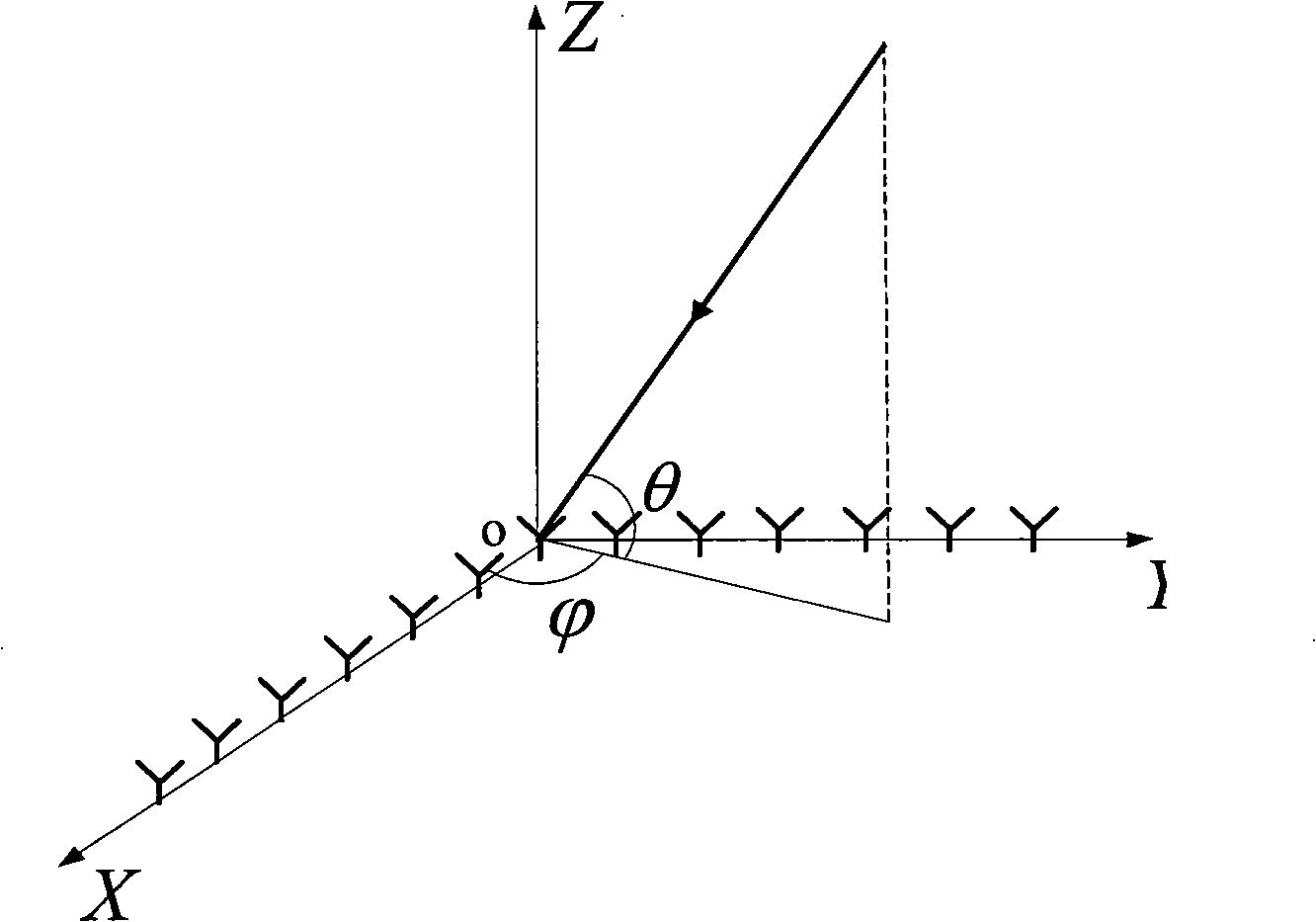
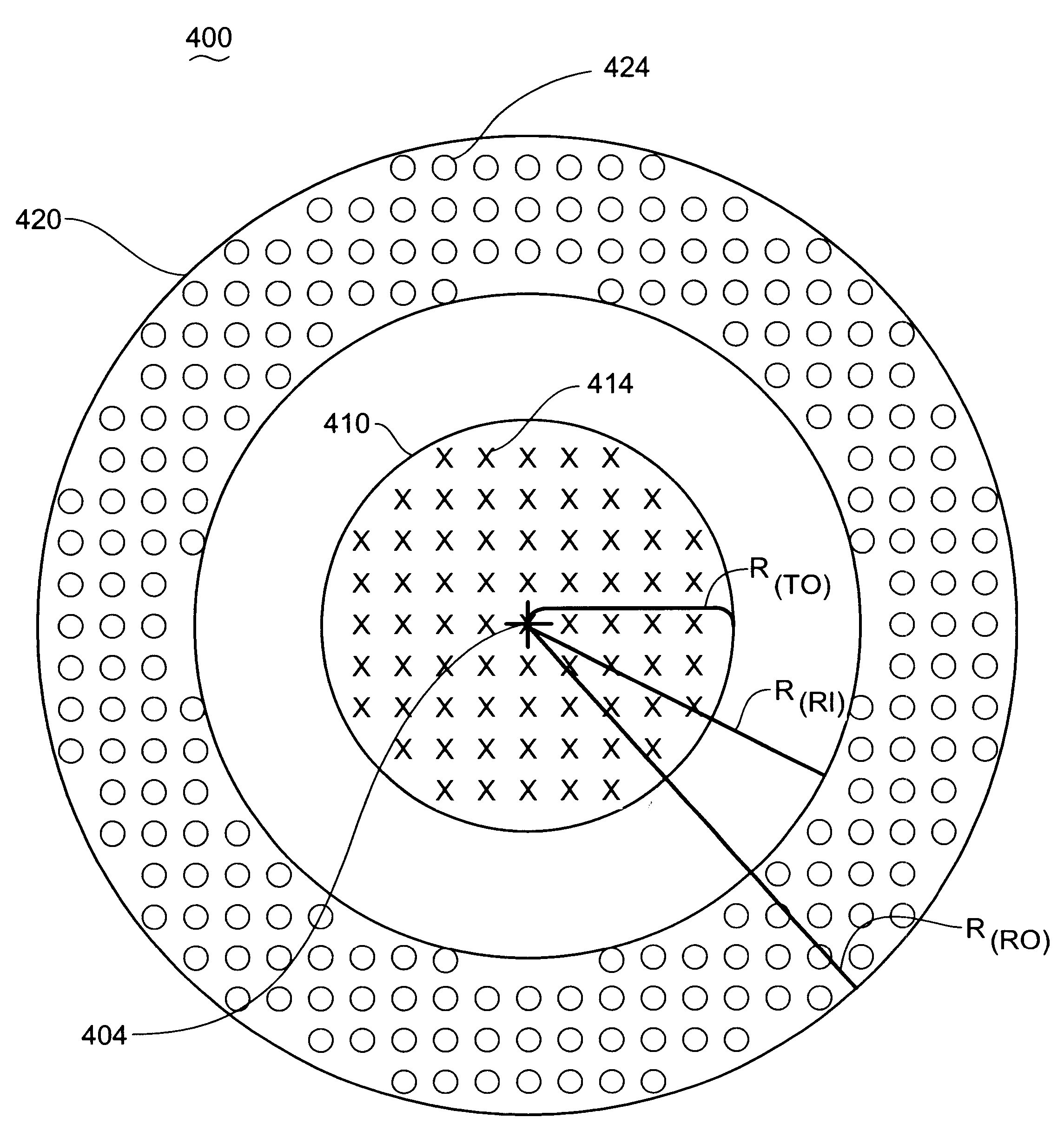
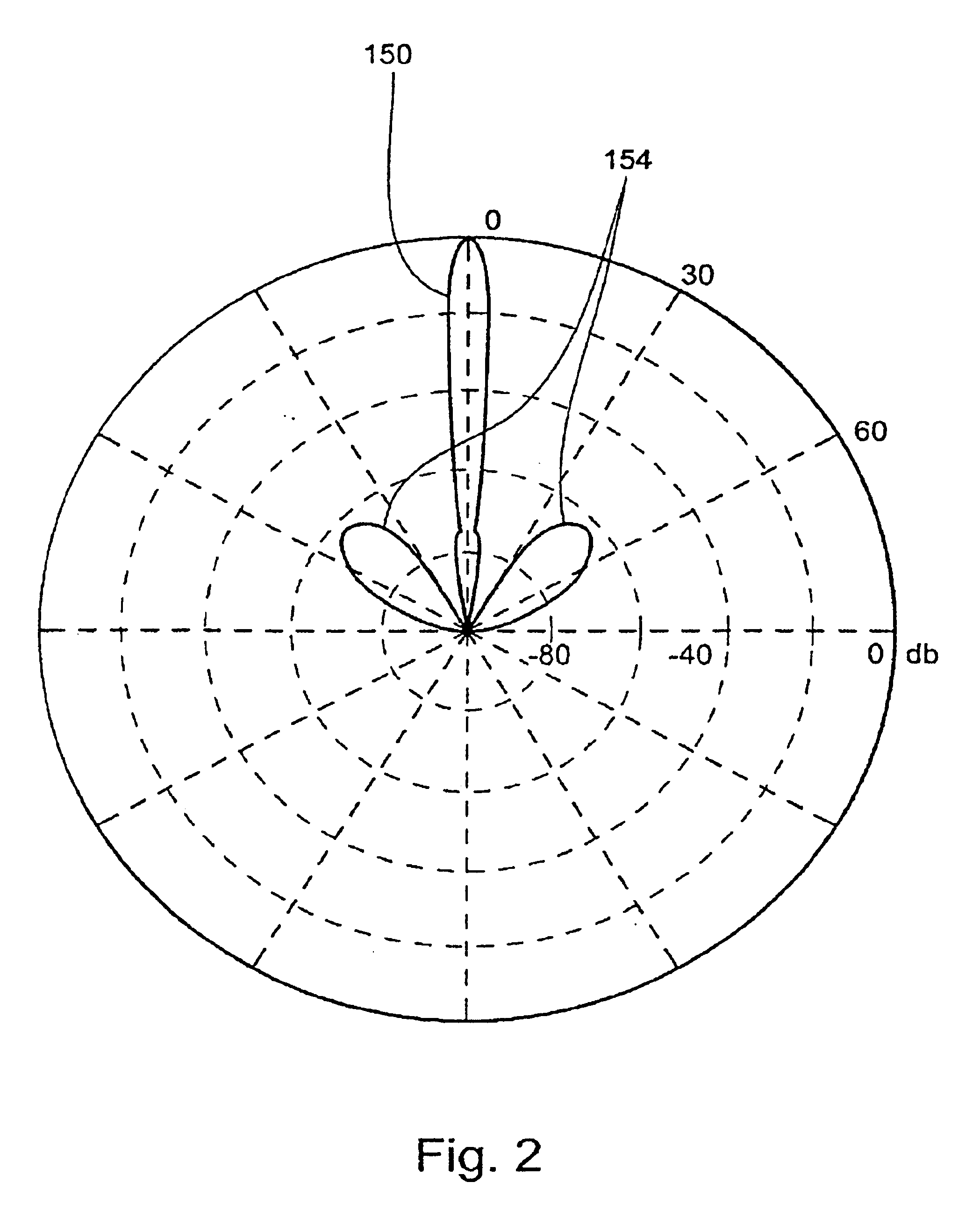
Patents
Literature
394 results about "Sparse array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
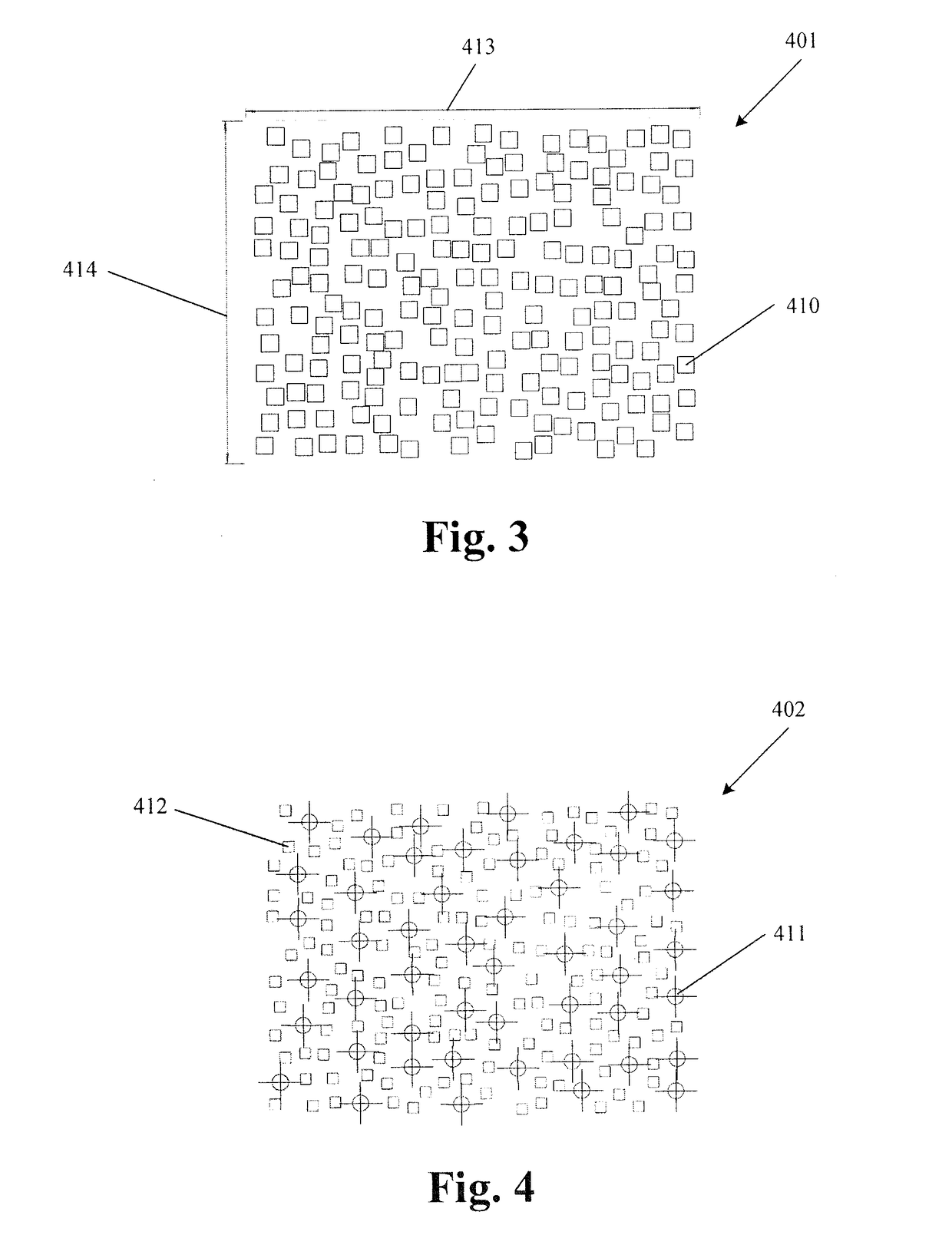
In computer science, a sparse array is an array in which most of the elements have the same value. The occurrence of zero elements in a large array is inefficient for both computation and storage. An array in which there is a large number of zero elements is referred to as being sparse. In the case of sparse arrays, one can ask for a value from an "empty" array position. If one does this, then for an array of numbers, a value of zero should be returned, and for an array of objects, a value of null should be returned. A naive implementation of an array may allocate space for the entire array, but in the case where there are few non-default values, this implementation is inefficient. Typically the algorithm used instead of an ordinary array is determined by other known features of the array. For instance, if the sparsity is known in advance or if the elements are arranged according to some function. A heap memory allocator in a program might choose to store regions of blank space in a linked list rather than storing all of the allocated regions in, say a bit array.
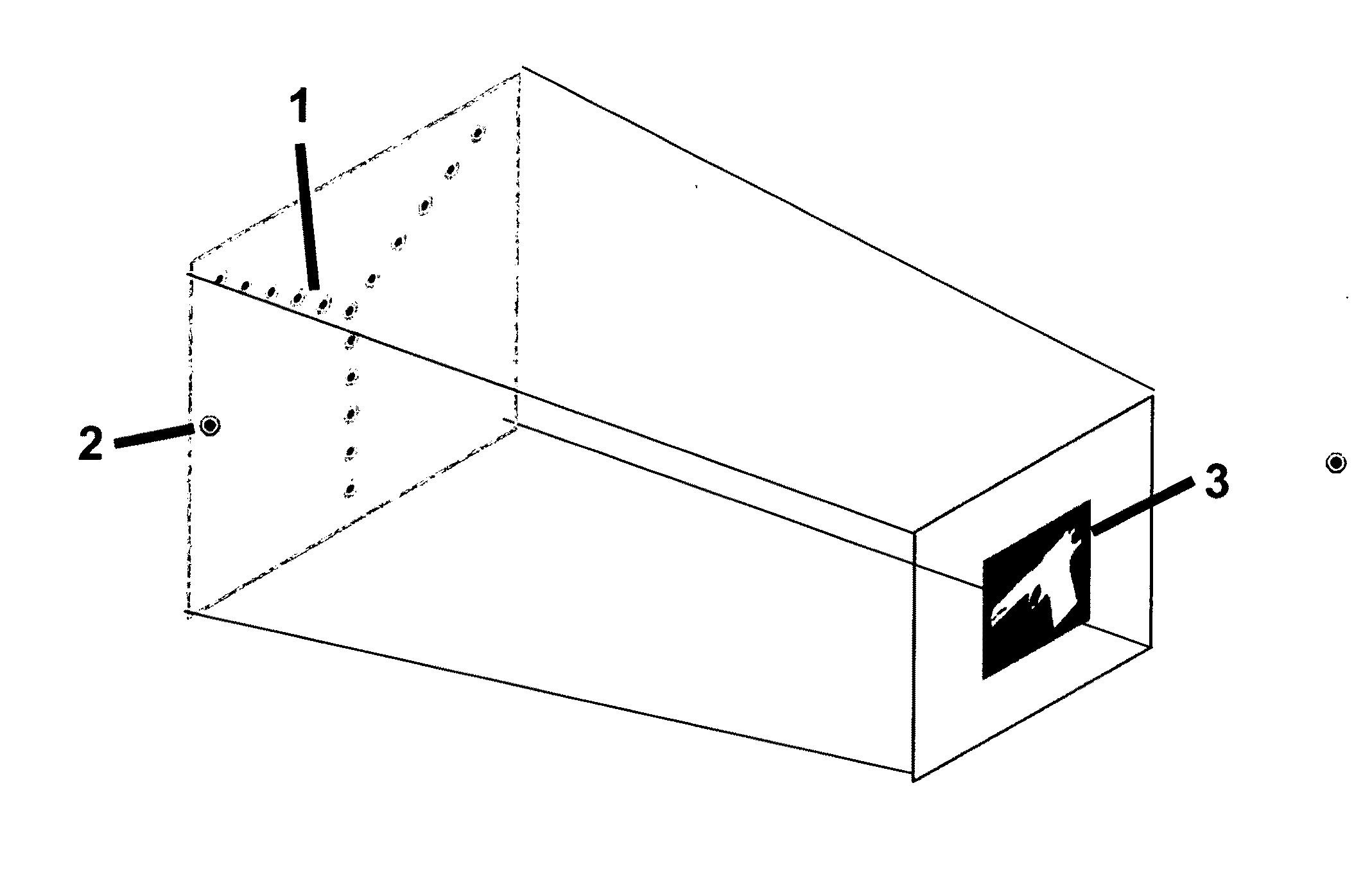
System and method for active protection of a resource
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
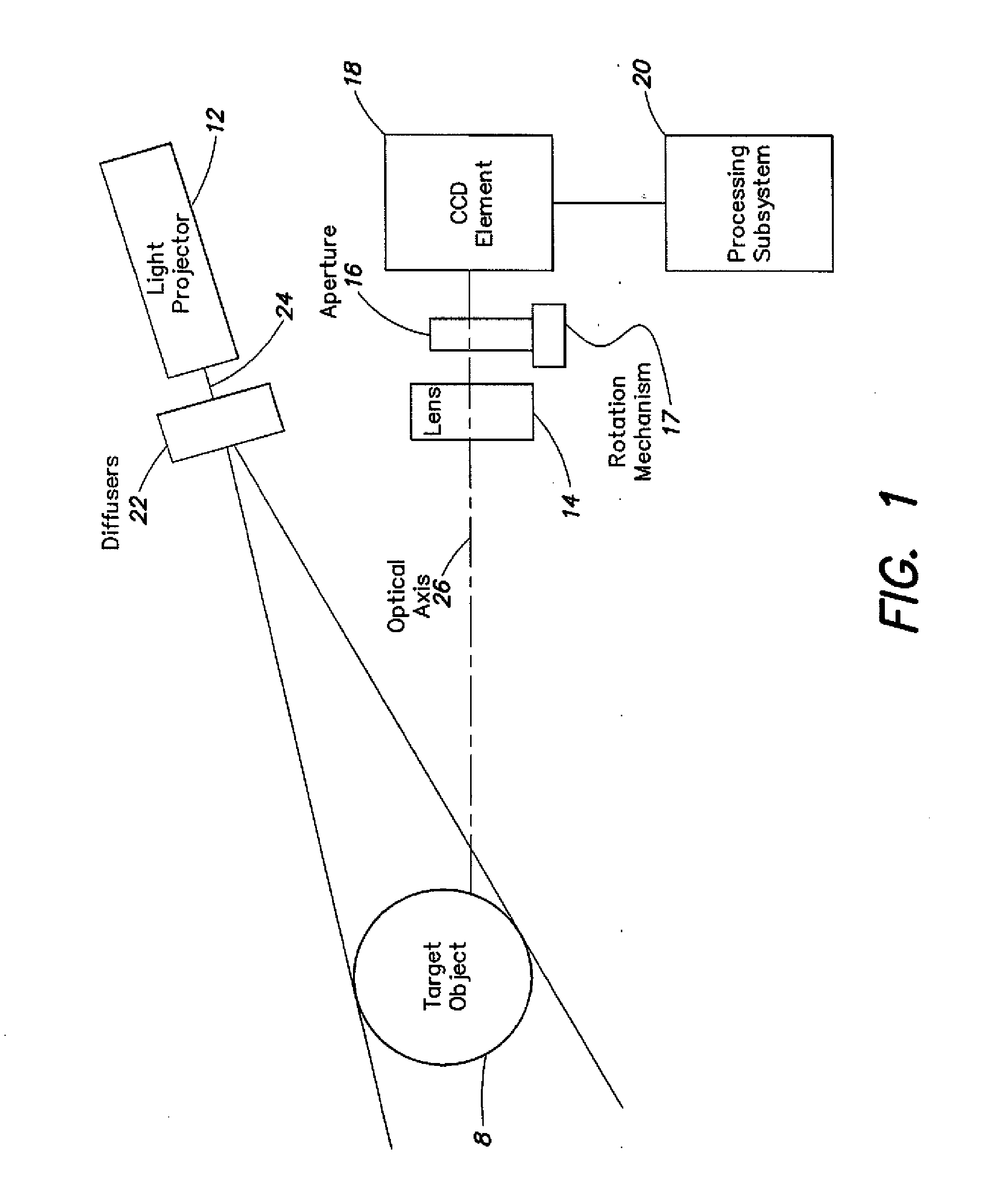
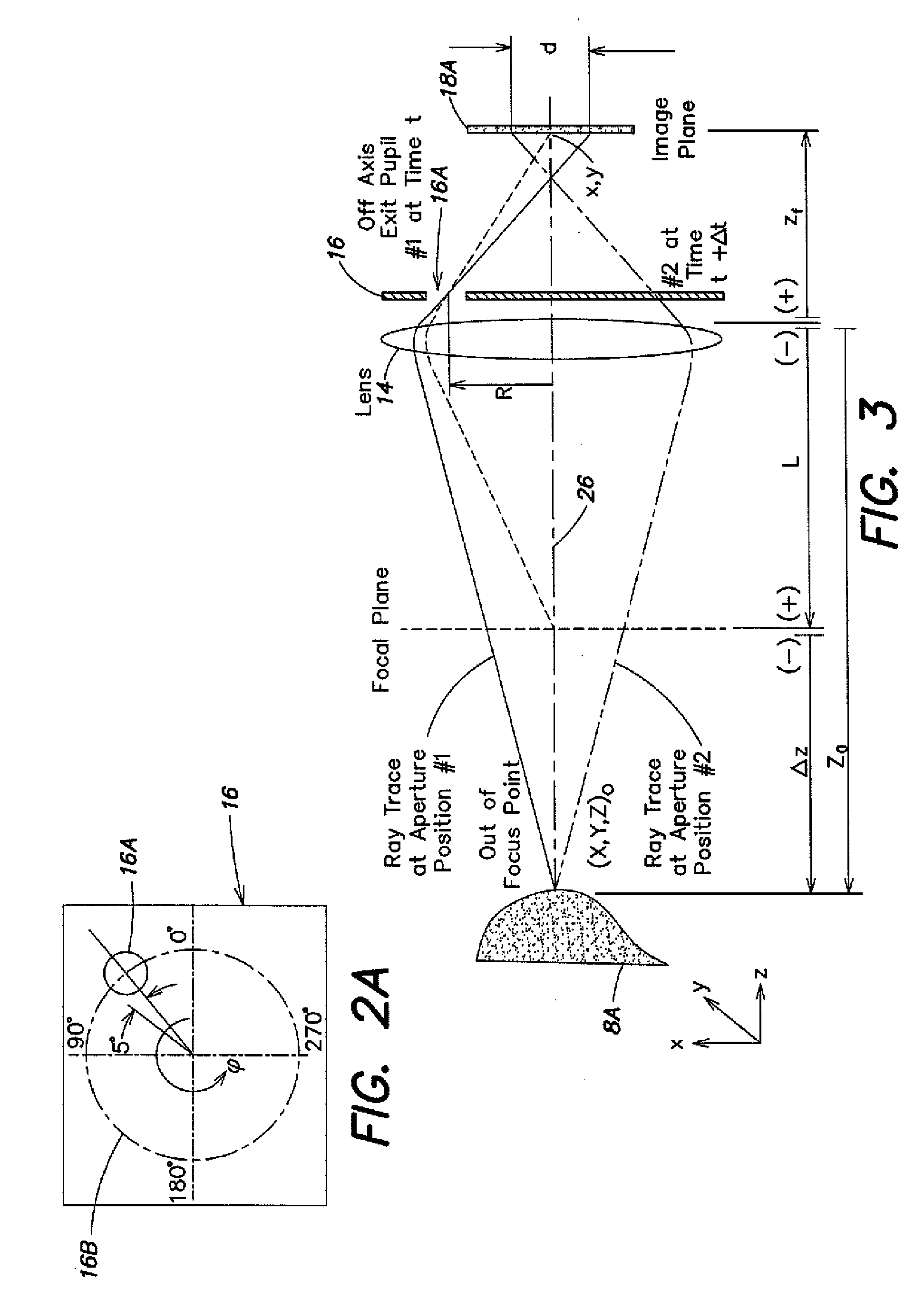
Method and system for high resolution, ultra fast 3-d imaging
InactiveUS20090016642A1Add depthHigh displacement accuracyTelevision system detailsImage analysisImage resolutionUltra fast
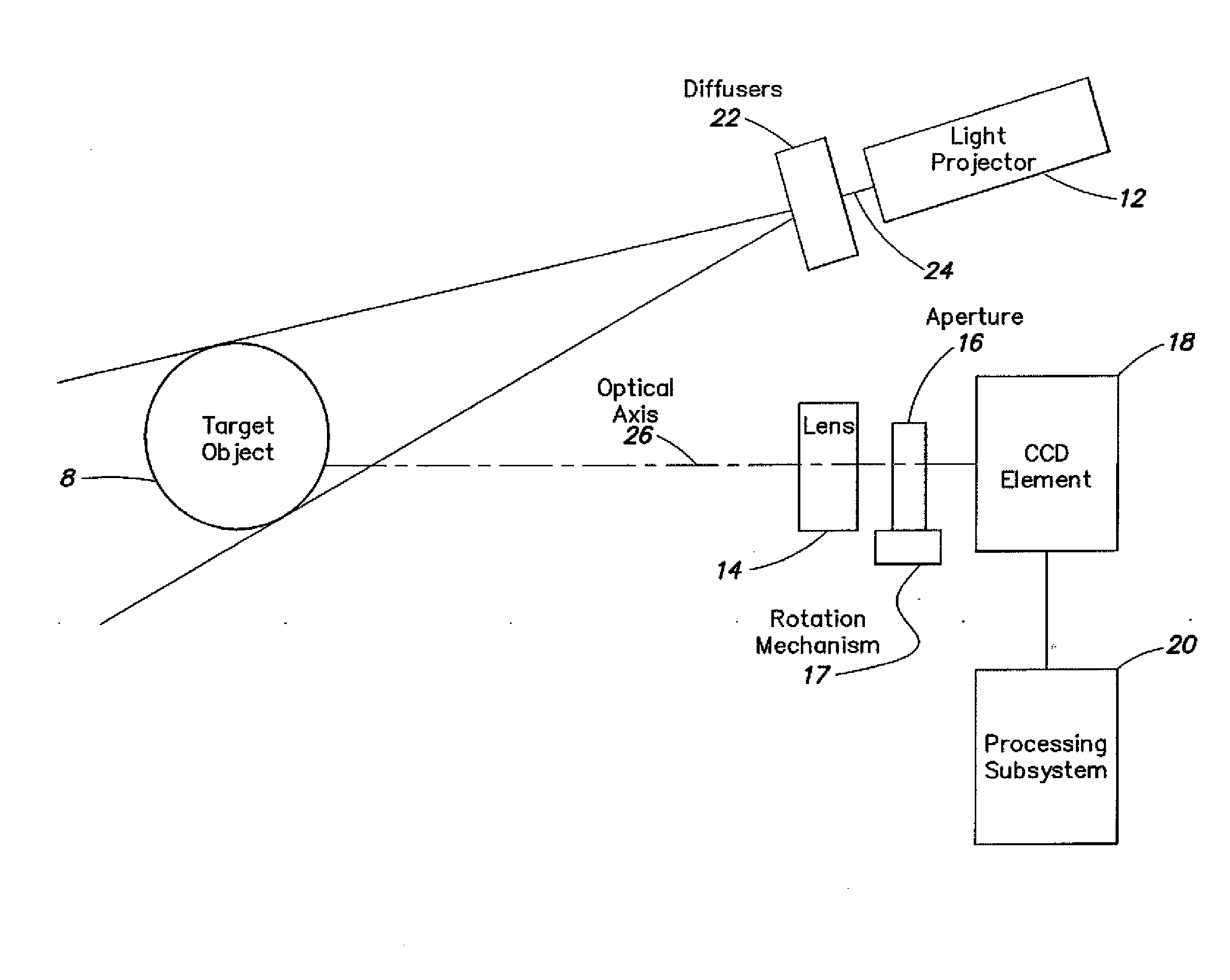
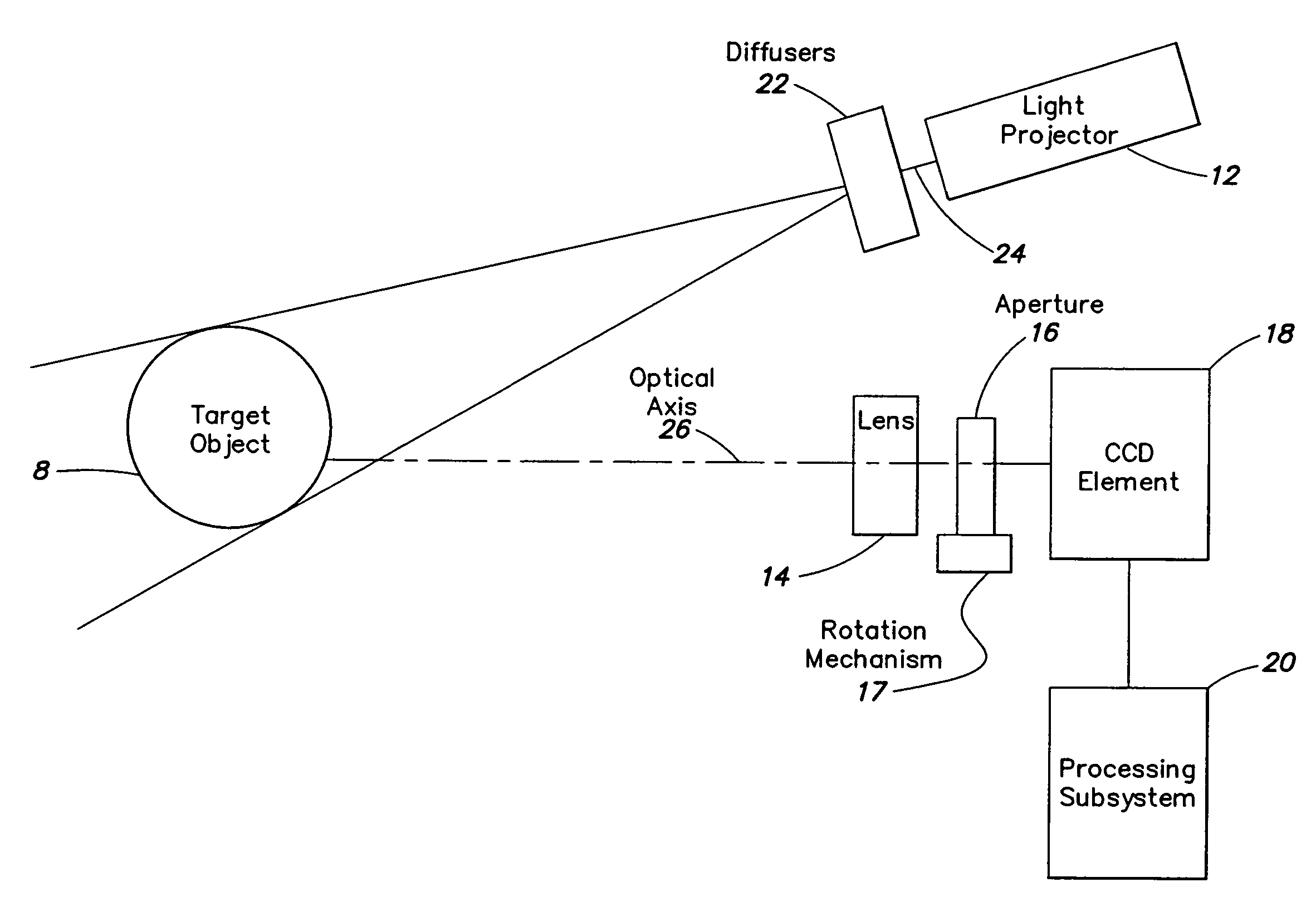
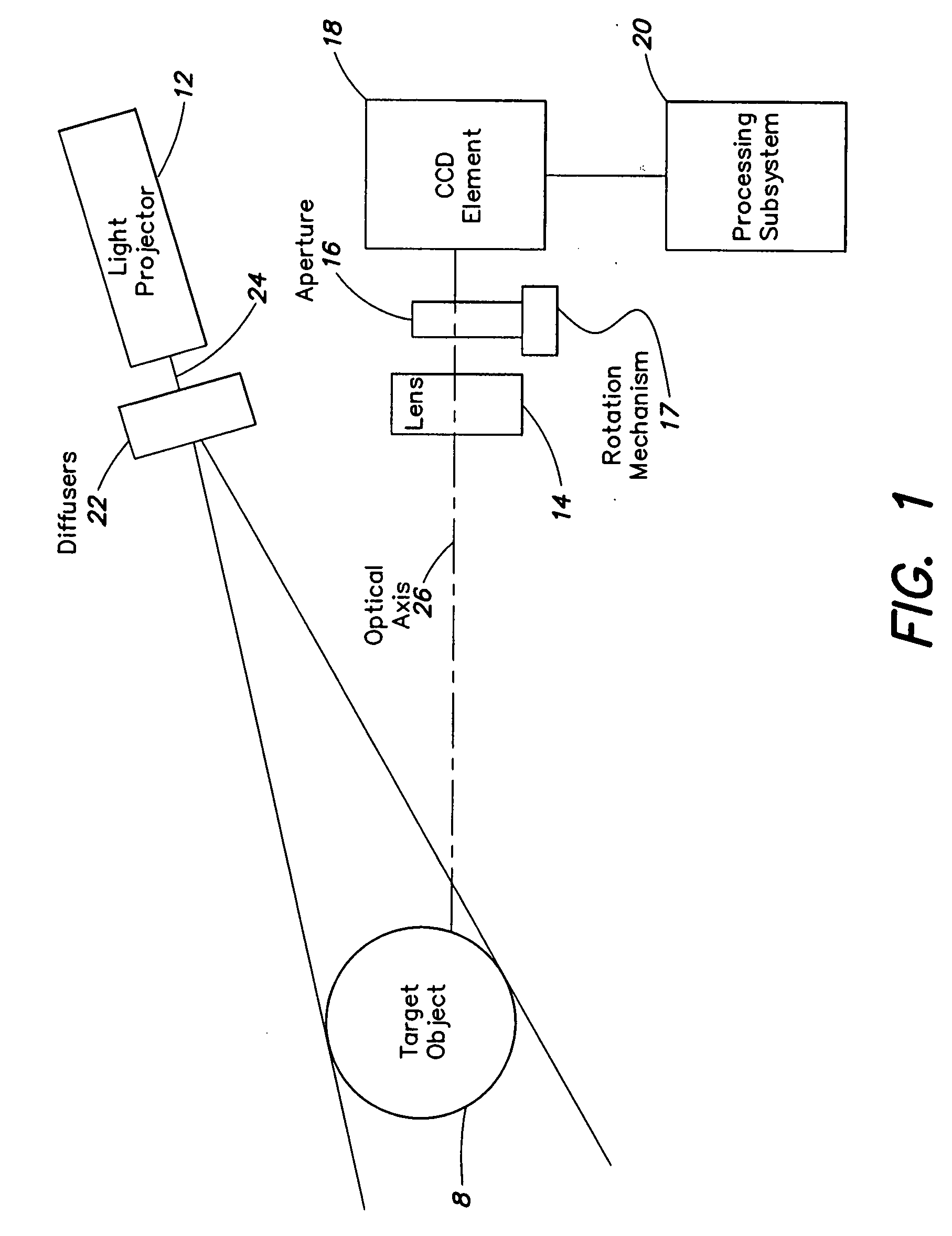
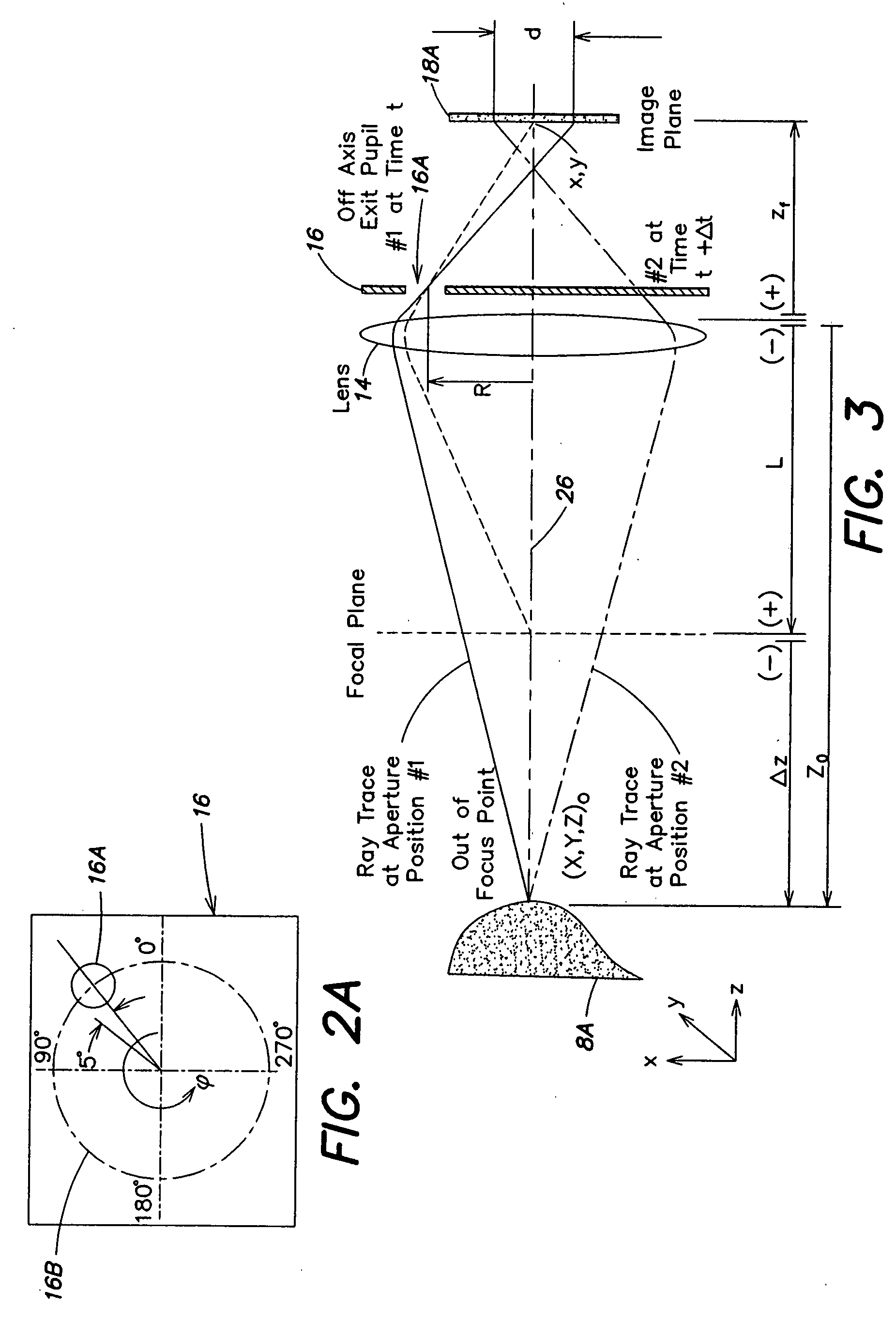
A high-speed three-dimensional imaging system includes a single lens camera subsystem with an active imaging element and CCD element, and a correlation processing subsystem. The active imaging element can be a rotating aperture which allows adjustable non-equilateral spacing between defocused images to achieve greater depth of field and higher sub-pixel displacement accuracy. A speckle pattern is projected onto an object and images of the resulting pattern are acquired from multiple angles. The images are locally cross-correlated using a sparse array image correlation technique and the surface is resolved by using relative camera position information to calculate the three-dimensional coordinates of each locally correlated region. Increased resolution and accuracy are provided by recursively correlating the images down to the level of individual points of light and using the Gaussian nature of the projected speckle pattern to determine subpixel displacement between images. Processing is done at very high-speeds by compressing the images before they are correlated. Correlation errors are eliminated during processing by a technique based on the multiplication of correlation table elements from one or more adjacent regions.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Three-dimensional photoacoustic imager and methods for calibrating an imager
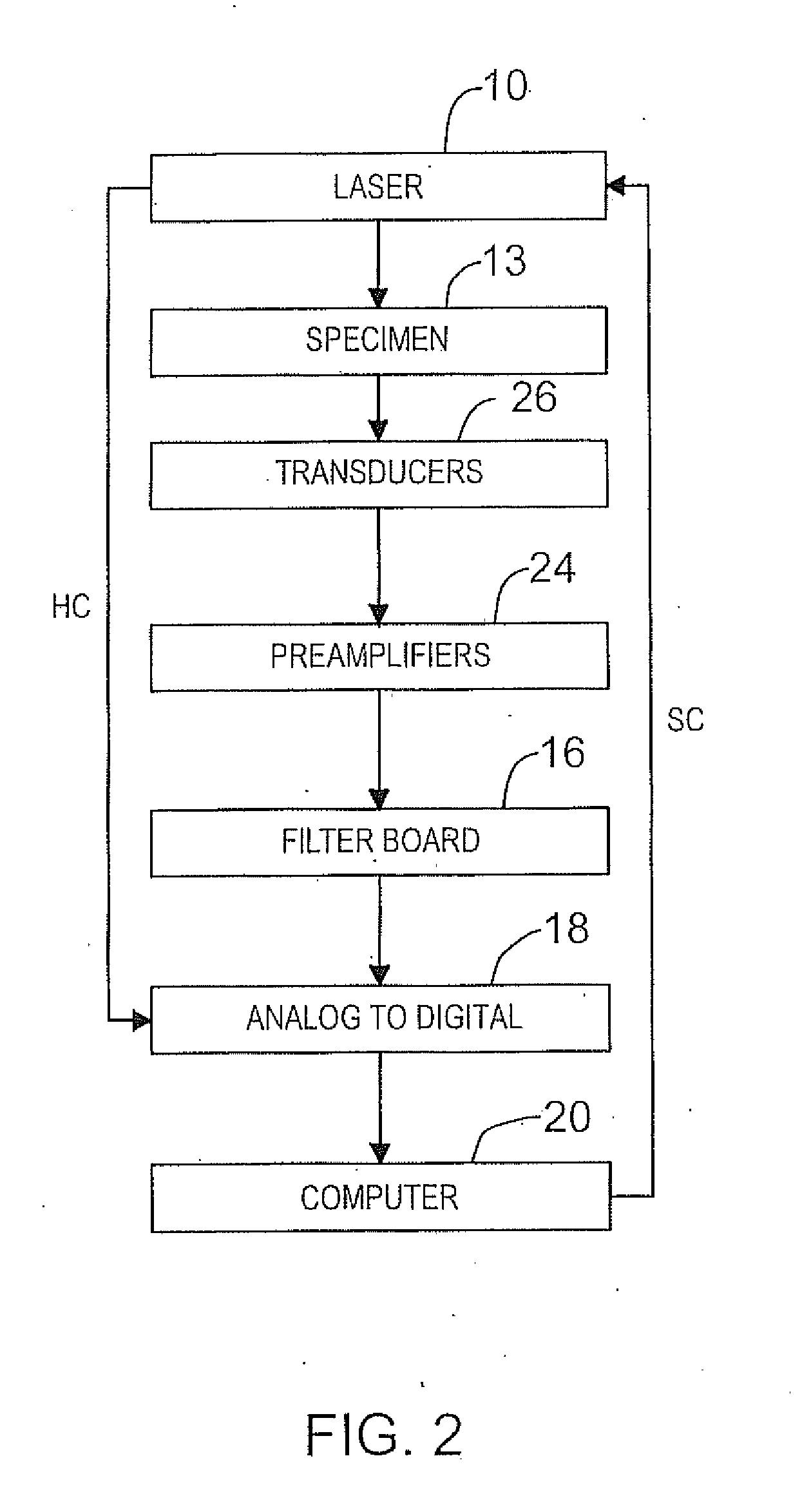
InactiveUS20100249570A1Illuminating subjectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesData acquisitionReconstruction algorithm
A photoacoustic imaging apparatus is provided for medical or other imaging applications and also a method for calibrating this apparatus. The apparatus employs a sparse array of transducer elements and a reconstruction algorithm. Spatial calibration maps of the sparse array are used to optimize the reconstruction algorithm. The apparatus includes a laser producing a pulsed laser beam to illuminate a subject for imaging and generate photoacoustic waves. The transducers are fixedly mounted on a holder so as to form the sparse array. A photoacoustic (PA) waves are received by each transducer. The resultant analog signals from each transducer are amplified, filtered, and converted to digital signals in parallel by a data acquisition system which is operatively connected to a computer. The computer receives the digital signals and processes the digital signals by the algorithm based on iterative forward projection and back-projection in order to provide the image.
Owner:MULTI MAGNETICS
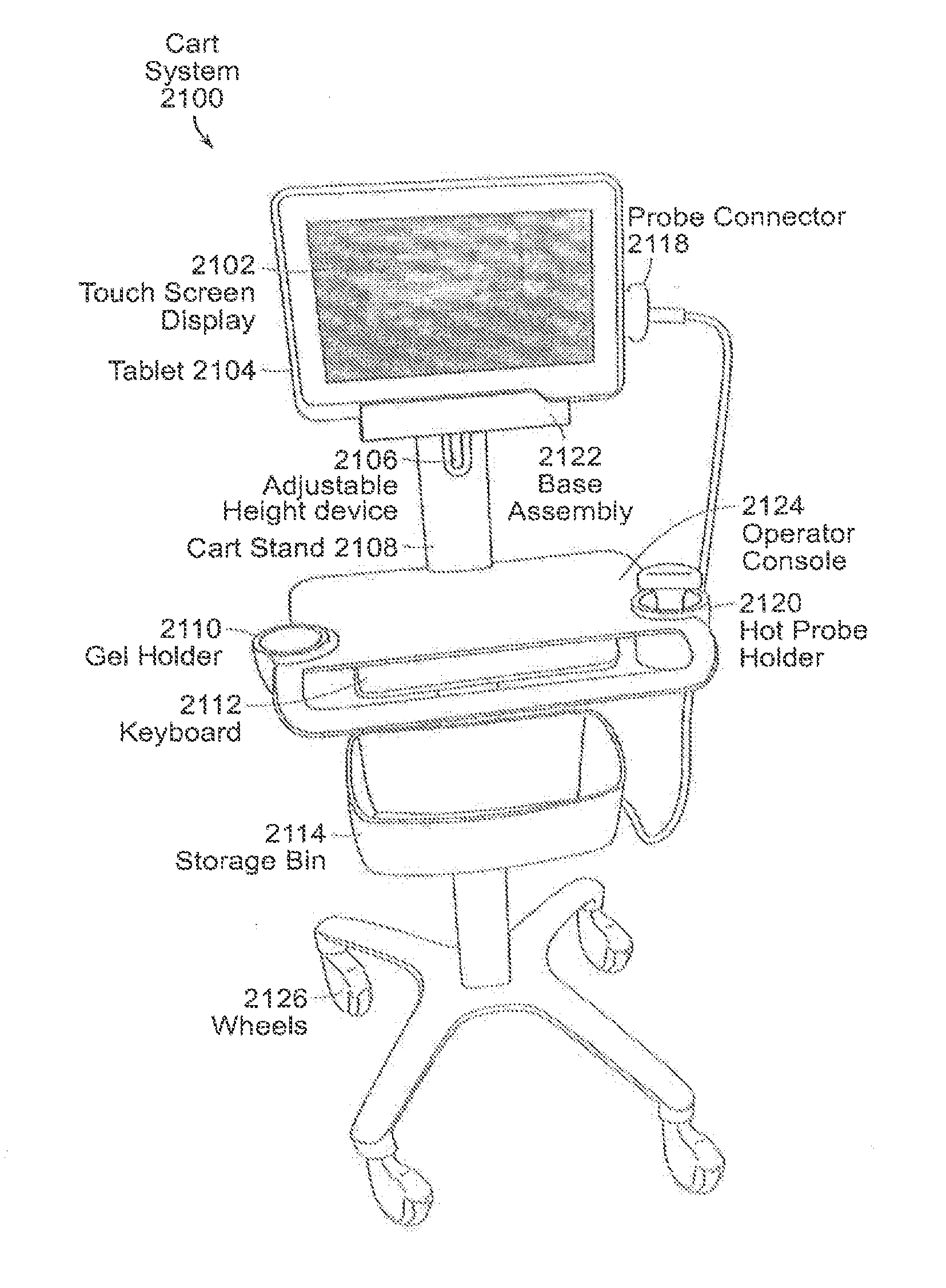
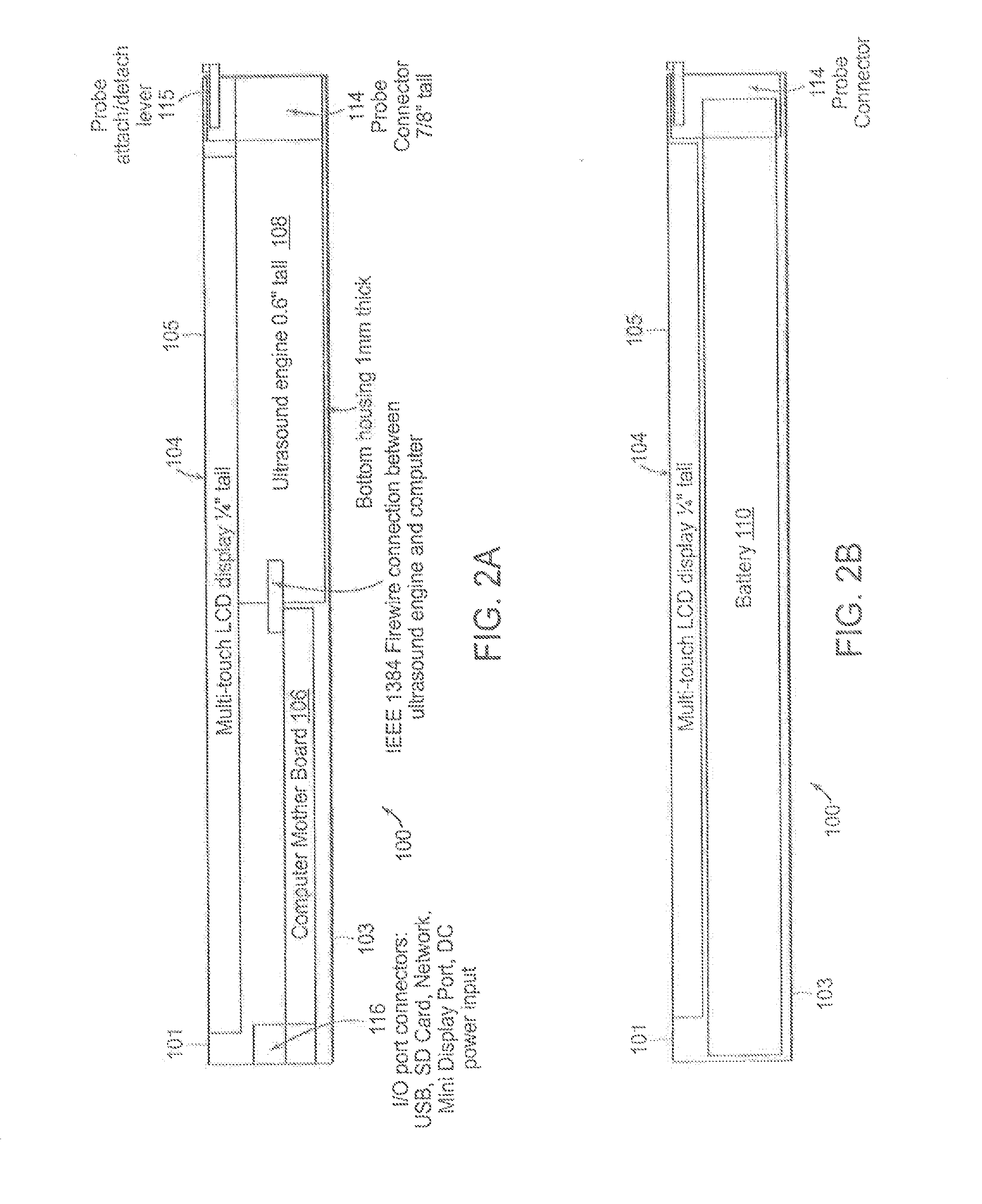
Tablet ultrasound system
ActiveUS20140121524A1Minimize packaging sizeMinimized footprintSolid-state devicesTomographyUltrasonographySonification
Exemplary embodiments provide systems and methods for portable medical ultrasound imaging. Preferred embodiments utilize a tablet touchscreen display operative to control imaging and display operations without the need for using traditional keyboards or controls. Certain embodiments provide ultrasound imaging system in which the scan head includes a beamformer circuit that performs far field sub array beamforming or includes a sparse array selecting circuit that actuates selected elements. Exemplary embodiments also provide an ultrasound engine circuit board including one or more multi-chip modules, and a portable medical ultrasound imaging system including an ultrasound engine circuit board with one or more multi-chip modules. Exemplary embodiments also provide methods for using a hierarchical two-stage or three-stage beamforming system, three dimensional ultrasound images which can be generated in real-time.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
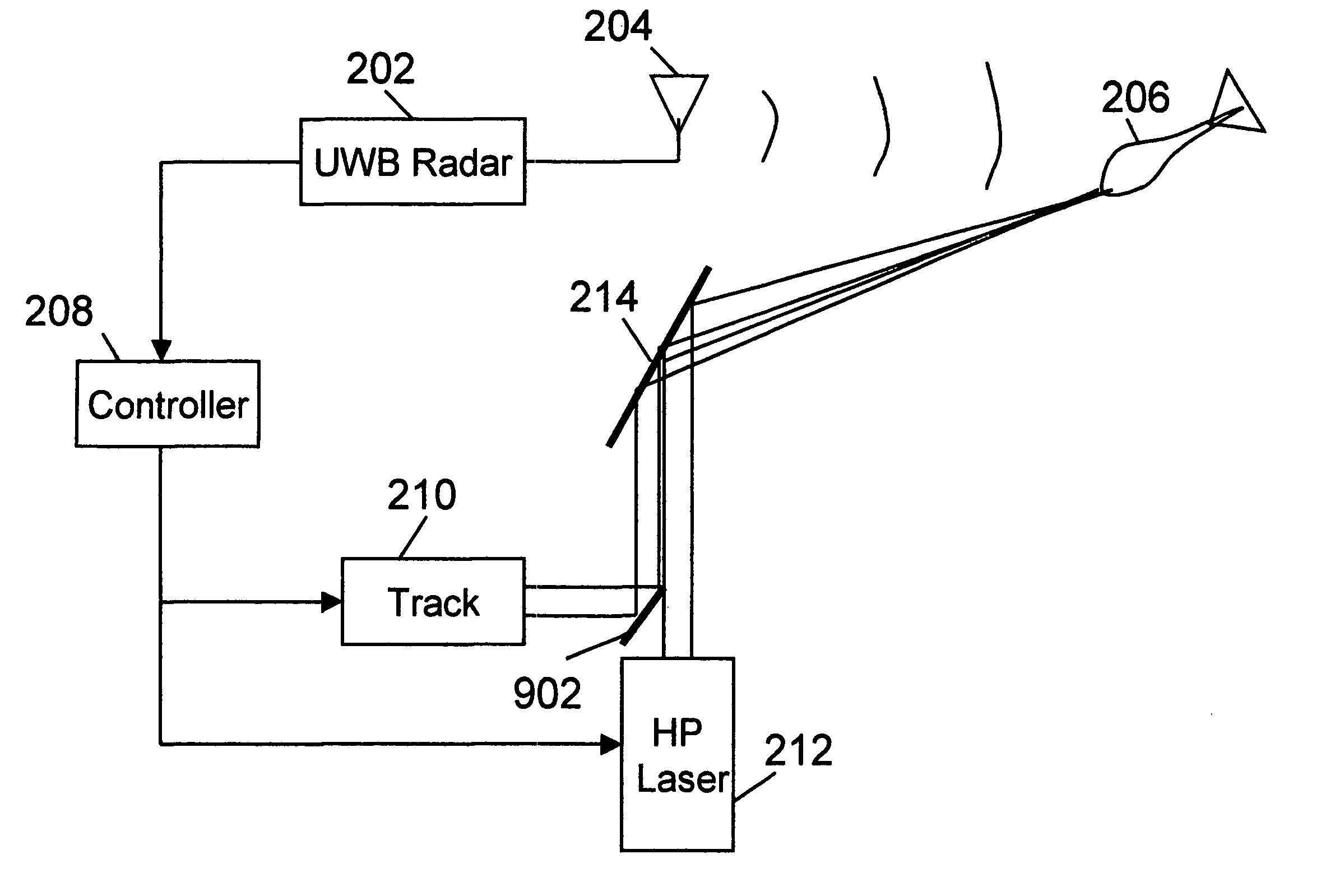
System and method for ultra wideband subarray beam steering
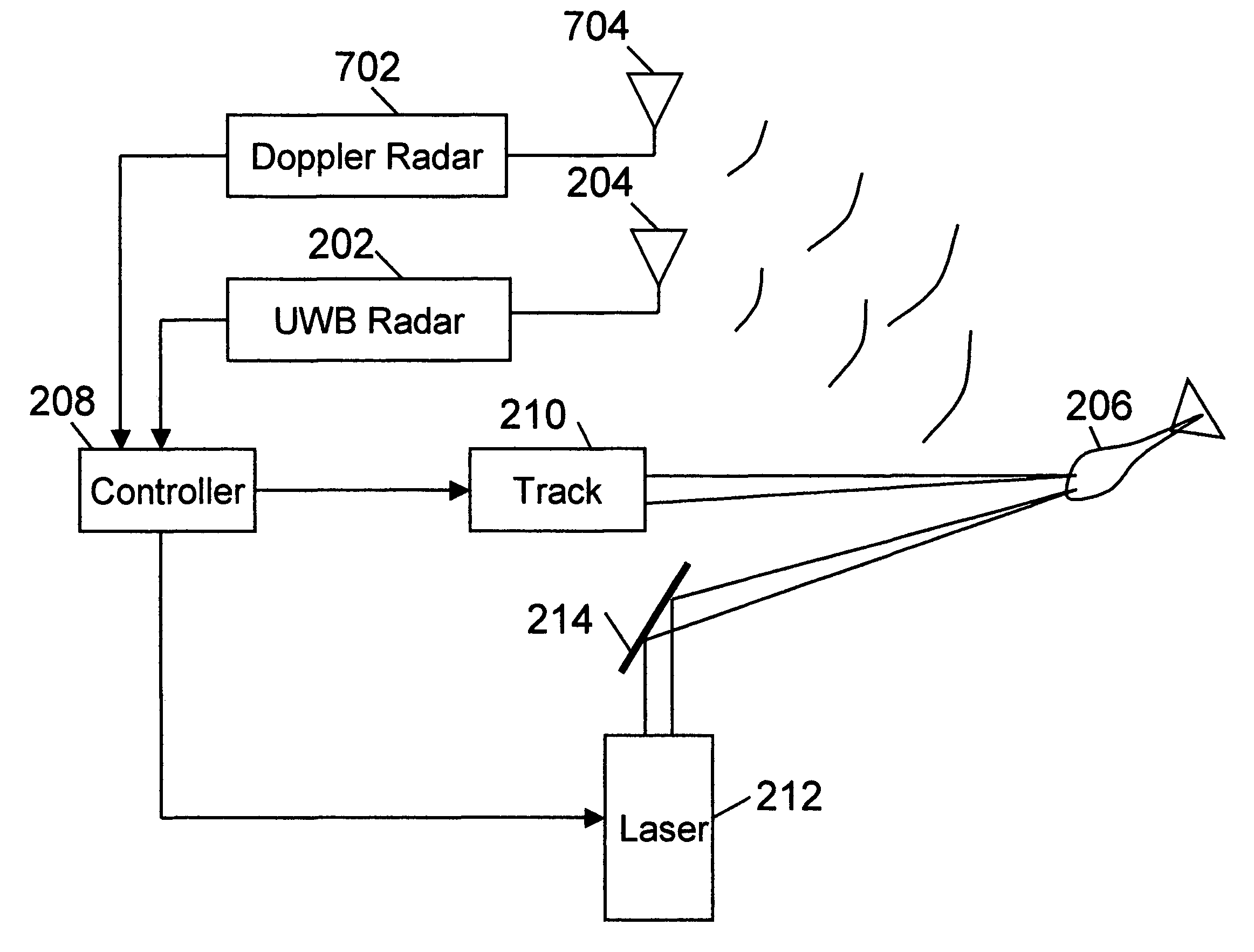
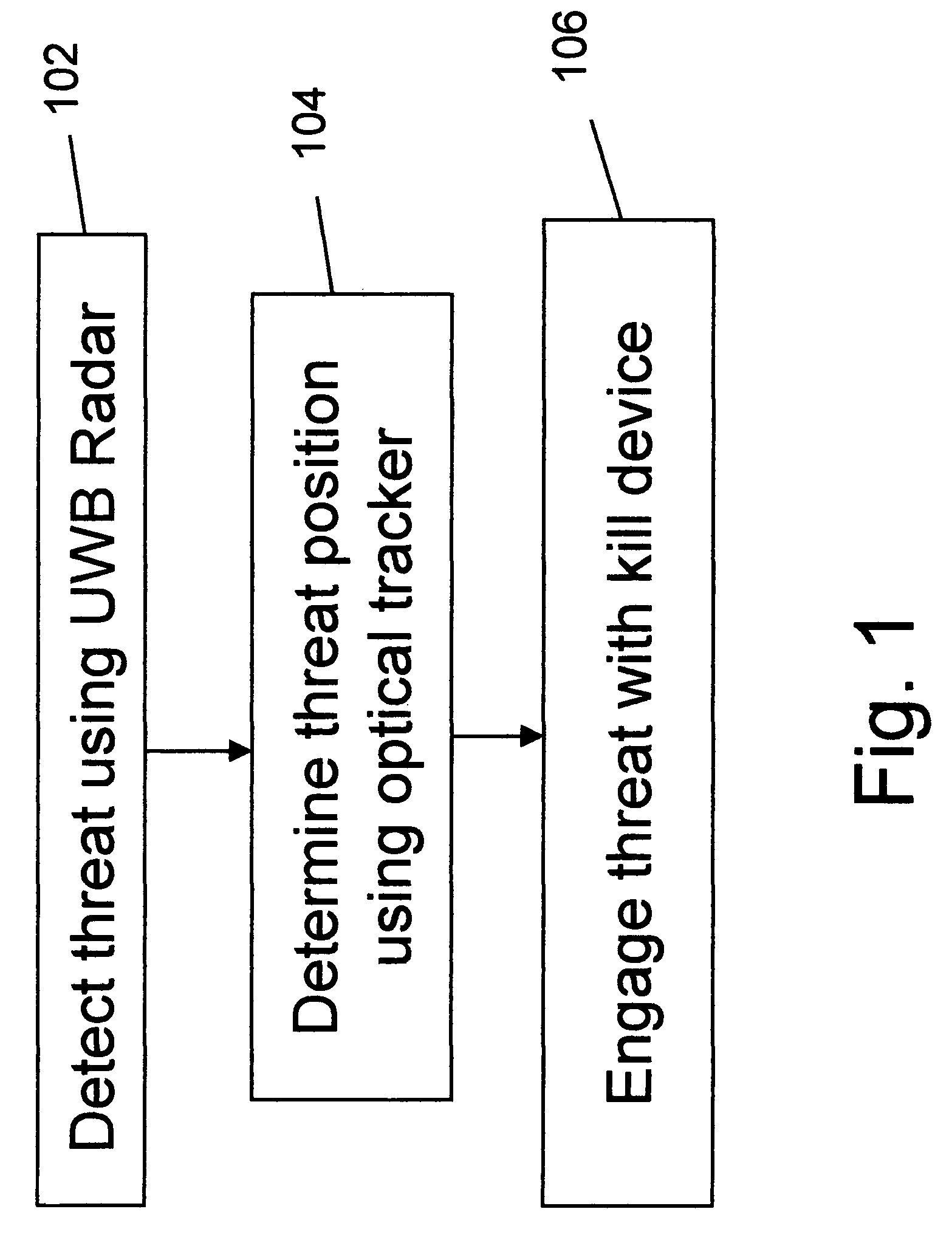
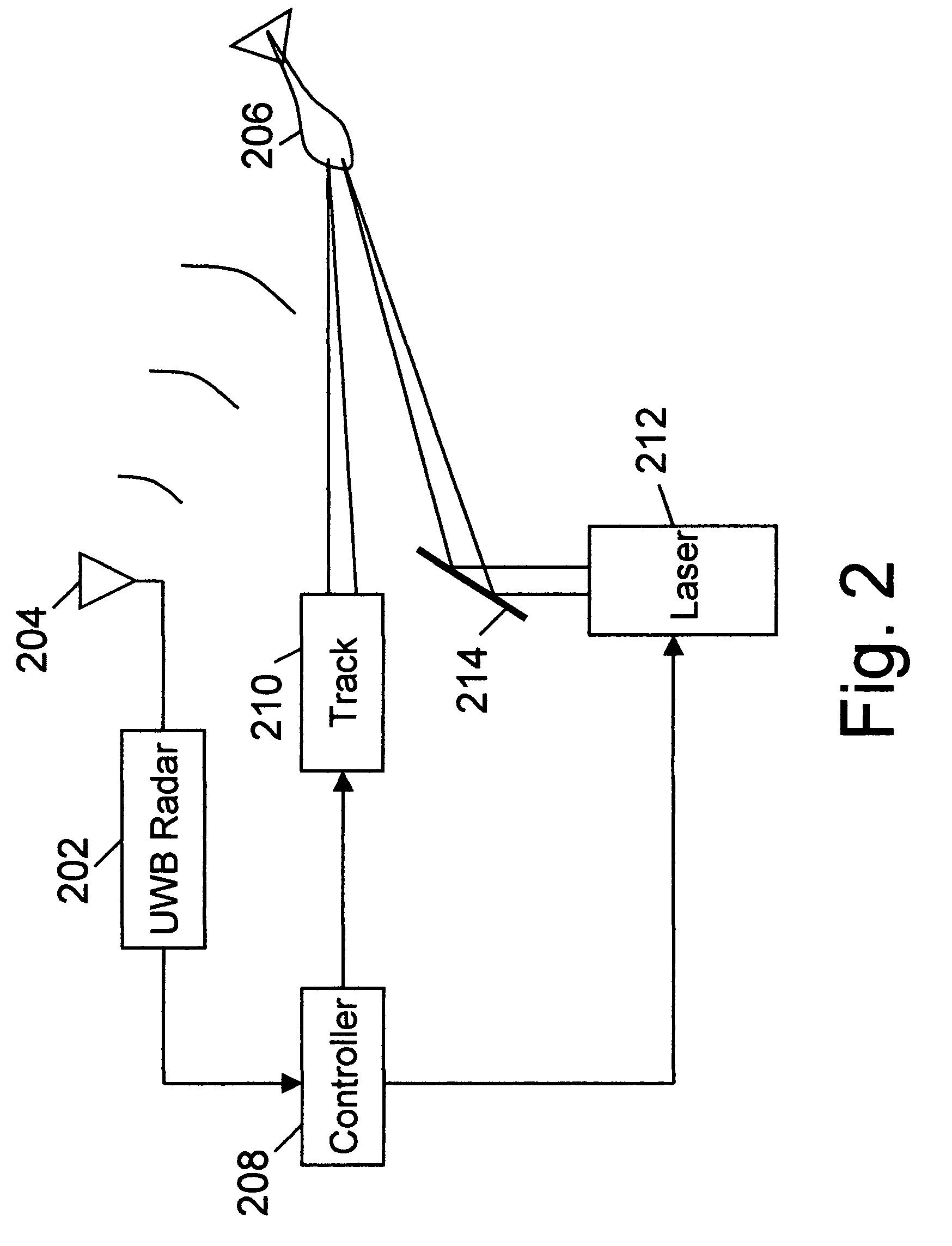
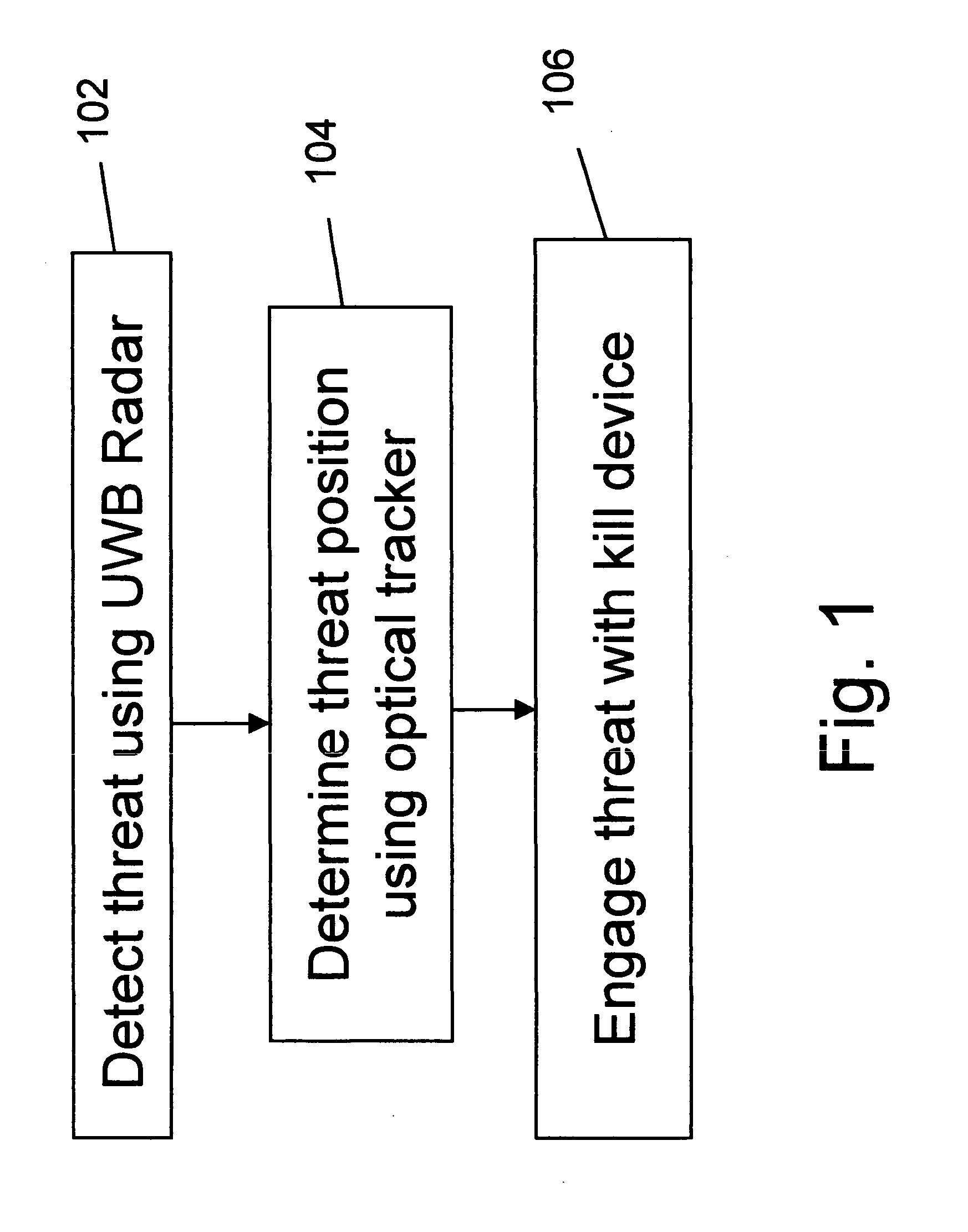
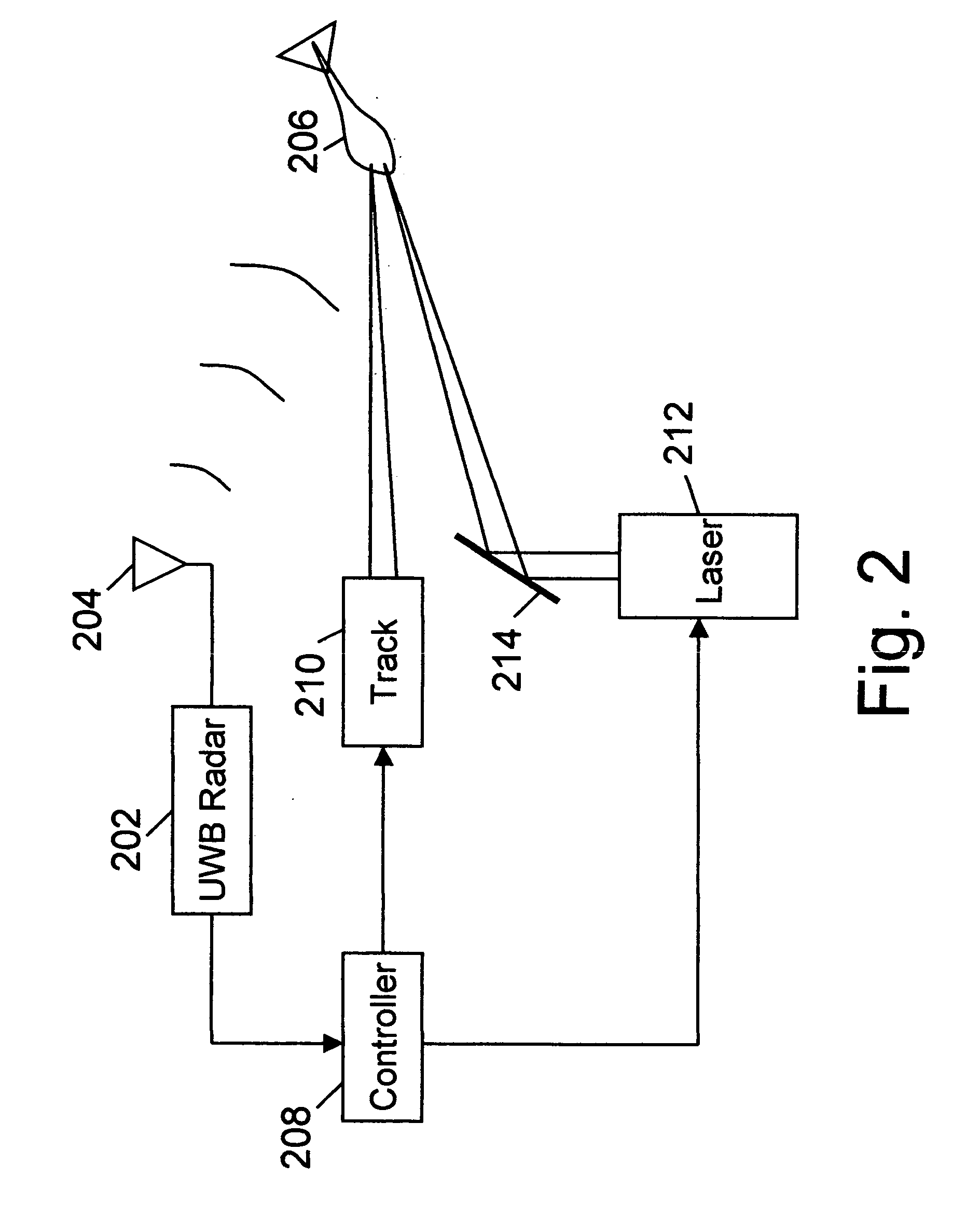
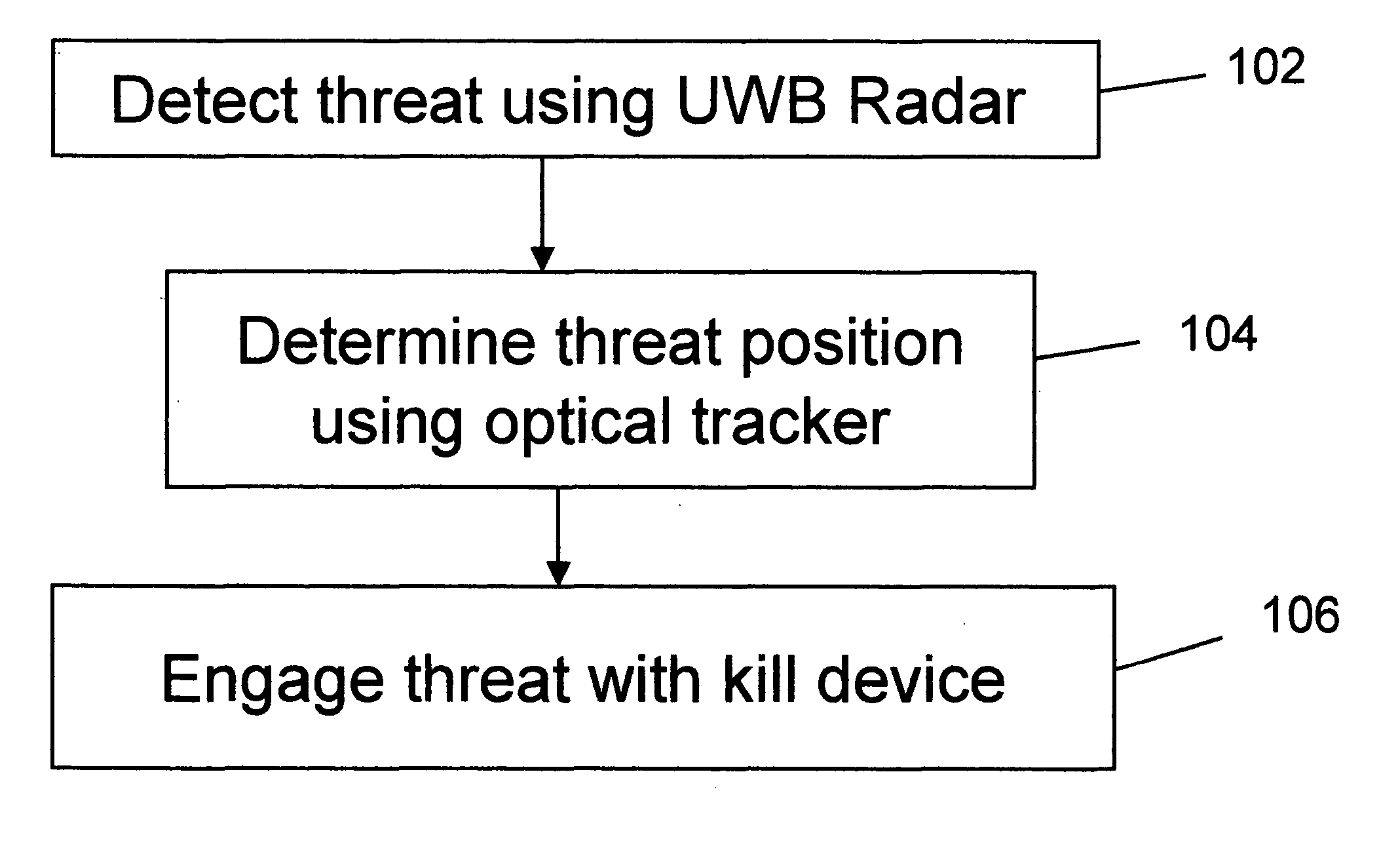
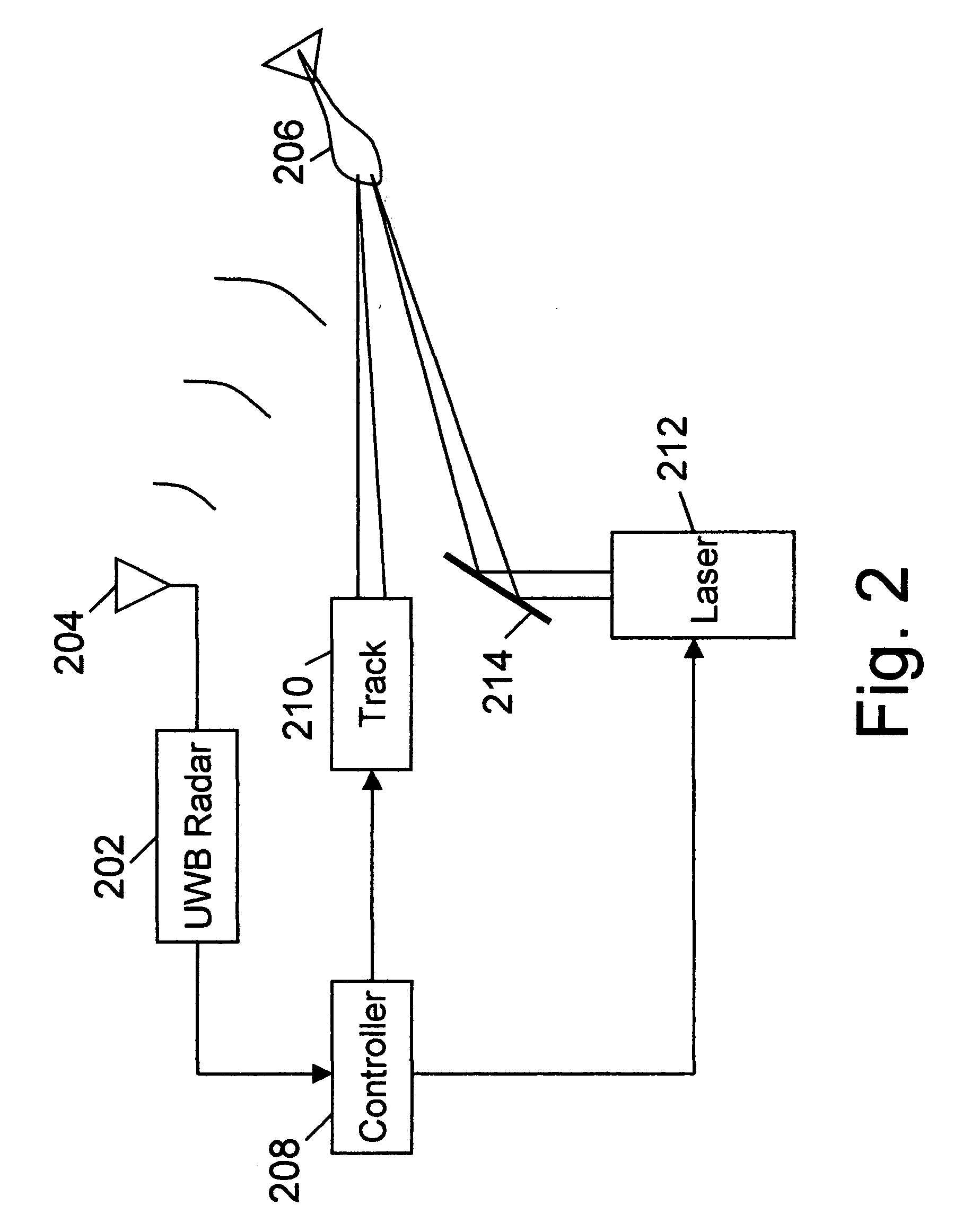
An active protection system comprising an ultra wideband (UWB) radar for threat detection, an optical tracker for precision threat position measurement, and a high powered laser for threat kill or mitigation. The UWB radar may use a sparse array antenna and may also utilize Doppler radar information. The high powered laser may be of the optically pumped solid state type and in one embodiment may share optics with the optical tracker. In one embodiment, the UWB radar is used to focus the high power laser. Alternative interceptor type kill mechanisms are disclosed. In a further embodiment, the kill mechanism may be directed to the source of the threat. In a further embodiment, an antenna array is steered by using subarray groups having fixed timing within the group and variable timing from group to group.
Owner:TIME DOMAIN
Method and system for high resolution, ultra fast 3-D imaging
InactiveUS20080031513A1Add depthHigh displacement accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionRapid imagingImage resolution
A high-speed three-dimensional imaging system includes a single lens camera subsystem with an active imaging element and CCD element, and a correlation processing subsystem. The active imaging element can be a rotating aperture which allows adjustable non-equilateral spacing between defocused images to achieve greater depth of field and higher sub-pixel displacement accuracy. A speckle pattern is projected onto an object and images of the resulting pattern are acquired from multiple angles. The images are locally cross-correlated using a sparse array image correlation technique and the surface is resolved by using relative camera position information to calculate the three-dimensional coordinates of each locally correlated region. Increased resolution and accuracy are provided by recursively correlating the images down to the level of individual points of light and using the Gaussian nature of the projected speckle pattern to determine subpixel displacement between images. Processing is done at very high-speeds by compressing the images before they are correlated. Correlation errors are eliminated during processing by a technique based on the multiplication of correlation table elements from one or more adjacent regions.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for intrusion detection using a time domain radar array
InactiveUS20080165046A1High resolutionImprove performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainUltra-wideband
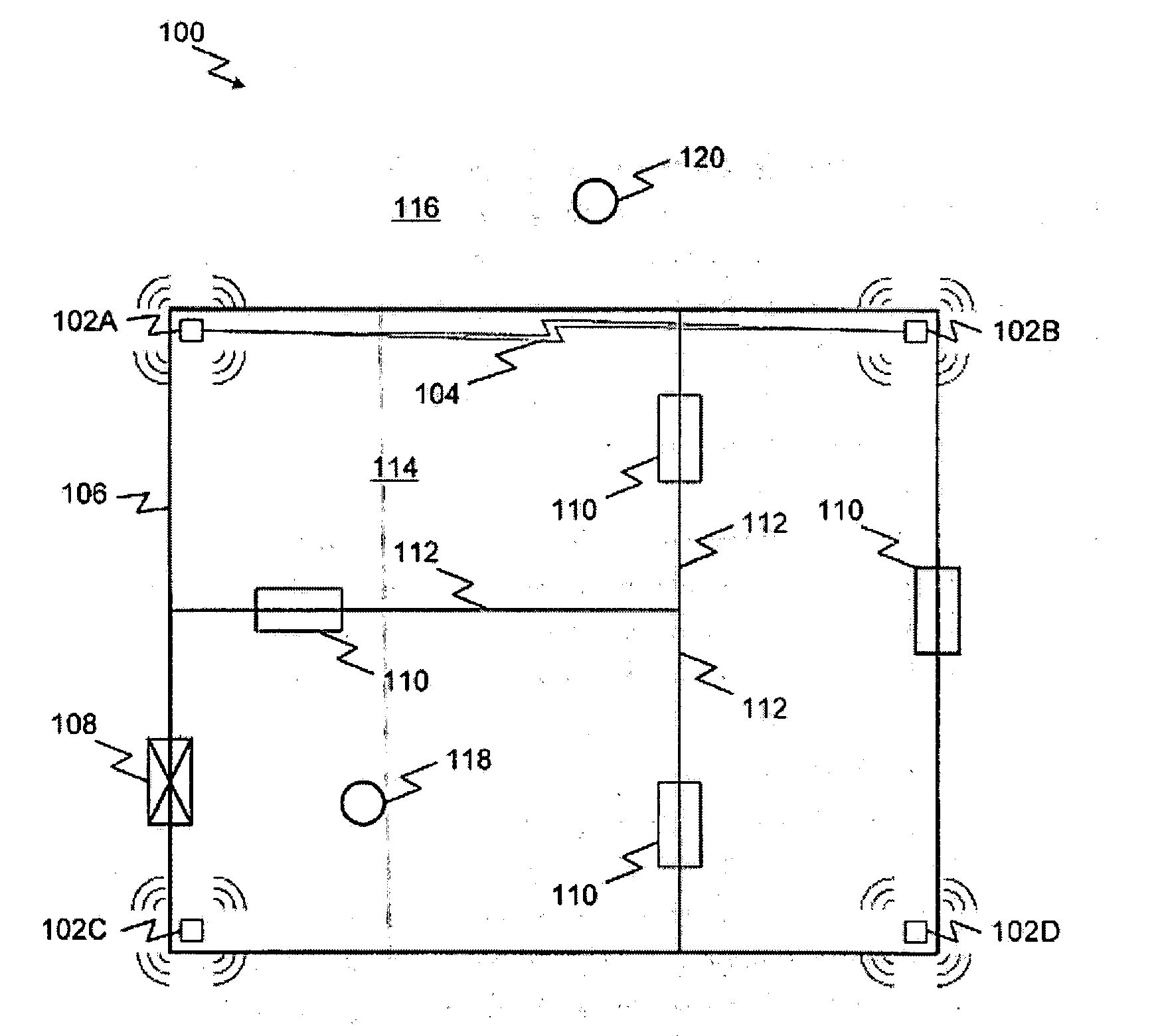
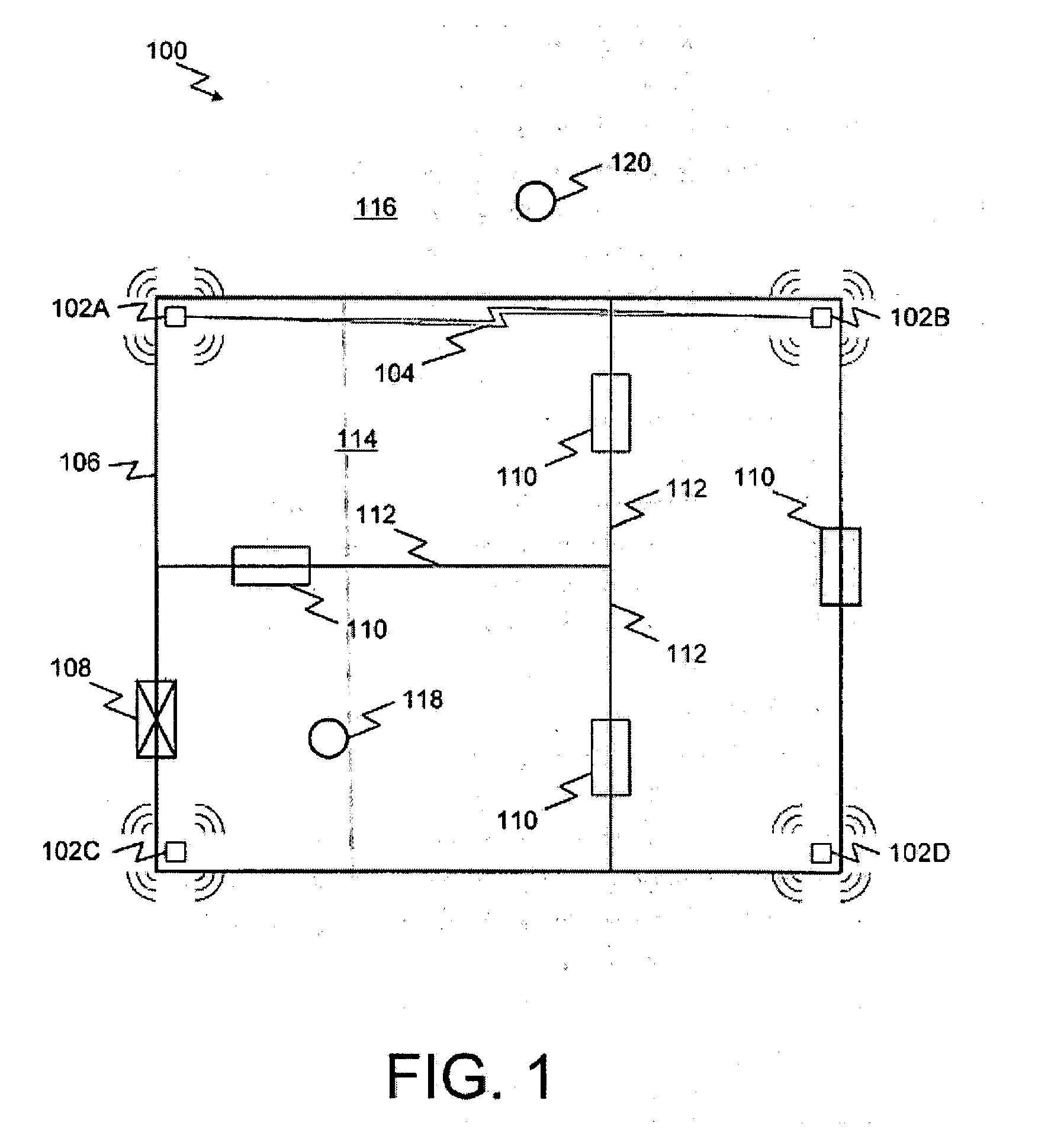
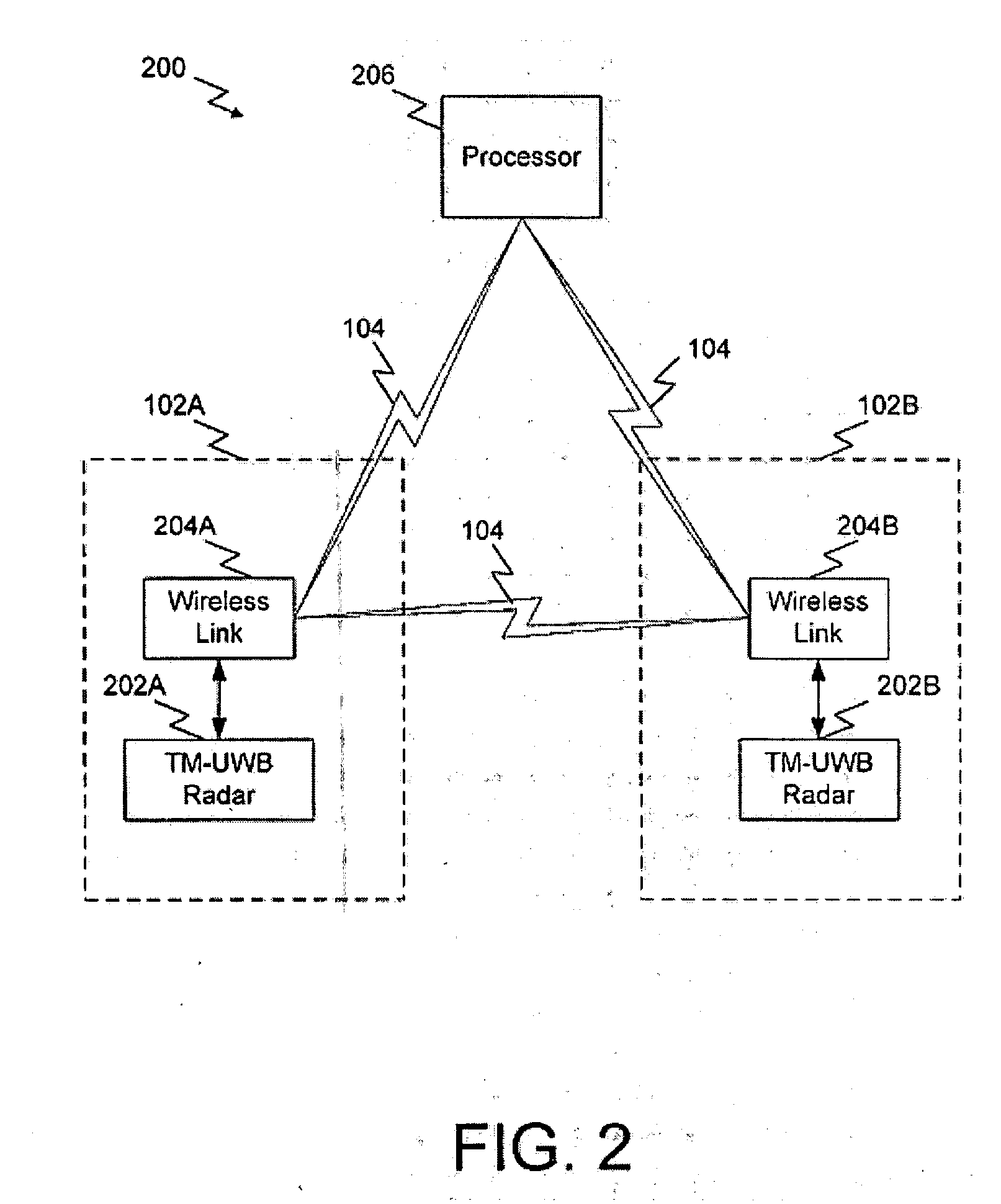
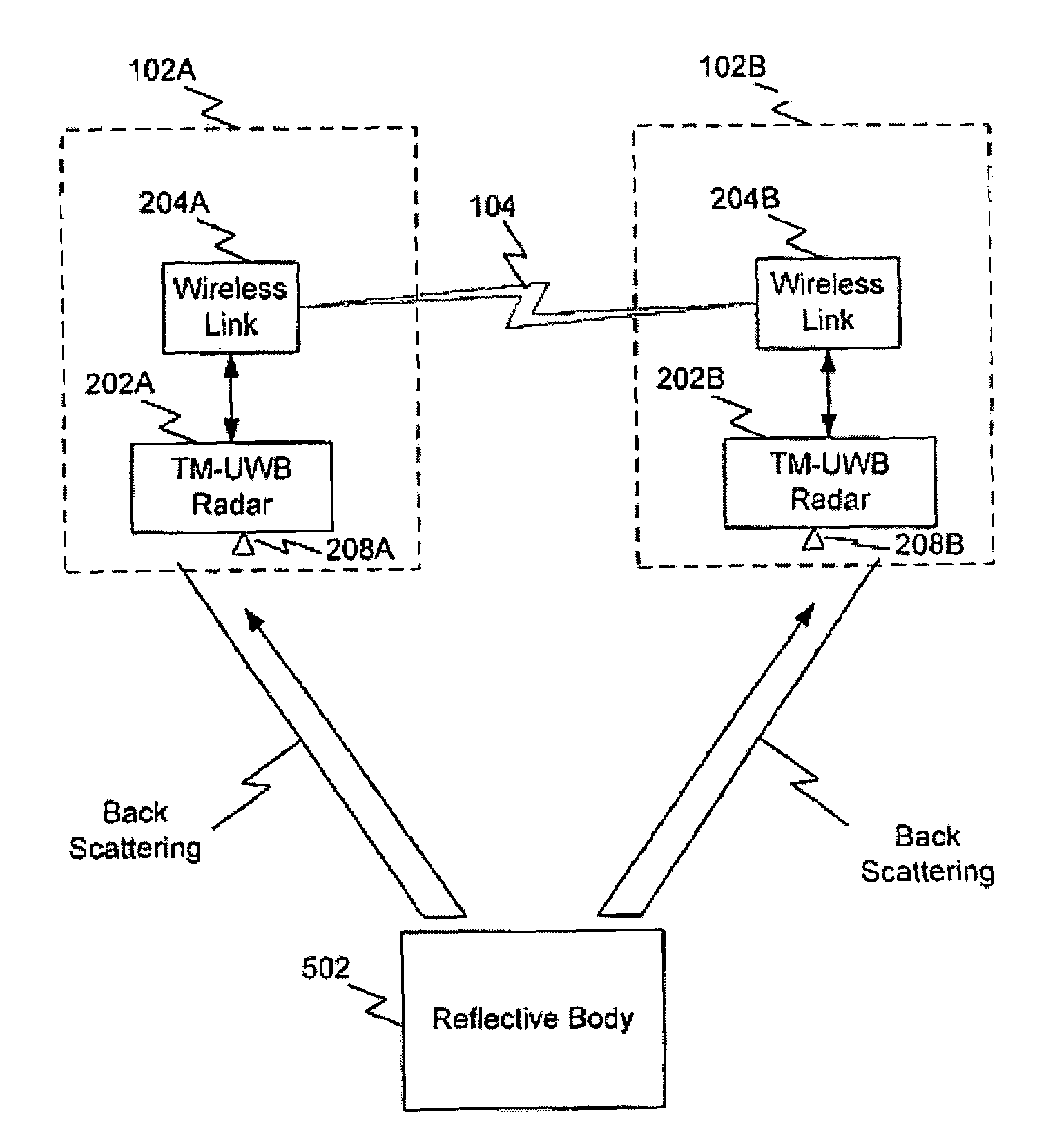
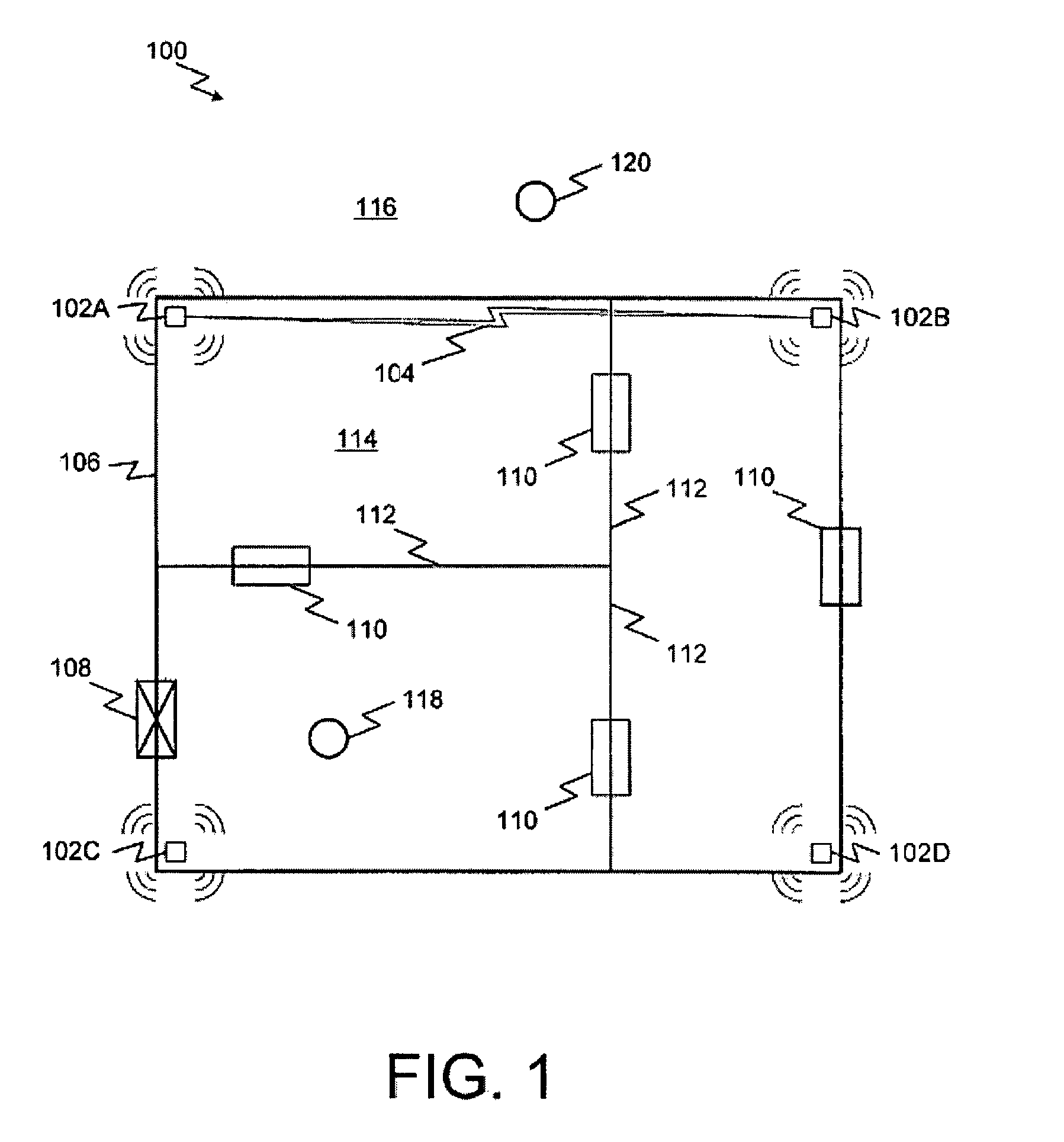
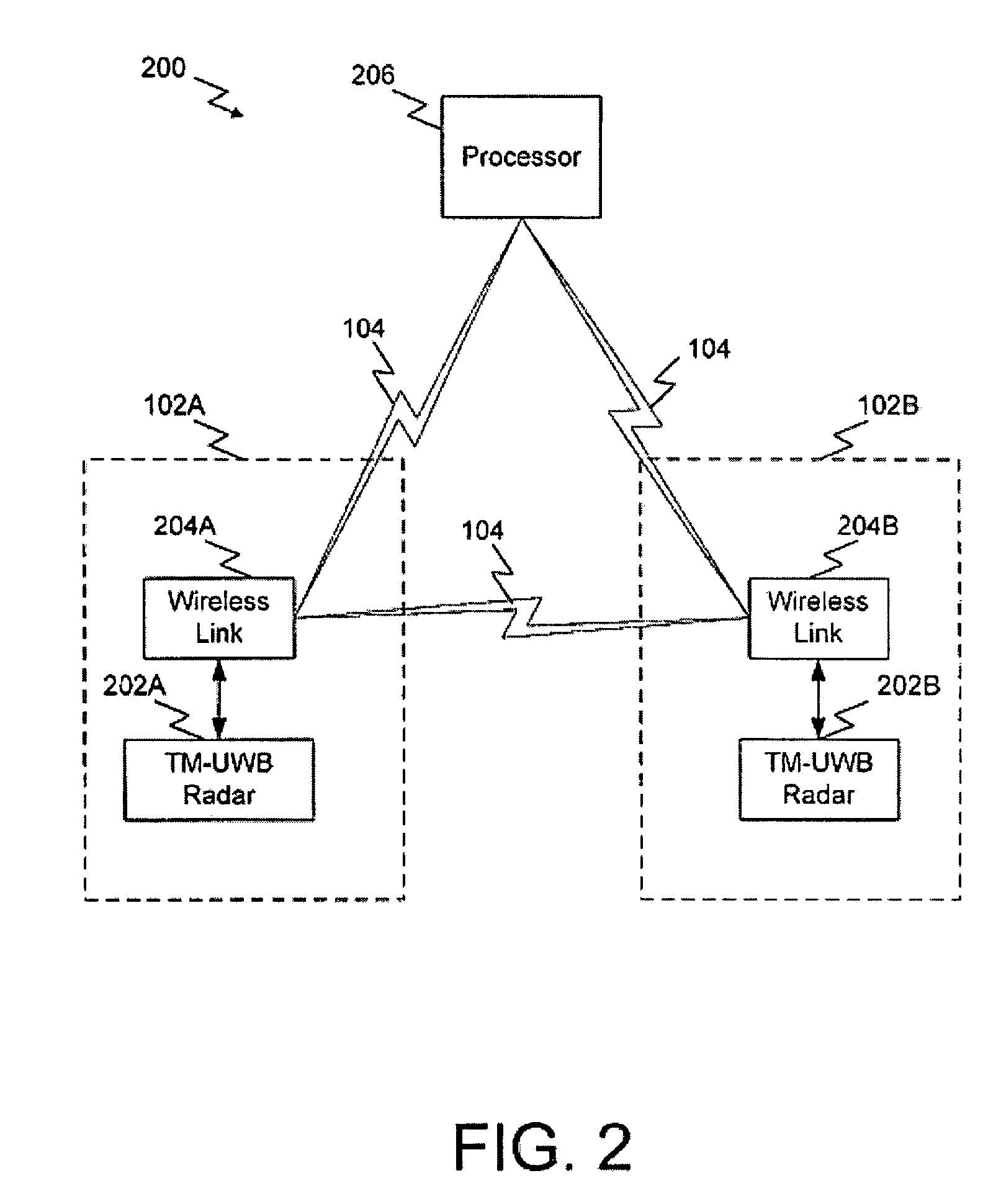
A system and method for highly selective intrusion detection using a sparse array of ultra wideband (UWB) radars. Two or more UWB radars are arranged in a sparse array around an area to be protected. Each UWB radar transmits ultra wideband pulses that illuminate the area to be protected. Signal return data is processed to determine, among other things, whether an alarm condition has been triggered. High resolution radar images are formed that give an accurate picture of the area to be protected. This image is used to detect motion in a highly selective manner and to track moving objects within the protected area. Motion can be distinguished based on criteria appropriate to the environment in which the intrusion detection system operates.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
Ultrasound 3D imaging system
InactiveUS20120179044A1Reduce the amount requiredImproved harmonic imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationEngineering
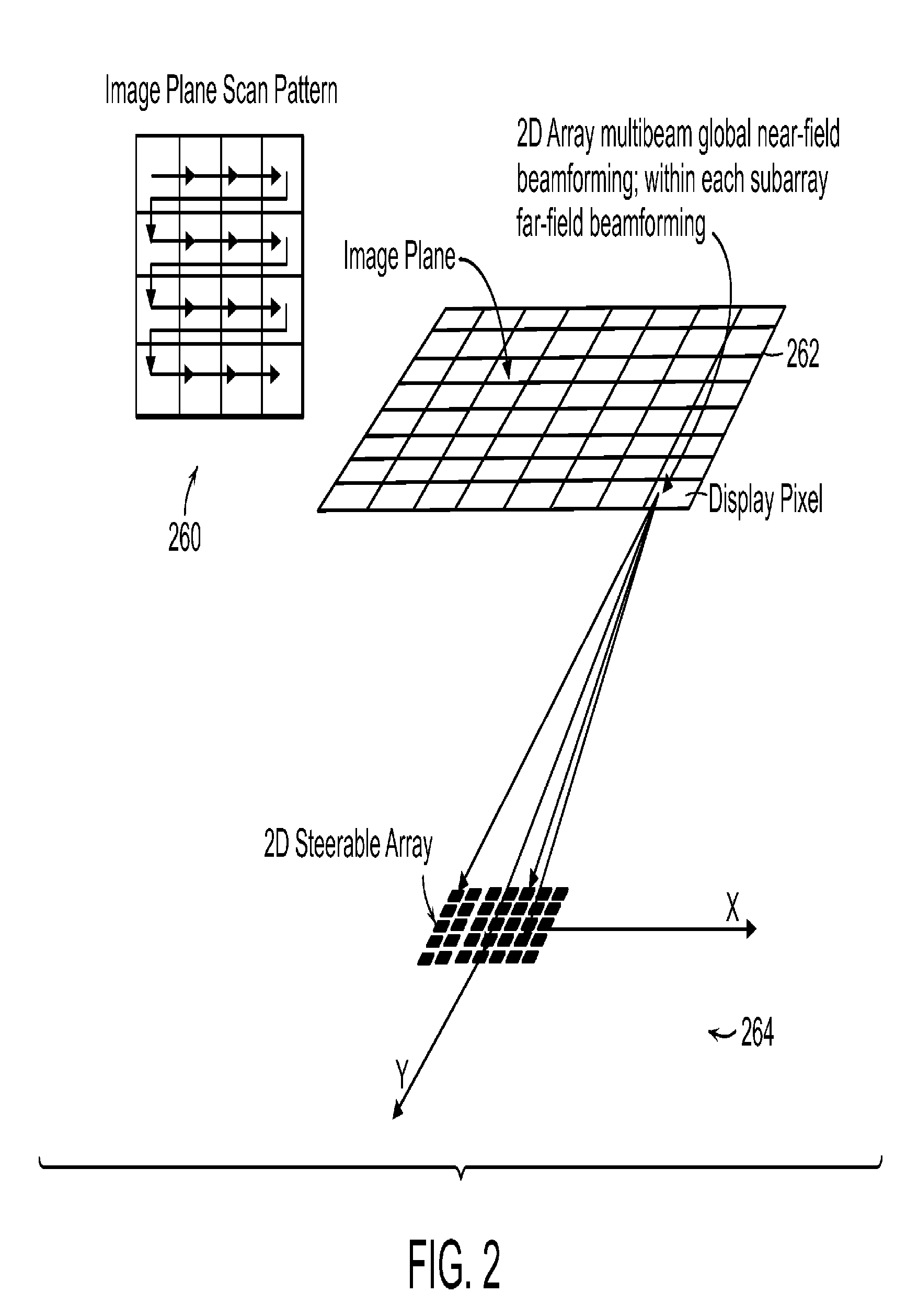
The present invention relates to an ultrasound imaging system in which the scan head includes a beamformer circuit that performs far field subarray beamforming or includes a sparse array selecting circuit that actuates selected elements. When using a hierarchical two-stage or three-stage beamforming system, three dimensional ultrasound images can be generated in real-time. The invention further relates to flexible printed circuit boards in the probe head. The invention furthermore relates to the use of coded or spread spectrum signalling in ultrasound imaging systems. Matched filters based on pulse compression using Golay code pairs improve the signal-to-noise ratio thus enabling third harmonic imaging with suppressed sidelobes. The system is suitable for 3D full volume cardiac imaging.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
Ultrasound 3D imaging system
ActiveUS20100174194A1Minimizing energyEliminate periodicityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSonification
The present invention relates to an ultrasound imaging system in which the scan head either includes a beamformer circuit that performs far field subarray beamforming or includes a sparse array selecting circuit that actuates selected elements. When used with second stage beamforming system, three dimensional ultrasound images can be generated.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
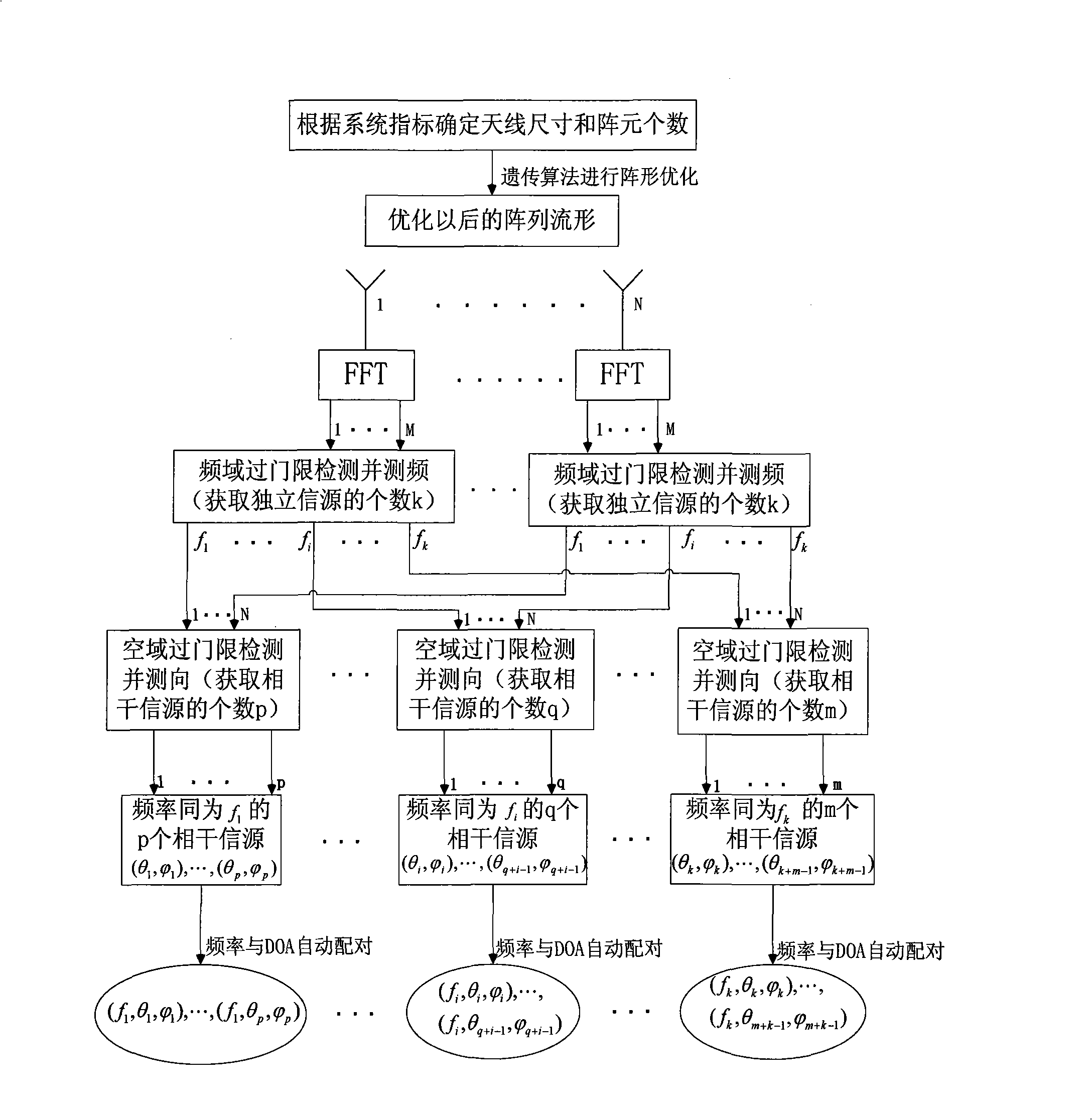
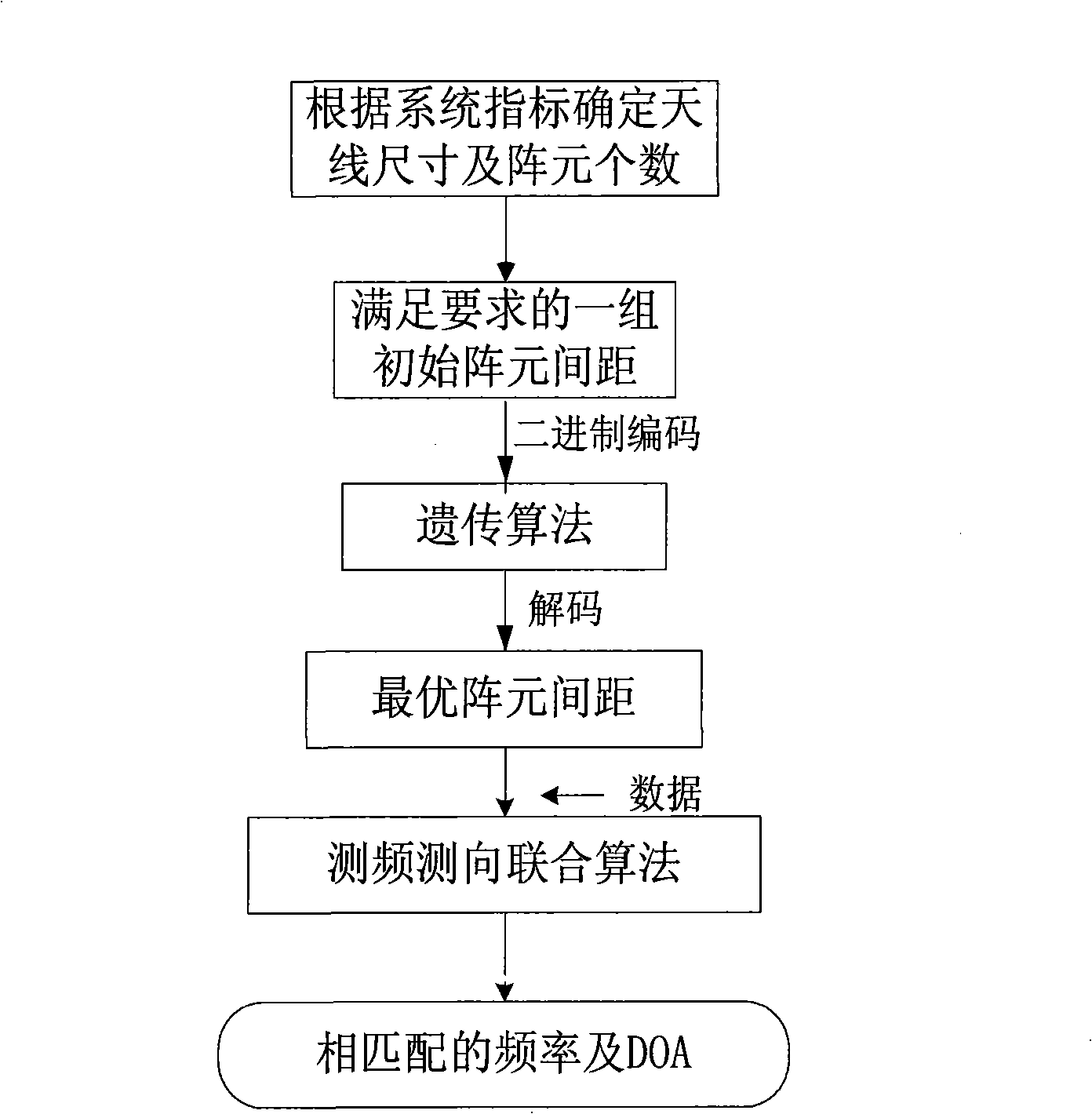
Method for optimizing space between broad band phased array elements and measuring frequency and direction of frequency domain multiple targets
InactiveCN101349742AImproved DF resolutionSolve the direction finding ambiguity problemRadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFrequency measurementsArray element
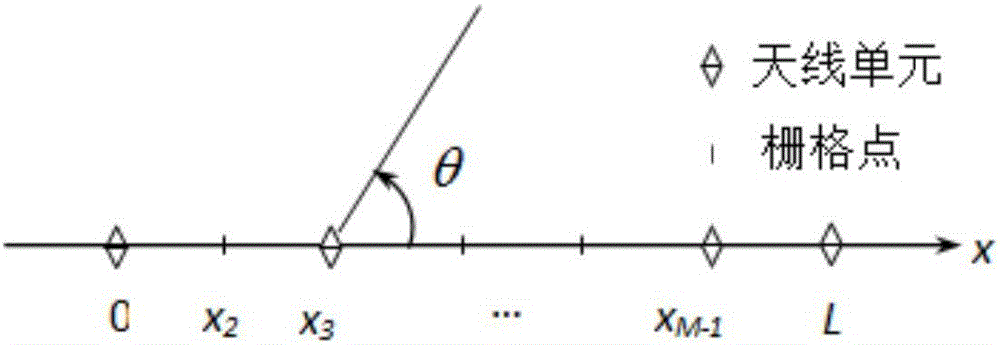
The invention discloses a method for matrix element distance optimization and frequency domain multi target frequency and direction measurement of wideband phased arrays, for realizing the direction measurement of multiple targets having narrow band coherence and irrelevance of a wideband receiver, resolving the contradiction between the direction measurement resolution and unambiguous direction measurement of sparse array, and realizing more accurate target detection under a certain channel error. The method comprises the steps of: first using uneven array, using genetic algorism to optimize the distance of array elements to satisfy the higher direction measurement resolution and high direction measurement accuracy of spatial unambiguous condition; based on the optimized array, realizing the frequency domain multi target frequency and direction measurement algorism as a DOA evaluation algorism which processes frequency domain accumulation, frequency domain check and frequency measurement for the data of each array element channel and realizes frequency automatic match. The algorism adopts array optimization, frequency domain peak snapshot frequency and direction measurement joint algorism. The invention can be applied for the multi narrow band target accurate frequency and direction measurement of wideband receivers in the airborne and satellite-borne electronic reconnaissance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Two-dimensional ultrasonic array with asymmetric apertures
InactiveUS6783497B2Avoids cost and inherentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationMedical imaging
Owner:VON RAMM OLAF PH D +1
System and method for active protection of a resource
An active protection system comprising an ultrawideband radar for threat detection, an optical tracker for precision threat position measurement, and a high powered laser for threat kill or mitigation. The uwb radar may use a sparse array antenna and may also utilize Doppler radar information. The high powered laser may be of the optically pumped solid state type and in one embodiment may share optics with the optical tracker. In one embodiment, the UWB radar is used to focus the high power laser. Alternative interceptor type kill mechanisms are disclosed. In a further embodiment, the kill mechanism may be directed to the source of the threat.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
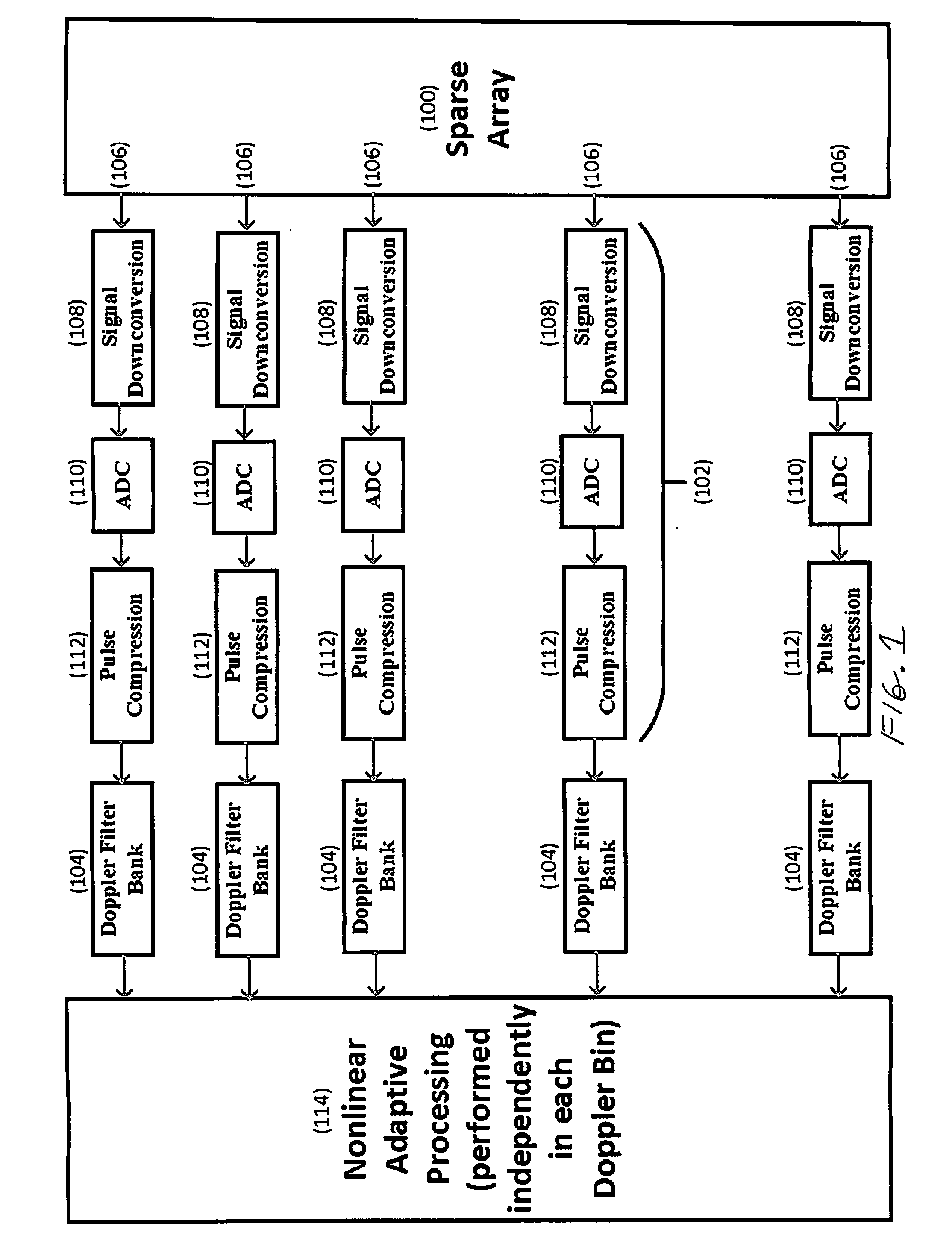
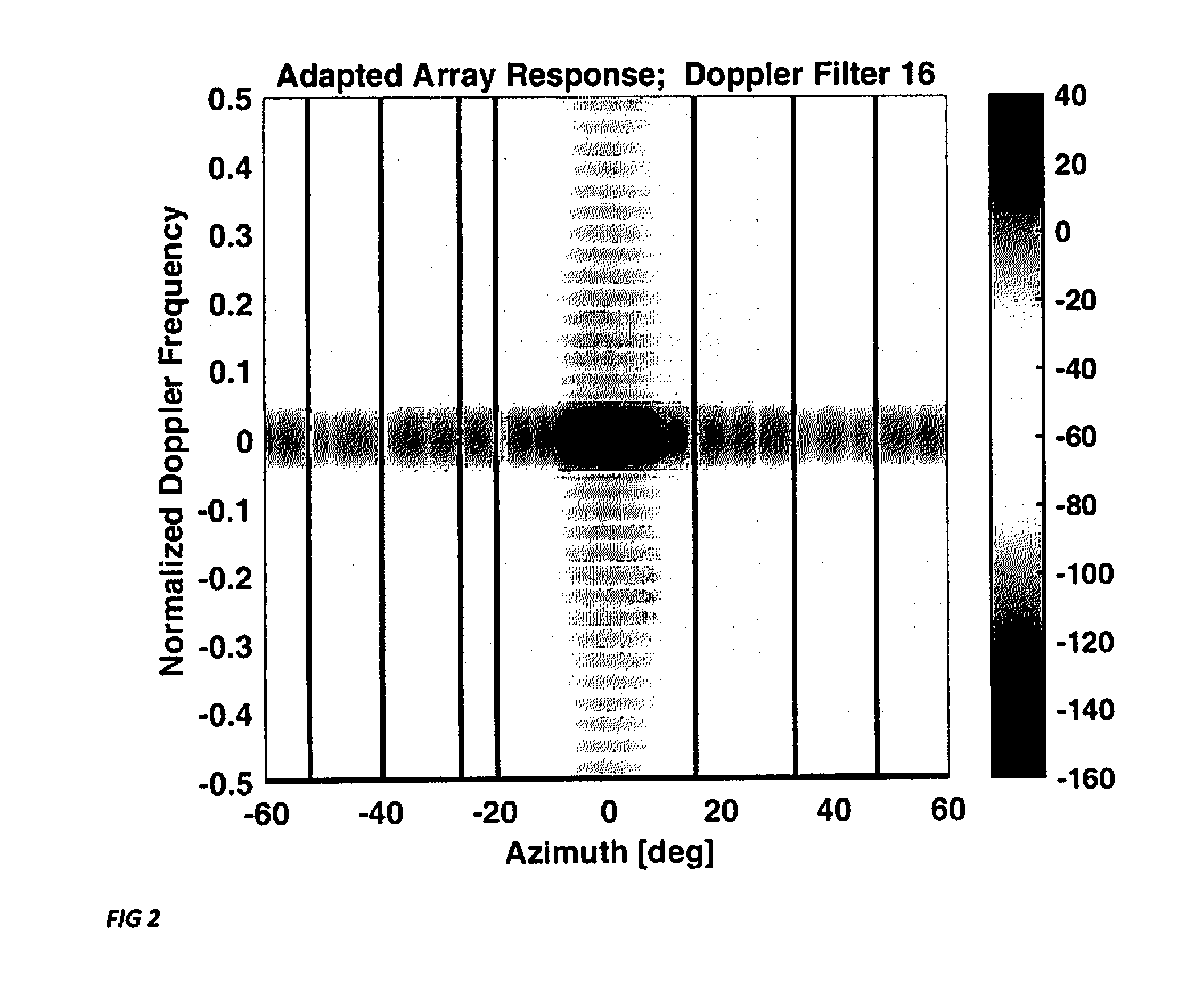
Sparse Space-Time Adaptive Array Architecture
InactiveUS20160091598A1Reduce impactReduce signalingCommunication jammingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCoprime arrayEngineering
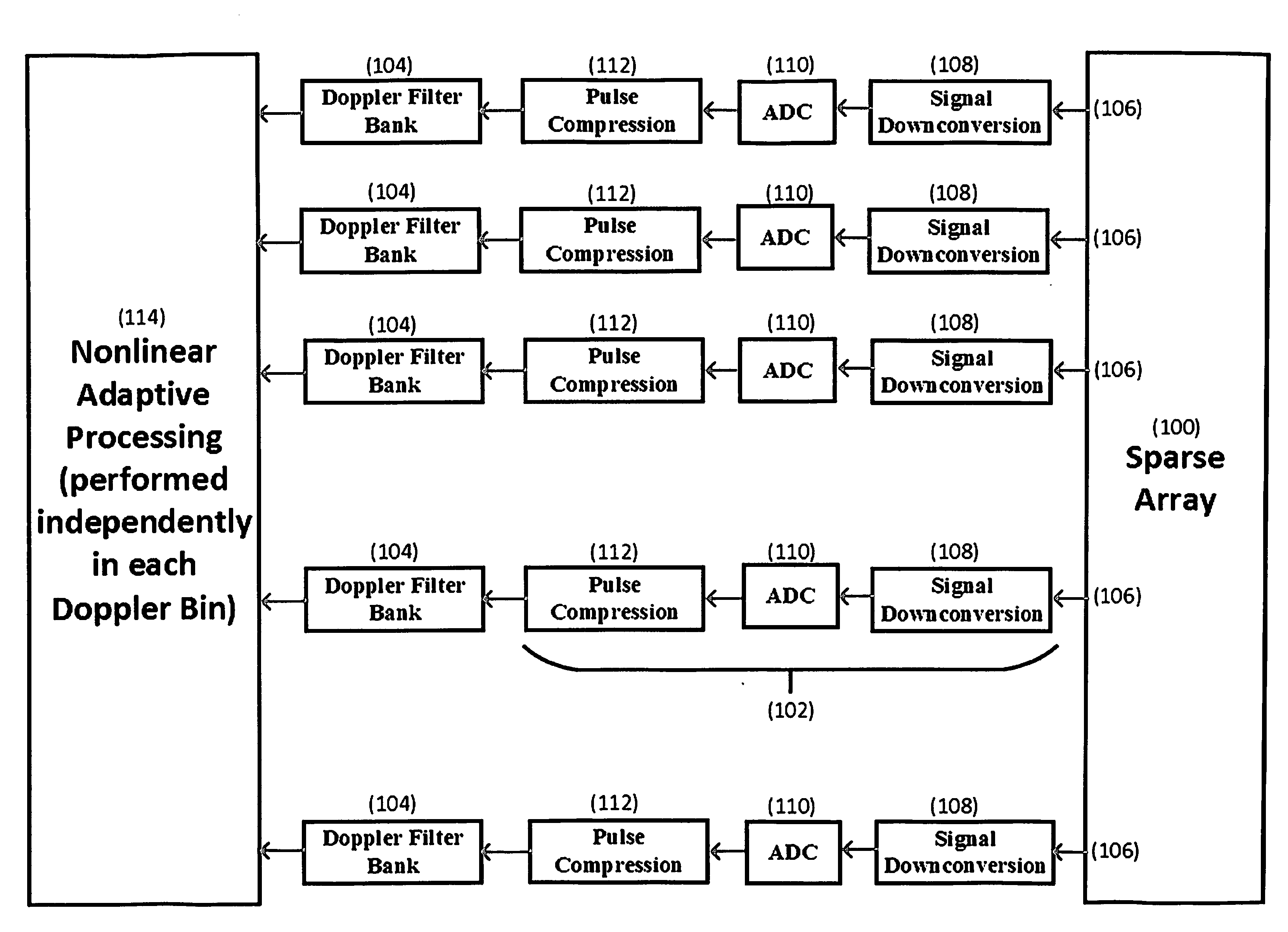
A sparse multichannel array includes a plurality of array elements, a receiver behind each array element, and a Doppler filter bank behind each receiver, whereby within each Doppler bin is placed spatial nulls at selected angles of undesired interference. The invention enables Doppler processing to be performed on sparse arrays, such as nested or coprime arrays, used in nonlinear adaptive beamforming to mitigate the impact of unintentional interference and hostile jamming on the received signal.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Ultrasound 3D imaging system
ActiveUS20130261463A1Minimizing energyEliminate periodicityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationEngineering
The present invention related to an ultrasound imaging system win which the scan head includes a beamformer circuit that performs far field subarray beamforming or includes a sparse array selecting circuit that actuates selected elements. When using a hierarchical two-stage or three-stage beamforming system, three dimensional ultrasound images can be generated in real-time. The invention further relates to flexible printed circuit boards in the probe head. The invention furthermore related to the use. of coded or spread spectrum signaling in ultrasound imagining systems. Matched filters based on pulse compression using Golay code pairs improve the signal-to-noise ratio thus enabling third harmonic imaging with suppressed sidelobes. The system is suitable for 3D full volume cardiac imaging.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
System and method for generating and directing very loud sounds
An improved system and method for controlling and directing sound waves is provided. A fuel-oxidant mixture is supplied to at least one detonator having at least one spark initiator. The fuel-oxidant mixture flows through the at least one detonator and into the closed end of at least one detonation tube also having an open end. The timing at least one spark initiator is controlled to initiate at least one spark within the at least one detonator while the fuel-oxidant mixture is flowing through the at least one detonator thereby initiating a detonation wave at the closed end of the at least one detonation tube. The detonation wave propagates the length of the at least one detonation tube and exits the open end of the at least one detonation tube as a sound wave. When multiple detonation tubes are detonated with controlled timing, the resulting sound waves are directed to a desired location. Sound waves can be directed from groups of detonation tubes and from a sparse array of detonation tubes.
Owner:SOUNDBLAST TECH
System and method for intrusion detection using a time domain radar array
InactiveUS7592944B2High resolutionImprove performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainUltra-wideband
A system and method for highly selective intrusion detection using a sparse array of ultra wideband (UWB) radars. Two or more UWB radars are arranged in a sparse array around an area to be protected. Each UWB radar transmits ultra wideband pulses that illuminate the area to be protected. Signal return data is processed to determine, among other things, whether an alarm condition has been triggered. High resolution radar images are formed that give an accurate picture of the area to be protected. This image is used to detect motion in a highly selective manner and to track moving objects within the protected area. Motion can be distinguished based on criteria appropriate to the environment in which the intrusion detection system operates.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
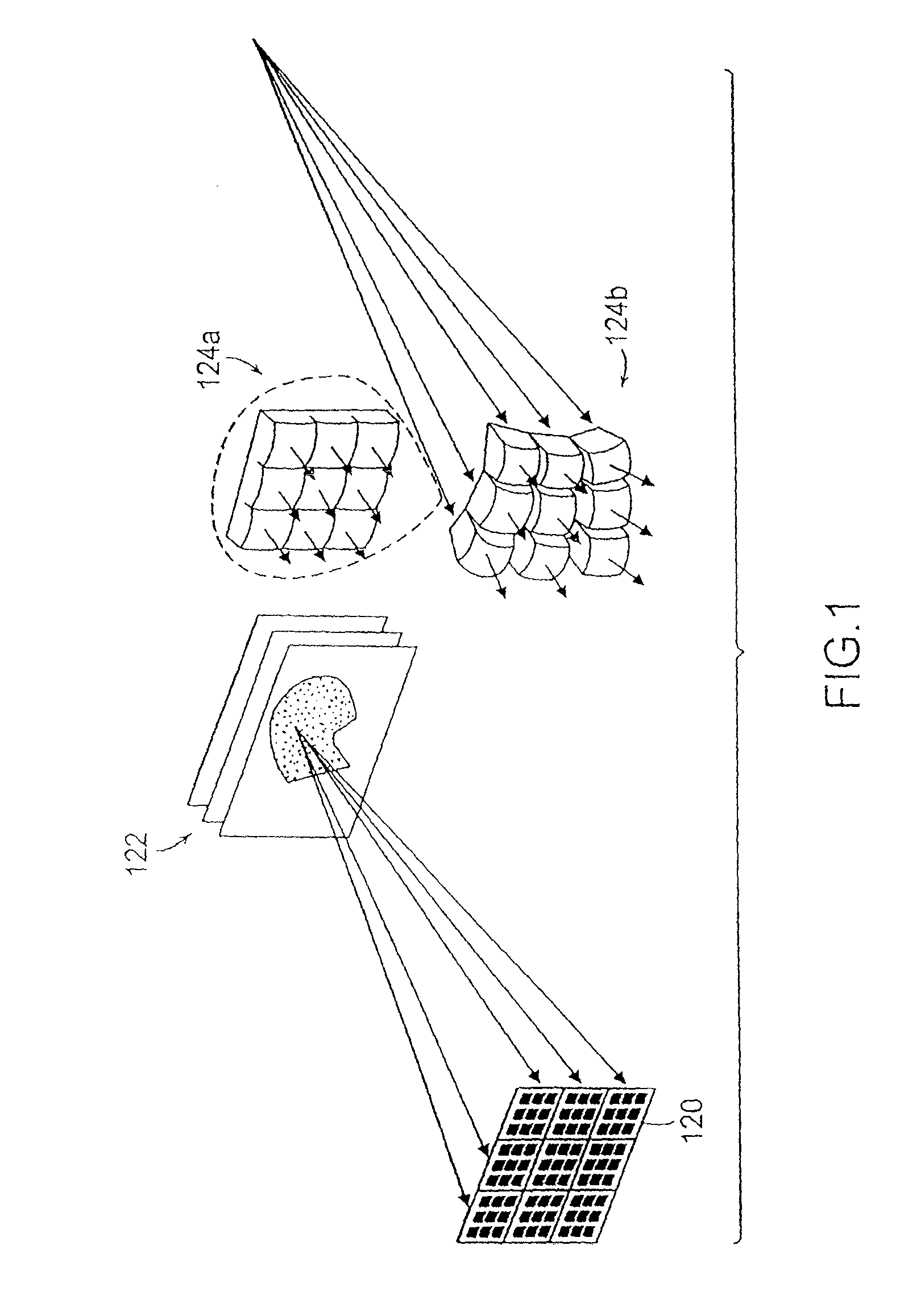
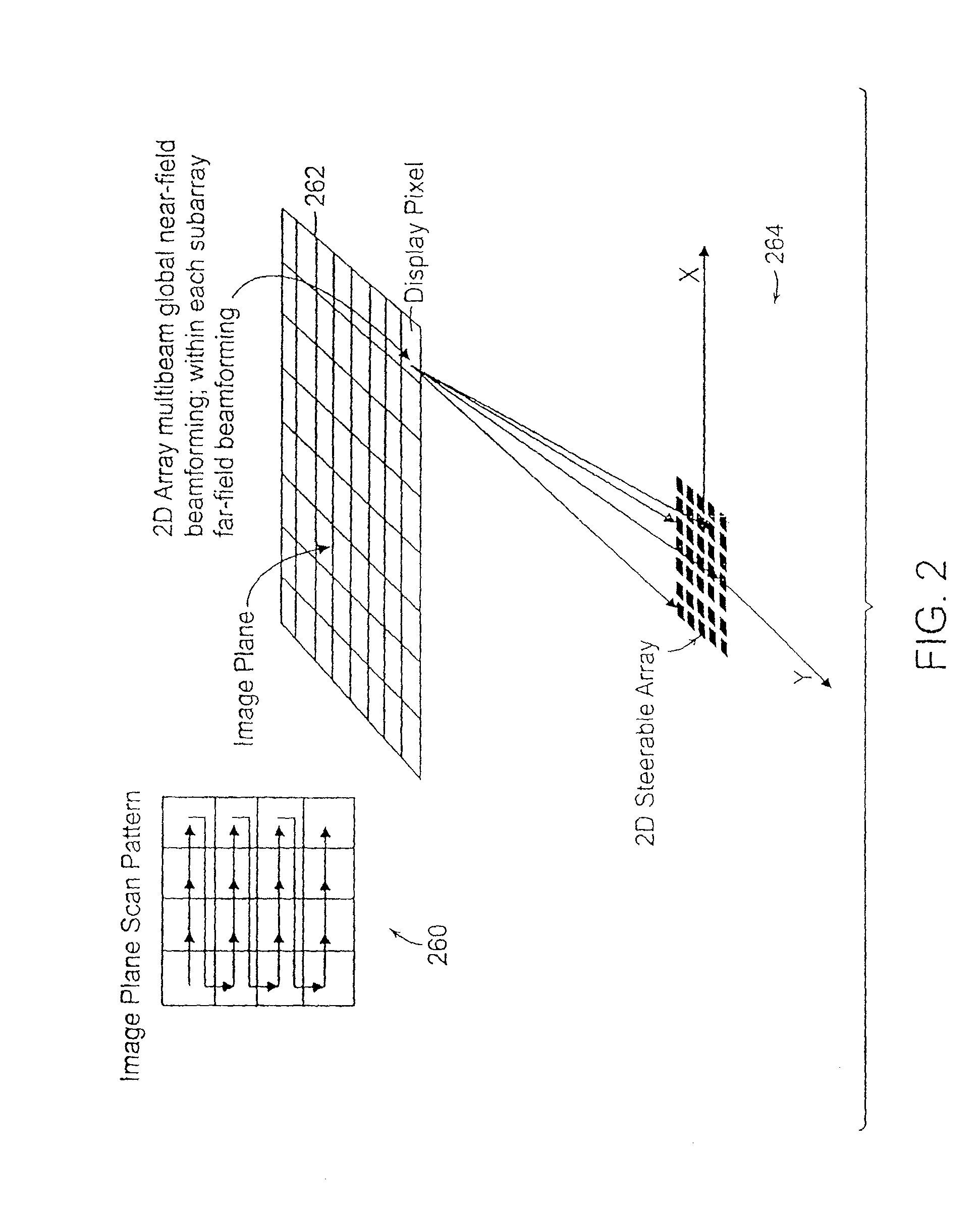
Near eye wavefront emulating display
ActiveUS20180131926A1Eliminate aberrationsComfortable form factorPicture reproducers using projection devicesSteroscopic systemsSmall form factorDisplay device
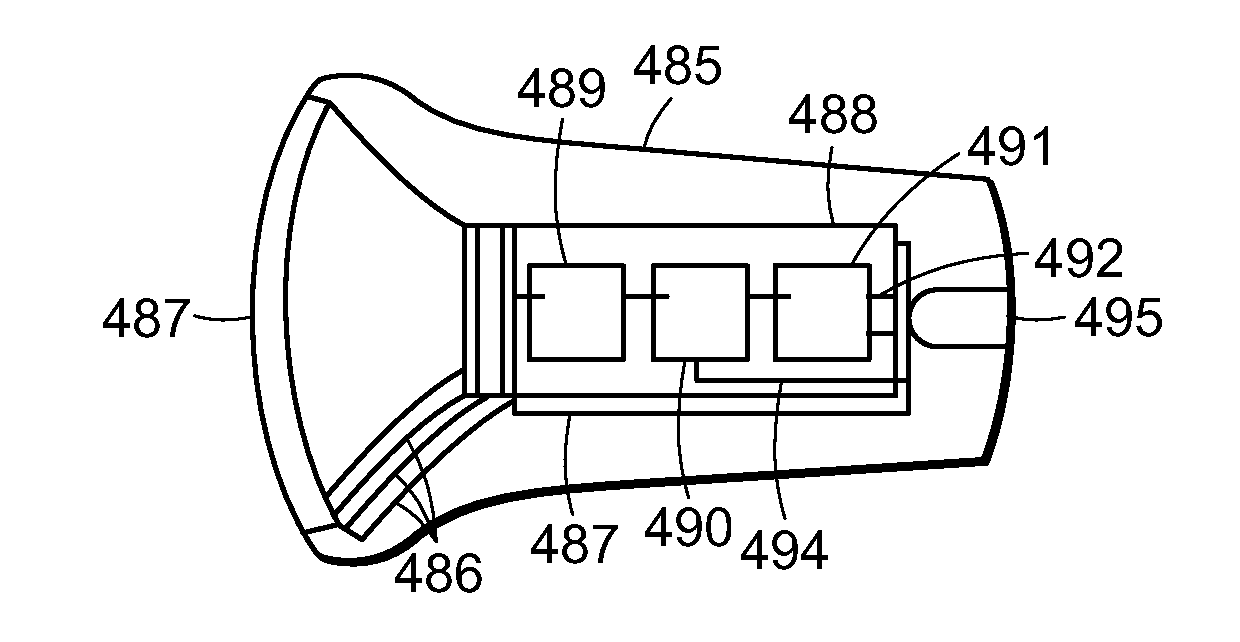
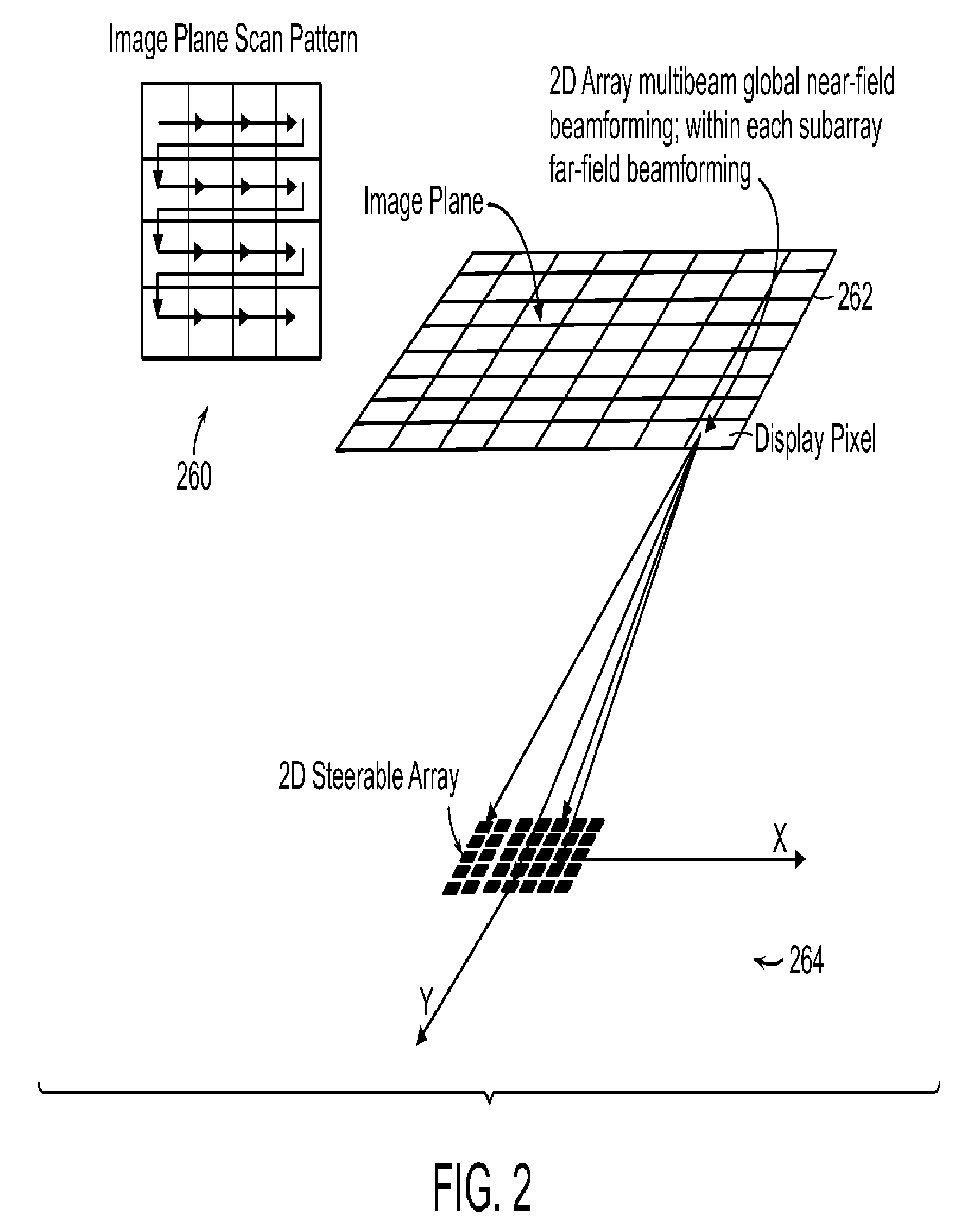
A near eye display device includes a sparse array of intensity modulated light beam emission and steering points disposed on a transparent lens, capable of forming a wide field of view composite image directly on the retina with variable degrees of apparent depth controlled by an image forming timing signal. The active regions of the beam emission and steering elements is configured so as not to generate optical aberrations of transmitted ambient light that is apparent to the eye. The display may be applied to small form factor stereoscopic head worn display systems and used in conjunction with Augmented Reality software applications.
Owner:MANOR FINANCIAL INC
Sparse sub-array and sparse array element antenna array integrated arranging method based on heredity algorithm
ActiveCN106099393AFlexible formationFlexible divisionAntenna arraysGenetic algorithmsSide lobePeak value
The invention belongs to the technical field of antenna array arranging optimization, especially to an optimal arranging method of antenna arrays of a sub-array level, and relates to a sparse sub-array and sparse array element antenna array integrated arranging method based on a heredity algorithm. A sub-array level array idea and sparse array element arrangement are combined to establish an arranging model, the peak side-lobe level (PSLL) of the antenna array is set as a fitness function to establish an optimization model, and the heredity algorithm is employed to solve the optimal result of the optimization model. The combination of the sub-array level array idea and the sparse array element arrangement are combined to overcome the landform problem, sub-arrays can be flexibly divided for arrangement. The optimization method combining sparse sub-arrays and sparse array elements effectively lowers PSLL, which is substantially reduced when compared with a molecule array arranging method. The convergence speed of the method is five to ten times that of a conventional sparse array arranging method, and the convergence speed is substantially improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Two-dimensional ultrasonic array with asymmetric apertures
InactiveUS20030220554A1Increase costAvoids compromiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationMedical imaging
A sparse array that uses a small fraction of a fully populated array but yields a radiation pattern that is suitable for high quality medical imaging. The sparse array consists of two or more separate zones for transmitting and receiving as opposed to the overlapping arrays of the prior art. More specifically, a preferred embodiment sets forth an inner array of transmit elements with a narrow effective aperture and a separate non-overlapping outer array of receive elements with a wide effective aperture. The combination of asymmetric apertures is particularly useful for parallel processing applications. This abstract is provided as a tool for those searching for patents, and not as a limitation on the scope of the claims.
Owner:VON RAMM OLAF PH D +1
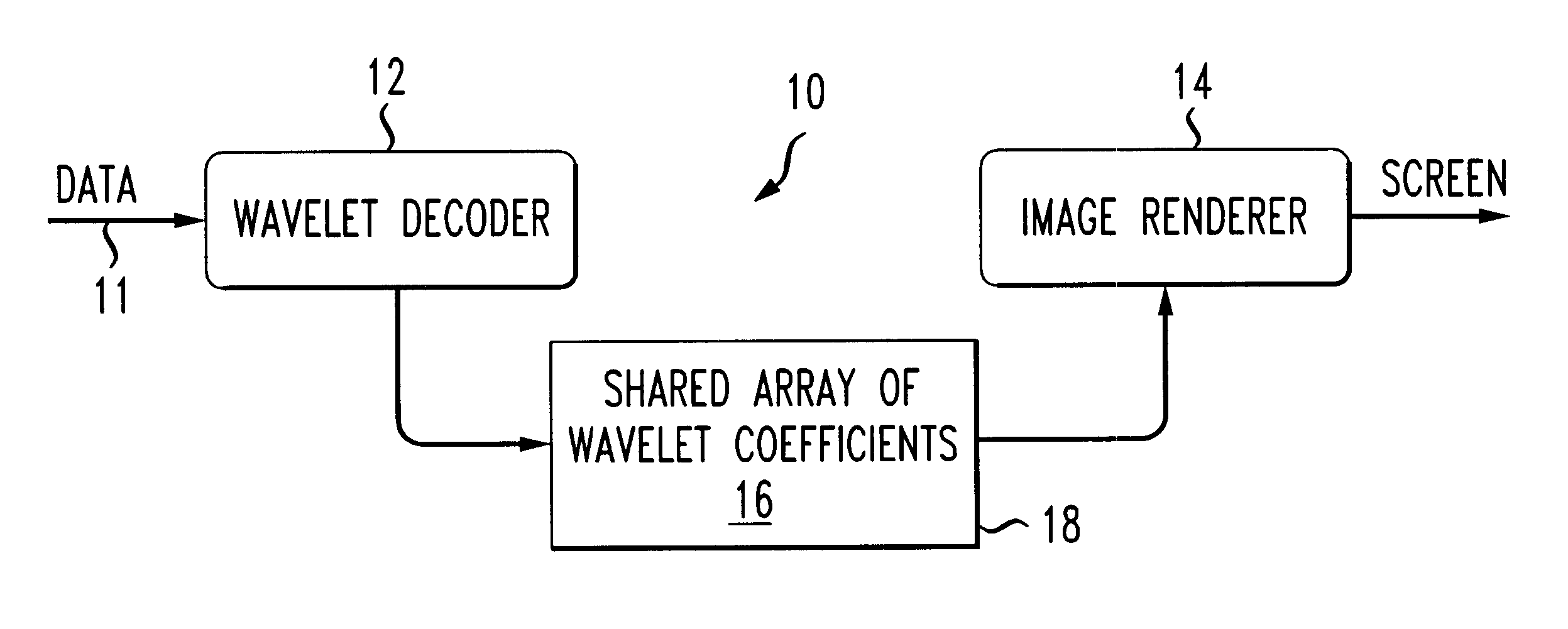
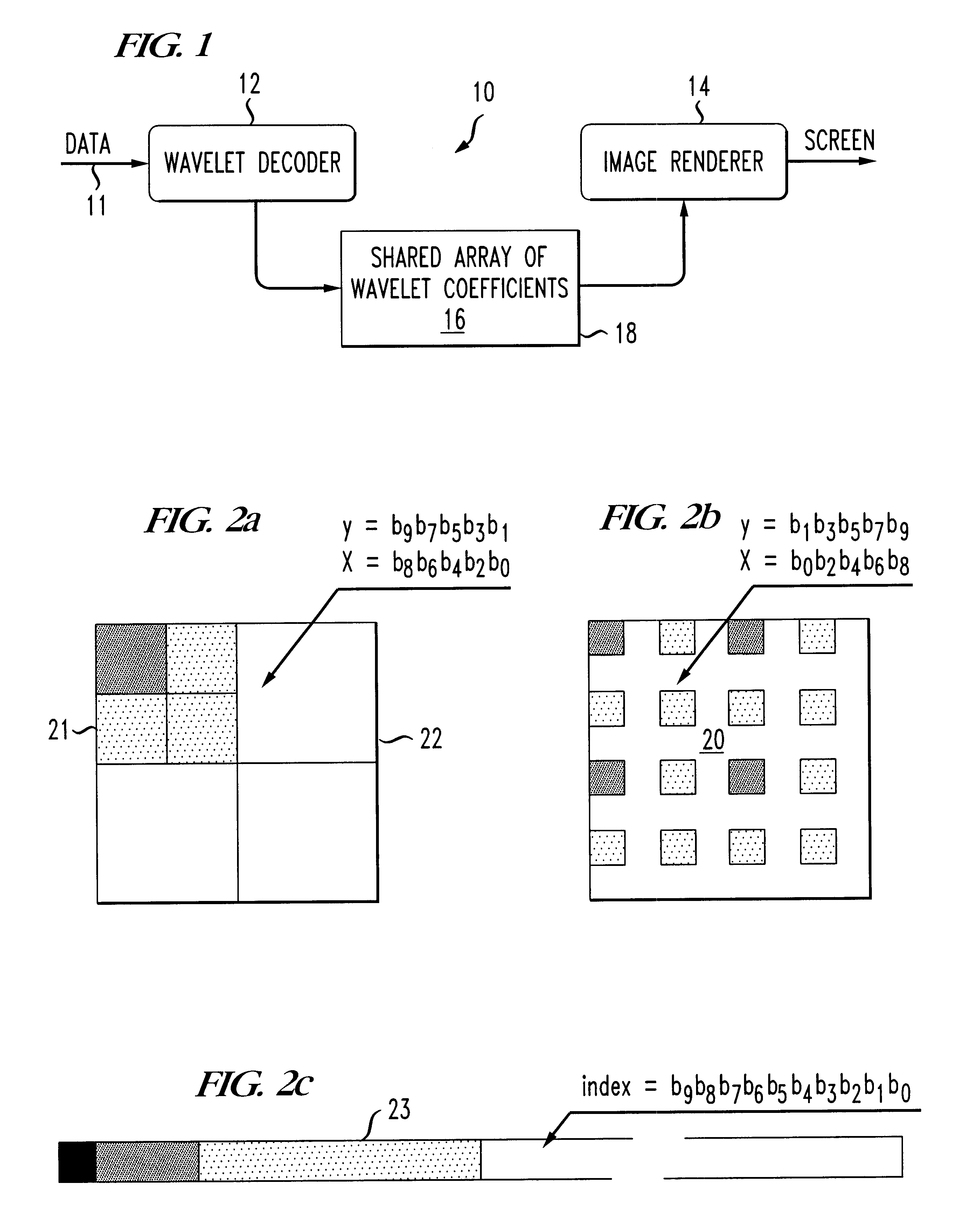
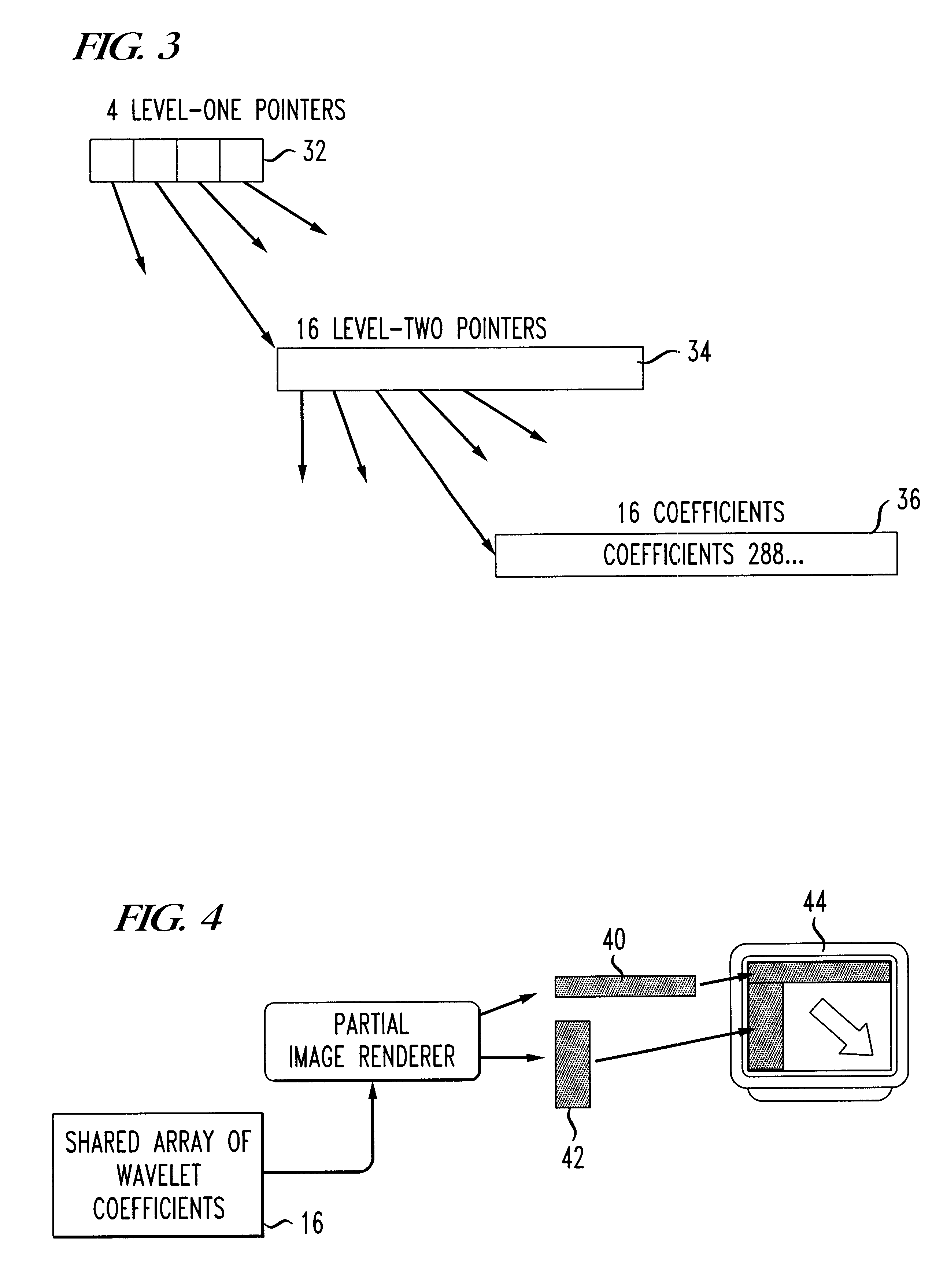
Progressive image decoder for wavelet encoded images in compressed files and method of operation
InactiveUS6587588B1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningArray data structureGray level
A progressive image display decoder and method of operation for wavelet encoded images achieves reduced memory storage requirements for wavelet transform coefficients and reduced execution time in displaying the image thereby overcoming the limitations of the prior art. Conveniently, a wavelet image format, typically DjVu IW44 facilitates progressive rendering and smooth scrolling of large color or gray level images with limited memory requirements. The progressive wavelet decoder is composed of two components. The first component decodes the incoming image data and updates an array of wavelet coefficients. The second component applies an inverse wavelet transform to the array of wavelet coefficients for the purpose of reconstructing the image. The operation of the first component (the decoder) is triggered by the incoming compressed image data. The received data is decoded and is used to apply updates to an array of wavelet coefficients. Each update improves the accuracy of the coefficients and therefore improves the fidelity of the reconstructed image. The coefficient array is composed of several two-dimensional arrays (one for each of the color components) having one entry corresponding to each 32x32 blocks in the image. Each entry contains 1024 wavelet coefficients organized as a sparse array with two levels of indirection. The operation of the second component (the renderer) is typically triggered when enough data has been received to display an updated version of the image, or when the user performs an action which requires displaying a new part of the image. In the latter case, the renderer only reconstructs the pixel values for the parts of the image, which are needed. A further reduction of the computation time is obtained by using "lifting" for implementing a fast inverse wavelet transform.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
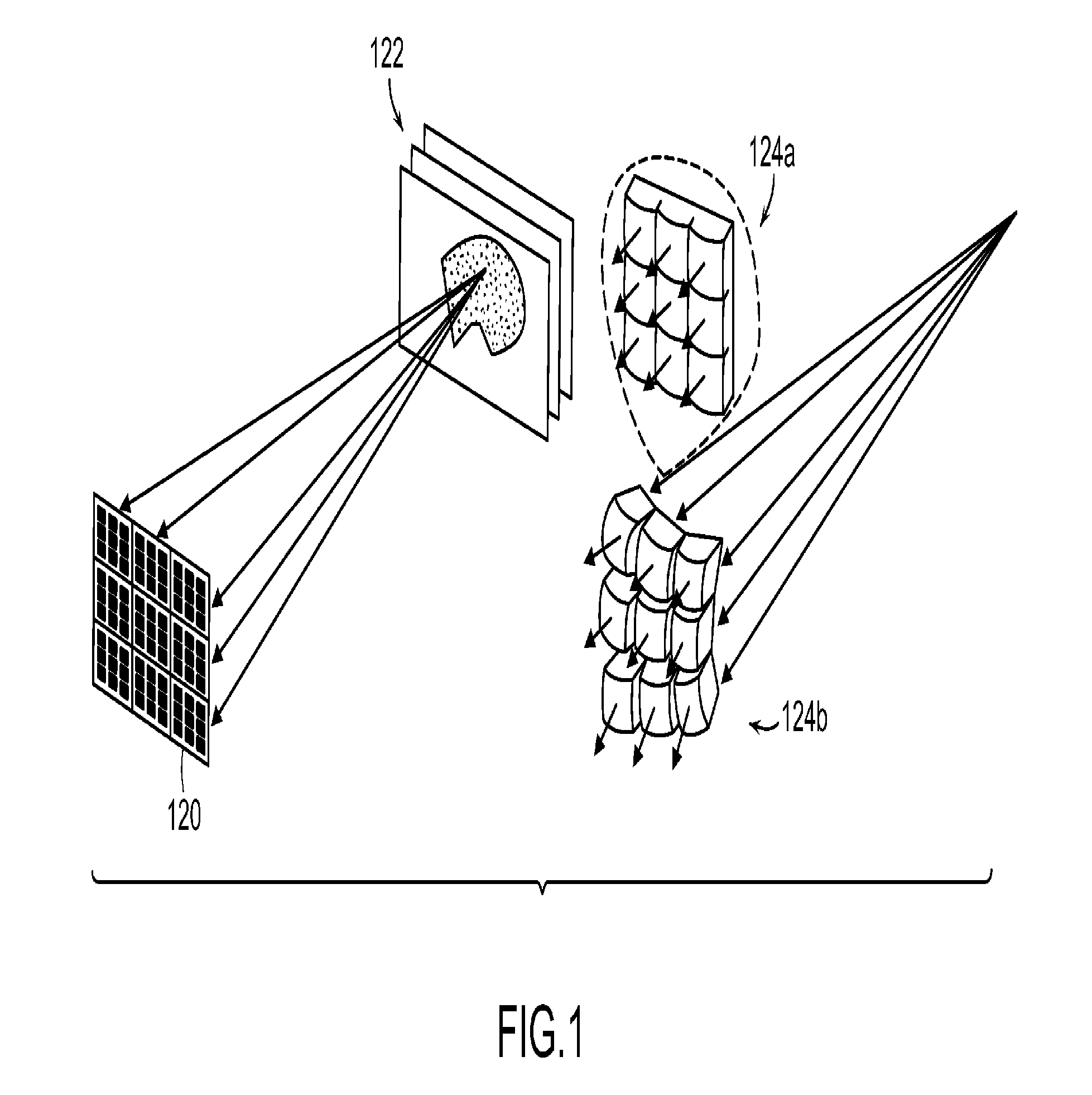
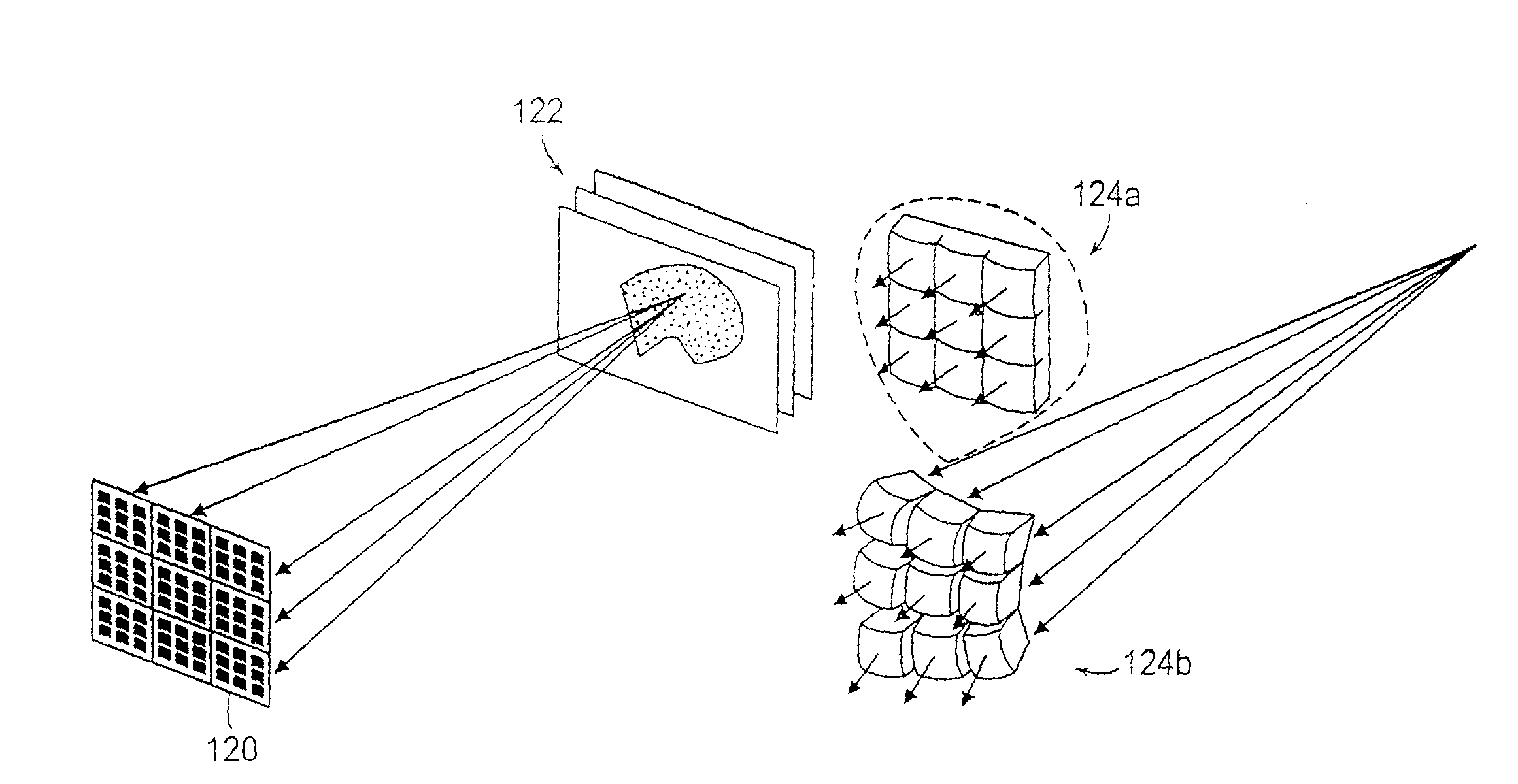
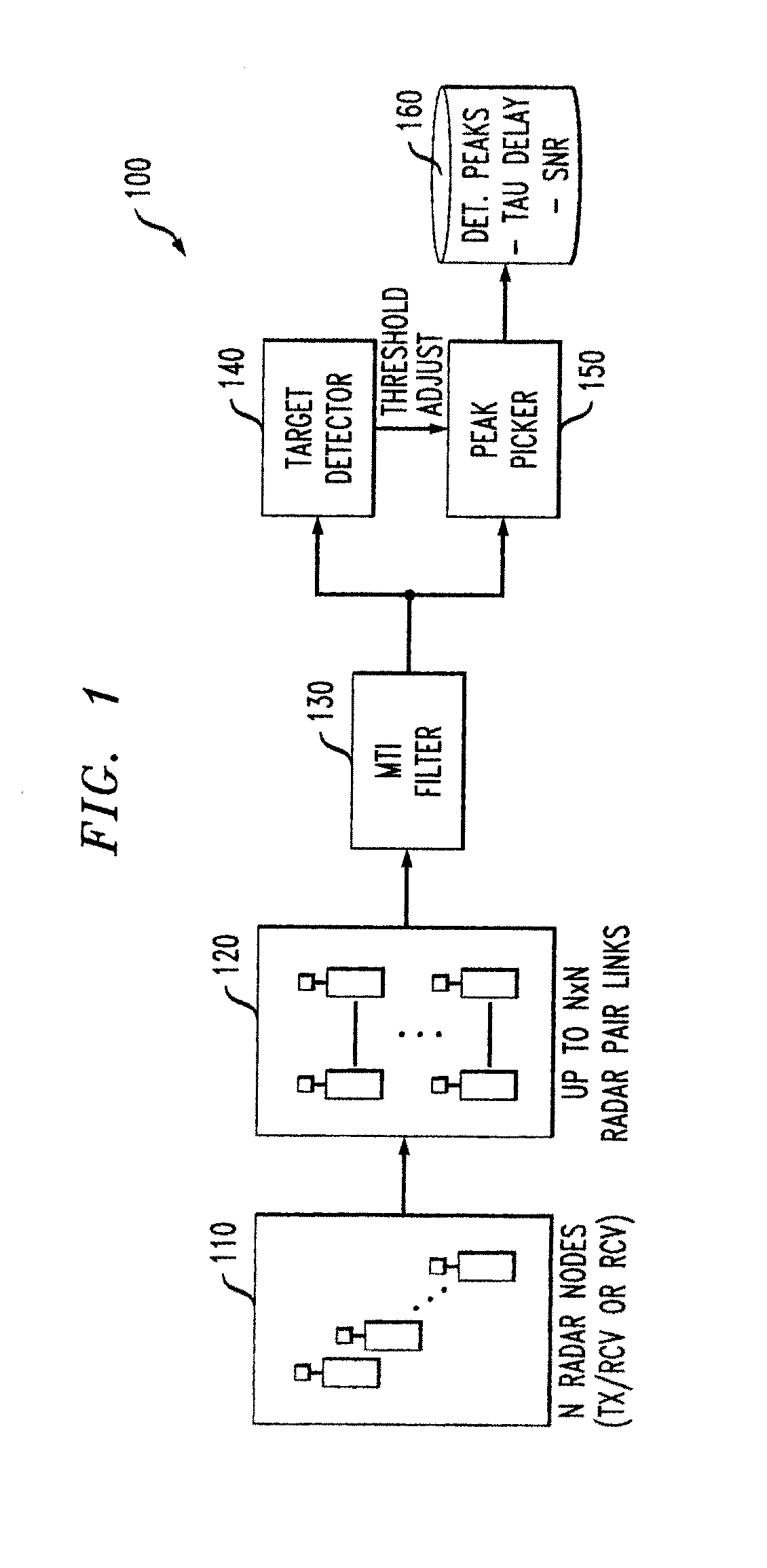
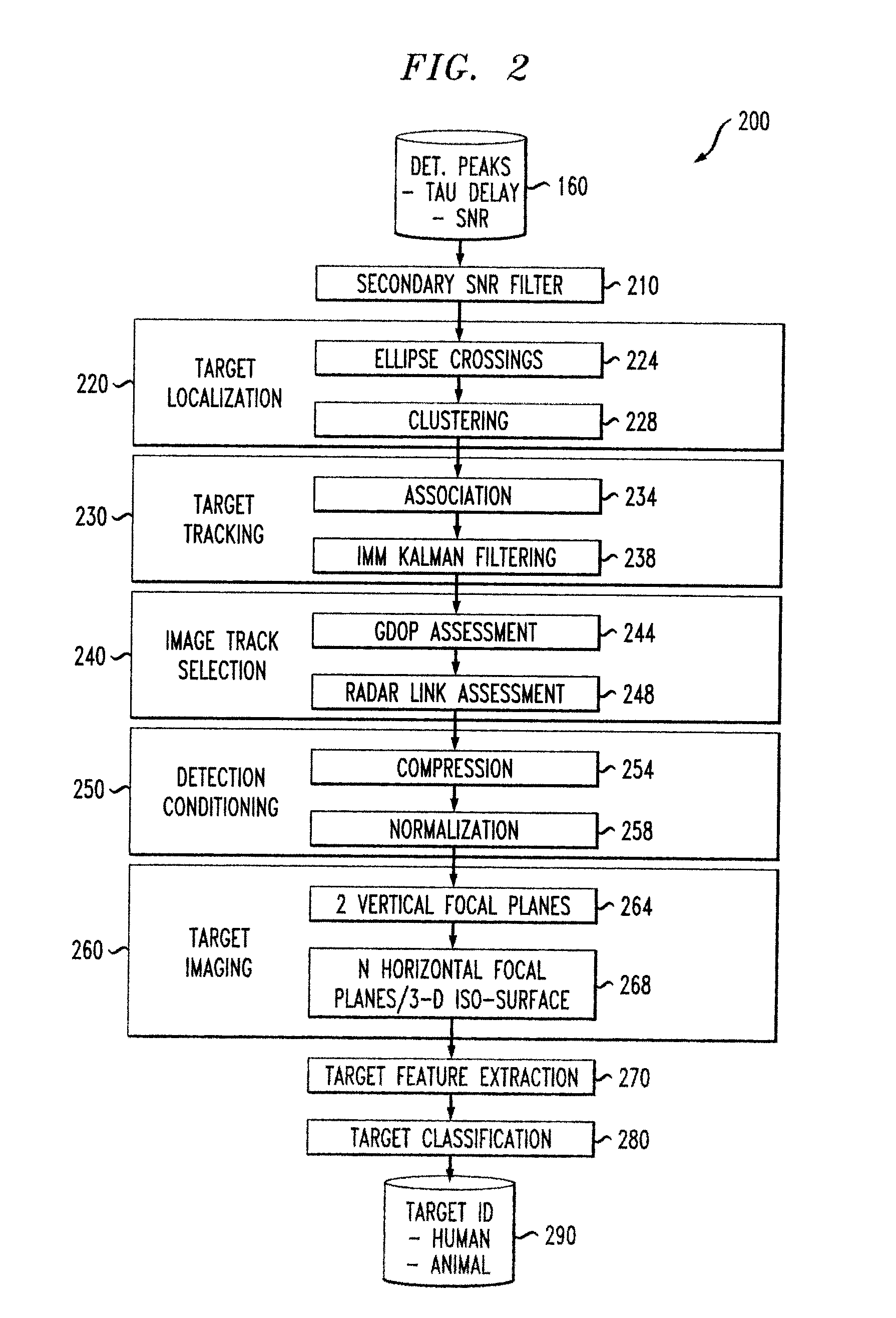
Sparse Array RF Imaging for Surveillance Applications
Techniques are provided for sparse array RF imaging for surveillance applications. The present invention enables object image identification using a sparsely populated array of distributed radio nodes deployed and operated as a radar detection, tracking and identification application. Three-dimensional object images are formed, from which estimates of extent and shape can be extracted for objects that are detected in the vicinity of the deployed radar array. In addition, techniques are provided for the identification and / or classification of vehicles, humans and fauna through feature extraction from the formed three-dimensional images.
Owner:APPLIED PHYSICAL SCI CORP
Ultrasound imaging with sparse array probes
ActiveUS20170209121A1Slow frame rateSufficient capturingOrgan movement/changes detectionMechanical vibrations separationUltrasound imagingVolumetric imaging
Sparse arrays of transducer elements may be beneficial in providing ultrasound transducer probes with a wide total aperture while containing a manageable number of transducer elements. Sparse arrays made with bulk piezoelectric materials or with arrays of micro-elements can be effectively with ping-based multiple aperture ultrasound imaging techniques to perform real-time volumetric imaging.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
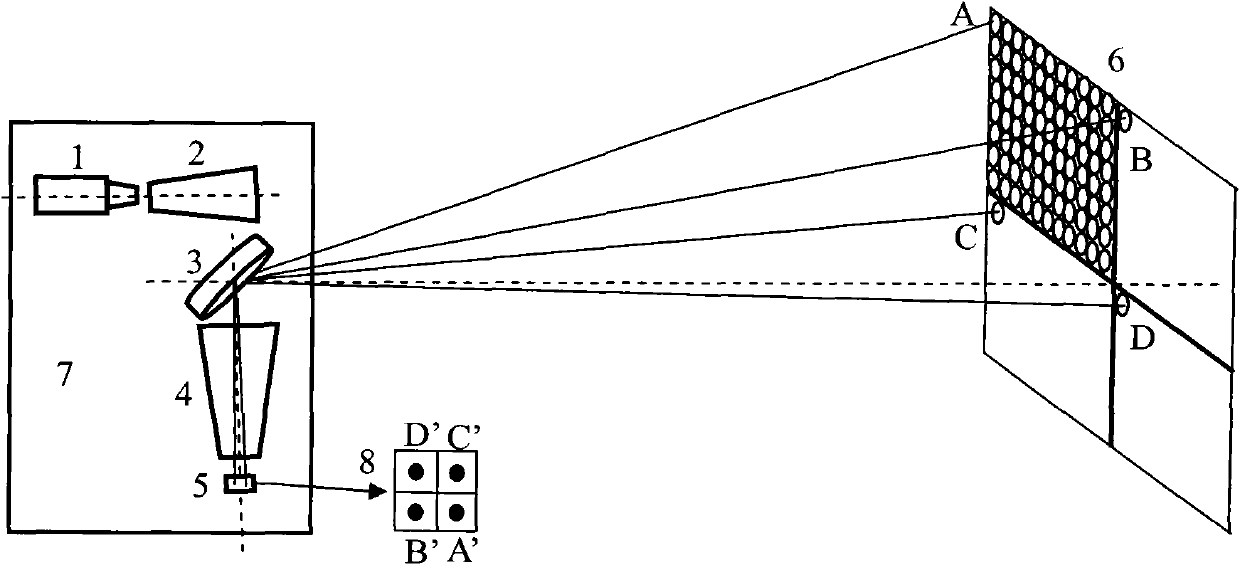
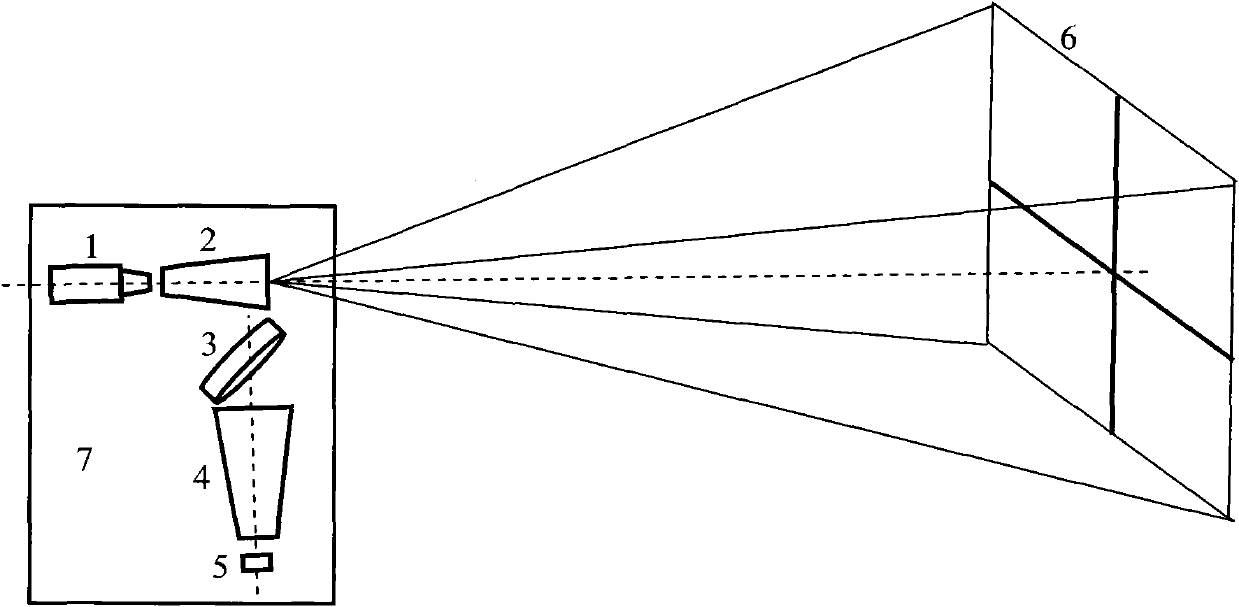
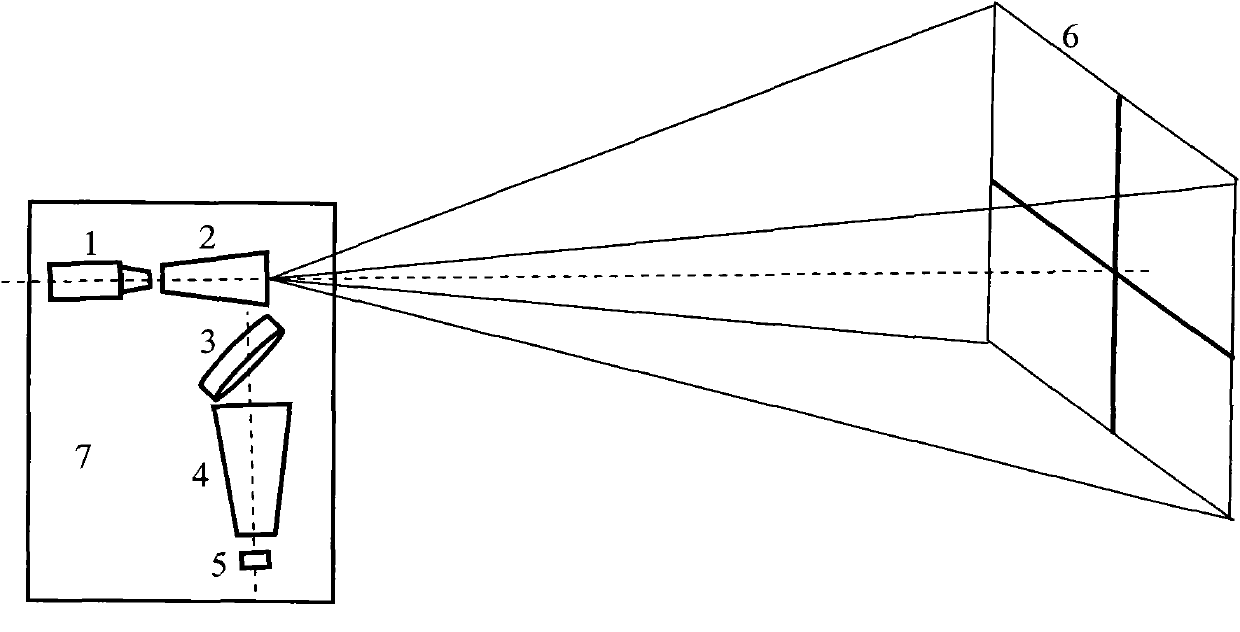
Implementation method for sparse array high-speed three-dimensional imaging lidar
ActiveCN102565808ASimple structureImprove reliabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationElectricityRadar
The invention relates to the field of three-dimensional imaging lidars, and aims to overcome the deficiencies of the prior art and provide an implementation method for a sparse array high-speed three-dimensional imaging lidar. In the implementation method, convenient and easily-obtained single detectors are utilized to form a sparse array detection system through sparse arrangement, piezoceramic low-angle quick scanning is combined to realize quick photoelectric conversion in a target echo signal subzone and solve the problems in high-speed three-dimensional imaging of the lidar. The invention is characterized in that an imaging detection optical system comprises a piezoceramic two-dimensional vibrating mirror (3), a laser receiving system (4) and the sparse array detection system (5). The invention has the advantages as follows: motor-free rotational scanning is realized, the whole structure is simple and the reliability is improved; the array detection has high imaging frame frequency and can satisfy high-speed measurement; devices are easy to obtain; and the transmit-receive separation layout has a low requirement for emitted light, and the installation is convenient.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
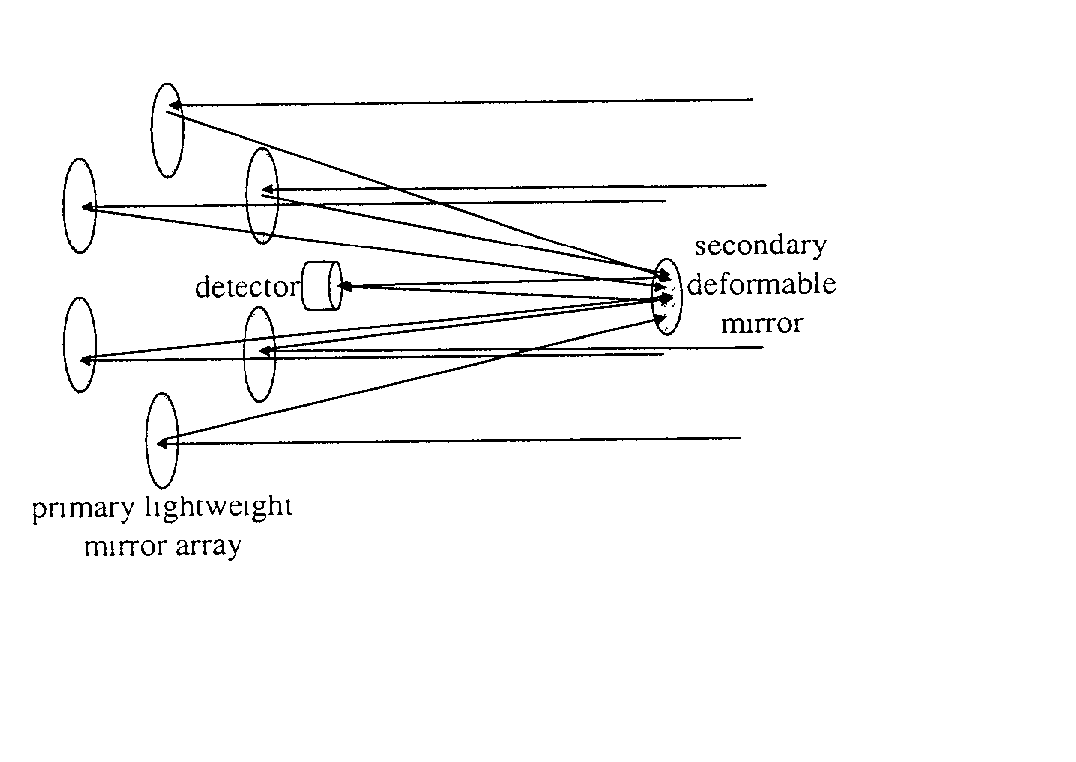
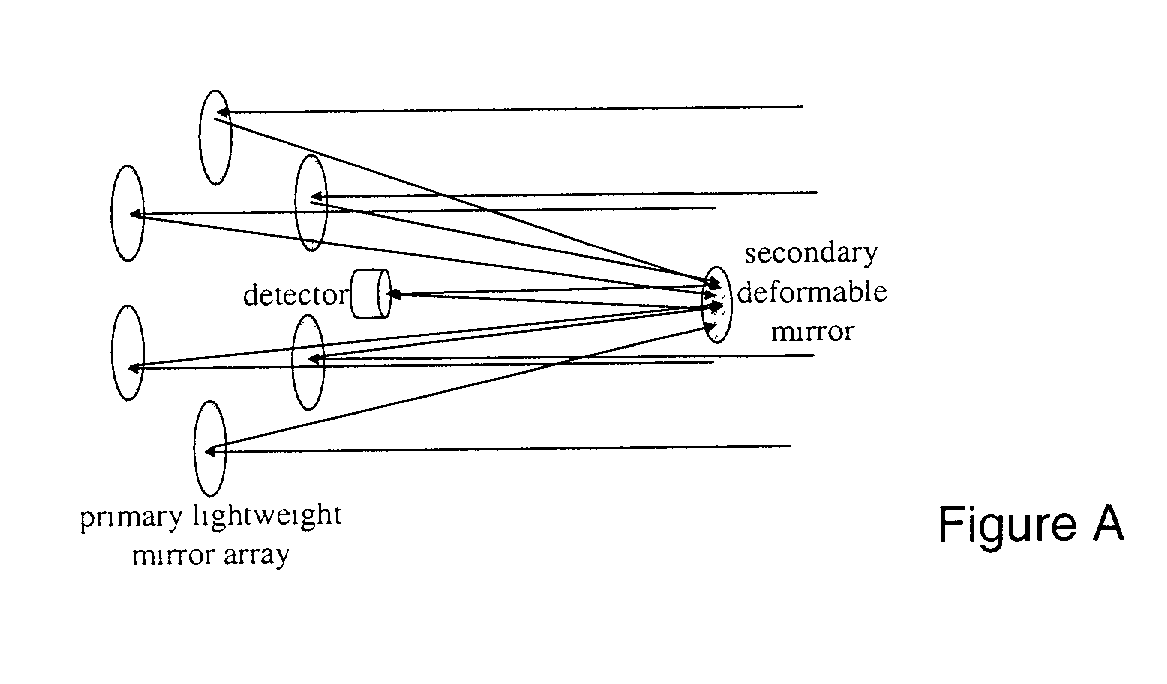
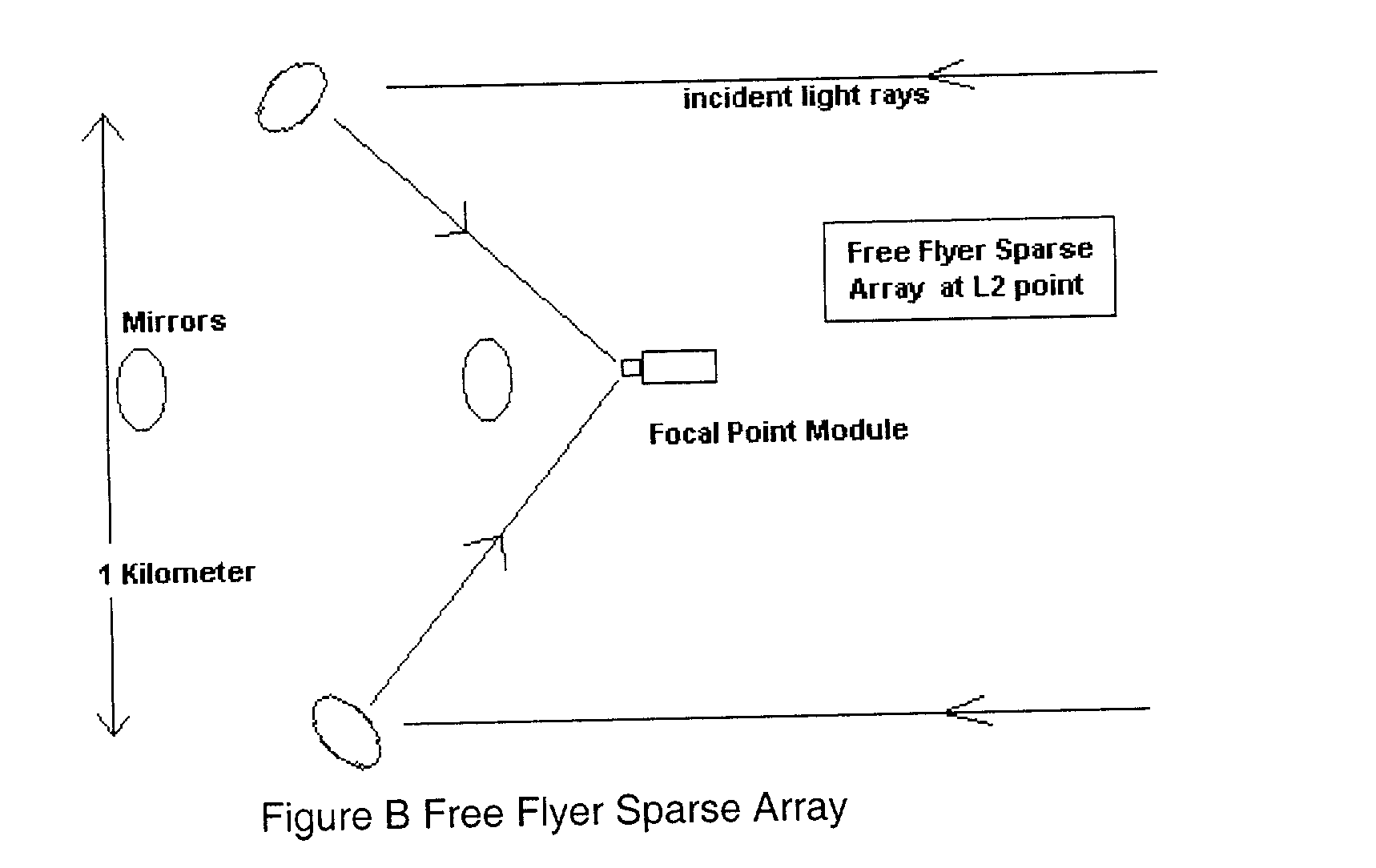
Telescope sparse array not requiring the use of laser interferometry
InactiveUS20030227696A1Rapid Strehle ratio maximizationHigh resolutionMirrorsTelescopesLight beamClassical mechanics
Recent schemes have been accepted by NASA in its TPF program for simple sparse arrays. But these methods require a great deal of interferometric control of tip tilt and other motion. But with this invention we just need (actuated) flats on a parabola with a central focal point module. The mirrors will be on the order of a kilometer distant from that module so that tip tilt can be sensed (and then controled) by sensors on the module that also detect beam pointing. The actual (high SNR) star the planet is orbiting can be used for rapid Strehle ratio maximization so that NO laser interferometry is needed at all. Fine mirror control can be done by variable reflectivity of the backside of the mirrors. The mirrors can be placed at L2 so that their orbits are all the same. A lot of this multi space craft control has already been accomplished with the ESA "Cluster".
Owner:MAKER DAVID JOEL
MIMO radar antenna array sparse arraying method
ActiveCN104849696AReduce the numberImprove spatial resolutionWave based measurement systemsArray elementLinear arrays
The invention discloses a MIMO radar antenna array sparse arraying method, which is based on almost difference sets and difference bases, and establishes a MIMO radar transmitting / receiving array rapidly through enumeration shifting process. When all transmitting array elements transmit orthogonal signals simultaneously and receiving array elements receive echo signals simultaneously, a virtual array with even space can be established equivalently by utilizing a phase center approximation principle; number of the transmitting / receiving array elements is given, the continuous aperture maximization of the equivalent virtual array can be realized according to the MIMO radar antenna array sparse arraying method, thereby improving spatial resolution of a MIMO radar system significantly; and the continuous apertures of the virtual array are given, and the minimization of number of the transmitting / receiving array elements can be realized according to the MIMO radar antenna array sparse arraying method, thereby reducing hardware cost of the system significantly. The MIMO radar antenna array sparse arraying method has small computational complexity, and is applicable to establishment of MIMO radar sparse linear arrays and planar array.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
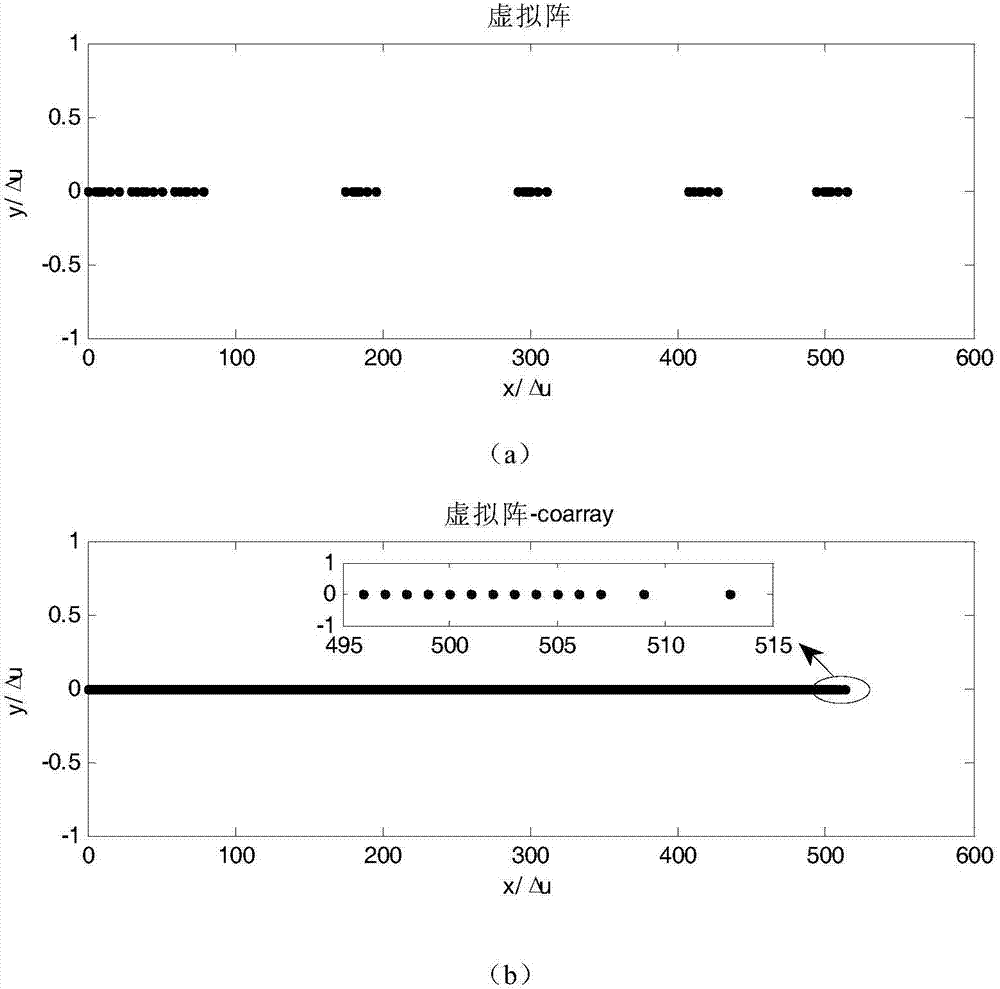
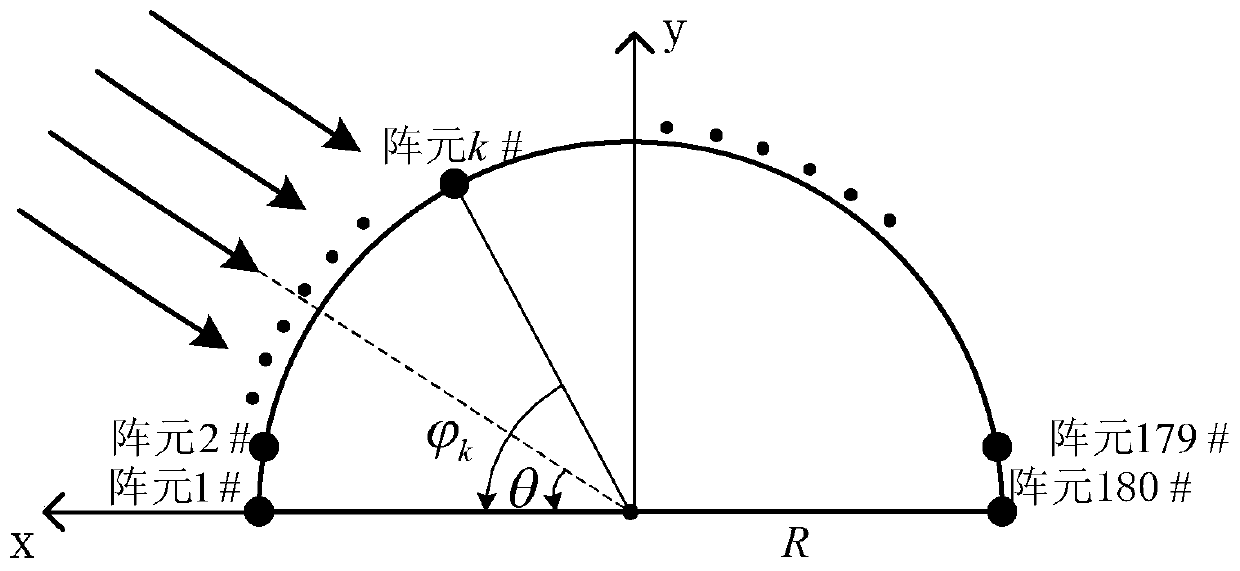
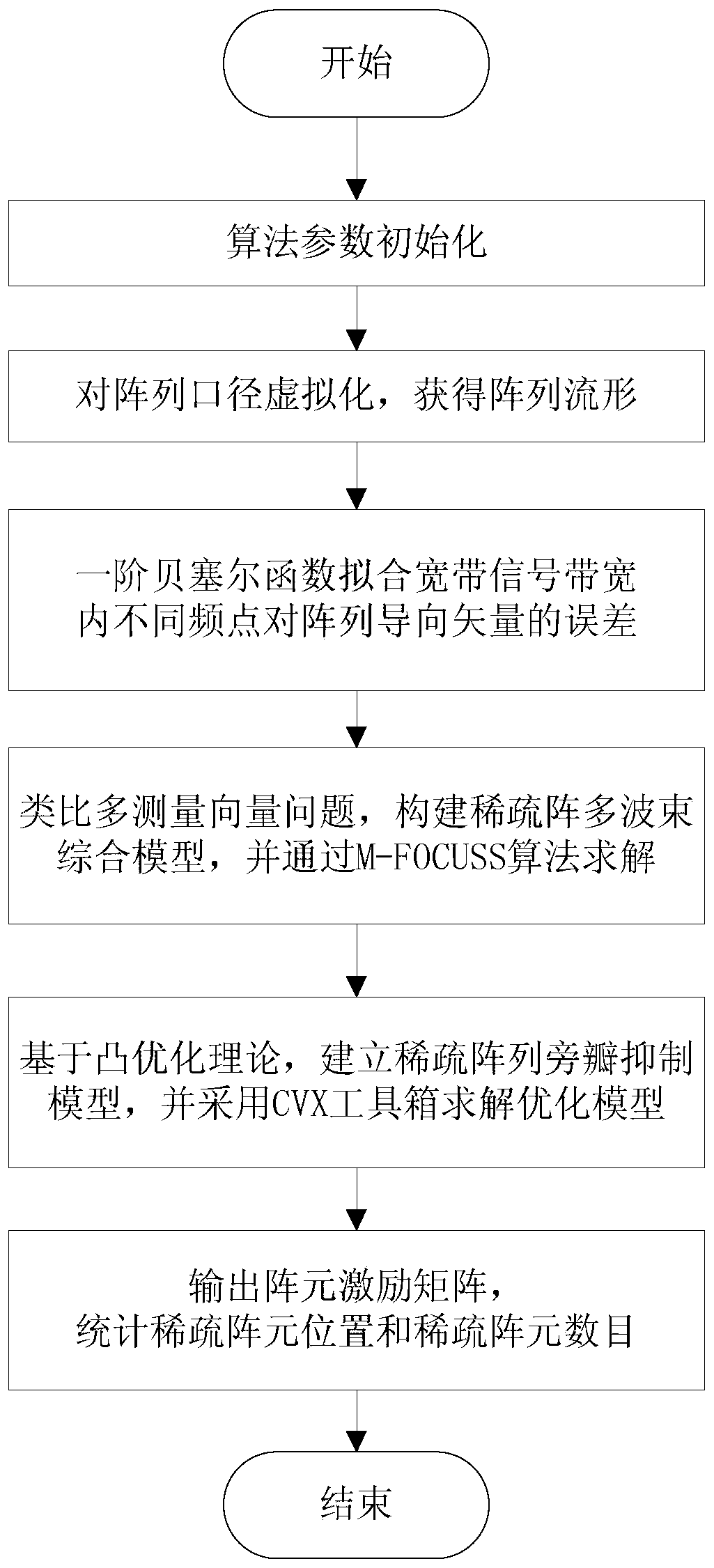
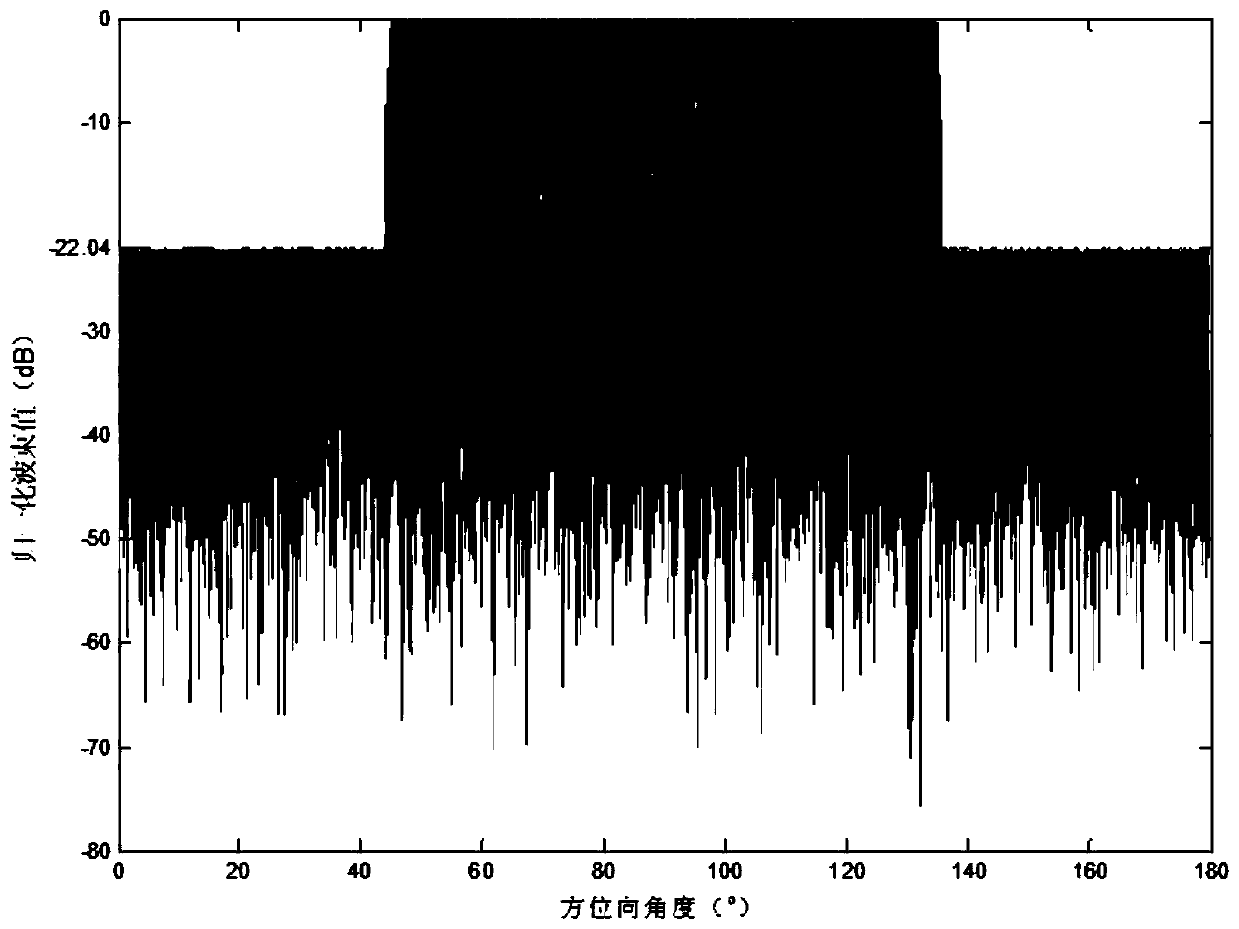
Array sparse method for broadband non-frequency-variable multi-beam imaging sonar
InactiveCN109959917AEnables wideband multi-beamformingAvoid getting stuck in local optimaWave based measurement systemsSparse methodsWeight coefficient
The invention discloses an array sparse method for a broadband non-frequency-variable multi-beam imaging sonar. With the Bessel function, fitting of influences on array guiding vectors by different frequency points in the broadband signal bandwidth is performed and a broadband signal multi-beam forming model under the far-field situation is established; on the premise that the formed multiple beams approximate a reference beam, a minimum number of effective array elements are searched and multiple sets of weighting coefficients are calculated; a highly nonlinear sparse array optimization problem is transformed into a sparse signal reconstruction problem in the compressed sensing theory, a reconstruction weighting coefficient is calculated iteratively by an underdetermined system localizedsolution algorithm, and a sparse array structure is determined; a convex optimization theory is introduced so as to form a plurality of low-side-lobe beams and a multi-beam array sparse side-lobe suppression model for array element excitation is established. According to the invention, the main lobes of a plurality of formed beams are not extended with changes of signal operating frequencies; andpeak side-lobe levels of multiple beams formed by the sparse array are reduced effectively.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
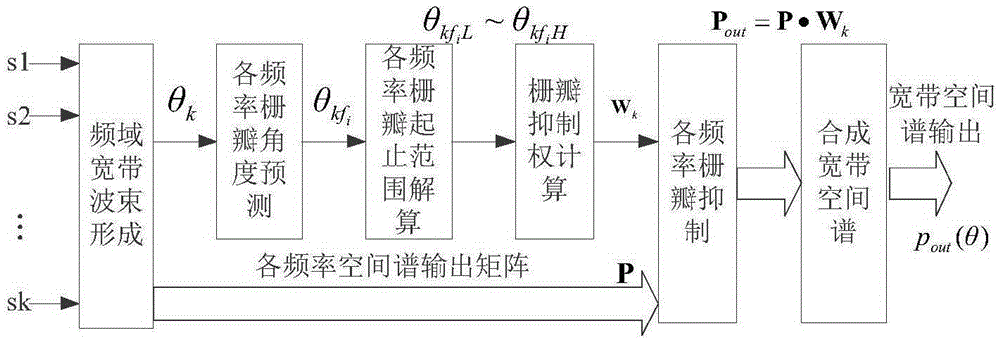
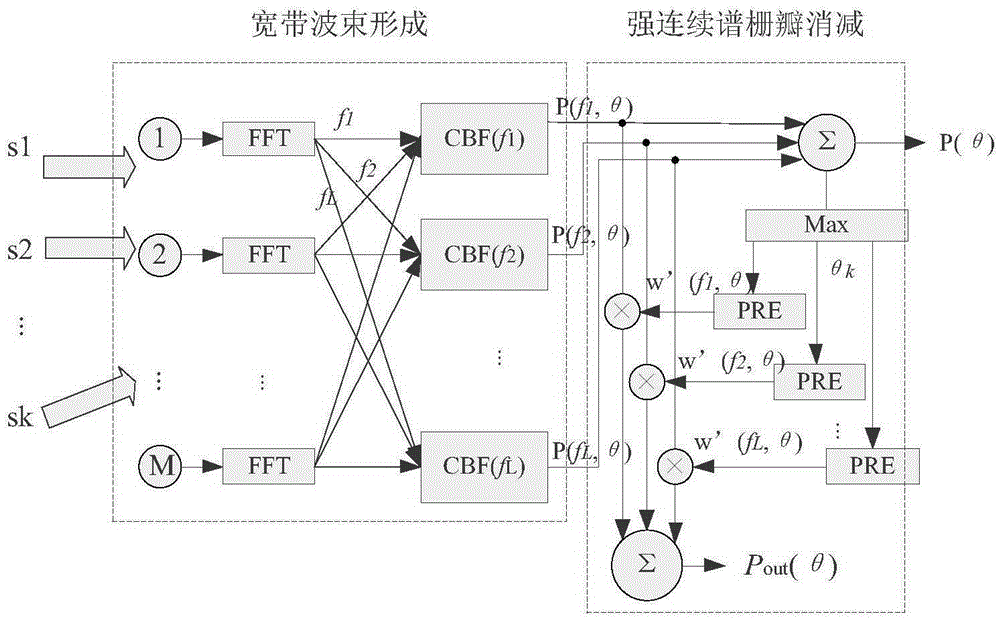
Sparse array broadband beamforming grating lobe suppressing method
ActiveCN105334508AImprove practicalityLow application costWave based measurement systemsWeight coefficientTarget signal
The invention provides a sparse array broadband beamforming grating lobe suppressing method. The method comprises a step 1 of performing frequency-domain broadband beamforming on array signals received by multiple array elements of a sparse array; a step 2 of predicting a grating lobe angle by using the orientation [theta]k of a strong interference target signal obtained in the step 1; a step 3 of resolving the start-stop range of the grating lobe of each frequency point according to the grating lobe angle [theta]kfj obtained in the step 2 and the main lobe width of each frequency point; a step 4 of computing a grating lobe suppression weight coefficient matrix Wk according to a grating lobe range obtained in the step 3; and a step 5 of suppressing the gratin lobe by using the grating lobe suppression weight coefficient matrix Wk obtained in the step 4 and a spatial spectrum output matrix P of each frequency point obtained in the step 1; and a step 6 of adding the spatial spectrum output matrix Pout after the grating lobe suppression in order to perform broadband spatial spectrum synthesis. The method solves broadband beamforming grating lobe influences caused by a common equal-interval sparse array and is used in signal processing field.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
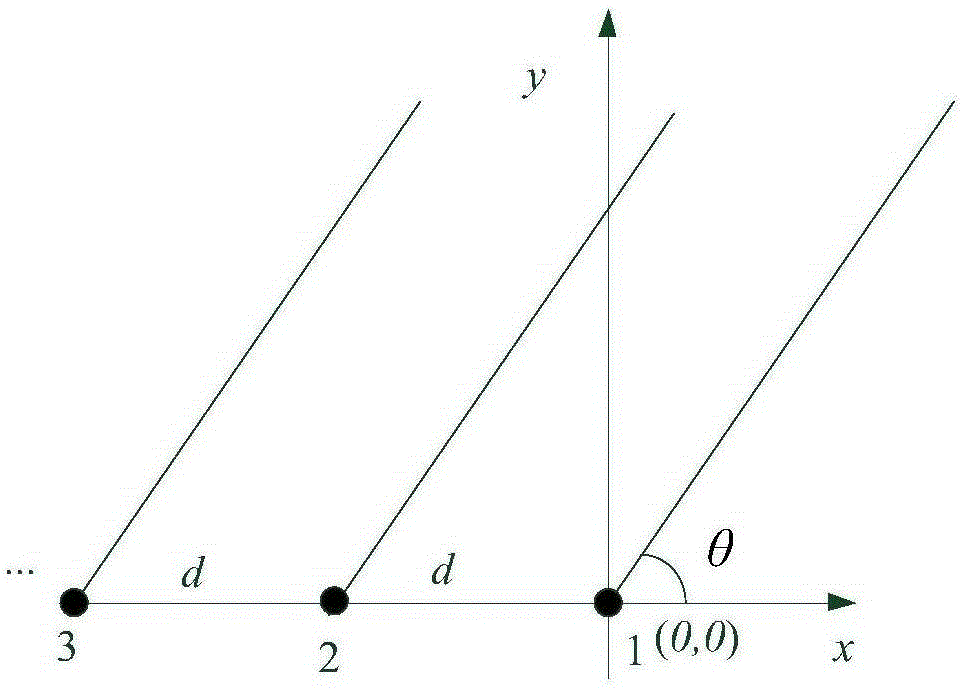
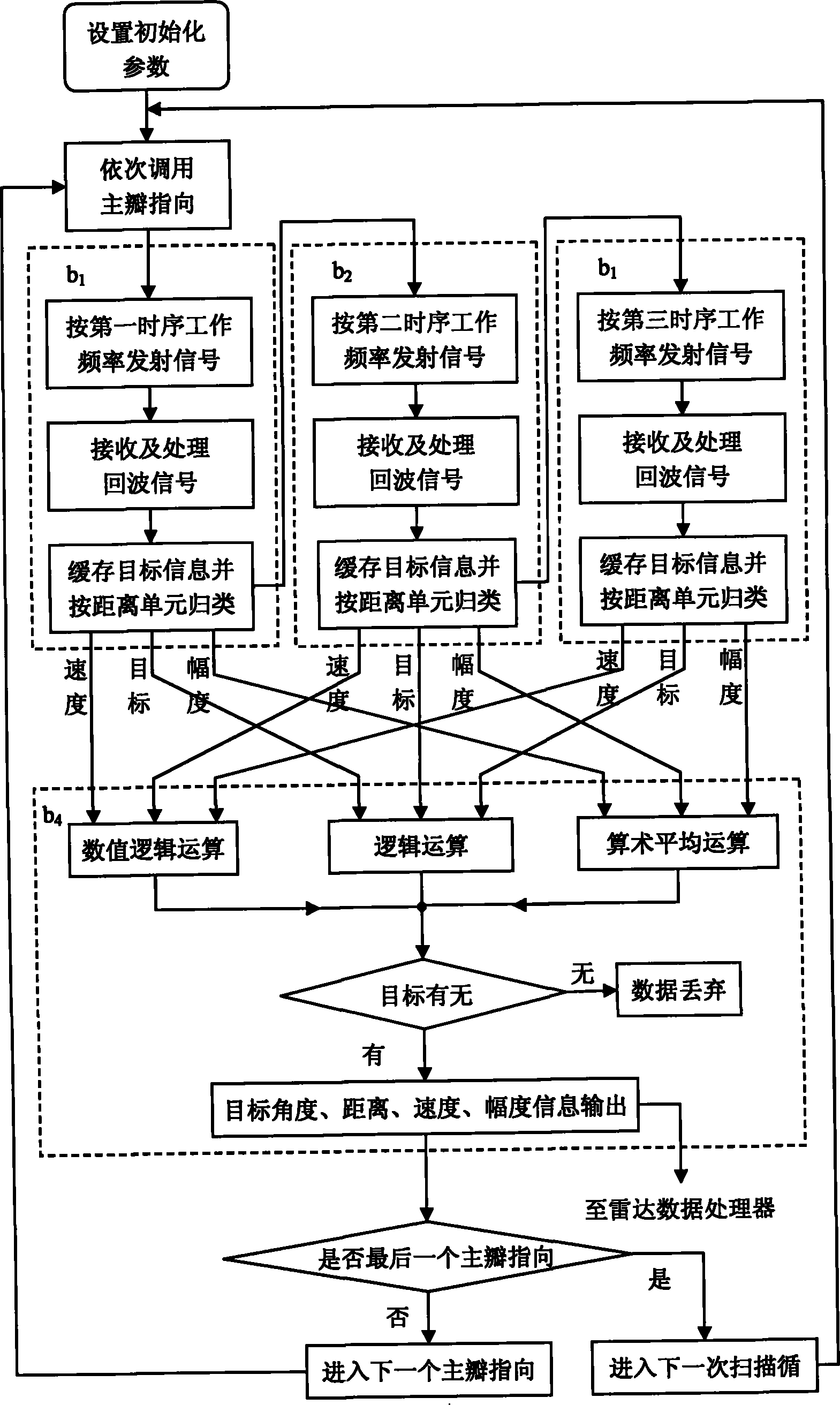
Method for suppressing uniform ultra-sparse array antenna beam pointing fuzziness
InactiveCN101813764ARemove blurReduce adverse effectsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPulse numberArray element
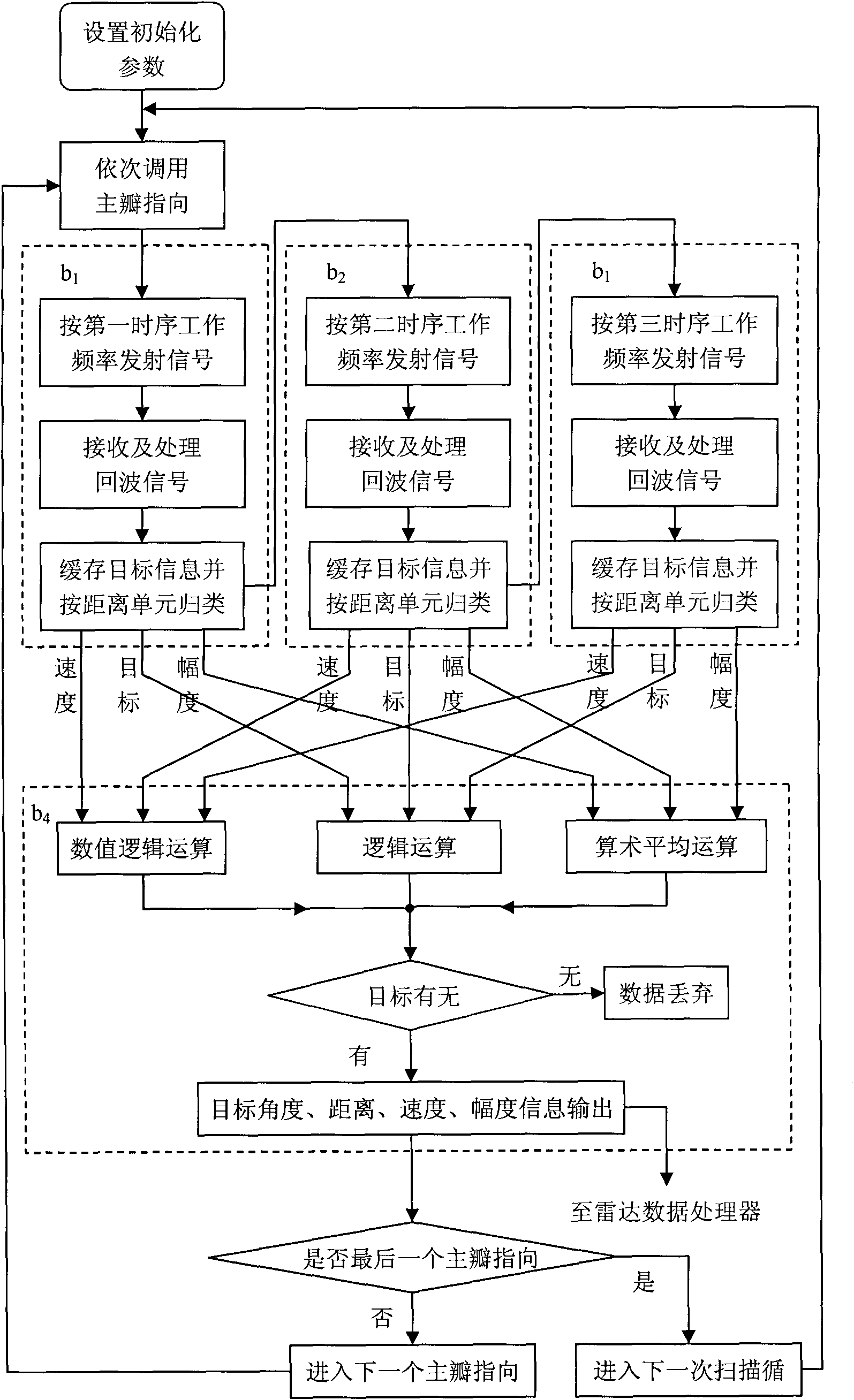
The invention belongs to a method for processing uniform ultra-sparse array antenna beam pointing fuzziness in the radar technology. The method comprises the steps of; performing initialization processing; performing directional transmission and reception by a first main lobe according to the set reference working frequency and two associated working frequency and pulse number in turn and performing comprehensive processing on the acquired three groups of target information so as to determine the existence of the target and removing pointing fuzziness caused by a grating lobe; when the target exists, inputting the angle and distance, speed and magnitude value of the target into a radar data processor together; and then repeatedly performing the processing on other main lobes so as to finish detection of the target on the pointing position of each main lobe. In the method, the angle range without grating lobe fuzziness is two times wider than that of two pieces of background technology and the array element number is reduced by over 50 percent, so that the method for the suppressing the uniform ultra-sparse array antenna beam pointing fuzziness is characterized in that: adverse impact of the grating lobe on the radar measured angle can be removed to the full extent; the antenna array element number and corresponding channel number of large-aperture uniform array radar are effectively reduced; the system cost is reduced, the application range is enlarged, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
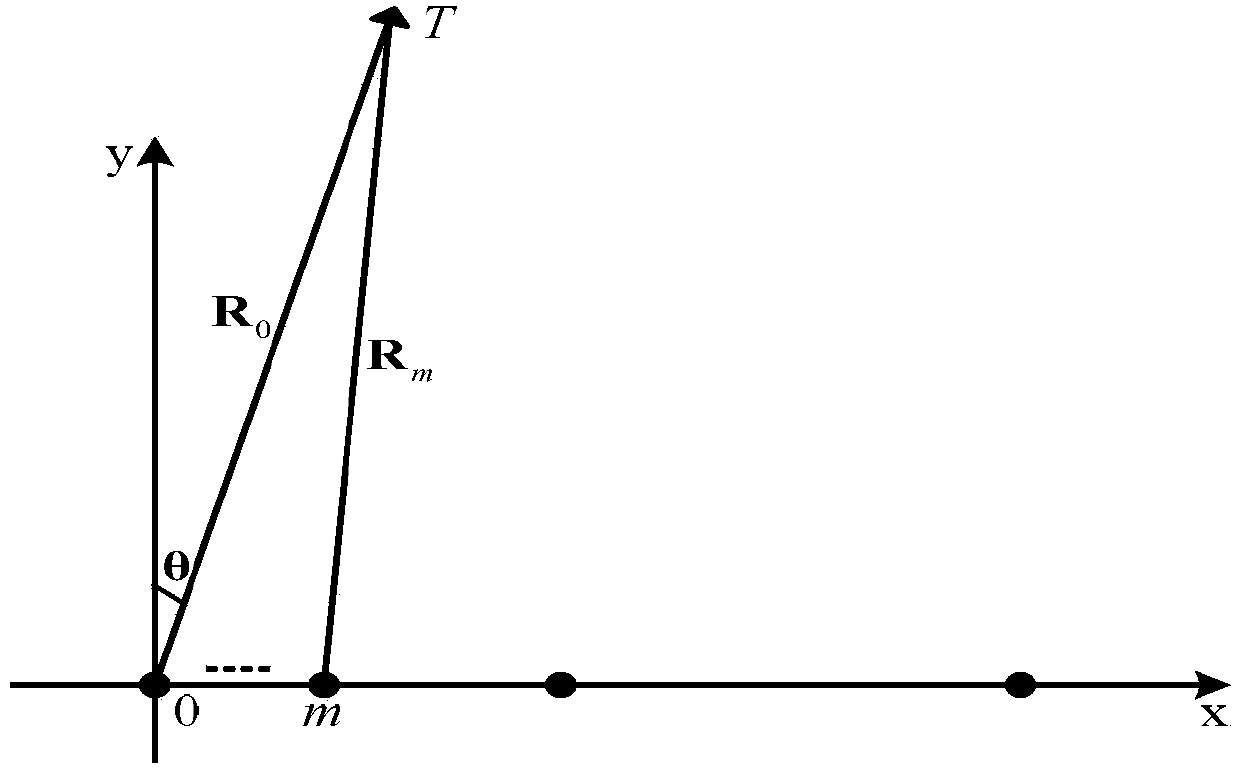
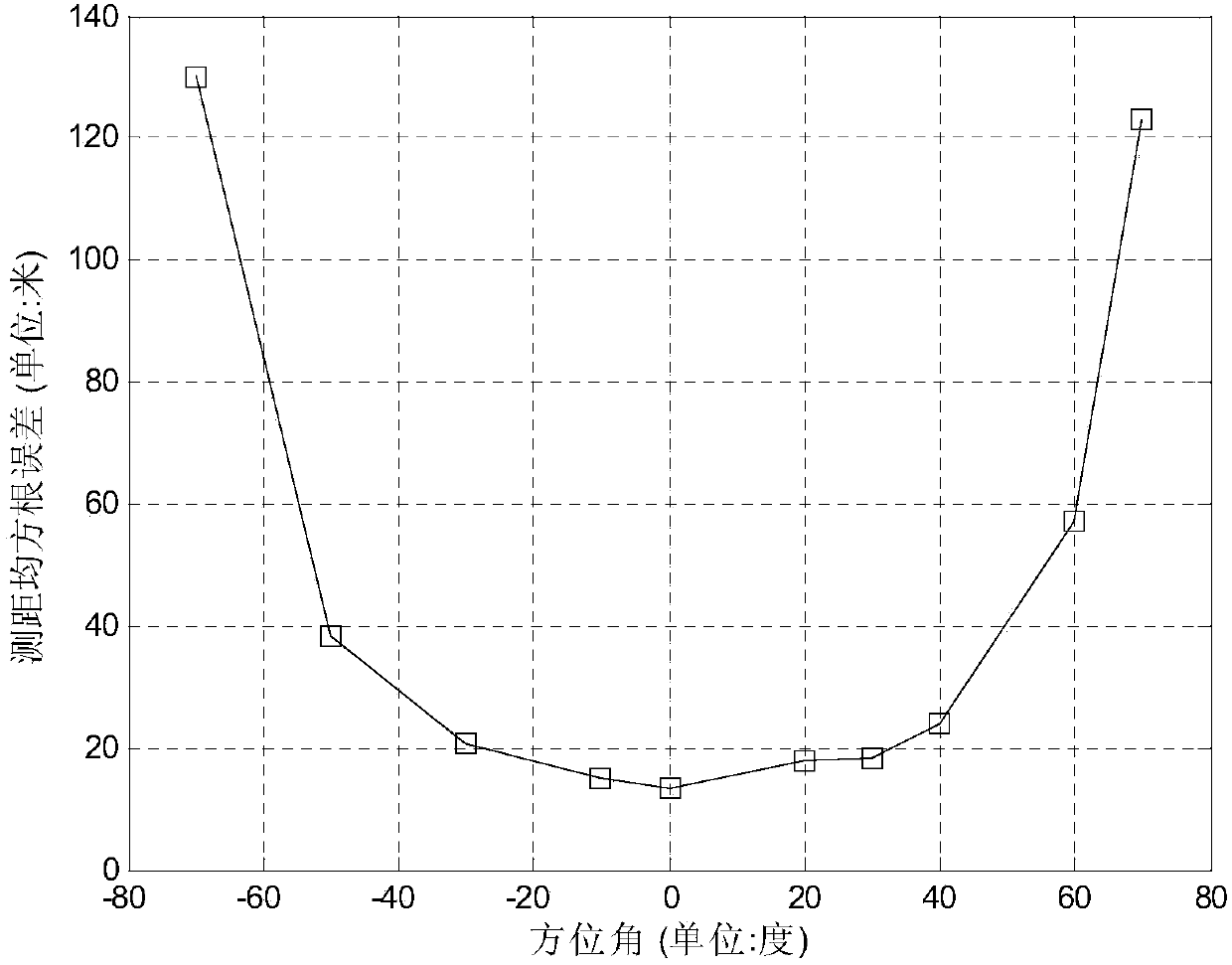
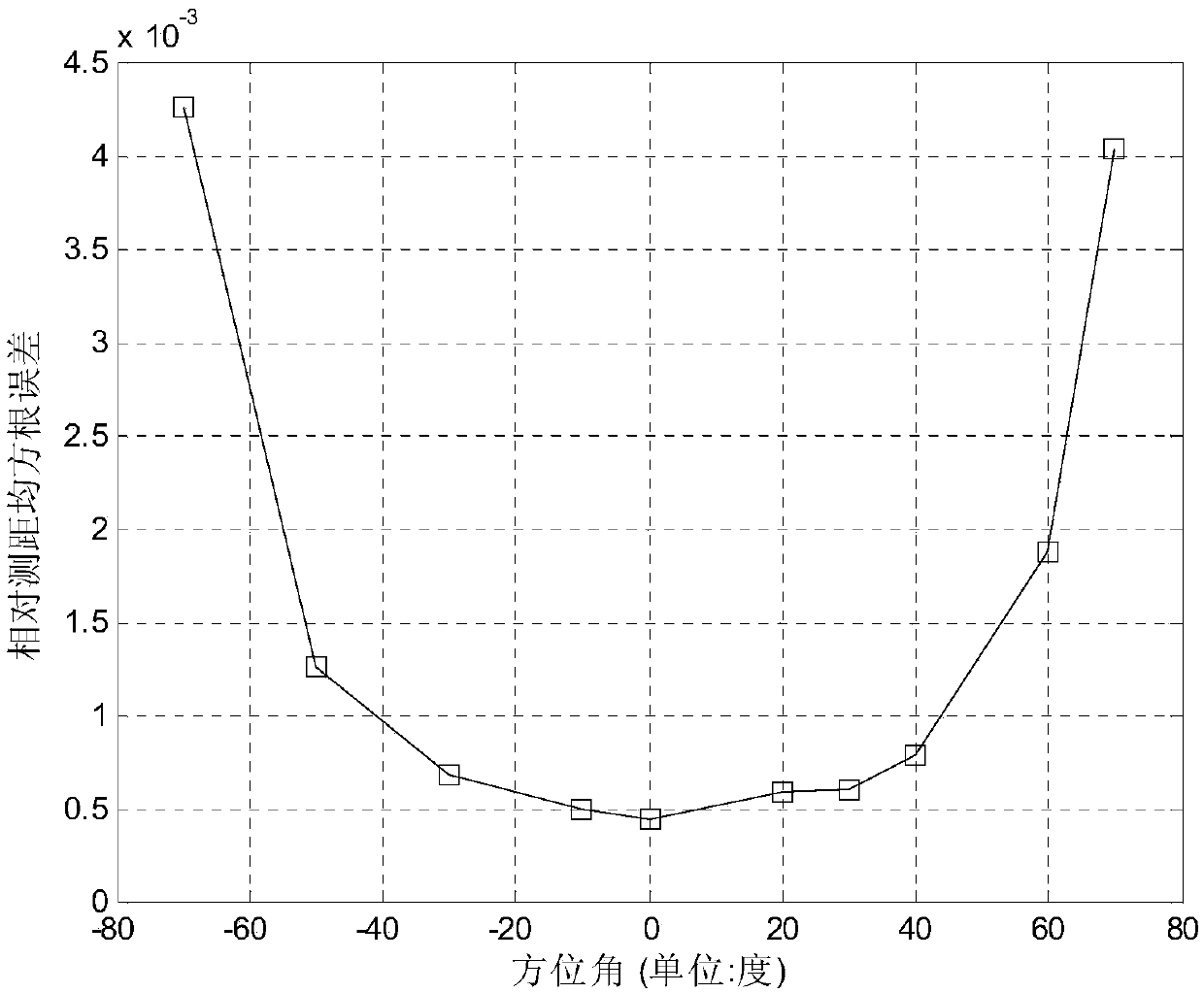
Ranging passive location method under azimuth angle prior condition based on linear sparse arrays
ActiveCN104181499ARapid deploymentRealize distance measurement and positioningPosition fixationMultiple signal classificationSingle station
The invention provides a ranging passive location method under an azimuth angle prior condition based on linear sparse arrays. The features of a multi-station system and a single-station system of passive location are combined, on the basis that observing stations are arrayed in a small space range in a linear sparse array mode, the observing stations are used for receiving data phase information, and near-field radiation source ranging location is achieved. On the basis of meticulous analysis of a structure of observed data phase information, prior azimuth angle information is used for carrying out phase compensation on a phase fuzzy part existing in the observed data phase information, a non-phase fuzzy part existing in the observed data phase information is used for establishing an array signal model, and estimation of near-field radiation source distance is completed based on a MUSIC algorithm.
Owner:齐鲁电科山东科技成果转化有限公司
Sparse array millimeter wave imaging system
InactiveUS20090289833A1Reduce system costLower frame rateAntenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionMillimetre wave
An active millimeter-wave imaging system that can provide a means of surmounting the deficiencies of earlier millimeter-wave systems, as well as lowering the system cost substantially. Earlier systems have employed large numbers of individual millimeter-wave receivers in either focal plane arrays or frequency scanned antenna arrays, and these systems have suffered from low frame rate, poor contrast, and relatively low resolution. By employing a sparse array of millimeter-wave transmitters and receivers, covering a relatively large, flat, physical aperture, a low cost and high resolution system can be achieved. By employing active millimeter-wave illumination, contrast and frame rate issues can be mitigated, at long ranges (10's of meters). A new approach, termed Fourier Telescopy, allows the illuminating signals to interrogate the various spatial frequencies of the target, and the image to be reconstructed from these various spatial frequency components.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com