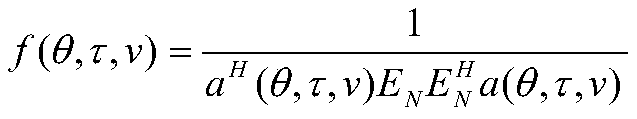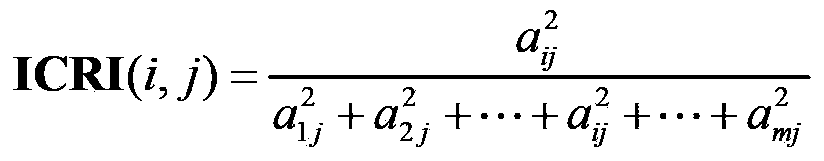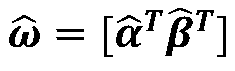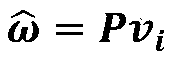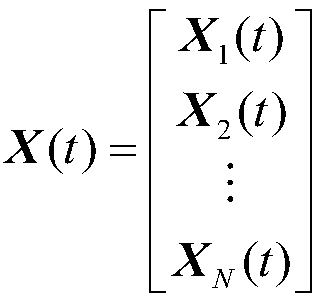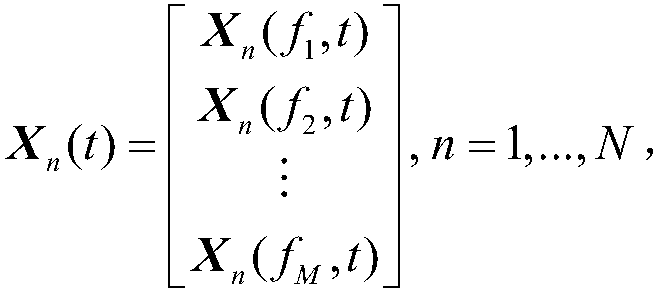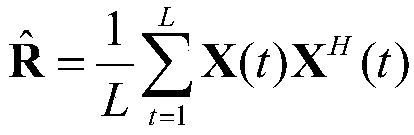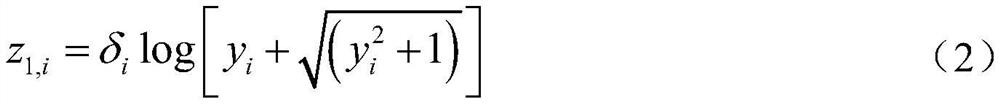Patents
Literature
59 results about "Subspace decomposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Data analytic engine towards the self-management of complex physical systems
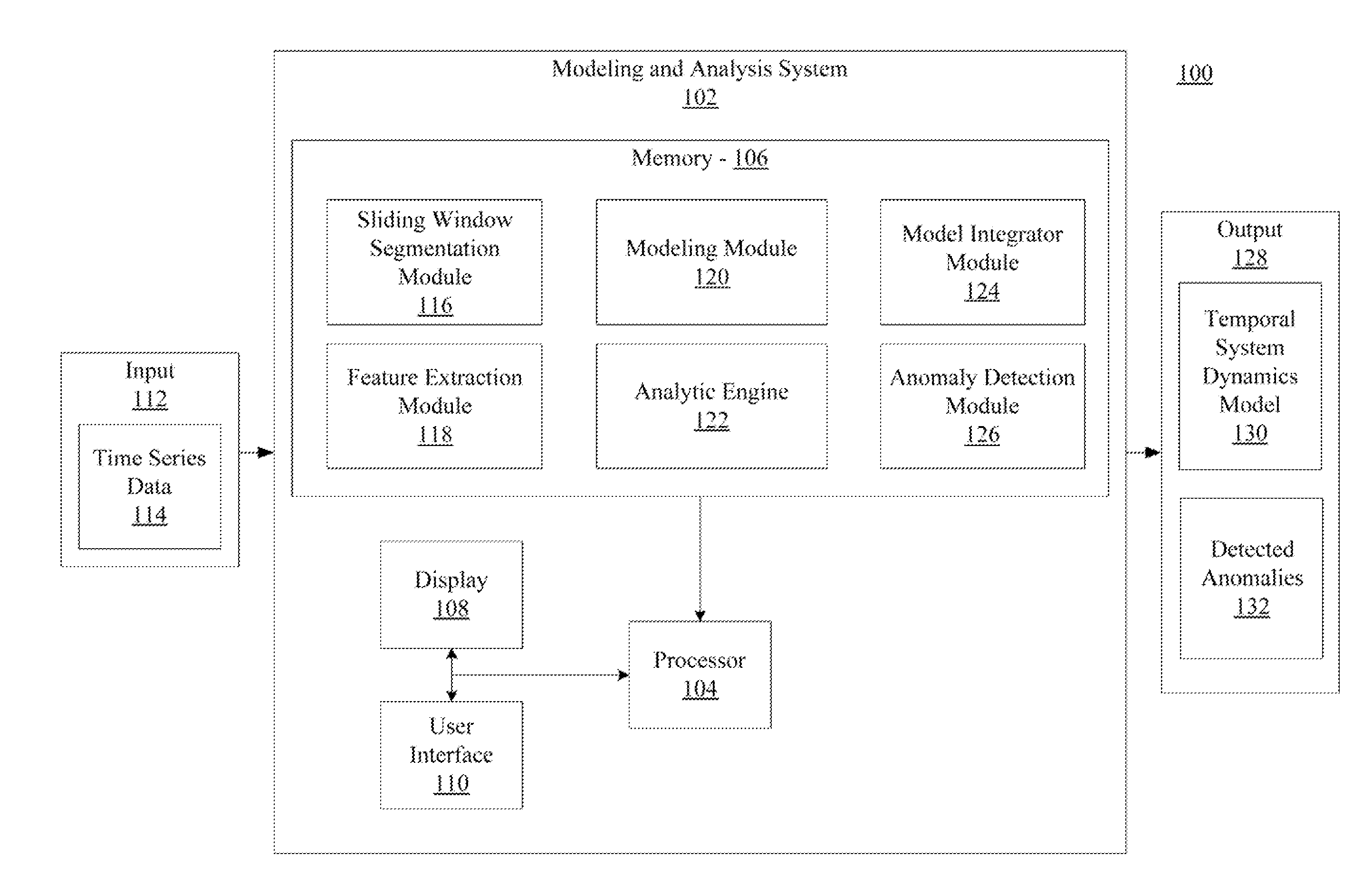
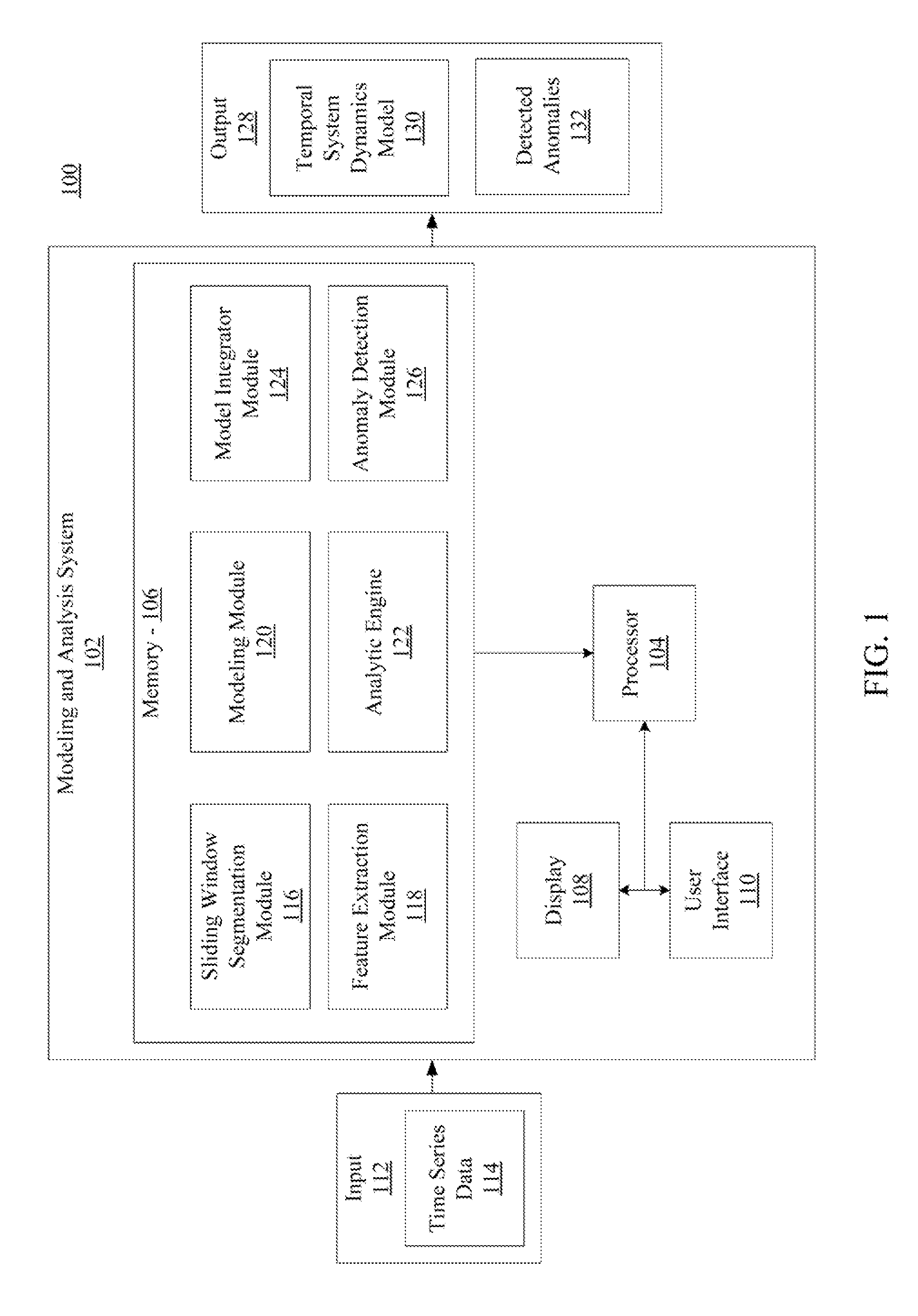
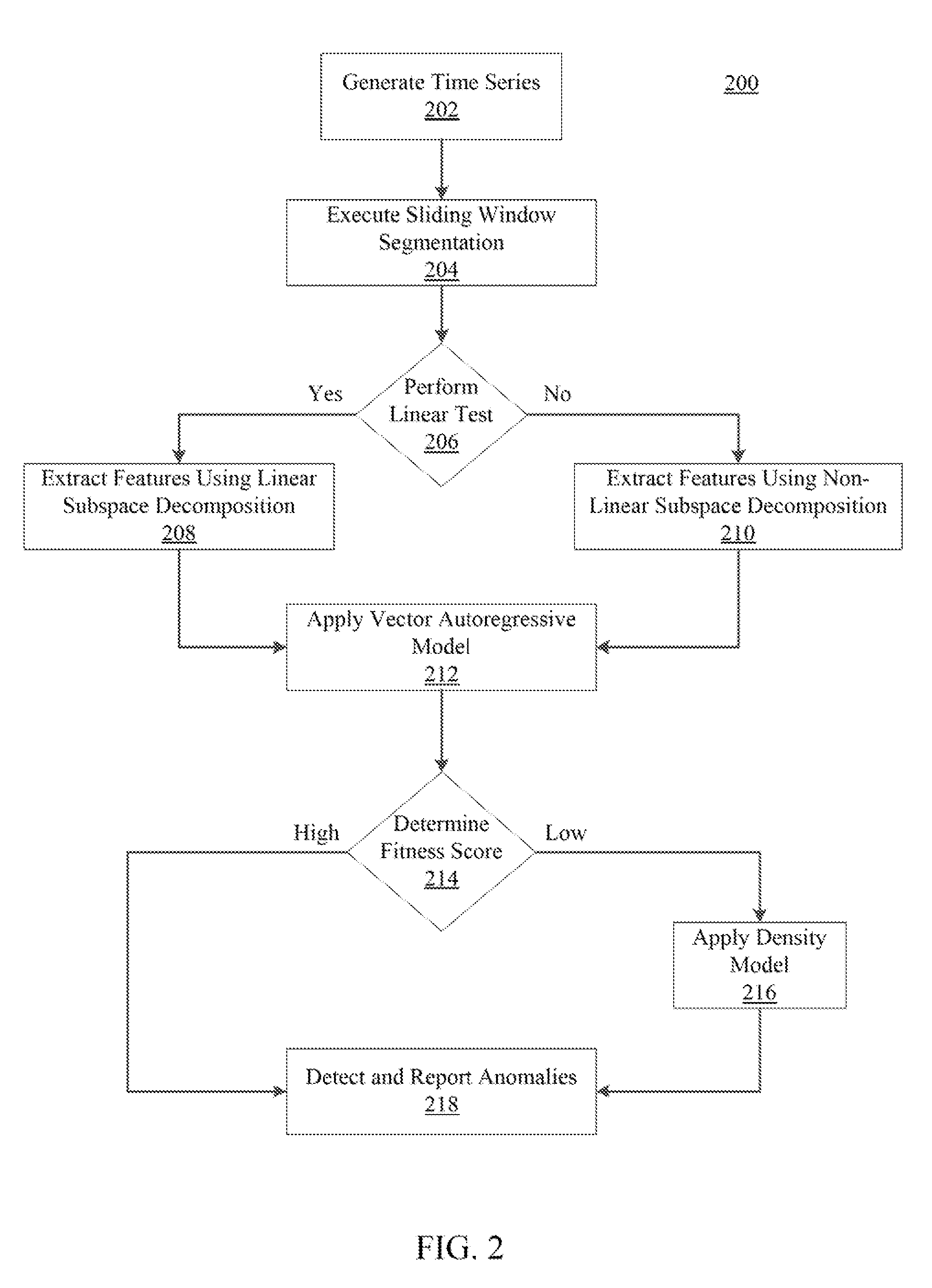
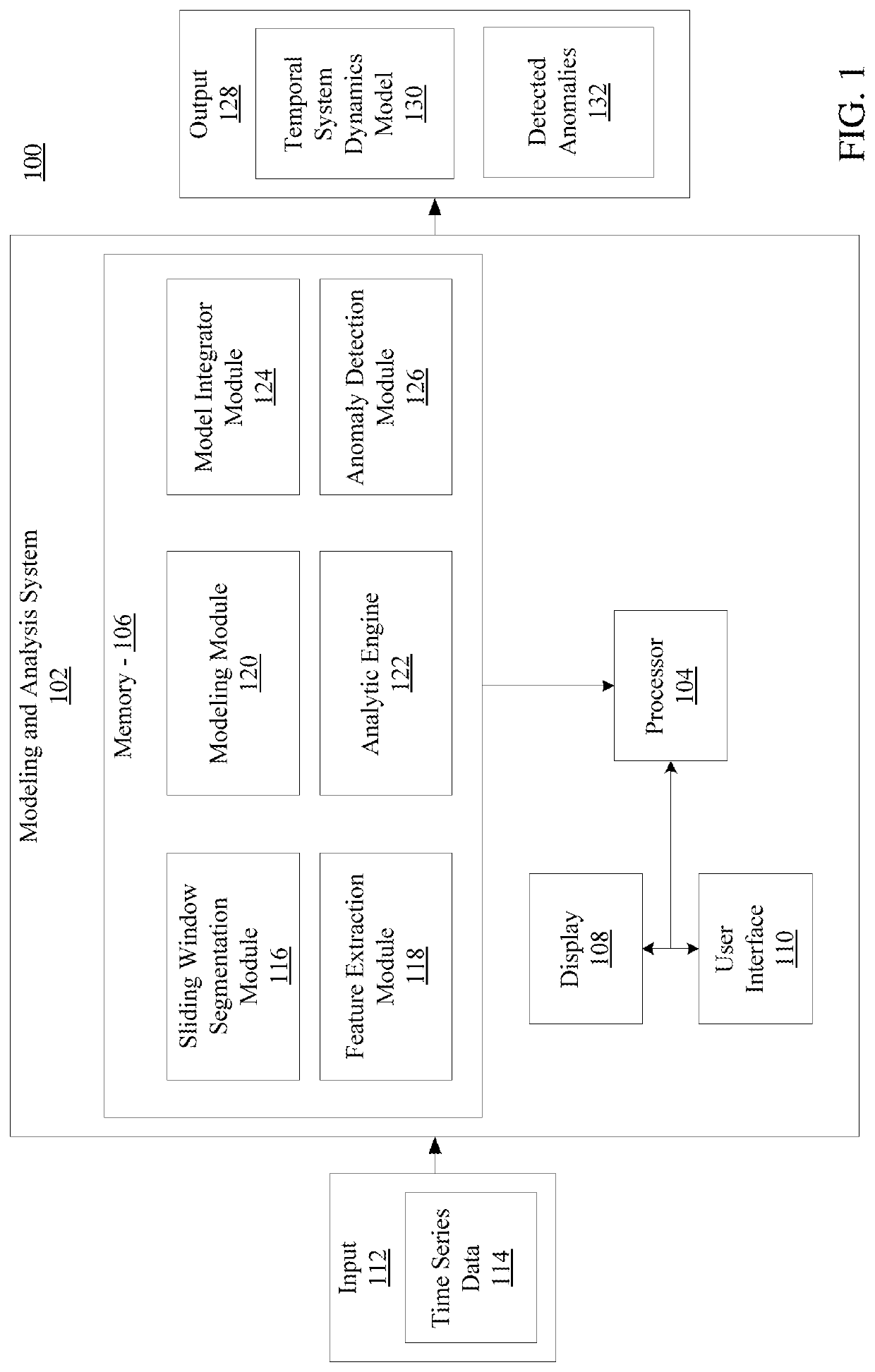
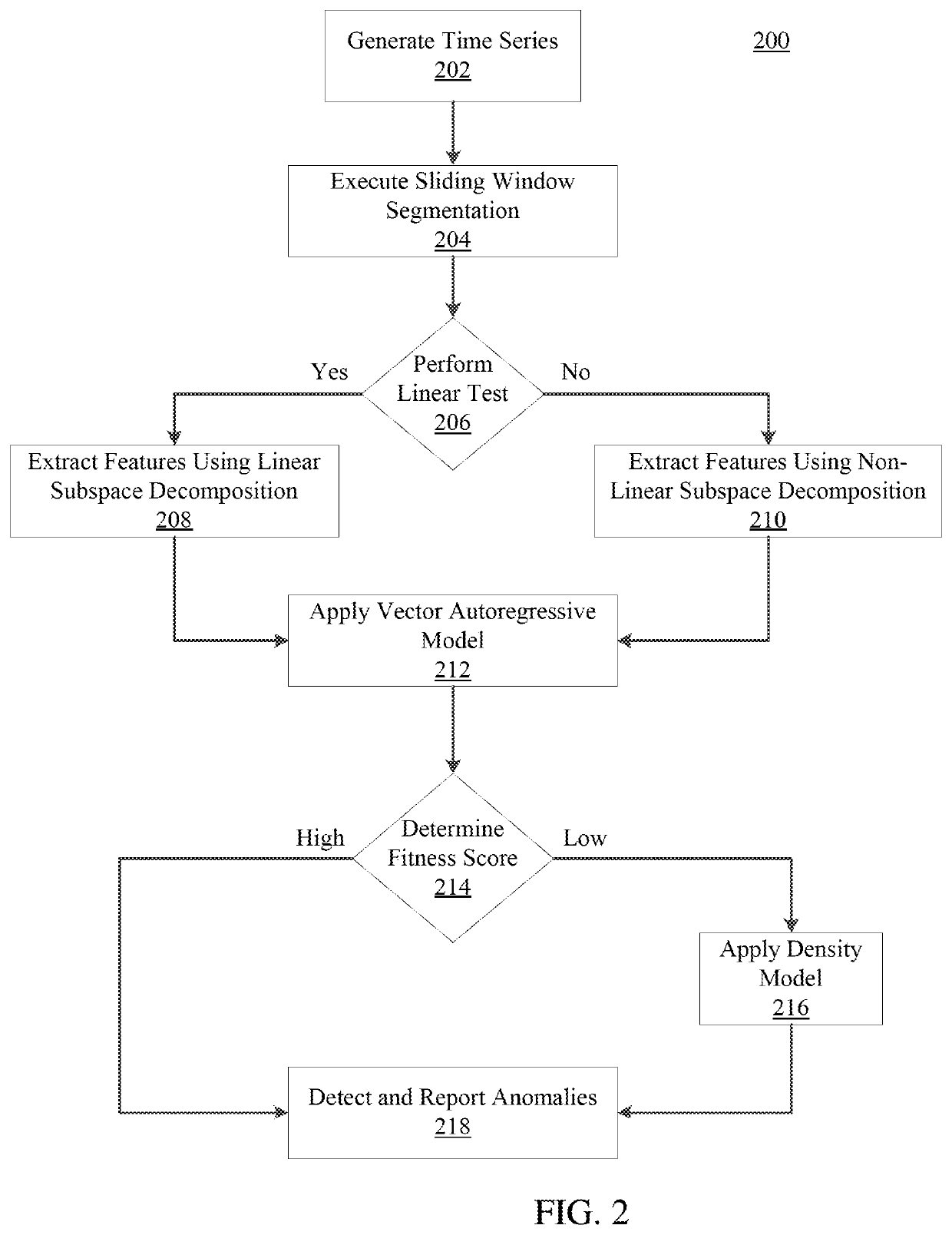
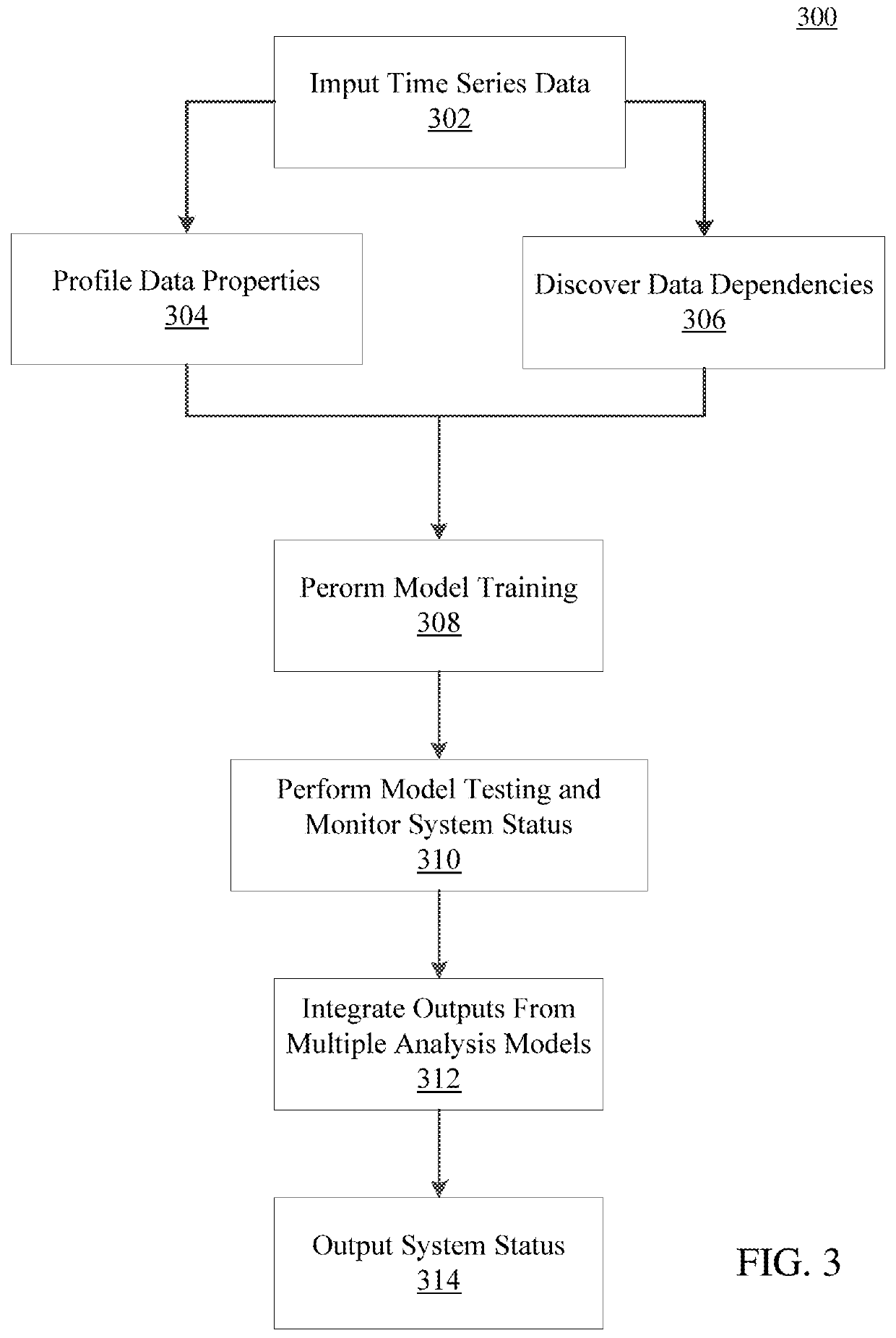
Systems and method for modeling system dynamics, including extracting features representative of a temporal evolution of a dynamical system, further including deriving one or more vector trajectories by performing sliding window segmentation of one or more time series; applying a linear test to determine whether the one or more vector trajectories are linear or nonlinear; and performing linear or nonlinear subspace decomposition on the vector trajectory based on the linear test. The system and method may generate a system evolution model from the extracted features of the dynamical system and determine a fitness score of the system evolution model.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
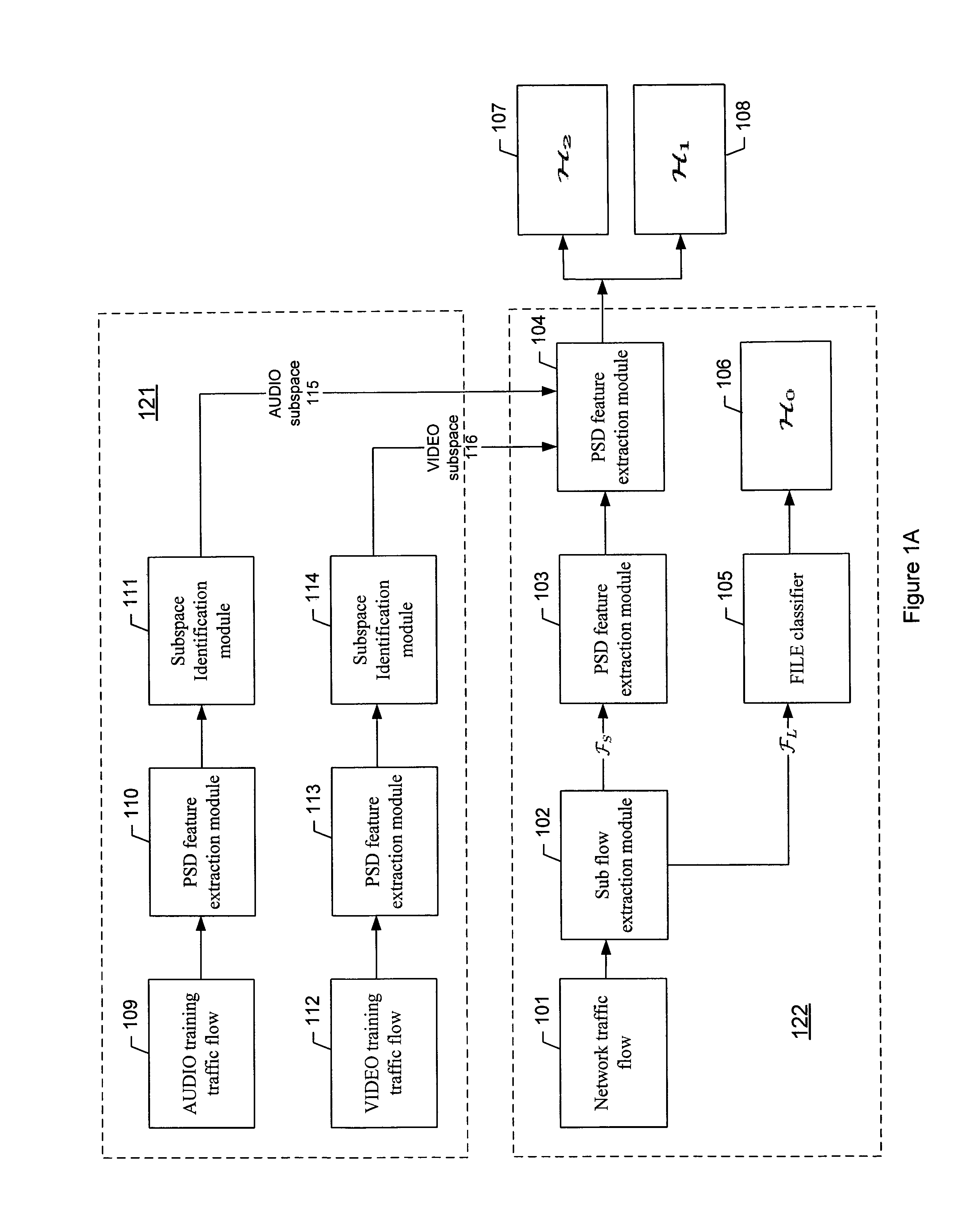
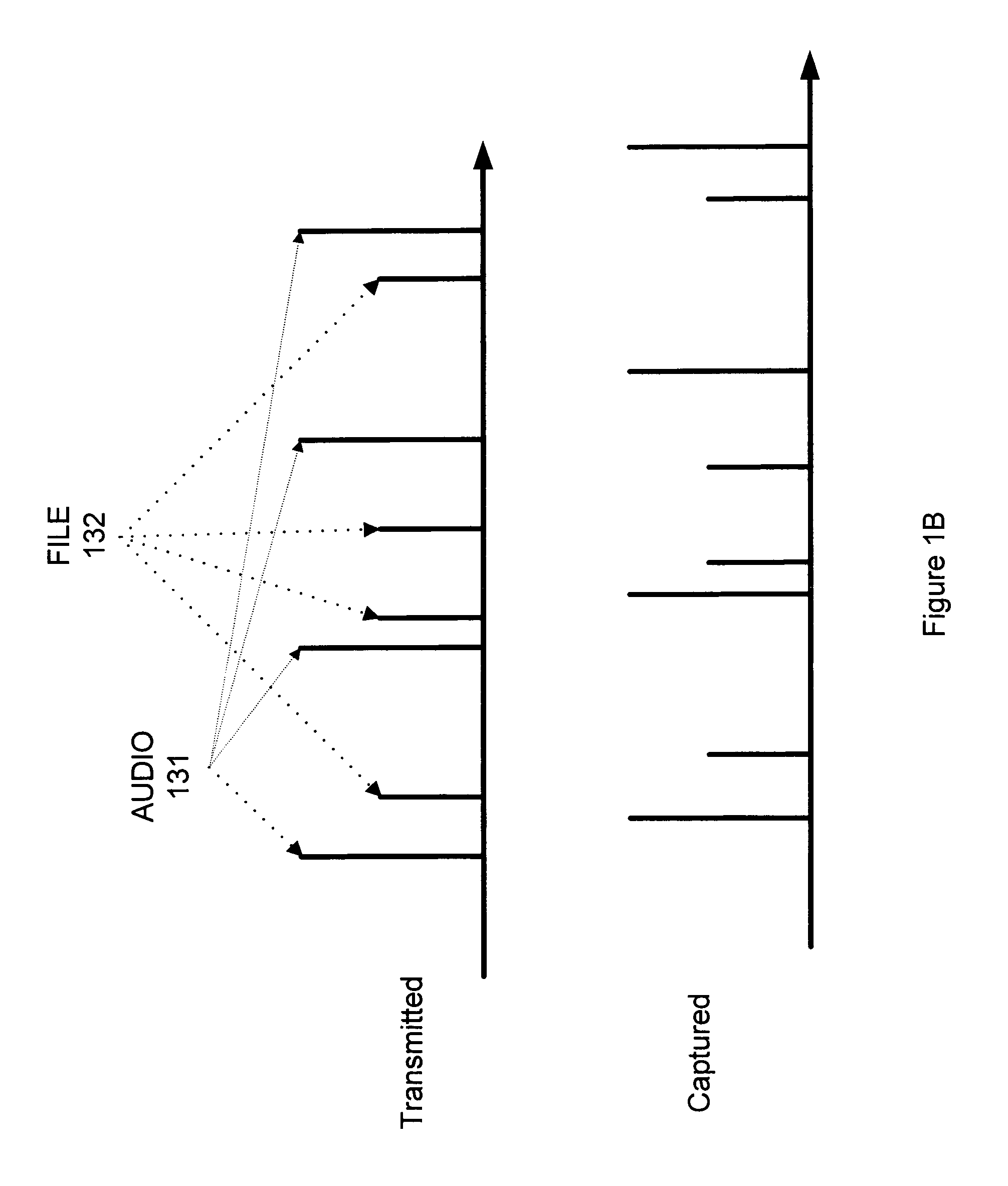
Method for real time network traffic classification
ActiveUS7684320B1Length minimizationEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTraffic capacityFeature vector
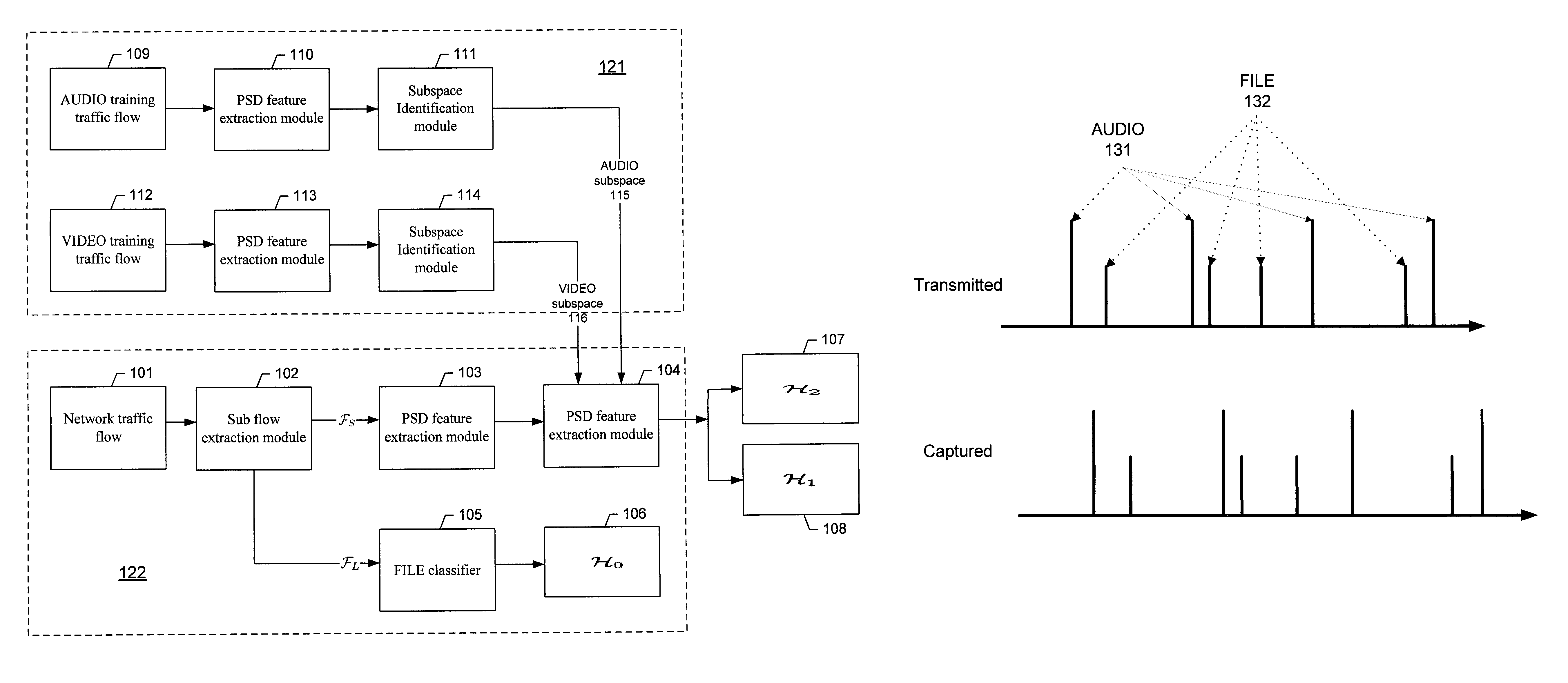
A method is provided to classify network traffic flows in real-time using spectral analysis techniques to extract regularities inside the network traffic flows. In one embodiment of the invention, subspace decomposition on power spectral density feature vectors and minimum coding length criterion are utilized for training traffic flows of different classifications. Experimental results are shown to demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the invention.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
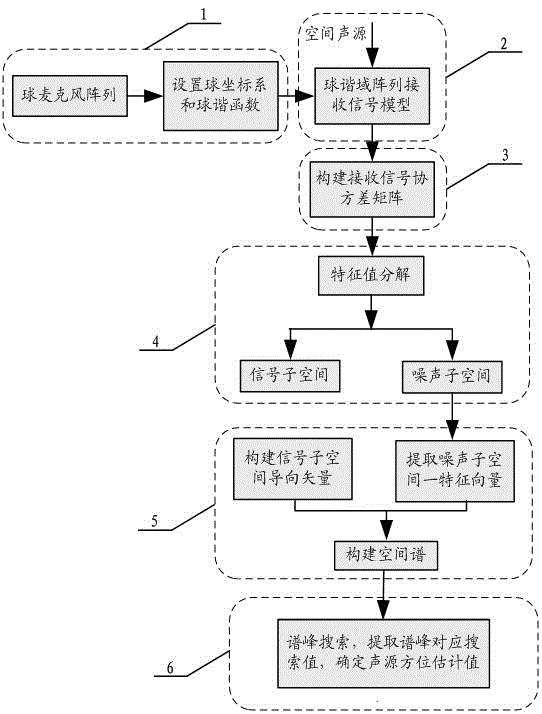
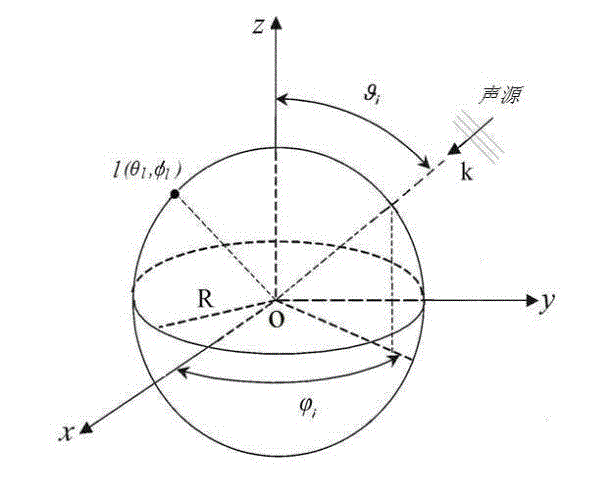
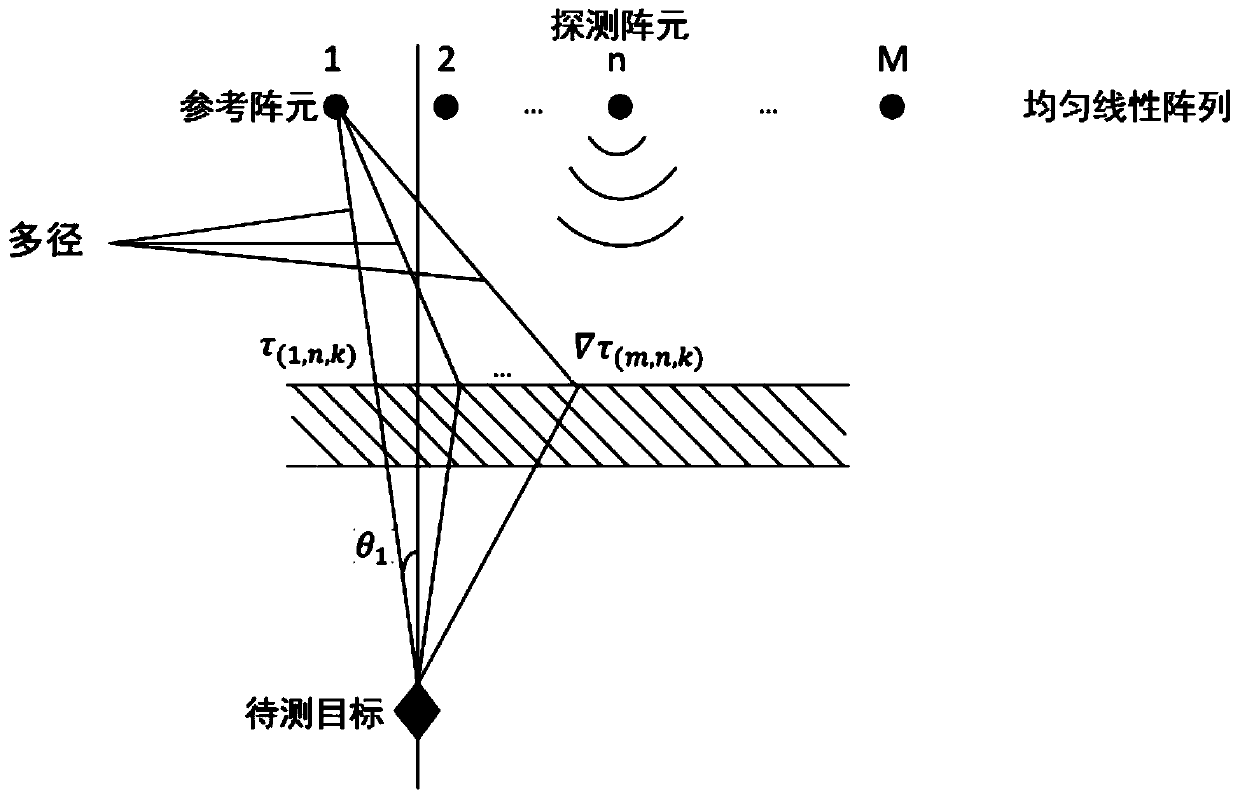
Multi-sound-source locating method based on spherical microphone array
The invention discloses a multi-sound-source locating method based on a spherical microphone array, and the method comprises the following steps of firstly conducting spherical harmonics decomposition for high-order sound fields collected by a spherical microphone array, and building a noise-contained sound source signal model received by a spherical harmonics domain array; then expressing a covariance matrix of data received by the array; classifying the covariance matrix according to a subspace decomposition method to obtain two mutually-orthogonal signal subspace and noise subspace; utilizing the orthogonality of the signal subspace and the noise subspace to define a guide vector of the signal subspace, and extracting one characteristic vector of the noise subspace to build a space azimuth spectrum; and finally searching a spectrum peak position of an azimuth spectrum function, and determining a space azimuth of a sound source. The method utilizes a three-dimensional space rotary symmetric structure of the spherical microphone array to adequately sample the sound field, so that the operation quantity is remarkably reduced through the high-resolution spectrum estimation and dimensional-reduced noise subspace, the sound source azimuth is accurately estimated, and the method can be widely applied to the fields such as a voice signal processing field.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
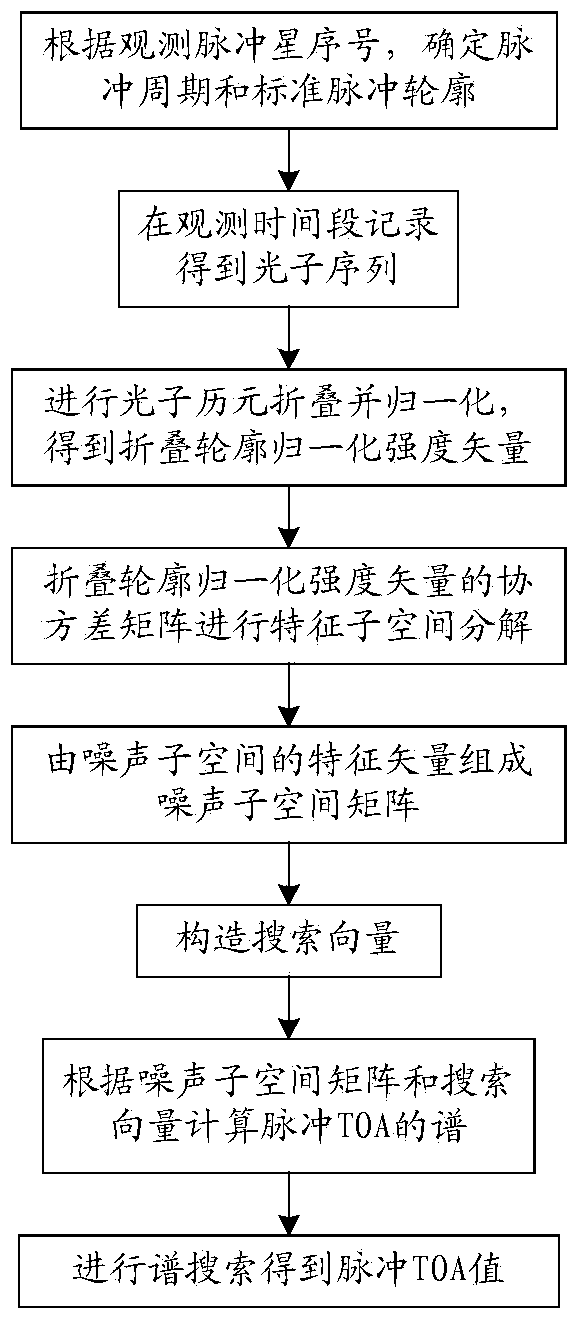
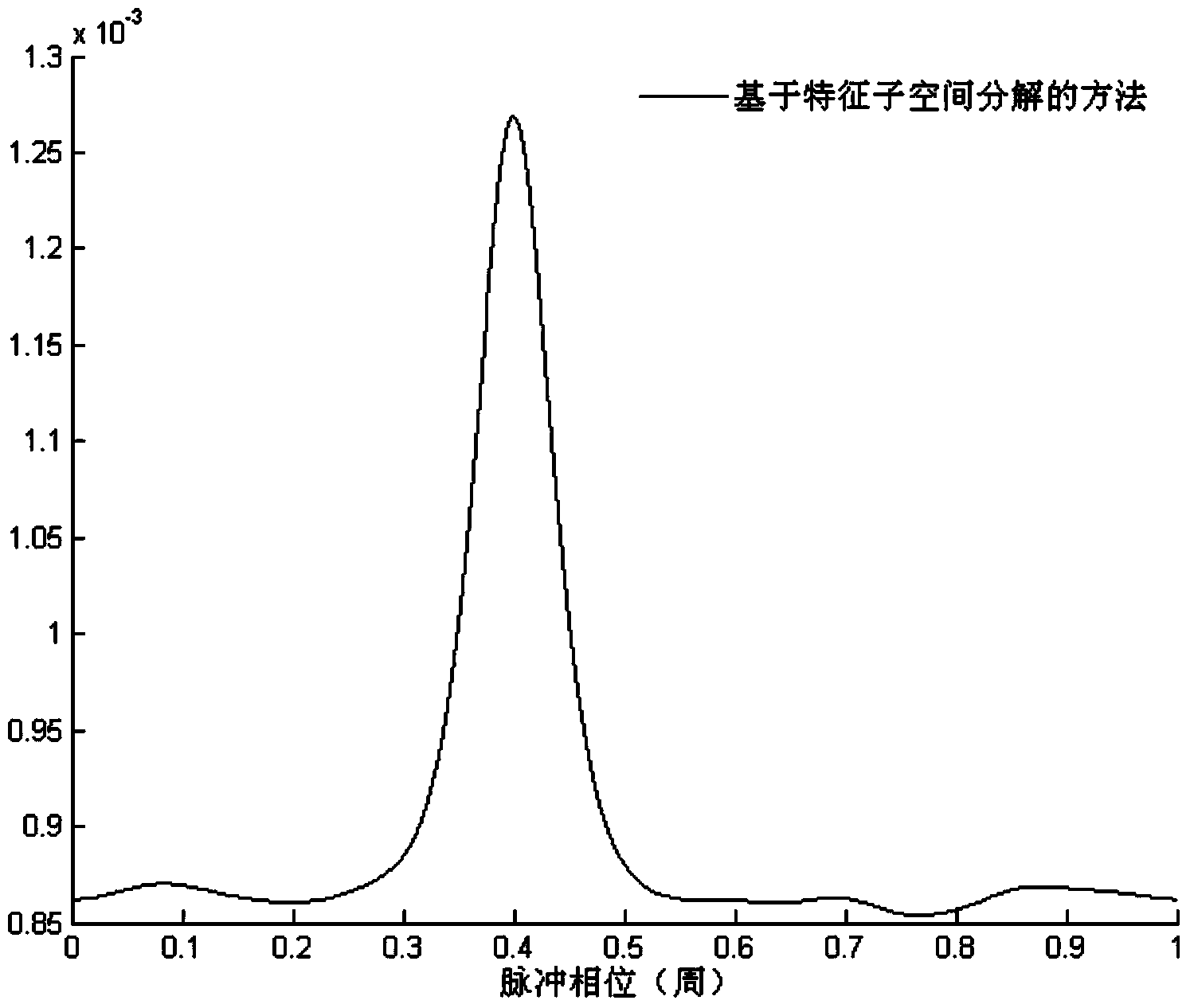
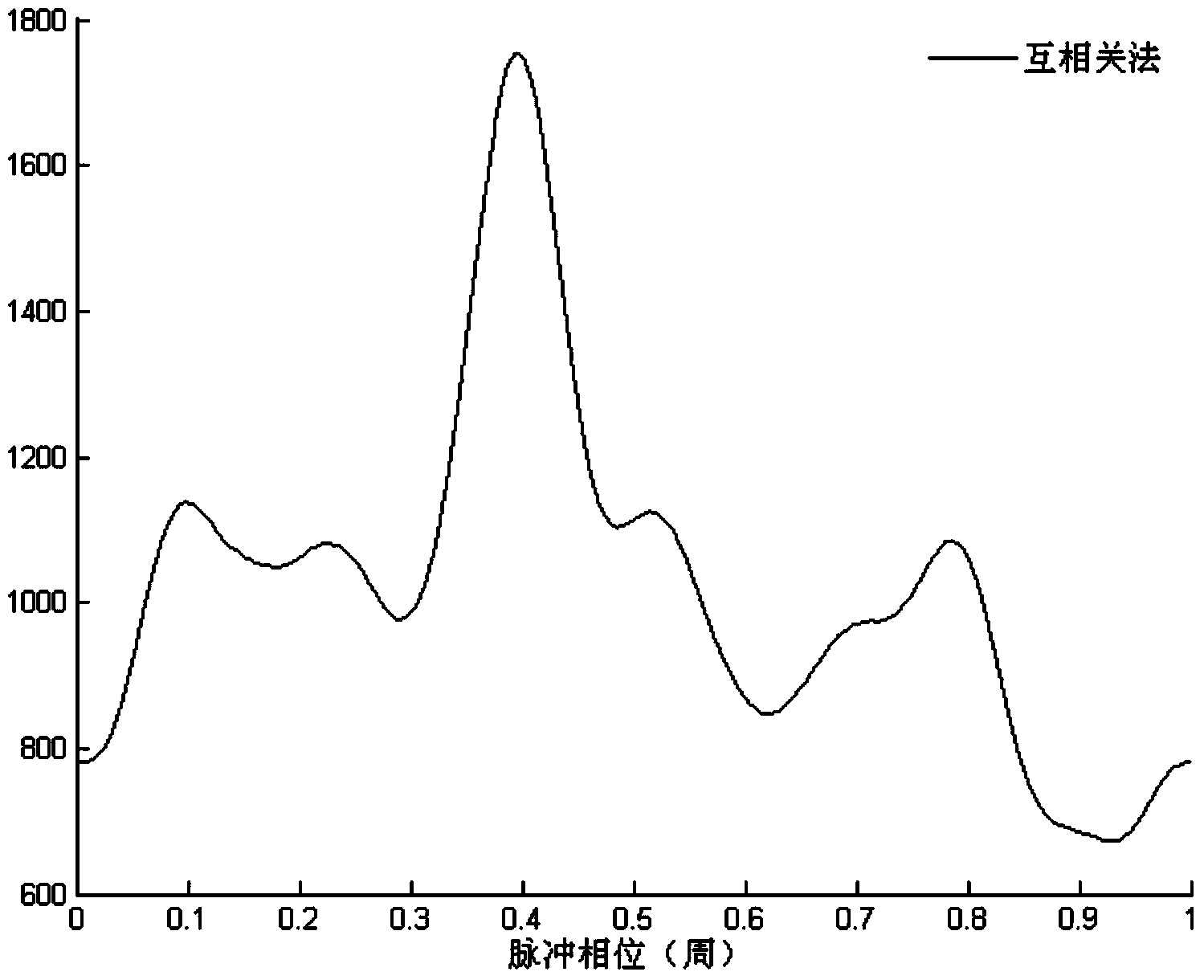
Determination method of pulse TOA of X-ray pulsar-based navigation
ActiveCN104296755AImprove the determination accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationSoft x rayX-ray
The invention relates to a determination method of pulse TOA of X-ray pulsar-based navigation. The method comprises the steps of firstly, performing pulse contour folding in a selected folding cycle according to a photon sequence obtained within the observation time, performing normalization so as to obtain a normalized intensity vector, then performing feature subspace decomposition on a covariance matrix of the normalized intensity vector, so as to obtain a noise subspace matrix, constructing a searching vector according to a standard pulse contour, then obtaining a spectrum of the pulse TOA from the noise subspace matrix and the searching vector, and searching a spectrum peak value of the spectrum of the pulse TOA, so as to obtain a value of the pulse TOA. According to the method, the pulse TOA is determined on the basis of the feature subspace decomposition, so that the calculation accuracy of the pulse TOA can be effectively increased, and the pulse contour folding is adopted, so that the approximation degree of a pulse contour estimated value and the standard pulse contour is increased, thereby increasing the calculation accuracy of the pulse TOA within the observation time.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method of virtual two-order array extension
InactiveCN107092007AEstimate performance impactImproved estimated resolution capabilitiesRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsComputation complexityWireless transmission
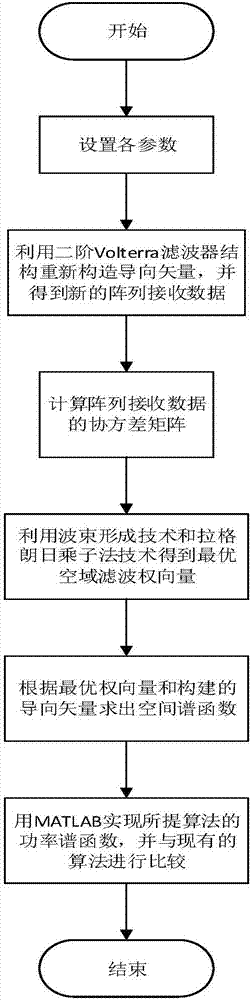
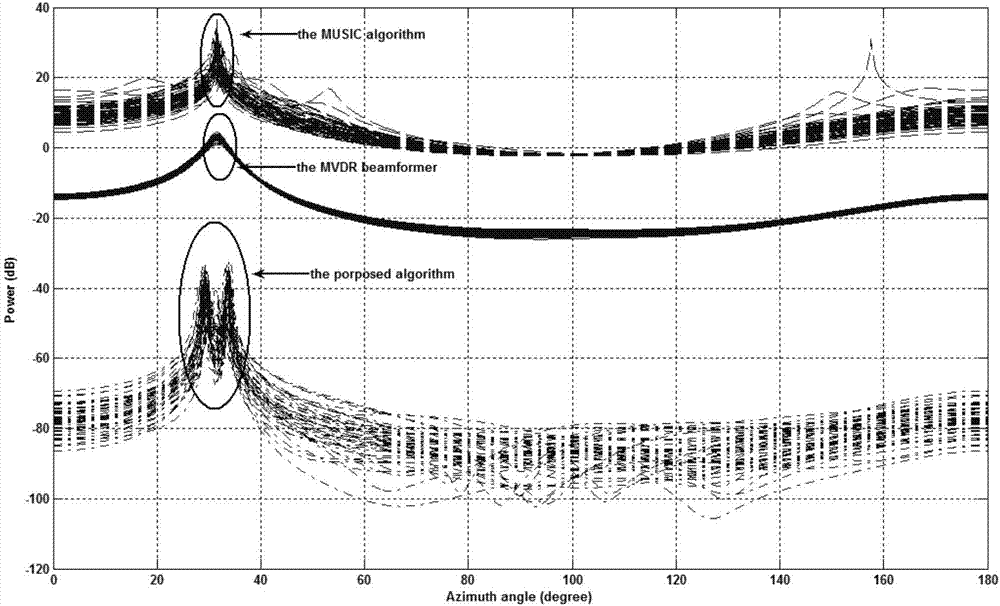
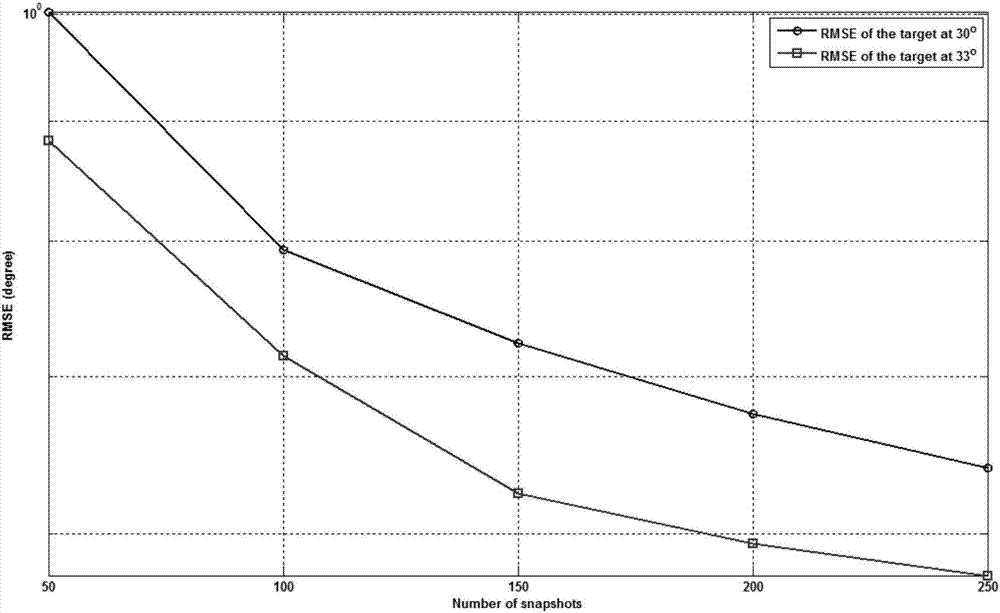
The invention discloses a direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method of virtual two-order array extension, belonging to the processing category of receiving an antenna array signal of a wireless transmission signal. In particular, the method is a method that a steering vector is constructed to be a virtual Volterra filter structure and the beamforming technology and the Lagrange multiplier method technology are combined to carry out direction of arrival (DOA) estimation. The steering vector is constructed to be the virtual Volterra filter structure and the beamforming technology and the Lagrange multiplier method technology are combined to carry out direction of arrival (DOA) estimation. According to the algorithm, the DOA estimation under the condition of an unknown number of signal sources can be realized and does not rely on subspace decomposition. The influence of the wrong estimation of the number of the signal sources on the performance of DOA estimation is avoided, the DOA estimation resolution ability is improved, and the computational complexity is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
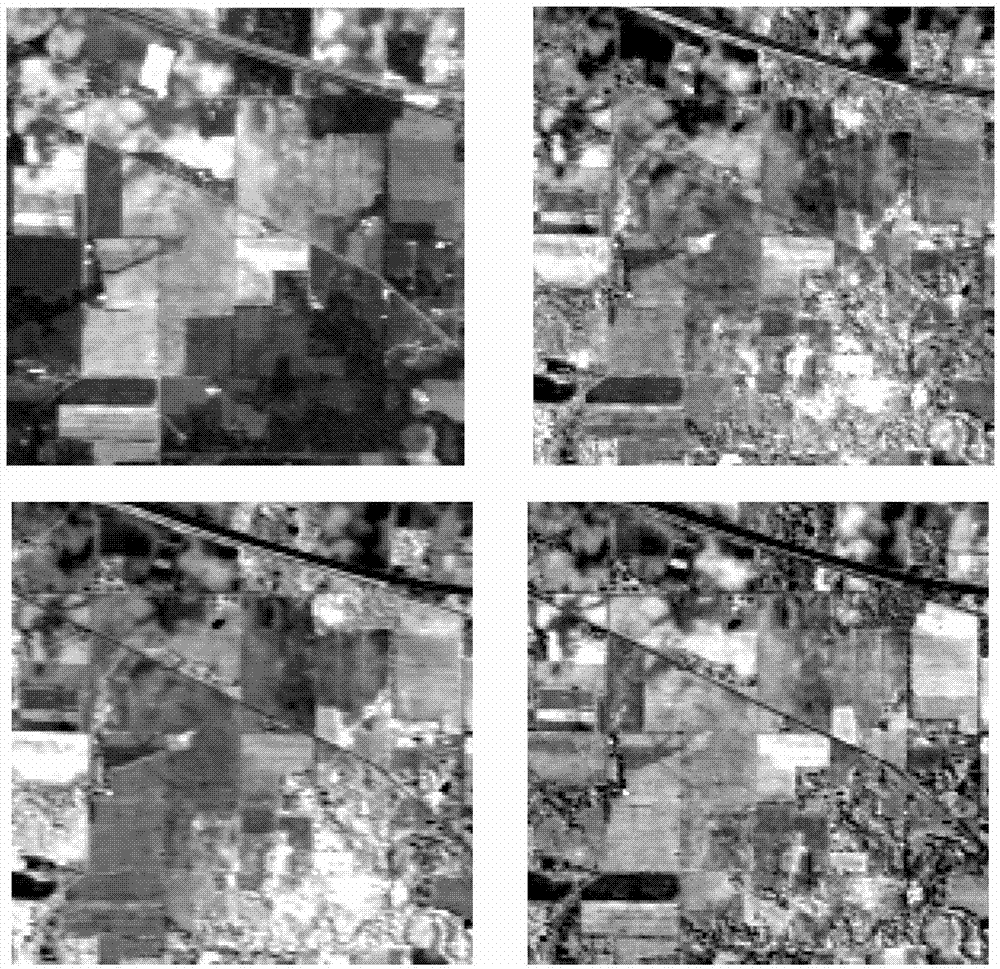
Intelligent classification method for high-spectrum remote sensing image
ActiveCN103366189AShorten operation timeImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineCombined method
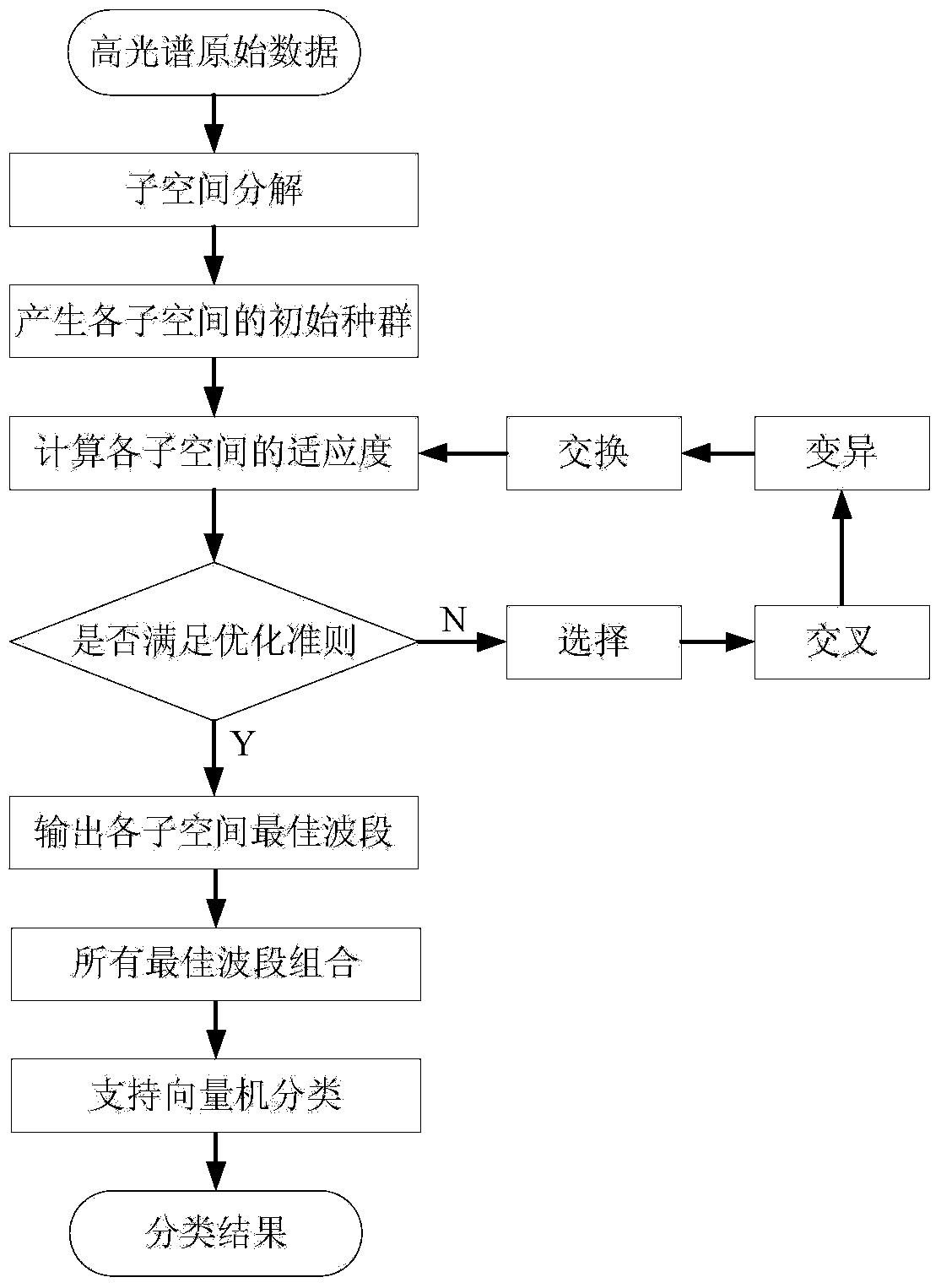
The invention discloses an intelligent classification method for a high-spectrum remote sensing image. The intelligent classification method for the high-spectrum remote sensing image comprises the following steps of: carrying out subspace decomposition on the high-spectrum image; then, selecting a proper waveband with a combined method of a simulated annealing algorithm and a genetic algorithm in each subspace; combining all wavebands selected by the subspaces; and finally, carrying out SVM (support vector machine) classification on all pieces of waveband information subjected to comprehensive dimension reduction.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
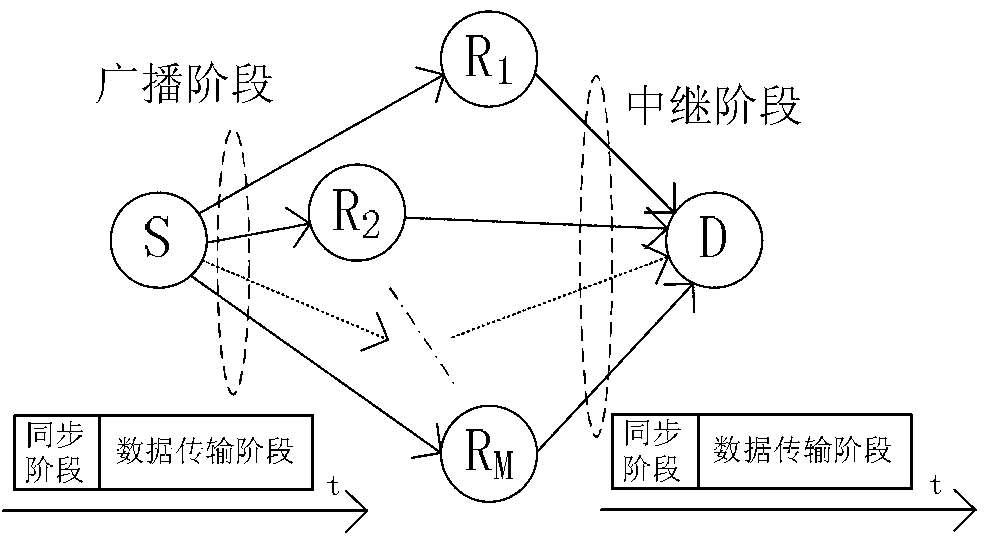
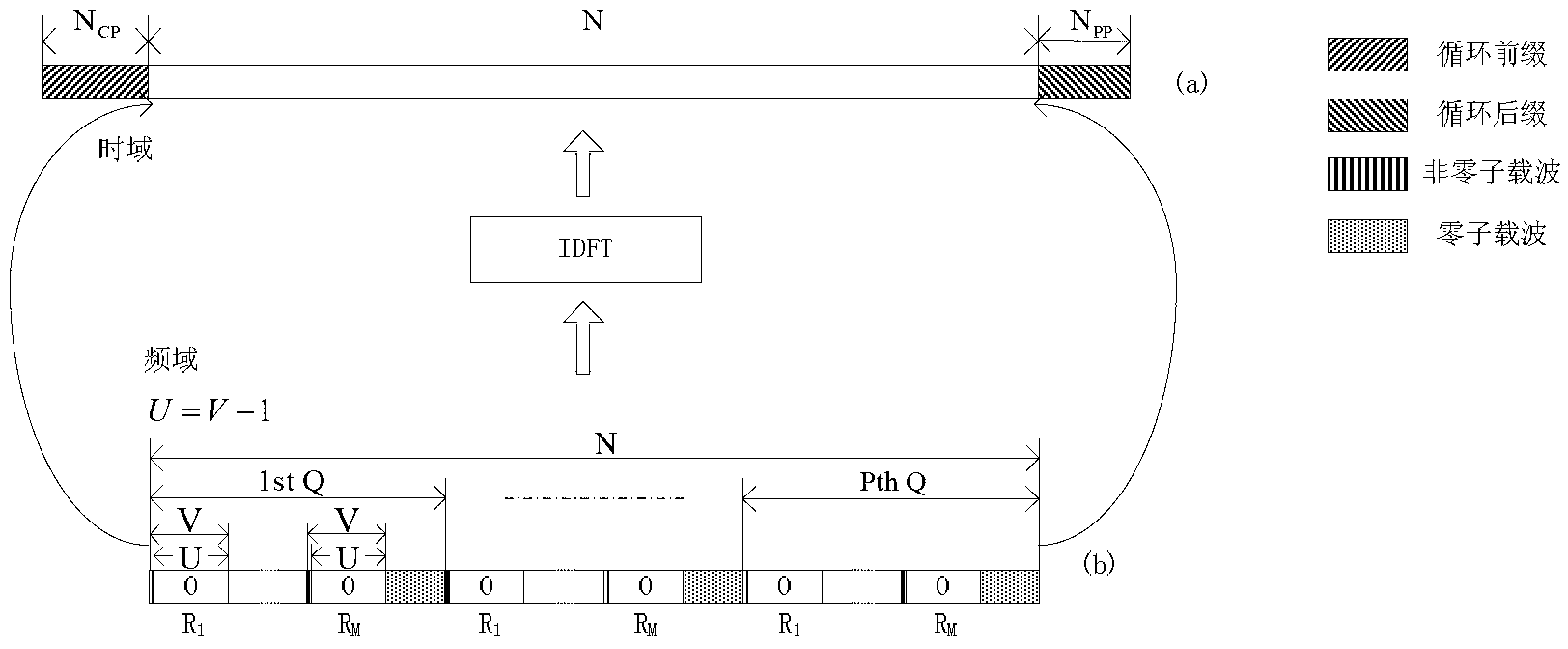
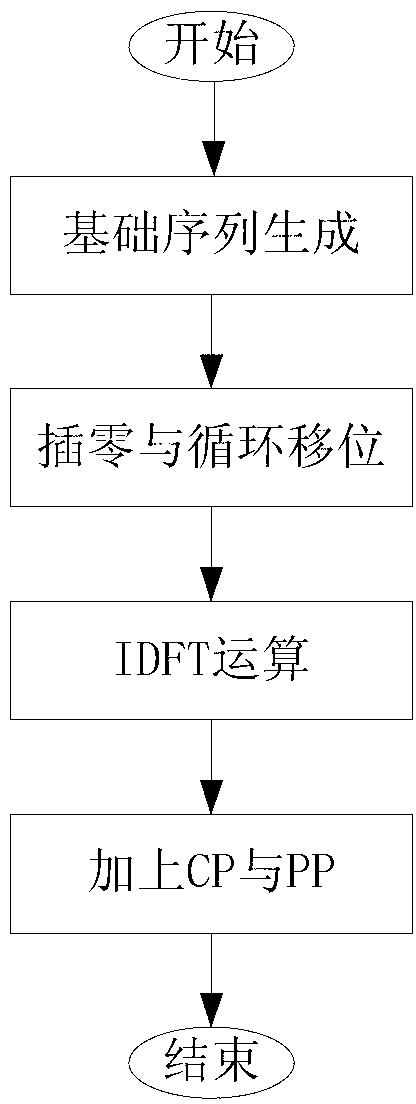
Synchronization sequence construction method in super cellular mobile communication device-to-device technology
ActiveCN102938754AReduce complexityImprove estimation performanceMulti-frequency code systemsComputation complexityCyclic prefix
The invention discloses a synchronization sequence construction method in the super cellular mobile communication device-to-device technology, wherein the frequency domain synchronization sequences corresponding to each relay terminal node are all composed of periodic subcarrier groups, each subcarrier group comprises one non-zero subcarrier, and other subcarriers are all zero subcarriers. In the synchronization sequence constructed according to the method provided by the invention, a cyclic prefix is in the front of the sequence and a cyclic postfix is in the back of the sequence, influence of multi-path delay and timing difference of different trunk links on the performance of the synchronization algorithm is avoided, a cross-correlation operation and the corresponding weighted averaging can be performed for a receiving sequence and a transmitting sequence so as to get the timing estimation, and the frequency offset estimation is obtained by a subspace decomposition method. The method provided by the invention effectively solves the problem of multiple time bias and multiple frequency offset specially existing in a cooperative device-to-device scene in the cellular / super cellular mobile communication system, and is low in computation complexity, excellent in estimation performance and capable of effectively avoiding occurrence of abnormal value of frequency offset estimation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
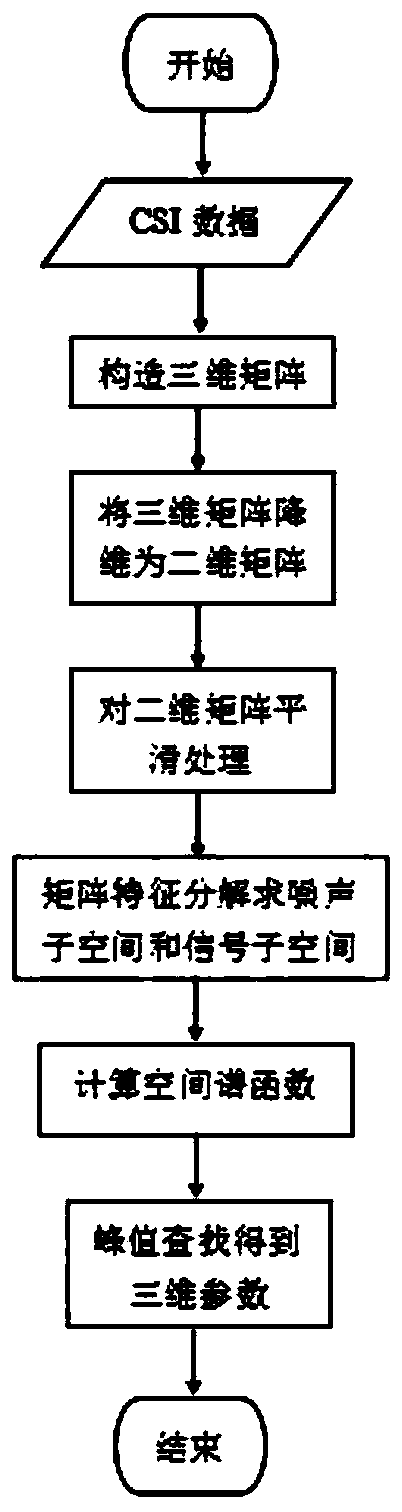
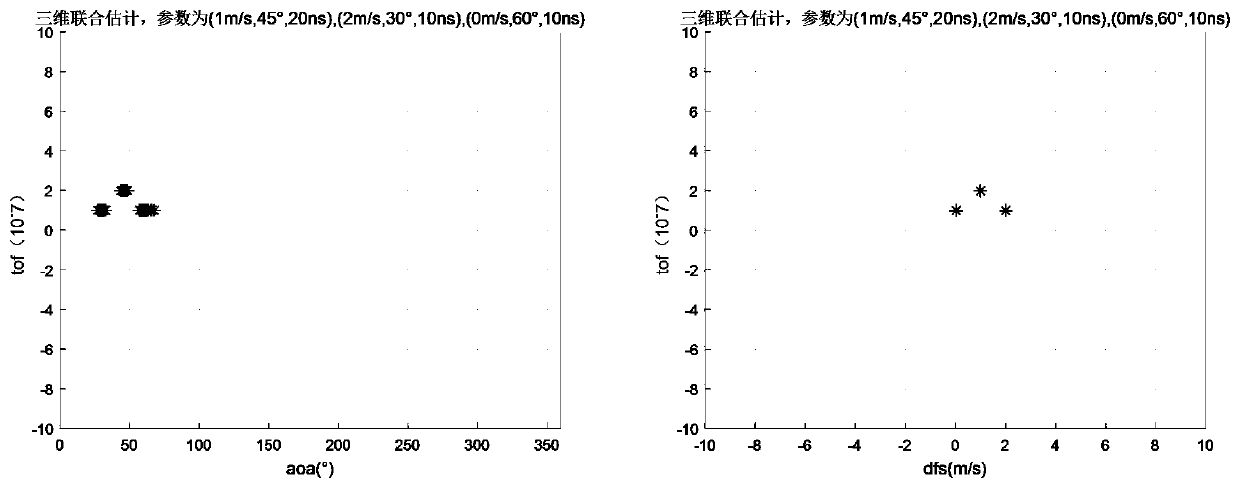
Three-dimensional joint estimation method based on Wi-Fi channel state information
ActiveCN109738861AGuaranteed irrelevanceImprove Joint Estimation AccuracyPosition fixationDecompositionSignal subspace
The invention provides a three-dimensional joint estimation method based on Wi-Fi channel state information (CSI). Firstly, in order to overcome the limitation of the number of antennas and the channel bandwidth to a two-dimensional joint estimation model, the obtained channel state information forms a three-dimensional matrix from three dimensions of subcarriers, the antennas and data packets; secondly, dimensional reduction processing is performed on the three-dimensional matrix, and smooth processing between the subcarriers, the antennas and the data packets is performed on the basis; and finally, signal subspace decomposition and noise subspace decomposition are performed on the smoothed matrix to construct a spectral function. Based on the spectral function, three-dimensional joint search of an angle of arrival (AoA), time of flight (ToF) and doppler frequency shift (DFS) is performed. A designed three-dimensional joint estimation algorithm can still achieve high estimation precision under the conditions of a small number of antennas and a narrow channel bandwidth, and provides a theoretical basis for application such as accurate indoor tracking and positioning.
Owner:重庆派明科技有限公司
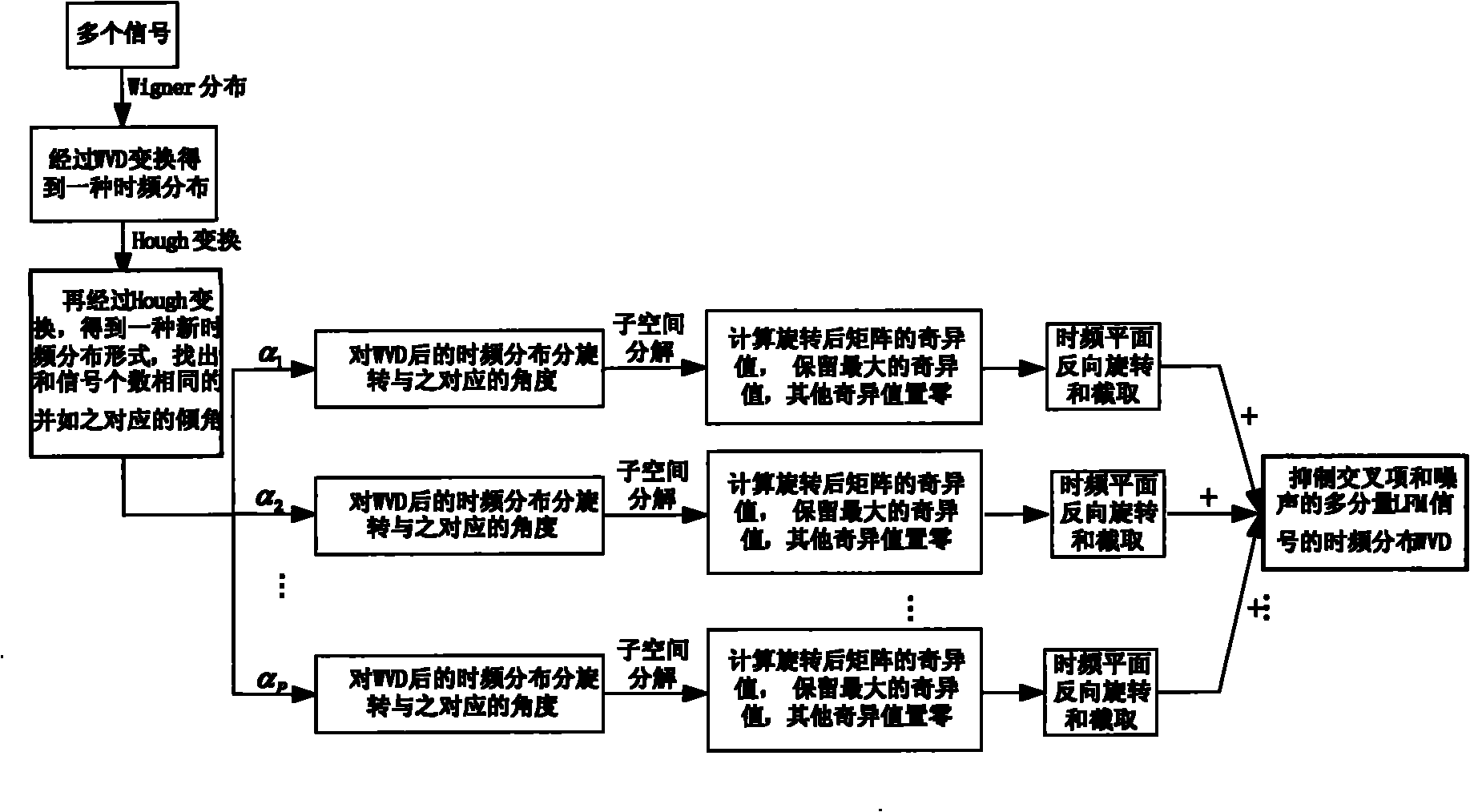
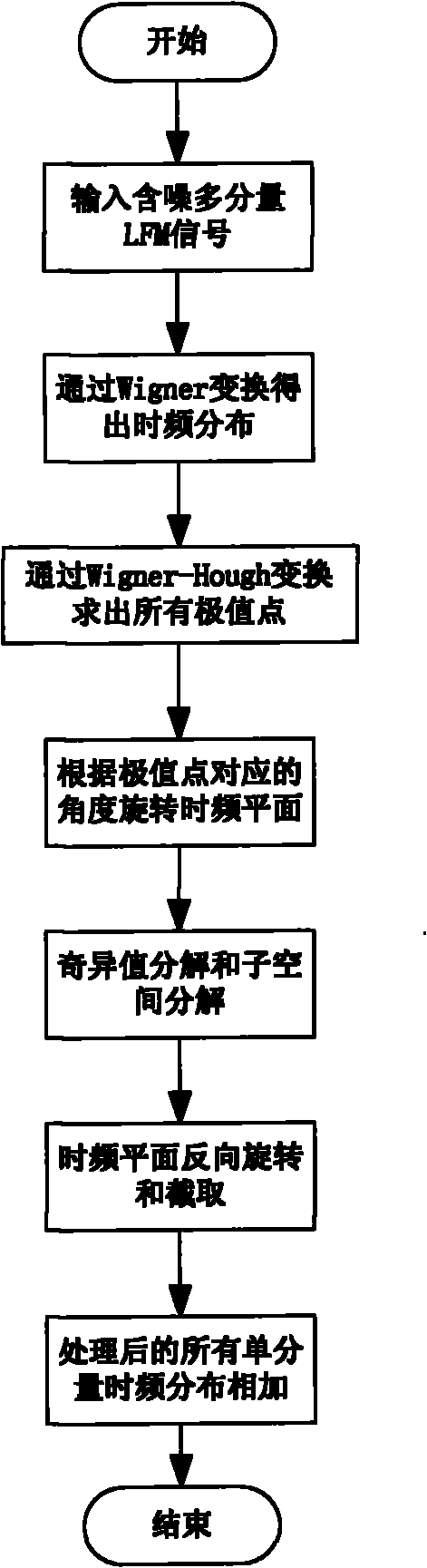
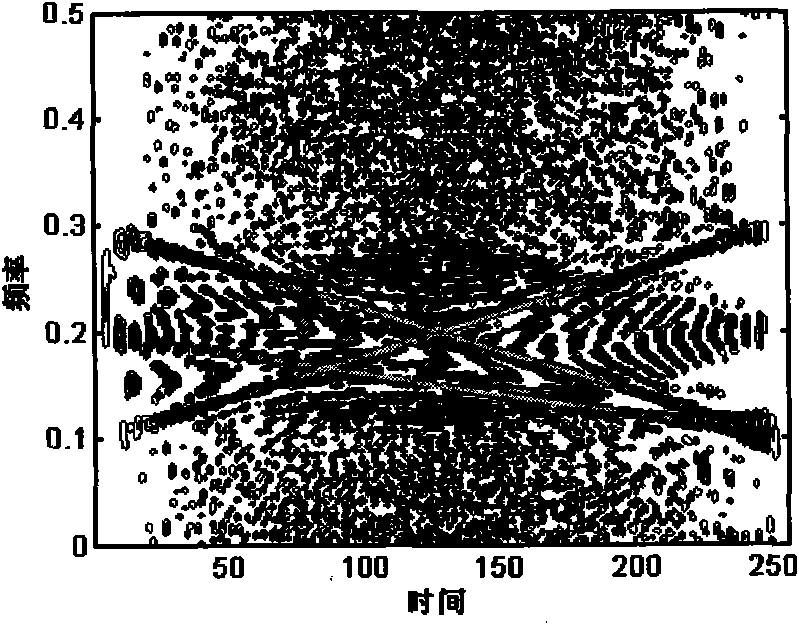
Method for inhibiting cross terms in time-frequency division of multi-component linear frequency modulation (LFM) signals
ActiveCN102158443APreserve time-frequency characteristicsAvoid the effects of cross termsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSingular value decompositionSignal subspace
The invention discloses a method for inhibiting cross terms in the time-frequency distribution of multi-component linear frequency modulation (LFM) signals based on subspace decomposition, which belongs to the technical field of signal processing. In the method, a time-frequency distribution matrix comprising noises and the cross terms is decomposed into signal subspaces and noise subspaces by utilizing singular value decomposition (SVD)-based subspace decomposition. For the problem that the linear modulation signals occupy relatively more bandwidths to make singular values are reduced at relatively lower rates and cannot be separated from the noises effectively, an angle of inclination of the time-frequency distribution of the signals can be obtained by utilizing Wigner-Hough transform. The time-frequency distribution of the signals is rotated according to the obtained angle so as to be parallel to a time base. The method is characterized in that: the singular values are rapidly decreased to zero, and then the signal sub-spaces can be separated effectively. By the method, the cross terms and the noises in the time-frequency distribution of the multi-component LFM signals are inhibited without reducing time-frequency resolution; therefore, the method is vast in application prospect.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
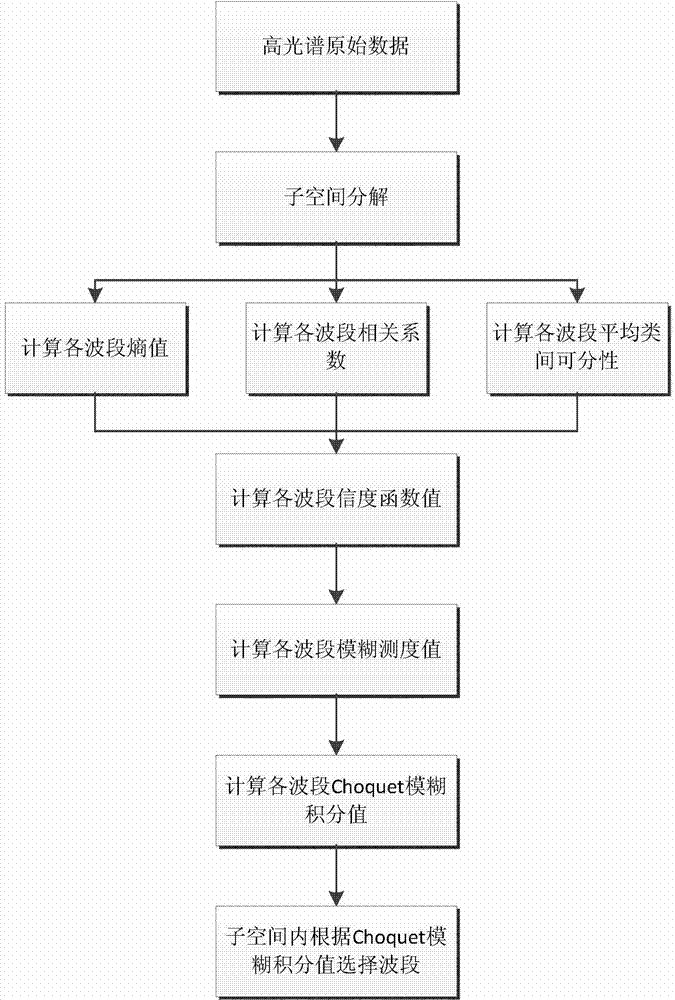
Multi-index fused hyperspectral remote sensing image dimensionality reduction method
InactiveCN103886334AAvoid lossReasonable distributionCharacter and pattern recognitionCorrelation coefficientComputer science
The invention discloses a multi-index fused hyperspectral remote sensing image dimensionality reduction method. Dimensionality reduction can be efficiently and rapidly achieved through a band selection method. At first, subspace decomposition is carried out on obtained hyperspectral remote sensing images, the entropy and the standard distance between mean values of a band and correlation coefficients between bands are fused by means of a method based on Choquet fuzzy integral in each subspace, and then band selection is carried out according to unified indexes to achieve data dimension reduction.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
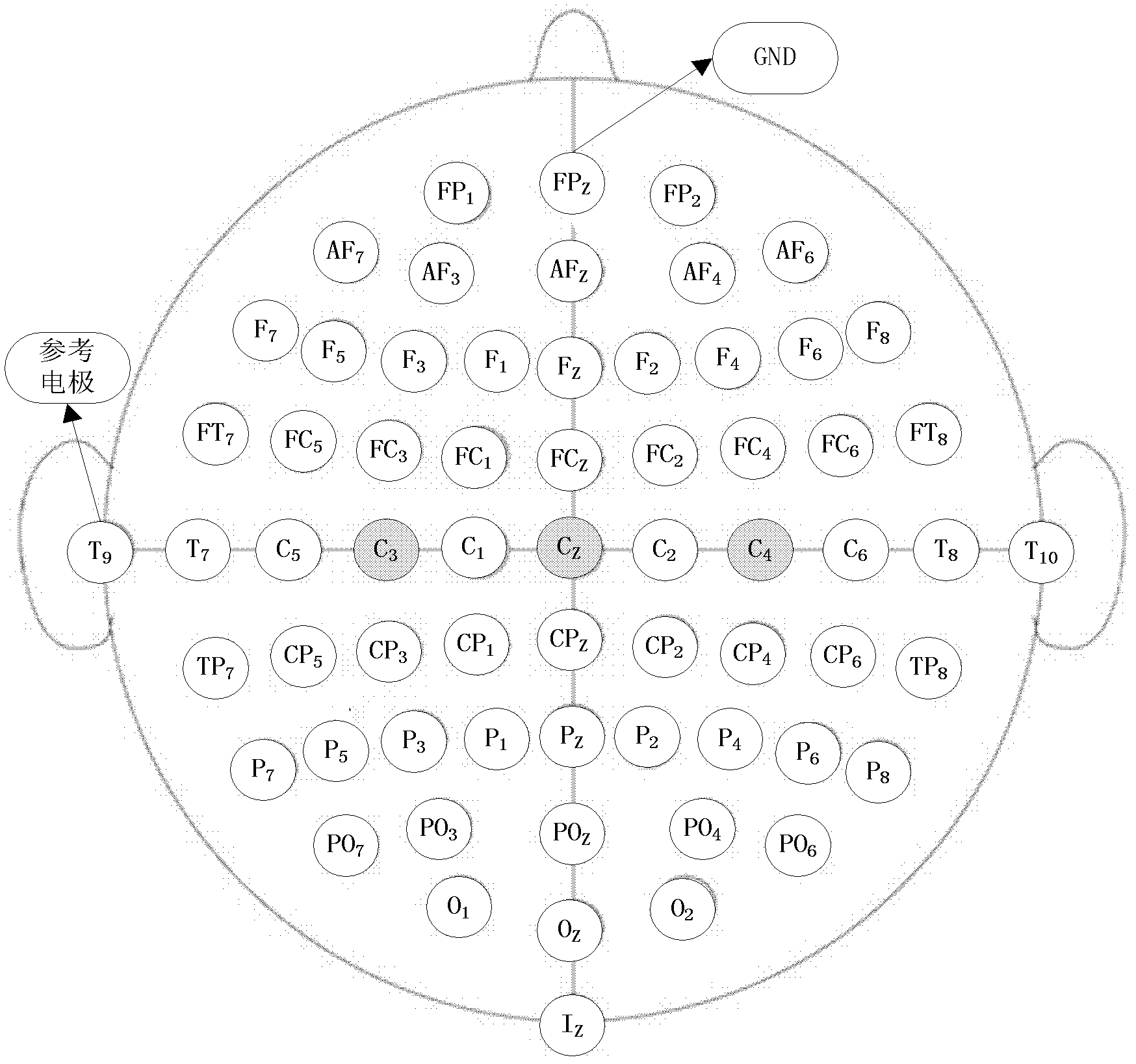
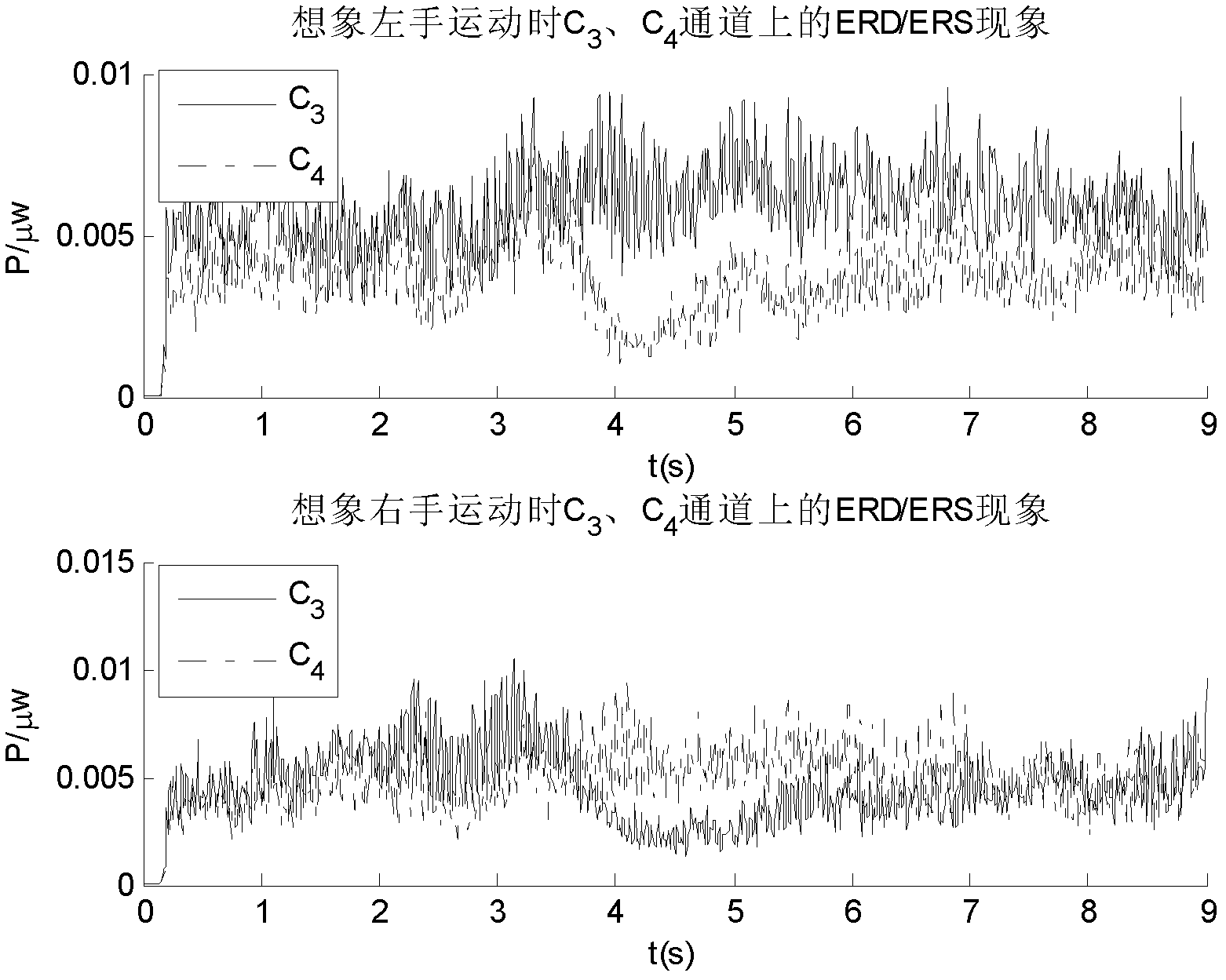
Electroencephalography signal characteristic extraction method based on small training samples
InactiveCN102306303AEasy to useImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSmall sampleBrain computer interfacing
The invention relates to a characteristic extraction method of imagining action potential in a BCI (Brain-Computer Interface) device and particularly relates to a characteristic extraction method combining a regularization method and a CSSD (Common Special Subspace Decomposition) algorithm. In the method provided by the invention, regularization parameters are led; a covariance matrix of training data of a target experimenter and a covariance matrix of training data of an auxiliary experimenter are combined to form a regularization covariance matrix under the action of the regularization parameters; a regularization space filter is constructed; and characteristic analysis is carried out on the test data of the target experimenter by utilizing the regularization space filter. By using the method in the invention, the problems that characteristic value is unstable, classification accuracy rate is low and the like in the CSSD algorithm are solved when a small-sample problem is processed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
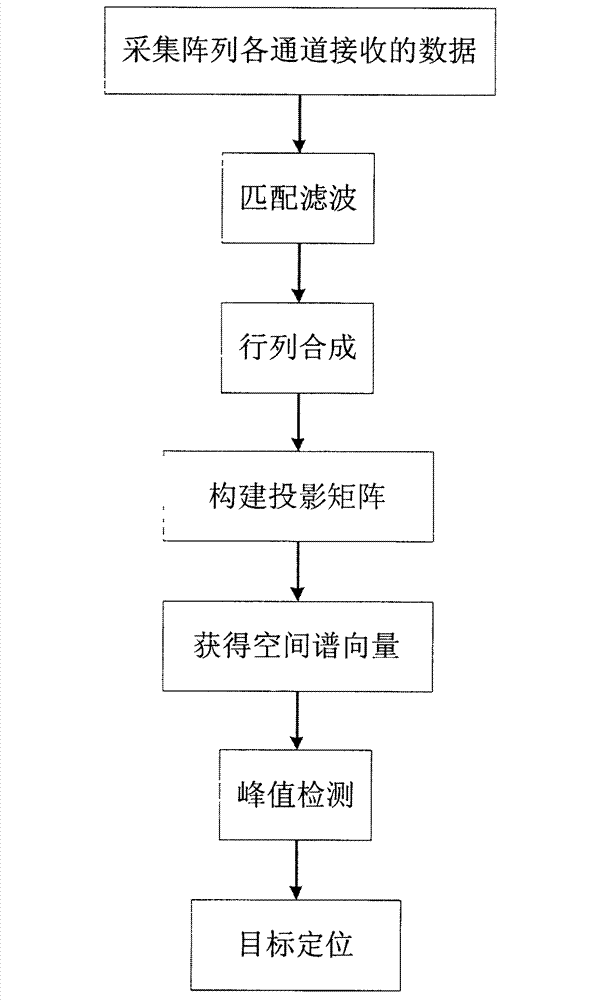
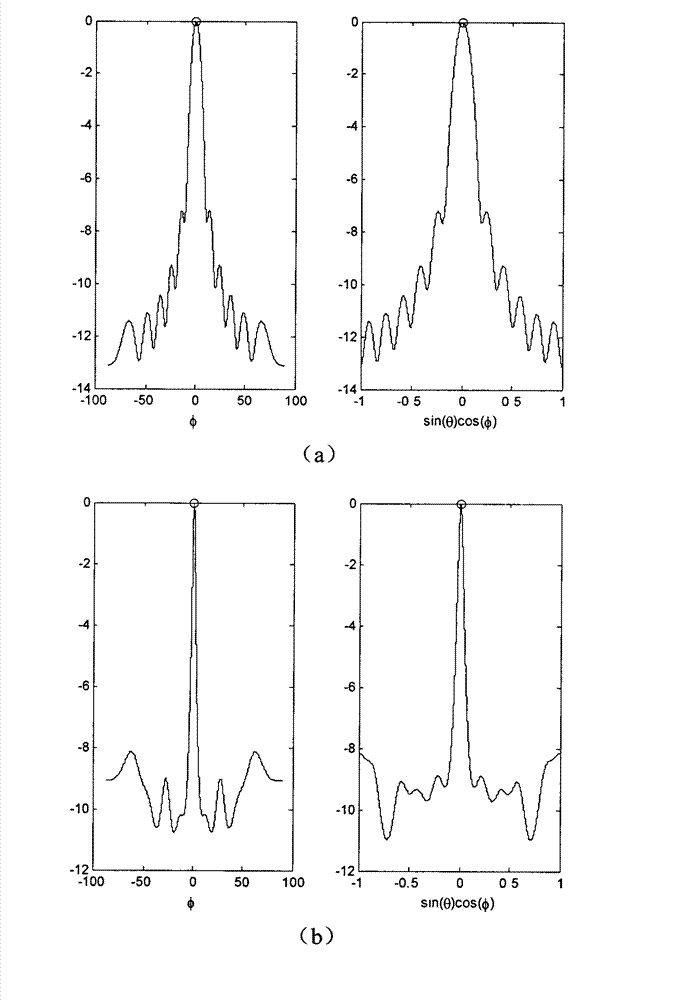
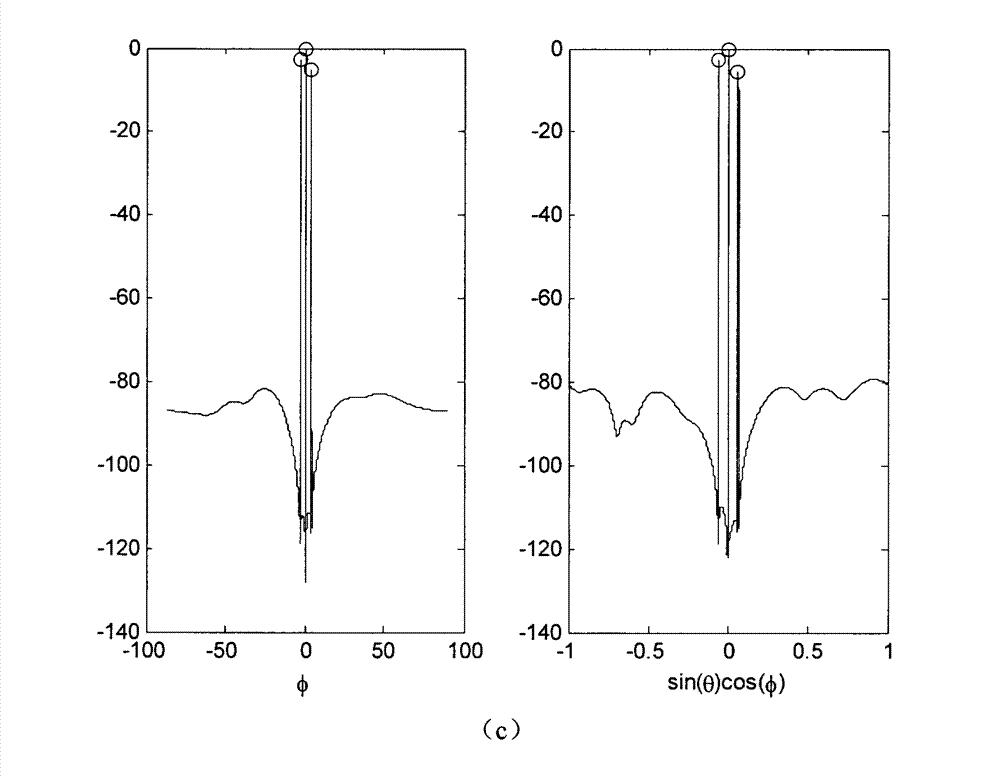
High-resolution sonar location method based on sparsity of objective space
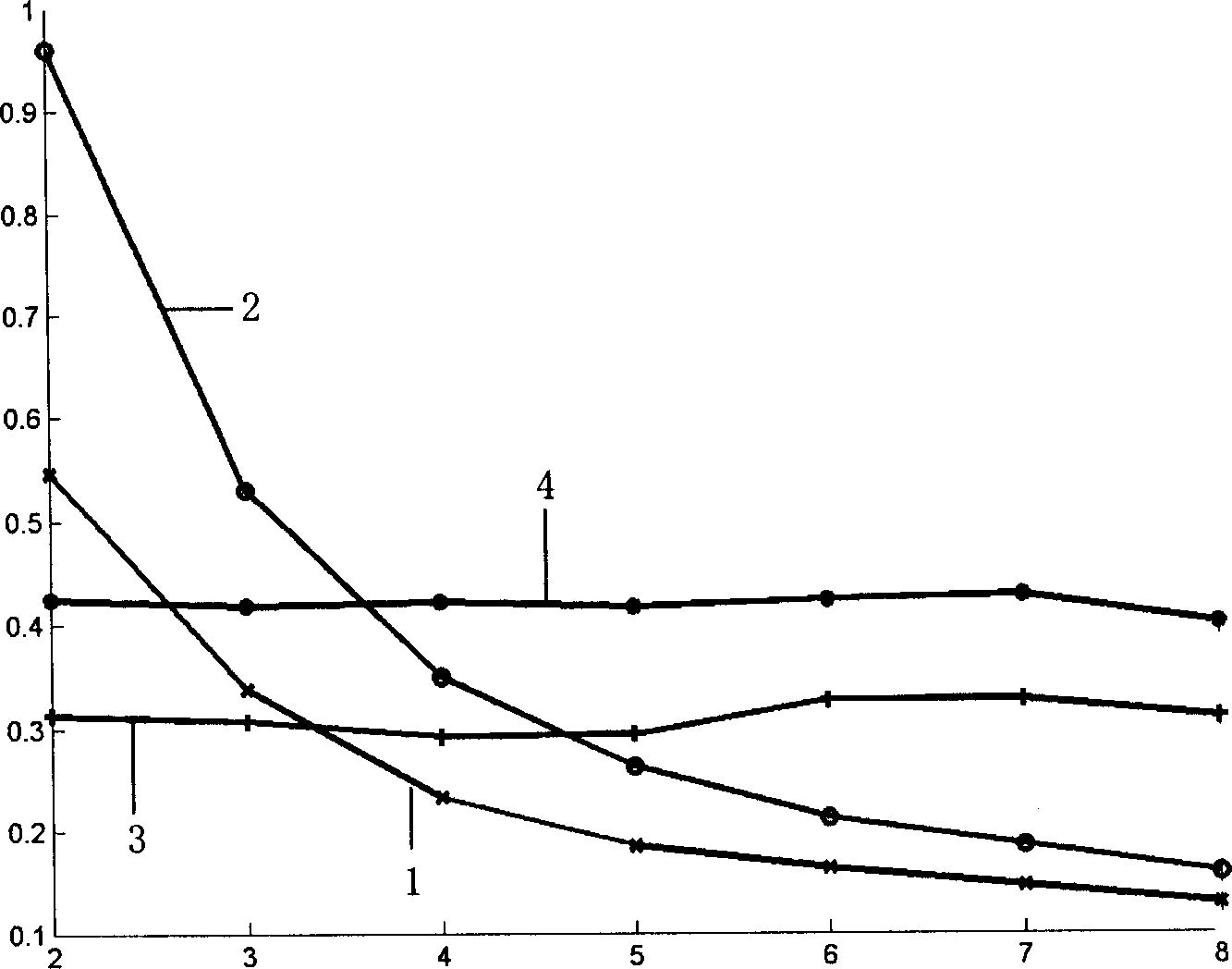
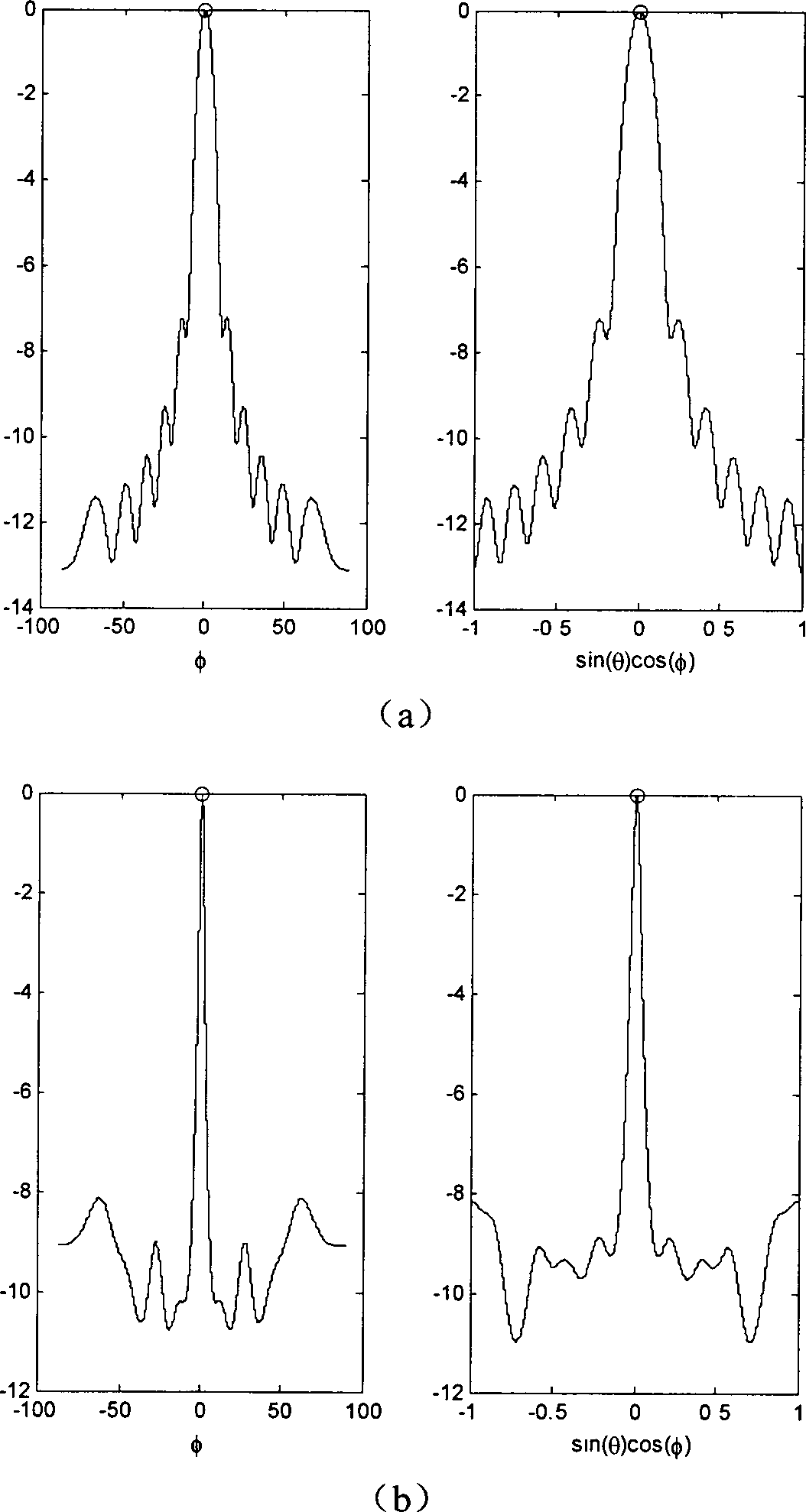
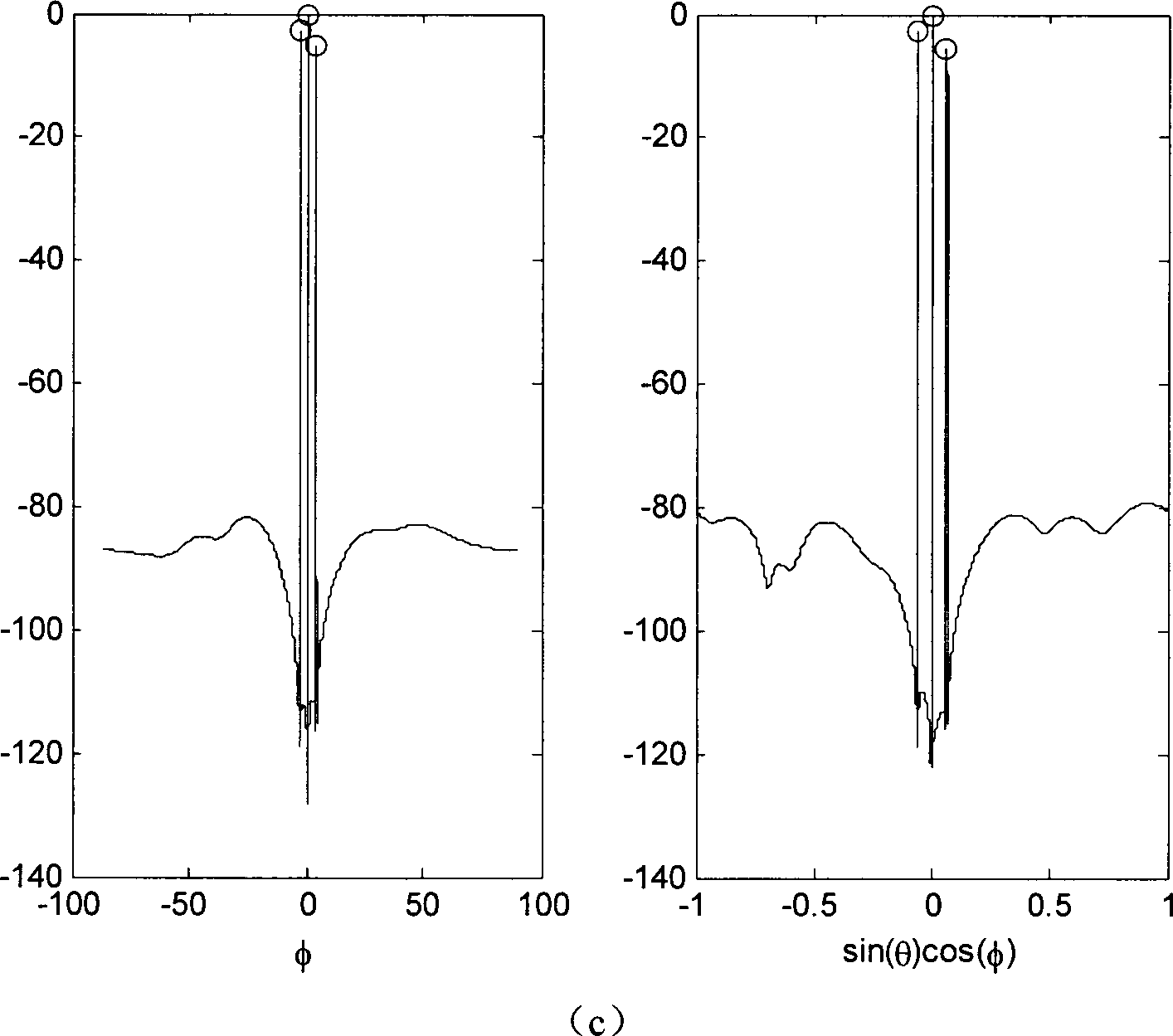
InactiveCN103116162AAchieve simultaneous positioningOvercoming dependenciesAcoustic wave reradiationHat matrixPeak value
The invention discloses a high-resolution sonar location method based on a sparsity of an objective space and mainly solves the problems that a limited array aperture causes insufficient spatial resolution and a signal source coherence causes an inaccurate estimation of an objective location and calculating work of subspace decomposition and data volume are considerable in the prior art. According to the method, a projection matrix which is from a spatial spectrum vector quantity to a ranks synthesis data vector is constructed. By taking advantage of the apriori information of the sparsity of the space target and obtaining data of large signal to noise ratio through a matched filtering, the spatial spectrum vector quantity is carried out with peak detection through an iterative computation to obtain the high-resolution spatial spectrum vector quantity. The objective location can be achieved by taking advantage of the received index value of a peak element through the calculation to gain an objective azimuth angle and an objective pitch angle. The location method has the advantages of being low in the needed data size and calculated amount in the iterative process, suitable for a hardware implementation, high in angular accuracy and improving markedly the spatial resolution.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
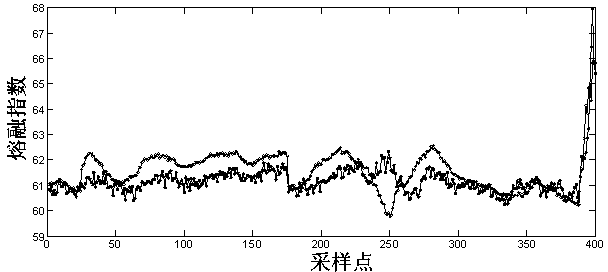
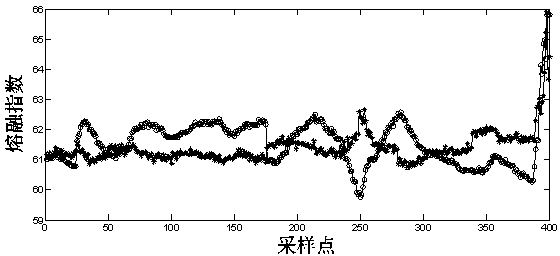
Melt index online detection method based on subspace independent component regression model
InactiveCN103390103ARealize online estimationImprove soft sensor accuracySpecial data processing applicationsData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a melt index online detection method based on a subspace independent component regression model. The melt index online detection comprises the following steps of firstly selecting key variables influencing the variation of melt indexes as input variables, and utilizing values of the melt indexes obtained through laboratory analysis as output variables; by utilizing a subspace decomposition algorithm, based on variable contribution degree indexes, dividing modeling dataset into a plurality of subspaces, and respectively establishing an independent component regression analysis model for each subspace dataset; and integrating and synthesizing information of different sub models to realize online soft measurement of the melt indexes in a polypropylene production process. Compared with the traditional independent component regression analysis method, the melt index online detection method based on the subspace independent component regression model, which is disclosed by the invention, can improve the soft measurement estimation precision of the melt indexes in the polypropylene production process, and also improve the robustness of a soft measurement model.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
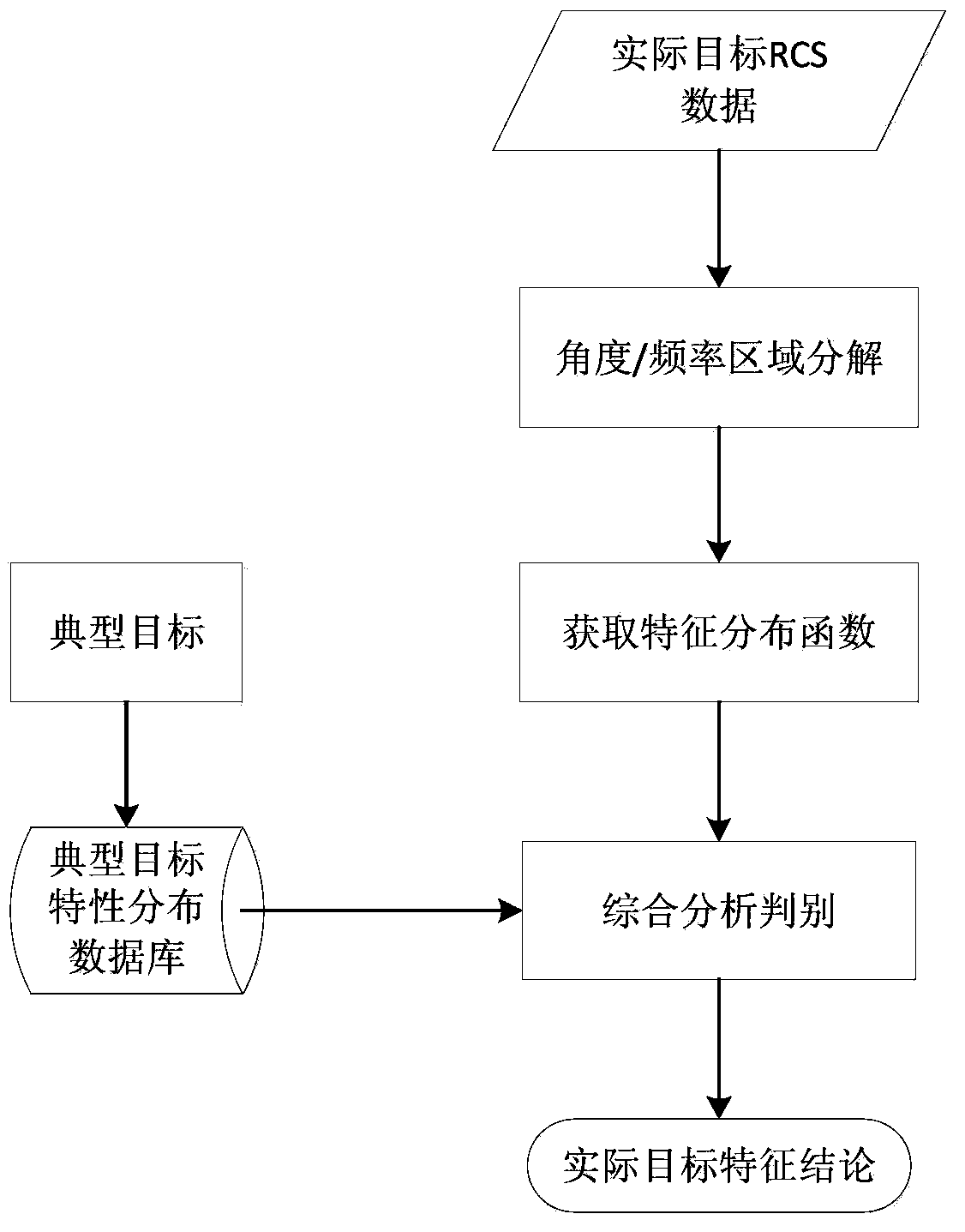
A method for rapidly extracting RCS information in a wide angle range of a target
ActiveCN103675782AStrong anti-noise abilityAdaptableWave based measurement systemsReference databaseElectrical field strength
The invention belongs to the technical field of signal characteristic control and specifically relates to a method for rapidly extracting RCS information in a wide angle range of a target. The method comprises following steps of: measuring backscattering cross sections of different incidence angles of a typical target in order to obtain a statistical distribution function of the scattering electric field intensity of the typical target; establishing a typical structural scattering database in combination with common typical target and structural characteristic distribution on that basis, wherein the typical structural scattering database is to be used as a reference database; inputting a wide-angle range RCS data to be analyzed of a real target; performing angle / frequency subspace decomposition on RCS data inputted in the step 2 according to a real operating bandwidth of a certain kind of radar and a possibly-generated observation angle variation range of an aircraft; obtaining a characteristic distribution function of a certain subspace of the real target decomposed in the step 3; and achieving rapid determination of a target type or a main scattering characteristic according to the typical target characteristic database established in the step 1 and the characteristic distribution function of the certain subspace of the real target obtained in the step 4.
Owner:中国航天科工集团第二研究院二〇七所
Single vector hydrophone based measurement method for acoustic reflection coefficient of large-sample underwater acoustic material
ActiveCN109001297AEfficient separationEfficient extractionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidSound sourcesCore component
The invention provides a single vector hydrophone based measurement method for acoustic reflection coefficient of a large-sample underwater acoustic material. The method mainly comprises the followingsteps: (1) eliminating diffraction sound at the edge of a sample; (2) constructing a signal processing model; (3) separating direct sound from reflected sound; (4) obtaining the acoustic reflection coefficient. On the one hand, broadband narrow pulse is adopted as a form of a transmission signal, time-frequency characteristics of the signal are easy to control, the diffraction sound at the edge of the sample can be separated in time, and the influence of the diffraction sound can be avoided; on the other hand, a single vector hydrophone is regarded as a three-element receiving array, and an array signal processing algorithm of subspace decomposition is adopted for processing measurement data, data processing is convenient and fast, and better real-time property is achieved; besides, a conventional sound source and a vector hydrophone are used as core components of measurement, a traditional large-scale transmitting and receiving matrix is not needed, a huge and complicated measurementsystem is saved, few test steps are taken, and the acoustic reflection coefficient of a concerned frequency band can be obtained by one transmission, so that measurement efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
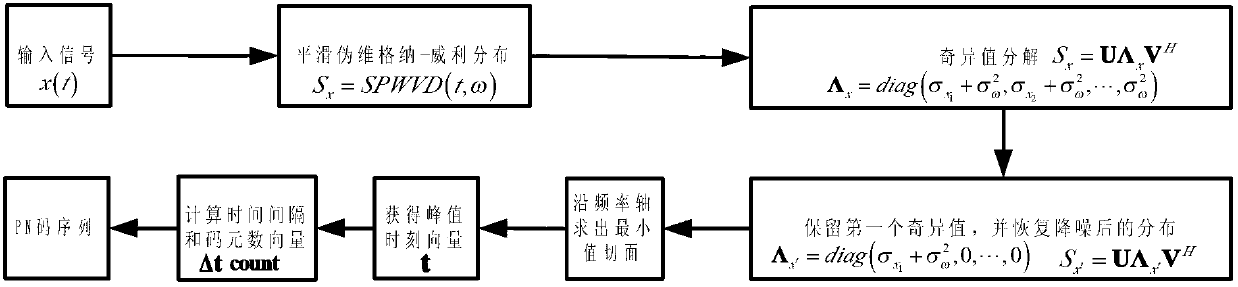
Modified smoothed pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution-based (MSPWVD-based) blind estimation method for pseudo code sequence of pseudo-random Bi-phase code-linear frequency modulation (PRBC-LFM) composite signal
ActiveCN102571671AAccurate estimateReduce distractionsMulti-frequency code systemsSingular value decompositionSystems design
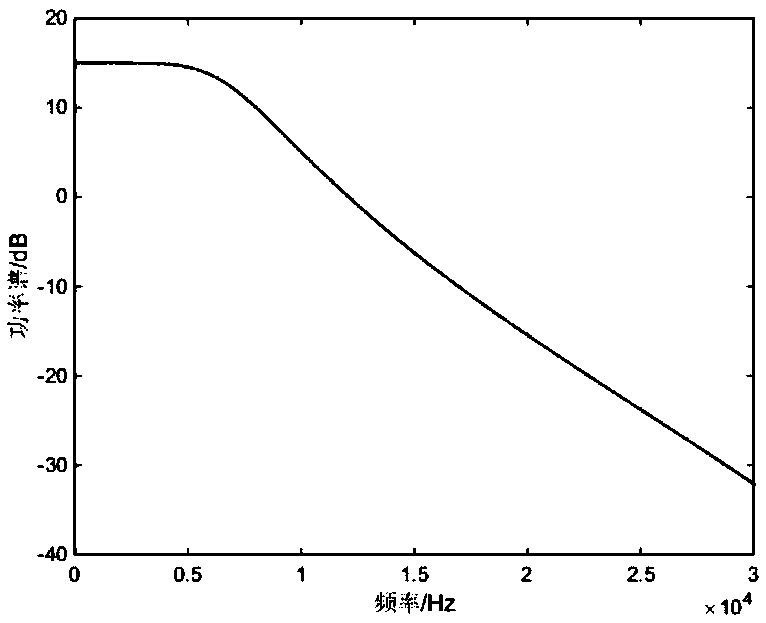
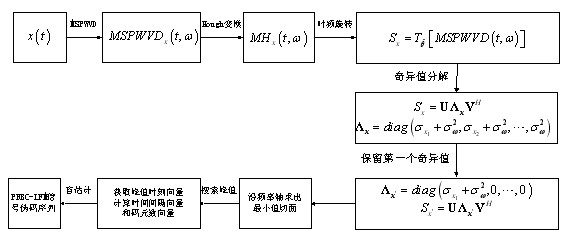
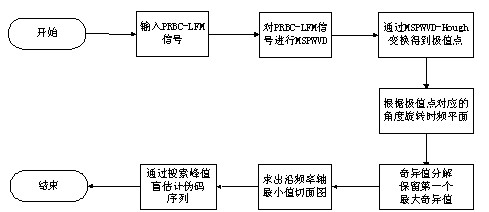
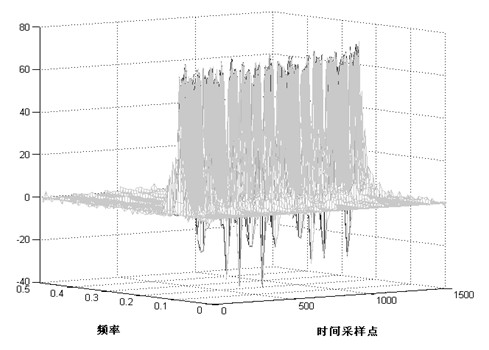
The invention asks for protecting a modified smoothed pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution-based (MSPWVD-based) blind estimation method for a pseudo code sequence of a pseudo-random Bi-phase code-linear frequency modulation (PRBC-LFM) composite signal and belongs to the field of signal processing. According to the method, time-frequency analysis is performed on the PRBC-LFM composite signal by adopting modified smoothed pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution (MSPWVD), and thereby, the time-frequency concentration is enhanced while the cross-term interference of the signal is effectively reduced, and the precision of estimating the pseudo-noise (PN) code sequence of the PRBC-LFM composite signal is increased. Firstly, the minimum section of the MSPWVD time-frequency diagram of the signal is obtained from the MSPWVD time-frequency diagram of the signal; the phase jump site of an estimated pseudo code is obtained through detecting the peak position in the minimum section, and finally, the estimation on the original sequence or the antitone sequence of the PN code of the signal is obtained. Meanwhile, by combining with an MSPWVD-Hough transformation and subspace decomposition (singular value decomposition-SVD) method, the influences of cross terms are further reduced and the influence of the noise is further restrained. According to the method, the PN code sequence can be accurately estimated at low signal to noise ratio to successfully obtain the estimation on the parameter of the PN code of the PRBC-LFM composite signal, and thereby, the capacity of monitoring, managing, detecting and disturbing the PRBC-LFM composite signal and designing a related new-system system is improved. The MSPWVD-based blind estimation method for the pseudo code sequence of the PRBC-LFM composite signal has a wide application prospect.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
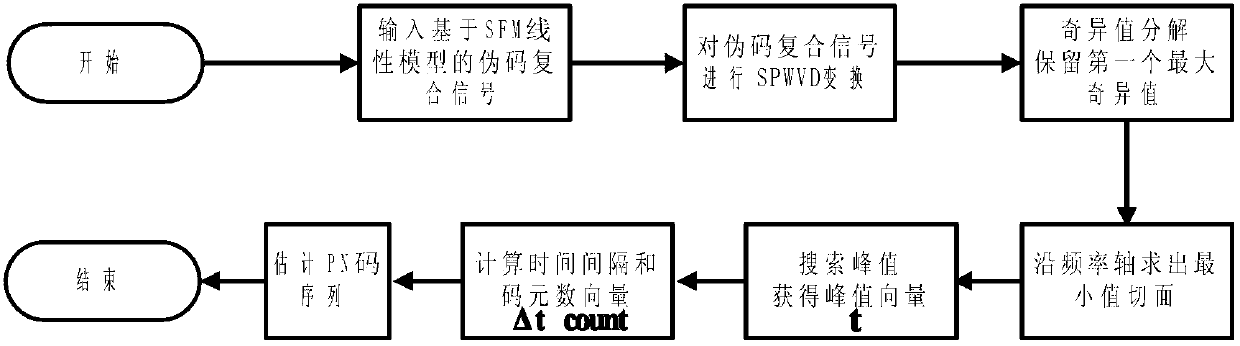
Method for estimating pseudo-code sequence of pseudo-code phase modulation and sinusoidal frequency modulation (SFM) compound signal based on linear module
ActiveCN103281266AEasy to monitorEasy to manageBaseband system detailsSingular value decompositionTime–frequency analysis
The invention provides a method for estimating the pseudo-code sequence of a pseudo-code phase modulation and sinusoidal frequency modulation (SFM) compound signal based on a linear module and belongs to the field of signal processing. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out Jacobi-Anger expansion on a sinusoidal frequency modulation signal, converting a nonlinear SFM (Sinusoidal Frequency Modulation) signal model into a linear signal model, acquiring the non-negative part of the linear signal according to the special symmetrical property of a Bessel function, and then compounding a pseudo-code phase modulation signal; adopting smooth pseudo Wigner distribution to carry out time-frequency analysis on the pseudo-code phase modulation compound signal, and combining an SVD (Singular Value Decomposition) subspace decomposition method to lower cross terms and noise; and determining the minimum tangent plane of an SPWVD (Smooth Pseudo Wigner-Ville Distribution) contour map processed by SVD denoising and enhancement along a frequency axis, and detecting peak value positions and phase jump information to finish accurate blind estimate on the PN code sequency of the pseudo-code phase modulation compound signal. The method has the advantages that PN (Pseudo Noise) codes can be accurately estimated under the condition of a low signal-to-noise ratio, so that the capability of improving management and interfering the pseudo-code phase modulation compound signal can be more effectively improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
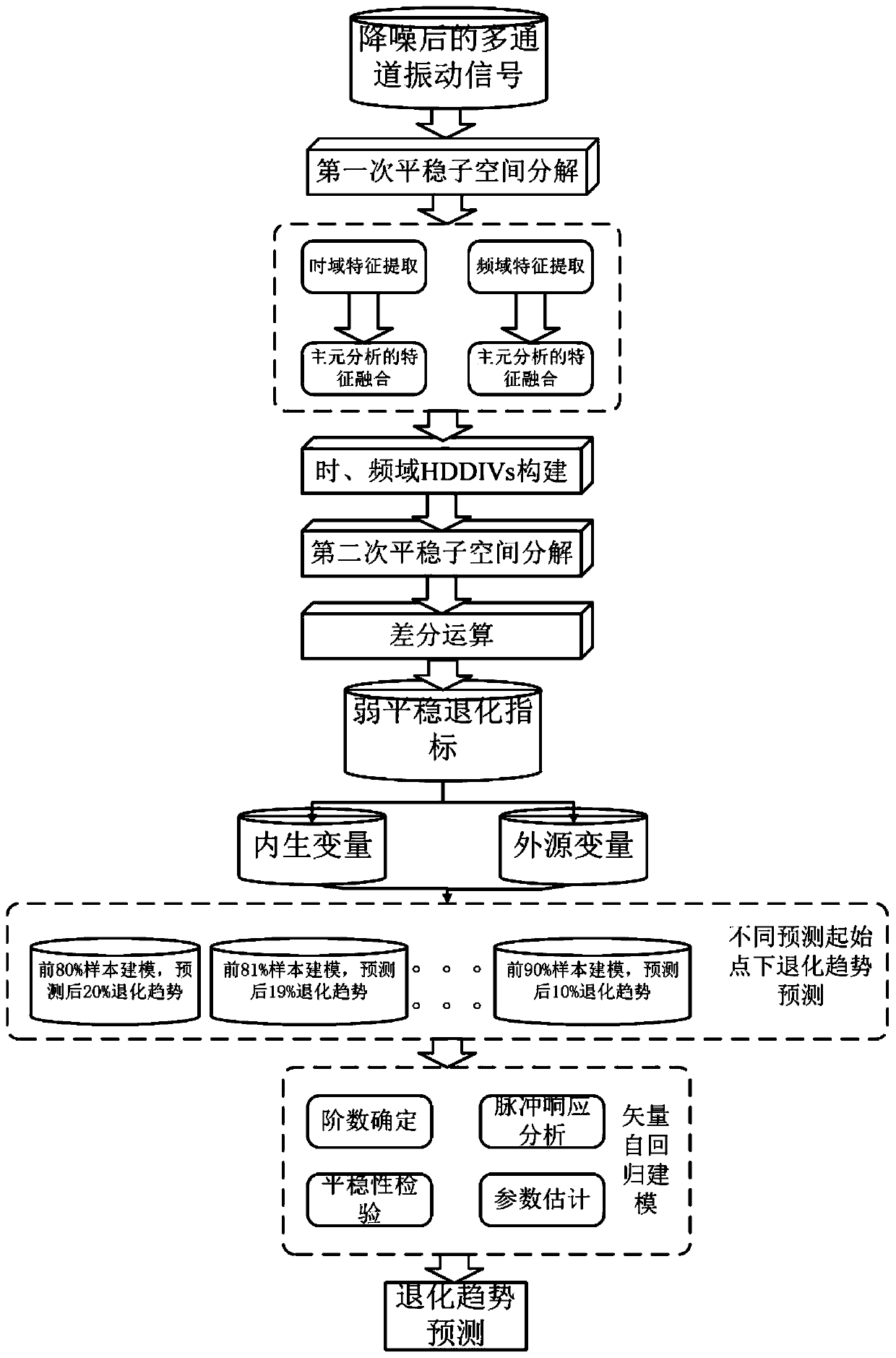
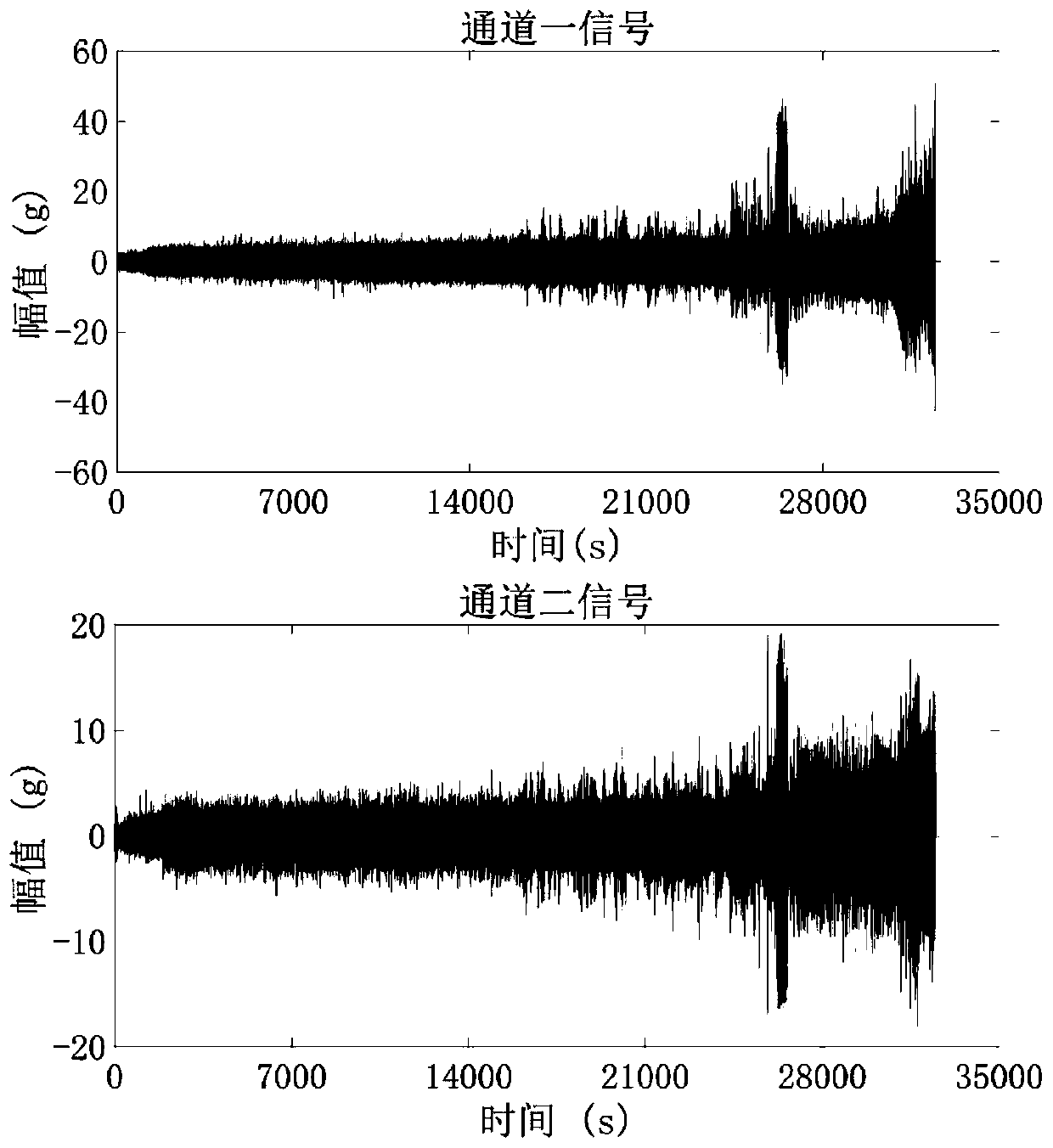
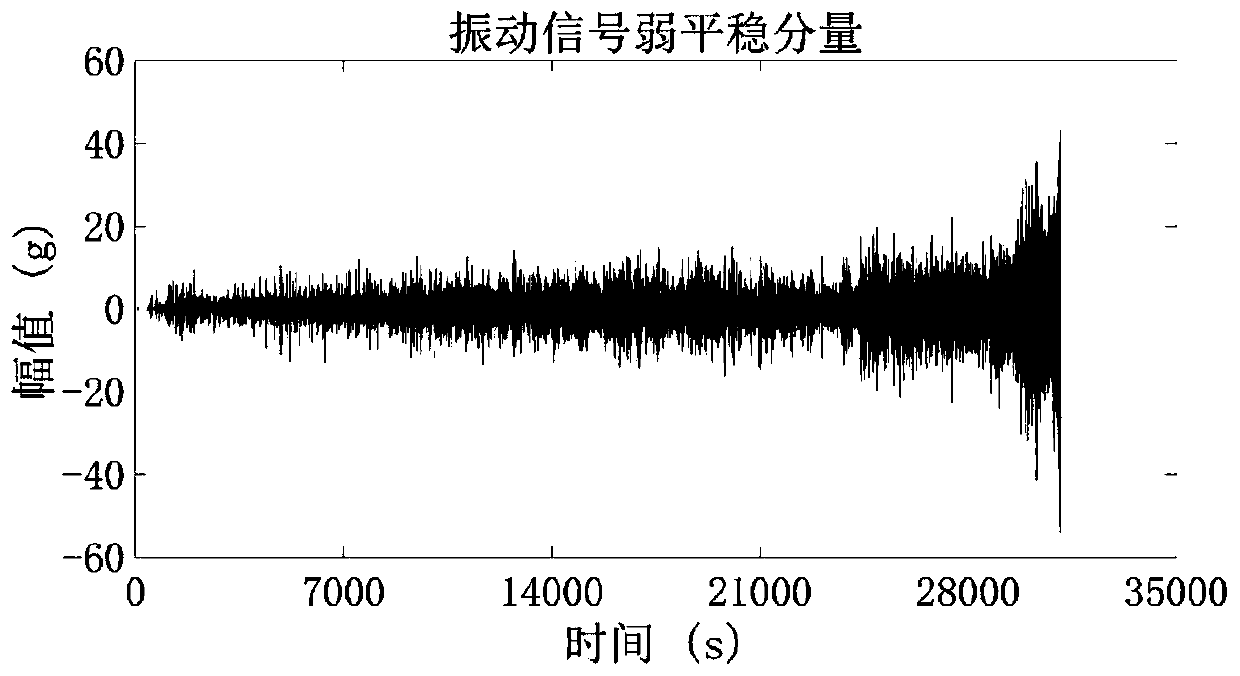
Rotary machine degradation trend prediction method based on steady subspace exogenous vector autoregression
ActiveCN111291918ACalculation speedHigh precisionForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainIndicator vector
The invention discloses a rotary machine degradation trend prediction method based on steady subspace exogenous vector autoregression, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out first stationary subspace decomposition on denoised multi-channel signals to extract vibration stationary components; extracting time-domain and frequency-domain degradation characteristic quantities andobtaining a high-dimensional degradation index vector group through characteristic fusion; performing second stationary subspace decomposition and differential operation on the high-dimensional degradation index vector group in the time domain and the frequency domain to extract weak stationary components in the degradation indexes as rotary machine degradation indexes; carrying out stability test and impulse response analysis on the degradation indexes, determining endogenous and exogenous variables and model orders, determining vector autoregression model parameters through maximum likelihood estimation, and finally carrying out degradation trend estimation on the rotary machine at different prediction starting points. The degradation trend prediction model obtained by the method not only has good generalization ability under small sample learning, but also is rapid in calculation and strong in releasability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
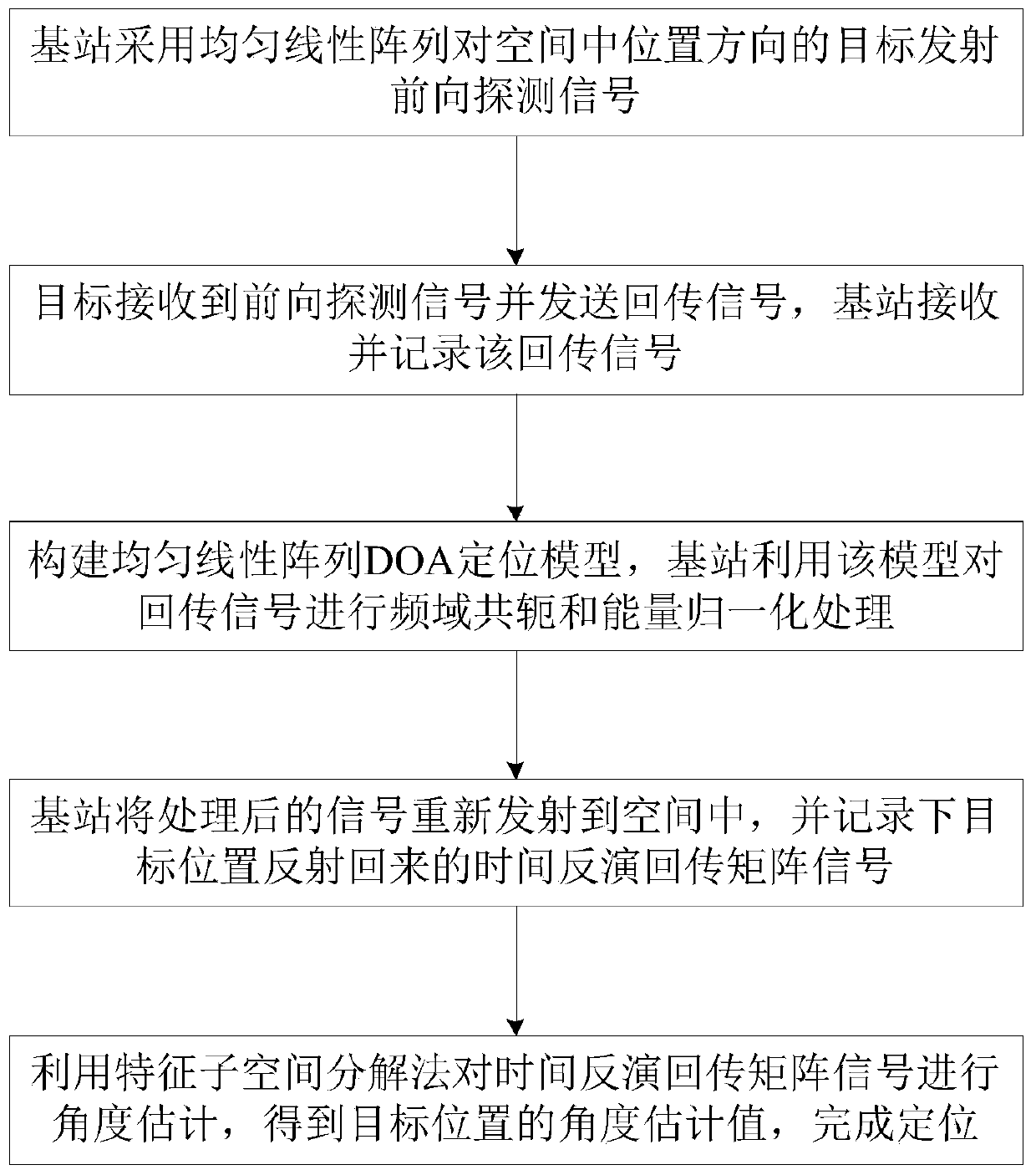
DOA positioning method based on time reversal
InactiveCN111107626AImprove accuracyDisadvantages of suppressing multipath effectsPosition fixationWireless communicationLinear arraysLinear array
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, in particular to a DOA positioning method based on time reversal, which comprises the following steps: a base station transmitsa forward detection signal to a target in a position direction in space by adopting a uniform linear array; the target receives the forward detection signal and sends a return signal, and the base station receives and records the return signal; constructing a uniform linear array DOA positioning model, and performing frequency domain conjugation and energy normalization processing on the returnedsignal by the base station by utilizing the model; the base station retransmits the processed signal to the space, and records a time reversal backhaul matrix signal reflected by the target position;carrying out angle estimation on the time reversal backhaul matrix signal by utilizing a characteristic subspace decomposition method to obtain an angle estimation value of the target position. According to the invention, the positioning service with higher accuracy can be provided.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Noise subspace estimation method based on application of sliding window determination in MWF
ActiveCN109100749ADecomposition is accurate and reliableImprove anti-interference abilitySatellite radio beaconingPattern recognitionMaximum eigenvalue
The invention relates to a noise subspace estimation method based on the application of sliding window determination in MWF. In the method, according to the characteristics of MWF and in combination with the maximum eigenvalue operation of a small matrix, a method for order determination by using a sliding window is provided, so that a noise subspace can be estimated robustly, and an optimal signal to interference plus noise ratio is obtained more stably. By adoption of the method, the interference subspace decomposition can be more accurate and reliable so as to obtain a better anti-interference effect.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
An image classification and recognition method for depth feature estimation based on subspace decomposition
ActiveCN109902720AProcessing speedEasy to handleCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorImage extraction
The invention relates to an image classification and recognition method for depth feature estimation based on subspace decomposition. The method comprises the steps of S1, obtaining an unshielded image and an additional image pair of a training set; S2, extracting a depth feature vector from each input image; S3, calculating the difference between the depth feature vectors of the occluded image and the depth feature vectors of the unoccluded image in the additional image pair to obtain an error vector; S4, forming a first subspace by using the calculated depth feature vectors of all the unshielded images, forming a second subspace by using the error vectors, and forming a cascade dictionary based on the first subspace and the second subspace; S5, calculating a coefficient matrix based on the cascade dictionary; S6, training a classifier based on all column vectors of the first subspace; And S7, performing classification and identification on the to-be-identified image based on the cascade dictionary, the coefficient matrix and the classifier. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of wide application range and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Multi-radiation sources passive direct time difference positioning method based on subspace decomposition
ActiveCN109239653AOvercome estimationOvercome discriminationPosition fixationInformation processingAlgorithm
The present invention relates to the technical field of signal and information processing, and to a multi-radiation sources passive direct time difference positioning method based on subspace decomposition. The method adopts a passive direct time difference positioning method, does not estimate intermediate parameters, avoids introducing intermediate parameters estimation error and intermediate parameters matching between multiple stations, so that solves the problem that a two-step method is no longer applicable in the scene of locating a plural of time-frequency overlapping radiation sources, and as for resolution problem of multiple radiation sources, the method adopts a super-resolution positioning method based on subspace decomposition to improve resolution of positioning.
Owner:TONG FANG ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH +1
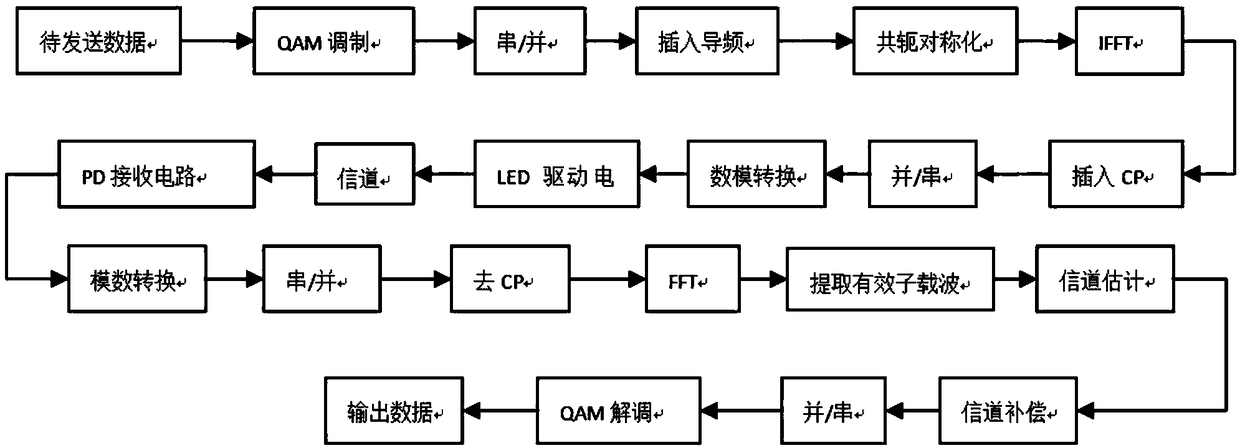
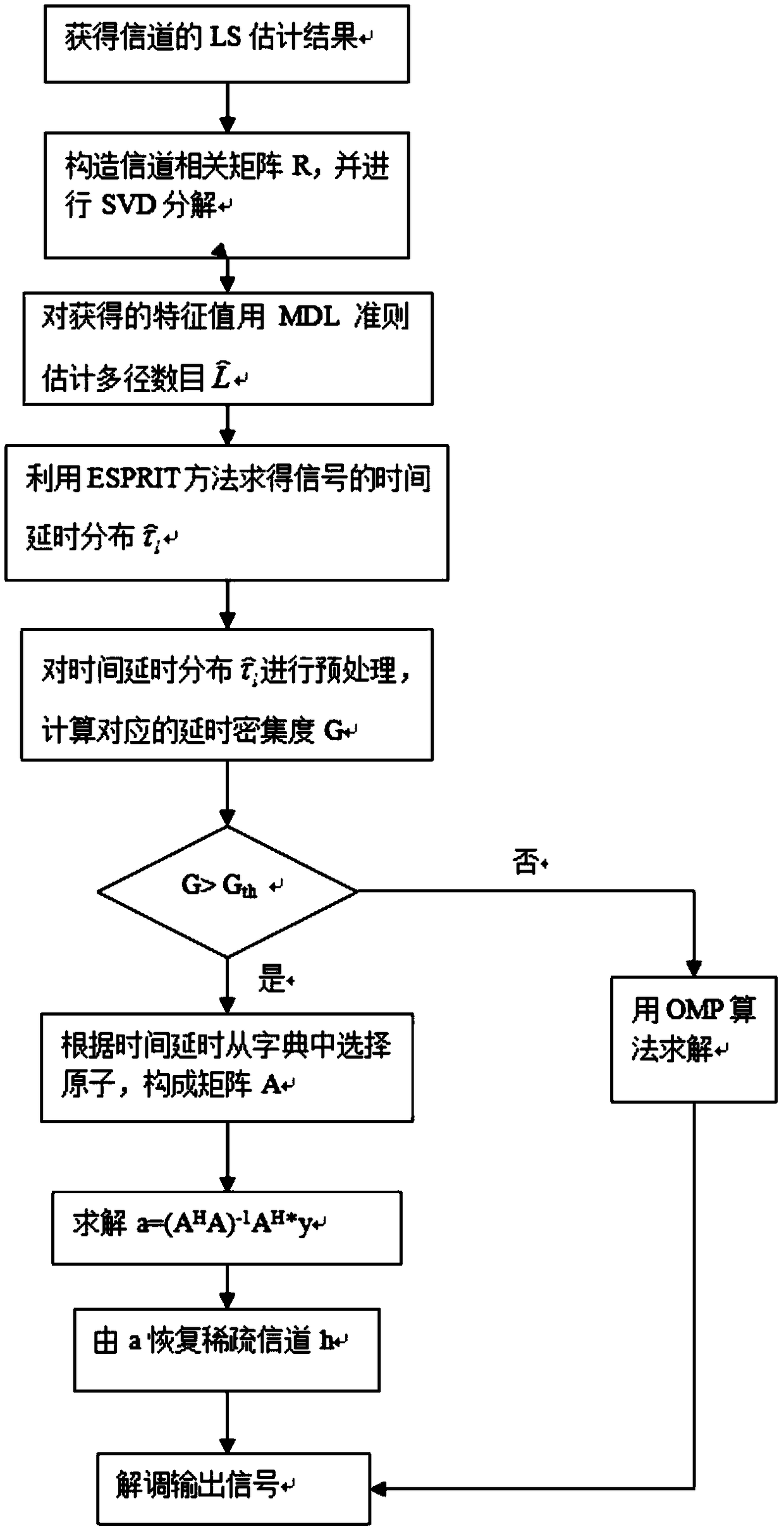
Channel estimation method and device based on compressed sensing theory
ActiveCN109347770AImprove accuracyImprove bit error performanceBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsChannel densityDecomposition
The invention discloses a channel estimation method and device based on a compressed sensing theory. The method comprises the following steps of estimating channel responses at pilot positions according to received pilot signals, and obtaining an LS estimation result of a channel; constructing a channel correlation matrix according to the LS estimation result, and carrying out SVD decomposition onthe channel correlation matrix, thereby obtaining sets of eigenvalues and eigenvectors; estimating the channel multipath number through utilization of an MDL criterion according to the eigenvalues; solving a delay distribution parameter of the channel according to the eigenvectors and the channel multipath number; and computing a channel density measurement value G according to the delay distribution parameter obtained through estimation, and for a given density measurement threshold Gth, solving the channel. According to the method and the device, relatively precise time delay is provided through utilization of a classical subspace decomposition method; channel sensitivity represented by a classical OMP method is improved; according to a provided improvement method, resolution capabilityof the method for the channel time delay is improved theoretically; channel estimation accuracy is further improved; and system reliability is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Method of direction of arrival (DOA) estimation under low snapshot number based on M estimation
InactiveCN109696651AOvercoming the problem of decreased estimation accuracyImprove performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsObservation dataCovariance matrix
The invention provides a method of direction of arrival (DOA) estimation under a low snapshot number based on M estimation, which comprises the steps of 1, setting an antenna array, and obtaining an observation data vector of the antenna array; 2, calculating a covariance matrix of the observation data vector at the snapshot number T; 3, carrying out trace regularization on the sample covariance matrix to obtain a trace-regularized matrix; 4, carrying out Toeplitz correction on the trace-regularized matrix to obtain a target matrix; 5, calculating a contraction coefficient for matrix contraction estimation according to the trace-regularized target matrix; 7, constructing a new covariance matrix according to the contracted target matrix and the contraction coefficient; 7, setting the new covariance matrix as the sample covariance matrix, repeating the step 2 to the step 6 until the final estimation is obtained; and 8, calculating the direction of arrival of the signal by adopting a subspace decomposition method according to the obtained covariance matrix.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
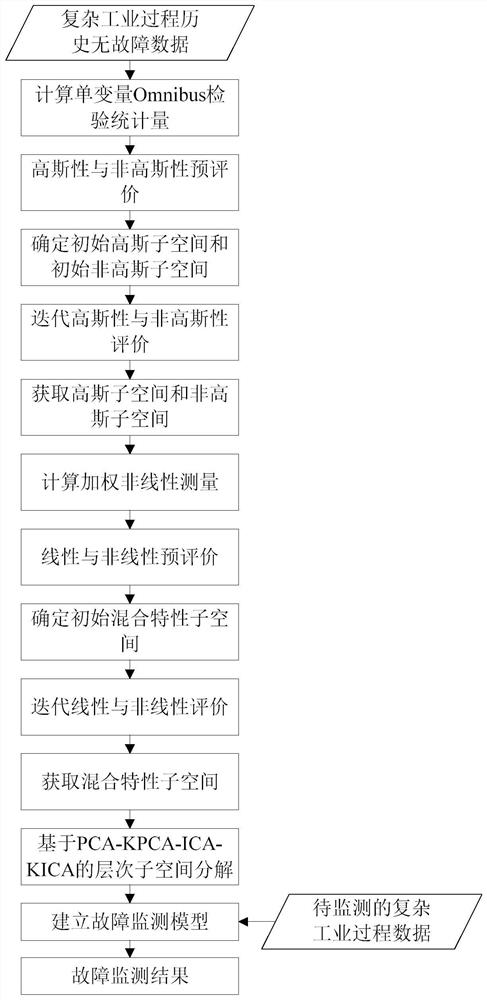
Hierarchical fault monitoring method based on mixed characteristic evaluation and subspace decomposition
ActiveCN112817291AImprove product qualityProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringPattern recognitionLinear correlation
The invention relates to a hierarchical fault monitoring method based on mixed characteristic evaluation and subspace decomposition, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining mixed characteristic subspaces, including a Gaussian linear subspace, a Gaussian nonlinear subspace, a non-Gaussian linear subspace and a non-Gaussian nonlinear subspace, of a complex industrial process through the mixed characteristic evaluation; and establishing a fault monitoring model based on a hierarchical subspace decomposition method of PCA-ICA-KPCA-KICA, and performing fault monitoring by using comprehensive statistics and a hierarchical monitoring strategy. According to the method, Omnibus inspection, weighted nonlinear measurement and hierarchical subspace decomposition based on PCA-ICA-KPCA-KICA are combined, the problem of mixed characteristic coexistence of a complex industrial process is considered, and the limitation that an existing fault monitoring method depends on prior process knowledge or does not consider Gaussian, non-Gaussian, linear correlation and nonlinear correlation coexistence is overcome, and the method has theoretical and practical significance for monitoring abnormal working conditions and improving product quality.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
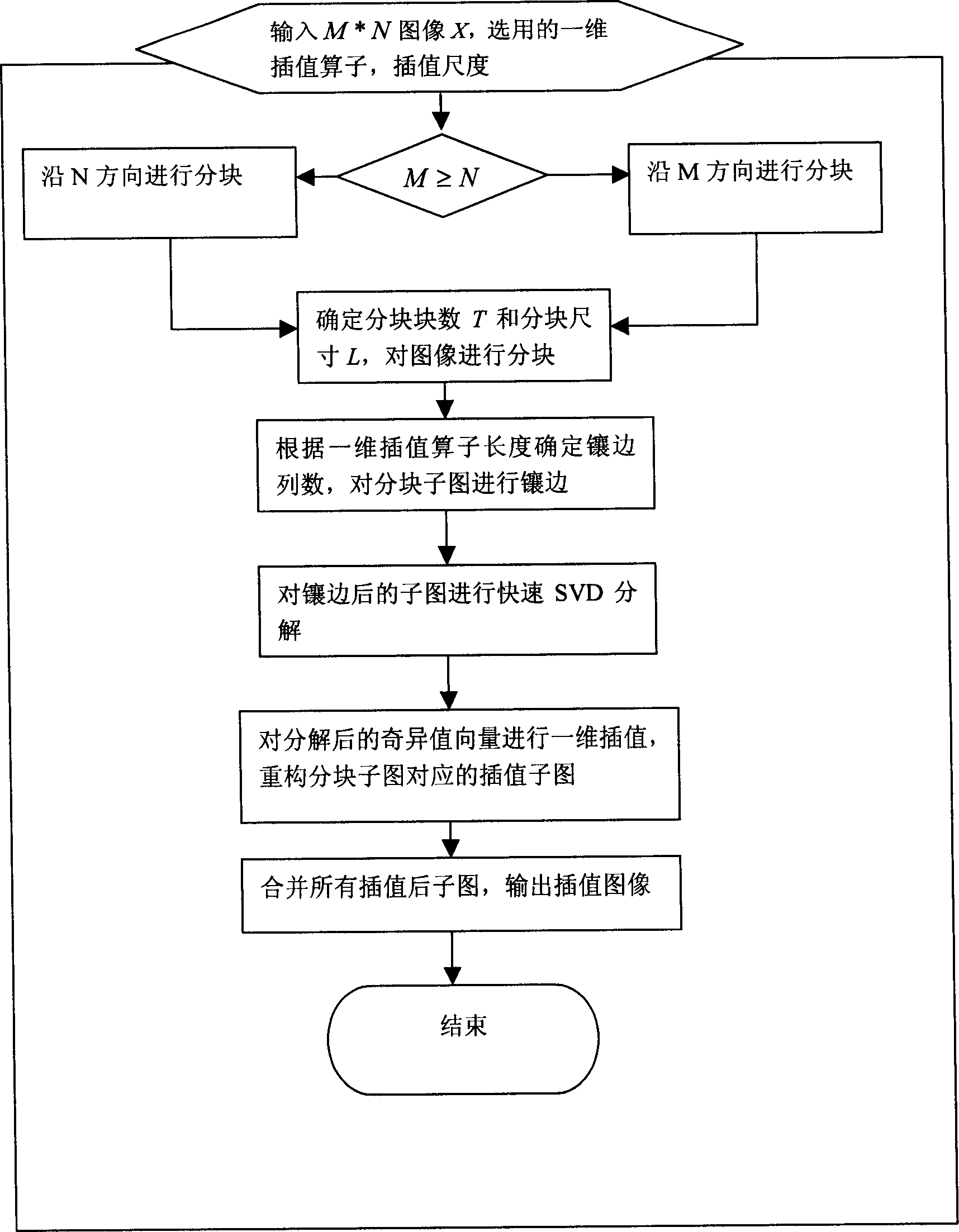
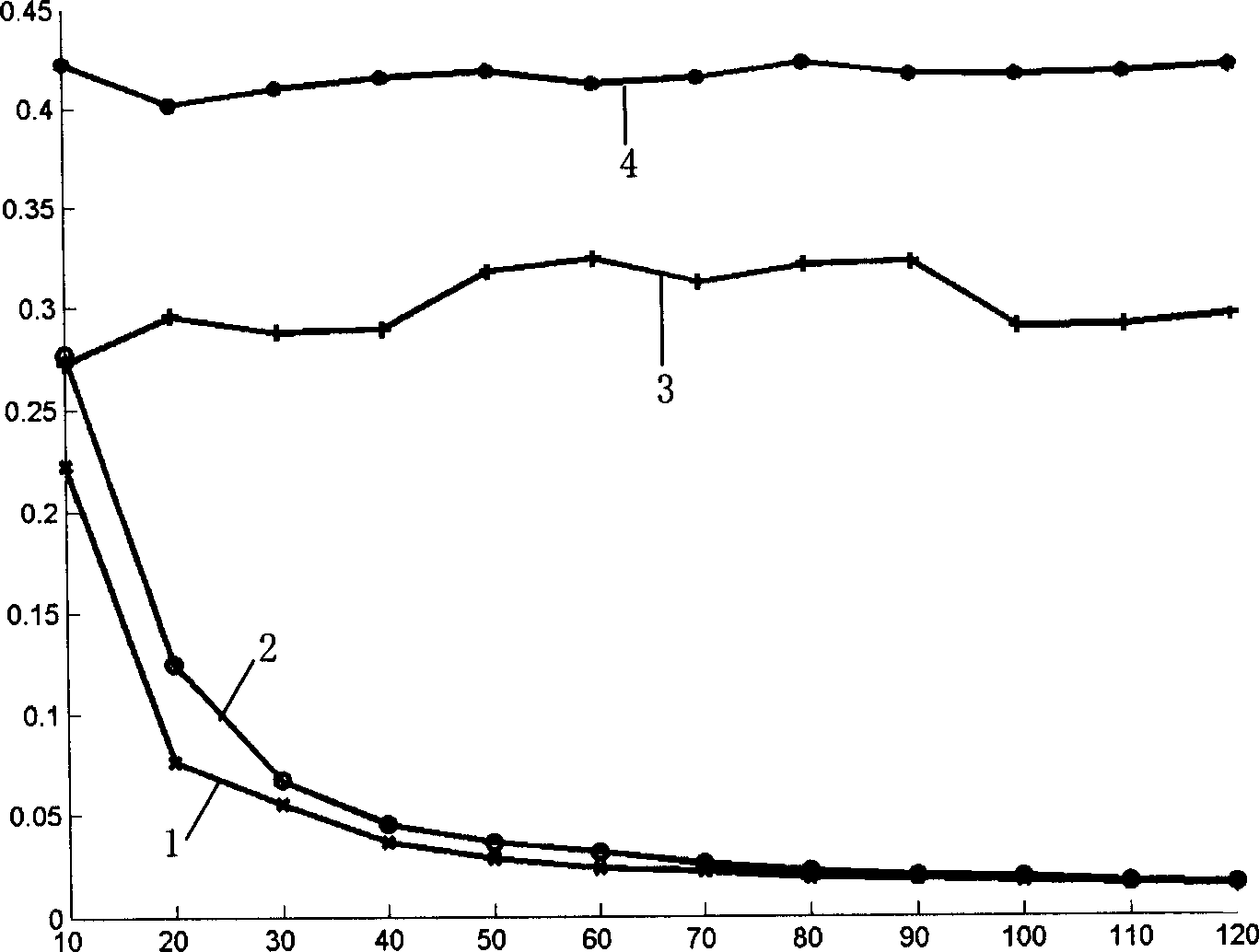
Large scale enlarging method with high performance for digital image based on subspace decomposition
InactiveCN1416103AImage enhancementComplex mathematical operationsSingular value decompositionDissolution
High efficient digit image large size amplification method based on subspace dissolution characterizes in converting two-dimension image interpolation into several singular vectors one-dimension interpolation containing singular value dissolution, singular value vector one-dimension interpolation and singular value restructure successively and greatly reducing the interpolation complexity by split, the ratio is reduced along with the increase of amplification of the operation time of this invented method and that of the image two-dimension three-interpolation method in a same image dimension and split dimension, such as a split dimesnion is 16*8, amplified dimension is 120 inch, if image three times interpolation is 1, image linear interpolation time is 0.42, image latest interpolation time is 0.295.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
High-resolution sonar positioning method based on sparsity of target space
InactiveCN103116162BAchieve simultaneous positioningOvercoming dependenciesAcoustic wave reradiationHat matrixPeak value
The invention discloses a high-resolution sonar location method based on a sparsity of an objective space and mainly solves the problems that a limited array aperture causes insufficient spatial resolution and a signal source coherence causes an inaccurate estimation of an objective location and calculating work of subspace decomposition and data volume are considerable in the prior art. According to the method, a projection matrix which is from a spatial spectrum vector quantity to a ranks synthesis data vector is constructed. By taking advantage of the apriori information of the sparsity of the space target and obtaining data of large signal to noise ratio through a matched filtering, the spatial spectrum vector quantity is carried out with peak detection through an iterative computation to obtain the high-resolution spatial spectrum vector quantity. The objective location can be achieved by taking advantage of the received index value of a peak element through the calculation to gain an objective azimuth angle and an objective pitch angle. The location method has the advantages of being low in the needed data size and calculated amount in the iterative process, suitable for a hardware implementation, high in angular accuracy and improving markedly the spatial resolution.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Radar target detection method combined with time domain and spatial domain on basis of feed network
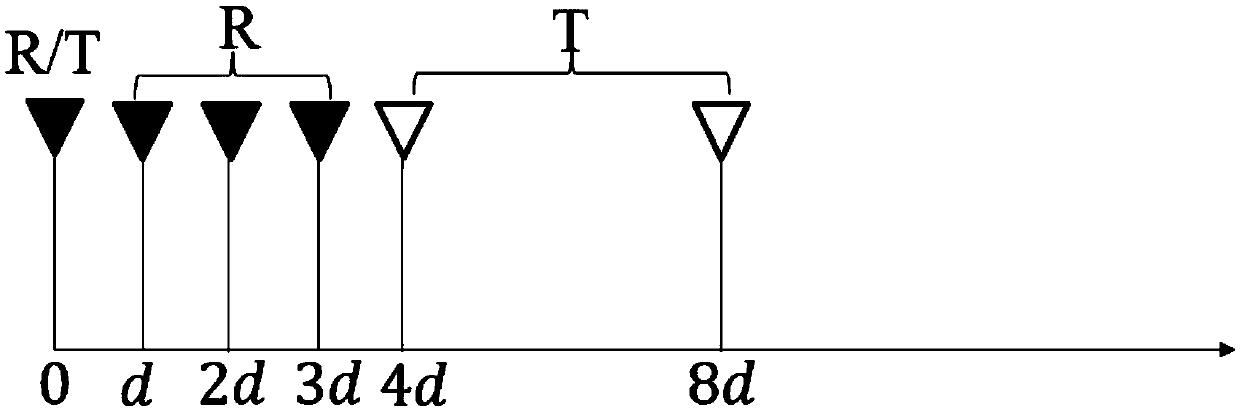
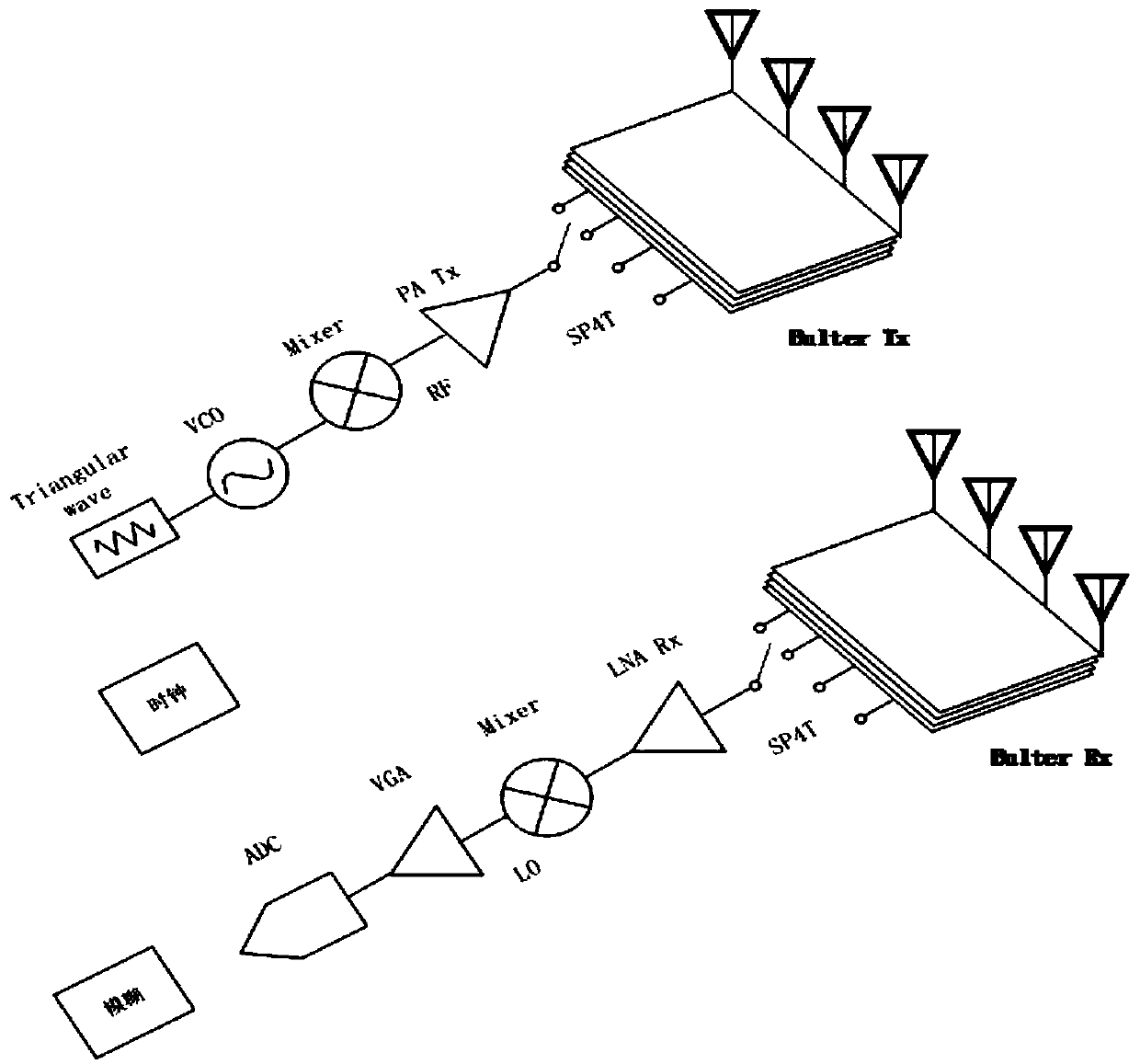
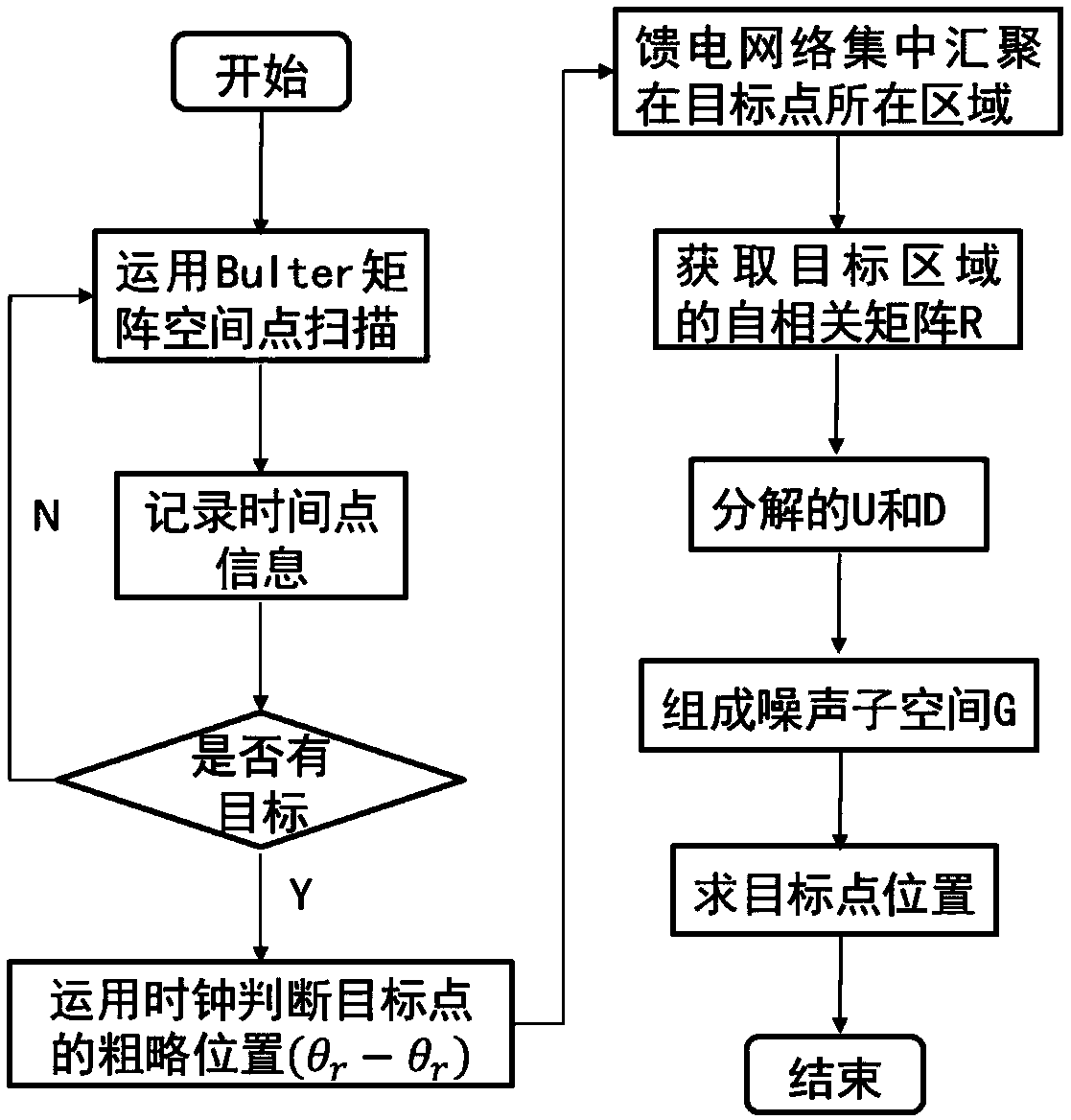
ActiveCN109001690ABeamforming for long range detectionComprehensive positioningWave based measurement systemsTime domainAlgorithm
The invention discloses a radar target detection method combined with a time domain and a spatial domain on basis of a feed network. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing the time characteristic of the feed network to explore a general orientation of a target point in the space; using the time signal to acquire a coarse position of the target point position; focusing on the antenna signal; and acquiring specific position information of the target point by using the phase relation between the received signals and a subspace decomposition algorithm. According to the radar target detection method combined with a time domain and a spatial domain on basis of a feed network in the invention, a bulter feed network is used for achieving beam scanning at the time domain stage; compared with one beam, the beamforming detection distance is further away in a fixed specific direction; the spatial domain stage scanned by using the algorithm is realized by using an algorithm; more target points can be positioned within an angle range; and the target point information can be identified more accurately.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Data analytic engine towards the self-management of complex physical systems
ActiveUS10914608B2Hardware monitoringCharacter and pattern recognitionAnomaly detectionPhysical system
Systems and methods for anomaly detection in complex physical systems, including extracting features representative of a temporal evolution of the complex physical system, and analyzing the extracted features by deriving vector trajectories using sliding window segmentation of time series, applying a linear test to determine whether the vector trajectories are linear, and performing subspace decomposition on the vector trajectory based on the linear test. A system evolution model is generated from an ensemble of models, and a fitness score is determined by analyzing different data properties of the system based on specific data dependency relationships. An alarm is generated if the fitness score exceeds a predetermined number of threshold violations for the different data properties.
Owner:NEC CORP
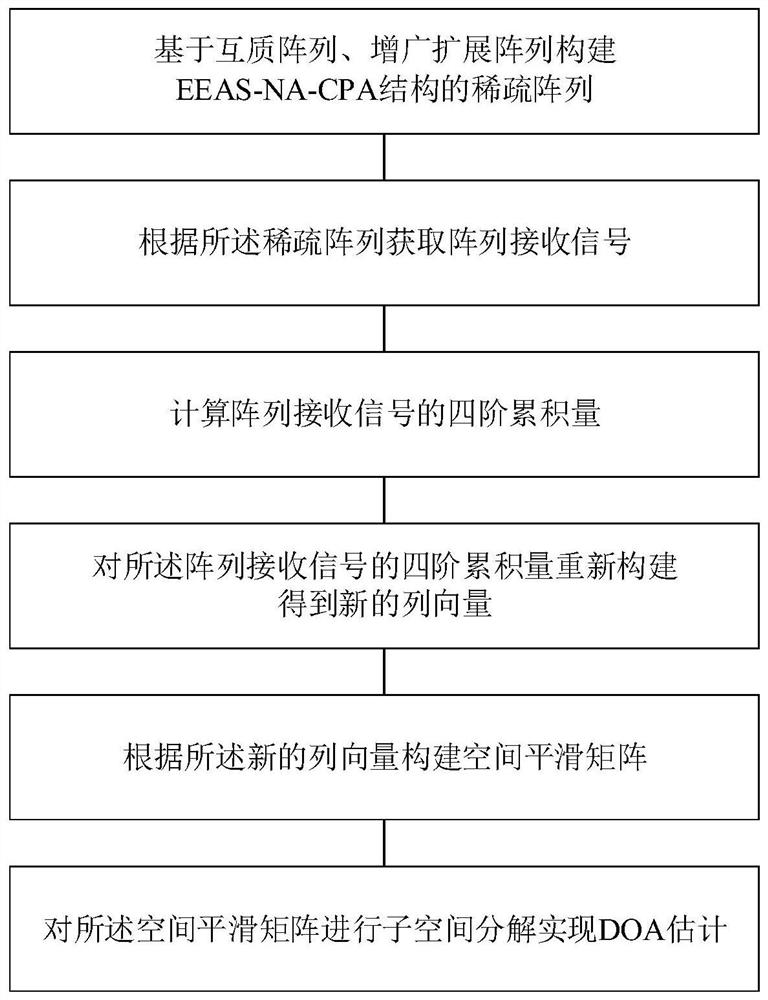
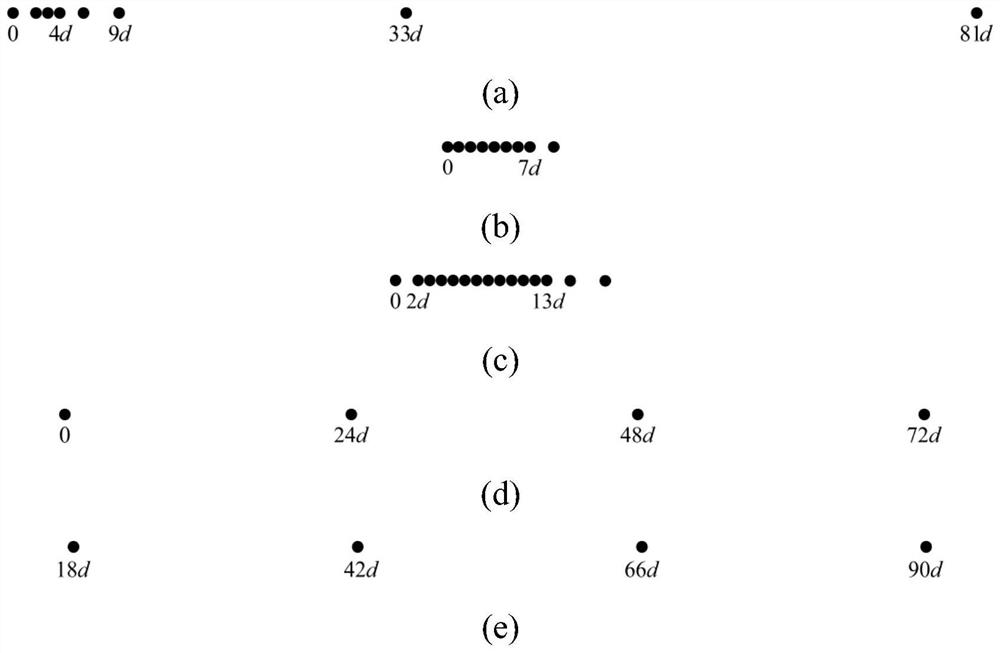
Four-order cumulant DOA estimation method based on co-prime array and augmented extension array
ActiveCN112904271AComprehensive detectionDetected moreRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsHigh level techniquesThinned arrayEngineering
The invention discloses a four-order cumulant DOA estimation method based on a co-prime array and an augmented extension array. The method comprises the following steps of constructing a sparse array of an EEAS-NA-CPA structure based on the co-prime array and the augmented extension array, acquiring an array receiving signal according to the sparse array, calculating a fourth-order cumulant of an array receiving signal, reconstructing the fourth-order cumulant of the array receiving signal to obtain a new column vector, constructing a spatial smoothing matrix according to the new column vector, and performing subspace decomposition on the spatial smoothing matrix to realize DOA estimation. According to the method, the EEAS-NA-CPA can obtain a larger continuous lag number, more signal sources can be detected with higher precision, and the DOA estimation based on the EEAS-NA-CPA structure can obtain better performance.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com