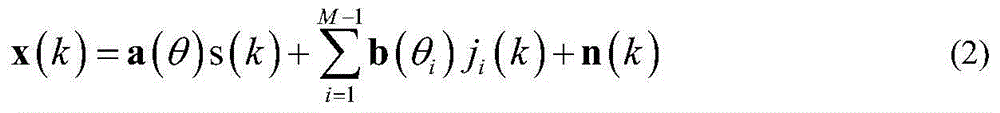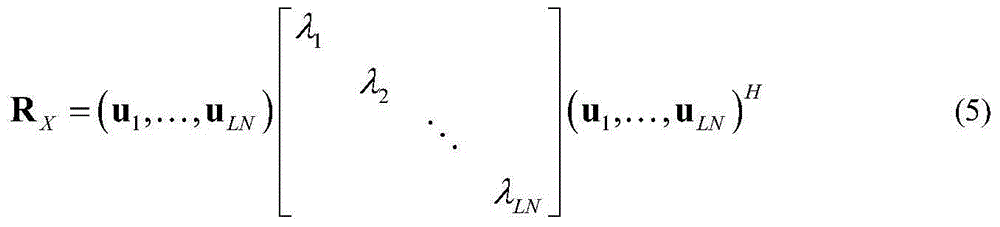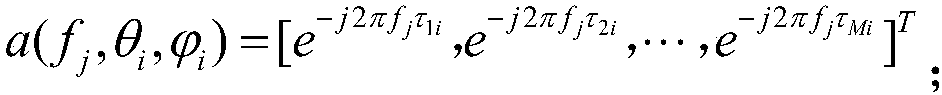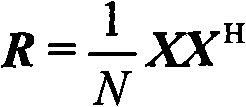Patents
Literature
175 results about "Data covariance matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
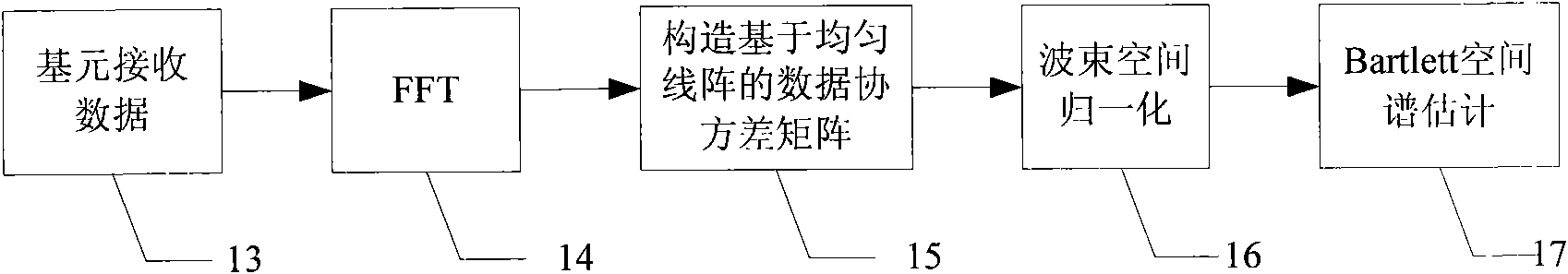
Application Year
Inventor
Covariance Matrix is a measure of how much two random variables gets change together. It is actually used for computing the covariance in between every column of data matrix. The Covariance Matrix is also known as dispersion matrix and variance-covariance matrix.
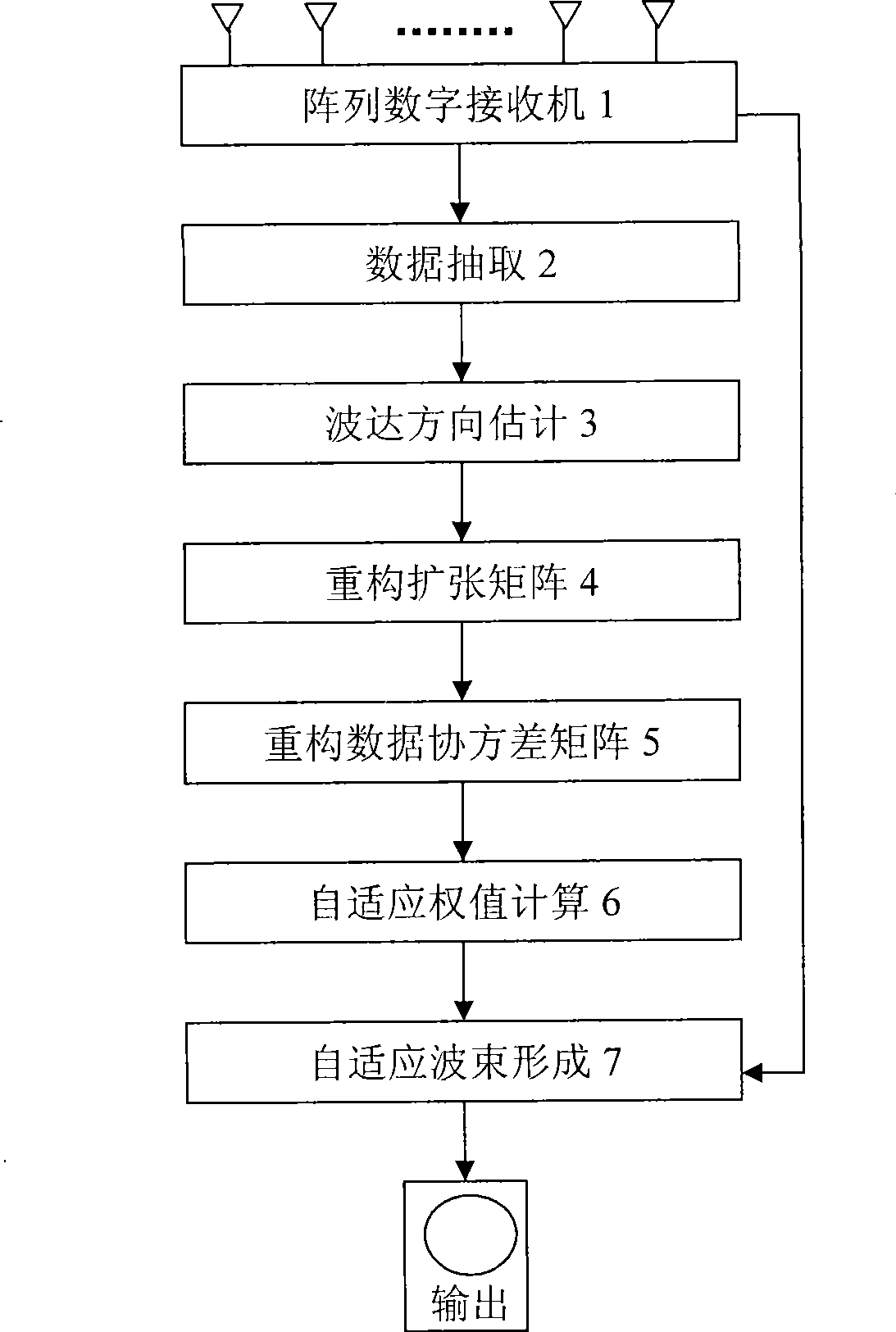
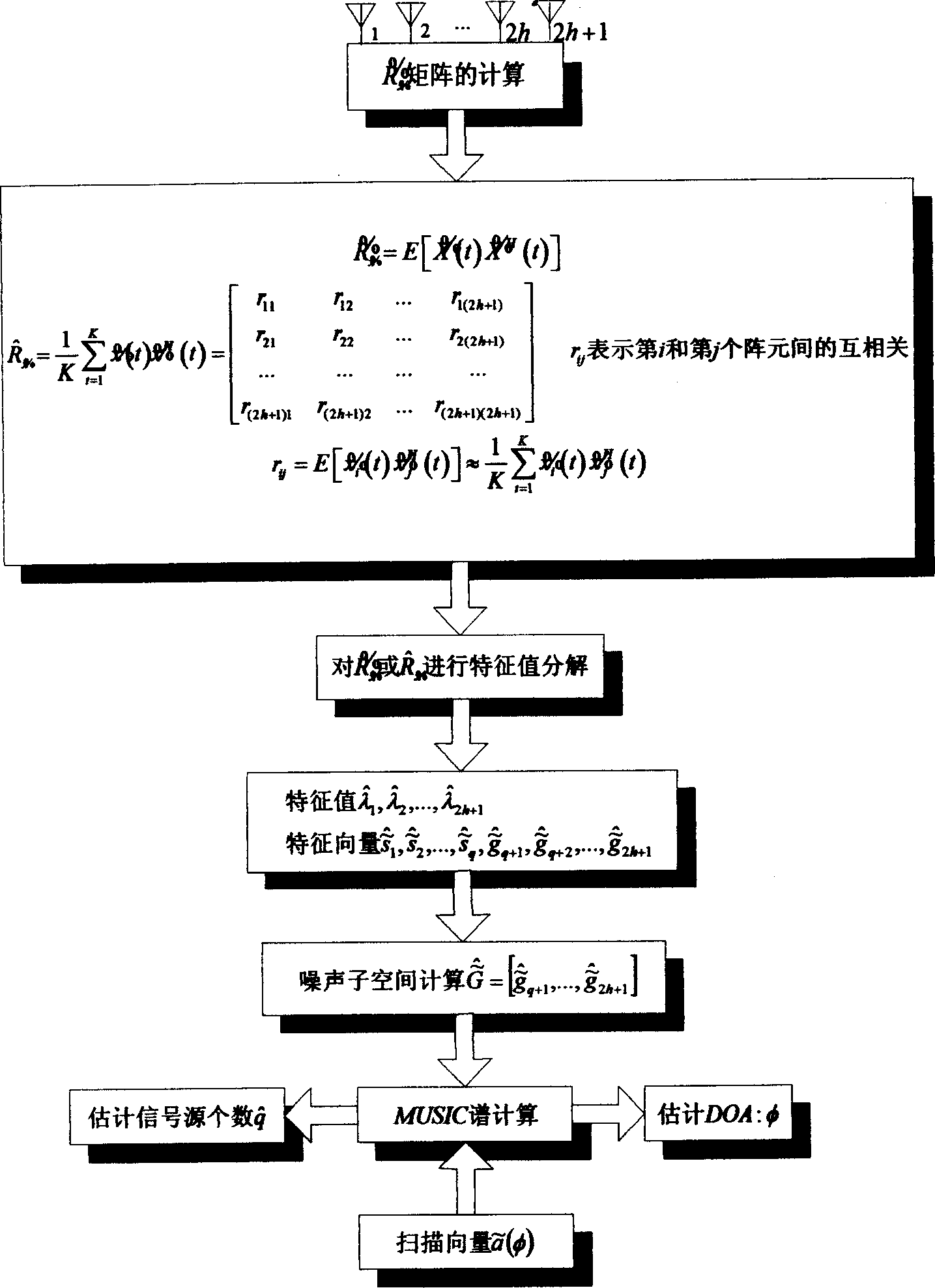
Self-adapting special interference restraint technology for phased array radar
InactiveCN101482610AEnhanced inhibitory effectSuppress complex interferenceWave based measurement systemsRadarAnalog signal
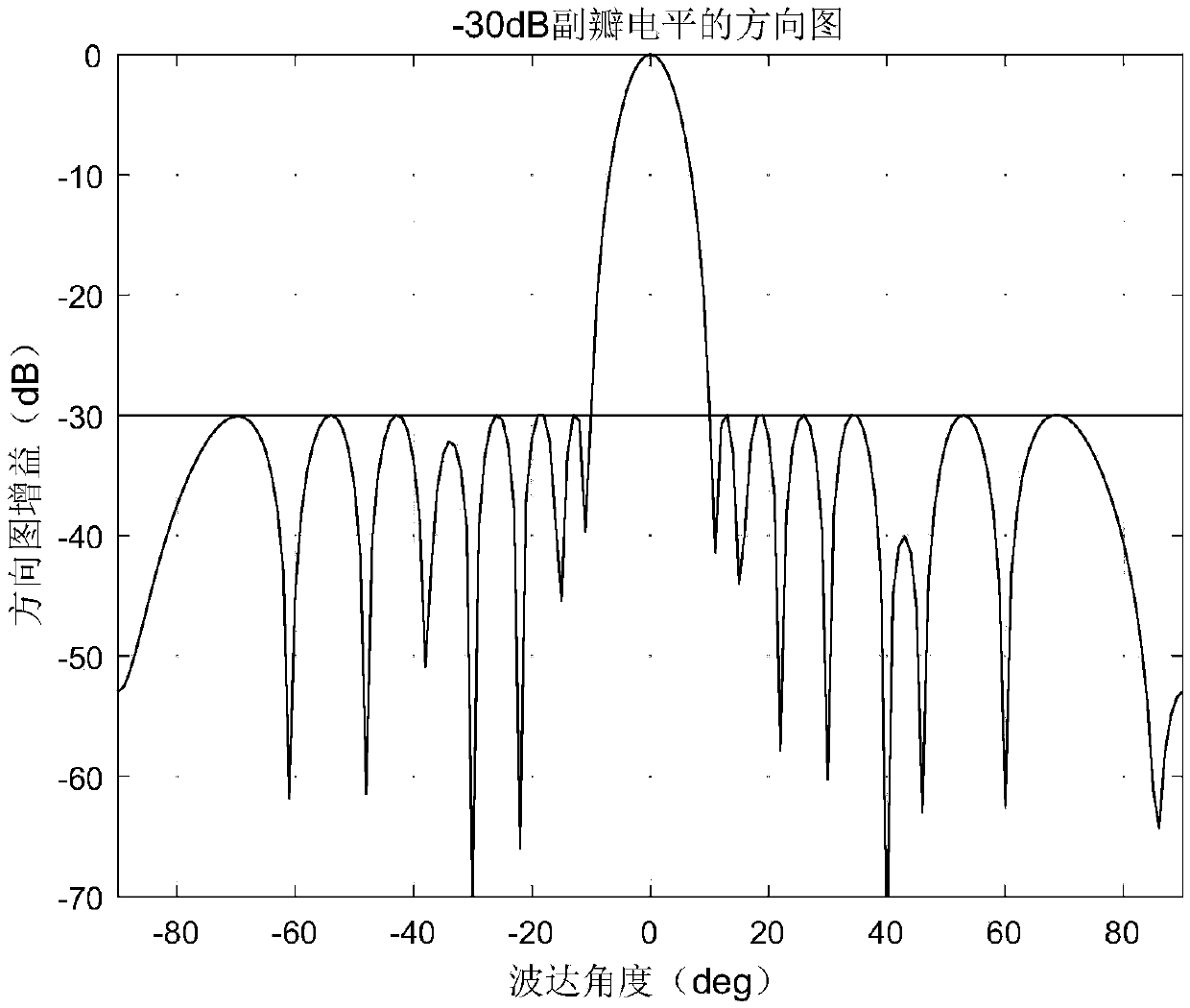
The invention discloses a self-adapting special interference suppressing technology aim at phased array radar. The conventional phased array radar can suppress the noise to inhibit the interference by self-adapting, firstly the interference data received by the radar receiver can be learned then to form a zero point on the interference direction. The zero point depth and width generated by the conventional processing method all can be influenced by the array error and are not suitable for the special interferences, such as the dense cheating interference, the movement interference, the fast transforming clearance type interference or the composite interference and so on complicated interference forms. Adopting the ultra-lower secondary lobe aerial is the most effective anti-interference method, but under the present technology and technological level, the over-high secondary lobe requirement for the phased array aerial is impractical. The invention can implement the estimations of the interference source number and the orientation by the space spectrum estimating technology firstly, and then can construct the interfering data covariance matrix by using the analog signals, then can obtain the self-adapting minor lobe cancellation weight vector calculated by the self-adapting method, thereby forming the wide zero point and deep zero defect self-adapting directional diagram to inhibit the complicated interferences. The technology of the invention can be used for the signal processing system of the phased array radar, the implementing is simple, and the invention has wide practical application prospects.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE RADAR COLLEGE
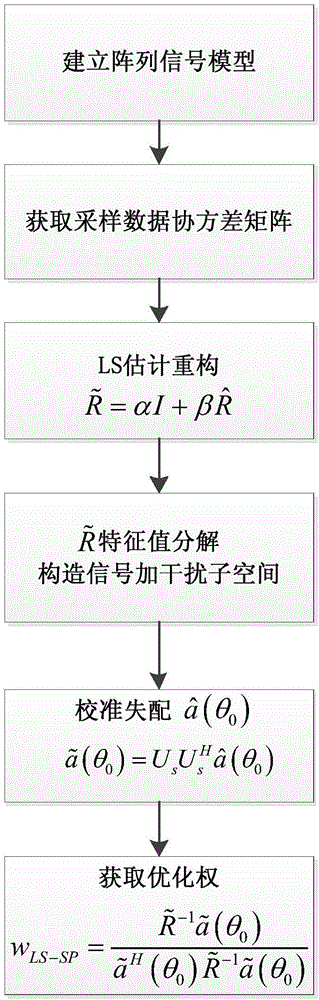
Algorithm for reconstructing robust Capon beamforming based on covariance matrix
InactiveCN106569181ASimple designAvoid cancellationWave based measurement systemsLinear contractionAlgorithm
The invention belongs to the field of signal processing. The invention provides an improved Capon beamforming algorithm for the problem that the performance of a conventional Capon beamforming algorithm is significantly degraded, wherein the problem is caused by estimation errors of an array steering vector or inaccurate estimation of a data covariance matrix. On the basis that a reception data covariance matrix is reconstructed based on linear contraction estimation, a mismatch steering vector is projected to an updated subspace by updating the signal and interfering subspace, so as to acquire the optimal reception right. The algorithm maintains a high gain in the true wave incoming direction and assumed wave incoming direction of a desired signal, which avoids signal cancellation. Compared with other algorithms, the algorithm can more accurately point to the true direction of the desired signal. The algorithm is robust for steering vector mismatch caused by the observation error of the signal arrival direction.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
DOA (direction of arrival) estimation method based on nested minimum redundant array
ActiveCN105403856ALarge apertureEasy to implementRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsRadarImage resolution
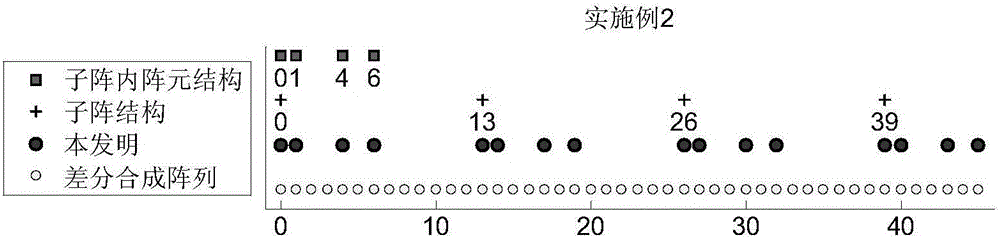
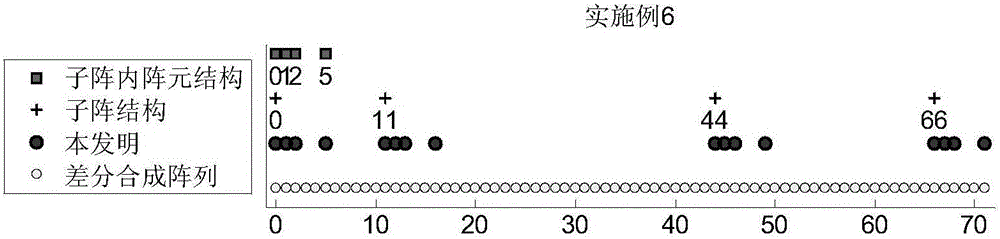
The invention discloses a DOA (direction of arrival) estimation method based on a nested minimum redundant array, and mainly solves the problem of low DOA estimation resolution when the number of targets is greater than the number of array elements in the prior art. An implementation process of the method comprises the following steps: 1, giving a total array element number to built a nested minimum redundant array (NMRA), 2, obtaining received data X(t) of the NMRA according to the NMRA, 3, estimating a covariance matrix R<XX> of the NMRA according to the X(t), vectorizing the R<XX>, removing repeated elements, and then obtaining differential synthesis array received data Z<c>, 4, dividing Z<c> into a plurality of sub array received data, calculating a covariance matrix of each sub array received data, performing forward and backward smooth average, and then obtaining rank recovery data covariance matrix R<SS>, and 5, performing eigenvalue decomposition on the R<SS>, and then obtaining a DOA estimation angle. The method has the advantages of the large aperture, the high degree of freedom and good DOA estimation angle measurement performance in the same condition, and can be applied to radar target signal detection or power estimation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
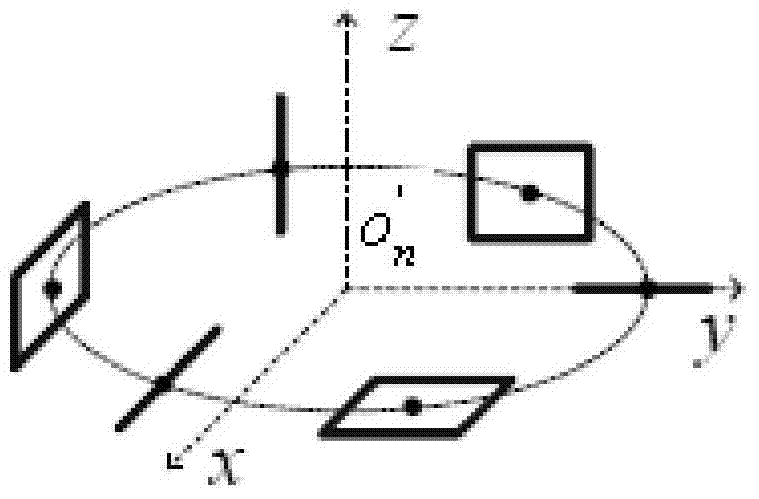
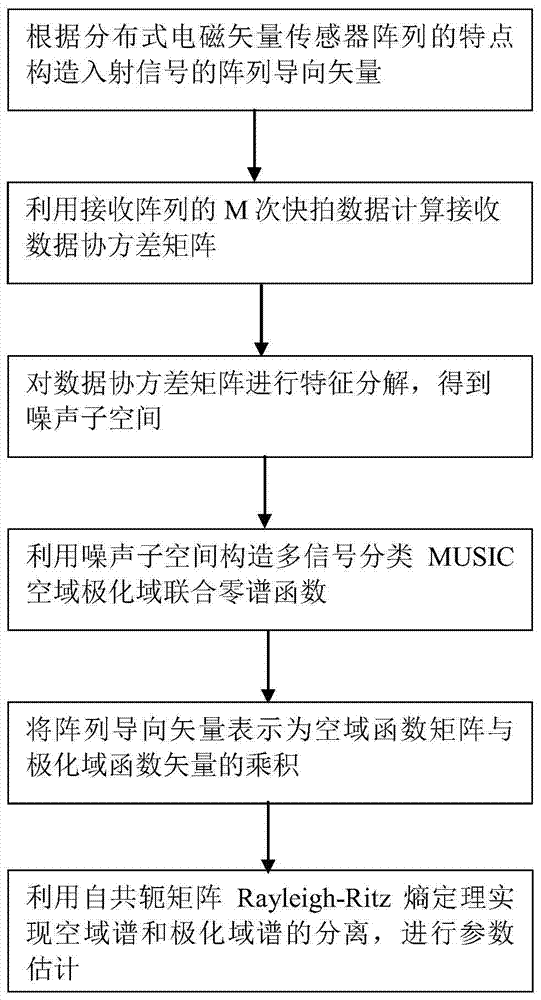
Method for estimating parameters of space stretching electromagnetic vector sensor array
InactiveCN103941221AReduce difficultyReduce complexityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSignal subspaceDomain combination
The invention provides a method for estimating parameters of a space stretching electromagnetic vector sensor array. The method comprises the steps of receiving K unrelated incoming signals through a receiving array, and constructing guide vectors of the incoming signals corresponding to the array; expressing the guide vectors of the incoming signals as a product of a spatial domain function array and a polarizational domain function vector; computing a covariance matrix of the received data; analyzing features of the covariance matrix of the received data to obtain signal subspace and noise subspace; constructing a multi-signal classified MUSIC spatial-polarizational domain combination zero spectrum function, and maximizing the spatial-polarizational domain combination zero spectrum function; performing MUSIC dimension reduction process to separate a spatial domain spectrum and a polarizational domain spectrum by means of the self-conjugate moment Rayleigh-Ritz entropy theorem, performing traversal search within value ranges of variables and estimating signal parameters. By means of the method, four-dimensional MUSIC search is transformed into two-dimensional spatial domain search and two-dimensional polarizational domain search, and therefore, calculated quantity is decreased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
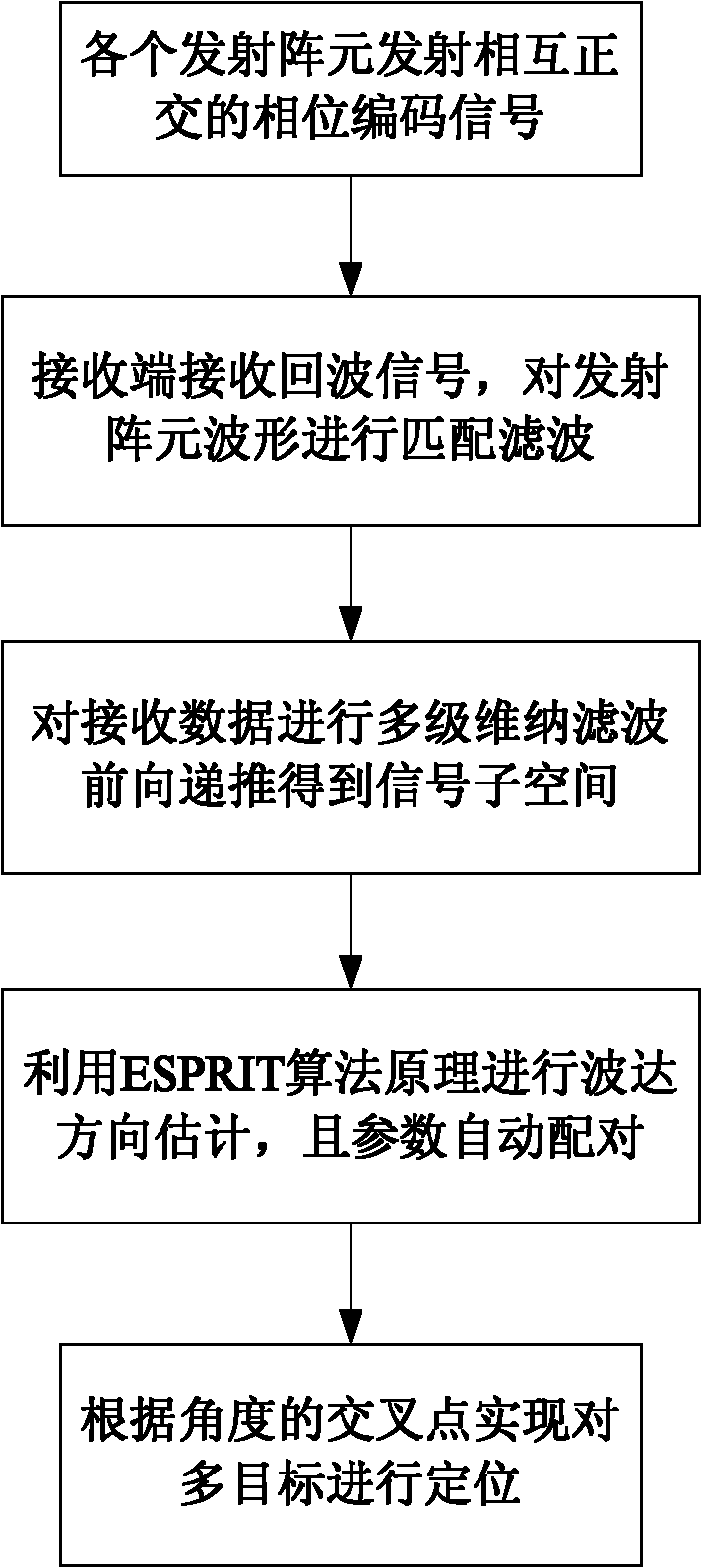
Multi-target positioning method of bistatic multi-input multi-output radar
InactiveCN102135617AAvoid decompositionFast convergenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputComputation complexity
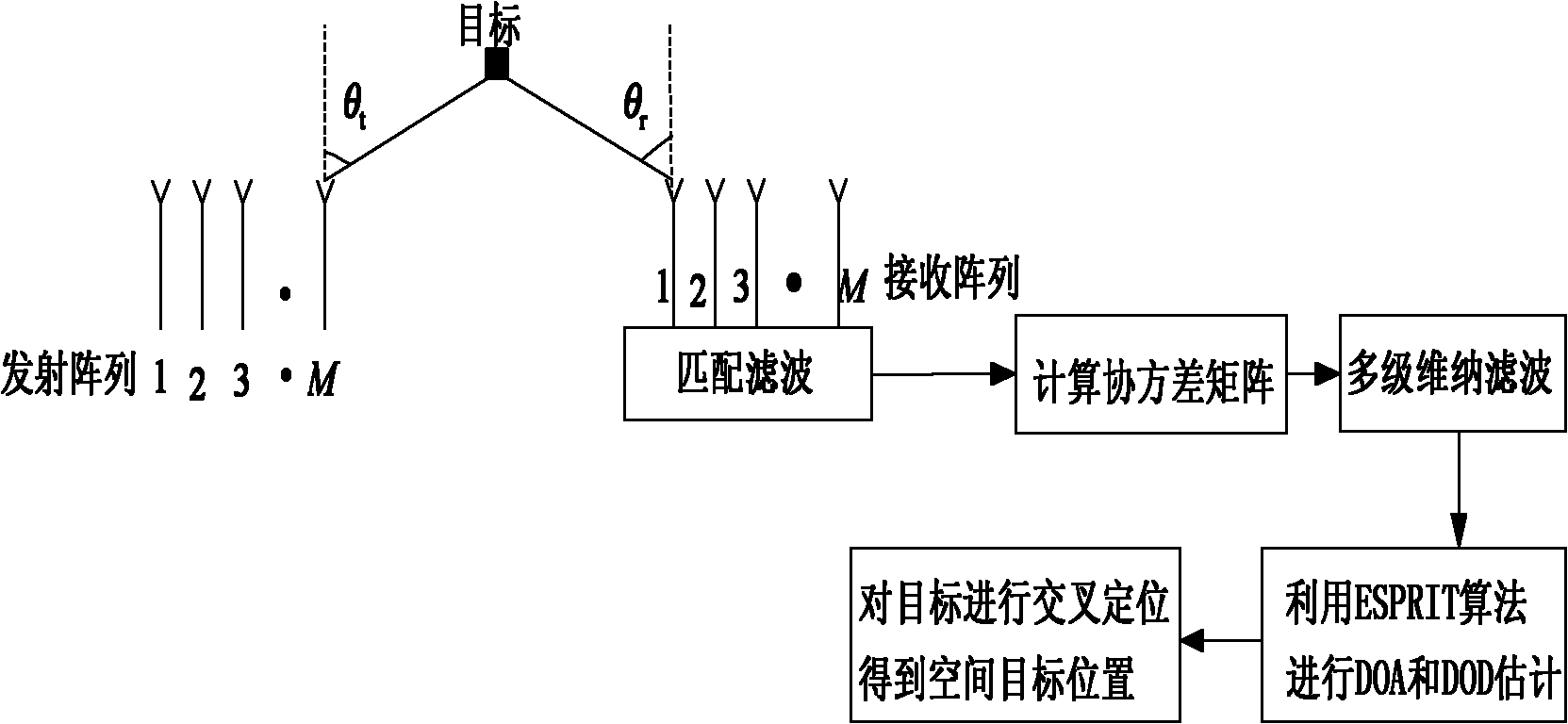
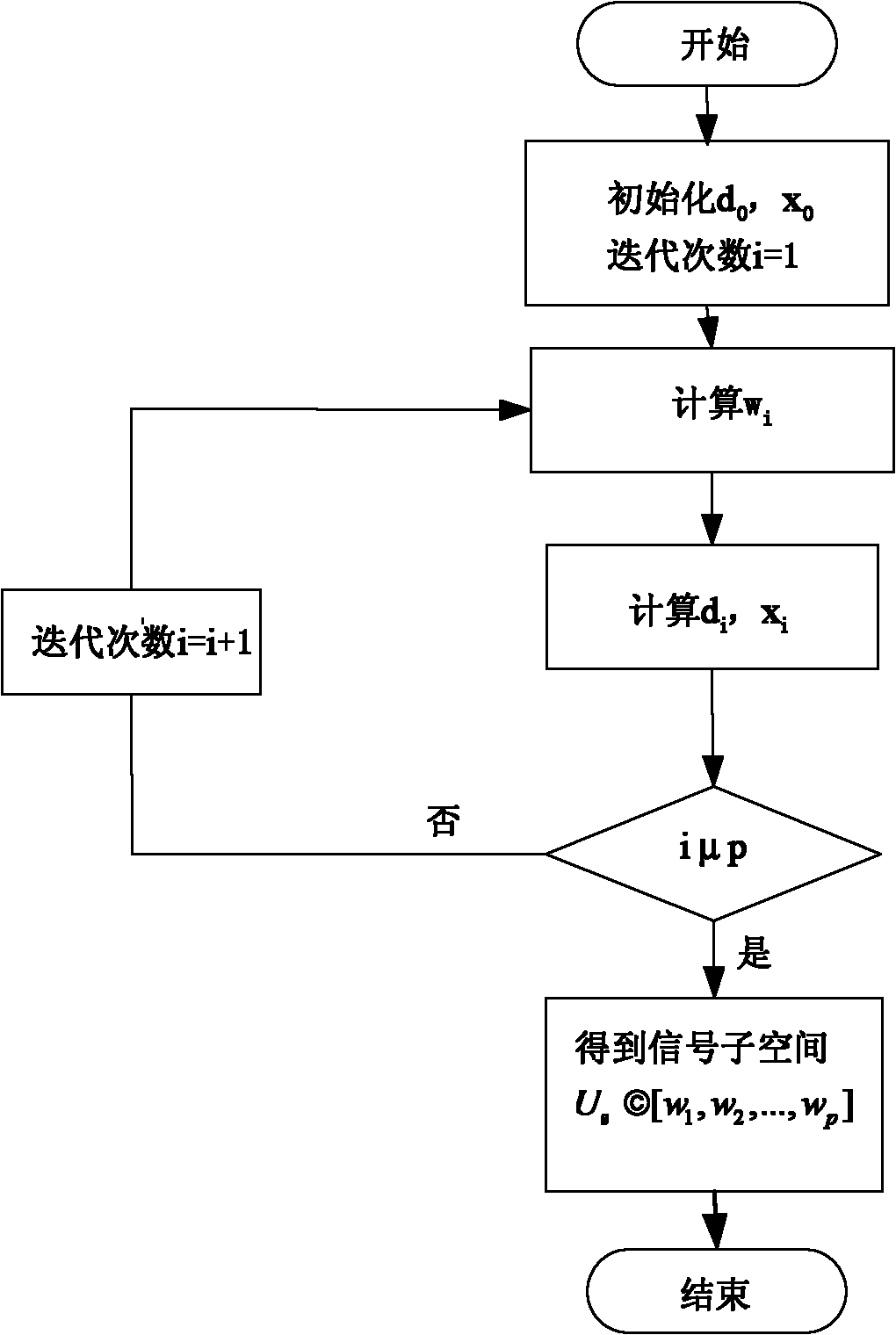
The invention provides a multi-target positioning method of a bistatic multi-input multi-output radar, comprising the following steps of: (1) transmitting mutually orthogonal phase-coded signals by M transmitting array elements, and receiving the phase-coded signals by N receiving array elements, wherein the distances of the M transmitting array elements and the N receiving array elements are all of half wavelengths; (2) carrying out matched filtering on the received phase-coded signals by a matched filter of a receiver of each receiving array element; (3) carrying out multistage Wiener filtering on a matched signal data covariance matrix space, and carrying out forward recursion to obtain a signal subspace; (4) carrying out high-resolution DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation by using an ESPRIT algorithm, wherein a pairing algorithm is used for carrying out the automatic pairing on two-dimensional parameters; and (5) realizing multi-target positioning according to cross points at two angles so as to obtain the positions of space targets. The multi-target positioning method provided by the invention has the advantages of low computation complexity, high computation speed, high estimation accuracy and can be used for positioning the sea-surface or low-altitude targets during tracking and guidance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Estimation method for radio orientation incoming wave direction based on TD-SCMA
InactiveCN1523372APosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsEstimation methodsSignal classification
The invention is a DOA estimating method to realize circle-angle positioning based on TD-SCMDA standard, firstly adopting multiple signal classifying and correcting algorithms to realize the DOA estimation of intelligent antenna circle-angle positioning; aiming at TD-SCMDA antenna being uniform circle array, converting the array cell-space uniform circle array into mode-space virtual uniform line array; according to eigenvalue and eigenvector characteristic of the data covariance matrix of the virtual line array, advancing a MUSIC algorithm based on mode-space virtual uniform line array and deriving the MUSIC algorithm power chart for the virtual line array and the general implementation algorithm for the mode-space MUSIC algorithm; according to the character of MUSIC algorithm inapplicable to the DOA estimation of relative signal source, advancing the correcting MUSIC algorithm based on the mode-space virtual uniform line array; finally aiming at the problem that the array aperture is small and that the resistance to array cell error disturbance is bad, caused by MUSIC algorithm, advancing four-order cumulant MUSIC algorithm and four-order cumulant correcting MUSIC algorithm based on the mode-space virtual uniform line array.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
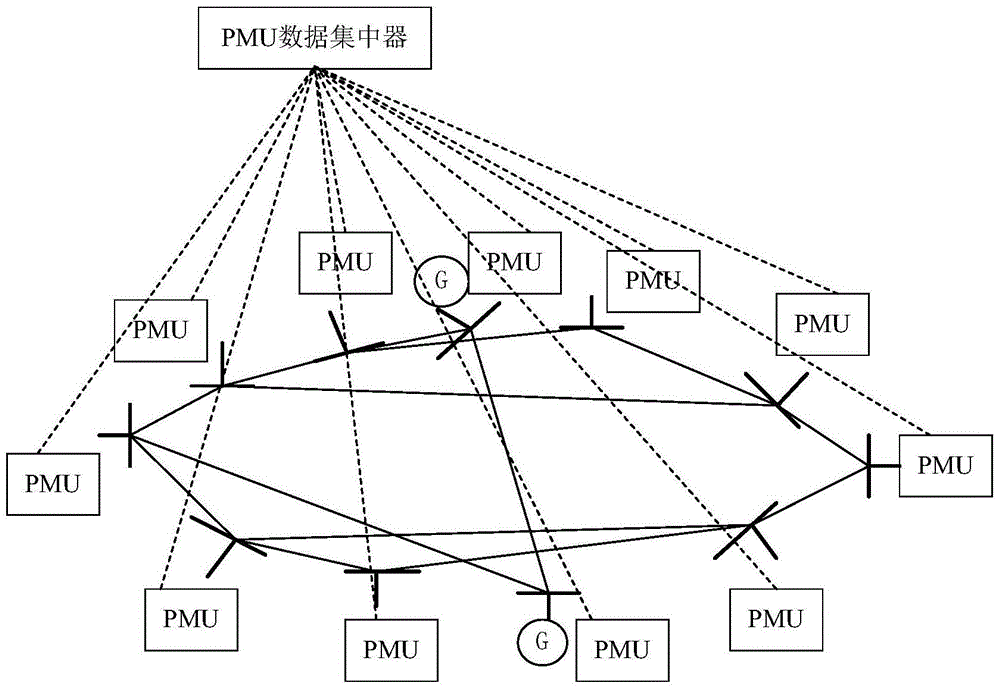
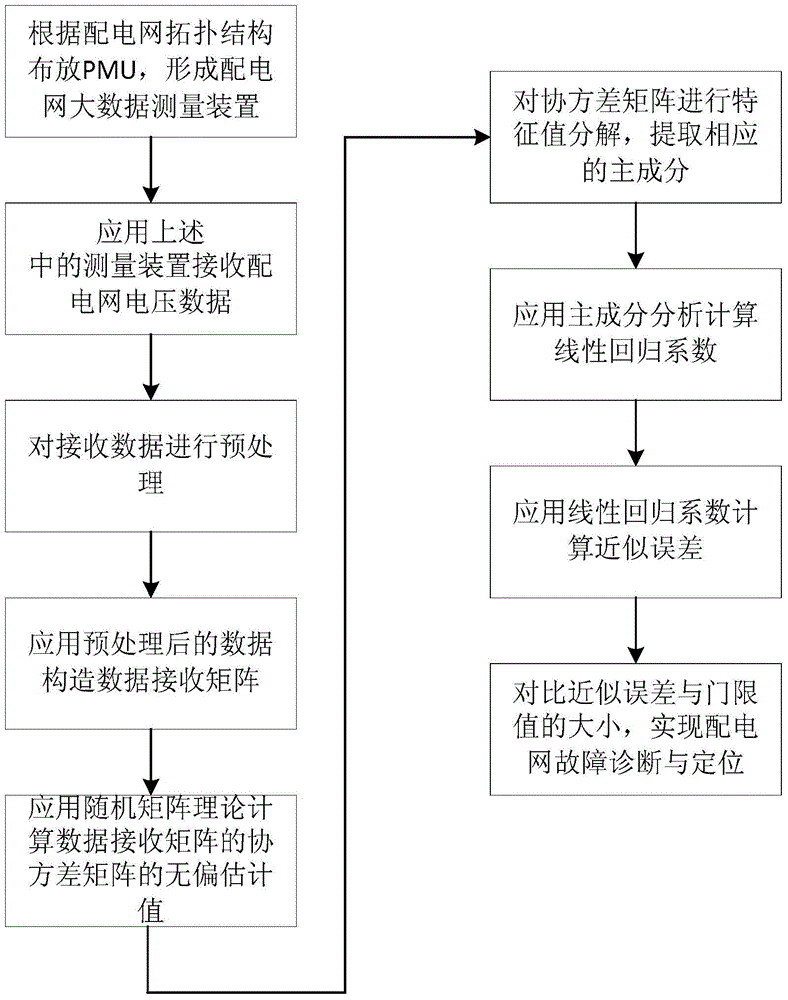
Big data fault detection and positioning method for power distribution network
ActiveCN105699804AOvercoming the problem of large estimation biasImprove applicabilityFault location by conductor typesSystems intergating technologiesPrincipal component analysisSmart grid
The invention provides a big data fault detection and positioning method for a power distribution network, and belongs to the field of intelligent power grids. The method comprises the steps: receiving voltage sampling data of the power distribution network through employing PMUs (Phasor Measurement Units); carrying out the preprocessing of voltages received by all PMUs, and constructing a receiving matrix; obtaining an unbiased estimated value of a receiving data covariance matrix through employing a random matrix theory; carrying out the eigenvalue decomposition of the covariance matrix, and obtaining a corresponding principal component; calculating a linear regression coefficient through employing PCA (Principal Component Analysis); comparing a relative approximation error and a threshold value, and achieving the fault detection and positioning of the power distribution network. The method provided by the invention solves a problem that the conventional covariance matrix estimation is biased under the measurement of a plurality of PMUs, and can achieve the real-time fault detection and positioning of the power distribution network.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Direction-of-arrival estimation method based on nested subarray array
ActiveCN105824002ALarge apertureEasy to implementRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsEstimation methodsRadar
The invention discloses a direction-of-arrival estimation method based on a nested subarray array, and mainly solves the problem existing in the prior art that the degree of freedom, array aperture and array density are not high. The realization process includes the steps of: 1. giving the total number of array elements, and determining the number of subarrays and the number of array elements in each subarray; 2. selecting a uniform linear array or minimum redundancy array or nested linear array structure according to the number of array elements in each subarray; 3. selecting a uniform linear array or minimum redundancy array or nested linear array structure according to the number of the subarrays; 4. constructing a nested subarray array according to a selected array element structure in each subarray and subarray structure; 5. obtaining received data X(t) according to the nested subarray array; 6. obtaining differential synthesis array received data zc according to X(t), and then obtaining a rank recovery data covariance matrix RSS; and 7. decomposing characteristic values of the RSS to obtain a direction-of-arrival estimation angle. The direction-of-arrival estimation method provided by the invention has the advantages of flexible array configuration and good direction-of-arrival estimation angle measurement performance under the same conditions, and can be used for radar target signal detection or power estimation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Quick beamforming method capable of improving array resolution and gain
InactiveCN101609150AImprove resolutionOvercoming demandsAcoustic wave reradiationComputation complexityComputation process
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
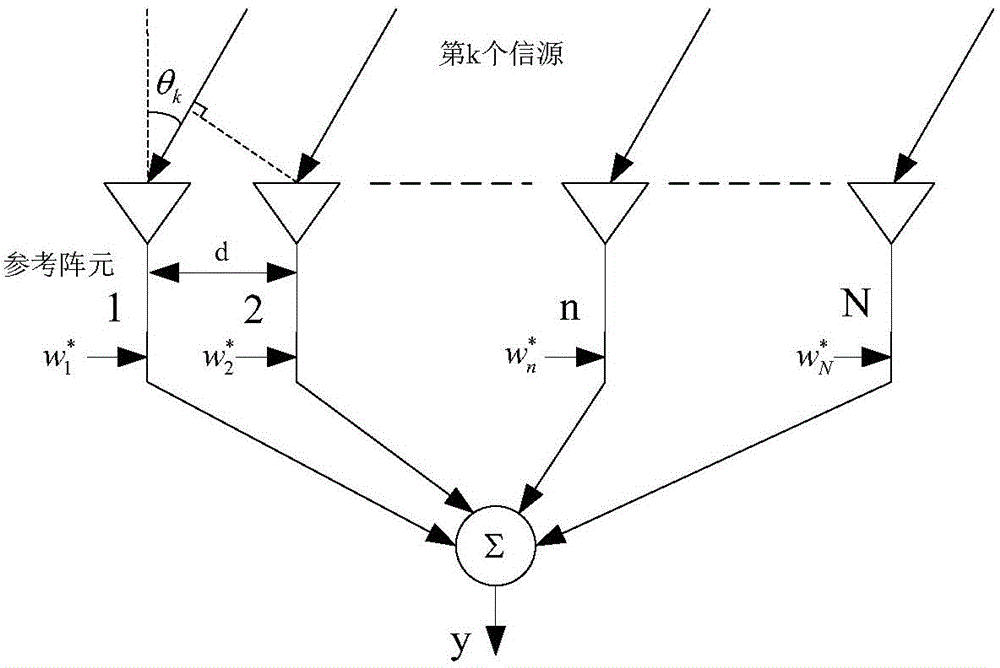
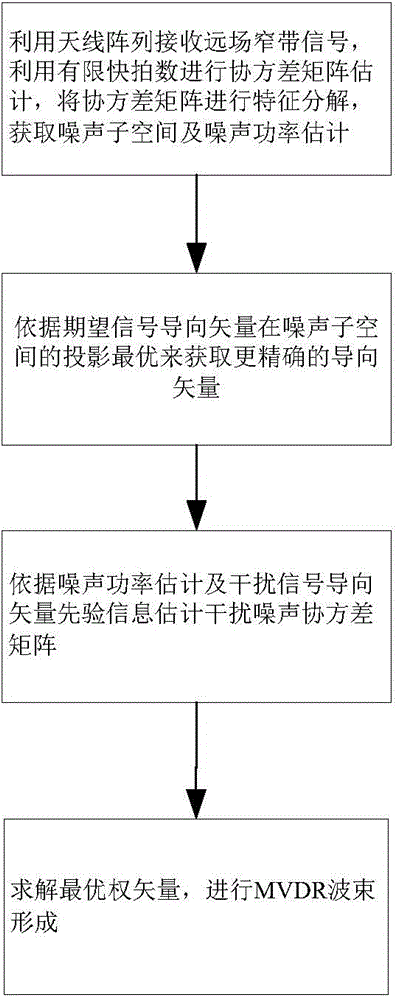
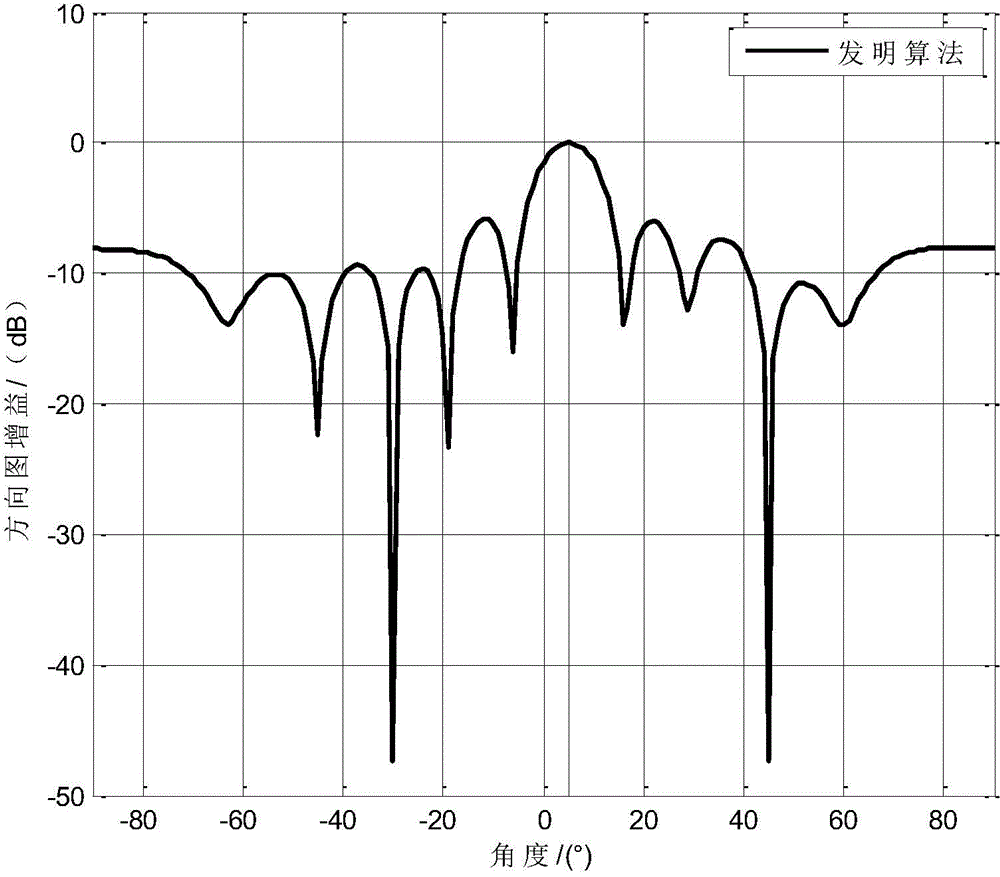
A method for forming steady beam based on interfering noise covariance matrix estimation
InactiveCN104408278AStrong robustnessAvoid signal cancellationSpecial data processing applicationsPrior informationDecomposition
The present invention relates to the field of self-adaption beam forming during array signal processing, in particular, relates to a method for forming a steady beam based on an interfering noise covariance matrix estimation. The present invention includes using an antenna array to receive a distant field narrowband incident signal, using a limited snapshot number to estimate the covariance matrix for receiving data, then performing characteristic decomposition on the covariance matrix for receiving data, wherein prior information of the number of an incident signal source can be obtained via a method of estimating the number of the signal source; optimally obtaining a more accurate desired signal steering vector at a projection of a noise subspace according to an estimated desired signal steering vector, and performing estimation obtaining of the interfering noise covariance matrix according to interference signal steering vector prior information and an estimated noise power so as to perform beam forming. The present invention first performs the interfering noise covariance matrix estimation to get rid of the component of the desired signal in the training data, which can avoid the generation of signal cancellation.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Pilot and data signals for MIMO systems using channel statistics
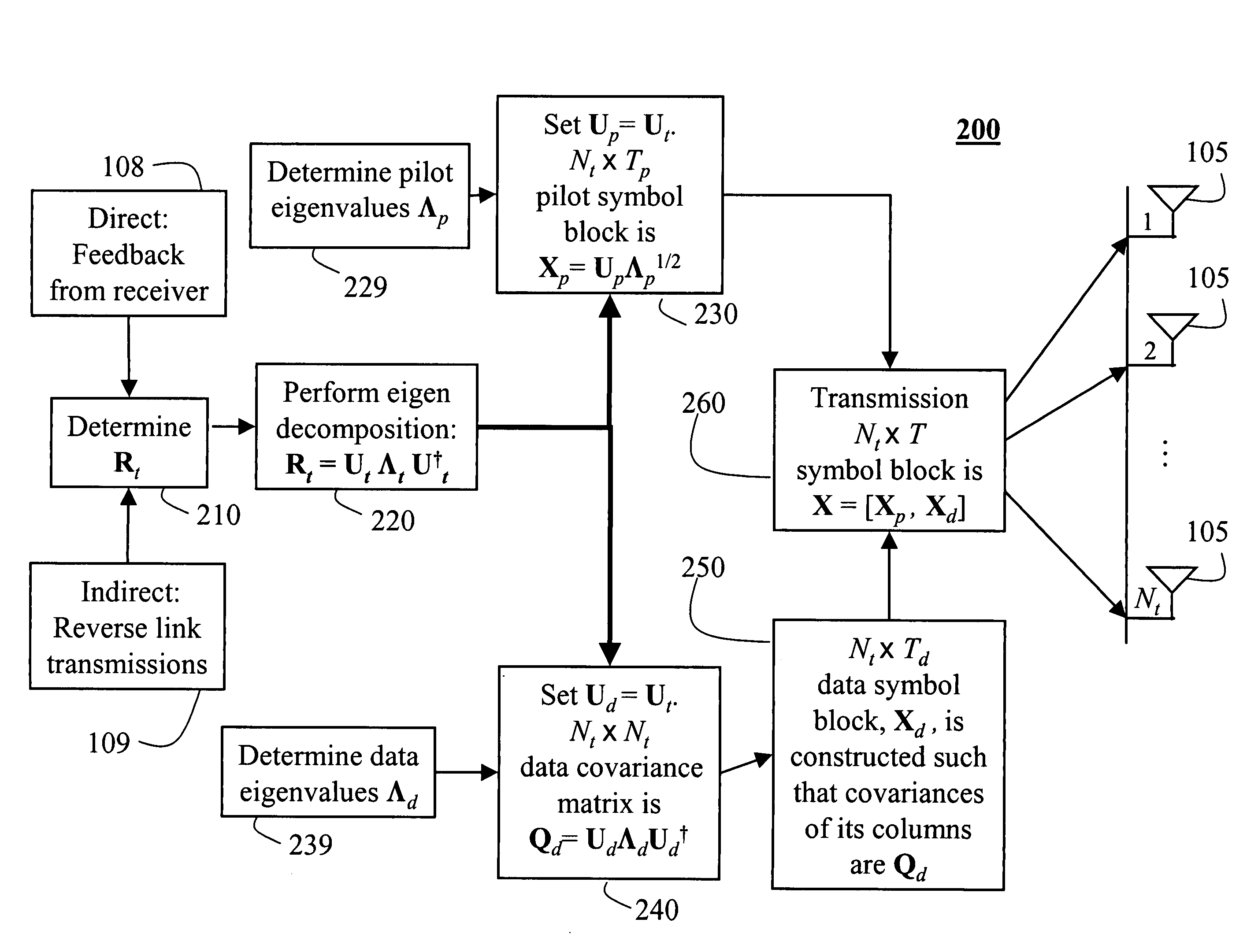
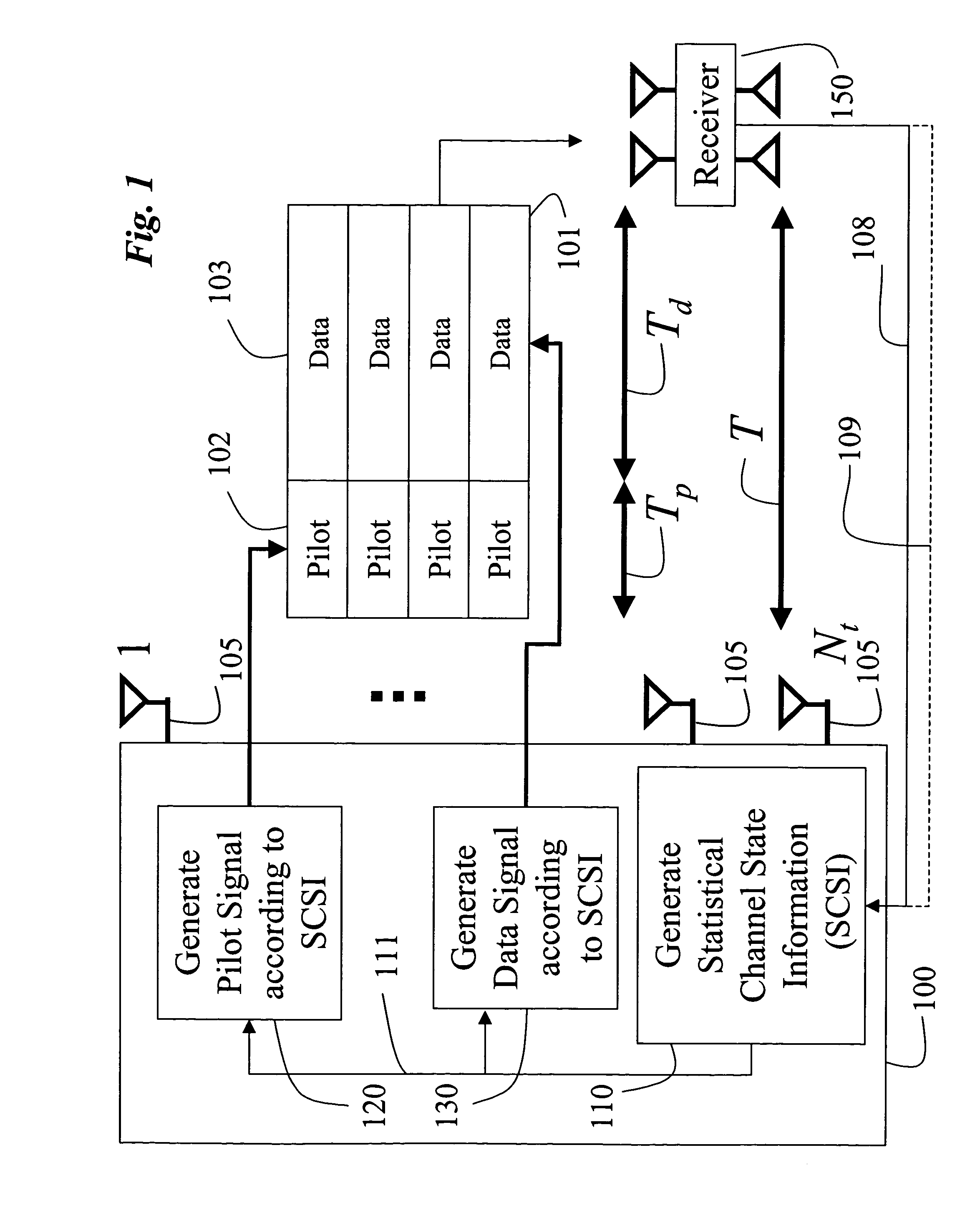
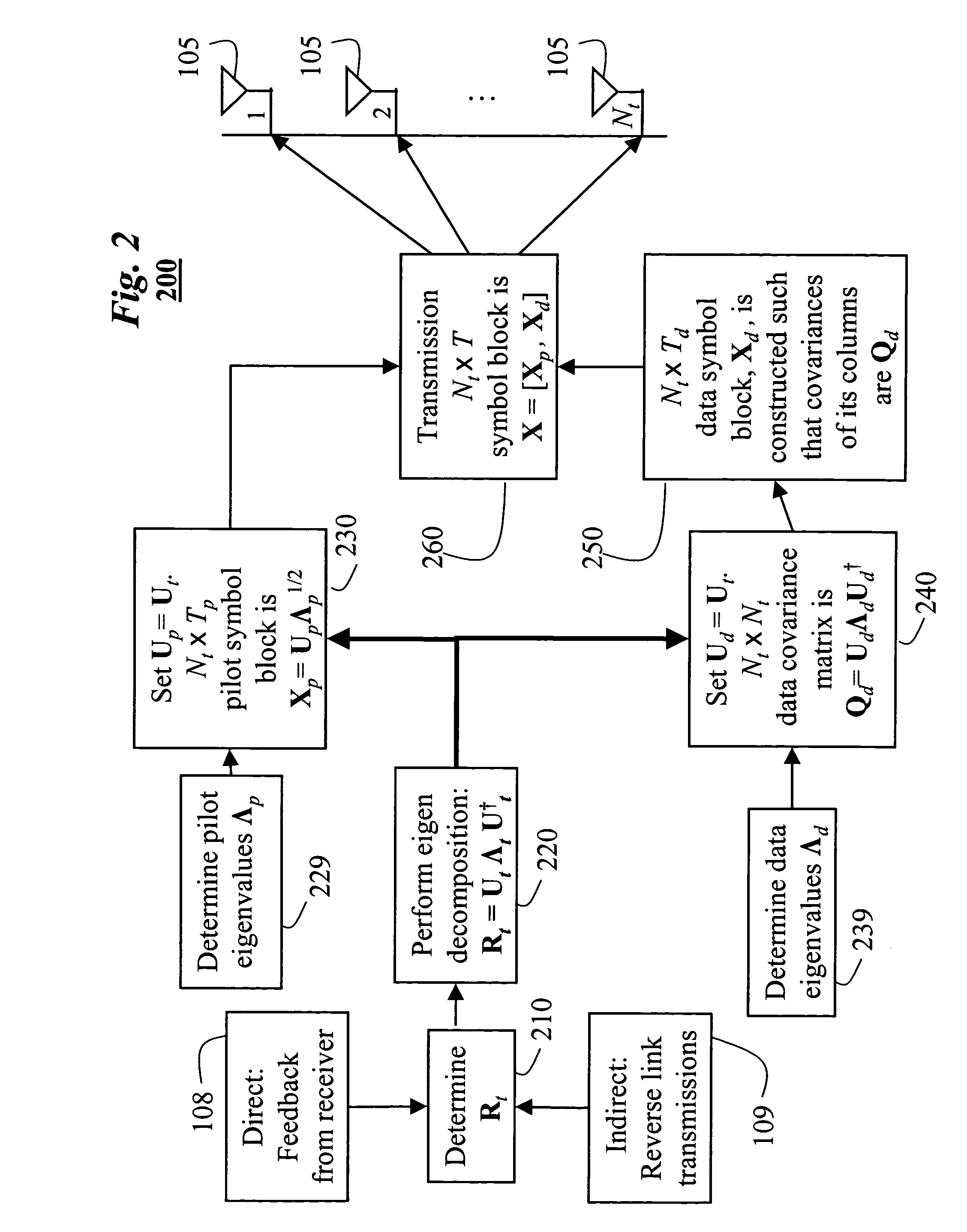
InactiveUS20060018402A1Improve data transfer rateSimplify complexityPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemChannel statistics
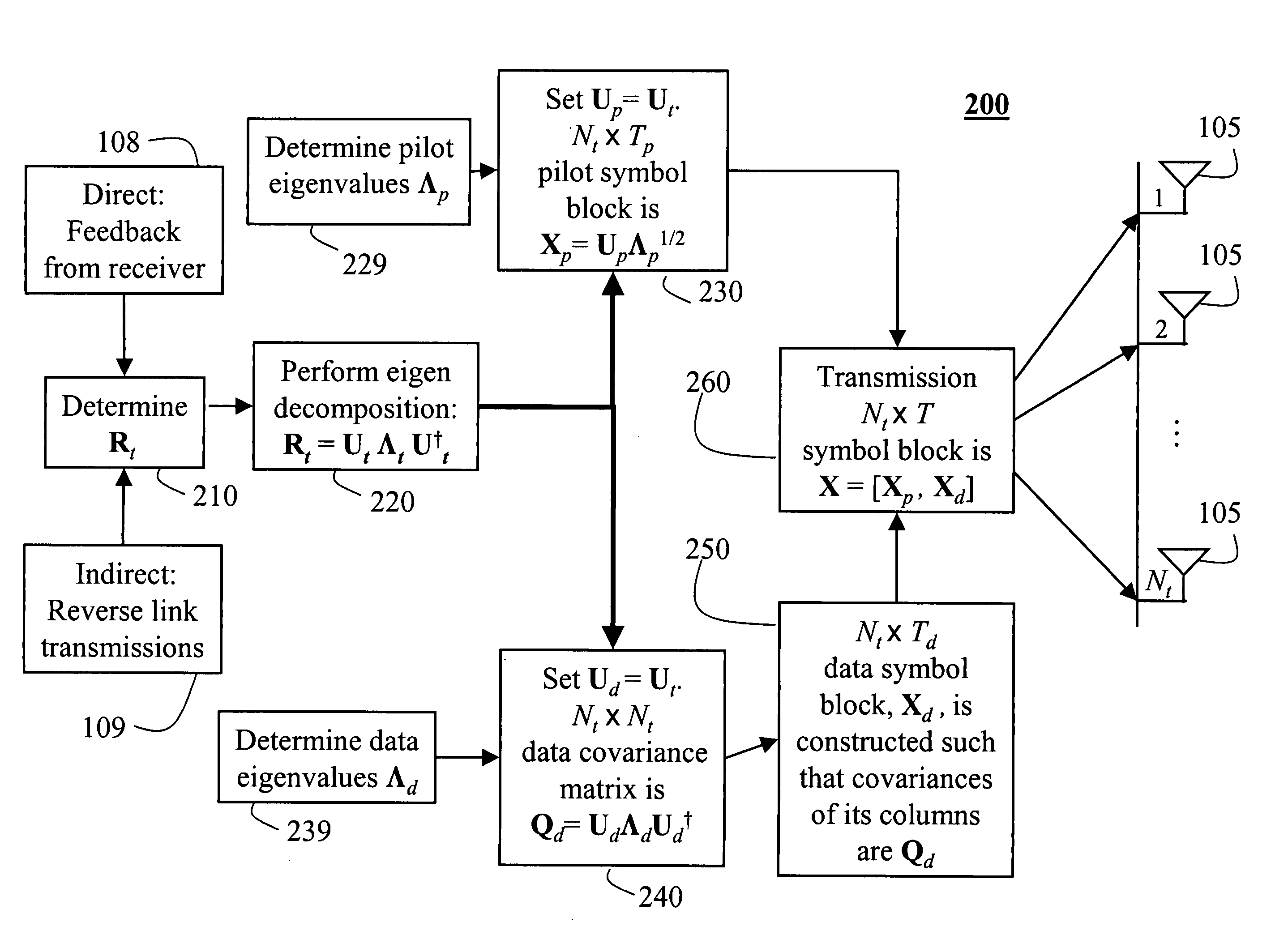
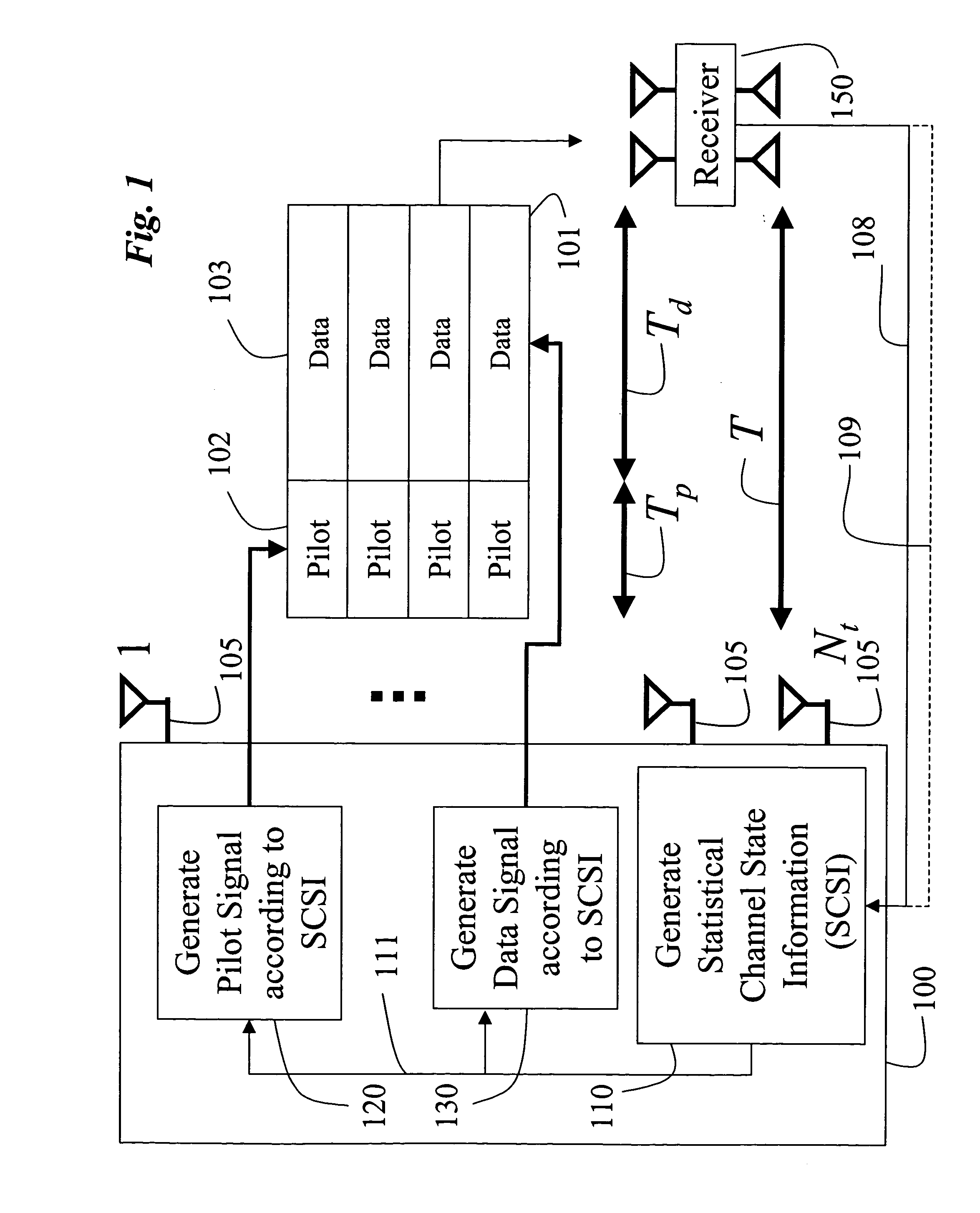
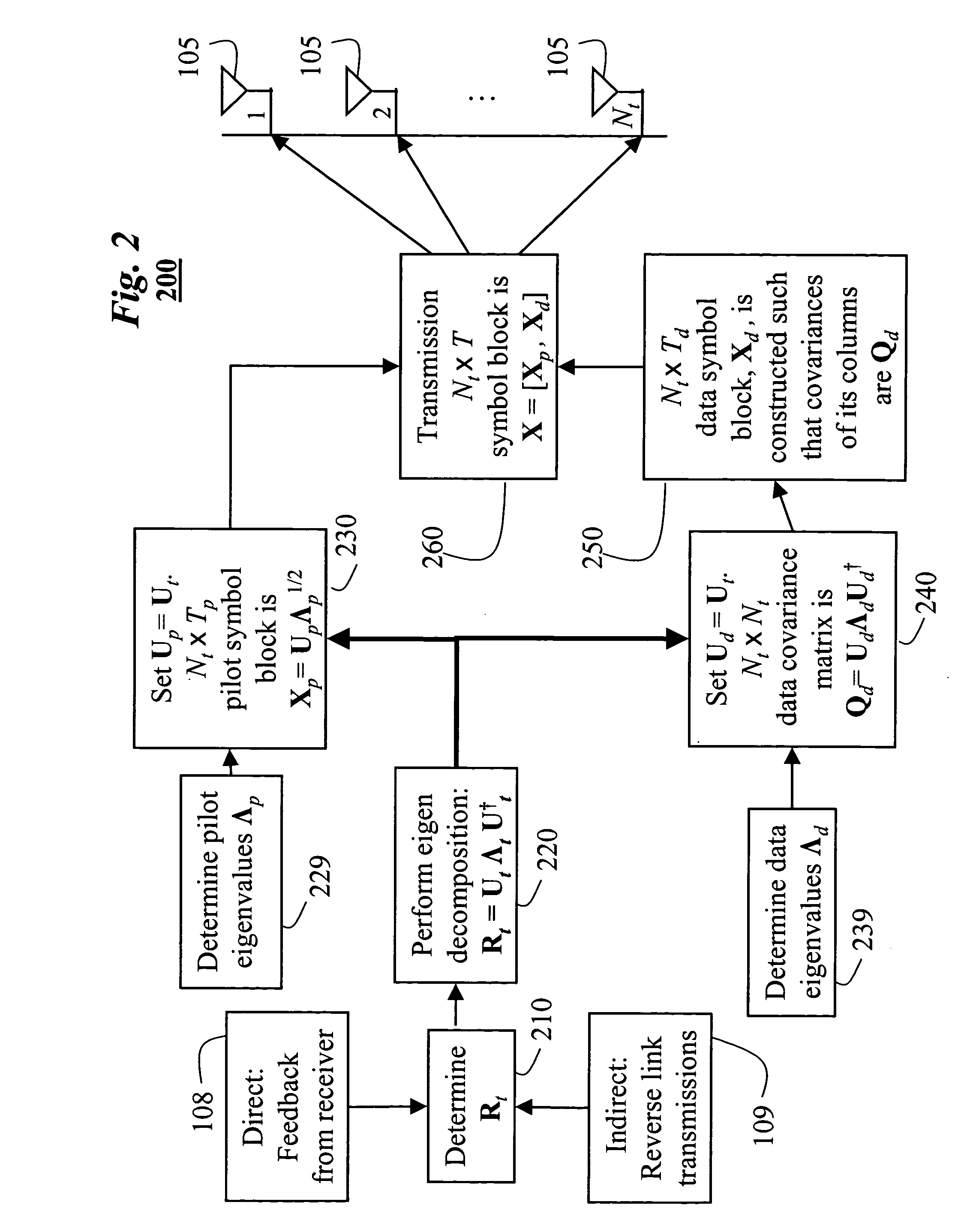
A method generates signals in a transmitter of a multiple-input, multiple-output wireless communications system. The transmitter includes Nt transmit antennas. A transmit covariance matrix Rt determined using statistical state information of a channel. The transmit covariance Rt matrix is decomposed using transmit eigenvalues Λt to obtain a transmit eigenspace Ut according to Rt=UtΛtU†t, where † is a Hermitian transpose. A pilot eigenspace Up is set equal to the transmit eigenspace Ut. A Nt×Tp block of pilot symbols Xp is generated from the pilot eigenspace Up and pilot eigenvalue Λp according to Xp=UpΛp1 / 2. A data eigenspace Ud is set equal to the transmit eigenspace Ut. In addition, a Nt×Nt data covariance matrix Qd is generated according to UdΛdU†d, where Λd are data eigenvalues. A Nt×Td block of data symbols is generated, such that an average covariance of each of the columns in the block of data symbols Xd equals the data covariance matrix Qd. The block of pilot and data symbols form the signals to be transmitted.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
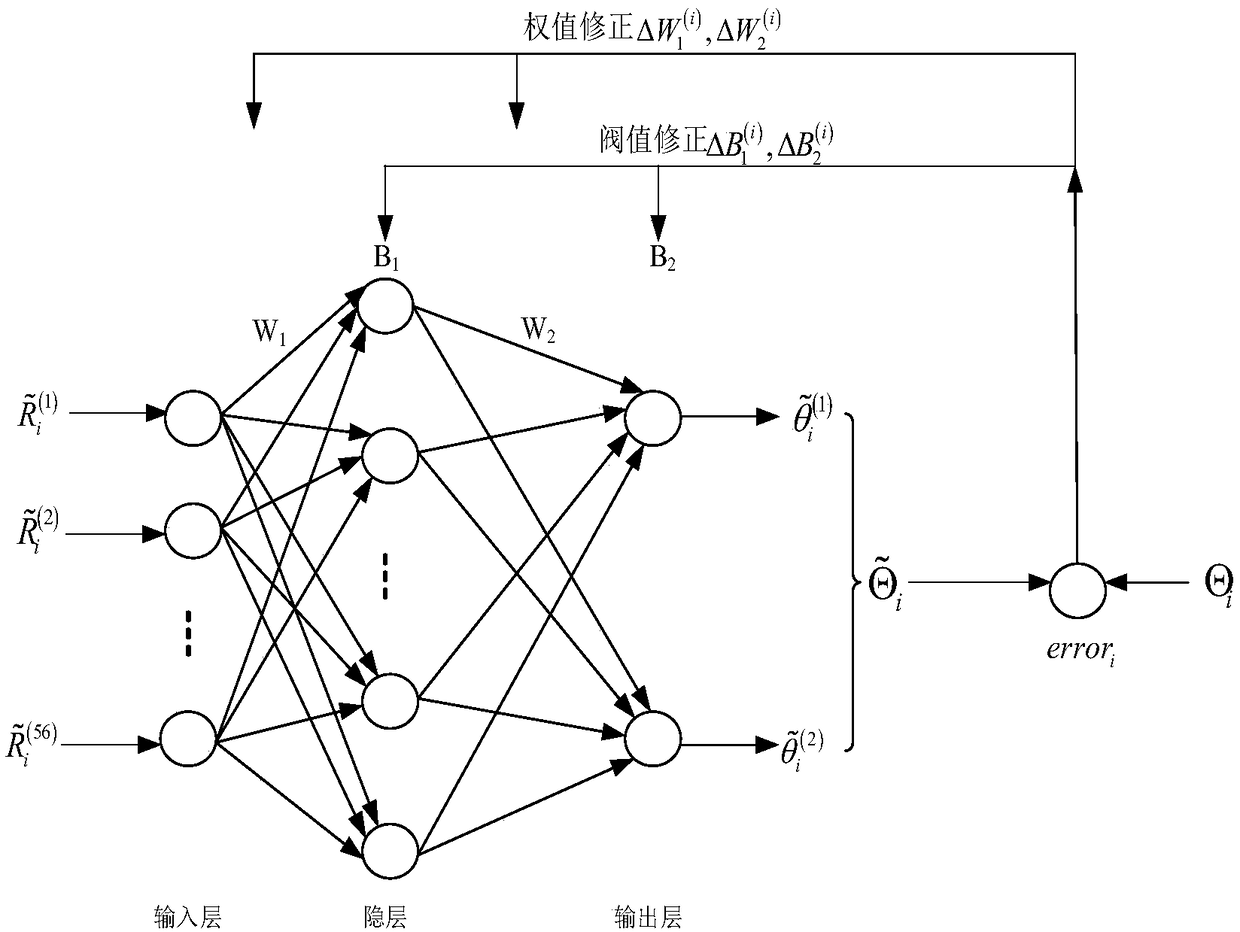
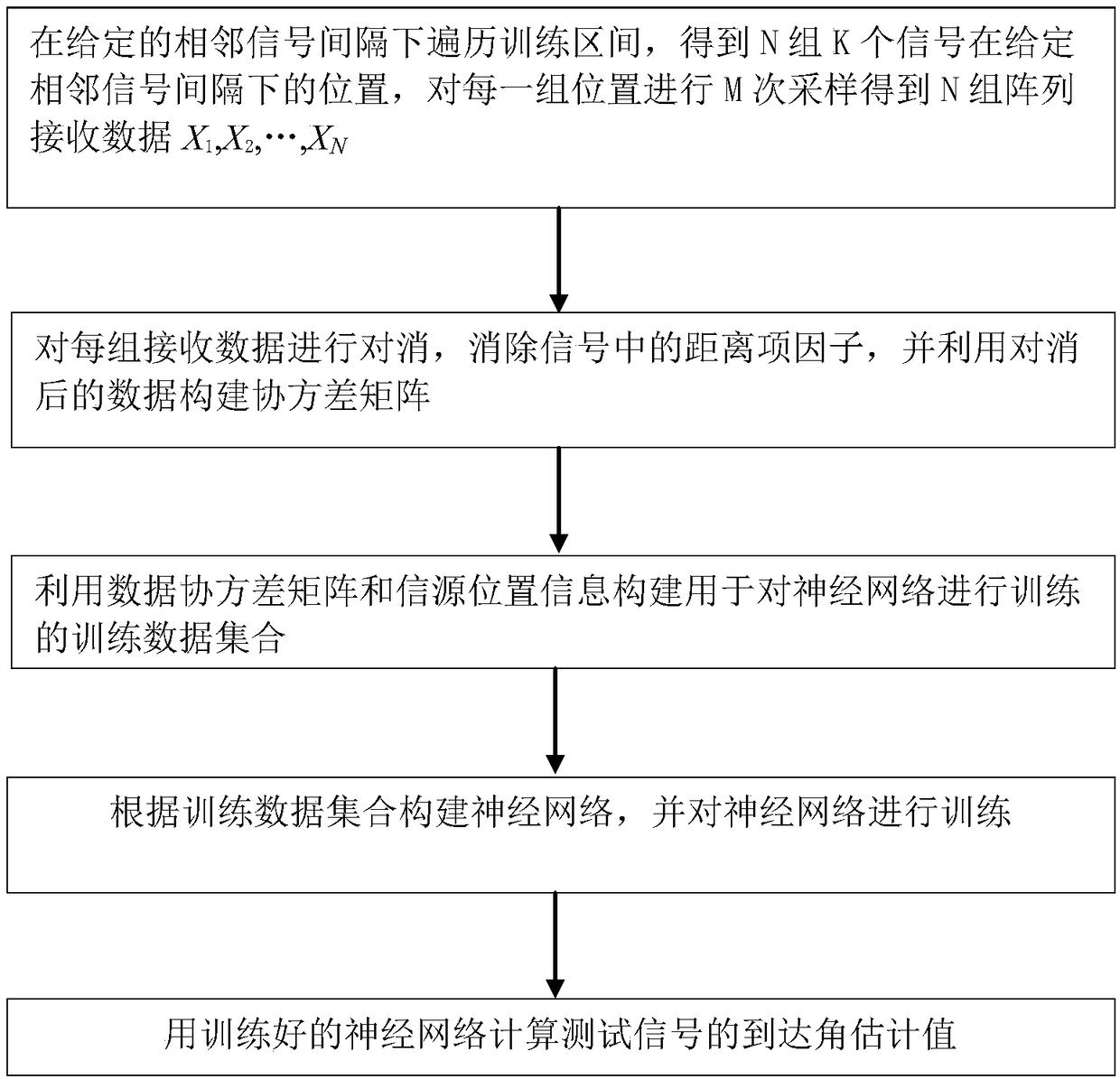
Near-field source arrival angle estimation method based on neural network
ActiveCN109085531AImprove generalization abilityImprove data processing speedRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsNeural learning methodsSensor arrayPattern recognition
A near-field source arrival angle estimation method based on a neural network comprises the steps that sampling data generated by K signals in a training interval are received by an array to calculatethe receiving data of the array, the signals are integrally rotated to acquire a next group of receiving data until the training interval is traversed; the covariance matrix of all groups of receiving data is established; a training data set is established through the covariance matrix and the arrival angles of the signals; the neural network is trained through the training data set; testing dataare calculated by sampling data generated by testing signals in testing angle intervals in the training interval are received by a sensor array, after one group of testing data are acquired, the signals are rotated to acquire the next group of testing data, the covariance matrix of all the groups of testing data is established, and normalization is conducted to obtain a normalized data covariancematrix; and the data of the normalized data covariance matrix are input into the neural network to calculate the arrival angle estimated value of the testing signals.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
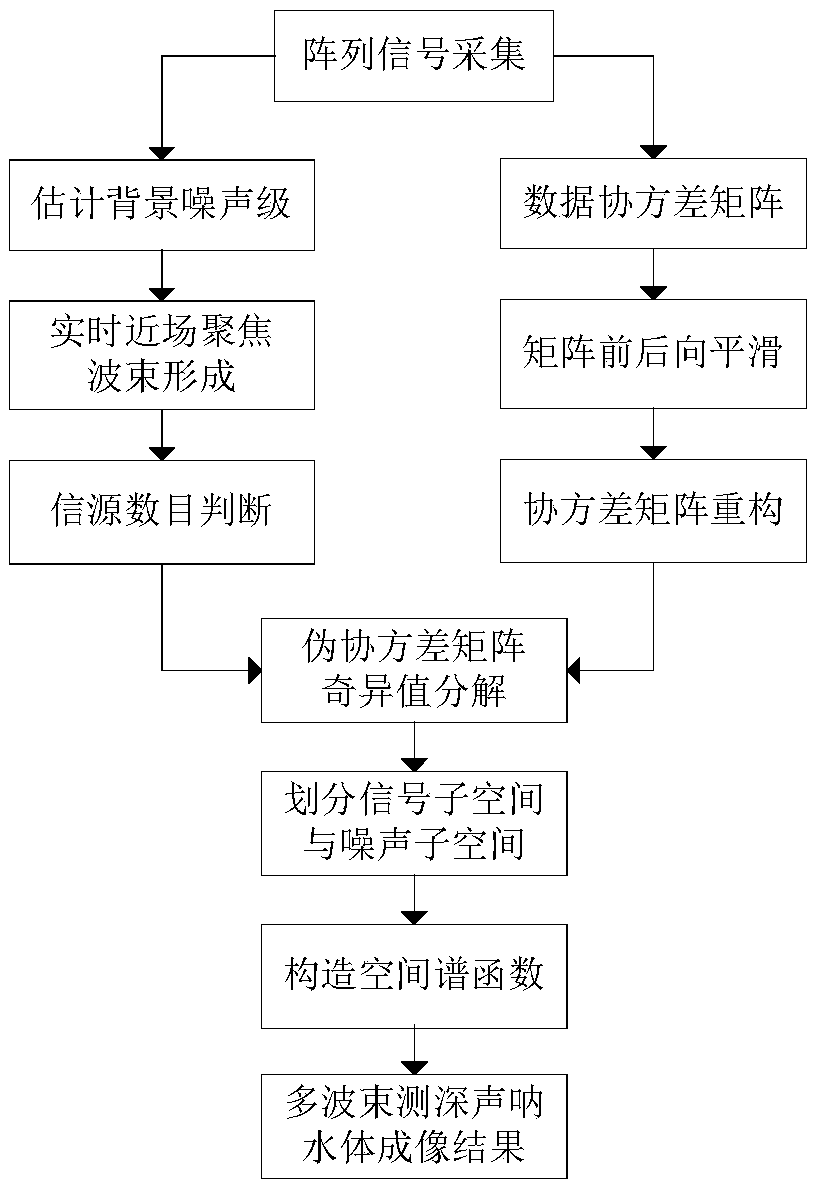
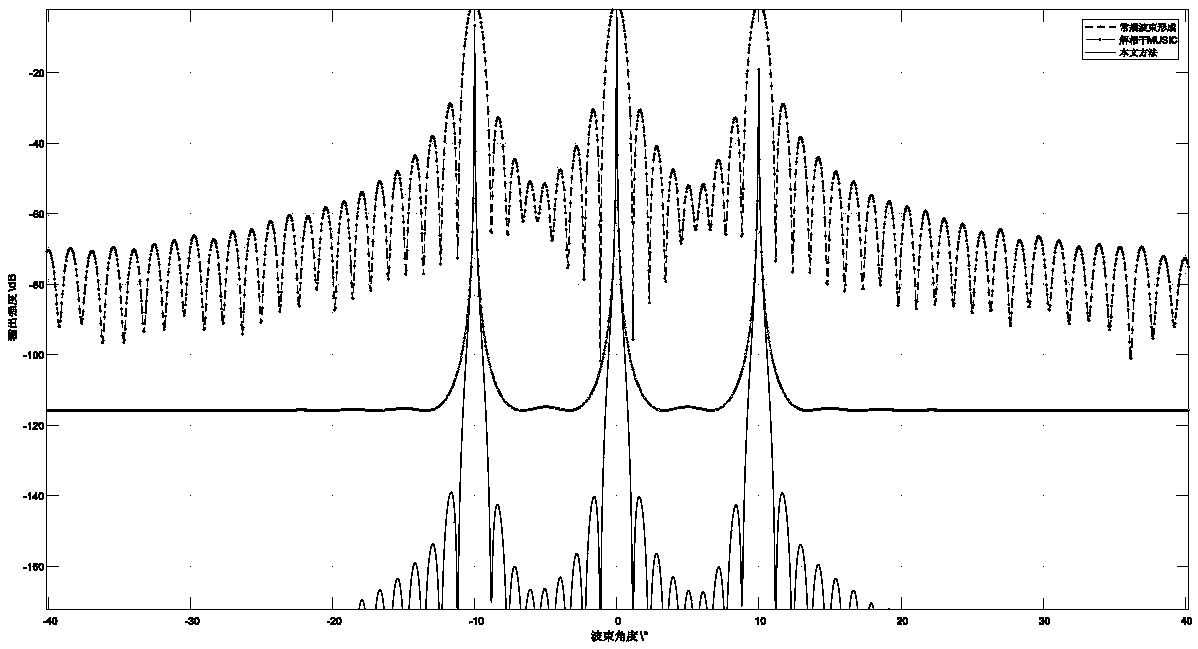
Multi-beam sounding sonar water body imaging beamforming algorithm
ActiveCN109283536AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityMeasuring open water depthWater resource assessmentSingular value decompositionSonar imaging
A multi-beam sounding sonar water body imaging beamforming algorithm relates to the field of signal processing. The multi-beam sounding sonar water body imaging beamforming algorithm mainly comprises:compensating for the propagation loss of the acoustic wave according to a time gain curve in each detection sampling time, and obtaining a background noise level of the current detected water area after time averaging; performing near-field focusing beamforming on the signal and estimating the number of sources under the current snapshot sequence number according to the current background noise level; performing covariance matrix estimation on a signal vector with a snapshot number of 1, and obtaining a new pseudo covariance matrix by reconstructing the data covariance matrix after the forward and backward smoothness; performing singular value decomposition on the pseudo-covariance matrix, using conventional beamforming output results and an array manifold to construct a spatial spectralfunction, and obtaining a multi-beam sounding sonar water body imaging result. The algorithm can be widely applied to the multi-beam sounding sonar water body imaging function, can effectively suppress the background noise of the multi-beam sounding sonar water body imaging, and can improve the sonar imaging quality.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
GPS (global positioning system) multipath mitigation method based on robust beam forming algorithm
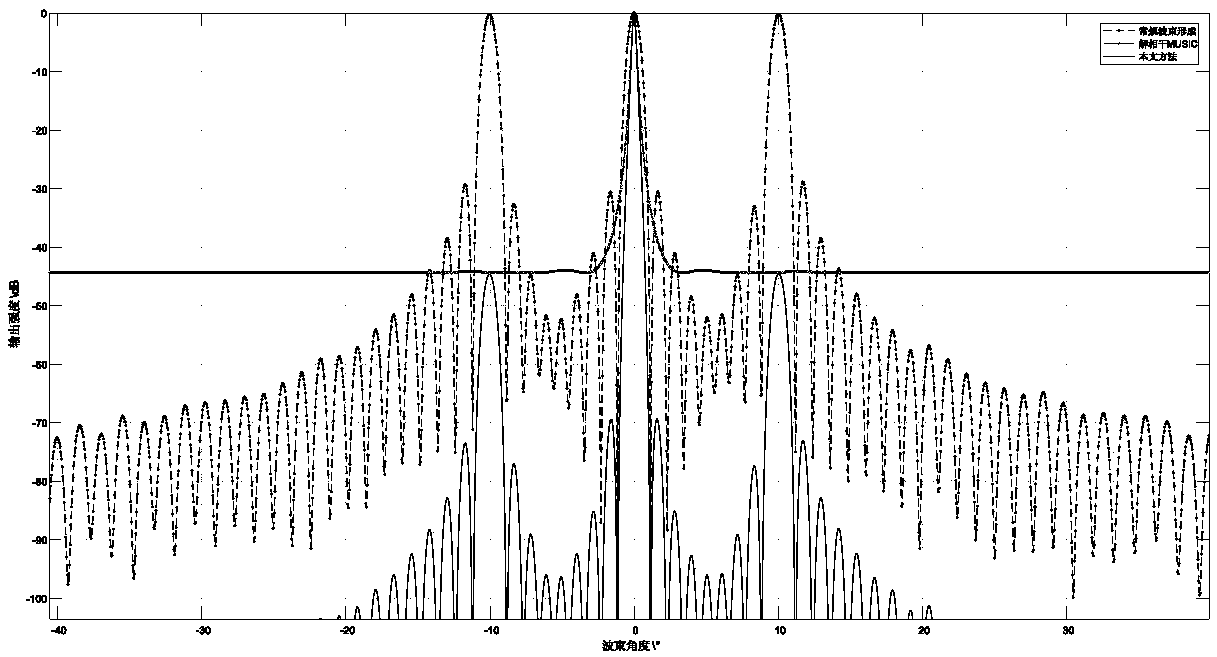
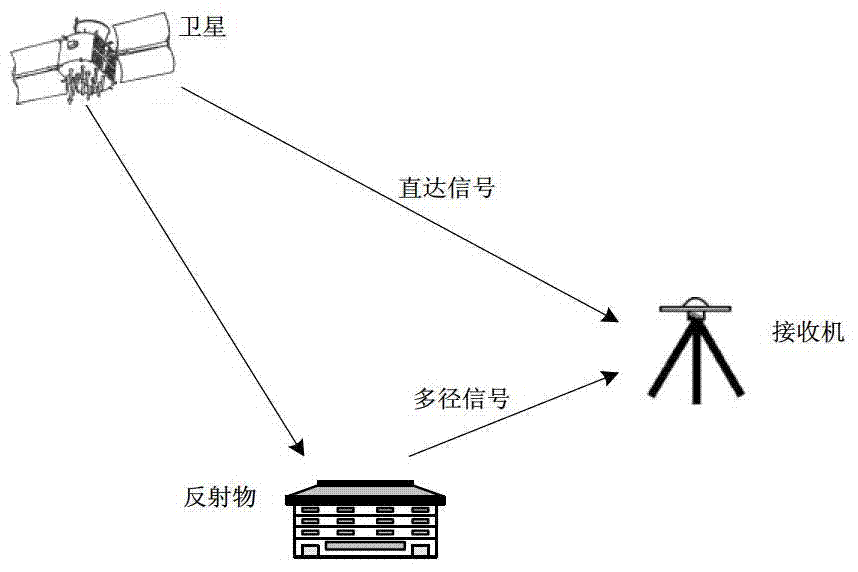
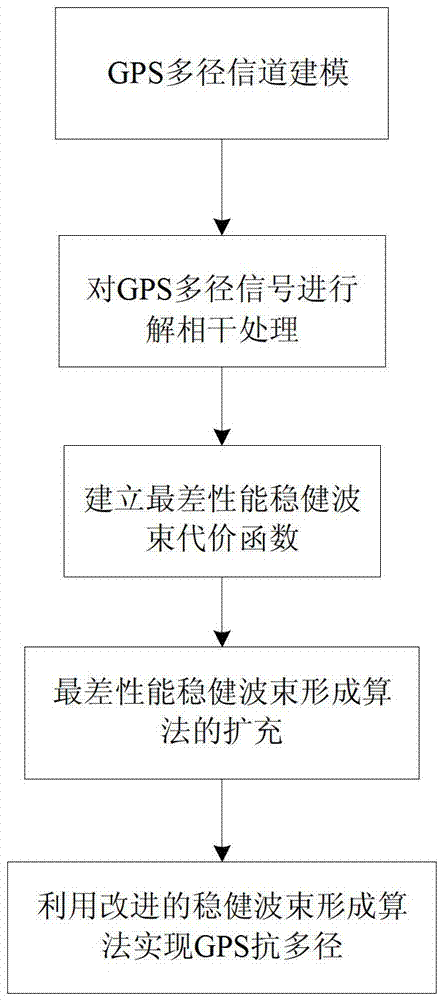
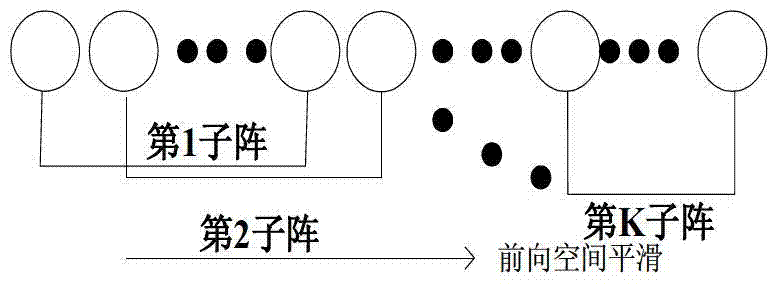
InactiveCN103245956AReduce the numberReduce correlationSatellite radio beaconingGlobal Positioning SystemCoherent processing
The invention discloses a GPS (global positioning system) multi-path mitigation method based on a robust beam forming algorithm, which comprises the following steps: step I, modeling a GPS multipath channel by adopting a uniform linear array; step II, performing decorrelation on received signals by adopting the forward-backward spatial-smoothing technology, so as to obtain a new data covariance matrix and the optimal weight of a Capon beam former; step III, on the basis of the step II, establishing a cost function of the worst-case performance optimization robust beam forming algorithm, so as to solve the optimal weight under steering vector mismatch; step IV, on the basis of the step III, exerting uncertainty constraint on other array response errors, so as to obtain an improved model for the worst-case performance optimization robust beam forming algorithm; and step V, according to the model determined in the step IV, calculating to obtain the optimal weight vector of the Capon beam former, and determining the loading capacity by utilizing the Newton iteration method.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
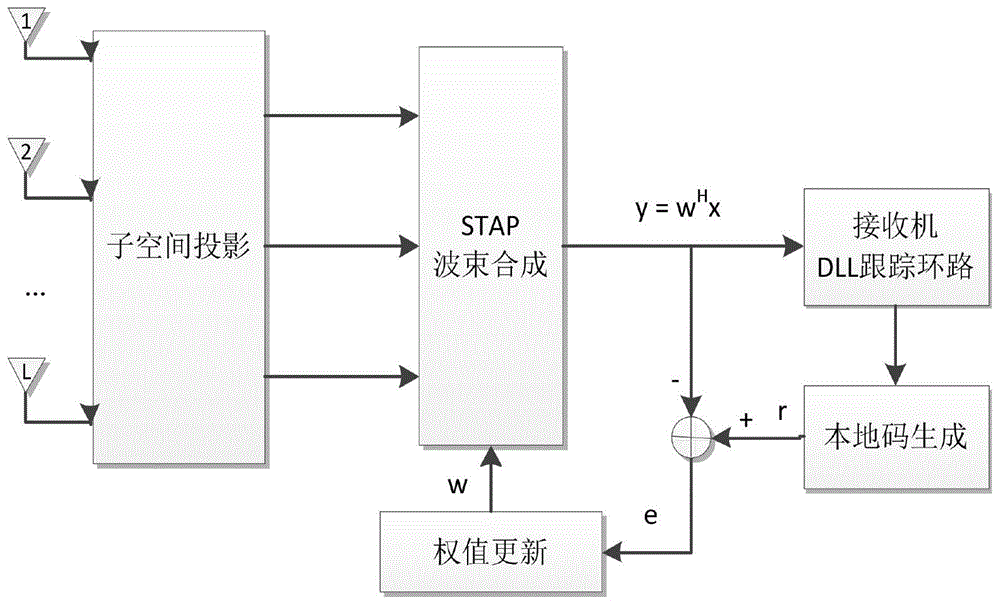
Navigation receiver STAP algorithm through which subspace projection is performed before beam forming
The invention discloses a navigation receiver STAP algorithm through which subspace projection is performed before beam forming. Firstly, SVD is performed on a received data covariance matrix, characteristic vectors corresponding to large characteristic values form an interference subspace, characteristic vectors corresponding to small characteristic values form a noise subspace, received data vectors are projected to the noise subspace so that interference suppression can be formed, and then, local pseudo codes of navigation signals are used as reference signals for performing beam forming on array weight so that a main beam of an array antenna can point to the incoming wave direction of the navigation signals. The navigation receiver STAP algorithm through which subspace projection is performed before beam forming has the advantages of increasing the array output signal interference and noise ratio and improving signal tracking precision.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Pilot and data signals for MIMO systems using channel statistics
InactiveUS7443925B2Improve data transfer rateSimplify complexityPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemChannel statistics
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Co-primer array non-grid DOA estimation method under non-negative sparse Bayes learning framework
ActiveCN109444810AReduce computational complexityDerivation is simpleRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsExpectation–maximization algorithmComputation complexity
The invention provides a co-primer array non-grid DOA estimation method under a non-negative sparse Bayes learning framework, and belongs to the field of research on a high-resolution direction finding method in signal processing. The method includes the steps that firstly, a co-primer array received data covariance matrix is vectorized, a virtual received signal model is established, then a non-negative sparse Bayes model is established based on the characteristic that virtual incident signal elements in the model are not negative, hyper-parameters and a grid point set are iteratively updatedthrough an expectation-maximization algorithm, finally, a signal power spectrum is established according to the finally-updated grid point set and the finally-updated hyper-parameters, and then an estimated DOA is determined through spectrum peak searching. By means of the method, the operation process is converted to a real number field from a complex number field, and therefore the computationcomplexity can be reduced to a certain degree. In addition, by the application of a co-primer array, undetermined DOA estimation can be achieved, the limitation of the number of array elements in themaximum estimable information source number is broken through, thus, the hardware cost can be reduced to a certain degree, and certain engineering application value is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for estimating direction of arrival of MIMO radar based on nested array
ActiveCN106707257AEasy to implementIncrease freedomWave based measurement systemsRadarImage resolution
The invention discloses a method for estimating the direction of arrival of MIMO radar based on a nested array, which mainly solves a problem that the early radar is low in resolution for the direction of arrival and small in number of recognized signal sources. Implementation of the method comprises the steps of 1) building a nested array based MIMO radar model, and acquiring a target return signal; 2) performing snapshot sampling, matched filtering and vectorization on the target return signal in sequence, and acquiring vectorized receiving data y; 3) estimating a covariance matrix Ryy of the receiving data y, and performing vectorization on the covariance matrix Ryy to acquire an observation vector z; 4) removing repeated elements of the observation vector z to acquire virtual differential array receiving data z1; 5) dividing the virtual differential array receiving data z1 into N1 pieces of subarray receiving data, and acquiring a rank-recovery receiving data covariance matrix Rss; 6) performing eigenvalue decomposition on the rank-recovery receiving data covariance matrix Rss to acquire a noise subspace EN; and 7) acquiring the direction of arrival according to a spectral function formed by the noise subspace EN. The method disclosed by the invention improves the degree of freedom and the resolution of an MIMO radar system, and can be applied to radar target orientation detection.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Ultrasonic receiving array orientation method for transformer partial discharge positioning
InactiveCN103995221ASmall apertureEasy to handleTesting dielectric strengthSorting algorithmTransformer
The invention discloses an ultrasonic receiving array orientation method for transformer partial discharge positioning. According to the method, an ultrasonic receiving array which is arranged along the array edge or the center line of a planar array and is in an L shape or in a cross shape is used. The method comprises the steps that broadband focusing and array expansion are combined, focusing operation is conducted on an ultrasonic array receiving signal of a broadband first, a broadband ultrasonic signal generated through partial discharge is segmented according to time, a focusing matrix is calculated through noiseless data, and the signal is focused on the same frequency band; then, virtual expansion is conducted on the array through a fourth order cumulant algorithm, and a data covariance matrix of the array after virtual expansion is replaced by an unexpanded fourth order cumulant matrix which is formed in sequence of an original array; at last, the partial discharge incoming wave direction of the array after virtual expansion is estimated through a multi-signal sorting algorithm.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
DOA estimation method based on DFT under nested array
InactiveCN107505602AImprove estimation performanceReduce complexityWave based measurement systemsPhase shiftedNested arrays
The invention discloses a DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method based on a DFT (Discrete Fourier Transform) under a nested array, which belongs to the field of array signal processing. First, a receiving data covariance matrix is vectorized to get receiving data with the number of array elements expanded. Then, the initial DOA is estimated through a DFT method. Finally, the precise DOA is estimated by searching for the optimal phase shift in a very small area. The method of the invention has better DOA estimation performance, a complete degree of freedom and lower complexity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
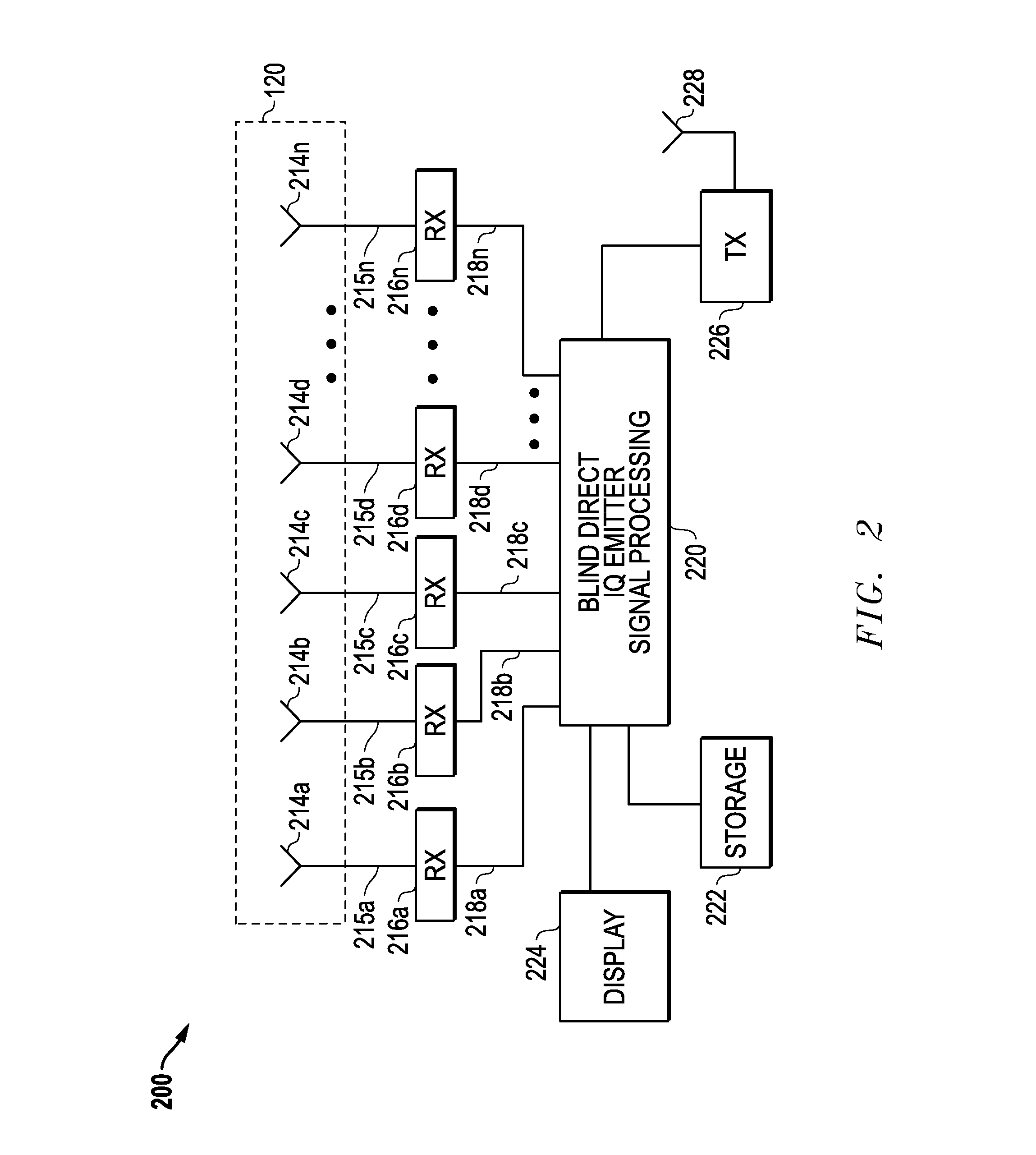
Systems And Methods For Direct Emitter Geolocation
ActiveUS20140327571A1Optimize locationFacilitates visual identificationRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPosition fixationSignal waveGeolocation
Systems and methods are disclosed for locating signal wave (SW) emitter / s using at least one moving signal collection platform. The disclosed systems and methods may be employed in one embodiment to estimate the signal energy transmitted from a grid of locations (such as a map) using collected IQ data (or other raw data representation such as IQ data covariance matrix), and without requiring computation of any intermediate geolocation-observable measurements (such as angle-of-arrival, direction-of-arrival, etc.). In a further embodiment, the disclosed systems and methods may be implemented in a blind manner (i.e., transmitted emitter signal / s are unknown and processed blindly) to geolocate SW emitters using a single SW signal collection platform (e.g., at relatively large standoff distances in some implementations) without relying on a known signal modulation or operation of multiple simultaneous SW signal collection platforms.
Owner:L3HARRIS TECH INTEGRATED SYST LP
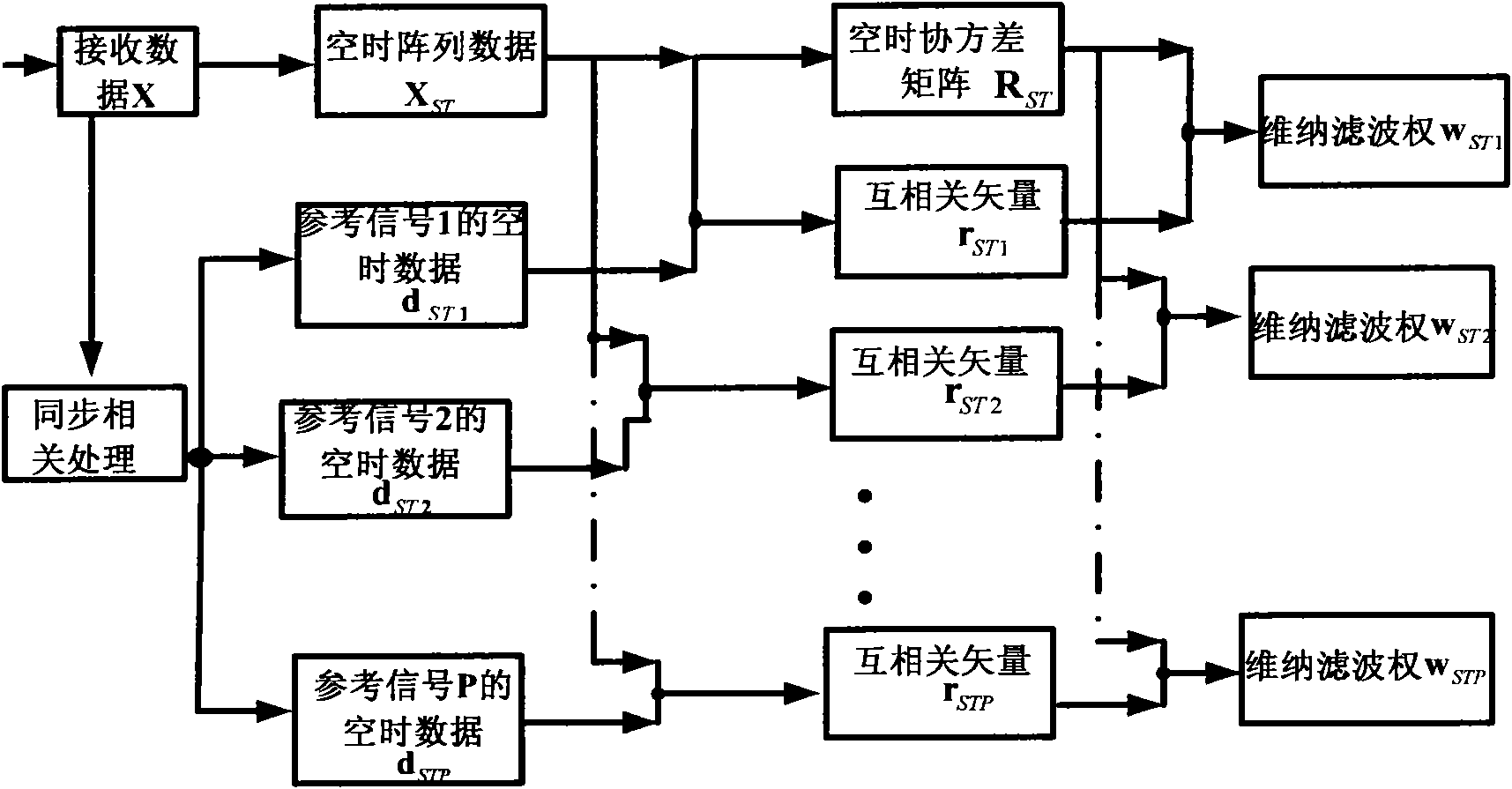
Space-time blind self-adapting anti-jamming method based on waveform characteristics
ActiveCN101807977AAchieving Blind Adaptive Anti-jammingImprove anti-interference abilityRadio transmissionError prevention/detection by diversity receptionAnti jammingSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a space-time blind self-adapting anti-jamming method based on waveform characteristics, which mainly solves the problem that the anti-jamming capability is lowered or even out of service in the presence of array manifold errors in the existing method. The method comprises the following steps that: data received by each matrix element realize the preliminary anti-jamming bythe space-domain sampling covariance matrix inversion method to synchronize a correlation peak so as to synchronize the data received by the matrix element with reference signals; the data received by the matrix element pass through a delay structure to output space-time array data, the space-time array data are used to estimate transformed space-time reference signals formed in a way that the space-time covariance matrix passes the synchronized reference signals through the delay structure, and the space-time reference signals and the space-time array data are used to estimate a cross-correlation vector rST; and the space-time data covariance matrix and the cross-correlation vector rST are used to calculate a space-time Wiener weight wST to carry out the space-time blind self-adapting anti-jamming. The invention has the advantage of strong anti-jamming capability, and can be used for the space-time anti-jamming under the condition that array manifold errors exist and satellite signals or the interfered arrival direction is unknown.
Owner:XIAN CETC XIDIAN UNIV RADAR TECH COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION INST CO LTD
Interpolation transformation and beam forming-based far-field coherent signal DOA estimation method
ActiveCN107315162AGuaranteed accuracyReduce computational complexityPosition fixationComputation complexityFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to an interpolation transformation and beam forming-based far-field coherent signal DOA estimation method. According to the method, firstly, an interpolation matrix is adopted to convert a non-uniform linear array covariance matrix into a covariance matrix of a virtual uniform linear array. Data on the covariance matrix of the virtual array are subjected to noise pre-whitening to obtain img file = 'DDA 00013602494400000000000011.T'wi = '67 'he = '71 '. After that, img file = 'DDA 00013602494400000000000011.T'wi = '43 'he = '70 ' is subjected to spatial smoothing treatment to resolve the phase coherence, so that a coherence-resolved data covariance matrix is obtained. The coherence-resolved data covariance matrix is processed through constructing a cost function, and then the estimated value of the DOA of a far-field coherent signal is obtained. According to the invention, on the premise that the precision is guaranteed, the operations of feature decomposition, frequency spectrum searching and the like which are complicated in operation, can be avoided. The method is low in calculation complexity, simple and effective. Meanwhile, based on the method, the application range is popularized from a uniform linear array to any linear array, and from a non-coherent signal source to a coherent signal source. Therefore, the method is wider in application range.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
MIMO radar target blind detection method based on characteristic values under correlated noise background
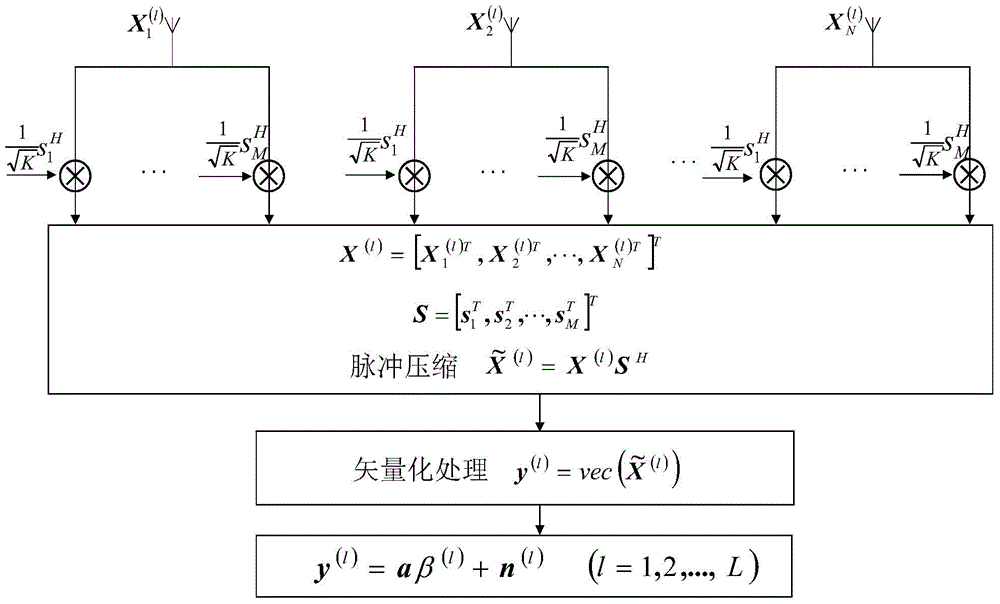
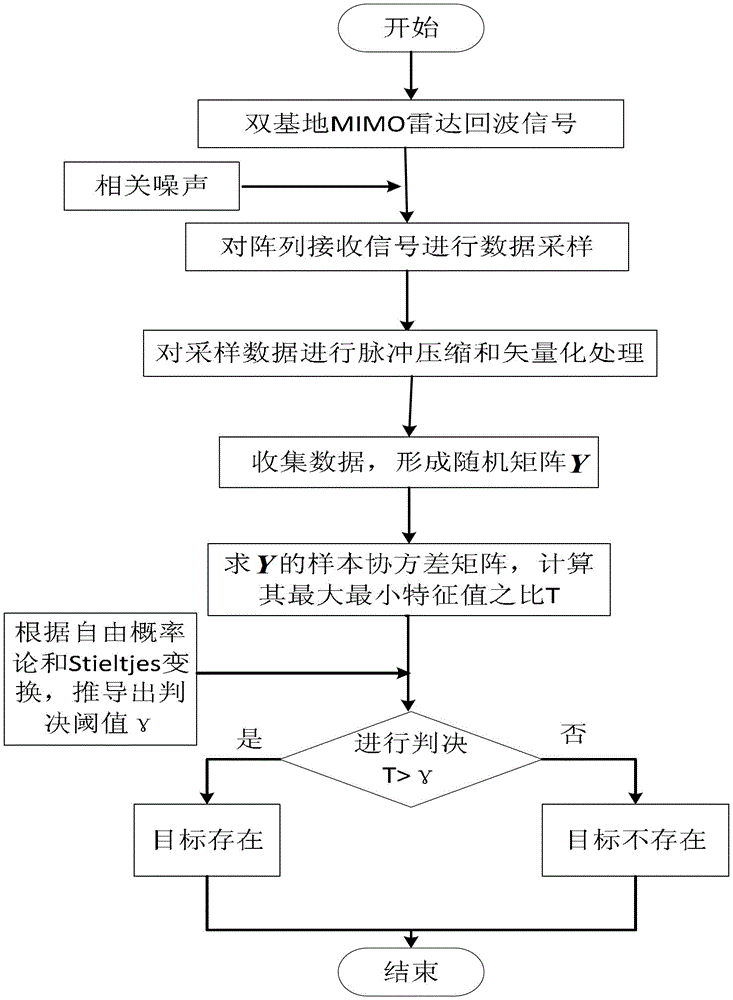
ActiveCN104360334AImprove robustnessSolve the defect of object detection performance degradationWave based measurement systemsPattern recognitionObservation data
The invention provides an MIMO radar target blind detection method based on characteristic values under a correlated noise background. The method is suitable for large-array bistatic MIMO radar with the receiving and transmitting number of array elements and the snapshot number being close. The method comprises the steps that a random matrix theory is used as a tool, the defects that in the prior art, the snapshot number is insufficient and the target detection performance under the correlated noise background is lowered are overcome, and a random matrix model of observation data is established by echo signals under the correlated noise background; the ratio of the maximum characteristic value and the minimum characteristic value of an echo data covariance matrix is calculated to be used as the detection statistical magnitude; the freedom probability theory and Stieltjes conversion are used for deriving a threshold value expression of target detection under the correlated noise background; the threshold value is used as a judgment threshold for detecting a target. Simulation experiments show that the method is suitable for blind detection under the condition that a noise variance and a target scattering matrix are unknown, and the robustness of target detection under the correlated noise environment is obviously improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Array direction-finding method and device thereof for aiming at broadband OFDM communication signal
ActiveCN107255793AImplement Direction of Arrival EstimationExcellent super-resolution direction finding performanceMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesMulti-frequency code systemsSignal subspaceMultiple signal classification
The invention relates to the direction finding technology of the broadband array signal processing field. The array direction-finding method of the invention comprises steps of choosing a focusing reference frequency point, decomposing an OFDM signal received by an array and performing DFT processing to obtain a broadband array signal, using a constraint condition that an error between an array flow pattern after focusing and a reference frequency point array flow pattern and an array flow pattern matrix to calculate a focusing matrix corresponding to a frequency point, performing focusing conversion on array reception data in every sub-time-frame to obtain a single frequency point data covariance matrix according to the focusing matrix so as to obtain a covariance matrix relating to the reference frequency point, calculating a mathematic mean value R of each reference frequency point covariance matrix, performing characteristic value decomposing on the R to obtain a signal sub-space and a noise sub-space so as to obtain a space spectrum expression of a broadband MUSIC algorithm and performing searching according to a space spectrum expression to obtain an angle position corresponding to P maximum value points which is an estimation value of a direction of a broadband OFDM signal incoming wave.
Owner:SOUTHWEST CHINA RES INST OF ELECTRONICS EQUIP
Nested array direction-of-arrival estimation method based on off-grid sparse Bayesian learning
ActiveCN108459296AAutomatically find noise varianceExact angle estimateDirection findersNested arraysEstimation methods
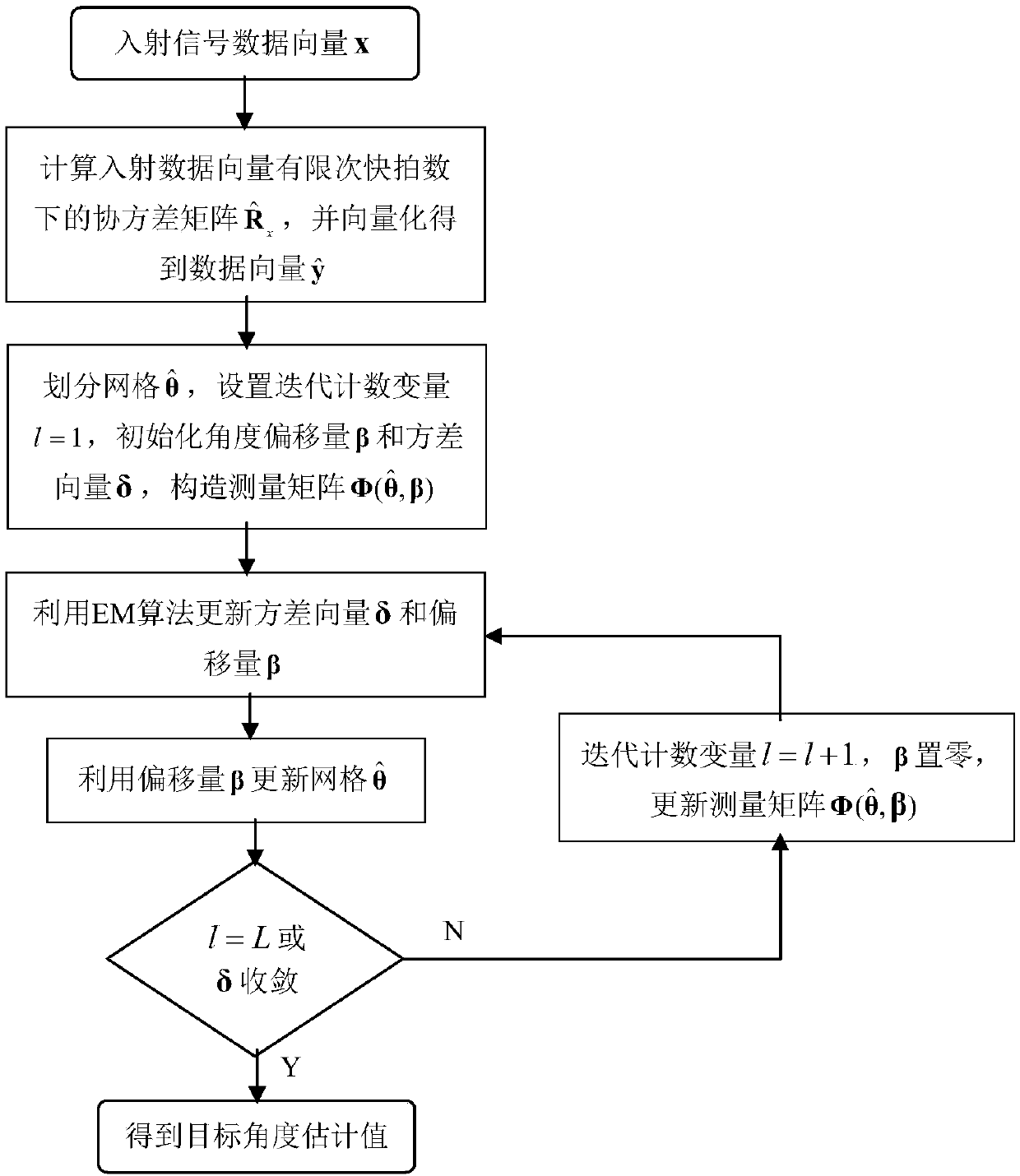
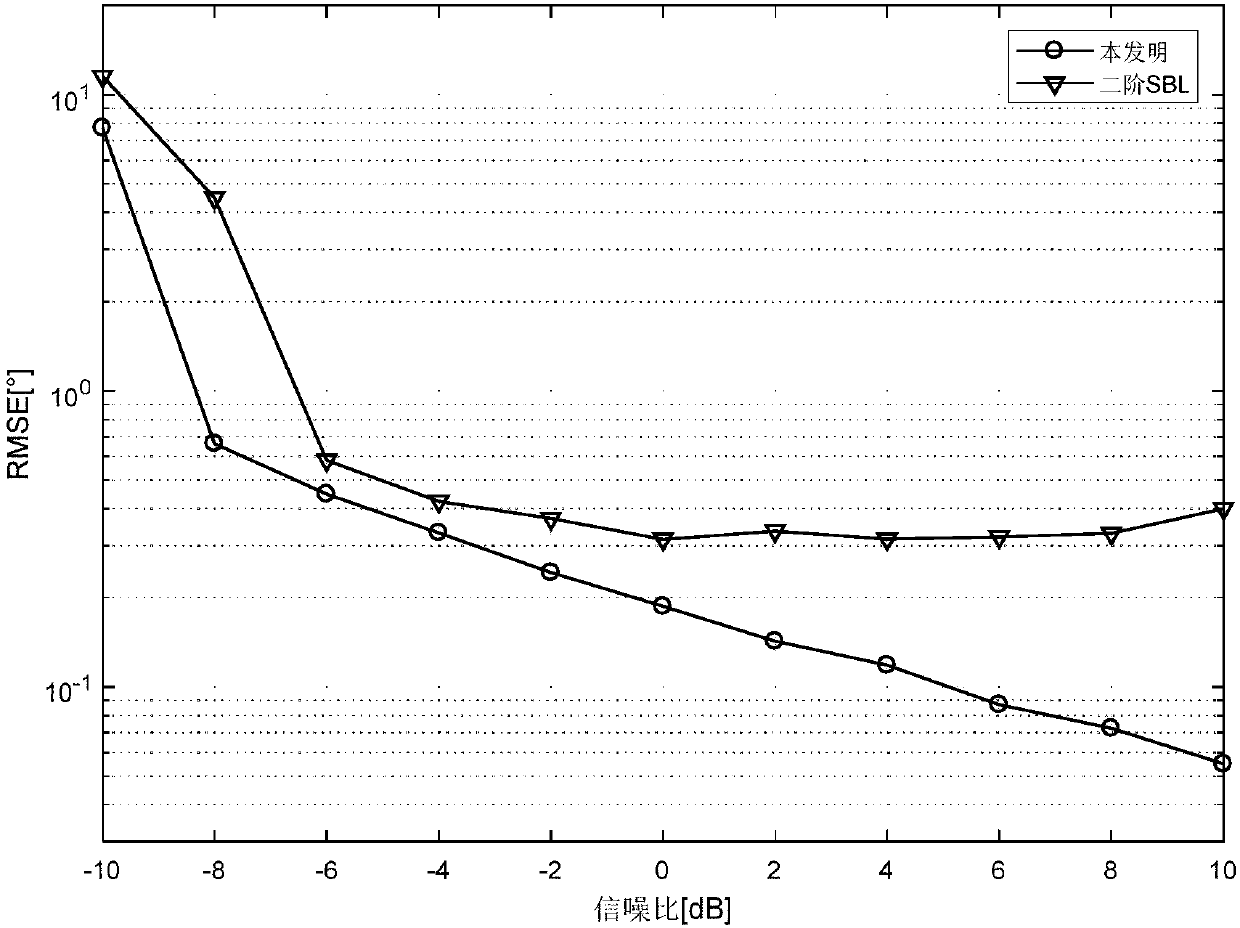
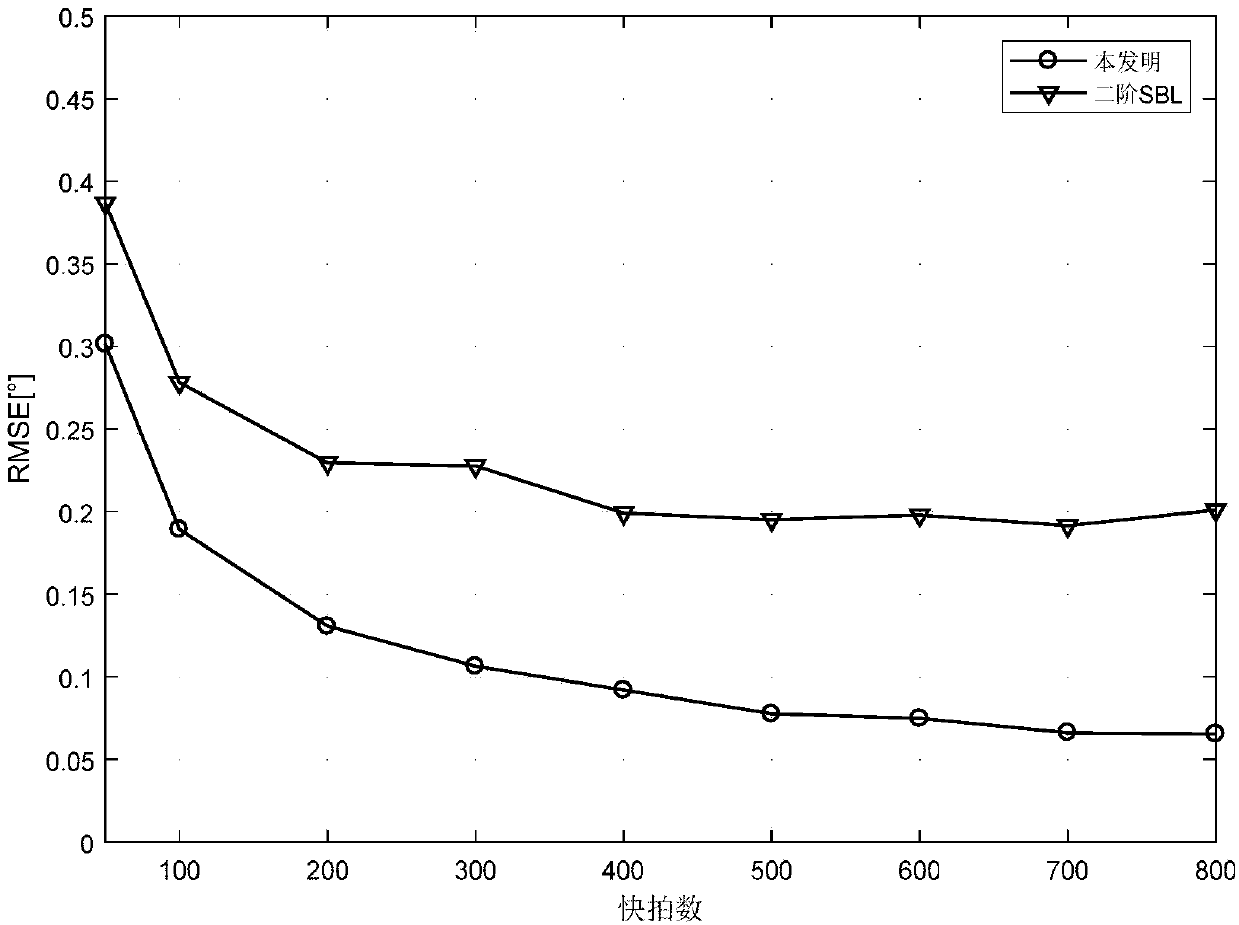
The invention discloses a nested array direction-of-arrival estimation method based on off-grid sparse Bayesian learning. The method comprises: step one, matching filtering is carried out on a narrowband Gaussian signal received by a nested array to obtain a data vector x(t) including DOA information at a t time; step two, with the x(t), a received data covariance matrix R^x under a T snapshot number is calculated and vectorization is carried out on the R^x to obtain a one-dimensional data vector Y^; step three, K^ grid points theta^={theta^i}<K^>i=1 are divided uniformly in a range [-pai / 2,pai / 2], a counting variable I of the number of times for iteration is set to be 1, a variance vector delta and an e angle offset vector beta are initialized, and a measuring matrix phi (theta^, beta) isconstructed; step four, a variance vector theta and an angle deviation value beta in a (K^+1) dimension are updated by using an EM criterion; step five, the grid theta^ is updated by using the beta value obtained at the step four; step six, whether the counting variable I of the number of times for iteration reaches an upper limit L or the delta converges is determined; if not, the counting variable I of the number of times for iteration conforms to a formula: 1=1+1, wherein the beta is equal to 0; updating is carried out on the phi (theta^, beta) by using the updated grid theta ^, and the step four is performed; and step seven, spectral peak searching is carried out on the variance vector delta to obtain angles corresponding to K maximum points, so that a final estimation value of the target angle is obtained.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Non-uniform array design and direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method
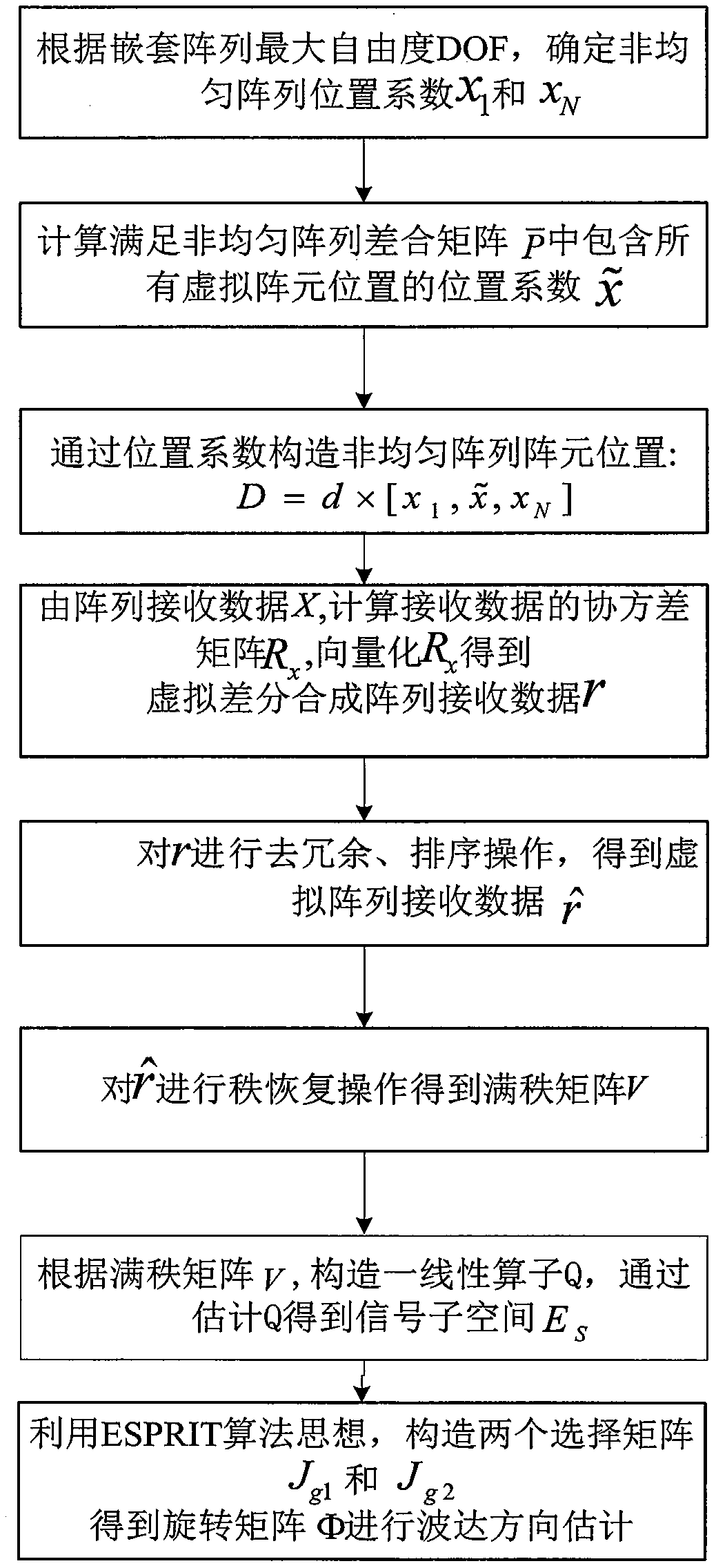
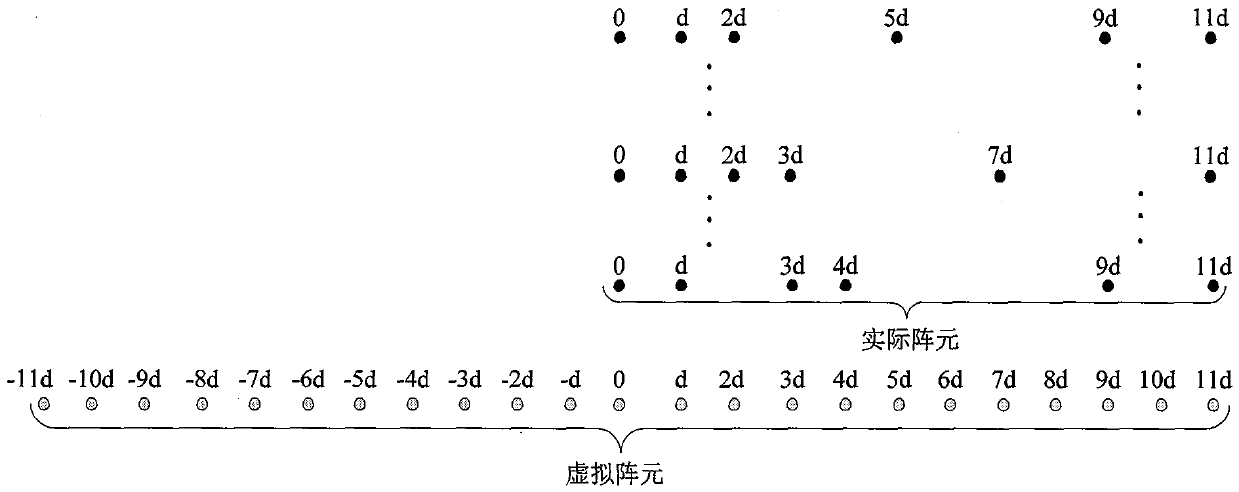
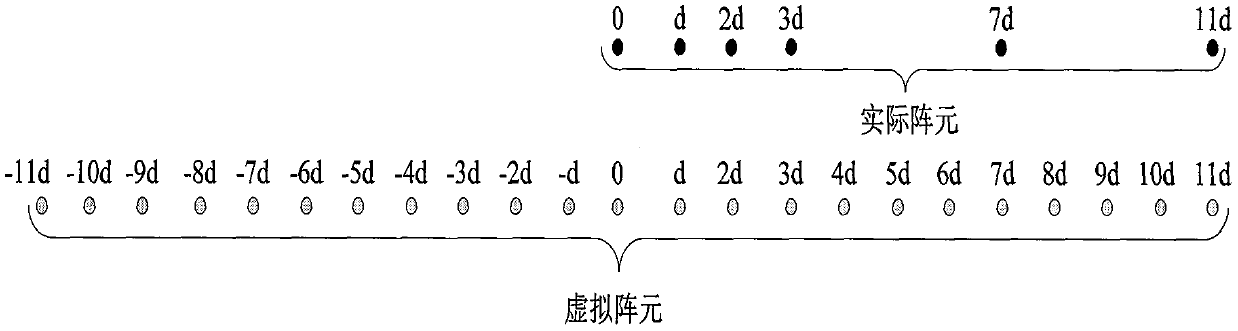
ActiveCN110082708ASuitable for engineering realizationLarge apertureRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsHigh level techniquesComputation complexityDecomposition
The invention discloses a non-uniform array design and direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method and mainly aims at solving the problems that arrangement is inflexible and computation complexity isrelatively high in the prior art. A realization process of the method comprises the following steps: according to maximum freedom degree of a nested array, determining head and tail position coefficients of a non-uniform array; calculating position coefficients of all the virtual array element positions meeting the non-uniform array and contained in a differential synthetic matrix; according to the position coefficients, finally obtaining positions of array elements of the non-uniform array; according to received data, calculating a data covariance matrix and vectorizing, so that received data r of a virtual differential synthetic array is obtained; performing redundancy elimination on the r and sorting to obtain received data of a virtual array, and then obtaining a non-singular matrix vof the virtual array; constructing a linear operator, and obtaining a signal subspace by estimating the linear operator; and constructing a selection matrix to obtain a rotation matrix, and finally estimating a direction of arrival by virtue of the rotation matrix. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that array configuration is flexible, characteristic decomposition does notneed to be performed on the data covariance matrix and spectral peak search does not need to be performed on the whole airspace angle under the same conditions.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Self-adaption anti-coherent interference technology based on characteristic component rejection
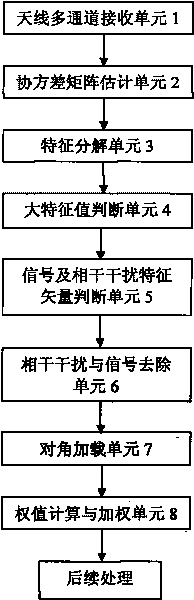
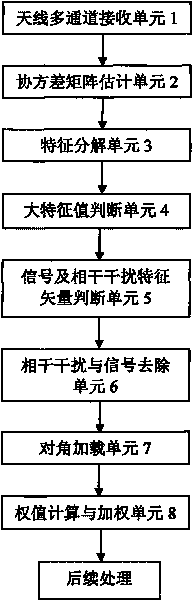
InactiveCN101726730AAvoid cancellationNo lossWave based measurement systemsDecompositionTarget signal
The invention discloses a self-adaption anti-coherent interference technology based on characteristic component rejection. Firstly, characteristic decomposition is carried out on an antenna multichannel receiving data covariance matrix to judge the number of a big characteristic value; then, the characteristic vector corresponding to signals and coherent interference is searched in a characteristic vector group corresponding to the big characteristic value so as to subtract the characteristic vector from the covariance matrix; finally, diagonal loading is carried out on the covariance matrix removing signals and coherent interference components, and the loaded matrix is used for calculating a self-adaption weight, data is weighed, and specific steps are disclosed in the drawing. The method of the invention avoids cancellation of desired signals while inhibiting incoherent interference, does not have array aperture loss and does not need to master the direction priori information of coherent interference. The method only relates to characteristic decomposition and inversion operation but does not relate to high-order cumulant operation, so that the method has simple steps and small calculation amount; the device is simple and has low cost. In addition, the method of the invention receives and utilizes the coherent interference as a wanted signal so as to improve the receiving gain of a target signal, thus owning better receiving performance. The method of the invention can be realized only by downloading a program to a general signal processing board, is easy to popularize and only needs to programme on a programmable signal processing board; thus, the system is convenient to upgrade while the system structure is not changed. The method of the invention can be widely applied to a system with various kinds of receiving channel structures and has popularization and application value.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE RADAR COLLEGE
Beam forming method based on covariance matrix reconstruction and steering vector correction
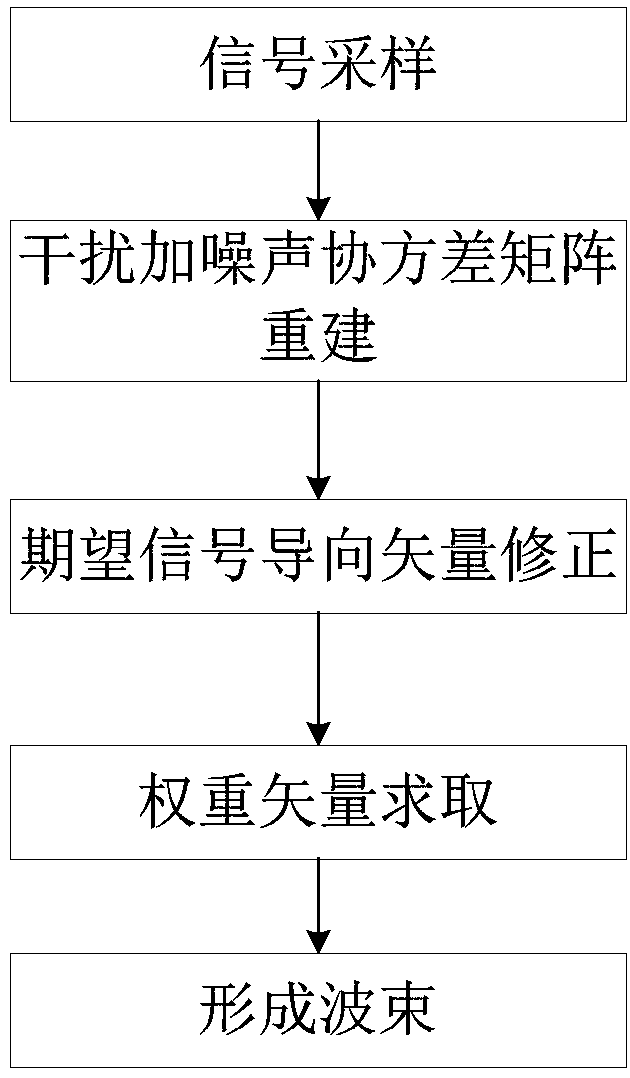
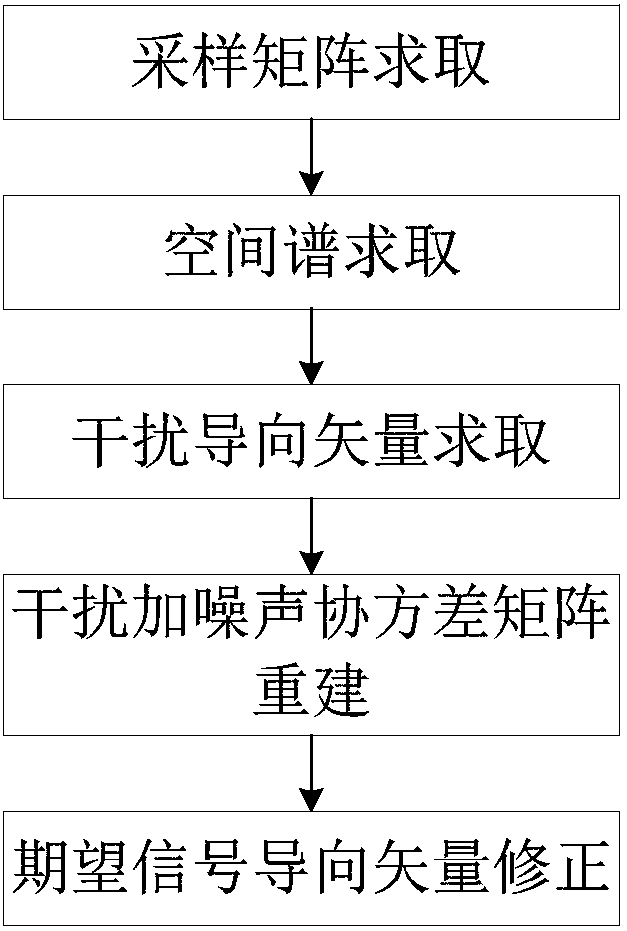
InactiveCN108445486AImprove robustnessLower performance requirementsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarSide lobe
The invention discloses a beam forming method based on covariance matrix reconstruction and steering vector correction. The method comprises steps of (1) sampling a received signal of a radar array toobtain a received signal vector; (2) according to the sampled received signal vector, obtaining a received data covariance matrix and a spatial spectral distribution, and then obtaining an interference steering vector by a spherical constraint method, and reconstructing an interference-noise covariance matrix; (3) correcting a desired signal steering vector according to the reconstructed interference-plus noise covariance matrix; (4) according to the reconstructed covariance matrix and the corrected desired signal steering vector, solving a MVDR model with added side lobe constraints by a convex optimization method to obtain a global optimal weight vector; and (5) multiplying the received signal vector by the global optimal weight vector to obtain a robust low-sidelobe adaptive beam. Thebeam forming method of the present invention not only has good robustness but also has low side lobes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Reservoir simulation fast matching method based on dimension reduction strategy
ActiveCN105808311AHigh precisionImprove efficiencySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAlgorithmModel parameters
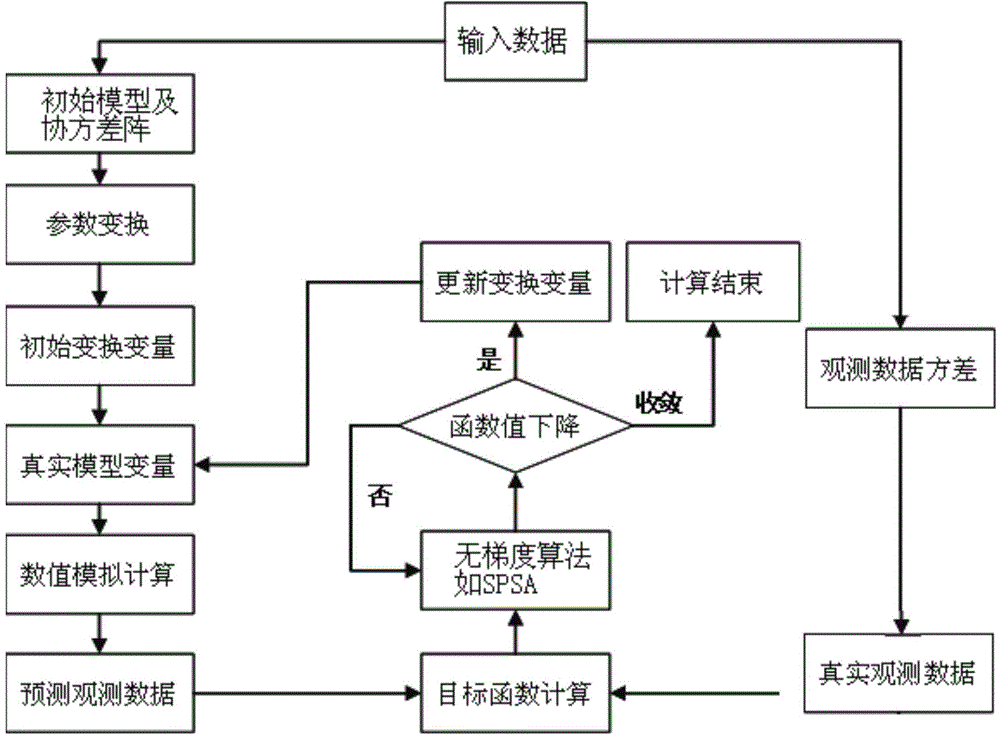
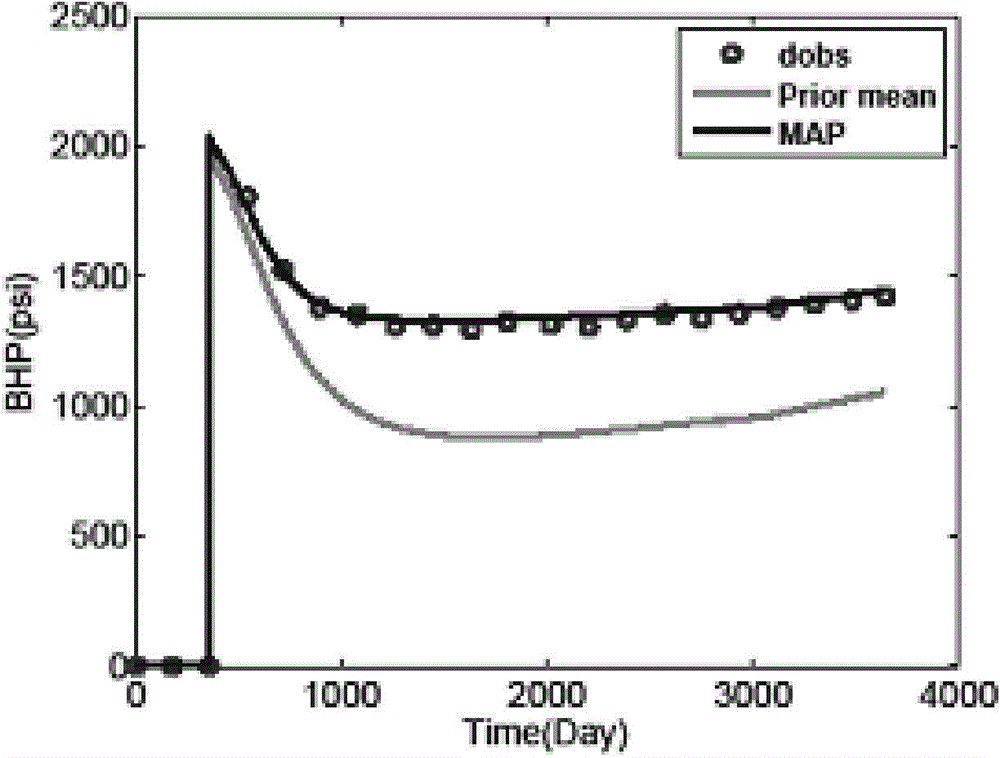
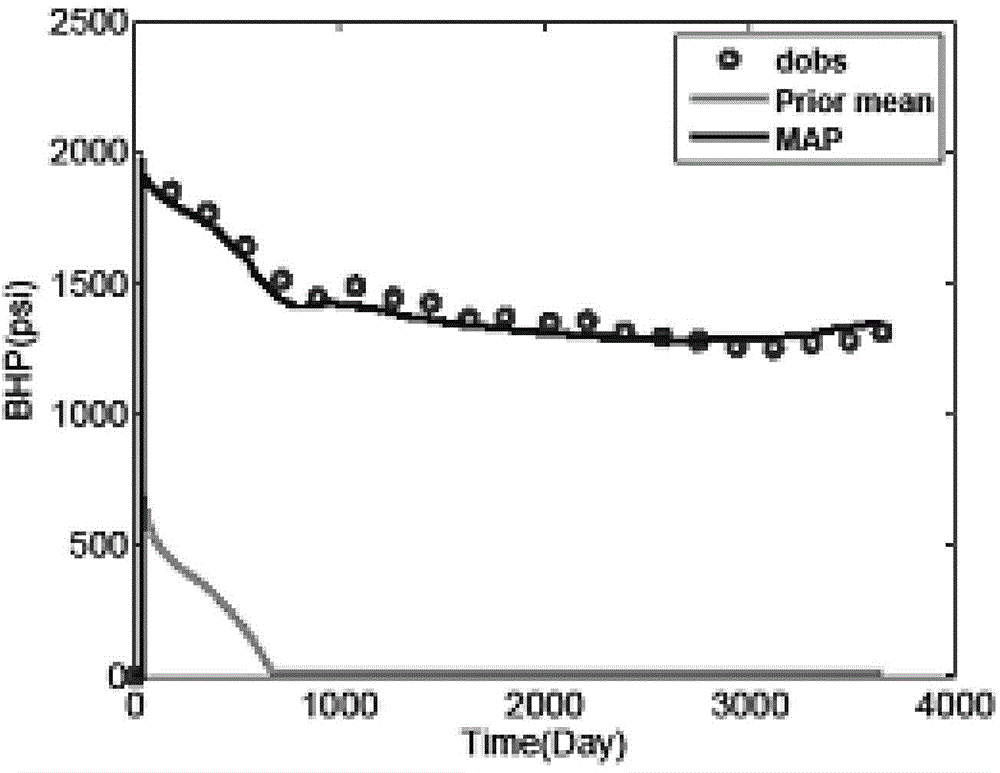
The present invention is a fast fitting method for reservoir simulation based on a dimensionality reduction strategy; the specific steps of the method are: Step 1, input data: input prior reservoir model m pr , Model covariance matrix C M , real observed dynamic data d obs , Observation data covariance matrix C D ; Step 2, establish the objective function O(m) to be optimized: use the prior reservoir model m pr and the model covariance matrix C M Combining with the historical fitting method, establish the objective function O(m) to be optimized; step 3, carry out dimension reduction processing on the objective function O(m) to be optimized, and obtain the historical fitting objective function O(p); step 4, use the The history fitting objective function O(p) obtains the model parameter m of the real reservoir.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com