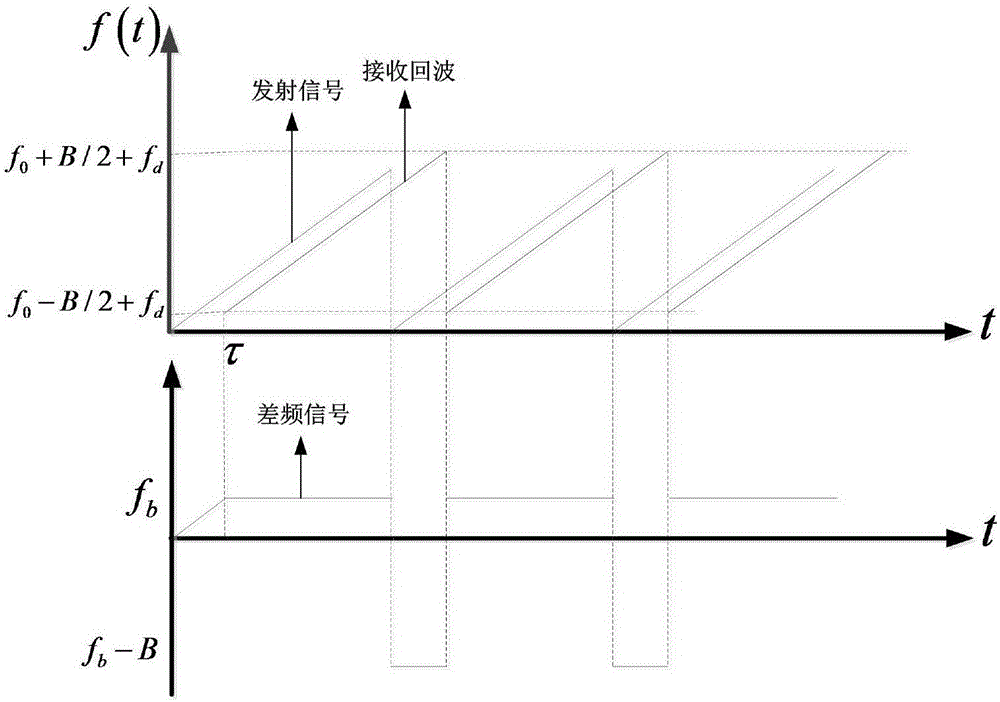
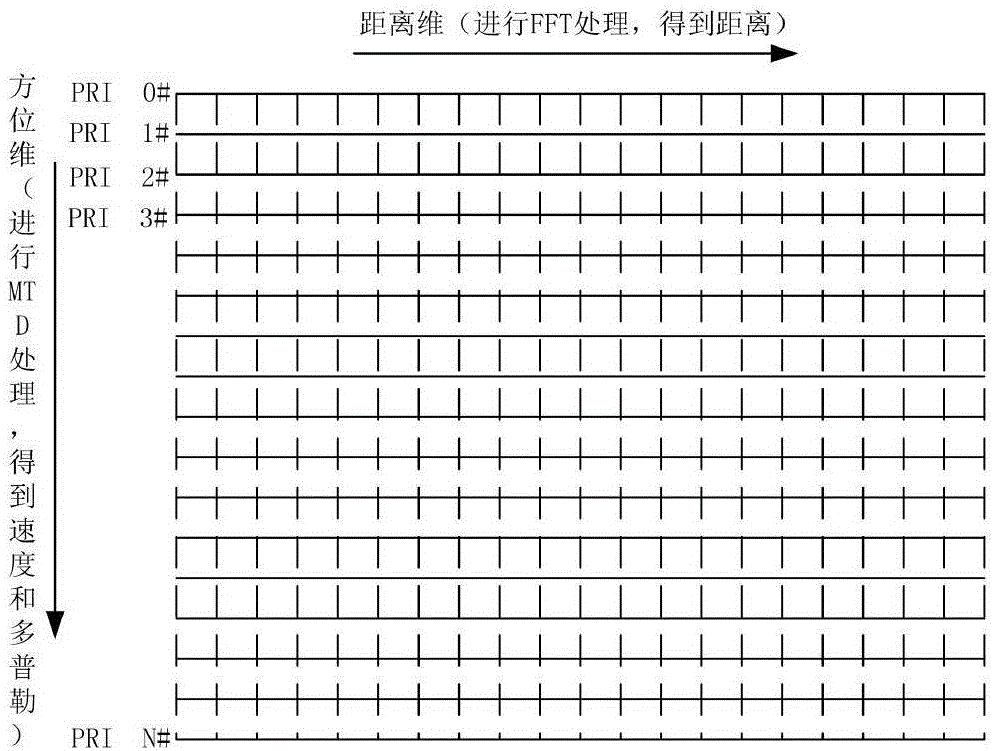
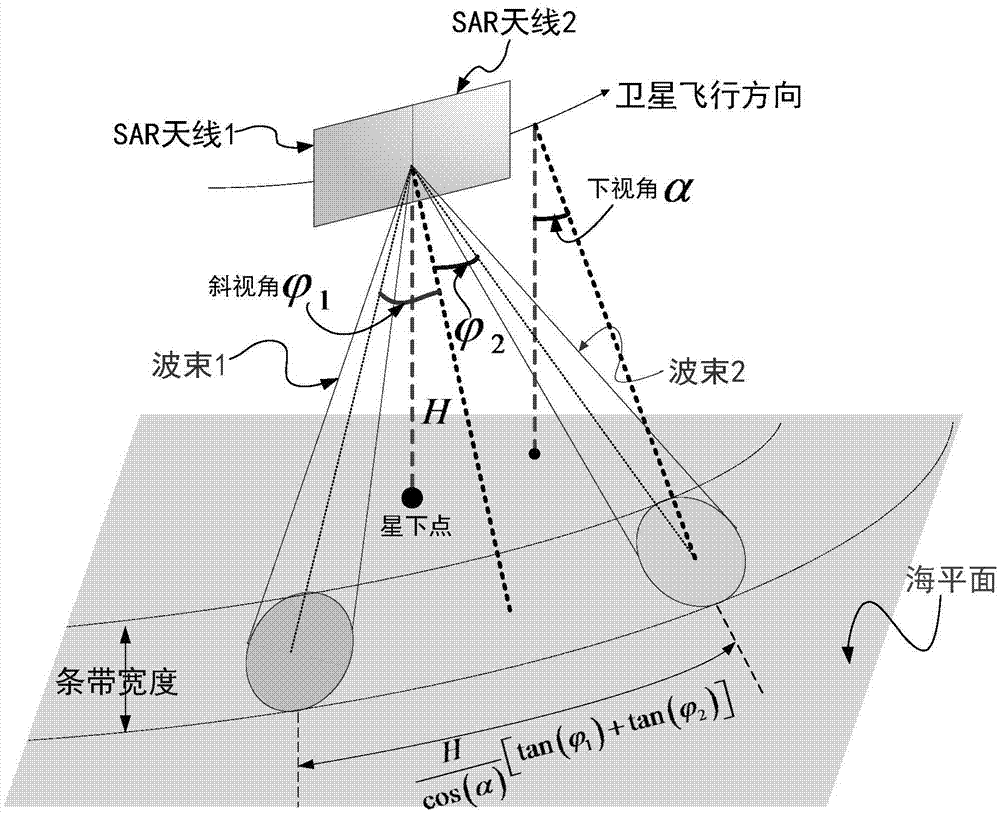
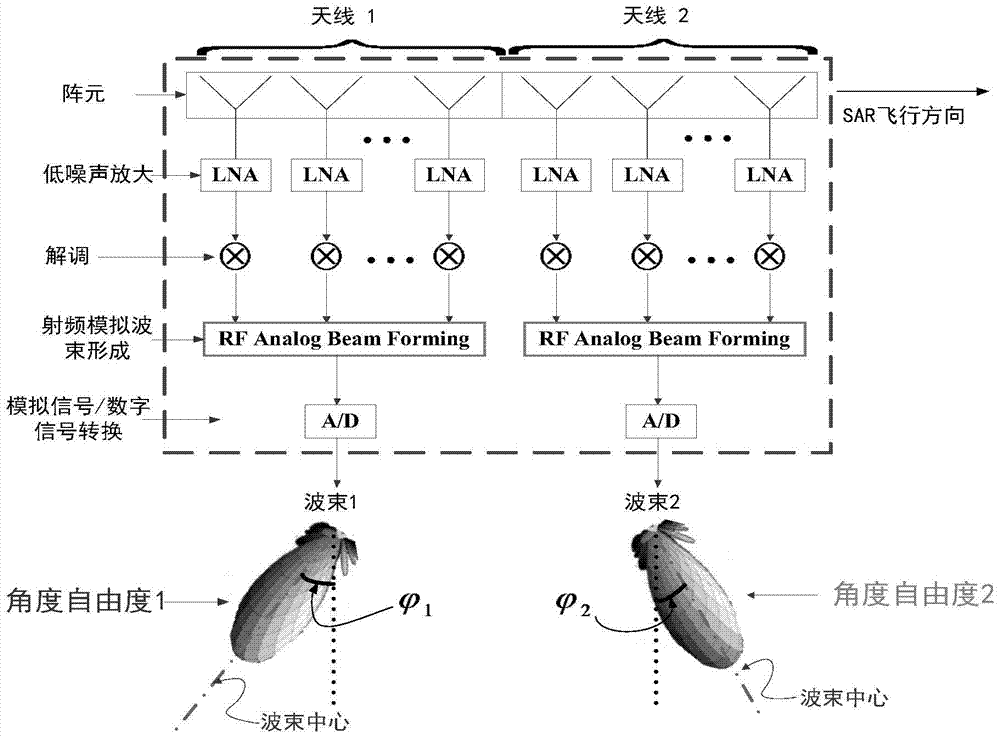
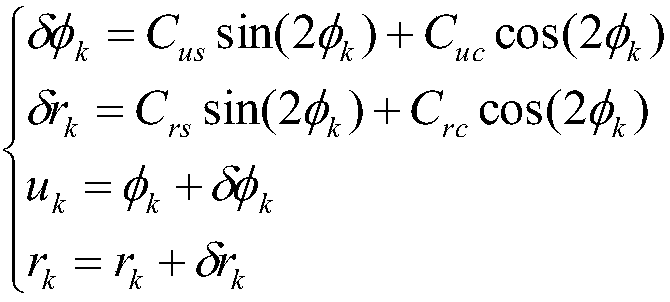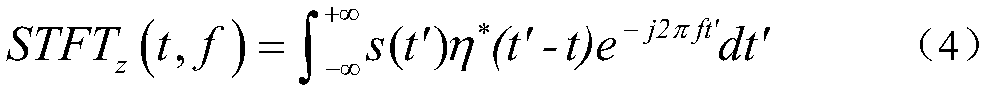Patents
Literature
205 results about "Radial velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The radial velocity of an object with respect to a given point is the rate of change of the distance between the object and the point. That is, the radial velocity is the component of the object's velocity that points in the direction of the radius connecting the object and the point. In astronomy, the point is usually taken to be the observer on Earth, so the radial velocity then denotes the speed with which the object moves away from or approaches the Earth.
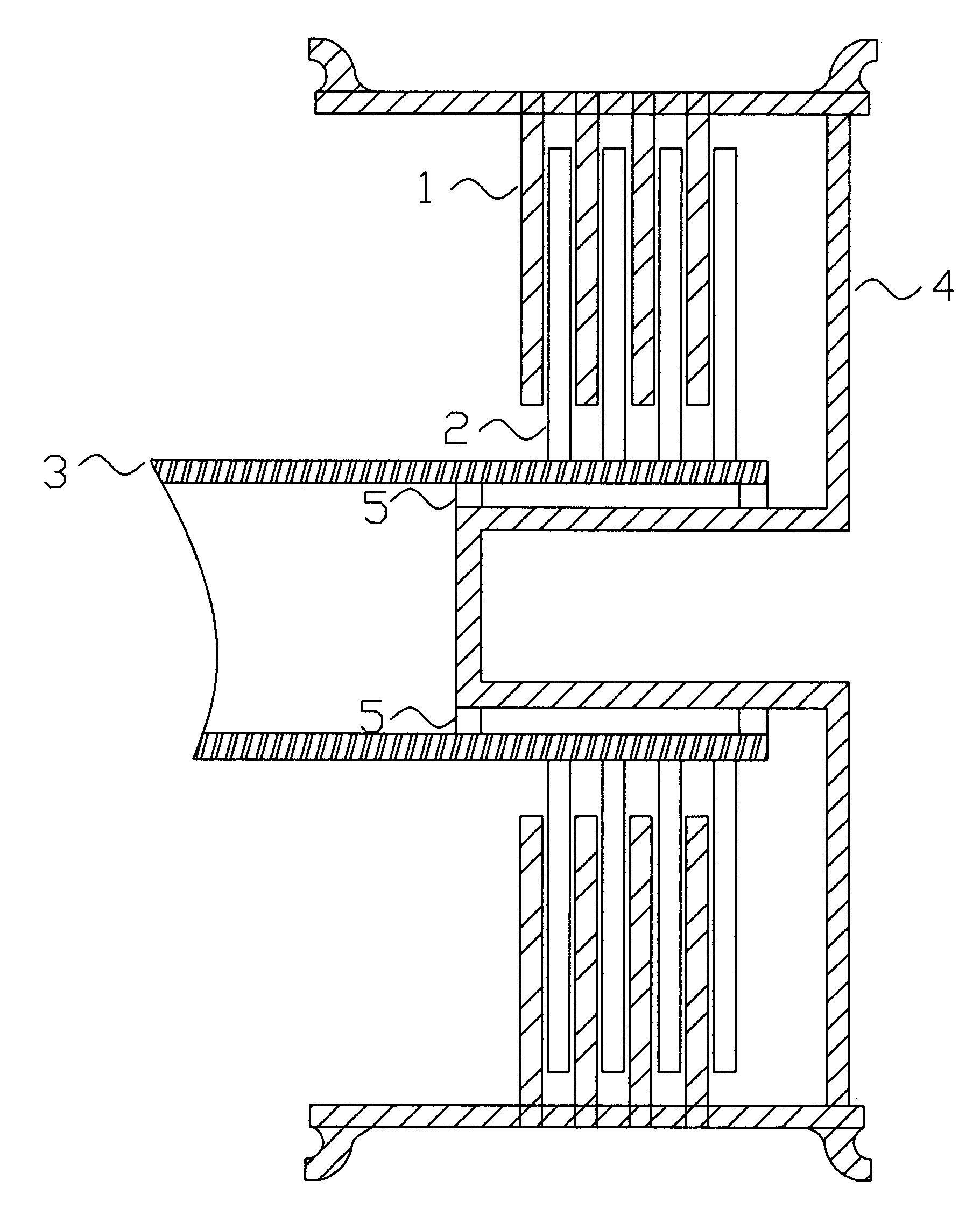
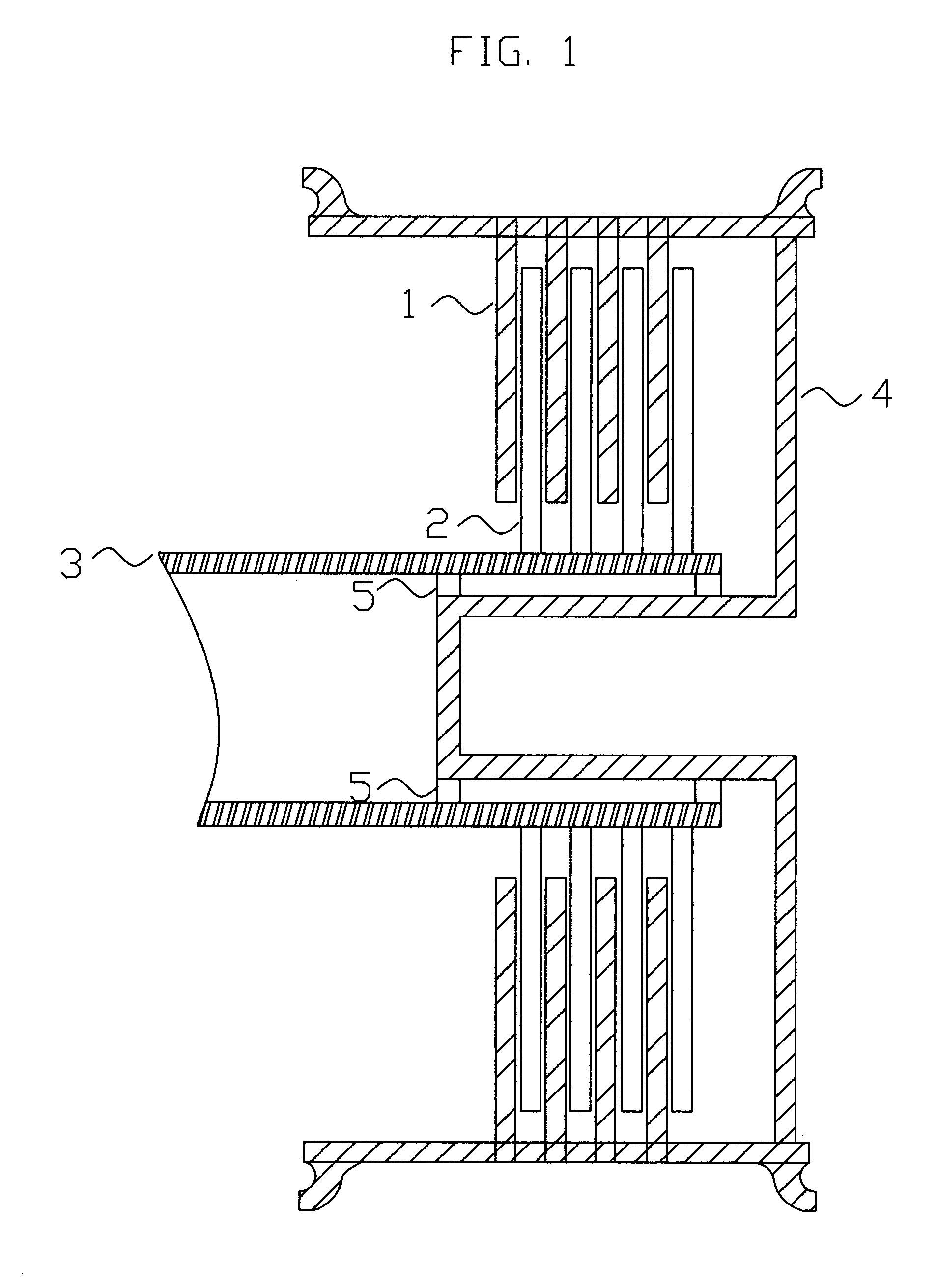
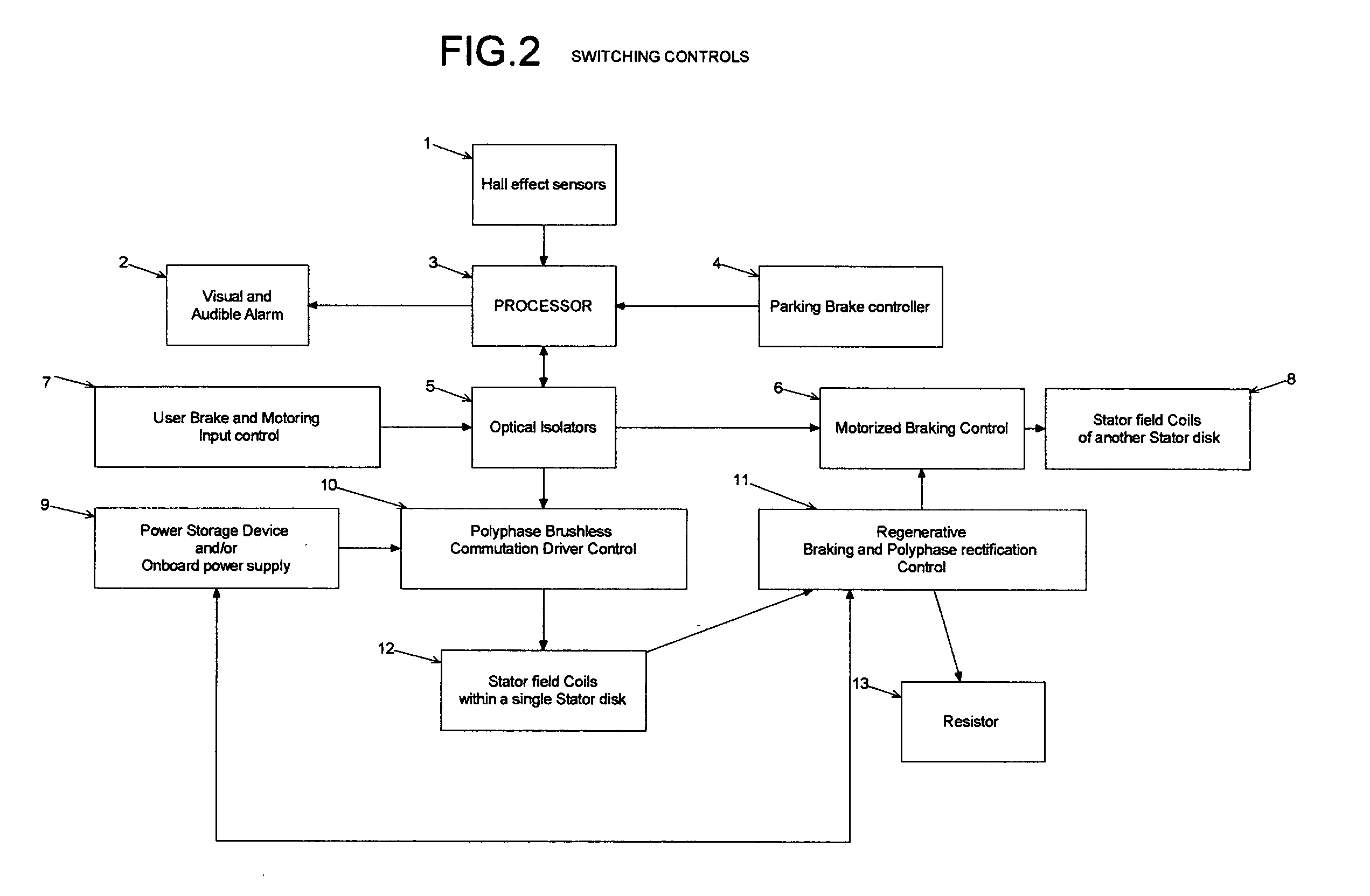
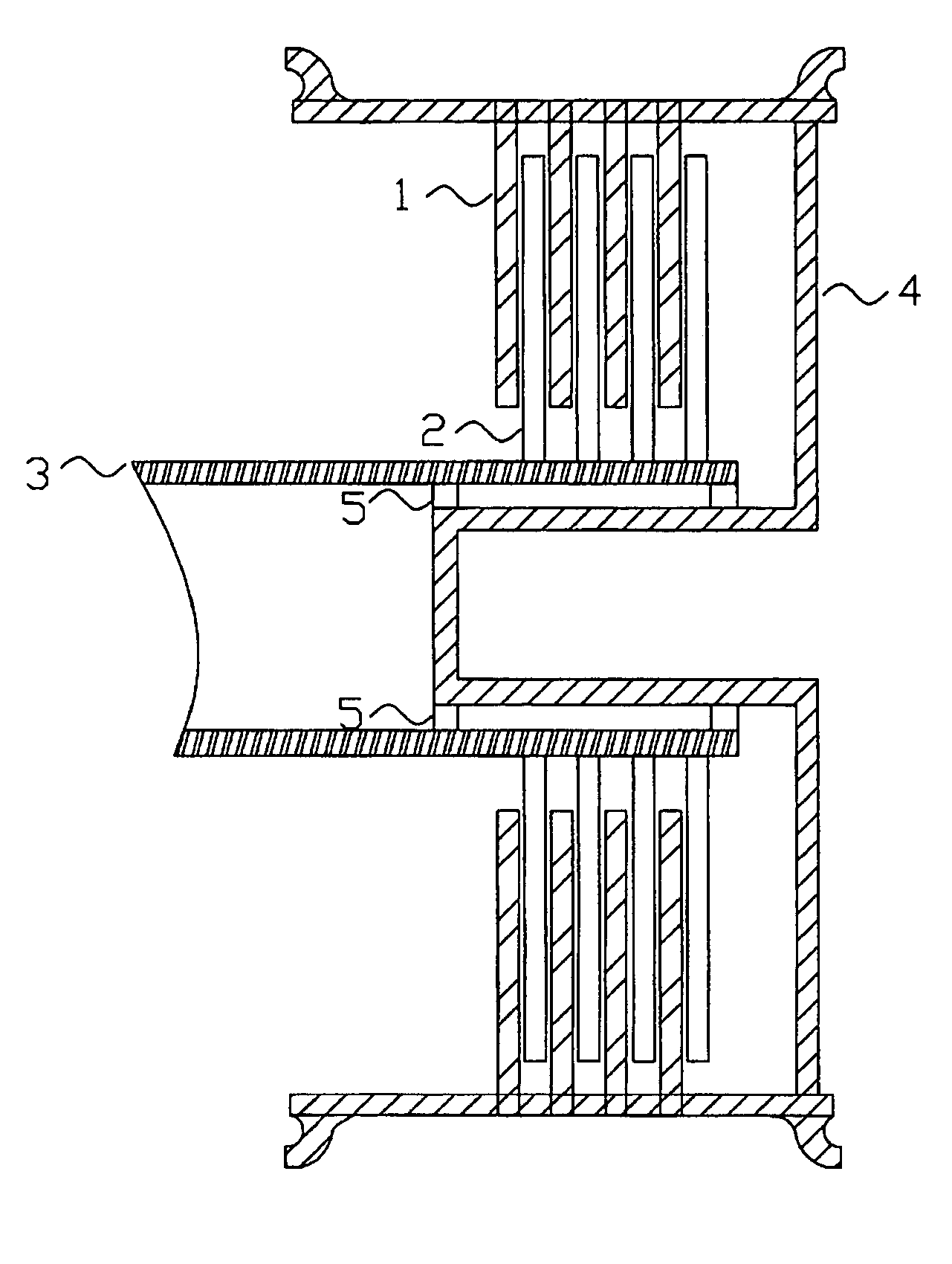
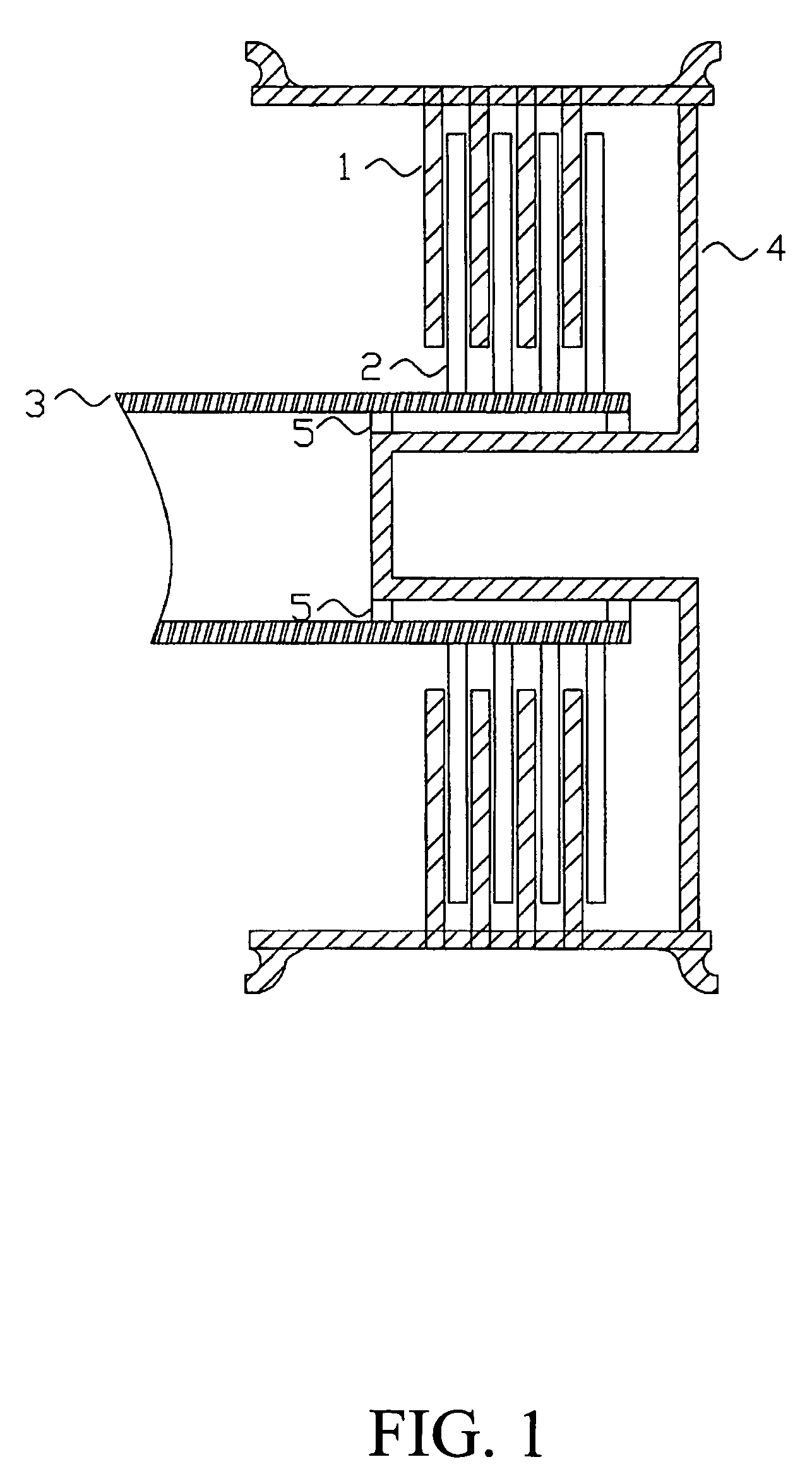
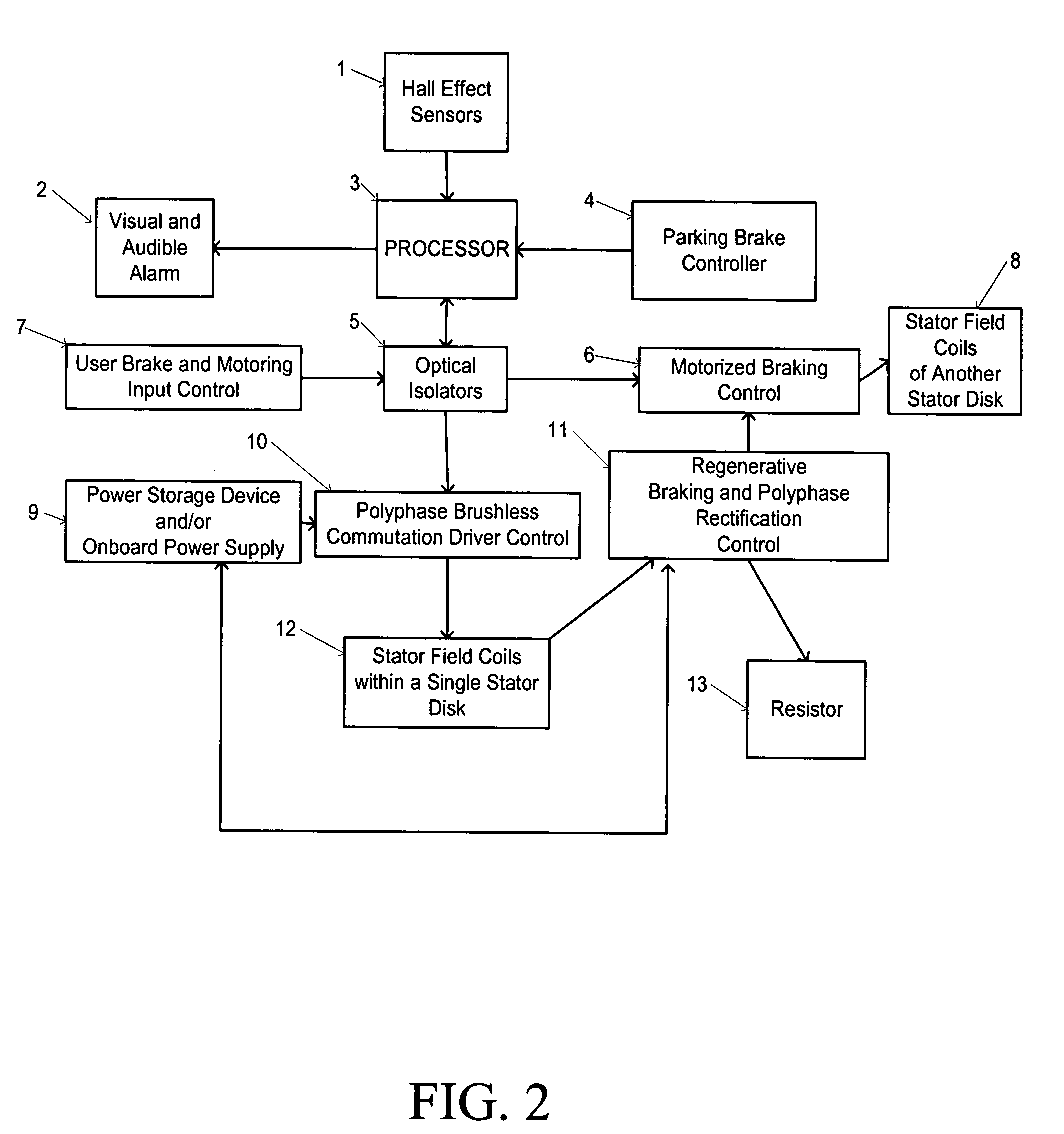
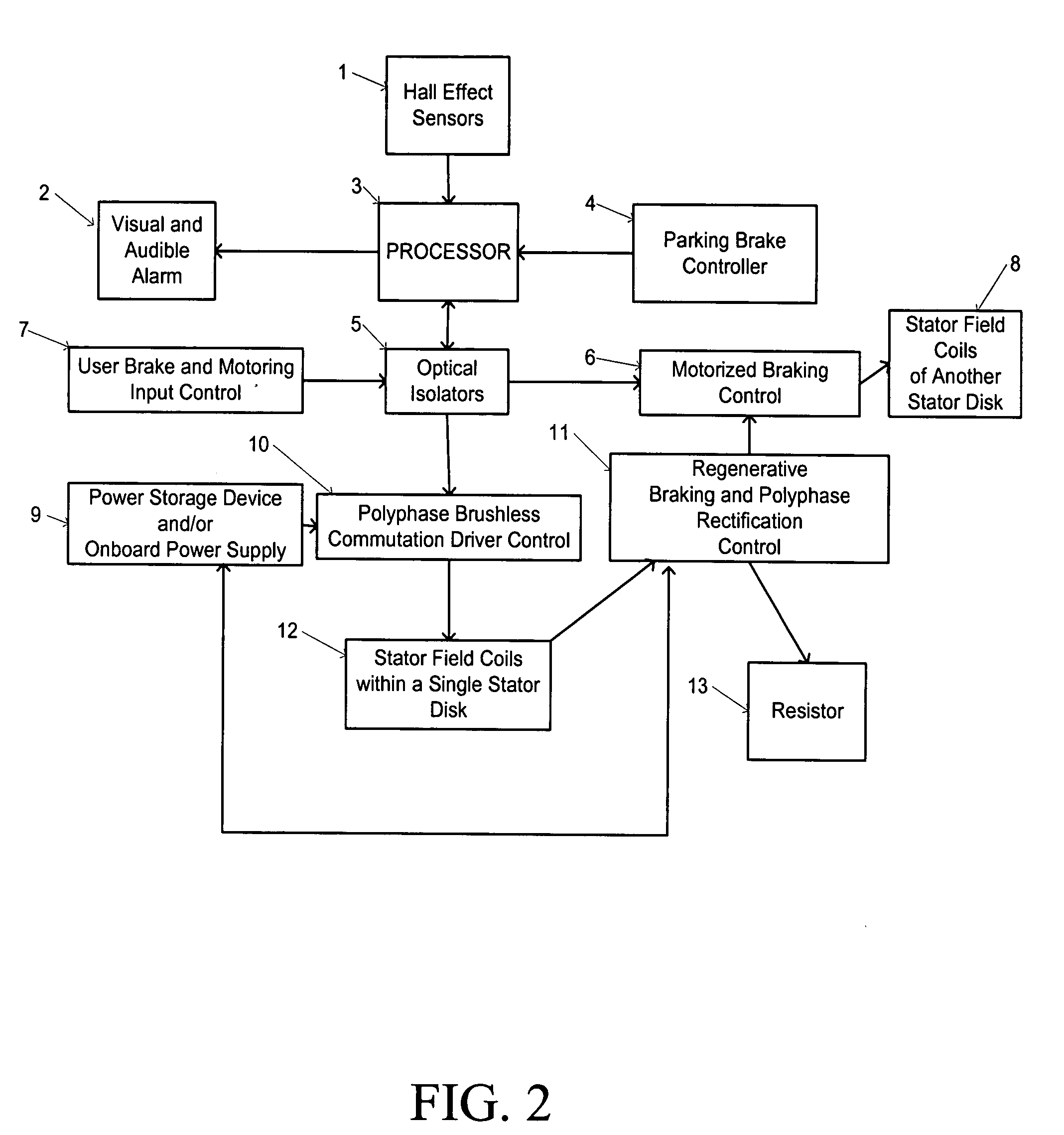
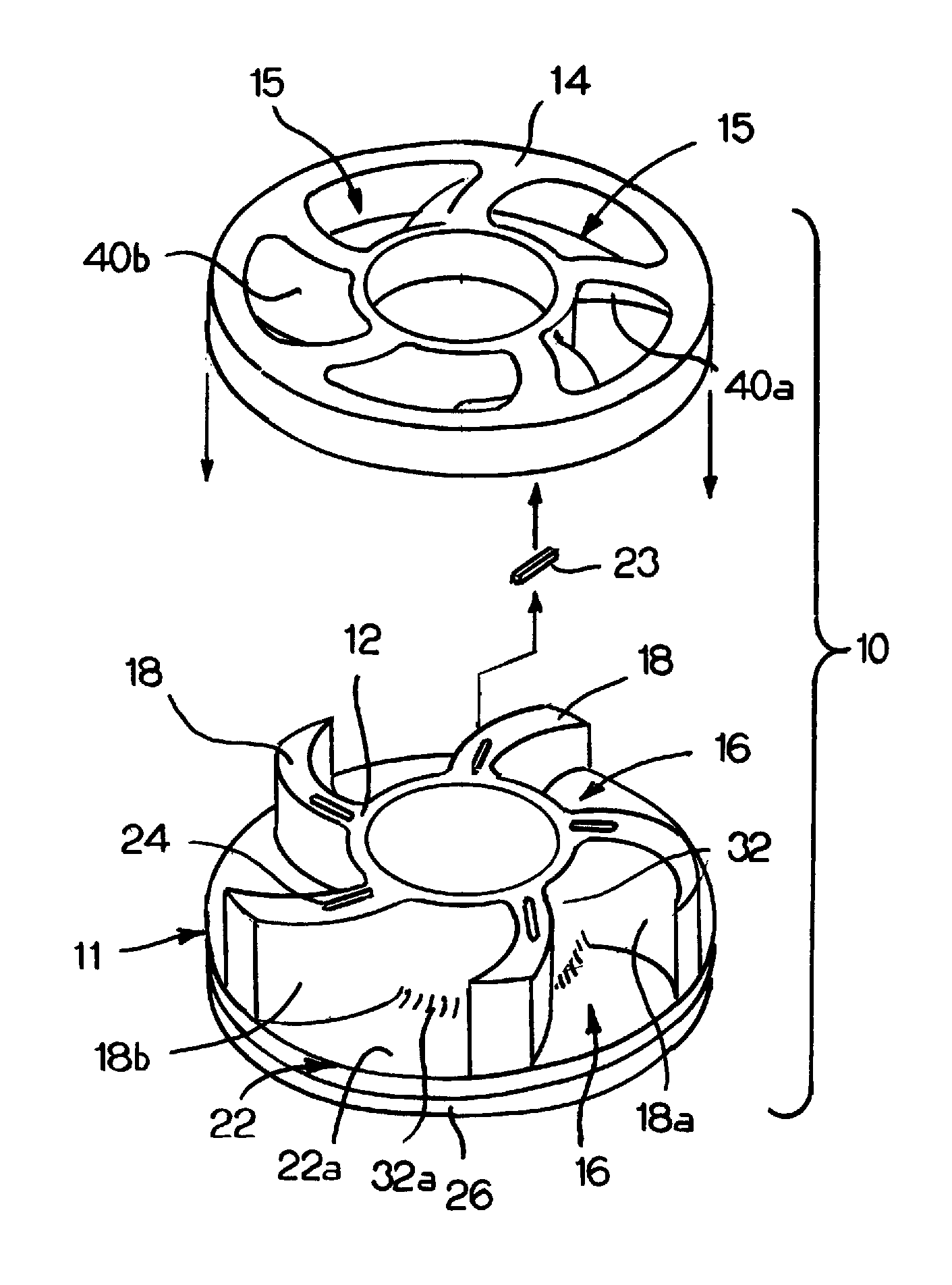
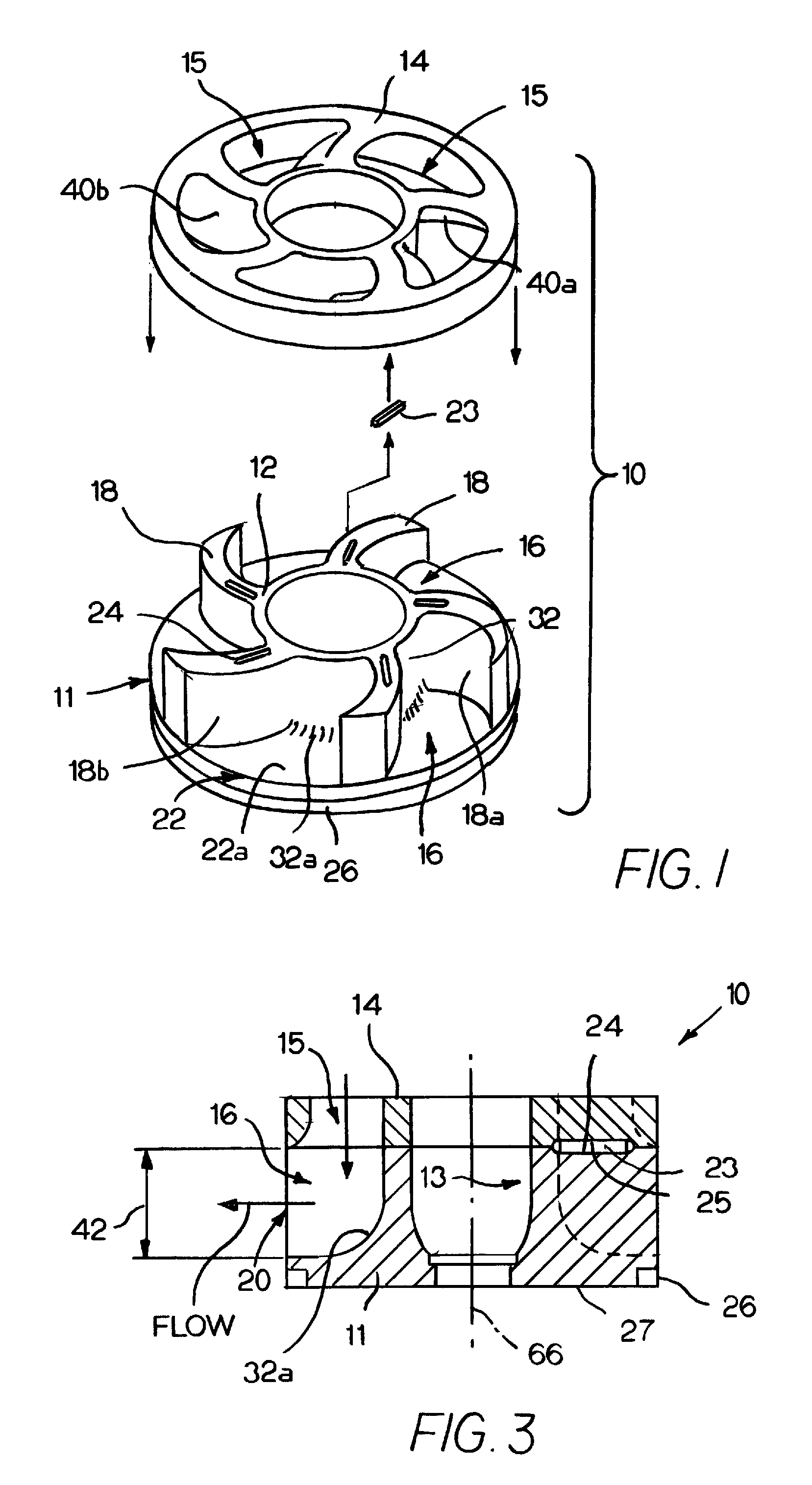
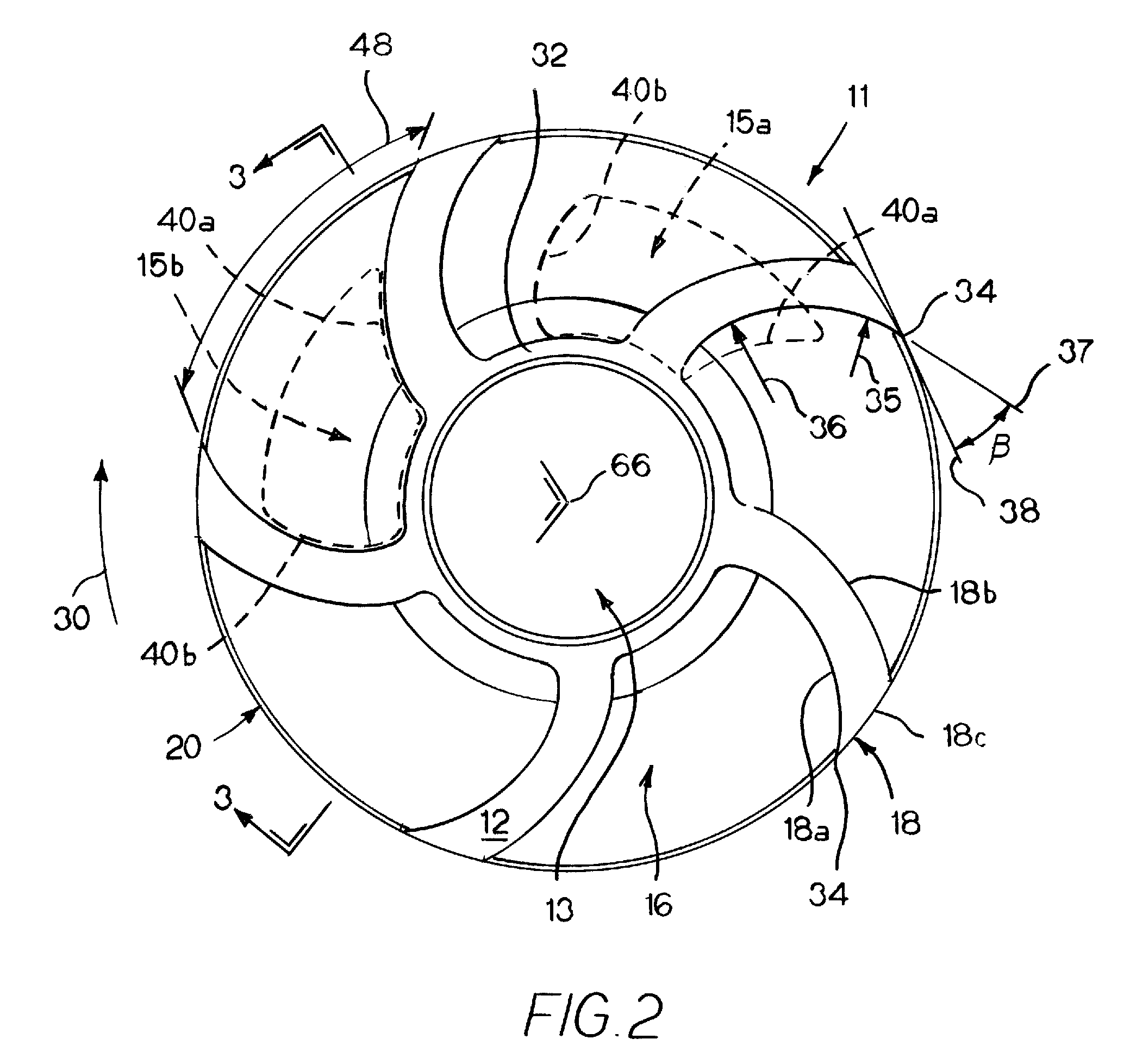
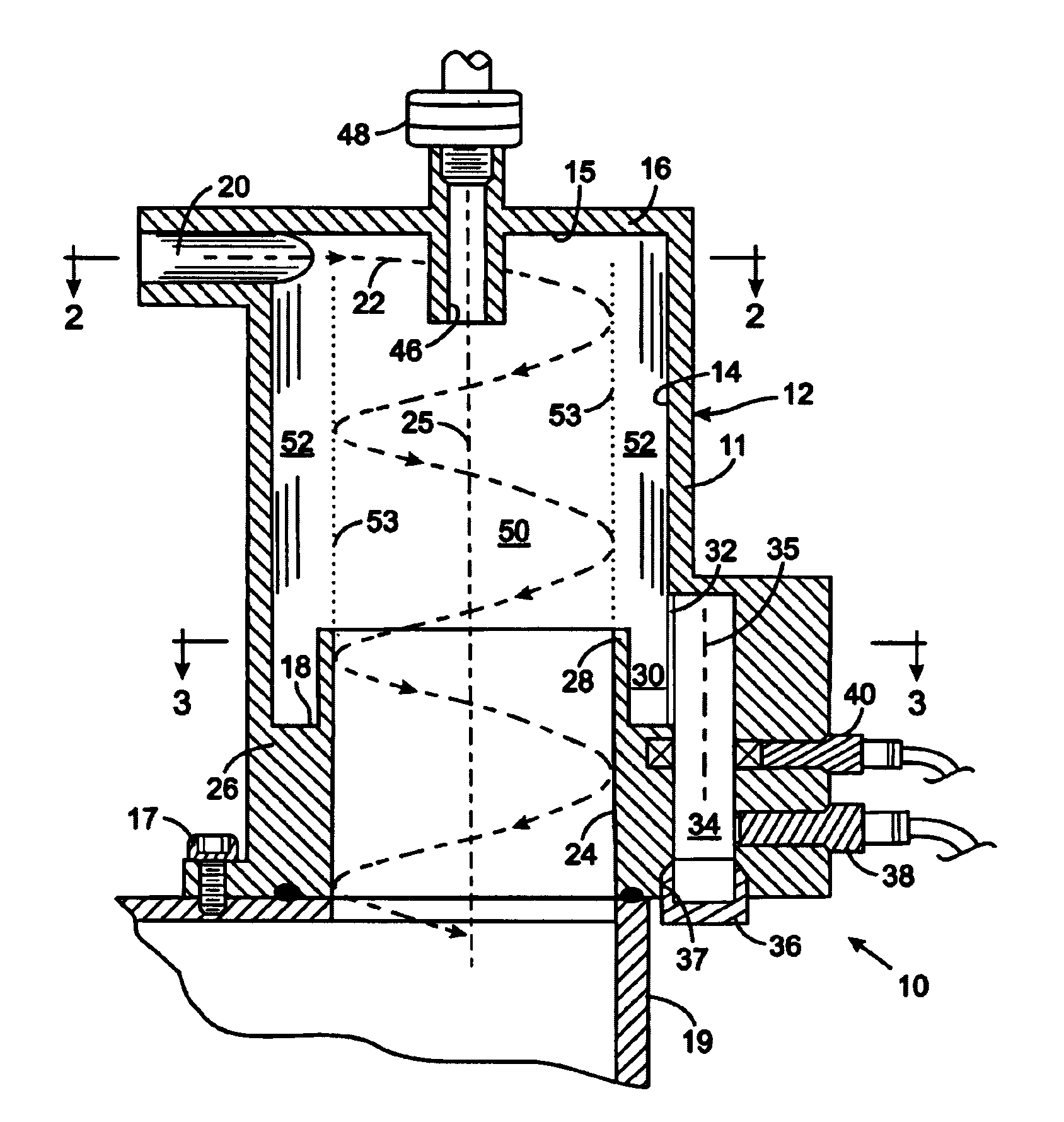
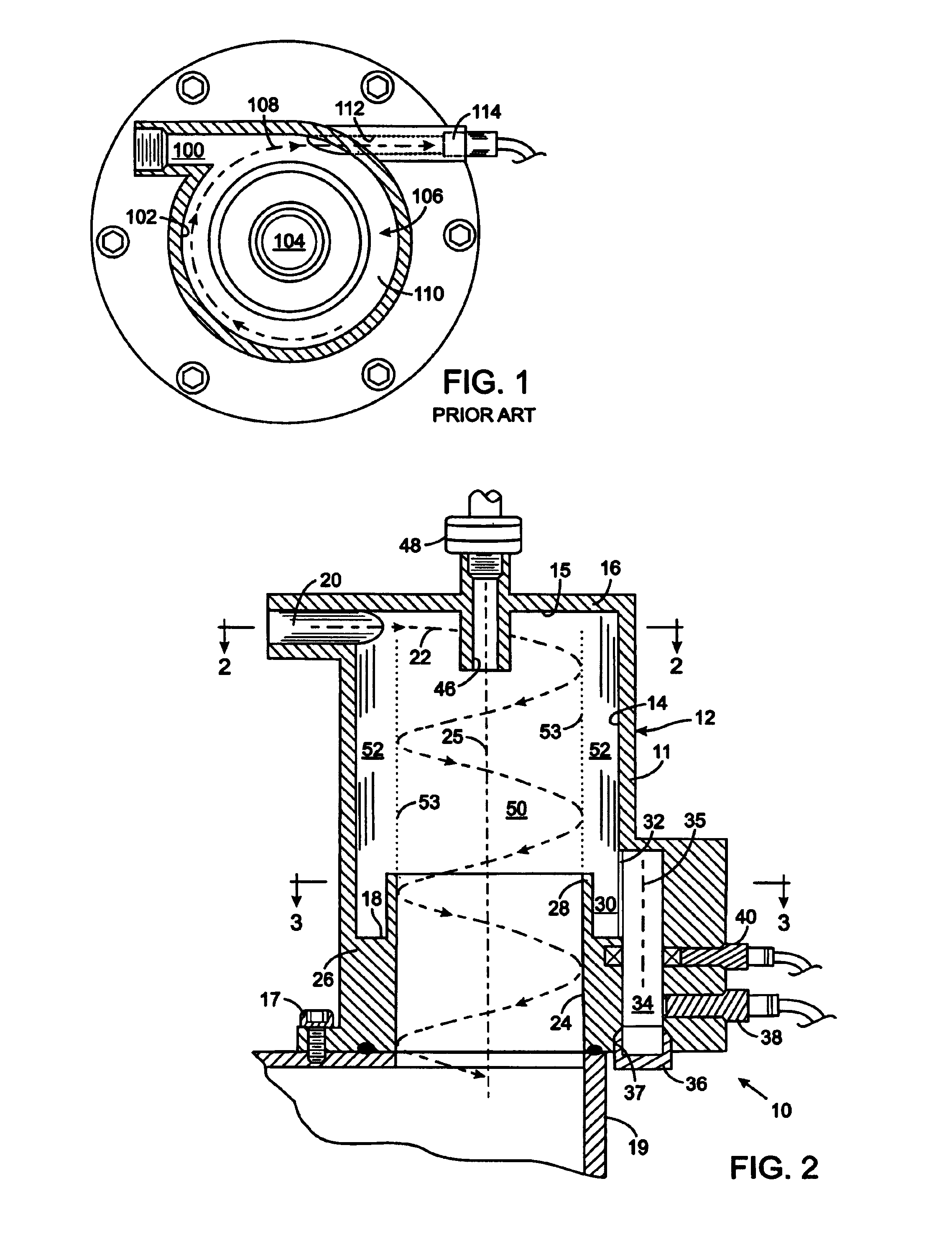
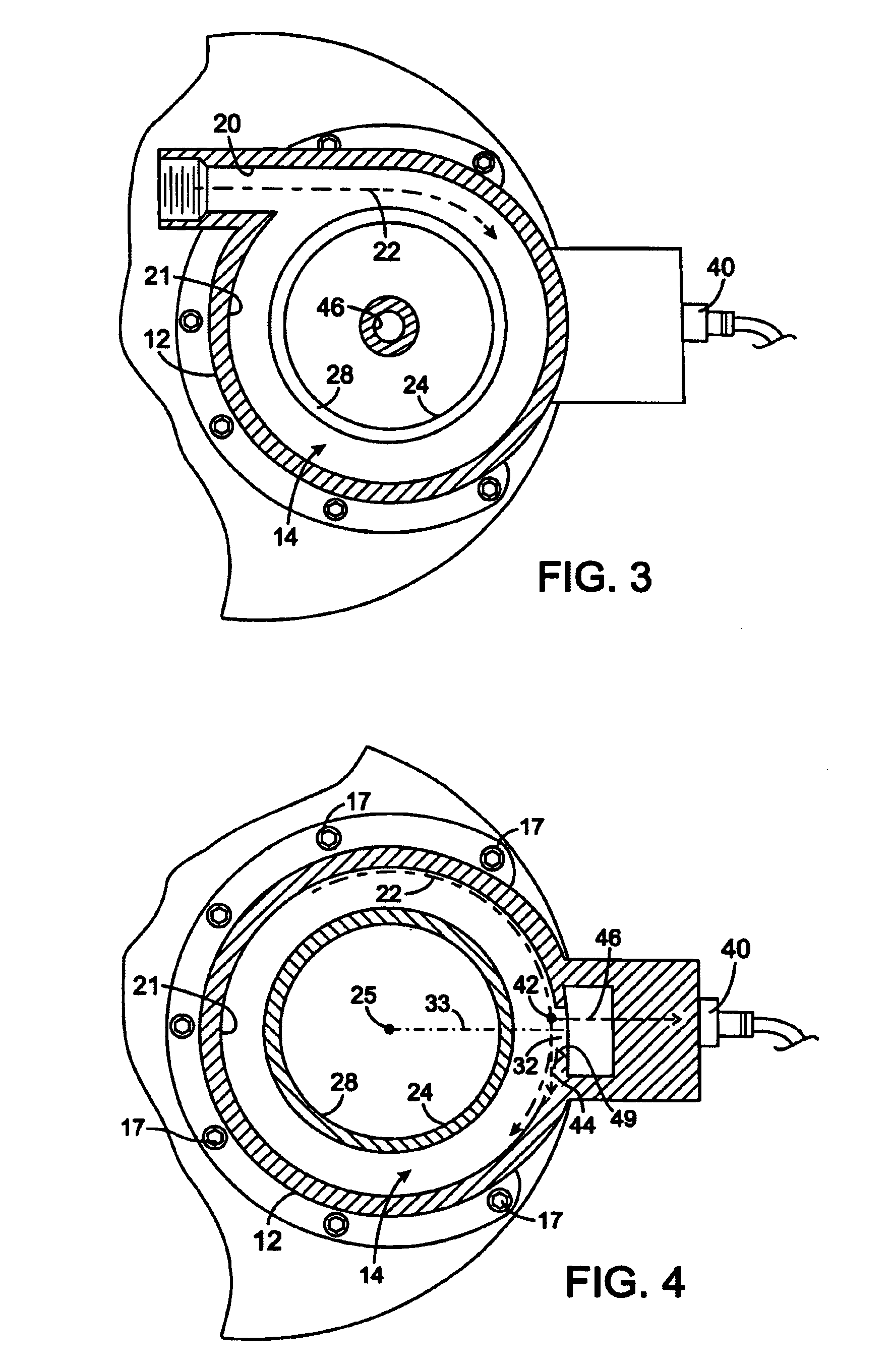
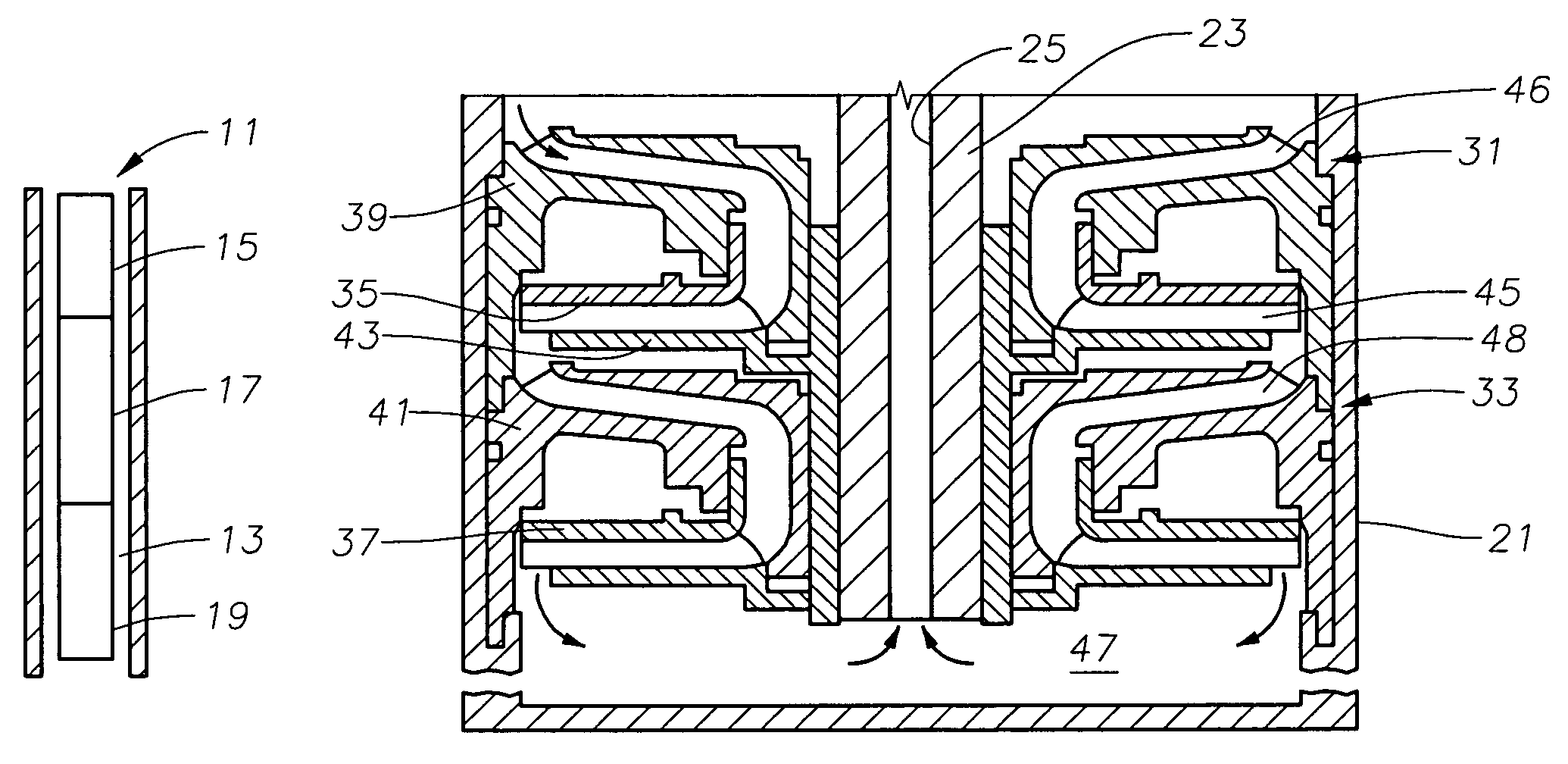
Landing gear method and apparatus for braking and maneuvering
ActiveUS20050224642A1Improve braking effectIncrease flexibilityEnergy efficient operational measuresElectric devicesEngineeringElectric power
Aircraft landing gear comprised of a wheel hub motor / generator disks stack, includes alternating rotor and stator disks mounted with respect to the wheel support and wheel. The wheel hub motor / generator can provide motive force to the wheel when electrical power is applied, which may be applied prior to touch-down thus decreasing the difference in relative velocities of the tire radial velocity with that of the relative velocity of the runway thus greatly reducing the sliding friction wear of said tire. After touchdown the wheel hub motor / generator may be used as a generator thus applying a regenerative braking force and / or a motorized braking action to the wheel. The energy generated upon landing maybe dissipated through a resistor and / or stored for later use in providing a source for motive power to the aircraft wheels for the purpose of taxiing and ground maneuvers of said aircraft.
Owner:DELOS AEROSPACE
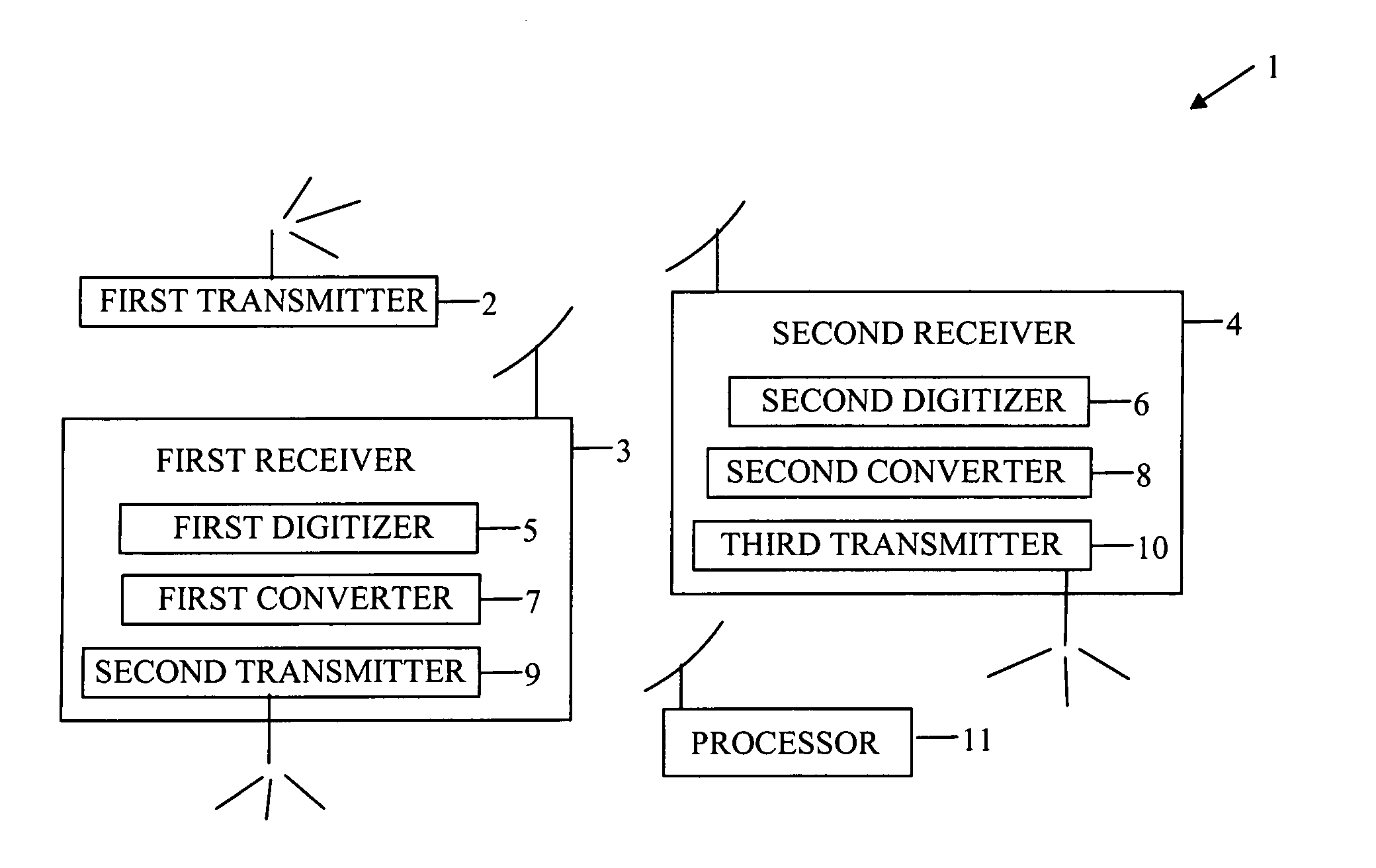
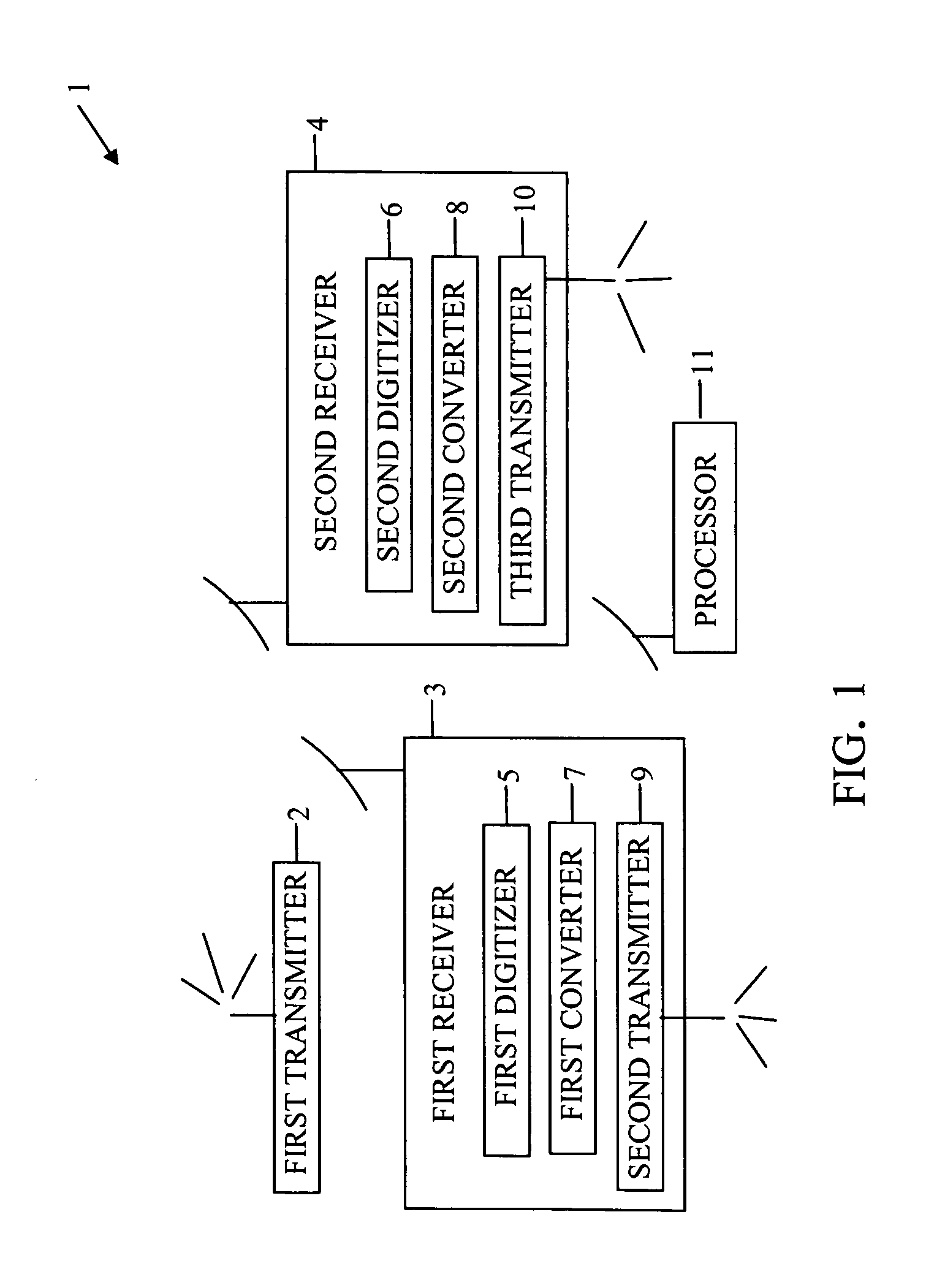
Device for and method of geolocation
ActiveUS7893875B1More precisionDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationGeolocationEngineering
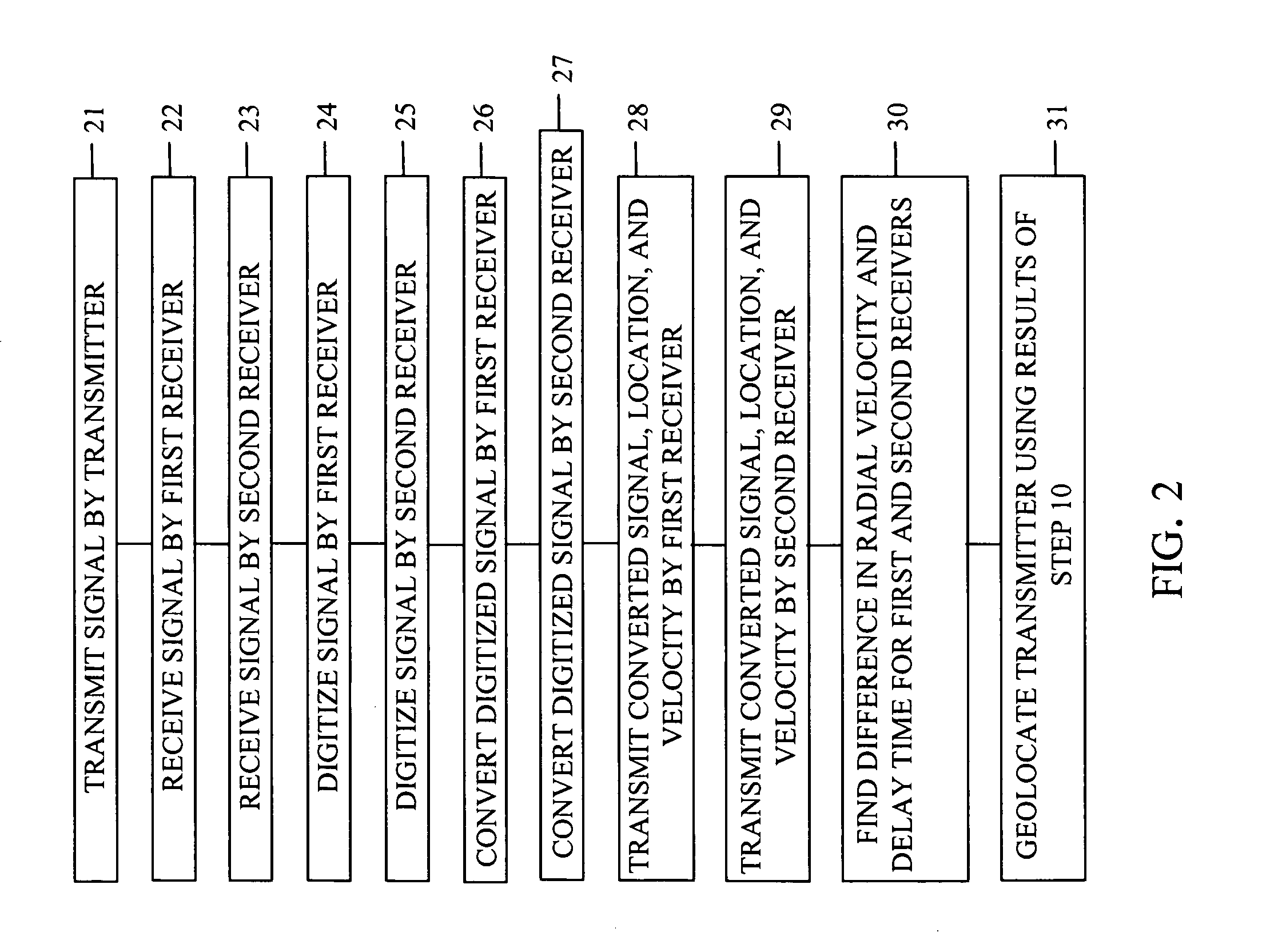
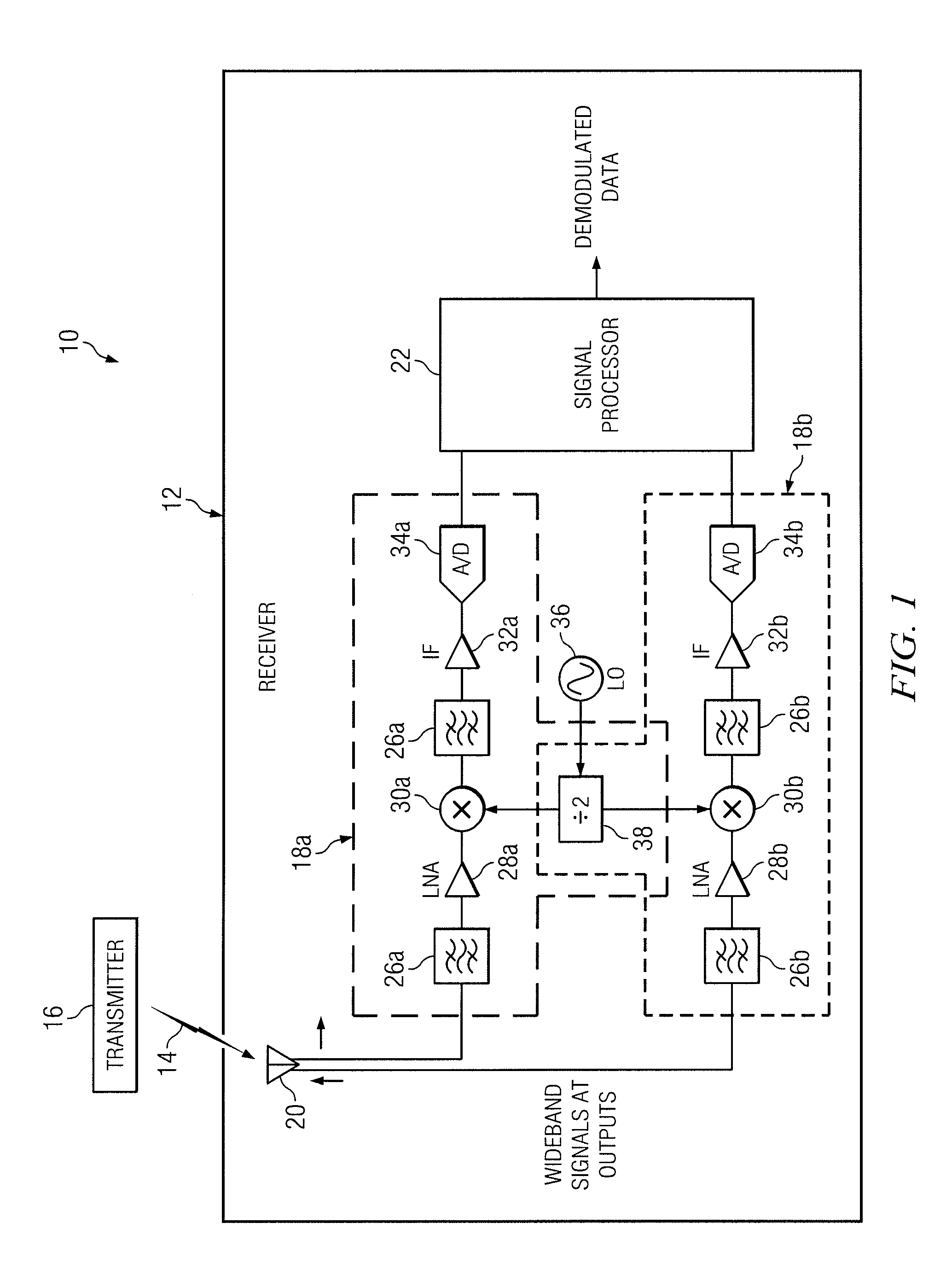
A device and method of geolocating a transmitter. First and second receivers, in motion, receive a signal from the transmitter. Digitizers in the receivers digitize the signal. Converters in the receivers for converting the digitized signals to complex-valued signals. Transmitters on the receivers transmit their digitized signals, locations, and velocities at the time the signal was received to a processor. A central processing unit on the processor determines a difference in radial velocities of the receivers relative to the transmitter. The difference in radial velocities and delay time between the signals received at the receivers are used to geolocate the transmitter.
Owner:NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY
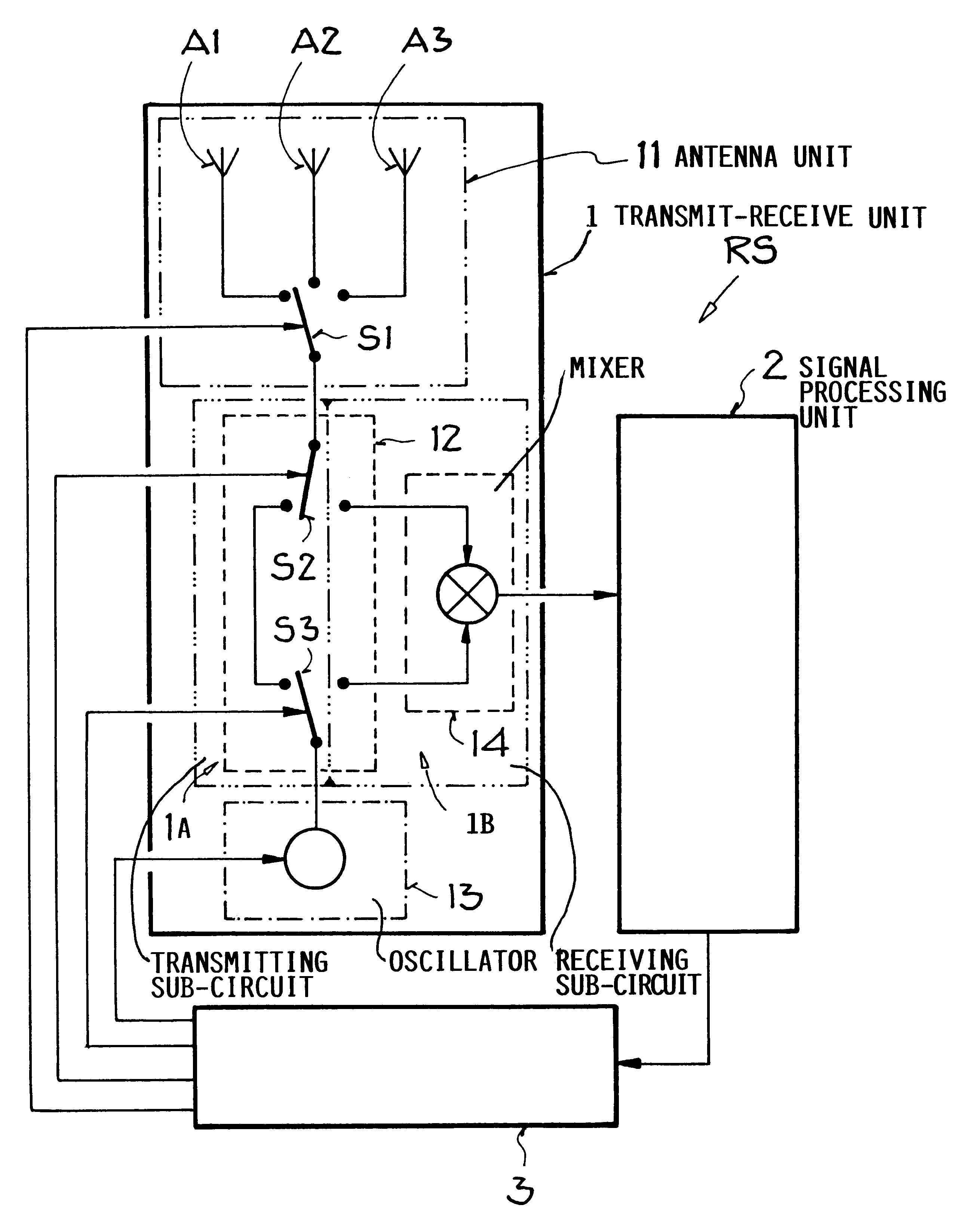
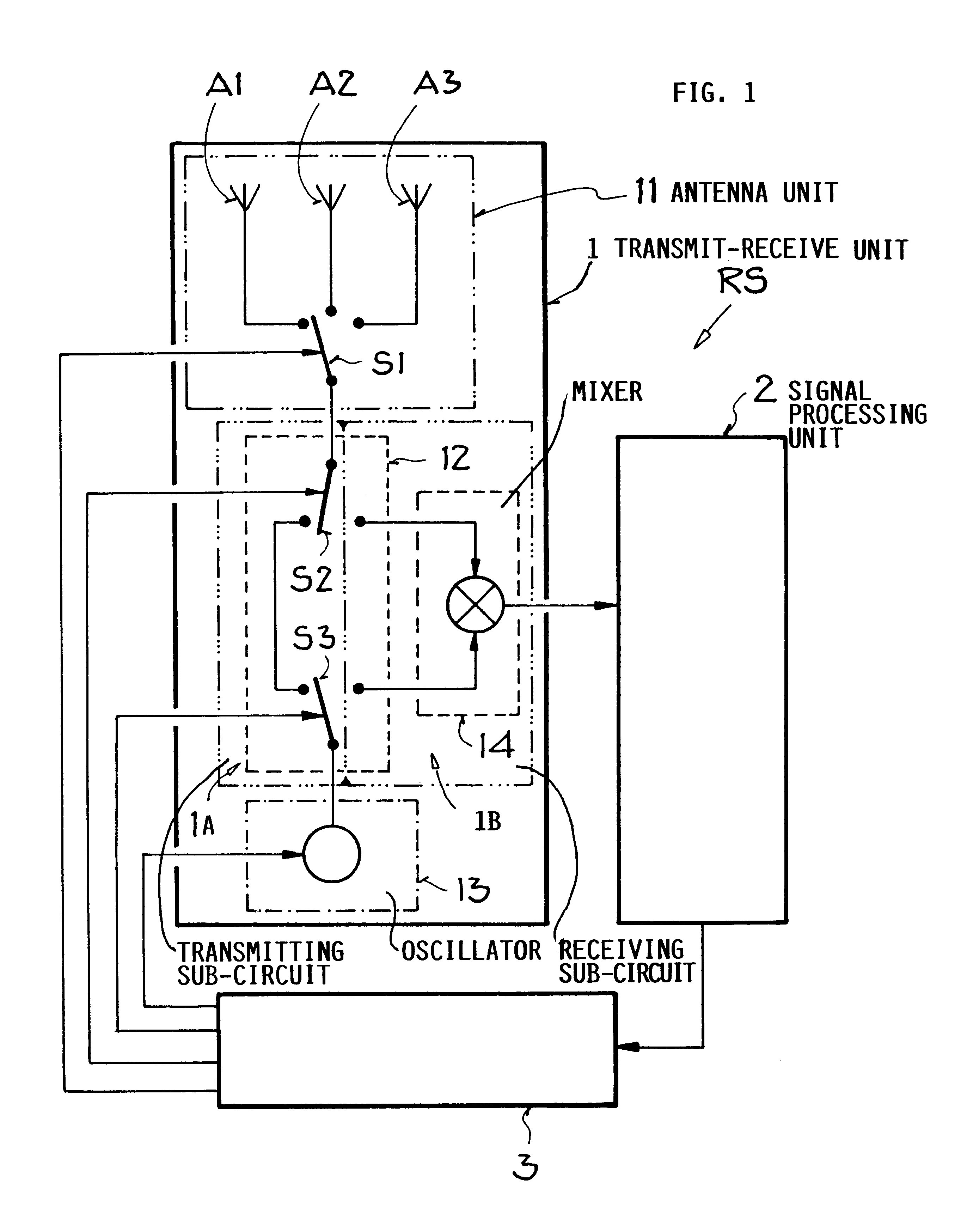
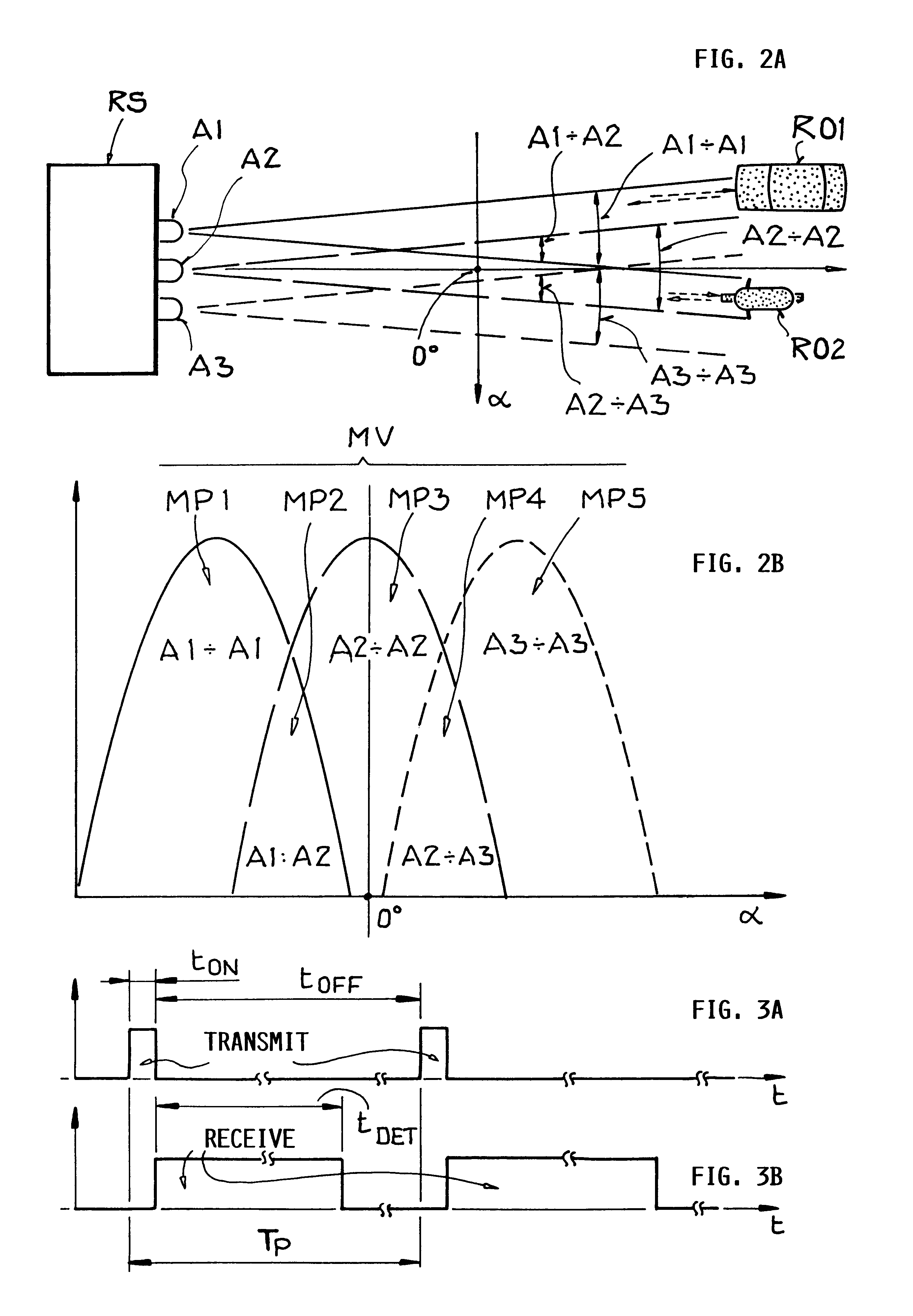
Method for operating a radar system
InactiveUS6147638AAvoid disadvantagesLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsPhase difference
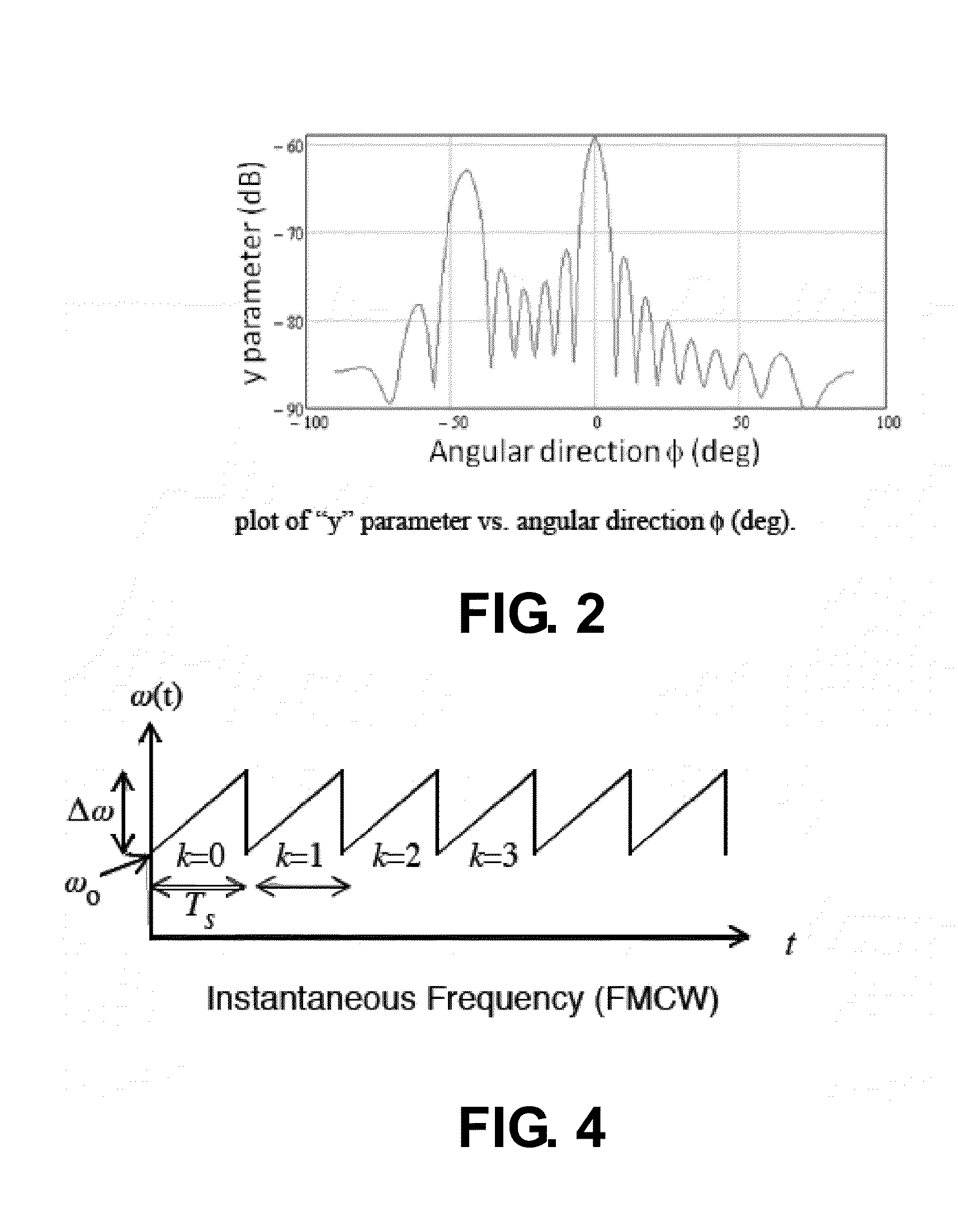
In a method for operating a radar system, the object is to determine by simple means and at low cost the distance and / or the radial velocity of at least one target object with high resolution. For this purpose, in each measuring phase of the measurement process in the "pulse FMCW radar system", switchover between a transmission mode and a receiving mode is effected a multiple number of times and at short intervals of time. In the transmission mode, all receiving units of the radar system are switched off, while a pulse-shaped (frequency-modulated) transmission signal with time-successive transmission pulses having a specific pulse-on time and a specific carrier frequency is emitted from at least one transmitter unit of the radar system. In receiving mode, all transmitter units are switched off in the pulse-off times of the transmission pulses, while from at least one receiver unit all reflection signals originating from the last emitted transmission pulse are detected as received signal from the entire observation range before emission of the next transmission pulse. The distance and / or the radial velocity of the reflection objects is determined indirectly by the signal processing unit of the radar system by evaluation of the frequency difference and / or phase difference between the transmission signal and the received signal.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE DISTANCE CONTROL SYST
Coded aperture beam analysis method and apparatus
ActiveUS20130169485A1Low probability of interceptLower performance requirementsDirection-finding diversity systems using radio wavesPosition fixationLight beamAntenna element
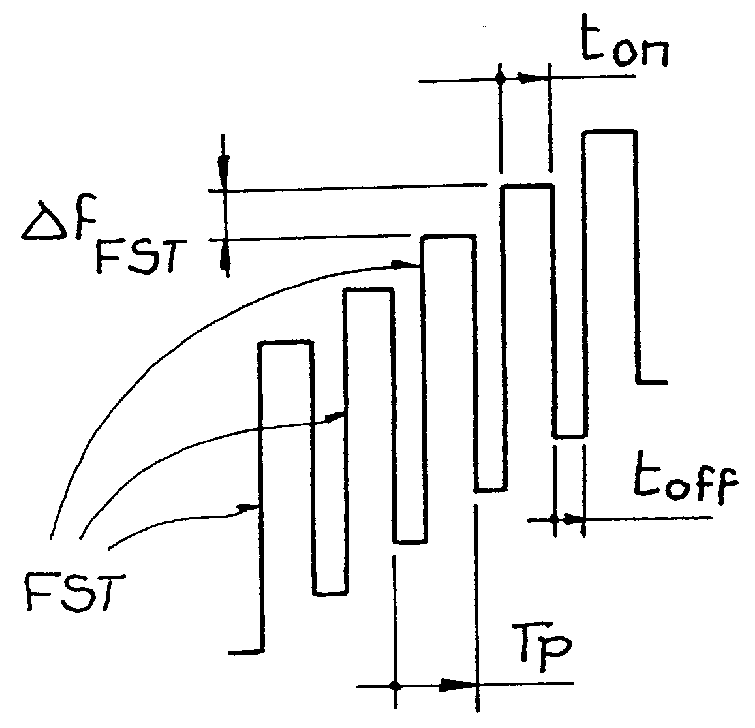
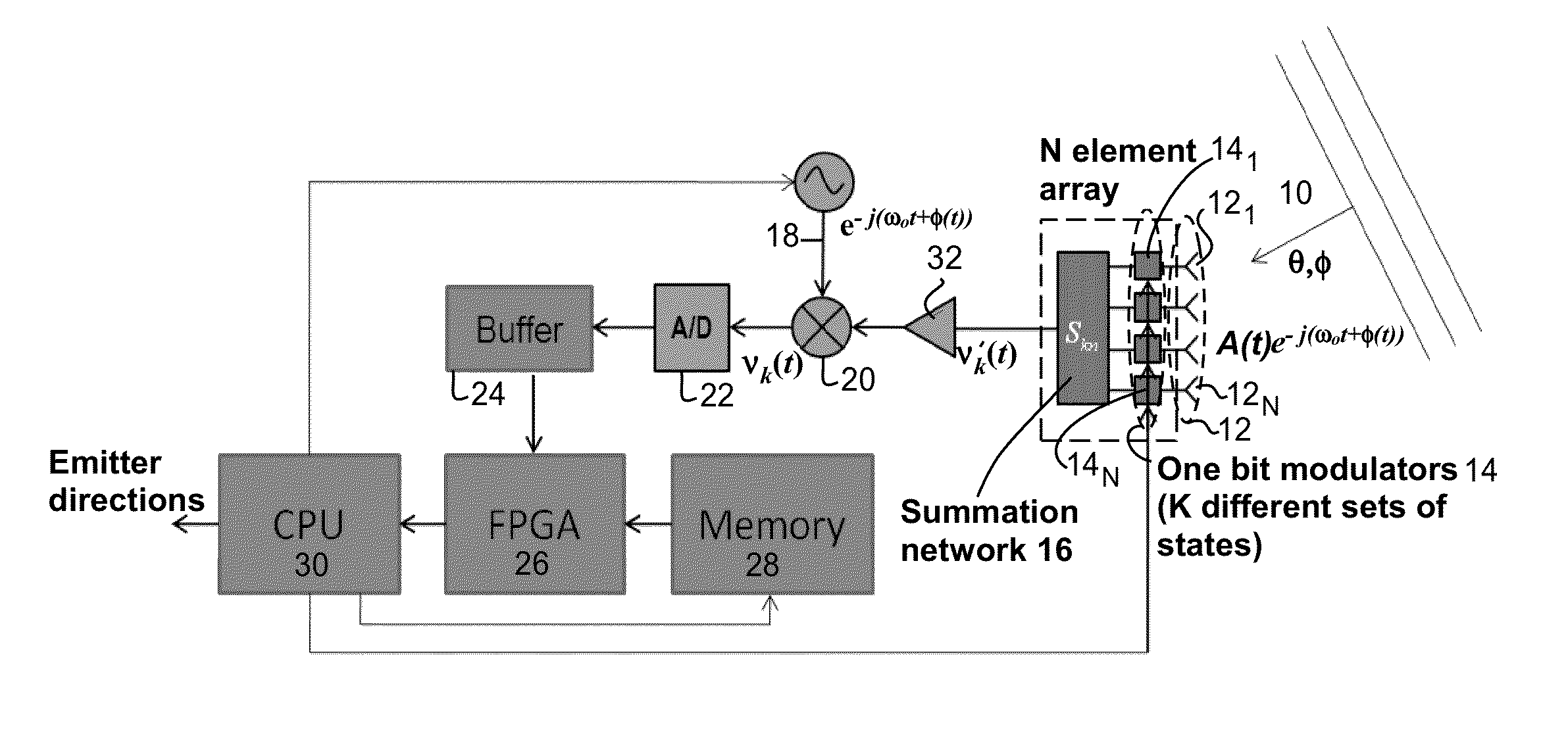
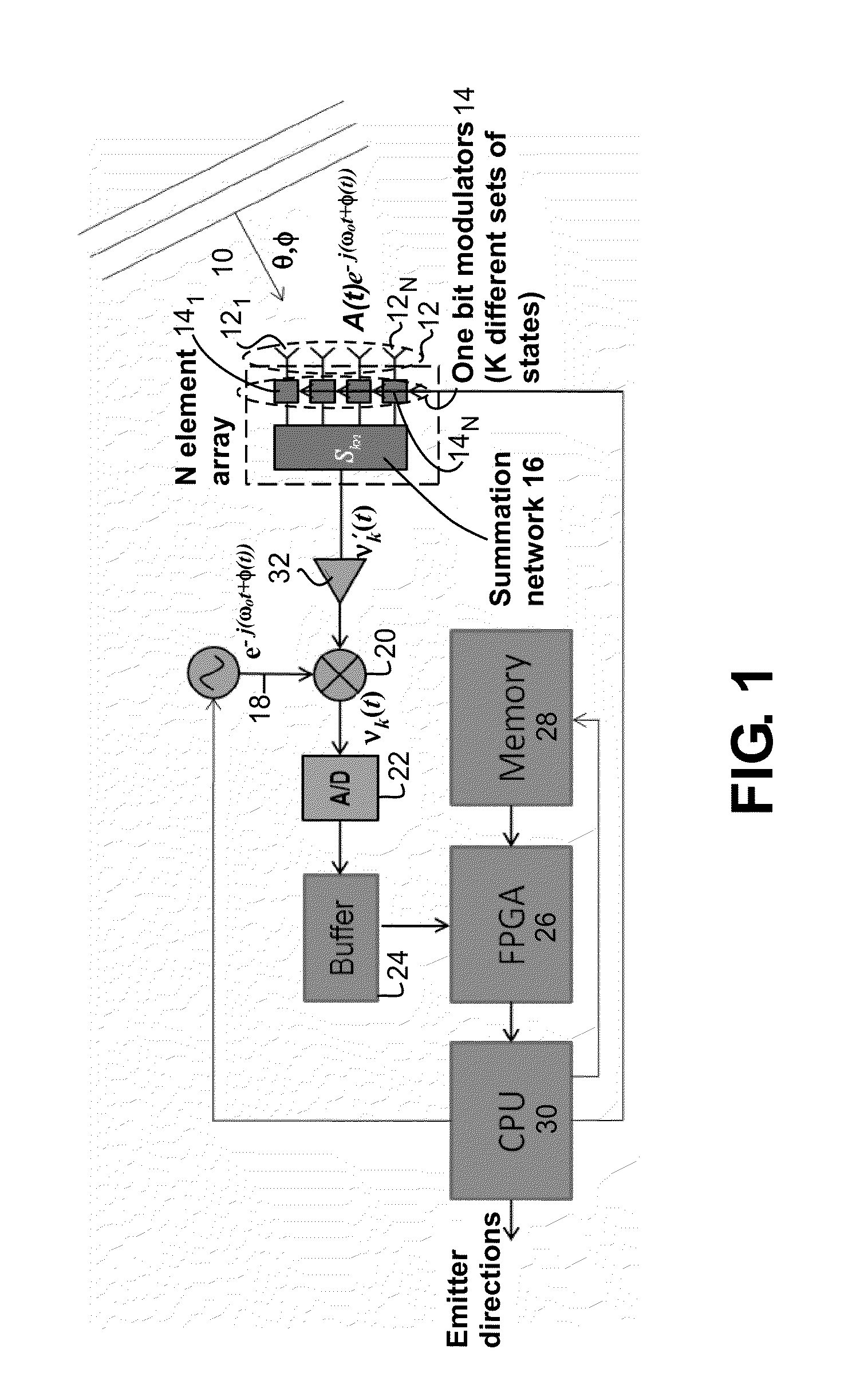
A method and apparatus for determining the range, radial velocity, and bearing angles of scattering objects reflecting RF signals or for determining the range, radial velocity, and bearing angles of sources RF signals. An array of antenna elements is utilized, the array of antenna elements each having an associated two state modulator wherein transmitted and / or received energy is phase encoded according to a sequence of multibit codes, the bits of the multibit codes each preferably having two states with approximately a 50% probability for each of the two states occurring within each given multibit code in said sequence of multibit codes, thereby allowing the determination of range, radial velocity, and bearing angles through digital computation after the scattered signals have been received.
Owner:HRL LAB
Landing gear method and apparatus for braking and maneuvering
InactiveUS7226018B2Reduce wearImprove stabilityElectric devicesEnergy efficient operational measuresElectric generatorAirplane
Aircraft landing gear comprised of a wheel hub motor / generator disks stack, includes alternating rotor and stator disks mounted with respect to the wheel support and wheel. The invention can provide motive force to the wheel when electrical power is applied, e.g. prior to touch-down, thus decreasing the difference in relative velocities of the tire radial velocity with that of the relative velocity of the runway and reducing the sliding friction wear of the tire. After touchdown the wheel hub motor / generator may be used as a generator thus applying a regenerative braking force and / or a motorized braking action to the wheel. The energy generated upon landing maybe dissipated through a resistor and / or stored for later use in providing a source for motive power to the aircraft wheels for taxiing and ground maneuvers of the aircraft. Methods and apparatuses for nose gear steering and ABS braking using the disclosed invention are described.
Owner:DELOS AEROSPACE
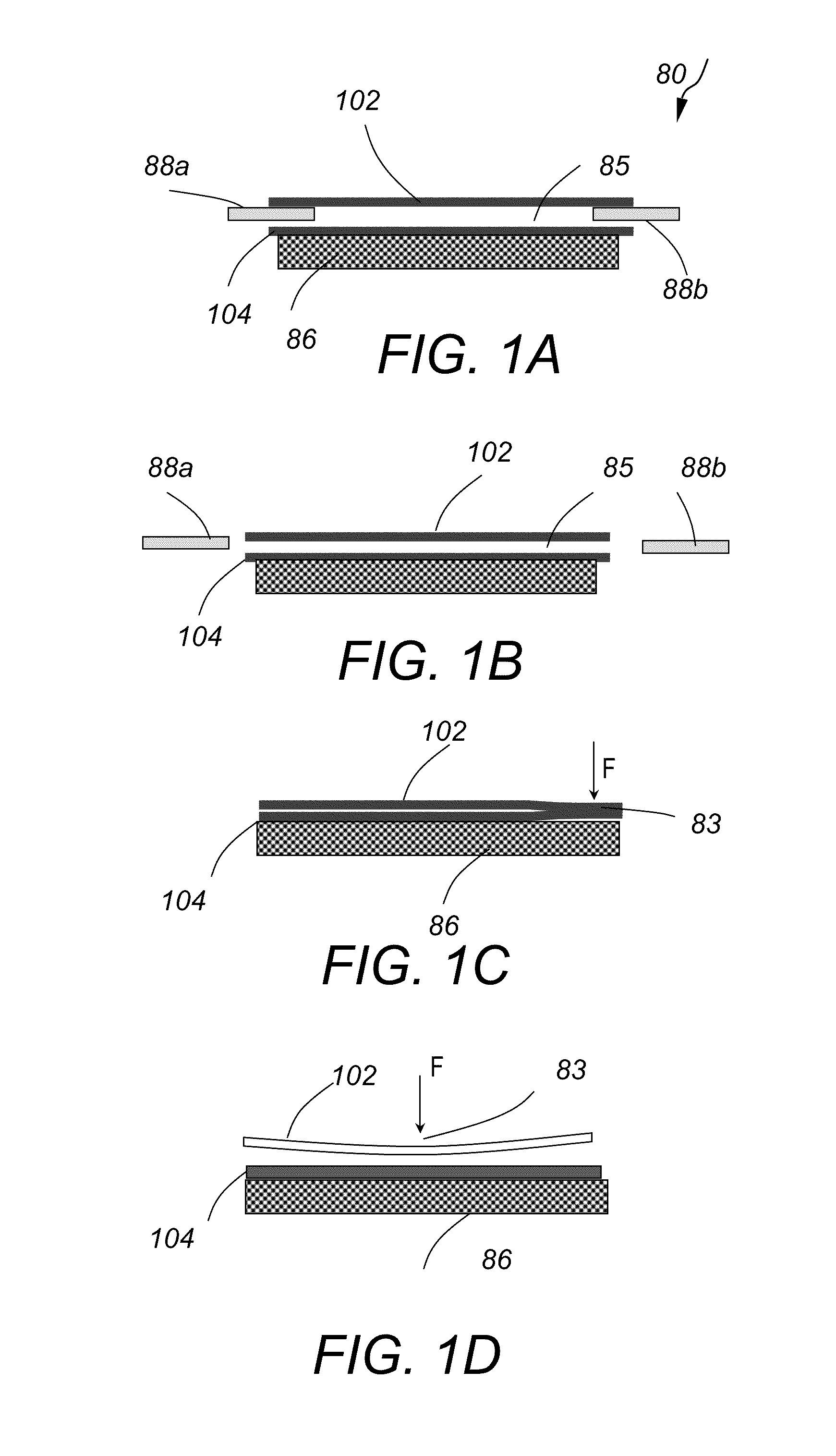
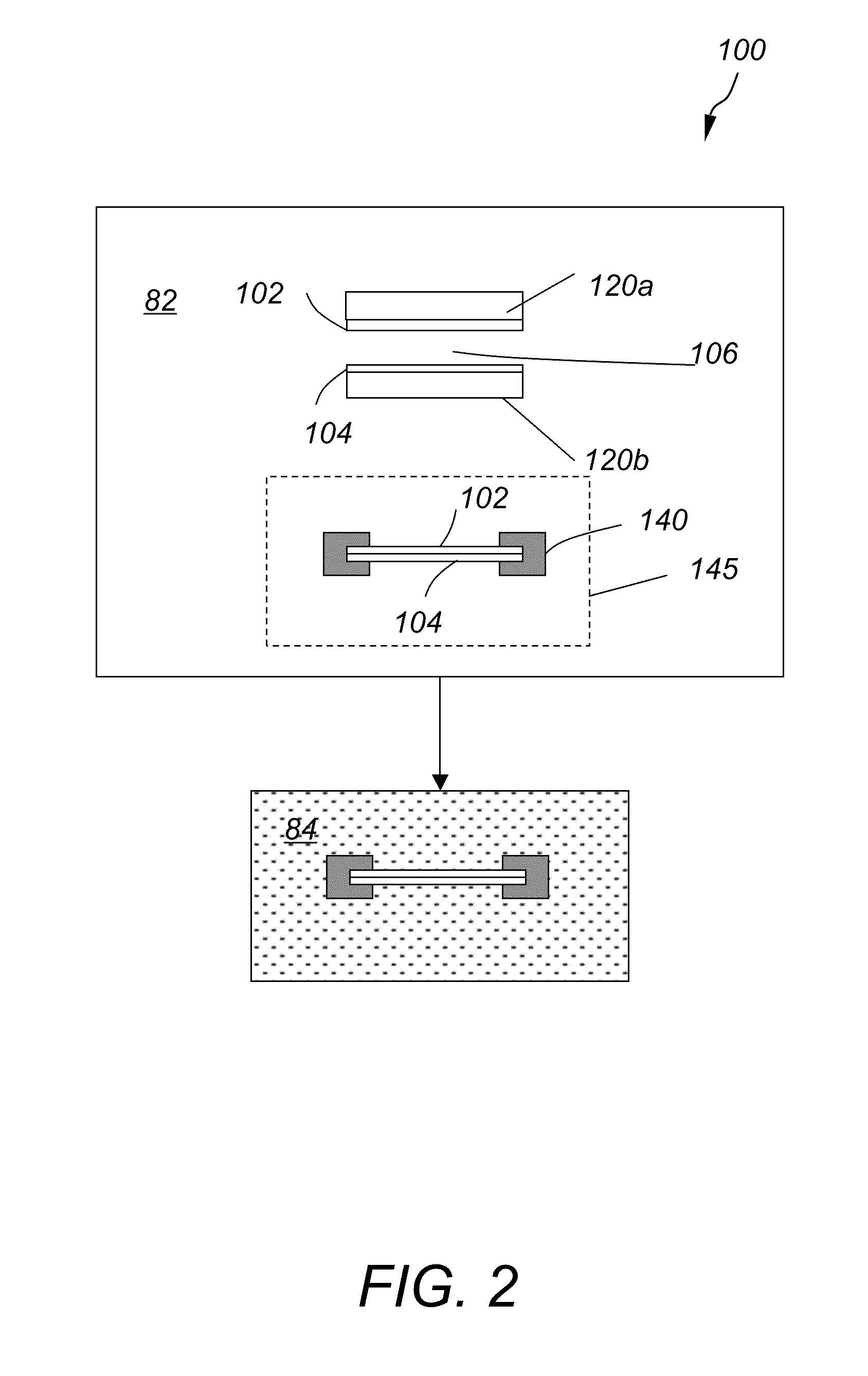
Method and apparatus for wafer bonding with enhanced wafer mating
ActiveUS20100122762A1Reduce pressureAccuracy in alignmentPrinted circuit assemblingMechanical working/deformationWafer dicingEngineering
An improved wafer-to-wafer bonding method includes aligning an upper and a lower wafer and initiating a bond at a single point by applying pressure to a single point of the upper wafer via the flow of pressurized gas through a port terminating at the single point. The bond-front propagates radially across the aligned oppositely oriented wafer surfaces at a set radial velocity rate bringing the two wafer surfaces into full atomic contact by controlling the gas pressure and / or controlling the velocity of the motion of the lower wafer up toward the upper wafer.
Owner:SUSS MICRO TEC LITHOGRAPHY
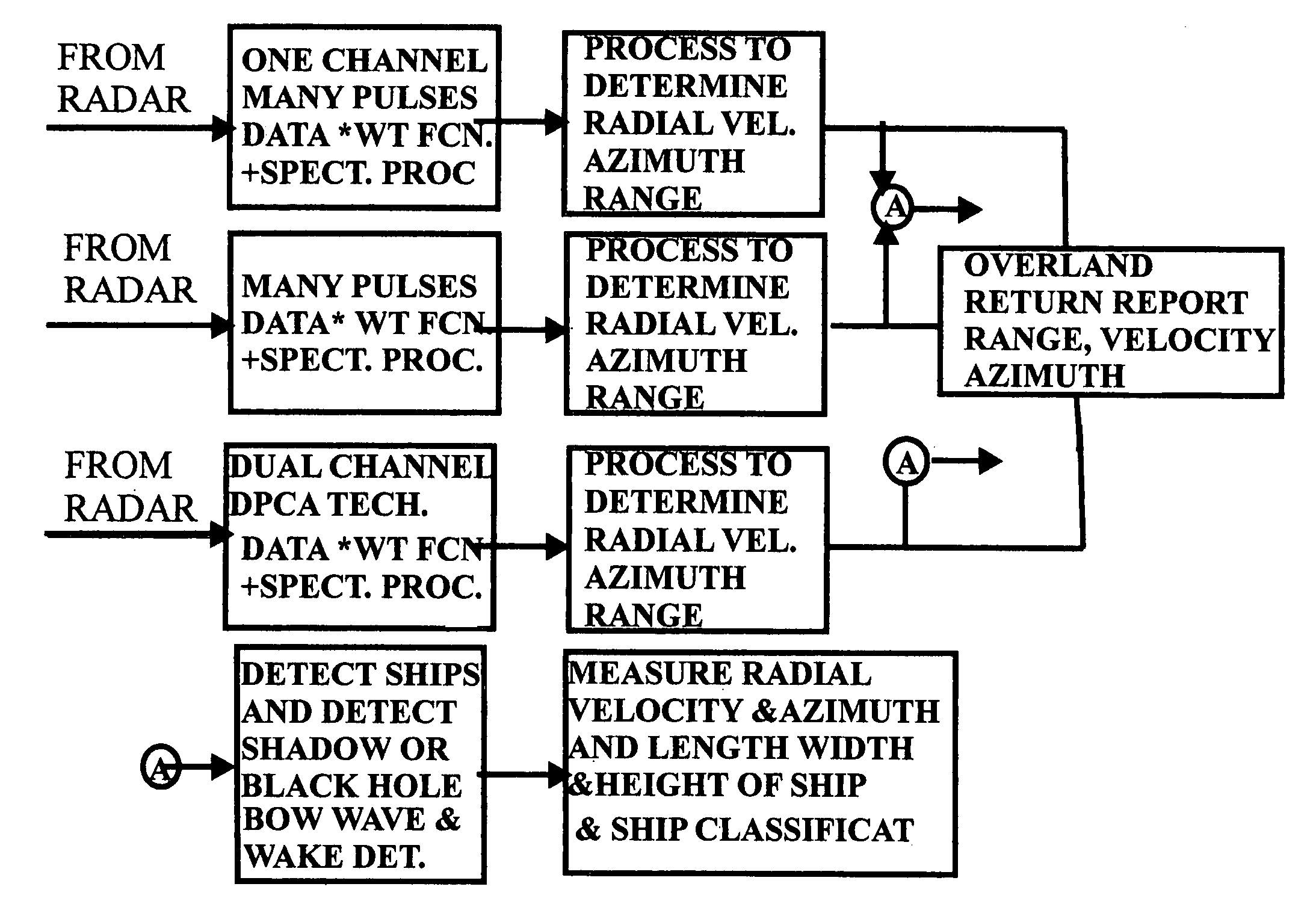
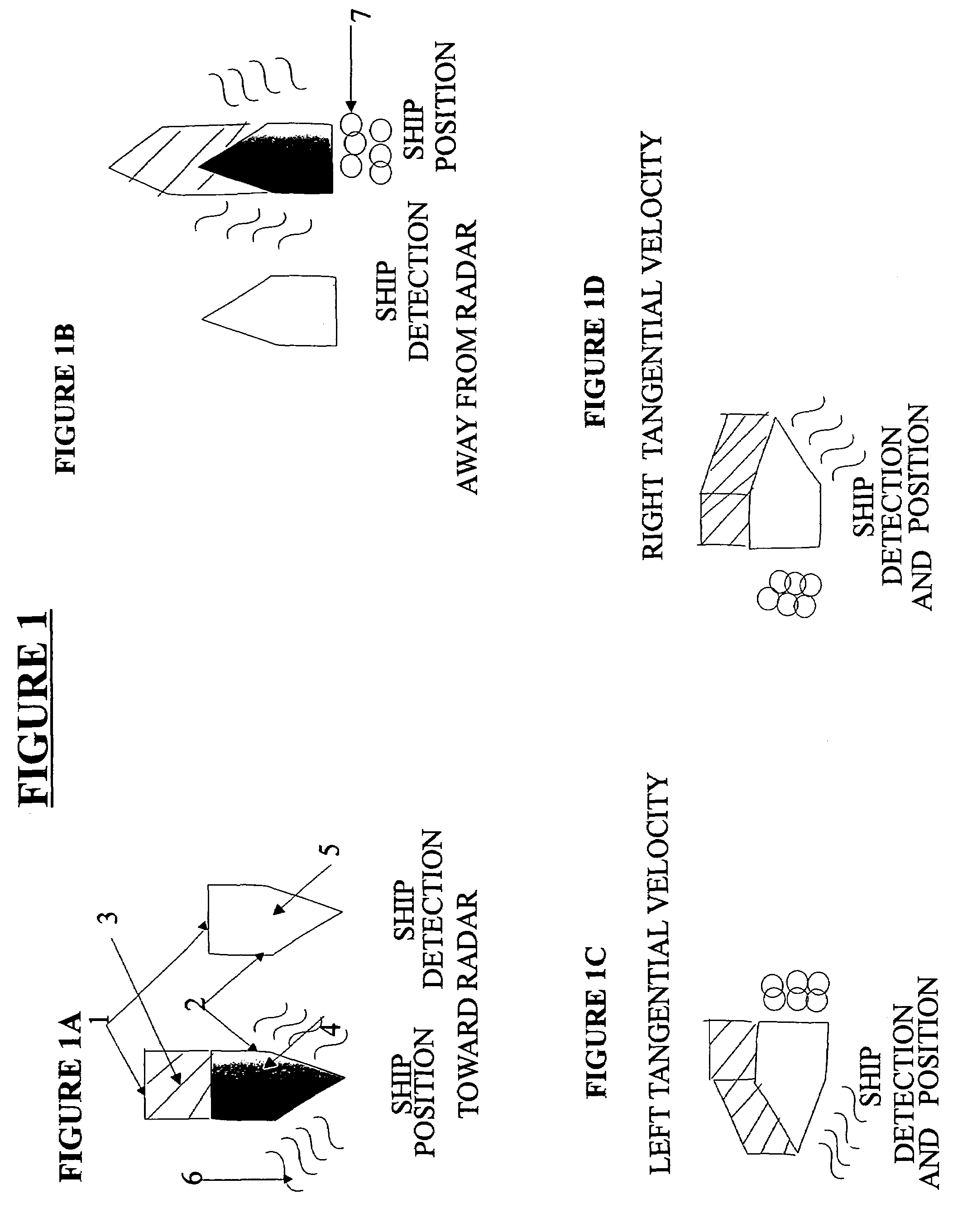
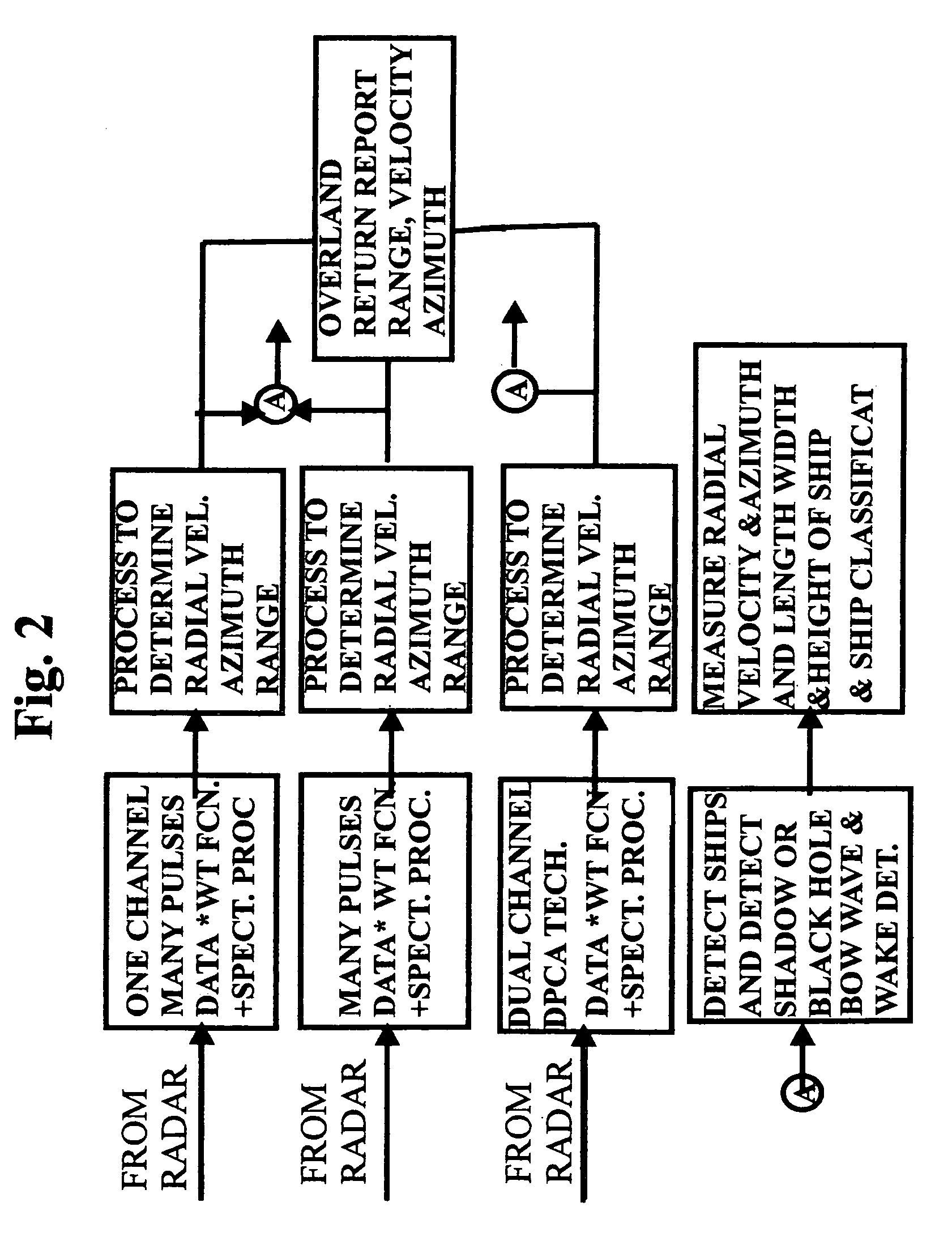
Unique space time adaptive system (USS)
A method of detecting radar returns and measuring their parameters with or without clutter present and no clutter cancellation employed which includes transmitting at least one pulse; processing the returns surpassing a threshold detected in one range azimuth bin and by processing and separating out the returns based on their different range and azimuth. Another method includes transmission of many pulses and has minimum of one channel return surpassing detected threshold, which is detected in one range Doppler bin. The method also includes processing and thereby separating out the returns based on their different radial velocity and or azimuth and comparing the returns to a database of expected returns and adaptively processing returns that do not correspond to the expected returns. The method identifies the non-corresponding returns as indicative of at least one of clutter, land sea interface, clutter discretes and antenna sidelobe returns each without utilizing clutter cancellation.
Owner:CATALDO THOMAS J
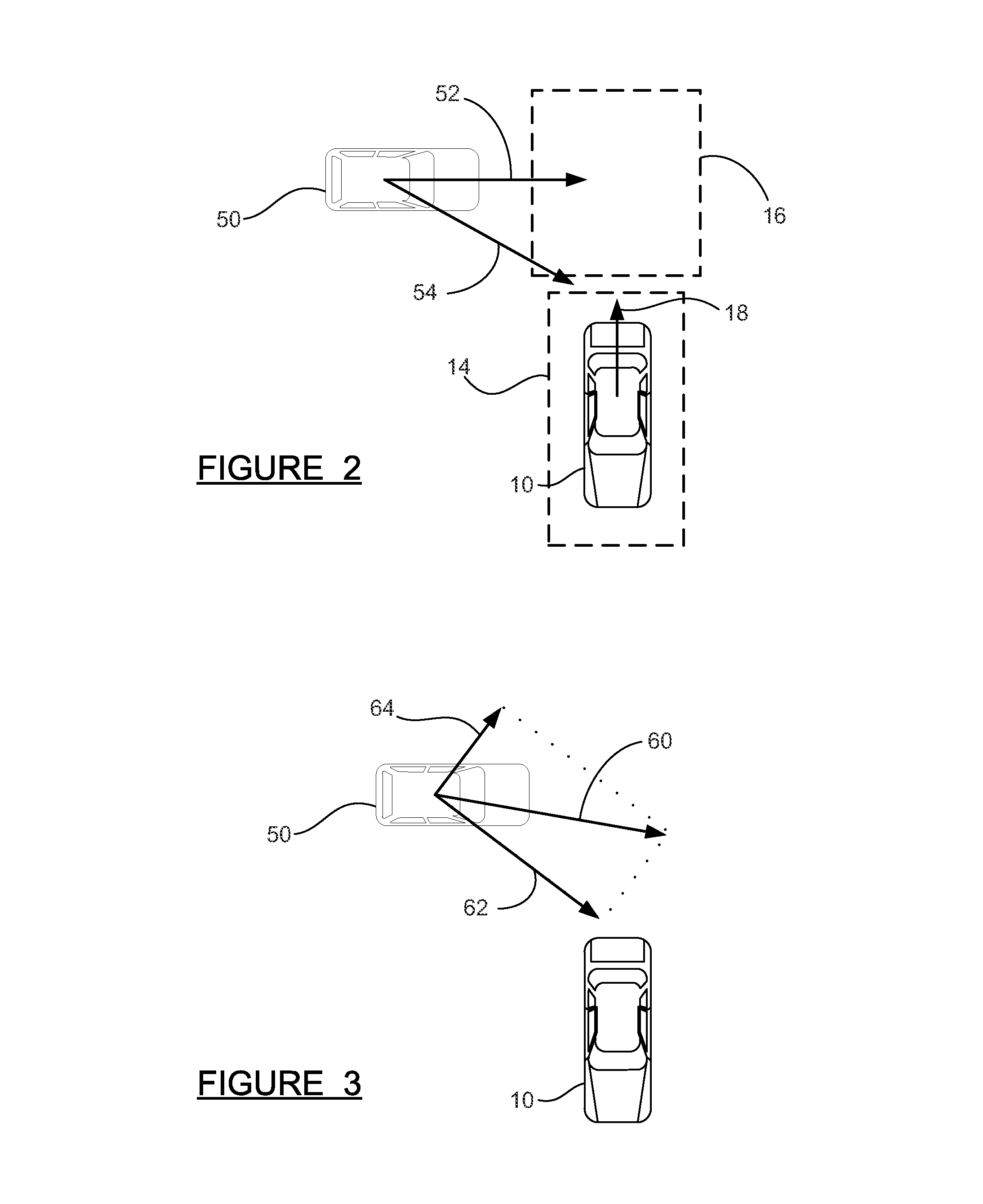
Fusion method for cross traffic application using radars and camera
ActiveUS20160291149A1Accurate estimateAutomatic initiationsSignalling/lighting devicesAutomatic brakingRadar
A method and system are disclosed for tracking objects which are crossing behind a host vehicle. Target data from a vision system and two radar sensors are provided to an object detection fusion system. Salient points on the target object are identified and tracked using the vision system data. The salient vision points are associated with corresponding radar points, where the radar points provide Doppler radial velocity data. A fusion calculation is performed on the salient vision points and the radar points, yielding an accurate estimate of the velocity of the target object, including its lateral component which is difficult to obtain using radar points only or traditional vision system methods. The position and velocity of the target object are used to trigger warnings or automatic braking in a Rear Cross Traffic Avoidance (RCTA) system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method of operating a multi-antenna pulsed radar system
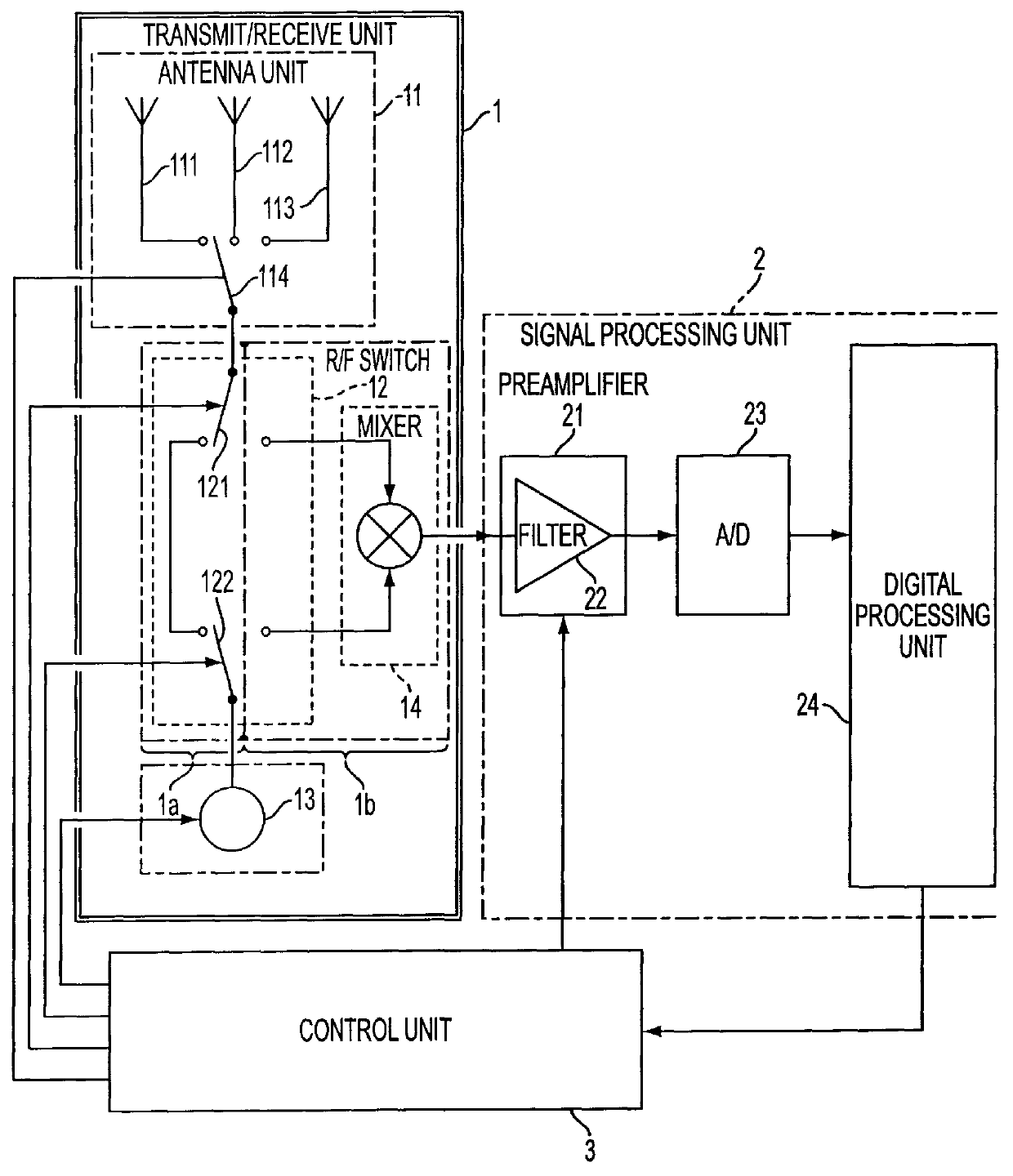
InactiveUS6184819B1Increase angular measuring accuracy and performance capacityReduce size and complexity and costDirection findersRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMobile vehicleRadar systems
A method for operating a radar system using at least two antennas provides an increased angular resolution for determining the angular position, radial velocity, and / or distance to a reflection object. A plurality of successive measuring phases are carried out in at least one measuring process. In each measuring phase, operation is repeatedly switched between a transmitting operation in which a transmitted signal pulse is emitted, and a receiving operation in which reflection signals are detected as received signals in the pulse pause interval between successive transmitted pulses. In at least one measuring phase, two different neighboring antennas of the radar system are used respectively as the transmitting antenna for emitting the transmitted signal and as the receiving antenna for detecting the reflected signal. In this manner, the respective receiving antenna monitors only the angular range of overlap between the emitted beam of the transmitting antenna and the field of view of the receiving antenna. The information provided by the detected signals in this overlapping angular range achieves an increased angular resolution. The method is particularly suitable for operating a separation distance warning system for a motor vehicle.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE DISTANCE CONTROL SYST
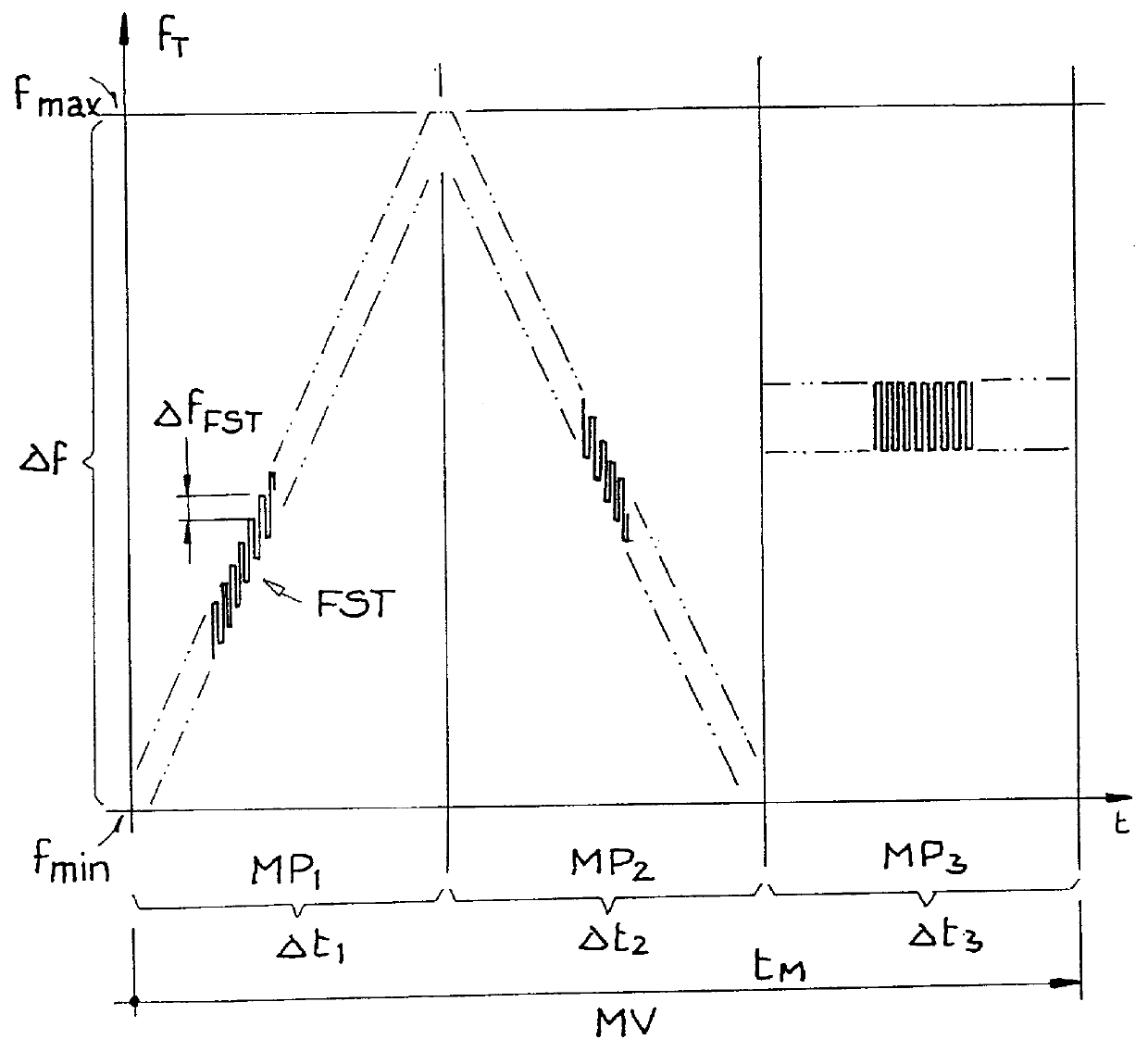
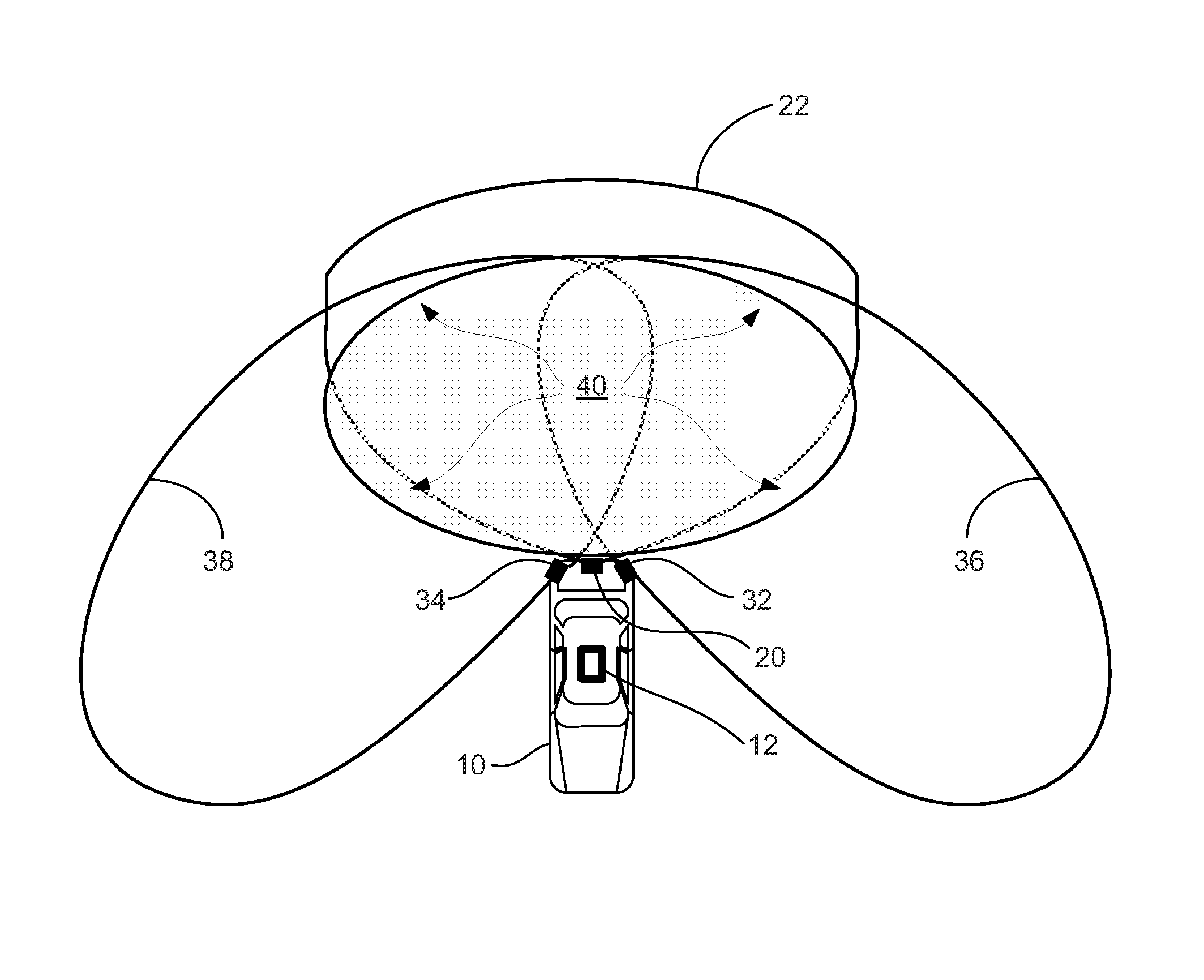
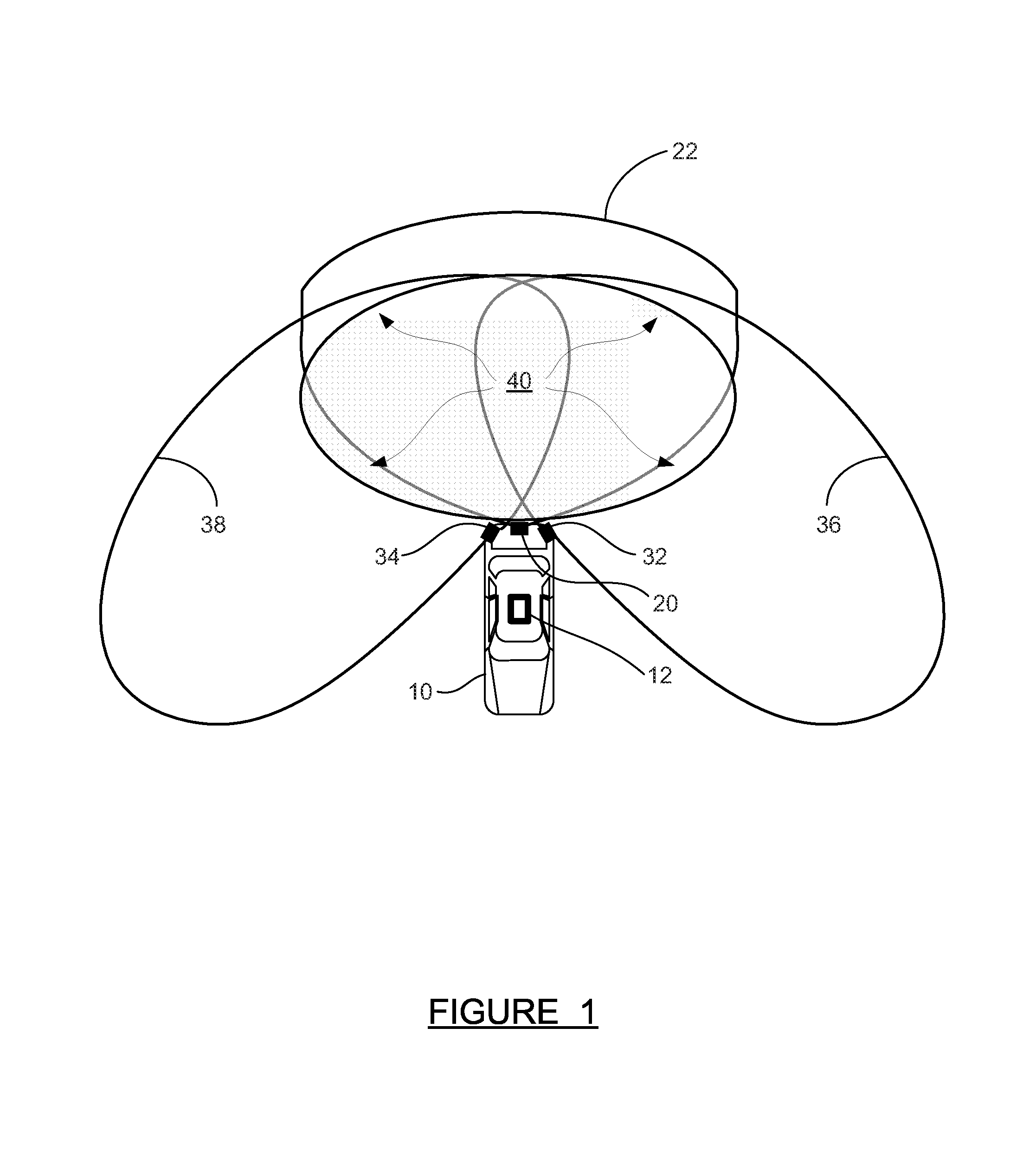
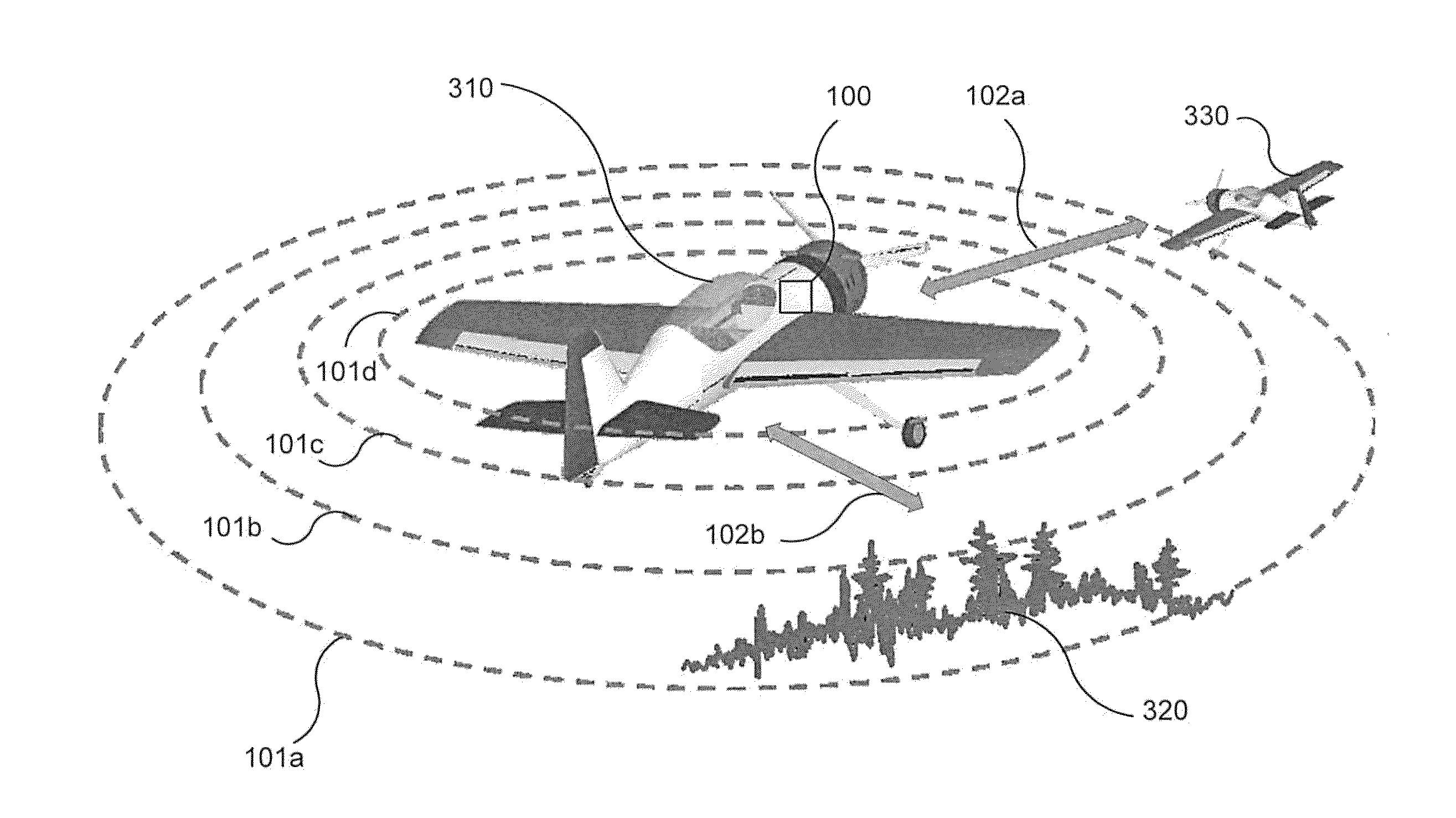
Sense-and-avoid systems and methods for unmanned aerial vehicles
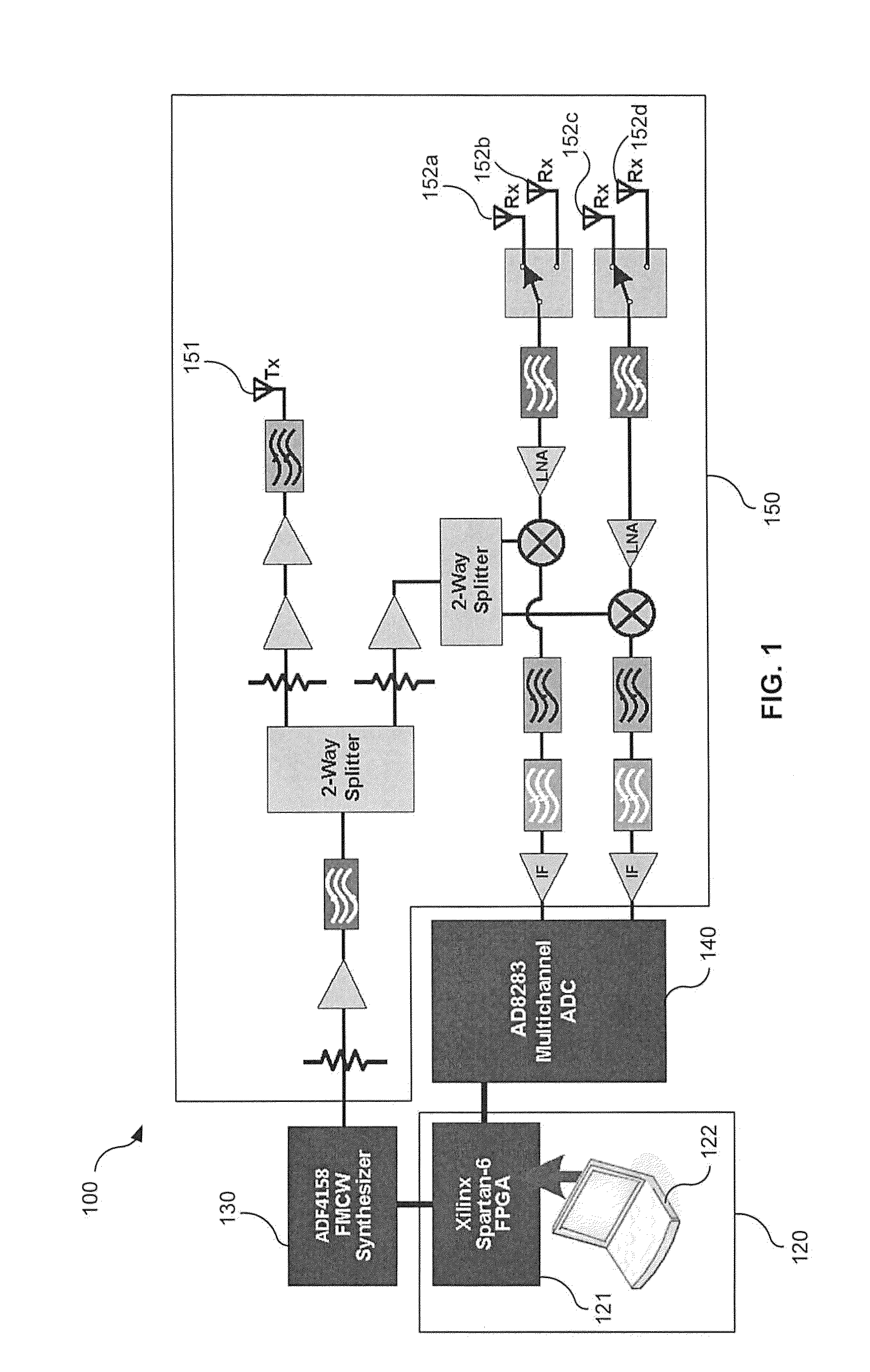
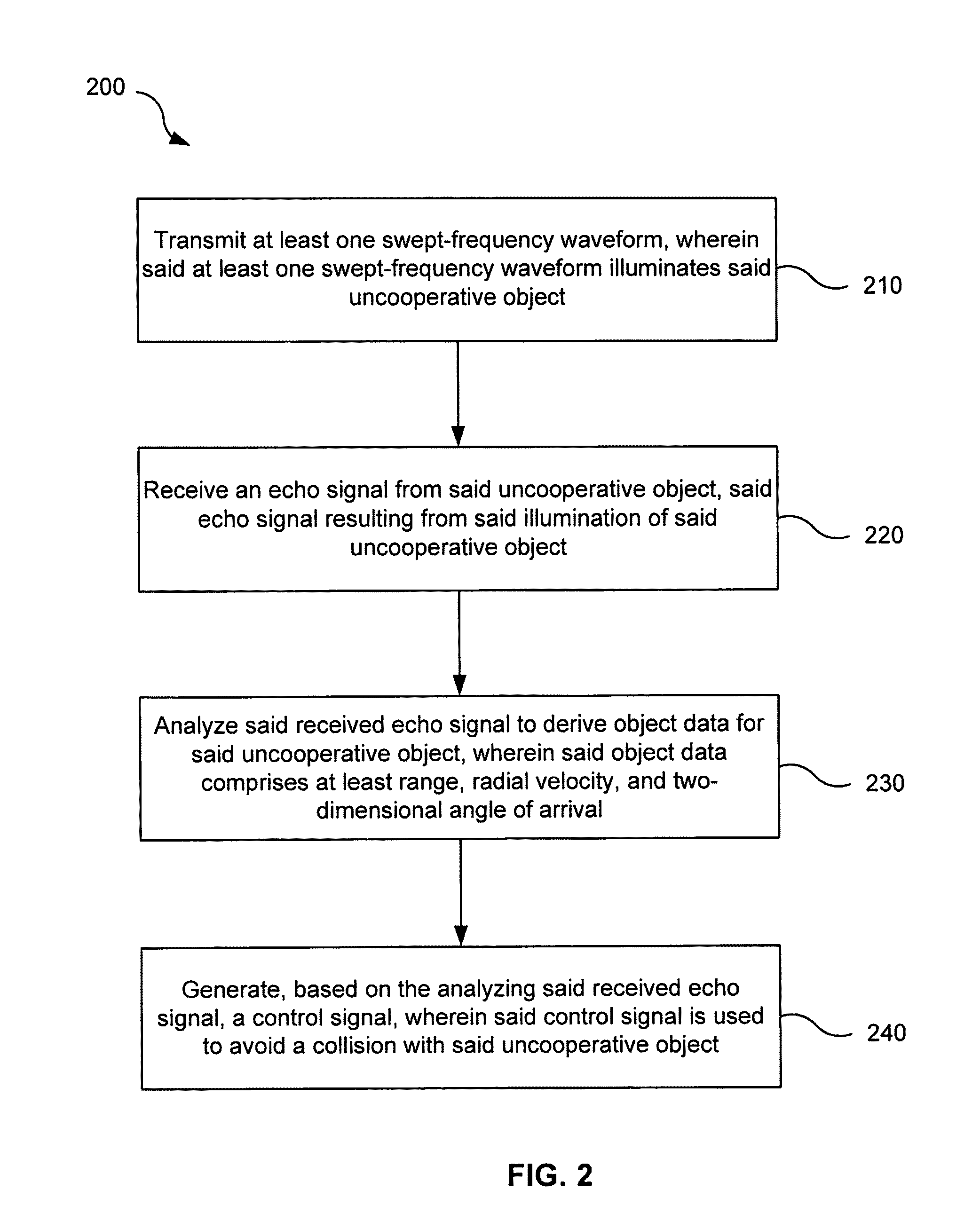
A sense-and-avoid system, for an unmanned air vehicle (UAV), configured to detect and estimate the relative position and velocity of a nearby object and to enable determination whether the nearby object poses a collision threat to the UAV. In one embodiment, the sense-and-avoid system is provided with a frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) synthesizer adapted to generate at least one swept-frequency waveform. The sense-and-avoid system may also be included with an RF subassembly. In some embodiments, the RF subassembly may include at least one transmit antenna adapted to transmit the at least one swept-frequency waveform. The at last one swept-frequency waveform may illuminate the nearby object. The sense-and-avoid system may be further provided with a plurality of receive antennas adapted to receive an echo signal from the nearby object. In some embodiments, the echo signal results from the illumination of the nearby object by the swept-frequency waveform. Additionally, the sense-and-avoid system may be provided with a signal processor configured to analyze the received echo signal and to derive object data for the nearby object. The object data may include at least range, radial velocity, and two-dimensional angle of arrival.
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF
Landing gear method and apparatus for braking and maneuvering
InactiveUS20060038068A1Reduce wearImprove stabilityEnergy efficient operational measuresElectric devicesElectric powerElectric generator
Owner:DELOS AEROSPACE
High flow/high efficiency centrifugal pump having a turbine impeller for liquid applications including molten metal
ActiveUS7896617B1Increase the cross-sectional areaHigh speedSpecific fluid pumpsPropellersParticulatesSolid particle
A centrifugal pump having a turbine impeller having a plurality of curved vanes. The vanes curve from the inlet end to the outlet end in the direction of pumping rotation of the impeller, such that the leading wall of each vane re-directs a portion of the radial velocity of the fluid flowing through the passage to increase the total tangential velocity provided by the impeller. Each curved passage has cooperating inlet and outlet areas and a smooth curved shape to ensure that the radial velocity of the liquid does not decrease dramatically while flowing through the passage, while ensuring that any solid particulates and contaminants entering the impeller will pass therethrough.
Owner:MORANDO JORGE A
Three-phase cyclonic fluid separator with a debris trap
An apparatus separates liquid, gas and solid components of a mixture in a fluid system. An inlet for receiving the mixture opens into a separation chamber tangentially with a cylindrical side wall and a gas outlet has an opening in a first end wall adjacent the inlet to allow gas to exit the separator. A fluid outlet is located in an opposing second end wall. A debris passage extends through the cylindrical side wall and oriented so that the radial velocity of the particles within the separation chamber directs the particles through the debris passage. The debris passage leads to a particle collection chamber in which the particles accumulate. Unlike prior separators that relied on the tangential velocity of the particles, the present apparatus utilizes the greater radial velocity to drive the particles from the separation chamber into the particle collection chamber.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Pressurized bearing system for submersible motor
Pressurized lubricant is used for stabilizing shaft bearings in an electrical submersible pump motor. A lubricant pump is located within the motor housing. The lubricant pump has a set of impellers attached to a lower end of the shaft and rotating with the shaft, the impellers being located in the flow path of the lubricant. A diffuser is located upstream of and adjacent each impeller. The impellers increase the radial velocity of the lubricant, and this velocity is converted into a pressure head at the impeller outlet. The lubricant flows through the first diffuser, through the first impeller, through the second diffuser, and then flows through the second impeller and out into a reservoir. The shaft has an axial flow passage with an outlet at each bearing. The outlet has at least three ports arranged symmetrically around the shaft for discharging lubricant into a clearance between the shaft and bearing to create a fluid film.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Mesocyclone identification method based on Doppler radar echo images
InactiveCN102645679AReduce complexityReduce false alarm rateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationElevation angleMesocyclone
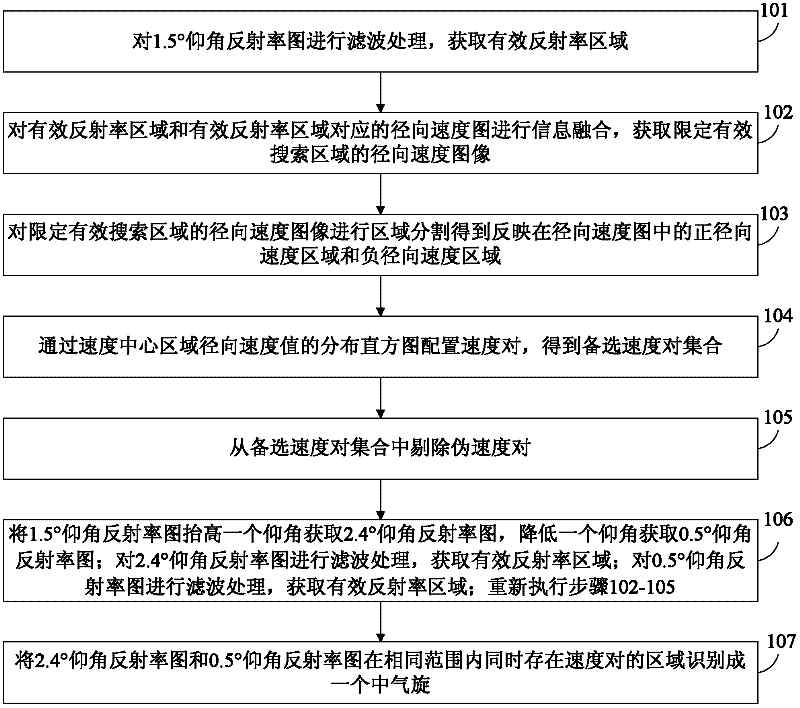
The invention discloses a mesocyclone identification method based on Doppler radar echo images. The mesocyclone identification method comprises the following steps of: filtering reflectivity images with 0.5-degree, 1.5-degree and 2.4-degree elevation angles to acquire an effectively reflectivity area; blending information on the effective reflectivity area into radial velocity images with same elevation angles to acquire radial velocity images of a limited searching area; segmenting the radial velocity images into which the information on the effective reflectivity area is blended, and screening positive and negative velocity center areas in the radial velocity images; configuring all possible velocity pairs through distribution histograms of radial velocity values of the velocity center areas so as to obtain a velocity pair set; and eliminating pseudo velocity pairs from the velocity pair set, and identifying the mesocyclone. By the mesocyclone identification method, the complicity of time and space is reduced, most of false mesocyclones are eliminated, the identification rate is increased, the misstatement rate is reduced, the working efficiency is improved; moreover, the method has the characteristic of not limiting the cyclone direction and structure information of the mesocyclone, so the identification result is more comprehensive.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for processing non-meteorological noise in radar echoes
InactiveCN101706571AEffective filteringLarge vertical changeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationSkyRadar
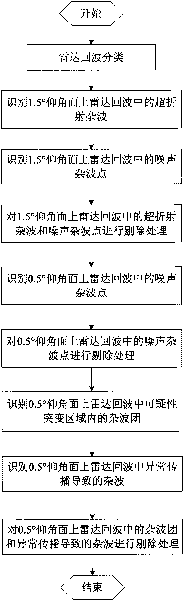
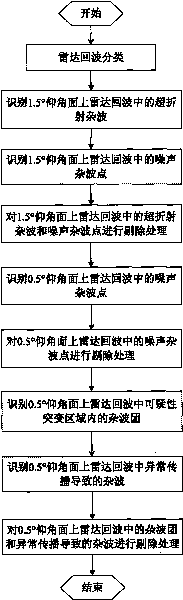
The invention discloses a method for non-meteorological noise in radar echoes, which comprises the steps of: identifying noise areas existing on an 1.5 DEG elevation plane and an 0.5 DEG elevation plane by simply classifying the radar echoes, then analyzing reflectivity factor values of the echoes and then orderly referring radial velocity values and spectrum width values; performing a best noise rejection strategy on different noises after the noise areas are correctly identified; directly adopting a rejection strategy for noises under the conditions of clear sky and no precipitation echoes at peripheries; and adopting an approximate value filling mechanism for noises which are mixed in the precipitation echoes or are adjacent to the precipitation echoes so as to achieve better rejection effect.
Owner:宁波市气象服务中心
Method of moving-target relocation and velocity ambiguity resolution based on velocity synthetic aperture radar (VSAR) system
ActiveCN102565784AInaccurate speed estimationGood precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
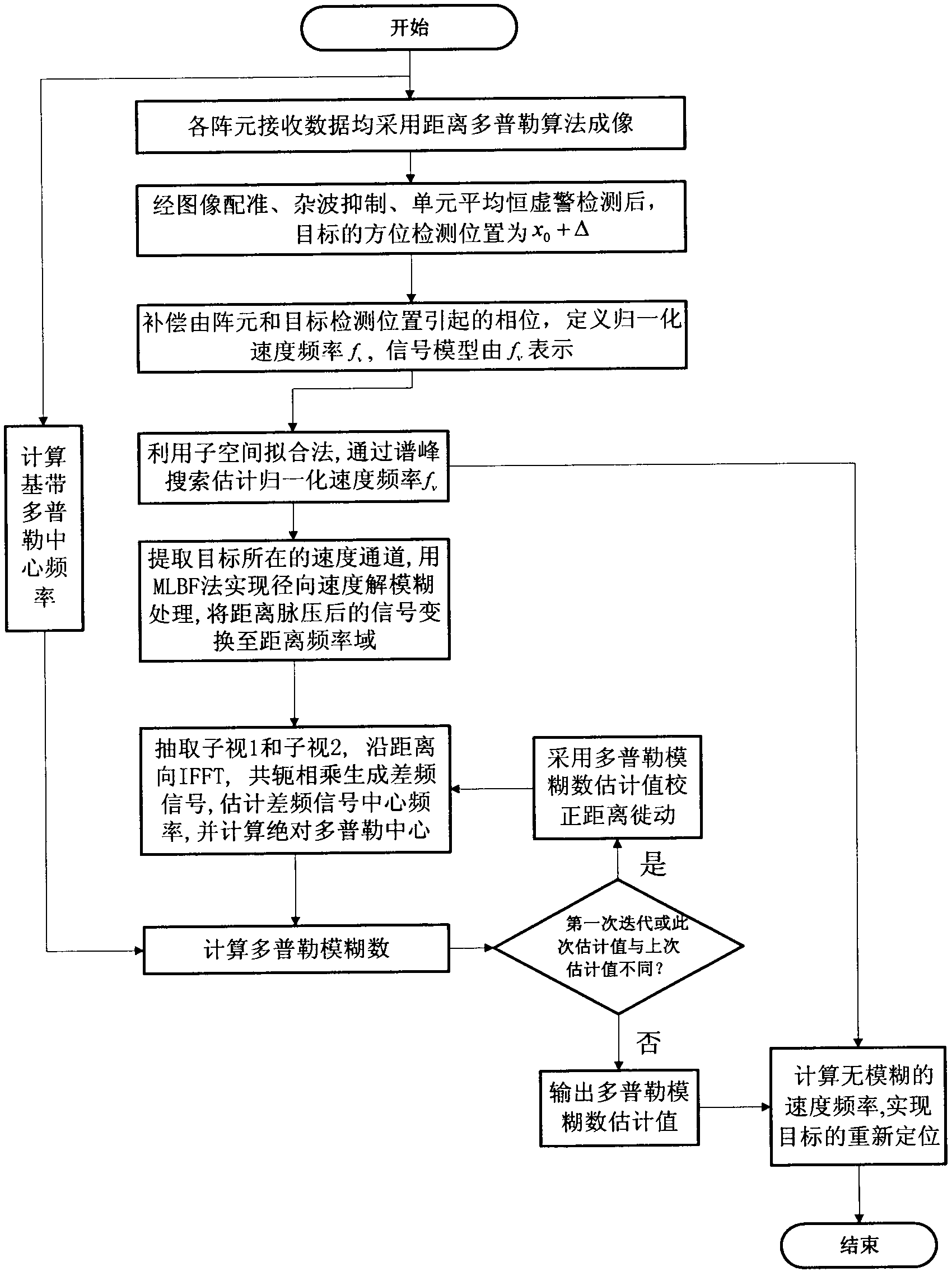
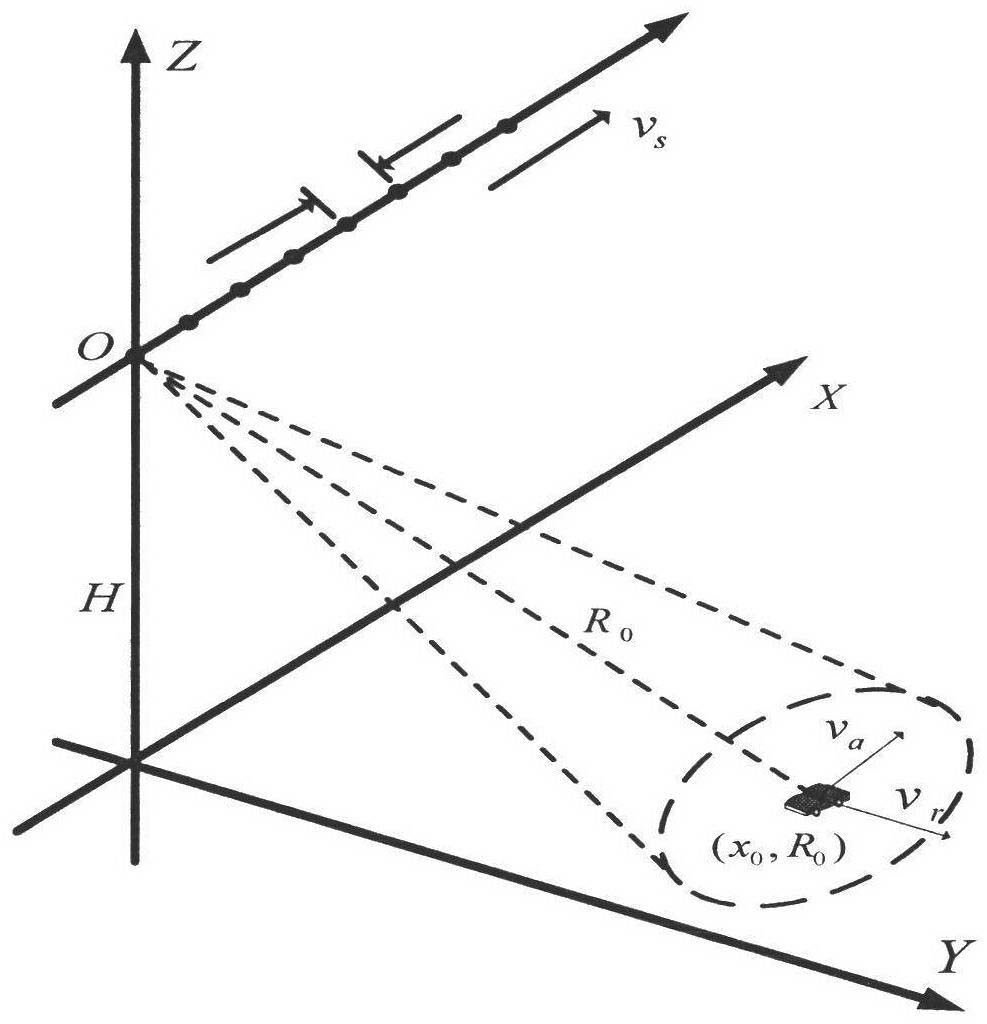
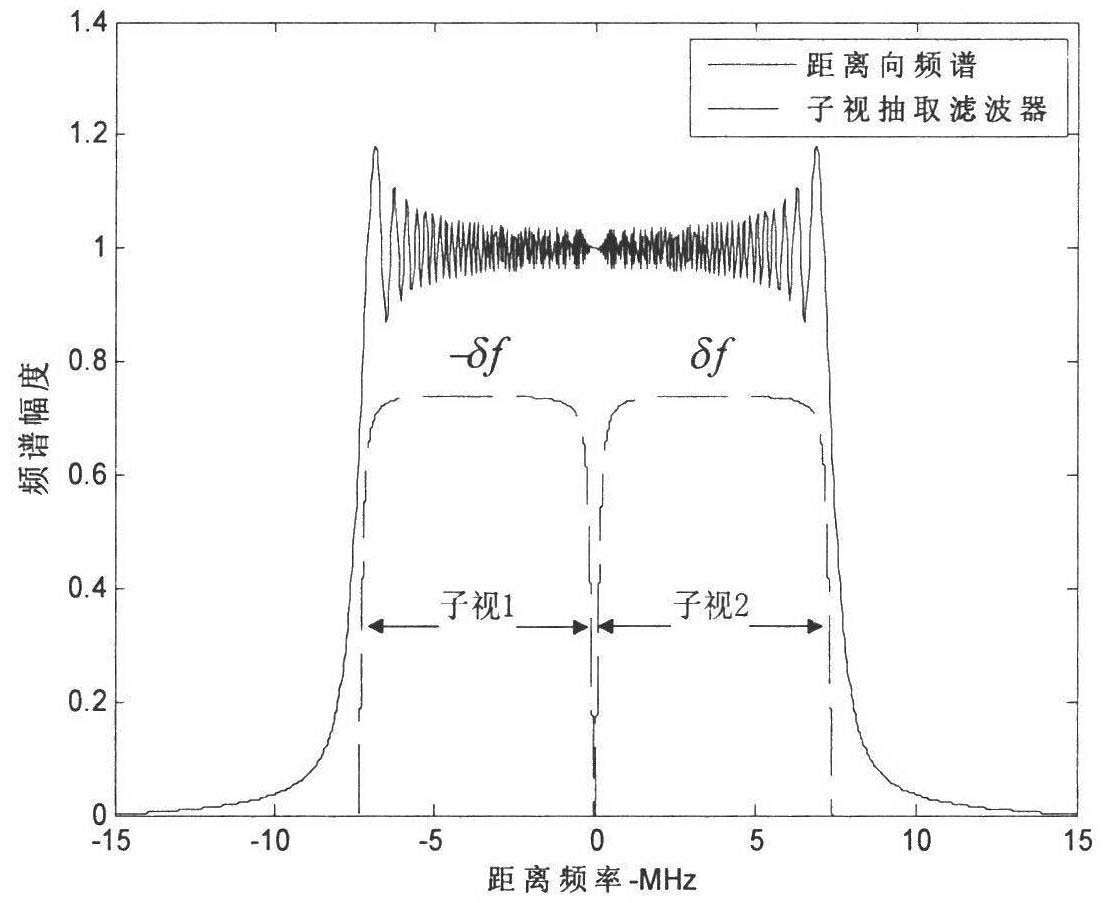
The invention discloses a method of moving-target relocation and velocity ambiguity resolution based on a velocity synthetic aperture radar (VSAR) system, which mainly solves the problems that the velocity estimation accuracy of a moving target is low and the velocity of a fast moving target is ambiguous in the radar detection system. According to the method of moving-target relocation and velocity ambiguity resolution based on the VSAR system, the process includes perform range-doppler algorithm imaging to received data of each of array elements of the VSAR system; detecting the moving target and recording the corresponding position of the moving target after image registration, clutter suppression and cell average constant false alarm detection processing; using subspace fitting algorithm to estimate normalized velocity frequency after phase compensation so that the velocity estimation accuracy is effectively improved; extracting speed channel of the target, using multi-look differential frequency method to estimate doppler ambiguity number; calculating radial velocity of non-ambiguity according to the ambiguity numbers and estimate value of the velocity frequency and achieving an accurate location of the target. According to the method of moving-target relocation and velocity ambiguity resolution based on the velocity synthetic aperture radar (VSAR) system, the estimation accuracy and the detection performance are improved. Due to the fact that the ambiguity resolution processing is merely required for 2-3 iterations, the calculation is reduced, the accurate probability of understanding doppler ambiguity is improved and the effectiveness of the method is proved in a simulation experiment.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
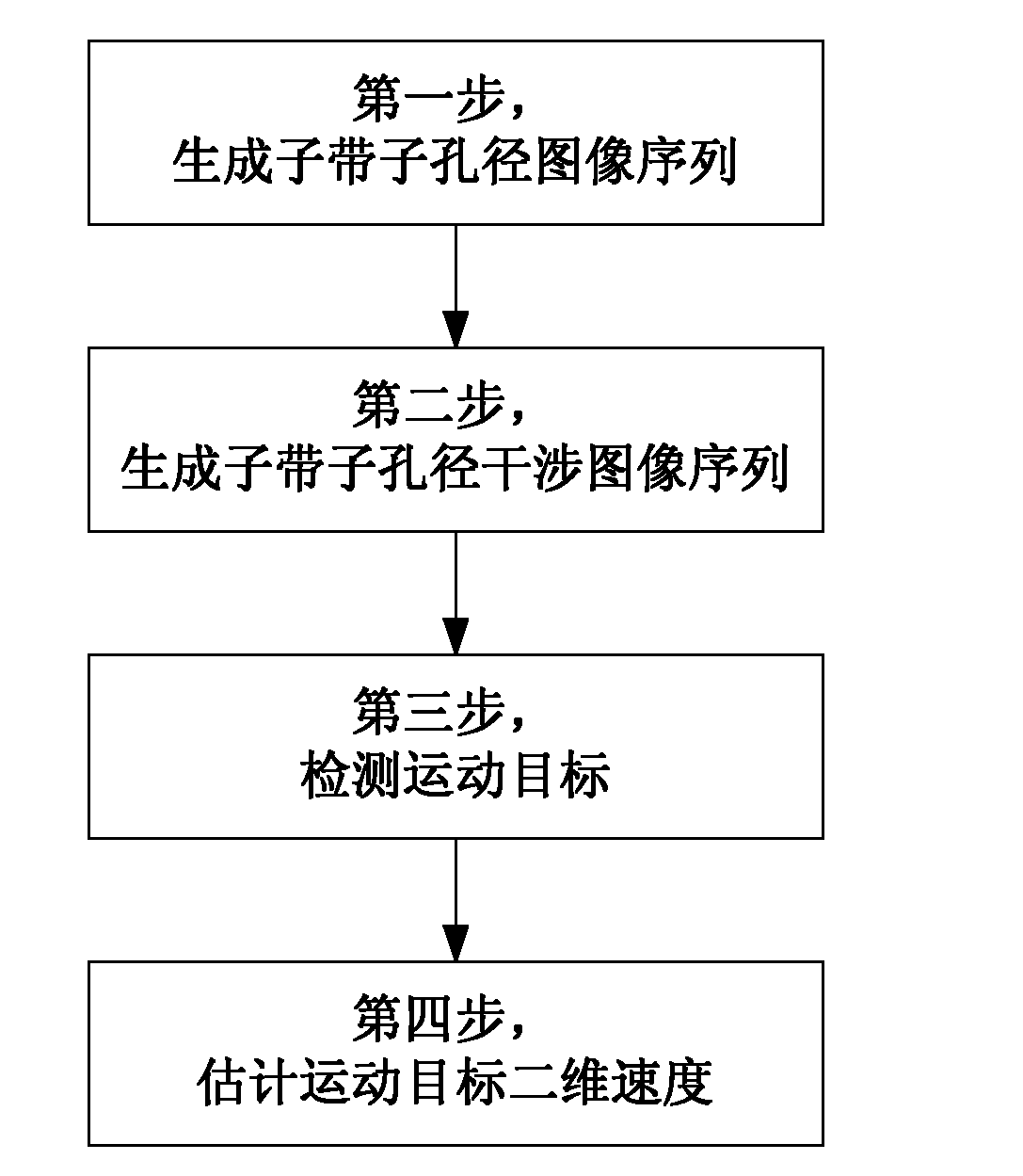
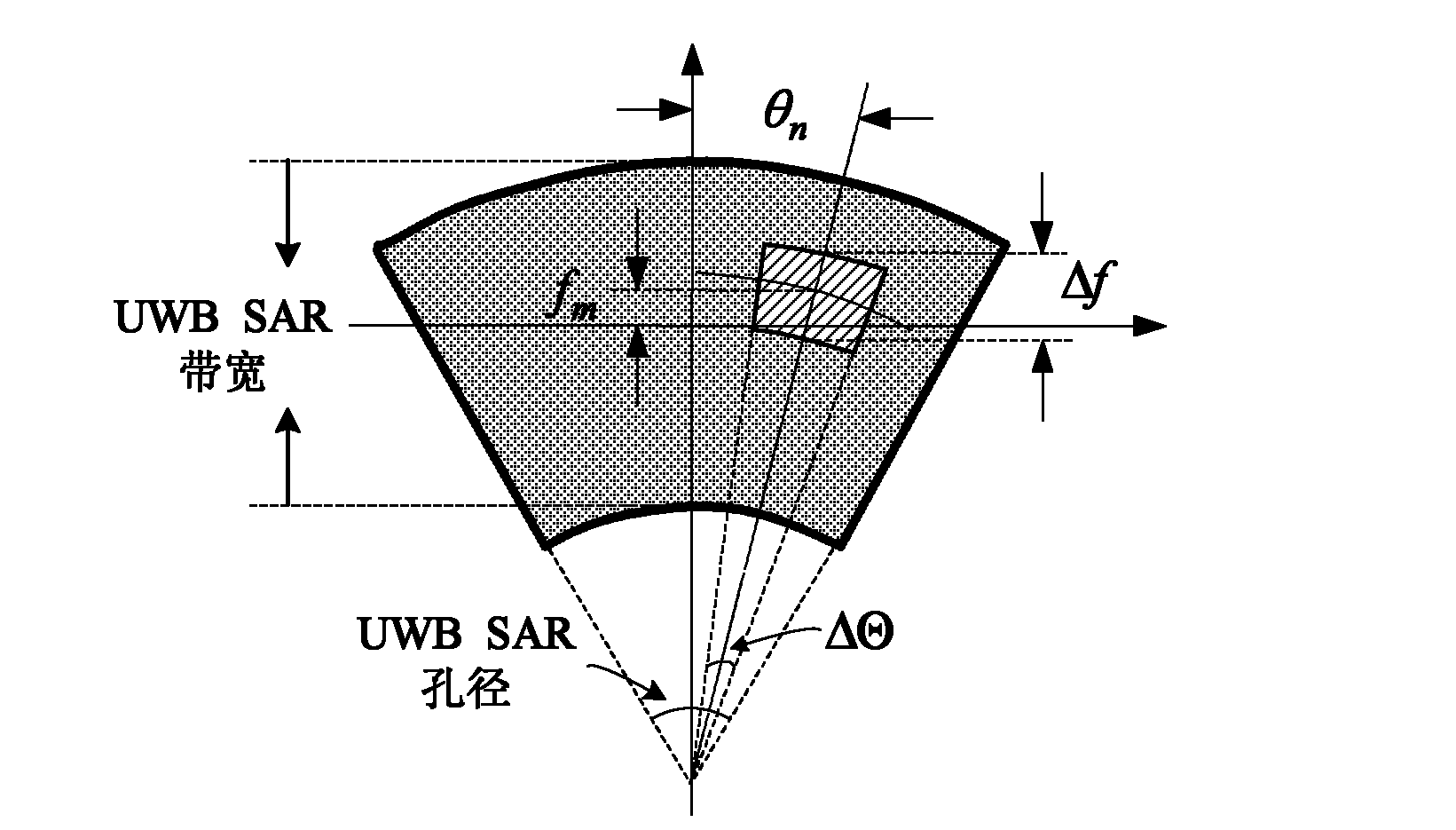
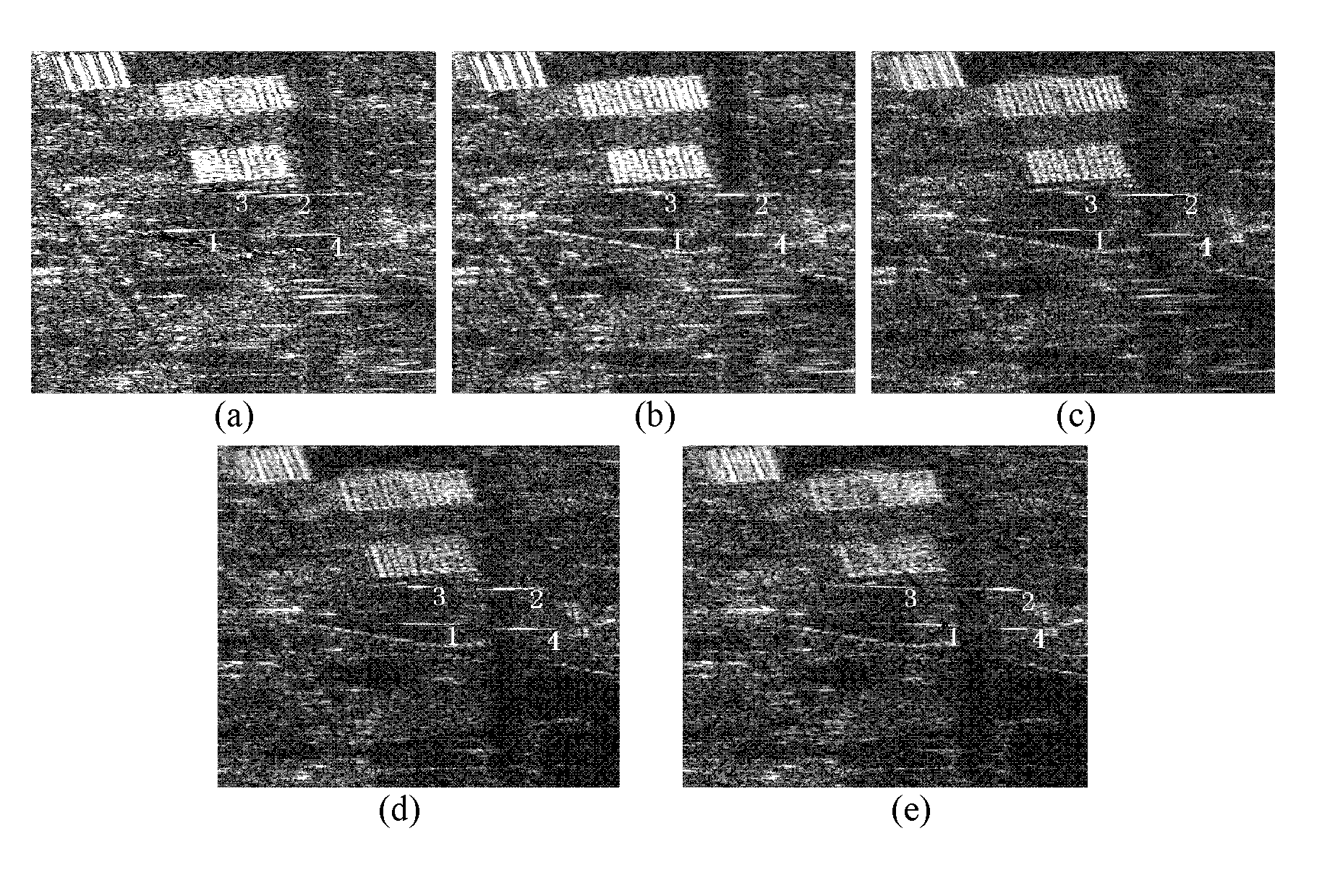
Ground moving target detection and parameter estimation method
InactiveCN102508244ABlind Speed EliminationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEstimation methodsSynthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a ground moving target detection and parameter estimation method. The technical scheme realizes the moving target detection and two-dimensional velocity estimation by combining with an interference image sequence with multiple sub-bands and sub-apertures on the basis of a three-way ultra-wide bandwidth (UWB) synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image. The specific steps of the method are as follows: 1, generating a sub-band sub-aperture image sequence; 2, generating a sub-band sub-aperture interference image sequence; 3, detecting the moving target; and 4, estimating the two-dimensional velocity of the moving target. By using the ground moving target indication and parameter estimation method provided by the invention, the moving target and a static target can be distinguished on an imaging position and a phase position; the radial velocity of the moving target can be estimated clearly; and the azimuth speed and distance speed can also be estimated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Fully-coherent continuous-wave Doppler radar and distance measurement and velocity measurement method thereof
ActiveCN106405541AWith no distance blind spot rangingEliminate the effects ofRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBlind zoneFree distance
The invention discloses a fully-coherent continuous-wave Doppler radar and a distance measurement and velocity measurement method thereof. According to the fully-coherent continuous-wave Doppler radar and the distance measurement and speed measurement method thereof, difference-frequency complex signals obtained by mixing echo signals and transmitted signals are acquired; according to the modulation characteristics of distance difference-Doppler frequency and target distance-velocity, a distance-dimension FFT and azimuth-dimension MTD-combined two-dimensional joint detection method is adopted to independently obtain fuzziness-free radial velocity information based on a plurality of coherent high-repetition frequency modulation signals; Doppler information introduced by velocity is removed from the frequency-domain information in the distance dimension, so that the influence of distance-velocity coupling can be eliminated, and therefore, accurate distance information can be obtained. The fully-coherent continuous-wave Doppler radar and the distance measurement and velocity measurement method thereof of the invention have coherent radar velocity measurement function and a continuous-wave radar distance blind zone-free distance measurement function and can satisfy requirements for distance blind zone-free and simultaneous distance measurement and velocity measurement, real-time performance, miniaturization and low power consumption.
Owner:SUZHOU TUSHI ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
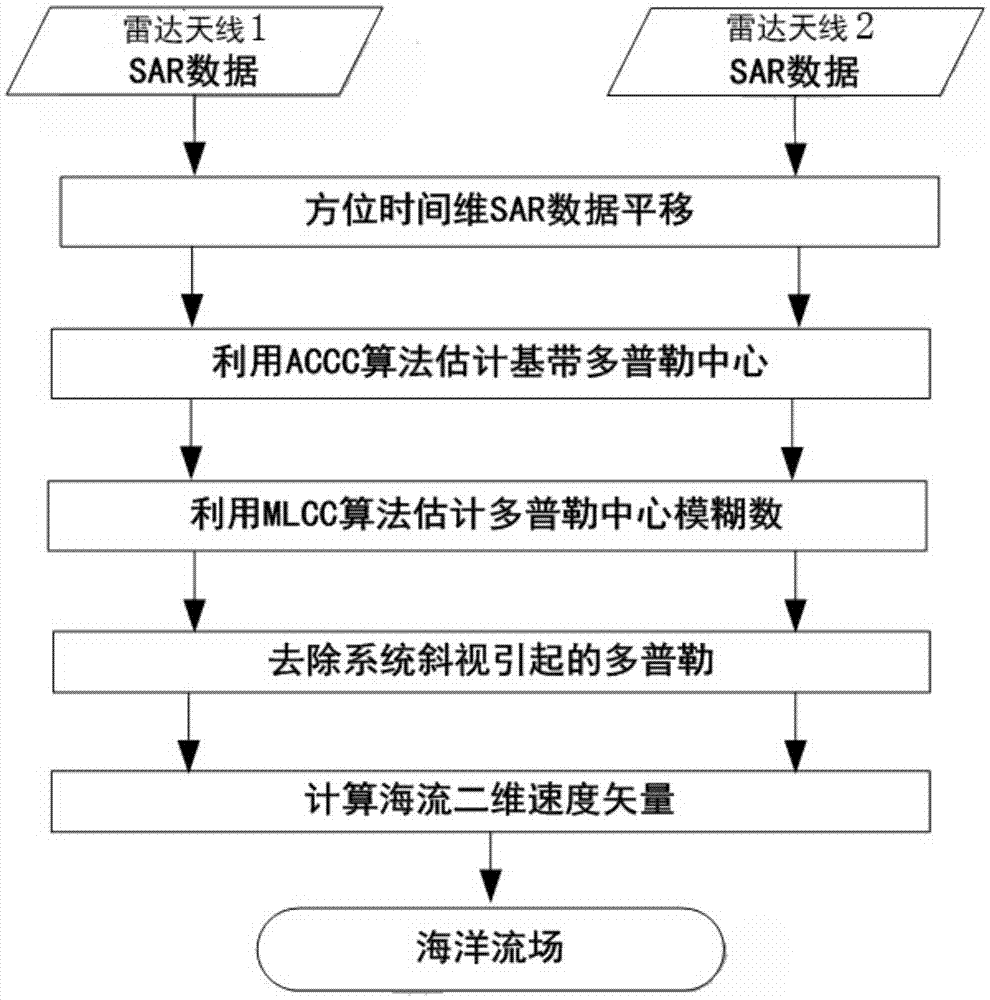
Ocean current field inversion satellite-borne SAR system based on angle diversity, and method thereof
ActiveCN105445730AComprehensive understanding of temporal and spatial changesNot subject to weather conditionsClimate change adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionNatural satelliteShore
The invention discloses an ocean current field inversion satellite-borne SAR system based on angle diversity, and a method thereof. The satellite-borne SAR system comprises two radar antennas which are arranged in the flying direction of a satellite, wherein the two radar antennas respectively generate two radar wave beams; and the two wave beams have different squint angles and can irradiate the same area on the ocean surface in different time. The method comprises: utilizing the satellite-borne SAR system and taking a doppler center frequency as the observation variable to perform inversion on an ocean current field; and obtaining a complete velocity vector of an ocean current, that is, the ocean current information obtained through inversion not only includes the radial velocity information of the ocean current but also includes the azimuth velocity information. Compared with a traditional ocean surface current field inversion means, such as field observation and shore-base radar observation, the ocean current field satellite-borne SAR system based on angle diversity can realize inversion of a worldwide ocean current field, can comprehensively know about temporal and spatial variation of the ocean current, and can work all day long and all weather without limitation of meteorological conditions.
Owner:中科星图维天信科技股份有限公司
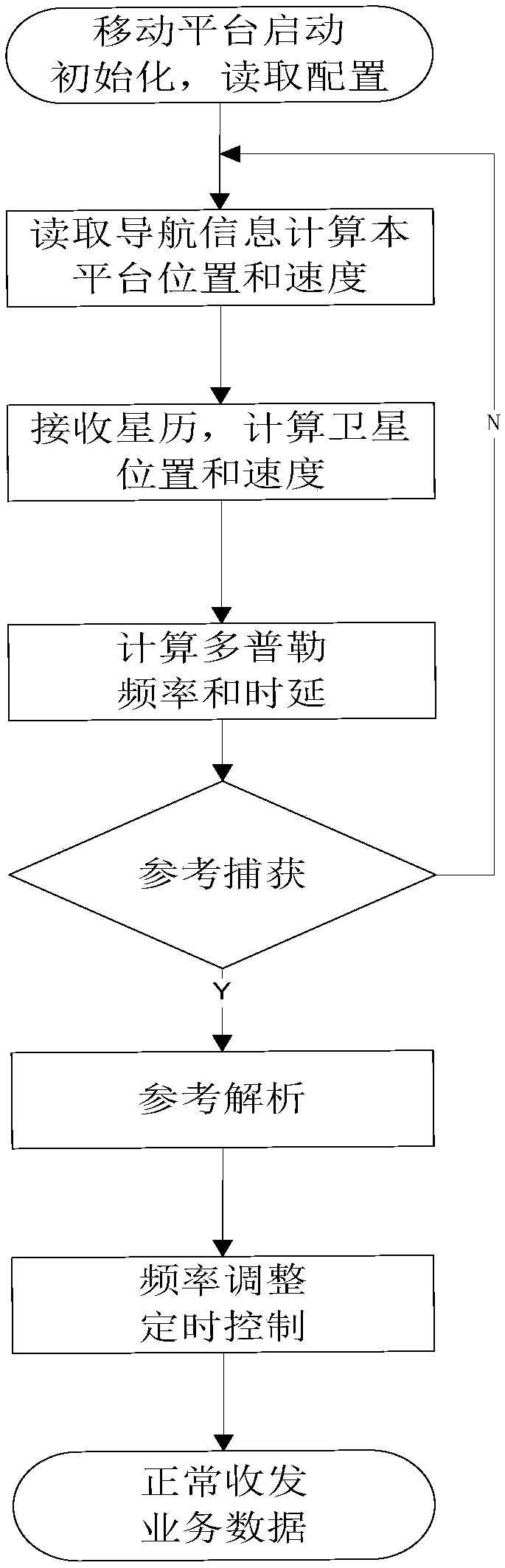
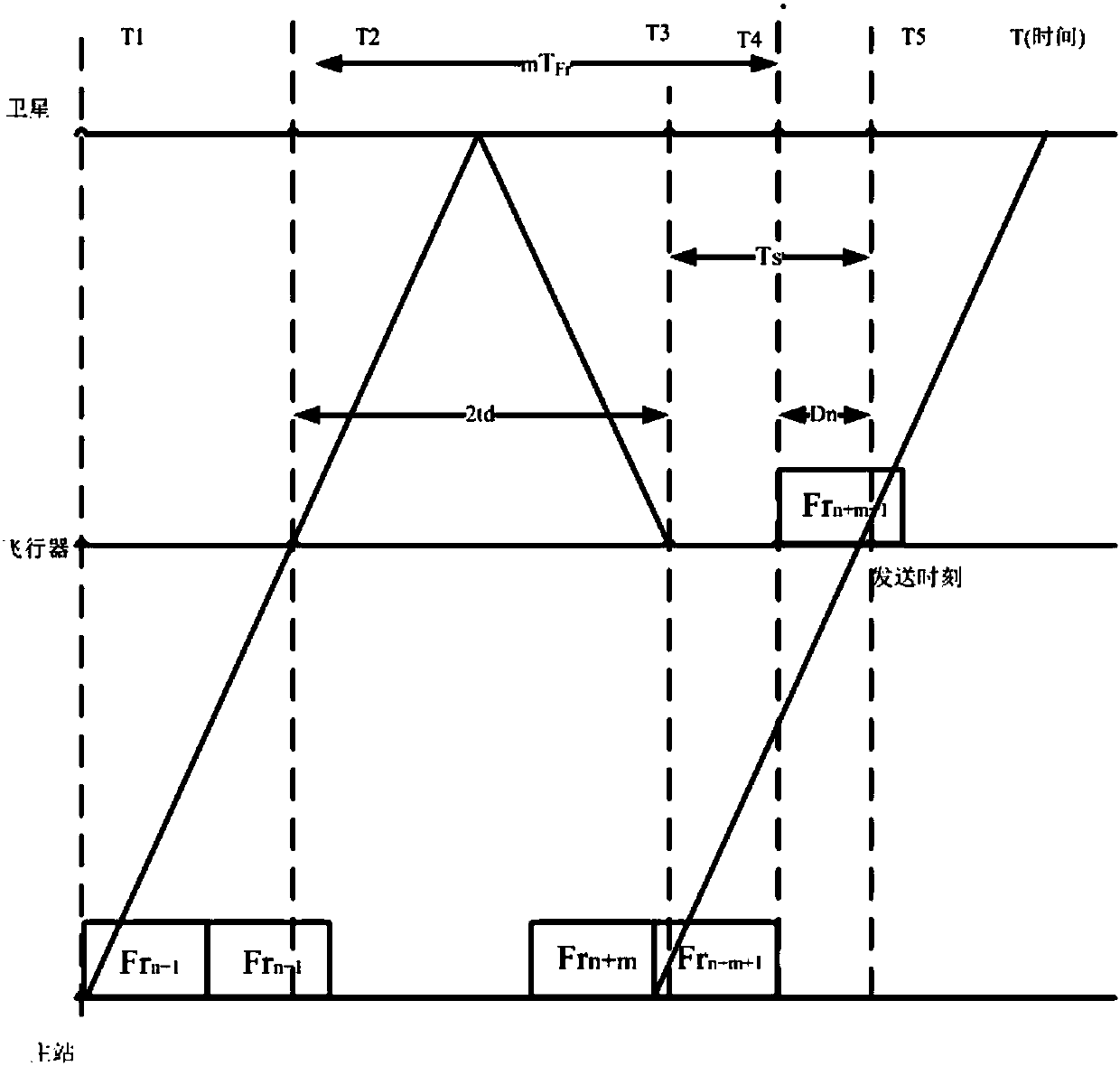
High-speed mobile platform TDMA satellite communication synchronization control method based on ephemeris
The invention provides a high-speed mobile platform TDMA satellite communication synchronization control method based on ephemeris. A radial velocity and location of a satellite relative to an earth station are obtained by using high-precision satellite ephemeris information, a platform location and a radial velocity are obtained through the navigation information of the platform, the speeds of the two components are superposed, the platform roughly estimate a distance measurement distance between the two components according to the positions of the two components according to a result compensation frequency deviation, and the platform compensates a timing deviation according to real distance measurement information and finally meets the synchronization requirements. By adoption of the high-speed mobile platform TDMA satellite communication synchronization control method provided by the invention, the Doppler frequency and delay variation caused by the high-speed movement of low orbitsatellites and the platform can be compensated.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Radon transform-based moving object imaging method, device and electronic device
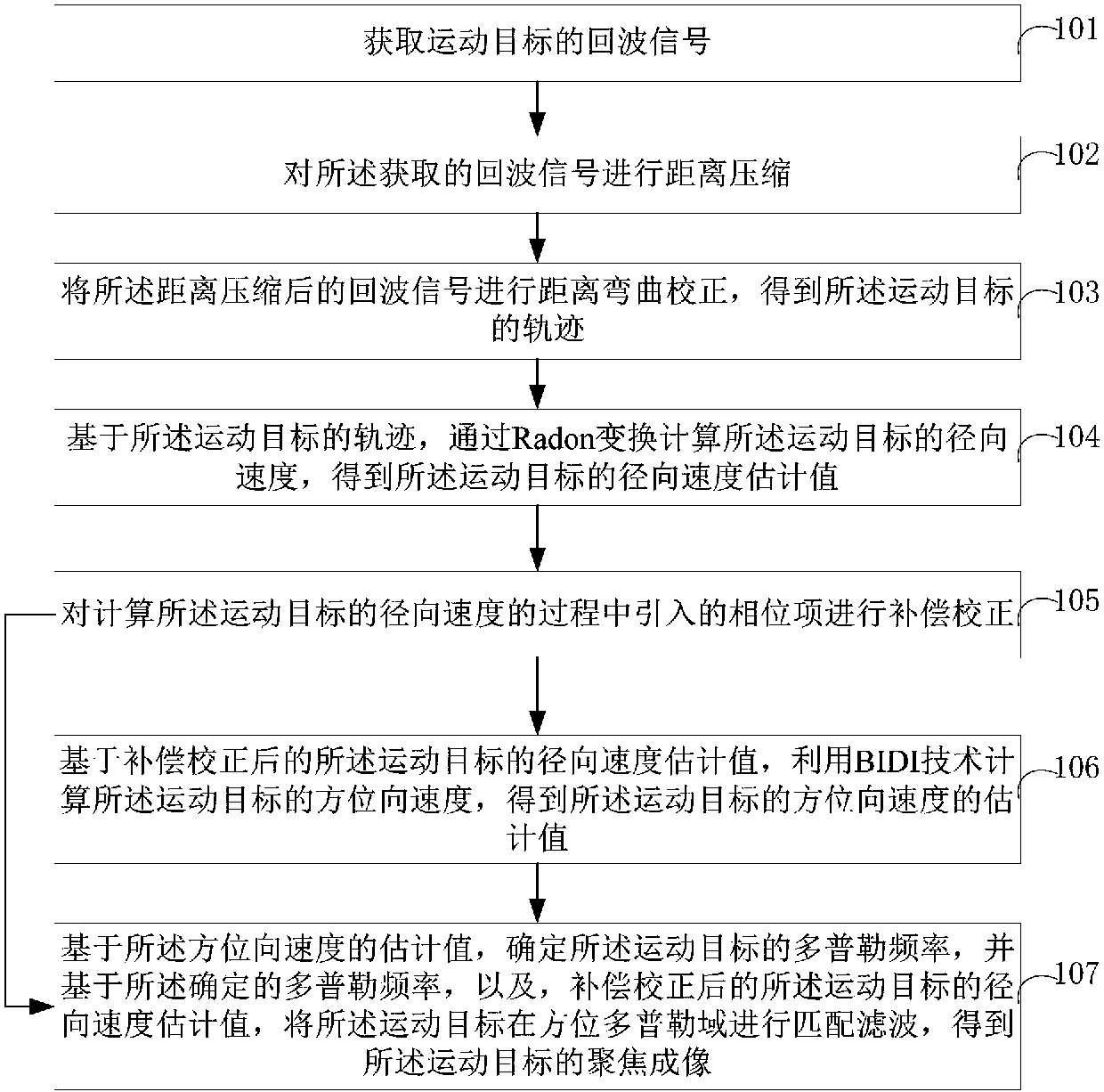
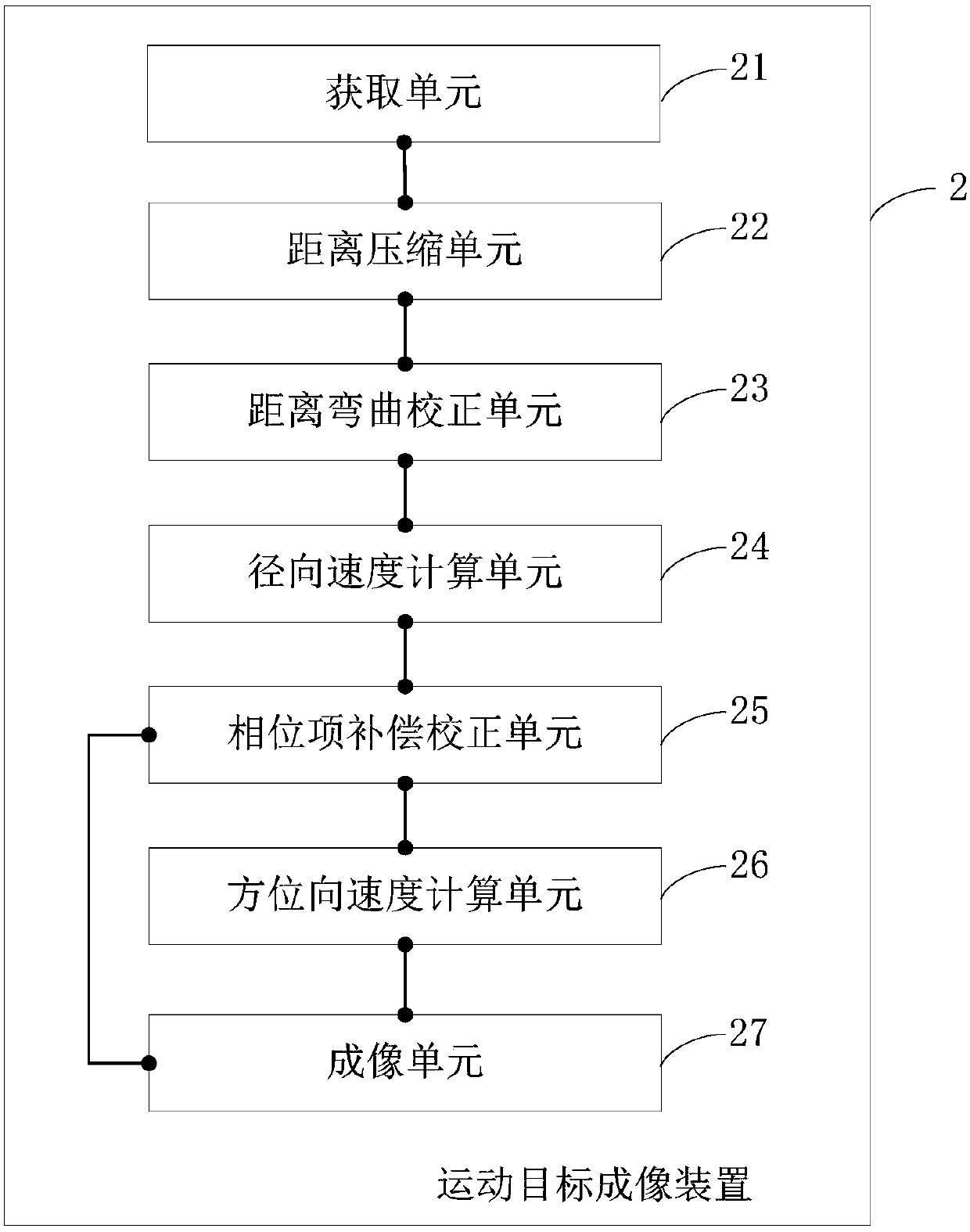
ActiveCN108051809AImprove accuracySolve the problem of azimuth sidelobe asymmetryRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarRadon transform
The present invention belongs to the radar identification technological field and provides a Radon transform-based moving object imaging method, a Radon transform-based moving object imaging device, an electronic device, and a computer-readable storage medium. The imaging method includes the following steps that: the echo signals of a moving object are obtained; distance compression is performed on the acquired echo signals; distance bending correction is performed; the radial velocity of the moving target is calculated through Radon transform; a phase term introduced into a calculation process is compensated and corrected; and the azimuth velocity of the moving target is calculated through using a BIDI technique; and matched filtering is performed on the moving target in the azimuth Doppler domain, so that the focused imaging of the moving target can be obtained. With the imaging method of the invention adopted, the accuracy of the positioning and imaging result of the moving target can be improved.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TIEDAO UNIV
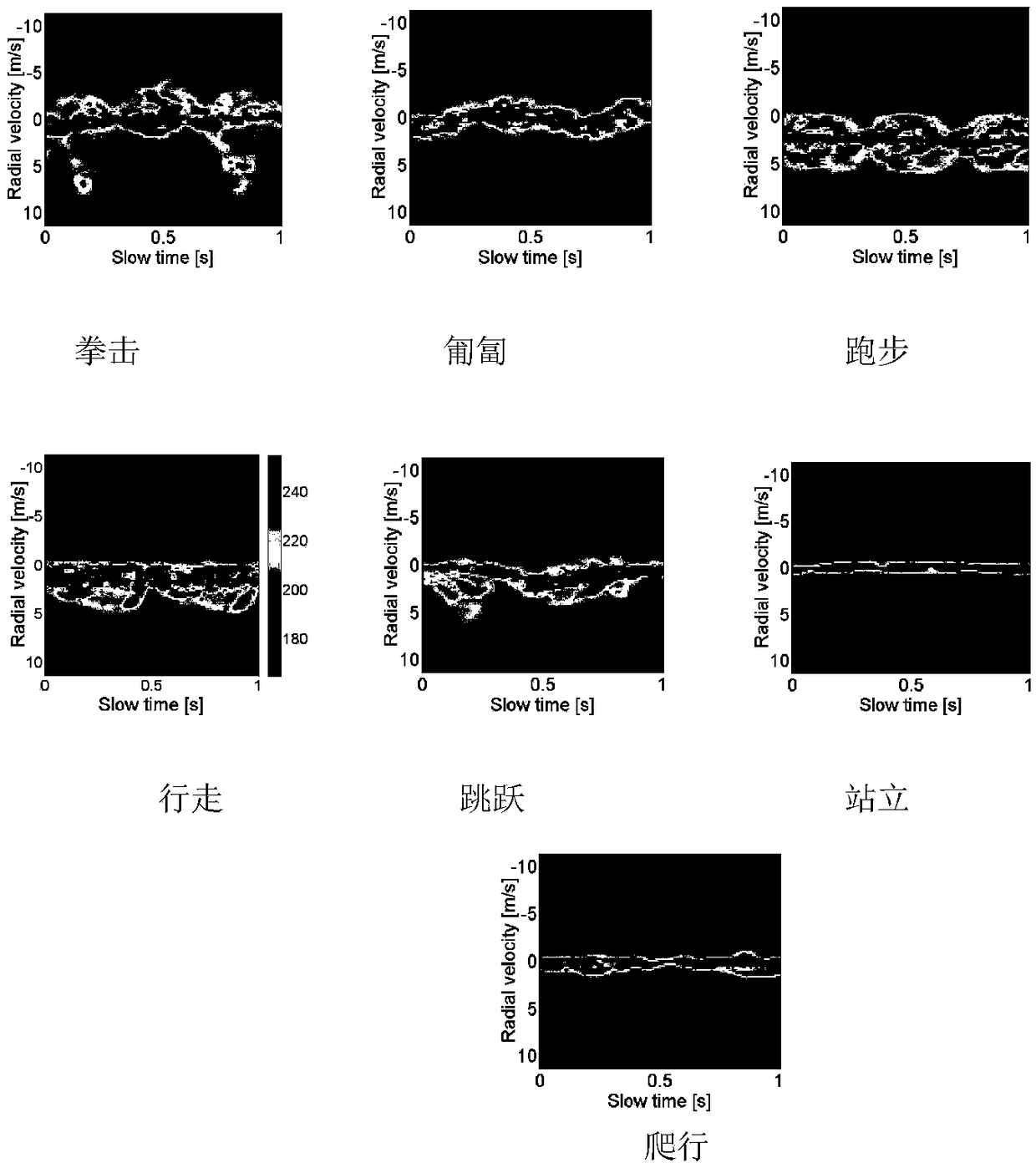
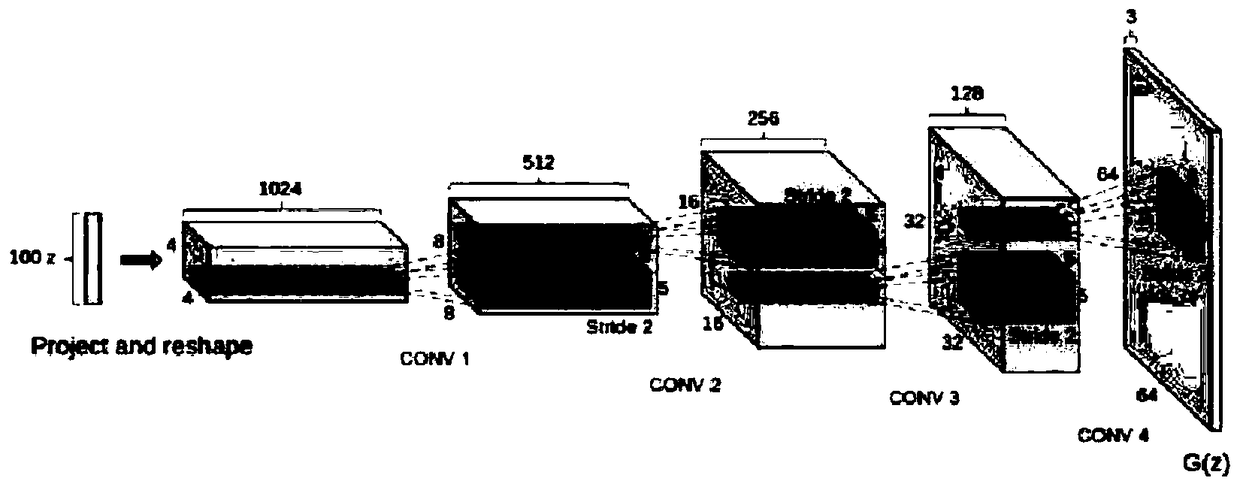
Deep convolutional adversarial neural network-based human body action radar image classification method
InactiveCN108664894AData augmentationFew failed imagesCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyNerve network
The invention relates to a deep convolutional adversarial neural network-based human body action radar image classification method. The method comprises the steps of constructing a data set; realizingradar image data enhancement through a DCGAN: establishing the DCGAN, using the network to individually learn each radar spectrogram, generating new radar spectrograms according to characteristics learned by the network, expanding training set samples under the condition of a certain data amount, adjusting parameters by the network to ensure that fewest failure images are generated, and expandingthe data set to the maximum extent, thereby realizing the data enhancement; and extracting upper, middle and lower envelopes in each radar image to serve as eigenvectors, taking the three eigenvectors as inputs of a support vector machine classifier, and classifying radar image data by utilizing a support vector machine, wherein the upper and lower envelopes represent echo radial velocities of human limbs, the middle envelope represents an echo radial velocity of a human trunk.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
NMR MAS inflow bernoulli bearing
ActiveUS7170292B2Improve stabilityIncrease stiffnessMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic measurementsAxial pressureHydrostatic pressure
An improved axial gas bearing for a gas-driven NMR MAS sample rotor is disclosed that utilizes inward flow with a low rotational component over a rotor conical end. A conical flow region is formed between the rotor conical end and a conical stator bearing surface such that the included angle defining the stator surface is not less than the included angle defining the rotor conical end. Gas is injected radially inward with a significant axial rearward component from a number of small holes at high velocity from the periphery into the conical flow region. Compared to the radial velocity components, the tangential flow components of the injected gas are small and preferably opposed to the direction of the rotor rotation. The high and accelerating negative radial velocities may result in significant Bernoulli effect, such that the mean axial pressure over the conical rotor end may be less than atmospheric pressure for a given axial clearance, but as the clearance decreases, the hydrostatic effects exceed the Bernoulli effects and the mean axial pressure over the conical rotor end may then exceed atmospheric pressure by a substantial amount. Thus, a self-stabilizing axial bearing is formed with improved stability and stiffness for rotor surface speeds up to at least 80% of the speed of sound. Motive power required to spin the rotor may be provided by a radial-inflow microturbine at the opposite end of the rotor in a way that is readily compatible with automatic sample change.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Method for Classifying Moving Vehicles
ActiveUS20140049420A1Road vehicles traffic controlRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMobile vehicleFrequency spectrum
A method for classifying vehicles in which an angle-resolving radar device yields measurement signals which have frequencies corresponding to a Doppler shift and which originate from measured vehicles and from which radial distances, object angles and radial velocities can be derived. The frequencies of the acquired measurement signals are stored as functions over the measurement time period, and a spectrogram is formed for every vehicle therefrom. Subsequently, the spectrograms are checked for assessment regions with maximum bandwidth of the frequency. These assessment regions are compared with assessment regions of stored spectrograms for different vehicle classes and associated with the most similar such that the measured vehicles are classified.
Owner:JENOPTIK ROBOT GMBH
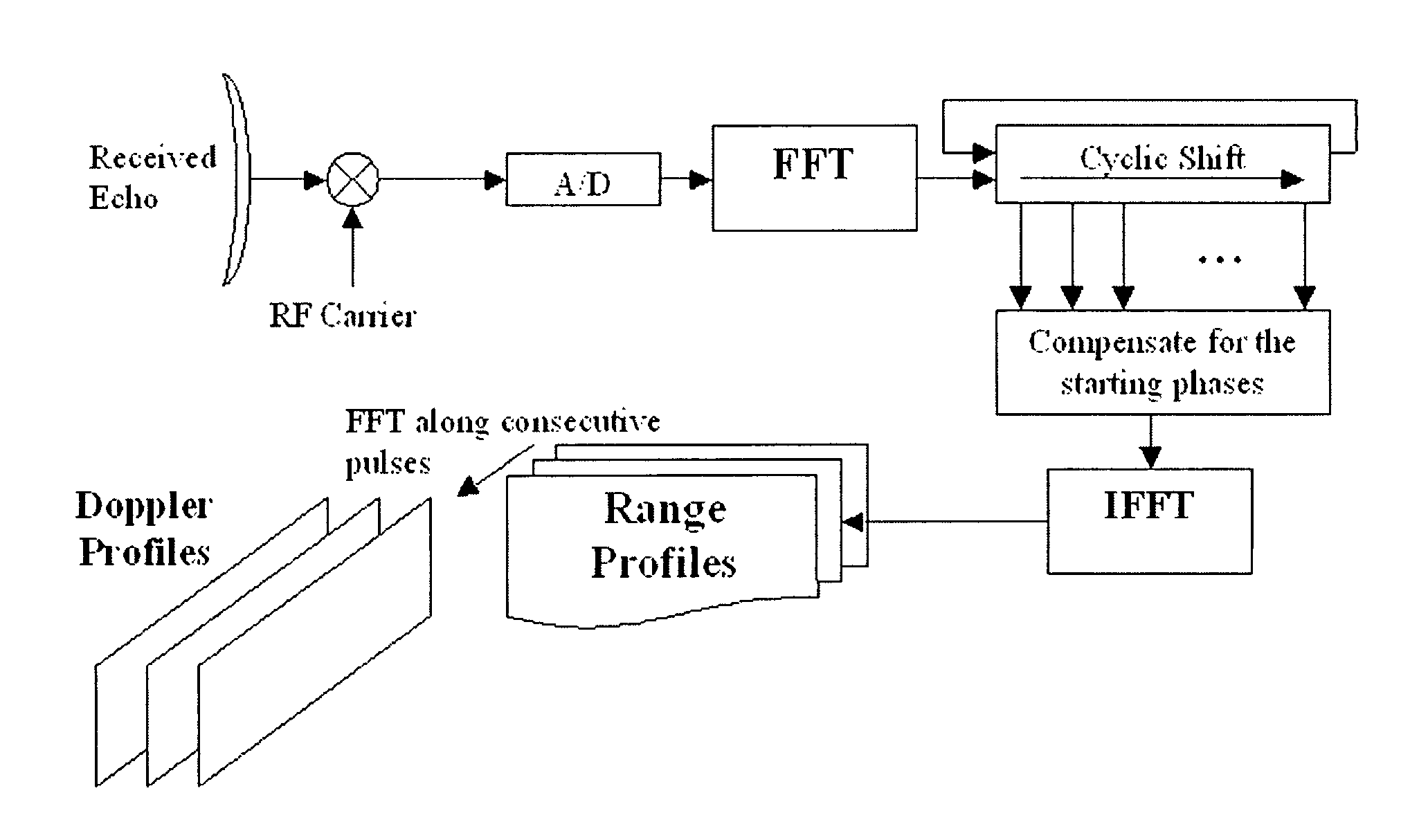
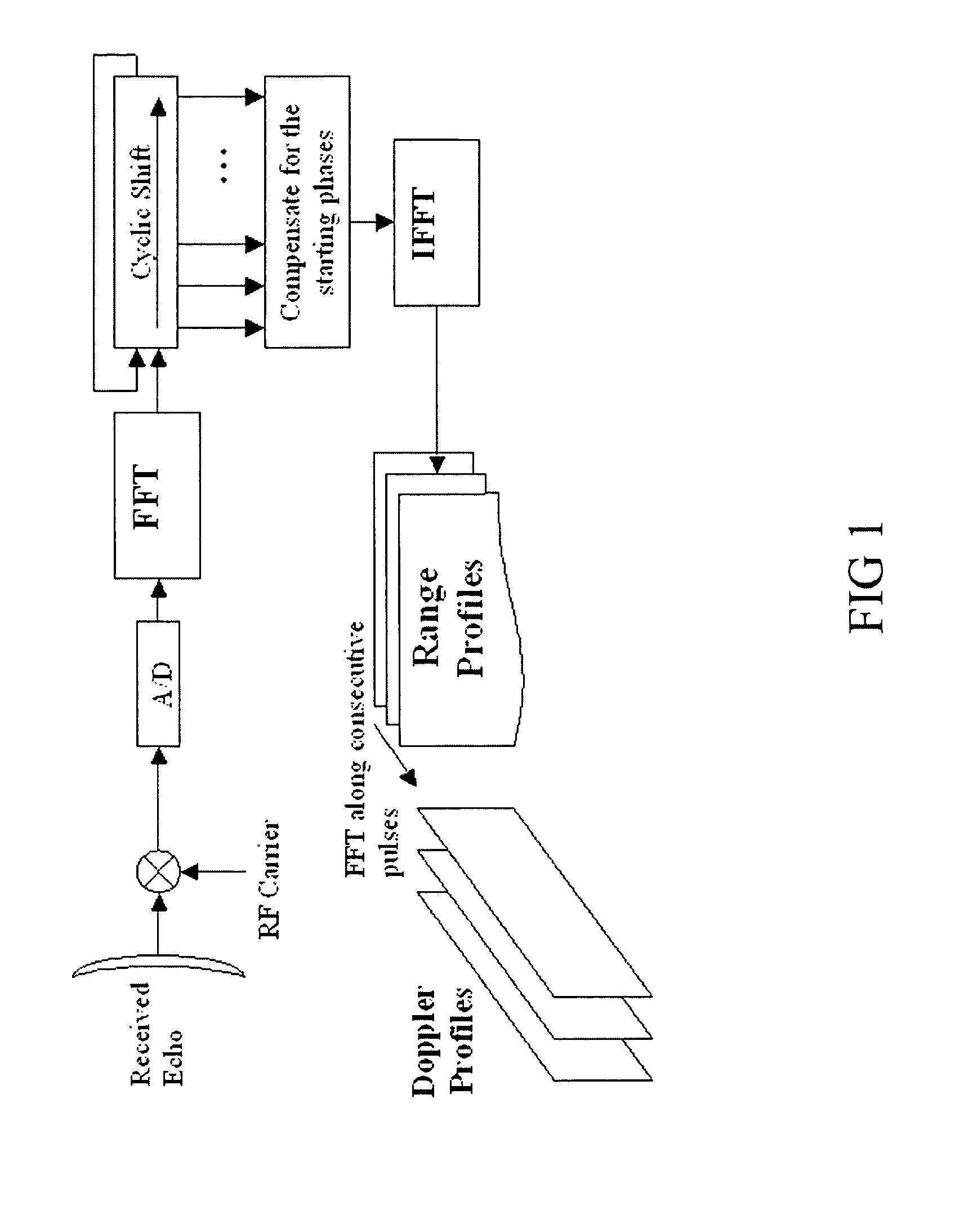
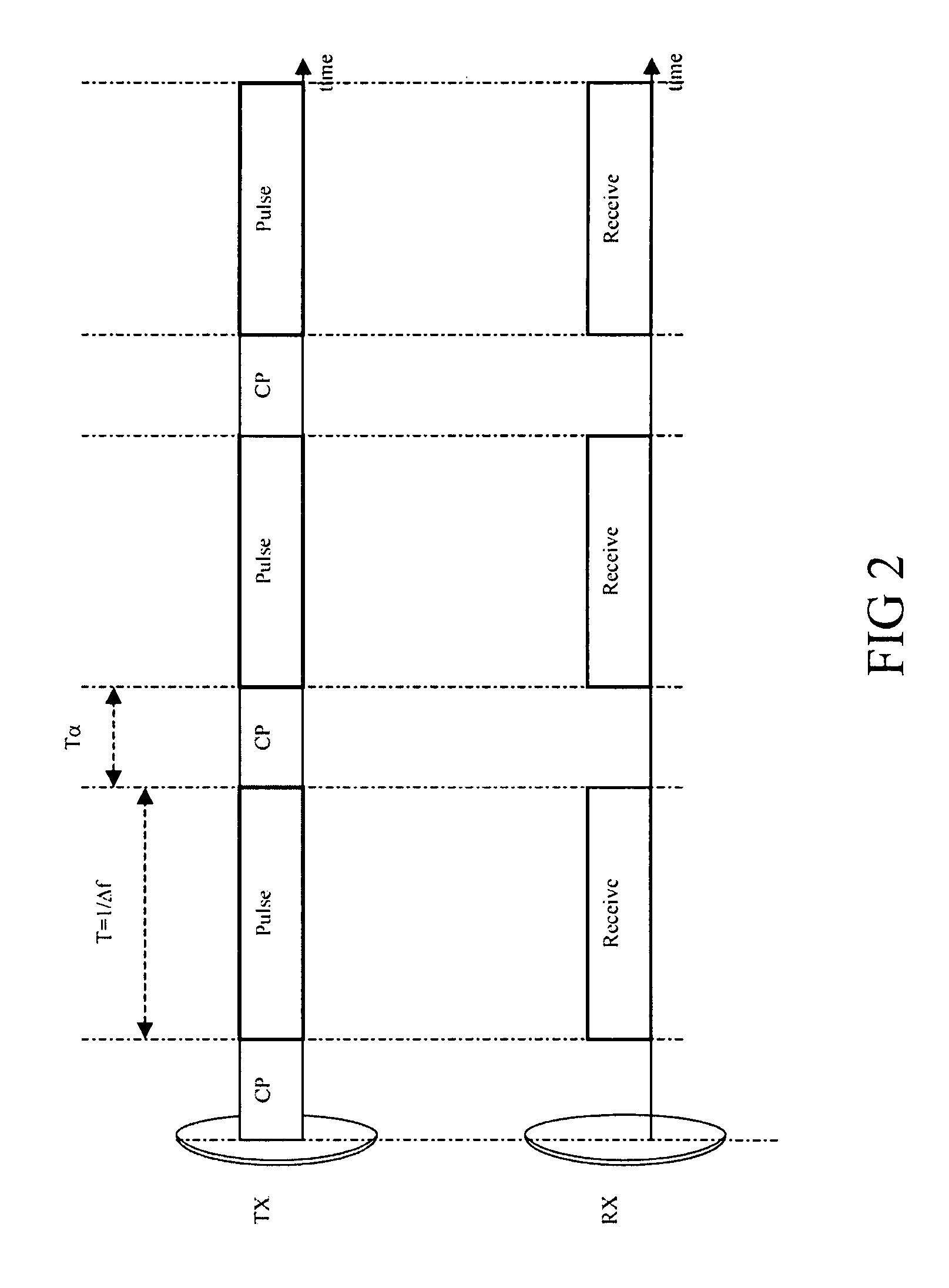
Method for measuring the radial velocity of a target with a doppler radar
InactiveUS8081105B2Resolve ambiguityModulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexRadarCarrier signal
An embodiment of the invention includes a step of transmitting an OFDM waveform including several frequency carrier signals transmitted simultaneously, the frequency carrier signals being coded in order to improve the Doppler response. An embodiment of the invention includes a step of receiving the echoed waveform from the target. The initial phase of each frequency carrier signal is recovered from the echoed waveform. The recovered initial phase of each frequency carrier signal is cyclically shifted in order to compensate for the Doppler effect and subsequently decoded. A compressed pulse is synthesized from the decoded initial phases.
Owner:THALES NEDERLAND BV
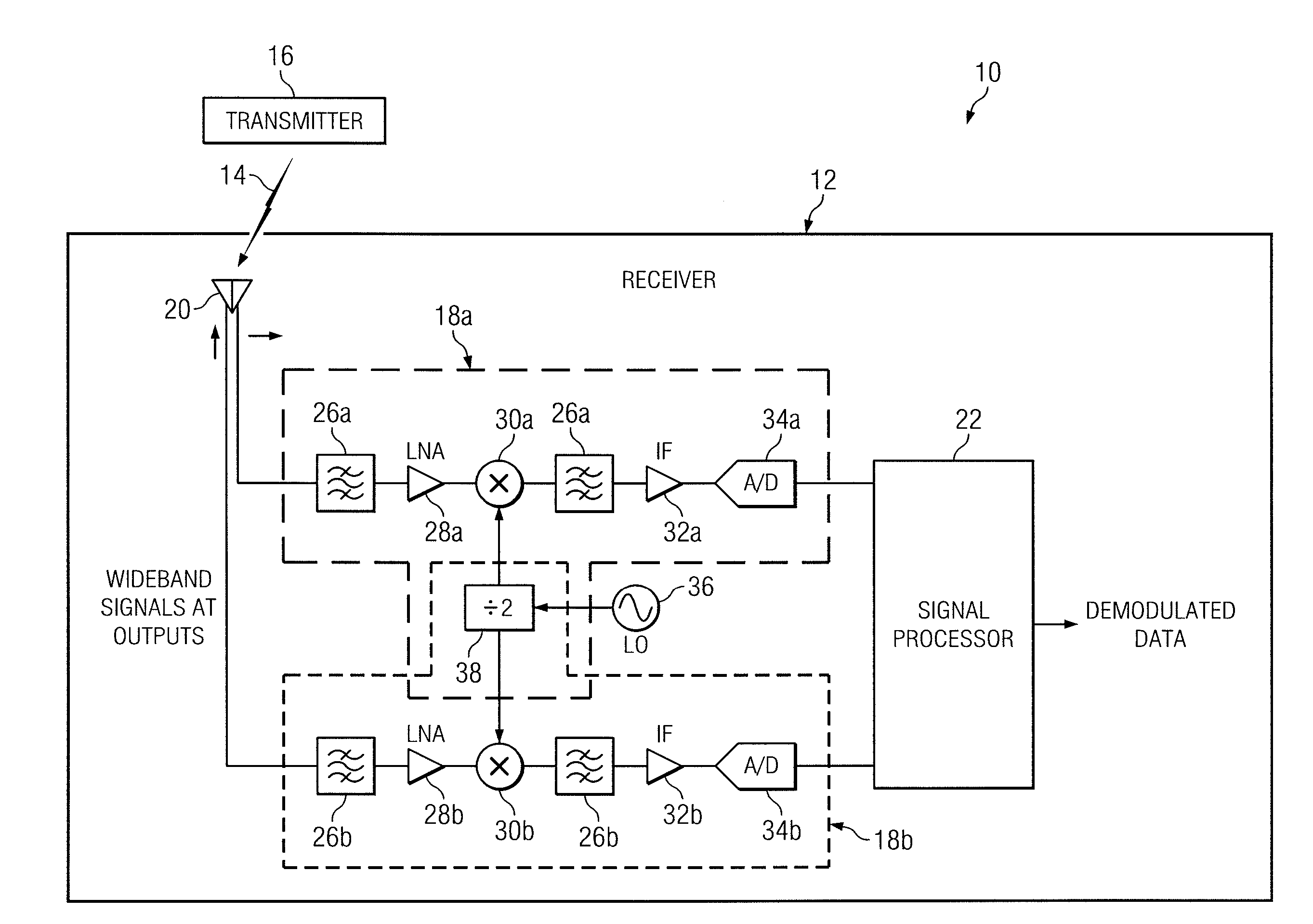
Cross Domain Modulation Scheme for a Wireless Communication Link
ActiveUS20110019630A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems can be reduced eliminatedMultiplex communicationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
In certain embodiments, a wireless communication link includes a wireless receiver that receives a circular polarized signal from a remotely configured transmitter. The circular polarized signal has a polarization vector that rotates at a radial velocity. The wireless receiver determines a phase deviation in the radial velocity of the polarization vector and demodulates information from the circular polarized signal according to the determined phase deviation. The phase deviation is caused by a frequency deviation of the circular polarized signal generated by the transmitter.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and system for determining navigation parameters of an aircraft
ActiveUS20120212369A1Easy to useSpeed/acceleration/shock instrument detailsSatellite radio beaconingRadio navigationMarine navigation
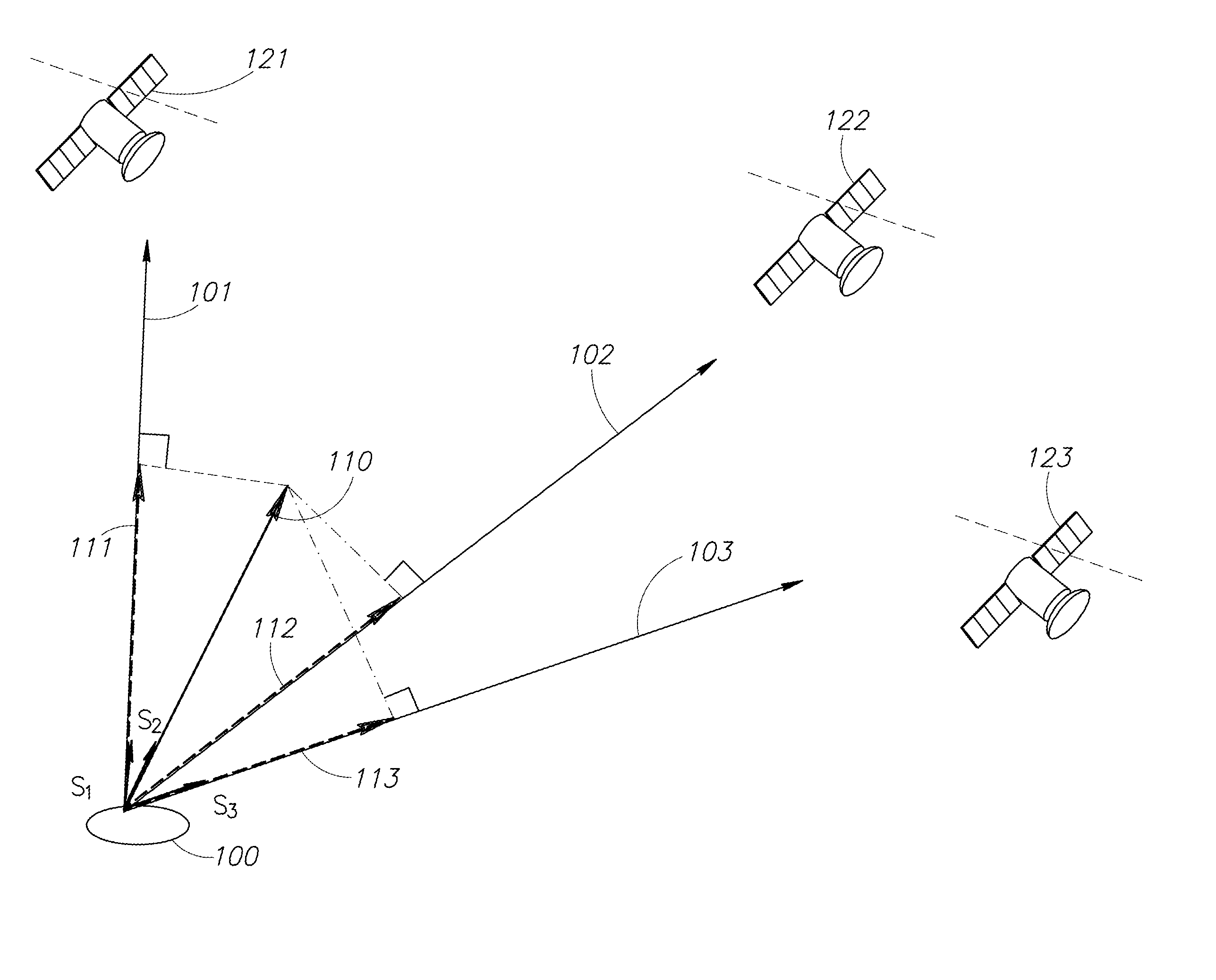
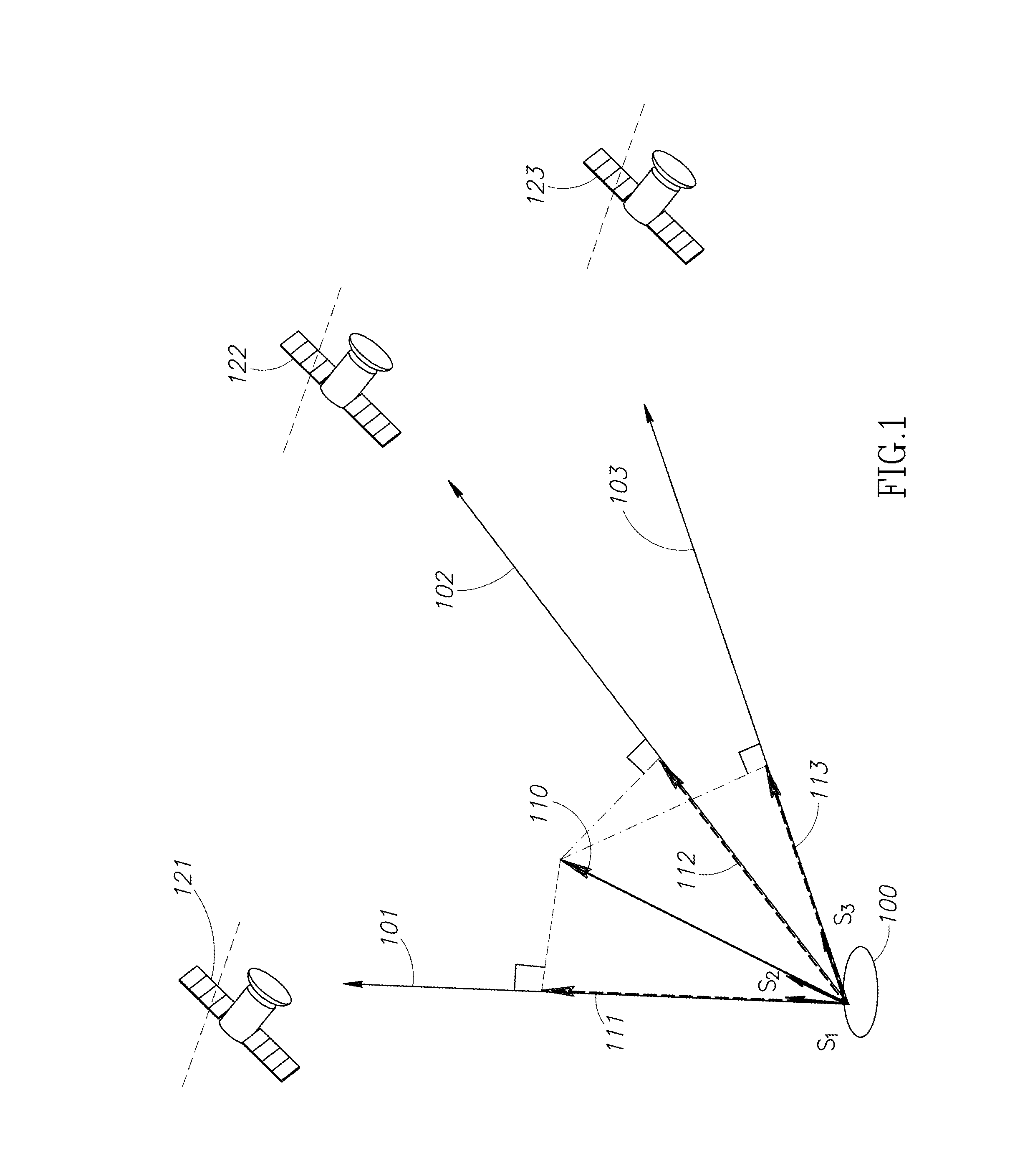
Method for determining navigation parameters of an aircraft, characterized in that it consists at least in determining the geographic speed {right arrow over (V)}, expressed in a given local fixed coordinate system {{right arrow over (i)}, {right arrow over (j)}, {right arrow over (k)}}, based on the measurements m, of carrier phase increments Δφi of the radio navigation signals originating from a plurality of radio navigation satellites in sight of said aircraft, each of said measurements mi constituting an estimate of the relative speed of said aircraft relative to said satellite projected onto the sight axis linking the aircraft to the satellite, each of said measurements m, being compensated by the apparent radial speed of the satellite.
Owner:THALES SA
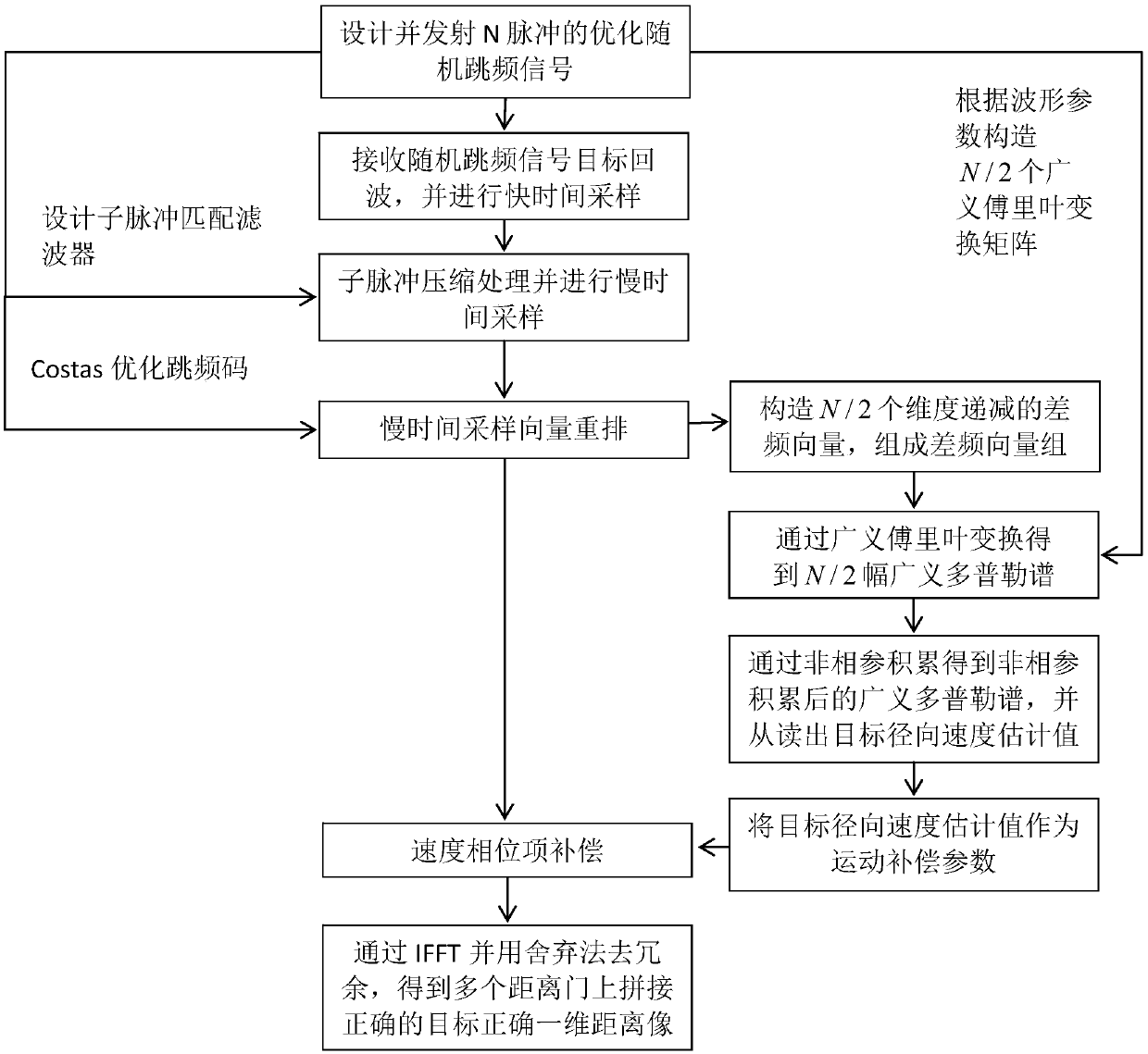
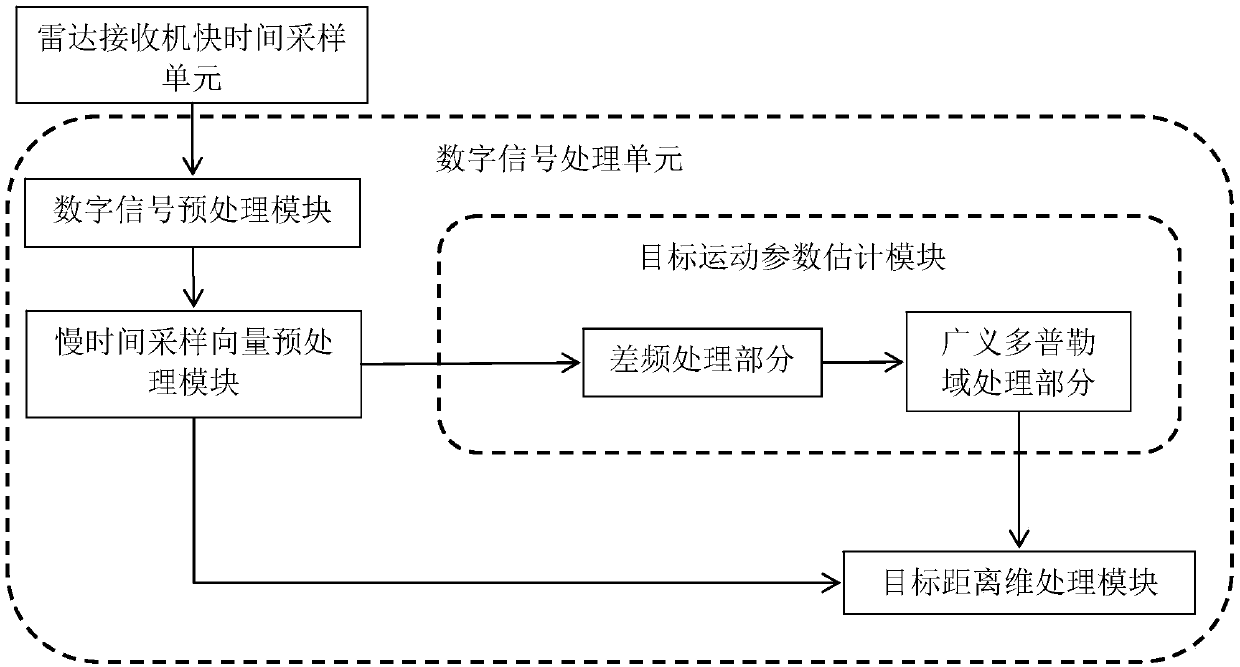
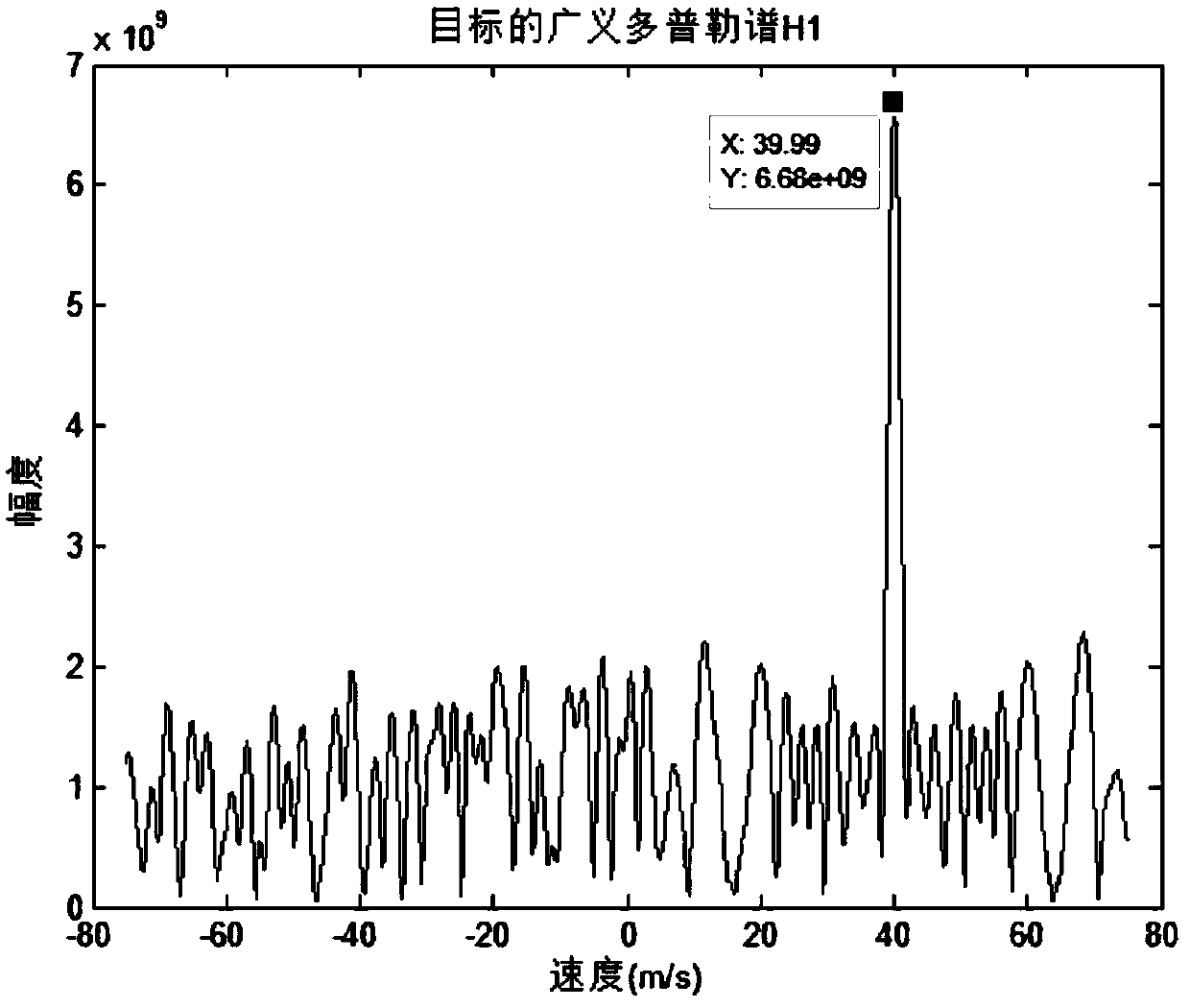
Target motion parameter estimation method for random frequency hopping radar
ActiveCN109061589ASmall amount of calculationCoherent accumulation time is shortICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCoherent integrationRange gate
The invention proposes a target motion parameter estimation method for a random frequency hopping radar, and solves the problem that the existing speed measurement scheme has a long accumulation time,a large calculation amount and a poor anti-noise performance. The method comprises the main steps of: designing a waveform parameter for transmitting a random frequency hopping signal and receiving atarget echo; preprocessing digital signals; preprocessing the slow time sampling vector; constructing a difference frequency vector group; constructing a Doppler domain generalized Fourier transformmatrix group; carrying out the generalized Doppler transform and non-coherent processing; carrying out motion compensation processing; and carrying out the coherent integration of distance dimensionsand de-redundance processing to obtain a one-dimensional range profile with the correct target in the plurality of range gates. According to the target motion parameter estimation method for the random frequency hopping radar, a set of dimension decreasing difference frequency vectors are constructed from the target echoes, generalized Doppler processing is performed on each difference frequency vector, and an estimated value of the target radial velocity can be read in the generalized Doppler spectrum after non-coherent integration. The method is short in accumulation time, small in calculation amount and good in anti-noise performance, and is used for target detection and pulse accumulation of the random frequency hopping radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
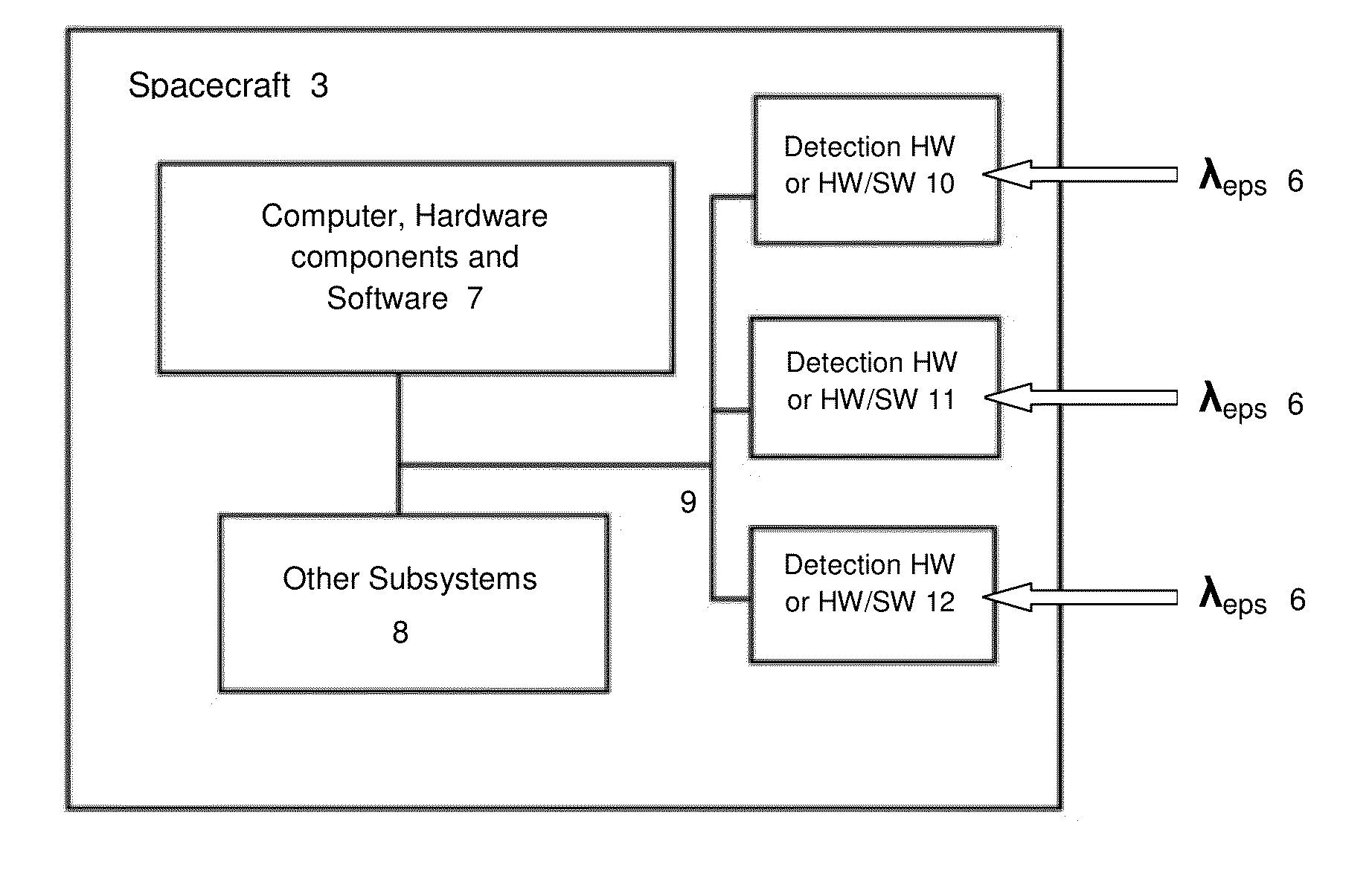
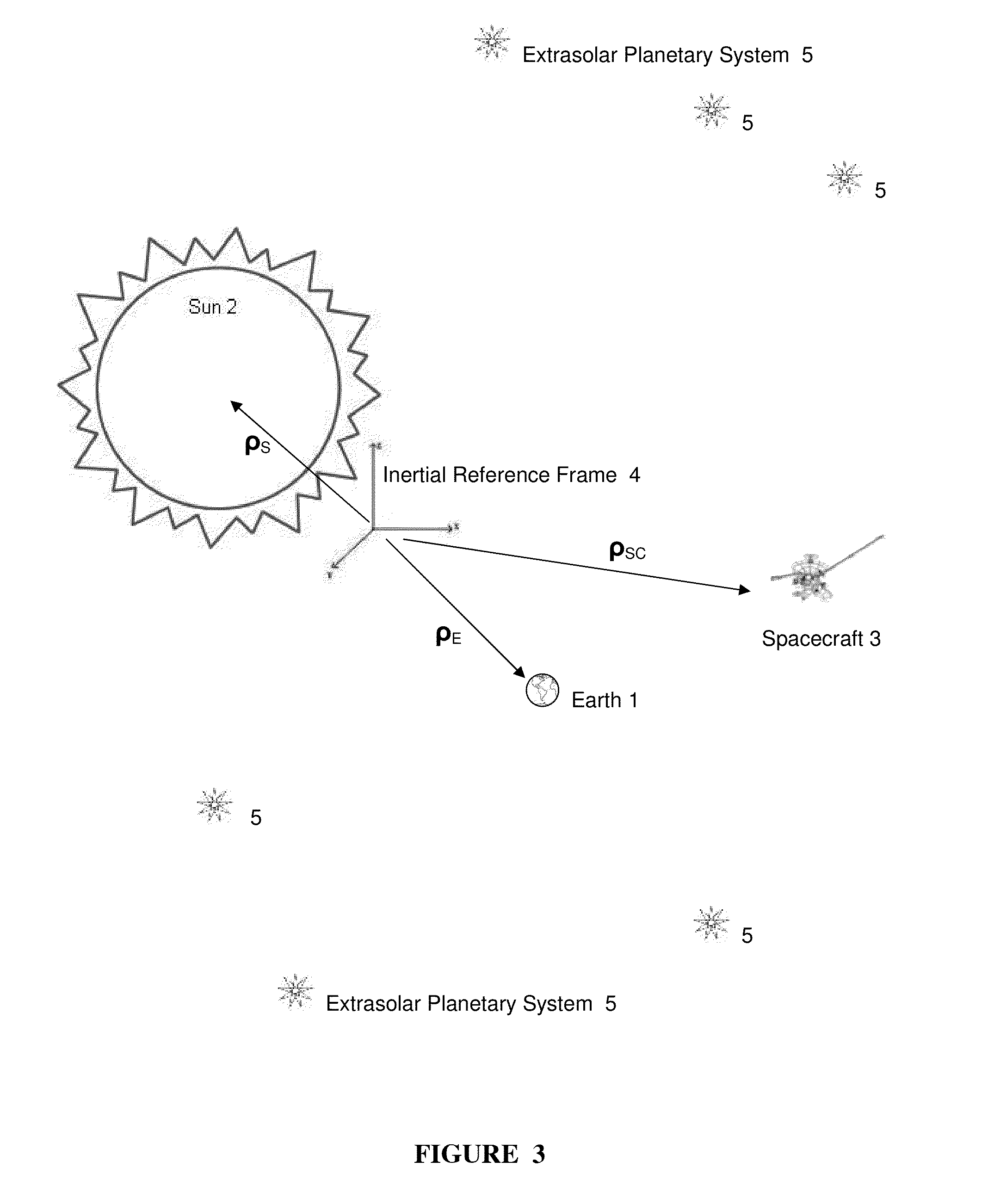
Apparatus, system and method for spacecraft navigation using extrasolar planetary systems
InactiveUS20130006449A1Stable and highly predictable natural signal patternReducing resourceCosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationAbsorption cellEngineering
Owner:HINDMAN GEORGE WILLIAM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com