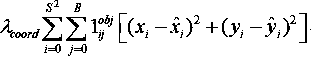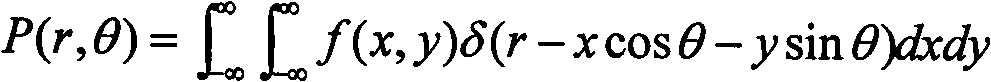Patents
Literature
203 results about "Radon transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the Radon transform is the integral transform which takes a function f defined on the plane to a function Rf defined on the (two-dimensional) space of lines in the plane, whose value at a particular line is equal to the line integral of the function over that line. The transform was introduced in 1917 by Johann Radon, who also provided a formula for the inverse transform. Radon further included formulas for the transform in three dimensions, in which the integral is taken over planes (integrating over lines is known as the X-ray transform). It was later generalized to higher-dimensional Euclidean spaces, and more broadly in the context of integral geometry. The complex analog of the Radon transform is known as the Penrose transform. The Radon transform is widely applicable to tomography, the creation of an image from the projection data associated with cross-sectional scans of an object.
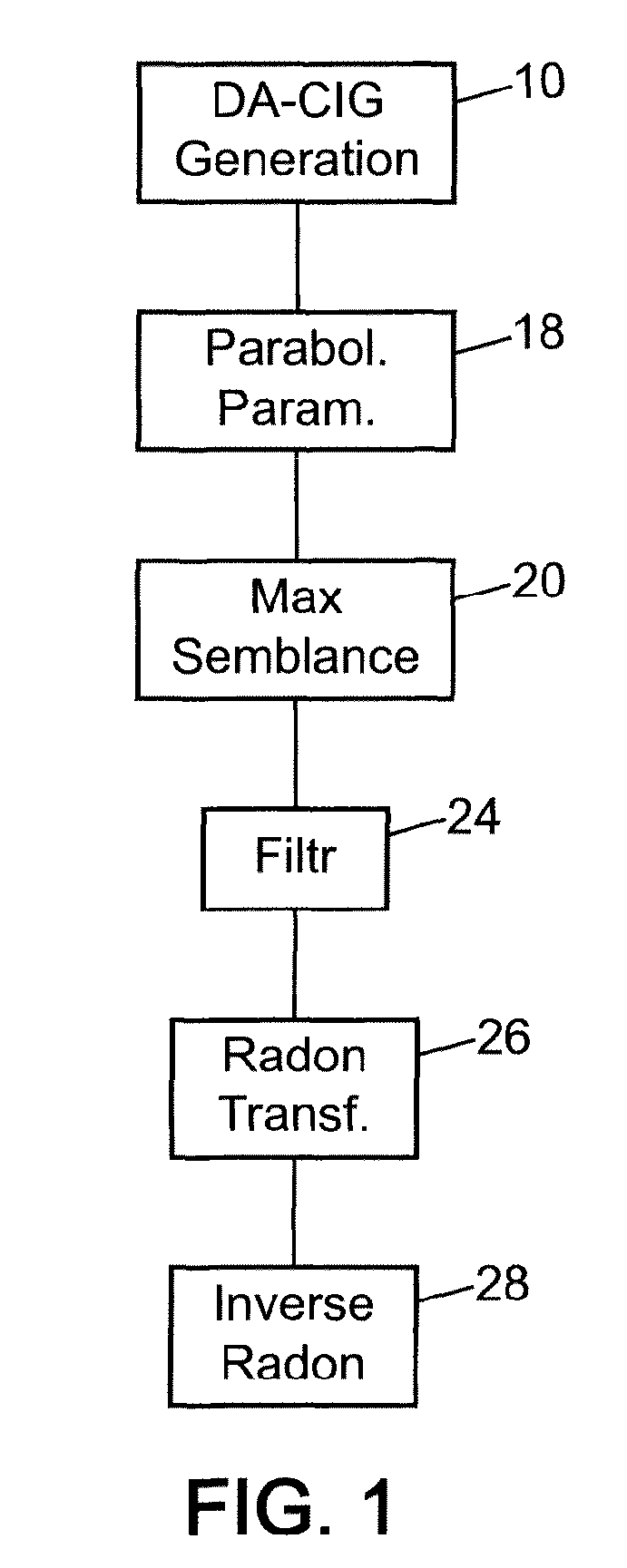
Dispersion extraction for acoustic data using time frequency analysis
ActiveUS20090067286A1Efficient identificationSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingSensor arrayDispersion curve
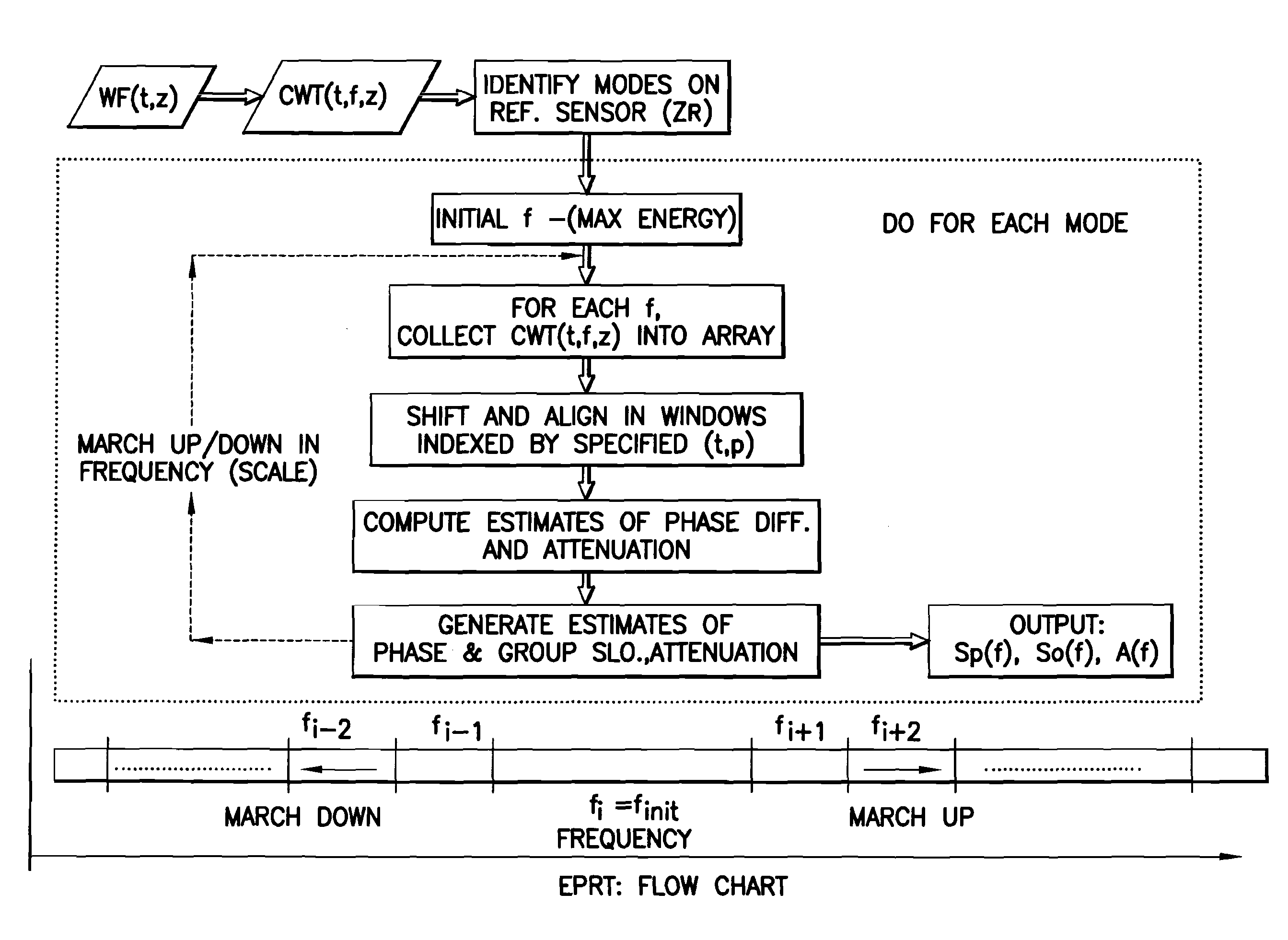
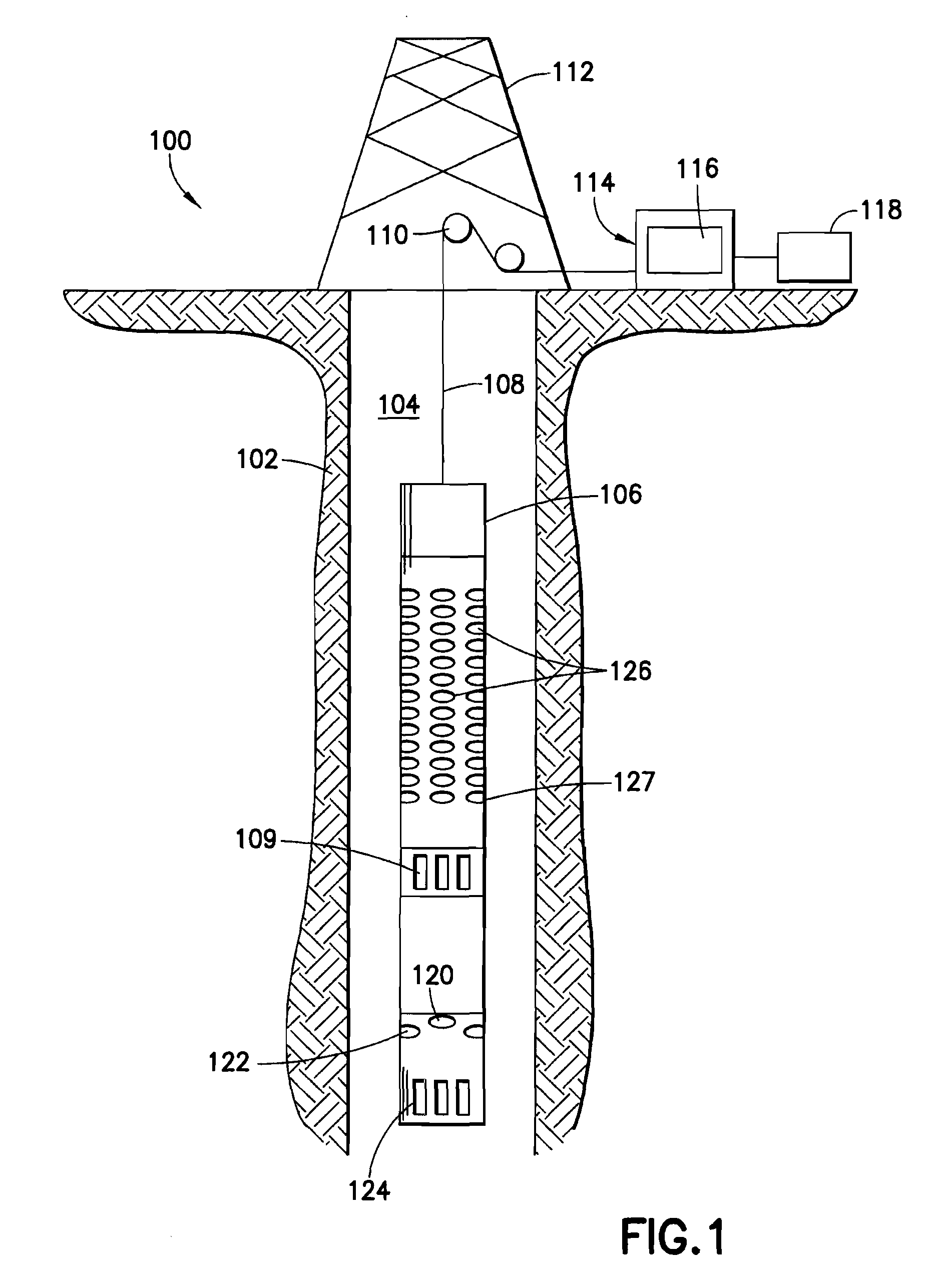
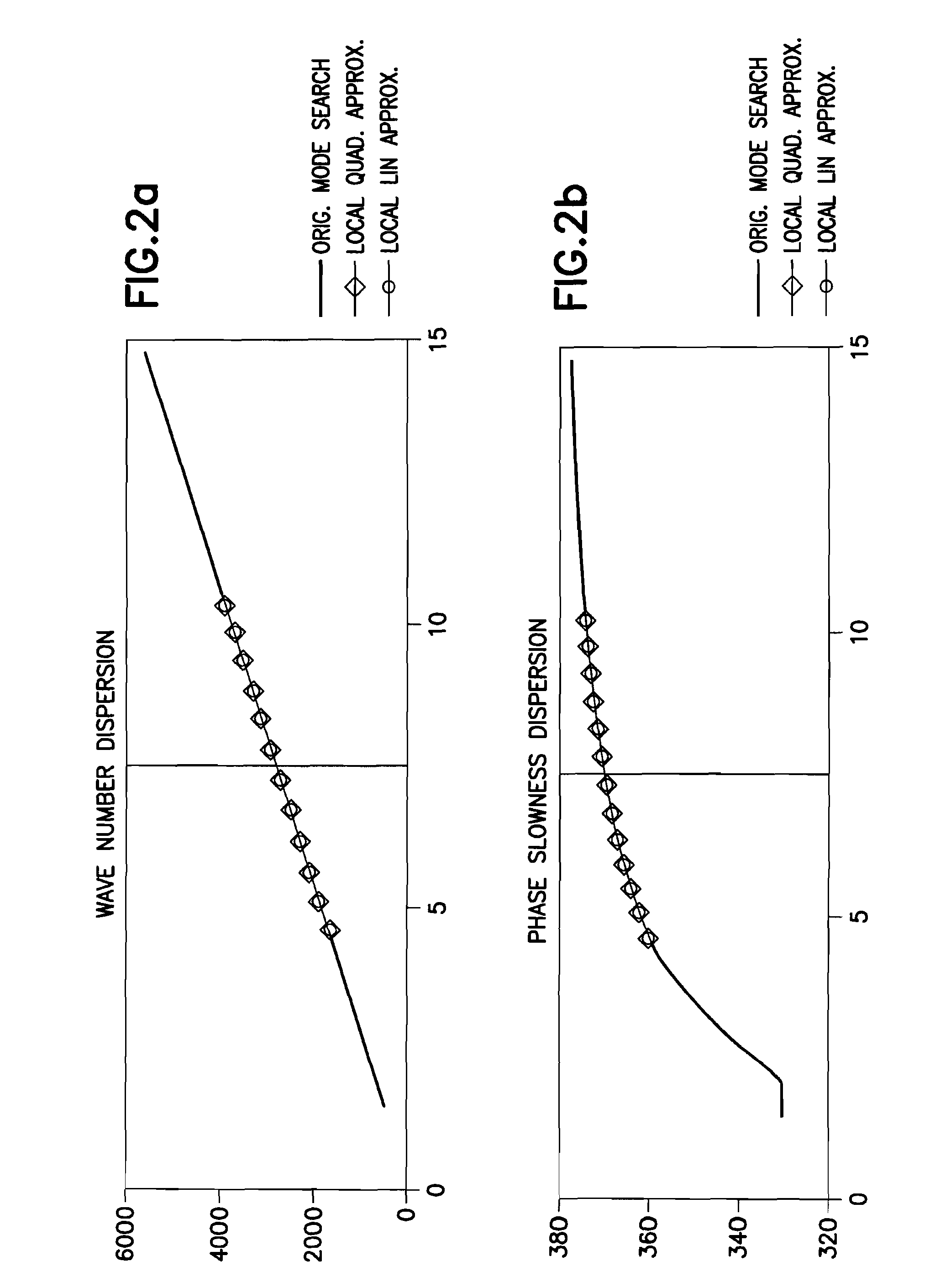
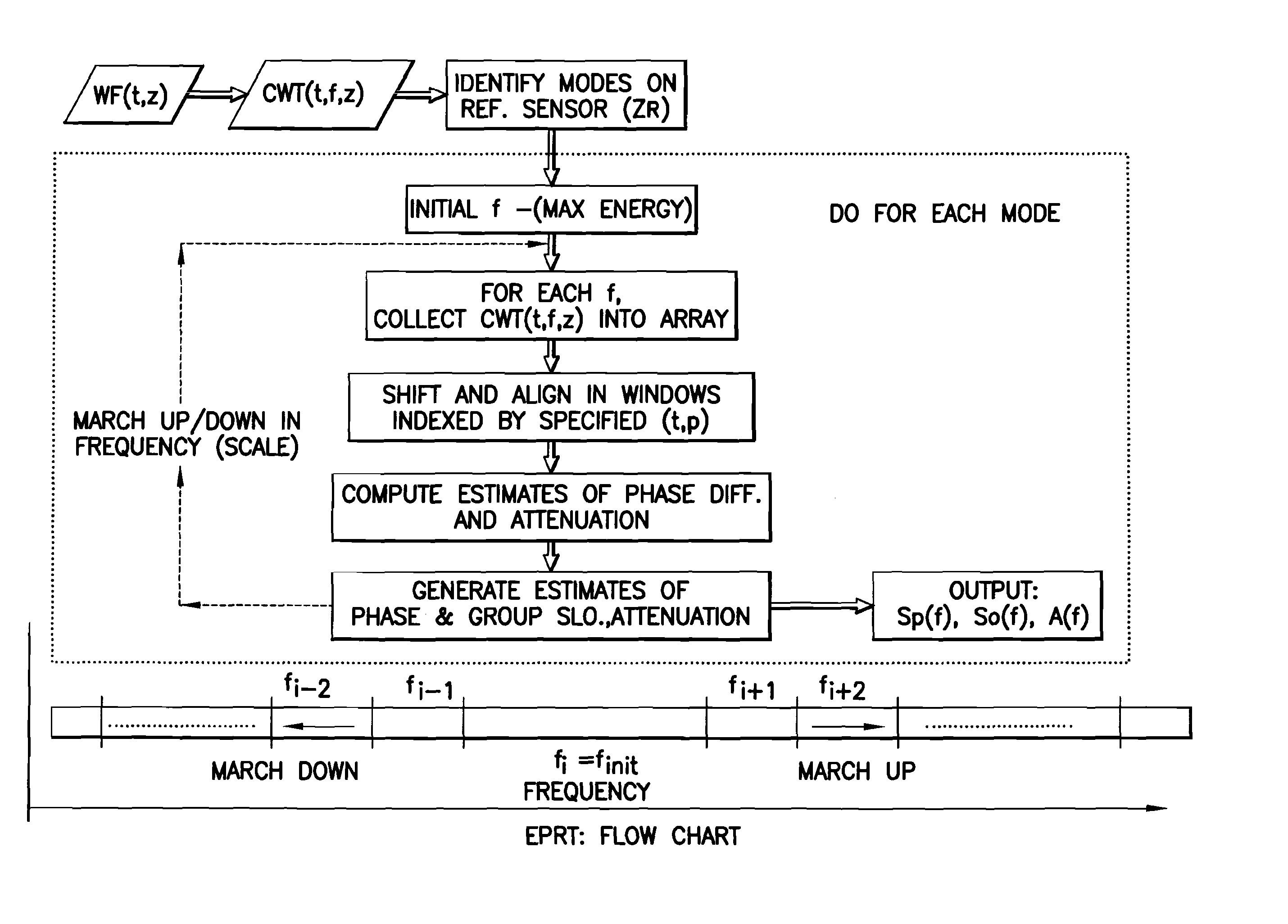
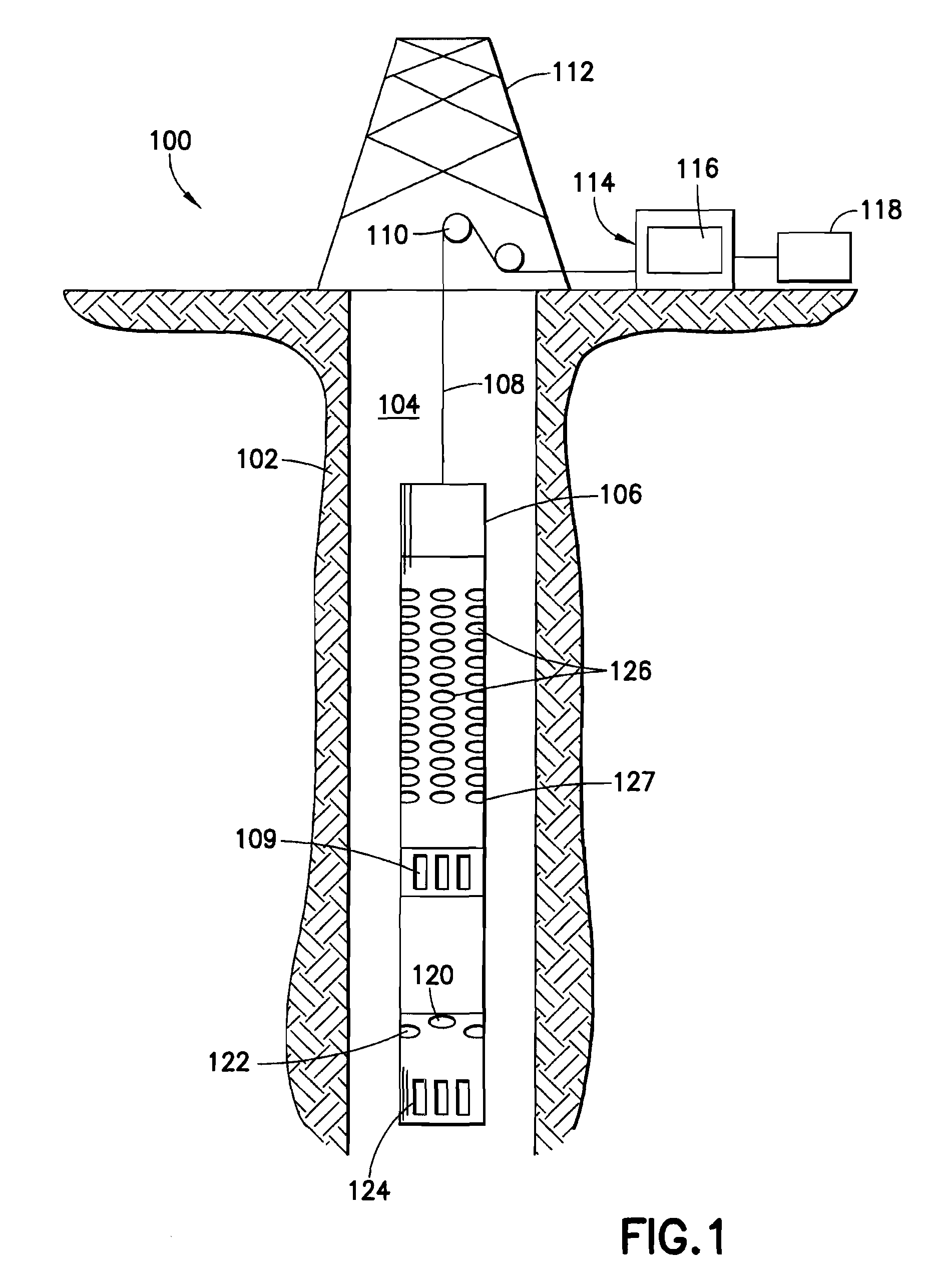
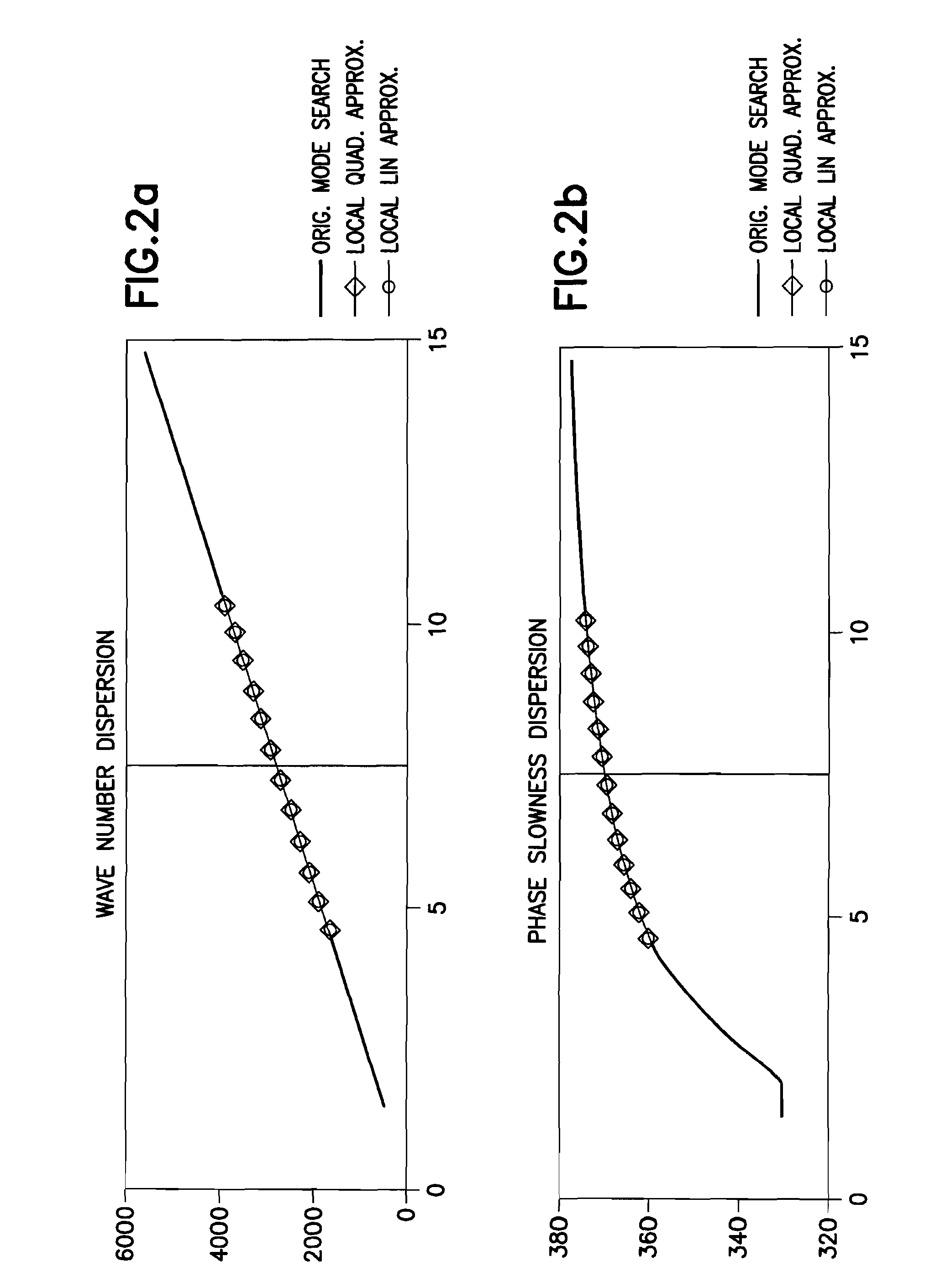
This invention pertains to the extraction of the slowness dispersion characteristics of acoustic waves received by an array of two or more sensors by the application of a continuous wavelet transform on the received array waveforms (data). This produces a time-frequency map of the data for each sensor that facilitates the separation of the propagating components thereon. Two different methods are described to achieve the dispersion extraction by exploiting the time frequency localization of the propagating mode and the continuity of the dispersion curve as a function of frequency. The first method uses some features on the modulus map such as the peak to determine the time locus of the energy of each mode as a function of frequency. The second method uses a new modified Radon transform applied to the coefficients of the time frequency representation of the waveform traces received by the aforementioned sensors. Both methods are appropriate for automated extraction of the dispersion estimates from the data without the need for expert user input or supervision
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Image processing method for image distortion automatic correction
InactiveCN1937698AGuaranteed no distortionRealize Distortion CorrectionPictoral communicationWord identificationMathematical model
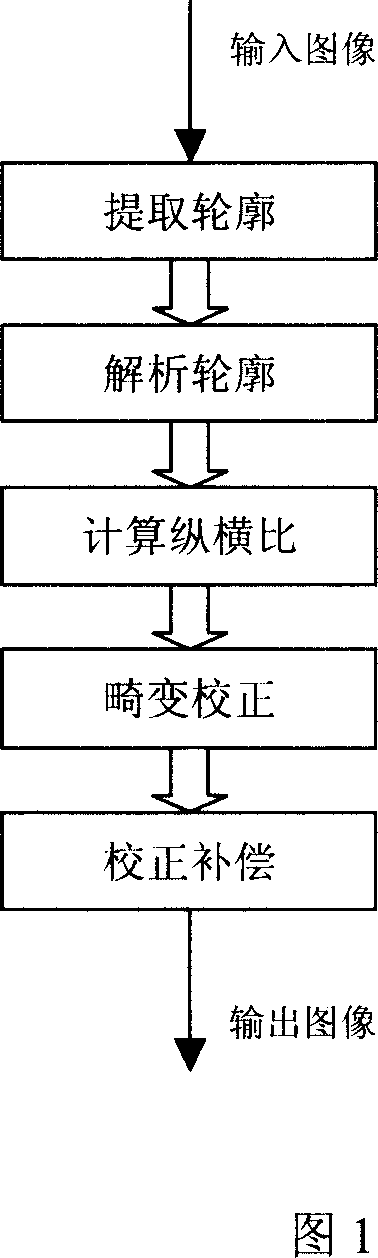
A image processor of automatic calibrating aberration makes use of radon transforming to pick up four sides profiles of business cards and texts, with profile vertex message, we can calibrate the image aberration and establish internal mathematics module of shot equipment and equation groups of business cards and texts aspect ratio parameter, then solve equation groups to get the rectangle object's aspect ratio and apply it to calibrate images to prevent distortion. At last, the invention can identify the image inversion by words identification for judging if it is necessary to circumvolve the calibrated images to get the perfect calibration results. It is very easy to calibrate images without manual practice , we can utilize the invention in most of the imaging equipments ,such as medical imaging, supervising equipment, mobile, digital camera ,digital vision and so on, no wonder that every user can do the operation very easily.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
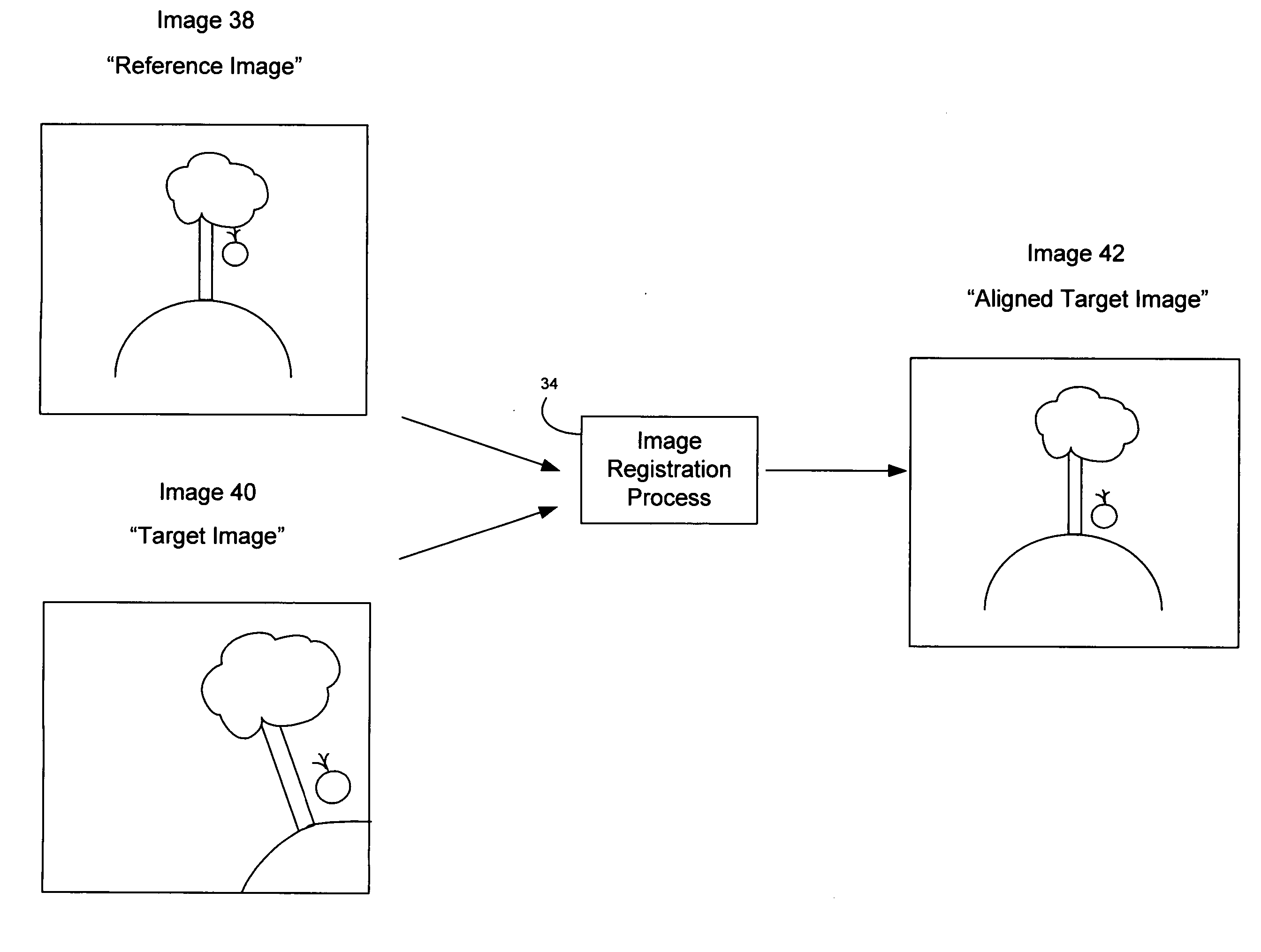
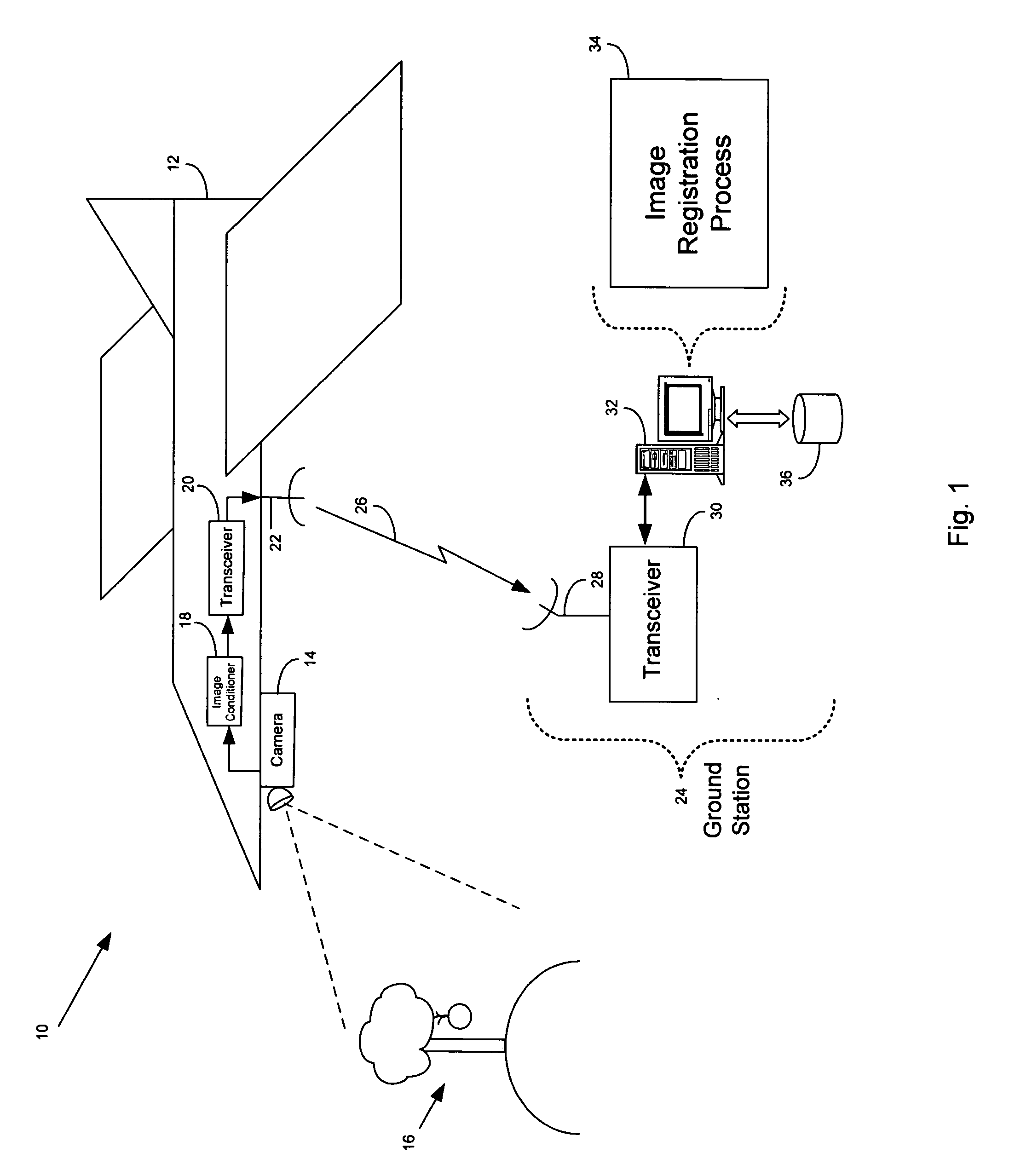
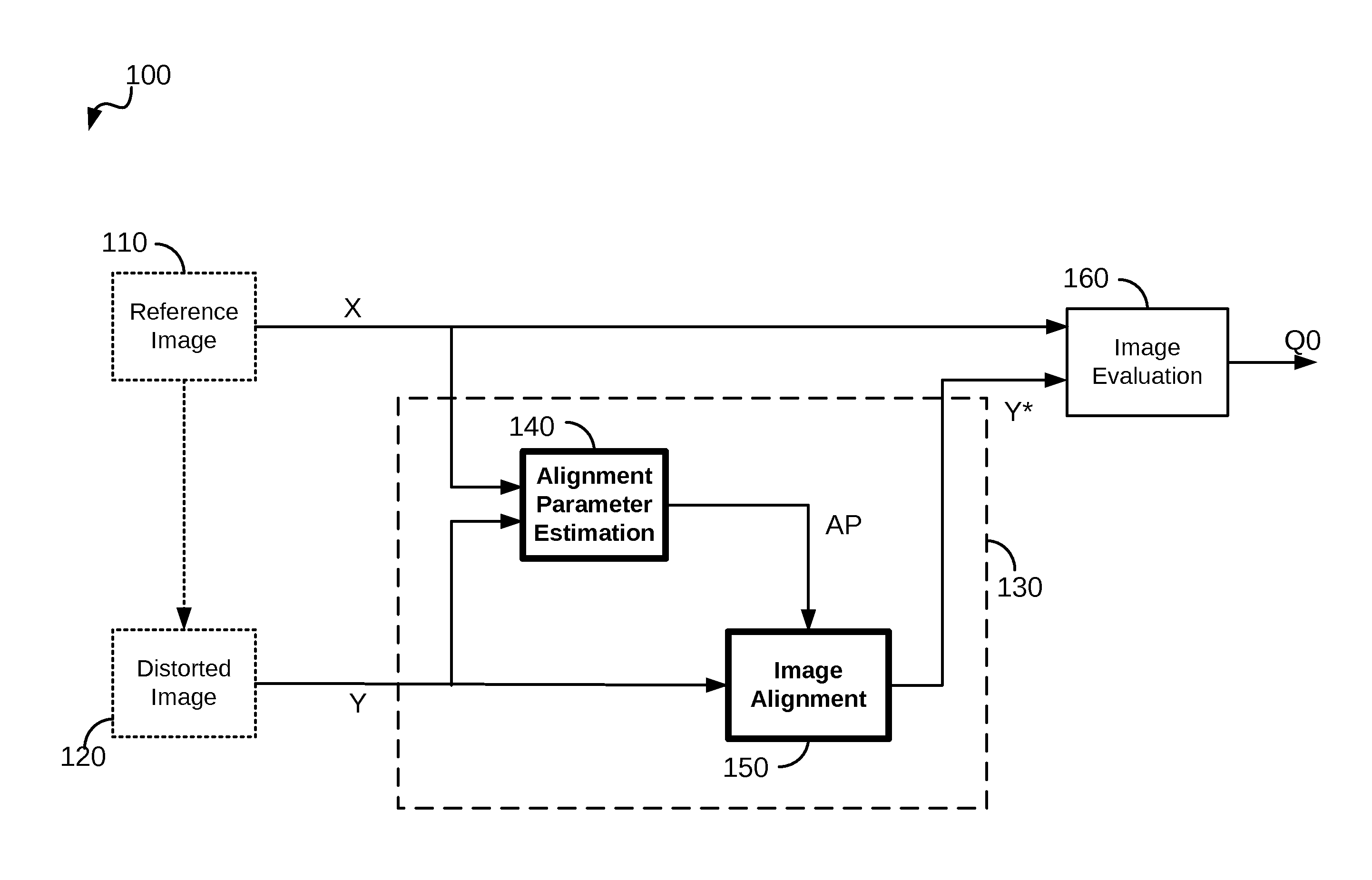
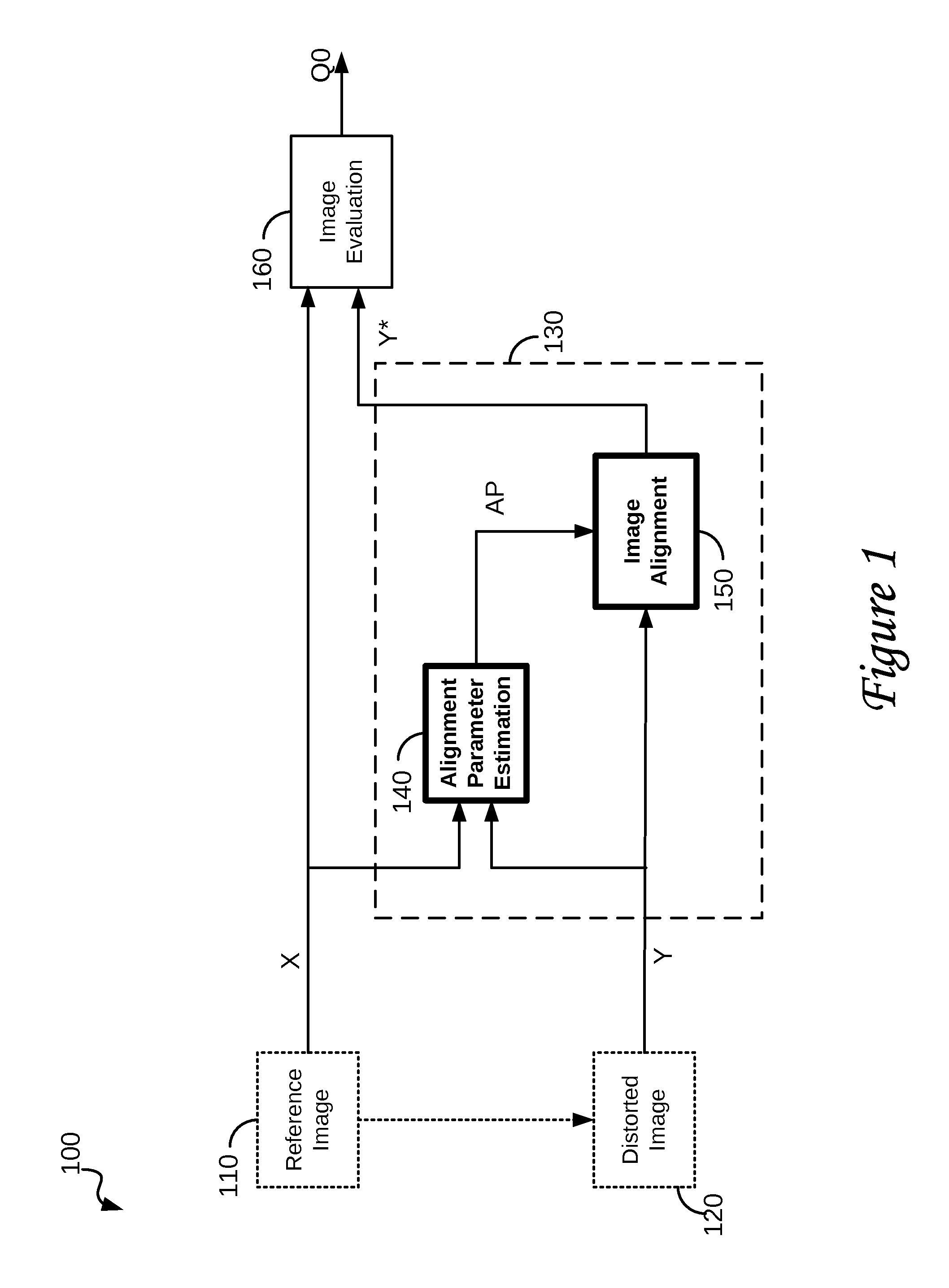
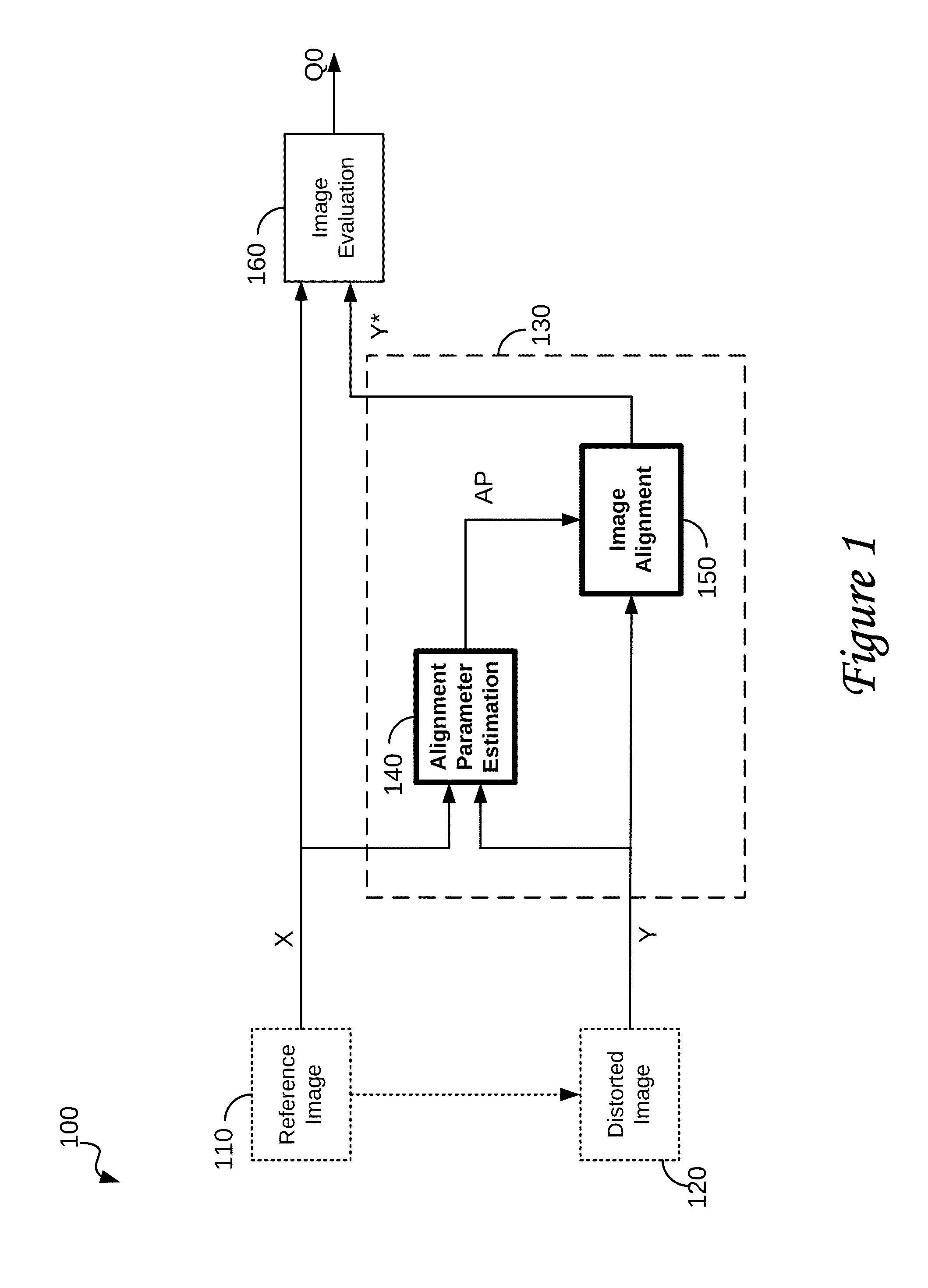
Image registration system and method
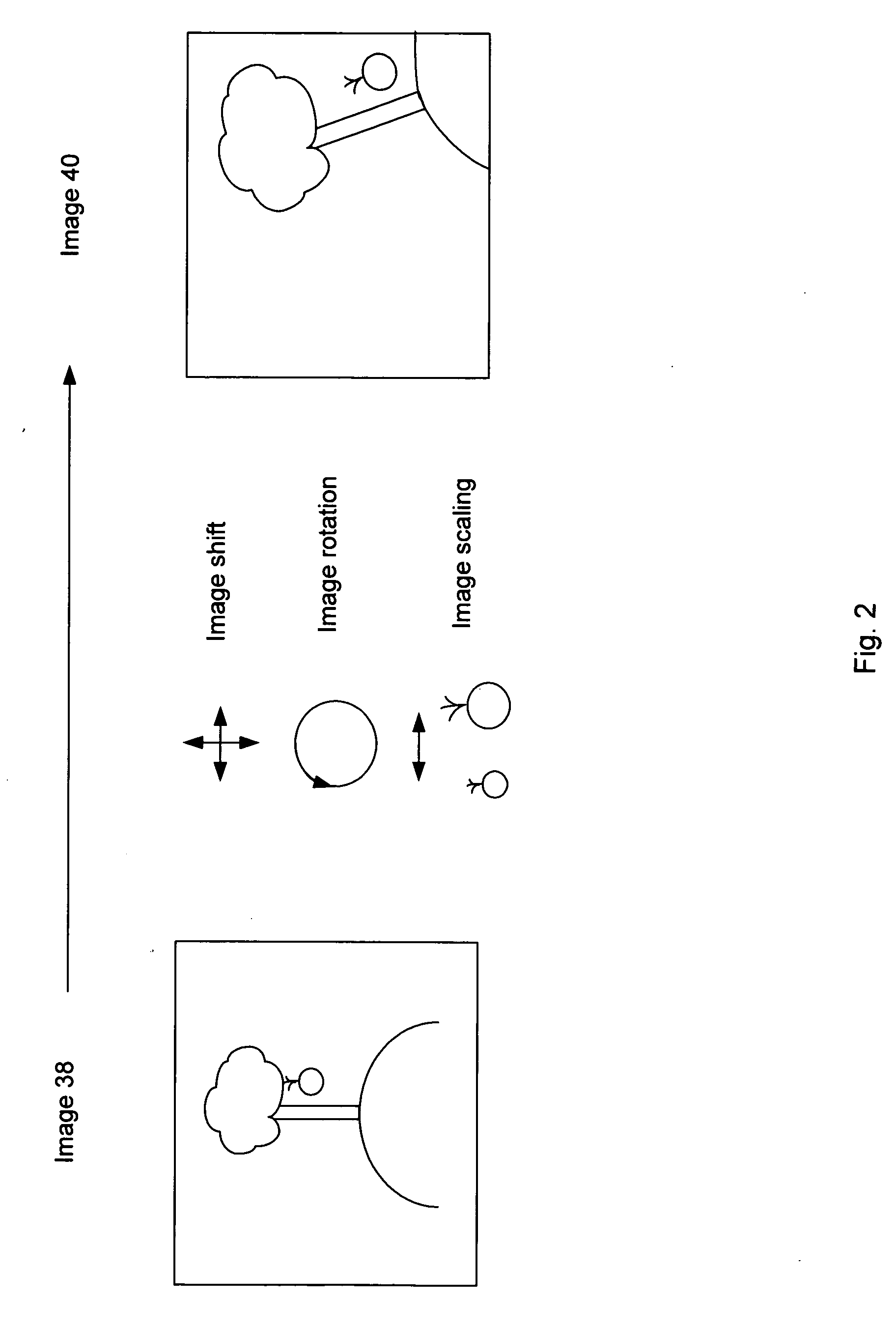
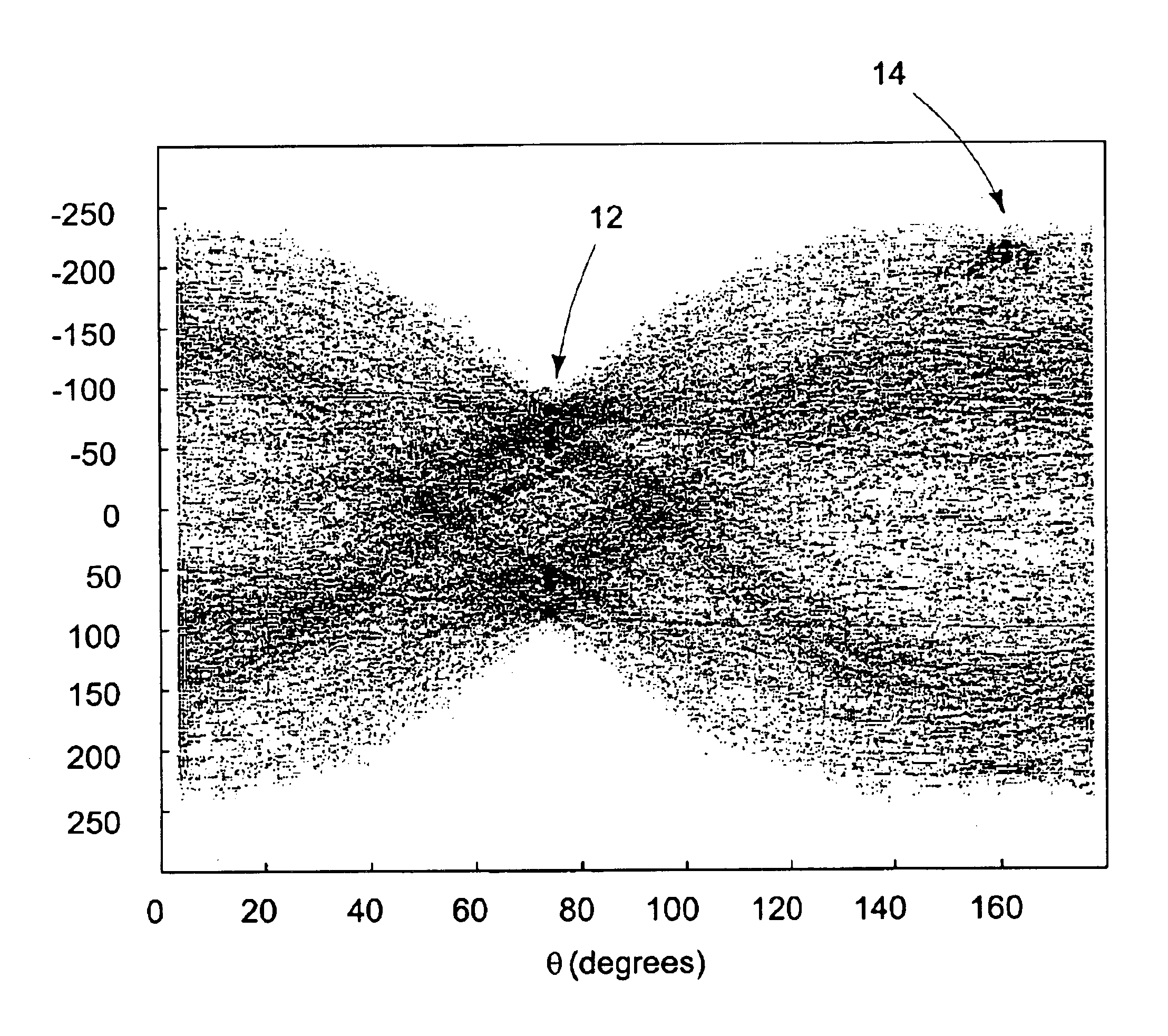
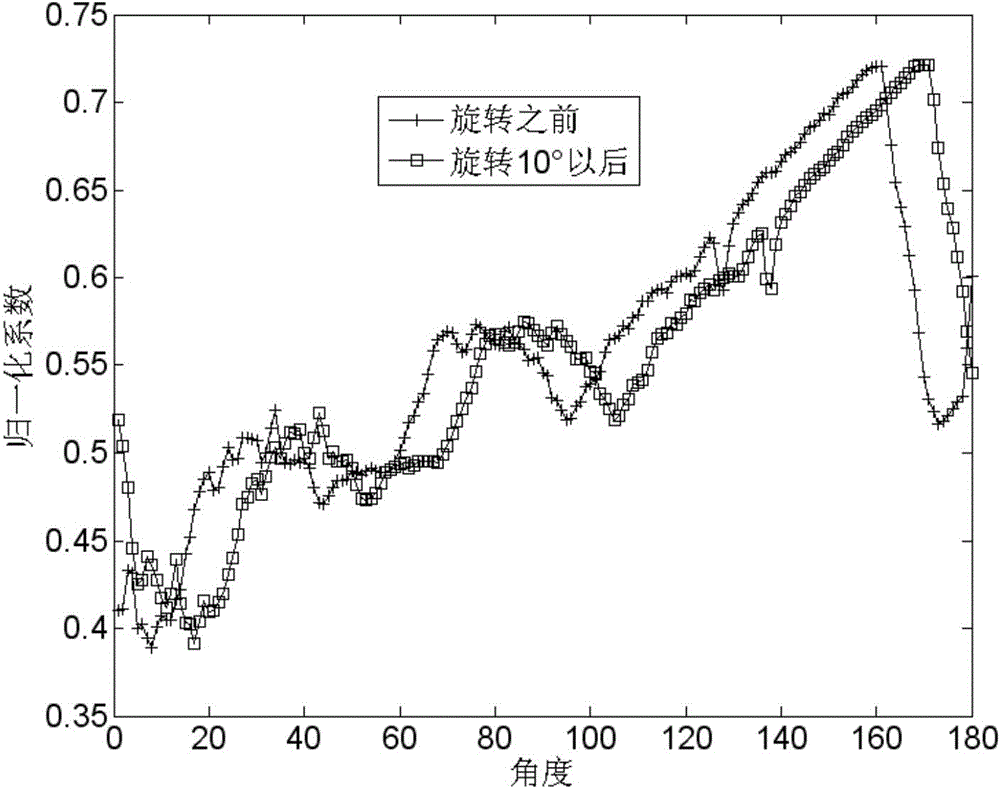
A method of characterizing alignment between two images includes receiving a first data set representative of a reference image, receiving a second data set representative of a target image, processing the first and second data sets that includes calculating an autocorrelation of the first data set to obtain a third data set that is substantially absent information representative of a relative shift between the reference image and the target image, and processing the third data set that includes calculating a Radon transform of the autocorrelation of the first data set to obtain a fourth data set that includes information representative of a relative rotational difference between the reference image and the target image.
Owner:PHOTON RES ASSOCS
Method and system for determining image transformation
InactiveUS6959098B1Character and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationDecoding methodsRadon transform
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
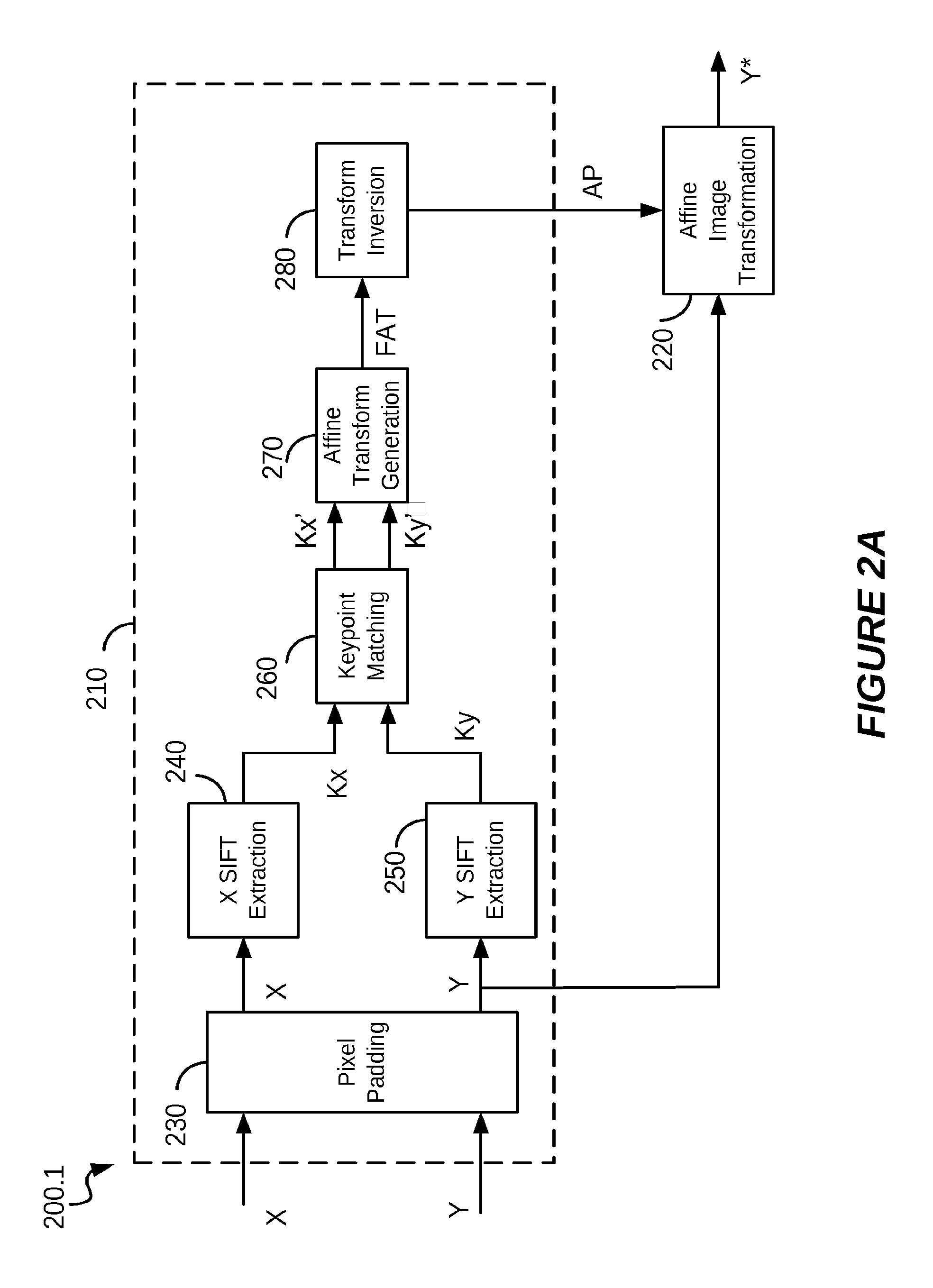
Image registration method and system robust to noise
ActiveUS20130163896A1Improved image registration methodStrengthen the systemImage analysisGeometric image transformationFast Fourier transformComputer graphics (images)
An image registration method is disclosed for processing a distorted image into a registered image that is aligned with reference to an original image. Distortions from the original image may include scaling, rotation, and noise. The method is based on correlating Radon transforms of both images to determine the rotation angle, and the scaling factor is determined by dividing averages of the overall luminance of each image on the assumption that any added noise will cancel. The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is used to estimate global spatial shifts. In one embodiment, the distorted image is first scaled to the size of the original image before being rotated. In another embodiment, the original image is first scaled to the size of the distorted image before rotating the distorted image, and finally scaling it to match the original image. A corresponding system for image registration is also provided.
Owner:ECOLE DE TECH SUPERIEURE
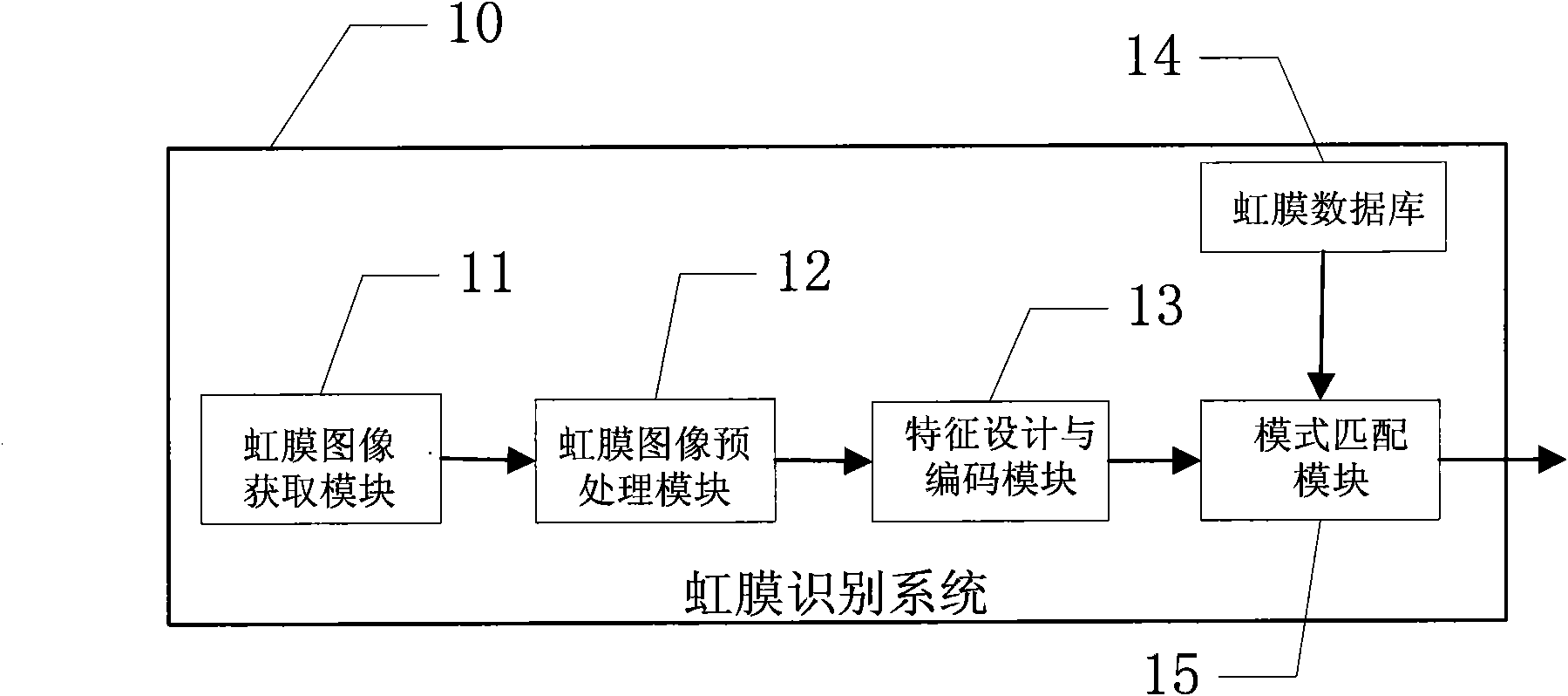
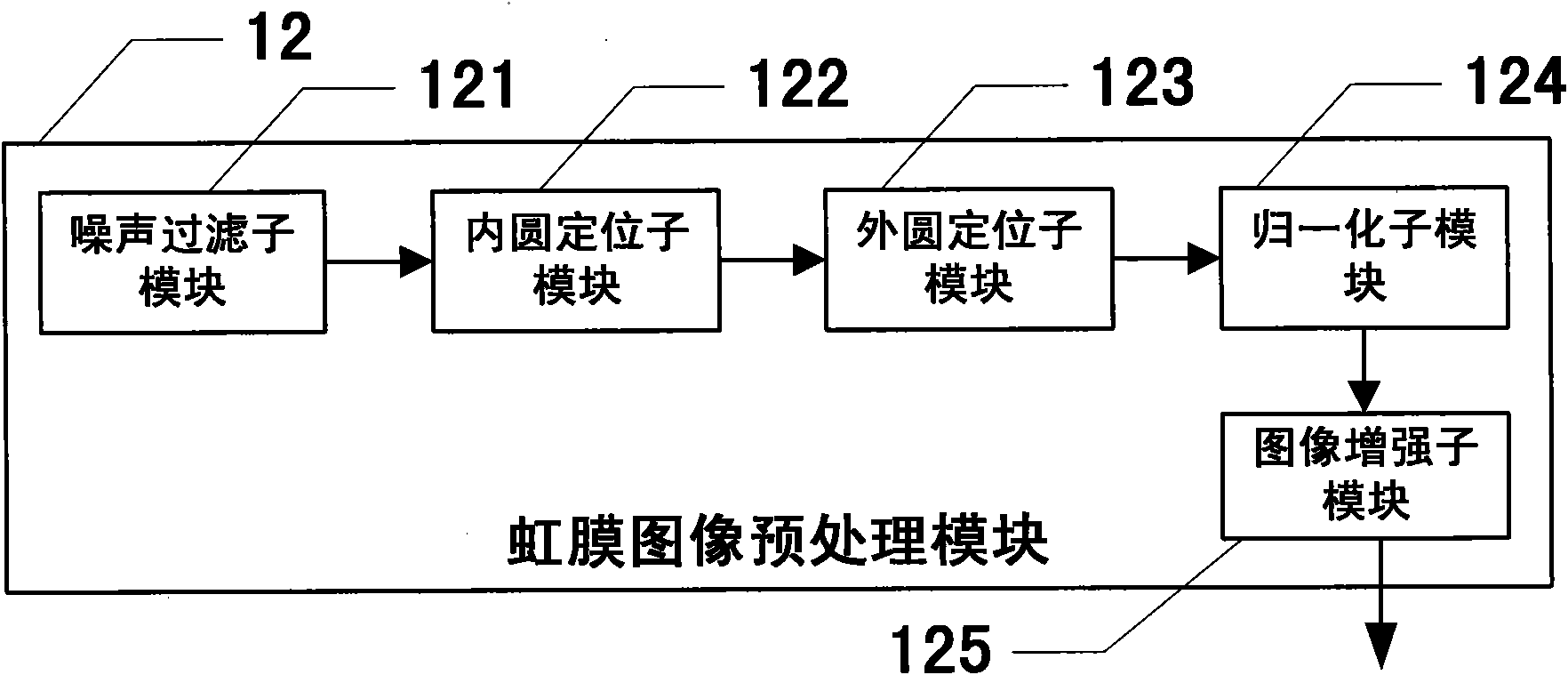
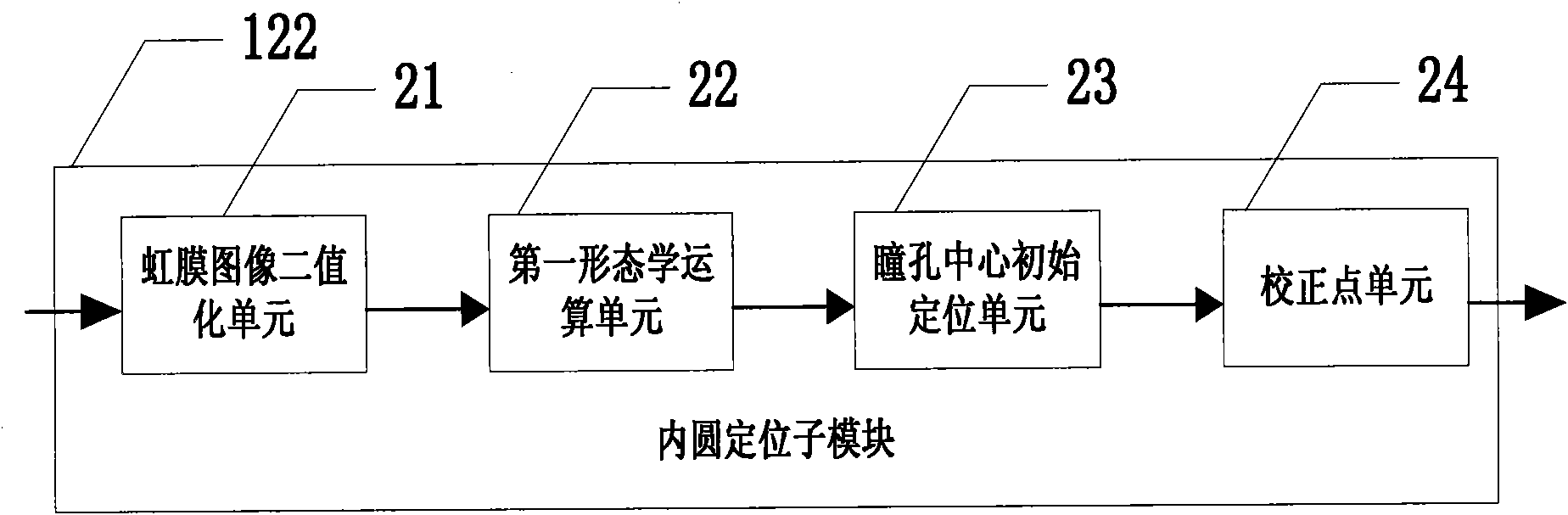
Iris positioning method and iris identification system
InactiveCN101916362AAvoid Blind SearchesFast positioningCharacter and pattern recognitionHough transformEyelid
The invention relates to the technical field of biometric identification and discloses an iris positioning method and an iris identification system. The method and the system are based on mathematical morphology, Radon transform, canny operator and hough transform. The algorithm comprises the positioning of an inner edge and an outer edge, wherein in the positioning of the inner edge, based on a gray projection method of line detection, a binarized image is processed by using the principle of the mathematical morphology so as to remove the interference of noise; and in the positioning of the outer edge, an iris image is processed by using the principle of the mathematical morphology at first, then an upper eyelid and a lower eyelid are detected by the Radon transform to remove the interference, and finally, an edge is extracted by a canny algorithm and the external edge of the iris is detected by the hough transform. Therefore, large area blind searching can be avoided so as to improve positioning speed.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
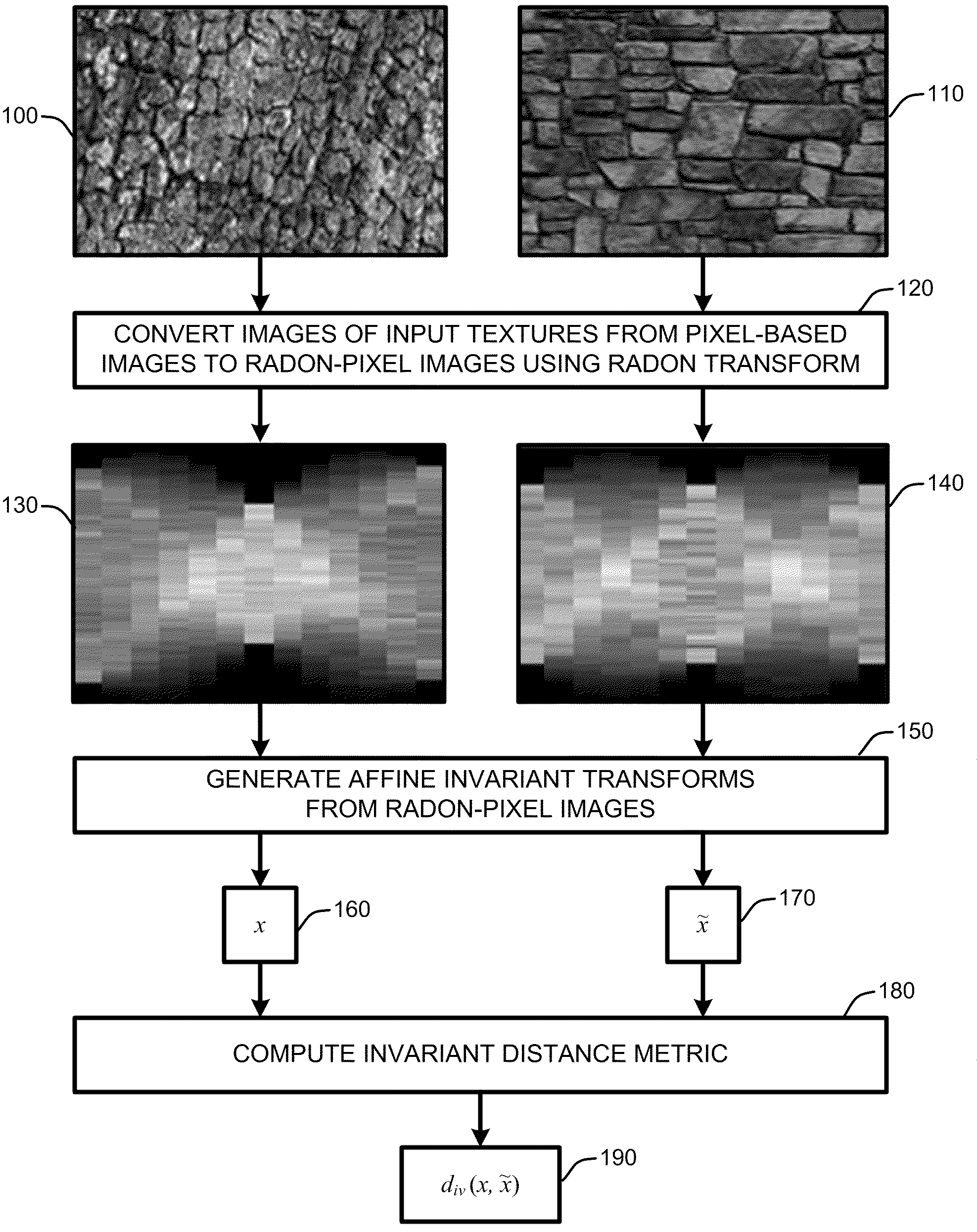
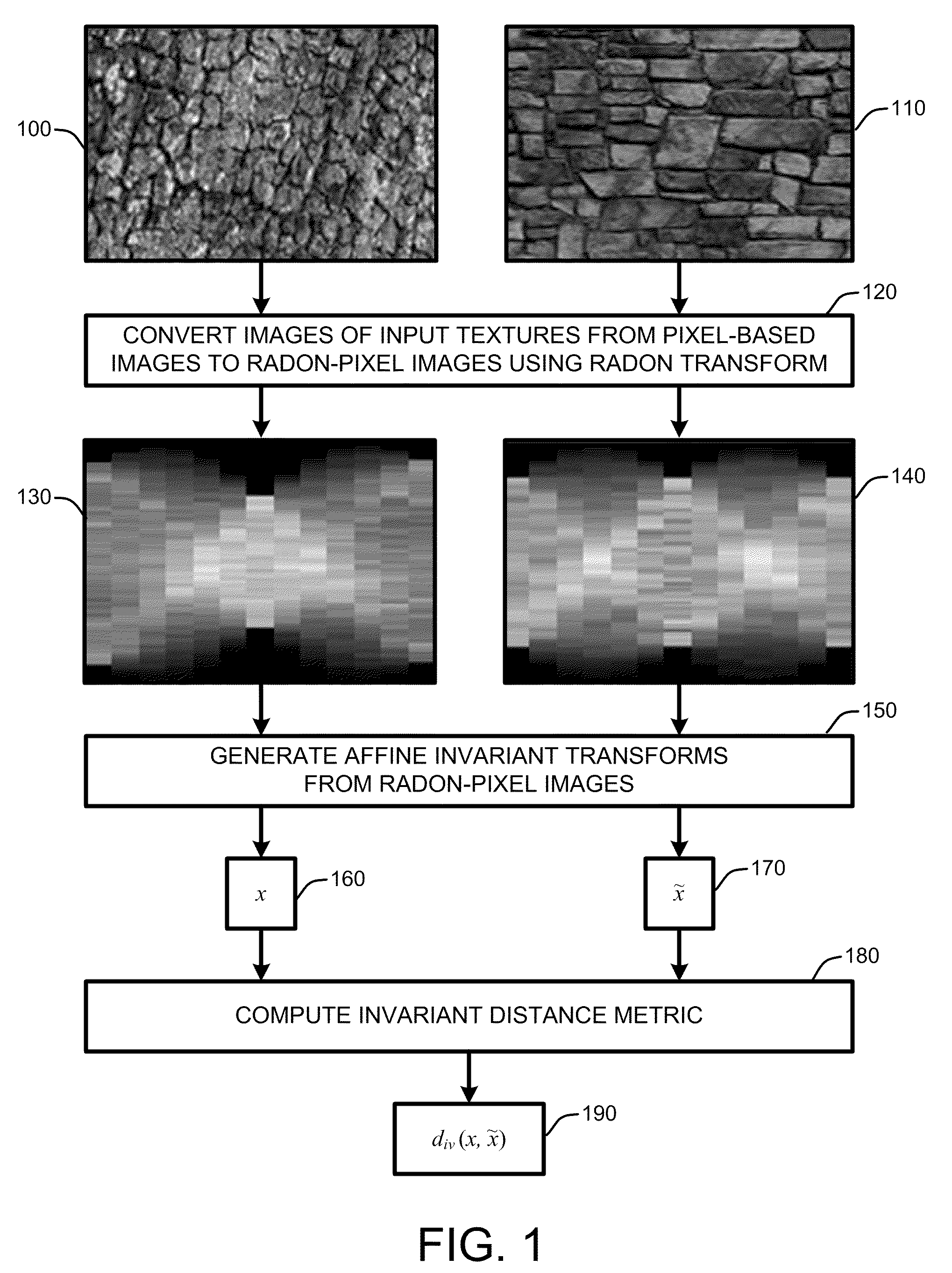
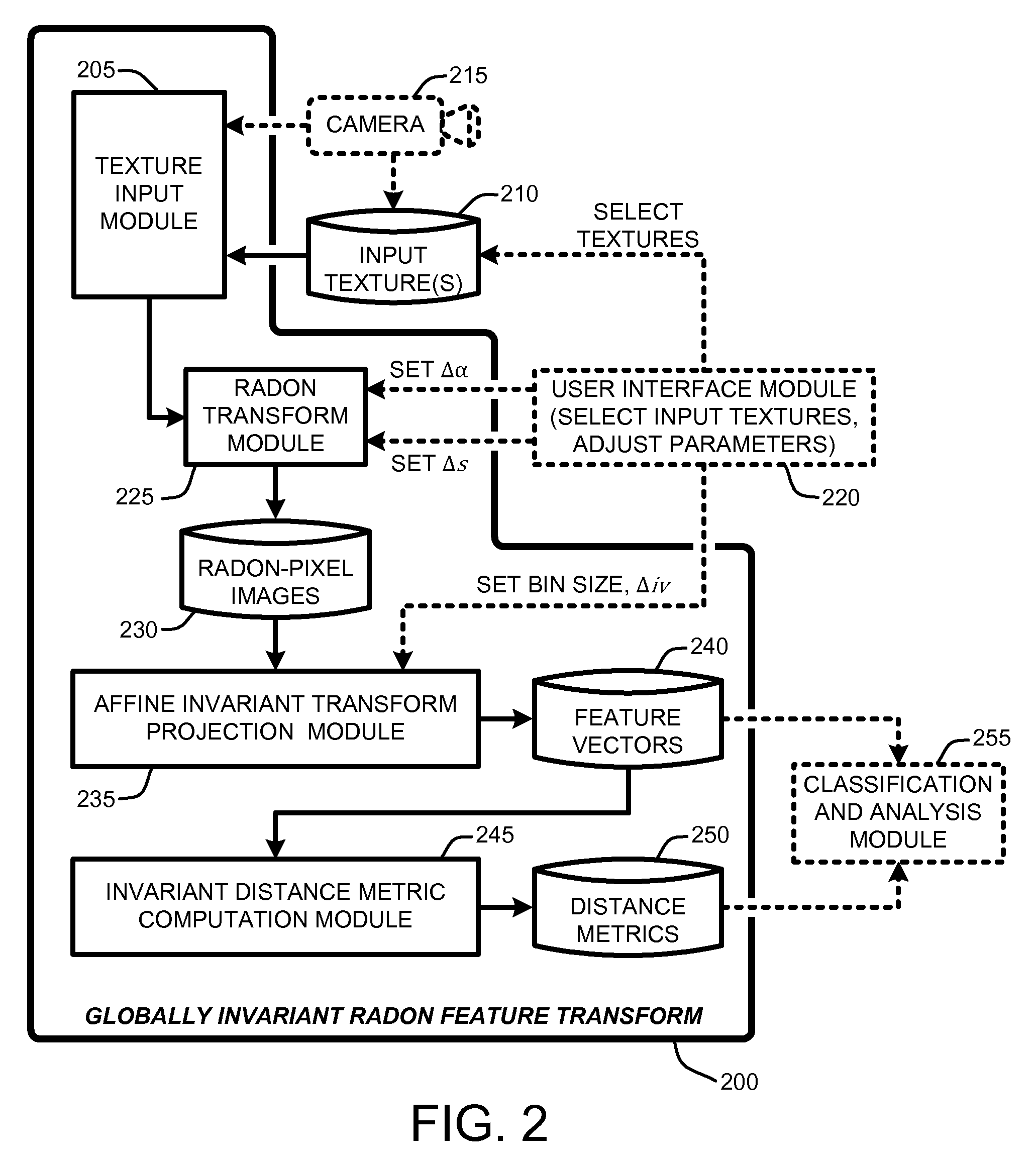
Globally invariant radon feature transforms for texture classification
InactiveUS20100067799A1Accurate textureHigh rateCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionRadon transform
A “globally invariant Radon feature transform,” or “GIRFT,” generates feature descriptors that are both globally affine invariant and illumination invariant. These feature descriptors effectively handle intra-class variations resulting from geometric transformations and illumination changes to provide robust texture classification. In general, GIRFT considers images globally to extract global features that are less sensitive to large variations of material in local regions. Geometric affine transformation invariance and illumination invariance is achieved by converting original pixel represented images into Radon-pixel images by using a Radon Transform. Canonical projection of the Radon-pixel image into a quotient space is then performed using Radon-pixel pairs to produce affine invariant feature descriptors. Illumination invariance of the resulting feature descriptors is then achieved by defining an illumination invariant distance metric on the feature space of each feature descriptor.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
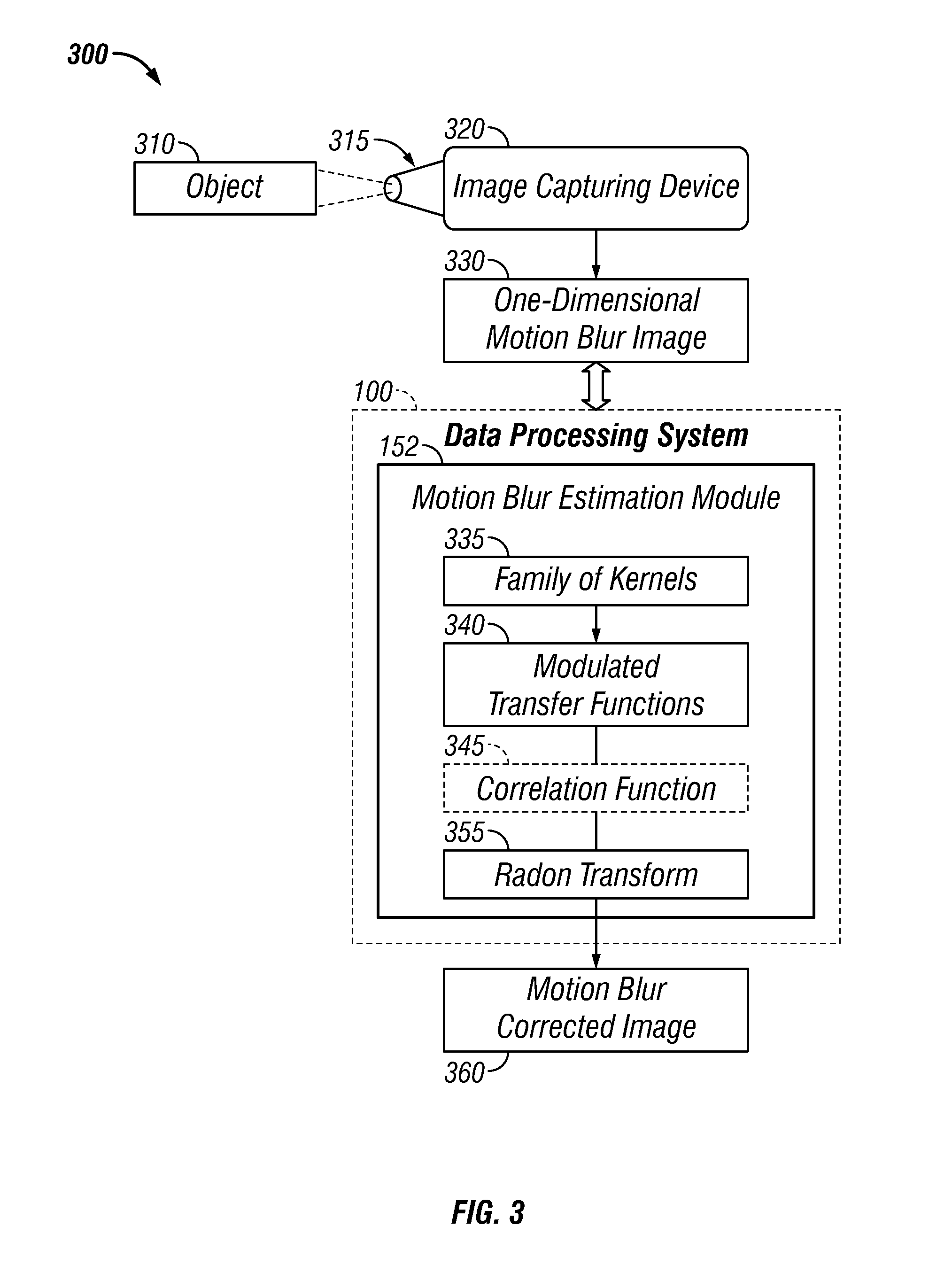
Fourier domain blur estimation method and system
ActiveUS20110096180A1Effective motion blur estimationEffective estimateImage enhancementTelevision system detailsEstimation methodsCorrelation function
A method and system for estimating motion blur of an image associated with a moving object. The direction of one-dimensional motion blur may be estimated by inspecting a power spectrum associated with the image. A radon transform with respect to the image power spectrum is computed in the direction of the motion blur. A family of kernels with respect to the one-dimensional motion blur may then be defined utilizing a shutter triggering sequence associated with an image capturing device. The family of kernels may be modeled utilizing a modulation transfer function (MTF). Each modulation transfer function may be compared with the radon transform of the power spectrum associated with the image via a correlation function. The kernel with highest correlation with respect to the radon transform of the image power spectrum may be employed for de-blurring the image.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
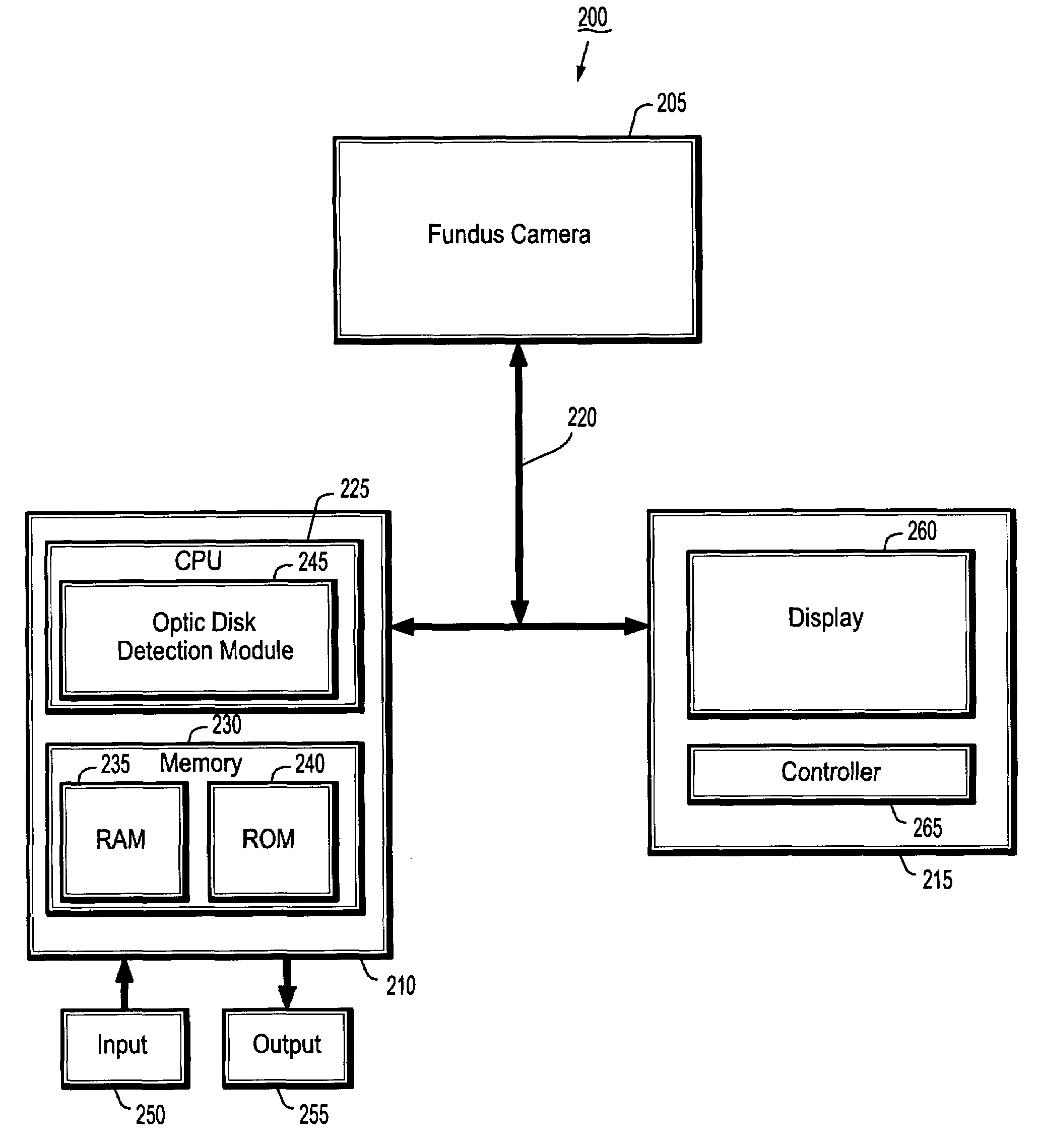
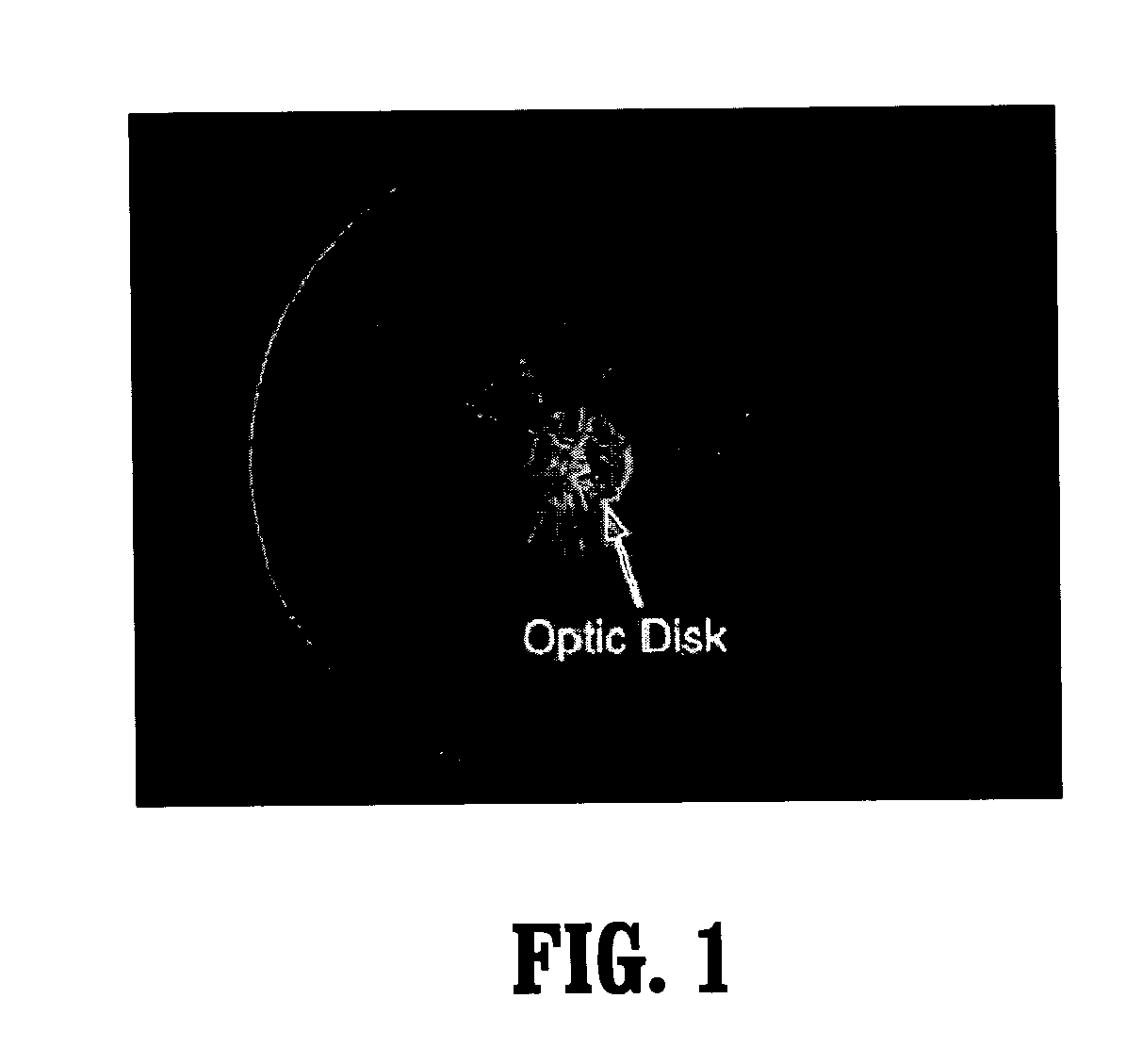
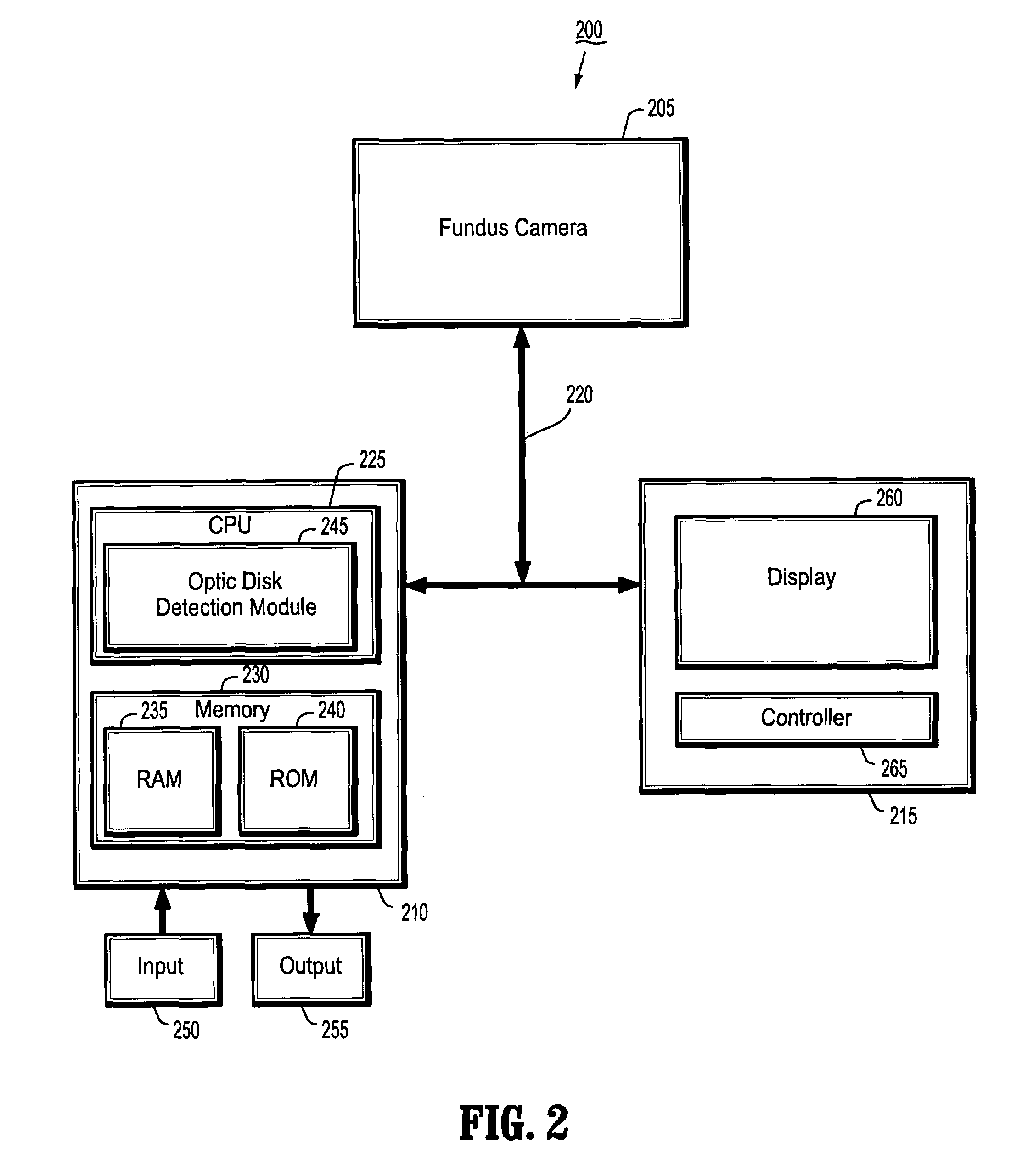
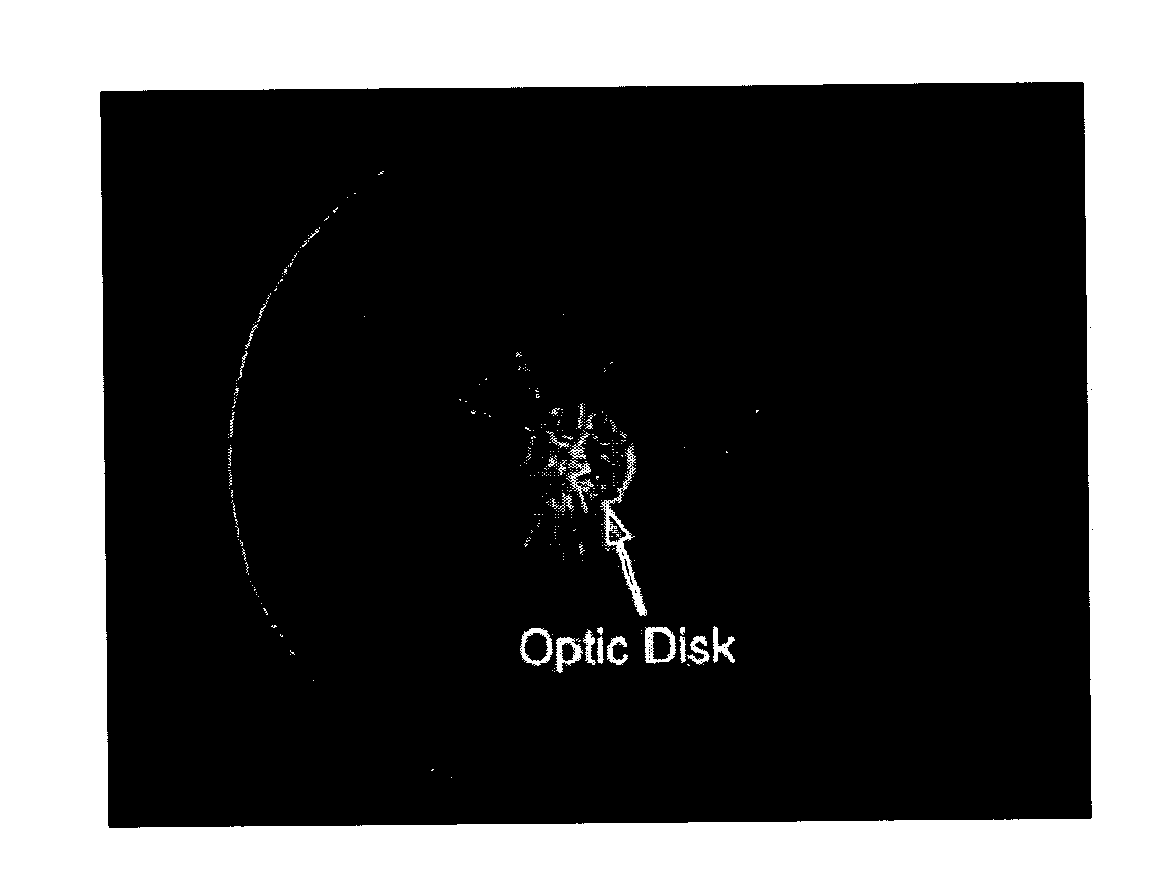
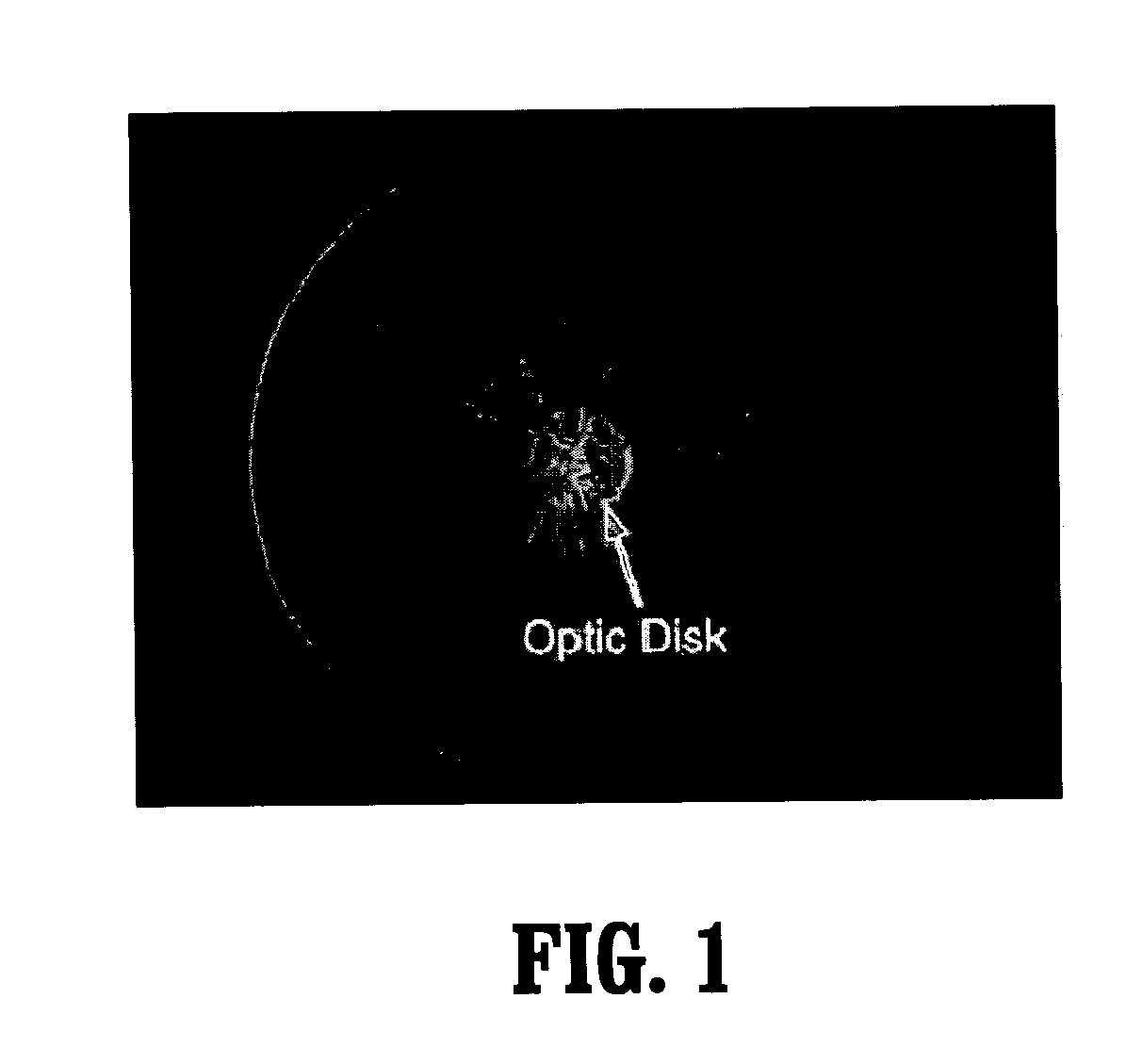
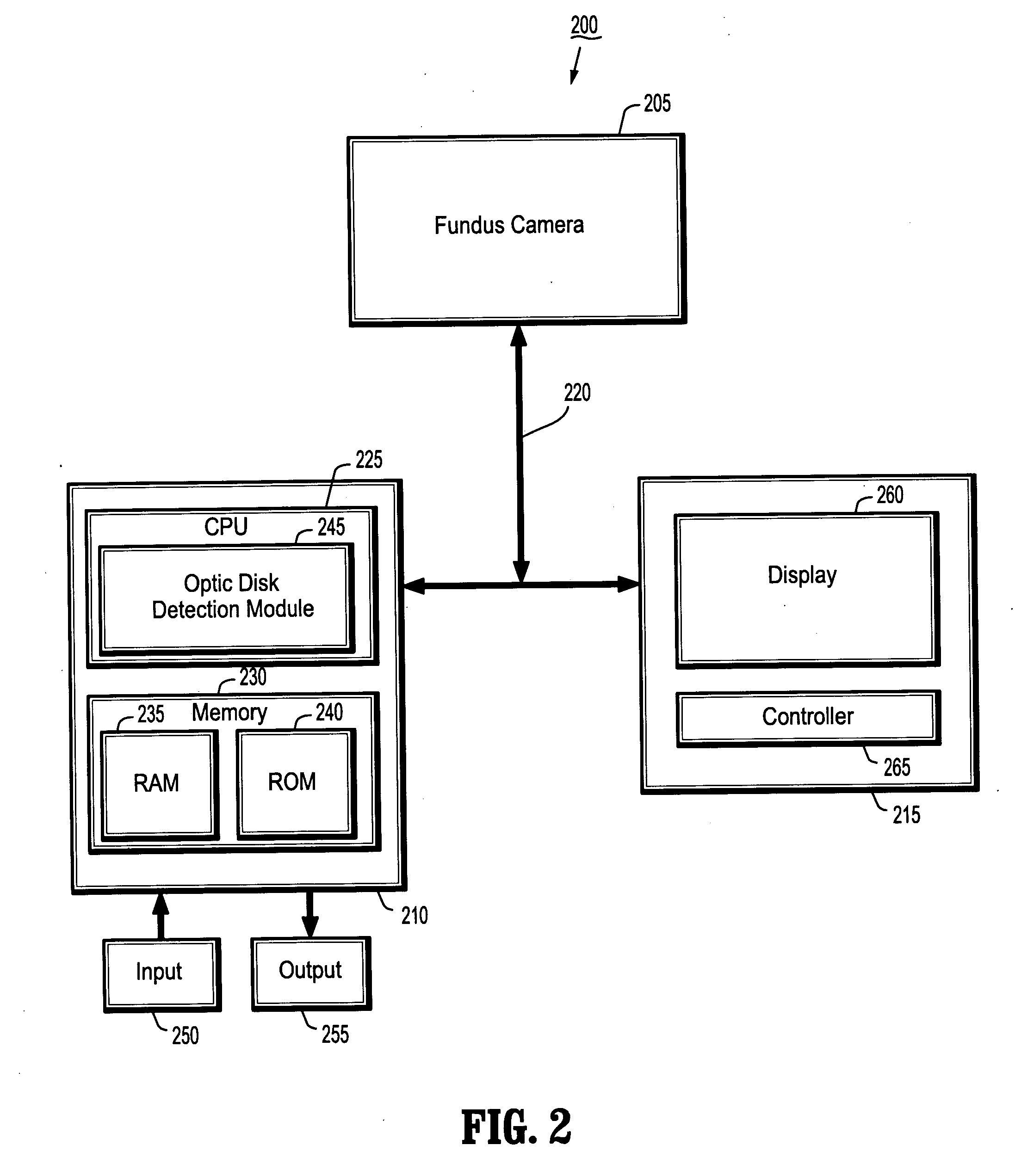
System and method for robust optic disk detection in retinal images using vessel structure and radon transform
A method for optic disk detection in retinal images, includes: extracting a vessel tree from a retinal image; locating an optic disk in the retinal image using the vessel tree; enhancing a contrast of the optic disk; removing vessels from the contrast enhanced optic disk; detecting a boundary of the optic disk with vessels removed by generating an edge map; projecting the edge map at a plurality of angles by using a radon transform; and estimating a radius and center of the optic disk using the projections.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
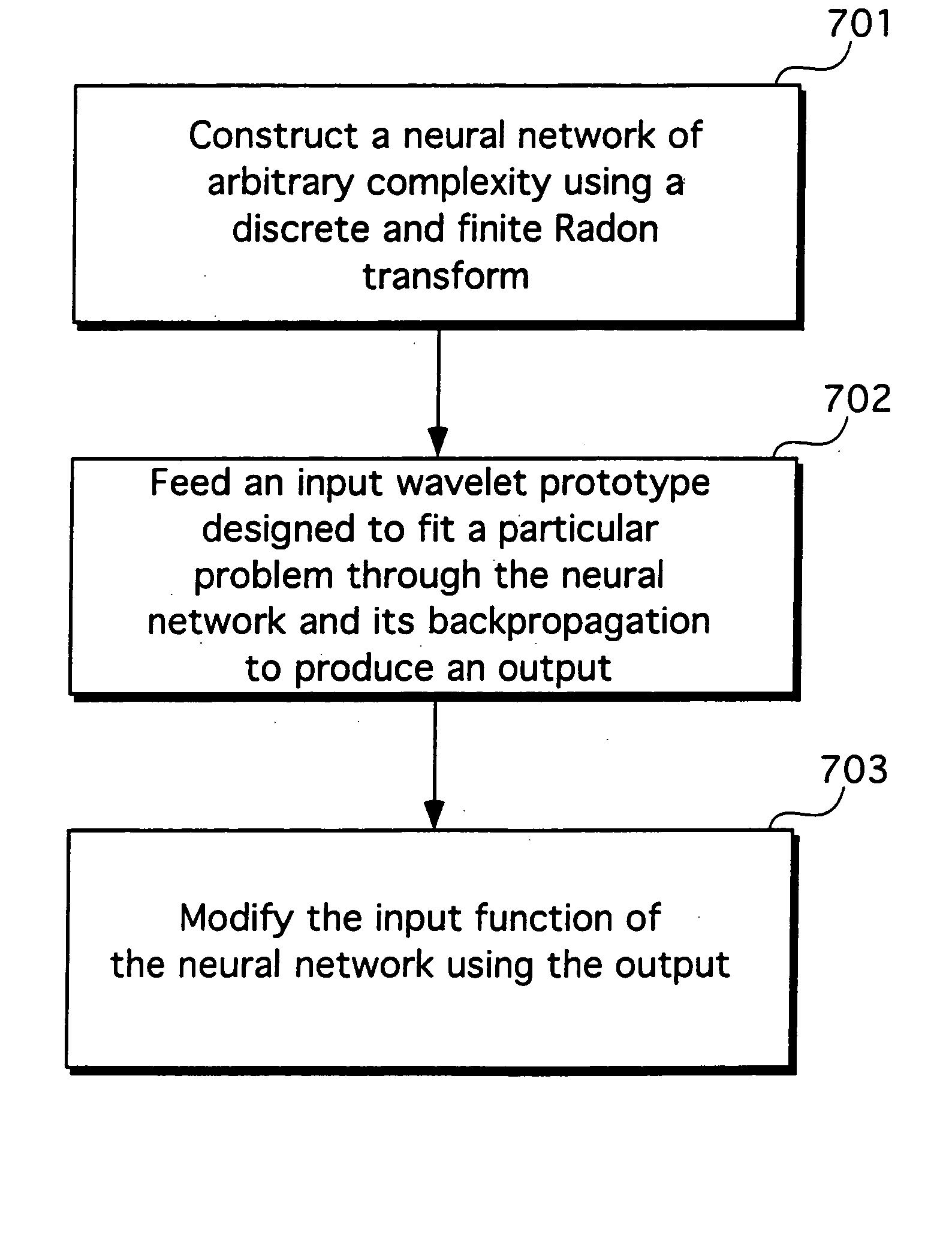
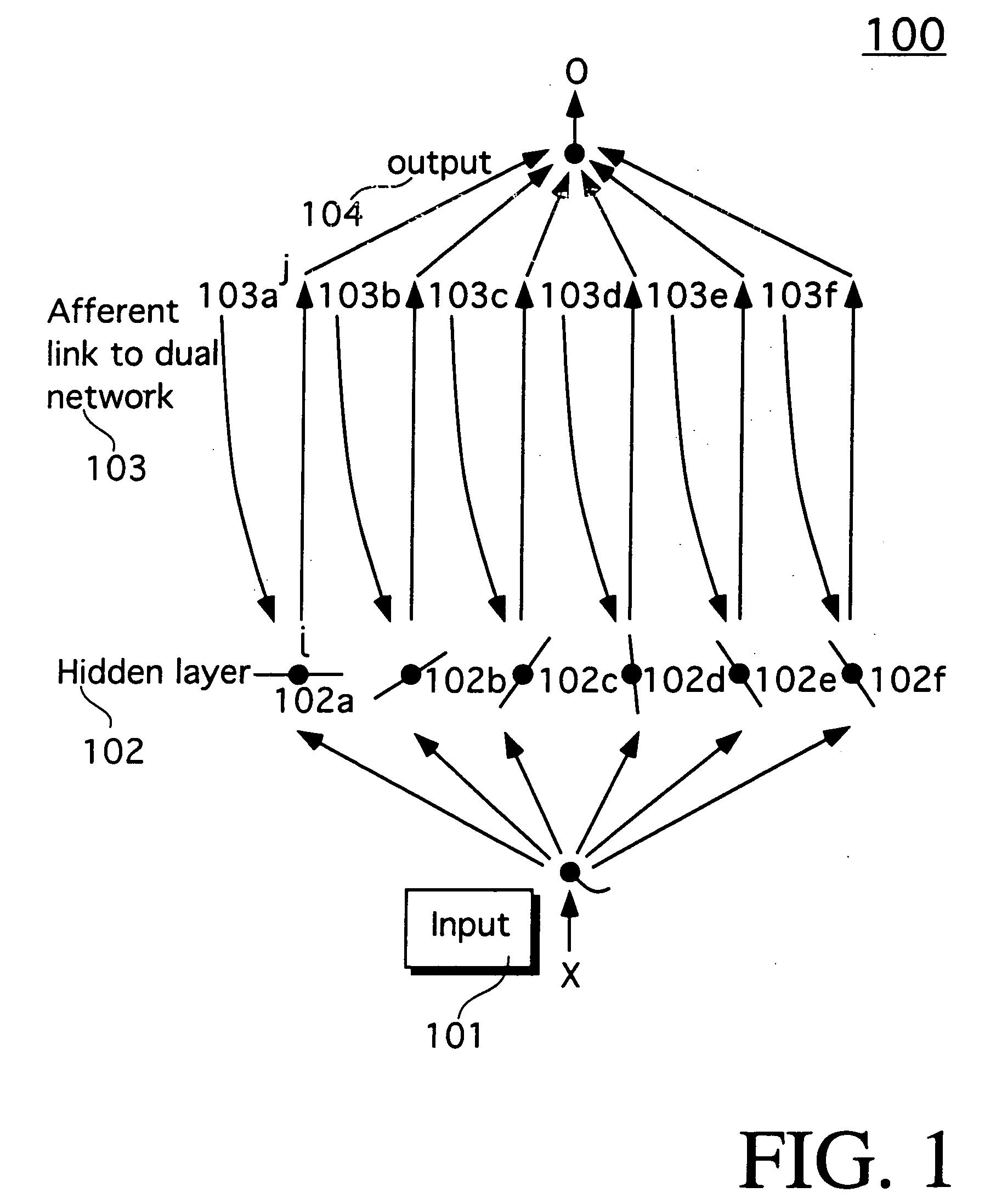
Method and apparatus of using neural network to train a neural network
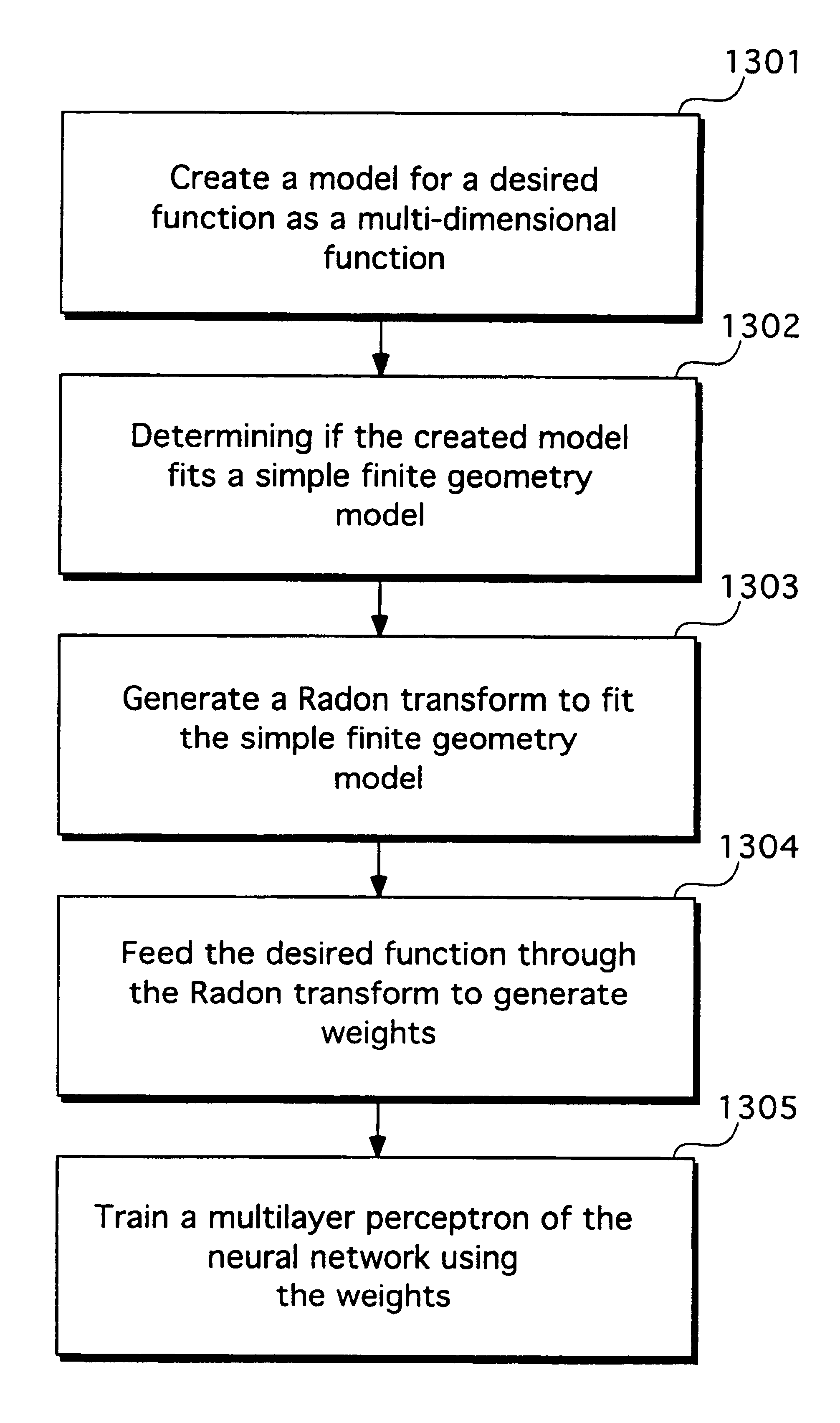
A method and apparatus of training a neural network. The method and apparatus include creating a model for a desired function as a multi-dimensional function, determining if the created model fits a simple finite geometry model, and generating a Radon transform to fit the simple finite geometry model. The desired function is fed through the Radon transform to generate weights. A multilayer perceptron of the neural network is trained using the weights.
Owner:RISING HAWLEY K III
System and Method For Robust Optic Disk Detection In Retinal Images Using Vessel Structure And Radon Transform
A method for optic disk detection in retinal images, includes: extracting a vessel tree from a retinal image; locating an optic disk in the retinal image using the vessel tree; enhancing a contrast of the optic disk; removing vessels from the contrast enhanced optic disk; detecting a boundary of the optic disk with vessels removed by generating an edge map; projecting the edge map at a plurality of angles by using a radon transform; and estimating a radius and center of the optic disk using the projections.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
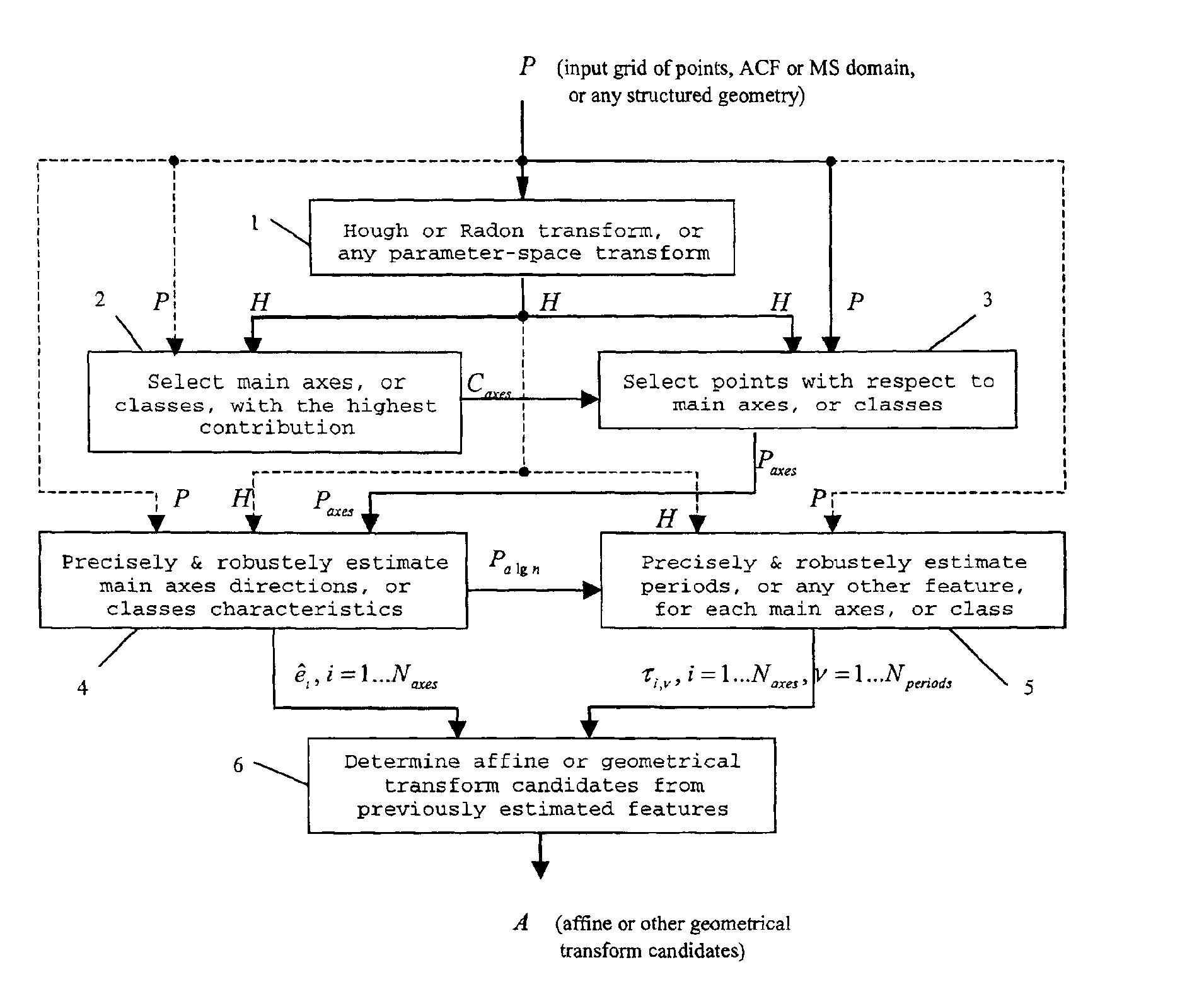
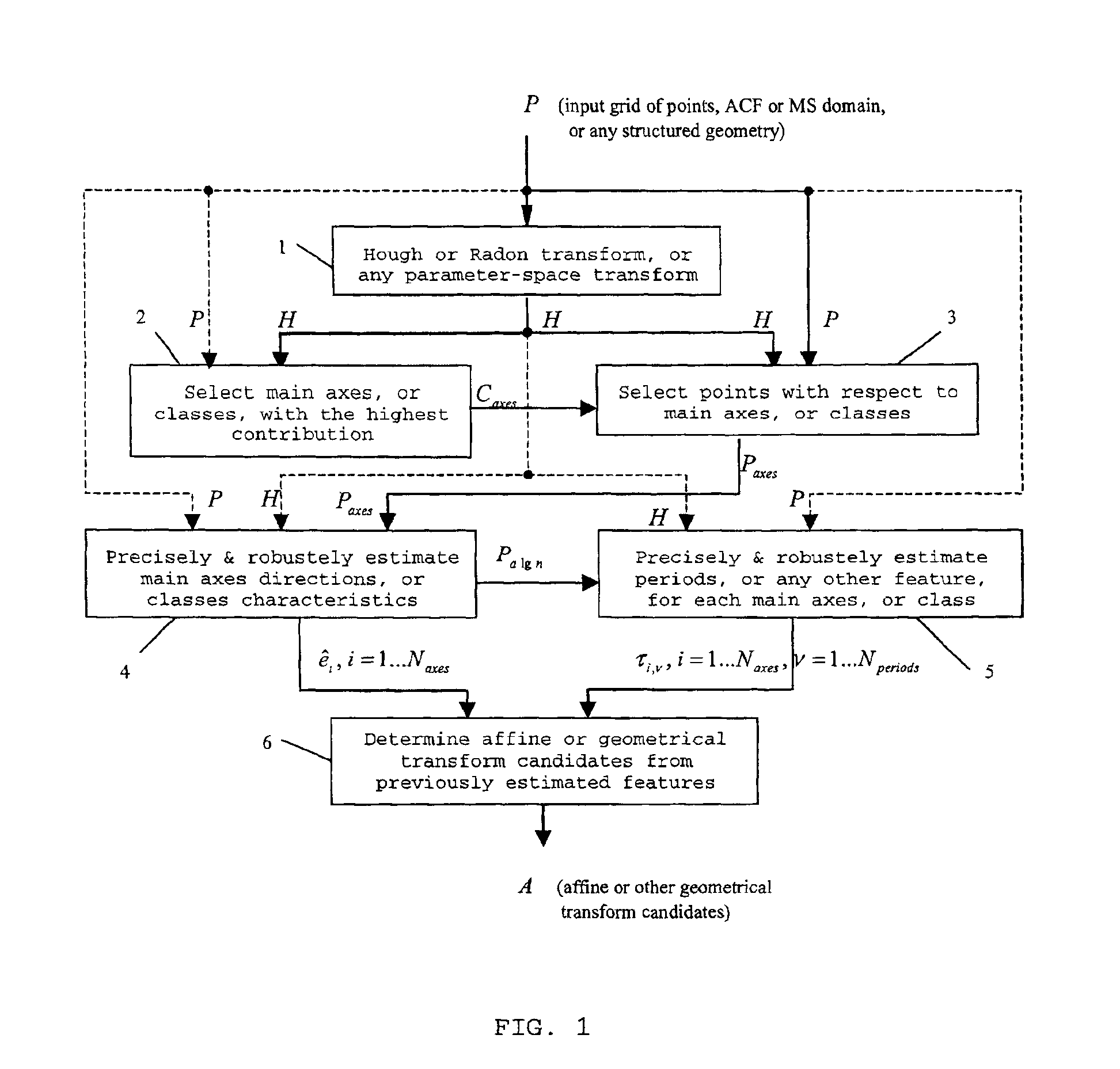
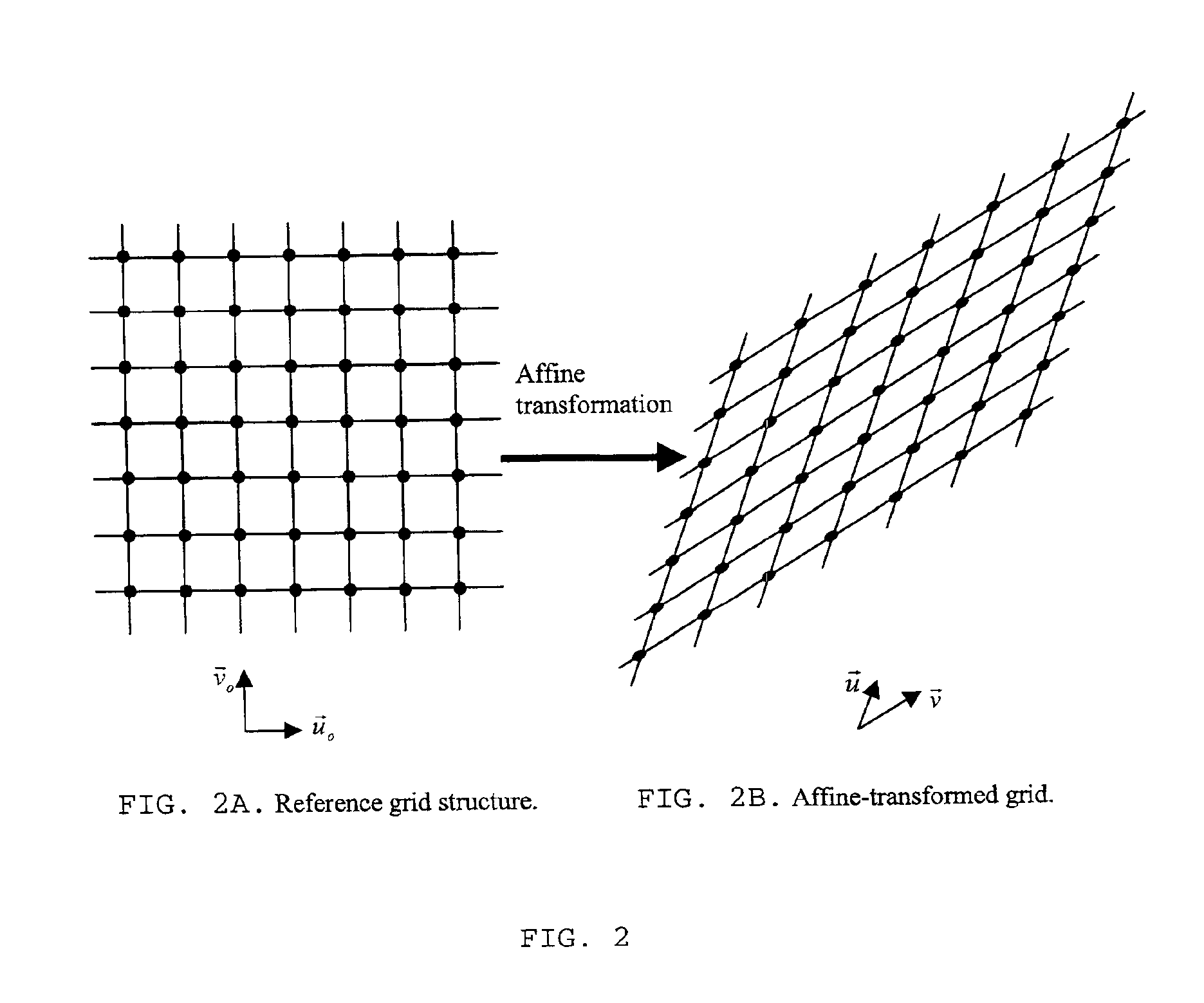
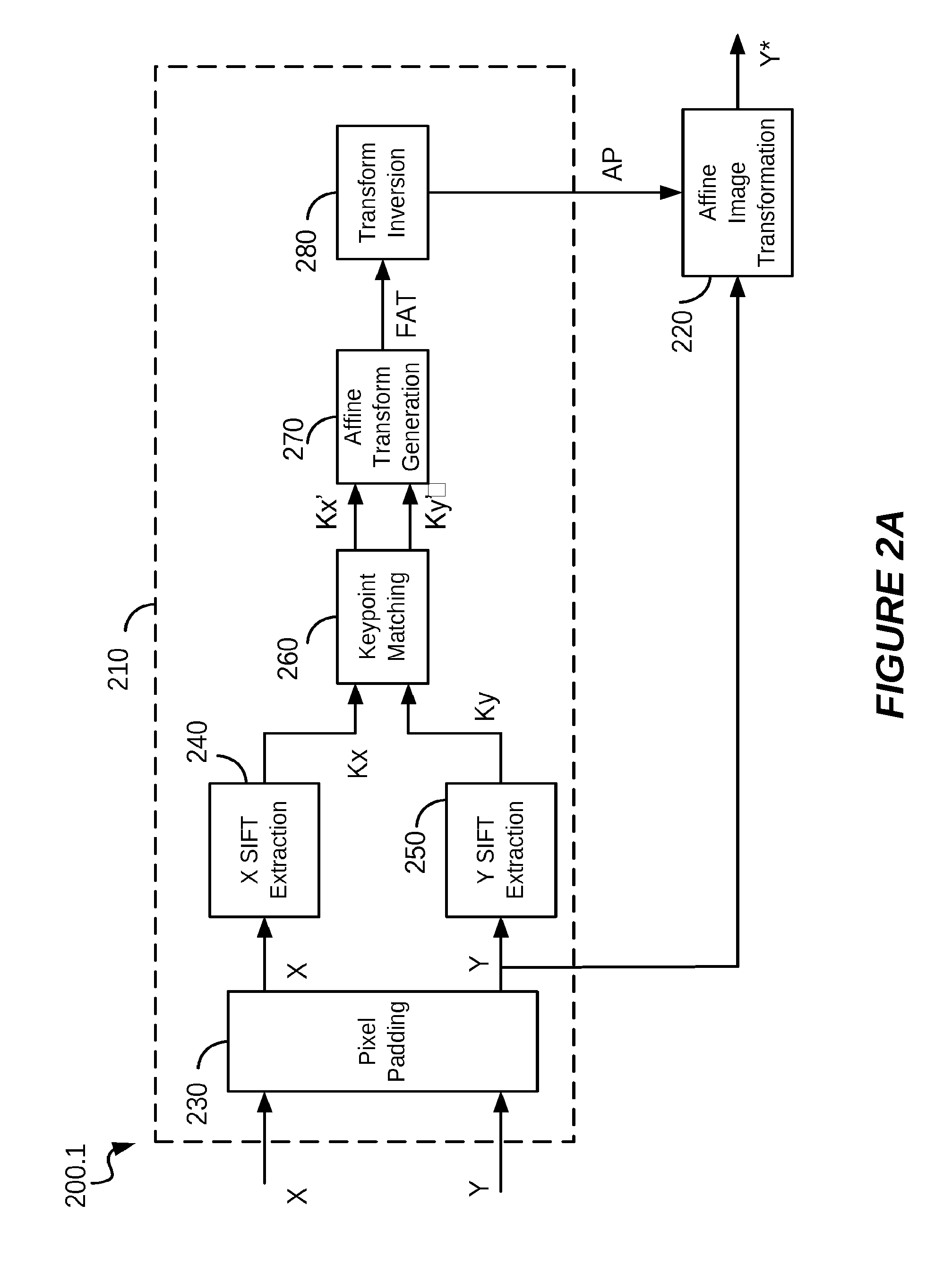
Method for the estimation and recovering of general affine transform
ActiveUS6904151B2Lack of precisionImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationHough transformRestoration method
The present invention relates to the methods of estimation and recovering of general affine geometrical transformations which were applied to data, extensible to any other defined class of geometrical transformations, according to the preamble of the dependent claims. The parameters of the undergone deformation are robustly estimated based on maxima given by a parametric transform such as Hough transform or Radon transform of some embedded information with periodical or any other known regular structure. The main applications of this invention are robust digital still image / video watermarking, document authentication, and detection of periodical or hidden patterns. In the case of periodical watermarks, the watermark can also be predistorted before embedding based on a key to defeat block-by-block removal attack.
Owner:DEGUILLAUME FREDERIC +2
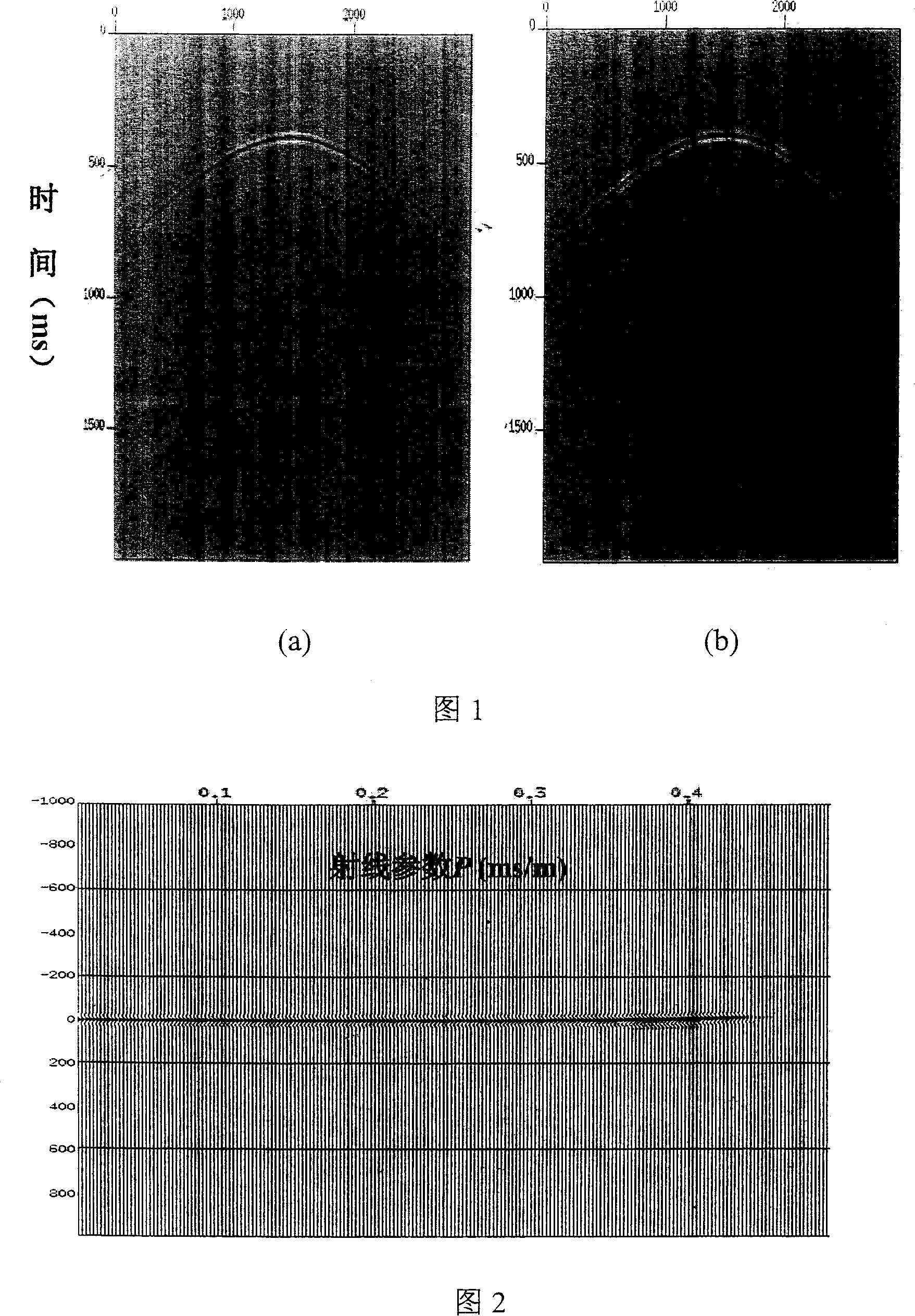
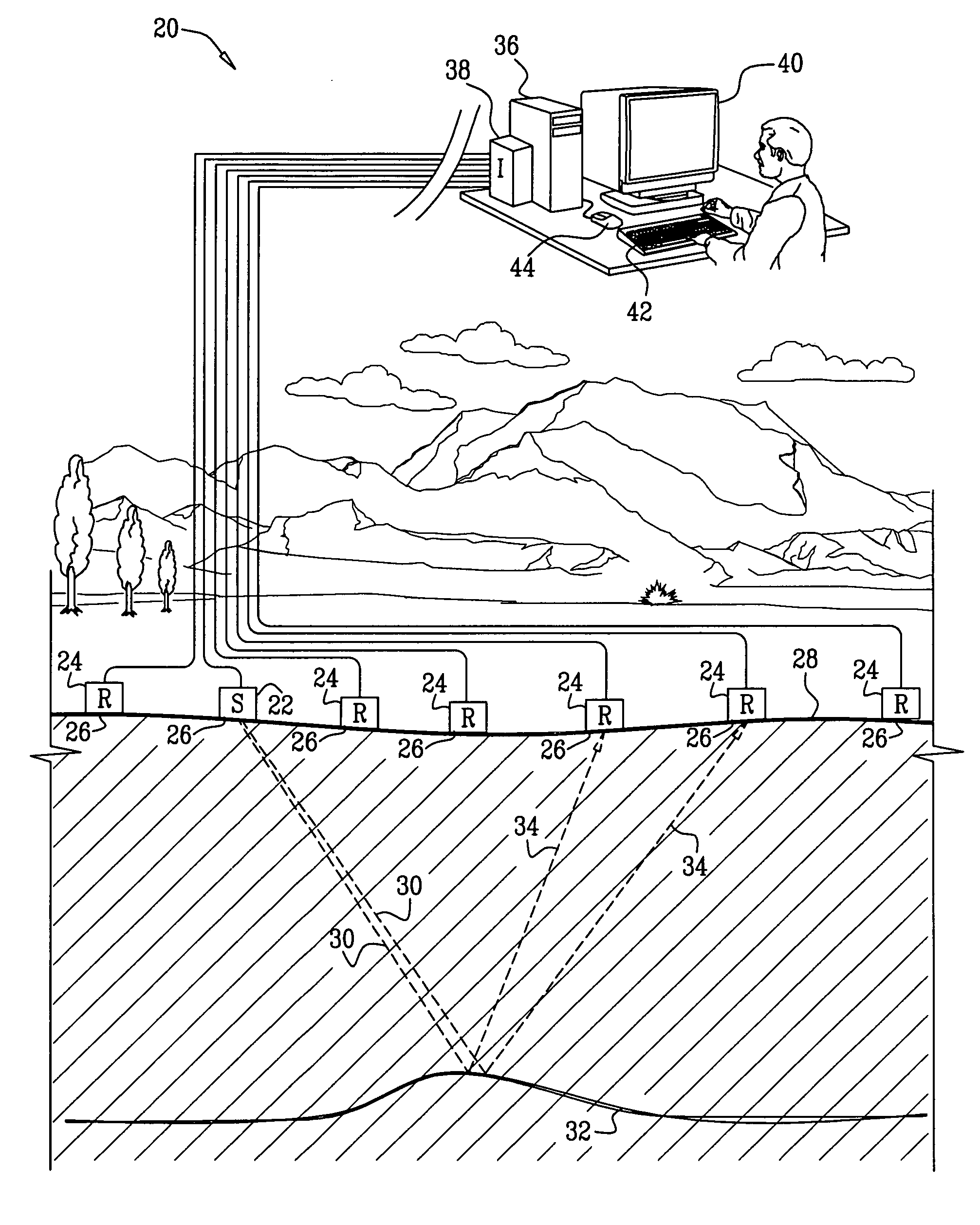
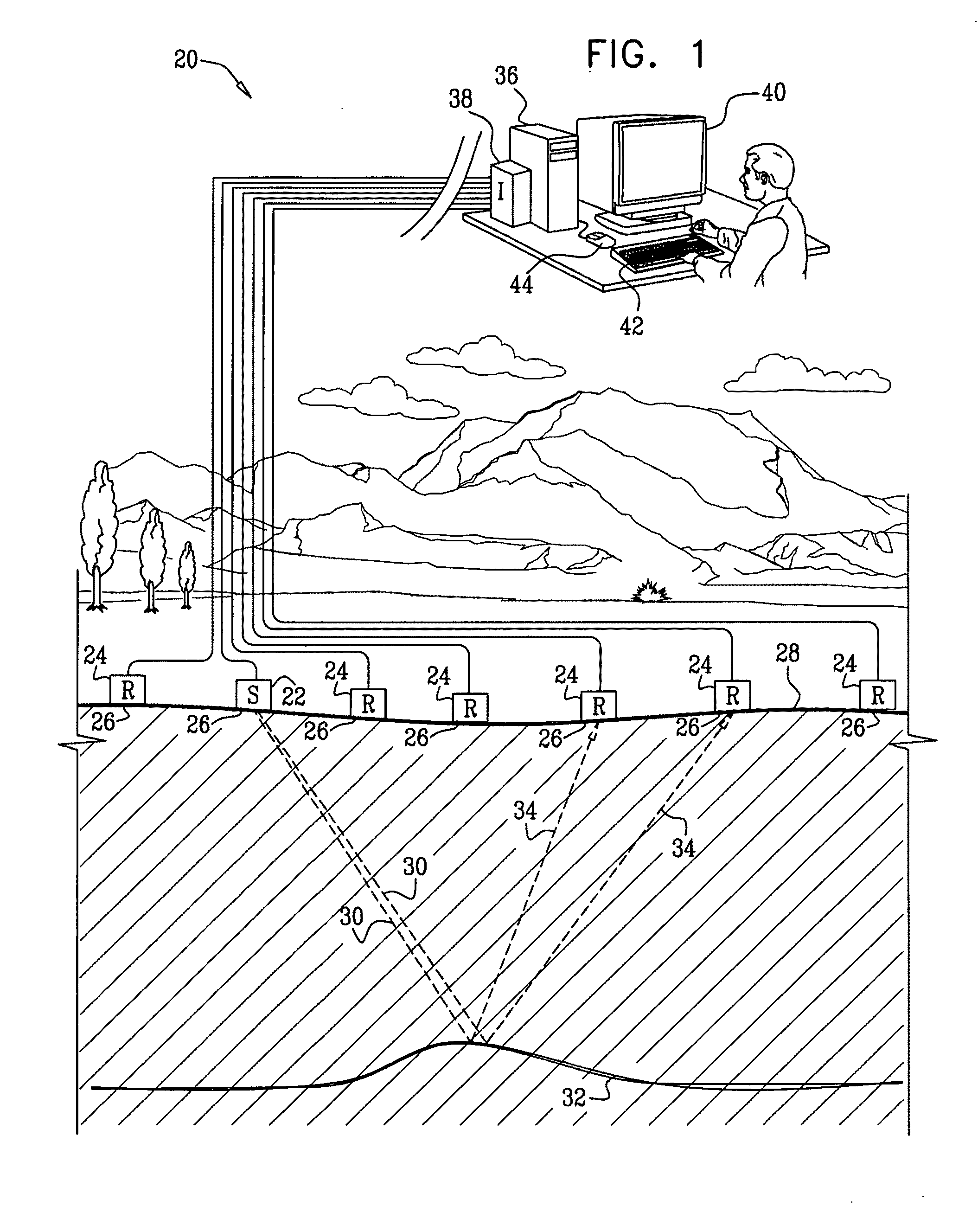
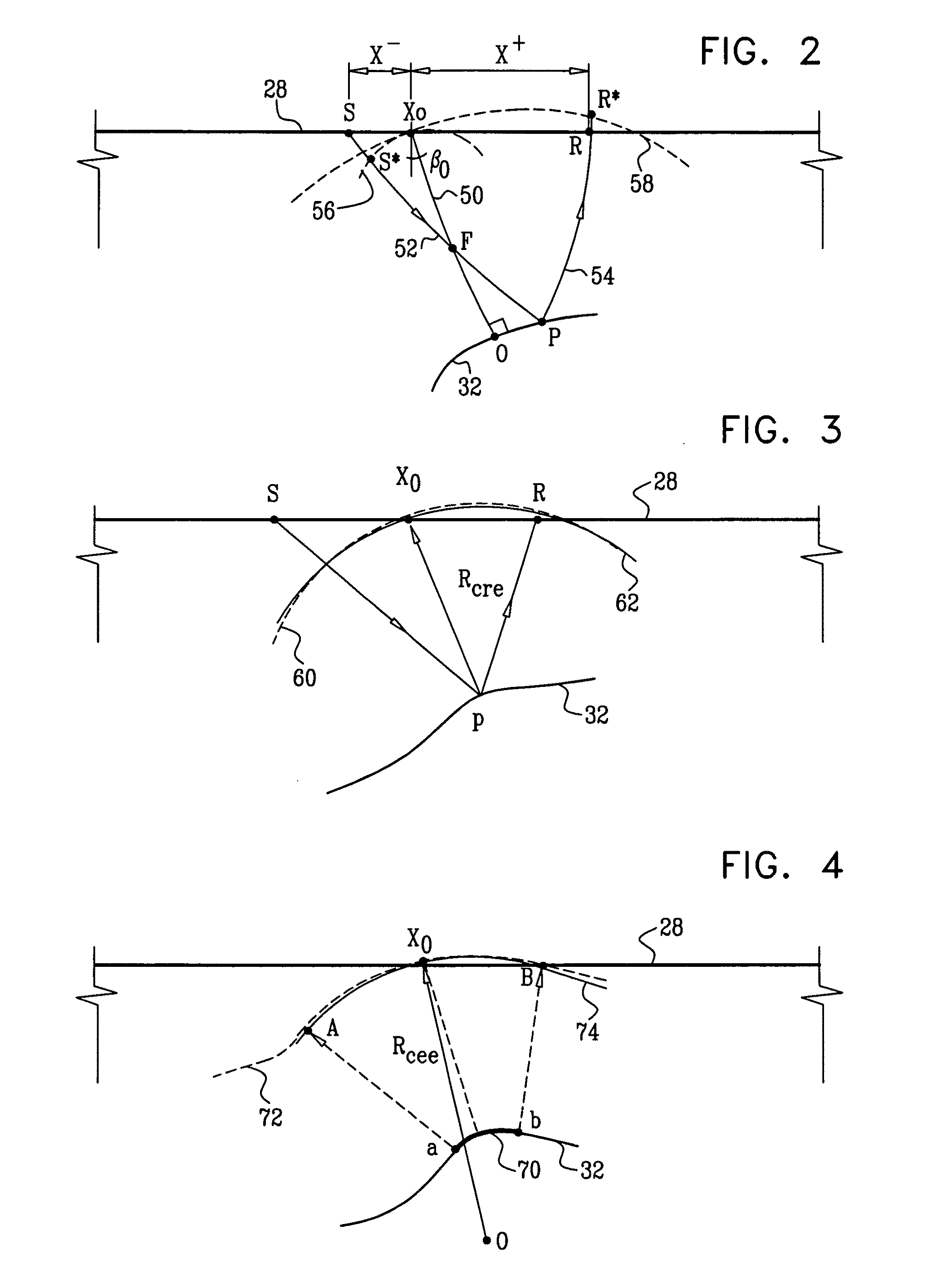
High accuracy depth domain prestack earthquake data inversion method
The invention relates to a pre stack seismic data inversion method of globe physical exploration high accuracy depth domain, which has the following steps: single shot records are collected; according to pre stack shot gather data and through radial line track or wave-field continuation focus, wave-field continuation focusing operators of all detecting wave points are pointed to and the focusing operator of each imaging point is obtained; the focusing operator and the single shot record are implemented in a migration aperture, and focus point shot gather corresponding to each shot is obtained; the focusing operator and common focus point gather are implemented cross correlation operation in time domain and space domain at the same time, and net point gather is obtained; the net point gather is implemented Radon transform, and CFP-AVP gather of corresponding imaging point is obtained; each imaging point gather is stacked, and the whole 2D document pre stack high accuracy analysis sectional plane is obtained. The CFP-AVP analysis in the invention has the advantages of wide application condition, reliable analysis sectional plane and sound effect of supercritical information inversion.
Owner:BGP OF CHINA NAT GASOLINEEUM CORP
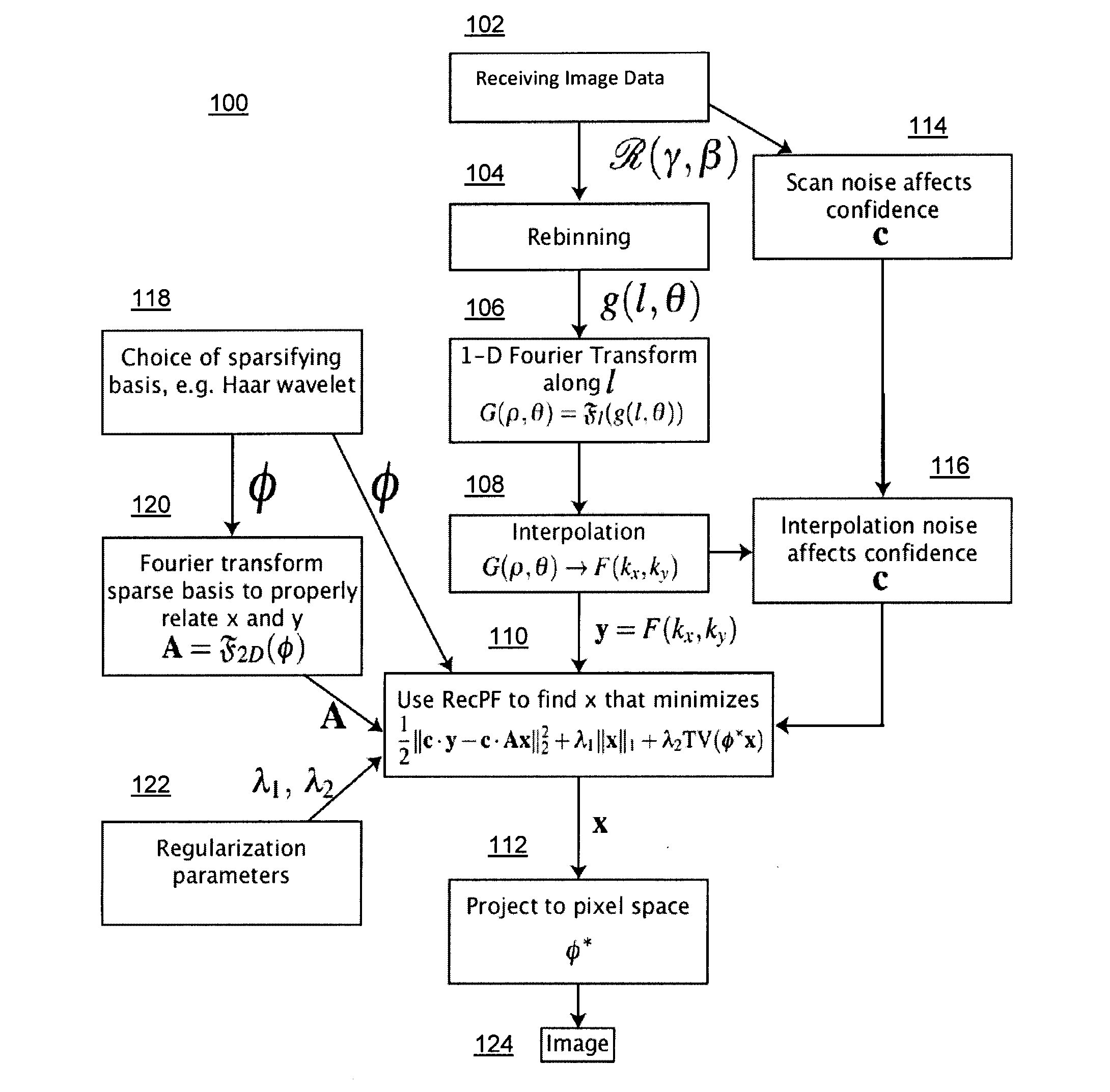
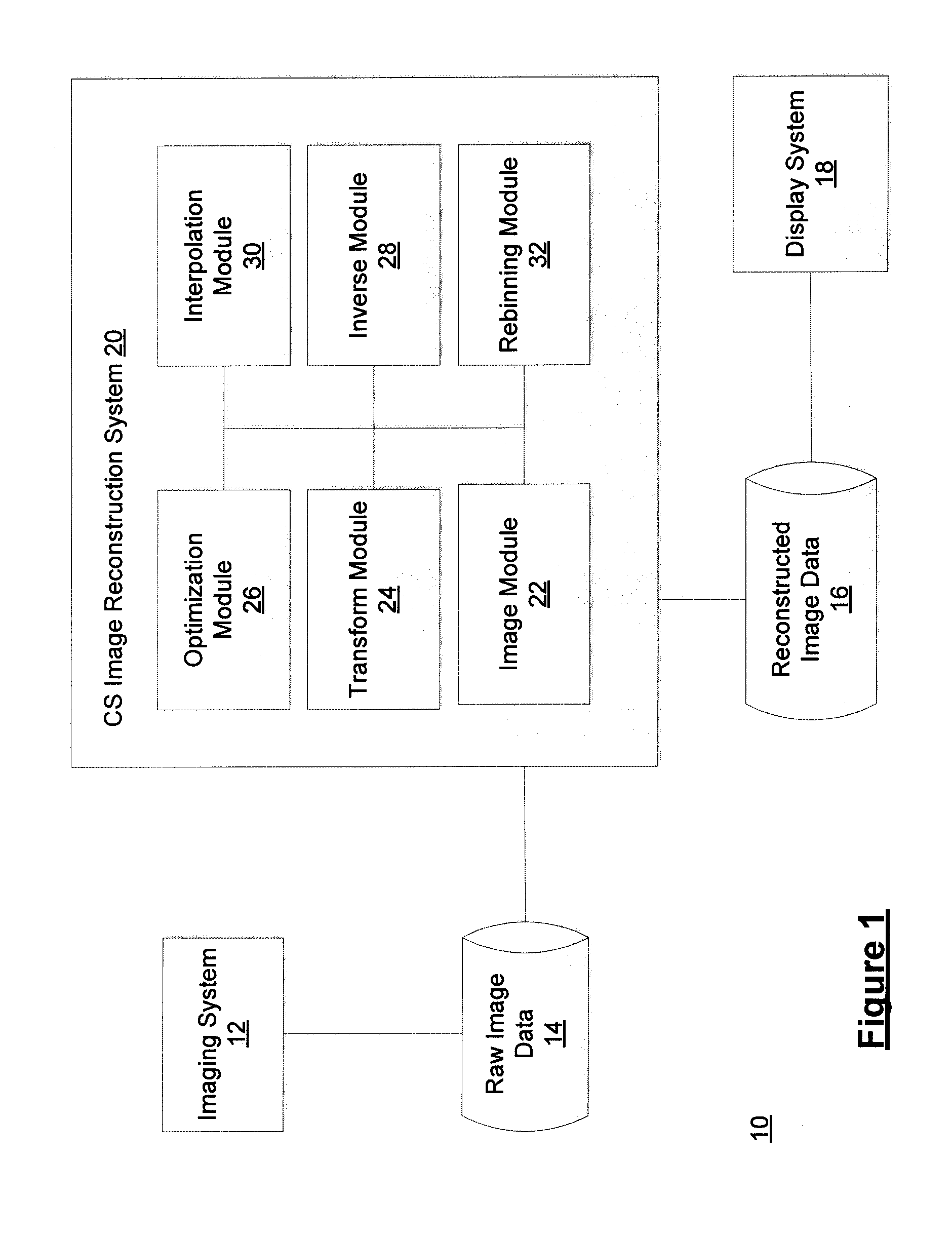
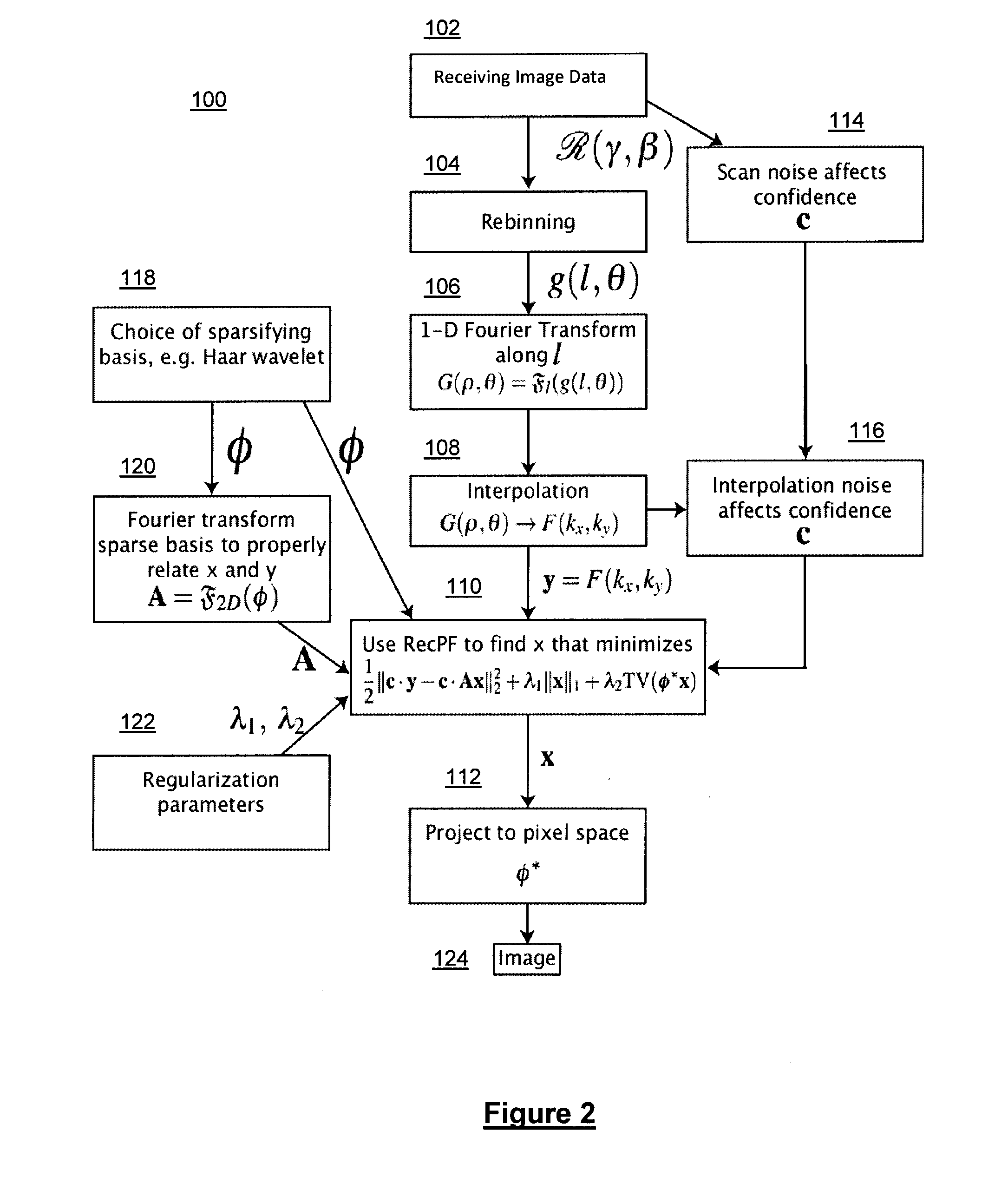
Method and system for compressed sensing image reconstruction
ActiveUS20150187052A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputation complexity
A Compressed Sensing (CS) based image reconstruction method and system is described herein which may be used to reduce the X-ray dose radiation in Computed Tomography (CT) or to decrease the scan duration in MR imaging (MRI). Methods and systems described herein may address problems that have hindered the clinical usage of CS, i.e. computation complexity and modeling problems. Using the described algorithm, high quality images may be recovered from undersampled data which may help to reduce the scan time and the exposed invasive radiations. Using the same set of data in conventional image reconstruction algorithms (e.g. Filtered Back Projection (FBP) in CT) may cause severe streak artifacts and may take significantly more time using Graphics Processing Units (GPU) and parallel clusters with the conventional CS-based methods. This method can be used other imaging modalities using Radon transform (such as C-Arm and electron tomography, for example).
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
True 3D cone-beam imaging method and apparatus
InactiveUS6865246B2Improve sampling performanceAccurate measurementReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadon transformRadiation attenuation
A three-dimensional image of an object scanned with a plurality of cone-beam projections from a number of source positions is reconstructed using a method wherein intermediate transform functions are obtained from two-dimensional images of radiation attenuation in the scanned object. The intermediate transform functions are then filtered over a set of parallel planes using a moving-frame technique. The second-order radial derivative of the Radon transform can then be backprojected to generate an intermediate, locally-reconstructed, three-dimensional image. After repetition of this process, the plurality of intermediate, locally reconstructed, three-dimensional images are summed to obtain an ultimate, reconstructed, three-dimensional image of the object. In particular embodiments, the source and detector are displaced along helical paths and radiation scans of the object are taken at multiple positions along the paths.
Owner:MIT TECH LICENSING OFFICE
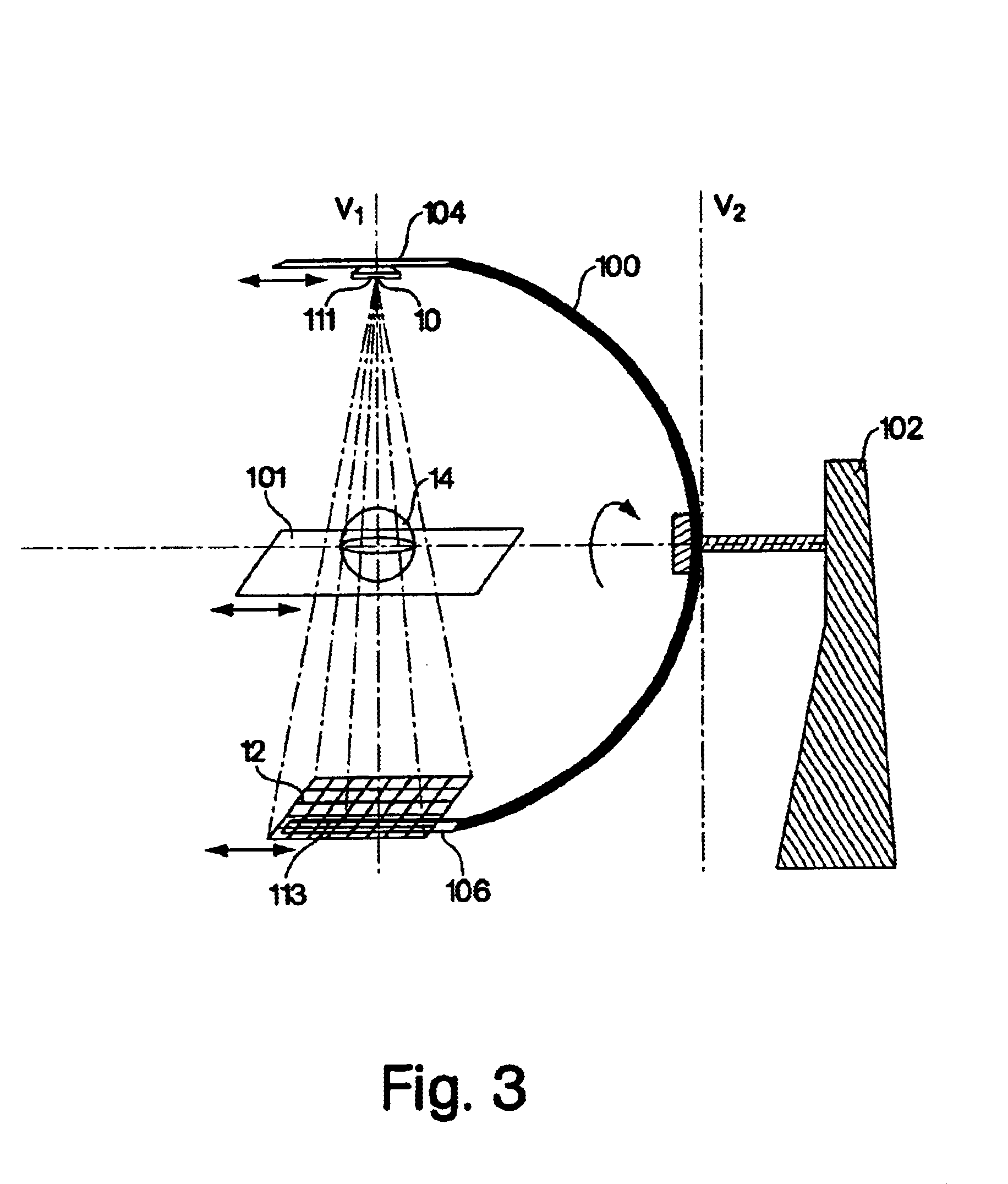
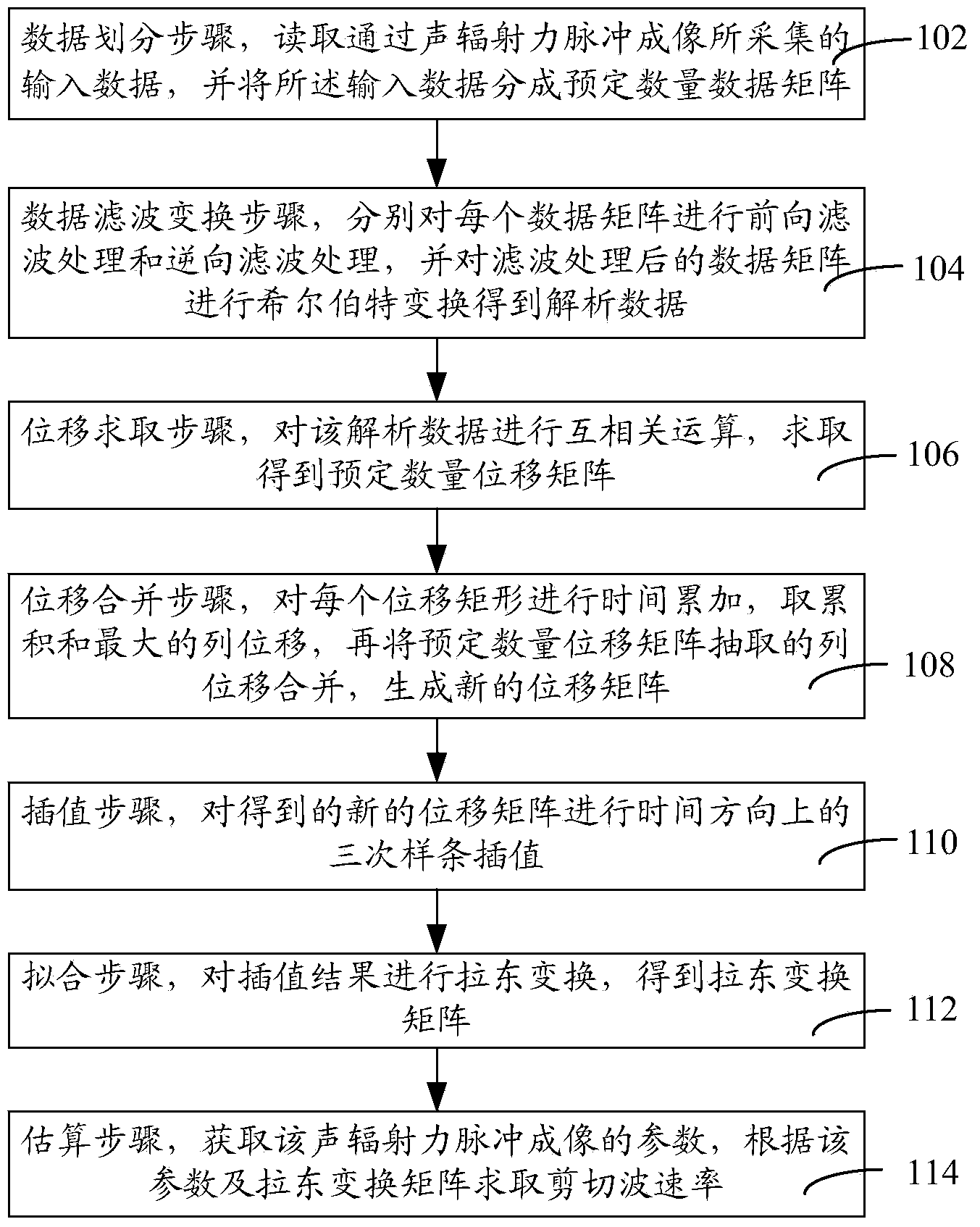
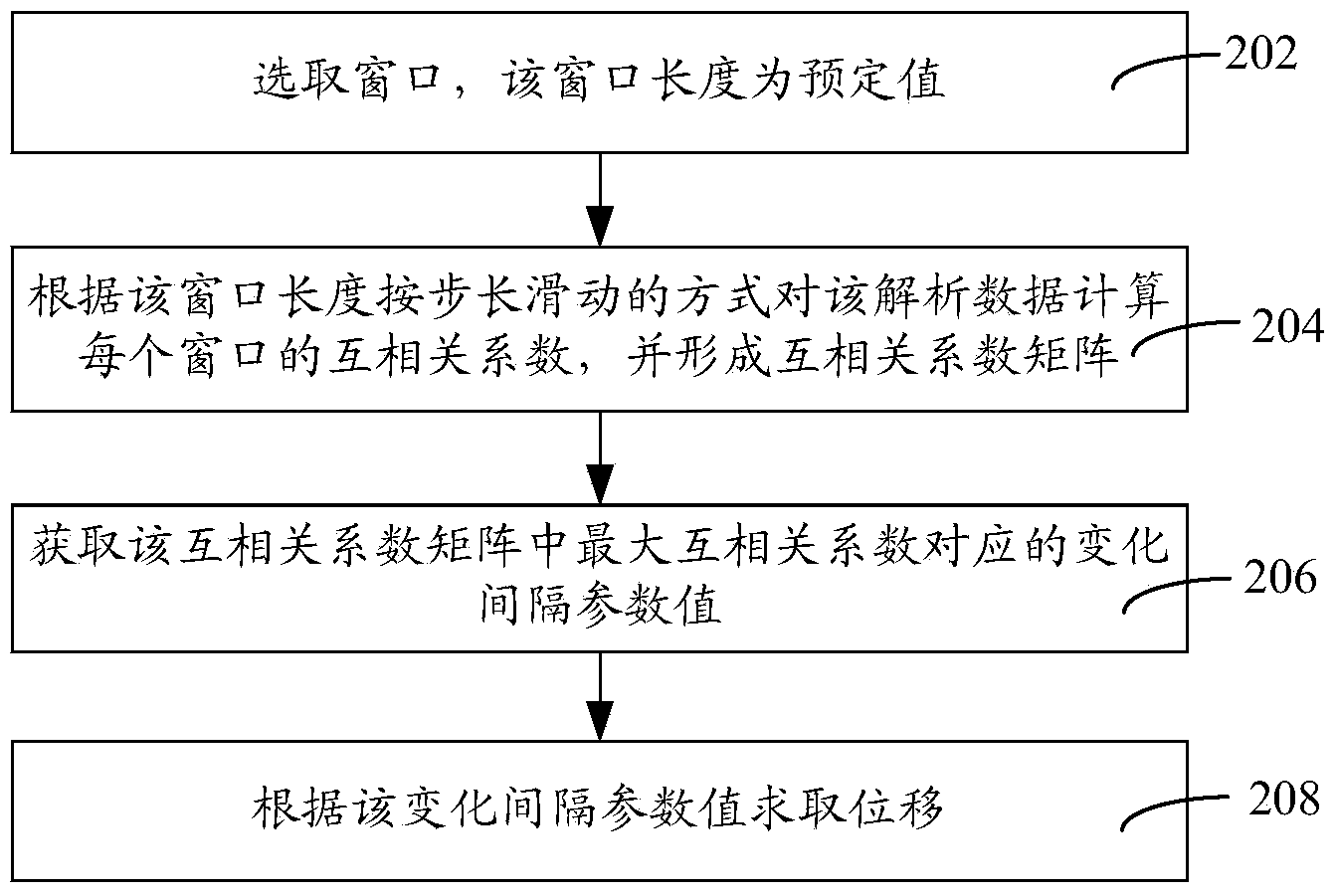
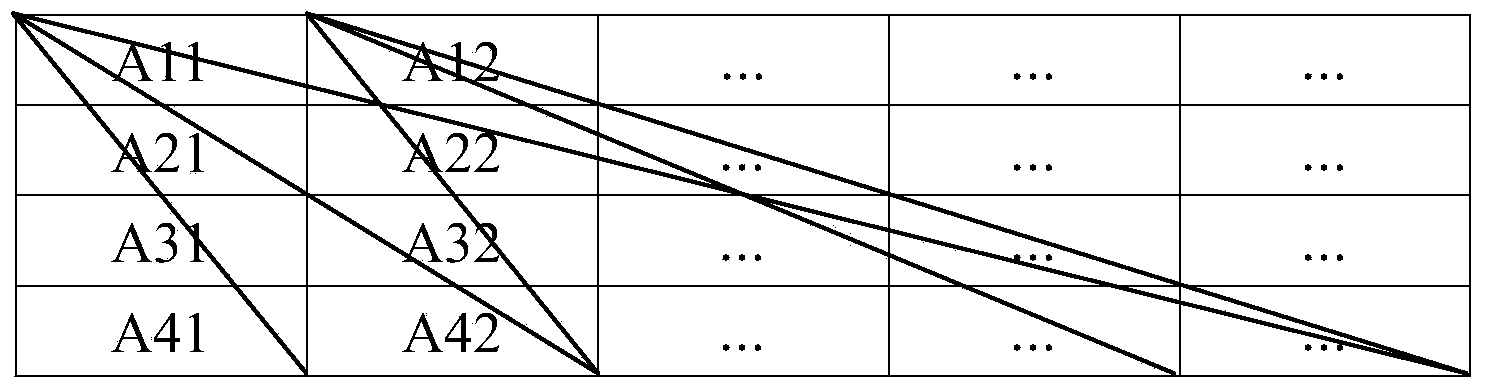
Method and system for estimating acoustic radiation force pulse imaging
ActiveCN103431874AAchieve a high degree of parallelismImprove efficiencyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsComputer scienceRadon transform
The invention relates to a method and a system for estimating acoustic radiation force pulse imaging. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: reading input data, and dividing the input data into a predetermined number of data matrixes; respectively carrying out forward filter processing and reverse filter processing on each data matrix, and carrying out Hilbert transform on the filtered data matrix to obtain analyzed data; carrying out cross-correlation algorithm on the analyzed data to obtain a predetermined number of displacement matrixes; accumulating various displacement matrixes, and obtaining a line displacement with the maximum accumulation sum to generate a new displacement matrix; carrying out spline interpolation on a new displacement matrix in the time direction three times; carrying out radon transform of an interpolation result to obtain a radon transform matrix; obtaining parameters of the acoustic radiation force pulse imaging, and obtaining the shear wave velocity according to the parameters and the radon transform matrix. According to the invention, errors generated by calculating displacement through cross-correlation are reduced; the calculation result is relatively accurate; furthermore, the infinitesimal displacement can be precisely estimated; the sensitivity is improved.
Owner:LEPU MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
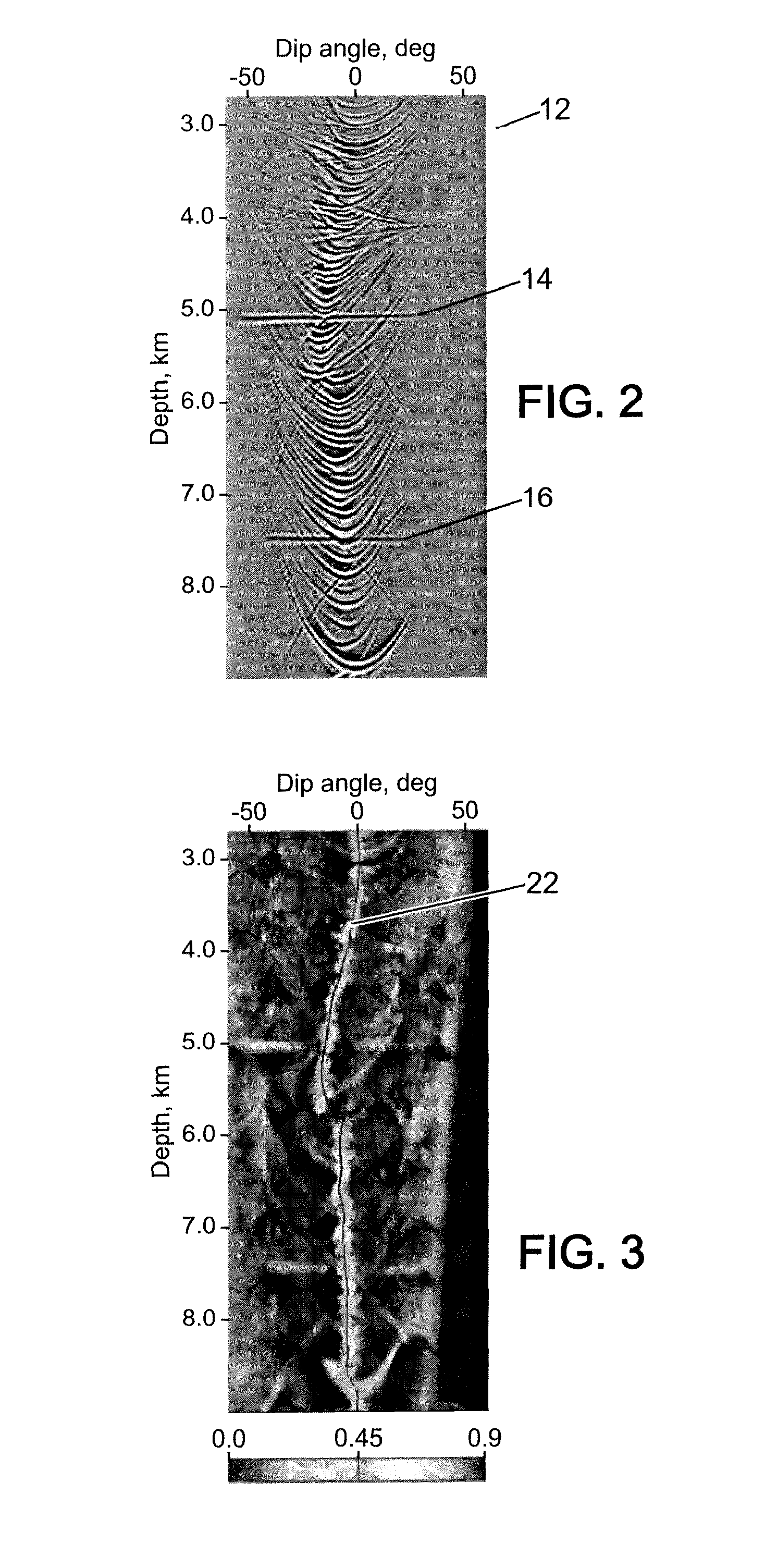
Wavefront-defined radon transform
ActiveUS20090248313A1Improve image qualityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingWavefrontImaging quality
A computer-implemented method for processing data includes accepting a first collection of traces corresponding to signals received over time due to reflection of seismic waves from subsurface structures. A Radon transform is defined with respect to a set of wavefront parameters of the seismic waves. The transform defines a summation of amplitudes of the seismic waves over trajectories defined by the wavefront parameters.The Radon transform is applied to the first collection of traces, so as to convert the first collection into a multidimensional data array that is defined as a function of at least two of the wavefront parameters. The multidimensional data array is processed to produce a second collection of traces having an improved imaging quality with respect to the first collection. The second collection of traces is processed to generate a seismic image of the subsurface structures at the improved imaging quality.
Owner:GEOMAGE 2003
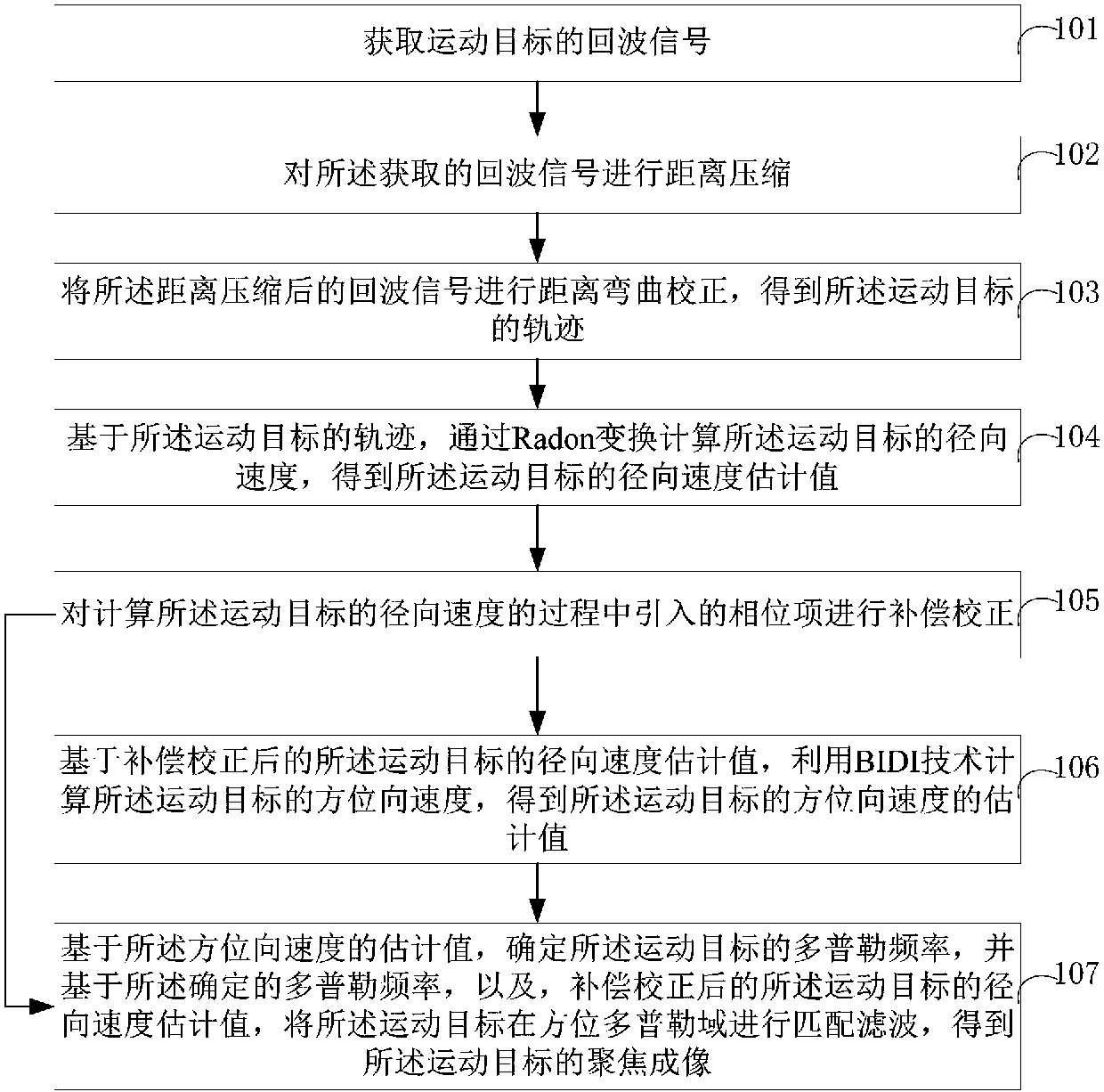
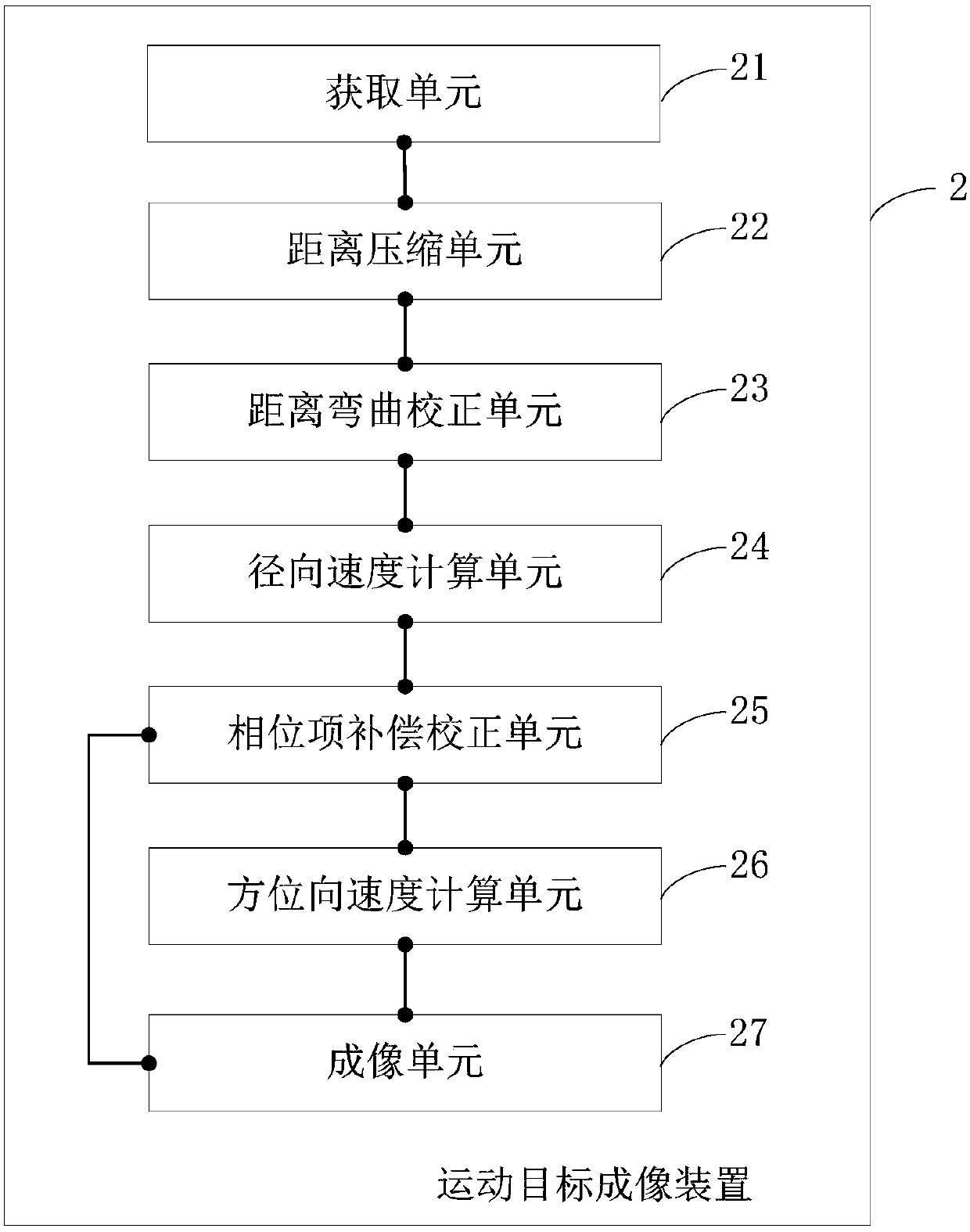
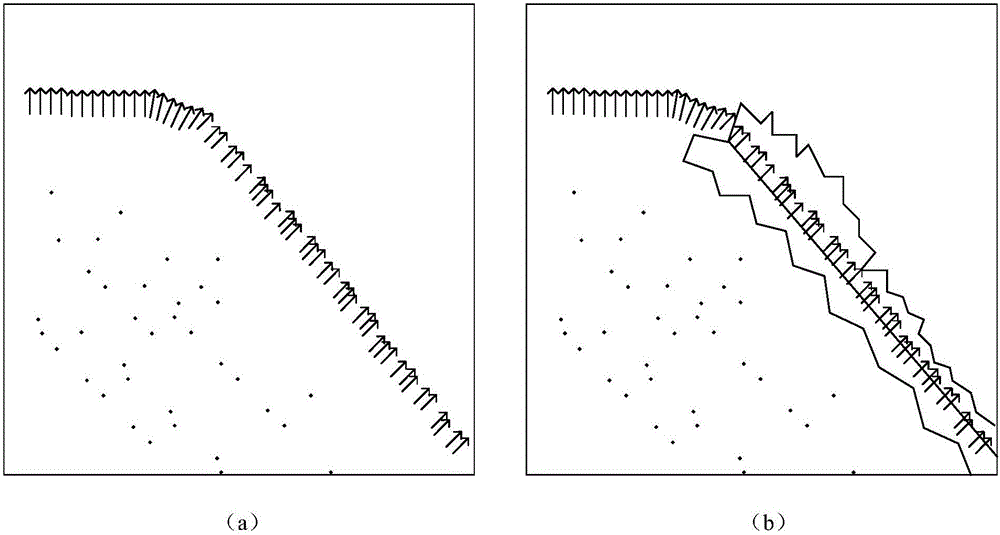
Radon transform-based moving object imaging method, device and electronic device
ActiveCN108051809AImprove accuracySolve the problem of azimuth sidelobe asymmetryRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarRadon transform
The present invention belongs to the radar identification technological field and provides a Radon transform-based moving object imaging method, a Radon transform-based moving object imaging device, an electronic device, and a computer-readable storage medium. The imaging method includes the following steps that: the echo signals of a moving object are obtained; distance compression is performed on the acquired echo signals; distance bending correction is performed; the radial velocity of the moving target is calculated through Radon transform; a phase term introduced into a calculation process is compensated and corrected; and the azimuth velocity of the moving target is calculated through using a BIDI technique; and matched filtering is performed on the moving target in the azimuth Doppler domain, so that the focused imaging of the moving target can be obtained. With the imaging method of the invention adopted, the accuracy of the positioning and imaging result of the moving target can be improved.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TIEDAO UNIV
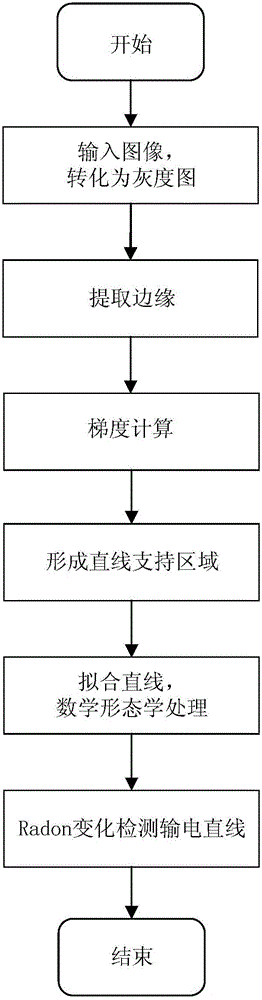
Unmanned aerial vehicle vision wire patrol method based on gradient constraint Radon transform
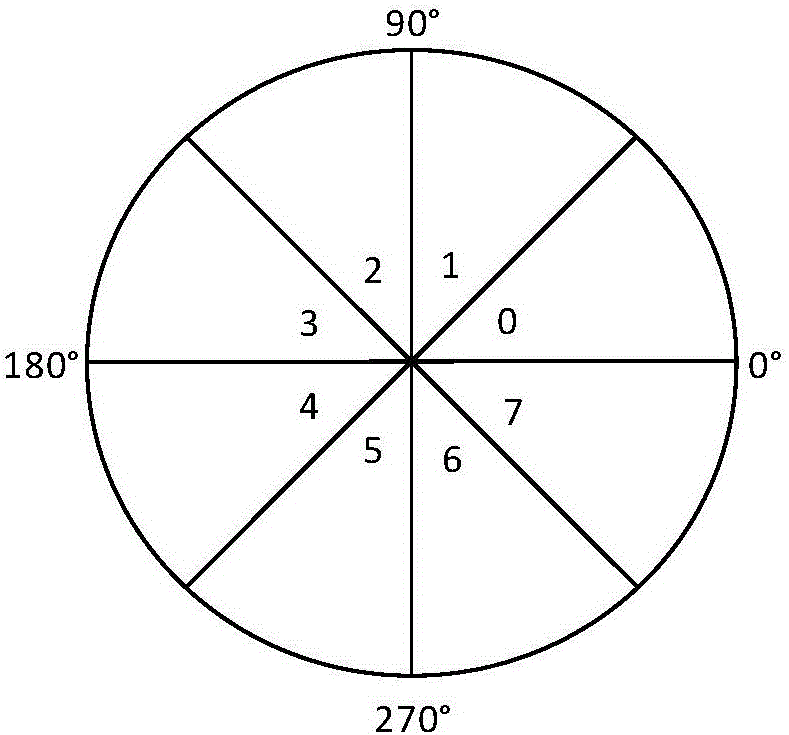
InactiveCN106056619AHigh resolutionAccurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisEdge extractionHigh tension line
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle vision wire patrol method based on gradient constraint Radon transform. The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining a high-voltage line image to be processed by utilizing an unmanned aerial vehicle image acquisition device and converting the obtained degraded image into a grayscale image F; 2) carrying out edge extraction on the grayscale image F to obtain an edge image F'; 3) carrying out gradient calculation on the edge image F' to obtain gradient magnitude Gk; 4) setting eight direction pixel points of the kth pixels in the edge image F' being ki, wherein i=0,1,...,7, and when the gradient magnitudes Gk of the adjacent two pixels ki are same, grouping the pixels to the same line support region; 5) for the line support region obtained in the step 4), carrying out fitting to obtain a straight line according with conditions, and carrying out follow-up processing on the fit straight line through mathematical morphology; and 6) detecting a power transmission line through Radon transform according to the fitting result obtained in the step 5). The method realizes detection accuracy of the power transmission line in the image, removes redundant edge information and improves accuracy of power transmission line identification.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
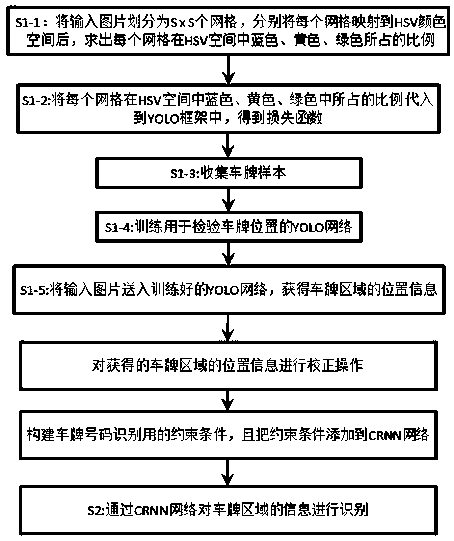
A license plate detection method based on depth learning
ActiveCN109271991AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed real-timeCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPattern recognitionMonitor equipment
The invention provides a license plate recognition method based on depth learning, which can self-adaptively obtain license plate characteristic information under different scenes, and simultaneouslyimproves the accuracy rate of license plate recognition. The invention adds the inherent color attribute of the license plate into the YOLO model to construct a license plate detection model with strong generalization ability and high detection and positioning accuracy, detects the passing picture taken by the input bayonet monitoring device, and obtains the area position of the license plate. Then, the inclined license plate area is corrected by Radon transform, and the license plate area is fine-tuned by color and edge. Finally, the fine-tuned license plate area is sent to CRNN network whichis constrained by license plate coding rules to recognize the license plate number.
Owner:TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT RES INST OF THE MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Nuclear imaging system using rotating scintillation bar detectors with slat collimation and method for imaging using the same
ActiveUS20050285042A1Maximizing geometric efficiencyMaximize efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographySingle photon imagingSpins
A gamma camera having a scintillation detector formed of multiple rotating bar detector modules arranged in a ring configuration, with synchronized spin motion of each module. Such a camera can be used for both PET (coincidence) and single photon imaging applications. Image reconstruction is obtained using either an inverse 3-D Radon transform or a 3-D fan-beam algorithm.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Imaging auto shutter roi
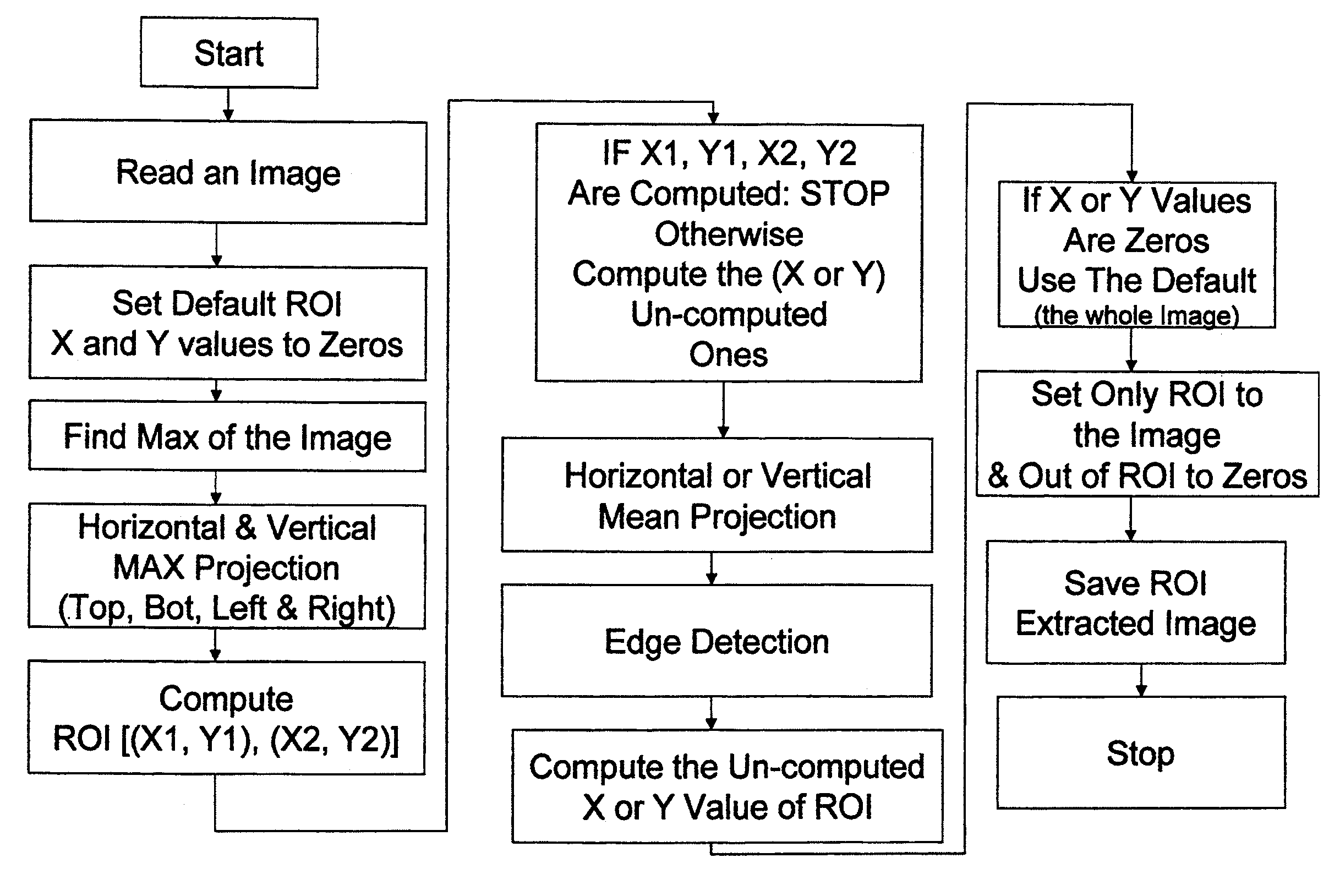
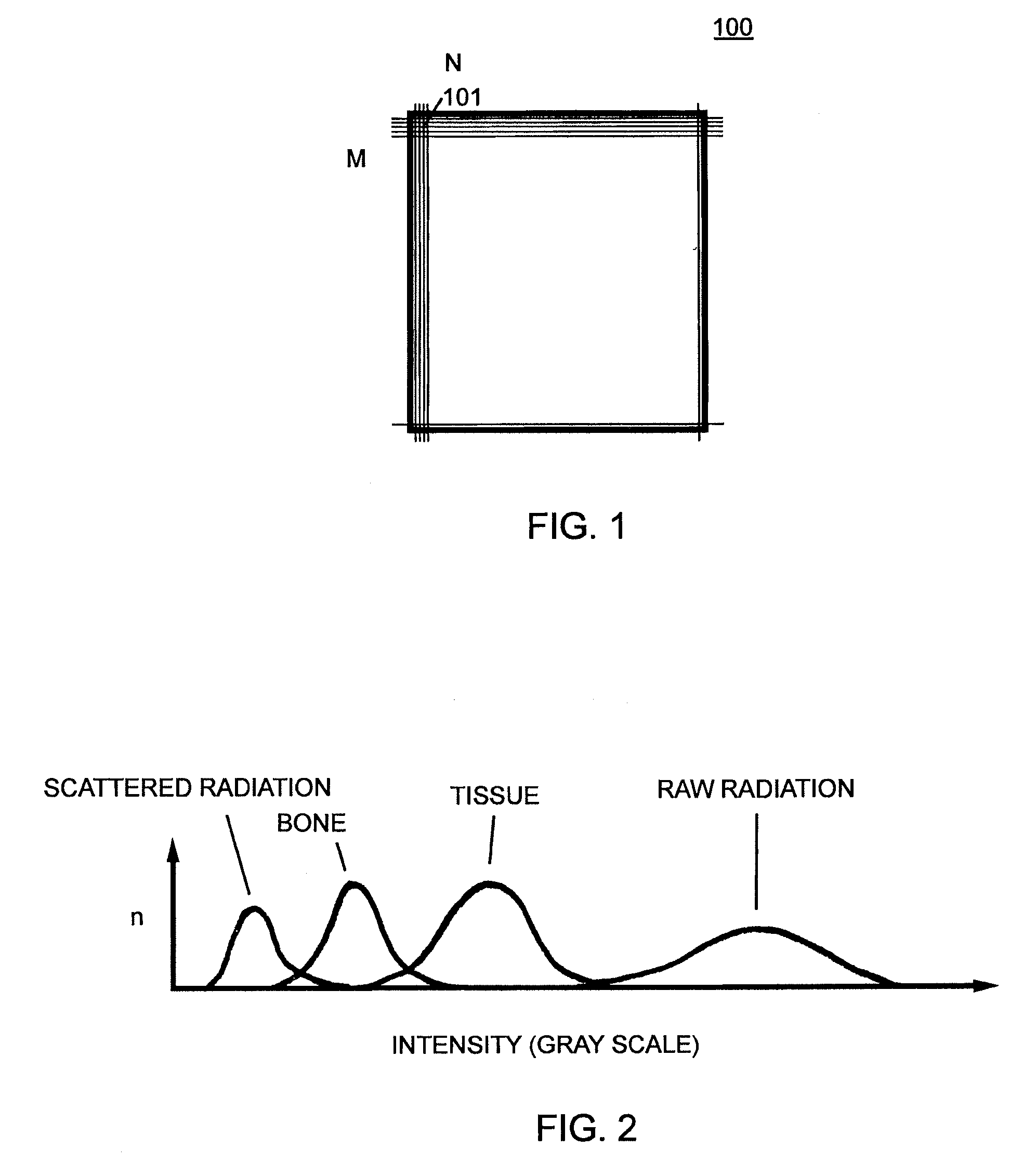
A method to identify a Region Of Interest (ROI) within an image includes the steps of: reading a digital image; finding predetermined brightness values; analyzing lines near a plurality of outer edges of the digital image; identifying an entire area of the digital image as the ROI if the found brightness values are also found in lines near the plurality of outer edges of the digital image; computing Radon transforms to generate one dimensional (1D) projections of the digital image if the found brightness values are not found in the lines; detecting a set of edges within the 1D projections; selecting edges from the set of edges; validating the selected edges to identify a set of validated edges; computing the ROI from the set of validated edges of the 1D projections; and saving the computed ROI to memory. A system to perform the method is also described.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Dispersion extraction for acoustic data using time frequency analysis
This invention pertains to the extraction of the slowness dispersion characteristics of acoustic waves received by an array of two or more sensors by the application of a continuous wavelet transform on the received array waveforms (data). This produces a time-frequency map of the data for each sensor that facilitates the separation of the propagating components thereon. Two different methods are described to achieve the dispersion extraction by exploiting the time frequency localization of the propagating mode and the continuity of the dispersion curve as a function of frequency. The first method uses some features on the modulus map such as the peak to determine the time locus of the energy of each mode as a function of frequency. The second method uses a new modified Radon transform applied to the coefficients of the time frequency representation of the waveform traces received by the aforementioned sensors. Both methods are appropriate for automated extraction of the dispersion estimates from the data without the need for expert user input or supervision.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus of using a neural network to train a neural network
A method and apparatus of training a neural network. The method and apparatus include creating a model for a desired function as a multi-dimensional function, determining if the created model fits a simple finite geometry model, and generating a Radon transform to fit the simple finite geometry model. The desired function is fed through the Radon transform to generate weights. A multilayer perceptron of the neural network is trained using the weights.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Methods and systems for processing a first image with reference to a second image
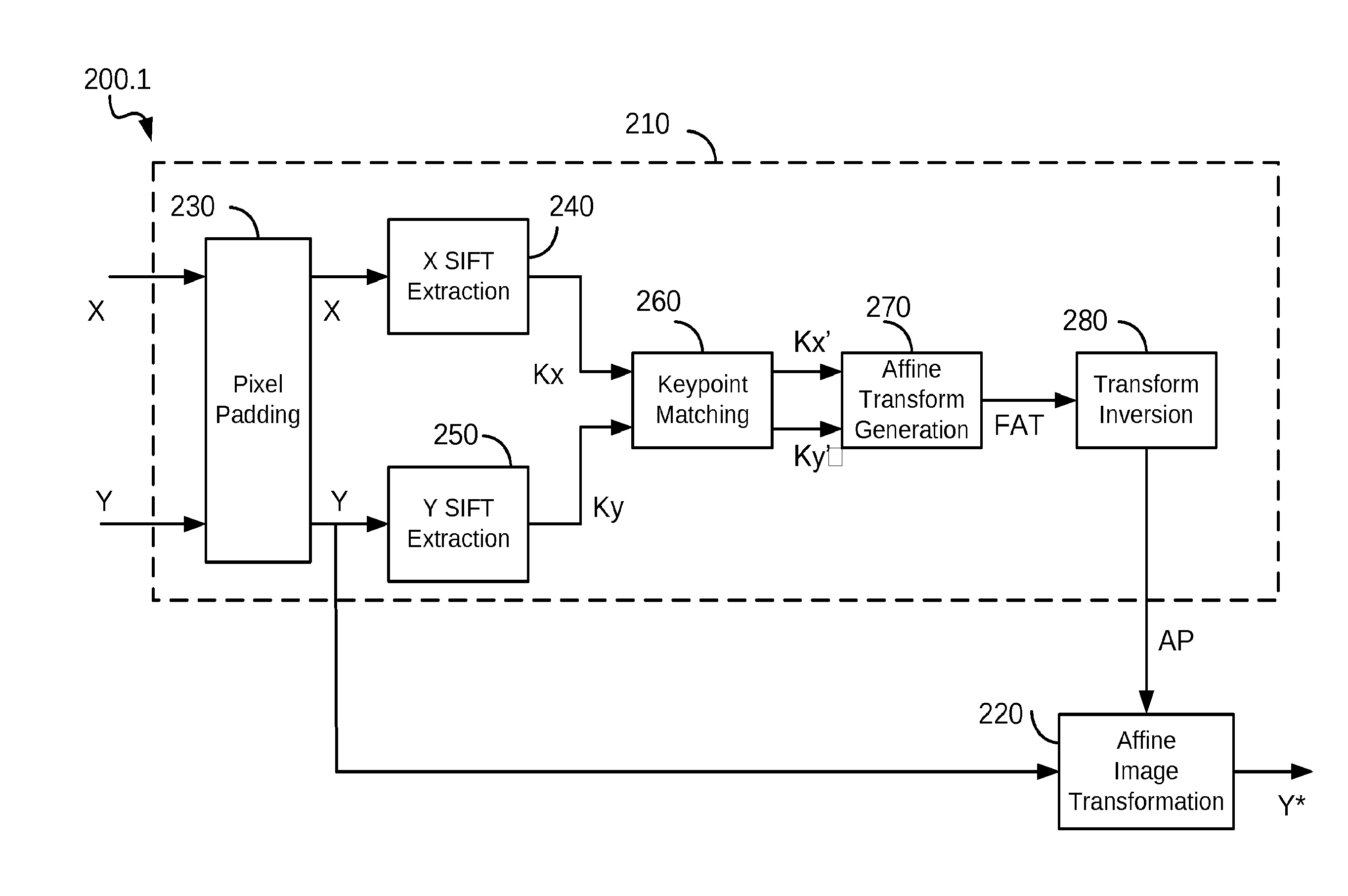
ActiveUS20130272627A1PowerfulImage analysisGeometric image transformationFast Fourier transformComputer graphics (images)
An image registration method is disclosed for processing a distorted image into a registered image that is aligned with reference to an original image. Distortions from the original image may include scaling, rotation, and noise. The method is based on correlating Radon transforms of both images to determine the rotation angle, and the scaling factor is determined by dividing averages of the overall luminance of each image on the assumption that any added noise will cancel. The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is used to estimate global spatial shifts. In one embodiment, the distorted image is first scaled to the size of the original image before being rotated. In another embodiment, the original image is first scaled to the size of the distorted image before rotating the distorted image, and finally scaling it to match the original image. A corresponding system for image registration is also provided.
Owner:ECOLE DE TECH SUPERIEURE
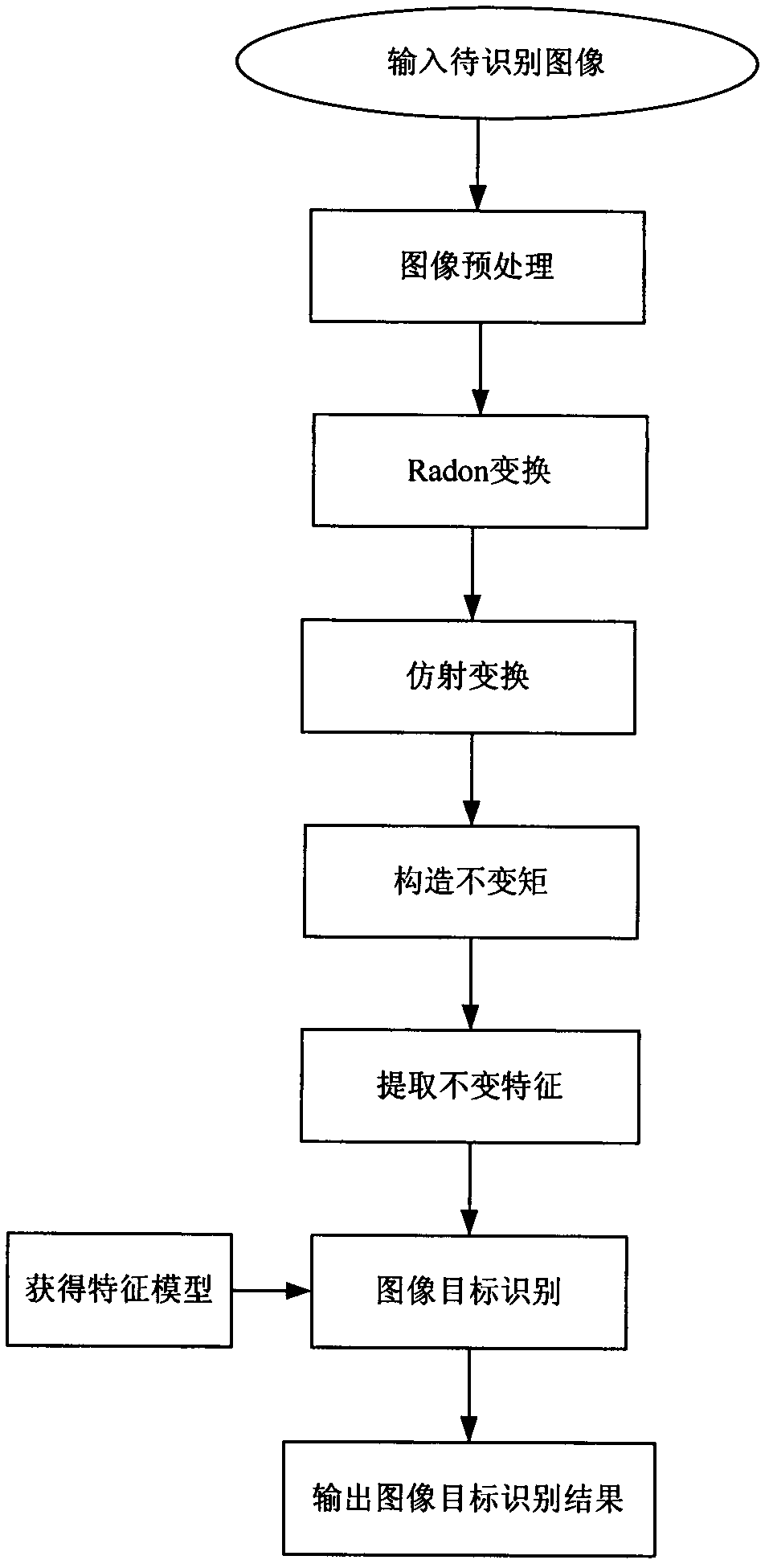
Invariant-moment target recognition method based on Radon transformation and polar harmonic transformation
InactiveCN102324045ASolve noise interferenceEmbody authenticityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionGoal recognition
The invention discloses an invariant-moment target recognition method based on Radon transformation and polar harmonic transformation, which comprises the steps of: 1) inputting an image to be recognized; 2) preprocessing the image; 3) conducting the Radon transformation; 4) conducting affine transformation; 5) constructing invariant moments; 6) extracting invariant features; 7) constructing a feature model; 8) conducting image target recognition; and 9) outputting an image target recognition result. By adopting the method, three new invariant moments, i.e. a Radon complex exponential invariant moment, a Radon sine and cosine invariant moment and a polar complex exponential invariant moment real and imaginary invariant moment are successfully constructed. By extracting the real part and the imaginary part of the invariant moments as the invariant features, the problem of noise interference can be effectively solved, the reality of the image can be better reflected and the accuracy of the image target recognition can be improved. The method disclosed by the invention has better applicability and stability, and can improve the overall performance of the invariant moments and the applicability and stability of the image target recognition.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Notch defect detection method for flexible IC package substrate line
ActiveCN108918526APrecise positioningEasy to detectOptically investigating flaws/contaminationBoundary contourLine width
The invention discloses a notch defect detection method for a flexible IC package substrate line. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining target prior knowledge; extracting a boundary contour of a line of a flexible IC package substrate image to be detected to obtain a contour map; using the target prior knowledge as the constraint condition of Radon transform to carry out Radon transform on the contour map, extracting the boundary line in the contour map, and calculating a standard line width or a standard line space between the contours through the boundary line; determining a notch defect on the contour and a curve portion on the contour by aiming at each contour in the contour map; comparing the distance between each pixel point in the curve portion of each contour and thecurved portion of the next contour with the standard line space or the line width between the contour and the next contour, and determining whether the pixel point in the curve portion of the contourhas the notch defect or not according to the comparison result. The method can accurately and quickly detect the notch defects of the linear portion and the curve portion.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
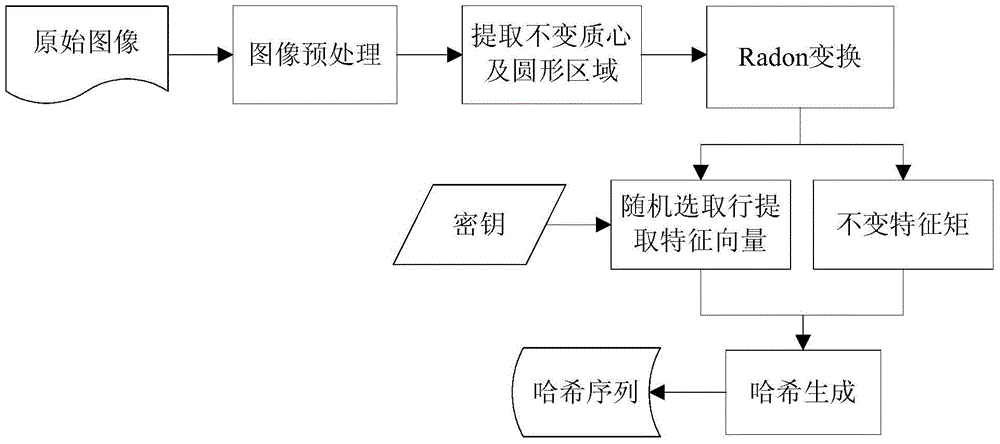
Robust image hashing method and device based on Radon transformation and invariant features
InactiveCN104091303AReduce computational complexityMeet robustness requirementsImage data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityCentroid algorithm
The invention relates to a robust image hashing method and device based on Radon transformation and invariant features, and belongs to the field of information safety. In terms of the problem that hashing cannot resist geometric attacks well, normalized preprocessing operation is carried out on images firstly, invariant feature points are generated by utilizing an unchanged centroid algorithm, the circular area around an unchanged centroid is selected, Radon transformation is carried out on the circular area to generate a coefficient matrix, multiple lines of coefficients are selected randomly from a transformation domain by utilizing a chaotic system, robust features of each line are extracted, the features of all lines are combined with the invariant moment features of the whole matrix to generate image hashing, and similarity comparison is carried out by utilizing Euclidean distance. By the adoption of the robust image hashing method and device based on the Radon transformation and invariant features, the problem that the false drop rate rises due to geometric attacks can be solved effectively; the problems that computation complexity is too high and hashing is too long can be solved according to hashing steps and hashing lengths. The method and device can be applied to the field of image content authentication, and can also be applied to image retrieval, image identification and other information safety fields.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
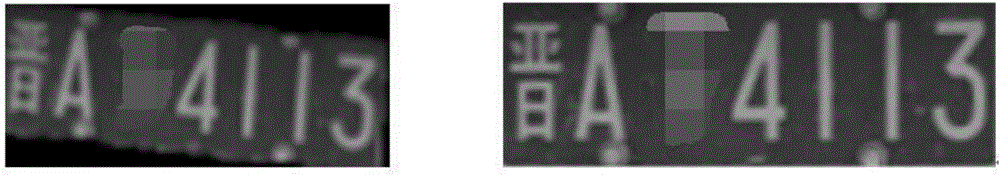
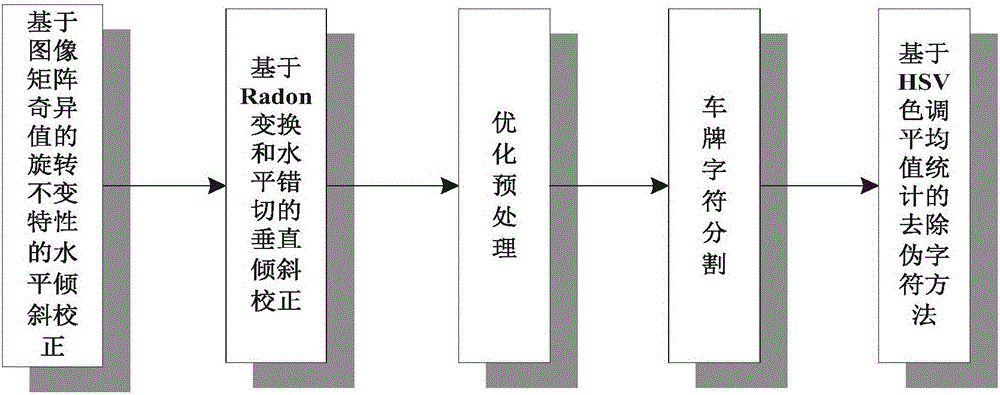
Variable-length license plate character segmentation method based on hybrid tilt correction and projection method
InactiveCN106529534AOptimizing Binarized ImagesEffective correctionCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageImage segmentation
The invention, which relates to the computer vision field, provides a variable-length license plate character segmentation method based on hybrid tilt correction and a projection method. The method comprises the following steps that: horizontal license plate correction is carried out by using rotation invariance of a singular value of an image matrix and vertical license plate correction is carried out based on a Radon transform and horizontal shearing principle, thereby completing hybrid tilt correction of the license plate effectively and rapidly; various optimization pretreatment is carried out before license plate character segmentation, wherein image gray processing based on a weighted average method, elimination of license plate background non-character interference regions at the left side and the right side of the license plate based on license plate left-right boundary positioning, improved binary processing operation by combination of a global threshold value, a local threshold and an RGB color image, and binary image optimization based on a morphological method are carried out for optimization pretreatment; character image segmentation is carried out by using H-S connected domain analysis and projection methods; and then pseudo characters are eliminated by using a hue average statistical method of HSV space.
Owner:HUNAN VISION SPLEND PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Method for analyzing seismic data
InactiveUS8948463B2Robust methodScene recognitionSeismic signal processingImaging FeatureAnalysis method
Owner:TOTAL PUTEAUX FR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com