Ground moving target detection and parameter estimation method
A technology for ground moving target and parameter estimation, which is applied in the field of synthetic aperture radar signal processing and can solve problems such as inability to detect moving targets, blind speed phenomenon, and distance velocity ambiguity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
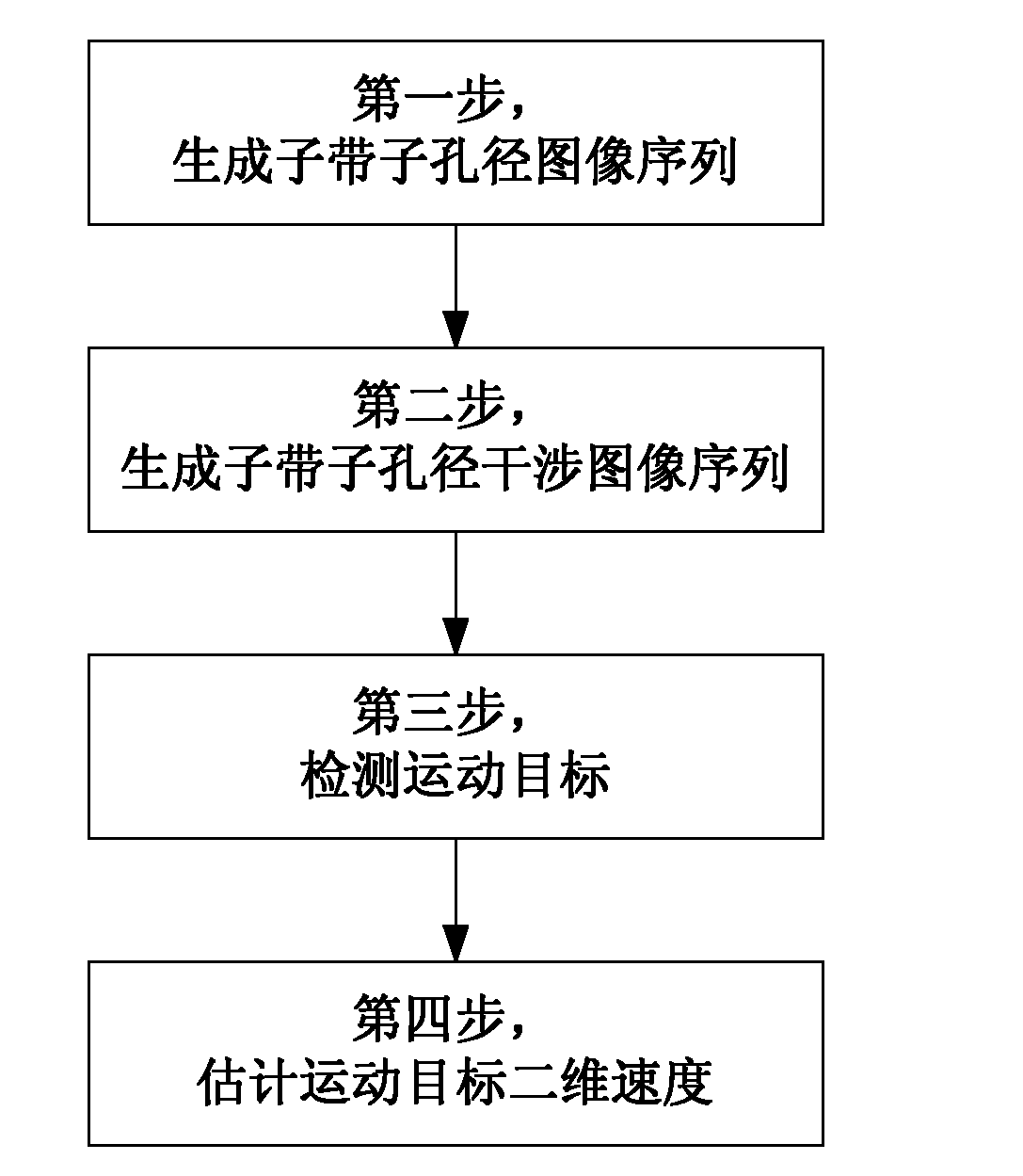
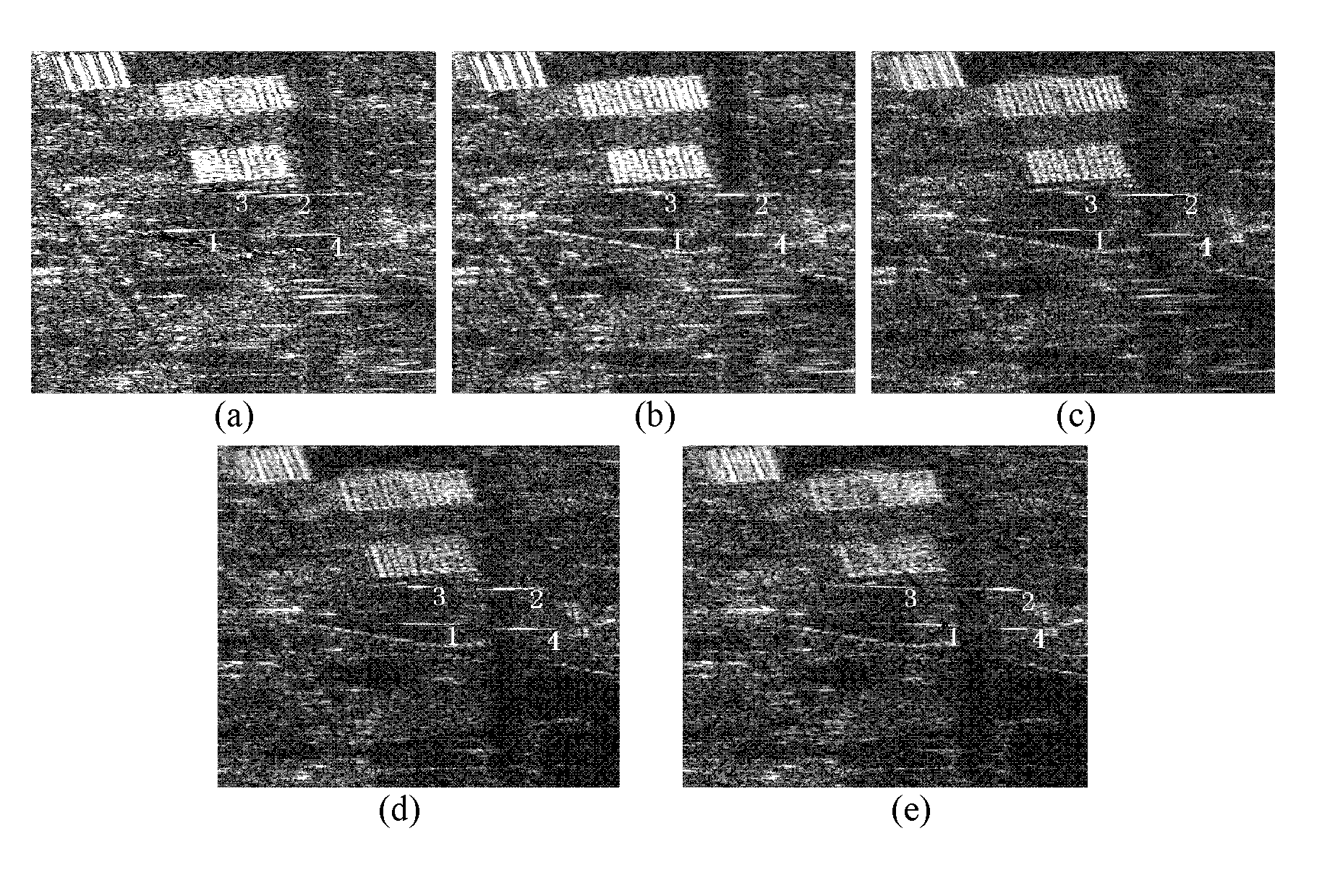
[0049] figure 1 It is the flow chart of the realization of the present invention. The whole process is mainly divided into four steps: the first step is to generate sub-band sub-aperture image sequence, the second step to generate sub-band sub-aperture interference image sequence, the third step to detect moving objects, and the fourth step to estimate the radial velocity and two-dimensional velocity of moving objects.
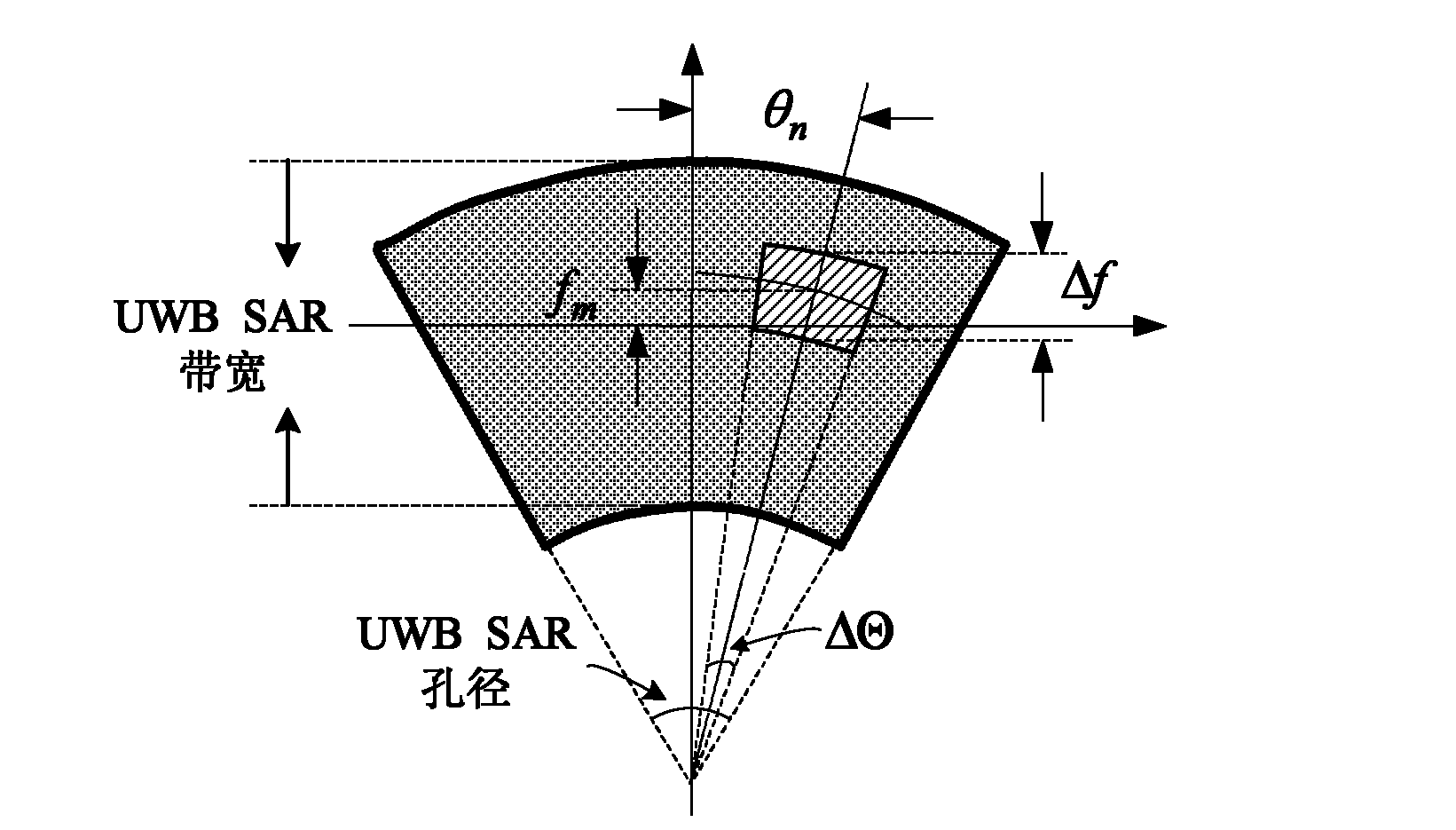
[0050] The first step is to pay attention to the selection of sub-band bandwidth, sub-aperture accumulation angle, sub-band center frequency, and sub-aperture viewing angle in the process of sub-band sub-aperture image generation. The relationship between resolution and defocusing of moving objects needs to be considered. If the target speed is high, a lower resolution is required, and the sub-band bandwidth and sub-aperture accumulation angle can be smaller; if the target speed is low, a higher resolution is required, and the sub-band bandwidth and sub-apert...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com