Patents
Literature
658 results about "Doppler effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Doppler effect (or the Doppler shift) is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842.
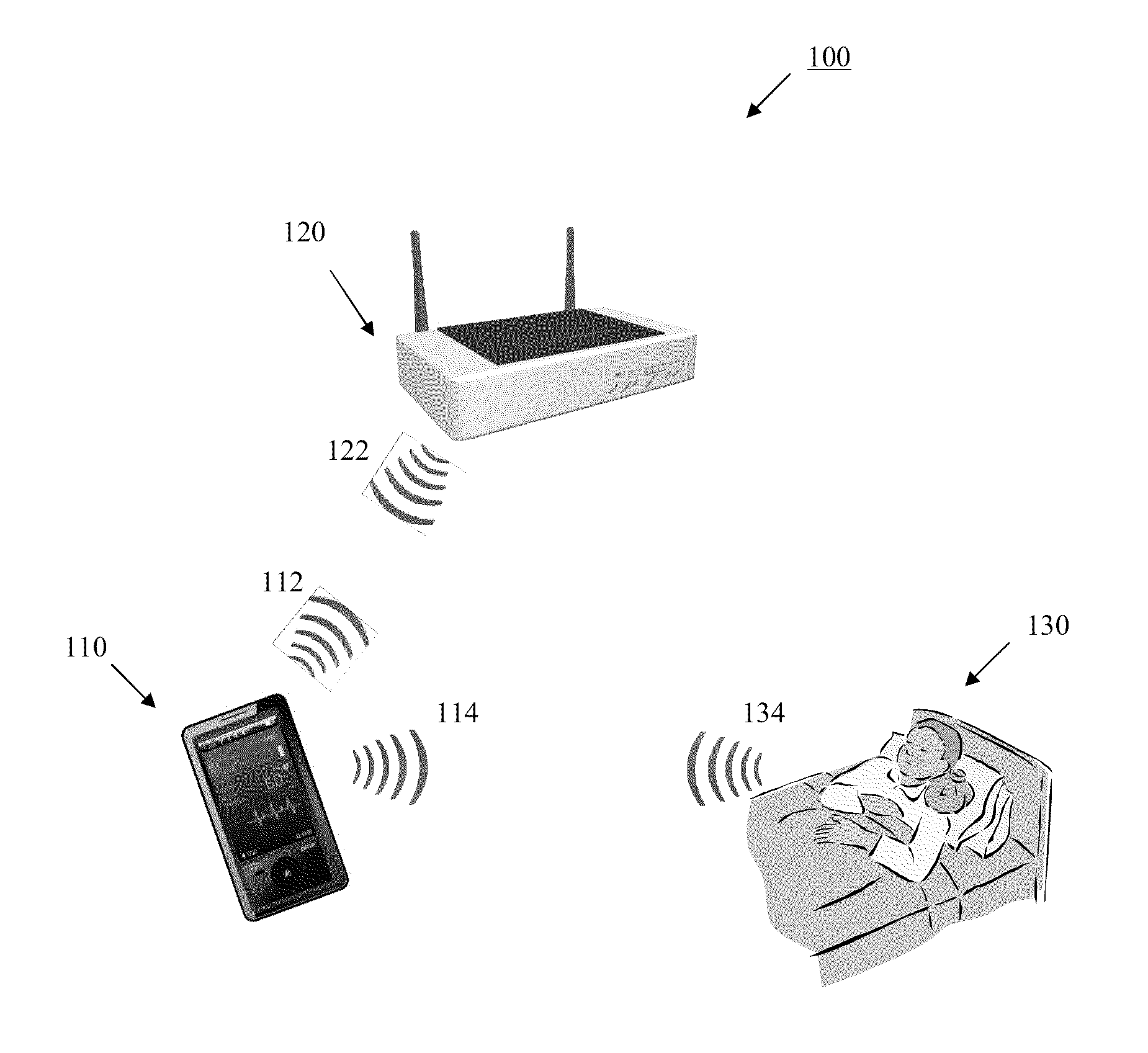
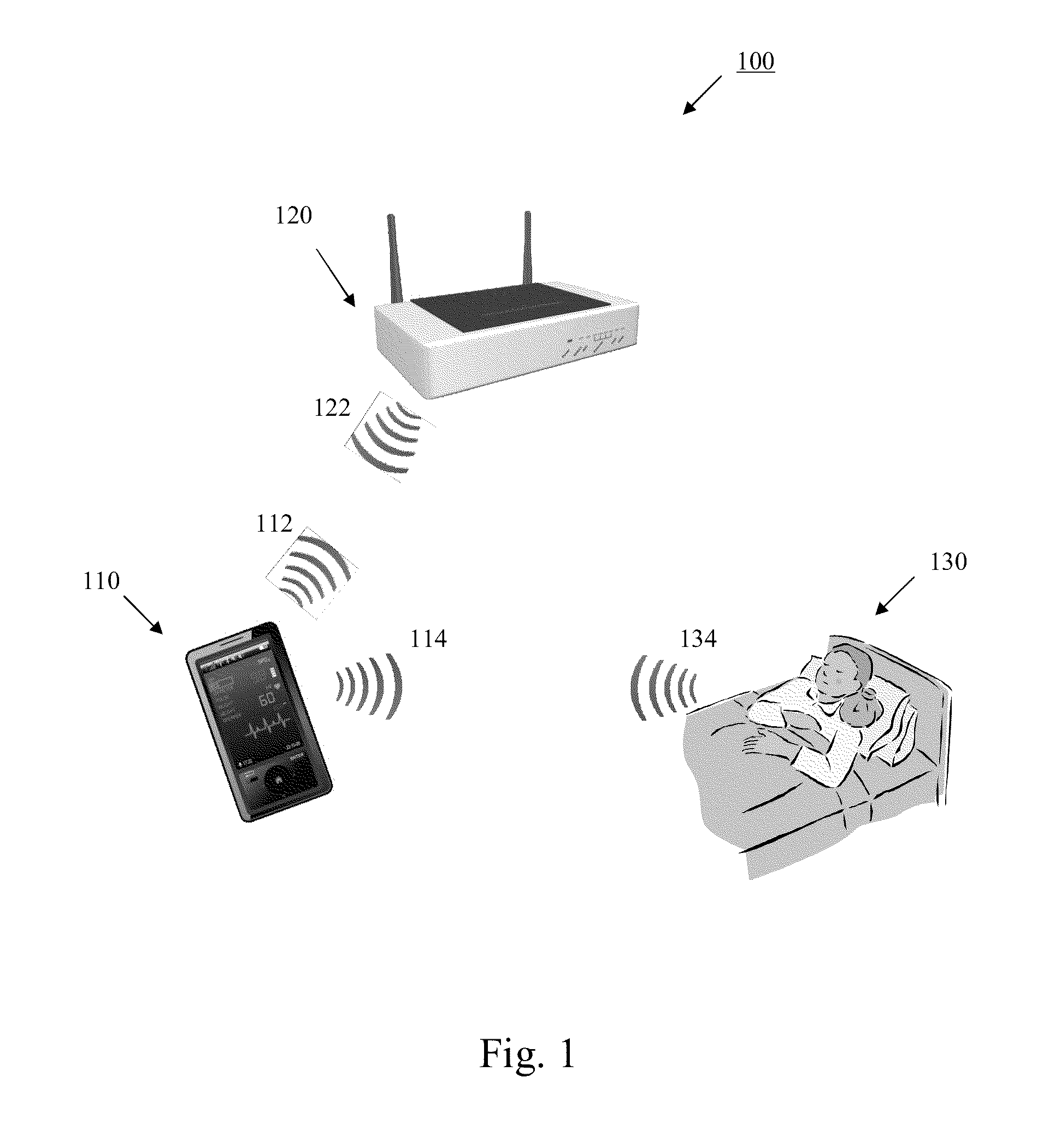
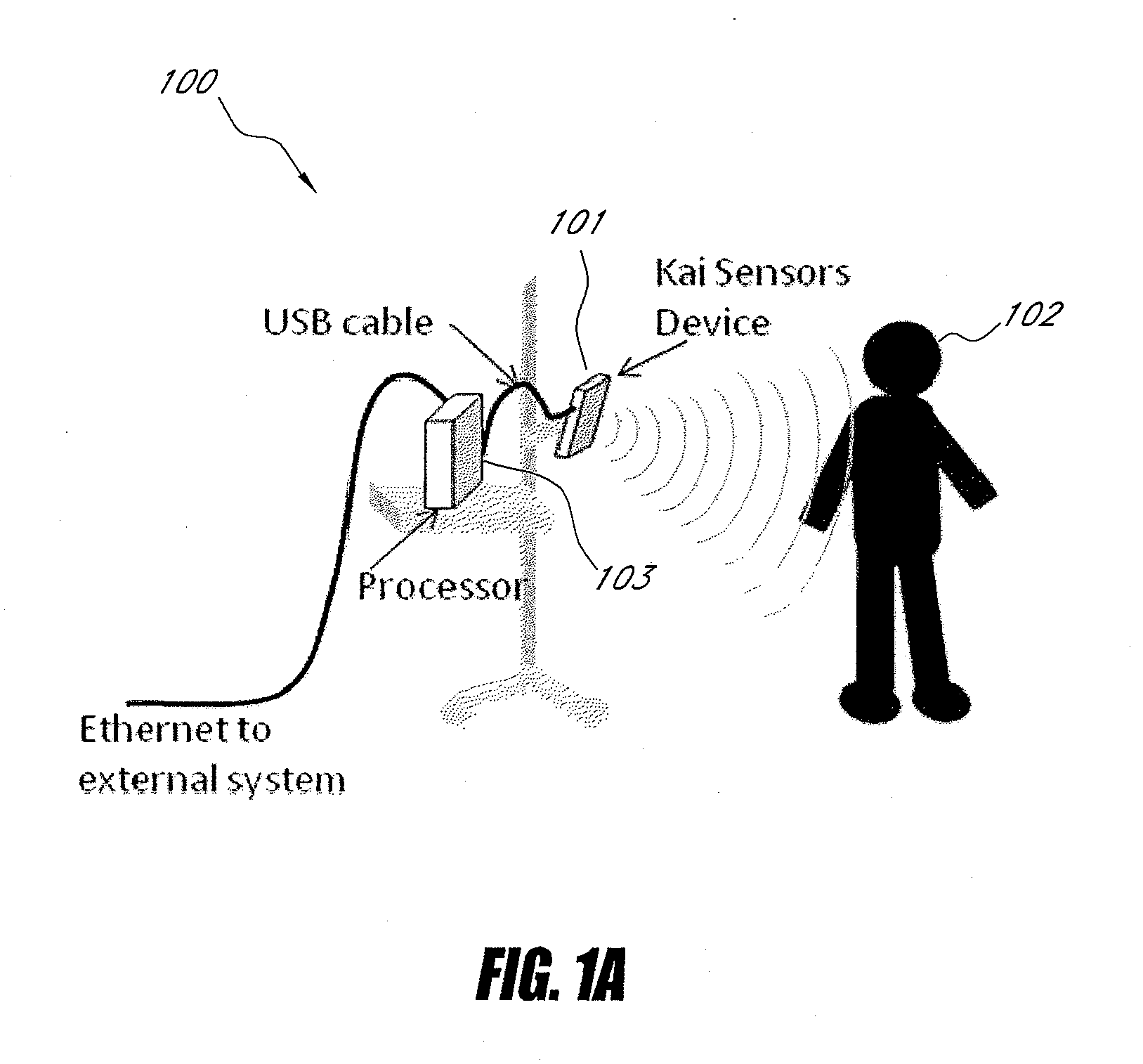
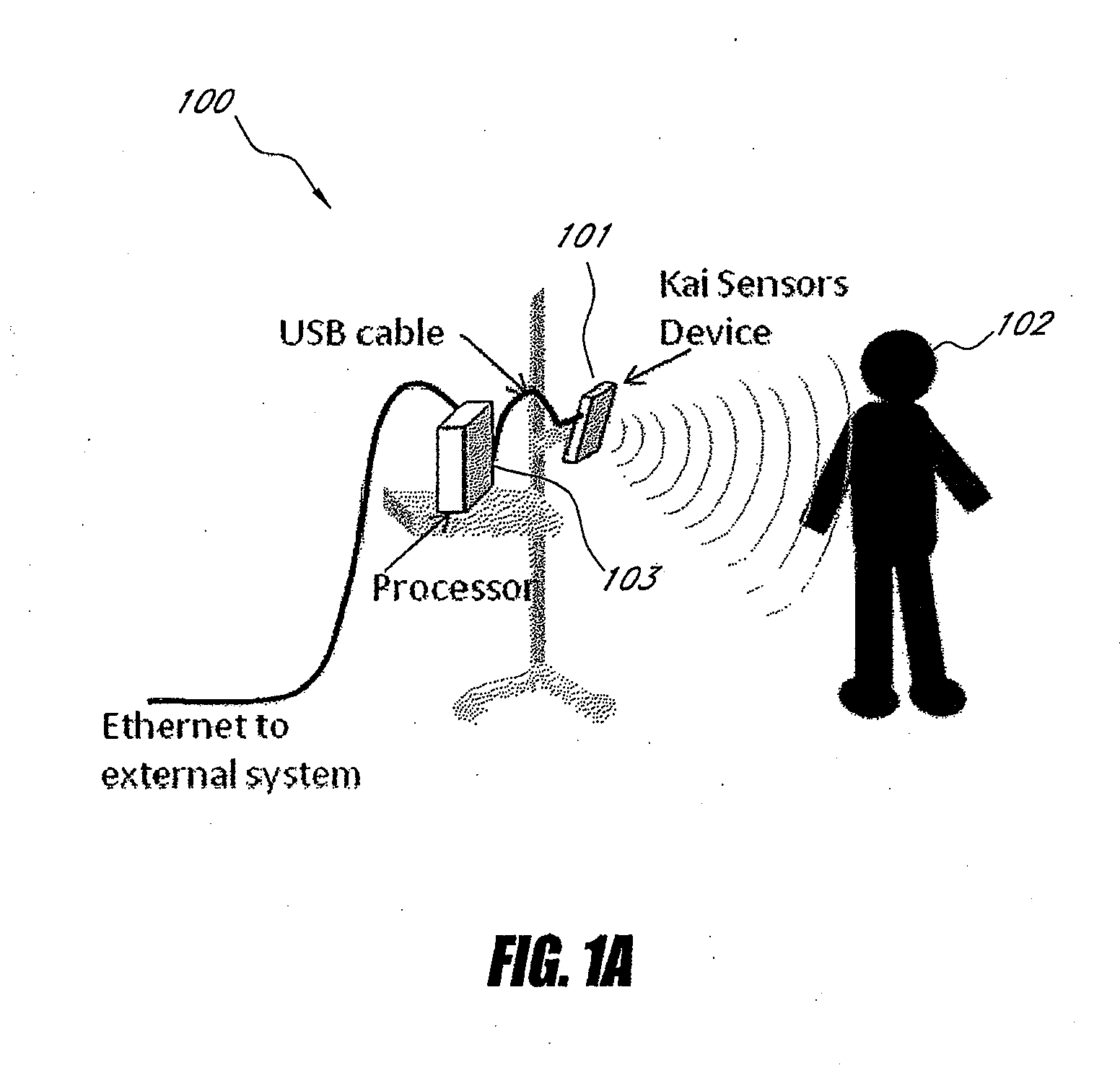
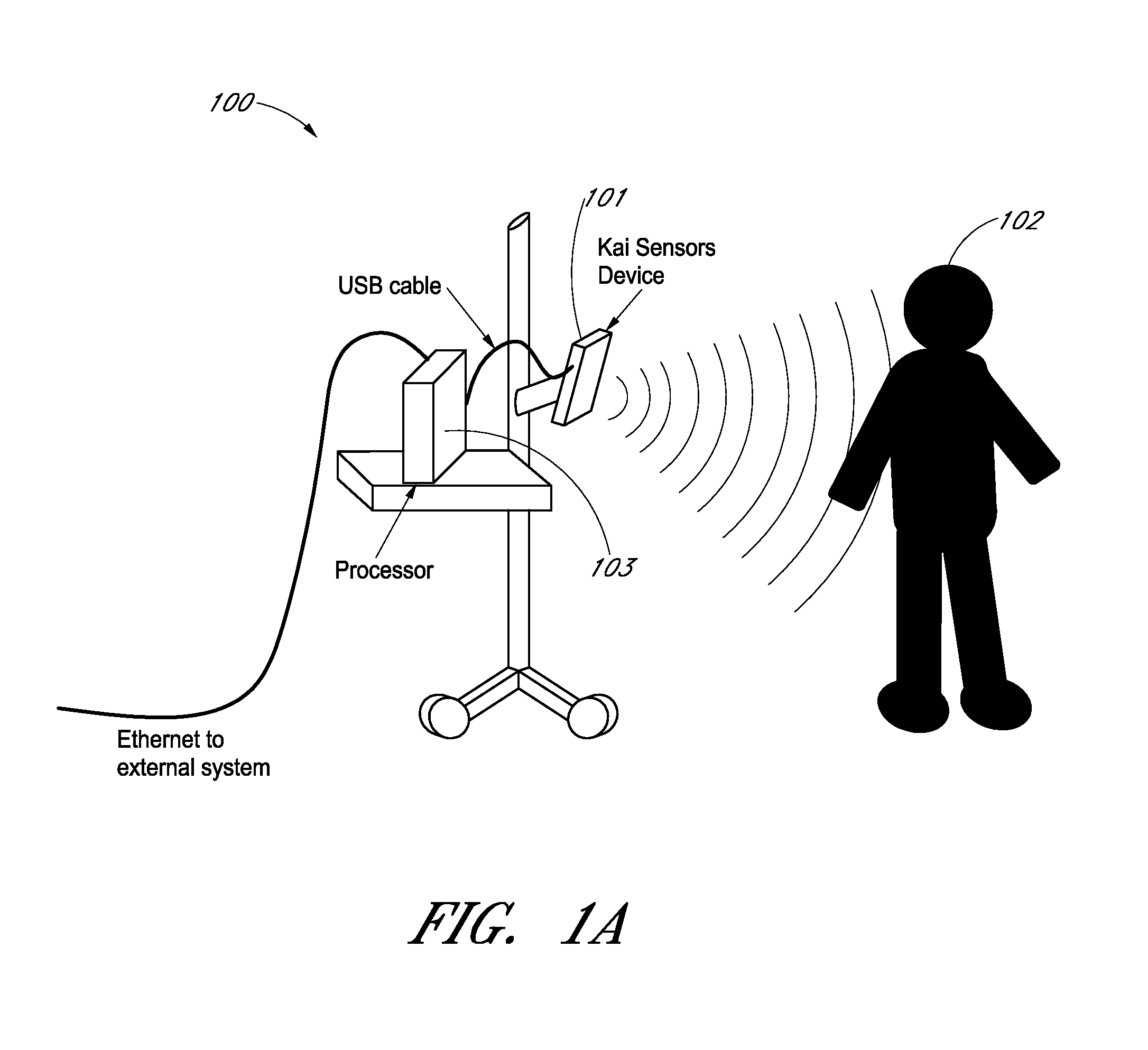
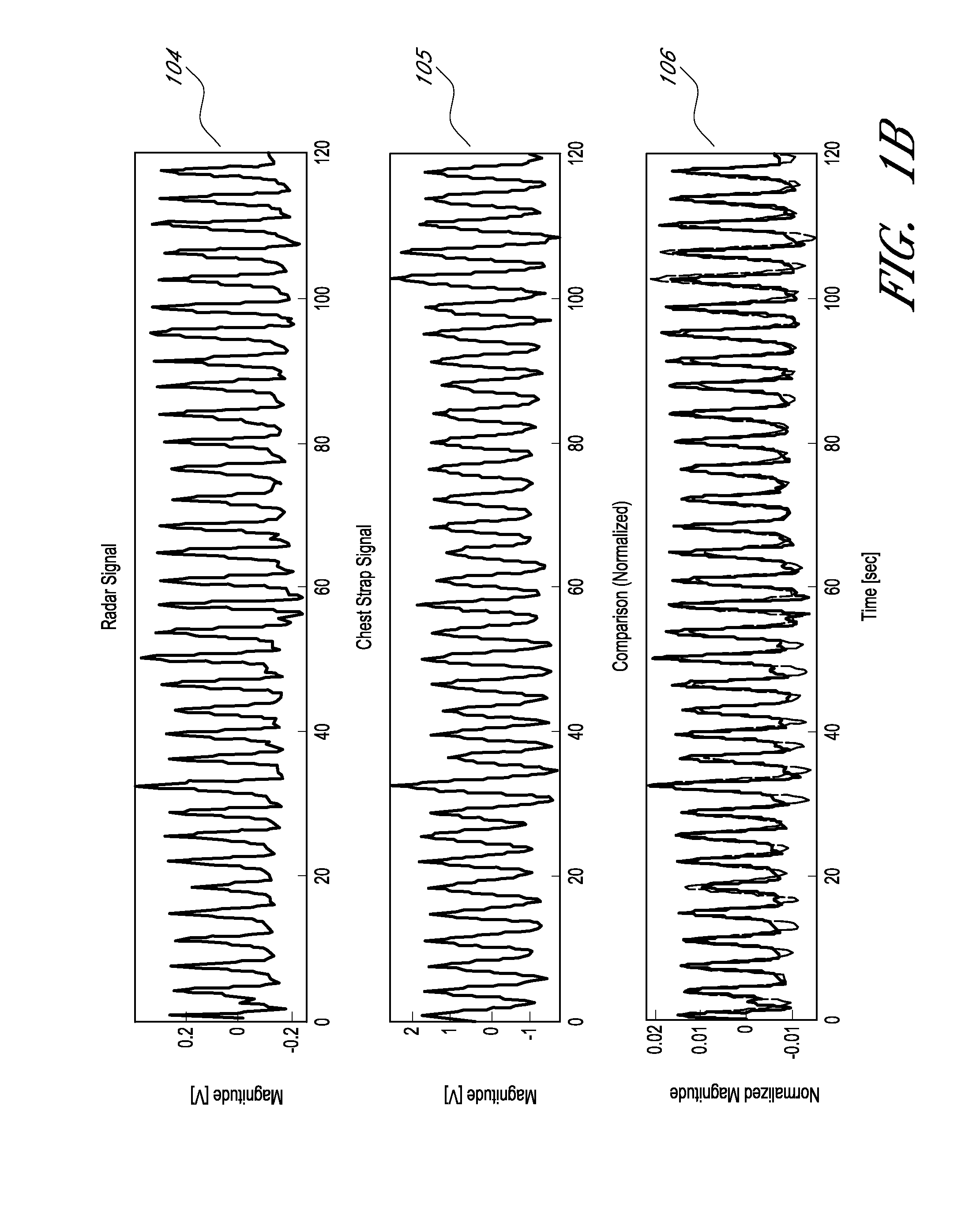
Wireless Physiology Monitor
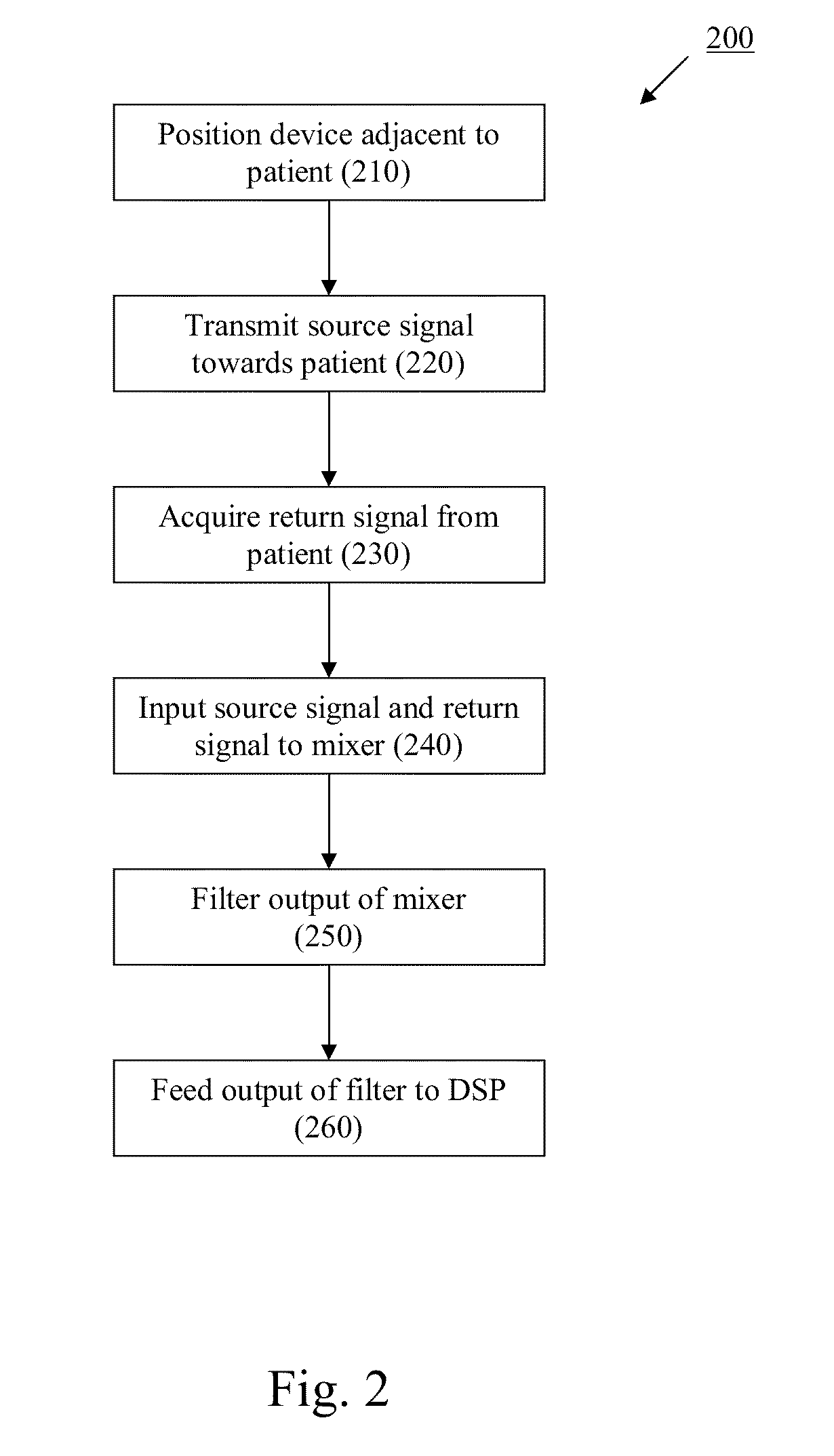
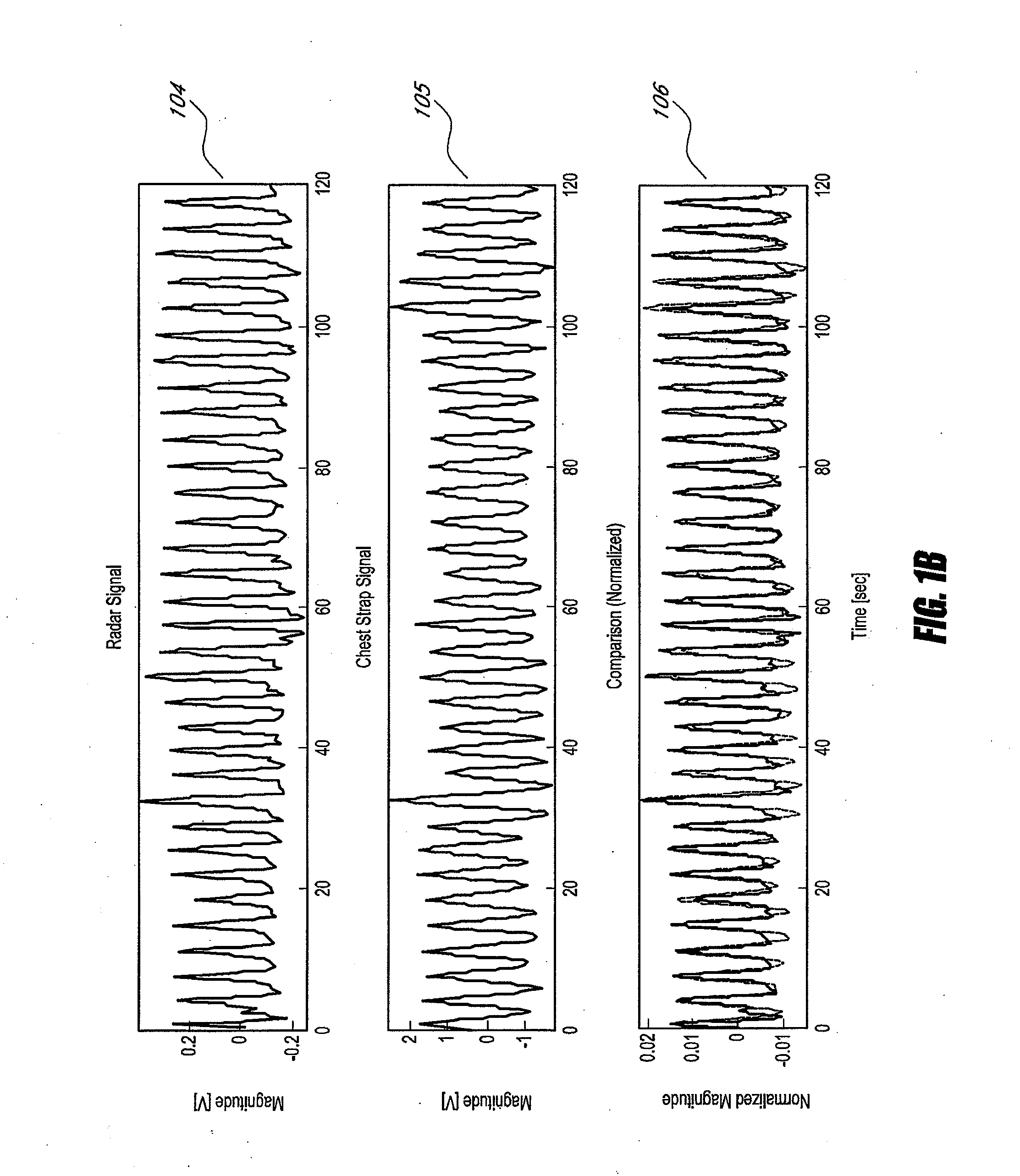
The present invention provides a new non-invasive technique for organ, e.g., heart and lung, monitoring. In at least one embodiment of the invention, a subject is radiated with a non-harmful and relatively low power electromagnetic source diagnostic signal normally associated with a communications protocol such as, but not limited to a version of the IEEE 802.11(x) family of protocols in the 2.4, 3.6, or 5 GHz spectrum bands. After passing through the patient, a return signal is acquired from the patient and compared to the original source signal. The differences between the source and modified signals are then analyzed to monitor the heart, e.g., measure heart rate and detect defects within the heart, and the lung. For example, using Doppler Effect principles, heart rate and motion can be measured from the differences in frequency, phase, and / or wavelength between the source signal and the modified signal reflected back from the heart moving within the patient.
Owner:MATHAI TOM +1
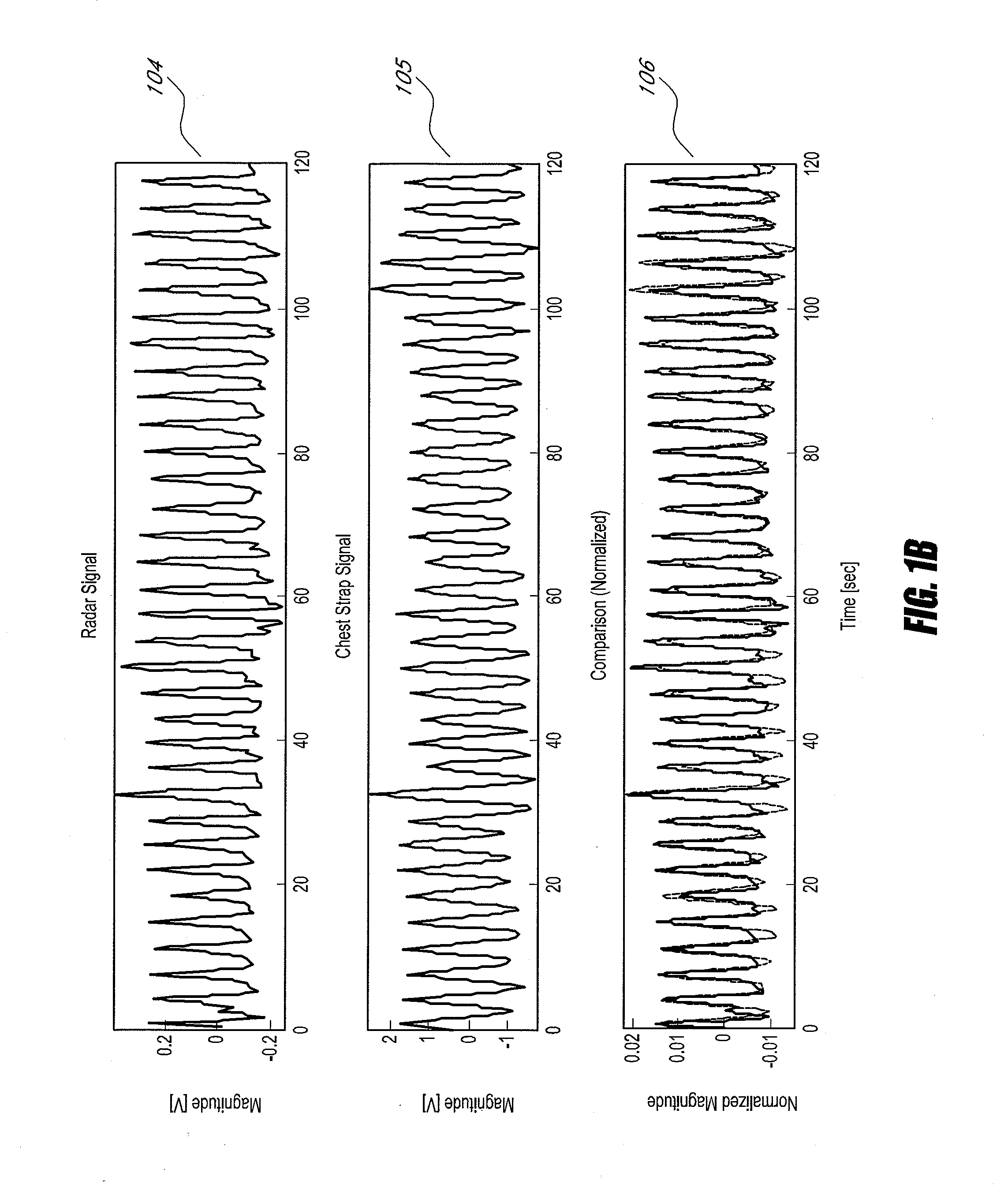
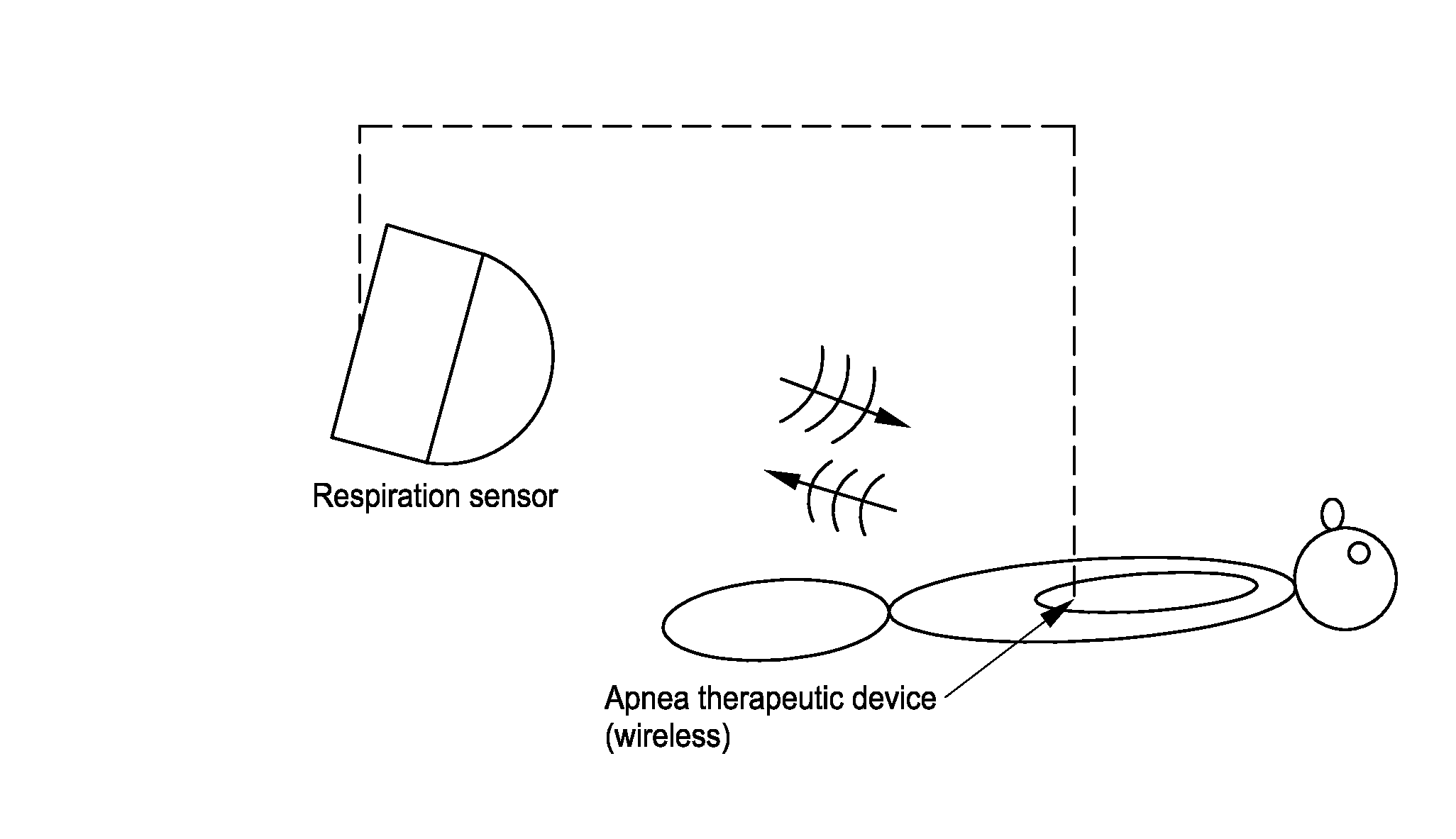
Systems and methods for non-contact multiparameter vital signs monitoring, apnea therapy, sway cancellation, patient identification, and subject monitoring sensors
InactiveUS20120022348A1Minimize signal powerElectrotherapyCatheterElectromagnetic radiationDigitization
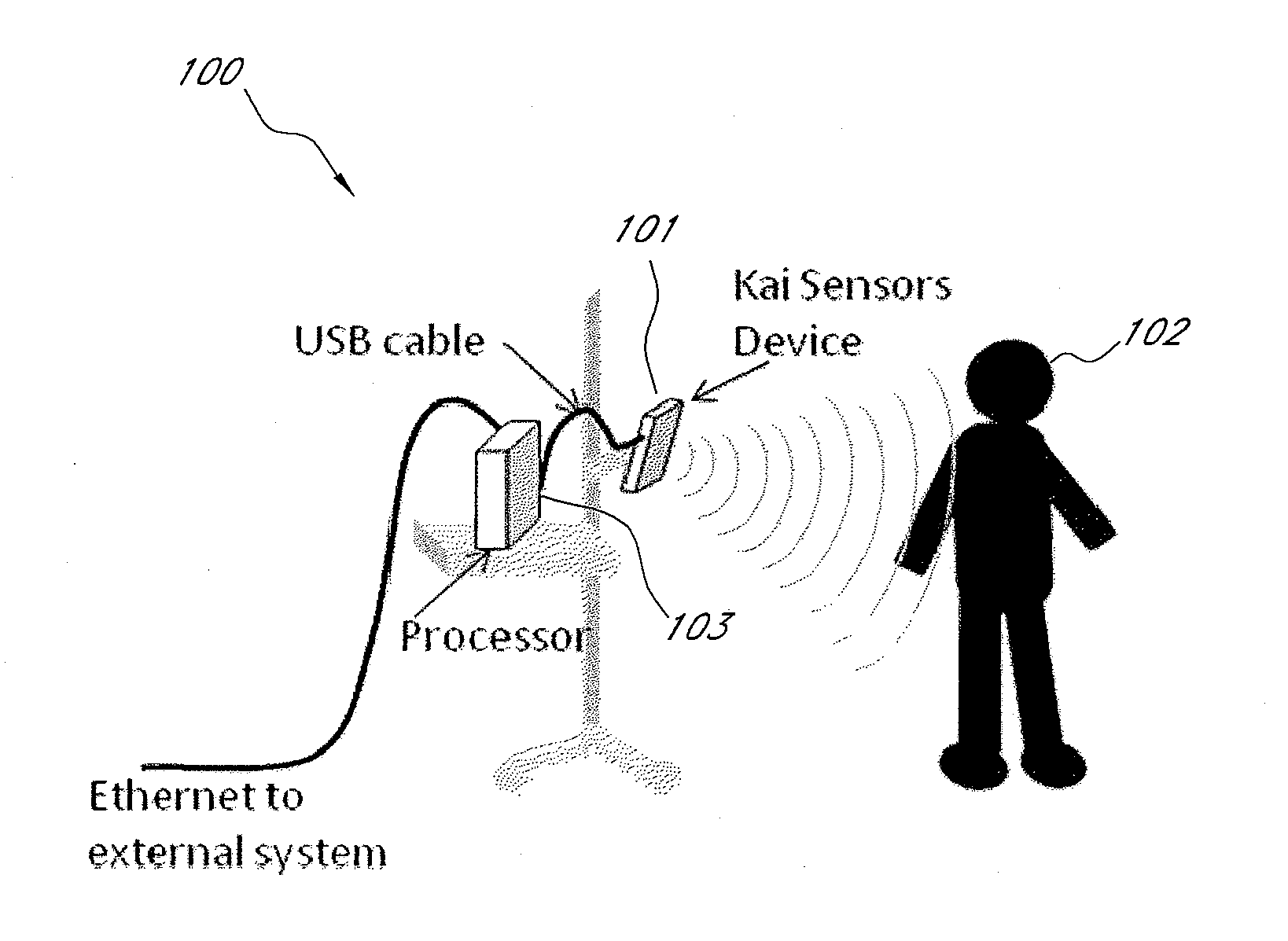
Aspects of the of the disclosure relate to a non-contact physiological motion sensor and a monitor device that can incorporate use of the Doppler effect. A continuous wave of electromagnetic radiation can be transmitted toward one or more subjects and the Doppler-shifted received signals can be digitized and / or processed subsequently to extract information related to the cardiopulmonary motion in the one or more subjects. The extracted information can be used, for example, to determine apneic events and / or to provide apnea therapy to subjects when used in conjunction with an apnea therapy device. In addition, methods of use are disclosed for sway cancellation, realization of cessation of breath, integration with multi-parameter patient monitoring systems, providing positive providing patient identification, or any combination thereof.
Owner:KAI MEDICAL
Systems and methods for non-contact multiparameter vital signs monitoring, apnea therapy, apnea diagnosis, and snore therapy
InactiveUS20130030257A1Minimize signal powerRestore muscle toneElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesMonitoring systemContinuous wave
Aspects of the of the disclosure relate to a non-contact physiological motion sensor and a monitor device that can incorporate use of the Doppler effect. A continuous wave of electromagnetic radiation can be transmitted toward one or more subjects and the Doppler-shifted received signals can be digitized and / or processed subsequently to extract information related to the cardiopulmonary motion in the one or more subjects. The extracted information can be used, for example, to determine apneic events and / or snoring events and / or to provide apnea or snoring therapy to subjects when used in conjunction with an apnea or snoring therapy device. In addition, methods of use are disclosed for sway cancellation, realization of cessation of breath, integration with multi-parameter patient monitoring systems, providing positive providing patient identification, or any combination thereof.
Owner:RESMED SENSOR TECH
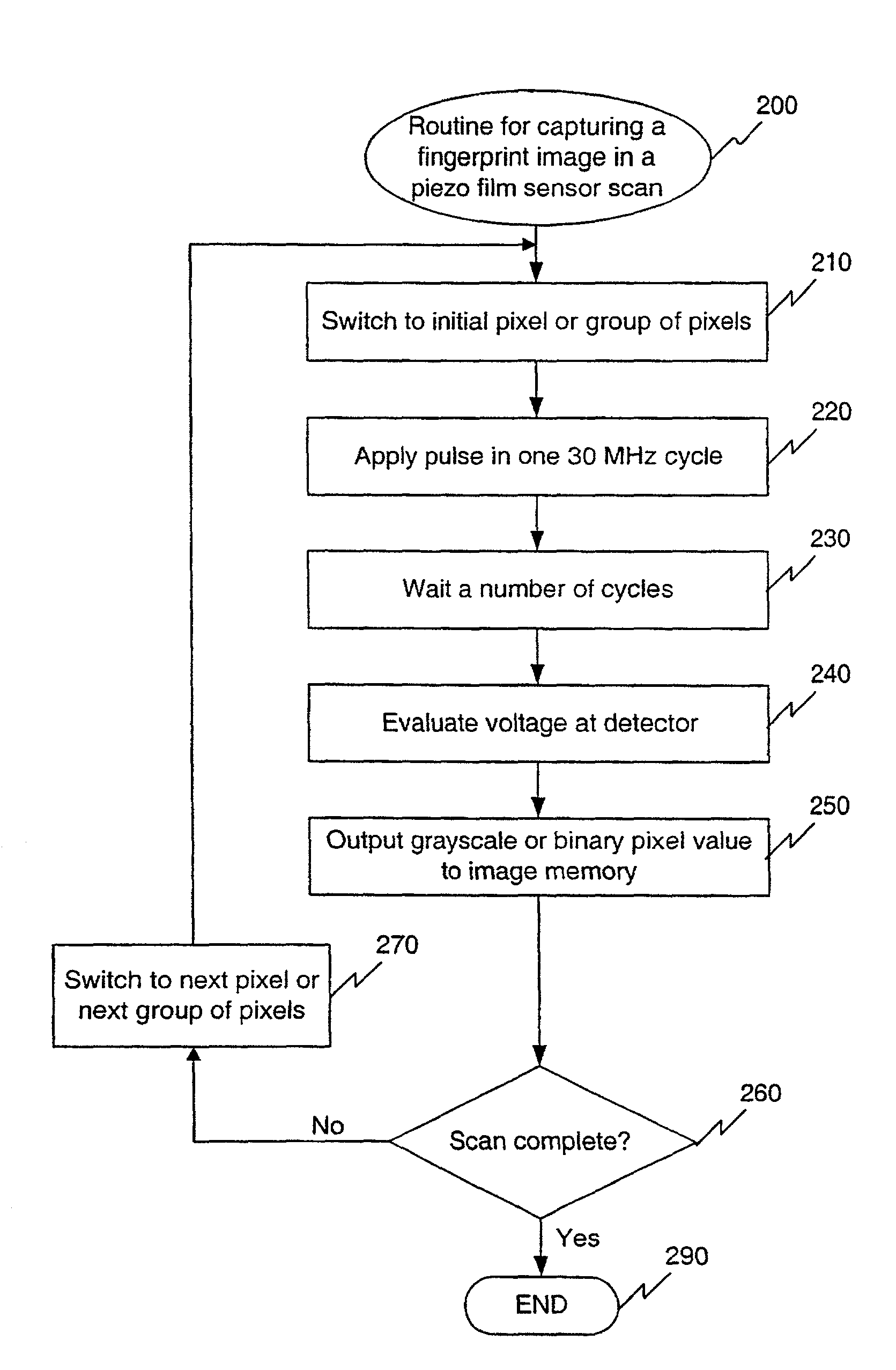
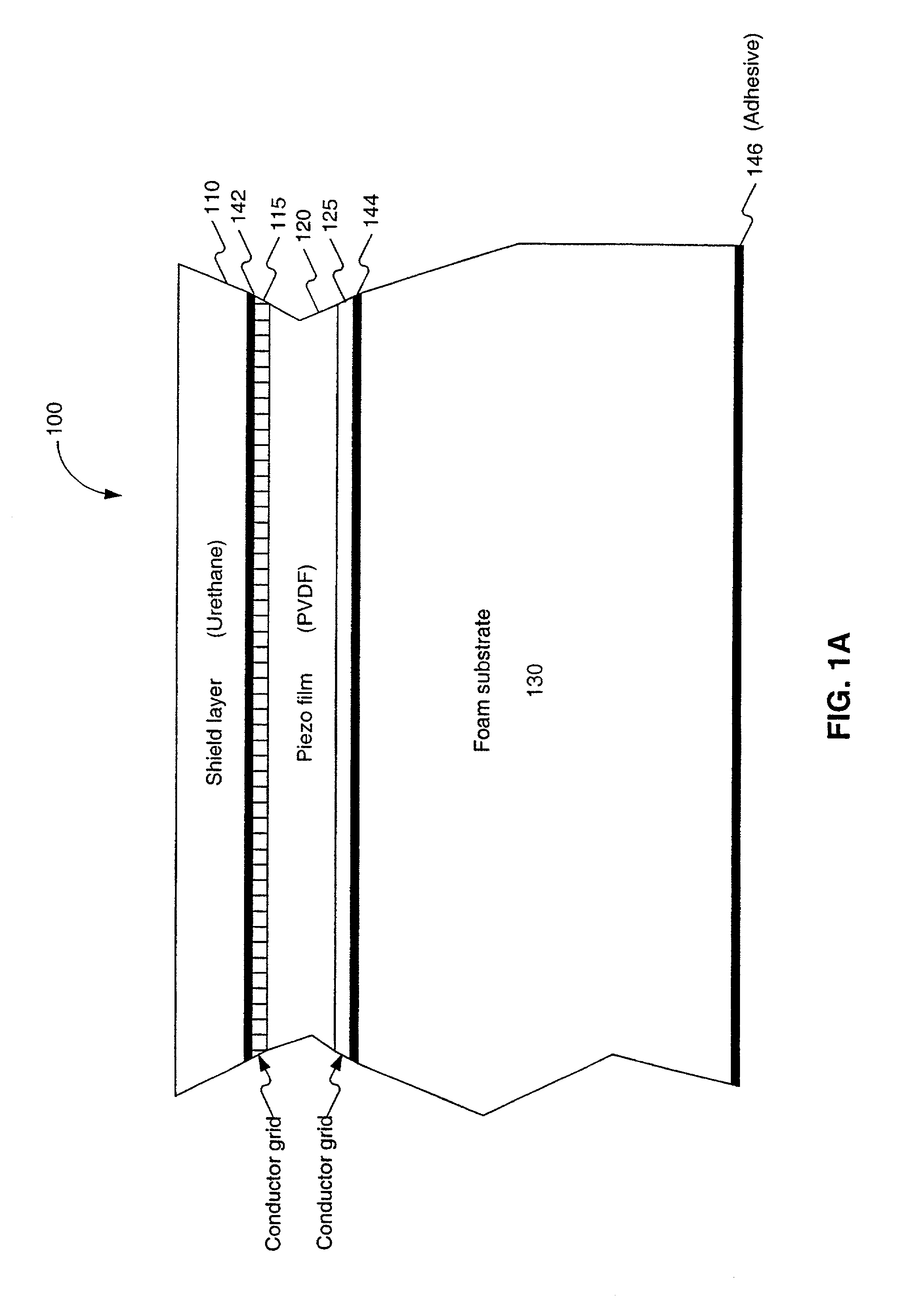
Biometric piezo scanner
InactiveUS20080175450A1Provide informationBlood flow measurement devicesPerson identificationSensor arrayElectrical conductor
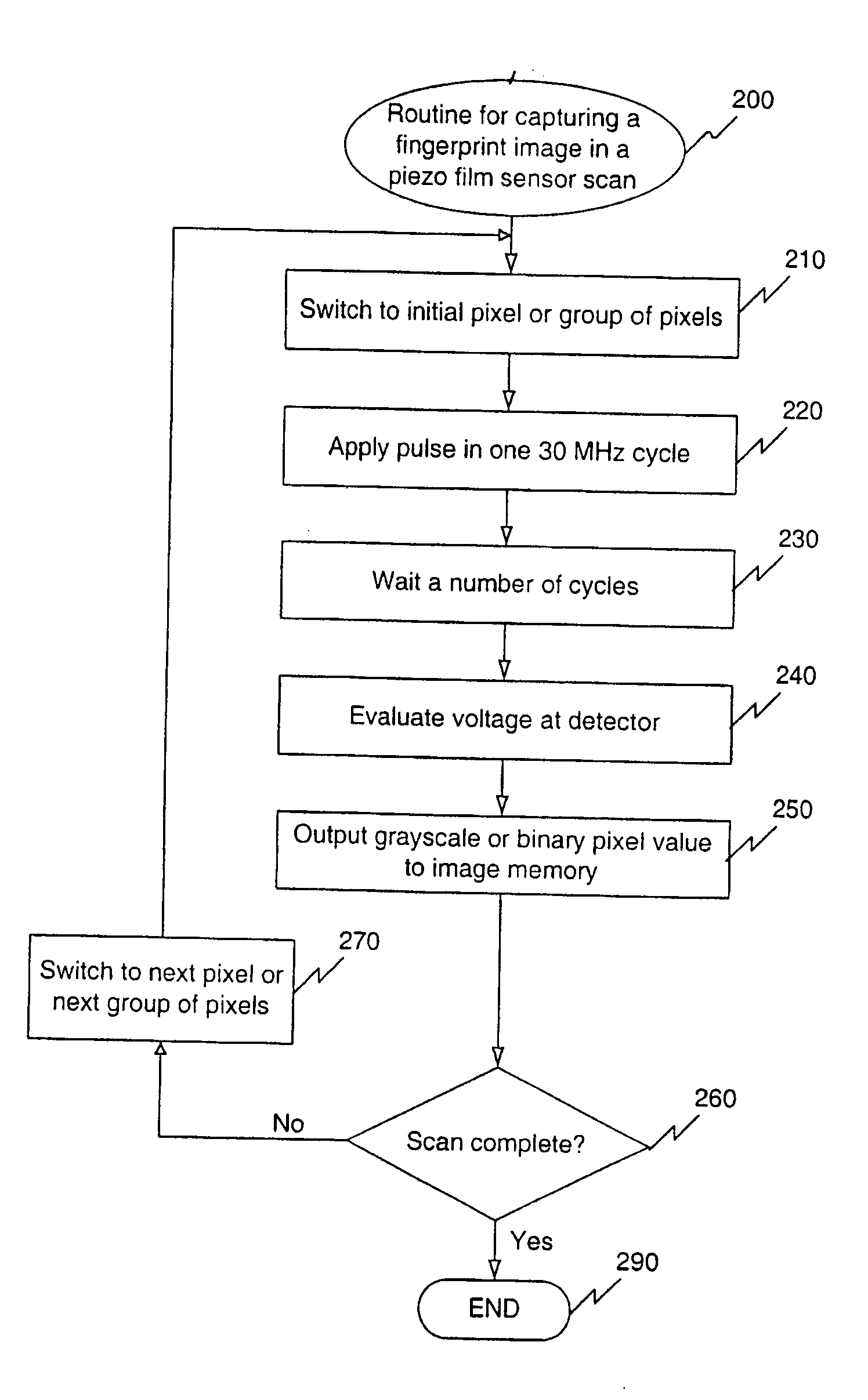
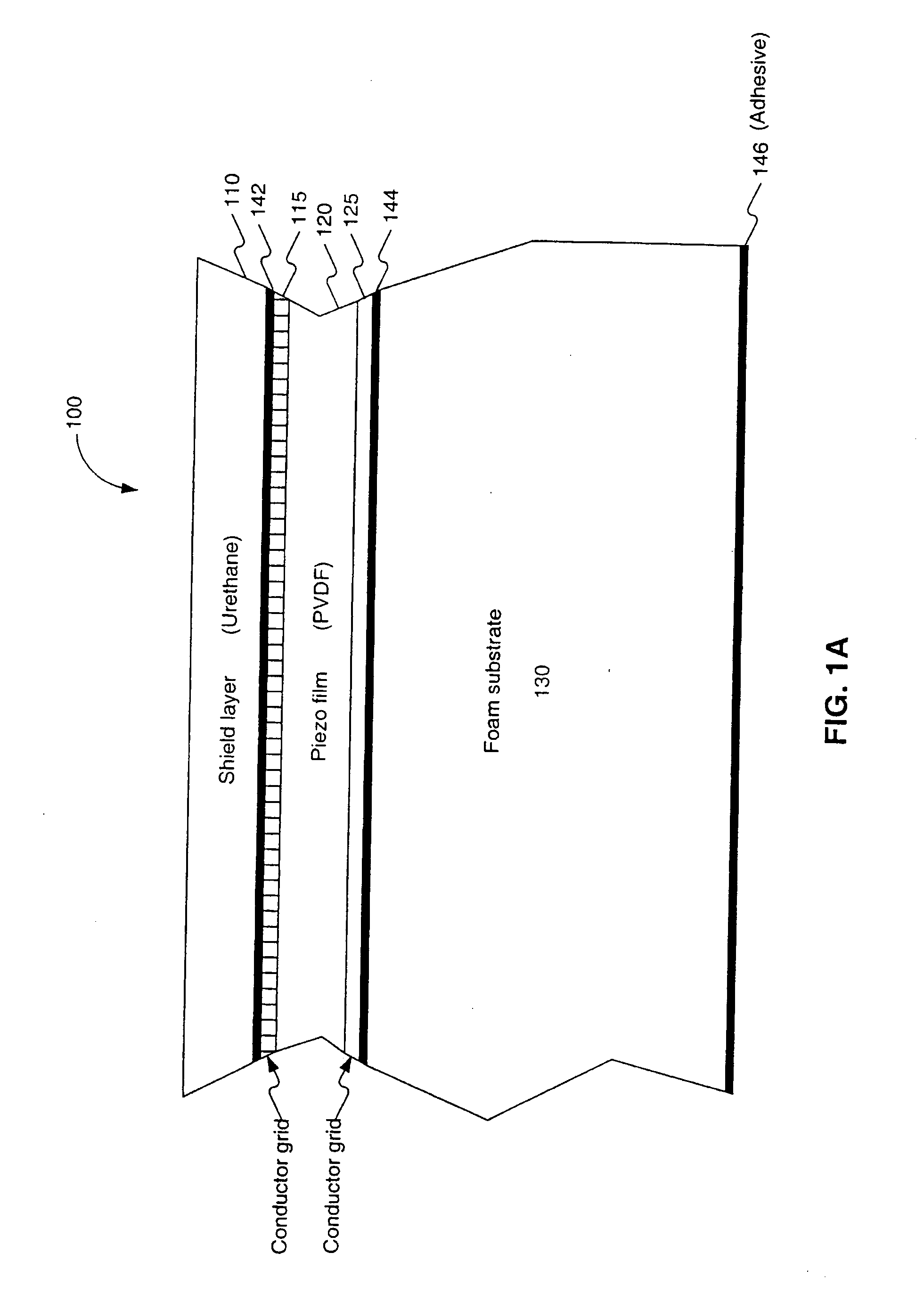
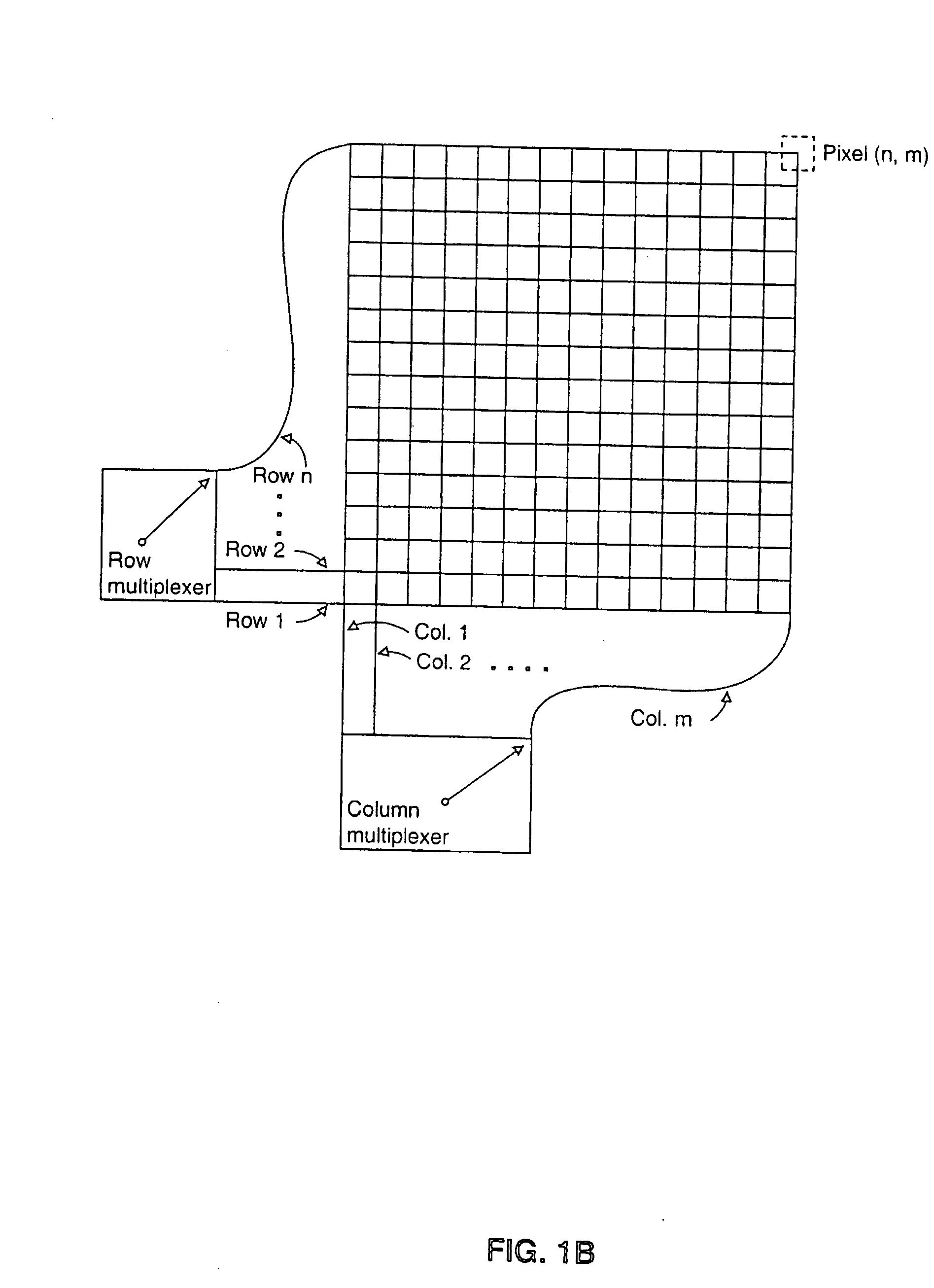
A piezoelectric thin film sensor array is used to scan and capture biometric data, for example, a fingerprint image. In one embodiment, a multi-layer structure includes a PVDF layer in between two conductor grids arranged orthogonally to one another. Urethane can be added to one side where a finger is placed. A foam substrate can be used as a support. In one feature, the PVDF, and grids can be peeled off like a label for easy replacement. Multiplexers are switched to scan the sensor. A single pixel or a group of pixels can be detected and output to an image memory. The presence of a fingerprint ridge is detected by virtue of a ring-down oscillation that arises from reflection when an electric field is applied to the piezoelectric thin film sensor array at a pixel in contact with the fingerprint ridge. For example, such a ring-down value associated with a fingerprint ridge can be detected at about 150 ns. (or 5 cycles at 30 MHZ). Other reflections indicative of additional biometrics (e.g. from tissue, blood, bone, fingernail, etc.) can also be detected. A Doppler effect due to reflections from circulating blood can also be detected. Such a Doppler effect can provide further information about direction and speed of blood circulation. An instantaneous pyroelectric effect can also be detected to indicate a live finger presence.
Owner:SONAVATION INC
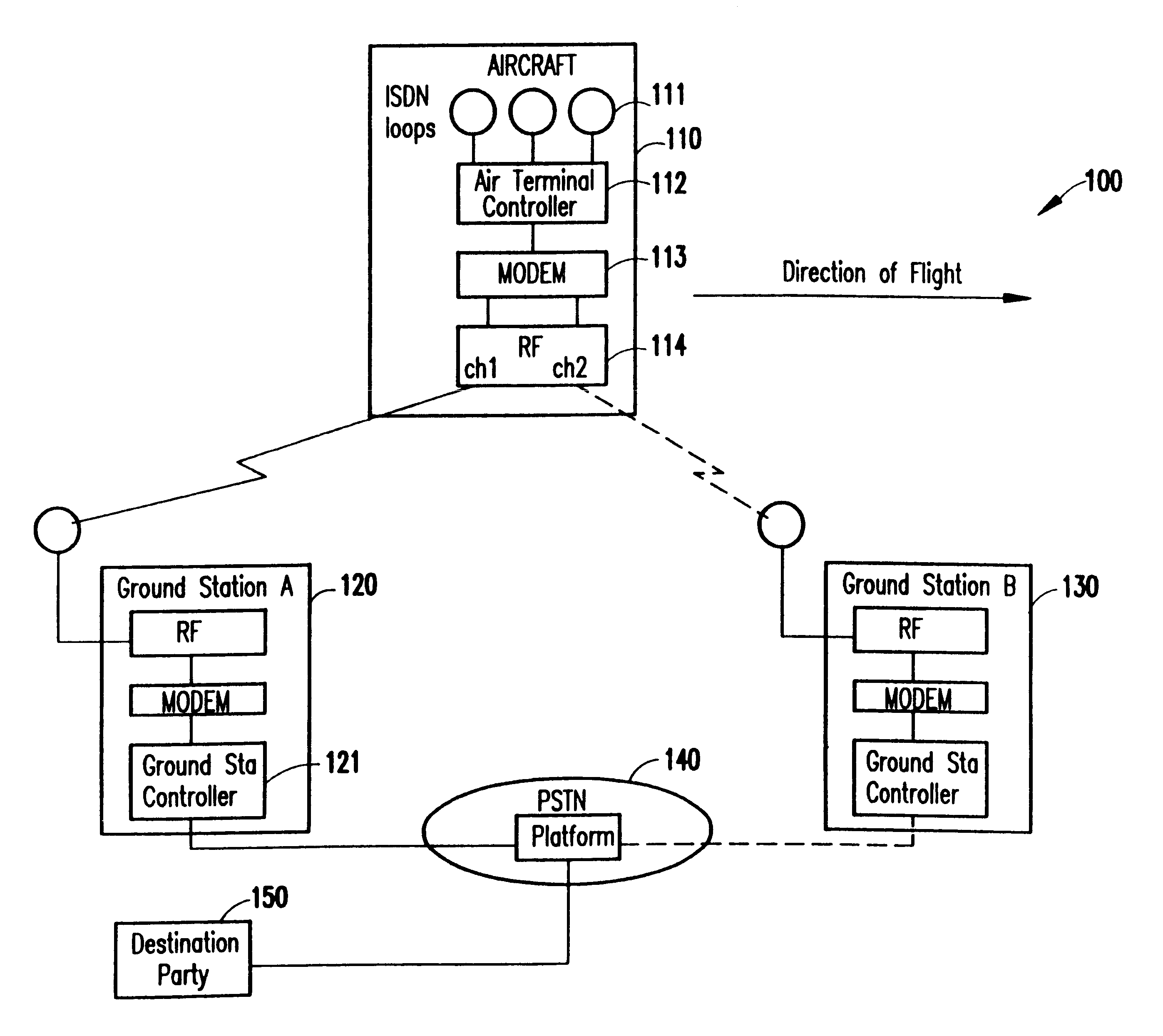
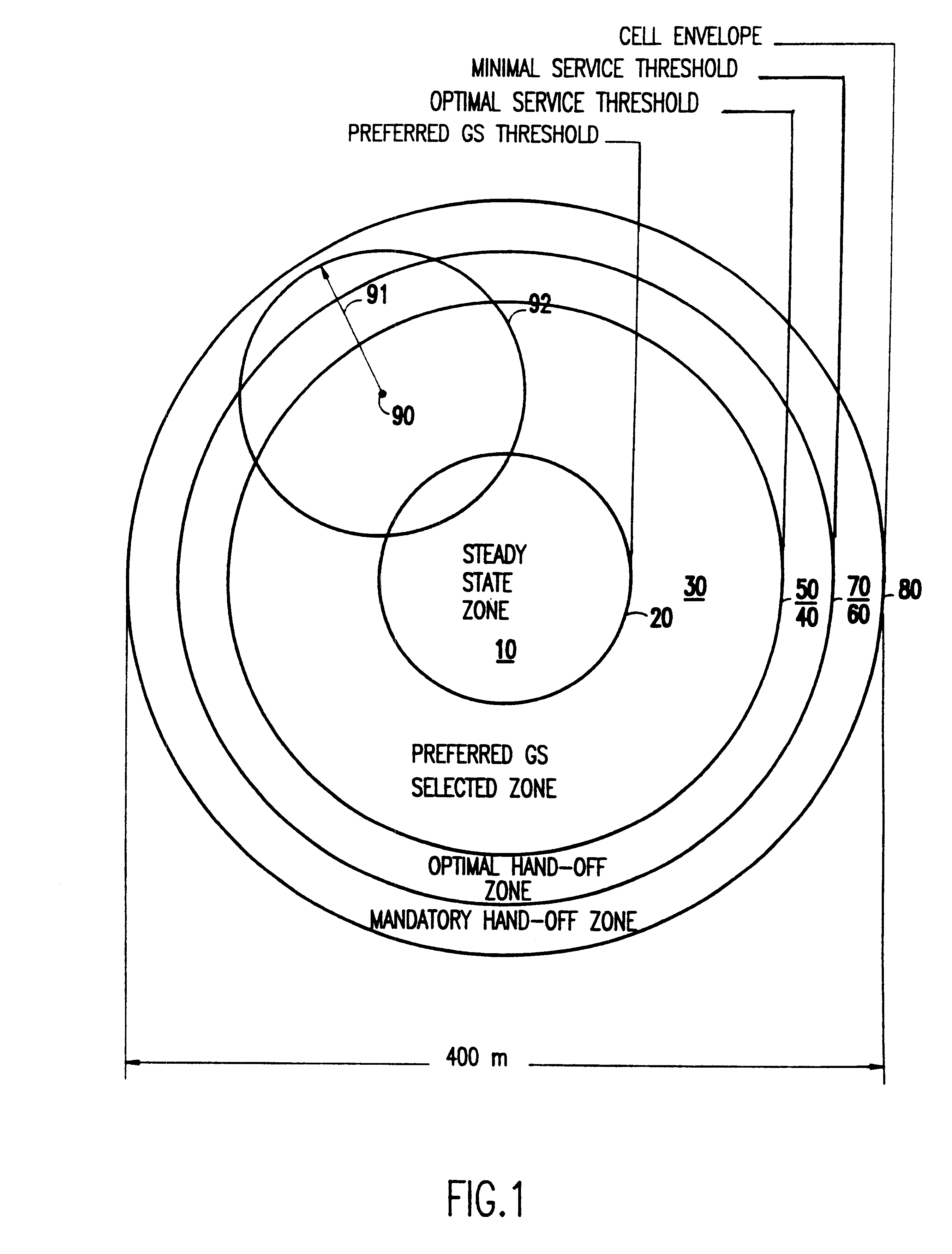
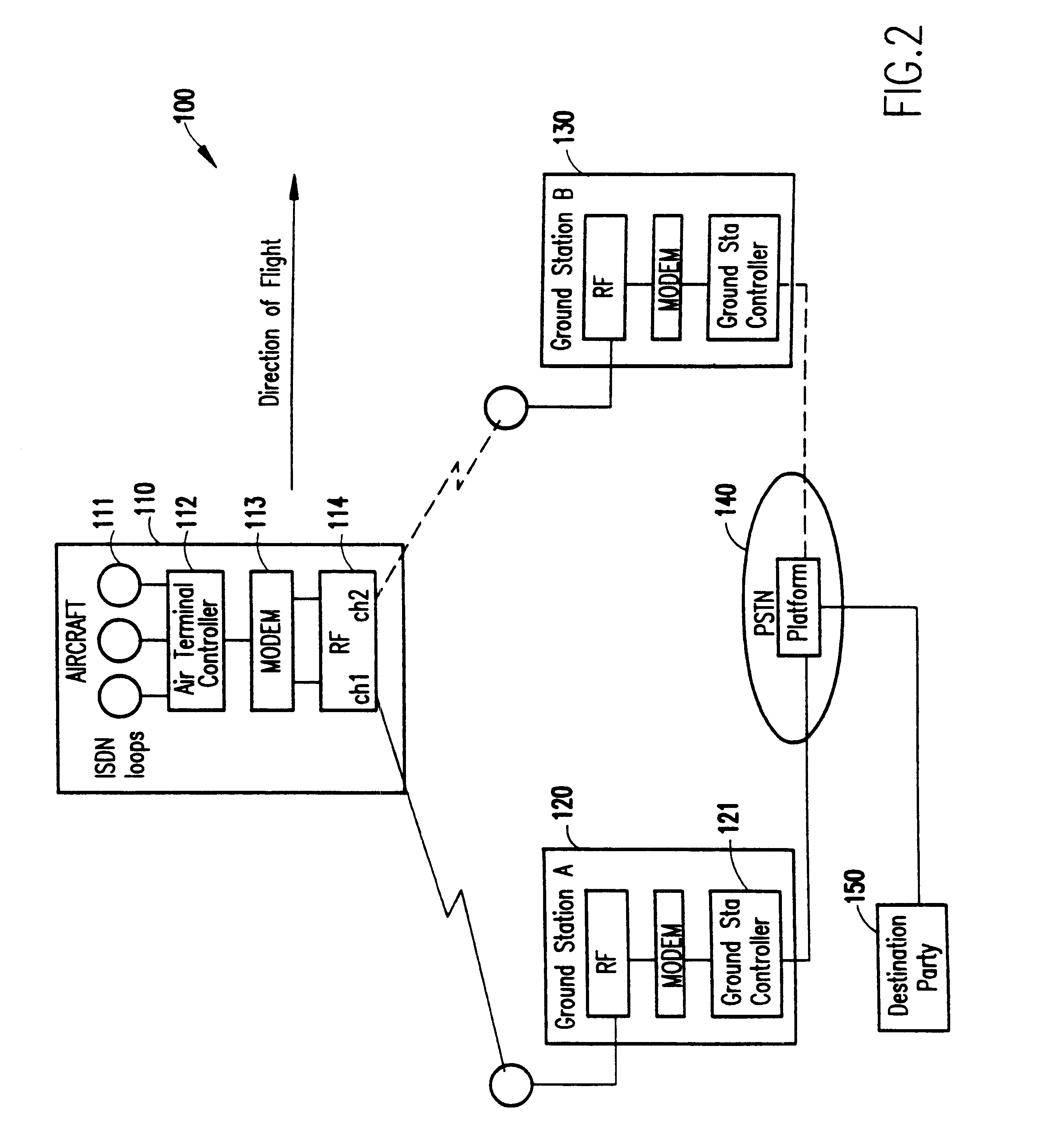
Seamless hand-off for air-to-ground systems
InactiveUS6393281B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionGround systemGround station
Seamless hand-off of air-to-ground telephony calls is achieved autonomously within an aircraft by using one of at least two radio links to search for additional ground stations. The search for candidate ground stations for hand-off is expedited by eliminating ground stations exhibiting zero or negative Doppler effects. Other values indicating quality of the link corresponding to the channel over which the search is conducted is compared with the quality of the call and an alternate call is established using the call identification code previously established for the call in progress. The hand-off of the call may then be easily conducted by transferring the voice signal to the channel over which the search was conducted. This is preferably done at a time when the transmission quality of the two channels would be approximately the same or the quality improved on the channel to which hand-off is made.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
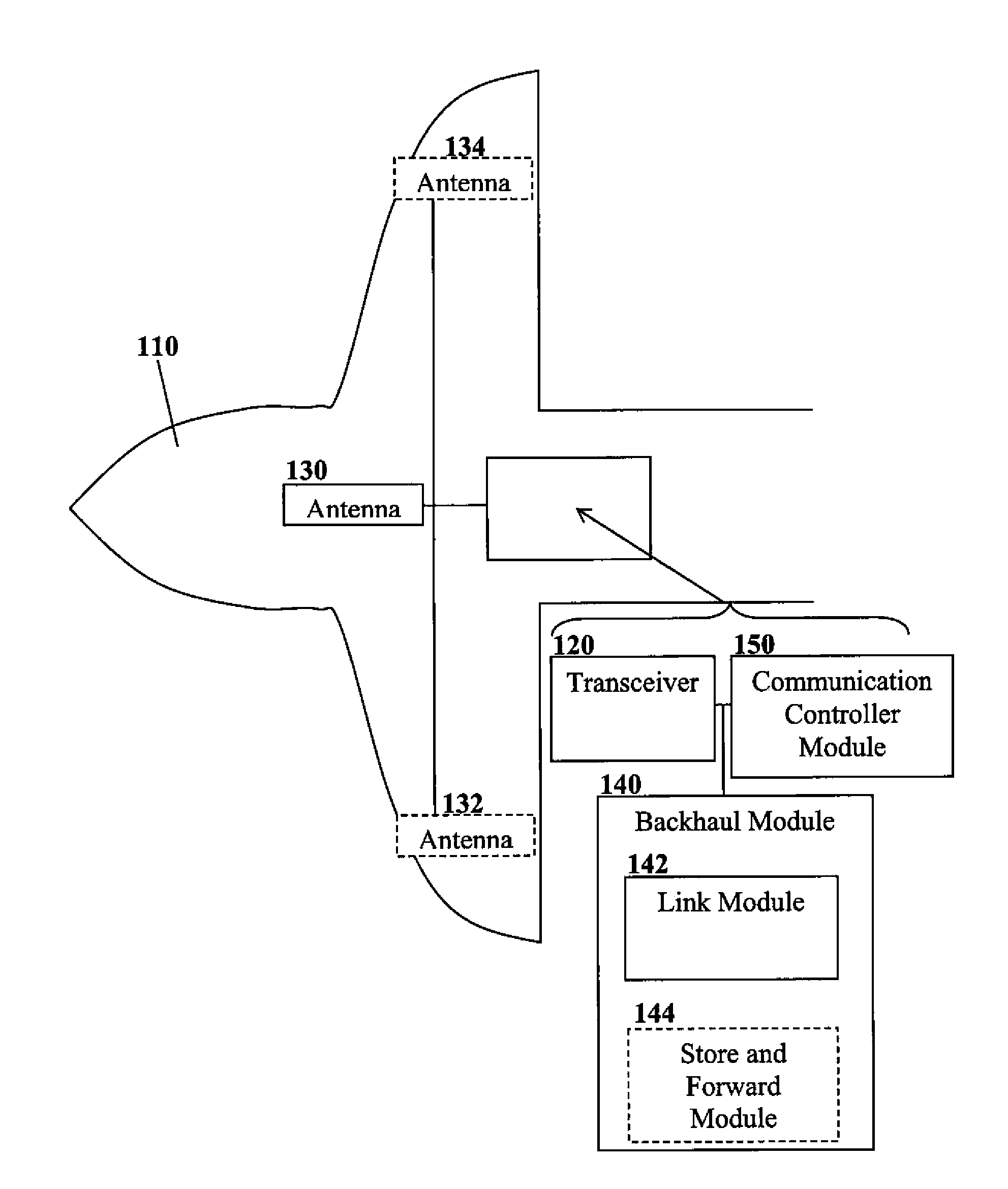
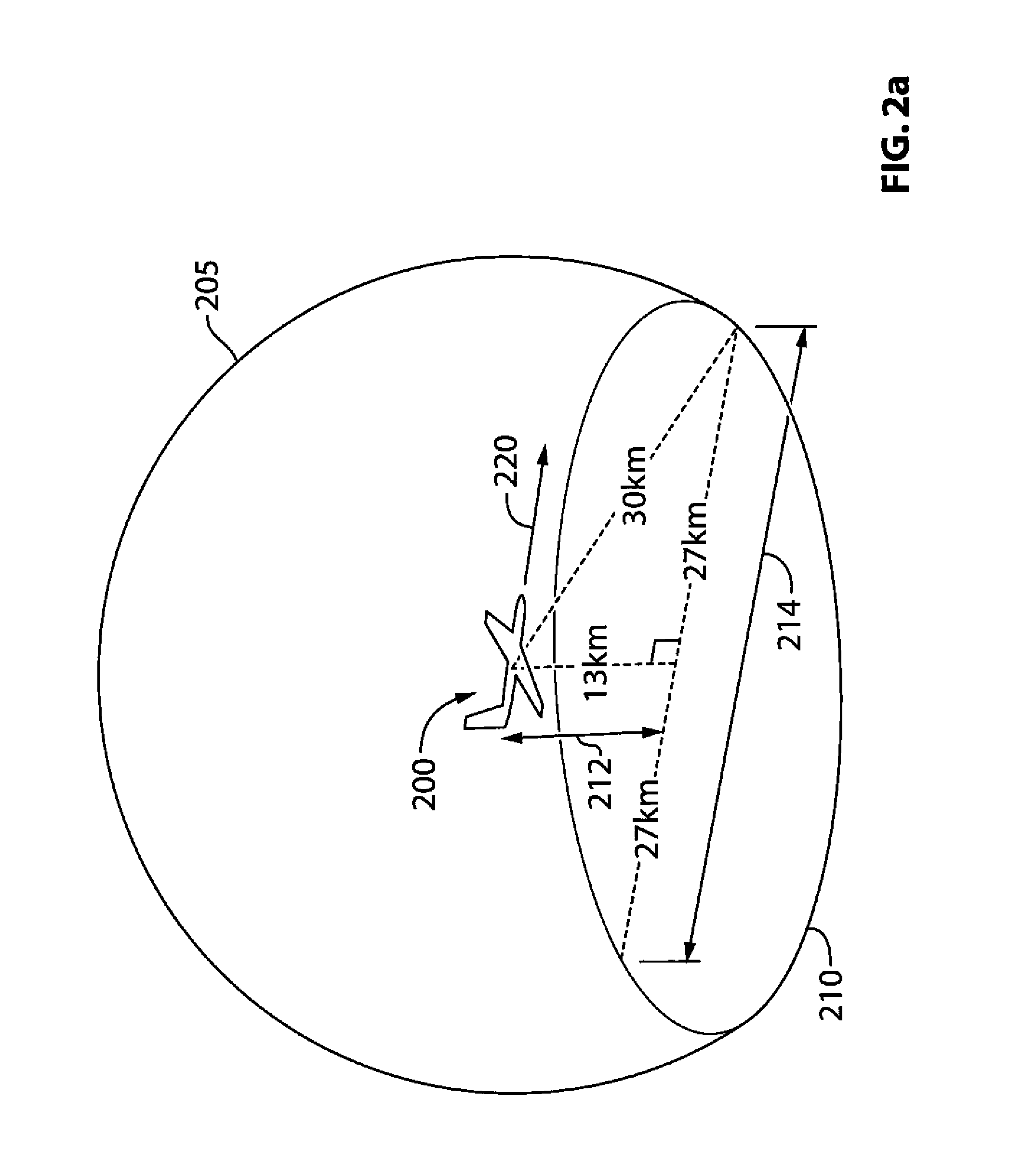
Airliner-mounted cellular base station
InactiveUS20130324070A1Eliminate the problemNetwork topologiesTelephonic communicationDual modeRadio access network
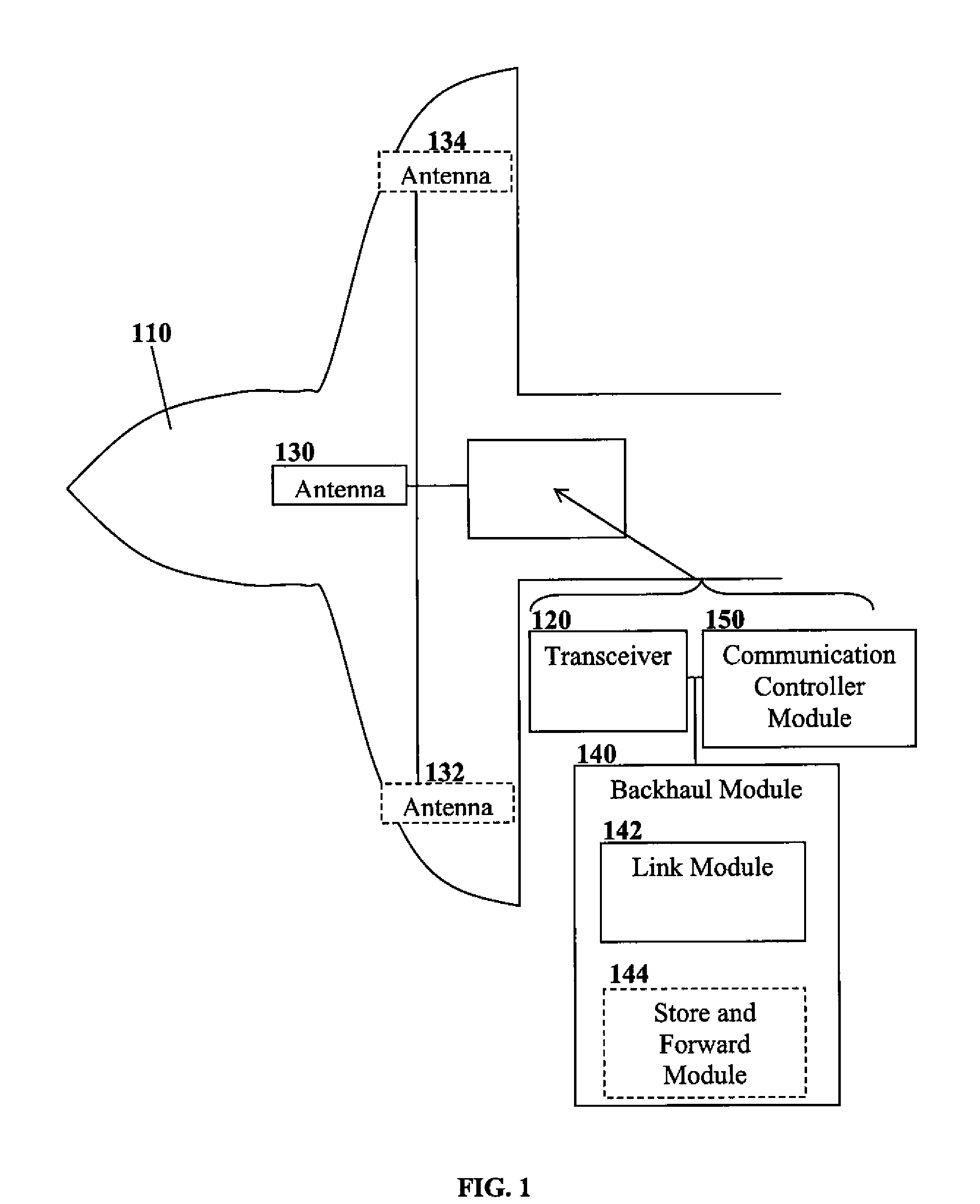
An aircraft-mounted base transceiver station (mBTS) for providing intermittent coverage in a cellular radio network. The mBTS utilizes the existing protocol of its terrestrial counterparts, thereby avoiding dual-mode devices and enabling common usage of terminal monitoring and device management systems for devices connected to a single radio access network even when outside terrestrial coverage areas. The aircraft follows a transient flight pattern, providing intermittent flyover connectivity for remote radio device such as machine-type devices. Connectivity may be store and forward. Channel usage may be adjusted to avoid interfering with terrestrial communication cells during flyover. Doppler effects due to aircraft speed may be accounted for. The mBTS may be configured to service in-range radio devices which are outside a Doppler-inhibited region and / or to prioritize communication with devices based on expected time outside the Doppler-inhibited region. An aircraft mounted antenna may have a radiation pattern focused toward devices outside the Doppler-inhibited region.
Owner:SIERRA WIRELESS
Apparatus for performing doppler correction in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS6965753B1Simple and inexpensive implementationRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringCommunications systemCarrier signal
Apparatus for Doppler correction in a wireless communications system, including a first frequency synthesizer for generating a carrier signal oscillating at a rate responsive to a first input, a counter coupled to the first input for generating a Doppler compensation signal, the counter having a clock input, and a second frequency synthesizer coupled to the clock input for generating a clock signal oscillating at a rate responsive to a rate input. The rate input is adjusted over time according to a predetermined sequence so that the Doppler compensation signal compensates for the Doppler effect experienced by, for example, ground-to-satellite communications in a satellite communications system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Double-frequency grating interferometer displacement measurement system
ActiveCN102937411AReduce volumeLight in massUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyGratingBeam splitter
The invention discloses a double-frequency grating interferometer displacement measurement system. The system comprises a double-frequency laser device, an interferometer, a measuring grating and an electrical signal processing portion. The measurement system achieves displacement measurement based on optical grating diffraction, the optical doppler principle and an optical beat frequency principle. The double-frequency laser device transmits double-frequency laser, the laser is divided into reference light and measuring light through a polarizing beam splitter, the measuring light transmits into a position of the measuring grating, positive and negative first-order diffraction occurs, diffraction light and the reference light form a beat frequency signal which contains displacement information in two directions at the position of a light detection unit, and linear displacement output is achieved through signal processing. According to the system, the sub-nanometer-grade or even higher grade of resolution ratio and accuracy can be achieved, and horizontal large-stroke displacement and horizontal displacement can be measured at the same time. The system has the advantages of being insensitive to the environment, high in measuring accuracy, small in volume and light in weight. The system serves as a lithography machine ultraprecise workpiece platform position measurement system, the comprehensive performance of the workpiece platform can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Systems and methods for non-contact multiparameter vital signs monitoring, apnea therapy, apnea diagnosis, and snore therapy
InactiveUS20140194793A1Minimize signal powerRestore muscle toneElectrotherapyStethoscopeMonitoring systemContinuous wave
Aspects of the of the disclosure relate to a non-contact physiological motion sensor and a monitor device that can incorporate use of the Doppler effect. A continuous wave of electromagnetic radiation can be transmitted toward one or more subjects and the Doppler-shifted received signals can be digitized and / or processed subsequently to extract information related to the cardiopulmonary motion in the one or more subjects. The extracted information can be used, for example, to determine apneic events and / or snoring events and / or to provide apnea or snoring therapy to subjects when used in conjunction with an apnea or snoring therapy device. In addition, methods of use are disclosed for sway cancellation, realization of cessation of breath, integration with multi-parameter patient monitoring systems, providing positive providing patient identification, or any combination thereof.
Owner:RESMED SENSOR TECH
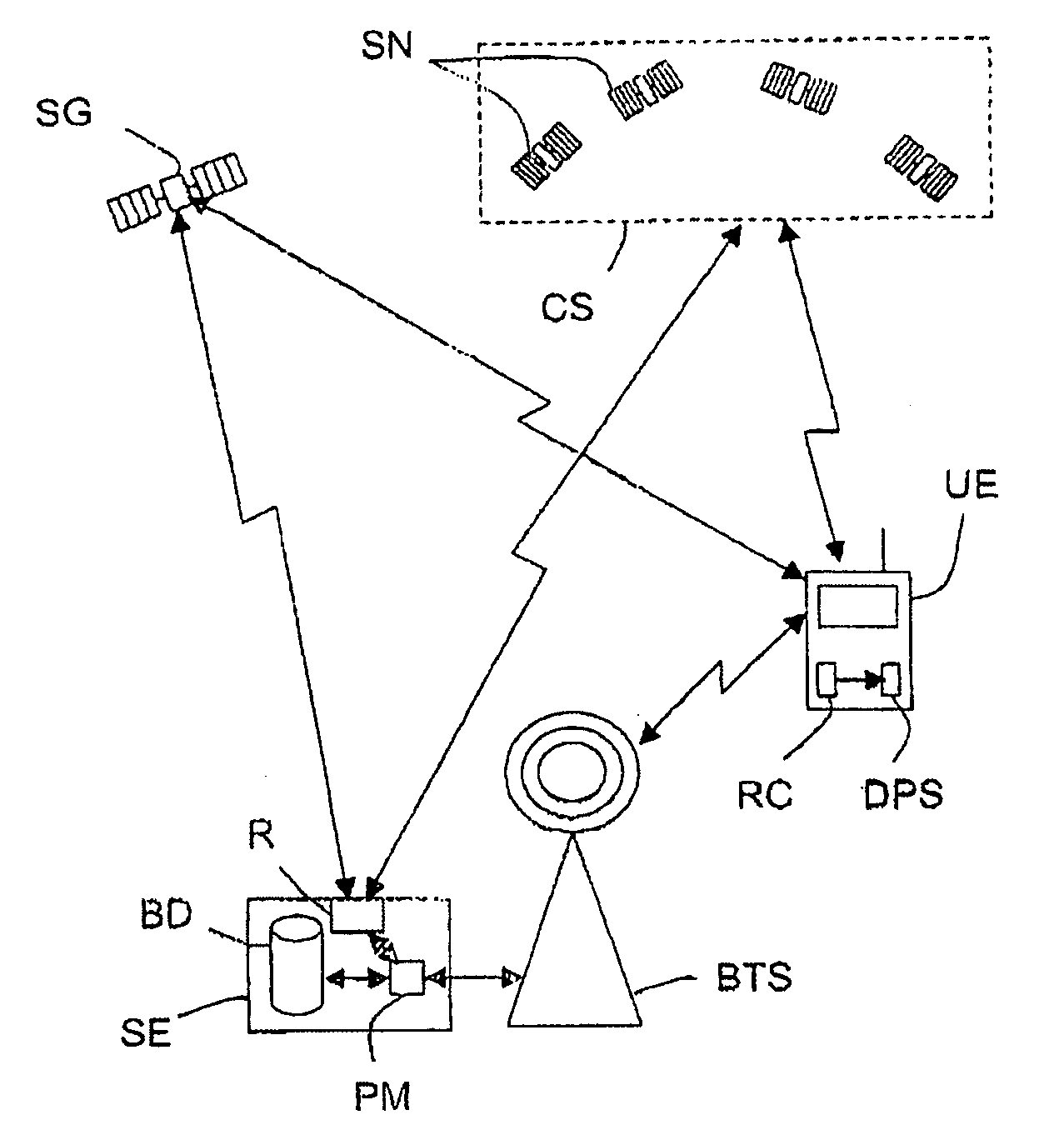
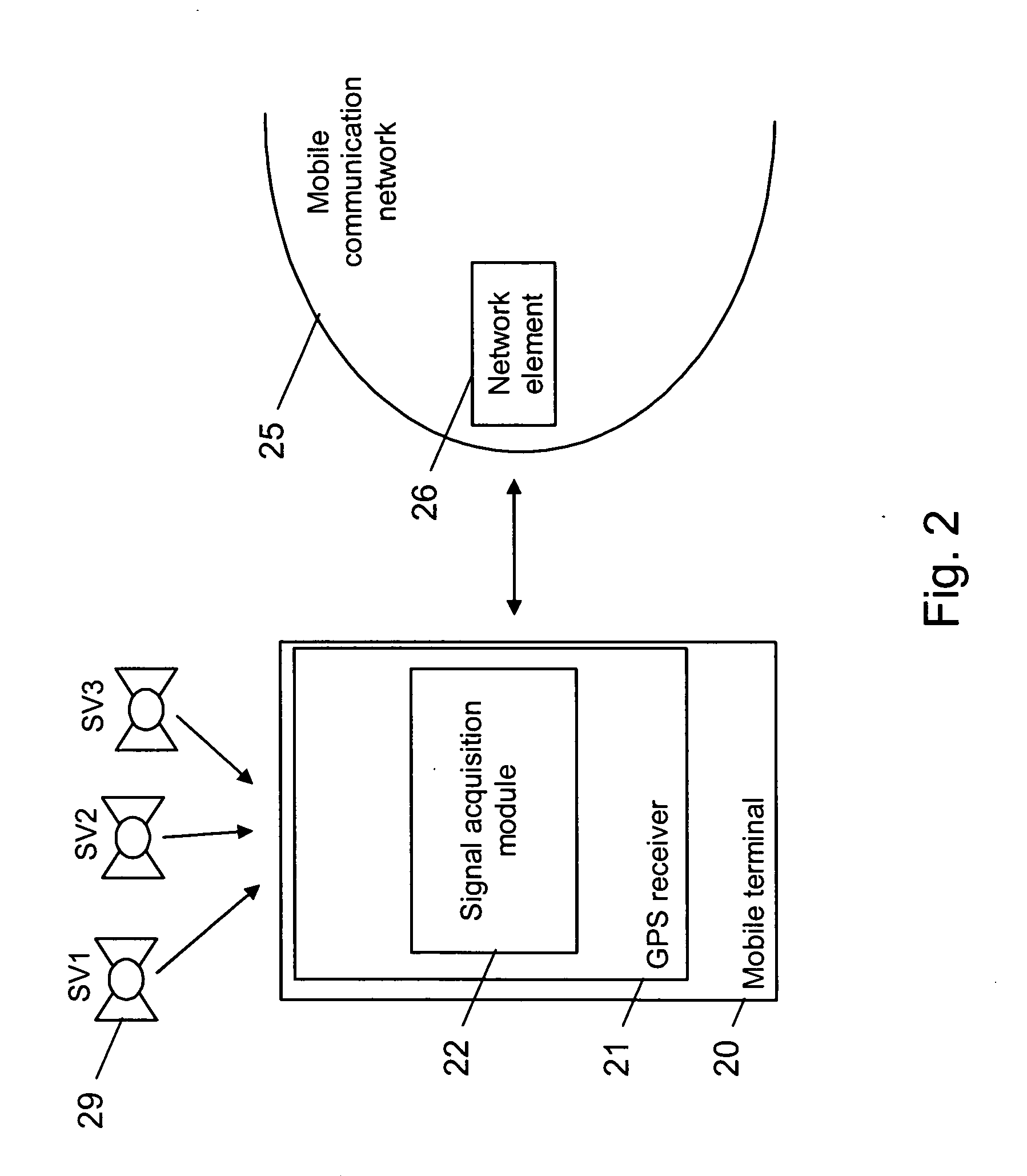
Determining mobile terminal positions using assistance data transmitted on request
InactiveUS20060238418A1Easy to detectImprove the level ofPosition fixationBeacon systemsPosition dependentComputer science
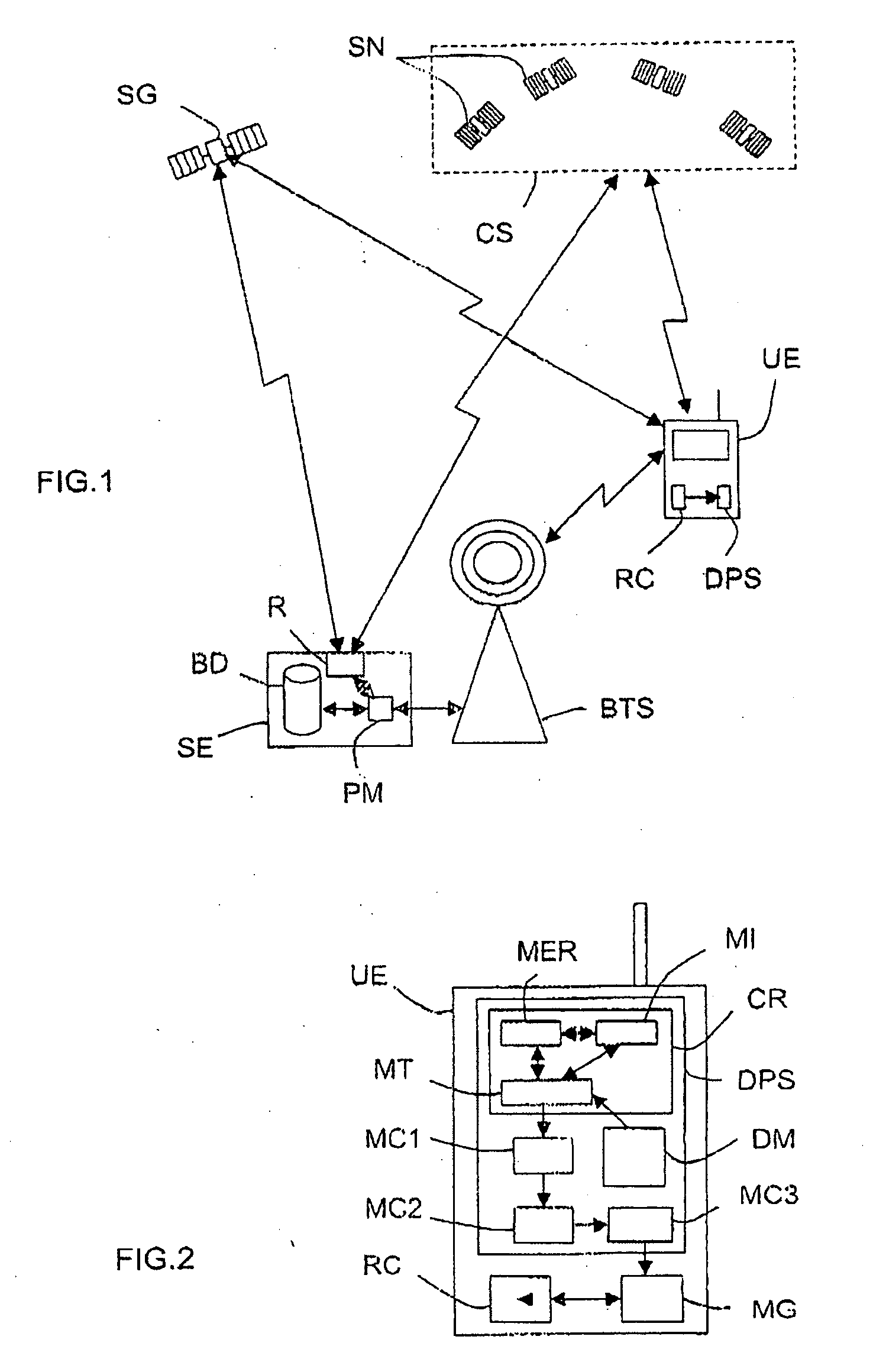
A mobile terminal (UE) comprises means (CR) for acquiring pseudo-random codes modulating signals received from positioning satellites (SN) in view belonging to a constellation (CS) and related to a reference time, and computation means (MC1-MC3) for determining its position received from the acquired codes and from navigation data contained in the signals. The acquisition means (CR), on receiving assistance data representing an approximate reference time and the approximate position of the terminal (UE), determine estimated positions of the satellites, estimated distances between the terminal and each of the satellites in view and associated Doppler effects as a function of pairs of hypotheses relating to the approximate reference time and the approximate position, and then determine a signal replica for each pair of hypotheses corresponding to the estimated positions and distances and to the associated Doppler effects over a selected time interval, and select the pair of hypotheses corresponding to the signal replica having the maximum correlation with the signal received during the time interval in order to determine the pseudo-random codes modulating the received signals.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
Devices and systems for measurement of position of drilling related equipment
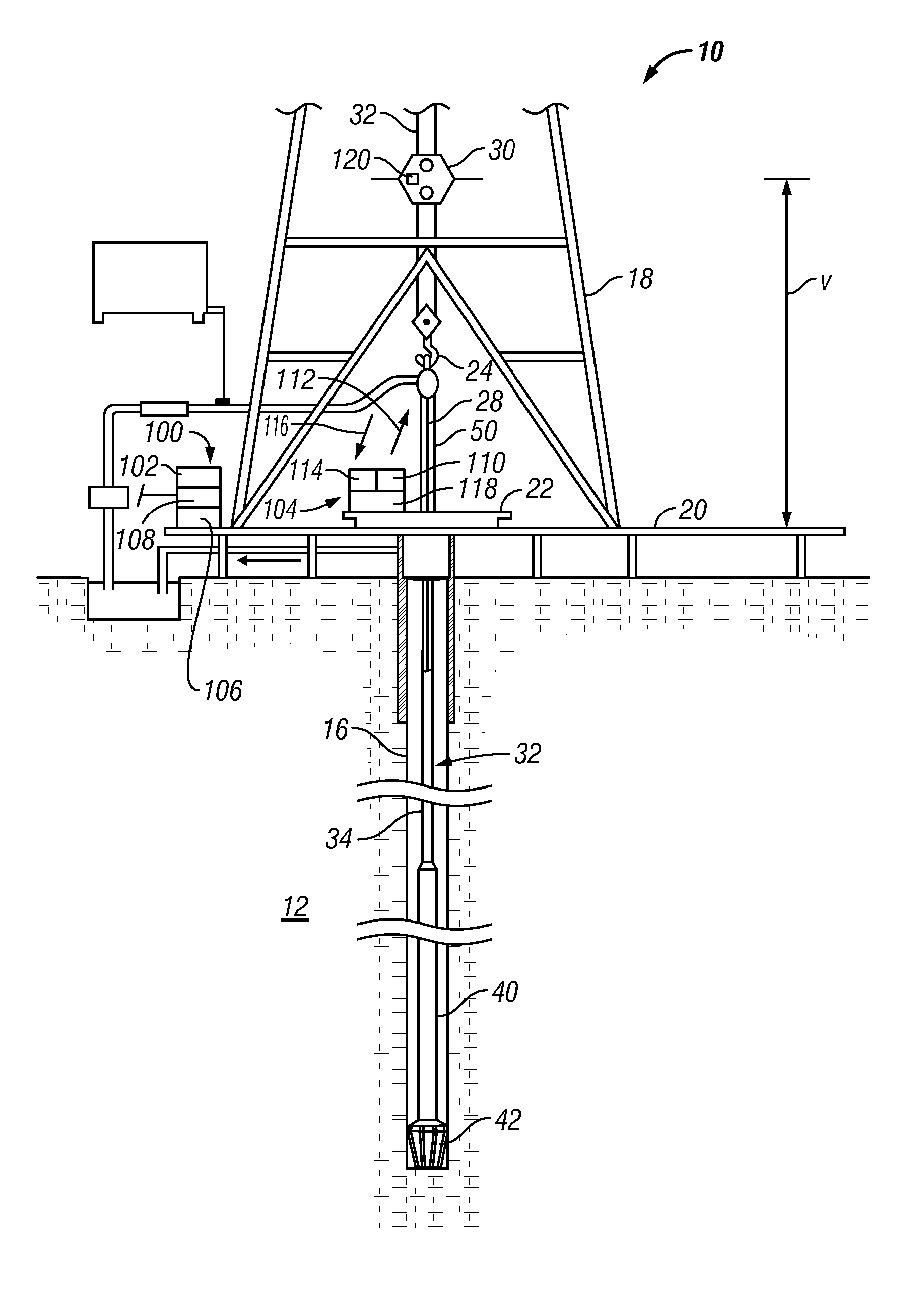
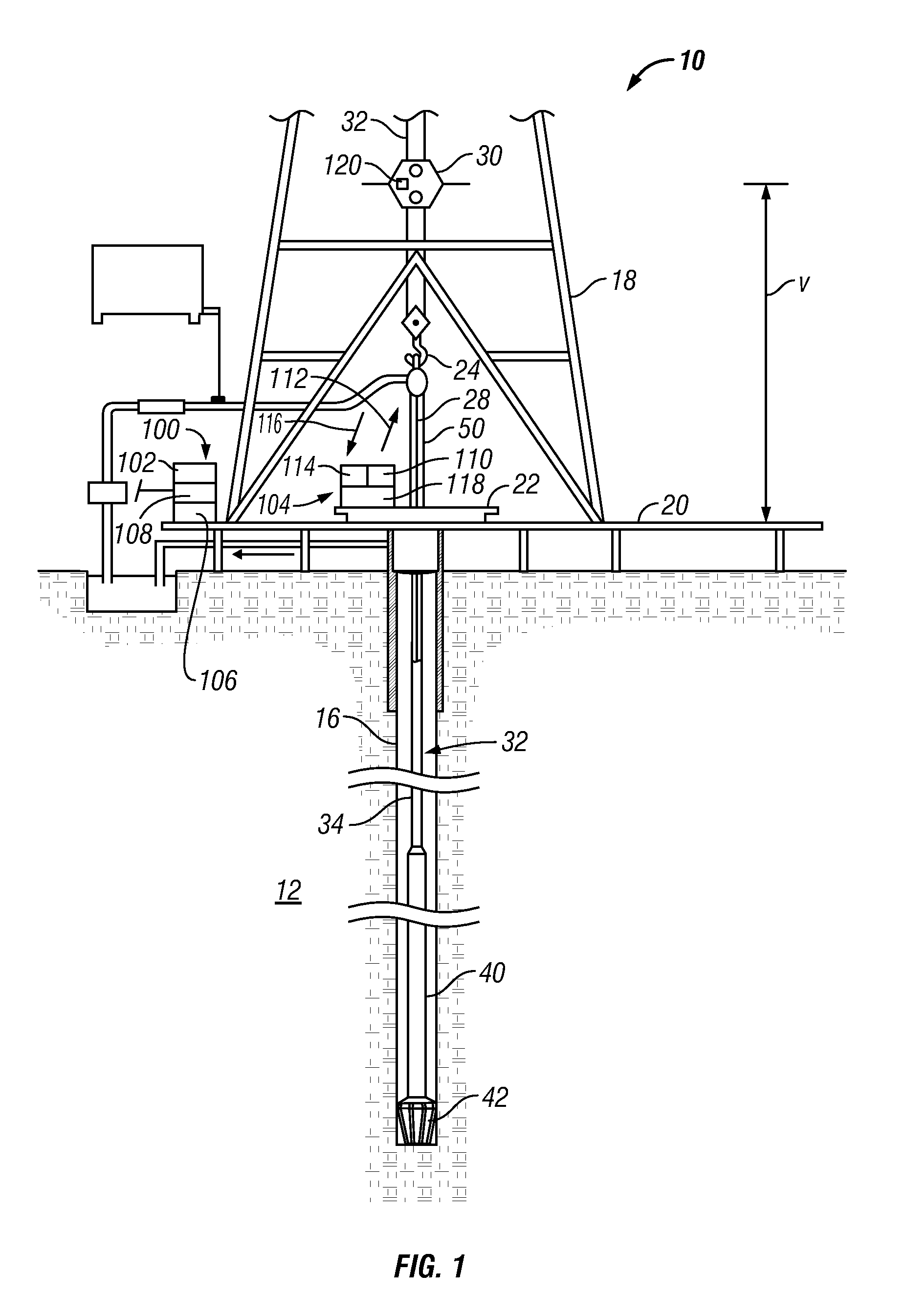
A depth measurement system for determining an absolute depth of a drill string uses a position acquisition device to determine a length value for a joint or stand being added to the drill string. The position acquisition device receives a signal from a target object associated with the added joint. The processed signal can be an optical signal, a radio signal, an acoustic signal, or other suitable signal. Using techniques such as time lapse, Doppler effect or phase shift, the depth measurement system determines a position parameter such as distance or position based on the received signal. Thereafter, the processor determines the absolute depth of the drill string by summing a length of each joint making up the drill string and correcting for the position of the newly added joint.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Methods and devices for determining the resonance frequency of passive mechanical resonators
ActiveUS7134341B2Accurately determineImprove accuracyVibration measurement in solidsFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsResonanceBlood pressure
Methods and systems for determining the resonance frequency of a resonator, using the Doppler effect. An interrogating sonic beam including a carrier frequency and one or more resonator exciting frequencies is directed at a resonator disposed in a measurement environment. Resonator vibrations are excited by the resonator exciting frequencies. The carrier frequency is modulated by the vibrating part(s) of the resonator. The returning signal is received and analyzed to determine the amplitude of the Doppler shifted sideband frequencies. The resulting data is processed to determine the resonator's resonance frequency. Using calibrated resonating sensors having a resonance frequency that varies as a function of a physical parameter in a measurement environment, the method and systems allow determining the value of the physical variable from the sensor's resonance frequency. The methods and systems may be used, inter alia, to determine intraluminal blood pressure in various parts of a cardiovascular system, the pressure of intra-cranial fluids, the pressure of fluids in various bodily cavities by using implantable calibratable resonating pressure sensors. The methods and systems may also be used for determining the pressure in various industrial measurement environments and enclosures. Methods and systems are provided for detecting the sensor and for centering the interrogating beam on the sensor.
Owner:MICROTECH MEDICAL TECH
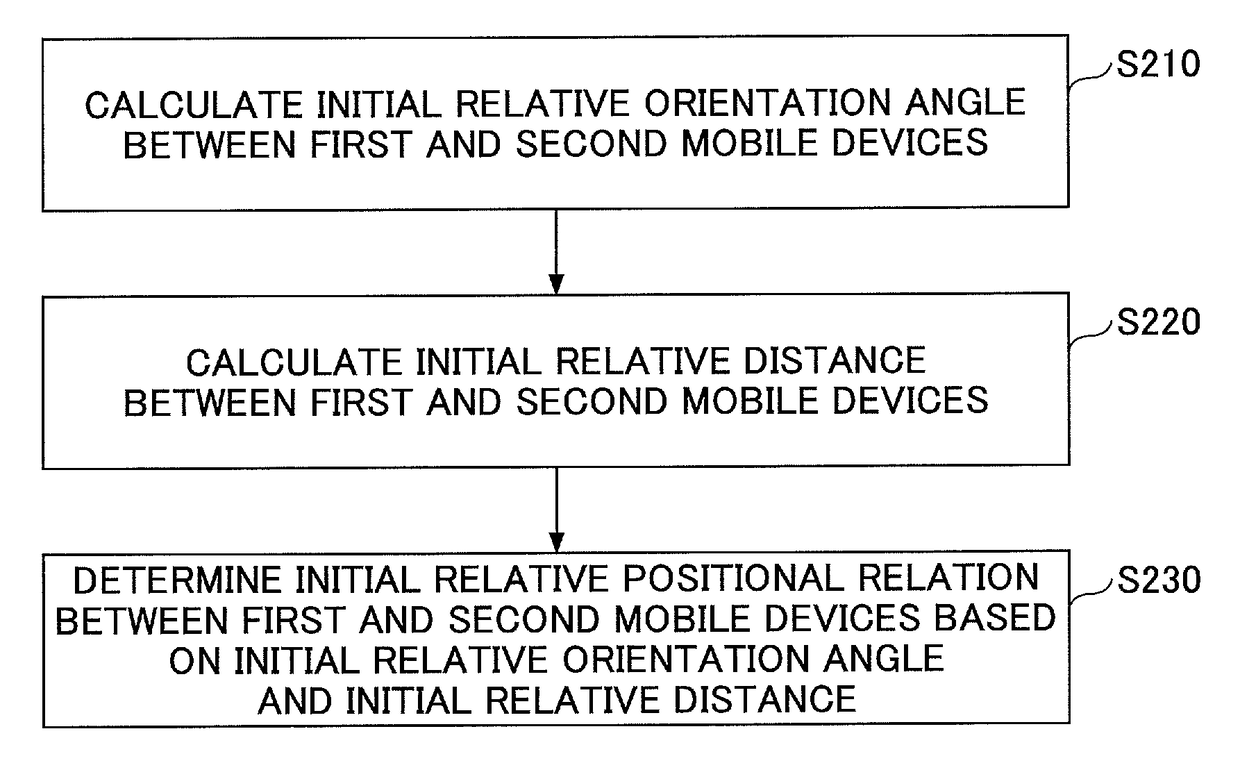
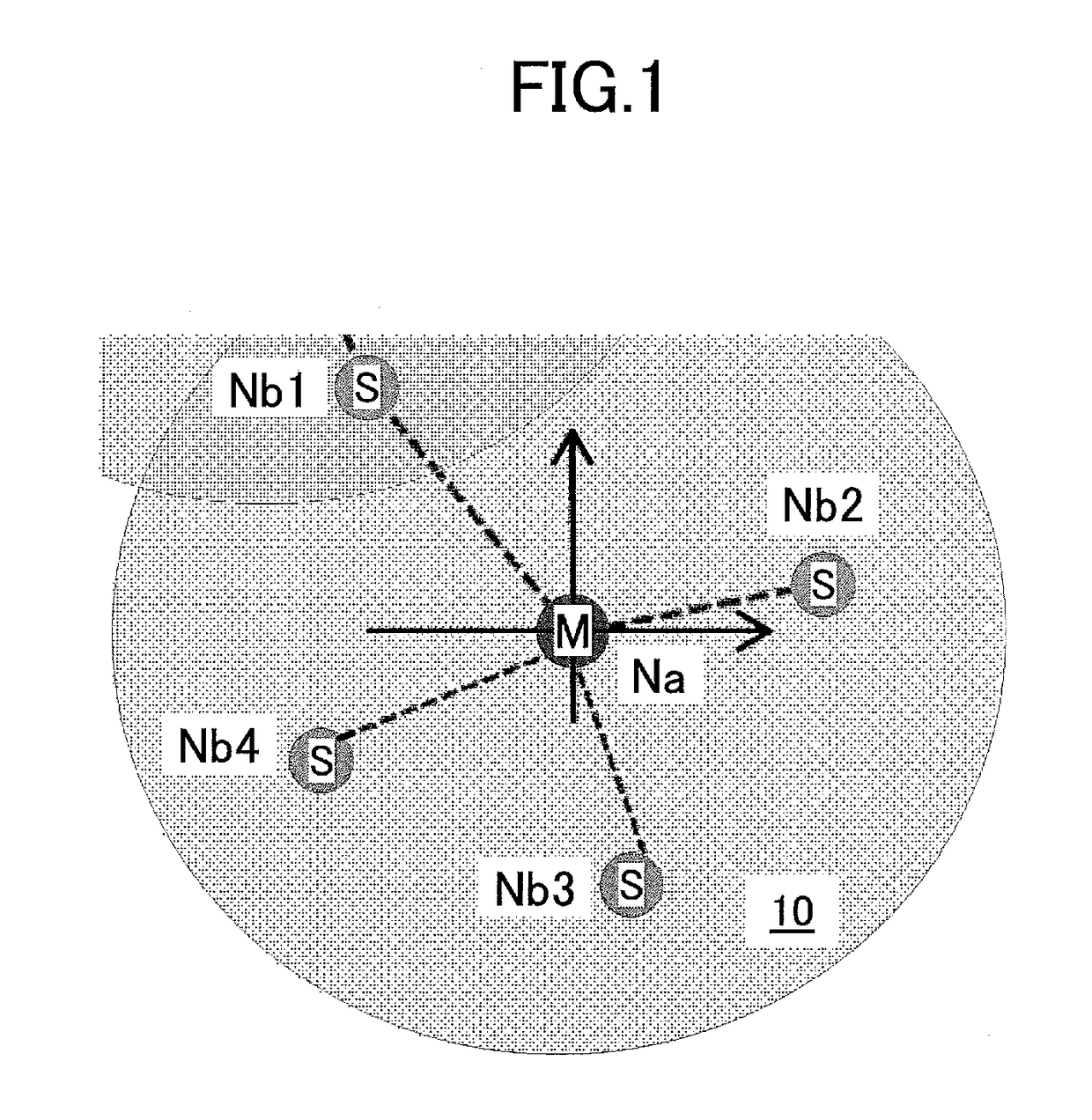
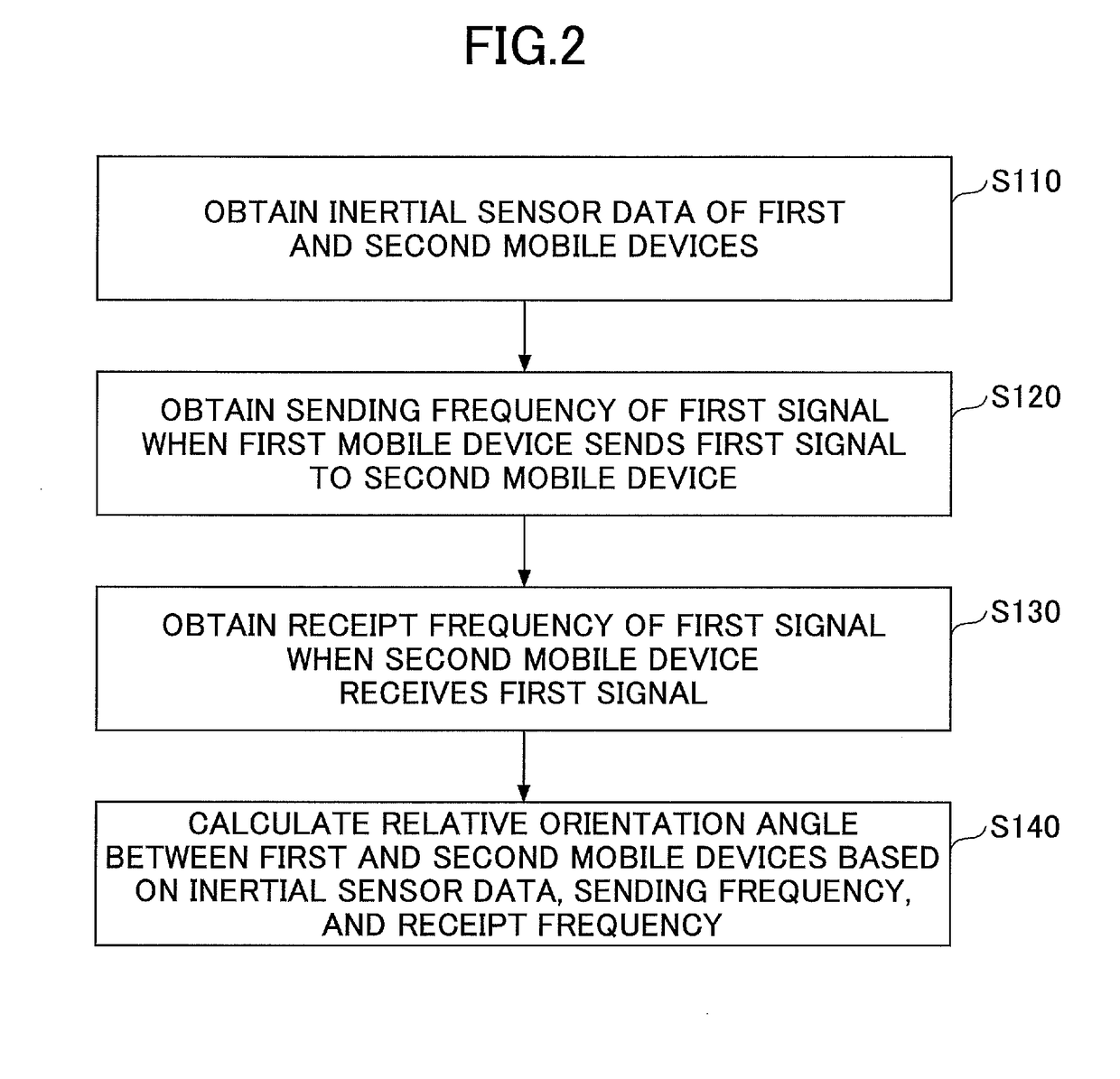
Relative orientation angle calculation method and device as well as relative positioning method
ActiveUS9772396B2Position fixationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMobile deviceRelative bearing
Disclosed is a relative orientation angle calculation method comprising steps of obtaining inertial sensor data of first and second mobile devices, the first mobile device being capable of sending a first signal to the second mobile device; obtaining a sending frequency that the first signal has when the first mobile device sends the first signal to the second mobile device; obtaining a receipt frequency that the first signal has when the second mobile device receives the first signal sent from the first mobile device, the first signal receiving influence of the Doppler effect in a sending process in which the first signal is sent to the second mobile device from the first mobile device; and calculating, based on the inertial sensor data, the sending frequency, and the receipt frequency, a relative orientation angle between the first and second mobile devices.
Owner:RICOH KK
Airliner-mounted cellular base station
An aircraft-mounted base transceiver station (mBTS) for providing intermittent coverage in a cellular radio network. The mBTS utilizes the existing protocol of its terrestrial counterparts, thereby avoiding dual-mode devices and enabling common usage of terminal monitoring and device management systems for devices connected to a single radio access network even when outside terrestrial coverage areas. The aircraft follows a transient flight pattern, providing intermittent flyover connectivity for remote radio device such as machine-type devices. Connectivity may be store and forward. Channel usage may be adjusted to avoid interfering with terrestrial communication cells during flyover. Doppler effects due to aircraft speed may be accounted for. The mBTS may be configured to service in-range radio devices which are outside a Doppler-inhibited region and / or to prioritize communication with devices based on expected time outside the Doppler-inhibited region. An aircraft mounted antenna may have a radiation pattern focused toward devices outside the Doppler-inhibited region.
Owner:SIERRA WIRELESS
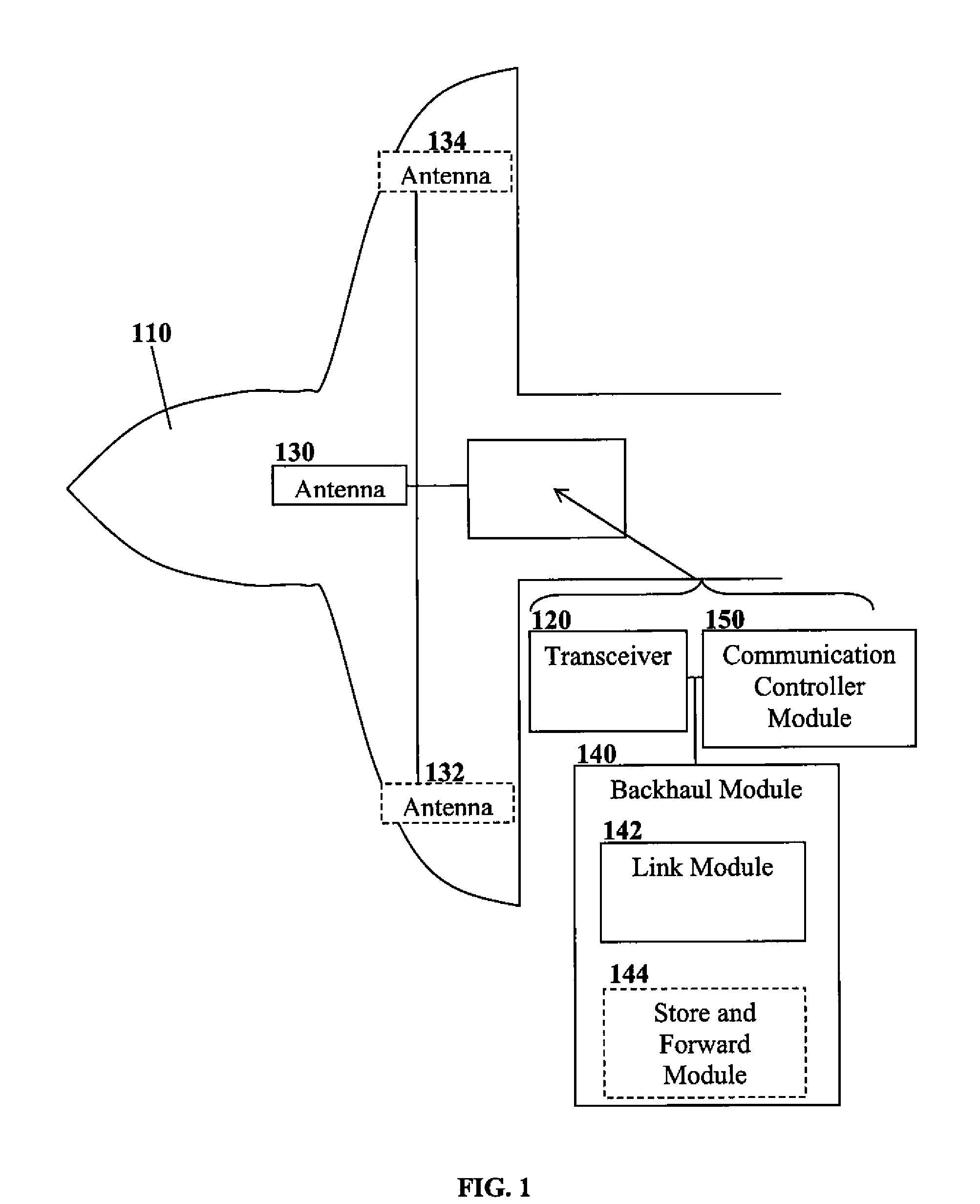
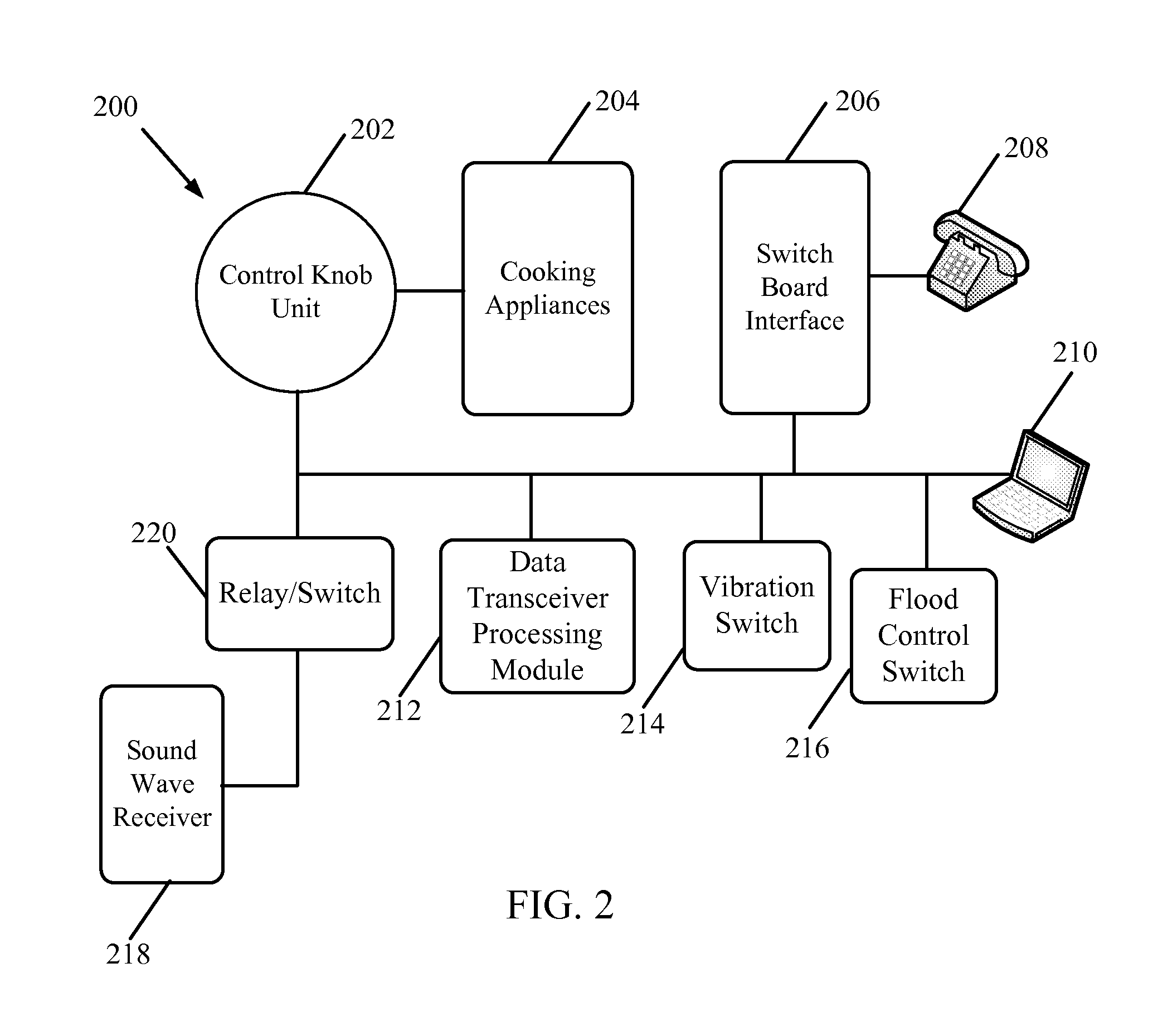
Systems and methods for automation of a control knob unit
InactiveUS20120325197A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesDomestic stoves or rangesTransceiverProcess module
A system and method for automatically rotating a control knob unit on an appliance or other device to an Off position upon the occurrence of a safety event is provided. The control knob unit may be secured to and engaged with an operational shaft on the appliance which controls the flow of gas or power to the appliance. The system may include one or more detectors (or detector modules) that are configured to emit a signal upon an occurrence of the event, such as a fire, which may be an early indication of a developing emergency. The signal may be in the form of an audible alert, such as sound (or sound waves). A data transceiver processing module may receive a plurality of sound waves and analyze the plurality of sound waves for a variation in frequency (or Doppler Effect) to determine if any of the sound waves originate from the one or more detector modules.
Owner:LEGASPI FERDINAND VILLEGAS +2
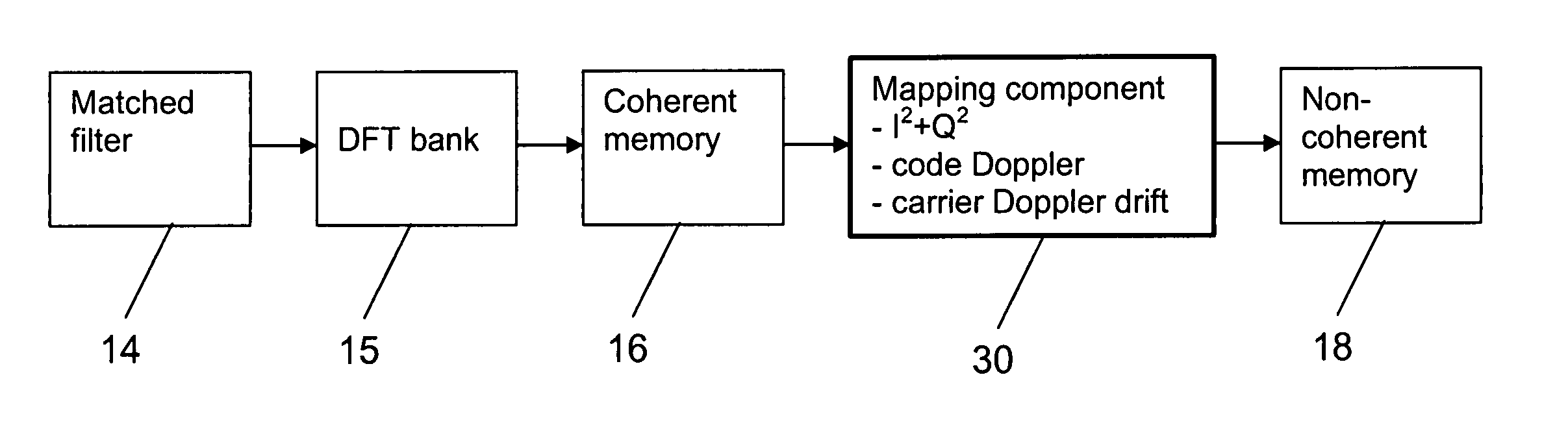
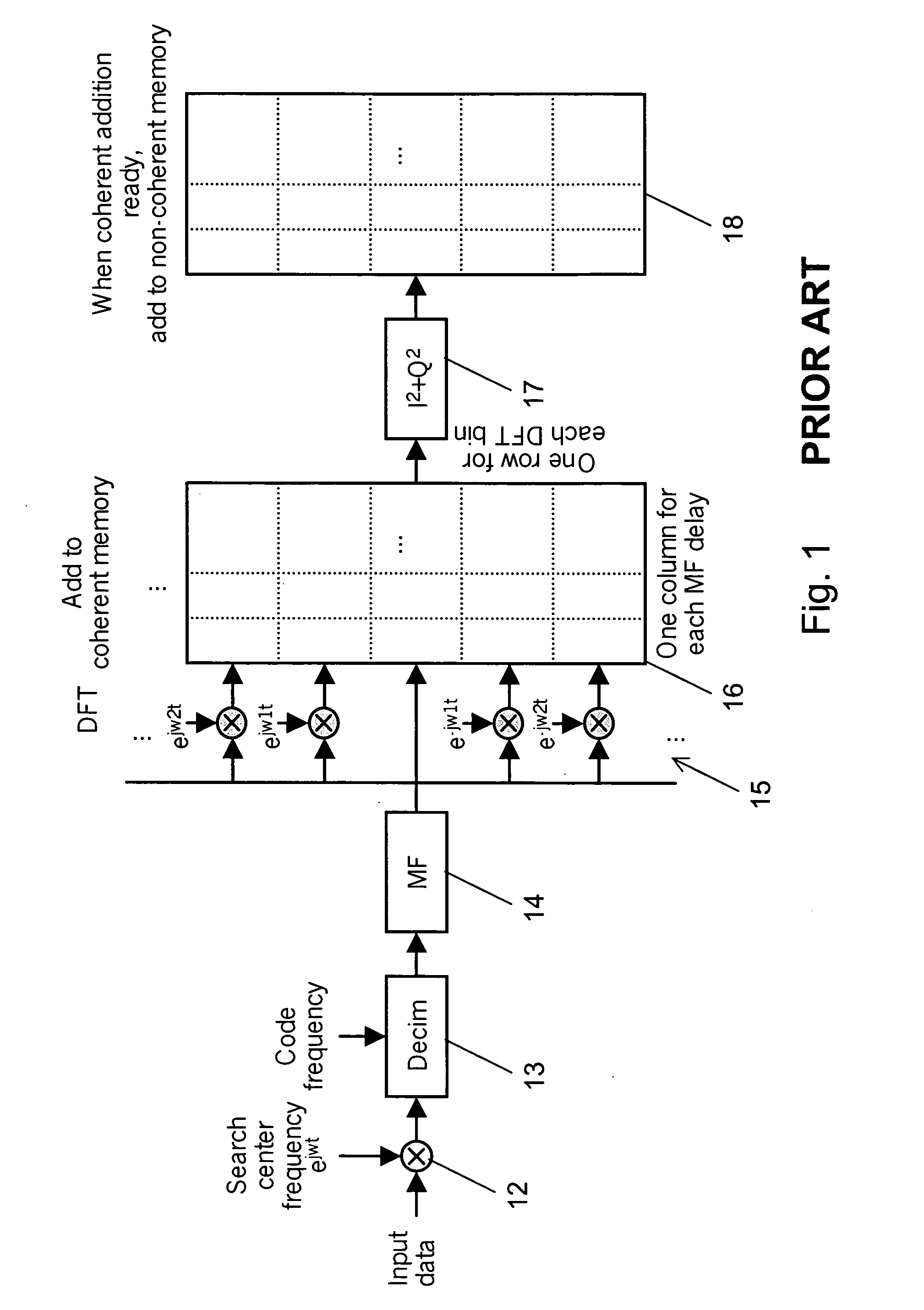
Determination of a code phase
InactiveUS20060133463A1Long integration timeHigh sensitivityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSatellite radio beaconingFrequency compensationCarrier signal
The invention relates to determining a correct code phase of a received, code modulated carrier signal using a correlation portion, a frequency compensation portion, a coherent memory and a non-coherent memory. In order to compensate for a code Doppler effect and / or a carrier Doppler drift effect, a mapping portion maps correlation values either to the coherent memory or to the non-coherent memory. Alternatively, the mapping portion maps correlation values stored in the coherent memory or in the non-coherent memory to new positions. The mapping depends on a frequency compensation applied by the frequency compensation portion and elapsed integration time, and / or on a drift of a frequency offset in correlation values output by said correlation portion.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
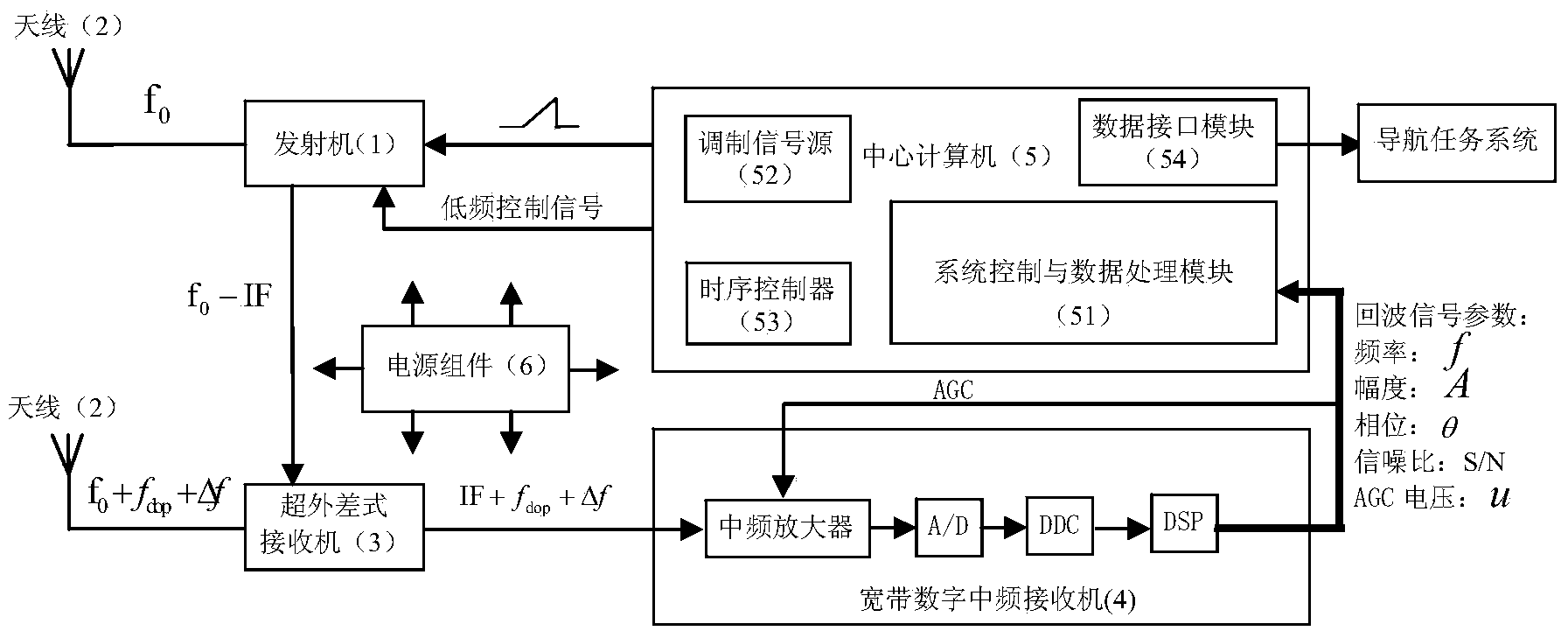
Onboard automatic speed measuring and height measuring radar system and speed measuring and height measuring method
InactiveCN104237877ARealize synchronous processingRealize the function of measuring speed and height at the same timeSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses an onboard automatic speed measuring and height measuring radar system and a speed measuring and height measuring method. The system comprises an antenna, a transmitter, a superhet receiver, a broadband digital intermediate-frequency receiver, a center computer and a power module. The transmitter generates four sawtooth wave linear frequency modulation radio-frequency signals and achieves space symmetric configuration through the antenna; the superhet receiver and the broadband digital intermediate-frequency receiver complete echo signal digital demodulation together and calculate the frequency, amplitude, phase and signal-to-noise ratio information of echo signals; the center computer separates the speed information and the height information of the same echo beam by applying Doppler principle directivity based on the space symmetry and the timing sequence relevance of four beams, and the information is used for calculating the flight speed value and the flight height value of an aircraft. According to the onboard automatic speed measuring and height measuring radar system and the speed measuring and height measuring method, the same radar can be used for automatically measuring the speed and the height, the structure of an aircraft avionics system is simplified, the measuring precision is high, and the onboard automatic speed measuring and height measuring radar system and the speed measuring and height measuring method can be used for measuring carrier aircraft flight parameters.
Owner:SHAANXI CHANGLING ELECTRONICS TECH
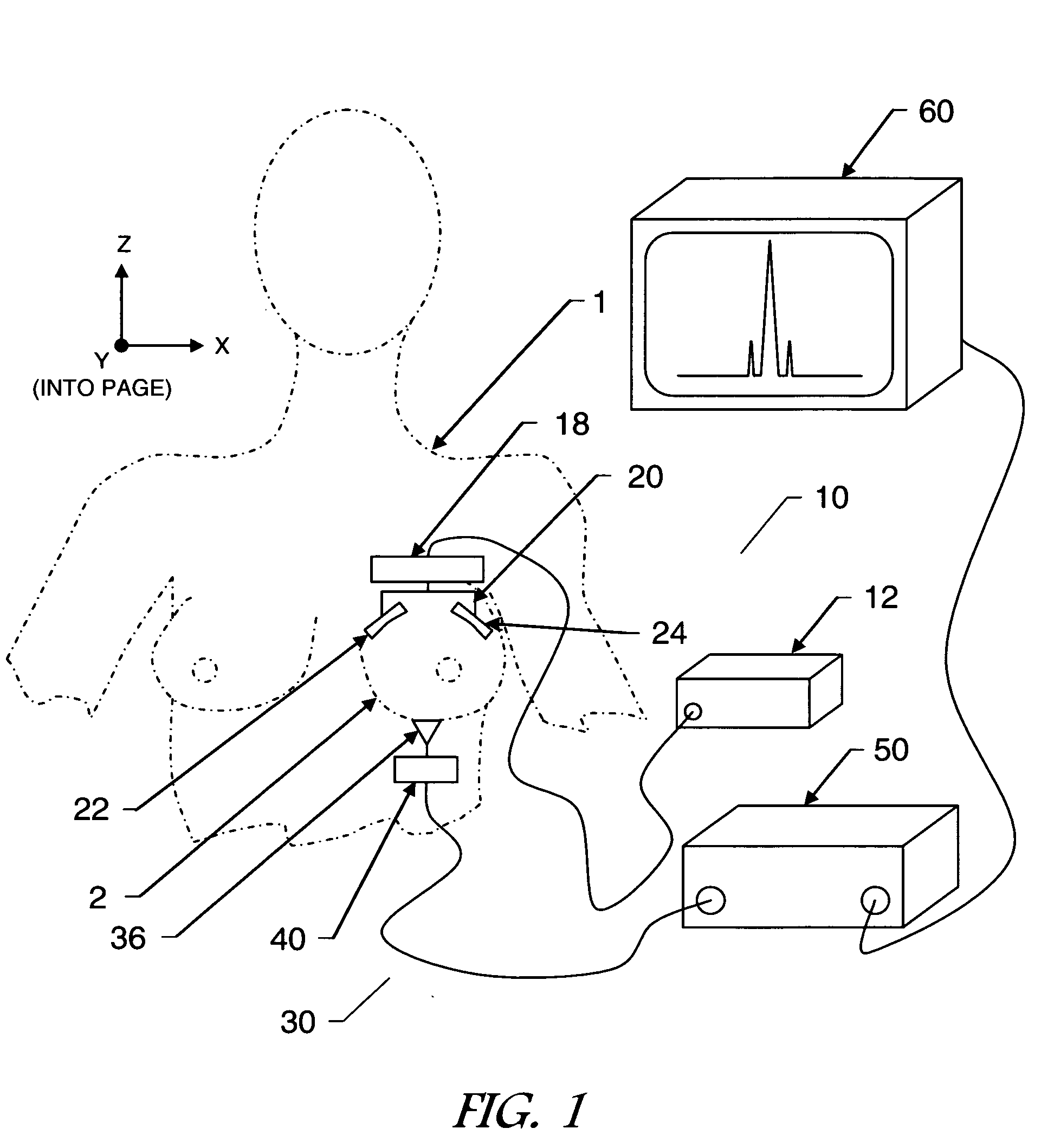
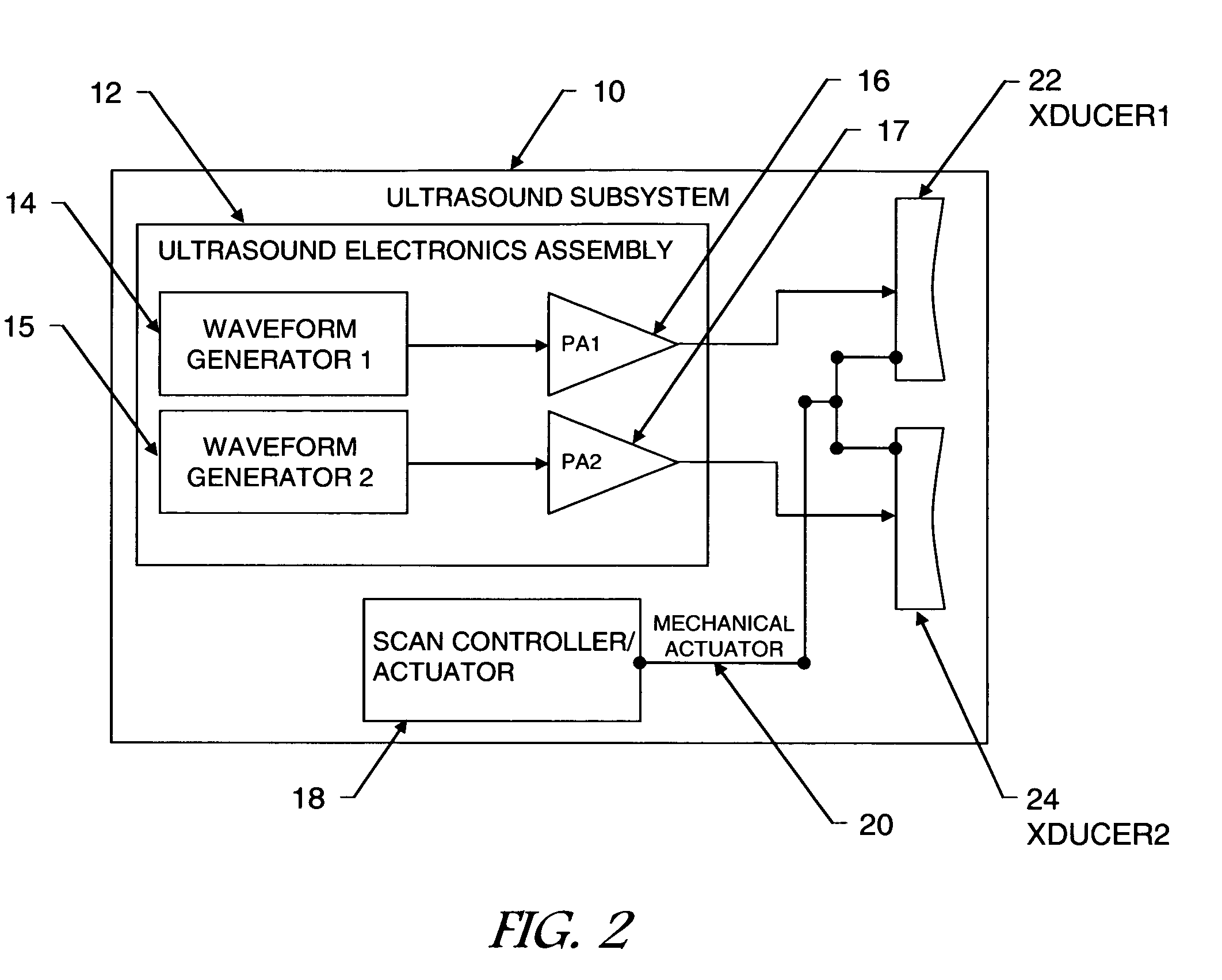
Multi-modality system for imaging in dense compressive media and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20090281422A1Improve permeabilityHigh resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsFrequency waveMicrowave
A multi-modality system and method for performing detection, characterization and imaging of materials and objects in dense compressive media, such as in medical soft tissue applications, is disclosed. Medical tissue applications include but are not limited to the detection and diagnosis of breast tumors. Generally, an ultrasound subsystem is employed to excite a region in the dense compressive media and a microwave subsystem is employed to collect detection, characterization and imaging information from the excited region. In one preferred embodiment, multiple focused oscillating high-frequency ultrasound wave beams are transmitted into the media. The resultant low beat-frequency wave creates a force inducing motion in the materials and objects in the media. A radio-frequency microwave subsystem detects that motion and produces images based upon the Doppler effects of the excited materials and objects.
Owner:ULTRAWAVE LABS
Biometric piezo scanner
InactiveUS7236616B1Doppler effectProvide informationBlood flow measurement devicesPerson identificationSensor arrayElectrical conductor
A piezoelectric thin film sensor array is used to scan and capture biometric data, for example, a fingerprint image. In one embodiment, a multi-layer structure includes a PVDF layer in between two conductor grids arranged orthogonally to one another. Urethane can be added to one side where a finger is placed. A foam substrate can be used as a support. In one feature, the PVDF, and grids can be peeled off like a label for easy replacement. Multiplexers are switched to scan the sensor. A single pixel or a group of pixels can be detected and output to an image memory. The presence of a fingerprint ridge is detected by virtue of a ring-down oscillation that arises from reflection when an electric field is applied to the piezoelectric thin film sensor array at a pixel in contact with the fingerprint ridge. For example, such a ring-down value associated with a fingerprint ridge can be detected at about 150 ns. (or 5 cycles at 30 MHZ). Other reflections indicative of additional biometrics (e.g. from tissue, blood, bone, fingernail, etc.) can also be detected. A Doppler effect due to reflections from circulating blood can also be detected. Such a Doppler effect can provide further information about direction and speed of blood circulation. An instantaneous pyroelectric effect can also be detected to indicate a live finger presence.
Owner:SONAVATION INC
Doppler radar-based non-contact type vibration measuring method
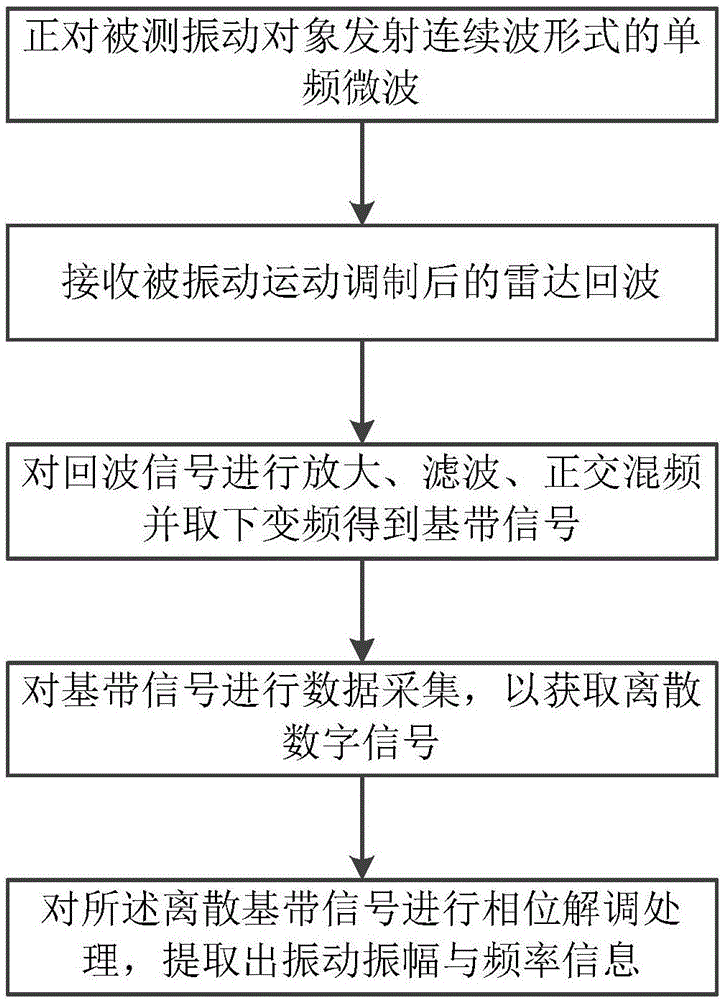
ActiveCN106644030AReduce power consumptionCompact structureSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansVibration amplitudeData acquisition
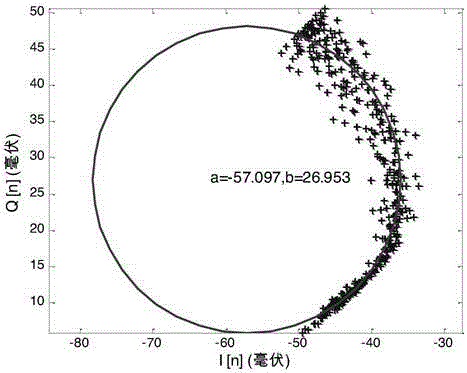
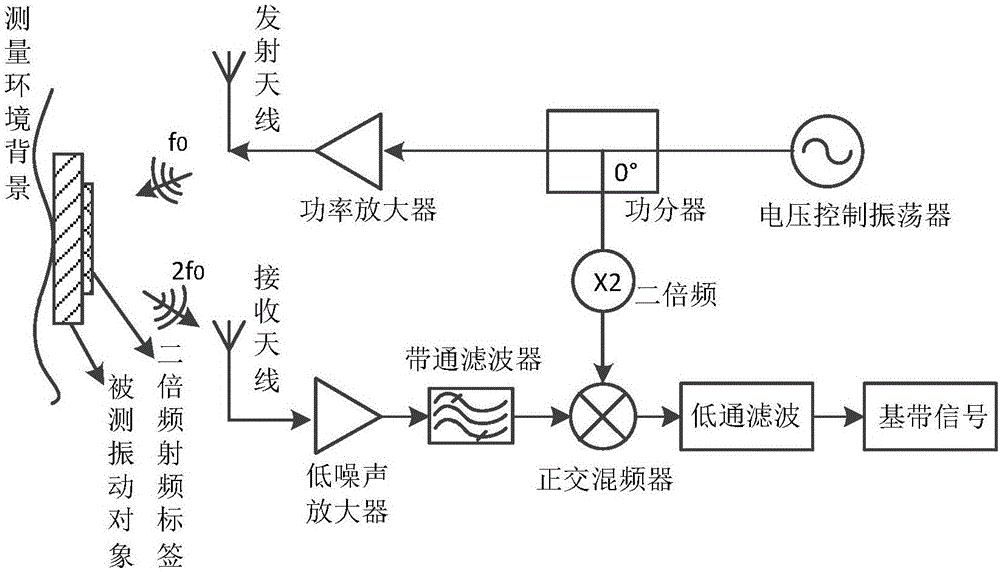
The invention discloses a Doppler radar-based non-contact type vibration measuring method. The method includes the following steps: S1. directly facing a measured vibration object to emit single-frequency microwaves in the form of continuous waves, and receiving radar echoes after modulation by vibration motion; S2. performing amplifying, filtering and quadrature mixing on echo signals and taking down conversion signals to obtain two paths of baseband signals I(t) and Q(t); S3. performing data collection on the baseband signals to obtain discrete digital signals; and S4. performing phase demodulation processing on the discrete baseband signal I[n] and Q[n], and extracting vibration amplitude and frequency information. The Doppler radar-based non-contact type vibration measuring method provided by the invention uses a microwave radar to perform non-contact type vibration measurement based on a Doppler effect, has good low frequency measurement sensitivity, is high in environmental adaptation, and can perform accurate vibration measurement under the condition of containing a barrier. The microwave radar used by the method is compact in structure and low in cost and has relatively low power consumption, thereby providing a solution to integration of a large-scale vibration measuring system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Doppler factor estimation and compensation method of mobile underwater acoustic communication
ActiveCN107911133AAccurate estimateImprove estimation accuracyMulti-frequency code systemsComputation complexityRadio channel
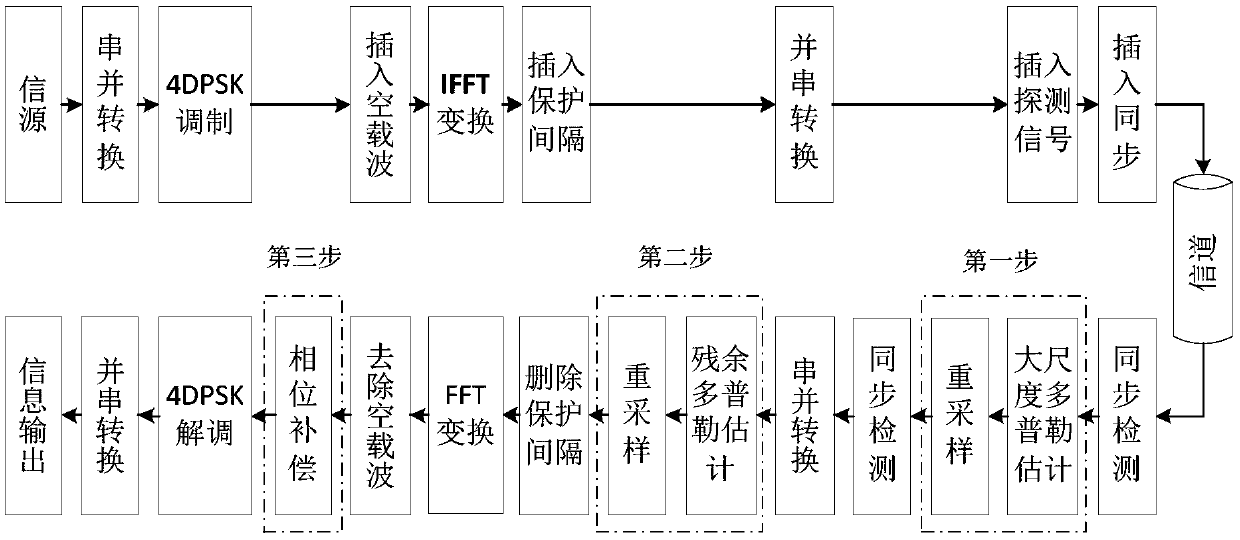
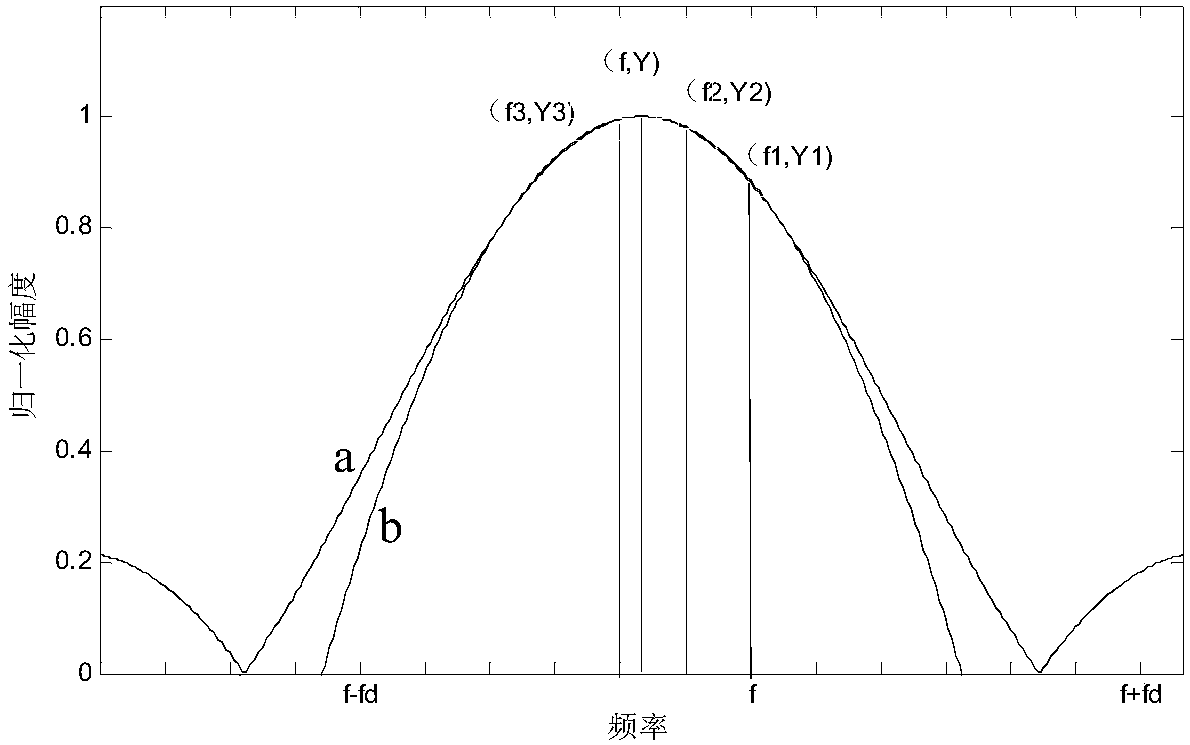
The invention discloses a Doppler factor estimation and compensation method of mobile underwater acoustic communication, related to underwater acoustic communication. The Doppler factor estimation andcompensation method of the mobile underwater acoustic communication comprises the following steps: 1) large scale Doppler estimation and compensation; 2) residual Doppler estimation and compensation;and 3) Doppler phase rotation compensation. In order to accurately and efficiently estimate the Doppler factor in the mobile underwater acoustic communication environment, overcome the more obvious Doppler effect compared with the terrestrial radio channel and eliminate the adverse effects on the underwater acoustic OFDM communication system of the Doppler effect, a Doppler factor estimation andcompensation method of the mobile underwater acoustic communication considering both the accuracy and the computationcomplexity is needed. Because the estimation is carried out in the frequency domainand aims at the characteristics of the underwater acoustic channel, the Doppler factor estimation and compensation method of the mobile underwater acoustic communication, especially the Doppler factor estimation and compensation method applied to the mobile underwater acoustic OFDM system is more suitable for the fast changing mobile underwater acoustic channel based on the traditional Doppler estimation and compensation. The estimation accuracy is high; and meanwhile, the computation complexity is reduced appropriately, therefore, the practicability is excellent.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Clutter rejection in a passive radar receiver of OFDM signals
InactiveUS6924763B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsOrthogonal multiplexPassive radarCovariance matrix
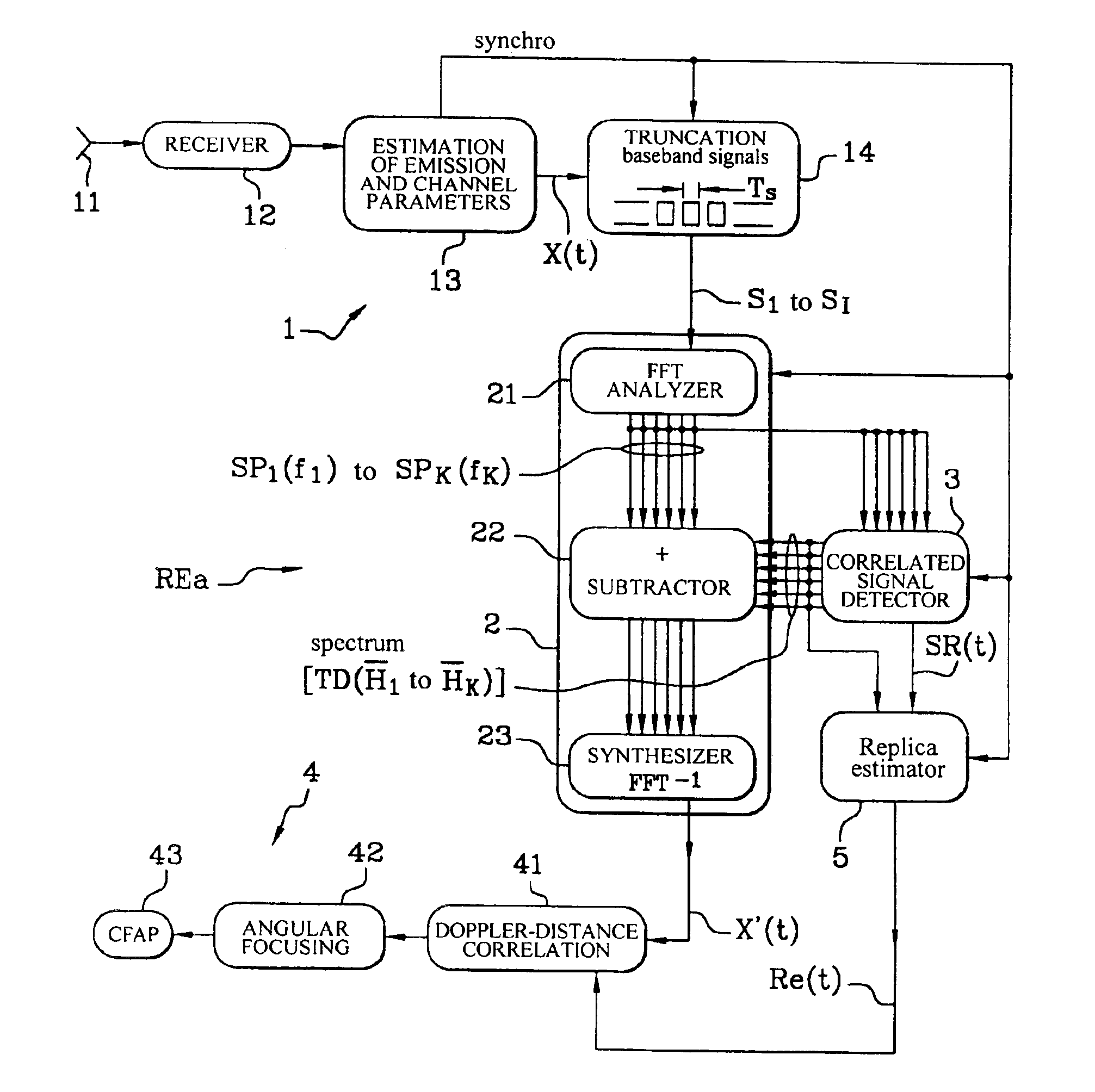
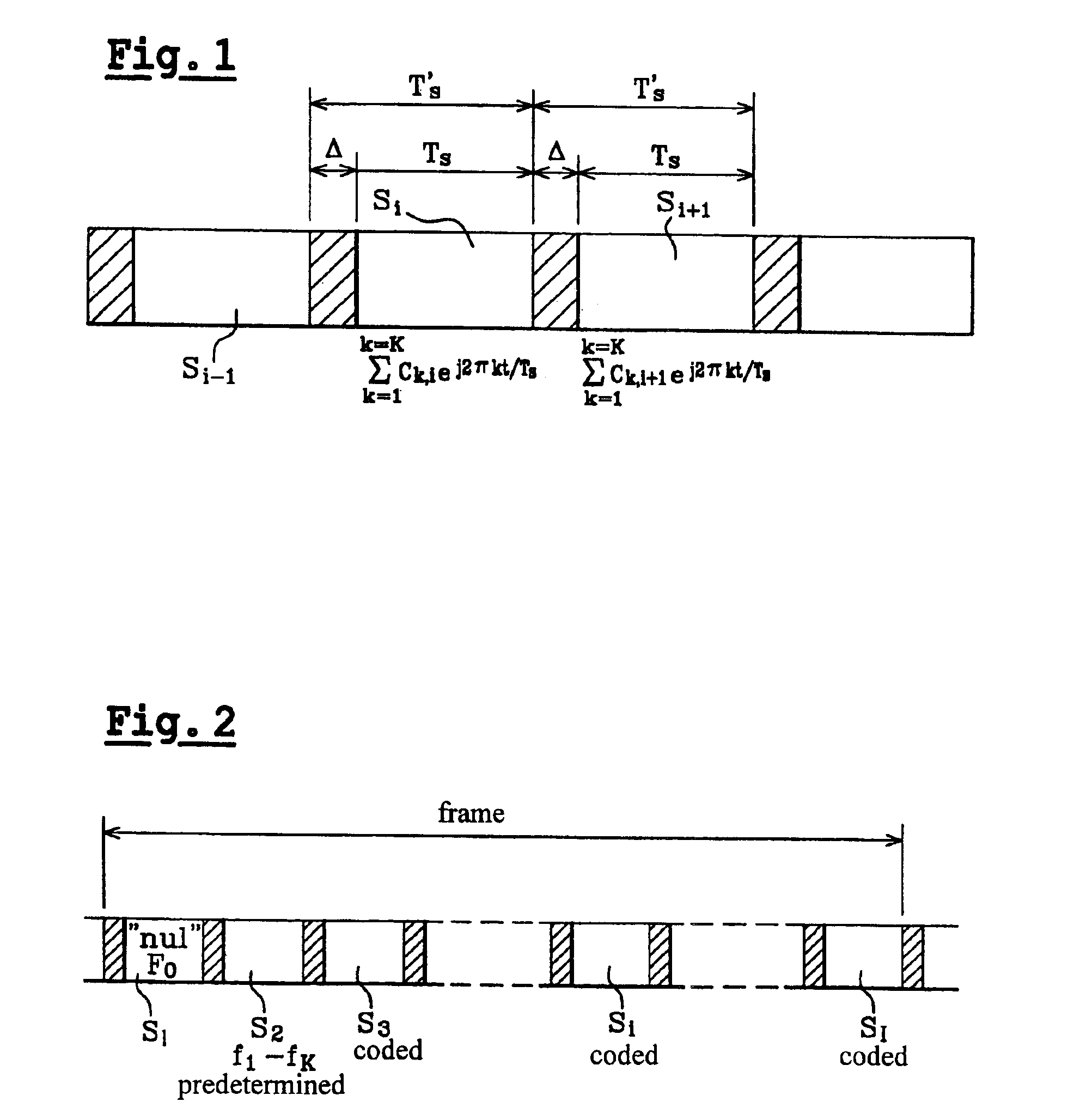
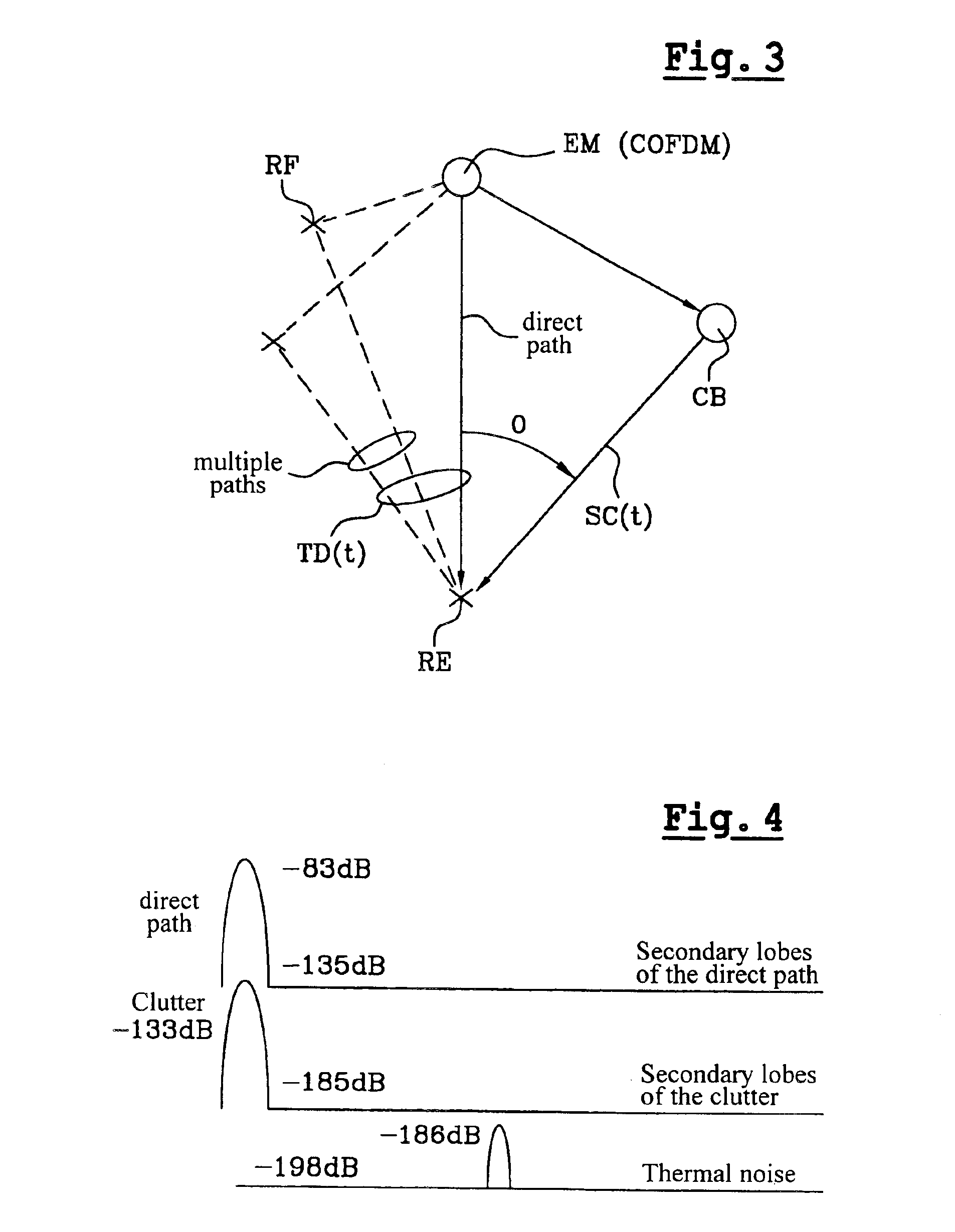
The invention concerns a passive radar receiver for a received orthogonal frequency division multiplex-type signal consisting of symbol frames each emitted on coded orthogonal carriers. After formatting the received signals into digital symbols (S1 S1), a filtering circuit (2) eliminates by subtraction or using a covariance matrix, in the symbol signal at least unwanted signals with null Doppler effect so as to apply a filtered signal (X′) including essentially signals backscattered by mobile targets to a Doppler-distance correlator (4).
Owner:OFFICE NAT DETUD & DE RECH AEROSPATIALES
Method for re-establishing moving sound source by adopting moving equivalent source method
InactiveCN101539455AEliminates the effects of the Doppler effectRealization of sound field reconstructionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementEquivalent source methodSound sources
A method for re-establishing a moving sound source by adopting a moving equivalent source method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of measuring Doppler effect-contained sound pressure data in a moving sound source radiation sound field; establishing a transmission relationship between vibration speed and radiation sound pressure under Doppler effect-contained measured sound pressure and sound source static situation by the moving equivalent source; removing the influence of the Doppler effect according to the transmission relationship; and realizing the positioning identification and sound field re-establishment of the moving sound source. The moving sound source applicable to the method can be any shapes including plane, cylindrical surface or spherical surface; and the method is developed on the basis of a near-field acoustical holography reconstruction algorithm based on the equivalent source, has good computation stability, high computation precision and simple execution.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
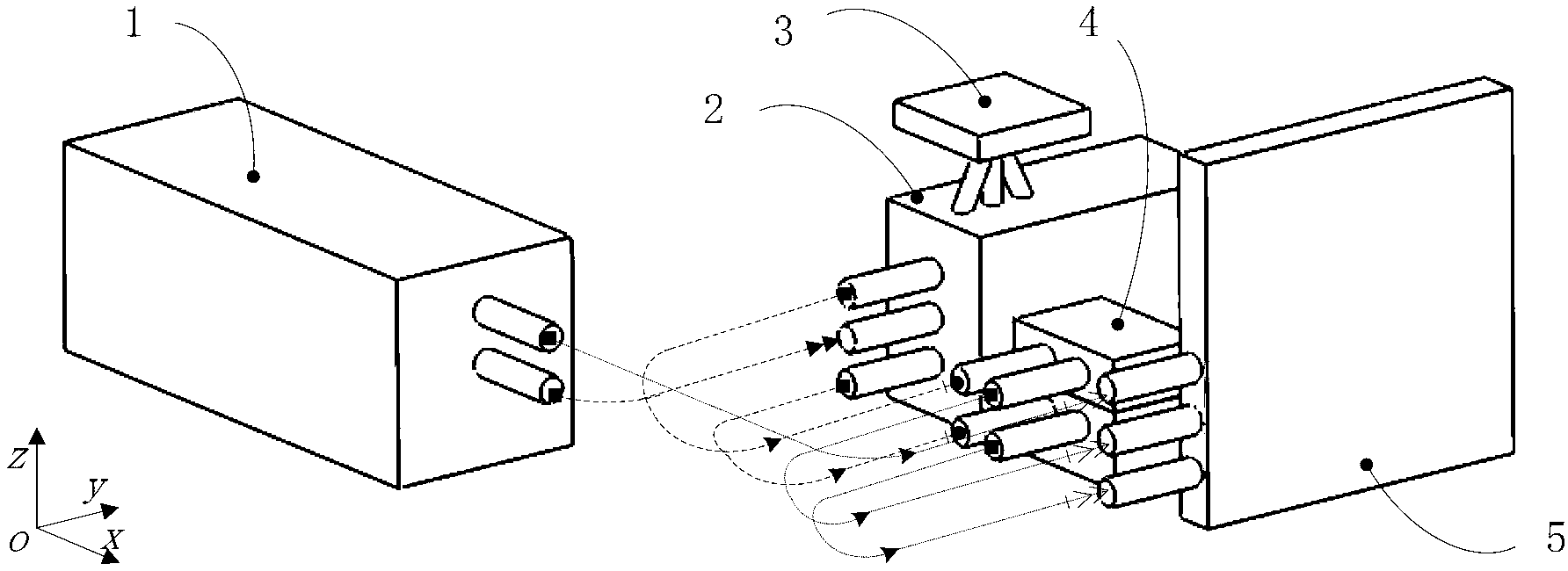
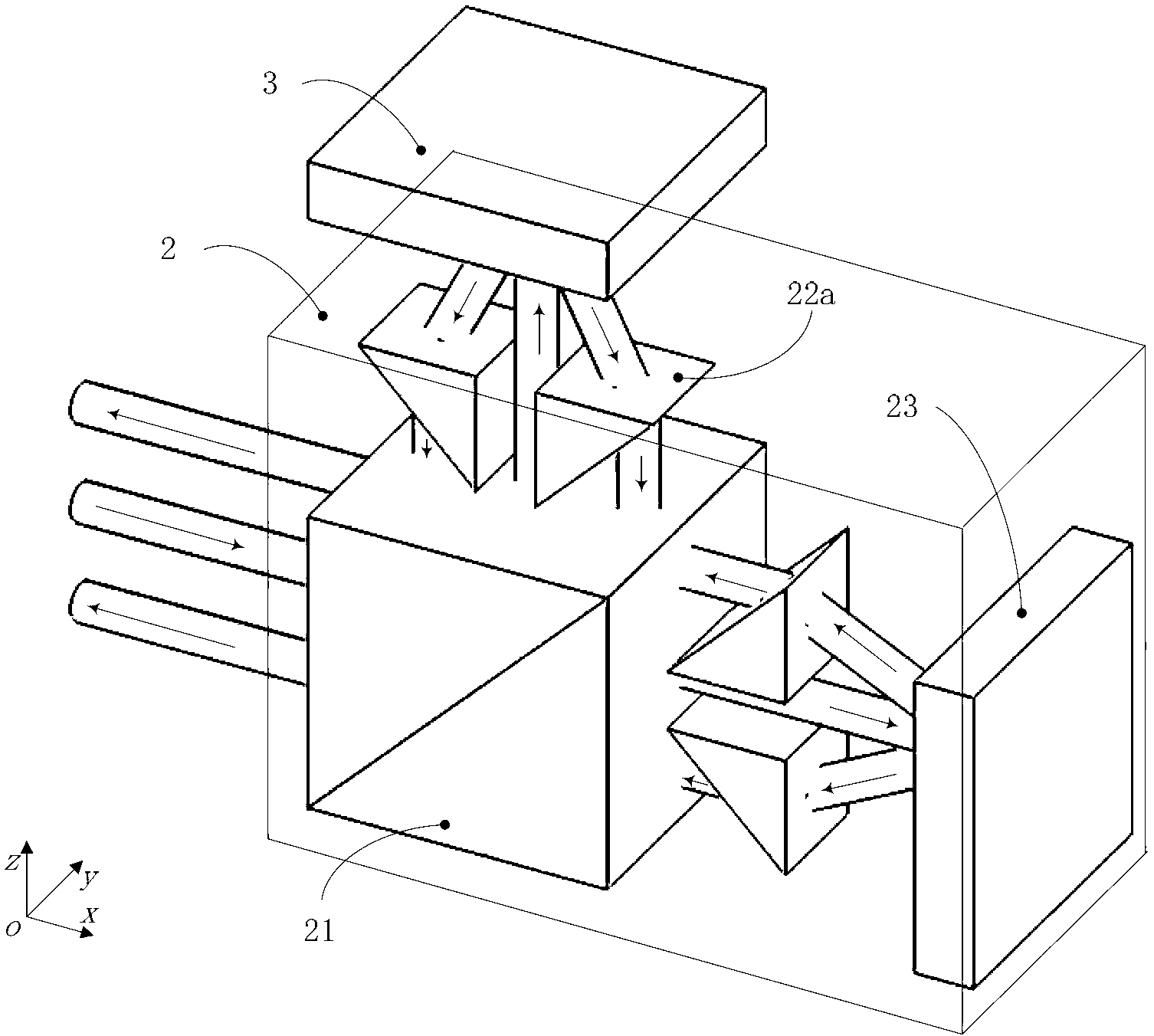
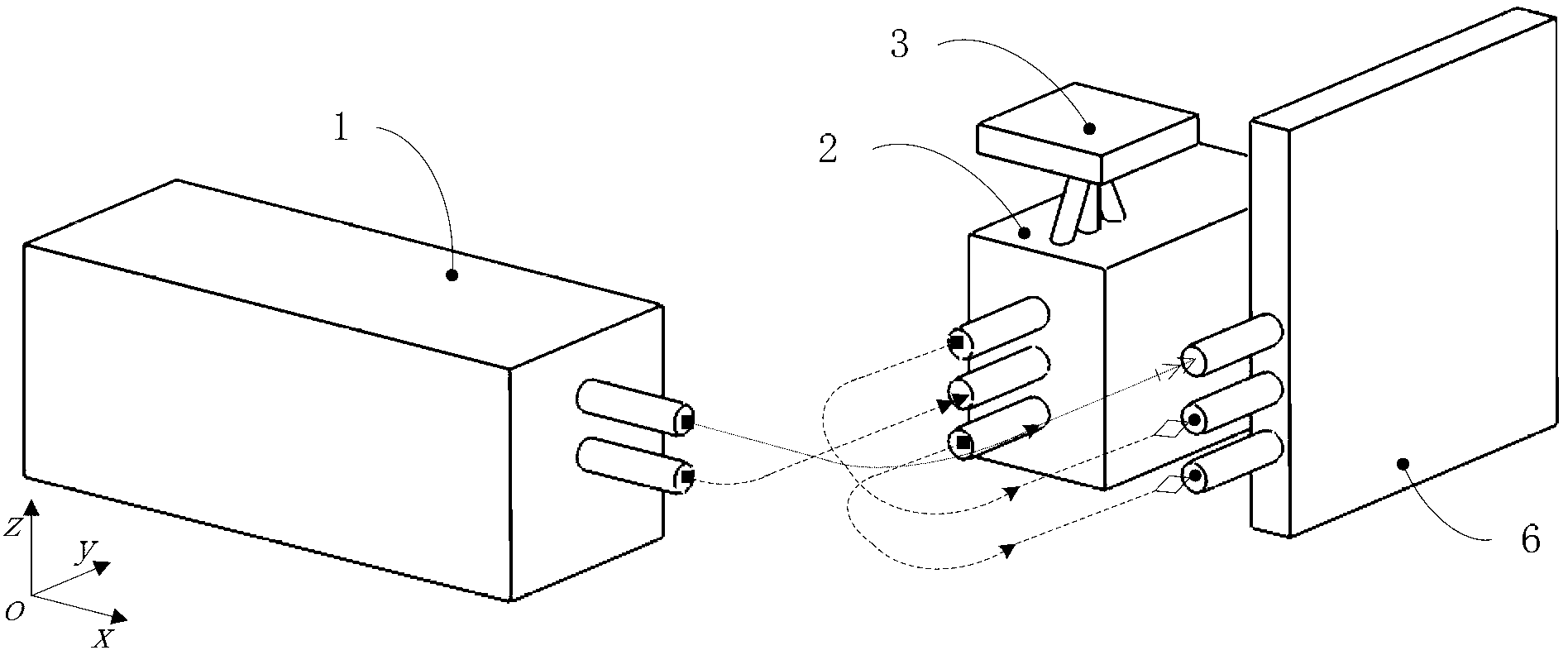
Two-degree-of-freedom heterodyne grating interferometer displacement measurement system and method
The invention provides a two-degree-of-freedom heterodyne grating interferometer displacement measurement system and method. The system comprises a double-frequency laser device, a grating interferometer, a measuring grating, a receiver and a signal processing unit. The grating interferometer comprises a lateral displacement light splitting prism, a polarization light splitting prism, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a reflecting mirror and an optical fiber coupler. The method realizes displacement measurement based on grating diffraction, the optical Doppler effect and the optical-beat frequency principle. Laser of the double-frequency laser device is incident to the interferometer and the measuring grating and then optical signals are outputted to the signal processing unit. When the interferometer and the measuring grating perform two-degree-of-freedom linear relative movement, the system can output two linear displacements; the measurement system adopts Littrow incident conditions, a measurement target has large passive movement tolerance and two linear displacements can be measured simultaneously so that precision can reach the nanoscale and higher scale; and the measurement system has advantages of short light path, small size, compact structure, low weight and low requirement for the measuring grating and is suitable for two-degree-of-freedom high-precision long-stroke displacement measurement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
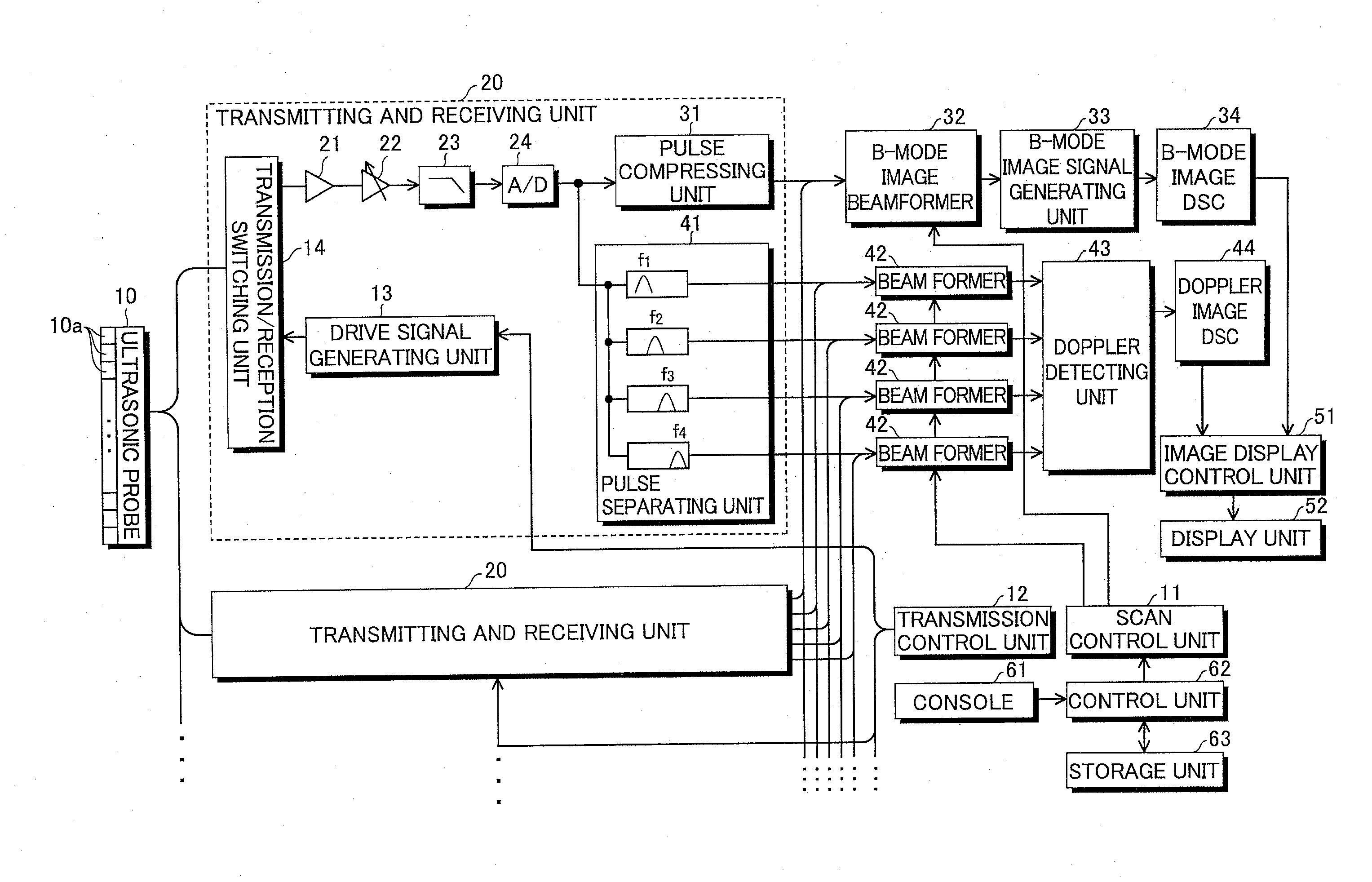
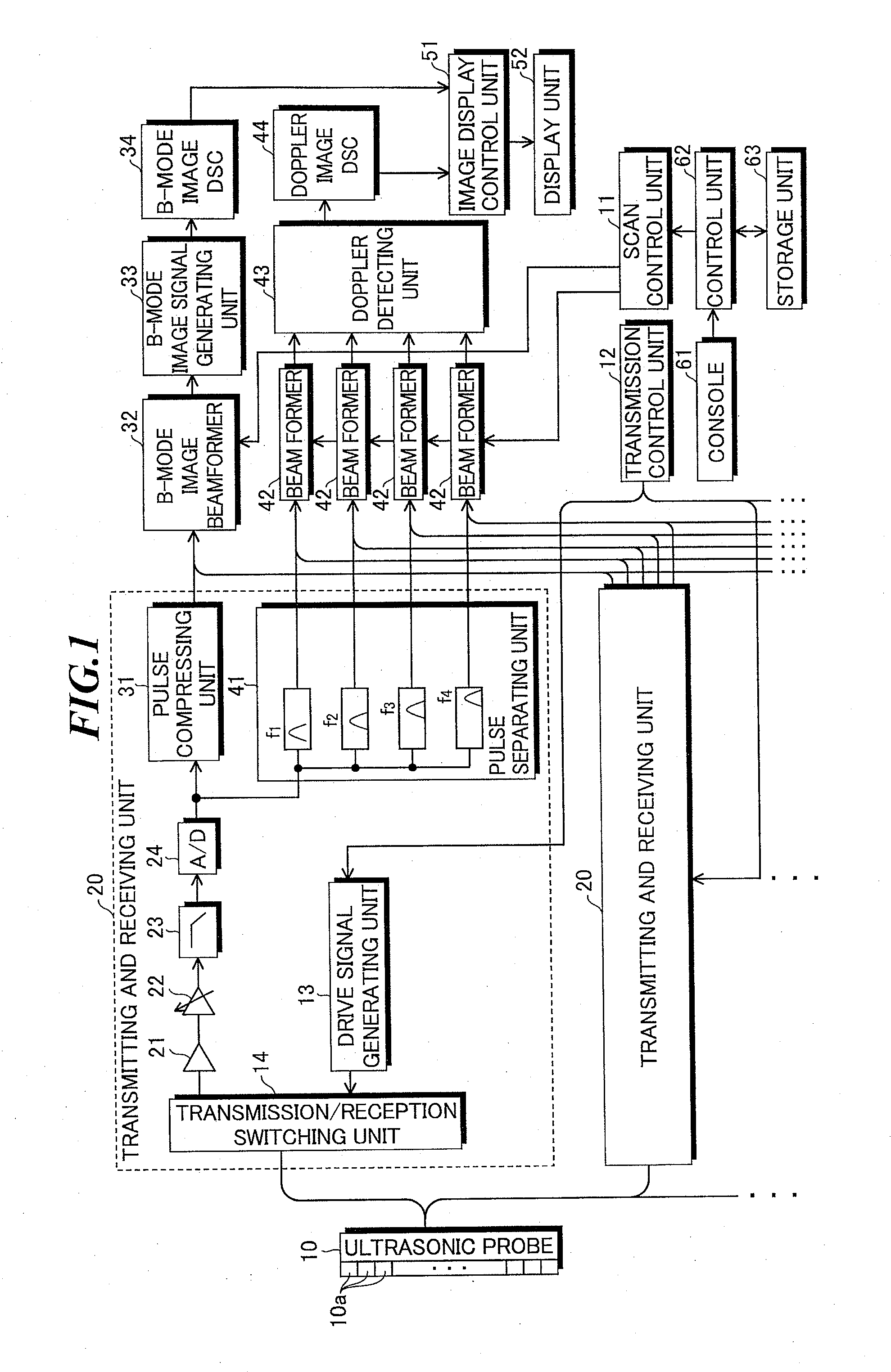
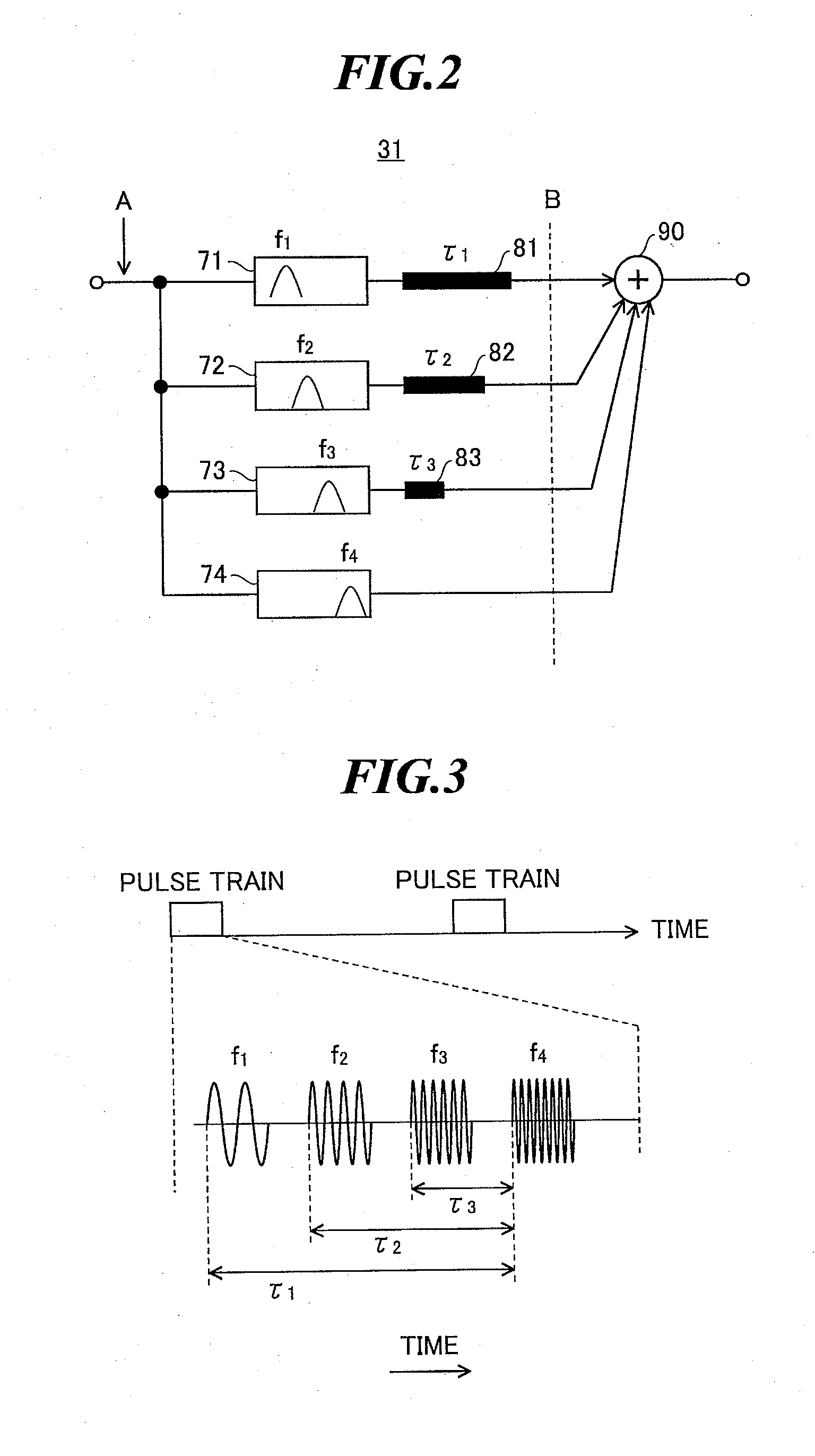
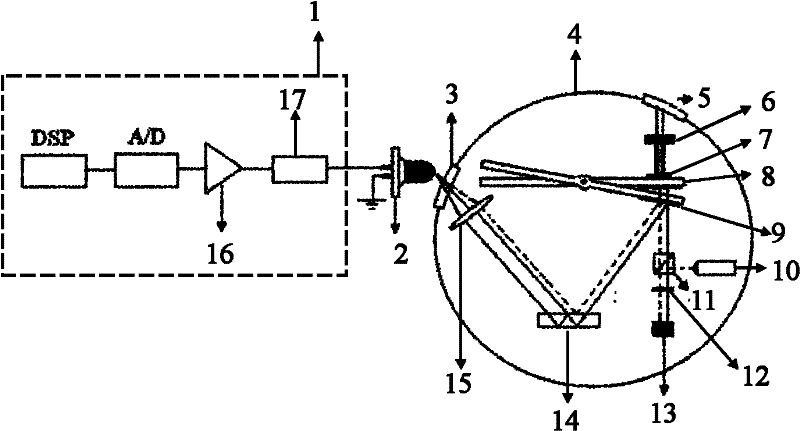
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS20100280379A1Reduce build timeIncrease frame rateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsColor dopplerSonification
An ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus in which an image generation time can be reduced and a frame rate can be improved even in a color mode in which a two-dimensional color Doppler image obtained due to Doppler effect is combined with a B-mode image. The ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus includes an ultrasonic probe, a transmission system signal processing unit for supplying drive signals to the ultrasonic probe to transmit pulse trains, each including plural pulses respectively having frequency components of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing waves orthogonal to one another and having different center frequencies from one another, in the same direction, and a reception system signal processing unit for pulse-compressing the plural pulses having different frequency components included in each reception signal outputted from the ultrasonic probe which has received the pulse trains from the same direction, and generating a B-mode image signal based on the compressed pulse.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Positional Audio in a Vehicle-to-Vehicle Network
InactiveUS20090226001A1Road vehicles traffic controlRadio transmission for post communicationDriver/operatorUsability
In a vehicle-to-vehicle network, a driver may listen to audio generated by other drivers participating in the network. The usability of the audio is enhanced by determining the relative positions of the providing and the receiving vehicles and then distributing received audio to specific speakers in the audio system of the receiving vehicle to create an impression that the sound originates from a source on the line between the two vehicles. The audio distributed to different speakers in the vehicle changes as the relative positions of the two vehicles changes. Volume changes and Doppler effects can be added to the audio if the two vehicles are converging or diverging.
Owner:IBM CORP
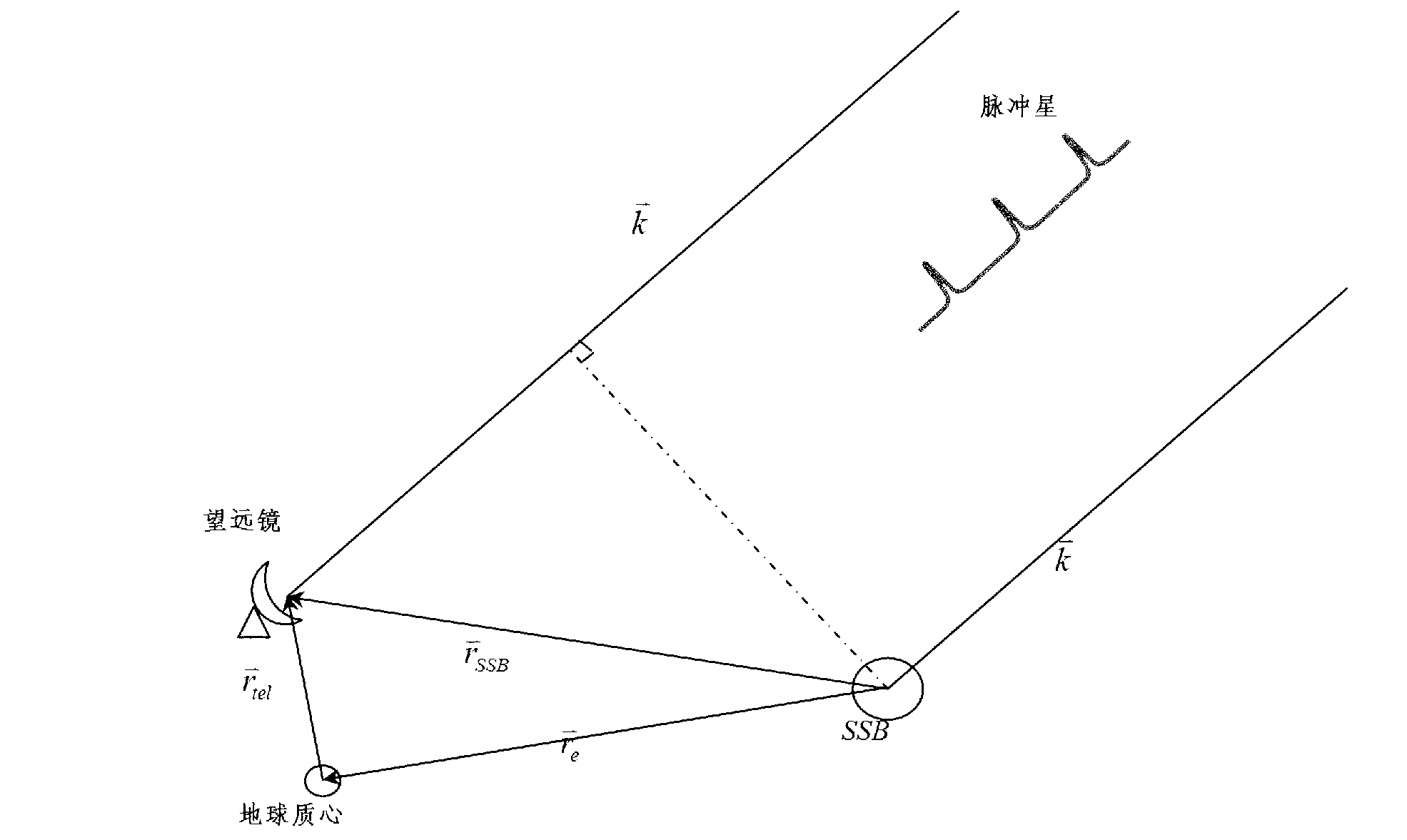
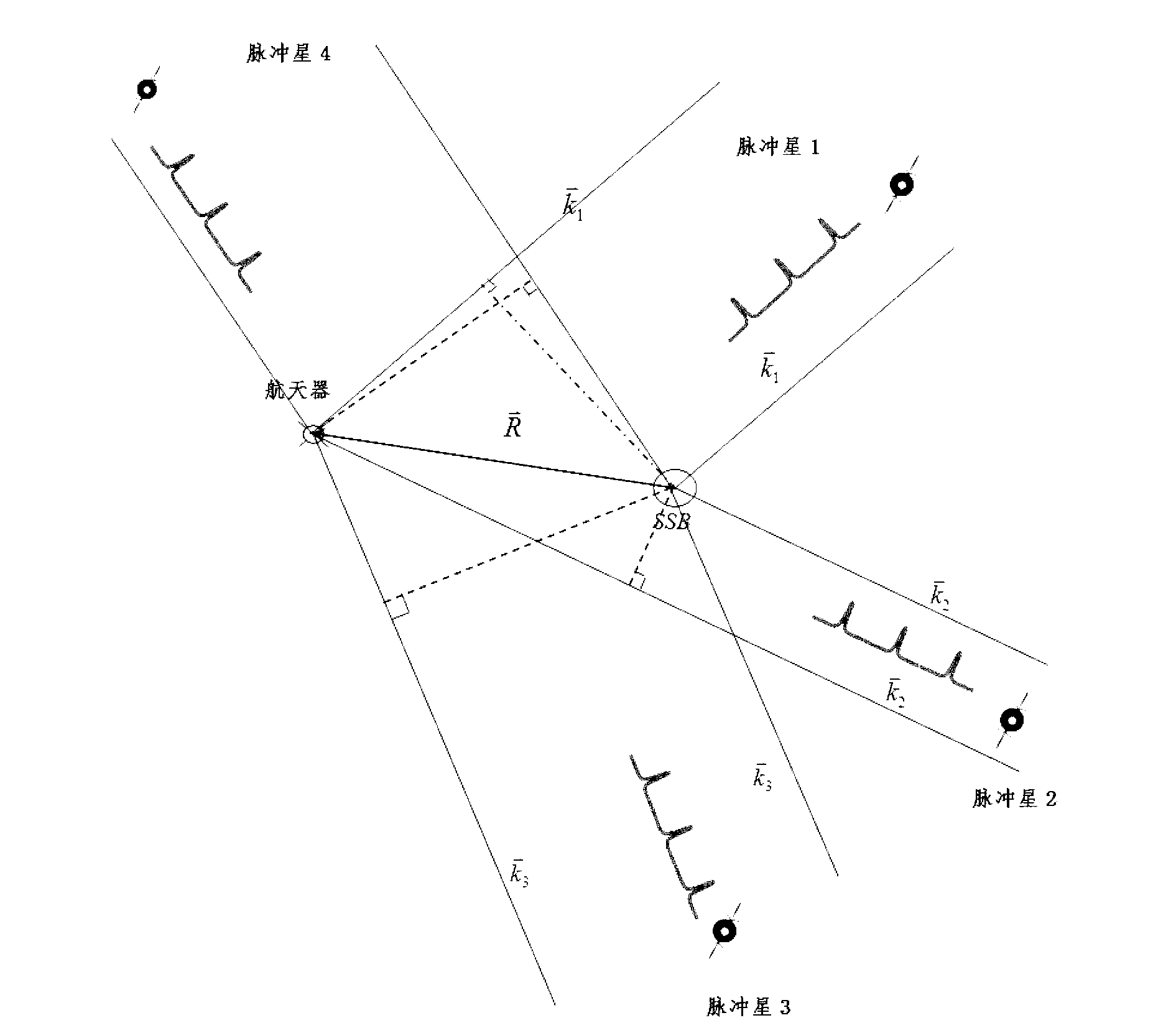
Pulsar navigation method with single detector
InactiveCN103017774AReduce loadHigh implementabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationArrival timeShapiro delay
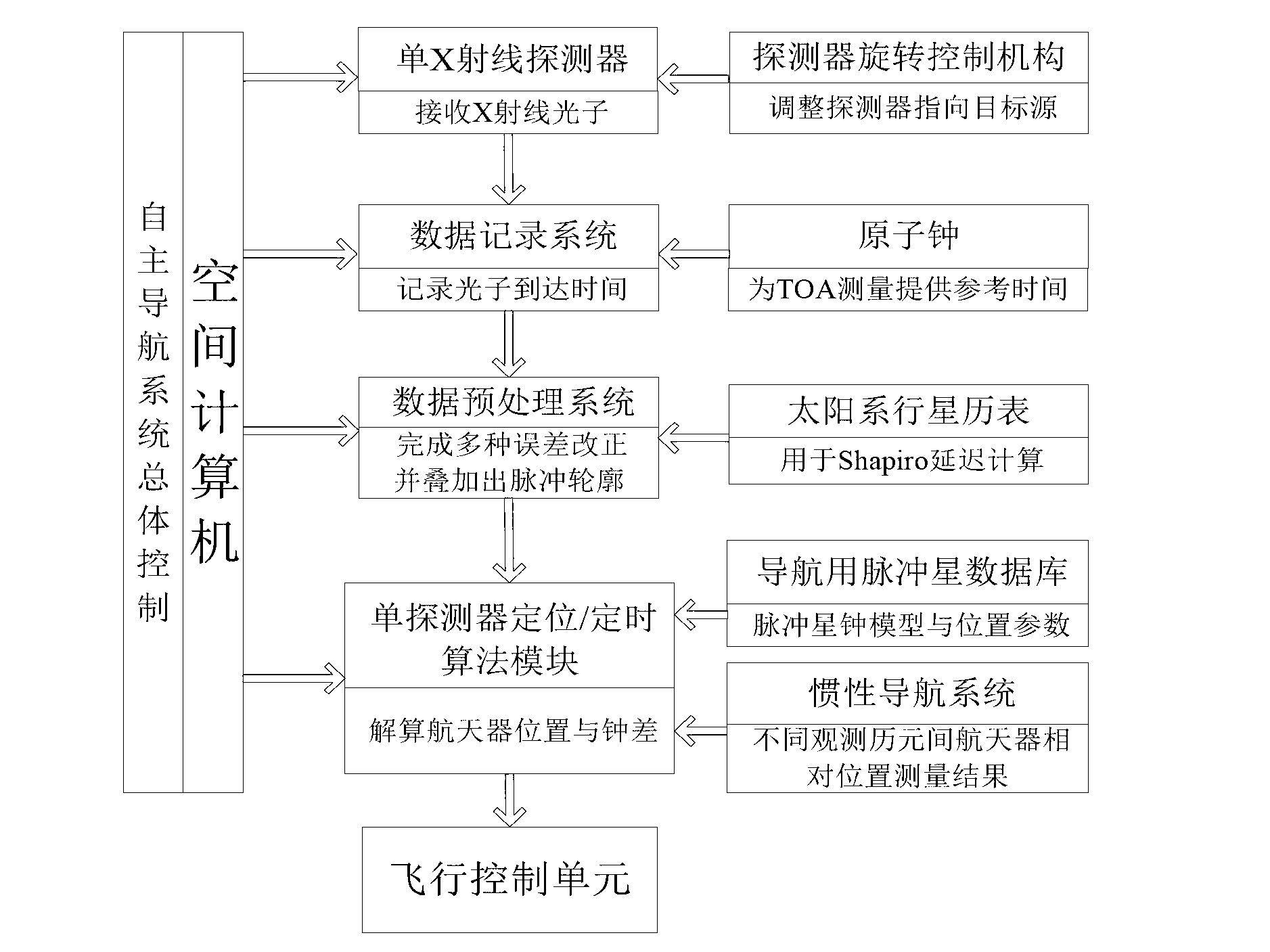
The invention provides a pulsar navigation method with a single detector, which comprises the steps that an X-ray detector on a spacecraft receives X-ray photons from four millisecond pulsars one by one and measures times when the X-ray photons arrive at the X-ray detector; the arrival times are saved as original observation signals; a doppler effect, a relativistic effect and Shapiro delay correction are performed; the arrival time of a pulse profile datum point is obtained; an observation equation of each corresponding pulsar is formed; and independent timing and positioning of the spacecraft are realized after resolving. The pulsar navigation method can accomplish absolute positioning of the pulsars with the single detector, and the positioning accuracy is high without secular error accumulation.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
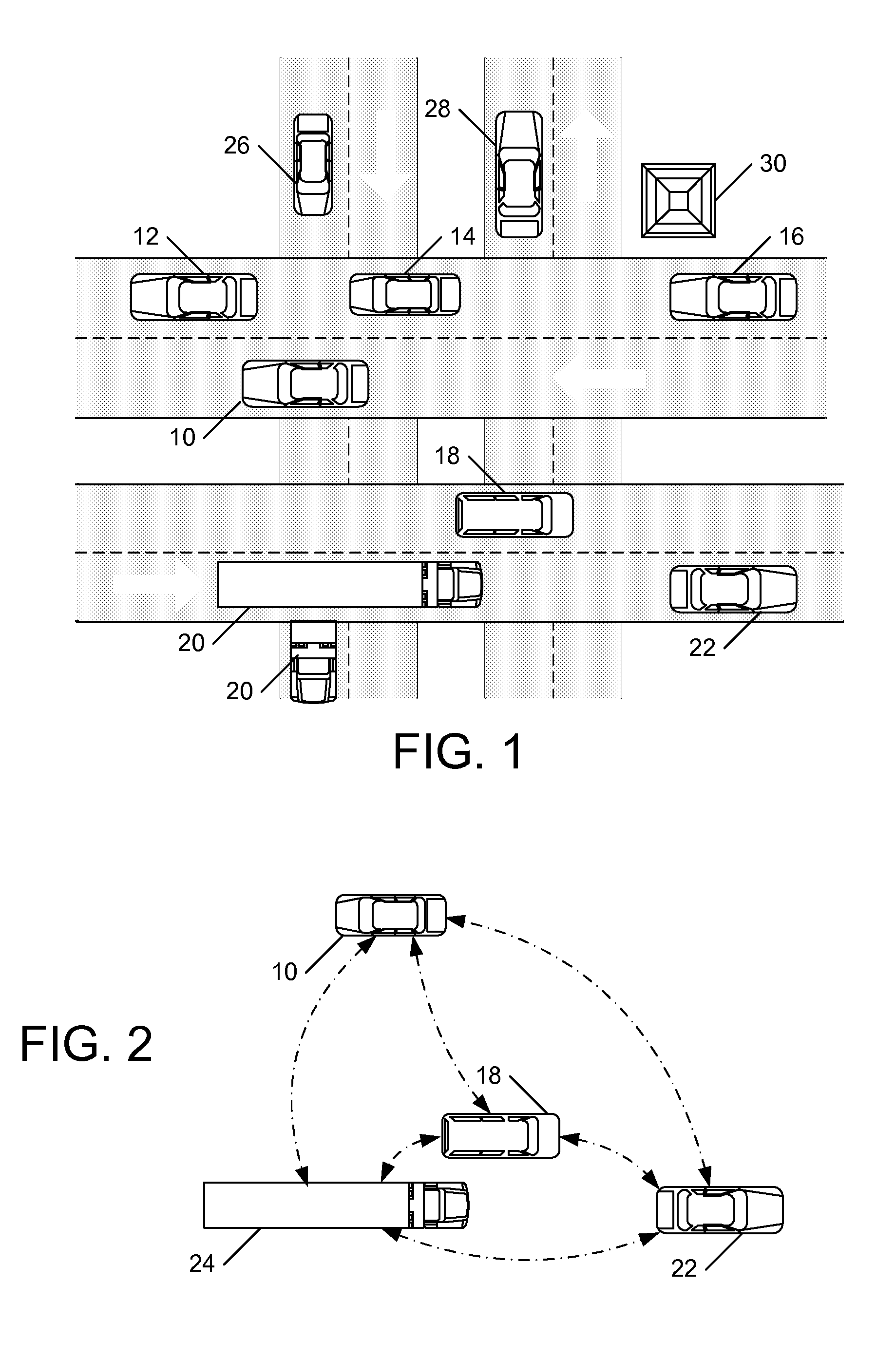
Detecting misbehavior in vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) comminications
ActiveUS20160335897A1Improve security levelSeverely disruptedSynchronisation arrangementParticular environment based servicesIn vehicleReal-time computing
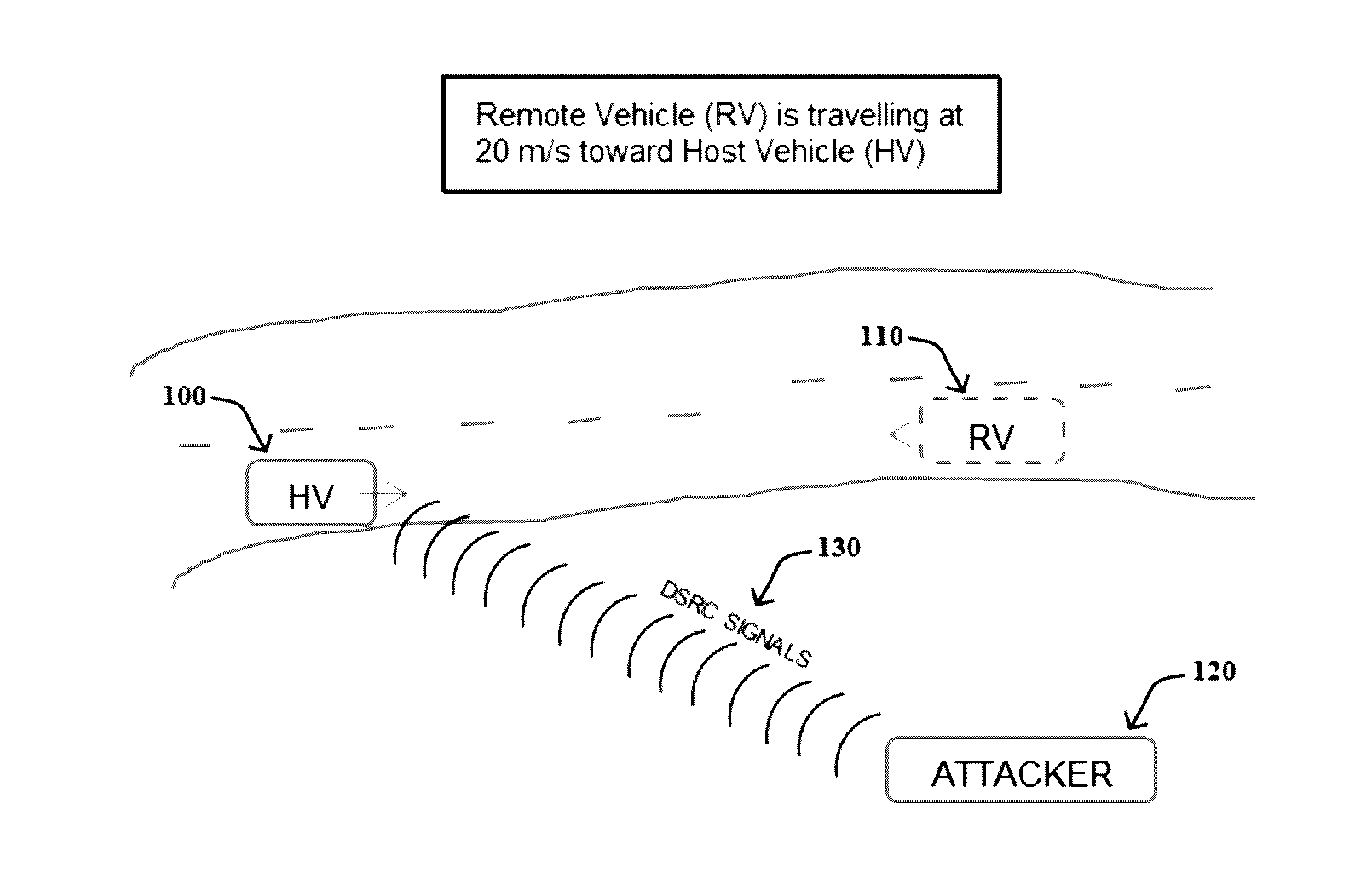
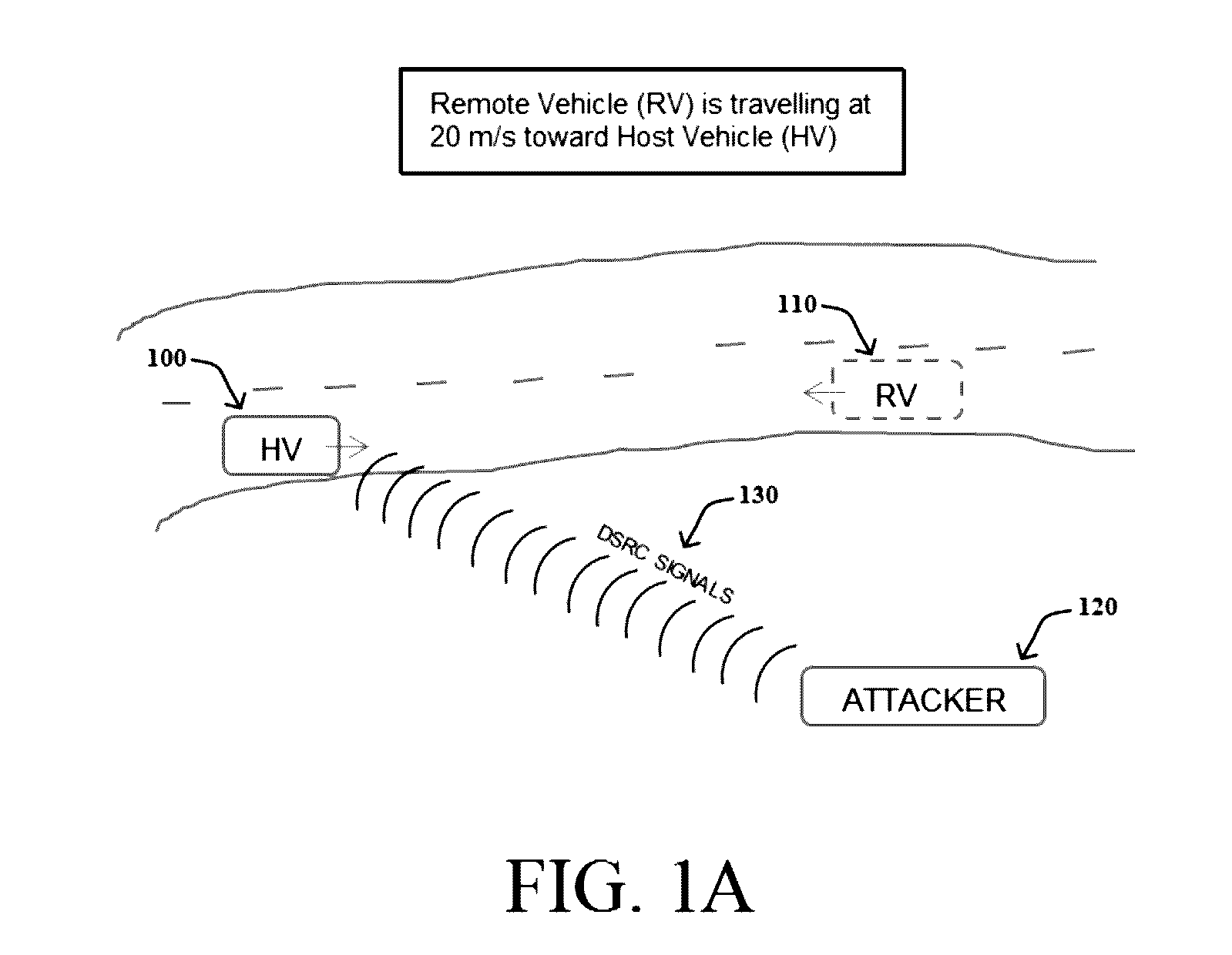
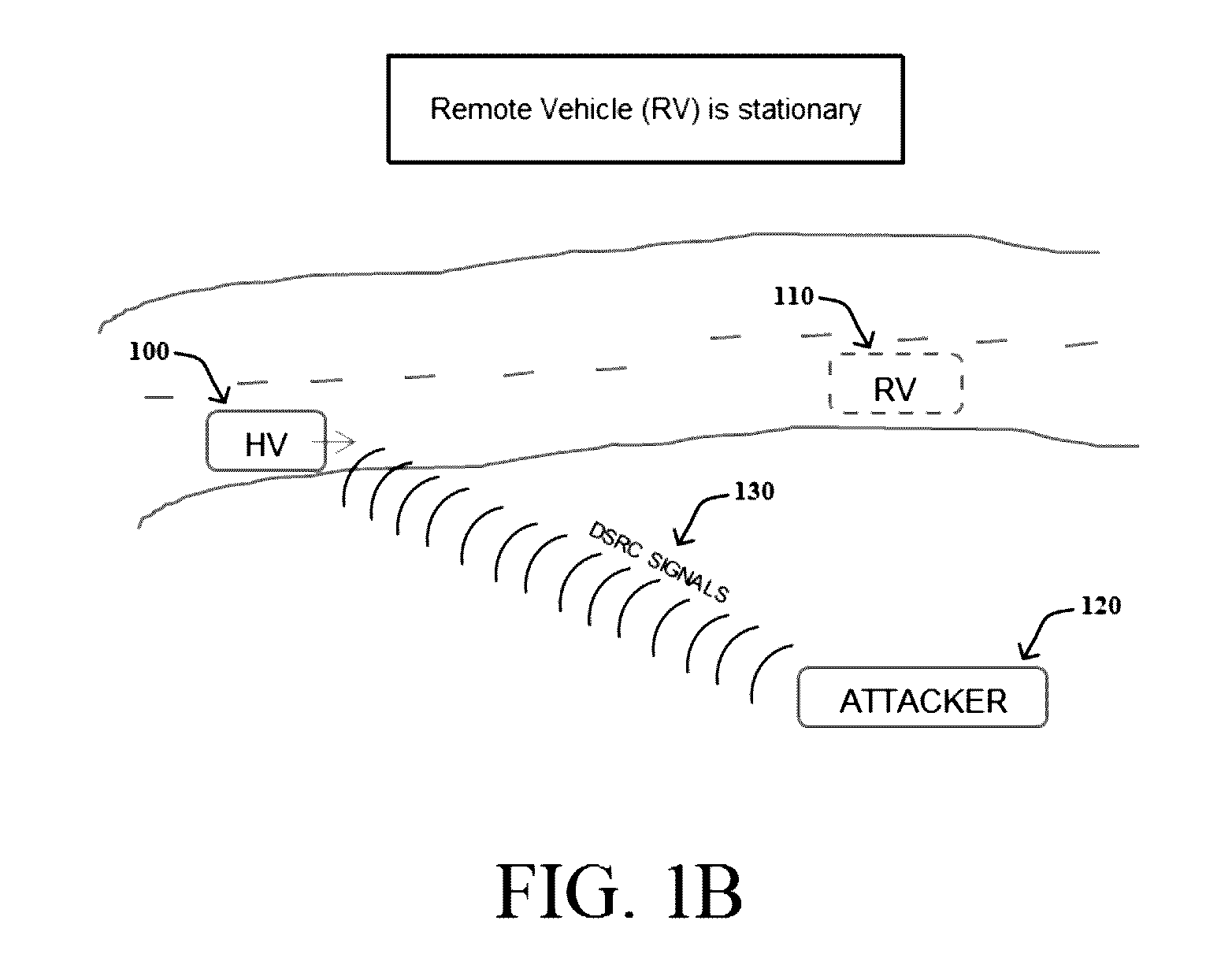
A method includes: receiving, at a host vehicle, a plurality of messages transmitted using Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) communications indicating a heading angle and a speed of a remote vehicle; calculating an expected change in frequency of the plurality of messages received at the host vehicle based on the heading angle and the speed of the remote vehicle; measuring an actual change in frequency of the plurality of messages received at the host vehicle due to the Doppler effect; comparing the expected change in frequency to the actual change in frequency; and determining that the plurality of messages were not transmitted from the remote vehicle when a difference between the expected change in frequency and the actual change in frequency exceeds a predefined frequency change threshold.
Owner:HYUNDAI AMERICA TECHN CENT +2
Two-DOF (degree of freedom) heterodyne grating interferometer displacement measurement system
ActiveCN103307986AMeasuring light path is shortLow environmental sensitivityInterferometersUsing optical meansGratingBeam splitter
A two-DOF (degree of freedom) heterodyne grating interferometer displacement measurement system comprises a two-frequency laser, a grating interferometer, a measuring grating, a receiver, and an electronic signal processing part. The grating interferometer comprises a polarizing beam splitter, a reference grating and a refraction element. The measurement system measures displacement according to optical grating diffraction, optical Doppler Effect and optical beat frequency principle. A two-frequency laser beam emitted by the two-frequency laser enter the grating interferometer and the measuring grating before two light signals are output to the receiver, and the signals are sent to the electronic signal processing part. When the grating interferometer is in two-DOF linear relative motion with the measuring grating, the system can output two linear displacements. The measurement system allows for sub-nano or higher resolution and precision, and can measure two linear displacements simultaneously. The measurement system has the advantages of insensitivity to environment, high measurement precision, small size, light weight and the like, and after the measurement system is used as a lithography machine ultra-precision workpiece bench position measurement system, comprehensive performances of a workpiece bench can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Multi-laser-beam heterodyne micro-impulse-measuring device and method
InactiveCN102175376ASolve efficiency problemsSolve the errorApparatus for force/torque/work measurementWorking fluidIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a multi-laser-beam heterodyne micro-impulse-measuring device and a multi-laser-beam heterodyne micro-impulse-measuring method and relates to the technical field of micro impulse detection. By the device and the method, the problems of low energy coupling efficiency and big system error in the current small-impulse-measuring system are solved and the micro impulse measurement is carried out on the basis of a laser heterodyne technology and a Doppler effect. The method comprises the steps of: converting the micro impulse generated under the action of the laser and a target into a rotating angle of a torsional pendulum; then introducing a scanner into the measuring light path to attach an optical frequency to each of the light signals entering at different time points, so that a reflected light from the front surface of a planer standard lens and a transmitted light reflected by the front surface and the back surface of the planer standard lens for many times generate a multi-beam heterodyne interfering signal under an interfering condition; and thus modulating the change information of the rotating angle of a standard beam into the frequency difference of a medium-frequency heterodyne signal successfully. With polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and 2 percent of carbon (C) as working fluid, the micro impulse generated under the action of the laser and the working fluid is simulatively measured by using a torsional pendulum method and the measurement result shows that the maximum relative error of the measurement is less than 2.3 percent.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com