Patents
Literature
5093 results about "Wavelength-division multiplexing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
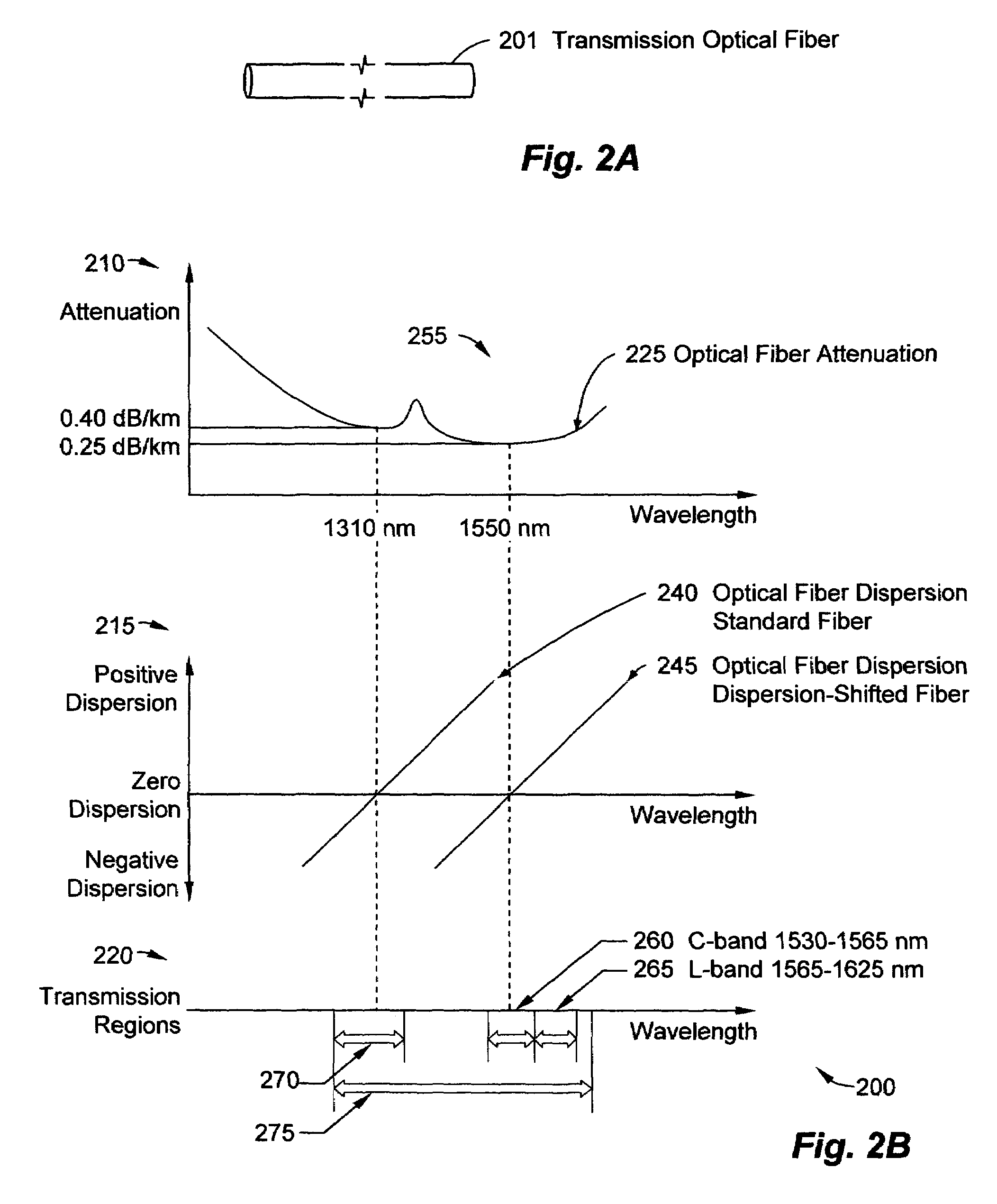
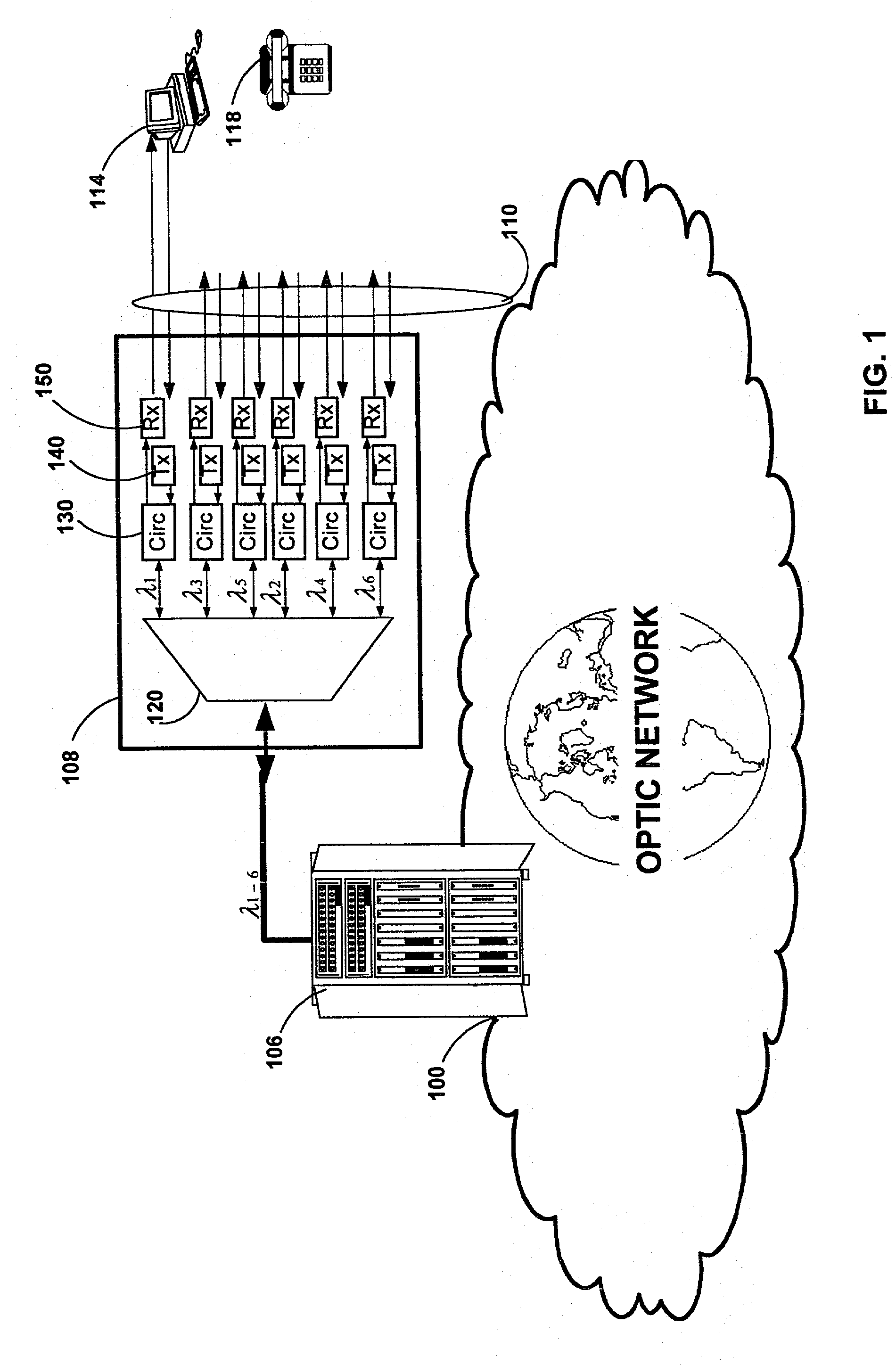
In fiber-optic communications, wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) is a technology which multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths (i.e., colors) of laser light. This technique enables bidirectional communications over one strand of fiber, as well as multiplication of capacity.
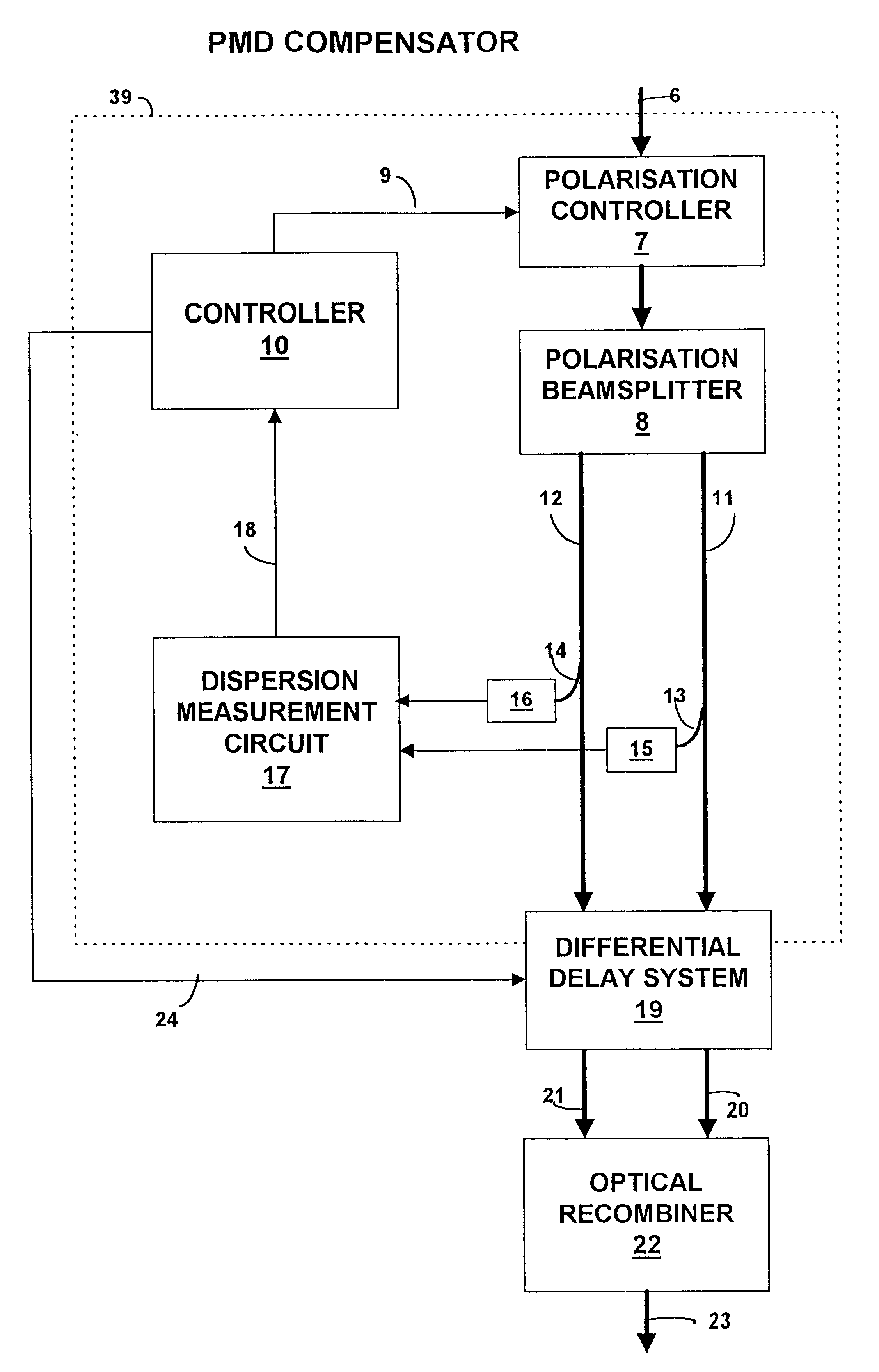
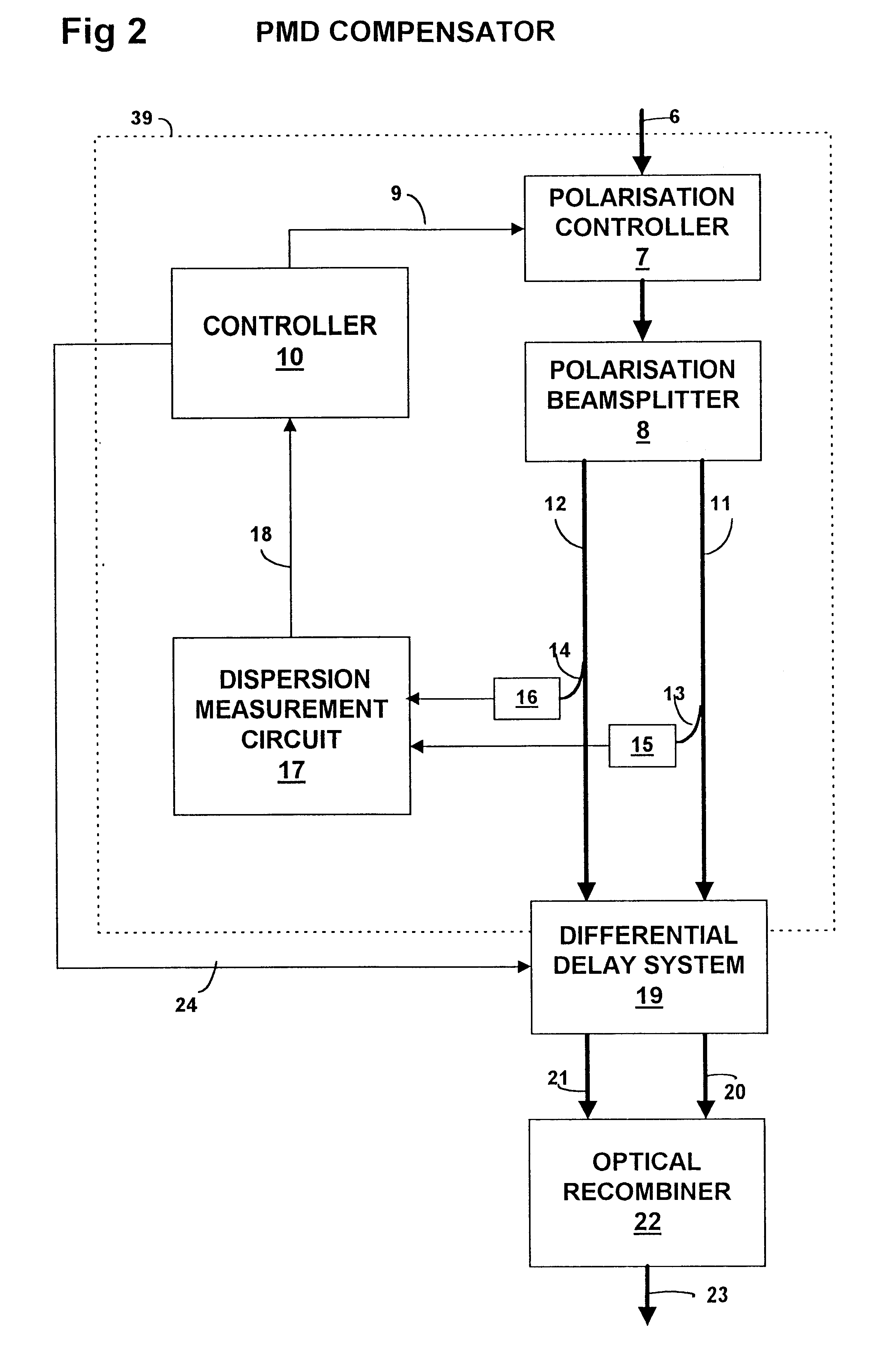
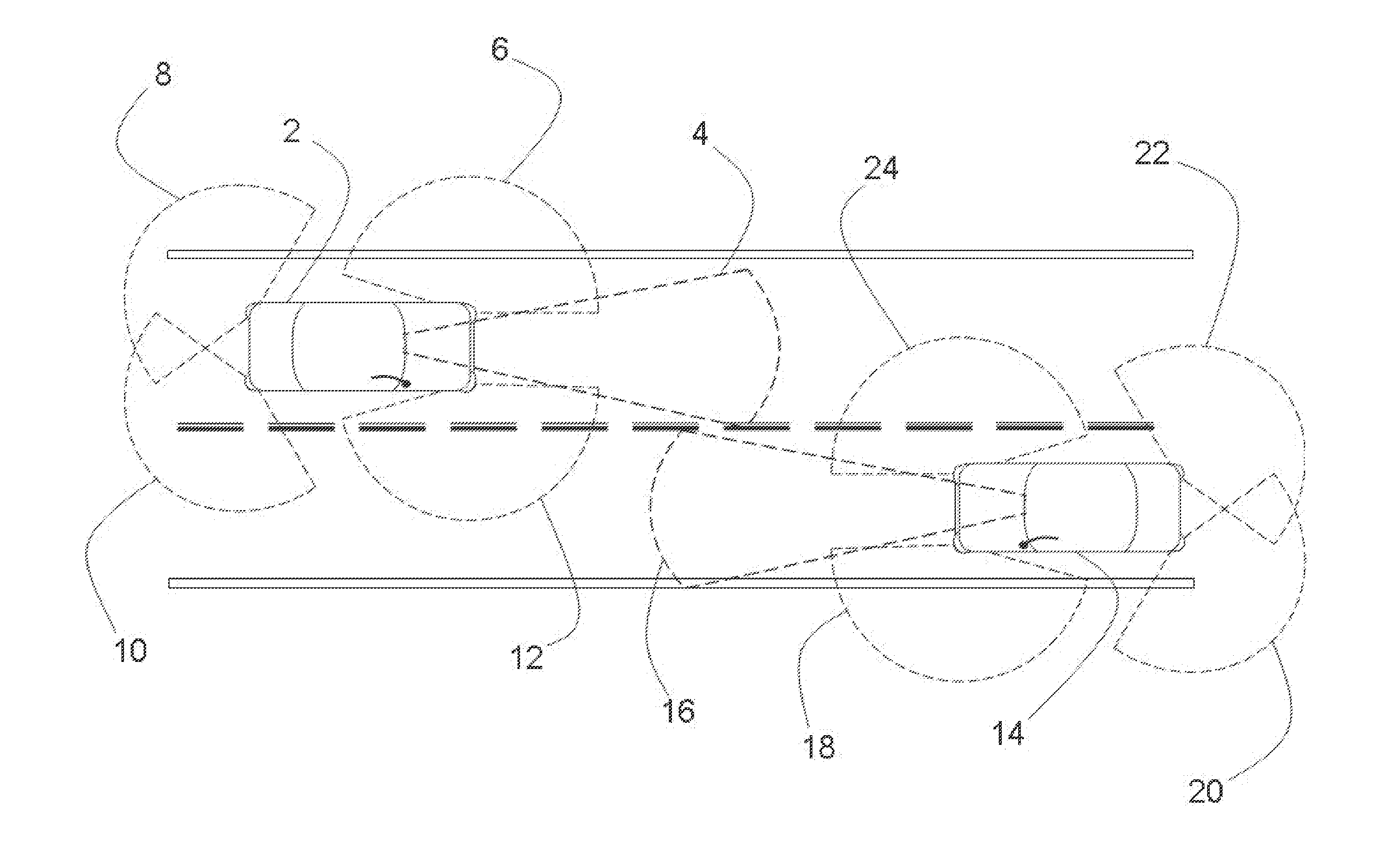
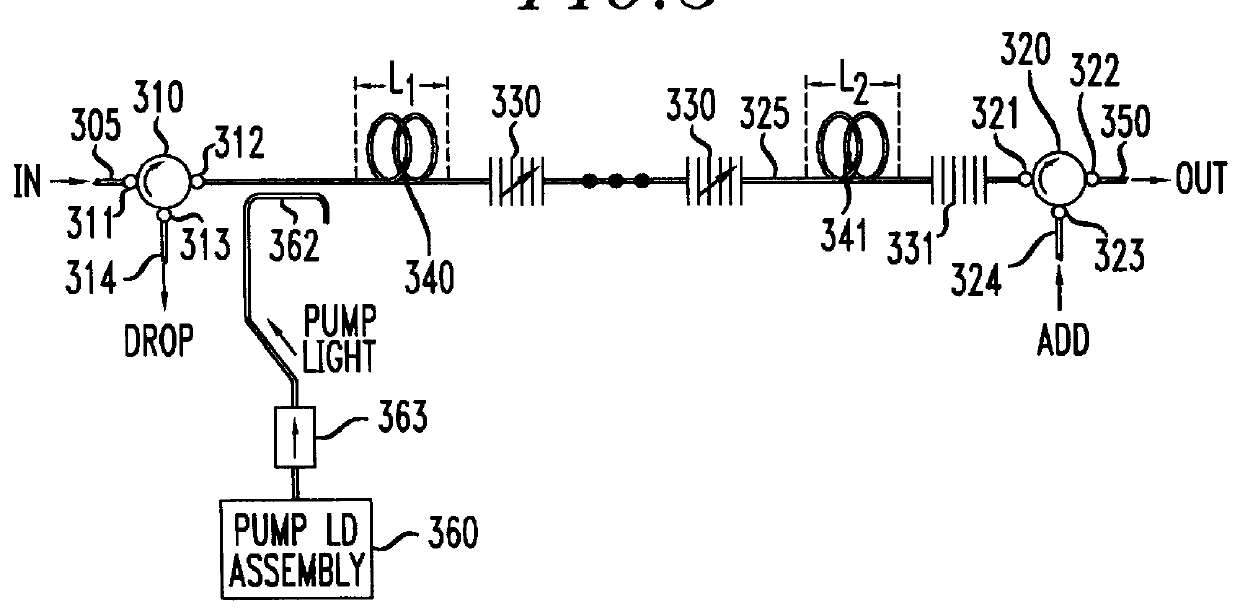
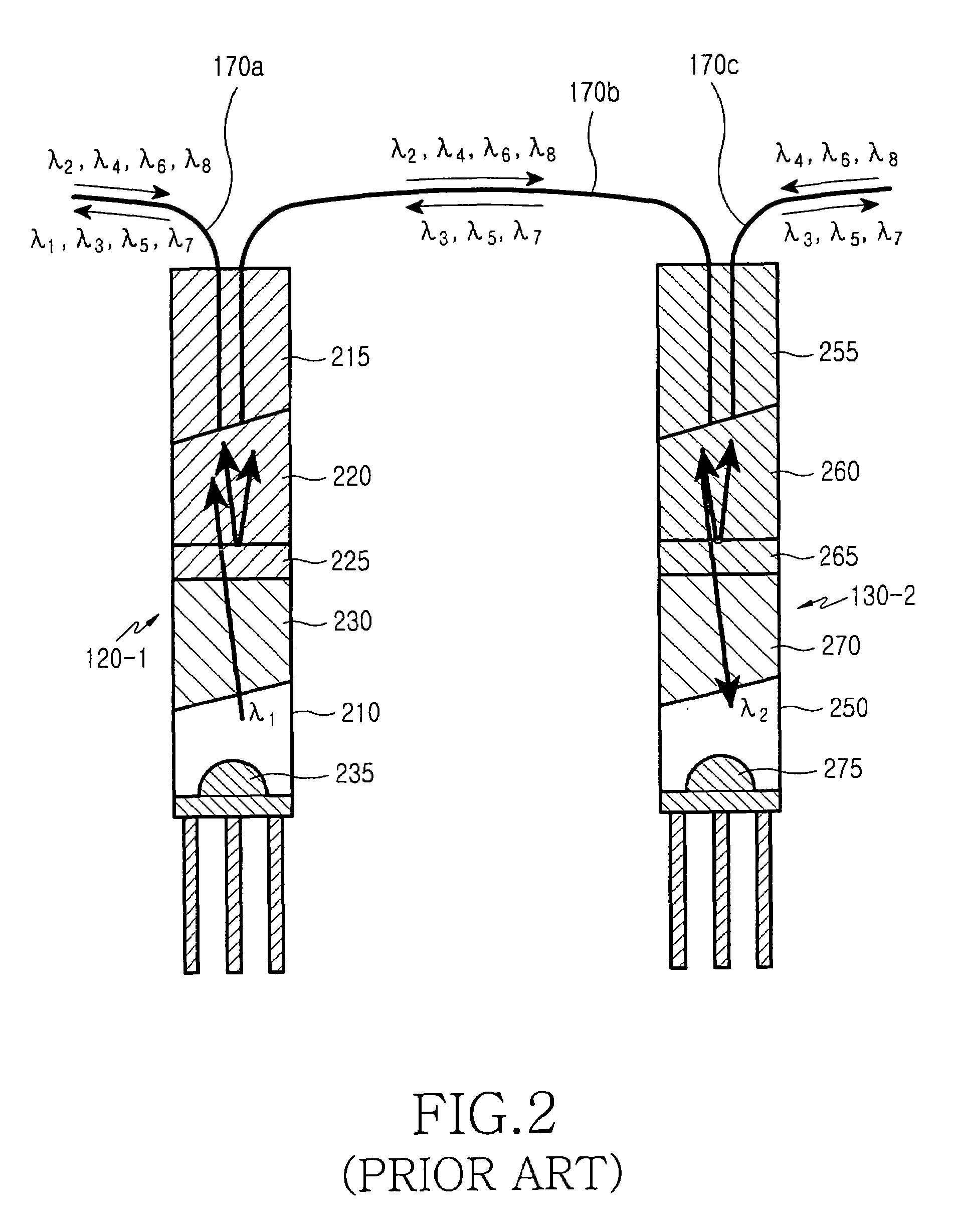
Polarization mode dispersion compensation
InactiveUS6271952B1Producing strainTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsGratingCommunications system
Polarization mode dispersion in an optical signal transmitted through a waveguide of a communications system is compensated by separating the dispersed signal into components corresponding to principal polarization states. The components are delayed by respective delays differing by a delay increment which is controlled to correspond to the dispersion delay and the delayed components are recombined to provide a dispersion compensated optical output signal. Each of the delays is provided by an chirped Bragg reflector forming part of a delay line, the Bragg reflectors comprising optical fibres with chirped intracore index gratings. Transducers or temperature controllers acting on one of the fibres allows dimensional control of the grating periodicity such that the position of Bragg reflection is variable. Wavelength division multiplexed optical signals are compensated using sampled gratings which allow a common Bragg reflection position for each wavelength.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
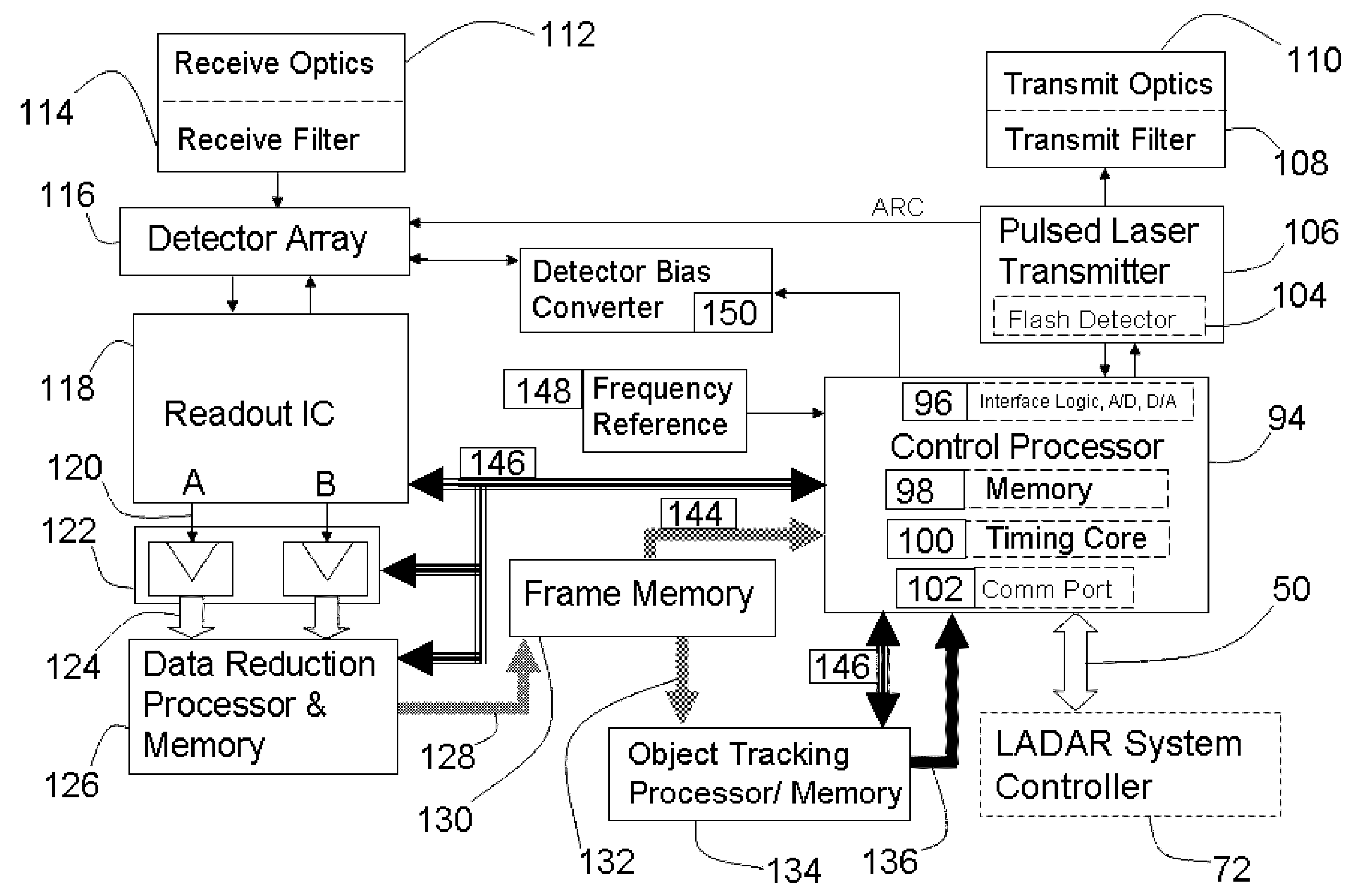
Ladar sensor for a dense environment
ActiveUS20160003946A1Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationDiscriminatorFloating point
A multi-ladar sensor system is proposed for operating in dense environments where many ladar sensors are transmitting and receiving burst mode light in the same space, as may be typical of an automotive application. The system makes use of several techniques to reduce mutual interference between independently operating ladar sensors. In one embodiment, the individual ladar sensors are each assigned a wavelength of operation, and an optical receive filter for blocking the light transmitted at other wavelengths, an example of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). Each ladar sensor, or platform, may also be assigned a pulse width selected from a list, and may use a pulse width discriminator circuit to separate pulses of interest from the clutter of other transmitters. Higher level coding, involving pulse sequences and code sequence correlation, may be implemented in a system of code division multiplexing, CDM. A digital processor optimized to execute mathematical operations is described which has a hardware implemented floating point divider, allowing for real time processing of received ladar pulses, and sequences of pulses.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
Methods and apparatus for filtering an optical fiber
InactiveUS6222970B1Improve responseReduce sensitivityCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh energyPhotonics
Filtering of optical fibers and other related devices. High-energy methods for depositing thin films directly onto the ends of optical fibers can be used to produce high-quality, high-performance filters in quantity at a reasonable cost. These high-quality filters provide the high performance needed for many demanding applications and often eliminate the need for filters applied to wafers or expanded-beam filtering techniques. Having high-quality filters applied directly to optical fiber and faces permits production of high-performance, micro-sized devices that incorporate optical filters. Devices in which these filters may be used include spectroscopic applications including those using fiber optic probes, wavelength division multiplexing, telecommunications, general fiber optic sensor usage, photonic computing, photonic amplifiers, pump blocking and a variety of laser devices.
Owner:CIRREX SYST
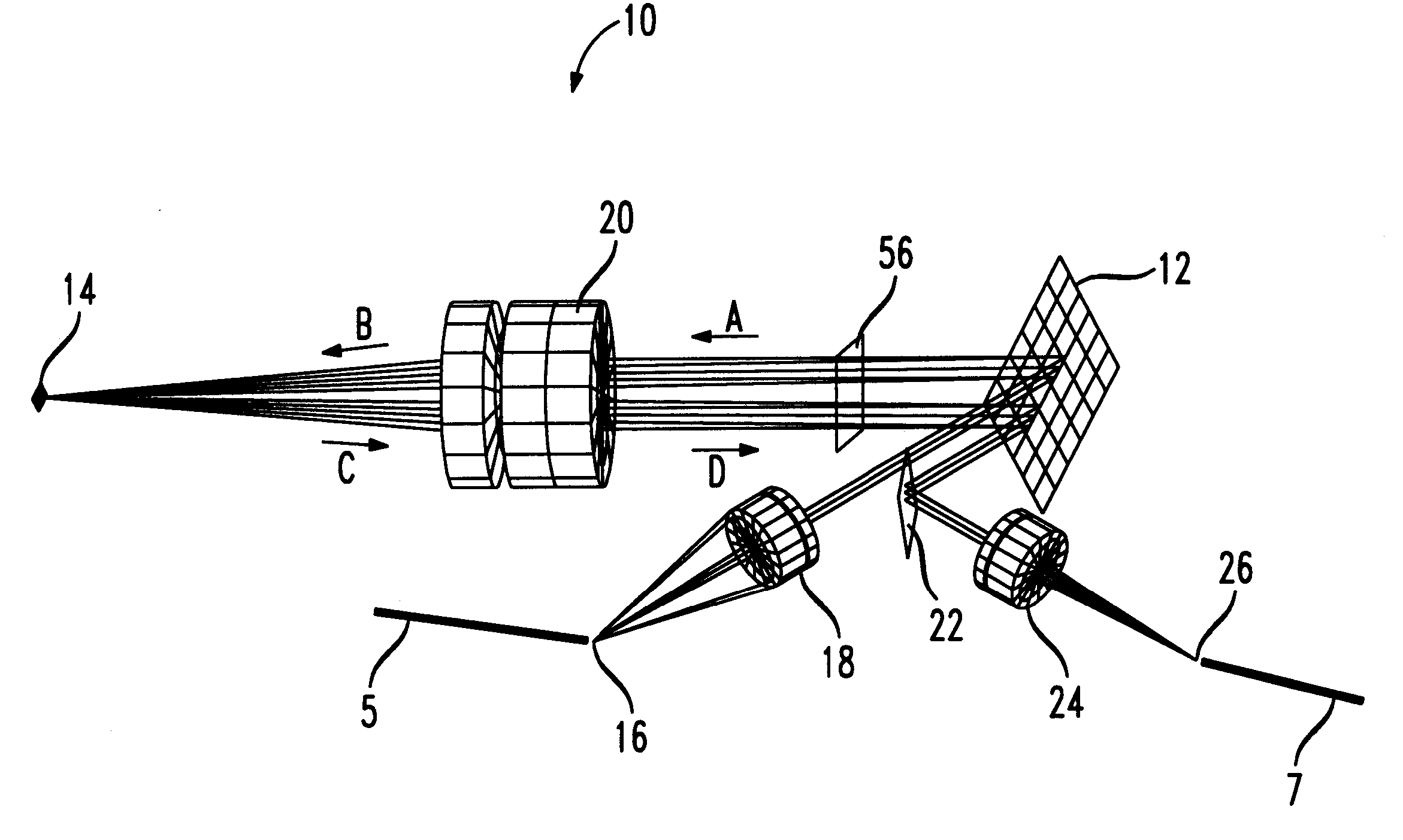
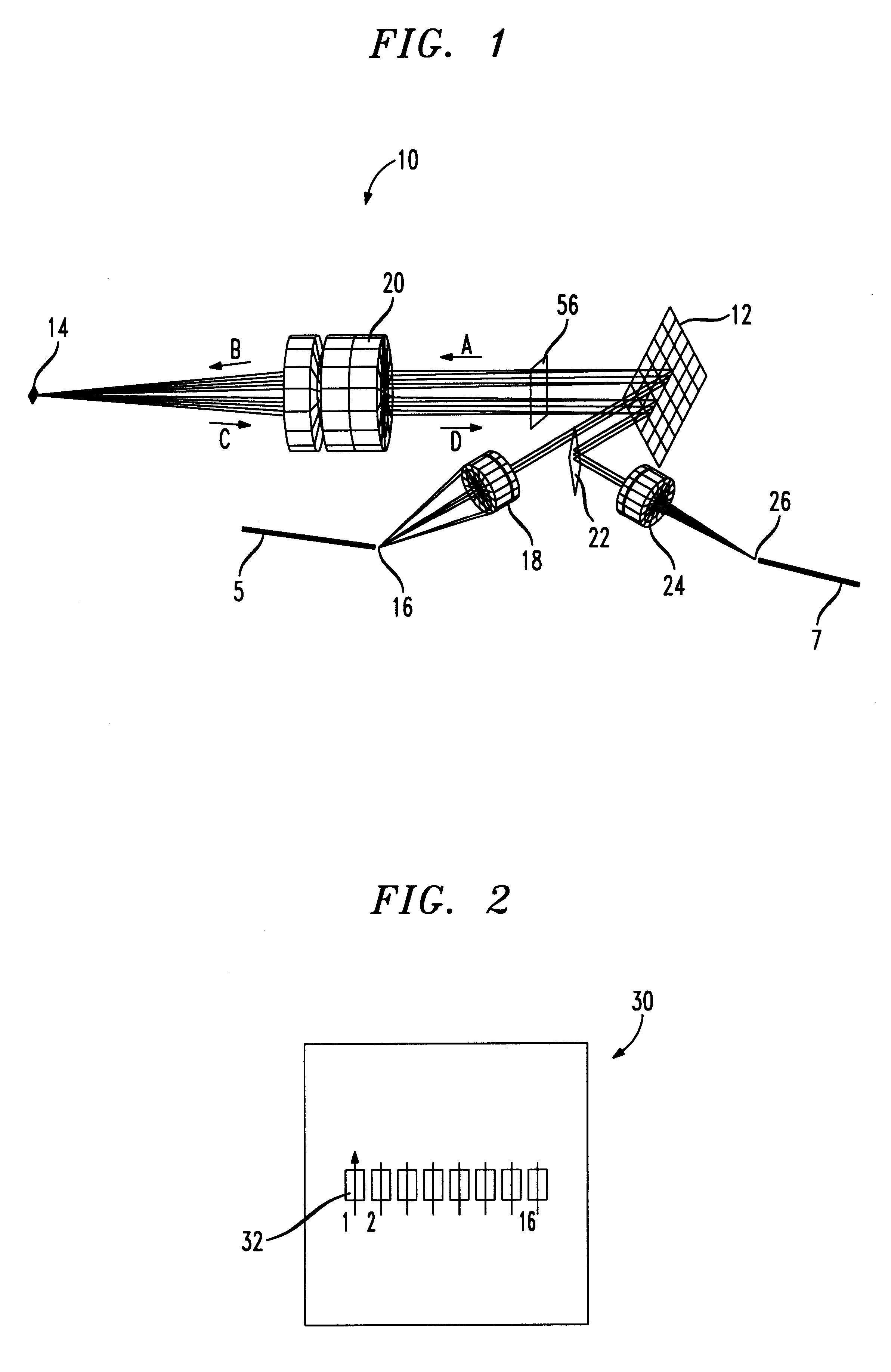
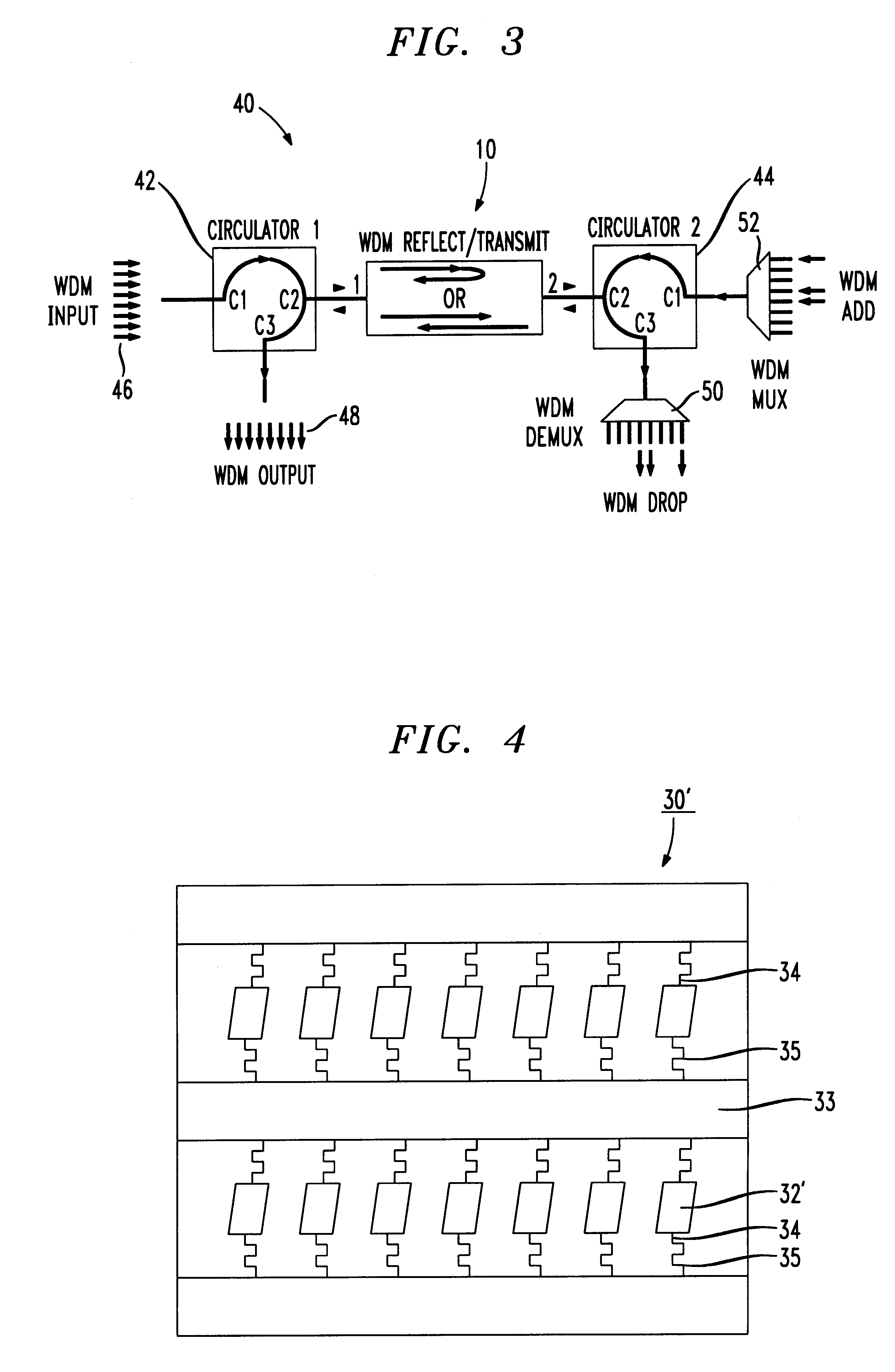
Reconfigurable wavelength division multiplex add/drop device using micromirrors
InactiveUS6204946B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemGrating
A WDM add / drop device for use in an optic communications system for adding and dropping optical wavelengths from a multiple-wavelength optical system. The device includes a set of lenses, a planar grating wavelength multiplexer and a micromirror array switchable for individual wavelengths of the multiple-wavelength signal between a transmit mode and a reflect mode. The grating angularly demultiplexes a multiple-wavelength optical signal in a first direction and the individual wavelengths are processed by the micromirror array and directed to the grating in a second direction. The micromirror array will either reflect select wavelengths to a first port or transmit select wavelengths to a second port. In a preferred embodiment, ports on a first multiport circulator input the multiple-wavelength optical signal to the WDM add / drop device and output the multiple-wavelength optical signal from the WDM add / drop device. A second multiport circulator provides to-be-added wavelengths to the WDM add / drop device and removes to-be-dropped wavelengths from the WDM add / drop device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
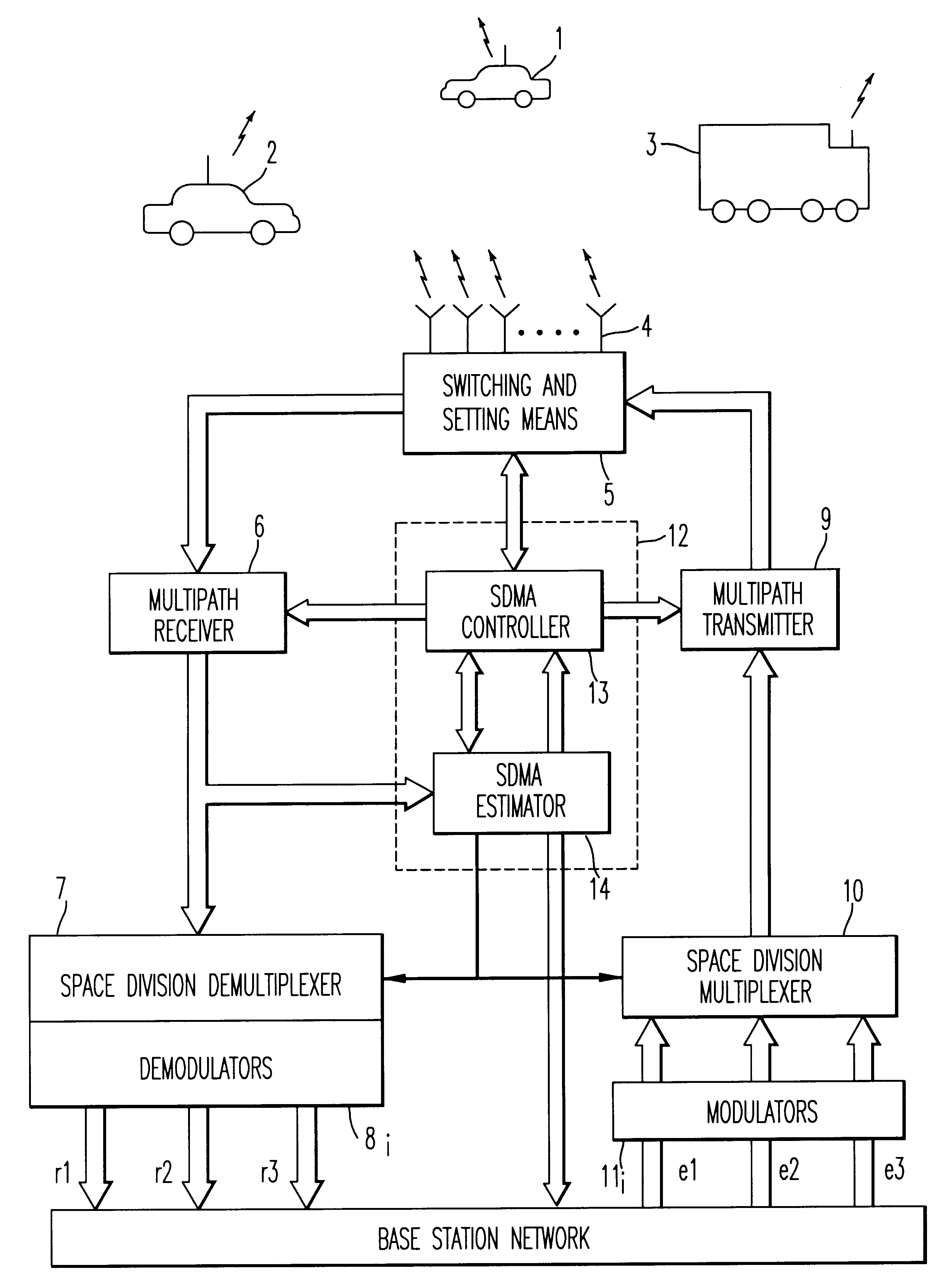
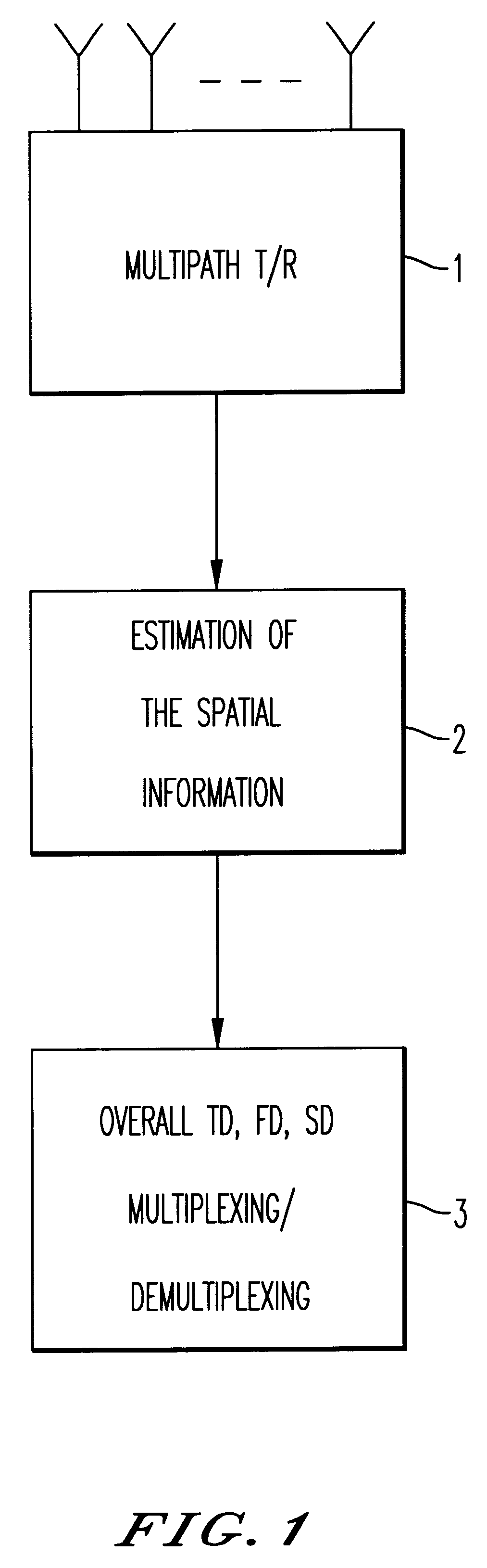
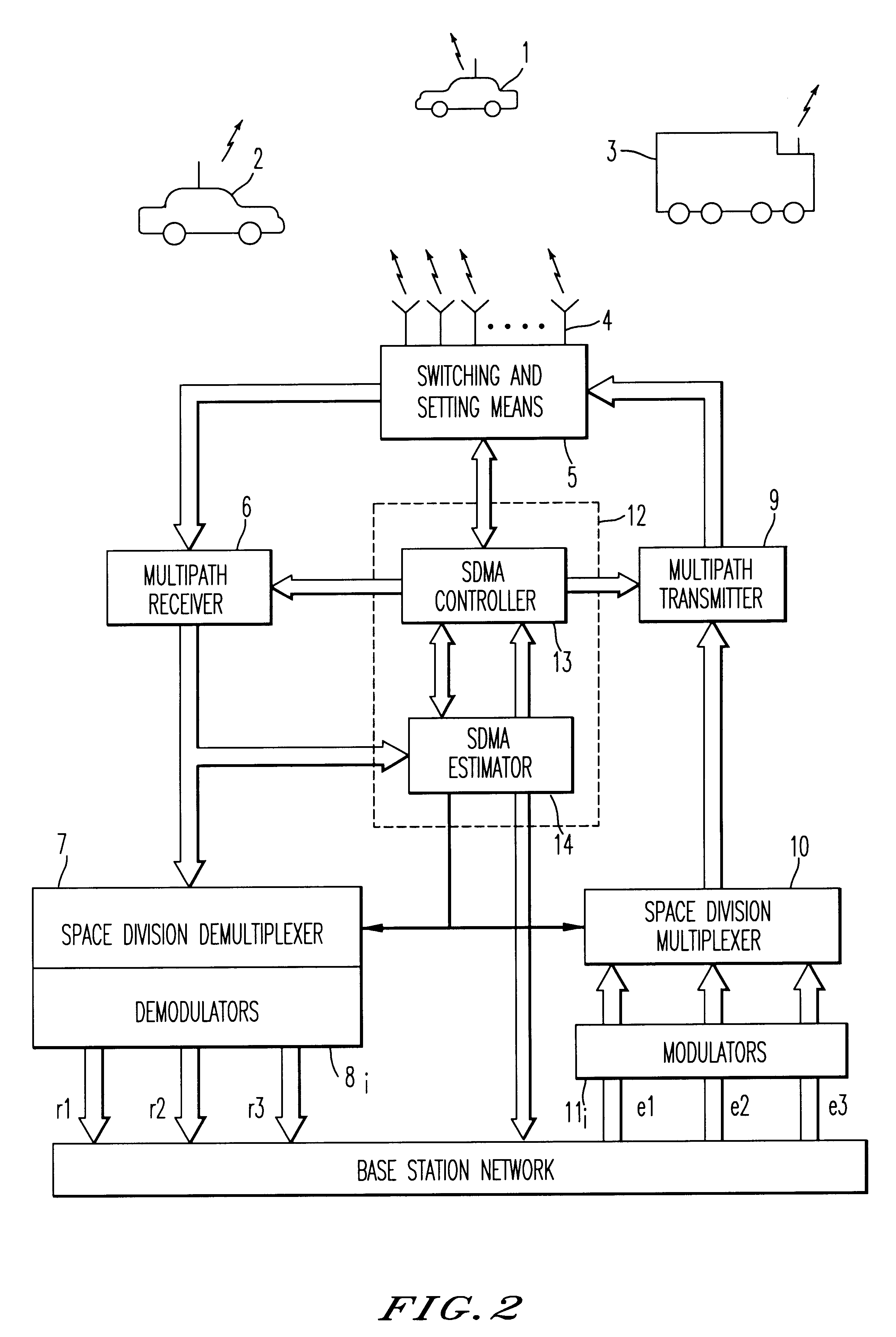
Method and device for space division multiplexing of radio signals transmitted in cellular radio communications
InactiveUS6240098B1Space can be allowedImprove performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
A method and apparatus for spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing of radio signals. A multichannel transmitter and receiver is integrated in a base station and coupled to an antenna array. Using digital radio signals containing previously known or non-Gaussian sequences and arranged in frames, the spatial information about each mobile unit is estimated on the basis of the signal received by the receiver for the reception and transmission frequencies. This is done by known sequences or by blind source separation methods. The respective paths of each mobile unit with the power above a predetermined threshold is isolated by spatial filtering in the presence of multiple channel paths in order to provide spatial demultiplexing. Simultaneously, the intended signal is transmitted in the direction of the main path of each mobile unit while protecting each mobile unit from signals transmitted in the direction of other mobile units by spatial filtering with cancelling constraints in order to provide spatial multiplexing.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
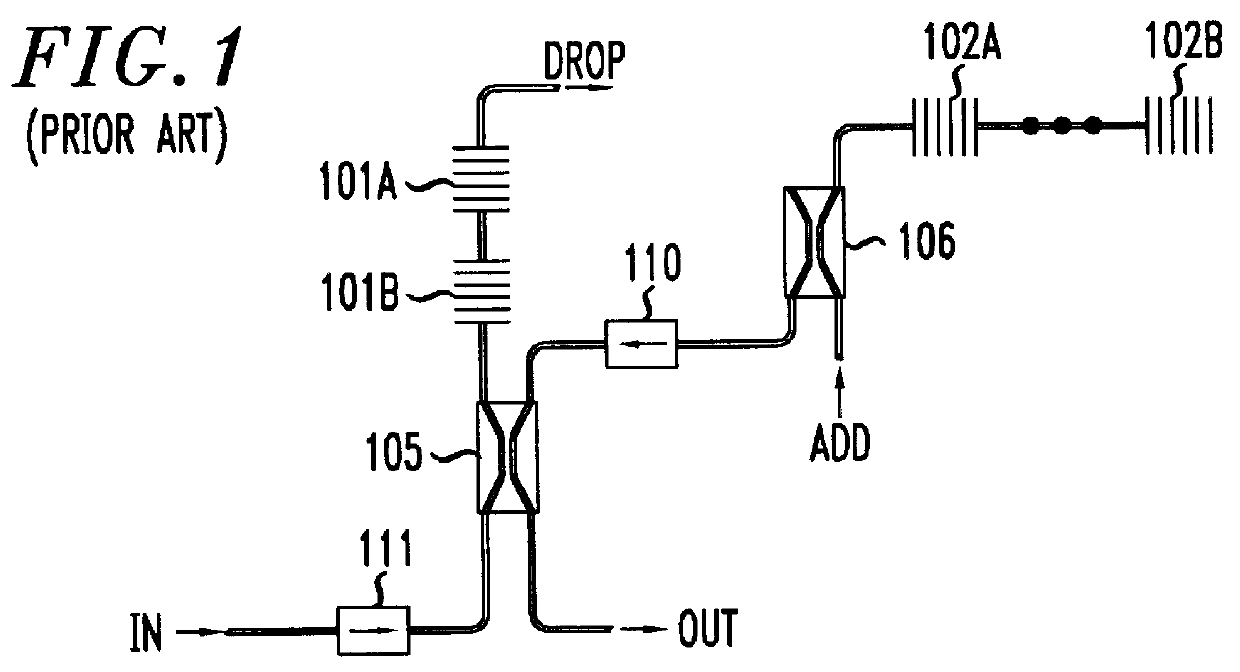
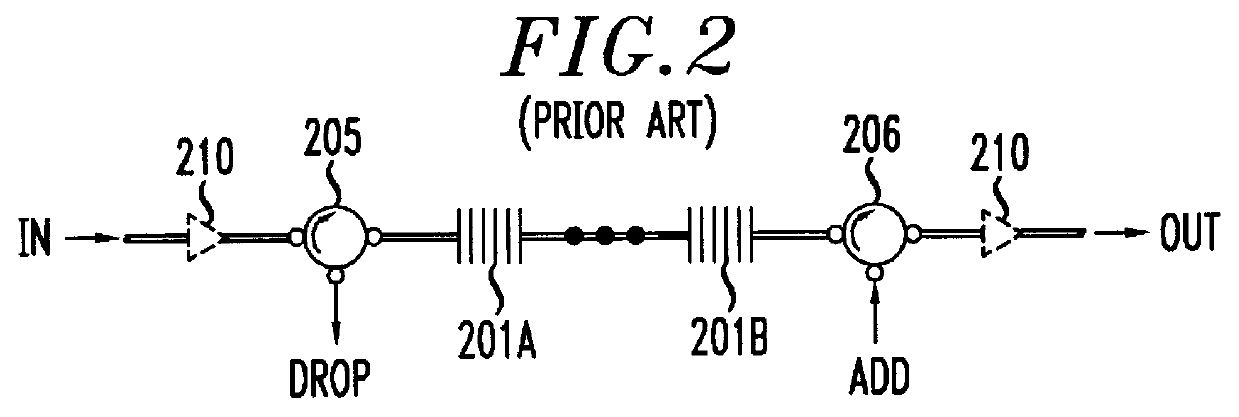
Wavelength-selective and loss-less optical add/drop multiplexer
InactiveUS6122095ALoss can be compensatedOvercomes shortcomingRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberGrating
A loss-less, optical add / drop multiplexer according to the present invention includes a rare earth-doped fiber amplifier integrated with a wavelength-selective fiber path coupled between two directional optical transfer devices for selectively adding and dropping optical signals from a multi-wavelength signal, such as a wavelength division multiplexed optical signal. One or more fiber gratings are disposed along the length of the rare earth-doped fiber amplifier or between segments of the rare earth-doped fiber so that at least one grating is used for reflecting each optical signal that is expected to be added to or dropped from the multi-wavelength optical signal. By using this configuration, appropriate amplification is provided to compensate for losses in the add, drop, and through paths.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
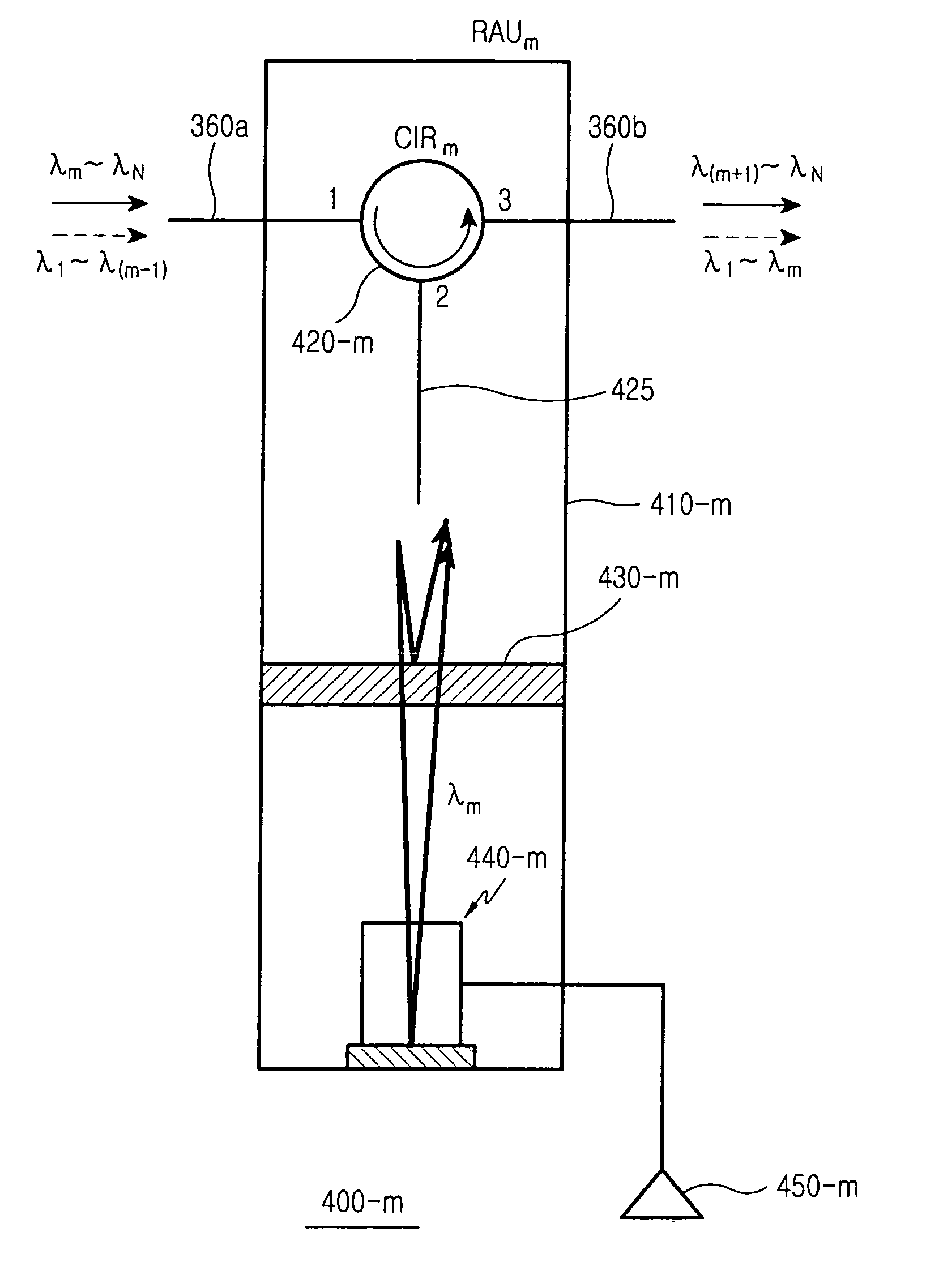
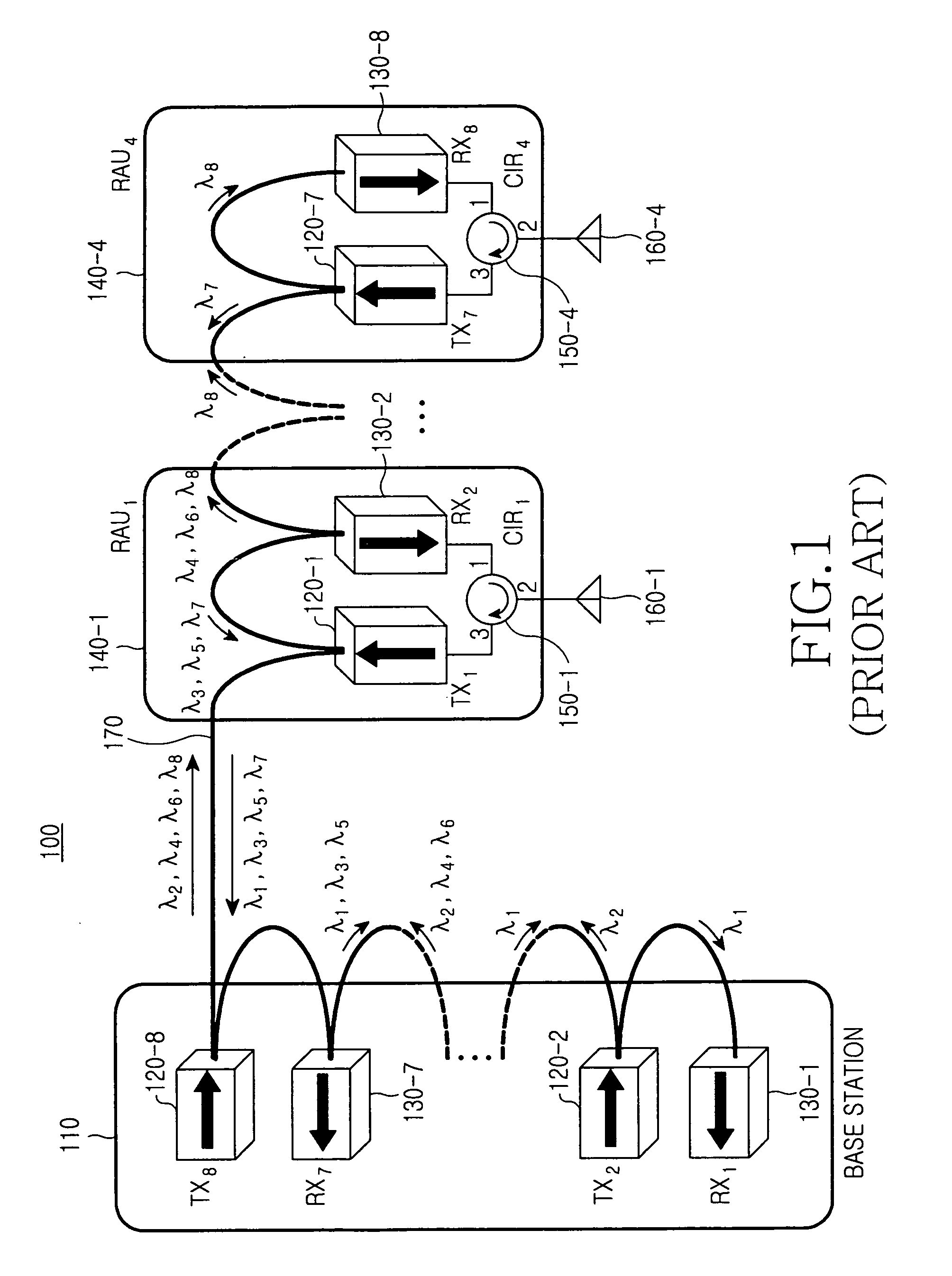
Remote antenna unit and wavelength division multiplexing radio-over-fiber network
InactiveUS7269311B2Simple structureLow costCoupling light guidesRadio-over-fibreElectricityRadio over fiber
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
LADAR sensor for a dense environment
A multi-ladar sensor system is proposed for operating in dense environments where many ladar sensors are transmitting and receiving burst mode light in the same space, as may be typical of an automotive application. The system makes use of several techniques to reduce mutual interference between independently operating ladar sensors. In one embodiment, the individual ladar sensors are each assigned a wavelength of operation, and an optical receive filter for blocking the light transmitted at other wavelengths, an example of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). Each ladar sensor, or platform, may also be assigned a pulse width selected from a list, and may use a pulse width discriminator circuit to separate pulses of interest from the clutter of other transmitters. Higher level coding, involving pulse sequences and code sequence correlation, may be implemented in a system of code division multiplexing, CDM. A digital processor optimized to execute mathematical operations is described which has a hardware implemented floating point divider, allowing for real time processing of received ladar pulses, and sequences of pulses.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
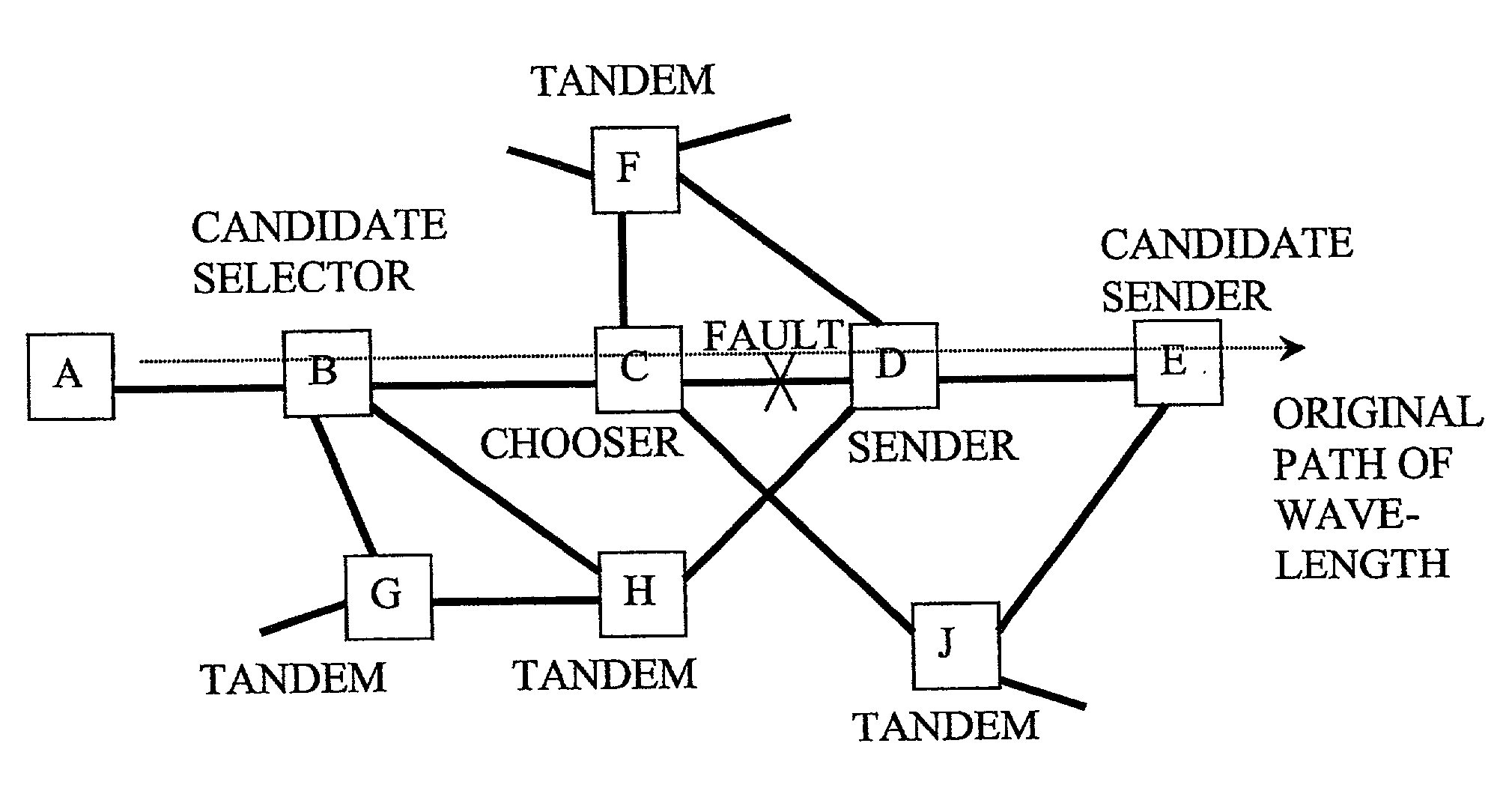
Fast restoration in optical mesh network
InactiveUS20020191247A1Easy to operateImprove good performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringOptical mesh networkRouting table
A wavelength division multiplexed optical network has a restoration process to re-route one or more of the wavelengths, by dynamically determining possible restoration routes, and re-routing each wavelength along a chosen one of the possible restoration routes. A distributed dynamic search for restoration routes down to the optical layer, for wavelengths, gives faster and more scalable restoration than reconfiguring routing tables and enables much better utilisation of bandwidth than using predetermined restoration paths.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
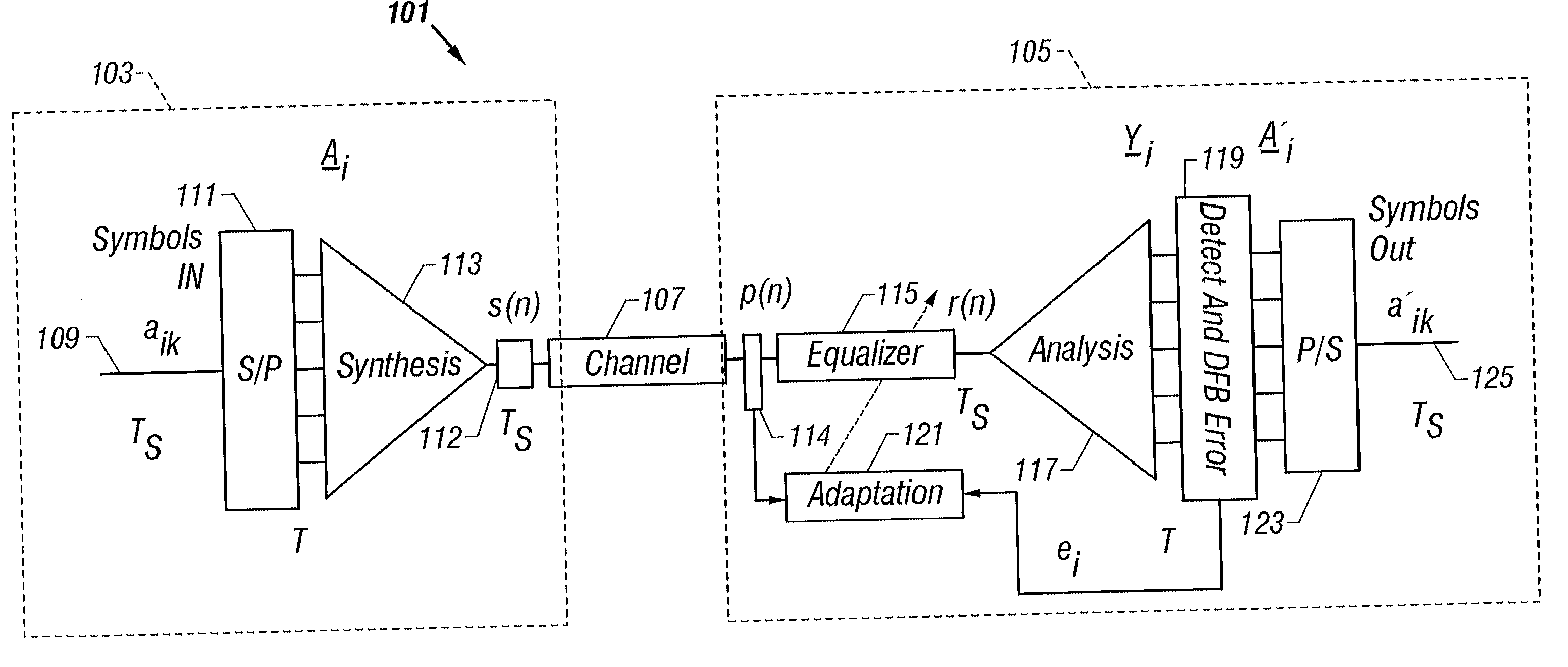
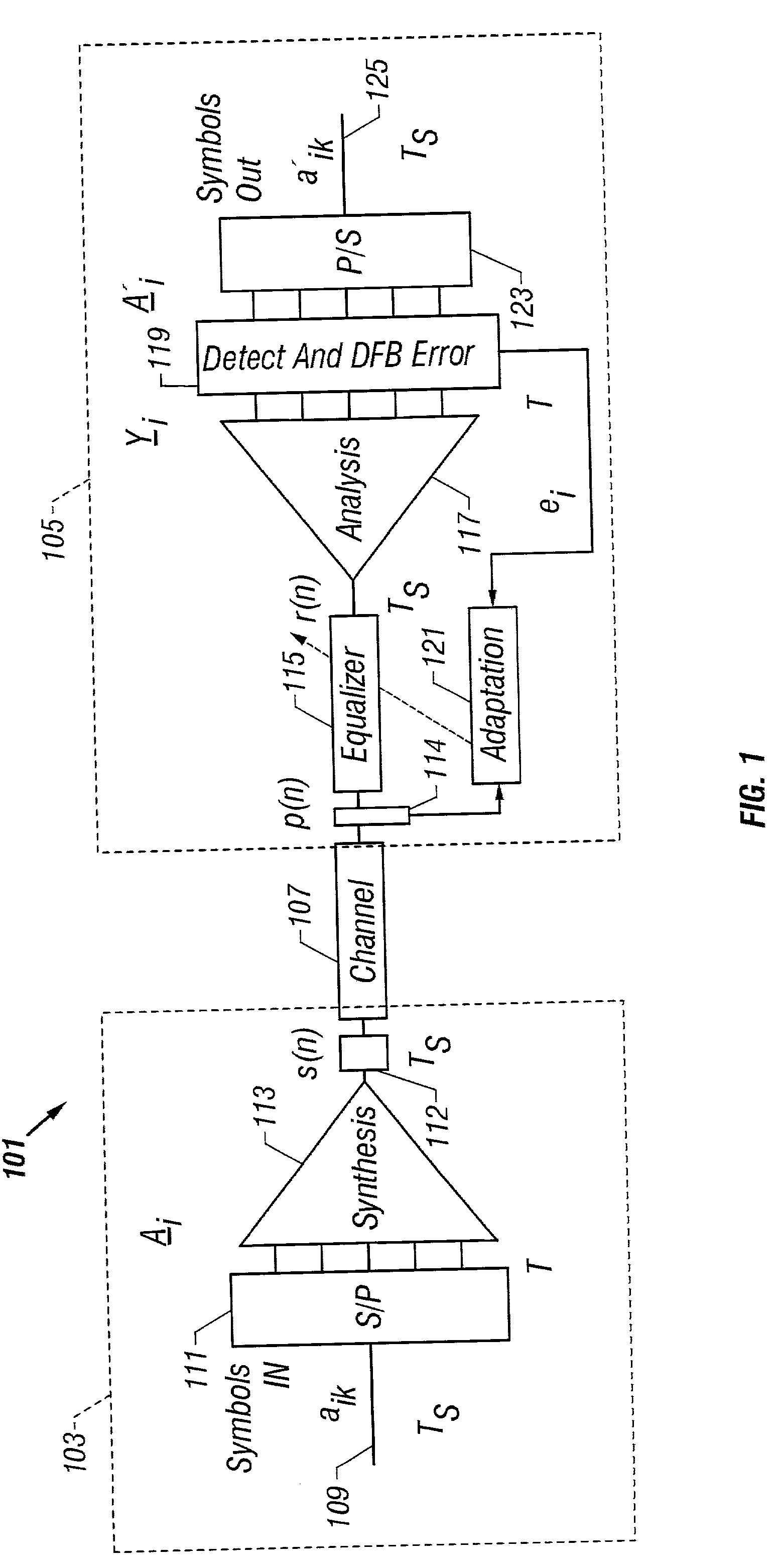
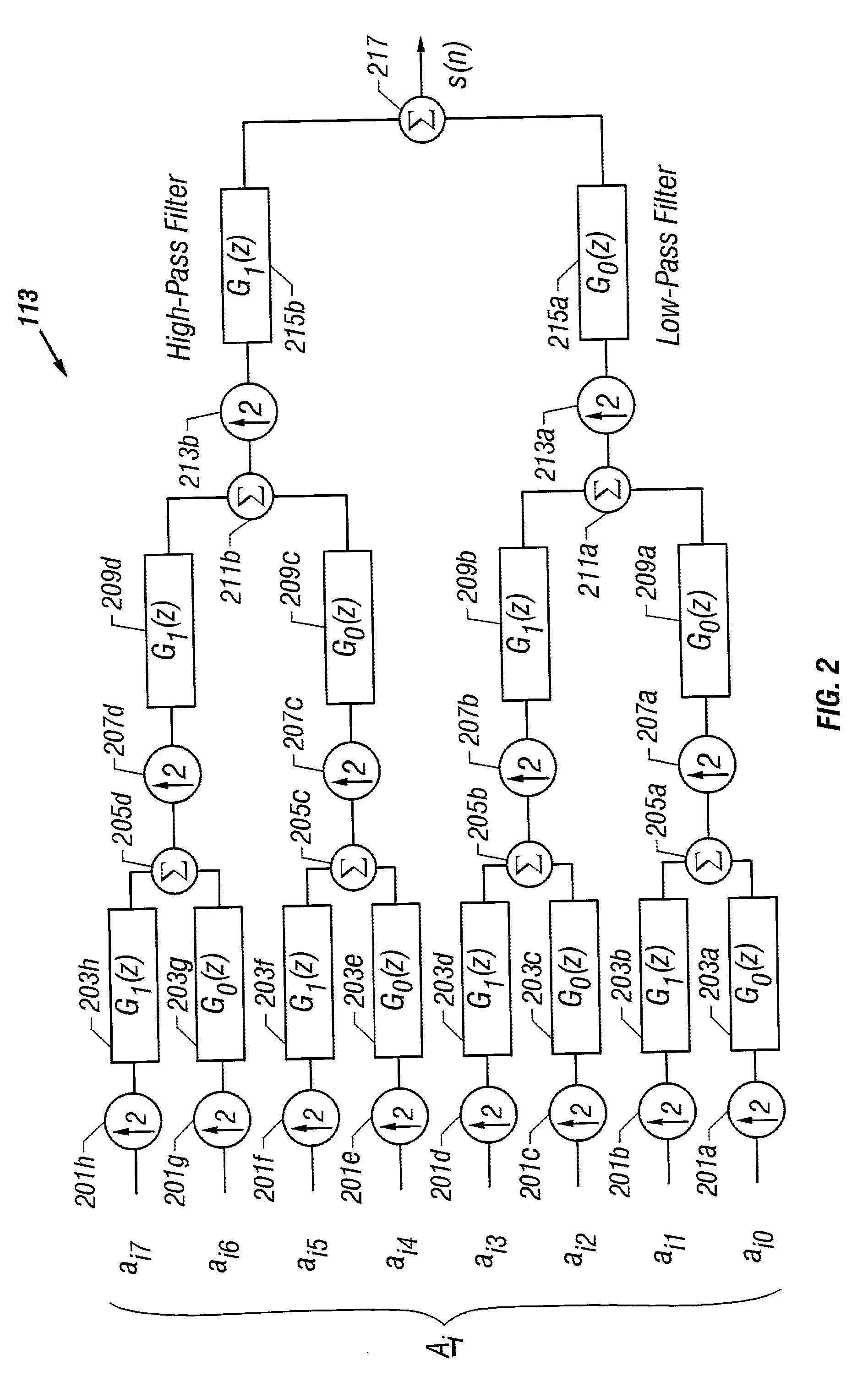
Communication system using orthogonal wavelet division multiplexing (OWDM) and OWDM-spread spectrum (OWSS) signaling
InactiveUS20020181388A1Multiple-port networksPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMultiplexingBroadband pulse
An orthogonal wavelet division multiplexing (OWDM) communication system including a synthesis section and a channel interface. The synthesis section includes a filter pair bank with multiple inputs and an output that provides an OWDM signal. Each input receives a corresponding symbol of a supersymbol, where the symbols are from a selected modulation scheme. The synthesis section generates the OWDM signal as a combination of weighted OWDM pulses, where each weighted OWDM pulse represents of a symbol of the supersymbol. An OWDM Spread Spectrum (OWSS) communication system that uses broad-time and broadband pulses generated from a family of OWDM pulses together with a set of orthogonal PN code vectors. The OWSS pulses are mutually orthogonal and allow multi-user operation. Each user is assigned an OWSS pulse corresponding to a particular PN code. OWSS enables high rate operation for wireless channels with the use of an equalizer with FE and DFE sections.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +2
Integrated bi-directional axial gradient refractive index/diffraction grating wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS6011884AIncreased durabilityImprove the environmentLaser detailsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingMultiplexer
A wavelength division multiplexer is provided that integrates an axial gradient refractive index element with a diffraction grating to provide efficient coupling from a plurality of input optical sources (each delivering a single wavelength to the device) which are multiplexed to a single polychromatic beam for output to a single output optical receiver. The device comprises: (a) means for accepting optical input from at least one optical source, the means including a planar surface; (b) a coupler element comprising (1) an axial gradient refractive index collimating lens having a planar entrance surface onto which the optical input is incident and (2) a homogeneous index boot lens affixed to the axial gradient refractive index collimating lens and having a planar but tilted exit surface; (c) a diffraction grating, such as a Littrow diffraction grating, on the tilted surface of the homogeneous index boot lens which combines a plurality of spatially separated wavelengths from the optical light; and (d) means to output at least one multiplexed, polychromatic output beam, the means including a planar surface. The device may be operated in the forward direction as a multiplexer or in the reverse direction as a demultiplexer.
Owner:AUXORA
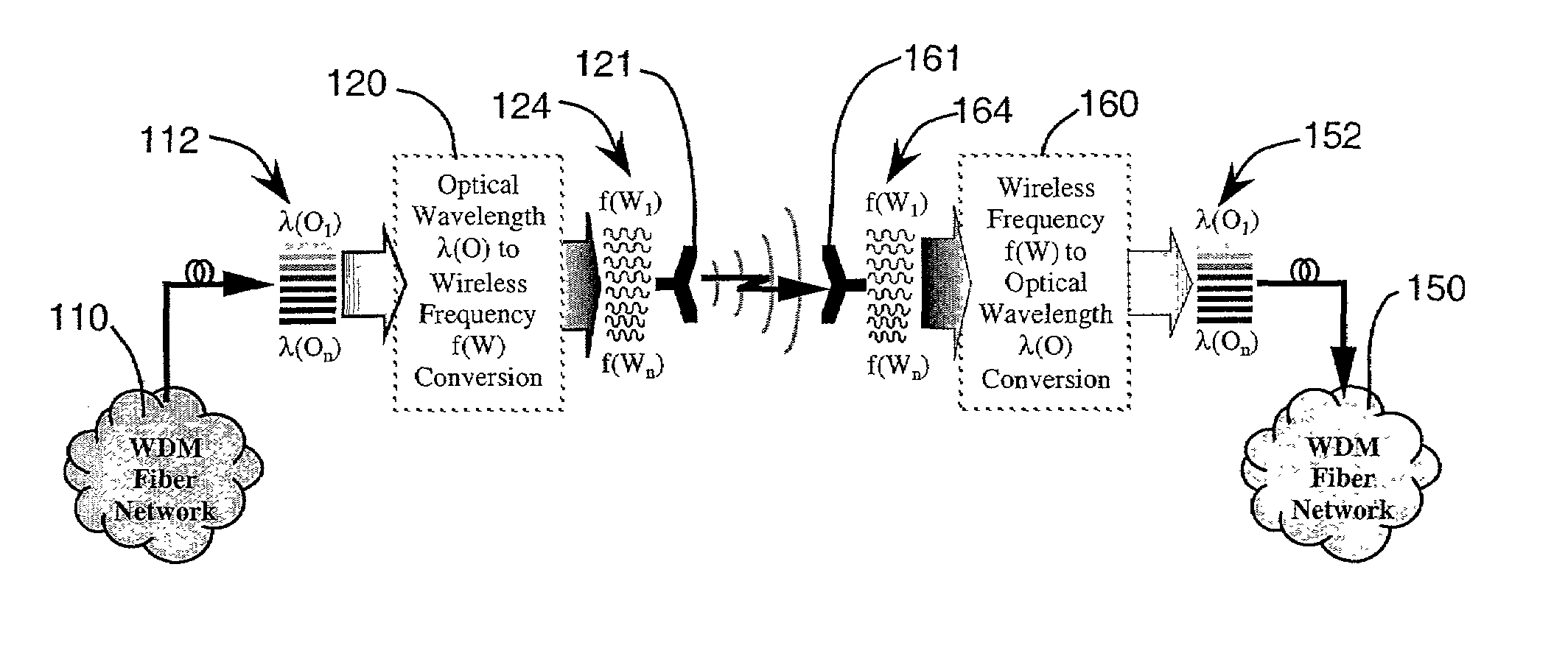
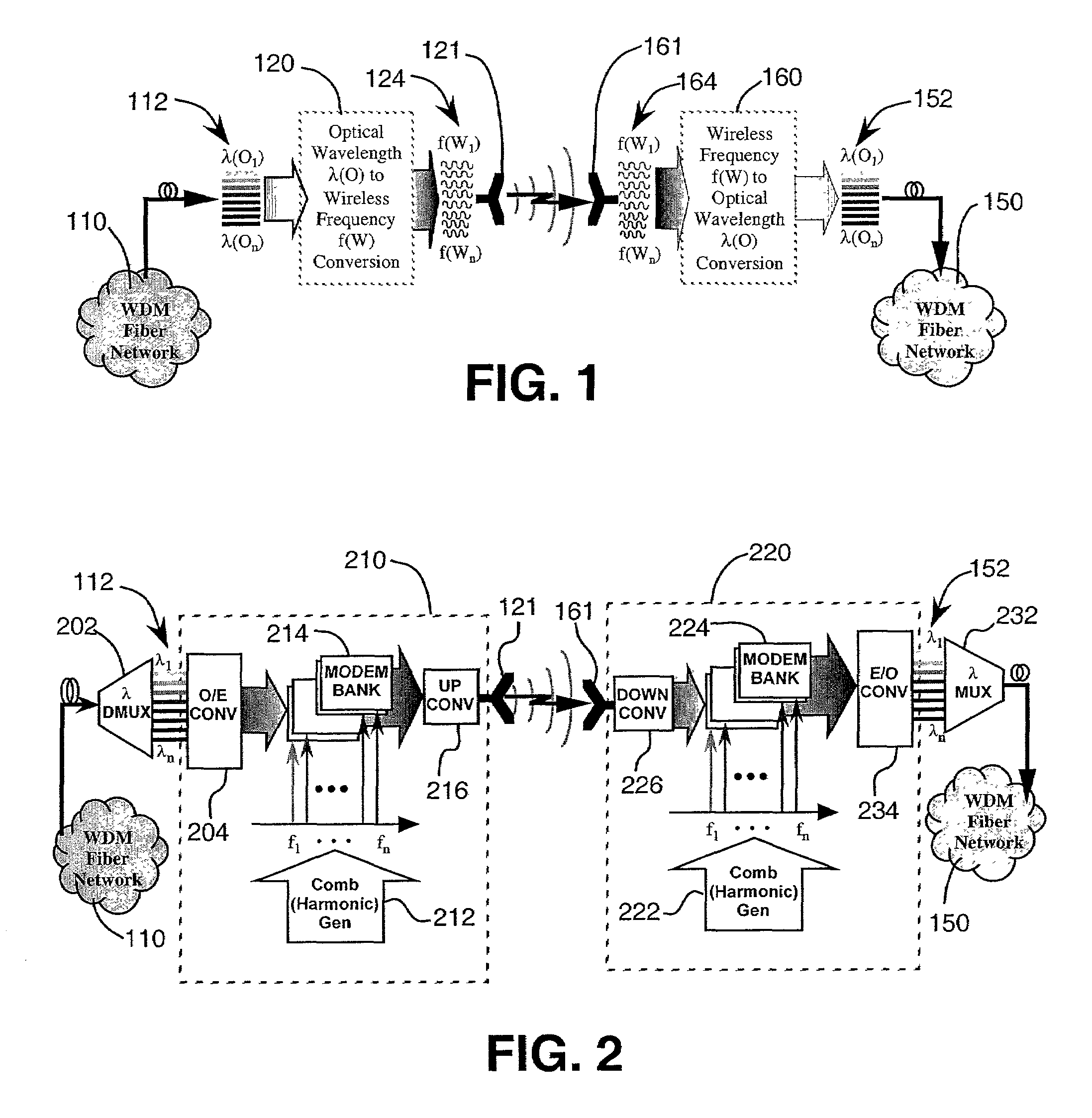
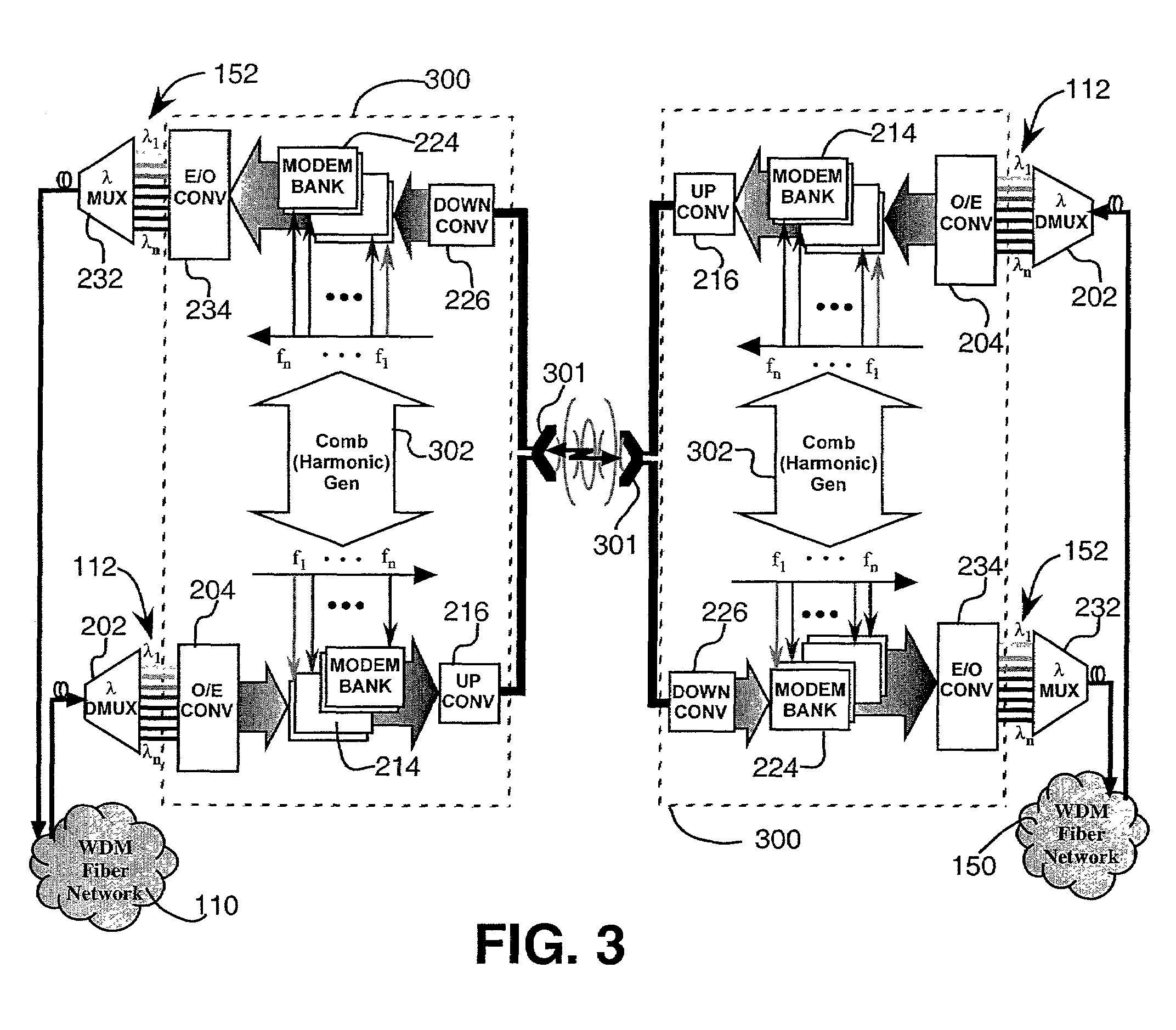
Wireless wavelength division multiplexed system
InactiveUS7409159B2Sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransceiverLocal Multipoint Distribution Service
A system and method for linking optical wavelength division multiplexed (OWDM) networks by using wireless communications. Each optical channel in a OWDM network is coupled to a wireless wavelength division multiplexing (WWDM) channel by a WWDM transceiver, which transmits and receives data between OWDM networks. The WWDM transceiver may transmit and receive data in RF bands, where the assignment of different OWDM channels to different frequencies within the RF bands may depend upon the data rate or service supported by the OWDM channel. WWDM systems may also support communications between OWDM networks and individual users, such as those in a local multipoint distribution service.
Owner:HRL LAB
Power and optical frequency monitoring system and transmission system of frequency-modulated optical signal
InactiveUS20020154372A1Realized easily and economicallyAvoid performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransport systemMonitoring system
The present invention relates to a monitoring system that observes the power and optical frequency of a frequency-modulated optical signal, which is utilized in the communication network employing the WDM (wavelength division multiplexing) method. The monitoring system comprises demultiplex means for demultiplexing the frequency-modulated optical signal outputted from a transmitter including frequency-modulation means, photo-detection means for converting the output of demultiplex means into an electrical signal, and extraction means for extracting the power and optical frequency of an optical signal by measuring the magnitude of an amplitude-modulated tone.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
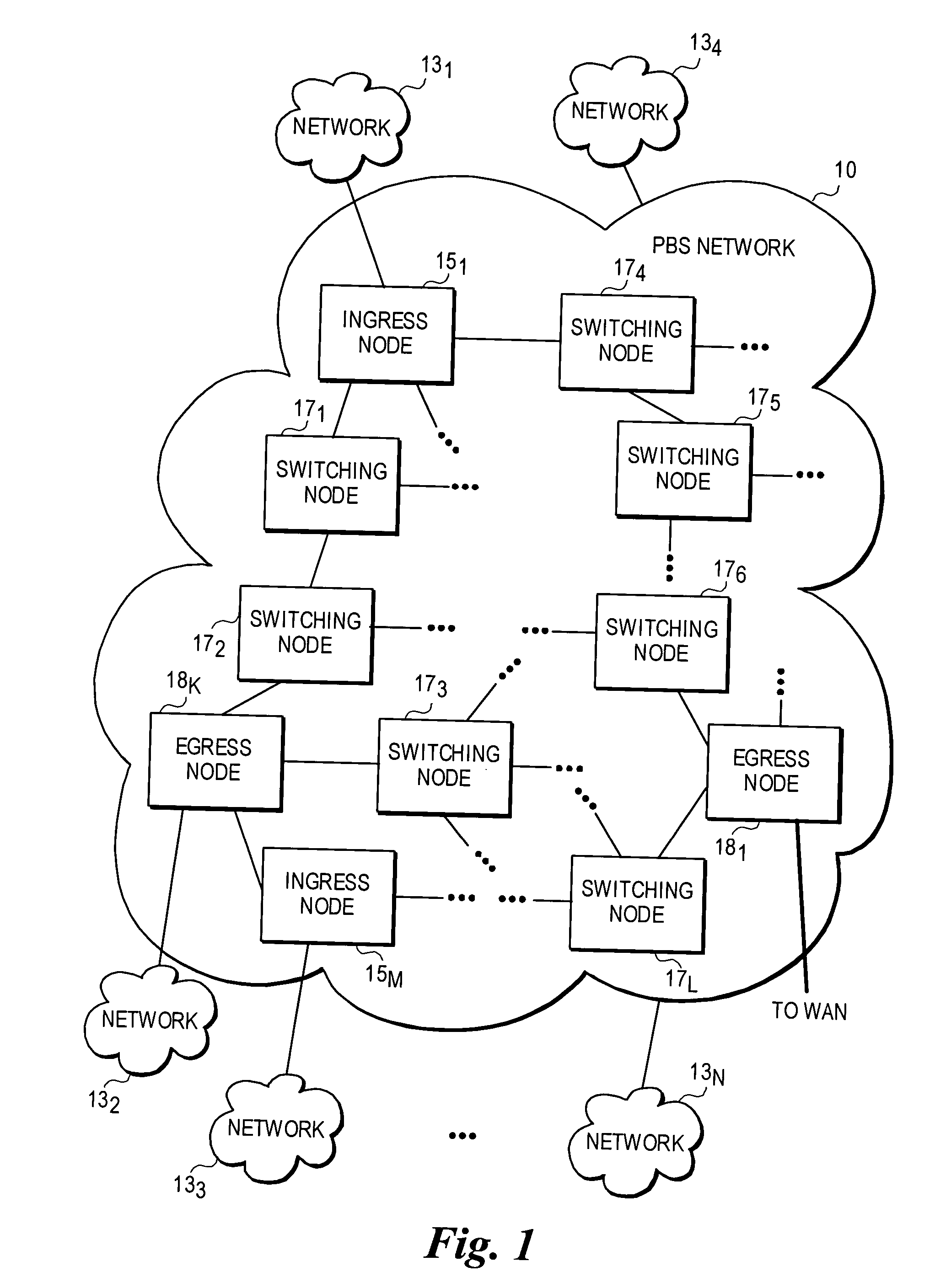
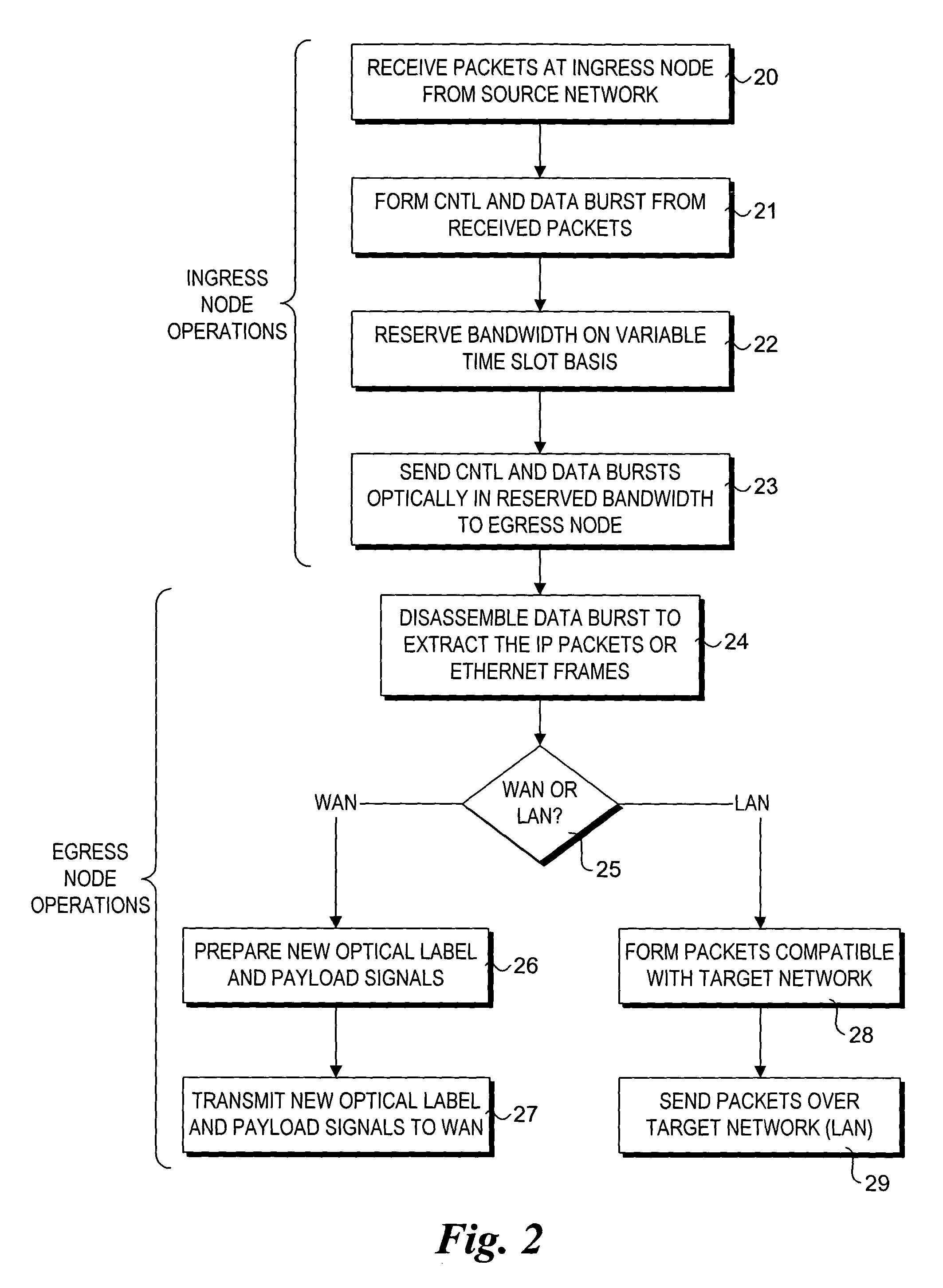
Method and system to recover resources in the event of data burst loss within WDM-based optical-switched networks
InactiveUS20050063701A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexExchange networkEdge node
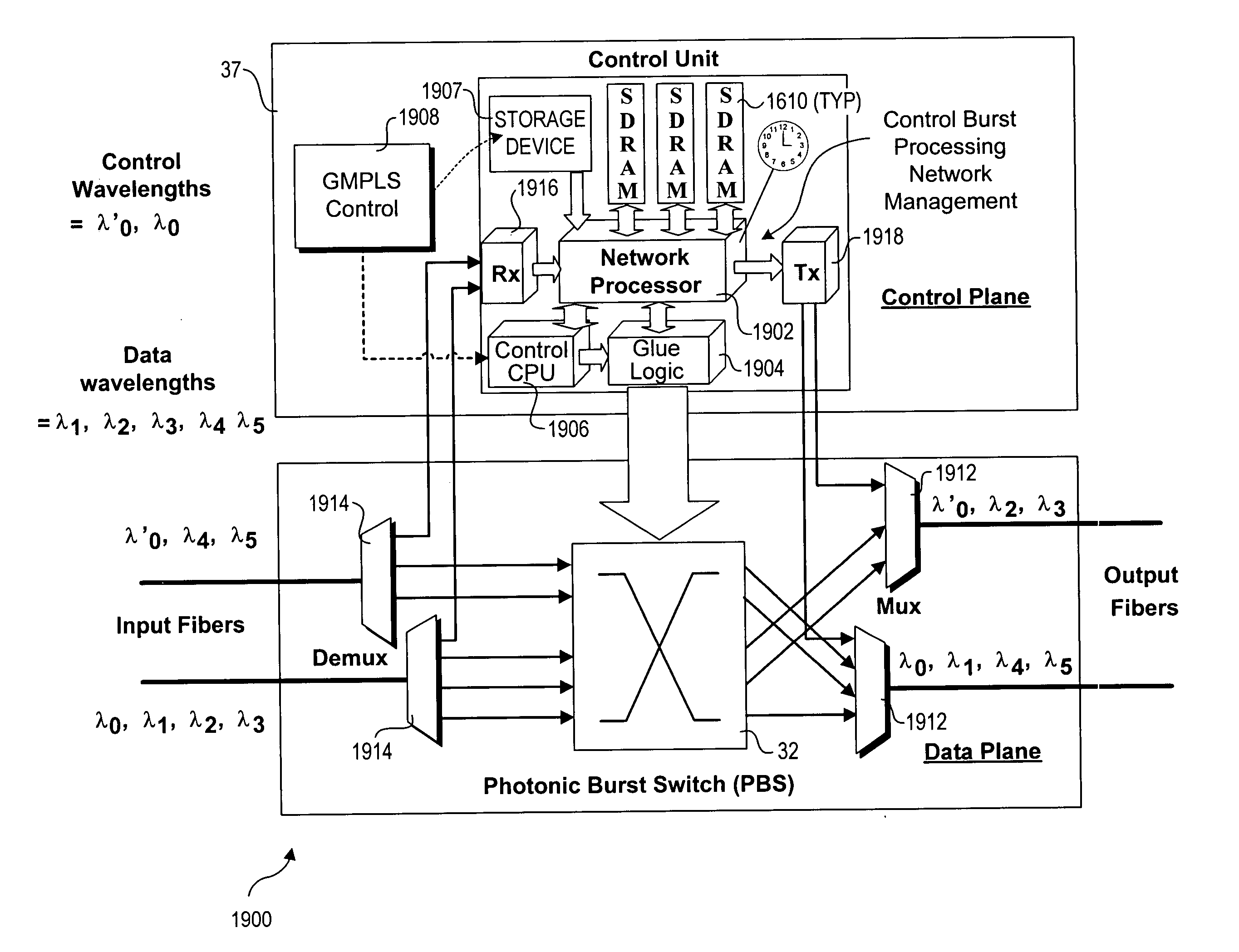
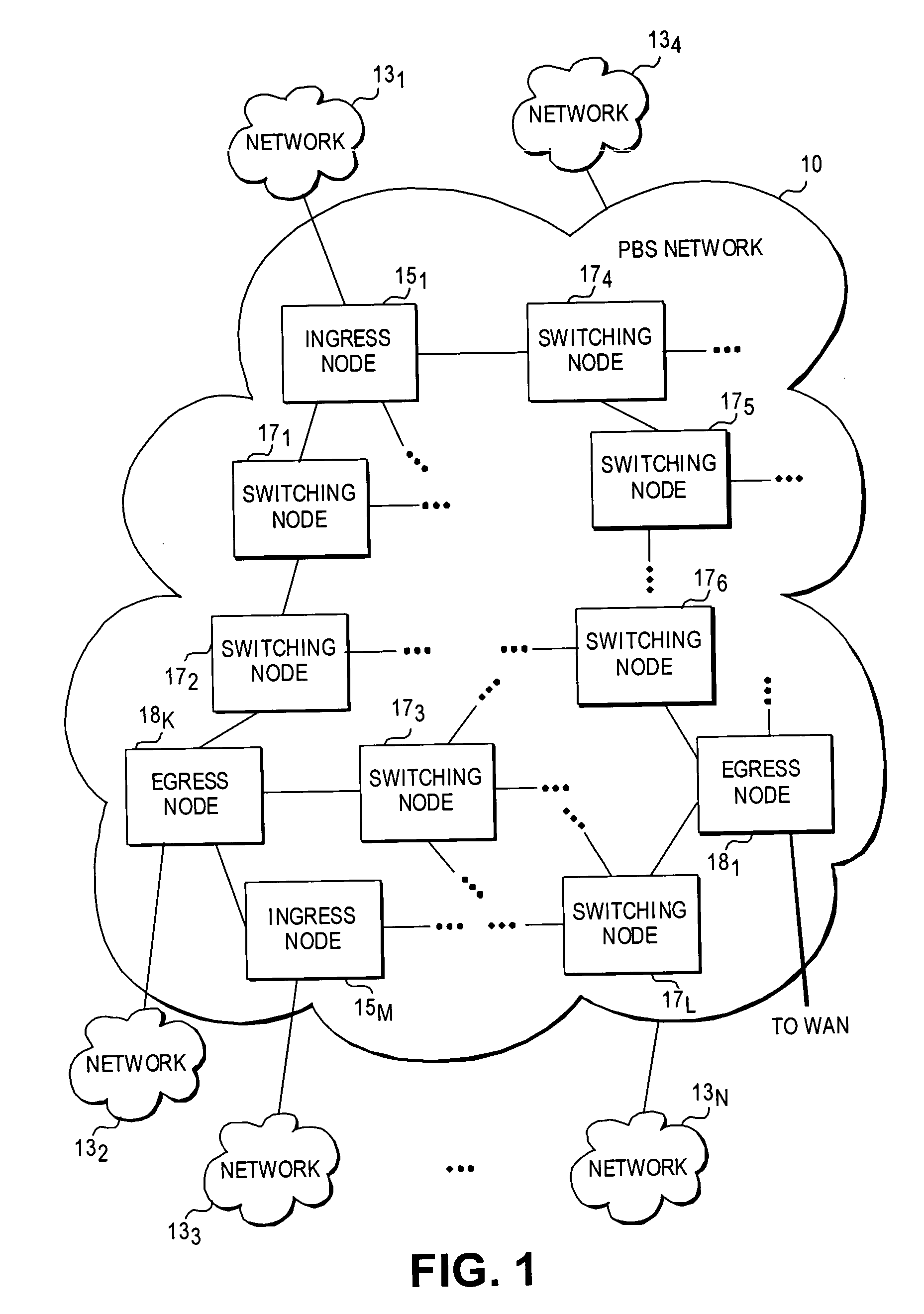
A mechanism for recovering reserved resources in a wavelength-division-multiplexed based photonic burst switched (PBS) network in response to resource non-availability. The PBS network includes edge and switching nodes, which optically communicate information formatted into PBS control and data burst frames. Each PBS data burst frame is associated with a PBS control burst frame. A PBS control burst is sent to reserve resources along a lightpath comprising a concatenation of lightpath segments linked between in ingress edge nodes, switching nodes and egress edge nodes. During a subsequent data burst, an unavailable resource is detected at one of the switching nodes. In response, a resource cancellation message (RCM) comprising a control burst is sent to upstream and / or downstream nodes along the lightpath. Upon receiving the RCM, the corresponding resource reservation is cancelled, freeing the network resources for subsequent bandwidth reservations and access.
Owner:INTEL CORP
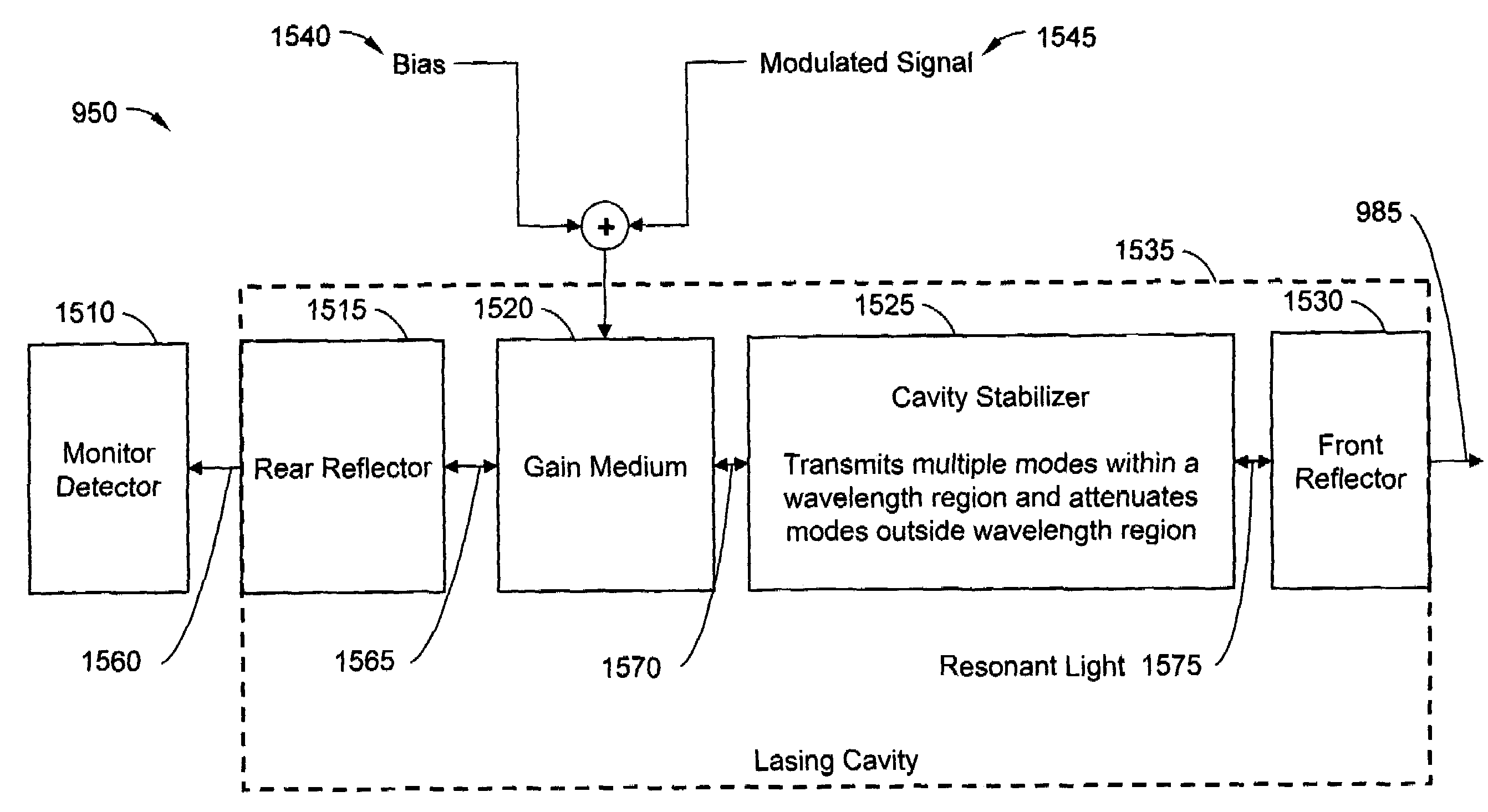
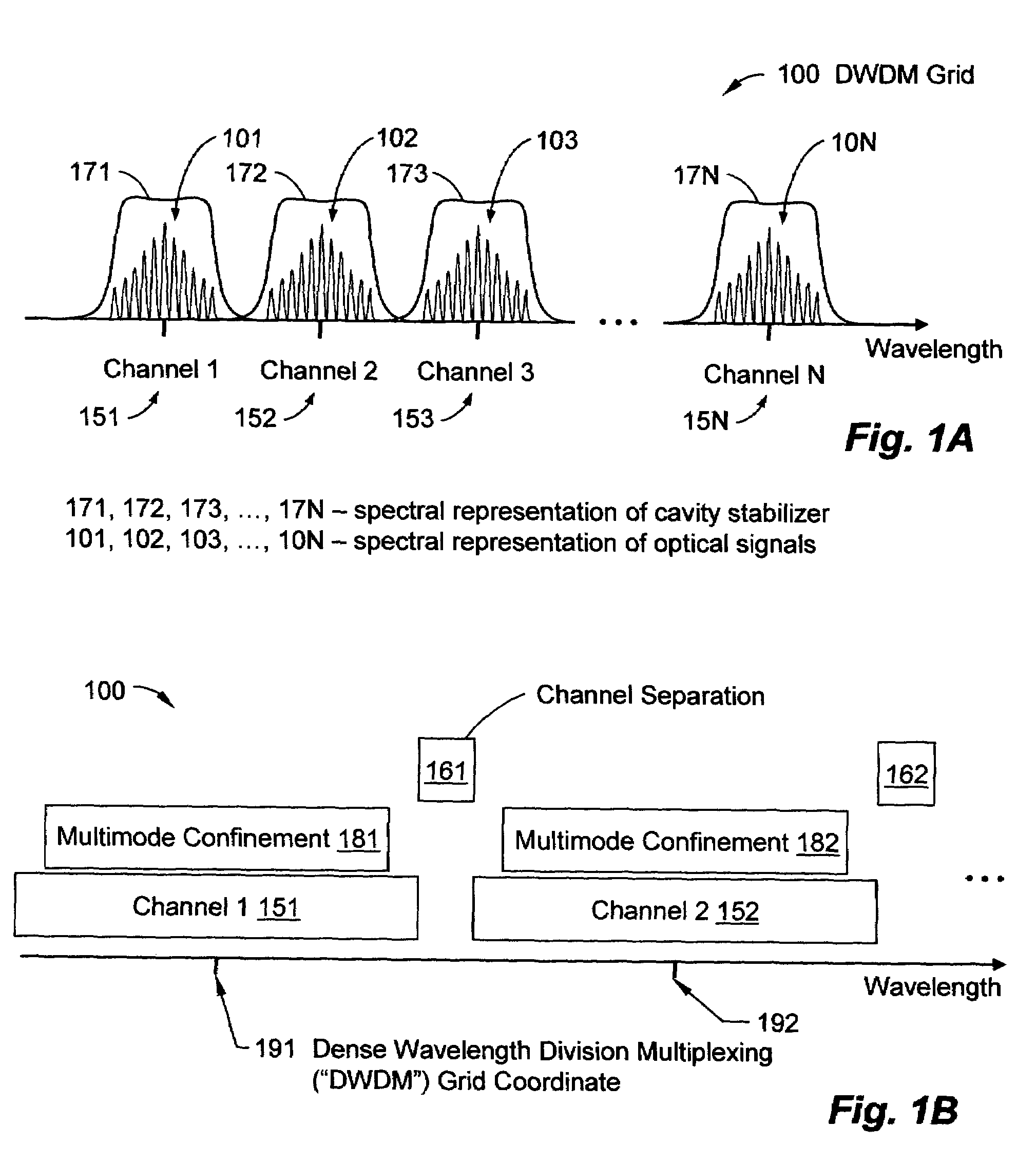
Robustly stabilizing laser systems
InactiveUS7565084B1Optical mode multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersPattern matchingBeam steering
A robustly stabilized communication laser can output a multimode optical signal remaining aligned to a coordinate of a dense wavelength division multiplexing (“DWDM”) grid while responding to a fluctuating condition or random event, such as, without limitation, exposure to a temperature fluctuation, stray light, or contamination. Responsive to the fluctuating condition, energy can transfer among individual modes in a plurality of aligned longitudinal modes. Modes shifting towards a state of misalignment with the DWDM coordinate can attenuate, while modes shifting towards a state of alignment can gain energy. Fabrication processes and systems and light management, such as beam steering, epoxy scaffolds, spectral adjustments, mode matching, thermal expansion control, alignment technology, etc. can facilitate nano-scale control of device parameters and can support low-cost fabrication.
Owner:CIRREX SYST
Method and apparatus for filtering an optical beam
InactiveUS20020126345A1Compact form factorEasy to tuneLaser optical resonator constructionPolarisation multiplex systemsExternal cavity laserMesh grid
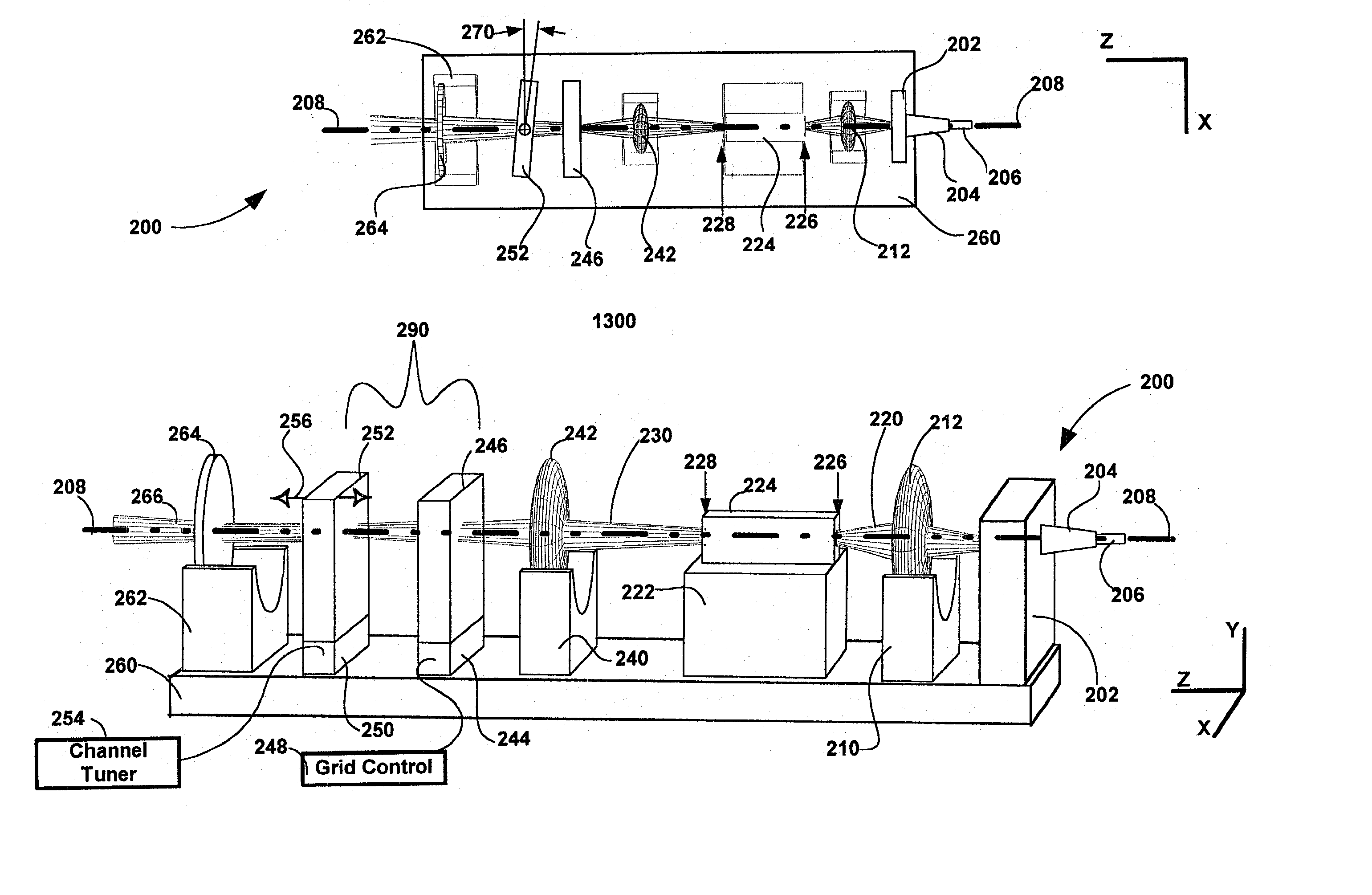
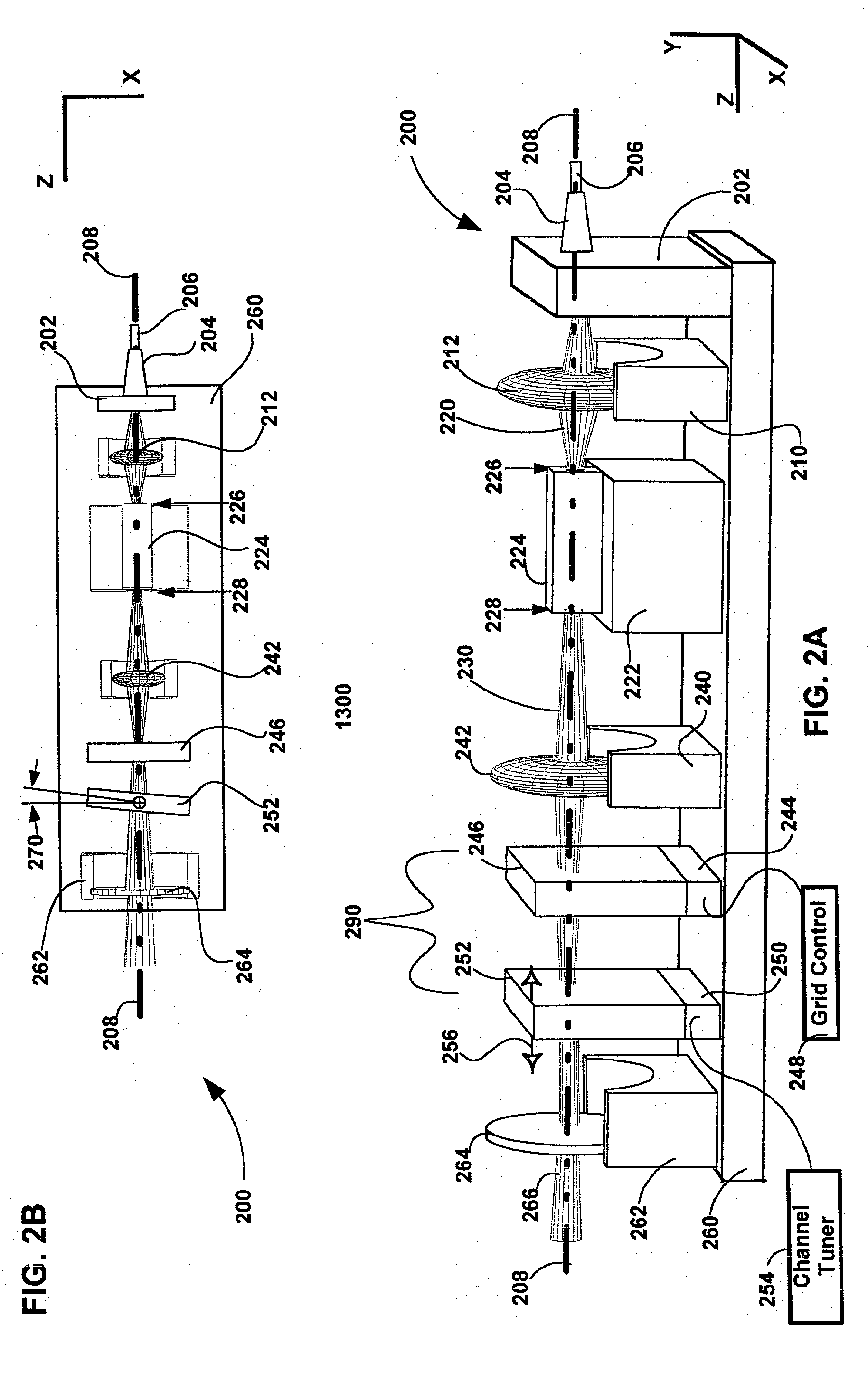
The invention pertains to wavelength-agile optical filters suitable for wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) optical communications networks. More particularly, the invention pertains to optical filters with a wavelength reference that can be remotely switched to arbitrarily selectable channels on a standard grid, and to re-configurable optical communications networks employing same. The present invention provides a communication apparatus with a tunable filter which may be used in a wide range of applications including tuning an external cavity laser (ECL), selecting a wavelength for an add / drop multiplexer and providing channel selection and feedback for a wavelength locker. The filter may be utilized as a discrete component or in combination with circulators, wavelength lockers and gain medium. The filter may be implemented in whole or in part as part of a gain medium. The tunable filter exhibits a compact form factor and precise tuning to any selected wavelength of a predetermined set of wavelengths comprising a wavelength grid. The tunable filter may thus be utilized in telecom applications to generate the center wavelengths for any channel on the ITU or other optical grid.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Diffraction grating for wavelength division multiplexing/demultiplexing devices
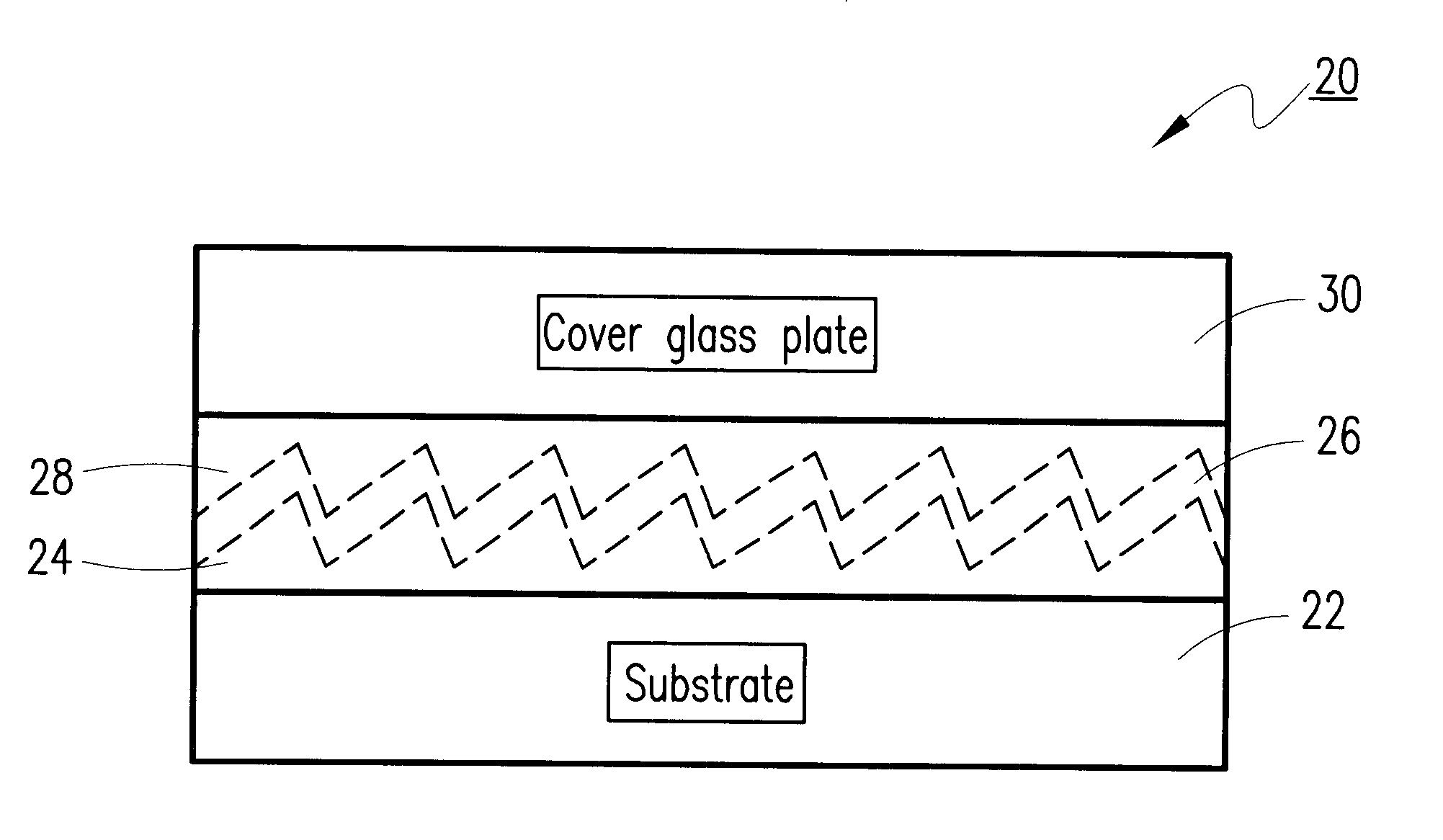
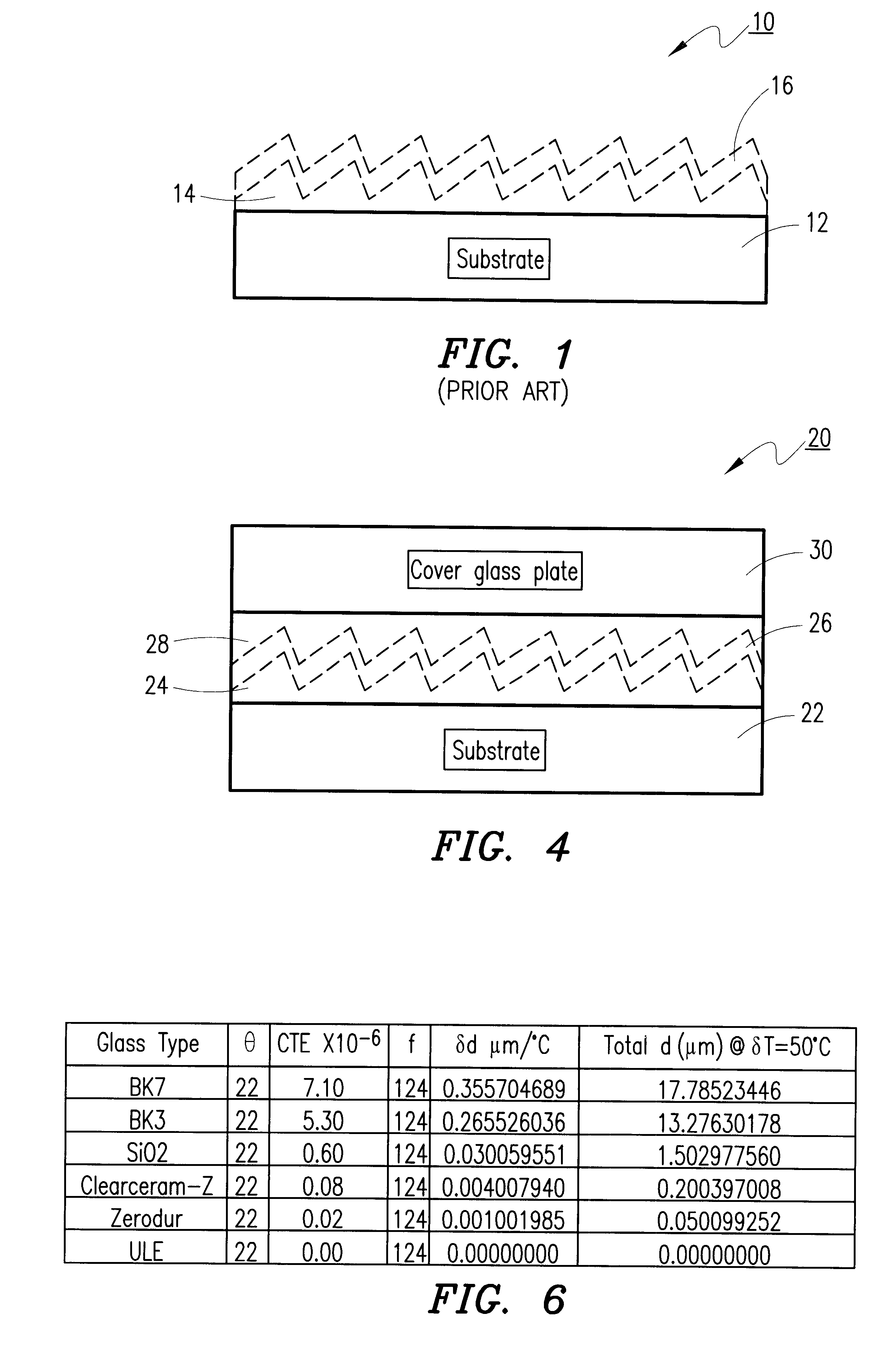
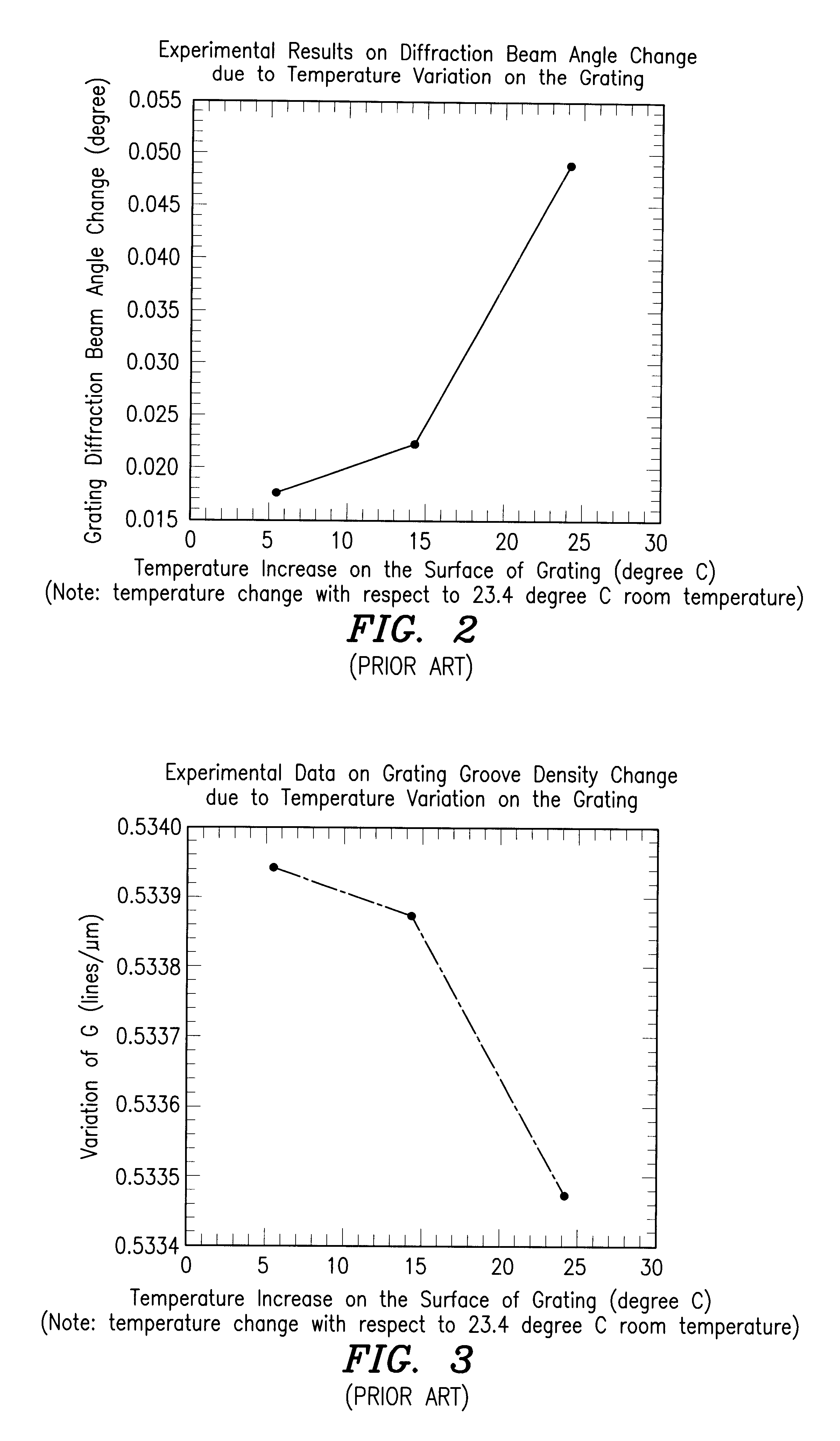
An improved diffraction grating for wavelength division multiplexing / demultiplexing devices is disclosed. The improved diffraction grating has a glass substrate, a polymer grating layer located adjacent to the glass substrate, and a metal coating layer located adjacent to the polymer grating layer. The improvement comprises a polymer coating layer located adjacent to the metal coating layer, and a glass cover located adjacent to the polymer coating layer, wherein the polymer coating layer and the glass cover compensate for thermal characteristics associated with the polymer grating layer and the glass substrate, respectively.
Owner:AUXORA
Integrated bi-directional dual axial gradient refractive index/diffraction grating wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS6137933AIncreased durabilityImprove the environmentCoupling light guidesExit surfaceWavelength-division multiplexing
A wavelength division multiplexer / demultiplexer is provided that integrates axial gradient refractive index elements with a diffraction grating to provide efficient coupling from a plurality of input optical sources (each delivering a single wavelength to the device) which are multiplexed to a single polychromatic beam for output to a single output optical source. The device comprises: (a) means for accepting an optical input from at least one optical source, the means including a planar surface; (b) a first coupler element comprising (1) a first axial gradient refractive index collimating lens having a planar entrance surface onto which the optical input is incident and (2) a first homogeneous index boot lens affixed to the first collimating lens and having a planar exit surface from which optical light exits; (c) a diffraction grating formed on the planar exit surface which combines a plurality of angularly separated diffracted wavelengths from the optical light; (d) a reflecting element for reflecting the plurality of diffracted wavelengths; (e) a second coupler element comprising (1) a second homogeneous index boot lens having a planar entrance surface onto which said plurality of diffracted wavelengths is incident and (2) a second axial gradient refractive index collimating lens affixed to the second homogeneous index boot lens; and (f) means for outputting at least one multiplexed, polychromatic output beam to an optical receiver, the means including a planar back surface. The device may be operated in either the forward or the reverse direction.
Owner:AUXORA
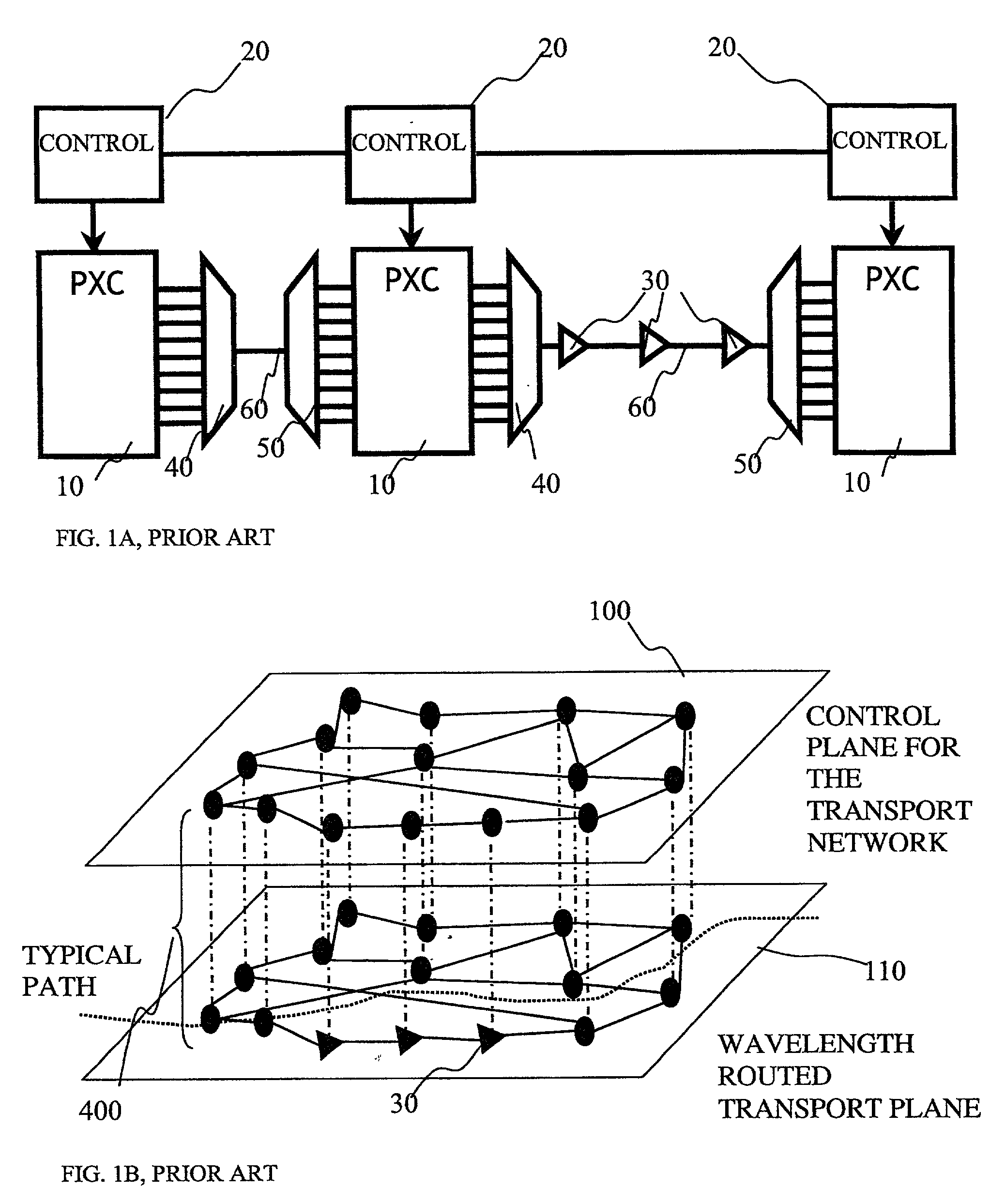
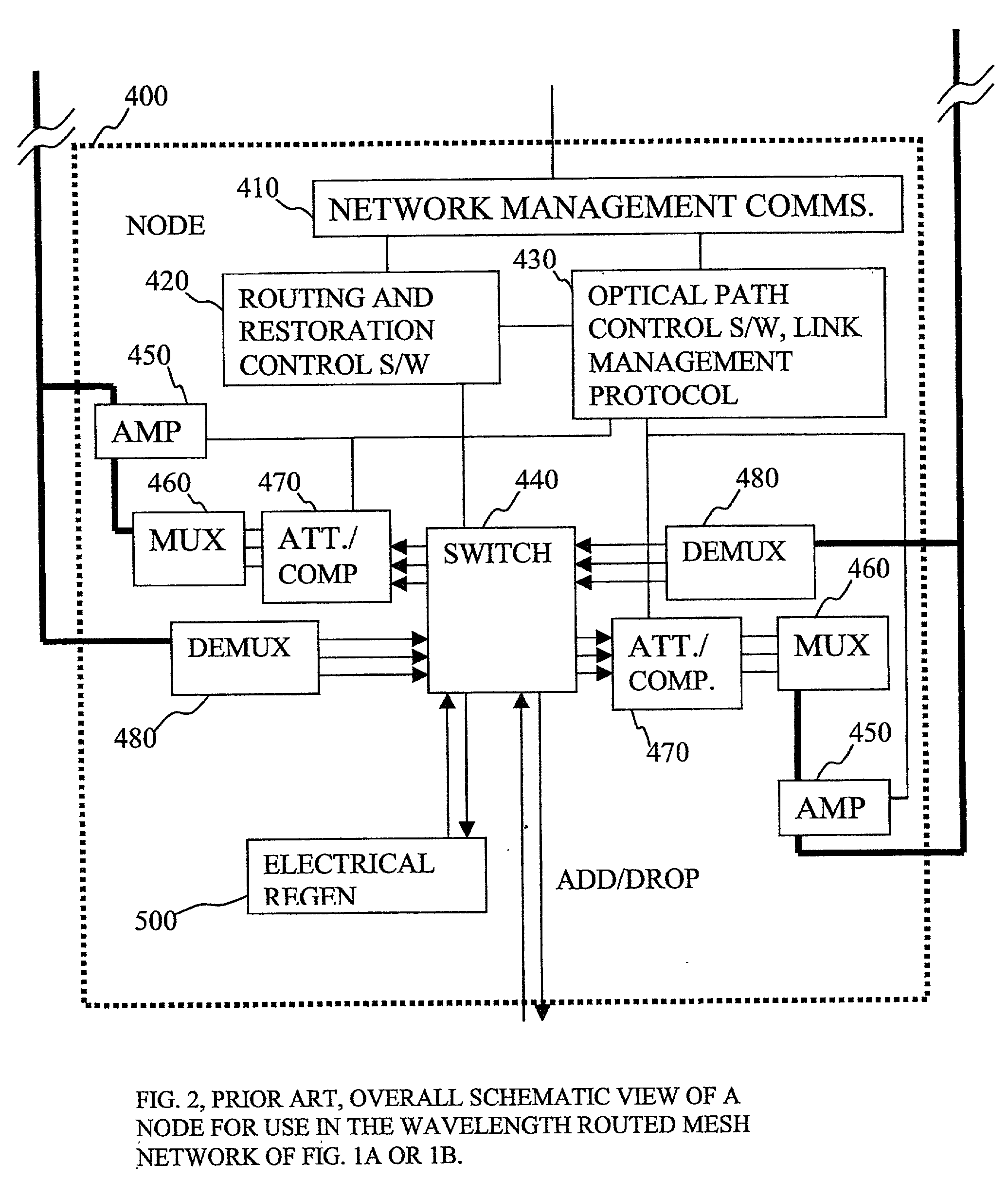
Photonic node, photonic nodes for transmission and reception, and method of restoring traffic upon occurrence of link failure in optical path network
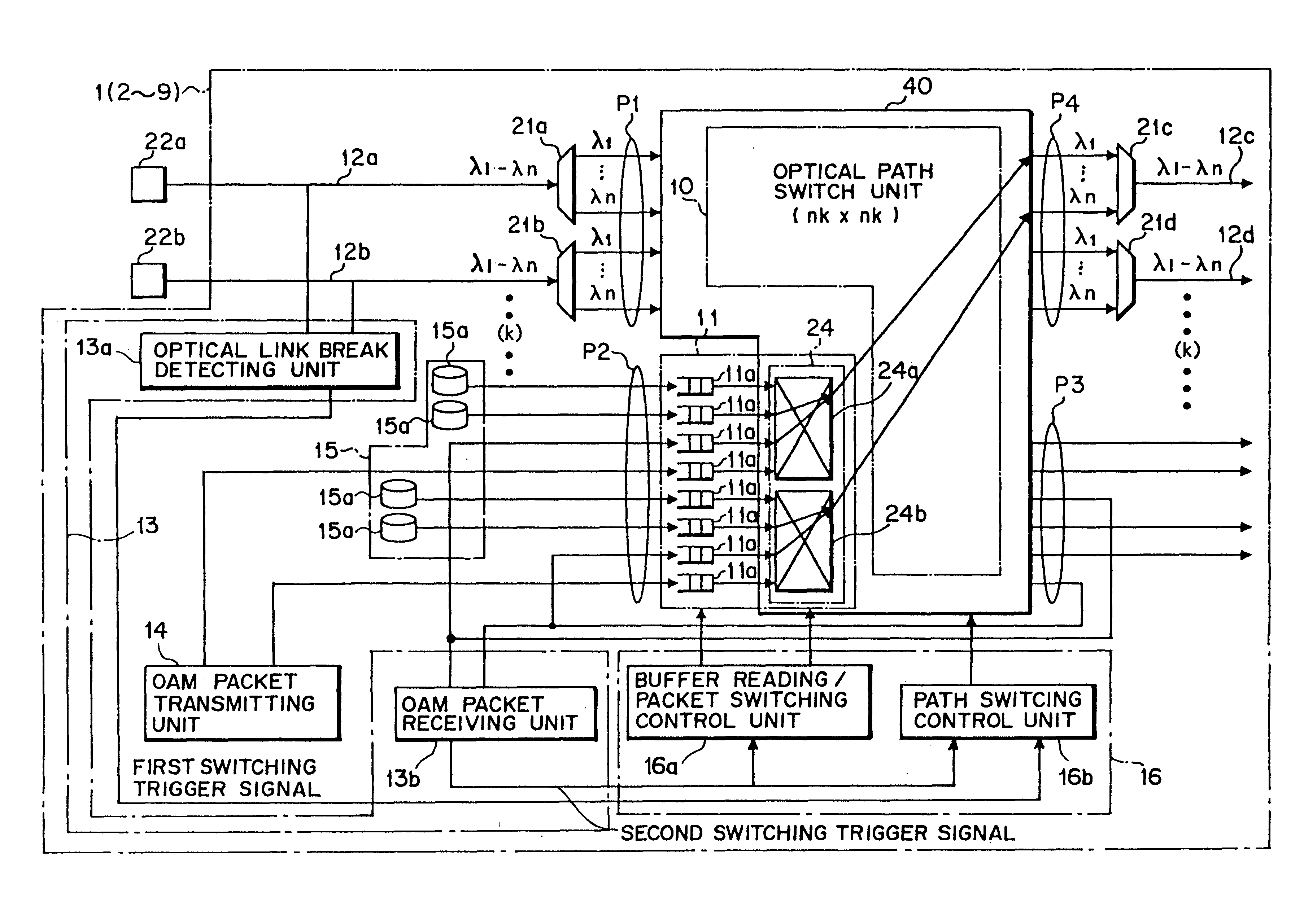
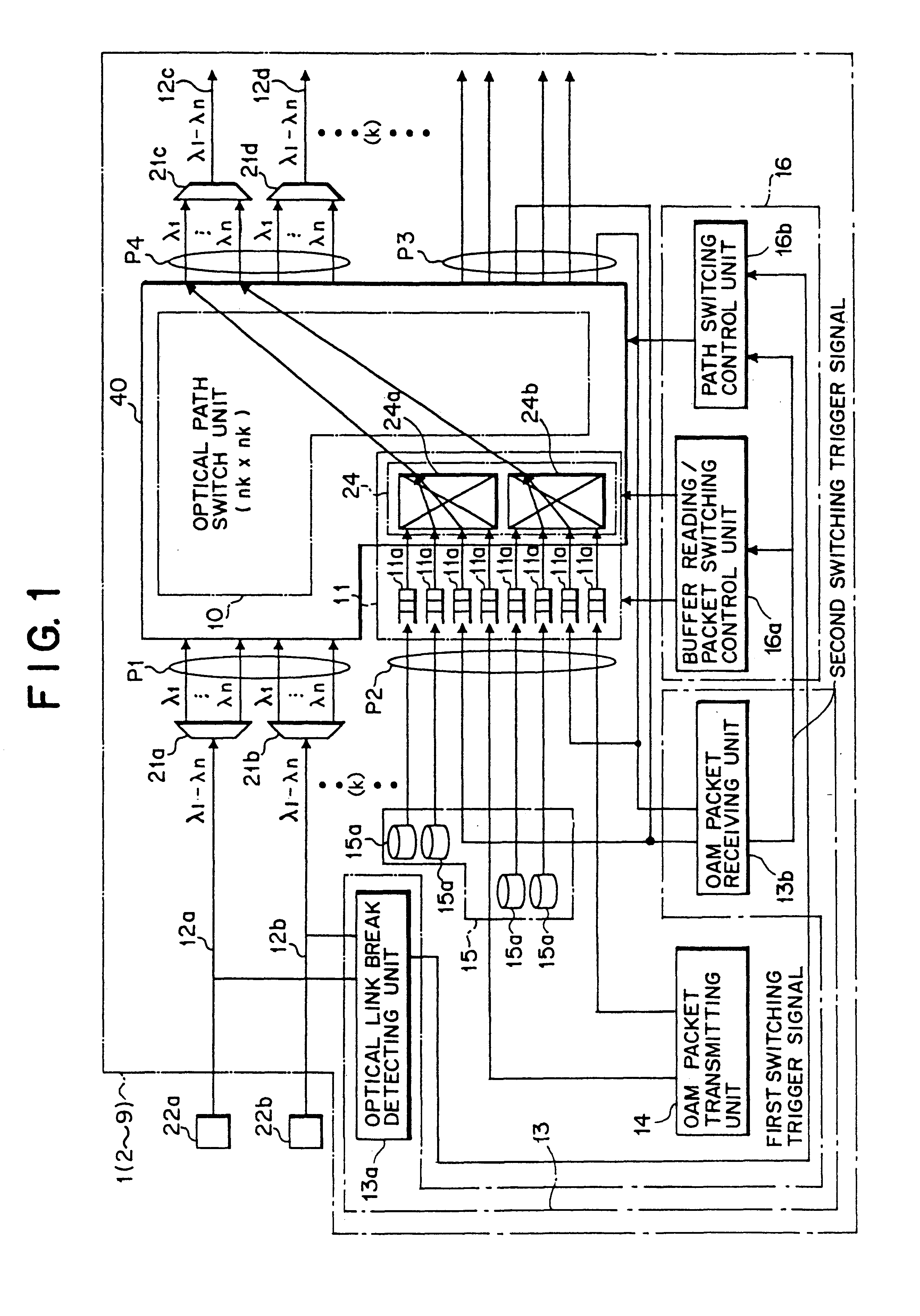
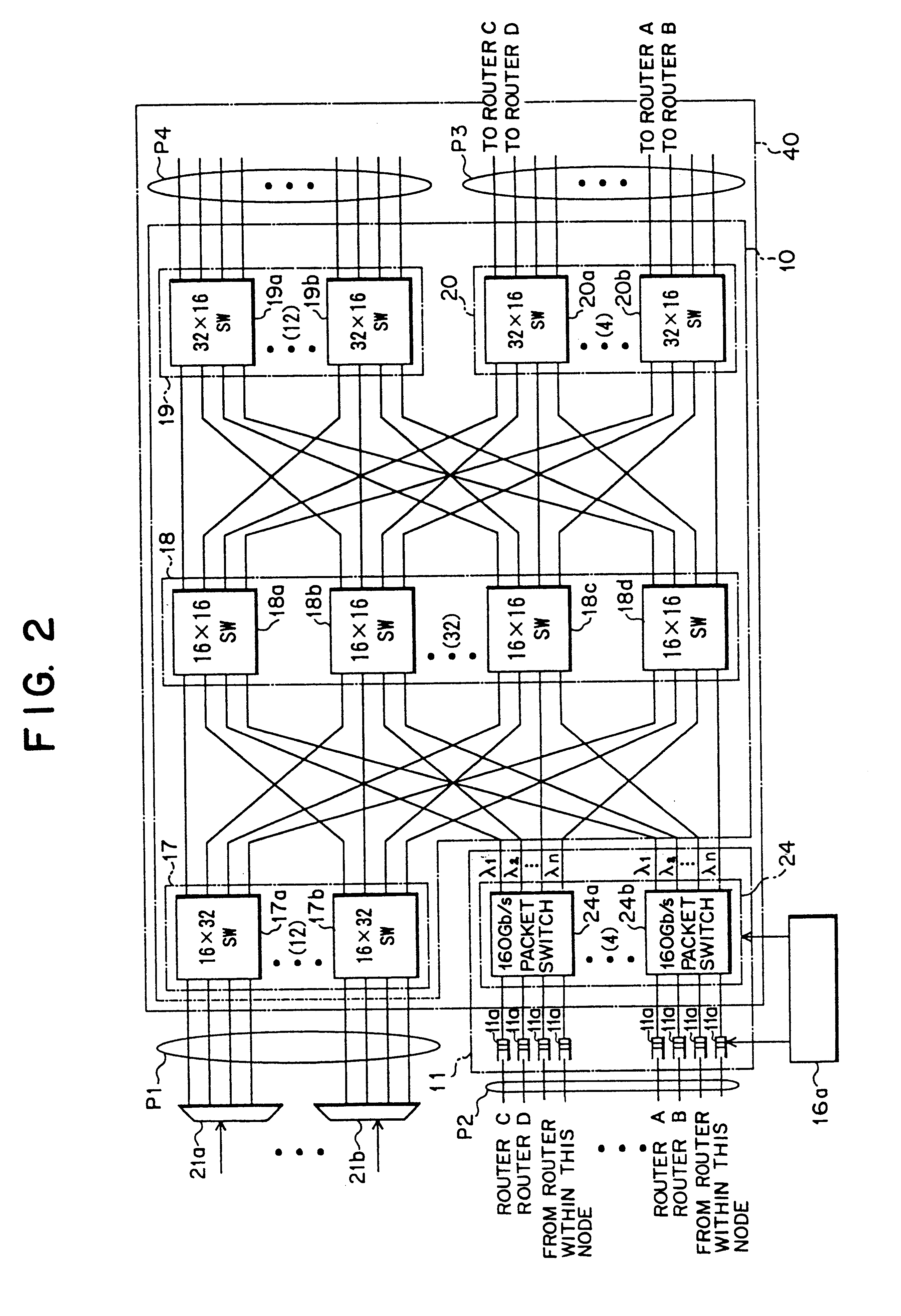
The present invention relates to a technology of an IP node for transferring IP packets accommodated in a wavelength division multiplexing optical signal. The optical IP node of the present invention includes a space switch unit supplied with a wavelength division multiplexing optical signal and a packet with another node destination and generating an optical signal with the self node destination and multiplexing the optical signal with another node destination and an optical signal caused by the packet together and generating the multiplexed signal, link failure detecting unit connected to an input side and an output side of the space switch unit, detecting link failure and generating a detection signal, an OAM packet transmitting unit for generating a monitoring packet at a predetermined time interval, and a traffic restoration control unit connected to the link failure detecting unit, selecting each optical signal depending on the wavelength in response to reception of the detection signal, switching the optical path and generating the optical signal. Each of the optical IP nodes carries out optical path switching on the wavelength division multiplexing optical signal and assignment of an IP packet to be transmitted to an optical signal and switching of the assignment. Thus, the number of optical wavelengths utilized for transmission can be reduced and the size of the optical IP node can be made small.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Reservation protocol signaling extensions for optical switched networks
InactiveUS20050030951A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexPhotonicsSignaling protocol
An architecture and method for performing coarse-grain reservation of lightpaths within wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) based photonic burst-switched (PBS) networks with variable time slot provisioning. The method employs extensions to the RSVP-TE signaling protocol, which uses various messages to reserve resources. A resource reservation request is passed between nodes during a downstream traversal of the lightpath route connecting a source node to a destination node via one or more switching nodes, wherein each node is queried to determine whether it has transmission resources (i.e., a lightpath segment) available during a future scheduled time period. Soft reservations are made for each lightpath segment that is available using information contained in a corresponding label. If all lightpath segments for a selected route are available, a reservation response message is sent back upstream along the route from the destination node to the source node. In response to receiving the response, the soft reservations are turned into hard reservations at each node.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Three-dimensional optical waveguide, method of manufacturing same, optical module, and optical transmission system
InactiveUS20030161573A1Intuitive adjustmentLow costLaser detailsCoupling light guidesOptical ModulePlanar substrate
A three-dimensional optical waveguide is formed by laminating planar substrates such as a plurality of lens substrates and, an isolator substrate and a wavelength division multiplexing filter, the optical substrates at least include a waveguide substrate having a waveguide and a reflecting surface. In the three-dimensional optical waveguide, the planar substrates are positioned by markers integrally formed on at least two of the planar substrates. Light directed into the waveguide is reflected by a reflecting surface and passes through the lens substrates and the isolator substrate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
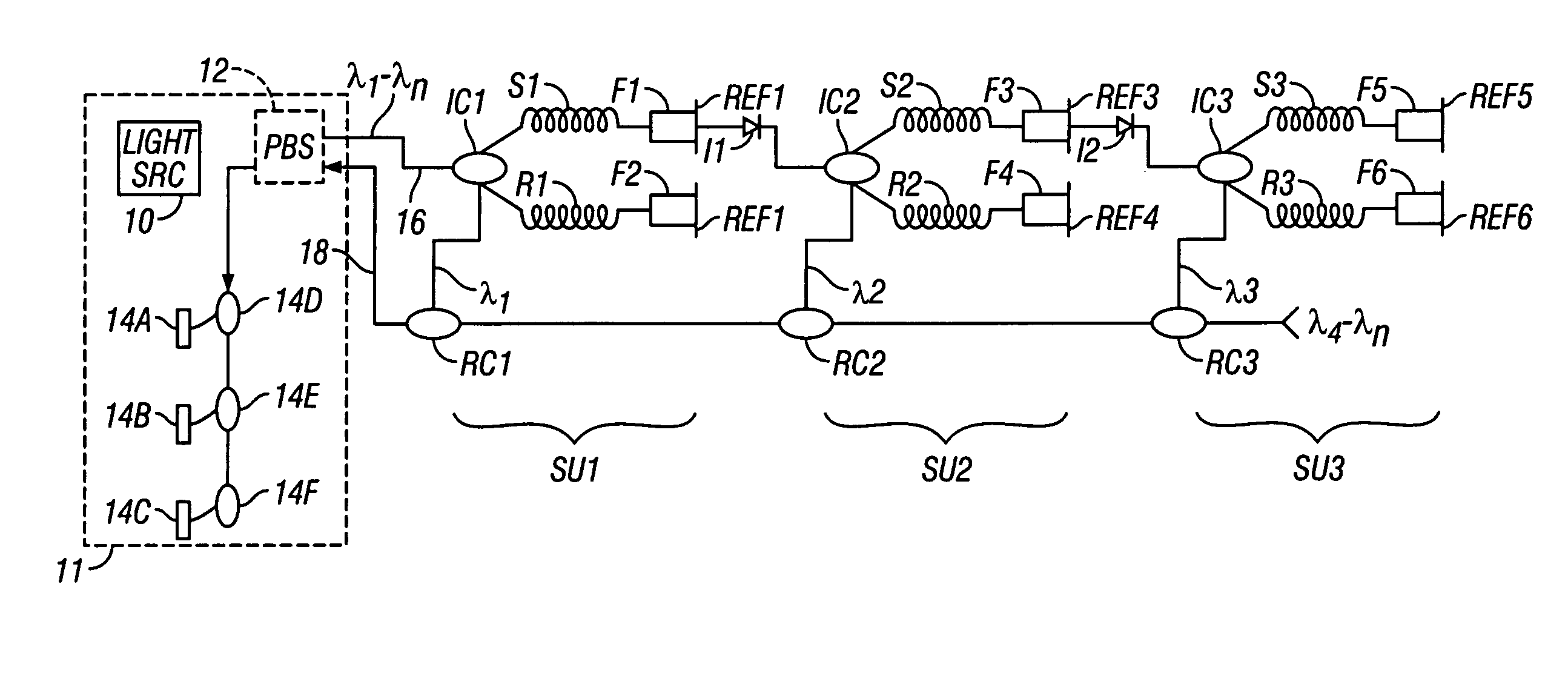
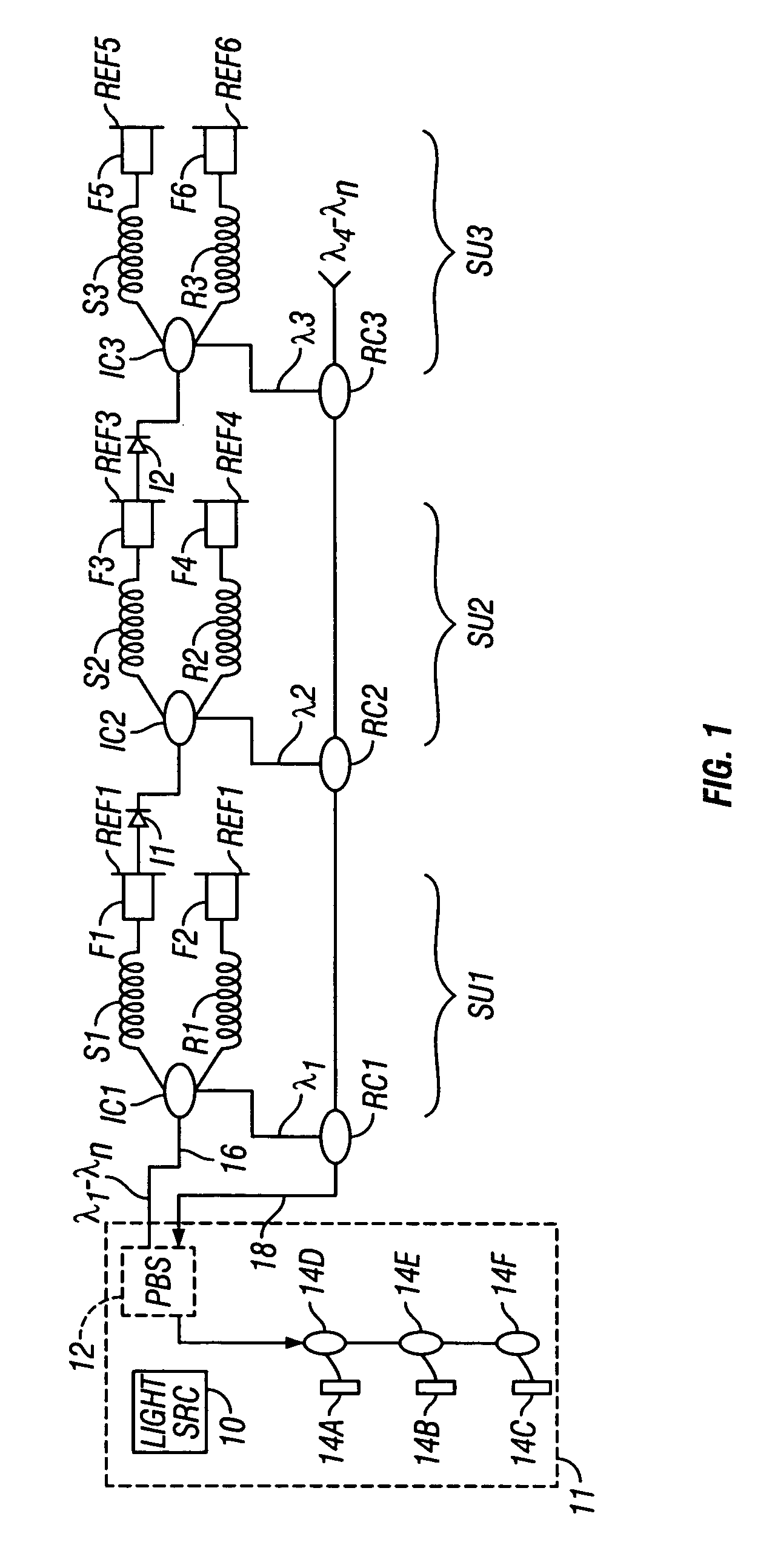
Frequency division and/or wavelength division multiplexed recursive fiber optic telemetry scheme for an optical sensor array
ActiveUS20060038115A1Radiation pyrometrySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSensor arrayLength wave
An optical fiber sensor array is disclosed which includes a first sensor fiber and a first reference fiber coupled at one end thereof to one side of a first optical coupling. A first wavelength selective reflector is coupled to the other end of each of the first sensor fiber and the first reference fiber. A second sensor fiber is coupled at one end to one side of a second optical coupling. The other side of the second optical coupling is coupled to an opposite side of one of the first wavelength selective reflectors coupled on one side to the first sensor fiber and the first reference fiber. The array also includes a second wavelength selective reflector coupled to the other end of each of the second sensor fiber and the second reference fiber. The second wavelength selective reflectors are operative at a wavelength different from an operative wavelength of the first wavelength selective reflectors.
Owner:GEOSPACE TECH
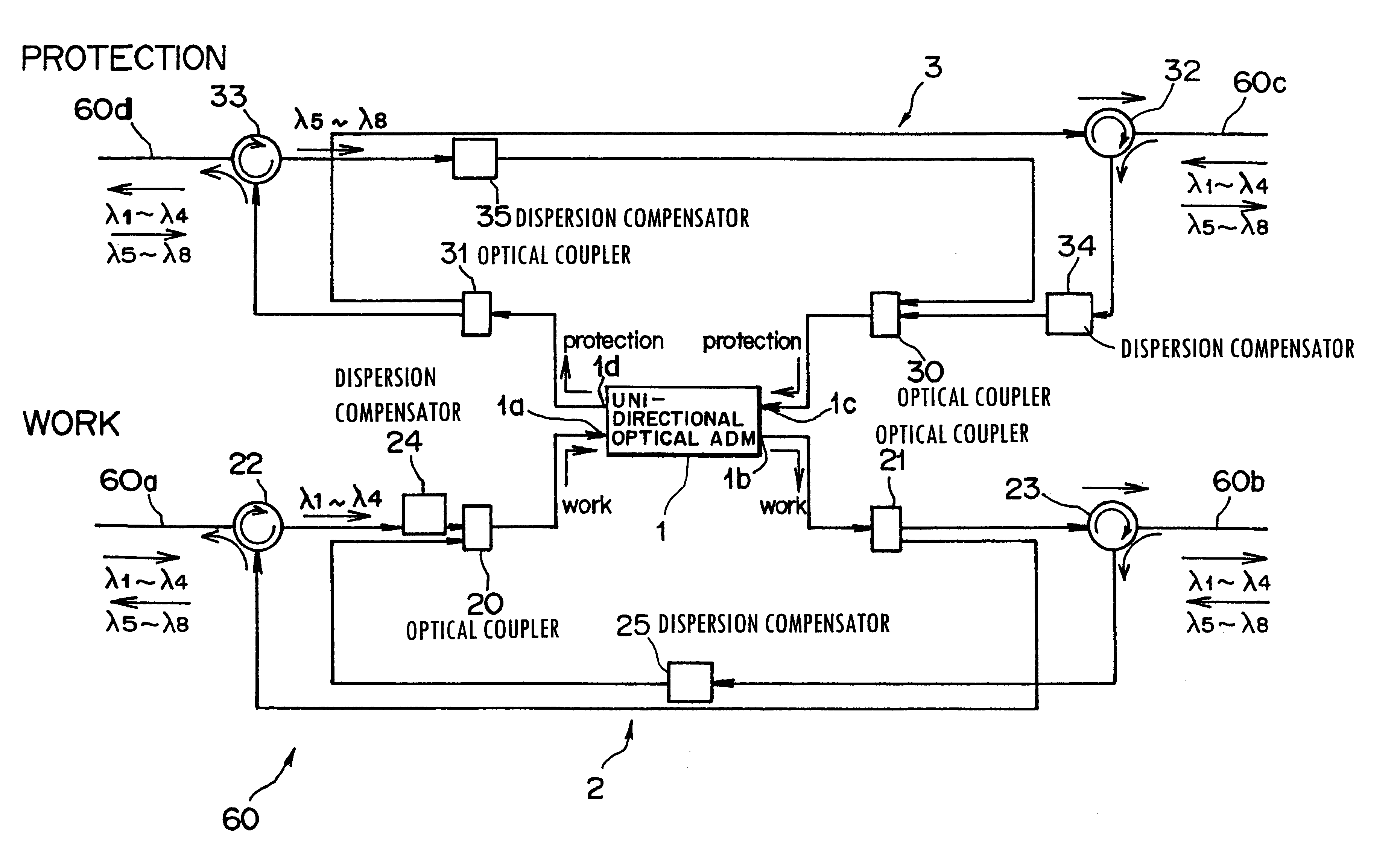
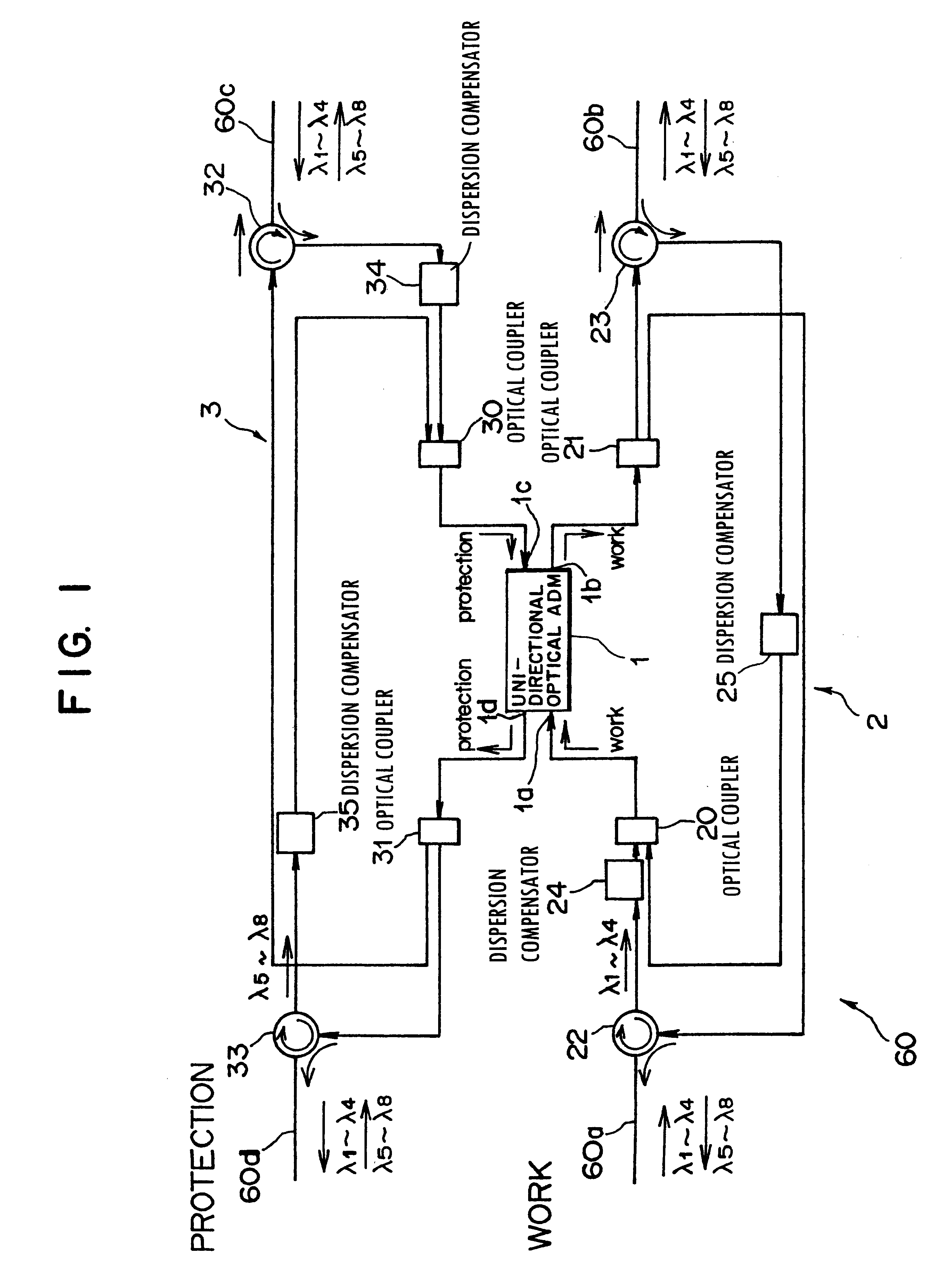
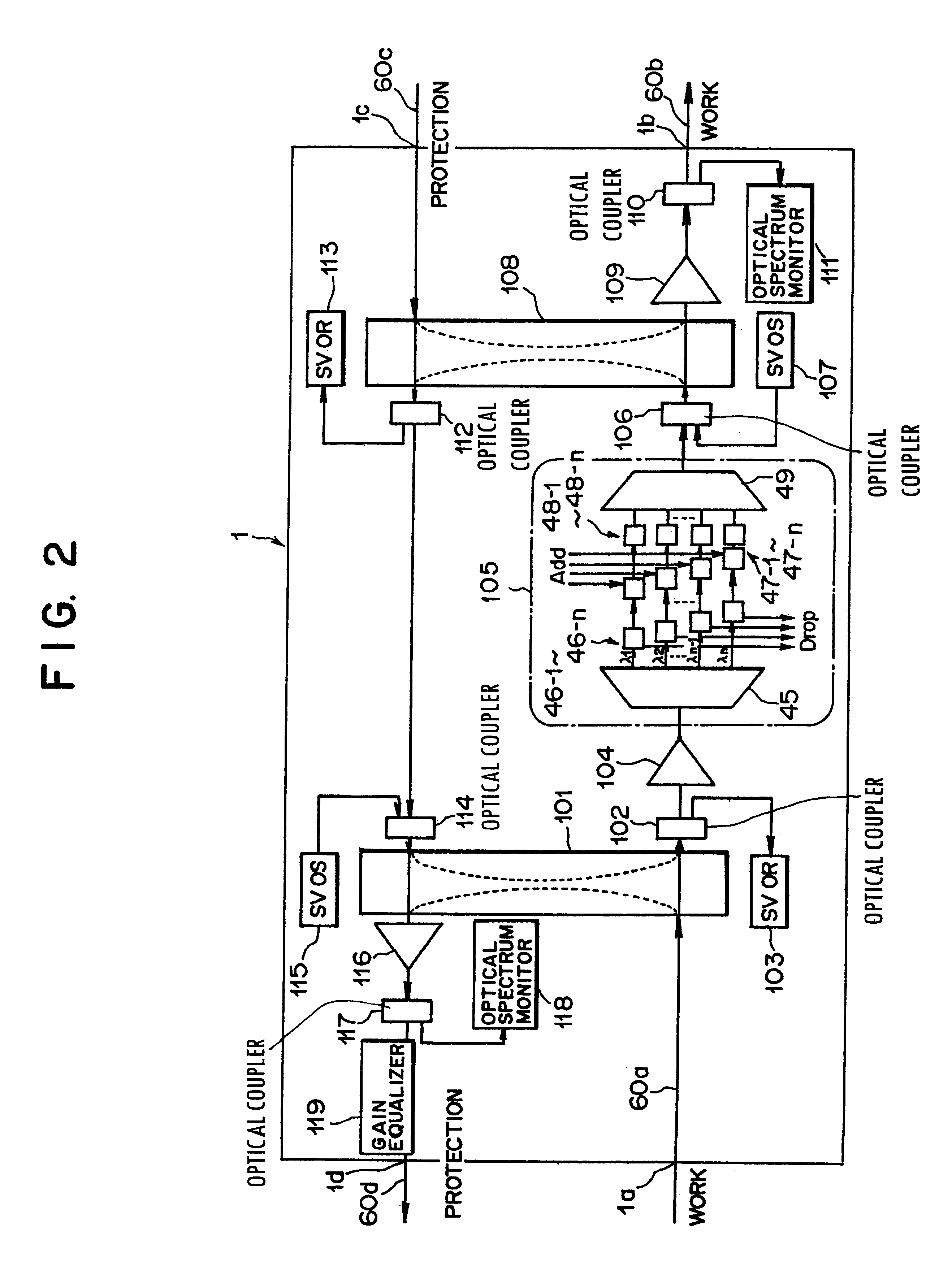
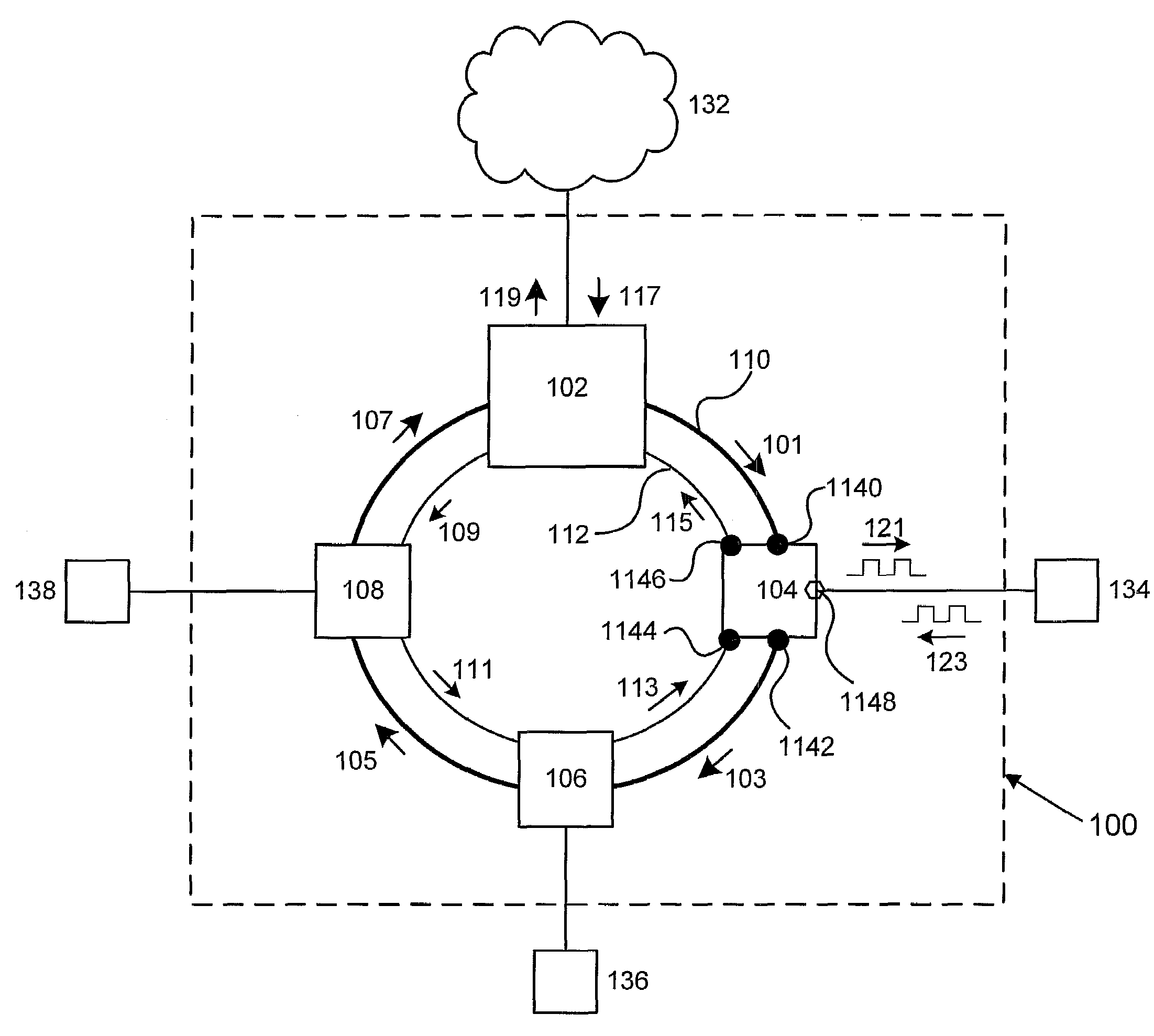
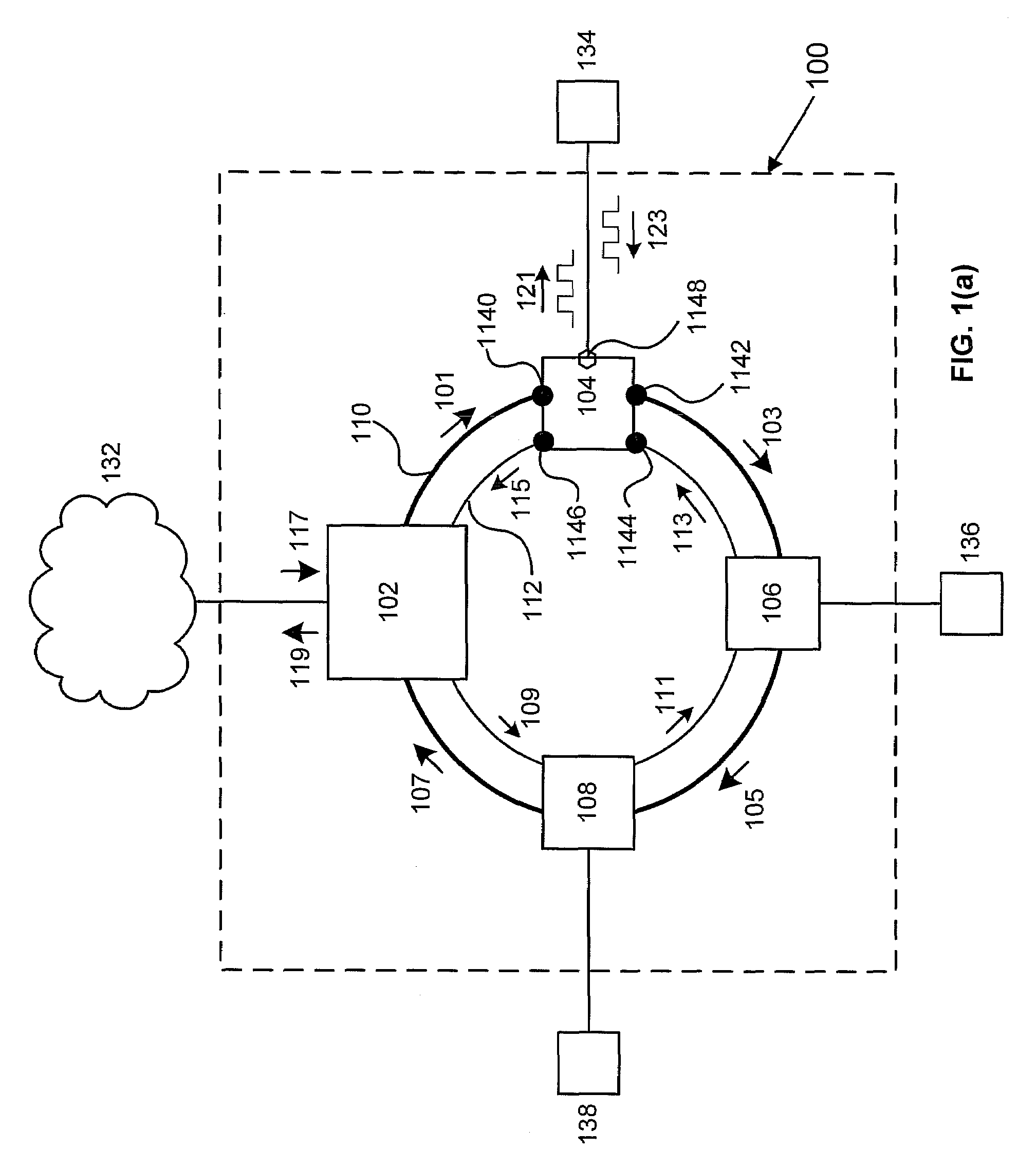
Optical transmission device for bi-directional optical communication
InactiveUS6278536B1Low costWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationEngineeringOptical communication
This invention discloses an optical transmission device used for bi-directional optical communications. The optical transmission device comprises a uni-directional optical signal processing unit for performing specified optical signal processing for optical signals transmitted in a single direction and a uni-direction / bi-direction changing unit for unifying the flows of clockwise and counterclockwise optical signals in a single direction, inputting these flow-unified optical signals to the uni-directional optical signal processing unit and dividing the flow of optical signals from the uni-directional optical signal processing unit between clockwise and counterclockwise directions. Bi-directional wavelength-division multiplexing optical communications can be performed by unifying the transmission routes (flows) of optical signals transmitted in two ways in a single direction and using the existing optical transmission device for uni-directional optical communications.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
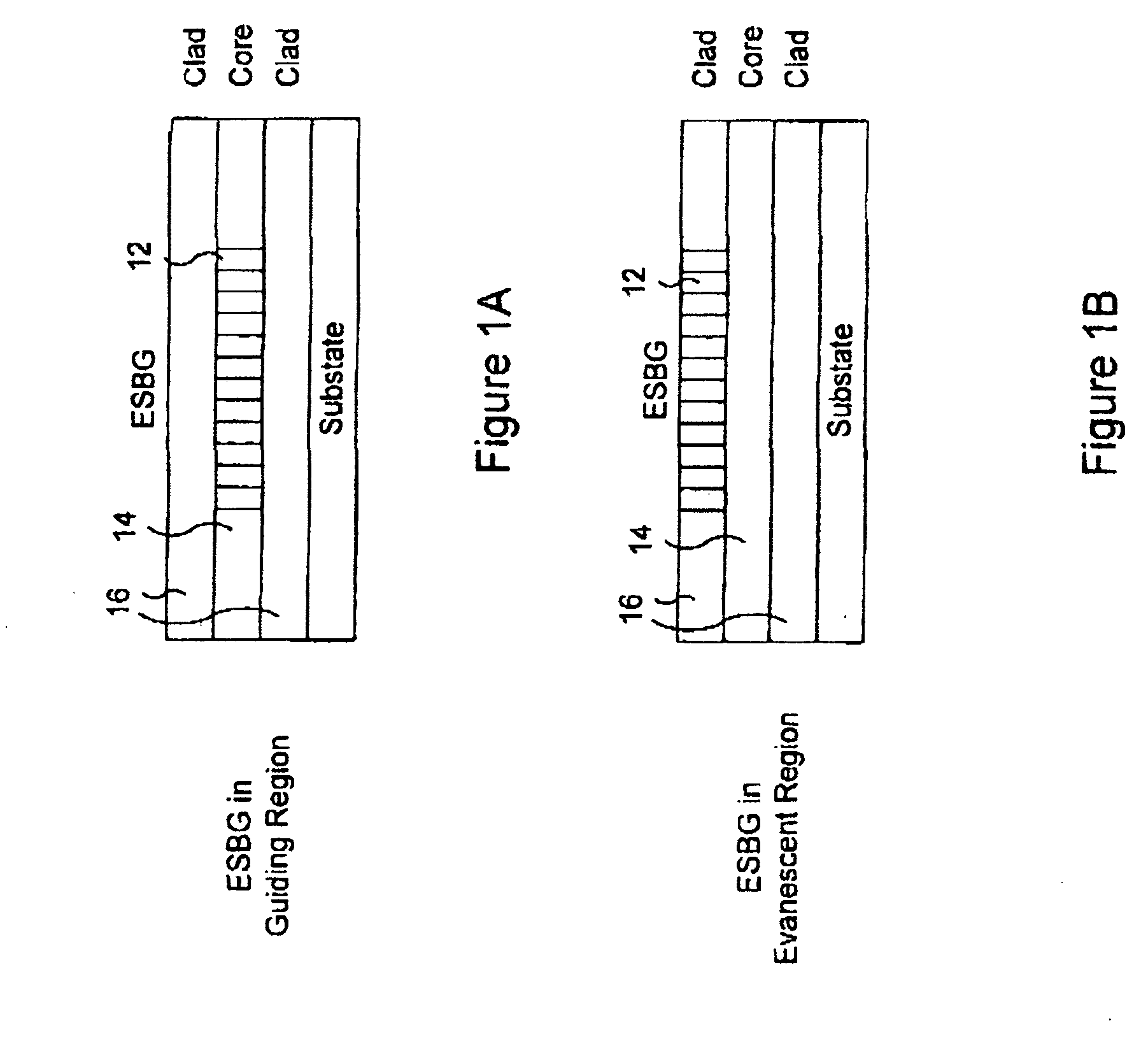
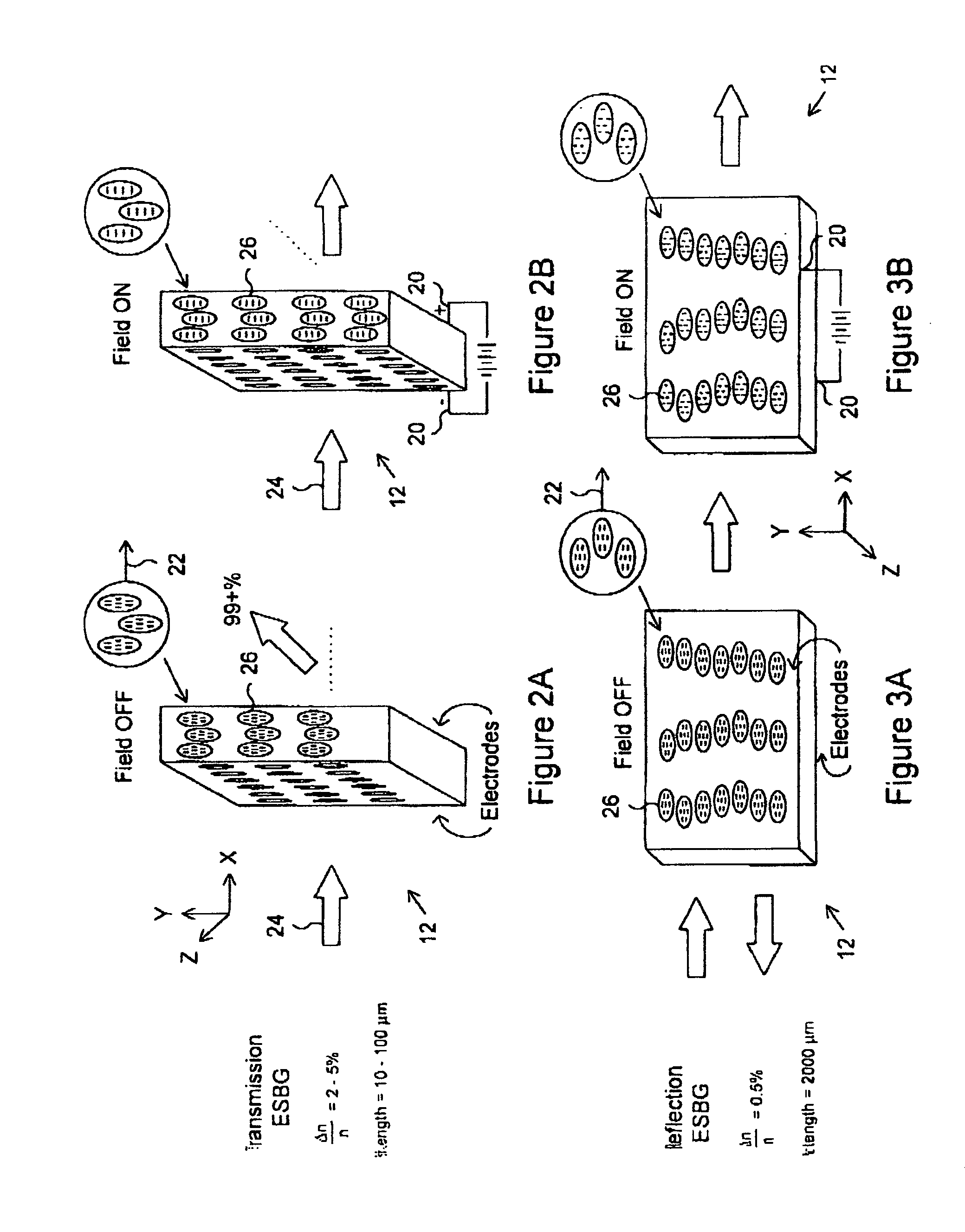
Switchable optical components
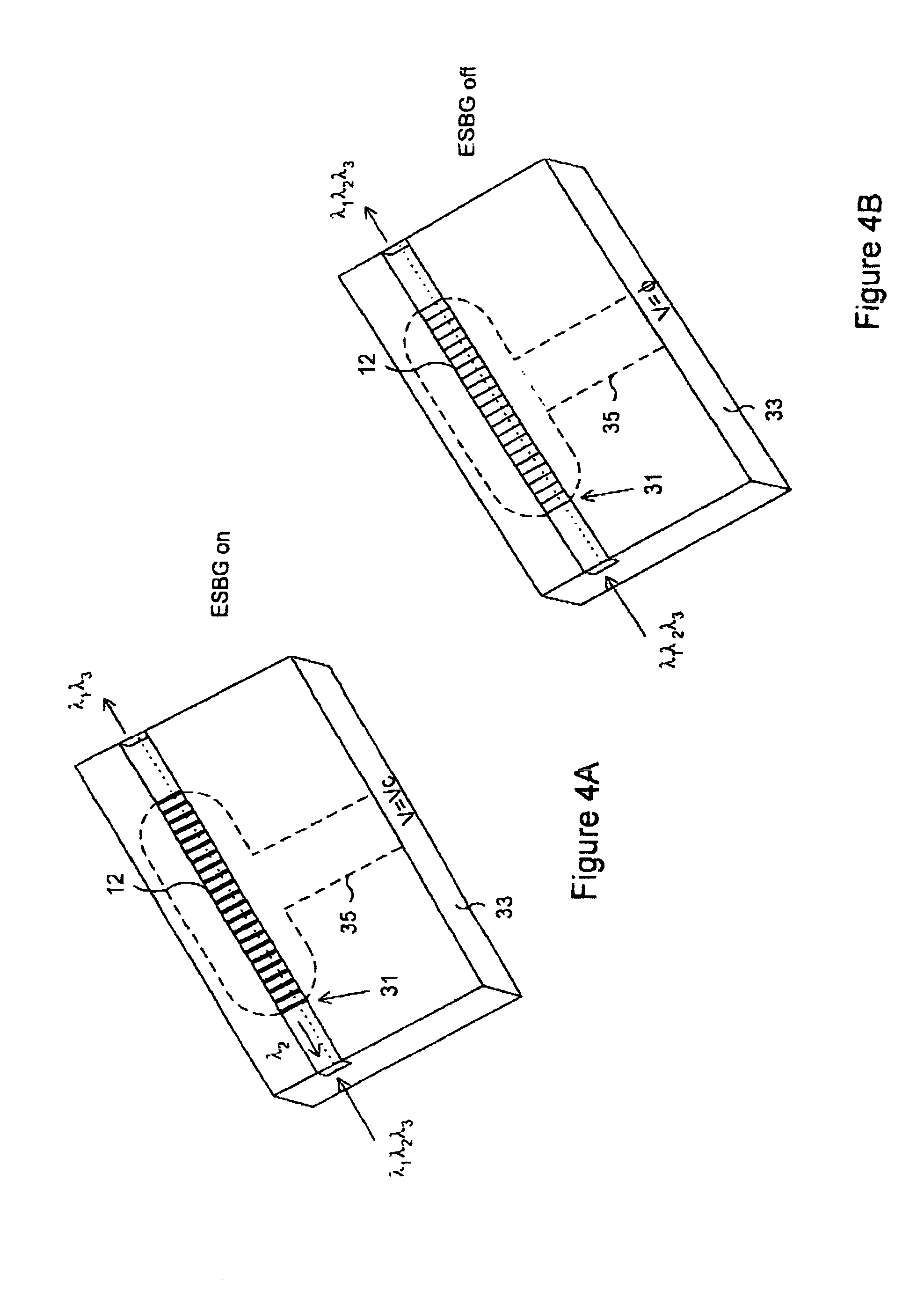
This invention relates to a number of components, devices and networks involving integrated optics and / or half coupler technology, all of which involve the use of electronically switchable Bragg grating devices and device geometries realized using holographic polymer / dispersed liquid crystal materials. Most of the components and devices are particularly adapted for use in wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) systems and in particular for use in switchable add / drop filtering (SADF) and wavelength selective crossconnect. Attenuators, outcouplers and a variety of other devices are also provided.
Owner:DOMASH LAWRENCE H +1
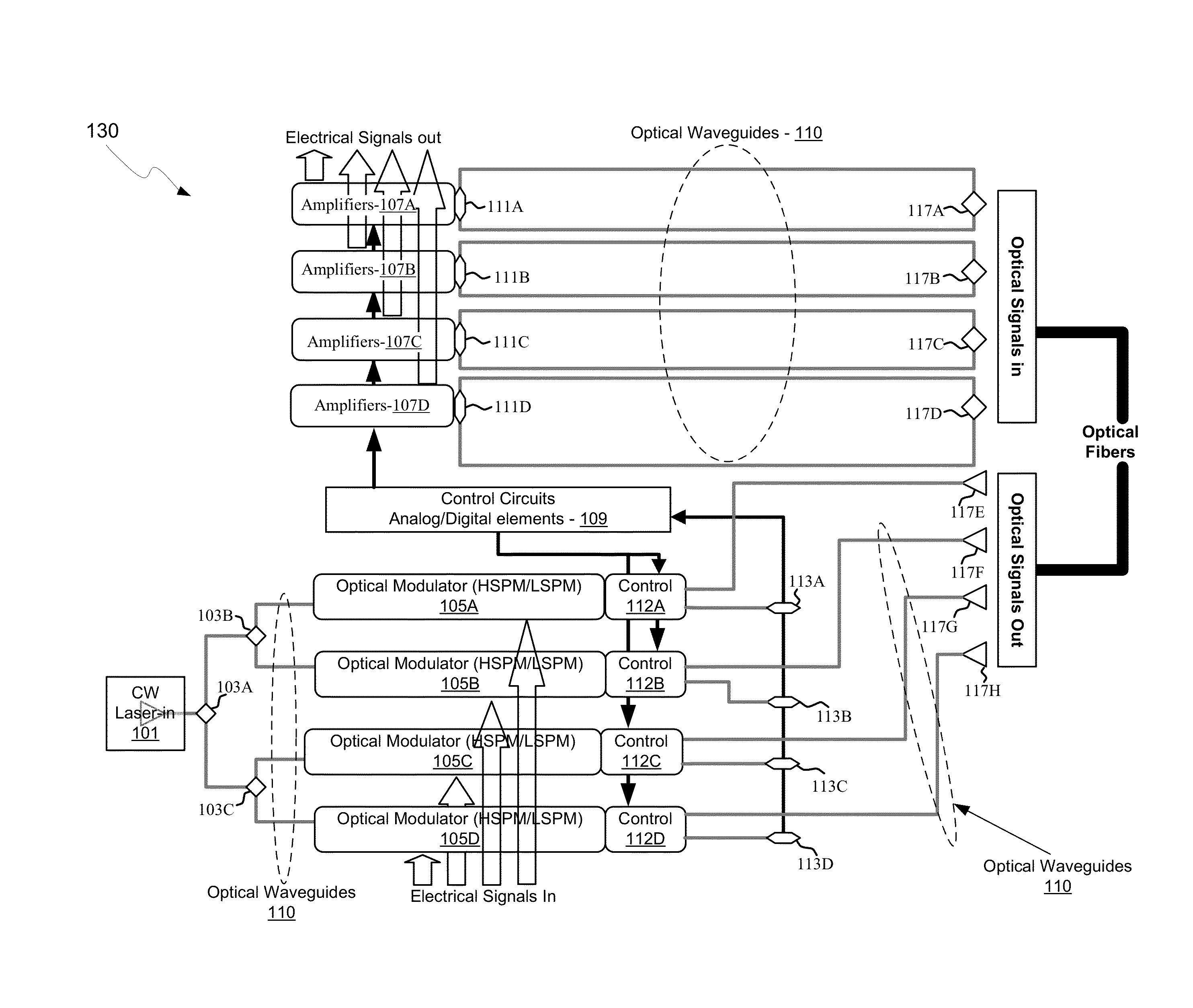
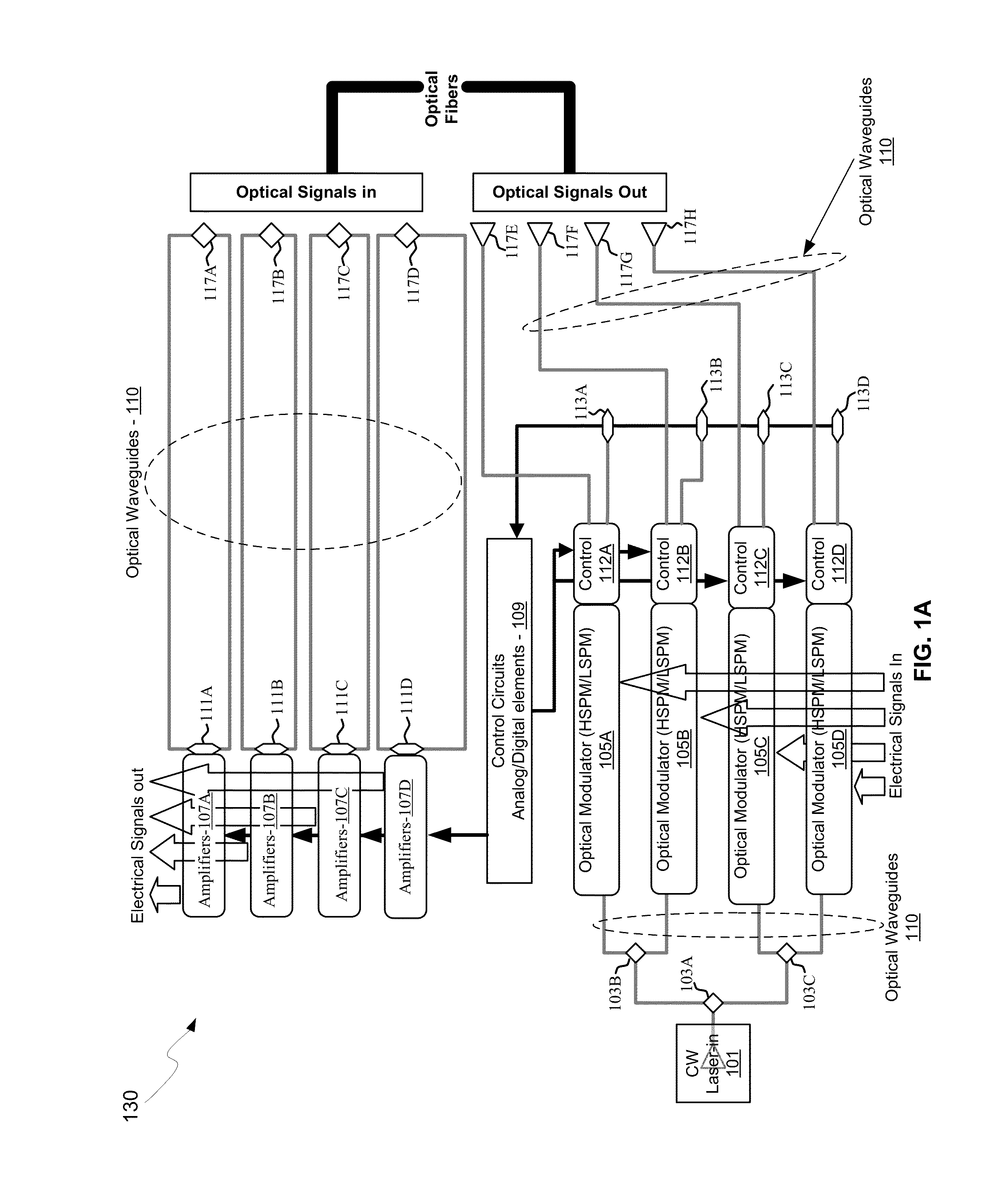
Method And System For Silicon Photonics Wavelength Division Multiplexing Transceivers
Methods and systems for silicon photonics wavelength division multiplexing transceivers are disclosed and may include, in a transceiver integrated in a silicon photonics chip: generating a first modulated output optical signal at a first wavelength utilizing a first electrical signal, generating a second modulated output optical signal at a second wavelength utilizing a second electrical signal, communicating the first and second modulated output optical signals into an optical fiber coupled to the chip utilizing a multiplexing grating coupler in the chip. A received input optical signal may be split into a modulated input optical signal at the first wavelength and a modulated input optical signal at the second wavelength utilizing a demultiplexing grating coupler in the chip. The first and second modulated input optical signals may be converted to first and second electrical input signals utilizing first and second photodetectors in the chip.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
MIMO-OFDM-Based Flexible Rate Intra-Data Center Network
ActiveUS20140056371A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSecret communicationData centerEngineering
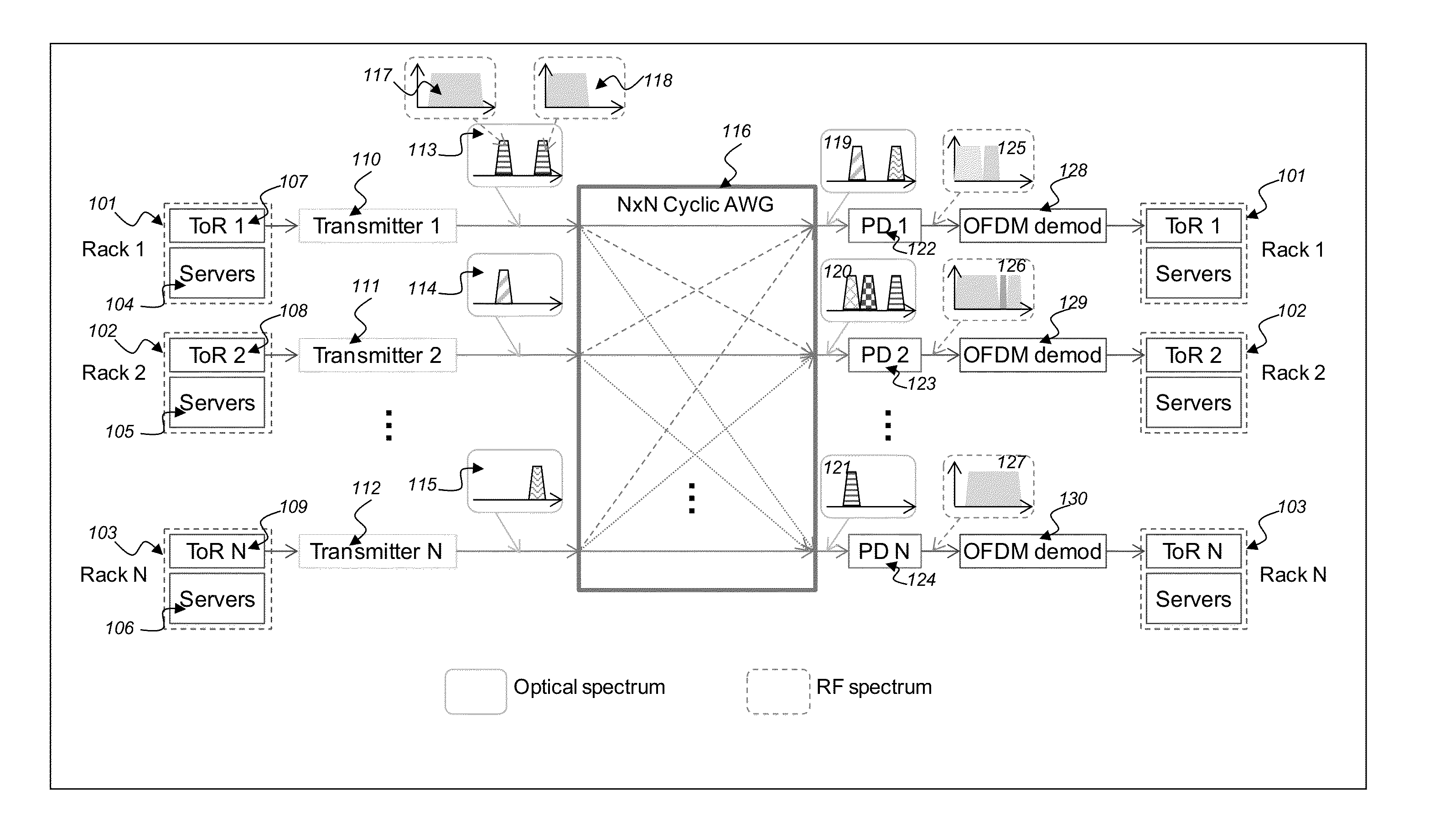
An optical network includes receiving inter-rack traffics from transmitter racks, converting by transmitters the inter-rack traffics to respective wavelength division multiplexing WDM optical signals, receiving and routing by a cyclic interleaver the optical signals from the transmitters to output ports in a cyclic manner, converting respective routed optical signals from the cyclic interleaver into respective electrical signals, and demodulating OFDM formats from respective converted optical signals containing signals for respective receiver racks.
Owner:NEC CORP
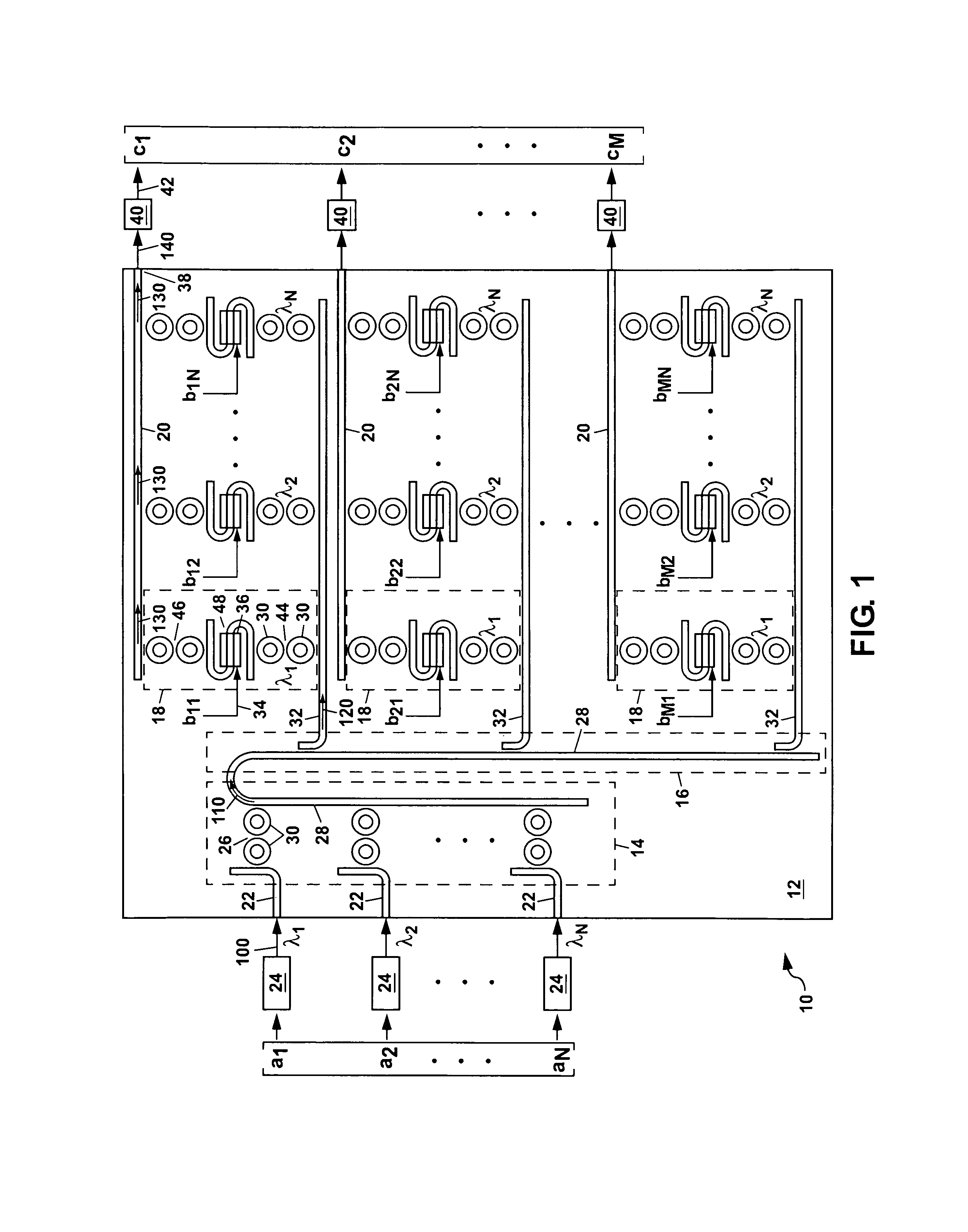
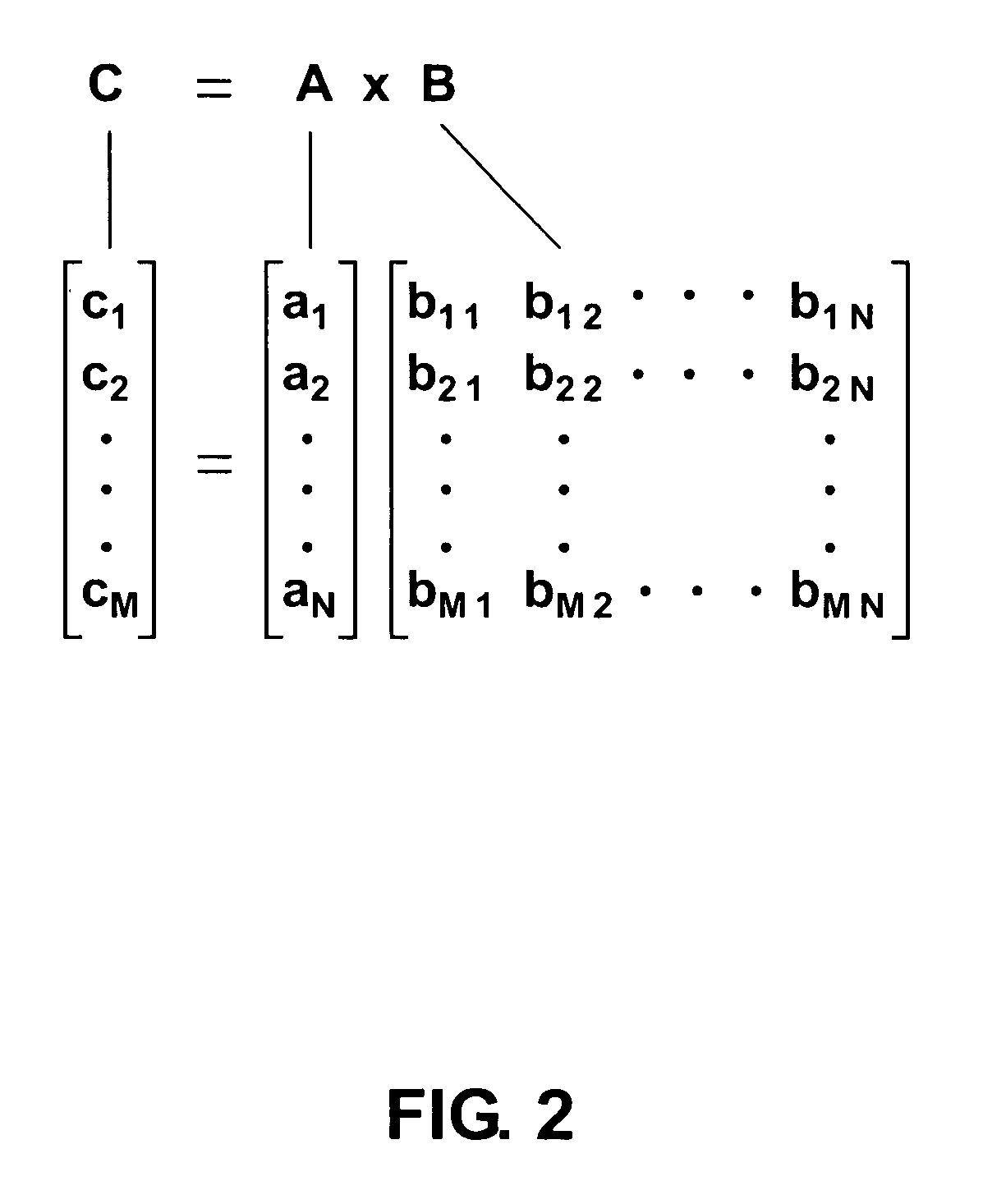
Integrated optic vector-matrix multiplier
ActiveUS8027587B1Computing operations for integration/differentiationWavelength-division multiplex systemsMatrix multiplierLength wave
A vector-matrix multiplier is disclosed which uses N different wavelengths of light that are modulated with amplitudes representing elements of an N×1 vector and combined to form an input wavelength-division multiplexed (WDM) light stream. The input WDM light stream is split into N streamlets from which each wavelength of the light is individually coupled out and modulated for a second time using an input signal representing elements of an M×N matrix, and is then coupled into an output waveguide for each streamlet to form an output WDM light stream which is detected to generate a product of the vector and matrix. The vector-matrix multiplier can be formed as an integrated optical circuit using either waveguide amplitude modulators or ring resonator amplitude modulators.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access Based Optical Ring Network
ActiveUS20090092389A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission path divisionData streamCarrier signal
A fiber optic network transmits data between a hub node and a plurality of local nodes connected by at least one unidirectional fiber ring. Downstream data streams are carried on wavelength-division-multiplexed optical carriers from the hub node to the local nodes. An optical carrier corresponding to a specific wavelength carries downstream data streams to a specific local node. Downstream data streams are multiplexed onto an optical carrier via orthogonal frequency division multiplexing. A parallel signal detector in each local node detects all downstream optical carriers. A signal processing module demultiplexes the data stream from the optical carrier having the specific wavelength corresponding to the local node. An upstream data stream is multiplexed via orthogonal frequency division multiplexing onto an upstream optical carrier having the same specific wavelength and transmitted from the local node to the hub node. Upstream data awaiting transmission is allocated to specific subcarriers and time slots.
Owner:NEC CORP
Opto-electronic distributed crossbar switch
InactiveUS6597824B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesCrossbar switchLaser transmitter
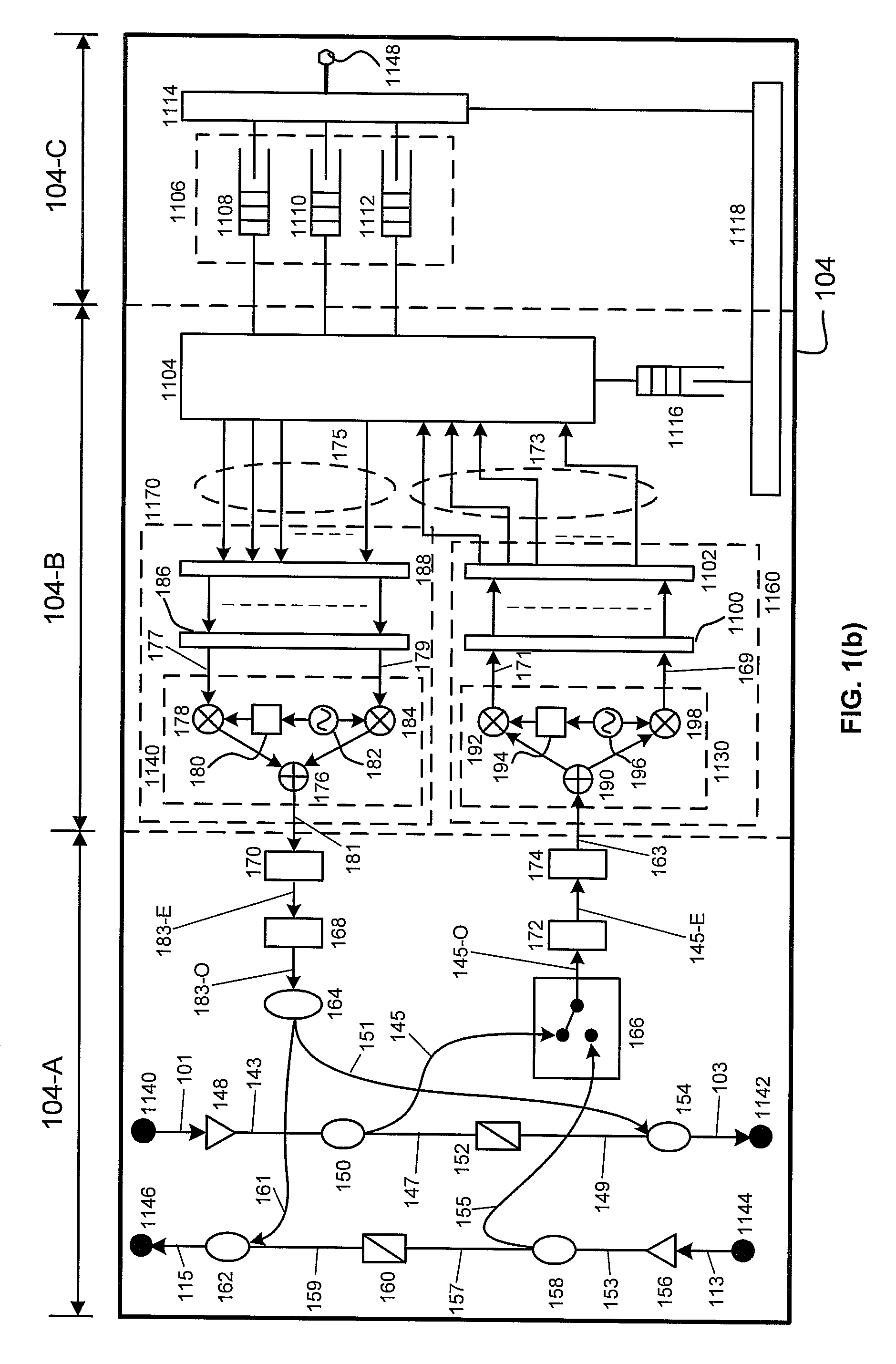
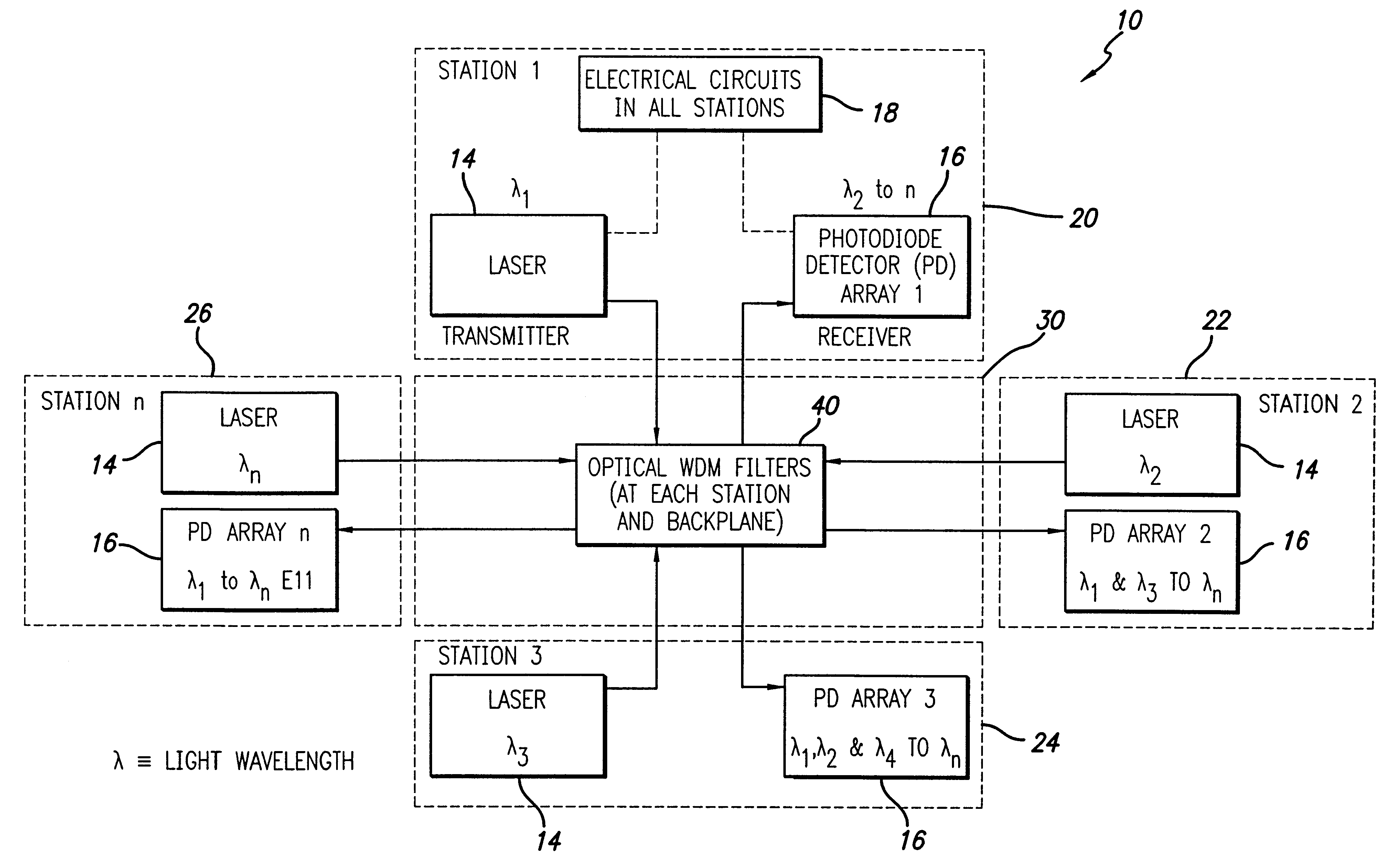
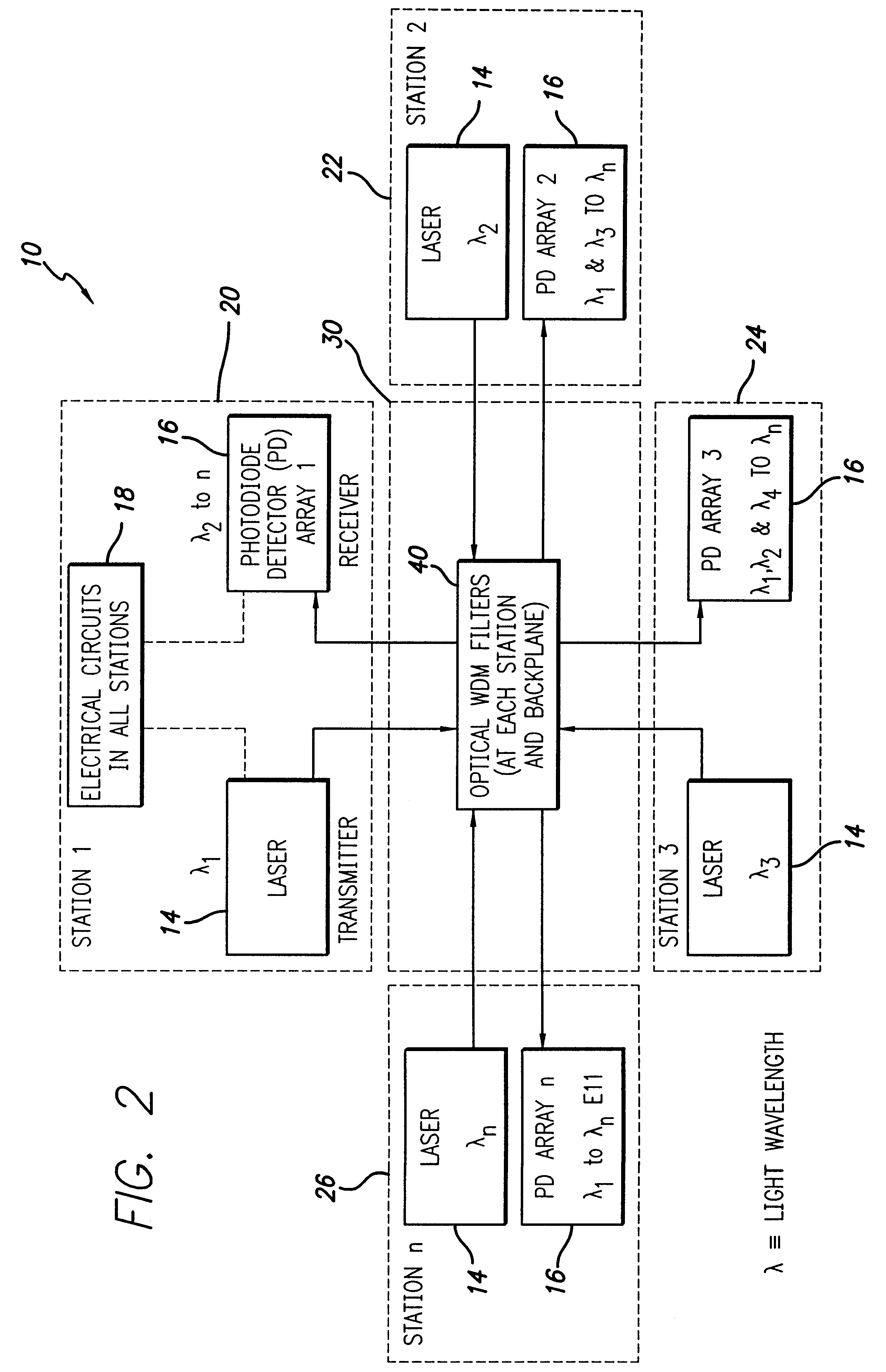
The invention is an optoelectronic (OE) crossbar switch (10) for both digital and analog signals, used either separately or combined, whose functions are reconfigurable and distributed. The invention allows multiple senders to be connected with multiple receivers simultaneously. The invention uses optical filters for wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing (WDM and WDD). A single fiber module input / output port carries multiple bi-directional signals that are optically filtered out in the module using WDM / WDD filters (12) at each sender / receiver and then selected after optical filtering using photodiode detectors (15) as detectors and switches. Laser transmitters (14), photodiode detectors (15), and smart electronics (18) are used to implement the crossbar switch functions. In addition to optical filters, the use of time division multiplexing (TDM) and code division multiple access (CDMA) implemented either electrically or optically are taught to increase the number of independent users that the distributed switch handles. The switch can be cascaded with other switches using optical bridging circuits (100) to create a scaleable interconnect fabric. An arbitration technique can be used which allows signals to be sent only when the intended receiver is capable of accepting these signals.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
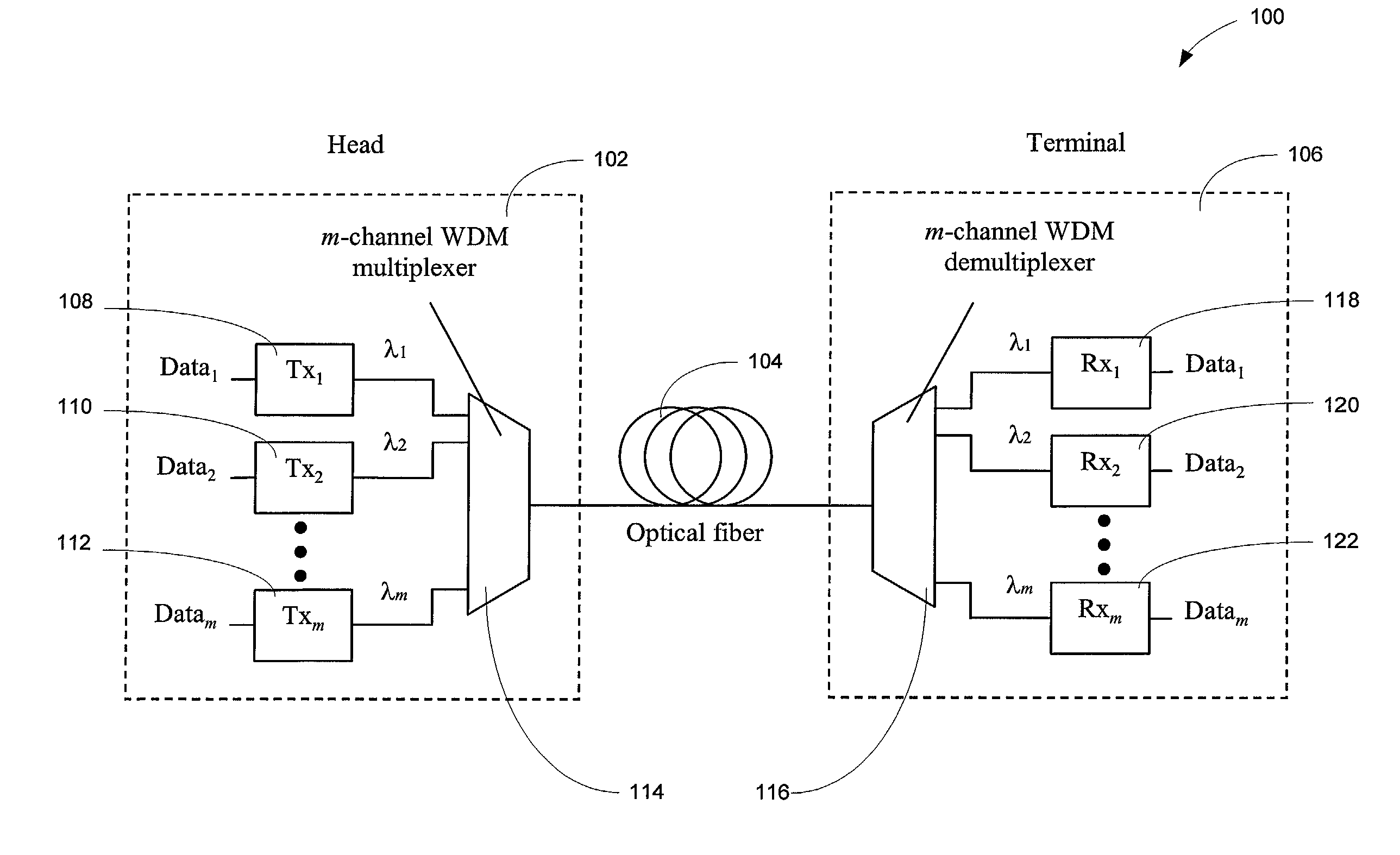
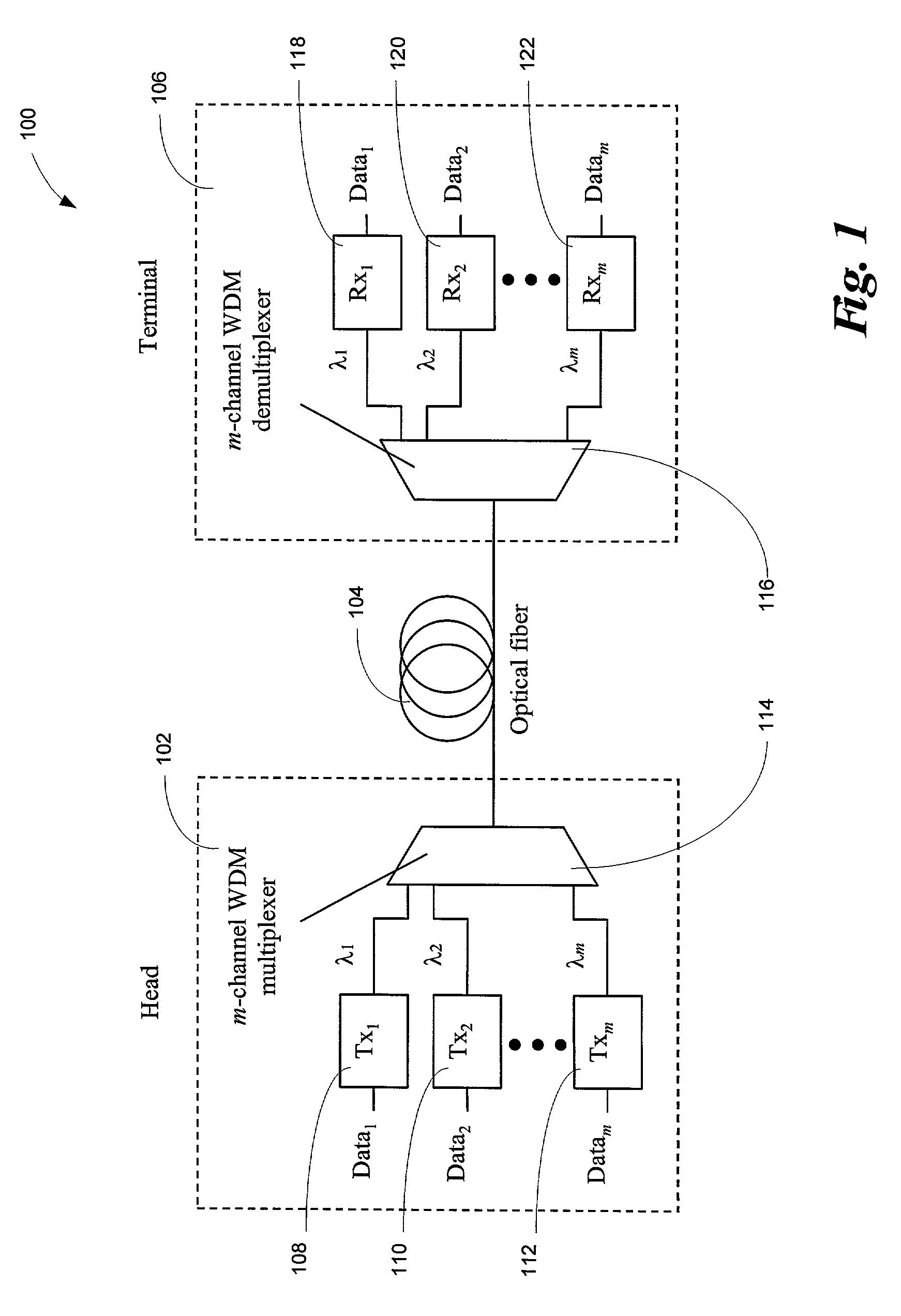
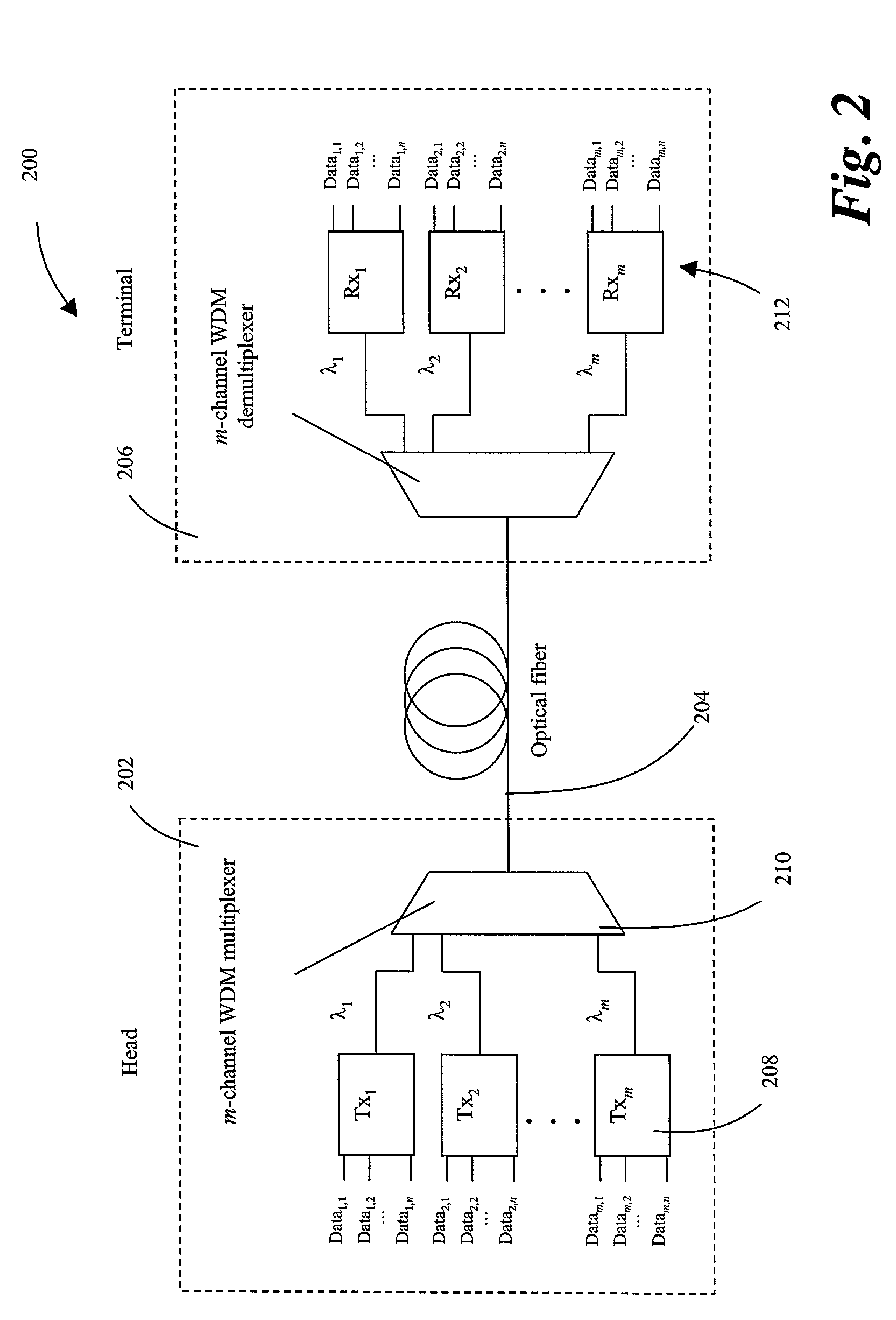
Increasing data throughput in optical fiber transmission systems
InactiveUS7173551B2Increase channel data throughput rateImprove spectral efficiencyElectric signal transmission systemsError preventionFiberFrequency spectrum
Data throughput rates are increased in an optical fiber communication system without requiring replacement of the existing optical fiber in a link. Channel throughput is increased by upgrading the components and circuitry in the head and terminal of an optical fiber communication system link. Aggregate throughput in a fiber optic link is increased beyond the range of conventional Wavelength Division Multiplexed (WDM) upgrades, while precluding the necessity of replacing existing fiber plants. The increase in system throughput is achieved by using advanced modulation techniques to encode greater amounts of data into the transmitted spectrum of a channel, thereby increasing the spectral efficiency of each channel. This novel method of increasing transmission capacity by upgrading the head and terminal of the system to achieve greater spectral efficiency and hence throughput, alleviates the need to replace existing fiber plants. Spectrally efficient complex modulation techniques can be supported by interface circuits with an increased level of signal processing capability in order to both encode multiple bits into a transmitted symbol and decode the original data from the received symbols.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com