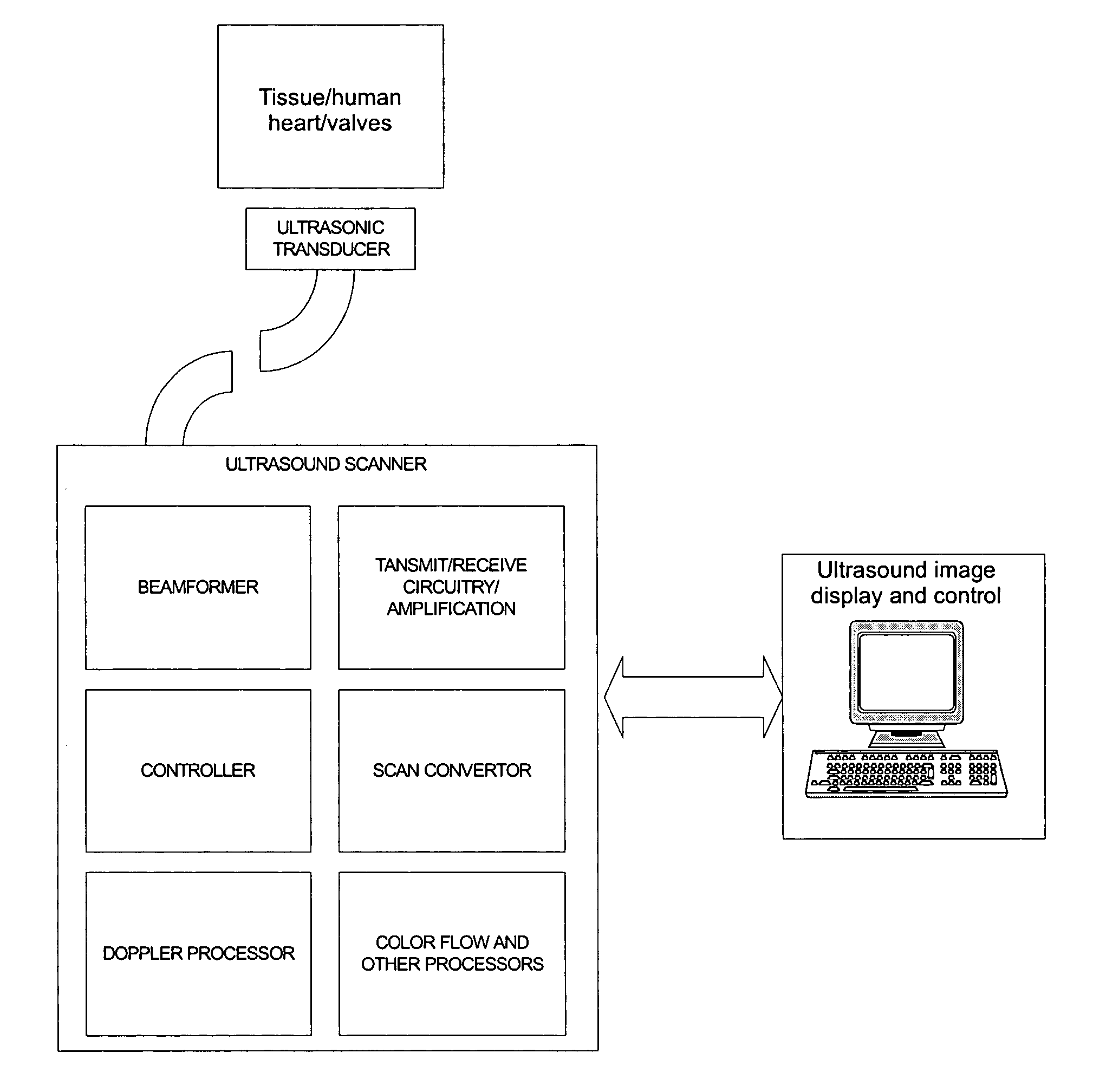
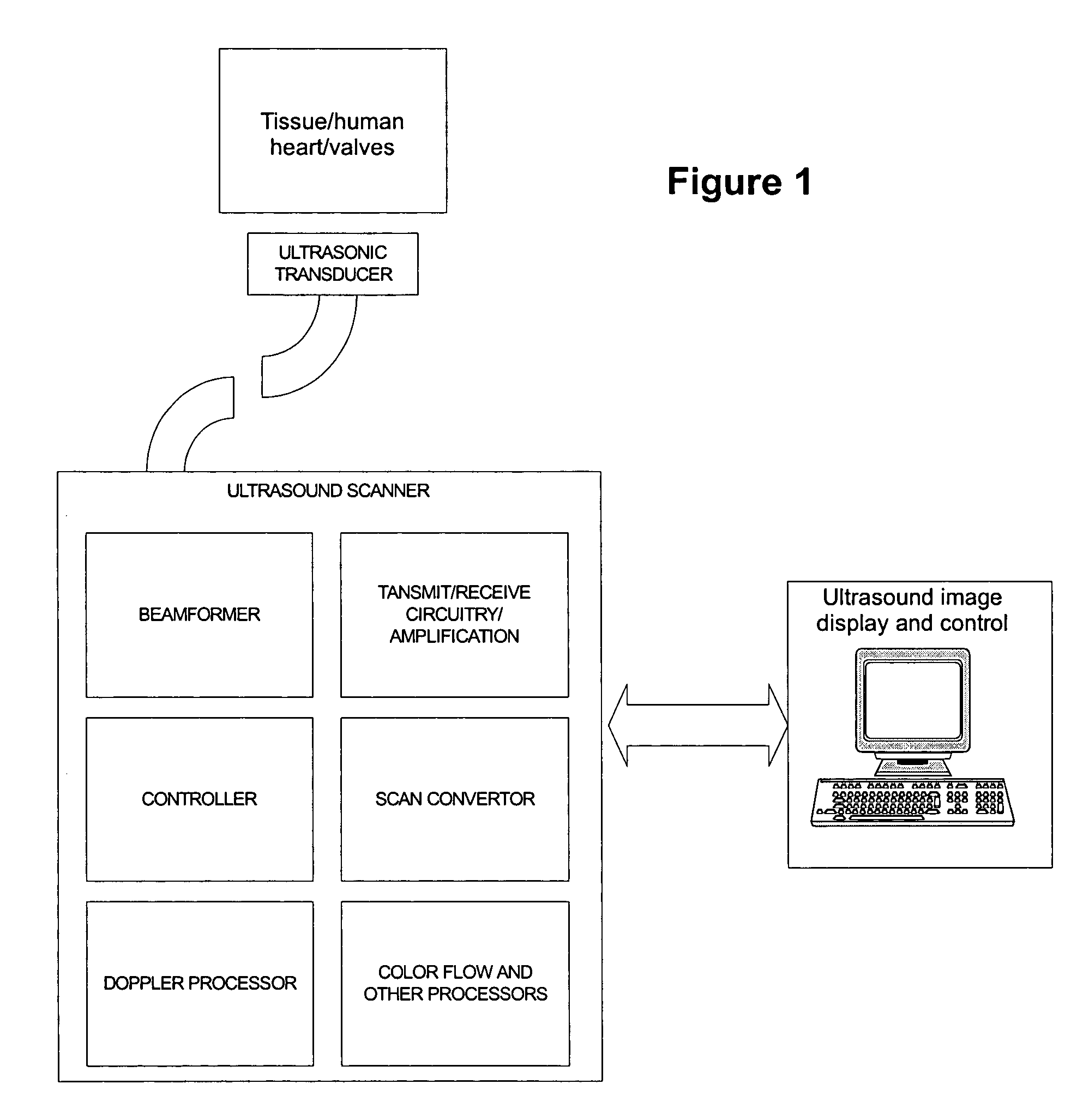
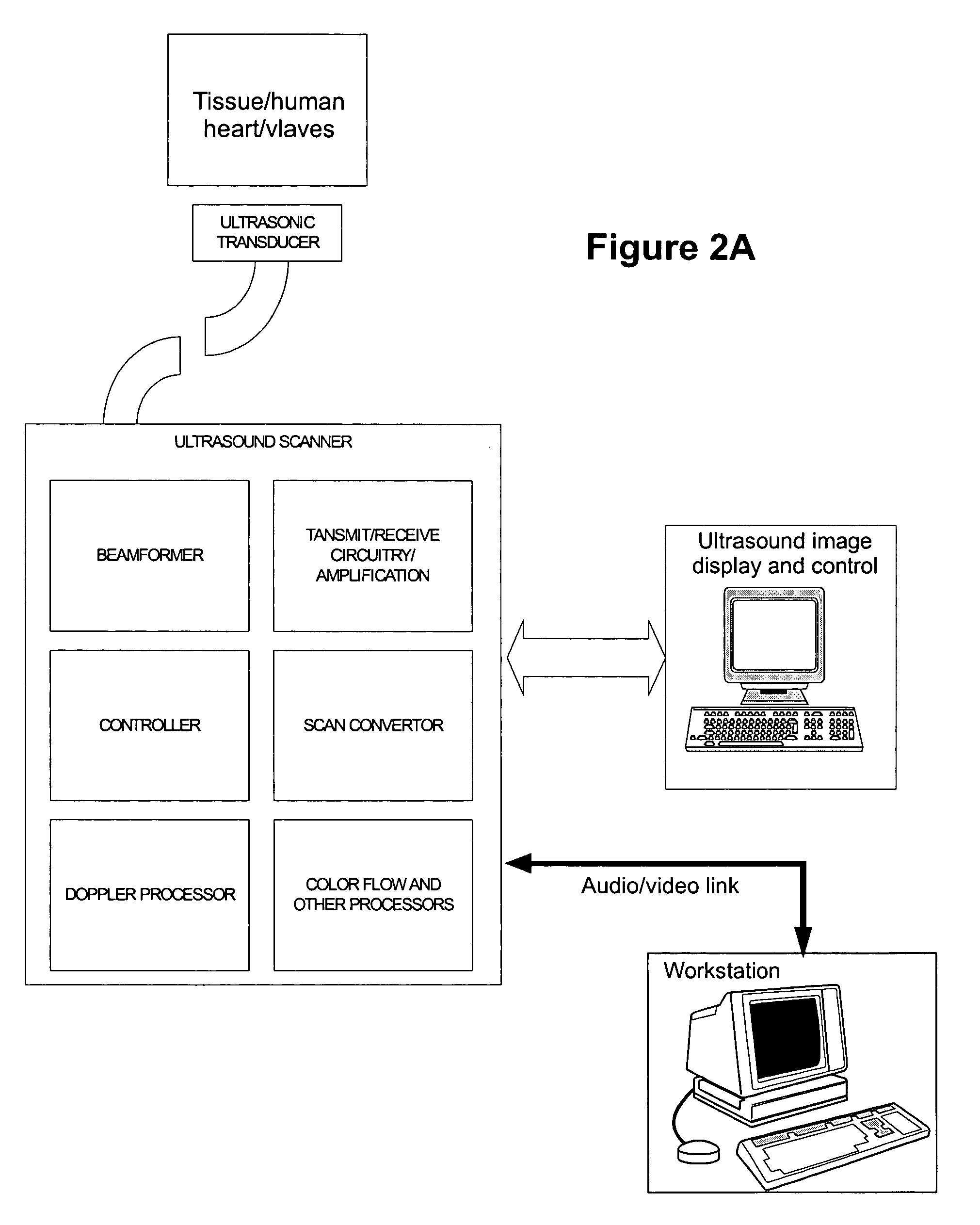
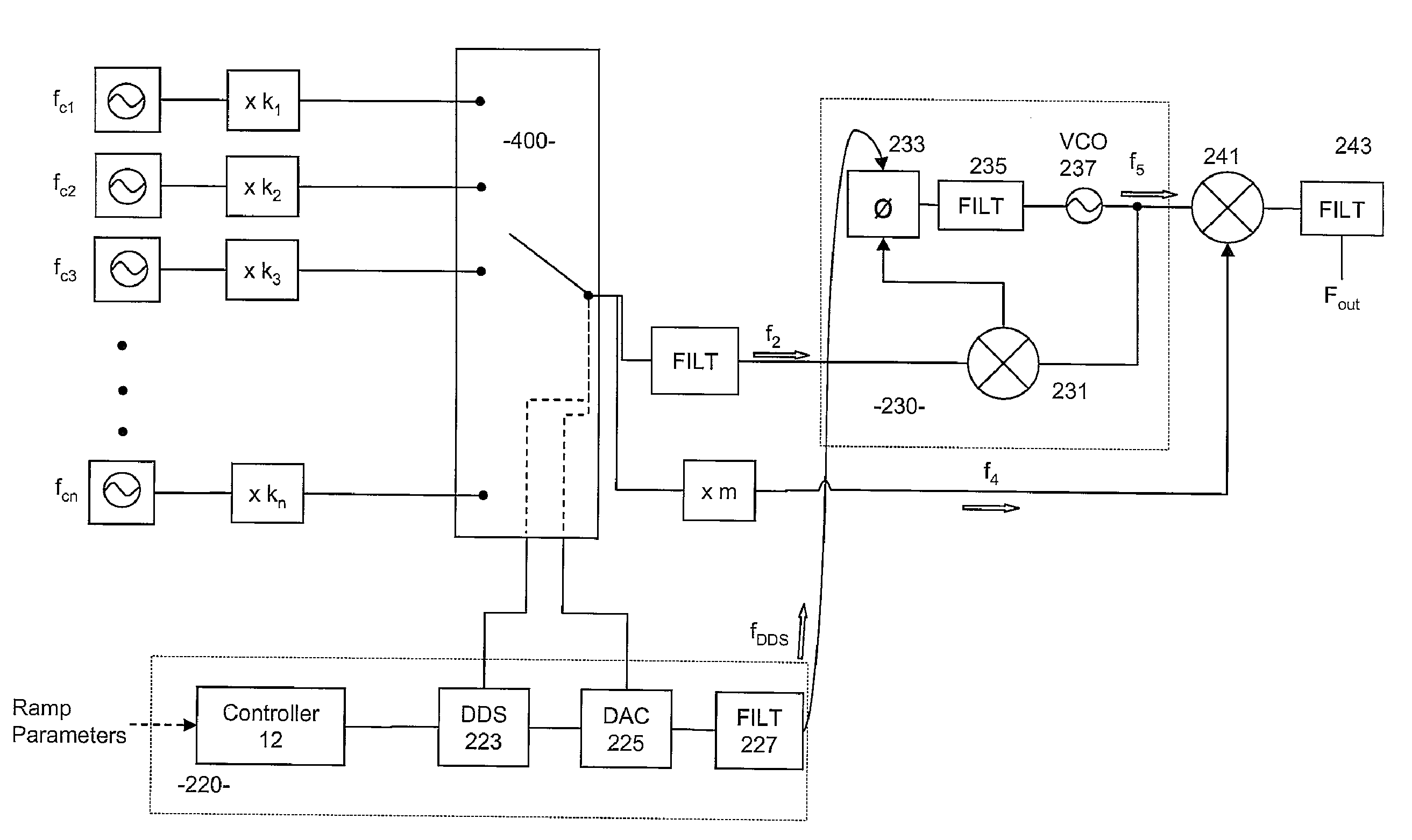
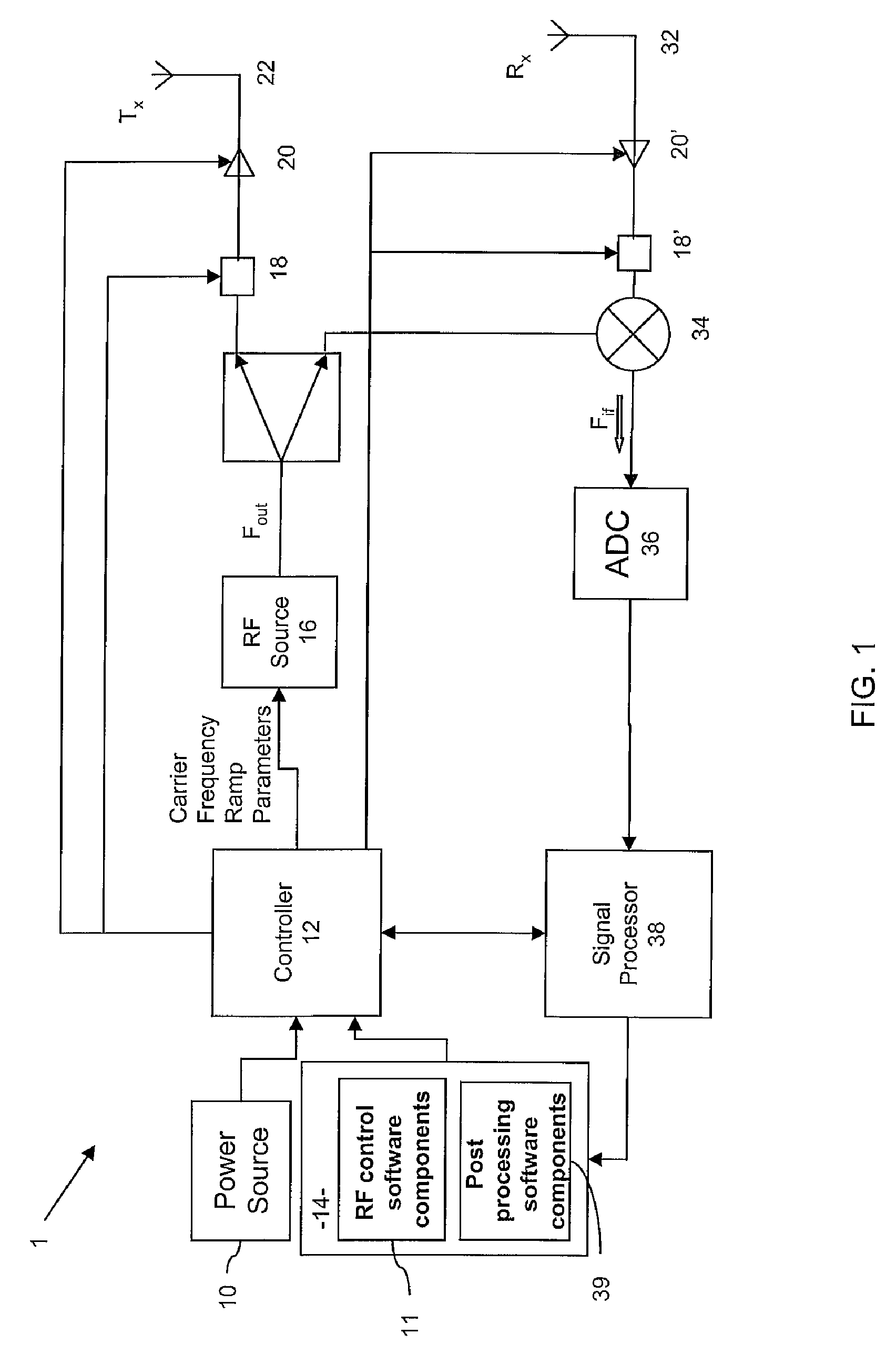
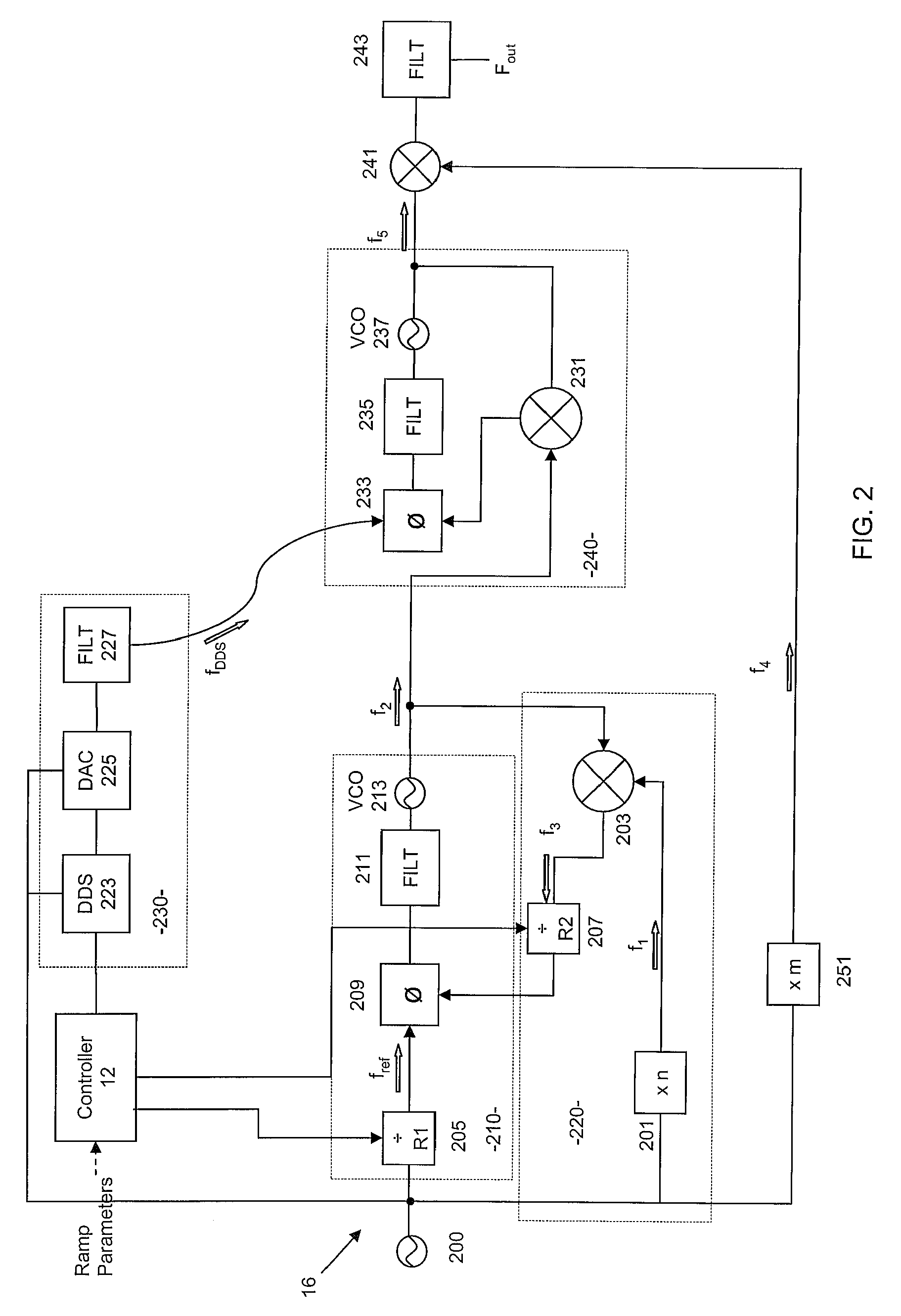
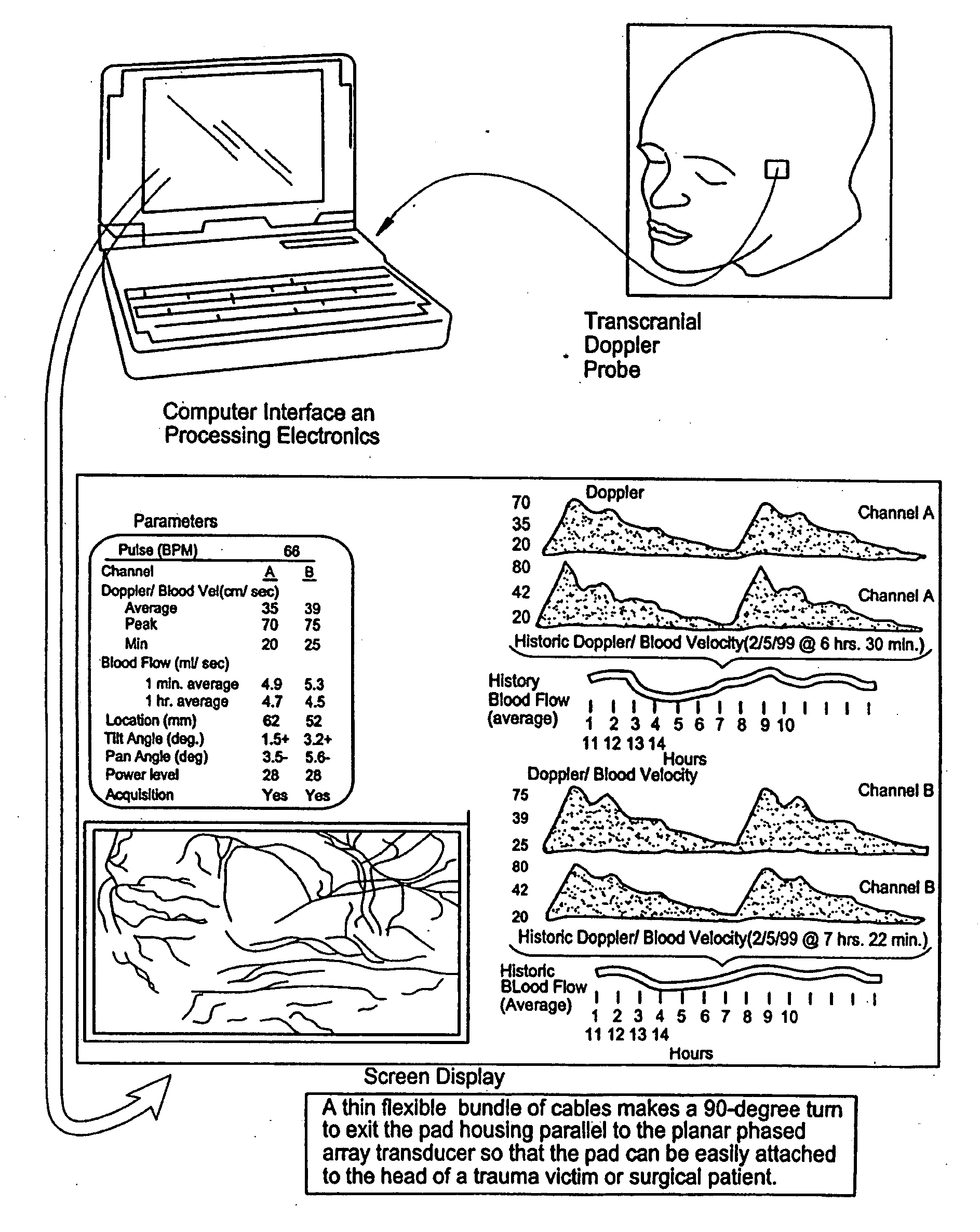
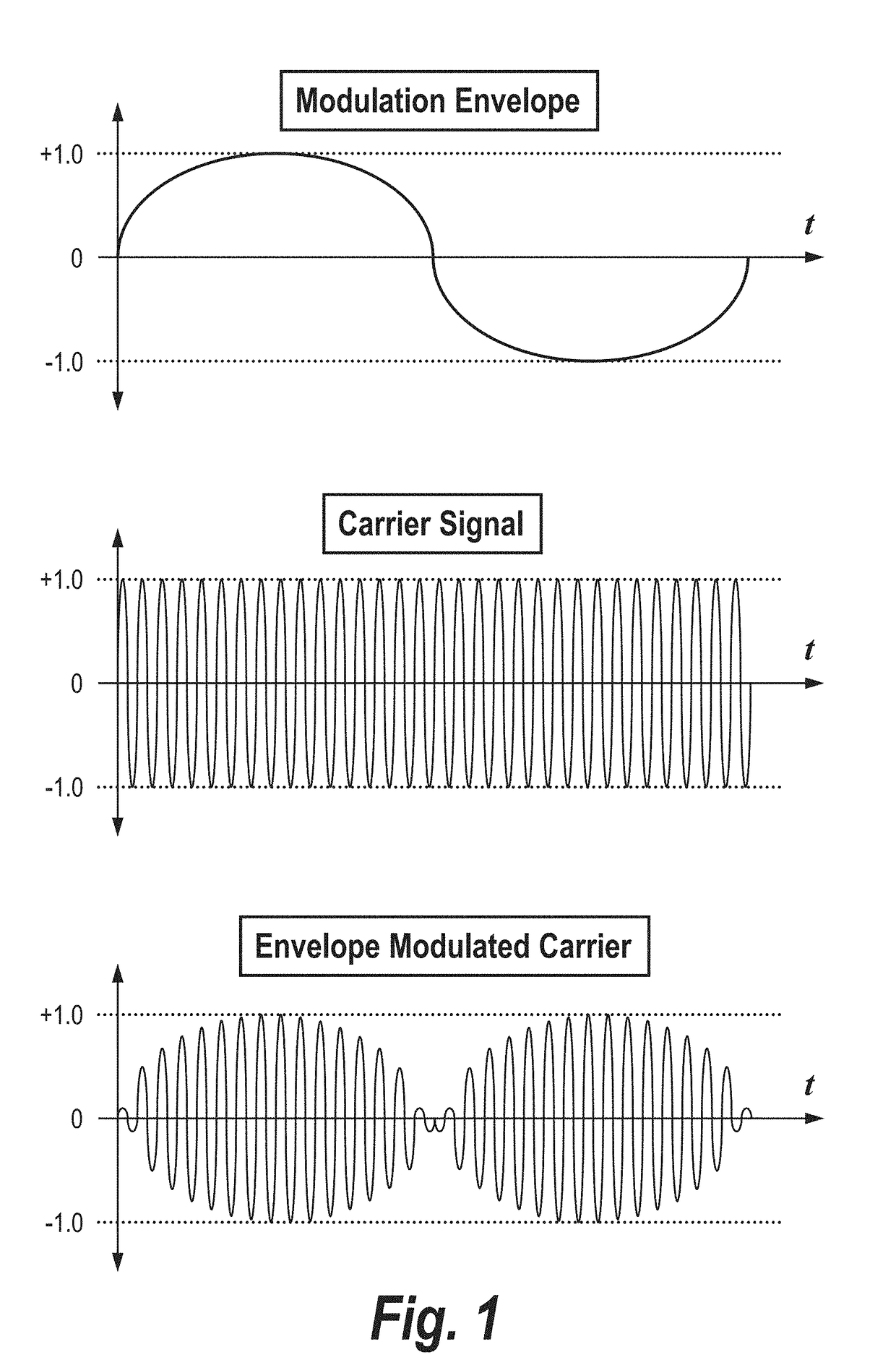
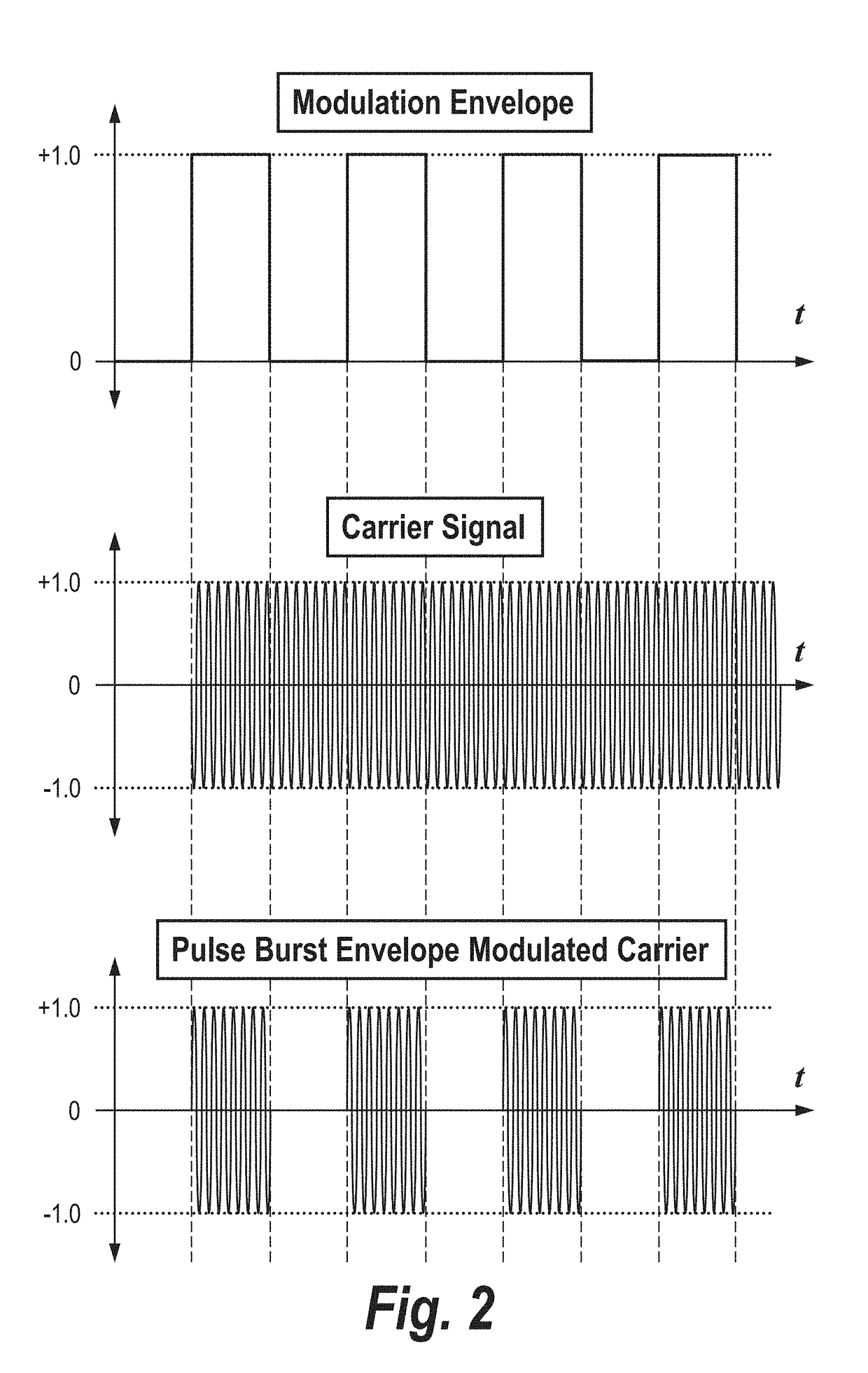
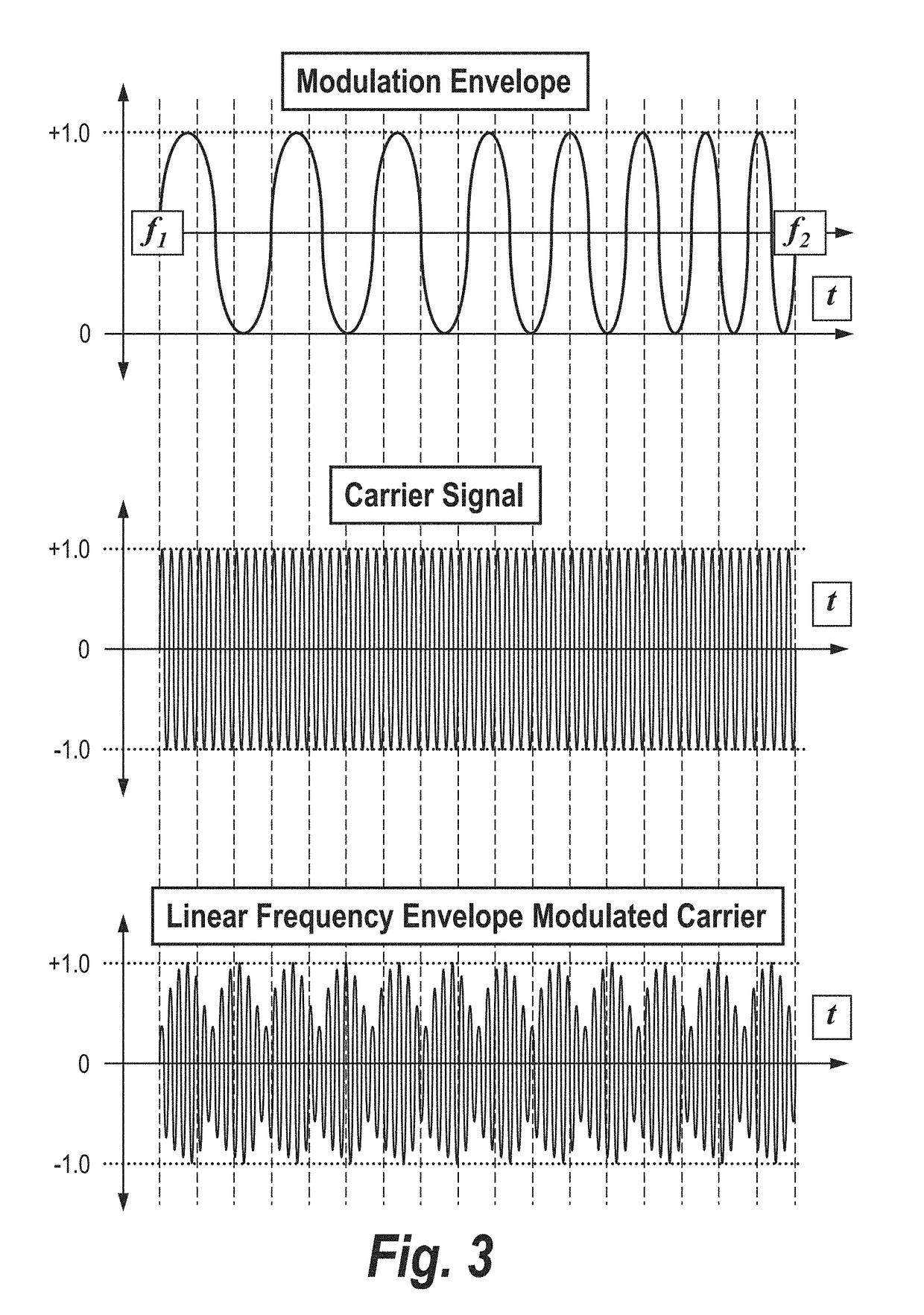
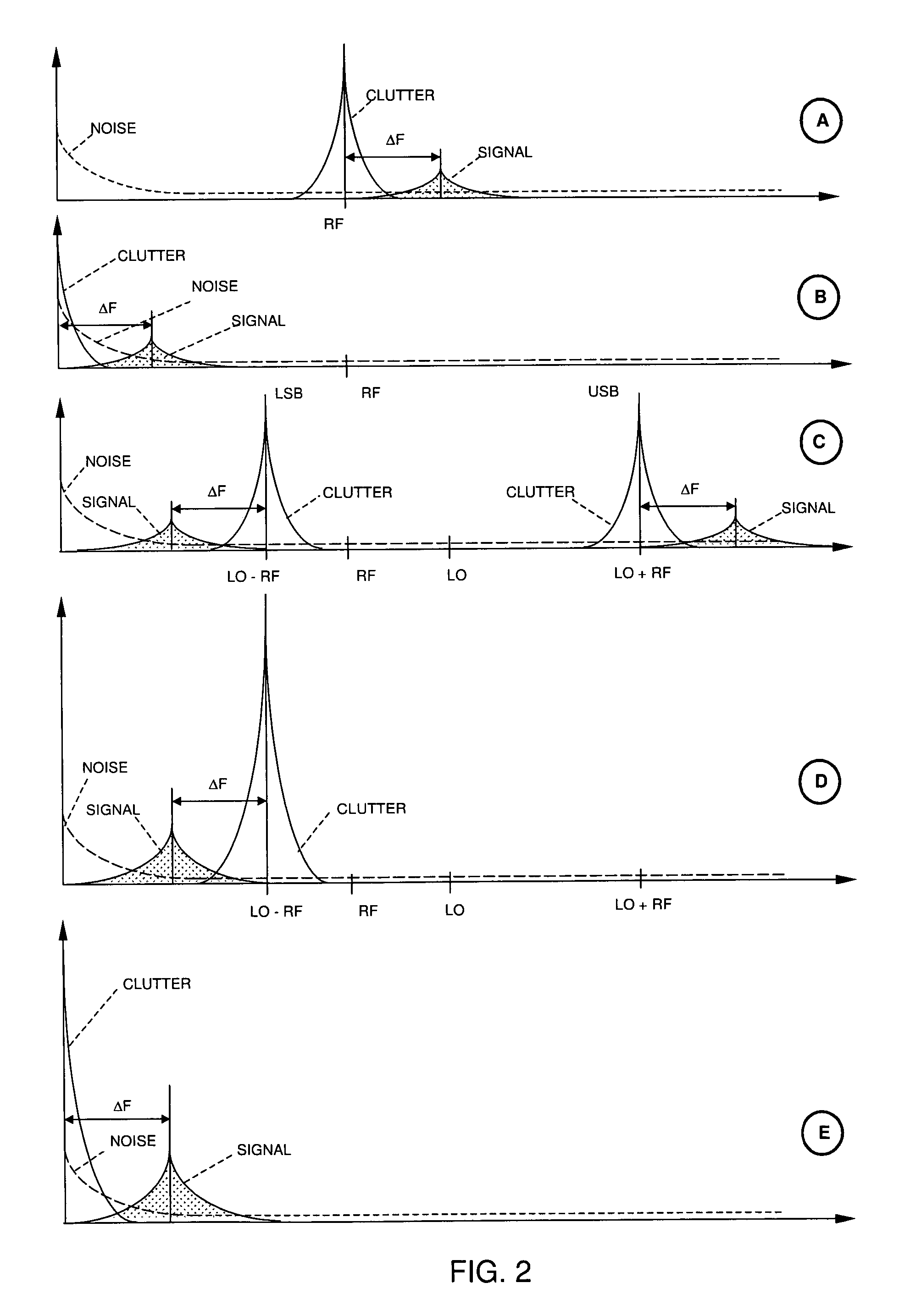
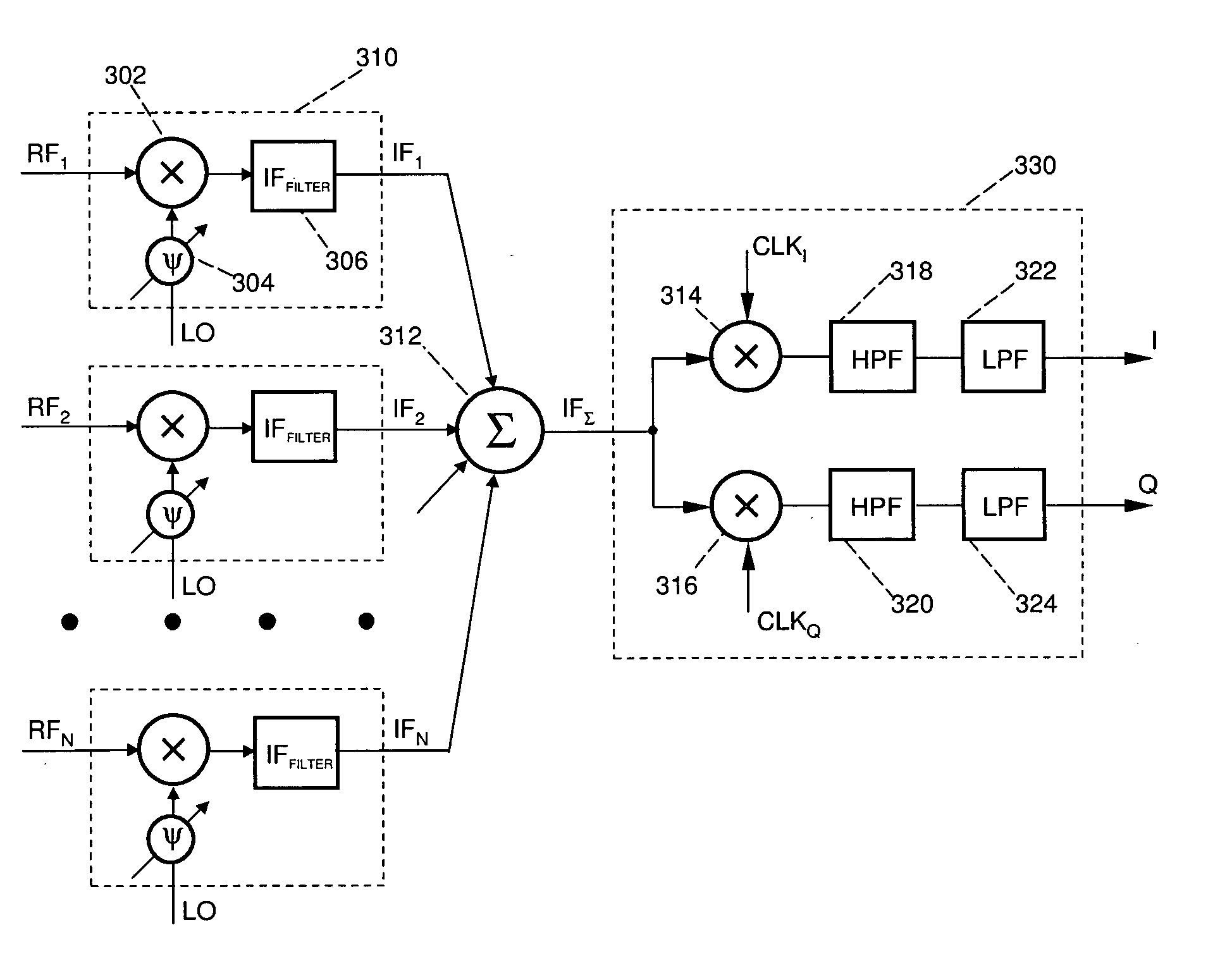
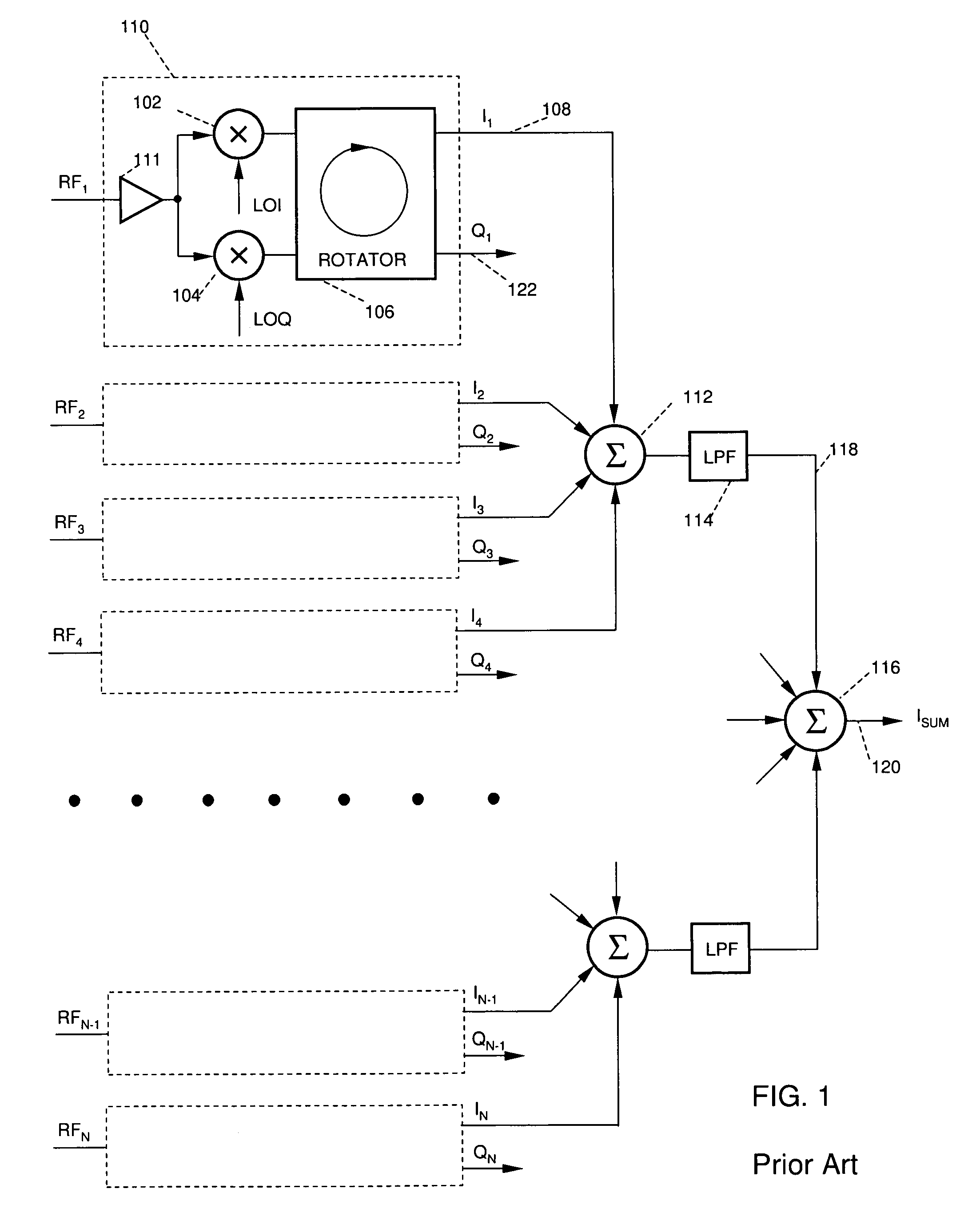
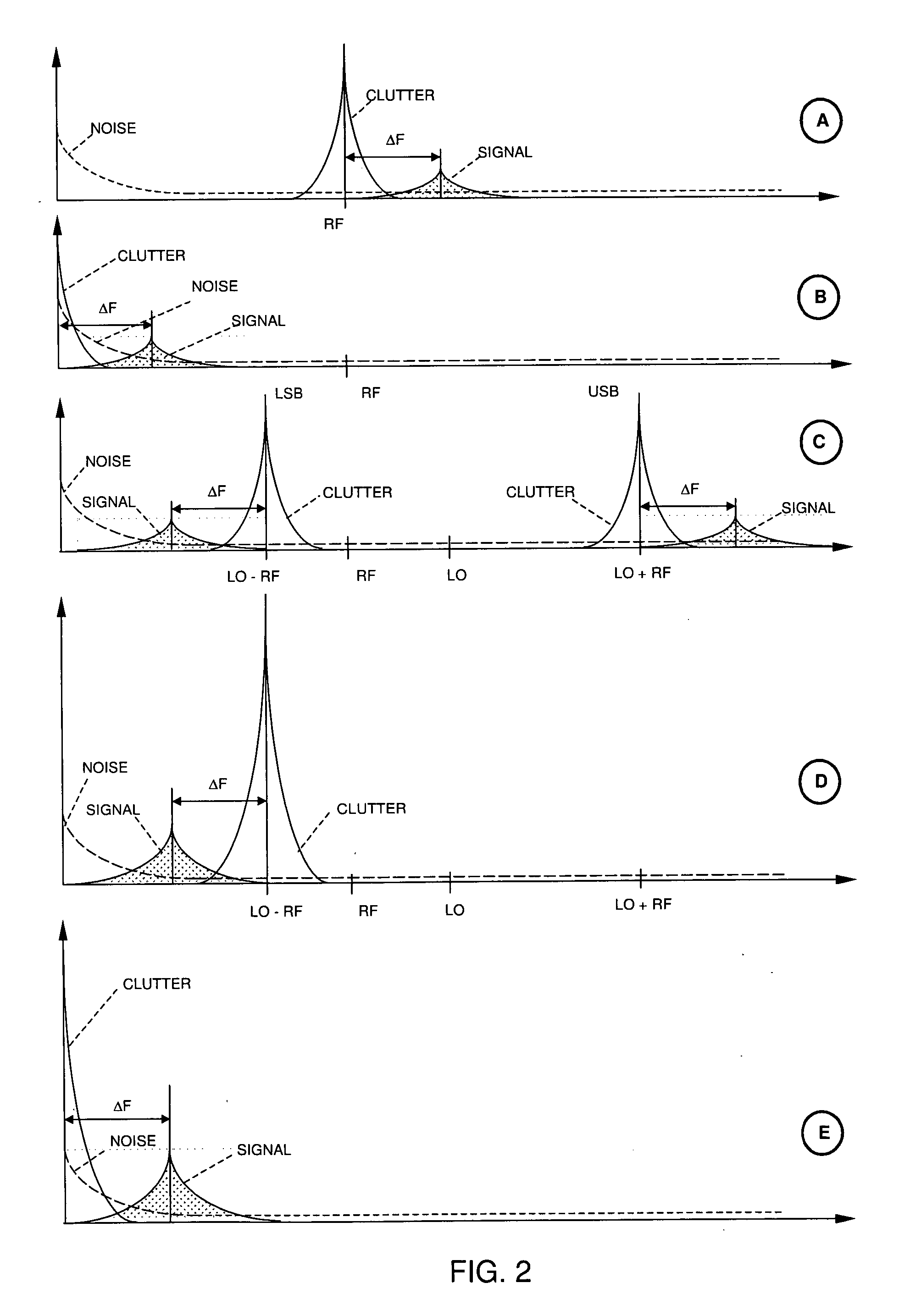
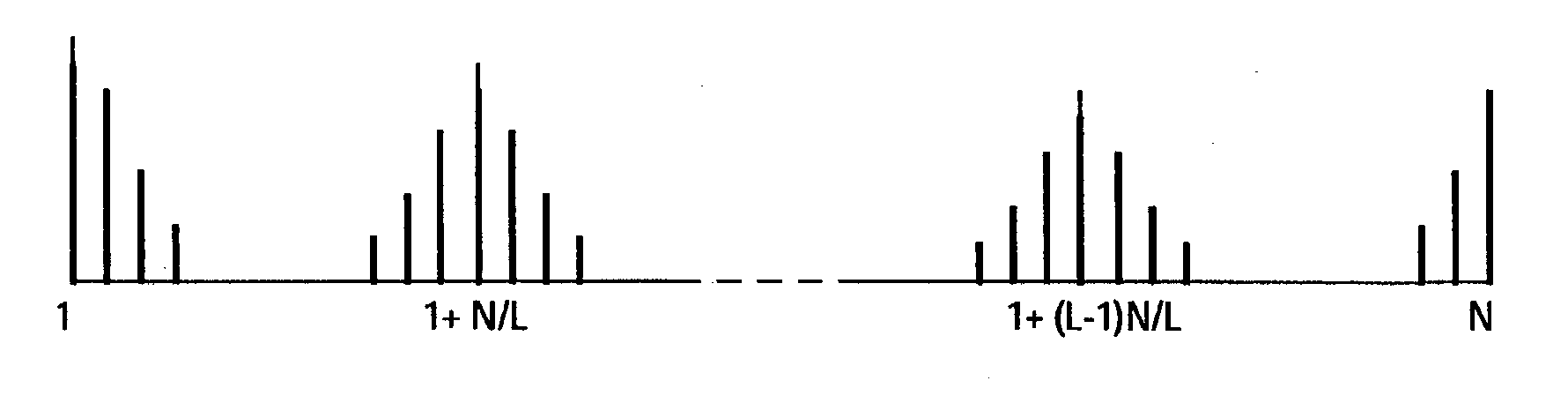Patents
Literature
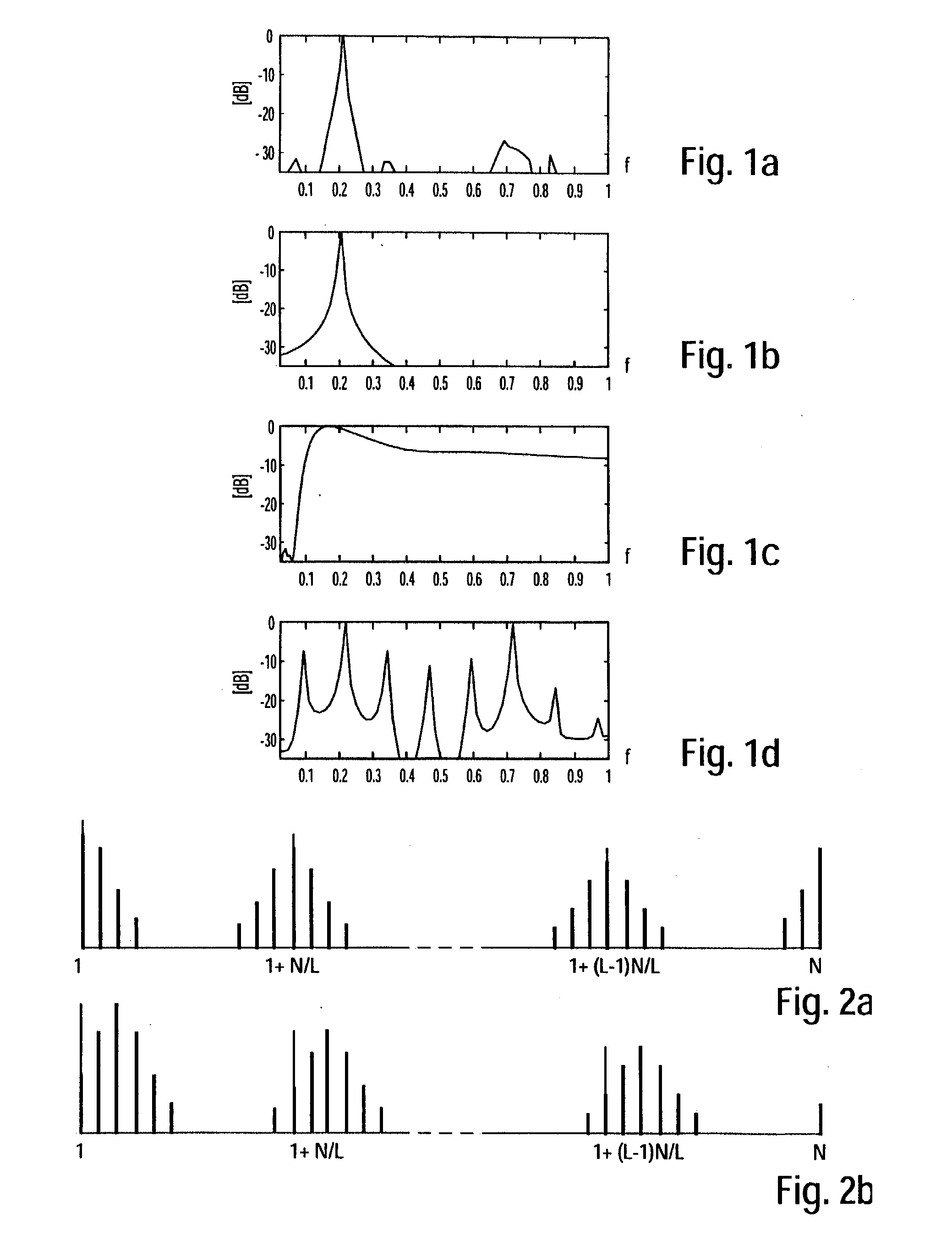
117 results about "Doppler processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
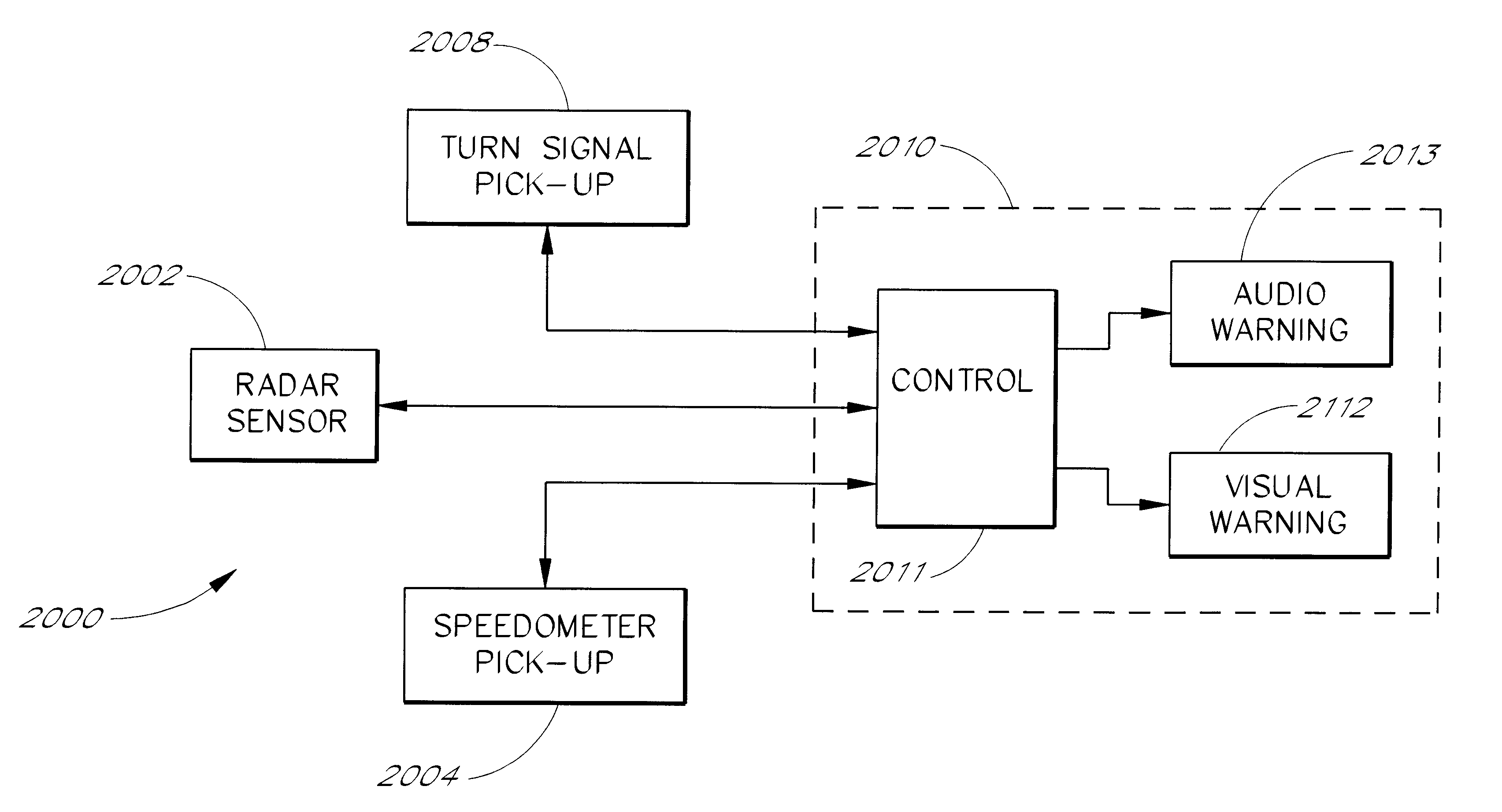
High performance vehicle radar system
InactiveUS6400308B1Road vehicles traffic controlAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDriver/operatorRadar systems
A radar system is described for use in vehicular applications. The radar system is particularly suited to backup warning systems and lane-change warning systems. The radar minimizes many of the problems found in the prior art by providing programmable delays and programmable gain. The radar uses a range search algorithm to detect and sort targets at various ranges within the field of view of the radar. Each target range corresponds to a particular delay and gain setting. The radar searches for targets at the various ranges by running a target search algorithm. For each target range, the search algorithm causes the proper time delay and gain setting. Targets within the selected range are detected and catalogued. Speed of the targets is obtained through Doppler processing. A display is used to warn the driver of the vehicle of the presence of targets at the various ranges. The warning may be visual and / or audible. When used in a lane-change system, issuance of an audible warning is based on the speed of the vehicle.
Owner:AMERIGON INC
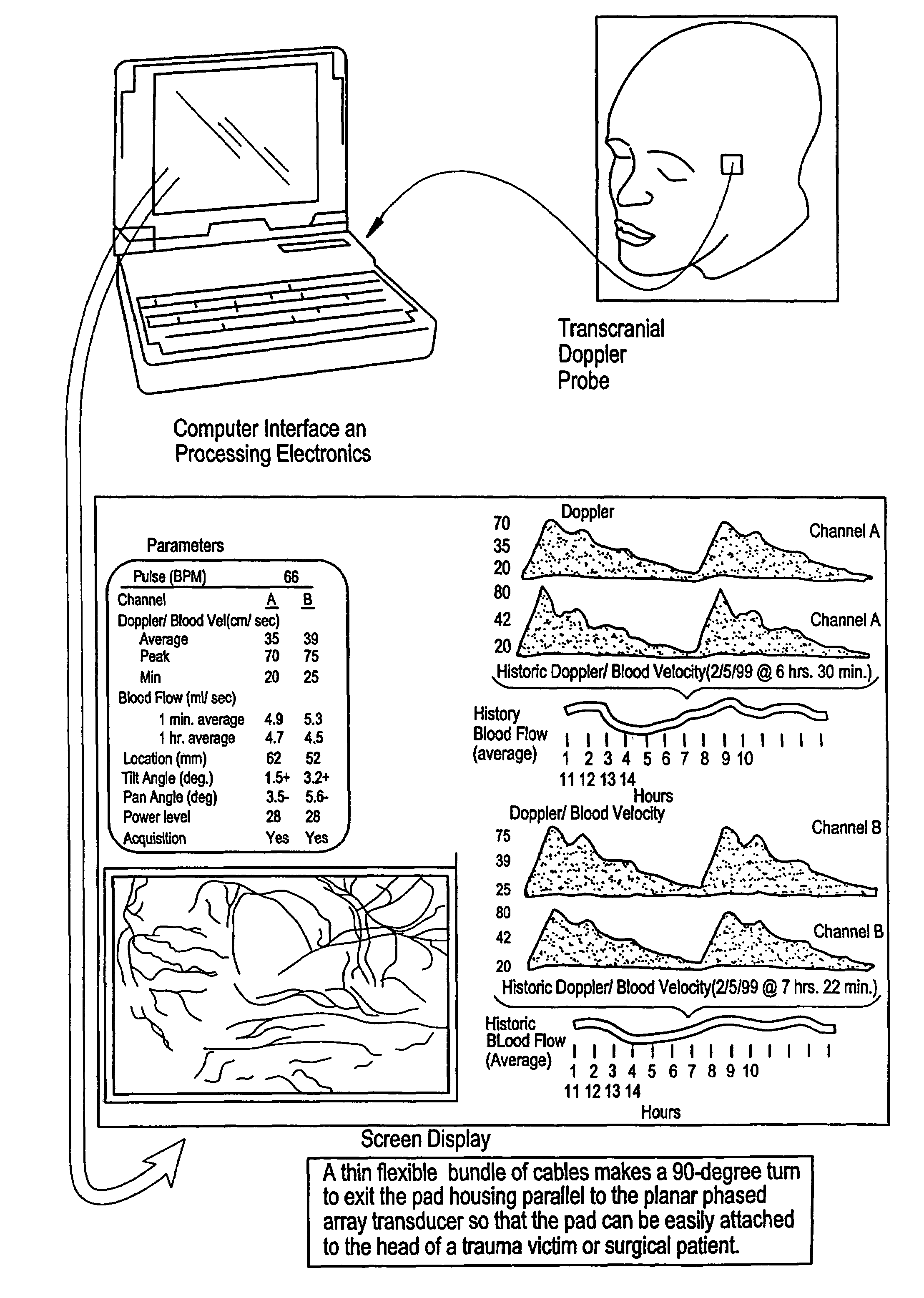
Transmitter patterns for multi beam reception
InactiveUS7399279B2High resolutionSmall sizeBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsThinned arrayDisplay device
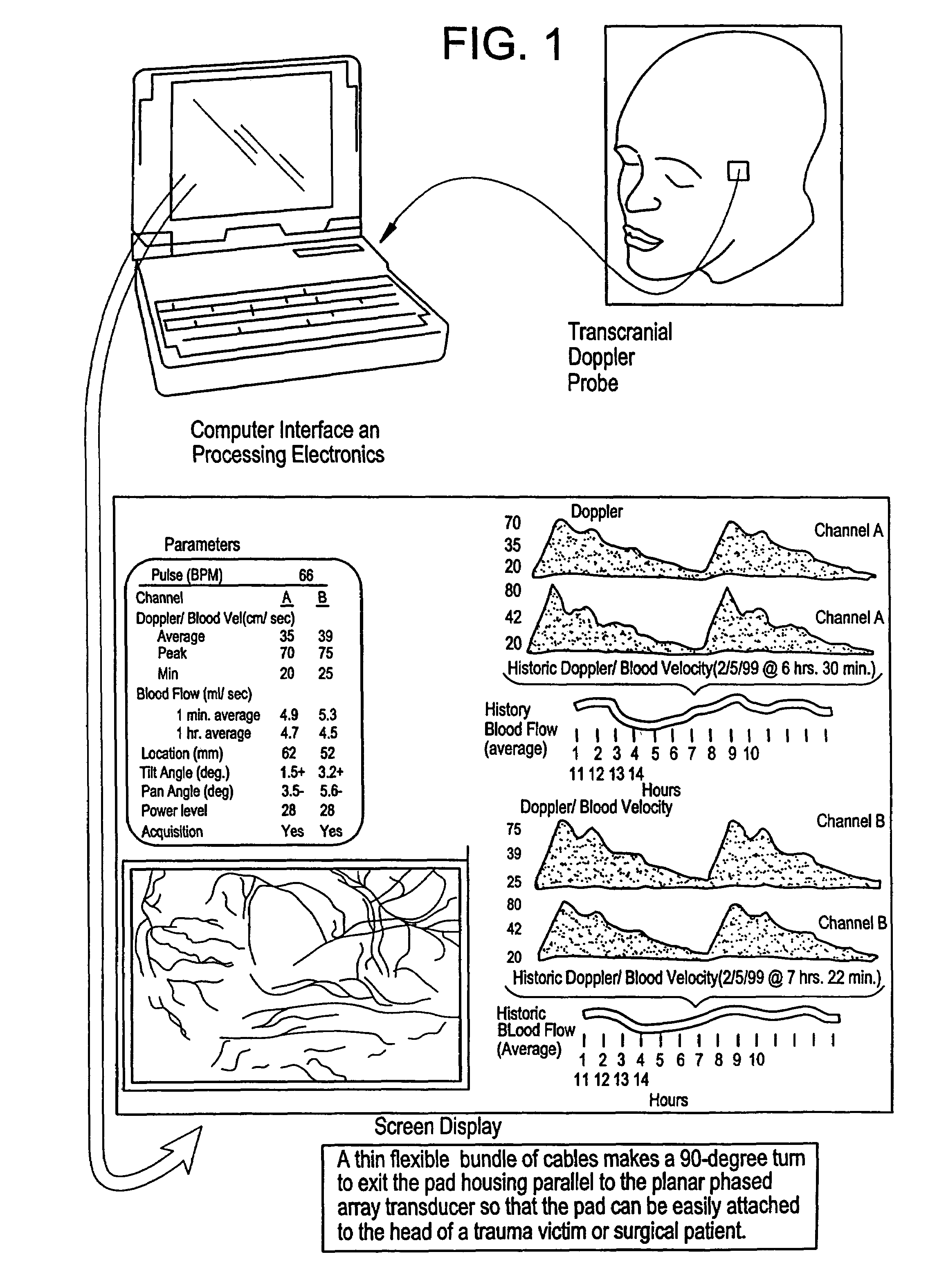
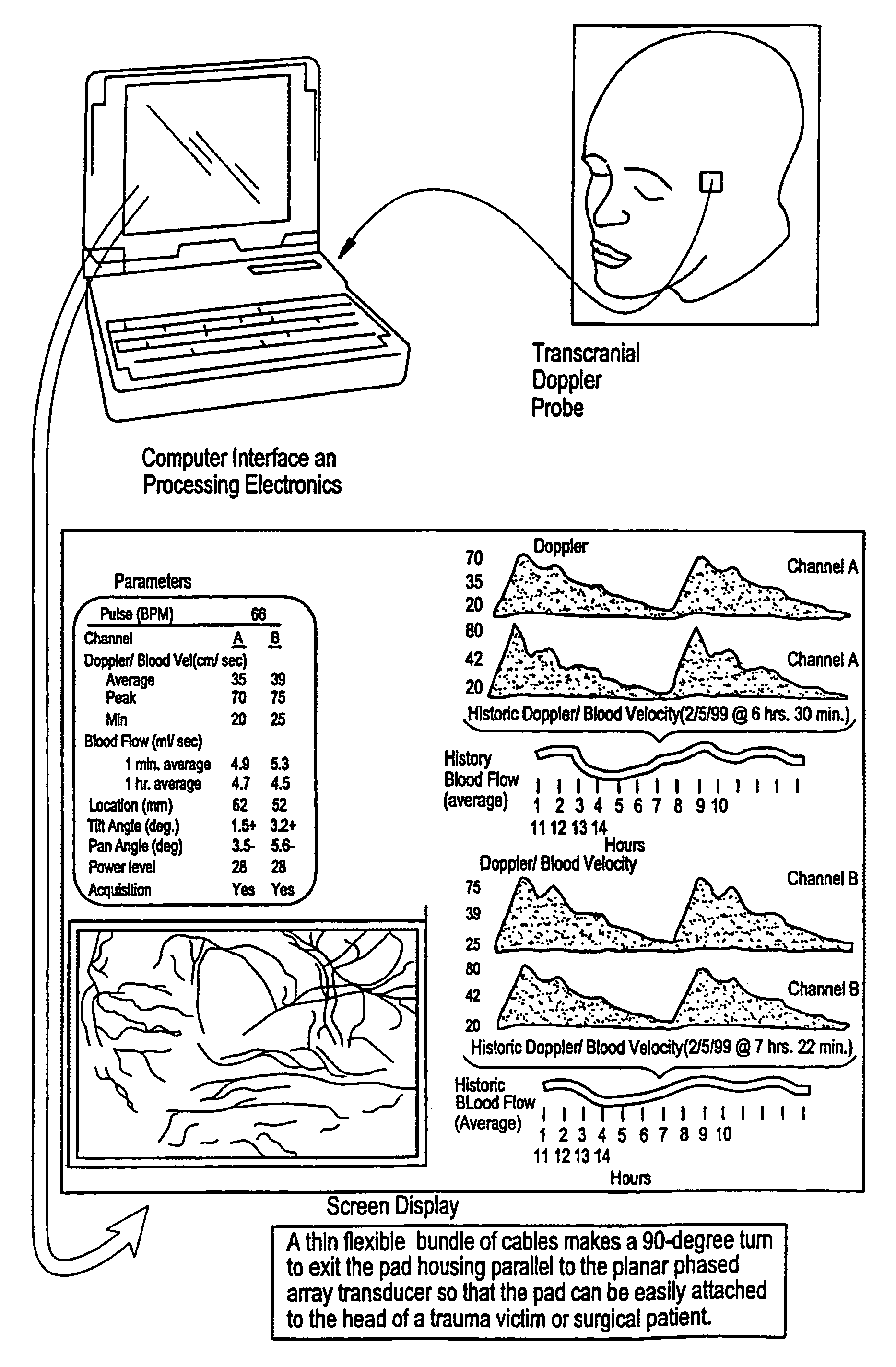
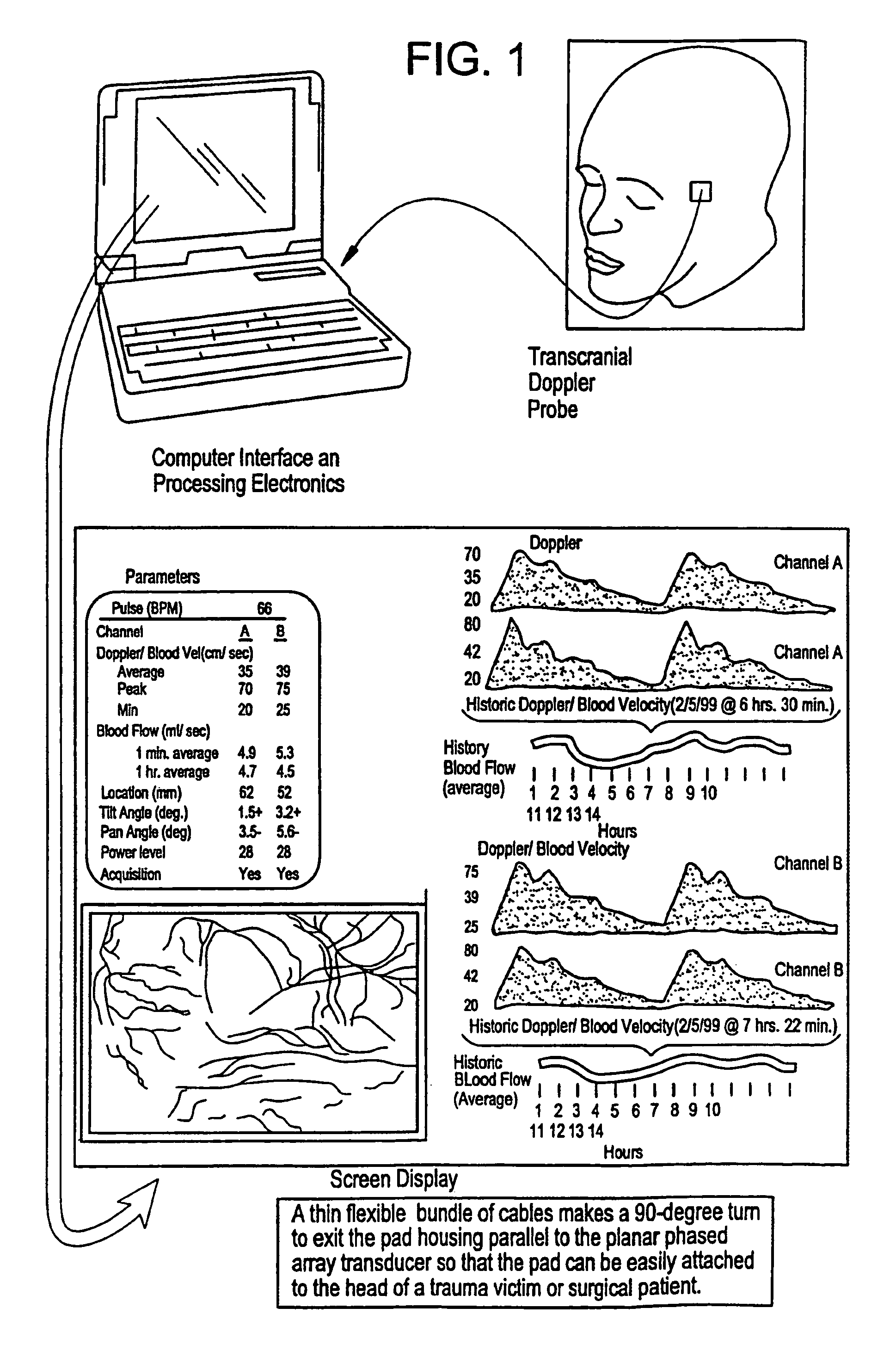
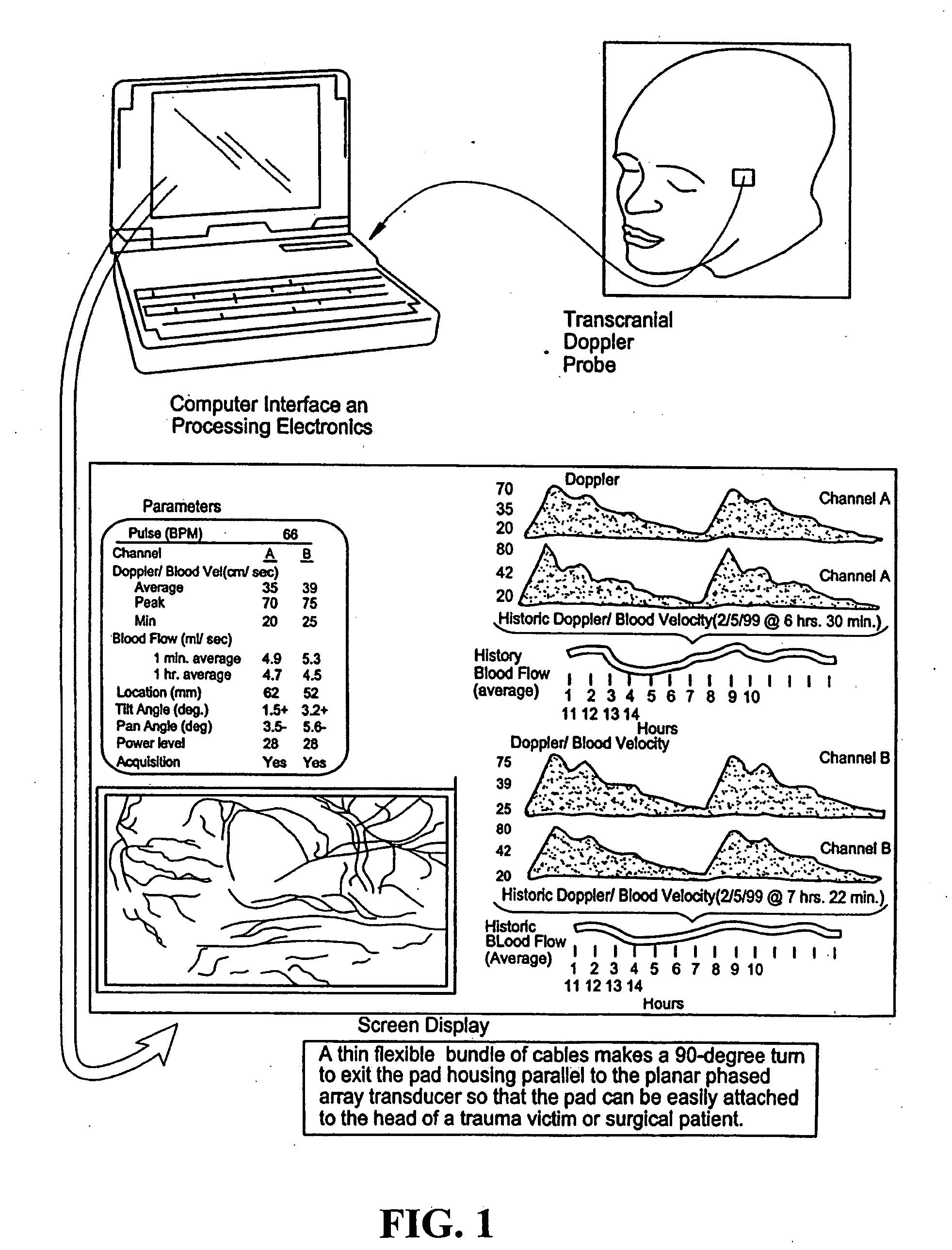
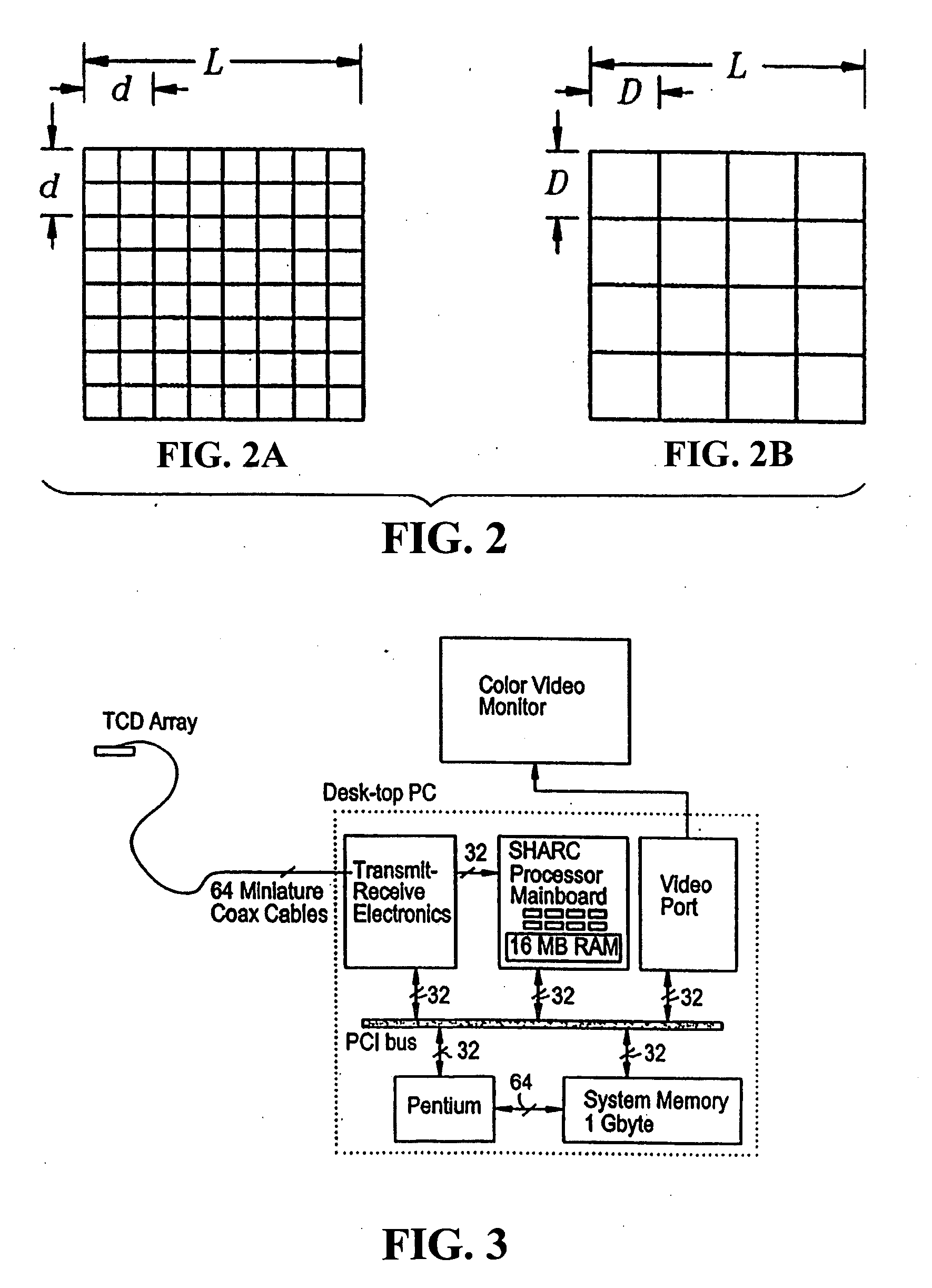
Provided herein is a method for use in medical applications that permits (1) affordable three-dimensional imaging of blood flow using a low-profile easily-attached transducer pad, (2) real-time blood-flow vector velocity, and (3) long-term unattended Doppler-ultrasound monitoring in spite of motion of the patient or pad. The pad and associated processor collects and Doppler processes ultrasound blood velocity data in a three dimensional region through the use of a planar phased array of piezoelectric elements. The invention locks onto and tracks the points in three-dimensional space that produce the locally maximum blood velocity signals. The integrated coordinates of points acquired by the accurate tracking process is used to form a three-dimensional map of blood vessels and provide a display that can be used to select multiple points of interest for expanded data collection and for long term continuous and unattended blood flow monitoring. The three dimensional map allows for the calculation of vector velocity from measured radial Doppler.A thinned array (greater than half-wavelength element spacing of the transducer array) is used to make a device of the present invention inexpensive and allow the pad to have a low profile (fewer connecting cables for a given spatial resolution). The full aperture is used for transmit and receive so that there is no loss of sensitivity (signal-to-noise ratio) or dynamic range. Utilizing more elements (extending the physical array) without increasing the number of active elements increases the angular field of view. A further increase is obtained by utilizing a convex non-planar surface.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
Device and method for mapping and tracking blood flow and determining parameters of blood flow
InactiveUS7534209B2Small sizeBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationDisplay device
Provided herein is a method for use in medical applications that permits affordable three-dimensional imaging of blood flow using a low-profile easily-attached transducer pad, real-time blood-flow vector velocity, and long-term unattended Doppler-ultrasound monitoring in spite of motion of the patient or pad. The pad and associated processor collects and Doppler processes ultrasound blood velocity data in a three dimensional region through the use of a planar phased array of piezoelectric elements. The invention locks onto and tracks the points in three-dimensional space that produce the locally maximum blood velocity signals. The integrated coordinates of points acquired by the accurate tracking process is used to form a three-dimensional map of blood vessels and provide a display that can be used to select multiple points of interest for expanded data collection and for long term continuous and unattended blood flow monitoring. The three dimensional map allows for the calculation of vector velocity from measured radial Doppler.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
Method and System For Estimating Cardiac Ejection Volume And Placing Pacemaker Electrodes Using Speckle Tracking
InactiveUS20070167809A1Eliminate error of inputReduce duplicationBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsEcg signalSystole
A method and system for estimating the volume of blood ejected from a cardiac ventricle or atrium uses ultrasound to track speckle patterns in the heart. The process utilizes the M-mode to estimate volume differences in a view of the ventricle or atrium over time using speckle pattern motion to estimate volume differences between systole and diastole. Alternatively, the ultrasound speckle tracking method may be used in combination with Doppler processing techniques or to obtain temporal flow profiles across flow cross-sectional areas, from which the flow volume is computed. The method can also measure the phase delay of motion of sites on the cardiac wall relative to each other or relative to an ECG signal.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method and system for using ultrasound in cardiac diagnosis and therapy
InactiveUS7211045B2Optimize locationHigh energyBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterCatheterBlood vessel
A method and system for estimating the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle of the heart to a succeeding chamber / conduit, or vice-versa, while imaging the intersection of such structures is described. The process utilizes either the M-mode to estimate volume differences in a view of the ventricle over time or Doppler processing techniques to obtain flow profiles across intersections (e.g., valves), or blood vessels, which are then utilized to calculate output. This process can be combined with ECG guidance / triggering to measure / track changes in output from beat to beat, or during the course of an evaluation or therapeutic procedure. This process can be specifically used for the placement of permanent pacemaker electrodes.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
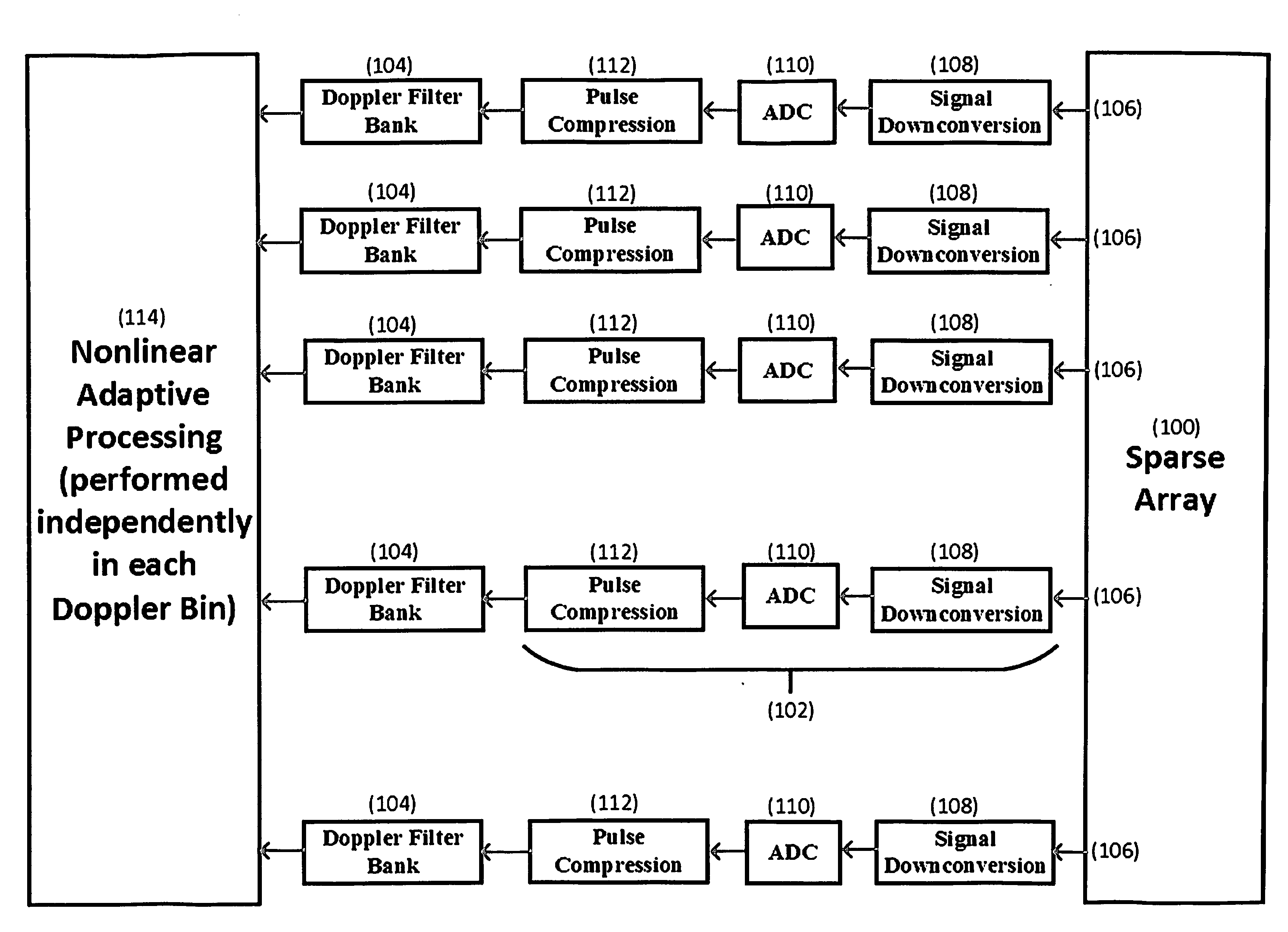
Sparse Space-Time Adaptive Array Architecture
InactiveUS20160091598A1Reduce impactReduce signalingCommunication jammingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCoprime arrayEngineering
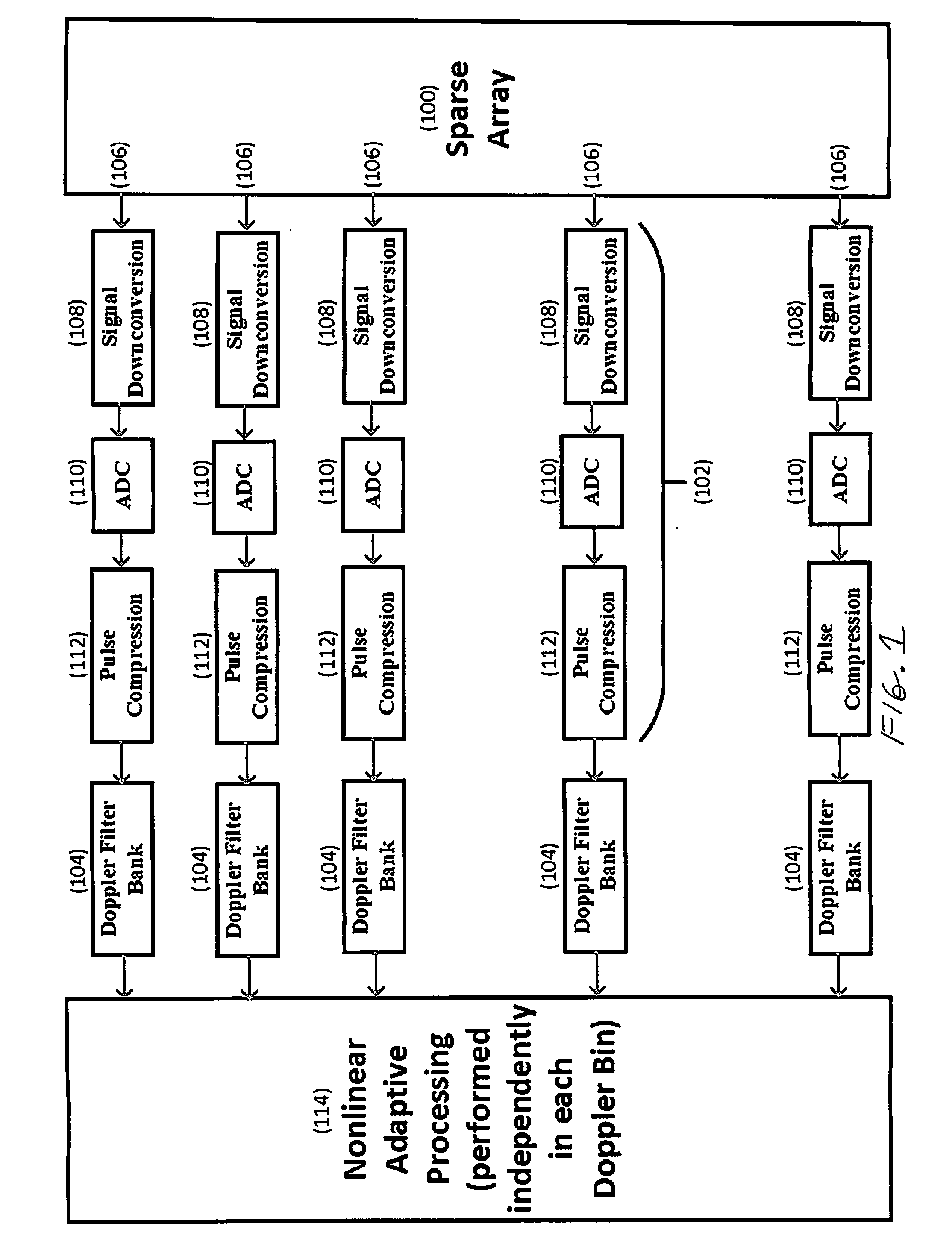
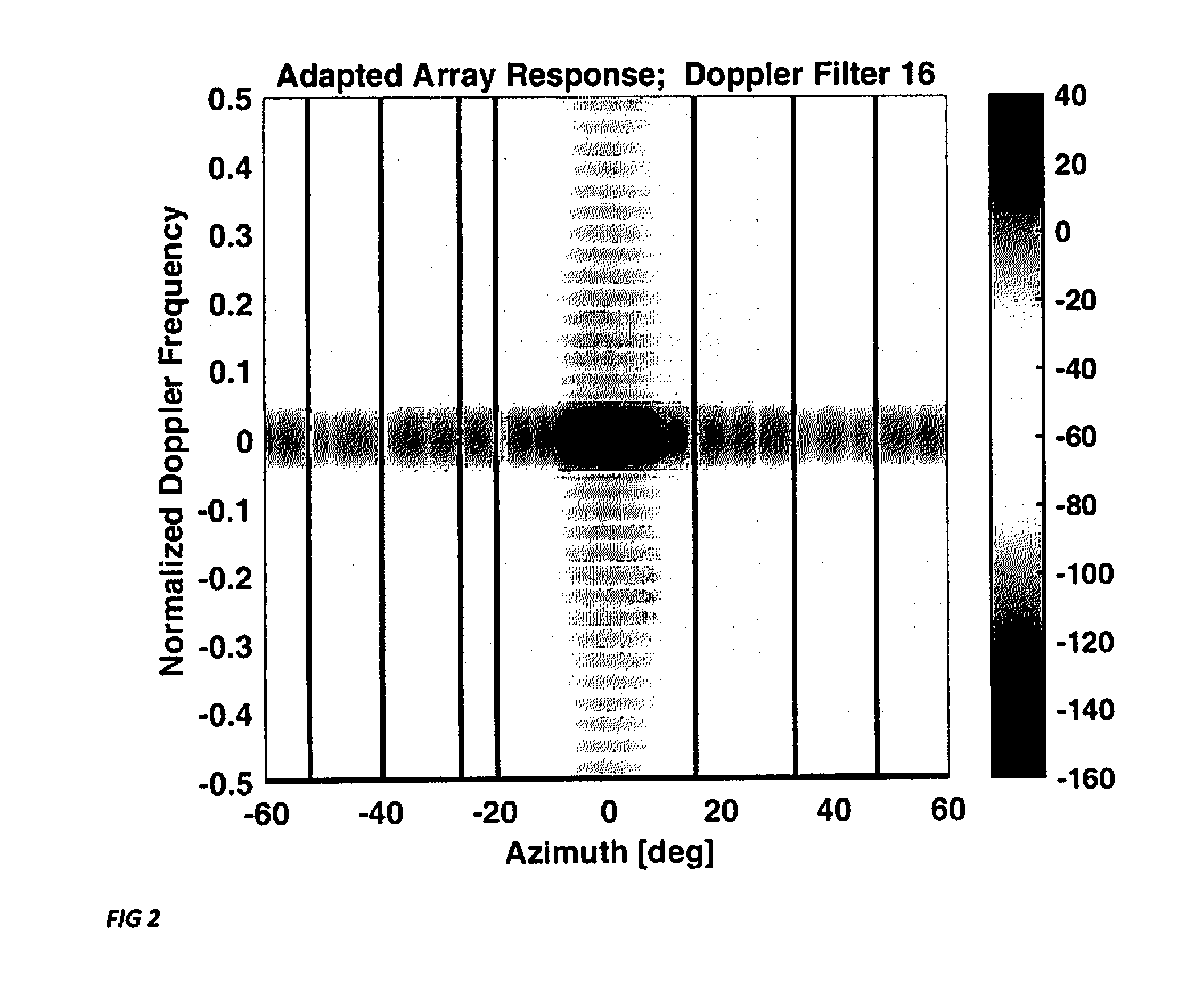
A sparse multichannel array includes a plurality of array elements, a receiver behind each array element, and a Doppler filter bank behind each receiver, whereby within each Doppler bin is placed spatial nulls at selected angles of undesired interference. The invention enables Doppler processing to be performed on sparse arrays, such as nested or coprime arrays, used in nonlinear adaptive beamforming to mitigate the impact of unintentional interference and hostile jamming on the received signal.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
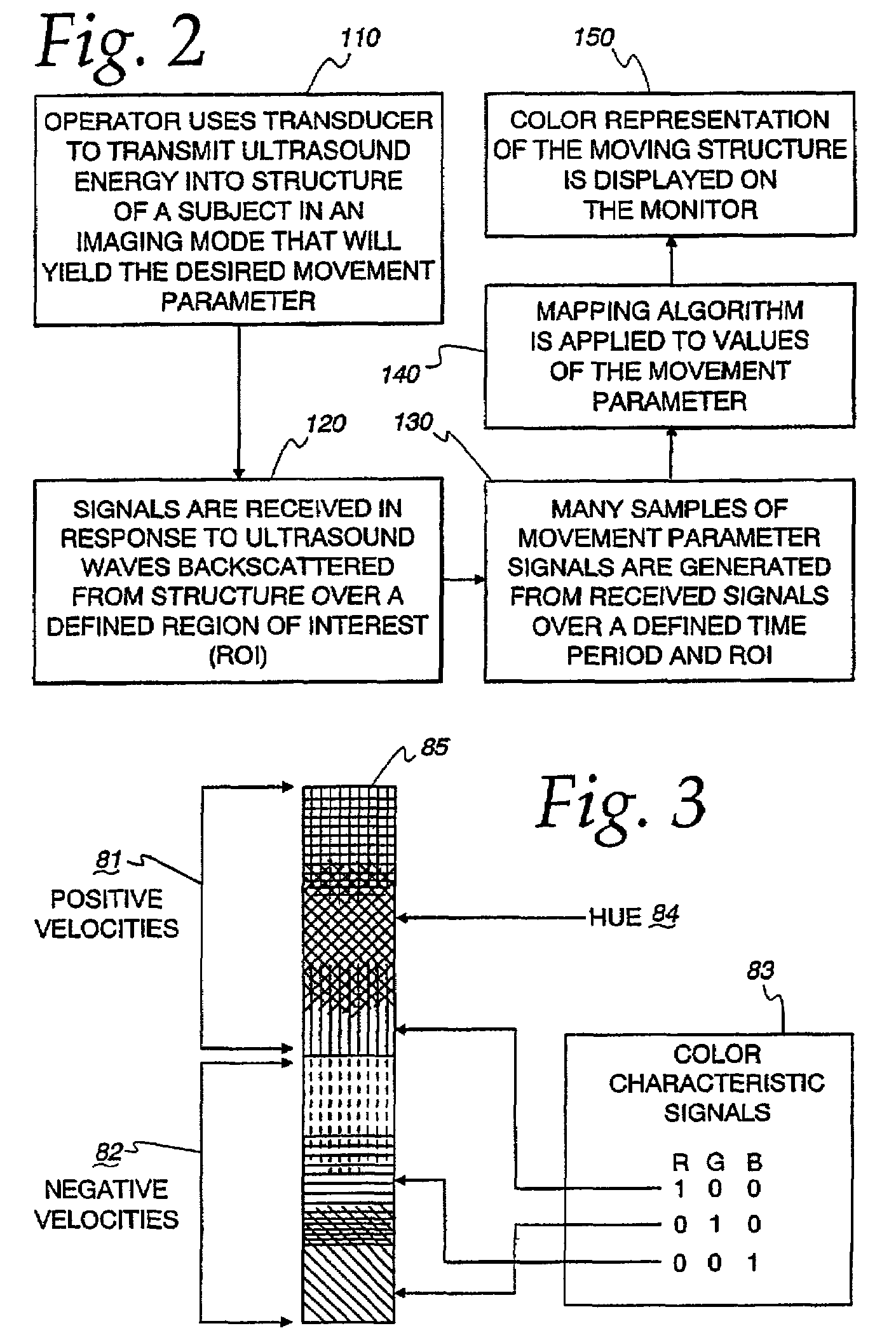
Ultrasound color characteristic mapping
ActiveUS7245746B2Improve visualizationEasily visualizedElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionCardiac wallMotion parameter
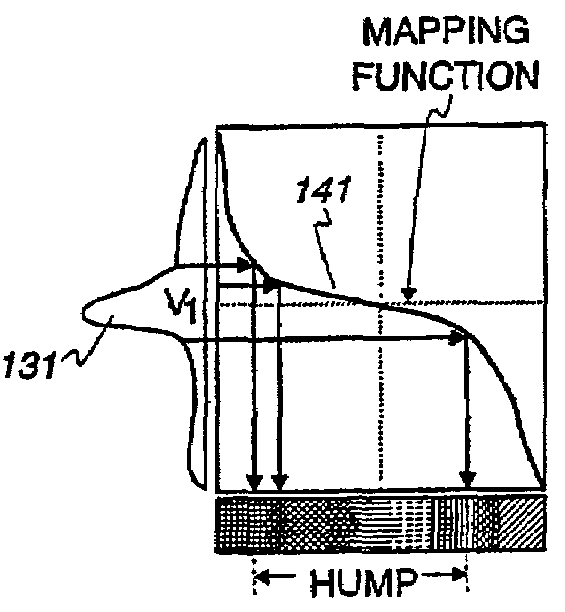
An ultrasound machine is disclosed that displays a color representation of moving structure, such as a cardiac wall tissue, within a region of interest on a monitor. The color representation is generated by displaying at least one color characteristic corresponding to a movement parameter of the structure, such as velocity or strain rate. The movement parameter is mapped to the color characteristic by apparatus comprising a front-end that generates received signals in response to ultrasound waves. A Doppler processor generates a set of parameter signals representing values of the movement parameter within the structure. A control processor adaptively generates a mapping function based on the distribution of the parameter signals to map the parameter signals to a set of color characteristic signals. A display processor applies the mapped values of the color characteristic legend to the values of the movement parameter representing the moving structure, to display a color representation on the monitor in response to the mapping function.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Multi-resolution fmcw radar detection method and radar implementing such a method
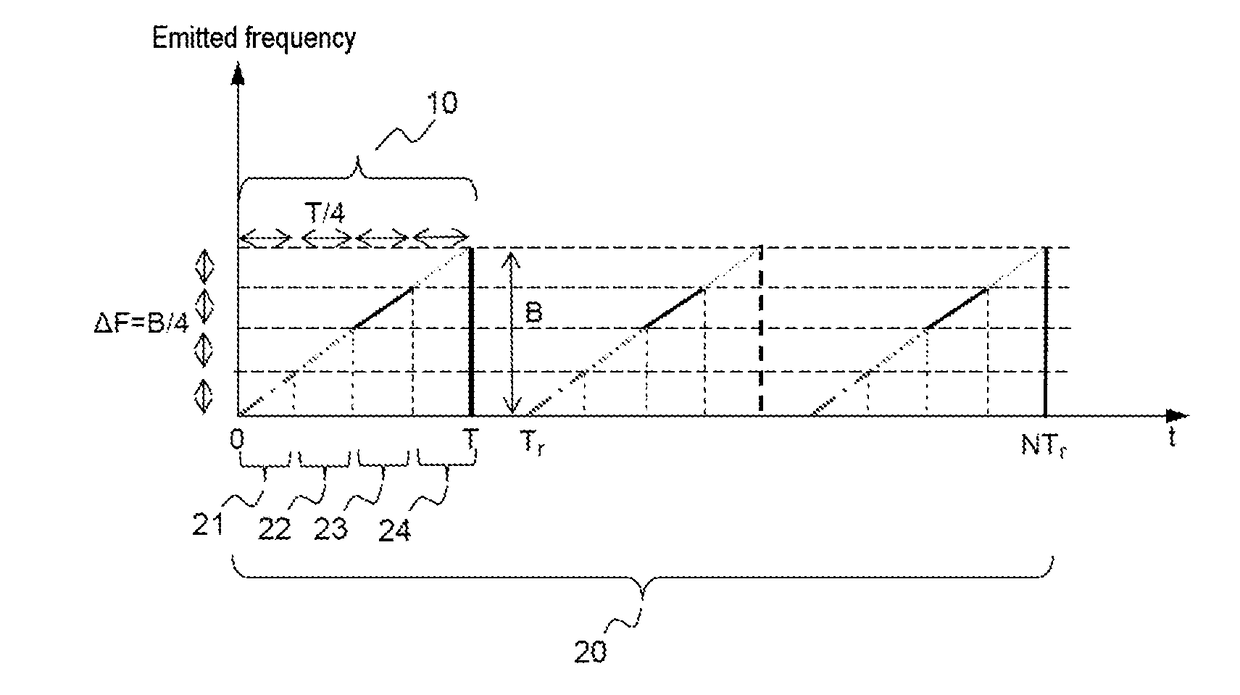
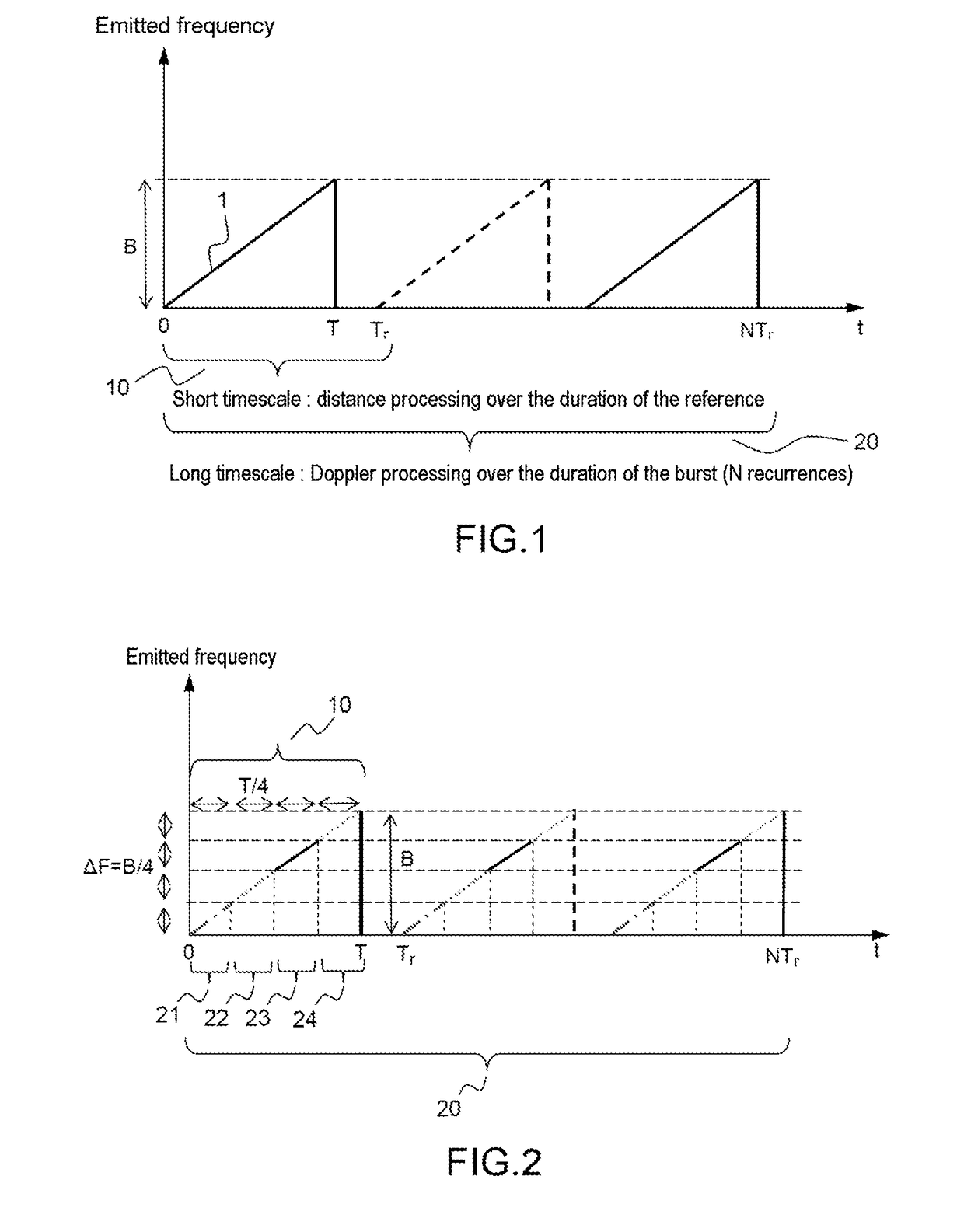
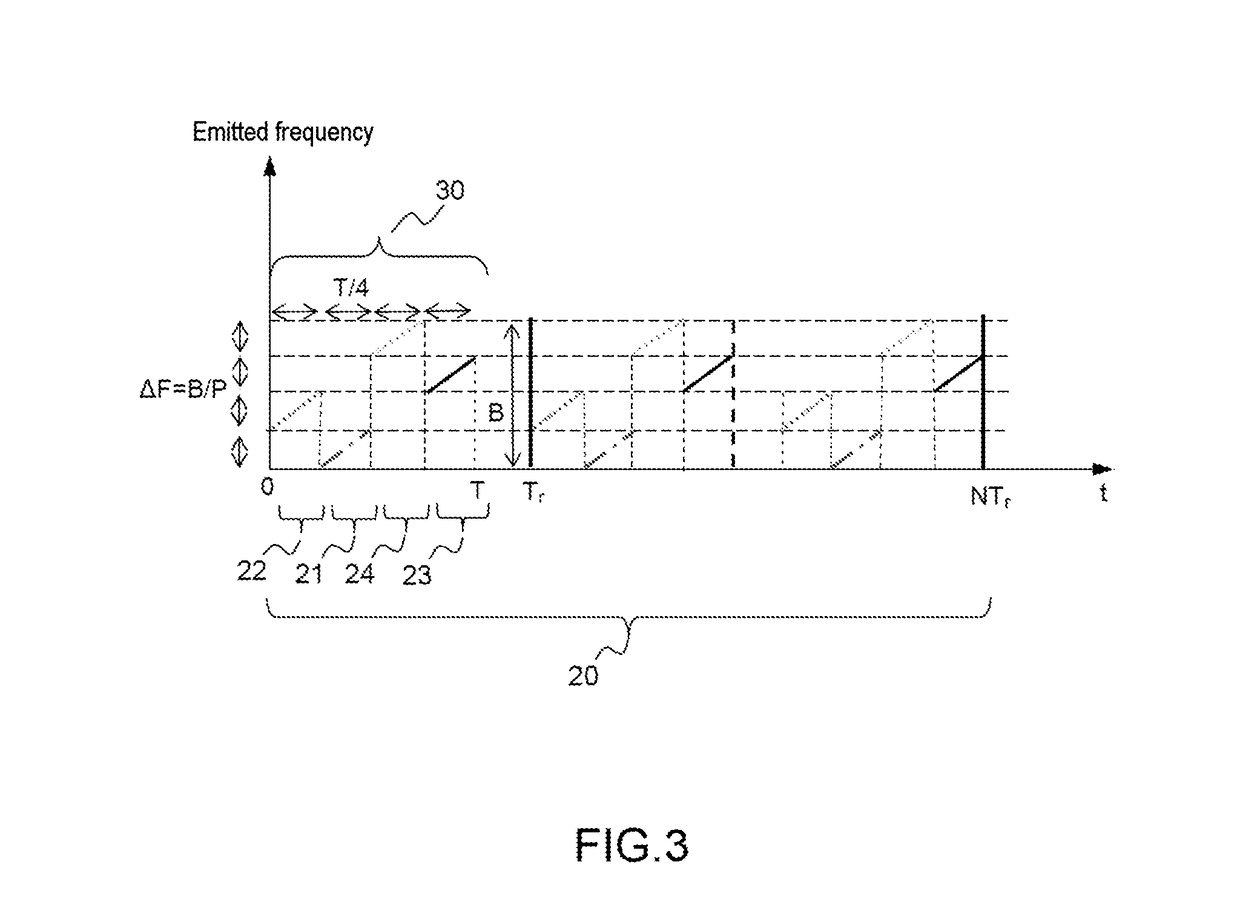
ActiveUS20180045819A1Reduce resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionRadar detection
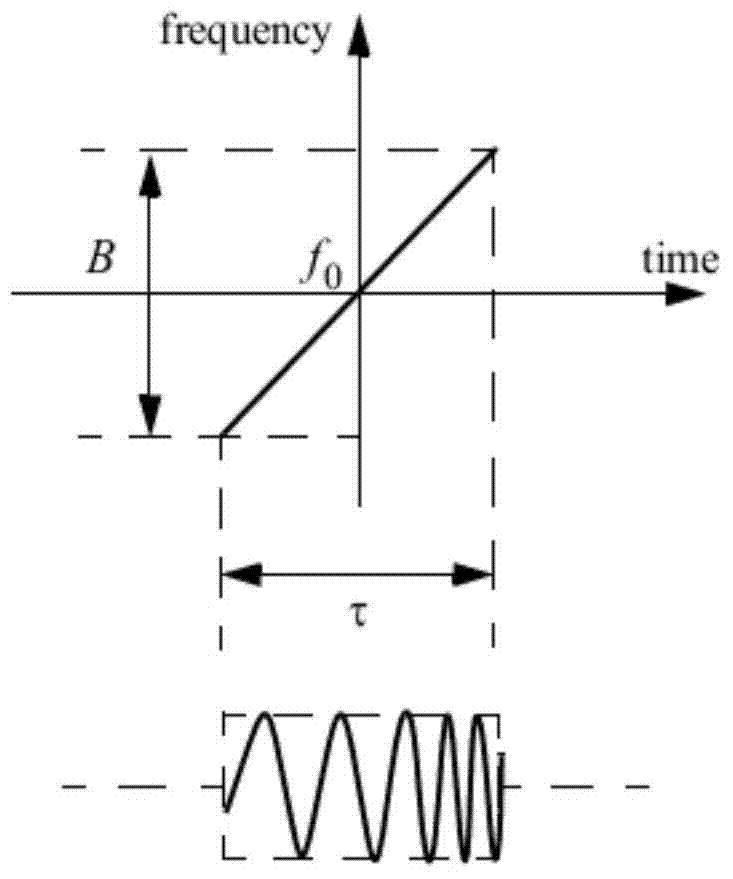
A detection method implementing an FMCW waveform is provided, the emitted waveform is formed of a recurring pattern of given period Tr covering an emission frequency band of given width B, each pattern being divided into a given number P of sub-patterns of duration Tr / P covering an excursion frequency band ΔF=B / P, the sub-patterns being mutually spaced by a frequency interval equal to ΔF. The radar performs: a first distance-compression processing operation carrying out a low-resolution distance compression at the scale of each recurring pattern on a fraction B / P of the emission band of width B corresponding to the frequency band covered by each of the sub-patterns; a Doppler processing operation on a given number N of successive recurrences so as to form P ambiguous distance-Doppler maps of low distance resolution, the maps being segmented into various speed domains; a second distance-compression processing operation of resolution that differs depending on the speed domain to which the relative speed of the target with respect to the radar belongs.
Owner:THALES SA
Radar system
ActiveUS7567202B2Easy to controlGenerate accuratelyAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Embodiments of the invention are concerned with a radar system, and relates specifically to scanning radar systems that are suitable for detecting and monitoring ground-based targets.In one aspect, the radar system is embodied as a scanning radar system comprising a frequency generator, a frequency scanning antenna, and a receiver arranged to process signals received from a target so as to identify a Doppler frequency associated with the target, wherein the frequency generator is arranged to generate a plurality of sets of signals, each set having a different characteristic frequency, the frequency generator comprising a digital synthesiser arranged to modulate a continuous wave signal of a given characteristic frequency by a sequence of modulation of patterns whereby to generate a said set of signals, and wherein the frequency scanning antenna is arranged to cooperate with the frequency generator so as to transceive radiation over a region having an angular extent dependent on the said generated frequencies.Embodiments of the invention thus combine digital synthesiser techniques, which are capable of precise frequency generation and control, with passive frequency scanning and Doppler processing techniques. This enables accurate control of range and of scan rates, and enables optimisation of range cell size for factors such as slow and fast target detection and Signal to Noise ratio, and thus enables detection of targets located at distances considerably farther away than is possible with known systems having similar power requirements.
Owner:BLIGHTER SURVEILLANCE SYST LTD
Devices and methods for tracking blood flow and determining parameters of blood flow
InactiveUS20080269609A1Small sizeBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationThinned array
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
Improved constant false alarm rate detecting method for ship-borne linear frequency modulation continuous wave radar
ActiveCN104237866AAccurate thresholdAvoid shadow effectWave based measurement systemsComputation complexityReference window
The invention discloses an improved constant false alarm rate detecting method for a ship-borne linear frequency modulation continuous wave radar and belongs to the field of signal processing. The method includes: the maximum value of each Doppler channel energy after Doppler treatment of each distance unit is used as the input of a two-dimensional reference window; judgment is performed twice, targets and backgrounds are preliminarily distinguished through the first judgment, and before the second judgment, the units judged as the targets by the first judgment are removed during energy average value calculation of the distance units. Compared with traditional CA_CFAR, the method has the advantages that the defect of mutual shielding of adjacent targets is overcome, the advantage of low calculation complexity of the traditional CA_CFAR is kept, and both detection performance and software-hardware implementation cost are considered.
Owner:WUHAN ZHONGYUAN ELECTRONICS GRP
Doppler tracking optical monopulse
A method and apparatus for finding a relative direction to, a radial speed of, and a distance to a target is described. A laser source illuminates the target and the Doppler shifted return beam is incident upon a window system at an angle and is transmitted therethrough. The magnitude of the transmitted Doppler shifted beam decreases due to Fresnel transmittance. Opposing photomixers then detect this transmitted Doppler shifted beam, thereby creating a pair of detection signals that are mixed with a local oscillator signal. The mixing process creates Doppler frequency signals that are subsequently processed to determine the radial speed of the target. Due to the Doppler frequency component of the signals, objects in the same direction, but moving at different radial speeds, can be discriminated, as the relative direction processing occurs after the Doppler processing.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Direct detection lidar system and method with synthetic doppler processing
ActiveUS20190086517A1Electromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase shiftedRadar systems
A detection system includes a signal transmitter for transmitting transmitted signals into a region and a receiver for receiving reflected signals generated by reflection of the transmitted signals and for generating receive signals indicative of the reflected signals. A processor coupled to the receiver receives the receive signals and processes the receive signals to generate detections of one or more objects in the region. The processing includes altering phase shift to generate phase-modulated signals from the receive signals and generating the detections from the phase-modulated signals.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
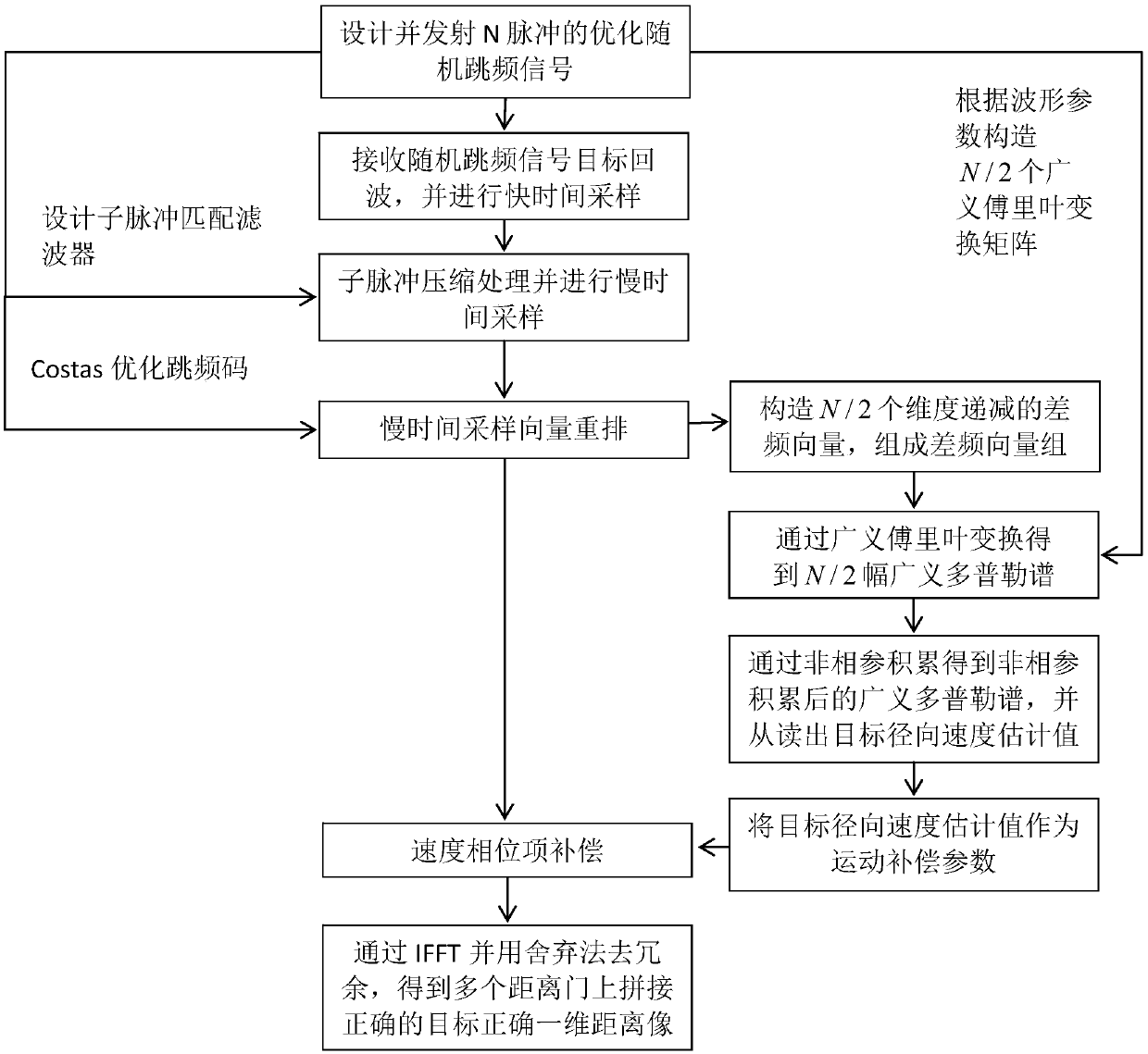
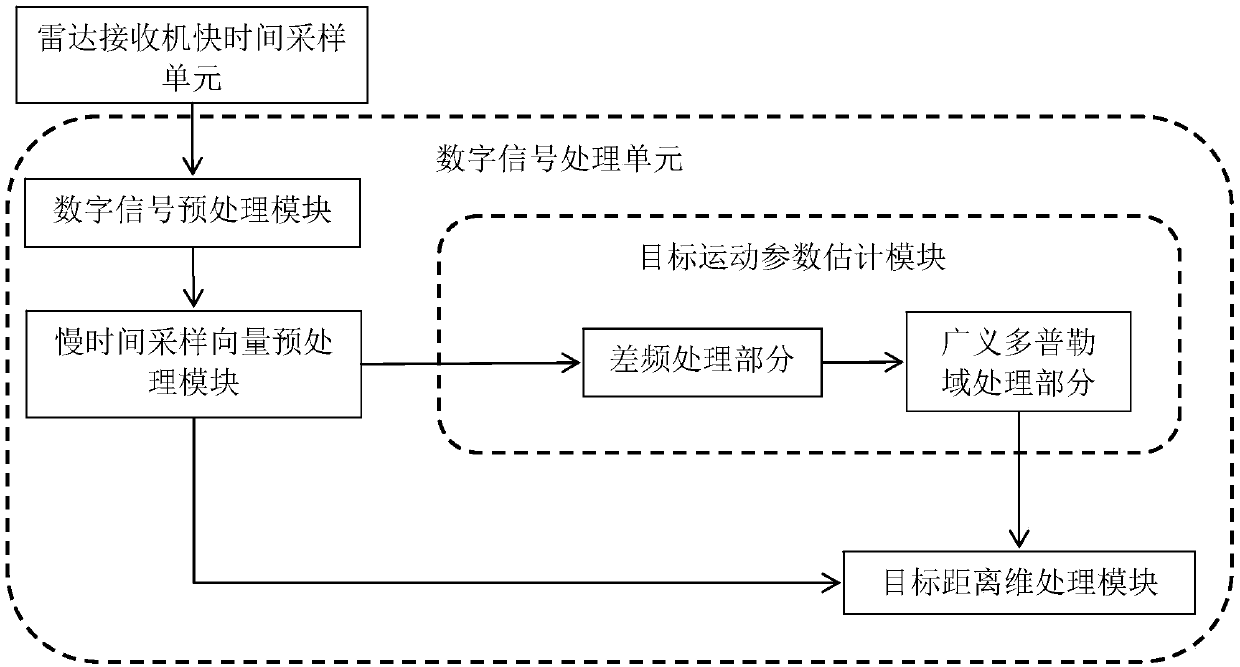
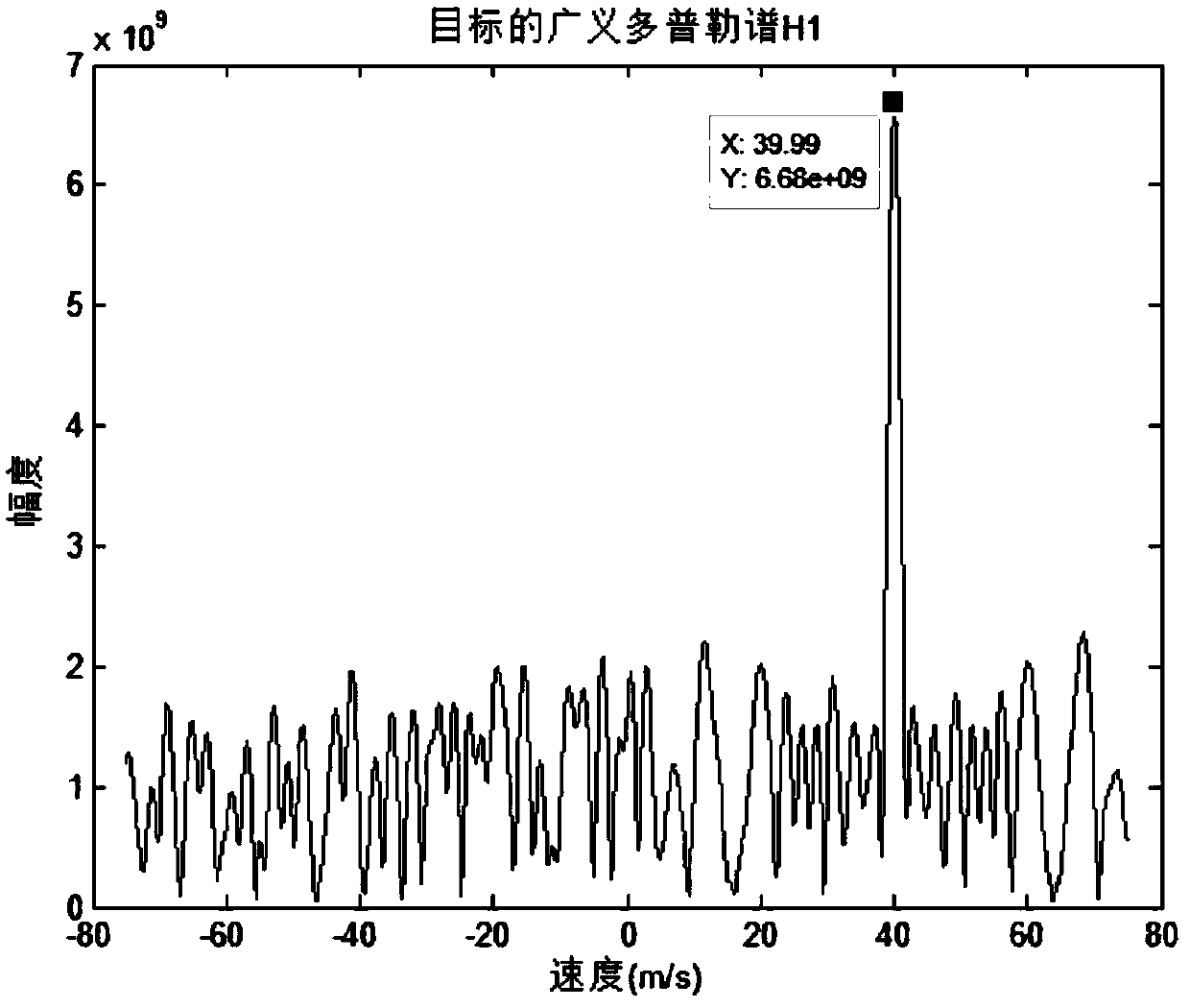
Target motion parameter estimation method for random frequency hopping radar
ActiveCN109061589ASmall amount of calculationCoherent accumulation time is shortICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCoherent integrationRange gate
The invention proposes a target motion parameter estimation method for a random frequency hopping radar, and solves the problem that the existing speed measurement scheme has a long accumulation time,a large calculation amount and a poor anti-noise performance. The method comprises the main steps of: designing a waveform parameter for transmitting a random frequency hopping signal and receiving atarget echo; preprocessing digital signals; preprocessing the slow time sampling vector; constructing a difference frequency vector group; constructing a Doppler domain generalized Fourier transformmatrix group; carrying out the generalized Doppler transform and non-coherent processing; carrying out motion compensation processing; and carrying out the coherent integration of distance dimensionsand de-redundance processing to obtain a one-dimensional range profile with the correct target in the plurality of range gates. According to the target motion parameter estimation method for the random frequency hopping radar, a set of dimension decreasing difference frequency vectors are constructed from the target echoes, generalized Doppler processing is performed on each difference frequency vector, and an estimated value of the target radial velocity can be read in the generalized Doppler spectrum after non-coherent integration. The method is short in accumulation time, small in calculation amount and good in anti-noise performance, and is used for target detection and pulse accumulation of the random frequency hopping radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Low-noise ultrasound method and beamformer system for doppler processing
ActiveUS7513873B2Low costImprove power efficiencyBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsLow noiseAnti-aliasing
An ultrasonic low-noise analog beamformer for Doppler acquisition achieves high sensitivity by translating the frequency of the ultrasound echoes to an intermediate frequency, which is well above of the 1 / f corner. This is accomplished by beamforming the downconverted RF signals instead of using their baseband representation. The baseband conversion, succeeding the beamformation, also incorporates the steps of clutter filtering and anti-aliasing. The invention is particularly suitable for low-voltage process technologies that support broadband applications.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Low-noise ultrasound method and beamformer system for doppler processing
ActiveUS20060079784A1Wide dynamic rangeLow costBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsLow noiseAnti-aliasing
An ultrasonic low-noise analog beamformer for Doppler acquisition achieves high sensitivity by translating the frequency of the ultrasound echoes to an intermediate frequency, which is well above of the 1 / f corner. This is accomplished by beamforming the downconverted RF signals instead of using their baseband representation. The baseband conversion, succeeding the beamformation, also incorporates the steps of clutter filtering and anti-aliasing. The invention is particularly suitable for low-voltage process technologies that support broadband applications.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Radar system
ActiveUS20080284651A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce frequencyAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Embodiments of the invention are concerned with a radar system, and relates specifically to scanning radar systems that are suitable for detecting and monitoring ground-based targets.In one aspect, the radar system is embodied as a scanning radar system comprising a frequency generator, a frequency scanning antenna, and a receiver arranged to process signals received from a target so as to identify a Doppler frequency associated with the target, wherein the frequency generator is arranged to generate a plurality of sets of signals, each set having a different characteristic frequency, the frequency generator comprising a digital synthesiser arranged to modulate a continuous wave signal of a given characteristic frequency by a sequence of modulation of patterns whereby to generate a said set of signals, and wherein the frequency scanning antenna is arranged to cooperate with the frequency generator so as to transceive radiation over a region having an angular extent dependent on the said generated frequencies.Embodiments of the invention thus combine digital synthesiser techniques, which are capable of precise frequency generation and control, with passive frequency scanning and Doppler processing techniques. This enables accurate control of range and of scan rates, and enables optimisation of range cell size for factors such as slow and fast target detection and Signal to Noise ratio, and thus enables detection of targets located at distances considerably farther away than is possible with known systems having similar power requirements.
Owner:BLIGHTER SURVEILLANCE SYST LTD
Navigation system for GPS denied environments
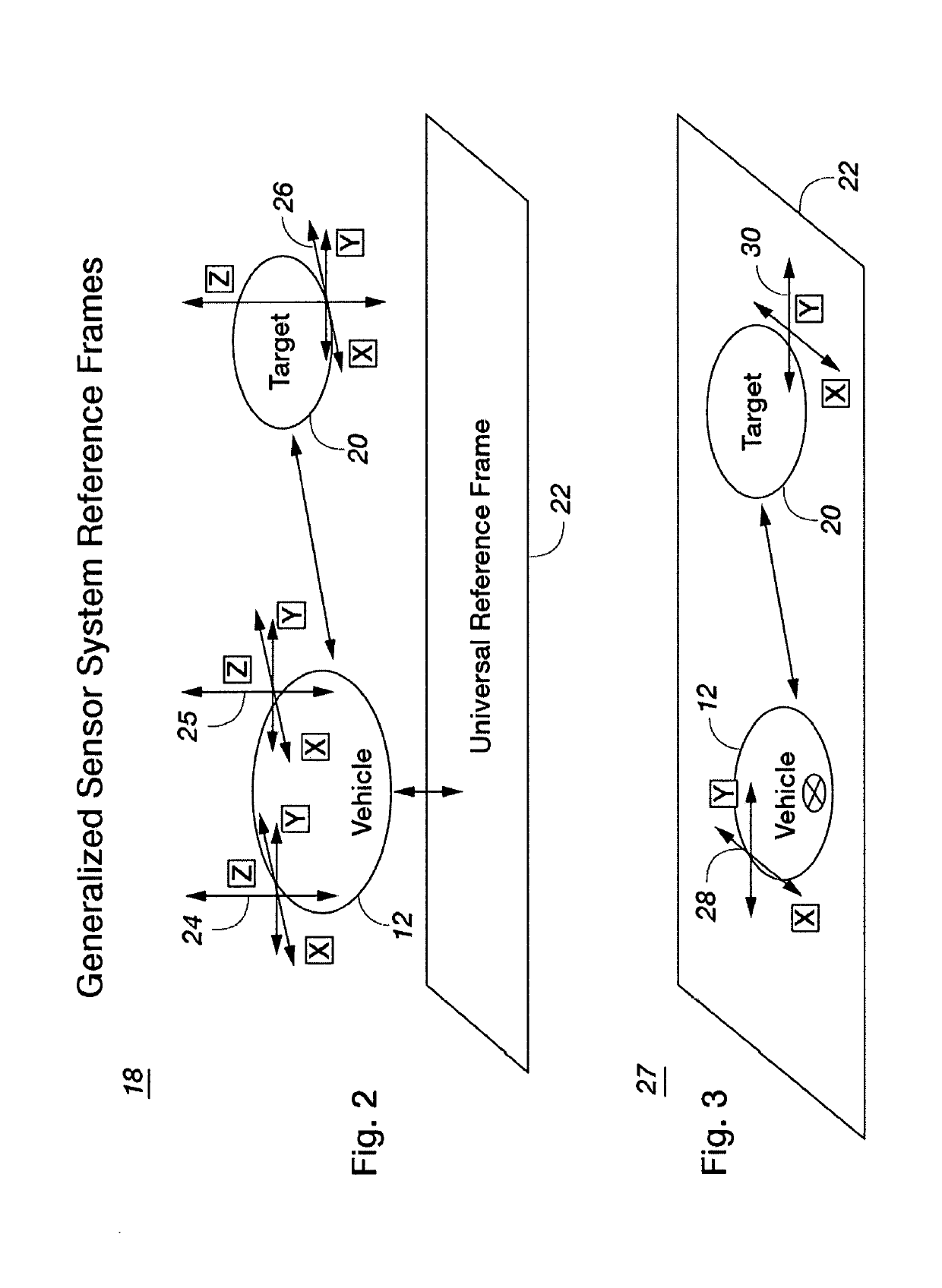
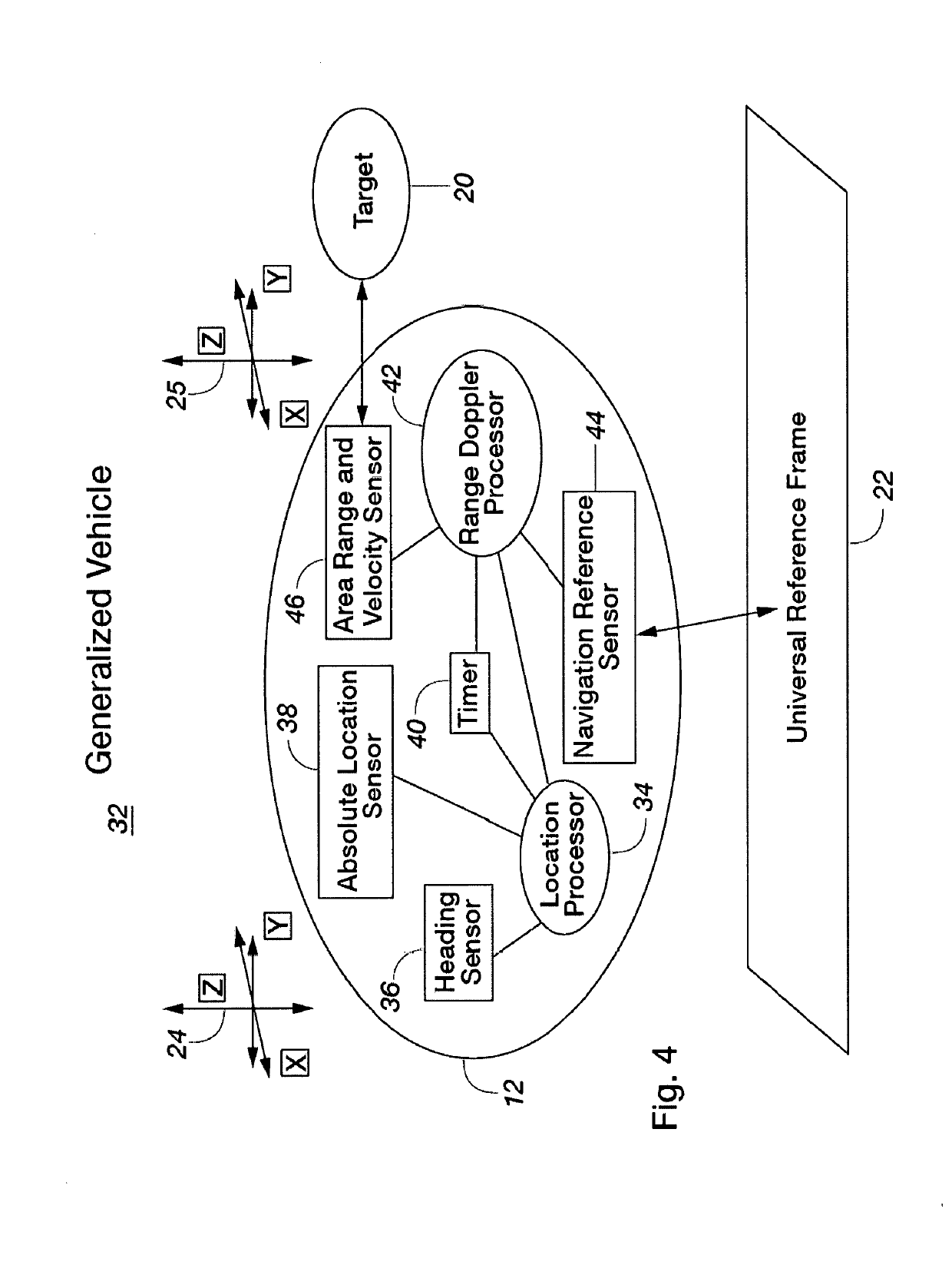
InactiveUS20200341117A1Eliminate systematic errorsImprove accuracyAutonomous decision making processElectromagnetic wave reradiationEngineeringNavigation system
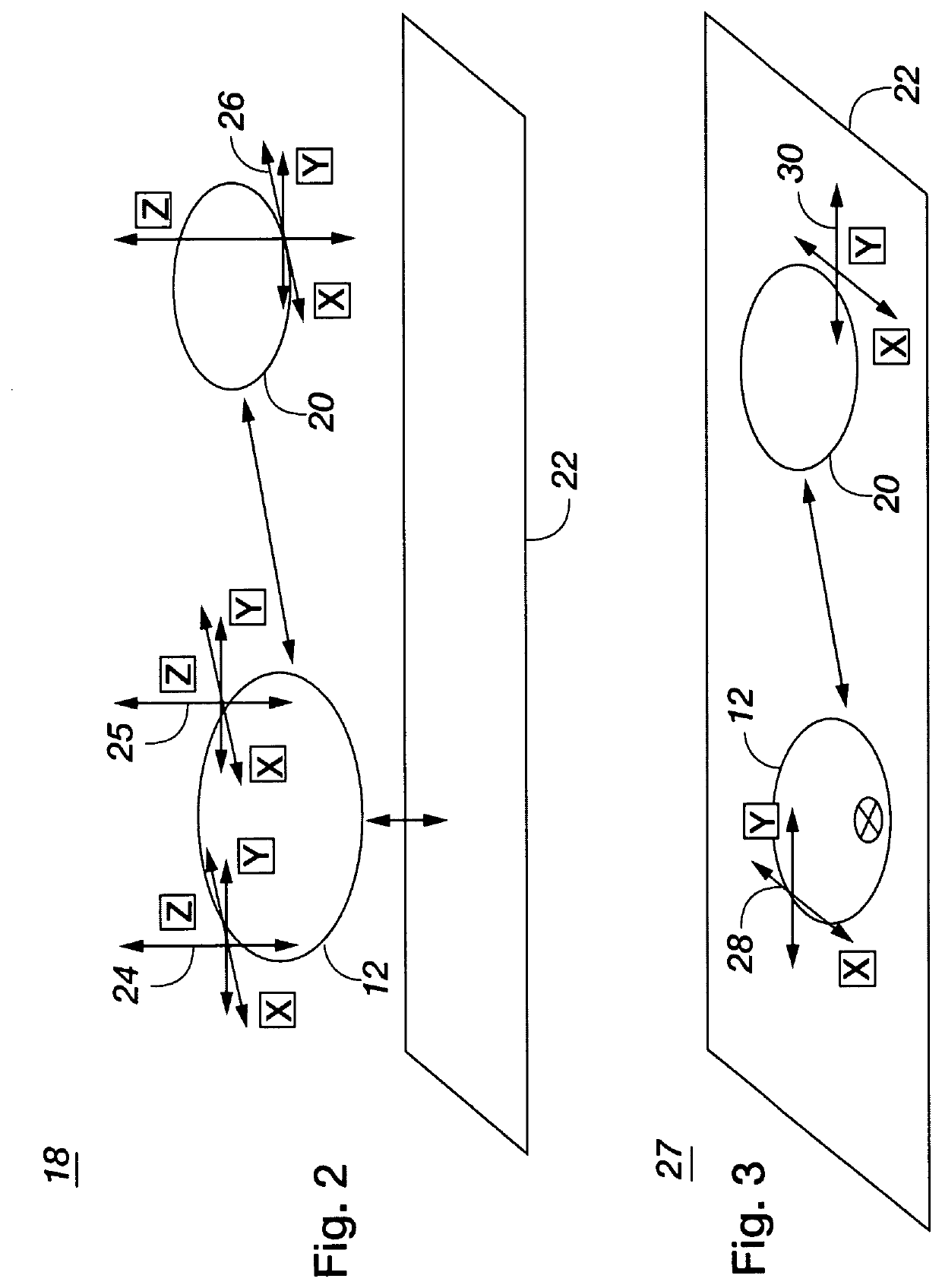
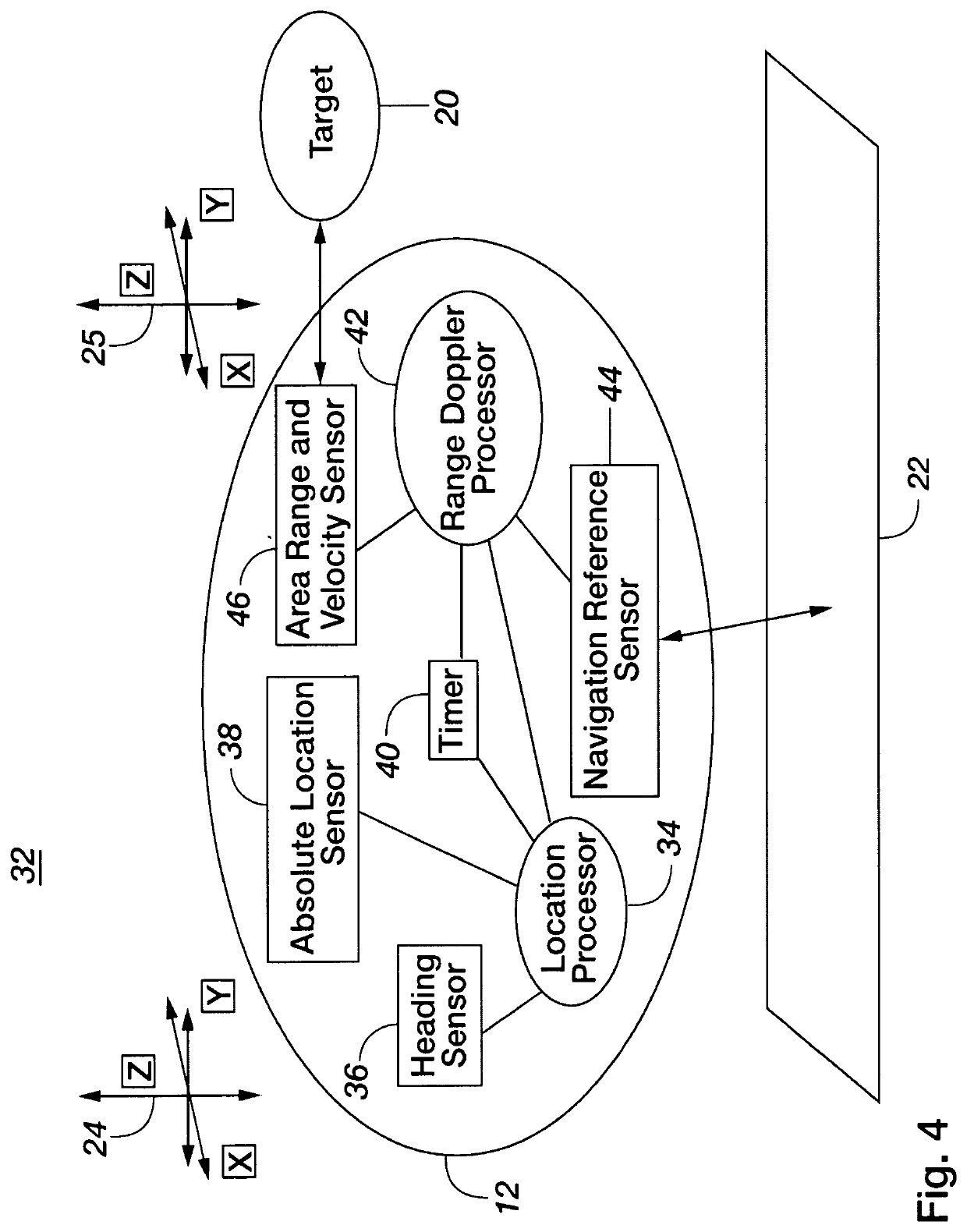
Methods and apparatus for providing self-contained guidance, navigation, and control (GN&C) functions for a vehicle moving through an environment on or near the ground, in the air or in space without externally provided information are disclosed. More particularly, one embodiment of the present invention includes a Heading Sensor (36), an Absolute Location Sensor (38), a timer (40), a Range Doppler Processor (42), a Navigation Reference Sensor (44), an Area Range and a Velocity Sensor (46) which provide enhanced navigation information about a universal reference frame (22) and one or more targets (20).
Owner:PSIONIC LLC
Signal processing method of conical scanning high-resolution microwave scatterometer
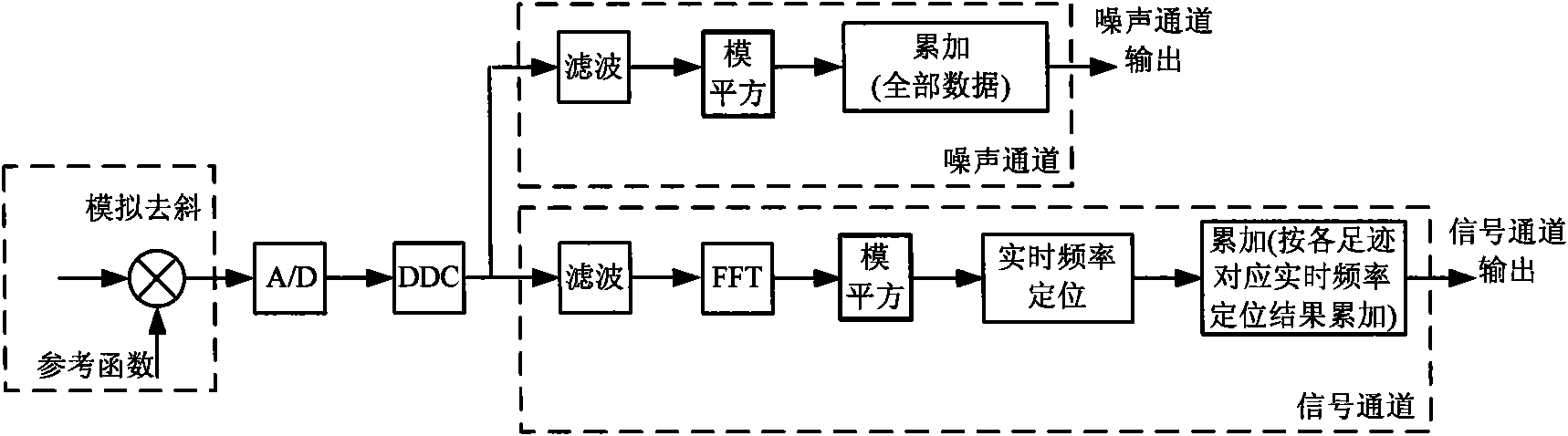
ActiveCN101672914AResolve orientation ambiguitySolve the distance problemRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationConical scanningScatterometer
The invention provides a signal processing method of a conical scanning high-resolution microwave scatterometer, which realizes azimuth high-resolution signal processing by the steps of echo (or internal calibration) signal acquiring, direct digital down-conversion (DDC) processing, narrowband distance filtering, distance de-chirping, distance fast Fourier transform (FFT), azimuth Doppler filtering, azimuth high-resolution processing (Doppler processing or deconvolution processing), modulus square processing, real-time frequency locating (required by fan beams but not by pencil beams), accumulating and the like. By adopting DBS or deconvolution processing in the azimuth direction, the method can improve the azimuth resolution and avoid adopting large-size antennae. The method solves the problem of distance ambiguity by adopting distance filtering and solves the problem of Doppler ambiguity by adopting azimuth filtering and can further decrease the size of the antennae so that the method can adopt DBS processing to improve the azimuth resolution in the form of small-size antennae.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Navigation system for GPS denied environments
ActiveUS20190302276A1Eliminate systematic errorsImprove accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation systemTimer
Methods and apparatus for providing self-contained guidance, navigation, and control (GN&C) functions for a vehicle moving through an environment on or near the ground, in the air or in space without externally provided information are disclosed. More particularly, one embodiment of the present invention includes a Heading Sensor (36), an Absolute Location Sensor (38), a timer (40), a Range Doppler Processor (42), a Navigation Reference Sensor (44), an Area Range and a Velocity Sensor (46) which provide enhanced navigation information about a universal reference frame (22) and one or more targets (20).
Owner:PSIONIC LLC
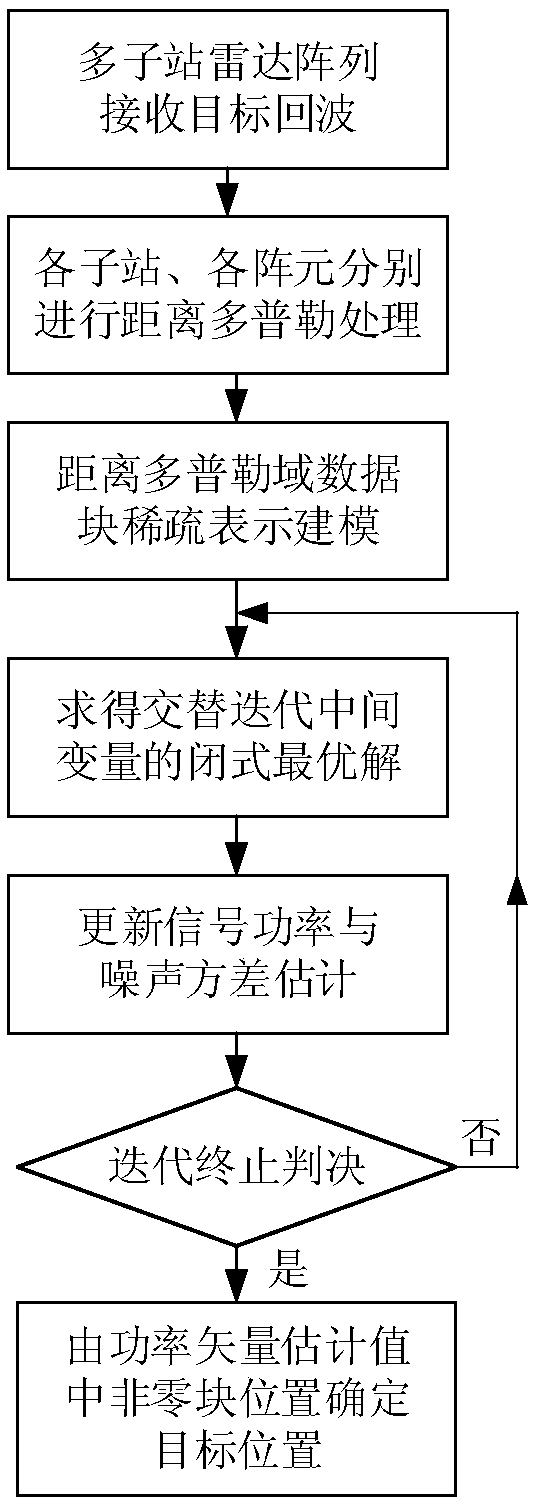
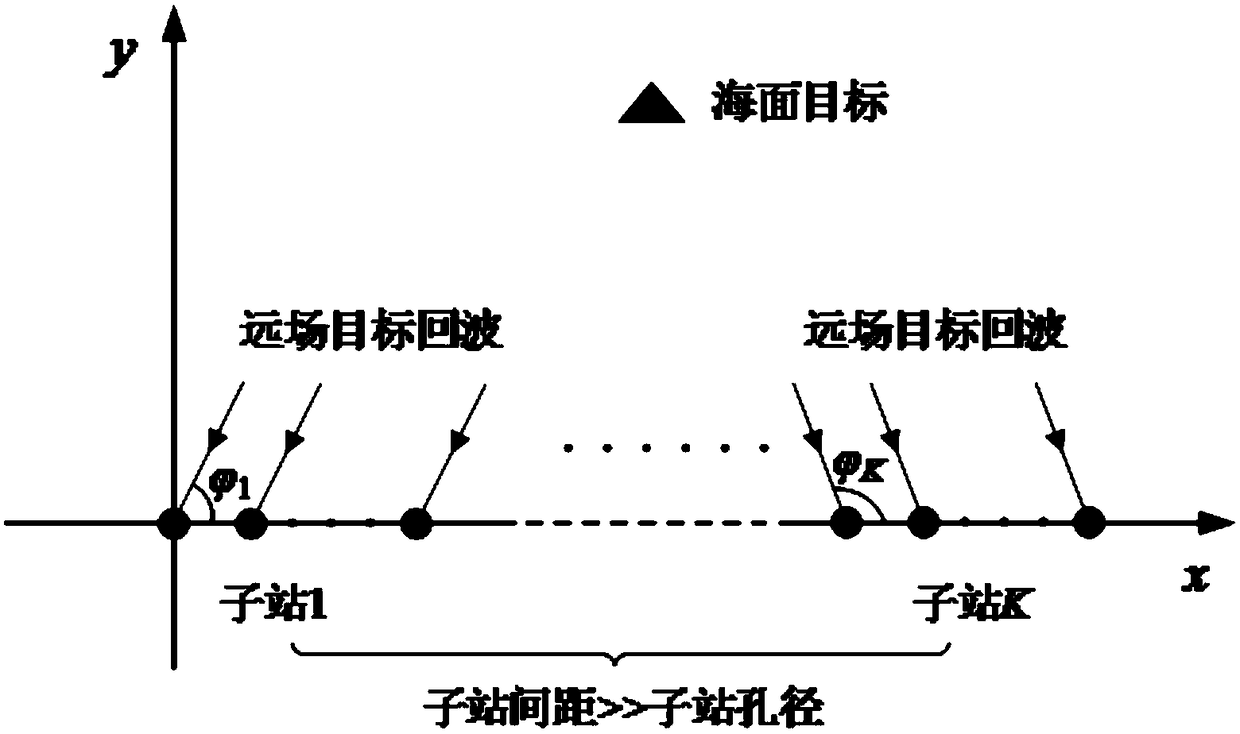
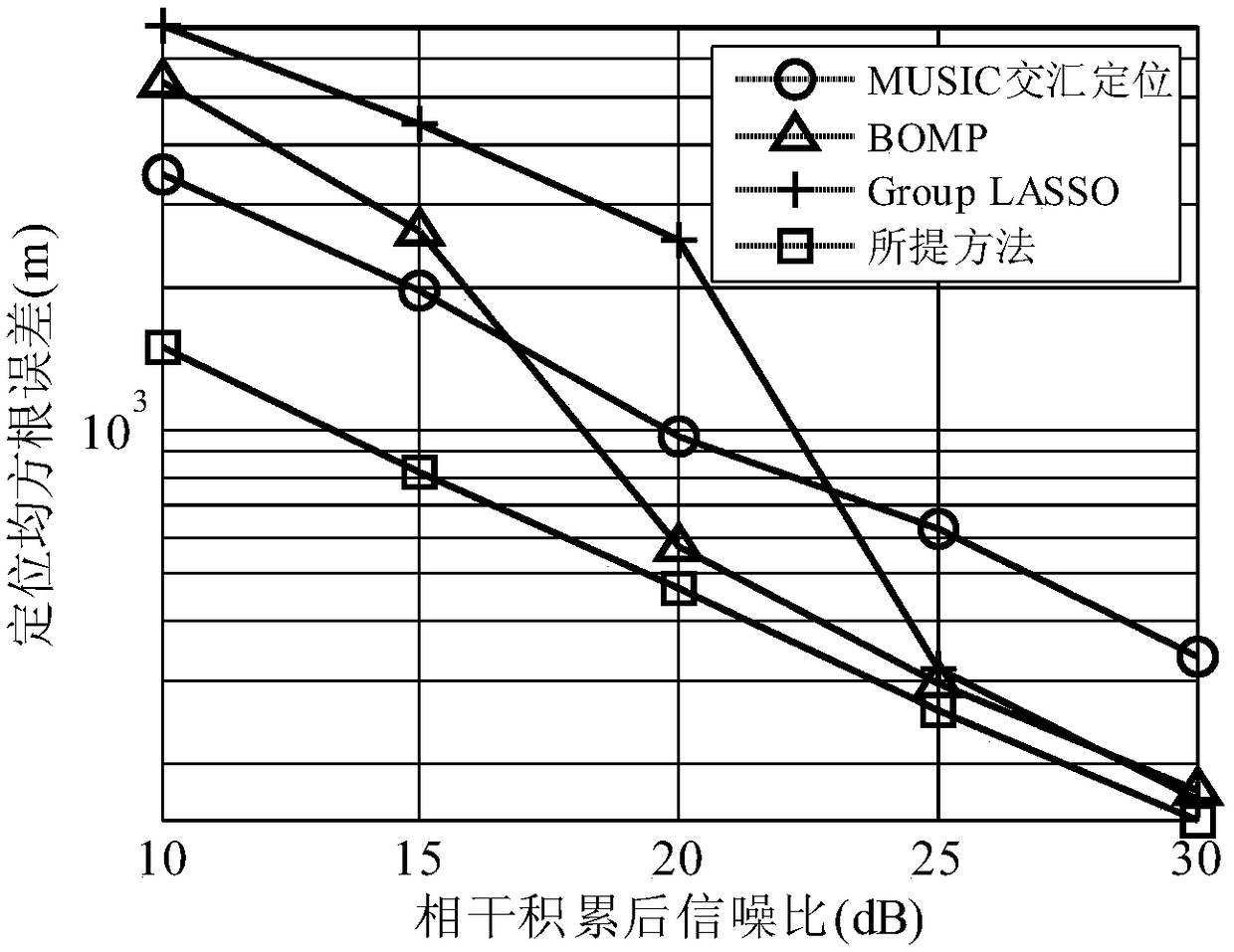
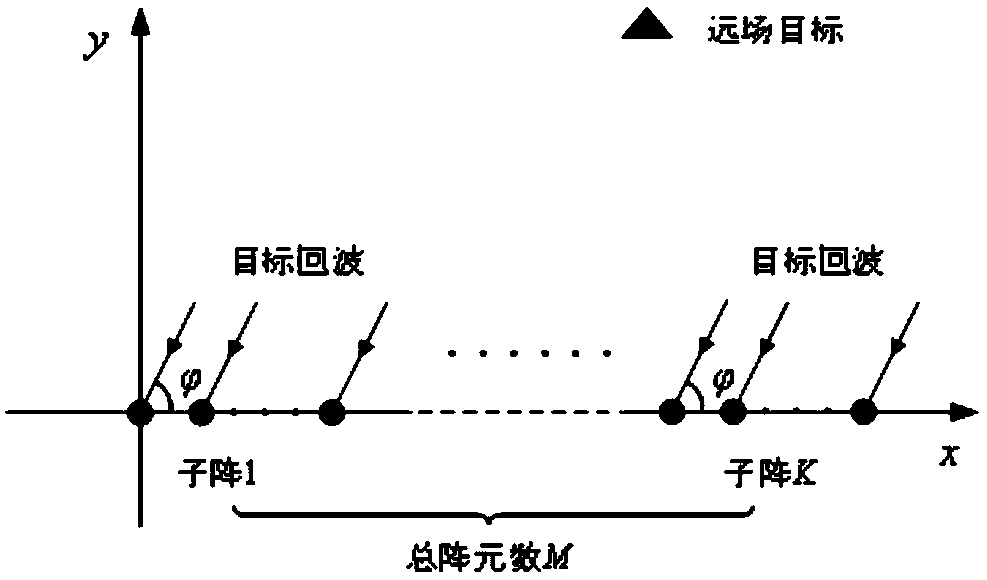
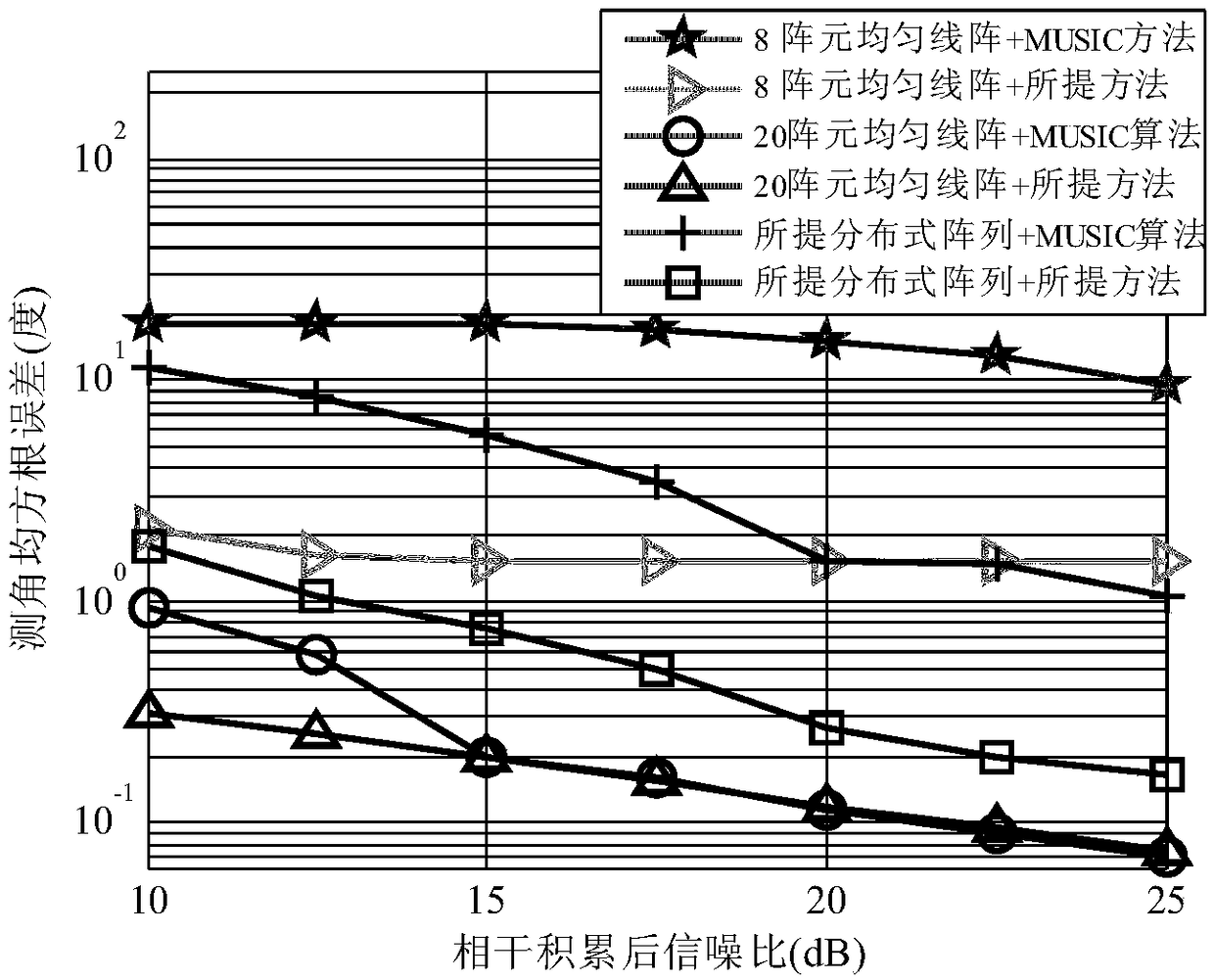
Large-aperture distributed multi-station target positioning method for high-frequency ground wave radar
ActiveCN109212527AImprove robustnessPrecise positioningICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionArray elementWave radar
The invention provides a large-aperture distributed multi-station target positioning method for a high-frequency ground wave radar. The large-aperture distributed multi-station target positioning method for the high-frequency ground wave radar comprises the steps of: (1), performing data snapshot extraction of a range Doppler processing domain of each receiving array element in each radar sub-station; (2), performing data block sparse-representation modelling and cost function construction; (3), performing alternative optimization solution of the signal power vector; and (4), obtaining a two-dimensional coordinate space spectrum, and realizing target positioning by utilizing the spectrum peak position. According to the target positioning method provided in the invention, only data snapshotof the single distance Doppler domain is at least needed; the known target number does not need to be prior; parameters do not need to be artificially adjusted; compared with the traditional radar multi-station target positioning method, the maximum target number is not limited by the array element number in the sub-station in the method; furthermore, the aperture advantage of the distributed multi-station array is effectively utilized; and the target positioning precision is relatively high.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
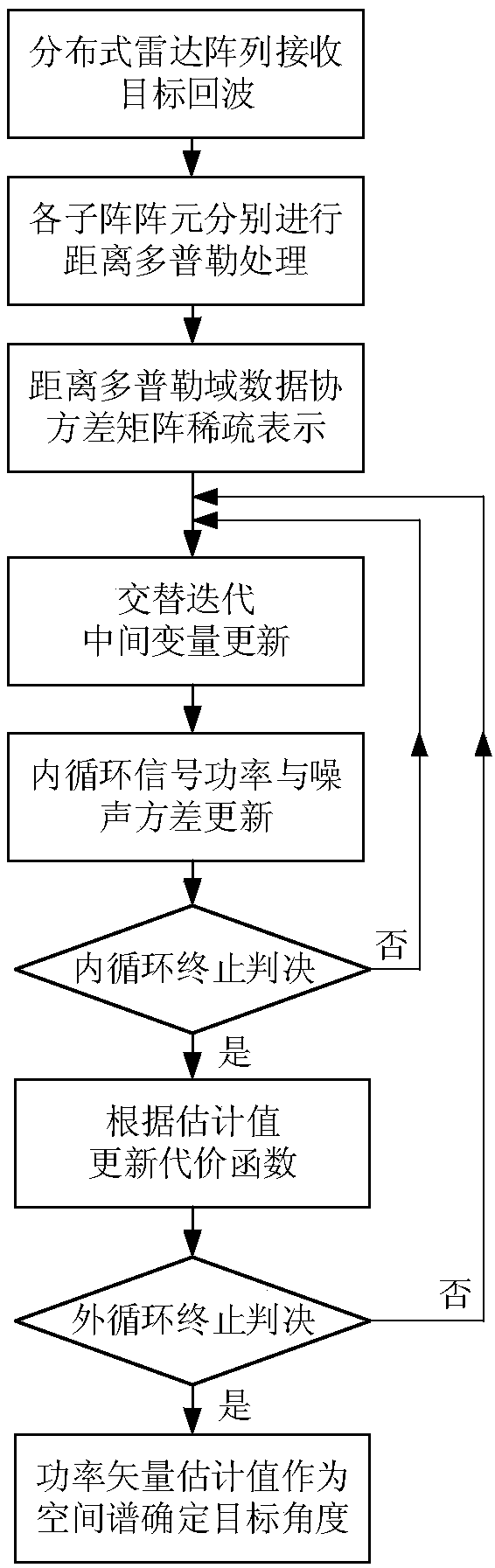
Distributed array target angle measurement method for high-frequency ground wave radar
ActiveCN109212526AReduce transfer volumeLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionArray elementOptimization problem
The invention provides a distributed array target angle measurement method for a high-frequency ground wave radar. The distributed array target angle measurement method for the high-frequency ground wave radar is characterized by comprising the steps of: (1), performing range Doppler processing on received echo of the array element of each radar sub-array; (2), performing data covariance matrix sparse-representation modelling; (3), performing conversion of an optimization problem to be solved; (4), performing internal cylinder to update a signal power estimation value; and (5), performing external cylinder to update a cost function, and finally obtaining target angle estimation. Compared with the traditional radar array, the distributed array adopted in the invention is flexible to arrangeand convenient to perform site selection; furthermore, the direction finding performance of the traditional array having relatively large aperture can be realized only through few array elements; according to the angle measurement method provided in the invention, only the single snapshot of a range Doppler domain is at least needed; the known target number and any artificial parameter adjustmentare unnecessary; and the direction finding performance is also obviously superior to that of the traditional radar angle measurement method.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Signal processing device, radar apparatus, target object method
ActiveUS20140062760A1Eliminate errorsReduce distractionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correctionSignal generator
A signal processing device is provided. The device includes an echo signal input unit for receiving echo signals resulted from transmission signals reflected on an object. The transmission signals are transmitted from a transmission source at transmission timings at predetermined time intervals, at least one of the transmission timings shifted from the other timings in time. The device includes a complex reception signal generator for generating complex reception signals, a phase calculator for calculating a phase change amount of the complex reception signals with respect to a reference phase, a phase corrector for phase-correcting the complex reception signals and outputting the corrected signals, and a Doppler processor for performing Doppler processing on the corrected signals and outputting the Doppler-processed signals as Doppler echo signals of the object.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
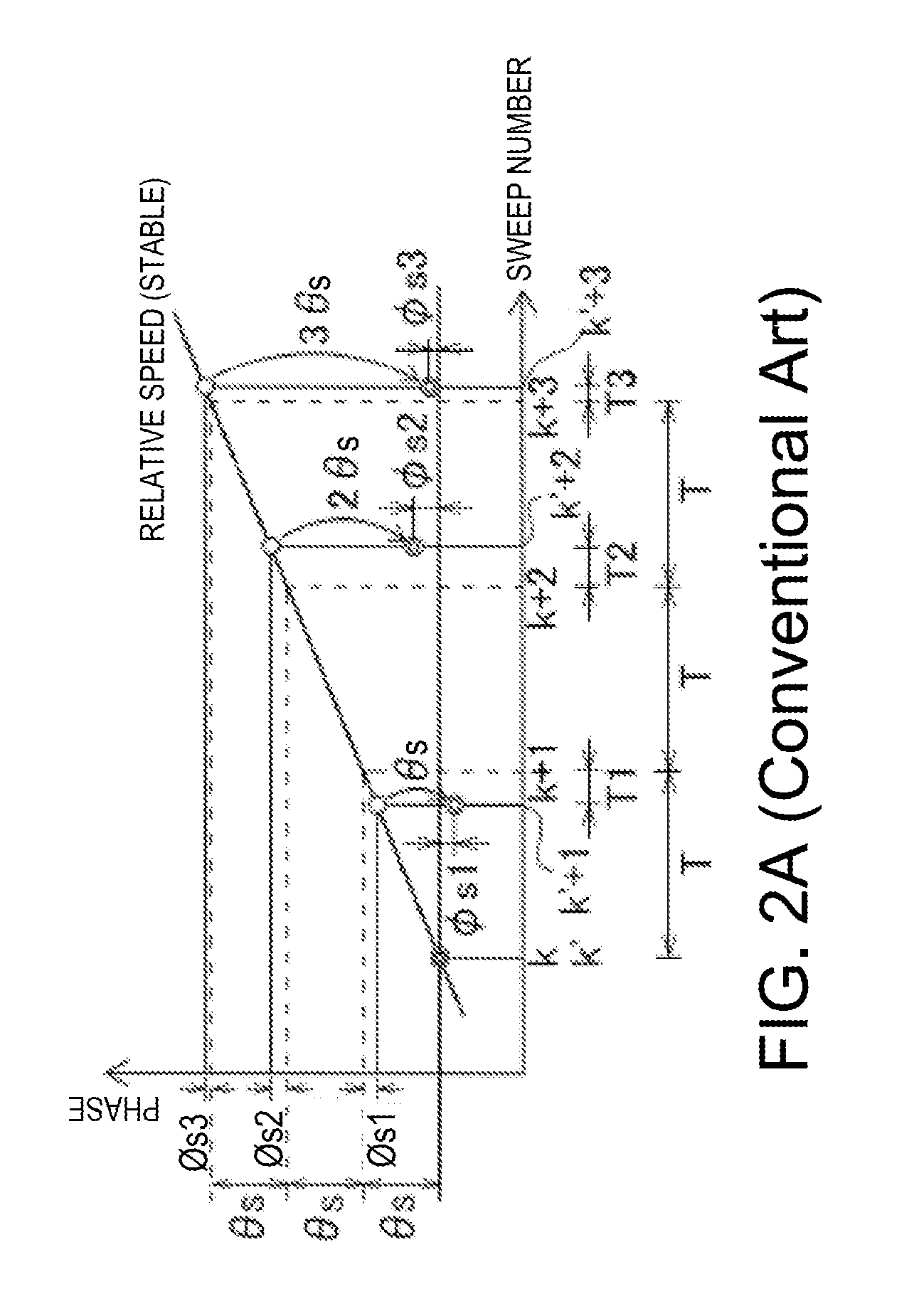
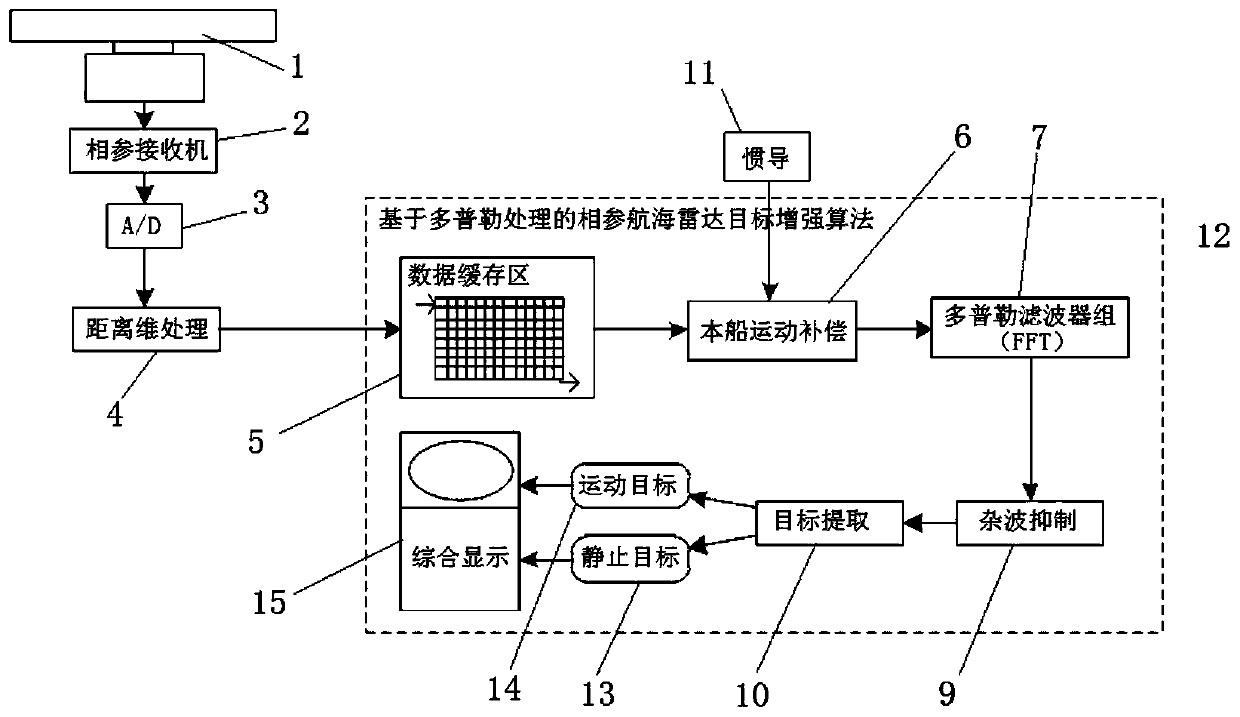
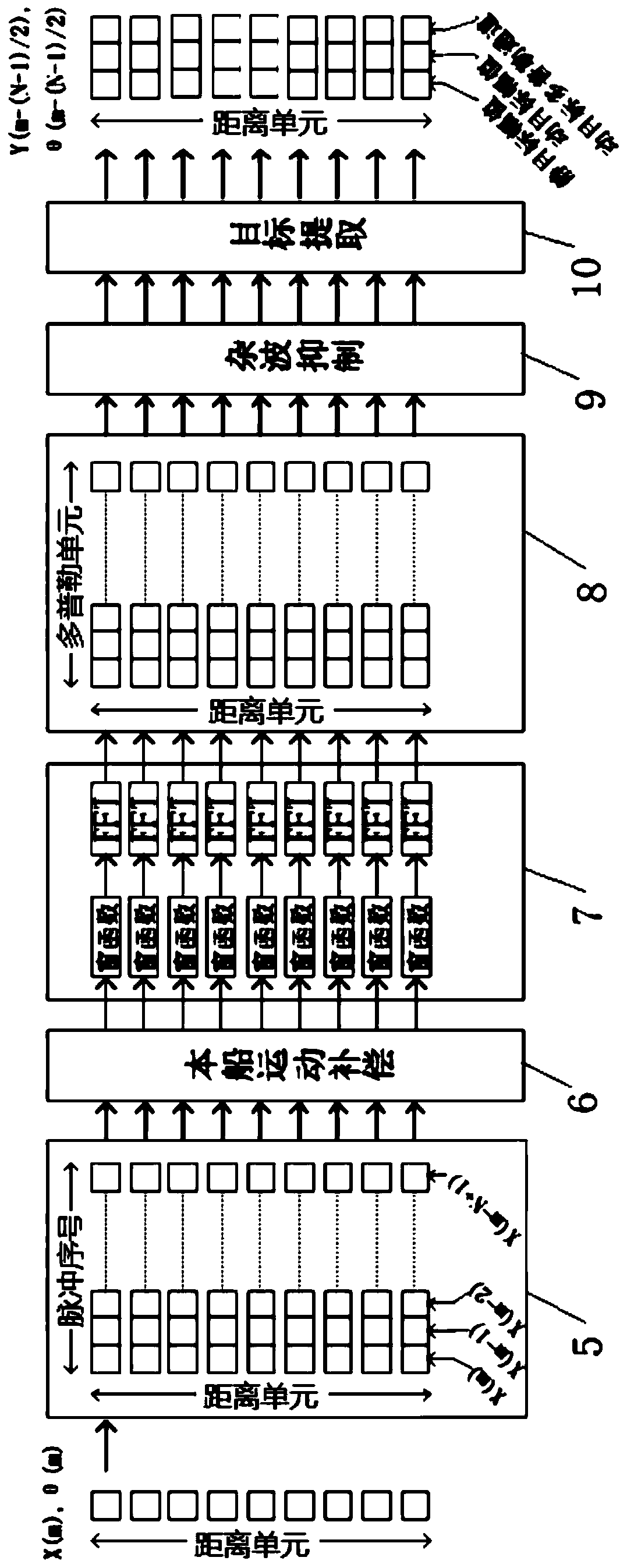
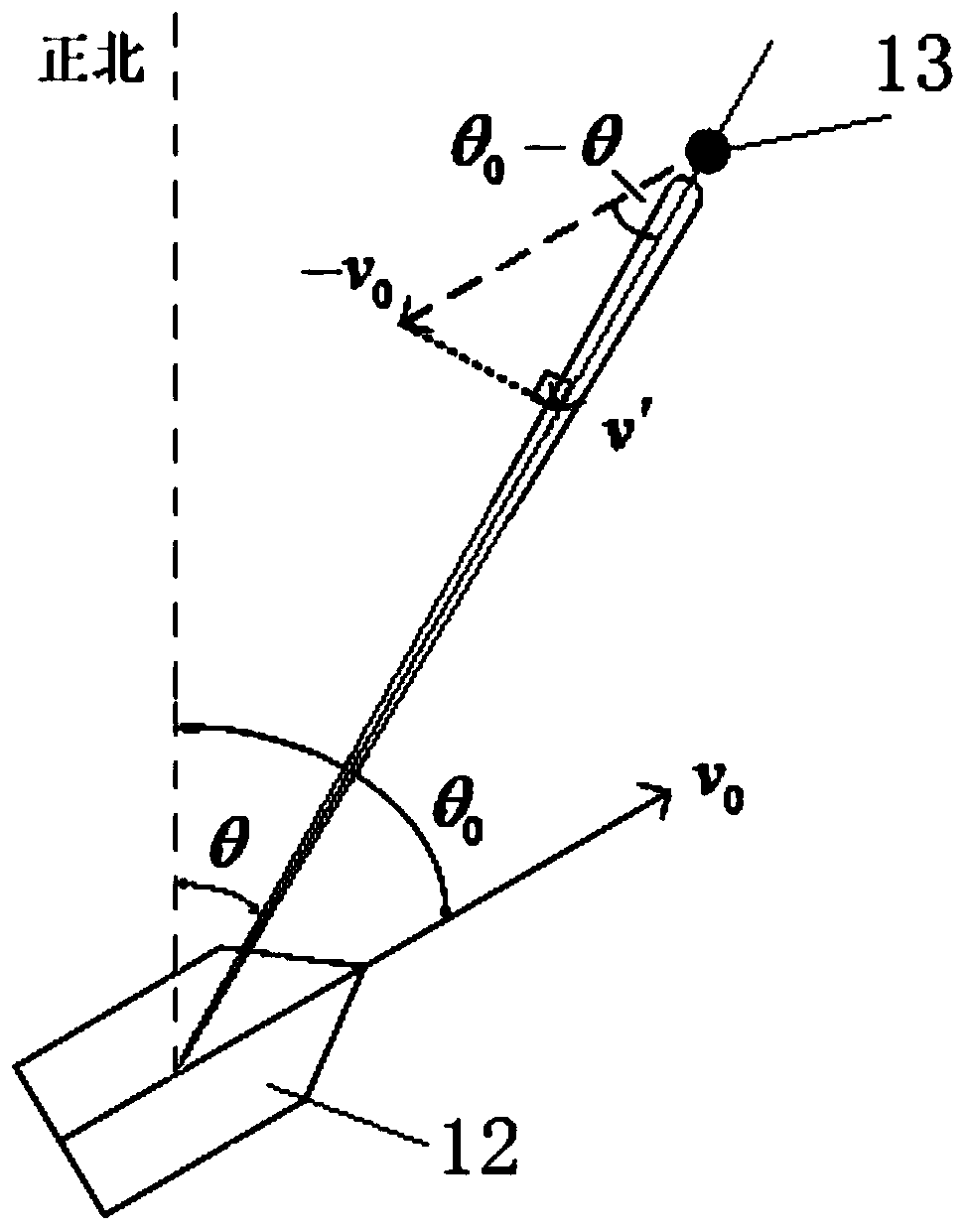
Coherent navigation radar target enhancement technology based on Doppler processing
PendingCN110703239AAchieving coherent accumulationSuppress motion clutterRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhysicsReceiver
The invention relates to a coherent navigation radar target enhancement technology based on Doppler processing. Based on a coherent receiver, a reasonable signal processing flow is designed, under thepremise of not changing the working mode comprising an antenna rotating speed and pulse repetition frequency of the existing navigation radar, Doppler processing is performed by using a data buffer area and by using a sliding window FFT method to form a distance-Doppler two-dimensional map, and present ship motion compensation is performed, so that a stationary target is located at a zero Dopplerchannel; then adaptive clutter suppression is performed, such as dynamic clutter of sea clutter and rain clutter; the stationary target and a moving target are respectively extracted and stored according to Doppler characteristics, and finally, echo images of the stationary target and the moving target are adjusted separately and displayed comprehensively by using double threshold detection and overlapping two-color maps. According to the coherent navigation radar target enhancement technology provided by the invention, the target detection capability under the condition of sea clutter is greatly improved by automatically suppressing the clutter, and the high-threat moving target is highlighted to give full play to the superior performance of coherent navigation radars.
Owner:上海广电通信技术有限公司
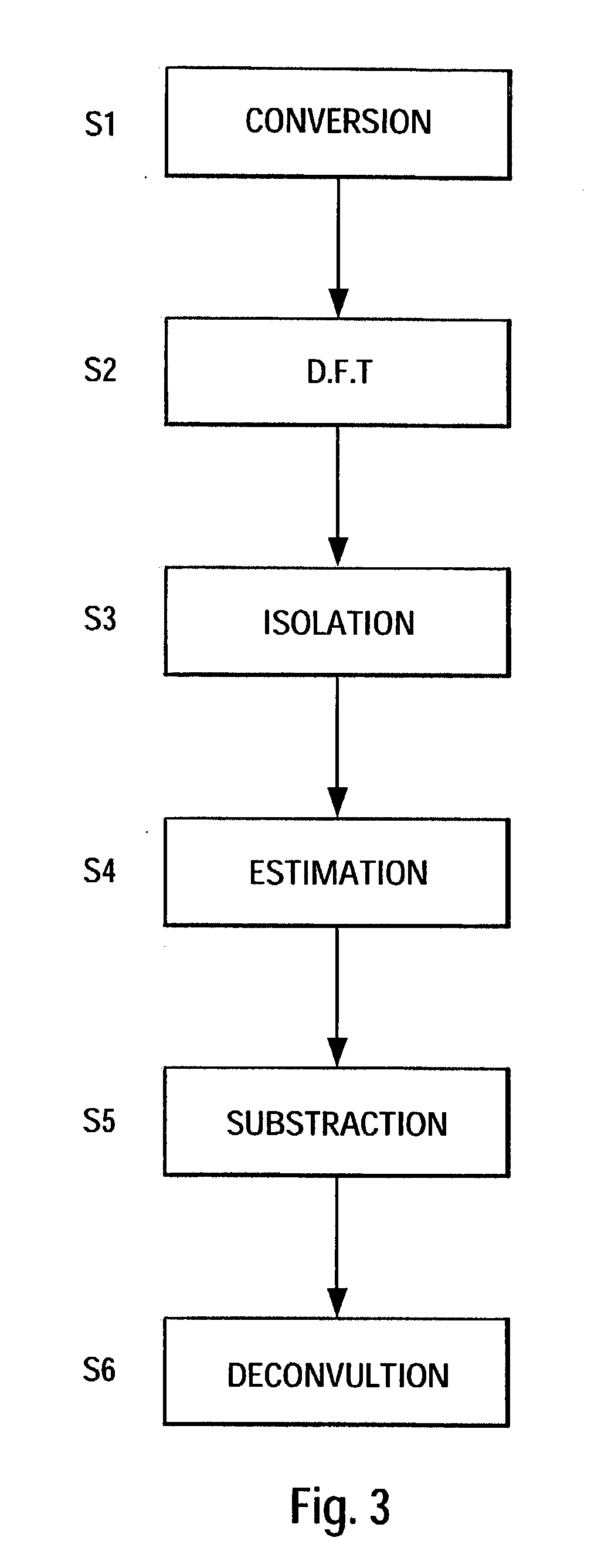
Irregular PRT deconvolution method and systems, and its uses
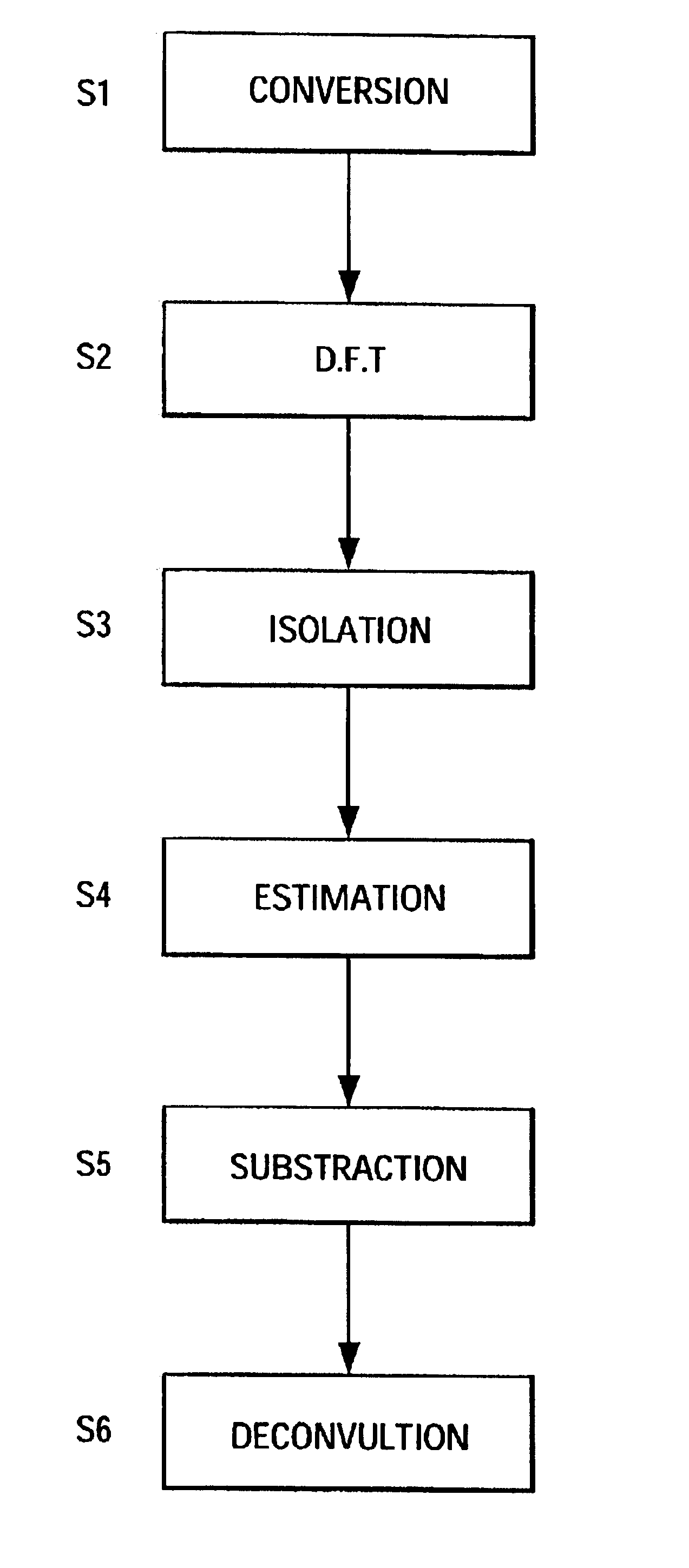
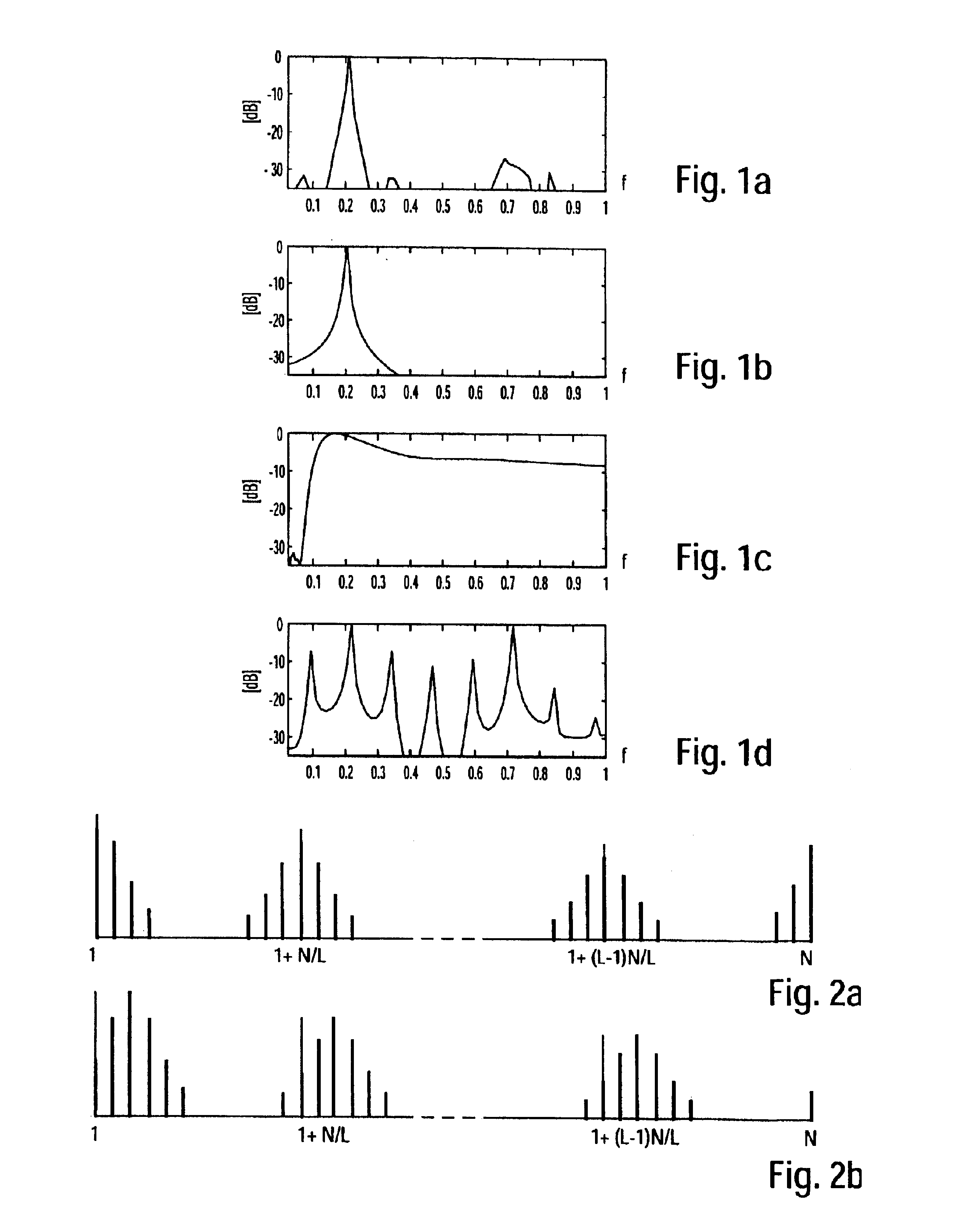
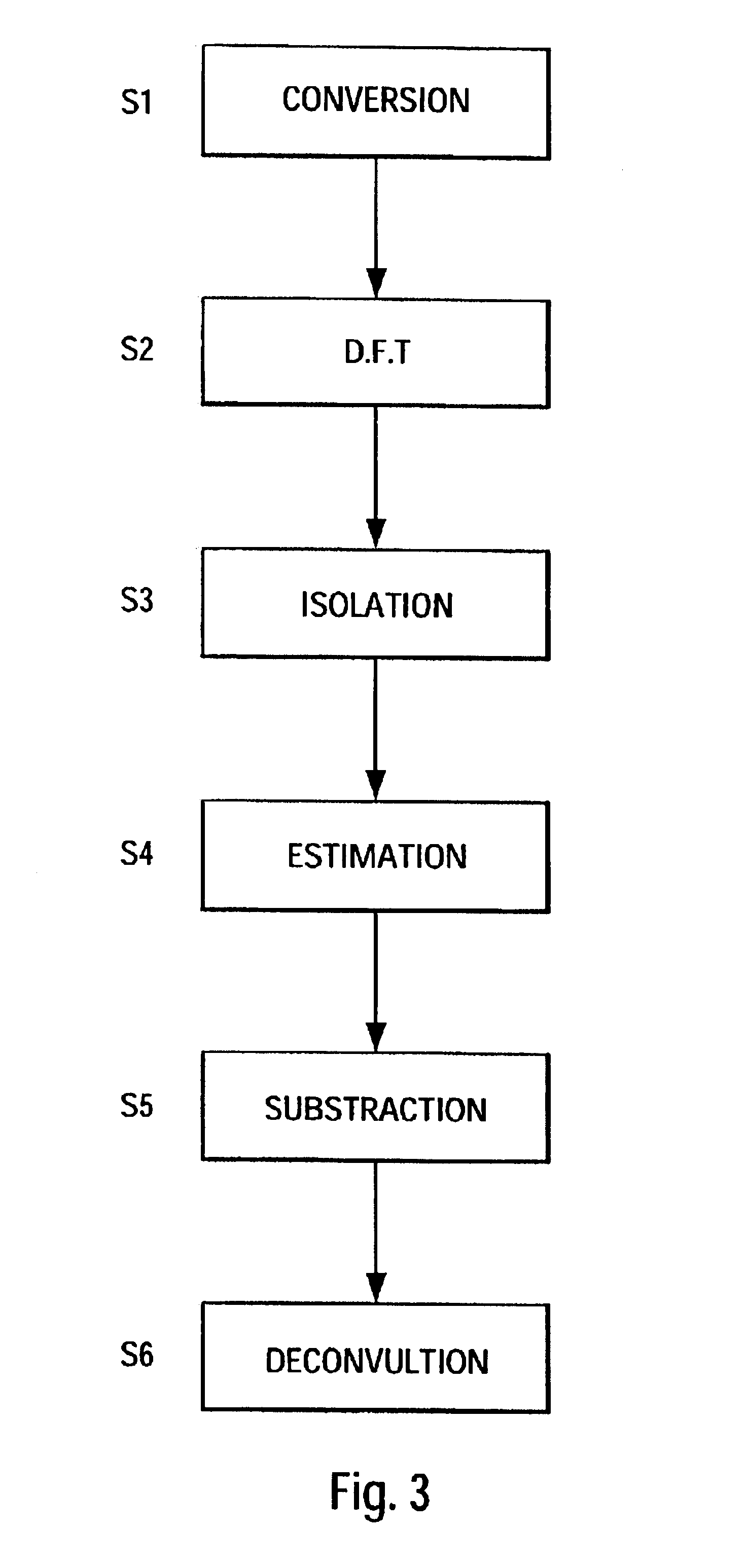
This invention relates to radar signal processing. In particular, this invention concerns Doppler processing and clutter filtering on irregular Pulse Repetition Time (PRT) sampled signal.This invention solves the above-mentioned drawbacks, in particular solving the velocity ambiguity and filtering any type of clutter, providing a deconvolution method which filter any kind of clutter even varying clutter like sea clutter, rain clutter . . .The deconvolution method of irregular pulse repetition time sampled signal x(tm), comprises the following steps:[S1] conversion of the irregular samples x(tm) to regular samples r(iTepsilon);[S2] computation of the spectrum dft(r) of these regular samples;[S3] isolation of the clutter spectra in dft(r) by assuming clutter spreads over more than a few range gates;[S4] estimation of the clutter spectral lines from the mean and the width of the isolated clutter spectra;[S5] subtraction of the estimated clutter spectra from the total spectrum dft(r);[S6] deconvolution of the remaining spectra.
Owner:THALES NEDERLAND BV
Irregular PRT deconvolution method and systems, and its uses
This invention relates to radar signal processing. In particular, this invention concerns Doppler processing and clutter filtering on irregular Pulse Repetition Time (PRT) sampled signal. This invention solves the above-mentioned drawbacks, in particular solving the velocity ambiguity and filtering any type of clutter, providing a deconvolution method which filter any kind of clutter even varying clutter like sea clutter, rain clutter . . . The deconvolution method of irregular pulse repetition time sampled signal x(tm), comprises the following steps: [S1] conversion of the irregular samples x(tm) to regular samples r(iTepsilon); [S2] computation of the spectrum dft(r) of these regular samples; [S3] isolation of the clutter spectra in dft(r) by assuming clutter spreads over more than a few range gates; [S4] estimation of the clutter spectral lines from the mean and the width of the isolated clutter spectra; [S5] subtraction of the estimated clutter spectra from the total spectrum dft(r); [S6] deconvolution of the remaining spectra.
Owner:THALES NEDERLAND BV
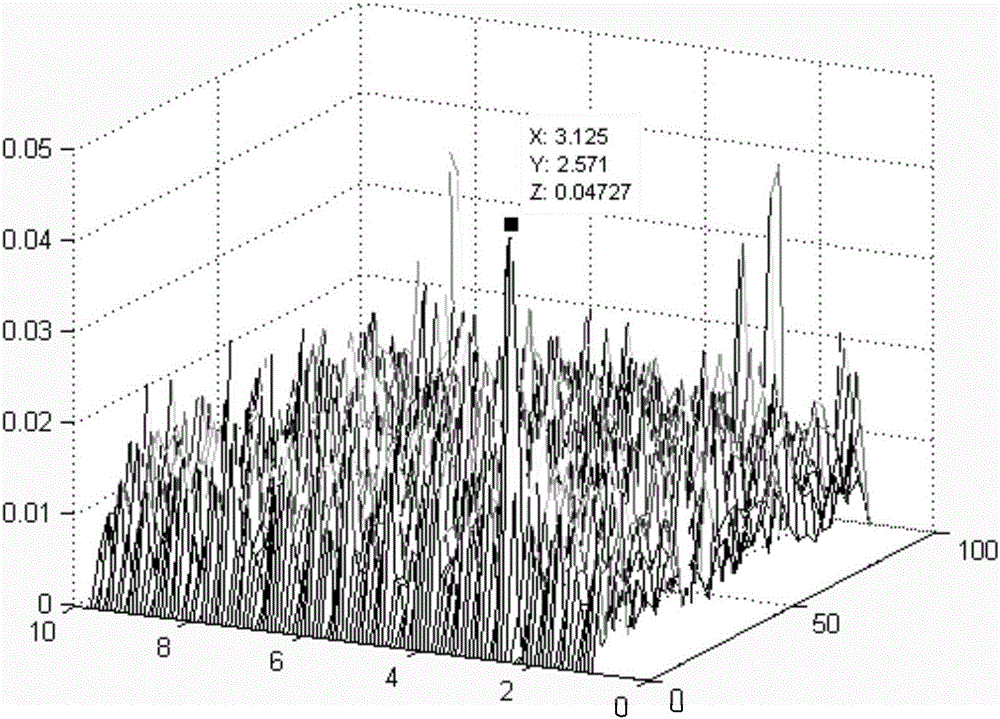
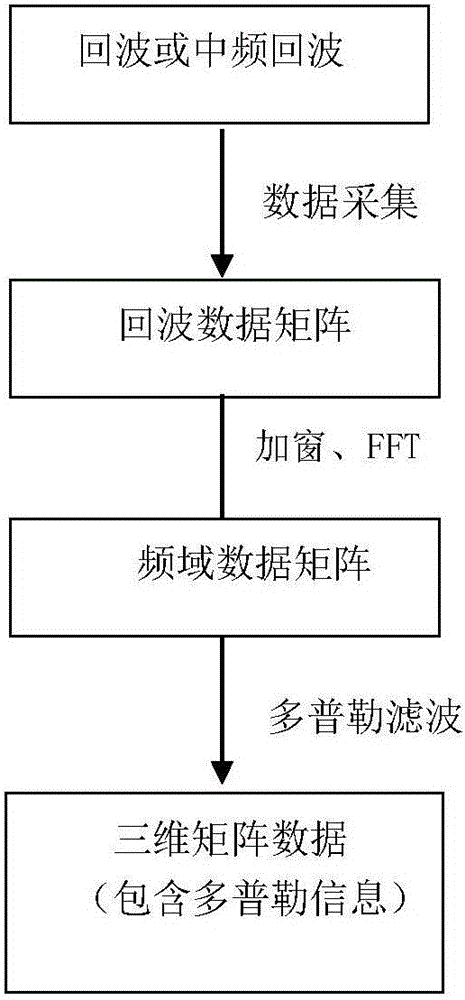
Method used for fast detecting and pulse Doppler radar pulse jitter estimating
ActiveCN106093896ADetermine the level of pulse jitterThe evaluation method is simpleWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsTarget signal
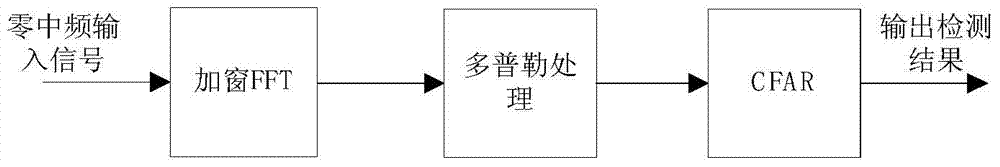
The invention discloses a method used for fast detecting and pulse Doppler radar pulse jitter estimating. The method comprises the steps that echo signal data of a stationary object or processed echo signal data are collected; windowing and Fourier transform in direction are carried out on the data to acquire a frequency-domain data matrix; Doppler filtering is carried out on the frequency-domain matrix data, and modular operation is carried out, so as to acquire a Doppler spectrum; the ratio of the zero-Doppler frequency amplitude of the acquired Doppler spectrum to the maximum non-zero Doppler frequency amplitude is acquired; and jitter amplitude is evaluated according to the ratio. According to the invention, the residual clutter intensity of a strong stationary target signal during Doppler processing can be evaluated, and the ability of jiggle target detection of a radar system is evaluated.
Owner:山东山科感测智慧科技有限公司
Amplitude-weighted spatial coherent processing for ladar system
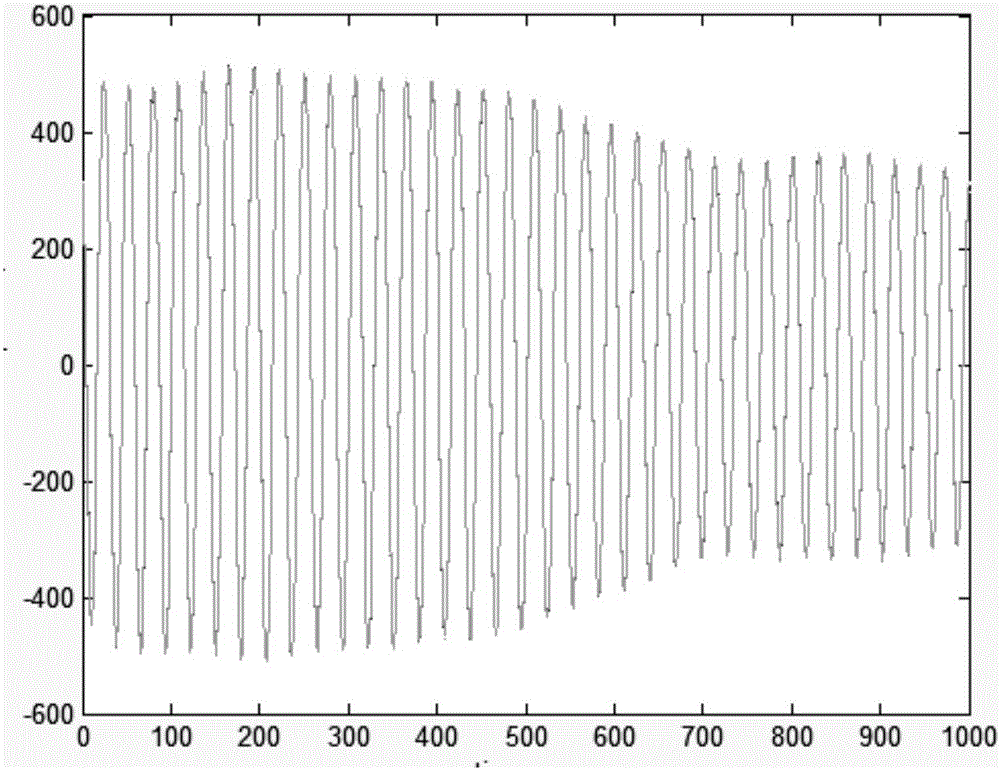
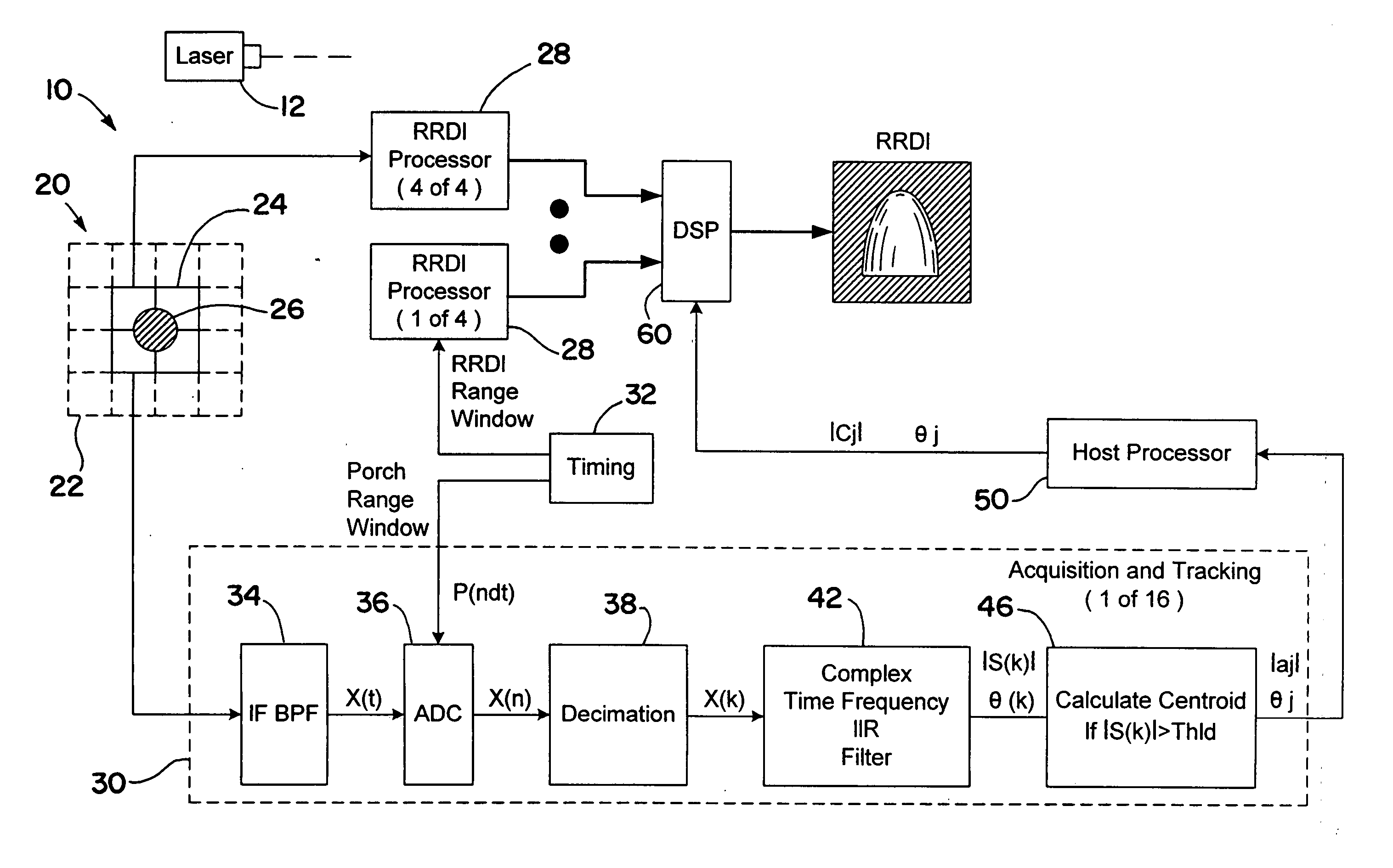
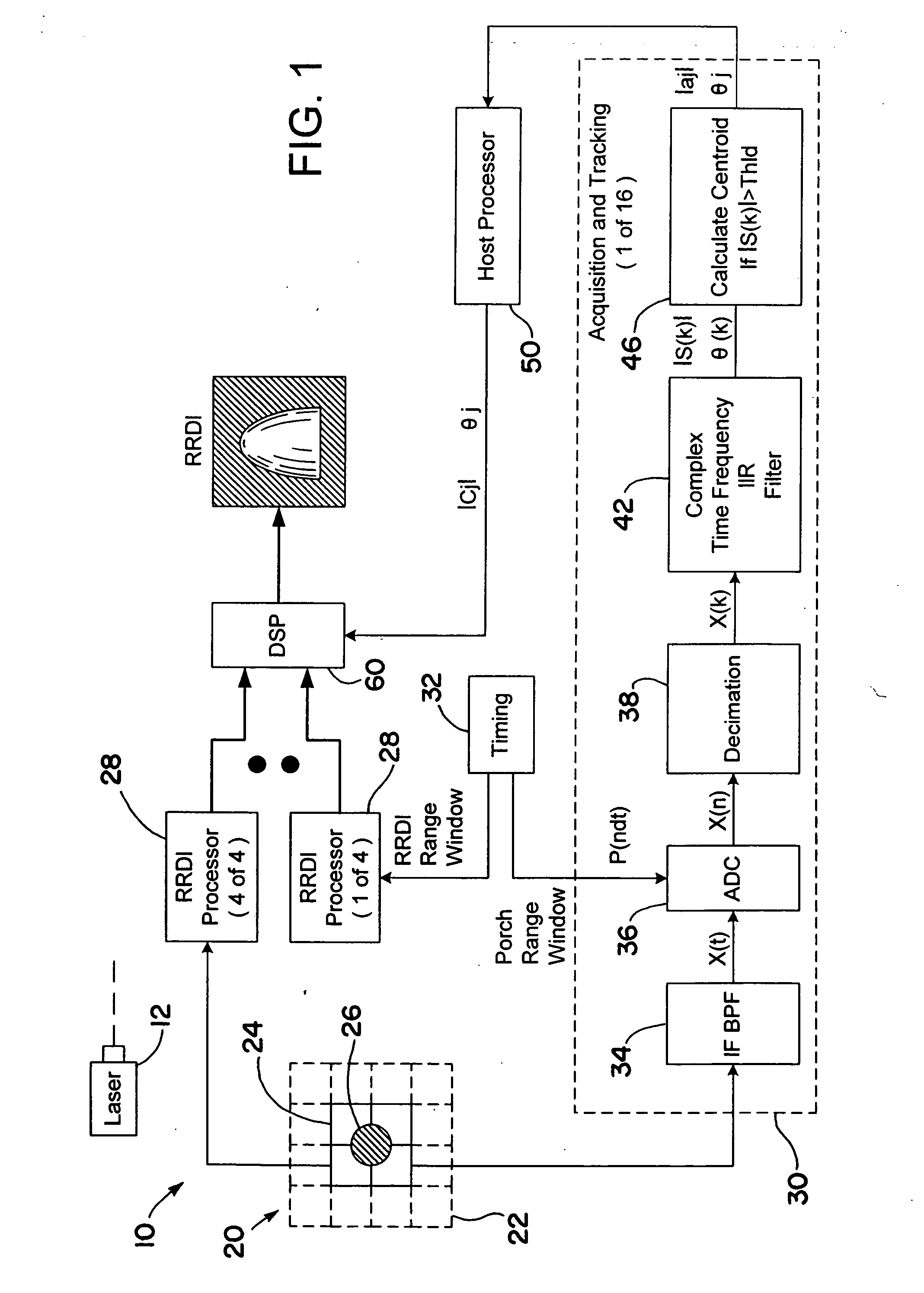
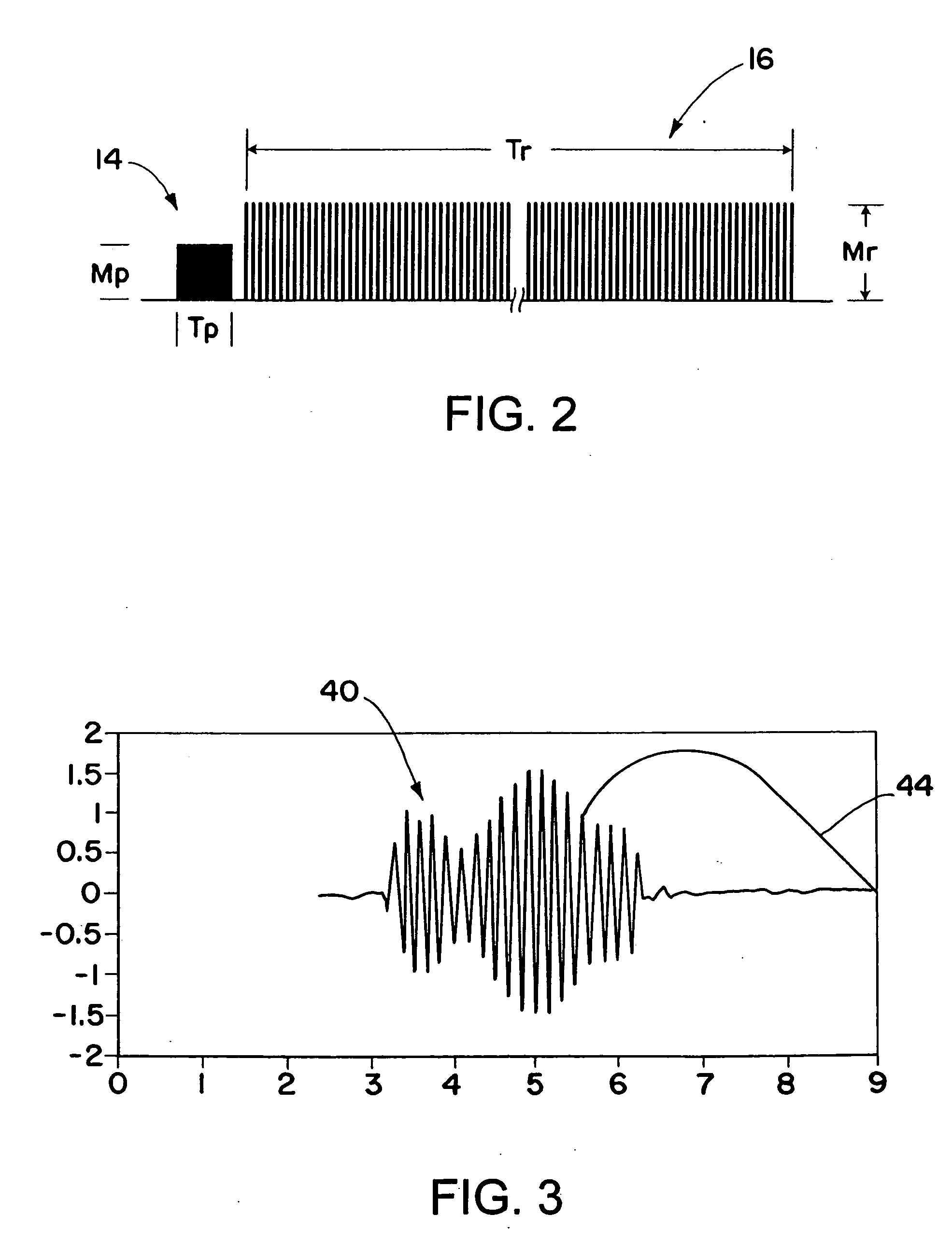
ActiveUS20070097352A1Improve carrier-to-noise ratioMaintain nearly constant the CNR of the resultant RRDIOptical rangefindersProfile tracingTime domainWeight coefficient
A laser radar (LADAR) system is provided with amplitude-weighted spatial coherent processing. An amplitude-weighted sum of time domain signals arising from several detectors within a detector array is formed and used for range doppler processing. Weighting coefficients are chosen to be proportional to the signal amplitude present for each of the separate signals from each detector within the array. The amplitude coefficients are determined using target returned energy arising from a continuous wave (CW) porch portion of the transmitted waveform. Amplitude-weighted spatial coherent processing improves the carrier-to-noise
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Ultrasonic diagnostic imaging system with spectral and audio tissue doppler
A spectral tissue Doppler processor for an ultrasound system produces Doppler phase shift estimates of sequences of signal samples from a sample volume with a short-lag autocorrelator. The autocorrelation products are summed and an arc tangent taken of each sum to produce angle estimates. The angle estimates, which are proportional to the tissue motion velocity, are plotted, smoothed, and displayed as a spectral tissue Doppler display. The angle estimates are also used to produce the audio Doppler signal which is frequency-adjustable by a user. The spectral Doppler display exhibits good time and velocity resolution for motion which is less than that of blood flow such as myocardial motion. Major causes of blurring, unevenness, and distortion are reduced or eliminated.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Skywave over-the-horizon radar transient interference suppression method based on robust principal component analysis
InactiveCN105116388ATransient Interference SuppressionSolve detection difficultiesWave based measurement systemsLightning strikeSkywave
The invention discloses a skywave over-the-horizon radar transient interference suppression method based on robust principal component analysis, and the problem of a poor interference suppression effect caused by the need of previous transient interference positioning in the prior art is mainly solved. The method comprises the steps of (1) using distance unit echo signals to construct Hankel matrixes in a plural form and decomposing the Hankel matrixes as a real part matrix and an imaginary part matrix, (2) calculating the sparse matrixes and the low rank matrixes corresponding to the real part matrix and the imaginary part matrix, (3) obtaining the echo signals to transient interference and noise suppression according to the low rank matrix of the real part and the low rank matrix of an imaginary part, (4) subjecting each distance unit in the step (1), (2) and (3) and carrying out Doppler processing to obtain echo distance Doppler information with transient interference and noise suppression. The complexity of the method is low, it can significantly suppress noise and transient disturbances multiple simultaneous presence can be used for sky wave or ground wave OTH radar interference lightning strike, meteor trails interference echo suppression and human impact of interference.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com