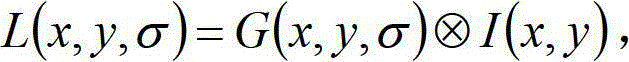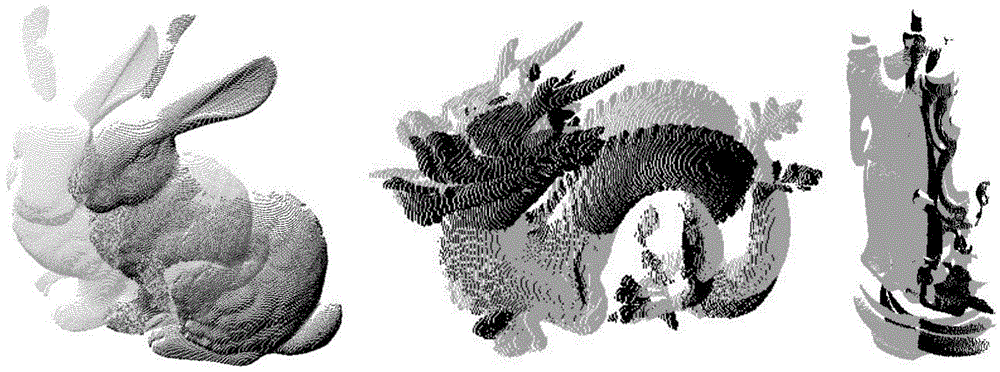Patents
Literature
1010 results about "Feature descriptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
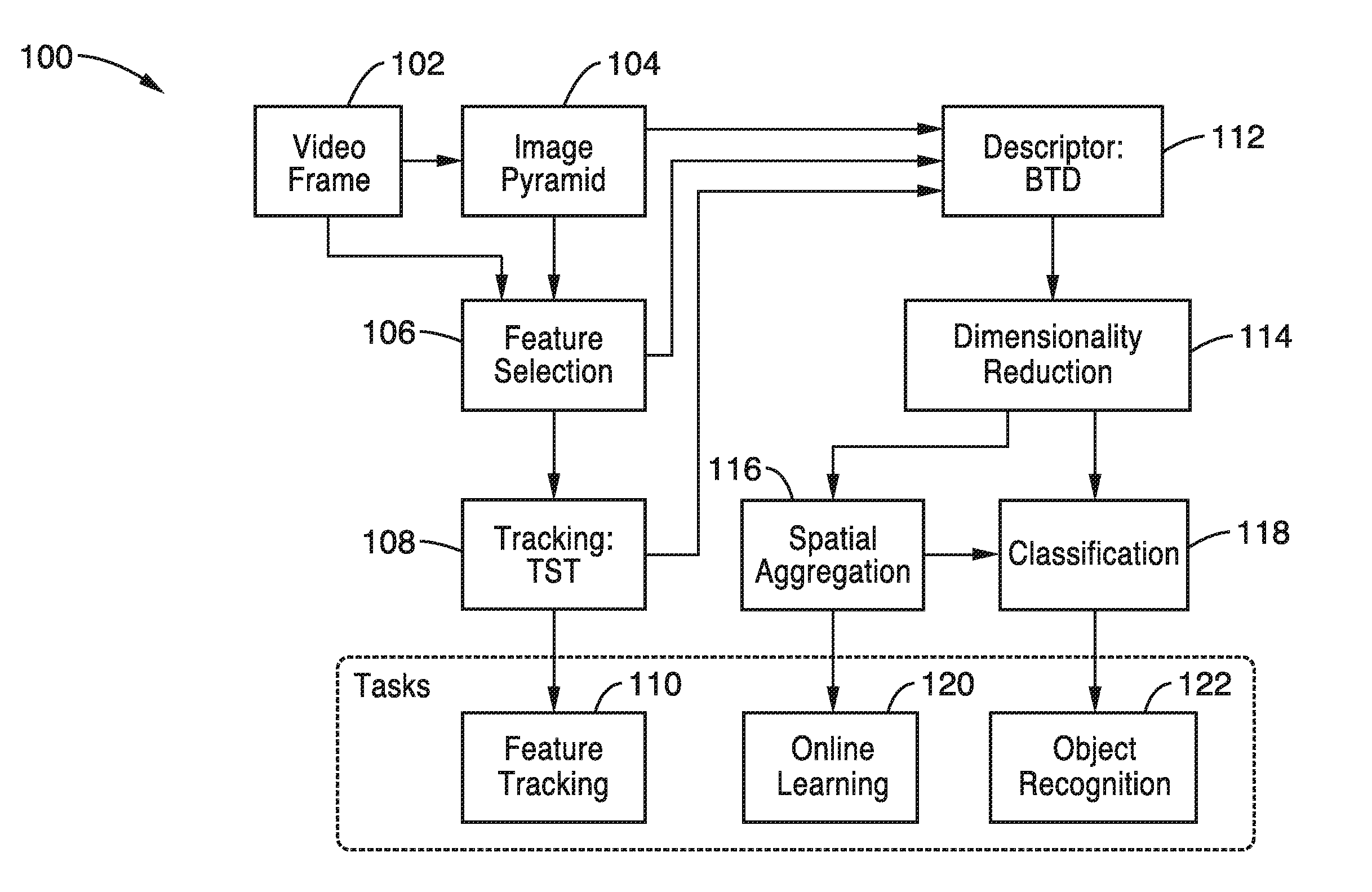
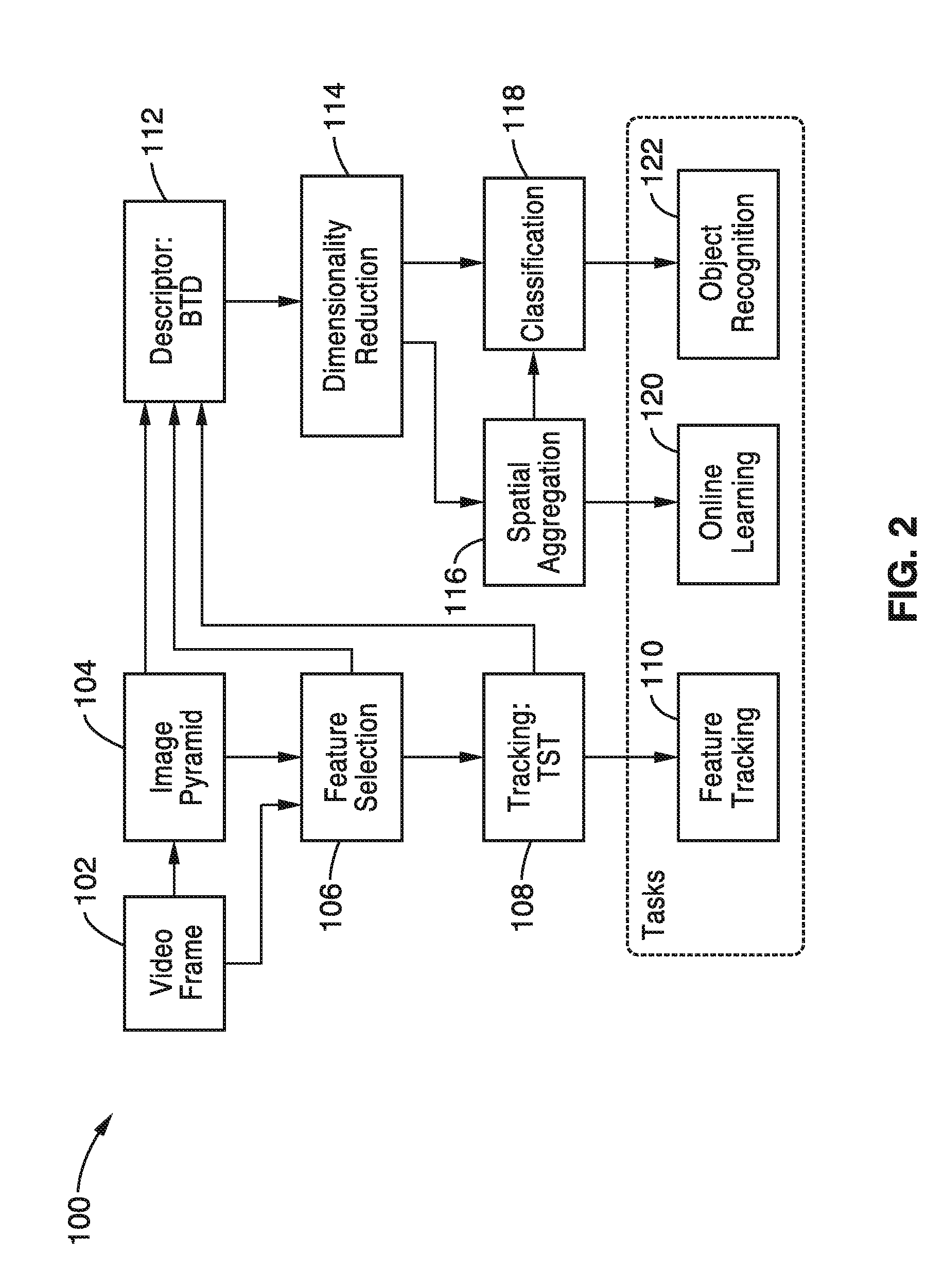
A feature descriptor is an algorithm which takes an image and outputs feature descriptors/feature vectors. Feature descriptors encode interesting information into a series of numbers and act as a sort of numerical "fingerprint" that can be used to differentiate one feature from another.
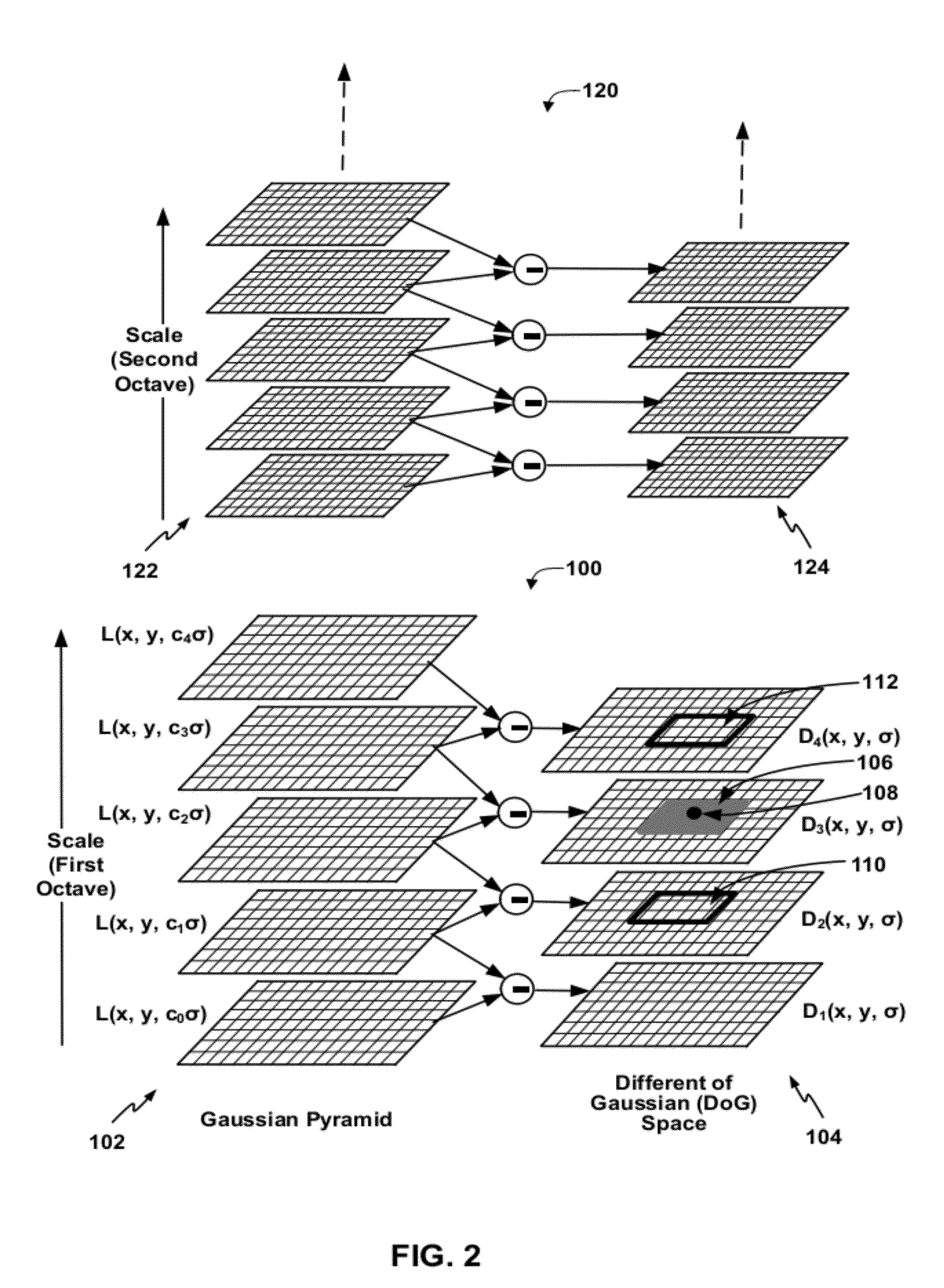
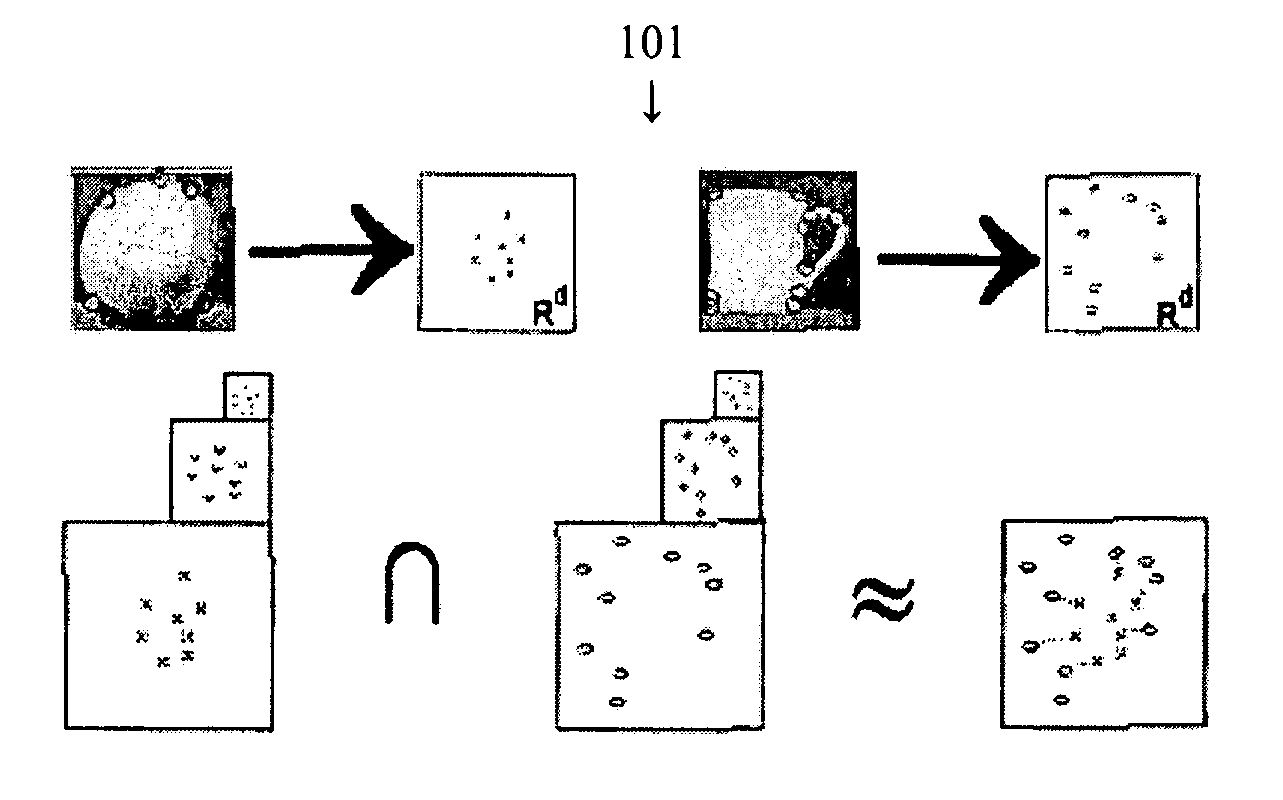
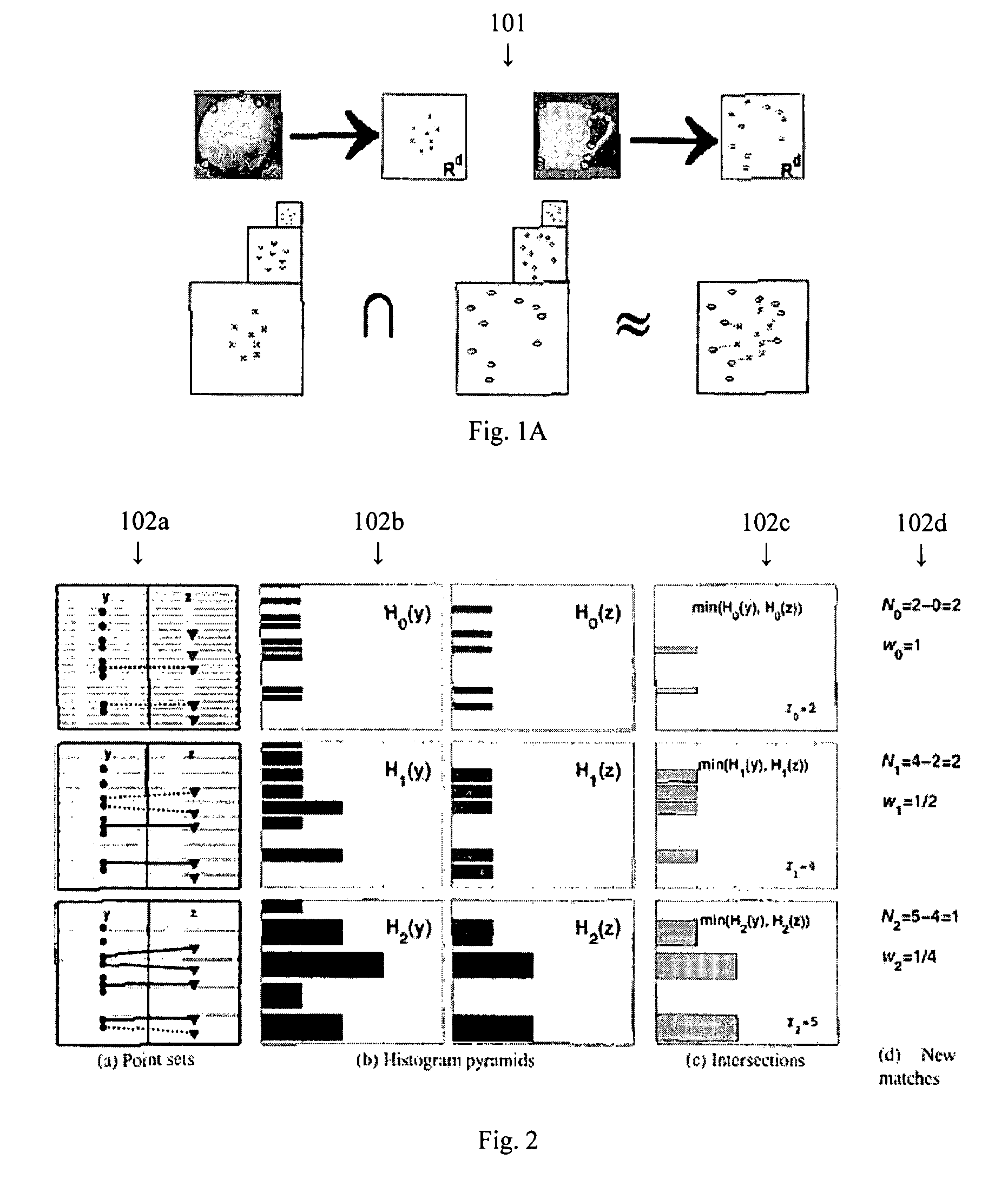
Pyramid match kernel and related techniques
InactiveUS20070217676A1Efficient and accurateFinish quicklyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorHigh dimensional
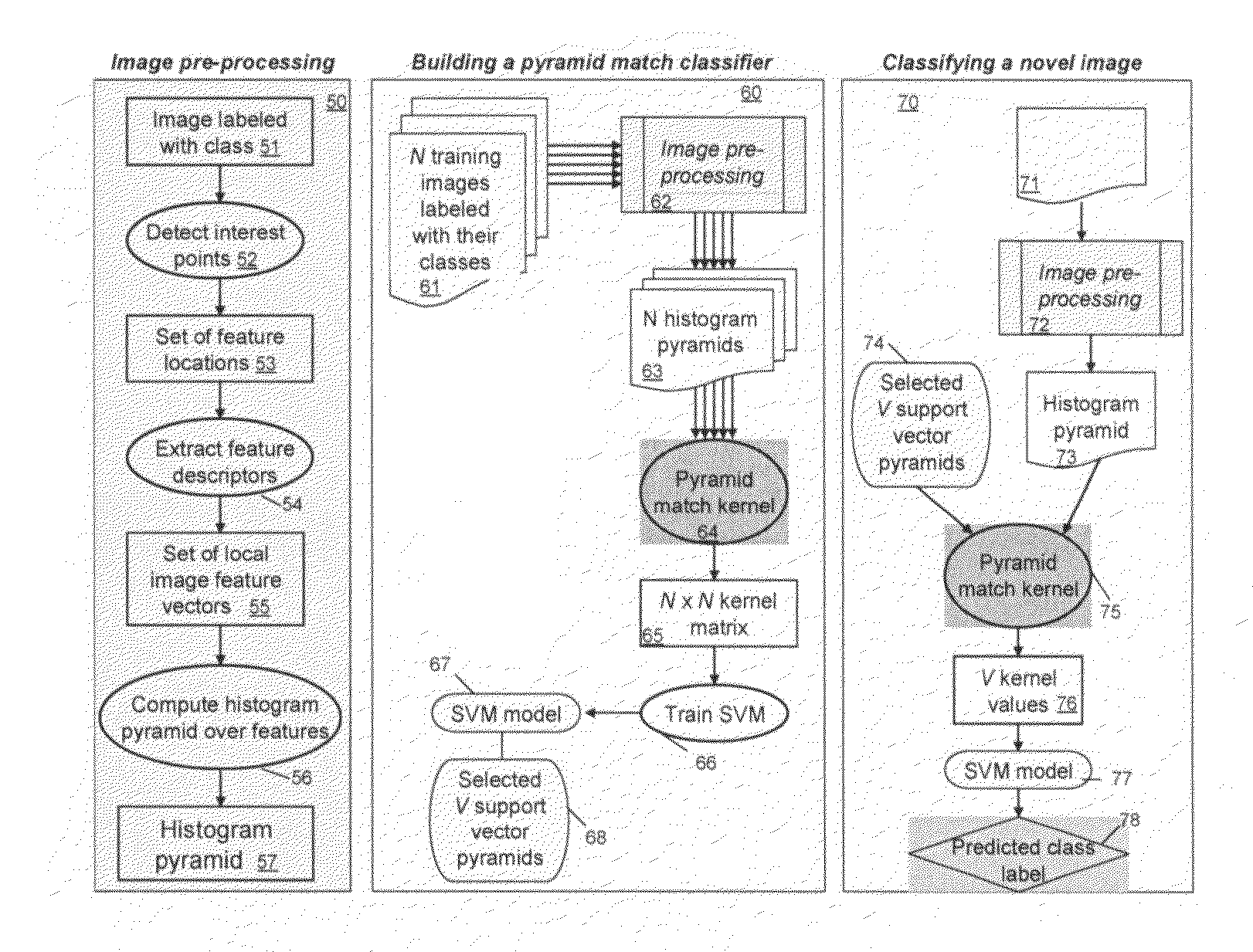
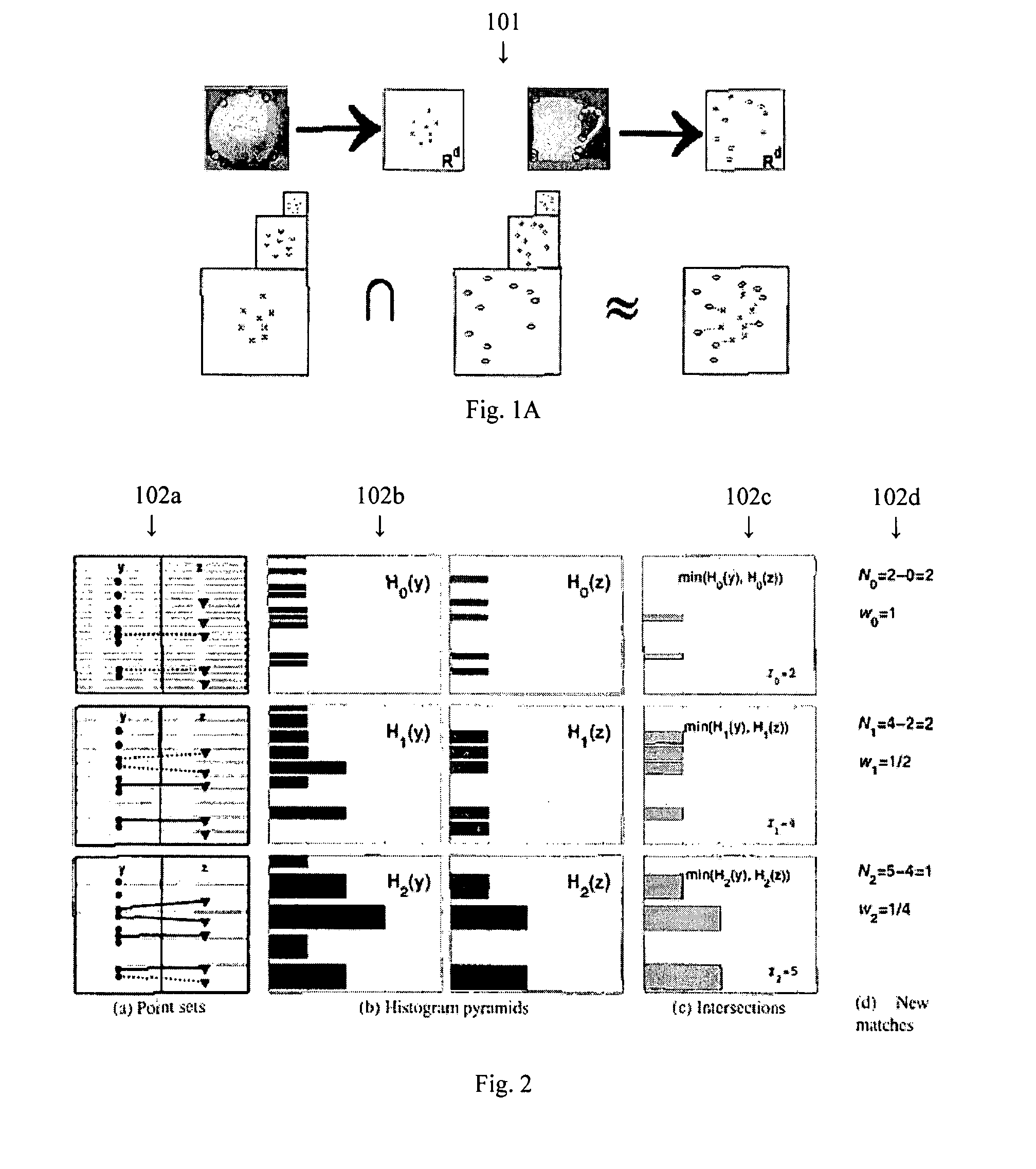
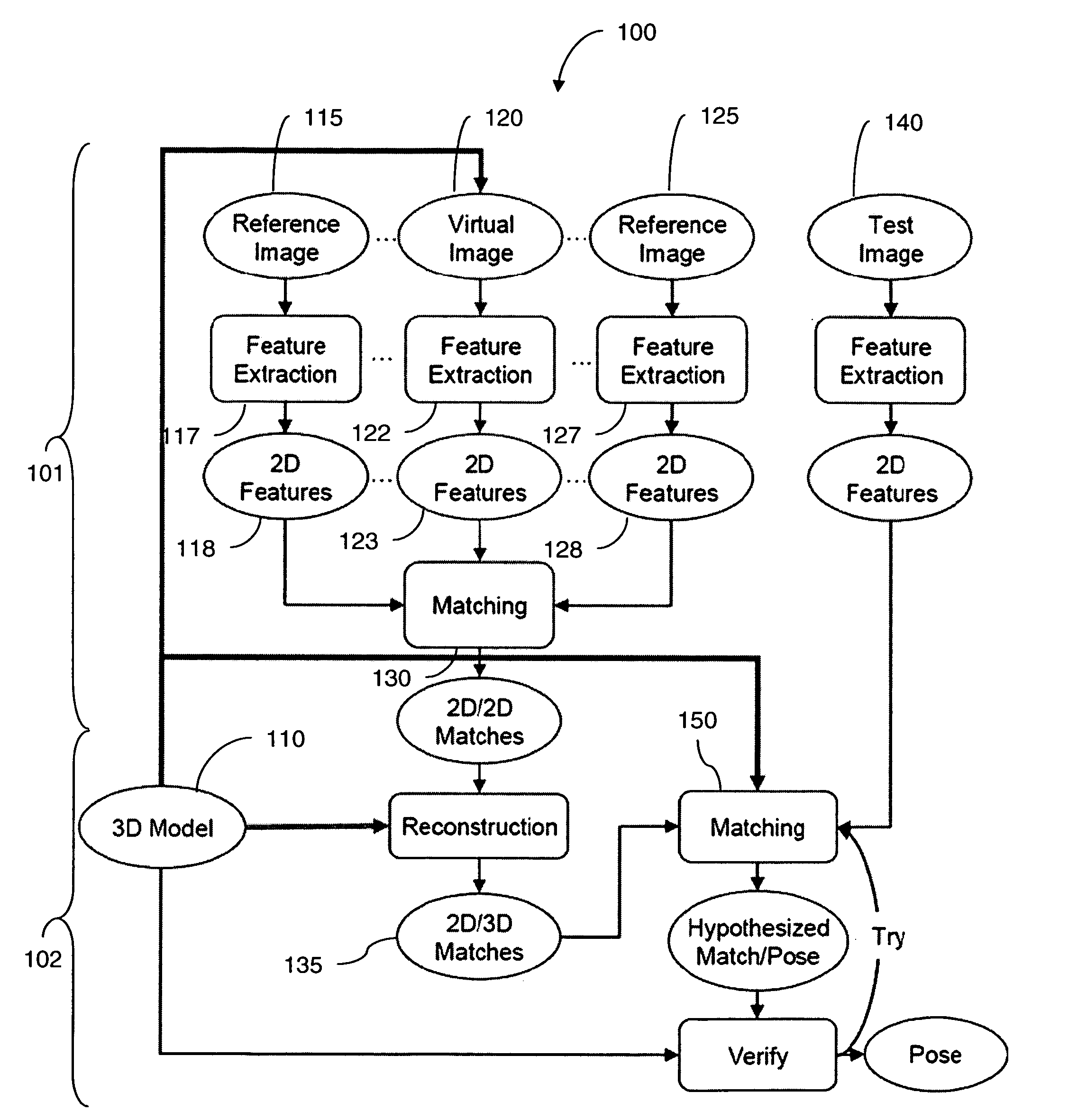
A method for classifying or comparing objects includes detecting points of interest within two objects, computing feature descriptors at said points of interest, forming a multi-resolution histogram over feature descriptors for each object and computing a weighted intersection of multi-resolution histogram for each object. An alternative embodiment includes a method for matching objects by defining a plurality of bins for multi-resolution histograms having various levels and a plurality of cluster groups, each group having a center, for each point of interest, calculating a bin index, a bin count and a maximal distance to the bin center and providing a path vector indicative of the bins chosen at each level. Still another embodiment includes a method for matching objects comprising creating a set of feature vectors for each object of interest, mapping each set of feature vectors to a single high-dimensional vector to create an embedding vector and encoding each embedding vector with a binary hash string.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
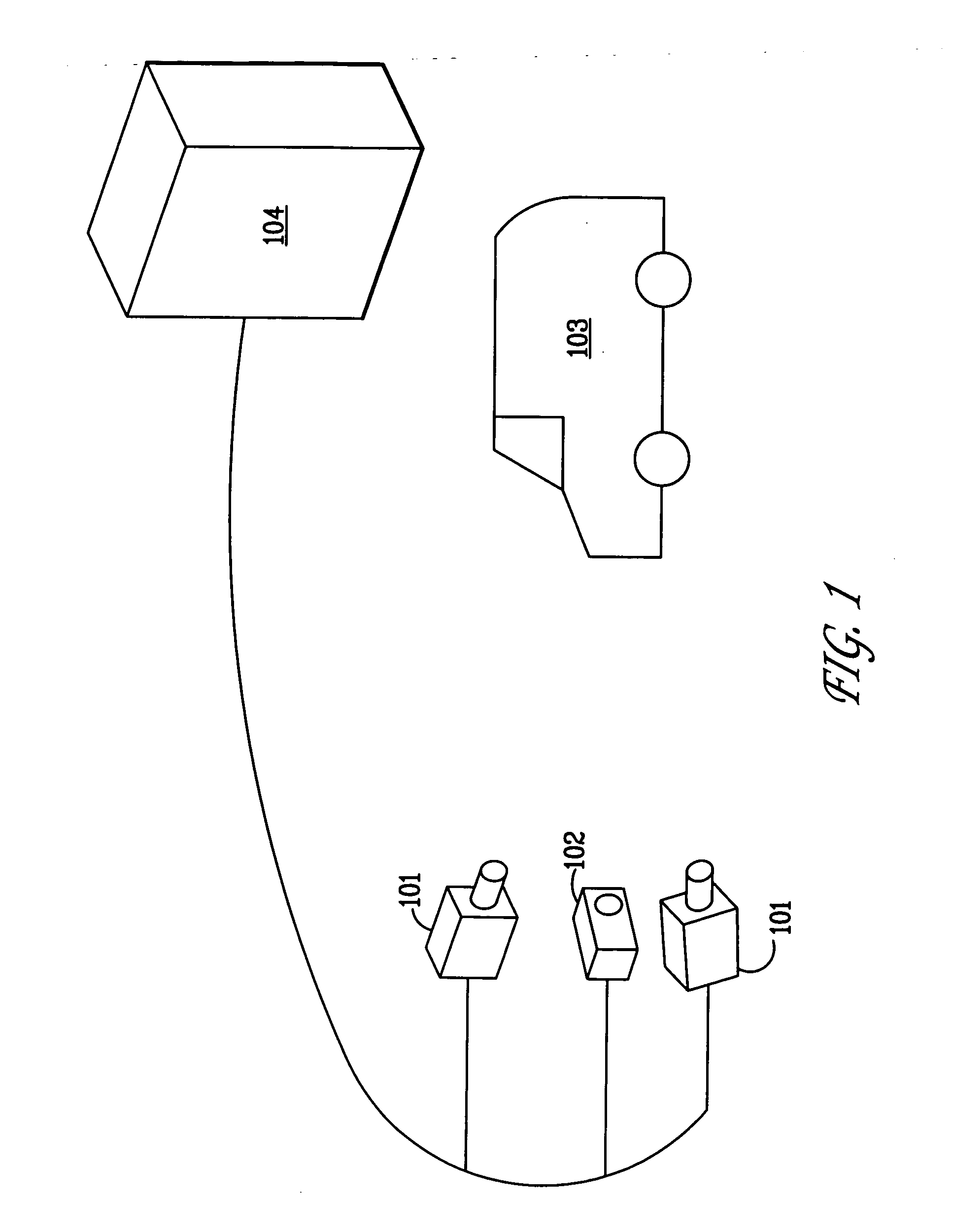
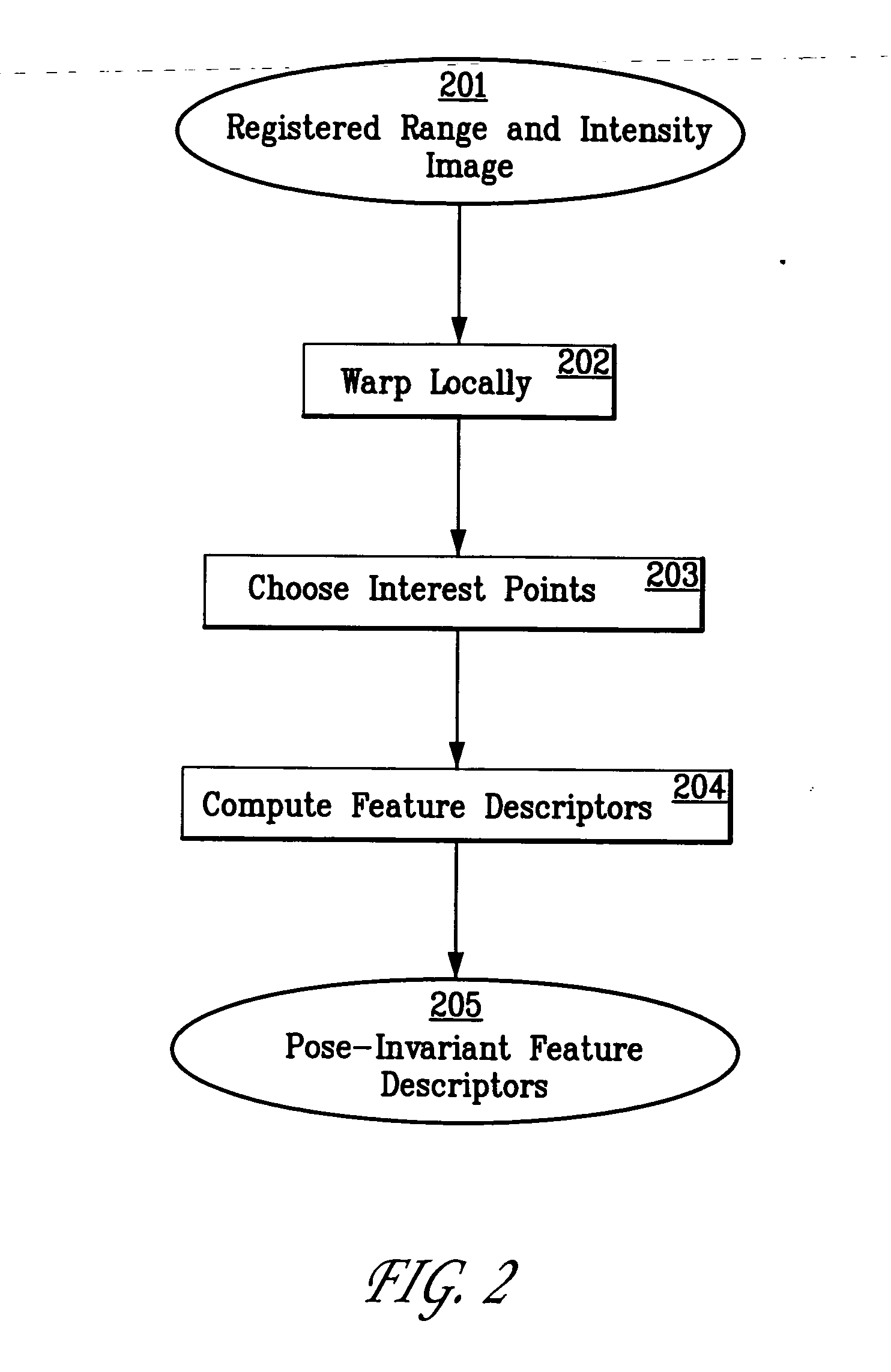
System and method for 3D object recognition using range and intensity
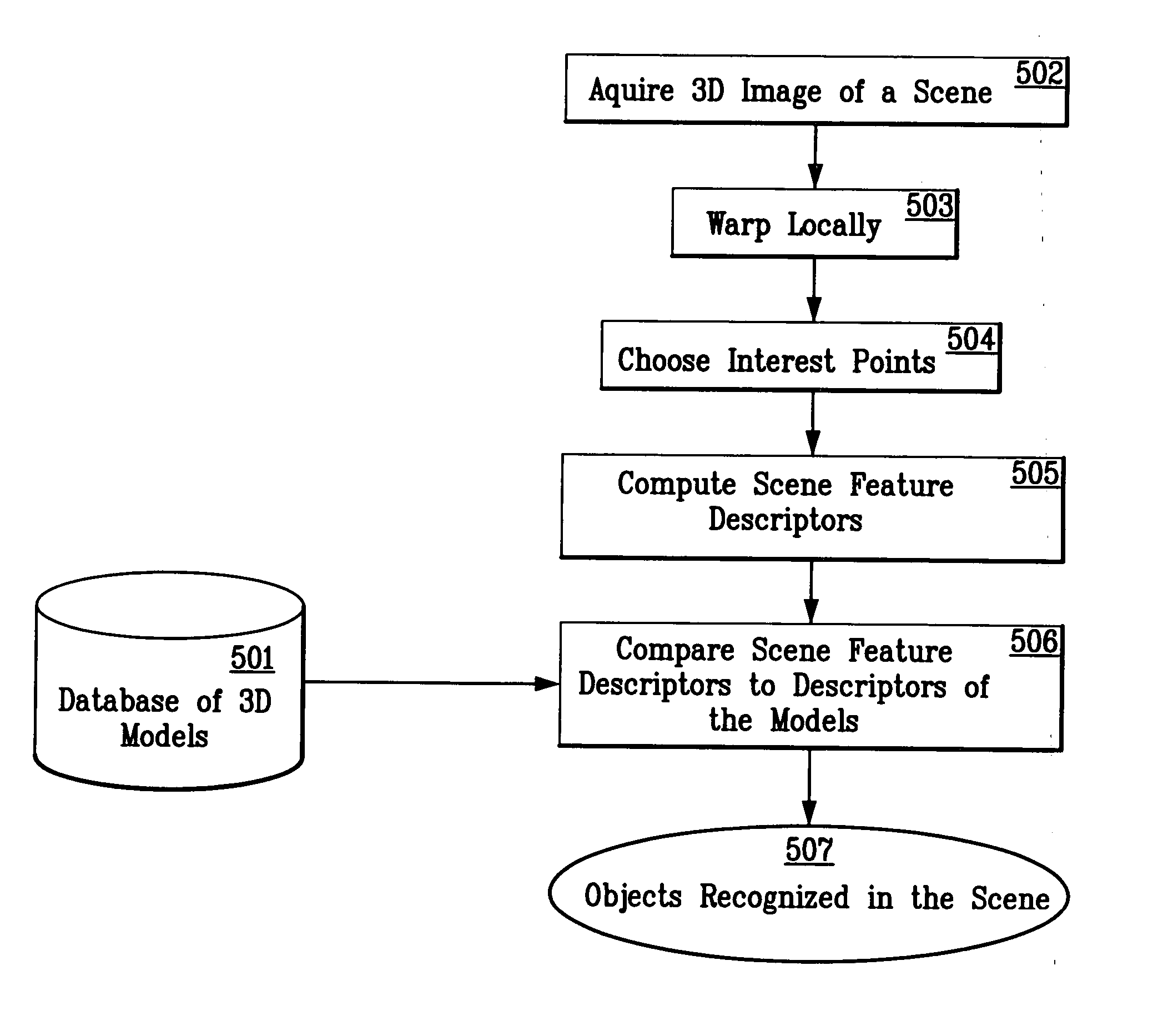
A system and method for performing object and class recognition that allows for wide changes of viewpoint and distance of objects is disclosed. The invention provides for choosing pose-invariant interest points of a three-dimensional (3D) image, and for computing pose-invariant feature descriptors of the image. The system and method also allows for the construction of three-dimensional (3D) object and class models from the pose-invariant interest points and feature descriptors of previously obtained scenes. Interest points and feature descriptors of a newly acquired scene may be compared to the object and / or class models to identify the presence of an object or member of the class in the new scene.
Owner:STRIDER LABS
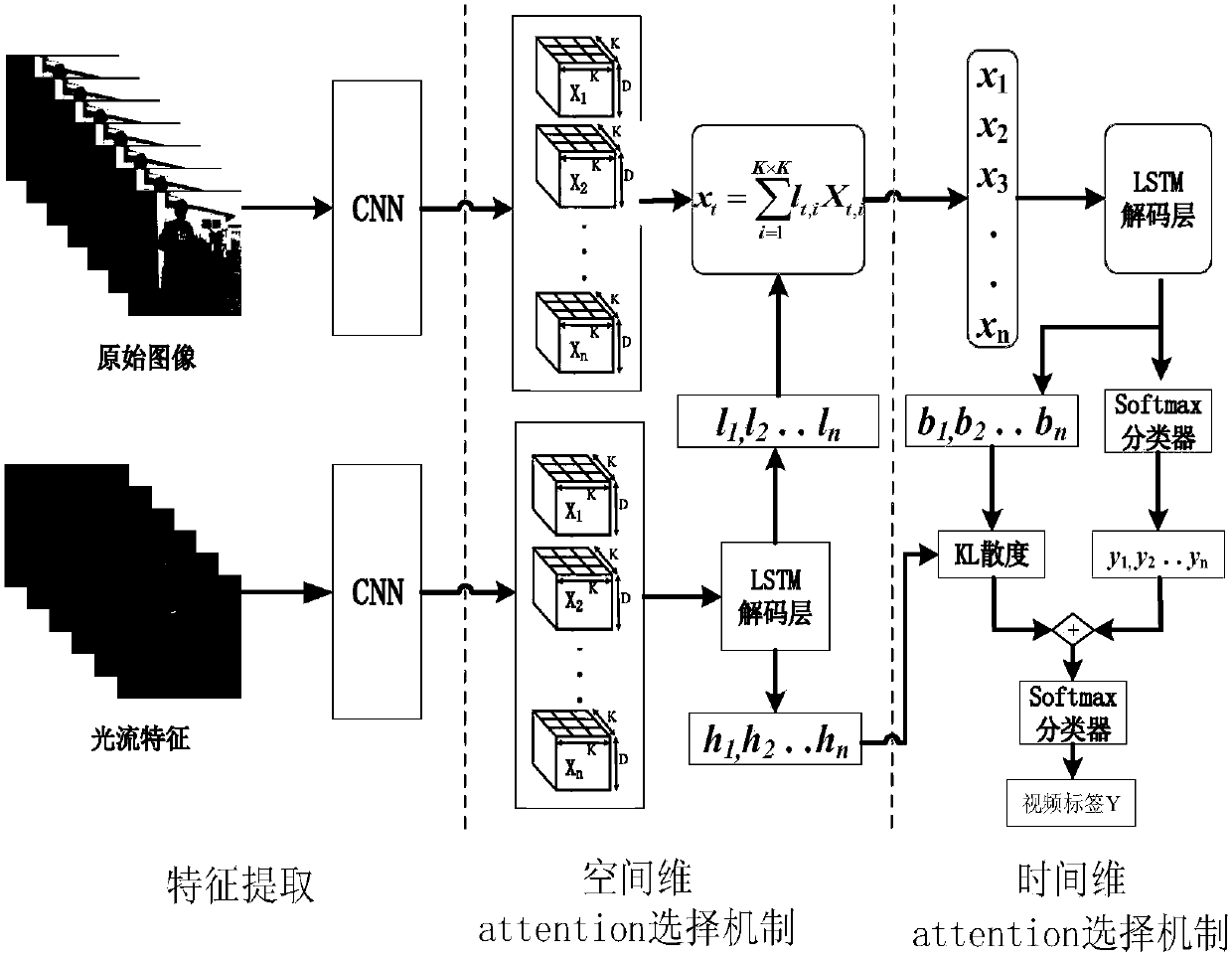
Human behavior recognition method integrating space-time dual-network flow and attention mechanism
ActiveCN107609460AImprove accuracyEliminate distractionsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesHuman behaviorPattern recognition
The invention discloses a human behavior recognition method integrating the space-time dual-network flow and an attention mechanism. The method includes the steps of extracting moving optical flow features and generating an optical flow feature image; constructing independent time flow and spatial flow networks to generate two segments of high-level semantic feature sequences with a significant structural property; decoding the high-level semantic feature sequence of the time flow, outputting a time flow visual feature descriptor, outputting an attention saliency feature sequence, and meanwhile outputting a spatial flow visual feature descriptor and the label probability distribution of each frame of a video window; calculating an attention confidence scoring coefficient per frame time dimension, weighting the label probability distribution of each frame of the video window of the spatial flow, and selecting a key frame of the video window; and using a softmax classifier decision to recognize the human behavior action category of the video window. Compared with the prior art, the method of the invention can effectively focus on the key frame of the appearance image in the originalvideo, and at the same time, can select and obtain the spatial saliency region features of the key frame with high recognition accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multi-image feature matching using multi-scale oriented patches
InactiveUS20050238198A1Quick extractionEasy to liftConveyorsImage analysisPattern recognitionNear neighbor
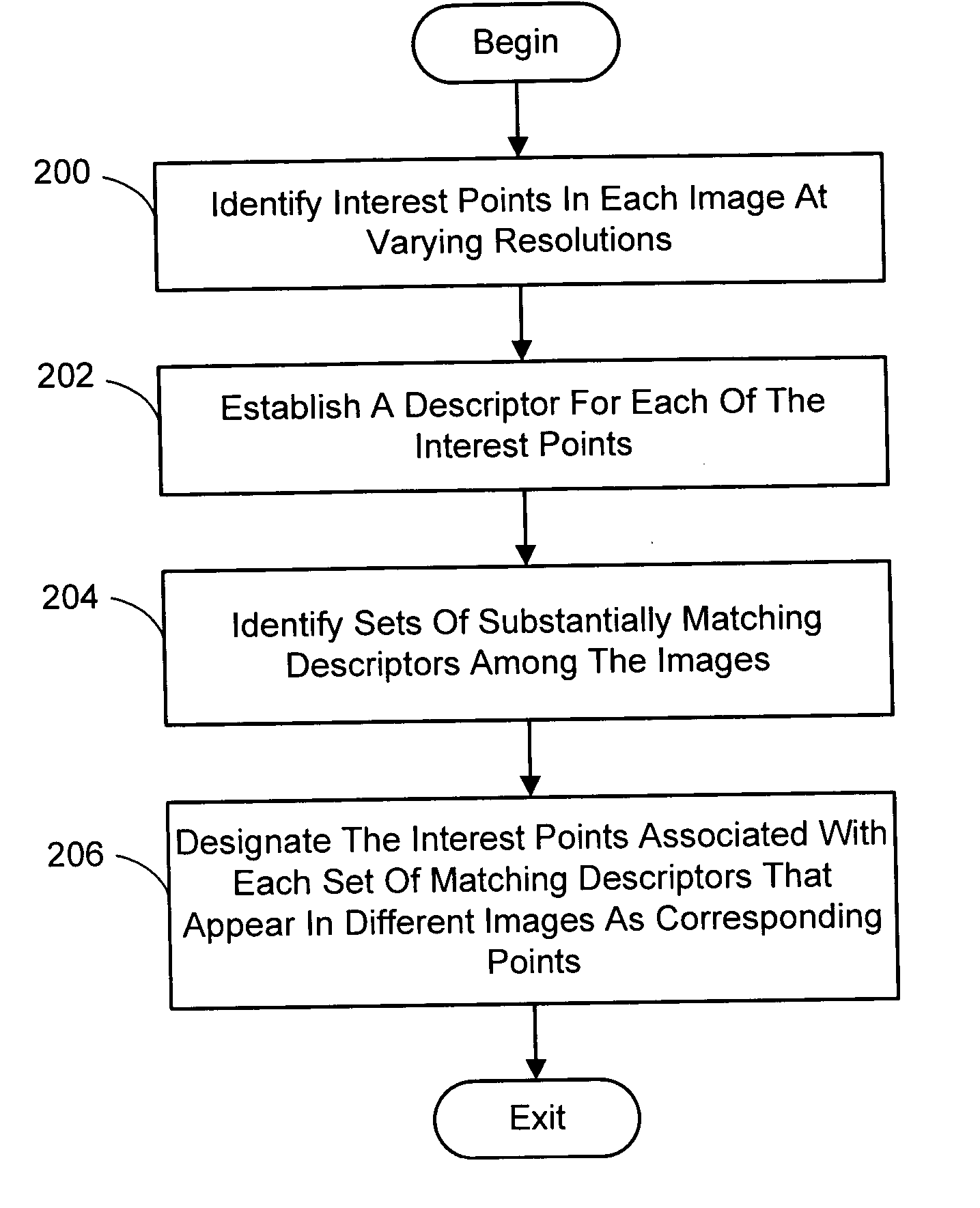
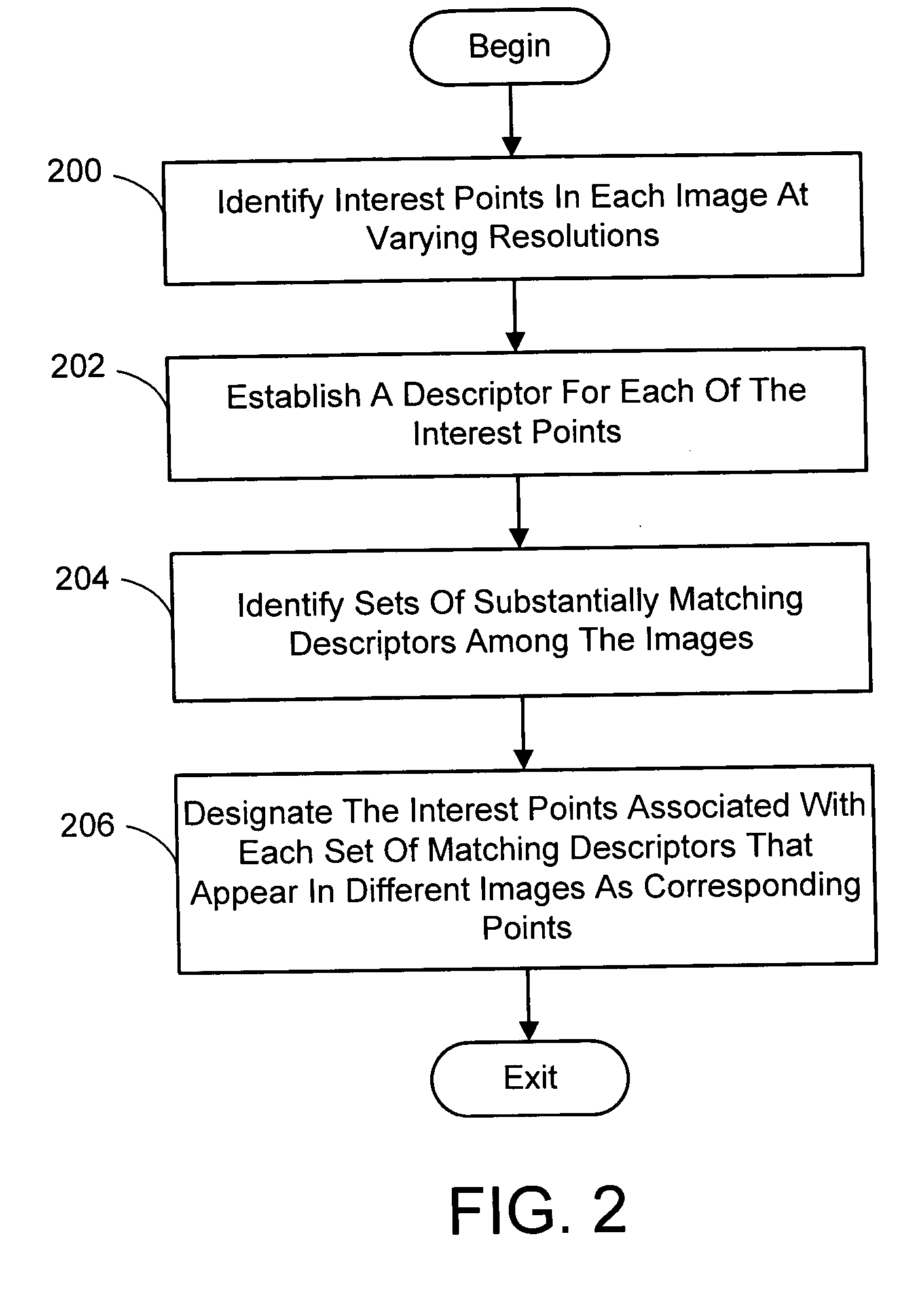
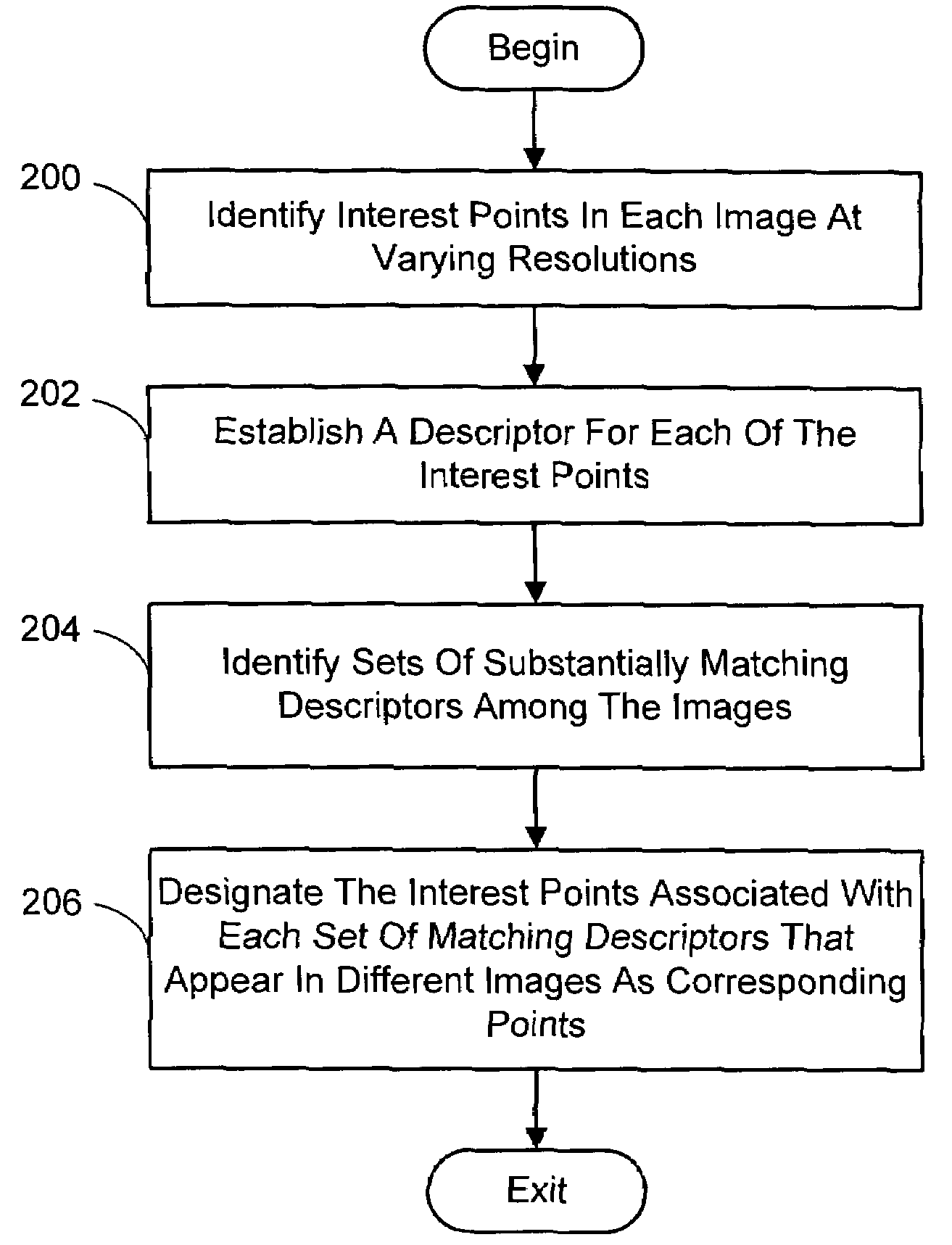
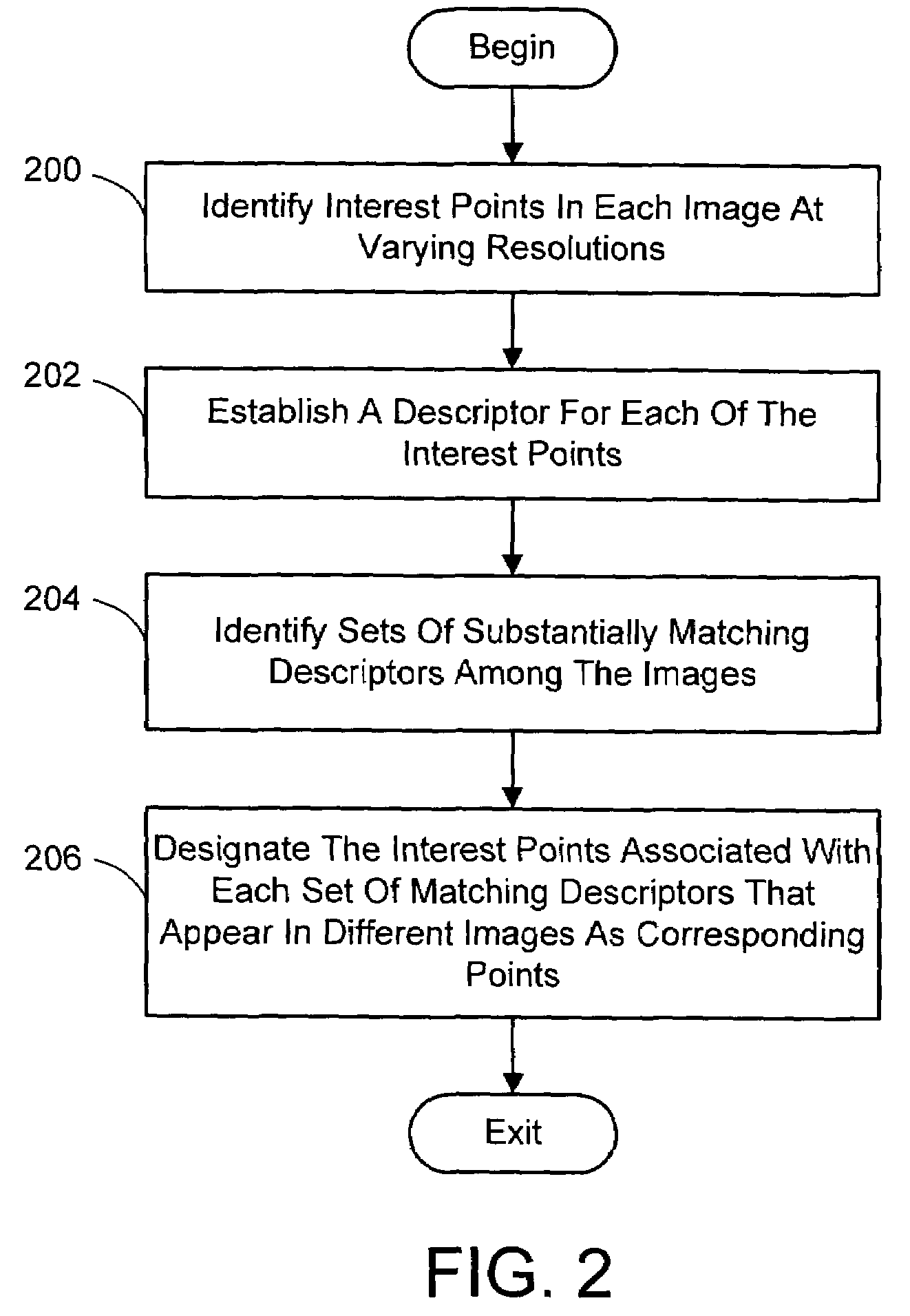
A system and process for identifying corresponding points among multiple images of a scene is presented. This involves a multi-view matching framework based on a new class of invariant features. Features are located at Harris corners in scale-space and oriented using a blurred local gradient. This defines a similarity invariant frame in which to sample a feature descriptor. The descriptor actually formed is a bias / gain normalized patch of intensity values. Matching is achieved using a fast nearest neighbor procedure that uses indexing on low frequency Haar wavelet coefficients. A simple 6 parameter model for patch matching is employed, and the noise statistics are analyzed for correct and incorrect matches. This leads to a simple match verification procedure based on a per feature outlier distance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
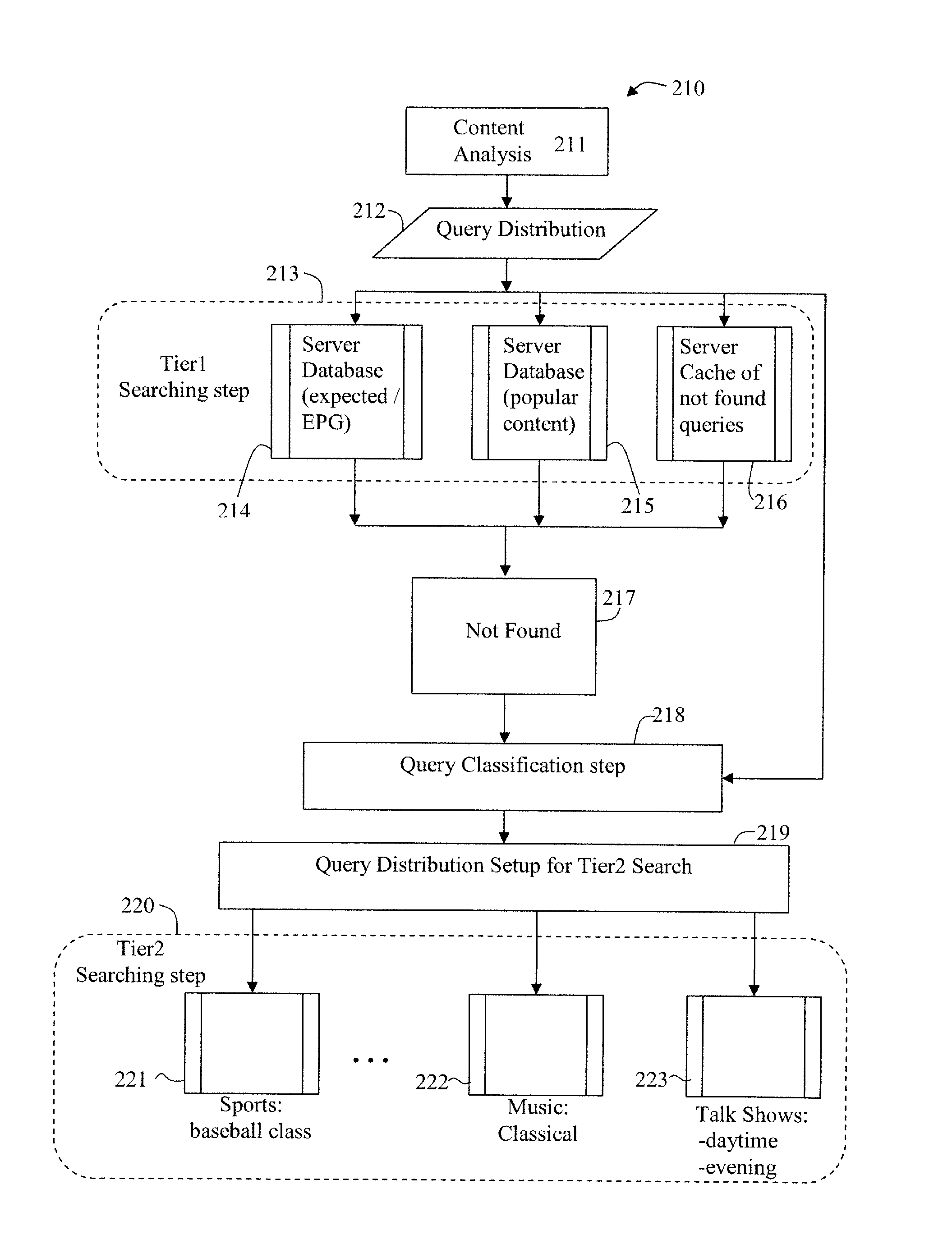
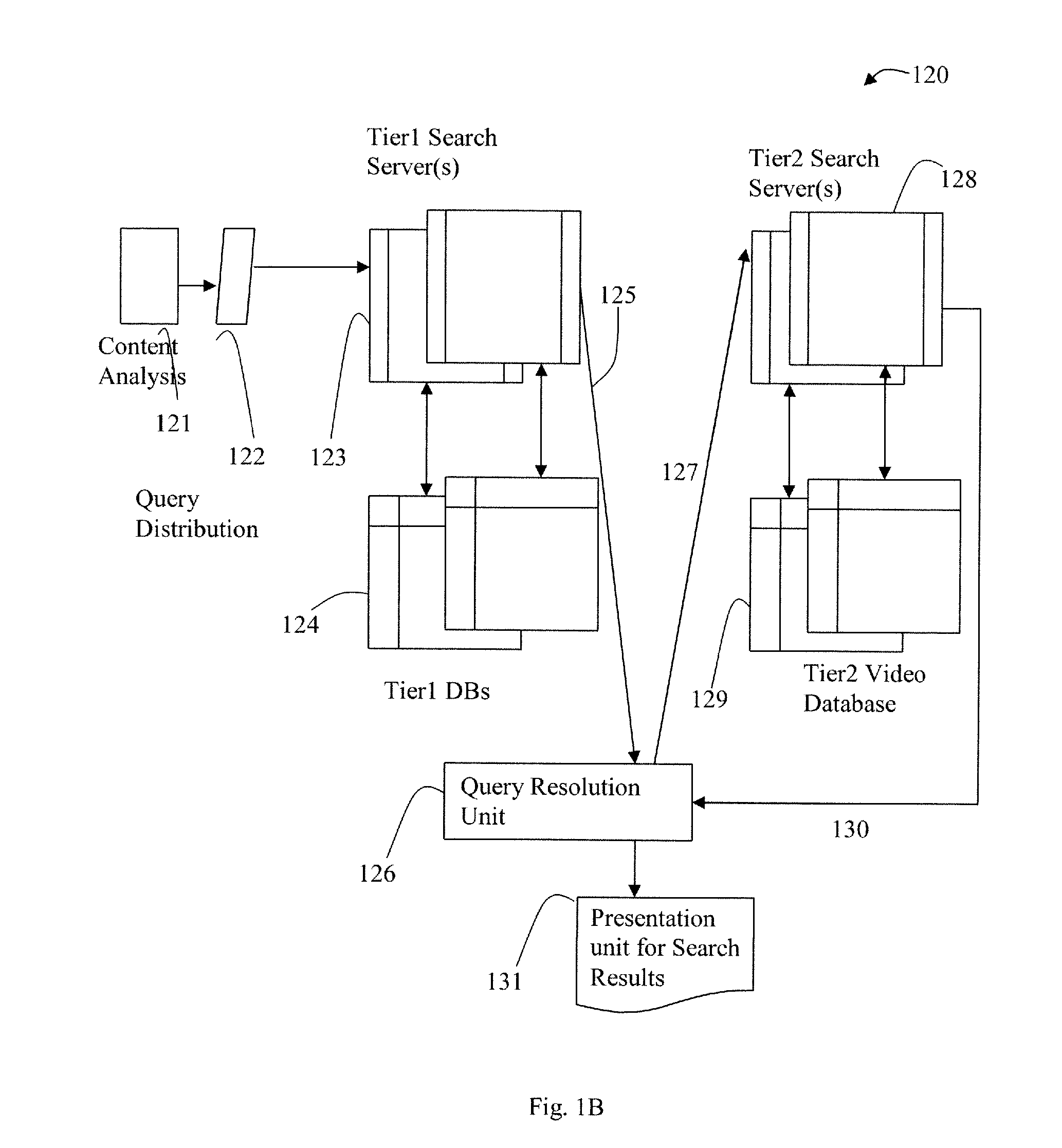
Distributed and Tiered Architecture for Content Search and Content Monitoring
ActiveUS20120095958A1Multimedia data indexingDigital data processing detailsTime segmentSchema for Object-Oriented XML
An efficient large scale search system for video and multi-media content using a distributed database and search, and tiered search servers is described. Selected content is stored at the distributed local database and tier1 search server(s). Content matching frequent queries, and frequent unidentified queries are cached at various levels in the search system. Content is classified using feature descriptors and geographical aspects, at feature level and in time segments. Queries not identified at clients and tier1 search server(s) are queried against tier2 or lower search server(s). Search servers use classification and geographical partitioning to reduce search cost. Methods for content tracking and local content searching are executed on clients. The client performs local search, monitoring and / or tracking of the query content with the reference content and local search with a database of reference fingerprints. This shifts the content search workload from central servers to the distributed monitoring clients.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
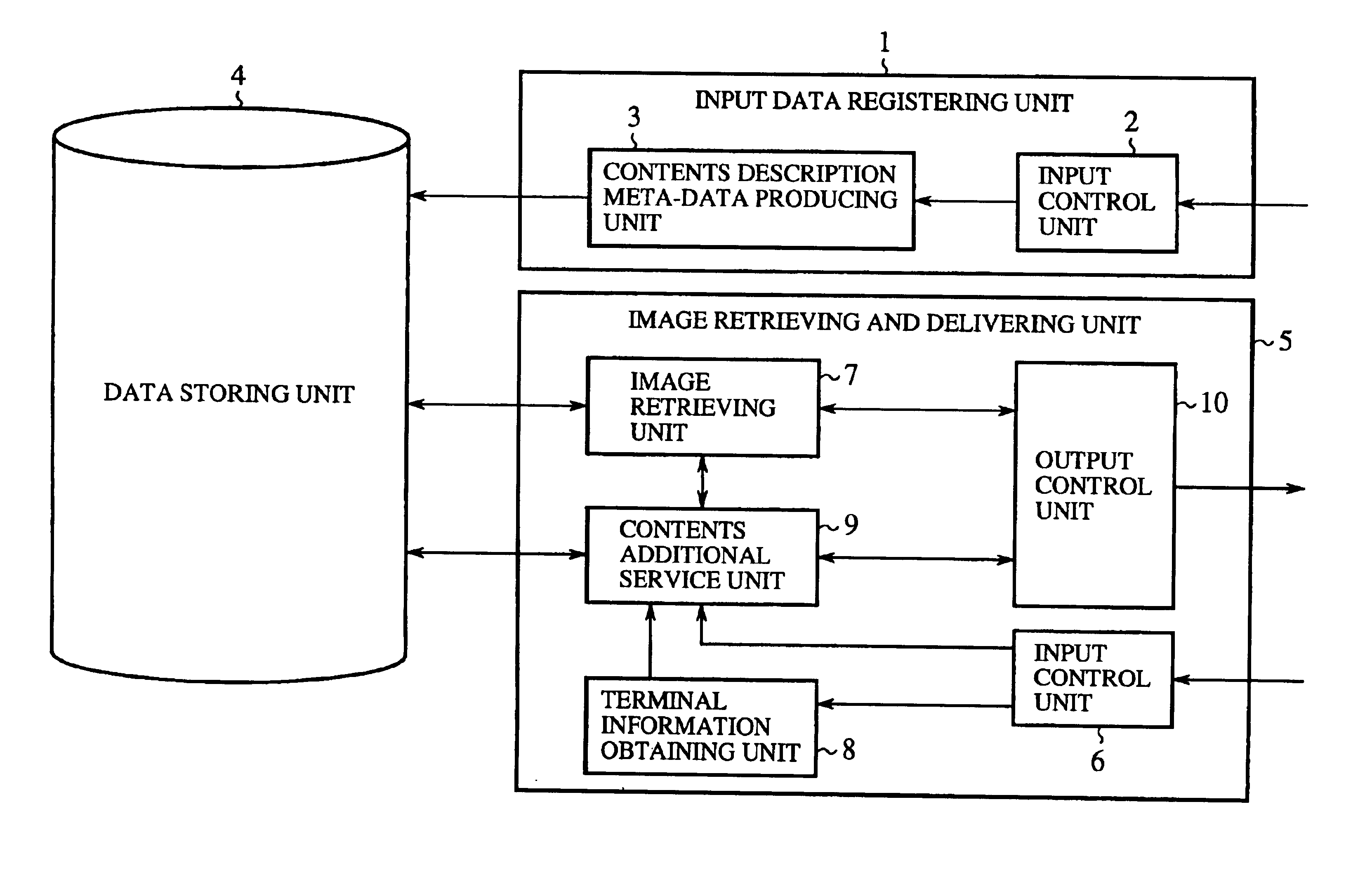
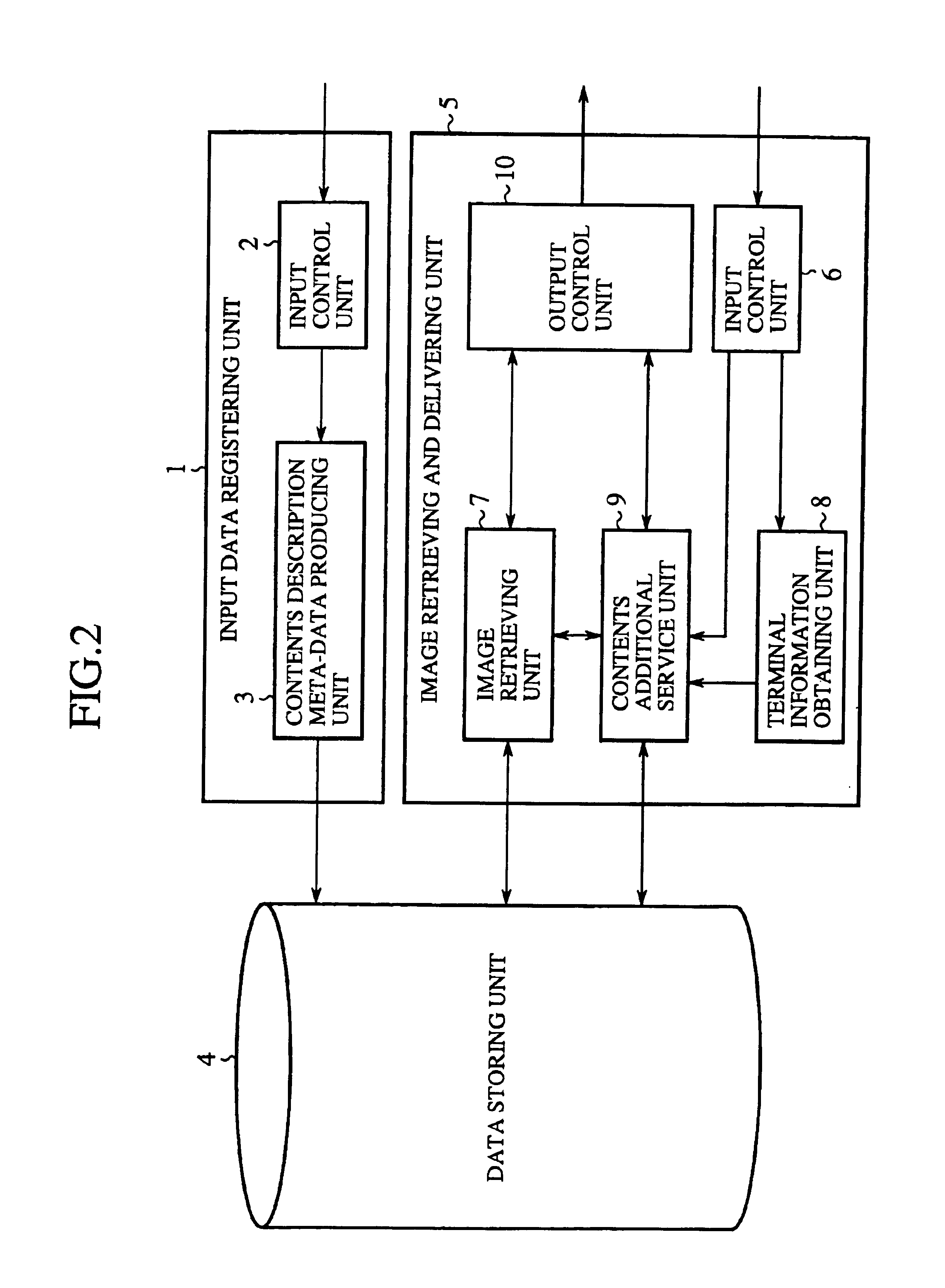
Image retrieving and delivering system and image retrieving and delivering method
InactiveUS7031965B1Easy retrievalEasy to displayData processing applicationsVideo data queryingUser inputComputer science
In an image retrieving and delivering system and an image retrieving and delivering method, a feature descriptor is retrieved from a data base, in which each of a plurality of images including a moving picture and a static picture is registered with a feature descriptor describing the feature of the image, according to a retrieval condition input by a user, a retrieval result satisfying the retrieval condition is obtained, and the retrieval result is edited and processed according to a delivery condition obtained from a user terminal in which the retrieval result is to be received.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
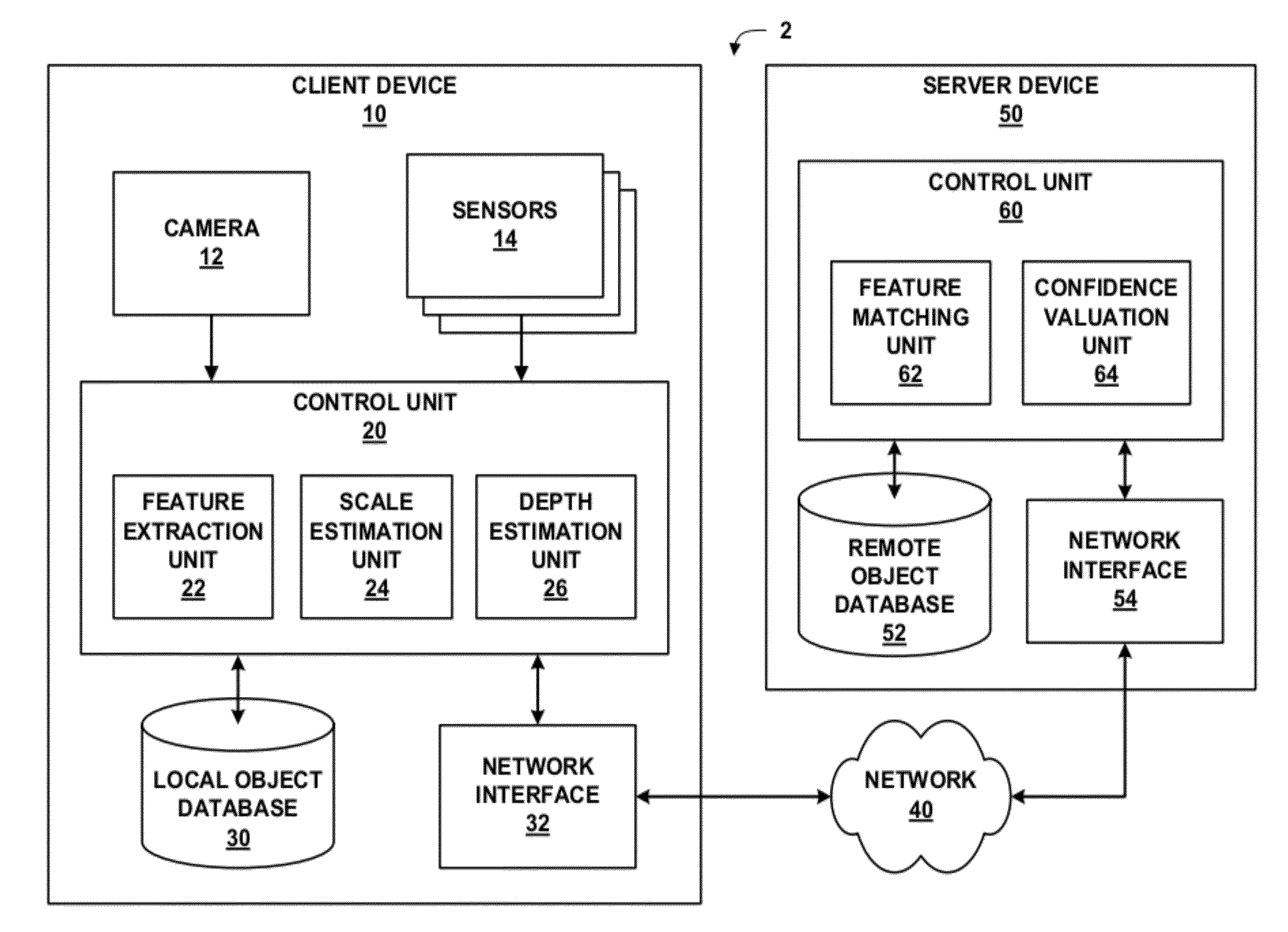
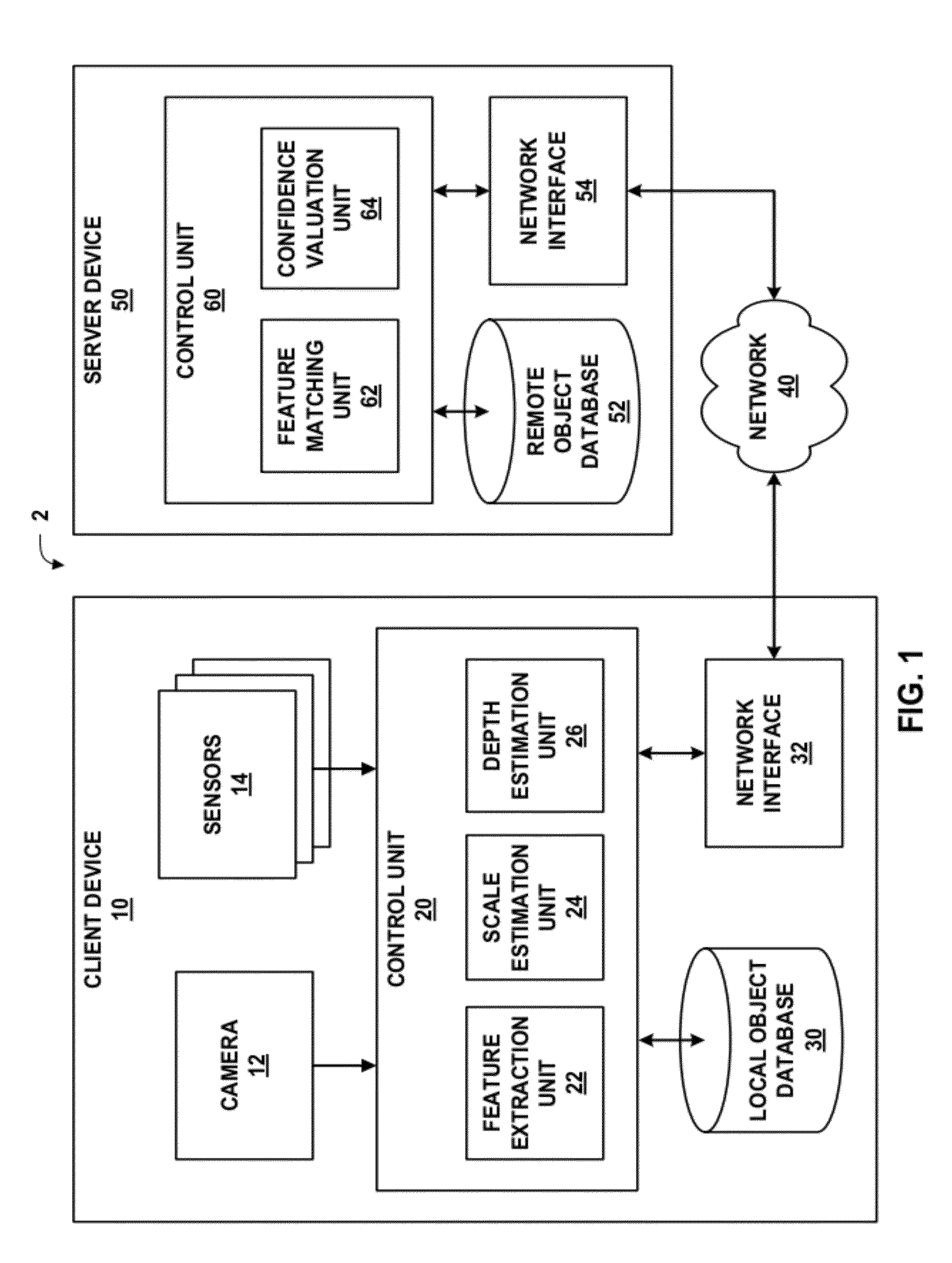
Object recognition using incremental feature extraction
ActiveUS20120027290A1Computational complexity is reducedCharacter and pattern recognitionOctaveDigital image
In one example, an apparatus includes a processor configured to extract a first set of one or more keypoints from a first set of blurred images of a first octave of a received image, calculate a first set of one or more descriptors for the first set of keypoints, receive a confidence value for a result produced by querying a feature descriptor database with the first set of descriptors, wherein the result comprises information describing an identity of an object in the received image, and extract a second set of one or more keypoints from a second set of blurred images of a second octave of the received image when the confidence value does not exceed a confidence threshold. In this manner, the processor may perform incremental feature descriptor extraction, which may improve computational efficiency of object recognition in digital images.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Pyramid match kernel and related techniques
InactiveUS7949186B2Search can be accomplished more quicklyFinish quicklyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorCluster group
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Simultaneous localization and mapping using multiple view feature descriptors
InactiveUS20050238200A1Efficiently build necessary feature descriptorReliable correspondenceThree-dimensional object recognitionKaiman filterKernel principal component analysis
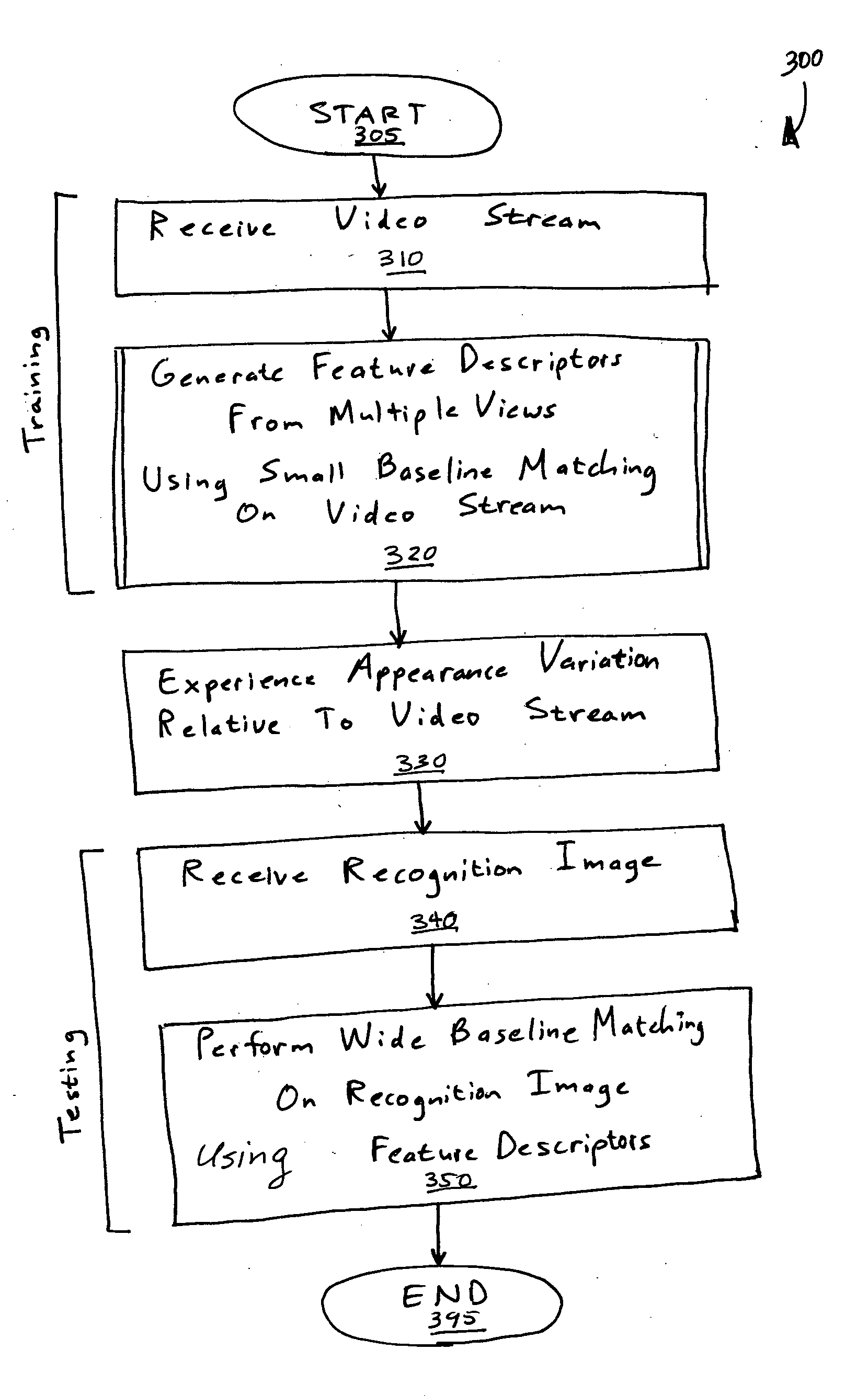
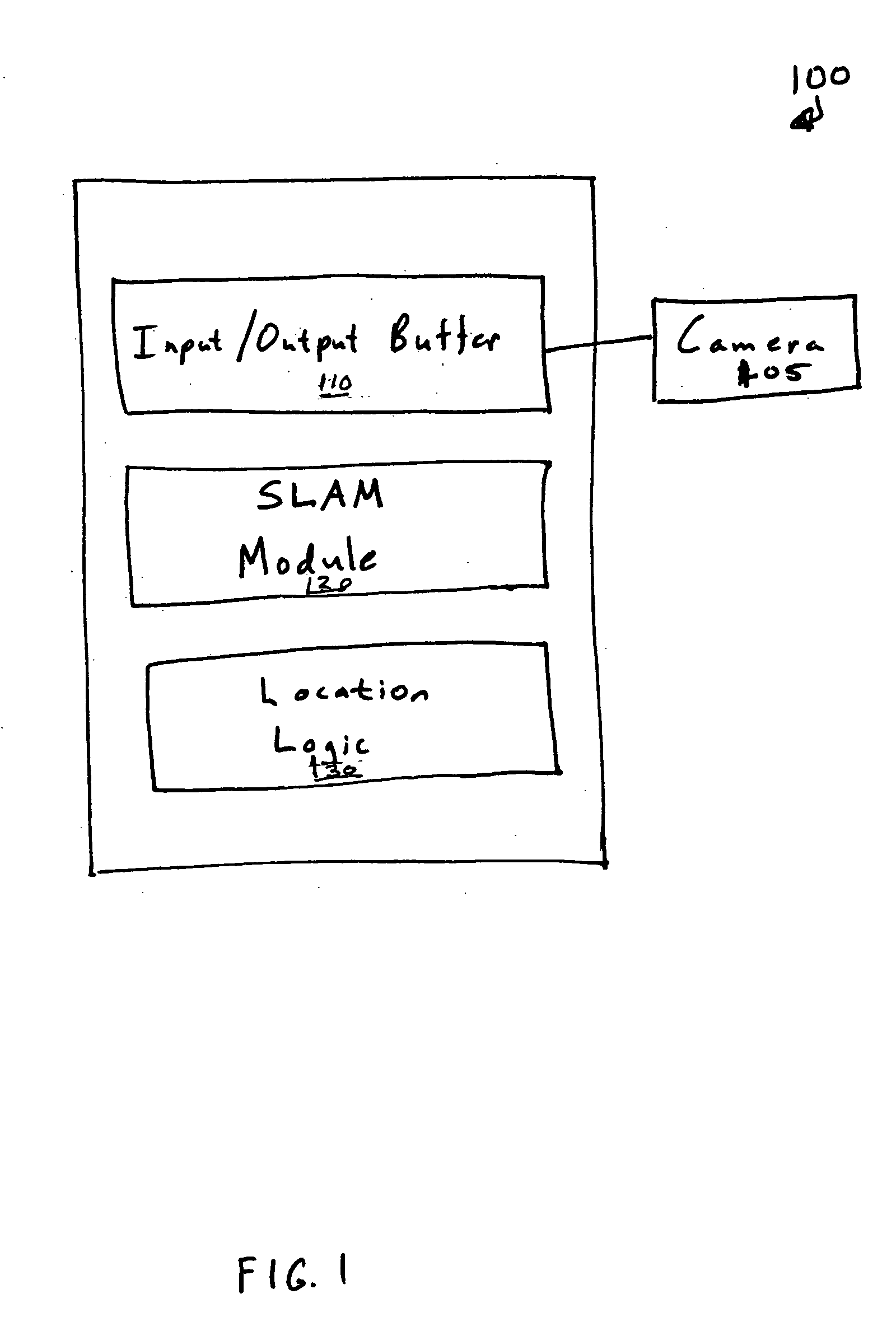
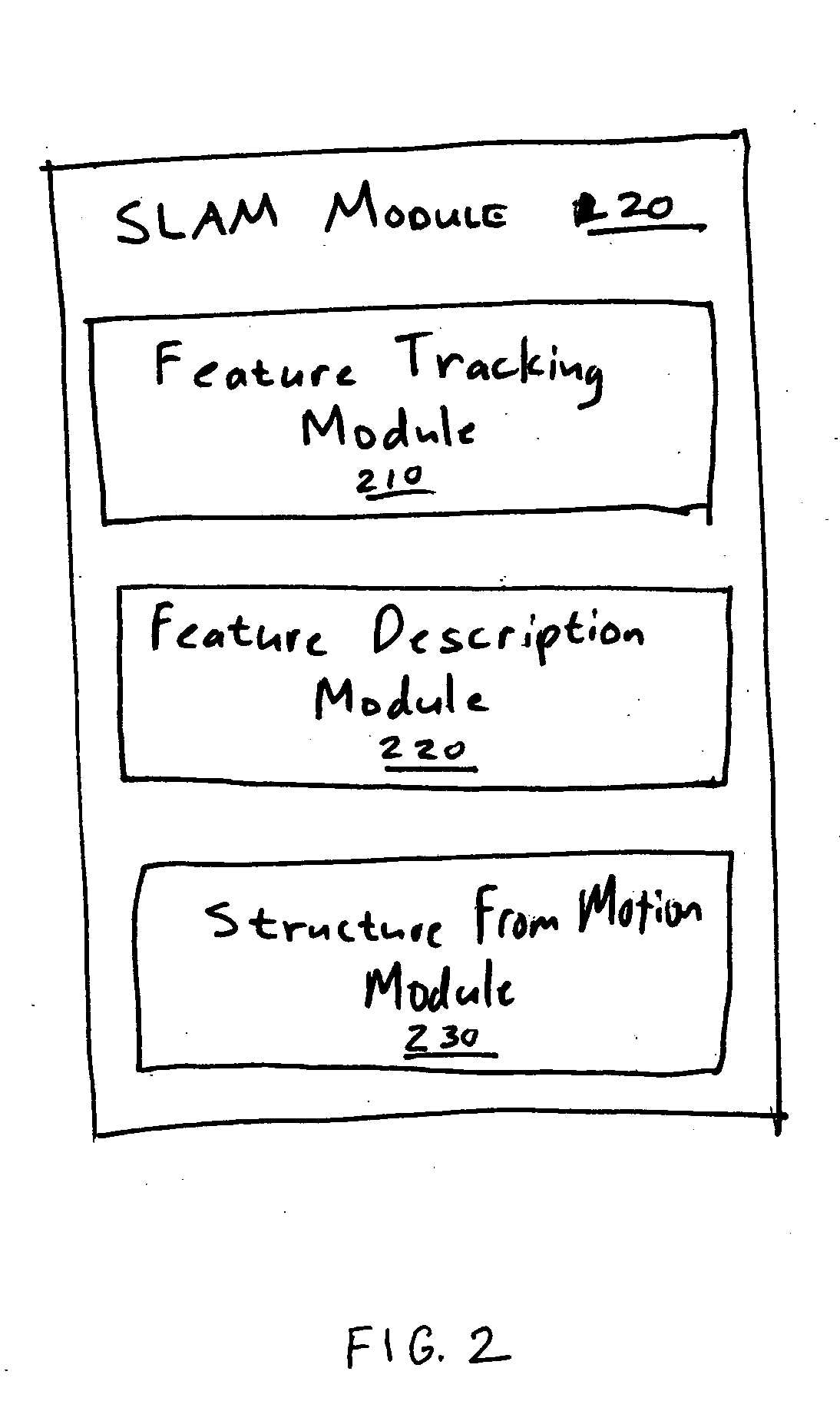
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) utilizes multiple view feature descriptors to robustly determine location despite appearance changes that would stifle conventional systems. A SLAM algorithm generates a feature descriptor for a scene from different perspectives using kernel principal component analysis (KPCA). When the SLAM module subsequently receives a recognition image after a wide baseline change, it can refer to correspondences from the feature descriptor to continue map building and / or determine location. Appearance variations can result from, for example, a change in illumination, partial occlusion, a change in scale, a change in orientation, change in distance, warping, and the like. After an appearance variation, a structure-from-motion module uses feature descriptors to reorient itself and continue map building using an extended Kalman Filter. Through the use of a database of comprehensive feature descriptors, the SLAM module is also able to refine a position estimation despite appearance variations.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Methods and Apparatus for Visual Search
ActiveUS20130121600A1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionBag of features
Each image of a set of images is characterized with a set of sparse feature descriptors and a set of dense feature descriptors. In some embodiments, both the set of sparse feature descriptors and the set of dense feature descriptors are calculated based on a fixed rotation for computing texture descriptors, while color descriptors are rotation invariant. In some embodiments, the descriptors of both sparse and dense features are then quantized into visual words. Each database image is represented by a feature index including the visual words computed from both sparse and dense features. A query image is characterized with the visual words computed from both sparse and dense features of the query image. A rotated local Bag-of-Features (BoF) operation is performed upon a set of rotated query images against the set of database images. Each of the set of images is ranked based on the rotated local Bag-of-Features operation.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Method and apparatus for tracking and recognition with rotation invariant feature descriptors
ActiveUS20110286627A1Sufficiently robustCheap computerImage enhancementImage analysisPyramidInvariant feature
Various methods for tracking and recognition with rotation invariant feature descriptors are provided. One example method includes generating an image pyramid of an image frame, detecting a plurality of interest points within the image pyramid, and extracting feature descriptors for each respective interest point. According to some example embodiments, the feature descriptors are rotation invariant. Further, the example method may also include tracking movement by matching the feature descriptors to feature descriptors of a previous frame and performing recognition of an object within the image frame based on the feature descriptors. Related example methods and example apparatuses are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA CORP +1
Fast object detection for augmented reality systems
InactiveUS20060233423A1Reduce dimensionalityMinimize impactImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionVisibilityViewpoints
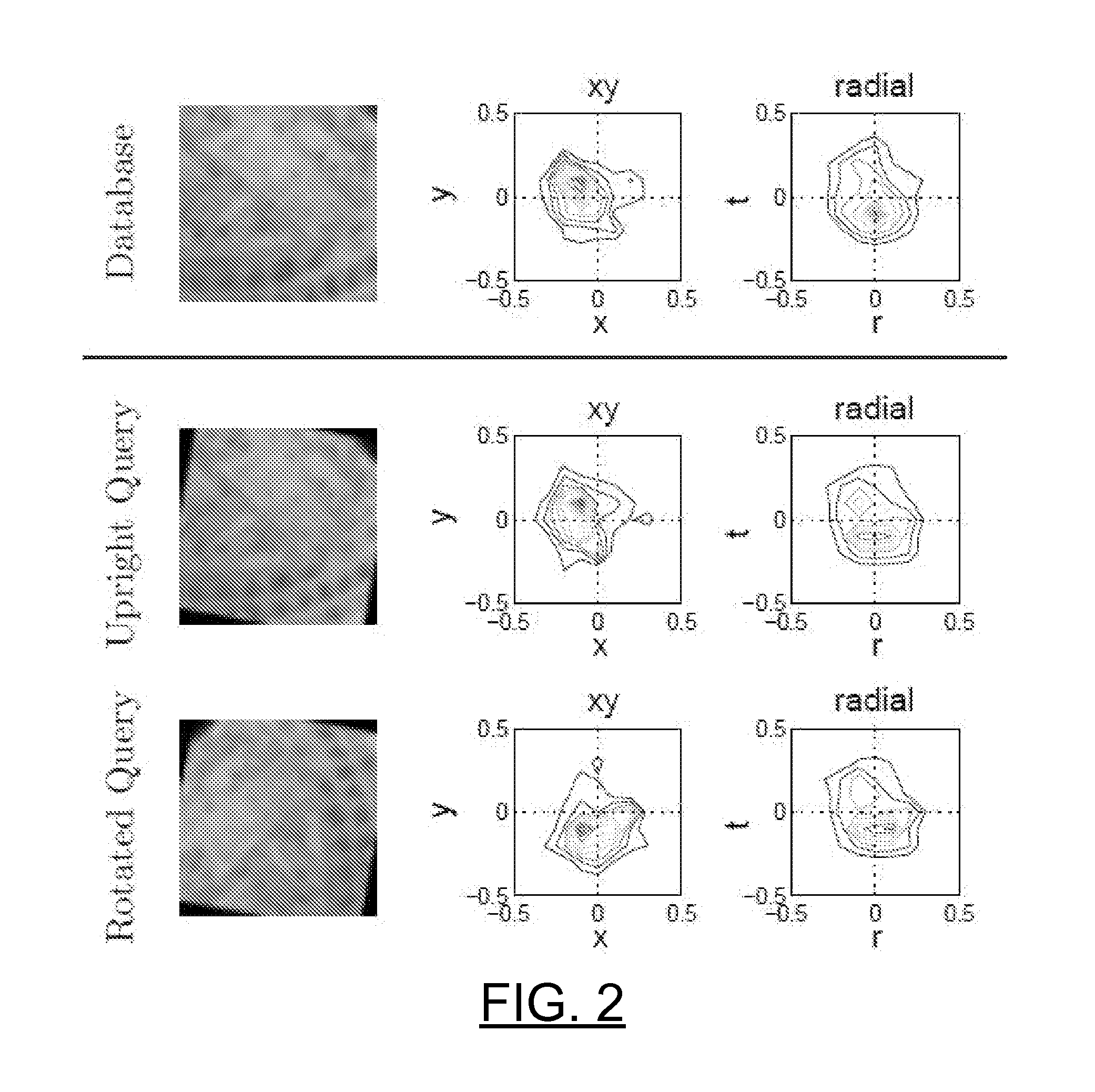
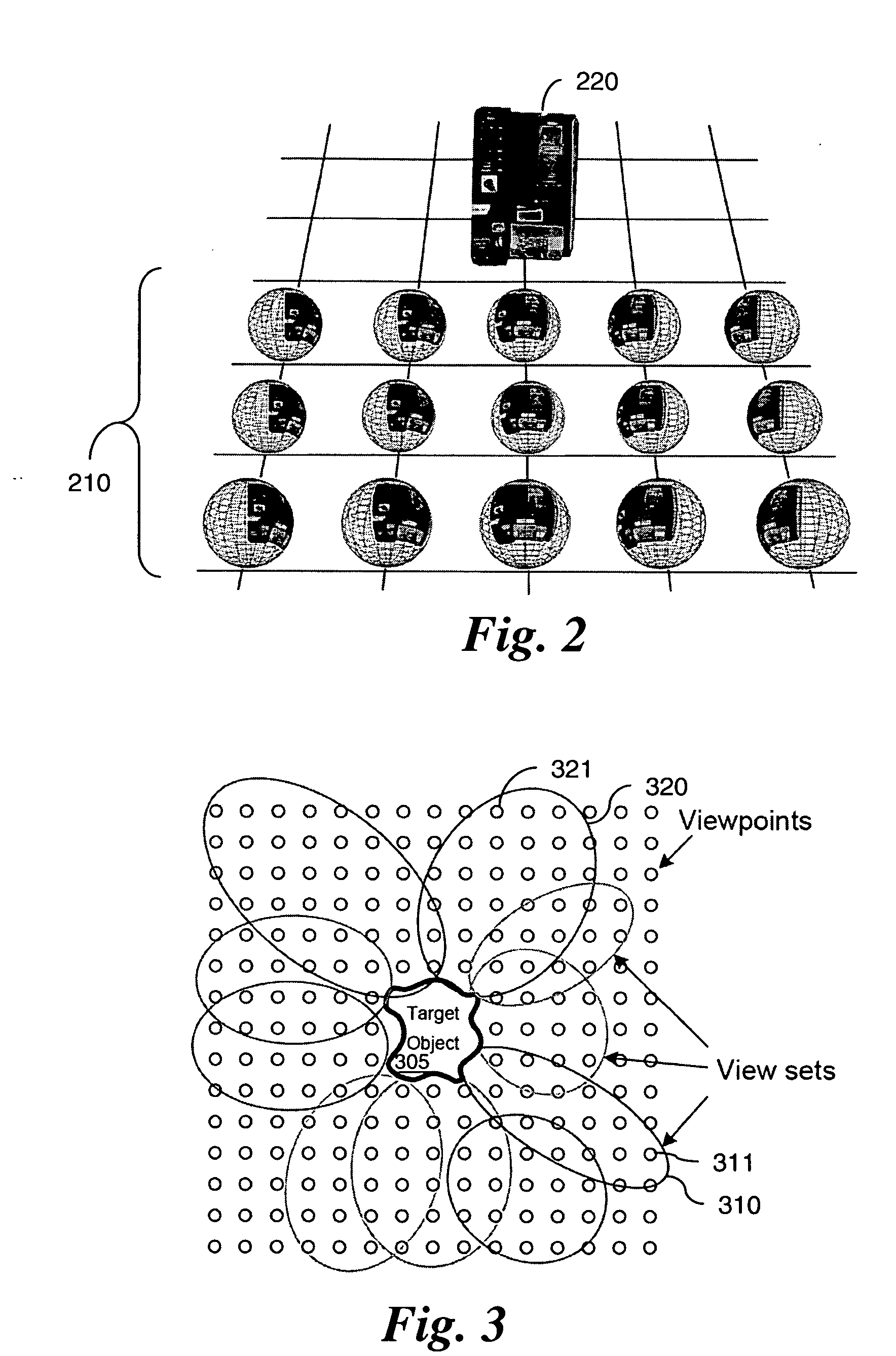
A detection method is based on a statistical analysis of the appearance of model patches from all possible viewpoints in the scene, and incorporates 3D geometry during both matching and pose estimation processes. By analyzing the computed probability distribution of the visibility of each patch from different viewpoints, a reliability measure for each patch is estimated. That reliability measure is useful for developing industrial augmented reality applications. Using the method, the pose of complex objects can be estimated efficiently given a single test image. In a fast method to detect objects in a given image or video sequence, a series of hierarchical feature descriptors permit balancing between the complexity of feature extraction and cost of combinatorial matching. The feature descriptors are derived from the 3D model of the object of interest along with the available calibrated real-life images or videos. The variability of the real-life images defines the granularity of the feature descriptors.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
Efficient image matching method based on improved scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) algorithm
InactiveCN102722731AImprove real-time performanceReduce overheadCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorScale-invariant feature transform
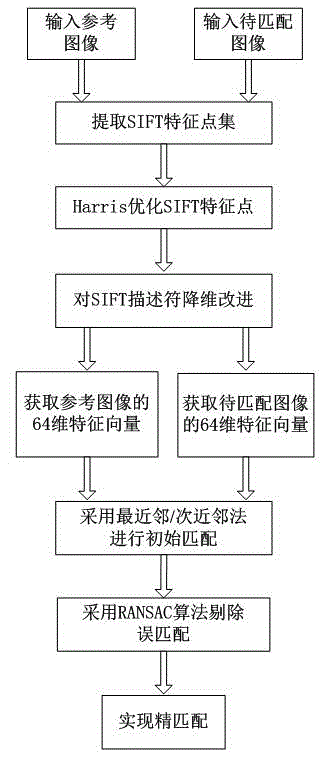
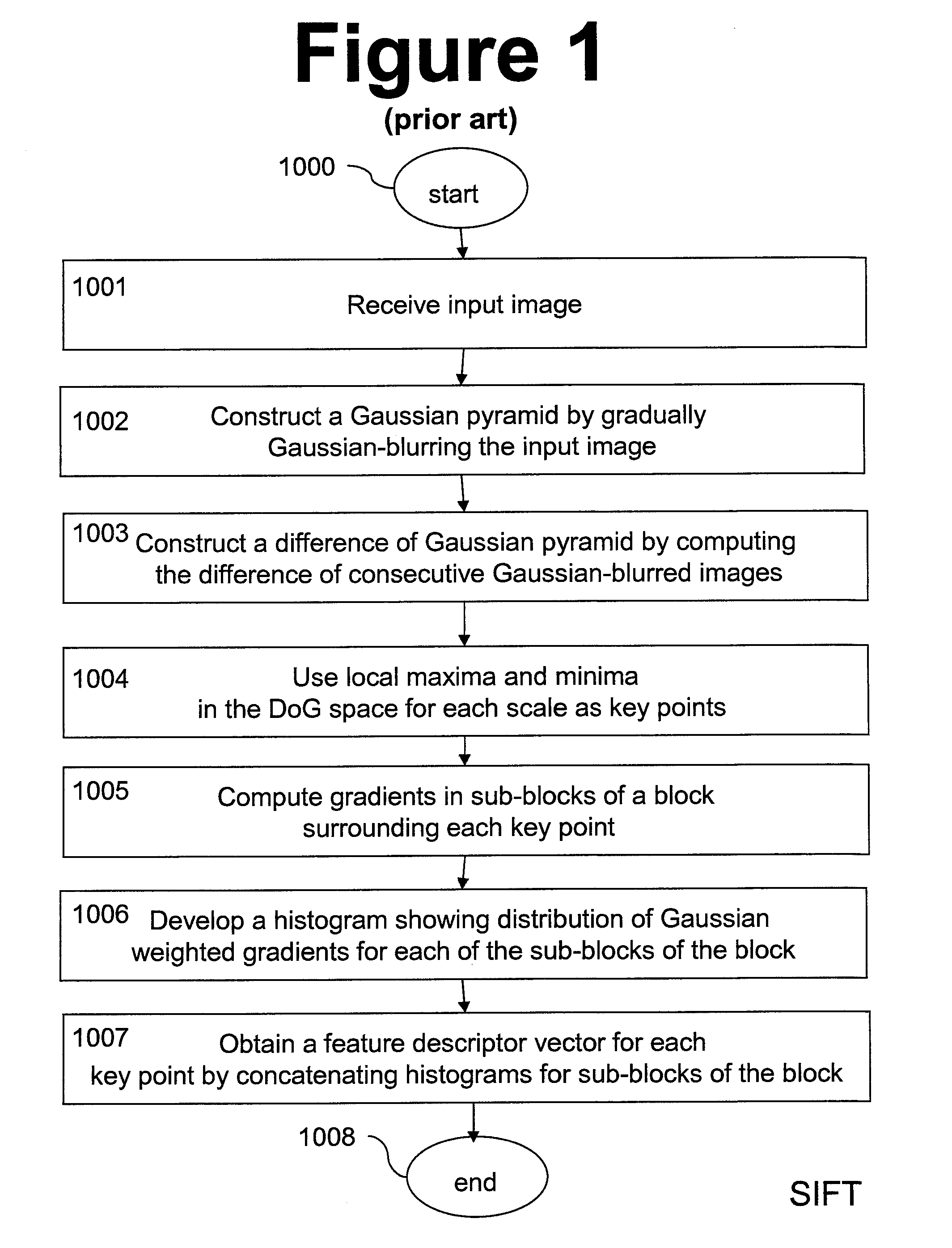
The invention discloses an efficient image matching method based on an improved scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting feature points of an input reference image and an image to be matched by using an SIFT operator; (2) by using a Harris operator, optimizing the feature points which are extracted by the SIFT operator, and screening representative angular points as final feature points; (3) performing dimensionality reduction on an SIFT feature descriptor, and acquiring 64-dimension feature vector descriptors of the reference image and the image to be matched; and (4) initially matching the reference image and the image to be matched by using a nearest neighbor / second choice neighbor (NN / SCN) algorithm, and eliminating error matching by using a random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm, so the images can be accurately matched. The method has the advantages that by selecting points which can well represent or reflect image characteristics for image matching, matching accuracy is ensured, and the real-time performance of SIFT matching is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method of providing image feature descriptors
InactiveUS20150294189A1Small sizeIncrease success rateCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging Feature
A method of providing a set of feature descriptors configured to be used in matching an object in an image of a camera is provided. The method includes: a) providing at least two images of a first object; b) extracting in at least two of the images at least one feature from the respective image, c) providing at least one descriptor for an extracted feature, and storing the descriptors; d) matching descriptors in the first set of descriptors; e) computing a score parameter based on the result of the matching process; f) selecting at least one descriptor based on its score parameter; g) adding the selected descriptor(s) to a second set of descriptors; and h) updating the score parameter of descriptors in the first set based on a selection process and to the result of the matching process.
Owner:APPLE INC
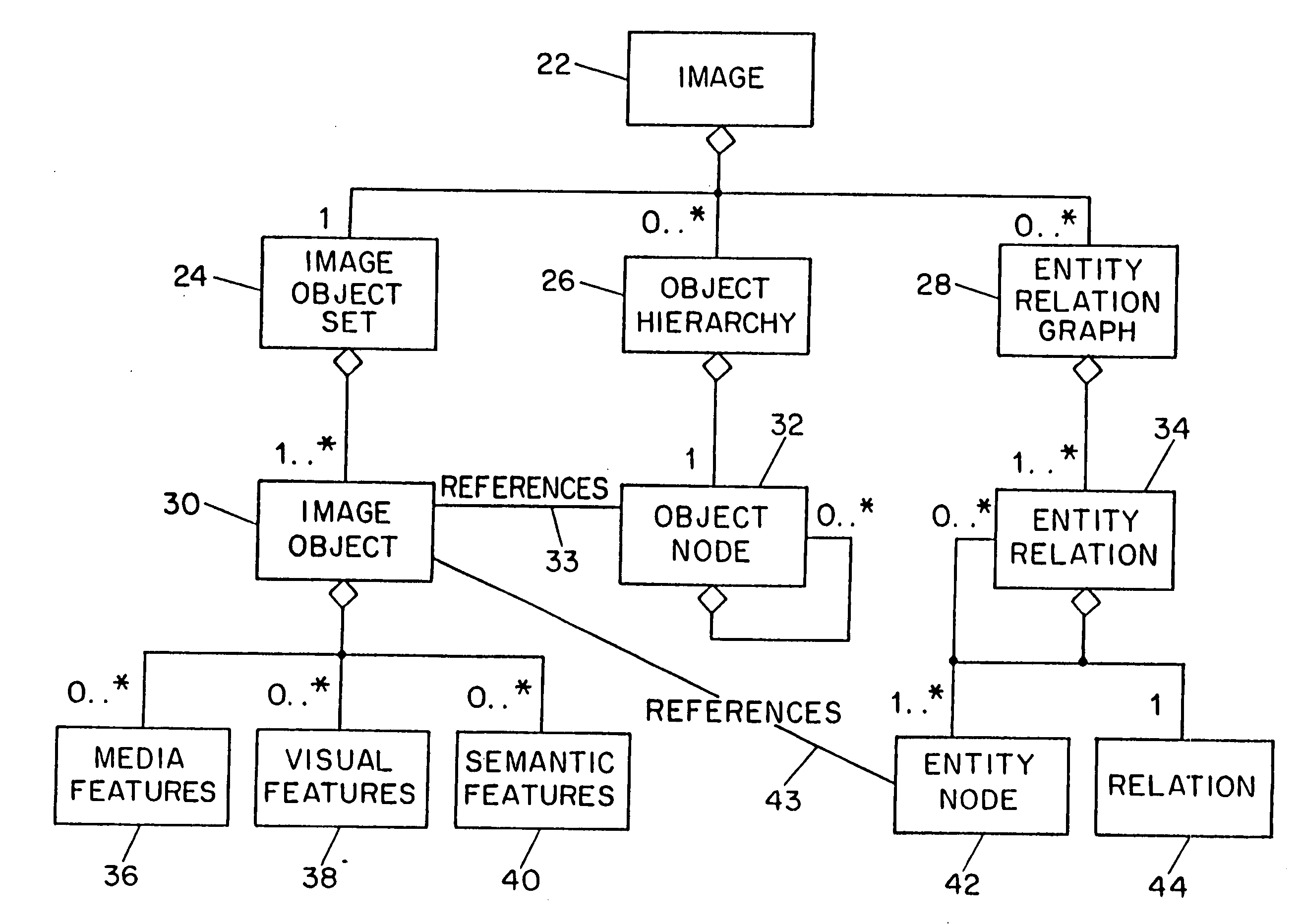
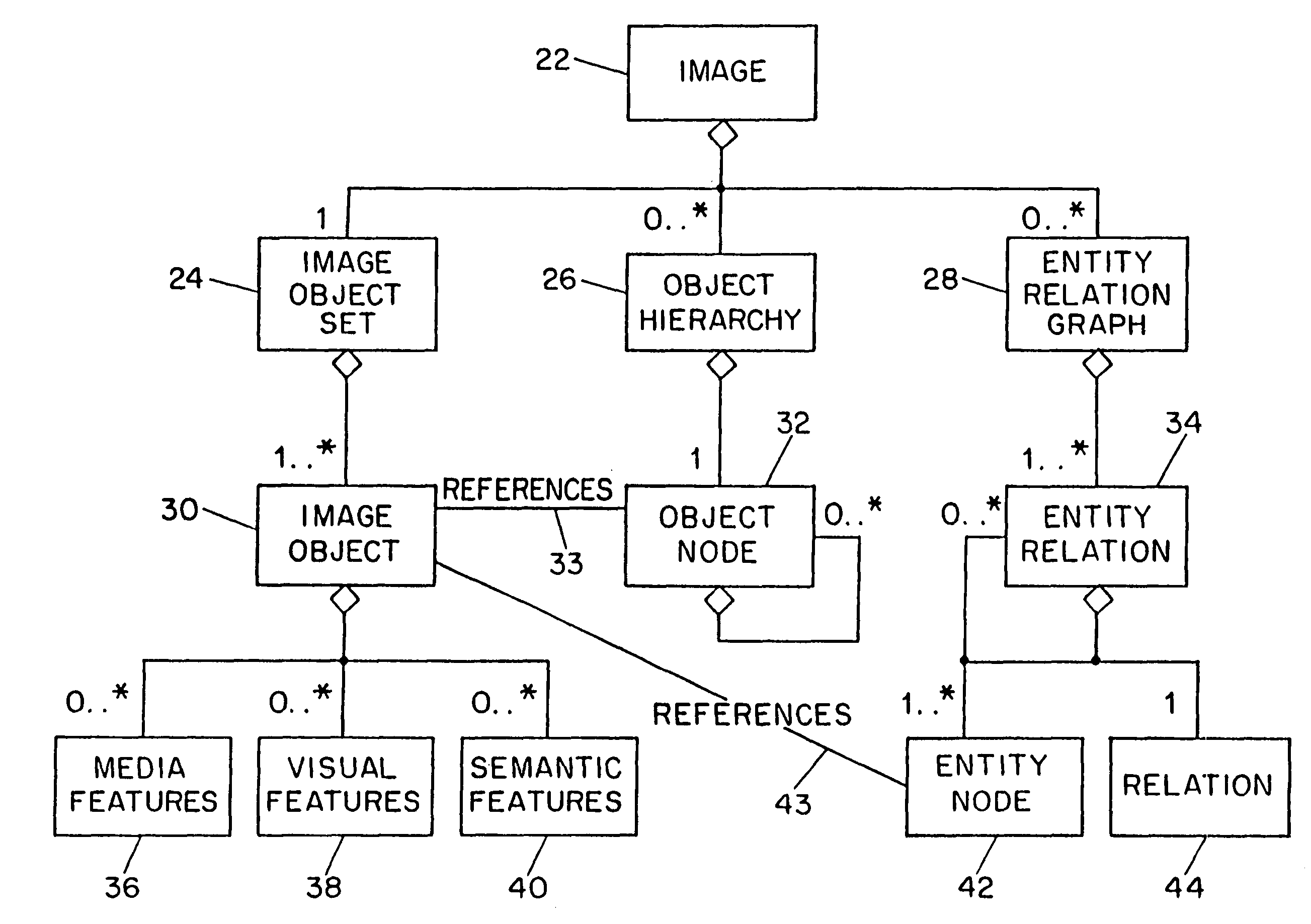
Image description system and method
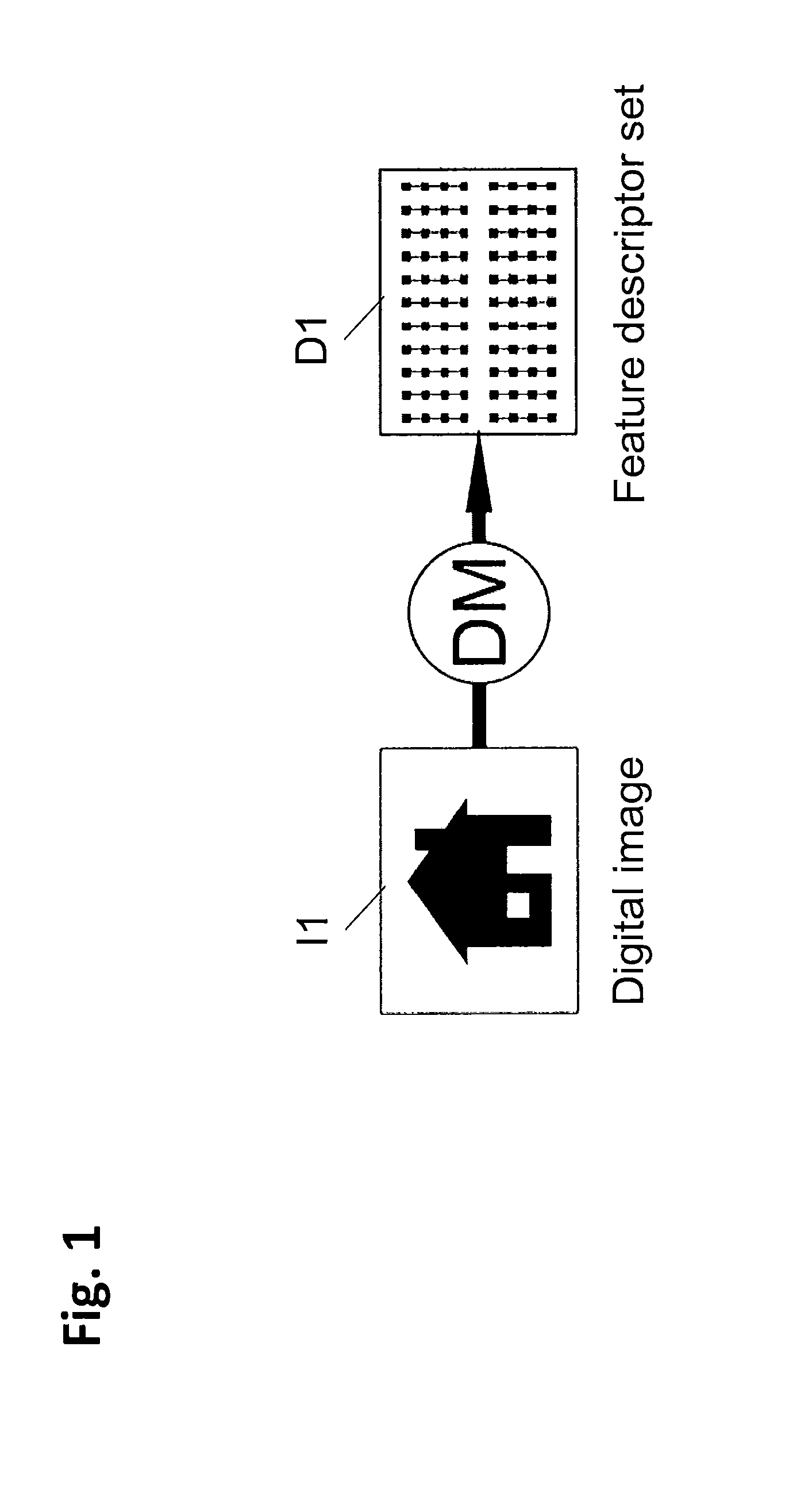
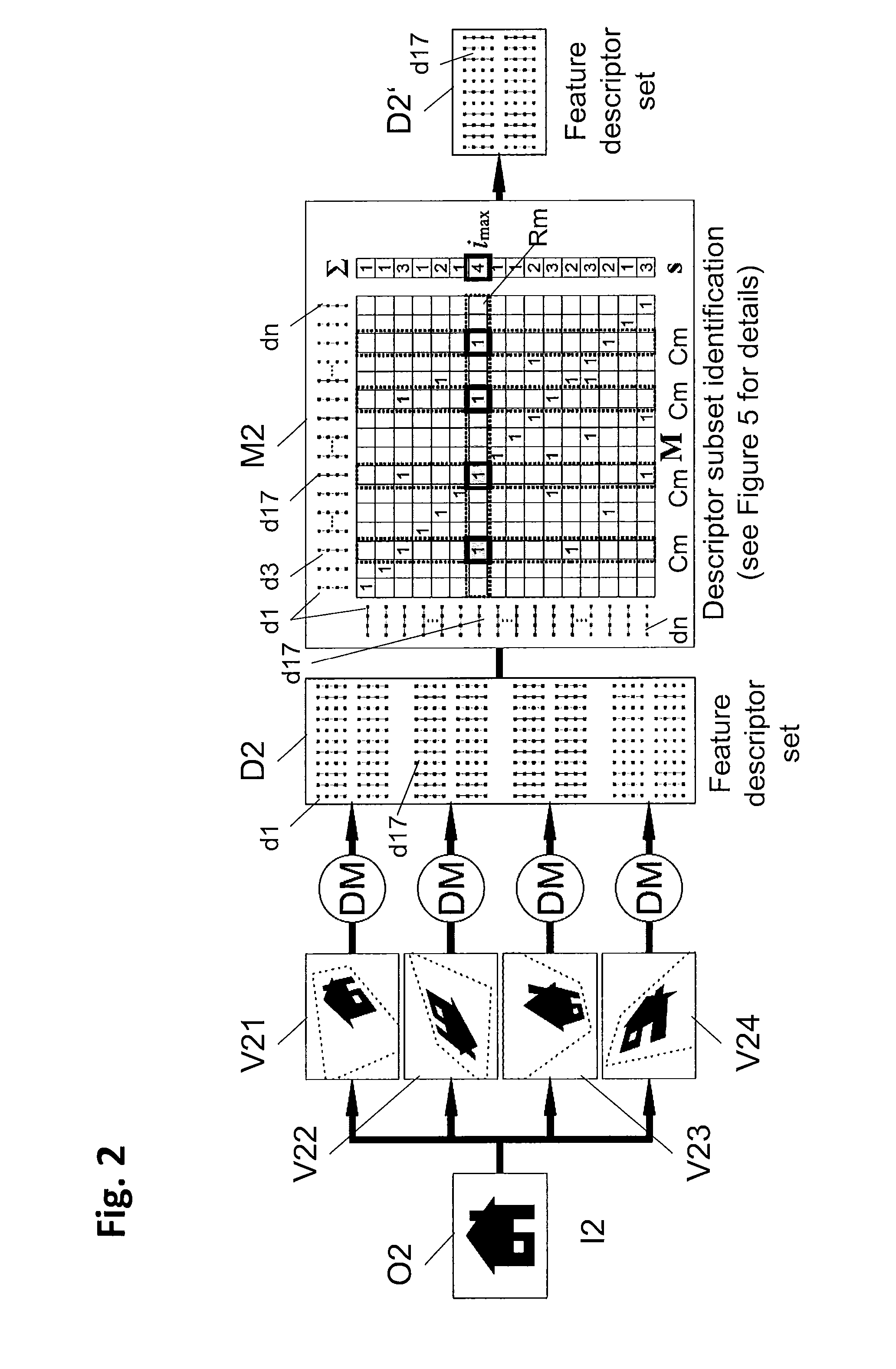
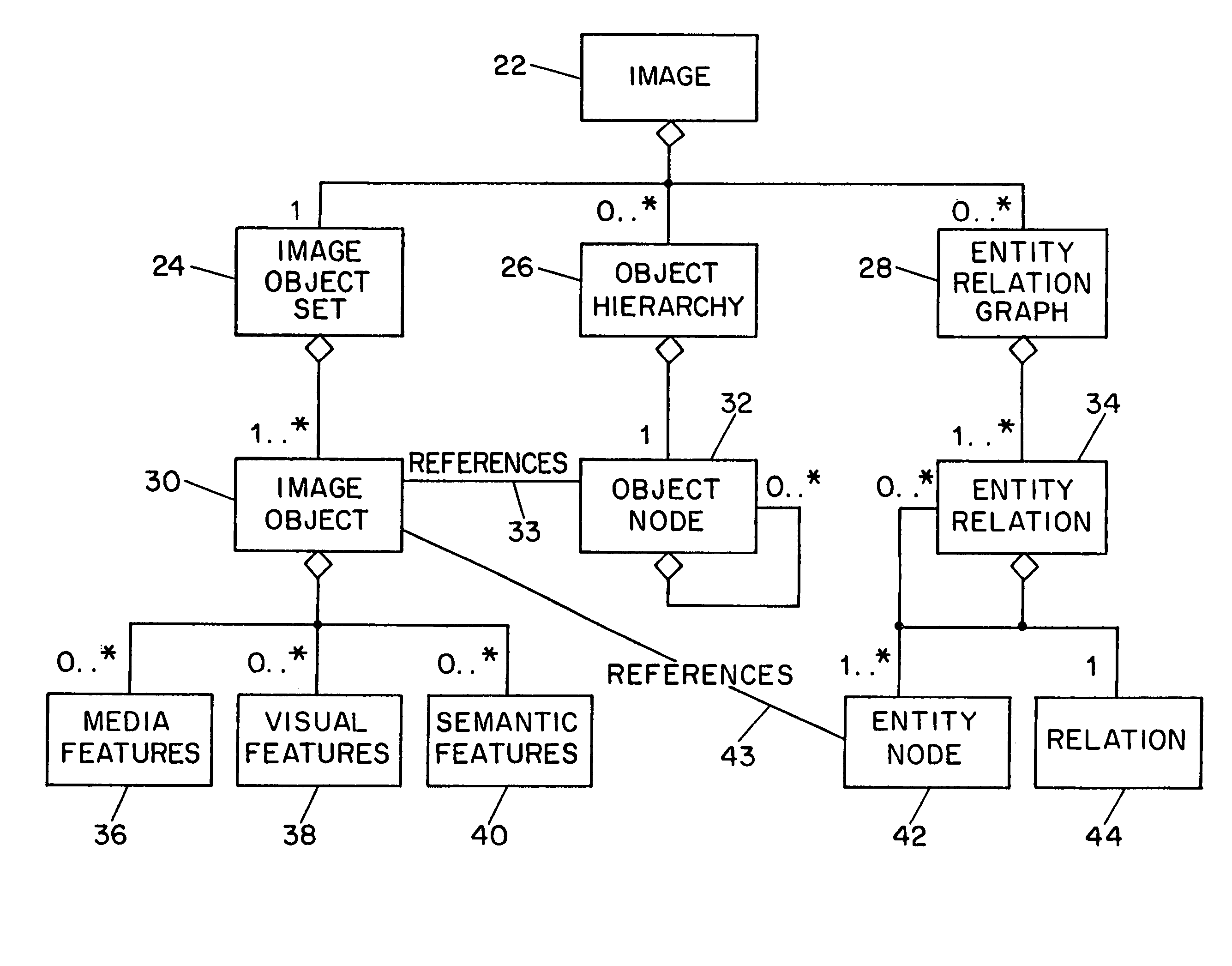
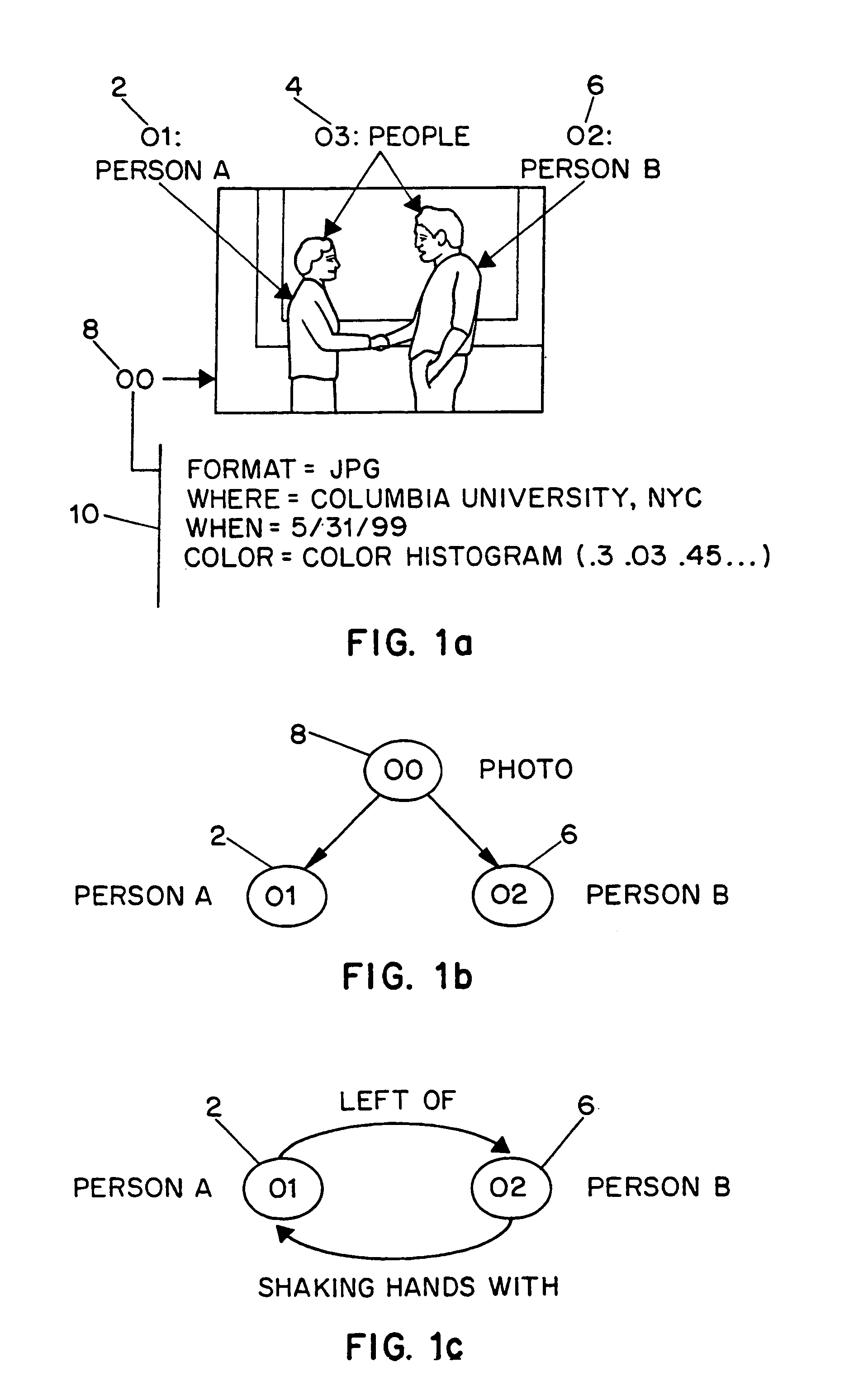
InactiveUS7254285B1Character and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationImage objectFeature descriptor
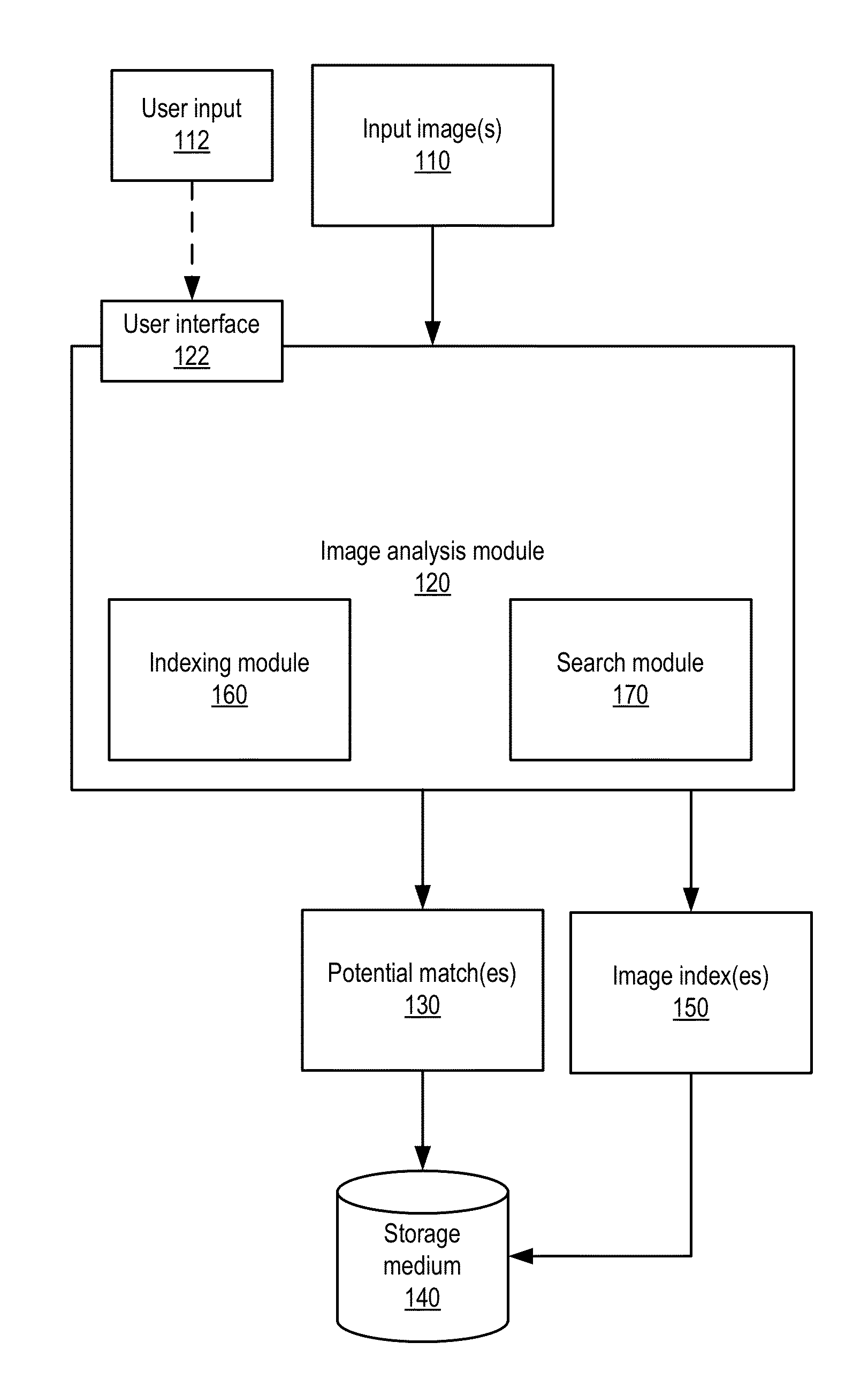
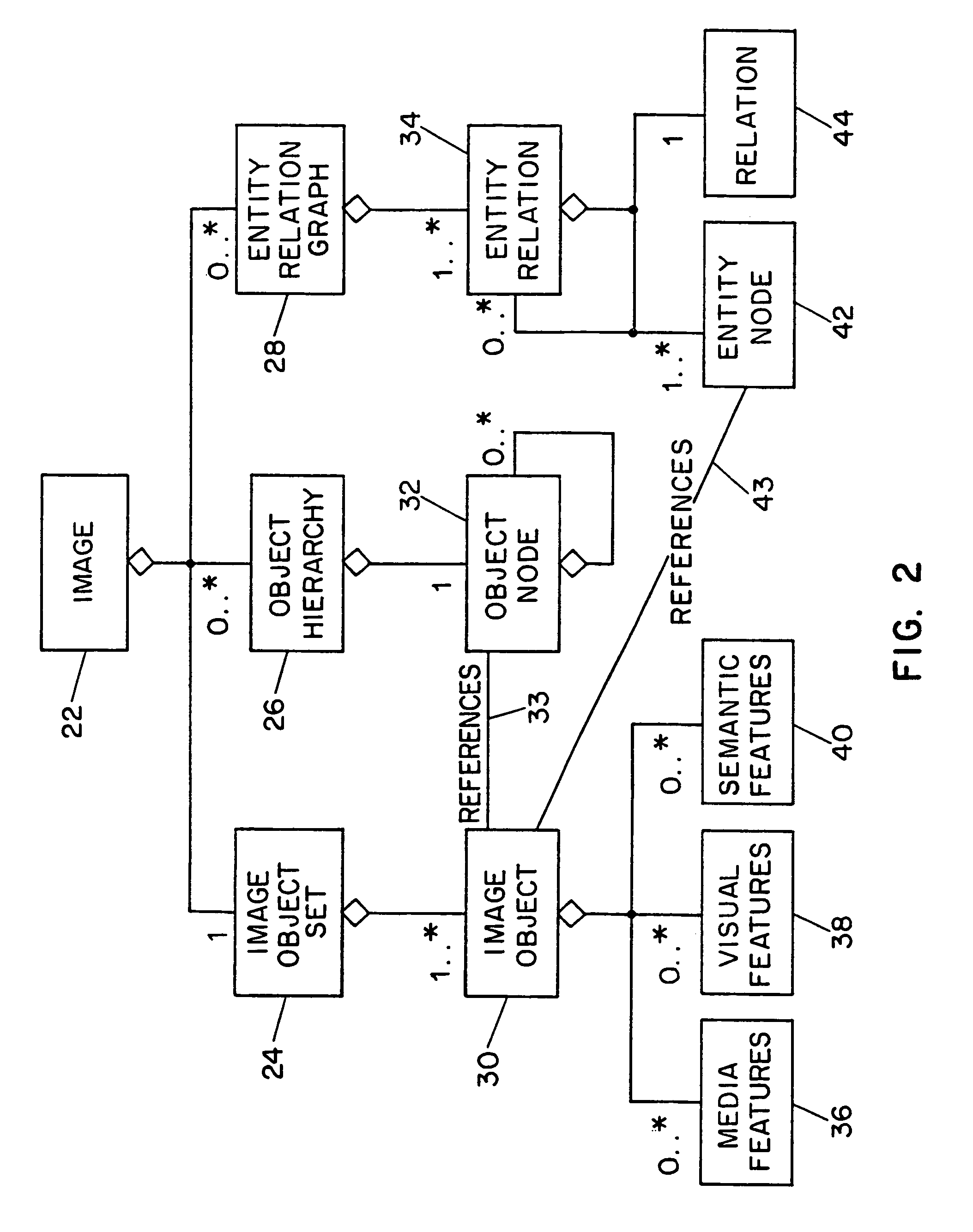
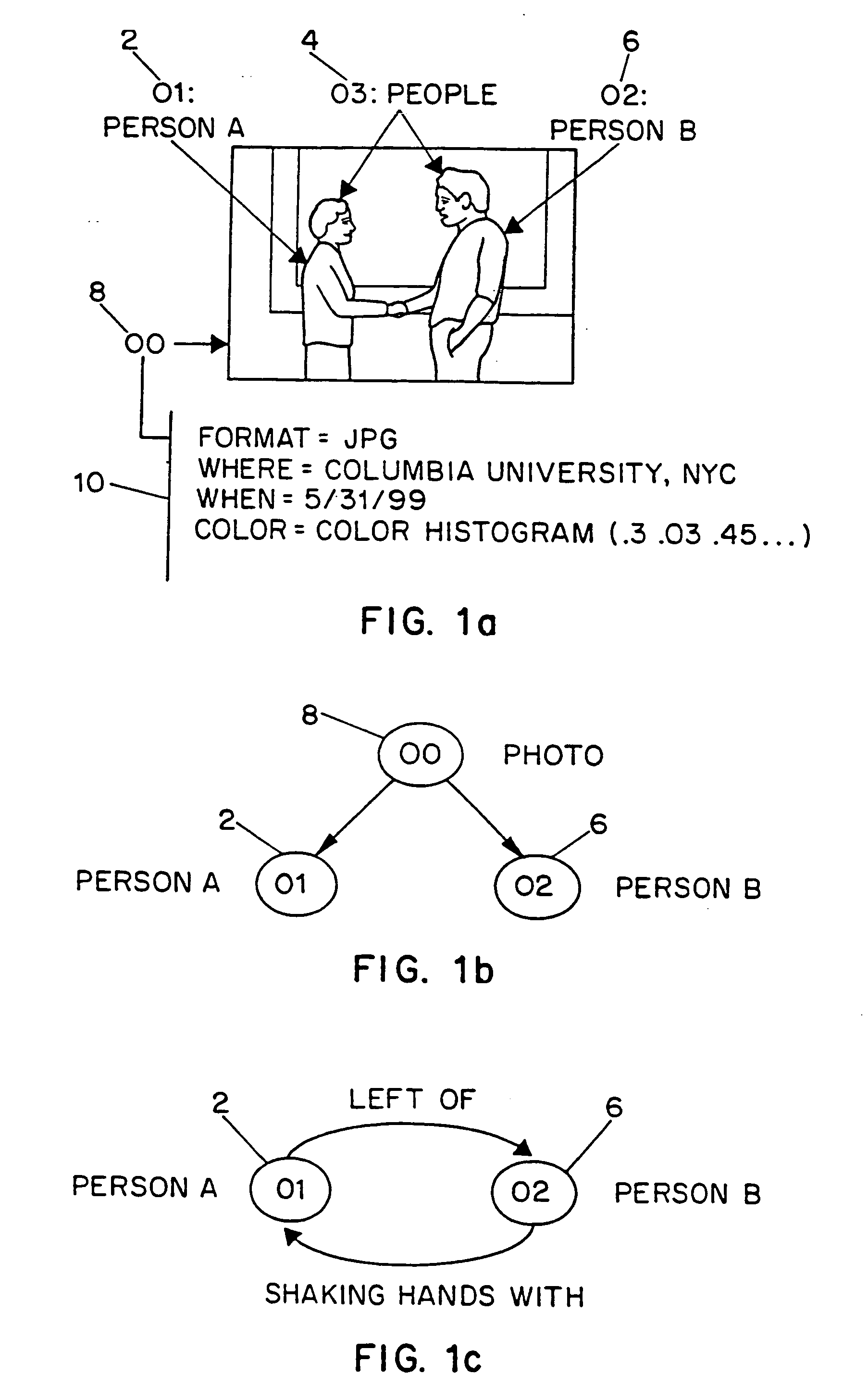
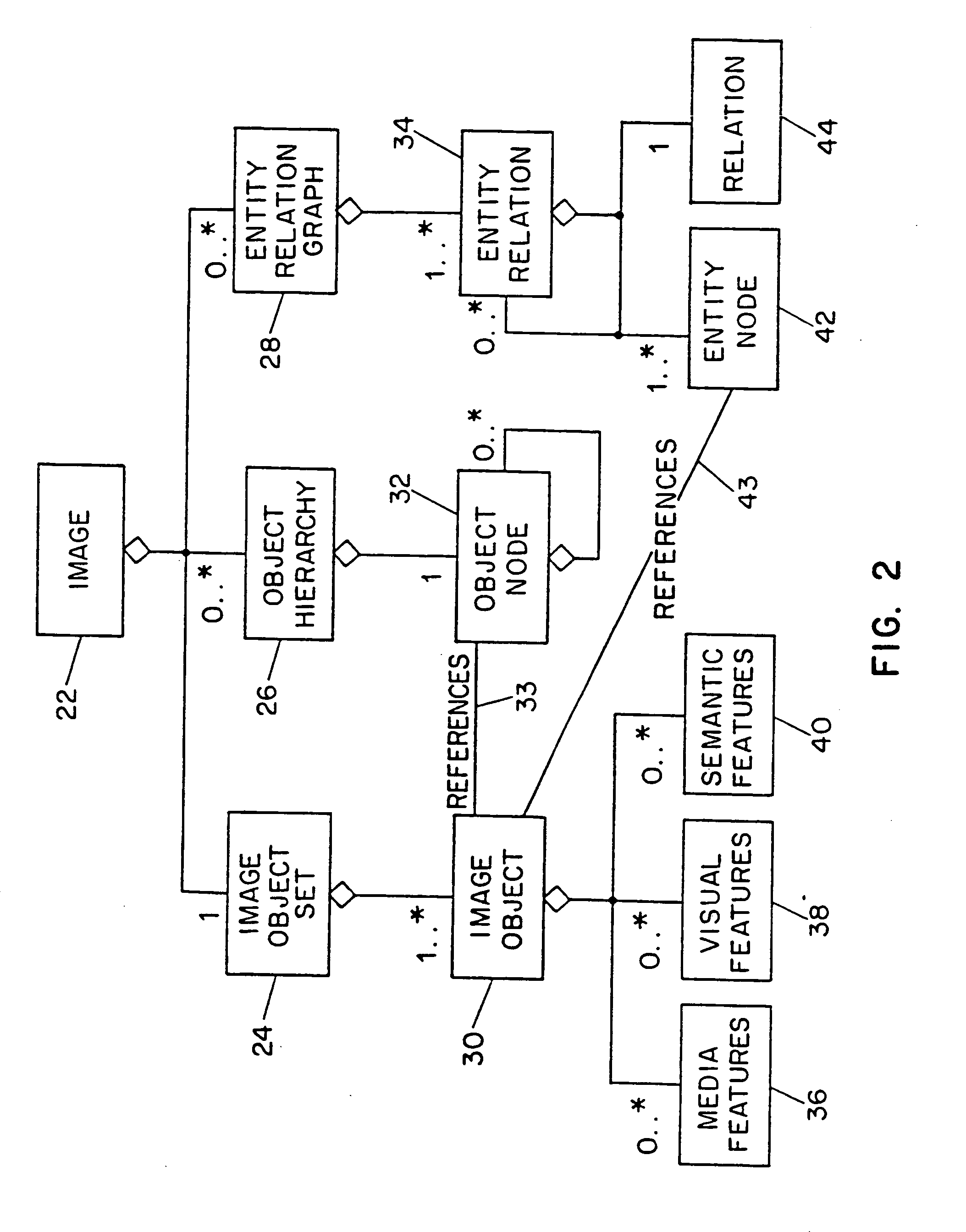
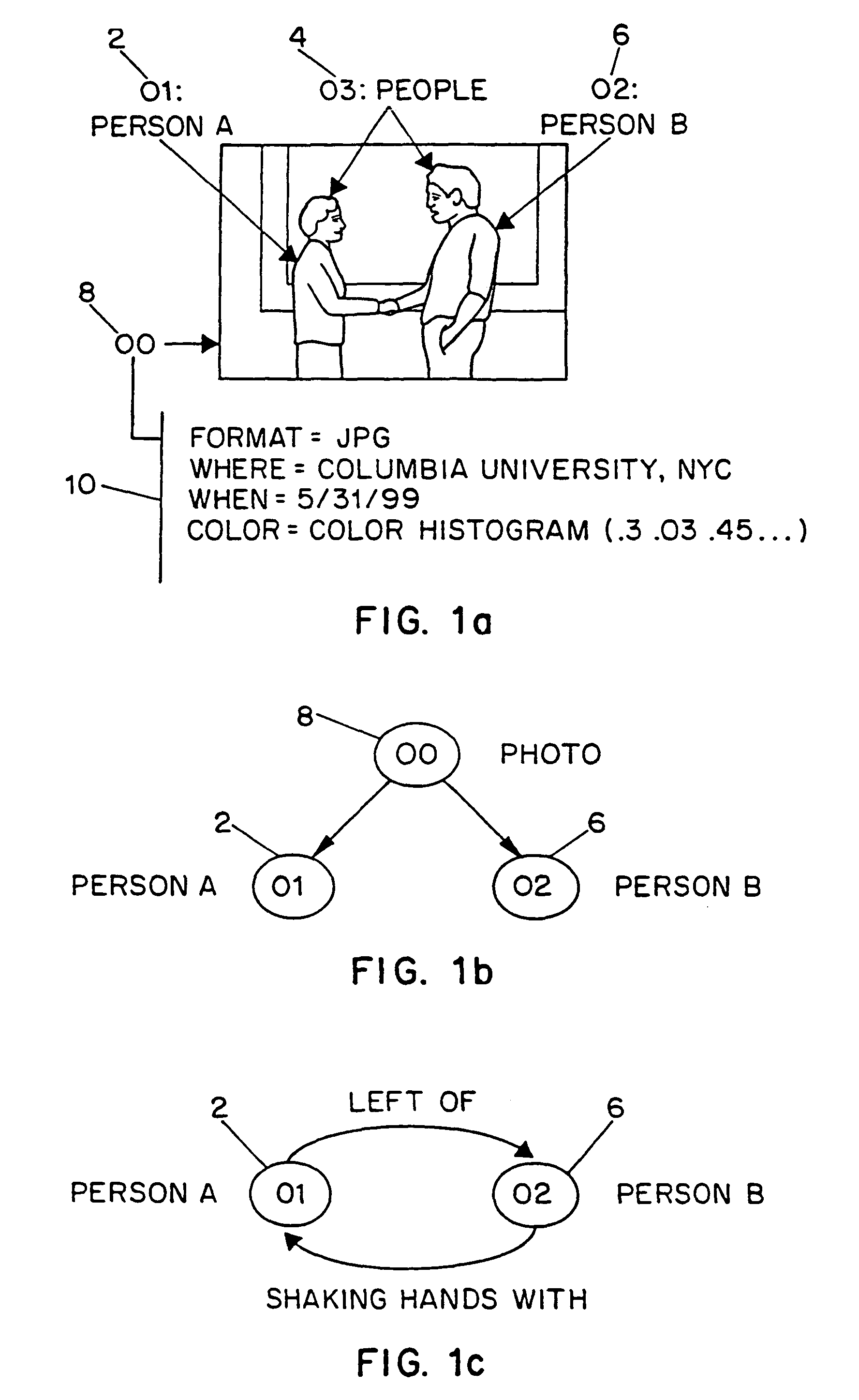
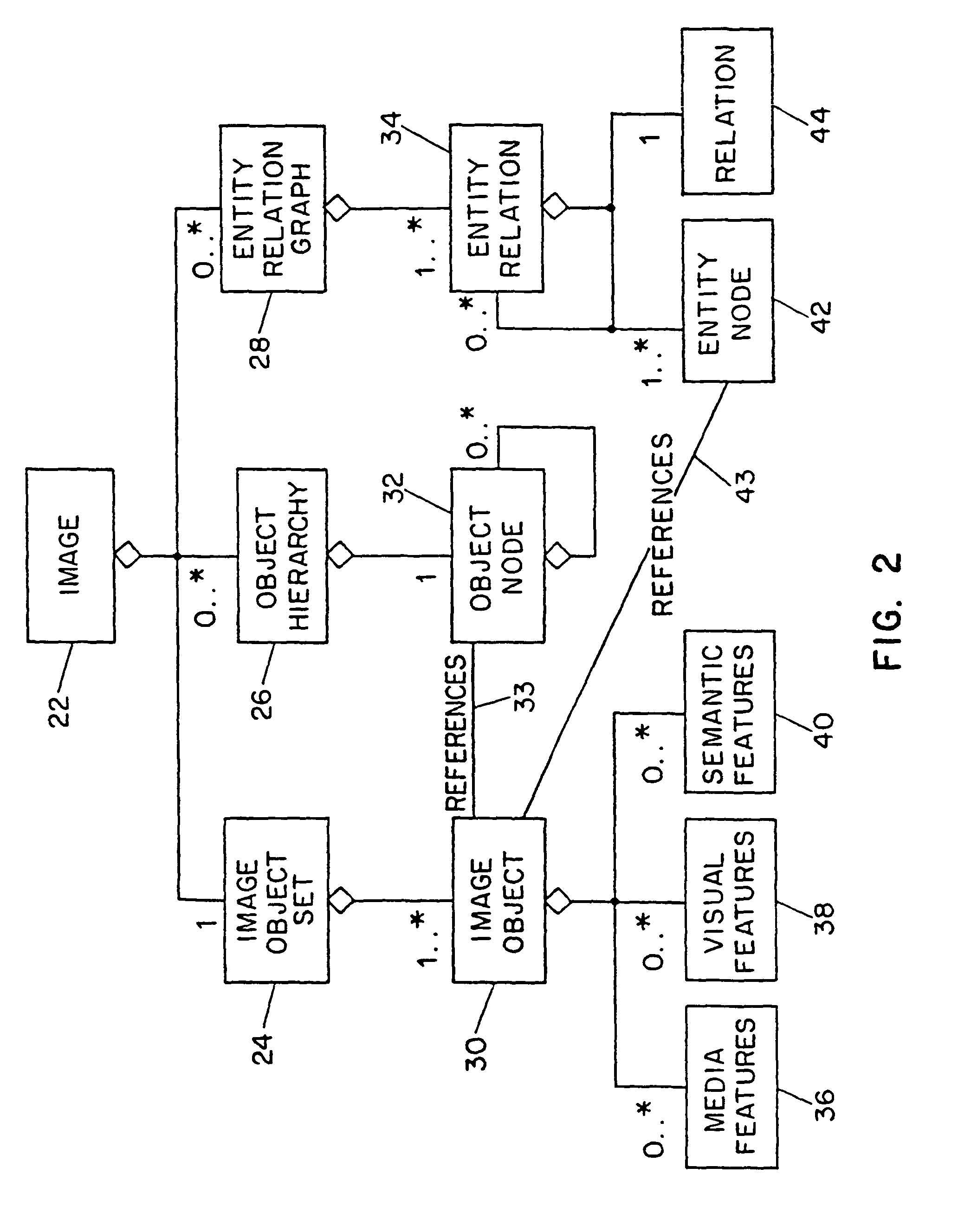
Systems and methods for describing image content establish image description records which include an object set (24), an object hierarchy (26) and entity relation graphs (28). For image content, image objects can include global objects (O0 8) and local objects (O1 2 and O2 6). The image objects are further defined by a number of features of different classes (36, 38 and 40), which in turn are further defined by a number of feature descriptors. The relationships between and among the objects in the object set are defined by the object hierarchy (26) and entity relation graphs (28). The image description records provide a standard vehicle for describing the content and context of image information for subsequent access and processing by computer applications such as search engines, filters, and archive systems.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Multi-image feature matching using multi-scale oriented patches
InactiveUS7382897B2Quick extractionEasy to liftConveyorsImage analysisPattern recognitionNear neighbor
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
End-to-end visual recognition system and methods
We describe an end-to-end visual recognition system, where “end-to-end” refers to the ability of the system of performing all aspects of the system, from the construction of “maps” of scenes, or “models” of objects from training data, to the determination of the class, identity, location and other inferred parameters from test data. Our visual recognition system is capable of operating on a mobile hand-held device, such as a mobile phone, tablet or other portable device equipped with sensing and computing power. Our system employs a video based feature descriptor, and we characterize its invariance and discriminative properties. Feature selection and tracking are performed in real-time, and used to train a template-based classifier during a capture phase prompted by the user. During normal operation, the system scores objects in the field of view based on their ranking.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
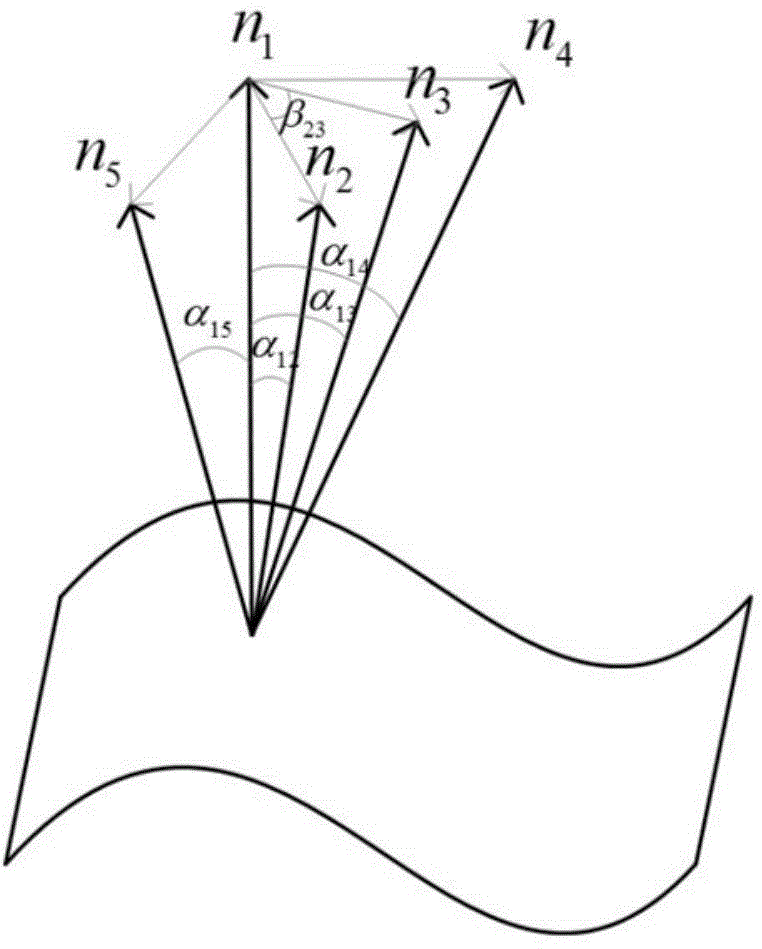
Novel descriptor for image corresponding point matching
ActiveUS20100080469A1Reduce complexityReduce dimensionalityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage gradientImage identification
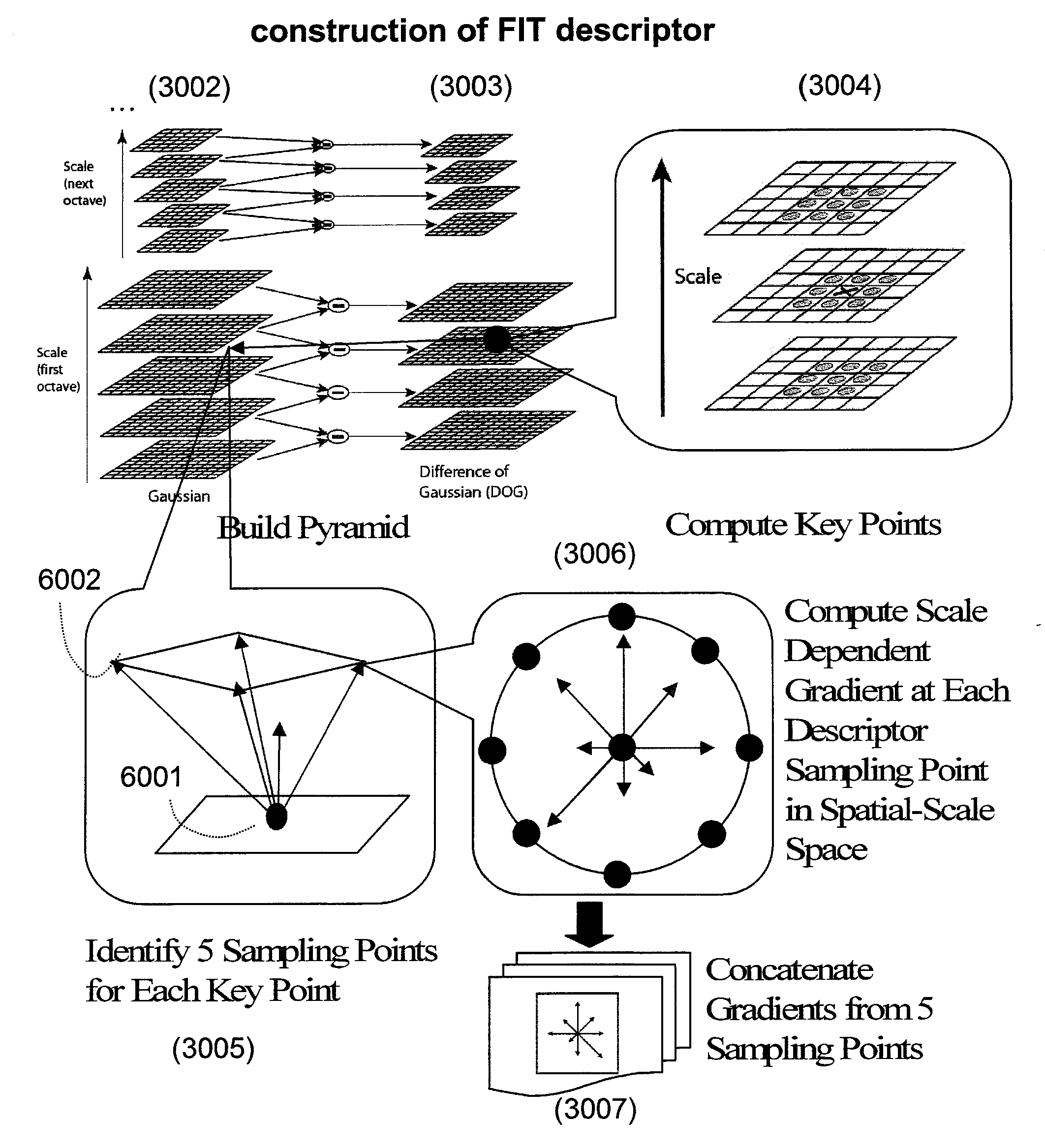
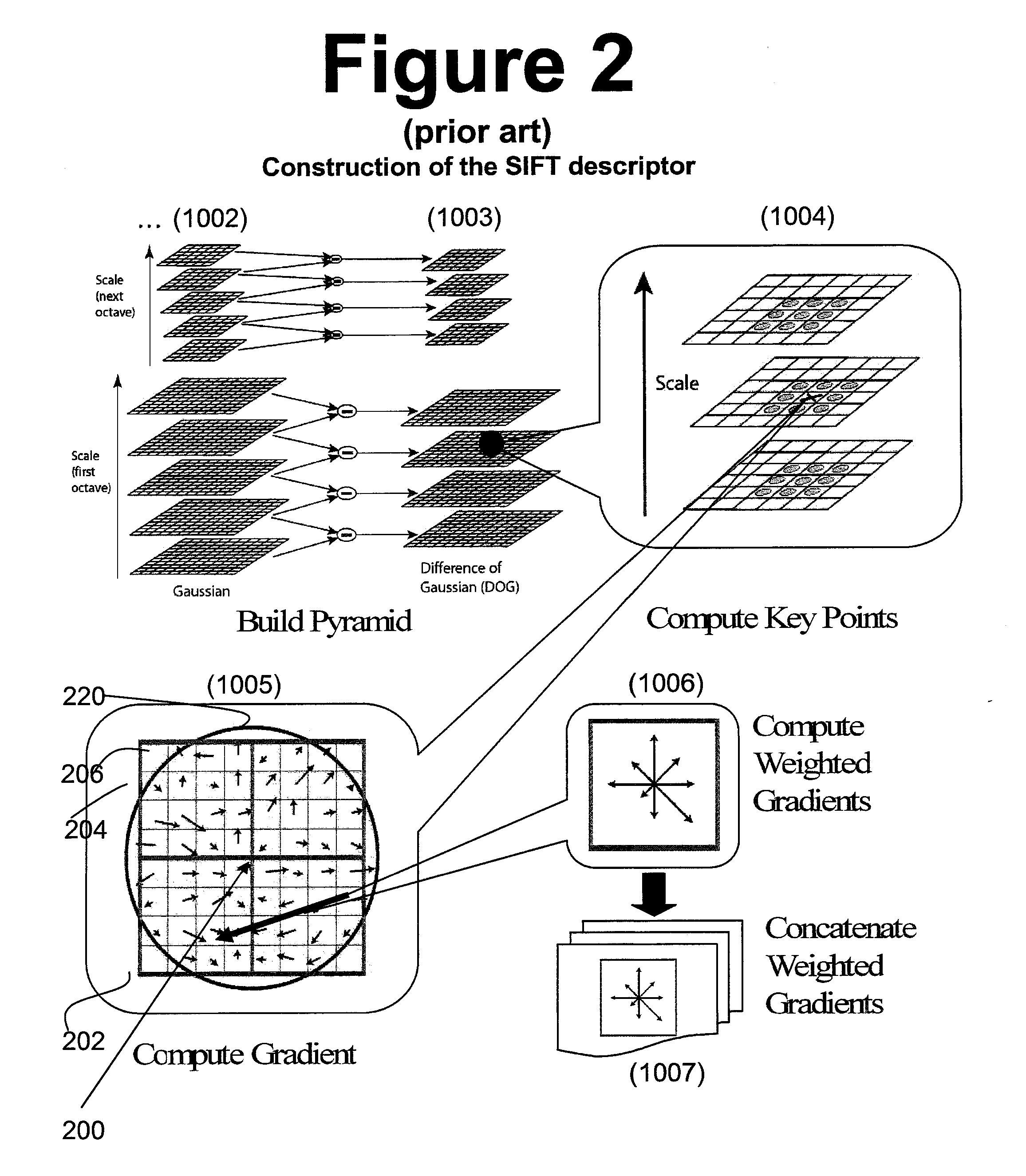
System and method of generating feature descriptors for image identification. Input image is Gaussian-blurred at different scales. A difference of Gaussian space is obtained from differences of adjacent Gaussian-blurred images. Key points are identified in the difference-of-Gaussian space. For each key point, primary sampling points are defined with three dimensional relative positions from key point and reaching into planes of different scales. Secondary sampling points are identified for each primary sampling point. Secondary image gradients are obtained between an image at a primary sampling point and images at secondary sampling points corresponding to this primary sampling point. Secondary image gradients form components of primary image gradients at primary sampling points. Primary image gradients are concatenated to obtain a descriptor vector for input image. Descriptor vector thus obtained is scale invariant and requires a number of additions equal to number of primary sampling points multiplied by a number of secondary sampling points.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
System And Method For Face Verification Using Video Sequence
ActiveUS20120070041A1Improve discriminationReduce computing costCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital data authenticationLocal binary pattern histogramFace verification
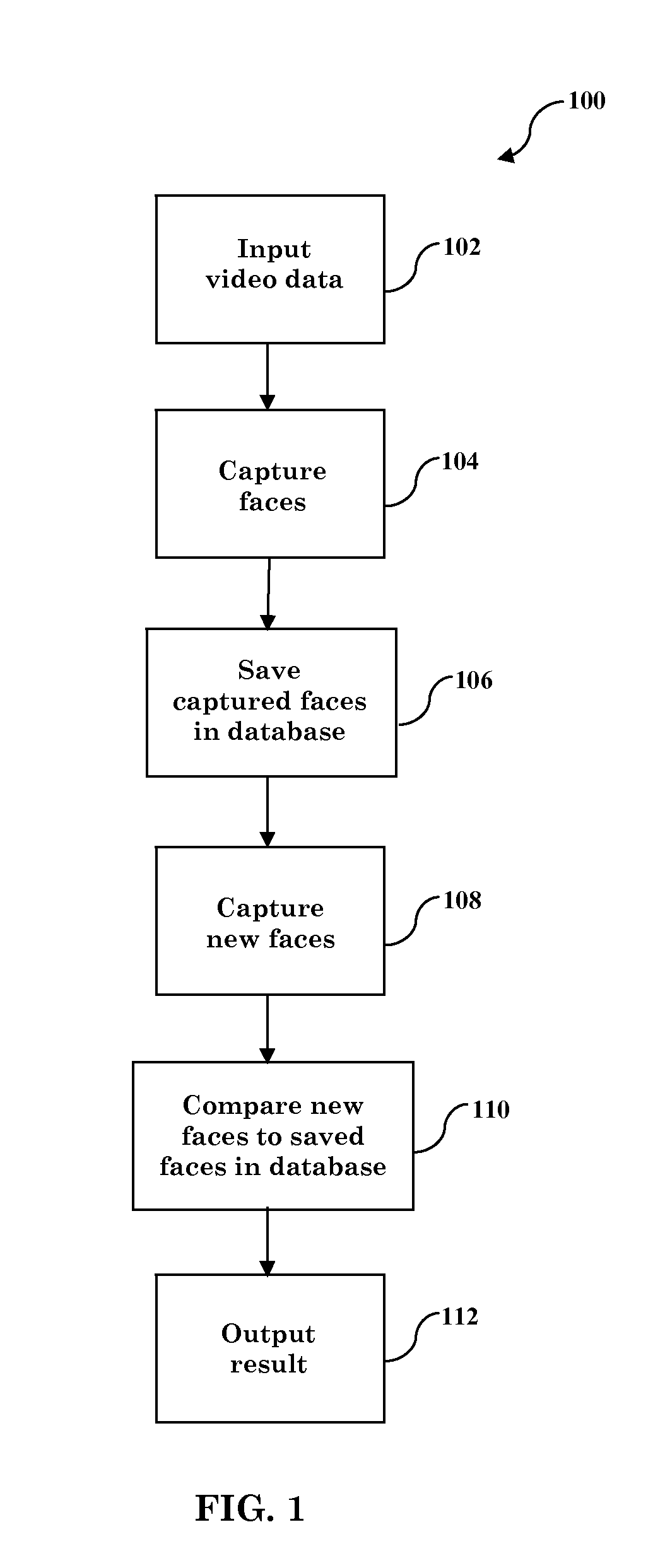
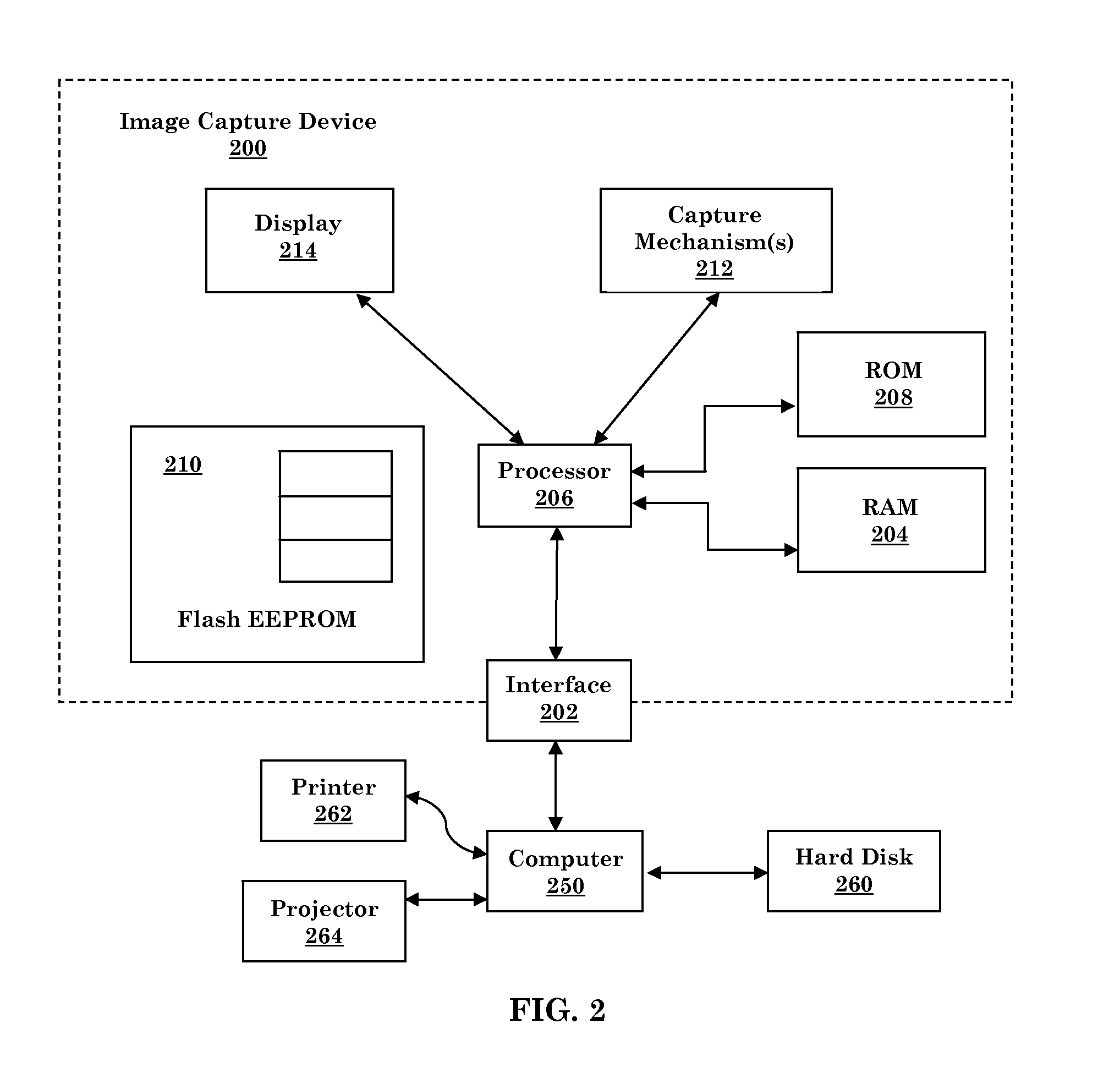
Face verification is performed using video data. The two main modules are face image capturing and face verification. In face image capturing, good frontal face images are captured from input video data. A frontal face quality score discriminates between frontal and profile faces. In face verification, a local binary pattern histogram is selected as the facial feature descriptor for its high discriminative power and computational efficiency. Chi-Square (χ2) distance between LBP histograms from two face images are then calculated as a face dissimilarity measure. The decision whether or not two images belong to the same person is then made by comparing the corresponding distance with a pre-defined threshold. Given the fact that more than one face images can be captured per person from video data, several feature based and decision based aggregators are applied to combine pair-wise distances to further improve the verification performance.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
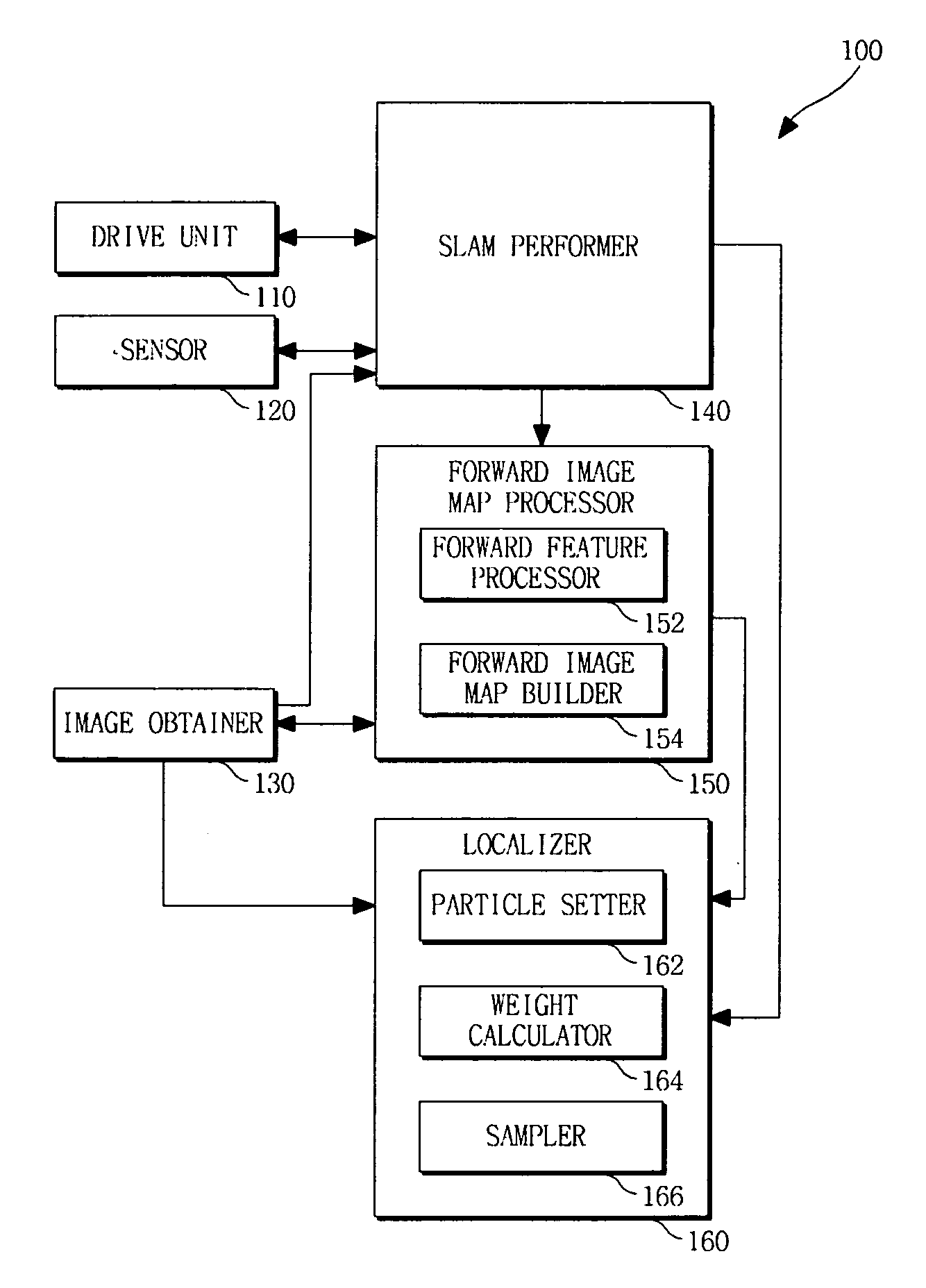
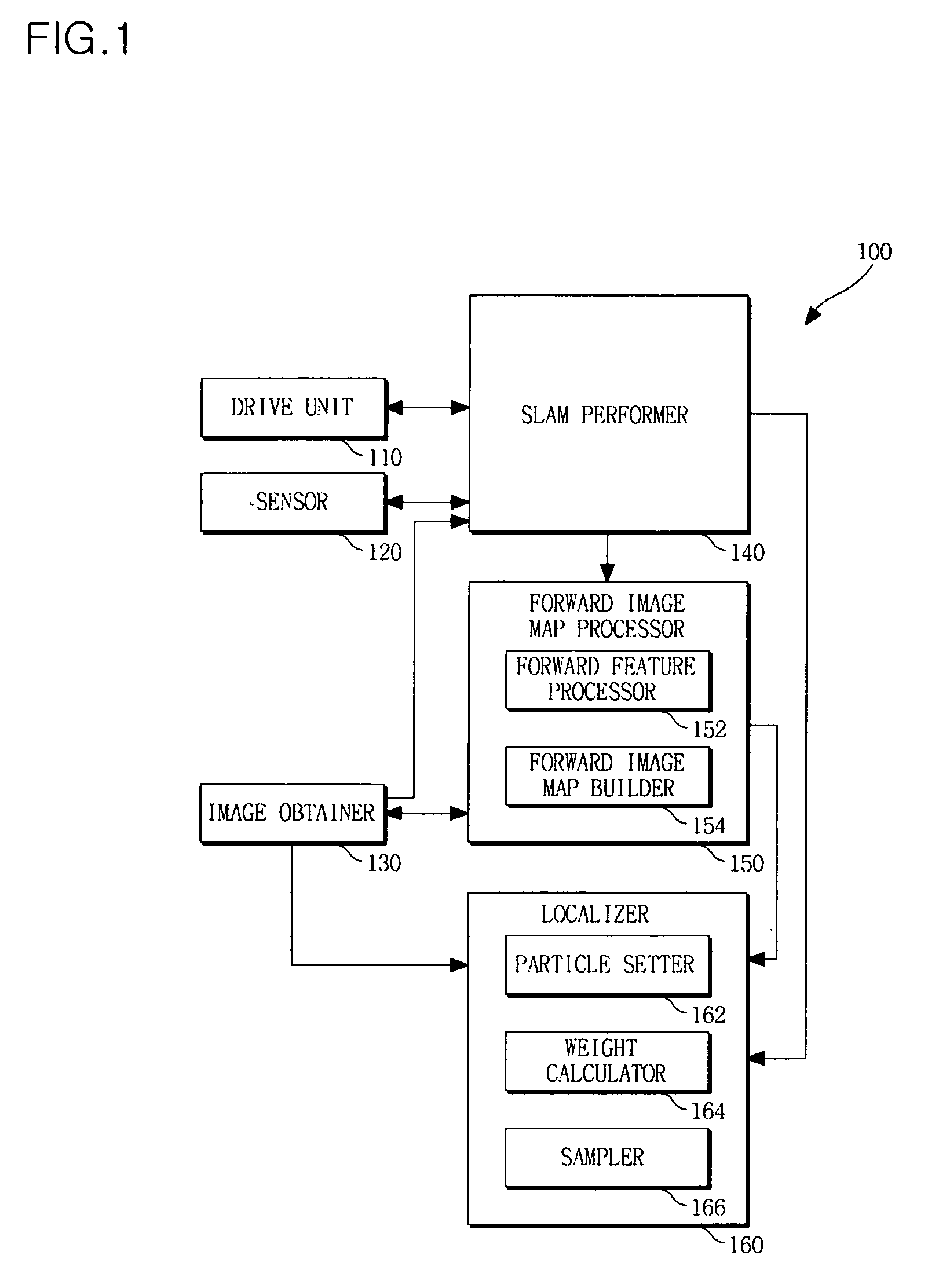
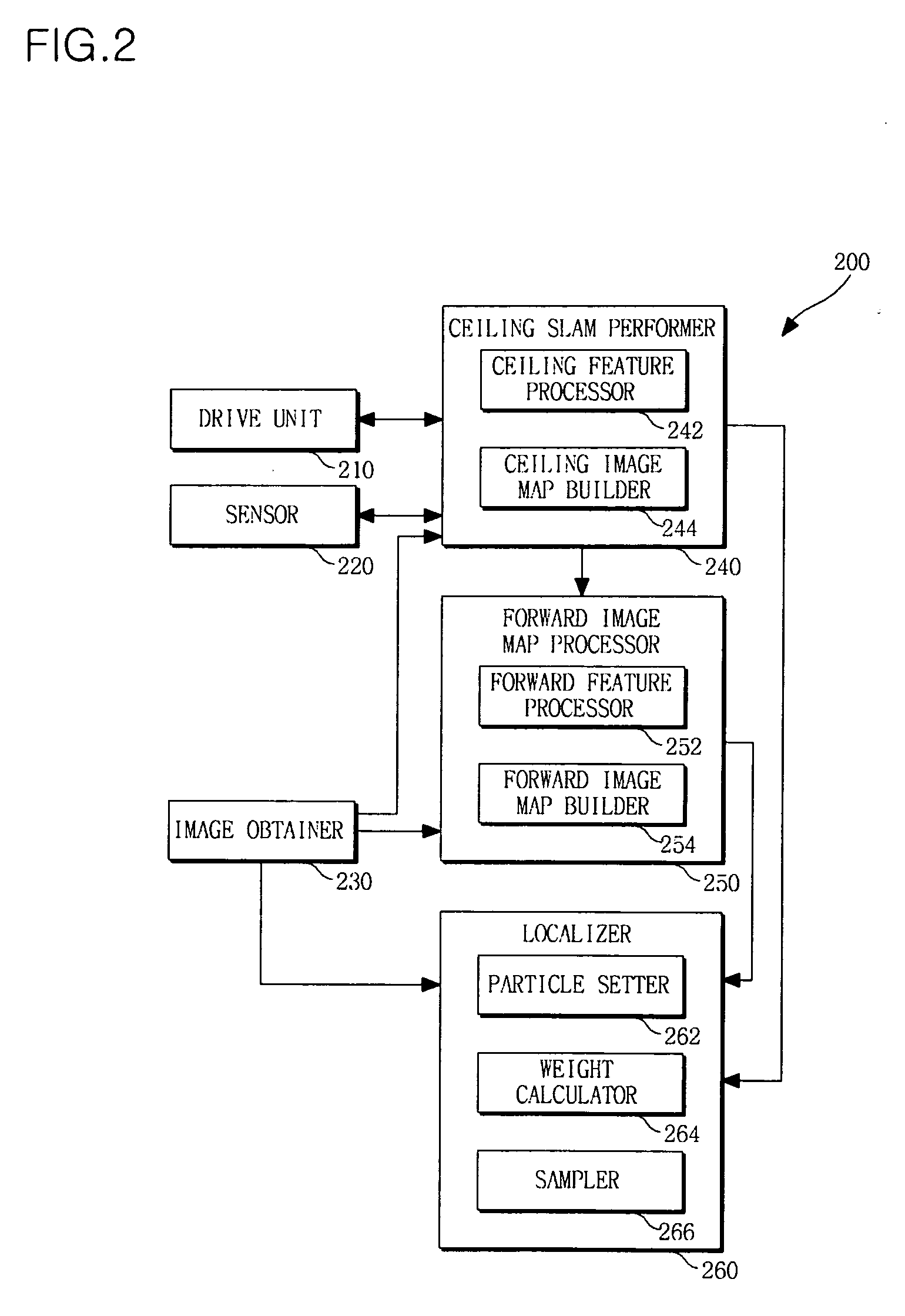
Apparatus and method for localizing mobile robot
ActiveUS20100070125A1Improve performanceWeight increaseImage enhancementImage analysisImage mapPositive direction
An apparatus and method for localizing a mobile robot are provided. The method includes building a forward image map including features extracted according to position at which the mobile robot takes forward images and feature descriptors of the extracted features, and localizing the mobile robot on the basis of features extracted from a newly input forward image and the built forward image map.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Video description system and method
InactiveUS20070245400A1Video data indexingAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsRelation graphEntity relation diagram
Systems and methods for describing video content establish video description records which include an object set (24), an object hierarchy (26) and entity relation graphs (28). Video objects can include global objects, segment objects and local objects. The video objects are further defined by a number of features organized in classes, which in turn are further defined by a number of feature descriptors (36, 38, and 40). The relationships (44) between and among the objects in the object set (24) are defined by the object hierarchy (26) and entity relation graphs (28). The video description records provide a standard vehicle for describing the content and context of video information for subsequent access and processing by computer applications such as search engines, filters and archive systems.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Scattered workpiece recognition and positioning method based on point cloud processing
InactiveCN108830902AAchieve a unique descriptionReduce the probability of falling into a local optimumImage enhancementImage analysisLocal optimumPattern recognition
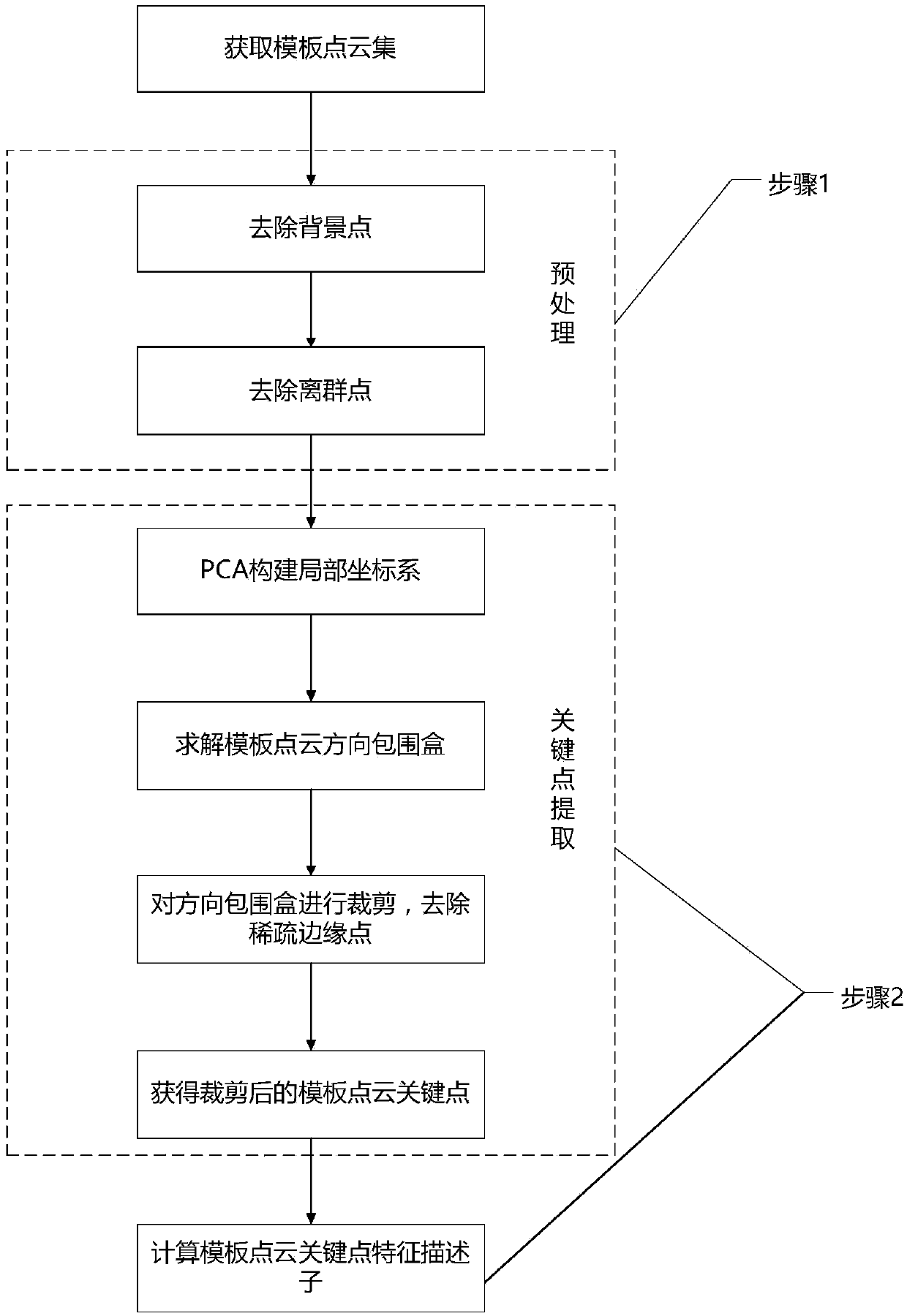
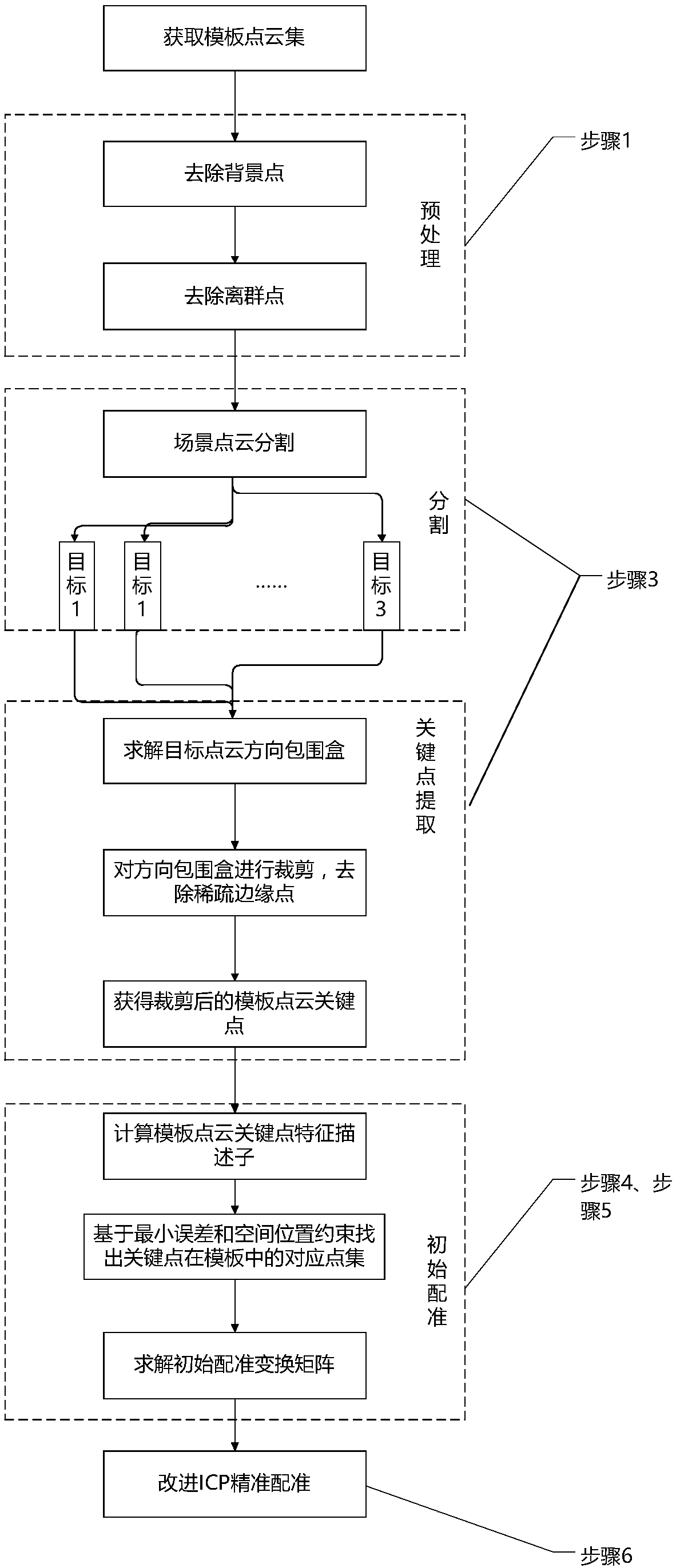
The invention discloses a scattered workpiece recognition and positioning method based on point cloud processing, and the method is used for solving a problem of posture estimation of scattered workpeics in a random box grabbing process. The method comprises two parts: offline template library building and online feature registration. A template point cloud data set and a scene point cloud are obtained through a 3D point cloud obtaining system. The feature information, extracted in an offline state, of a template point cloud can be used for the preprocessing, segmentation and registration of the scene point cloud, thereby improving the operation speed of an algorithm. The point cloud registration is divided into two stages: initial registration and precise registration. A feature descriptor which integrates the geometrical characteristics and statistical characteristics is proposed at the stage of initial registration, thereby achieving the uniqueness description of the features of a key point. Points which are the most similar to the feature description of feature points are searched from a template library as corresponding points, thereby obtaining a corresponding point set, andachieving the calculation of an initial conversion matrix. At the stage of precise registration, the geometrical constraints are added for achieving the selection of the corresponding points, therebyreducing the number of iteration times of the precise registration, and reducing the probability that the algorithm falls into the local optimum.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
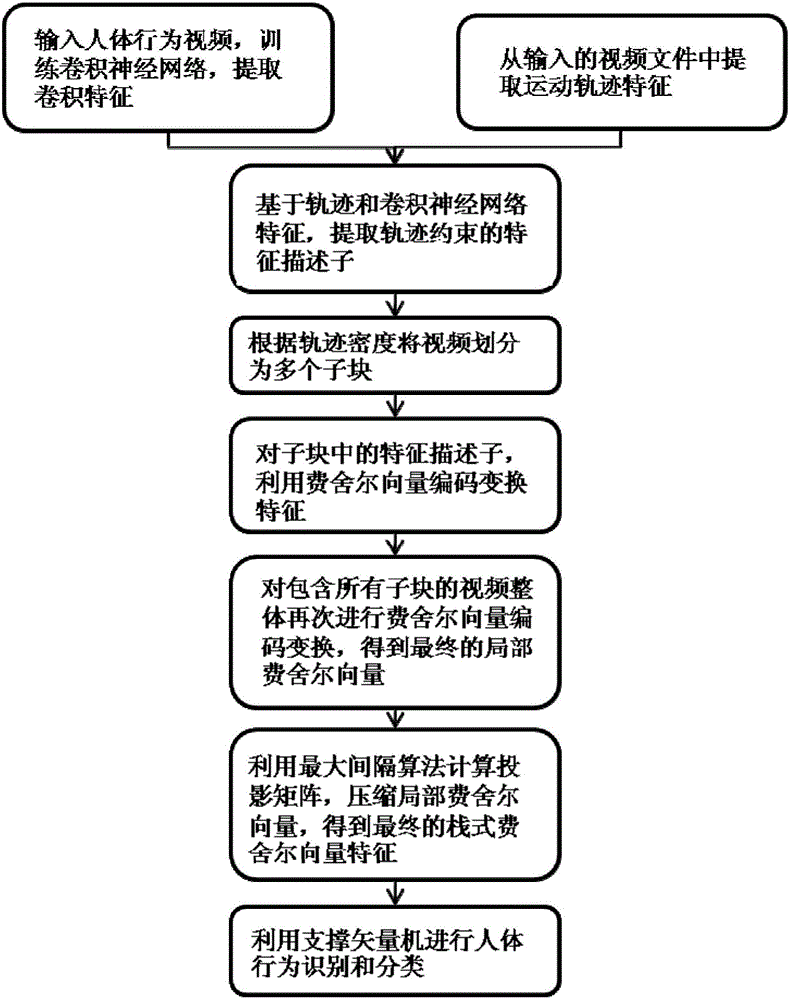
Track and convolutional neural network feature extraction-based behavior identification method
ActiveCN106778854AReduce computational complexityReduced characteristicsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesVideo monitoringHuman behavior
The invention discloses a track and convolutional neural network feature extraction-based behavior identification method, and mainly solves the problems of computing redundancy and low classification accuracy caused by complex human behavior video contents and sparse features. The method comprises the steps of inputting image video data; down-sampling pixel points in a video frame; deleting uniform region sampling points; extracting a track; extracting convolutional layer features by utilizing a convolutional neural network; extracting track constraint-based convolutional features in combination with the track and the convolutional layer features; extracting stack type local Fisher vector features according to the track constraint-based convolutional features; performing compression transformation on the stack type local Fisher vector features; training a support vector machine model by utilizing final stack type local Fisher vector features; and performing human behavior identification and classification. According to the method, relatively high and stable classification accuracy can be obtained by adopting a method for combining multilevel Fisher vectors with convolutional track feature descriptors; and the method can be widely applied to the fields of man-machine interaction, virtual reality, video monitoring and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
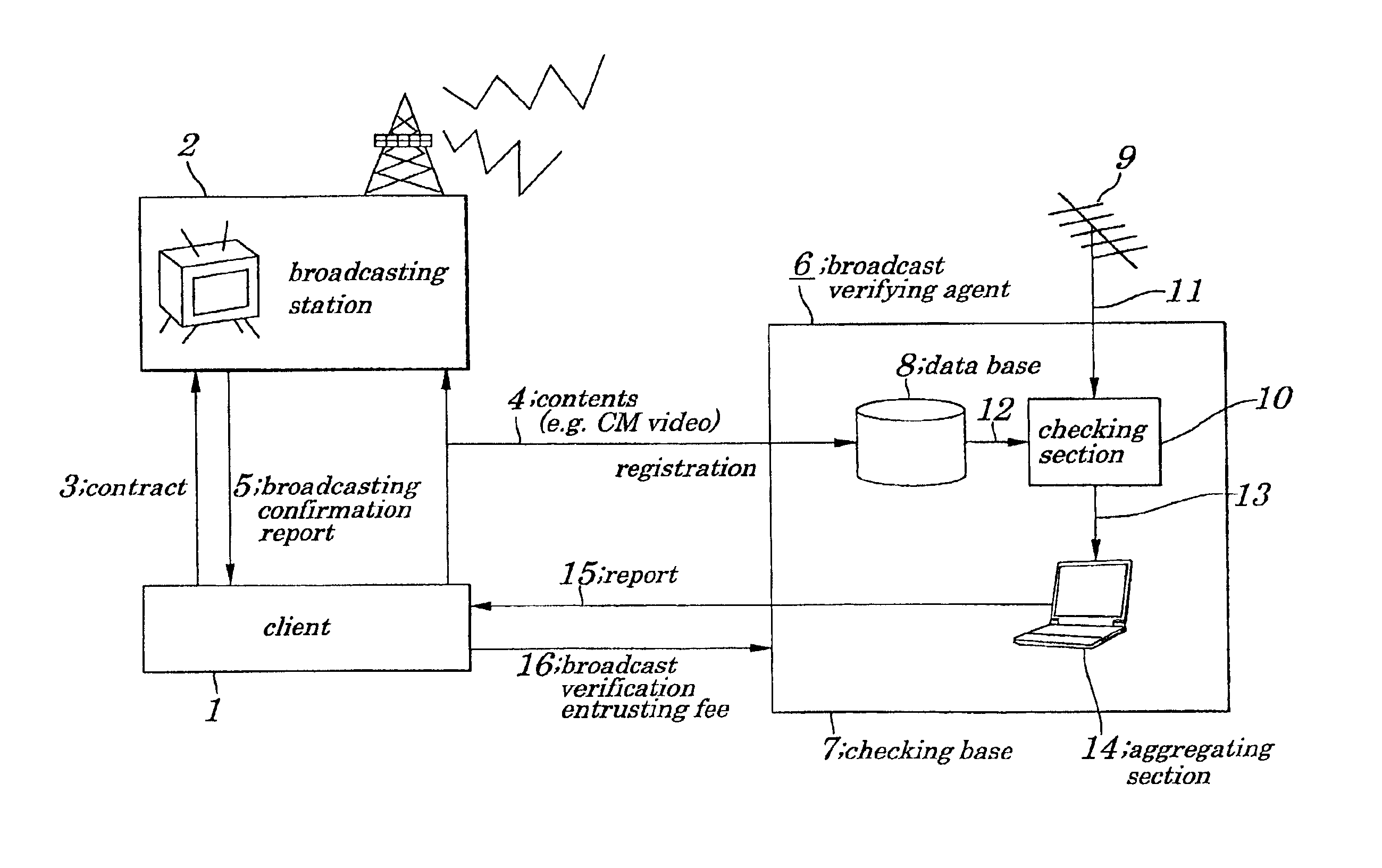
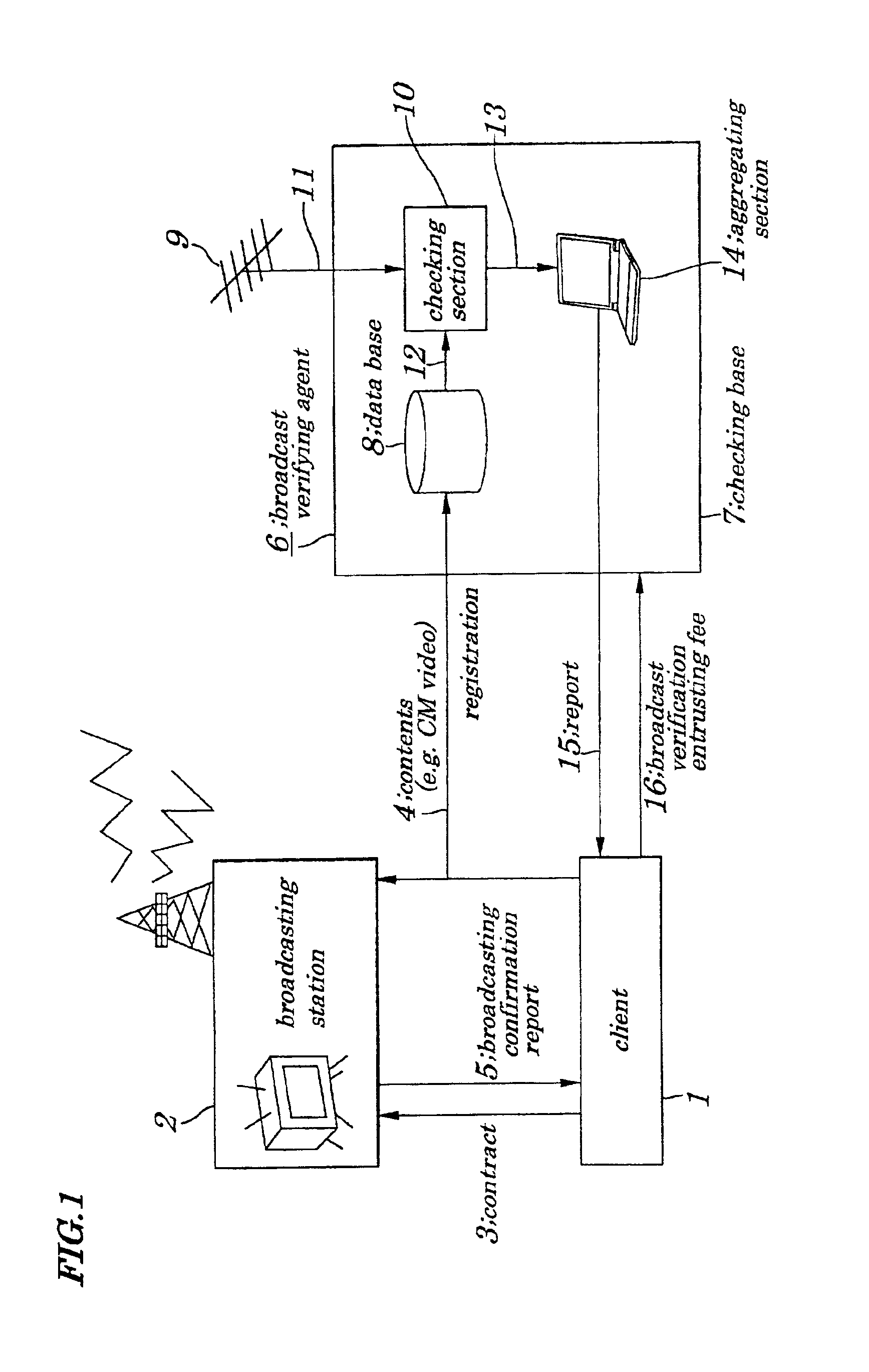
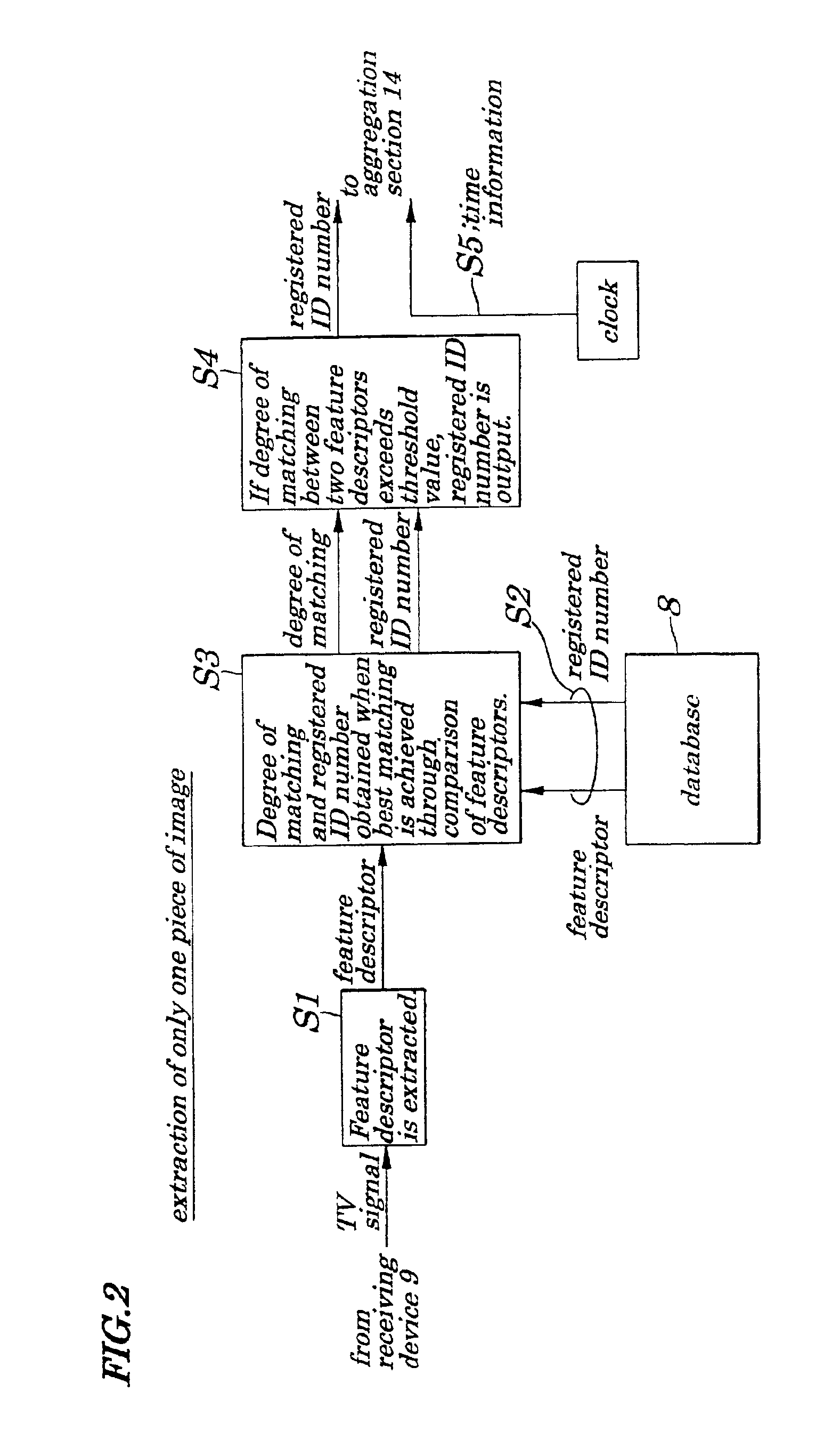
Broadcast verification system, broadcast verification method, broadcast verification apparatus and storage medium storing broadcast verification program
ActiveUS6880082B2Excellent in immediacy of operationEasy to detectUser identity/authority verificationAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast channelsThird party
A broadcast verification system is provided which enables broadcast verification to be performed by a third party being independent of a broadcasting station, without being assisted by another, at low costs and to be reported to a client.The client submits CM (Commercial Message) images to the broadcasting station and registers feature descriptors in a database. When the broadcasting station broadcasts the CM images in accordance with a contract, a receiving device in a checking base extracts contents from received broadcasting waves and a checking section compares feature descriptors of the contents with that of contents stored in the database. When there is coincidence between them, the checking section transmits comparison results to an aggregating section which creates a report including broadcast time, broadcasting channel, broadcasting state and submits it to the client. A broadcast verifying agent receives a broadcast verification entrusting fee.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
Video description system and method
InactiveUS8370869B2Video data indexingAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsRelation graphEntity relation diagram
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Visual Data Mining
ActiveUS20160239711A1Provide reliablyWeight optimizationDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionVisual perception
Method and system for finding targets within visual data, comprising receiving target object information. Generating a set of target object semantic attributes from the target object information. Identifying a plurality of candidate objects within visual data. Generating a set of low-level feature descriptors from the visual data for each candidate object. Generating from the set of low-level feature descriptors a set of candidate semantic attributes for each candidate object within the visual data. Identifying one or more portions of the visual data containing a candidate object, from the plurality of candidate objects, having a set of candidate object semantic attributes that match the set of target object semantic attributes. Providing an output indicating the identified one or more portions of the visual data.
Owner:VERITONE
Method and apparatus for sensor aided extraction of spatio-temportal features
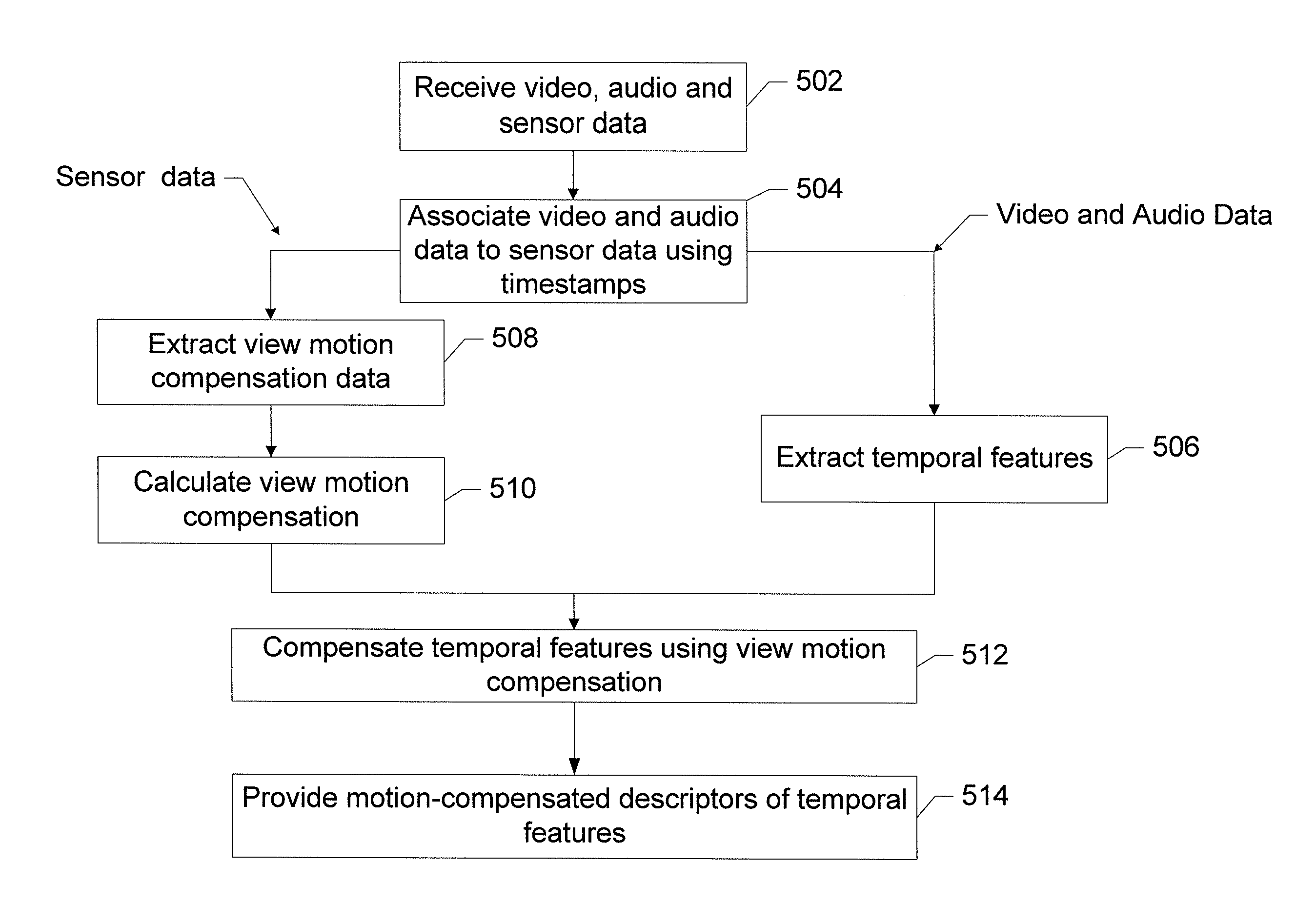
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided for extracting spatio-temporal features with the aid of sensor information. An exemplary method comprises receiving video data and auxiliary sensor data and associating the two with timestamp information. The method may also include segmenting an input data stream into stable segments and extracting temporal features from the associated video data. The method may further include extracting temporal features either form the whole video or only from the video data where little or no stable segments are detected and performing camera view motion compensation by using information provided by the auxiliary sensors for modifying the feature-descriptors.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Multi-scale normal feature point cloud registering method
ActiveCN104143210AEvenly distributedRecognizable3D-image renderingSingular value decompositionFeature vector
The invention relates to a multi-scale normal feature point cloud registering method. The multi-scale normal feature point cloud registering method is characterized by including the steps that two-visual-angle point clouds, including the target point clouds and the source point clouds, collected by a point cloud obtaining device are read in; the curvature of radius neighborhoods of three scales of points is calculated, and key points are extracted from the target point clouds and the source point clouds according to a target function; the normal vector angular deviation and the curvature of the key points in the radius neighborhoods of the different scales are calculated and serve as feature components, feature descriptors of the key points are formed, and a target point cloud key point feature vector set and a source point cloud key point feature vector set are accordingly obtained; according to the similarity level of the feature descriptors of the key points, the corresponding relations between the target point cloud key points and the source point cloud key points are preliminarily determined; the wrong corresponding relations are eliminated, and the accurate corresponding relations are obtained; the obtained accurate corresponding relations are simplified with the clustering method, and the evenly-distributed corresponding relations are obtained; singular value decomposition is carried out on the final corresponding relations to obtain a rigid body transformation matrix.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
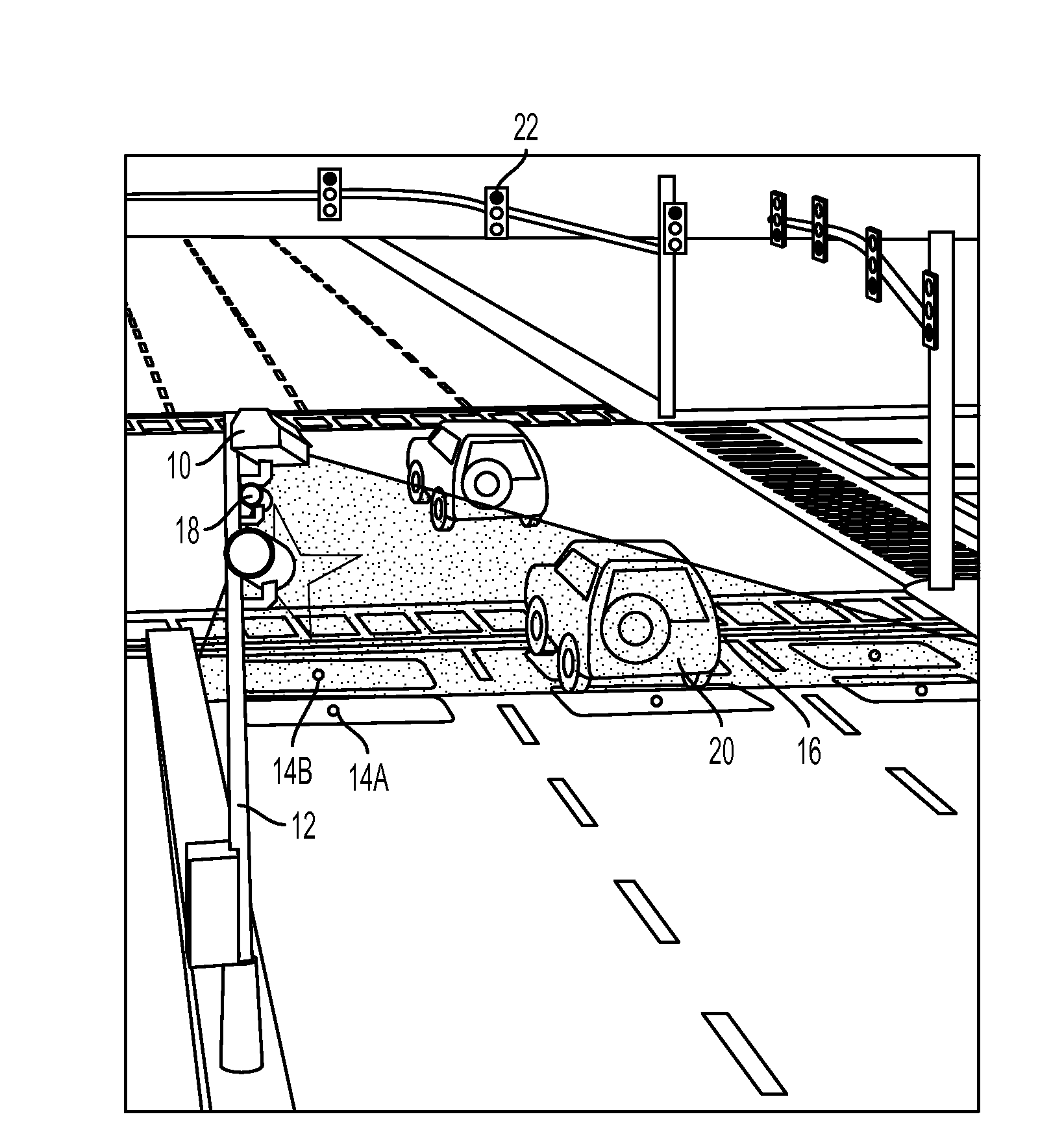
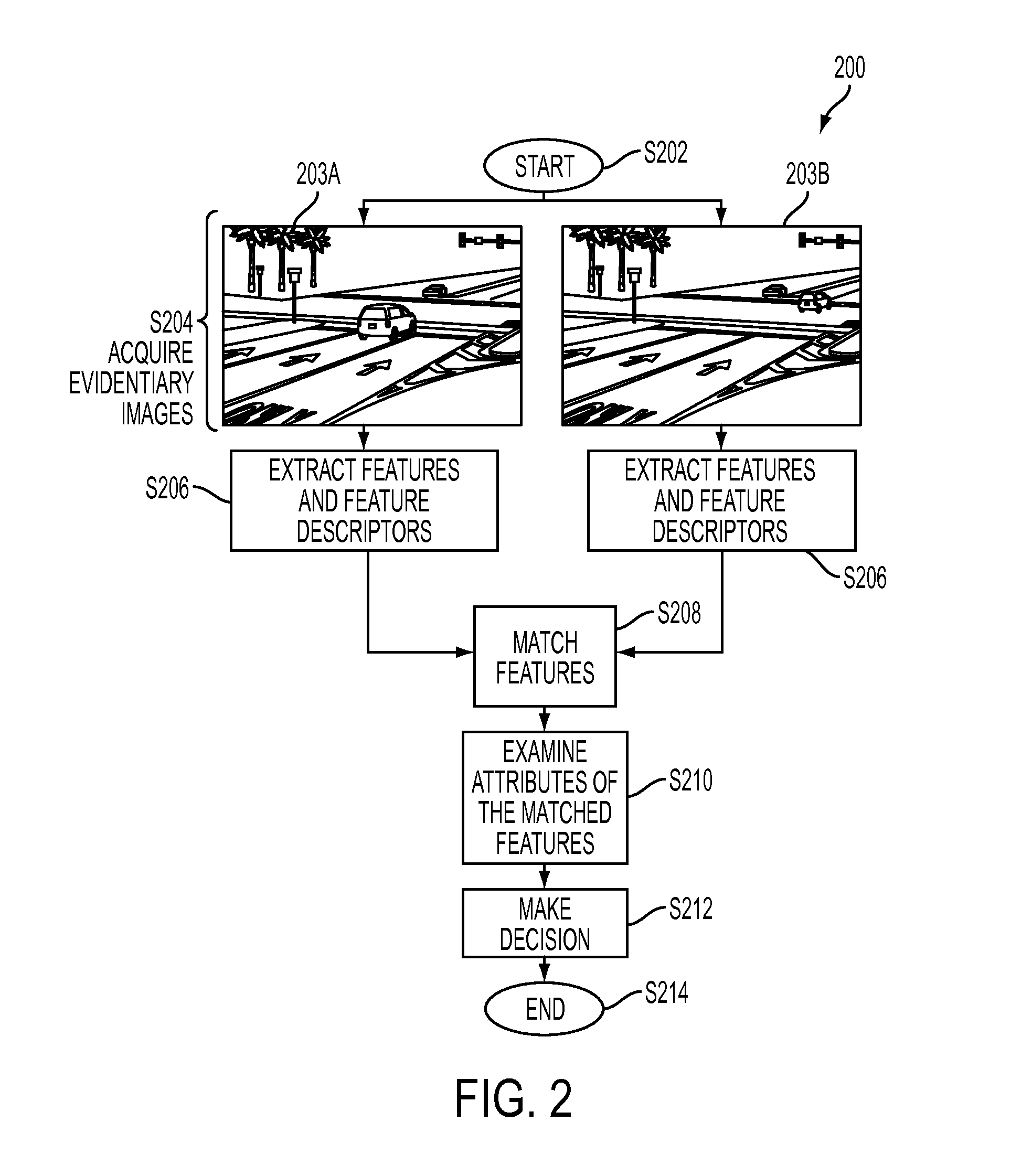
Short-time stopping detection from red light camera evidentiary photos
ActiveUS20150332588A1Road vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionRelationship extraction
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
Training method of human action recognition and recognition method
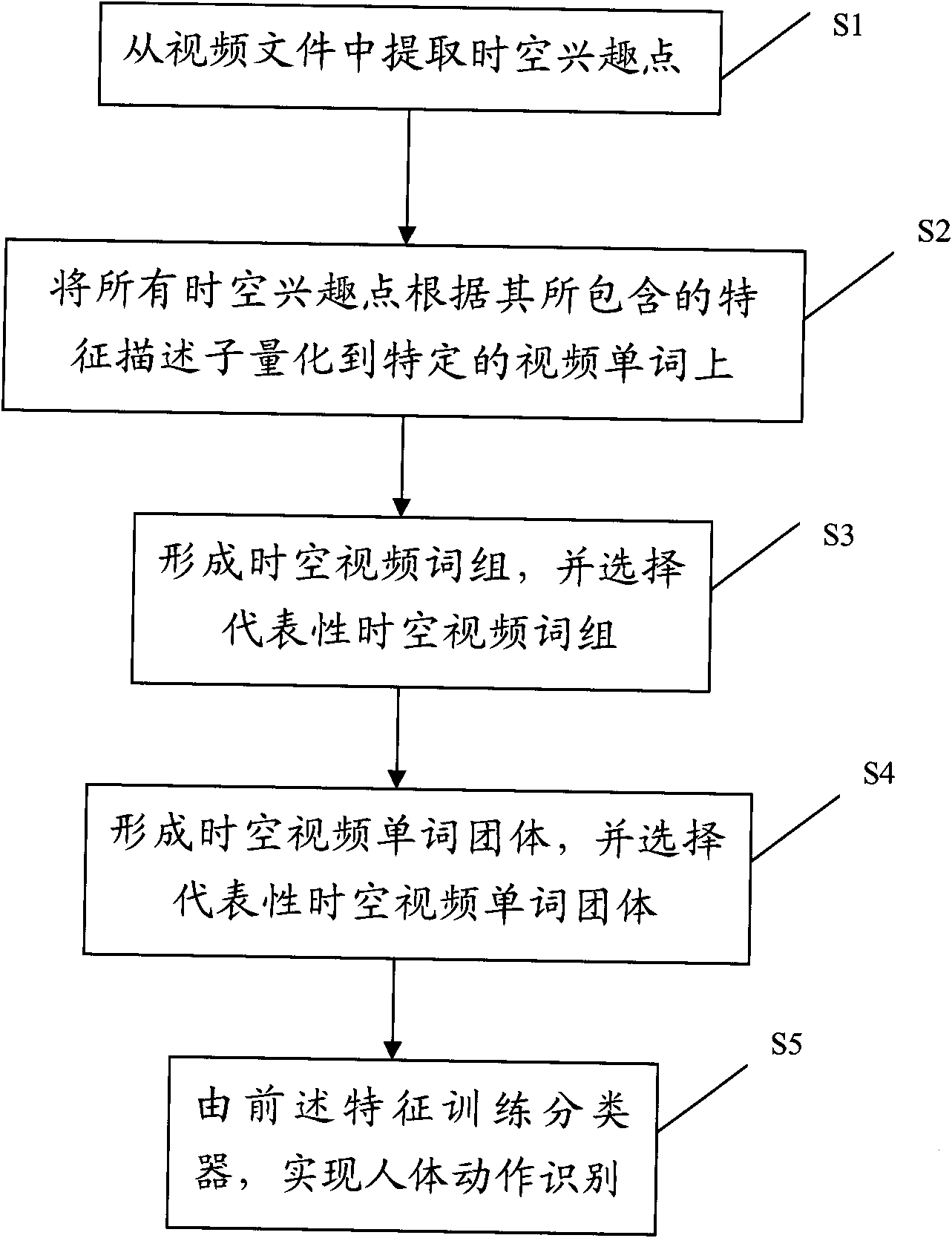
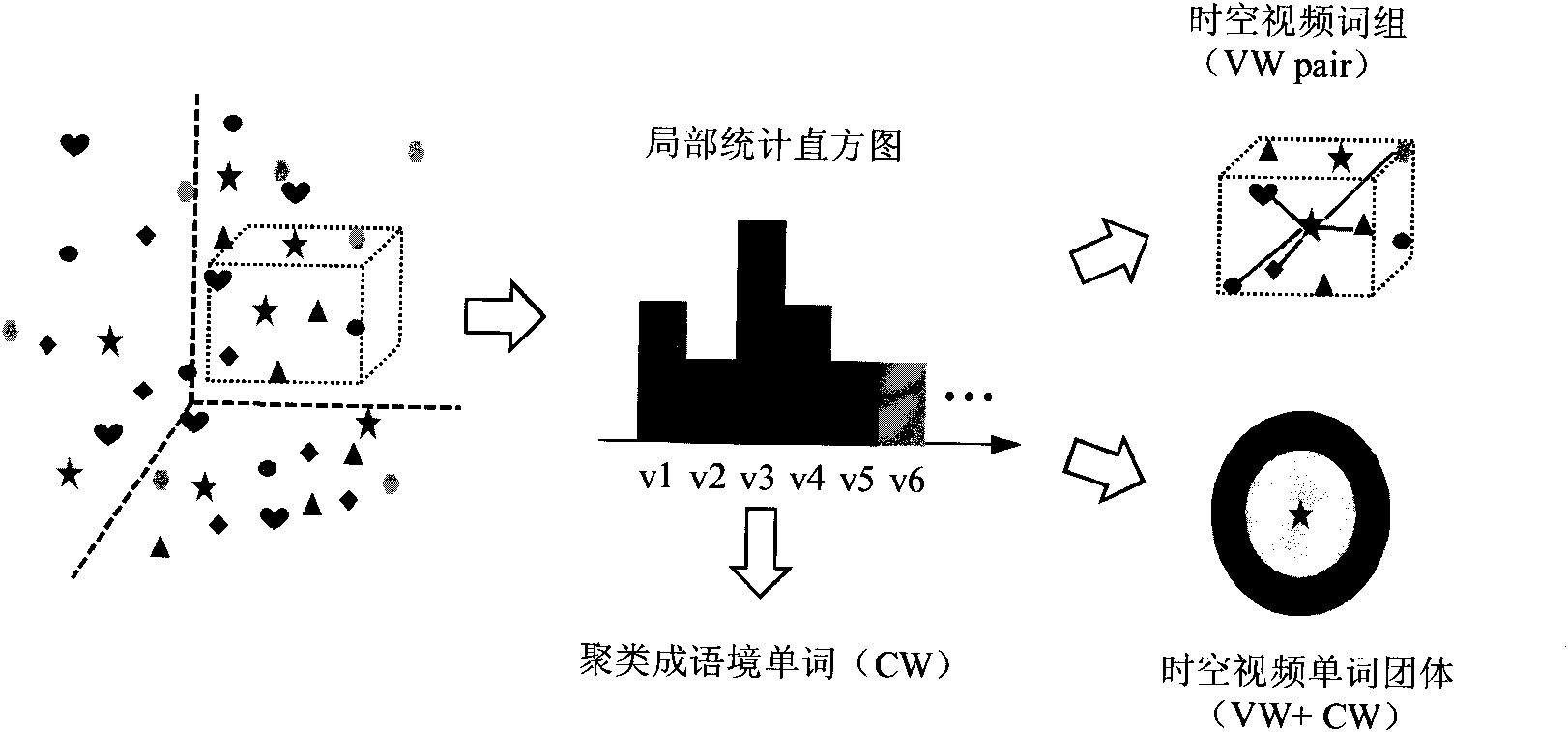
InactiveCN101894276AEfficient integrationCapture essential propertiesCharacter and pattern recognitionWord groupSpacetime
The invention provides a training method of human action recognition, comprising the following steps: extracting space-time interest points from a video file; quantizing all the space-time interest points to corresponding video words according to the feature descriptors contained by the space-time interest points and generating a statistical histogram for the video words; obtaining other video words in the space-time neighborhood of the video words according to the space-time context information in the space-time neighborhood of the video words and forming space-time video phrases by the video words and one of other video words which meets space-time constraint; clustering the space-time contexts in the space-time neighborhood of the video words to obtain context words and forming space-time video word groups by the video words and the context words; selecting the representative space-time video phrase from the space-time video phrases and selecting the representative space-time video word group from the space-time video word groups; and training a classifier by utilizing the result after one or more features in the video words, the representative space-time video phrase and the representative space-time video word group are fused.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com