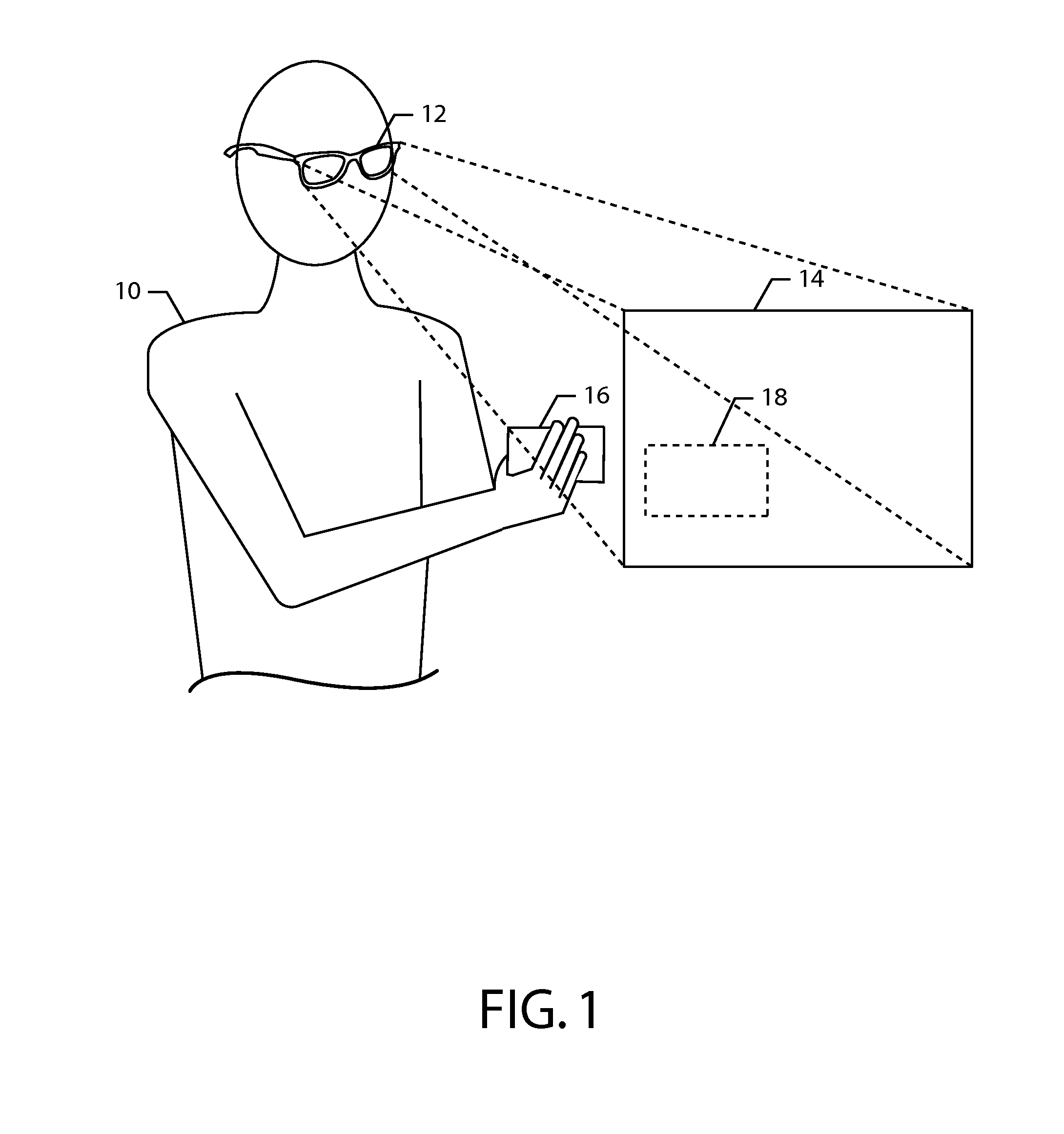
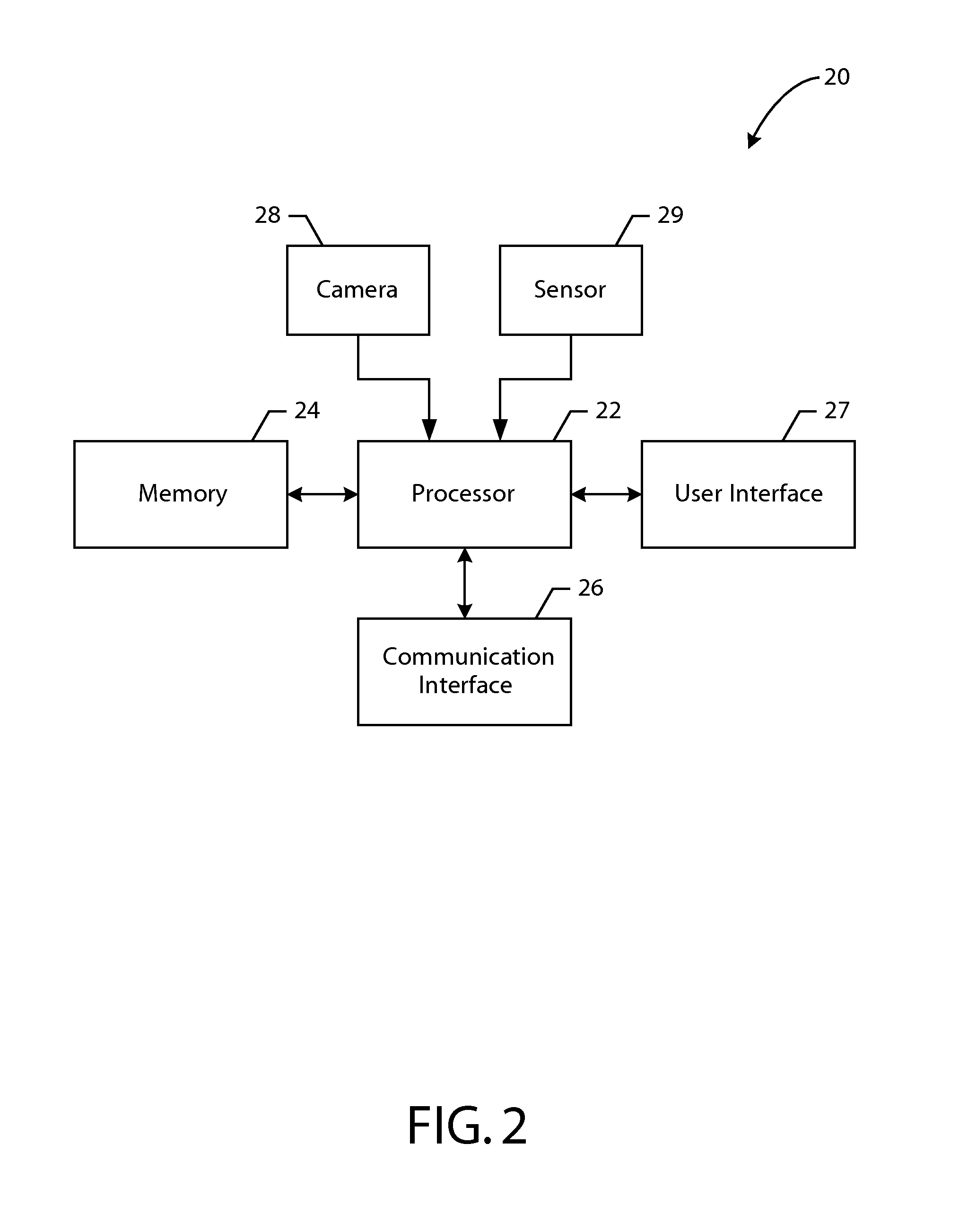
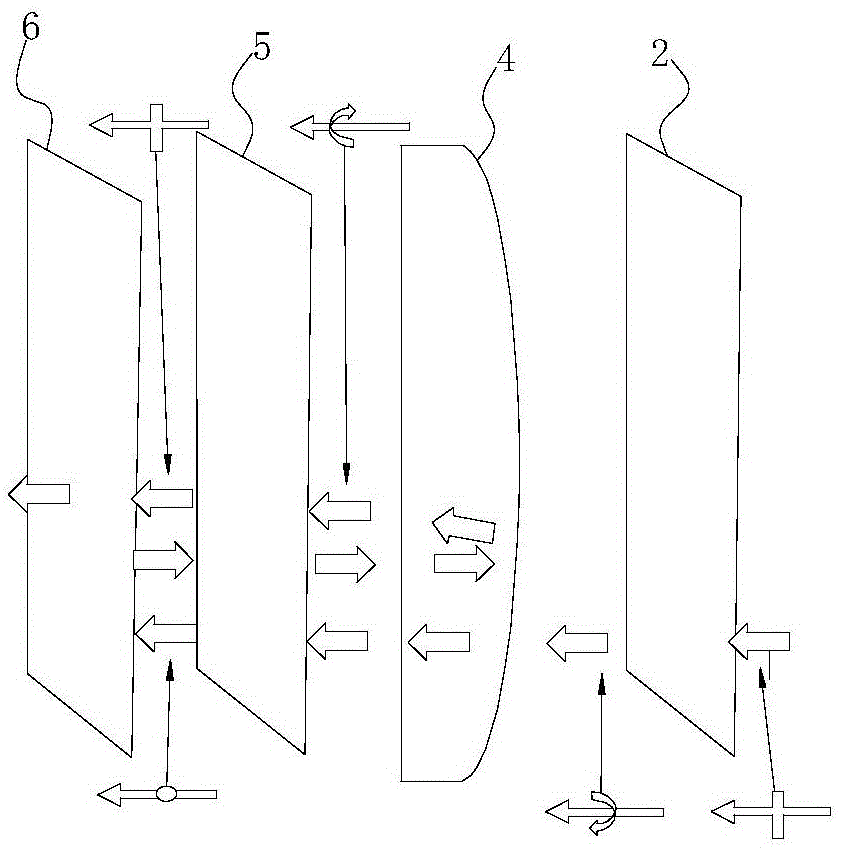Patents
Literature
849 results about "Near eye display" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
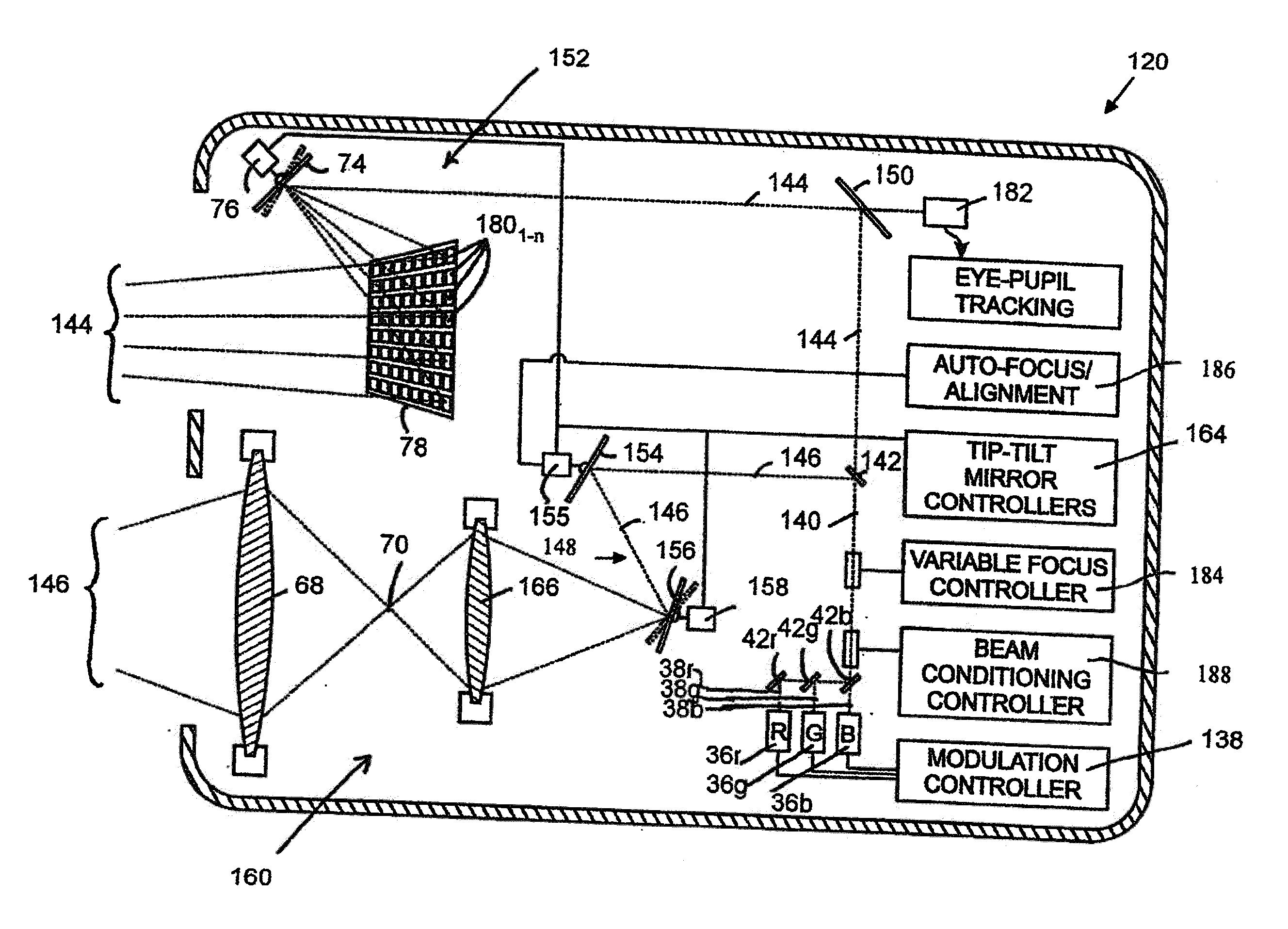
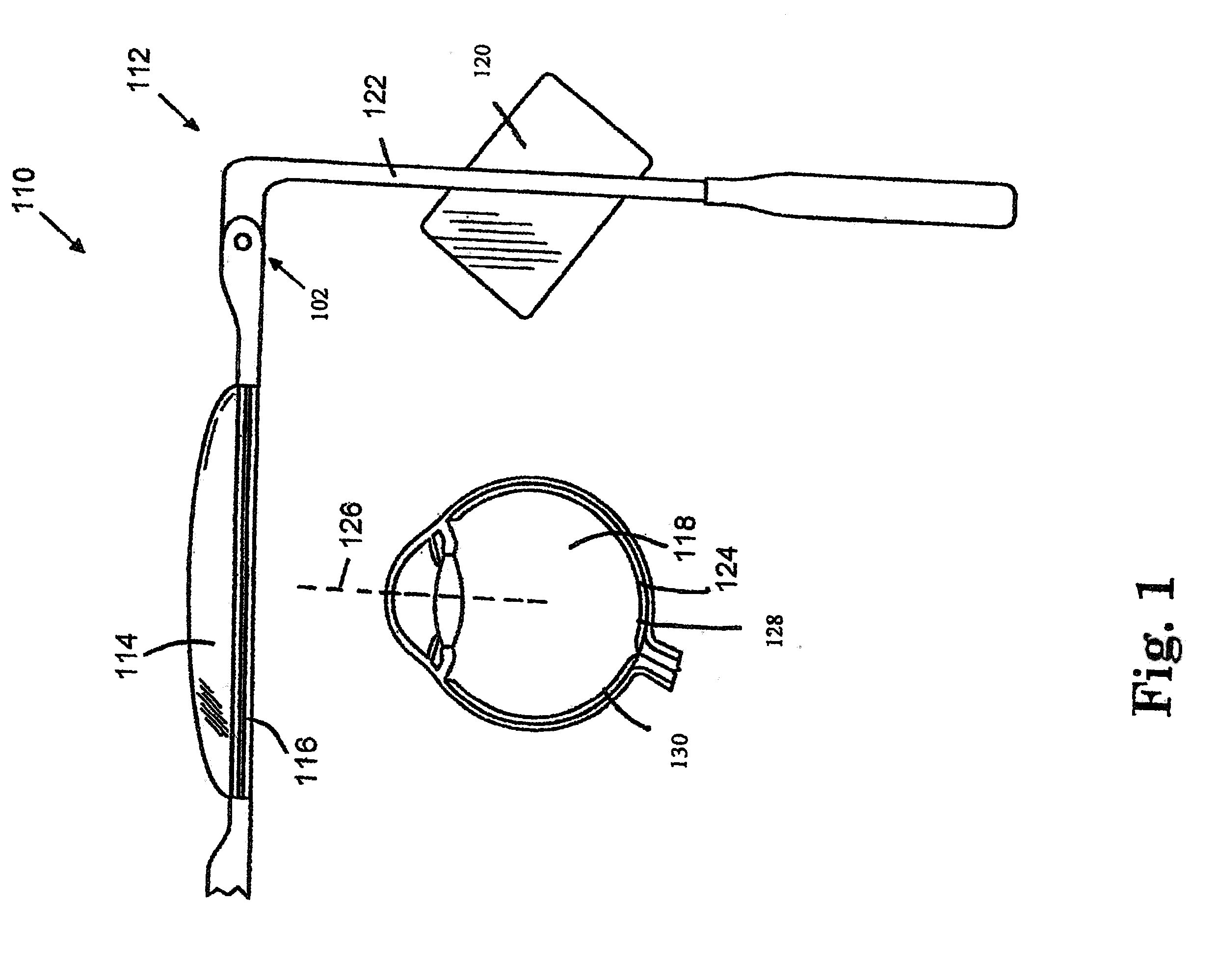
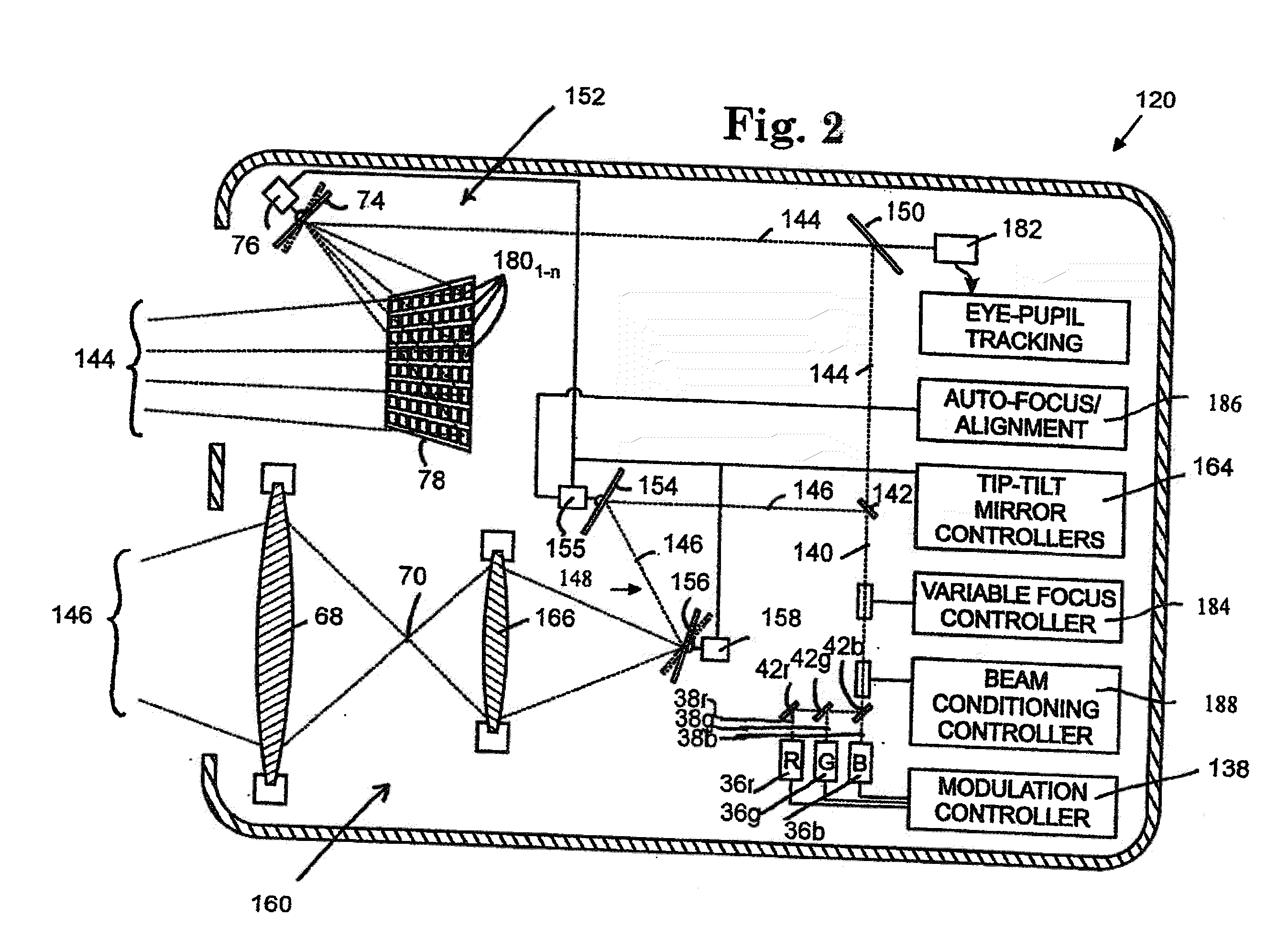
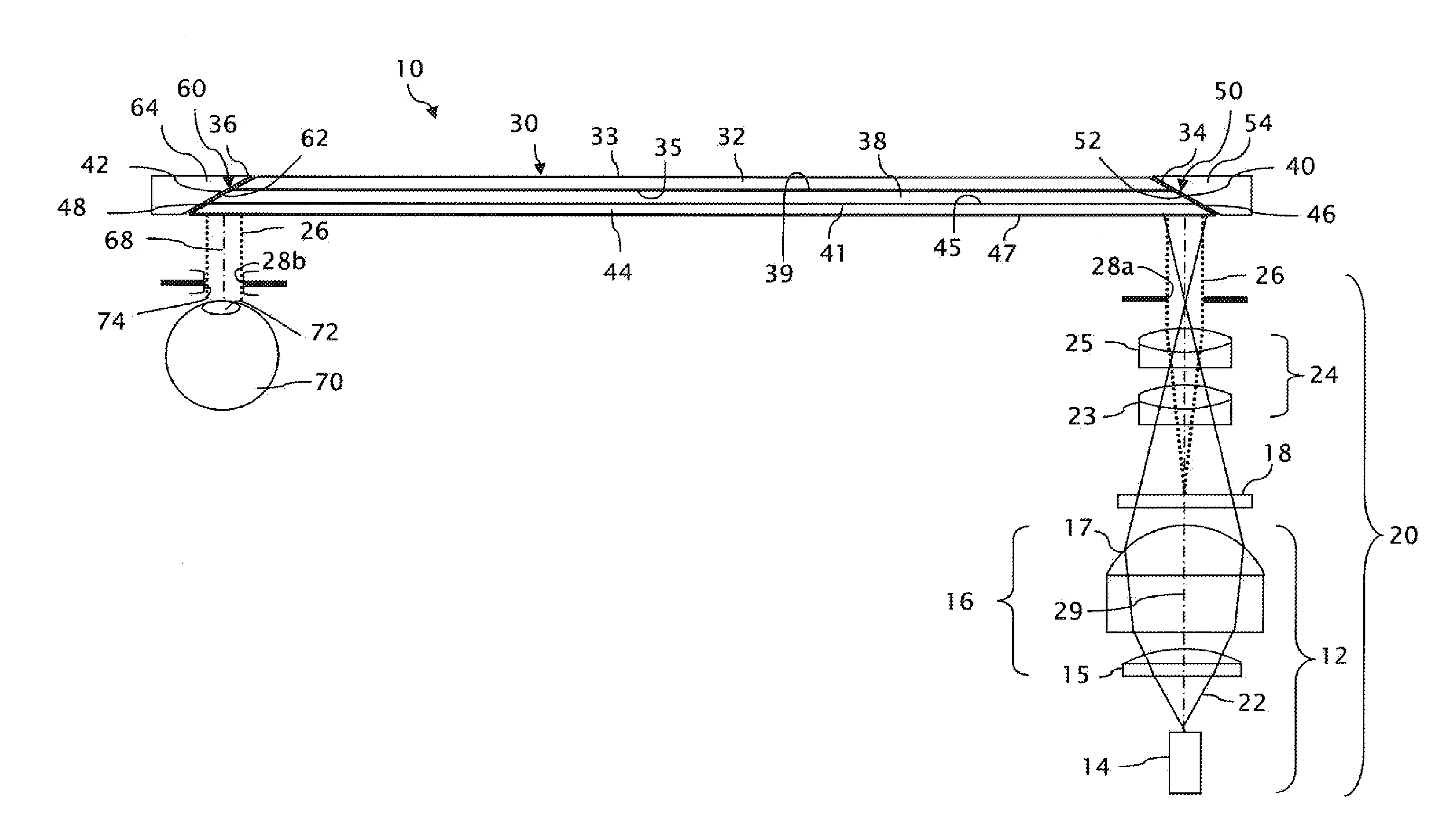
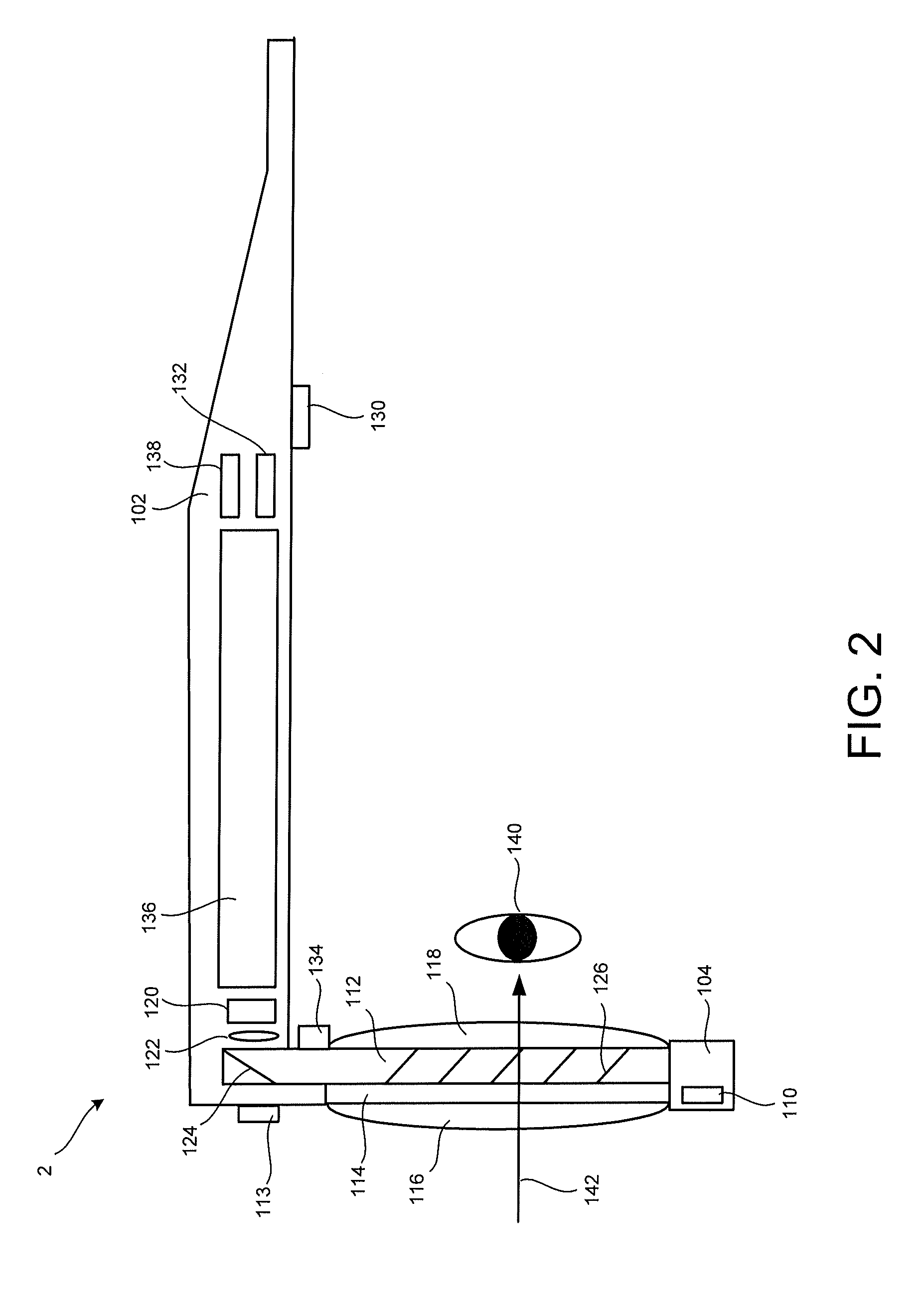
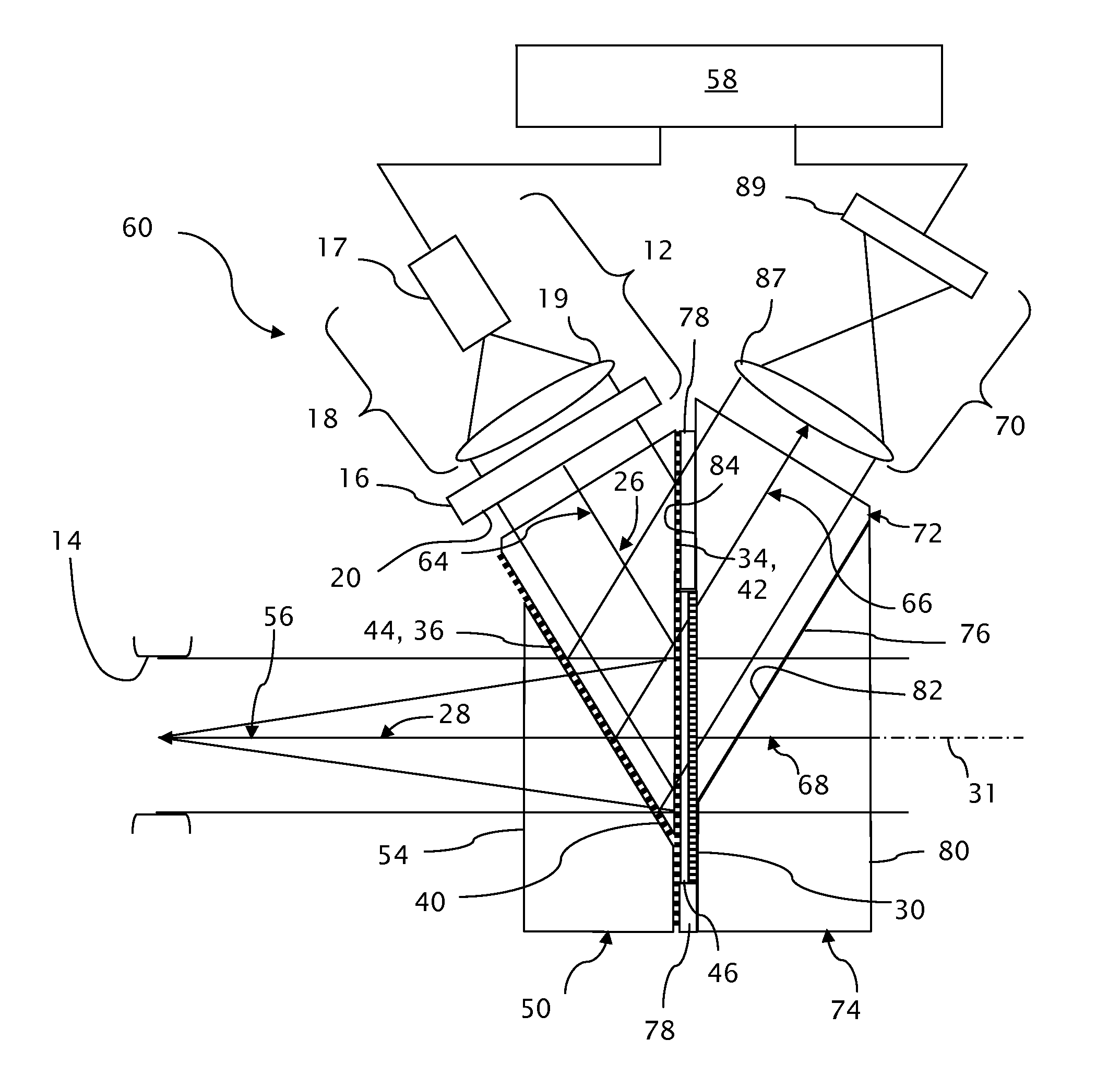
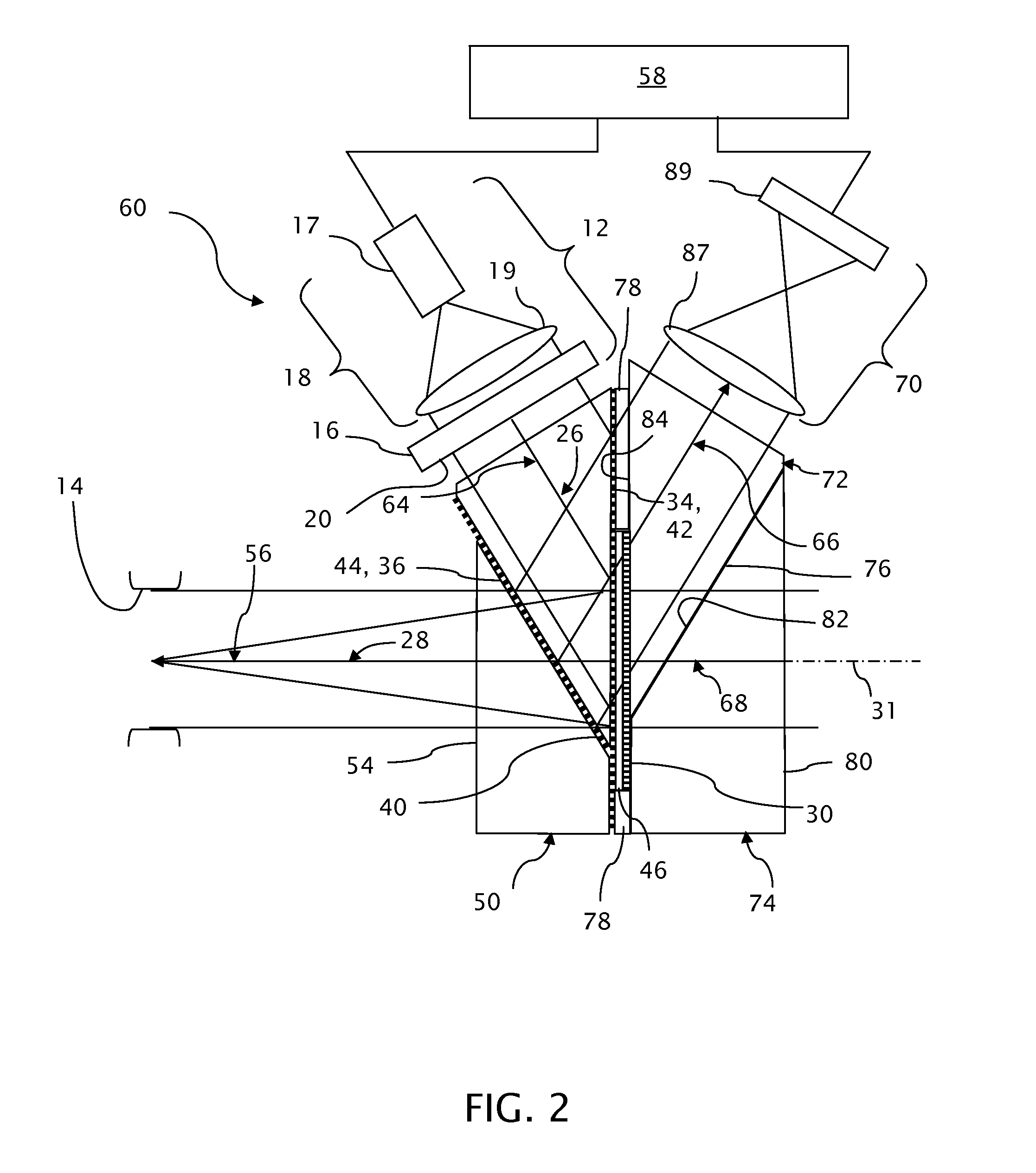
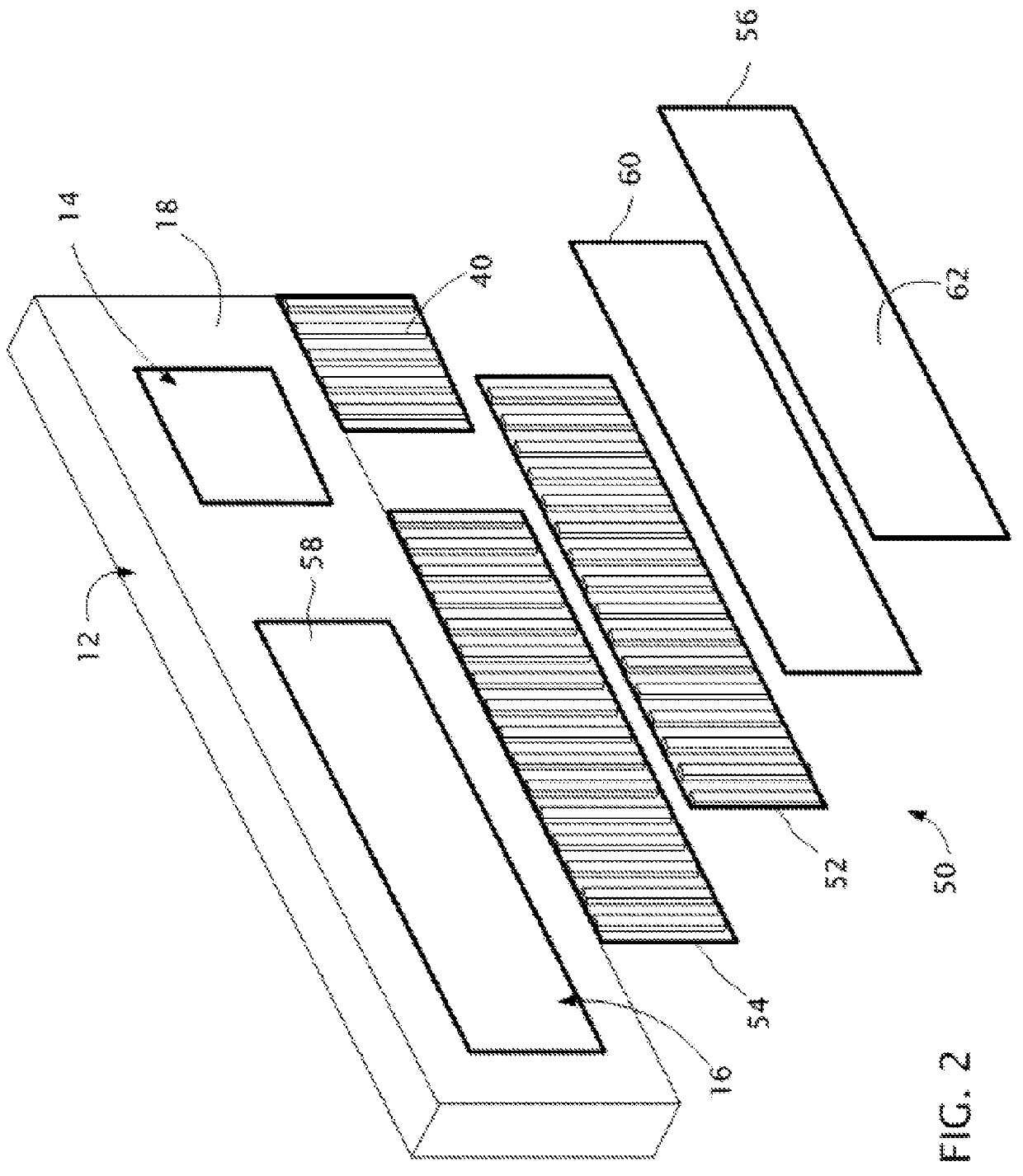
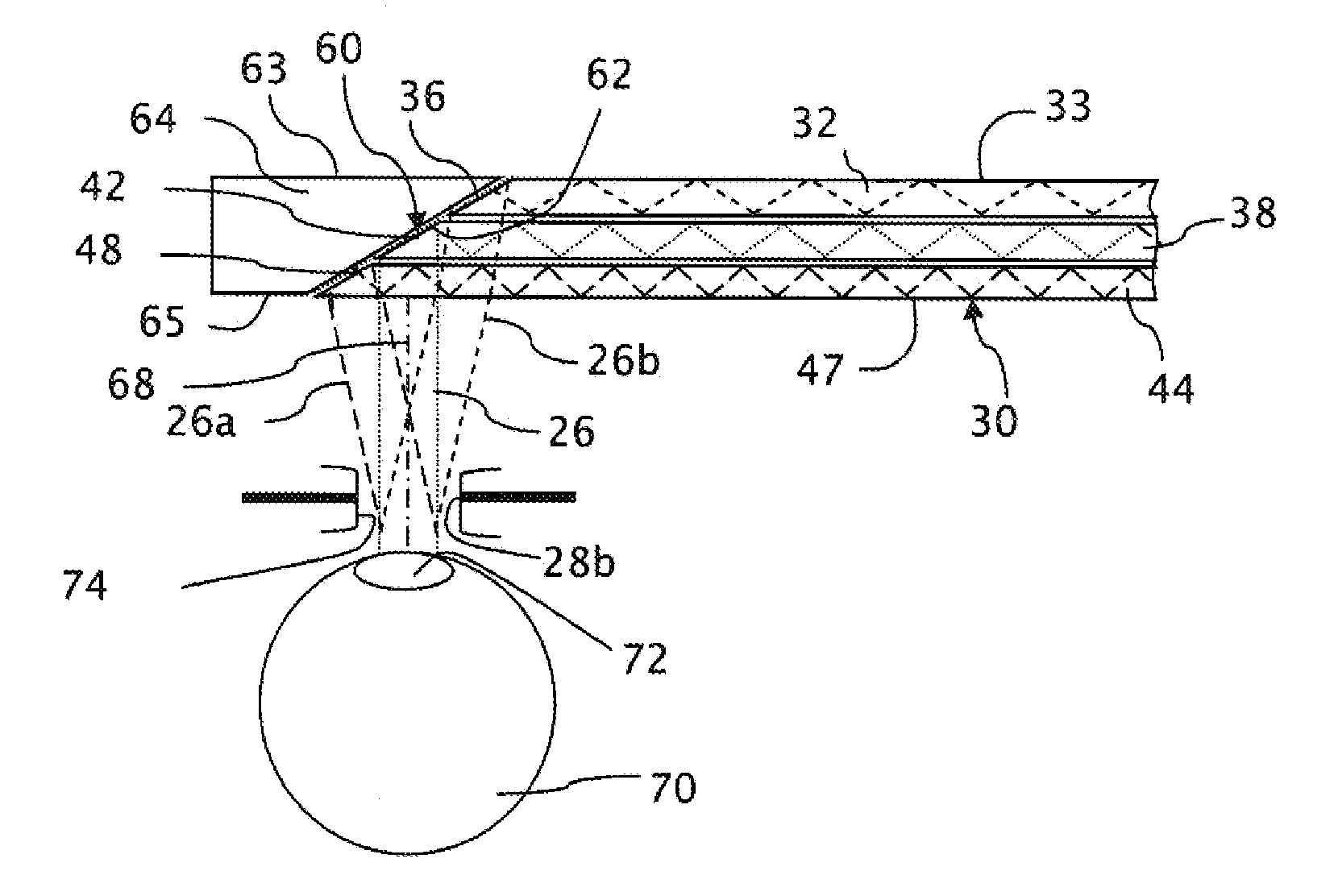
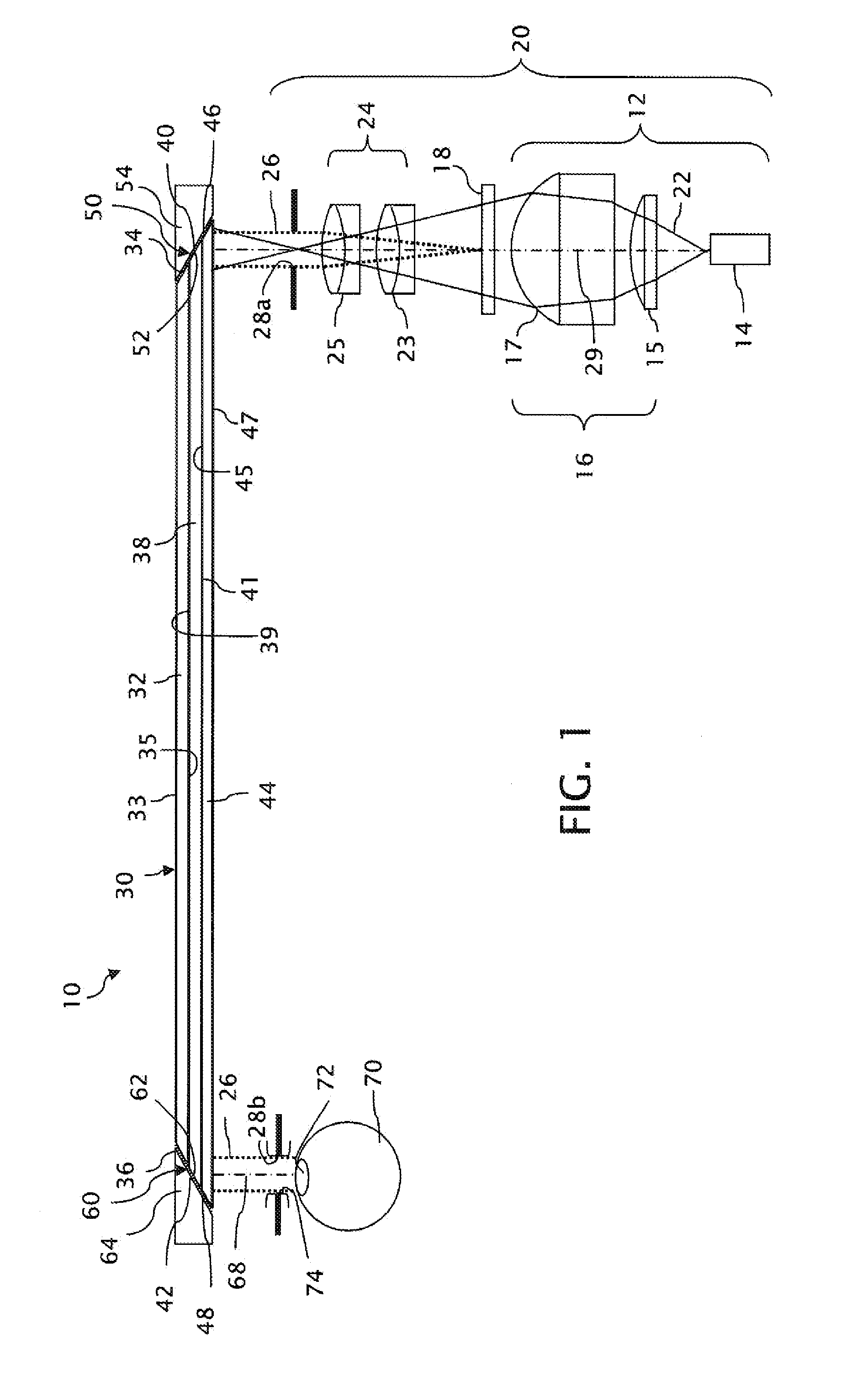
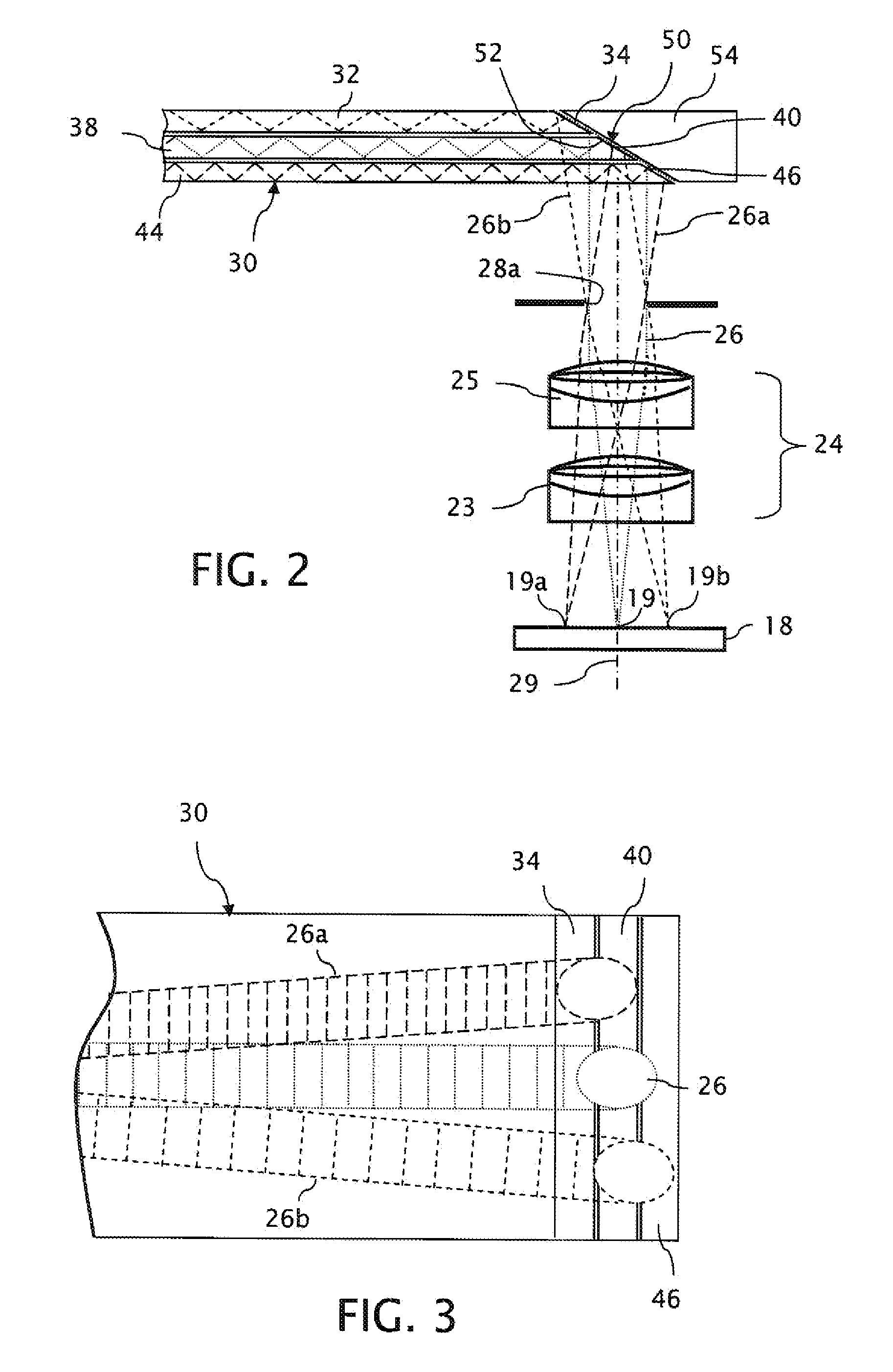
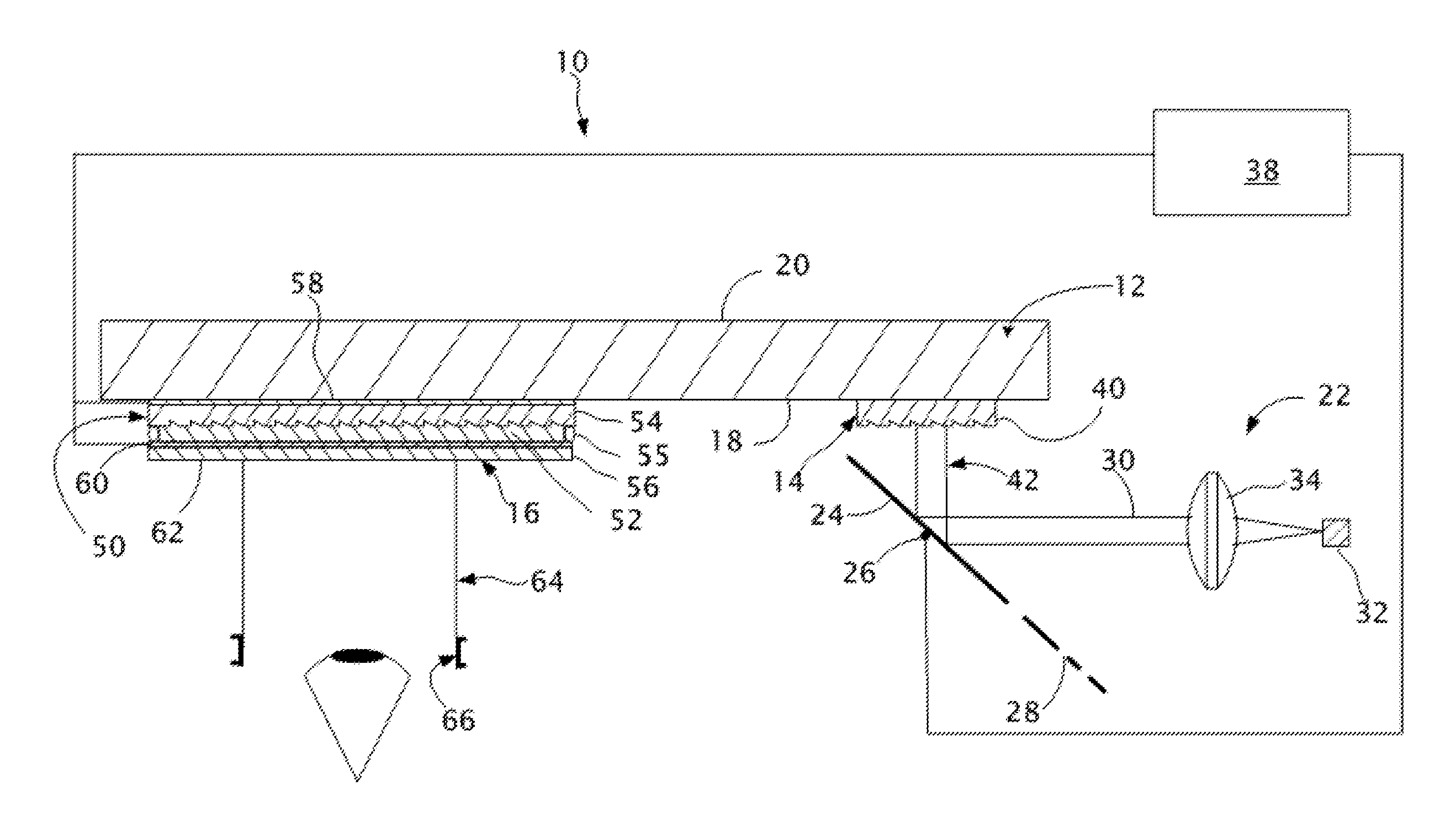
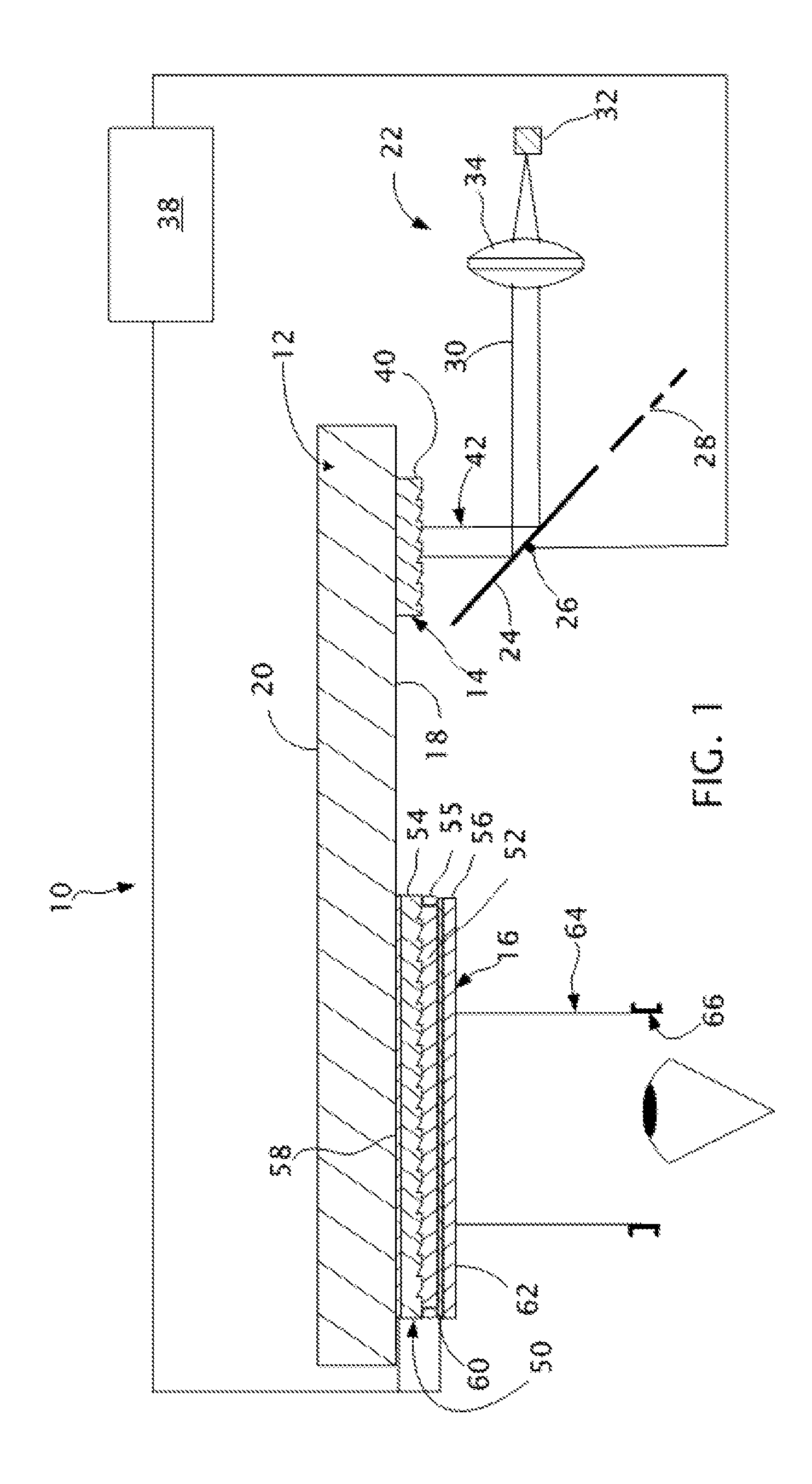
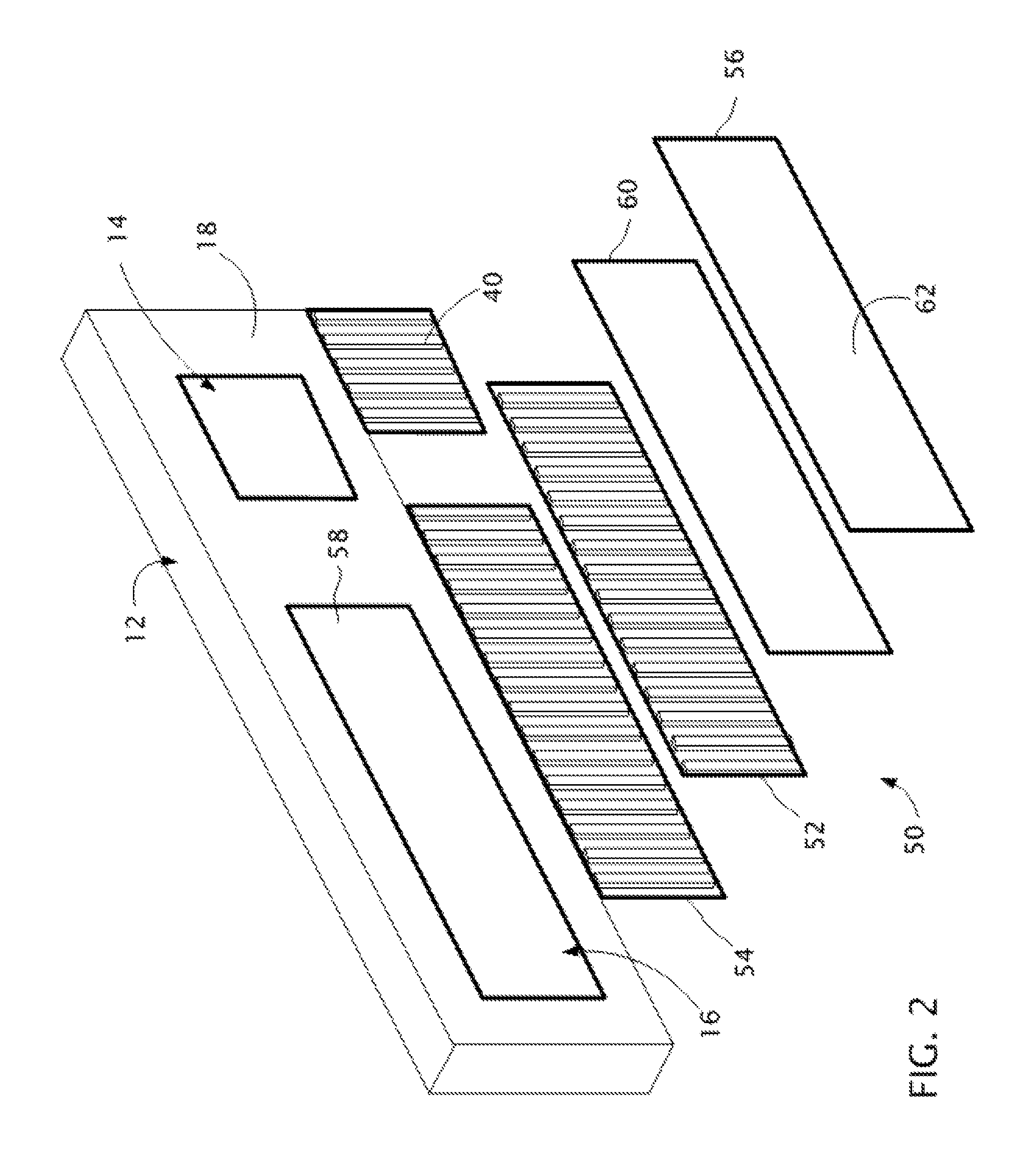
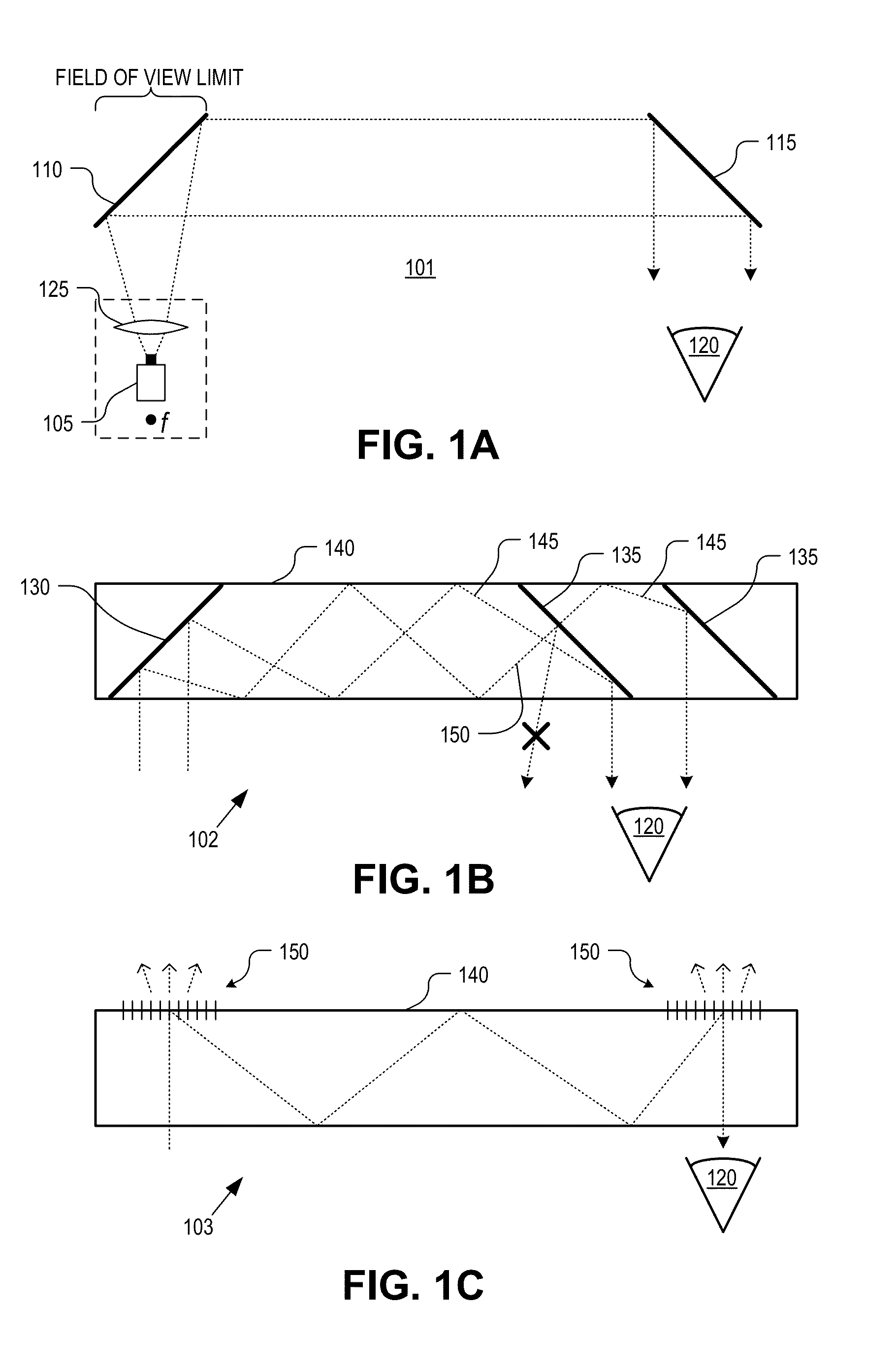
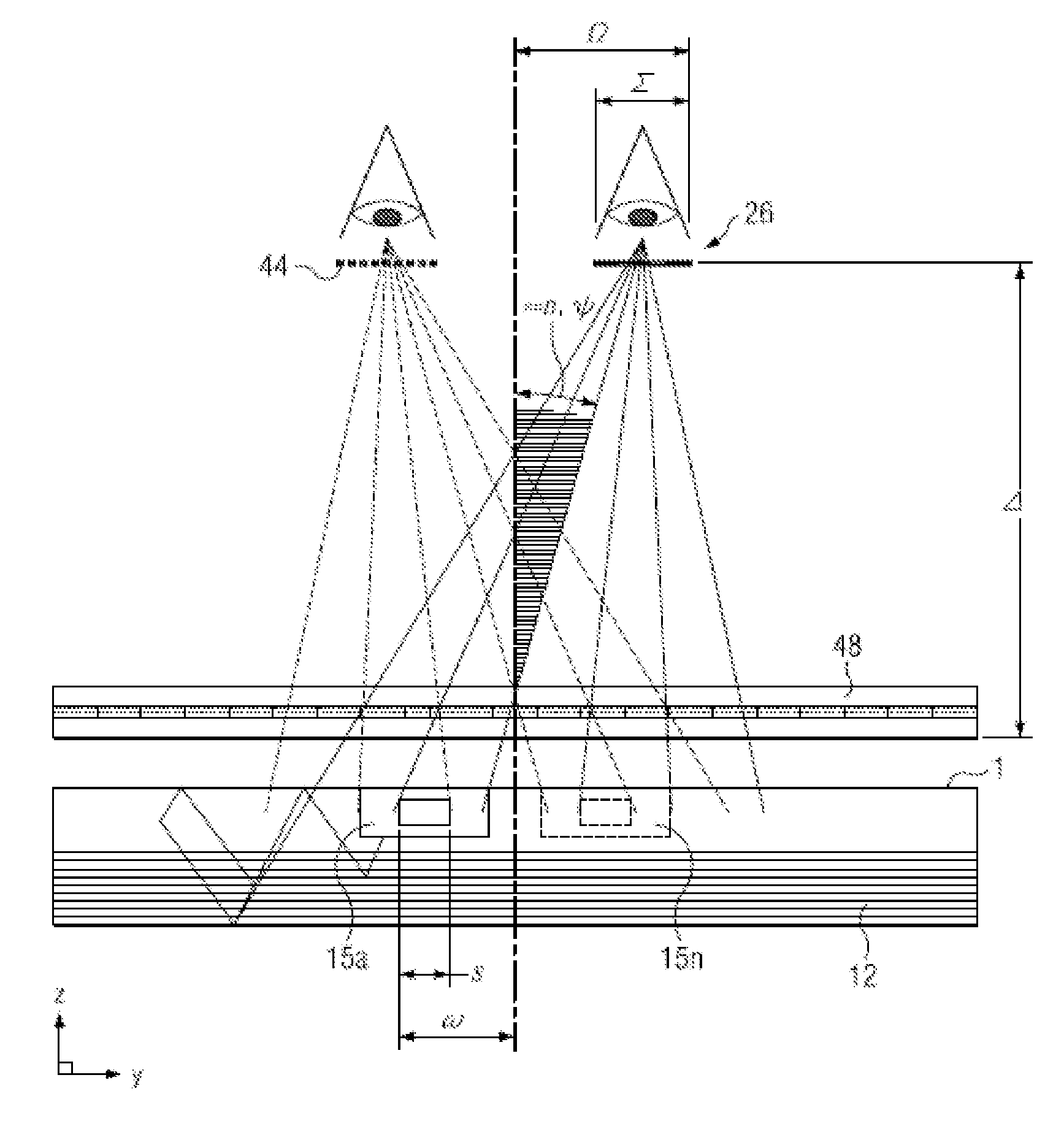
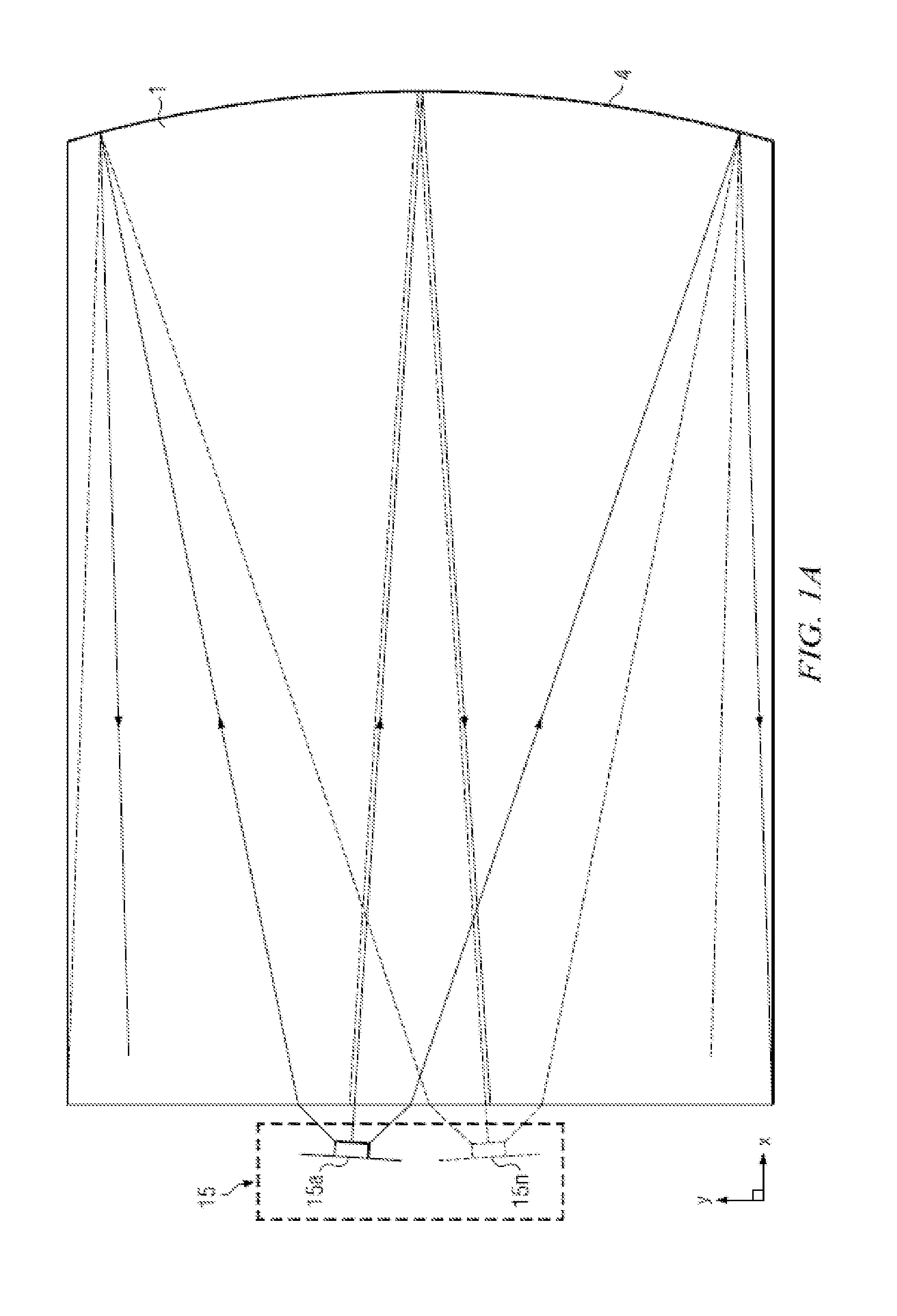
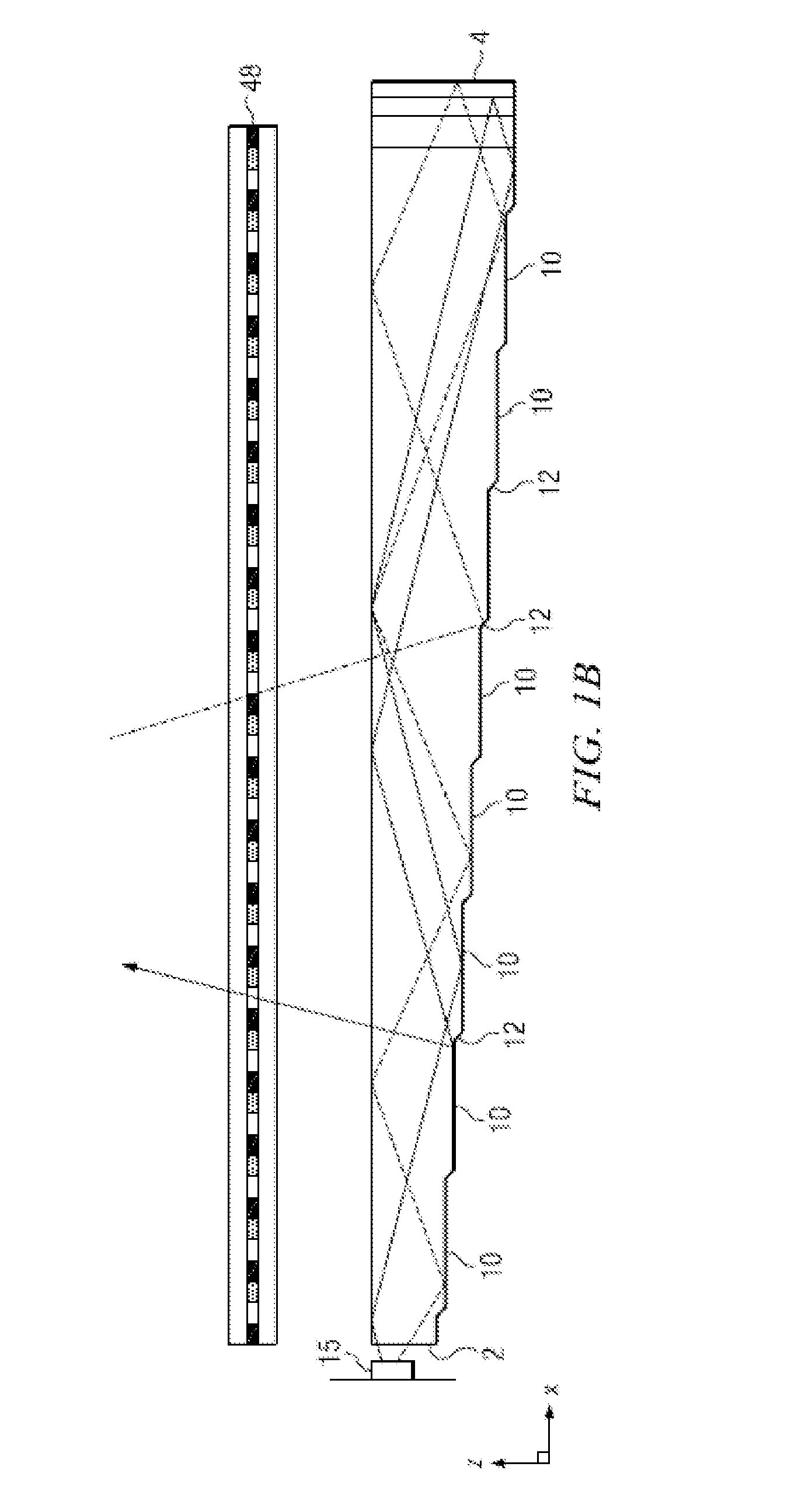
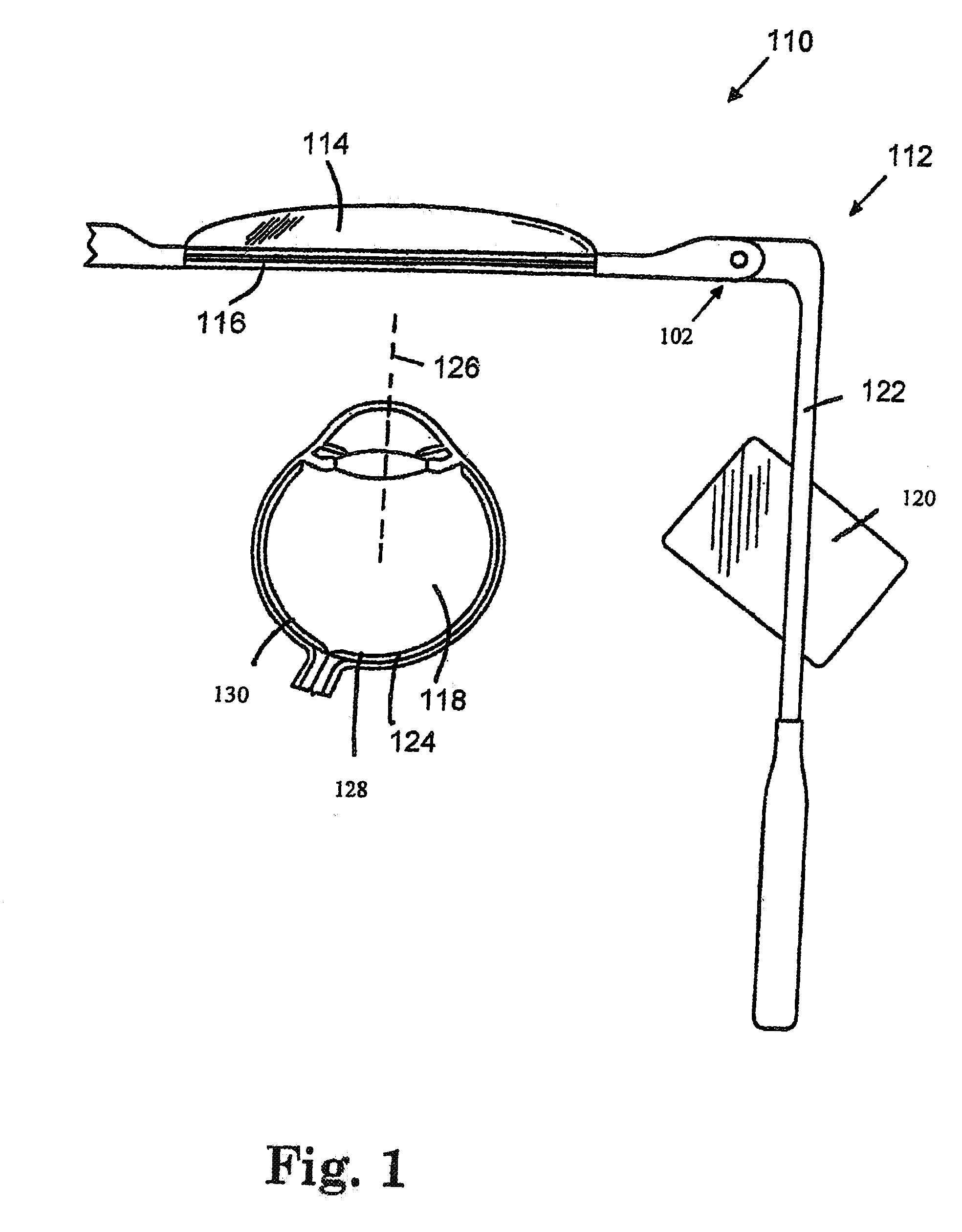
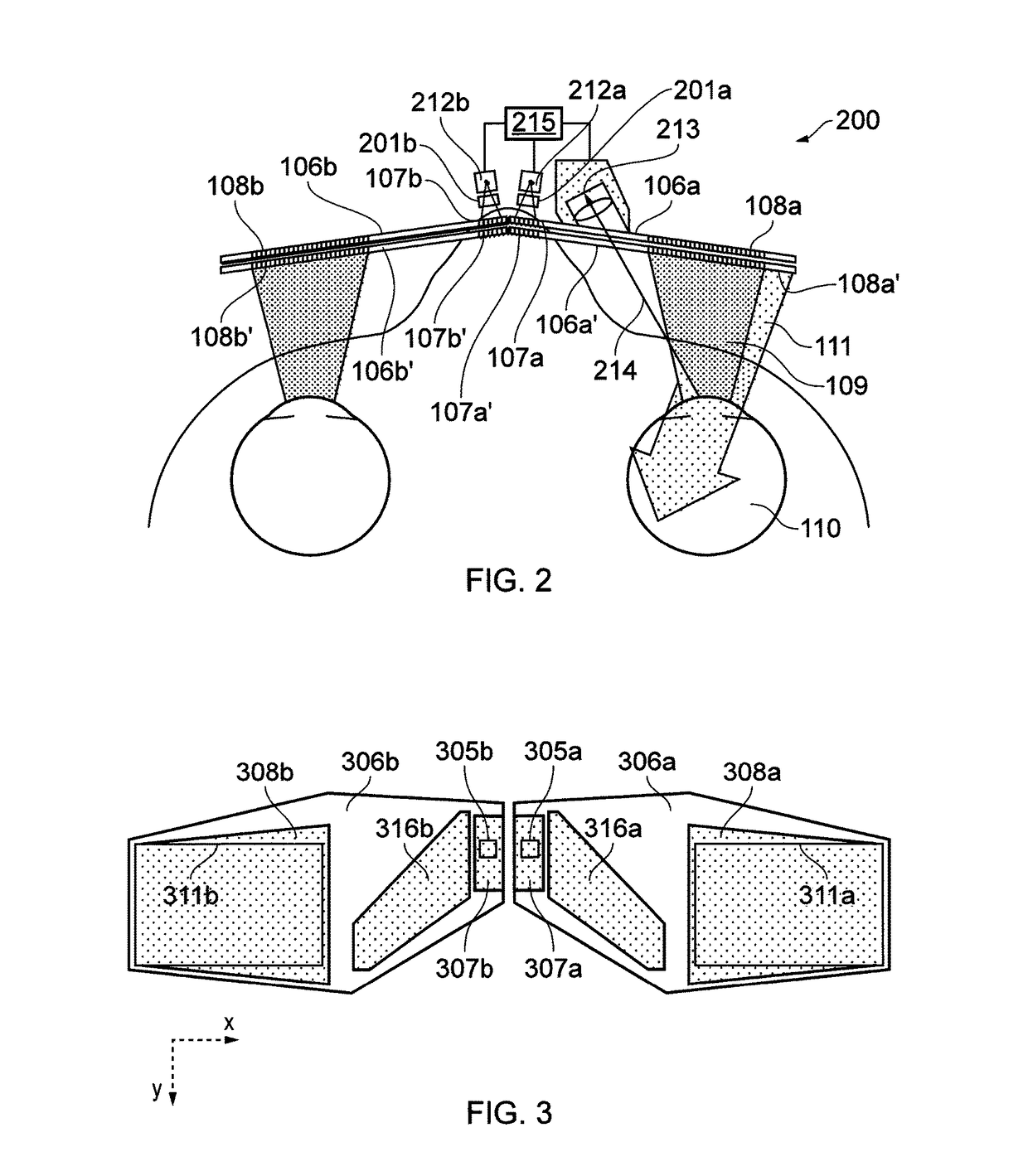
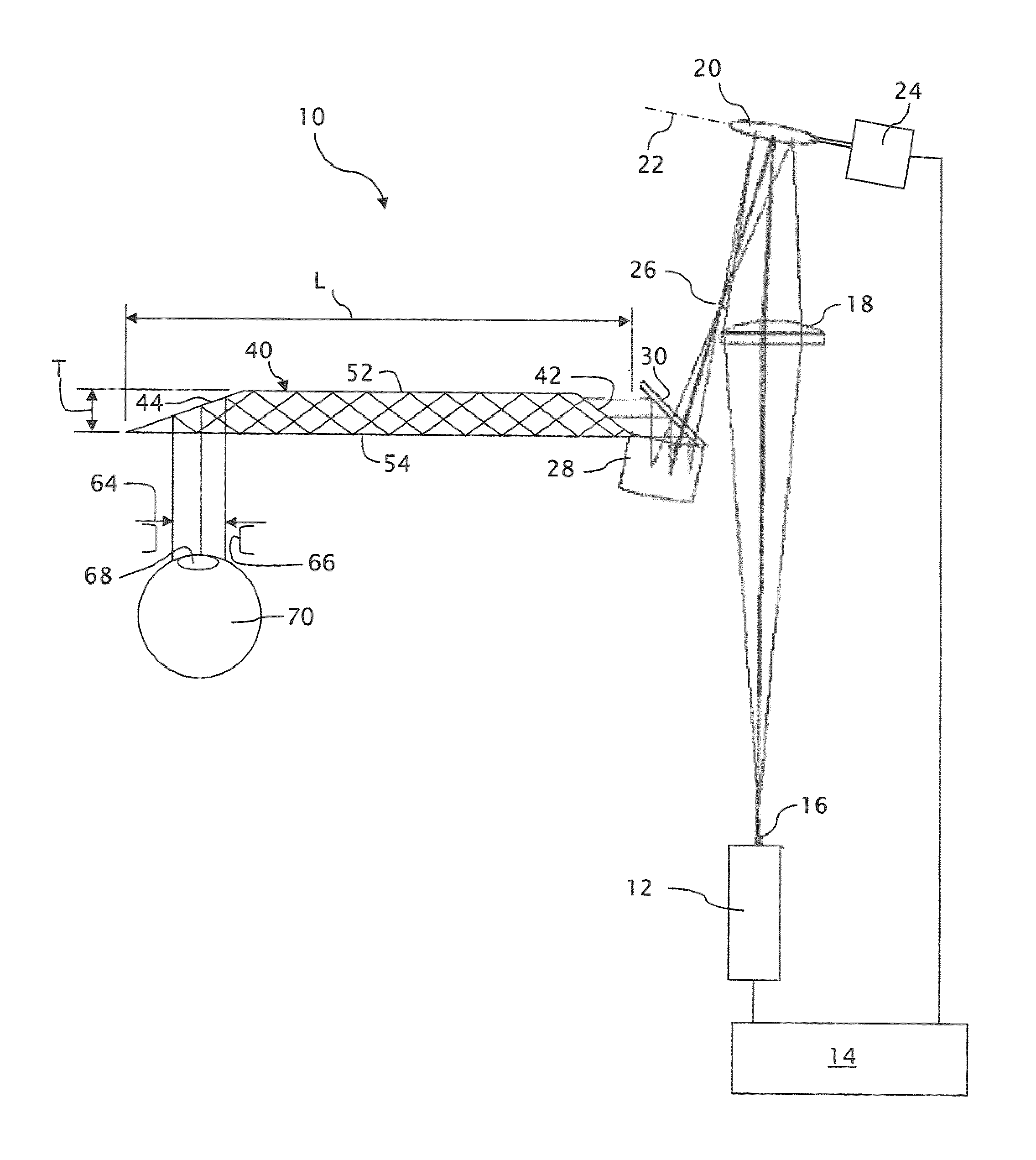
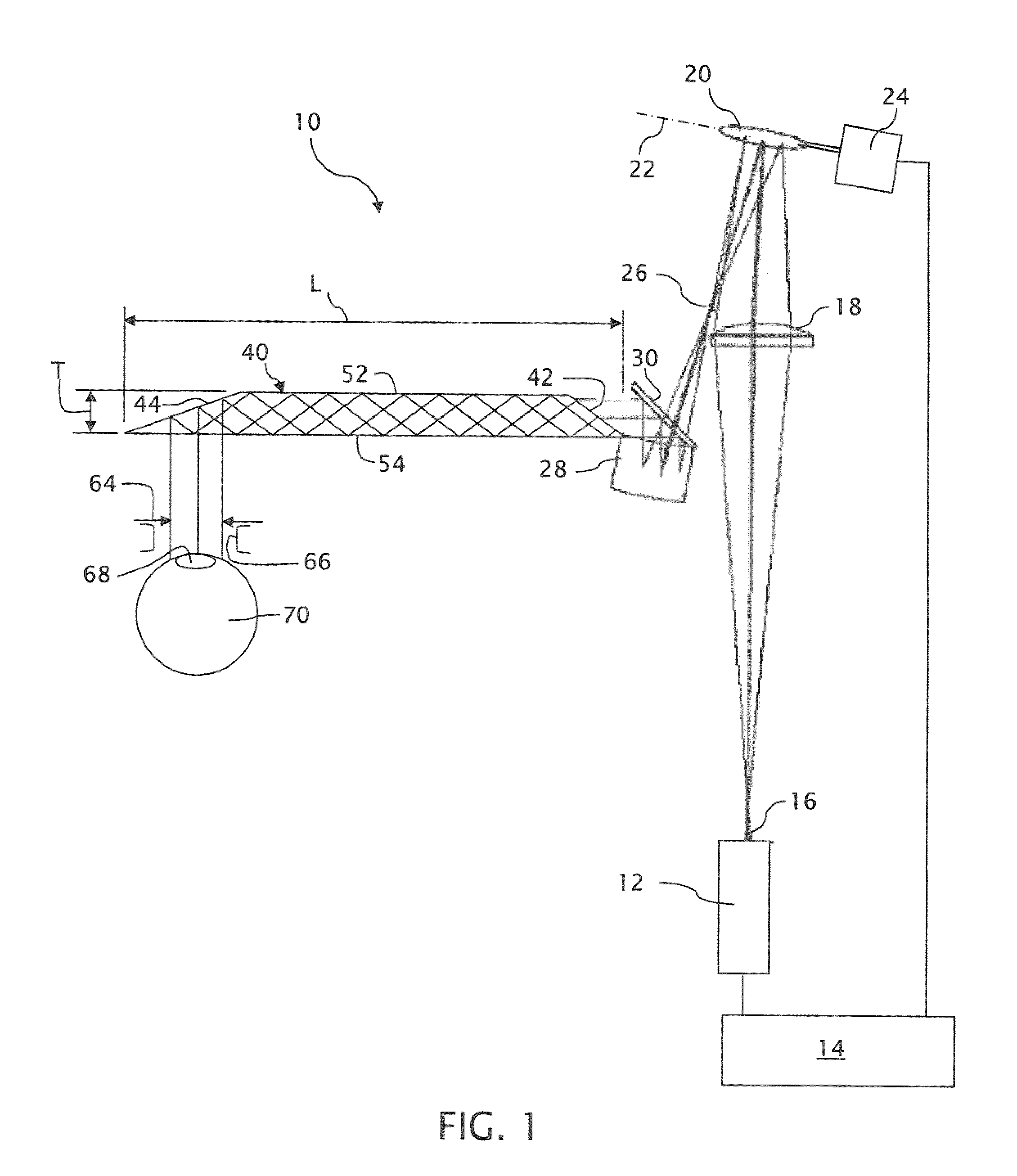
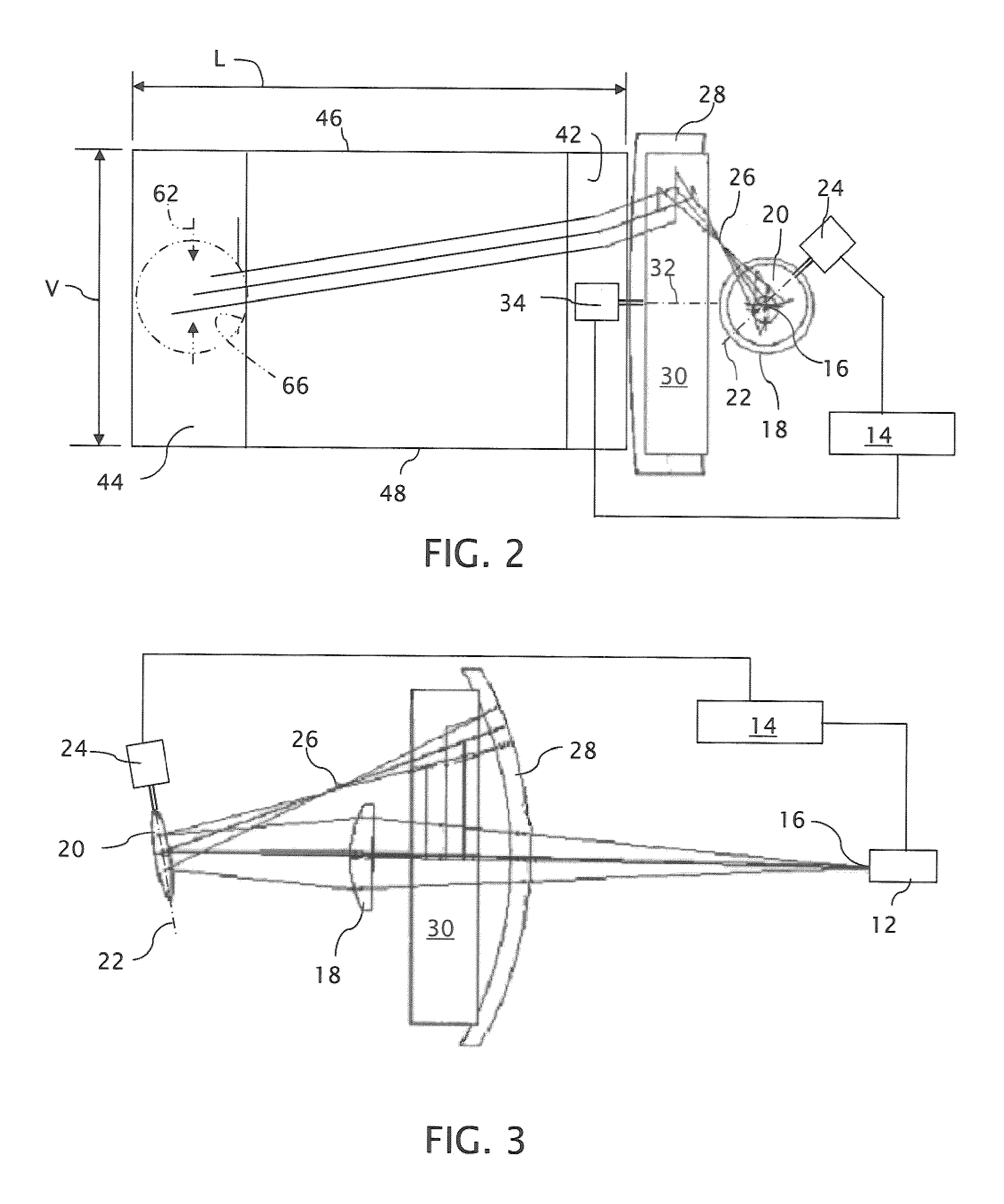
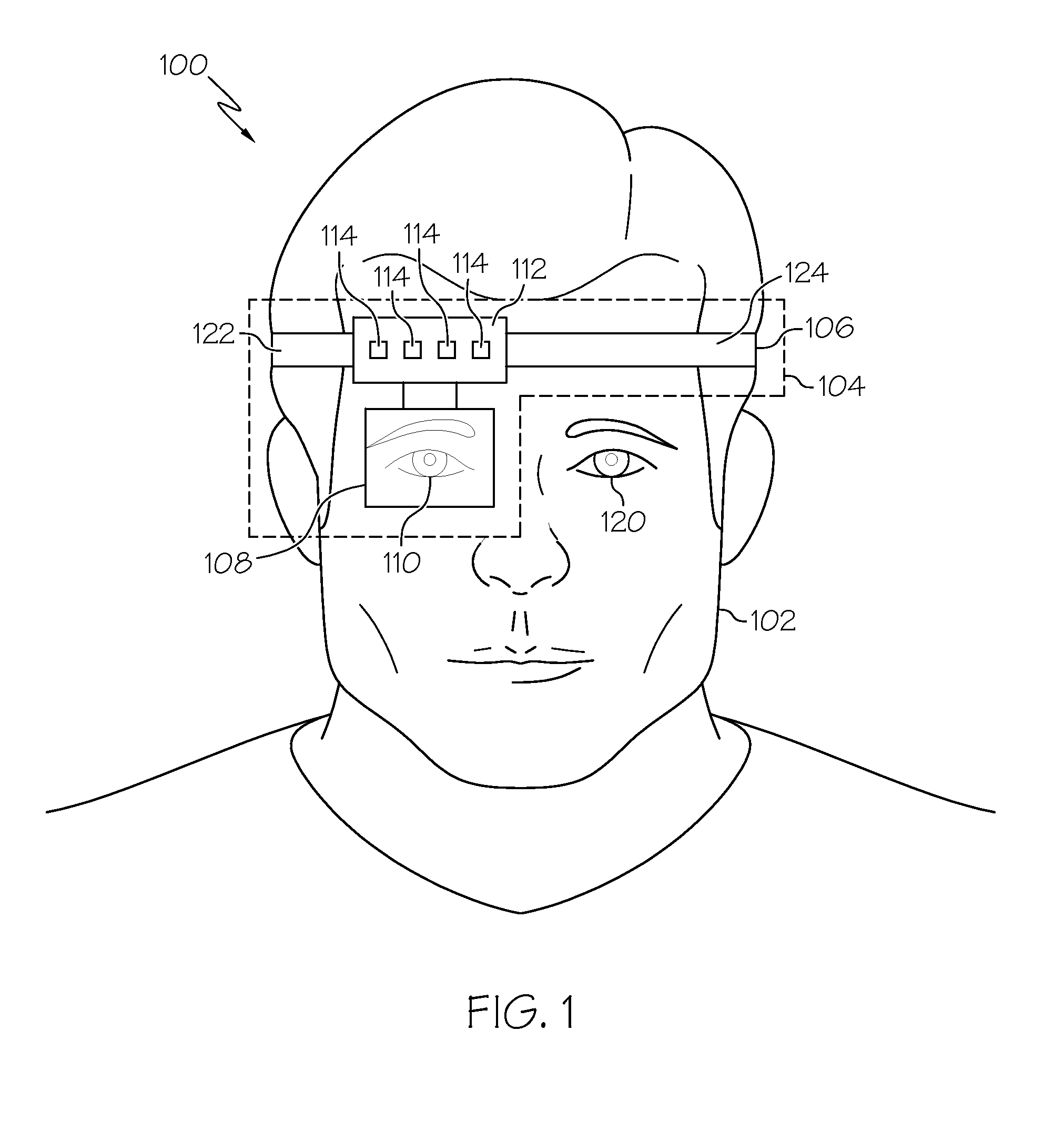
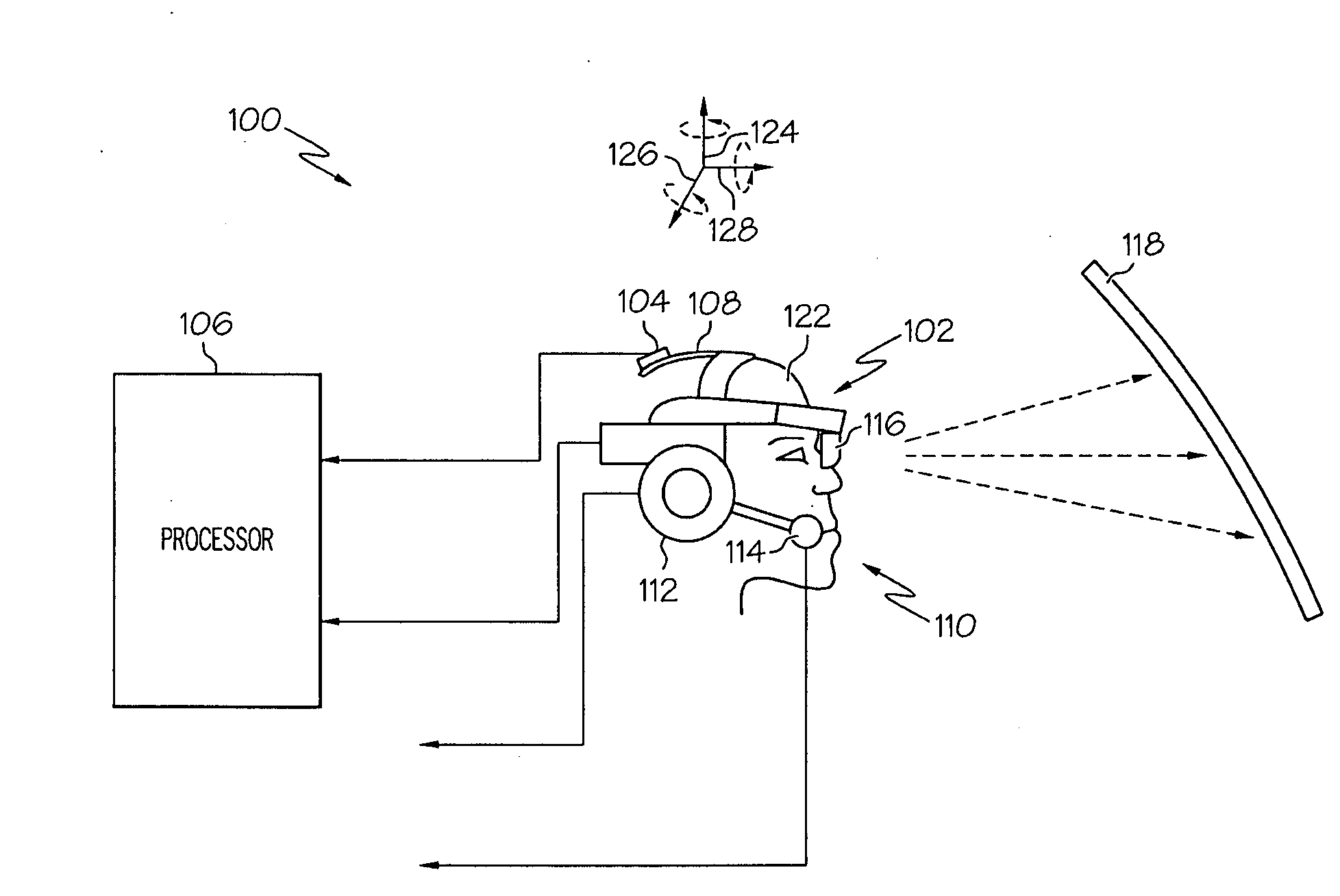
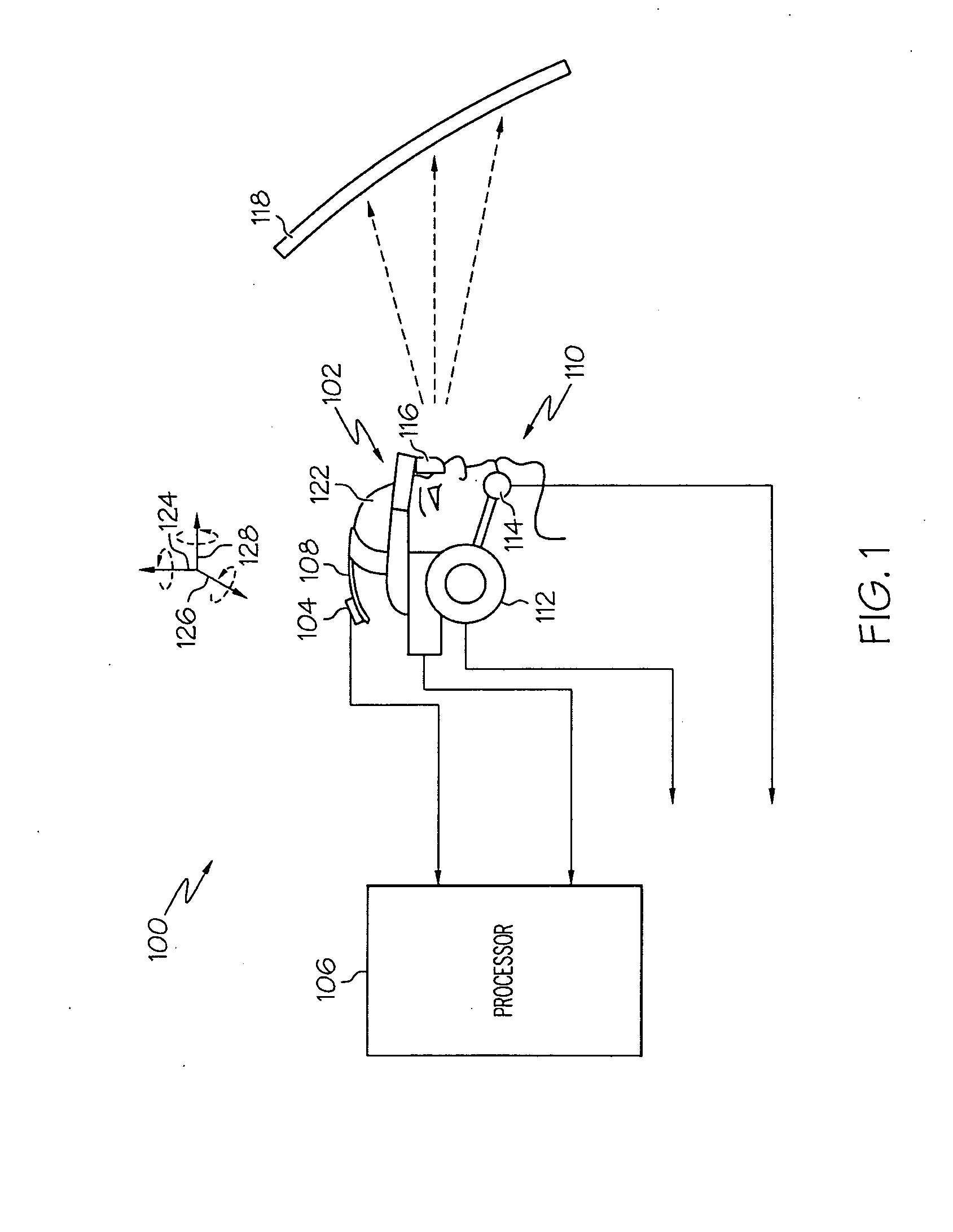
Near to Eye Display System and Appliance
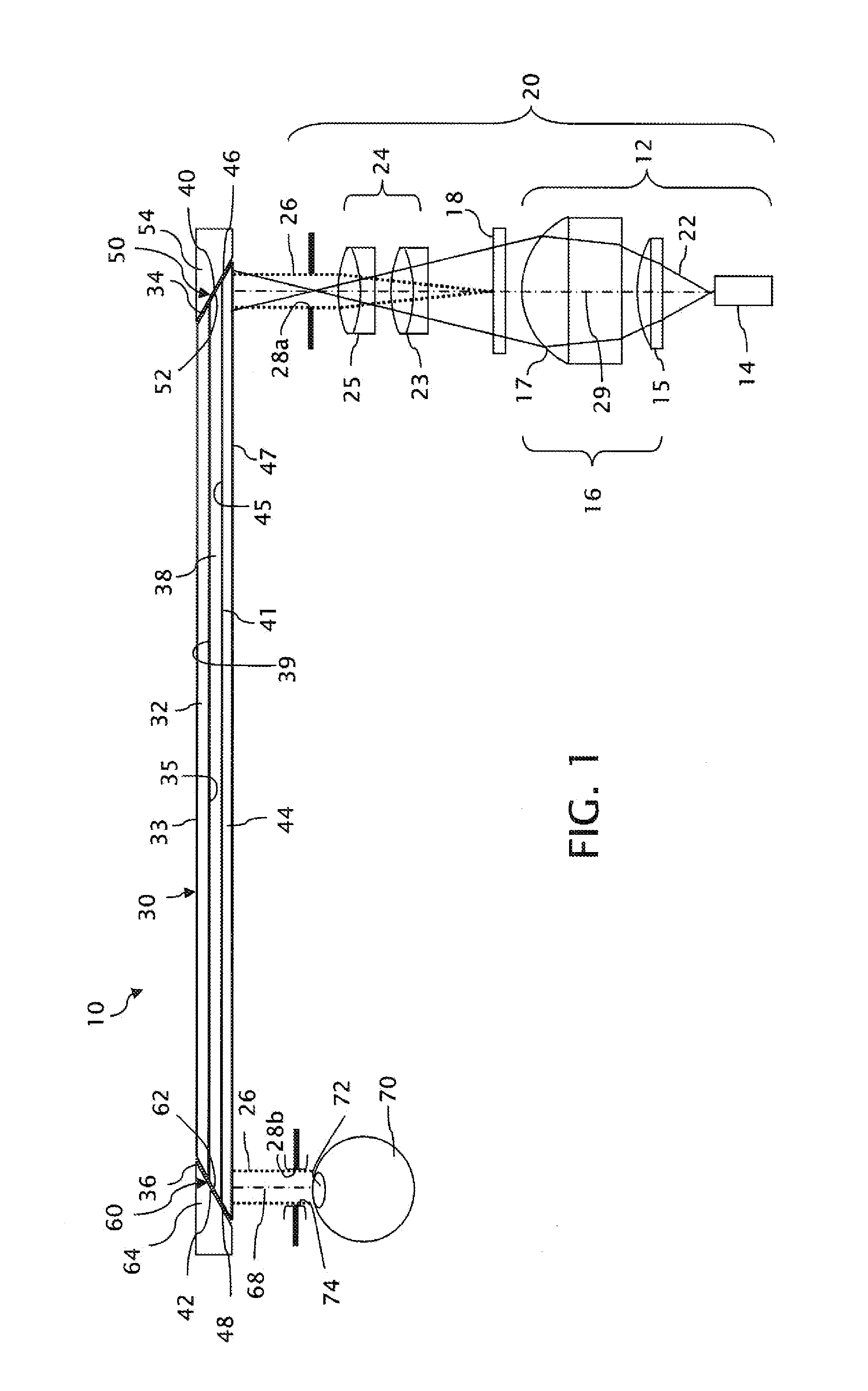
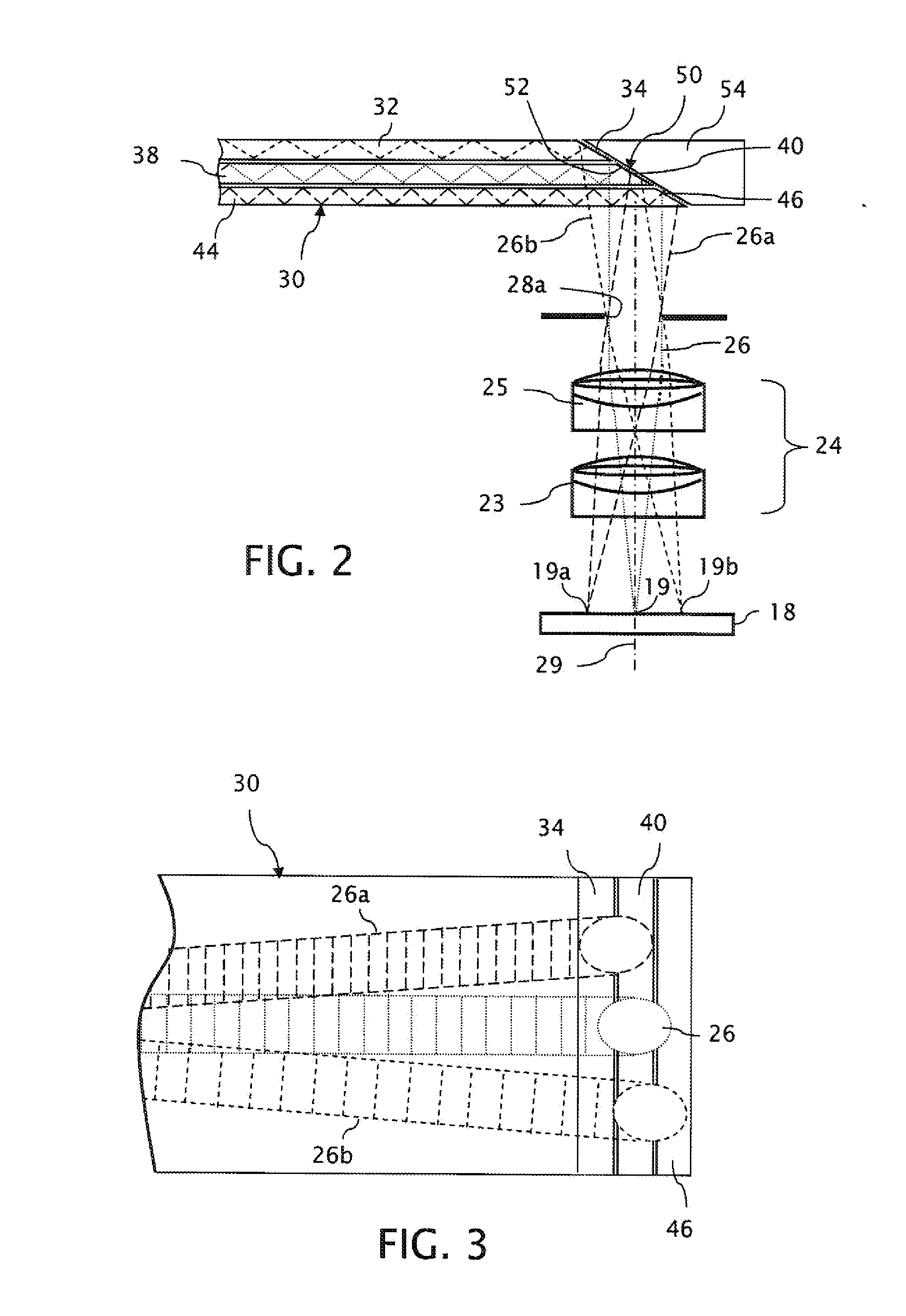
InactiveUS20100149073A1High resolutionCompact and economicalCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsLight beamPupil
A near-to-eye display system for forming an image as an illuminated region on a retina of at least one eye of a user is disclosed. The system includes a source of modulated light, a proximal optic positionable adjacent an eye of the user to receive the modulated light. The proximal optic has a plurality of groups of optically redirecting regions. The optically redirecting regions are configured to direct a plurality of beams of the modulated light into a pupil of the eye to form a contiguous illuminated portion of the retina of the eye. A first group of the optically redirecting regions is configured to receive modulated light from the source and redirect beams of the modulated light into the pupil of the eye for illumination of a first portion of the retina. A second group of the optically redirecting regions is configured to receive modulated light from the source and redirect beams of the modulated light into the pupil of the eye for illumination of a second portion of the retina.
Owner:CHAUM DAVID +2
Prismatic multiple waveguide for near-eye display
ActiveUS20120062998A1Compensation effectConvenient and accurateOptical articlesLaminationDisplay devicePupil
A near-eye display includes a compound waveguide for presenting viewers with virtual images visible within an eyebox at a limited relief distance from the compound waveguide. The compound waveguide is assembled from a plurality of waveguides that are at least partially optically isolated for conveying different portions of the virtual image. An input couple injects the different portions of the virtual image into predetermined combinations of the waveguides, and an output coupling ejects the different portions of the virtual image from the waveguides toward the eyebox in a form that at least partially constructs a pupil within the eyebox.
Owner:VUZIX
Comprehension and intent-based content for augmented reality displays
ActiveUS20120154557A1Improve experienceReduce appearance problemsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSee-through displayDisplay device
A method and system that enhances a user's experience when using a near eye display device, such as a see-through display device or a head mounted display device is provided. The user's intent to interact with one or more objects in the scene is determined. An optimized image is generated for the user based on the user's intent. The optimized image is displayed to the user, via the see-through display device. The optimized image visually enhances the appearance of objects that the user intends to interact with in the scene and diminishes the appearance of objects that the user does not intend to interact with in the scene. The optimized image can visually enhance the appearance of the objects that increase the user's comprehension. The optimized image is displayed to the user, via the see-through display device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
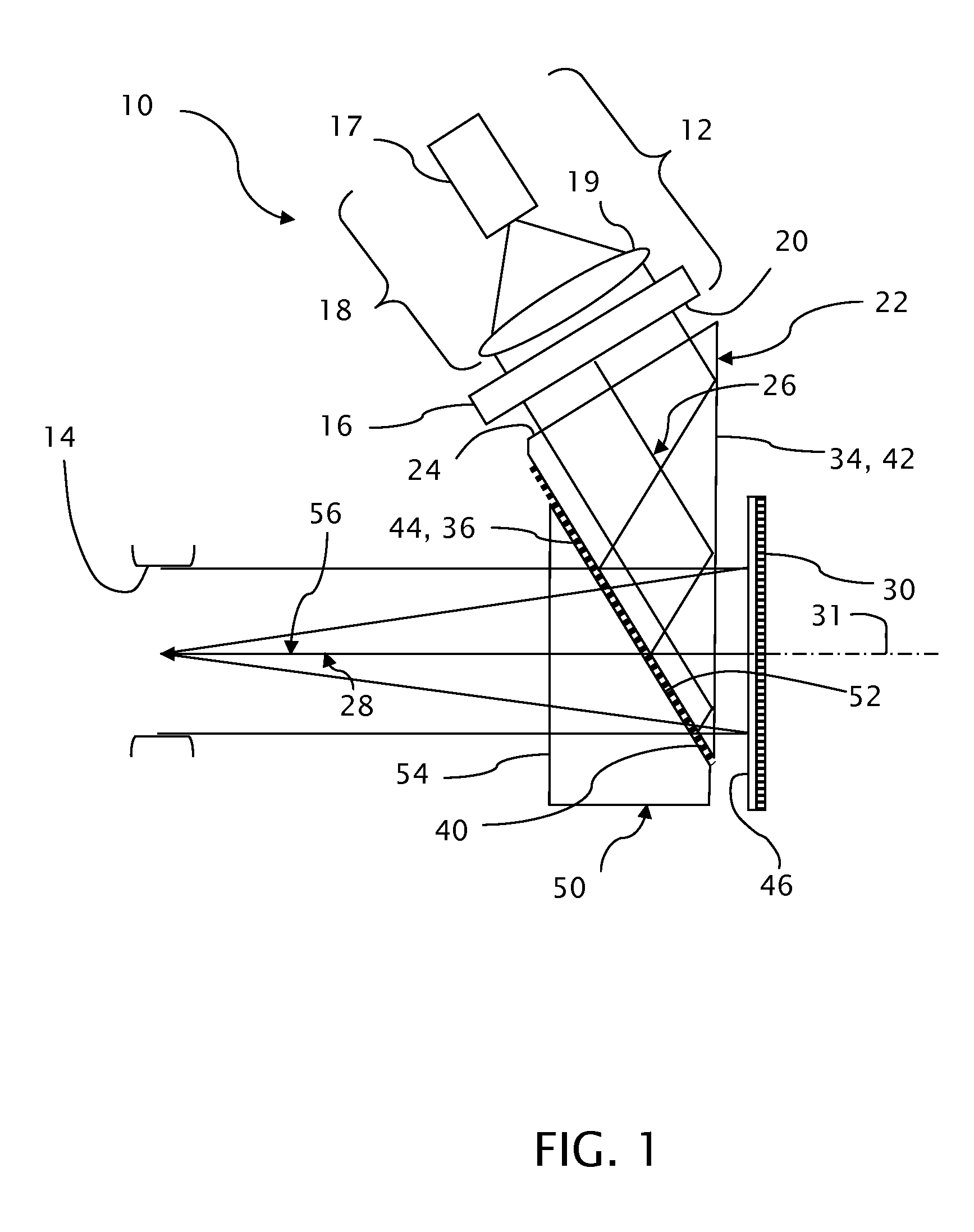
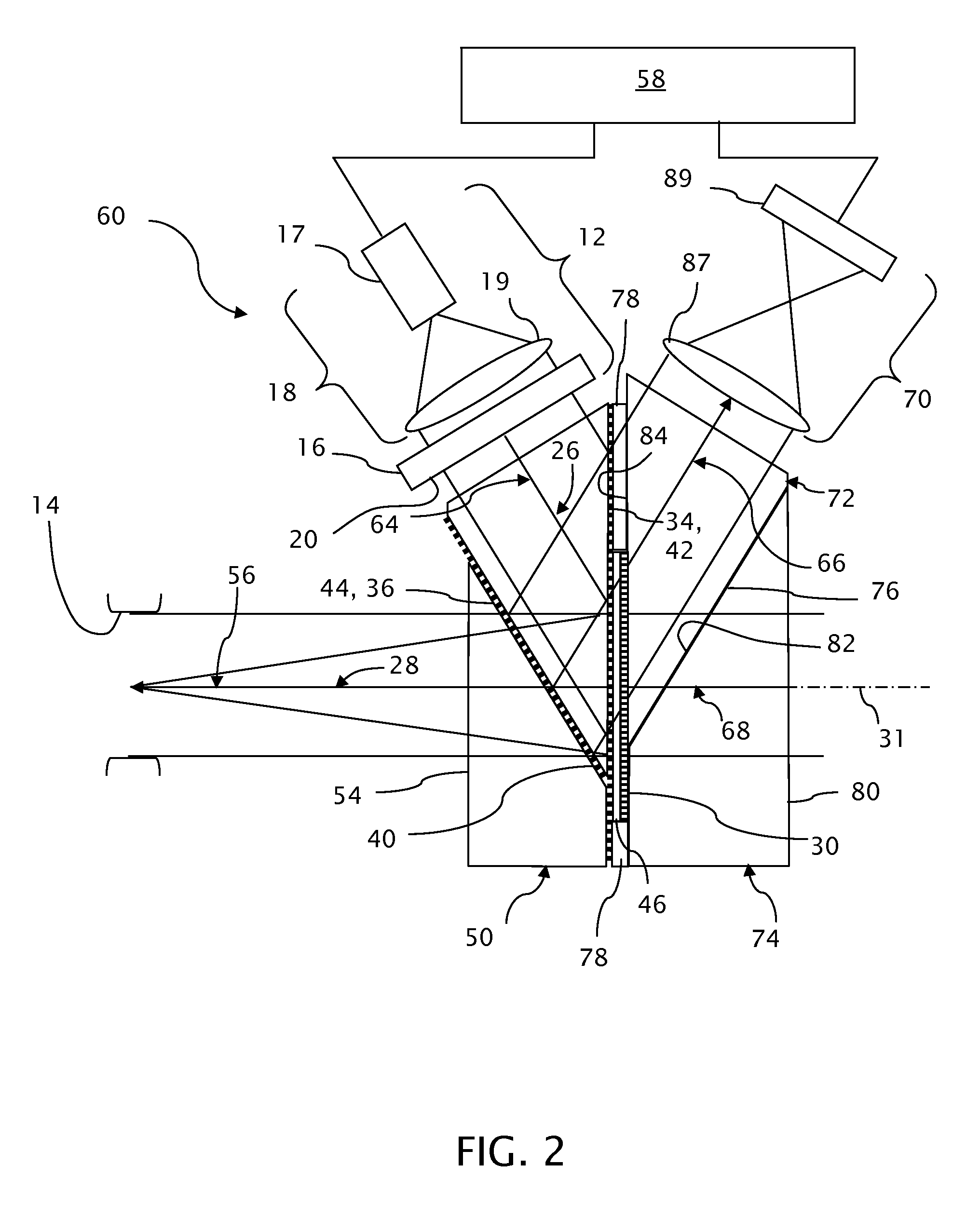
Near-eye display with on-axis symmetry
ActiveUS8376548B2Mitigate issueEffective overlapProjectorsNon-linear opticsSelective reflectionEye closure
A near-eye display projects virtual images from an image generator to an eyebox within which the virtual images can be seen by a viewer. A first optical path conveys image-bearing light from the image generator to a selectively reflective powered optic and a second optical path conveys the image-bearing light along a line of sight from the selectively reflective powered optic to the eyebox. First and second selectively reflective surfaces fold the first optical path with respect to the second optical path to locate the image generator out of the line of sight to the eyebox. The image generator is effectively inclined to the line of sight to the eyebox for reducing a thickness of the near-eye display. The selectively reflective powered optic is oriented normal to local overlapping portions of the first and second optical paths at the selectively reflective powered optic.
Owner:VUZIX
Near-eye display with on-axis symmetry
ActiveUS20120069413A1Mitigate issueEffective overlapProjectorsNon-linear opticsSelective reflectionDisplay device
A near-eye display projects virtual images from an image generator to an eyebox within which the virtual images can be seen by a viewer. A first optical path conveys image-bearing light from the image generator to a selectively reflective powered optic and a second optical path conveys the image-bearing light along a line of sight from the selectively reflective powered optic to the eyebox. First and second selectively reflective surfaces fold the first optical path with respect to the second optical path to locate the image generator out of the line of sight to the eyebox. The image generator is effectively inclined to the line of sight to the eyebox for reducing a thickness of the near-eye display. The selectively reflective powered optic is oriented normal to local overlapping portions of the first and second optical paths at the selectively reflective powered optic.
Owner:VUZIX
Dynamic apertured waveguide for near-eye display
ActiveUS20130051730A1Diffraction efficiencyGood image uniformityDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesDynamic apertureLight beam
A near-eye display of a type having an image generator for generating a succession of angularly related beams and waveguide for propagating the angularly related beams to an eyebox within which a virtual image is visible includes a controllable output aperture for such purposes as reconstructing a better defined pupil within the eyebox while also preserving the possibility for viewing the ambient environment from the eyebox through the controllable output aperture.
Owner:VUZIX
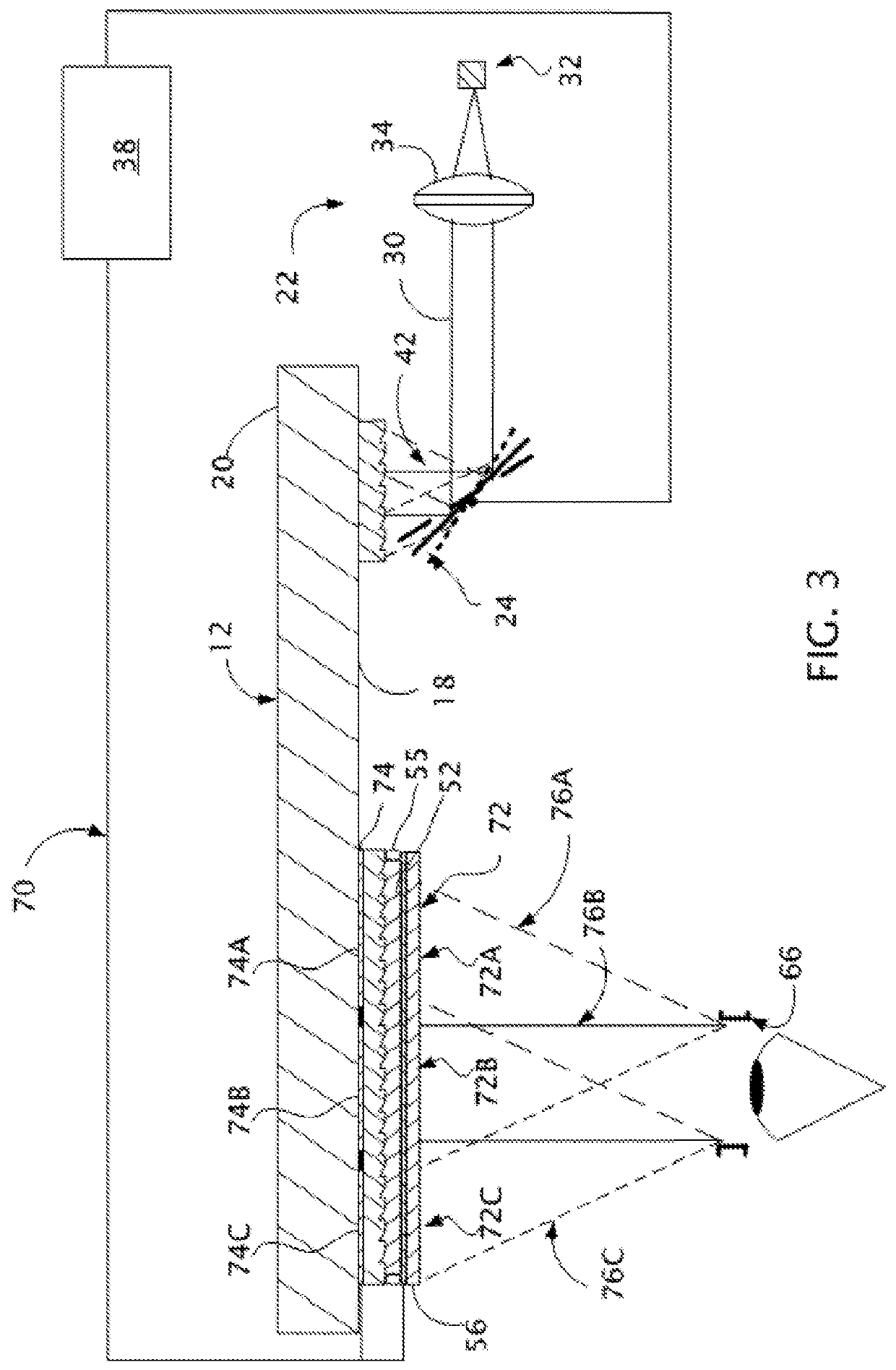
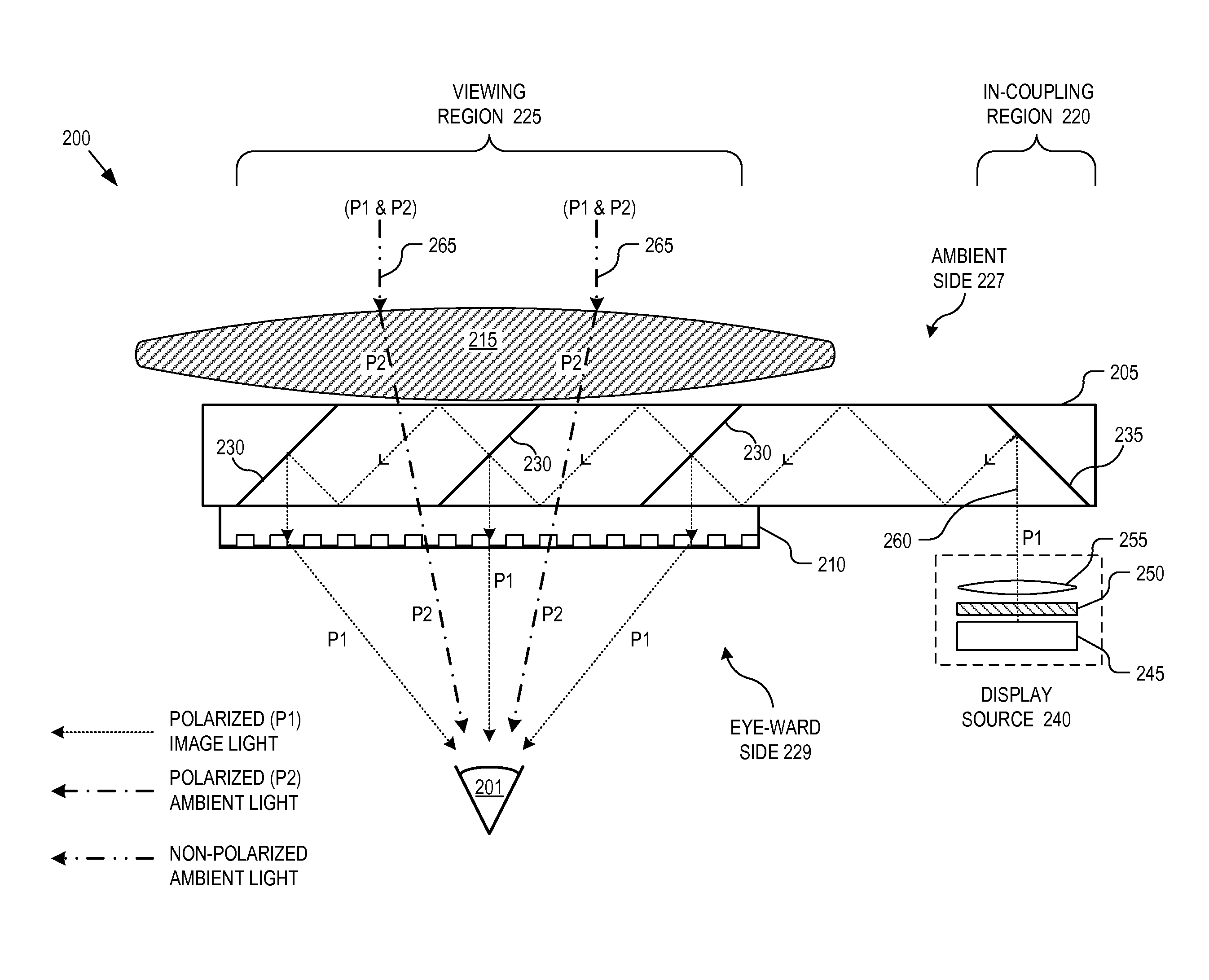
Near-to-eye display with diffractive lens
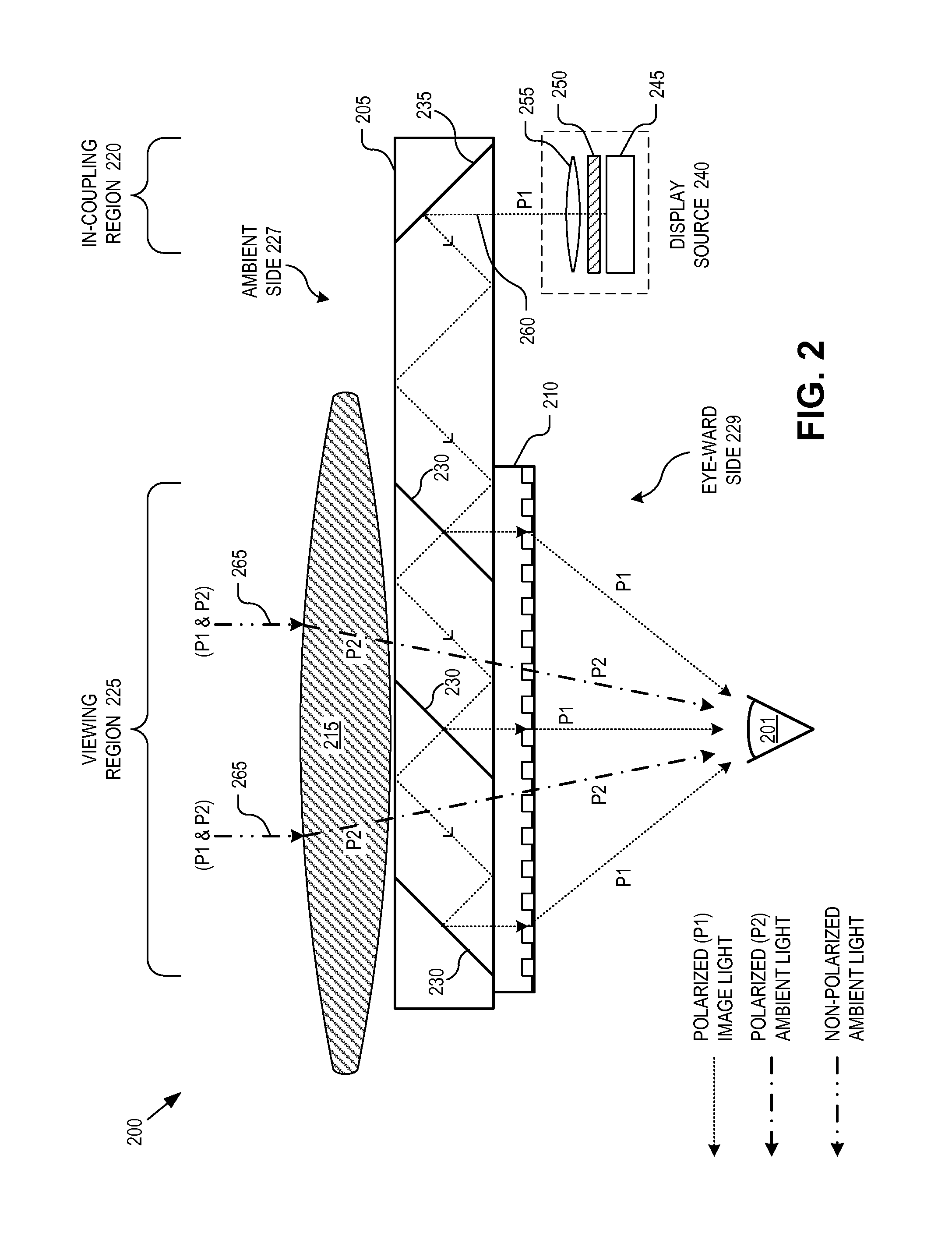
An eyepiece for a HMD includes a waveguide, an ambient light polarizer, and a wire grid polarizer with a diffraction lens having a lens function patterned into the wire grid polarizer. Polarized image light is guided between eye-ward and ambient sides of the waveguide from a display source to a viewing region of the waveguide where the polarized image light is directed out of the waveguide through the eye-ward side. The viewing region passes ambient light incident on the ambient side through to the eye-ward side. The ambient light polarizer is disposed adjacent to the ambient side to polarize the ambient light into polarized ambient light having a second polarization orthogonal to the first polarization. The wire grid polarizer is disposed adjacent to the eye-ward side along the viewing region. The wire grid polarizer is oriented to applying the lens function to the polarized image light via diffraction.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Curved near-to-eye display
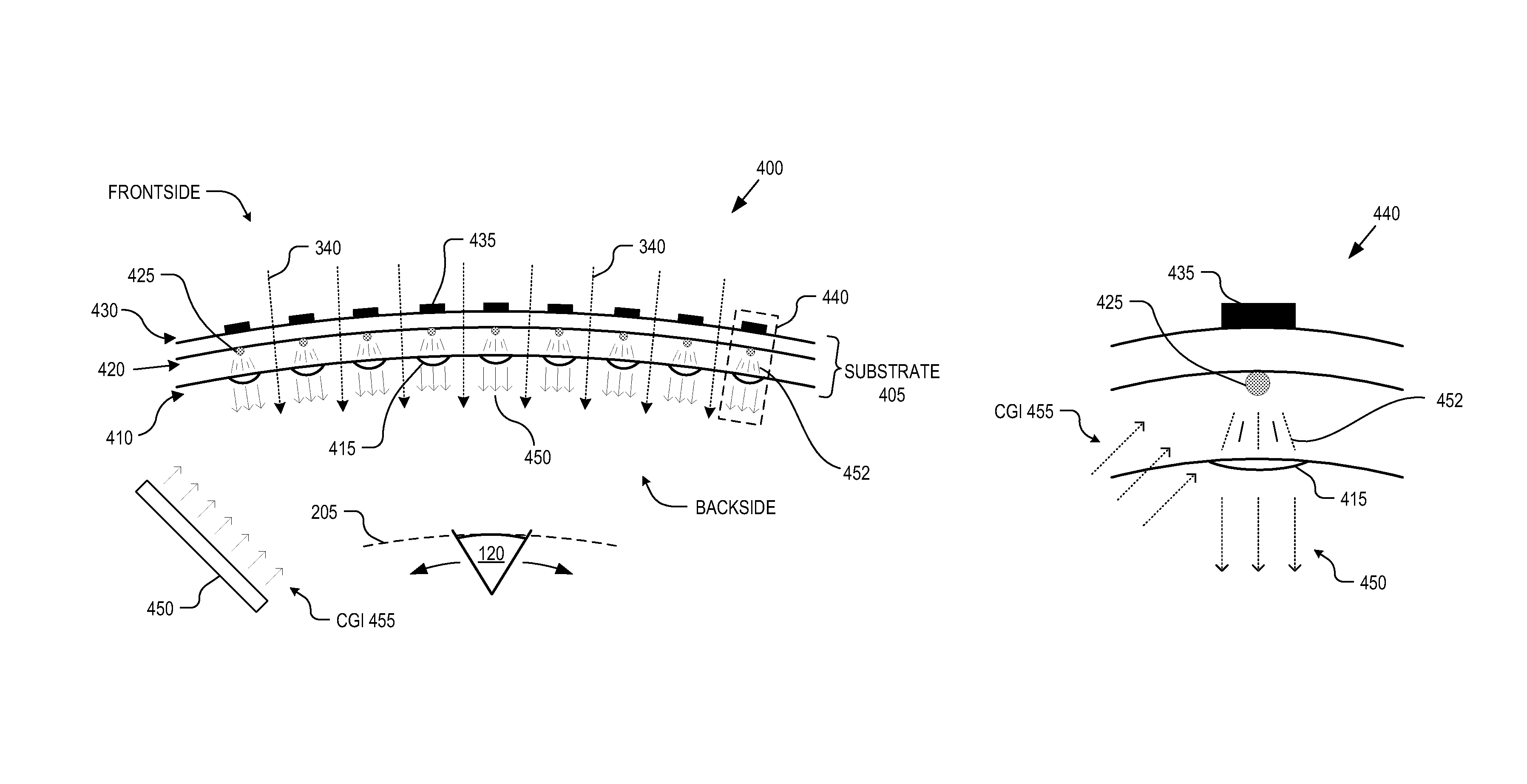
A display apparatus includes an array of microlenses disposed in or on a substrate. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes scattering centers disposed in or on the substrate and offset relative to the microlenses. The scattering centers are positioned substantially at focal points of the microlenses such that light incident upon a first side the substrate is scattered off of the scattering centers and collimated by corresponding ones of the microlenses before emission from the display apparatus. In another embodiment, the apparatus includes light emitting pixels disposed in or on the substrate and offset relative to the microlenses. The light emitting pixels are positioned substantially at focal points of the microlenses such that non-collimated light emitted from the light emitting pixels is collimated by the microlenses upon emission from the display apparatus.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Prismatic multiple waveguide for near-eye display
ActiveUS8649099B2Improve efficiencyReduces spatial separationOptical articlesAdhesivesDisplay devicePupil
A near-eye display includes a compound waveguide for presenting viewers with virtual images visible within an eyebox at a limited relief distance from the compound waveguide. The compound waveguide is assembled from a plurality of waveguides that are at least partially optically isolated for conveying different portions of the virtual image. An input couple injects the different portions of the virtual image into predetermined combinations of the waveguides, and an output coupling ejects the different portions of the virtual image from the waveguides toward the eyebox in a form that at least partially constructs a pupil within the eyebox.
Owner:VUZIX
Dynamic apertured waveguide for near-eye display
A near-eye display of a type having an image generator for generating a succession of angularly related beams and waveguide for propagating the angularly related beams to an eyebox within which a virtual image is visible includes a controllable output aperture for such purposes as reconstructing a better defined pupil within the eyebox while also preserving the possibility for viewing the ambient environment from the eyebox through the controllable output aperture.
Owner:VUZIX
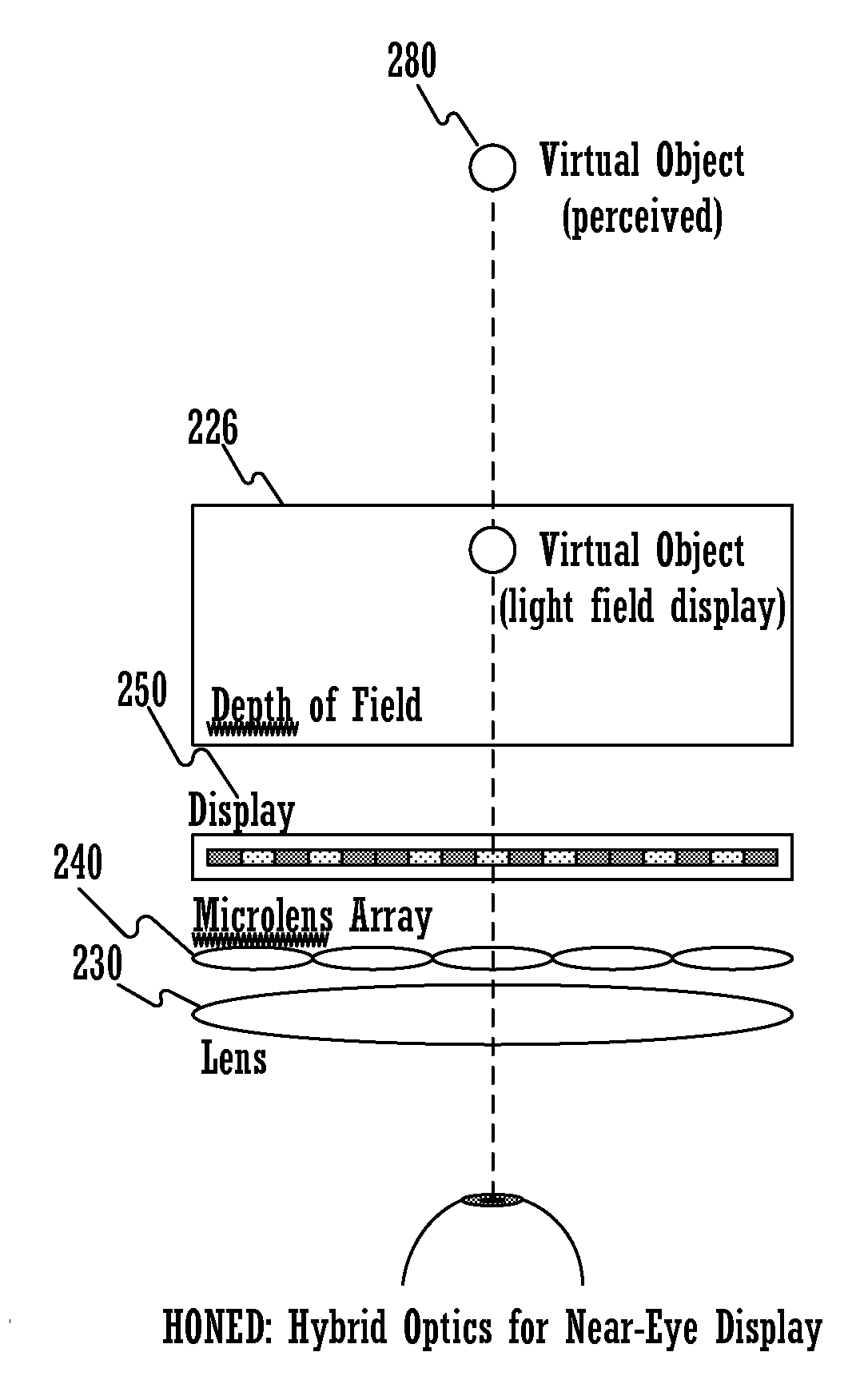
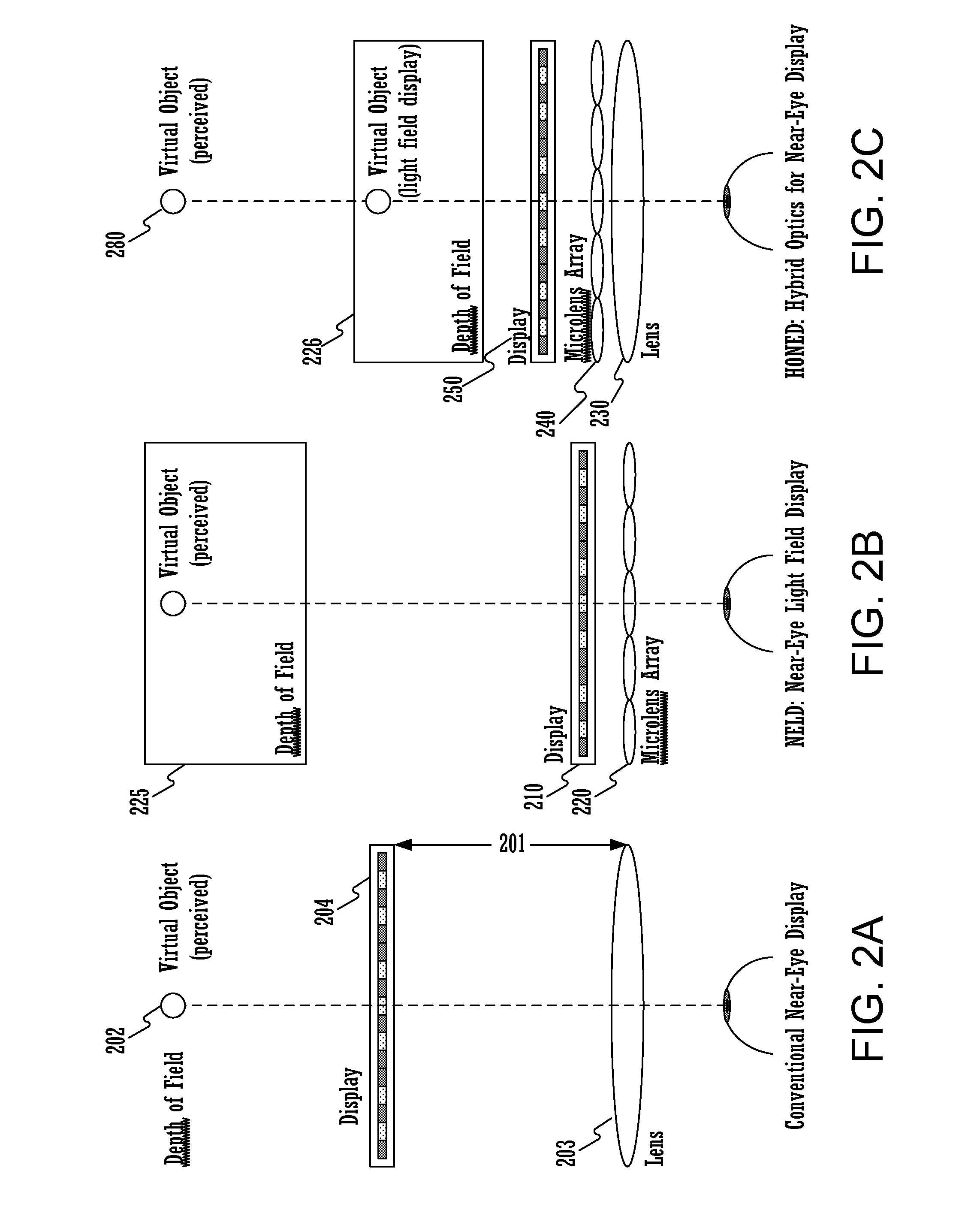
Hybrid optics for near-eye displays
ActiveUS20150049390A1Reduce depthGreat percentageStatic indicating devicesDetails for portable computersImage resolutionDisplay device
A method for displaying a near-eye light field display (NELD) image is disclosed. The method comprises determining a pre-filtered image to be displayed, wherein the pre-filtered image corresponds to a target image. It further comprises displaying the pre-filtered image on a display. Subsequently, it comprises producing a near-eye light field after the pre-filtered image travels through a microlens array adjacent to the display, wherein the near-eye light field is operable to simulate a light field corresponding to the target image. Finally, it comprises altering the near-eye light field using at least one converging lens, wherein the altering allows a user to focus on the target image at an increased depth of field at an increased distance from an eye of the user and wherein the altering increases spatial resolution of said target image.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Near-to-eye display having adaptive optics
An optical apparatus includes a light source, a deformable mirror, an actuator system, and a partially transparent mirror. The deformable mirror is positioned in an optical path of the image output from the light source. The actuator system is coupled to the deformable mirror to selectively adjust at least a curvature of the deformable mirror. The partially transparent mirror is positioned to be in front of the eye of the user when the optical apparatus is worn and optically aligned with the deformable mirror such that the image output from the light source positioned peripherally to the eye is reflected by the deformable mirror to the partially transparent mirror and reflected by the partially transparent mirror to the eye of the user.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Directionally illuminated waveguide arrangement
ActiveUS20140036361A1Function increaseCompact display structureMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideLight beam
Disclosed is a light guiding valve apparatus comprising an optical valve, a two dimensional light source array and a focusing optic for providing large area collimated illumination from localized light sources. A stepped waveguide may be a stepped structure, in which the steps may be extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. A two dimensional array of viewing windows may be produced. Such controlled illumination may provide for efficient, multi-user autostereoscopic displays with wide viewing freedom and low cross talk and near-eye displays that are substantially transparent.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
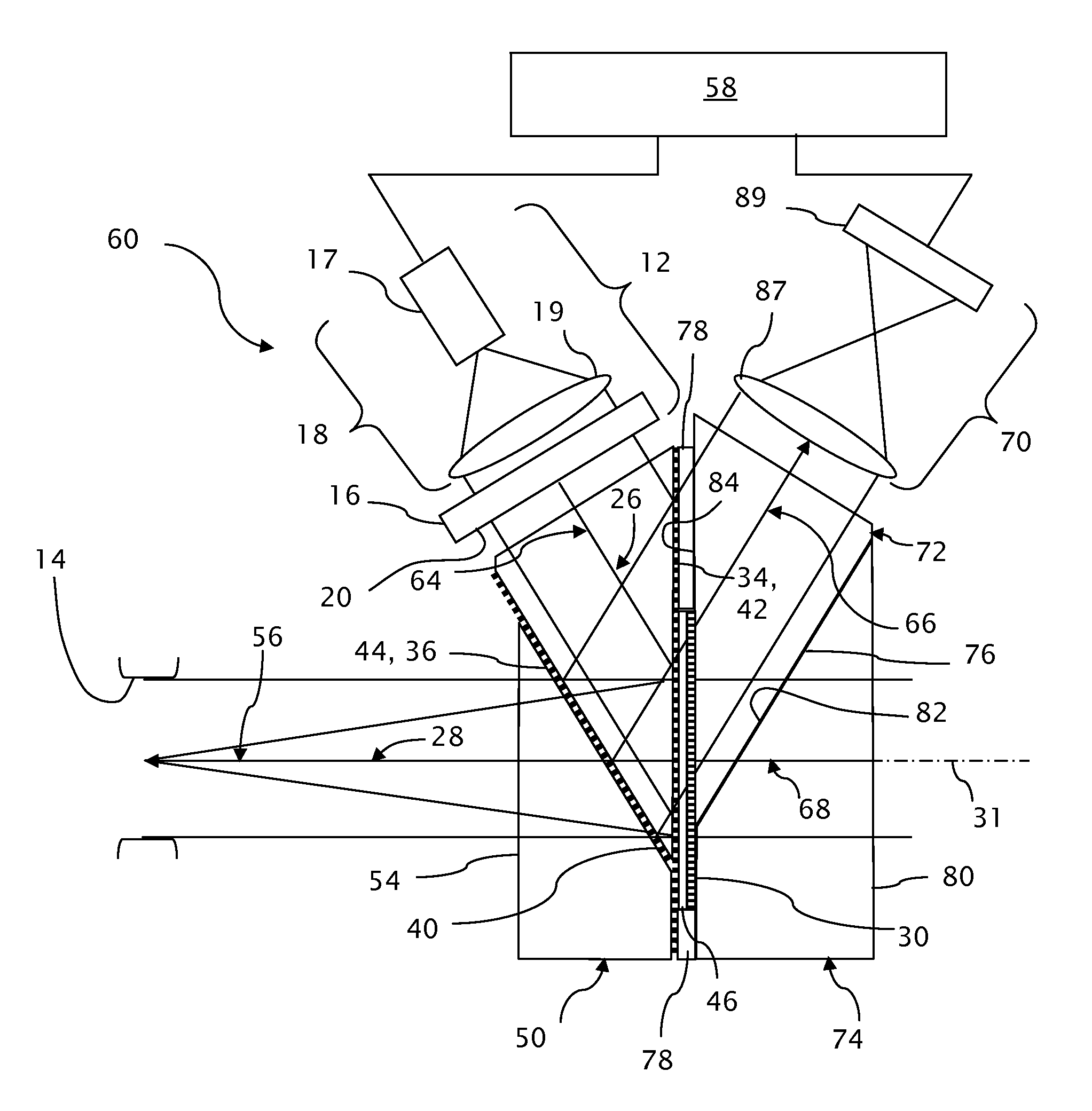
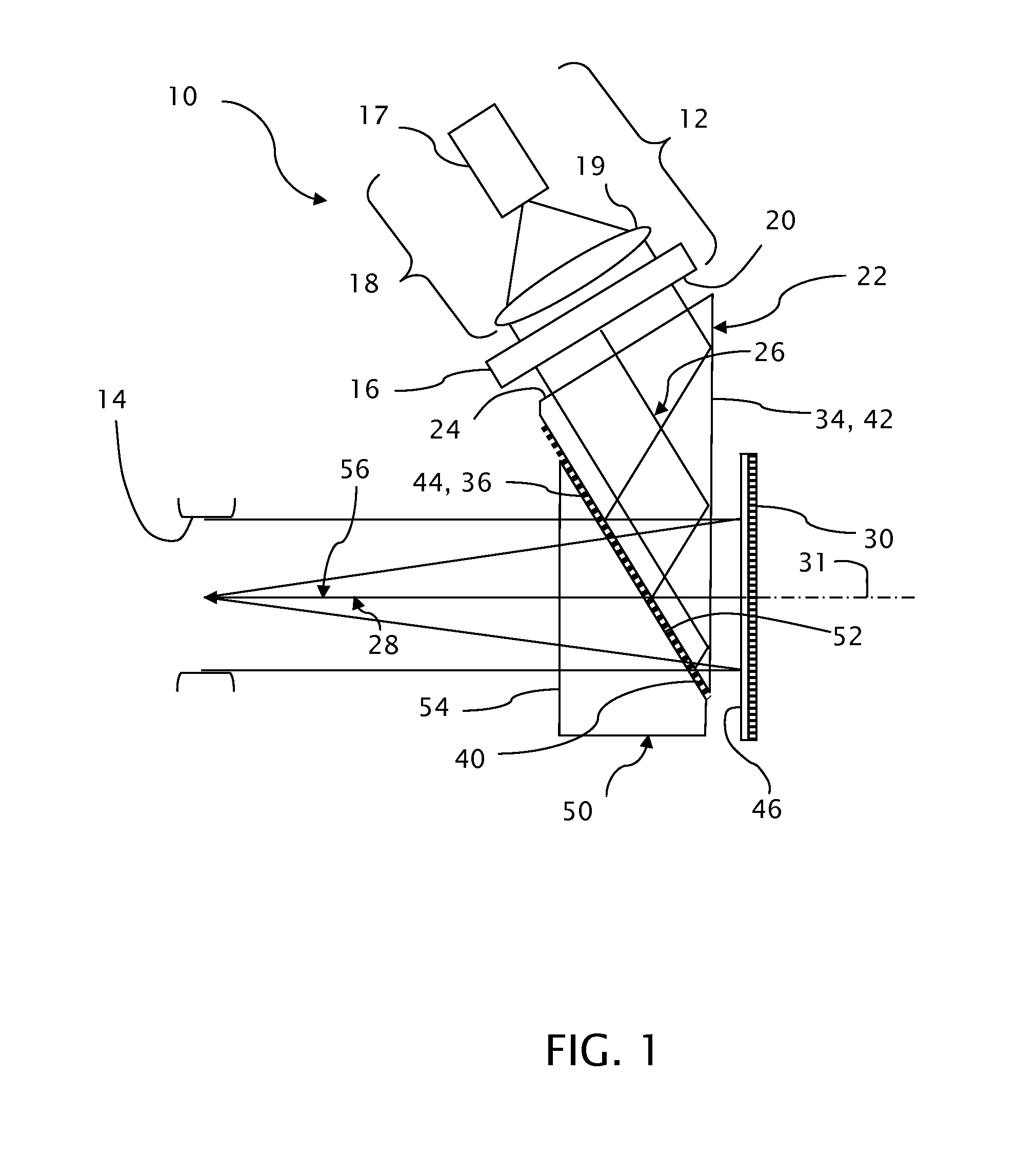
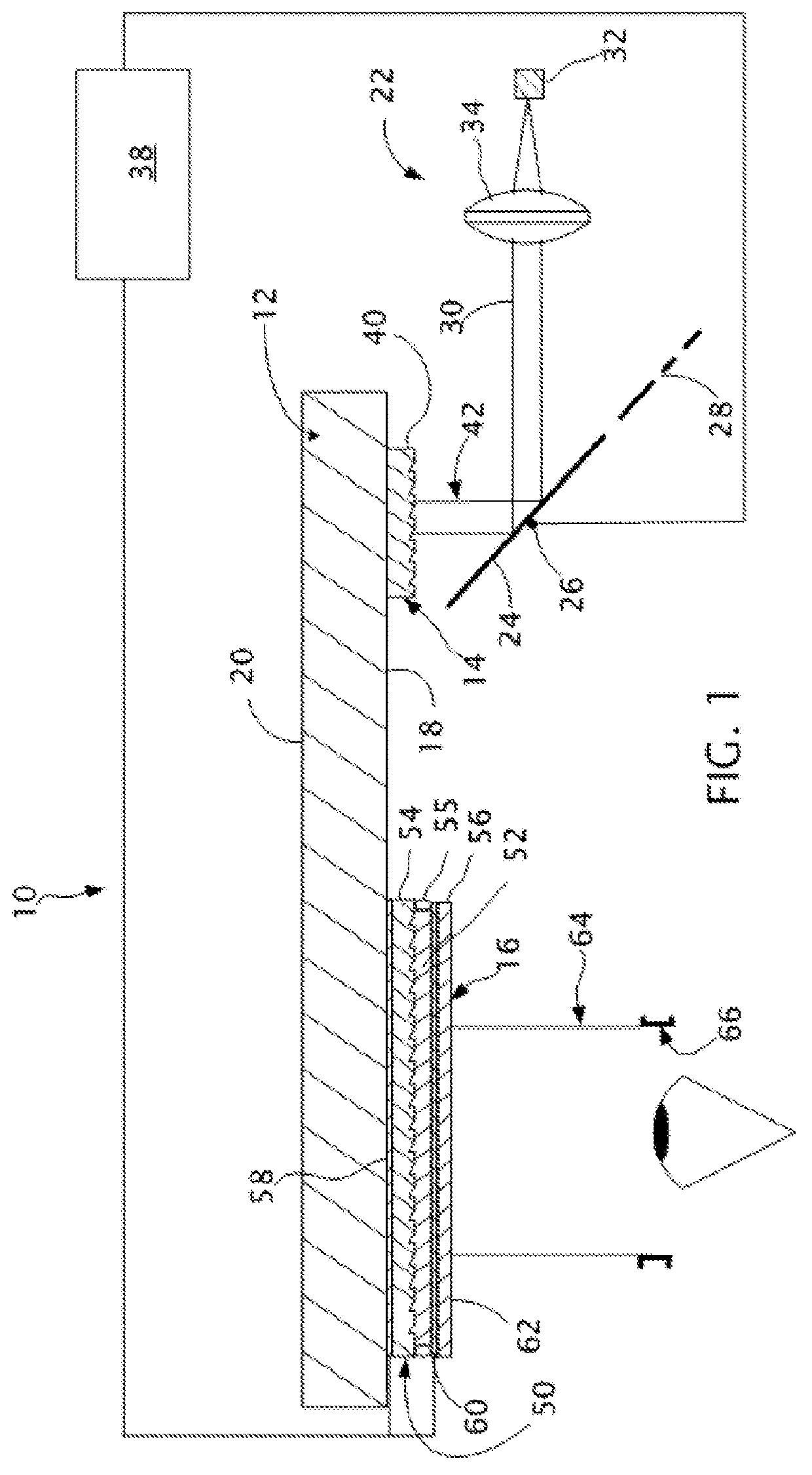
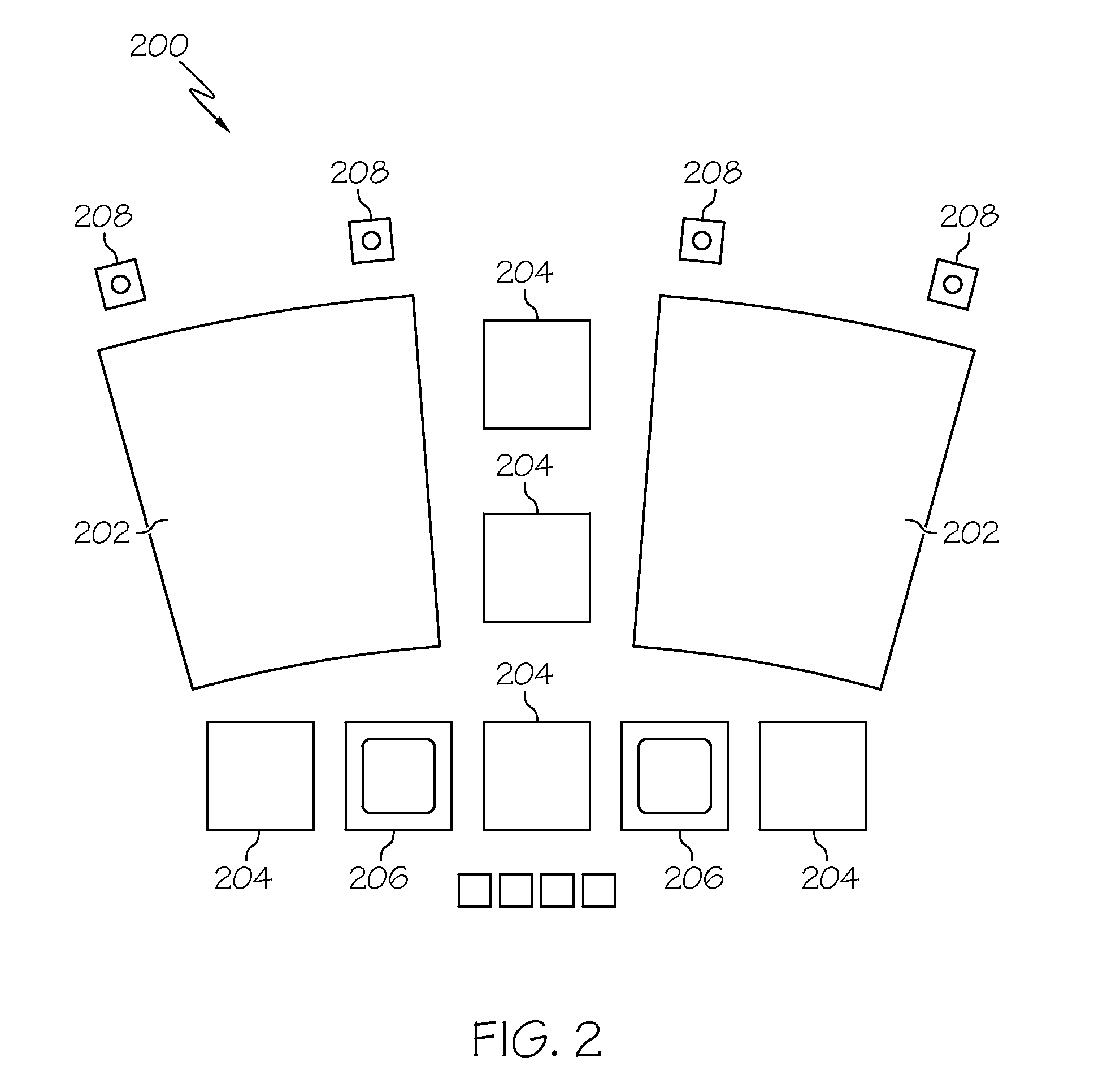
Near to eye display and appliance
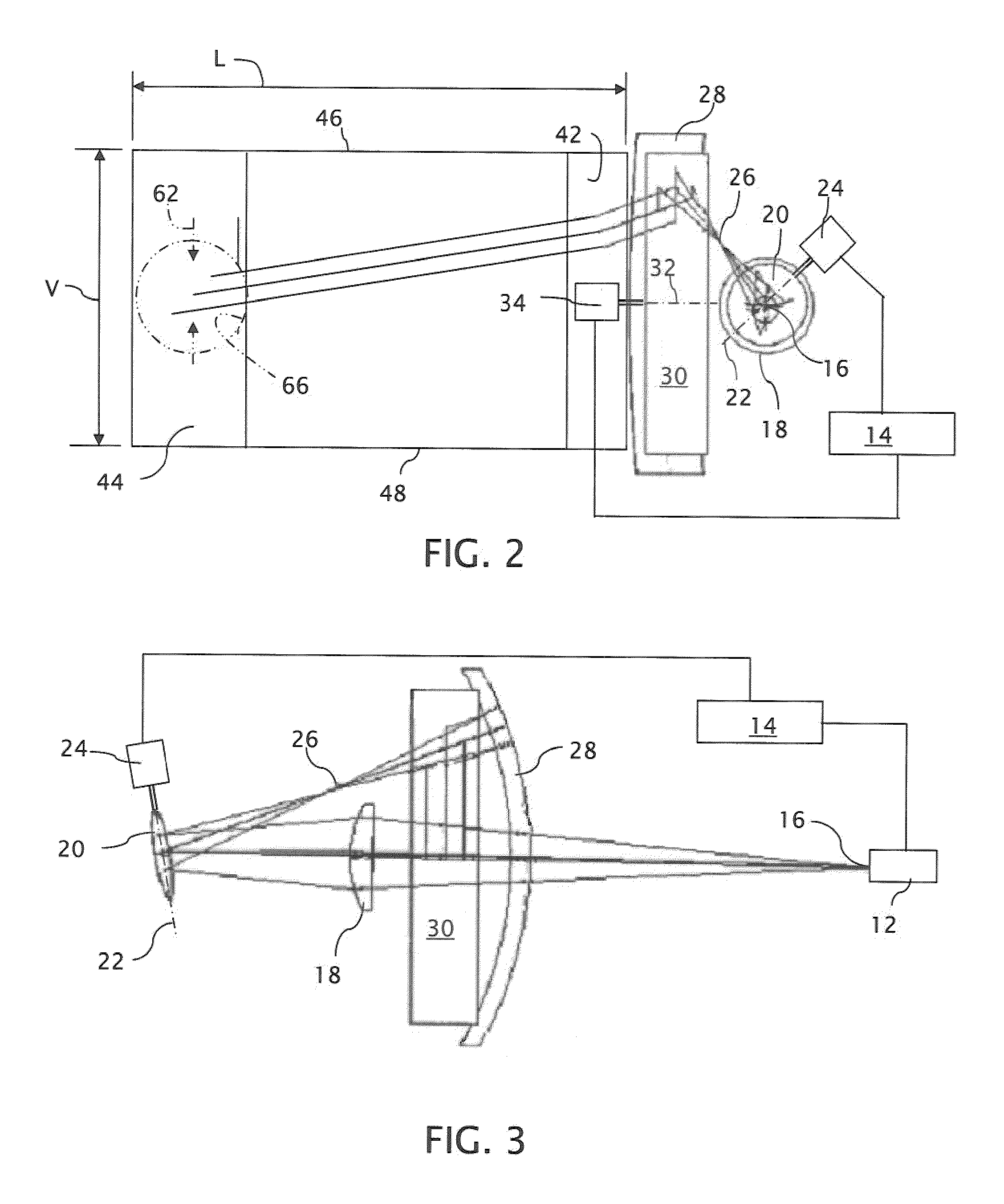
InactiveUS20150277123A1Easy to measureWide color gamutStatic indicating devicesColor television detailsLight beamDisplay device
A near-to-eye display system includes a source of modulated light, a proximal optic positionable adjacent an eye of the user to receive the modulated light. The proximal optic has a plurality of groups of optically redirecting regions. The optically redirecting regions are configured to direct a plurality of beams of the modulated light into a pupil of the eye to form a contiguous illuminated portion of the retina of the eye. A first group of the optically redirecting regions receives modulated light from the source and redirect beams of the modulated light into the pupil of the eye for illumination of a first portion of the retina. A second group of the optically redirecting regions receives modulated light from the source and redirect beams of the modulated light into the pupil of the eye for illumination of a second portion of the retina.
Owner:CHAUM DAVID +2
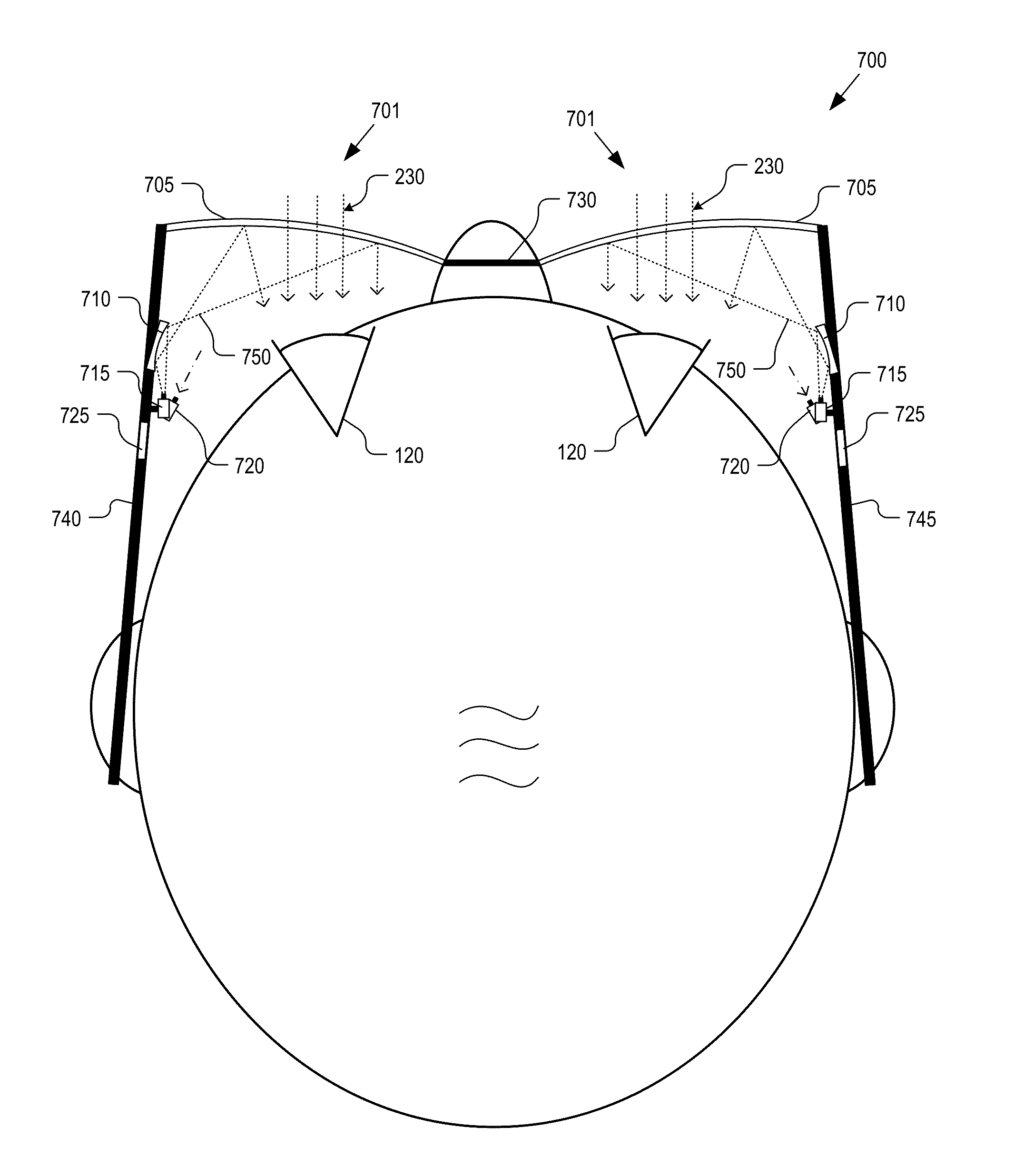
Apparatus for a Near-Eye Display
An apparatus for providing gaze tracking in a near-eye display. Certain examples provide an apparatus including a light modulator configured to receive light of a first range of wavelengths and generate an image beam therefrom. The light modulator is further configured to receive light of a second range of wavelengths and generate a probe beam therefrom. The apparatus also includes one or more light guides including one or more in-coupling element areas, and one or more out-coupling element areas. The one or more in-coupling element areas are configured to receive and in-couple the image beam and the probe beam into the one or more light guides. The one or more out-coupling element areas are configured to out-couple, from the one or more light guides: the image beam to a user's eye for user viewing, and the probe beam to the user's eye for detection of reflection therefrom.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Methods and devices for optical aberration correction
ActiveUS20160314564A1Reduce restrictionsSpectales/gogglesImage enhancementSide effectOptical Obstruction
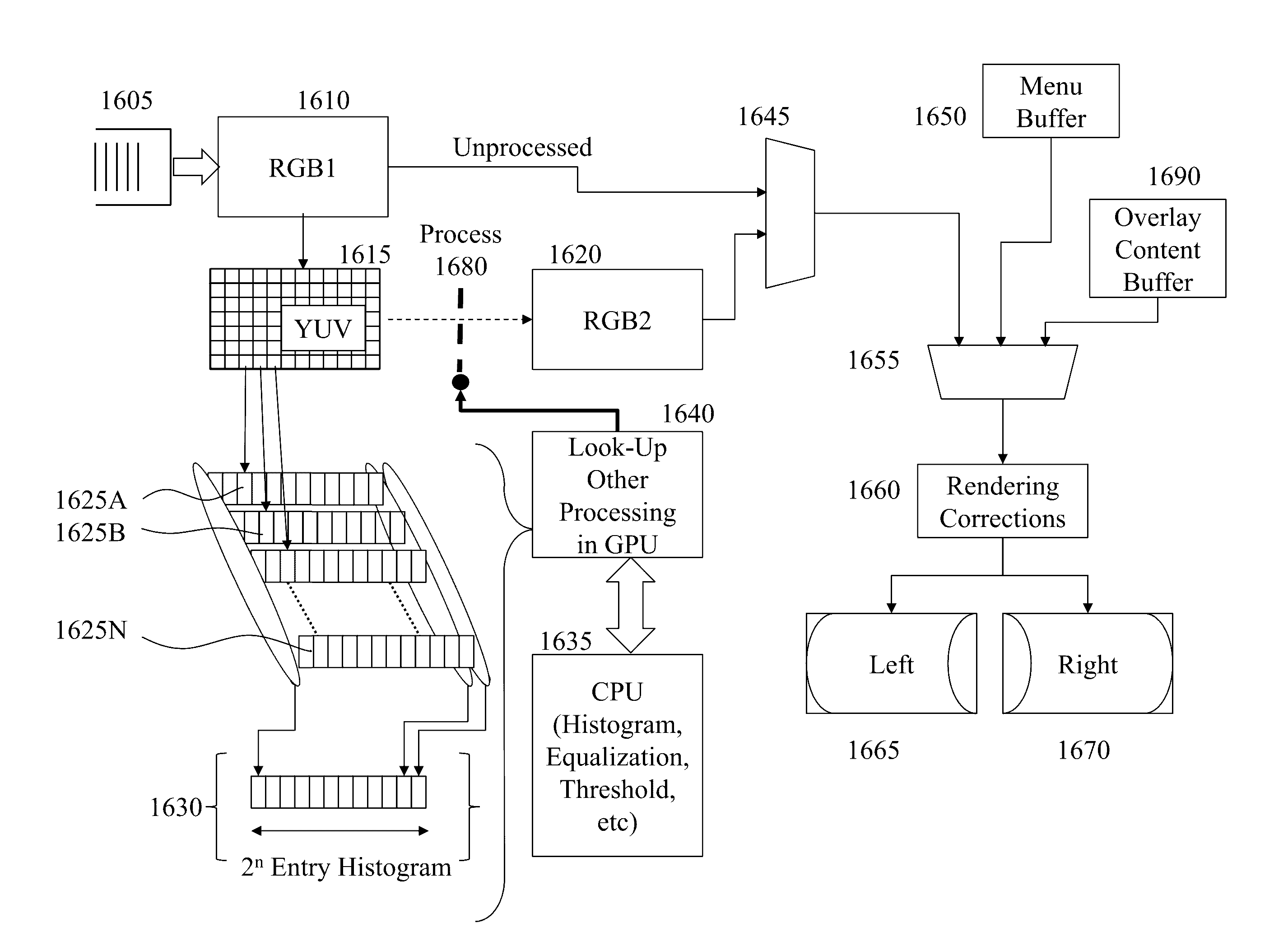
Near-to-eye displays within head mounted devices offer both users with and without visual impairments enhanced visual experiences either by improving or augmenting their visual perception. Unless the user directly views the display without intermediate optical elements then the designer must consider chromatic as well as other aberrations. Within the prior art the optical train is either complex through additional corrective elements adding to weight, cost, and size or through image processing. However, real time applications with mobile users require low latency to avoid physical side effects. Accordingly, it would be beneficial to provide near-to-eye displays mitigating these distortions and chromatic aberrations through pre-distortion based electronic processing techniques in conjunction with design optimization of the optical train with low weight, low volume, low complexity, and low cost. Further, it would be beneficial to exploit consumer grade low cost graphics processing units rather than application specific circuits.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
Controllable waveguide for near-eye display applications
ActiveUS9400395B2Quality improvementIncrease viewable areaMechanical apparatusProjectorsDisplay deviceLight beam
A near-eye display includes an image generator that generates angularly related beams over a range of angles for forming a virtual image and a waveguide that propagates the angularly related beams over a limited range of angles. An input aperture of the waveguide includes a plurality of controllable components that are selectively operable as diffractive optics for injecting subsets of the angularly related beams into the waveguide. An output aperture of the waveguide includes a plurality of controllable components that selectively operable as diffractive optics for ejecting corresponding subsets of the angularly related beams out of the waveguide toward an eyebox. A controller synchronizes operation of the controllable components of the output aperture with the propagation of different subsets of angularly related beams along the waveguide for ejecting the subsets of angularly related beams out of the waveguide for presenting the virtual image within the eyebox.
Owner:VUZIX
Method and apparatus for a near-to-eye display
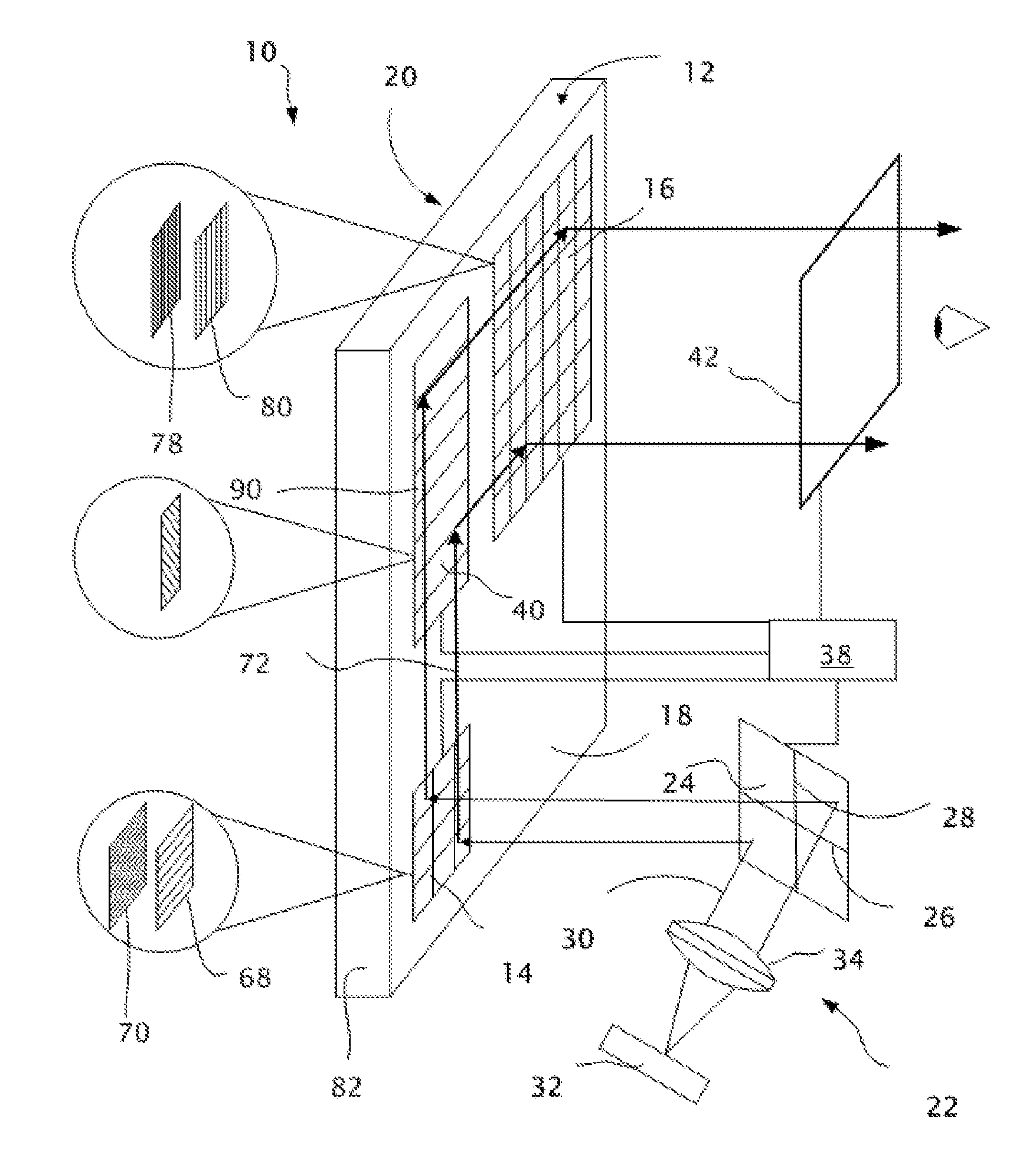
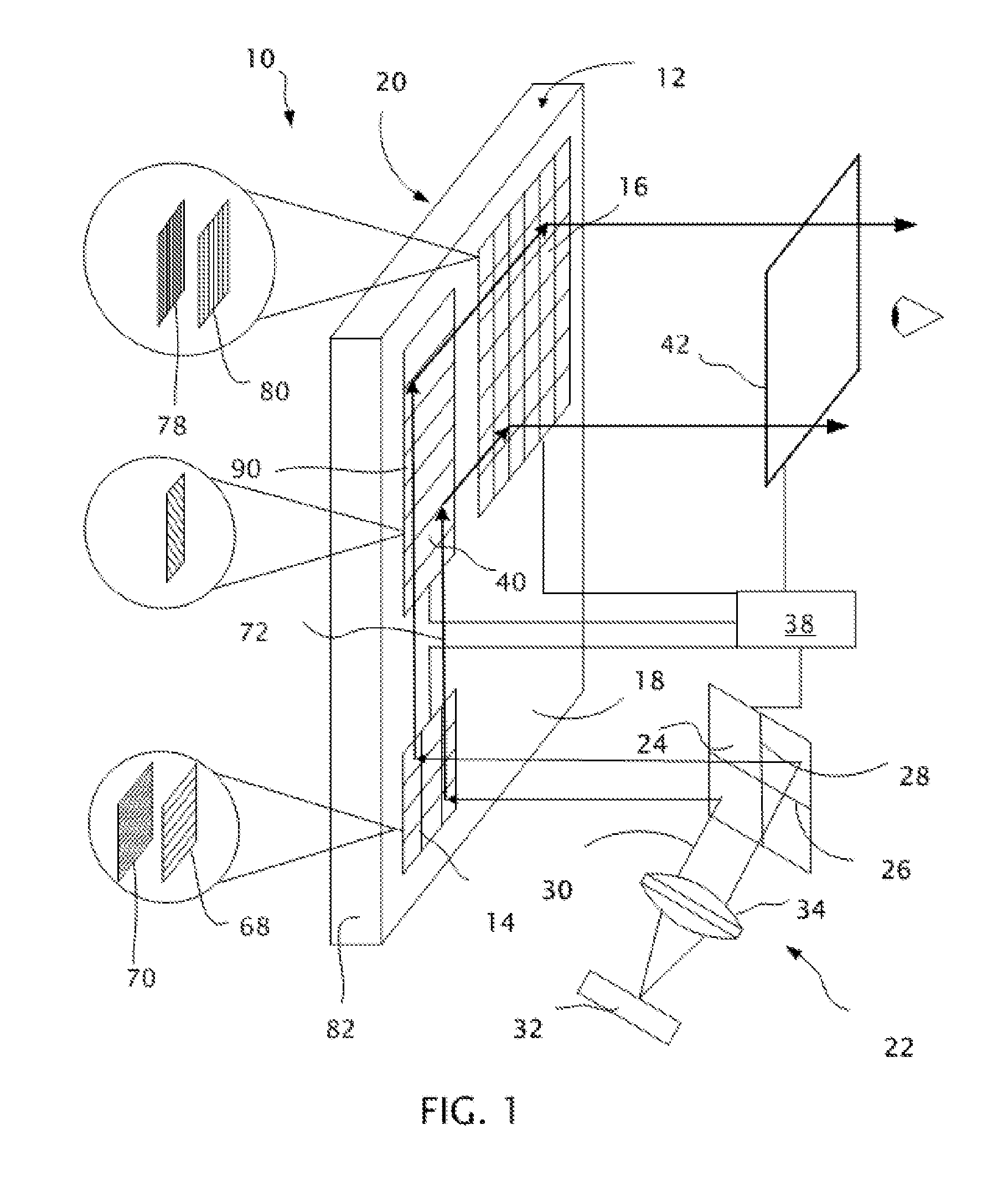
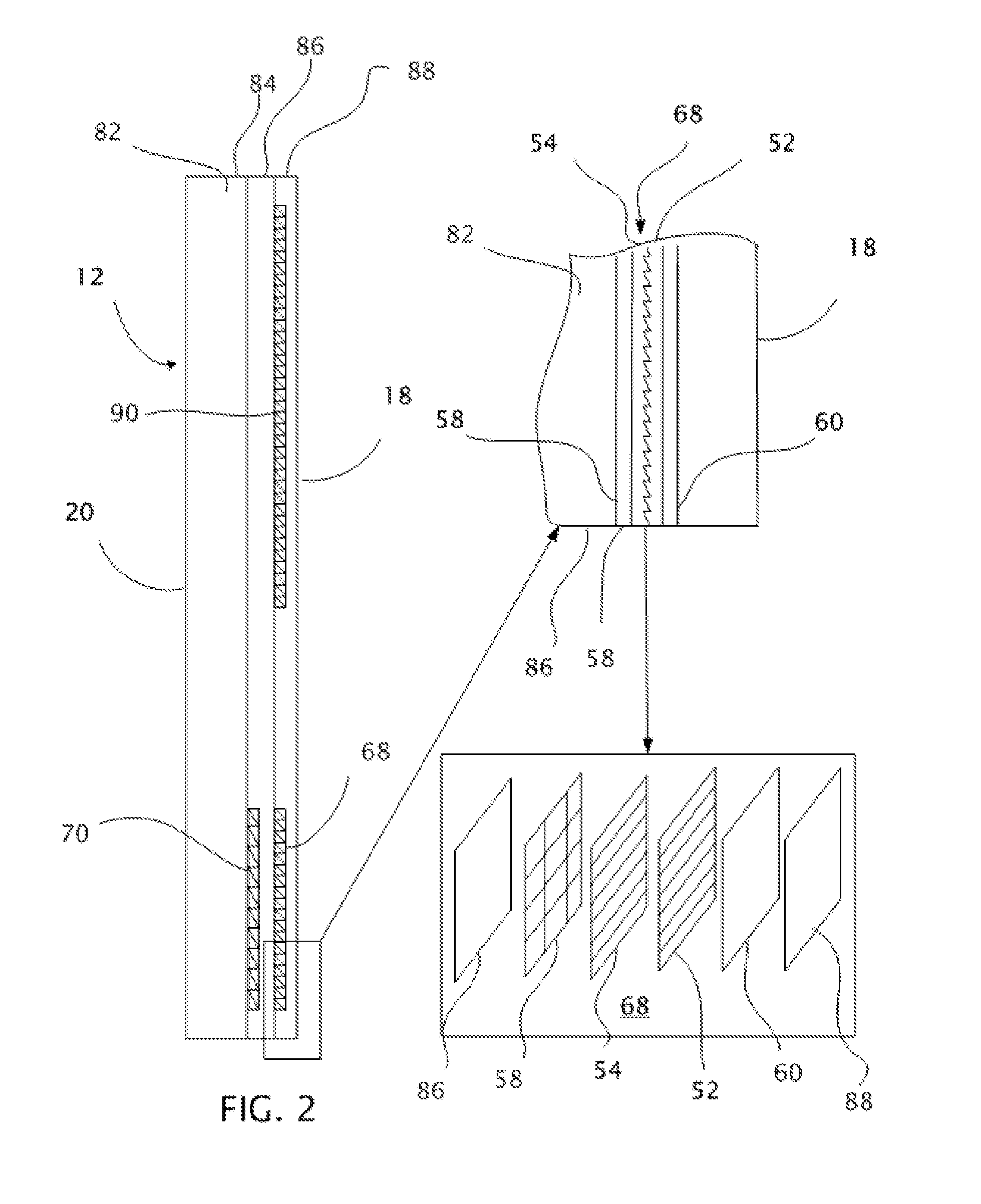
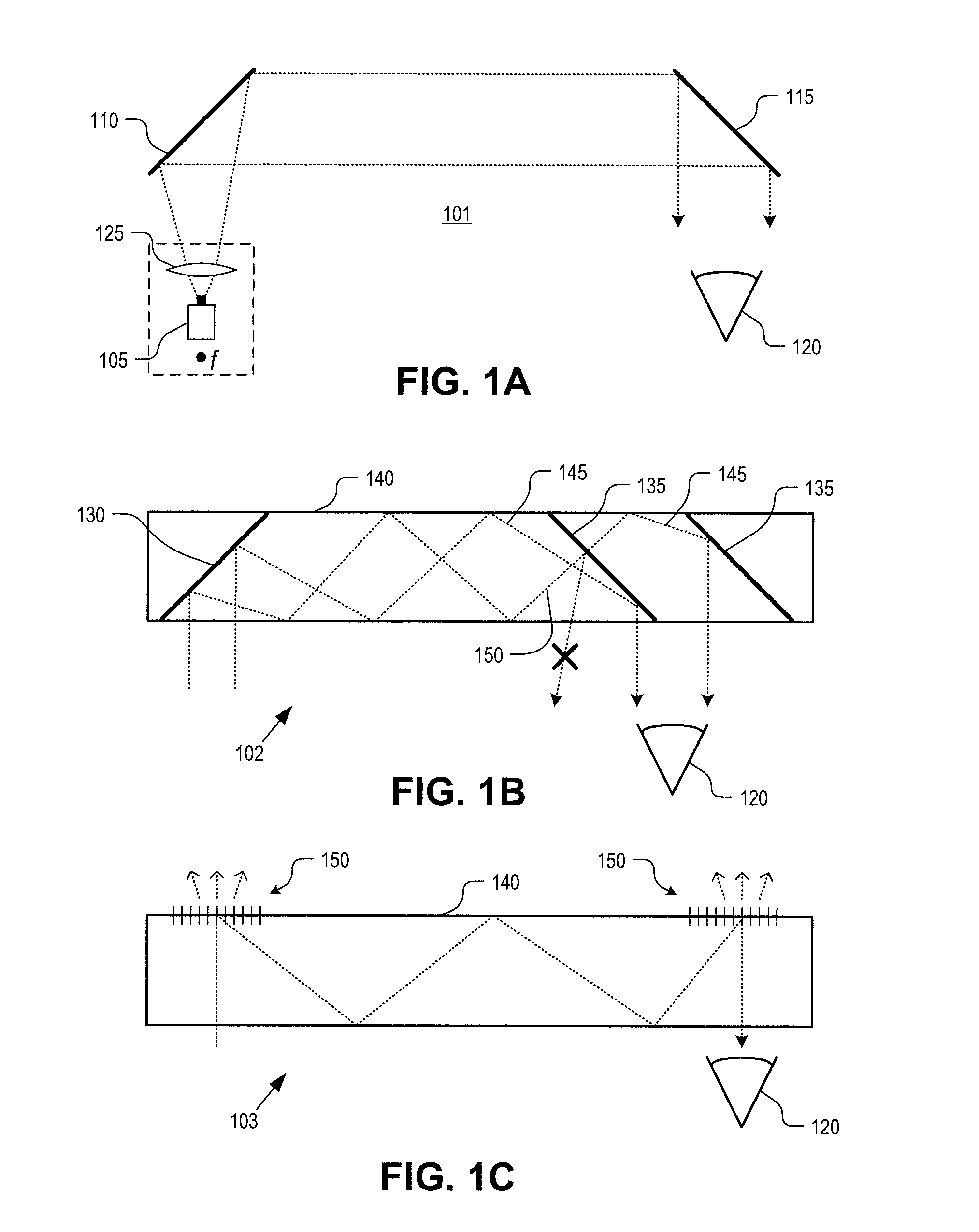
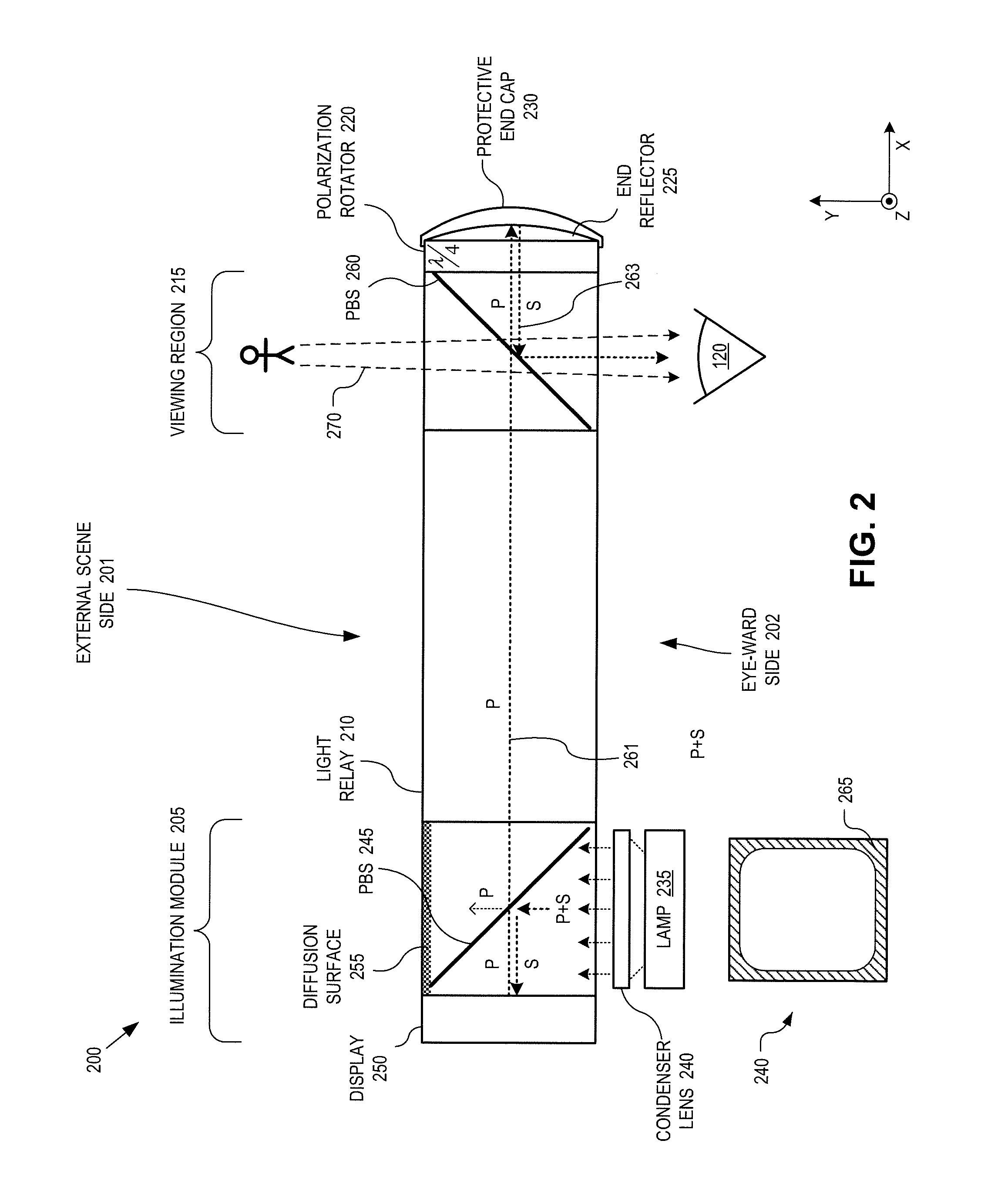
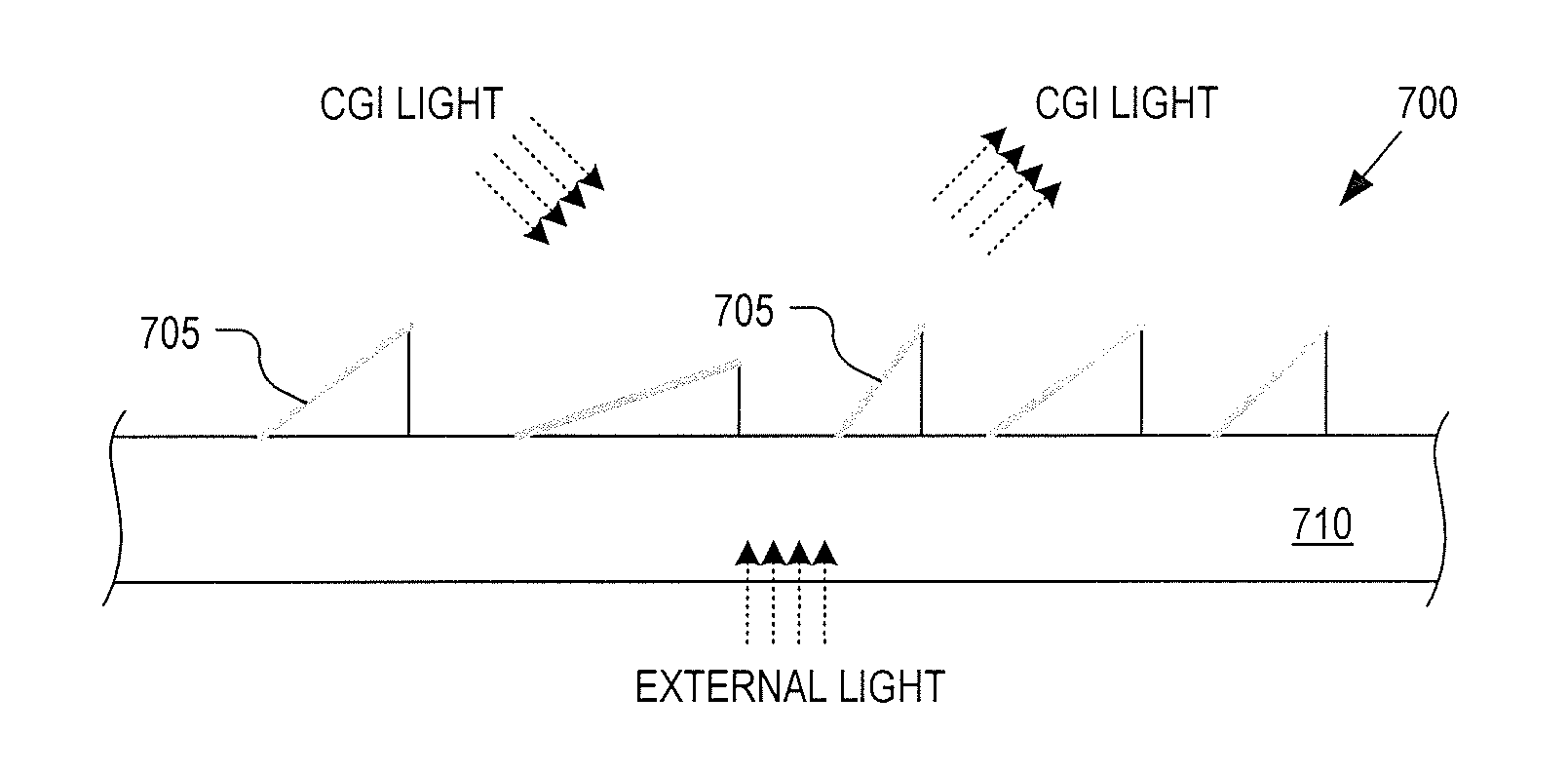
InactiveUS20130033756A1Reduce disagreementDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsBeam splitterEyepiece
An eyepiece for a head mounted display includes an illumination module, an end reflector, a viewing region, and a polarization rotator. The illumination module provides CGI light along a forward propagation path within the eyepiece. The end reflector is disposed at an opposite end of the eyepiece from the illumination module to reflect the CGI light back along a reverse propagation path within the eyepiece. The viewing is disposed between the illumination module and the end reflector and includes an out-coupling polarizing beam splitter (“PBS”). The out-coupling PBS passes the CGI light traveling along the forward propagation path and redirects the CGI light traveling along the reverse propagation path out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece. The polarization rotator is disposed in the forward and reverse propagation paths between the out-coupling PBS and the end reflector.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
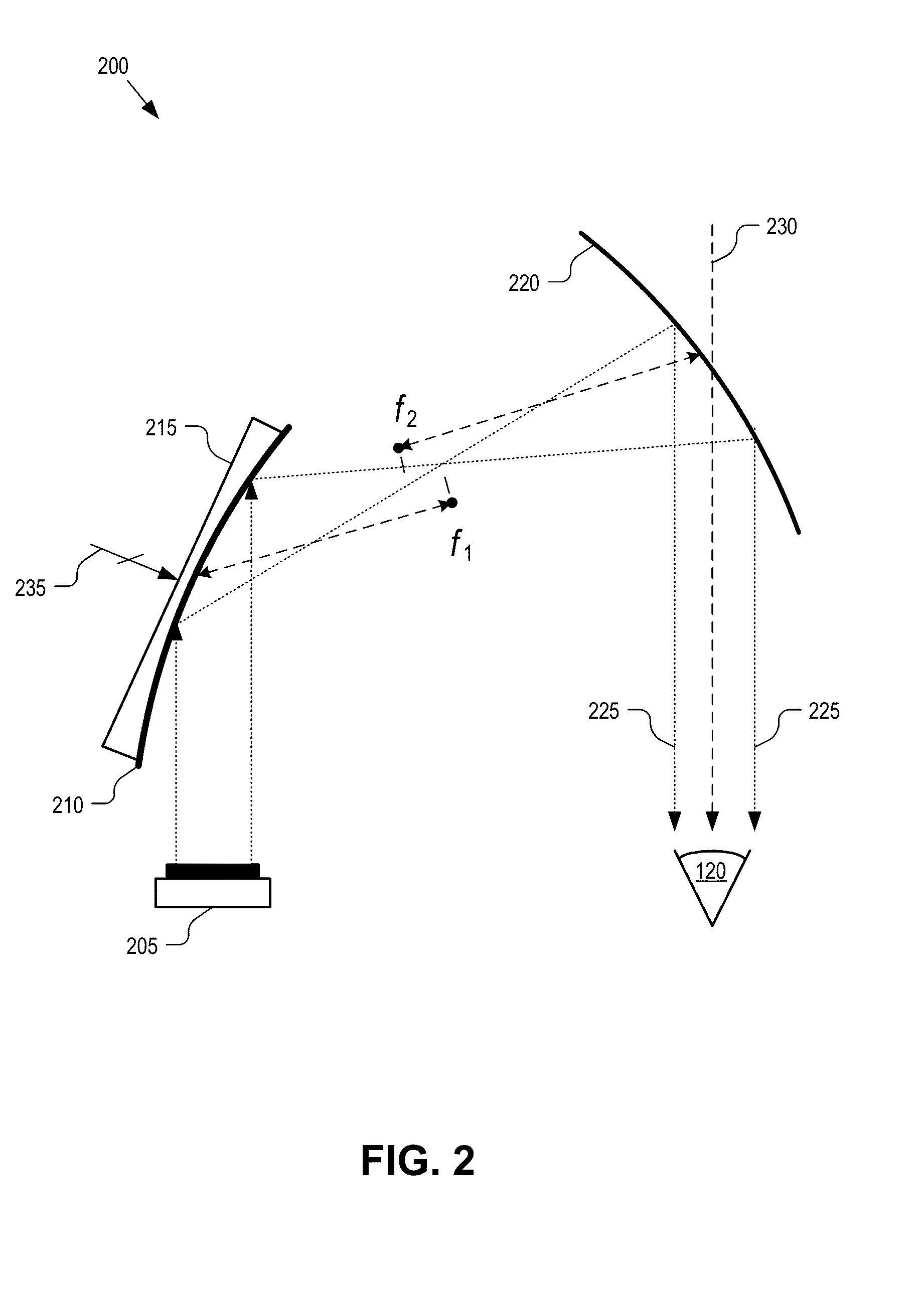
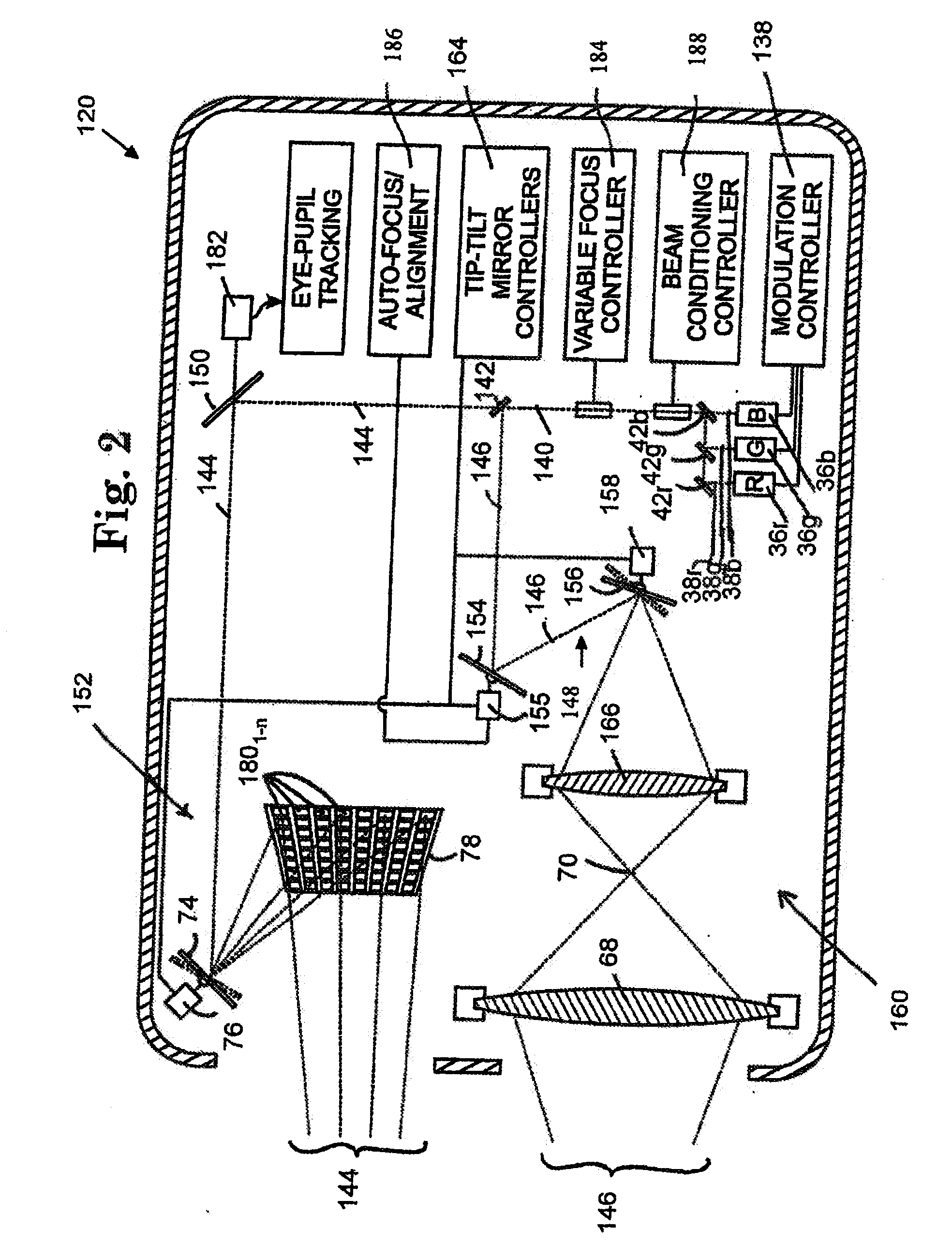
Compact near eye display with scanned image generation
ActiveUS20110134017A1Thickness minimizationSmall sizeStatic indicating devicesOptical light guidesLight beamDisplay device
A compact near eye display generates image segments for a first dimension of an intended image. Each of the image segments is transformed into angularly distinguished beamlets that converge through a first dimension pupil within an eyebox. A scanning optic angularly separates the angularly distinguished beamlets of different image segments for creating a second dimension pupil. The angularly distinguished and separated beamlets propagate along a waveguide in a form that minimizes the thickness of the display in front of a viewer's eye and limits the overall size of the optics required to support the projection of virtual images into the viewer's eye.
Owner:VUZIX
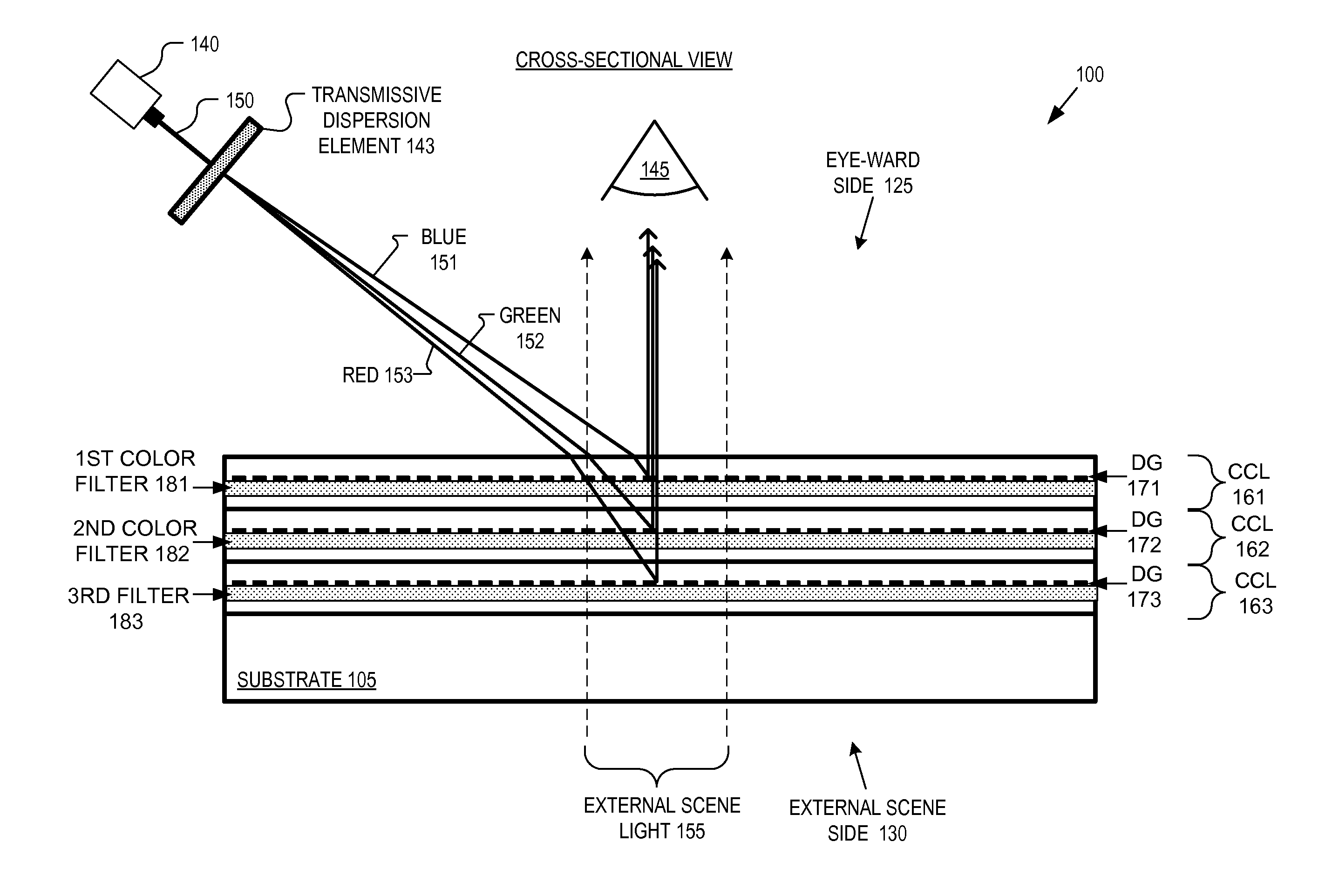
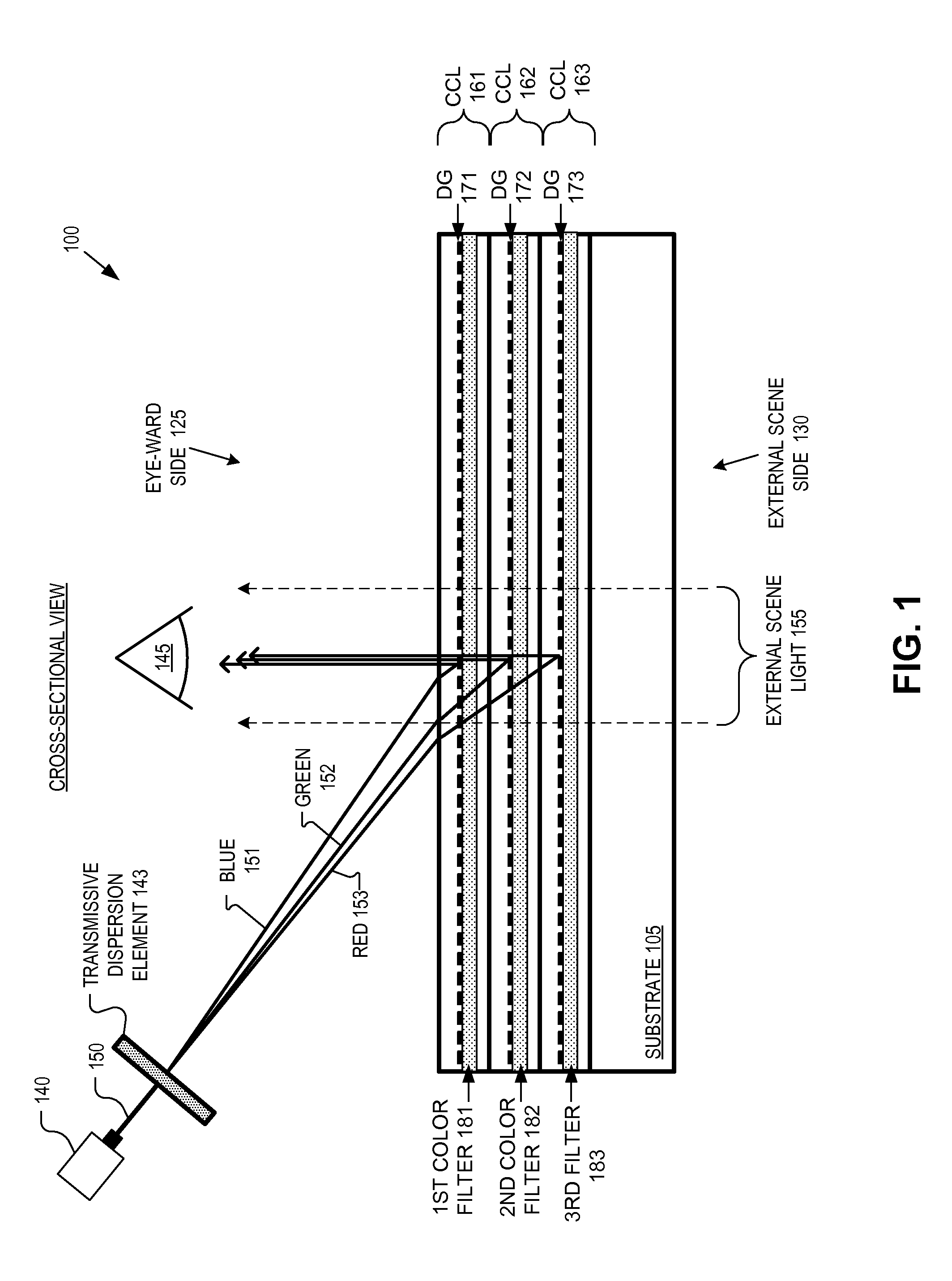
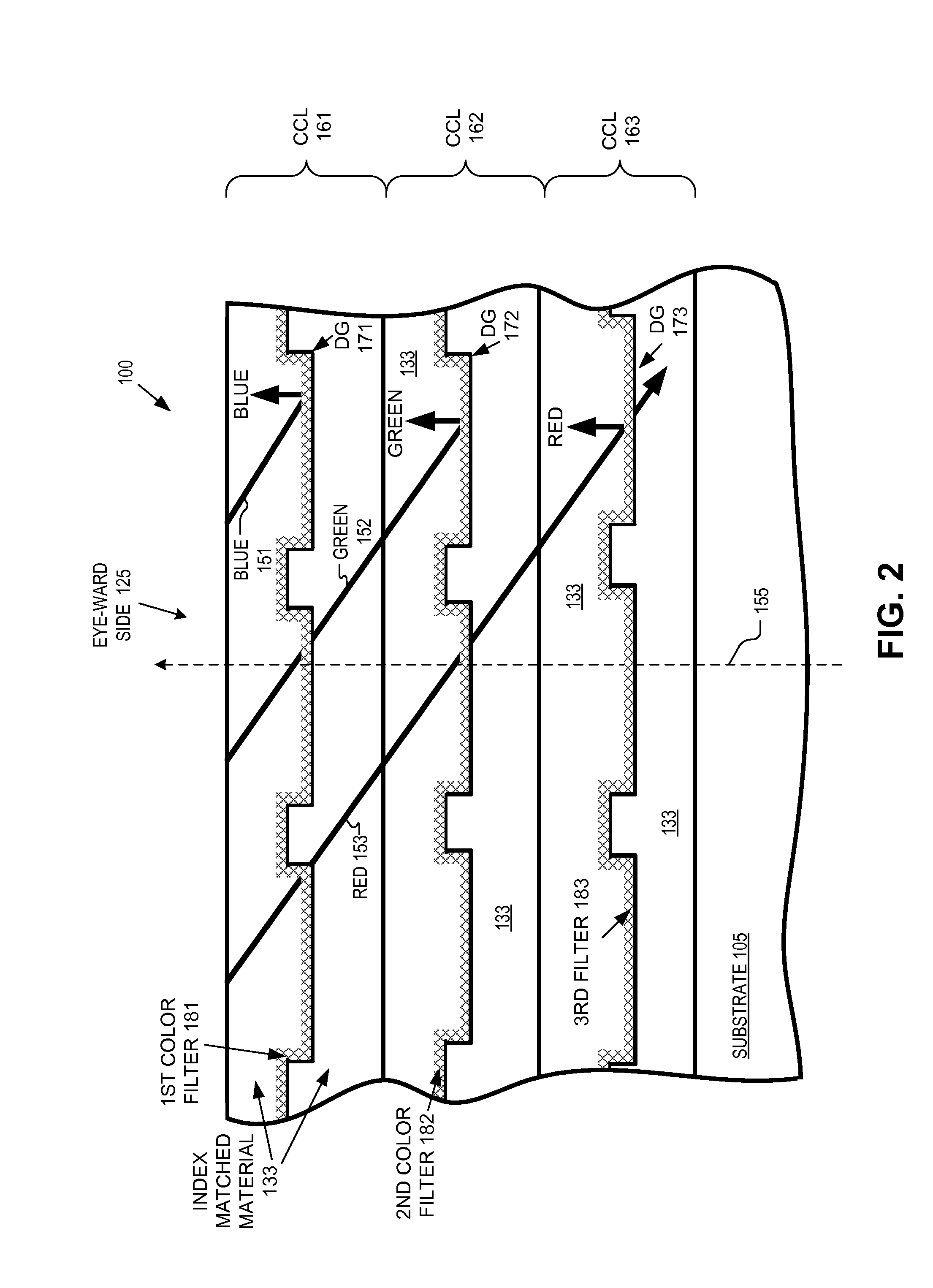
Optical combiner for near-eye display
An optical combiner includes a first, second, and third color combiner layer (“CCL”). The first CCL includes a first diffractive grating coated with a first filter configured to reflect a first color light and pass a second and a third color light. The second CCL includes a second diffractive grating coated with a second filter configured to reflect the second color light and pass the third color light. The third CCL includes a third diffractive grating coated with a third filter configured to partially reflect visible light. The diffractive gratings are each embedded in an index matched material and are angle-tuned diffractive gratings configured to receive image light at an angle and respectively reflect the first, second, and third color light in the image light at an order of diffraction that directs the light to an eye of a user.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Compact near eye display with scanned image generation
ActiveUS8698705B2Thickness minimizationSmall sizeCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical light guidesLight beamDisplay device
A compact near eye display generates image segments for a first dimension of an intended image. Each of the image segments is transformed into angularly distinguished beamlets that converge through a first dimension pupil within an eyebox. A scanning optic angularly separates the angularly distinguished beamlets of different image segments for creating a second dimension pupil. The angularly distinguished and separated beamlets propagate along a waveguide in a form that minimizes the thickness of the display in front of a viewer's eye and limits the overall size of the optics required to support the projection of virtual images into the viewer's eye.
Owner:VUZIX
Near-to-eye tracking for adaptive operation
A method and a system are provided for adaptive vehicle operation. The method includes the steps of sensing a position and an orientation of a near-to-eye display device worn by the vehicle operator, determining a direction of gaze of the vehicle operator in response to the position and the orientation of the near-to-eye display device, and selectively generating an alert signal in response to the direction of gaze of the vehicle operator.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
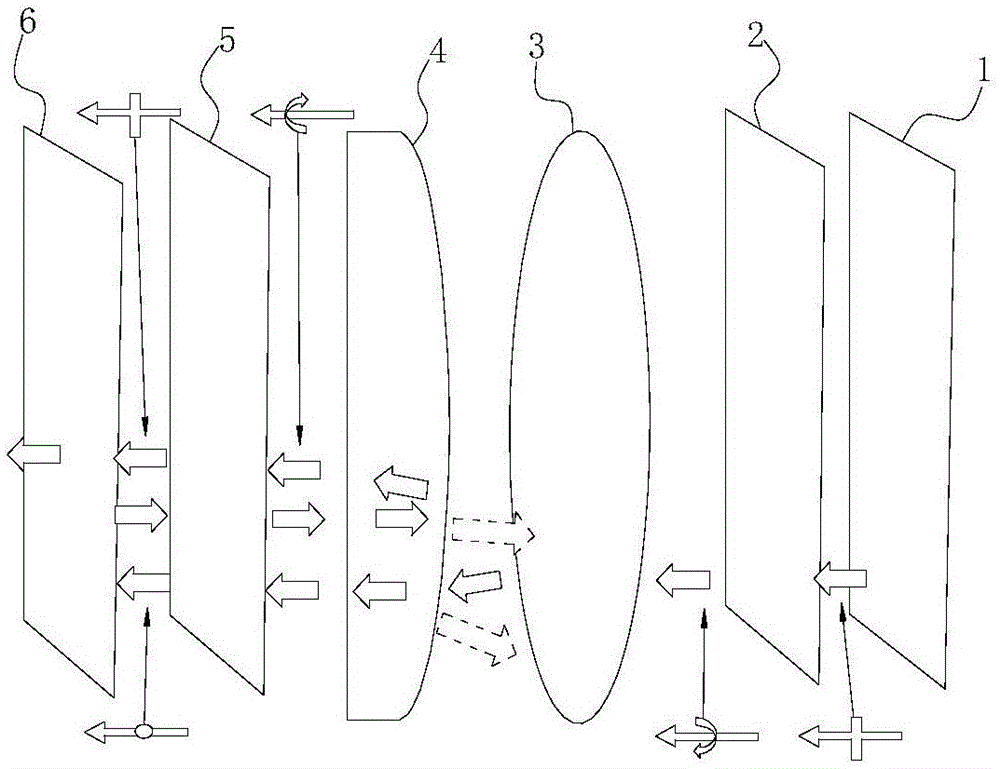
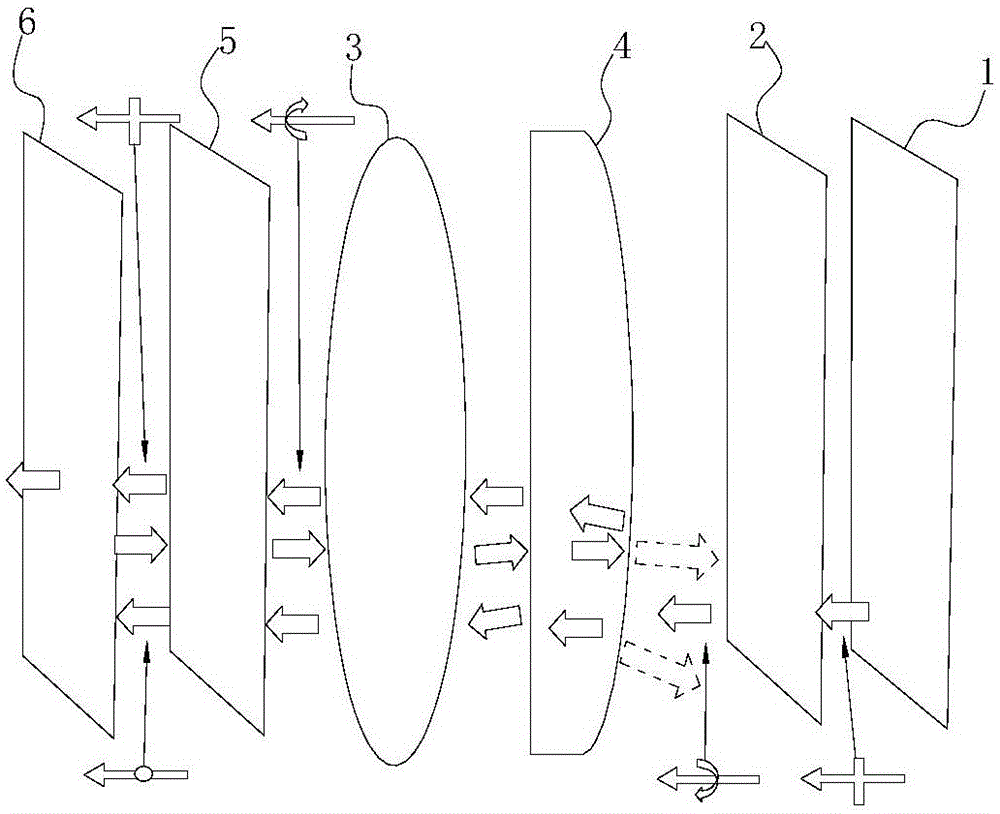
Short-distance optical magnification module group and near-to-eye display optical module group using the same
The invention relates to a short-distance optical magnification module group and a near-to-eye display optical module group using the same and aims at providing an optical magnification module group for realizing high-multiple magnification at a short distance less than 5cm and a near-to-eye display optical module group using the optical magnification module group to realize an extra-large field angle at a short distance less than 3cm. According to the invention, the near-to-eye display optical module group includes a first 45-degree phase delay plate (2), a partial-transmission partial-reflection curve-surface lens (4), a second 45-degree phase delay plate (5) and a reflective polarizing plate (6). In addition, the near-to-eye display optical module group includes a display screen (1) arranged at one side, far away from the partial-transmission partial-reflection curve-surface lens (4), of the first 45-degree phase delay plate (2).
Owner:SHENZHEN DLODLO TECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Light guide optical assembly
An optical assembly for optical aperture expansion combines facet reflective technology with diffractive technology. At least two diffractive components having opposite optical power (matching) are used, so that chromatic dispersion introduced by the first diffractive component will then be cancelled by the second diffractive component. The two diffractive components are used in combination with a reflective optical component to achieve more efficient aperture expansion (for near eye display), reducing distortions and noise, while also reducing design constraints on the system and individual components, as compared to conventional techniques. The assembly eliminates and / or reduces the need for polarization management, while enabling wider field of view. In addition, embodiments can have reduced nonuniformity, as compared to conventional single technology implementations, since the distortion patterns of the two technologies do not correlate.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Near-to-eye display with diffraction grating that bends and focuses light
A near-to-eye optical system includes an optically transmissive substrate having a see-through display region and a repeating pattern of diffraction elements. The repeating pattern of diffraction elements is disposed across the see-through display region of the optically transmissive substrate and organized into a reflective diffraction grating that bends and focuses computer generated image (“CGI”) light impingent upon the reflective diffraction grating. The see-through display region is at least partially transmissive to external ambient light impingent upon an exterior side of the optically transmissive substrate and at least partially reflective to the CGI light impingent upon an interior side of the optically transmissive substrate opposite the exterior side.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
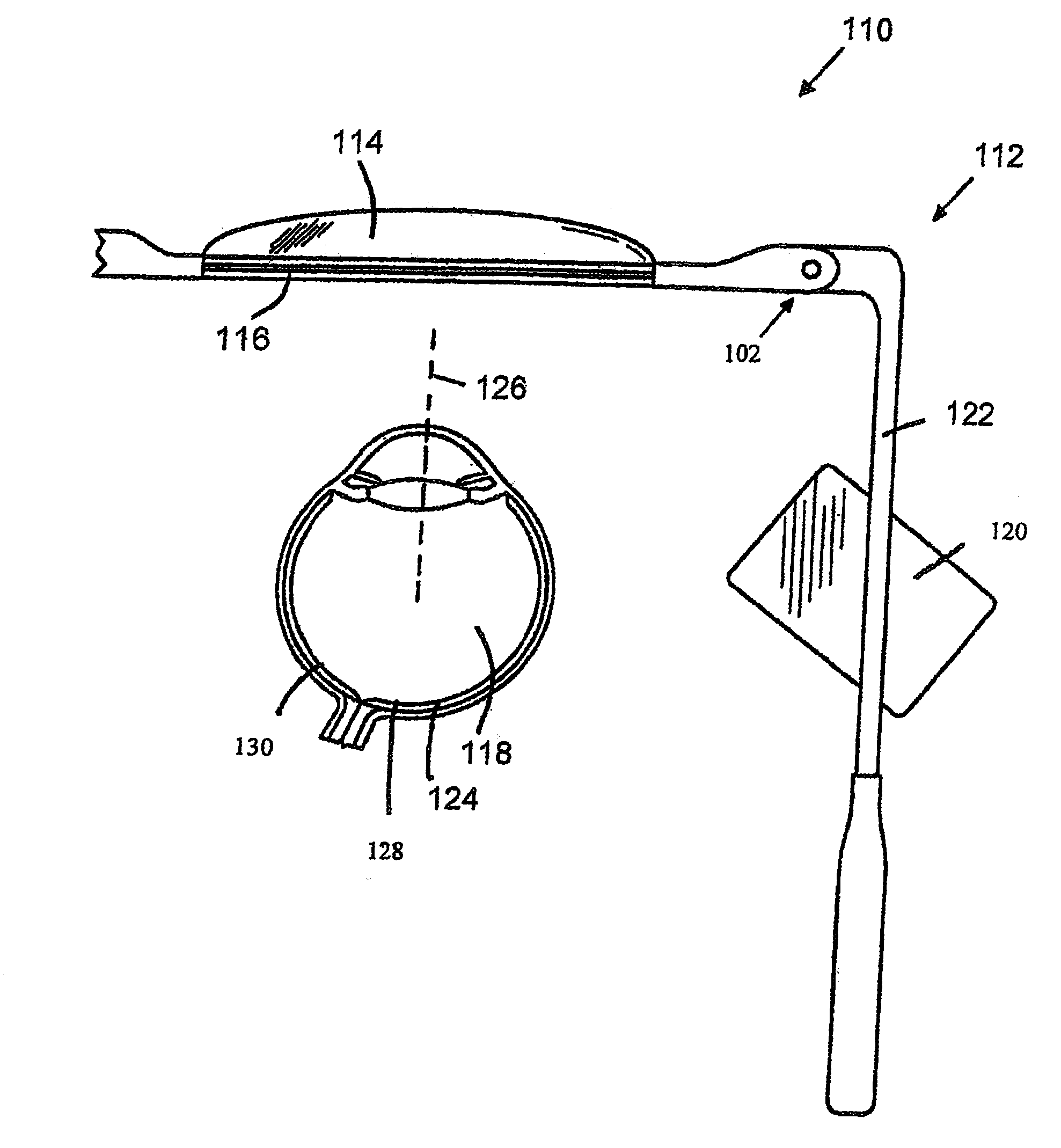
Apparatus and Method for a Bioptic Real Time Video System
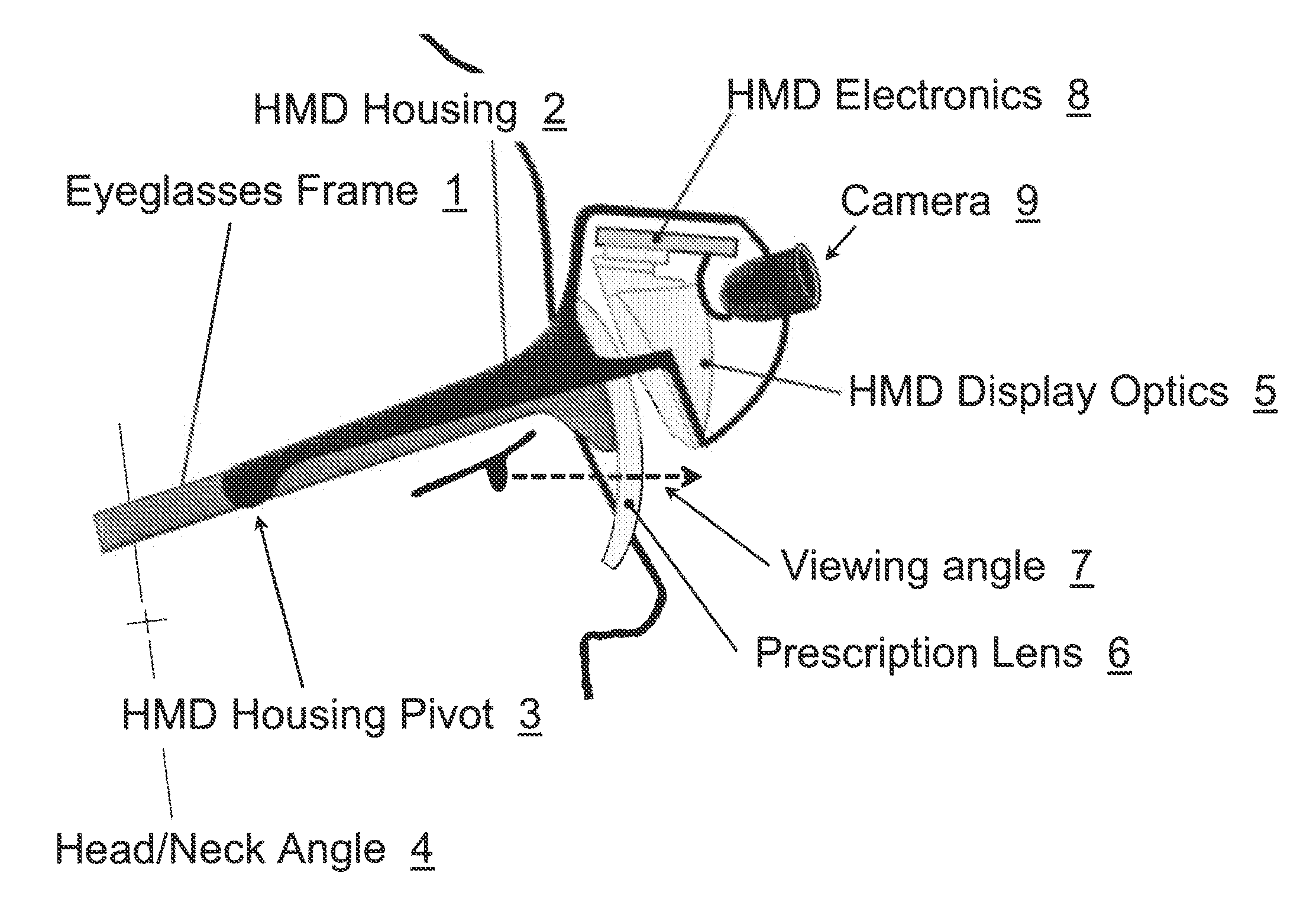
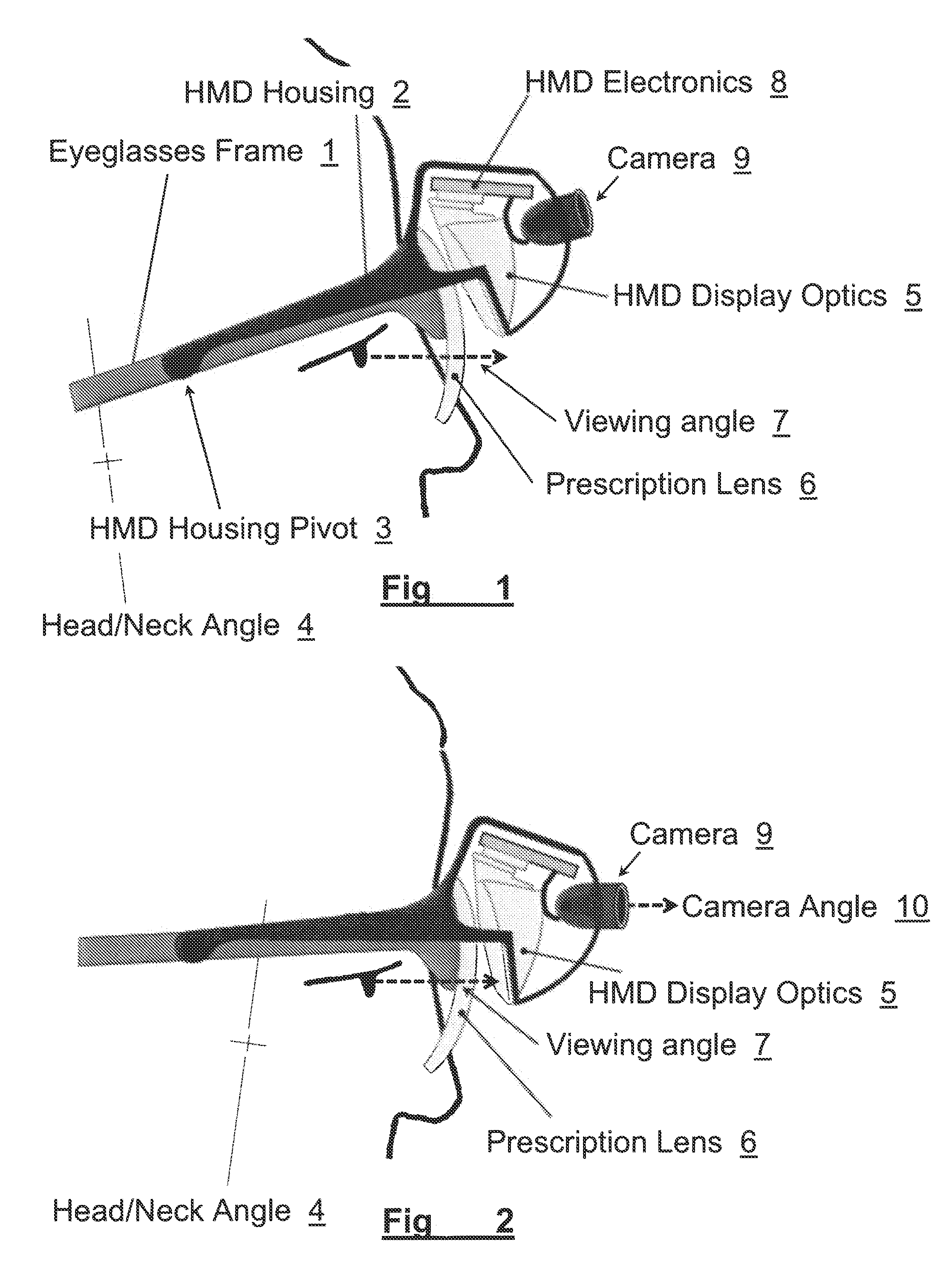
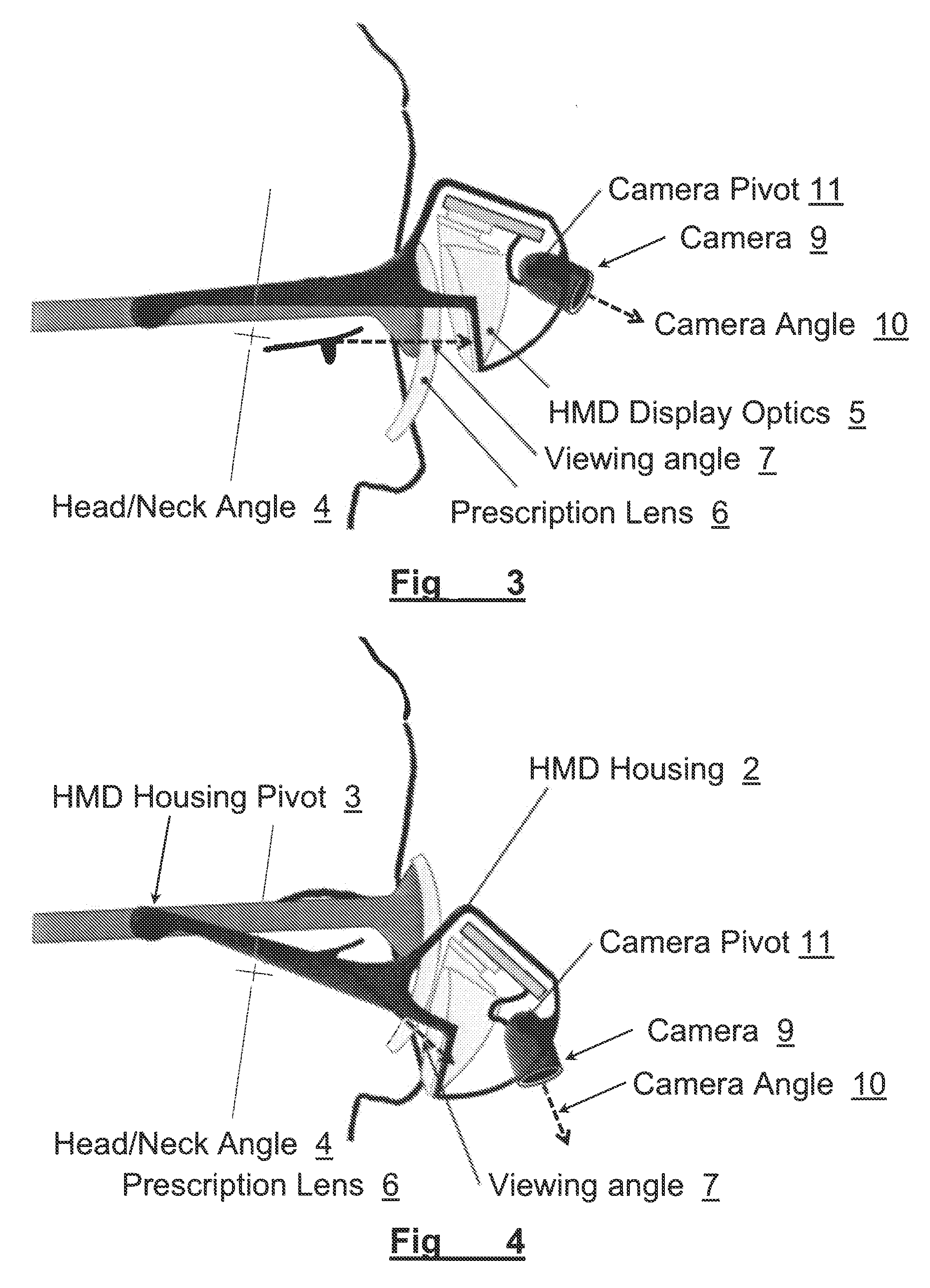
ActiveUS20120306725A1Improve usabilityWide field of viewCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A method and apparatus of displaying an electronic video image using a head-worn near-to-eye display in a non-immersive fashion, such that the wearer can choose, through simple adjustments of their neck and eye angles, to either look at the displayed video image or their natural environment. The invention also relates to the incorporation of prescription lenses into the optical chain of the near-to-eye display. The invention also relates to the use of motion and position sensors incorporated into the head-worn device to enable automatic stabilization of the video image. The invention also relates to the use of motion and position sensors incorporated into the head-worn device to automatically adjust the vertical angle of either the camera or the electronic display or both, by sensing the vertical angular position of the user's head.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
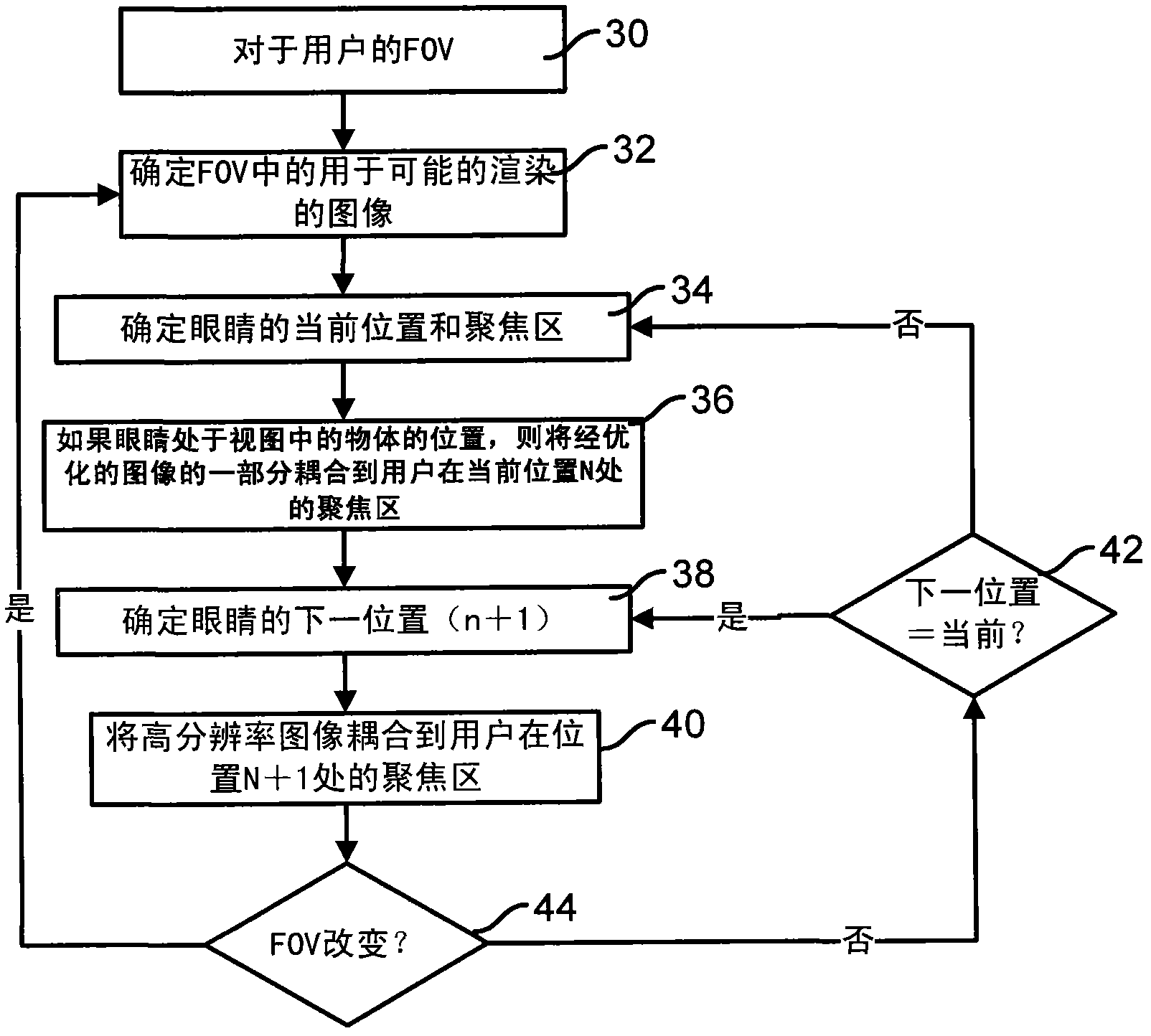
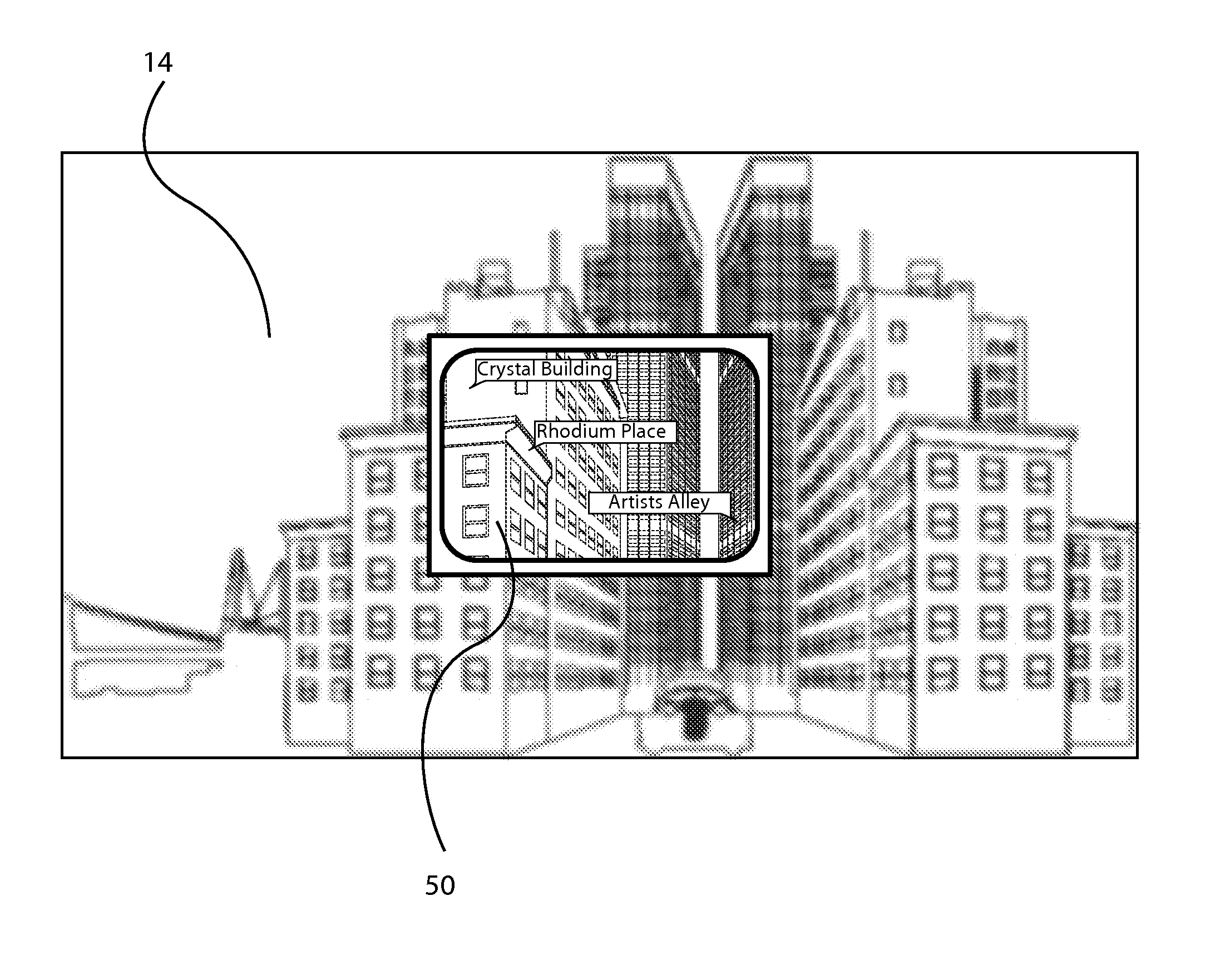
Optimized focal area for augmented reality displays
ActiveCN102591016AInput/output processes for data processingOptical elementsSee-through displayDisplay device
The invention relates to an optimized focal area for augmented reality displays, and provides a method and a system that enhances a user's experience when using a near eye display device, such as a see-through display device or a head mounted display device. An optimized image for display relative to a field of view of a user in a scene is created. The user's head and eye position and movement are tracked to determine a focal region for the user. A portion of the optimized image is coupled to the user's focal region in the current position of the eyes, a next position of the head and eyes predicted, and a portion of the optimized image coupled to the user's focal region in the next position.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
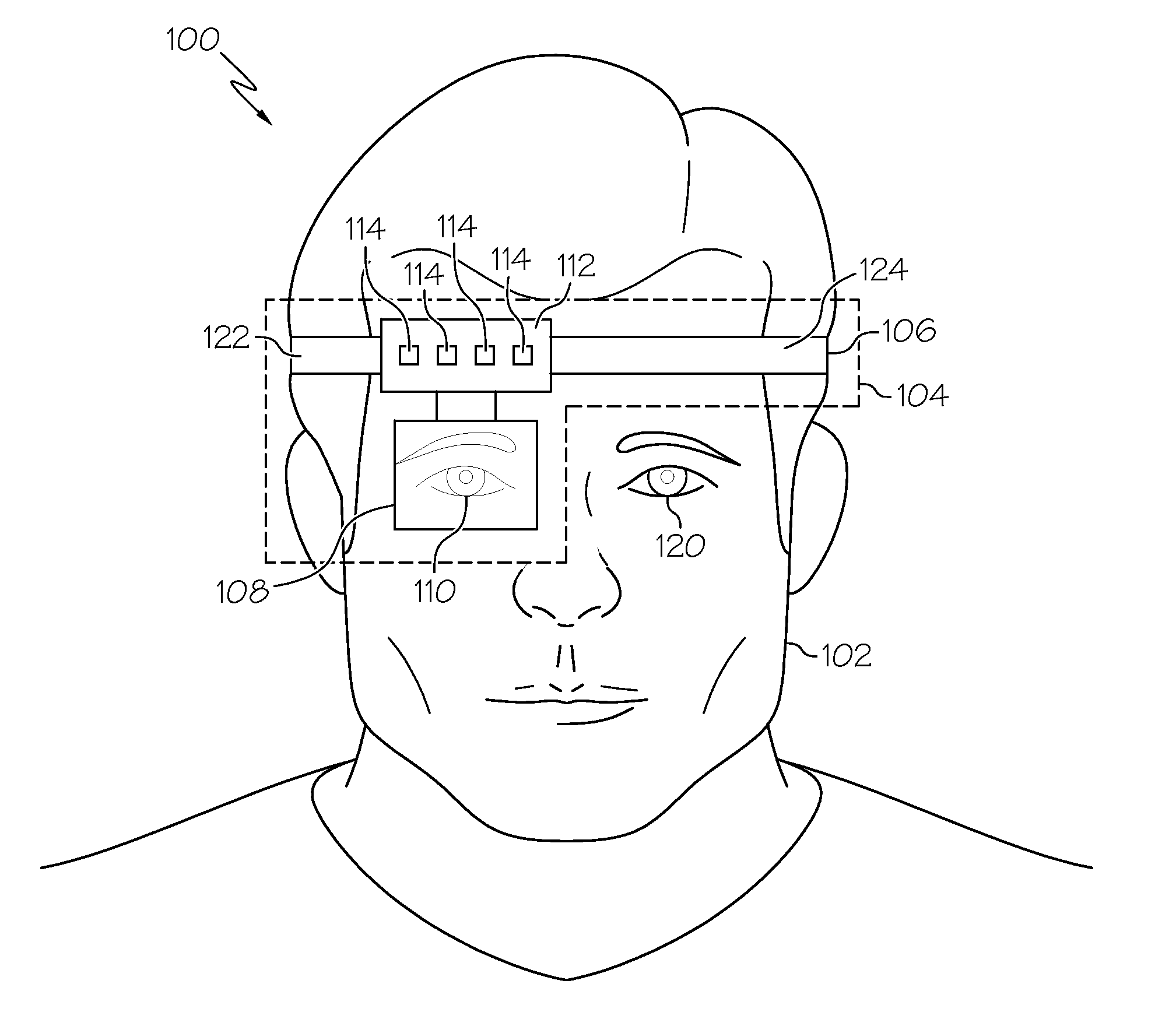
Near eye display prism optic assembly
An optical assembly uses a plastic prism with one flat surface and a collimating lens optic to provide the capability of imaging a color micro-display to the eye. The collimating optic and flat prism surface can allow for aberration-free diopter adjustment and an image with very low-magnitude, nearly-symmetric distortion. The collimating optic can also provide environmental protection of the prism involving an optical plastic device. The input illumination from the micro-display enters the prism, is reflected two times within the prism, exits the prism, and passes through the collimating optic before being viewed by the eye. Such an optical assembly can provide a field of view with eye-relief and exit pupil when viewing a full-color micro-display.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
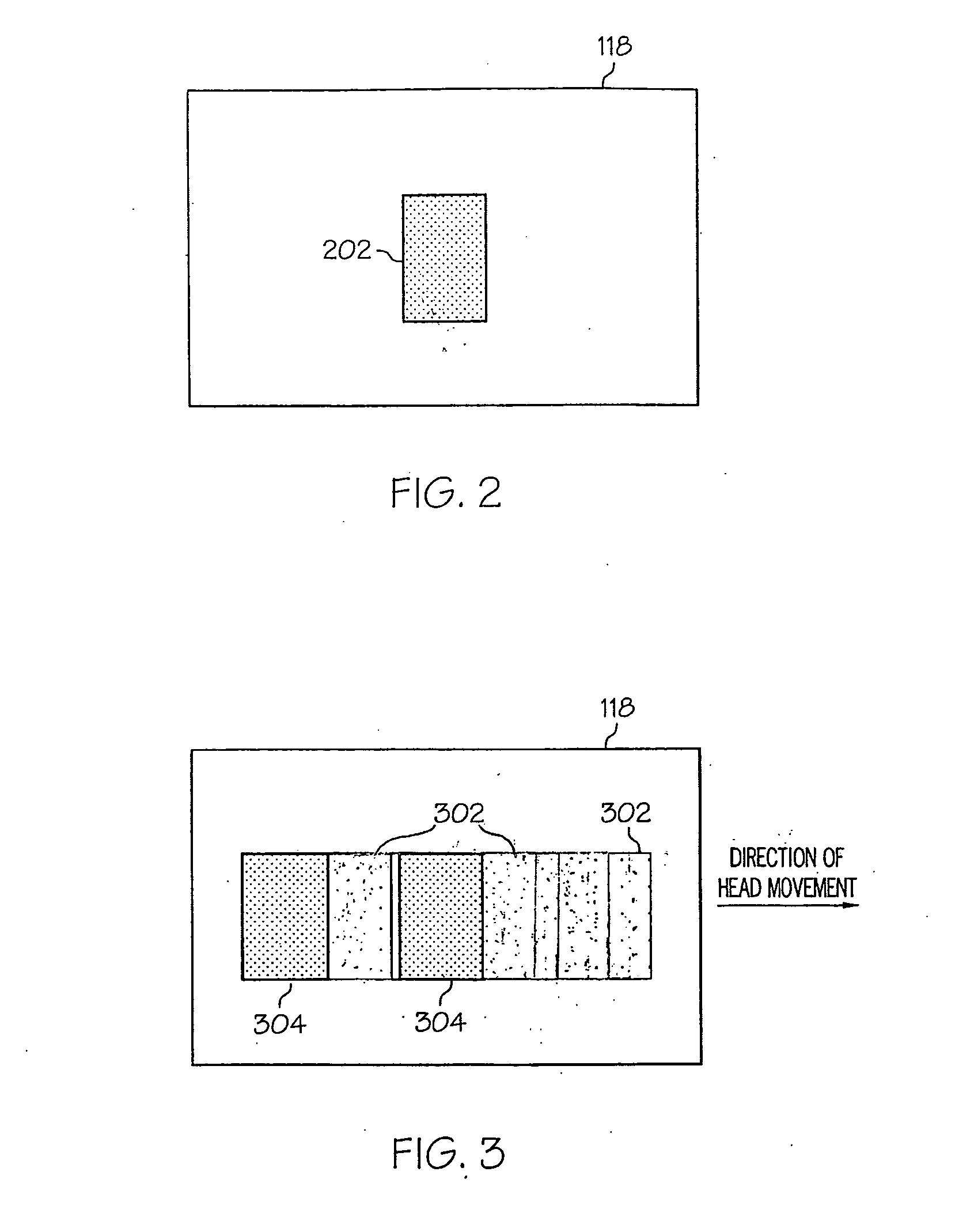
Near-to-eye display artifact reduction system and method
ActiveUS20100039353A1Reduce artifactsCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A near-to-eye (NTE) display system and method are provided for reducing artifact display in a NTE display that is worn, at least partially, on a viewer's head. The movement of the NTE display is sensed while displaying an image that comprises individual content frames on the NTE display. A characteristic of the individual content frames of the displayed image is varied based on the sensed movement.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus for augmenting an index generated by a near eye display
ActiveUS20130342569A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceComputer program
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided in order to augment an index image generated by a near eye display in order to more clearly present at least a portion of the index image. In the context of a method, a position of the mobile terminal relative to an index image generated by a near eye display is determined. The method also determines an image to be presented by the mobile terminal based upon the index image and the position of the mobile terminal relative to the index image. The method also causes the image to be presented by the mobile terminal. A corresponding apparatus and a computer program product are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com