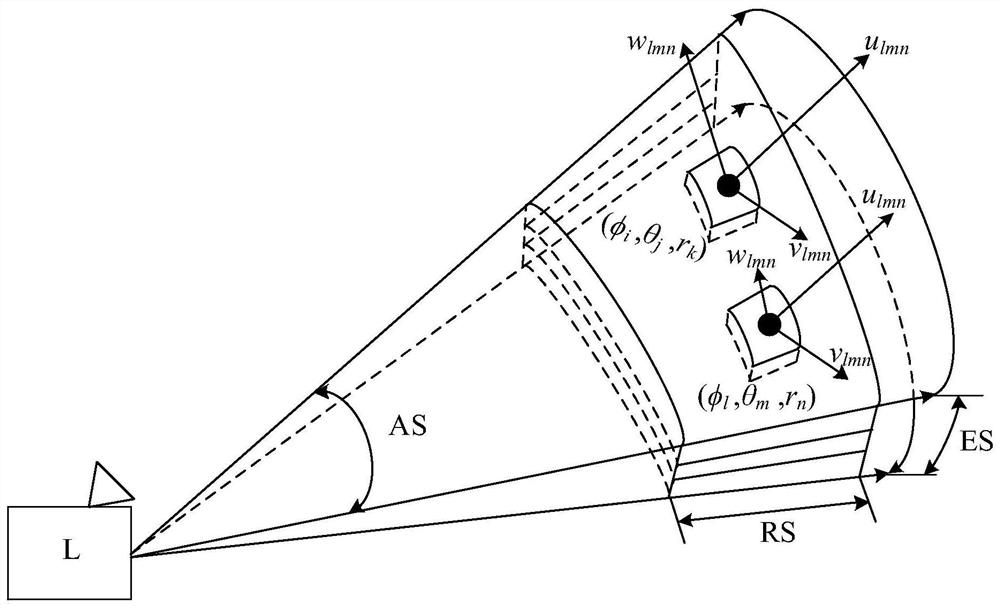
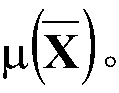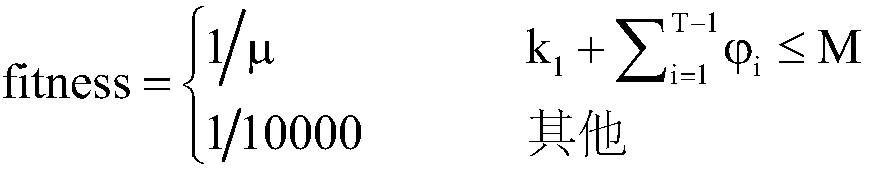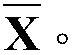Patents
Literature
35 results about "Partial fourier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
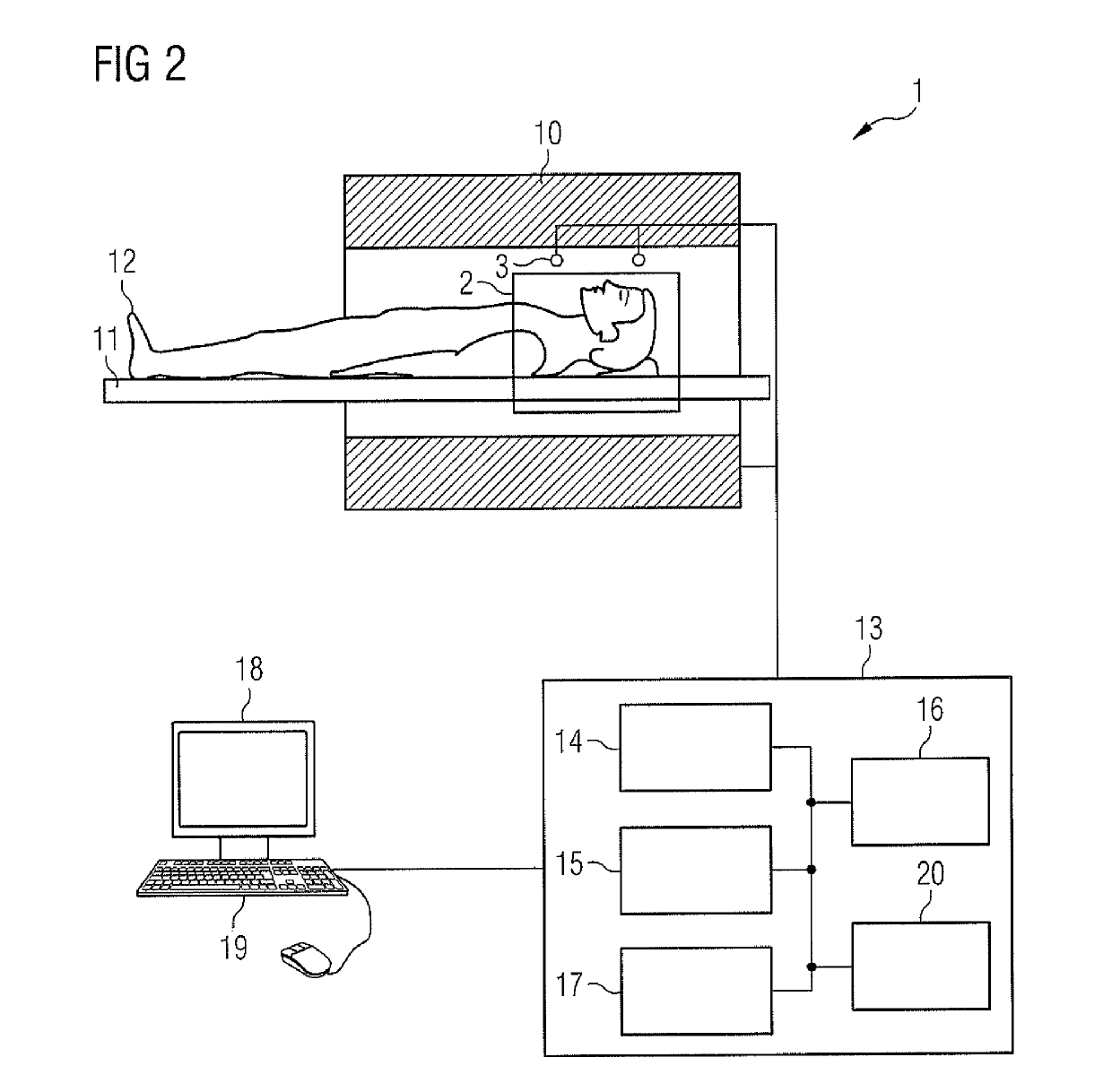
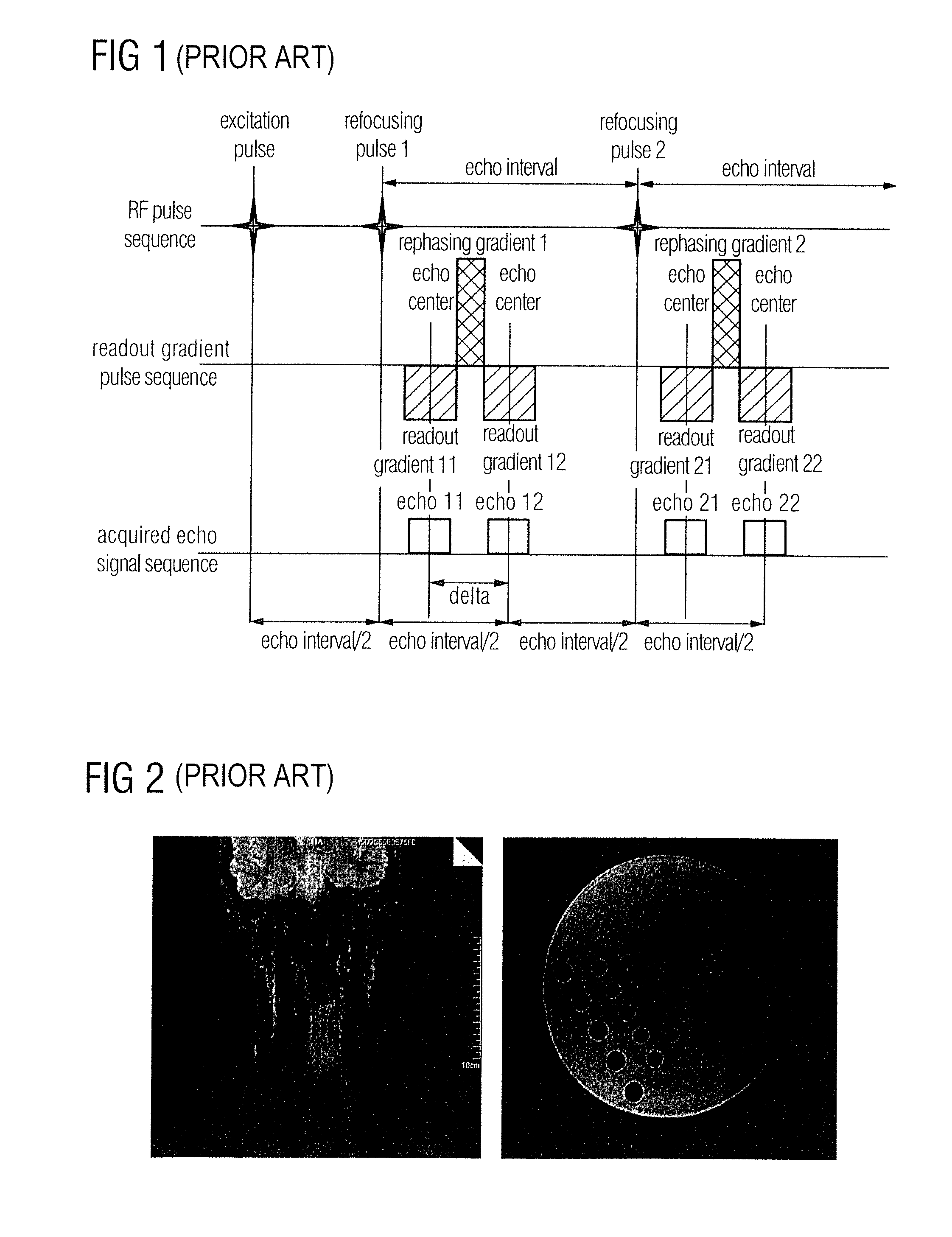
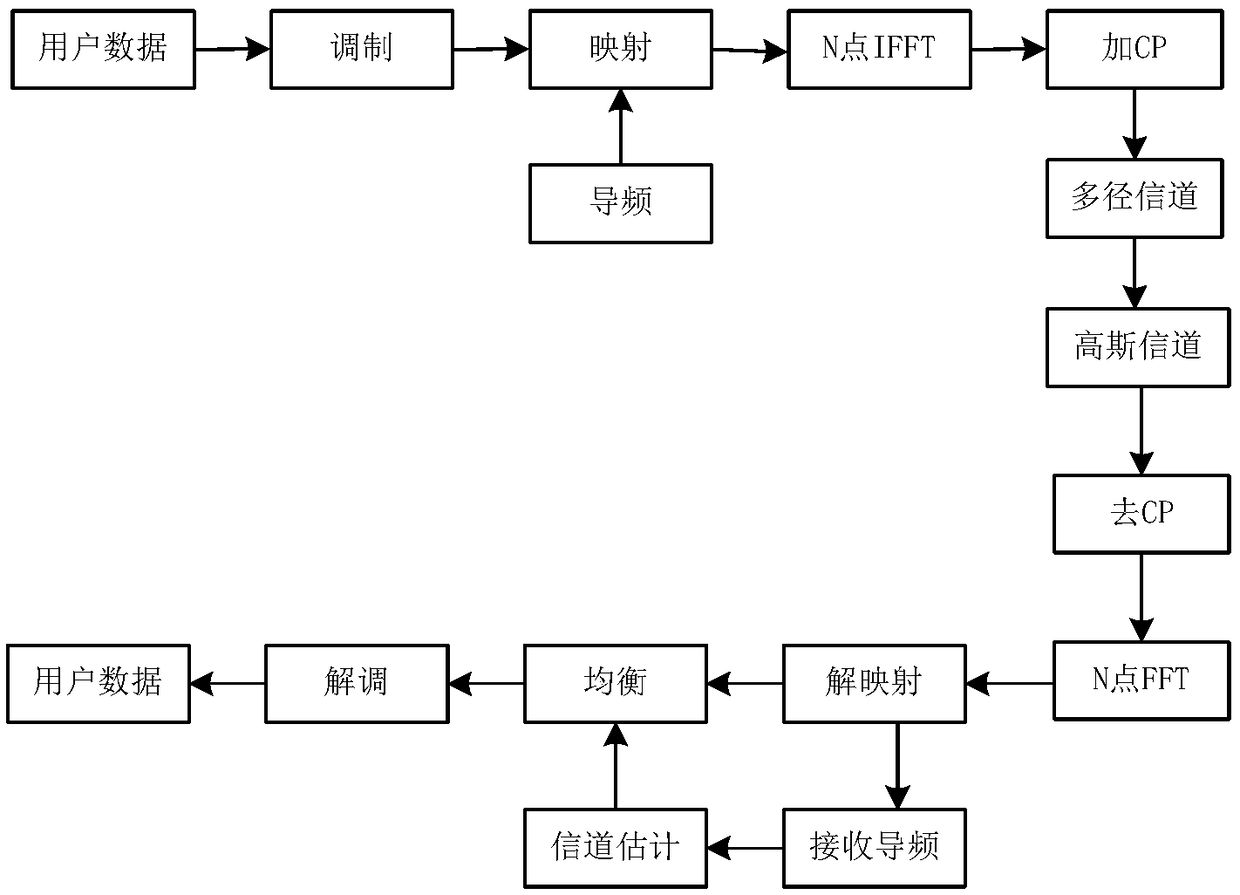
The partial Fourier technique is a modification of the Fourier transformation imaging method used in MRI in which the symmetry of the raw data in k-space is used to reduce the data acquisition time by acquiring only a part of k-space data. The symmetry in k-space is a basic property of Fourier transformation and is called Hermitian symmetry.
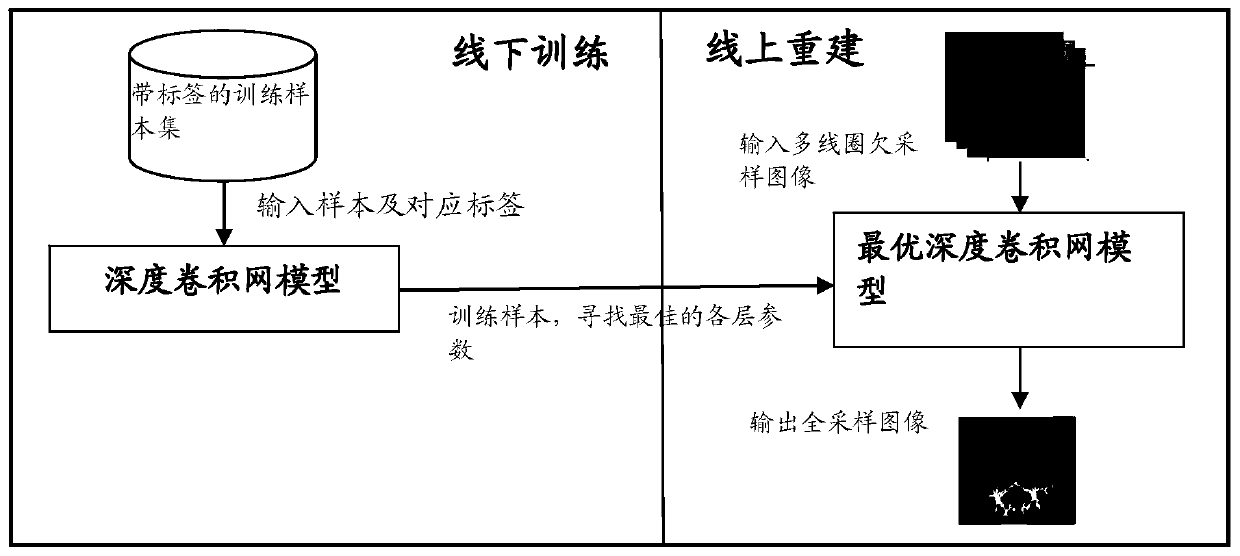
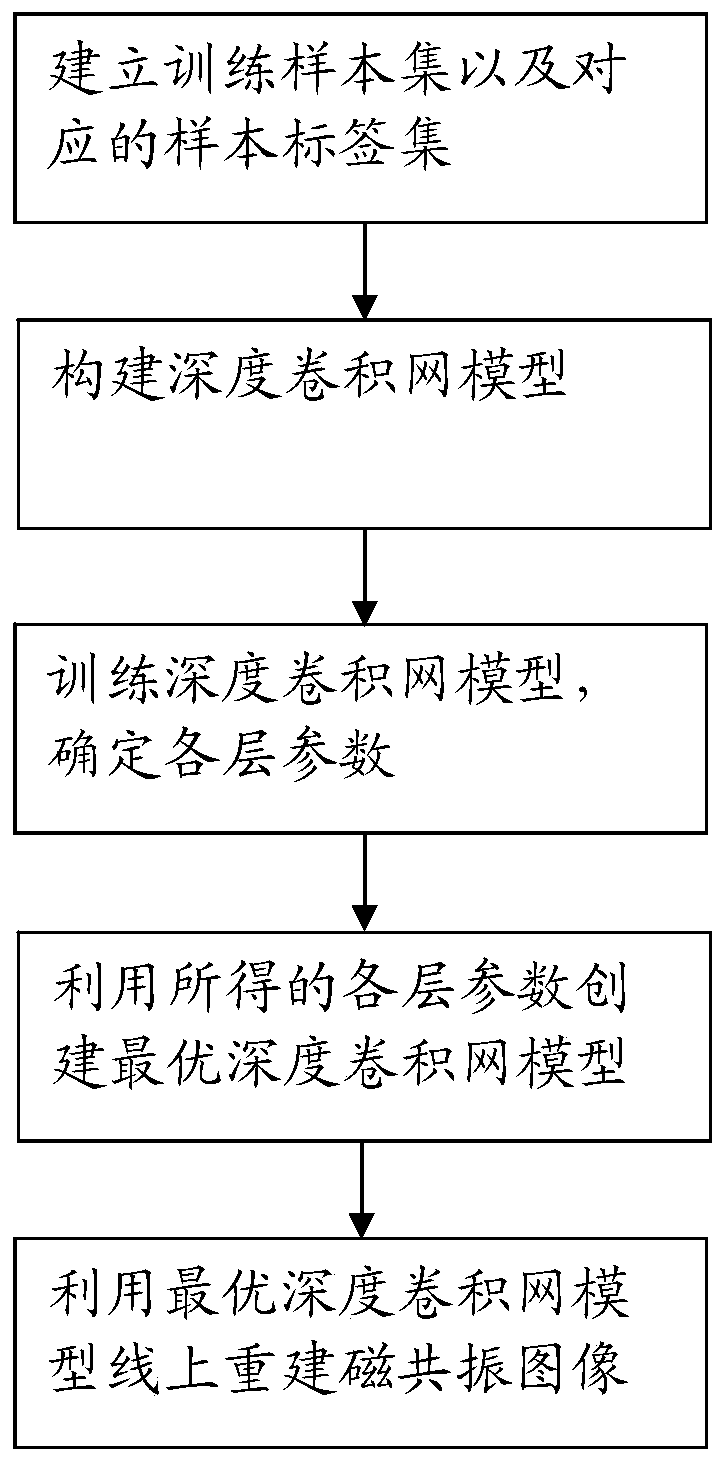
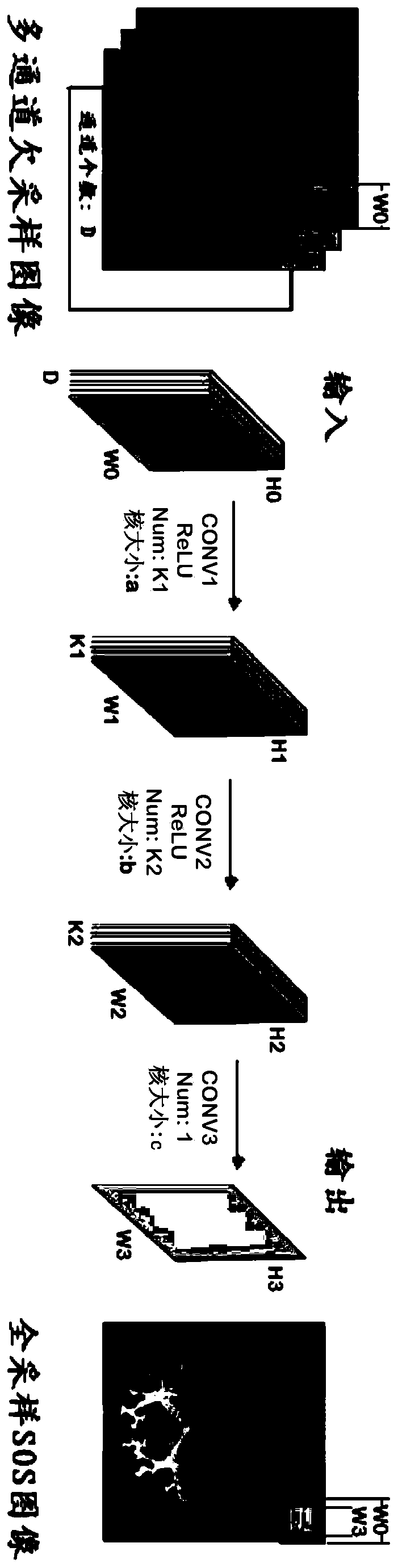
Fourier parallel magnetic resonance imaging method based on one-dimensional part of deep convolutional network
ActiveCN107064845AFast rebuildReduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAlgorithmNetwork model
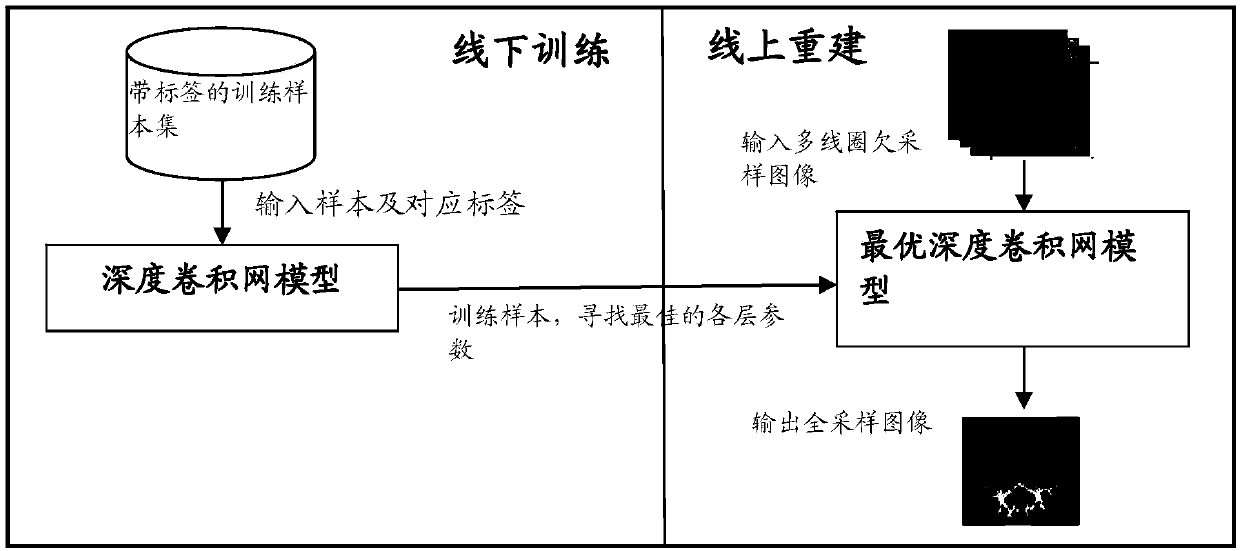
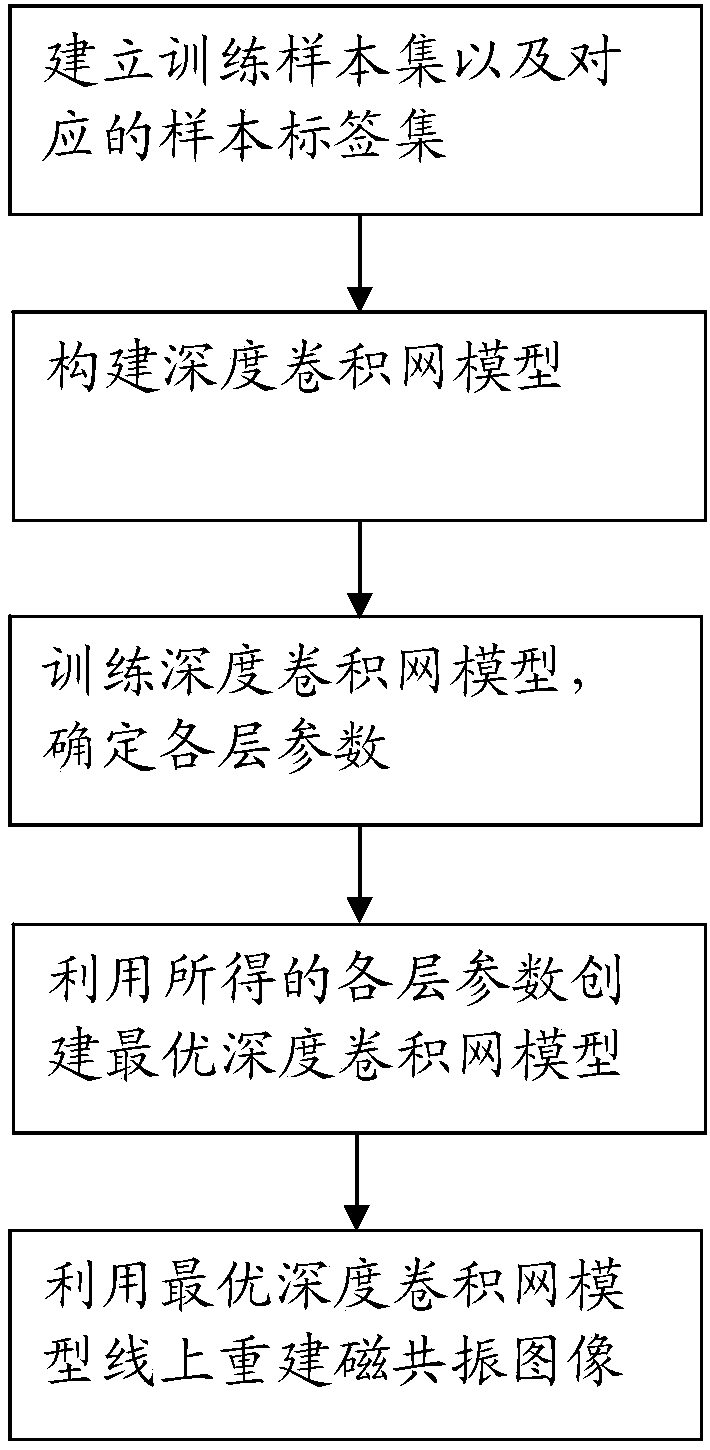
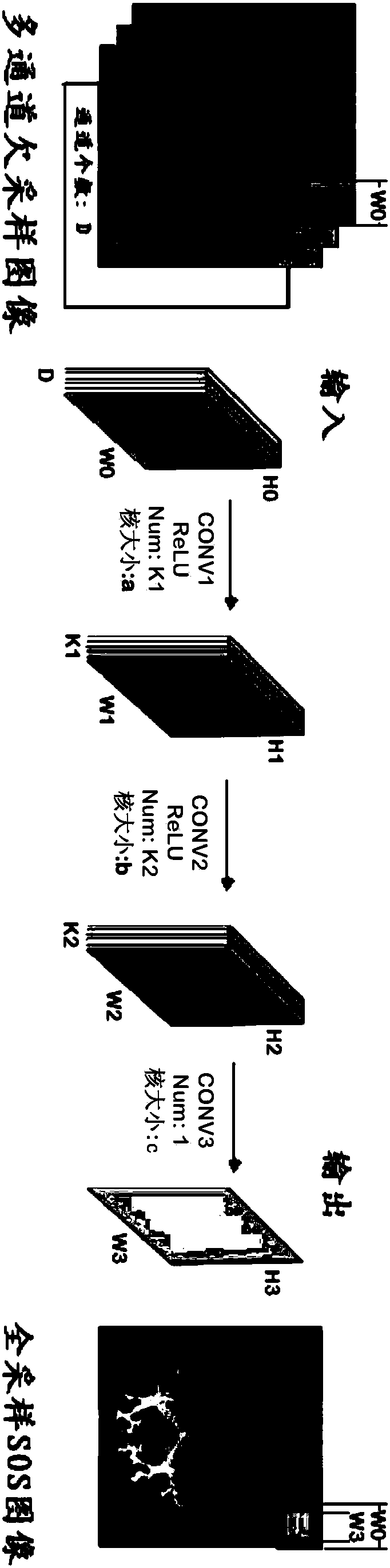
The invention relates to a Fourier parallel magnetic resonance imaging method based on a one-dimensional part of a deep convolutional network, and belongs to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging. The method comprises the following steps: a sample set for training and a sample label set are created; an initial deep convolutional network is built; a training sample of the sample set is input into an initial deep convolutional network model to perform forward propagation, an output result of the forward propagation is compared with an expect result in the sample label set, and training is performed using a gradient descent algorithm until various layer parameters maximizing the consistency between the output result and the expect result are obtained; an optimal deep convolutional network model is established by utilizing the obtained various layer parameters; and a multi-coil under-sampling image obtained through online sampling is input into the optimal deep convolutional network model, forward propagation is performed on the optimal deep convolutional network model, and a rebuilt single-channel whole-sampling image is output. A noise of the rebuilt image can be removed well, a magnetic resonance image having a good visual effect is rebuilt, and the Fourier parallel magnetic resonance imaging method has high practical value.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
System and method for reducing MR scan time using partial fourier acquisition and compressed sensing
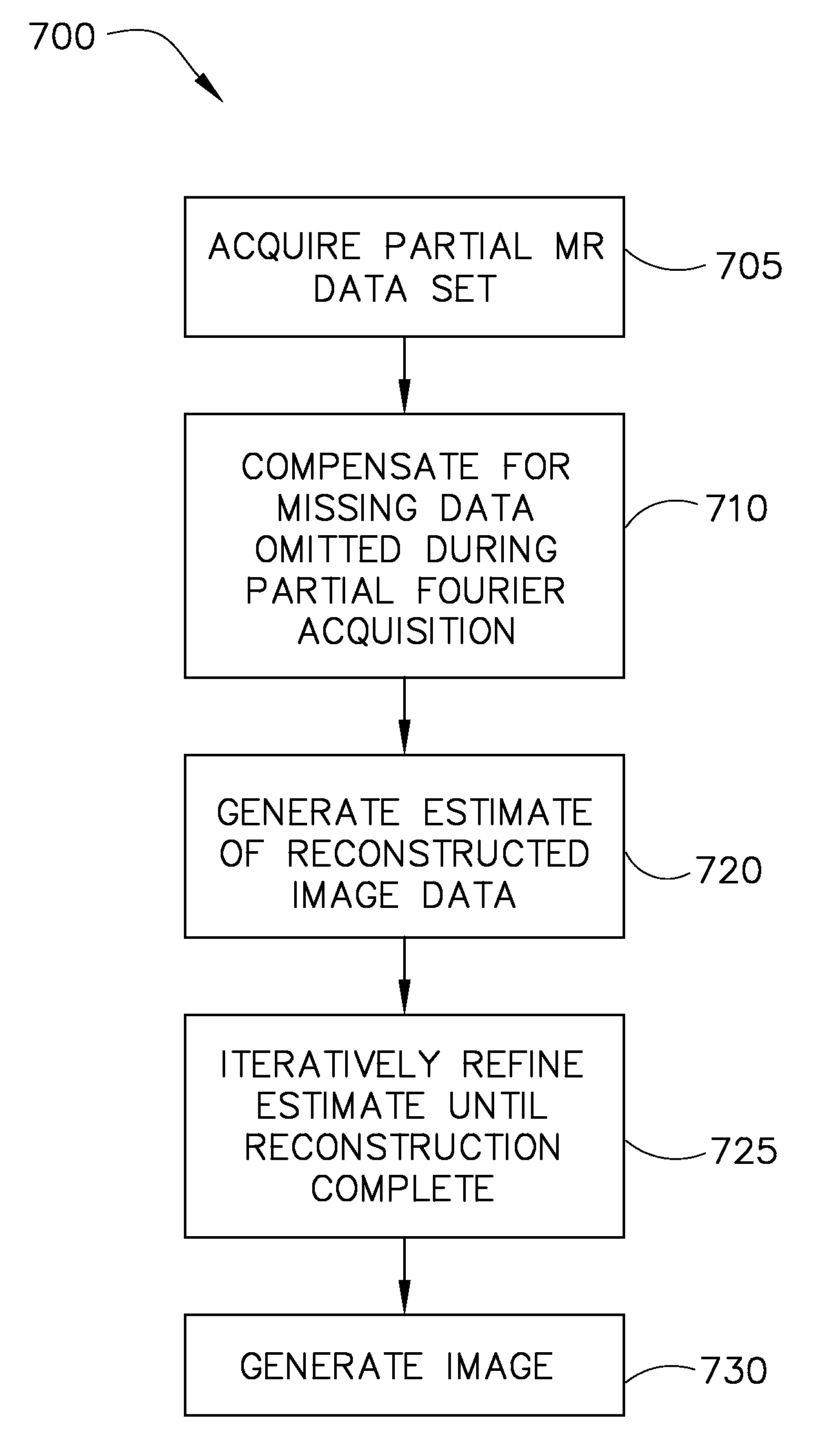
A system and method for reducing the scan time of an MR imaging system using a data acquisition technique that combines partial Fourier acquisition and compressed sensing includes a computer programmed to acquire a partial MR data set in k-space along a phase encoding direction, the data set having missing data in the phase encoding direction due to the omission of phase encoding steps. The computer is further programmed to generate an estimate of a reconstructed image, compensate the partial MR data set for the missing data, and reconstruct an MR image by iteratively minimizing the total squared difference between the k-space data of the estimate of the reconstructed image and the measured k-space data of the compensated partial MR data set.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
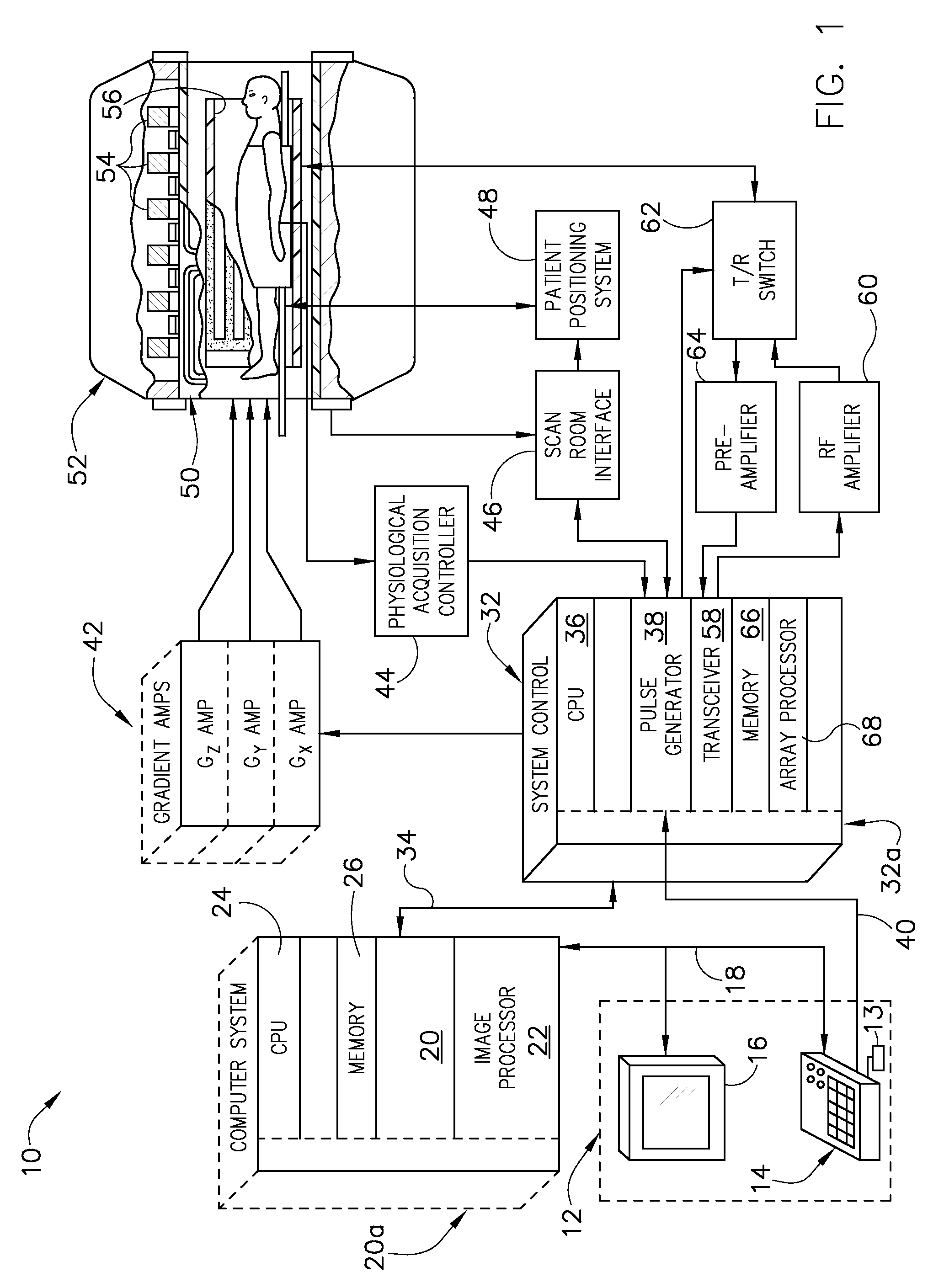
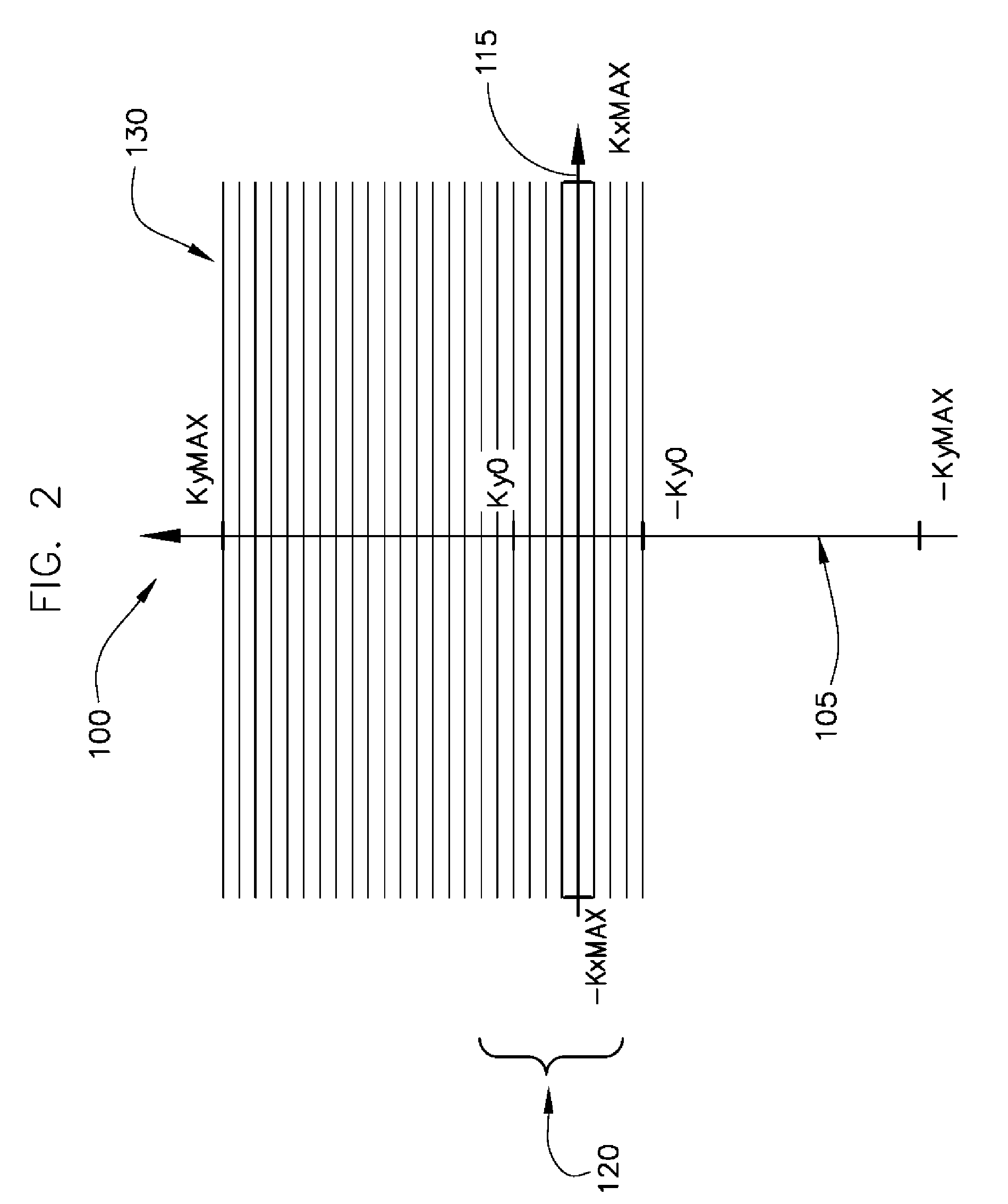
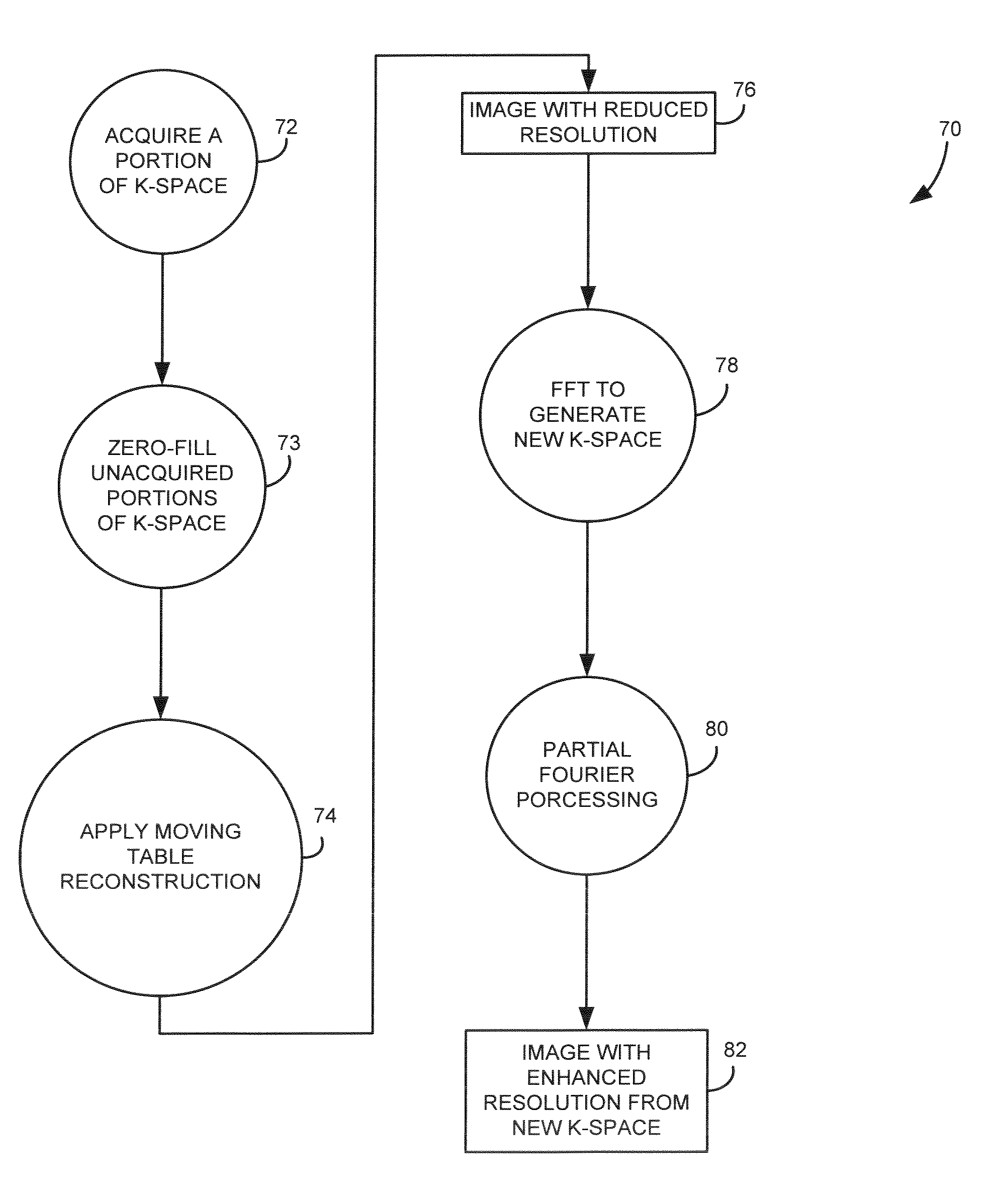
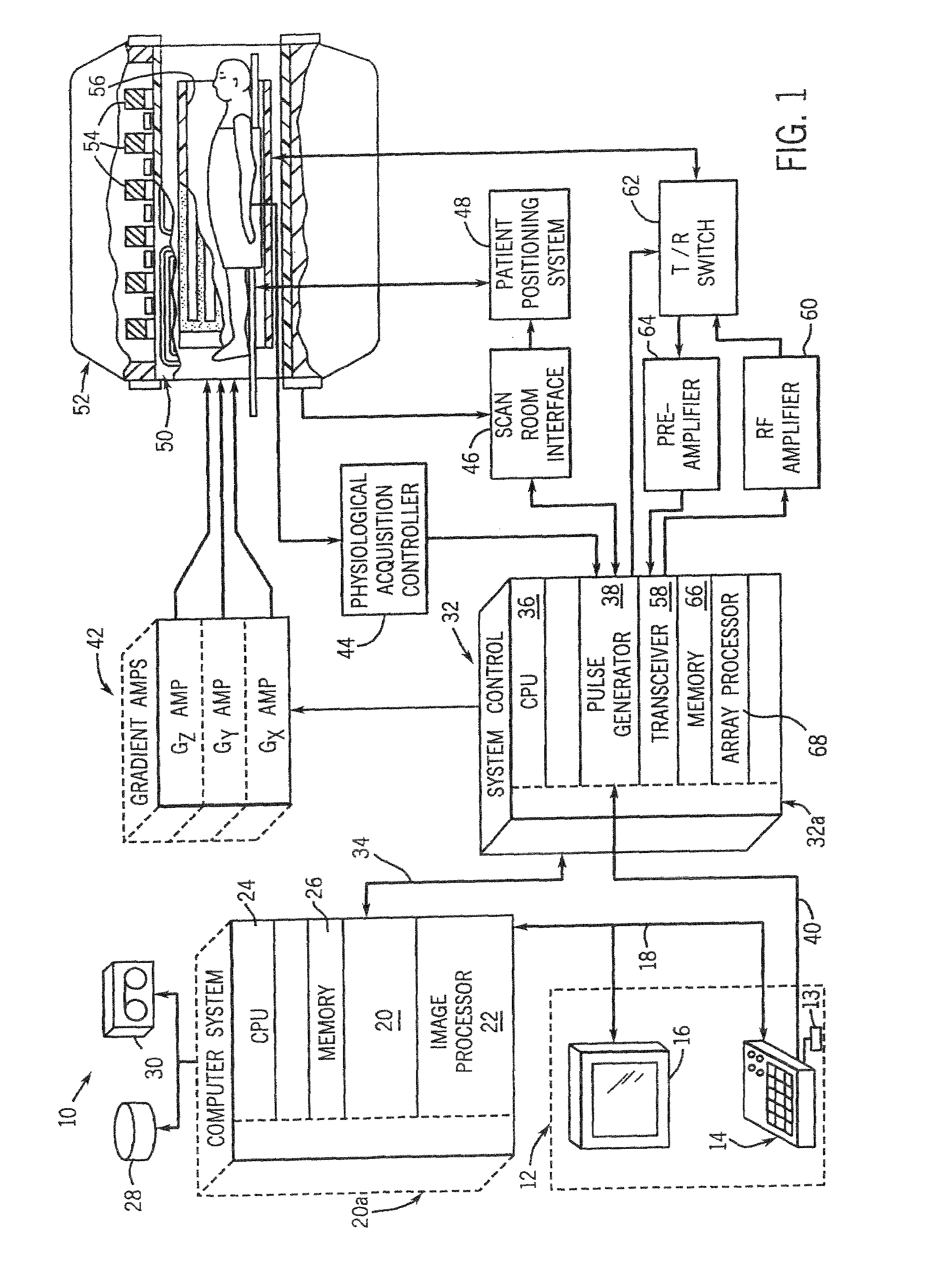
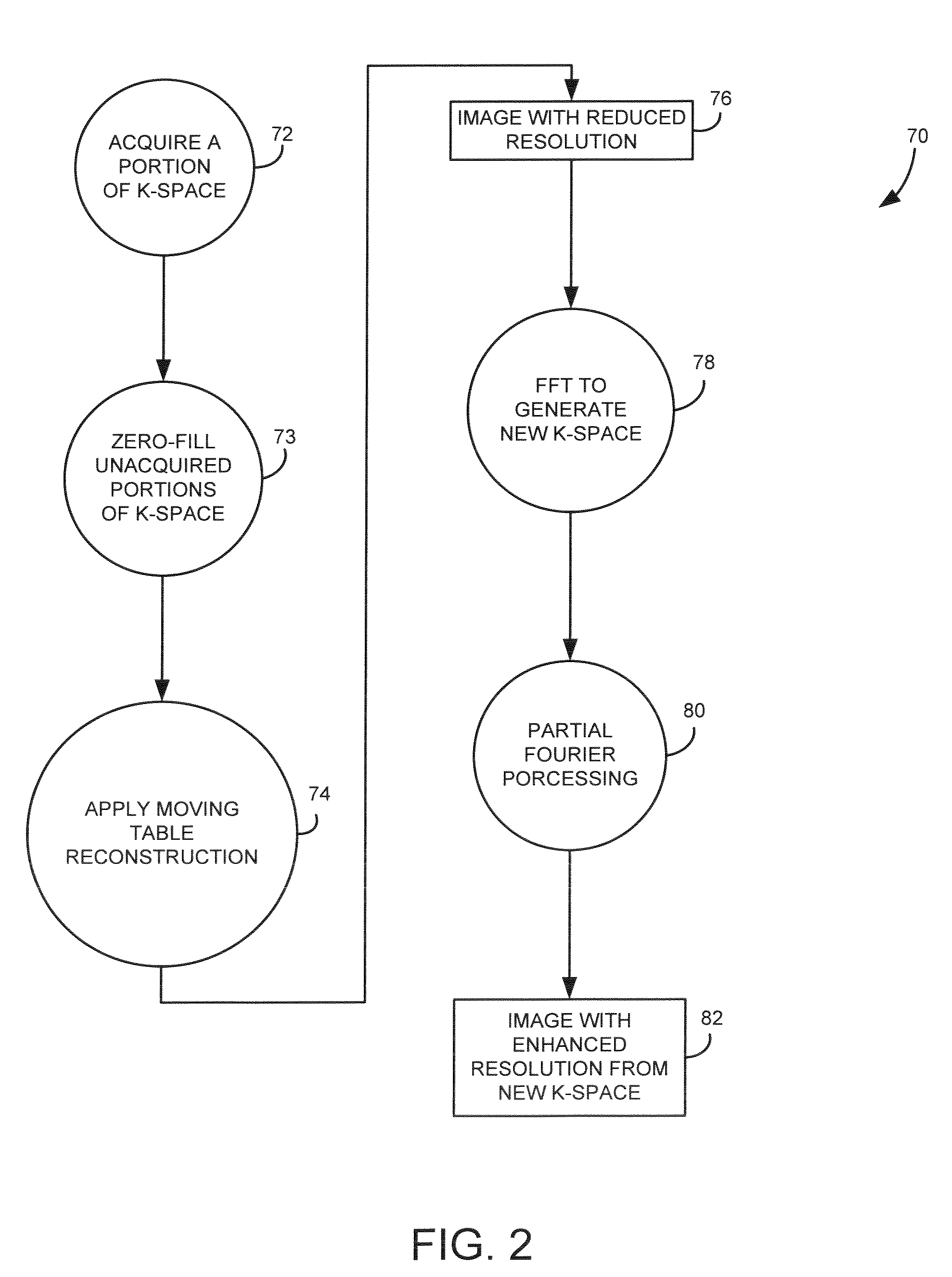
Method and system for moving table MRI with partial fourier imaging
InactiveUS6975113B1Overcomes drawbackMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionImage resolutionSpatial transformation
A method for moving table MR imaging with partial Fourier imaging is disclosed. MR data is acquired from a subject to partially fill k-space. The partially filled k-space is then reconstructed to form an image space having a first resolution. The image space is then transformed back into k-space followed by additional processing of the transformed k-space into an image space having a second resolution. A system to implement such a method is also disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
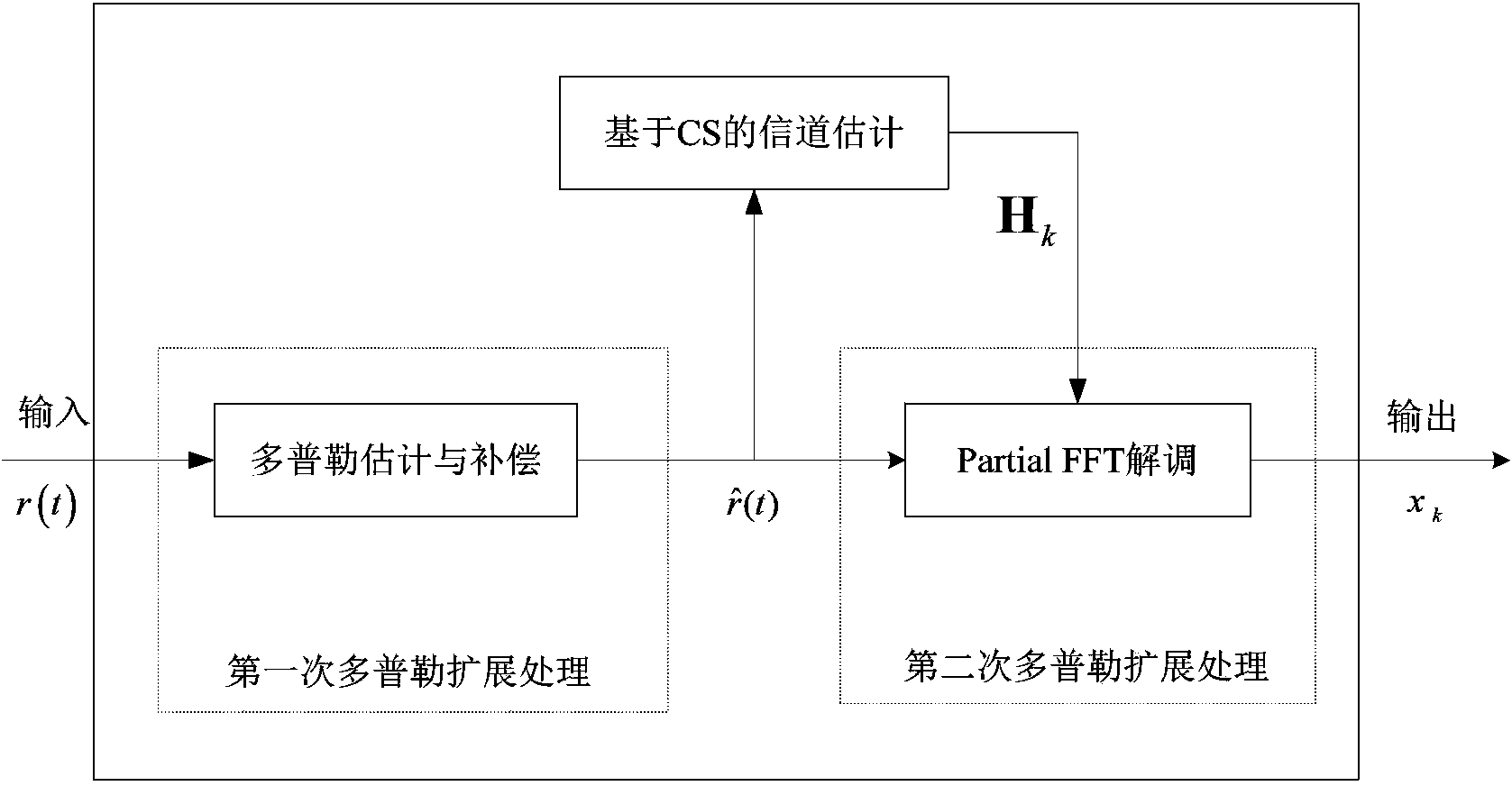
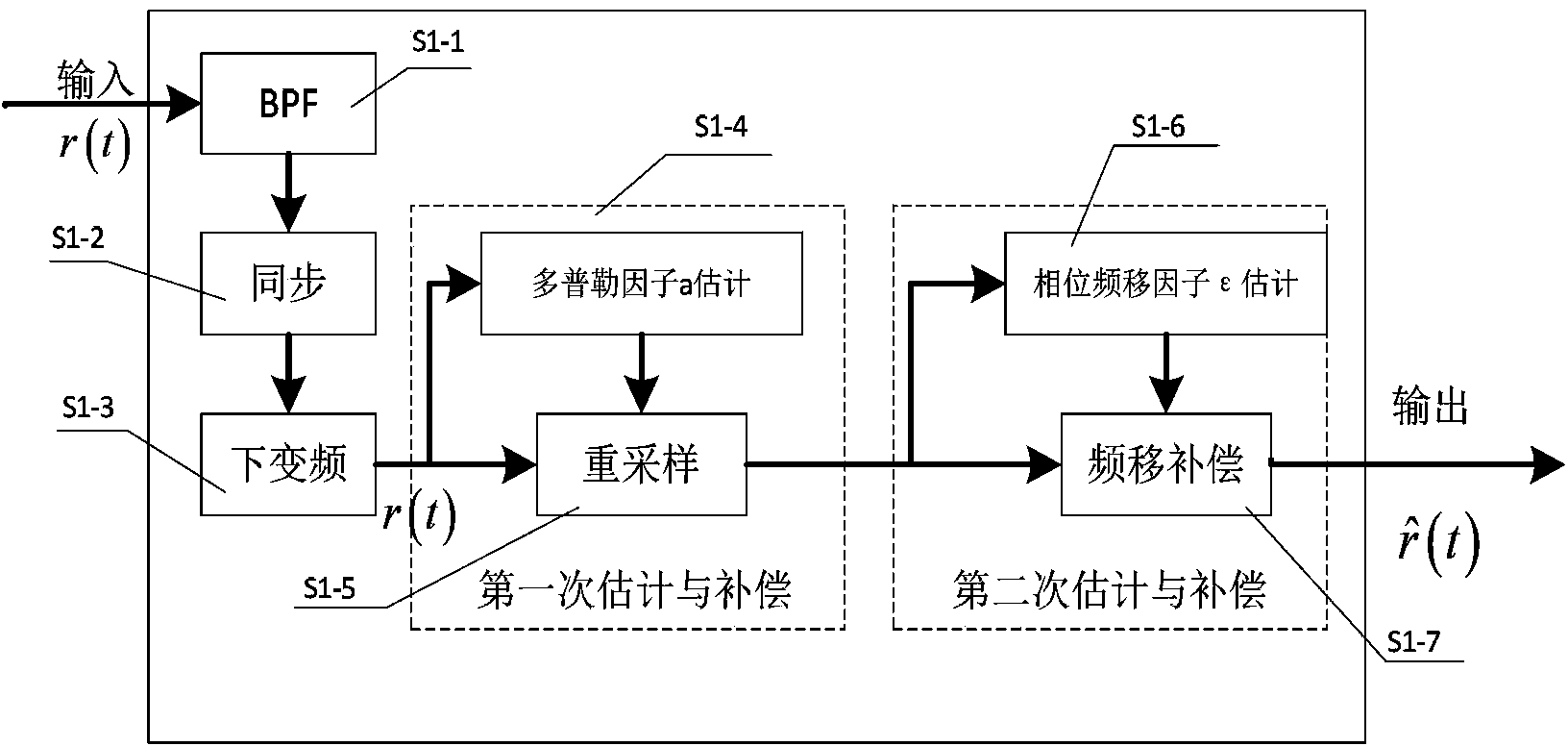
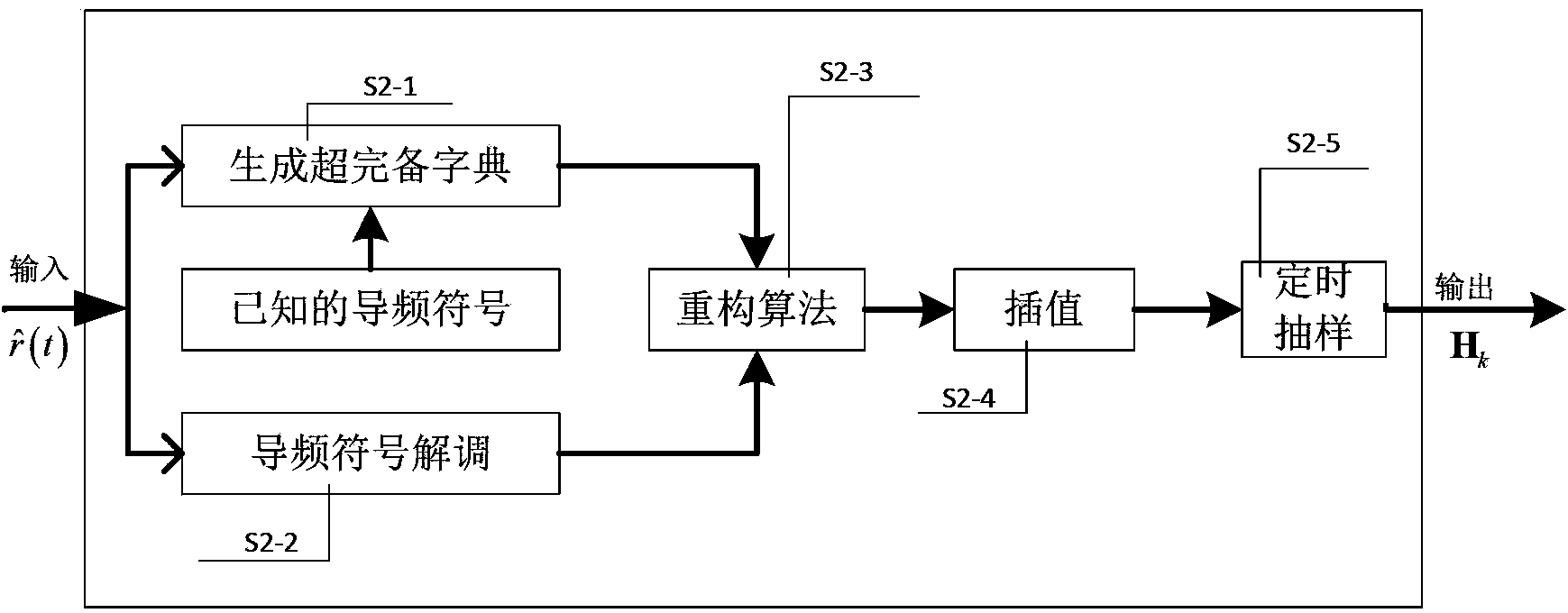
Method for processing Doppler expansion of underwater sound high-speed OFDM communication
InactiveCN103491046AReduce the impactAdaptableMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDoppler spreadFast Fourier transform
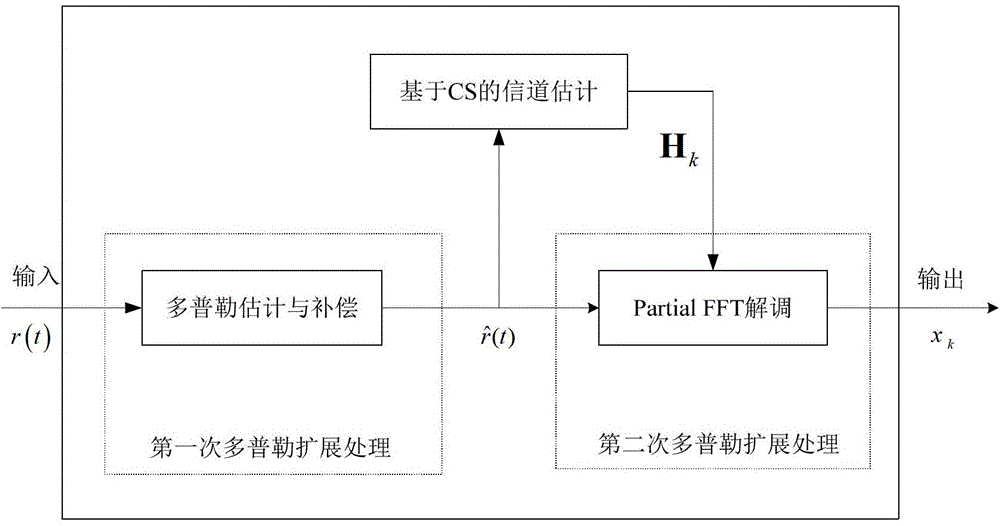
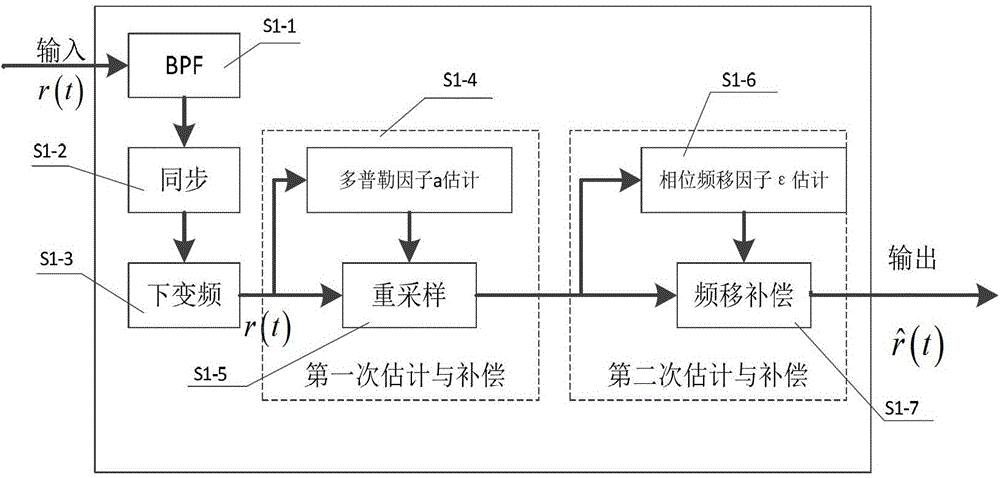
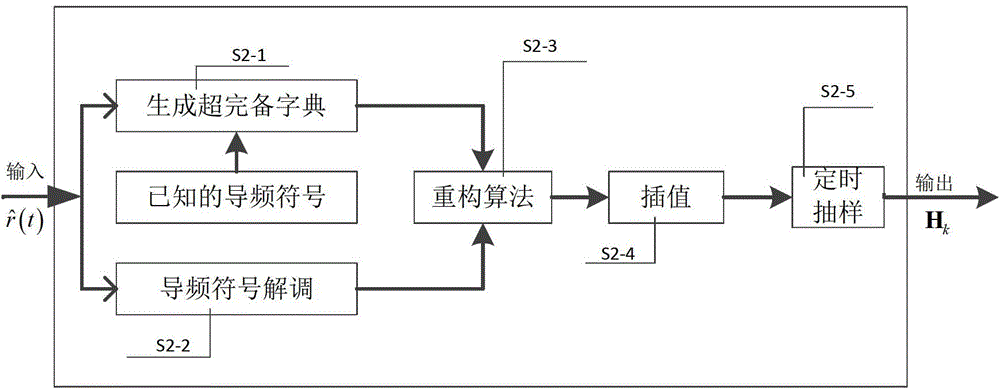
The invention discloses a method for processing Doppler expansion of underwater sound high-speed OFDM communication. The method relates to a Doppler estimation and compensation module, a channel estimation module based on compression sensing and a part fast Fourier transform demodulation module, wherein the key portion is the part fast Fourier transform demodulation module and output of the other two modules serves as input of the part fast Fourier transform demodulation module. According to the method for processing Doppler expansion of underwater sound high-speed OFDM communication, a traditional OFDM demodulation method is modified, part Fourier transform is firstly adopted to serve as a demodulation method and part of Doppler expansion can be eliminated in the process of demodulation; due to the fact that Doppler expansion is processed for twice, influence on signals by Doppler expansion can be reduced to a lower range and the method is particularly high in adaptation to a rapidly-changed underwater sound channel. Therefore, the high processing performance of Doppler expansion is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
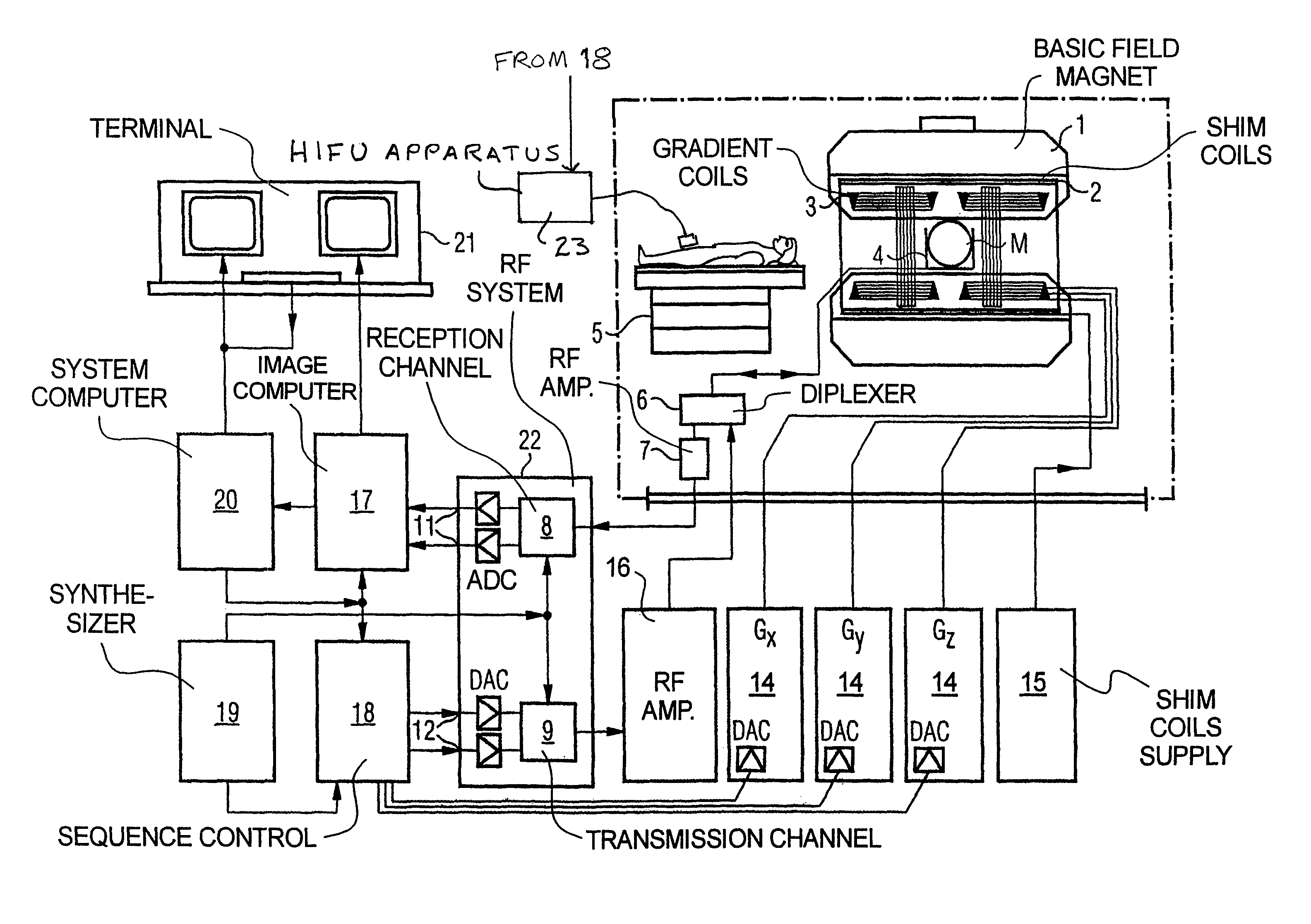
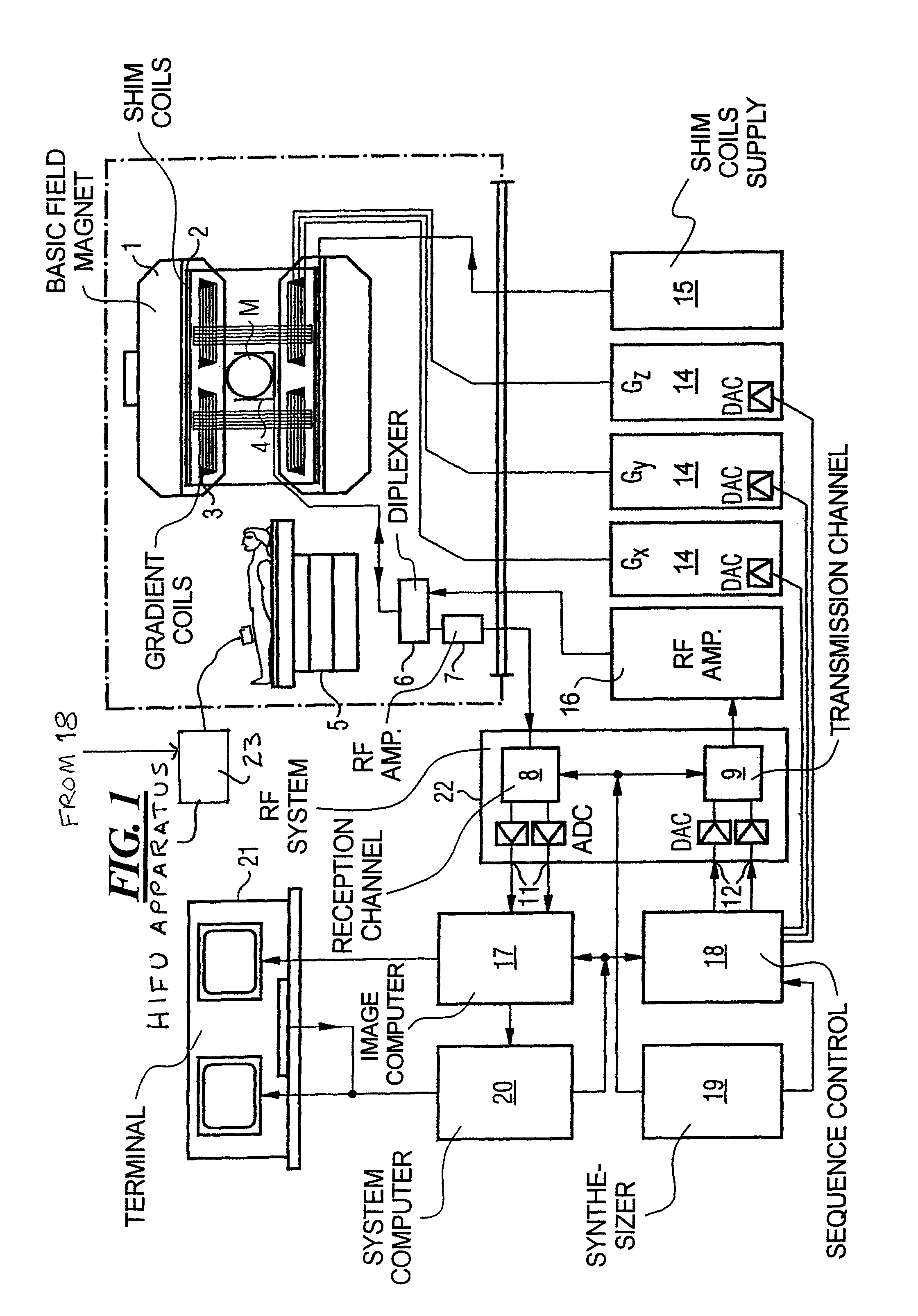
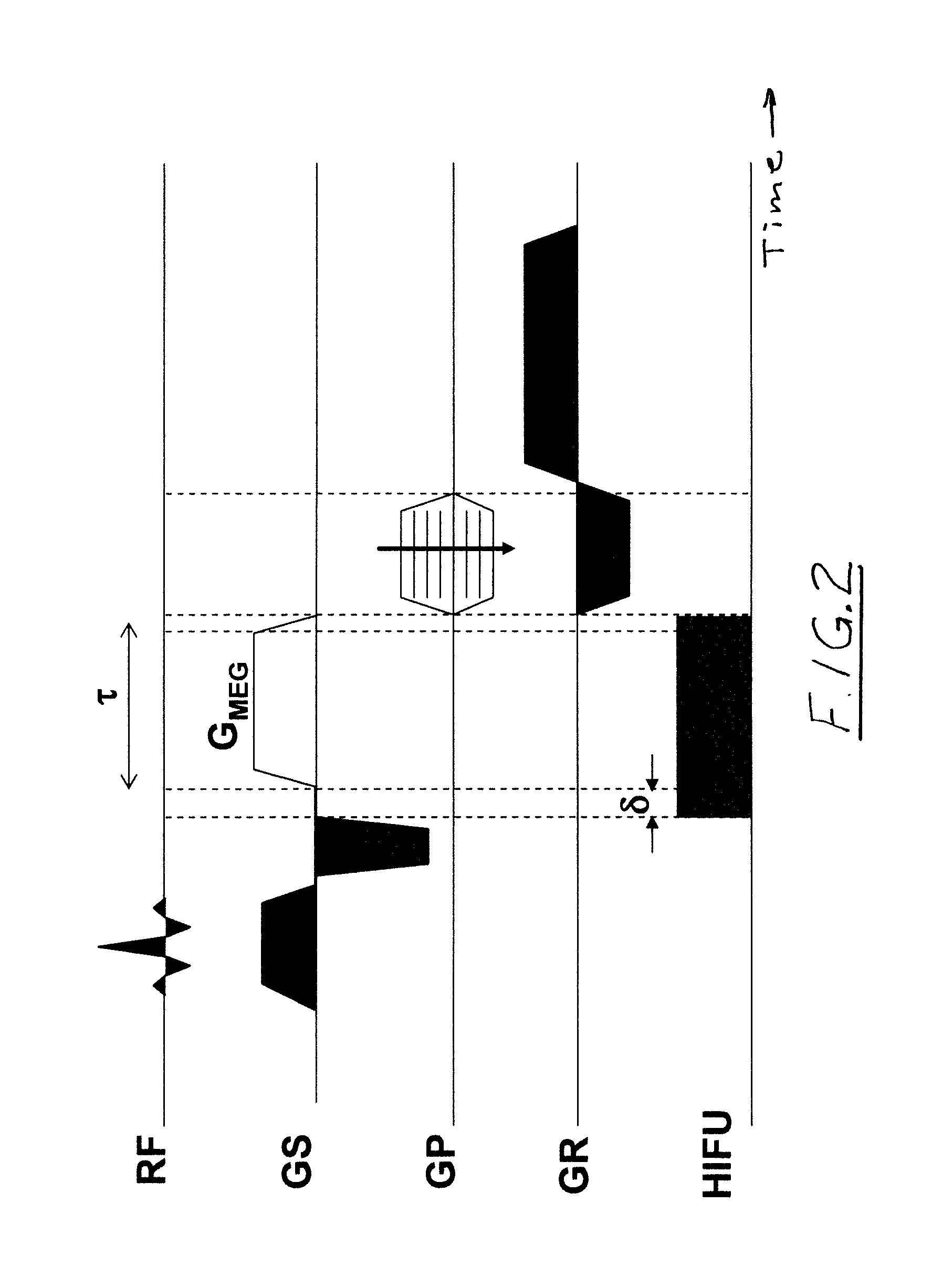
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound focusing under simultaneous temperature monitoring
ActiveUS20110248714A1Precise positioningHigh resolutionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRSonificationTissue heating
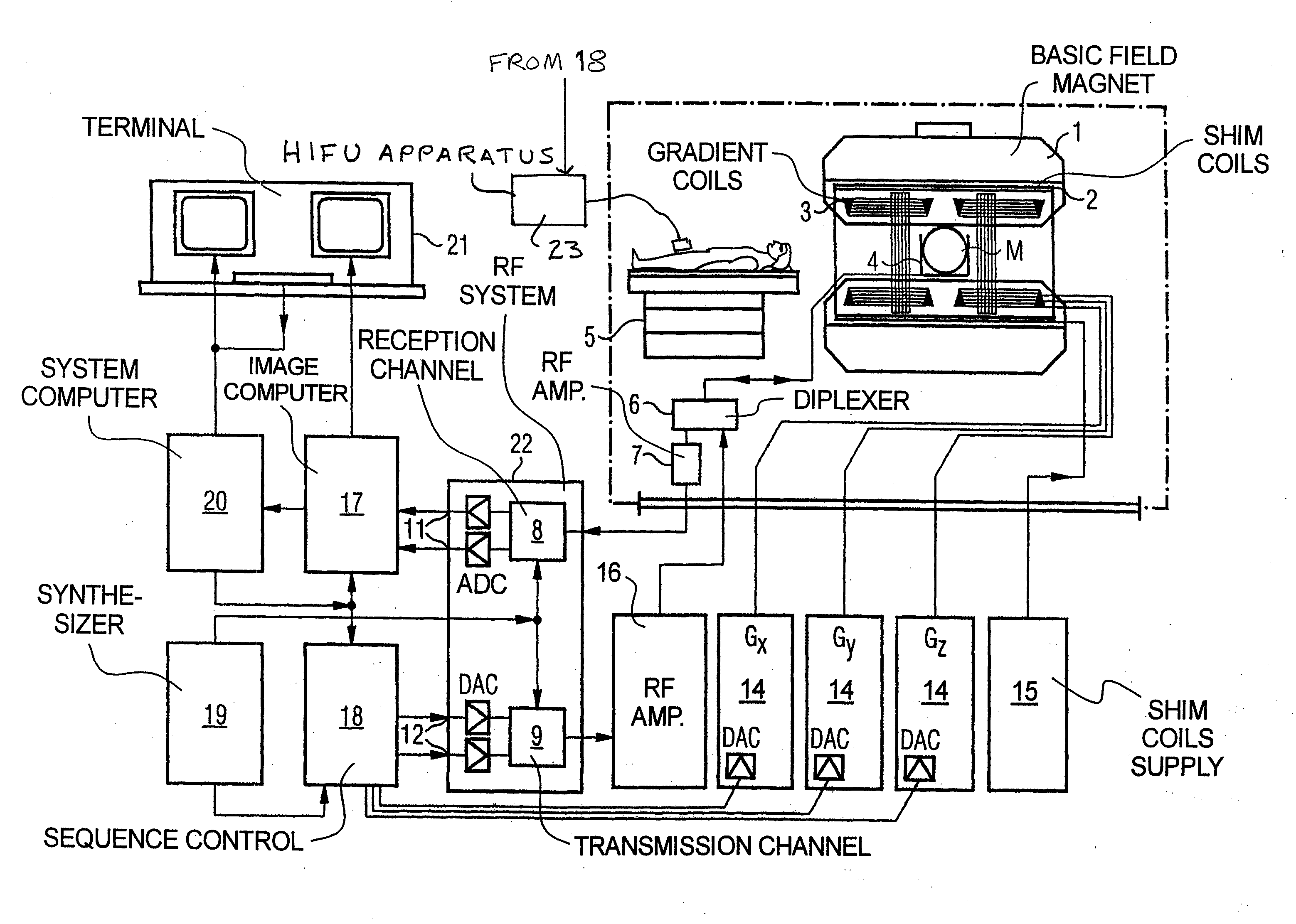
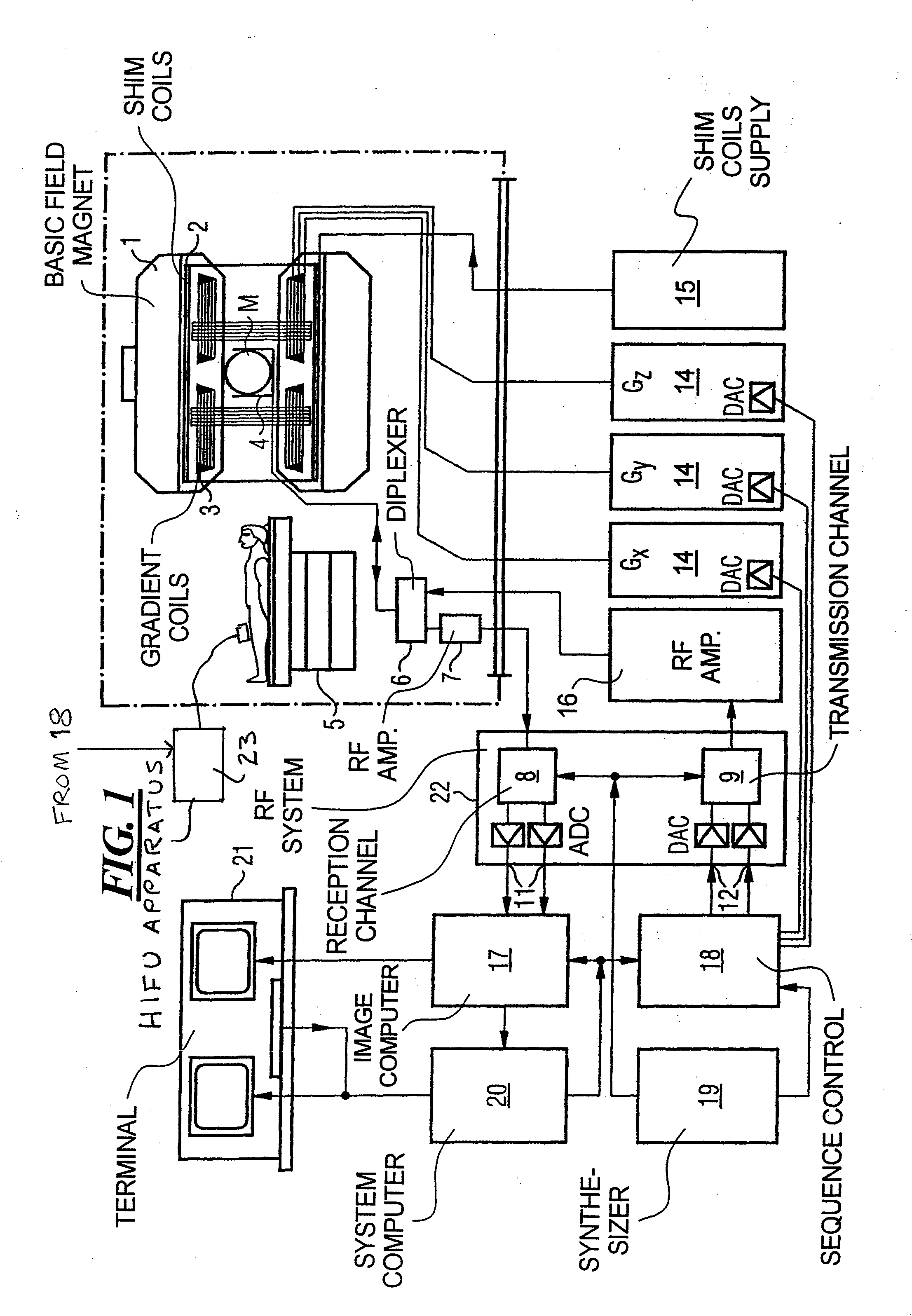
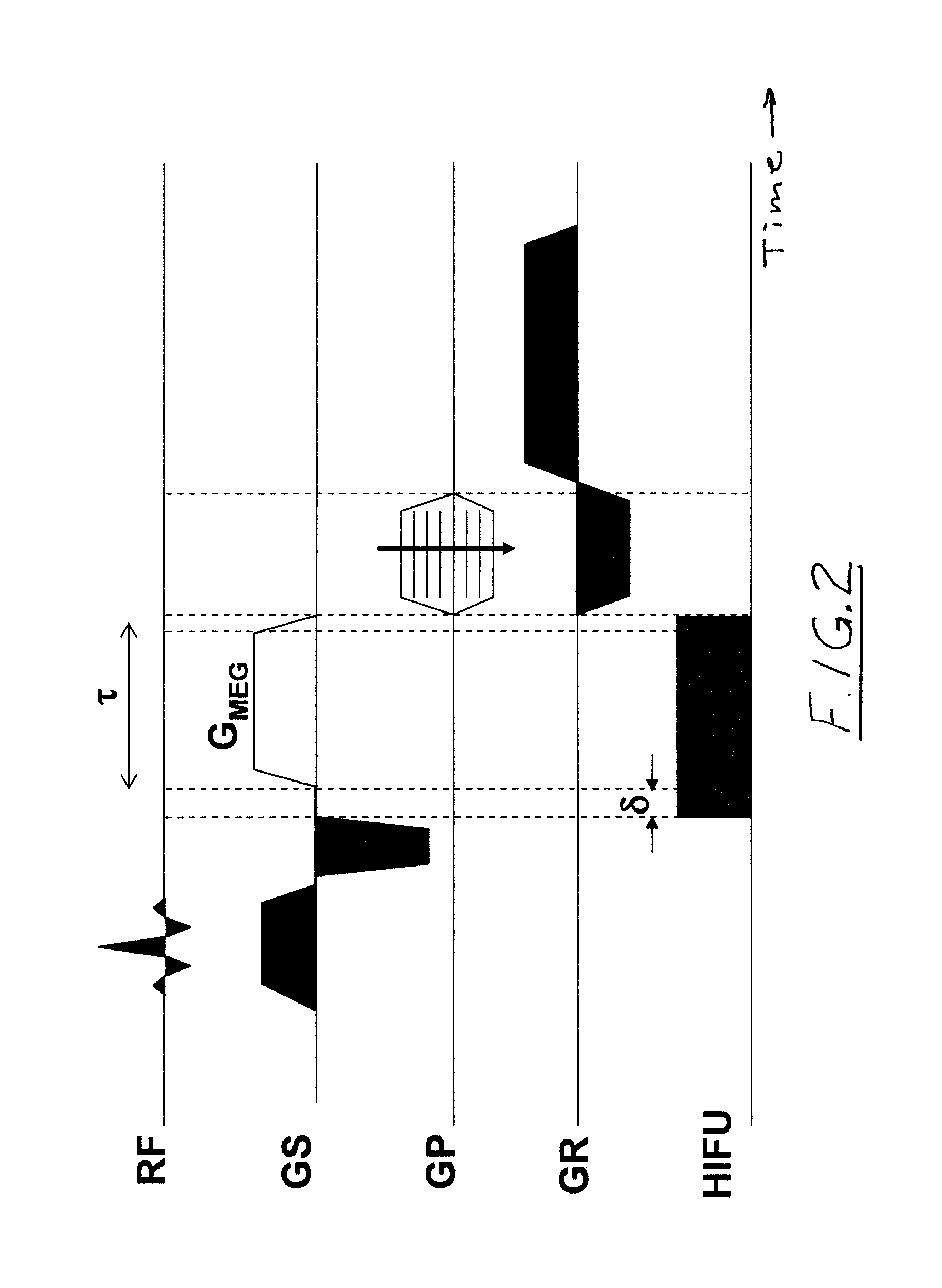
In a method and an apparatus for magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), precise localization of the focal point of the HIFU is determined by imaging an examination subject in parallel with GRE sequences that respectively include a positive monopolar gradient pulse and a negative monopolar gradient pulse, that respectively encode the acoustic radiation force (ARF)-induced phase shift that is induced by the simultaneous activation of HIFU during the sequences. A GRE phase image is reconstructed from each acquisition sequence, and a difference image is formed between the two GRE phase images, from which the HIFU focal point is determined. An average image is formed of the two GRE phase images from which PRFS temperature map is determined simultaneously to ARFI map. The use of parallel imaging and the use of partial Fourier reconstruction for reconstructing the GRE phase images allows the data to be acquired sufficiently rapidly so as to minimize the adverse effect of tissue heating that occurs with conventional longer-duration, and repetitious, techniques.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
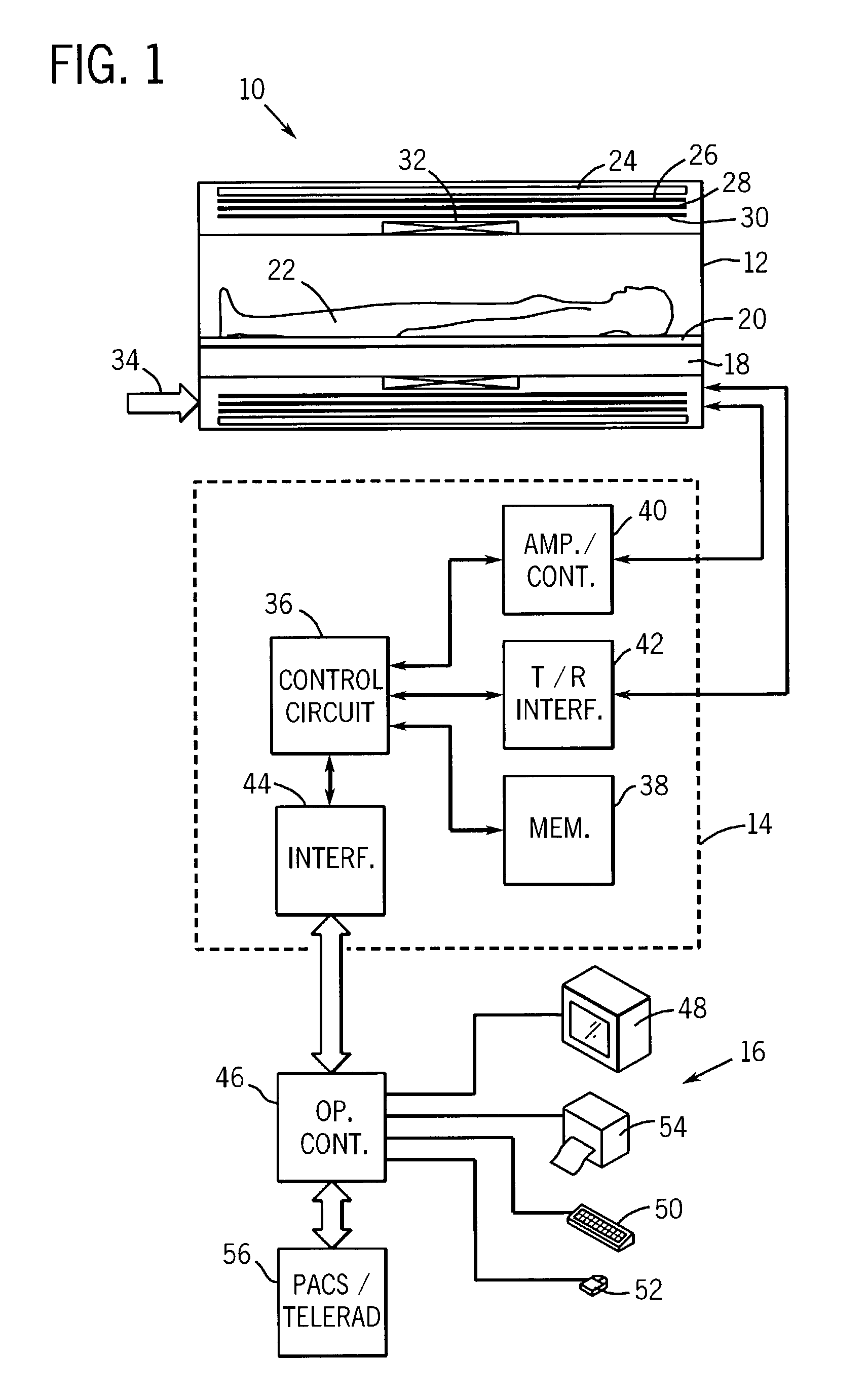
Data acquisition method and apparatus for MR imaging
An improved technique is described for acquiring MR image data such as needed for FSE-based Dixon imaging techniques. A gradient-induced echo shift is produced in the pulse sequences by a small gradient applied along the readout axis prior to a readout pulse. When necessary, another small pulse is applied along the readout axis, equal in area and opposite in polarity to the first, to compensate for the shifting effect. Similar pulses are applied for each acquisition window. While data with non-zero phase shifts between water and fat signals are collected as fractional echoes, no increase in echo spacing is necessary with the modified acquisition strategy. Images corresponding to different phase shifts are reconstructed using phase-sensitive partial Fourier reconstruction algorithms whenever necessary. These images are then used to separate different chemical species (such as water and fat) in the object to be imaged. Increased time efficiency is therefore achieved with the improved technique, with a significant reduction in degradation due to losses in slice coverage and increased image blurring and sensitivity to flow and motion due to T2-modulation along the echo train in conventional techniques.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
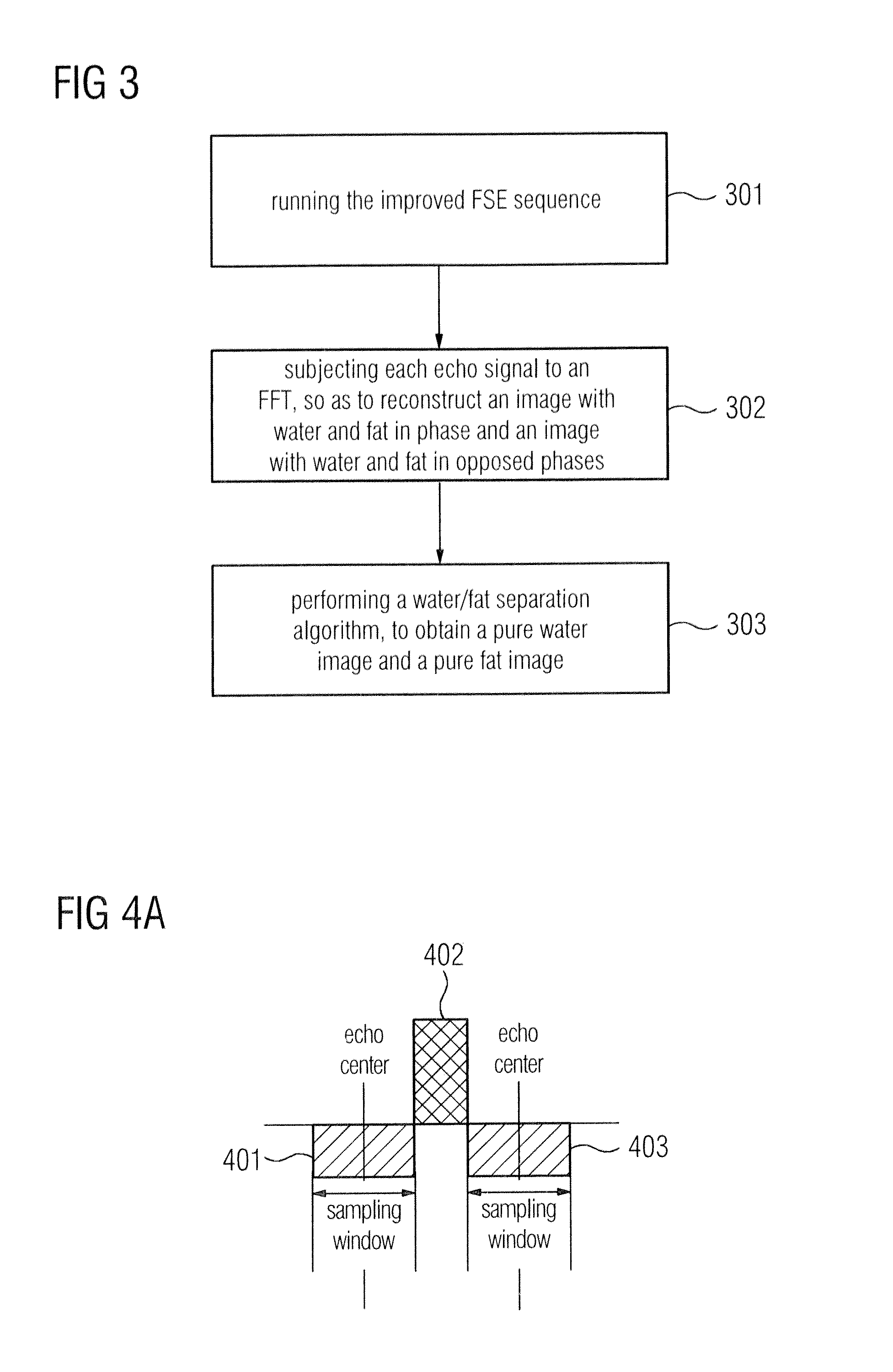
Imaging method and device for water/fat separation in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20130214783A1Momentum requirementReduce the amplitudeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFourier transform on finite groupsElectrical polarity
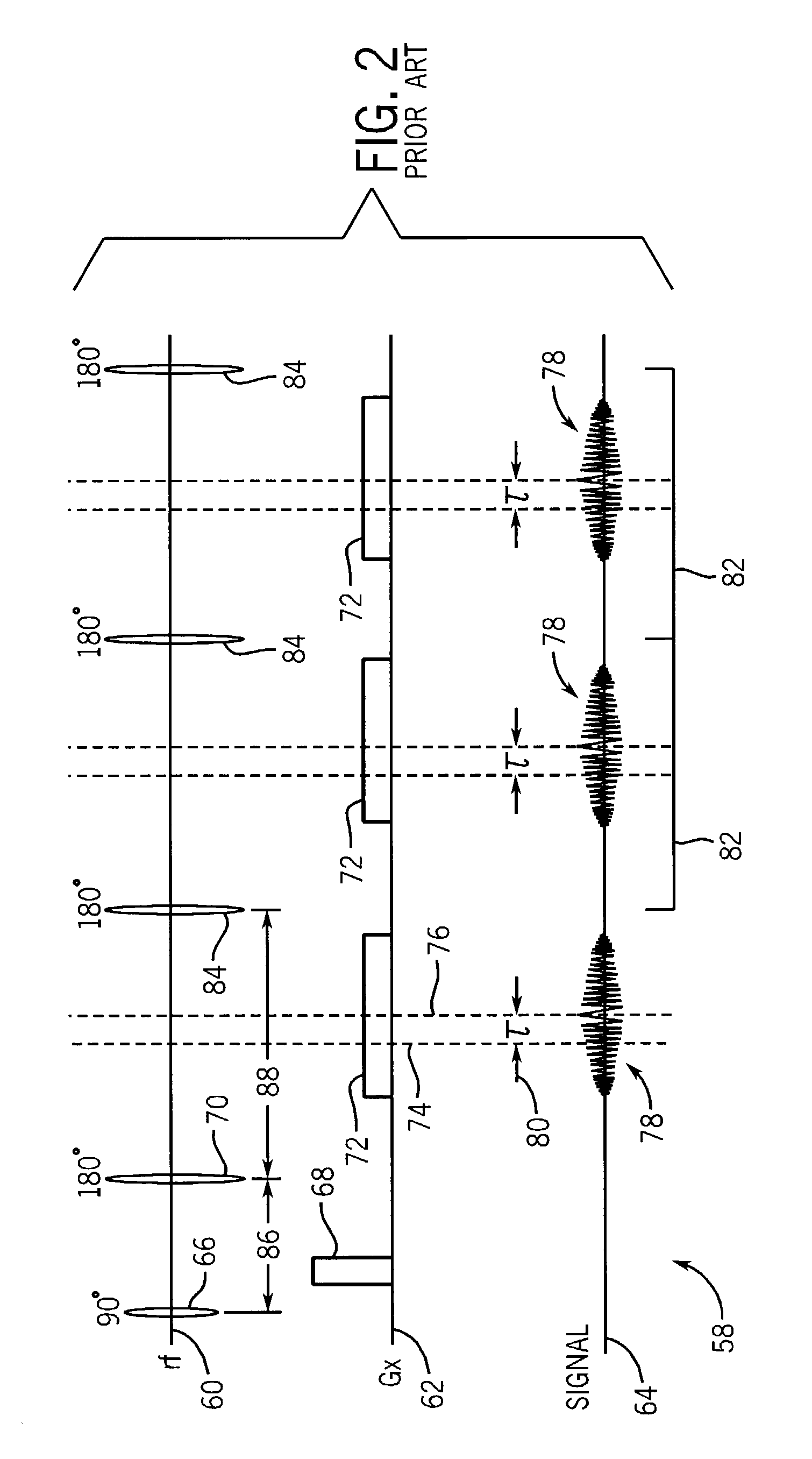
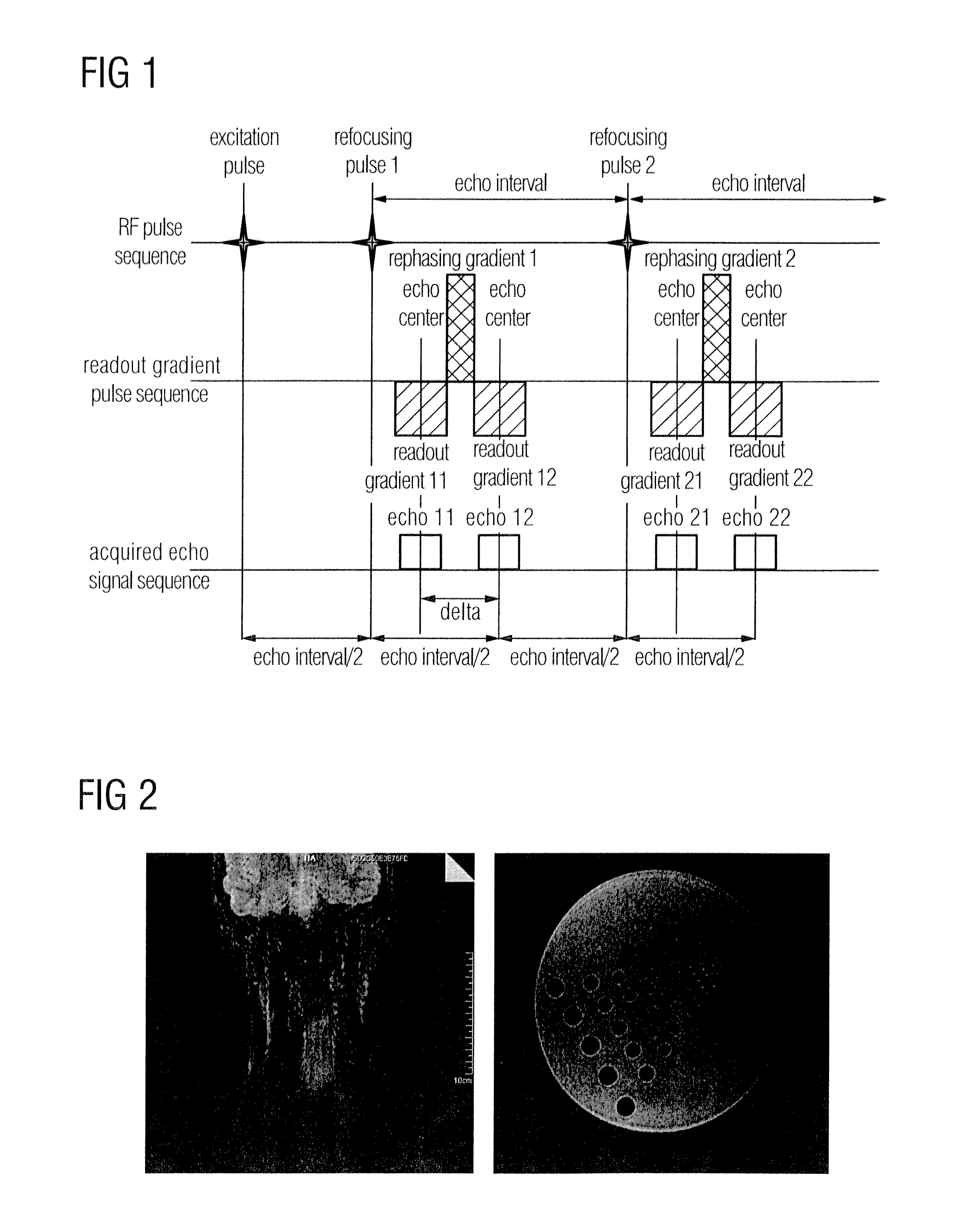
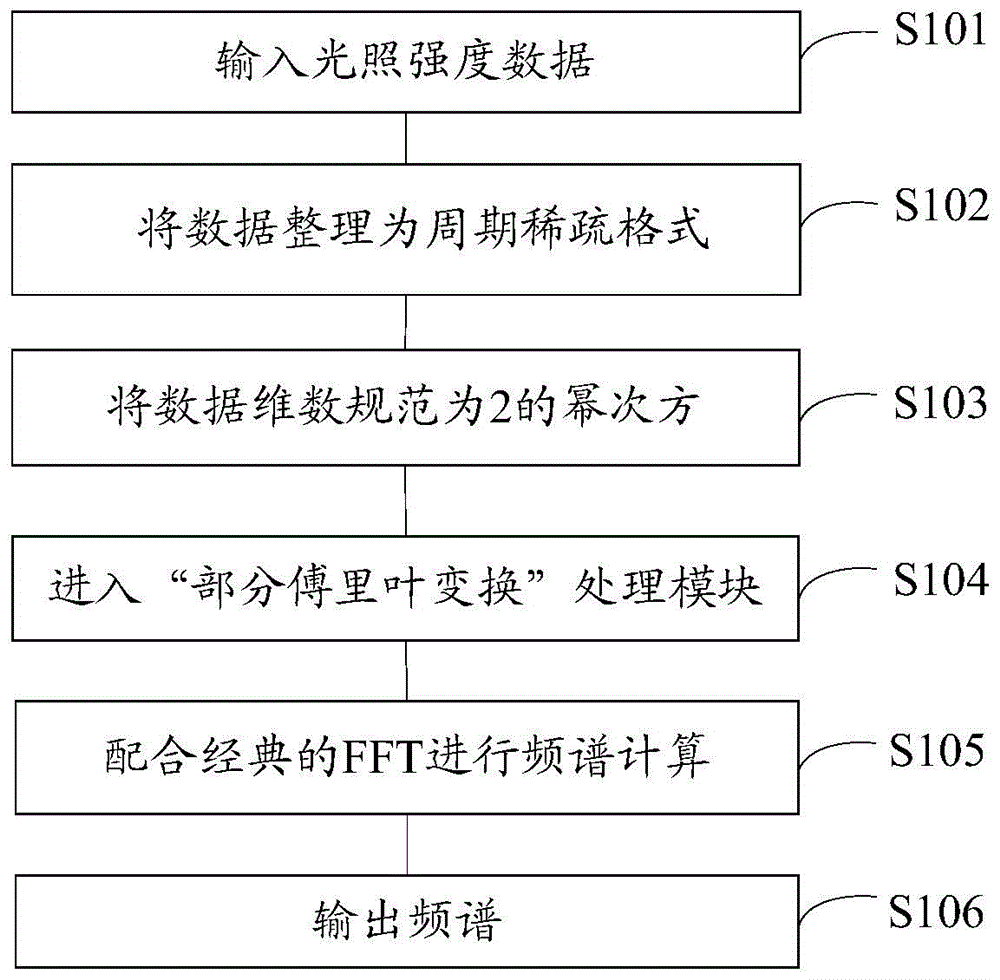
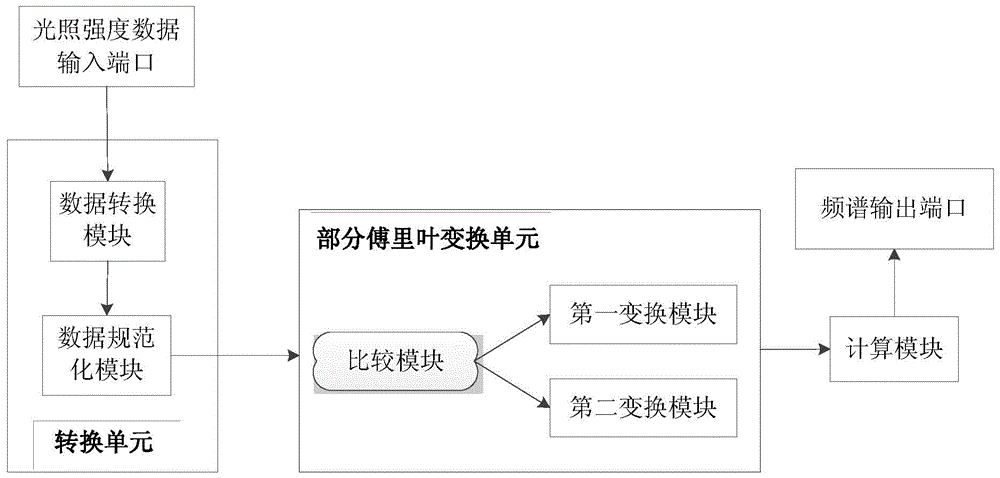
In an imaging method and device for water / fat separation in MRI using a two-point Dixon FSE sequence, each refocusing RF pulse corresponds to two readout gradients of the same polarity, each being center-divided into a smaller rear part and a larger front part, and one rephasing gradient of opposite polarity. In running the FSE sequence, each echo signal acquired is subjected to an FFT, to reconstruct an image with water and fat in phase and an image with water and fat in opposed phases. Data of each echo signal are subjected to a partial Fourier transform; and the in-phase water / fat image and the opposite-phase water / fat image are subjected to a water / fat separation algorithm, to obtain a pure water image and a pure fat image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Time-domain channel estimation method for MIMO OFDM downlink system
InactiveCN101364966AHigh precisionAvoid inhomogeneityMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCarrier signalFourier transform on finite groups
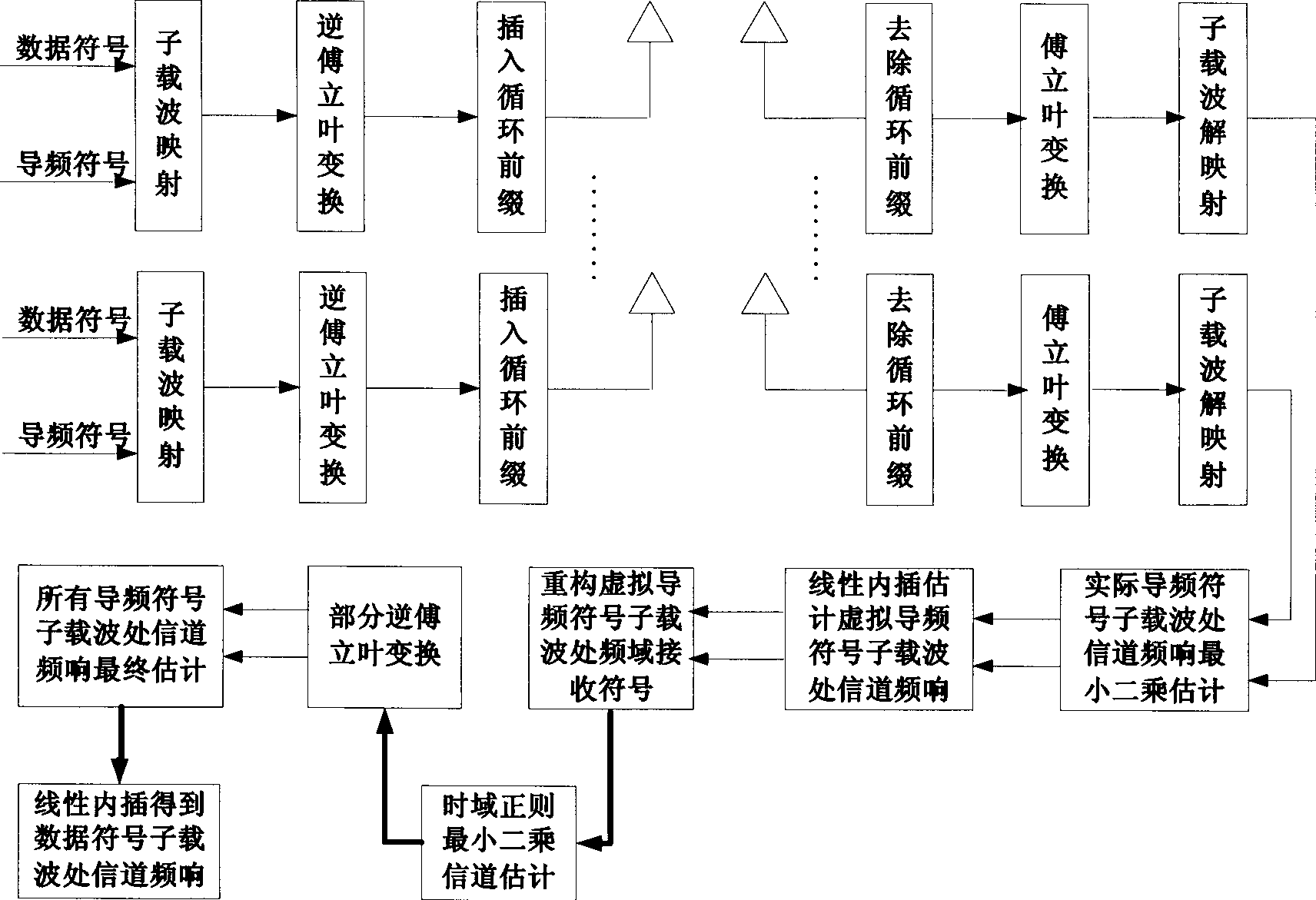
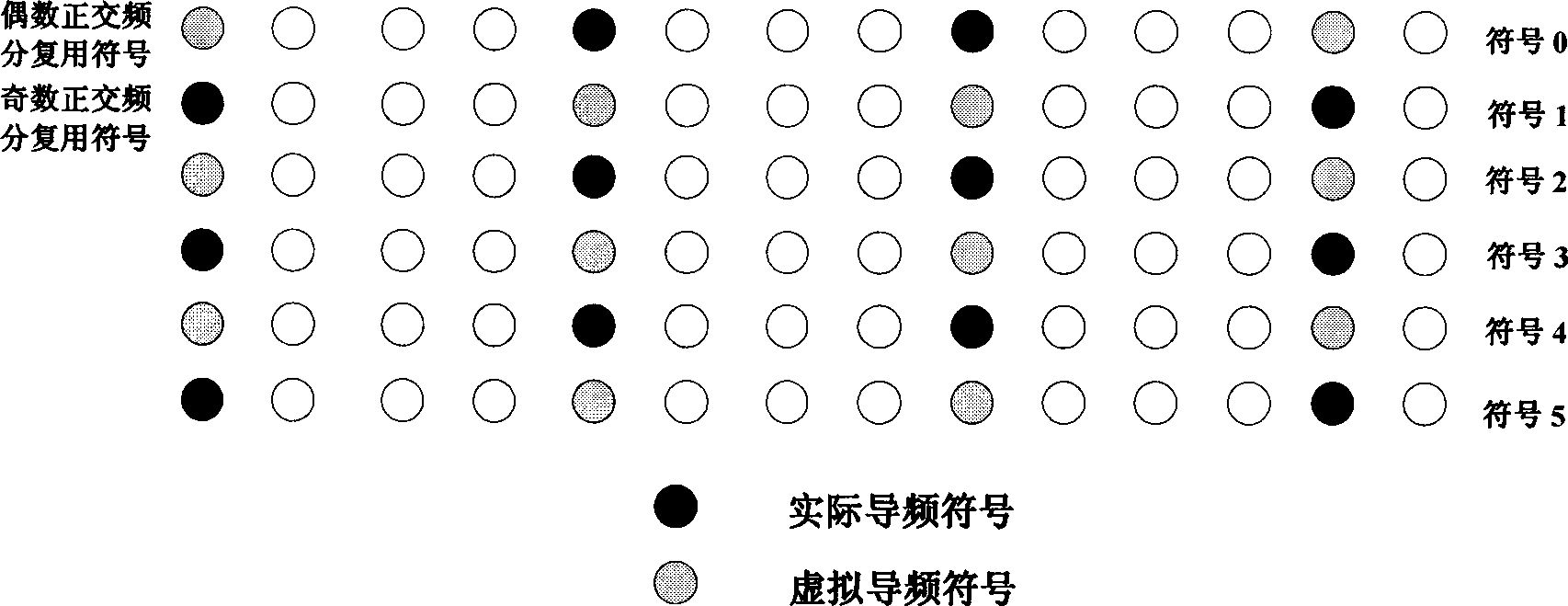
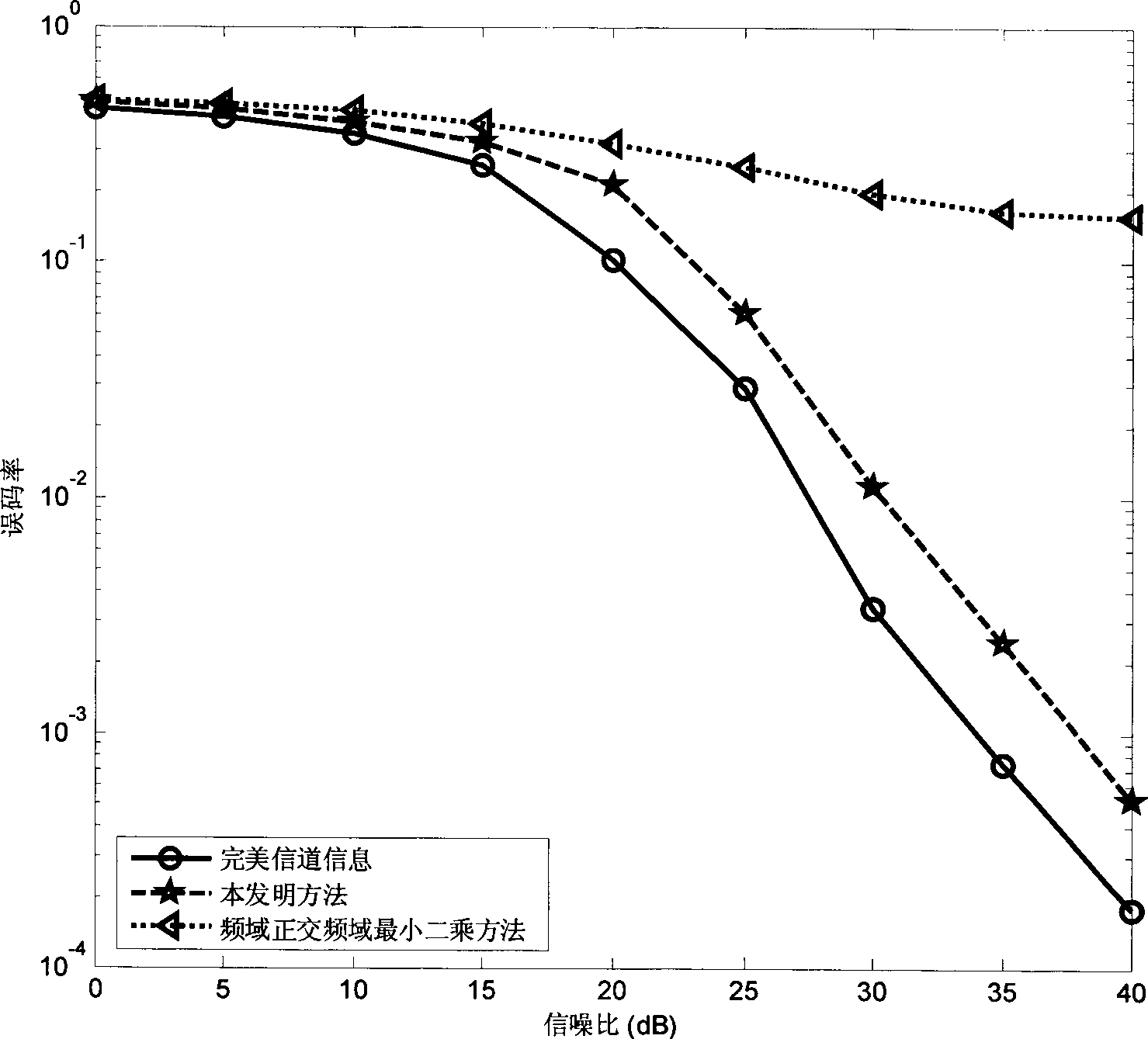
The invention relates to a time domain channel estimation method of a multiple-input multiple-output orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing down system. A pilot frequency symbol sequence using orthogonal virtual pilot frequency symbol and code domain is assumed to be used; firstly, a receiving terminal estimates the frequency response of each sub-channel at the actual pilot frequency symbol sub-carrier; then, the channel estimation for the virtual pilot frequency symbol sub-carrier is obtained through the linear interpolation of channel estimation of adjacent symbols used for orthogonal frequency division; the received symbol is re-constructed by utilizing the virtual pilot frequency symbol and the channel estimation thereof, the impulse response estimation of each sub-channel is obtained by ranking the received symbol of the actual pilot frequency symbol sub-carrier in ascending order according to the index value of the sub-carrier and then applying the least square method for time domain regularization, and the channel estimation of all the pilot frequency symbol sub-carriers is obtained after partial Fourier transformation; and finally, the channel frequency response of each user data symbol sub-carrier is obtained through the linear interpolation of channel estimation of the pilot frequency symbol sub-carrier. The invention has the advantages that the channel estimation precision is high, and larger quantity of transmitting antenna can be supported.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
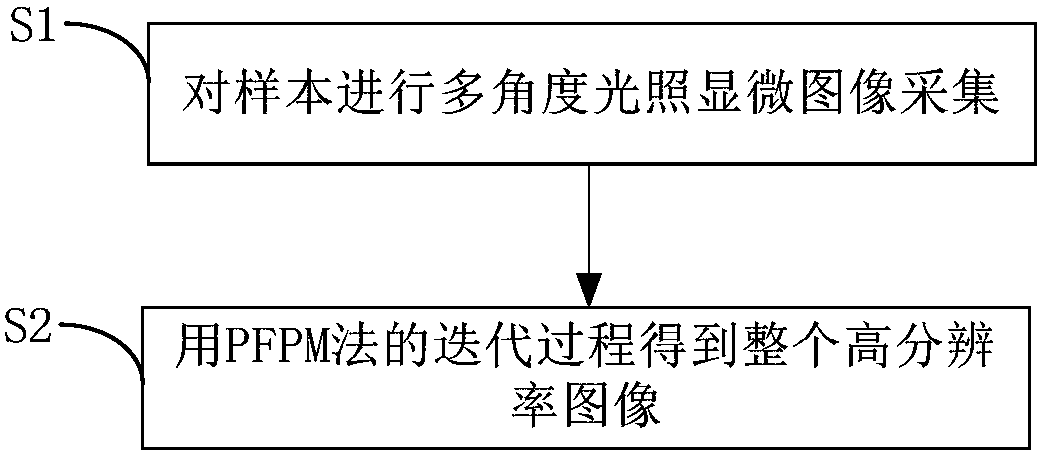
Microscopic imaging method based on partial Fourier space
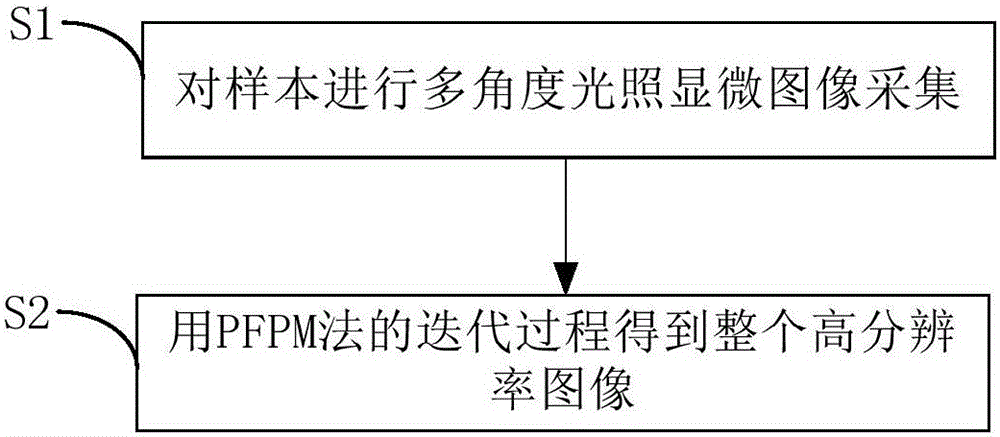
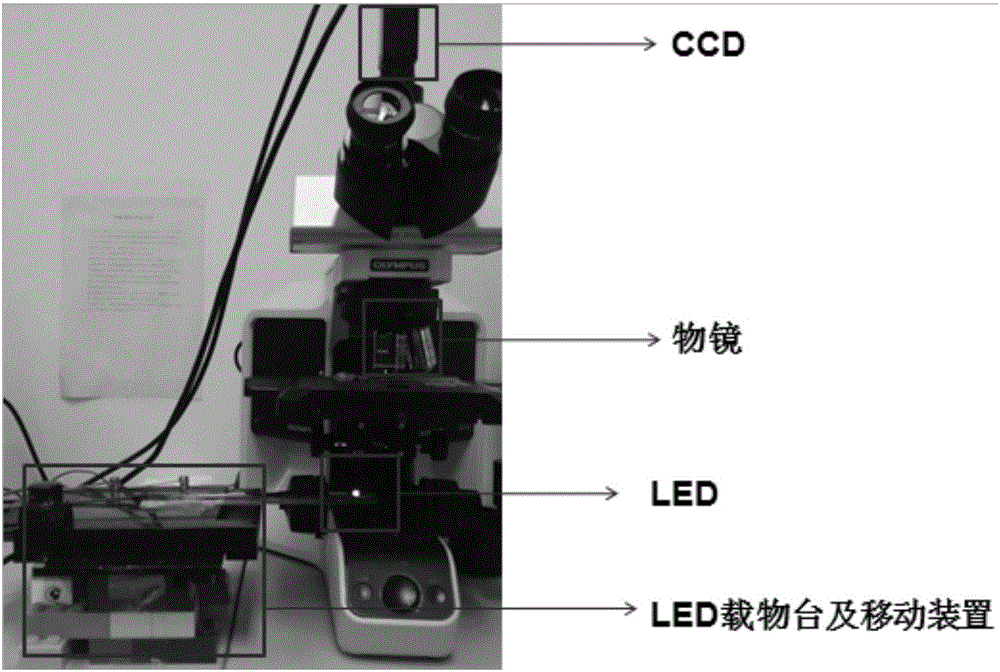
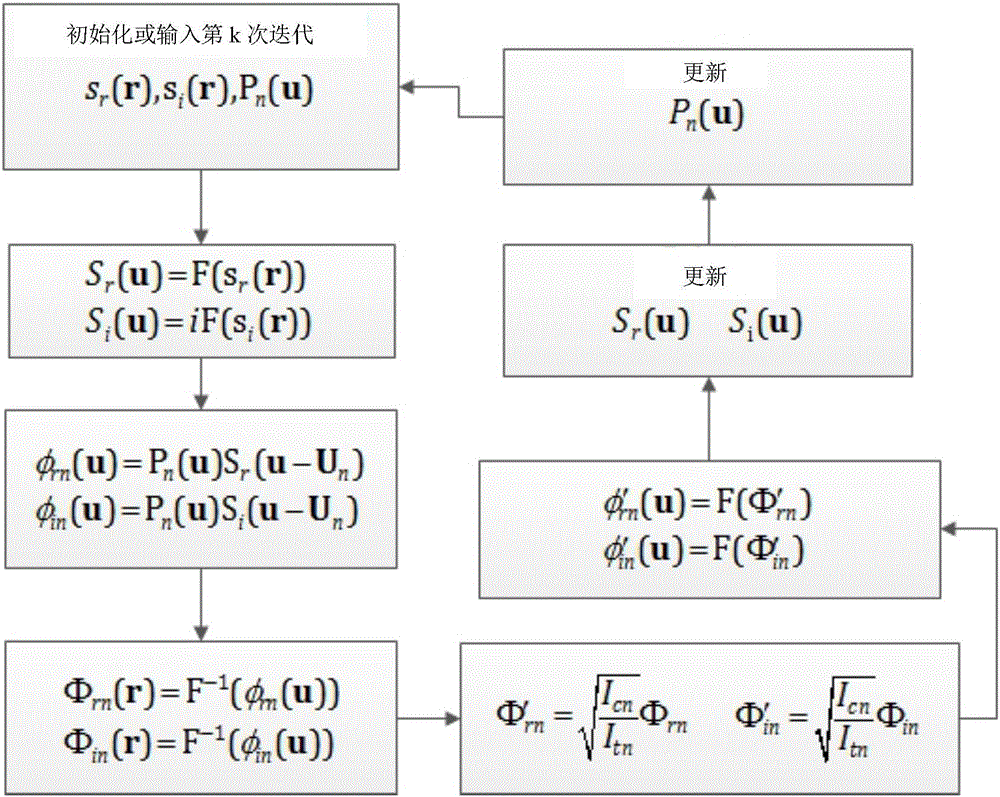
The invention discloses a microscopic imaging method based on a partial Fourier space, comprising the following steps: S1, collecting microscopic images of a sample under multi-angle lighting; and S2, getting a whole high-resolution image through an iteration process of a PFPM method. Step S1 includes collecting a central image of the sample and multiple images obtained under lighting of a half light matrix in a set range. Step S2 includes the sub steps of processing the central image to get an iterative initial figure of Fourier space, iteratively updating the multiple images one by one according to the iterative initial figure to complete a round of iteration, performing a plurality of rounds of iteration to get the Fourier space of the high-resolution image, and filling in the missing data according to the Fourier space of the high-resolution image and based on the conjugate symmetry of Fourier transform to generate a whole high-resolution image. Through the microscopic imaging method based on a partial Fourier space, the iteration speed is increased. The application scope of the microscopic imaging method based on a partial Fourier space is expanded.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for modulating an oqam type multi-carrier signal, and corresponding computer program and modulator
ActiveUS20140064407A1Increase speedEasy to implantMultiple carrier systemsTime domainFourier transform on finite groups
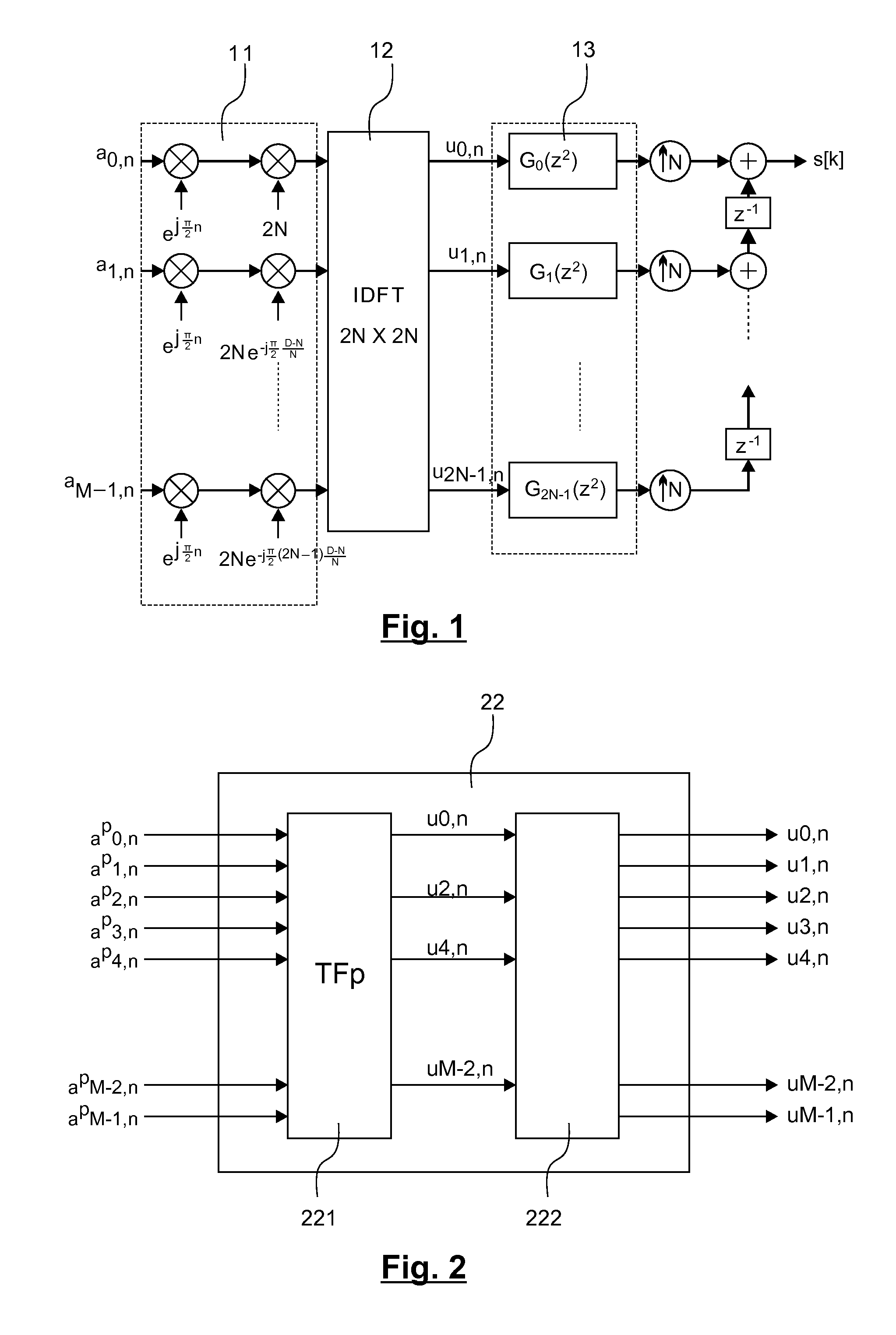
A modulator and modulation method are provided, which output an OQAM multi-carrier signal. The method implements a step of transforming, from the frequency domain to the time domain, a set of M symbols of real data so as to output M transformed symbols. The complete transformation includes the following sub-steps: applying a partial Fourier transform to the set of M symbols of real data, outputting a first subset of C transformed symbols, where C is strictly less than M; and obtaining, from the first subset, a second subset of (M-C) transformed symbols that is complementary to the first subset.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
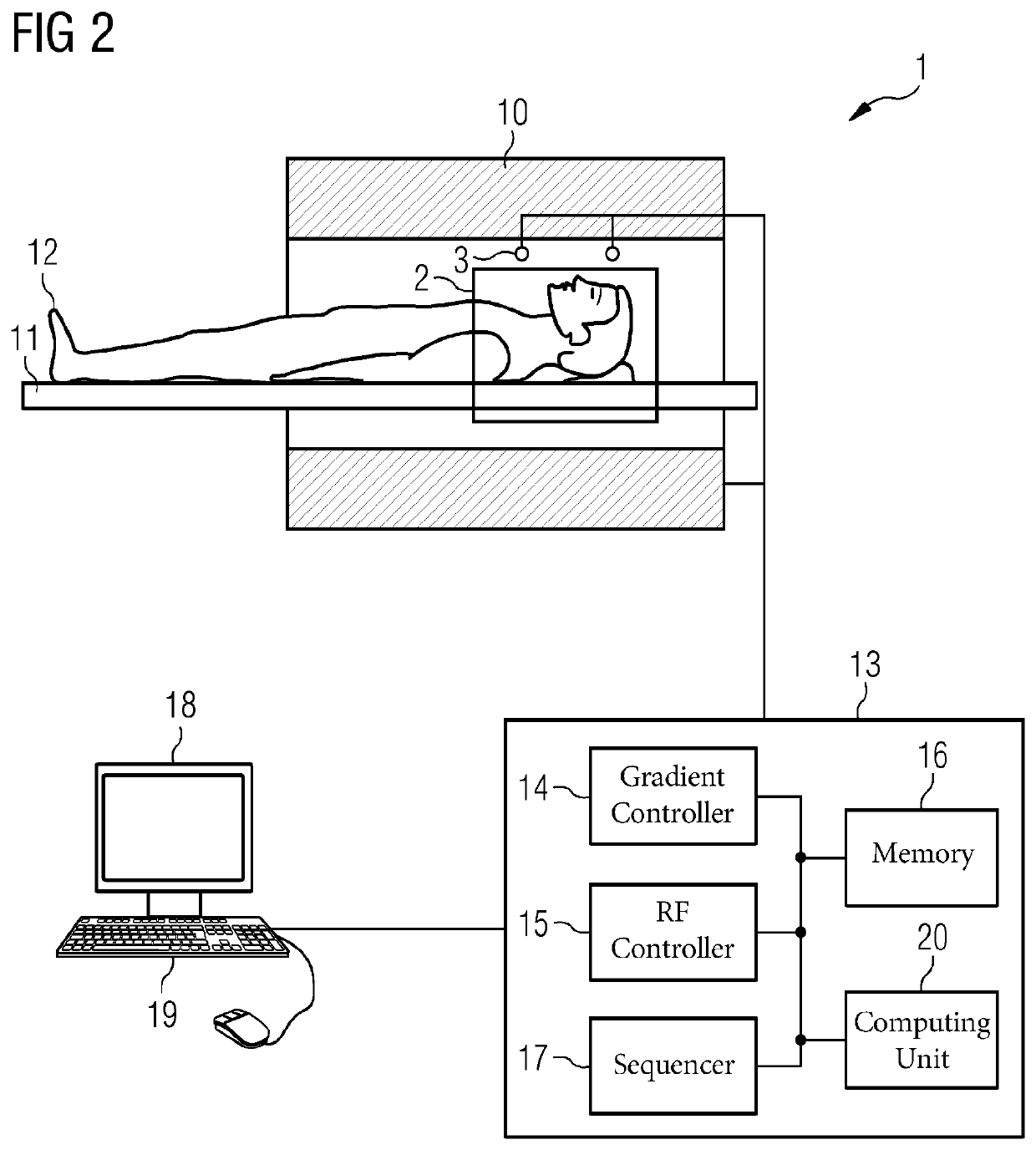
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS20190154784A1Faster MR scanning timeSimple methodMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase correctionStimulated echo
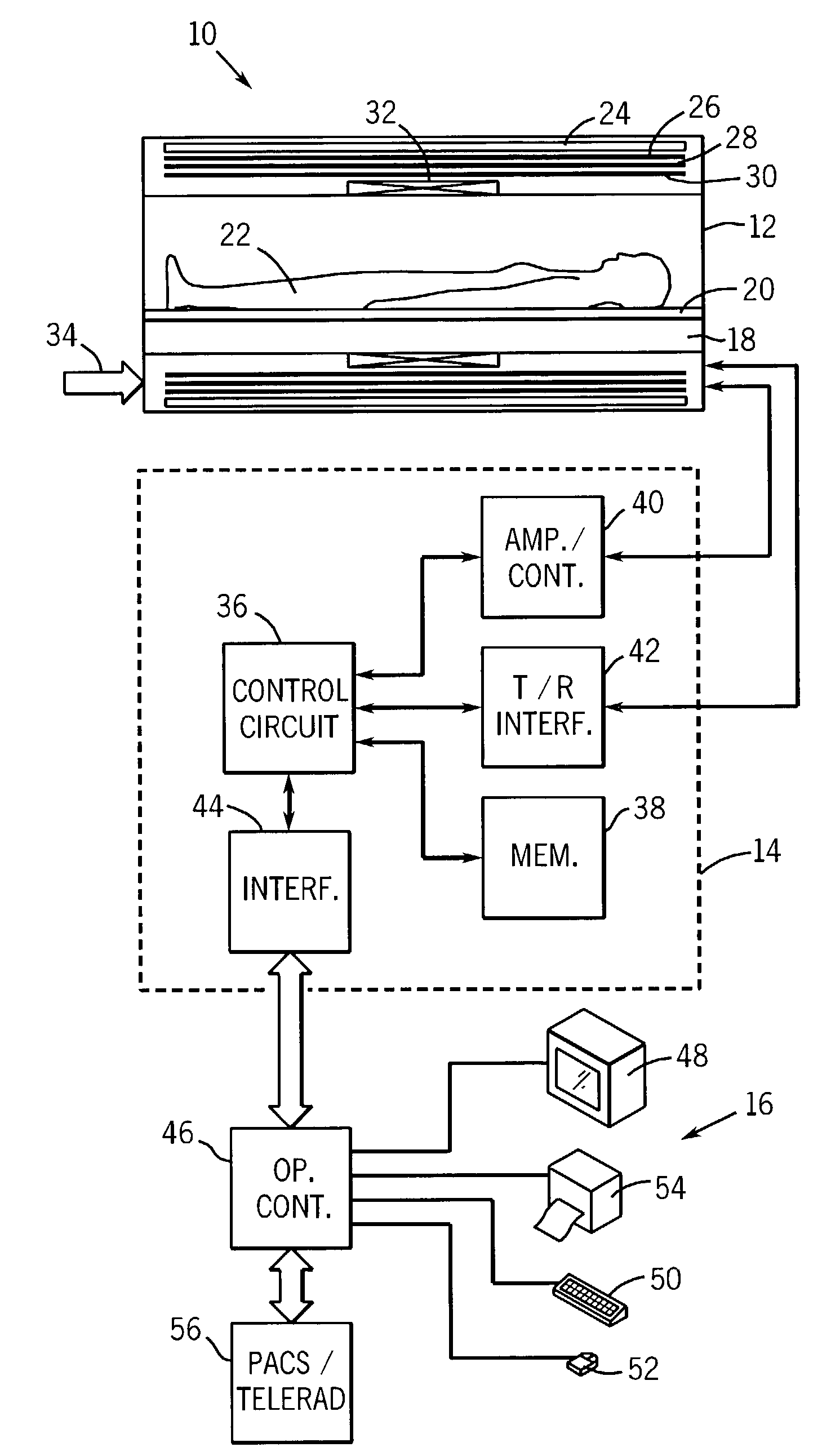
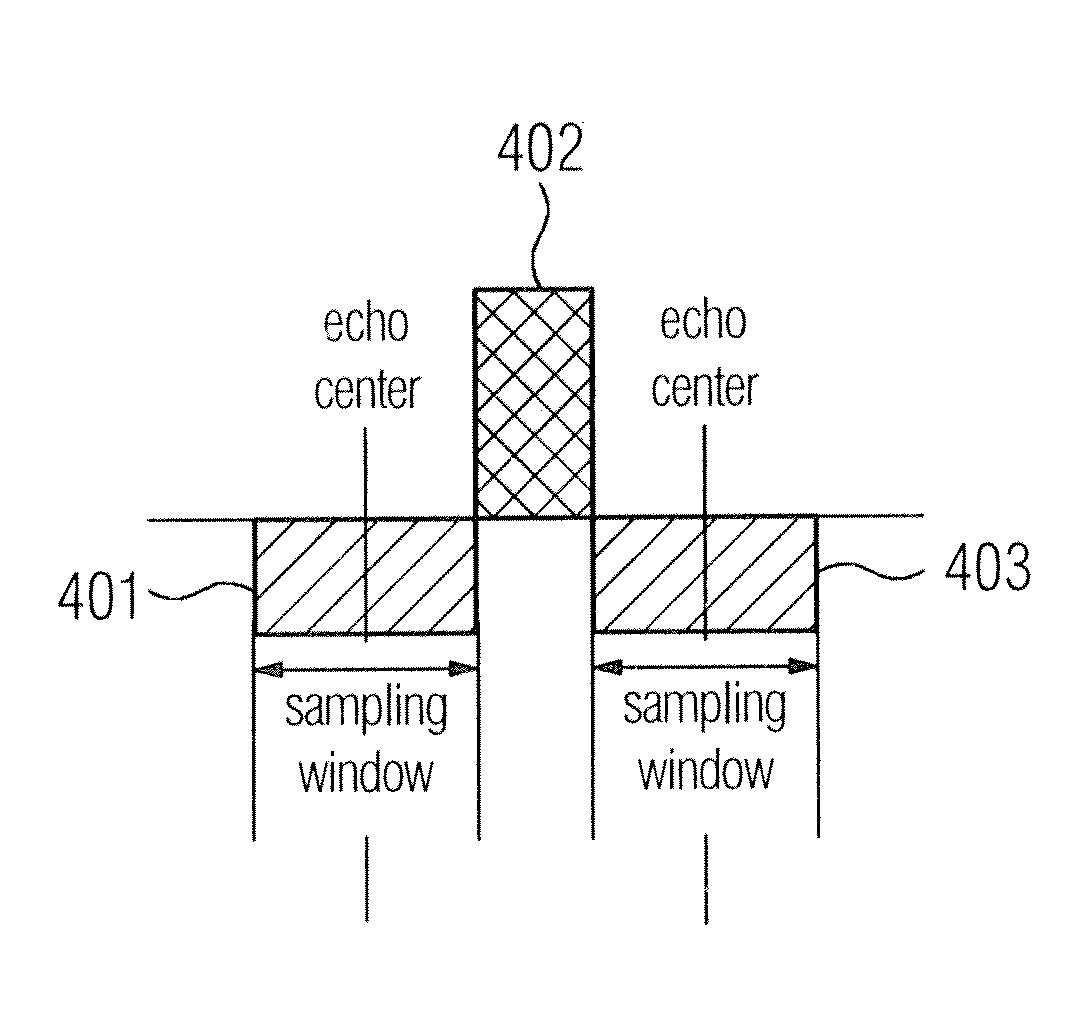
Magnetic resonance (MR) data are acquired by applying magnetic fields to an examination region concurrent with stimulated echo signals, such that trajectories, which are not straight lines, are generated in k-space. For this purpose, sequence of RF pulses is applied to generate the stimulated echo signals in the examination object, undersampled MR measurement data are detected during reception of the stimulated echo signals in the at least two receiving coils, along the curved k-space trajectories, and fully sampled MR measurement are generated from the undersampled MR measurement data using sensitivity information of the at least two receiving coils. Alternatively, the MR measurement data are fully sampled in a central region of k-space, and a region outside the central region is not fully sampled, and a phase correction with a Partial Fourier technique is executed on the MR measurement data using fully sampled MR measurement data from the central region of k-space.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for modulating an OQAM type multi-carrier signal, and corresponding computer program and modulator
ActiveUS9166858B2Reduce in quantityIncrease speedMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsTime domainFourier transform on finite groups
A modulator and modulation method are provided, which output an OQAM multi-carrier signal. The method implements a step of transforming, from the frequency domain to the time domain, a set of M symbols of real data so as to output M transformed symbols. The complete transformation includes the following sub-steps: applying a partial Fourier transform to the set of M symbols of real data, outputting a first subset of C transformed symbols, where C is strictly less than M; and obtaining, from the first subset, a second subset of (M-C) transformed symbols that is complementary to the first subset.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
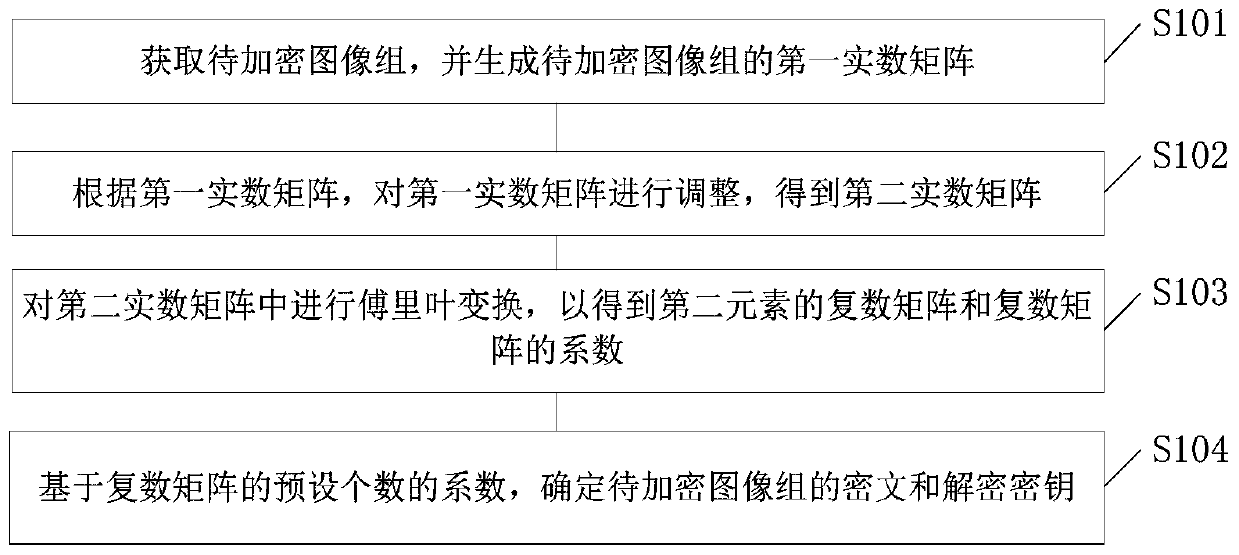
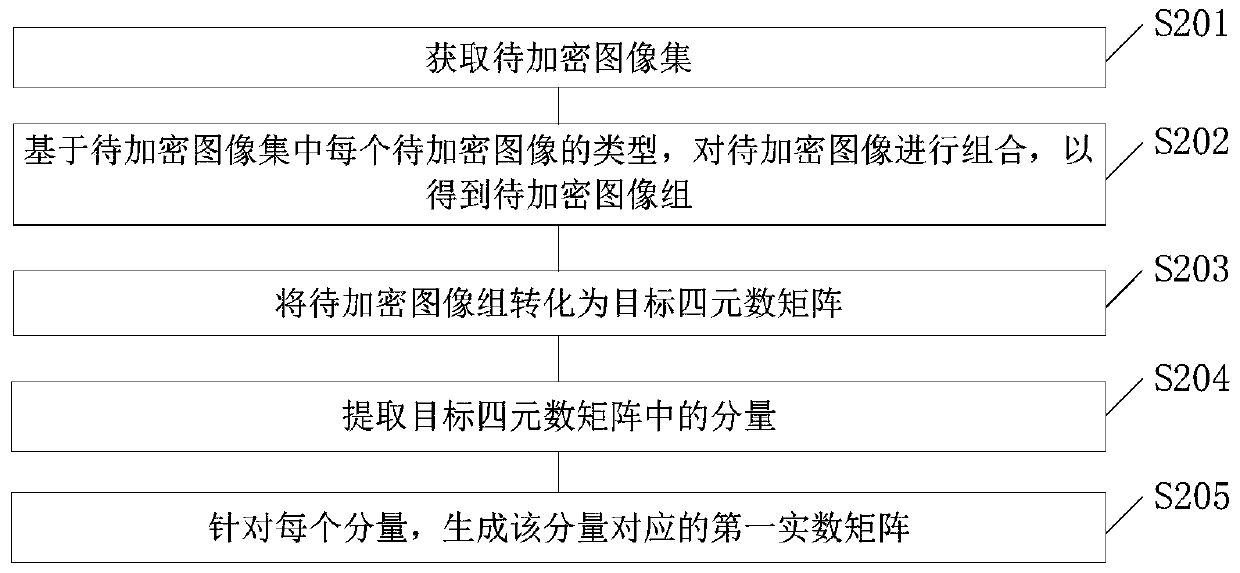
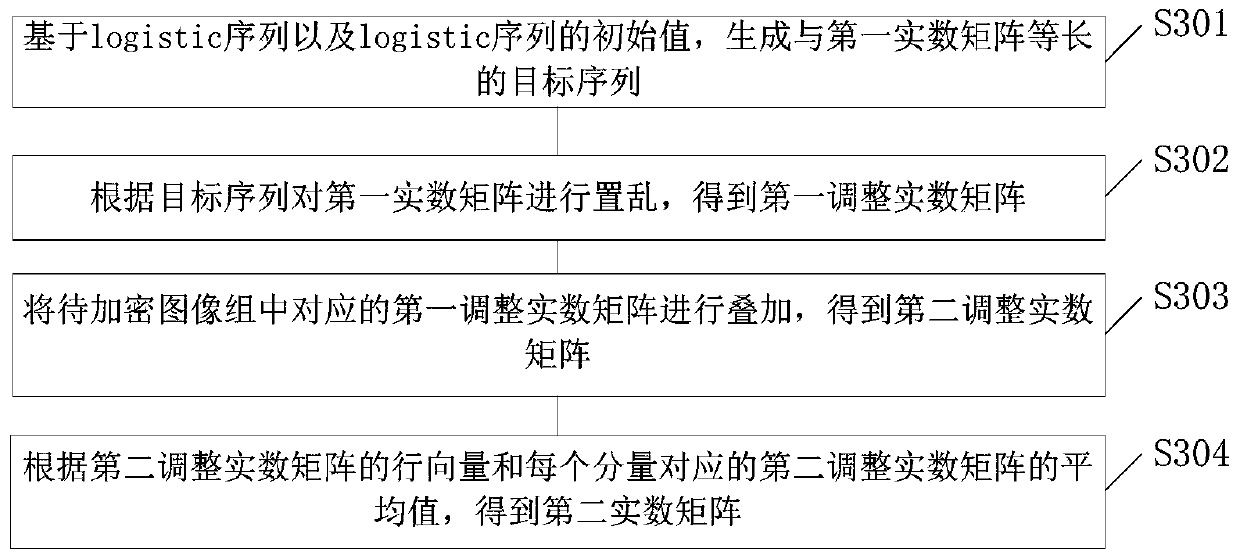
Image encryption method and device
ActiveCN110232284ASave storage spaceImprove encryption efficiencyDigital data protectionPictoral communicationCiphertextPartial fourier
The invention provides an image encryption method and device, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-encrypted image group, and generating a first real number matrix of the to-be-encrypted image group; adjusting the first real number matrix to obtain a second real number matrix; performing Fourier transform on the second real number matrix to obtain a complex number matrix of the second real number matrix and a coefficient of the complex number matrix; and determining a ciphertext and a decryption key of the to-be-encrypted image group based on a preset number of coefficients ofthe complex matrix. According to the embodiment of the invention, the Fourier coefficients of the to-be-encrypted image group are generated, and part of the Fourier coefficients are selected as the ciphertext and the secret key, so that the ciphertext storage space is reduced, multiple images are encrypted at the same time, and the encryption efficiency is improved.
Owner:南京研捷网络科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound focusing under simultaneous temperature monitoring
ActiveUS8427154B2Precise positioningReduces subsequent heatingMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSonificationTissue heating
In a method and an apparatus for magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), precise localization of the focal point of the HIFU is determined by imaging an examination subject in parallel with GRE sequences that respectively include a positive monopolar gradient pulse and a negative monopolar gradient pulse, that respectively encode the acoustic radiation force (ARF)-induced phase shift that is induced by the simultaneous activation of HIFU during the sequences. A GRE phase image is reconstructed from each acquisition sequence, and a difference image is formed between the two GRE phase images, from which the HIFU focal point is determined. An average image is formed of the two GRE phase images from which PRFS temperature map is determined simultaneously to ARFI map. The use of parallel imaging and the use of partial Fourier reconstruction for reconstructing the GRE phase images allows the data to be acquired sufficiently rapidly so as to minimize the adverse effect of tissue heating that occurs with conventional longer-duration, and repetitious, techniques.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
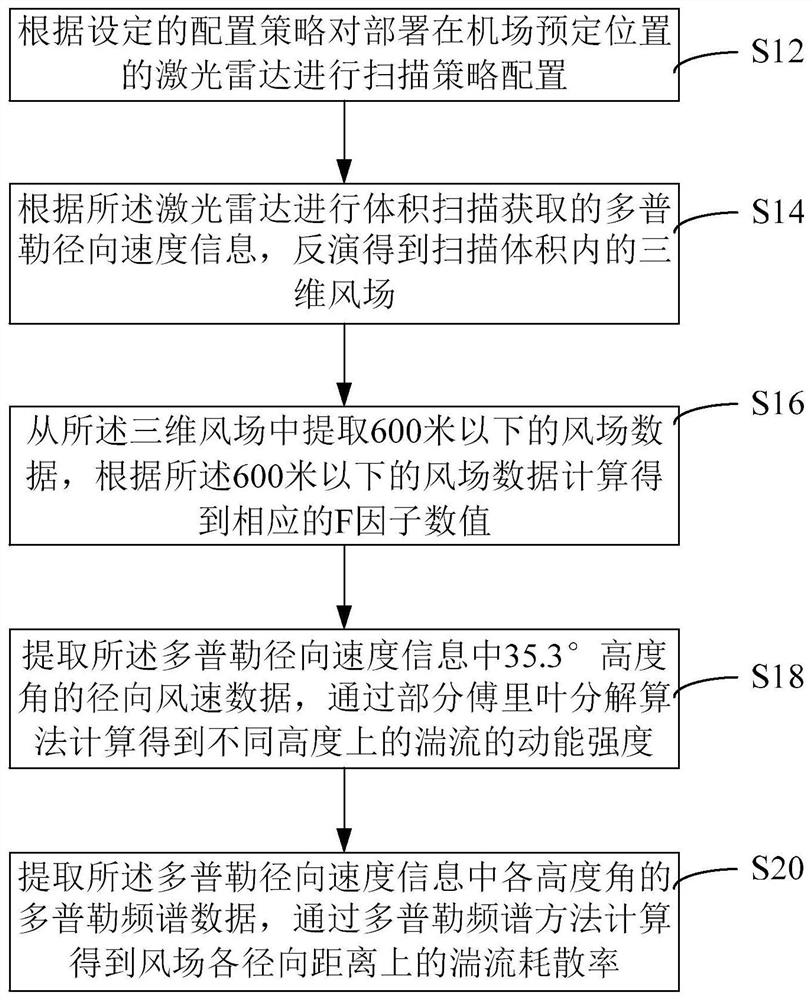
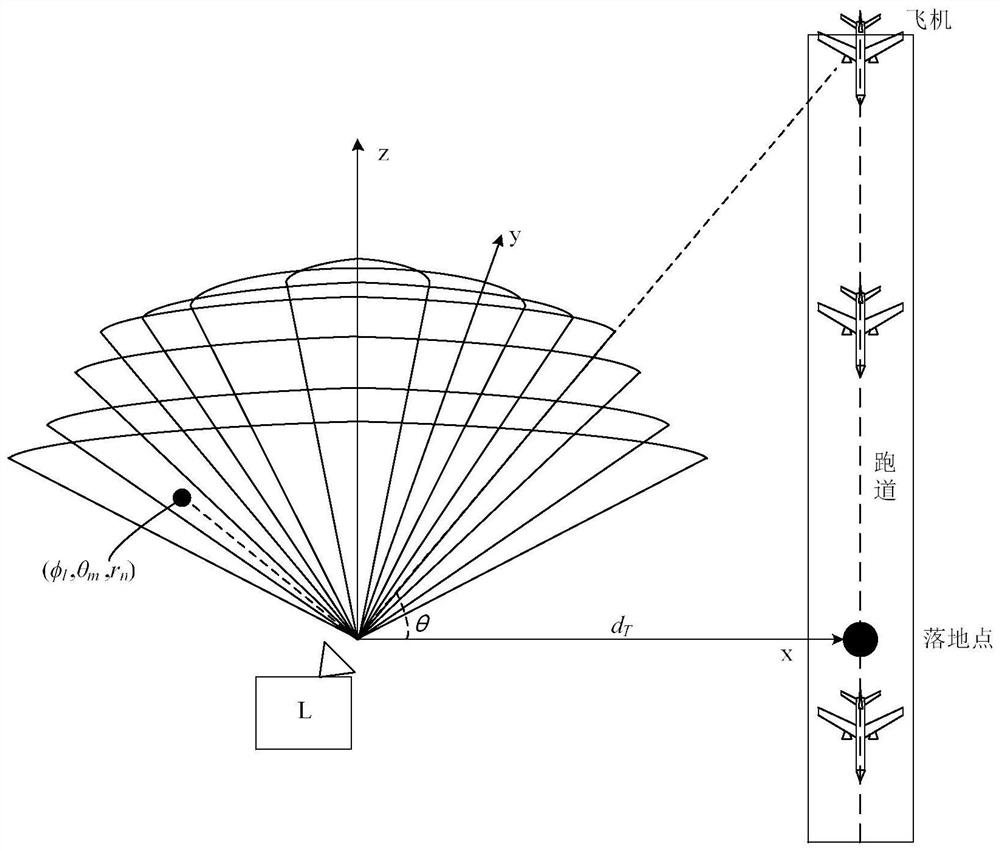
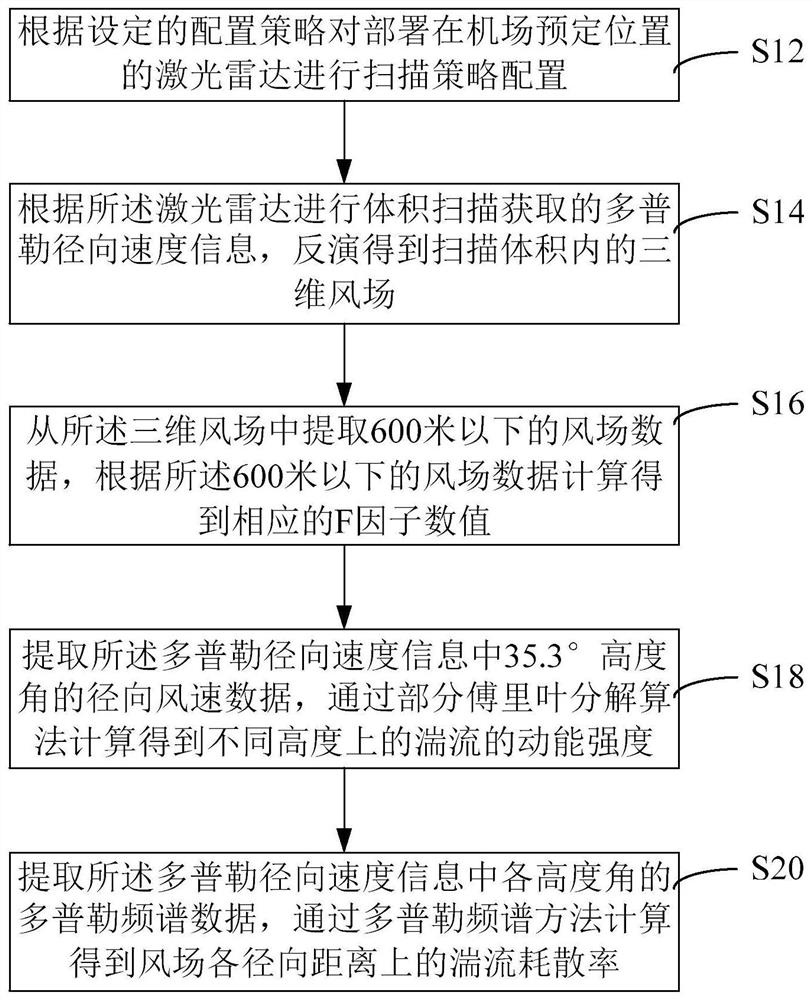
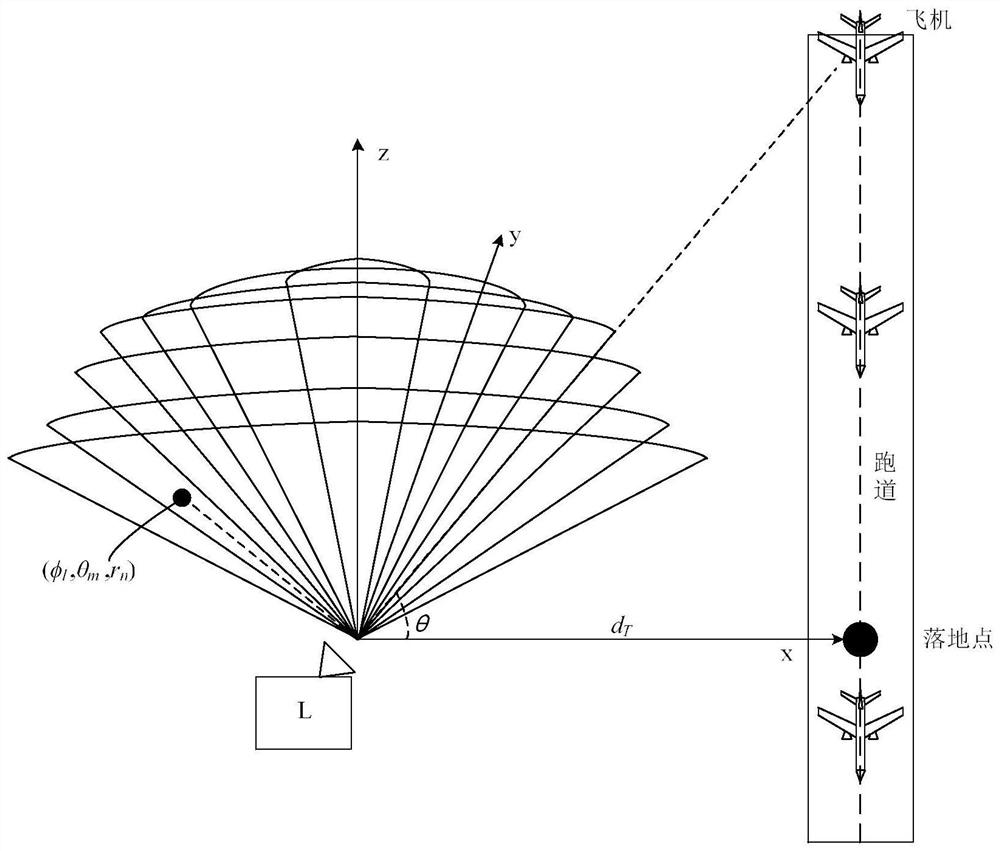
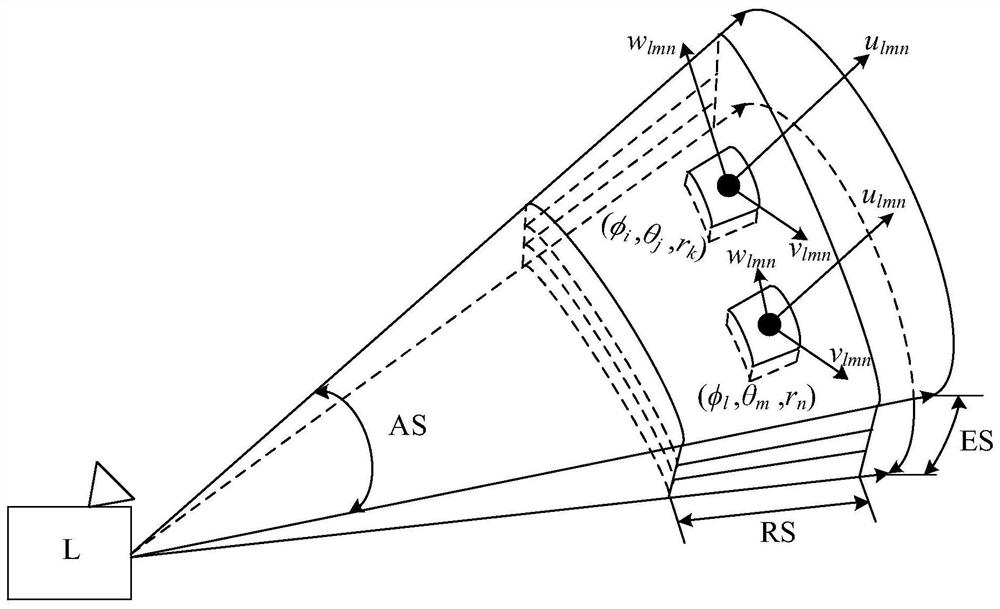
Airport wind field feature detection method and device based on laser radar and equipment
ActiveCN112965084AImprove detection abilityAccurate detectionFluid speed measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationElevation angleRadar
The invention relates to an airport wind field feature detection method and device based on a laser radar and equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out scanning strategy configuration on a laser radar deployed at a preset position of an airport according to a set configuration strategy; according to Doppler radial velocity information obtained by volume scanning of the laser radar, obtaining a three-dimensional wind field in the scanning volume through inversion; extracting wind field data below 600m from the three-dimensional wind field, and calculating to obtain a corresponding F factor value according to the wind field data below 600m; extracting radial wind speed data at an elevation angle of 35.3 degrees in the Doppler radial velocity information, and calculating to obtain kinetic energy intensity of turbulence at different heights through a partial Fourier decomposition algorithm; and extracting doppler spectrum data of each elevation angle in the Doppler radial velocity information, and calculating the turbulence dissipation rate of each radial distance of a wind field through a Doppler spectrum method. According to the method provided by the above technical schemes of the invention, the effect of relatively high comprehensive detection performance of the wind field is achieved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Pilot optimization method for compression sensing channel estimation of large-scale MIMO system
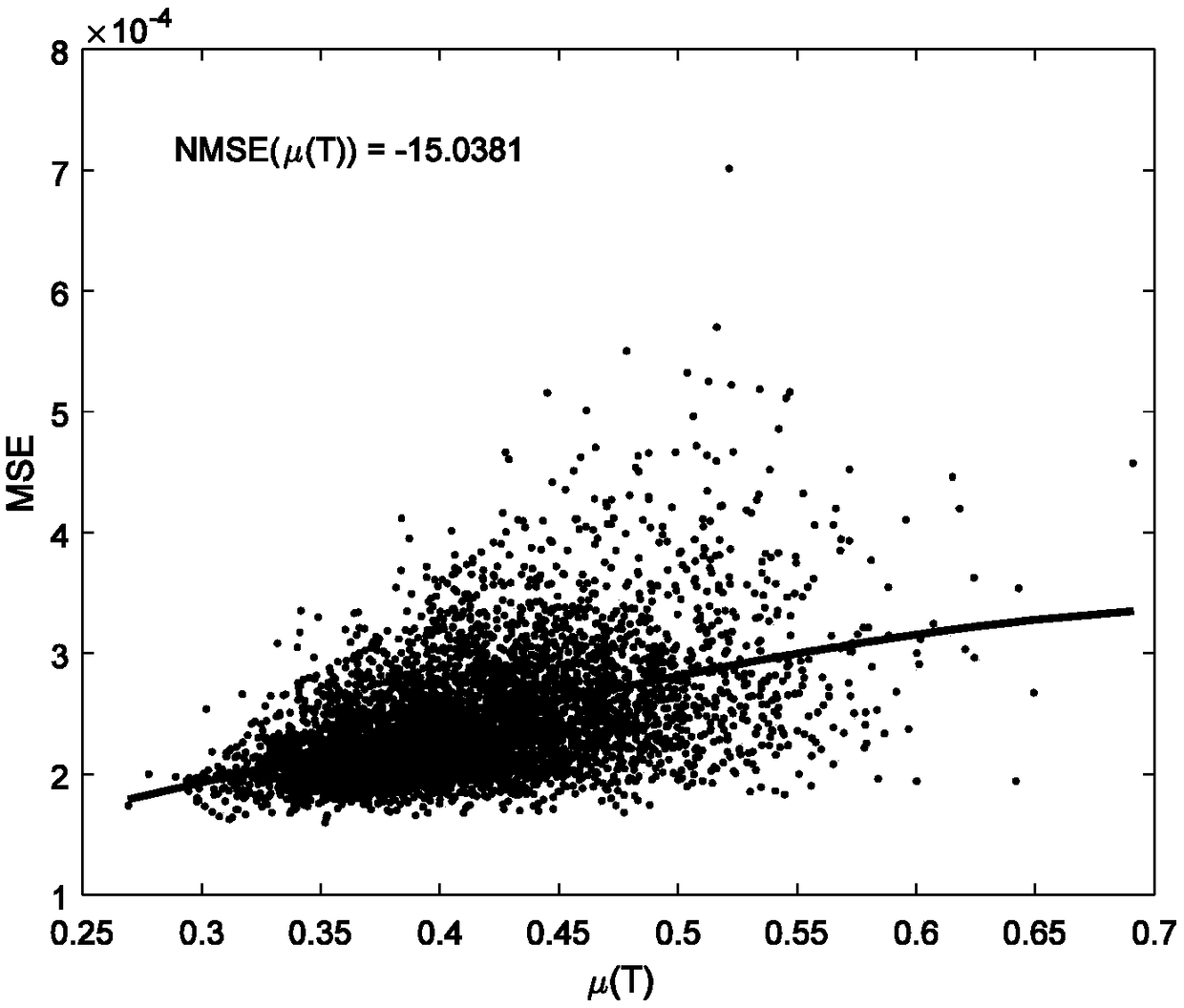
InactiveCN107171774AReduce mean square errorImprove estimation performanceBaseband system detailsRadio transmissionMean squareGenetic algorithm
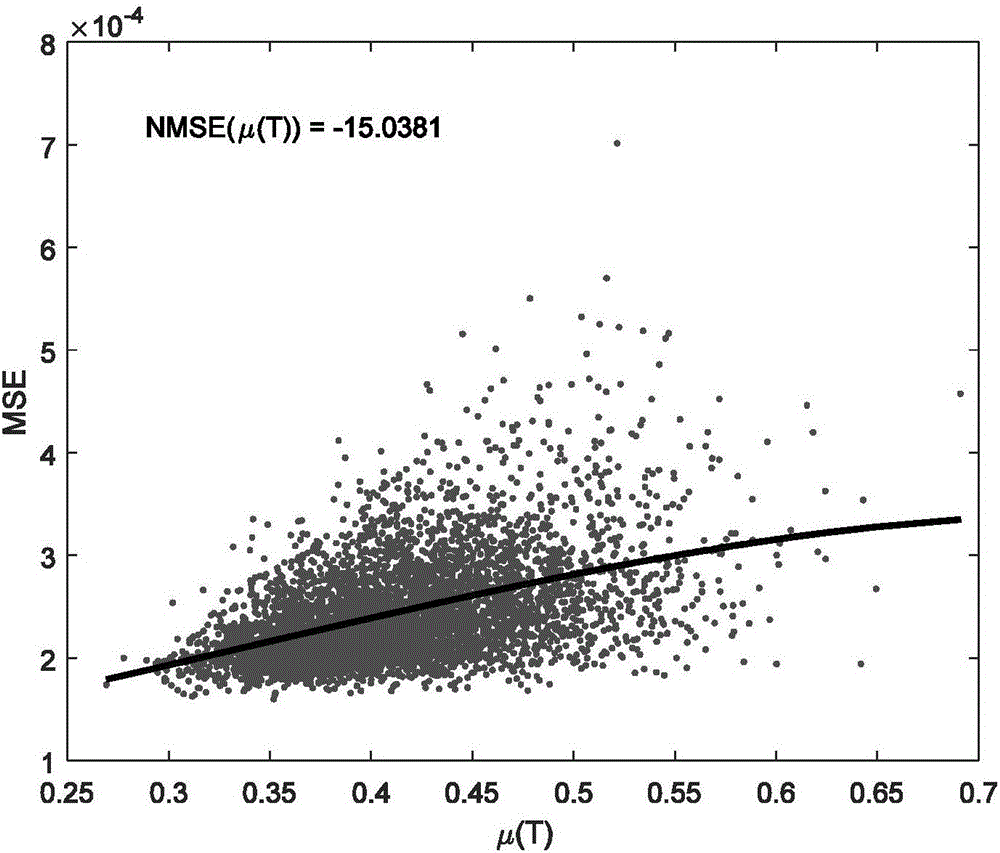
The invention discloses a pilot optimization method for compression sensing channel estimation of a large-scale MIMO system. A part of Fourier matrixes can be used as pilot matrixes; a minimum cross-correlation criterion is taken as the starting point; a pilot matrix optimization problem is modelled as a combined optimization problem; then, the combined optimization problem is solved by utilization of a genetic algorithm GA; and thus, an optimized pilot matrix having the minimum cross-correlation value is obtained. By means of the pilot optimization method disclosed by the invention, the fact that large-scale MIMO downlink channel estimation based on compression sensing has relatively low mean square error MSE can be ensured; and thus, the channel estimation performance can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
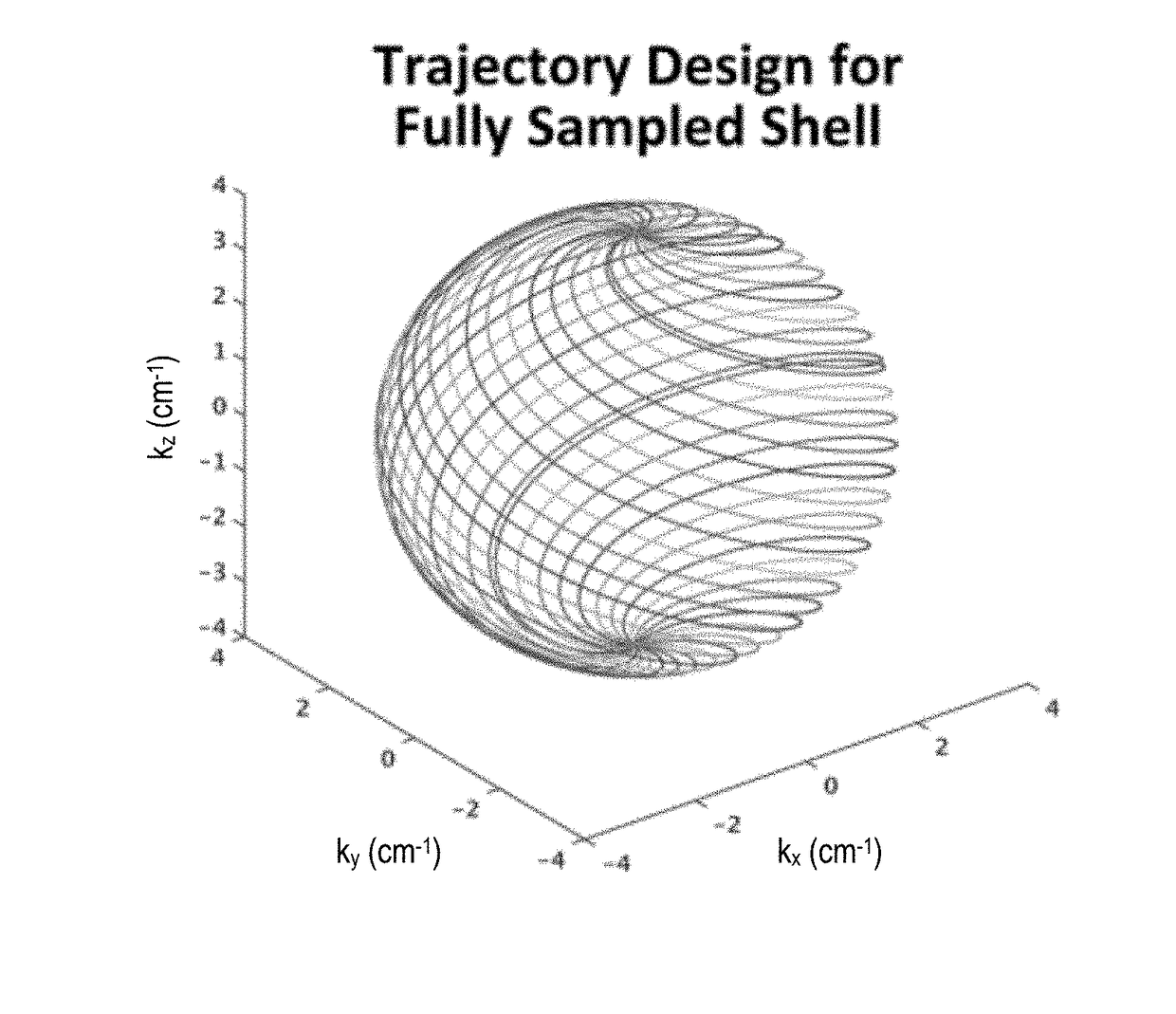
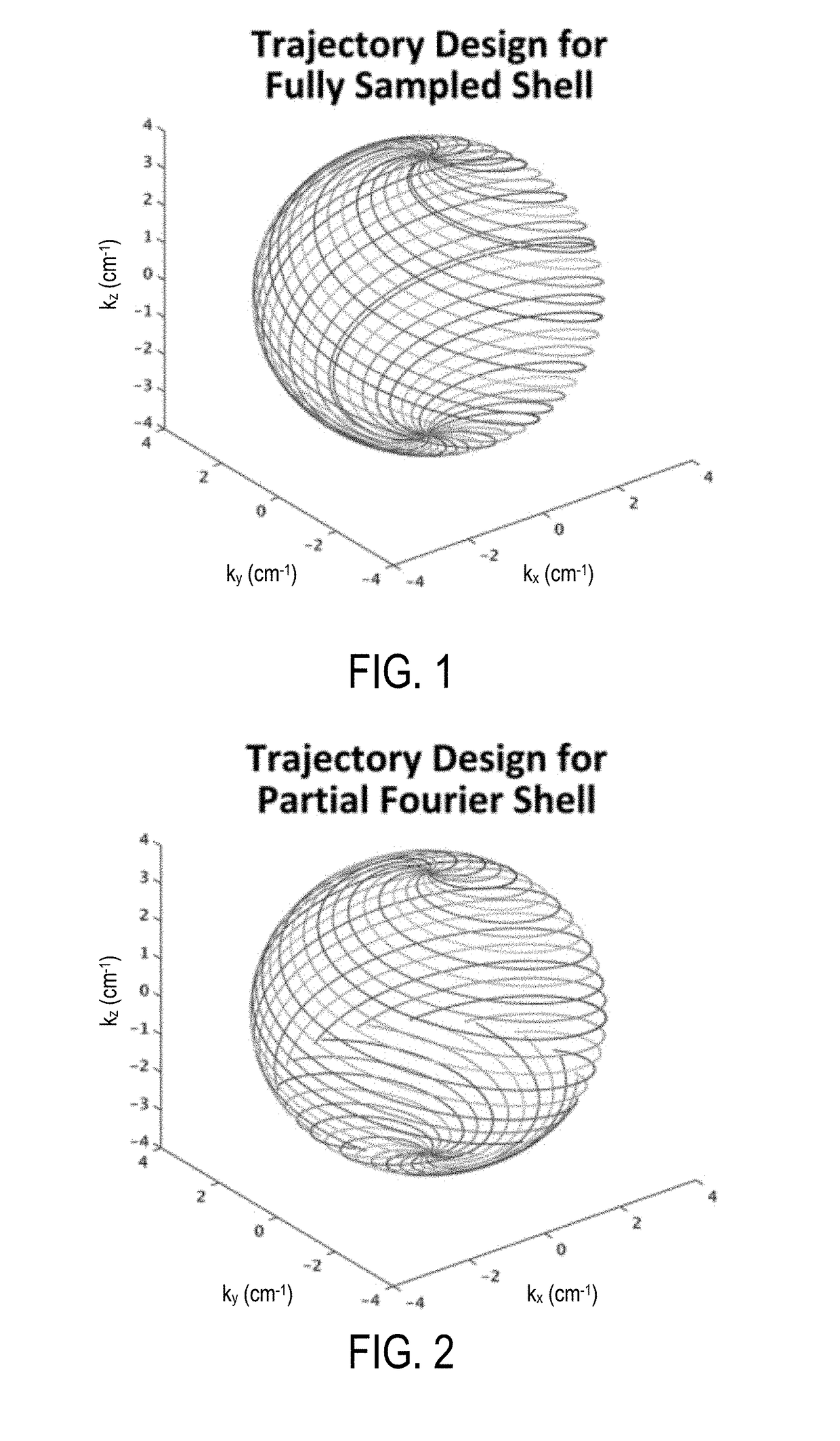
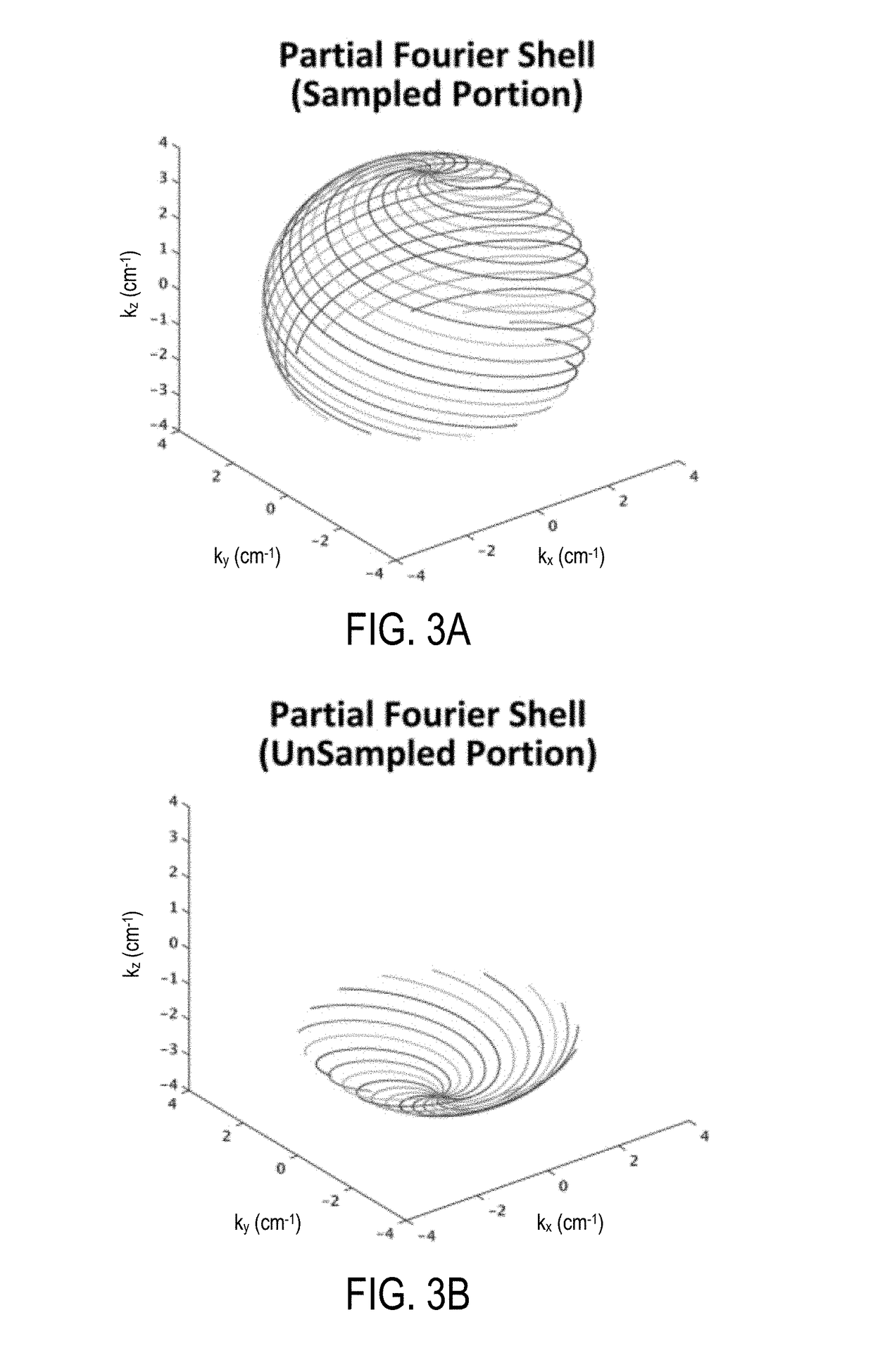
Partial fourier acquisition and reconstruction for k-space shells based magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20180292498A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsNon symmetricK space trajectory
An asymmetric 3D shells k-space trajectory design with partial Fourier acceleration is described. A non-iterative homodyne reconstruction framework is also described.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Imaging method and device for water/fat separation in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS9285447B2Reduce artifactsMomentum requirementMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical polarityFourier transform on finite groups
In an imaging method and device for water / fat separation in MRI using a two-point Dixon FSE sequence, each refocusing RF pulse corresponds to two readout gradients of the same polarity, each being center-divided into a smaller rear part and a larger front part, and one rephasing gradient of opposite polarity. In running the FSE sequence, each echo signal acquired is subjected to an FFT, to reconstruct an image with water and fat in phase and an image with water and fat in opposed phases. Data of each echo signal are subjected to a partial Fourier transform; and the in-phase water / fat image and the opposite-phase water / fat image are subjected to a water / fat separation algorithm, to obtain a pure water image and a pure fat image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
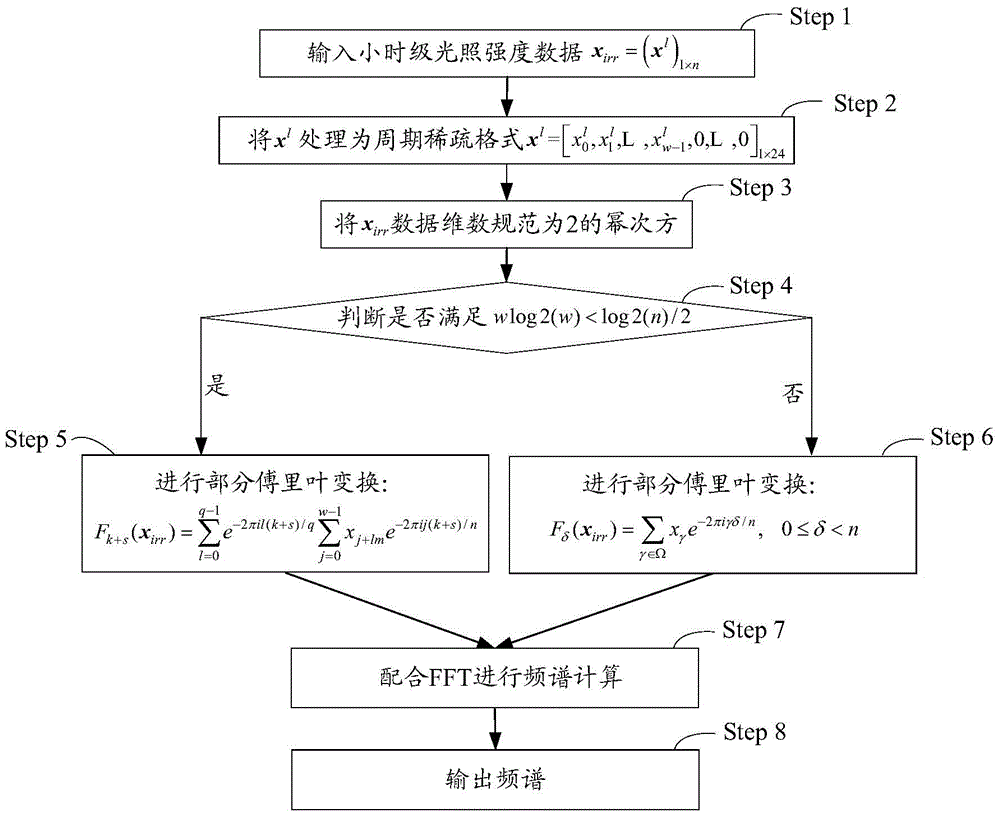
Spectral analysis calculation method and calculator for illumination intensity data
InactiveCN104156338AImprove computing efficiencyAvoid redundant calculationsComplex mathematical operationsFrequency spectrumDistribution characteristic
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
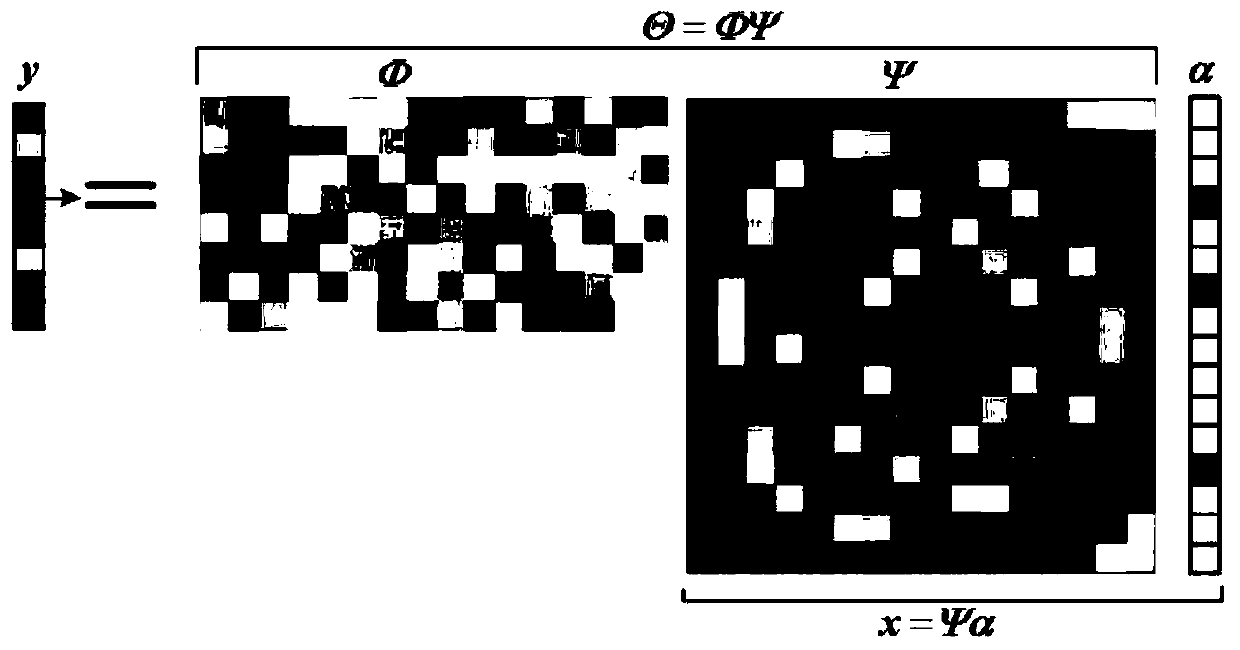
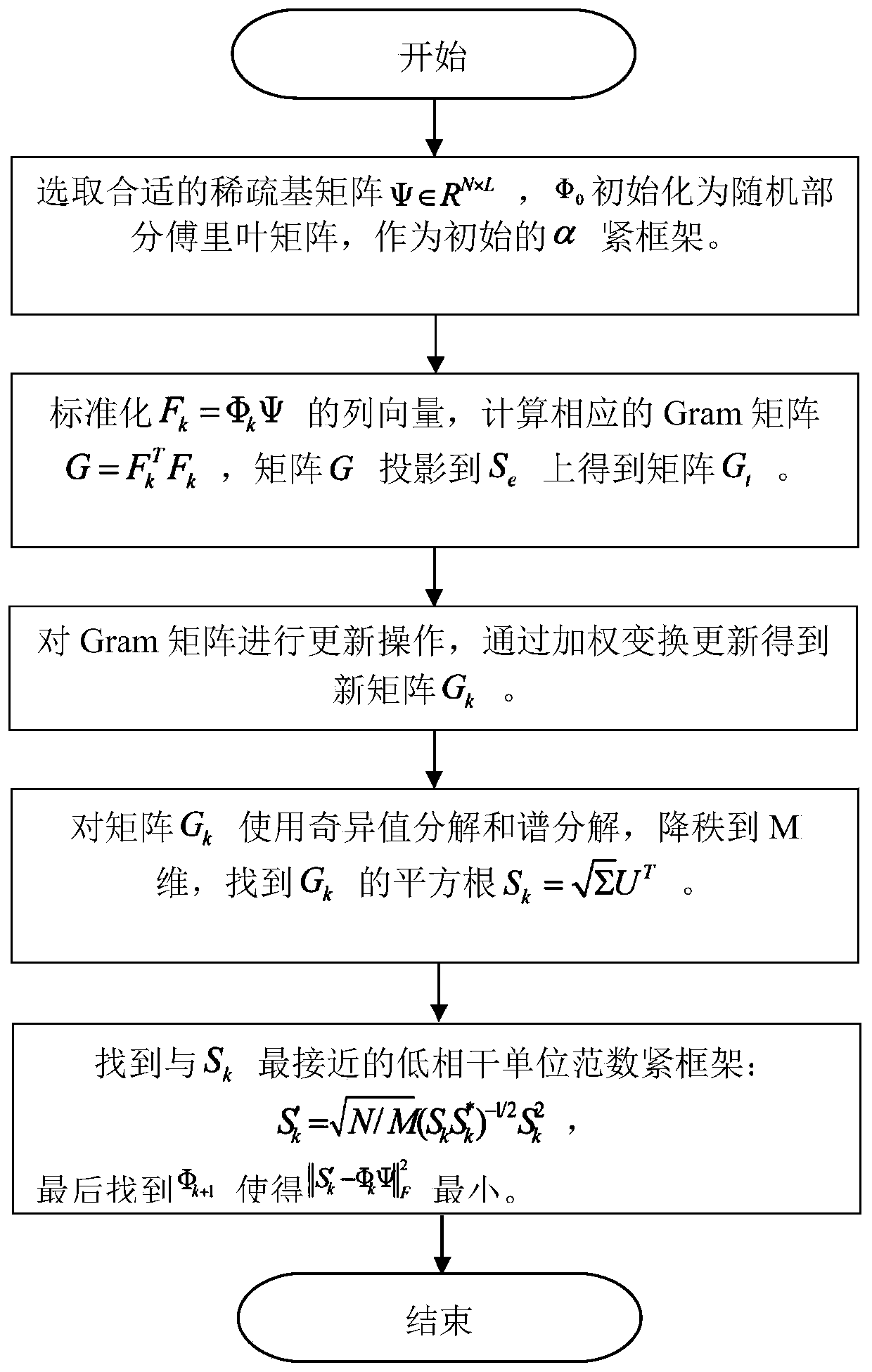
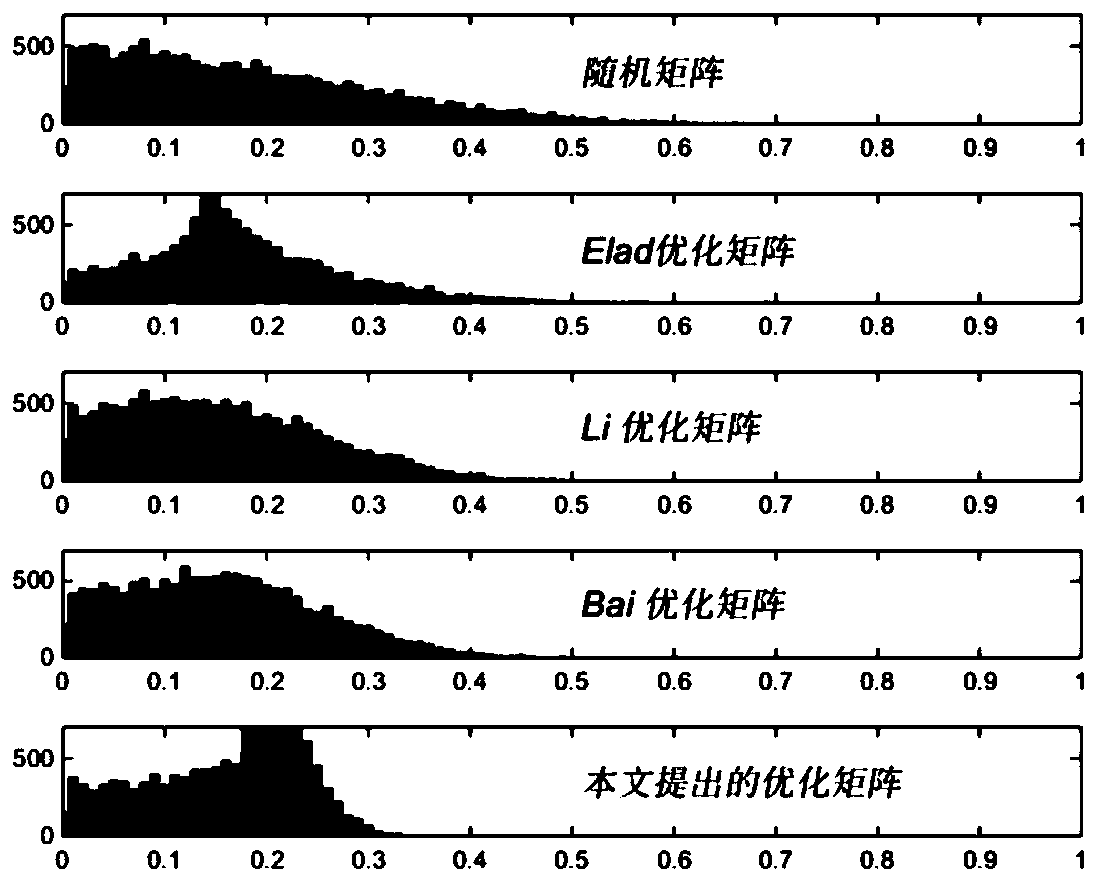
Observation matrix construction method based on low-coherence unit norm tight frame
ActiveCN111475768AAvoid the problem of difficult structureRobustImage memory managementImage acquisitionComputation complexityTight frame
The invention relates to an observation matrix construction method based on a low-coherence unit norm tight frame, and belongs to the technical field of signal processing, and the method comprises thesteps: S1, initializing an initial observation matrix phi 0 into a random part Fourier matrix, and enabling the initial observation matrix phi 0 to serve as an initial alpha tight frame F; s2, calculating a Gram matrix corresponding to the framework F, and projecting the matrix to a structure constraint set of a tight framework by using a contraction function to generate a new Gram matrix; s3, updating the Gram matrix through a weighted iteration process; s4, reducing the rank of the new Gram matrix, calculating the square root of the new Gram matrix, and finding out a tight frame closest toa unit norm tight frame; and S5, solving the optimal target function to obtain an observation matrix. According to the method, the mutual interference coefficient between the observation matrix and the sparse basis is reduced, the dependence degree on signal sparsity is reduced, the problem that an ETF frame is difficult to construct is avoided, the initial observation matrix is initialized into apart of Fourier matrix, the calculation complexity is reduced, and the pressure of storage and processing equipment is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Detection method, device and equipment of airport wind field characteristics based on lidar
ActiveCN112965084BImprove detection abilityAccurate detectionFluid speed measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadarWind field
This application relates to a lidar-based airport wind field feature detection method, device, and equipment. The method includes the steps of: configuring a scanning strategy for a lidar deployed at a predetermined location in the airport according to a set configuration strategy; The Doppler radial velocity information is inverted to obtain the three-dimensional wind field in the scanning volume; the wind field data below 600 meters is extracted from the three-dimensional wind field, and the corresponding F factor value is calculated according to the wind field data below 600 meters; The radial wind speed data of 35.3° altitude angle in the Doppler radial velocity information is calculated by the partial Fourier decomposition algorithm to obtain the kinetic energy intensity of the turbulent flow at different heights; the multiplicity of each altitude angle in the Doppler radial velocity information is extracted The Doppler spectrum data is used to calculate the turbulent dissipation rate at each radial distance of the wind field through the Doppler spectrum method. The above scheme achieves the effect of strong wind field comprehensive detection performance.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
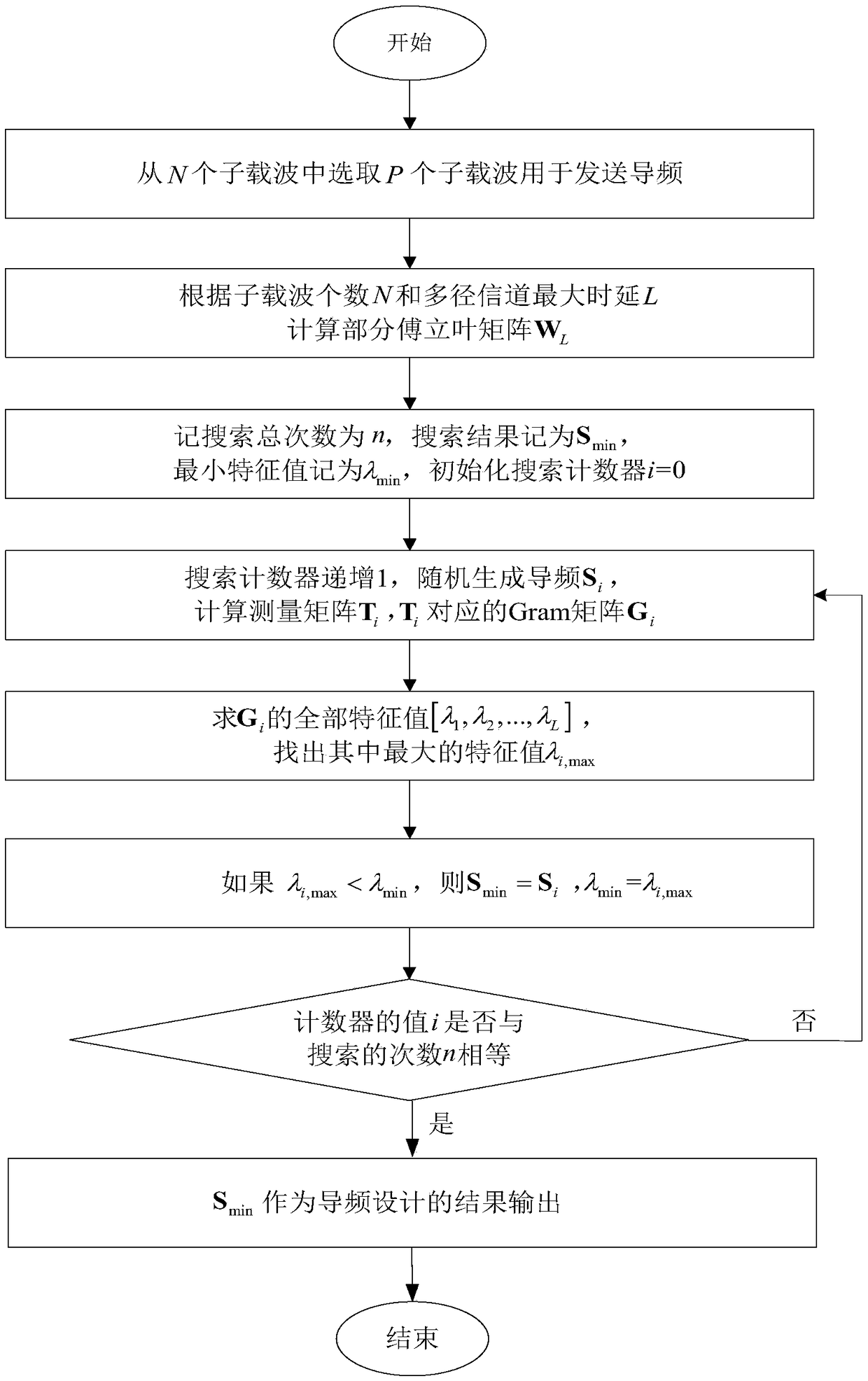
Pilot design method in compressed sensing channel estimation
ActiveCN106357581AImprove accuracyImprove performanceBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalEngineering
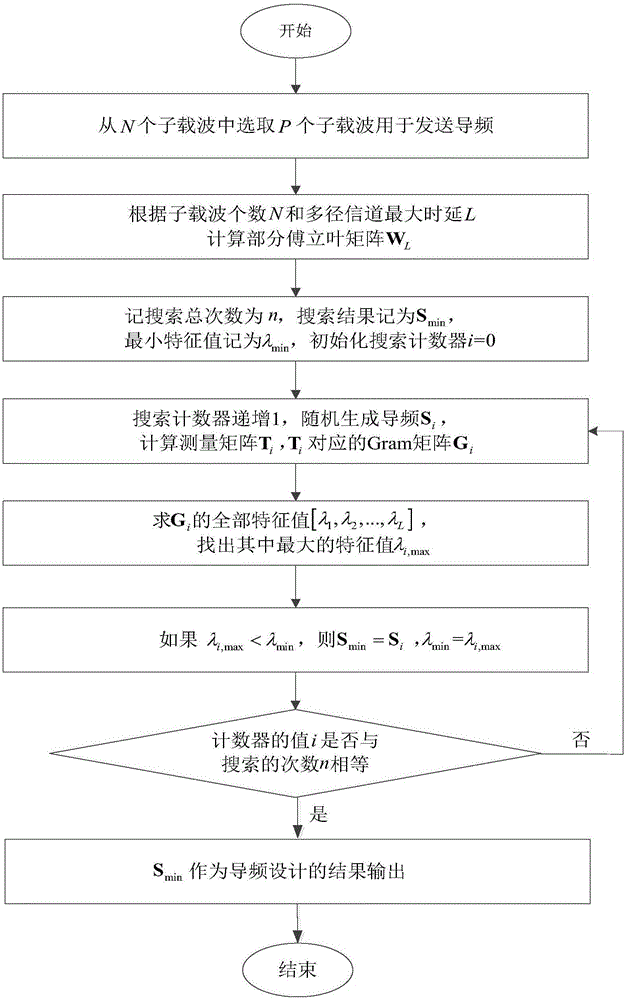
The invention discloses a pilot design method in compressed sensing channel estimation and mainly solves the problem that an existing design method cannot obtain a comparatively-good pilot pattern in limited-time searches. The method includes the steps of firstly, selecting P carrier positions from N subcarriers of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system to serve as a pilot pattern S; secondly, calculating a partial Fourier matrix WL according to the subcarrier number N and the maximum multipath delay L in the system; thirdly, using a random searching method to optimize the pilot pattern S, that is to say, using the partial Fourier matrix WL to calculate a measuring matrix T to obtain an optimized pilot patter Smin serving as the final pilot design result. Compared with an existing pilot design method, the pilot design method has the advantages that the method is good in search stability, better pilot can be obtained, and the method can be used for compressed sensing channel estimation and offline calculation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A method and system for calculating the interaction force between particles
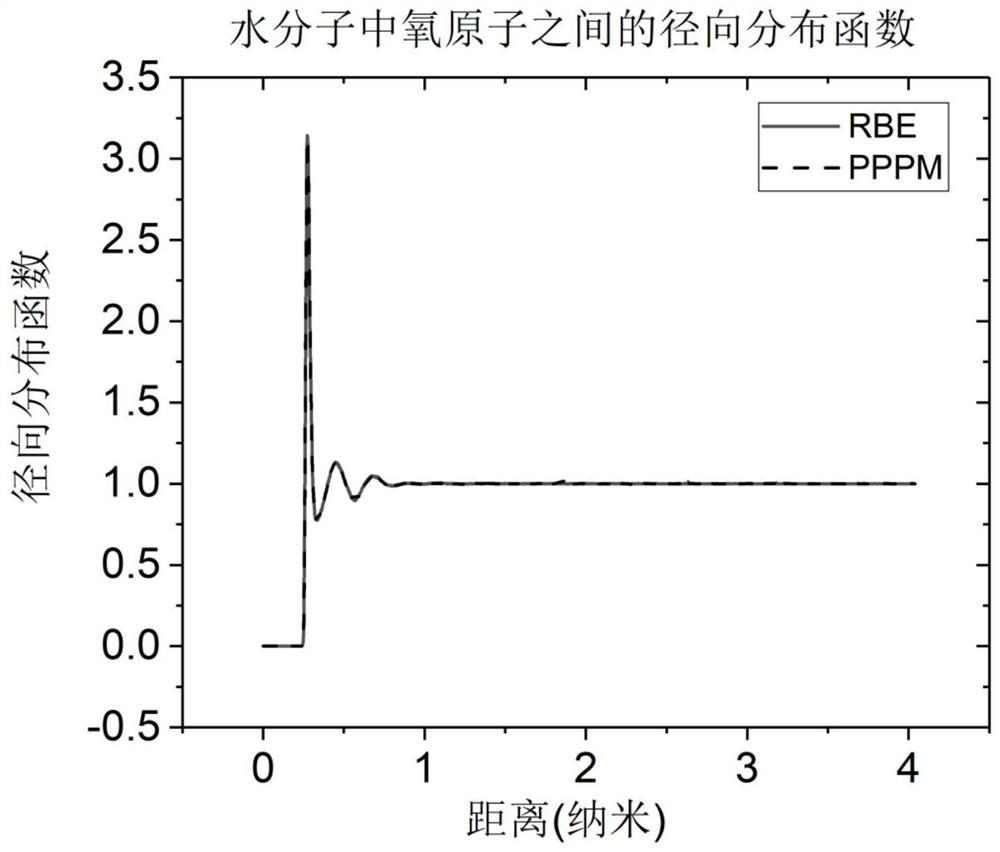
ActiveCN112733416BImprove efficiencyKinetic properties are maintainedDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringSmall data
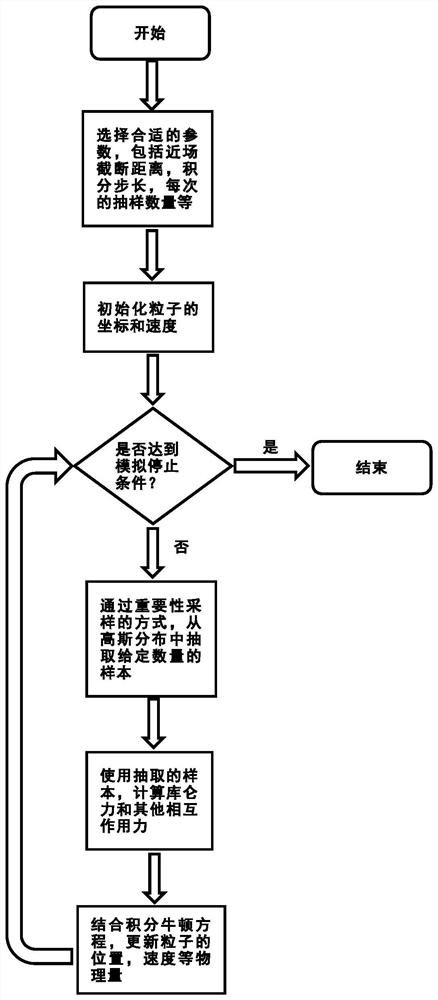
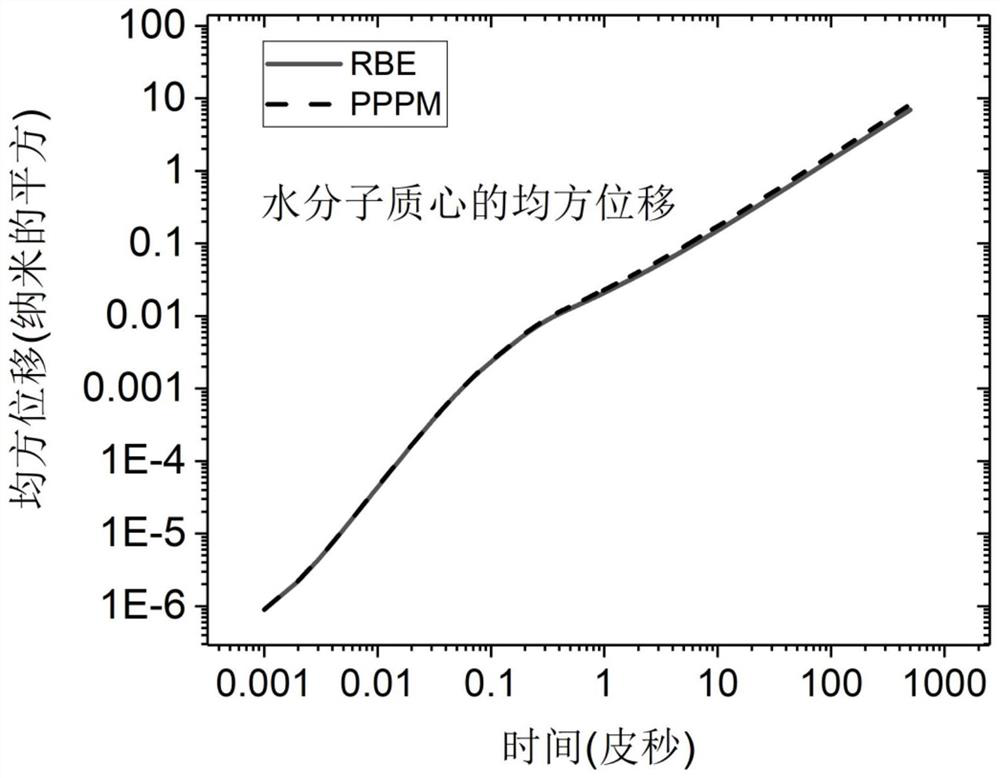
The invention discloses a method and a system for calculating the interaction force between particles, and relates to the technical field of molecular dynamics simulation systems. The charge distribution and the charged amount of the particle are used to obtain the Coulomb long-range force of the particle; wherein, the Fourier space corresponds to the function for calculating the Coulomb long-range force. Sampling methods include importance sampling, where fractional Fourier terms are randomly drawn on the order of hundreds or thousands. The method also includes obtaining the Coulomb short-range force according to Coulomb's law; obtaining the Leonard Jones force and bonding interaction force of the particle according to other parameters; finally obtaining the interaction force. The method can be used in molecular dynamics simulation to reduce computational time complexity and data traffic, thereby improving computational performance and parallel efficiency, and reducing communication consumption.
Owner:上海天鹜科技有限公司
Doppler extension processing method for underwater acoustic high speed ofdm communication
InactiveCN103491046BAdaptableEasy to handleMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDoppler spreadFast Fourier transform
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
1D Partial Fourier Parallel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method Based on Deep Convolutional Networks
ActiveCN107064845BFast rebuildReduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAlgorithmSample image
The invention relates to a Fourier parallel magnetic resonance imaging method based on a one-dimensional part of a deep convolutional network, and belongs to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging. The method comprises the following steps: a sample set for training and a sample label set are created; an initial deep convolutional network is built; a training sample of the sample set is input into an initial deep convolutional network model to perform forward propagation, an output result of the forward propagation is compared with an expect result in the sample label set, and training is performed using a gradient descent algorithm until various layer parameters maximizing the consistency between the output result and the expect result are obtained; an optimal deep convolutional network model is established by utilizing the obtained various layer parameters; and a multi-coil under-sampling image obtained through online sampling is input into the optimal deep convolutional network model, forward propagation is performed on the optimal deep convolutional network model, and a rebuilt single-channel whole-sampling image is output. A noise of the rebuilt image can be removed well, a magnetic resonance image having a good visual effect is rebuilt, and the Fourier parallel magnetic resonance imaging method has high practical value.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Magnetic resonance imaging using dataset undersampling
ActiveUS10823806B2Faster scan timeNegligible noise amplificationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase correctionStimulated echo
Magnetic resonance (MR) data are acquired by applying magnetic fields to an examination region concurrent with stimulated echo signals, such that trajectories, which are not straight lines, are generated in k-space. For this purpose, sequence of RF pulses is applied to generate the stimulated echo signals in the examination object, undersampled MR measurement data are detected during reception of the stimulated echo signals in the at least two receiving coils, along the curved k-space trajectories, and fully sampled MR measurement are generated from the undersampled MR measurement data using sensitivity information of the at least two receiving coils. Alternatively, the MR measurement data are fully sampled in a central region of k-space, and a region outside the central region is not fully sampled, and a phase correction with a Partial Fourier technique is executed on the MR measurement data using fully sampled MR measurement data from the central region of k-space.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Microscopic Imaging Method Based on Partial Fourier Space
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
A system and method for reconstruction of magnetic resonance images acquired with partial fourier acquisition
ActiveUS20220065967A1Improve efficiencyQuality improvementDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData setRadiology
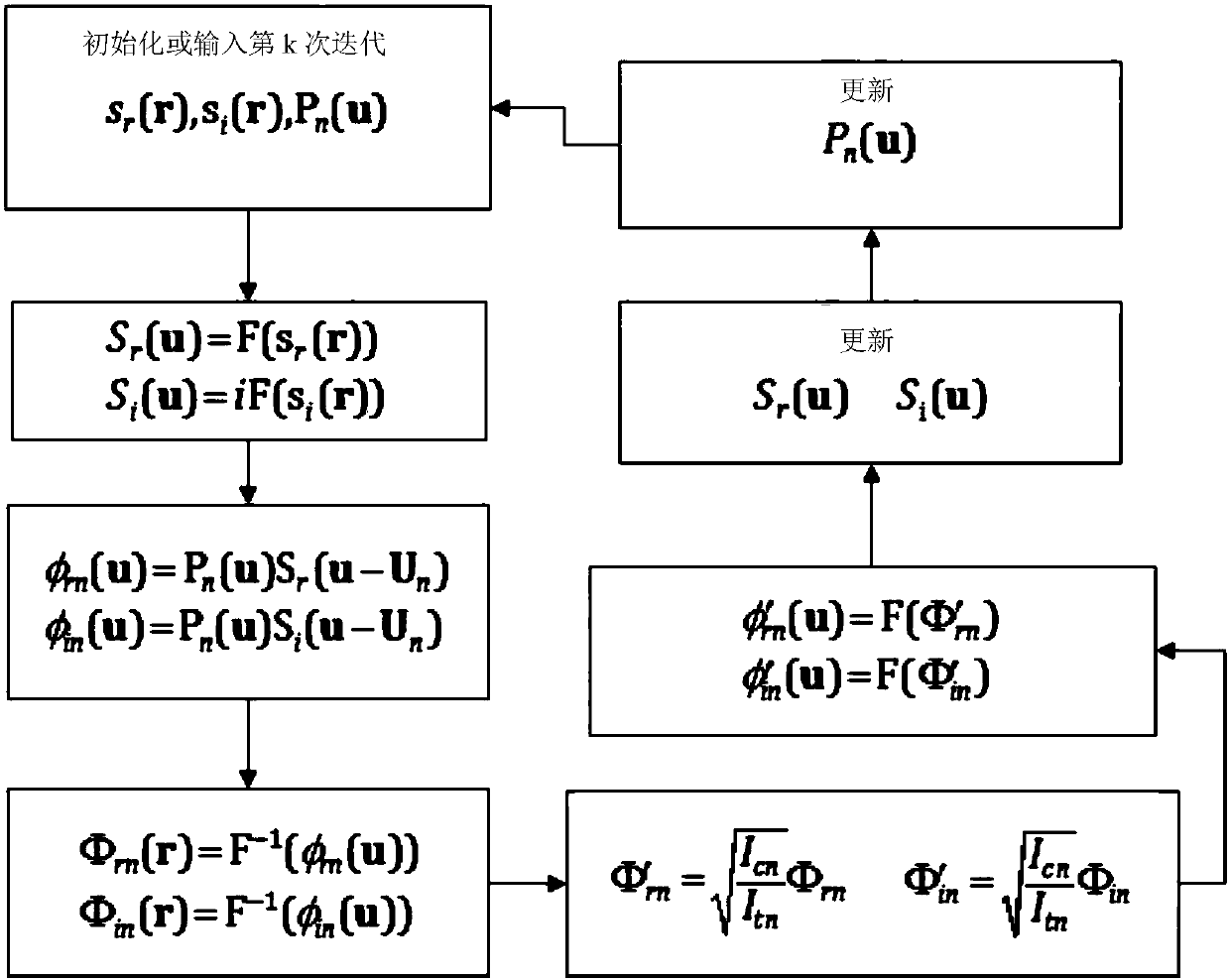
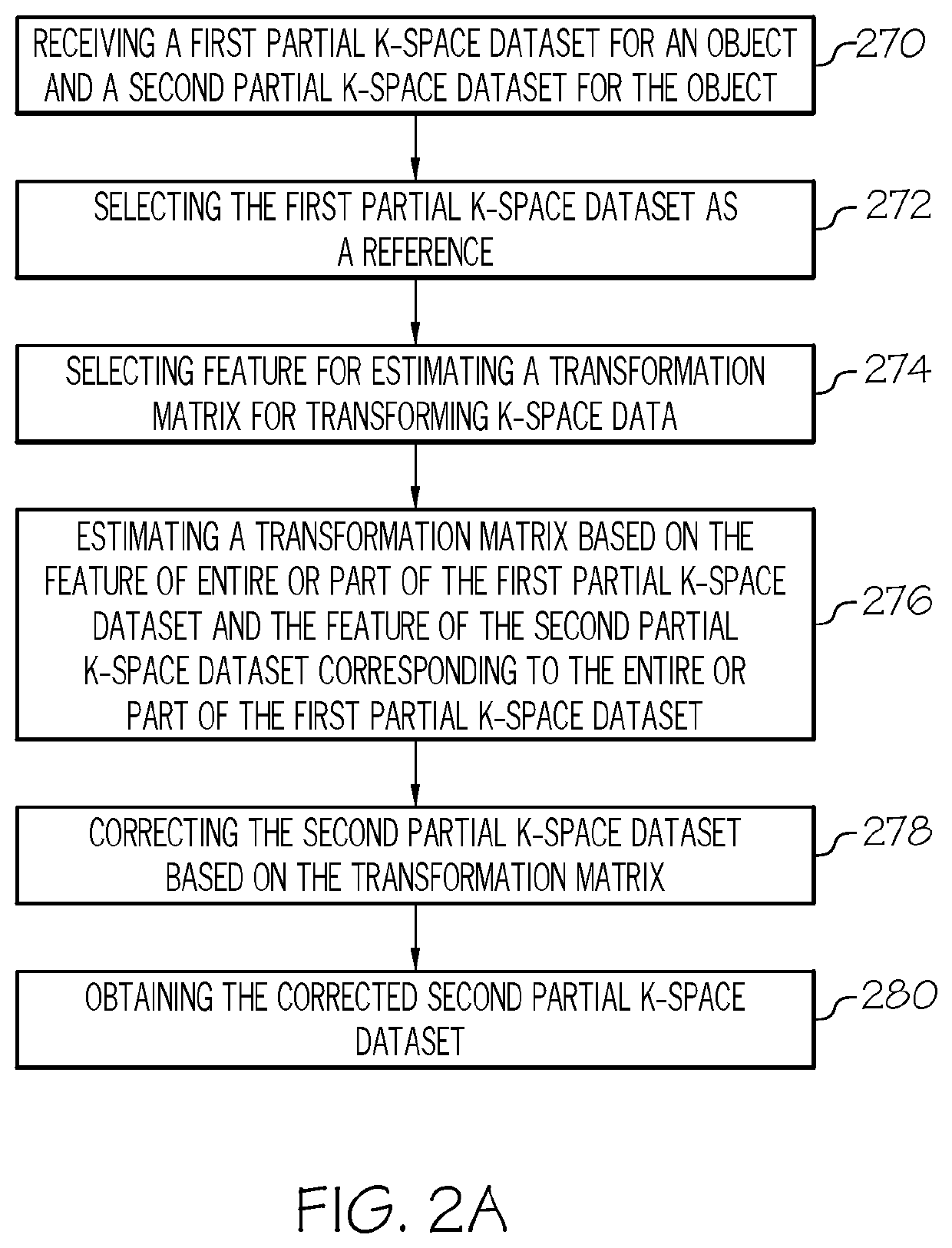
A method for k-space registration is provided. The method of k-space registration includes receiving a first partial k-space dataset for an object and a second partial k-space dataset for the object, selecting the first partial k-space dataset as a reference, selecting feature for estimating a transformation matrix for transforming k-space data, estimating a transformation matrix based on the feature of entire or part of the first partial k-space dataset and the feature of the second partial k-space dataset corresponding to the entire or part of the first partial k-space dataset, correcting the second partial k-space dataset based on the transformation matrix, and obtaining the corrected second partial k-space dataset. The present method is further used for partial Fourier reconstruction.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI +1
Pilot Design Method in Compressed Sensing Channel Estimation
ActiveCN106357581BImprove accuracyImprove performanceBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalEngineering
The invention discloses a pilot design method in compressed sensing channel estimation and mainly solves the problem that an existing design method cannot obtain a comparatively-good pilot pattern in limited-time searches. The method includes the steps of firstly, selecting P carrier positions from N subcarriers of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system to serve as a pilot pattern S; secondly, calculating a partial Fourier matrix WL according to the subcarrier number N and the maximum multipath delay L in the system; thirdly, using a random searching method to optimize the pilot pattern S, that is to say, using the partial Fourier matrix WL to calculate a measuring matrix T to obtain an optimized pilot patter Smin serving as the final pilot design result. Compared with an existing pilot design method, the pilot design method has the advantages that the method is good in search stability, better pilot can be obtained, and the method can be used for compressed sensing channel estimation and offline calculation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
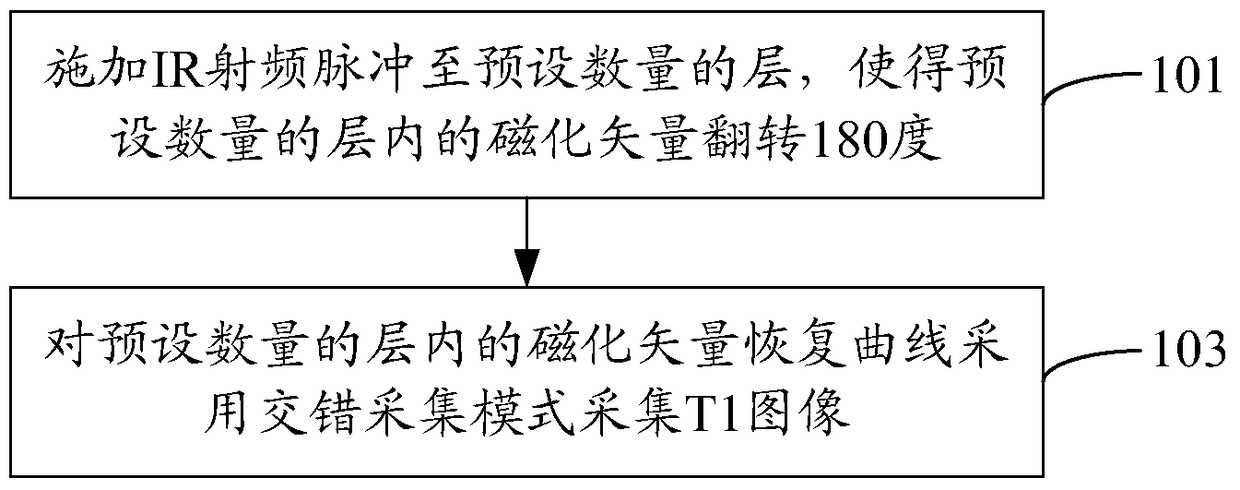
Method and device for measuring brain longitudinal relaxation value
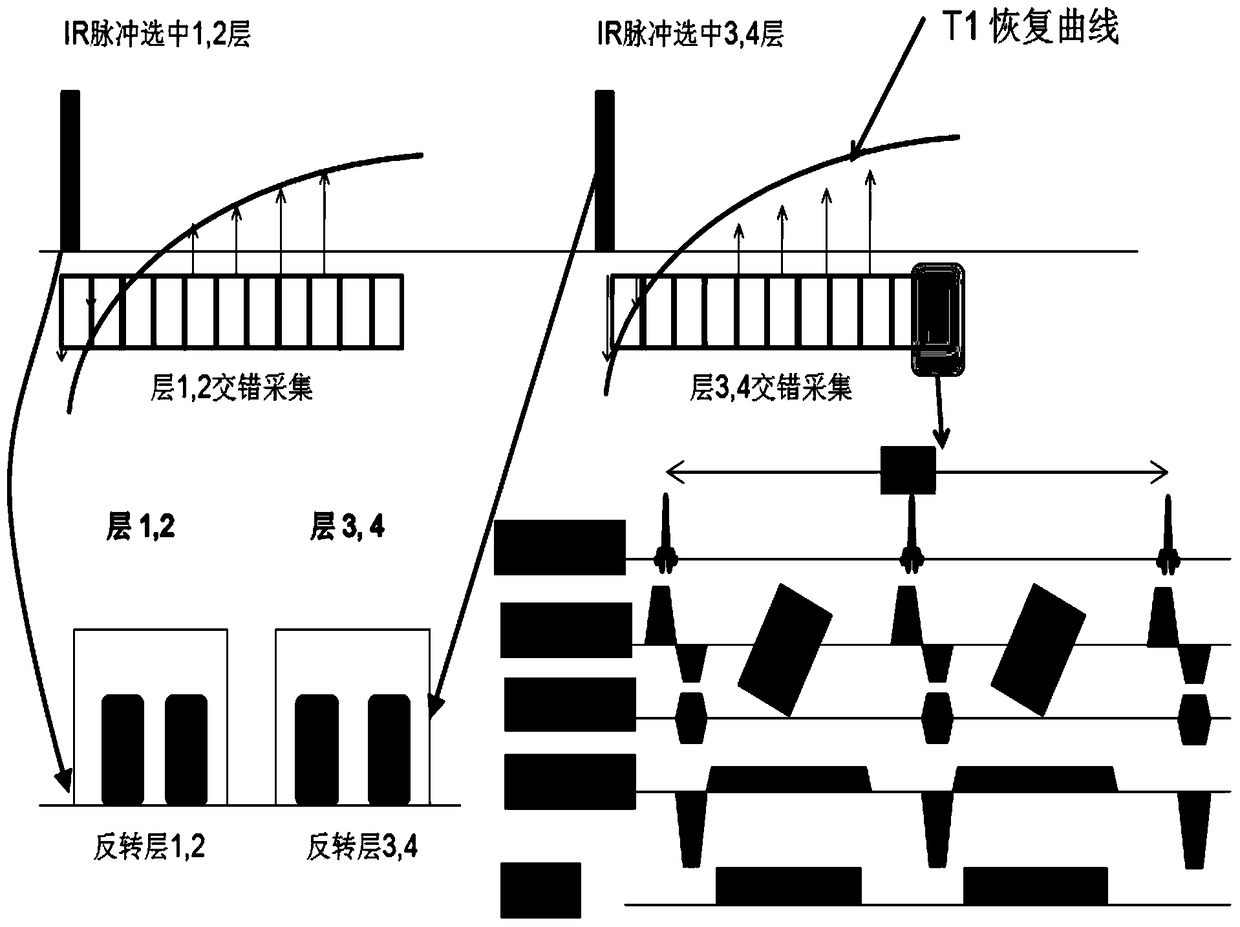
ActiveCN105496410BReduce acquisition timeLess likely to cause discomfortDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAcquisition timeBrain magnetic resonance
The invention provides a brain longitudinal relaxation value measuring method and an apparatus. The method comprises the following steps of applying an IR radio frequency pulse to a preset numbers of layers to enable a magnetized vector in the preset numbers of layers to turn over in 180-degree, and collecting a T1 image for a magnetized vector restoring curve in the preset numbers of layers via a staggered collection mode. The layer is an image layer formed via brain magnetic resonance scan; and parallel imaging and part Fourier transform accelerating technologies are employed during the T1 image collection by the staggered collection mode. T1 image collection time can be greatly shortened by the use of the above method and apparatus.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com