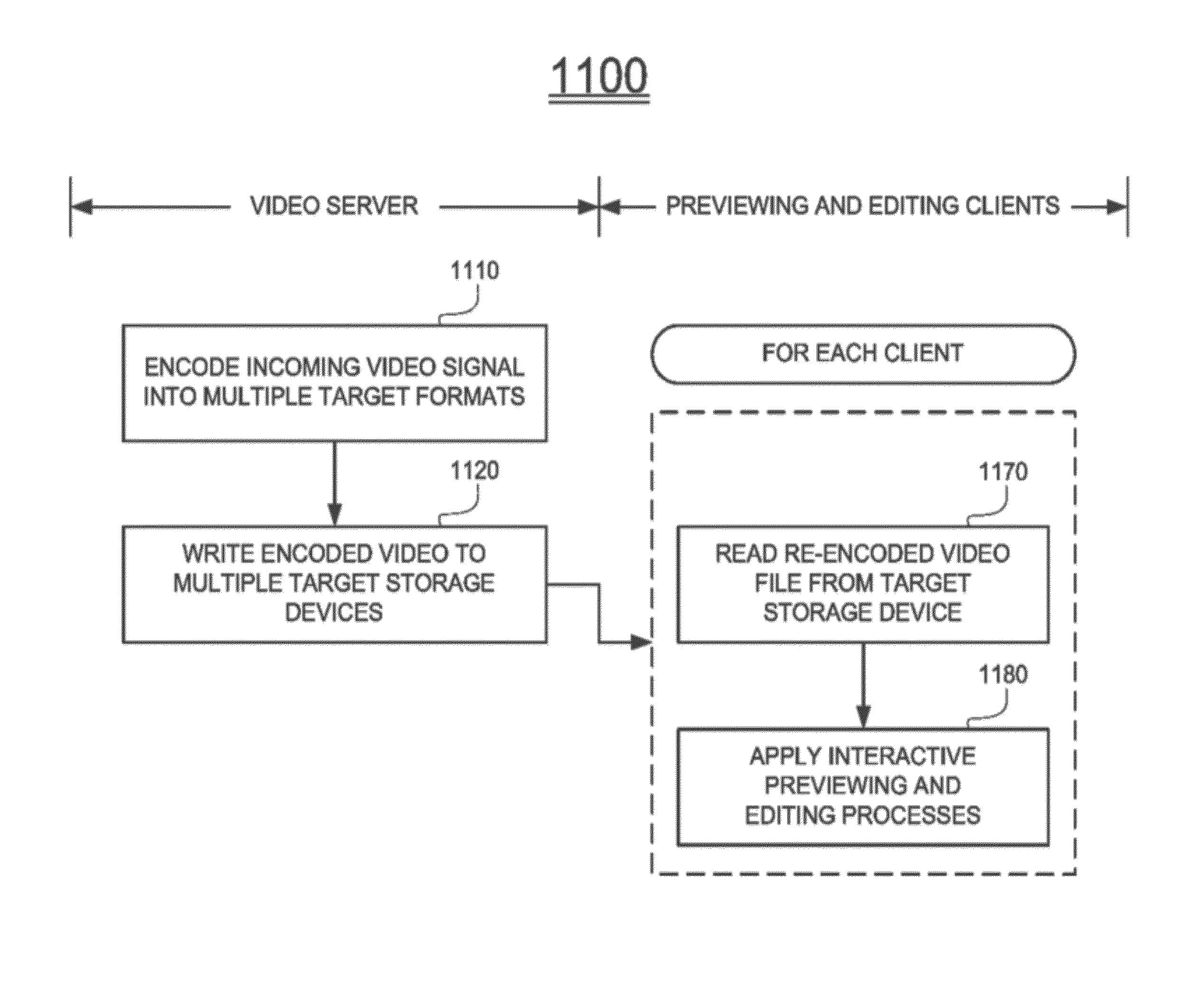
Ingest-once write-many broadcast video production system
InactiveUS20120266203A1High resolutionMultiple readTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionVideo serverImage resolution
A video ingest system, including a video server, including a receiver for receiving incoming video feeds, a video encoder for encoding incoming video feeds on-the-fly to one or more versions of high resolution video sample data, and to one or more versions of low resolution video sample data, and a transmitter for transmitting versions of the low resolution video sample data to respective ones of a plurality of storage units, and for transmitting high resolution video sample data to a broadcaster, a plurality of storage units, coupled communicatively with the video server, and a plurality of workstations, coupled communicatively with respective ones of the plurality of storage units, each workstation including a receiver for receiving a version of the low resolution video sample data from a storage unit, a video previewer for rendering the version of the low resolution video sample data, and a proxy video editor for generating edit instructions for the low resolution video sample data that is rendered by said video previewer.
Owner:DALET
Method and apparatus for editing heterogeneous media objects in a digital imaging device
InactiveUS7337403B2Ease useGuaranteed ease of operationElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsUnauthorized memory use protectionMedia typeDigital imaging
A method and apparatus for editing heterogeneous media objects in a digital imaging device having a display screen, where each one of the media objects has one or more media types associated therewith, such as a still image, a sequential image, video, audio, and text. The method aspect of the present invention begins by displaying a representation of each one of the media objects on the display screen to allow a user to randomly select a particular media object to edit. In response to a user pressing a key to edit a selected media object, one or more specialized edit screens is invoked for editing the media types associated with the selected media object. If the media object includes a still or a sequential image, then an image editing screen is invoked. If the media object includes a video clip, then a video editing screen is invoked. If the media object includes an audio clip, then an audio editing screen is invoked. And If the media object includes a text clip, then a text editing screen is invoked.
Owner:FLASHPOINT TECH
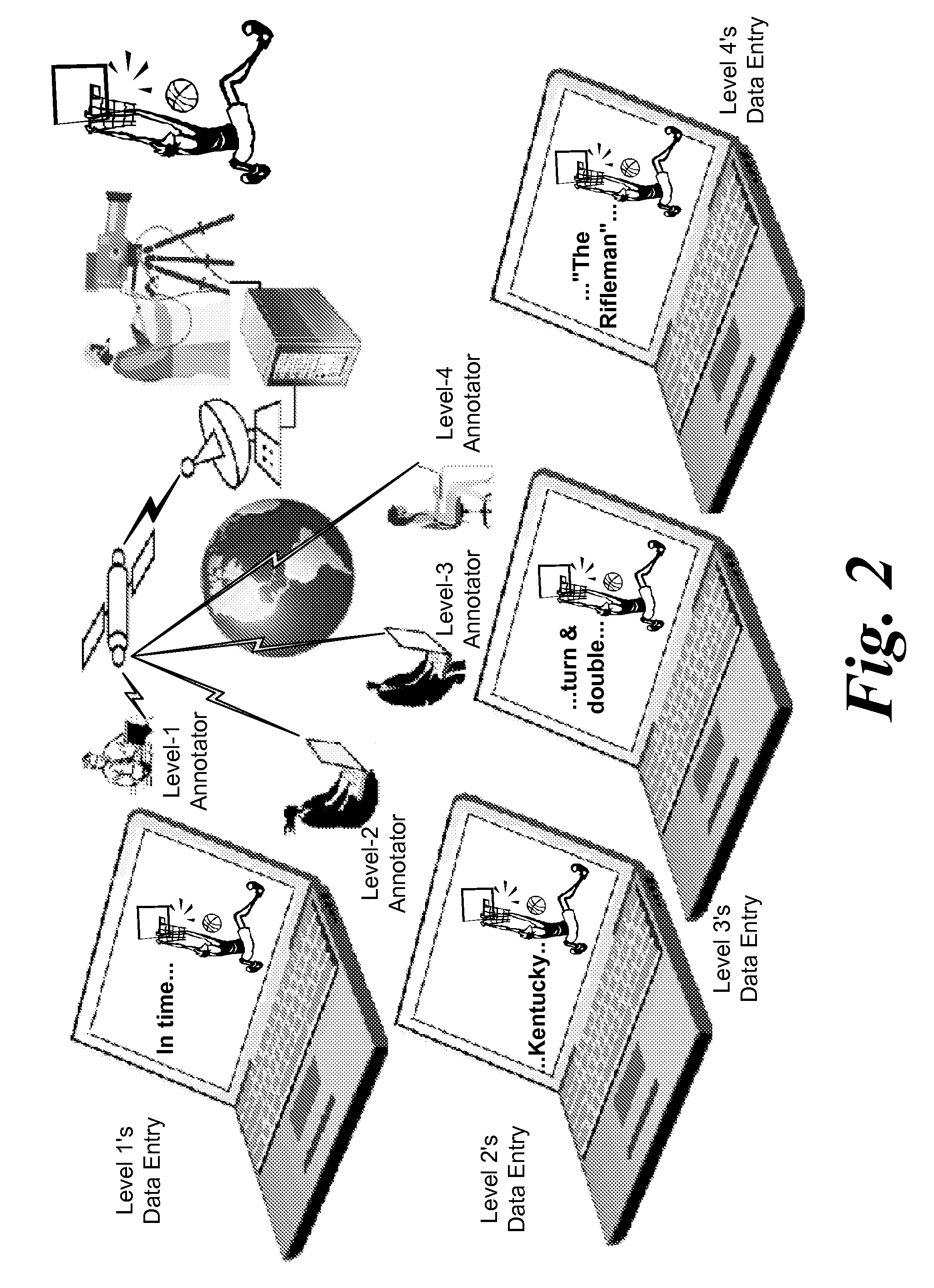
System and method for distributed and parallel video editing, tagging, and indexing
InactiveUS20090097815A1Efficient editingTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsClient-sideWorkflow engine
A system and method for having a media engine, client, workflow engine and server. The media engine takes digital or analog real-time video or video-on-demand as an input. Clients connect to the media engine, workflow engine and server. Depending on the client's capabilities, including software features, training and location, the workflow engine will drive required units of work to the client asking them to be fulfilled. This system enables efficient offline, real-time or faster than real-time editing, tagging and indexing of media by one or more clients at the same time. Unlimited numbers of users, tags and indexing functions to take place in parallel on a single video feed at the same time and managed through a rule based workflow engine.
Owner:SYNERGY SPORTS TECH
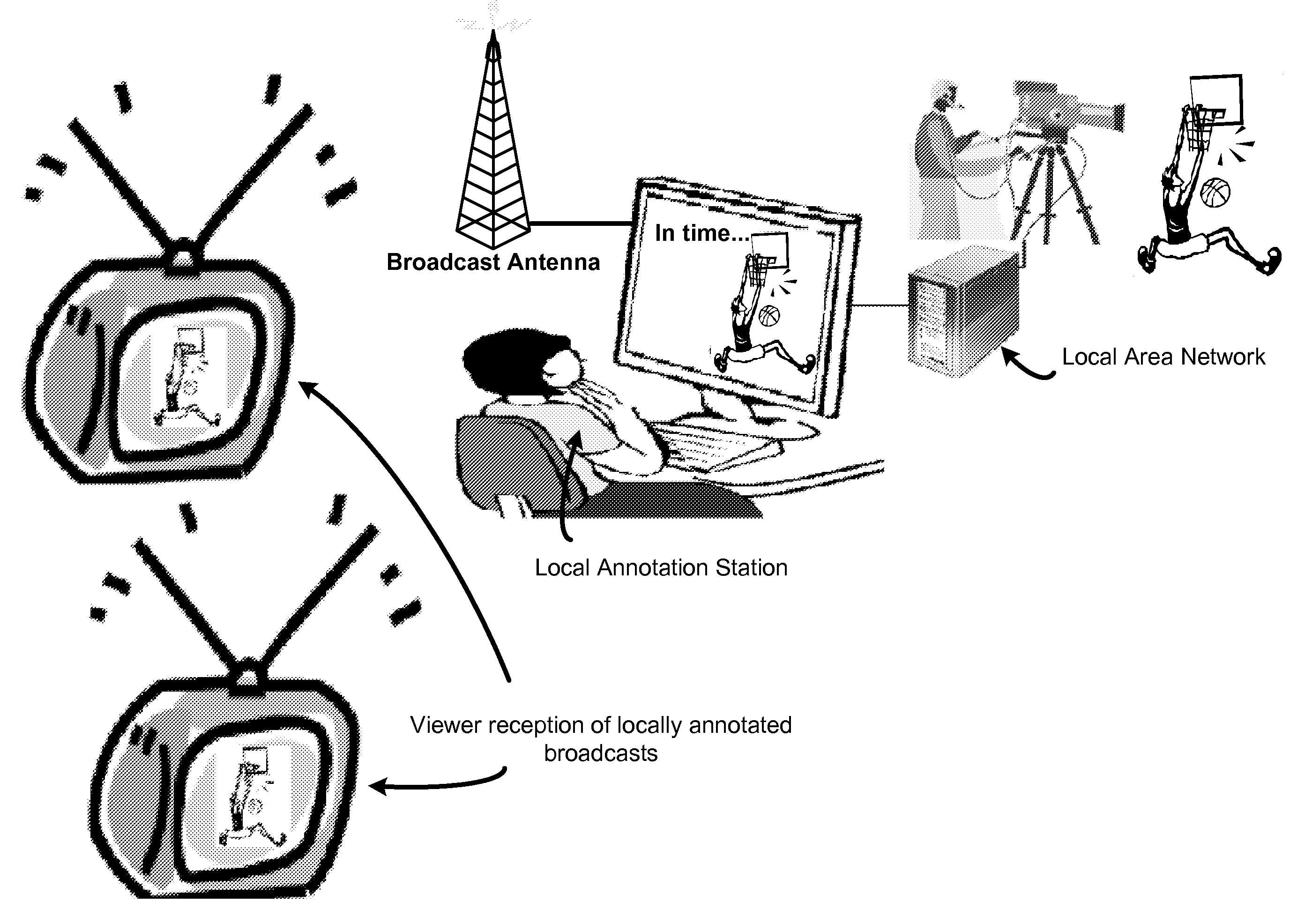
System and method for improved video editing
ActiveUS7352952B2Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsTheme parkAnnotation
Owner:MAGIX
Video-editing workflow methods and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20040131330A1Easy accessImprove the display effectTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImage resolutionThe Internet
Video-editing workflow methods and apparatus thereof are disclosed. A user drops off (or send) to a merchant that provides video-processing services the analog or digital videotape. The videotape can be processed (digitized if necessary) into both a high-resolution and low-resolution video stream. The low-resolution video stream could be provided to a customer either in the form of a CD / DVD or accessible for download from the Internet. While at home on a personal computer or consumer video edition device, the user could perform the edits and cuts on the low-resolution video stream. The edits to the video stream, which are very small, can then be sent into the video processing service and re-rendered on the high-resolution video stream.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
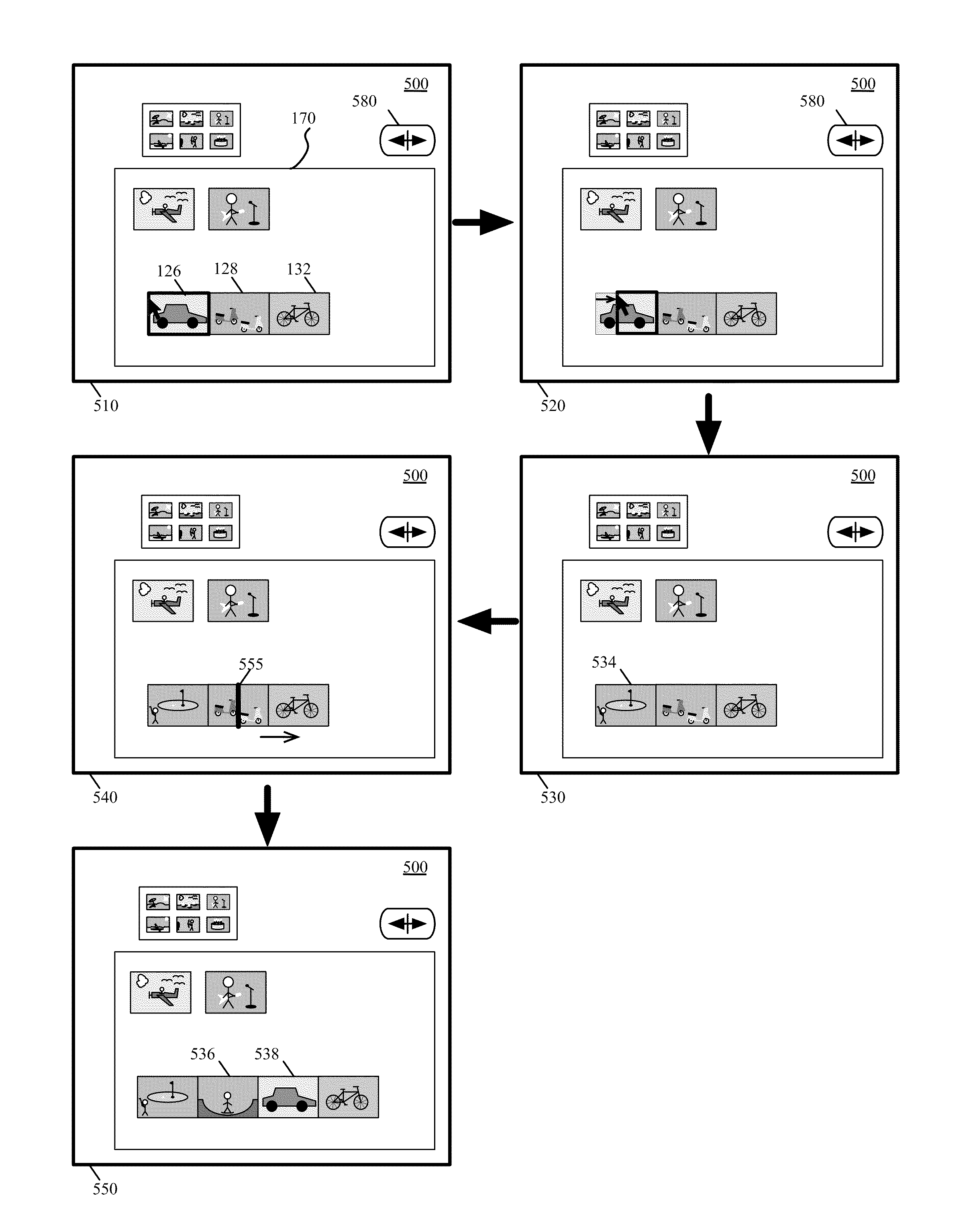
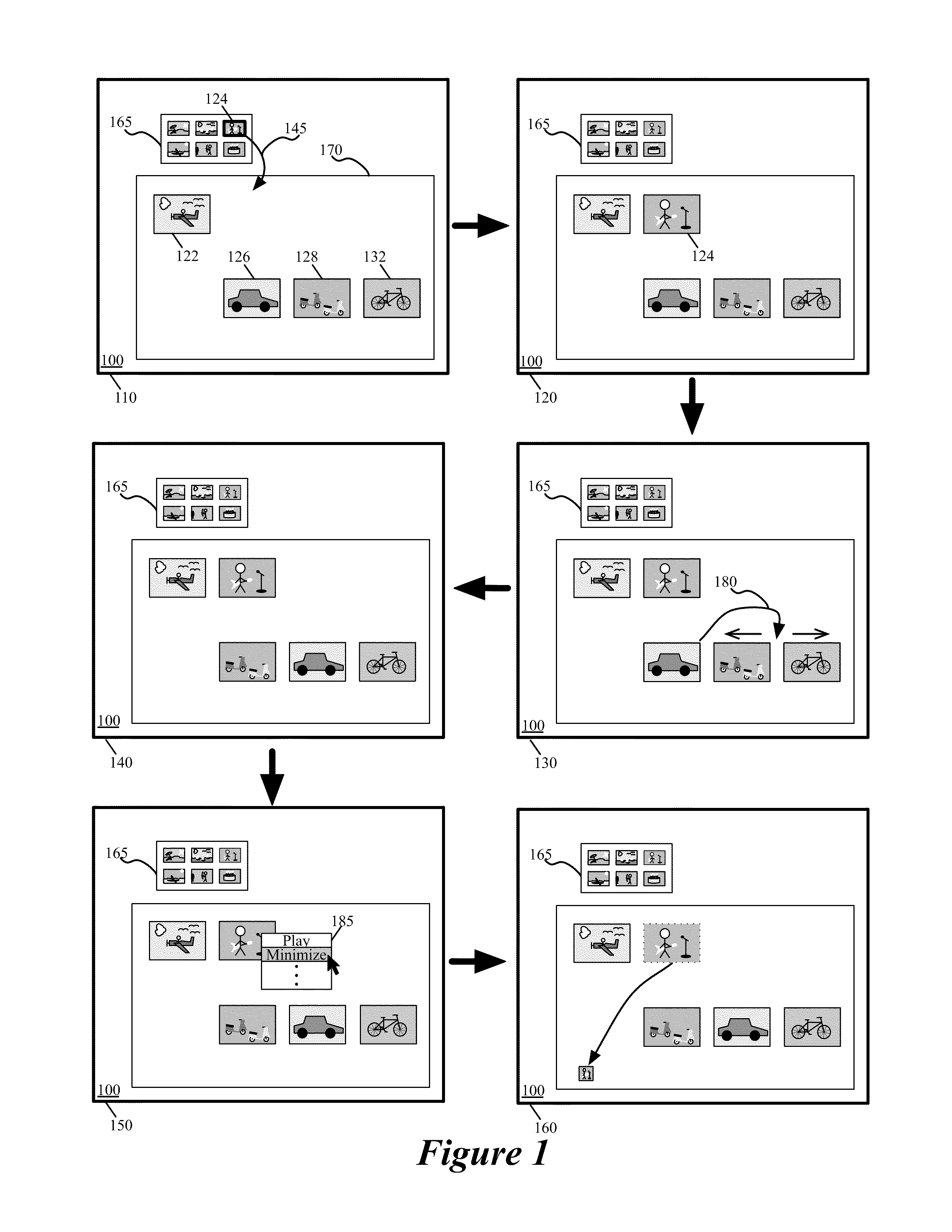
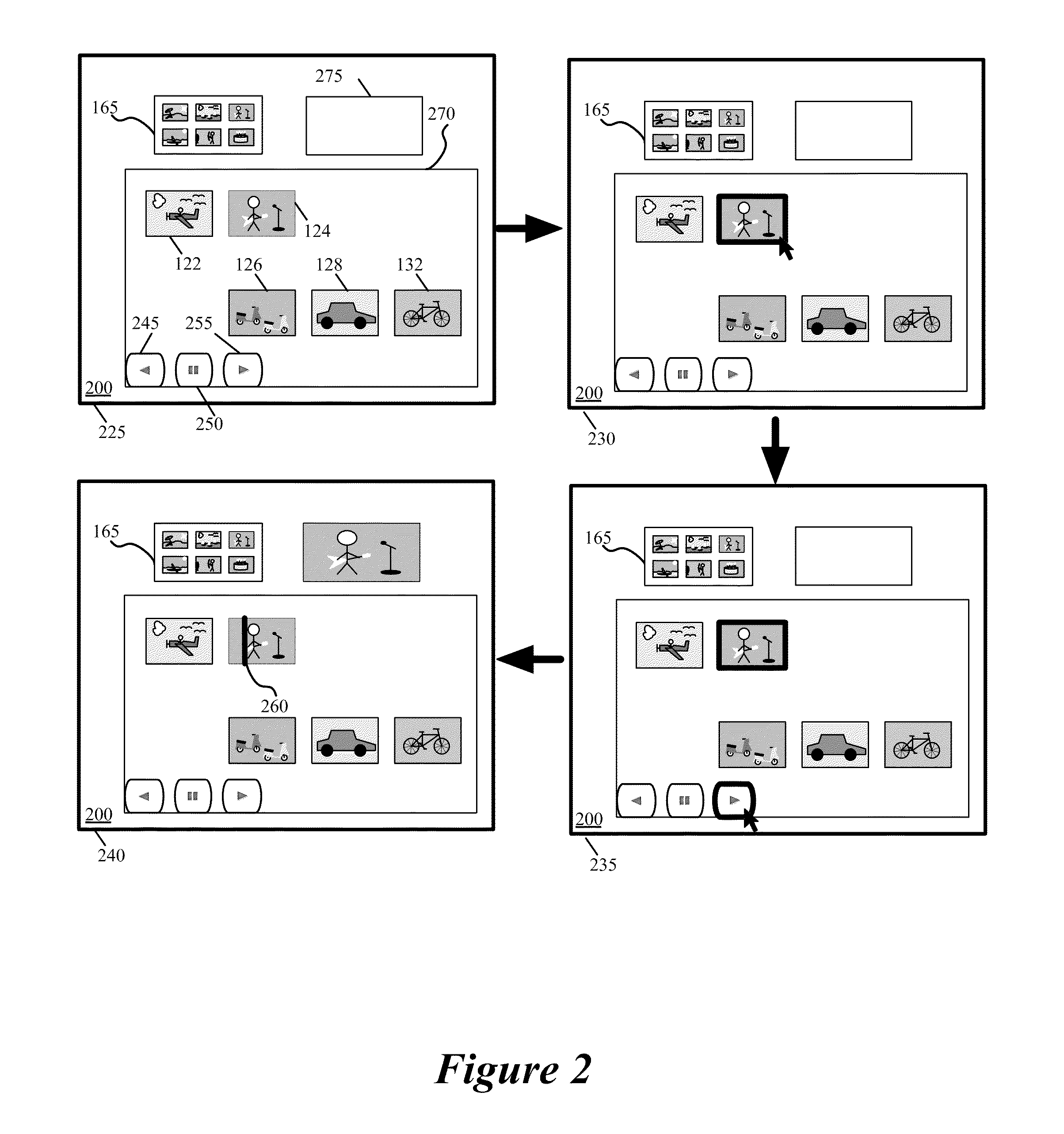
User interfaces for capturing and managing visual media
ActiveUS10645294B1Faster and efficient methodReduce cognitive loadImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMedia controlsMediaFLO
Media user interfaces are described, including user interfaces for capturing media (e.g., capturing a photo, recording a video), displaying media (e.g., displaying a photo, playing a video), editing media (e.g., modifying a photo, modifying a video), accessing media controls or settings (e.g., accessing controls or settings to capture photos or videos to capture videos), and automatically adjusting media (e.g., automatically modifying a photo, automatically modifying a video).
Owner:APPLE INC
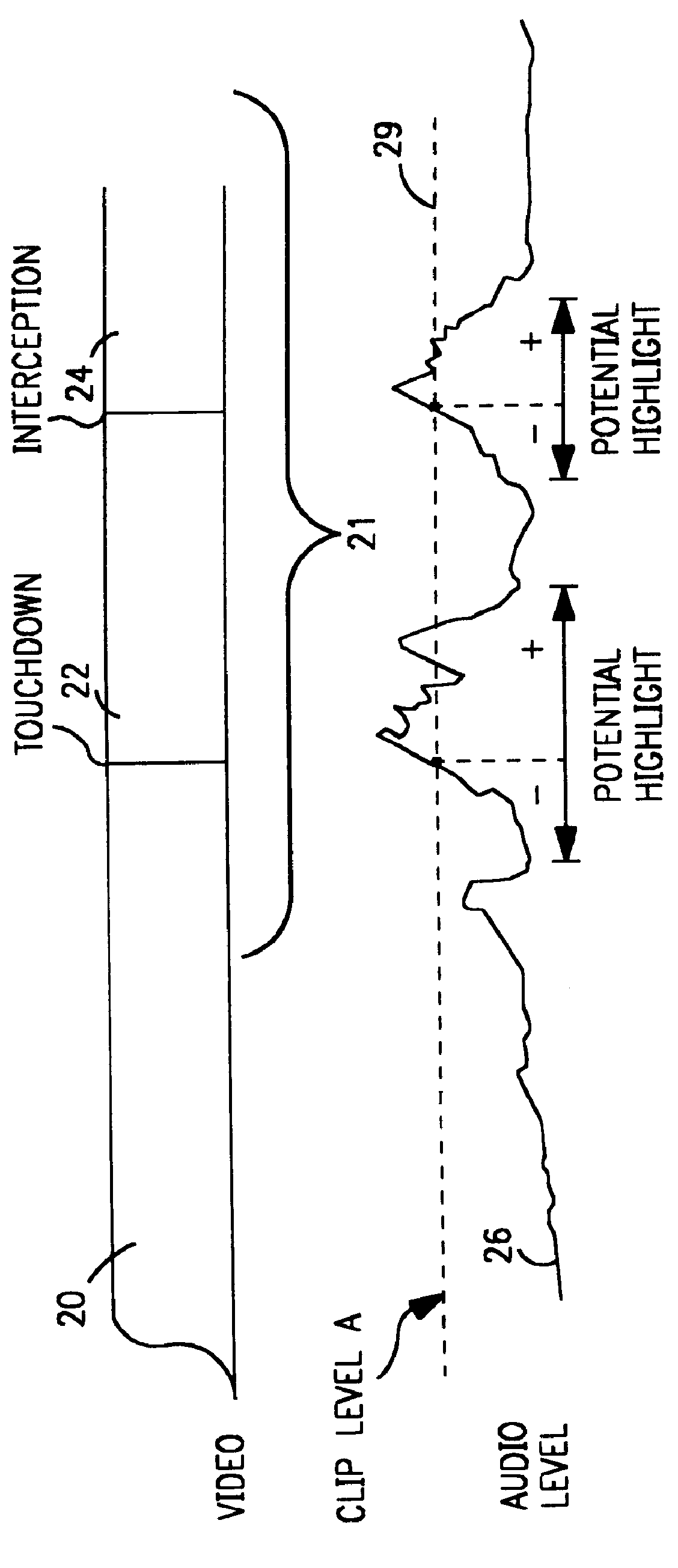
Multimedia search and indexing system and method of operation using audio cues with signal thresholds
A multimedia search and indexing system automatically selects scenes or events of interest from any media, i.e., video, film, sound for replay, in whole or in part, in other contexts. The entire audio track of a recorded event in video, film, sound, etc., is analyzed to determine audio levels within a set of frequency ranges of interest. Audio clip levels within the selected frequency ranges are chosen as audio cues representative of events of interest in the track. The selection criteria are applied to the audio track of the recorded event. An Edit Decision List (EDL) is generated from the analysis of the audio track. The list is representative of scenes or sounds of interest as clips for reuse. The clips are reviewed and accepted or rejected for reuse. Once selected, the clips are edited using industry standard audio and video editing techniques.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Dynamic video editing
InactiveUS20120017153A1Minimize the media clipsInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComposite mediaVideo editing
For a media-editing application, some embodiments provide tools for editing media clips, such as dynamic editing and playback of media clips. In some embodiments, dynamic editing allows a user of the media-editing application to perform operations on a media clip while the media clip is being played back. Examples of dynamic editing operations include tagging instances in time of the media clip, splitting the media clip into multiple media clips, trimming the ends of the media clip, and extending a trimmed media clip, among other operations. In addition, to composite media clips, some embodiments also allow the user to create sequences of media clips, reorder the media clips within sequences, stack sequences, and add or remove media clips from sequences. Some such embodiments allow the user to composite media clips while some or all of the media clips are being played back.
Owner:APPLE INC
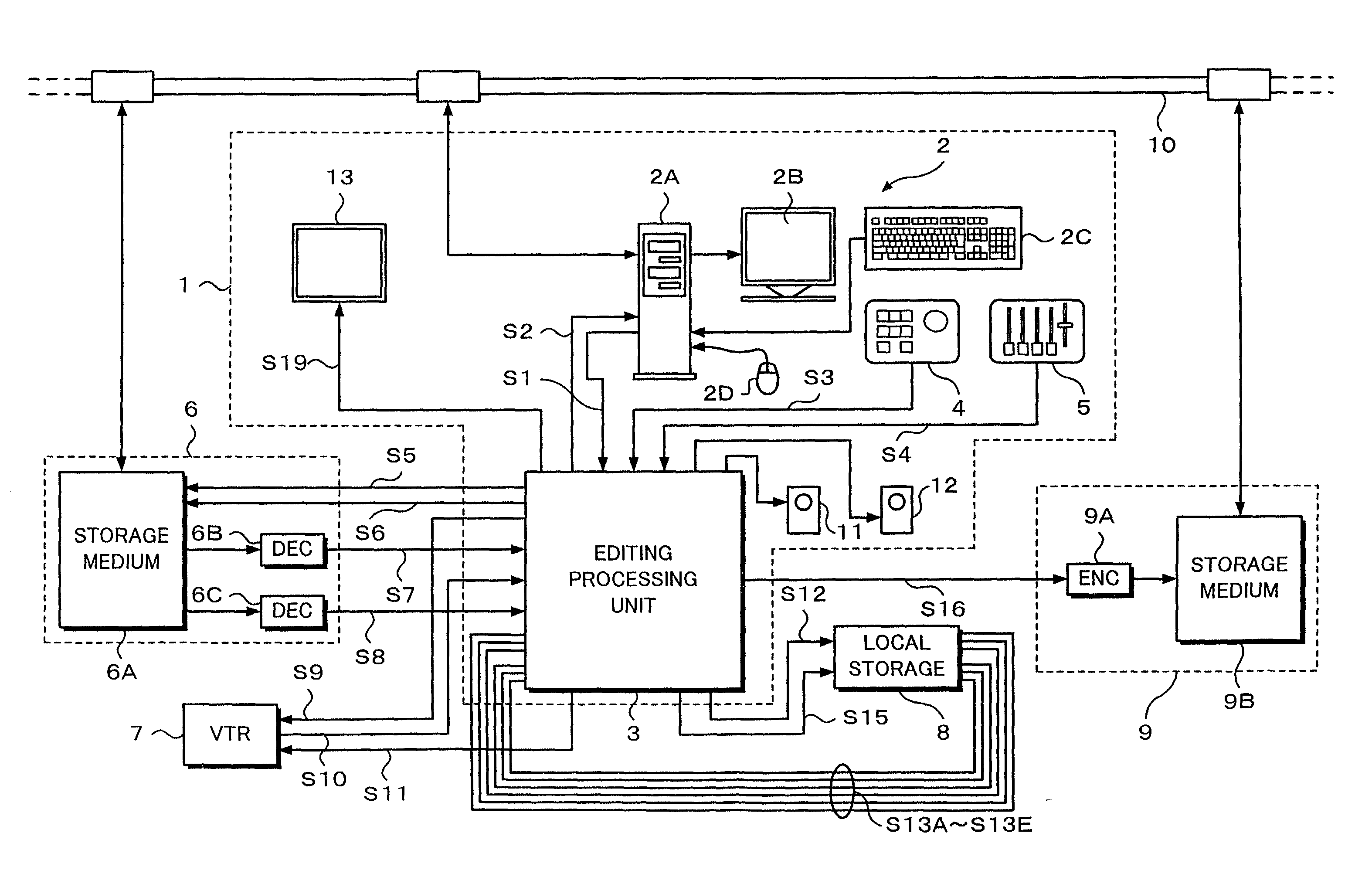
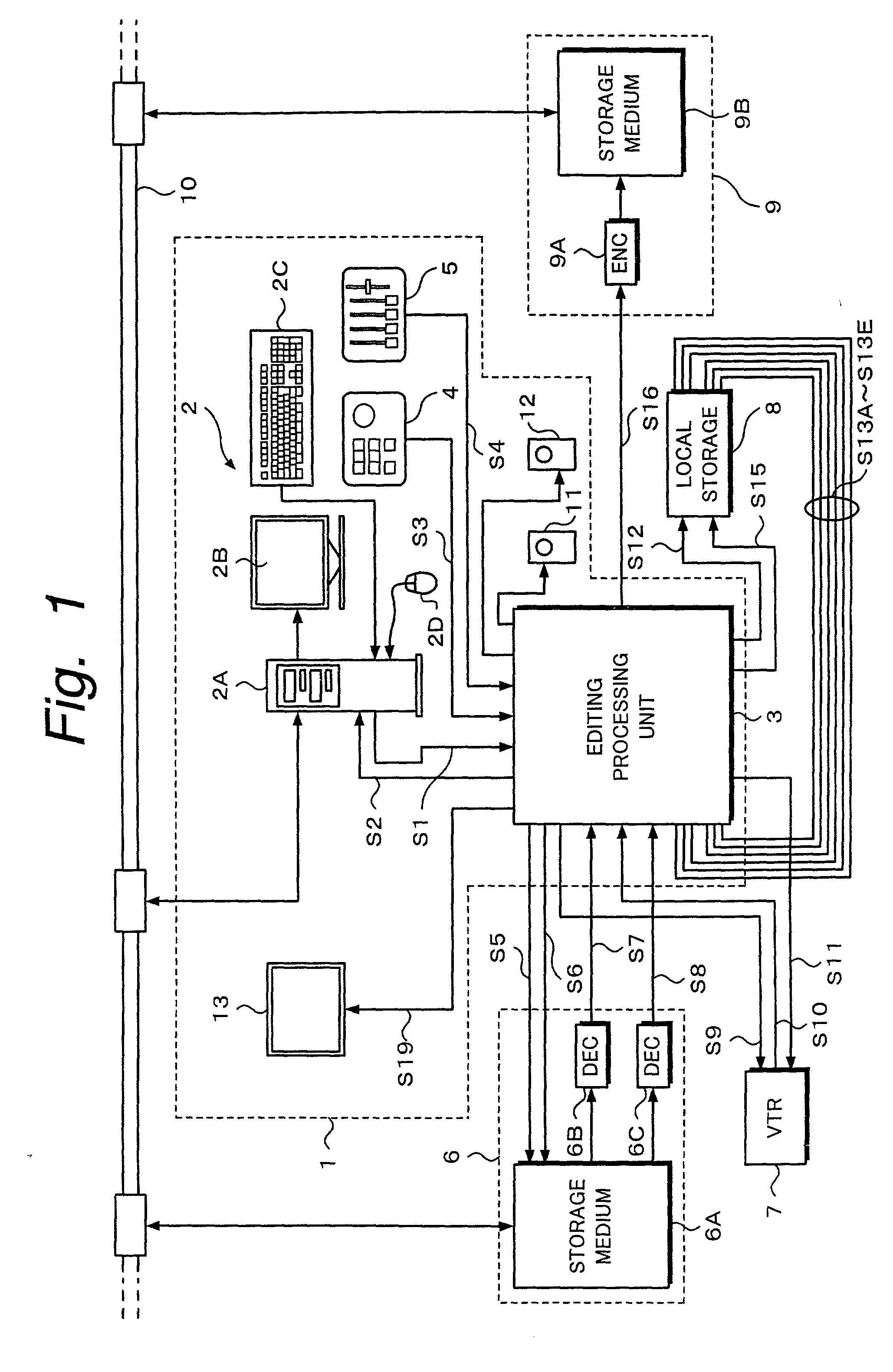
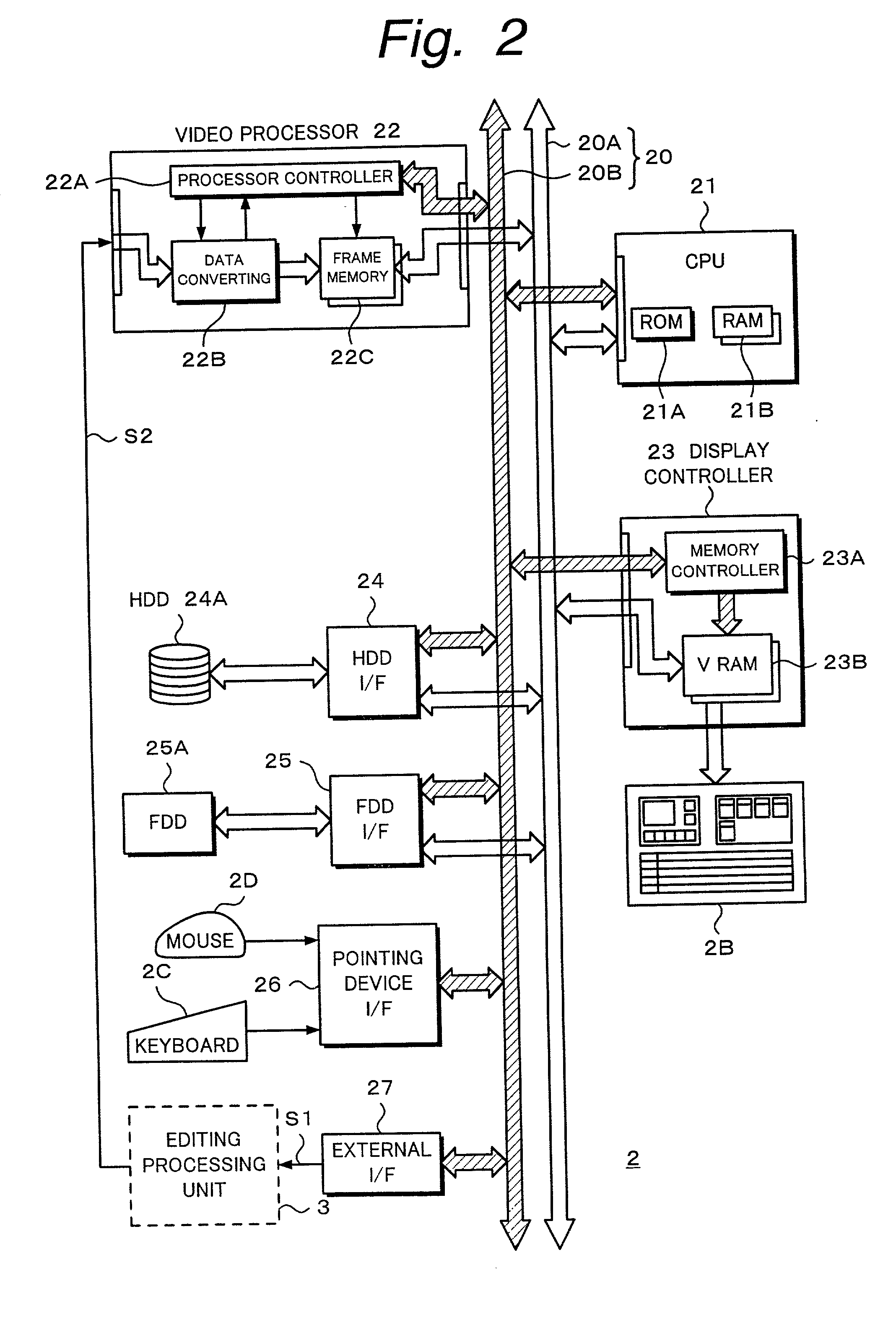
Editing apparatus having dedicated processing unit for video editing
InactiveUS20030086686A1Secure performanceRemove background noiseTelevision system detailsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsSource materialDisplay device
An editing apparatus is disclosed, that comprises an editing processing unit for processing a video signal and an audio signal supplied as source materials, and a computer for controlling the editing processing unit, wherein the computer comprises a controlling means for displaying a viewer window, a log window, and a program window on a display of the computer, the viewer window allowing the editing operator to decide an edit point while viewing a video image of a source material so as to produce an event, the log window displaying a clip image corresponding to an event that is set on the viewer window, the program window allowing the editing operator to arrange a plurality of events on a time line in a desired order so as to produce a program list, and wherein the controlling means displays an icon that represents by what source device each event arranged on the time line is produced.
Owner:SONY CORP
Process for creating a media sequence by coherent groups of media files
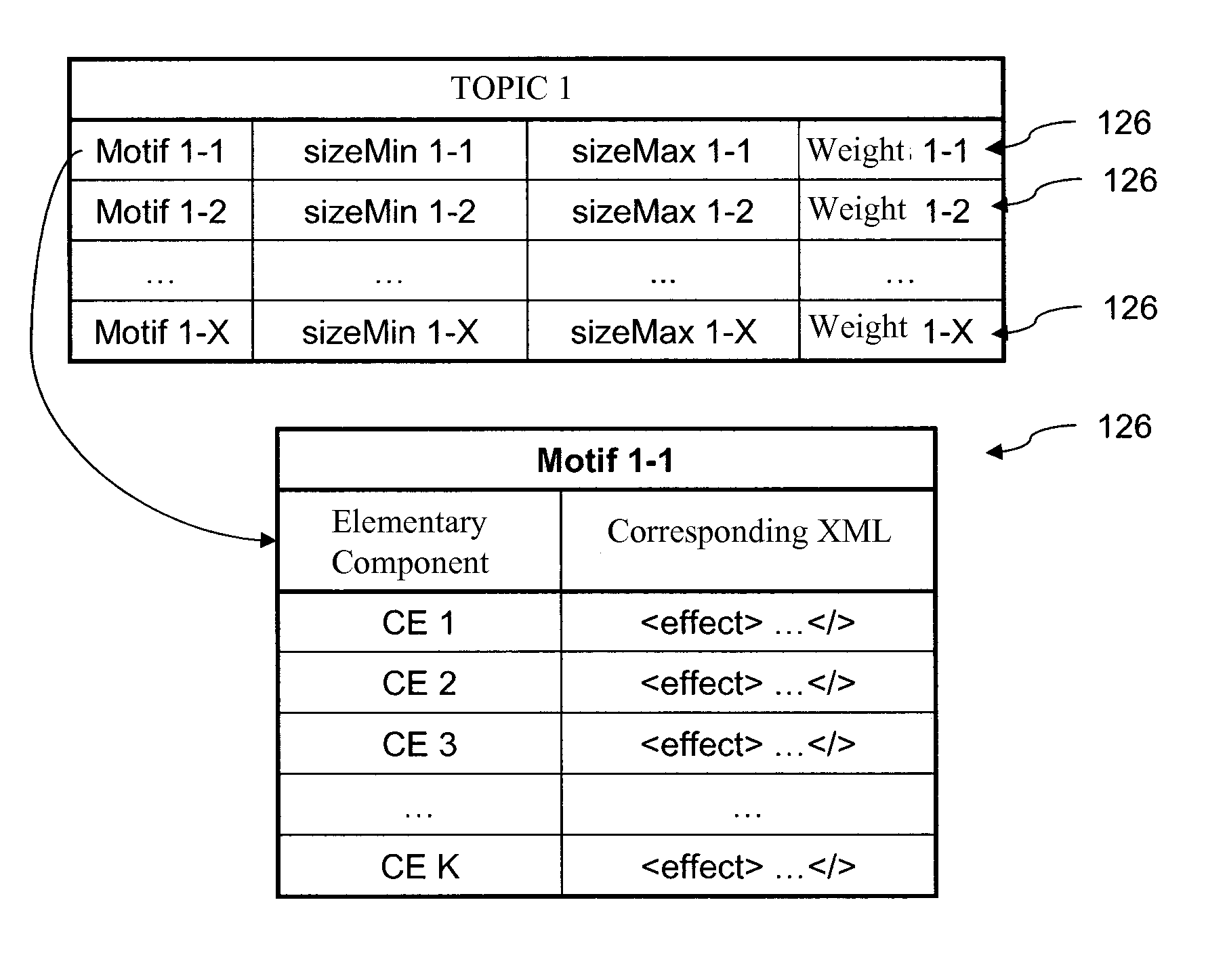
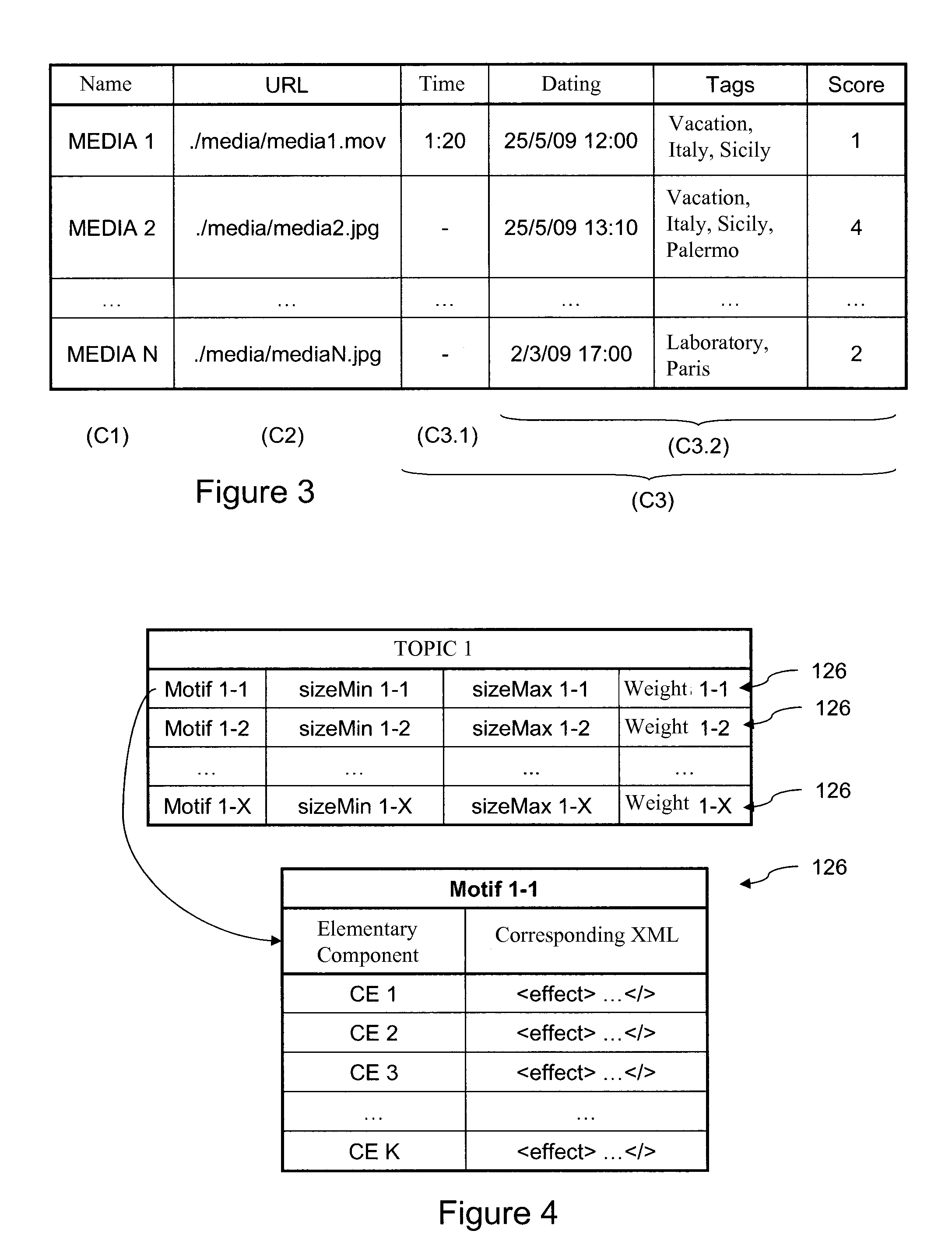
InactiveUS20110276864A1Volume andMedia file rendering of the group is reducedMultimedia data indexingMultimedia data queryingWeb serviceVideo editing
A process for creating a media sequence, for example video or audio, and an associated device includes the stages of:obtaining a selection of media files;regrouping the chosen media files into a plurality of groups according to at least one coherence criterion;selecting, for each group of media files assembled in this way, a media motif among a plurality of predefined media motifs, the chosen media motif being able to define a media rendering for the set of media files of the group; andassembling the media motifs selected in this way and their associated media files in such a way as to form at least one definition of the media sequence. The process can relate to automated video editing as implemented on Web servers.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Systems and methods for identifying media portions of interest
Systems and methods for video editing and playback are provided. In one implementation, a selected portion of a timeline for navigating media content can be repositioned and resized by user input actions received along various axes relative to the timeline. In another implementation, a plurality of signals associated with media content can be intelligently weighted based on user group historical attributes to identify portions of interest in the media content. In a further implementation, an experience map for media content is provided in which a representative signature for the content includes visual signal intensity representations and social interest concentrations over the length of the content. In another implementation, a subset of filters is determined for recommendation to a user based on one or more attributes associated with at least one of media content, the user, a group of users, or a user device.
Owner:BRIGHTSKY LABS
Video editing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060206526A1Improve user interactionElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsUsing non-detectable carrier informationComputer configurationData store
A computer video editing system and method in a network of computers is disclosed. The system and method include a datastore or other source of subject video data, a transcription module and an assembly member. The transcription module generates a working transcript of the corresponding audio data of subject source video data. The working transcript includes original source video time coding for the passages (statements) forming the transcript. The assembly member enables user selection and ordering of transcript portions. For each user selected transcript portion, the assembly member, in real-time, (i) obtains the respective corresponding source video data portion and (ii) combines the obtained video data portions to form a resulting video work. The resulting video work is displayed to users and may be displayed simultaneously with display of the whole original working transcript to enable further editing and / or user comment. A text script of the resulting video work is also displayed. The video editing system and method may be implemented in a local area network of computers, as a browser based application on a host in a global computer network, as well as on stand alone computer configurations with a remote or integrated transcription service. The subject video data may be from a video blog, email, a user discussion thread or other user forum based on a computer network.
Owner:PORTALVIDEO
Automatic video editing for real-time multi-point video conferencing
InactiveUS20060251384A1Automatically simulateTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsStationary objectUnique object
An “automated video editor” (AVE) automatically processes one or more input videos to create an edited video stream with little or no user interaction. The AVE produces cinematic effects such as cross-cuts, zooms, pans, insets, 3-D effects, etc., by applying a combination of cinematic rules, object recognition techniques, and digital editing of the input video. Consequently, the AVE is capable of using a simple video taken with a fixed camera to automatically simulate cinematic editing effects that would normally require multiple cameras and / or professional editing. The AVE first defines a list of scenes in the video and generates a rank-ordered list of candidate shots for each scene. Each frame of each scene is then analyzed or “parsed” using object detection techniques (“detectors”) for isolating unique objects (faces, moving / stationary objects, etc.) in the scene. Shots are then automatically selected for each scene and used to construct the edited video stream.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
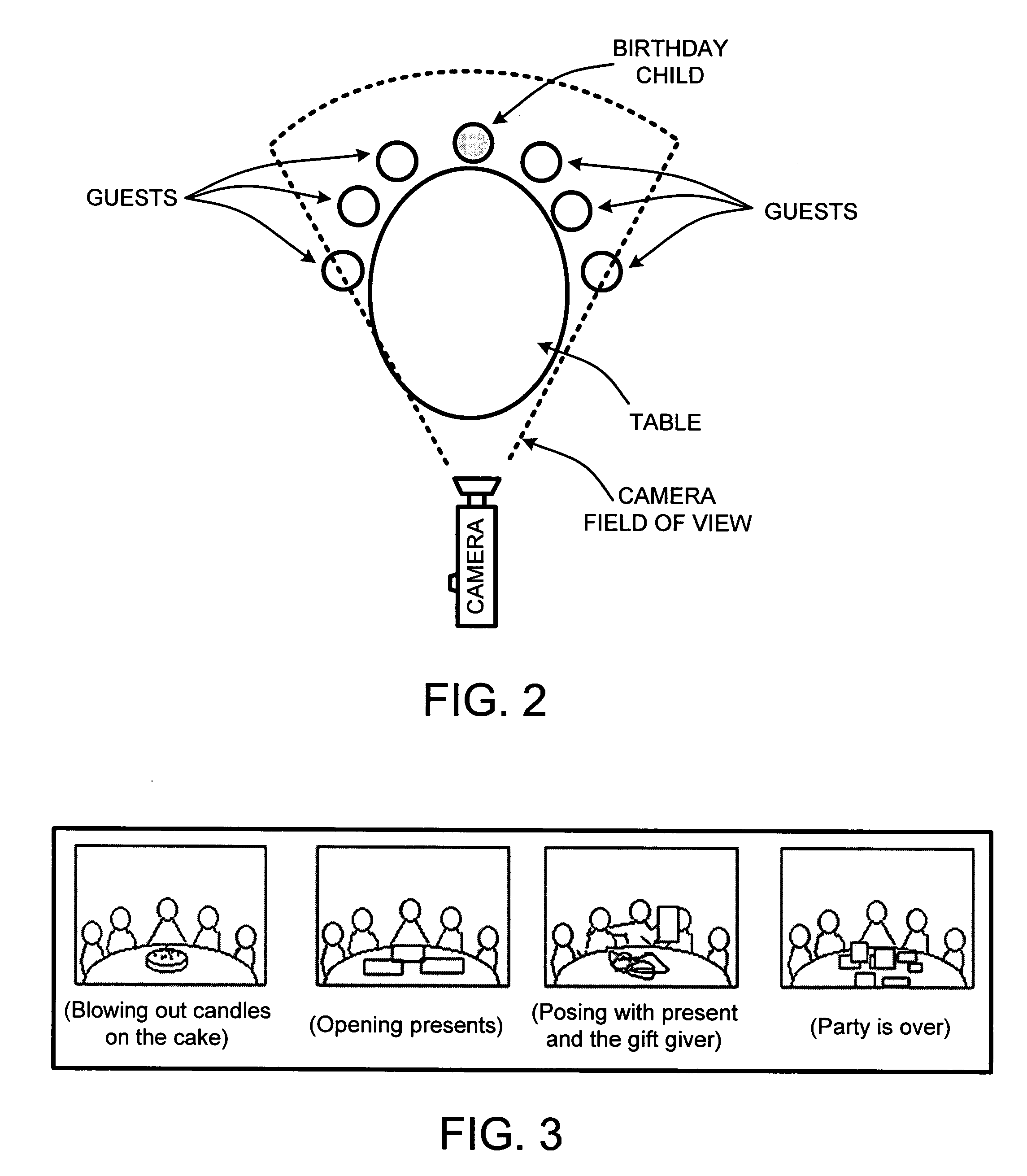
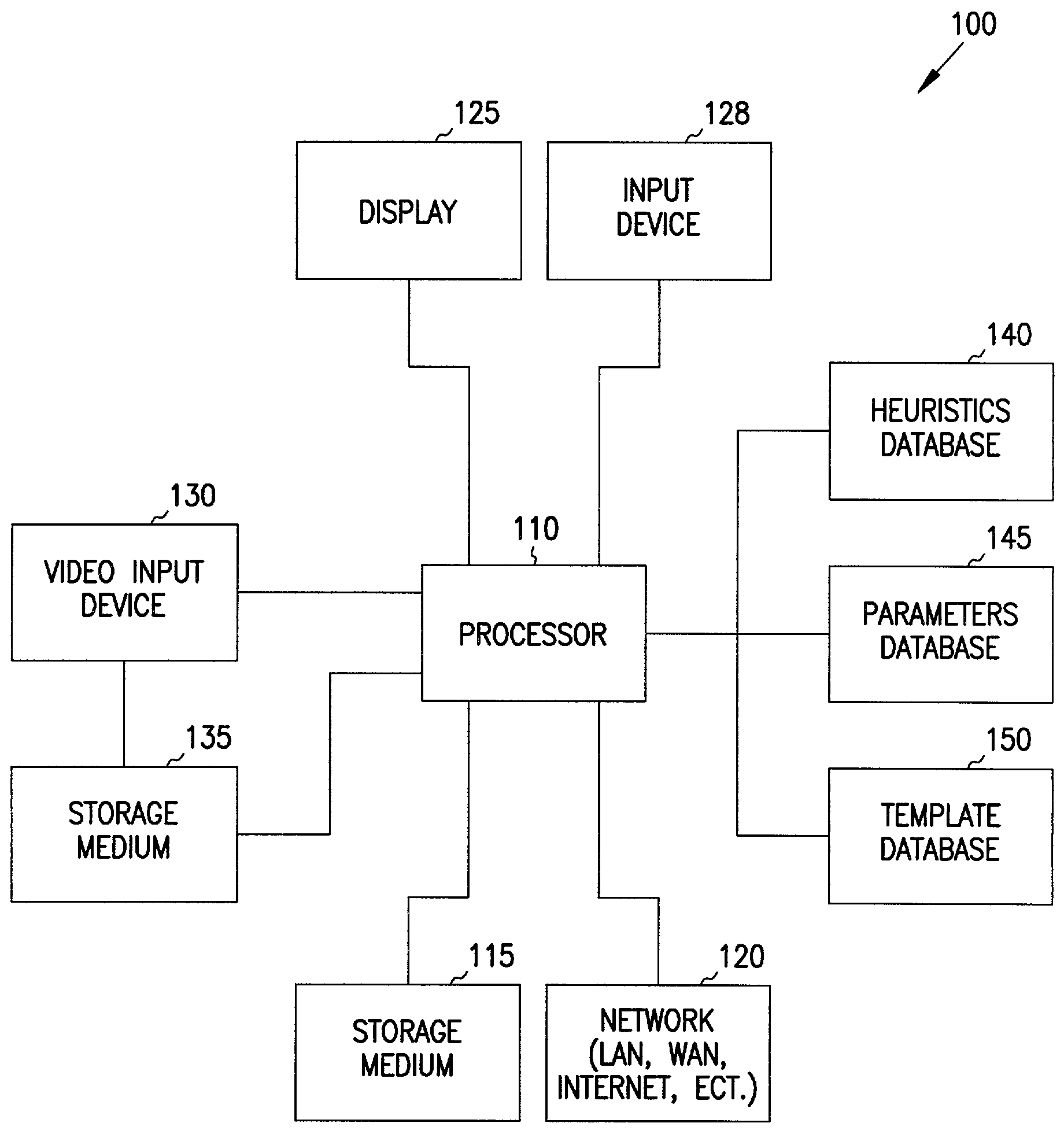
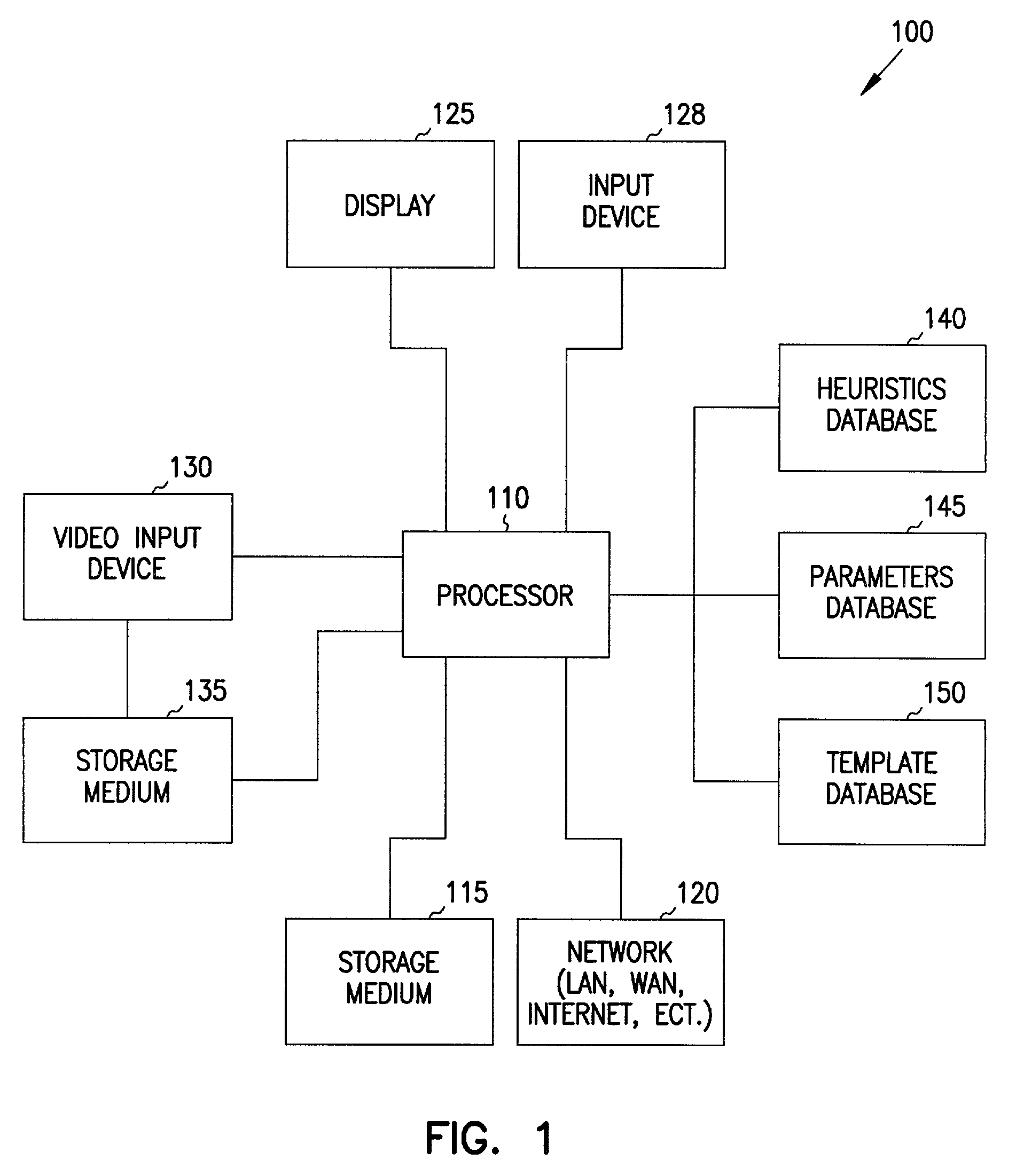
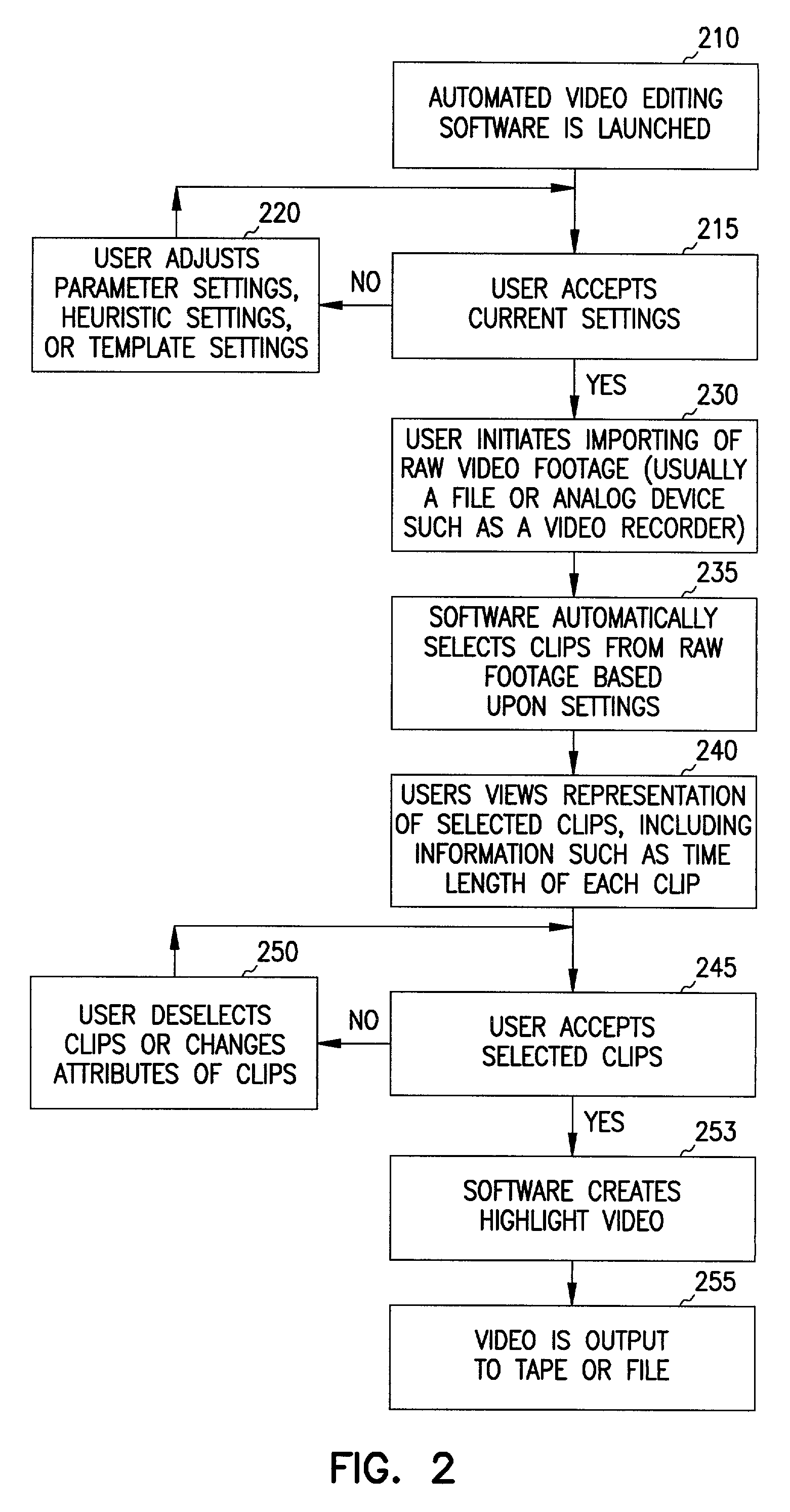
Automated video editing system and method
ActiveUS7248778B1Reduce quality problemsTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsHeuristicUser interface
A video editing system uses simple heuristics and parameters on video footage to provide a condensed version of the footage. The editing system automatically provides either a finished condensed version of the footage or selects a plurality of clips based on the heuristics and parameters. The clips are optionally further edited by a user to produce a condensed version. The condensed version is transferable to any desired media suitable for storing video. A user interface enables the user to select heuristics to identify video clips from the footage. Parameters are also be set to automatically edit the clips in a desired manner. Temporal combinations of heuristics and parameters form templates, which are used to assemble desired clips for selected types of events.
Owner:GATEWAY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com