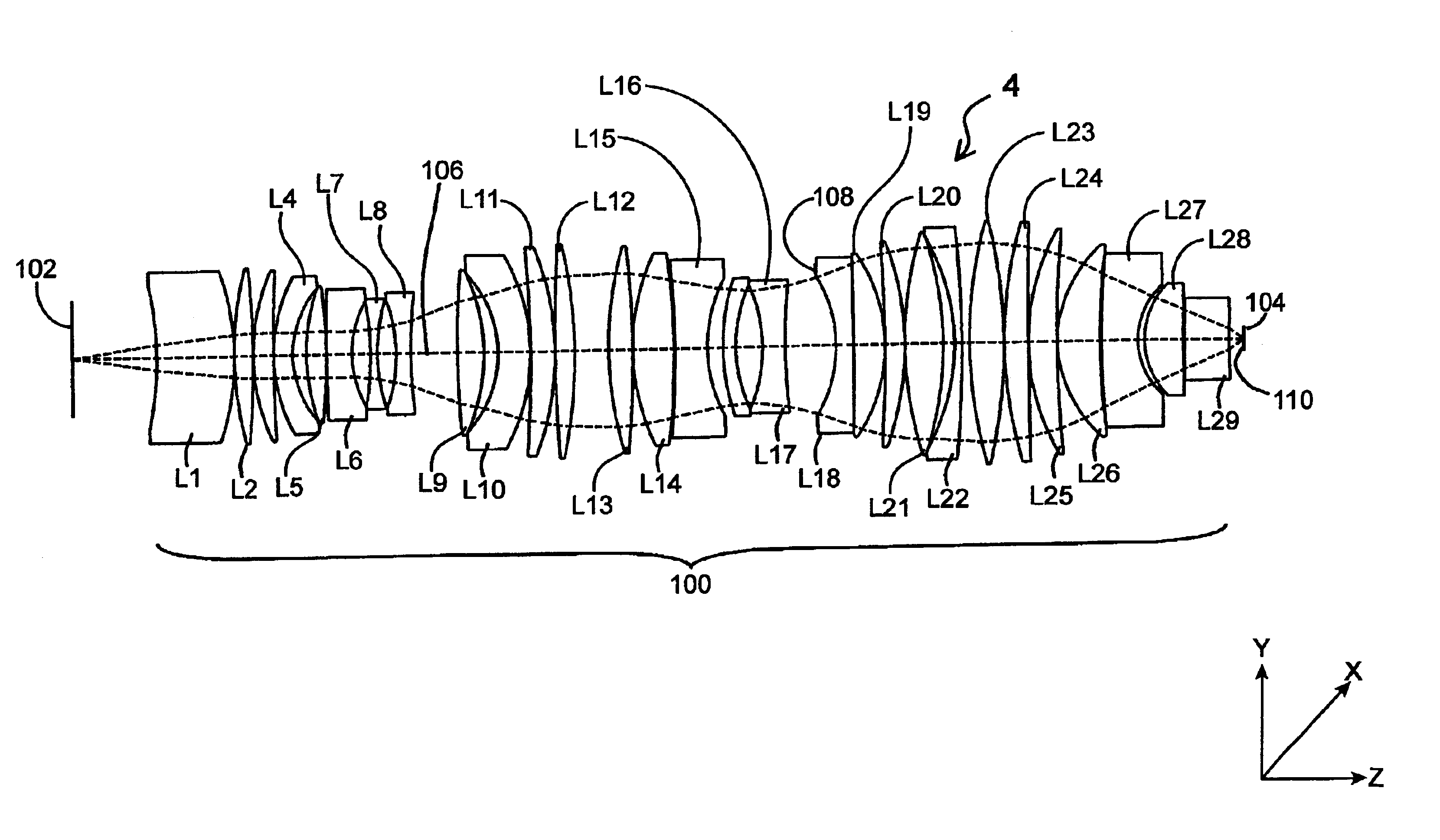
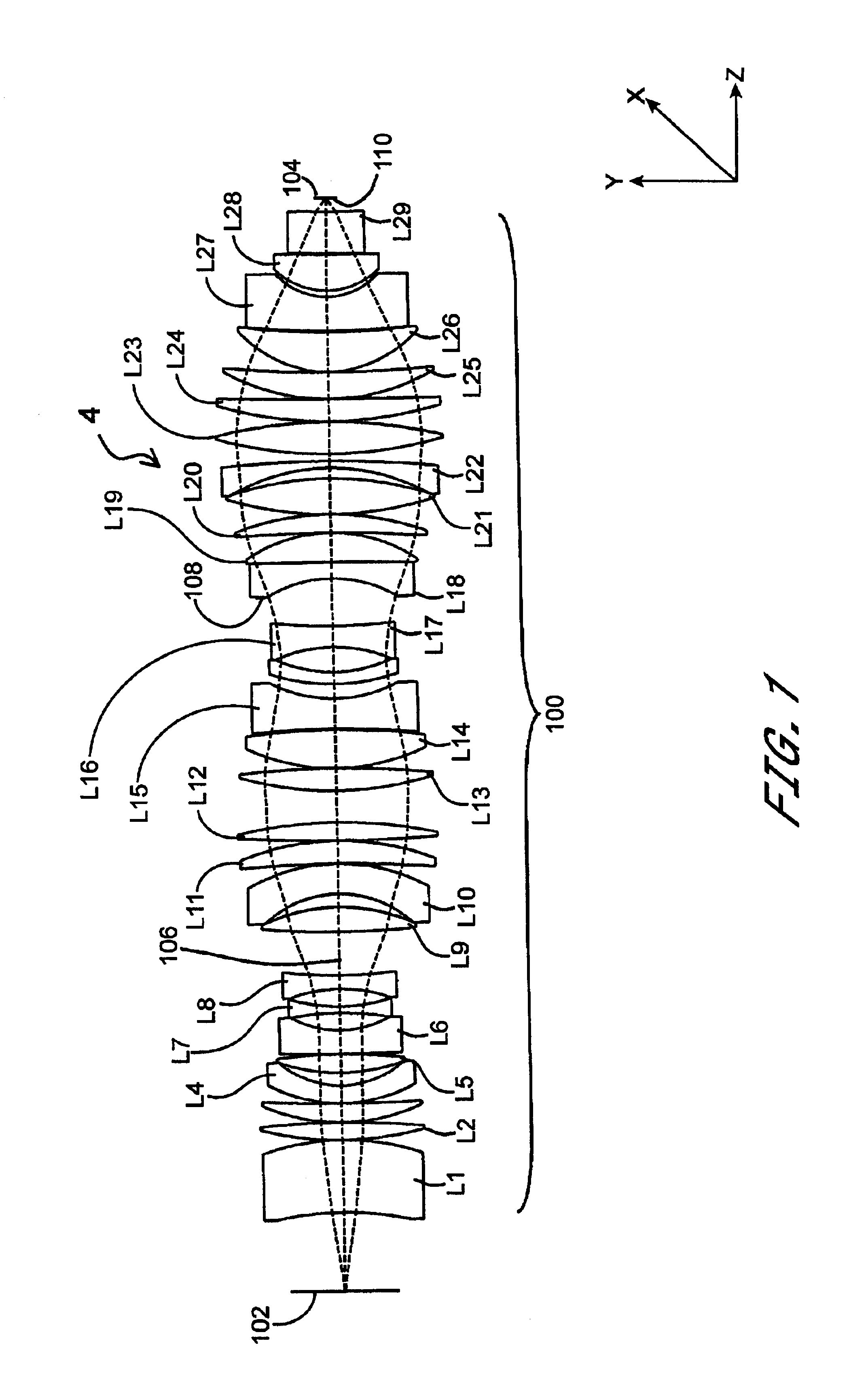
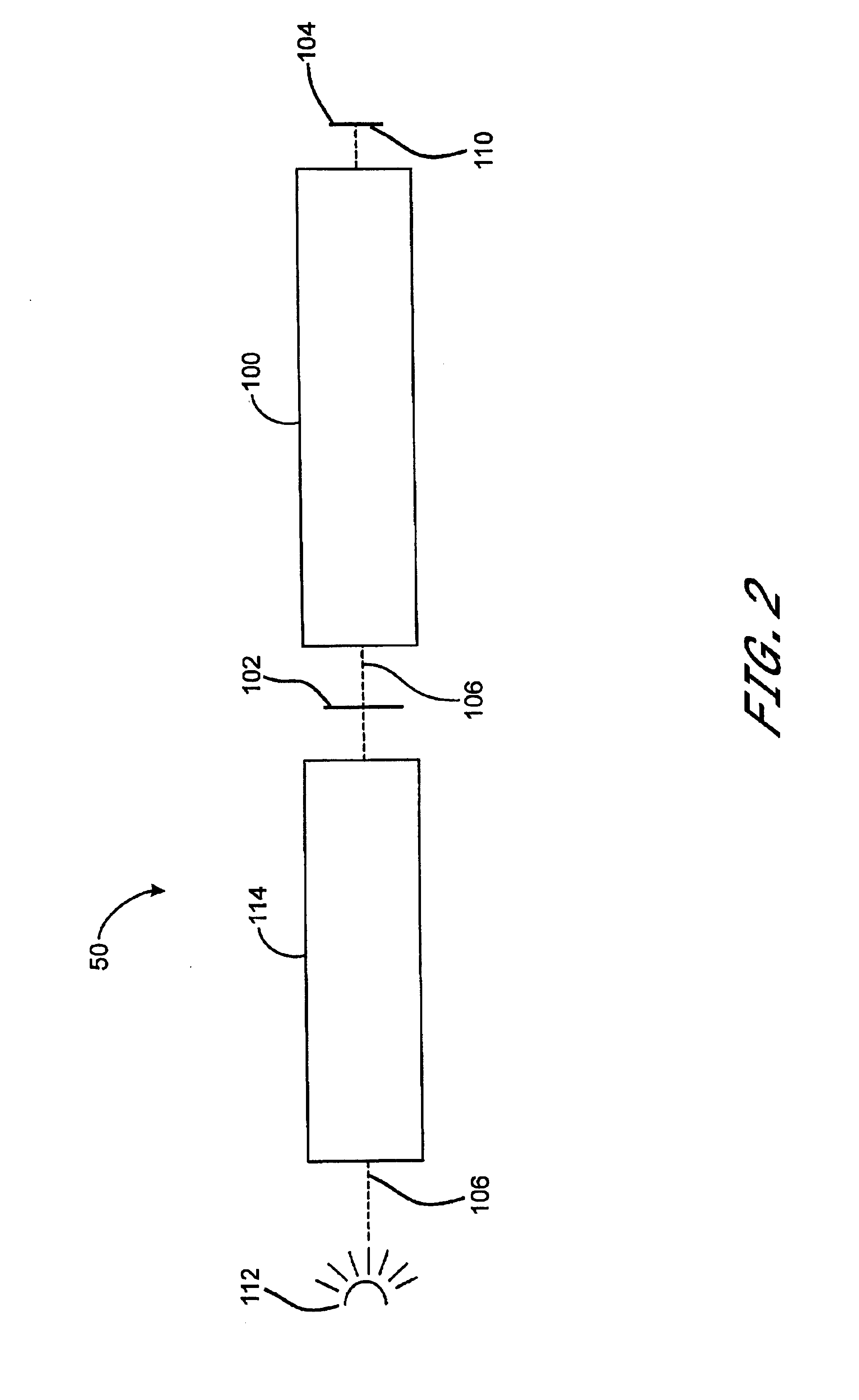
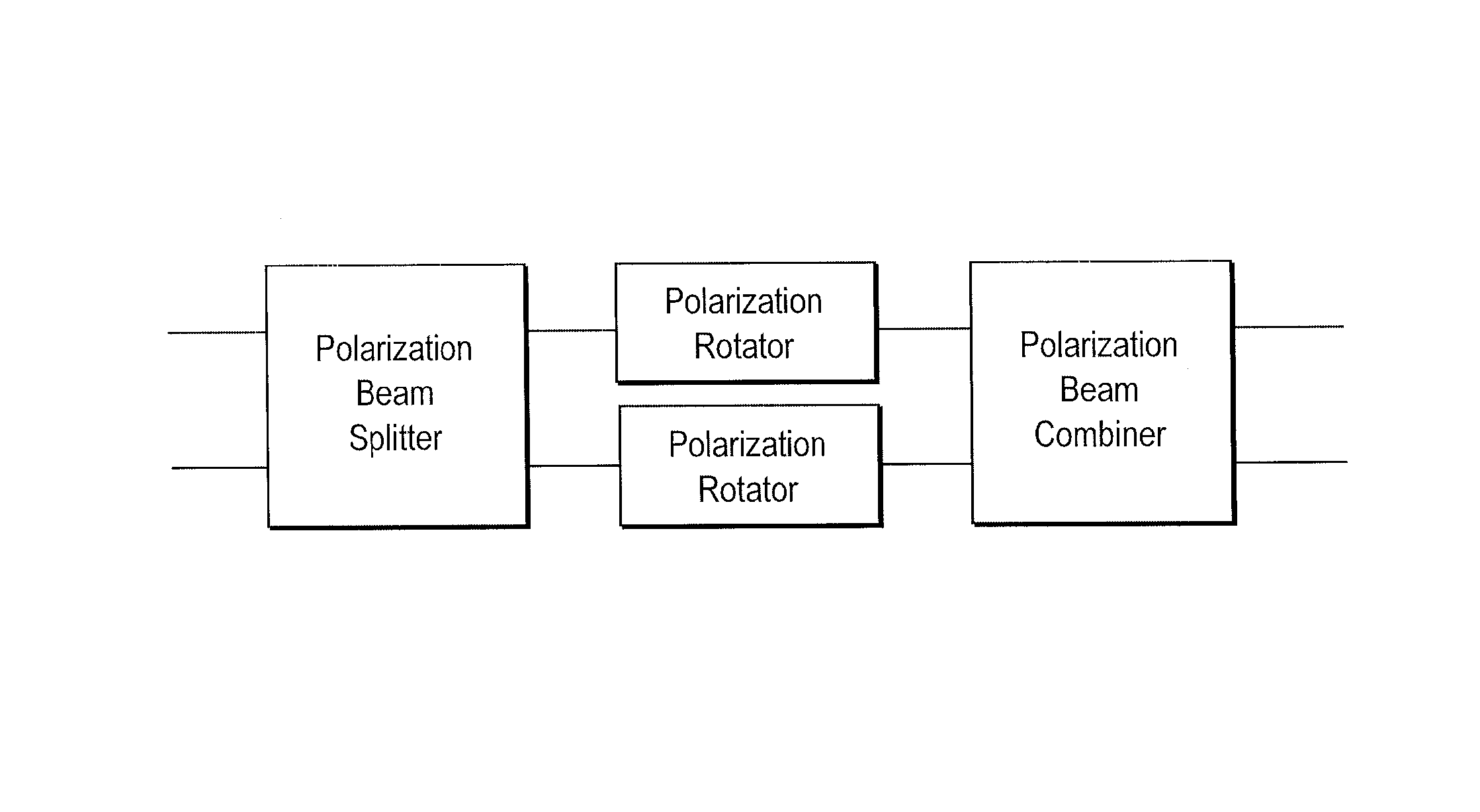
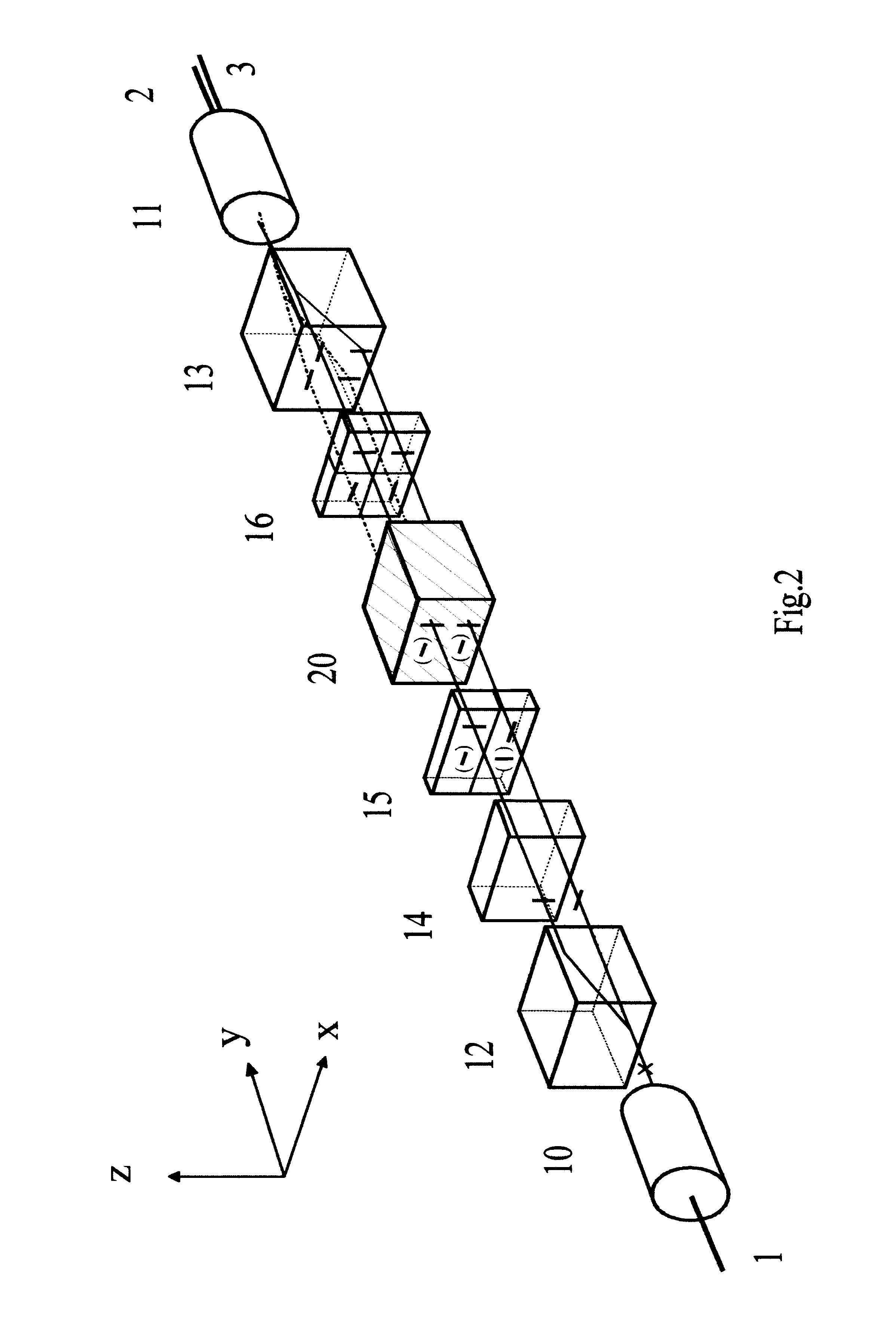
Patents
Literature
351 results about "Polarization rotator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A polarization rotator is an optical device that rotates the polarization axis of a linearly polarized light beam by an angle of choice. Such devices can be based on the Faraday effect, on birefringence, or on total internal reflection. Rotators of linearly polarized light have found widespread applications in modern optics since laser beams tend to be linearly polarized and it is often necessary to rotate the original polarization to its orthogonal alternative.
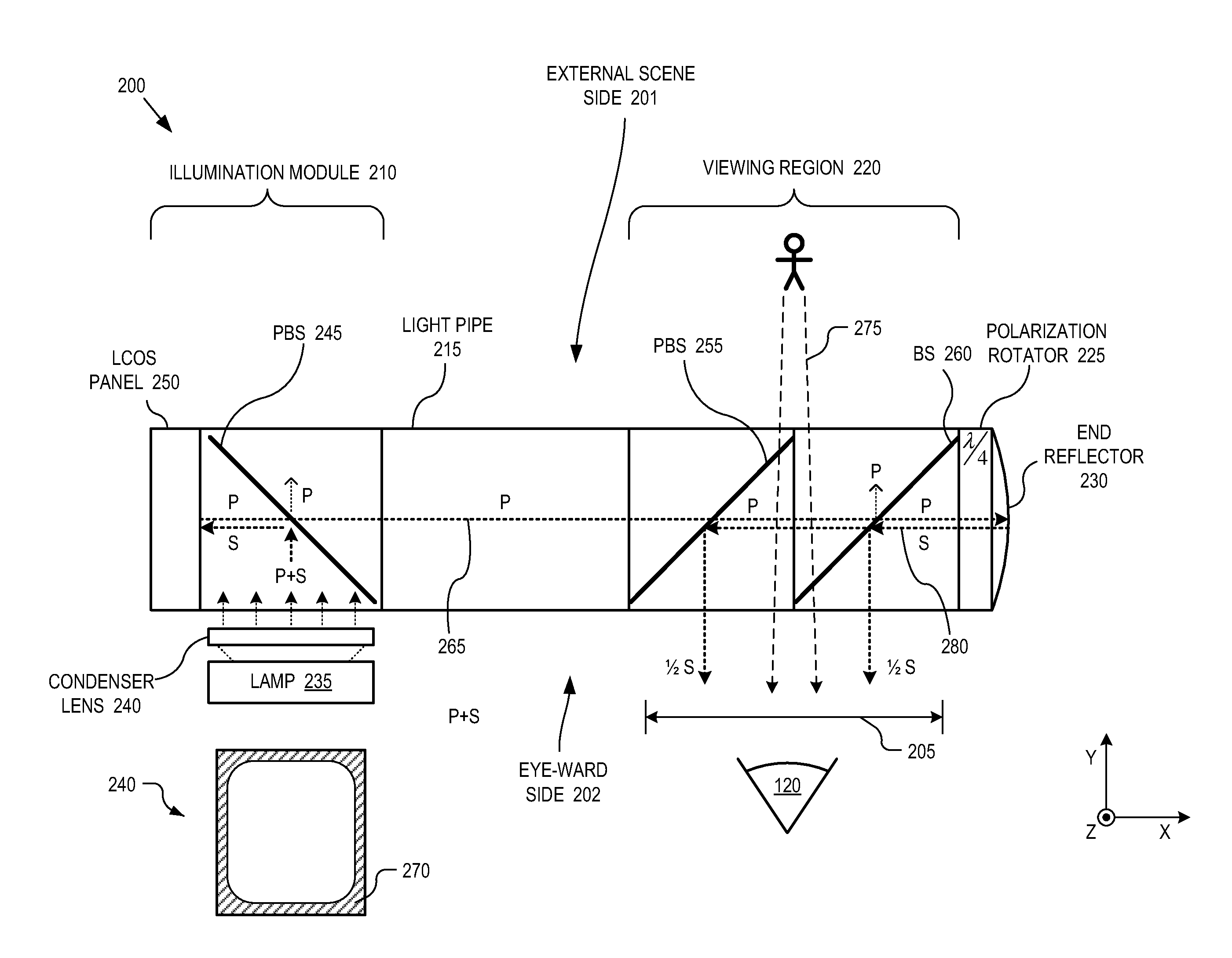
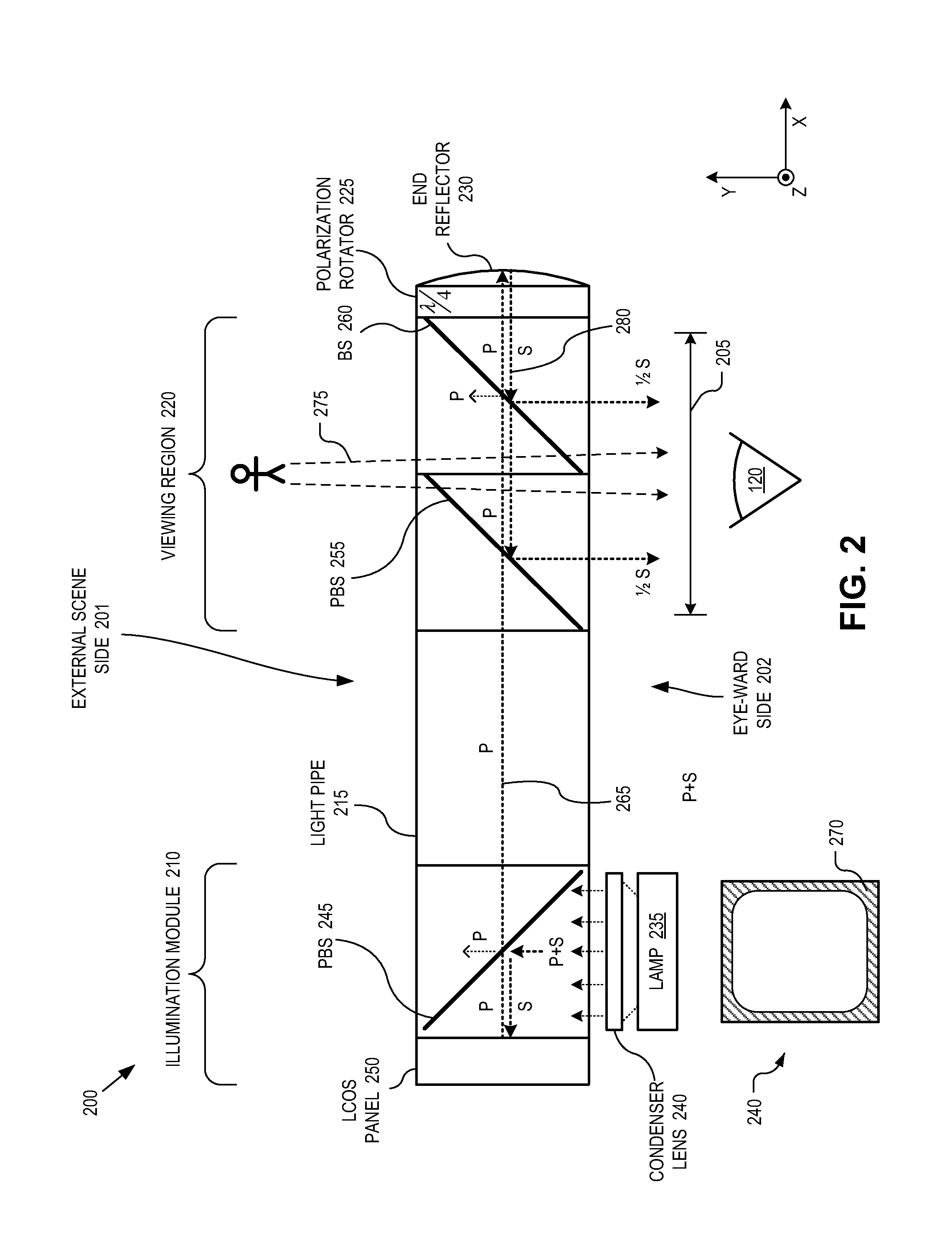
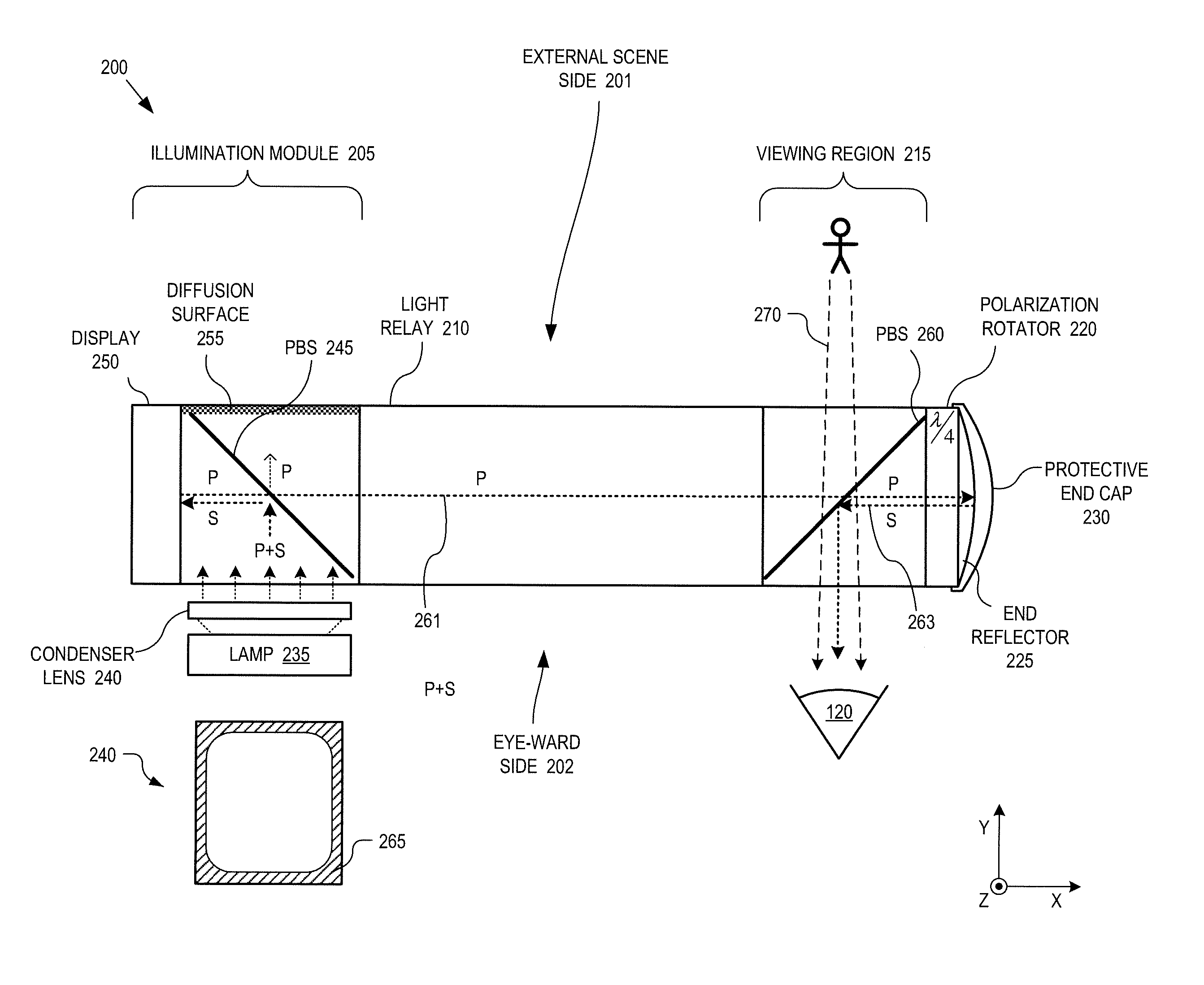
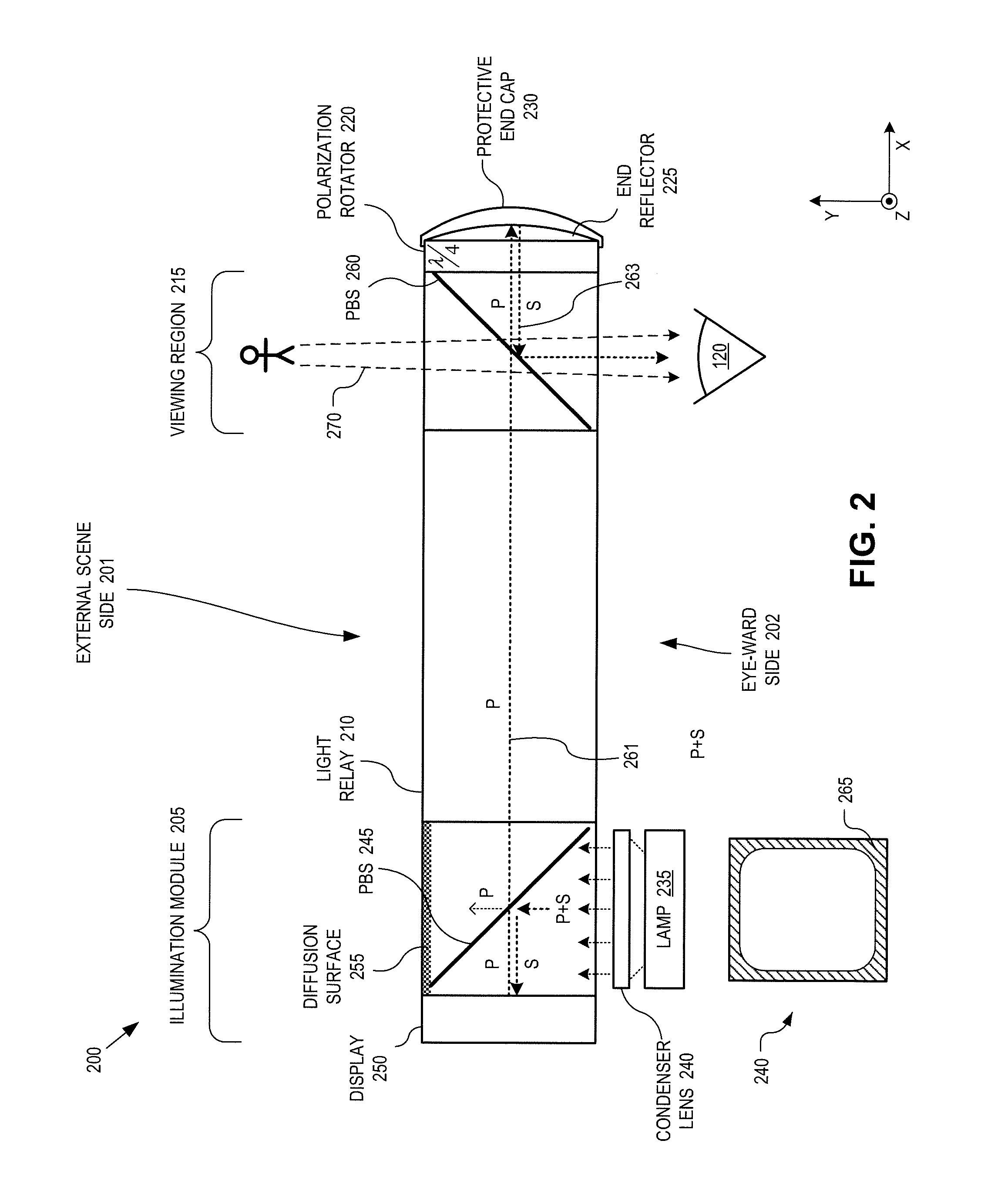
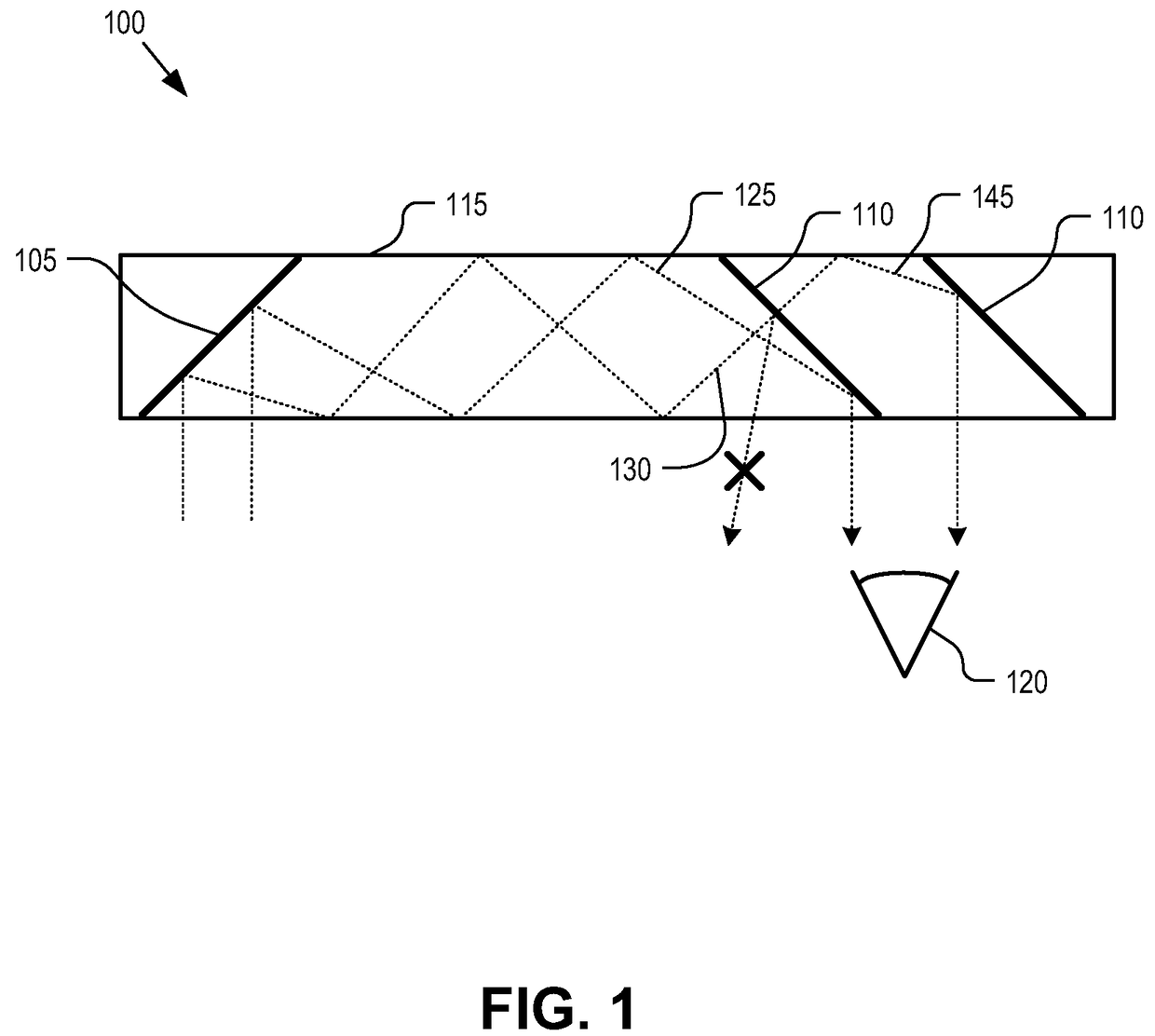
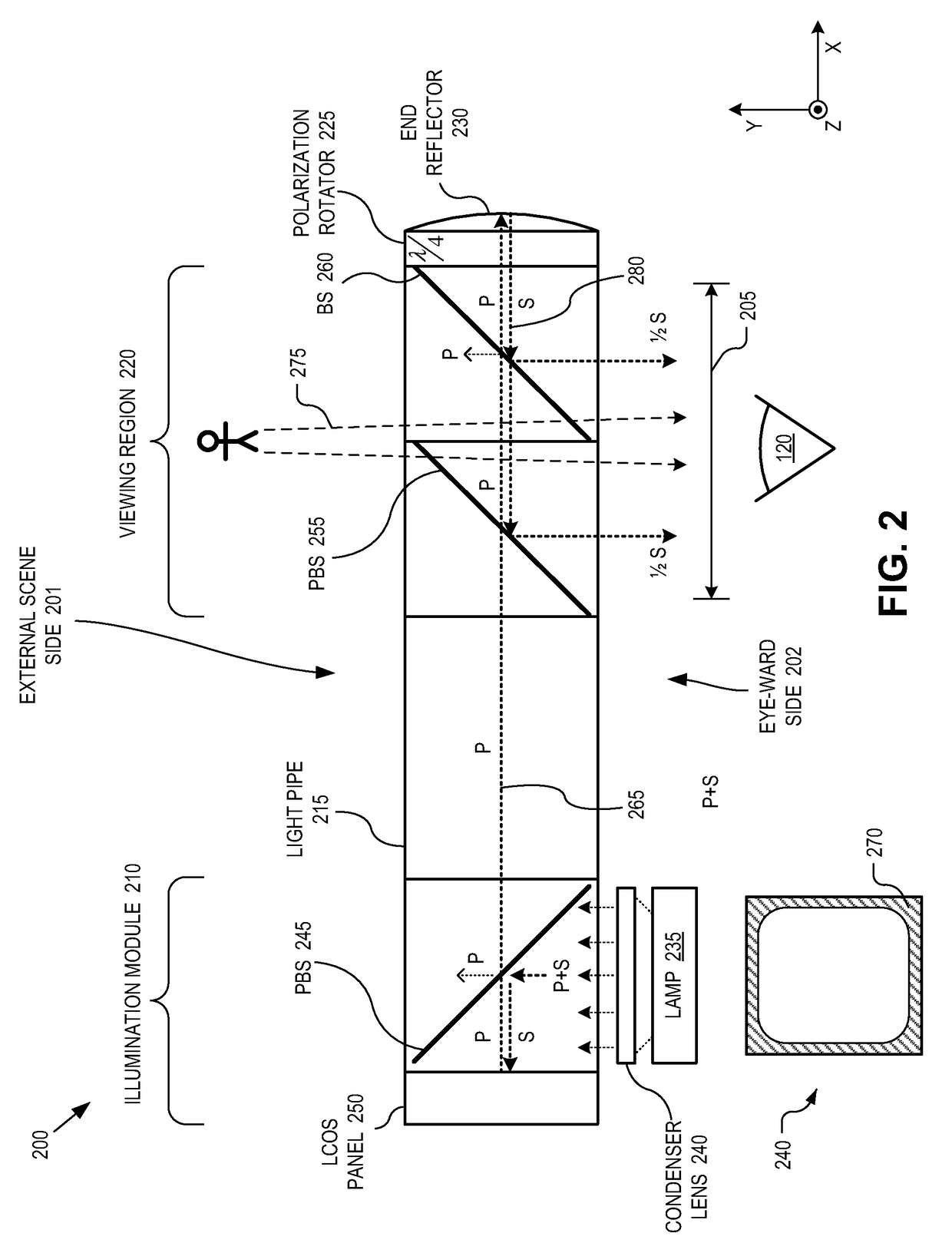
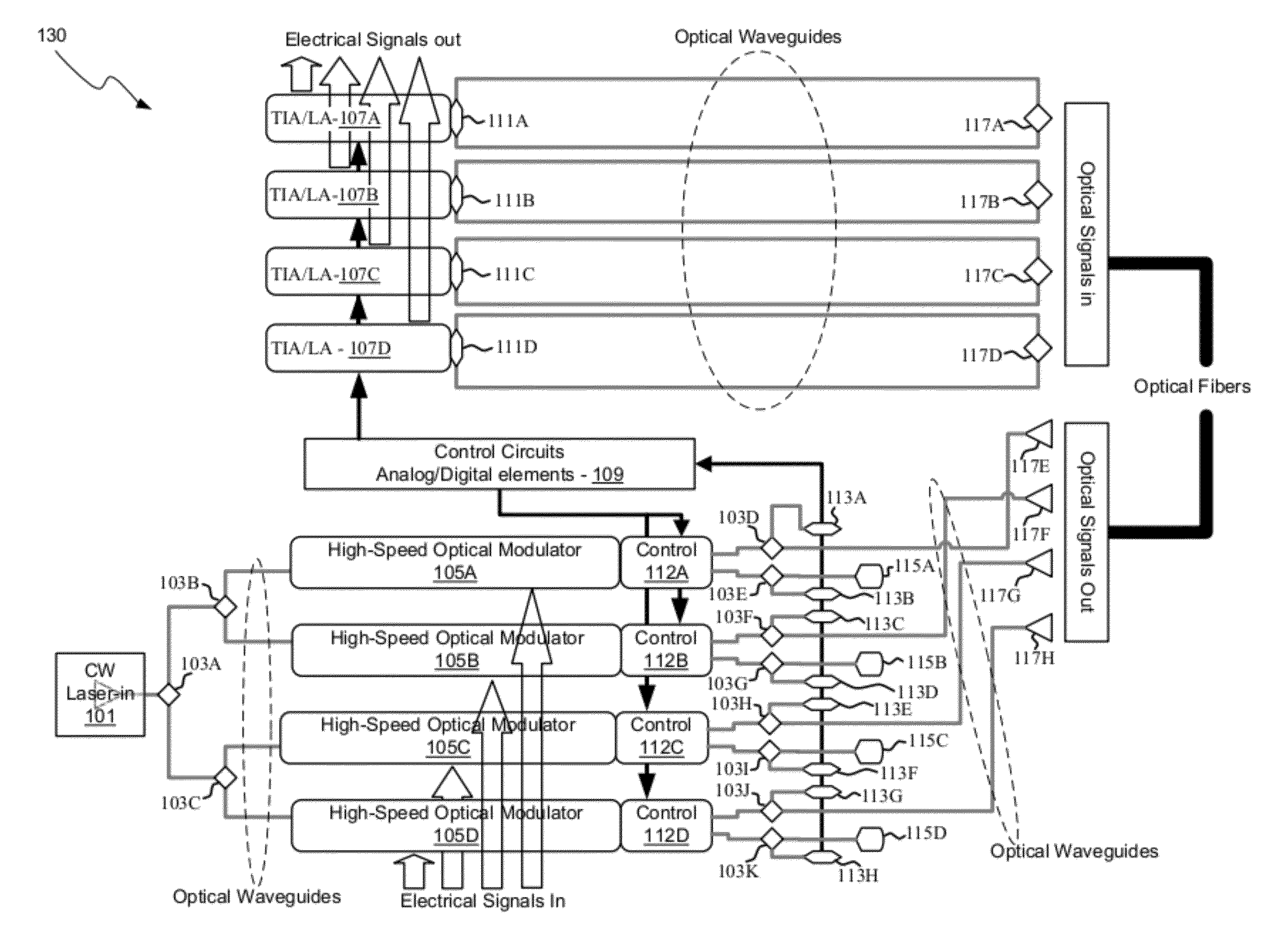
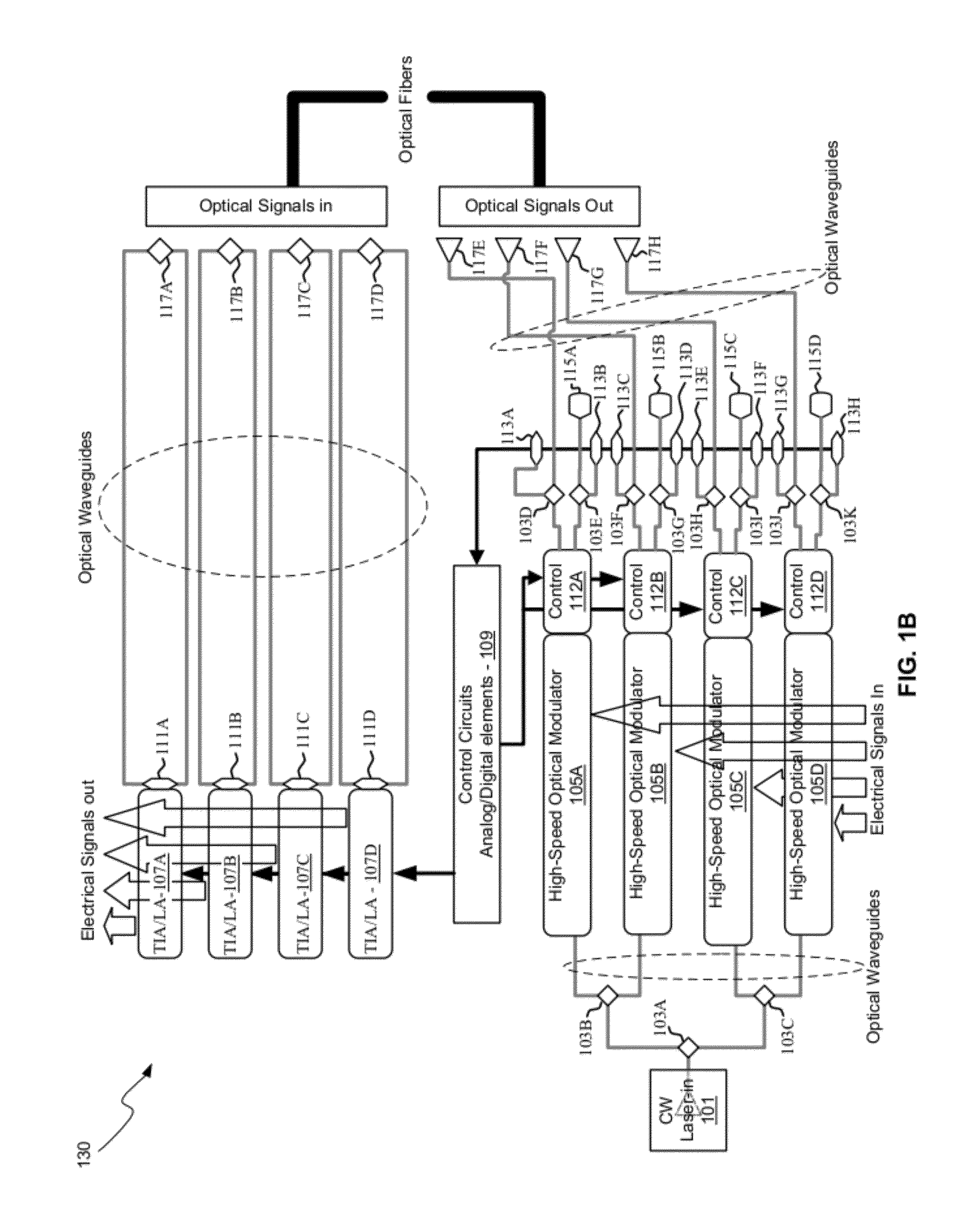
Eyepiece for near-to-eye display with multi-reflectors
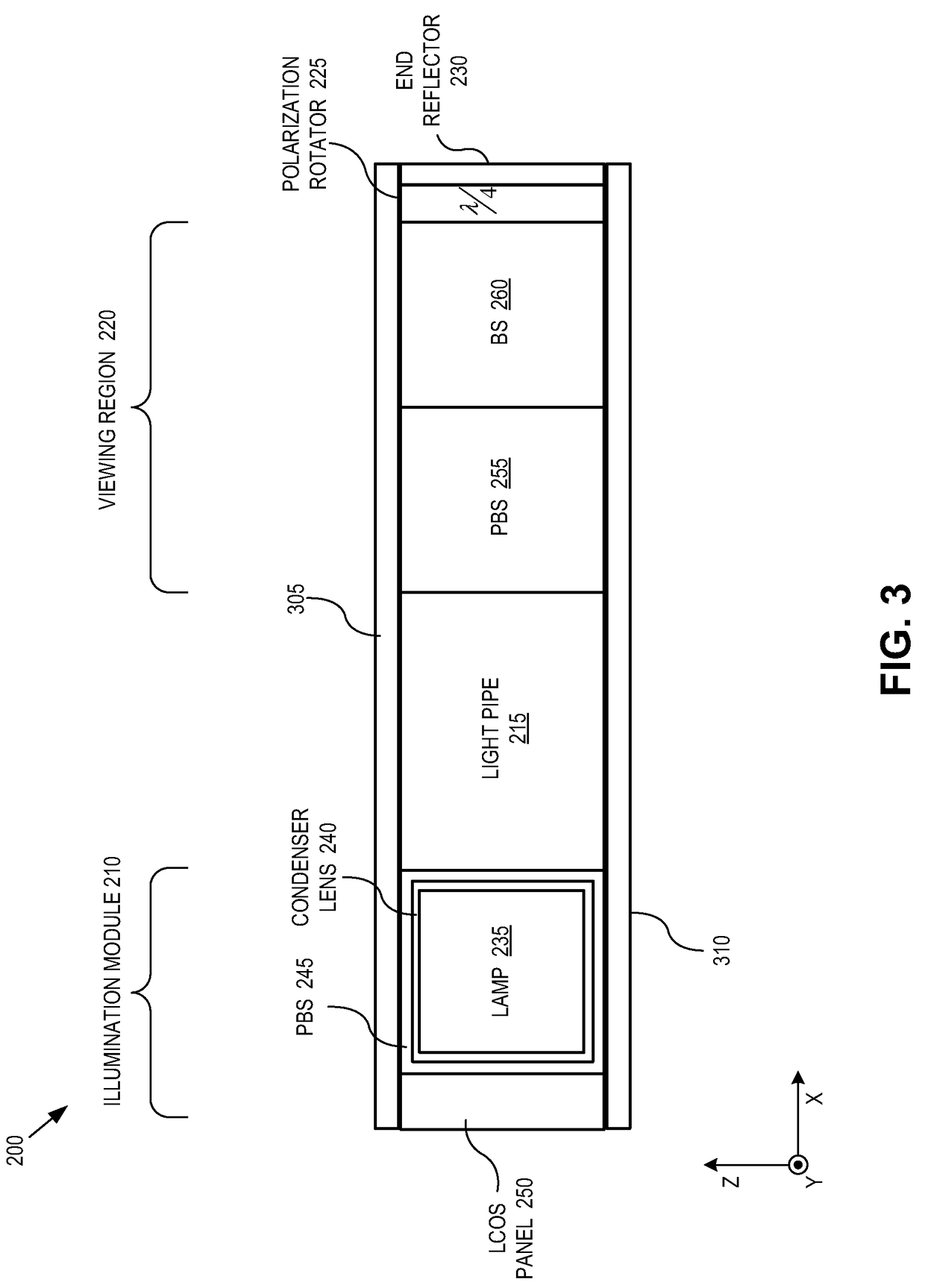
An eyepiece for a head mounted display includes an illumination module, an end reflector, a viewing region, and a polarization rotator. The illumination module includes an image source for launching computer generated image (“CGI”) light along a forward propagating path. The end reflector is disposed at an opposite end of the eyepiece from the illumination module to reflect the CGI back along a reverse propagation path. The viewing region is disposed between the illumination module and the end reflector. The viewing region includes a polarizing beam splitter (“PBS) and non-polarizing beam splitter (“non-PBS”) disposed between the PBS and the end reflector. The viewing region redirects the CGI light from the reverse propagation path out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece. The polarization rotator is disposed in the forward and reverse propagation paths of the CGI light between the viewing region and the end reflector.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Electronically dimmable optical device
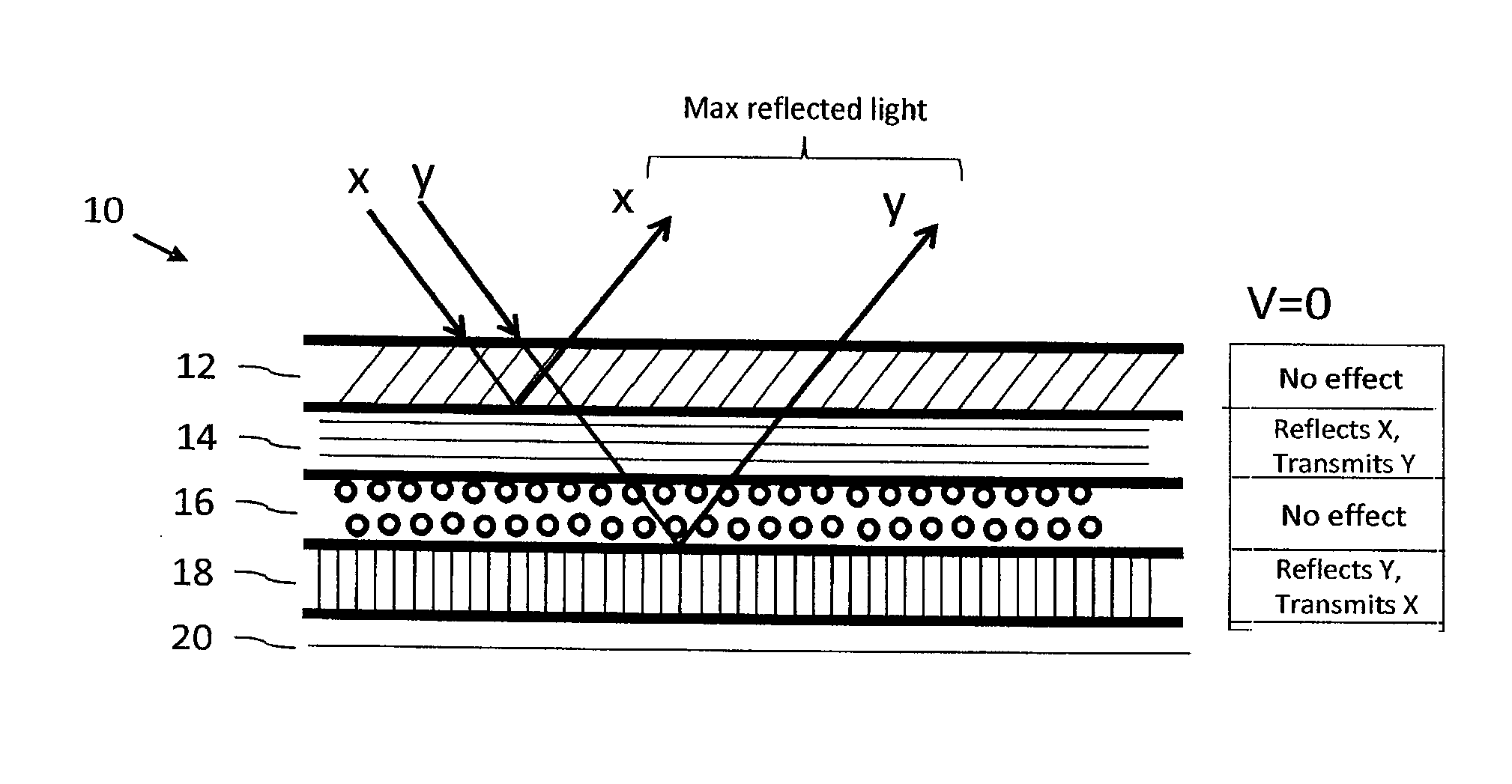
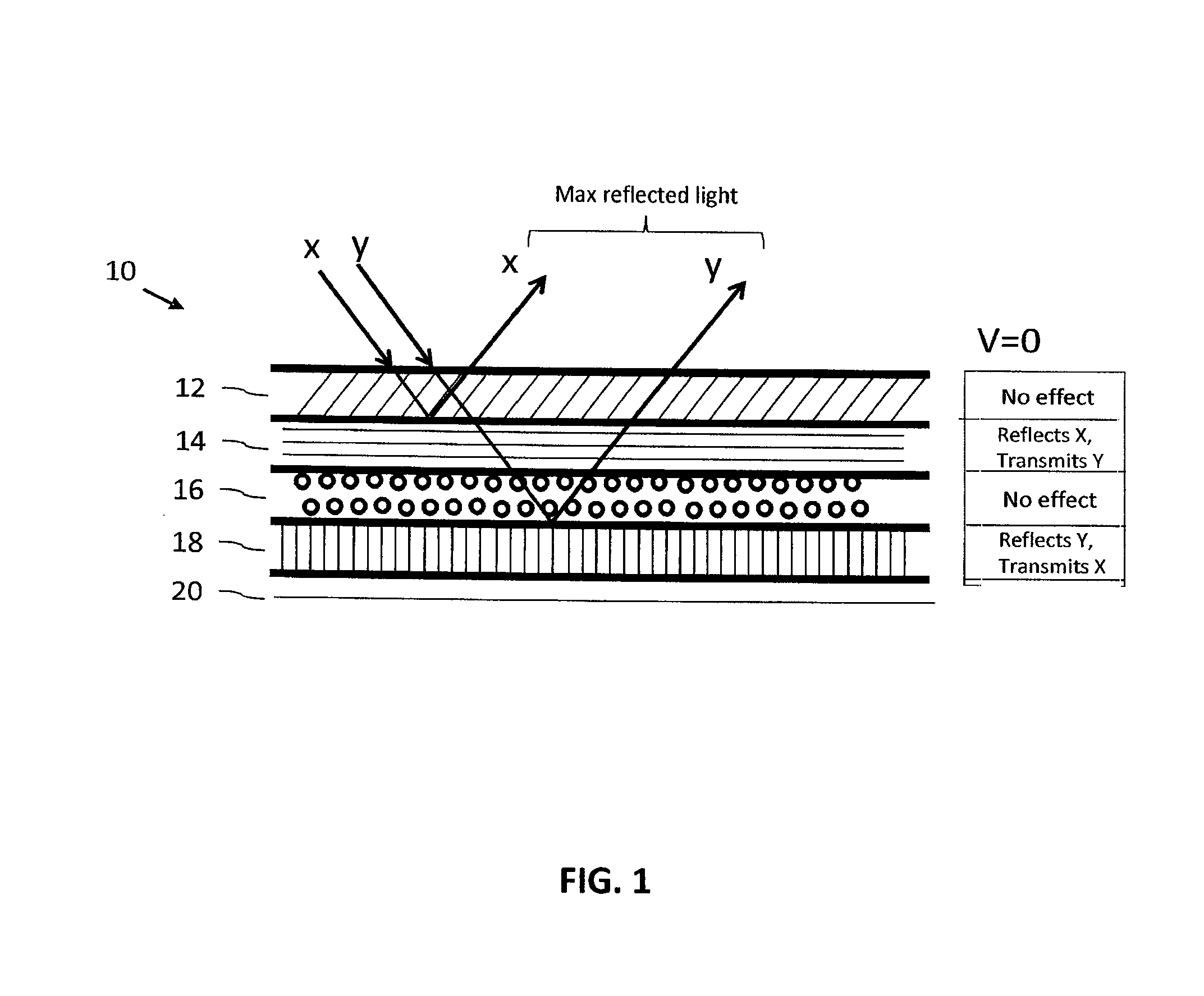
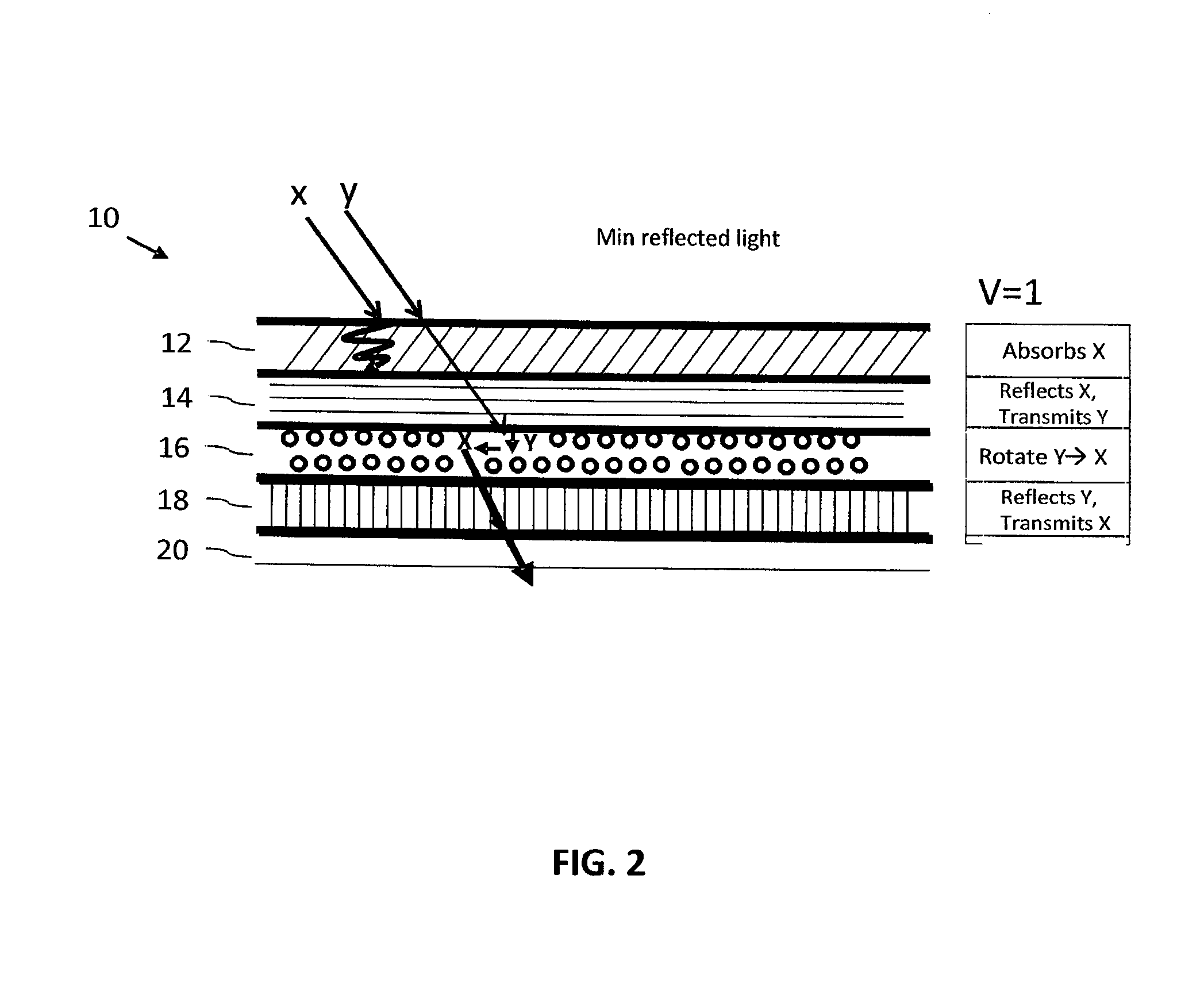
ActiveUS20140340728A1Varying levelReduce reflectivityPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsPolarizerOptoelectronics
An electronically dimmable optical device, including, in sequence, an active absorbing polarizer; a first static reflective polarizer; an active polarization rotator; and a second static reflective polarizer; configured so that the reflectivity and / or transmissivity of the device can be controlled (increased or decreased) by application of a voltage across the active absorbing polarizer and / or the active polarization rotator. One or more polarization levels can be selected by controlling the voltage at the active absorptive polarizer such that setting the active absorptive polarizer to a selected polarization level determines the brightness of an image produced by the device.
Owner:ALPHAMICRON INC
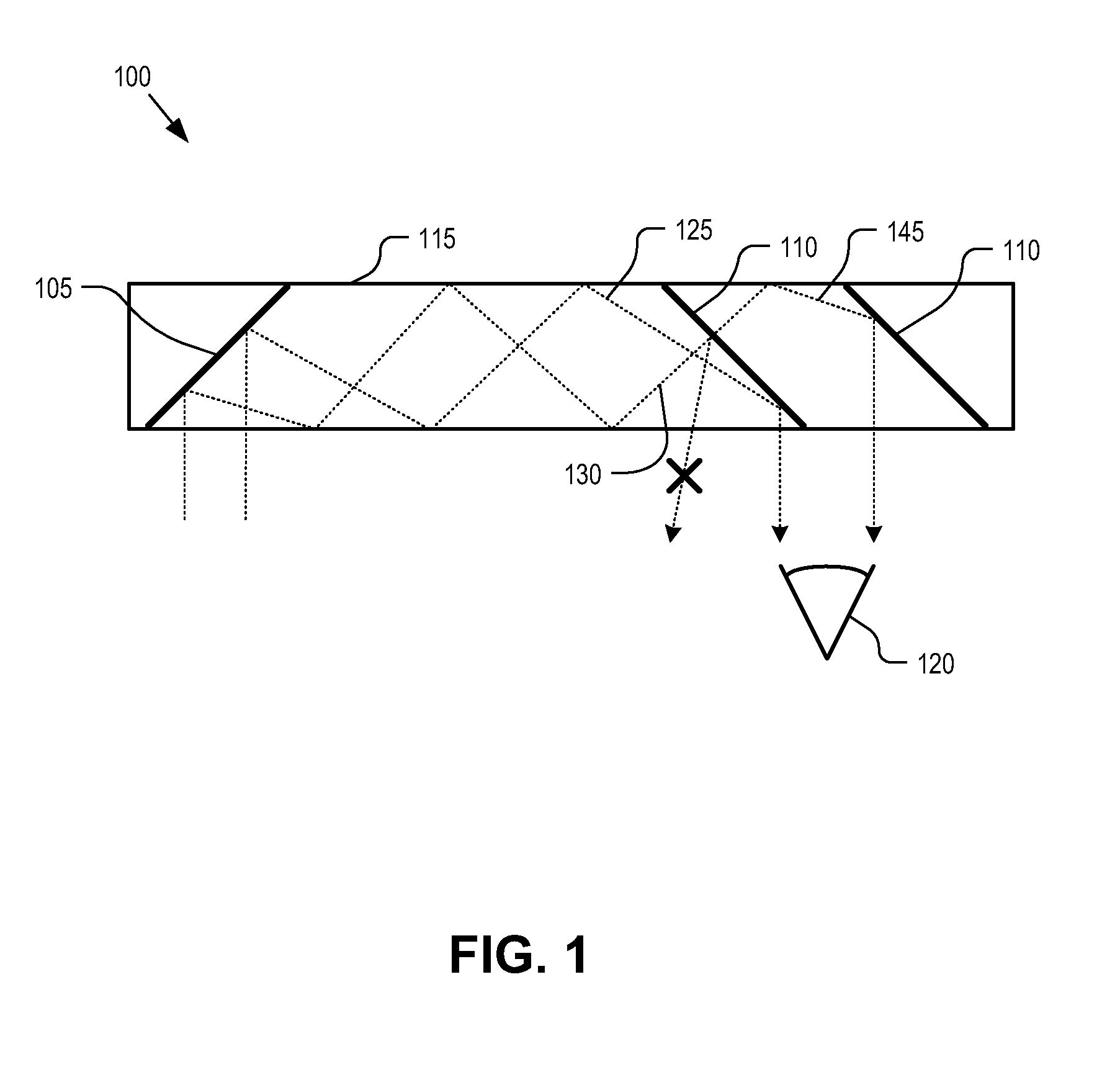
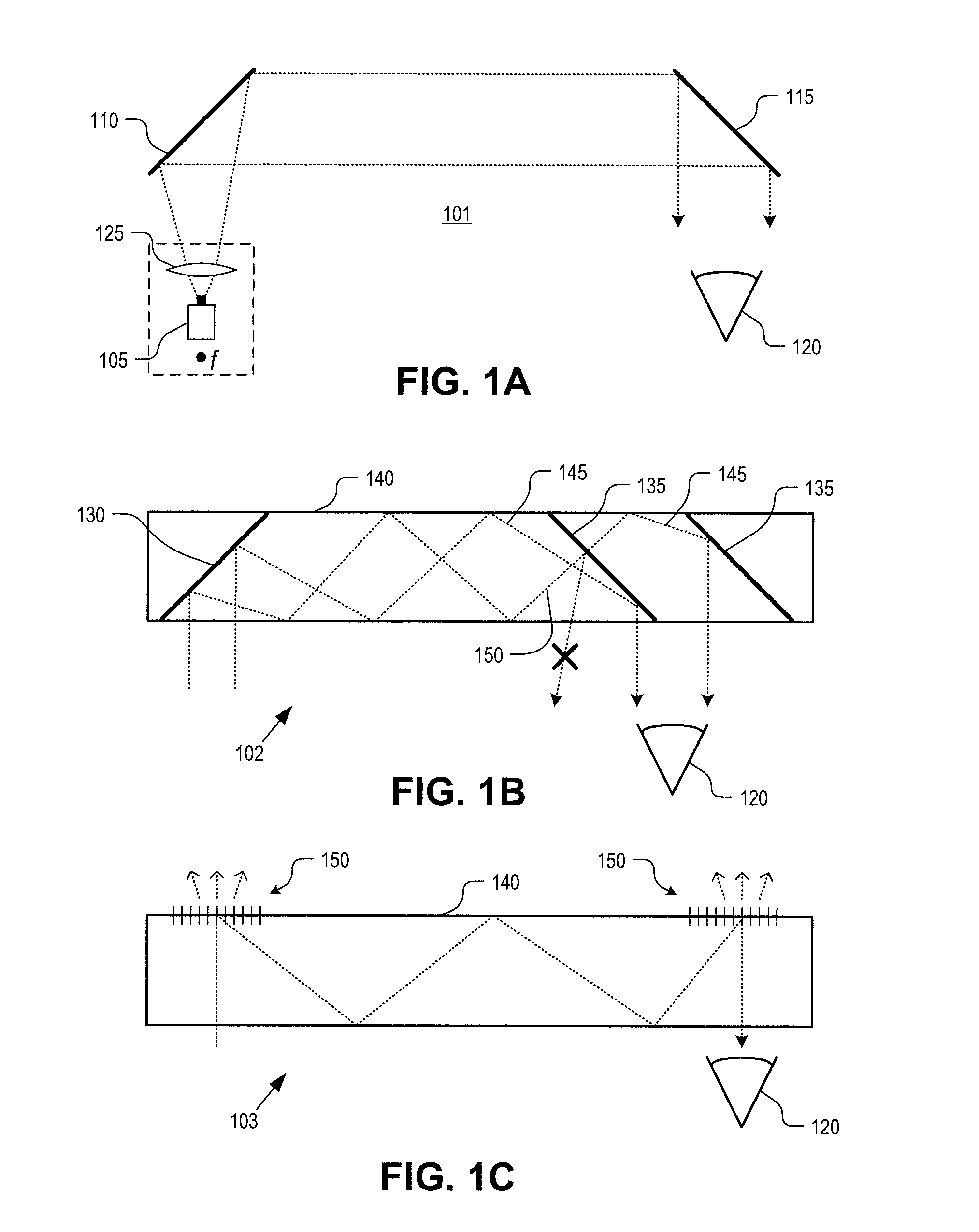
Method and apparatus for a near-to-eye display
InactiveUS20130033756A1Reduce disagreementDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsBeam splitterEyepiece
An eyepiece for a head mounted display includes an illumination module, an end reflector, a viewing region, and a polarization rotator. The illumination module provides CGI light along a forward propagation path within the eyepiece. The end reflector is disposed at an opposite end of the eyepiece from the illumination module to reflect the CGI light back along a reverse propagation path within the eyepiece. The viewing is disposed between the illumination module and the end reflector and includes an out-coupling polarizing beam splitter (“PBS”). The out-coupling PBS passes the CGI light traveling along the forward propagation path and redirects the CGI light traveling along the reverse propagation path out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece. The polarization rotator is disposed in the forward and reverse propagation paths between the out-coupling PBS and the end reflector.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and system for a light source assembly supporting direct coupling to an integrated circuit
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
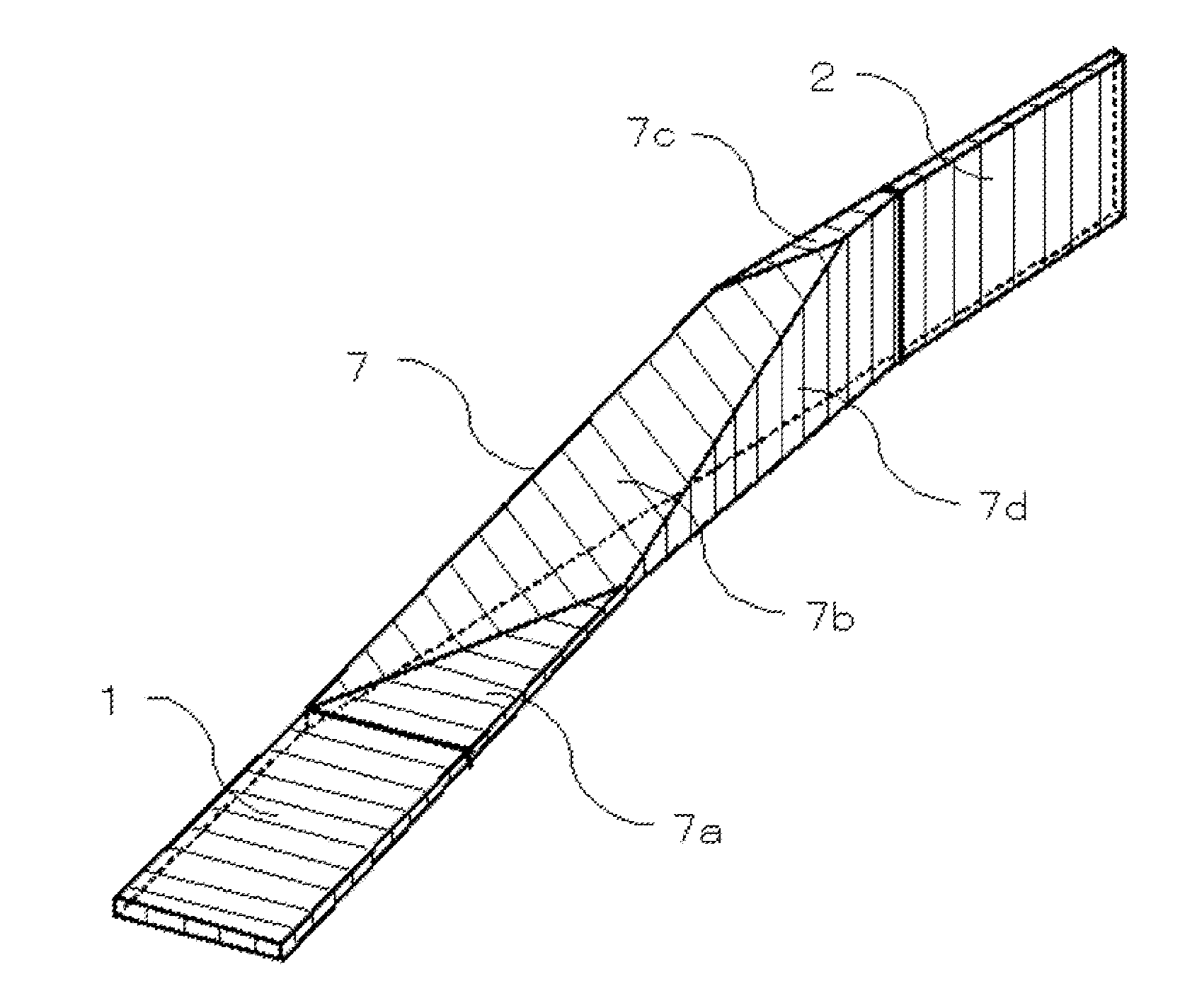
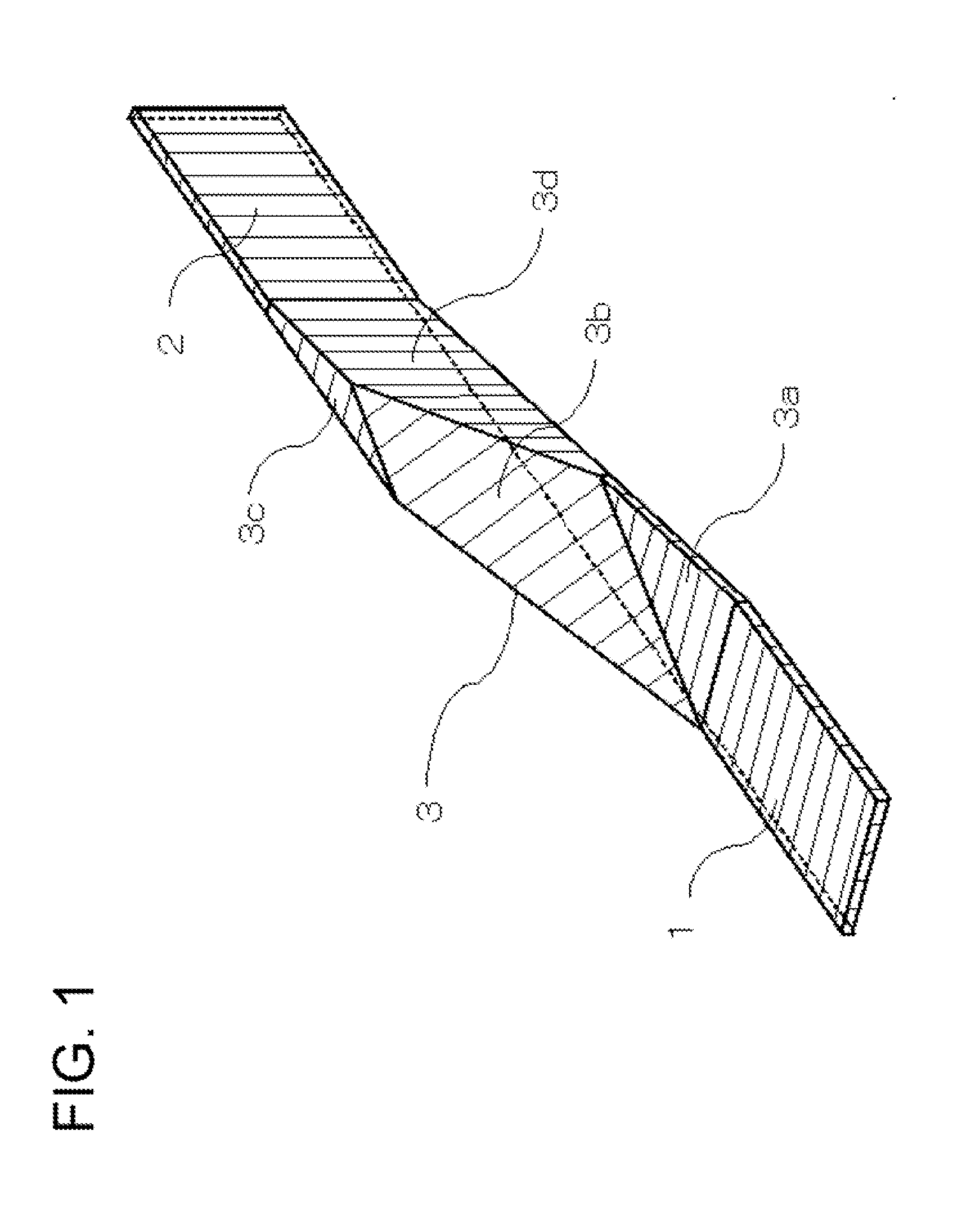
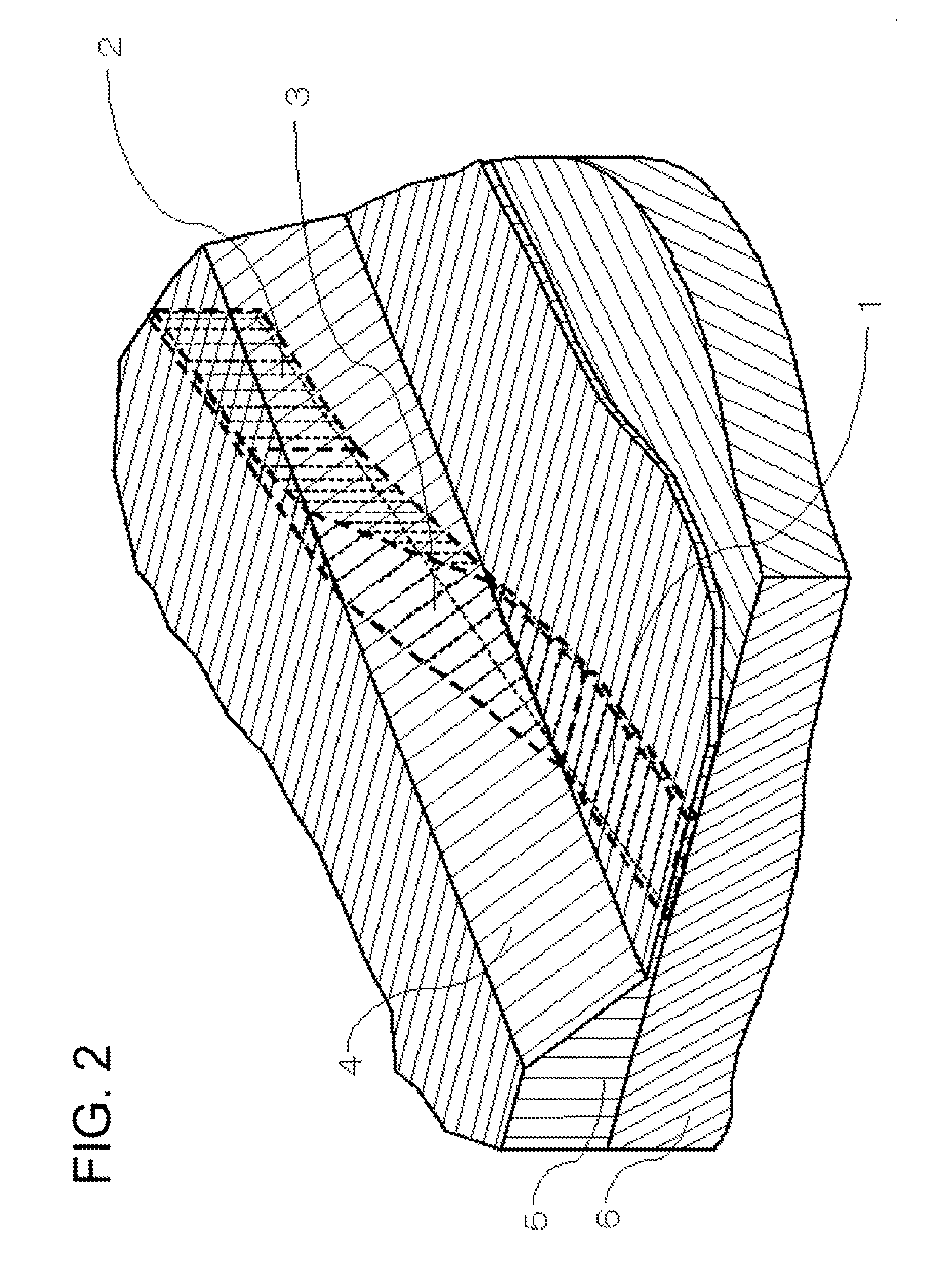
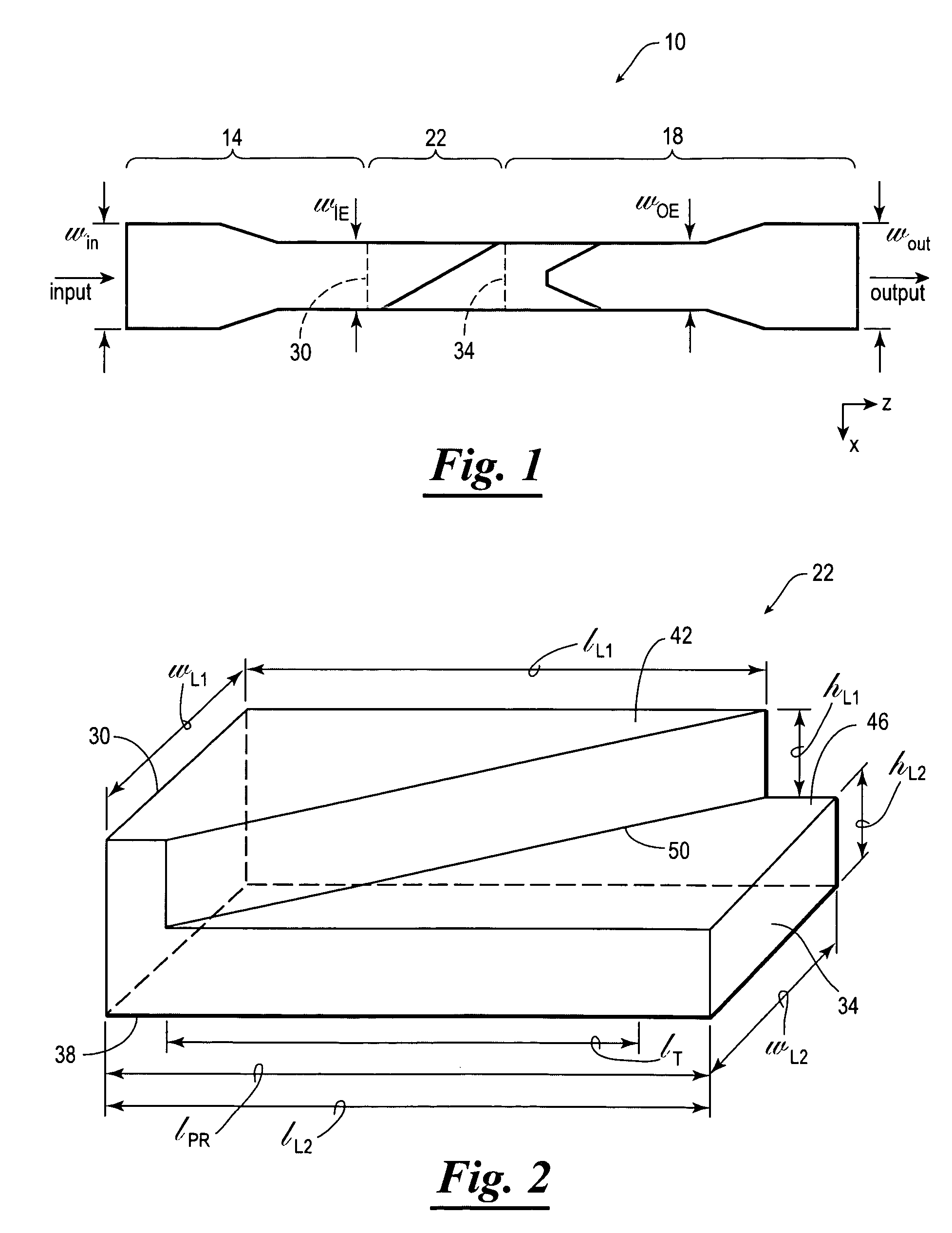
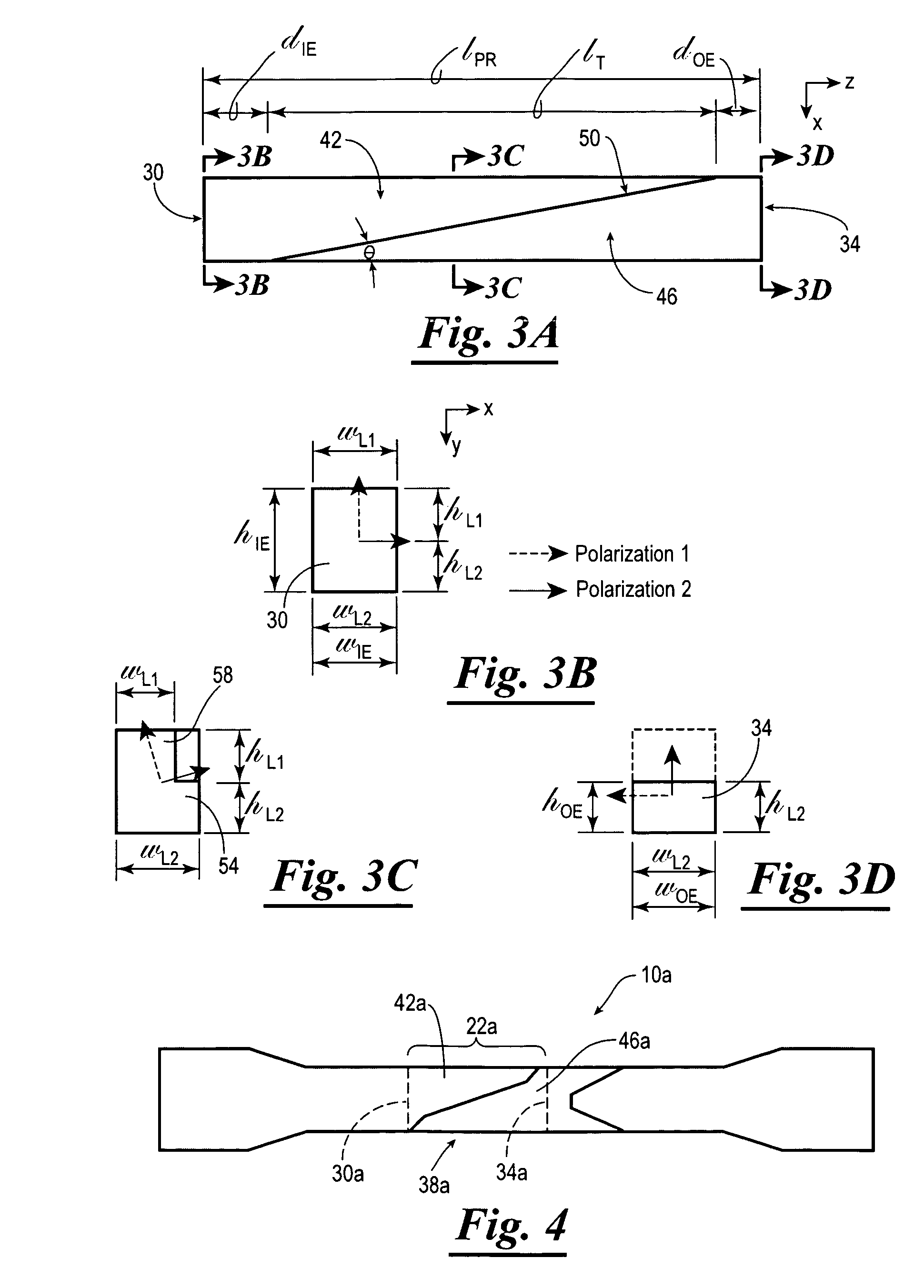
Polarization rotator and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100002989A1Eliminate trade-off relationshipHighly integratedCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideLarge aspect ratioWaveguide
An optical circuit comprises a first waveguide; a second waveguide; and a third waveguide that converts mode field and direction of polarization of light of said first waveguide at the same time to perform wave guiding to said second waveguide; wherein large aspect ratio directions of corresponding ends of a core of said first waveguide and a core of said second waveguide differ from each other.
Owner:NEC CORP
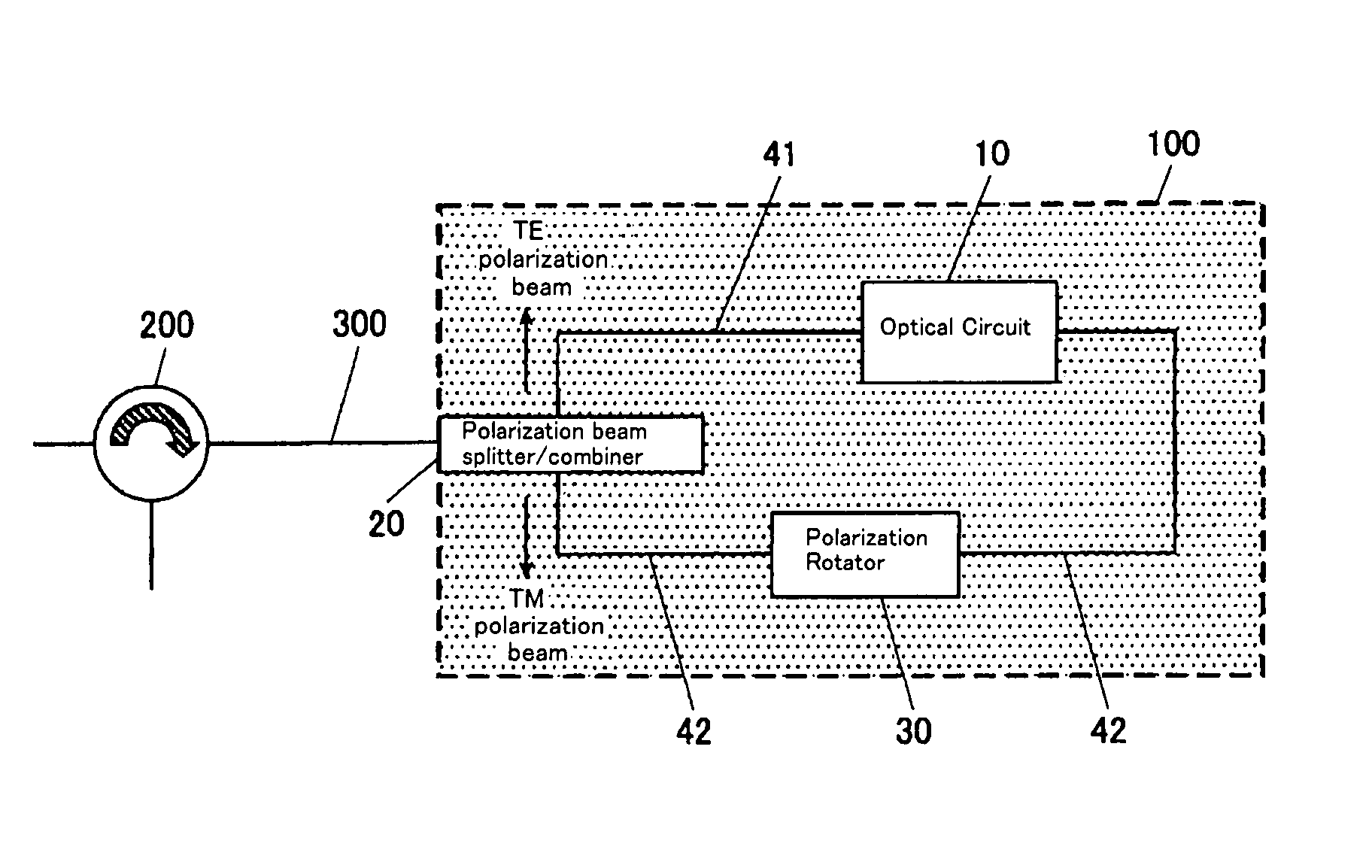
Optical Circuit Device
InactiveUS20080031566A1Reduce PDLExtinction ratio is not deterioratedOptical waveguide light guidePlanar substrateLight beam
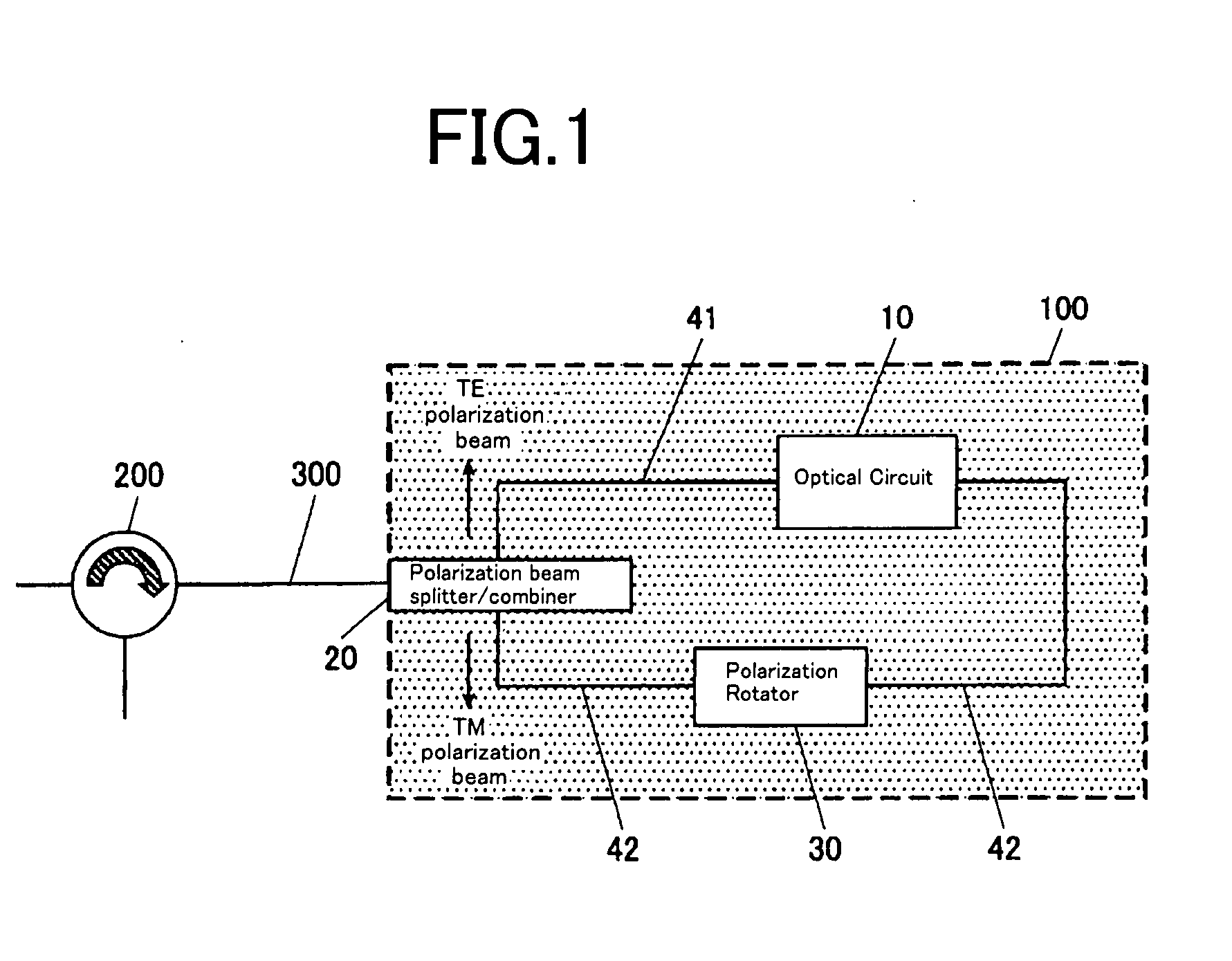
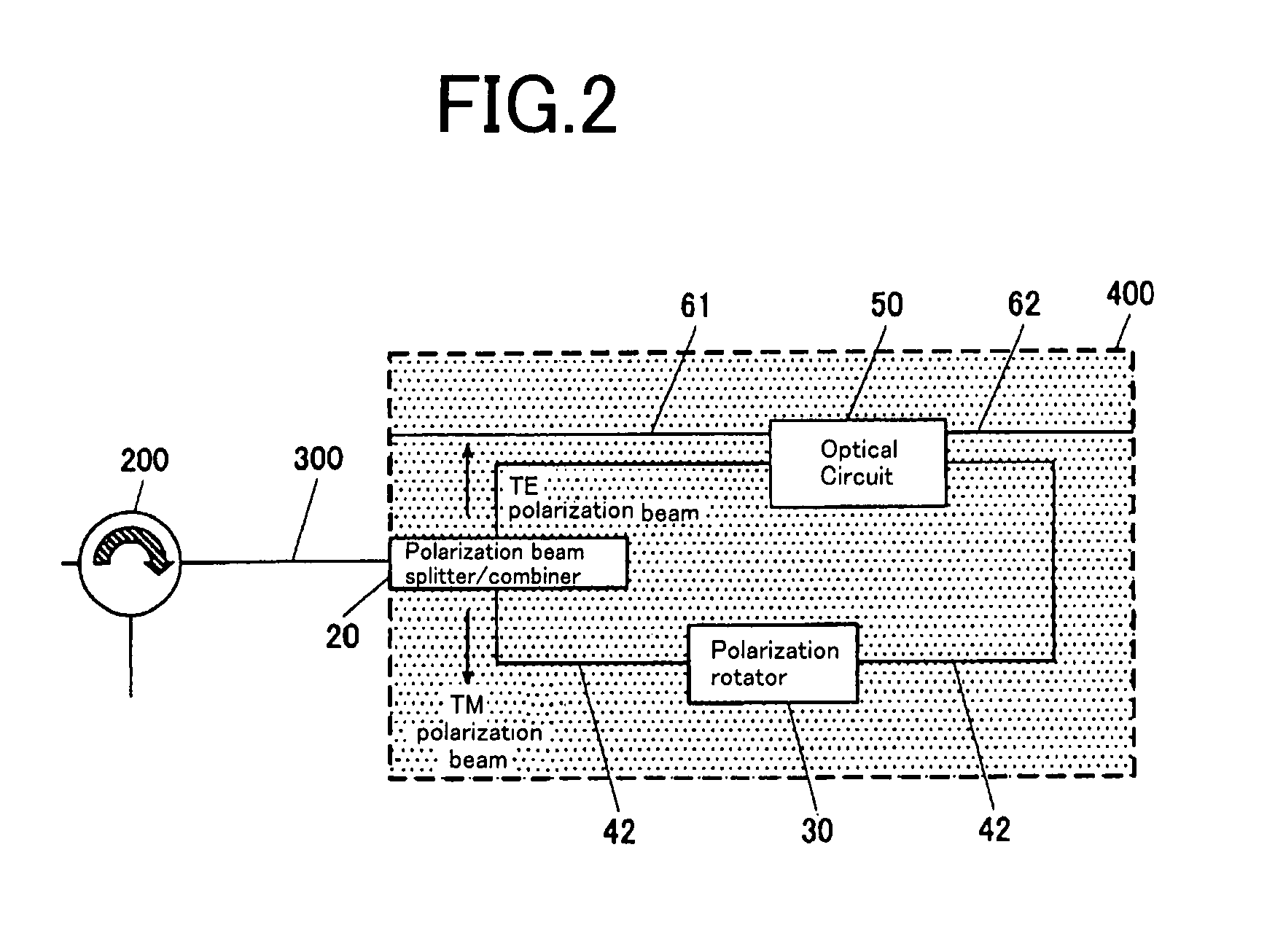
The present invention provide an optical circuit device having: an optical circuit; a polarization beam splitter / combiner for splitting an incoming light beam into two polarization beams and combining the two polarization beams into an outgoing light beam; a first optical waveguide and a second optical waveguide for connecting the optical circuit and the polarization beam splitter / combiner and receiving the two polarization beams independently; and a polarization rotator, arranged on the first optical waveguide, for rotating a polarization plane of one of the two polarization beams split by the polarization beam splitter / combiner so as to match a polarization plane of the other of the two polarization beams, the optical circuit, the polarization beam splitter / combiner, the first optical waveguide, the second optical waveguide and the polarization rotator being integrated on a planar substrate.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Fast switching camera aperture
A camera aperture includes a first polarizer and a second polarizer with a polarization 90° with respect to the first polarizer. The second polarizer has a through hole at a center. A polarizing rotator is disposed between the first polarizer and the second polarizer. A size of the aperture is changed when a voltage is applied selectively to the polarizing rotator.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
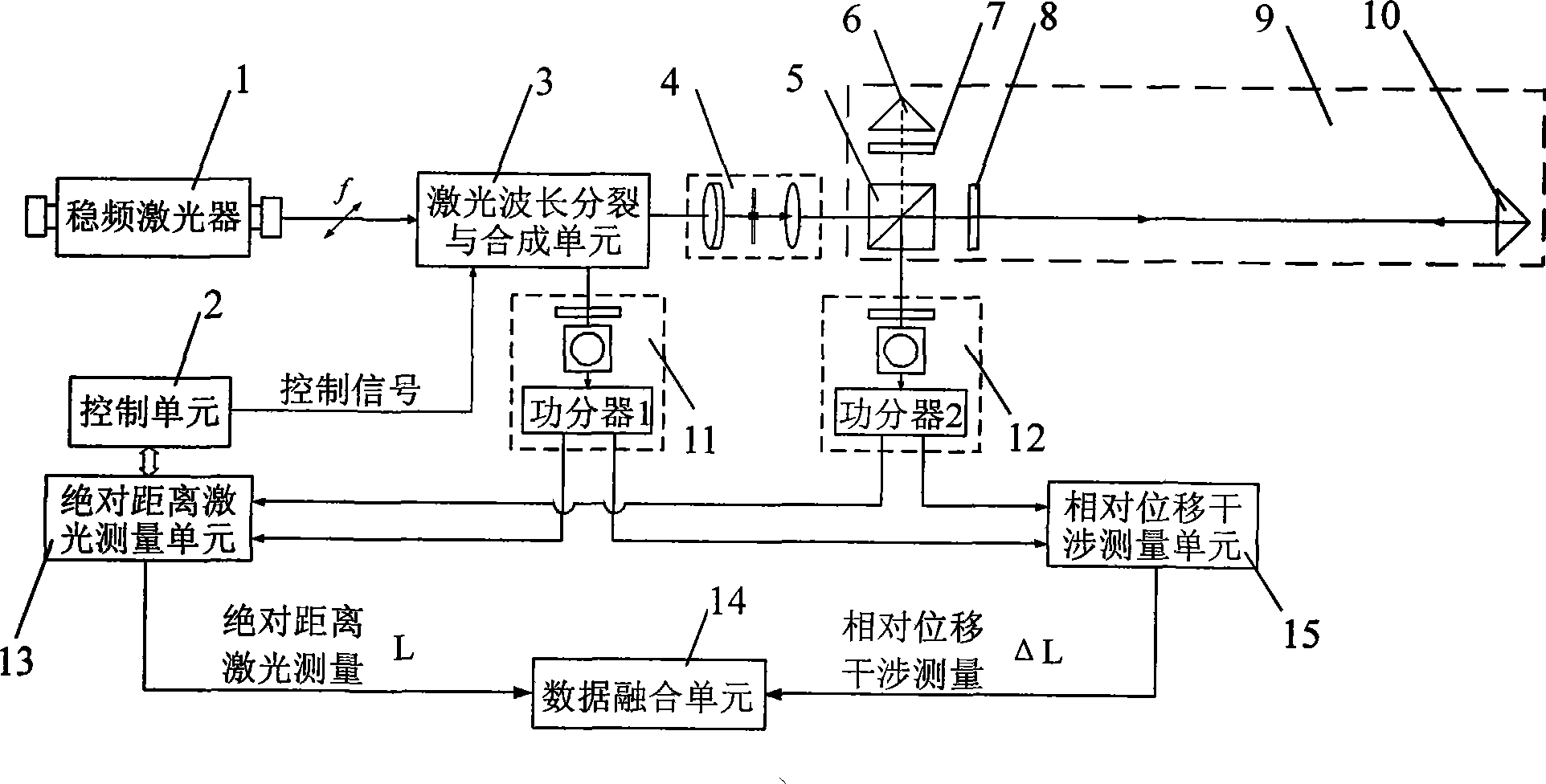
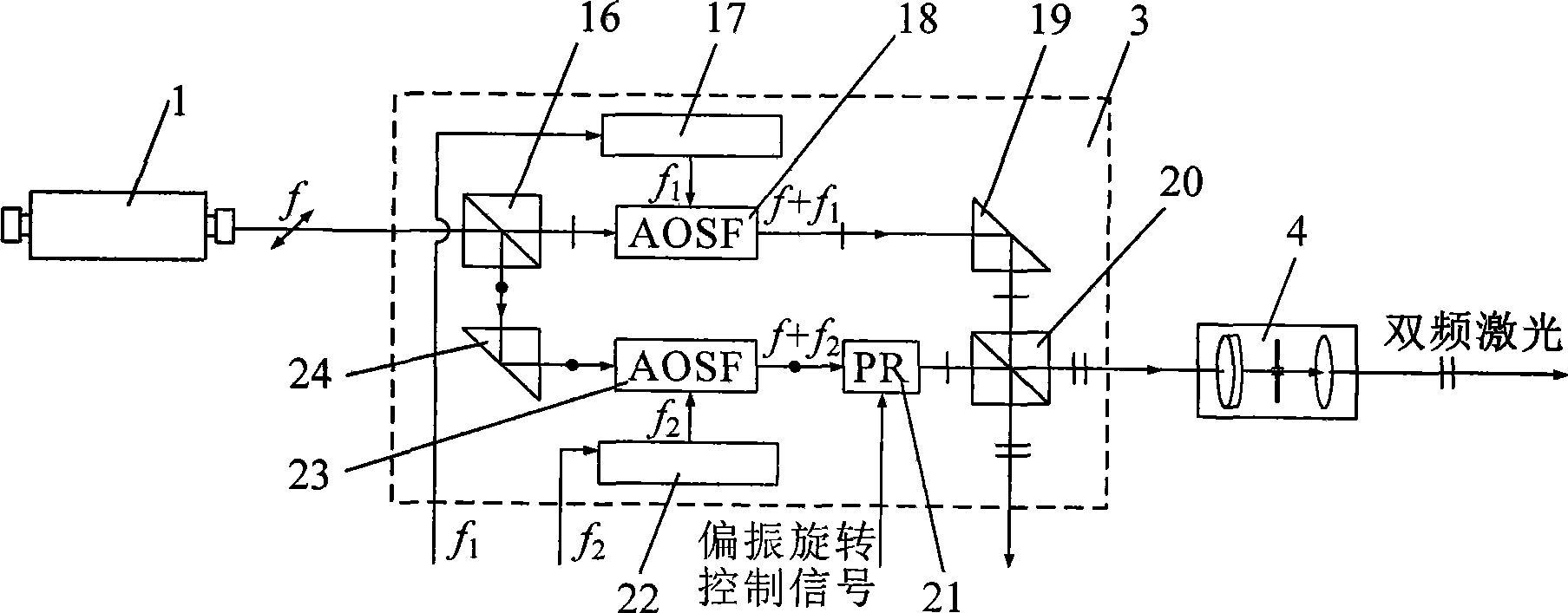
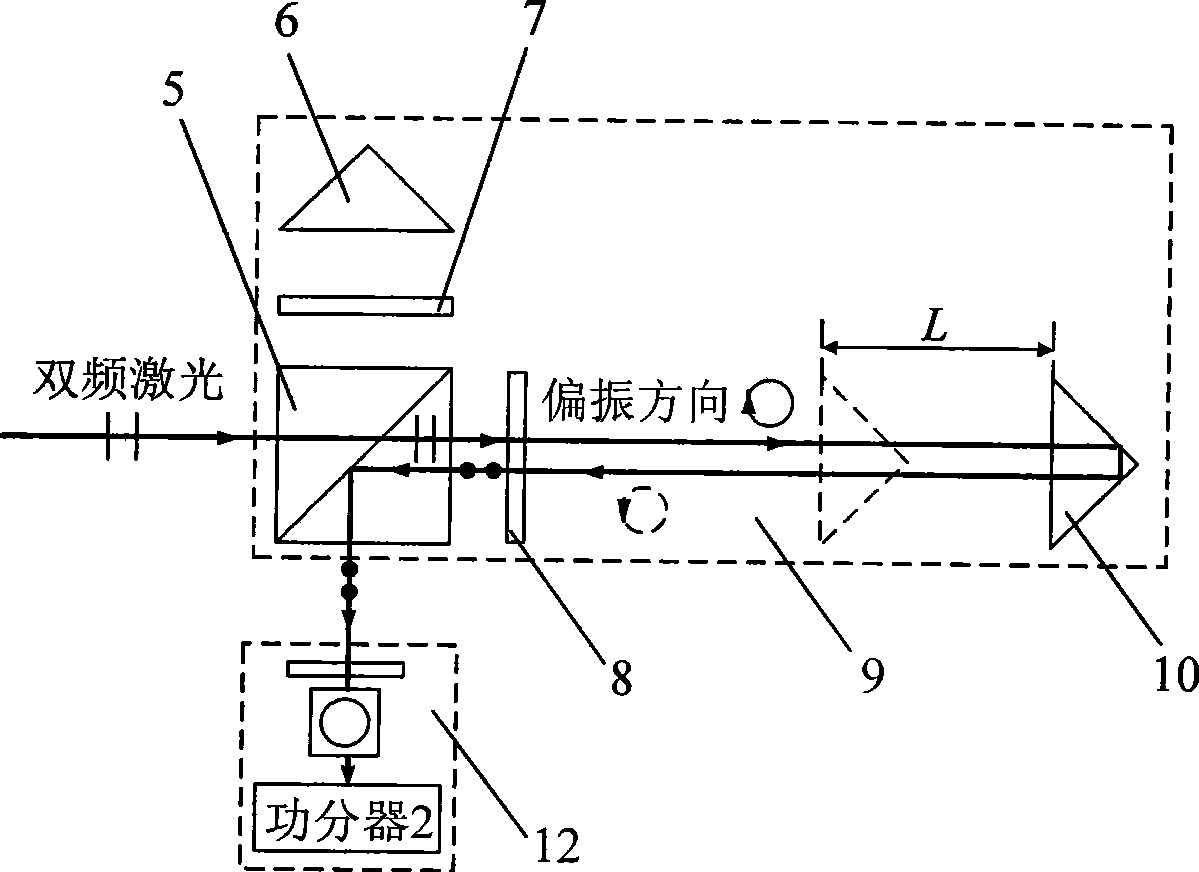
Dual-frequency laser ranging method and device based on polarization state regulation and wavelength synthesis
ActiveCN101533096AGood effectSimple structureElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingDual frequency
A dual-frequency laser ranging method and a device based on polarization state regulation and wavelength synthesis belong to the technical field of laser application. In absolute distance measurement and relative displacement measurement, the method adopts the same frequency stabilized laser as a measuring light source, realizes organic integration of absolute distance measurement and relative displacement dynamic measurement through the control of a polarization rotator and wavelength tuning of acoustooptic frequency shifters and simultaneously meets the requirements on extra long distance precise measurement and fast local displacement ultraprecise monitoring. The device comprises an acoustooptic frequency shifter A and an acoustooptic frequency shifter B, a reflecting mirror A and a reflecting mirror B, a frequency control unit A and a frequency control unit B, a polarization rotator, a polarization splitter B and a laser wavelength split and synthesis unit formed by partial optical splitters. The invention has the advantages of both extra long distance ultraprecise measurement capability and integral formation, etc.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Reducing aberration in optical systems comprising cubic crystalline optical elements
InactiveUS6844972B2Reduced polarization effectsLower latencyMaterial analysis by optical meansPolarising elementsCatadioptric systemDevice material
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more polarization rotators in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements. In one embodiment, all cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with identical three dimensional cubic crystalline lattice directions, a 90° polarization rotator divides the system into front and rear groups such that the net retardance of the front group is balanced by the net retardance of the rear group. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
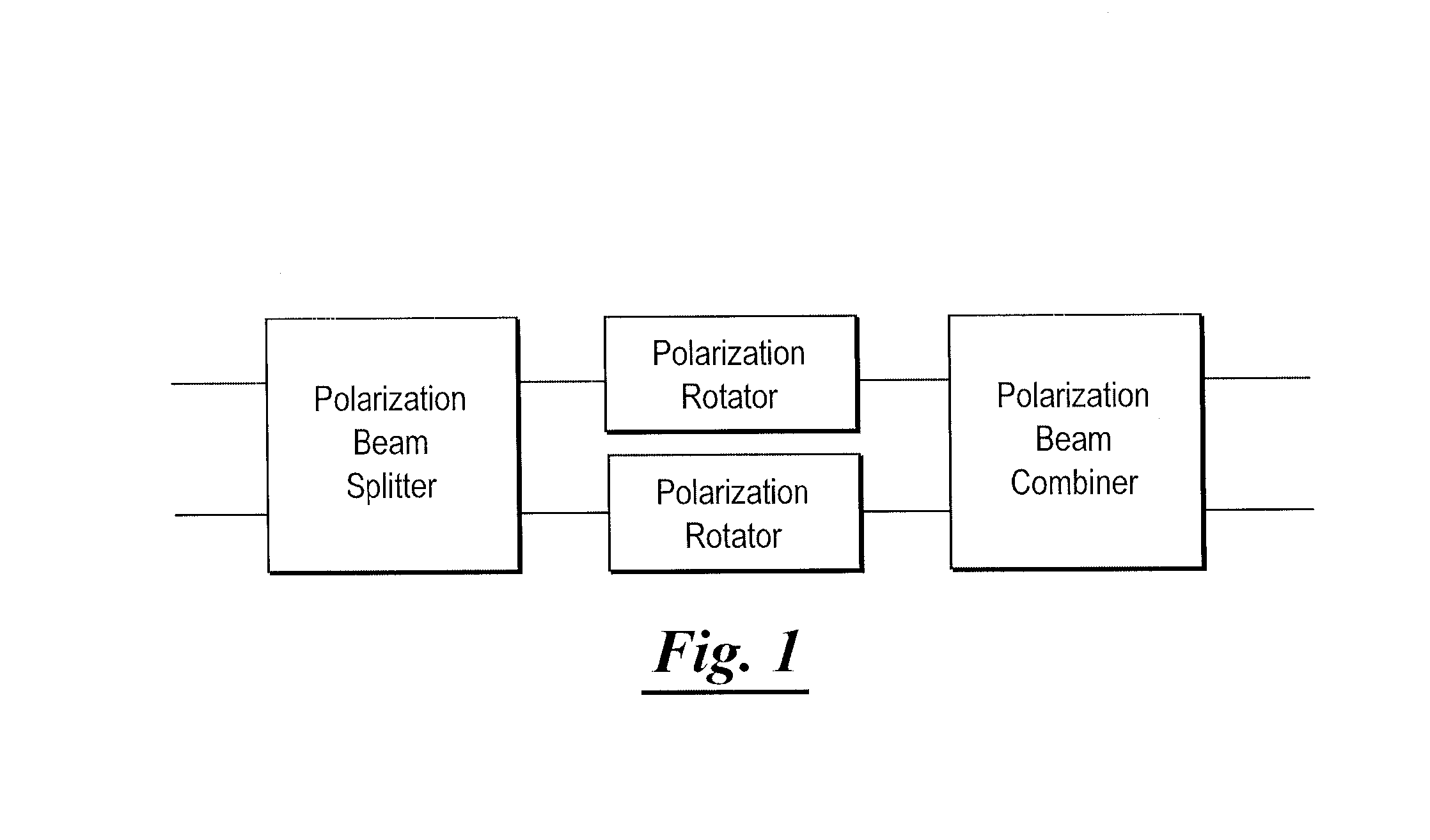
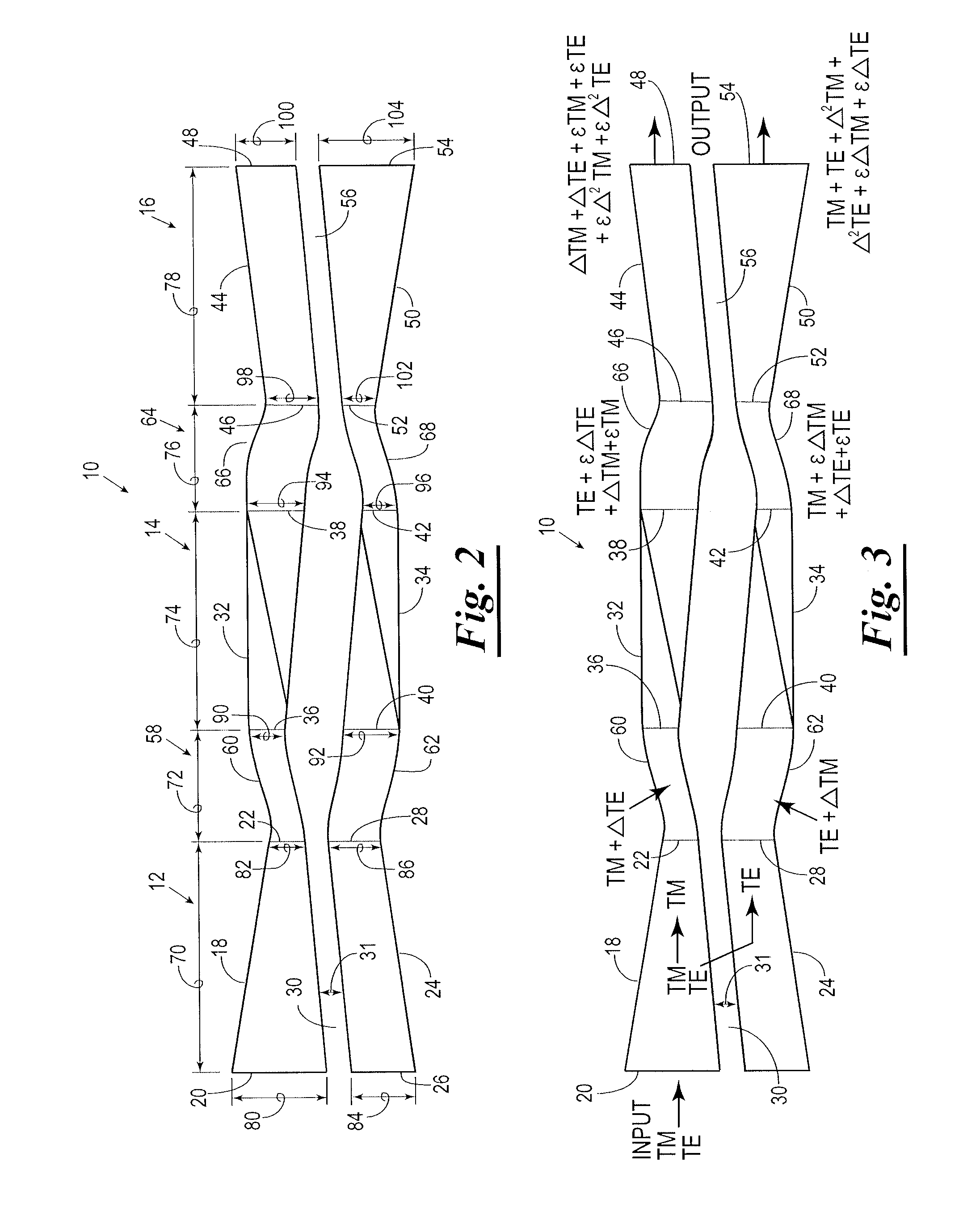
Polarization Beam Splitter-Polarization Rotator Structure
ActiveUS20080019637A1Easy to adaptCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsLight beamPolarization beam splitter
A polarization beam splitter-polarization rotator-polarization beam combiner optical structure comprising a pair of polarization rotators having a polarization beam splitter associated with the input ends of the two polarization rotators, and a polarization beam combiner associated with output ends of the two polarization rotators, and a method of purifying a light signal comprising TE and TM modes by disassociating the primary TE and TM modes from first order splitter and rotation error components.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
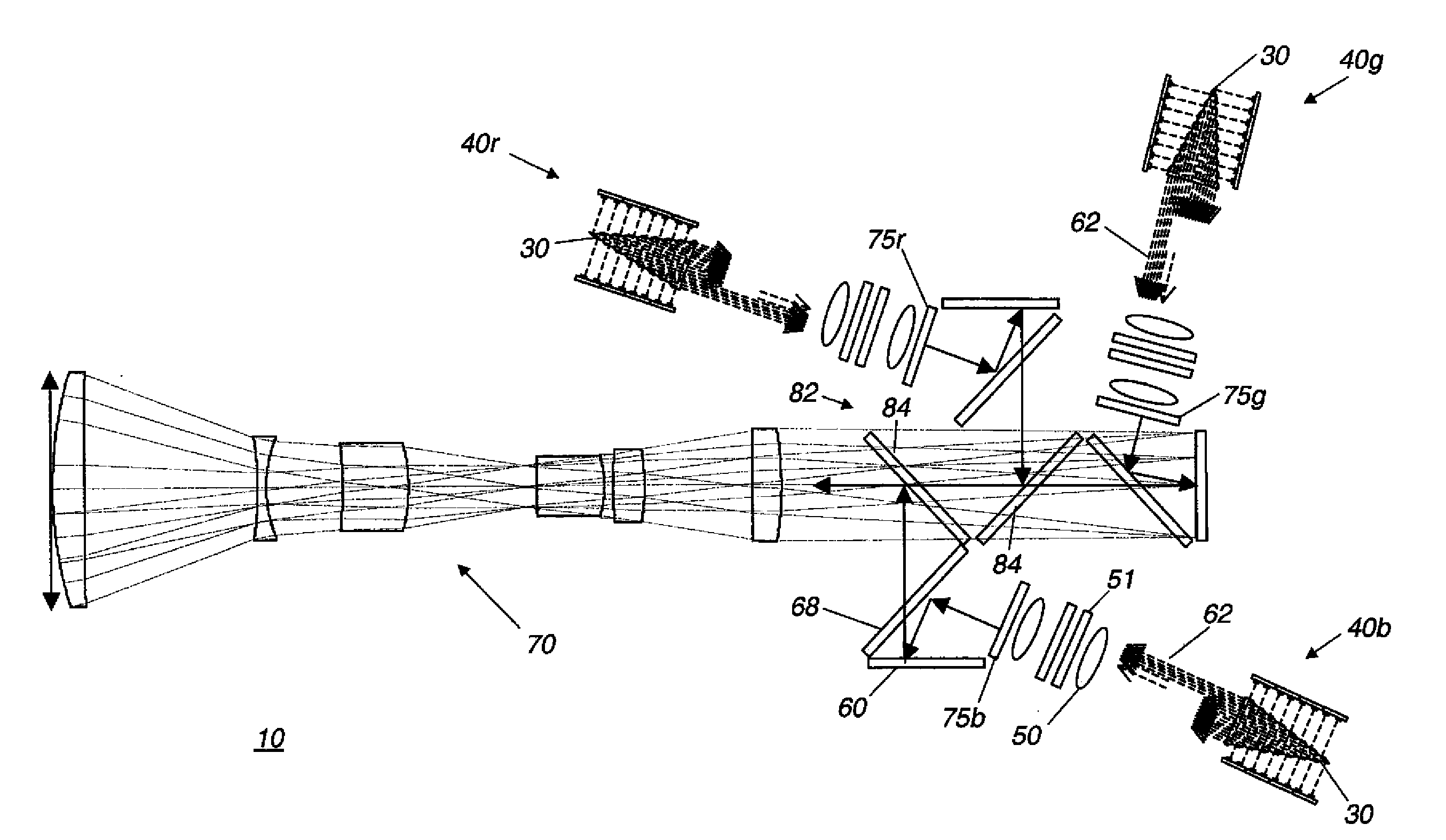
Stereo projection using polarized solid state light sources
InactiveUS7891816B2Improved etendue matchingProjectorsColor television detailsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
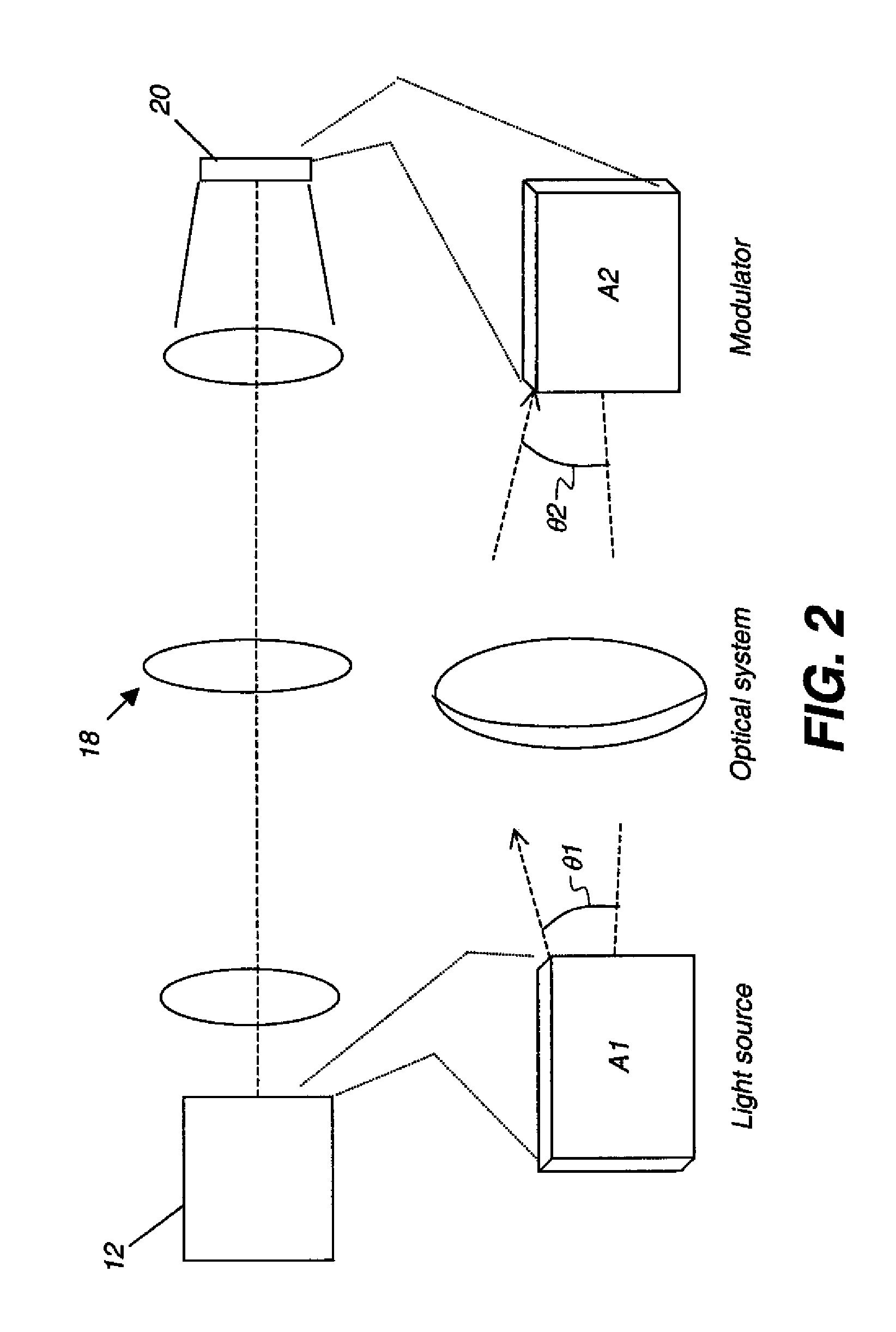
A stereoscopic digital image projector includes (a) a plurality of light modulation assemblies, each comprising: (i) at least one solid-state light source energizable to provide illumination having a first polarization axis; (ii) a polarization rotator disposed in the path of the polarized illumination from the solid-state light source(s) and actuable to controllably rotate the polarization axis from the solid-state light source(s) to a second polarized axis; (iii) a micro-electromechanical spatial light modulator in the path of the polarized illumination and energizable to modulate the polarized illumination to form a first modulated light from illumination of the first polarization state and to form a second modulated light from illumination of the second polarization state; and (b) a synchronizing means to temporally control the polarization rotation to match the appropriate image data on the spatial light modulator; and (c) projection optics for directing the first and second modulated light toward a display surface.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
Polarization rotator based on asymmetric vertical slot waveguide
InactiveCN103336330ABreak symmetryEliminates the problem of precise alignmentOptical light guidesSlot-waveguideNon symmetric
The invention discloses a polarization rotator based on an asymmetric vertical slot waveguide, which comprises an incident end waveguide used for leading in external incident light, a mode conversion waveguide used for converting TE / TM (Transverse Electric / Transverse Magnetic) mode incident light into TM / TE (Transverse Magnetic / Transverse Electric) mode emergent light, and an emergent end waveguide used for leading out a TM / TE mode, wherein the incident end waveguide, the mode conversion waveguide and the emergent end waveguide are asymmetric slot waveguides. With the adoption of the structure, the symmetry of a material is broken longitudinally, and the symmetry of a geometrical dimension is broken transversely, so that intrinsic modes of specific waveguides are mixed modes; the two intrinsic mixed modes can be converted mutually; and mutual conversion between a TE mode and a TM mode can be achieved finally. The polarization rotator can convert a TE / TM mode into the TM / TE mode by once etching, so that the manufacturing difficulty of a device is reduced greatly.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stereo projection using polarized solid state light sources
InactiveUS20090213330A1Improved etendue matchingProjectorsSteroscopic systemsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A stereoscopic digital image projector includes (a) a plurality of light modulation assemblies, each comprising: (i) at least one solid-state light source energizable to provide illumination having a first polarization axis; (ii) a polarization rotator disposed in the path of the polarized illumination from the solid-state light source(s) and actuable to controllably rotate the polarization axis from the solid-state light source(s) to a second polarized axis; (iii) a micro-electromechanical spatial light modulator in the path of the polarized illumination and energizable to modulate the polarized illumination to form a first modulated light from illumination of the first polarization state and to form a second modulated light from illumination of the second polarization state; and (b) a synchronizing means to temporally control the polarization rotation to match the appropriate image data on the spatial light modulator; and (c) projection optics for directing the first and second modulated light toward a display surface.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
Underwater video camera system based on polarization identification and method thereof
InactiveCN102116997AIncrease contrastImprove clarityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPolarizerOptical polarization
The invention relates to the technical field of optical instruments, in particular to an underwater video camera system based on polarization identification and a method thereof. The technical scheme is that the underwater video camera system comprises an underwater light source, a polarization modulation part and an image acquisition and processing part, wherein the underwater light source comprises a semiconductor laser, an optical filter, a polarizer, a polarization rotator and a beam expander; the polarization modulation part comprises an analyzer, a stepper motor, a stepper motor controller and an infrared detector; and the image acquisition and processing part comprises a high-frequency CCD (Charge Coupled Device) video camera, an image acquisition system and a computer. The underwater video camera system has the benefits that with the adoption of the underwater camera system and the method, the contrast degree and the definition of target imaging as well as the target detectionand the identification efficiency can be effectively improved; the polarization imaging can utilize the differences of different target back polarizations to eliminate the interference of background light; and as a means for identifying the target from messy background is provided, the method has remarkable advantage as compared with the commoner method for imaging and identifying the target by using light intensity.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Eyepiece for near-to-eye display with multi-reflectors
An eyepiece for a head mounted display includes an illumination module, an end reflector, a viewing region, and a polarization rotator. The illumination module includes an image source for launching computer generated image (“CGI”) light along a forward propagating path. The end reflector is disposed at an opposite end of the eyepiece from the illumination module to reflect the CGI back along a reverse propagation path. The viewing region is disposed between the illumination module and the end reflector. The viewing region includes a polarizing beam splitter (“PBS) and non-polarizing beam splitter (“non-PBS”) disposed between the PBS and the end reflector. The viewing region redirects the CGI light from the reverse propagation path out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece. The polarization rotator is disposed in the forward and reverse propagation paths of the CGI light between the viewing region and the end reflector.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
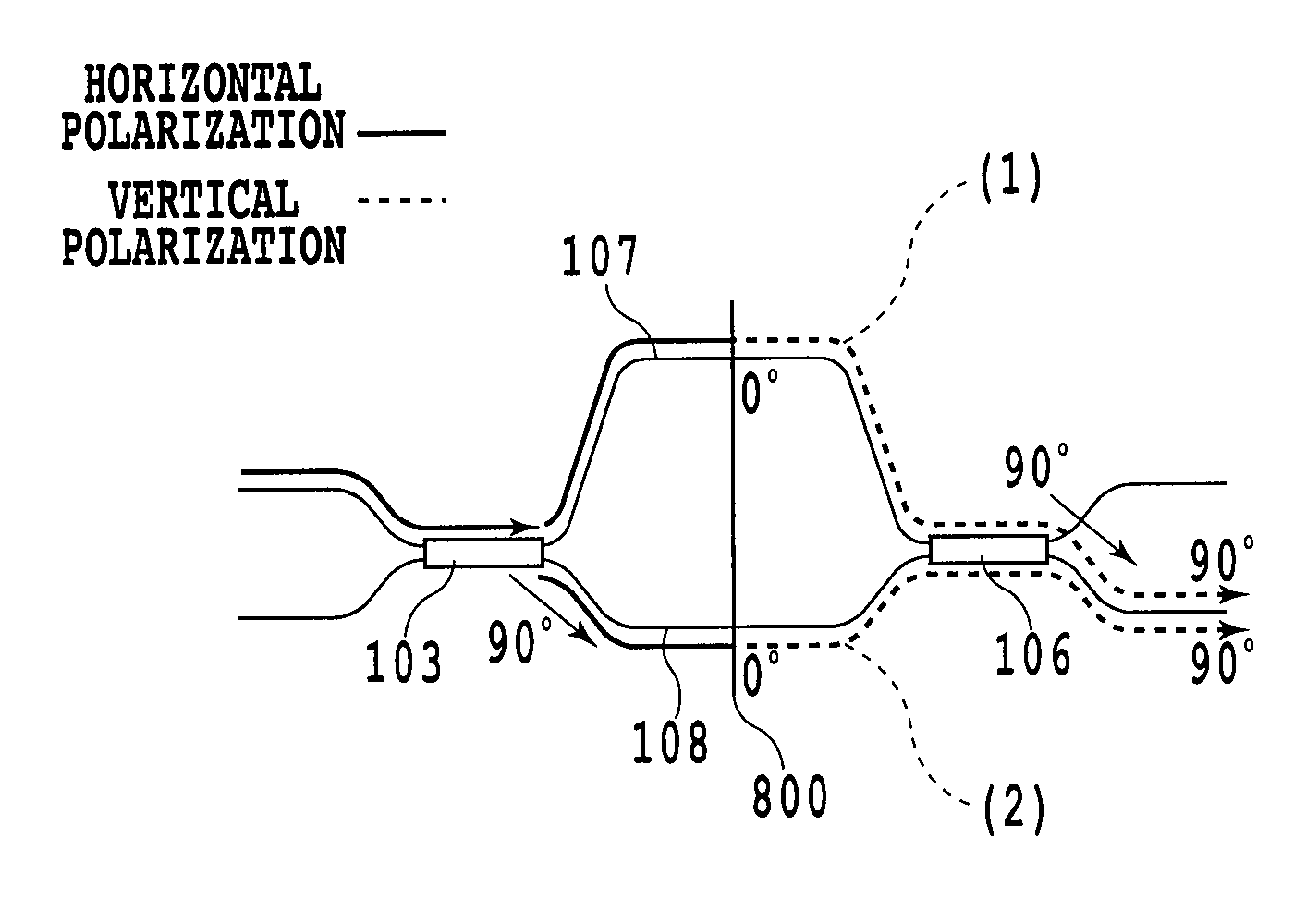
Polarization multiplexing transmitter and transmission system
InactiveUS20110170869A1Reduce equipment costsSmall sizePolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsTransfer systemMultiplexer
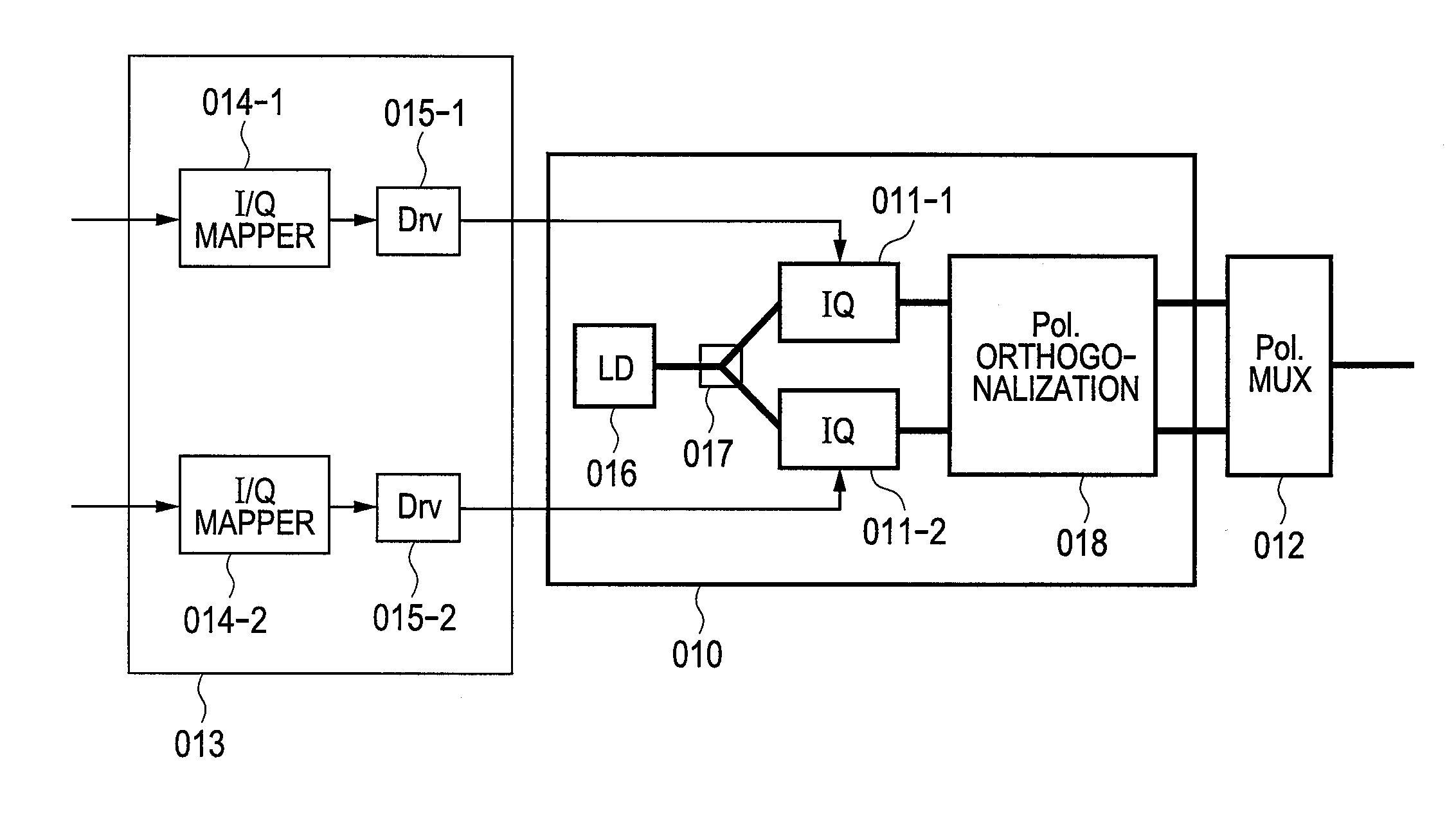
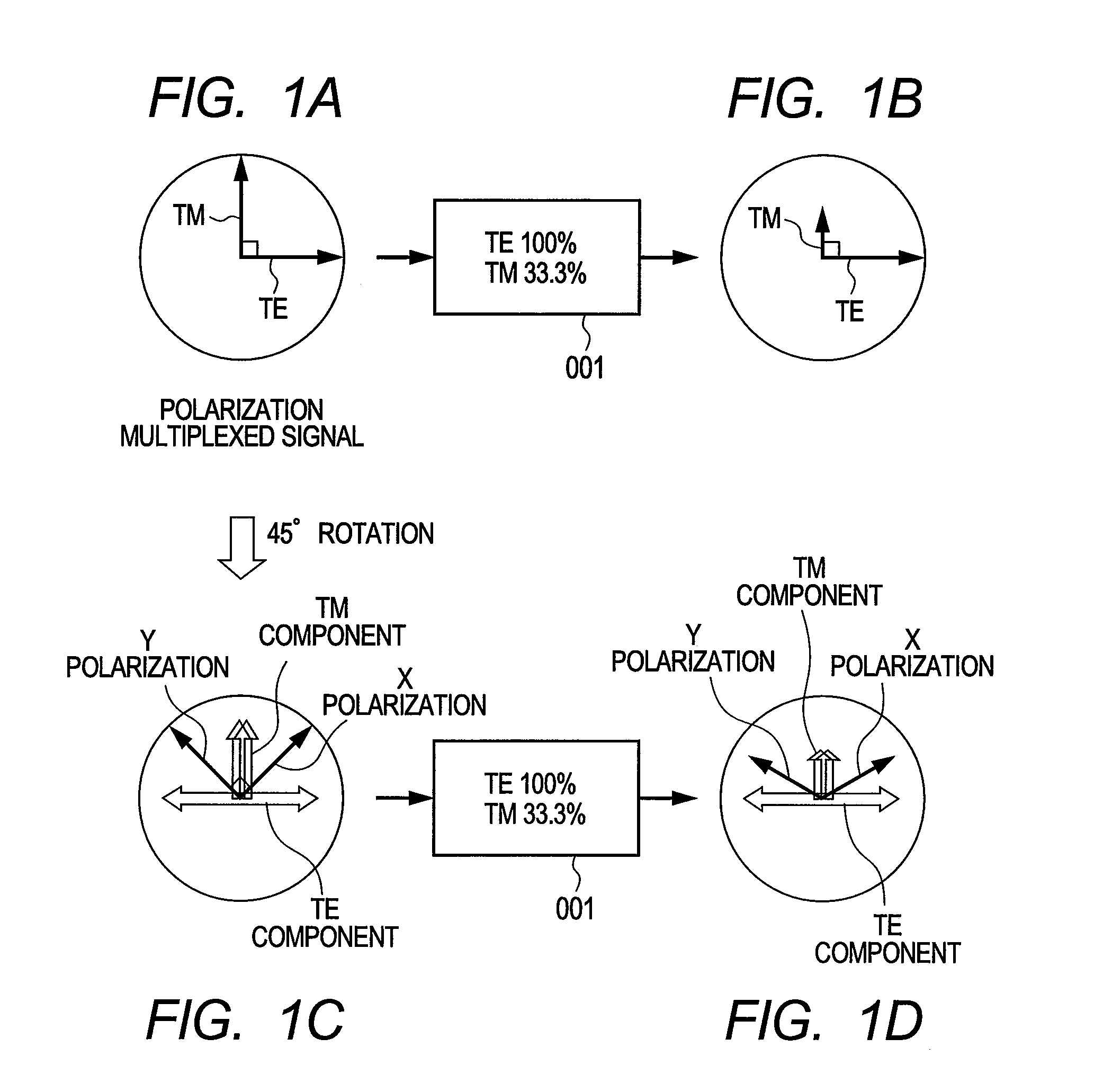
A polarization multiplexing transmitter which generates polarization-multiplexed signals which are arbitrarily polarization-scrambled at high speed, without adding a polarization modulator and a polarization scrambler. In the transmitter, an orthogonally polarized signal generator includes two optical modulators which modulate the electric fields of optical signals and generate two optical signals with mutually orthogonal polarized waves. The transmitter includes electric field mappers which convert two data strings into electric field signals, polarization mappers which give different polarized waves to the two signals, polarization rotators which rotate the polarized waves of the signals uniformly, a polarization multiplexer which multiplexes the two polarization-rotated signals, a polarization demultiplexer which demultiplexes the multiplexed signal into polarized wave components of optical signals generated by the orthogonally polarized signal generator, and a driver. The optical modulators are driven to make the two demultiplexed electric field signals consistent with the electric fields of optical signals modulated by the modulators.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method And System For A Light Source Assembly Supporting Direct Coupling To An Integrated Circuit
ActiveUS20120205524A1Radiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsGratingOptical table
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
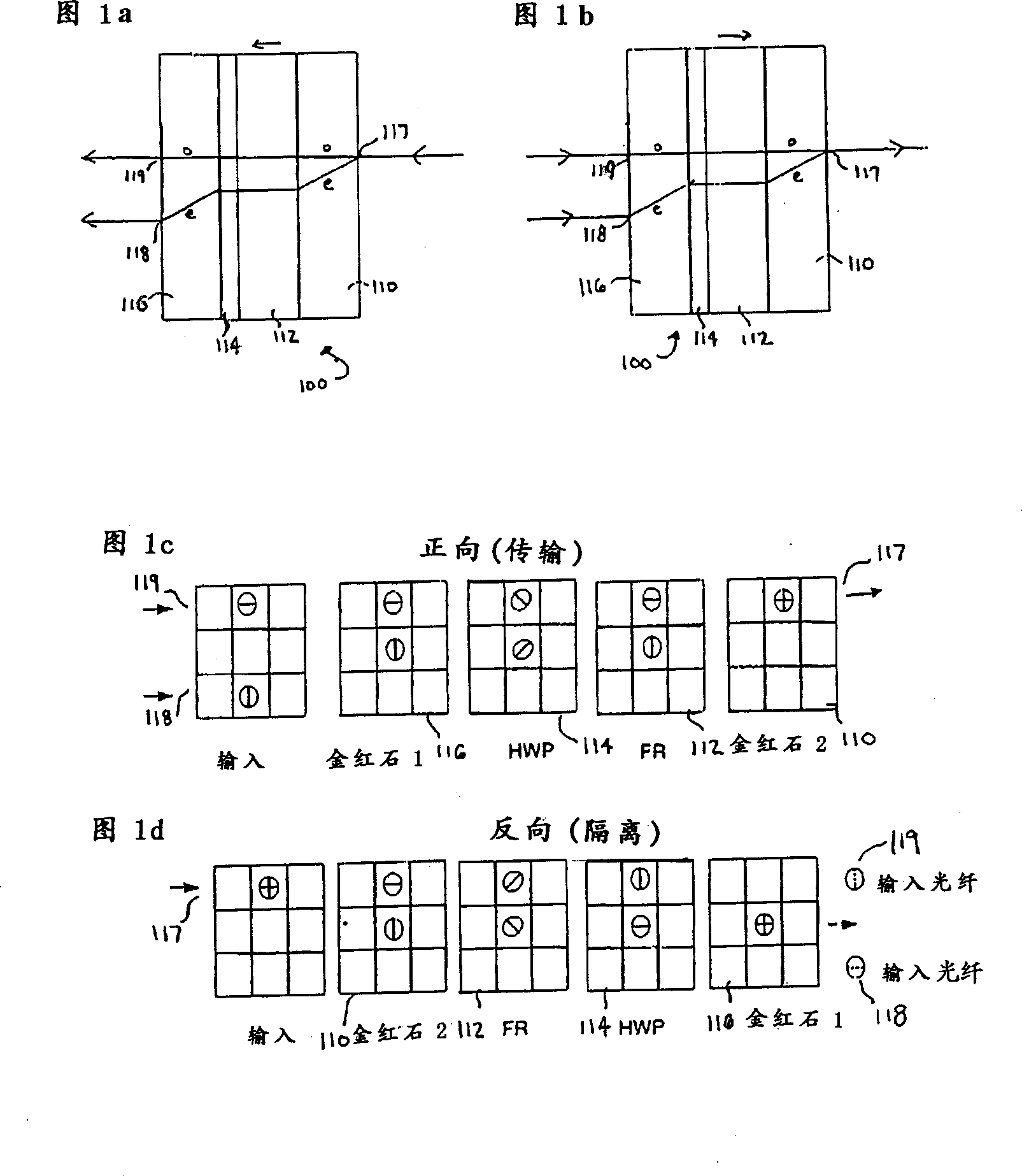
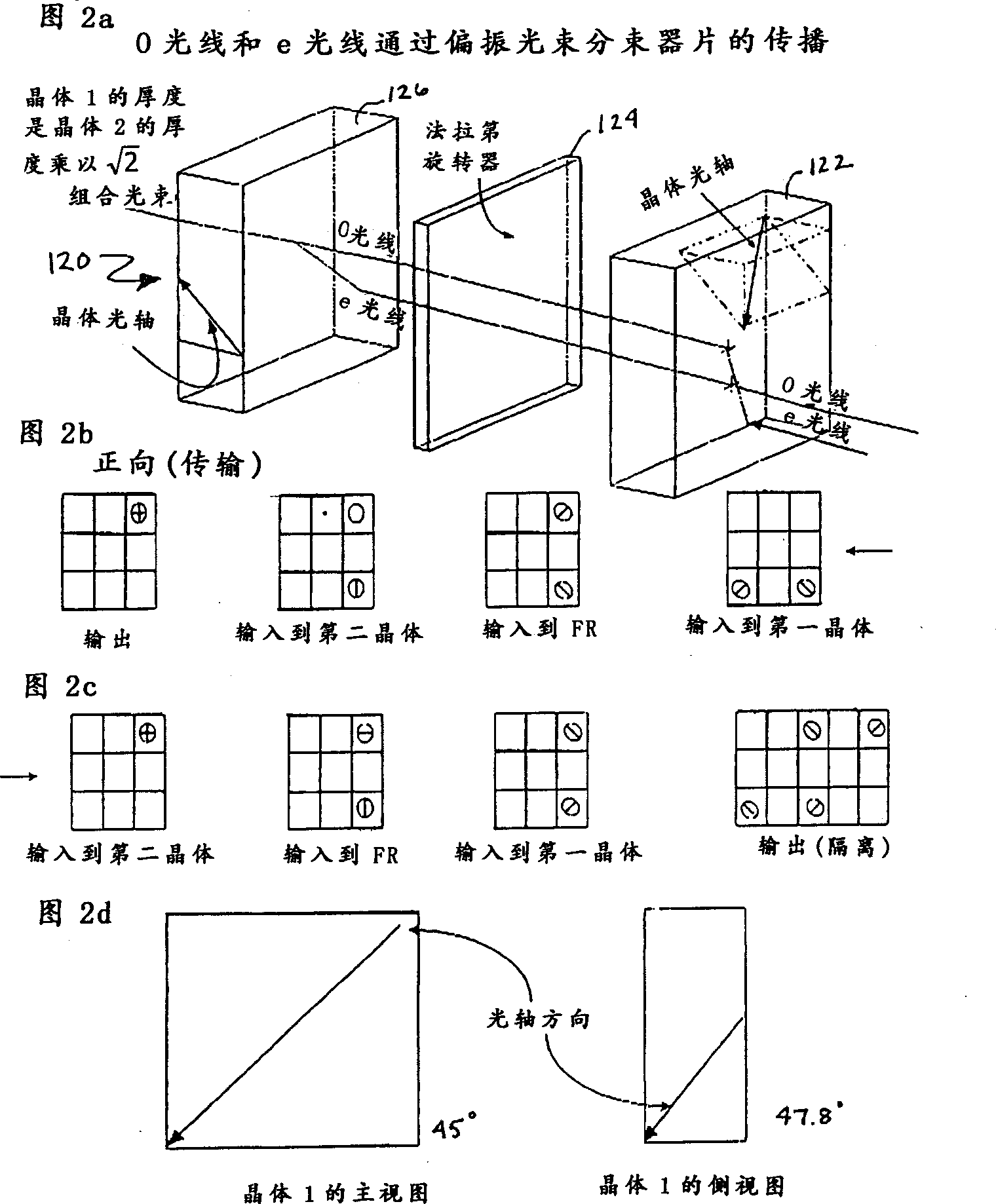
Bi-directional optical switch
The present invention provides improved optical switches in which no mechanical movement is required to direct optical pathways between plural fiber ports and light transmission is bi-directional. Advantageously, the inventive switches permit bi-directional light transmission. The inventive switches also incorporate light bending devices to allow two fibers to be coupled to the light beams using a single lens for compactness. In the inventive switch, an optical signal is spatially split into two polarized beams by a birefringent element, which passes through a polarization rotation device that comprises waveplates, walk-off elements, and an electrically controllable polarization rotator, and recombine into an output fiber, achieving polarization independent operation. The switches of the present invention rely on electro-magnetically or electro-optically switching the beam polarizations from one state to another to rapidly direct the light path.
Owner:AGILTRON
Device and method for an optical tunable polarization interface filter
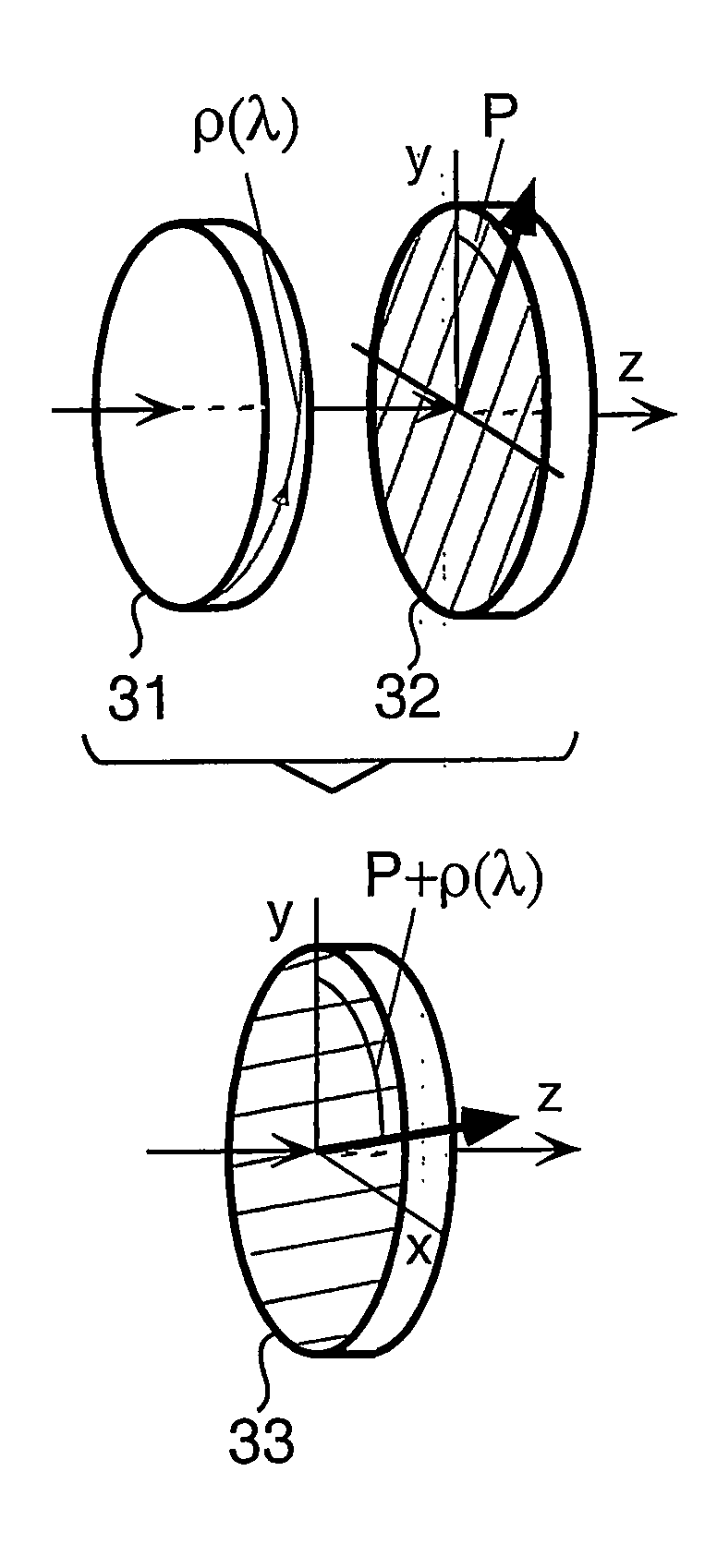
The tuner is a constituent component for constructing a tunable or switchable spectral filter, including single and multiple stage filters and filters without intermediate polarizer, over a wavelength range. It has elements arranged in cascade along a light beam axis including a dispersive polarization rotator that has its rotation angle ρ(λ) varying as a function of light wavelength λ over the wavelength range, an orientation-sensitive polarizing element and means for rotating the polarizing element or / and varying the rotation angle ρ(λ). The polarization rotator and the polarizing element are arranged in series in the spectral filter along the light beam axis with the polarizing element oriented at a predetermined orientation angle related to the structure of the spectral filter. The tuner is operated by rotating the polarizing element to change its orientation in the filter or / and by changing the rotation angle ρ(λ).
Owner:YE CHUN
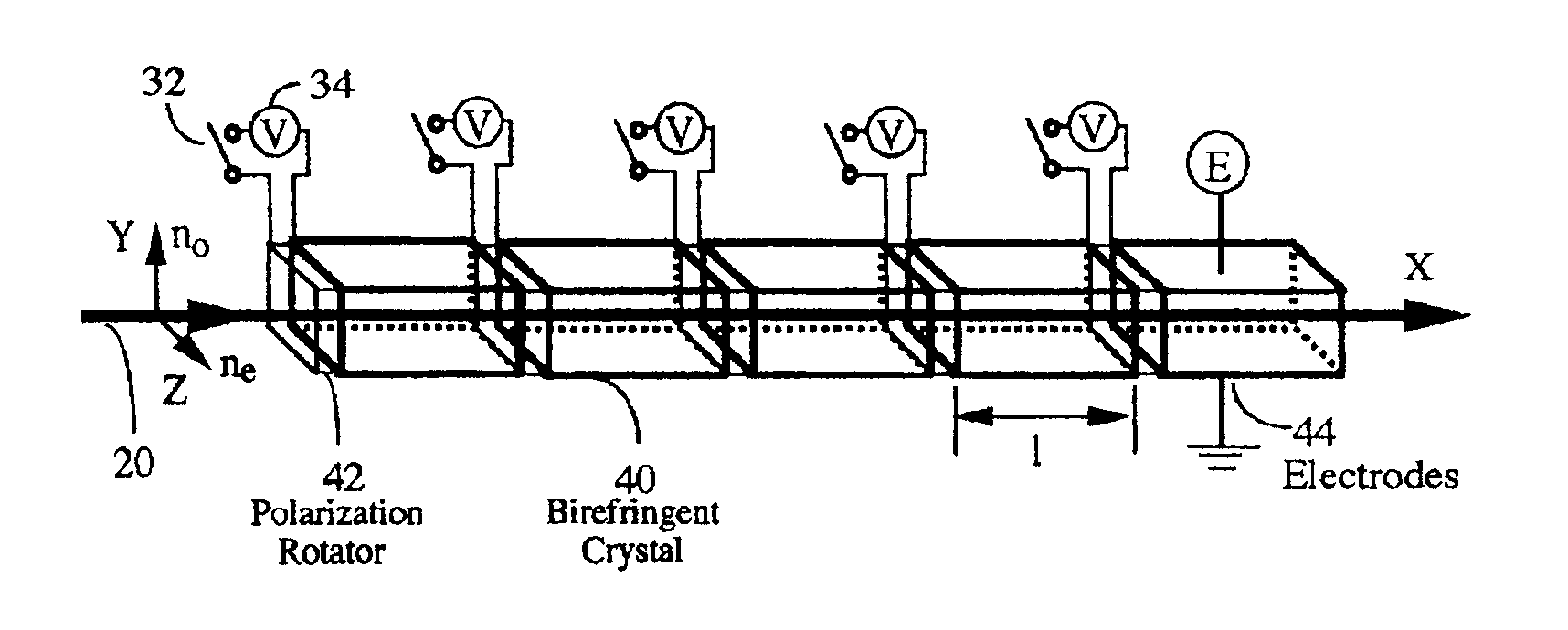
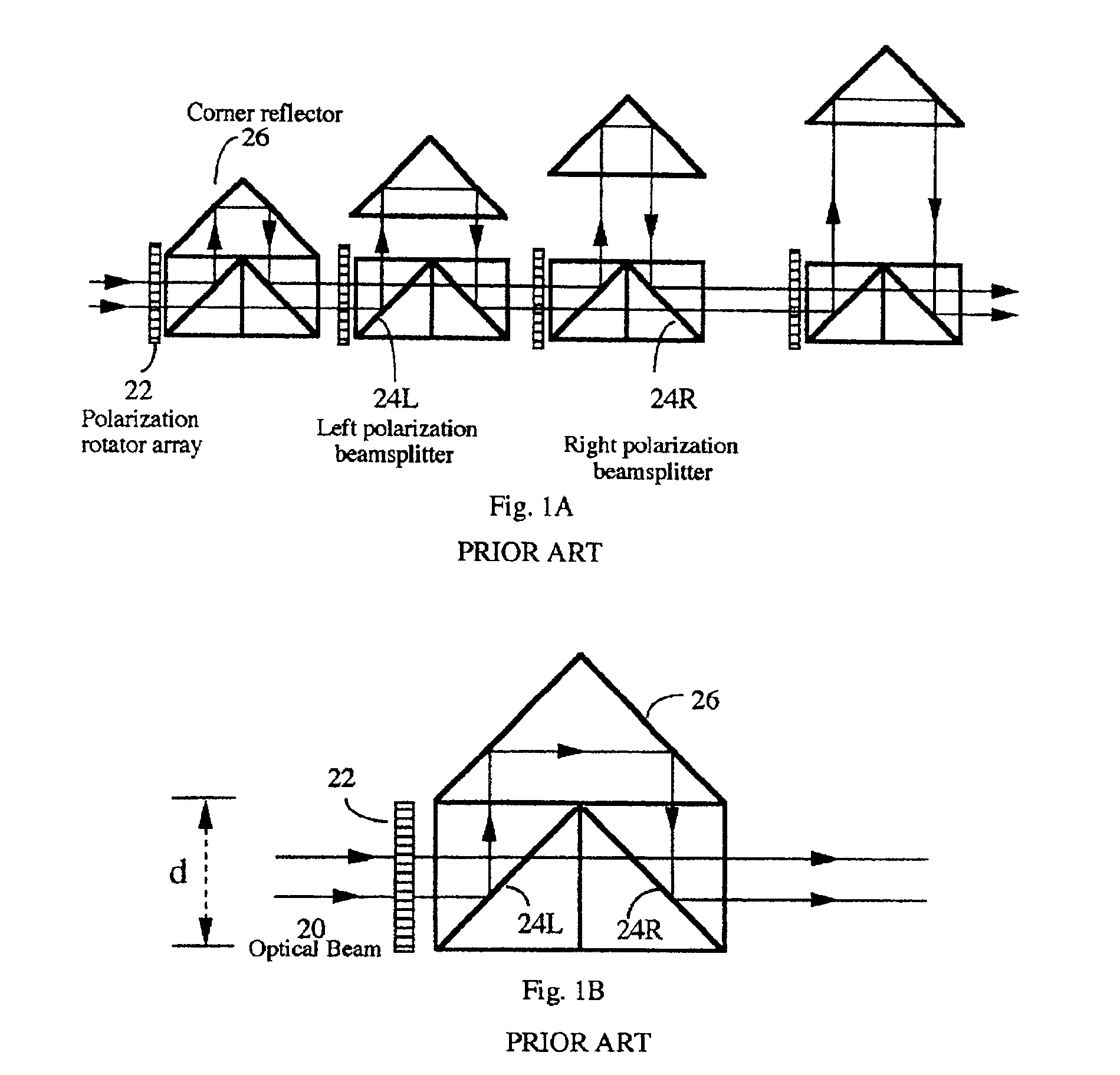
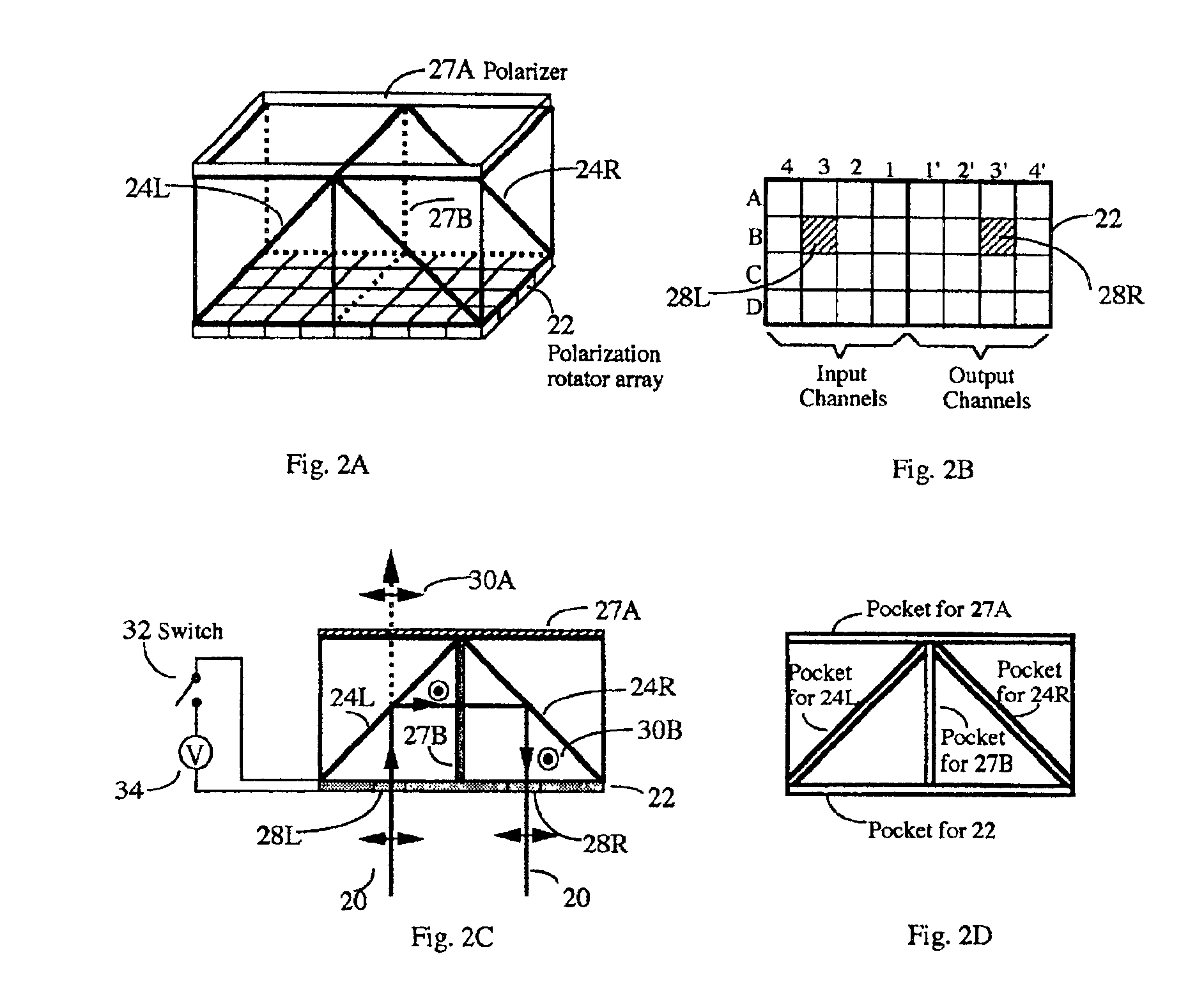
Photonic variable delay devices based on optical birefringence
Optical variable delay devices for providing variable true time delay to multiple optical beams simultaneously. A ladder-structured variable delay device comprises multiple basic building blocks stacked on top of each other resembling a ladder. Each basic building block has two polarization beamsplitters and a polarization rotator array arranged to form a trihedron; Controlling an array element of the polarization rotator array causes a beam passing through the array element either going up to a basic building block above it or reflect back towards a block below it. The beams going higher on the “ladder” experience longer optical path delay. An index-switched optical variable delay device comprises of many birefringent crystal segments connected with one another, with a polarization rotator array sandwiched between any two adjacent crystal segments. An array element in the polarization rotator array controls the polarization state of a beam passing through the element, causing the beam experience different refractive indices or path delays in the following crystal segment. By independently control each element in each polarization rotator array, variable optical path delays of each beam can be achieved. Finally, an index-switched variable delay device and a ladder-structured variable device are cascaded to form a new device which combines the advantages of the two individual devices. This programmable optic device has the properties of high packing density, low loss, easy fabrication, and virtually infinite bandwidth. The device is inherently two dimensional and has a packing density exceeding 25 lines / cm2. The delay resolution of the device is on the order of a femtosecond (one micron in space) and the total delay exceeds 10 nanosecond. In addition, the delay is reversible so that the same delay device can be used for both antenna transmitting and receiving.
Owner:GENERAL PHOTONICS CORP
Waveguide-type optical interferometer
ActiveUS20100104237A1Elimination of polarization dependenceEasy to mass produceSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsPolarization couplingOptical pathlength
In an optical interferometer, polarization dependence attributable to the optical path difference has conventionally been eliminated by inserting a half-wave plate at the center of the interferometer. However, light induced by polarization coupling produced in directional couplers used in the optical interferometer causes interference having different interference conditions from those of the normal light. Polarization rotators that effect any one of 90° rotation and −90° rotation of all states of polarization of incoming light are inserted in the optical interferometer, and thereby the interference conditions of light induced by polarization coupling are made the same as those of the normal light. Each of the polarization rotators is implemented by using two half-wave plates and by varying an angle of combination of these half-wave plates. Alternatively, each of the polarization rotators is implemented through a combination of one half-wave plate and a waveguide having birefringence properties.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
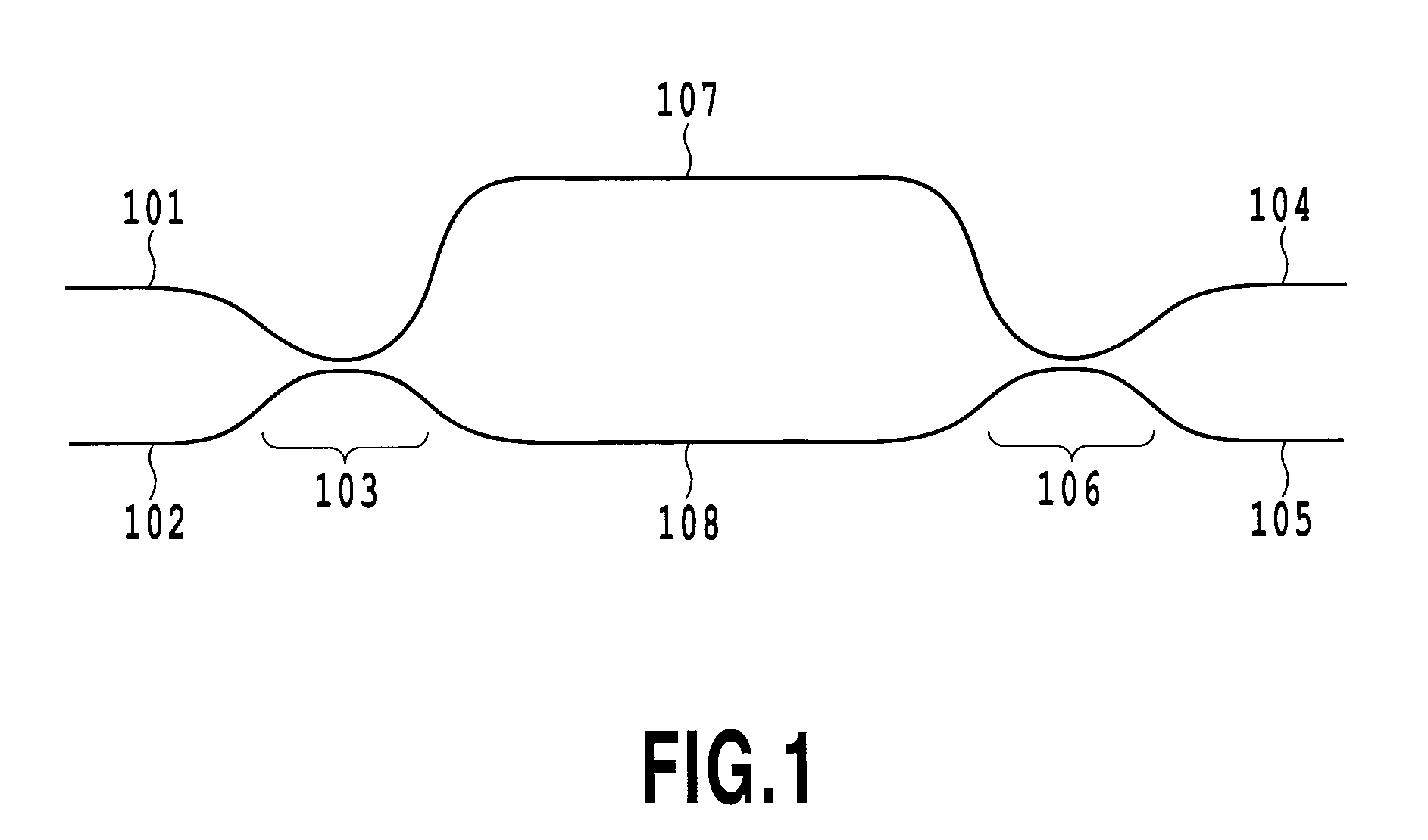
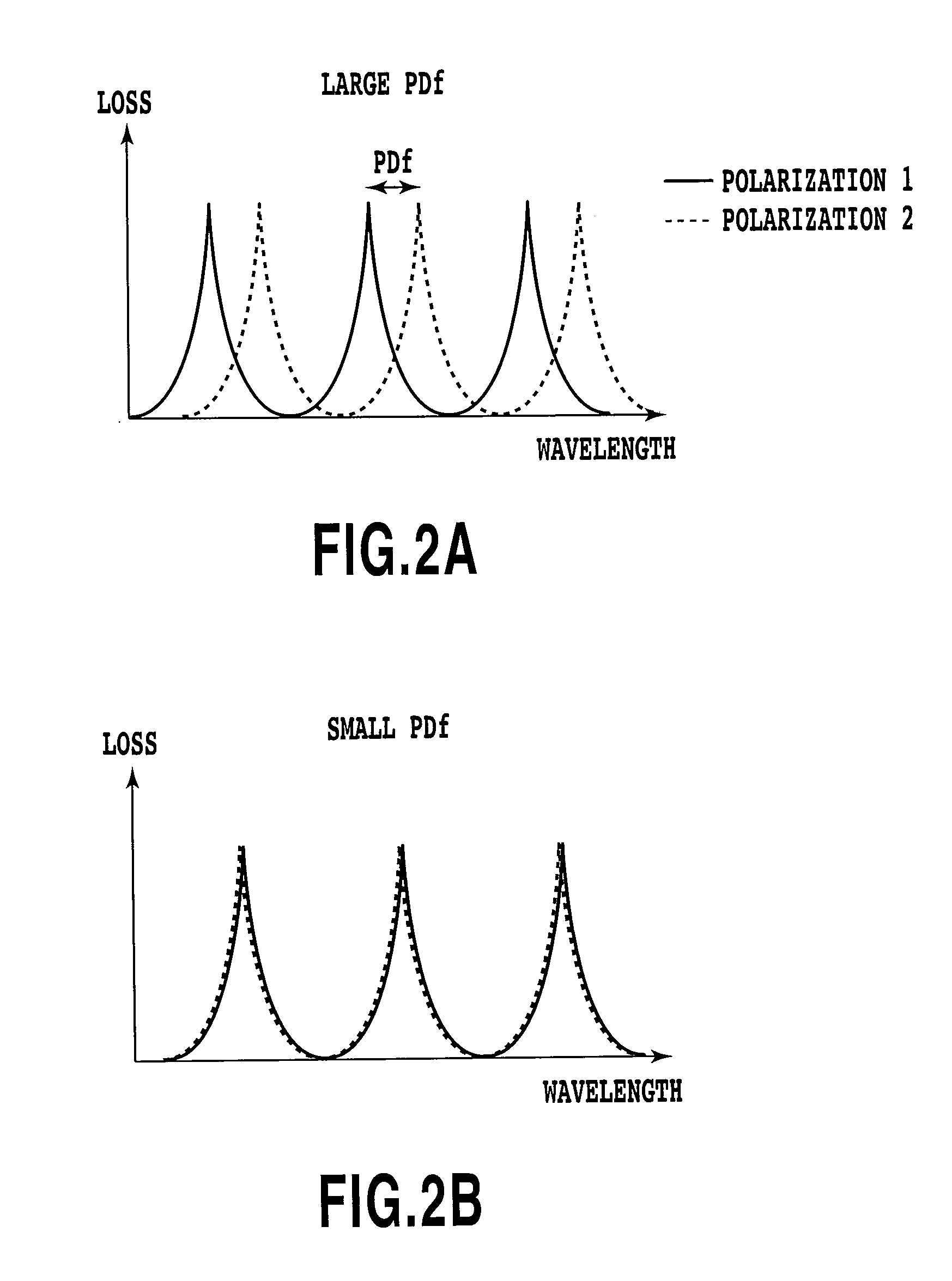
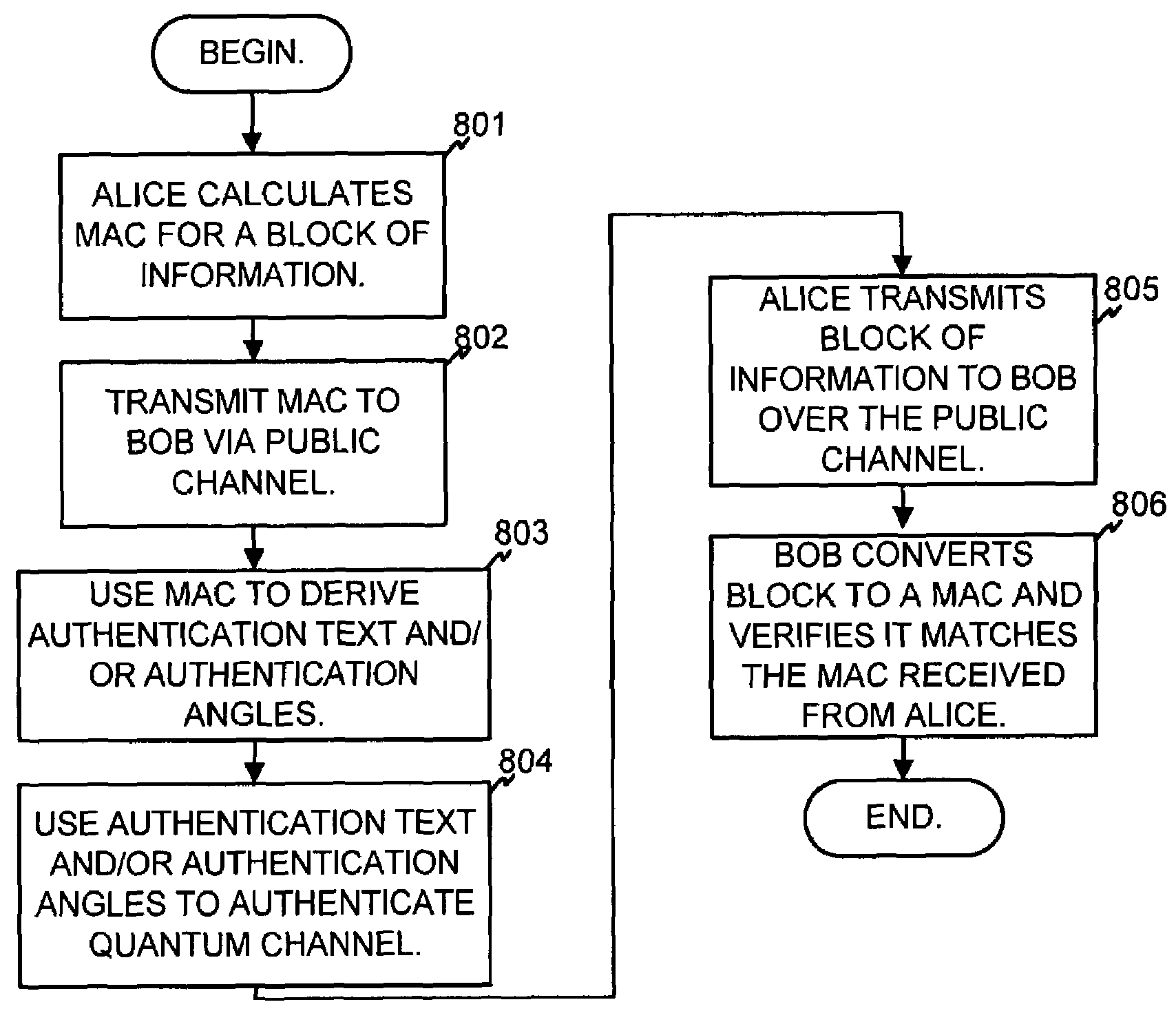
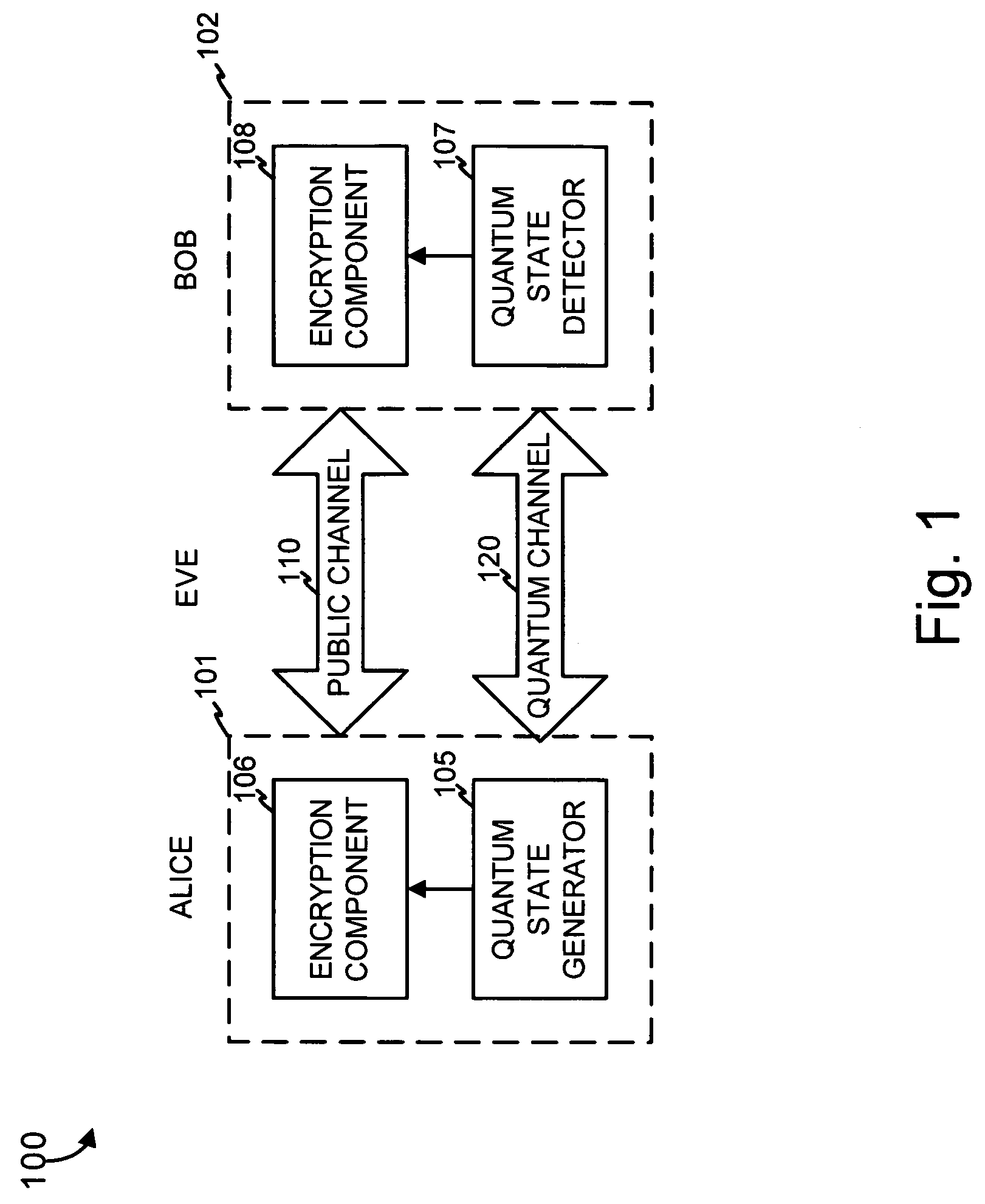
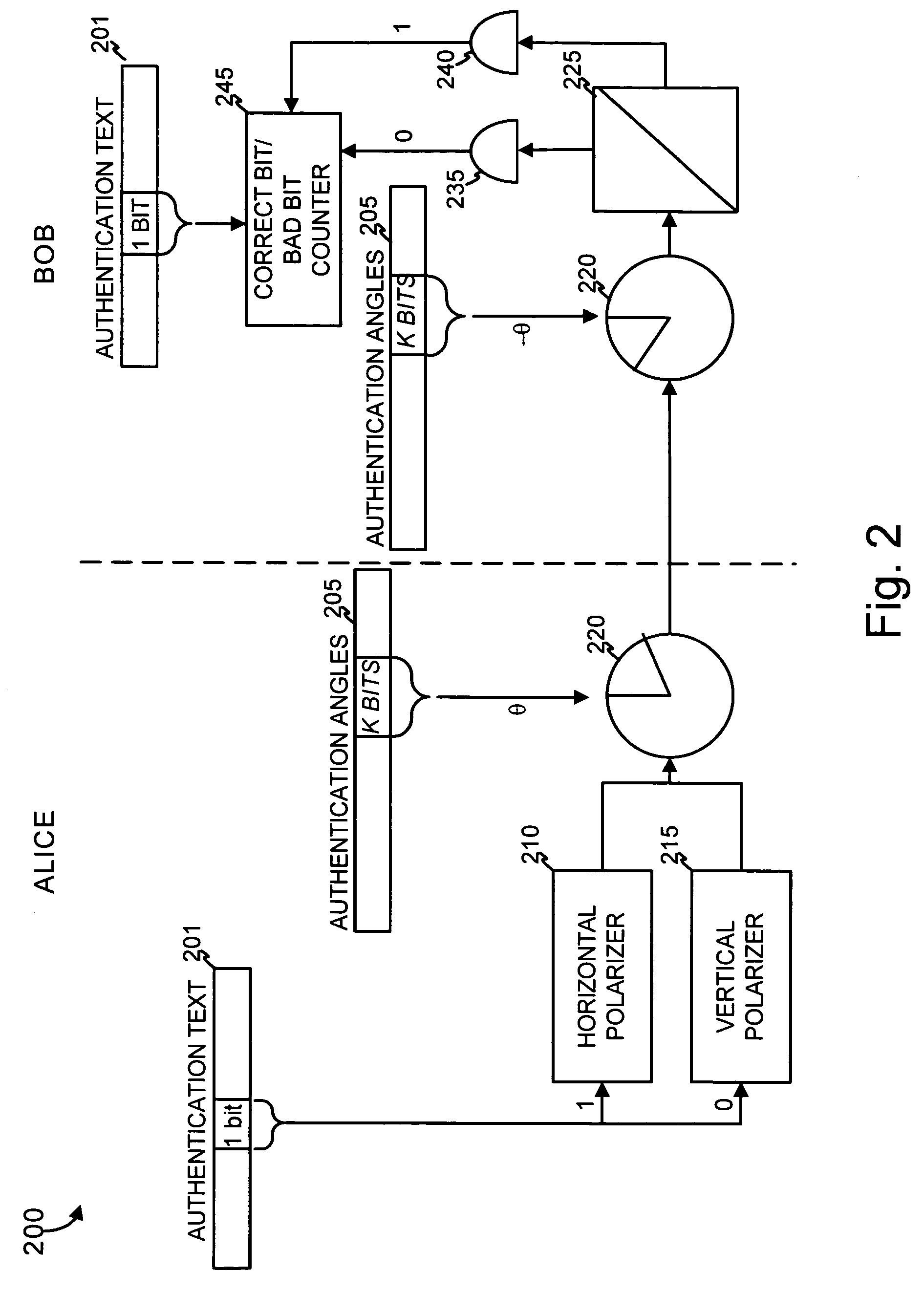
Authentication in a quantum cryptographic system
A quantum cryptographic device provides authentication services over the optical (quantum) channel and the public channel. In one implementation, polarizers generate optical pulses that have a polarization state based on a bit from a first bit sequence. A polarization rotator further rotates the polarization basis of the optical pulse by a rotation angle specified by one or more bits of a second bit sequence. A receiving device receives the modulated optical pulses, demodulates the pulses, and may determine whether the optical channel can be authenticated. In an alternate implementation, phase modulation, instead of polarization modulation, is used to similarly modulate the optical pulses.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP +1
Wavelength division multiplexing type silicon substrate optical receiving chip insensitive to polarization
ActiveCN104459881AFlat spectral responseLow wavelength dependent lossCoupling light guidesSpectral responseOpto electronic
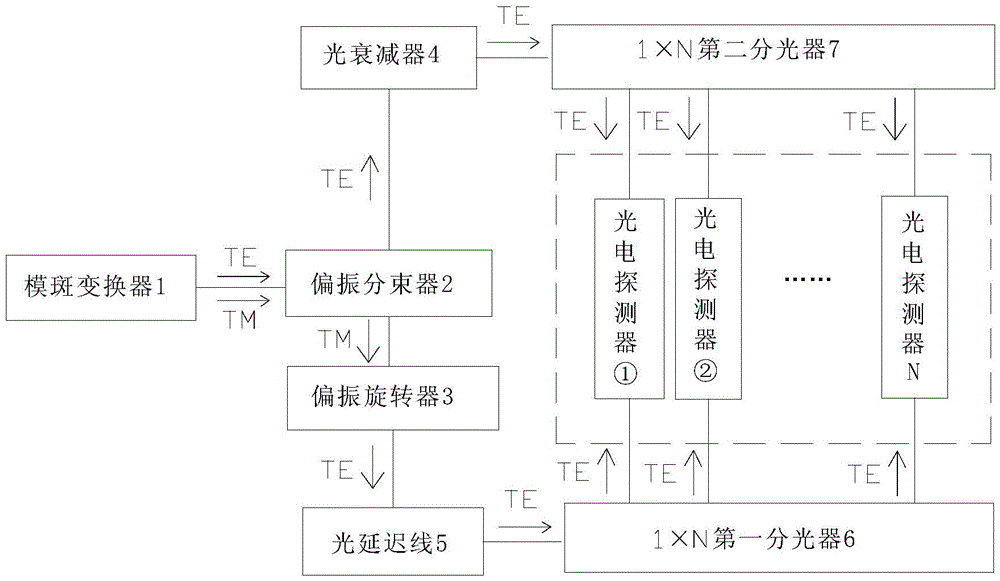
The invention discloses a wavelength division multiplexing type silicon substrate optical receiving chip insensitive to polarization. The optical receiving chip comprises a speckle convertor, a polarization beam splitter, two optical splitters and a plurality of photoelectric detectors. An optical signal in an optical fiber is coupled into the silicon substrate optical receiving chip by the speckle convertor, the optical signal is separated into TM model polarized light and TE model polarized light orthogonal with the TM model polarized light by the polarization beam splitter in a polarization mode, a TM model polarized light signal is converted into the TM model polarized light by a polarization rotator, the parts, with the same wavelength, in the optical signal in a first silicon waveguide and a second silicon waveguide are downloaded correspondingly through the first optical splitter and the second optical splitter respectively, and the two ends of each photoelectric detector correspond to one output end of the first optical splitter and one output end of the second optical splitter respectively. All the components on the silicon substrate optical receiving chip are small in size and low in optical insertion loss, and time domain synchronization and optical power balance are easy to achieve. Spectral response of all the components on the silicon substrate optical receiving chip is flat, the wavelength correlation loss is small, and the wavelength division multiplexing optical receiving function insensitive to polarization is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
2D/3D image display
InactiveCN1890988AEasy to manufacturePrecise alignmentDiffusing elementsSteroscopic systems3d imageDisplay device
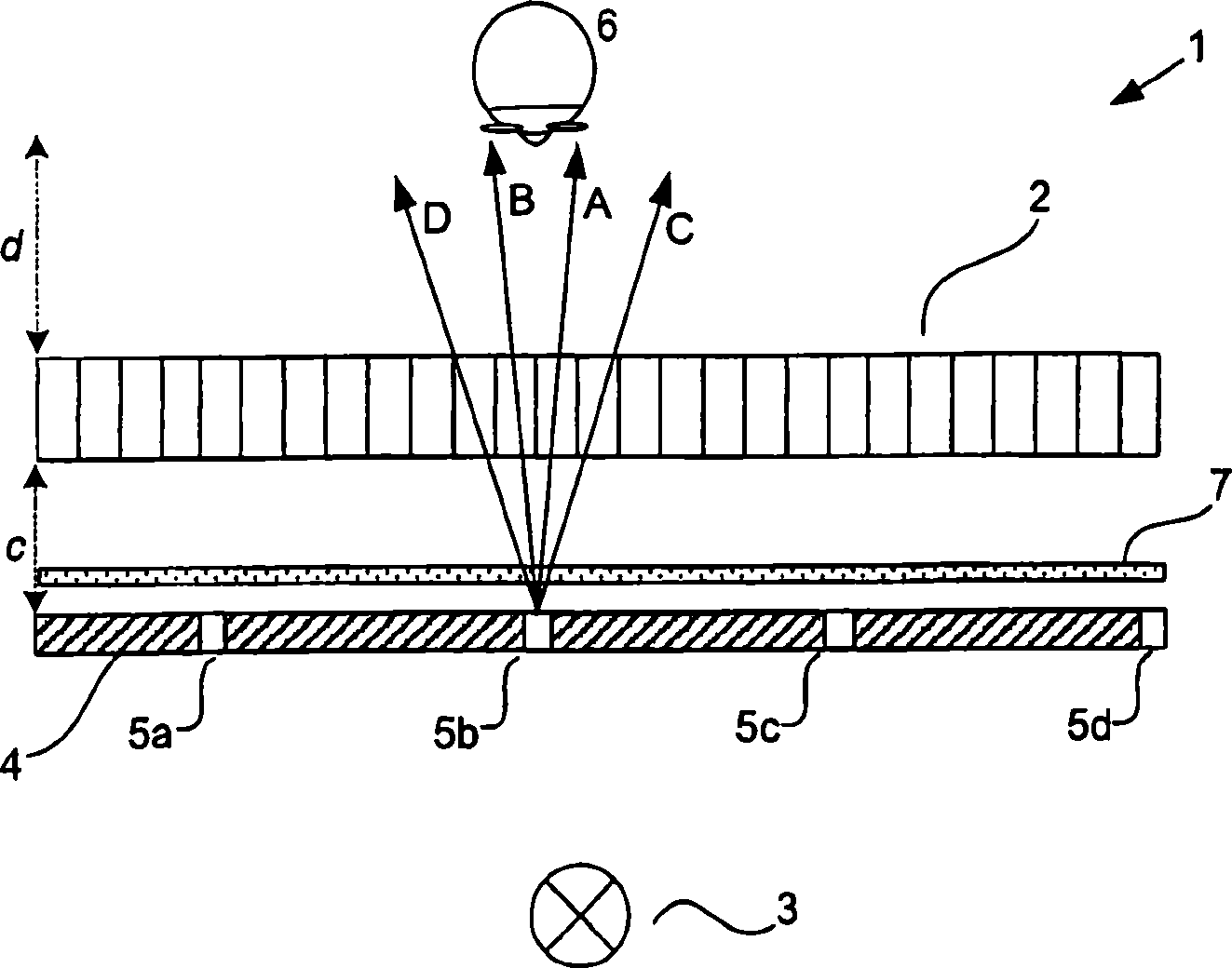
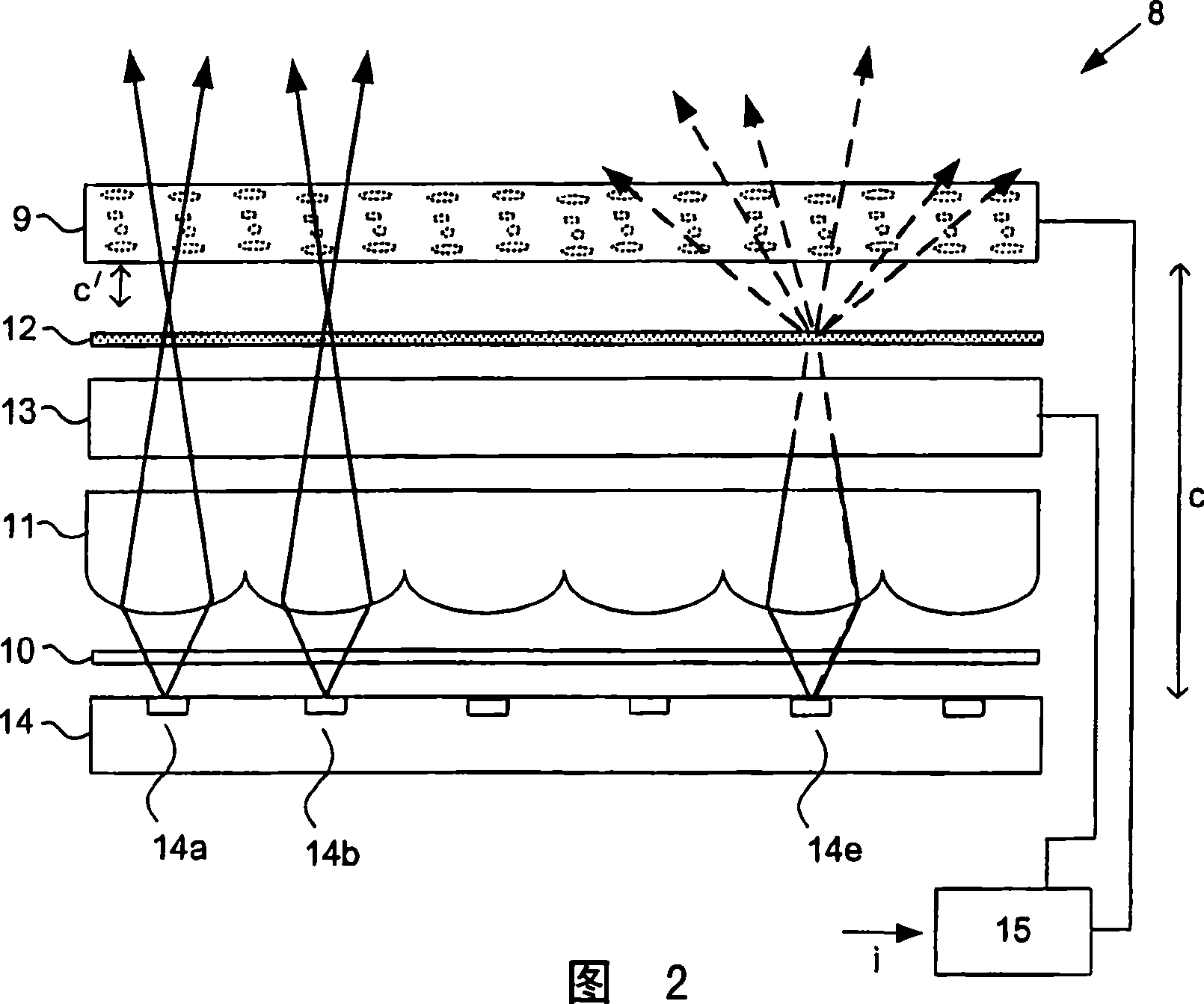
A display (8) comprises a display panel (9), a polariser (10), a polarisation rotator (13), and a scatterer (12) arranged to scatter light having a first polarisation as compared with light having a second polarisation. The display (8) can be switched between 2D and 3D modes by operating the polarisation rotator (13) accordingly. In 3D mode, the polarisation rotator (13) transmits light with relatively little or no change to its polarisation. Light transmitted by the scatterer (12) is then used to present a three-dimensional image (50). In 2D mode, the polarisation rotator (13) alters the polarisation of the light and light that is scattered by the scatterer (12) is used to present a two-dimensional image (51). The polarisation rotator (13) maybe arranged so that light incident on a first area thereof undergoes a different change in polarisation to light incident on a second area, in order to allow simultaneous presentation of 2D and 3D images (51, 50).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Compact tunable high-efficiency entangled photon source
InactiveUS20080063015A1Reduce pump powerEasy transferLaser detailsUsing optical meansWaveguidePhoton source
A compact, tunable, high-efficiency entangled photon source system that utilizes first and second periodically poled waveguides rather than bulk media in order to decrease the required pump power by up to several orders of magnitude. The first and second waveguides are arranged in respective arms of an interferometer. Each waveguide has partially reflecting ends, and are each placed on the Z-face of respective periodically poled KTP or LiNBO3 crystals to form respective first and second Fabry-Perot cavities. All waves (pump, idler, and signal) are co-polarized along the z-axis of the crystals. One of the waveguides is followed by a polarization rotator (shown as a half-wave-plate in the Figures) rotating the idler and signal wave polarization by 90 degrees. The outputs from two interferometer arms are combined by a polarization beam combiner and then split by a wavelength multiplexer into two spatially separated time-bin and polarization entangled beams. Another light source, a single frequency stabilized C-band laser (stabilization laser) is used to synchronize cavities spectral modes and phase-lock their outputs.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Systems and methods for photonic polarization-separating apparatuses for optical network applications
ActiveUS20130142476A1Carefully controlledCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsPhotonicsPolarization beam splitter
An integrated photonic polarization-separating apparatus includes a first waveguide polarization beam splitter (PBS) having a first port, a second port, a third port, and a fourth port and a first polarization rotator optically coupled to the first port of the first waveguide PBS. The apparatus also includes a first Faraday rotator optically coupled to the first polarization rotator and a second polarization rotator optically coupled to the second port of the first waveguide PBS. The apparatus further includes a second Faraday rotator optically coupled to the second polarization rotator and a second waveguide PBS having a first port, a second port, a third port, and a fourth port. The third port is optically coupled to the first Faraday rotator and the fourth port is optically coupled to the second Faraday rotator.
Owner:SKORPIOS TECH
Adiabatic polarization converter
The present invention relates to a waveguide structure, and methods for making the same. The waveguide structure has a polarization rotator for rotating the polarization of the electromagnetic signal, preferably by about ninety-degrees. In one embodiment, the polarization rotator has a midsection with a first level and a second level. The first level of the midsection has a width that decreases along the length of the first level, while the second level has a substantially constant width along the length of the second level. Further, the waveguide structure can include an input conditioning section and the output conditioning section to facilitate matching between the polarization rotator and other waveguide elements.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Beam splitter and beam combiner with isolated polarized beam
The present invention relates to an isolated polarization beam sputter or combiner, for joining light from different inputs into one common port, or for dividing a beam of light into orthogonal polarizations. In both modes of operation, the splitter / combiner provides isolation preventing transmission of light in a reverse direction. As a sputter, a beam of light is separated through a birefringent material into sub-beams of orthogonal polarization components, and each sub-beam is passed through a non-reciproca l polarization rotator to rotate the polarization so that a reflected beam, or other counter- transmitted light cannot return on the same path through the birefringent material to the source. As a combiner, two separate beams of light are launched with known orthogonal polarizations into a first birefringent material, passed through a non- reciprocal polarization rotator and then combined as orthogonal polarizations into a single output port.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Actively Q-switched laser system using quasi-phase-matched electro-optic Q-switch
A Q-switched laser system is disclosed. The laser system employs a quasi-phase-matched electro-optic (QPM EO) crystal as the laser Q-switch. When applied with a certain modulating electric field, the QPM EO crystal can function as a polarization rotator to rotate the polarization direction of the resonant laser beam in a polarization-dependent laser resonator, thereby switching the laser resonator between high-loss and low-loss cavity states to achieve laser Q-switching. Compared with traditional electro-optic Q-switched laser system, the disclosed laser system is characterized by a low switching-voltage, reduced cost, and compactness. A quasi-phase-matched electro-optically Q-switched wavelength-conversion and wavelength-tunable laser system is also disclosed. The disclosed laser system integrates a QPM electro-optic Q-switch and a QPM nonlinear wavelength converter in a single crystal substrate to perform a high-efficiency intracavity wavelength conversion. The disclosed laser system is therefore simple and compact and has lower system requirements on wall-plug power and higher overall conversion efficiency.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
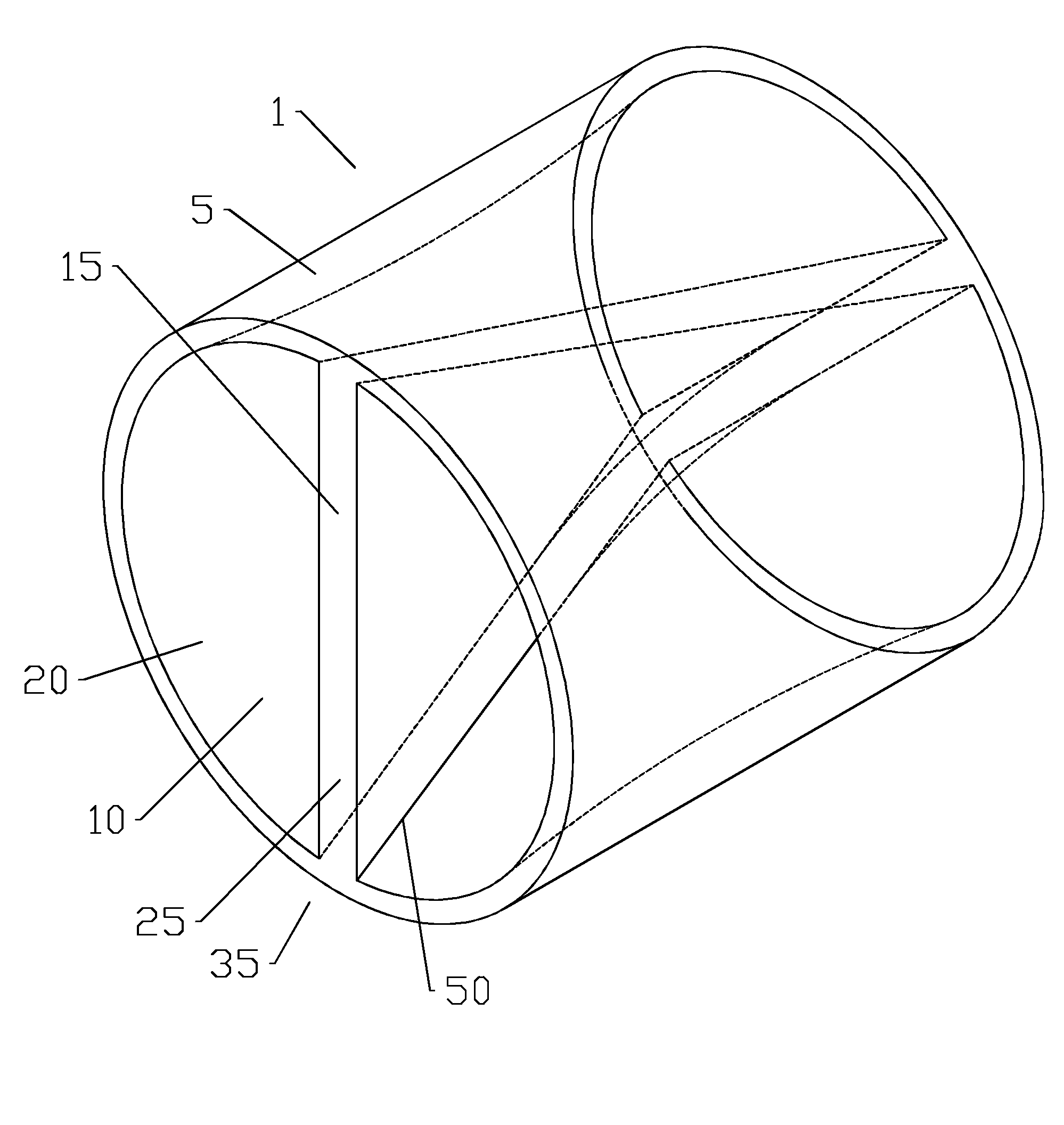
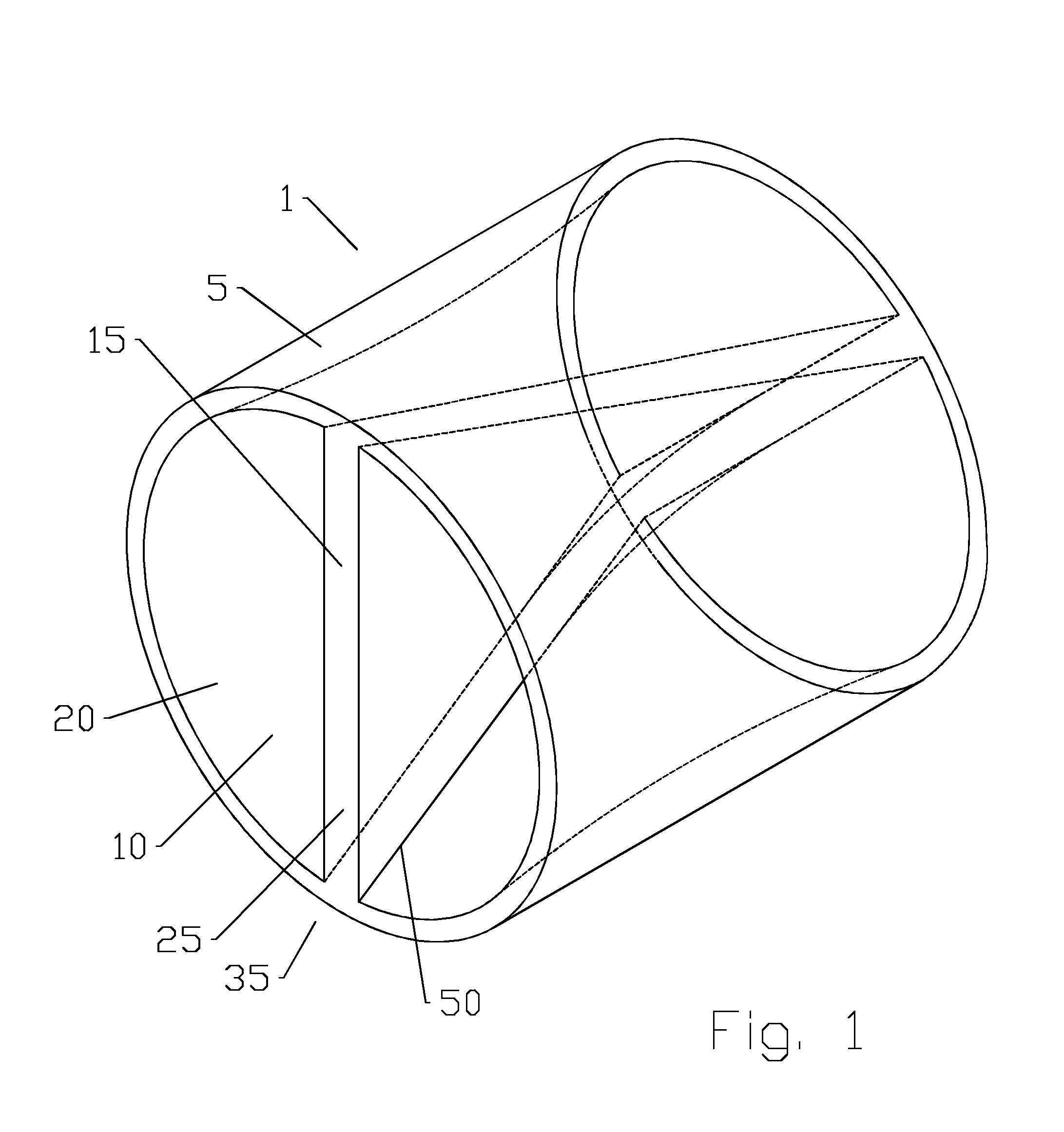
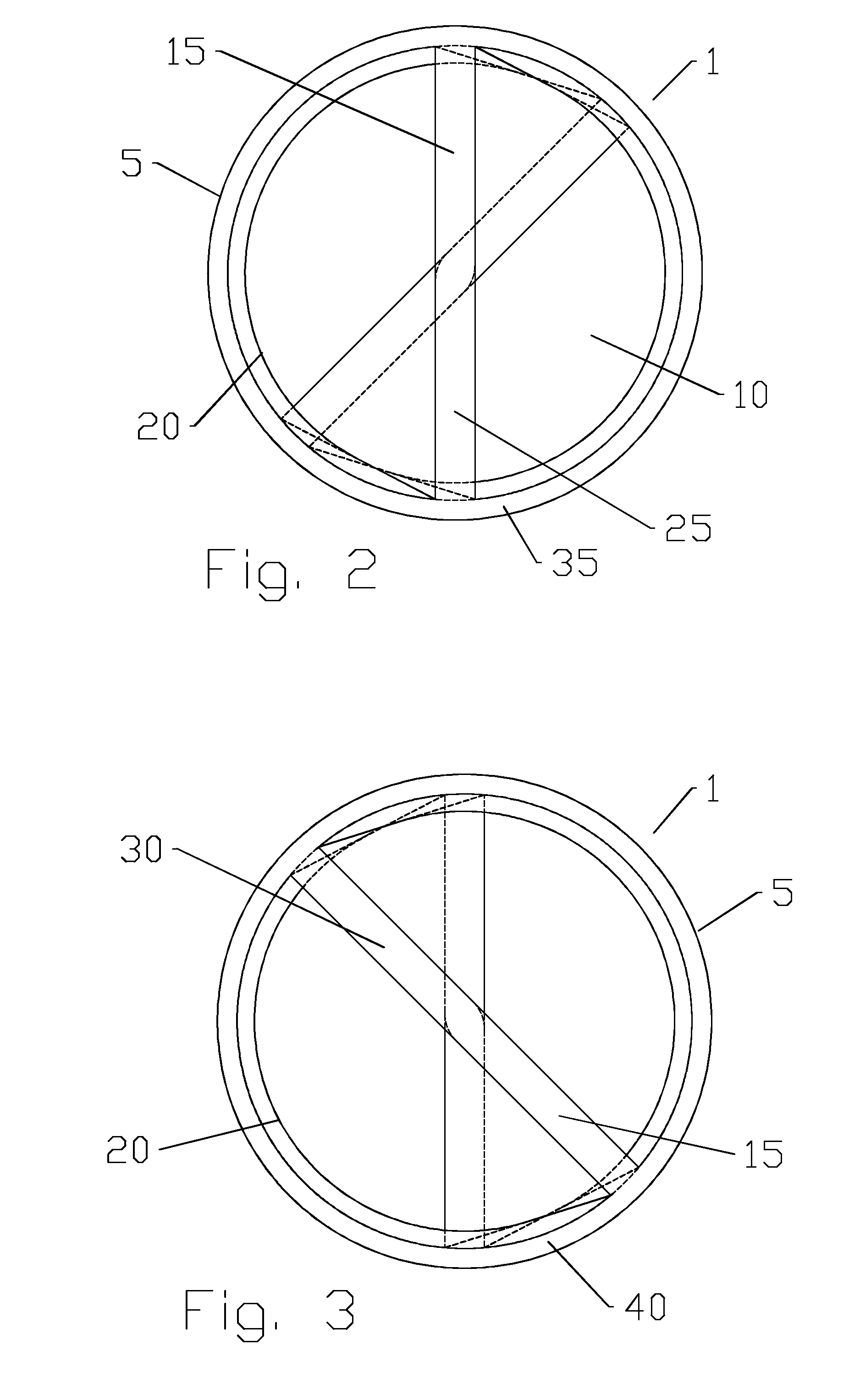
Twist septum polarization rotator
ActiveUS20140254976A1Reducing alignment and or sealing issueEfficient preparationPolarising elementsOptical articlesClassical mechanicsPolarization rotator
A waveguide polarization rotator is provided as unitary body with a first bore; a diametral first septum of the unitary body extending between sidewalls of the first bore. The first septum is twisted between a first end of the first septum and a second end of the first septum. The waveguide polarization rotator may be further provided in a matrix configuration with a plurality of second bores each with a diametral second septum of the unitary body extending between sidewalls of the second bores; a longitudinal axis of the first bore and each of the second bores parallel to one another. The waveguide polarization rotator may be manufactured via injection molding, casting or the like.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com