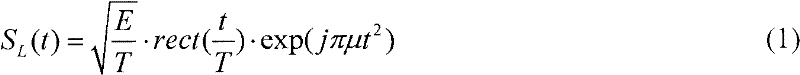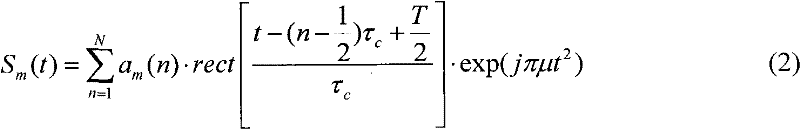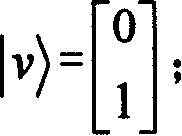Patents
Literature
887 results about "Phase coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
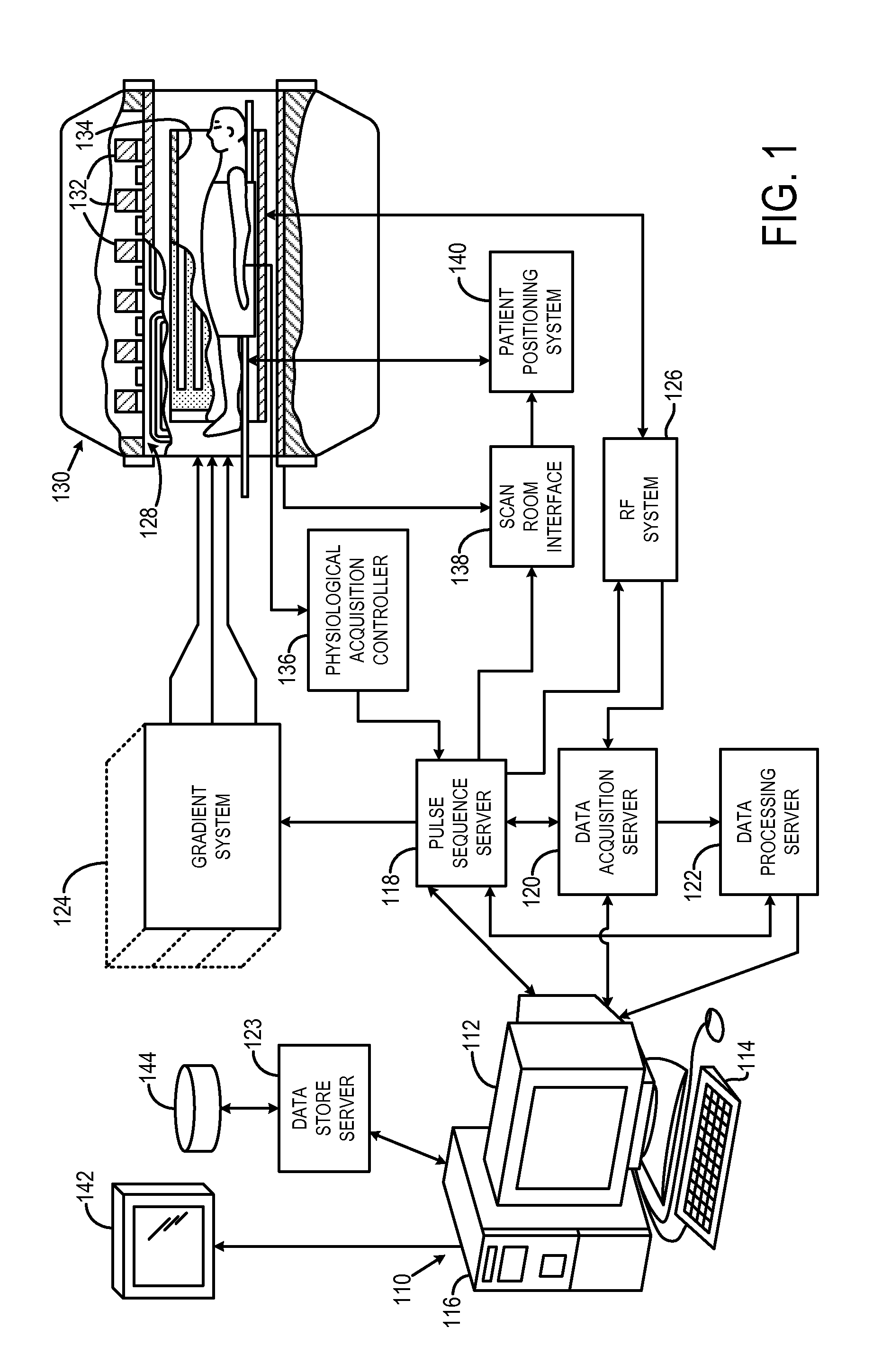
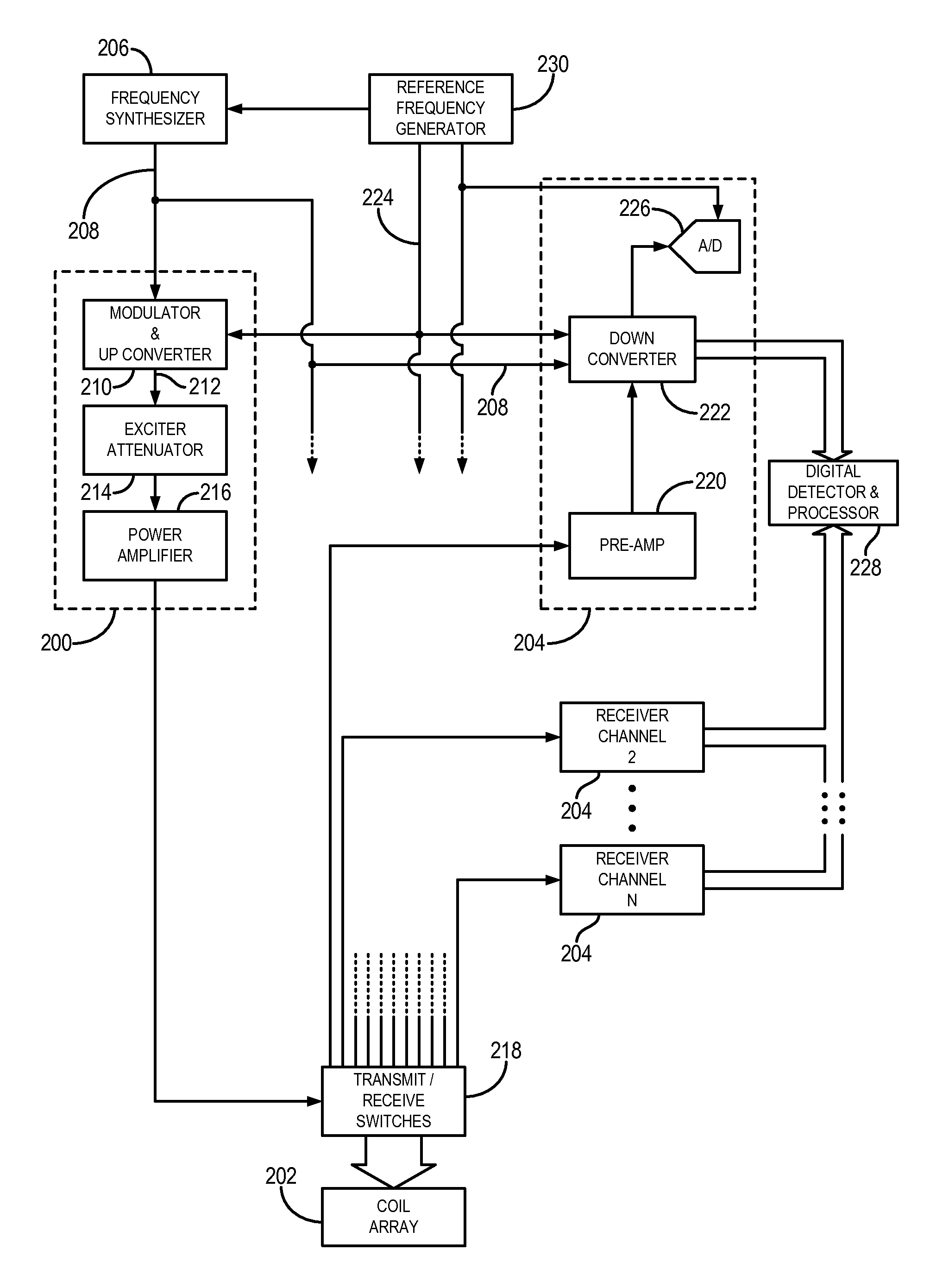
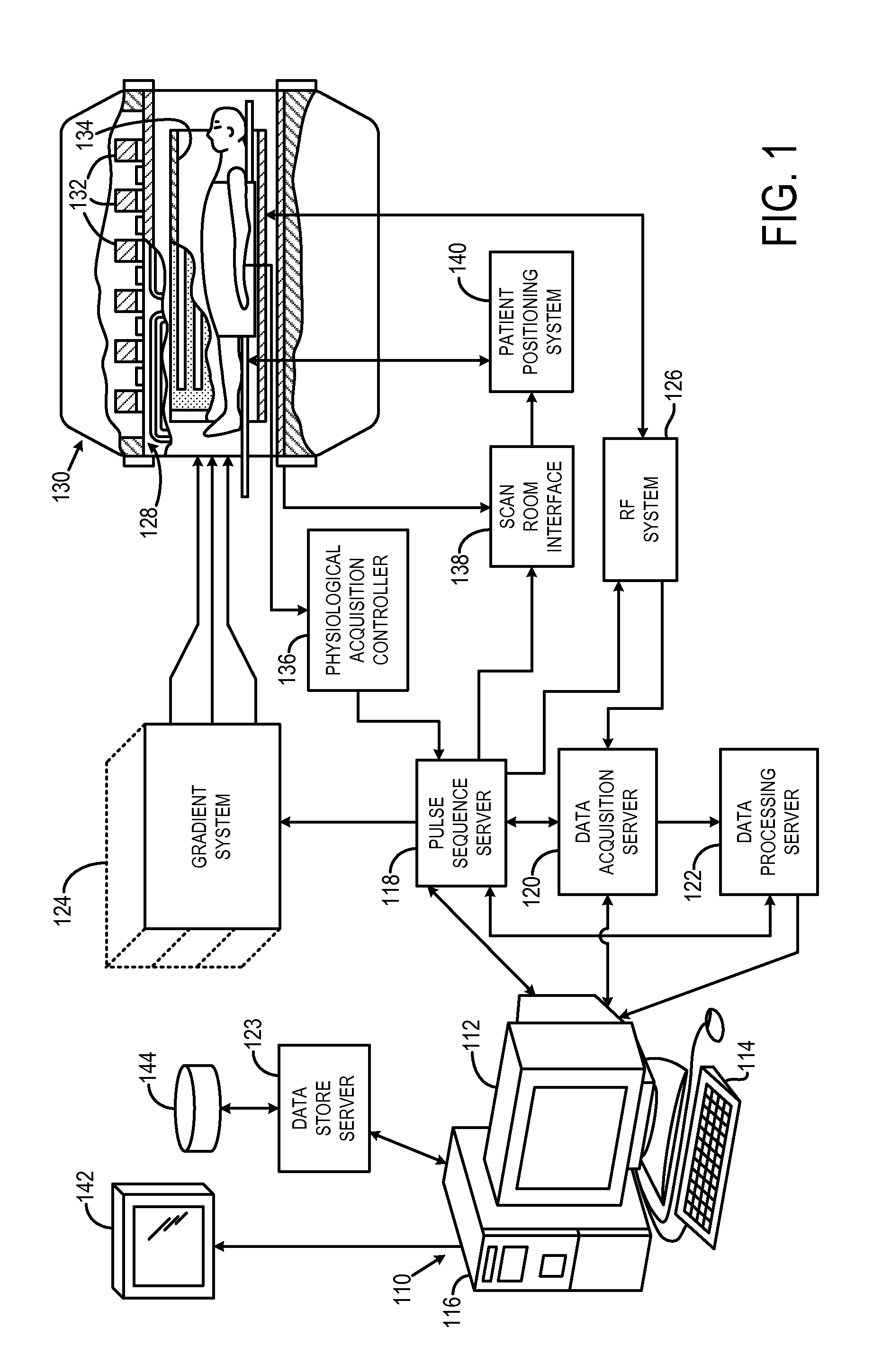
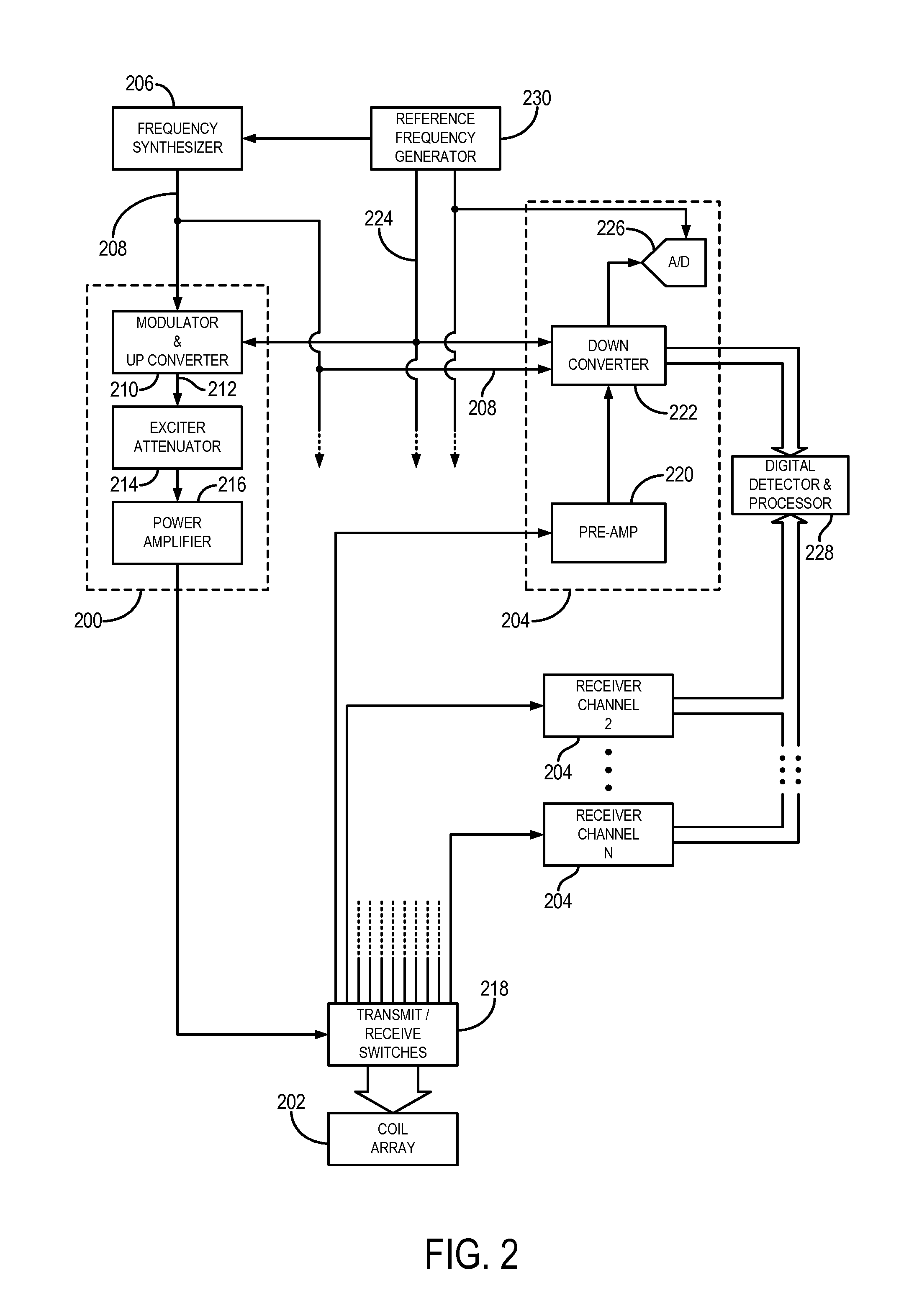
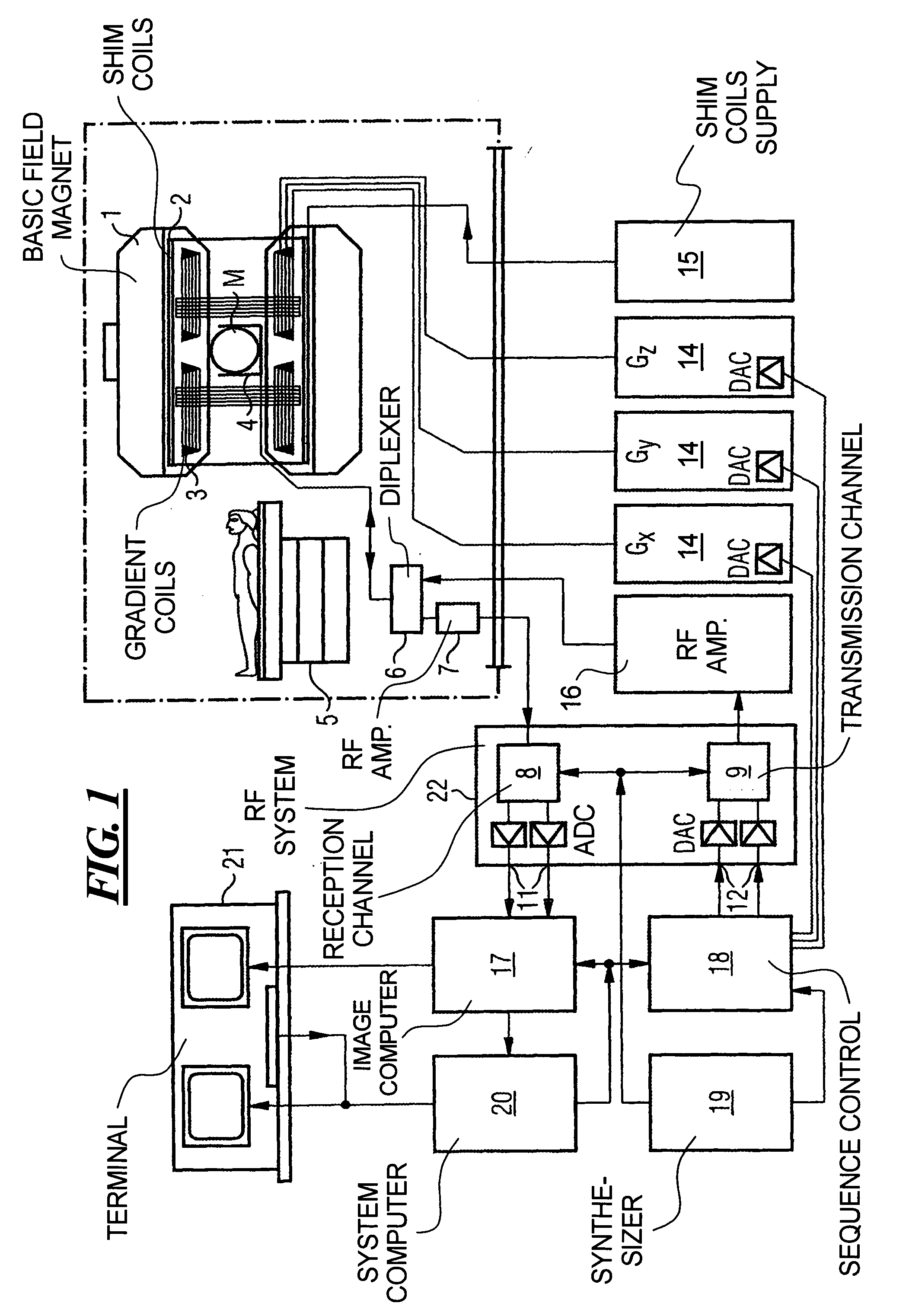
Coil array autocalibration MR imaging
InactiveUS6289232B1Shorten the timeEasy accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData spaceIn vivo
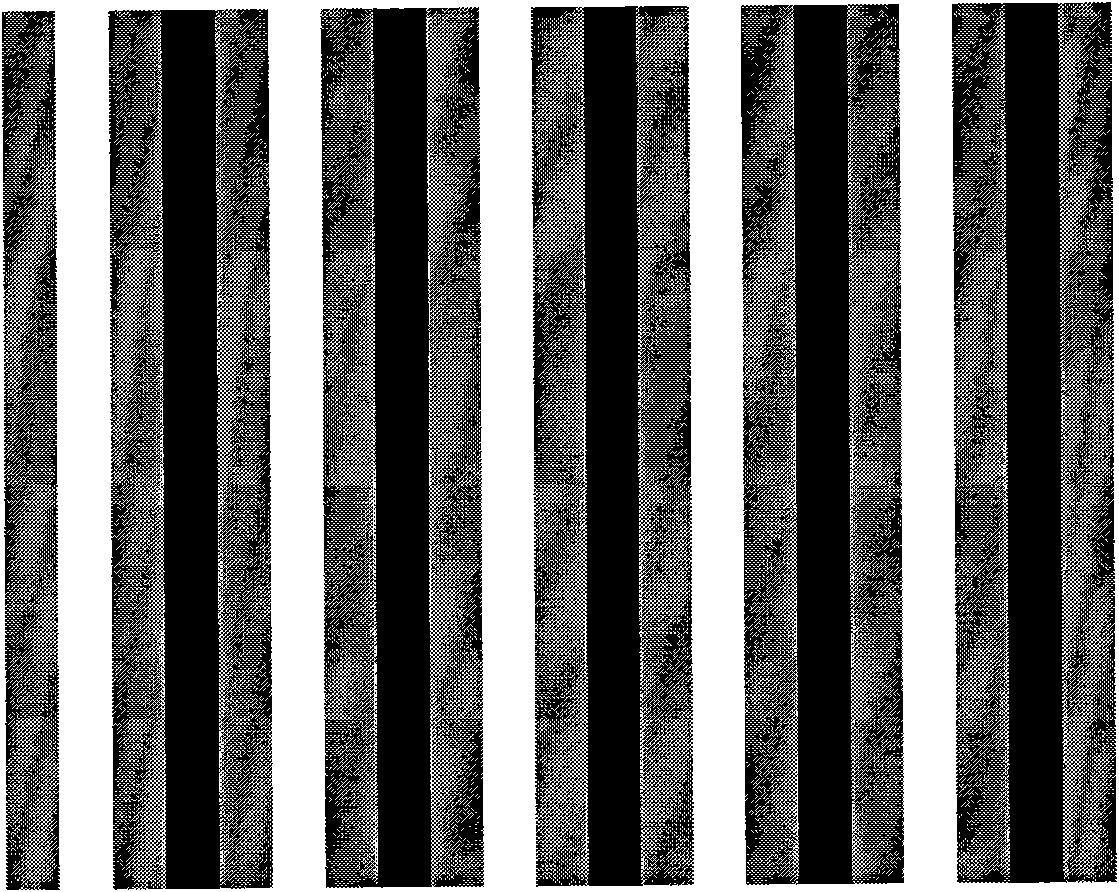
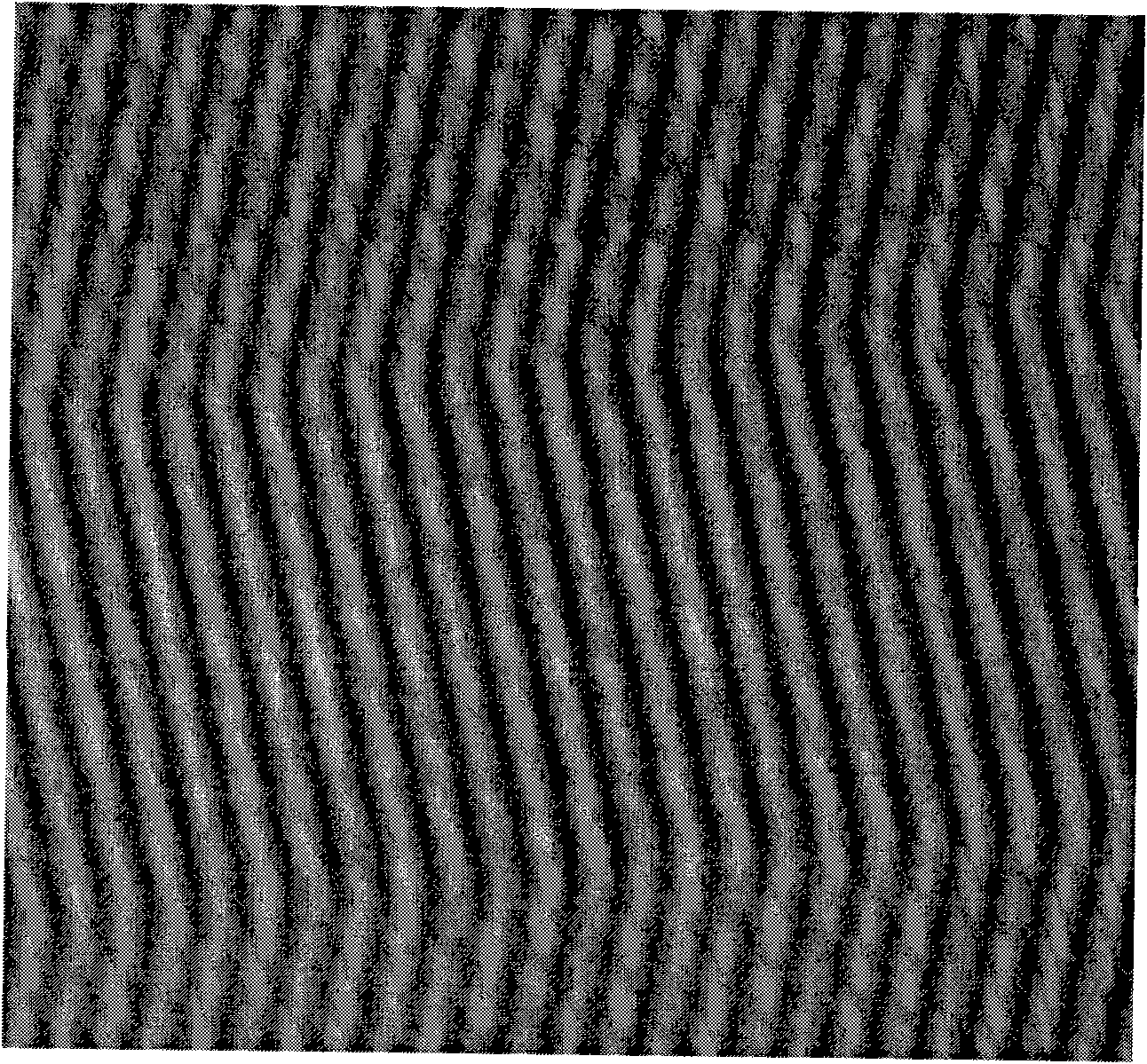
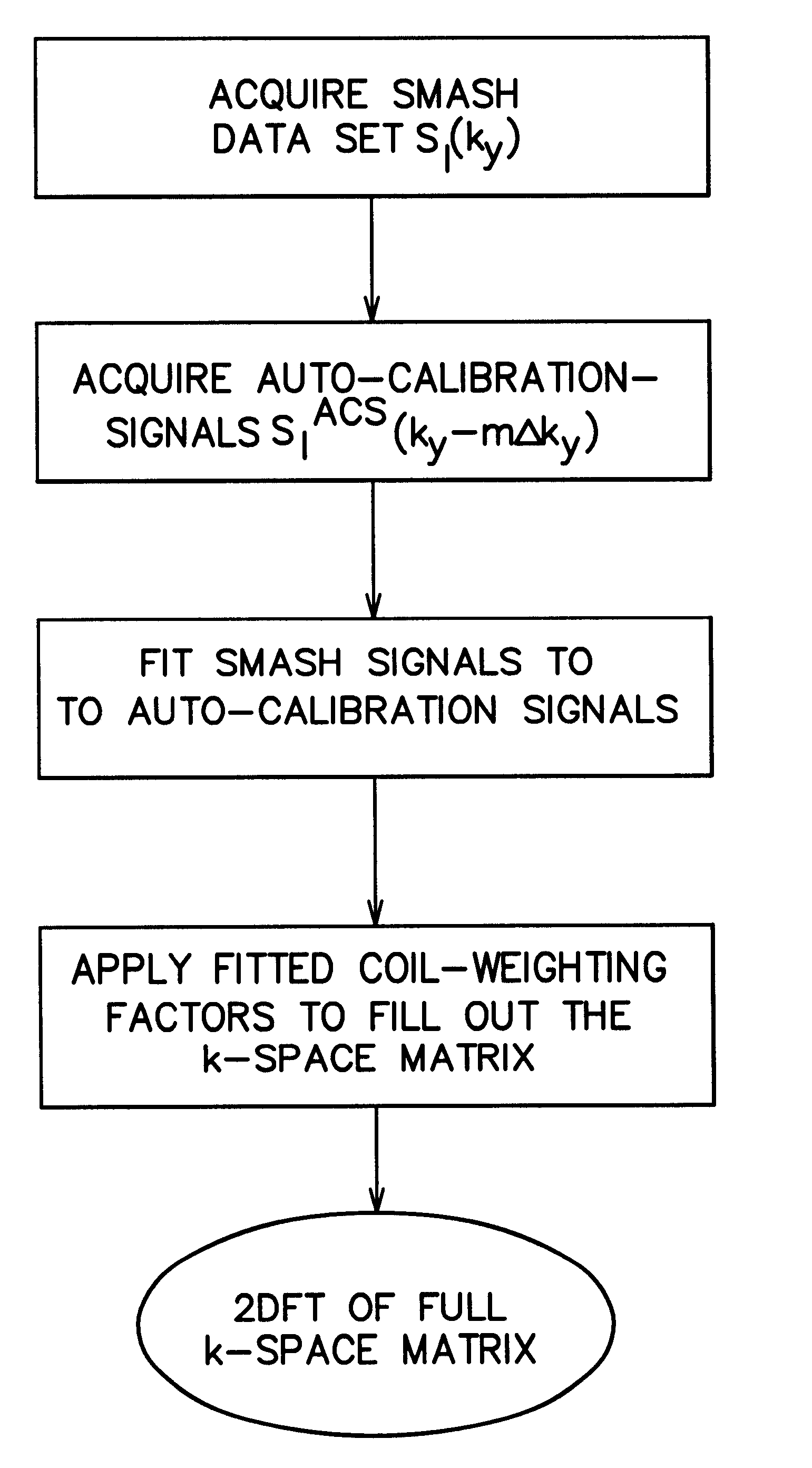
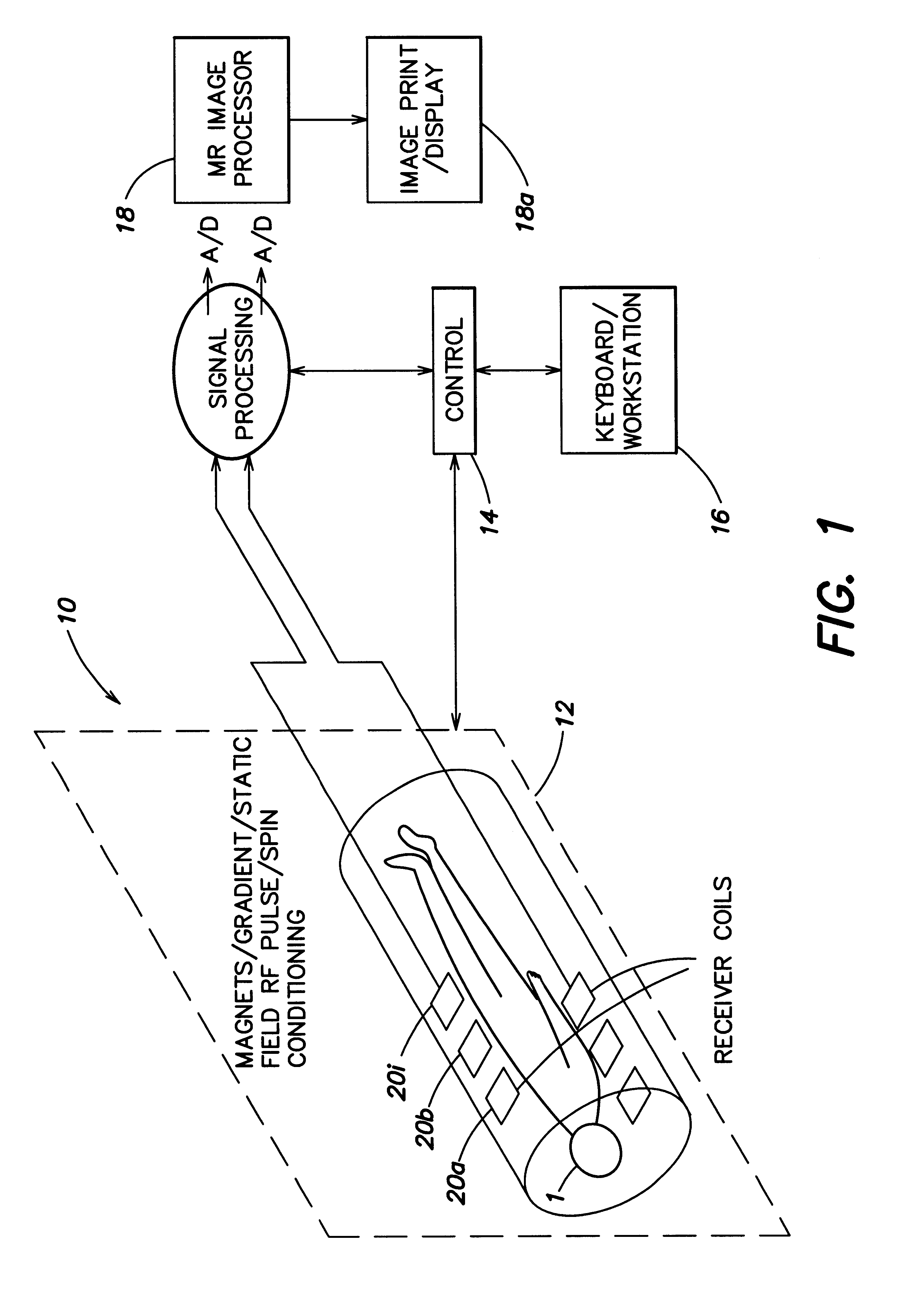
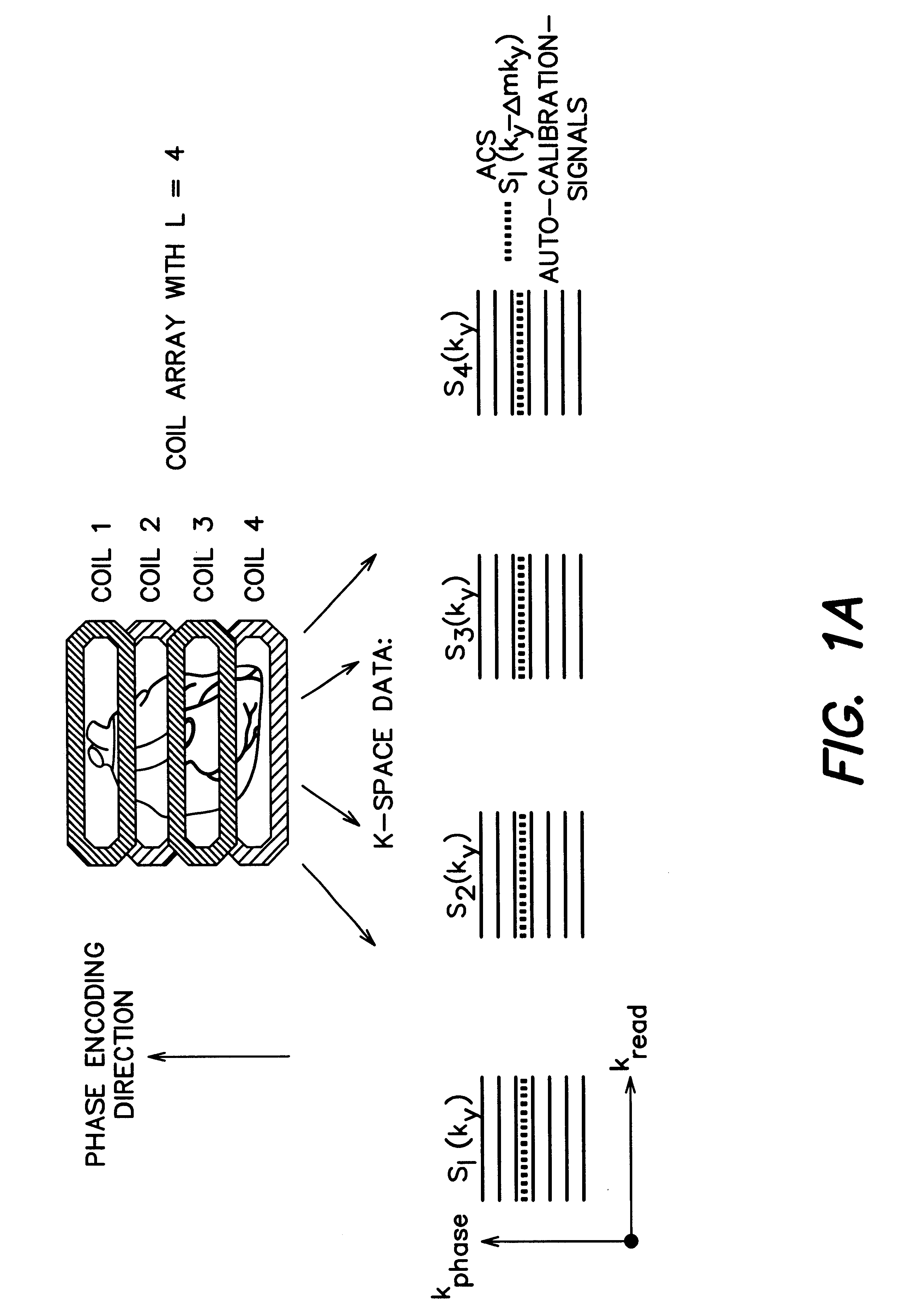
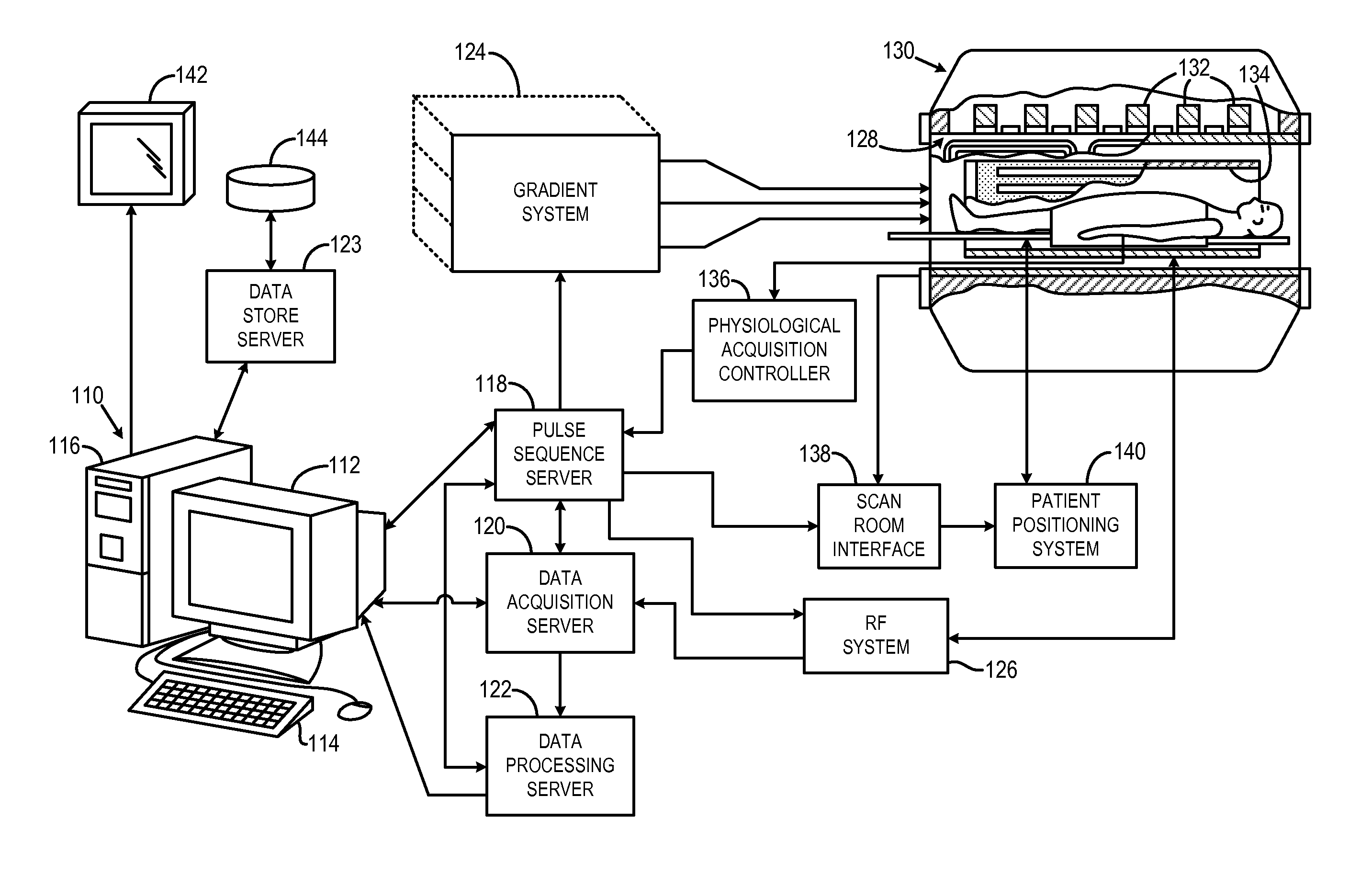
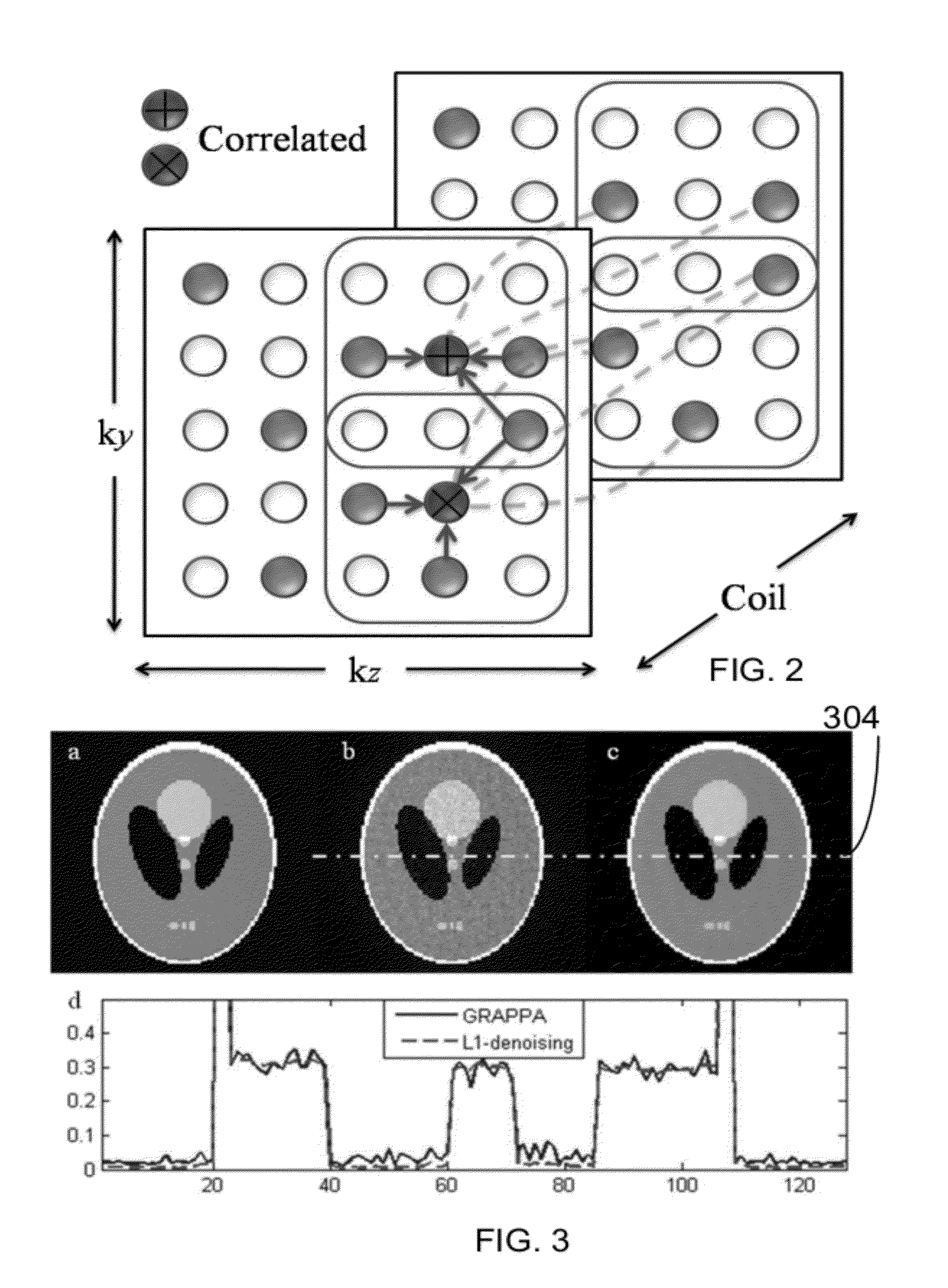
A magnetic resonance (MR) imaging apparatus and technique exploits spatial information inherent in a surface coil array to increase MR image acquisition speed, resolution and / or field of view. Magnetic resonance response signals are acquired simultaneously in the component coils of the array and, using an autocalibration procedure, are formed into two or more signals to fill a corresponding number of lines in the signal measurement data matrix. In a Fourier embodiment, lines of the k-space matrix required for image production are formed using a set of separate, preferably linear combinations of the component coil signals to substitute for spatial modulations normally produced by phase encoding gradients. One or a few additional gradients are applied to acquire autocalibration (ACS) signals extending elsewhere in the data space, and the measured signals are fitted to the ACS signals to develop weights or coefficients for filling additional lines of the matrix from each measurement set. The ACS lines may be taken offset from or in a different orientation than the measured signals, for example, between or across the measured lines. Furthermore, they may be acquired at different positions in k-space, may be performed at times before, during or after the principal imaging sequence, and may be selectively acquired to optimized the fitting for a particular tissue region or feature size. The in vivo fitting procedure is readily automated or implemented in hardware, and produces an enhancement of image speed and / or quality even in highly heterogeneous tissue. A dedicated coil assembly automatically performs the calibration procedure and applies it to measured lines to produce multiple correctly spaced output signals. One application of the internal calibration technique to a subencoding imaging process applies the ACS in the central region of a sparse set of measured signals to quickly form a full FOV low resolution image. The full FOV image is then used to determine coil sensitivity related information and dealias folded images produced from the sparse set.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
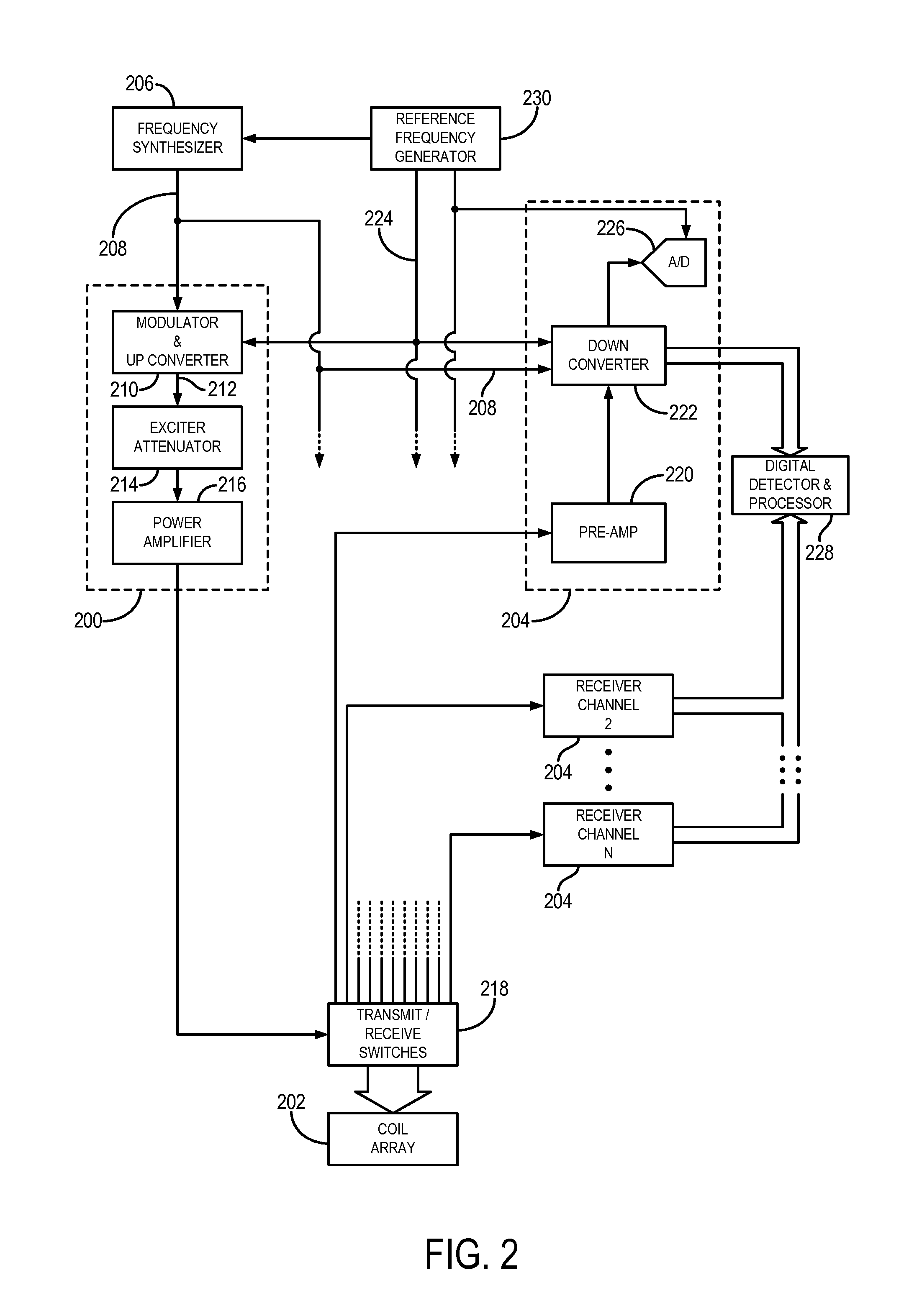
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110254548A1Reliable separationLarge possible separationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
A method for multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging, in which image data is acquired simultaneously from multiple slice locations using a radio frequency coil array, is provided. By way of example, a modified EPI pulse sequence is provided, and includes a series of magnetic gradient field “blips” that are applied along a slice-encoding direction contemporaneously with phase-encoding blips common to EPI sequences. The slice-encoding blips are designed such that phase accruals along the phase-encoding direction are substantially mitigated, while providing that signal information for each sequentially adjacent slice location is cumulatively shifted by a percentage of the imaging FOV. This percentage FOV shift in the image domain provides for more reliable separation of the aliased signal information using parallel image reconstruction methods such as SENSE. In addition, the mitigation of phase accruals in the phase-encoding direction provides for the substantial suppression of pixel tilt and blurring in the reconstructed images.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Holographic communications using multiple code stages
Owner:HOLO WAVE
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method and device based on tangential polarization
InactiveCN101907766ALow powerReduce bleachingMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageImage resolution
The invention discloses a super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method based on tangential polarization, comprising the following steps: carrying out 0-2pi vortex phase coding focus on tangential polarization exciting light, and obtaining an exciting spot below a diffraction limit on a fluorescence sample; adjusting tangential polarization STED laser and the phase coding tangential polarization exciting light to realize confluence and co-axis, focusing on the fluorescence sample to form a circle bread-shaped focusing spot the central point of which coincides with the central point of the exciting spot; adjusting the operating power of the STED laser to cause the area of a luminous point in the exciting spot to reach the super-resolution ratio; and collecting fluorescence emitted from the luminous point and carrying out detection processing to obtain a microimage with the super-resolution ratio. The invention also discloses a device for realizing the super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method based on tangential polarization. In the invention, on the premise of ensuring the super-resolution ratio, the working power of the STED is reduced greatly, thereby lowering bleaching of the sample and avoiding damage for the sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Systems and methods for thermophotonic dynamic imaging
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +2
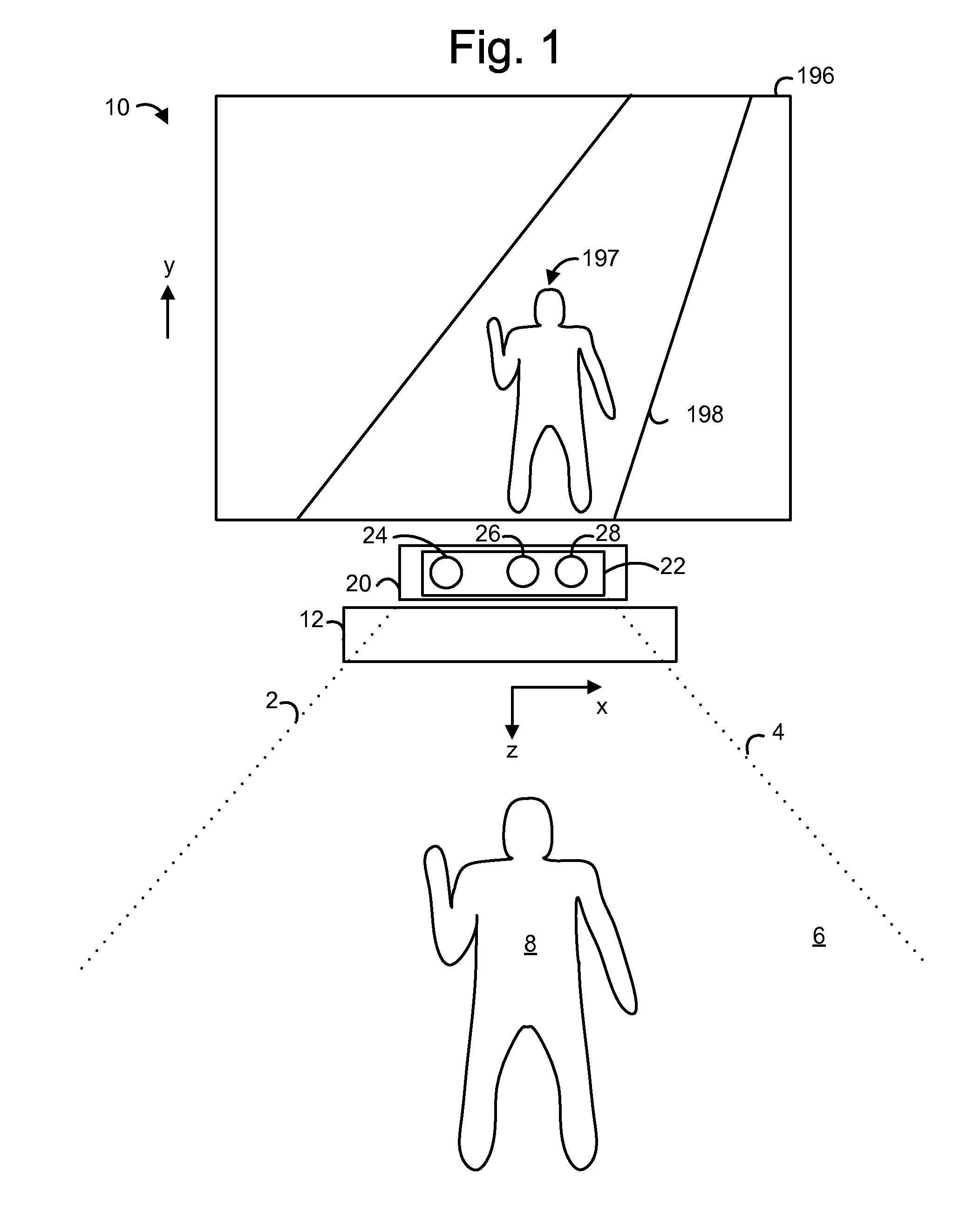
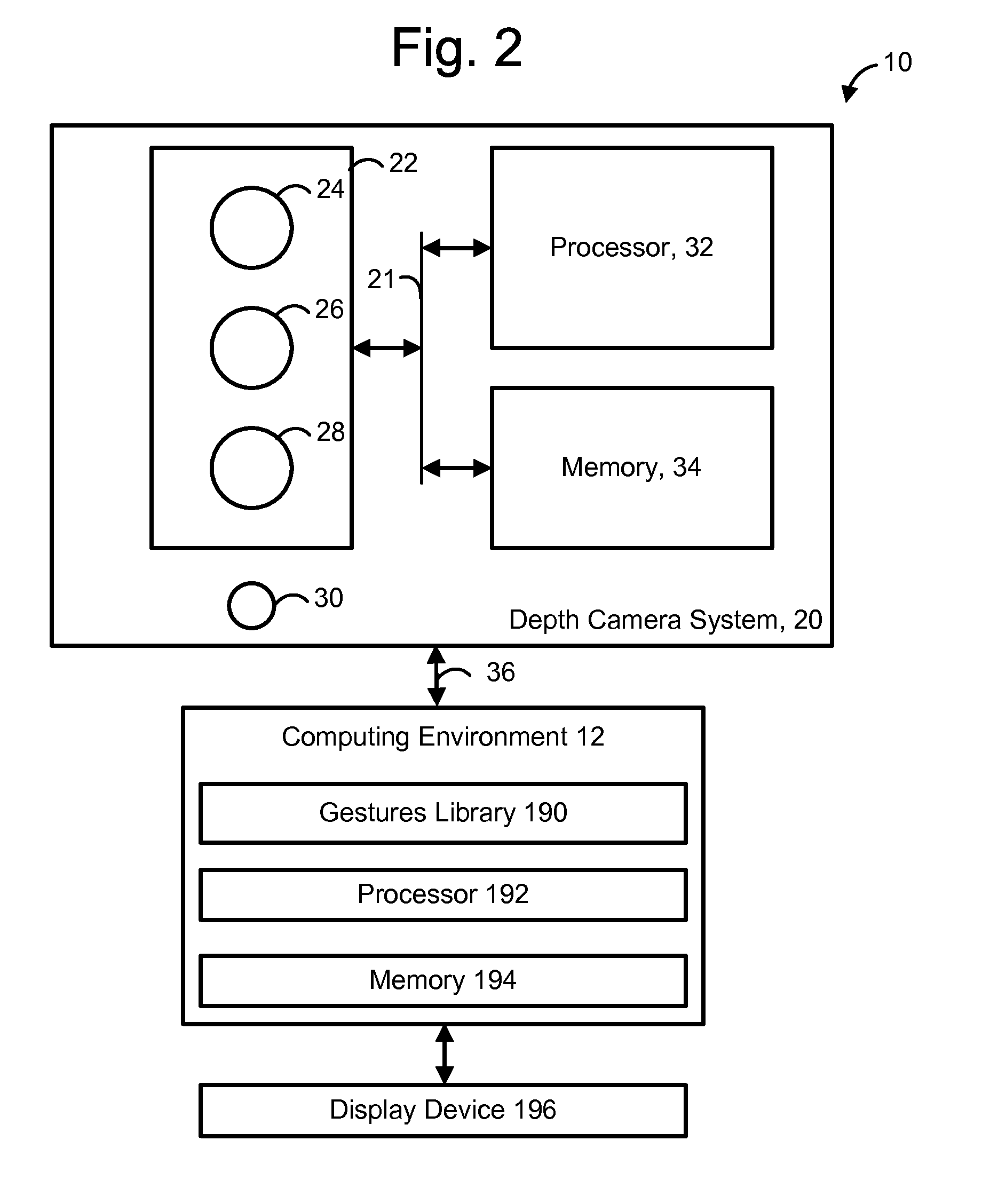
Use of wavefront coding to create a depth image
ActiveUS20110310226A1Well formedCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansDiffusion functionMotion capture
A 3-D depth camera system, such as in a motion capture system, tracks an object such as a human in a field of view using an illuminator, where the field of view is illuminated using multiple diffracted beams. An image sensing component obtains an image of the object using a phase mask according to a double-helix point spread function, and determines a depth of each portion of the image based on a relative rotation of dots of light of the double-helix point spread function. In another aspect, dual image sensors are used to obtain a reference image and a phase-encoded image. A relative rotation of features in the images can be correlated with a depth. Depth information can be obtained using an optical transfer function of a point spread function of the reference image.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Autocalibrating parallel imaging reconstruction method from arbitrary k-space sampling with reduced noise
ActiveUS20120092009A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel imagingReconstruction method
A computer implemented method for magnetic resonance imaging is provided. A 3D Fourier Transform acquisition is performed with two phase encode directions, wherein phase code locations are chosen so that a total number of phase encodes is less than a Nyquist rate, and closest distances between phase encode locations takes on a multiplicity of values. Readout signals are received through a multi-channel array of a plurality of receivers. An autocalibrating parallel imaging interpolation is performed and a noise correlation is generated. The noise correlation is used to weight a data consistency term of a compressed sensing iterative reconstruction. An image is created from the autocalibration parallel imaging using the weighted data consistency term. The image is displayed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
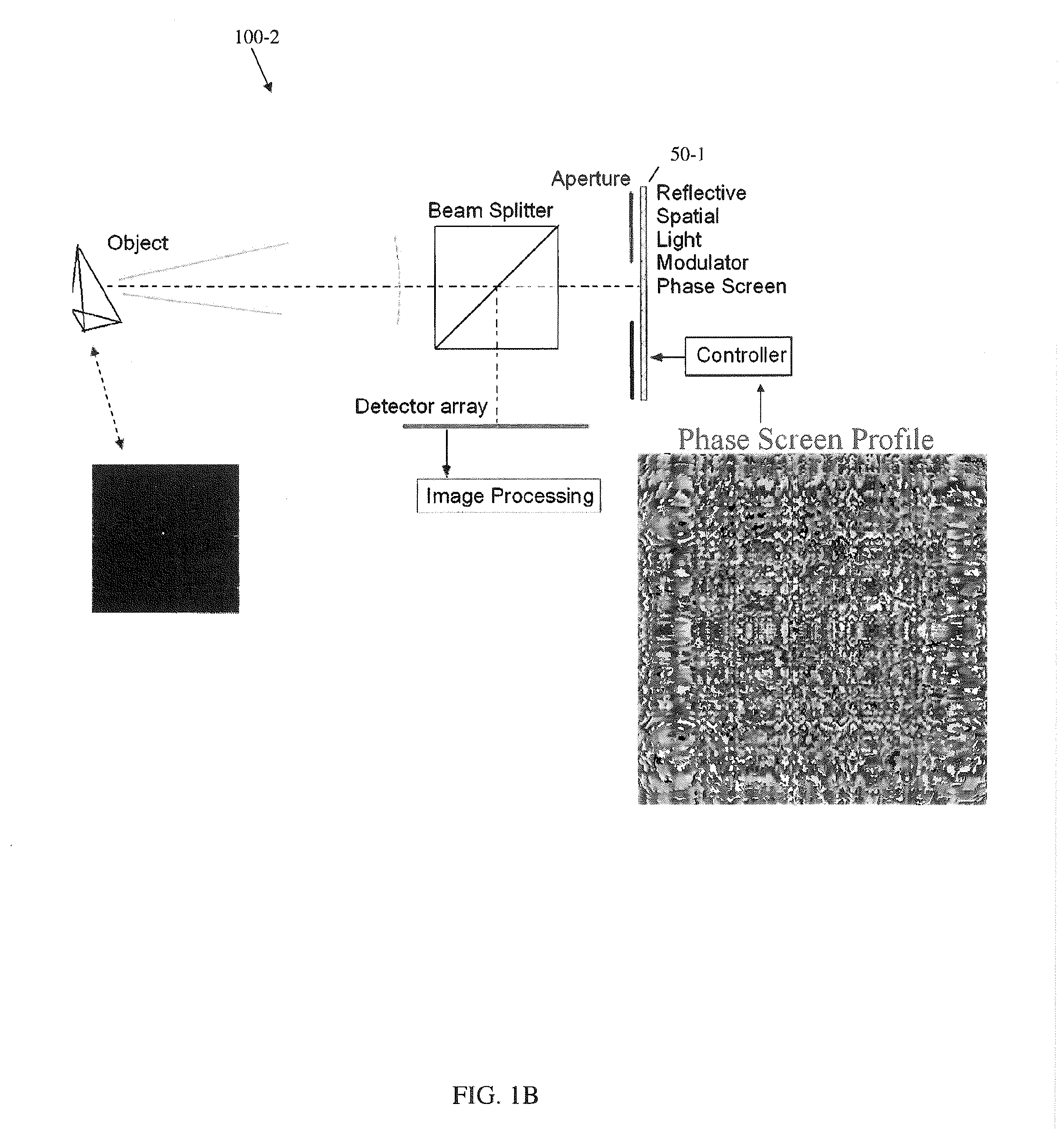
Method and apparatus for phase-encoded homogenized Fourier transform holographic data storage and recovery
InactiveUS20050134948A1Improves fidelity and efficiencyReduce cross-correlationRecord information storageActive addressable light modulatorSpatial light modulatorLight beam
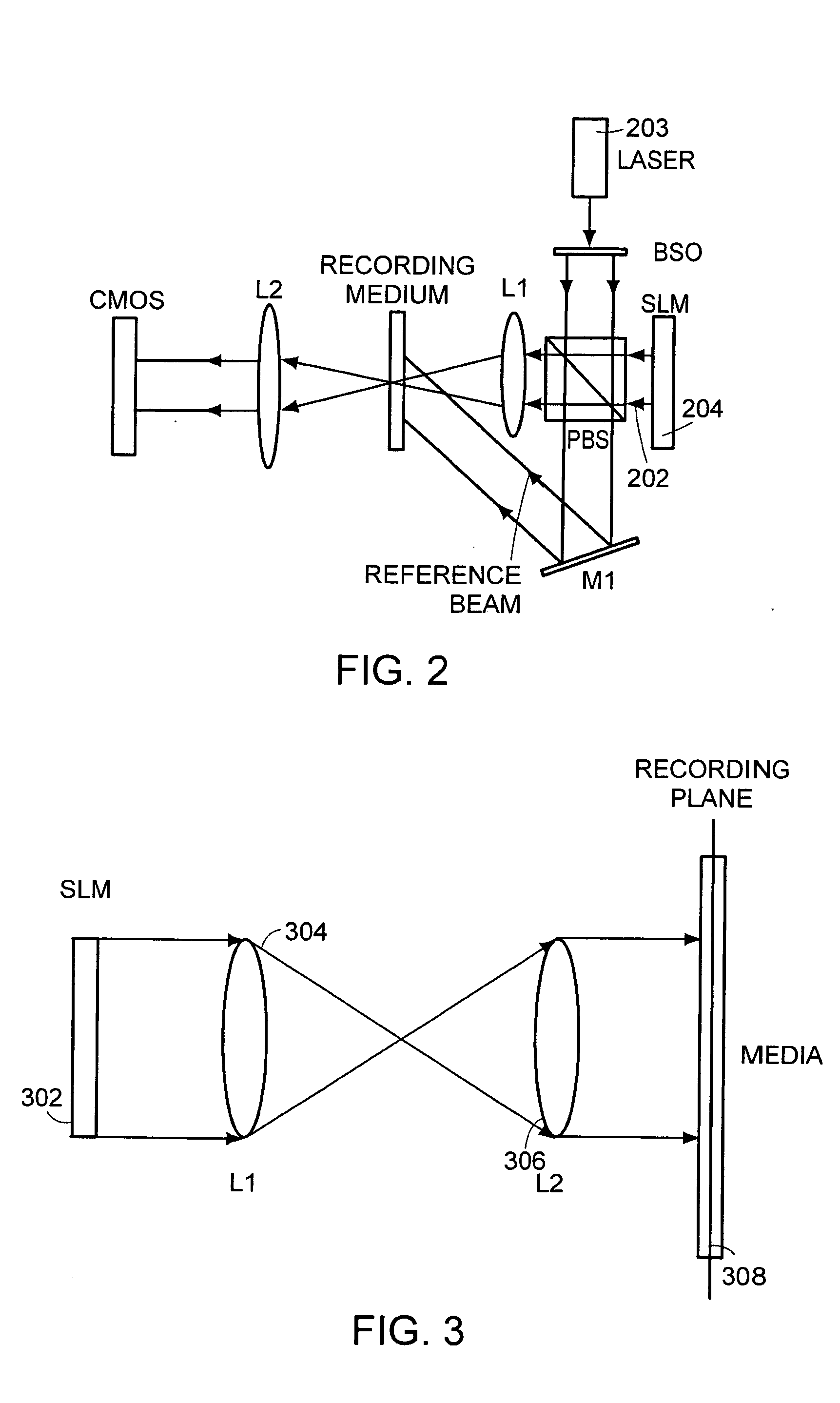
An apparatus for writing and reading holograms, comprising a spatial light modulator (SLM) operable in phase mode, having a plurality of pixels for generating an object beam that overlaps with a reference beam; a holographic recording medium (HRM) in the path of the object beam; and a first lens element disposed in the path of the object beam between the SLM and the HRM; wherein the HRM is disposed at or near the Fourier transform plane of the first lens element.
Owner:POSTECH CO LTD
Laser imaging radar device and distance measurement method thereof
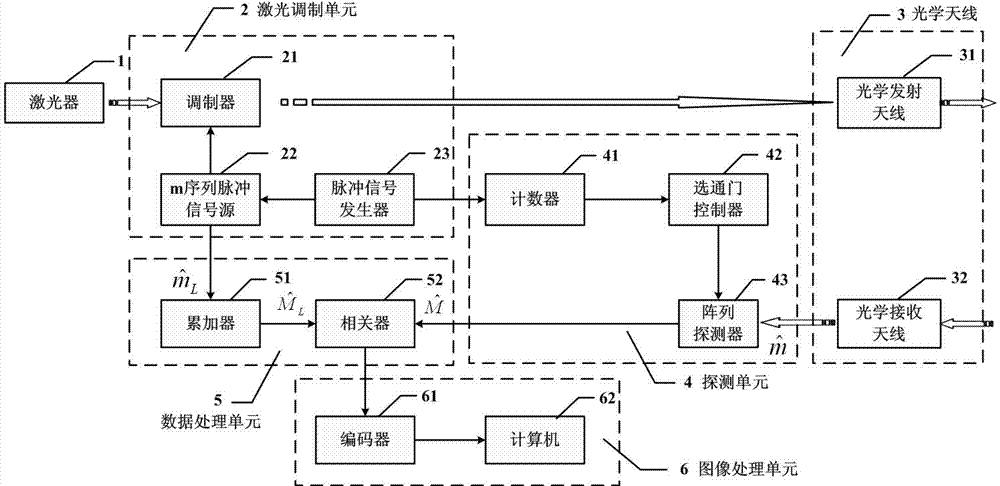
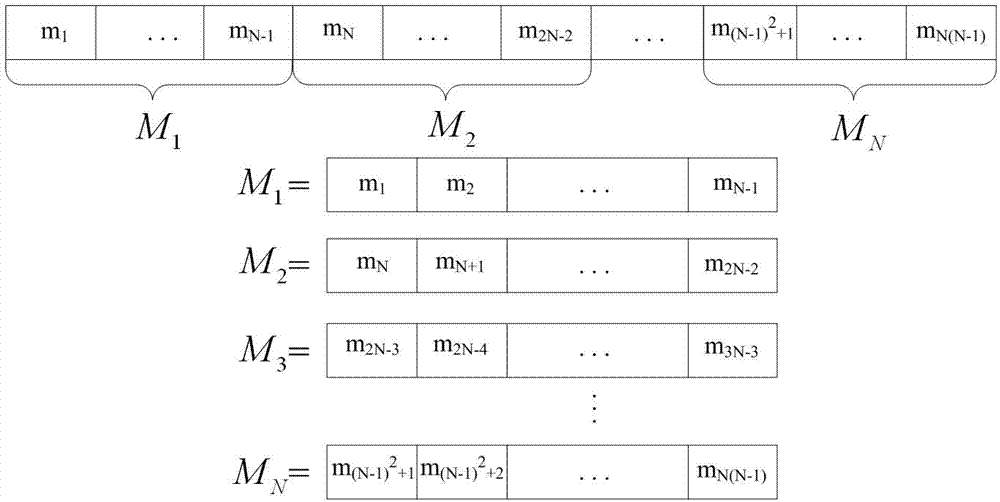
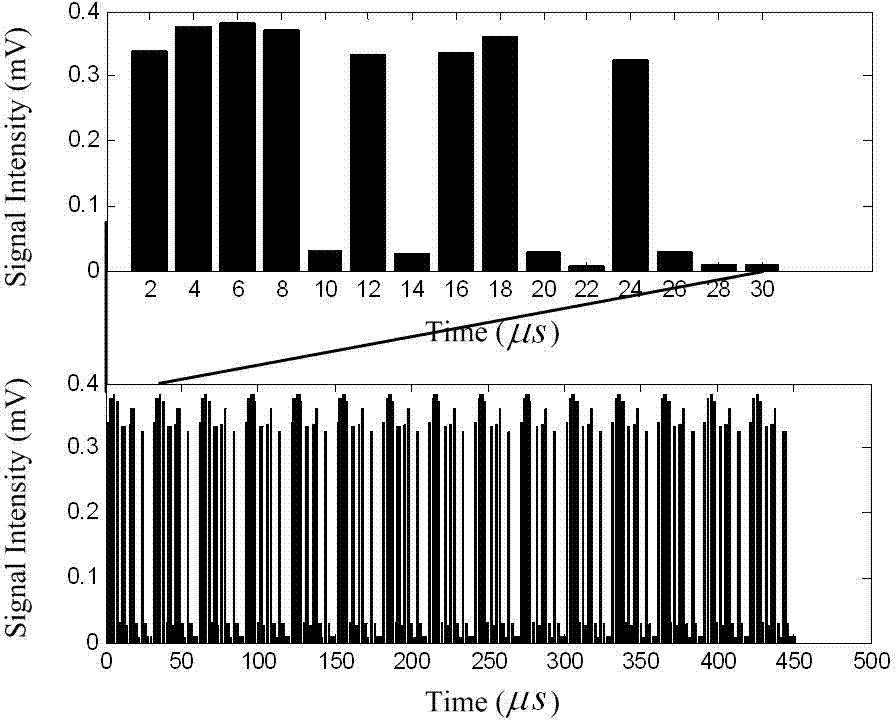
ActiveCN103616696AFast ranging speedProbe cycle shortenedElectromagnetic wave reradiationEngineeringRange gate
The invention provides a laser imaging radar device and a distance measurement method thereof. The laser imaging radar device and the distance measurement method thereof aims at the problem that an existing distance range gate laser imaging radar is low in distance resolution. The laser imaging radar device comprises a laser device, a laser modulation unit, an optical antenna unit, a detecting unit, a data processing unit and an image processing unit, wherein the detecting unit is composed of a counter, a gate controller and an array detector, and the data processing unit is composed of an accumulator and a correlator. According to the distance measurement method, an information loading process is carried out on laser signals with constant amplitude by using a phase code pulse amplitude modulation mode. The laser imaging radar device and the distance measurement method thereof have the advantages that the equipment and the method combine the advantages of long detecting distances of the distance ranging gate layer imaging radar and the advantage of high distance measurement resolution of the pulse phase coding mode, and meanwhile the detect of low distance measurement resolution of the distance ranging gate layer imaging radar and the detect of low imaging speed of the pulse phase coding mode are avoided.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
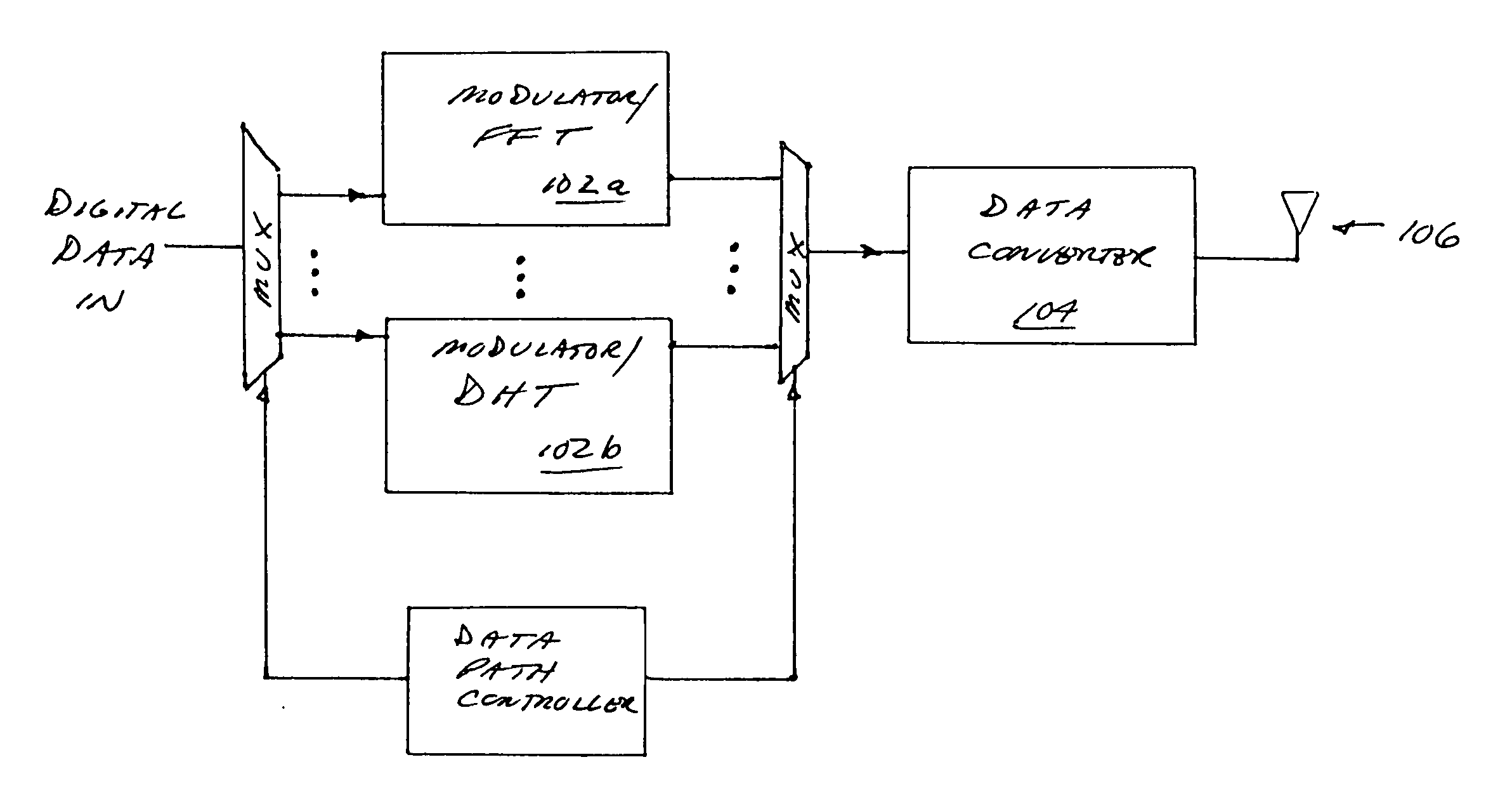
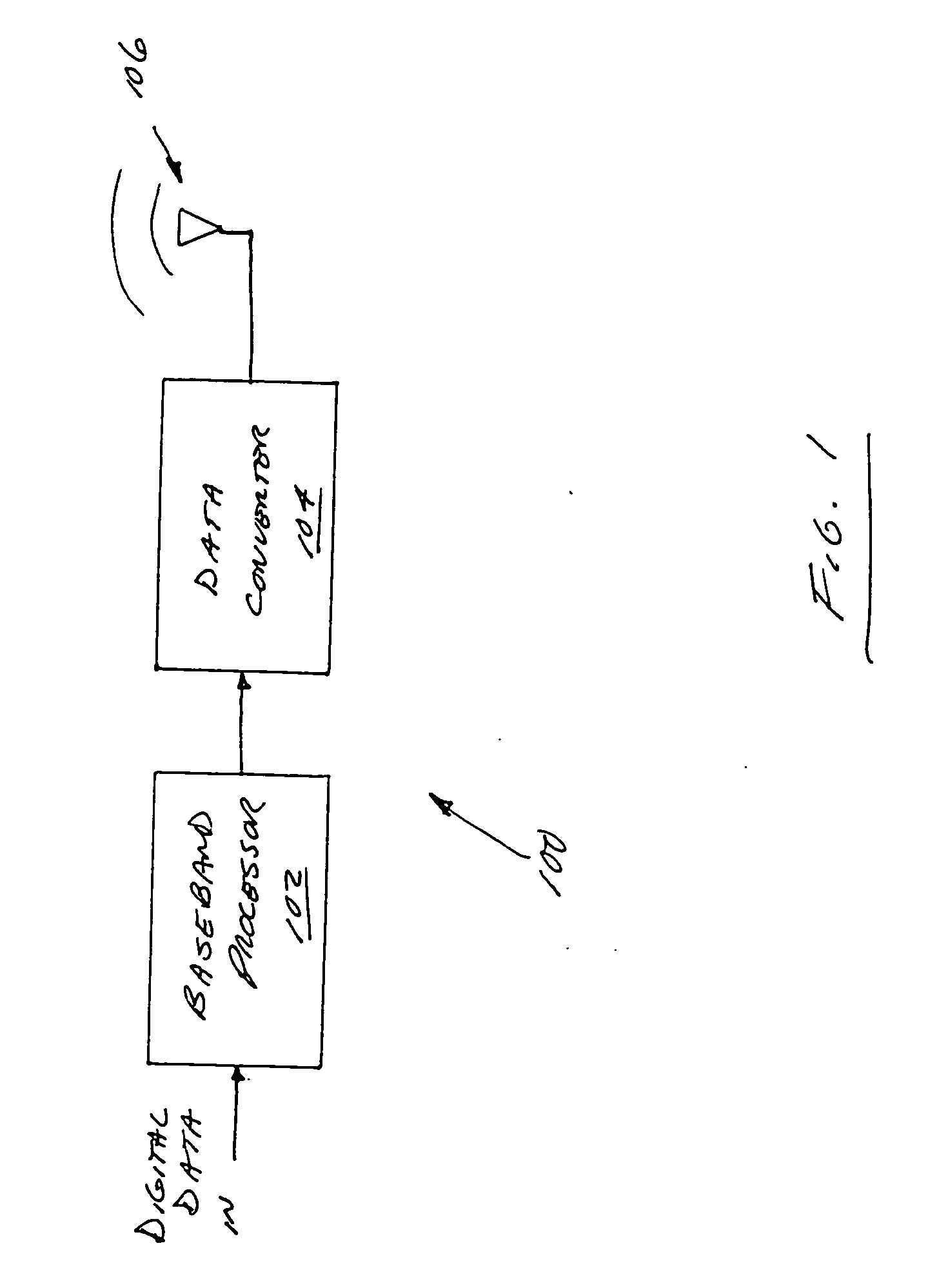
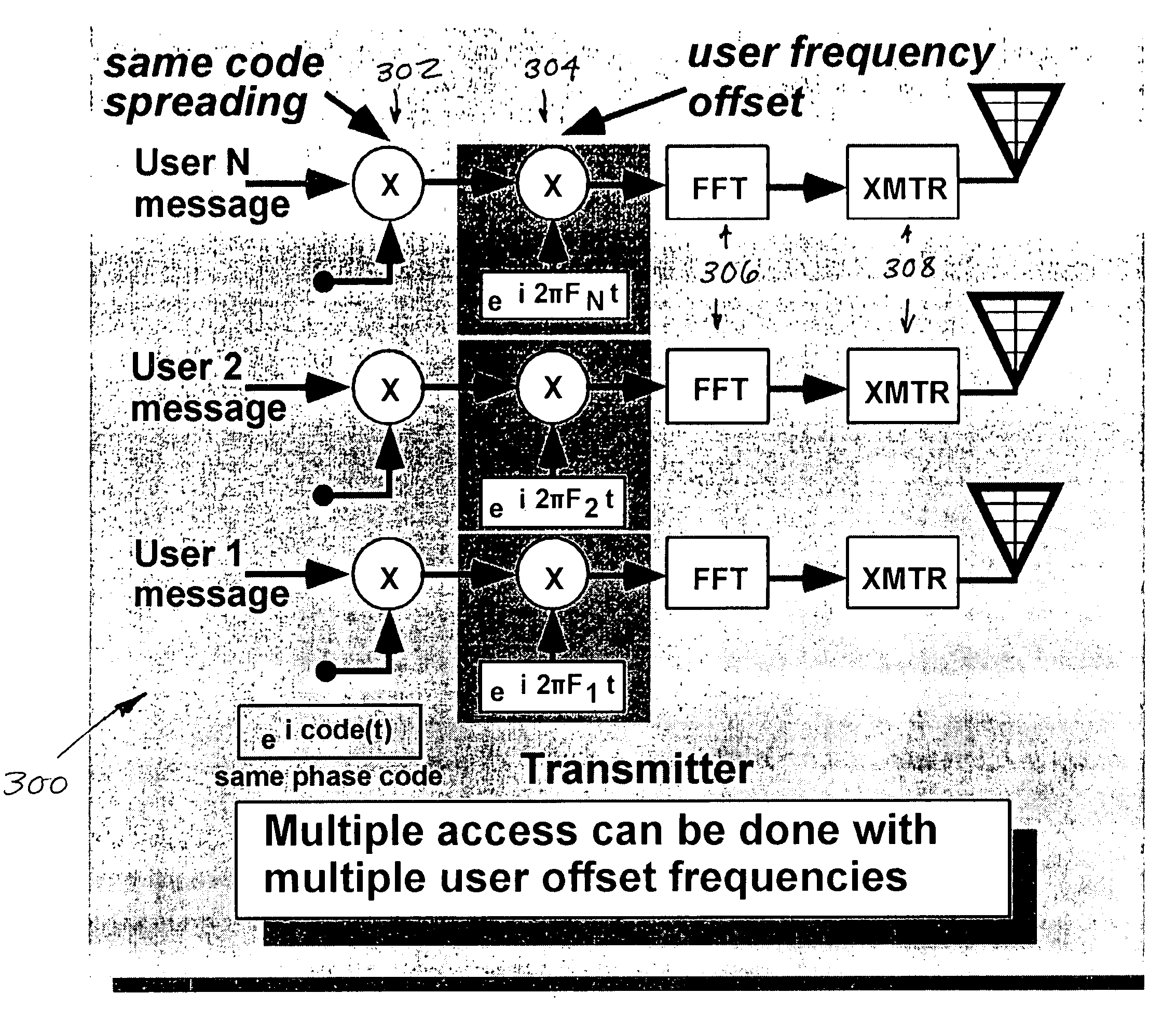
Scalable transform wideband holographic communications apparatus and methods
Improved apparatus and methods for utilizing holographic waveforms for a variety of purposes including communication. In one exemplary embodiment, the holographic waveforms are transmitted over an RF bearer medium to provide, inter alia, highly covert and robust communications. The baseband processor(s) are configured to selectively scale their architecture for performing the mathematical transforms (e.g., Fourier) or other operations (such as high speed phase-coding) in order to meet one or more operational requirements, such as reduced power consumption, changes in data rate, etc.
Owner:HOLOWAVE
Optical element, device, method, and applications
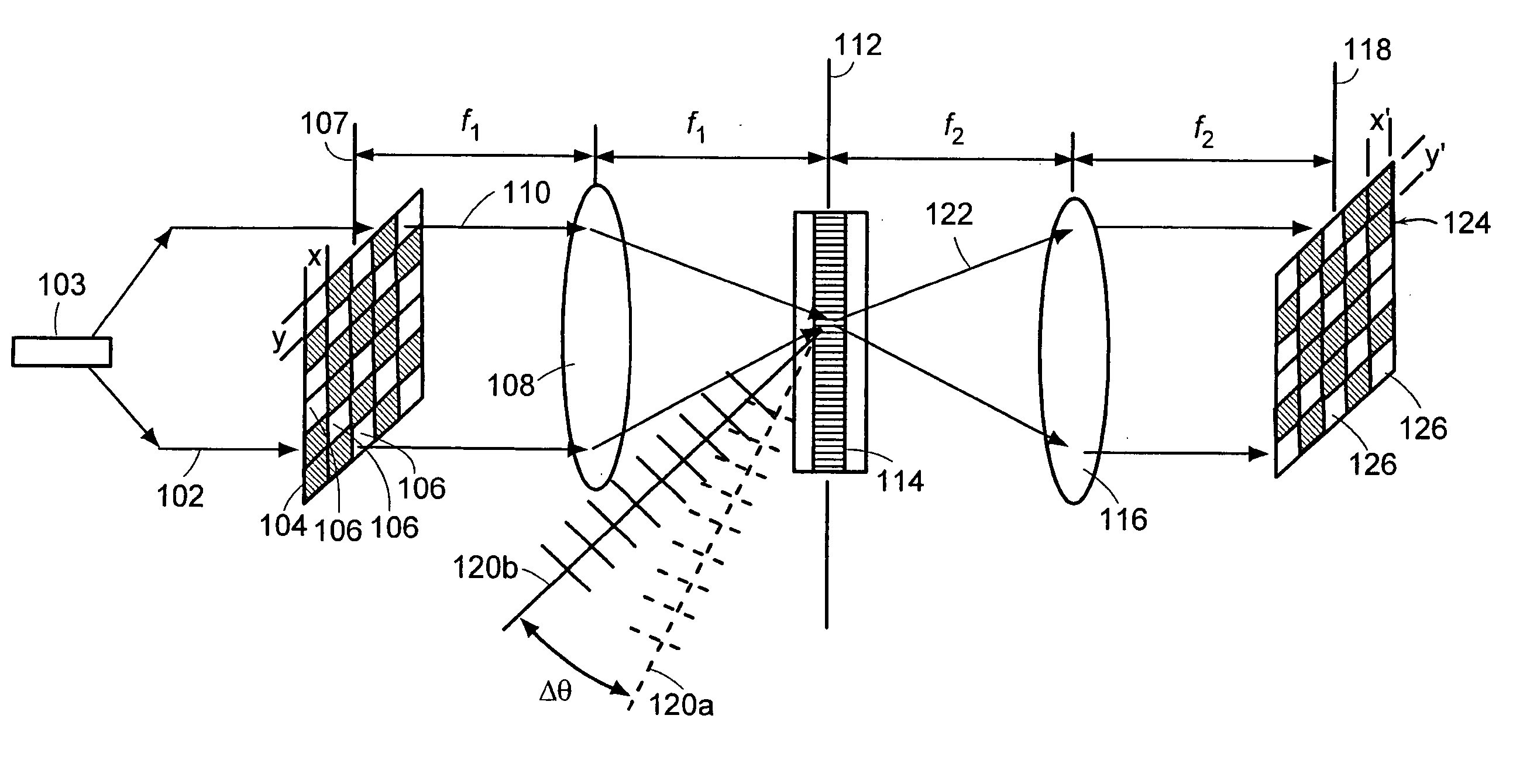
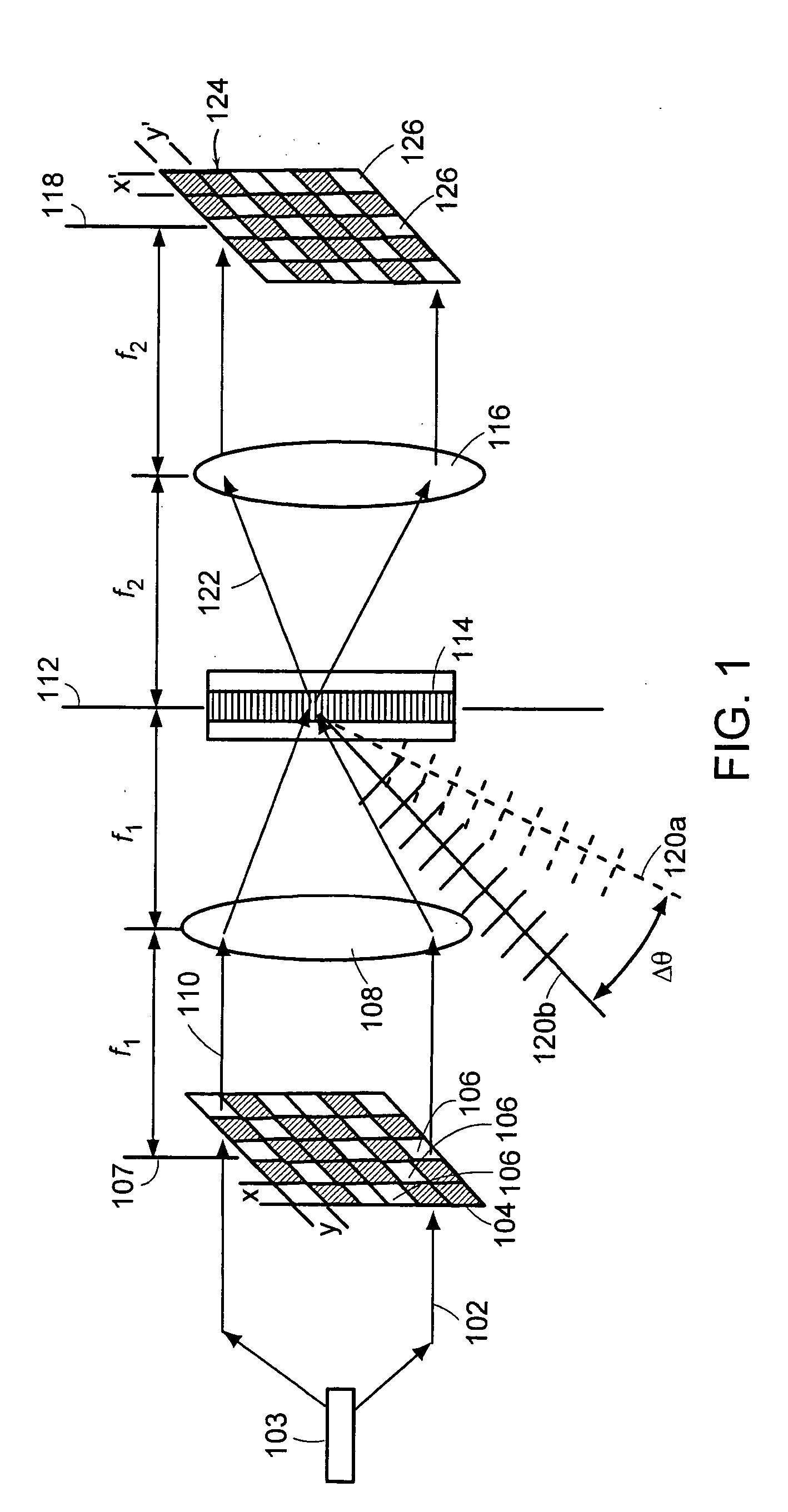
A novel phase-coded aperture, associated imaging system, and design method is disclosed. The optical imaging system includes a coded-aperture followed optically by a detector array and includes an image processor. A diffraction pattern in the form of a band-limited uniformly redundant array is formed on the detector array when focusable radiation from a point source in object space is modulation by the transmission function of the coded-aperture. Since diffraction effects cannot be ignored in the optical regime, an iterative phase retrieval method is used to calculate the phase-coded aperture transmission function. Correlation type processing can be applied for the image recovery.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Epoch-variant holographic communications apparatus and methods
Improved apparatus and methods for utilizing holographic waveforms for a variety of purposes including communication, ranging, and detection. In one exemplary embodiment, the holographic waveforms are transmitted over an RF bearer medium to provide, inter alia, highly covert communications, radar systems, and microwave data links. The bearer (i.e., carrier) is optionally frequency-hopped, and various pulse modulation techniques (including variation of the phase-coding clock epoch) applied in order to further increase communications efficiency and covertness. Methods of providing multiple access and high bandwidth data transmission are also disclosed. Improved apparatus utilizing these features; e.g., a wireless miniature covert transceiver / locator, are also disclosed.
Owner:HOLOWAVE
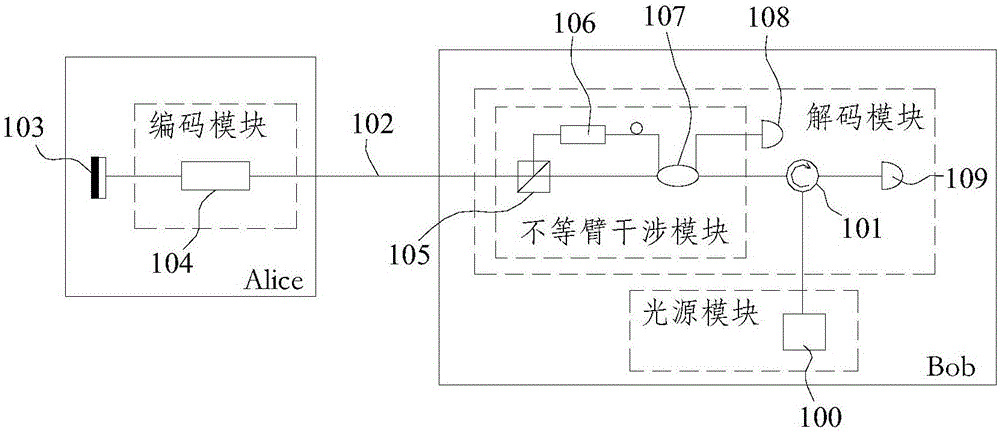
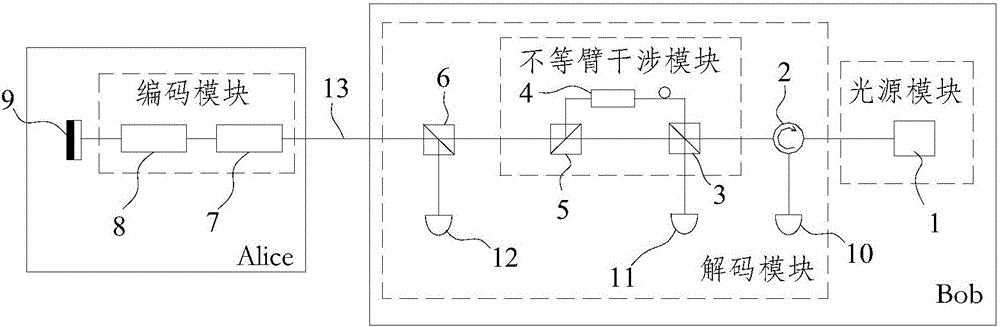
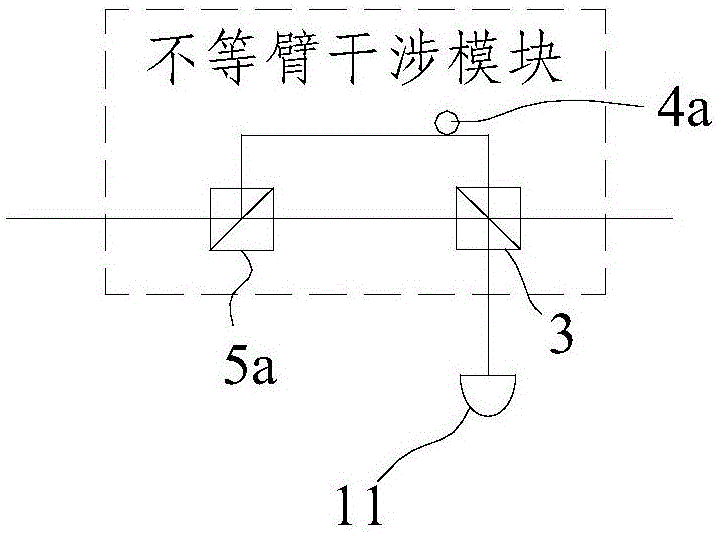
Plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system and method based on time-phase encoding, transmitting end and receiving end
ActiveCN106161011AImprove bit rateKey distribution for secure communicationCode moduleComputer architecture
The invention discloses a plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system and method based on time-phase encoding, a transmitting end and a receiving end. The plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system comprises the transmitting end and the receiving end which are in mutually optical connection, a coding module in the transmitting end comprises a Z basis vector time coding module coding optical signals according to any sequence and a phase coding module which is an X basis vector phase coding module, and a decoding module in the receiving end is matched with the coding module. The plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution method includes: after an Alice end receives and reflects optical signals from a Bob end, performing Z basis vector time coding and phase coding; sending the optical signals after going through Z basis vector time coding and phase coding to the Bob end for decoding and detecting, wherein phase coding refers to X basis vector phase coding. Improved time-phase coding is used, so that ultrahigh-contrast coding and decoding can be realized, and code generating rate can be increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENZHOU QUANTUM NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS8405395B2Reliable separationLarge possible separationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
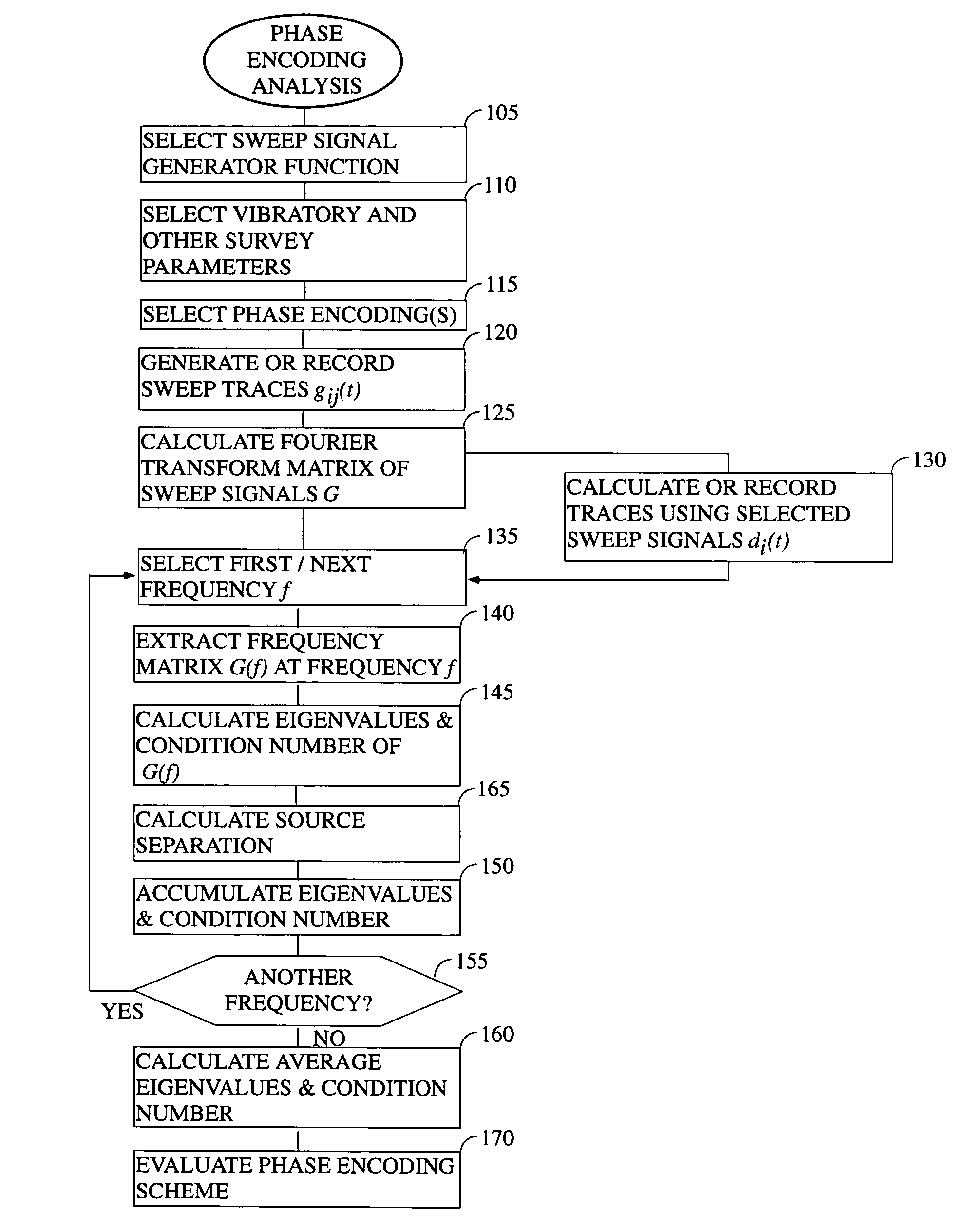
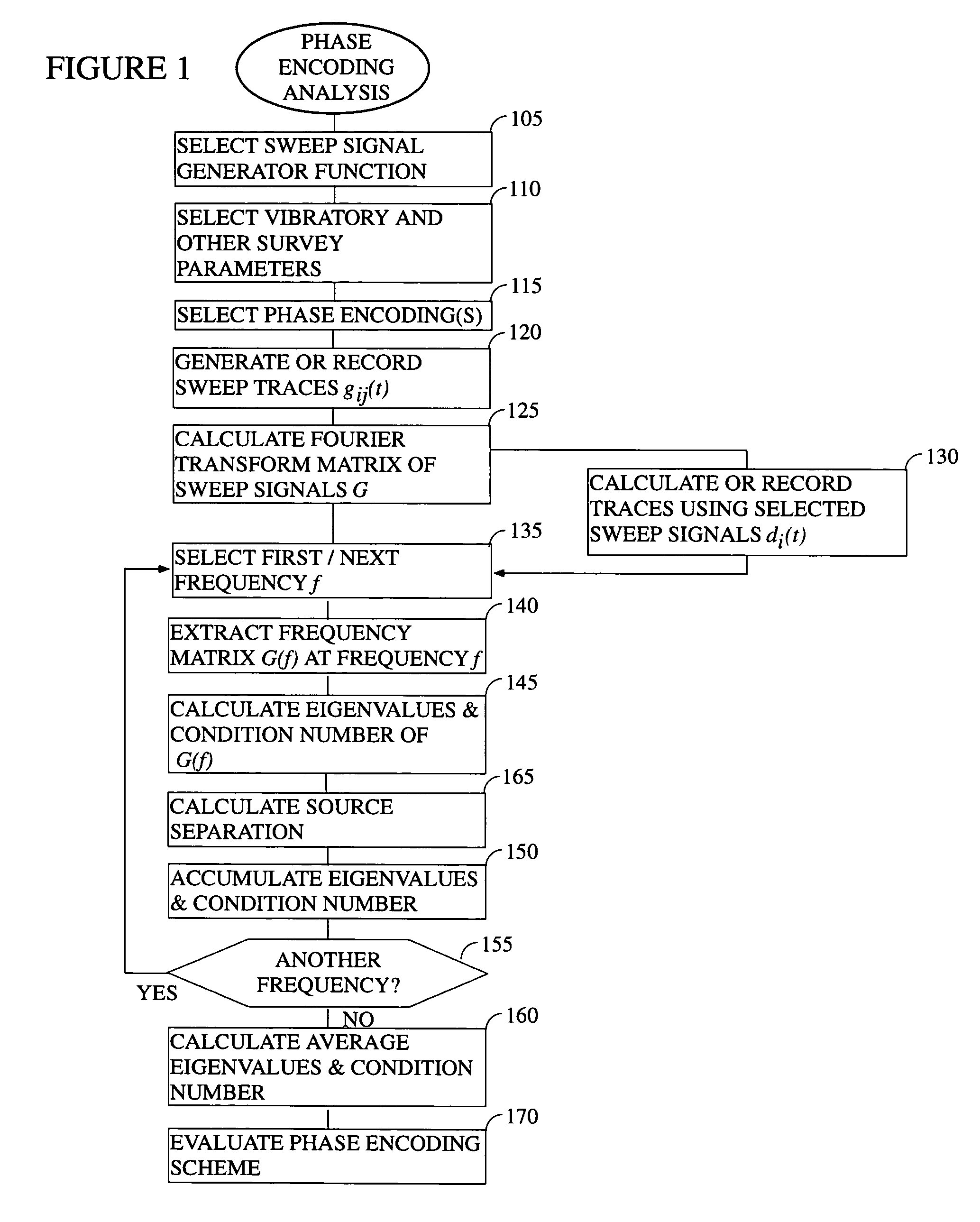
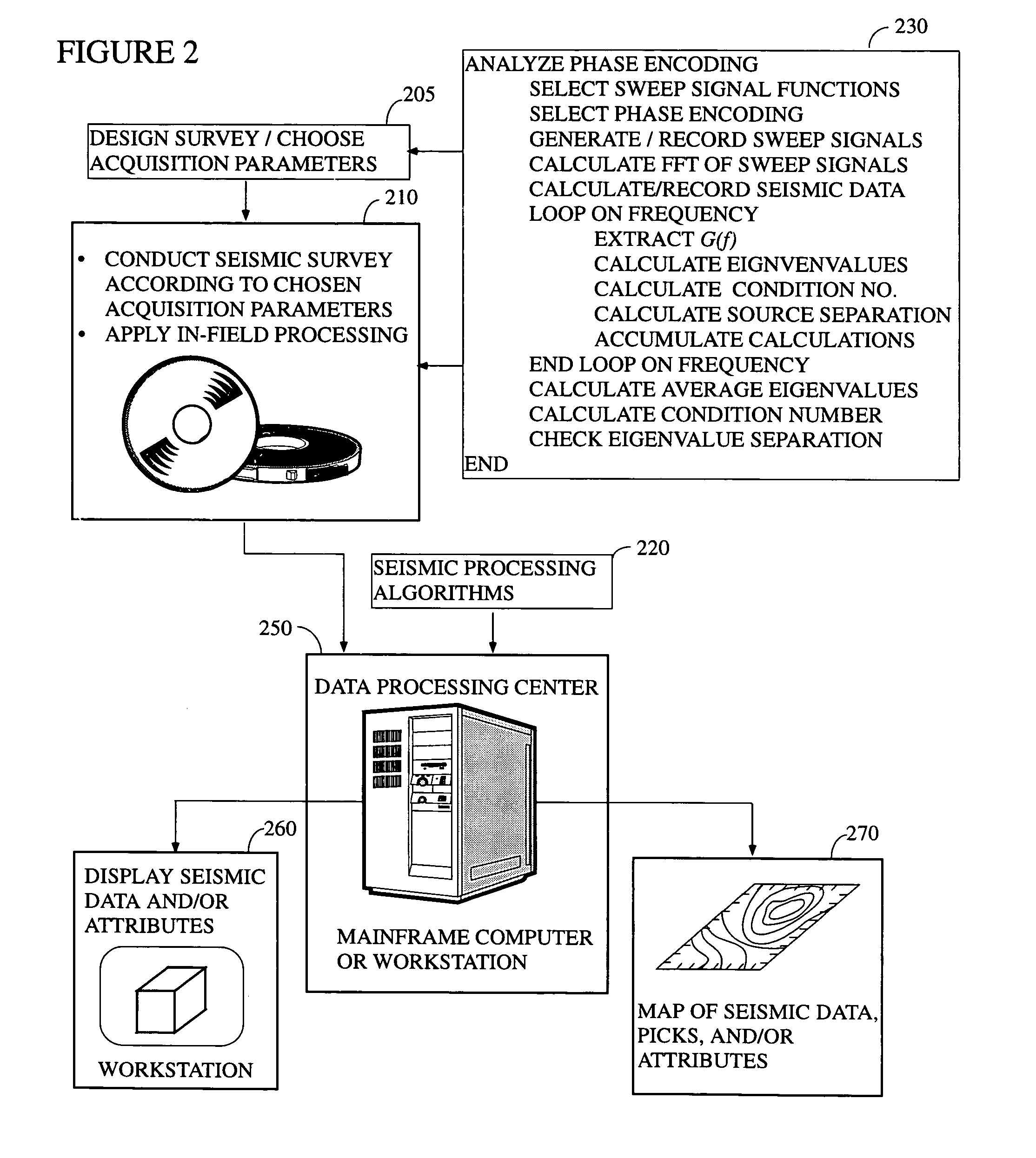
System and method of phase encoding for high fidelity vibratory seismic data
ActiveUS7295490B1Quality improvementMaintain good propertiesSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSingular value decompositionSeismic survey
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a method of determining whether a particular high fidelity vibratory seismic survey phase encoding is likely to be a good one based on an analysis of the eigenvalue structure (i.e., eigenvalues, eigenvalue separation, condition number, and model resolution matrix) of a matrix formed from the Fourier transforms of the sweep signals. Preferably, a singular value decomposition will be used to calculate the eigenvalues. Using this same approach, the condition number and eigenvalues of matrices that are associated with multiple proposed designs can be compared with each other to determine which is likely to be yield the best seismic data. This approach is preferably used either as a component of the advanced planning for a survey or in the field during pre-survey testing. The use of the instant approach to determine an optimal phase encoding scheme is also taught.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
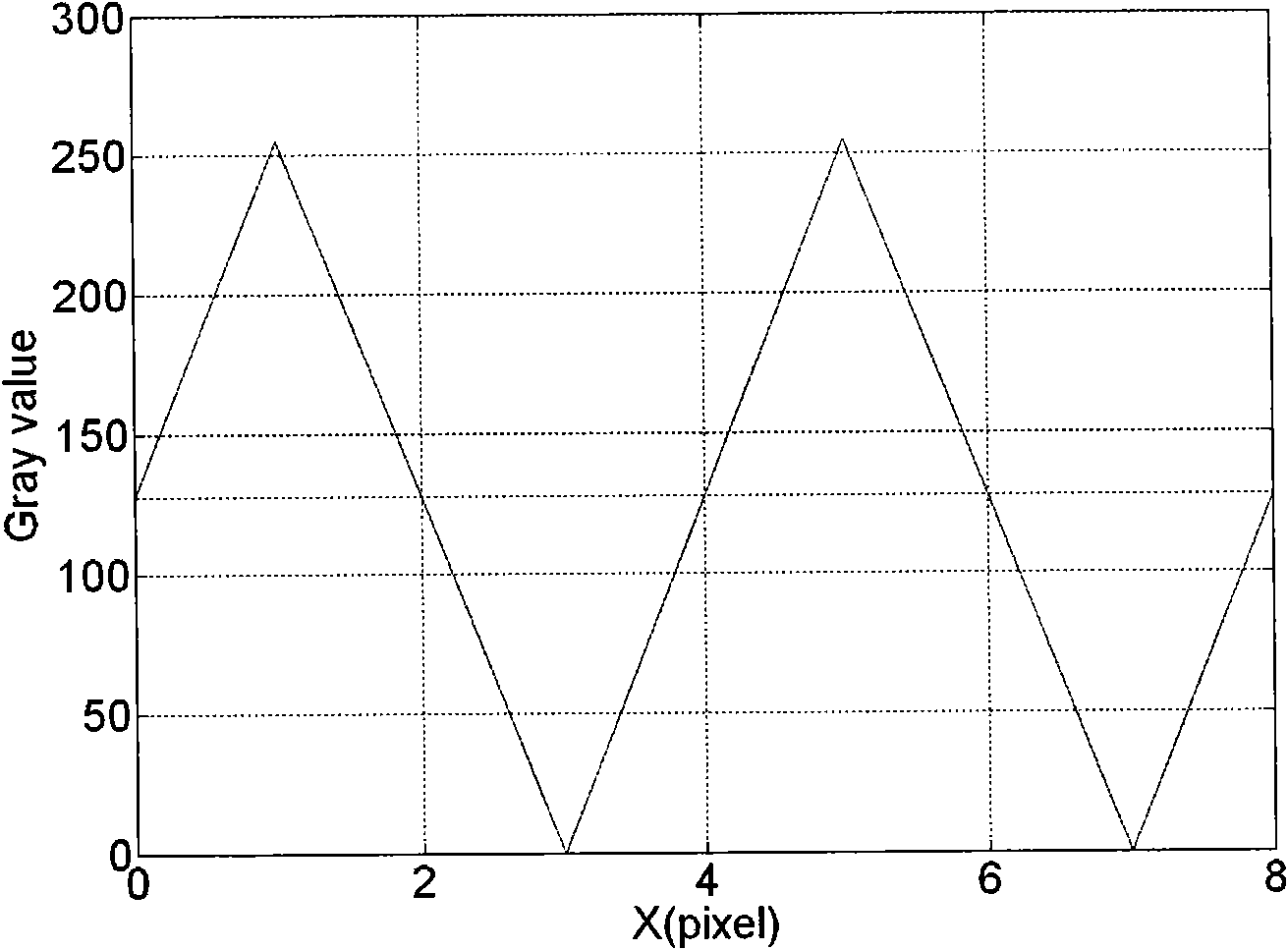
Optical three-dimensional measuring method based on phase coding technology
ActiveCN101881605AImprove anti-interference abilityGuaranteed correctnessUsing optical meansGratingInterference resistance
The invention relates to an optical three-dimensional measuring method based on a phase coding technology, belonging to the technical field of three-dimensional measurement. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) producing a grating coding stripe image by a computer; (2) projecting the grating coding stripe image by using digital projection equipment; and (3) acquiring the grating coding stripe image and performing coding solution and three-dimensional measurement by adopting a phase-shift algorithm. The method is characterized in that: the number of pixels in each grating period of the grating coding stripe image equals to the step number of the adopted phase-shift algorithm; the gray scale of the pixels in each grating period of the grating coding stripe image meets sine or cosine curve distribution, and the gray-scale value of the pixels are extreme points of the corresponding sine or cosine function. Compared with the traditional sine phase-shift coding method, the method has strong interference resistance to the nonlinear influence of gamma rays of the digital projection equipment, the coding has higher stability, reliability and correctness, and the method is important in the aspect of accurate measurement of an optical three-dimensional outline on the external surface of an object.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Authentication system and method
InactiveUS7317814B2Cheaply replicatedRaise security concernsRadiation pyrometryCo-operative working arrangementsSpatial light modulatorFourier transform on finite groups
An authentication system using a correlator that correlates an input with a reference wherein at least one of the input and reference comprises a phase volume mask having structures, preferably points, that are each less than about six microns in size and can have an aspect ratio (AR) greater than 1:1 so as to produce a phase encoded random pattern having millions of combinations in a mask that is as small as one square millimeter. The random pattern can be convolved with a second pattern, such as a biometric pattern, to produce a phase convolved mask. The correlator preferably is a nonlinear joint transform correlator that can use “chirp” encoding to permit the input to be located in a different plane than the reference. The correlator optically Fourier transforms images of the reference and input that are thereafter nonlinearly transformed and inverse Fourier transformed by a processor to determine the presence or absence of a correlation spike indicative of authenticity. A spatial light modulator (SLM) can be used as an input or reference and preferably is a liquid crystal panel having pixels or elements whose phase or grey scale intensity can be selectively controlled by a processor. The SLM can be used to display a biometric pattern, preferably scanned in real time from a person, that is correlated against an input or reference that can comprise a label on a card, a tag, or another object.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Modular generation method for multi-waveform radar signal
InactiveCN102073032AVersatileImprove compatibilityWave based measurement systemsData acquisitionEngineering
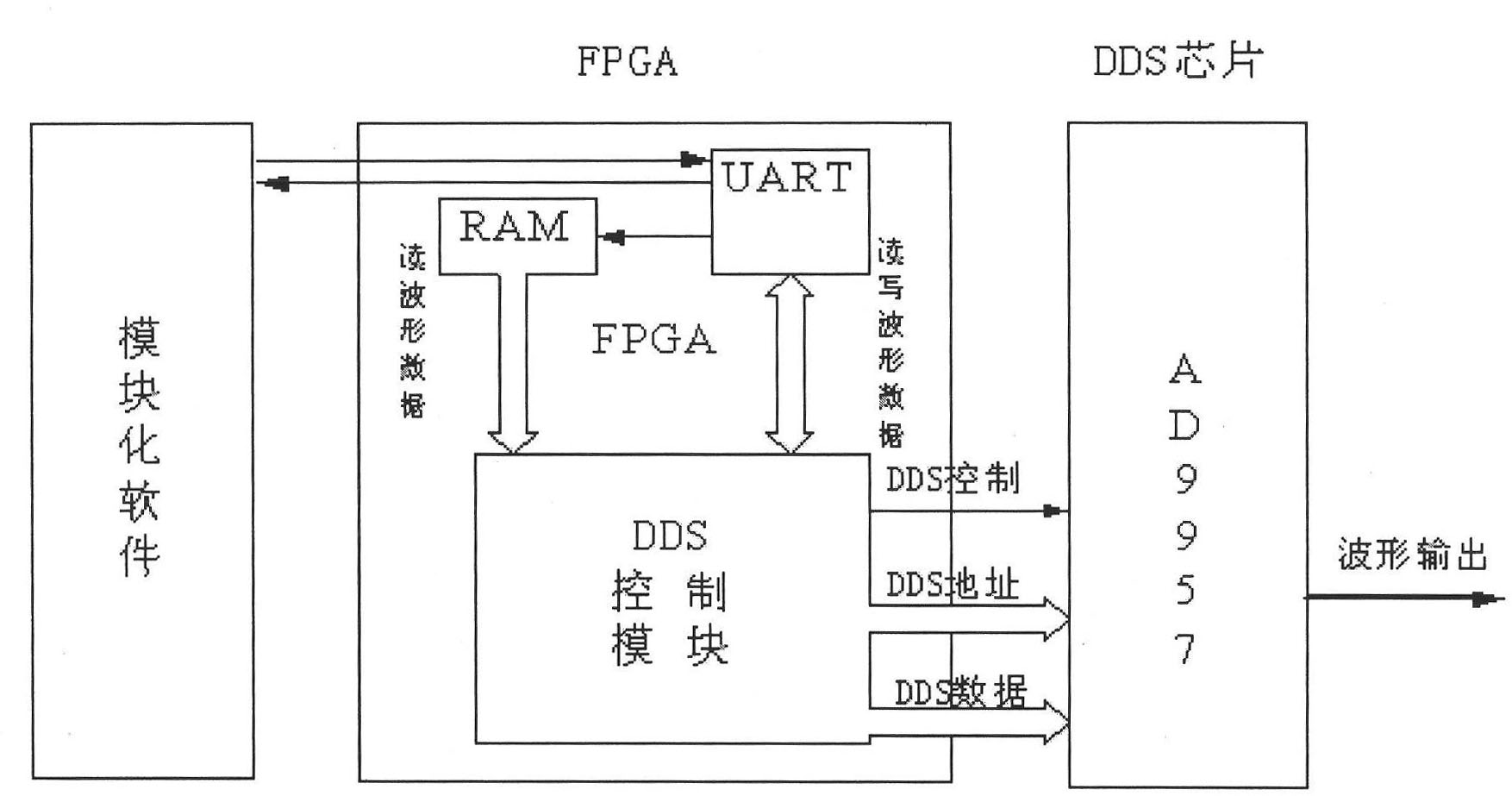
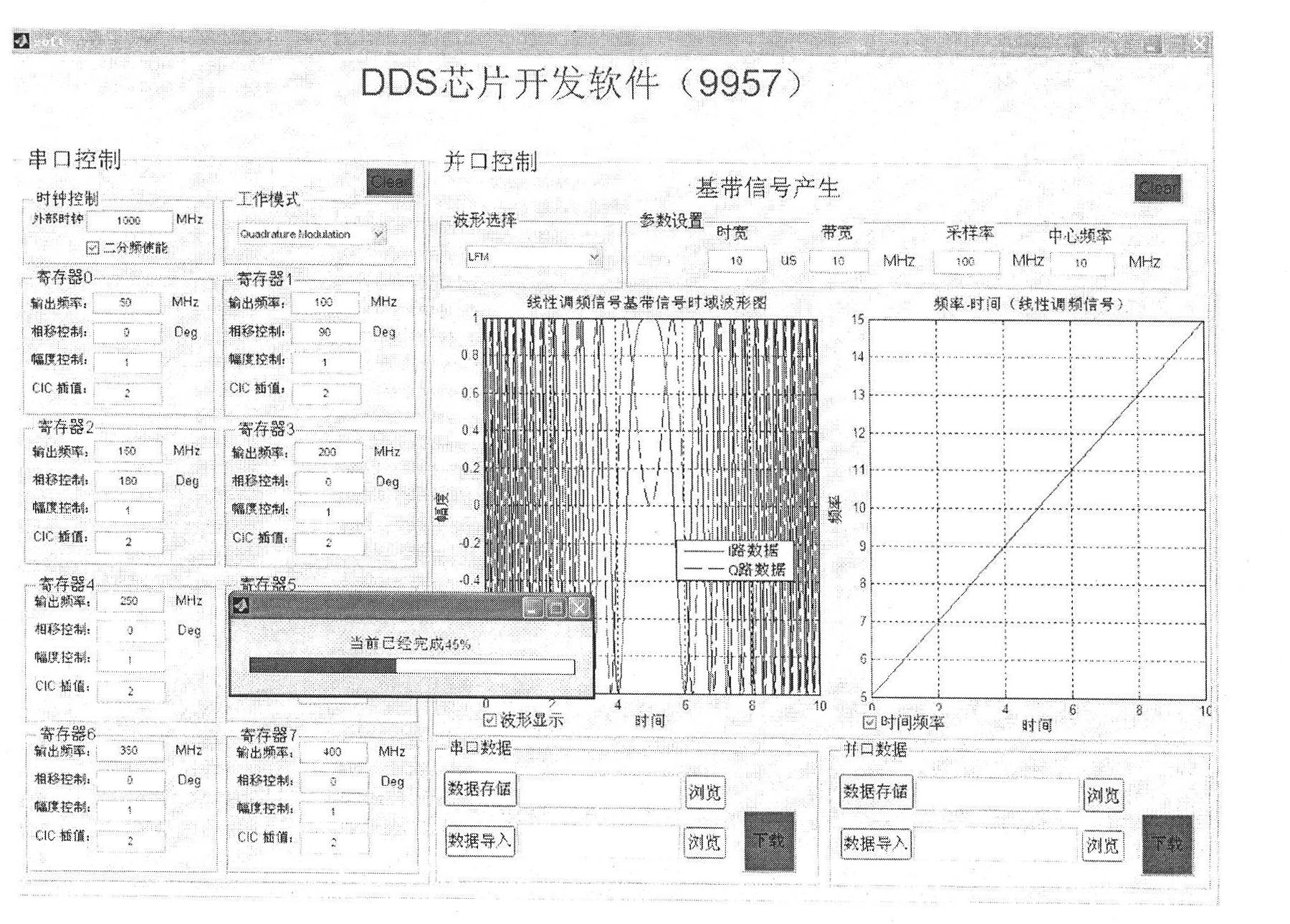
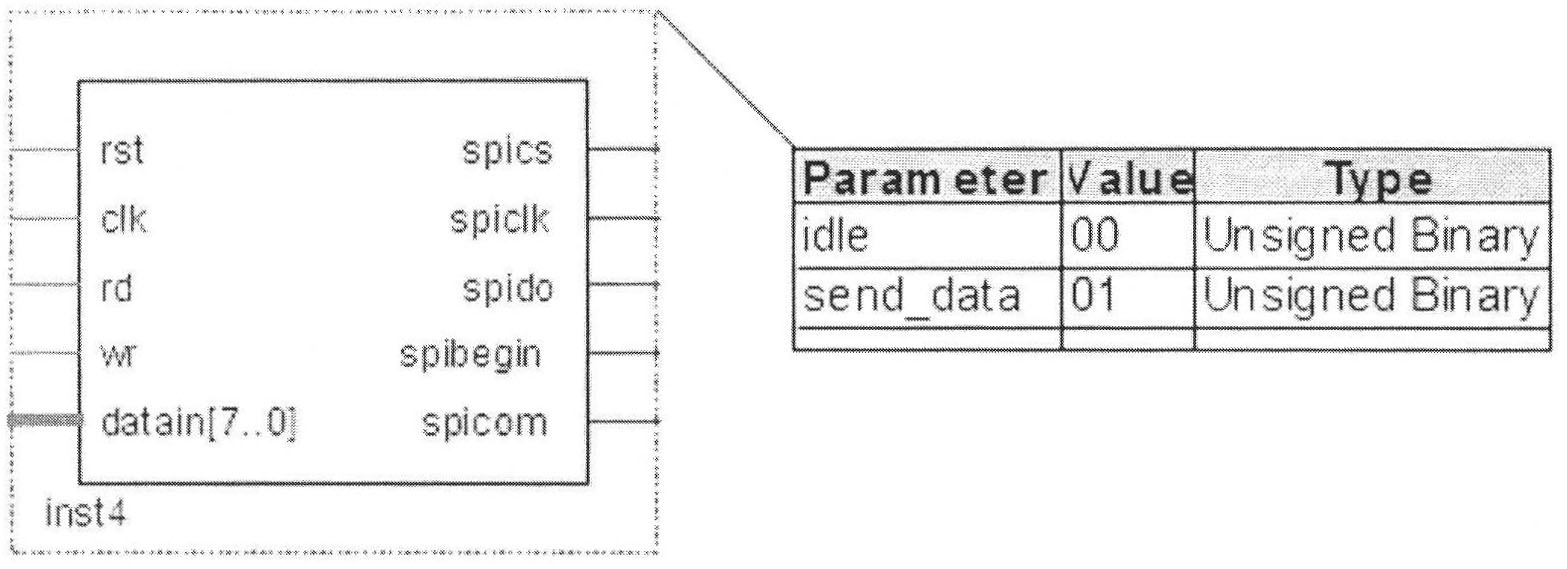
The invention relates to a modular generation method for a multi-waveform radar signal, which belongs to the technical field of radar frequency synthesis and is applied to the design of a direct digital frequency synthesis (DDS)-based frequency synthesizer. A multi-waveform radar signal module consists of modular software, a field programmable gate array (FPGA) and DDS chips. The modular software comprises a man-machine interactive interface and a modular serial port timing module, wherein the man-machine interactive interface performs relevant operation and storage of control parameters and waveform data of the DDS chips and performs data communication with the FPGA; and the modular serial port timing module generates modular serial port control timing which is suitable for the DDS series chips and completes data acquisition and updating by computer communication. The FPGA is provided with a random-access memory (RAM), a universal asynchronous receiver / transmitter (UART) and a DDS control module, and realizes the functions of data communication with a computer and the storage of the control parameters and waveform data of the DDS chips and DDS chip control. The DDS chips output various signals set by the parameters under the control of the FPGA. The modular software developed by the method configures different DDS chips, so various radar signals of point frequency, linear frequency modulation, nonlinear frequency modulation and phase encoding can be generated, and the software supports on-line programming and the real-time updating of the control parameters and waveform data of the DDS chips.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二〇六研究所
Apparatus of generating microwave phase coding signals in an optical manner
InactiveCN105162523AWide frequency adjustable rangeLarge time-bandwidth productPhase-modulated carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmissionOptical communicationFrequency shift
The invention discloses an apparatus of generating microwave phase coding signals in an optical manner, and relates to the microwave technology field and the optical communication technology field. The apparatus is mainly applied to generating pulse compression signals in pulse compression radar. By means of the frequency shift characteristics of two parallel Mach-Zehnder modulators, the optical wavelength modulated by coding signals and the optical wavelength after a frequency shift are coupled to each other and then are detected through a photoelectric detector, in this way, phase coding microwave signals can be generated. The apparatus can produce binary, quaternary or multi-nary phase coding microwave signals. The generated phase coding microwave signals are wide in frequency adjustable scope, and have a great time-bandwidth product. A conventional phase coding microwave signal generation mode in the electric field is restricted by the bottleneck of the rate and the bandwidth of an electronic device, and the cost of generation of high frequency signals is extremely high or high frequency signals cannot be produced, the time-bandwidth product is limited, the reconstructiblity and the frequency adjustability of a system are poor, etc. The apparatus of the invention helps to overcome the above problems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
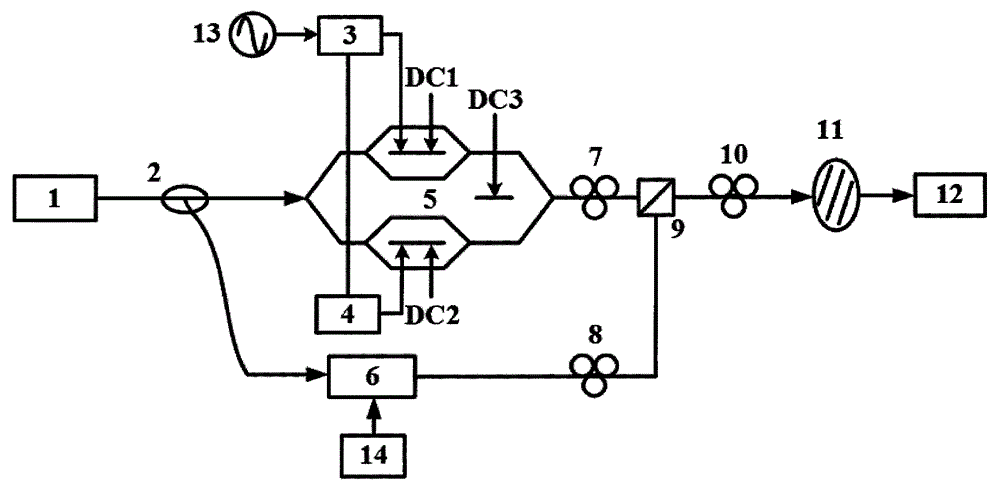
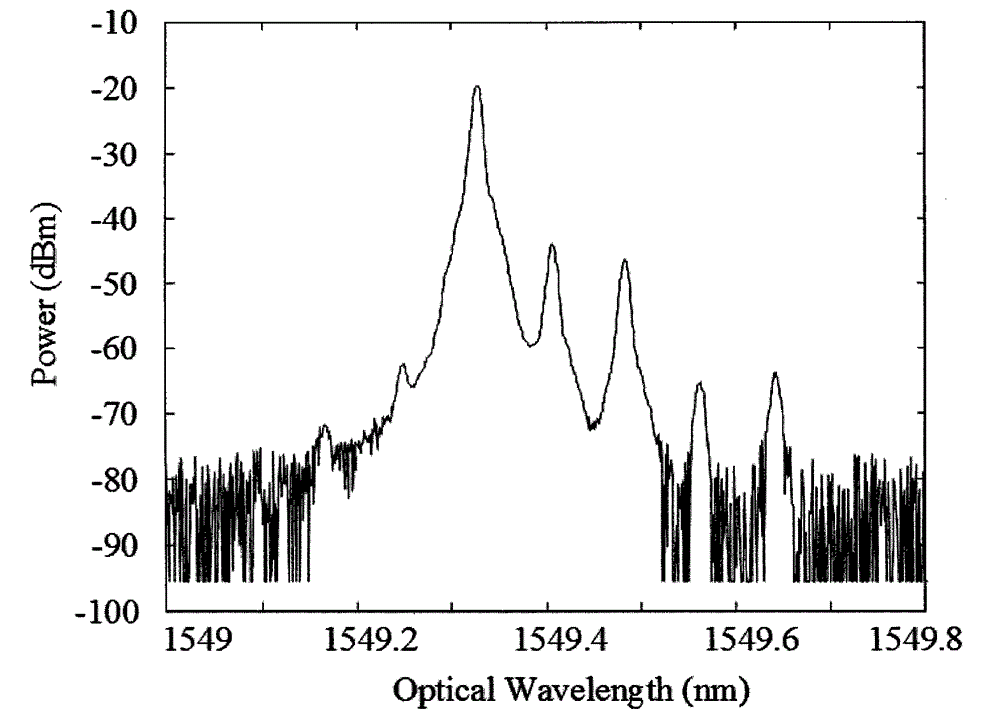
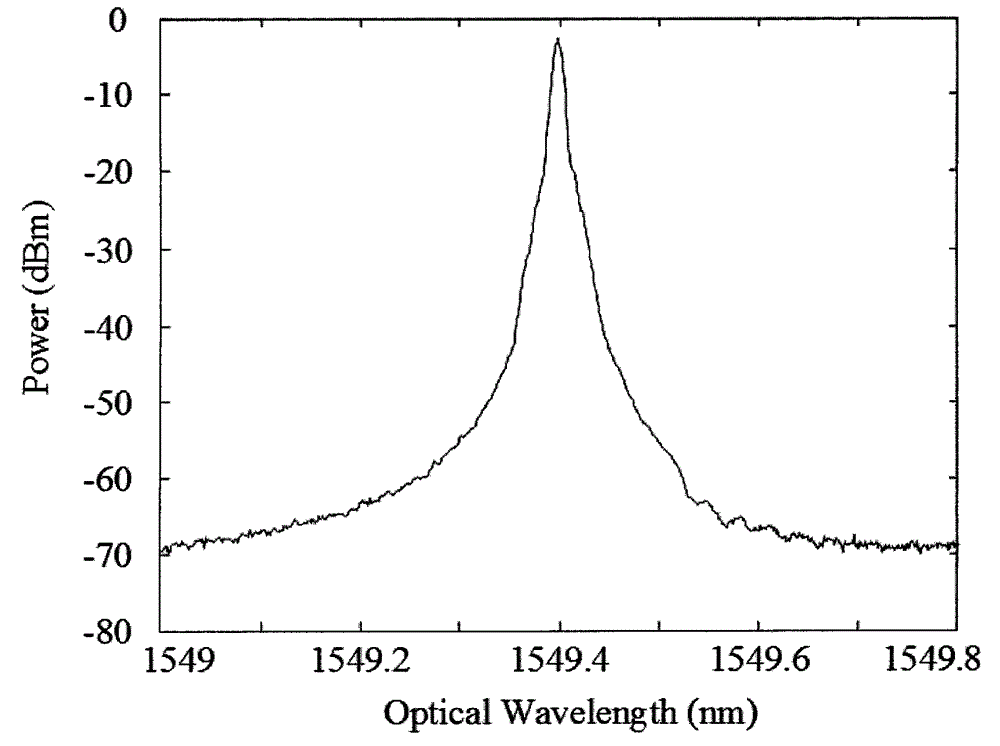
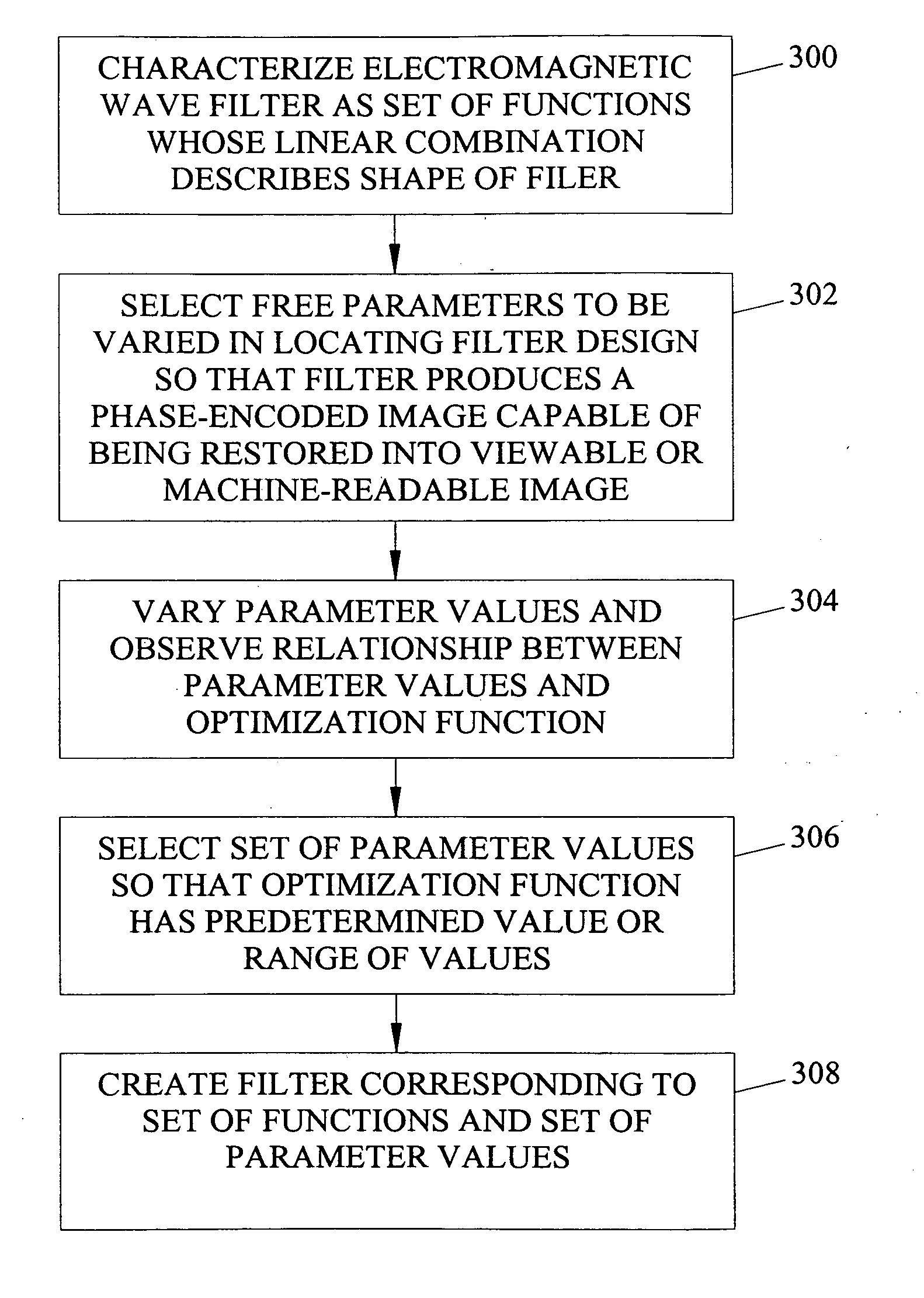
Methods and systems for designing electromagnetic wave filters and electromagnetic wave filters designed using same
InactiveUS20050204329A1Minimize spatially varying blurImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionSystems designComputational physics
Methods and systems for designing electromagnetic wave filters and electromagnetic wave filters designed using the methods and systems are disclosed. In one method, functions are selected whose linear combination define the surface of a filter for producing a desired phase-encoded image. Free parameter values are selected for the function and are varied. The values of the free parameters are observed with regard to an optimization function. Final values of the free parameters are selected based on the optimization function having a specific value or range of values.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
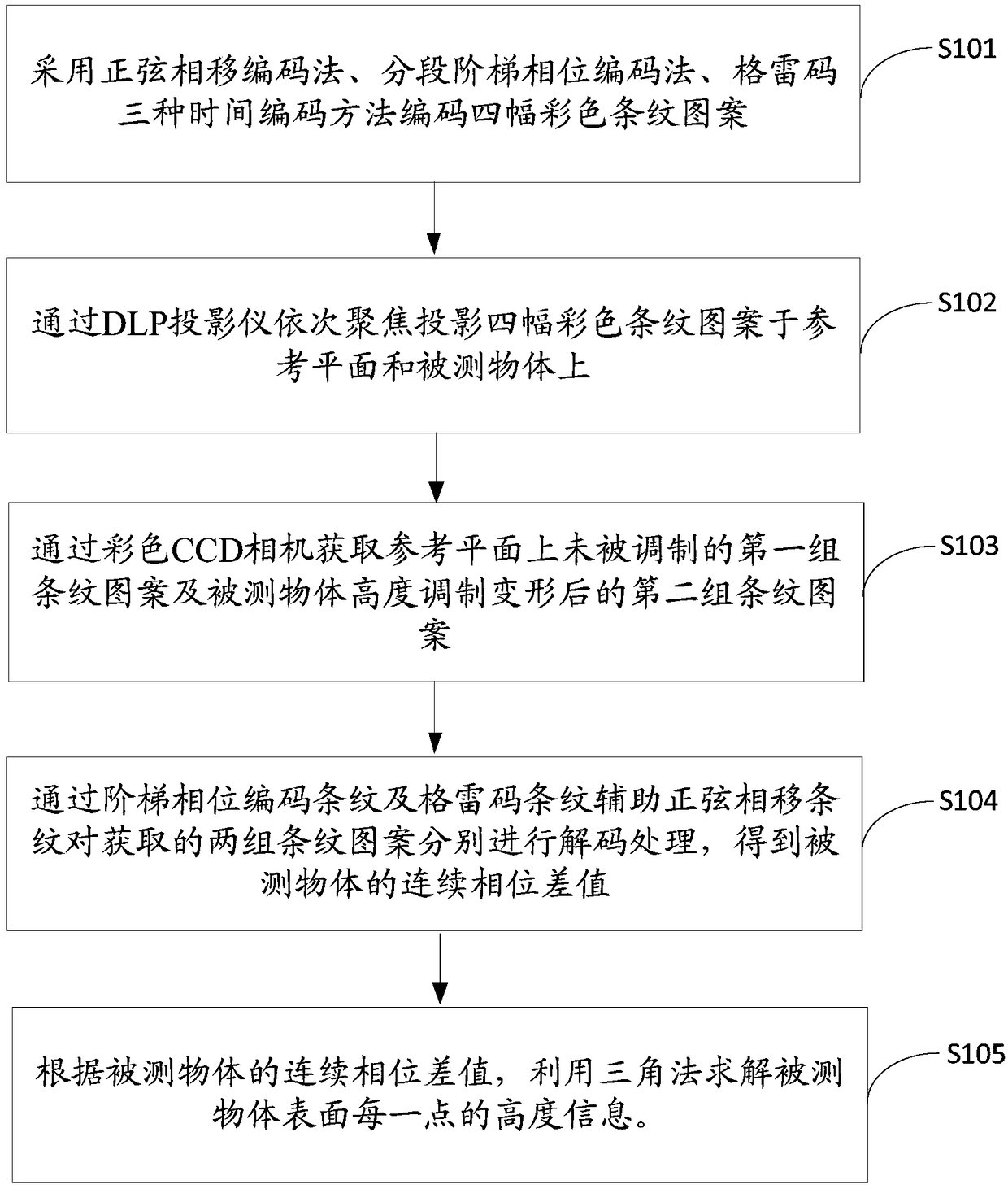
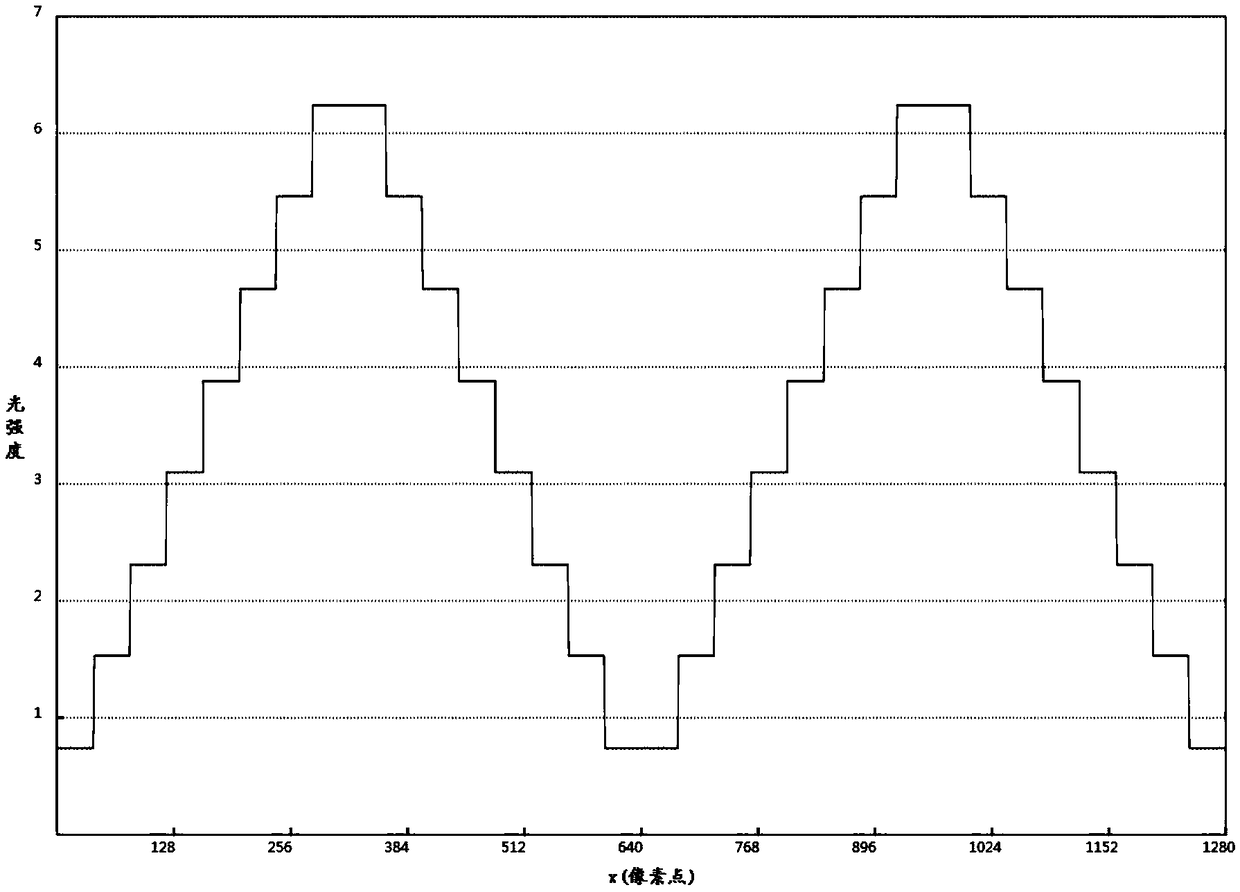
Color structured light three-dimensional measuring method, apparatus and device, and storage medium
The invention discloses a color structured light three-dimensional measuring method, apparatus and device, and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps of coding four color stripe patterns by adopting a sinusoidal phase shift coding method, a segmented step phase coding method and Gray codes; sequentially focusing and projecting the four color stripe patterns on a reference planeand a measured object through a DLP projector; acquiring the stripe patterns which are not modulated on the reference plane and after height modulation deformation of the measured object through a color CCD camera; performing decoding processing on the two groups of the stripe patterns to obtain a continuous phase difference value of the measured object; and solving three-dimensional height information of the surface of the measured object by utilizing a triangular method. Through the measuring method based on color composite coding which fuses sinusoidal phase shift coding, segmented step phase coding and the gray codes, the three-dimensional measurement can be realized by only four color patterns by means of a triangular principle; and therefore, the method is small in projection amount, high in processing speed and good in anti-jamming capability, and is suitable for fast and high-precision three-dimensional measurement of objects with the non-continuous surfaces in a static scene.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
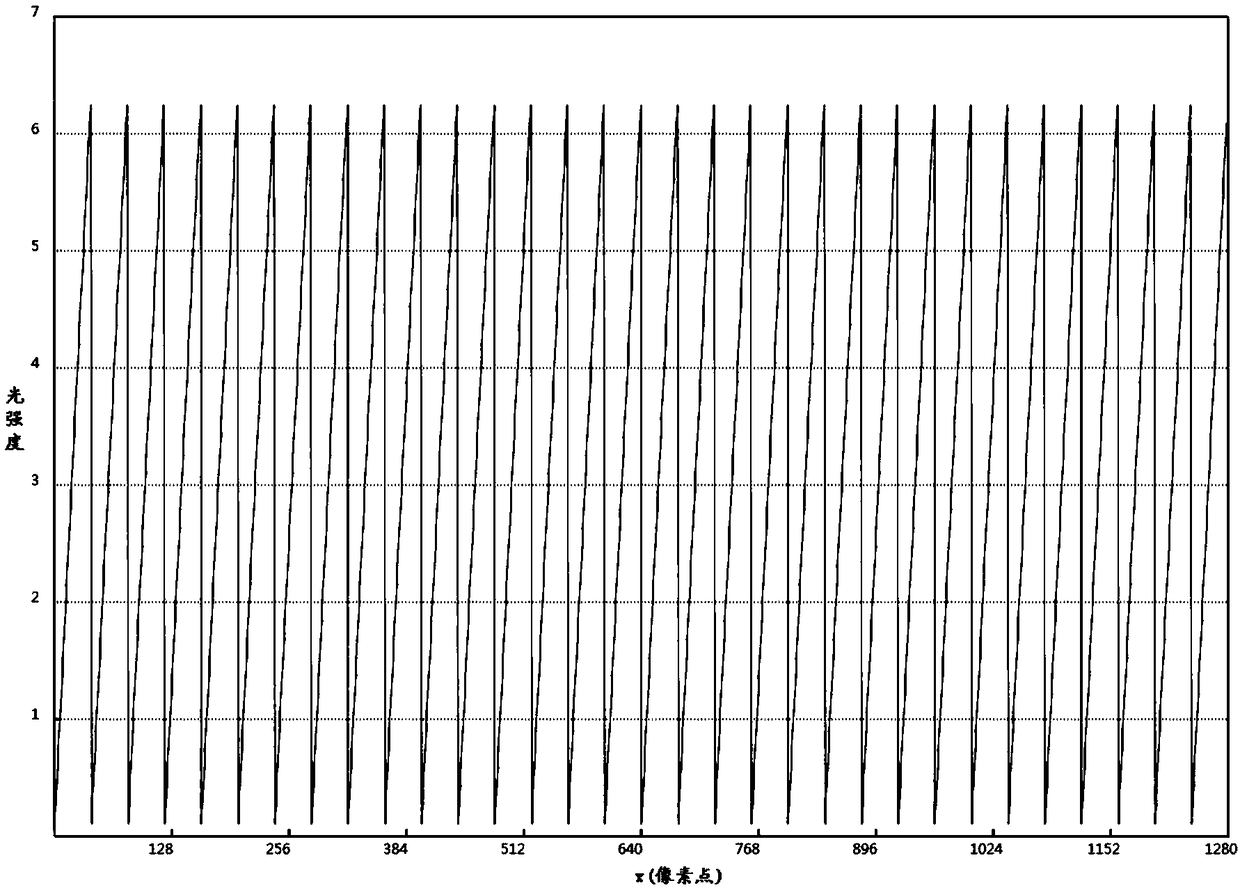
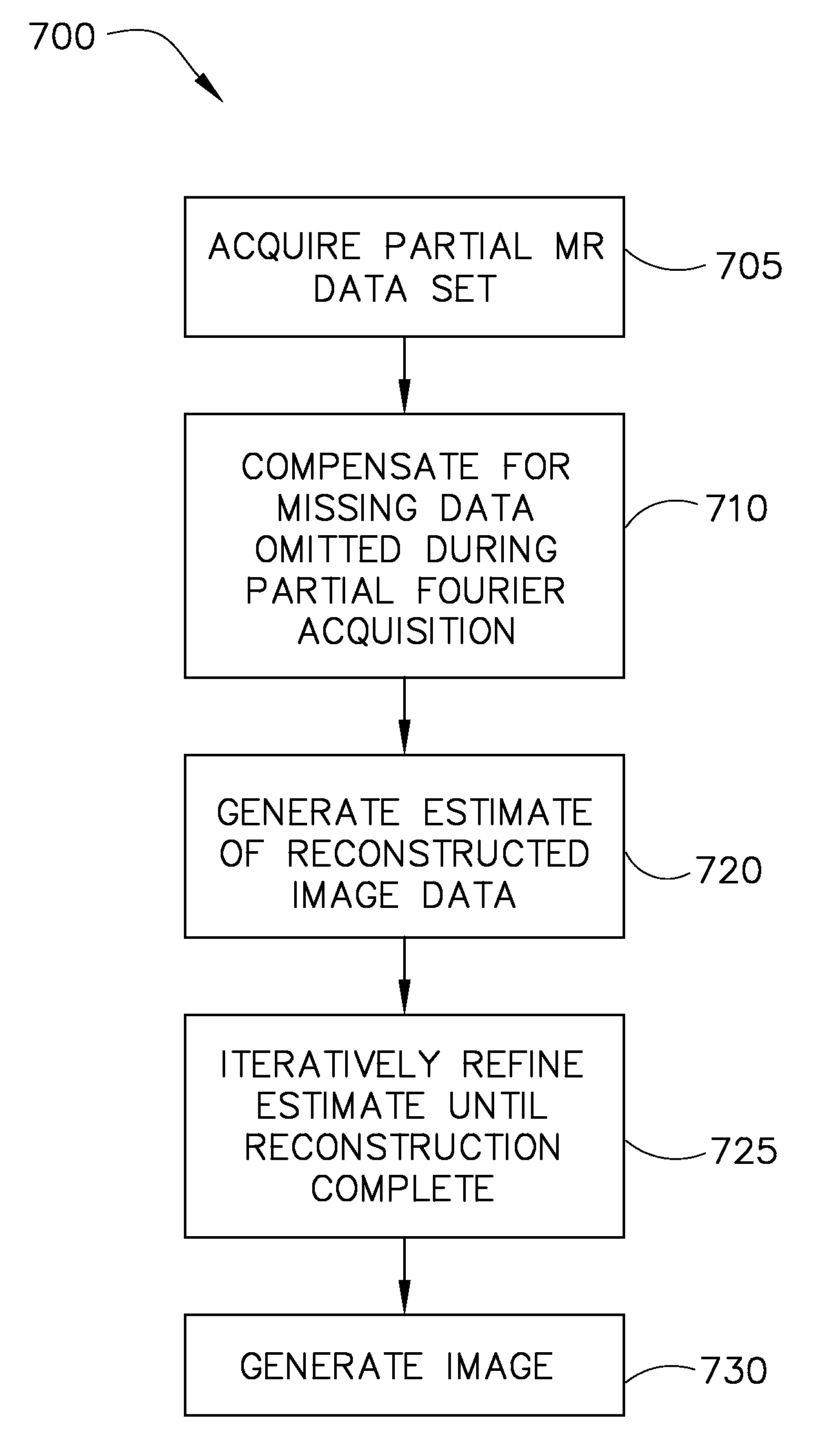
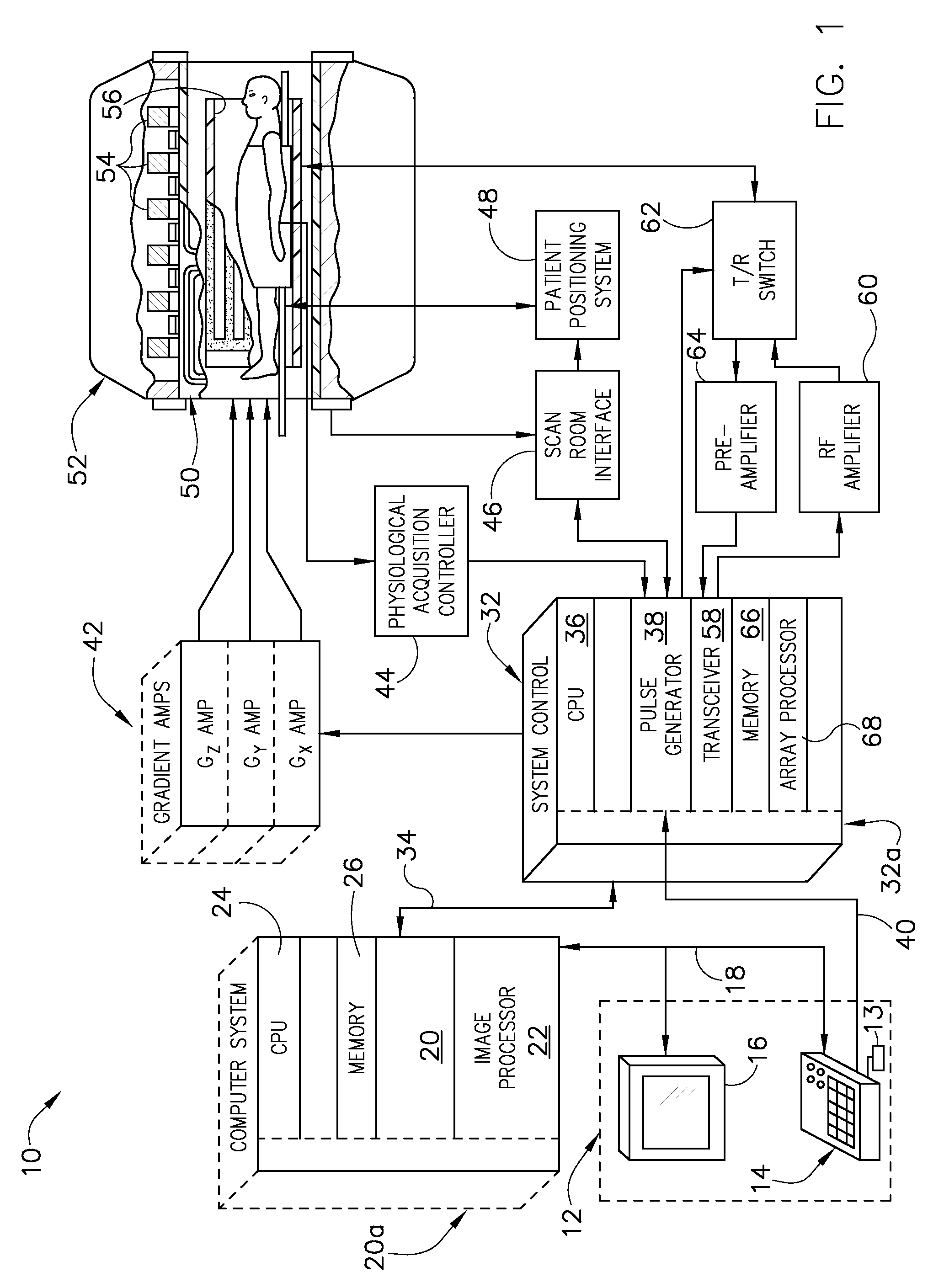
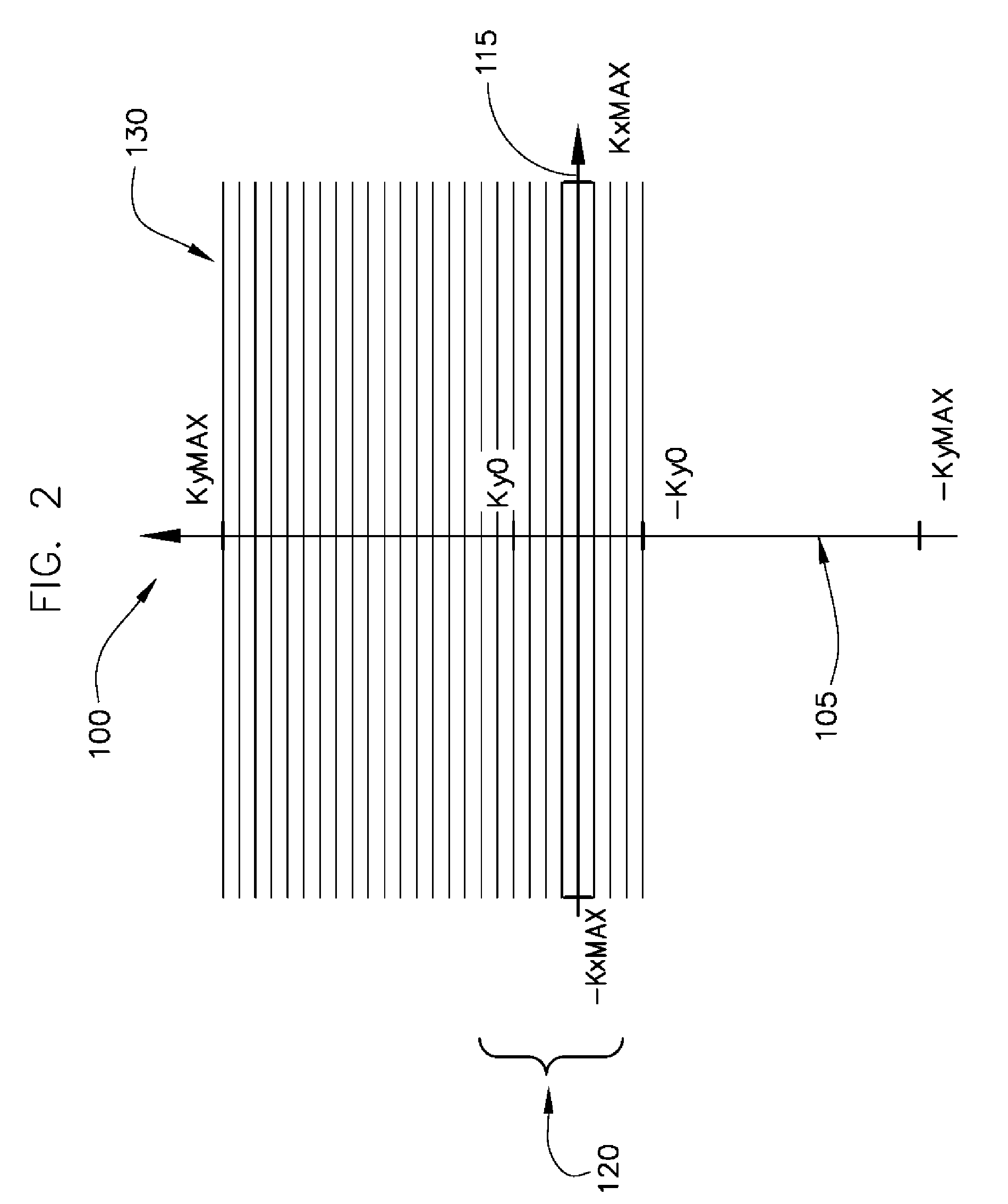
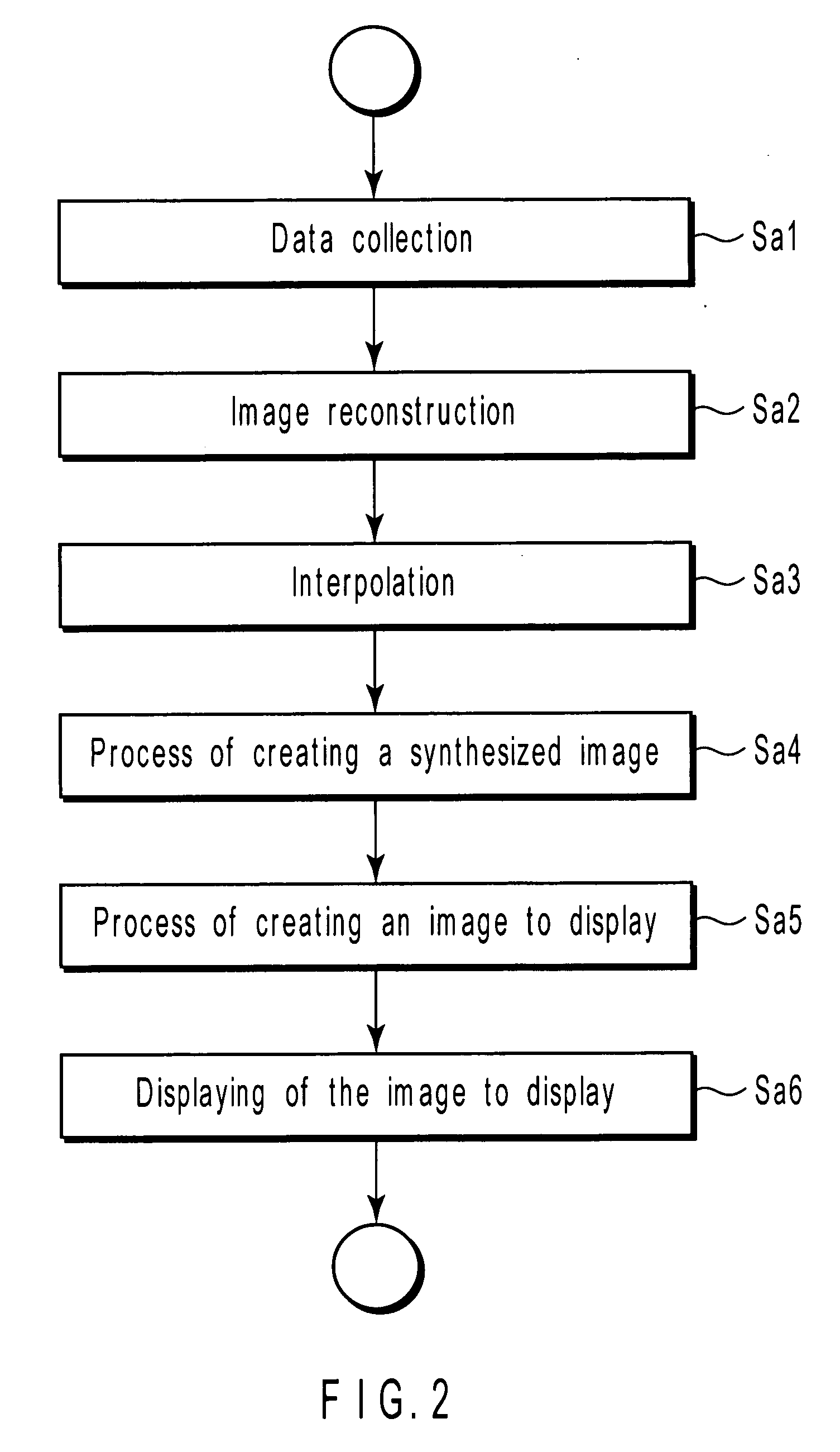
System and method for reducing MR scan time using partial fourier acquisition and compressed sensing
A system and method for reducing the scan time of an MR imaging system using a data acquisition technique that combines partial Fourier acquisition and compressed sensing includes a computer programmed to acquire a partial MR data set in k-space along a phase encoding direction, the data set having missing data in the phase encoding direction due to the omission of phase encoding steps. The computer is further programmed to generate an estimate of a reconstructed image, compensate the partial MR data set for the missing data, and reconstruct an MR image by iteratively minimizing the total squared difference between the k-space data of the estimate of the reconstructed image and the measured k-space data of the compensated partial MR data set.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rapid Inversion of Electromagnetic Reconnaisance Survey Data
ActiveUS20090306900A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceControlled source electro-magneticSituated computing
Method for rapid inversion of data from a controlled-source electromagnetic survey of a subterranean region. Selected (51) common-receiver or common-source gathers of the data are reformed into composite gathers (52) by summing their data. Each composite gather is forward modeled (in the inversion process) with multiple active source locations (53). Computer time is reduced in proportion to the ratio of the total number of composite gathers to the total number of original common-receiver or common-source gathers. The data may be phase encoded to prevent data cancellation. Methods for mitigating loss of far offset information by data overlap in the summing process are disclosed.
Owner:JOHN MEZZALINGUA ASSOC INC
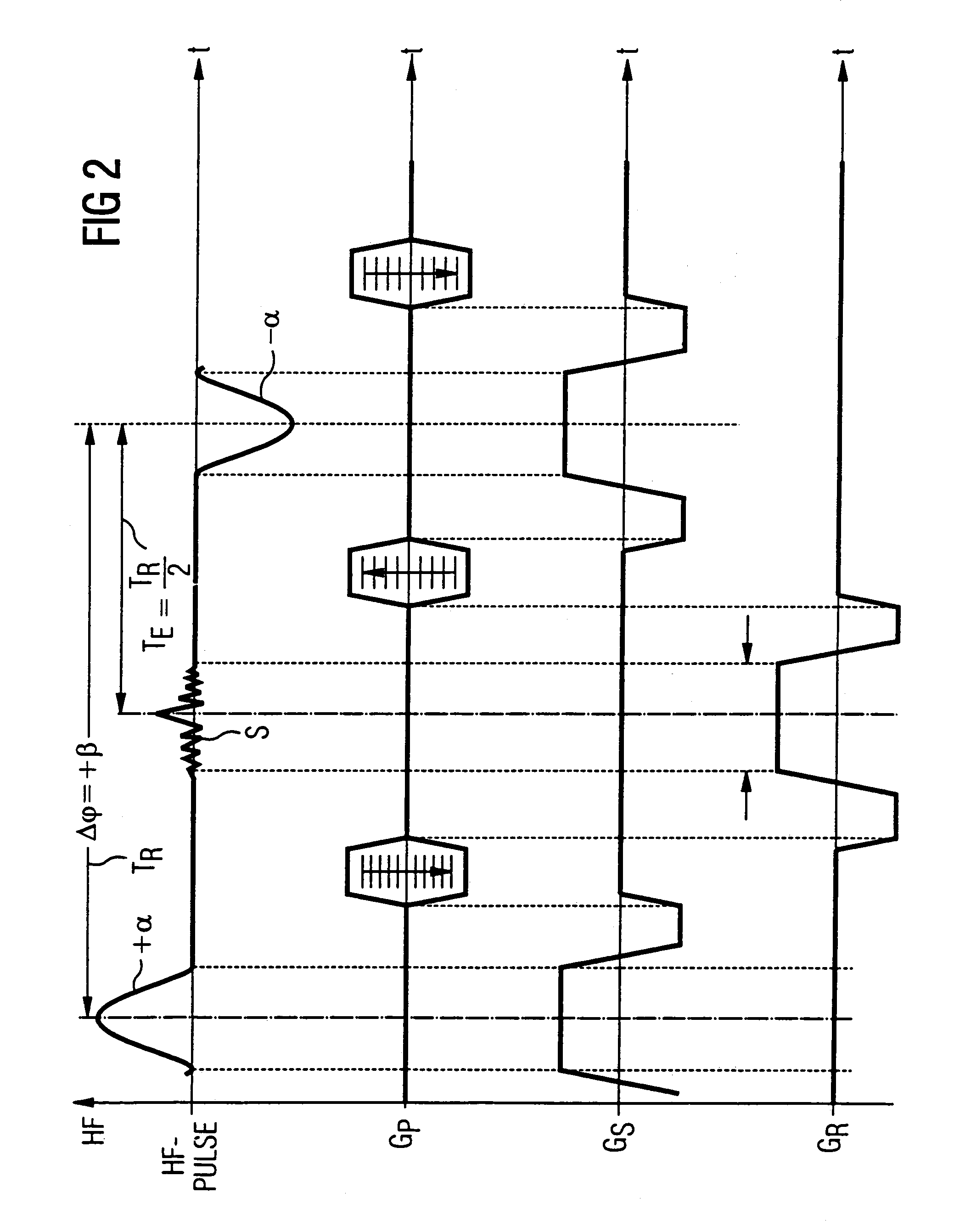
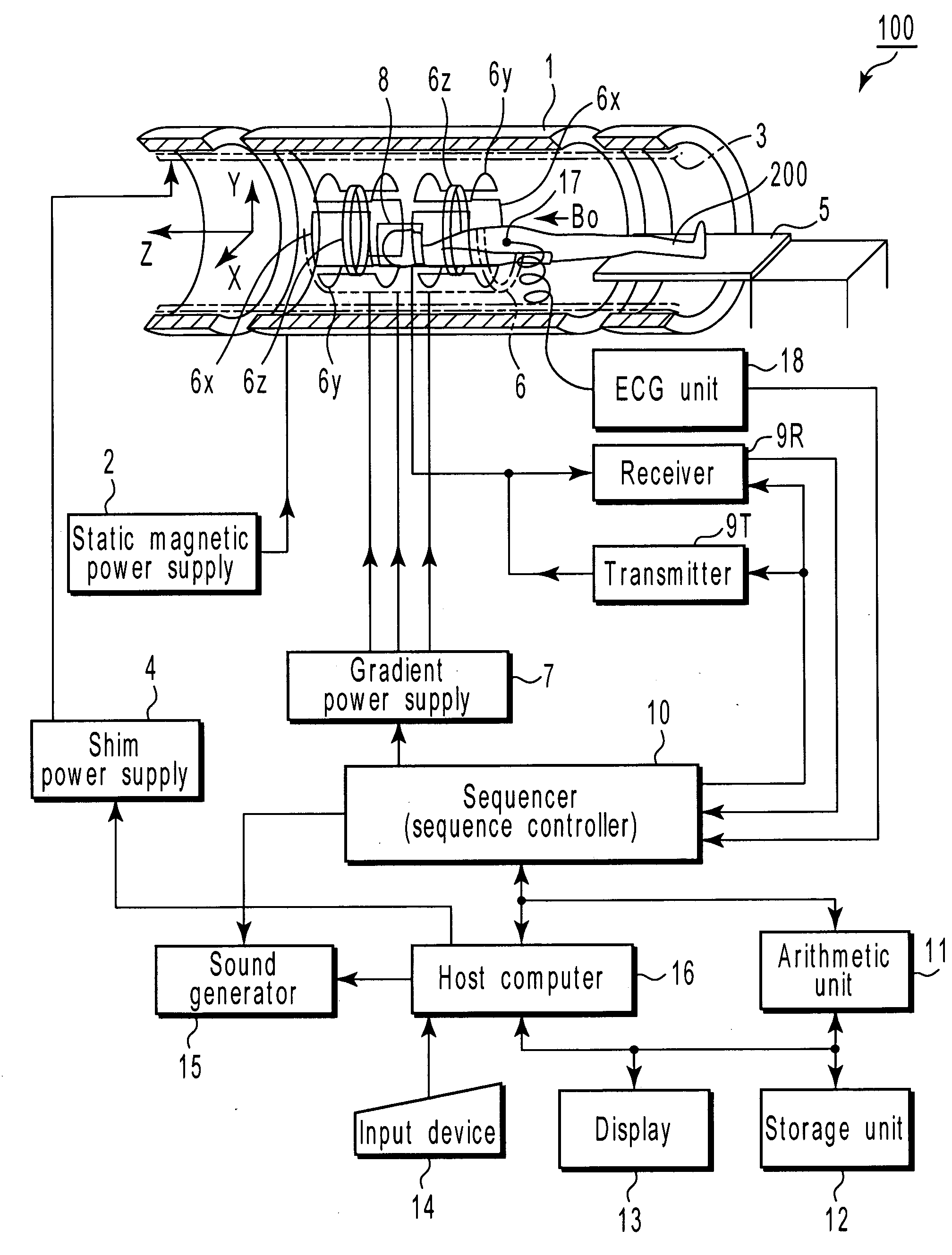
Magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method employing a true FISP sequence with improved off-resonant behavior of two spin ensembles
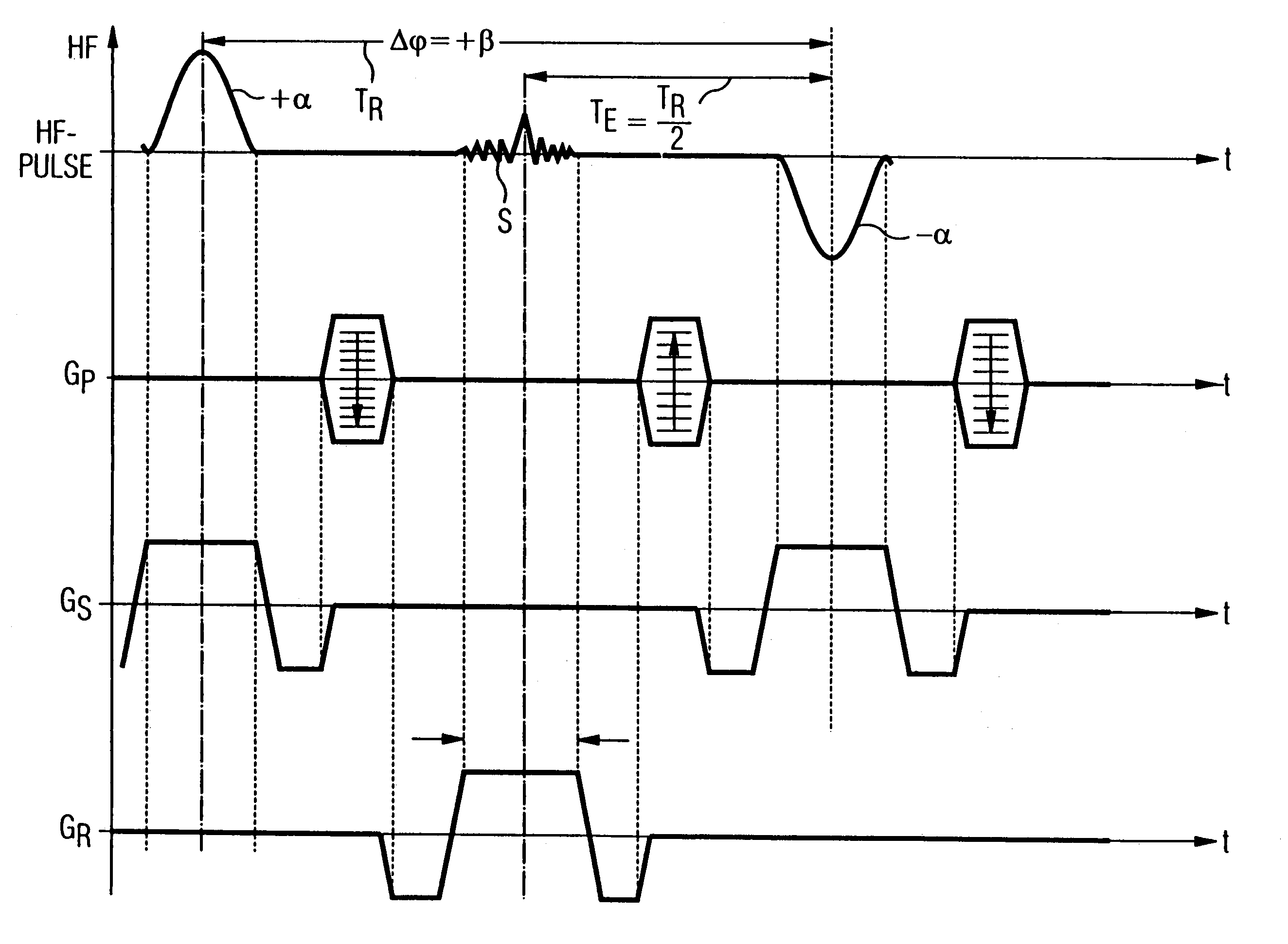
InactiveUS7020509B2Significant differenceImprove stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData setPhase Code
In a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus employing a FISP pulse sequence, the pulse sequence is repeated with a repetition time TR with different phase-coding gradient directions and with an alternating operational sign of the flip angle α. The gradient pulse trains are thereby completely balanced. A phase increment ΔΦ=β is generated in addition to the alternating operational sign of the flip angle α between successive excitation pulses, so that the steady state signals for a first and a second spin ensemble optionally have either identical or reversed signal polarities. A first dataset on the basis of identical signal polarities and a second dataset on the basis of reversed signal polarities are obtained by means of the free selection of the mutual signal polarities. A pure image of the first and the second spin ensembles is thus obtained by the addition and / or subtraction of the first and second datasets.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Frame synchronizing method for time-domain synchronous orthogonal frequency-division duplex receiver and system
Characters are that TDS - OFDM frame synchronization PN sequence adopted in the invention based on a group of displaced m sequence. Sliding correlation method is utilized to calculate correlativity between oversampled TDS - OFDM signal and local PN sequence. Peak detection is adopted to test correlative peak and location. Phase encoding for adjacent signal frames determines phase of PN sequence in each signal frame. Then, third correlative peak is utilized to determine whether signal is in real synchronization; if no, code capture program is restarted. Experimental verifies that after each frame is captured, timing error is ensured within minus or plus sampling interval / 2 in order to carry out timing track correctly.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
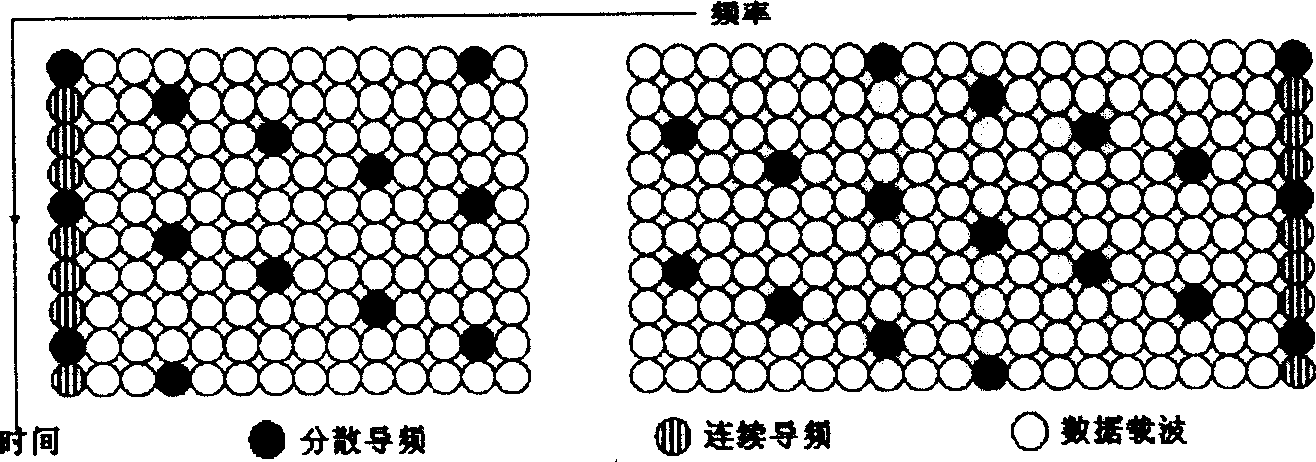
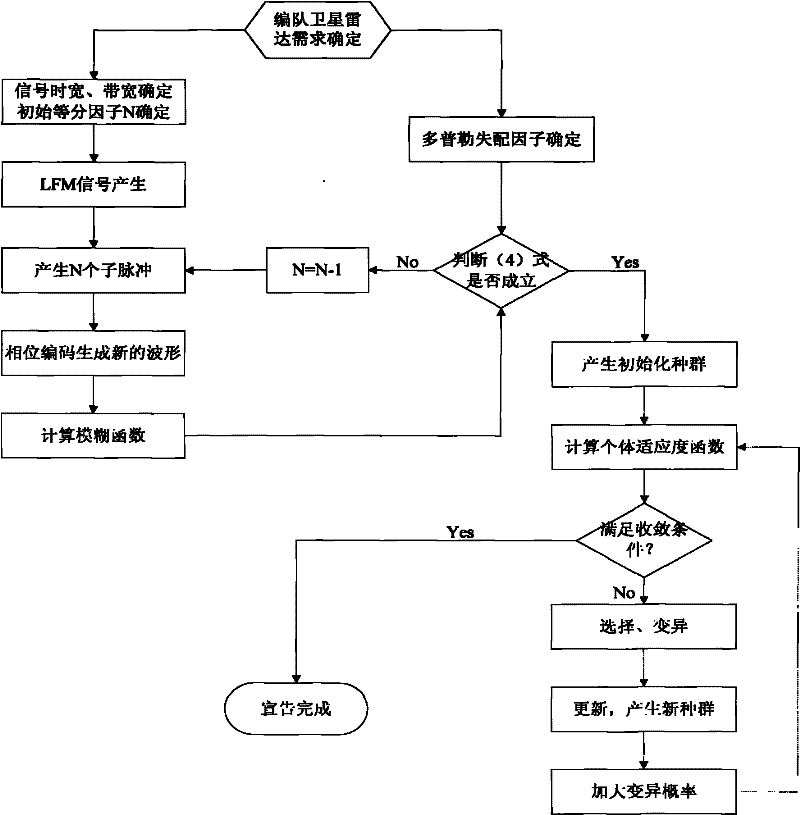
Orthogonal waveform designing method for formation flying satellites SAR (synthetic aperture radar)
InactiveCN102540187AReduce autocorrelation sidelobesReduce cross-correlation peaksRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarPeak value
The invention relates to a waveform design for a formation flying satellites SAR (synthetic aperture radar), and provides an orthogonal waveform designing method which is used for carrying out phase encoding for linear frequency modulation (LFM) signals. The orthogonal waveform designing method includes generating a linear frequency modulation signal at first, dividing the linear frequency modulation signal into N parts according to equal time intervals to form N sub-pulses, carrying out random phase encoding for each sub-pulse by M times according to the number M of the formation flying satellites, establishing an ambiguity function expression, calculating cluster tolerance xi meeting formation flying satellite synthetic aperture radar Doppler mismatch, finding out a critical N value meeting requirements by the aid of a searching comparison method, finally selecting energy and functions which are in autocorrelation and cross-correlation as cost functions, namely fitness functions in genetic algorithm, searching code values of phase encoding of the various sub-pulses by the aid of the genetic algorithm, and finding out orthogonal waveforms after optimization at last. The waveforms have low autocorrelation side lobes, cross-correlation peak values, bandwidth occupation ratio and Doppler mismatch, and excellently suppress echo signal interferences among different space-borne SARs.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Magnetic resonance parallel imaging method and magnetic resonance imaging system
ActiveCN106597333AReduce mistakesInhibition Sensitive FunctionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringIntermediate imageImaging quality
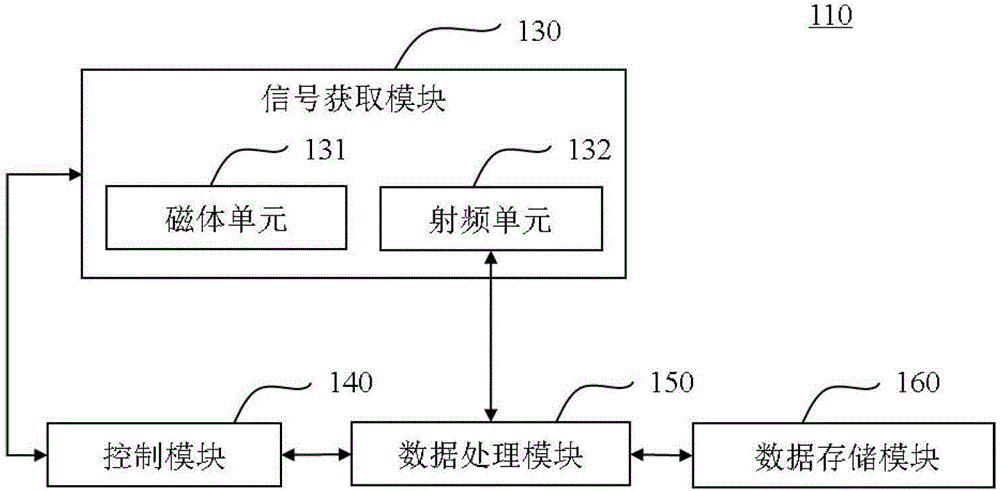
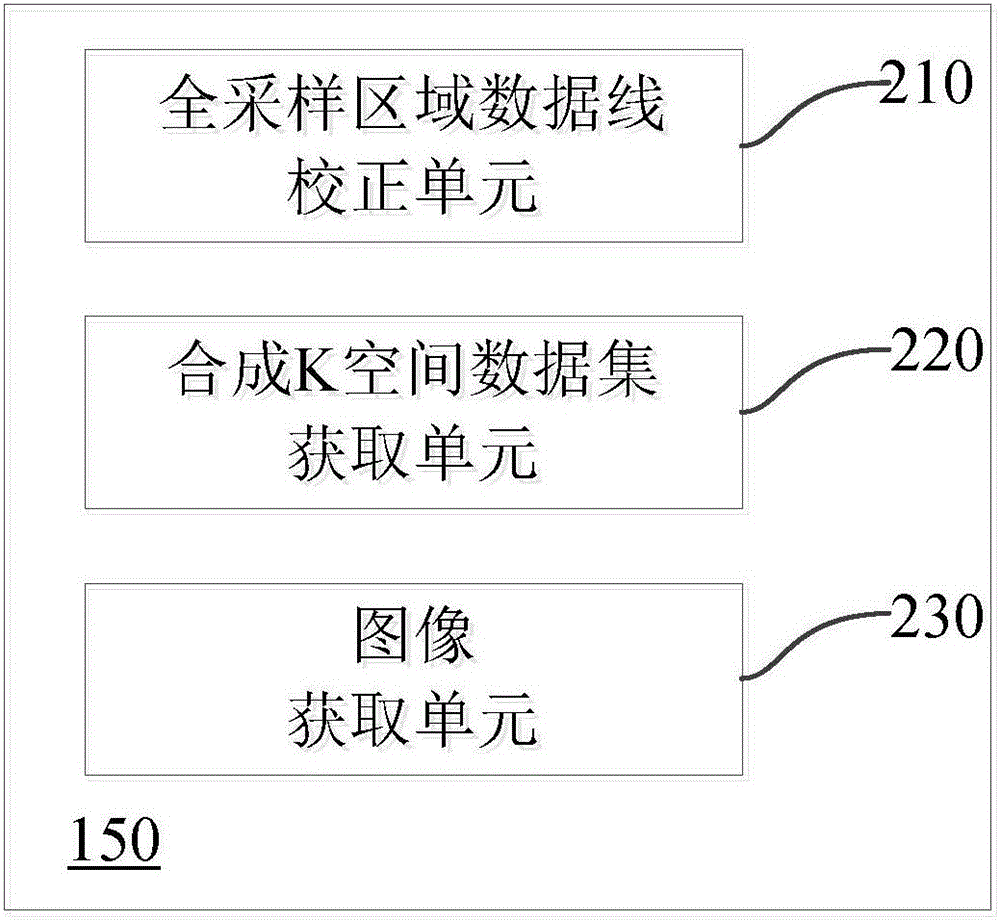
The application discloses a magnetic resonance parallel imaging method. The method comprises: a target region is excited by using a radio-frequency pulse and a plurality of RF coils are used for collecting a magnetic resonance signal of the target region; phase coding is carried out on the magnetic resonance signal to obtain a plurality of data lines and K space is filled with the plurality of data lines, wherein the K space includes an all-sampling region and an under-sampling region; an intermediate image is obtained based on the data lines in the all-sampling region and pretreatment is carried out on the intermediate image; on the basis of the intermediate image after pretreatment, a correction data line in the all-sampling region is obtained; according to the correction data line in the all-sampling region, data lines of the under-sampling region are reconstructed and a synthesized K space data set is obtained; and according to the synthesized K space data set, a magnetic resonance image of a target region of a subject is obtained. With the method, the motion artifact can be suppressed; and the image quality can be improved. In addition, the application also provides a magnetic resonance imaging system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
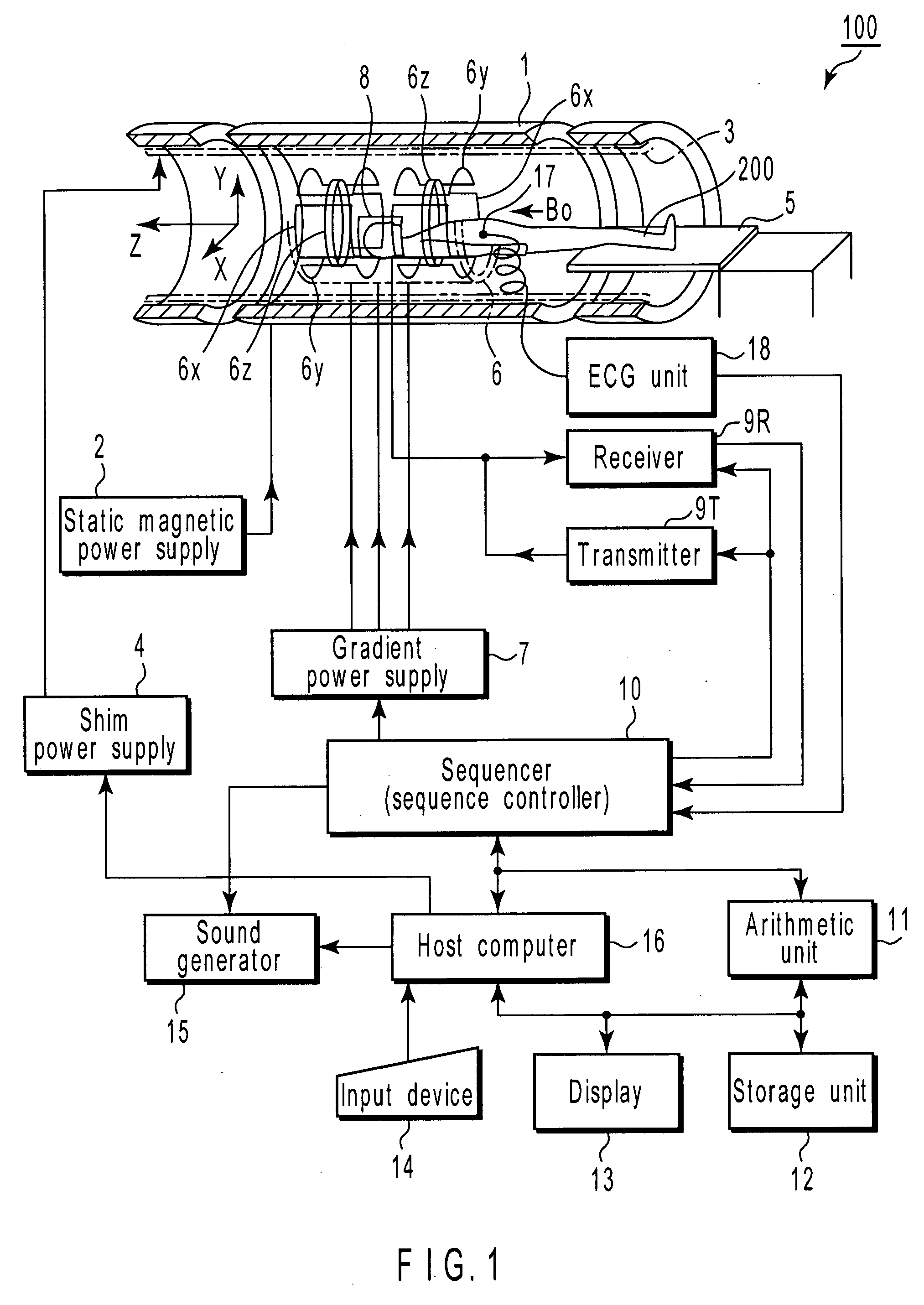
Magnetic-resonance image diagnostic apparatus and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20080071167A1Improve accuracyImprove abilitiesMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPulse sequenceImaging diagnostic
A magnetic resonance imaging diagnostic apparatus includes a generating unit which generates a slice gradient magnetic field, a phase-encode gradient magnetic field and a read-out gradient magnetic field that extend in a slice axis, a phase-encode axis and a read-out axis, respectively, a setting unit which sets a dephase amount for weighting a signal-level decrease resulting from flows in the arteries and veins present in a region of interest of a subject, with respect to at least one axis selected form the slice axis, phase-encode axis and read-out axes, and a control unit which controls the generating unit by using a pulse sequence for a gradient echo system, which includes a dephase gradient-magnetic-field pulse that corresponds to the dephase amount set by the setting unit for the at least one axis.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
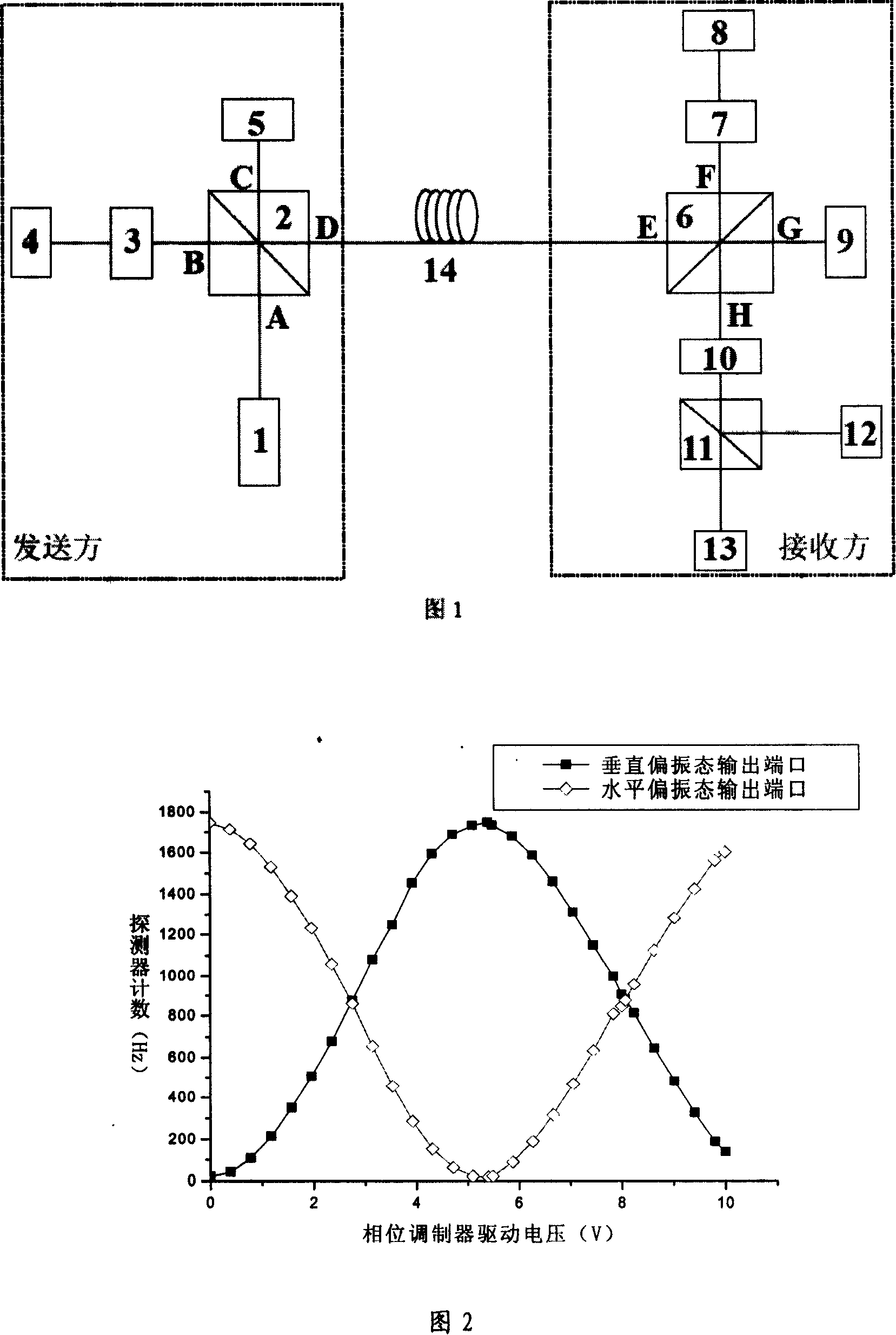
A quanta secret key distribution system for phase coding polarization detection
InactiveCN101150371ARealize unconditional security distribution systemSimple structureKey distribution for secure communicationCoupling light guidesBeam splittingQuantum channel
This invenion discloses a distribution system for quantum ciphered keys testing polarization of phase coding, in which, a transmitting party is connected with a receiving party by a quantum channel and either of which includes a same polarized beam splitting and merging device with four ports, the reflection port of which is connected with a phase modulator and a 90deg. rotation Faraday mirror orderly to form a long circuit and a transmission port of which is conneted with the 90deg. rotation Faraday mirror to form a short circuit, the incident port of the beam splitting and merging device is connected with a single photon source and the exit port is connected to a common port of a lambda / 2 wave plate and a three-port polarized splitting / merging device, the reflection and the transmission ports of which are connected with a single-photon detector.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiple-input-multiple-output radar waveform design method
ActiveCN104898113AEasy to detectImprove efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumMultiple input
A multiple-input-multiple-output radar waveform design method belongs to the radar communication technical field, and aims to provide a design method with lower related sidelobe and frequency spectrum inhibition depth, high efficiency, less consumption, high robustness, and excellent time frequency anti-interference performance; the method comprises the following steps: pre-evaluating an autocorrelation sidelobe inhibition fuzzy region according to a relative position between a strong scatterer and a to be measured object in a radar scene, thus forming a corresponding object function; analyzing MIMO radar waveform orthogonality constraint so as to form the object function satisfying the orthogonality constraint; pre-evaluating a frequency domain interference fuzzy frequency band zone according to scene prior information, thus forming the corresponding object function; forming a constant modulus phase coding waveform constrained condition; forming a loose alternative projection algorithm framework; solving a waveform design according to the loose alternative projection algorithm framework, thus providing three waveform optimization output modes. The loose alternative projection constant modulus waveform coding design enables the MIMO radar to have batter detection performance.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com