Nested array direction-of-arrival estimation method based on off-grid sparse Bayesian learning
A direction-of-arrival estimation and sparse Bayesian technology, which is applied in direction-determining orientators, radio wave measurement systems, and measurement devices, can solve the problems of effective array aperture loss, seriousness, and high computational complexity, and avoid array Aperture reduction, avoiding the effect of complex matrix transformations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
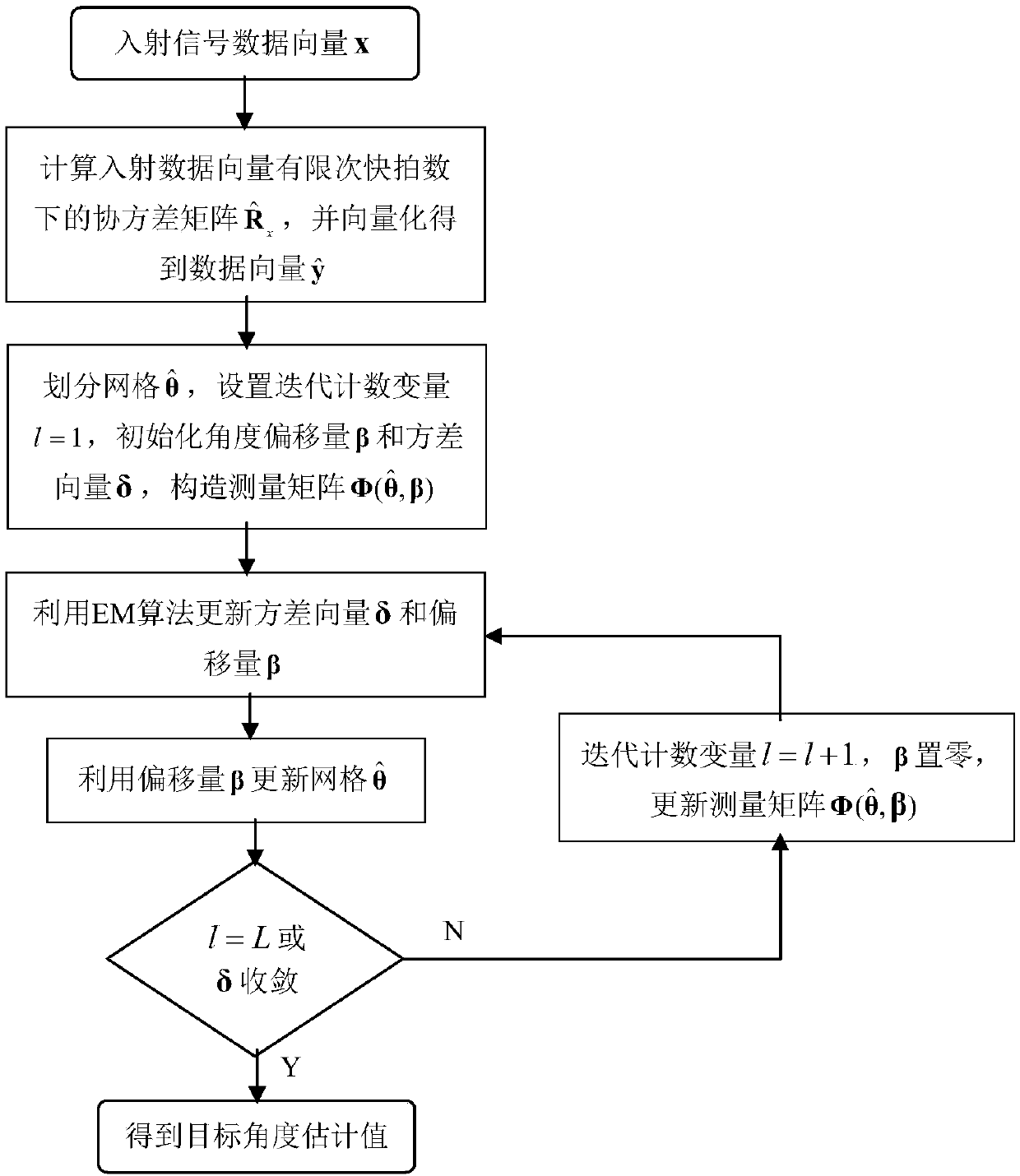
[0017] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0018] Such as figure 1 Shown, method of the present invention comprises the steps:
[0019] (1) After the far-field narrow-band Gaussian signal received by the nested array is matched and filtered, the data vector x(t)=As(t)+n(t) containing DOA information at time t is obtained, t=1,2,. ..,T, where:
[0020] T represents the number of snapshots;
[0021] s(t)=[s 1 (t),s 2 (t),...,s K (t)] T Represents K uncorrelated narrowband signals transmitted at time t, where s k (t) satisfy the mean value is 0, the variance is k=1,2,..., K complex Gaussian distribution, ( ) T means transpose;
[0022] A=[a(θ 1 ), a(θ 2 ),...,a(θ K )] represents an M×K-dimensional array flow pattern matrix, where M=M 1 +M 2 is the number of nested array elements, M 1 and M 2 Indicates the number of array elements in the inner and outer layers of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com