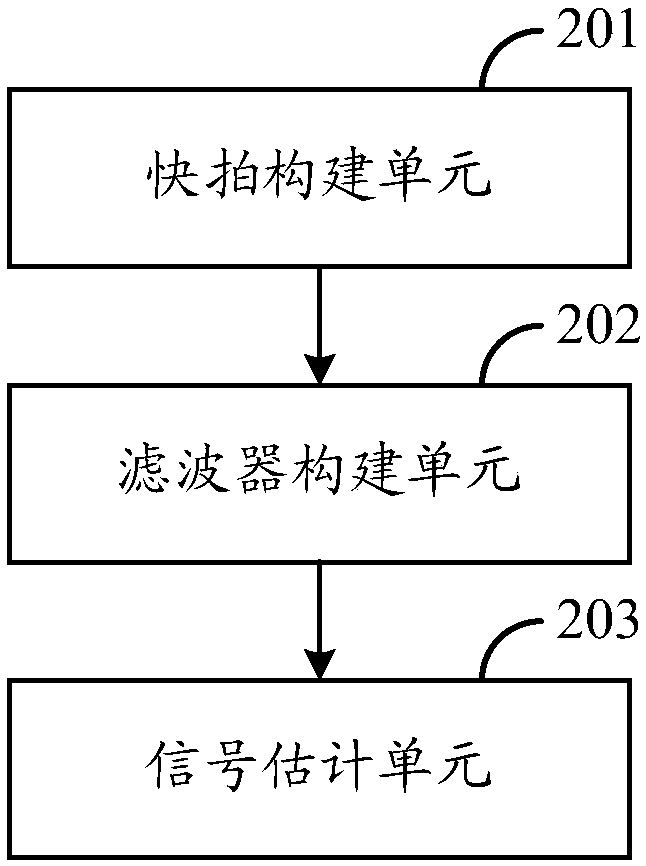
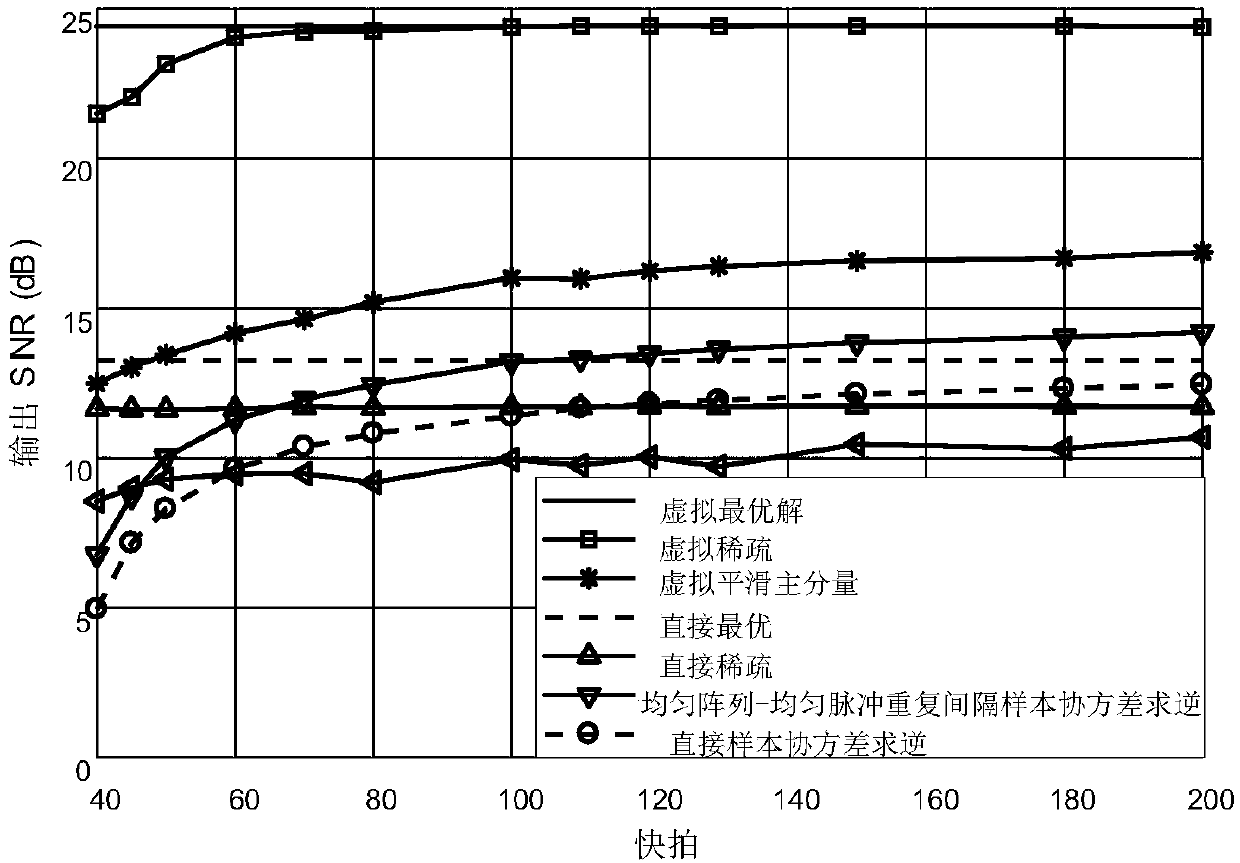
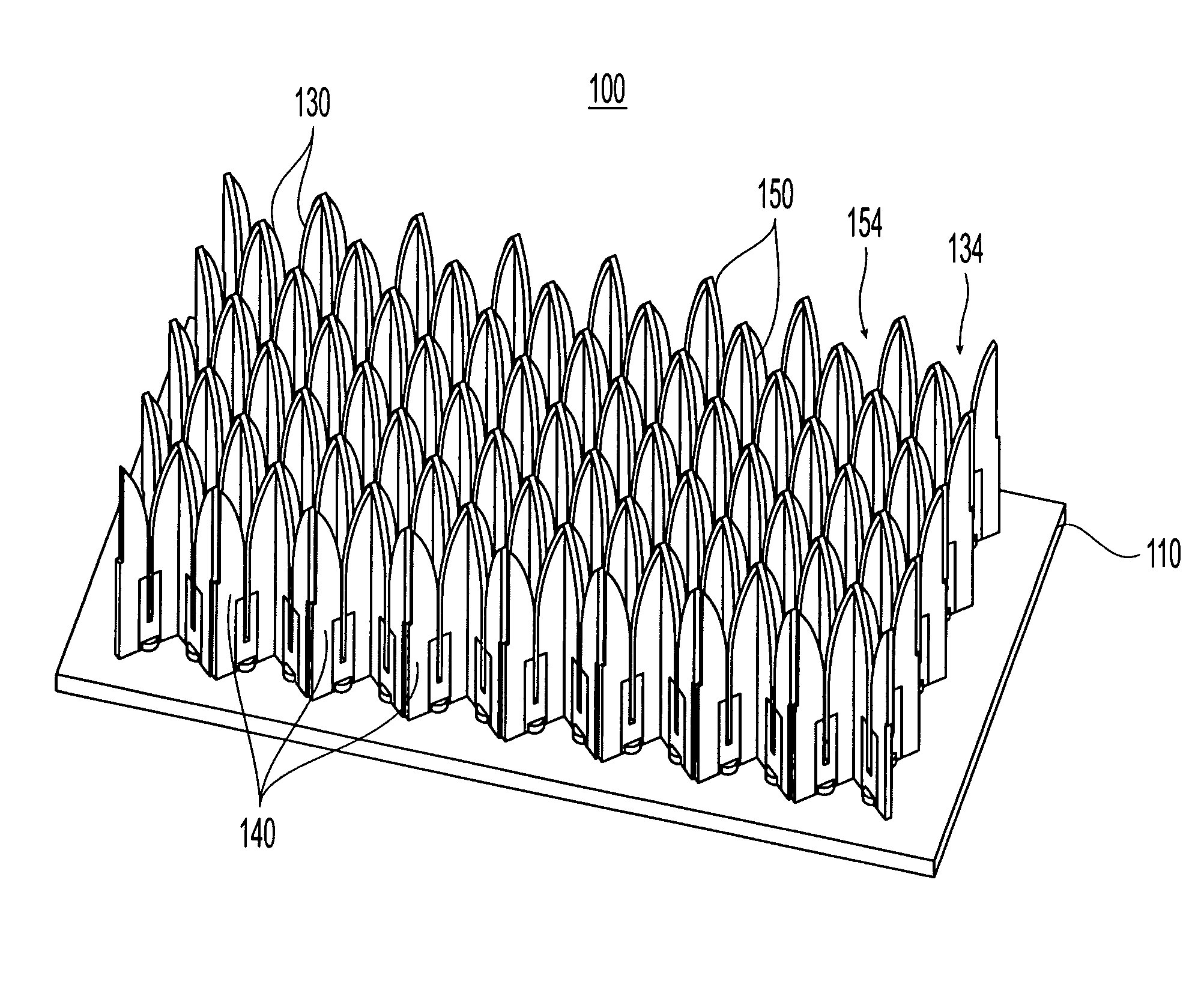
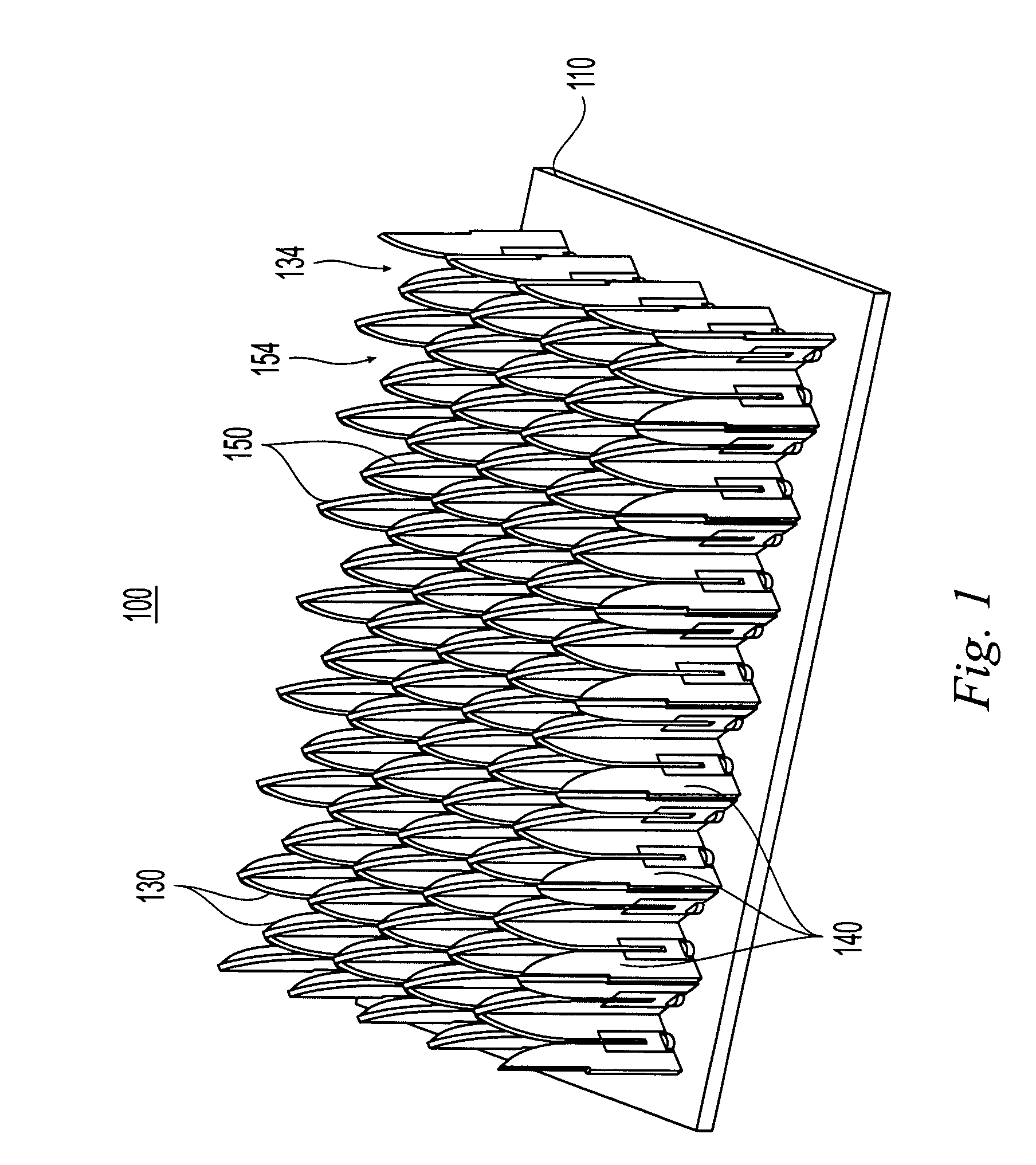
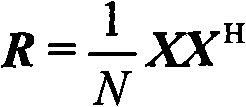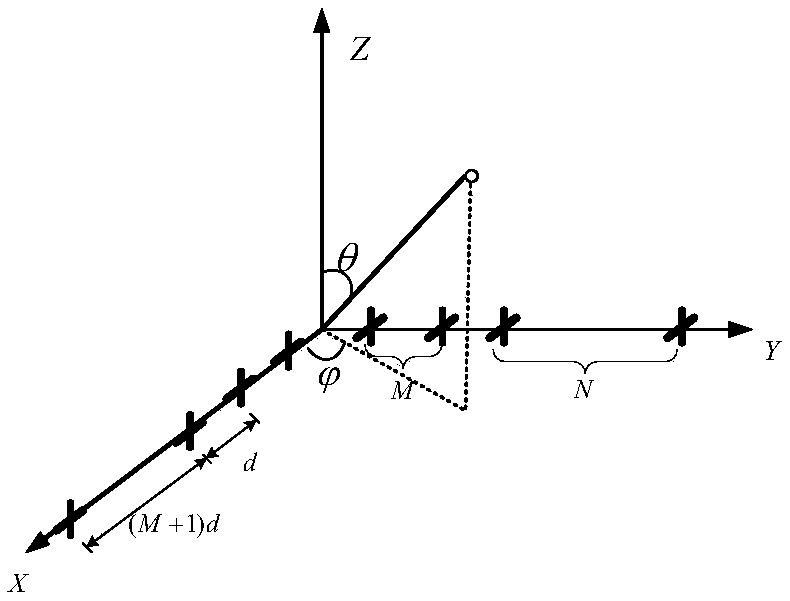Patents
Literature
109 results about "Array aperture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
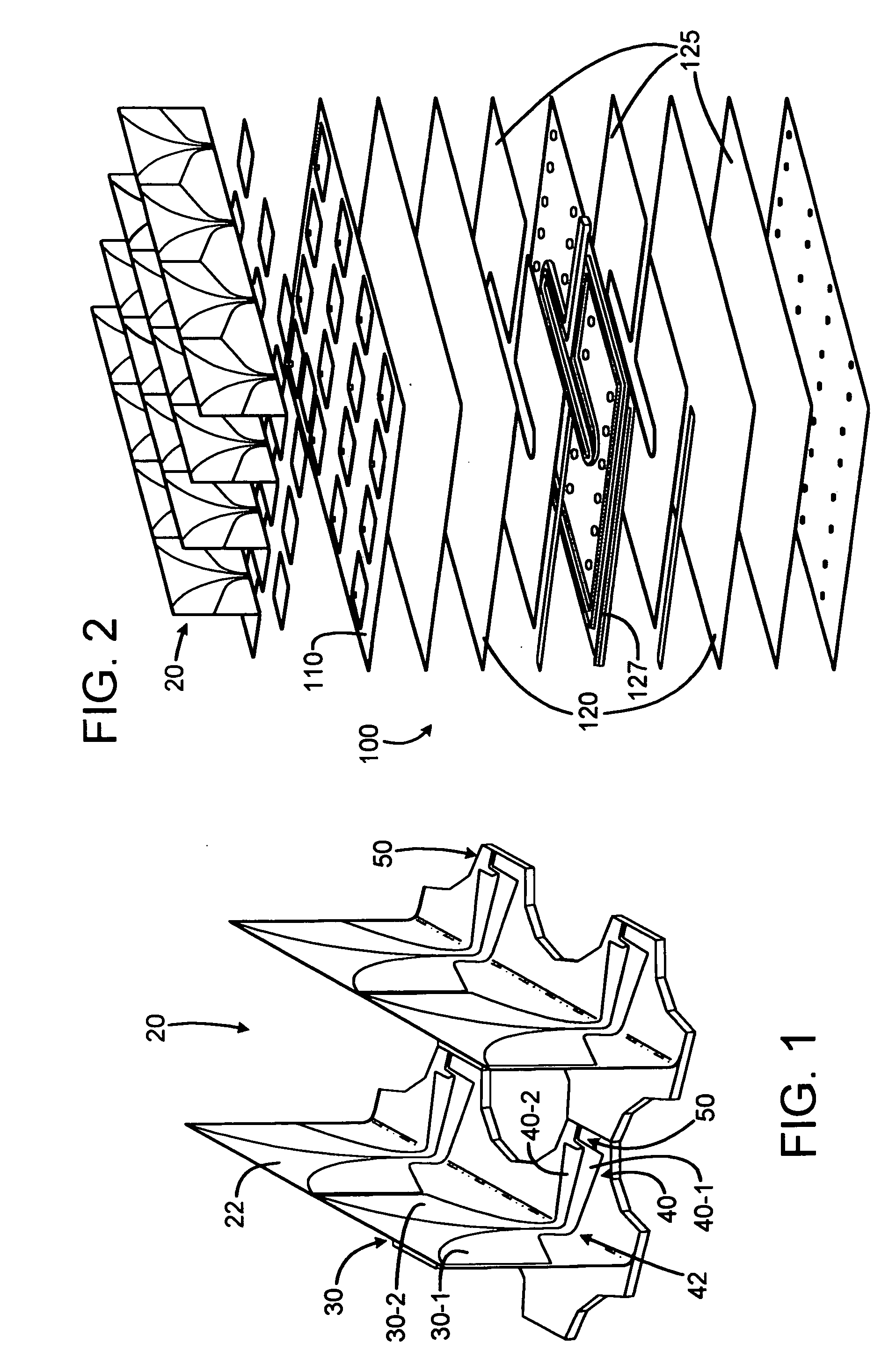
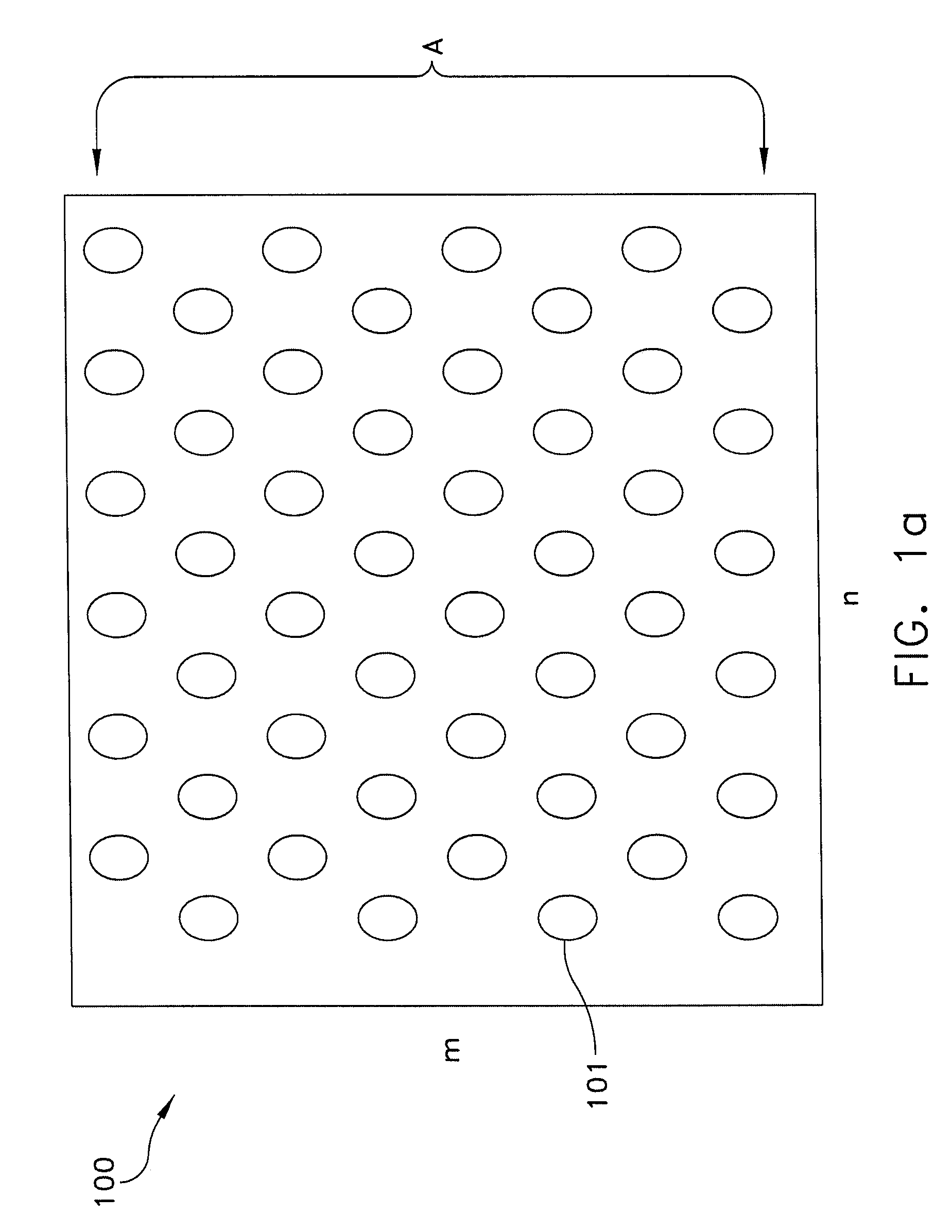
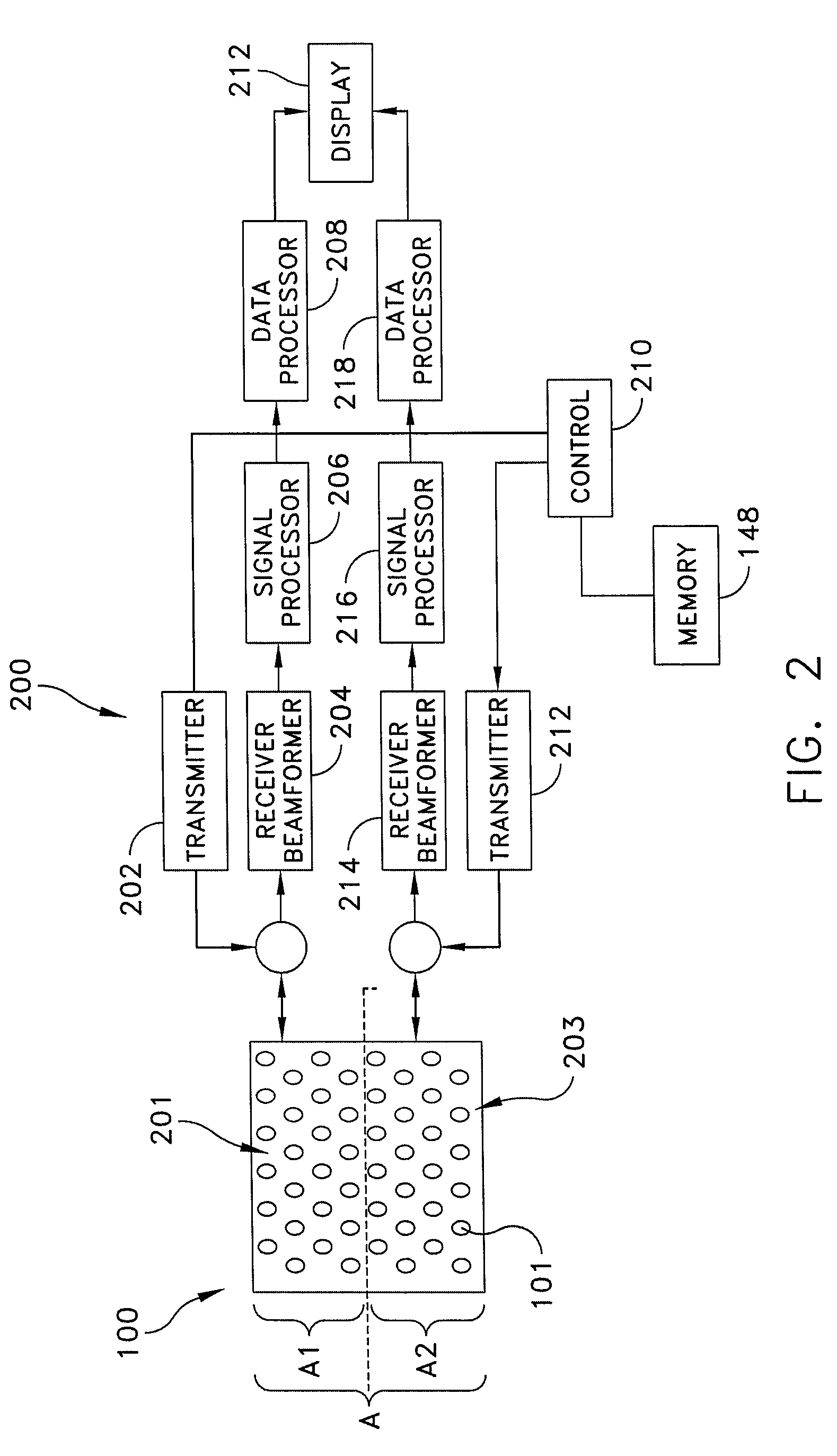
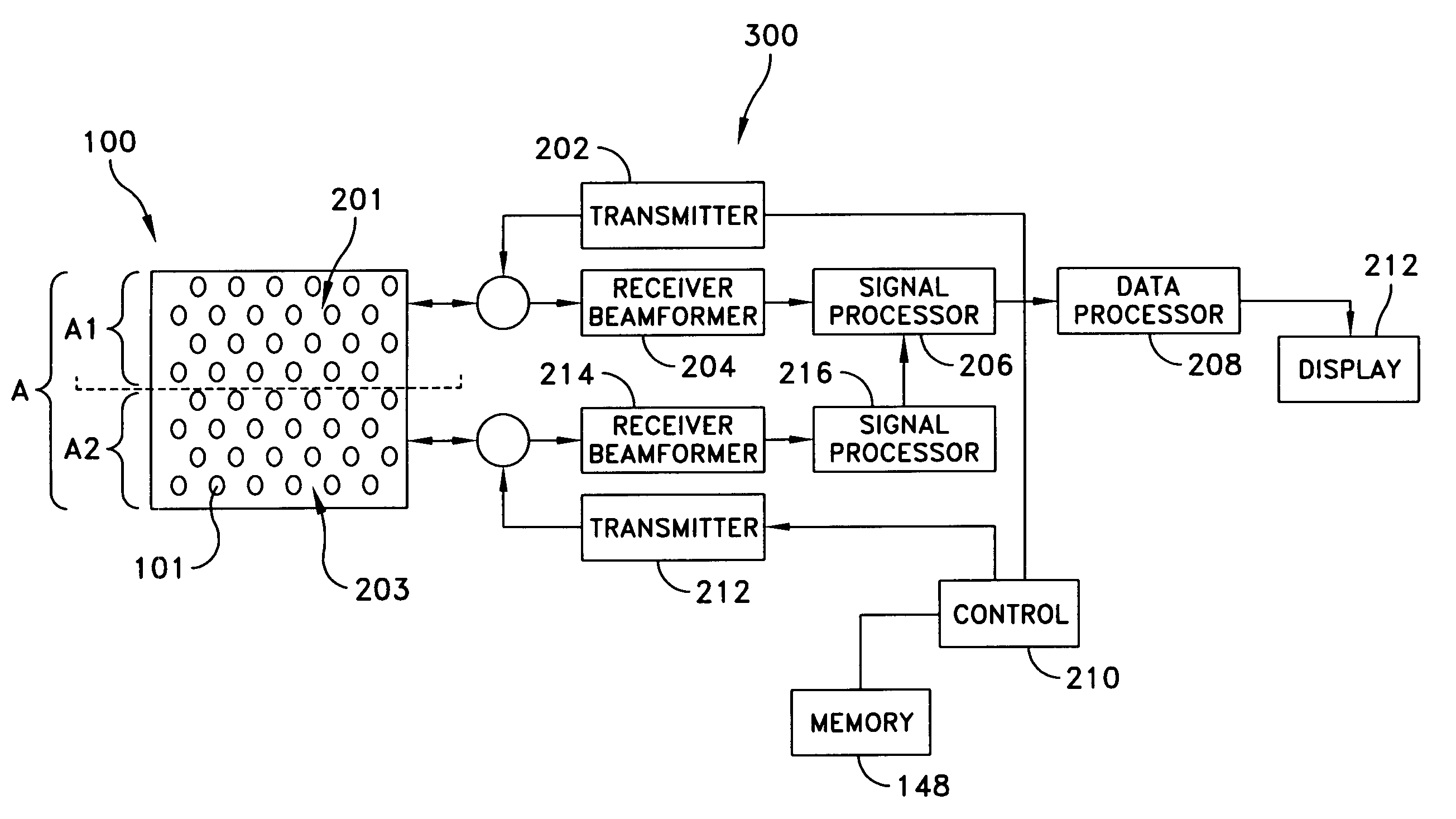
Dual frequency band ultrasound transducer arrays
ActiveUS7727156B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationArray aperture
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +4
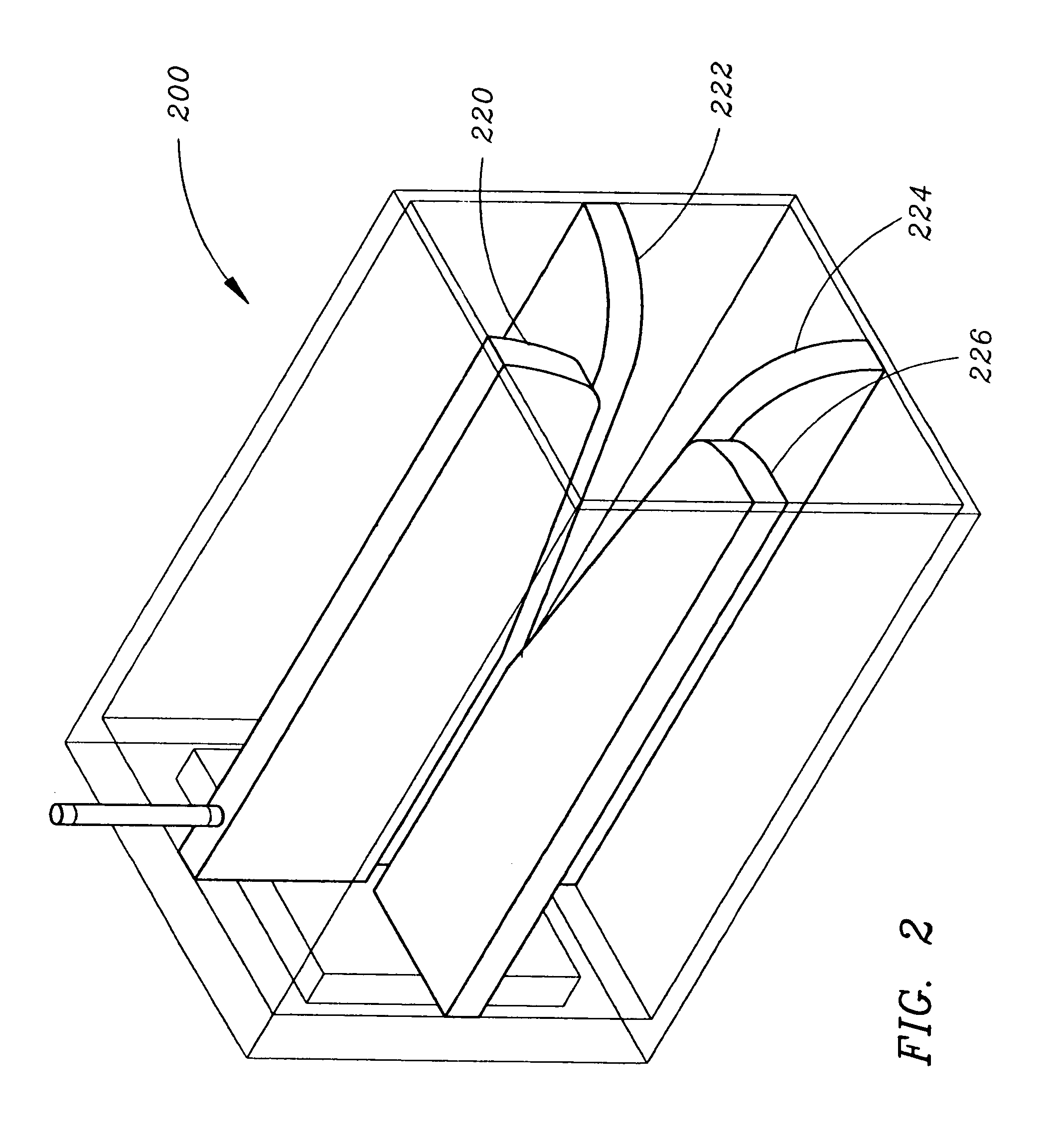
Radiator structures
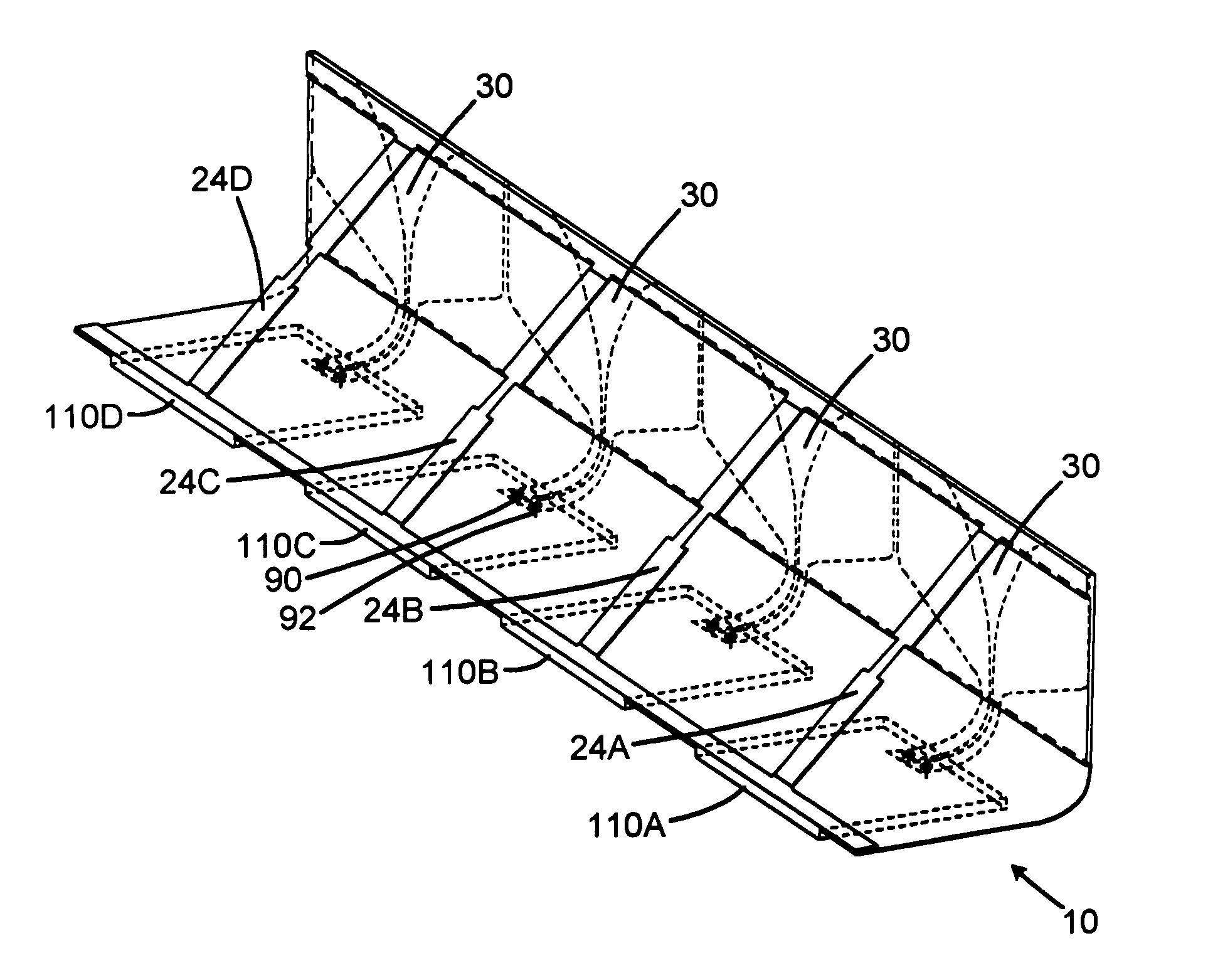
ActiveUS20050264448A1Antenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
A foldable radiator assembly includes a flexible dielectric substrate structure having a radiator conductor pattern formed therein. The flexible substrate structure can be flexible for movement between a folded position and a deployed position, or can be fixed in position by dielectric structures. An excitation circuit excites the radiator conductor pattern with RF energy. Strips of the radiator assemblies can be used to form an array aperture.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Split aperture array for increased short range target coverage
InactiveUS7423578B1Increase the number ofEffectively double the elevation beamwidthsIndividually energised antenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsControl signal
A phased array radar system comprising a plurality of radiating elements configured in a common array aperture for detecting and tracking targets; and a transmit and receive arrangement responsive to a first control signal for configuring the plurality of radiating elements to define a plurality of sub-apertures from the common array aperture for detecting and tracking short range targets, wherein the plurality of sub-apertures are independently steerable array apertures.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Dual frequency band ultrasound transducer arrays
ActiveUS20070035204A1Eliminate the effects ofUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationArray aperture
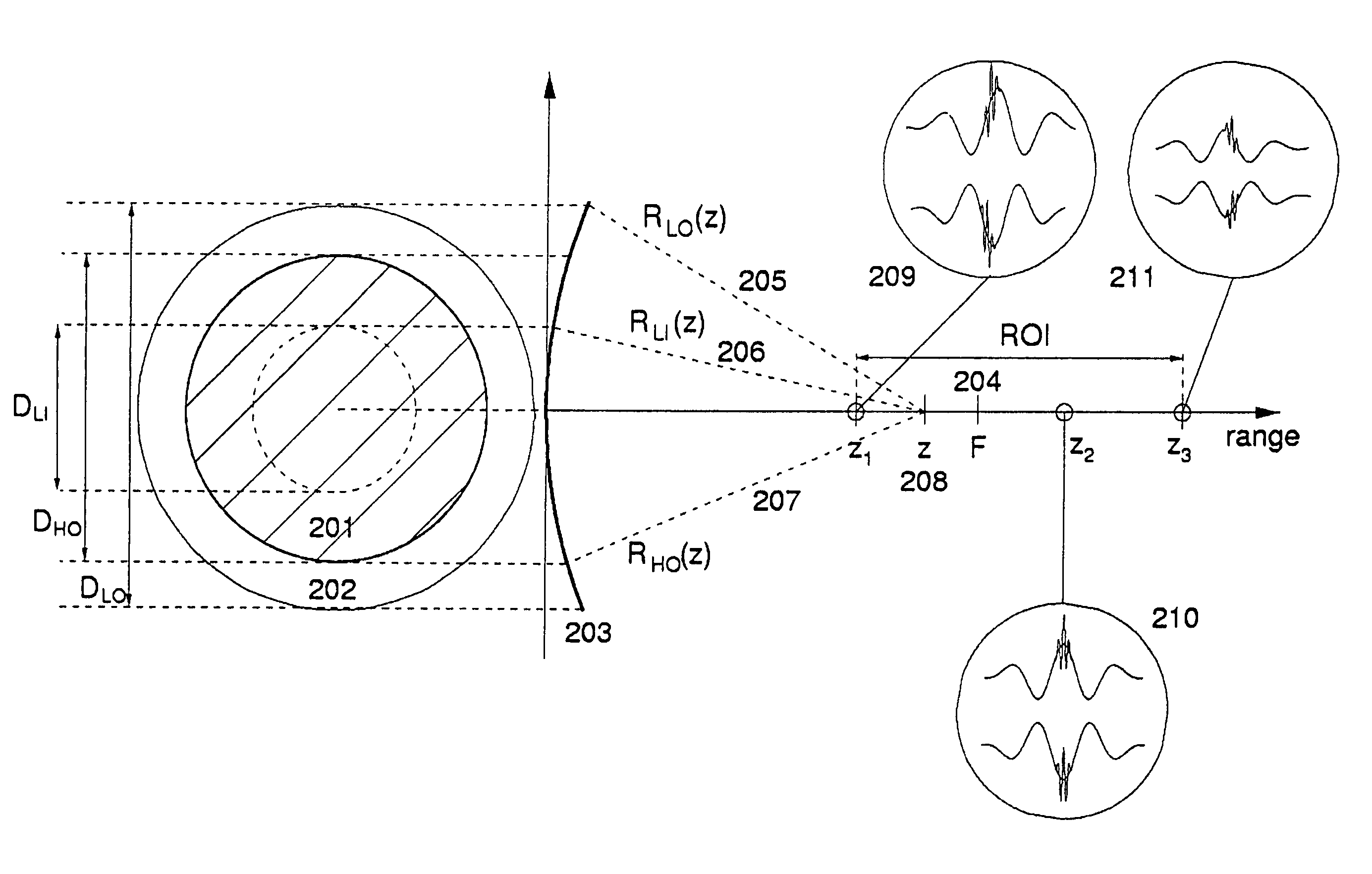
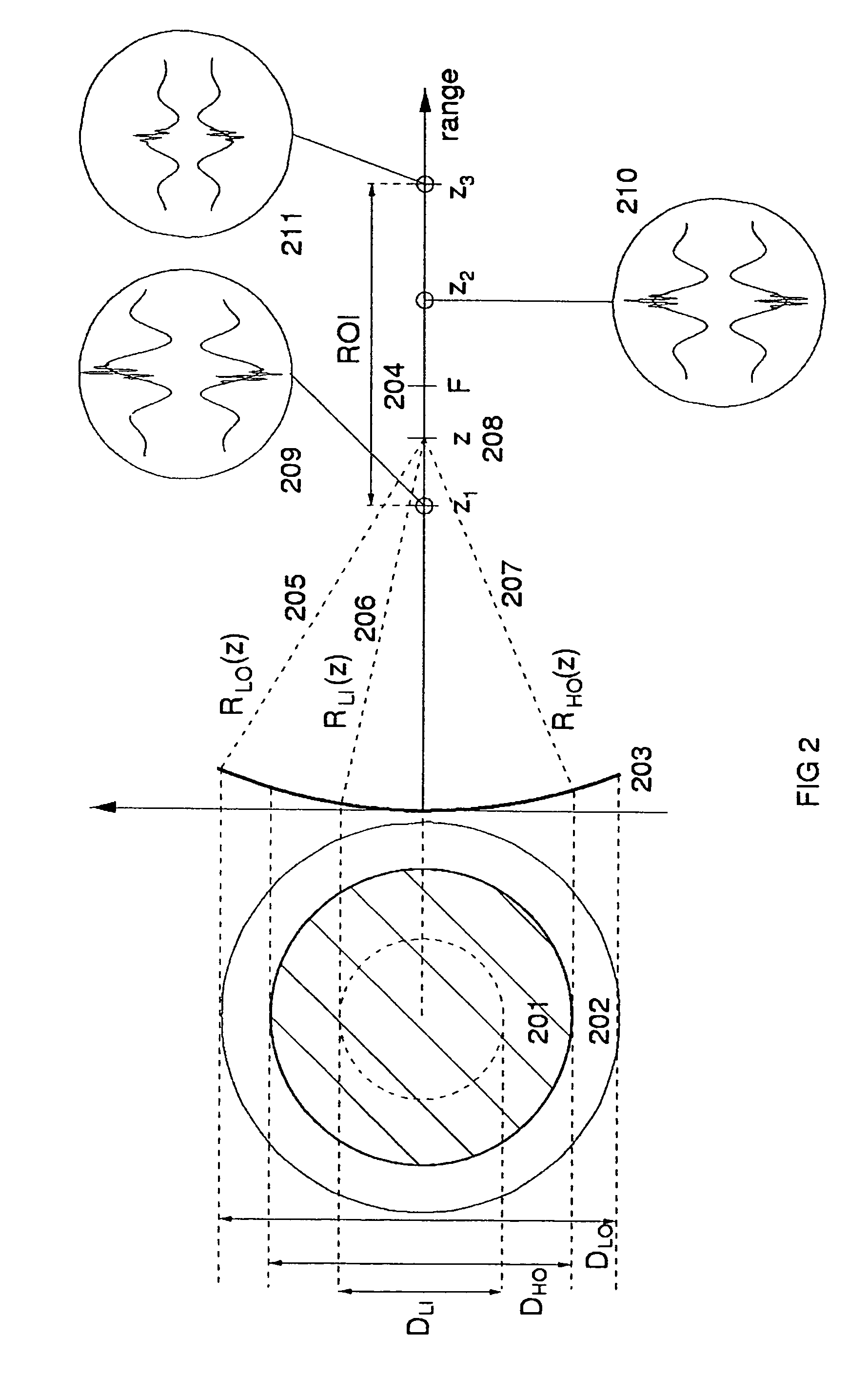
Ultrasound probes that transmits / receives ultrasound pulses with frequencies both in a low frequency (LF) and a high frequency (HF) band, where the radiation surfaces of said HF and LF bands at least have a common region. Several solutions for transmission (and reception) of LF and HF pulses through the same radiation surface are given. The arrays and elements can be of a general type, for example linear phased or switched arrays, or annular arrays or elements with division in both azimuth and elevation direction, like a 1.5D, a 1.75D and a full 2D array. The LF and HF element division and array apertures can also be different.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +4
Radiator structures
ActiveUS7057563B2Antenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
A foldable radiator assembly includes a flexible dielectric substrate structure having a radiator conductor pattern formed therein. The flexible substrate structure can be flexible for movement between a folded position and a deployed position, or can be fixed in position by dielectric structures. An excitation circuit excites the radiator conductor pattern with RF energy. Strips of the radiator assemblies can be used to form an array aperture.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Estimation method for radio orientation incoming wave direction based on TD-SCMA
InactiveCN1523372APosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsEstimation methodsSignal classification
The invention is a DOA estimating method to realize circle-angle positioning based on TD-SCMDA standard, firstly adopting multiple signal classifying and correcting algorithms to realize the DOA estimation of intelligent antenna circle-angle positioning; aiming at TD-SCMDA antenna being uniform circle array, converting the array cell-space uniform circle array into mode-space virtual uniform line array; according to eigenvalue and eigenvector characteristic of the data covariance matrix of the virtual line array, advancing a MUSIC algorithm based on mode-space virtual uniform line array and deriving the MUSIC algorithm power chart for the virtual line array and the general implementation algorithm for the mode-space MUSIC algorithm; according to the character of MUSIC algorithm inapplicable to the DOA estimation of relative signal source, advancing the correcting MUSIC algorithm based on the mode-space virtual uniform line array; finally aiming at the problem that the array aperture is small and that the resistance to array cell error disturbance is bad, caused by MUSIC algorithm, advancing four-order cumulant MUSIC algorithm and four-order cumulant correcting MUSIC algorithm based on the mode-space virtual uniform line array.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Direction-of-arrival estimation method based on nested subarray array
ActiveCN105824002ALarge apertureEasy to implementRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsEstimation methodsRadar
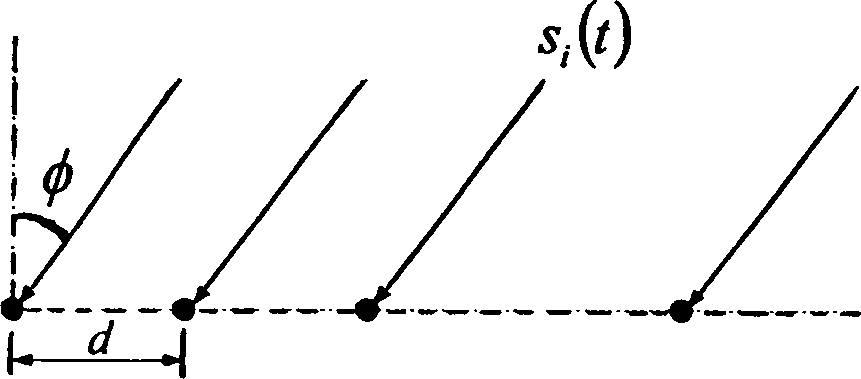
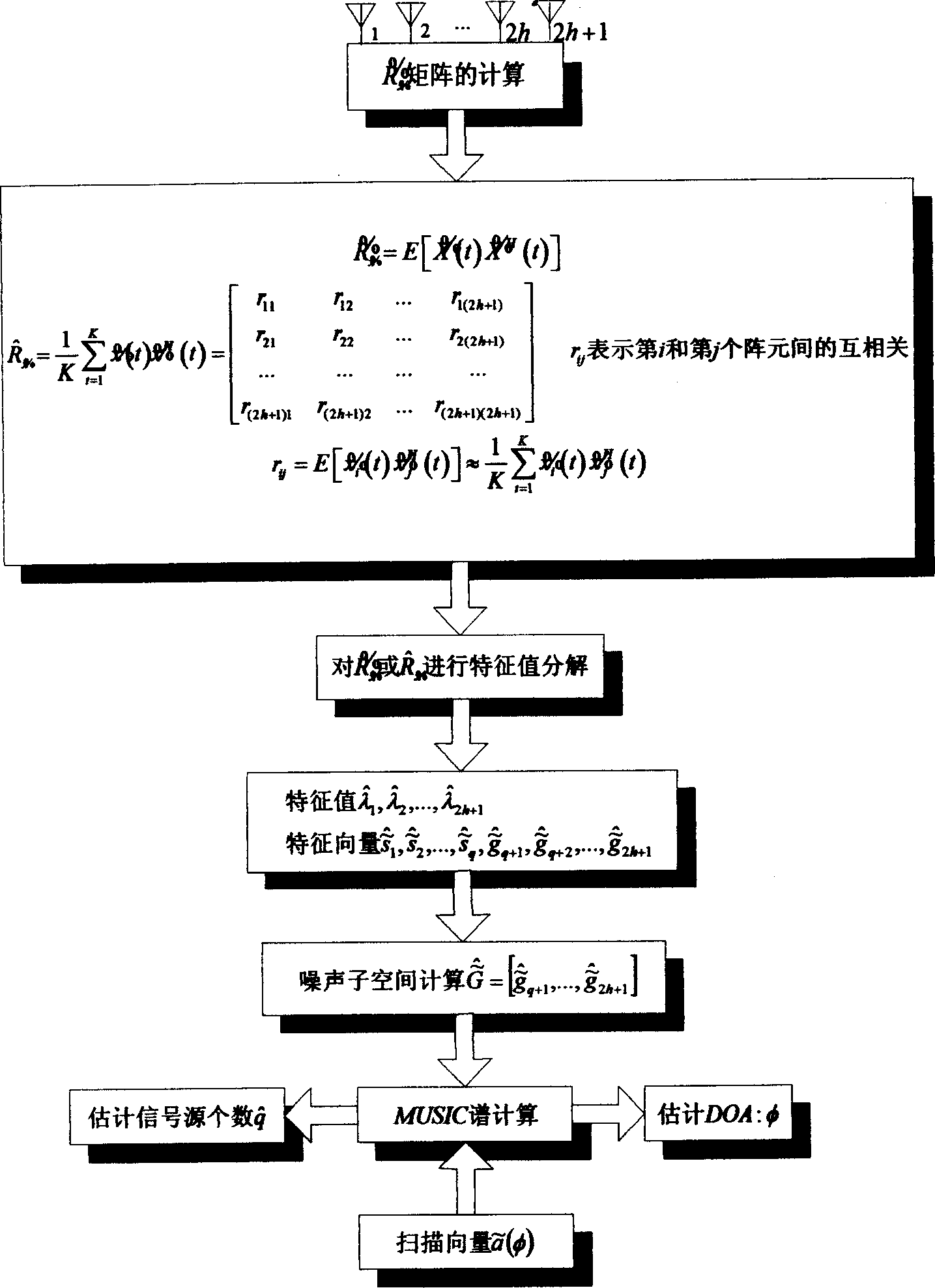
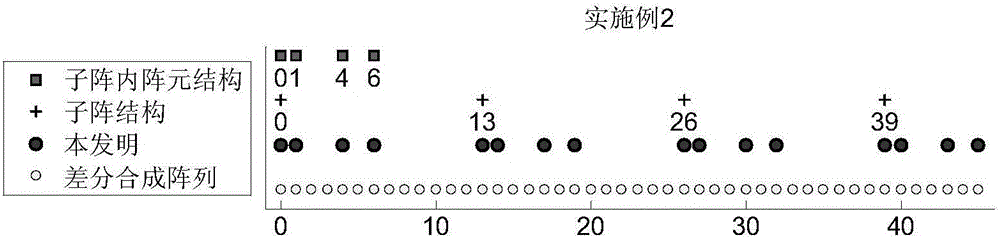
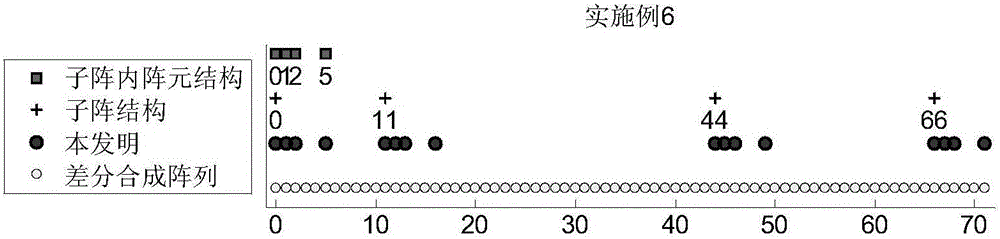
The invention discloses a direction-of-arrival estimation method based on a nested subarray array, and mainly solves the problem existing in the prior art that the degree of freedom, array aperture and array density are not high. The realization process includes the steps of: 1. giving the total number of array elements, and determining the number of subarrays and the number of array elements in each subarray; 2. selecting a uniform linear array or minimum redundancy array or nested linear array structure according to the number of array elements in each subarray; 3. selecting a uniform linear array or minimum redundancy array or nested linear array structure according to the number of the subarrays; 4. constructing a nested subarray array according to a selected array element structure in each subarray and subarray structure; 5. obtaining received data X(t) according to the nested subarray array; 6. obtaining differential synthesis array received data zc according to X(t), and then obtaining a rank recovery data covariance matrix RSS; and 7. decomposing characteristic values of the RSS to obtain a direction-of-arrival estimation angle. The direction-of-arrival estimation method provided by the invention has the advantages of flexible array configuration and good direction-of-arrival estimation angle measurement performance under the same conditions, and can be used for radar target signal detection or power estimation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Quick beamforming method capable of improving array resolution and gain
InactiveCN101609150AImprove resolutionOvercoming demandsAcoustic wave reradiationComputation complexityComputation process
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
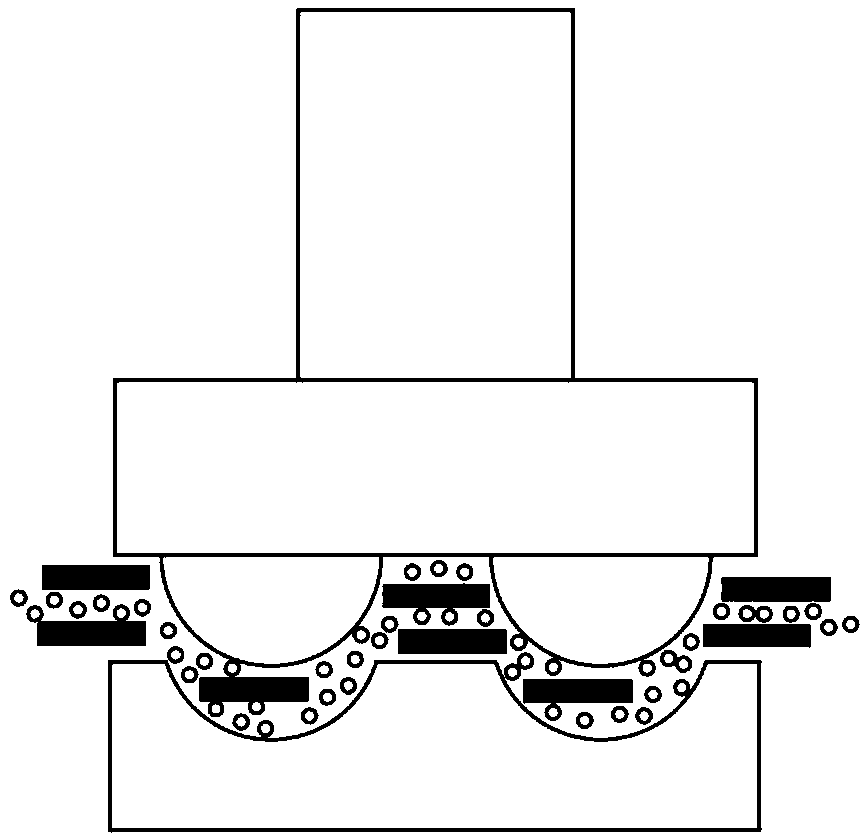
Micro semi-ring female die array-mode lapping and polishing method and device
ActiveCN105364641AImprove processing efficiencyEnsure consistencyLapping machinesLapping toolsMaterial removalGranularity
Disclosed is a micro semi-ring female die array-mode lapping and polishing method. The method includes the following steps that (1) a high-uniformity ultra-precise lapping and polishing die is manufactured, the upper end of a tool connecting rod is connected with a micro ultrasonic generator, the lower end of the tool connecting rod is connected with a positioning substrate, array apertures are formed in the positioning substrate, the size of the apertures is smaller than the diameter of precise spheres, spaces between the apertures and the precise spheres are filled with a binder, and part of the spheres is embedded into the apertures; and (2) the space between the high-uniformity ultra-precise lapping and polishing die and a substrate slice is filled with lapping and polishing liquid, the granularity of abrasive grains in the lapping and polishing liquid is nanoscale, the lapping and polishing die performs high-frequency micro ultrasonic vibration in the micro distance on the substrate slice, the ultrasonic vibration excites the abrasive grains in the lapping and polishing liquid to impact on the substrate slice at high speed, the lapping and polishing die performs feed movement downwards at set speed in the Z direction, and material removal of a micro semi-ring female die array is achieved. The invention further provides a micro semi-ring female die array-mode lapping and polishing device. The micro semi-ring female die array-mode lapping and polishing method and device can achieve the lapping and polishing effects of high efficiency, shape accuracy, shape uniformity and surface quality and low surface roughness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
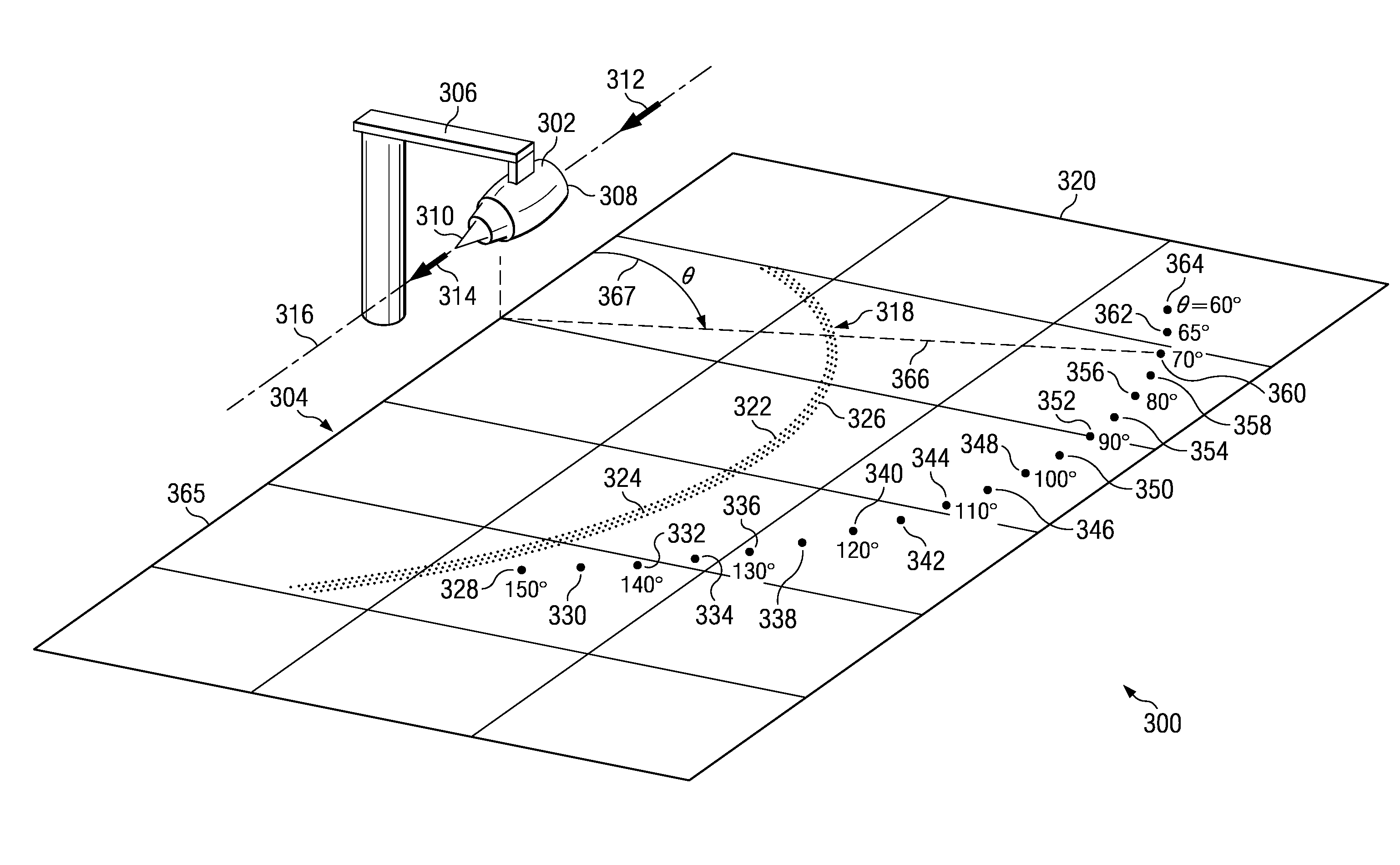
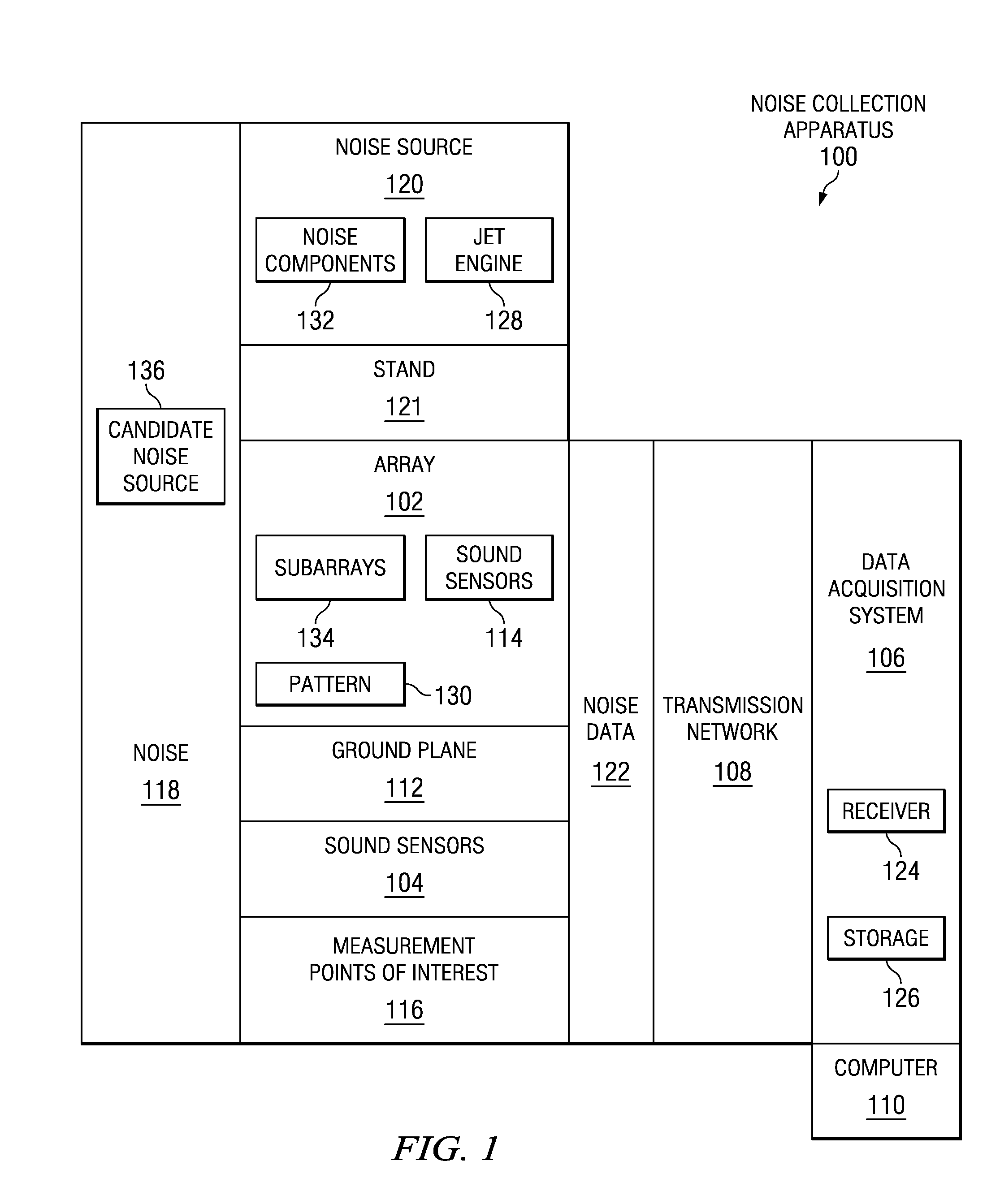
Method and apparatus for identifying noise sources
A computer implemented method and apparatus for identifying component breakdown of noise sources. Noise data is received for a noise source from an array of sound sensors. Measurement points of interest, candidate sound source points along an axis, and array aperture angles are identified. Sets of first and second bounding traces are identified from ray traces extending from the candidate noise source points towards the measurement points of interest using the array aperture angles. The bounding ray traces are rotated around the axis to form sets of first and second surfaces. Sets of first and second curves are identified from an intersection of the sets of first and second surfaces with the ground plane. Sound sensors are selected from the array using the curves to form subarrays. The component breakdown of noise generated by the noise source is identified using noise data from sound sensors in the subarrays.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
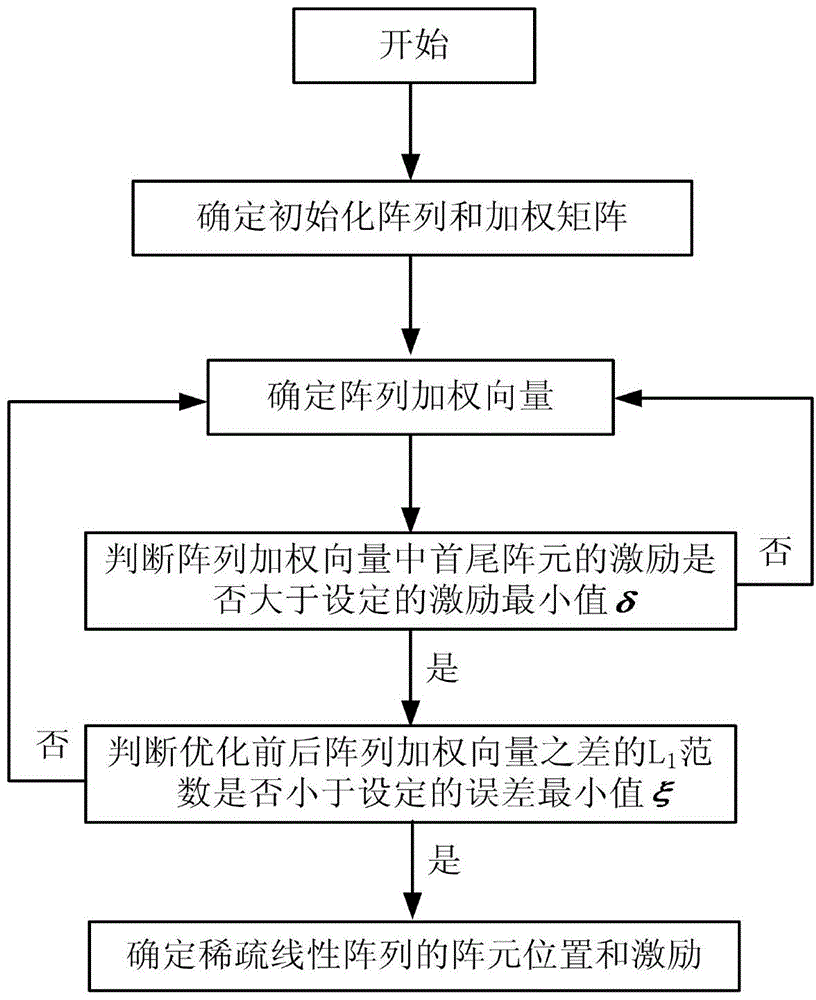
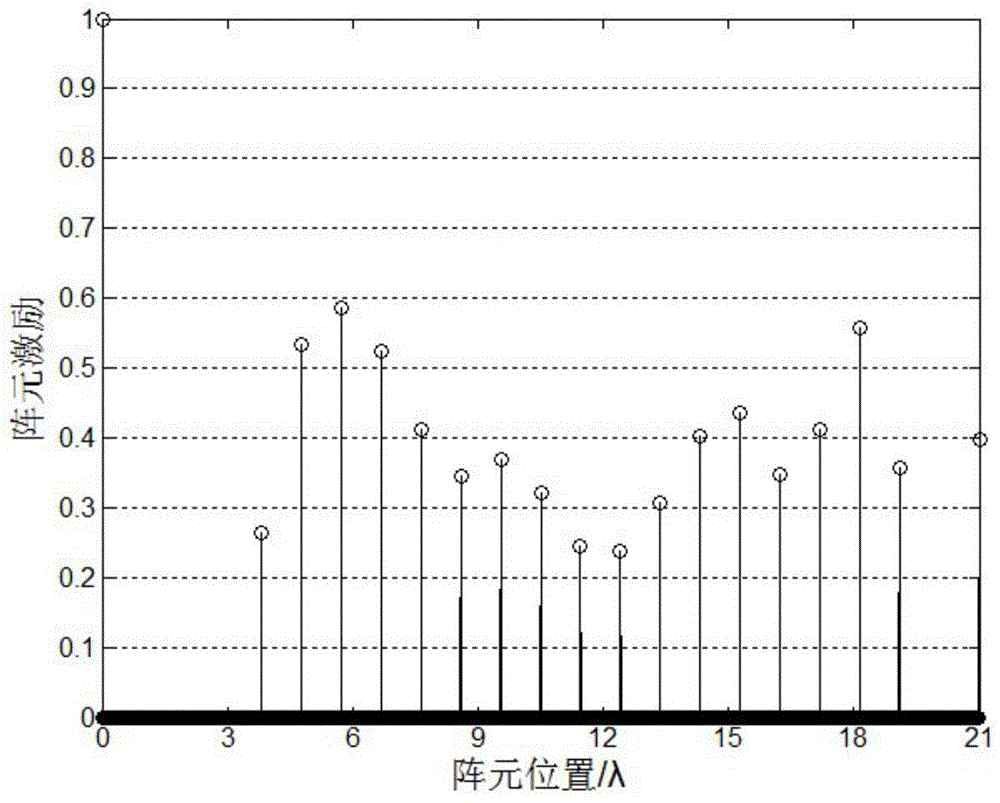
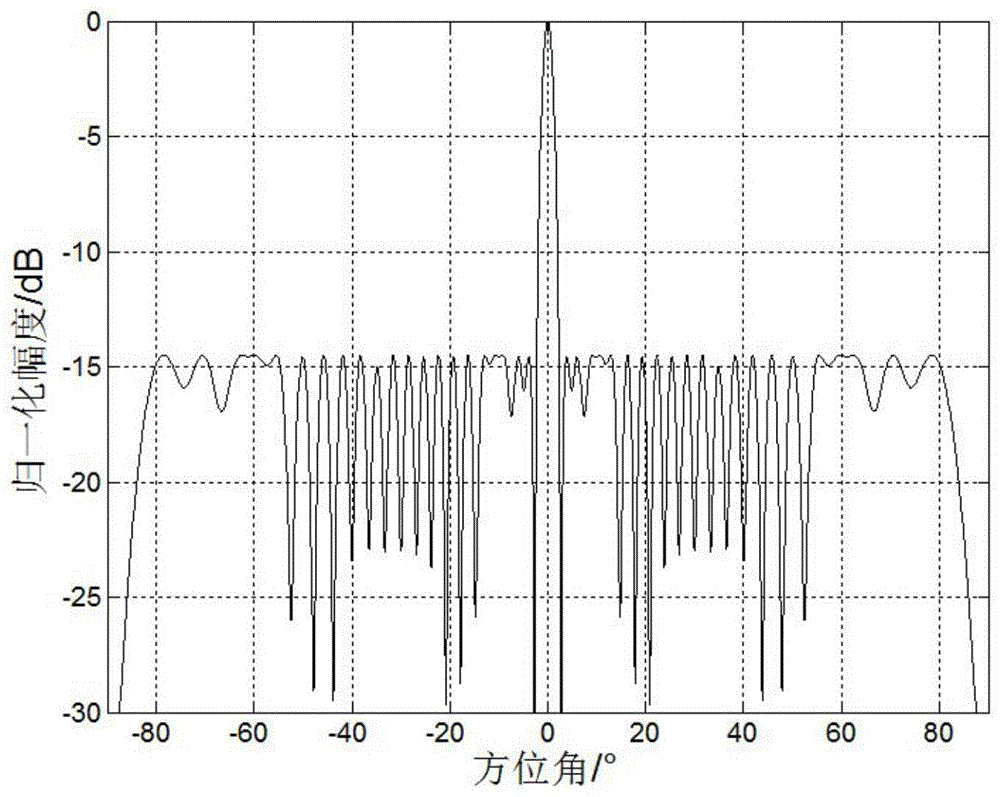
L1/2-norm-based sparse linear array optimization method
ActiveCN104392034AReduce sparsityMeet aperture requirementsSpecial data processing applicationsArray elementArray aperture
The invention relates to an L1 / 2-norm-based sparse linear array optimization method. The method is characterized by comprising the basic steps of determining an initial array and a weighting matrix, determining array weight vectors, judging whether the stimulus of head and tail array elements in the array weight vector is greater than a set stimulus minimum delta or not, judging whether an L1 norm for optimizing a difference between the previous and latter array weight vectors is smaller than a set error minimum xi or not, and determining the array element positions and stimulus of the sparse linear array. According to the method, the non-convex optimization problem of solution to an L1 / 2 norm is converted into a series of convex optimization problems of the L1 norm, so that a sparse array with lower sparsity can be obtained to reduce the number of actually required array elements on the premise of substantially keeping calculation unchanged; meanwhile, the head and tail array elements of the array are constrained and adaptively regulated under the condition of given array aperture, so that the problem of deficiency of the head and tail array elements of the sparse array in an iterative convex optimization process is well solved, and the method is particularly applied to the place of optimization of a large-sized antenna array.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Optical wave-front recovery for active and adaptive imaging control
InactiveUS20110157600A1Minimize wave-front sensingMinimize control timeOptical measurementsInterferometersWavefrontAdaptive imaging
An optical telescope system, method of actively, adaptively providing optical control to an array of articulated mirrors in a sparse aperture in the optical telescope system and a computer program product therefor. Array apertures are selected sequentially for imaging. Each aperture is temporally modulating at a unique / different frequency and, simultaneously, focal plane images are detected for each array aperture with known and separable temporal dependencies. The images are processed for the current set of said focal plane images to detect an image wavefront. The feeding back wavefront errors are fed back to aperture actuators for controlling the array.
Owner:NASA
Phase control focusing ultrasonic transducer array in high internsity
InactiveCN1562411AAchieve ultrasound focusRealize scanningUltrasound therapyElectricityPhase control
A high-intensity ultrasonic transducer array which phase-conrol fucusing is composed of a big-aperture rigid spherical crown body with a geometric radium close to maximal scan depth, a centrol hole for installing the probe of ultrasonography B and several small holes distributed in the mode of multi-layer regular ring array with unequal spacings, and several array cells inlaid in said holes. Its advantages are correct location, flexible focusing, small array aperture, and high grating lobe suppressing power and sonic intensity gain.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
TDM-MIMO radar system based on optimized sparse array and signal processing method thereof
ActiveCN110456334AGood precisionImprove design efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsArray element
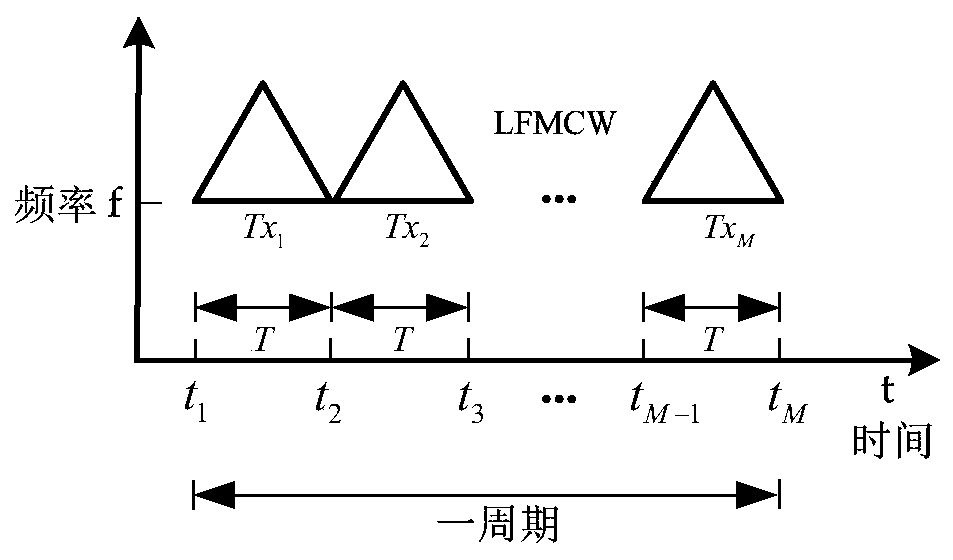
The invention discloses TDM-MIMO radar system based on an optimized sparse array and a signal processing method thereof. The system is based on a sparse array, and optimizes array distribution by using a genetic algorithm; and optimized array distribution lowers sidelobe level and improves energy use ratio. The system transmits an LFMCW signal by using a TDM technology without sending an orthogonal signal and matching filtering at a receiving end, thereby making radar system structure less complex. When the number of array elements is specific, DOA performance of the system is superior to thatof a traditional uniform linear array MIMO radar system; under the condition of identical array aperture, the system has the same DOA performance as the uniform linear array MIMO radar system, and has higher angular resolution and more concise structure. Further, the signal calibration processing method provided in the invention can improve accuracy and resolution of DOA estimation of a mobile target by the system effectively under a condition of low signal to noise ratio.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A differential evolution algorithm-based uniform area array sparse optimization method
PendingCN109885872ASimple structureFew control parametersBiological modelsComplex mathematical operationsArray elementAlgorithm convergence
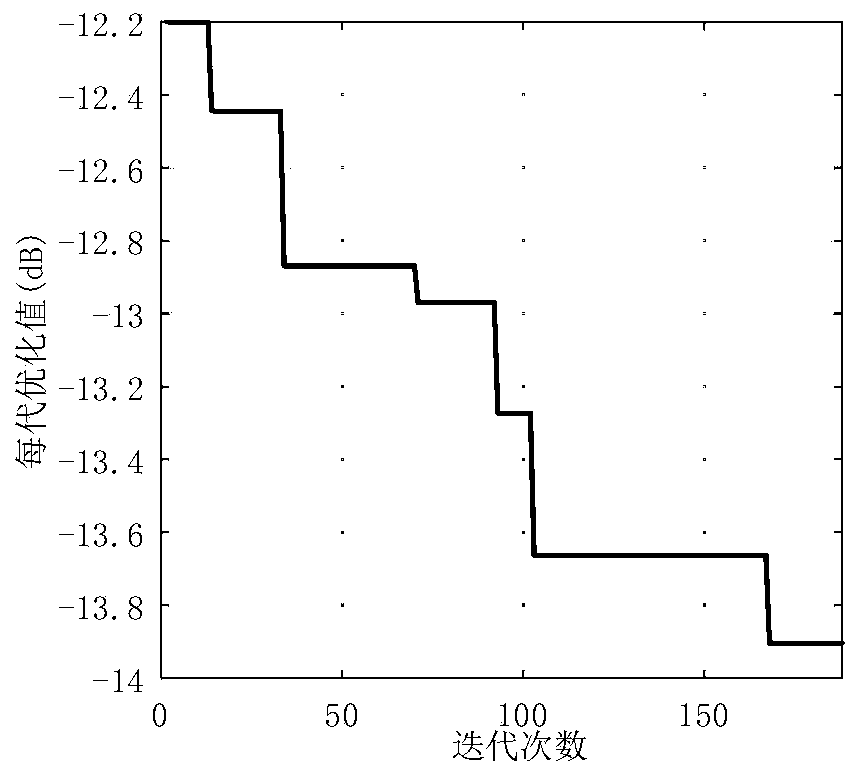
The invention discloses a differential evolution algorithm-based uniform area array sparse optimization method. At present, a phased array radar sparse array optimization technology lacks differentialevolution algorithm optimization under a uniform area array model. The method comprises the following steps of 1, converting a real number code in a differential evolution algorithm into a binary code; 2, constructing a fitness function by using the sum of the planar peak value side lobe levels; and 3, drawing a sparse array element distribution map through the binary codes obtained after optimization, and further obtaining a three-dimensional directional diagram of the sparse array. According to the method, based on a differential evolution algorithm, an array aperture, the number of array elements and an array element interval are taken as constraint conditions, and the minimum plane peak sidelobe level is taken as an objective function, so that a sparse array element position distribution map and a sparse array three-dimensional directional diagram are obtained. Simulation results show that the method has the advantages that constraint conditions are met, the directional diagram does not have obvious grating lobes and obvious mutual coupling influence in a visual area, the performance is good, and the algorithm convergence speed is high.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Harmony search algorithm-based linear sparse array grating lobe inhibition method
InactiveCN107844632AOptimization degrees of freedomImprove optimization efficiencyGeometric CADAntenna arraysArray elementArray aperture
The invention discloses a harmony search algorithm-based linear sparse array grating lobe inhibition method. The method comprises the steps of firstly, giving out a linear sparse array model comprising multiple constraints such as an array element number, an array aperture, an array element spacing and the like, and building an optimization model by taking the reduction of a PSLL of an array as anobjective function; and secondly, converting the array element spacing, namely an optimization independent variable into a new independent variable through a vector mapping method, building a linearsparse array grating lobe inhibition model with a higher optimization freedom degree on the premise of ensuring a feasible solution space to be unchanged, and performing optimization on the inhibitionmodel through an HS algorithm. Through iterative calculation, an optimal array layout for minimizing the sidelobe level of the array under the condition of meeting the multiple constraints is selected as an optimal solution, and an optimal direction graph is obtained according to the optimal array layout. The conversion of the optimization problem is performed by adopting the vector mapping method, so that the freedom degree of the problem is increased and the optimization efficiency is higher; the optimization is performed on the problem by adopting the HS algorithm, and through the iterative calculation, a better PSLL is obtained; and the method is high in convergence speed and good in robustness.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Dual frequency band ultrasound transducer arrays
InactiveCN101262960AMechanical vibrations separationAcoustic wave reradiationSonificationArray aperture
Ultrasound probes that transmits / receives ultrasound pulses with frequencies both in a low frequency (LF) and a high frequency (HF) band, where the radiation surfaces of said HF and LF bands at least have a common region. Several solutions for transmission (and reception) of LF and HF pulses through the same radiation surface are given. The arrays and elements can be of a general type, for example linear phased or switched arrays, or annular arrays or elements with division in both azimuth and elevation direction, like a 1.5D, a 1.75D and a full 2D array. The LF and HF element division and array apertures can also be different.
Owner:比约恩・A・J・安杰尔森
Coprime MIMO radar arrival direction estimation method based on multi-sample snapshots and set array signal discrete Fourier transform
ActiveCN109471086ALarge array apertureHigh resolution performanceWave based measurement systemsZero paddingComputation complexity
The invention discloses a coprime MIMO radar arrival direction estimation method based on multi-sample snapshots and set array signal discrete Fourier transform. The method mainly solves the problem that the calculation complexity of an existing method is high. The method comprises the steps that a homogeneous MIMO radar structure is established; reflected signals are received through a radar receiving sub-array, and modeling is carried out on radar output signals; the coprimey MIMO radar multi-sample snapshots and set array receiving signals are constructed; zero padding is carried out on themulti-sample snapshots and the set array receiving signals; the multi-sample snapshots and the set array receiving signals obtained after zero padding are subjected to sidelobe suppression; the multi-sample snapshots and the set array receiving signals obtained after filtering are subjected to discrete Fourier transform to construct a spatial spectrum; arrival direction estimation is conducted according to the obtained spatial spectrum. A larger array aperture is obtained under the condition that the number of physical array elements is certain, and the calculation complexity of arrival direction estimation is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
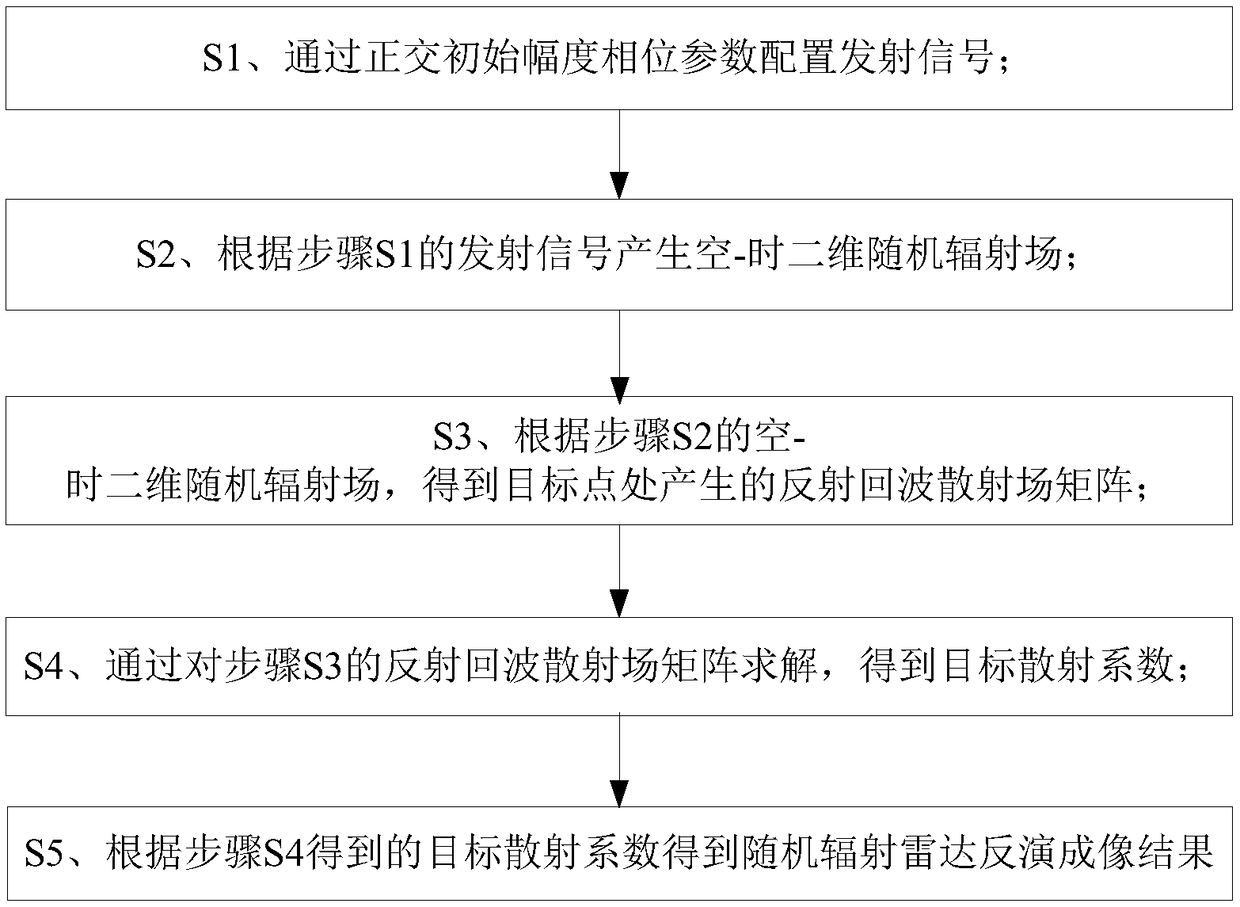
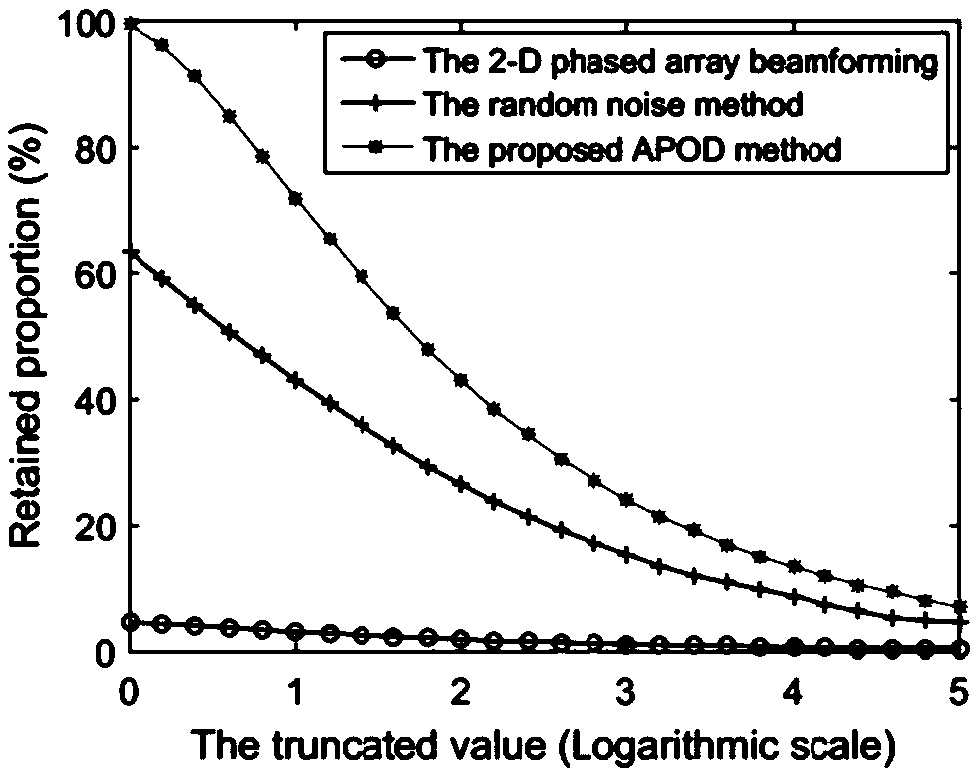
Stochastic radiation radar coincidence imaging method
ActiveCN108828593AGuaranteed OrthogonalityEnhance non-correlationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar imagingArray aperture
The invention discloses a stochastic radiation radar coincidence imaging method applied to the field of radar imaging technology. The invention aims to solve a problem of comparatively high matrix relevance of a radiation field under an array aperture with limited bandwidth since that the radiation field formed by a prior stochastic radiation field construction method has comparatively large redundant information. According to the invention, a space stochastic field is obtained through stochastic signals of a transmission space of a transmission antenna array and the radiation field changes stochastically over time on the basis of configured transmission signal parameters; distribution of a space-time two-dimensional stochastic radiation field is obtained according to the configuration ofan antenna array, parameters of transmission signals and target distance history and echo signals are obtained according to the distribution of the stochastic radiation field by a receiving antenna; and finally, a coincidence imaging result of a target scene is obtained according to the relation between the distribution of the stochastic radiation field and the echo signals. The method provided bythe invention ensures the orthogonality of stochastic amplitude and phase of transmission signals and enhances incoherence of an echo stochastic scattered field.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-band antenna system
The present invention is an improved antenna system. In an embodiment of the invention, the antenna system of the present invention may be a high-gain, low-profile wide-band antenna. Advantageously, the antenna system of the present invention may include a plate with reflecting elements to form a reflectarray antenna suitable for mounting on an aircraft. The reflectarray antenna of the present invention may be formed from a planar array of waveguides which may operate as a low loss, wide-band reflecting elements. Individual waveguides may be designed to scatter an incident field while impressing appropriate phase shifts in order to form a plane wavefront at the array aperture to produce a desired output signal. Waveguides may include ridges to employ vertical and horizontal polarization across a wide bandwidth operable at a high frequency, such as 10 GHz to 30 GHz.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
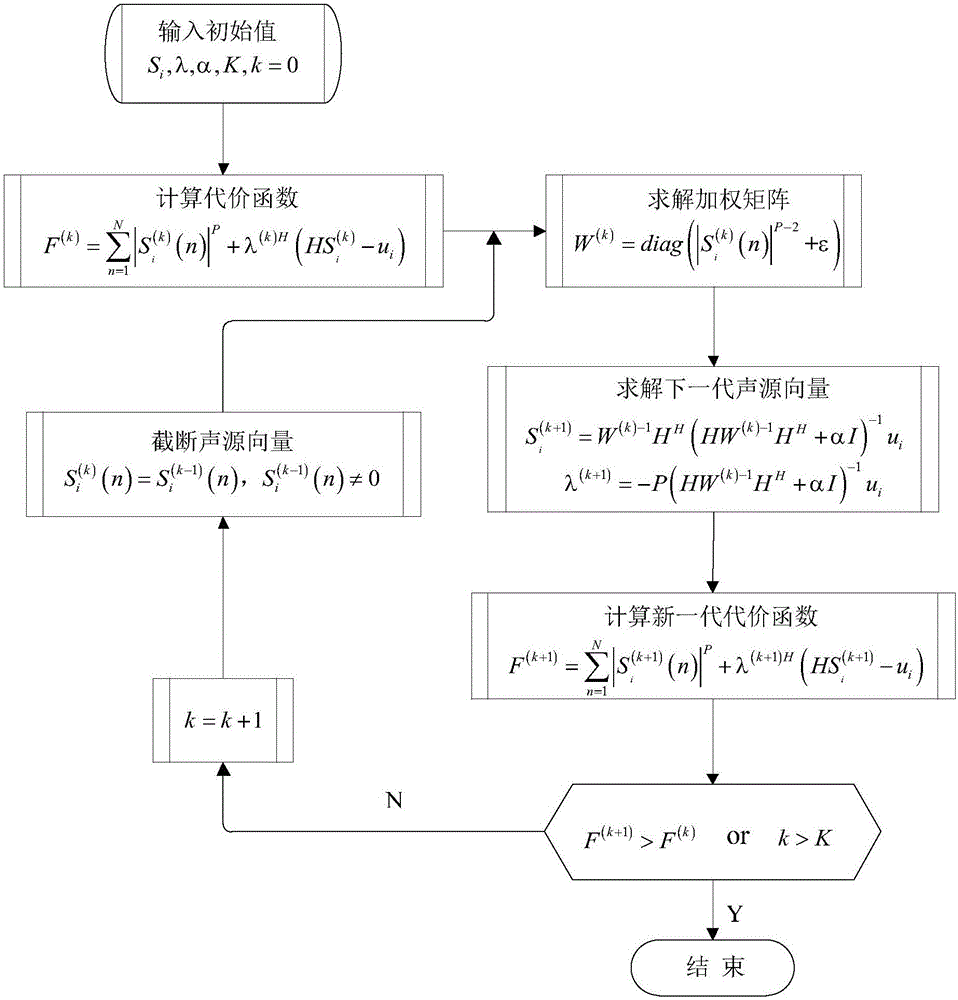
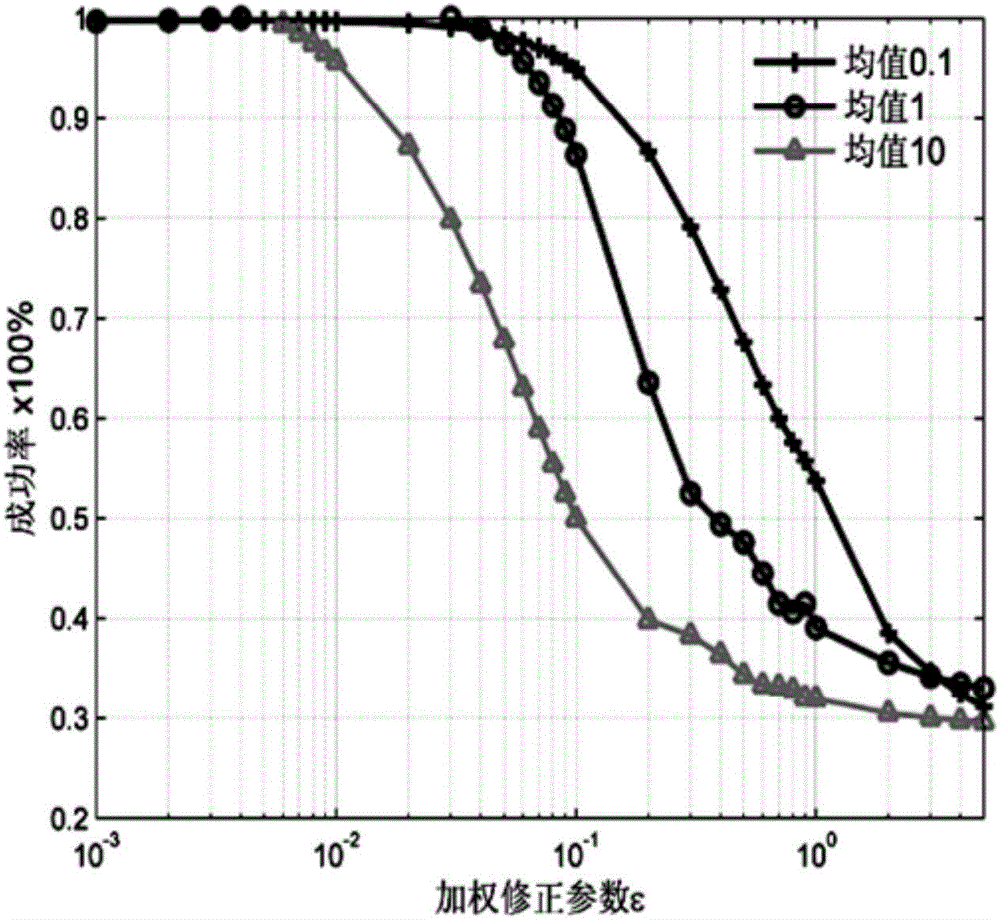
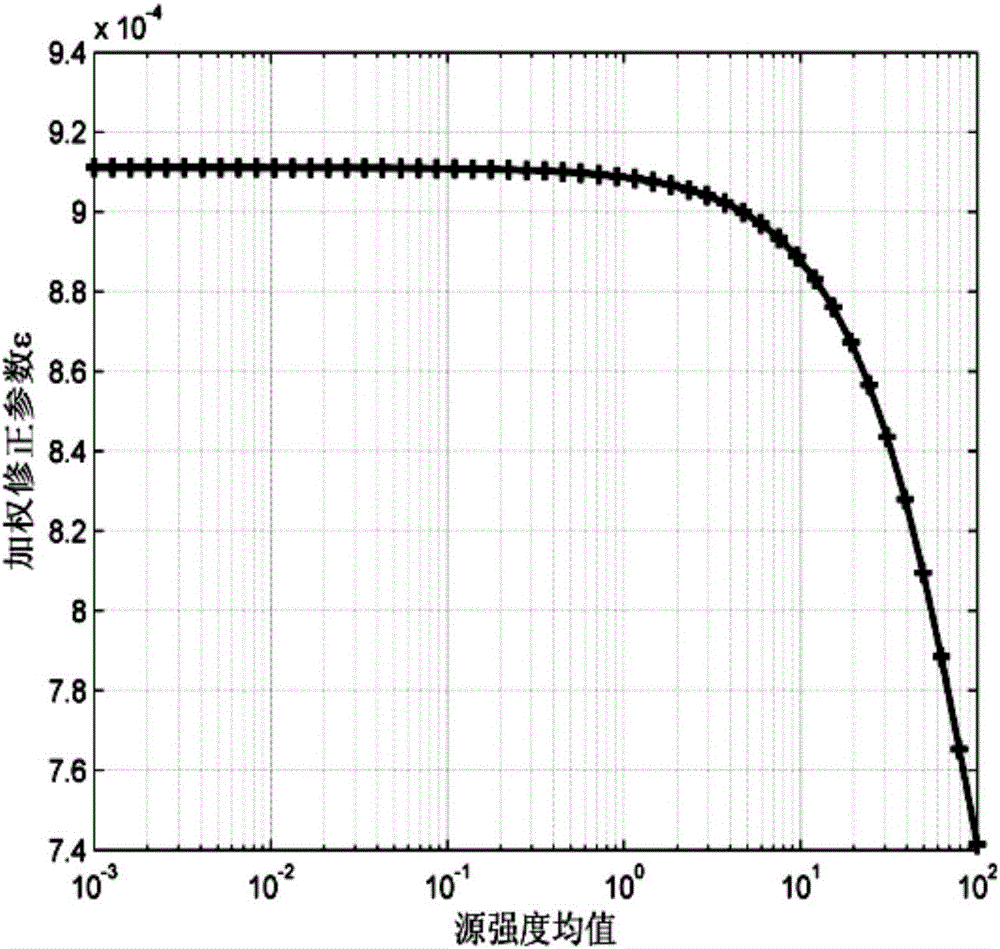
P-norm noise source positioning identification method based on weight correction parameter
InactiveCN106646376ASparsity concentrationAccurate estimatePosition fixationPattern recognitionSound source location
The invention discloses a P-norm noise source positioning identification method based on a weight correction parameter, relating to the technical field of noise source positioning. The positioning identification method includes step 1 eigenvalue decomposition sound source positioning recognition method; step 2 P-norm noise source signal reconstruction method; and step 3 selection of algorithm for weight correction parameter Epsilon. The characteristic subspace of each order and the subspace response function are obtained by characteristic decomposition, a subspace sound source vector reconstruction model is established for the characteristic subspace of each order, the reconstruction model is solved by the P-norm sparsity constraint of the weight correction parameter, the subspace sound source vector is forced to converge faster and more efficiently to the location of the real sparse source, and the more concentrated sparse solution of energy can be obtained; the effects of signal-to-noise ratio, measurement distance, array aperture and analysis frequency on the algorithm positioning performance are analyzed, the simulation result shows that the method can achieve the accurate estimation of the position and amplitude of different types of sound sources, and the stability is good.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Self-adaption anti-coherent interference technology based on characteristic component rejection
InactiveCN101726730AAvoid cancellationNo lossWave based measurement systemsDecompositionTarget signal
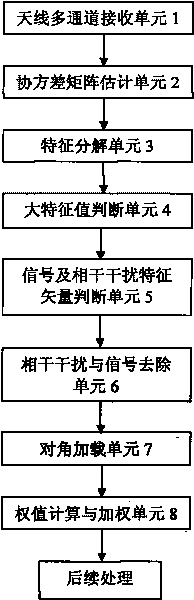
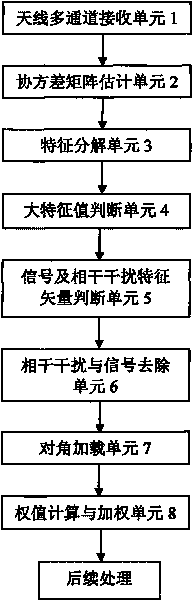
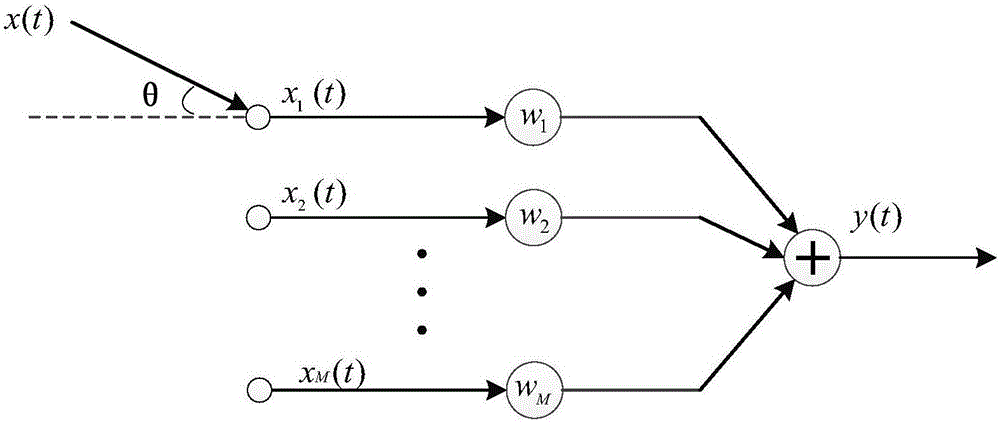
The invention discloses a self-adaption anti-coherent interference technology based on characteristic component rejection. Firstly, characteristic decomposition is carried out on an antenna multichannel receiving data covariance matrix to judge the number of a big characteristic value; then, the characteristic vector corresponding to signals and coherent interference is searched in a characteristic vector group corresponding to the big characteristic value so as to subtract the characteristic vector from the covariance matrix; finally, diagonal loading is carried out on the covariance matrix removing signals and coherent interference components, and the loaded matrix is used for calculating a self-adaption weight, data is weighed, and specific steps are disclosed in the drawing. The method of the invention avoids cancellation of desired signals while inhibiting incoherent interference, does not have array aperture loss and does not need to master the direction priori information of coherent interference. The method only relates to characteristic decomposition and inversion operation but does not relate to high-order cumulant operation, so that the method has simple steps and small calculation amount; the device is simple and has low cost. In addition, the method of the invention receives and utilizes the coherent interference as a wanted signal so as to improve the receiving gain of a target signal, thus owning better receiving performance. The method of the invention can be realized only by downloading a program to a general signal processing board, is easy to popularize and only needs to programme on a programmable signal processing board; thus, the system is convenient to upgrade while the system structure is not changed. The method of the invention can be widely applied to a system with various kinds of receiving channel structures and has popularization and application value.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE RADAR COLLEGE
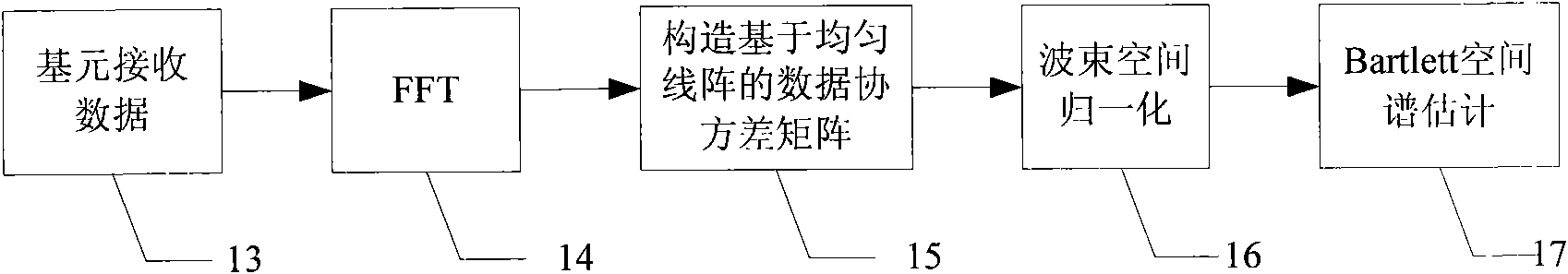
Sub-band processing method and frequency-space cascade broadband adaptive wave beam acquiring method
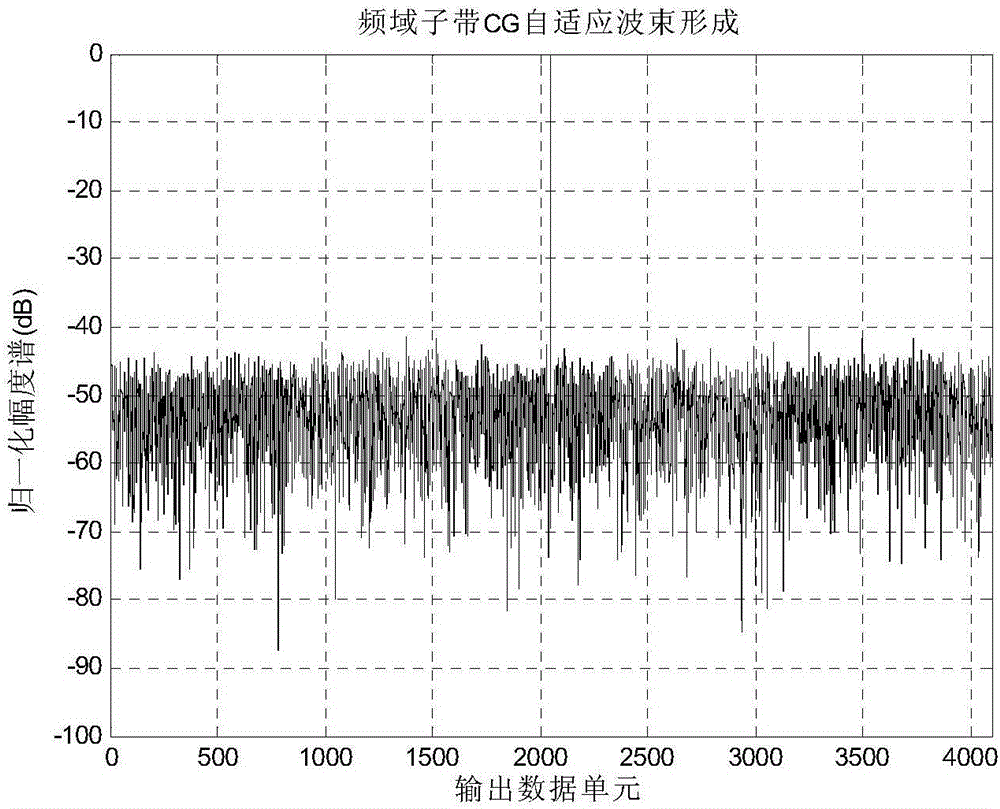
ActiveCN106301498ACompensation for transit timeSolve the problem of signal cancellationSpatial transmit diversityArray apertureConjugate gradient method
The invention discloses a sub-band processing method and a frequency-space cascade broadband adaptive wave beam acquiring method and aims to solve a broadband array aperture transition problem. The method comprises steps that firstly, each channel reception signal is converted from a time domain to a frequency domain through fast Fourier transform FFT, and aperture transition compensation of a broadband array is realized in the frequency domain; the broadband reception signals in the frequency domain are divided into sub-bands, sub-band pulse compression of the sub-bands is respectively carried out, adaptive spatial domain beam formation (ADBF) of each sub-band pulse compression data is carried out one distance unit by one distance unit, and ADBF weight is calculated through a conjugate gradient method (CG); fast Fourier transform FFT of each sub-band ADBF output signal is carried out to synthesize a broadband signal, and a broadband ADBF output signal is acquired through inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT). Through the method, broadband array ADBF aperture transition and signal cancellation problems are solved, operation efficiency is high, and project implementation is easy.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Split aperture array for increased short range target coverage
InactiveUS7737879B2Reduce sidelobe levelEffectively double the elevation beamwidthsAntenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsControl signal
A phased array radar system comprising a plurality of radiating elements configured in a common array aperture for detecting and tracking targets; and a transmit and receive arrangement responsive to a first control signal for configuring the plurality of radiating elements to define a plurality of sub-apertures from the common array aperture for detecting and tracking short range targets, wherein the plurality of sub-apertures are independently steerable array apertures and include an amplitude taper applied across each of the plurality of sub-apertures to reduce a peak sidelobe level.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
High-resolution sonar location method based on sparsity of objective space
InactiveCN103116162AAchieve simultaneous positioningOvercoming dependenciesAcoustic wave reradiationHat matrixPeak value
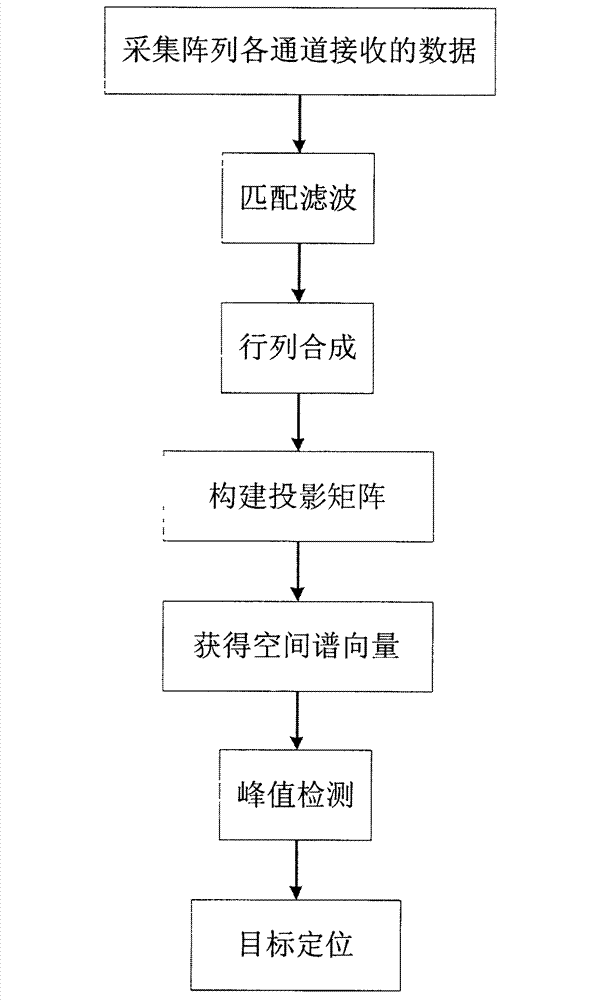
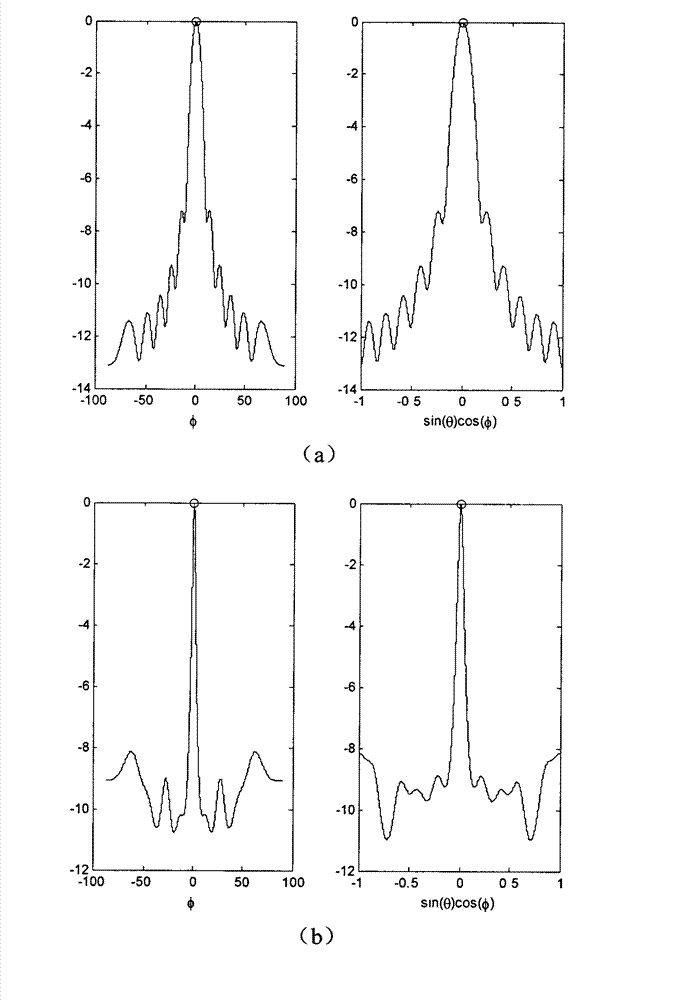
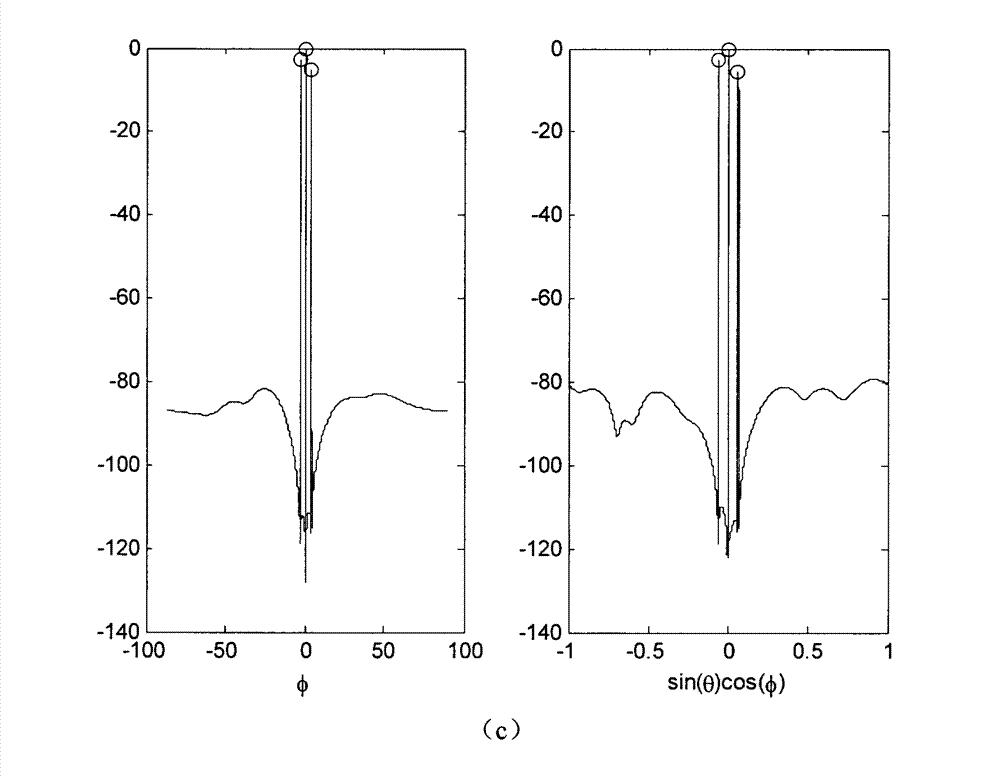
The invention discloses a high-resolution sonar location method based on a sparsity of an objective space and mainly solves the problems that a limited array aperture causes insufficient spatial resolution and a signal source coherence causes an inaccurate estimation of an objective location and calculating work of subspace decomposition and data volume are considerable in the prior art. According to the method, a projection matrix which is from a spatial spectrum vector quantity to a ranks synthesis data vector is constructed. By taking advantage of the apriori information of the sparsity of the space target and obtaining data of large signal to noise ratio through a matched filtering, the spatial spectrum vector quantity is carried out with peak detection through an iterative computation to obtain the high-resolution spatial spectrum vector quantity. The objective location can be achieved by taking advantage of the received index value of a peak element through the calculation to gain an objective azimuth angle and an objective pitch angle. The location method has the advantages of being low in the needed data size and calculated amount in the iterative process, suitable for a hardware implementation, high in angular accuracy and improving markedly the spatial resolution.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Sparse-based space-time adaptive processing method and system
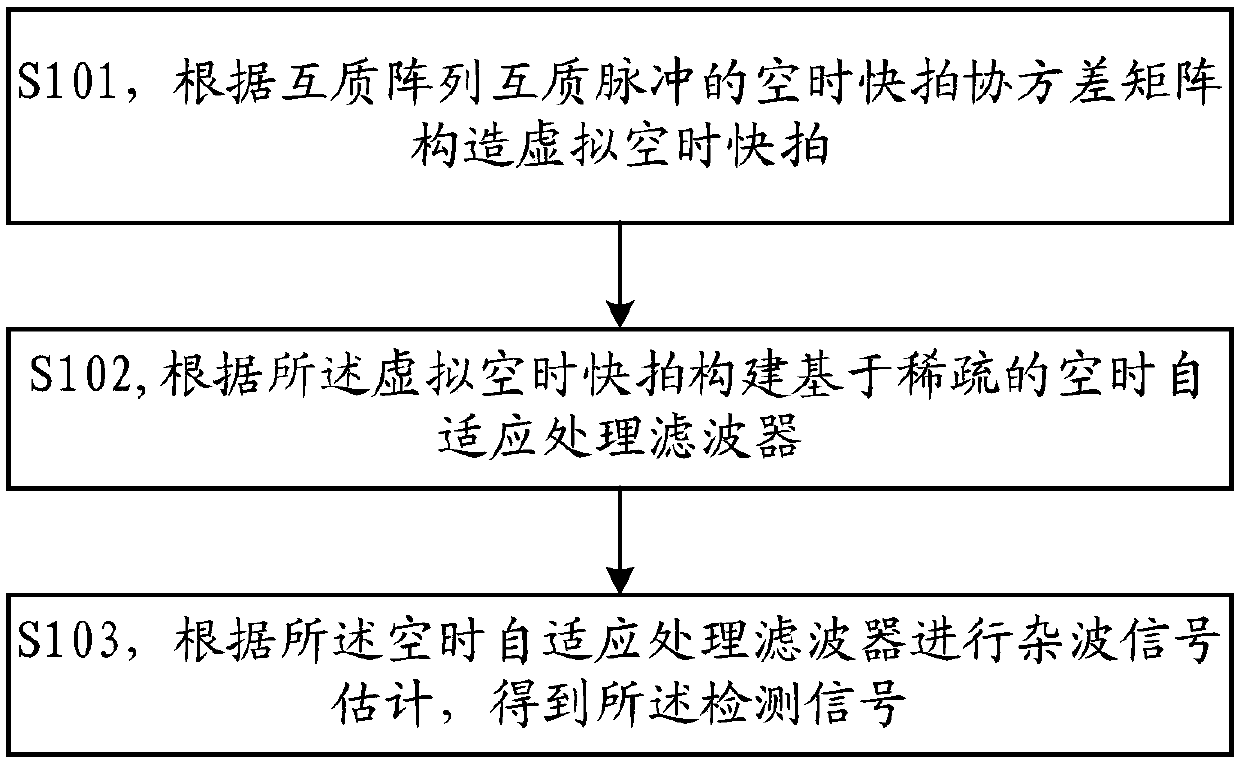
ActiveCN108802705AImprove estimation accuracyReduce the number of storiesWave based measurement systemsVirtual spaceSpace-time adaptive processing
The invention is applicable to the technical field of signal processing, and provides a sparse-based space-time adaptive processing method. The sparse-based space-time adaptive processing method comprises the steps: constructing a virtual space-time snapshot according to a space-time snapshot covariance matrix of a co-prime array - co-prime pulse; constructing a sparse-based space-time adaptive processing filter according to the virtual space-time snapshot; and according to the space-time adaptive processing filter, performing estimation of clutter signals to obtain a detection signal. One embodiment of the present invention provides a sparse-based space-time adaptive processing method with repetition interval of a co-prime array and a co-prime pulse. As the co-prime array can provide thecapability of a greater array aperture, and the O(MN) freedom degree can be realized by means of only M+N*1 physical sensors. Therefore, by means of the above advantages, the sparse-based space-time adaptive processing method can significantly improve the estimation accuracy of a direction of arrival (DOA), and applies the co-prime array to the space-time adaptive processor (STAP) field, thus greatly reducing the number of snapshots, and reducing the system cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Antenna array
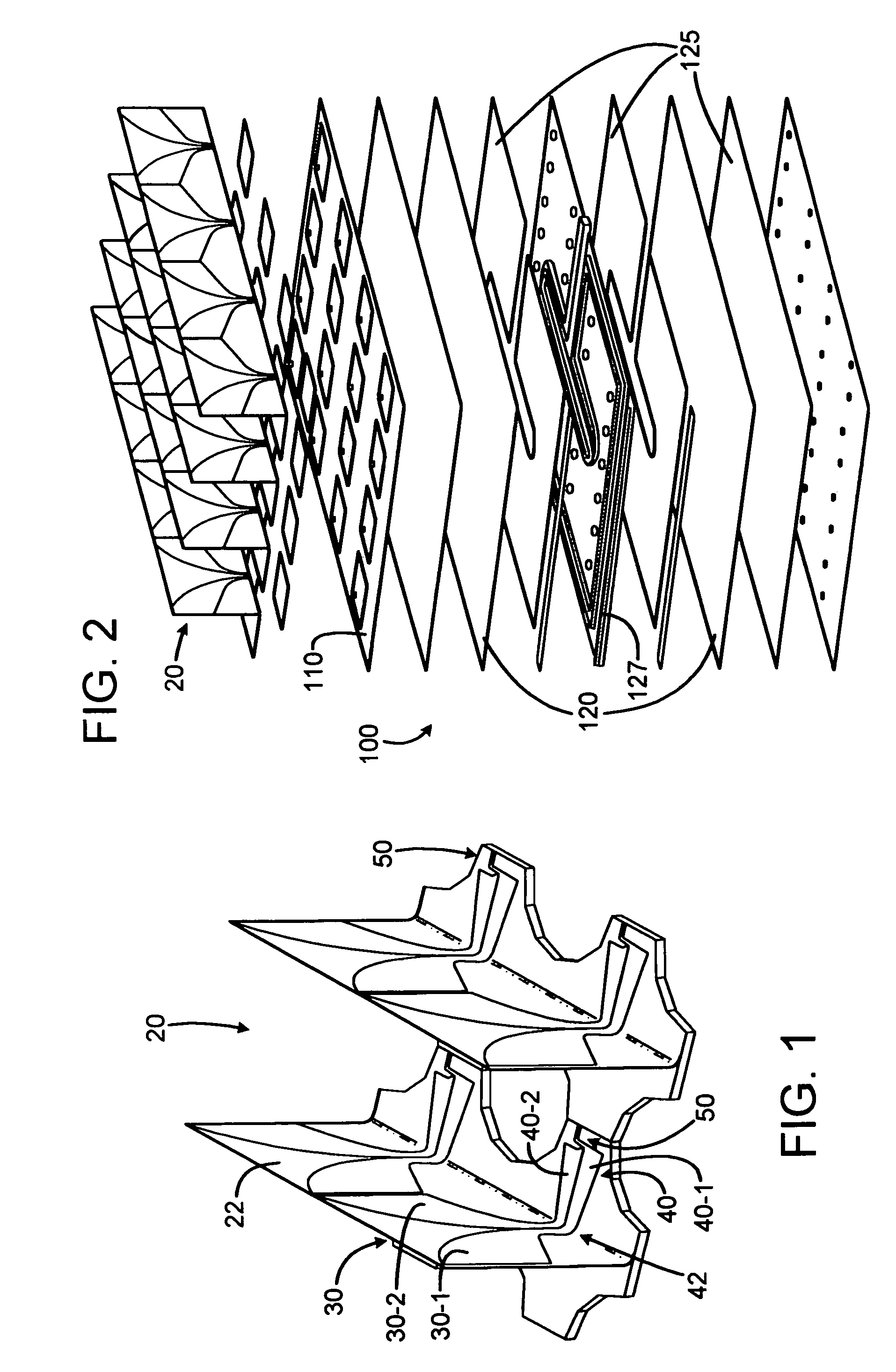
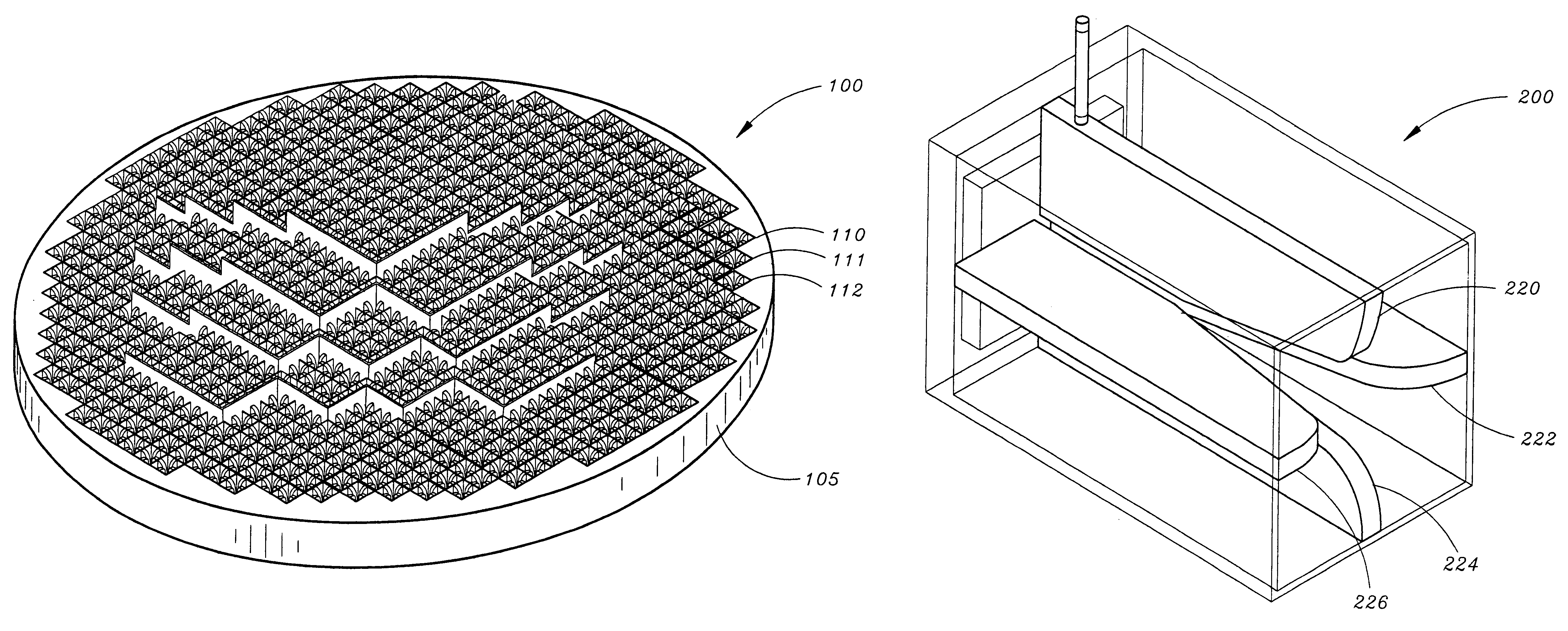
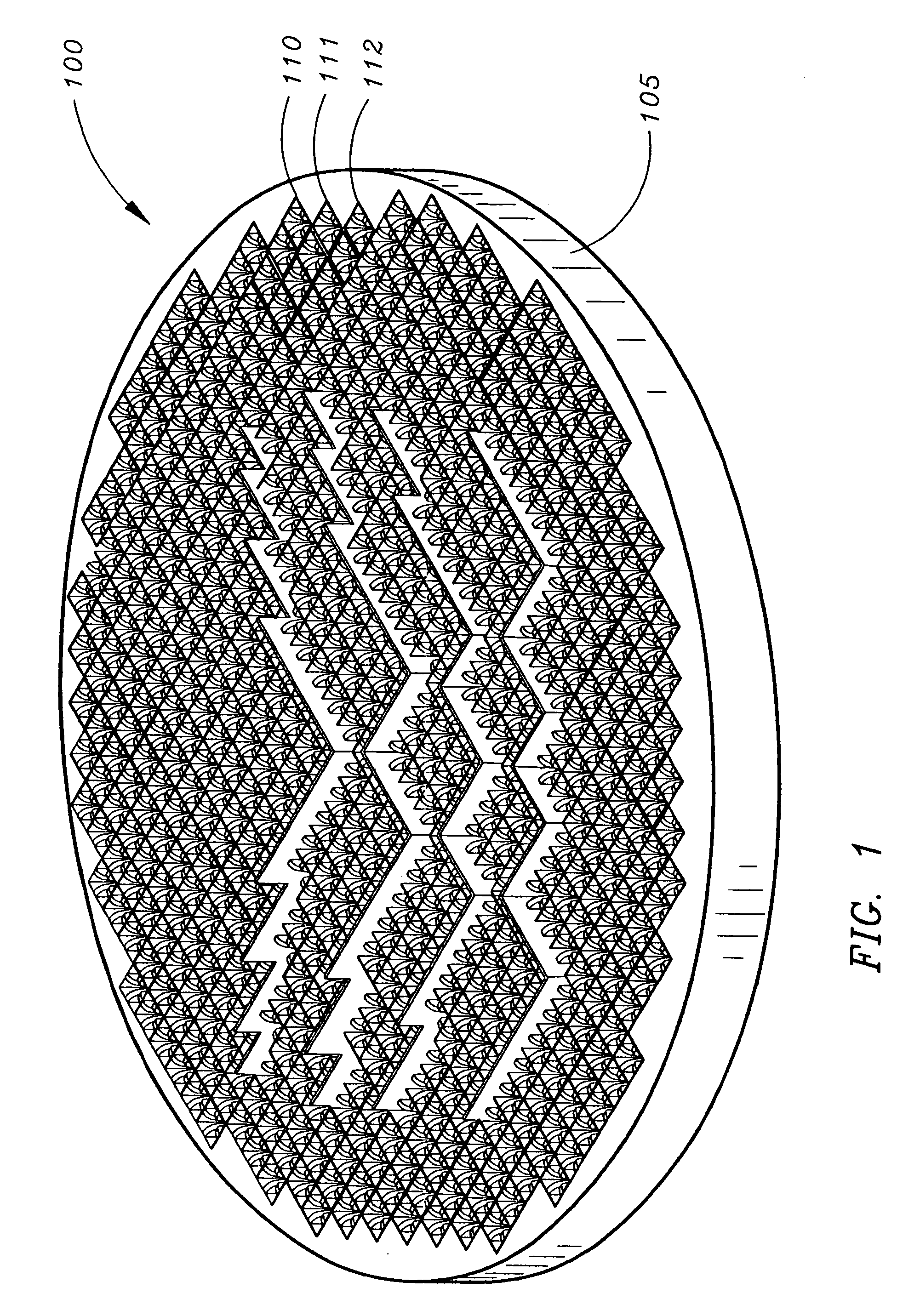
InactiveUS7106268B1Individually energised antenna arraysPolarised antenna unit combinationsHorn antennaArray aperture
TEM horn array apertures are disclosed, comprises a plurality of stamped sheet segments interconnected to form an “egg crate” like array. Each stamped sheet comprises a plurality of TEM horn antennas with a series of cooperating slots, enabling the sheets to be assembled into an “egg crate” design that allows quick and inexpensive building of a TEM horn antenna array. Moreover, the stamped sheet segments are structurally and dimensionally stable, and thus the assembled array may be connected to a guide plane without the need for additional aligning or structural elements. A method of assembling the array is also disclosed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
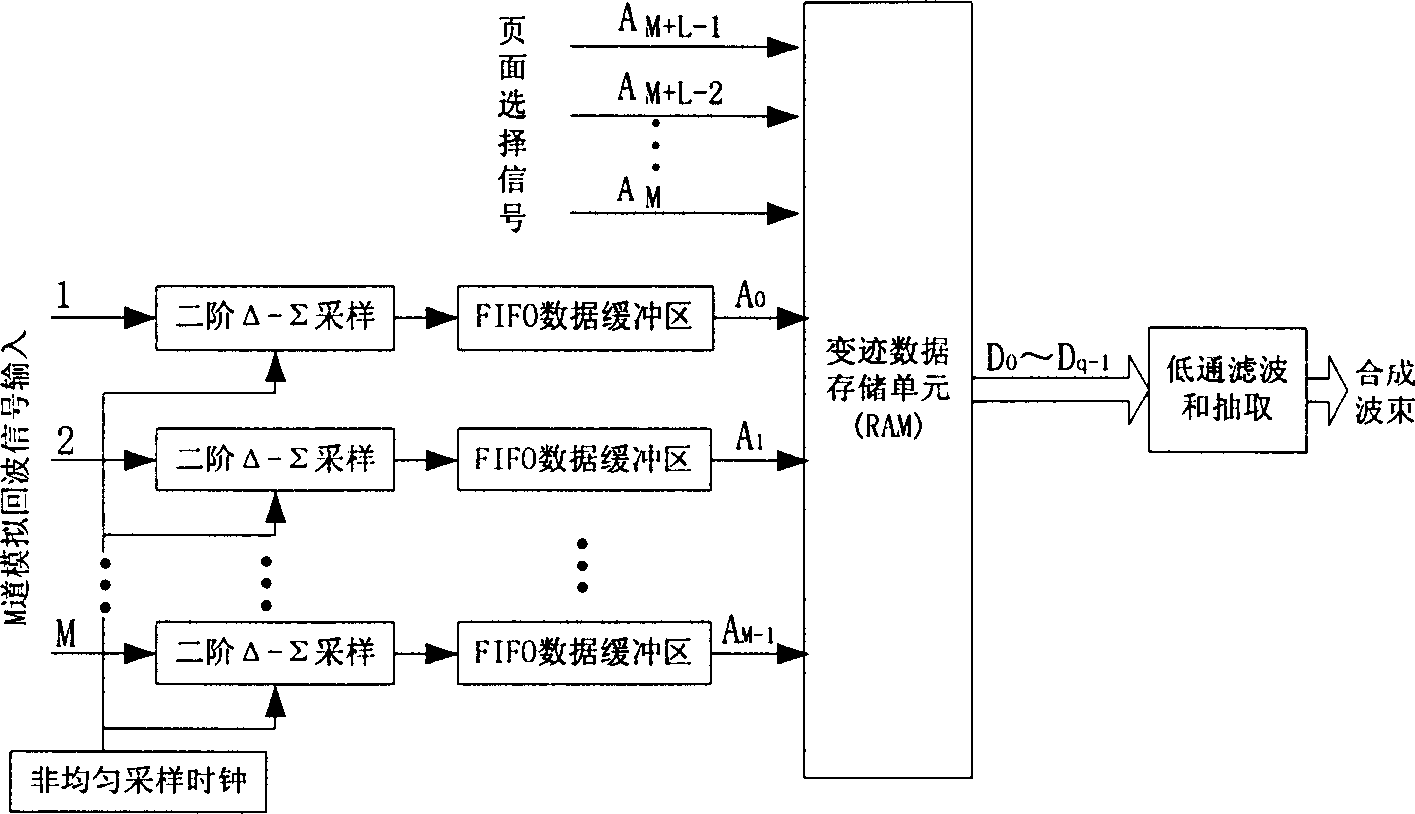
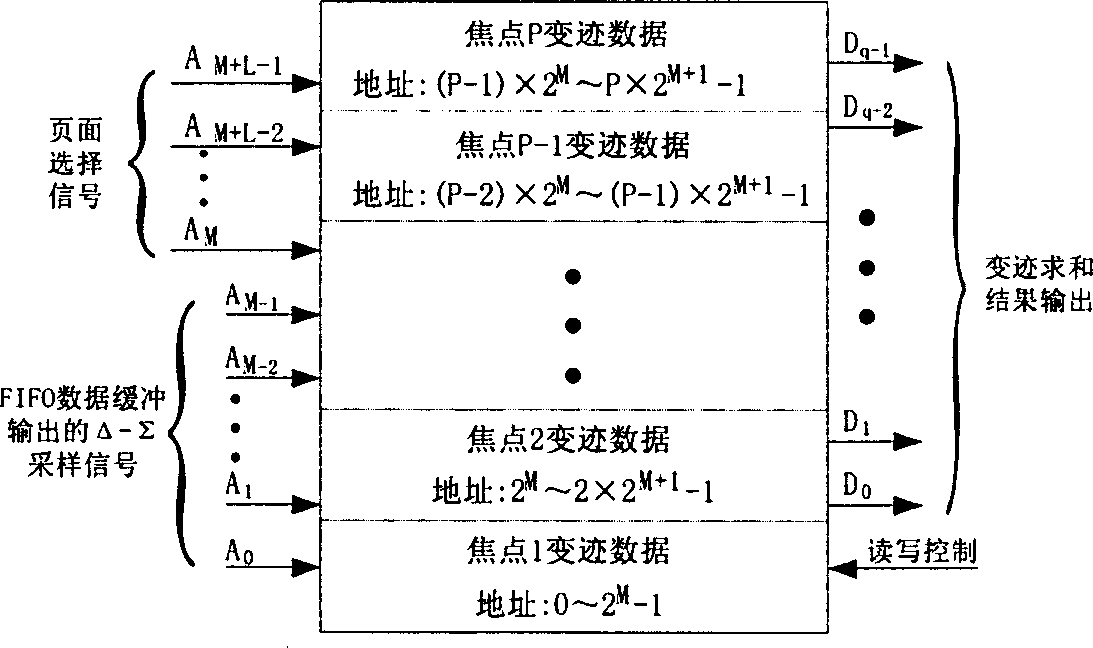
Ultrasonic dynamic receiving apodization method based on Ôû�-Ôêæ transformation
InactiveCN1431624AImprove ultrasound image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationImaging processingData stream
The method belongs to the technique areas of digital medical ultrasonic image processing. The characters are as follows. Based on non uniform sampling and delta-sigma transformation, the data storageunit is introduced to realize the dynamic receiving apodization by using the addressing method of multiple storage pages so as to restrain diffraction lobes caused by the array aperture and improve the quality of the ultrasonic image. The delta-sigma sampled data as the address of the apodization storage units are inputted. The apodization data of the focus P are stored into the related storage unit. Based on the page selection signal, the apodization data with different focus P are selected from the related storage units to form the output data stream, which form the composite wave after thelow pass filter and decimation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Low complexity DOA and polarization joint estimation method under electromagnetic vector nested L array
ActiveCN109375152AEstimate moreImprove spatial freedomPosition fixationDirection findersNested arraysEstimation methods
The invention provides a low complexity DOA and polarization joint estimation method under an electromagnetic vector nested L array. An electromagnetic vector sensor array and the nested L array are combined. Through introducing a spatial smoothing technology, smoothing processing is performed on a continuous virtual area array obtained after nested L array vectorization so as to obtain a virtualreceiving signal covariance matrix possessing a full rank characteristic. After a characteristic value is decomposed, a subspace class algorithm PM algorithm is used to realize signal DOA and polarization Information joint estimation. The electromagnetic vector sensor array can obtain the arrival angle information of the signal and can obtain the polarization information of the signal. The methodhas an important application value in the array signal processing field. In the method of the invention, space spectrum search is not needed, algorithm complexity is low, an obtained DOA estimation angle can realize automatic matching, the application of the nested array provides great array aperture support, and the high degree of freedom of a space and better parameter estimation performance arepossessed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Actual-value ESPRIT non-circular signal angle estimation method for single-base MIMO radar
ActiveCN108303683AReduce dimensionalityEasy to implement in real timeWave based measurement systemsComputation complexitySignal subspace
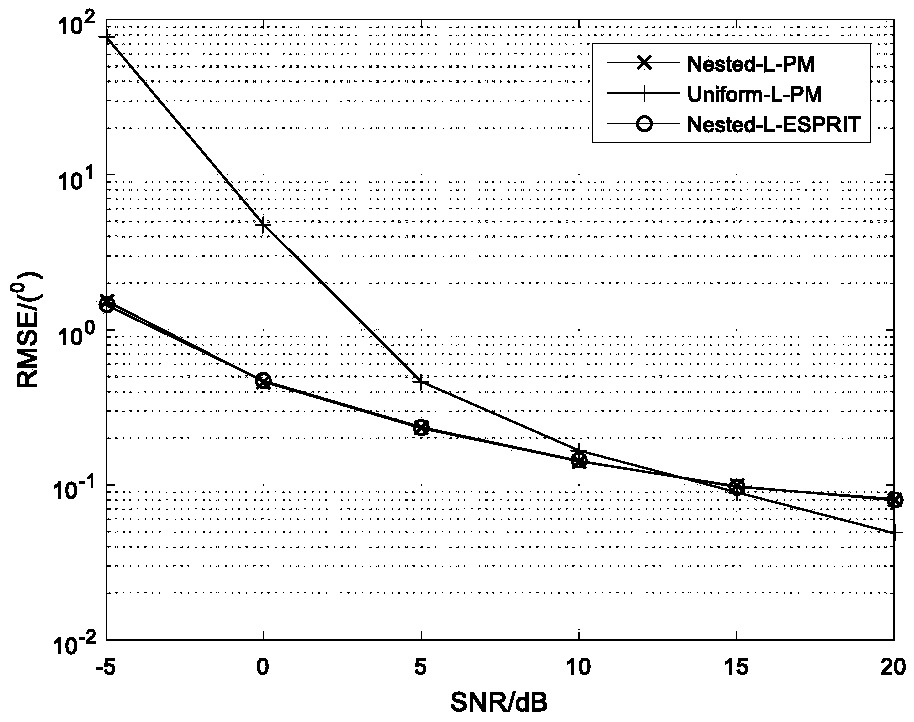
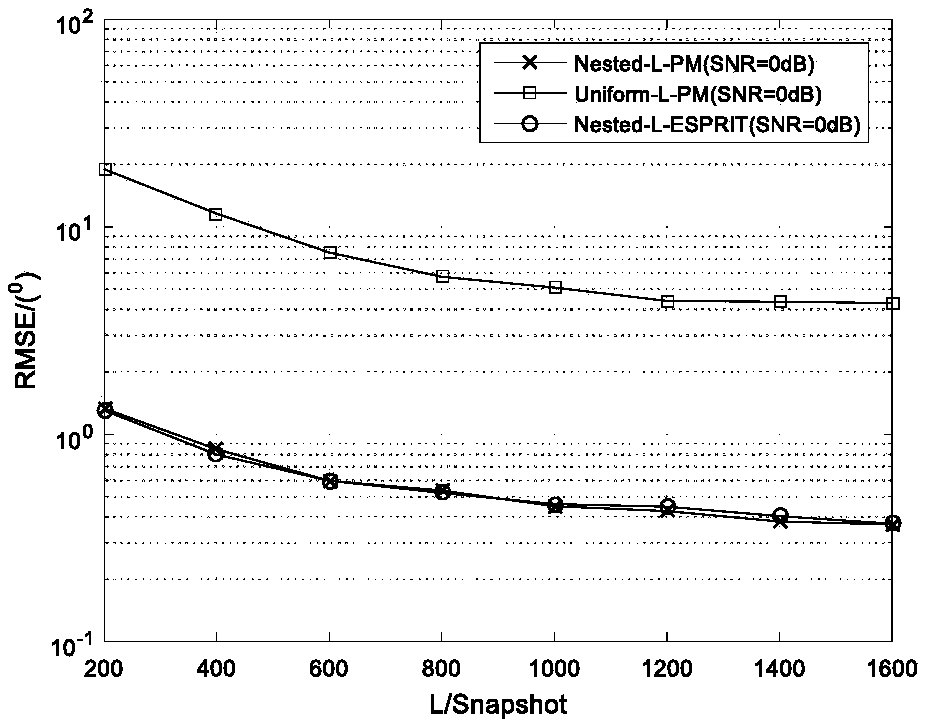
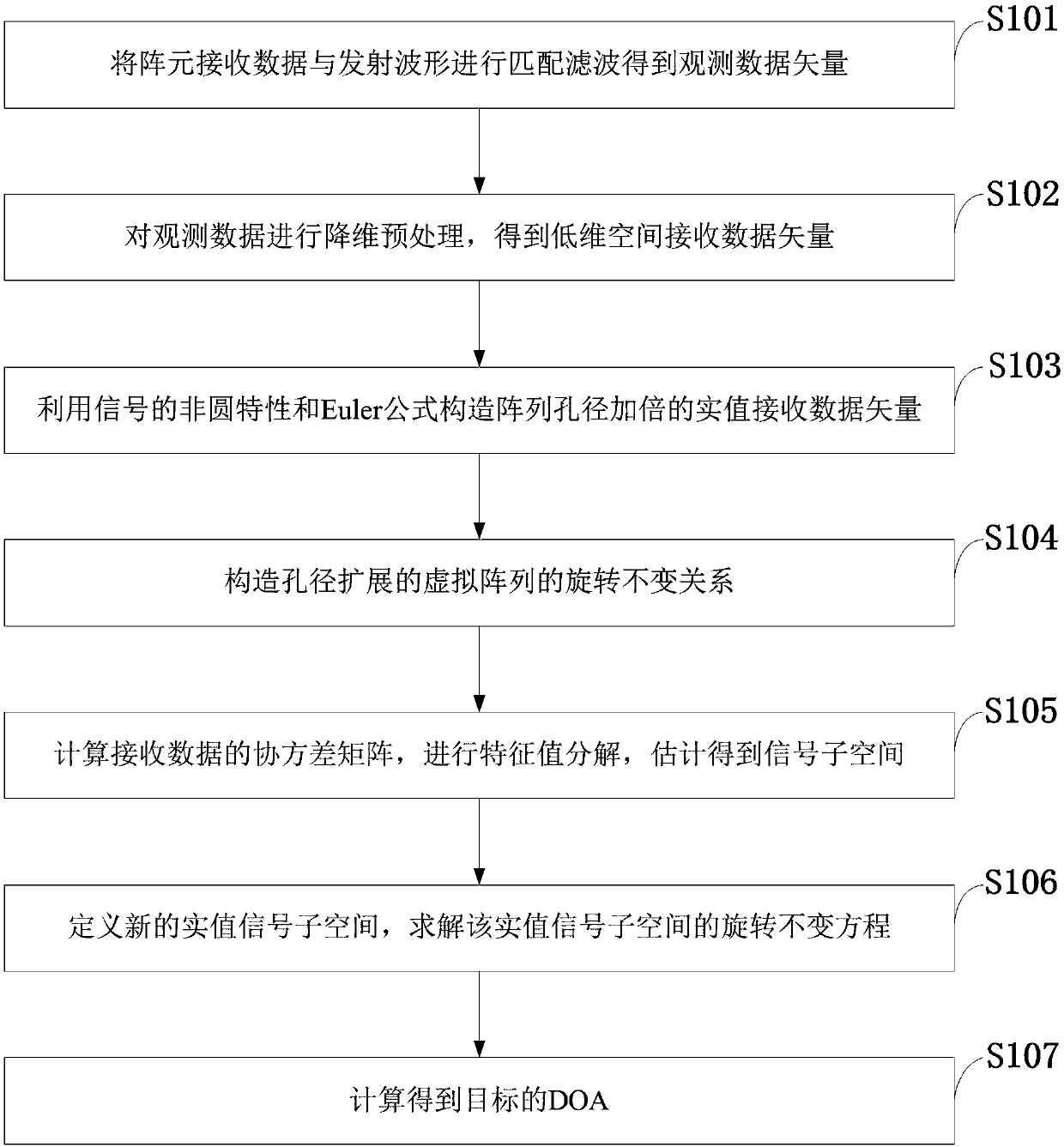
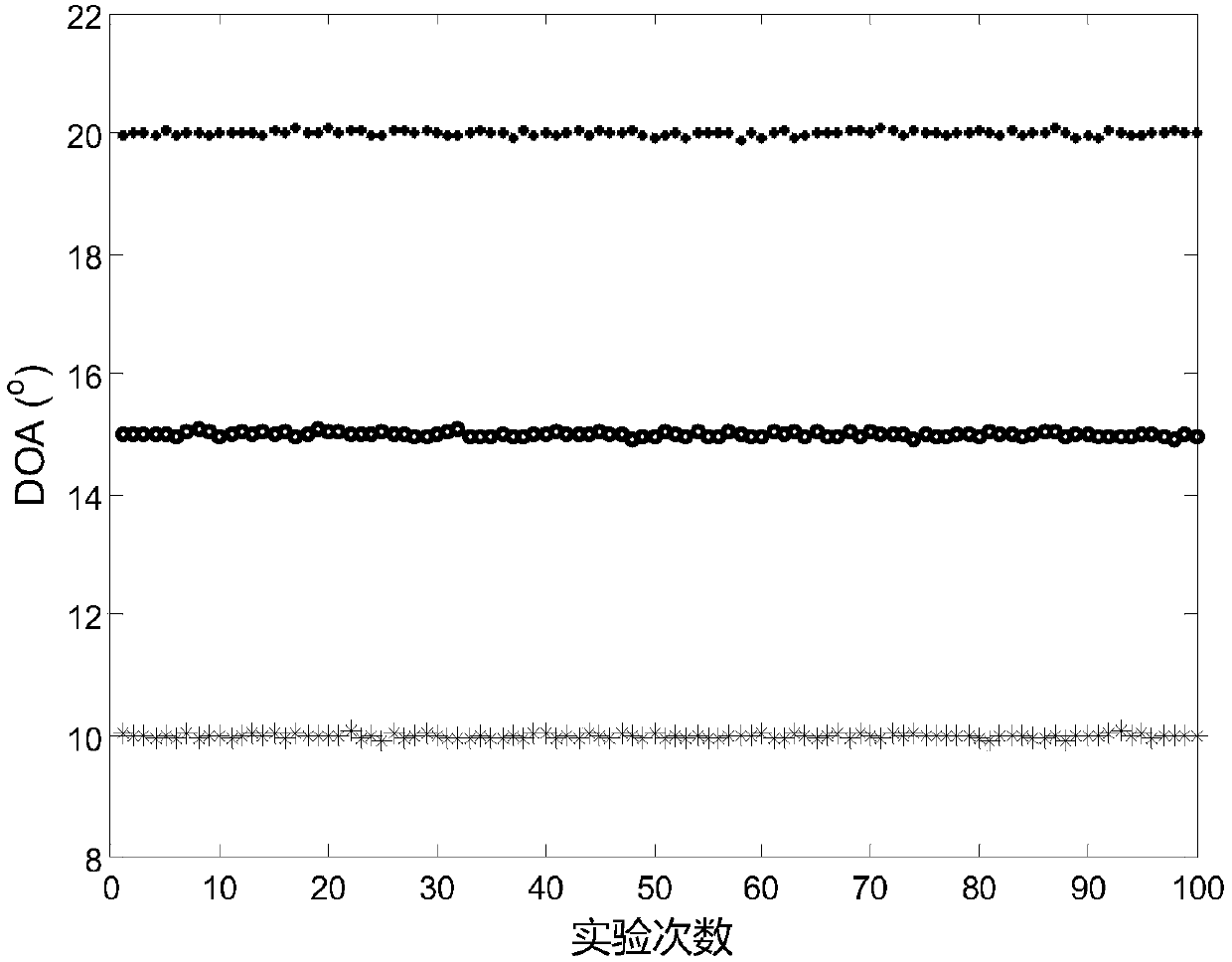
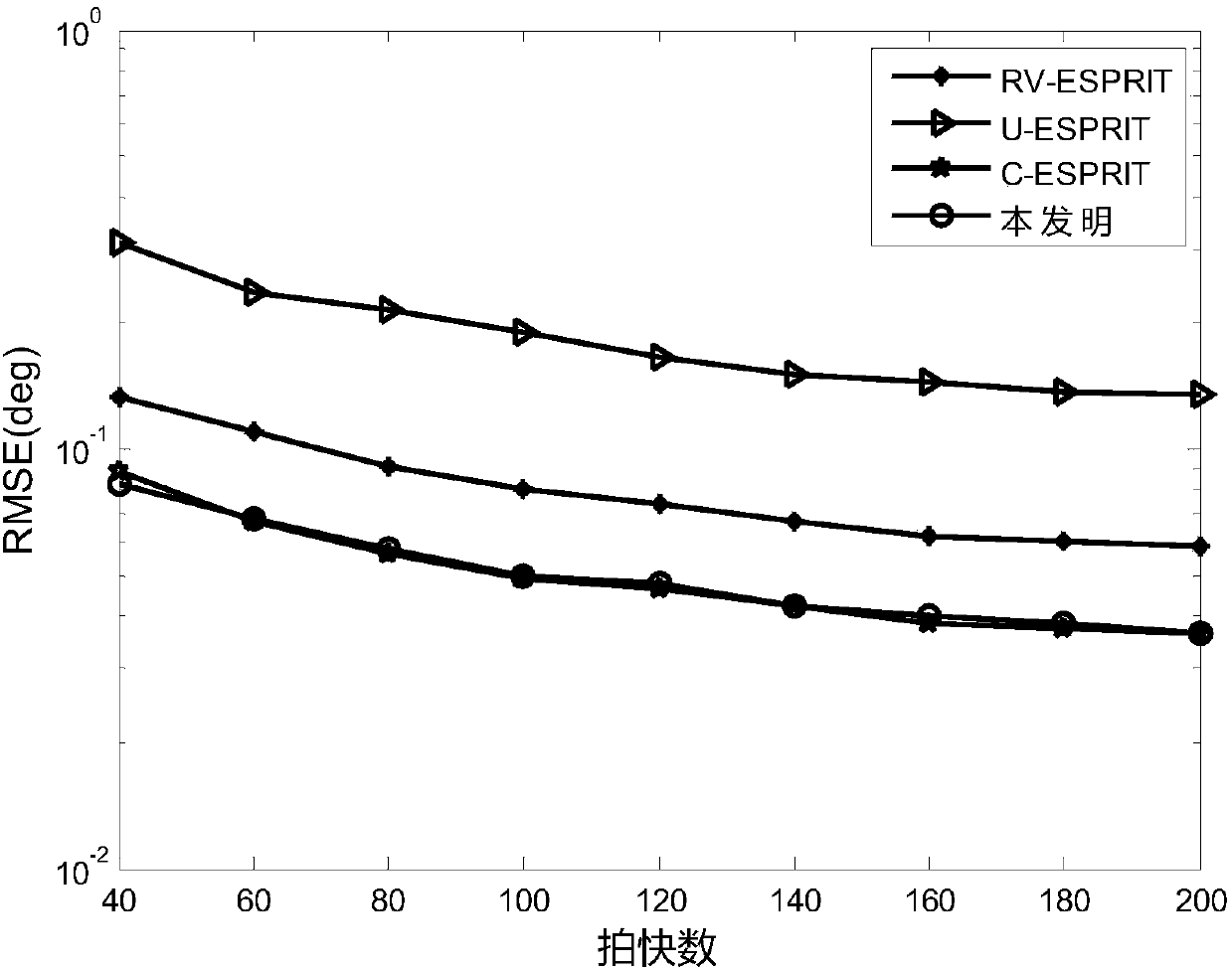
The invention, which belongs to the field of radar technology, discloses an actual-value ESPRIT non-circular signal angle estimation method for a single-base MIMO radar. Matched filtering is carried out on array element receiving data and a transmitted signal to obtain an observation data vector; dimensionality reduction preprocessing is carried out on the observation data to obtain a low-dimensional space receiving data vector; on the basis of a non-circular characteristic of the signal and an Euler formula, an actual-value receiving data vector with array aperture doubling is constructed; arotation invariance relationship of a virtual array with aperture extending is constructed; a covariance matrix of the extended receiving data is calculated and feature value decomposition is carriedout on the matrix, an actual-value signal sub space is estimated; new actual-value signal sub space is defined and a rotation invariance equation of the new actual-value signal sub space is calculated; and a DOA estimation value of the target is calculated. Therefore, the DOA estimation accuracy is improved obviously and the computational complexity of the ESPRIT algorithm is reduced substantially. The estimation method is suitable for the low-signal-to-noise-ratio and low-fast-beat-number occasions.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com