Patents
Literature
568 results about "Vital sign monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
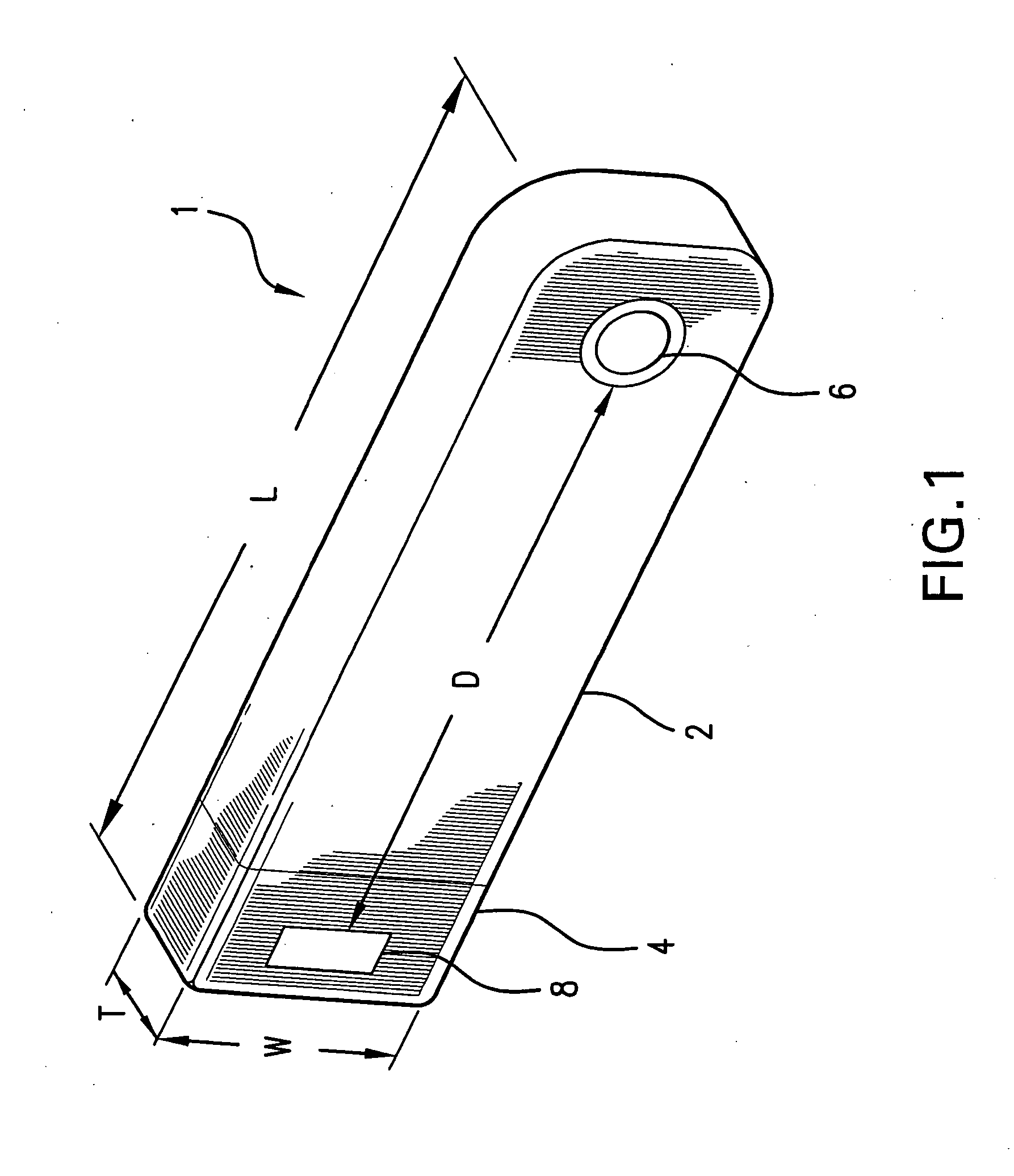
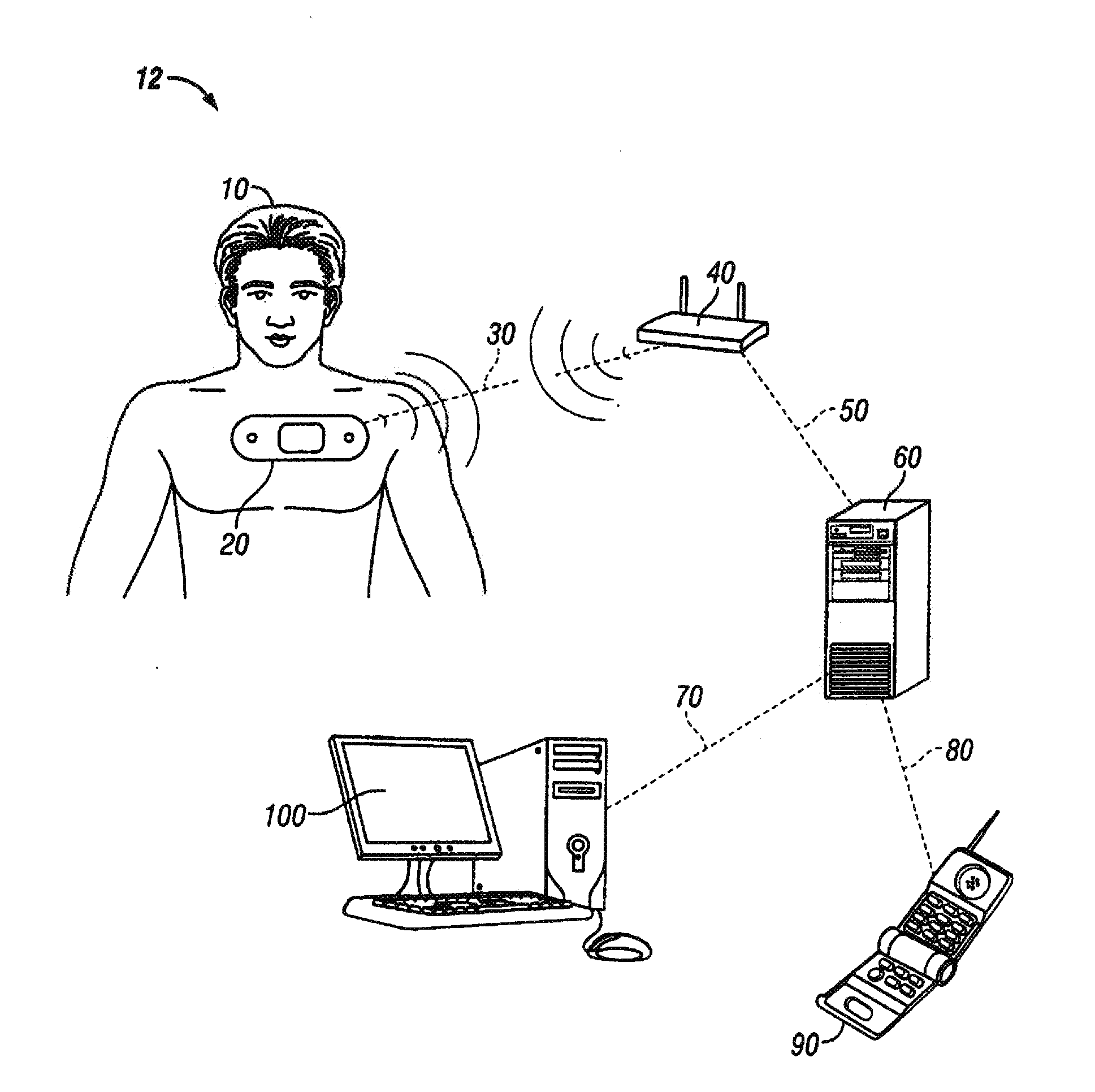
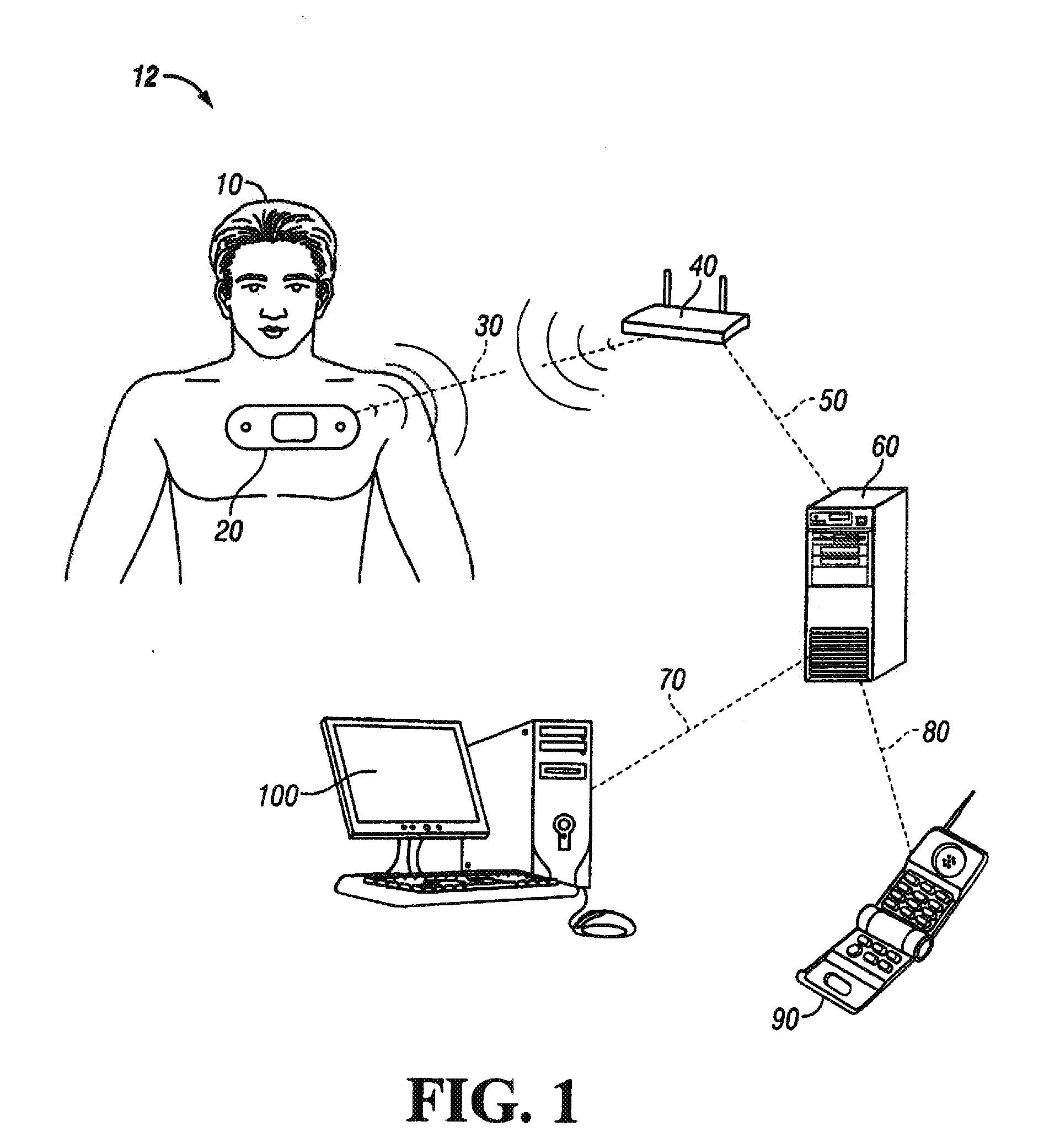
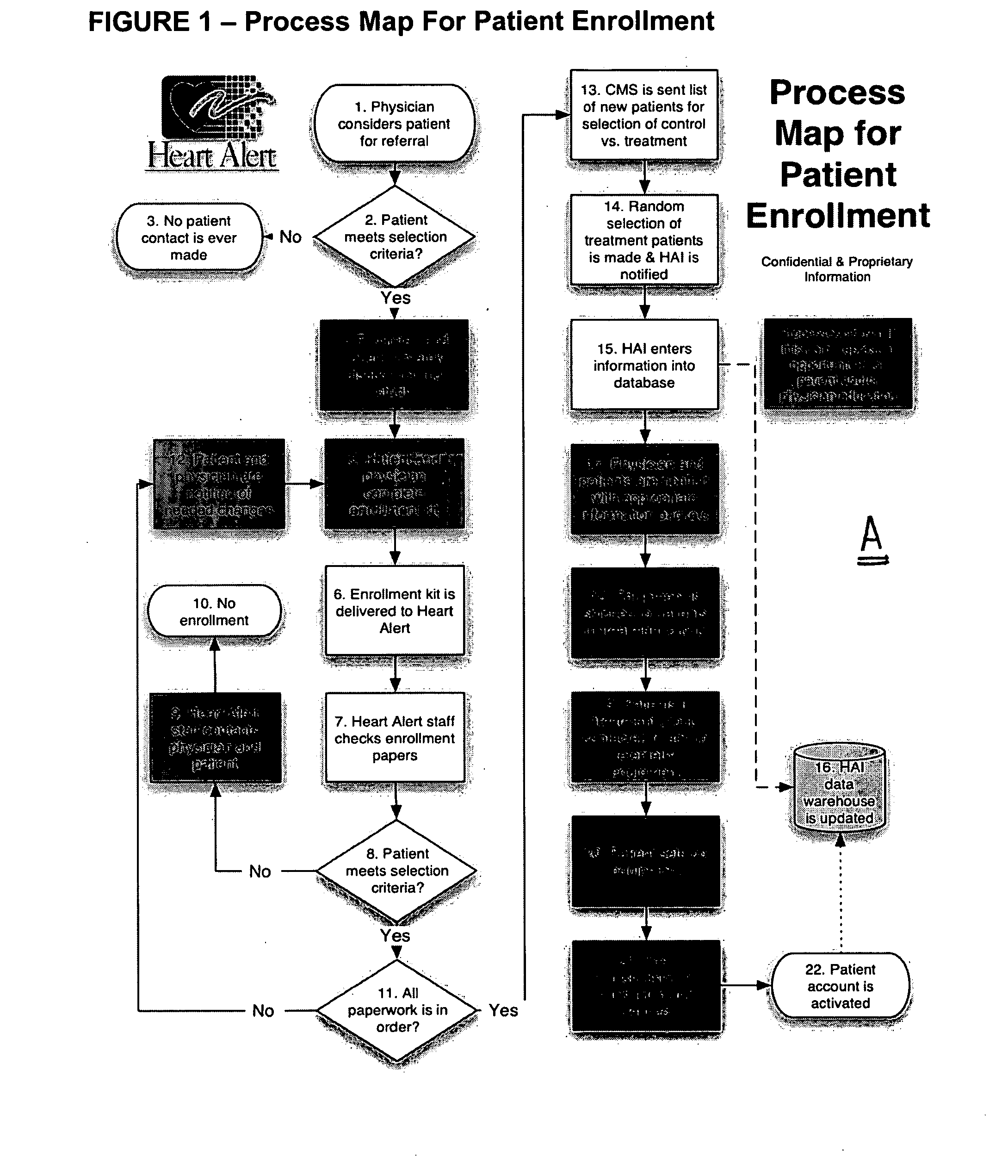
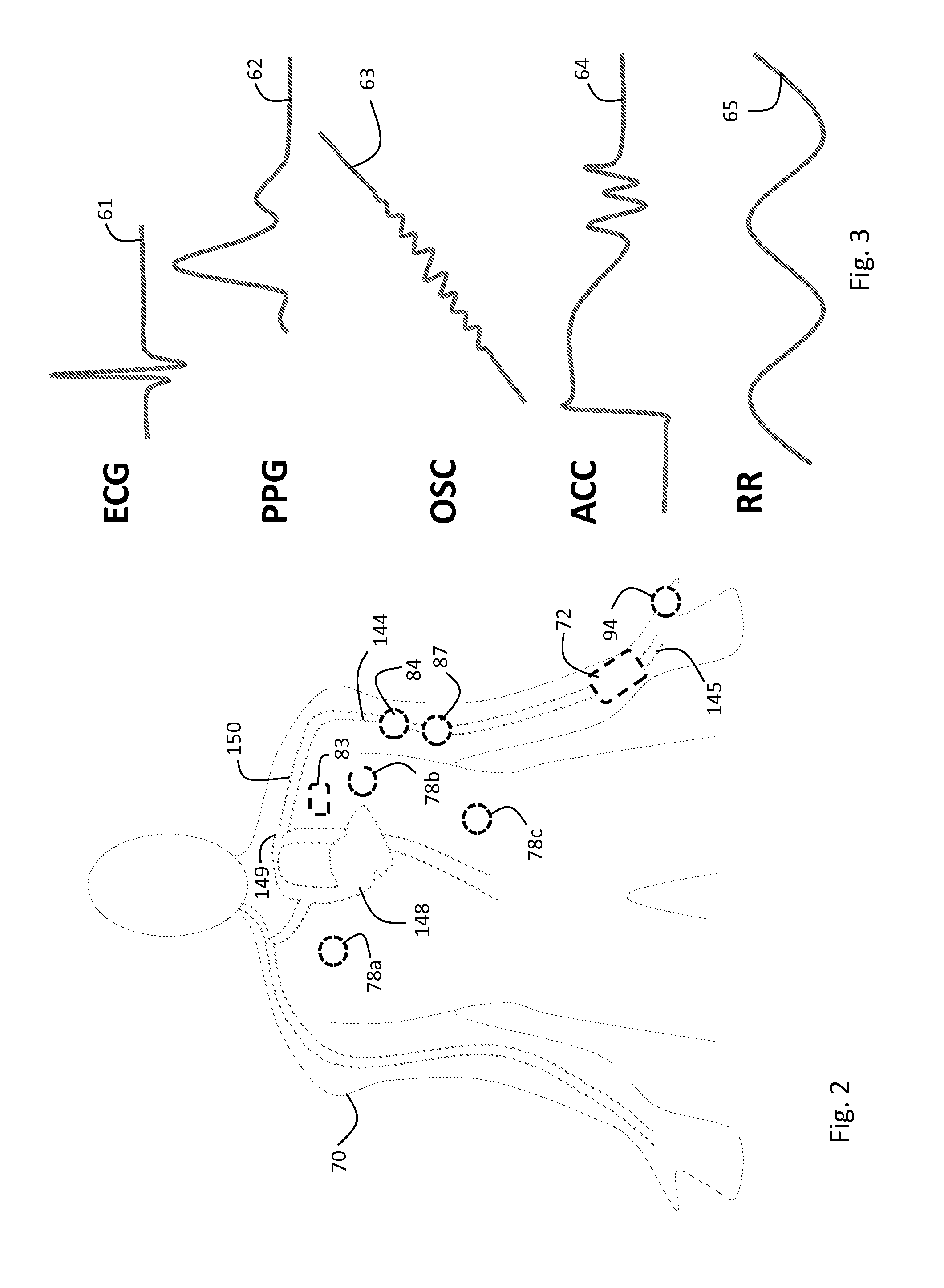
A vital signs monitor. An electroencephalography (EEG) monitor is used for detecting activity and irregularities within the brain. The fetal heart rate is monitored to ensure the baby is not stressed during labor and delivery.
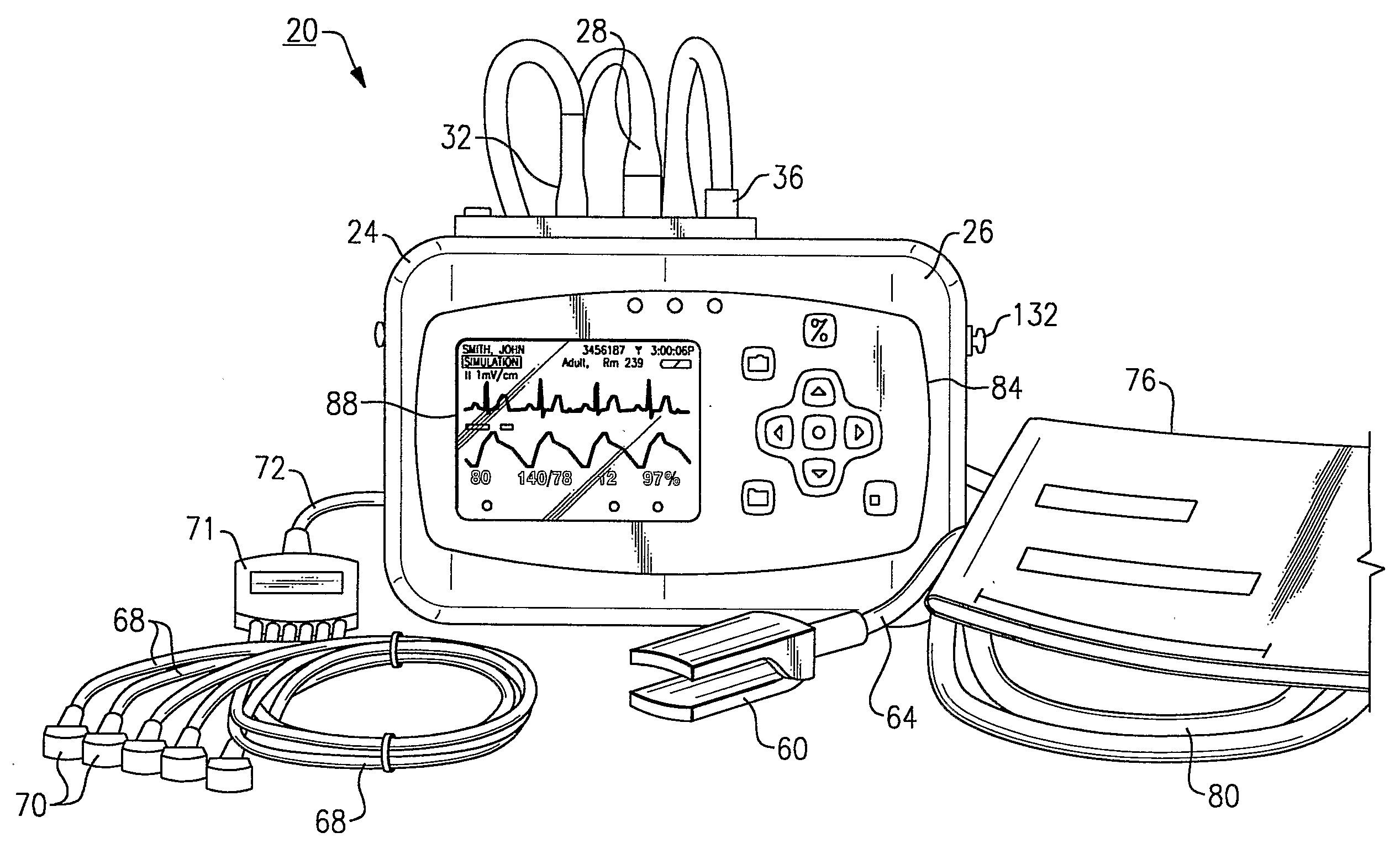
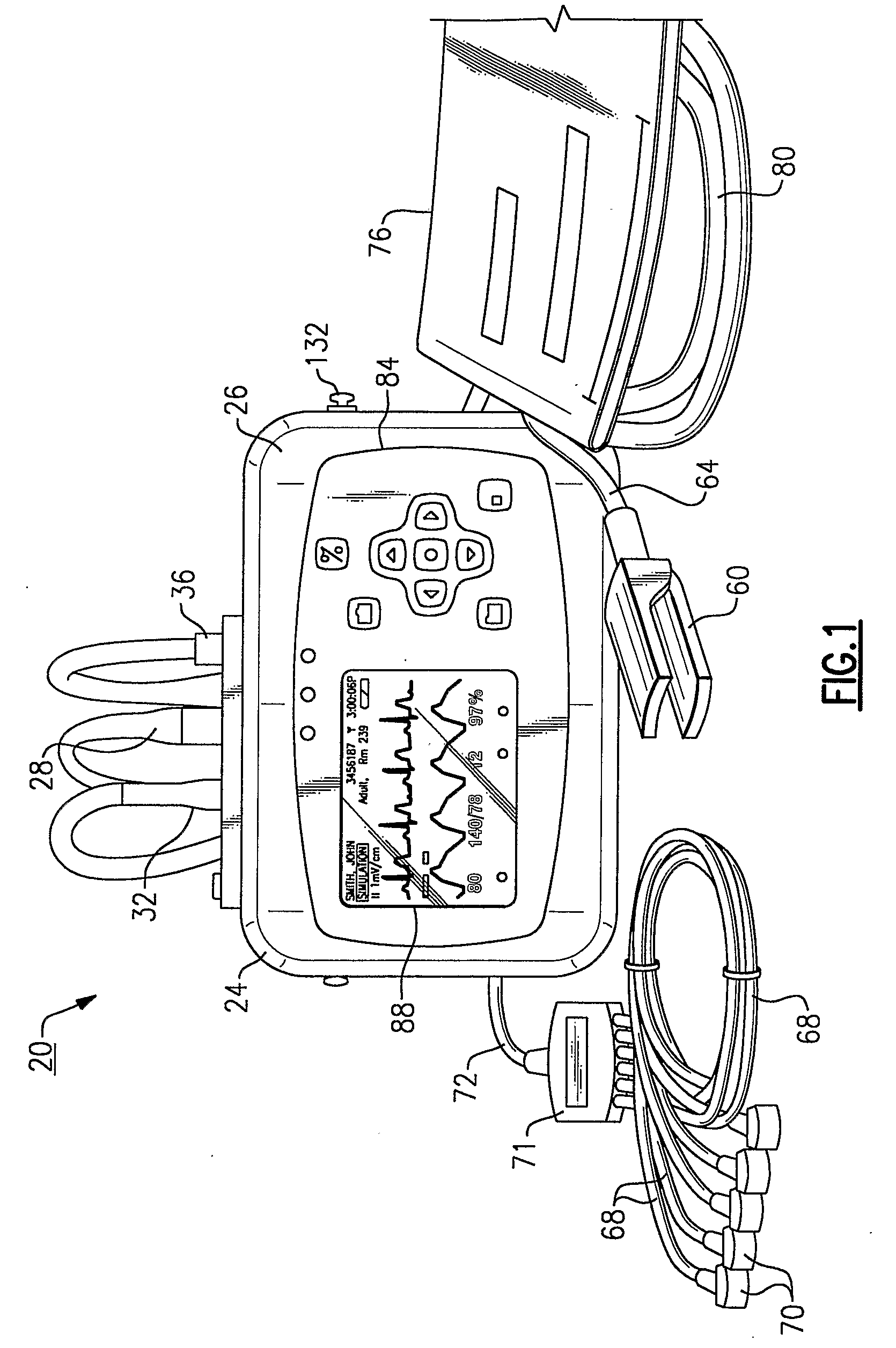
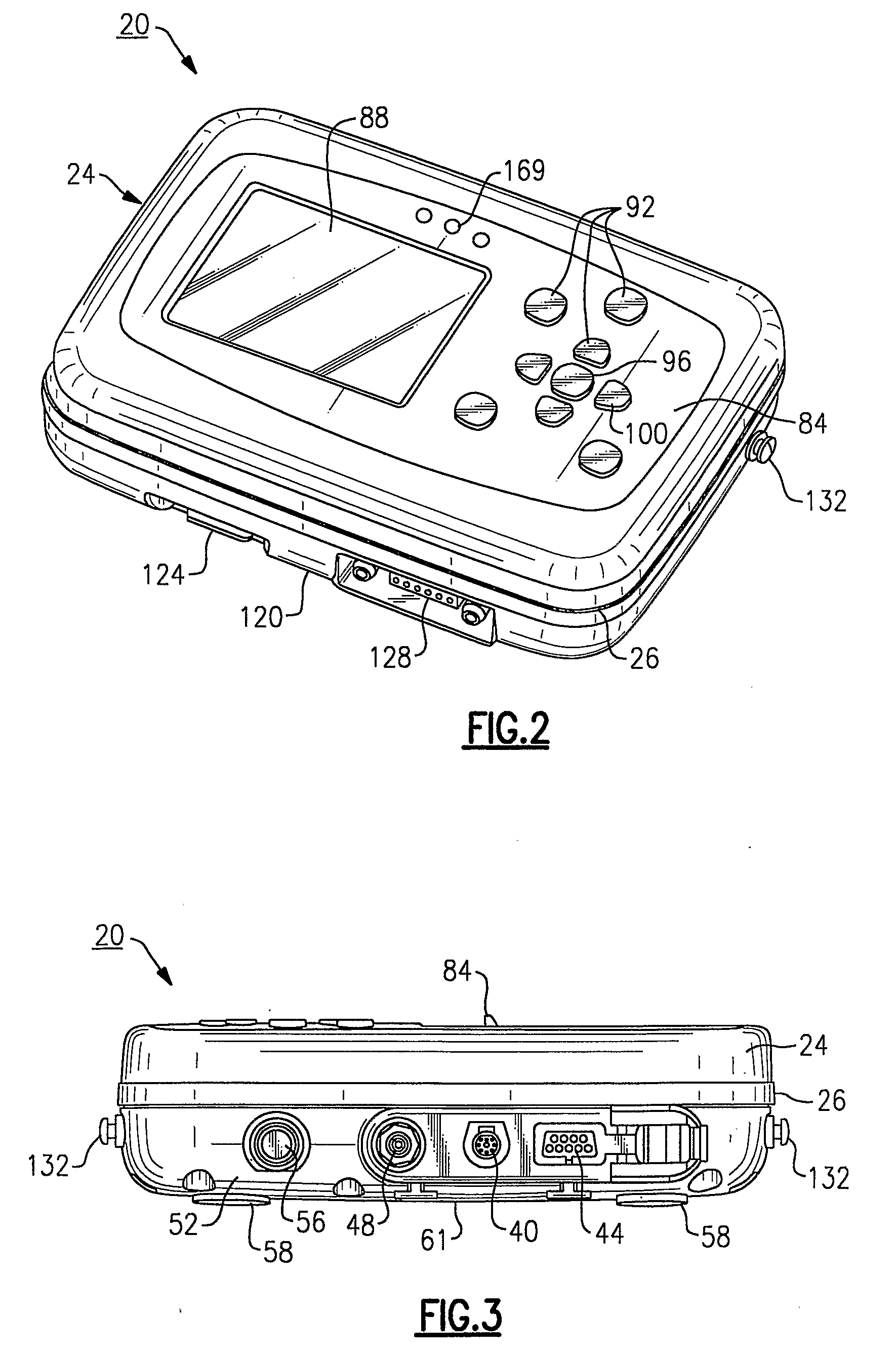
Vital Signs Monitor
ActiveUS20080281168A1Rugged in constructionEasy to useBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrocardiographyAmbulatoryEngineering
A multi-parametric vital signs monitoring device configured for use as an ambulatory and a bedside monitor wherein the device can be patient-wearable and is battery powered. The monitoring device can be used with a charging cradle to provide power to the device in lieu of the battery as a power source for bedside applications, in which the cradle further serves as an intermediary device to enable a data link with a PC or other peripheral device. The monitoring device can include a wireless radio to enable bi-directional transfer of patient-related data to a separate remote station.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
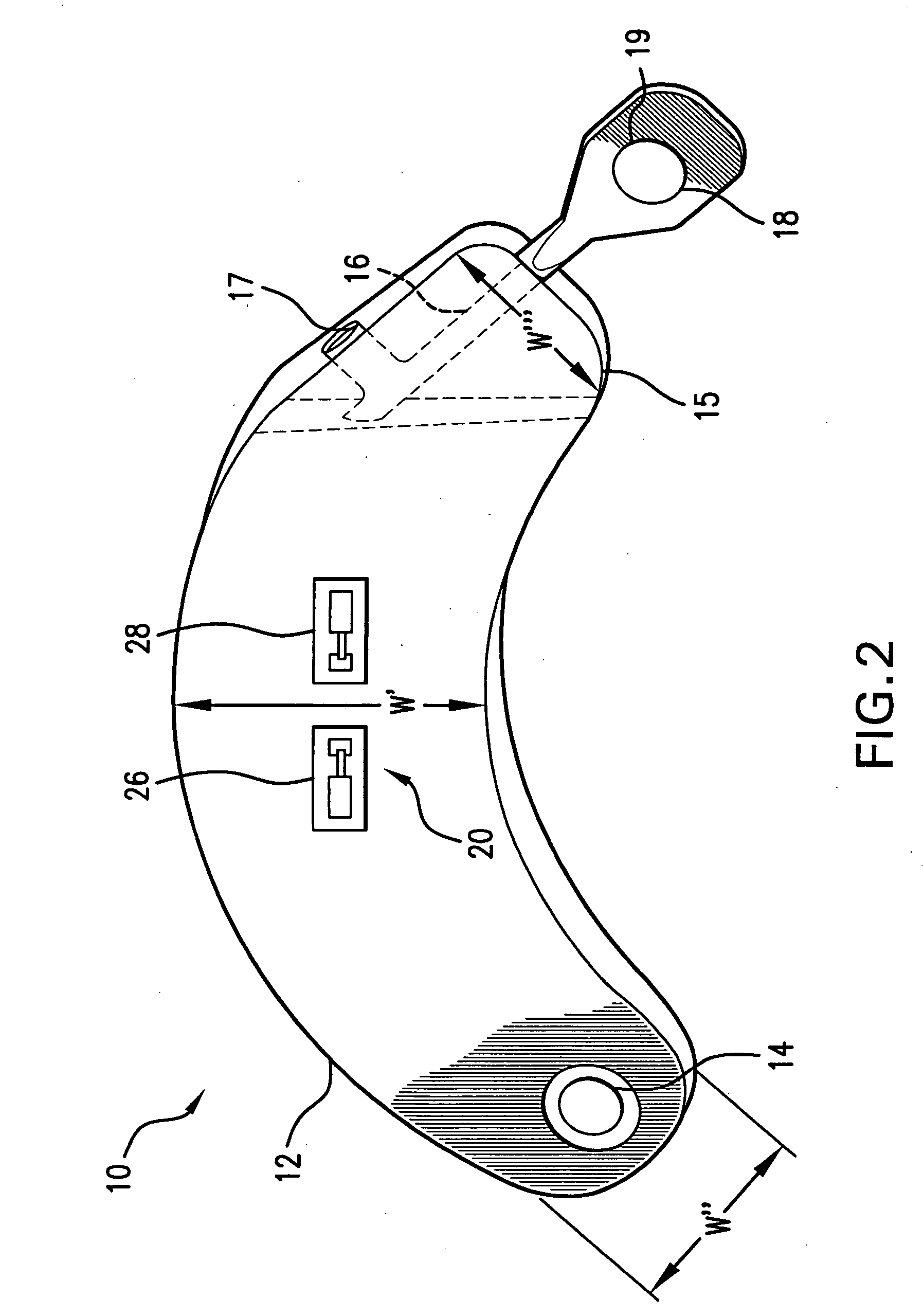
Implantable device for vital signs monitoring
InactiveUS20070016089A1Few suture requirementKeep the distanceElectrocardiographyCatheterSubcutaneous implantationDigital storage
An implantable medical device is provided for subcutaneous implantation within a human being. The implantable medical device includes a pair of electrodes for sensing electrical signals from the human being's heart. Electronic circuitry having digital memory is provided with the electronic circuitry designed to record the electrical signals from the heart. The electronics of the electronic circuitry are housed in a case having a tapered shape to facilitate implantation and removal of the implantable medical device.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST +1
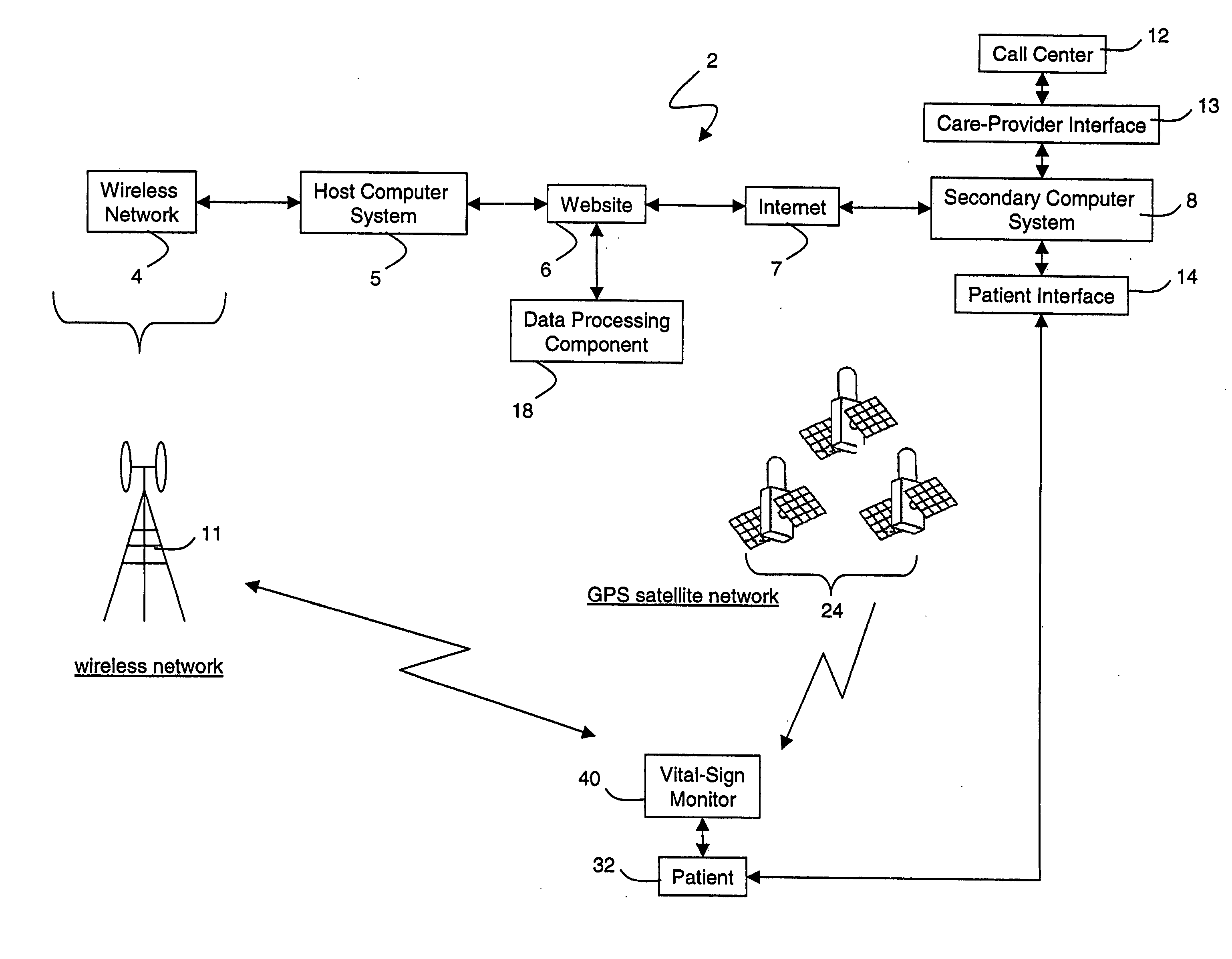
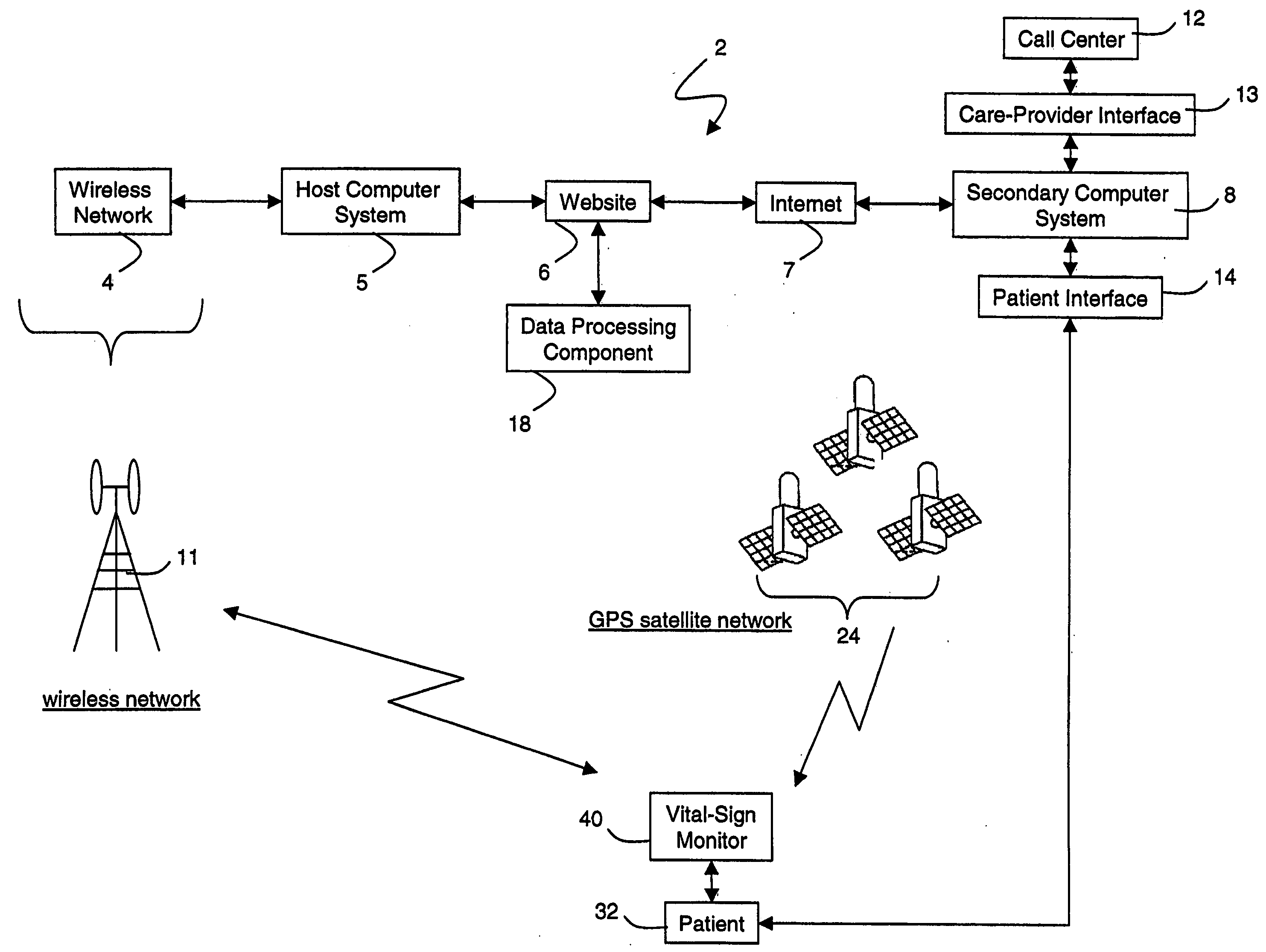
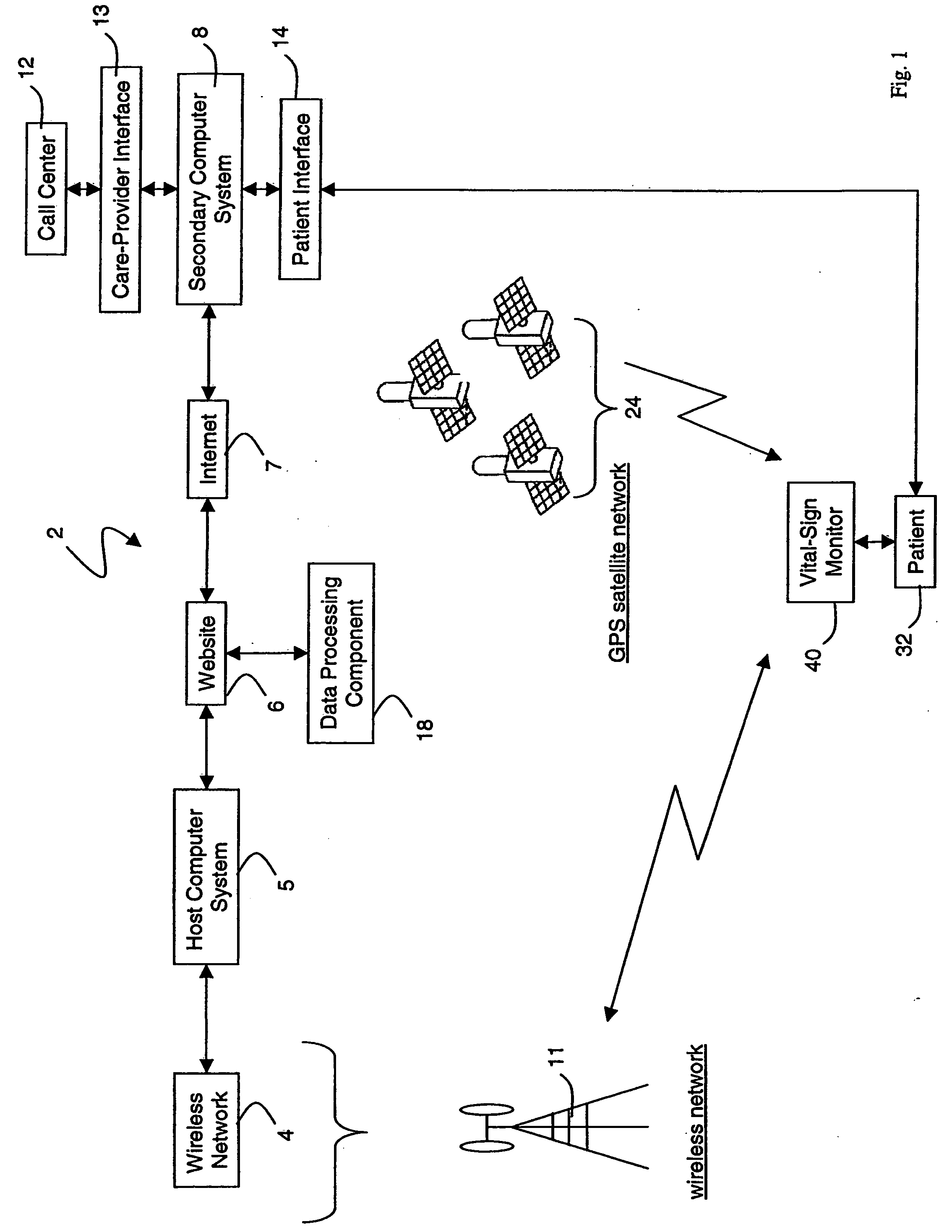
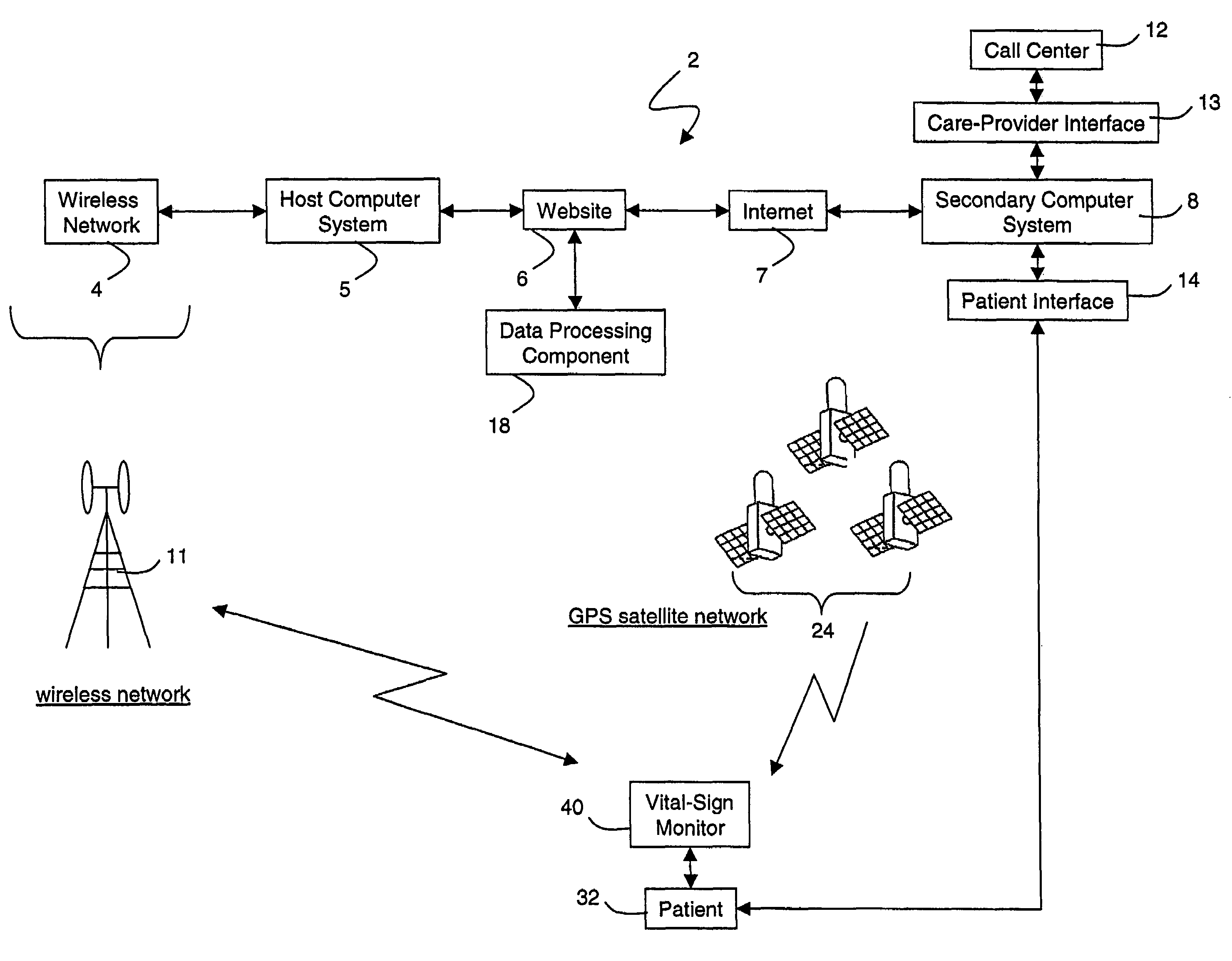
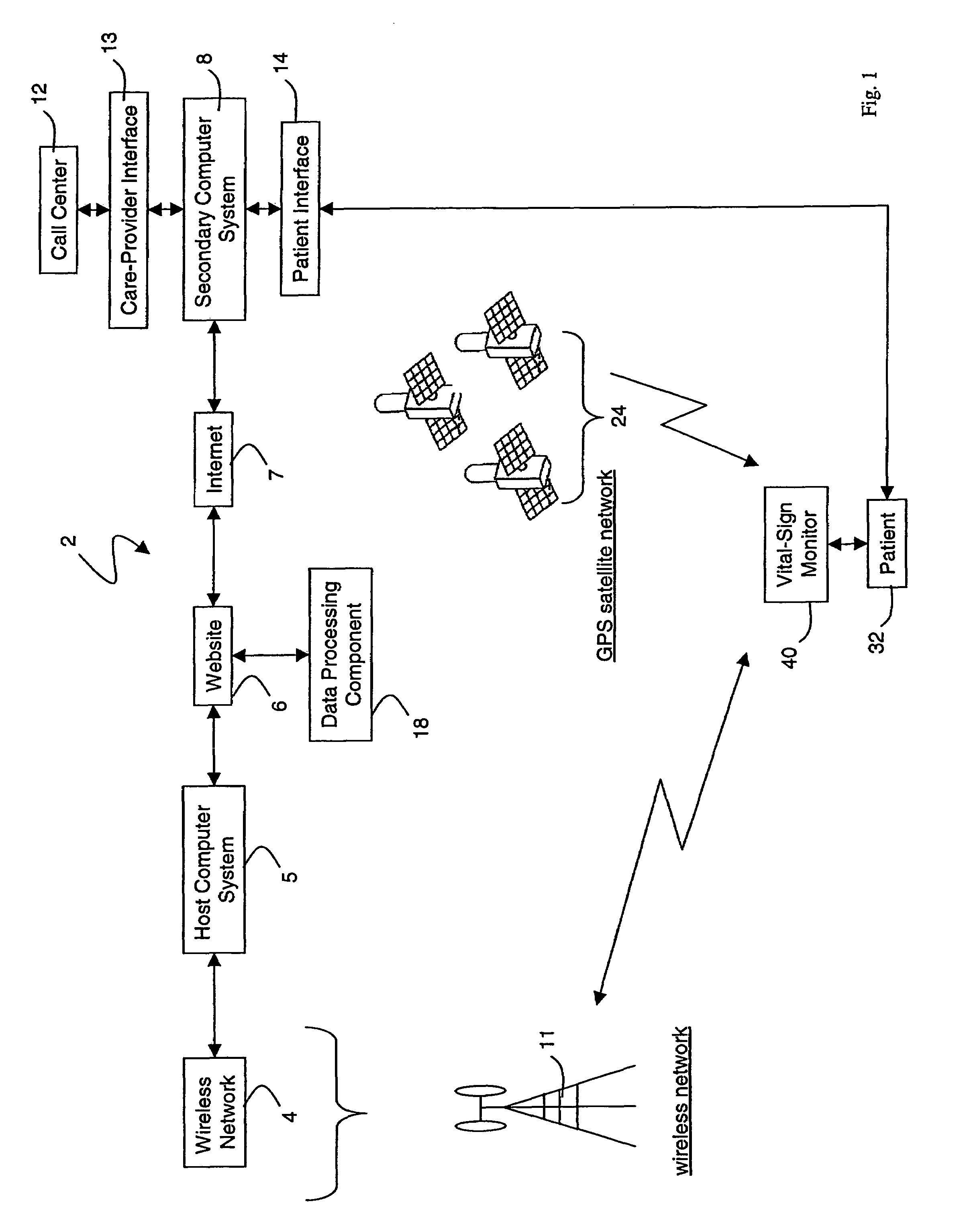
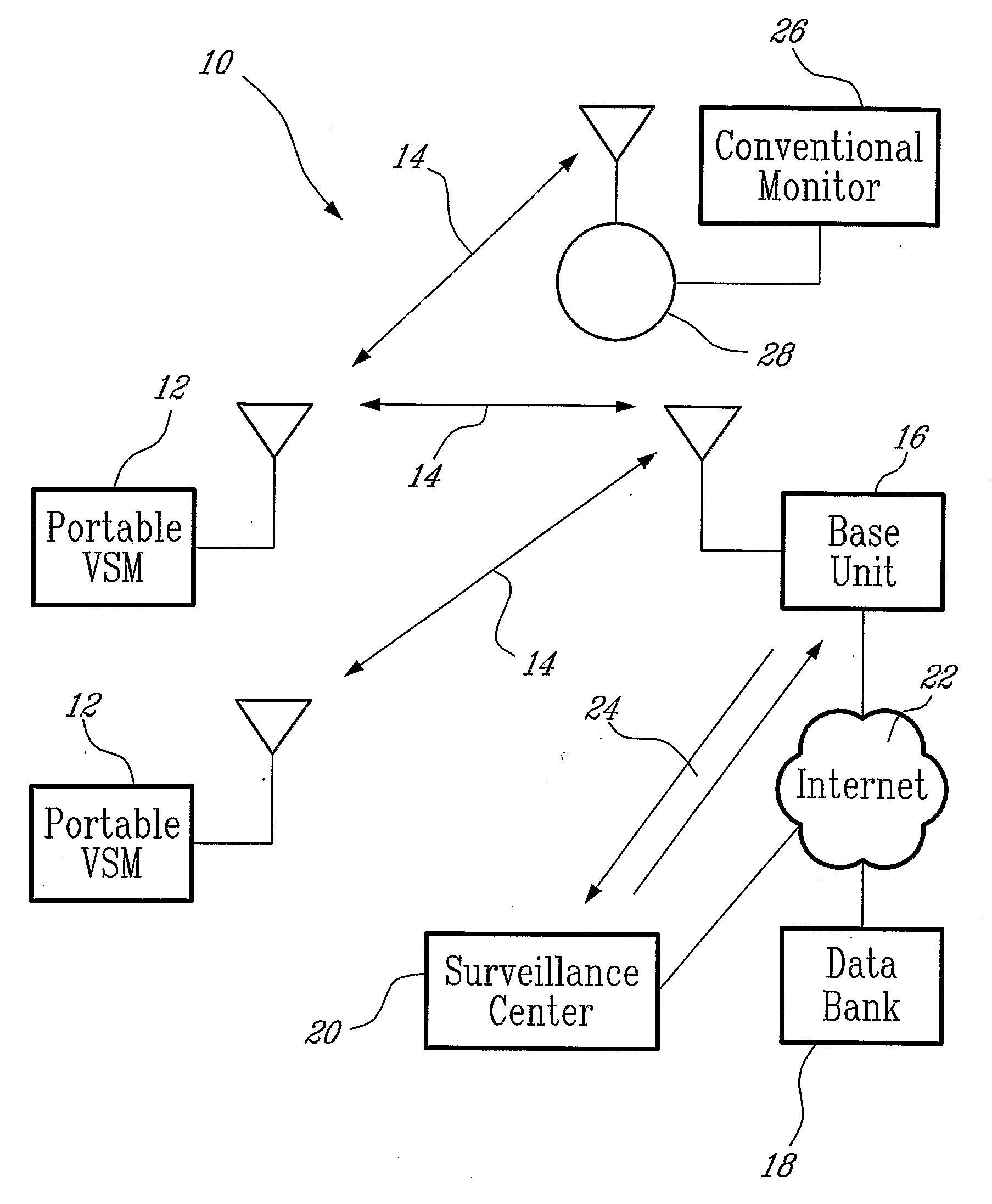
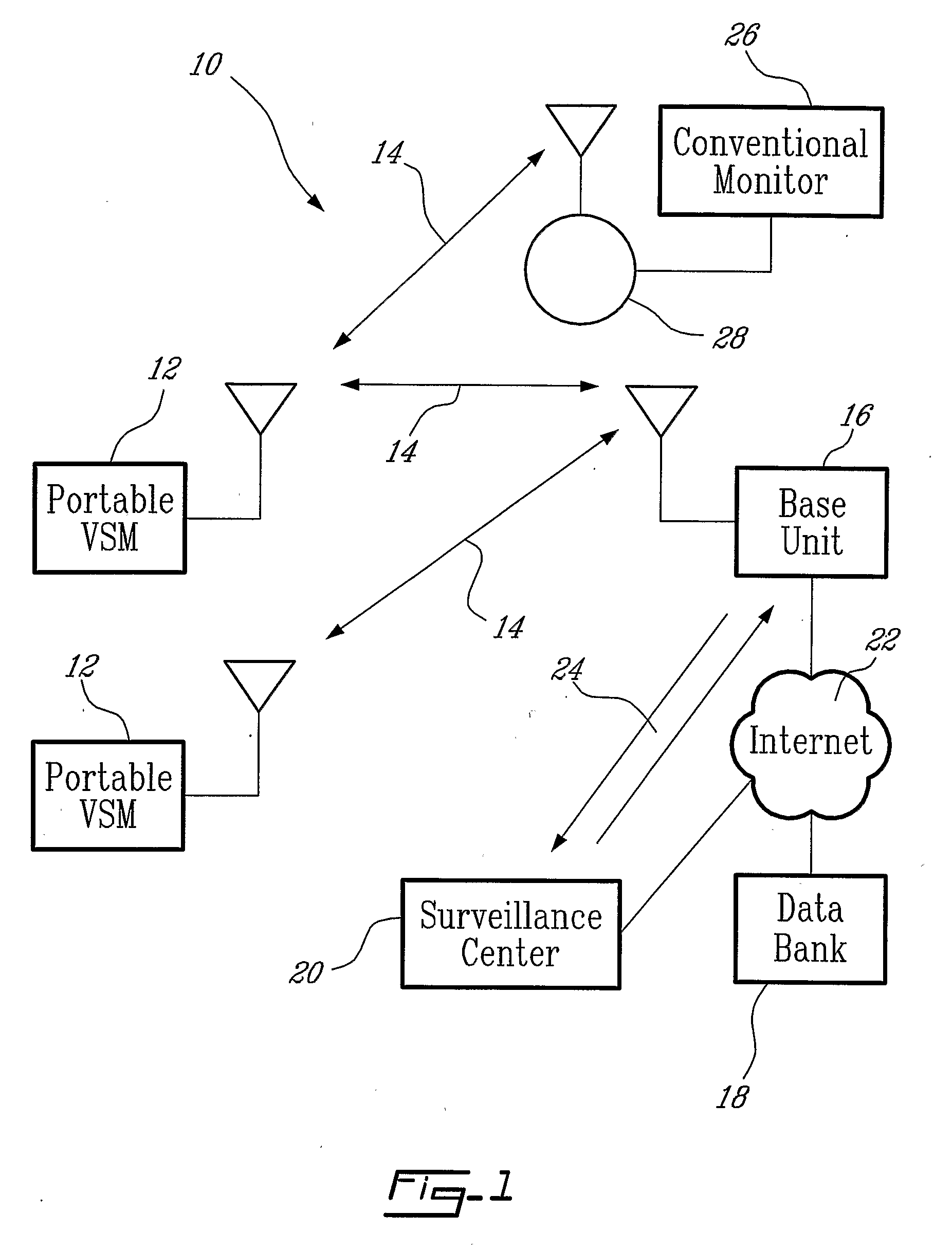
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
ActiveUS20050010087A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
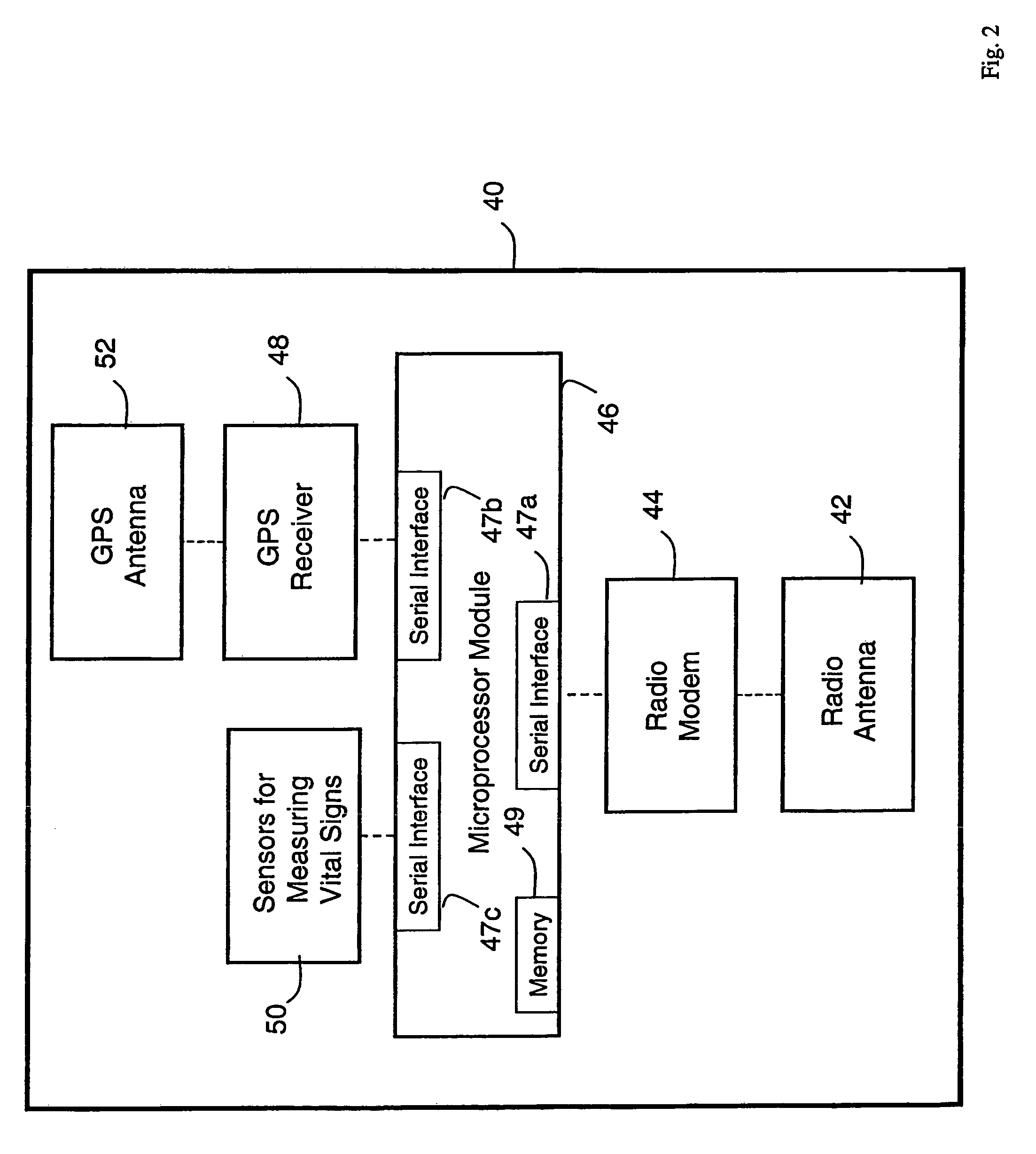
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
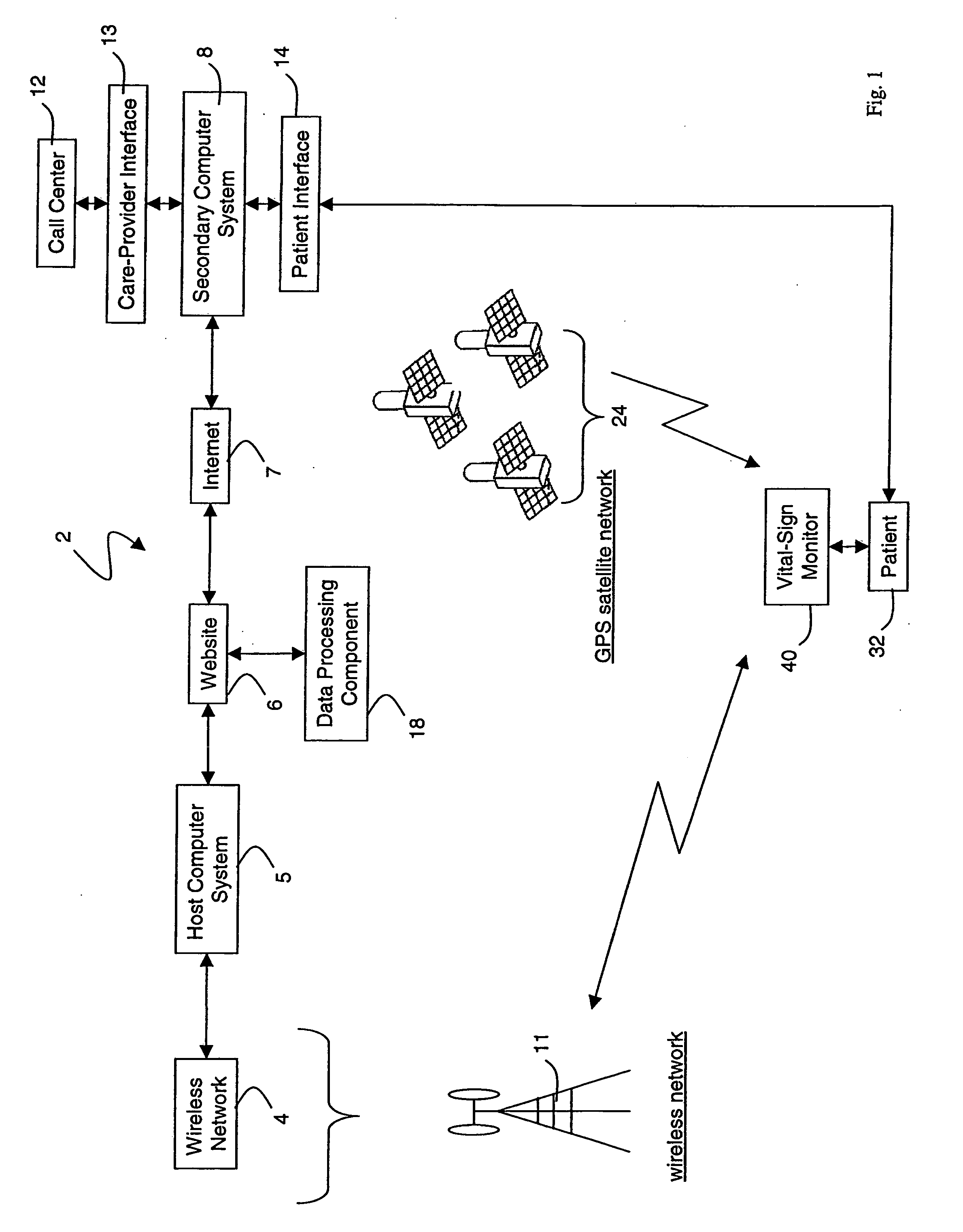
Wireless, internet-based, medical diagnostic system
InactiveUS20060142648A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsEmergency medicineGlobal Positioning System
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:TRIAGE DATA NETWORKS
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
ActiveUS7396330B2Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
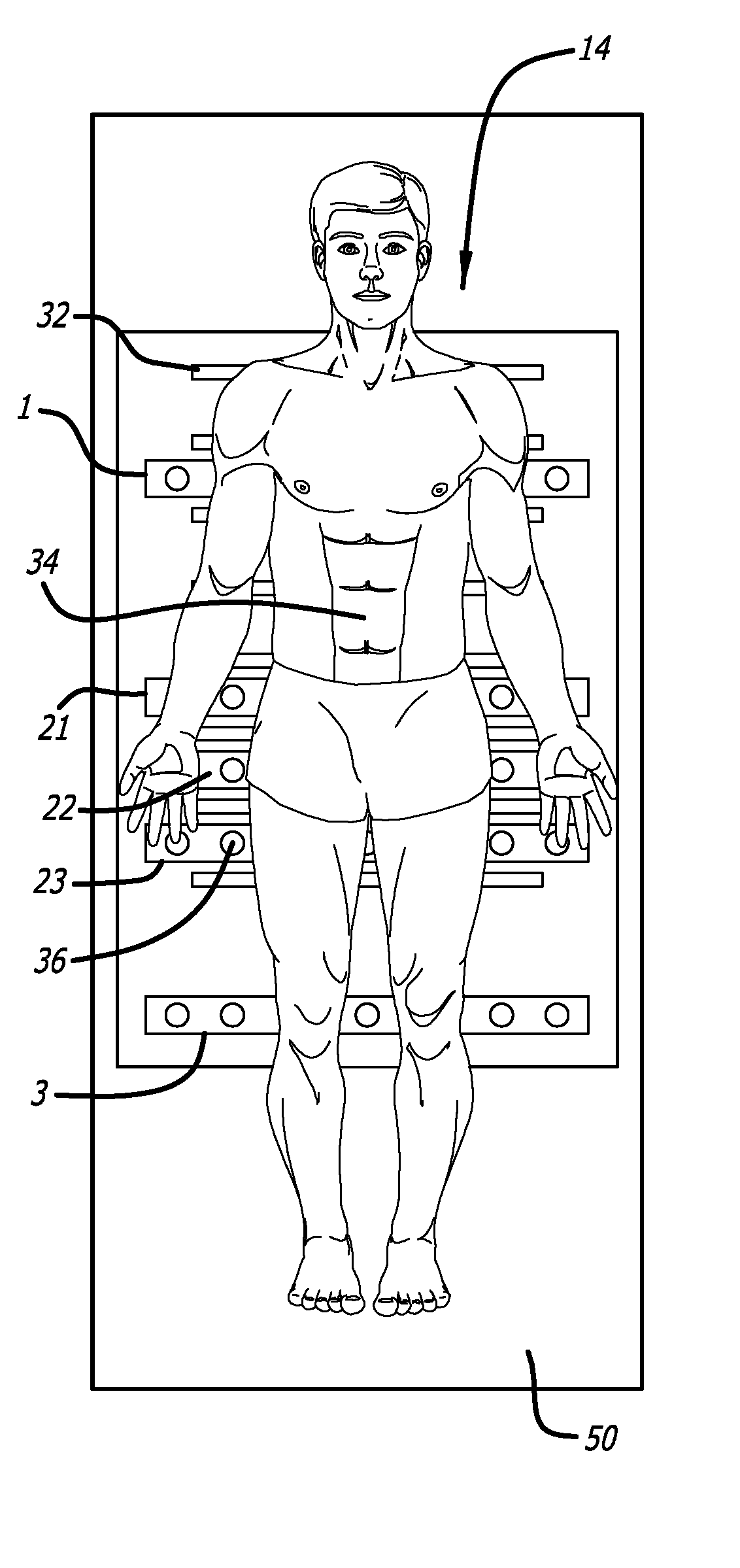
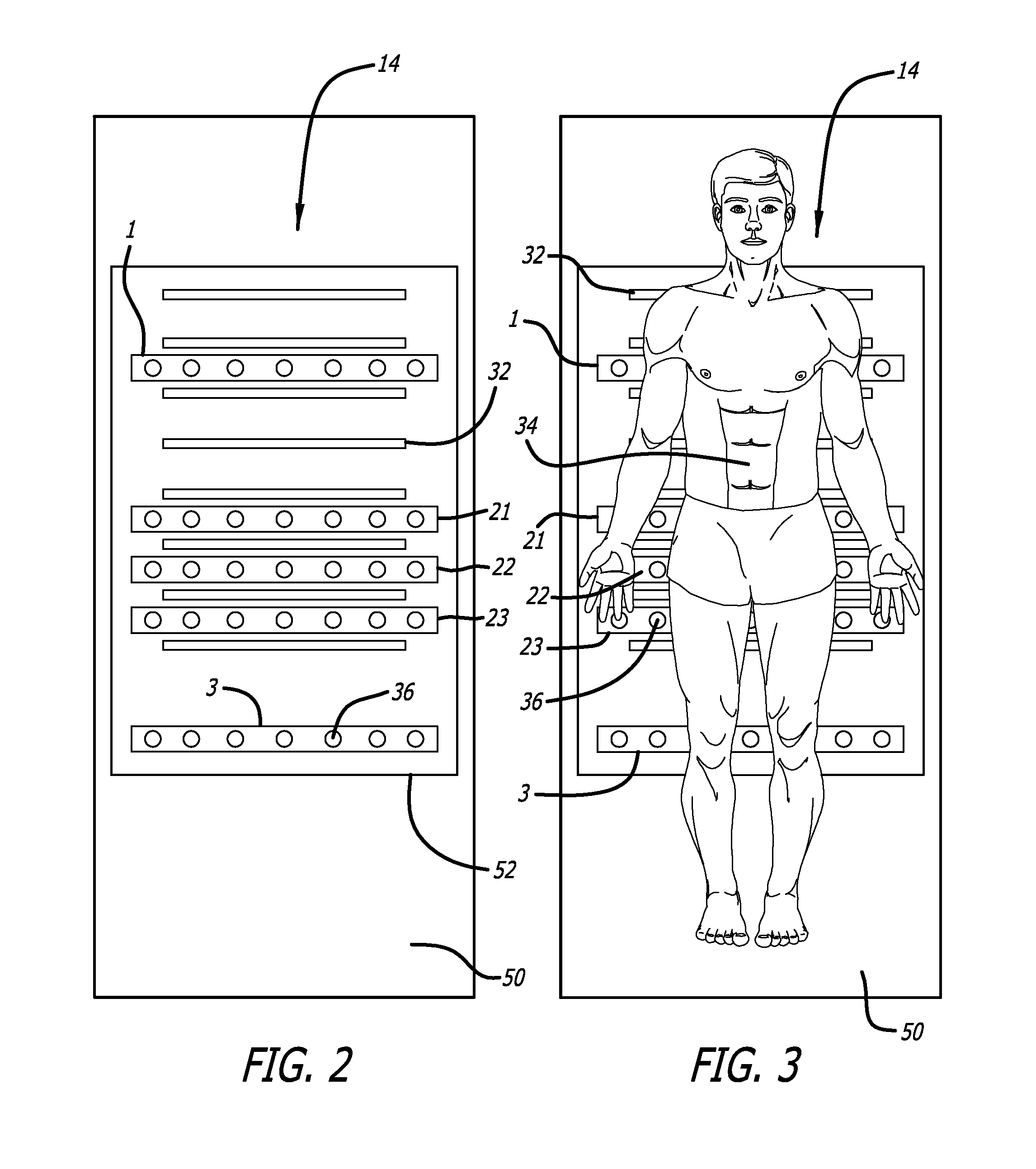
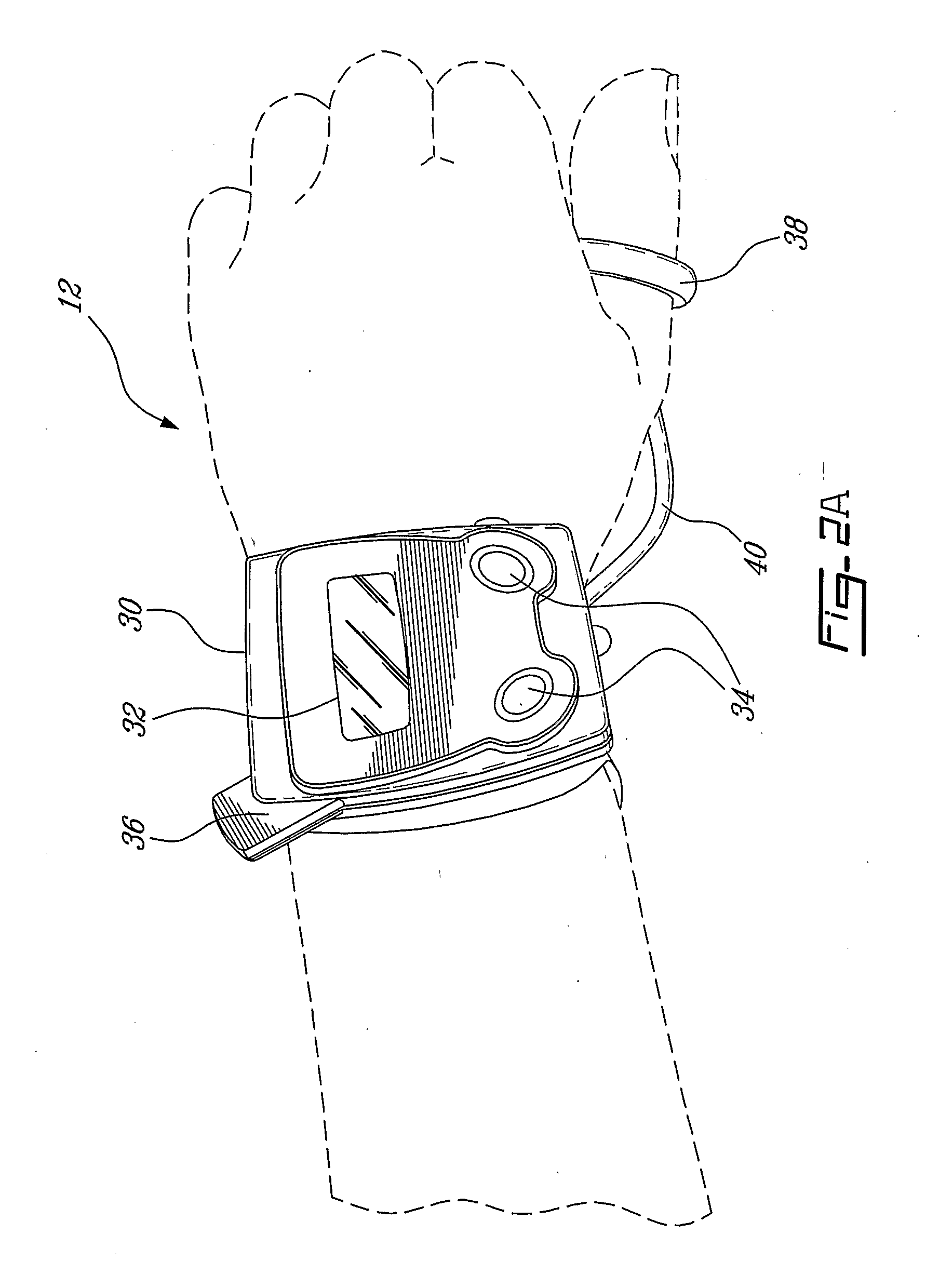
Body-worn vital sign monitor
InactiveUS20110224564A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionSensorsLocation information based serviceGraphical user interfaceDisplay device
The invention provides a body-worn vital sign monitor that measures a patient's vital signs (e.g. blood pressure, SpO2, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature) while simultaneously characterizing their activity state (e.g. resting, walking, convulsing, falling) and posture (upright, supine). The monitor processes this information to minimize corruption of the vital signs and associated alarms / alerts by motion-related artifacts. It also features a graphical user interface (GUI) rendered on a touchpanel display that facilitates a number of features to simplify and improve patient monitoring and safety in both the hospital and home.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
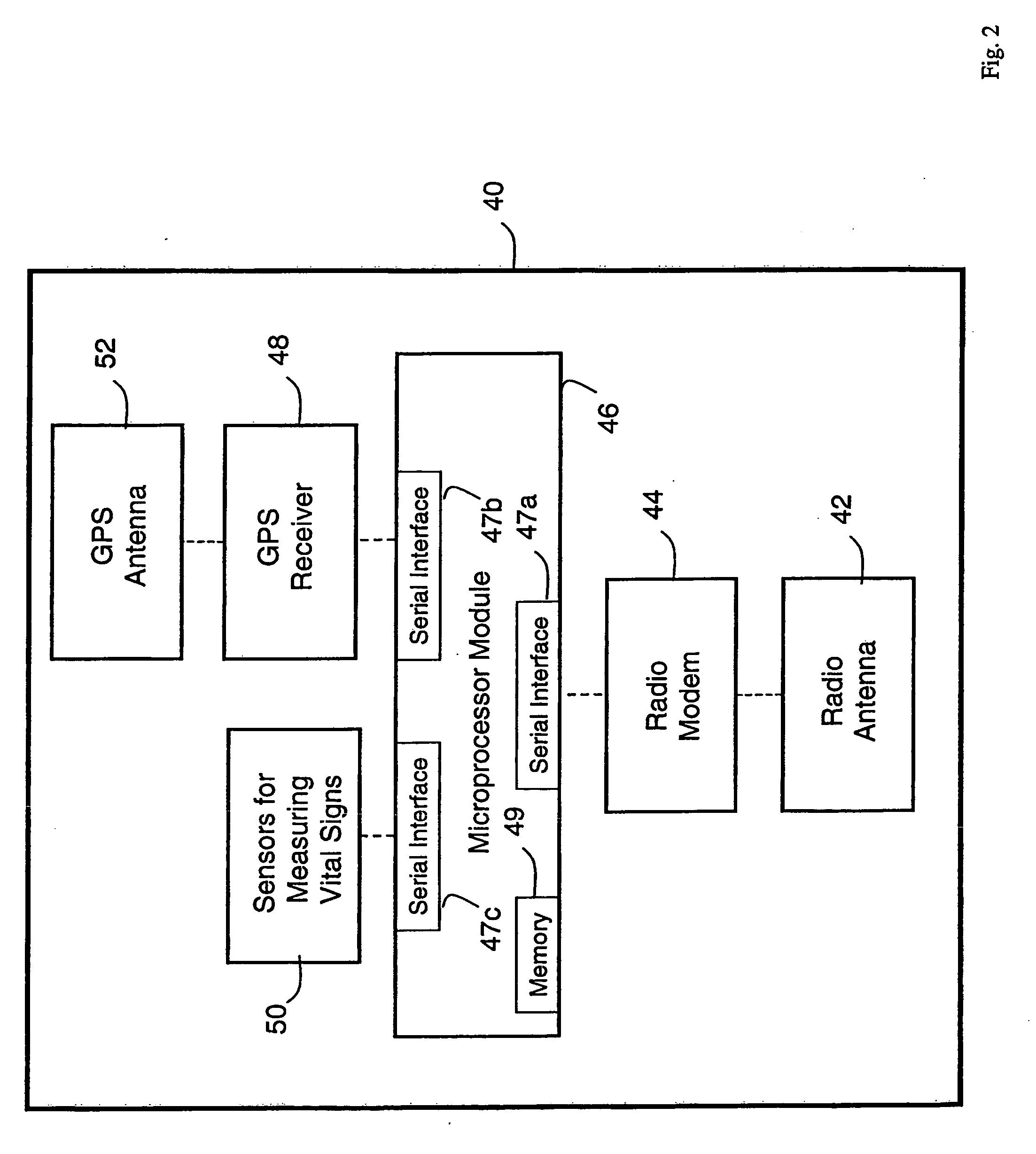
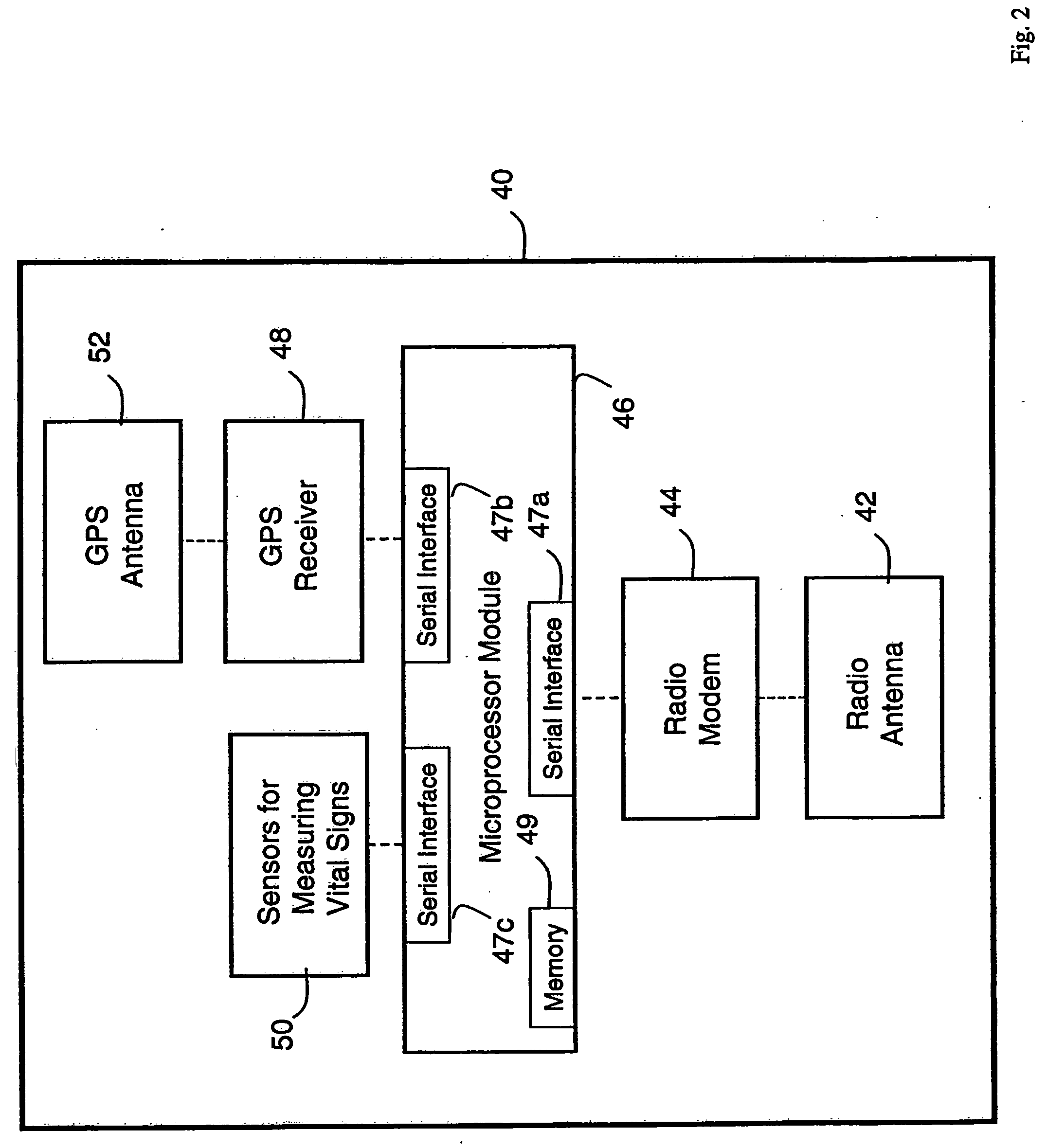
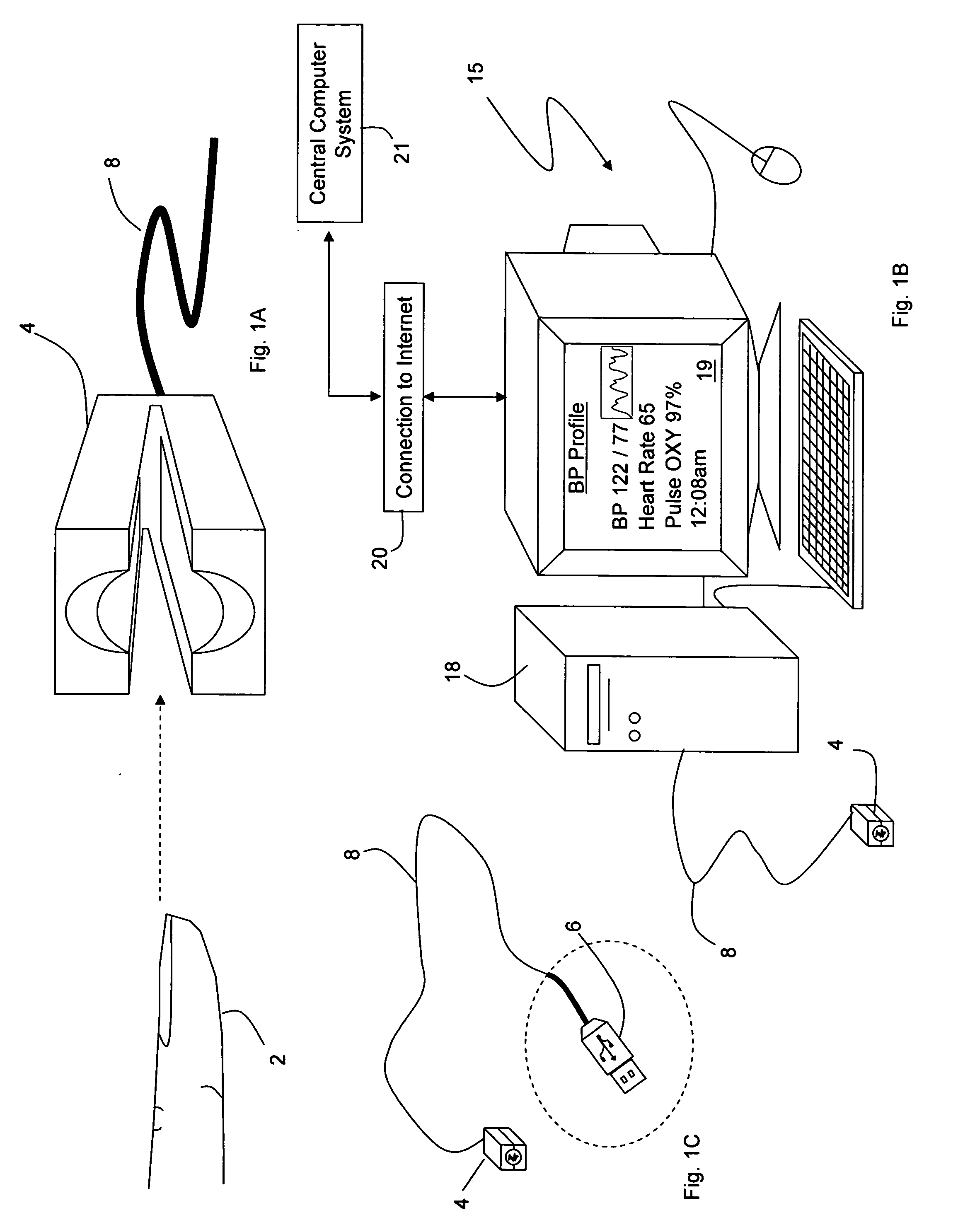
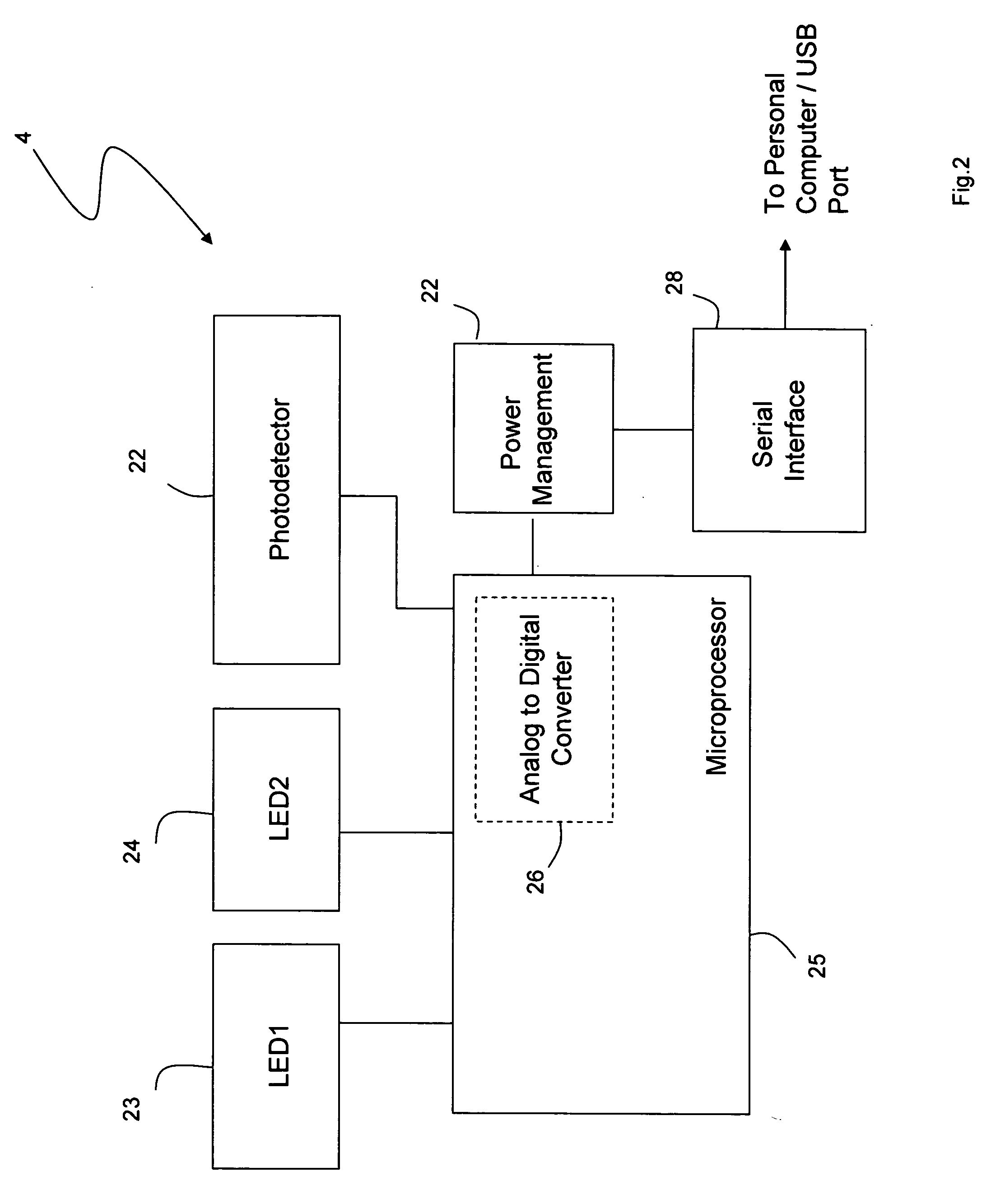
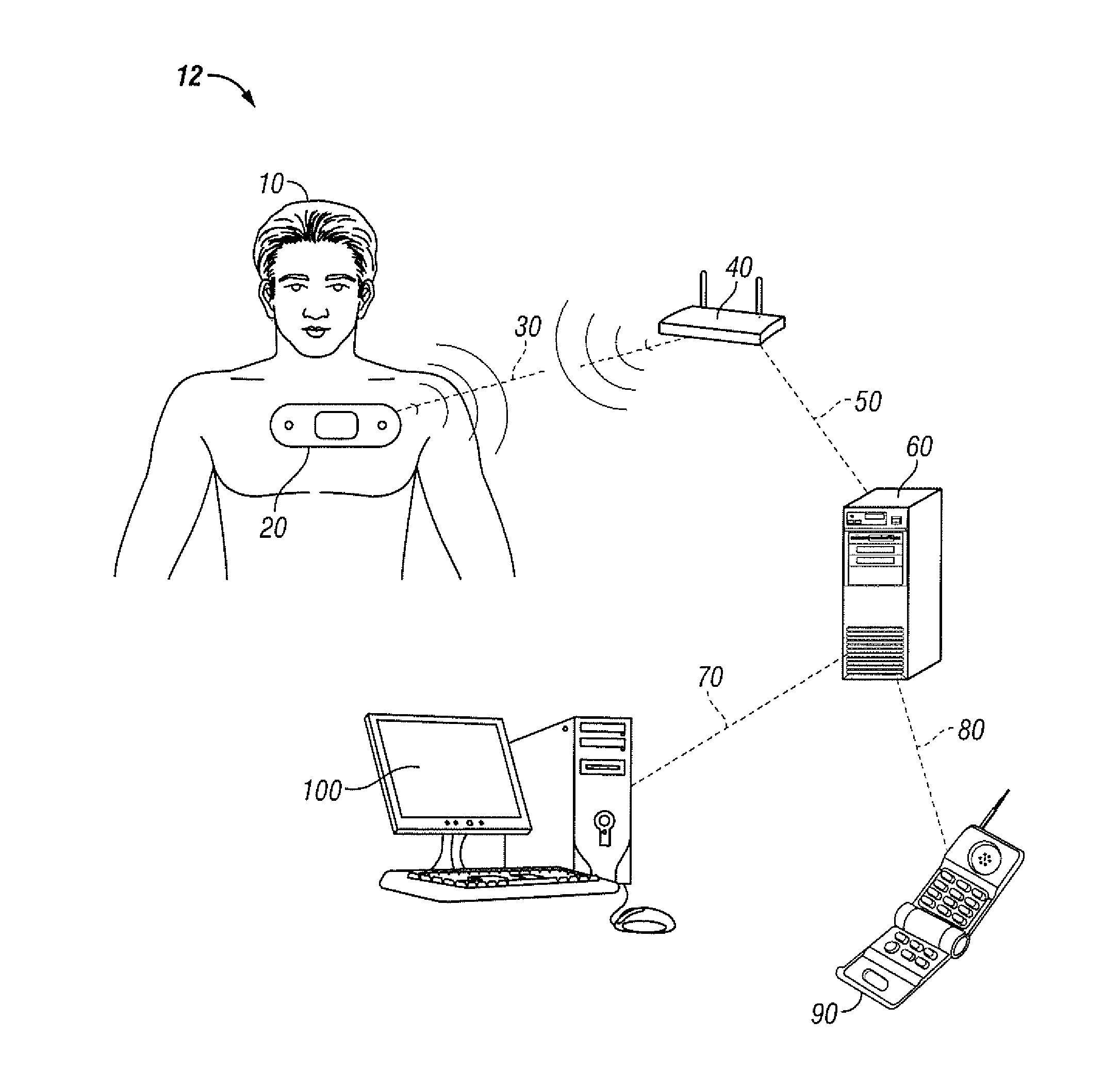
Personal computer-based vital signs monitor
InactiveUS20060084878A1Quickly and accurately measureSimple and low-cost systemCatheterSensorsOptical ModuleBlood pressure
The invention provides a system for measuring blood pressure from a patient that includes: 1) an optical module featuring systems for measuring signals from the patient, serial communication, and power management; 2) an external computing device configured to attach to the optical module, supply power to the optical module, and receive information from the optical module through the system for serial communication; and 3) an algorithm, operating on the external computing device, that processes information received through the system for serial communication to determine the patient's blood pressure.
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
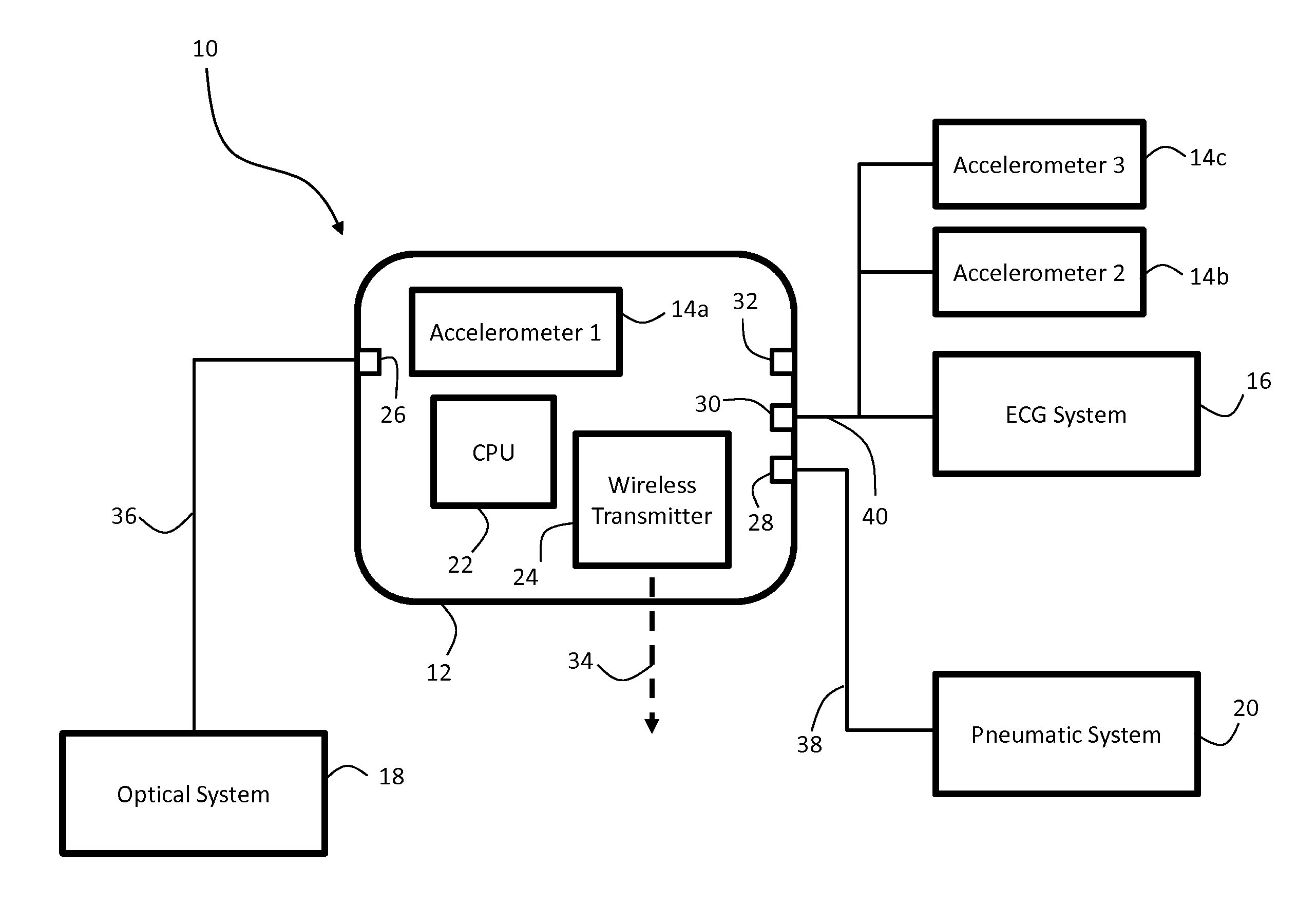
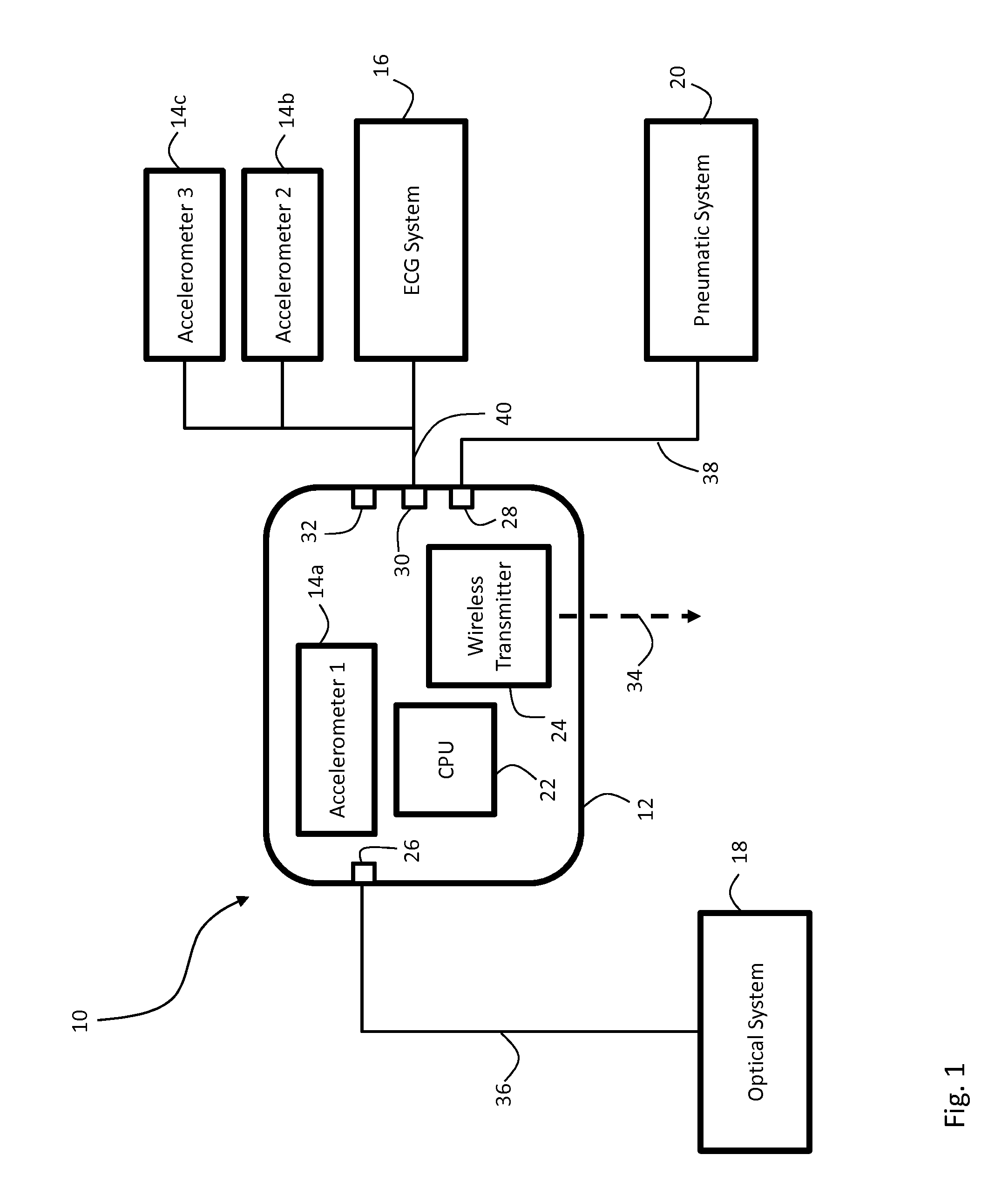
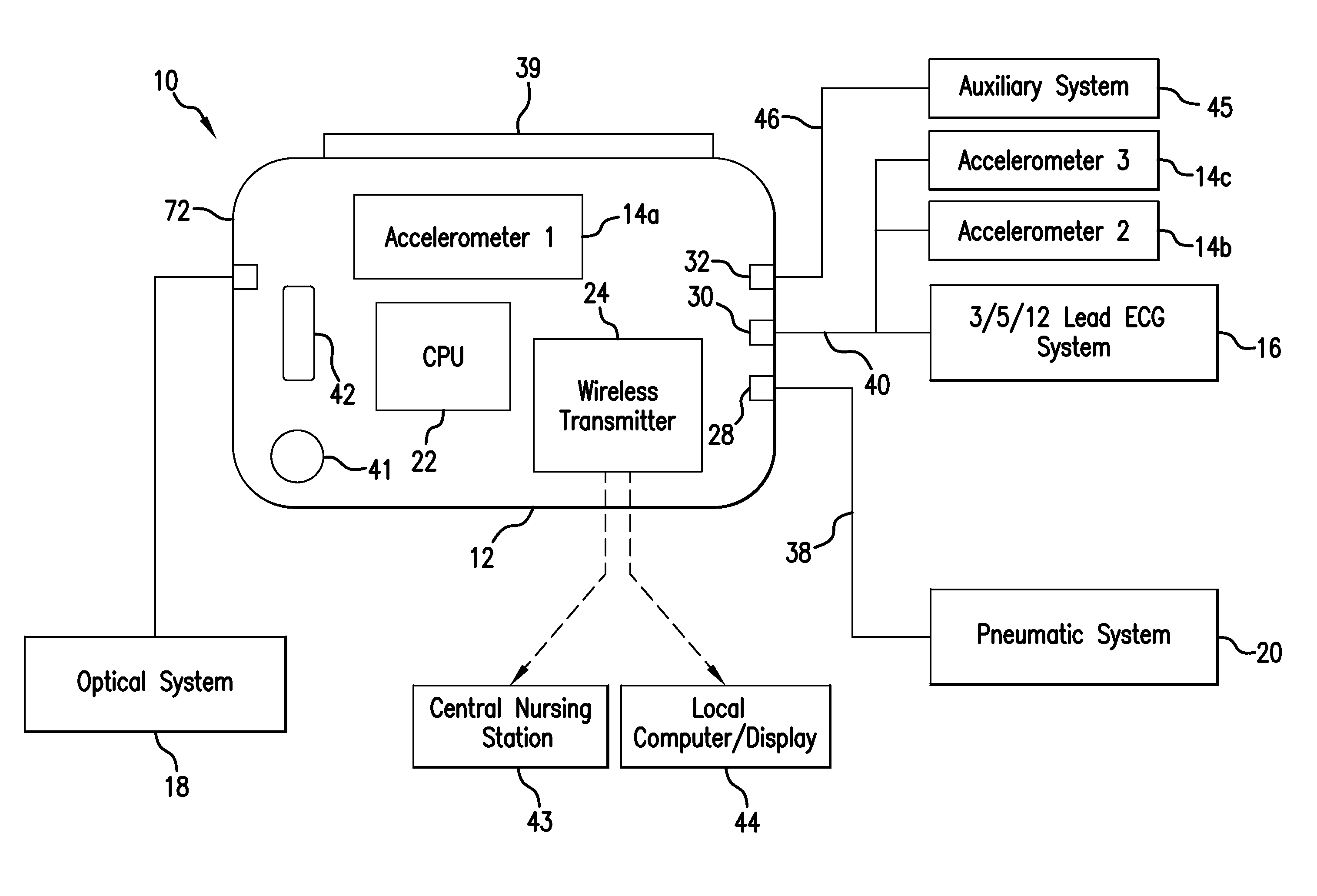
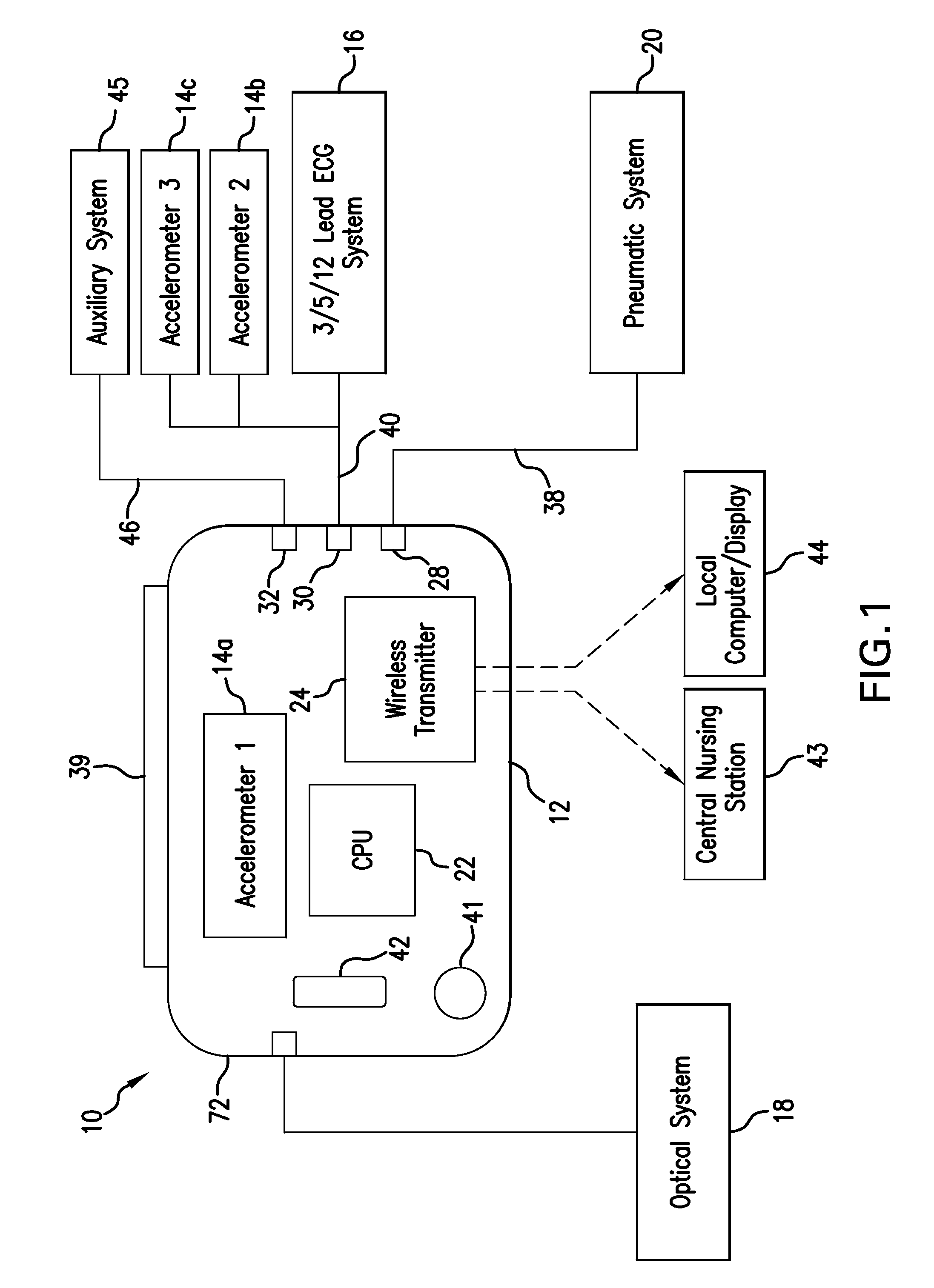
Vital sign monitoring system featuring 3 accelerometers
ActiveUS20100298650A1Useful characteristicElectrocardiographyPerson identificationAccelerometerMotion parameter
The invention provides a system and method for measuring vital signs (e.g. SYS, DIA, SpO2, heart rate, and respiratory rate) and motion (e.g. activity level, posture, degree of motion, and arm height) from a patient. The system features: (i) first and second sensors configured to independently generate time-dependent waveforms indicative of one or more contractile properties of the patient's heart; and (ii) at least three motion-detecting sensors positioned on the forearm, upper arm, and a body location other than the forearm or upper arm of the patient. Each motion-detecting sensor generates at least one time-dependent motion waveform indicative of motion of the location on the patient's body to which it is affixed. A processing component, typically worn on the patient's body and featuring a microprocessor, receives the time-dependent waveforms generated by the different sensors and processes them to determine: (i) a pulse transit time calculated using a time difference between features in two separate time-dependent waveforms, (ii) a blood pressure value calculated from the time difference, and (iii) a motion parameter calculated from at least one motion waveform.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
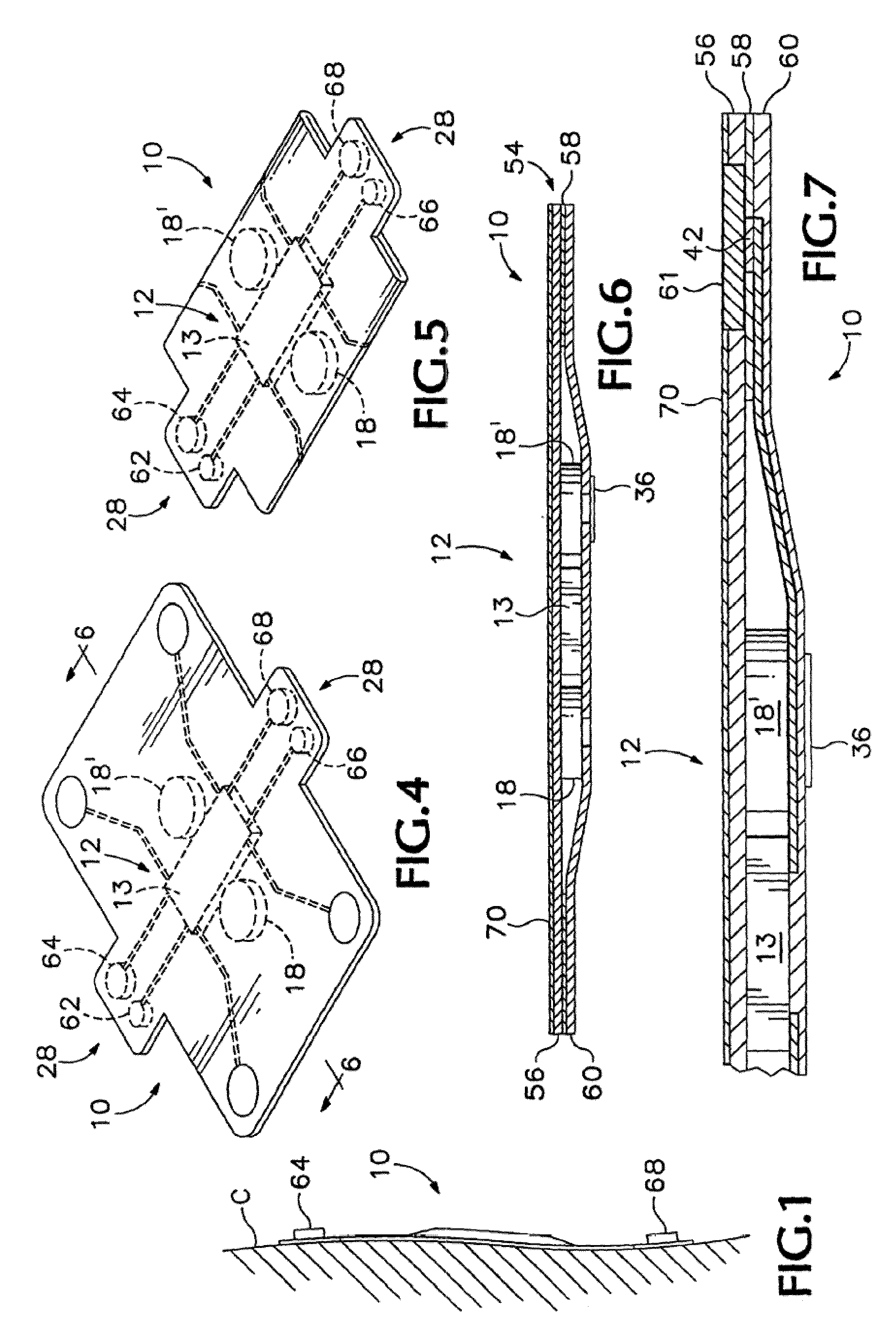
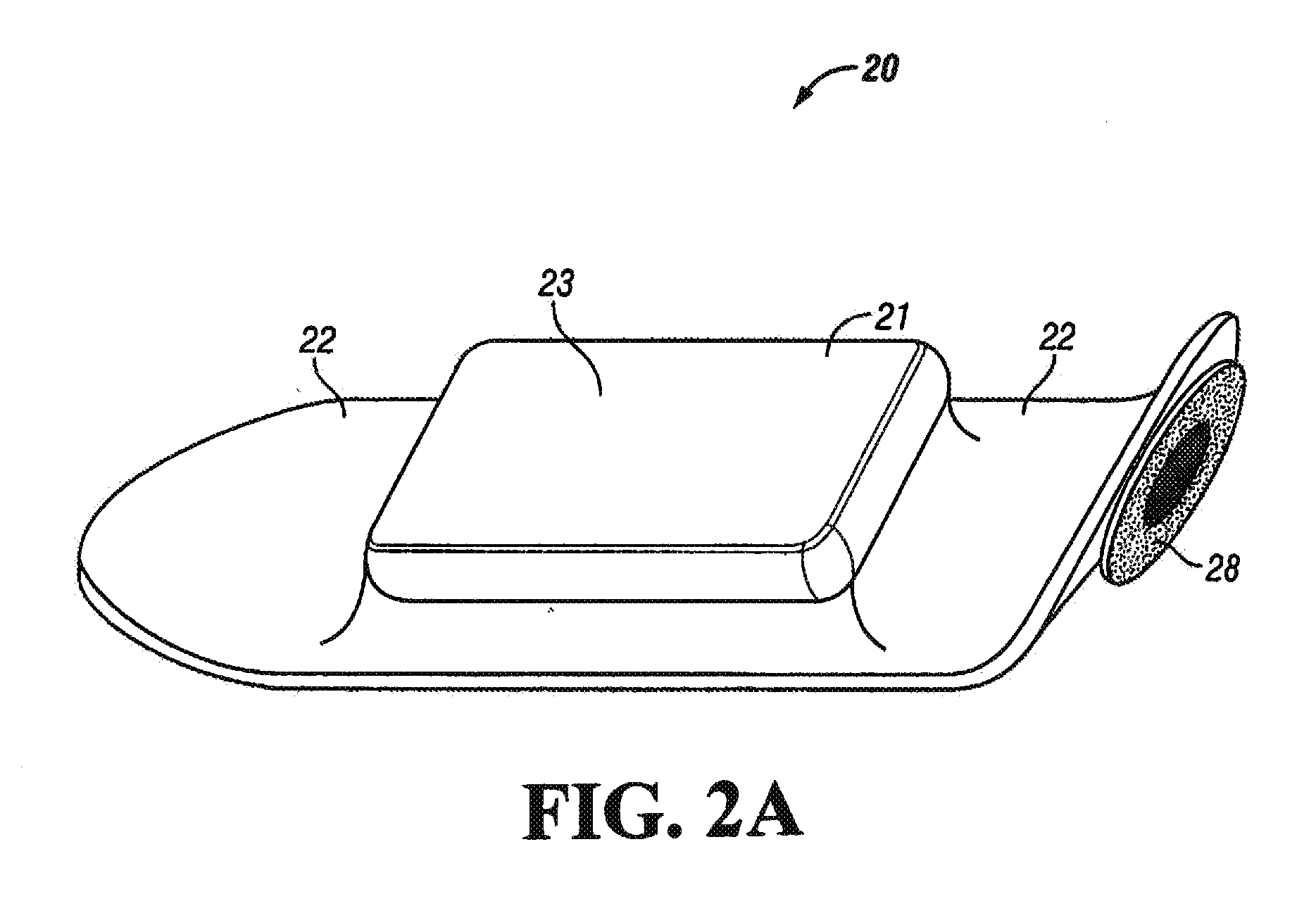
Body composition, circulation, and vital signs monitor and method
The invented non-invasive vital signs monitor is in a flexible, nominally flat planar form having integral gel electrodes, a sticky-back rear surface, an internal flex circuit capable of sensing, recording and playing out several minutes of the most recently acquired ECG waveform data and a front surface that includes an outplay port. The invented non-invasive body composition ‘risk’ monitor includes a measurement device for monitoring one or more variables including body fluid mass, dehydration, respiratory rate, blood pressure, bio-impedance, cardiography such as cardiac output, and body conformation parameters. The risk monitor may be provided in a lightweight carrying case into which the vital signs monitor plugs. Finally, a lightweight portable probe or transducer containing a transmissive or reflective electro-optical emitter and receptor in the infrared spectrum is fitted on a subject's finger or toe. Associated electronics energize and monitor the probe, detect cardio-rhythmic fluctuations therefrom, and process digital data over a prescribed window to produce a non-invasive, qualitative or quantitative measure of the subject's circulation. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, a simple tri-color LED array is used to indicate the subject's circulation as being normal, reduced, or borderline. Thus the vital signs, bio-impedance, and circulation monitors may be independent or they may be integrated into one portable, non-invasive device that can concurrently monitor and locally display or remotely convey important patient data including circulation data to a local subject or physician or to / from a remote patient medical data center via wireless telemetry for oversight, treatment and possible intervention by a remote physician.
Owner:SEMLER SCI
Blood-pressure monitoring device featuring a calibration-based analysis
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
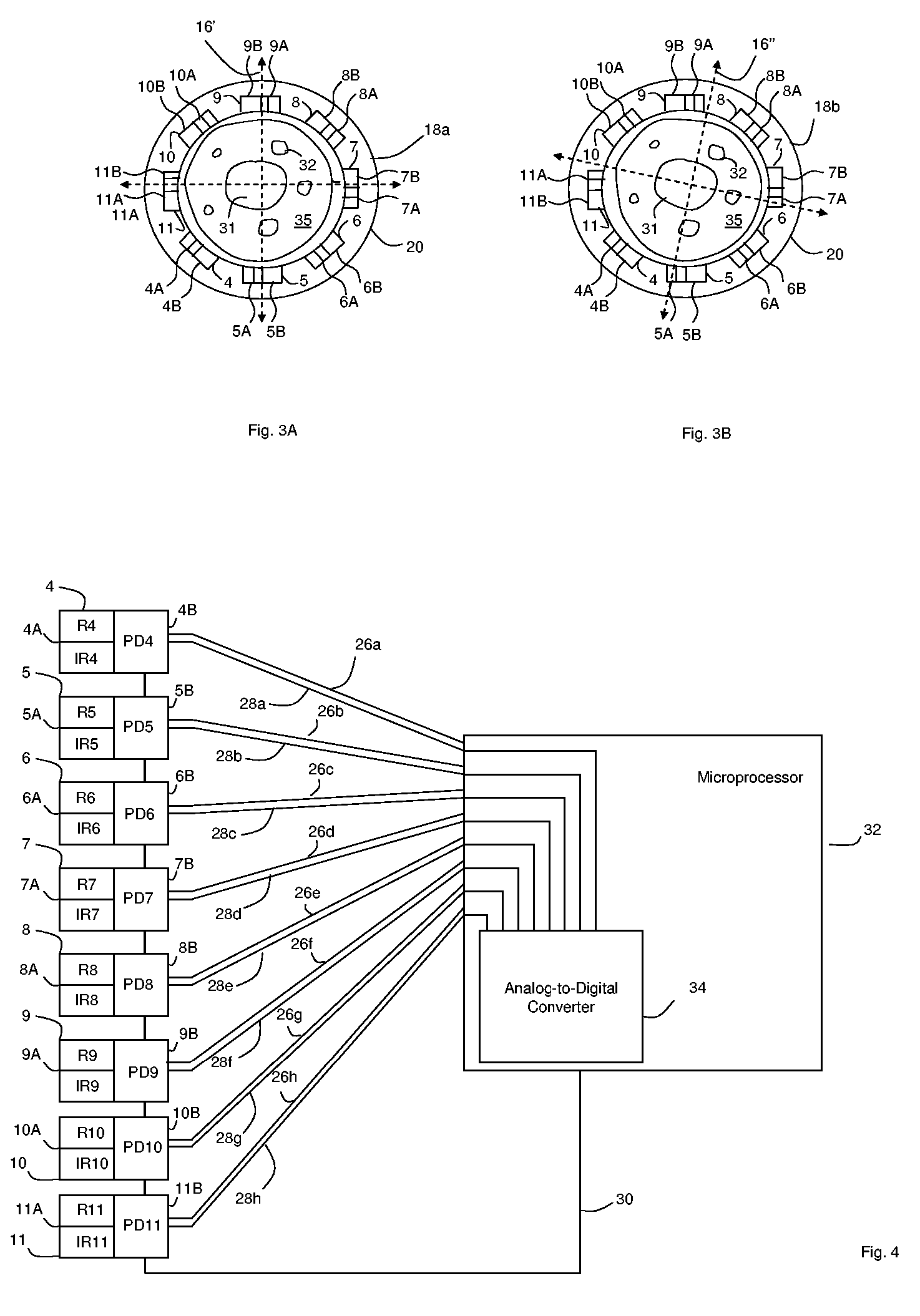
Optical sensors for use in vital sign monitoring
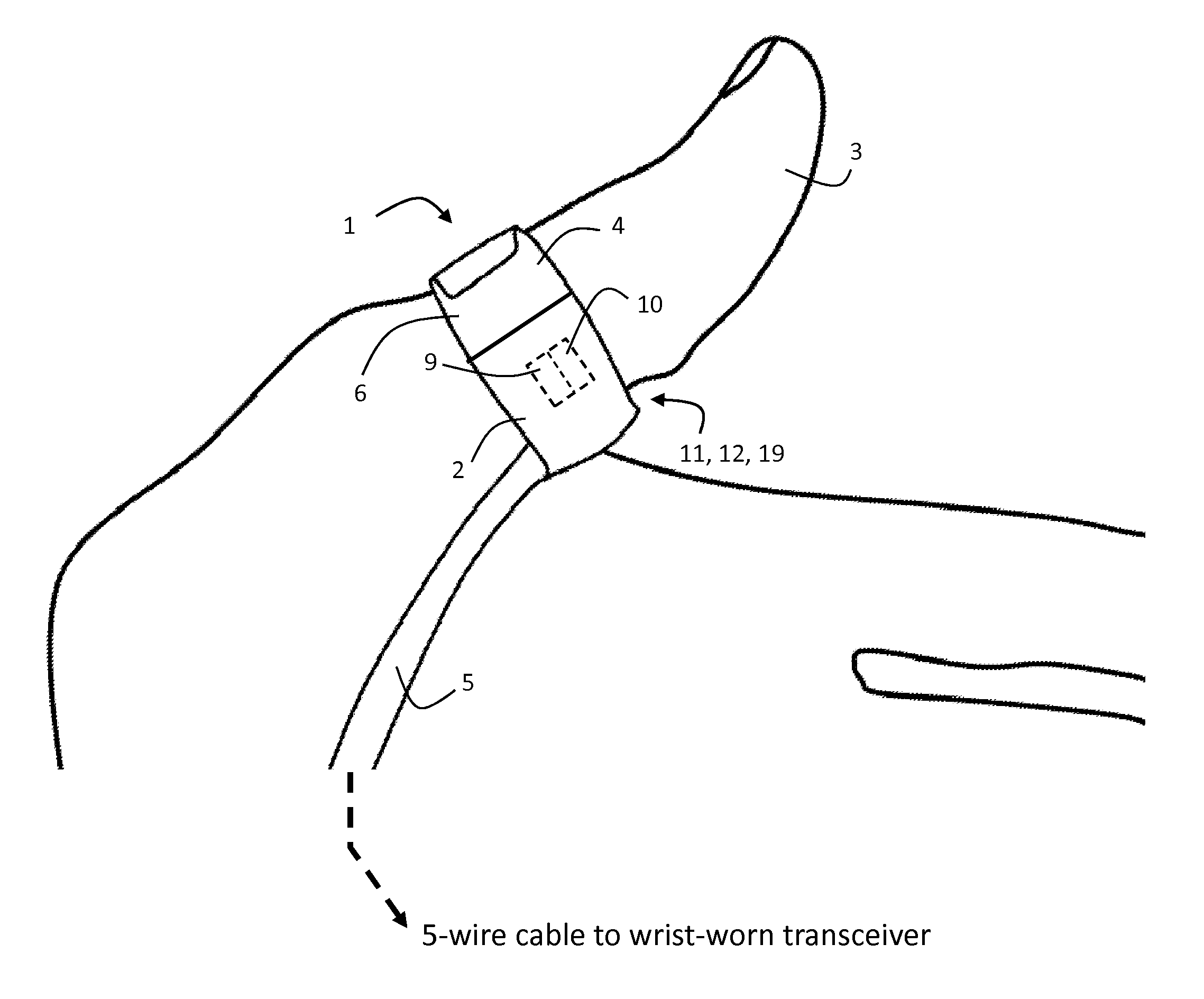
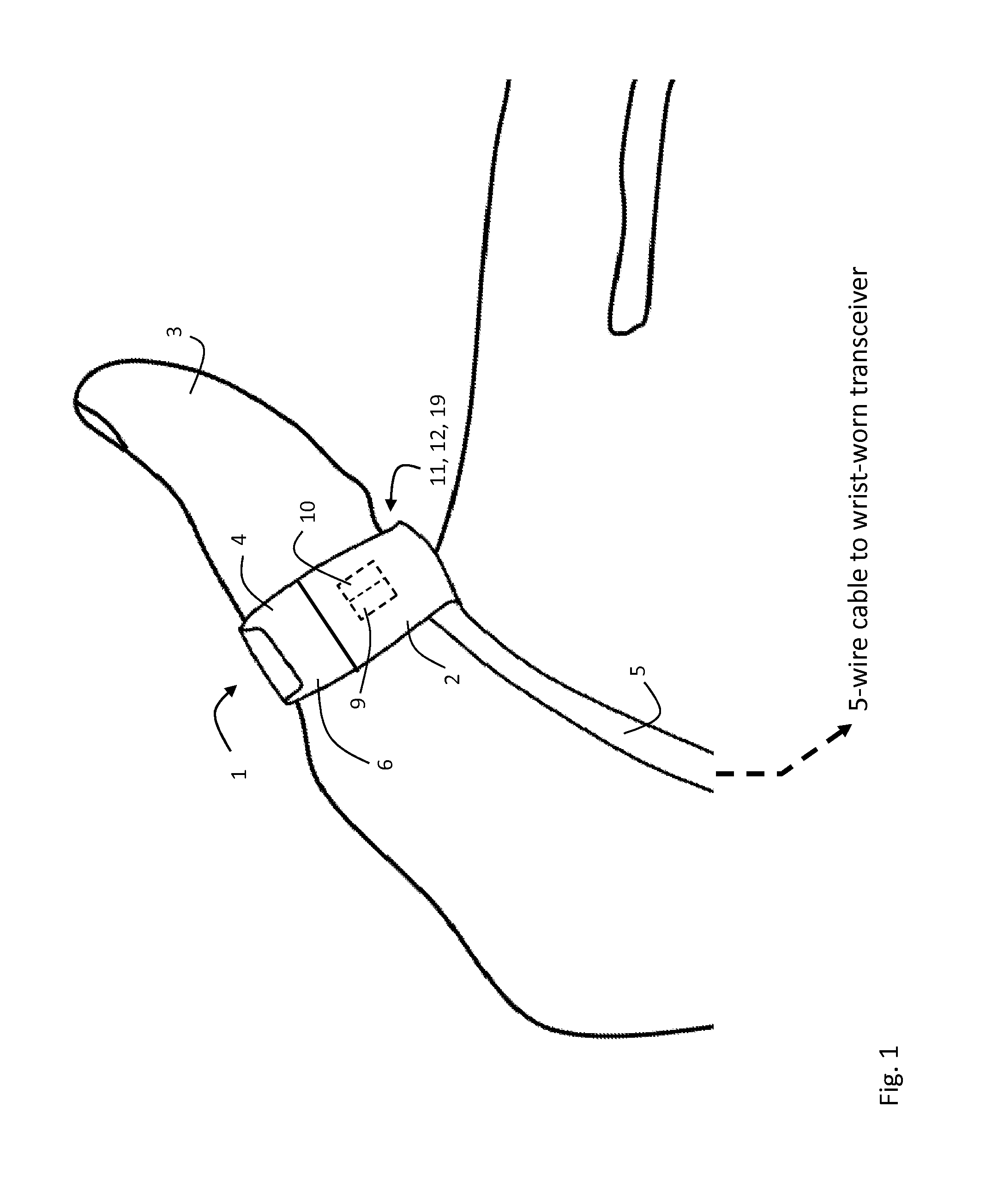
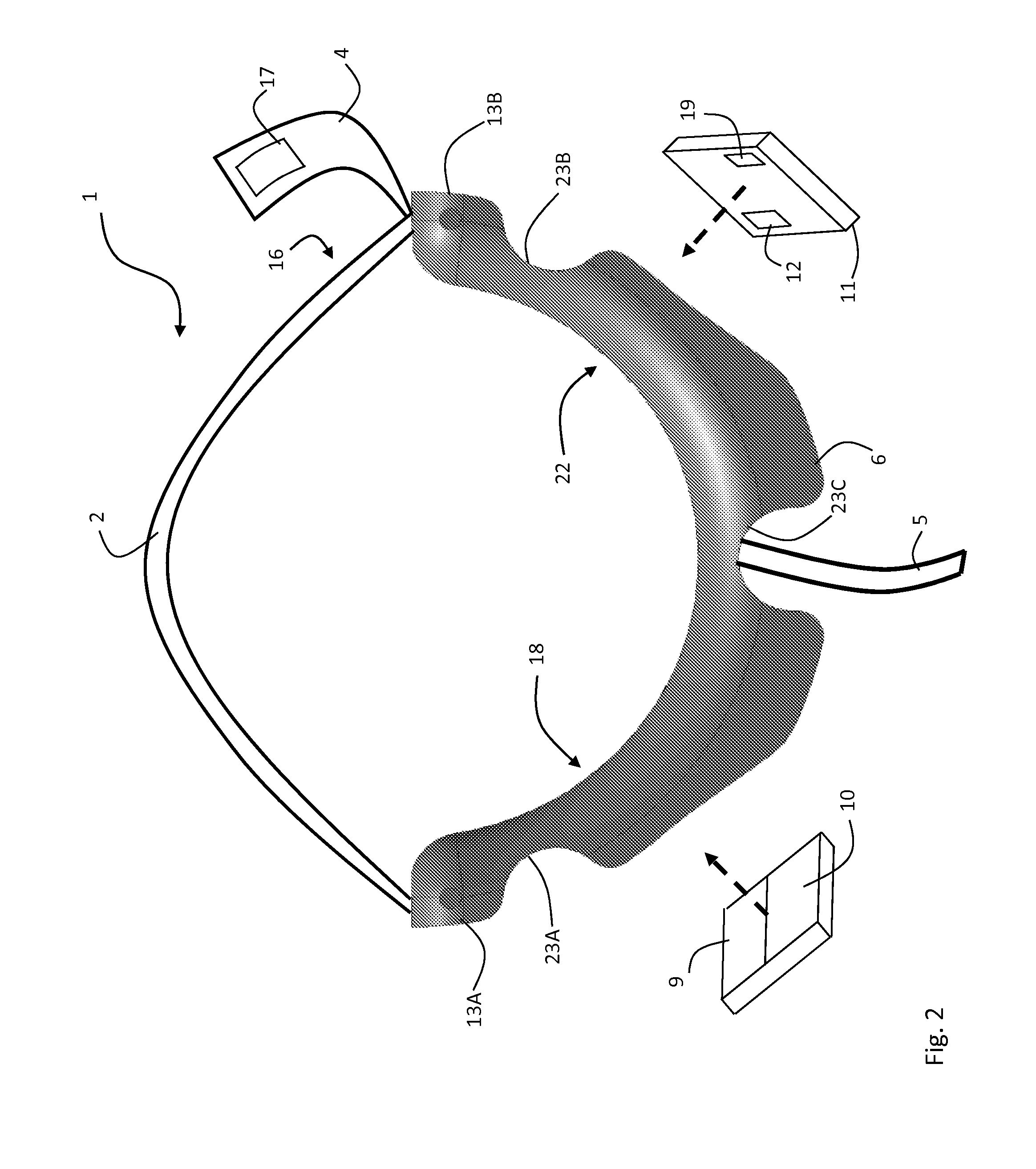
ActiveUS20120179011A1Accurate extractionImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsCable transmissionTransceiver
The invention provides a body-worn system that continuously measures pulse oximetry and blood pressure, along with motion, posture, and activity level, from an ambulatory patient. The system features an oximetry probe that comfortably clips to the base of the patient's thumb, thereby freeing up their fingers for conventional activities in a hospital, such as reading and eating. The probe secures to the thumb and measures time-dependent signals corresponding to LEDs operating near 660 and 905 nm. Analog versions of these signals pass through a low-profile cable to a wrist-worn transceiver that encloses a processing unit. Also within the wrist-worn transceiver is an accelerometer, a wireless system that sends information through a network to a remote receiver, e.g. a computer located in a central nursing station.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
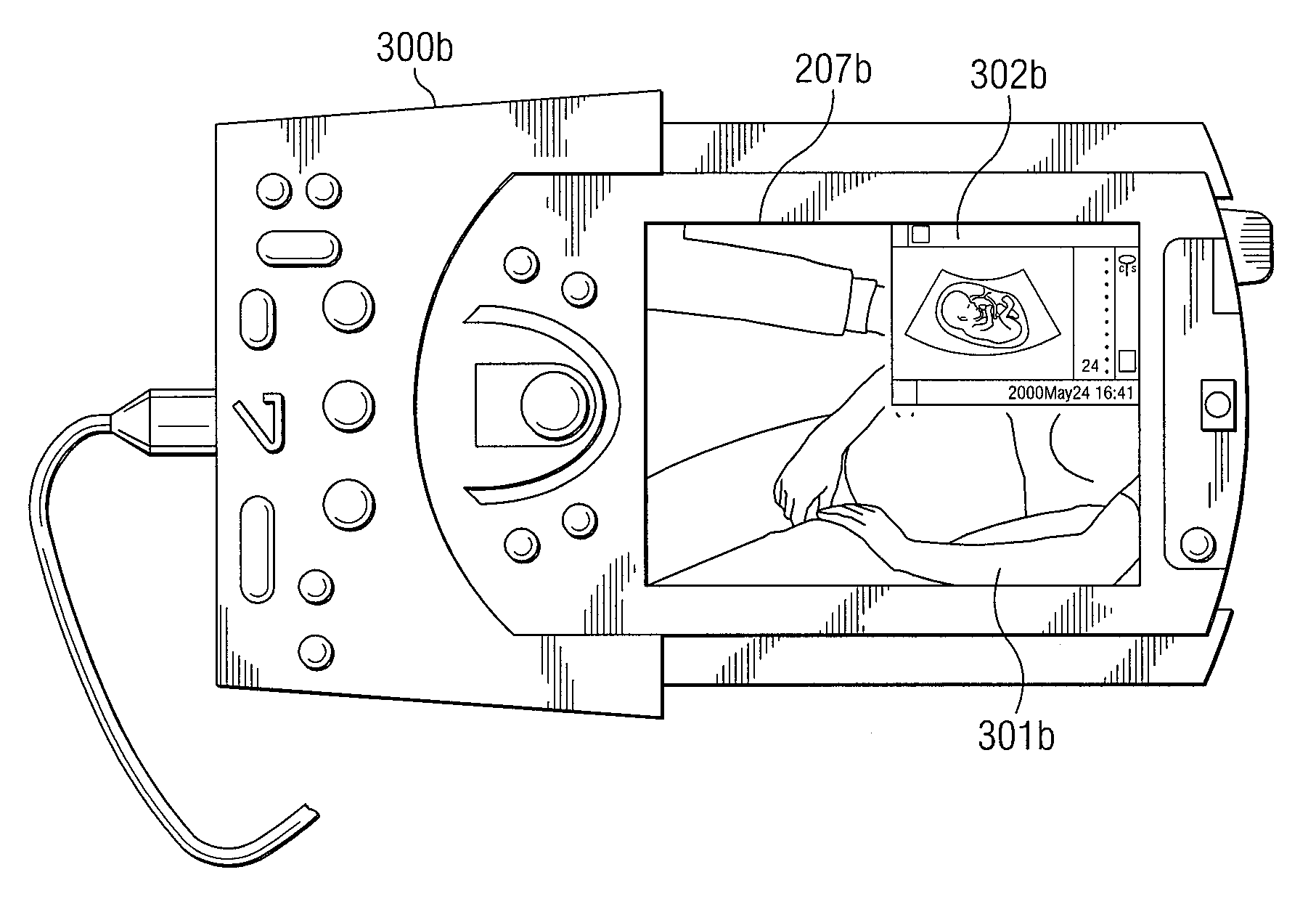
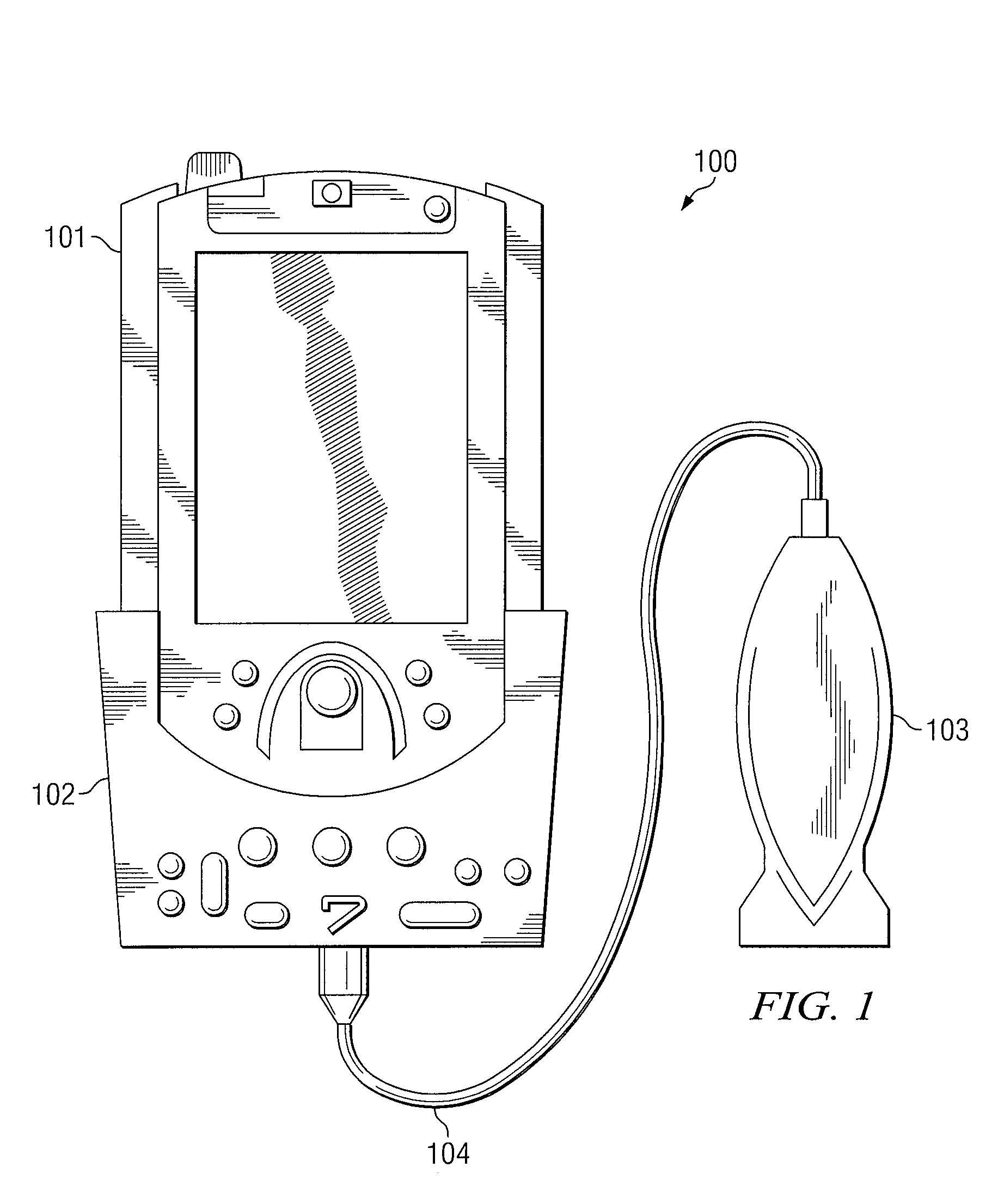
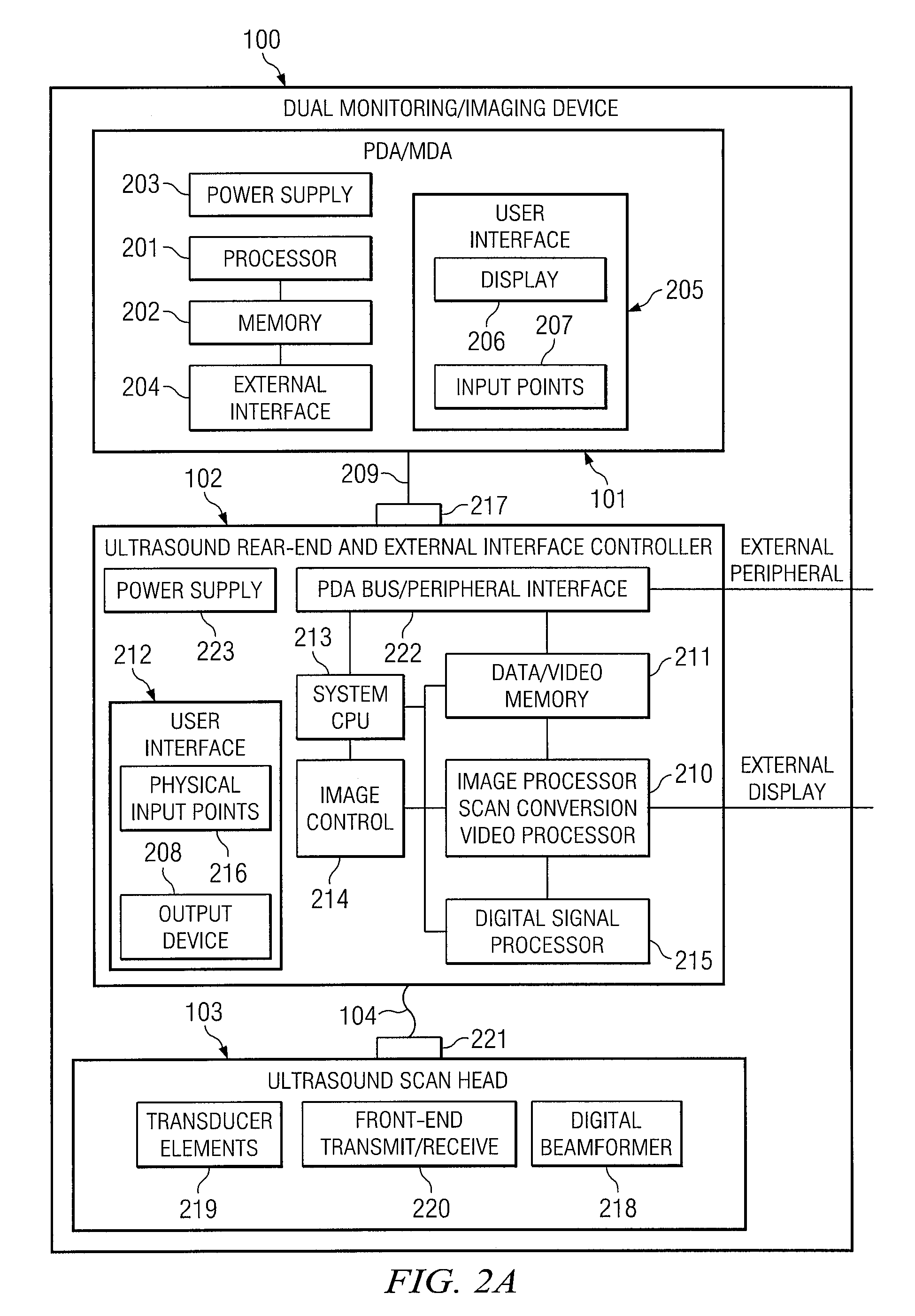
System and method supporting imaging and monitoring applications
ActiveUS7549961B1Suitable can be appliedDiagnostic recording/measuringTomographyReady to useEngineering
The present invention is directed to a system and method in which a portable medical device supports simultaneous imaging and monitoring applications. This portable device includes an external controller for receiving a PDA / MDA via a communication bus. An ultrasound scan head also is preferably attached to the external controller via an interconnect. In operation, real-time video feed of the patient may be acquired using the device and then displayed on the PDA / MDA. Using the ultrasound scan head in conjunction with the external controller, images may be acquired and displayed on the PDA / MDA, and vital sign monitoring of a single patient or multiple patients may be performed. Video feed, images and / or monitoring information may be transferred to a remote expert for review and analysis on the remote expert's communication device.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
Device, system and method for monitoring vital signs
ActiveUS20050228298A1Accurate measurementEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterAccelerometerPhotodetector
A monitoring device, method and system are disclosed herein. The monitoring device is capable of determine when a user's wrist is at rest using a motion sensor disposed within a wrist module that is attached to the user's wrist. When at rest, the monitoring device utilizes a vital sign monitor to determine a plurality of vital signs of the user. The vital sign monitor preferably comprises a light source and photodetector in communication with a pulse-oximetry circuit. The motion sensor is preferably an accelerometer.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
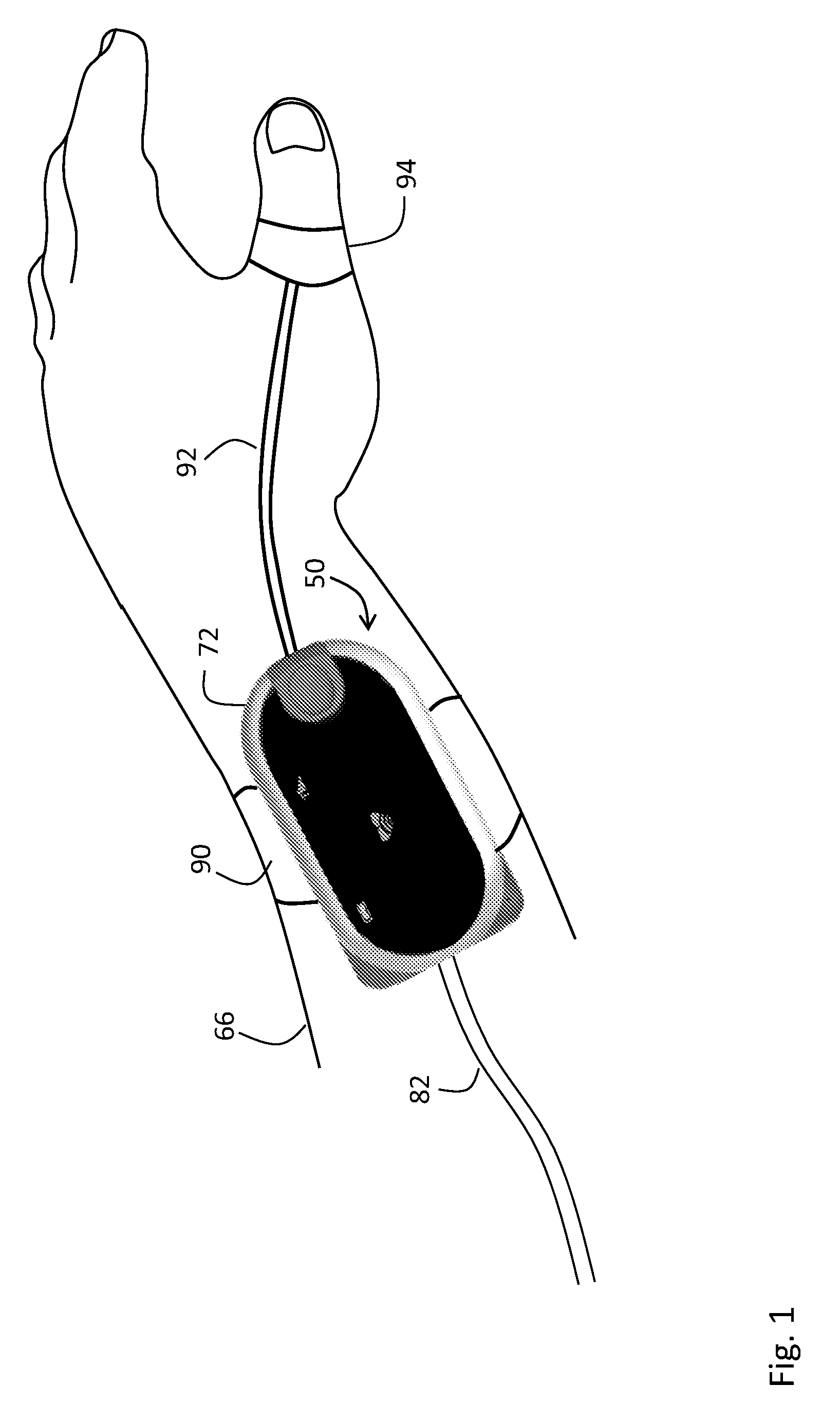
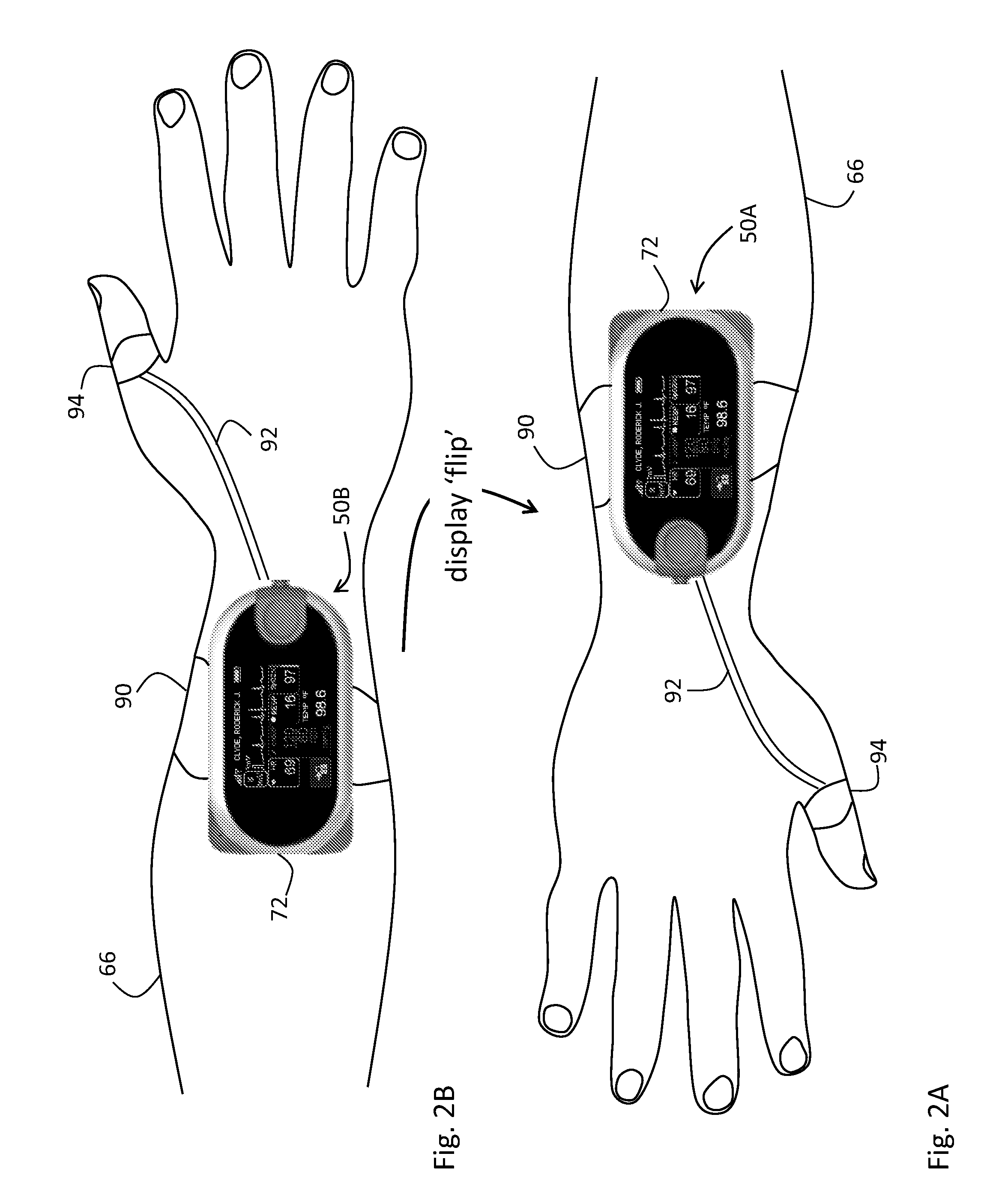
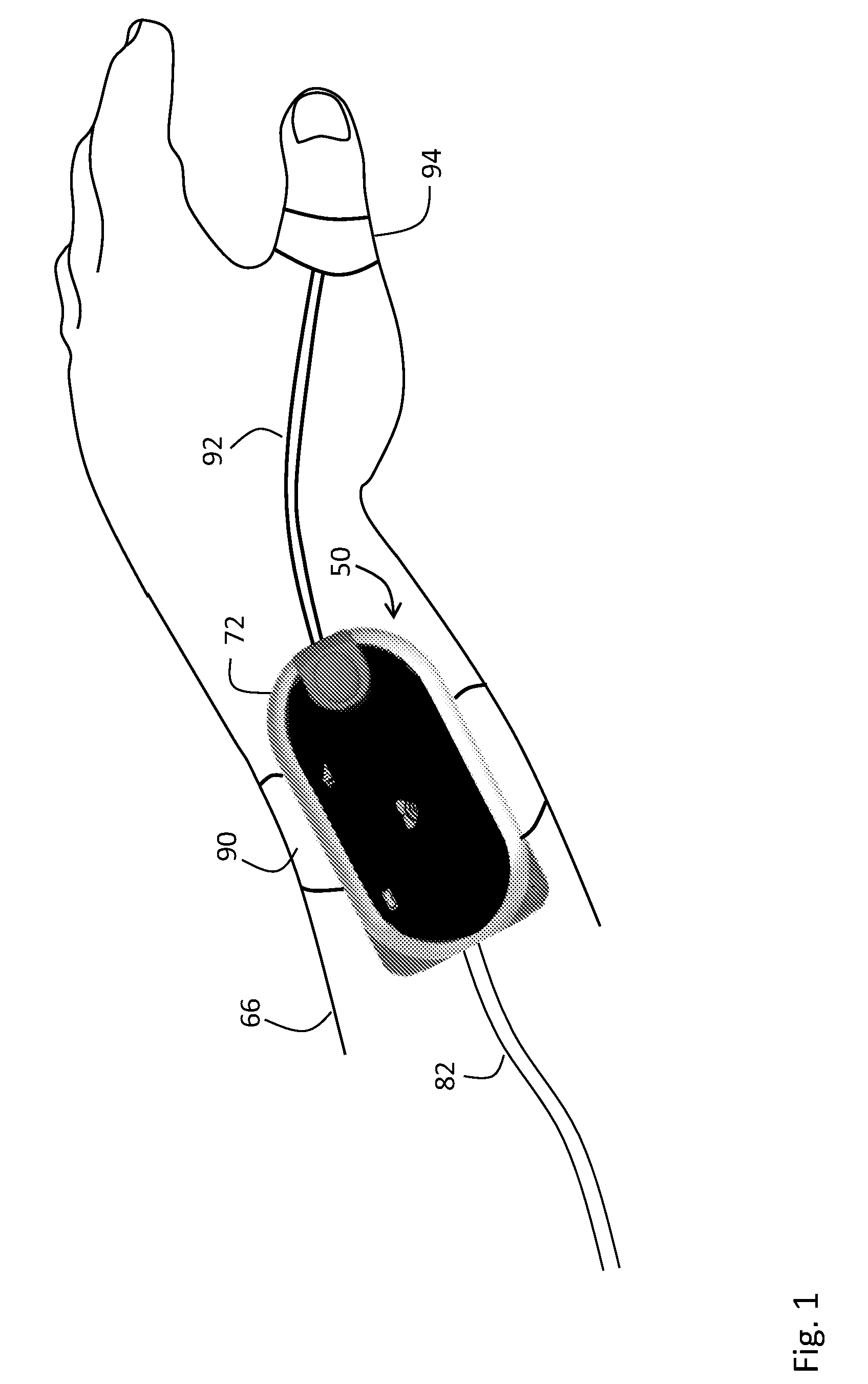
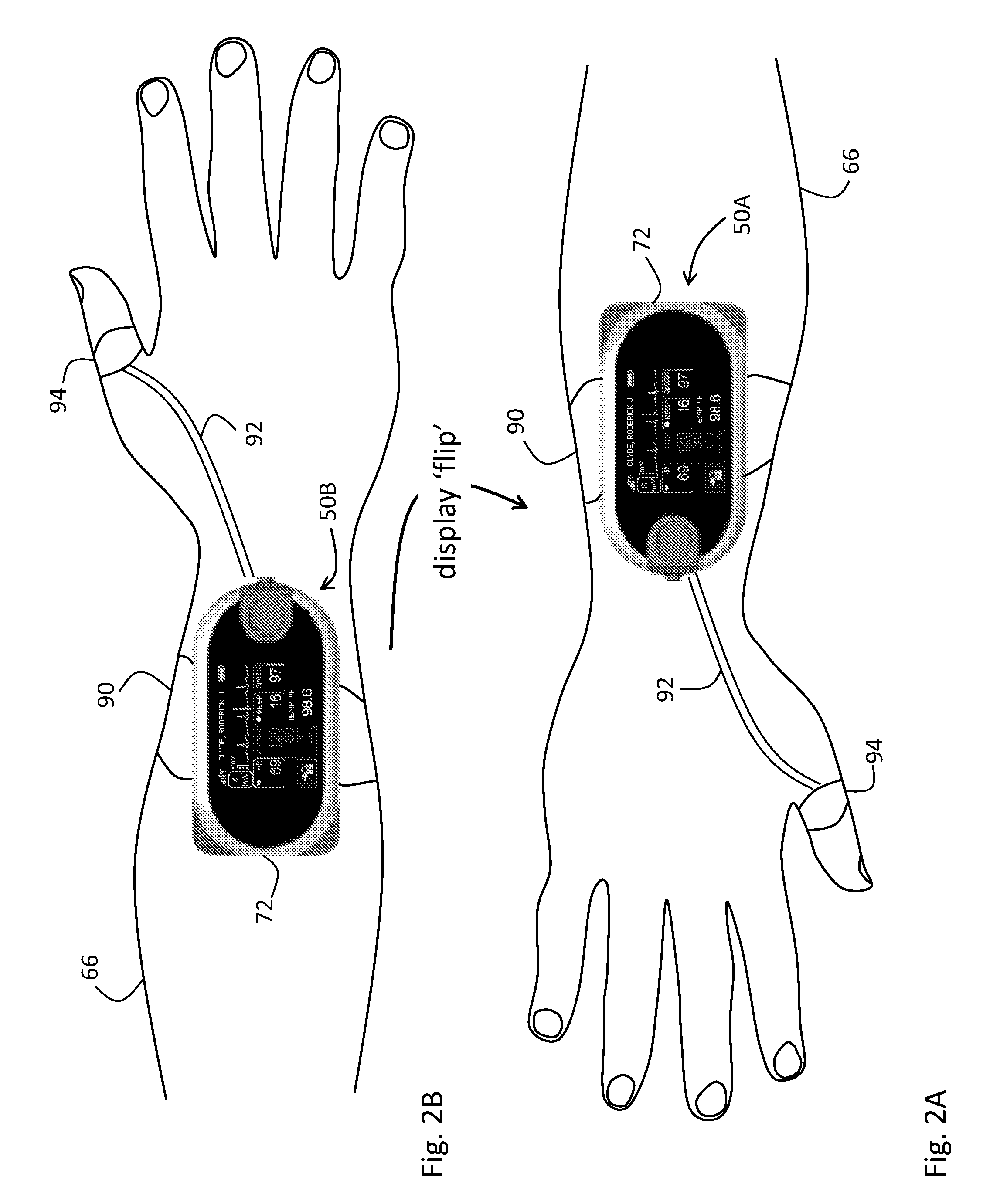
Body-worn vital sign monitor
ActiveUS20110224508A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionSensorsLocation information based serviceGraphical user interfaceDisplay device
The invention provides a body-worn vital sign monitor that measures a patient's vital signs (e.g. blood pressure, SpO2, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature) while simultaneously characterizing their activity state (e.g. resting, walking, convulsing, falling) and posture (upright, supine). The monitor processes this information to minimize corruption of the vital signs and associated alarms / alerts by motion-related artifacts. It also features a graphical user interface (GUI) rendered on a touchpanel display that facilitates a number of features to simplify and improve patient monitoring and safety in both the hospital and home.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
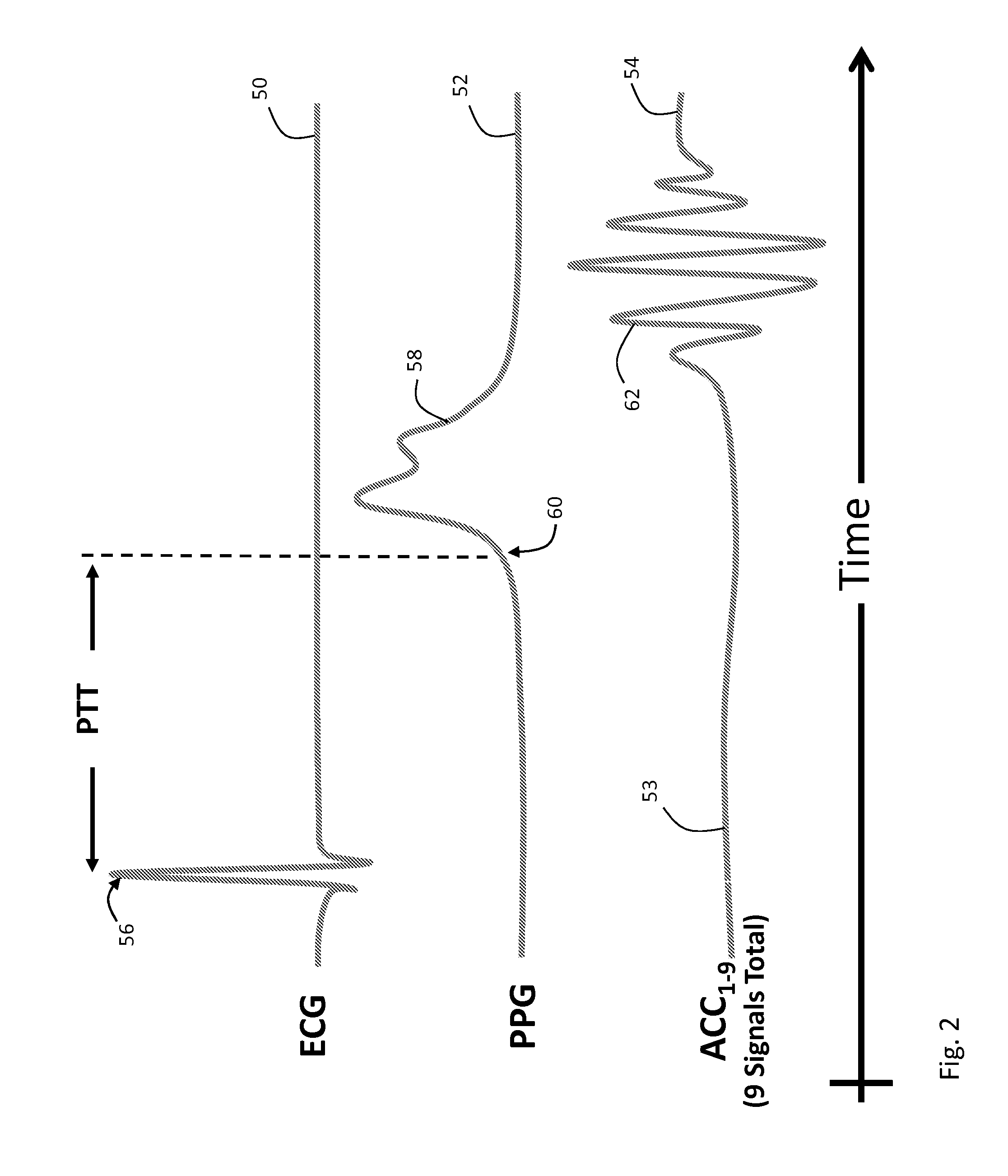
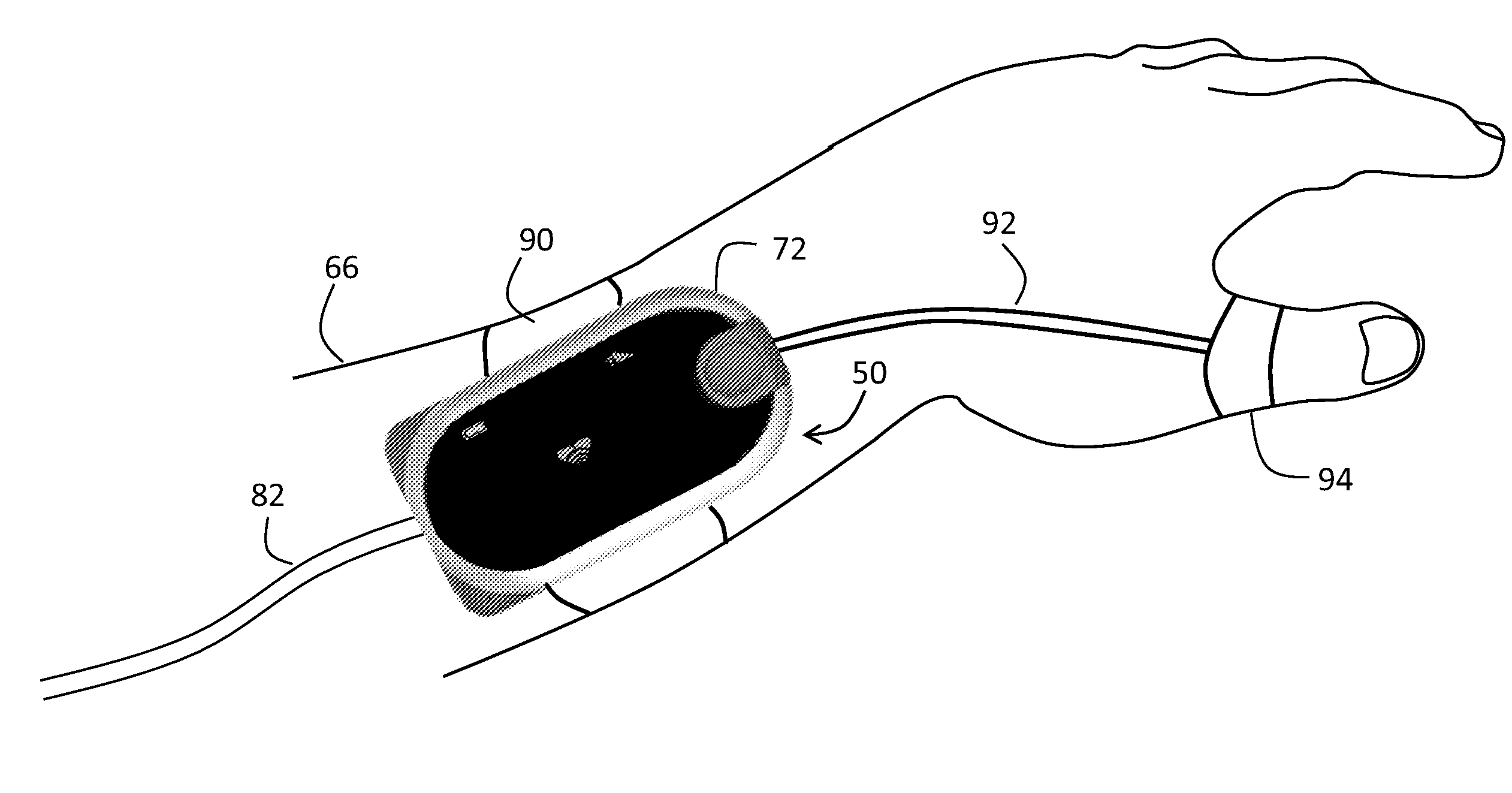
Vital sign monitor for measuring blood pressure using optical, electrical and pressure waveforms
ActiveUS20090018453A1Decreased blood flowEliminate amplitudeElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsContinuous measurementPhotodiode
A method and apparatus for continuous measurement of blood pressure, based on pulse transit time, which does not require any external calibration. This technique, referred to herein as the ‘composite technique’, is carried out with a body-won sensor that measures blood pressure and other vital signs, and wirelessly transmits them to a remote monitor. A network of disposable sensors, typically placed on the patient's right arm and chest, connect to the body sensor and measure a time-dependent electrical waveform, optical waveform, and pressure waveform. The disposable sensors typically include an armband that features an inflatable bladder coupled to a pressure sensor, at least 3 electrical sensors (e.g. electrodes), and an optical sensor (e.g., a light source and photodiode) attached to a wrist-worn band.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Bed exit and patient detection system
InactiveUS20080169931A1Accurate and reliable positioningEasy to useBedsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateMultiple inputSpeech sound
A bed exit and patient detection system especially adapted for use in the general medical or surgical floor area of a hospital or other healthcare facility as part of a vital signs monitoring and remote warning system includes a plurality of pressure sensors disposed in the patient's bed in a series of rectangular strips or zones that run laterally across the bed in the area of the patient's mid-back, hips and mid-legs, respectively. Each zone contains a plurality of sensors, arranged symmetrically about the centerline of the bed, with the corresponding sensors on opposite sides of the centerline in each zone being connected in parallel. The sensors are connected to a processor with multiple input channels that continuously monitors the sensor states to determine, from the pattern of sensor states observed, whether the patient is in bed, out of bed or is actively attempting to ext the bed at the sides or foot of the bed. At least three different sets of bed exit logic rules are available for user selection to configure the system for high, medium or low sensitivity, or bed exit privileges, for any particular patient. In some embodiments, the system also is capable of detecting when a patient is attempting to assume certain prohibited in-bed positions, such as sitting positions or slumping positions. An alarm in the form of a pre-recorded voice announcement or an alarm over a pre-existing nurse call system is provided when the sensor states are indicative of an out-of-bed or an exiting bed condition, or other prohibited in-bed positions, for a predetermined minimum period of time.
Owner:HOANA MEDICAL
Vital-signs monitor with encapsulation arrangement
A vital-signs monitoring device is disclosed. The vital-signs monitor includes a sensor that measures a physiological parameter of a patient, a circuit assembly containing vital-signs monitoring circuitry that analyzes the sensor measurements to generate vital sign signals, and a housing. The housing is designed to be worn by a patient and encapsulates the circuit assembly such that moisture and particulate matter is prevented from reaching the circuit assembly through the housing.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
Vital sign-monitoring system with multiple optical modules
The invention features a medical device that measures vital signs (e.g., blood pressure, pulse oximetry, and heart rate) from a patient using at least two optical modules. Each optical module typically features two light sources (red, infrared) and a photodetector. Both optical modules are configured to measure time-dependent signals describing the patient's flowing blood. A processor analyzes the time-dependent signals to determine the patient's vital signs. Once the vital signs are measured, a wireless transmitter in the body-worn device transmits them to an external device. Processing signals from least two optical modules compensates for motion-related artifacts and noise normally present in signals used to determine vital signs from a device featuring just a single optical module.
Owner:BANET DR MATTHEW JOHN
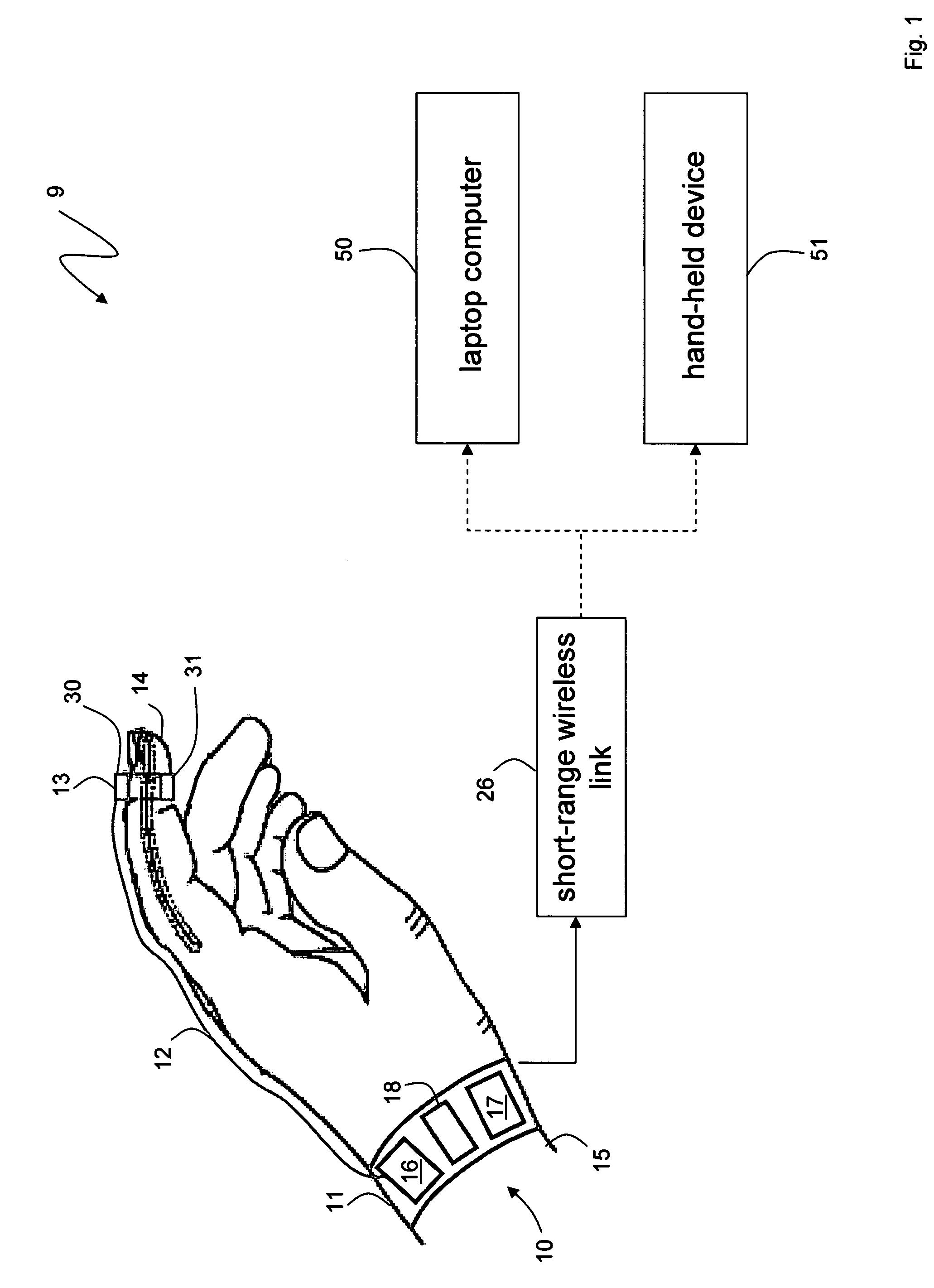
Wrist-type vital sign monitoring device and monitoring method thereof
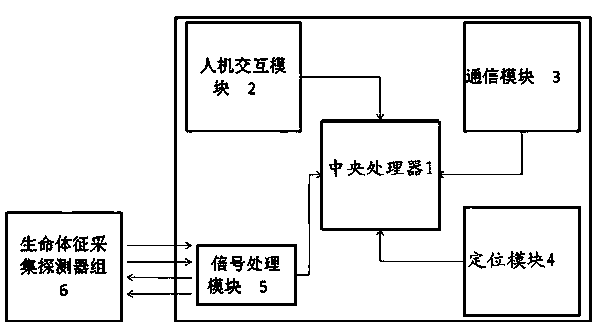
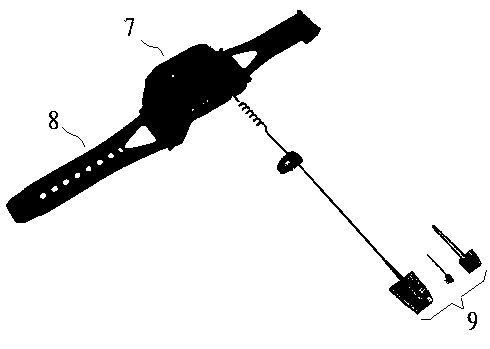
ActiveCN103417202AImprove convenienceTo achieve the practical purpose of real-time monitoringCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer moduleEngineering
The invention discloses a wrist-type vital sign monitoring device and a monitoring method thereof. A central processing unit, a human-computer interaction module, a communication module, a positioning module, a signal processing module and a vital sign collecting detector set are integrated in a wrist-type watch, and the wrist-type watch is worn on a wrist through a watchband. The vital sign collecting detector set comprises a plurality of physiological index sensors, and each physiological index sensor is arranged in the wrist-type watch in an integrated or detachably replaced mode. The portable device which has a positioning function and can monitor the physiological signal monitoring value of a user in real time is contrasted with pre-stored normal index parameters aiming at the user, and when a disease sign is found, the device sends out a prompt for the user and meanwhile sends the current related physiological signal monitoring values of the user, the physiological signal monitoring values in the recent period and the current geographical location information of the user to a service center, so that the precious time is earned for the user obtaining the timely salvation.
Owner:赵蕴博
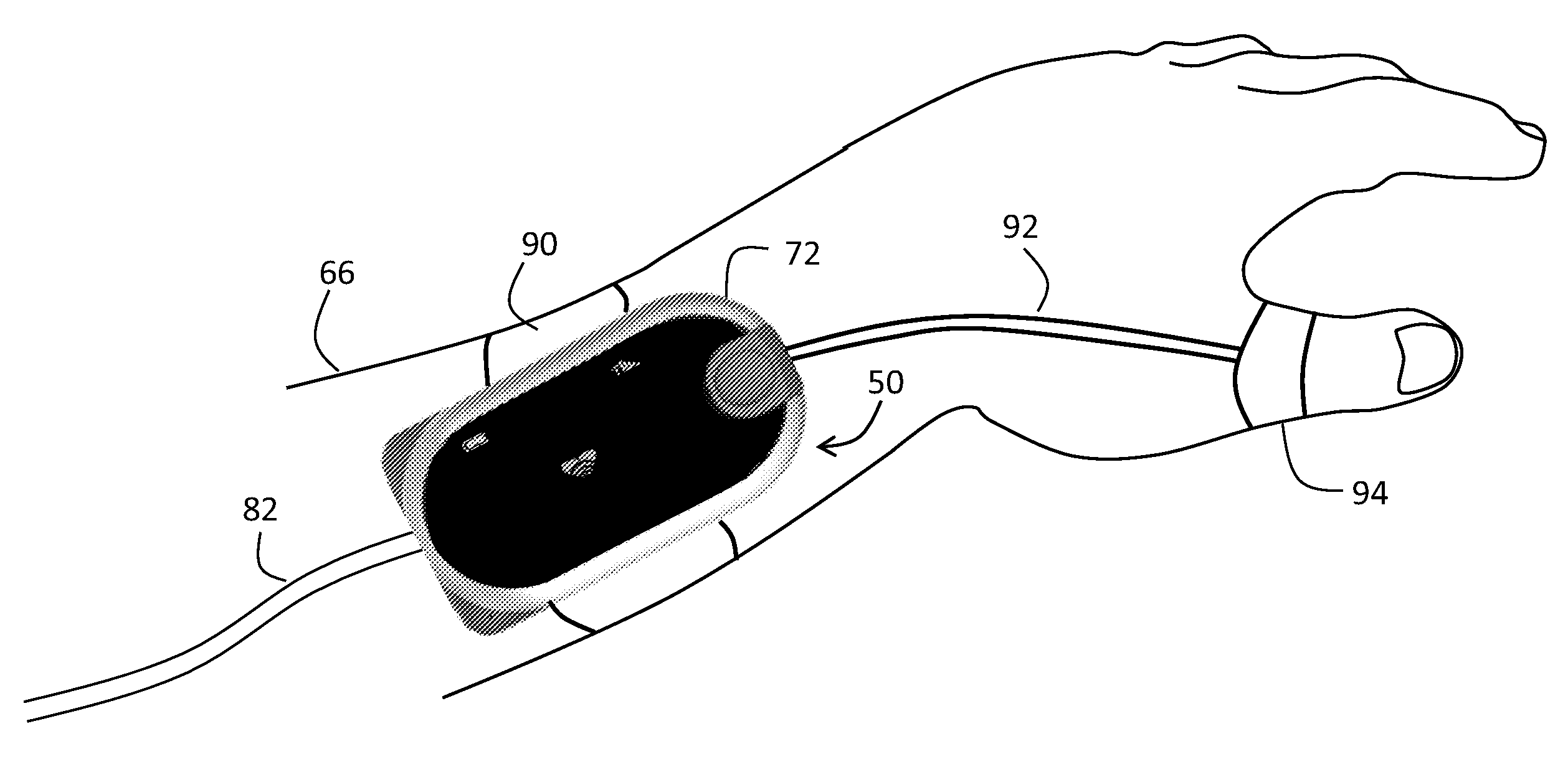
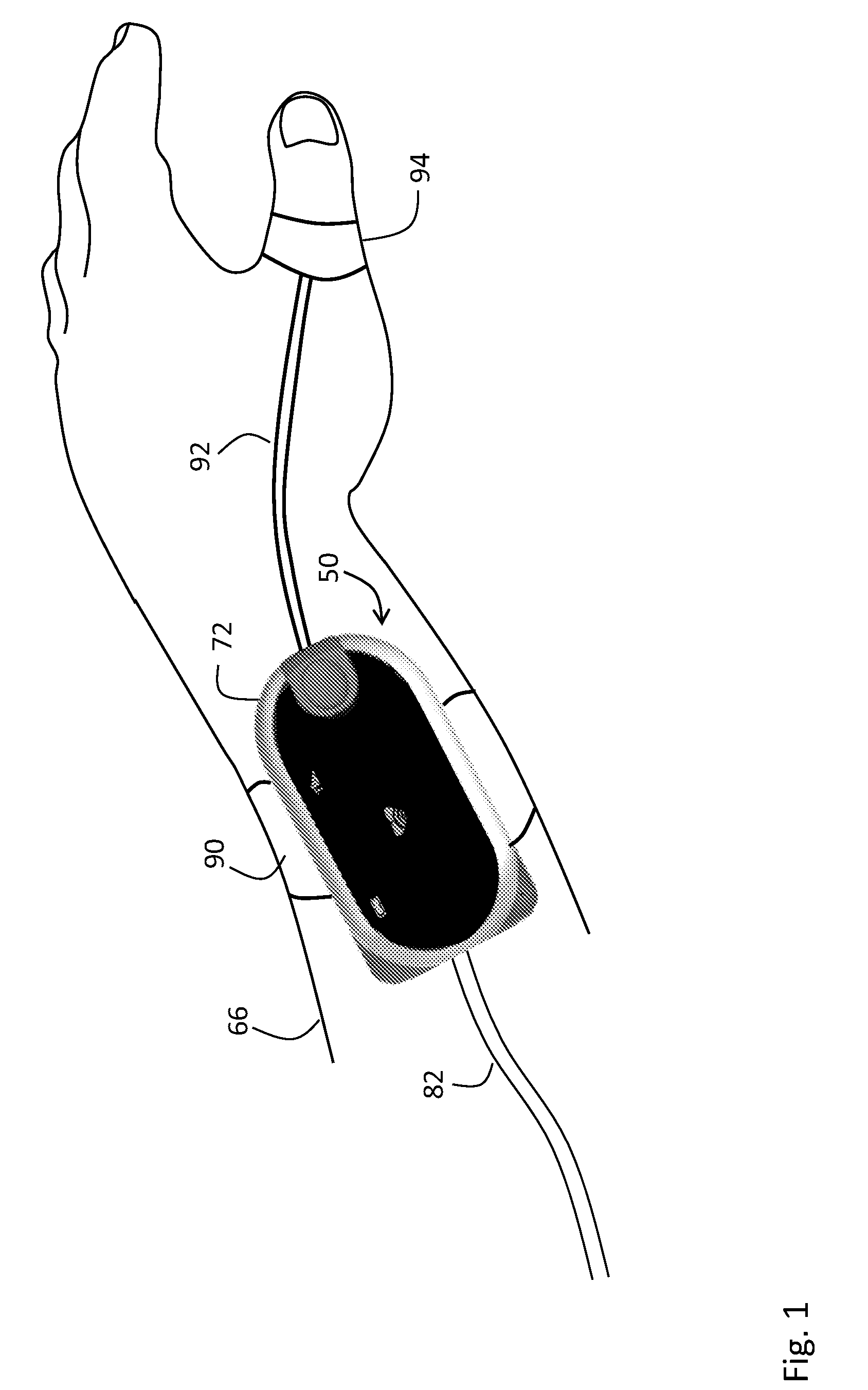
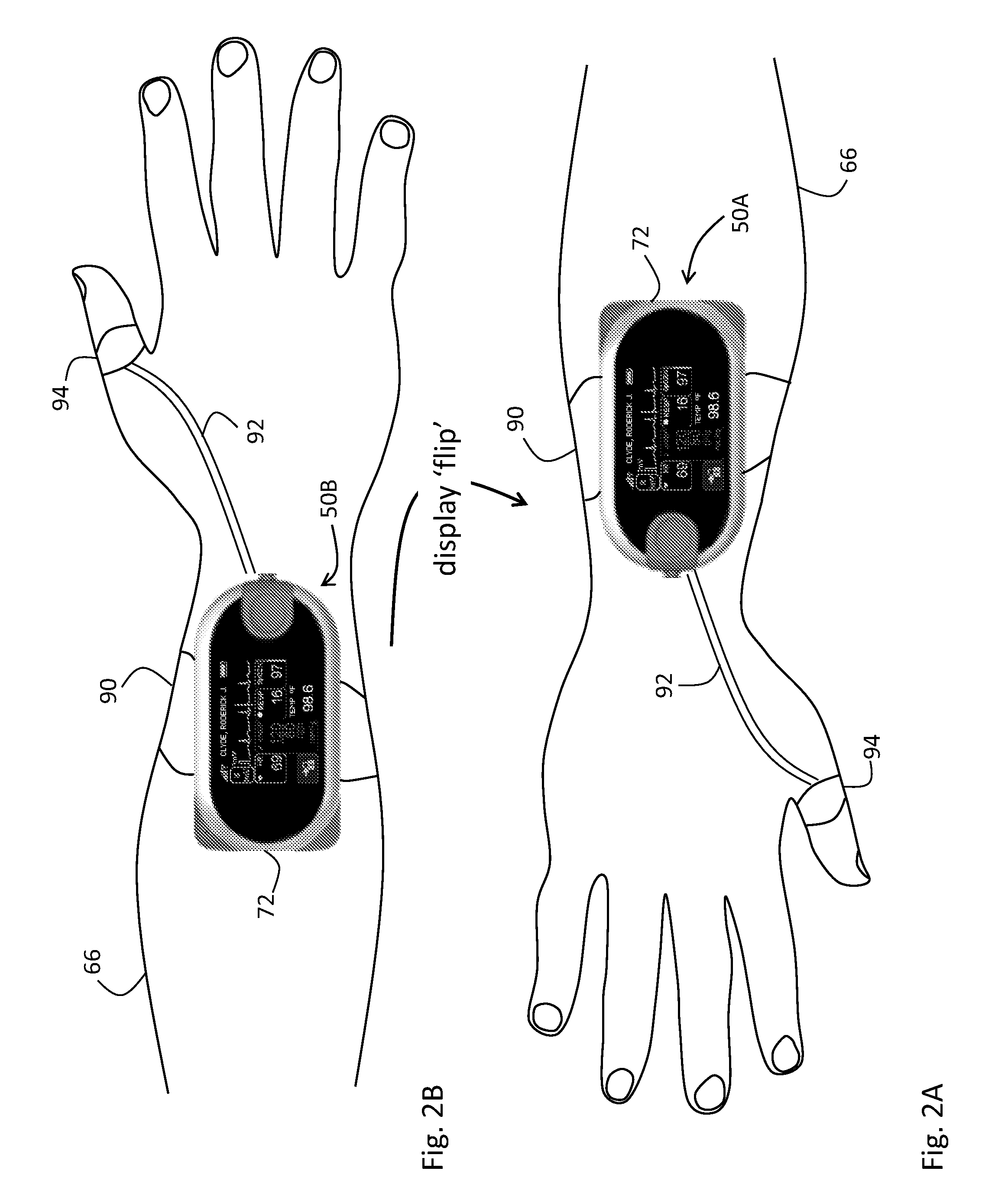
Rapidly deployable sensor design for enhanced noninvasive vital sign monitoring
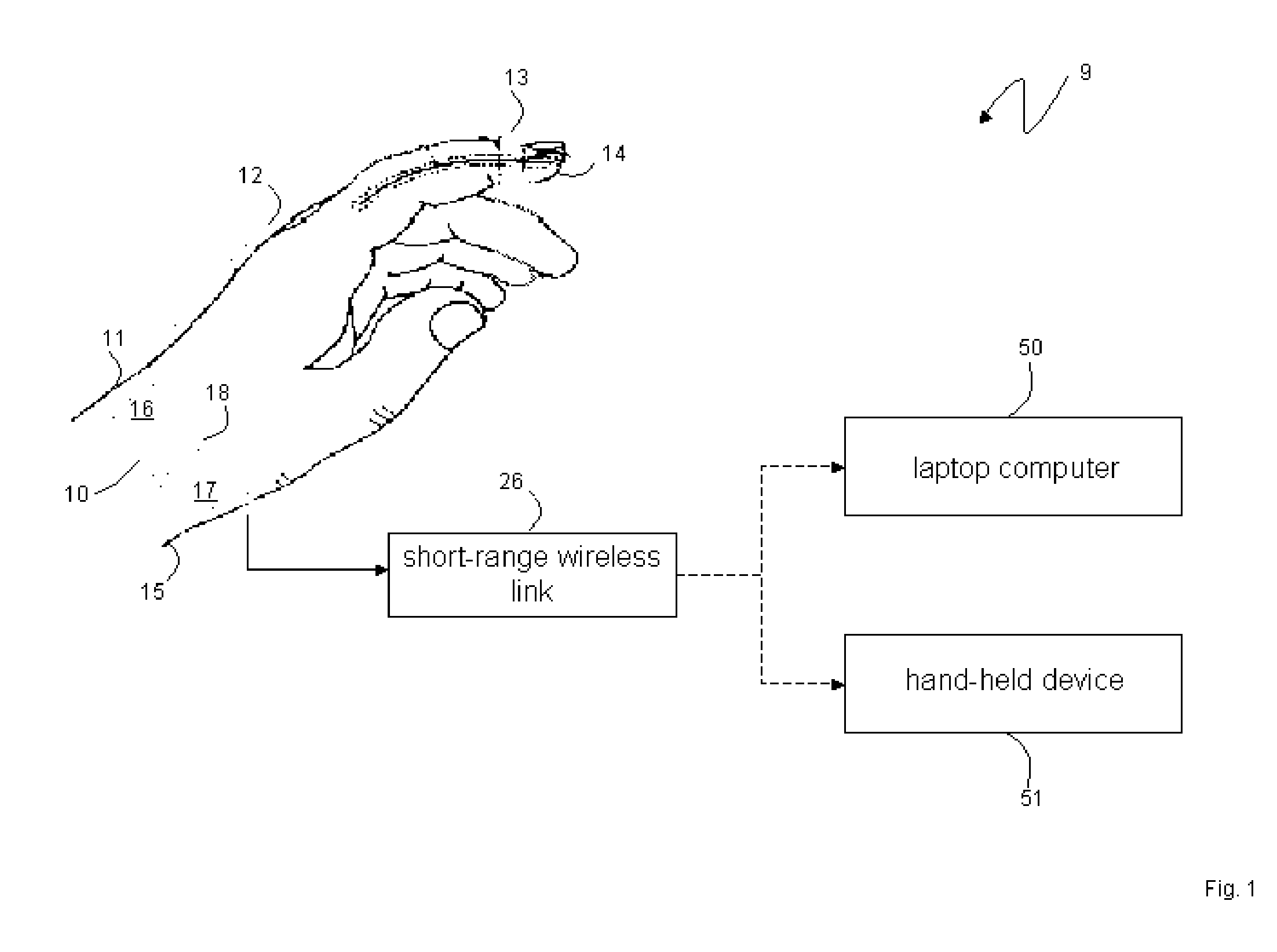
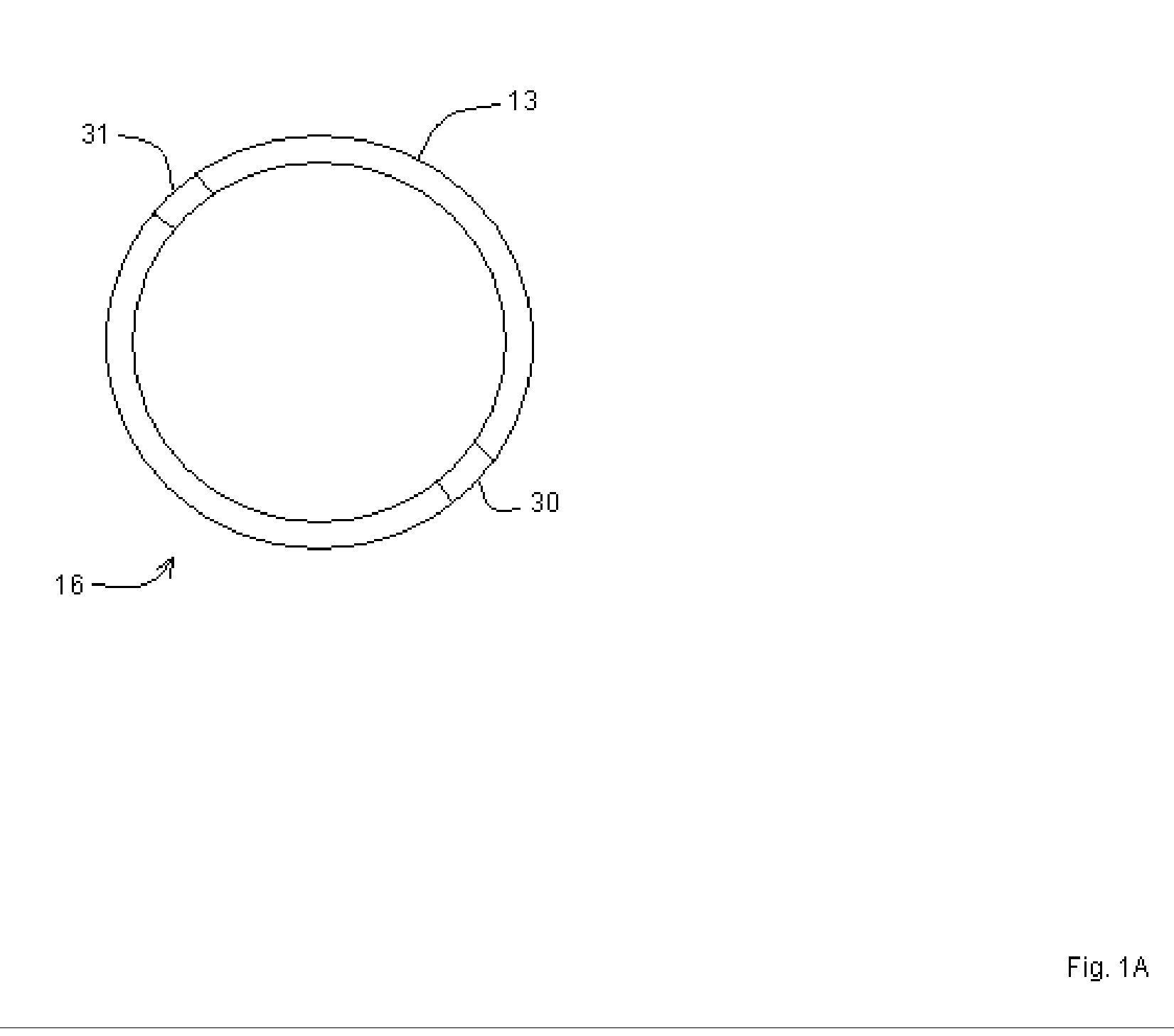
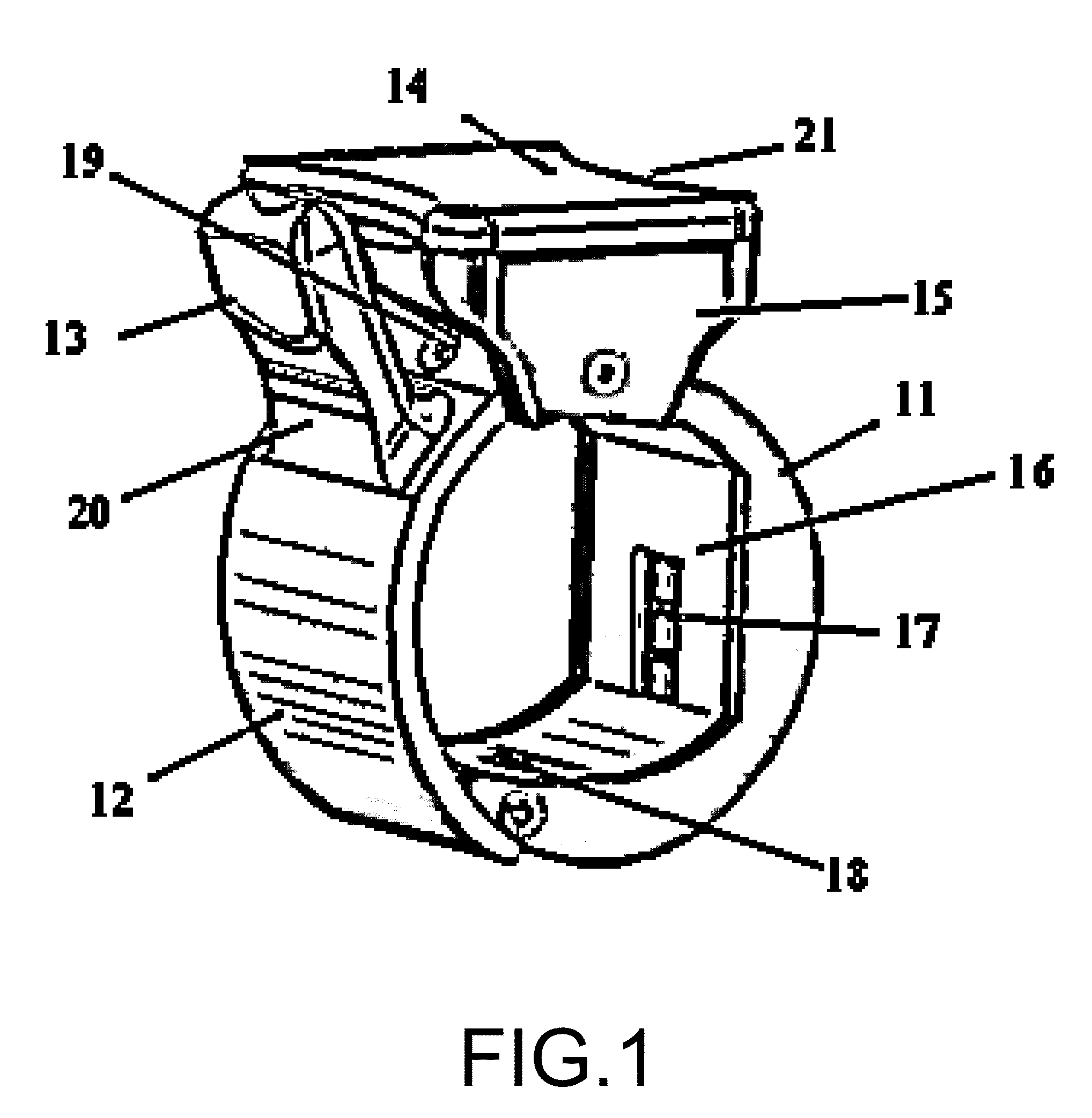
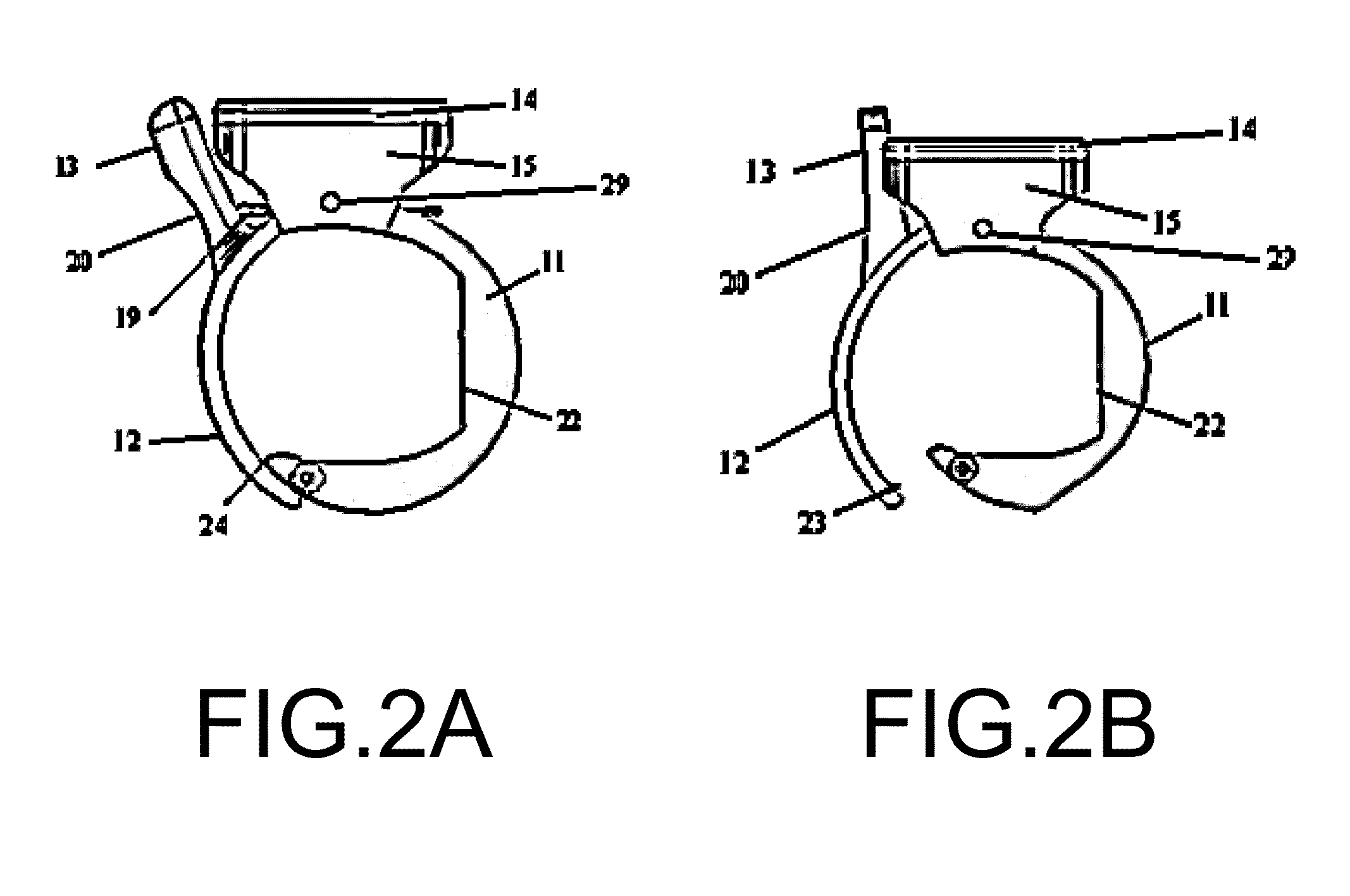
A new clip-type ring design for a rapidly-deployable triage sensor is described. The triage sensor is capable of measuring one or more parameters related to a patient's current health state. The device consists of two contoured halves which are designed to wrap around a finger like a ring. At least one of the halves is at least spring-loaded or motorized and is capable of opening or closing to allow for quick attachment to a wide range of finger shapes and sizes. The spring-loaded halves serve as both a means of securing the device to the patient as well as make it possible to measure patient health parameters such as systolic blood pressure, that are standard inputs to conventional triage methodologies. As data are acquired, the ring is able to transmit pertinent information wirelessly to medical responders for evaluation and decision making purposes.
Owner:SHALTIS DR PHILLIP ANDREW +1
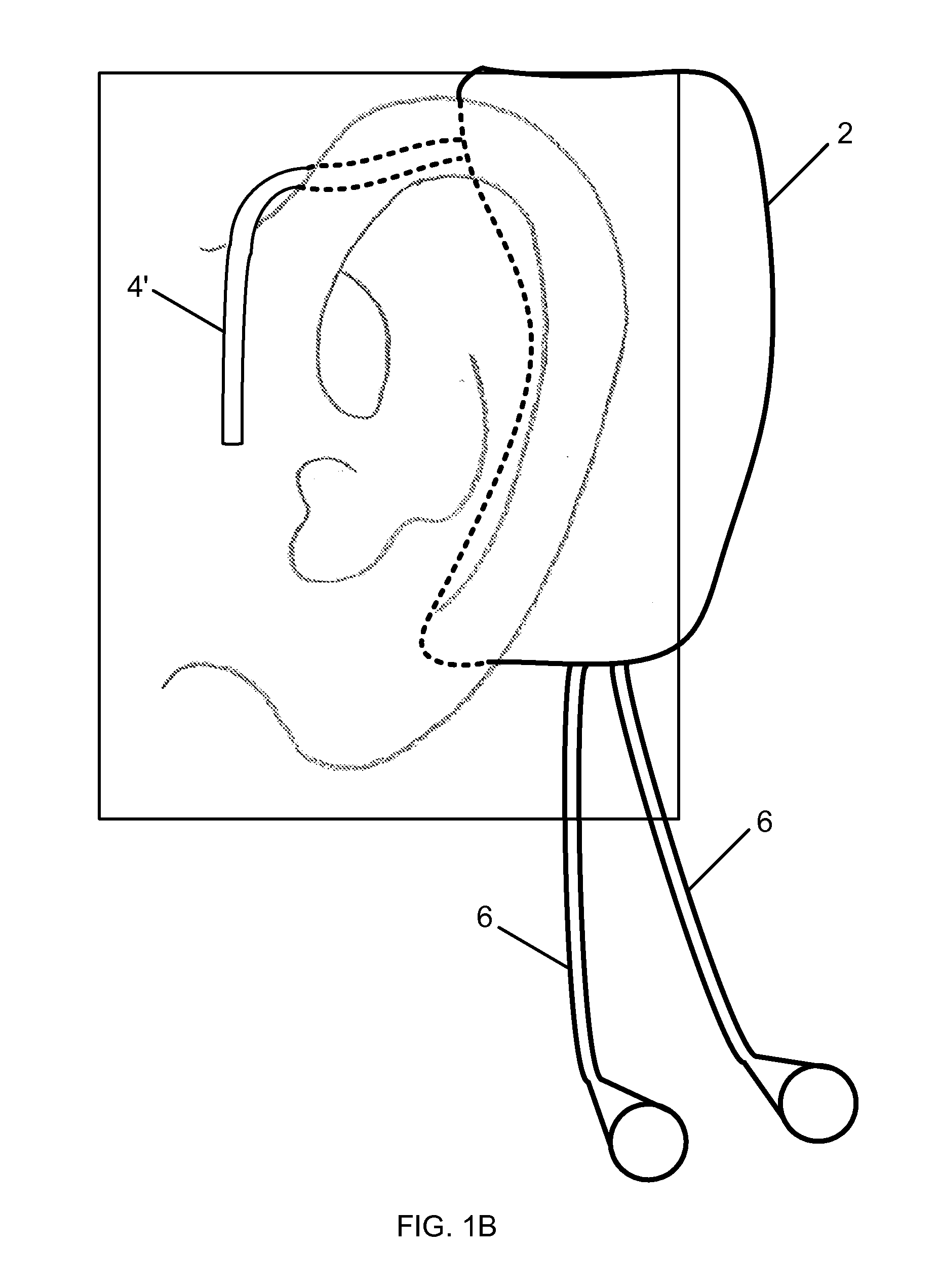
Wearable Vital Signs Monitor
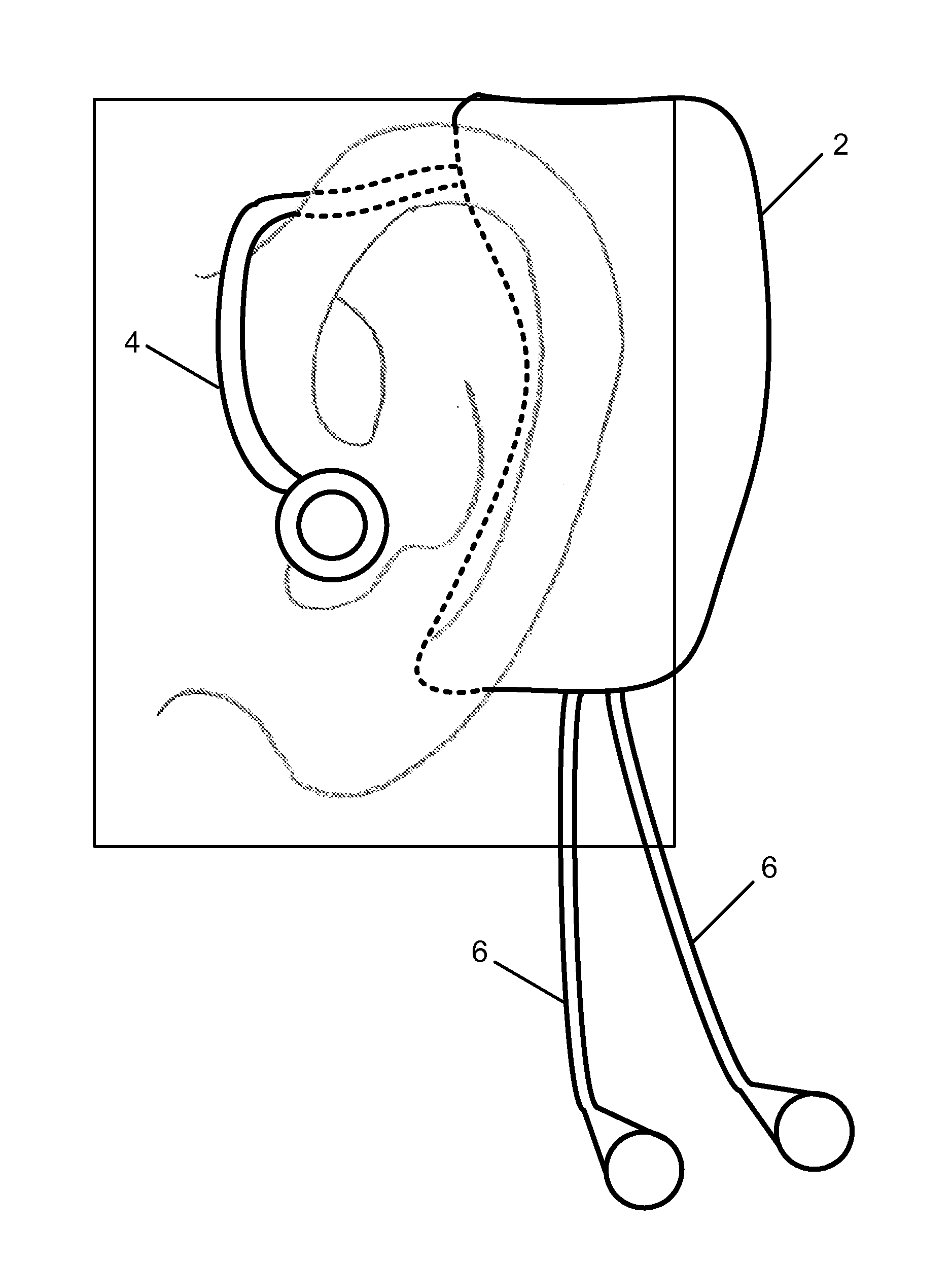
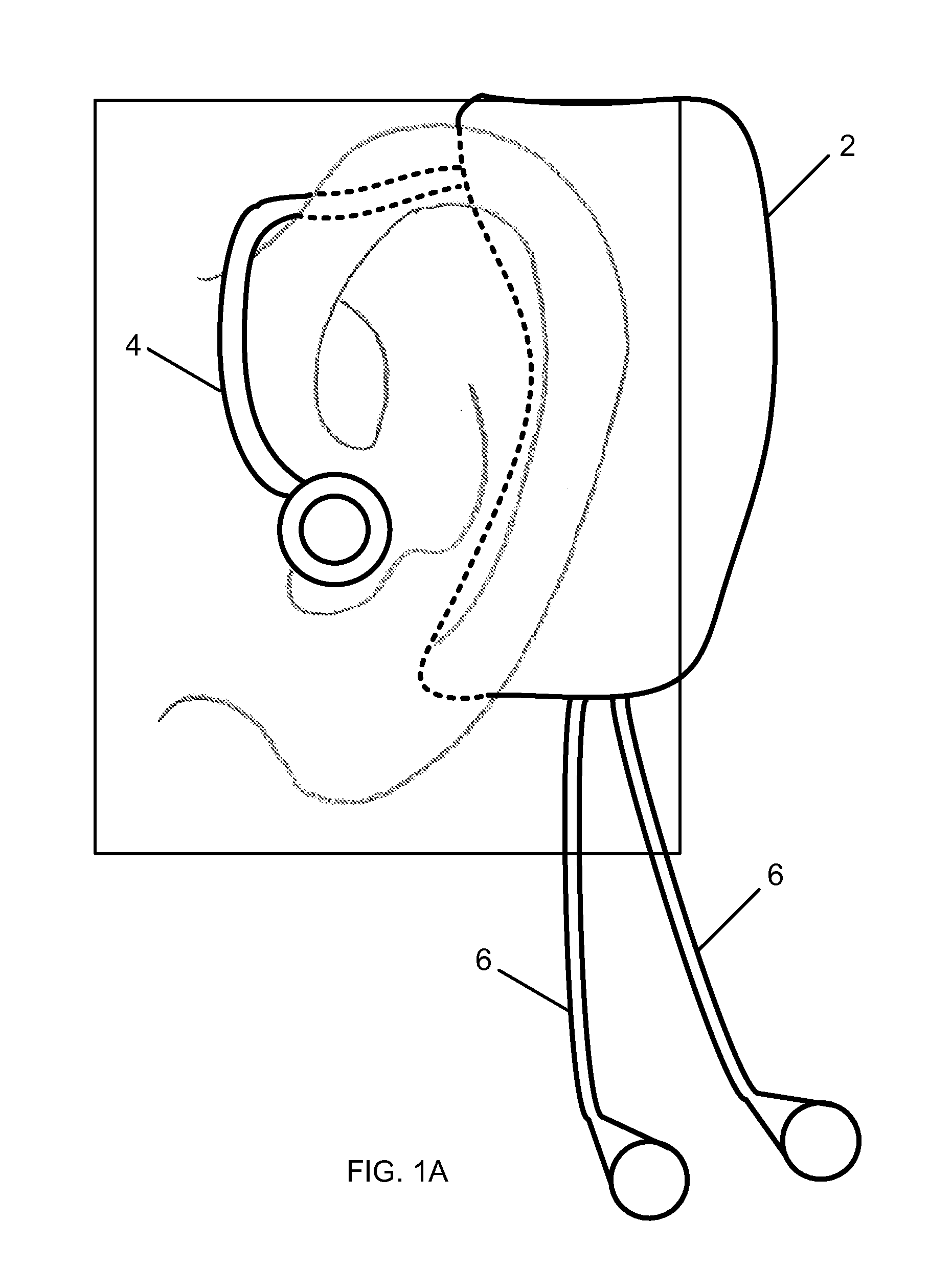
InactiveUS20120203077A1Reduce Interfering SignalsReduce power consumptionElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsAccelerometerComputer module
A method and monitor for monitoring vital signs. In one embodiment, the vital signs monitor includes a housing sized and shaped for fitting adjacent the ear of a wearer and an electronic module for measuring vital signs. The electronic module for measuring vital signs is located within the housing and includes a plurality of vital signs sensing modules in communication with a processor. The plurality of sensing modules includes at least two of the modules selected from the group of a ballistocardiographic (BCG) module, a photoplethysmographic (PPG) module, an accelerometer module, a temperature measurement module, and an electrocardiographic (ECG) module. In one embodiment, the processor calculates additional vital signs in response to signals from the plurality of vital signs sensing modules.
Owner:ROBERT F DUDLEY AS TRUSTEE OF THE QUANTTUS LIQUIDATING TRUST +1
Vital signs monitor with patient entertainment console
A system and device for monitoring at least one physiological parameter of a patient and selectively presenting entertainment media and at least one physiological parameter on a common display. The system and device comprises a patient monitor disposed to collect at least one patient physiological signal and processing at least one physiological signal to obtain at least one physiological parameter. A patient entertainment console with a processor programmed to receive at least one physiological parameter and programmed to control the patient entertainment console to selectively present entertainment media and at least one physiological parameter upon receiving a signal from an override means.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for reducing false alarms and false negatives based on motion and position sensing
InactiveUS20120029300A1Reduce and eliminate false positiveAvoid unnecessary trips or other actionsTelemedicineMedical automated diagnosisAccelerometerComputer science
Systems and methods of reducing false alarms associated with vital-sign monitoring are disclosed. One or more vital-sign readings of a patient are received. One or more acceleration readings from an accelerometer attached to the patient are received. At least one of motion and position of the patient are determined based at least in part on the one or more acceleration readings. An alarm condition determination procedure is modified if at least one of the motion and the position satisfies a predefined condition.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
Body-worn vital sign monitor
ActiveUS20110224557A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterGraphicsGraphical user interface
The invention provides a body-worn vital sign monitor that measures a patient's vital signs (e.g. blood pressure, SpO2, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature) while simultaneously characterizing their activity state (e.g. resting, walking, convulsing, falling) and posture (upright, supine). The monitor processes this information to minimize corruption of the vital signs and associated alarms / alerts by motion-related artifacts. It also features a graphical user interface (GUI) rendered on a touchpanel display that facilitates a number of features to simplify and improve patient monitoring and safety in both the hospital and home.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
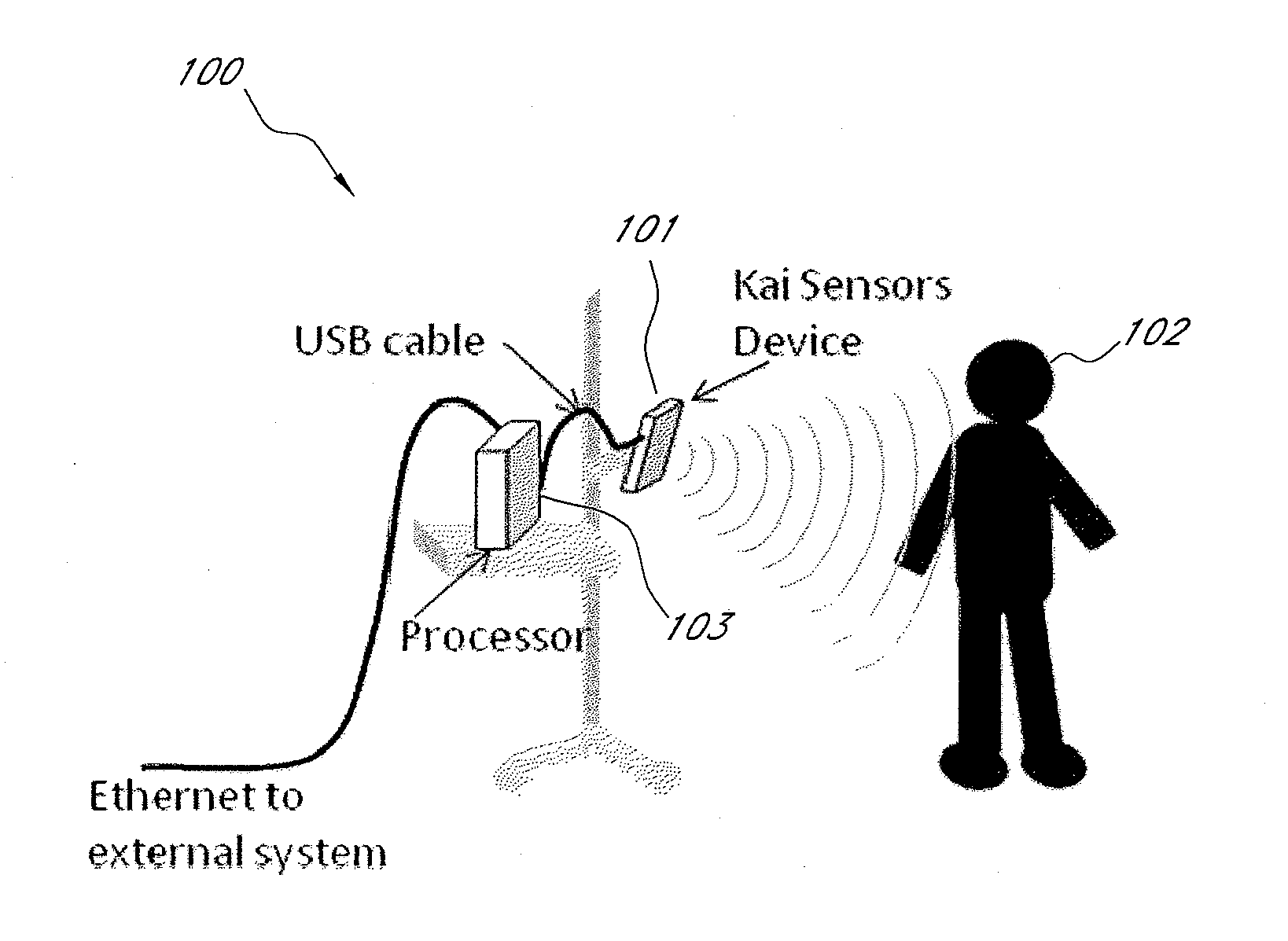
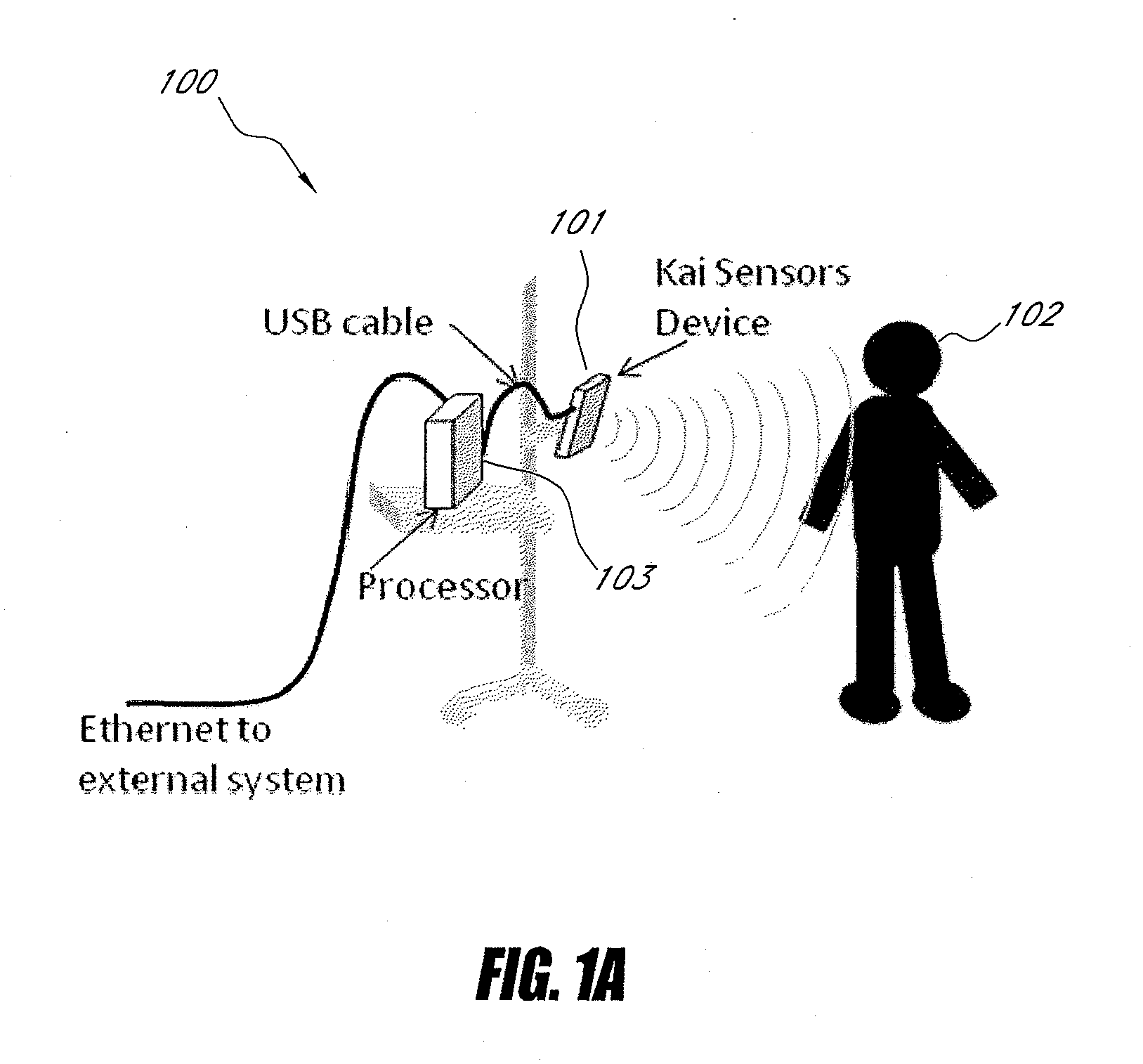
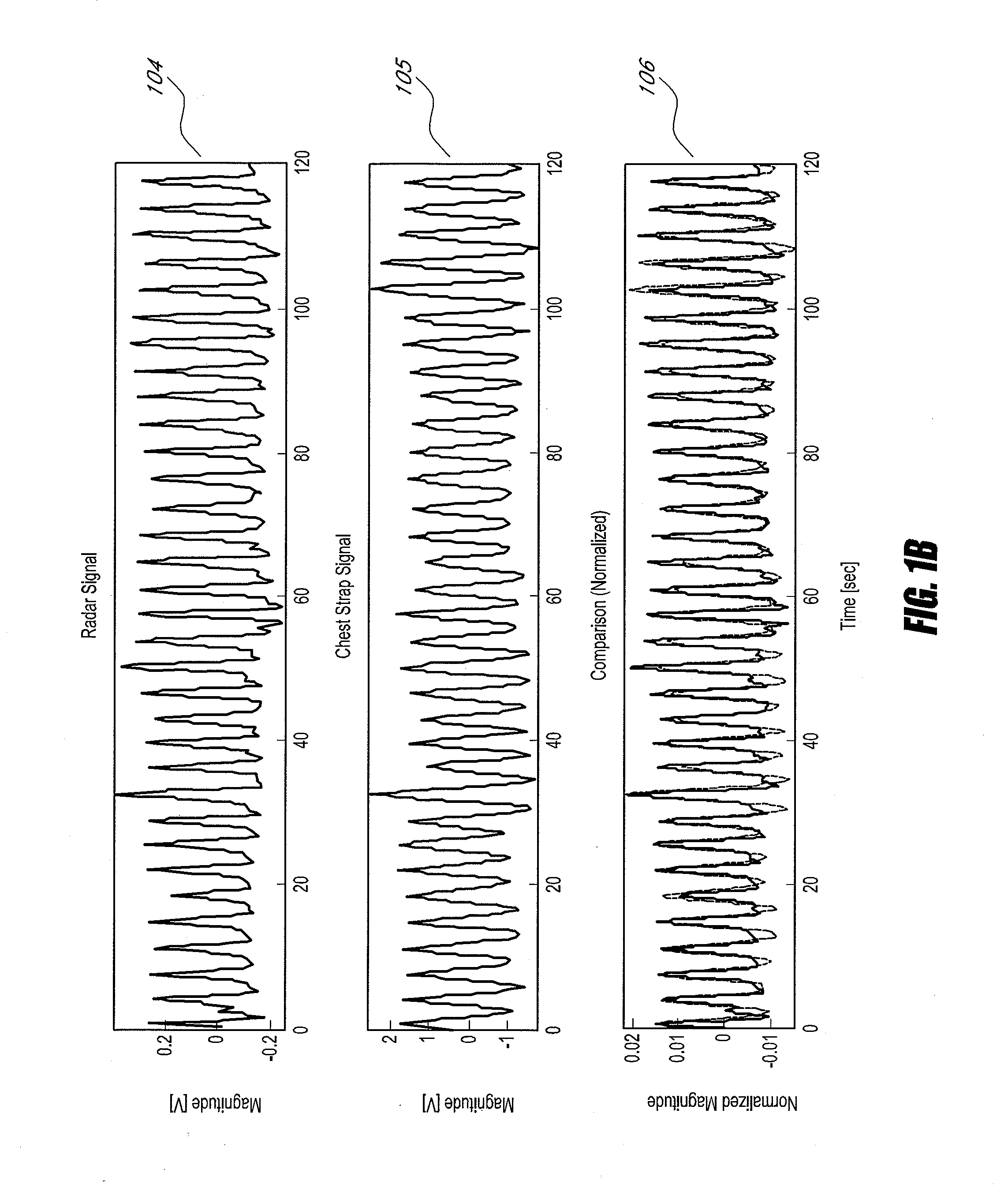
Systems and methods for non-contact multiparameter vital signs monitoring, apnea therapy, sway cancellation, patient identification, and subject monitoring sensors
InactiveUS20120022348A1Minimize signal powerElectrotherapyCatheterElectromagnetic radiationDigitization
Aspects of the of the disclosure relate to a non-contact physiological motion sensor and a monitor device that can incorporate use of the Doppler effect. A continuous wave of electromagnetic radiation can be transmitted toward one or more subjects and the Doppler-shifted received signals can be digitized and / or processed subsequently to extract information related to the cardiopulmonary motion in the one or more subjects. The extracted information can be used, for example, to determine apneic events and / or to provide apnea therapy to subjects when used in conjunction with an apnea therapy device. In addition, methods of use are disclosed for sway cancellation, realization of cessation of breath, integration with multi-parameter patient monitoring systems, providing positive providing patient identification, or any combination thereof.
Owner:KAI MEDICAL
Body-worn vital sign monitor
InactiveUS20110224556A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterGraphicsGraphical user interface
The invention provides a body-worn vital sign monitor that measures a patient's vital signs (e.g. blood pressure, SpO2, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature) while simultaneously characterizing their activity state (e.g. resting, walking, convulsing, falling) and posture (upright, supine). The monitor processes this information to minimize corruption of the vital signs and associated alarms / alerts by motion-related artifacts. It also features a graphical user interface (GUI) rendered on a touchpanel display that facilitates a number of features to simplify and improve patient monitoring and safety in both the hospital and home.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
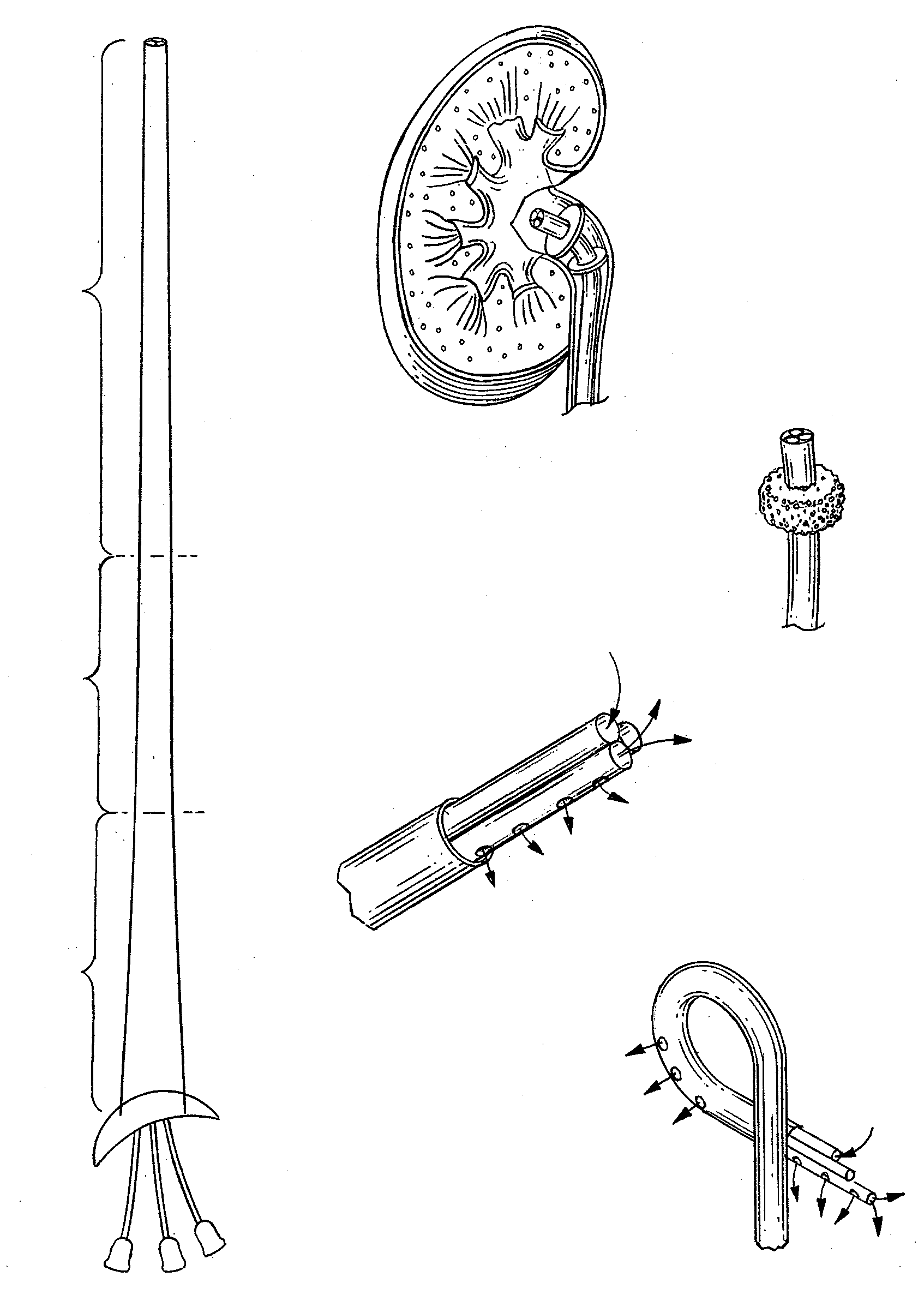
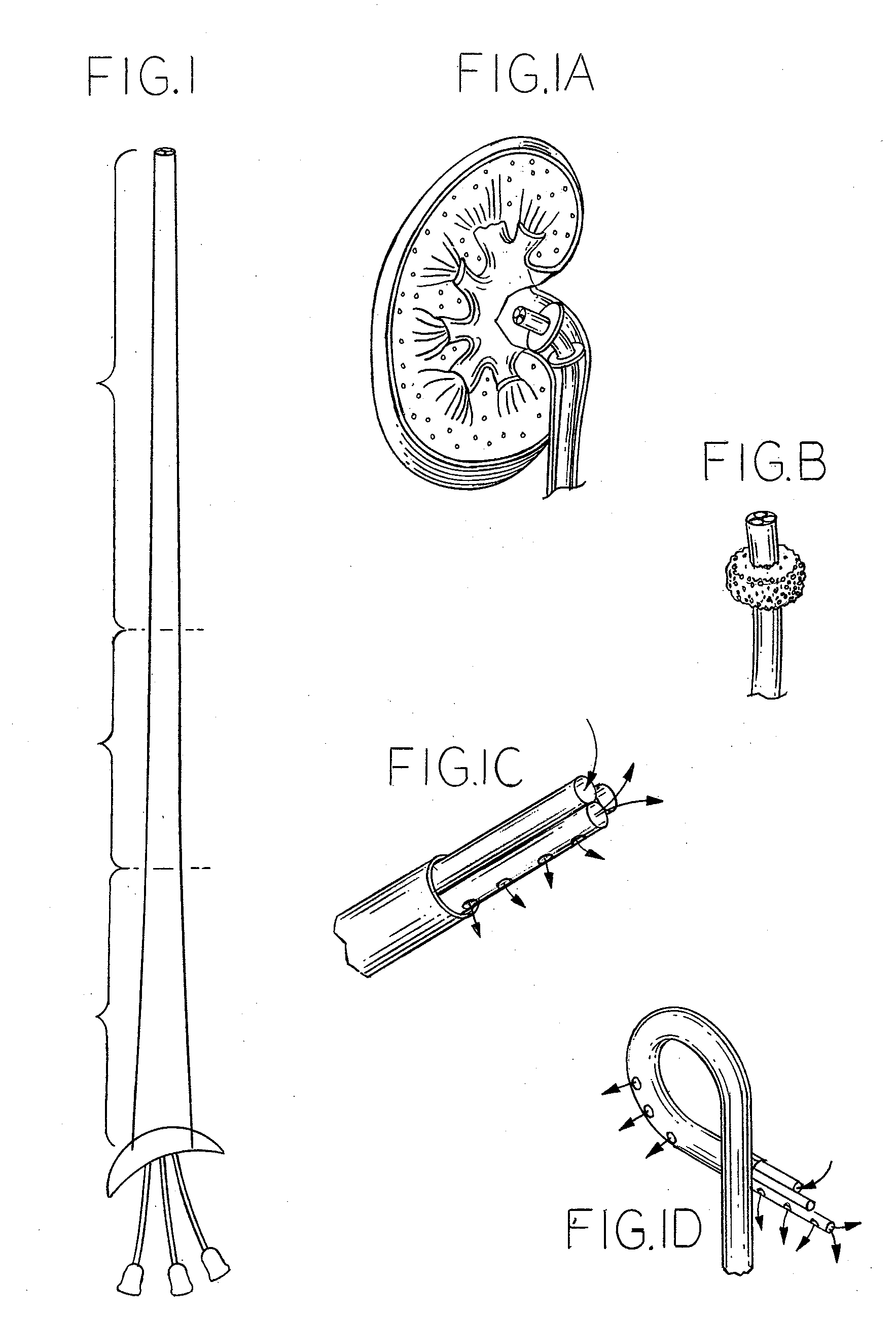
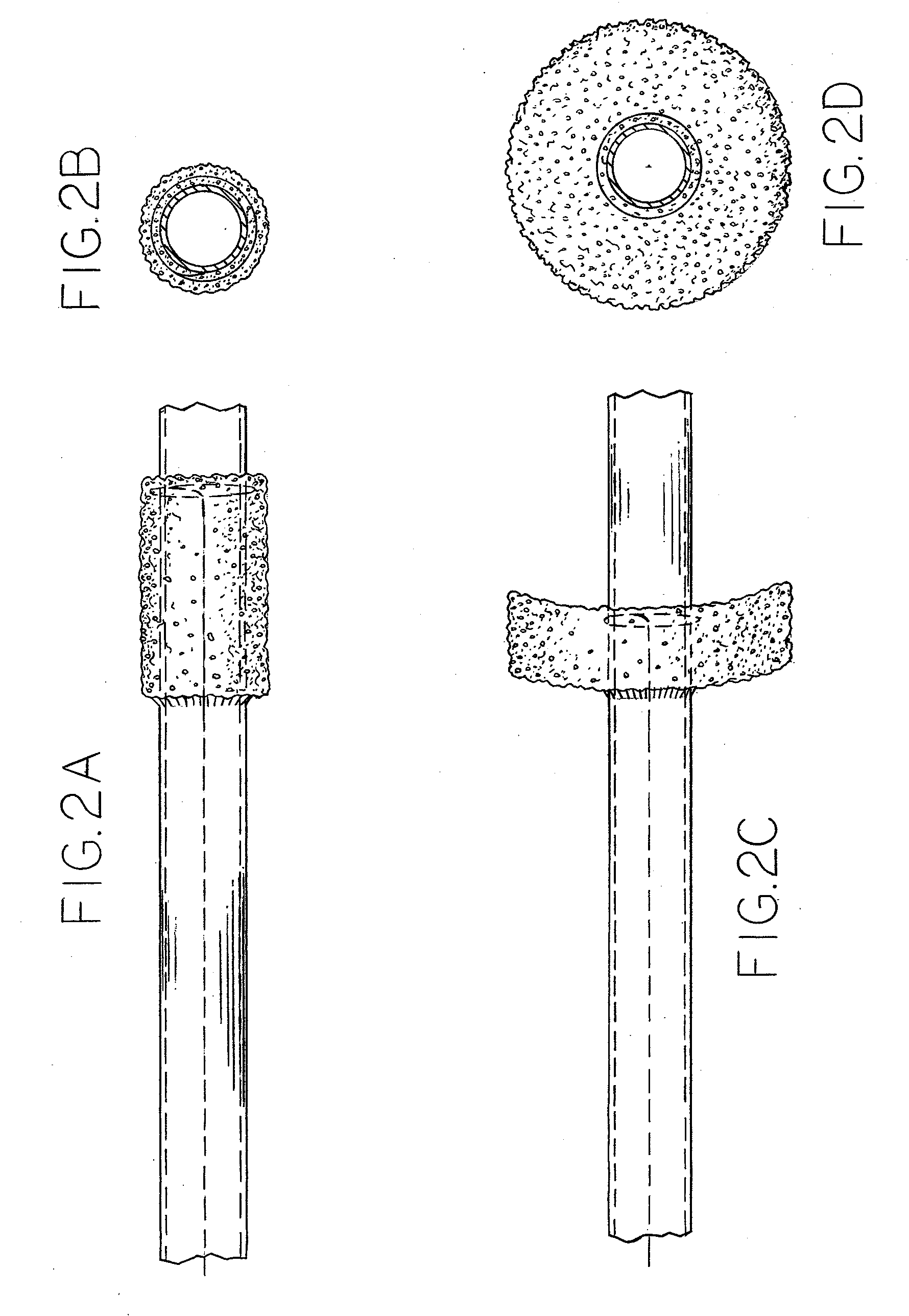
Process and System For Systematic Oxygenation and Renal Preservation During Retrograde Perfusion of the Ischemic Kidney
A delivery system to provide end organ oxygenation and even systematic oxygenation in the face of ischemic result. The deliver system including a retrograde oxygenation and perfusion stent. The stent employing at least two and possibly more channels to allow flow of the perfusate from the device to the renal pelvis then to a back out to a collection apparatus. The stent may include various vital sign monitors, such as a renal pressure monitor, temperature monitor, and even an oxygenation monitor. The stent may include an anchoring device to allow the stent to be anchored into the renal pelvis in a temporary way during the retrograde oxygenation process.
Owner:HUMPHREYS MITCHELL R
System and method for disease management
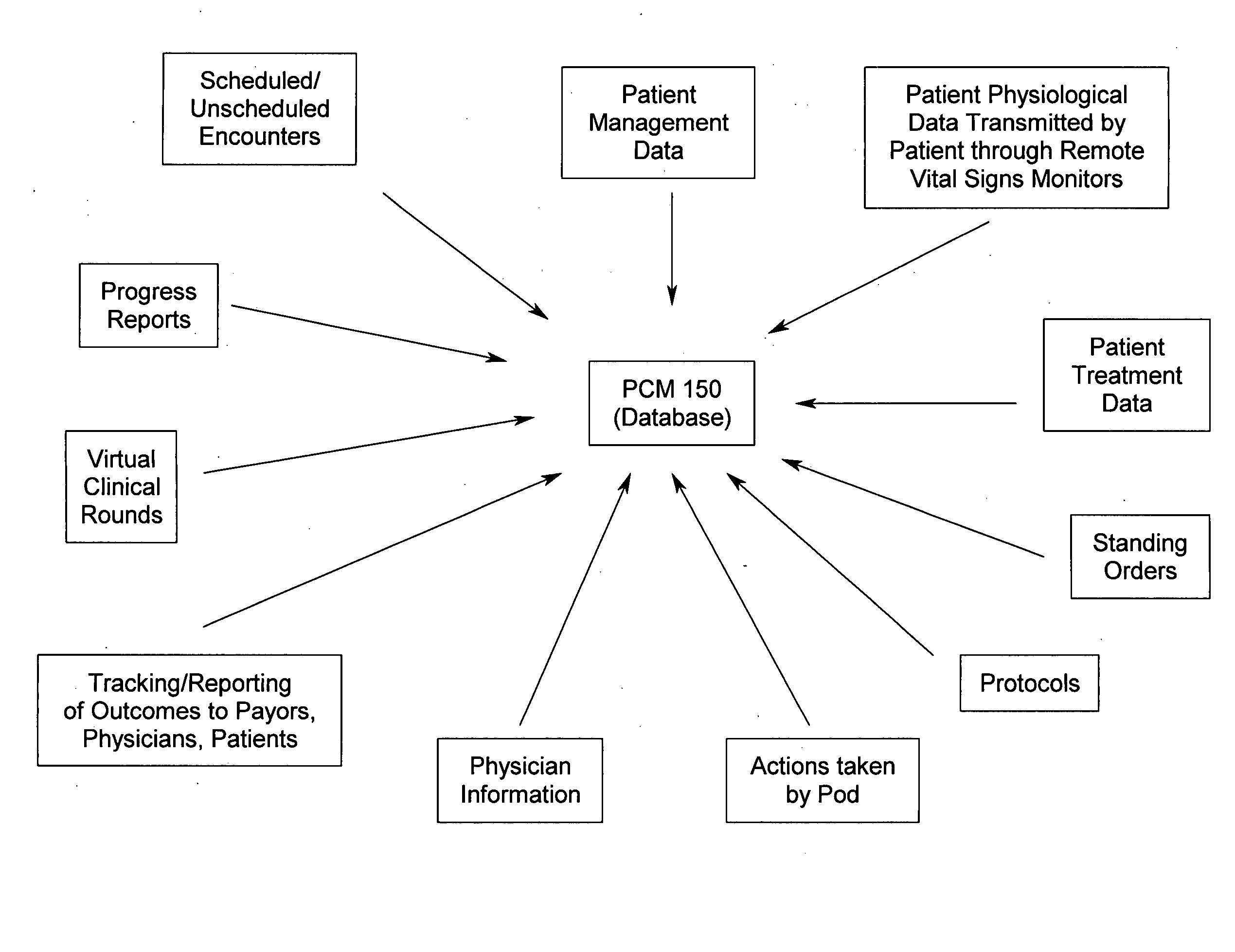
InactiveUS20050197545A1Increasing overall healthcare inefficiencies and financial lossImprove the quality of lifePhysical therapies and activitiesSurgeryIllness managementVital sign monitoring
A system and method for disease management that effectively eliminates unnecessary layers and / or intermediaries within the healthcare management system by enabling a disease management entity to operate as an extension of a physician's office, and thus, work closely with the patients and the patient's physicians to effectively empower patients towards self-care and a higher level of awareness and understanding of their disease process and treatment. The present system and method utilizes a team of highly trained healthcare professionals and technicians working together with patients and physicians, wherein remote vital sign monitoring equipment, software systems, and standing orders and treatment protocols, are utilized to effectively manage patients with chronic conditions. Additionally, as the disease management entity operates as an extension of a physician's office, the disease management entity is able to coordinate with a payor through the physician's office, and thus provide the payor with positive financial outcomes.
Owner:HOGGLE JOHN
Body-worn vital sign monitor
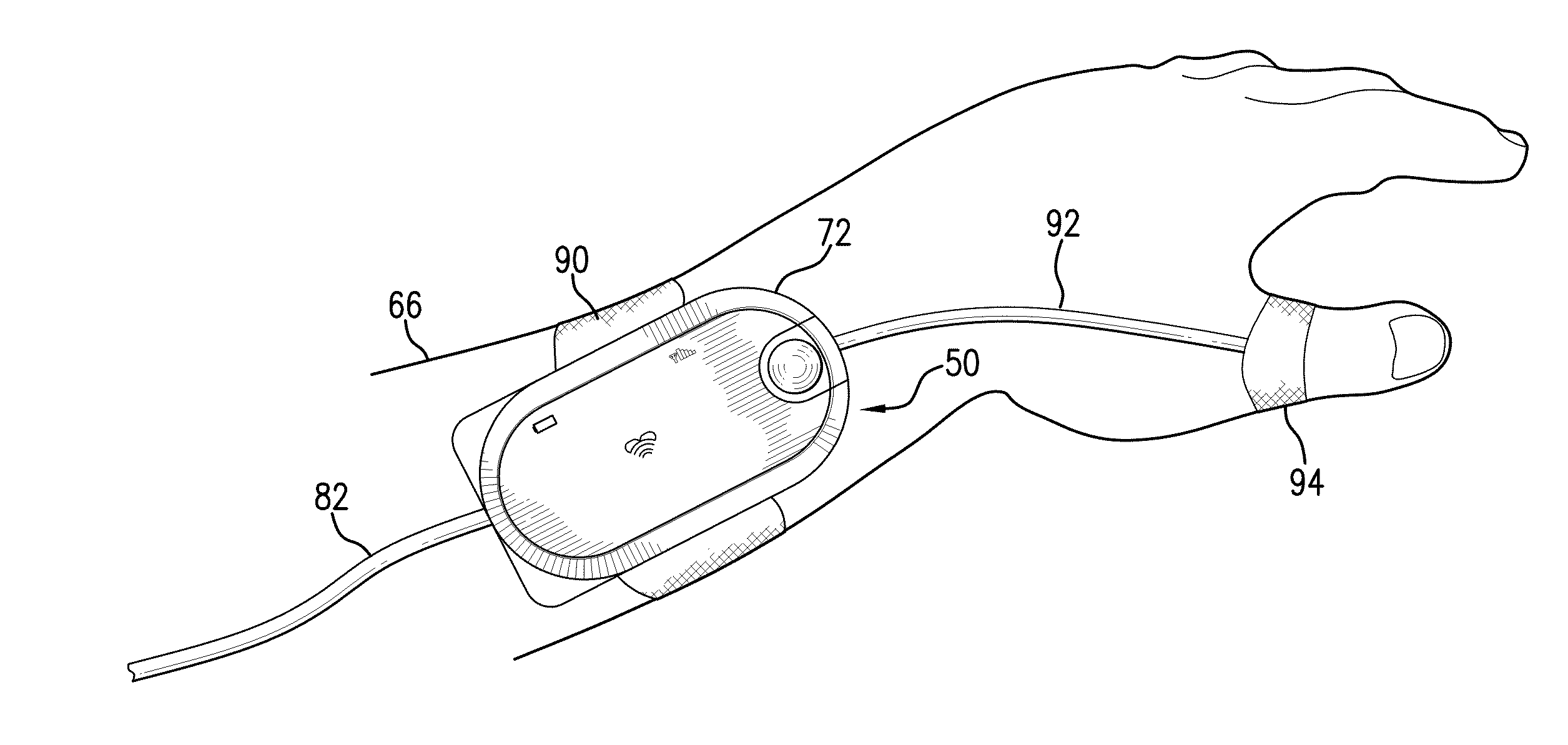
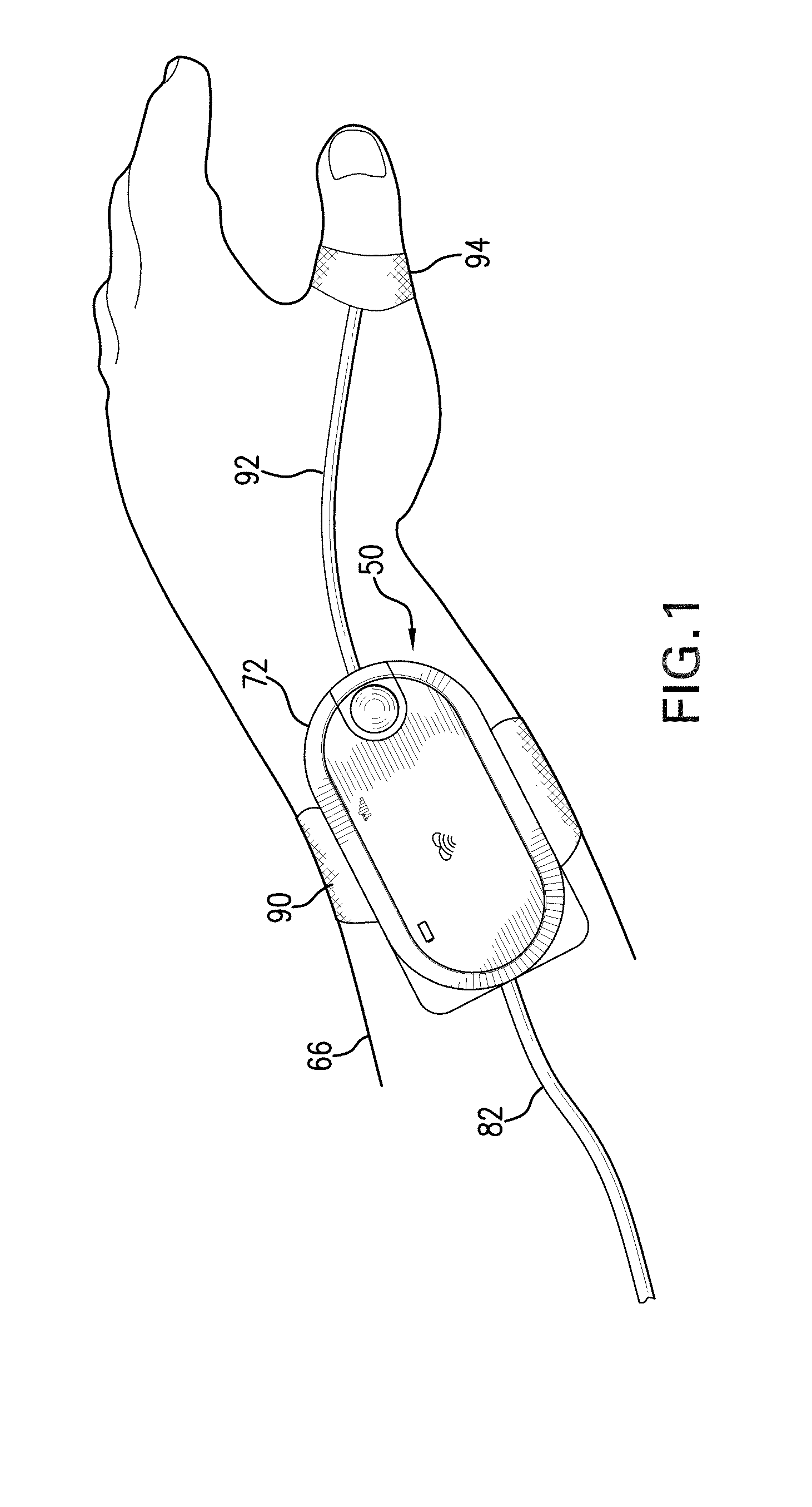
ActiveUS8527038B2Improve securityMinimize corruptionRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDigital dataTransceiver
The invention provides a body-worn monitor featuring a processing system that receives a digital data stream from an ECG system. A cable houses the ECG system at one terminal end, and plugs into the processing system, which is worn on the patient's wrist like a conventional wristwatch. The ECG system features: i) a connecting portion connected to multiple electrodes worn by the patient; ii) a differential amplifier that receives electrical signals from each electrode and process them to generate an analog ECG waveform; iii) an analog-to-digital converter that converts the analog ECG waveform into a digital ECG waveform; and iv) a transceiver that transmits a digital data stream representing the digital ECG waveform (or information calculated from the waveform) through the cable and to the processing system. Different ECG systems, typically featuring three, five, or twelve electrodes, can be interchanged with one another.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Vital sign monitor system and method
A portable vital sign monitor is provided which has a palm vital sign monitor unit carried by the patient, the unit comprising an optical probe positioned in the palm of the patient which measures at least one vital sign including SpO2 and pulse rate but not exclusively and only those vital signs. The detected vital signs are stored in memory and transmitted by wireless inter-connection to a communication base unit, which transmits the vital sign by a phone line, LAN, Internet, serial interface or the like to a data processing device / centre.
Owner:TELEMEDIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com