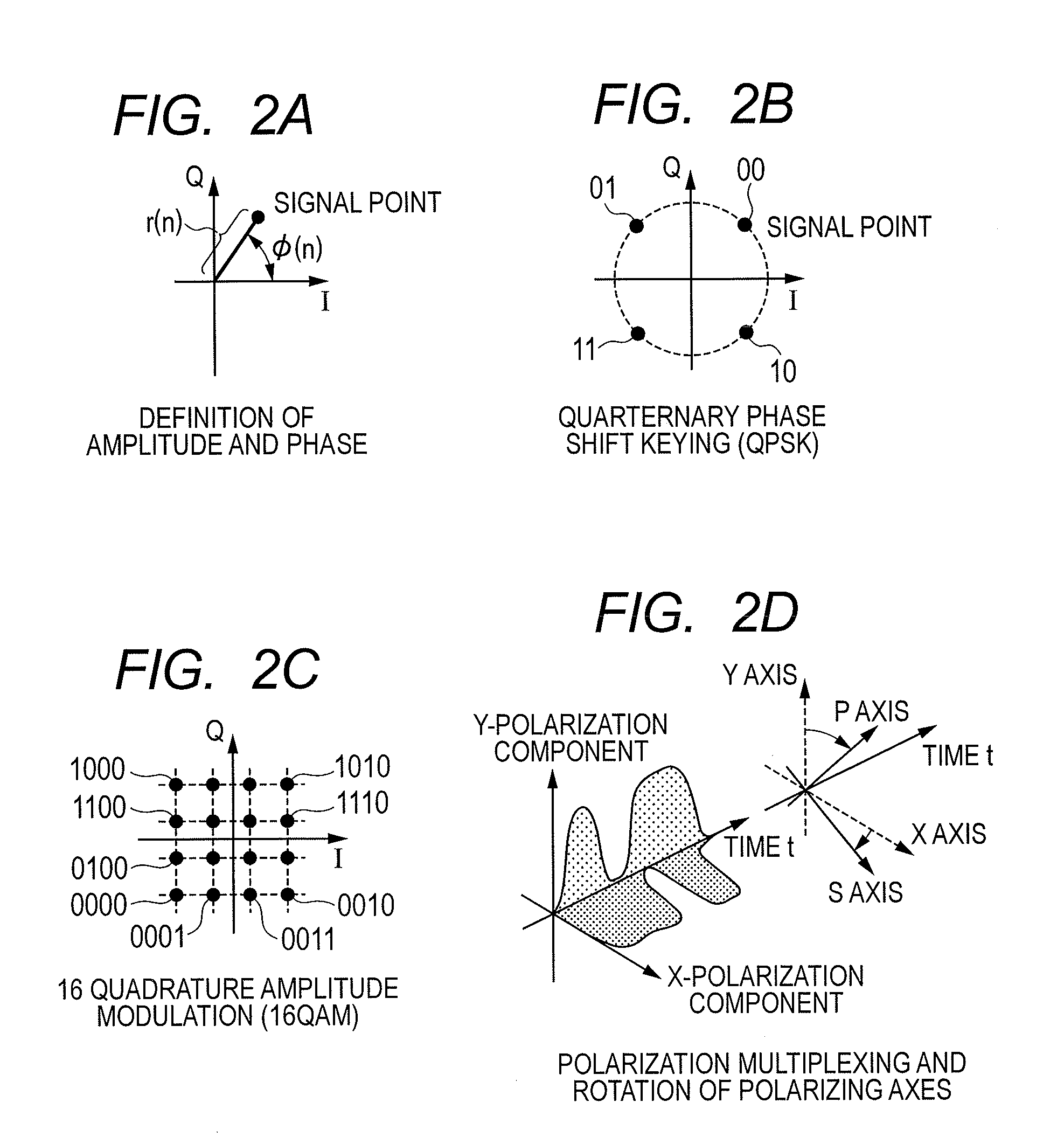
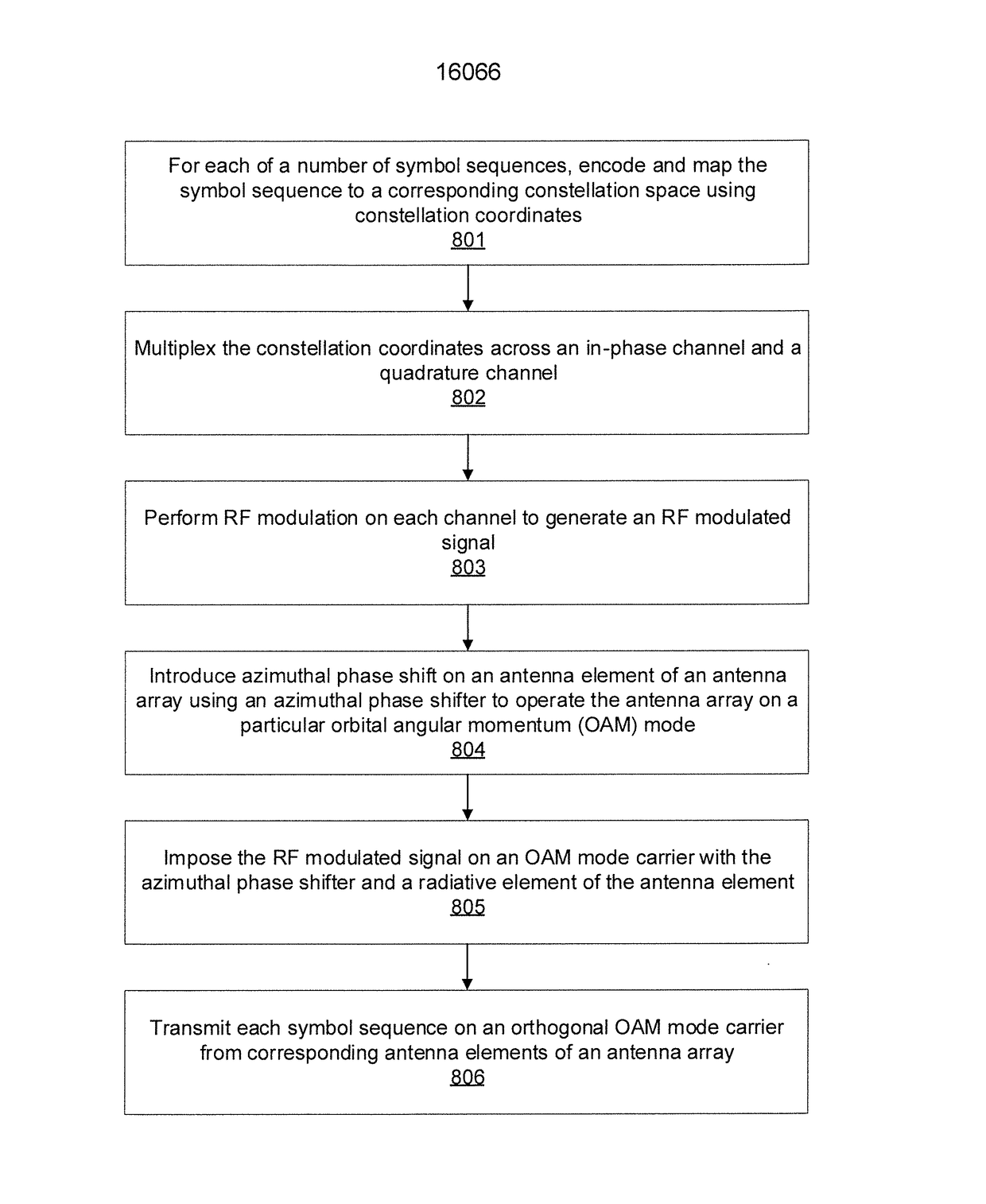
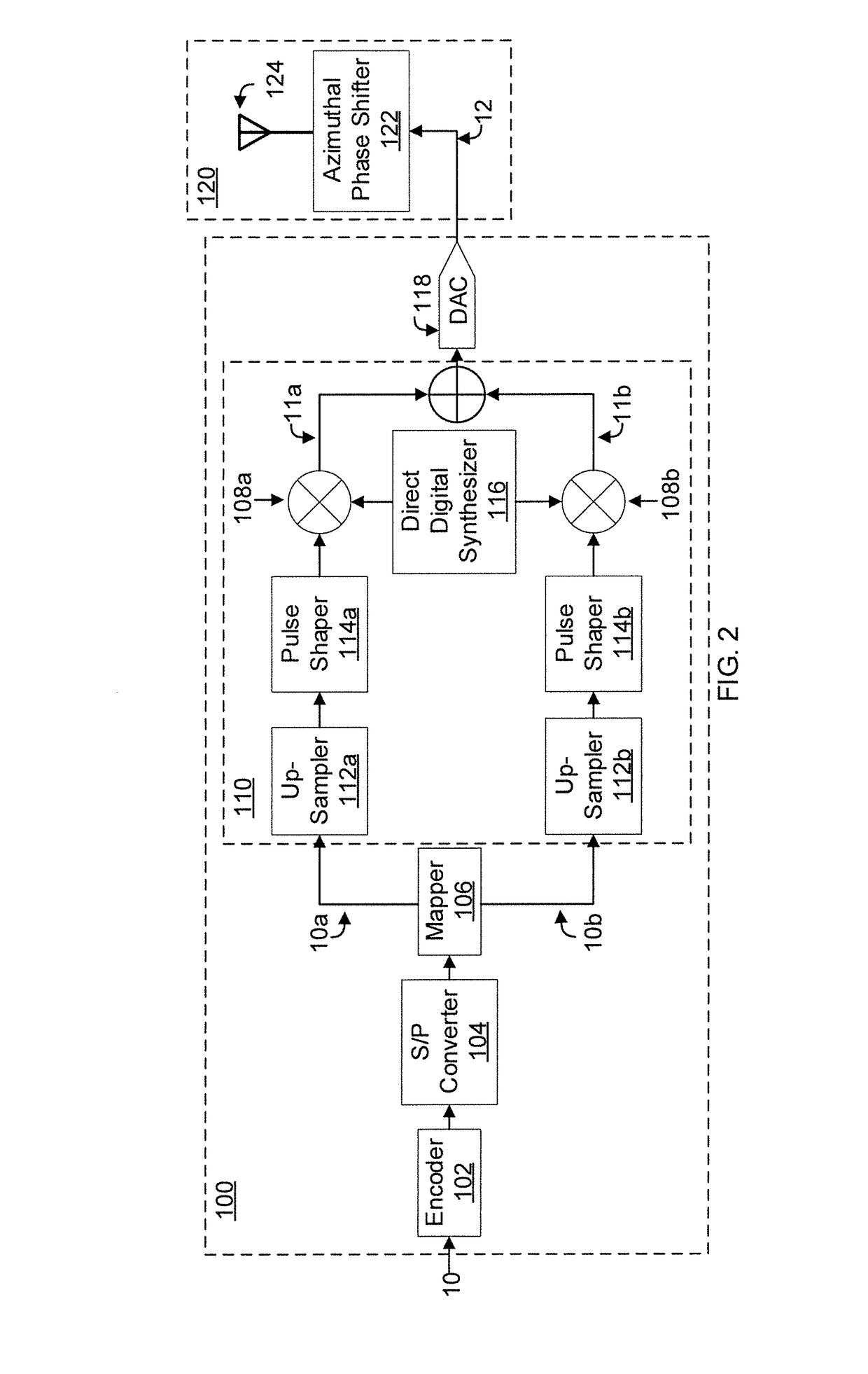
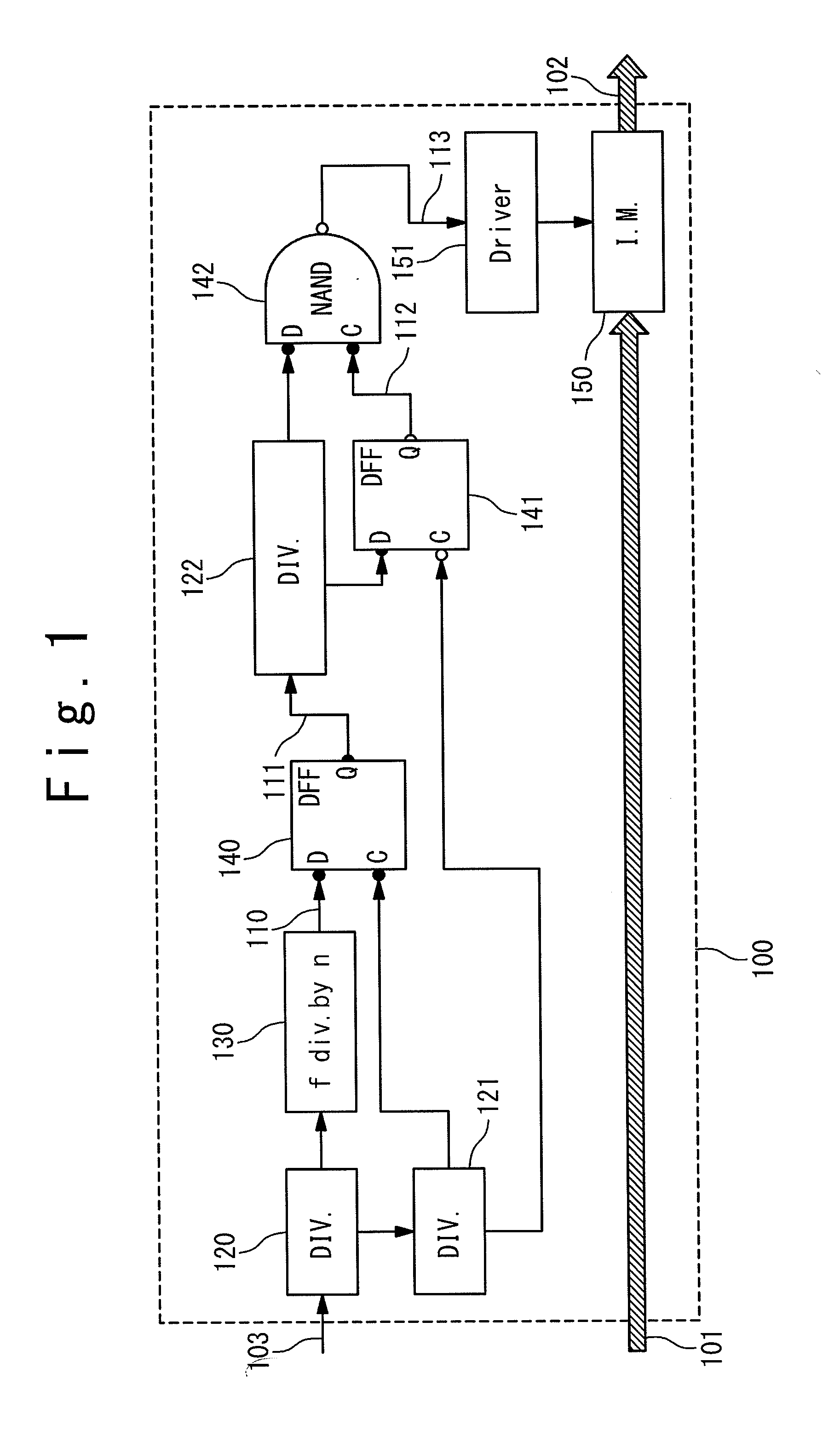
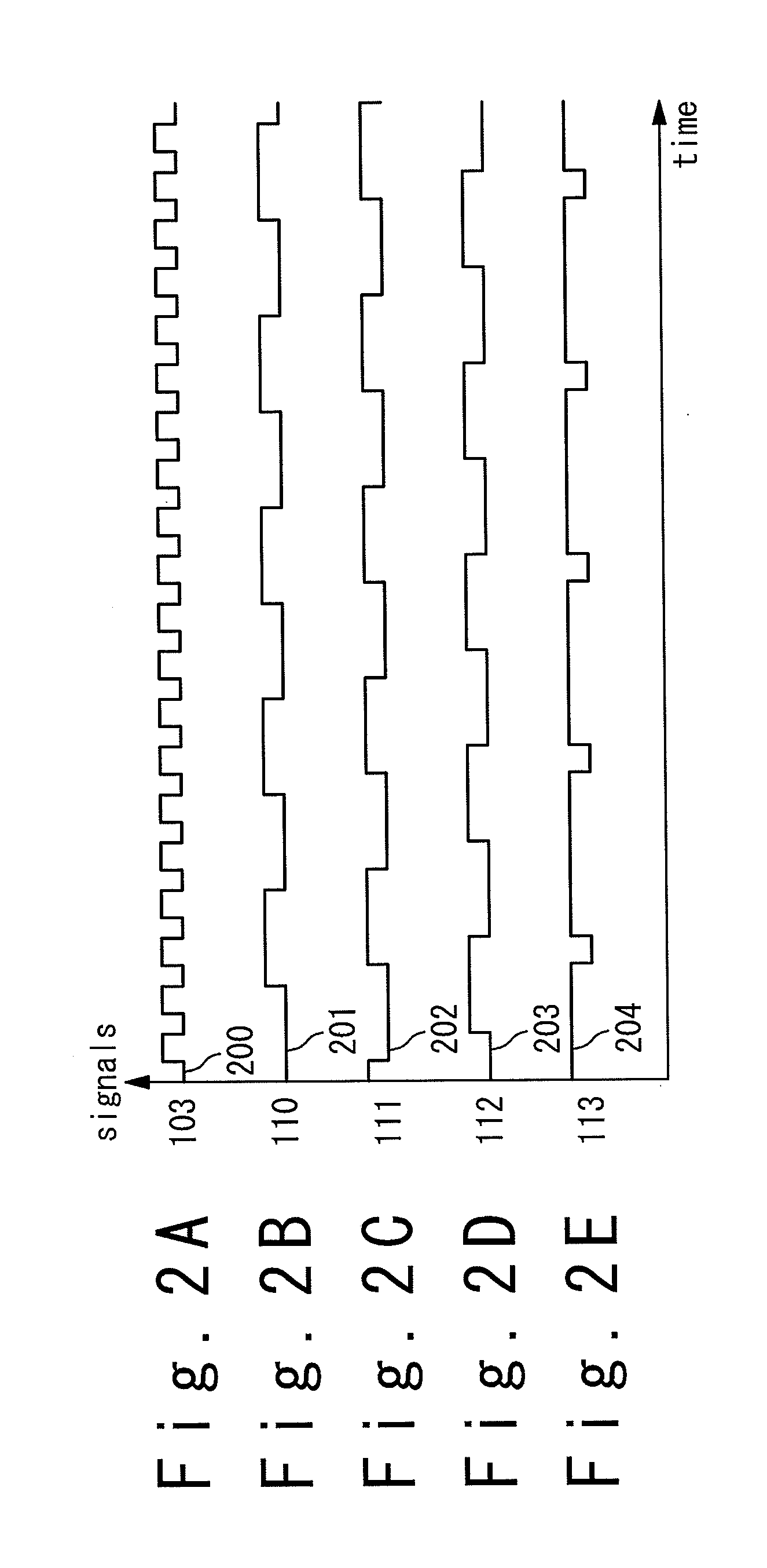
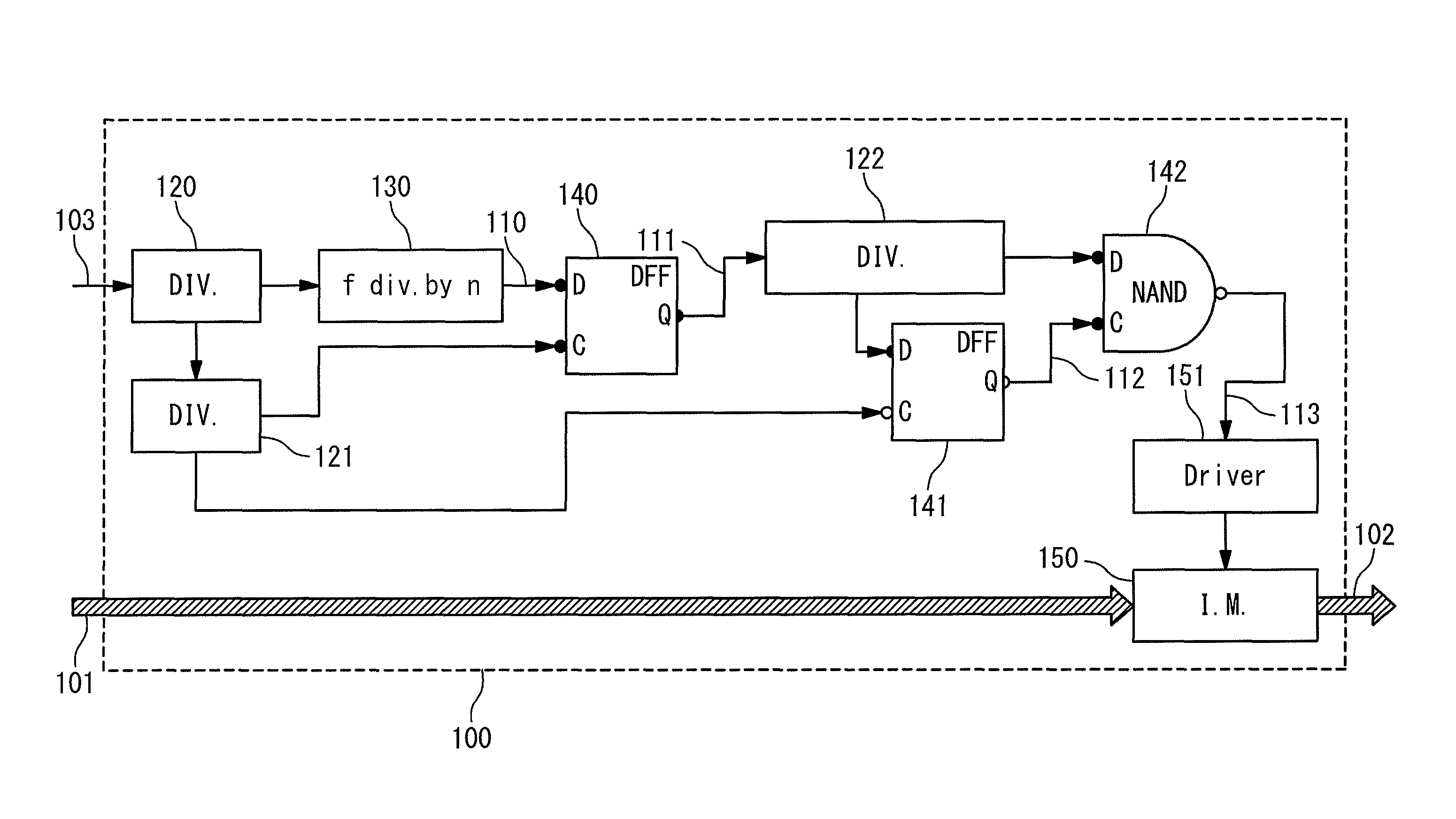
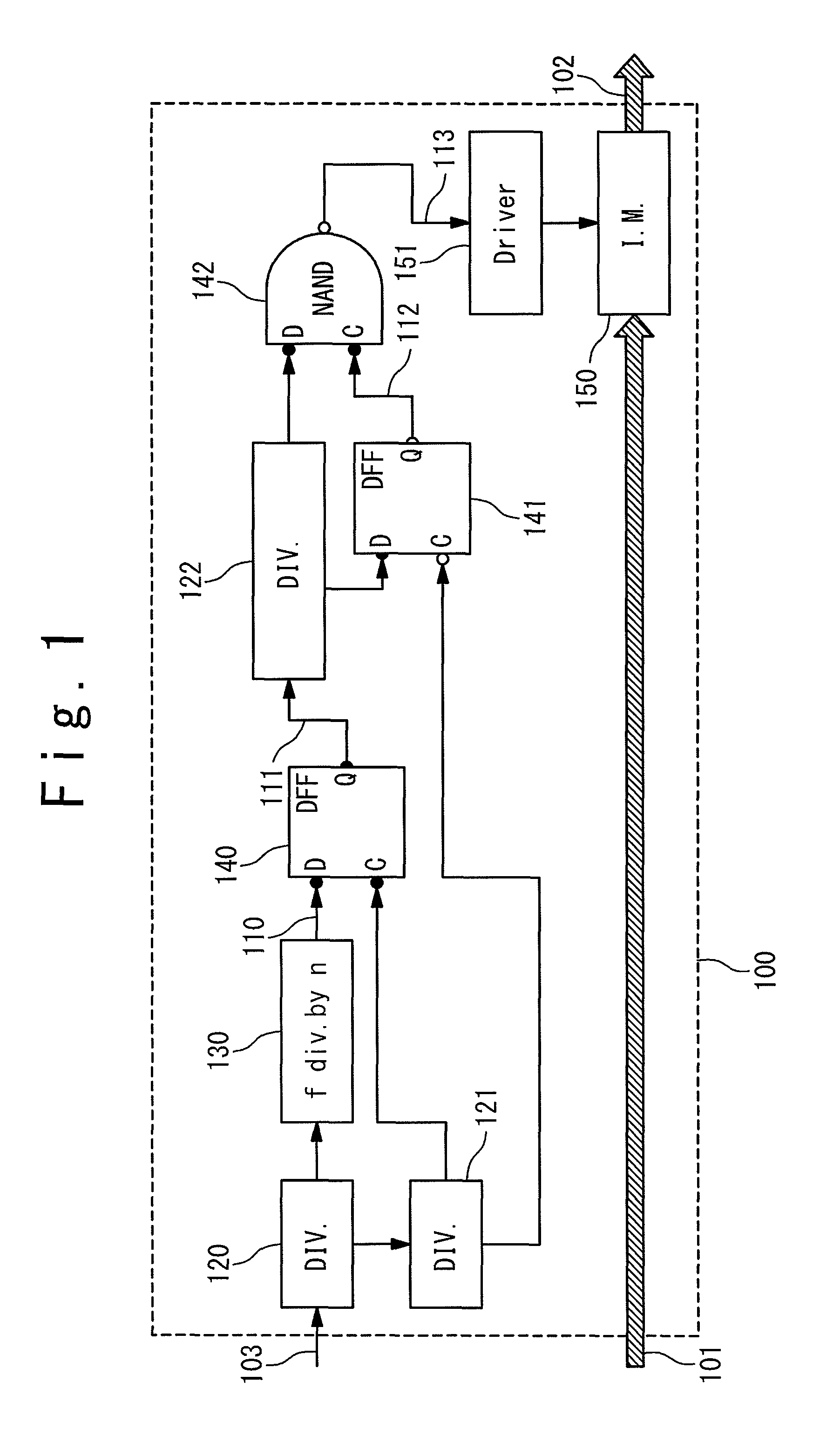
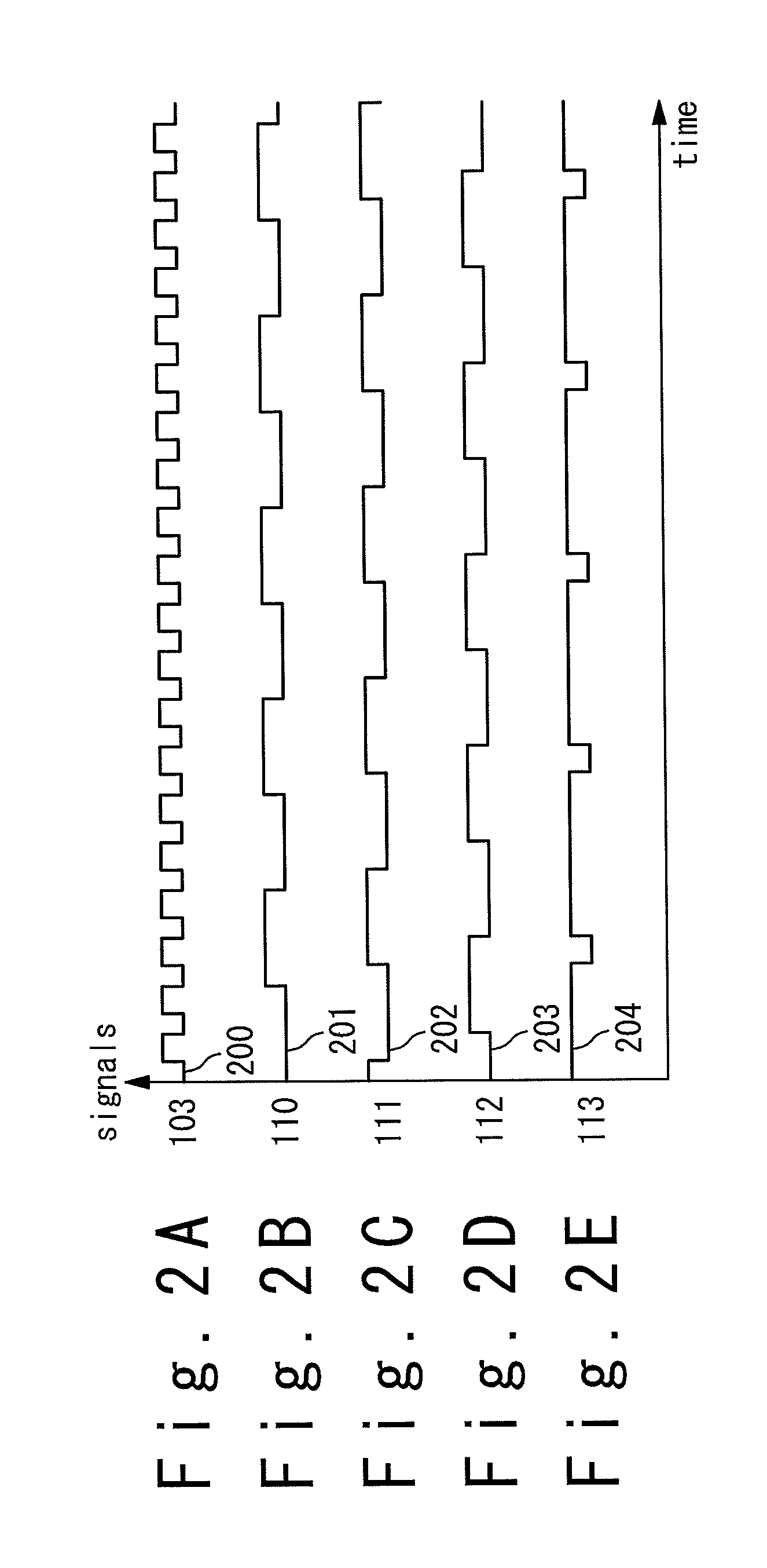
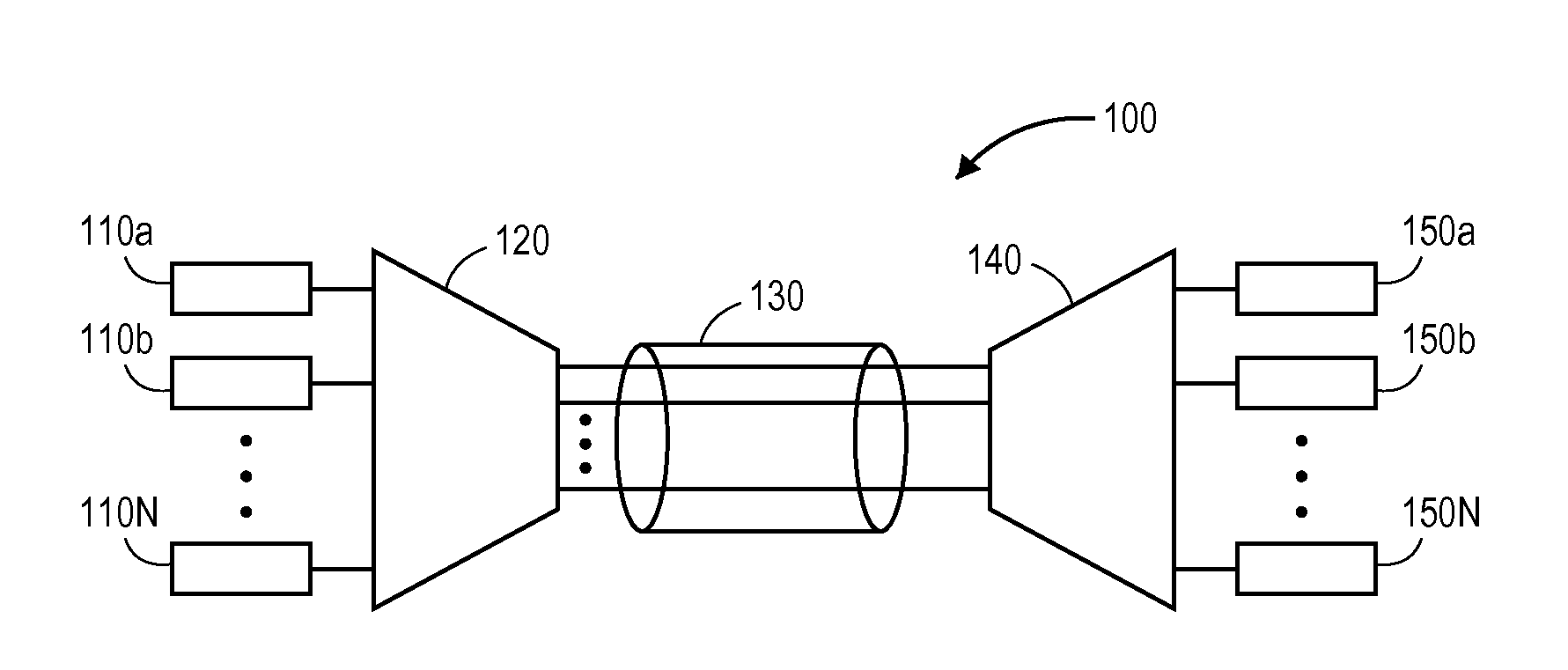
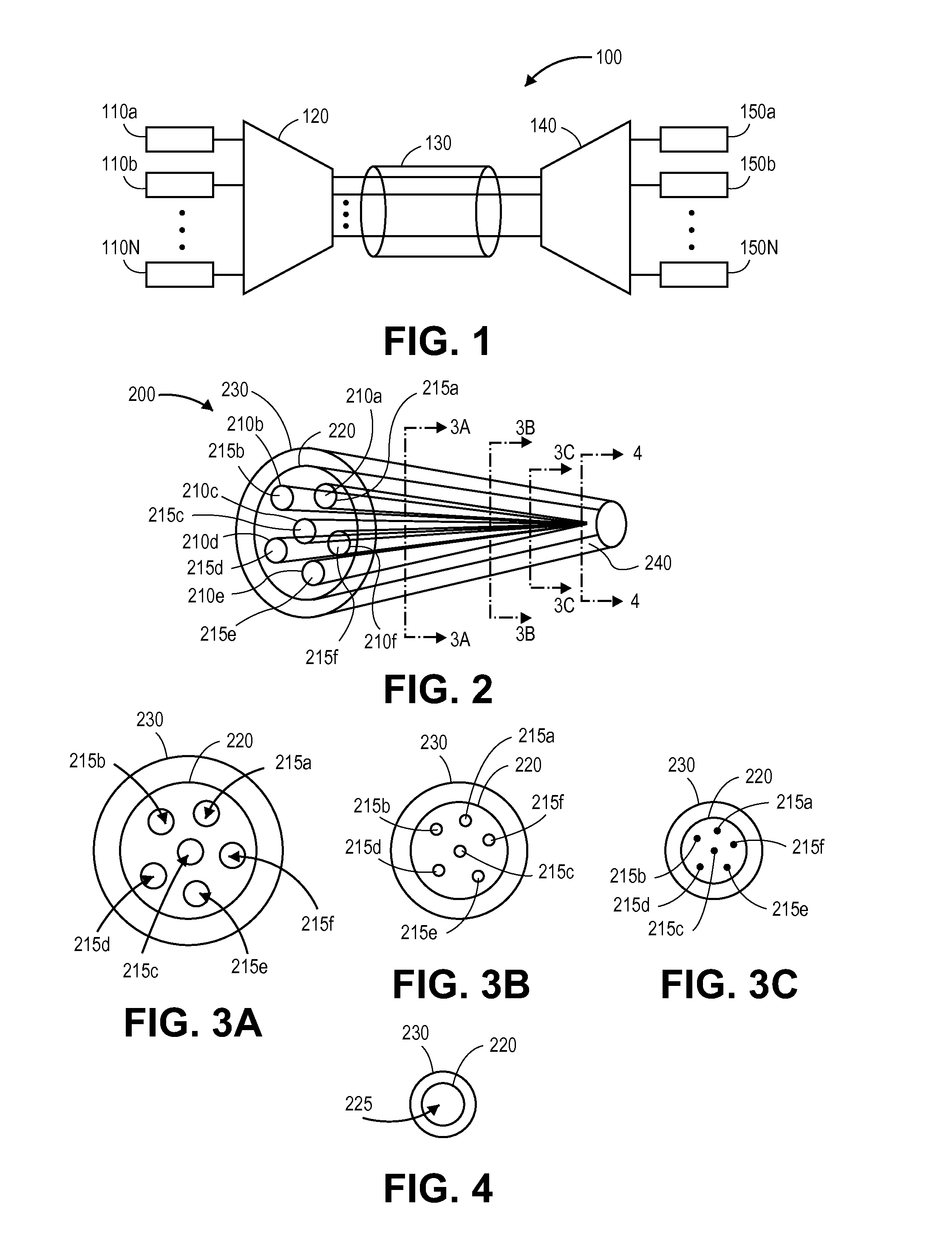
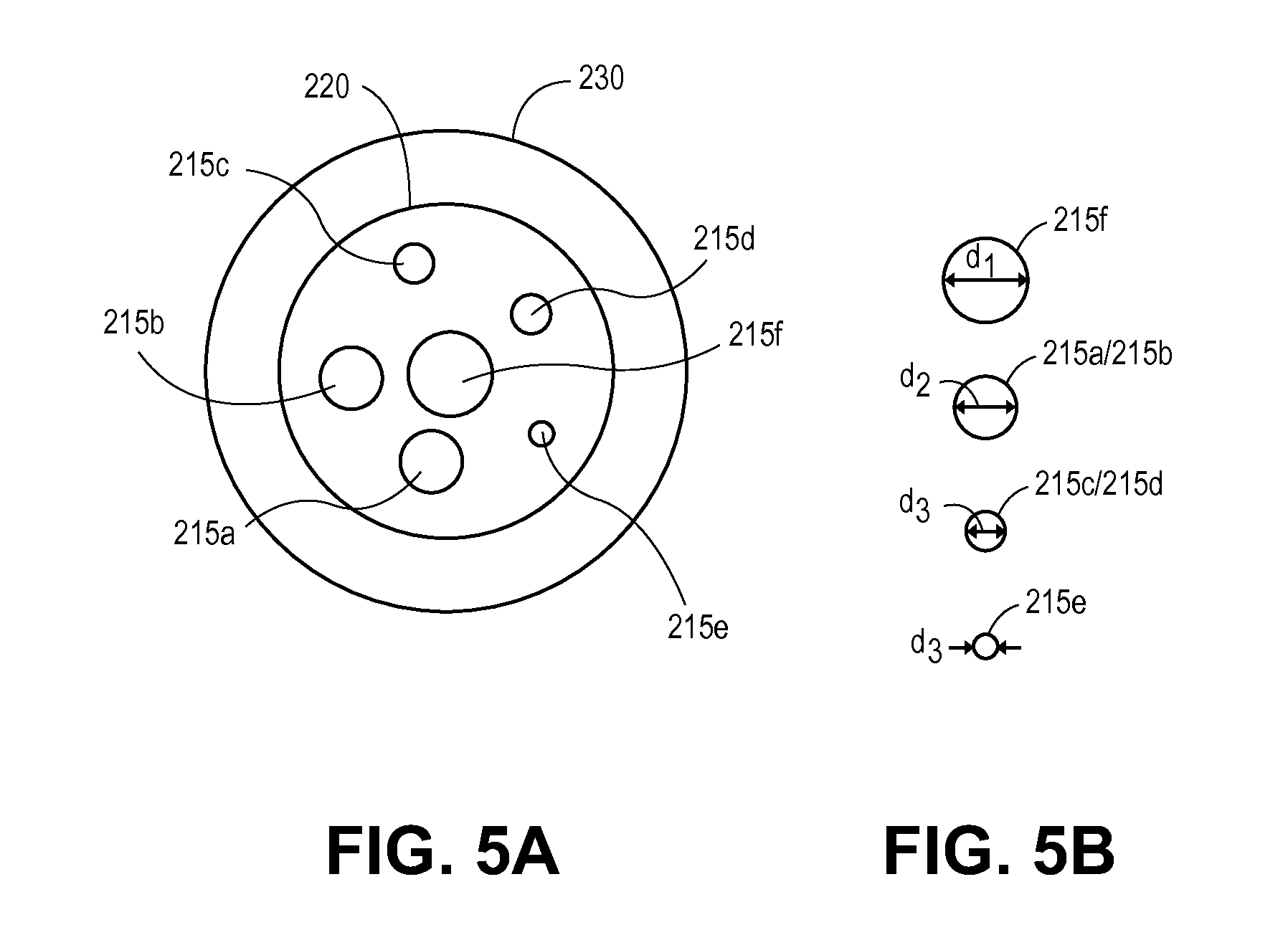
Patents
Literature
516results about "Optical mode multiplex systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
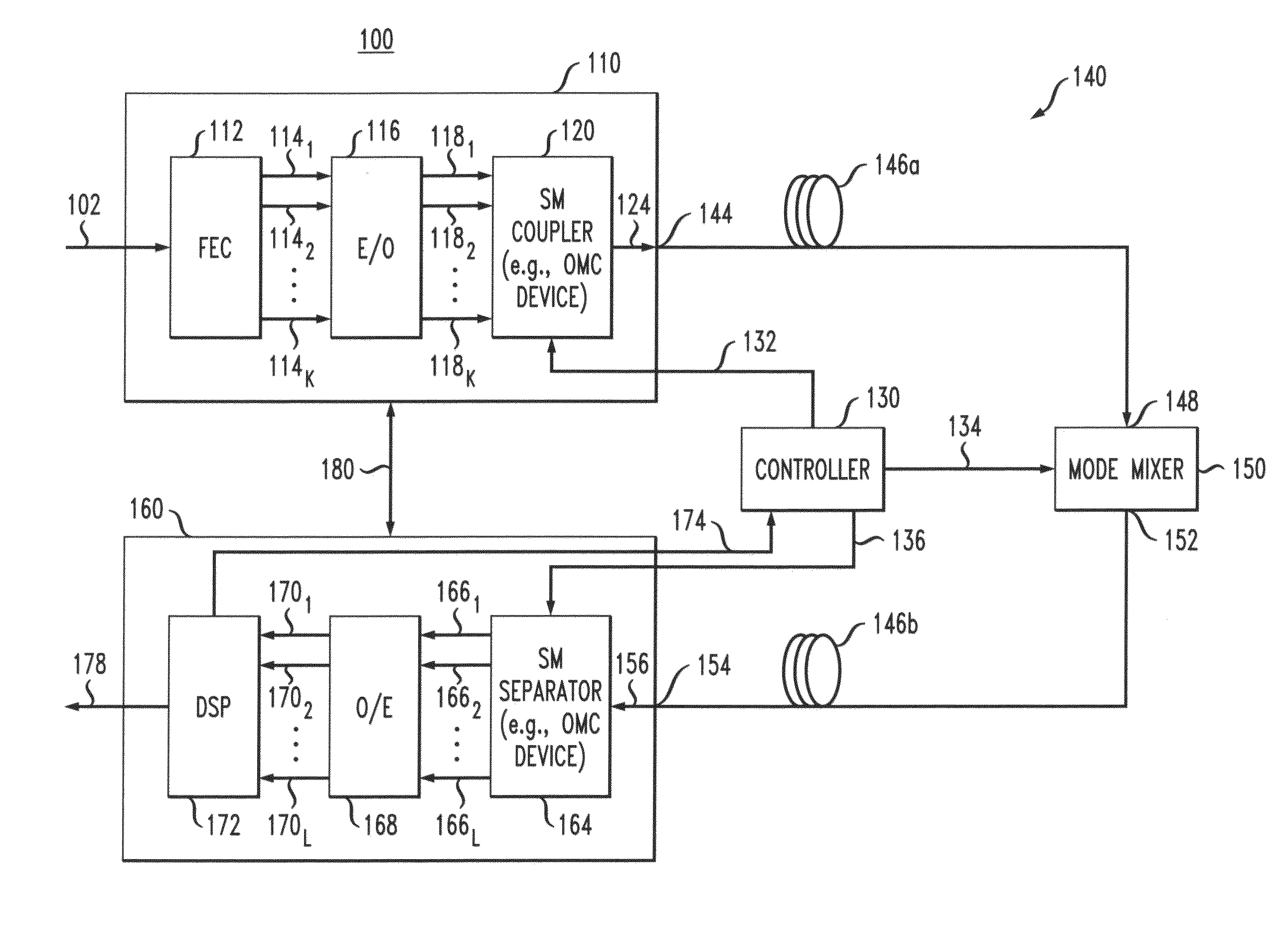
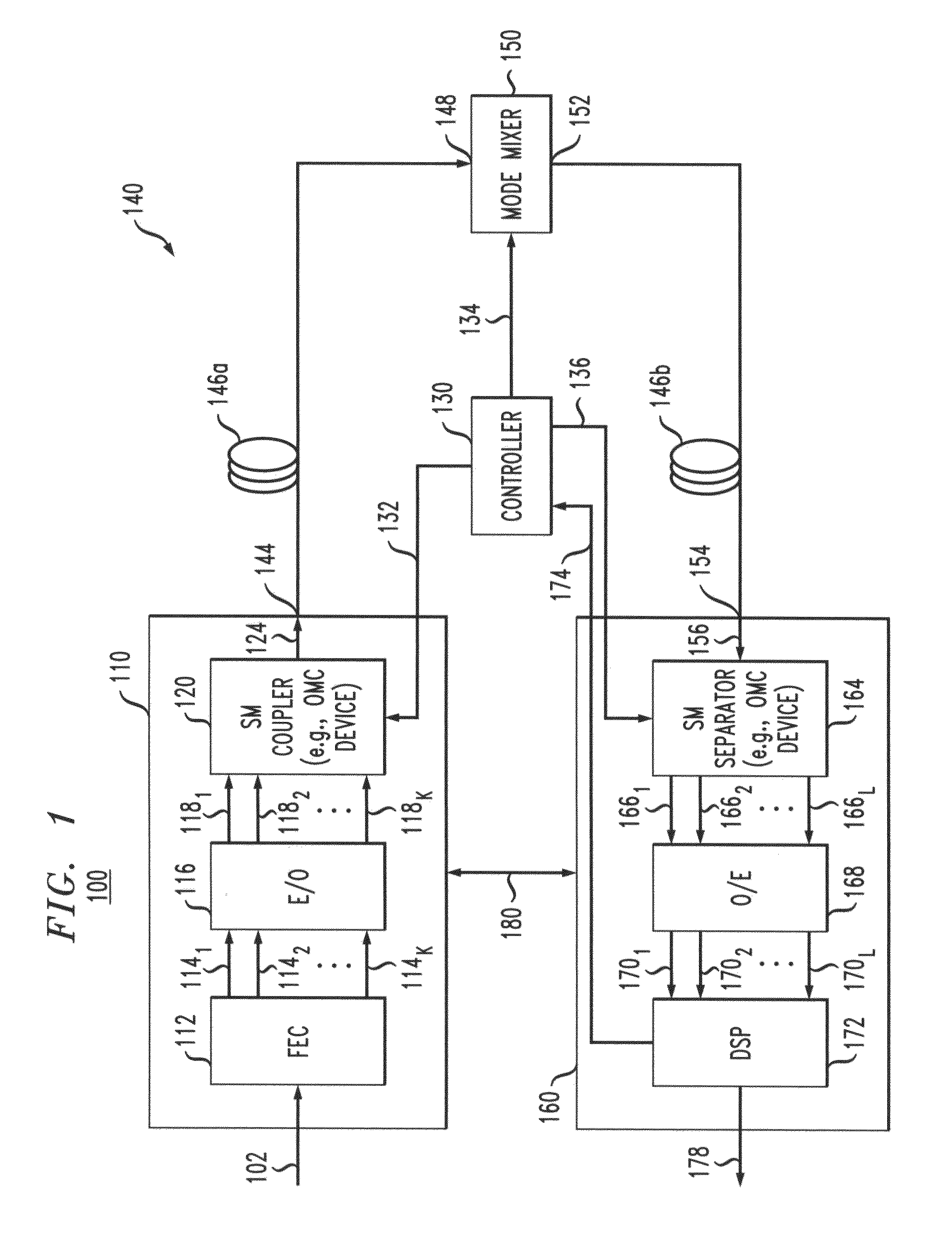
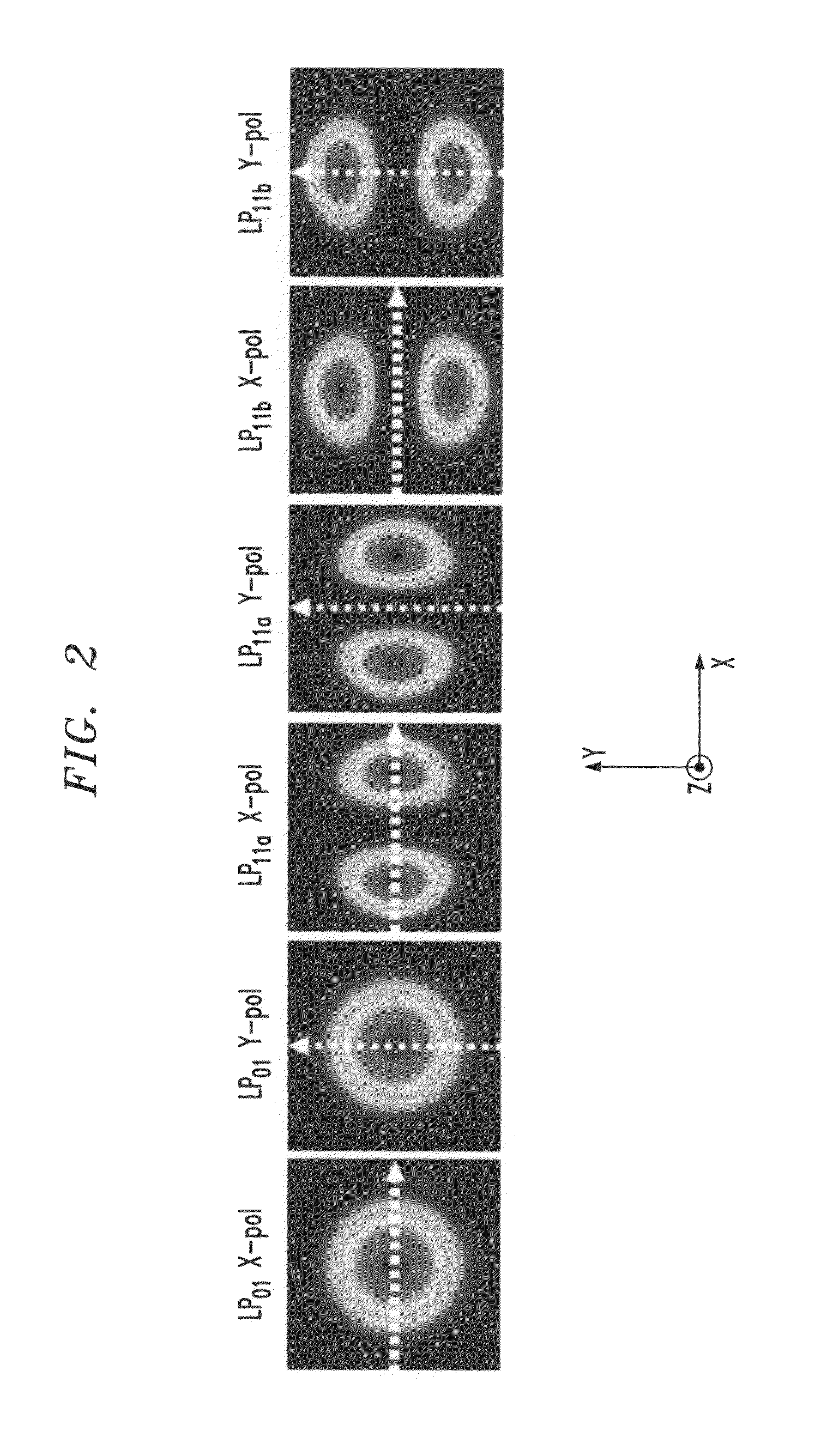
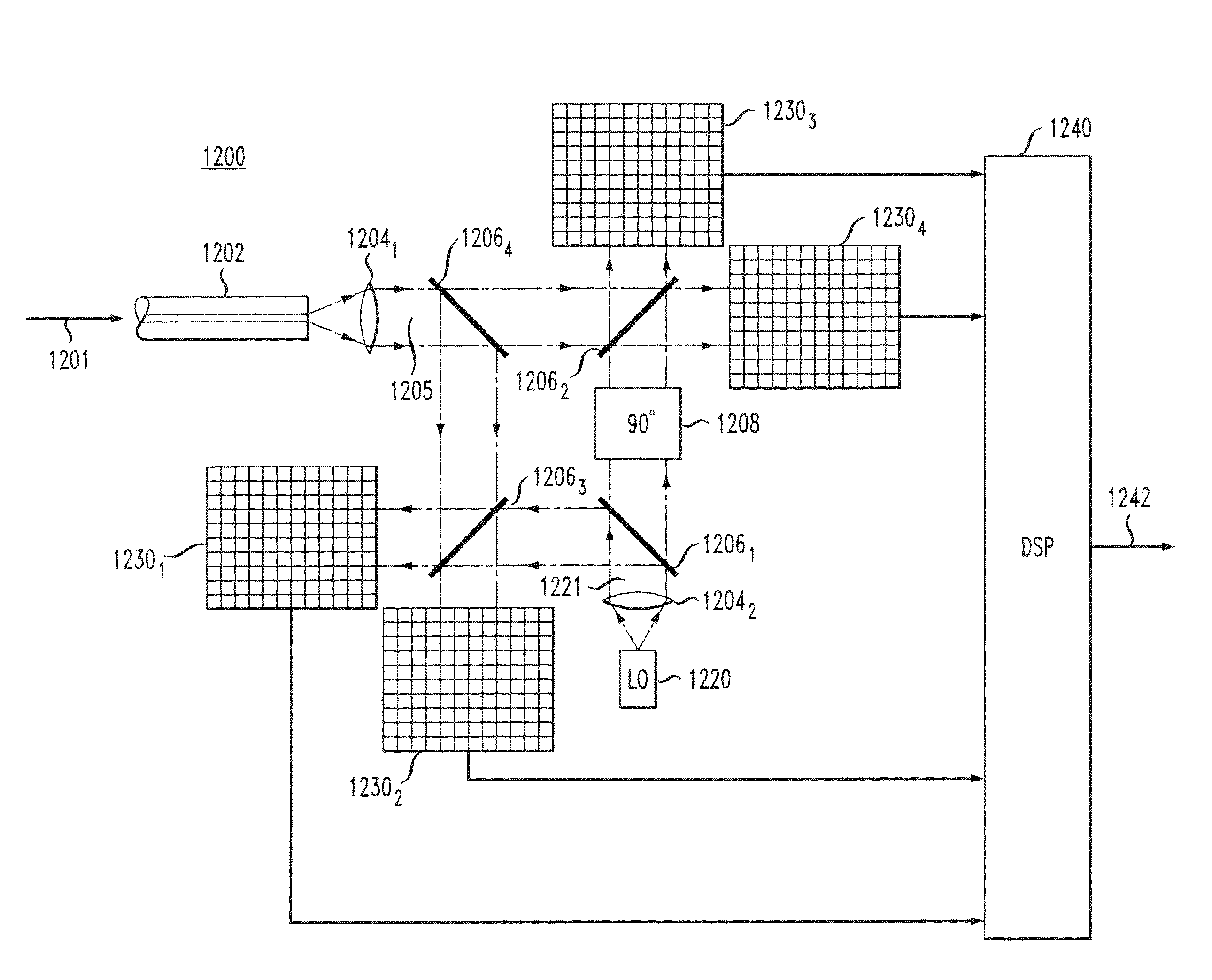
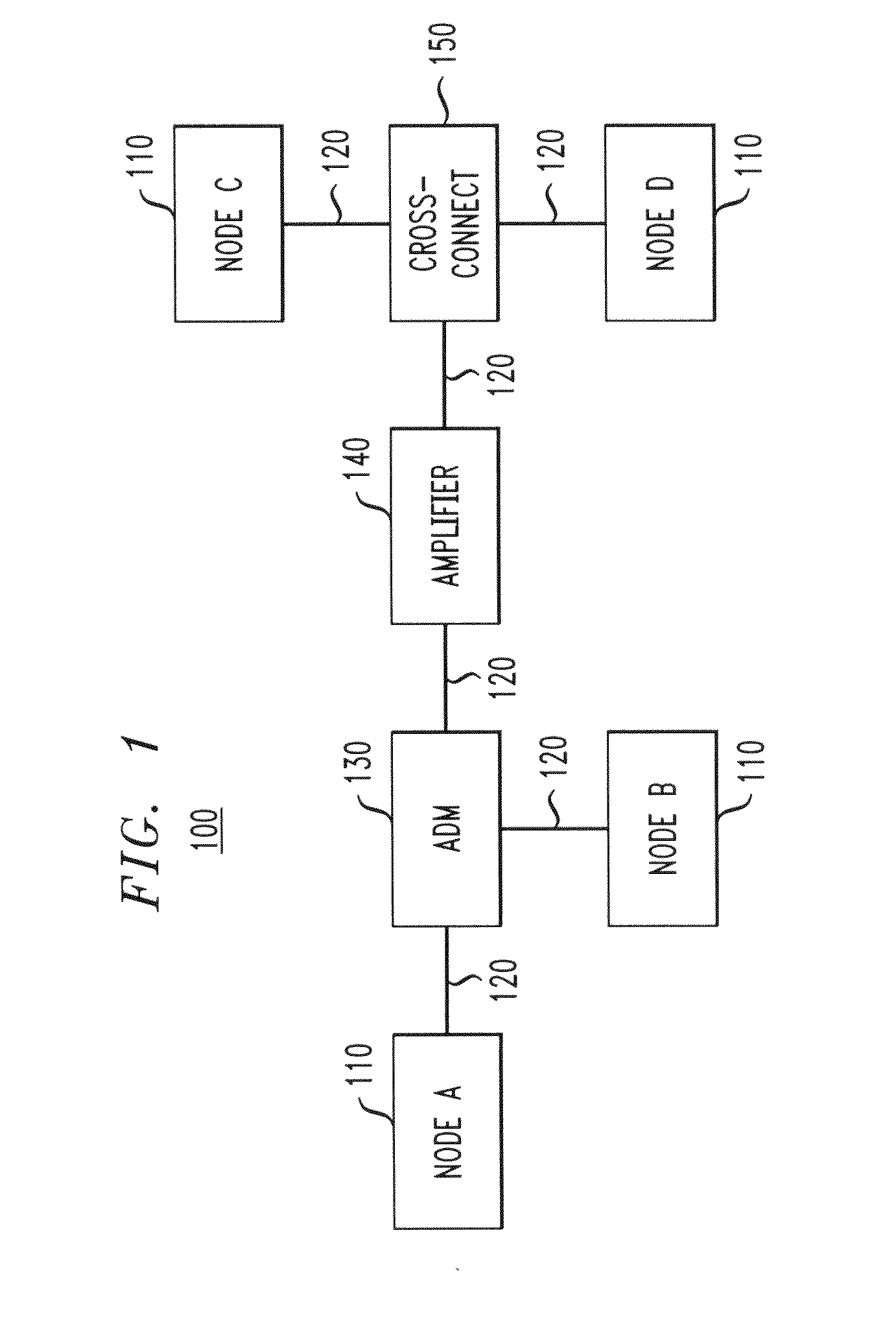
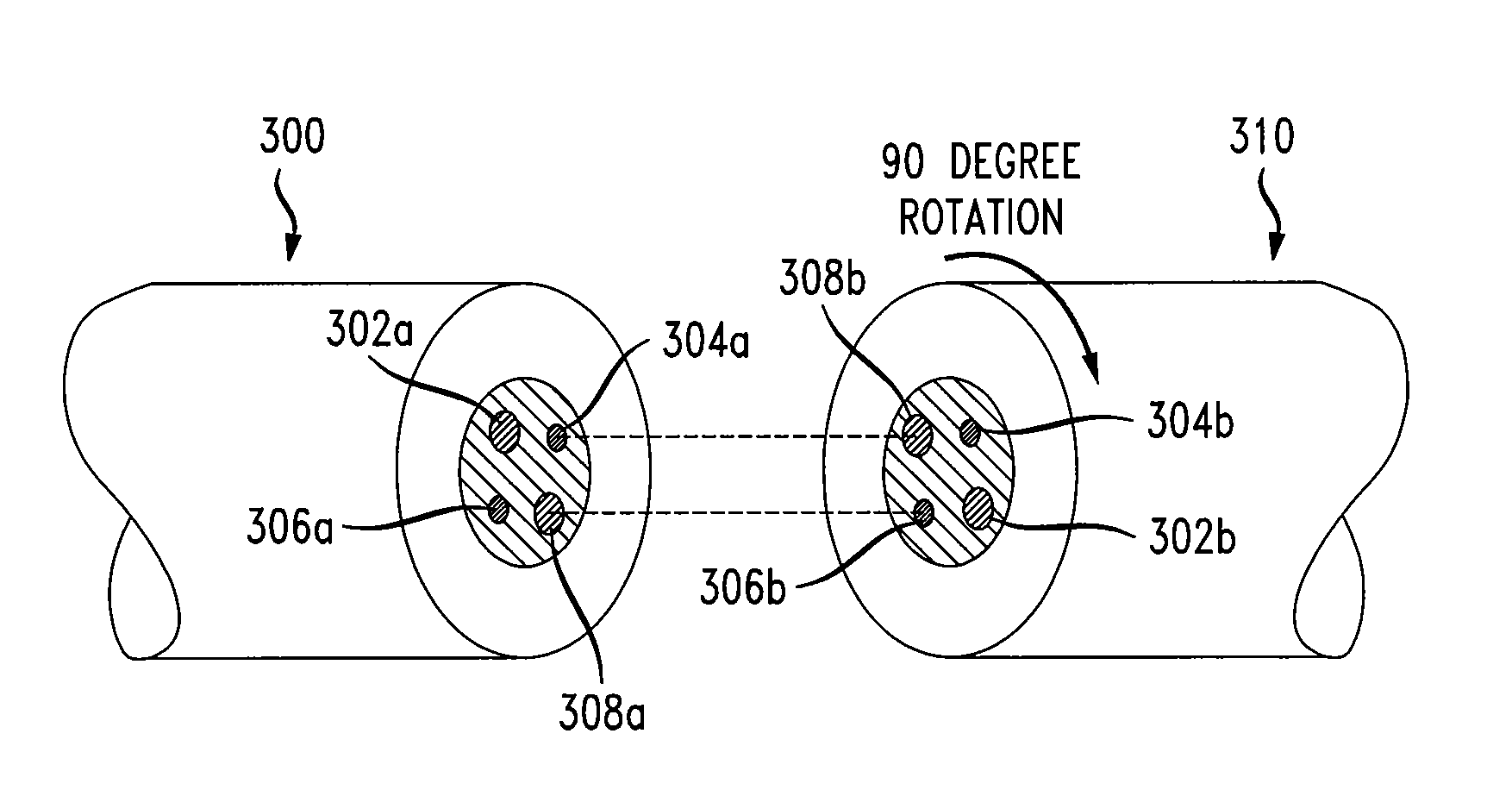
Intra-link spatial-mode mixing in an under-addressed optical MIMO system
ActiveUS20120224807A1Reduce frequencyReduce outage rateOptical mode multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesCoherence timeError correcting
The outage probability in an under-addressed optical MIMO system may be reduced by configuring an intra-link optical mode mixer to dynamically change the spatial-mode mixing characteristics of the link on a time scale that is faster than the channel coherence time. Provided that the MIMO system employs an FEC code that has a sufficient error-correcting capacity for correcting the amount of errors corresponding to an average state of the MIMO channel, this relatively fast dynamic change tends to reduce the frequency of events during which the number of errors per FEC-encoded block of data exceeds the error-correcting capacity of the FEC code.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Transverse-mode multiplexing for optical communication systems
ActiveUS20100329671A1Reverses effectOptical mode multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingCommunications system
An optical communication system having an optical transmitter and an optical receiver optically coupled via a multi-path fiber. The optical transmitter launches, into the multi-path fiber, an optical transverse-mode-multiplexed (TMM) signal having a plurality of independently modulated components by coupling each independently modulated component into a respective transverse mode of the multi-path fiber. The TMM signal undergoes inter-mode mixing in the multi-path fiber before being received by the optical receiver. The optical receiver processes the received TMM signal to reverse the effects of inter-mode mixing and recover the data carried by each of the independently modulated components.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
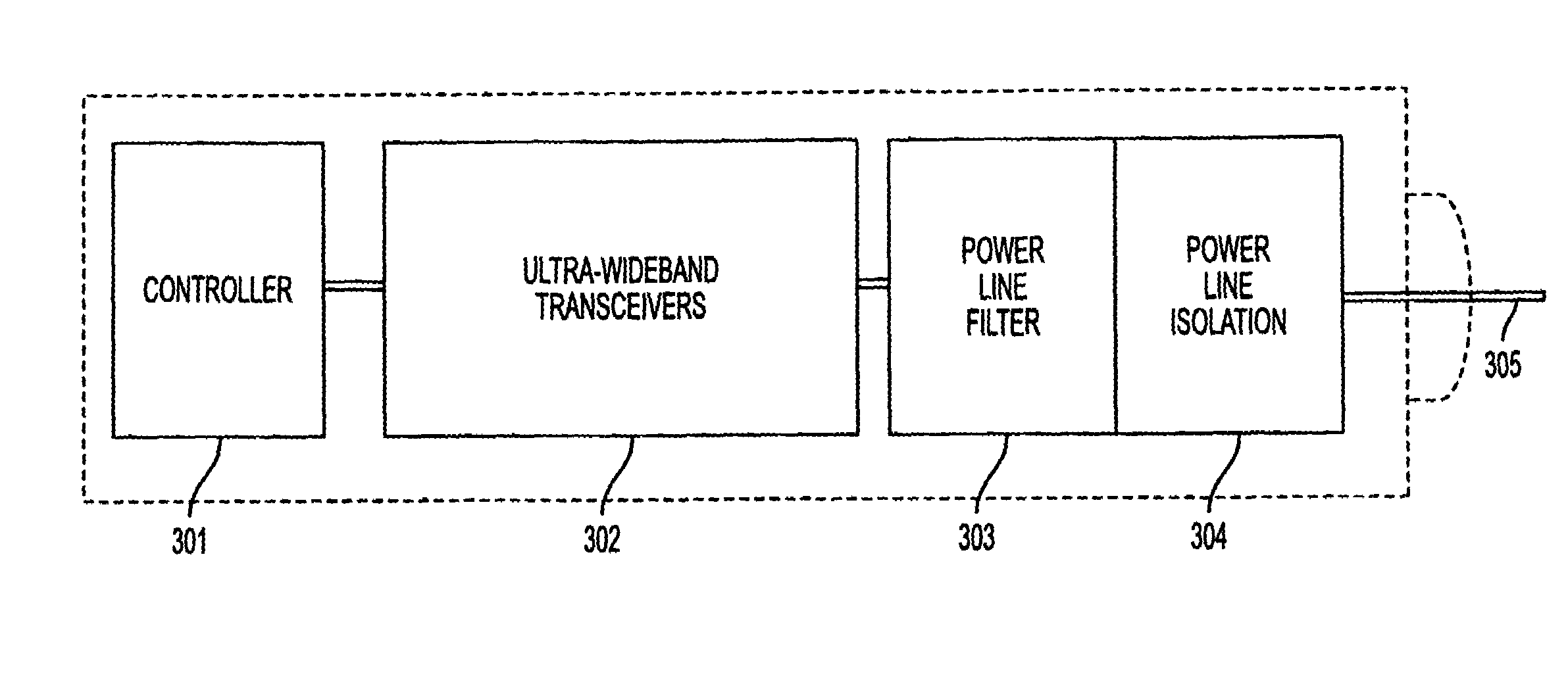
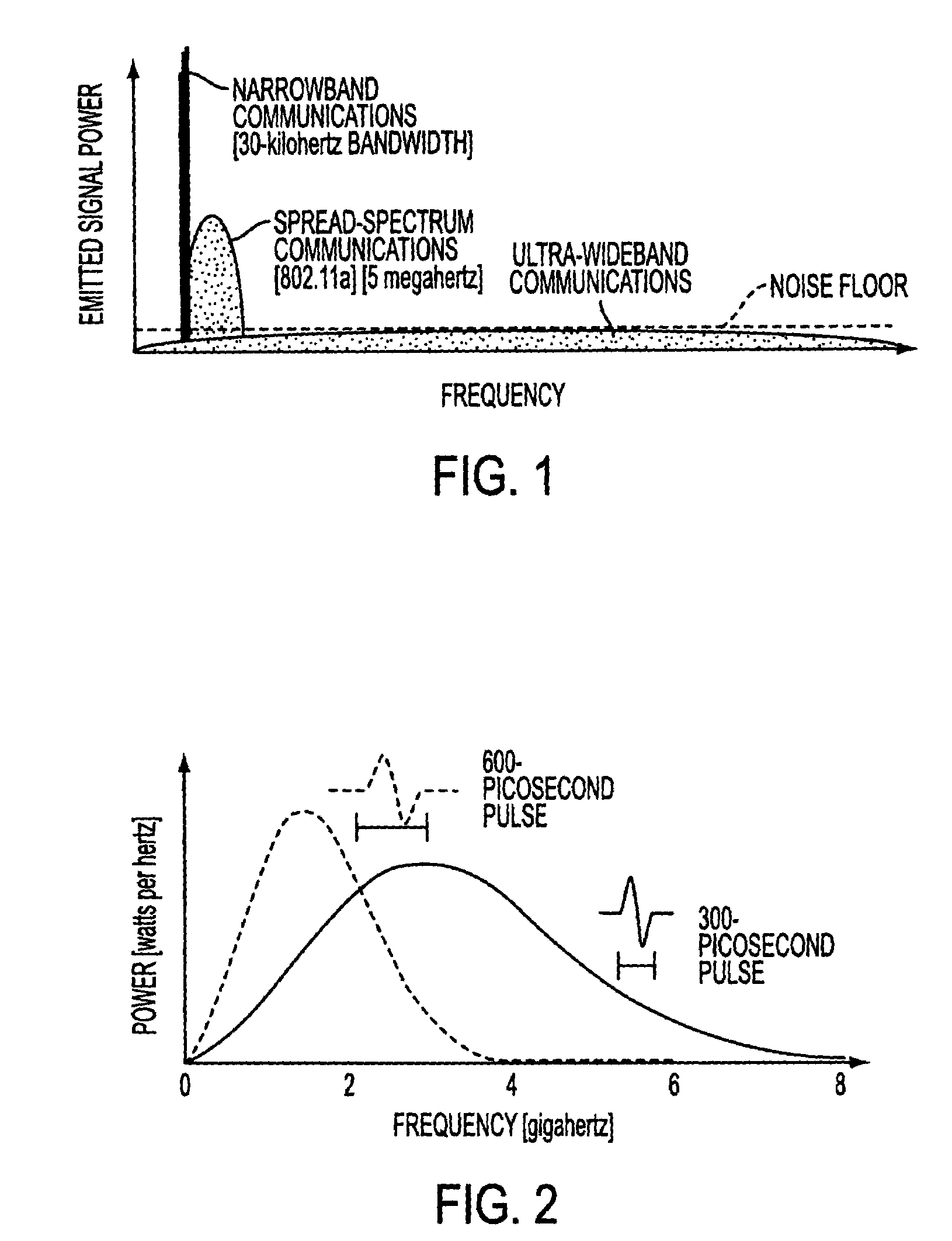
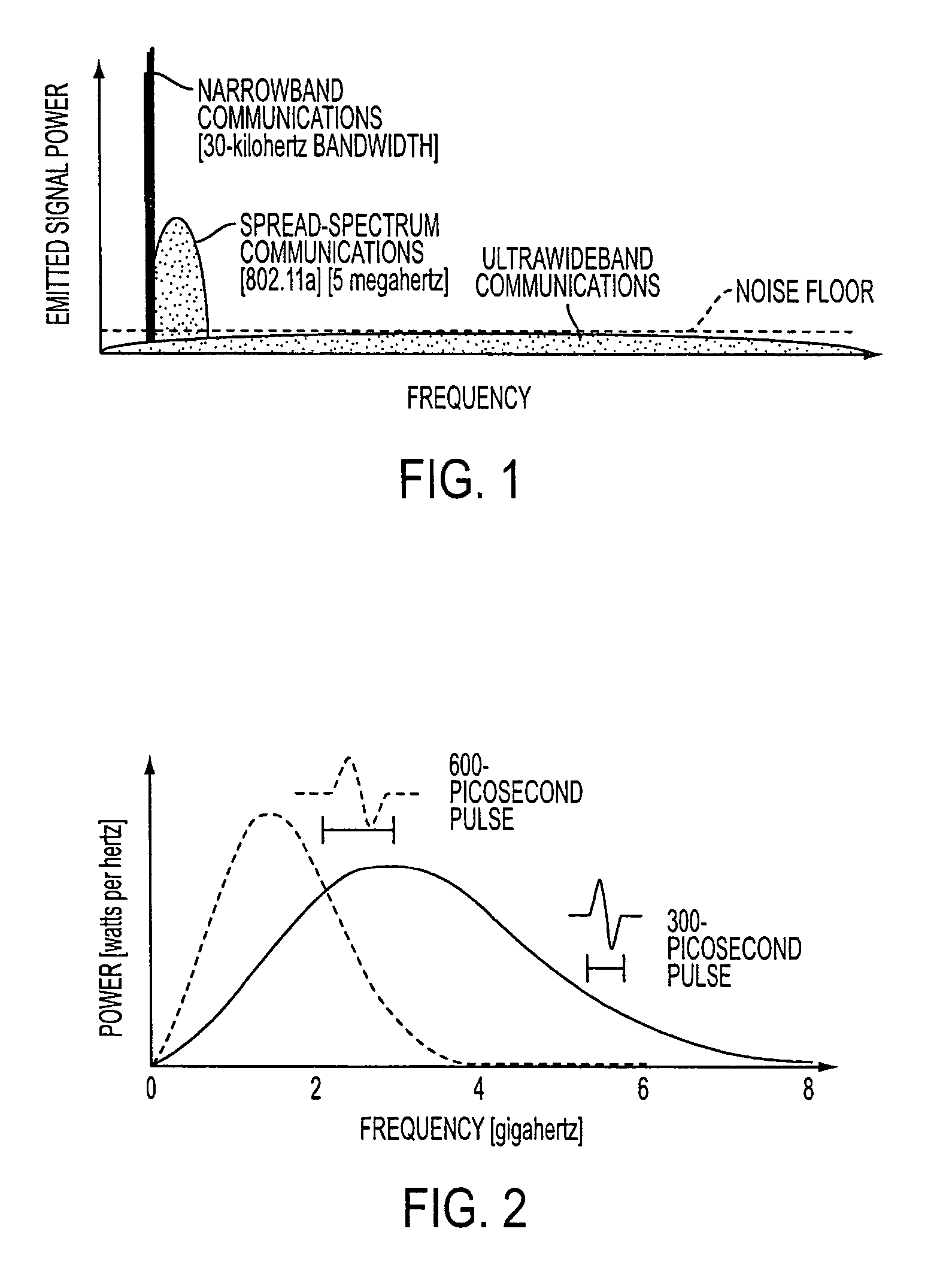
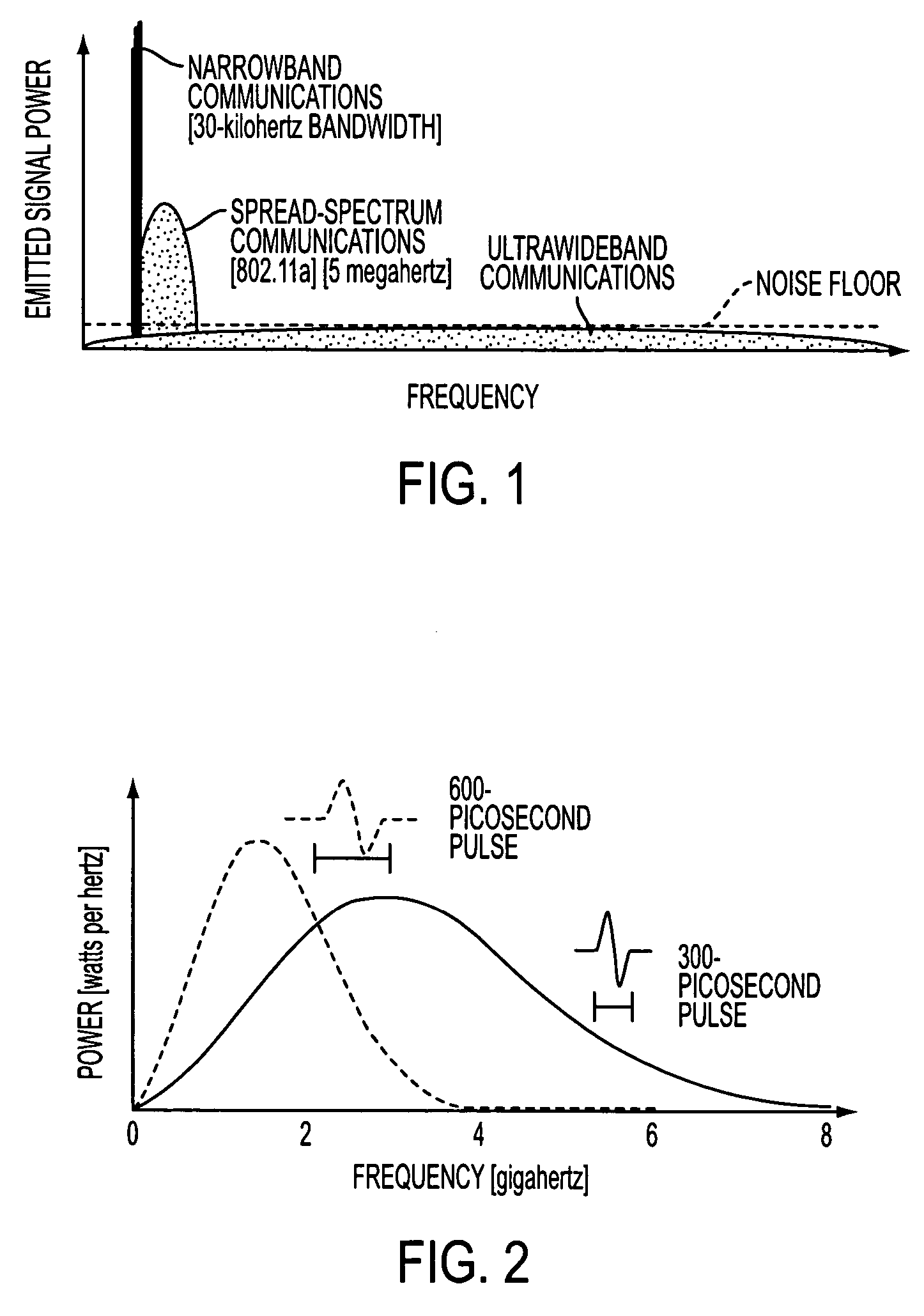
Ultra-wideband communication through local power lines
InactiveUS7027483B2Transmission/receiving by adding signal to waveBroadband local area networksUltra-widebandSubject matter
A system, method and apparatus structured to transmit a plurality of ultra-wideband pulses through an electric power medium is provided. One embodiment of the method comprises an ultra-wideband transmitter structured to transmit the plurality of ultra-wideband pulses through the electric power medium and an ultra-wideband receiver structured to receive the plurality of ultra-wideband pulses from the electric power medium. Another embodiment of the present invention comprises a power supply that provides ultra-wideband communications to devices that obtain power from the power supply. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
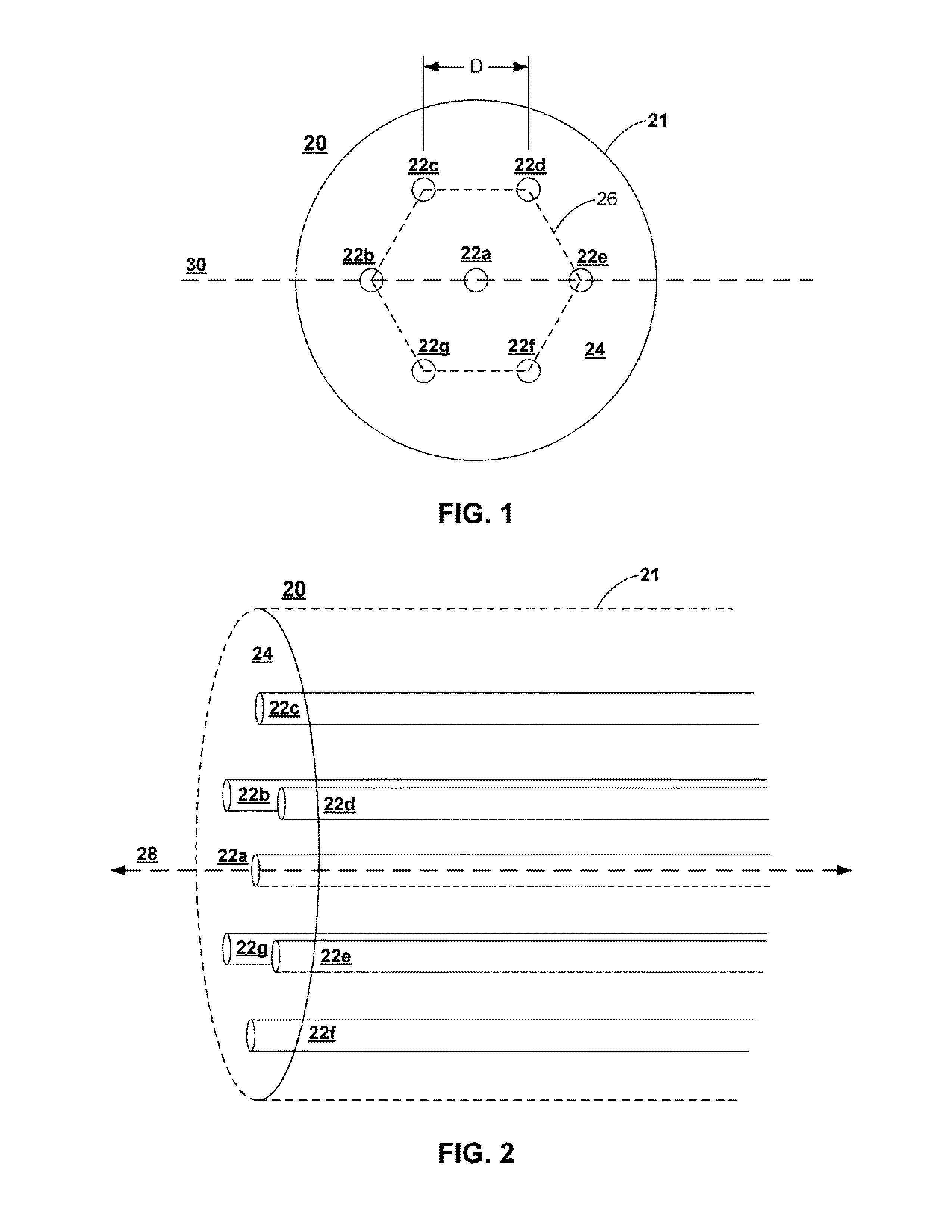
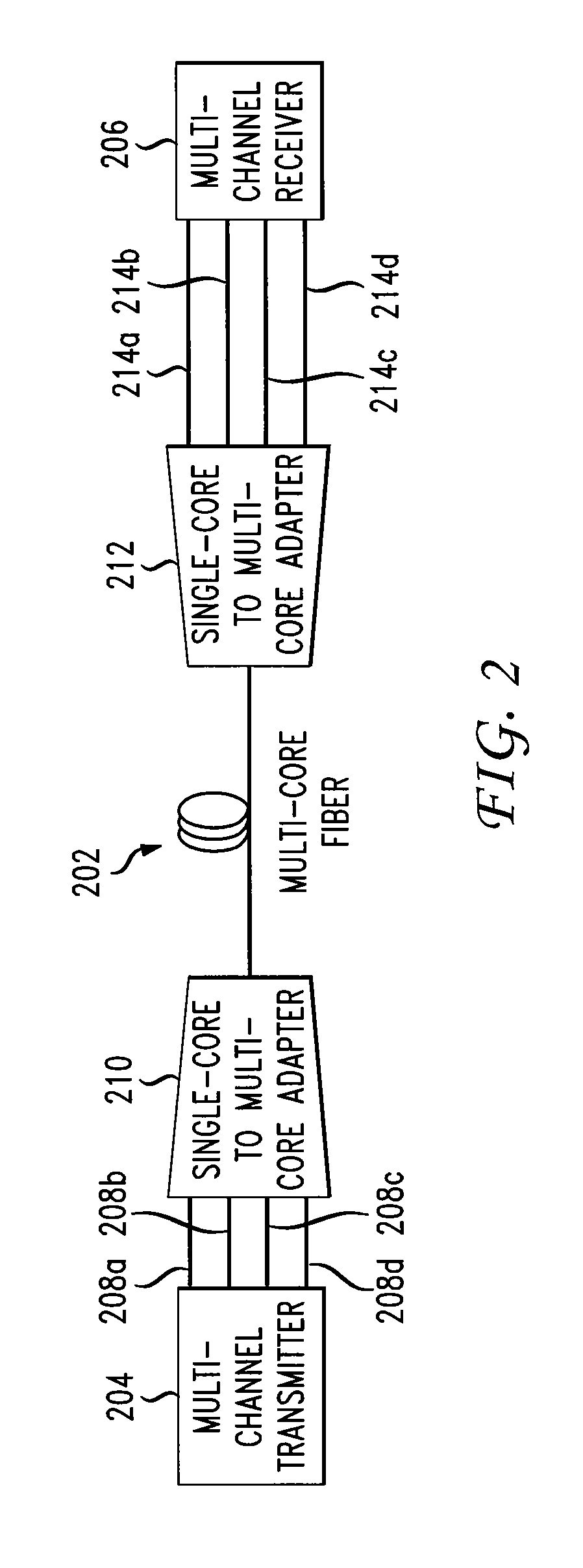
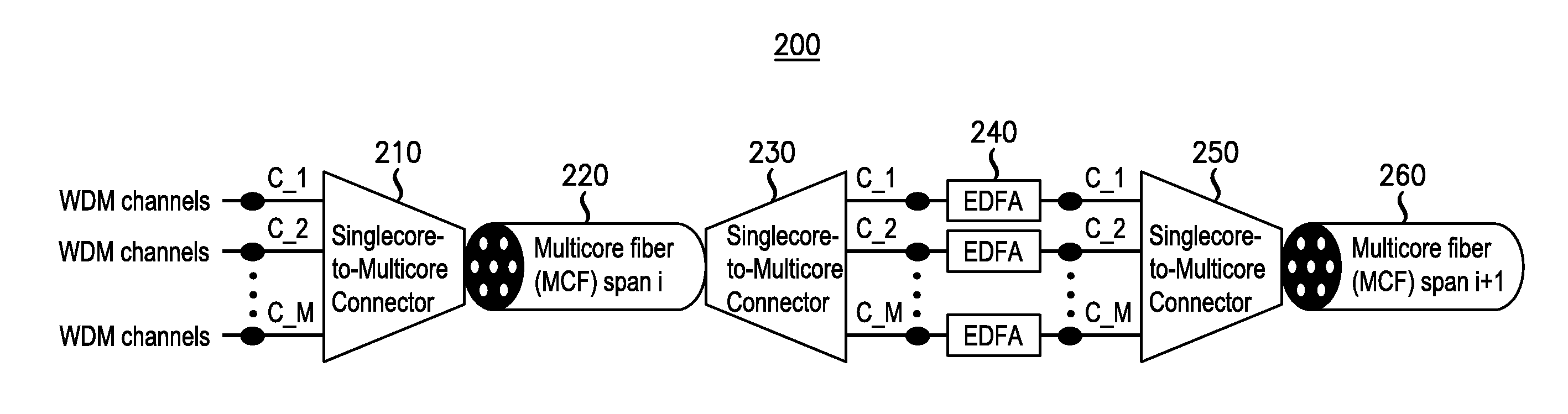
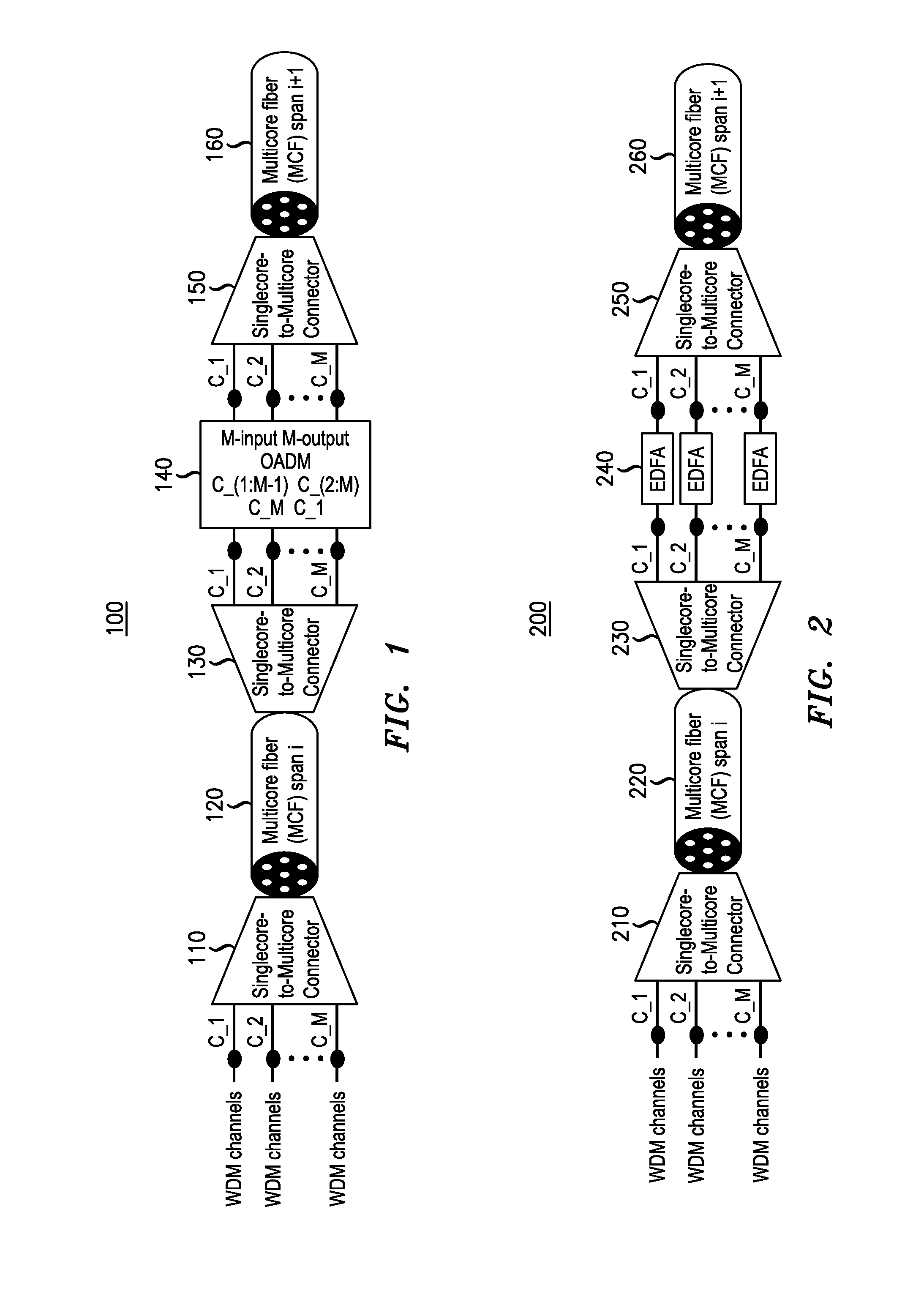
Multicore fiber transmission systems and methods
ActiveUS20110274435A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsAccess networkTransmission channel
An optical data link includes first and second pluralities of transmission devices, at least one of which is configured as an array. A multichannel transmission link has a first end connected to the first plurality of transmission devices and a second end connected to the second plurality of transmission devices so as to form a plurality of parallel transmission channels therebetween. The multichannel transmission link includes a multicore fiber with a plurality of individual cores having a configuration matching the array configuration of the at least one plurality of transmission devices. The multicore fiber has an endface connected directly to the at least one plurality of transmission devices, with the individual cores of the multicore fiber aligned with respective devices in the at least one plurality of transmission devices. Further described are access networks and core networks incorporating a transmission link comprising at least one span of a multicore fiber.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
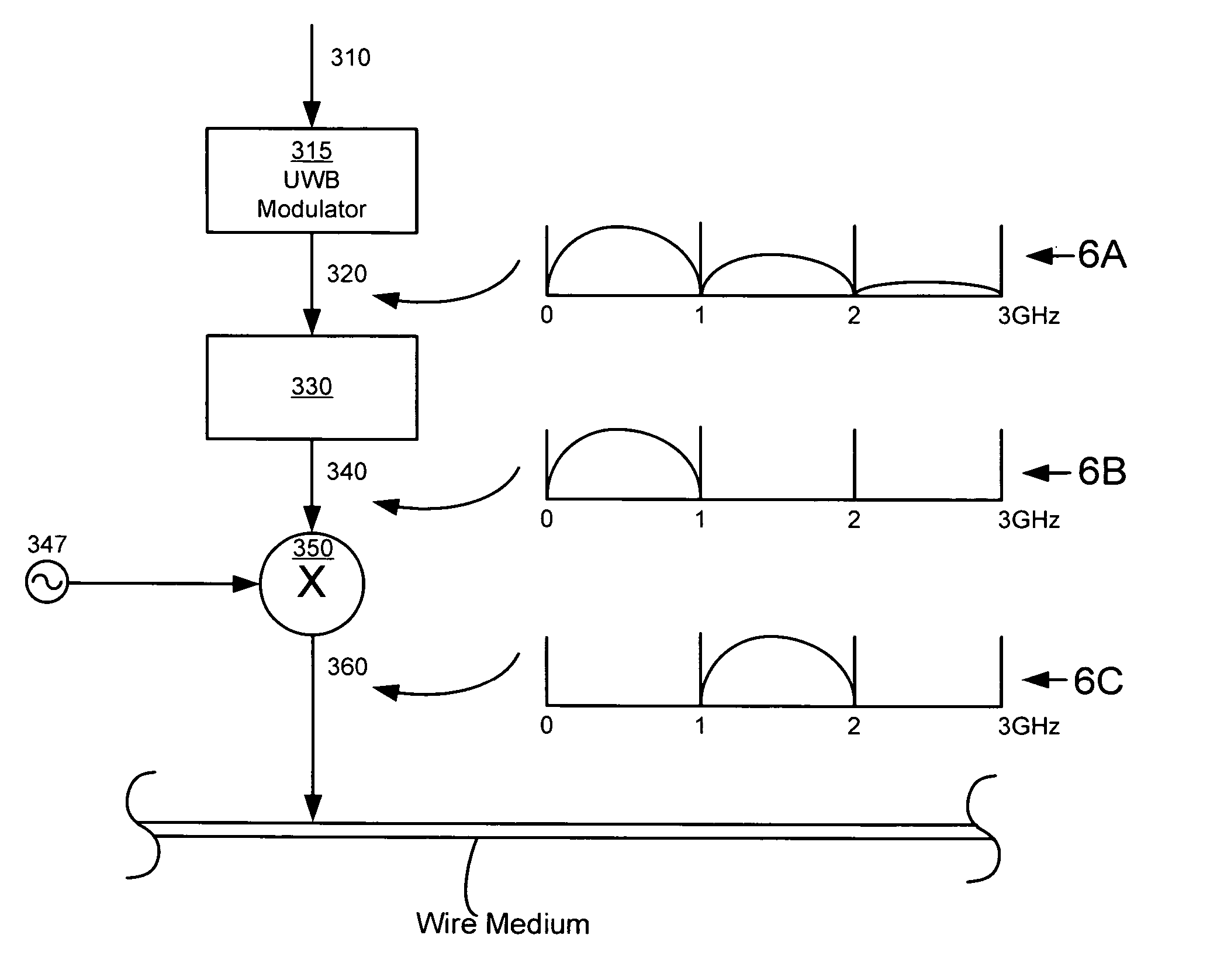
Ultra-wideband communication through a wire medium
InactiveUS7099368B2High bandwidthImprove rendering capabilitiesTransmission/receiving by adding signal to wavePolarisation multiplex systemsUltra-widebandSubject matter
Methods and apparatus for creating, transmitting and receiving ultra-wideband pulses through wire media are presented. One embodiment of the present invention transmits ultra-wideband pulses that occupy radio frequencies that are not used by other electromagnetic signals present in a wire medium of interest. Other embodiments of the invention may create, transmit, and receive ultra-wideband pulses that use radio frequency(s) that are not used by other signals present on wire media within a wire network of interest. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
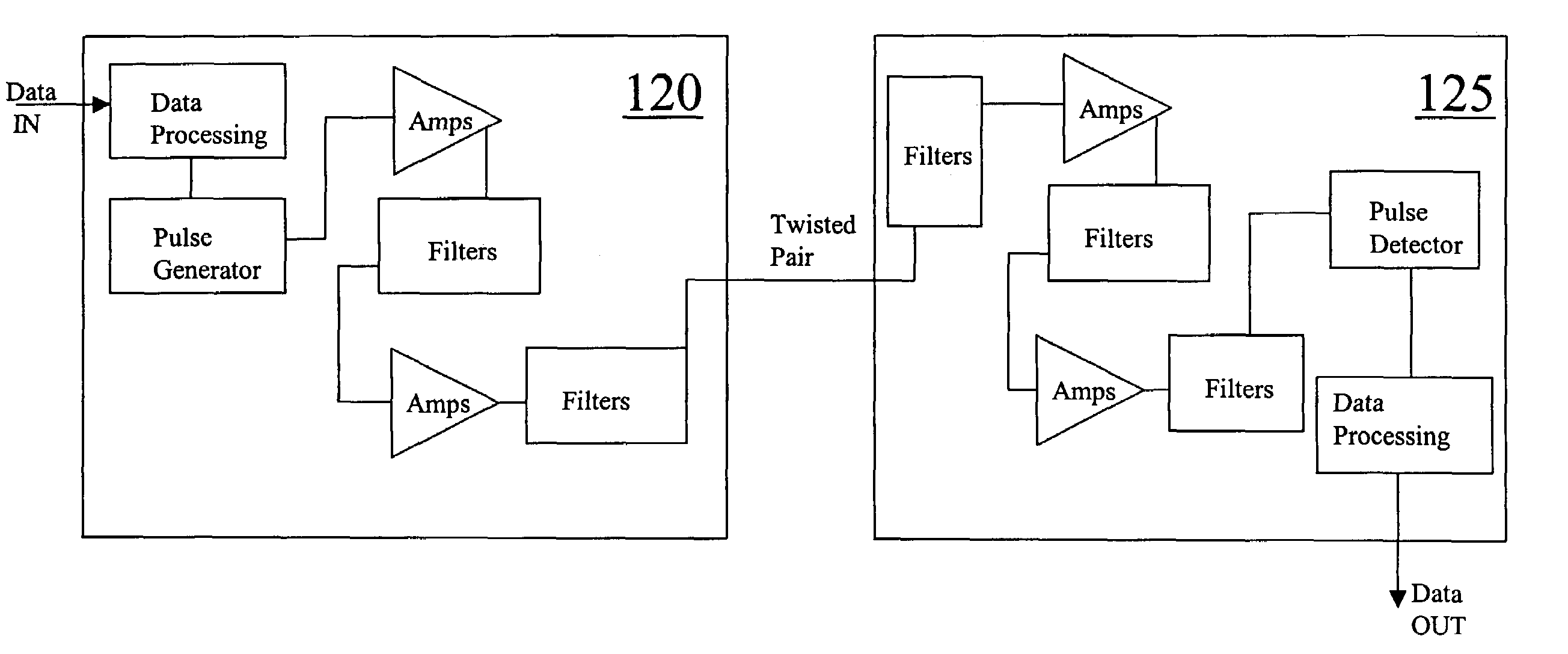
Ultra-wideband communication through twisted-pair wire media
InactiveUS7167525B2Transmission/receiving by adding signal to waveBroadband local area networksUltra-widebandBroadband pulse
Methods and apparatus that transmit ultra-wideband pulses through twisted-pair wire media are provided. One method includes transmitting an ultra-wideband pulse through the twisted-pair wire media at dissimilar time periods. Another method includes transmitting an ultra-wideband pulse through the twisted-pair wire media at dissimilar radio frequencies. Yet another method includes transmitting an ultra-wideband pulse through the twisted-pair wire media at dissimilar time periods and at dissimilar radio frequencies. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
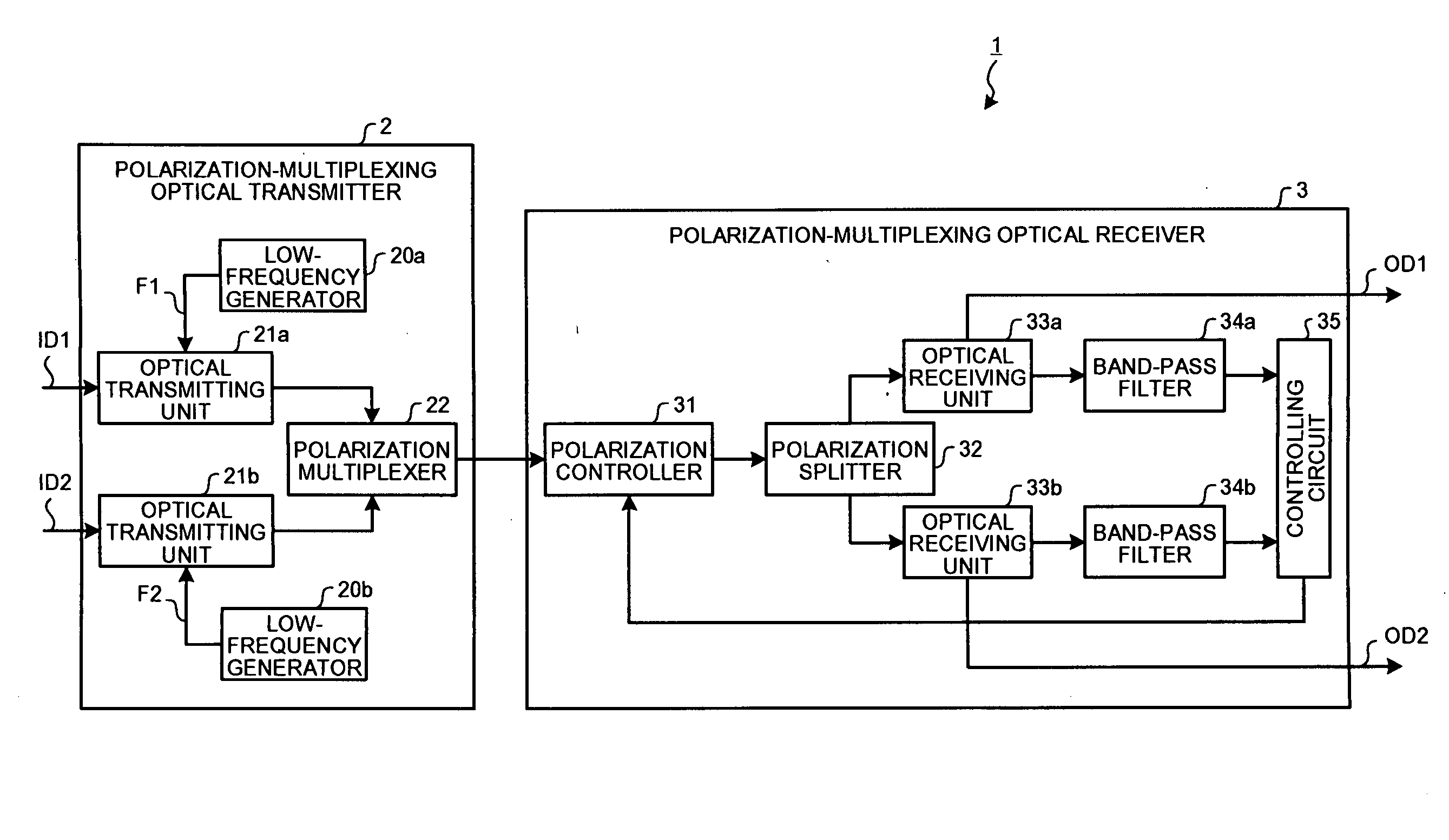
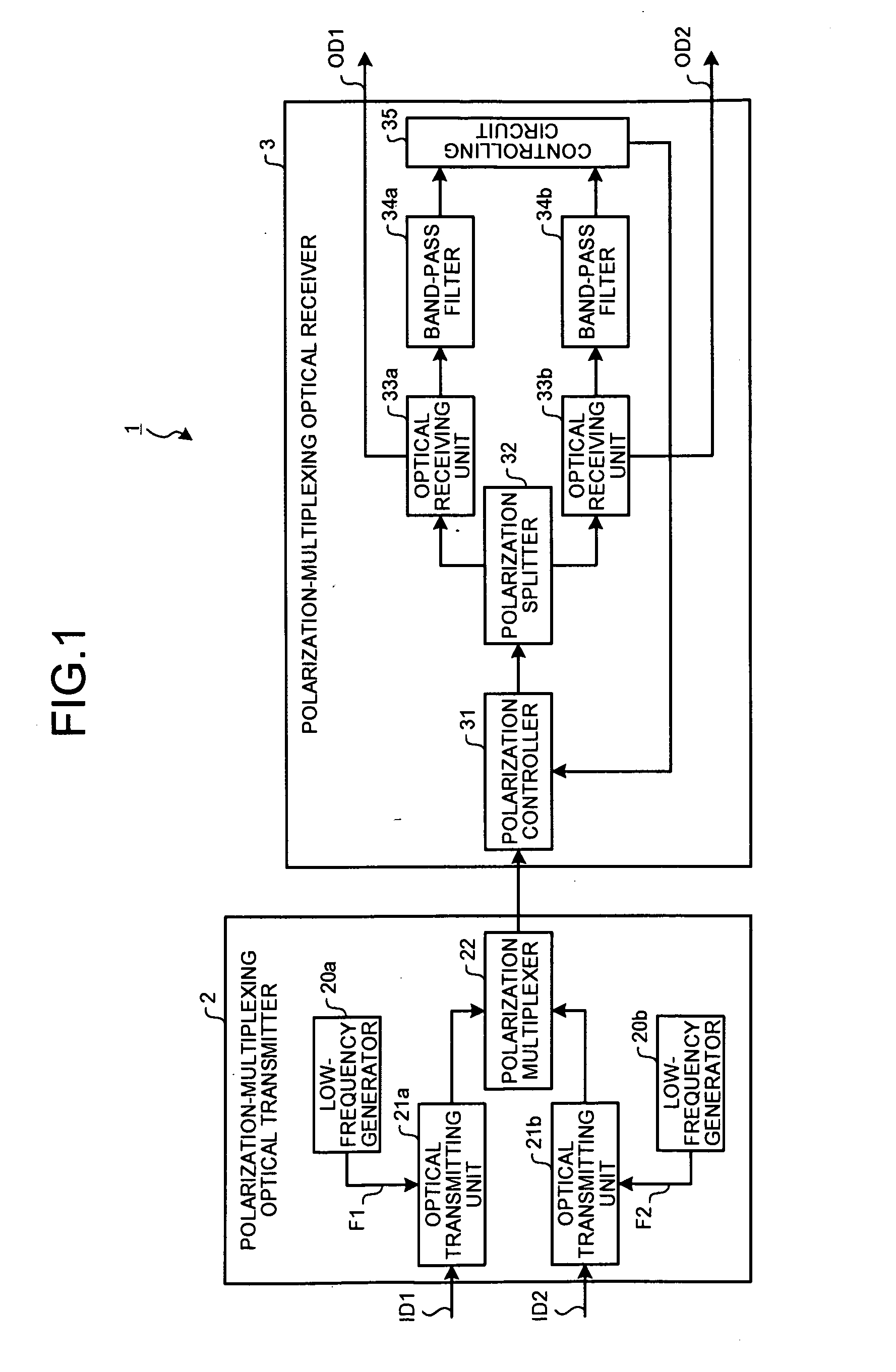
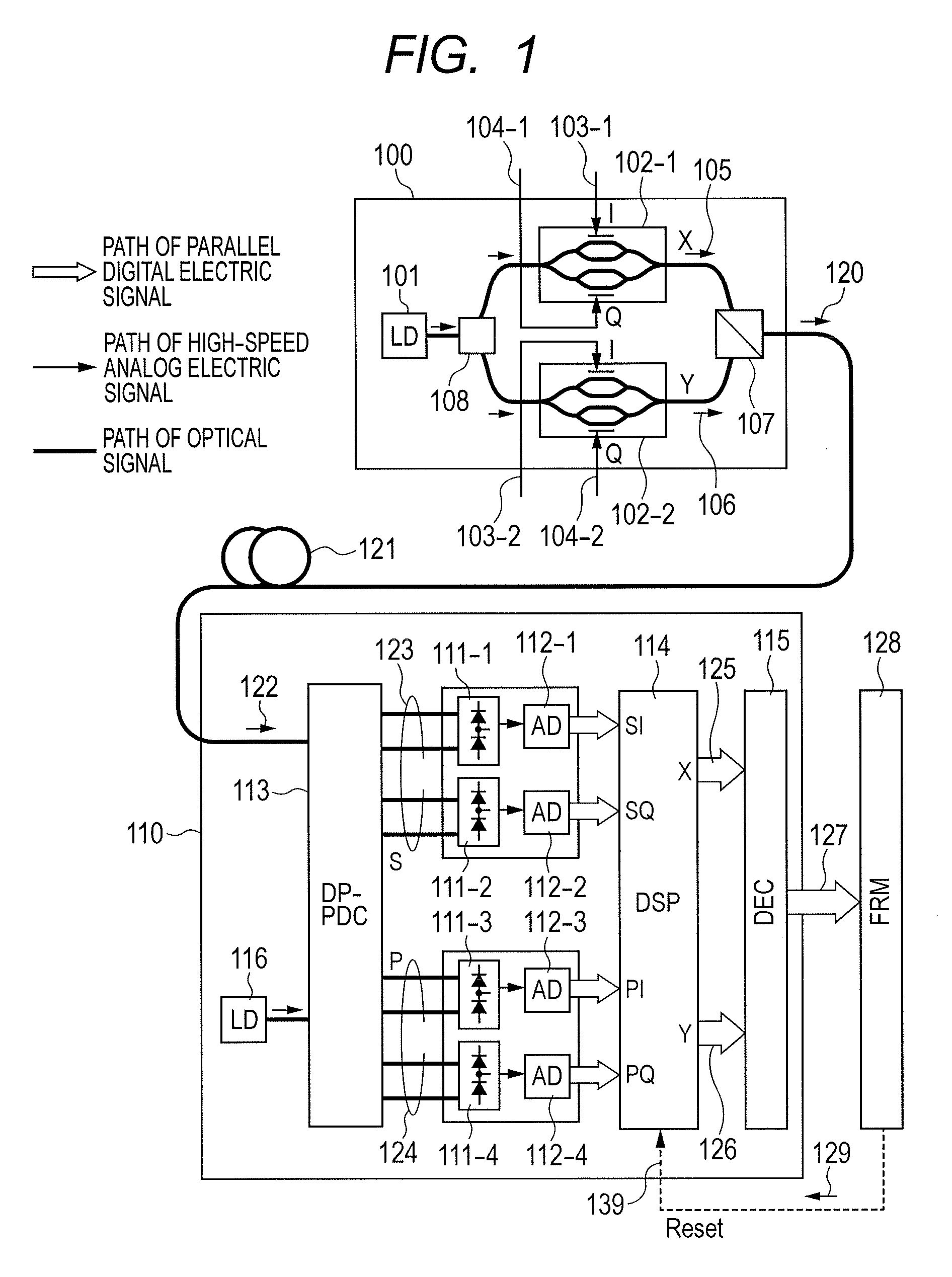
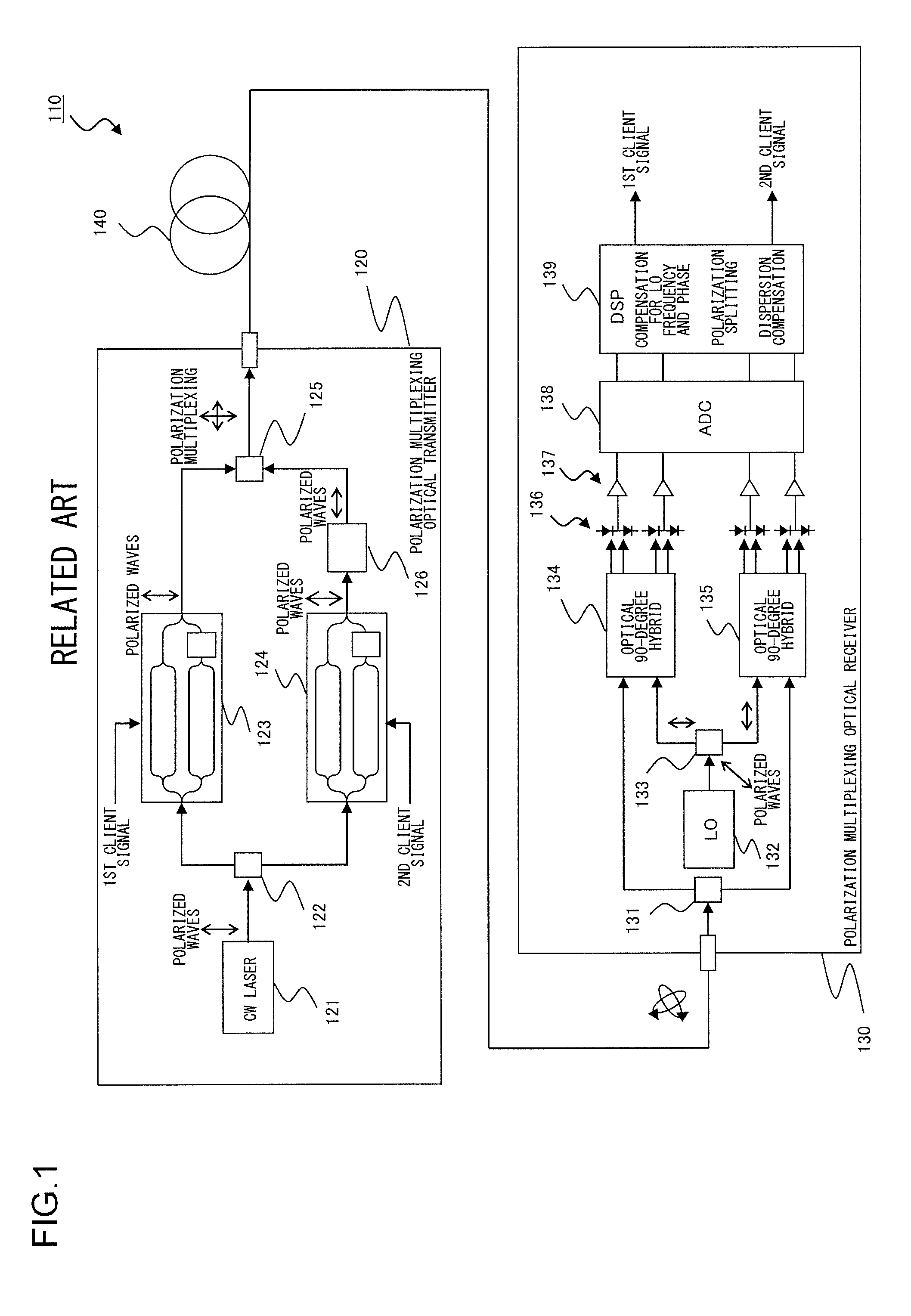
Polarization-multiplexing optical transmitter polarization-multiplexing optical receiver, polarization-multiplexing optical transceiving system, and controlling method thereof
InactiveUS20080232816A1Minimizes valueMaximizing and minimizing outputPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsPolarization multiplexedCarrier signal
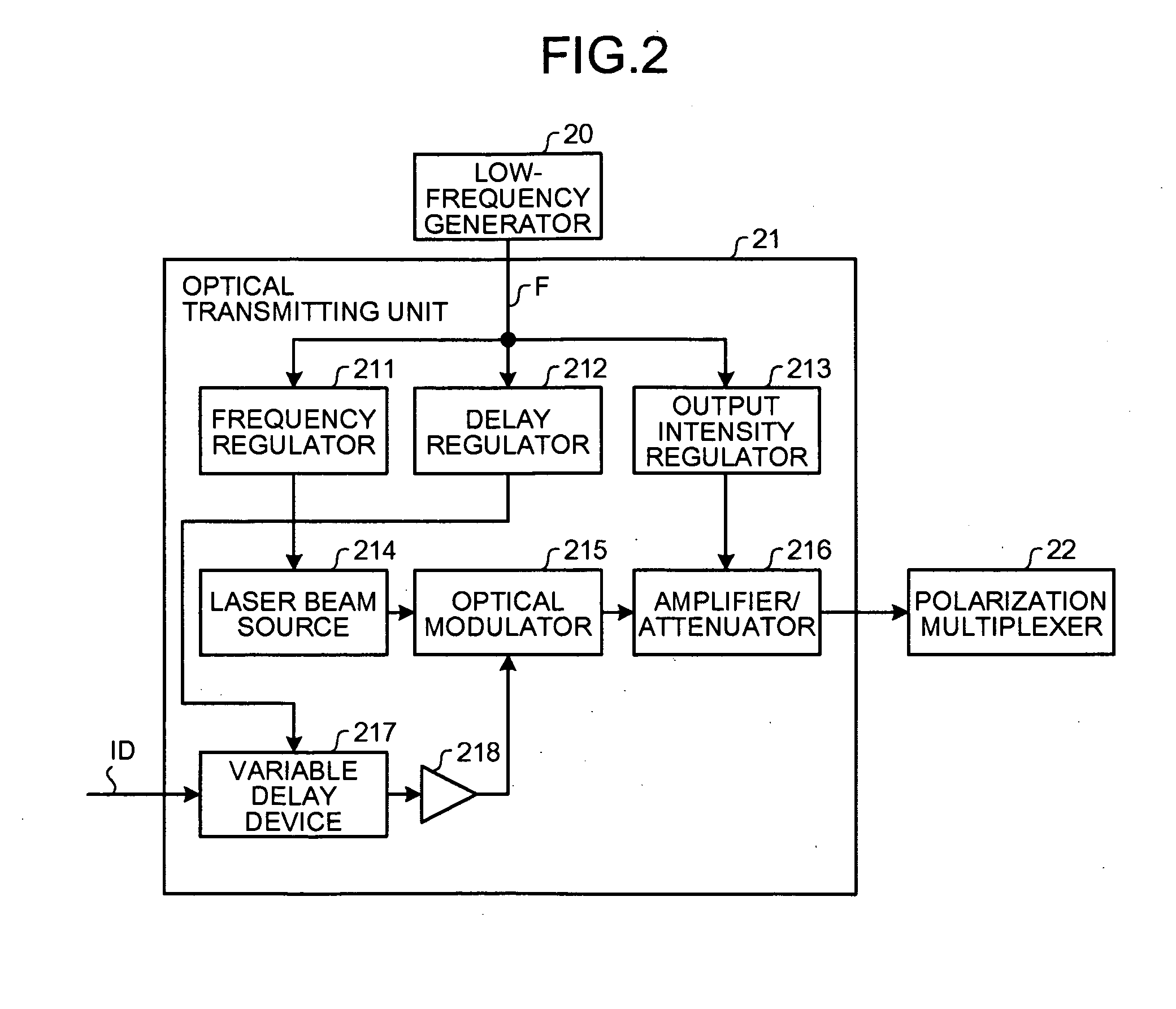
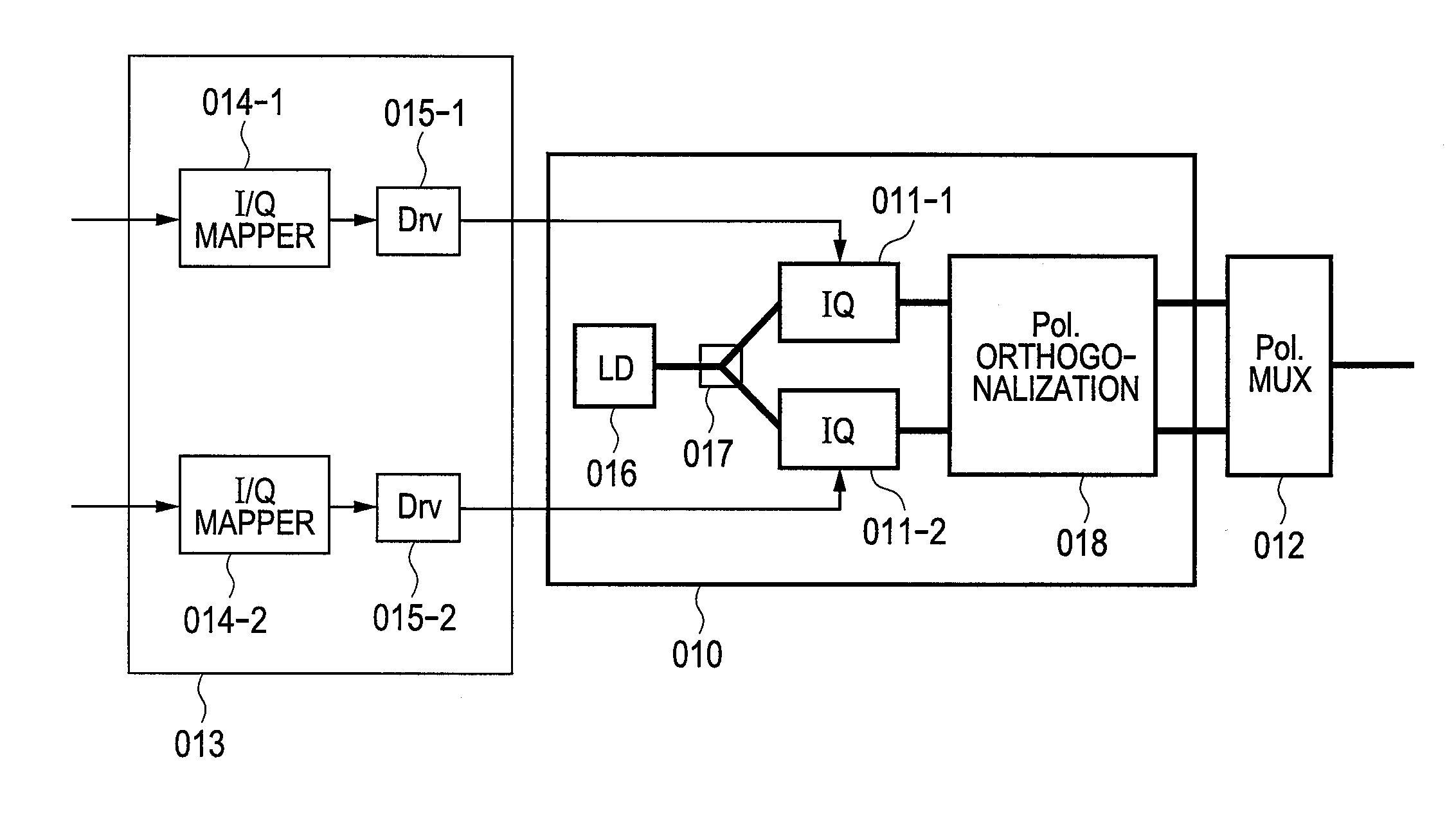
By using low-frequency signals, an optical transmitting unit modulates one of a wavelength, a transmission timing, and an intensity of light as a carrier wave. A polarization multiplexer synthesizes the output light signals, modulated by the optical transmitting unit, in polarization states orthogonal to each other and generates polarization-multiplexing signals. A polarization splitter splits by extracting two orthogonal polarization components from the polarization-multiplexing signals. The polarization states of the polarization-multiplexing signals are controlled by a polarization controller in an optical receiving unit. A band-pass filter extracts components transmitting through passbands from output signals of the optical receiving unit and outputs an intensity of the components. Based on the intensity output from the filter, a controlling circuit generates feedback control signals for maximizing a ratio of the components of the low-frequency signals and by using the feedback control signals, the polarization controller controls the polarization states of the optical multiplexing signals.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Visible ray communication system and method for transmitting signal
ActiveUS20110229147A1Improve communication qualityMore transmissionPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunication qualityCommunications system
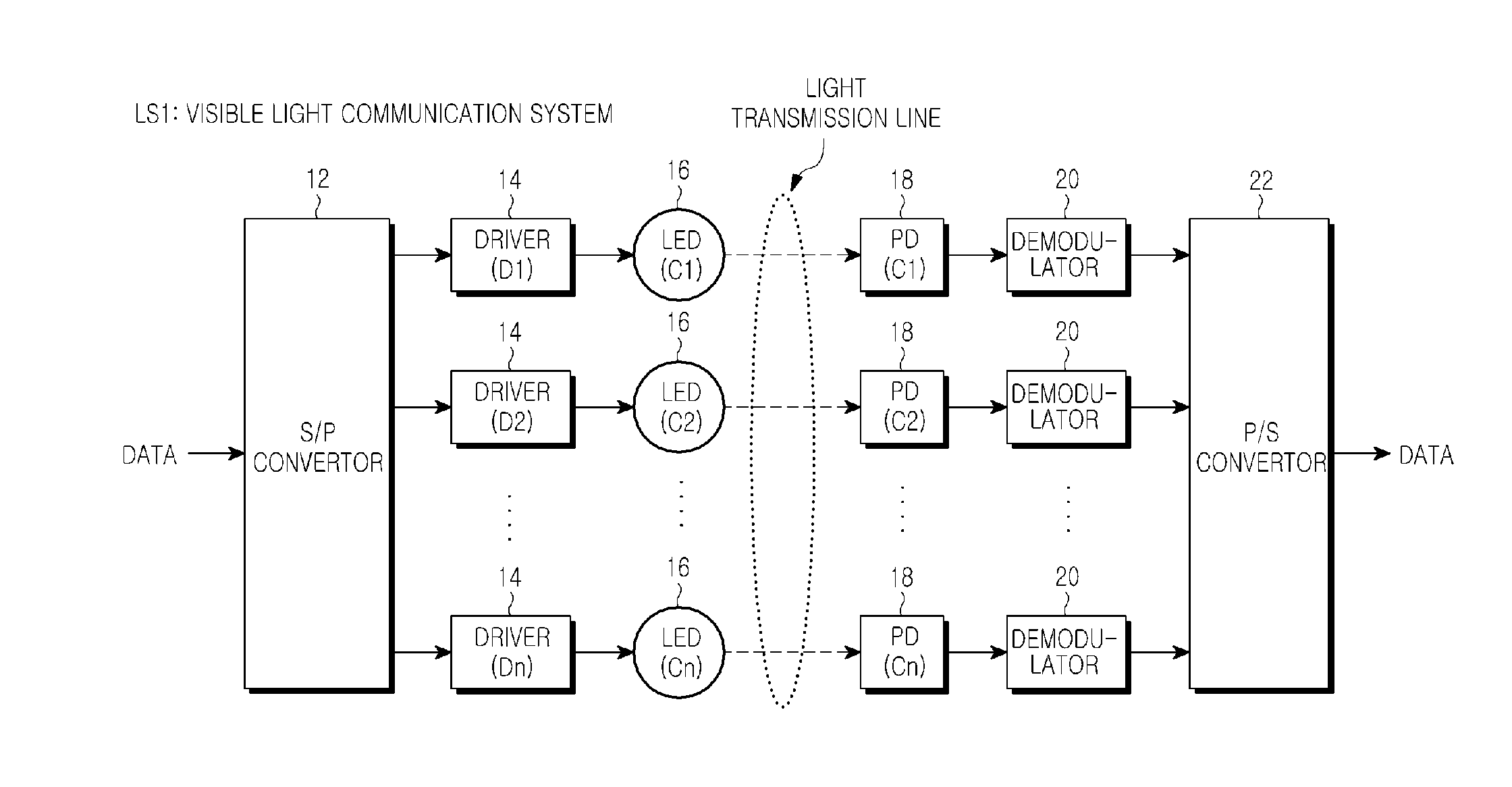
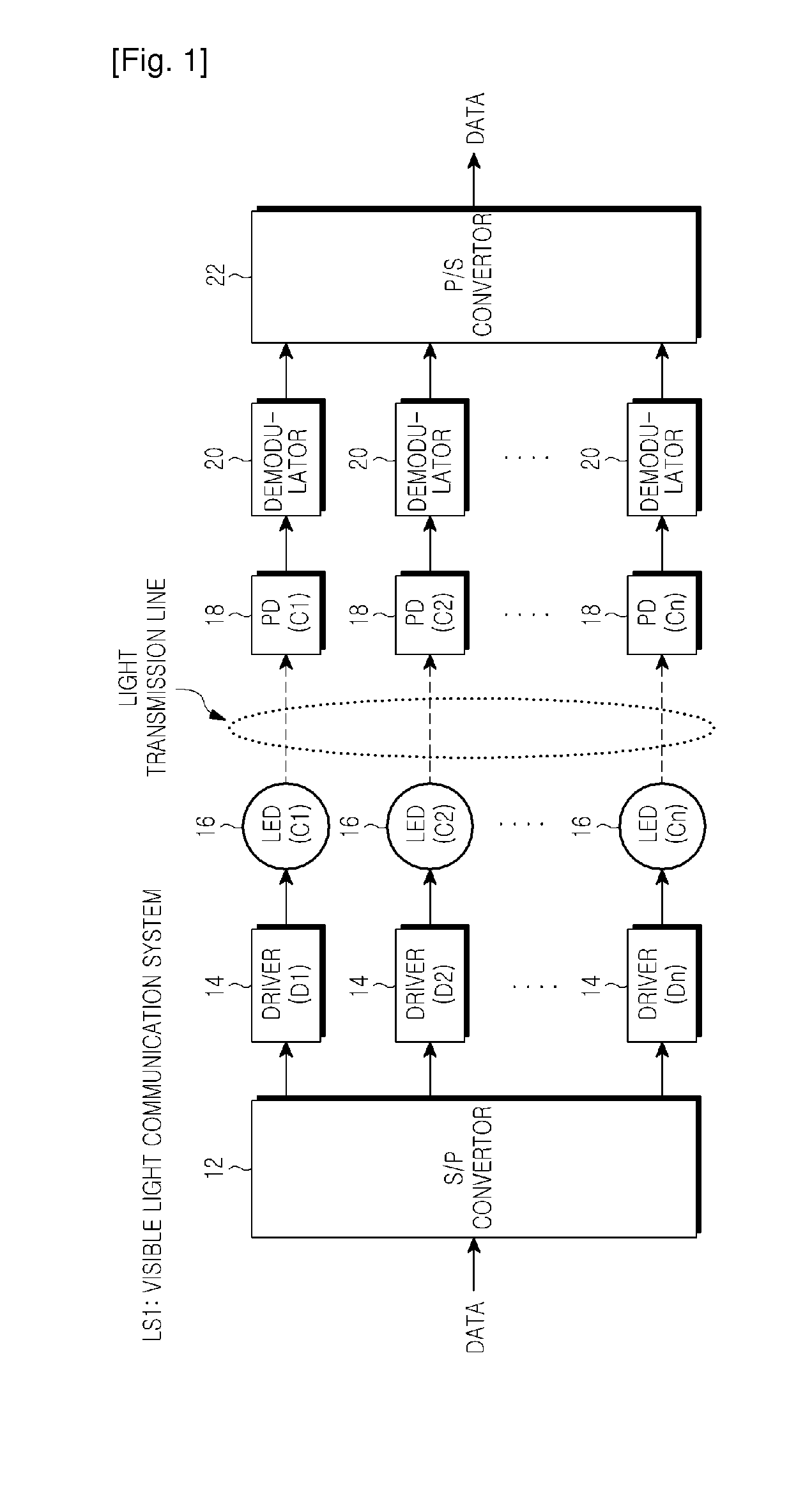
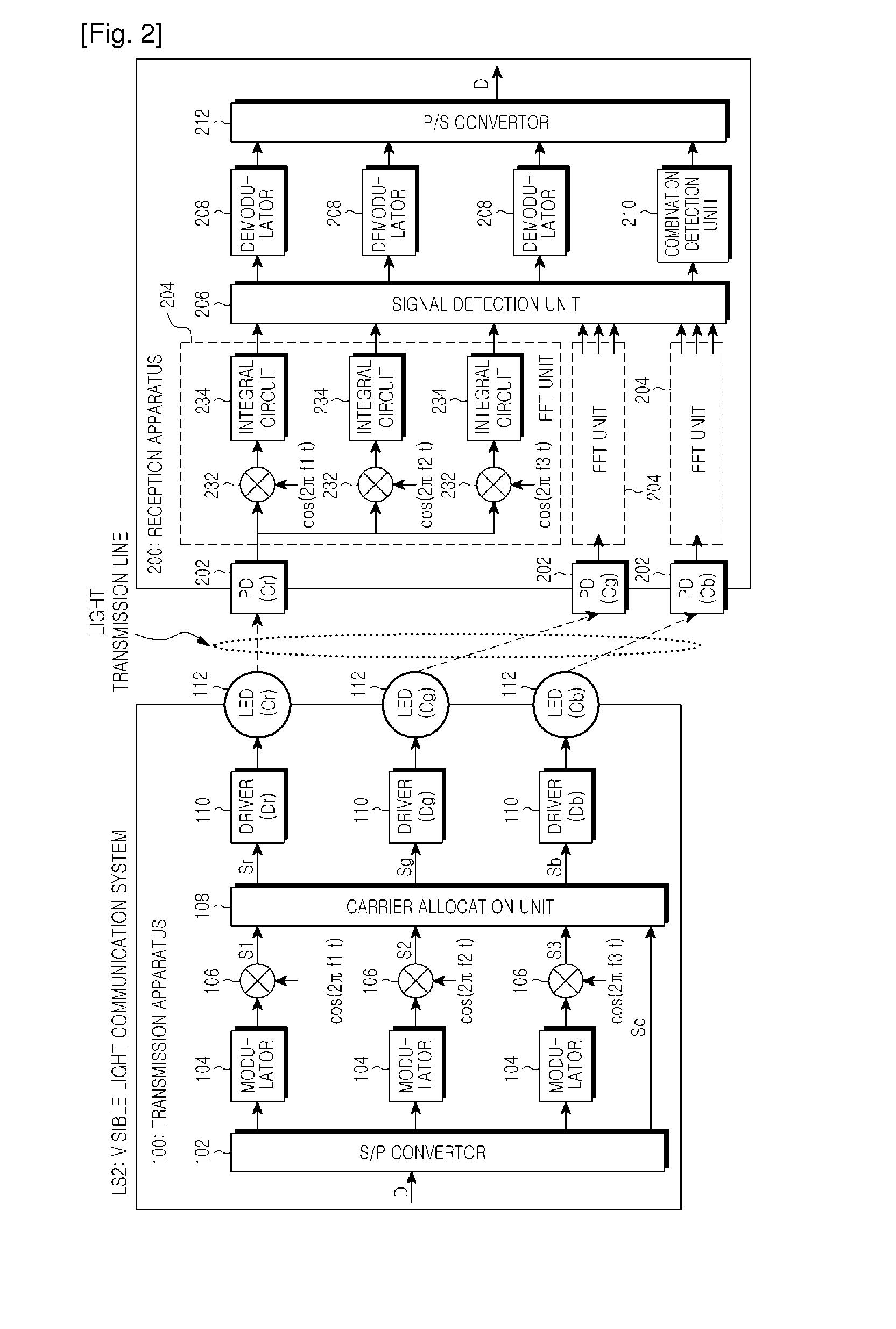
A visible ray communication system and method that improve transmission rate and remove an influence of inter-color interference to improve the communication quality. A transmission apparatus included in the visible ray communication system allocates each carrier signal component of an OFDM signal, which is modulated into transmission information, to a plurality of LEDs of different colors. The information is added to a combination of a carrier frequency and an LED wavelength, when a carrier signal is allocated to an, in addition to each carrier signal being modulated into the information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
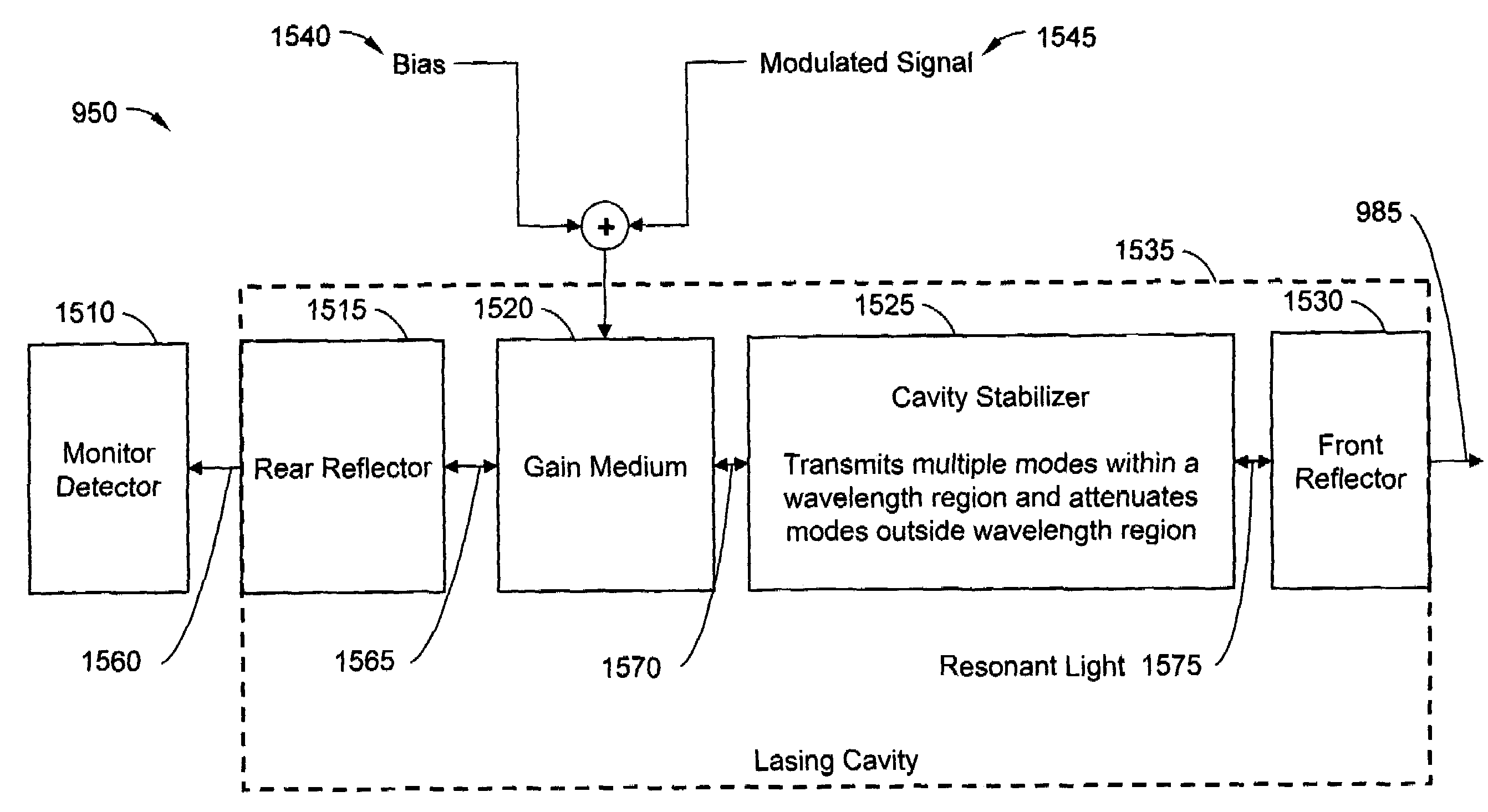
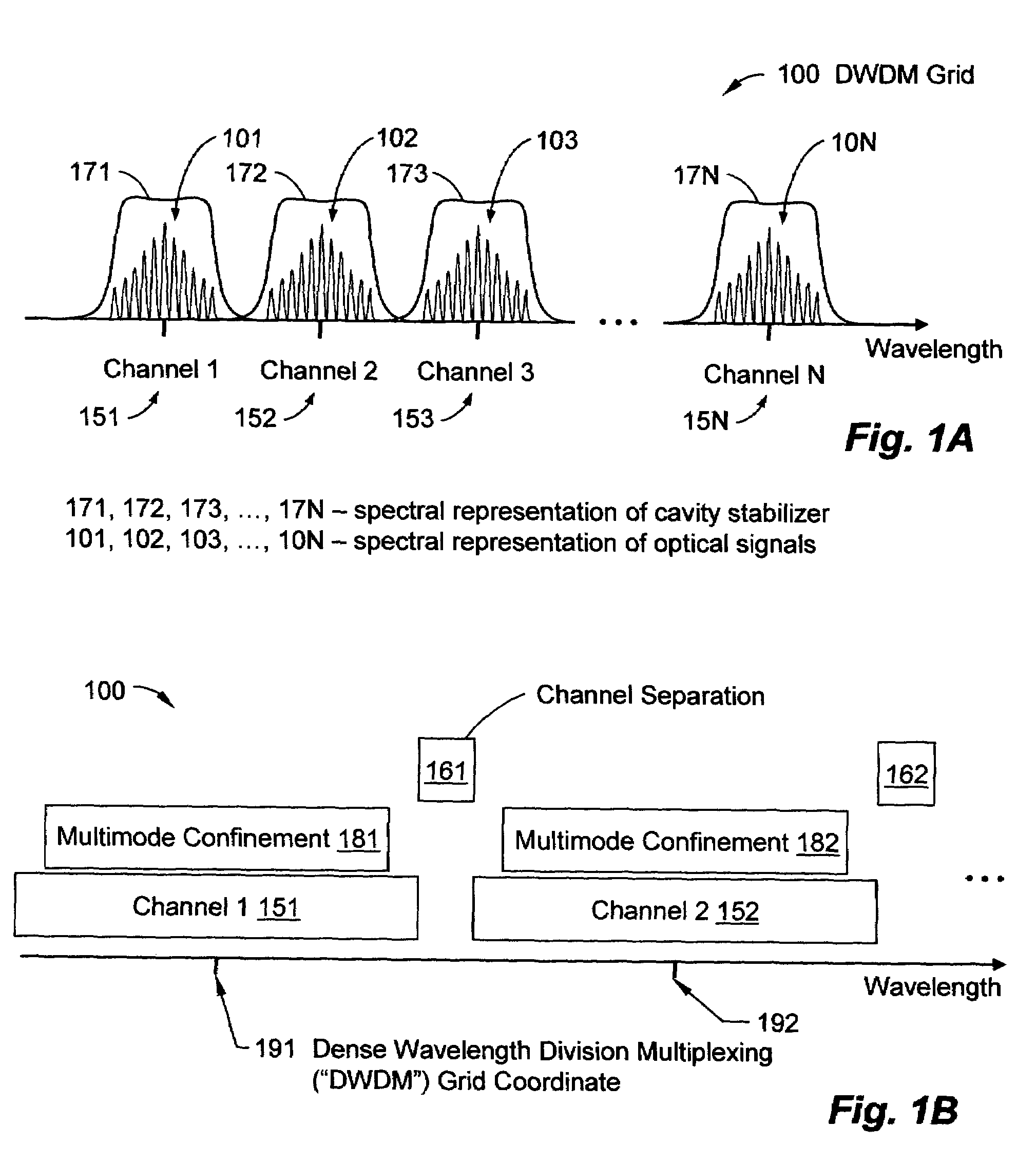
Robustly stabilizing laser systems
InactiveUS7565084B1Optical mode multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersPattern matchingBeam steering
A robustly stabilized communication laser can output a multimode optical signal remaining aligned to a coordinate of a dense wavelength division multiplexing (“DWDM”) grid while responding to a fluctuating condition or random event, such as, without limitation, exposure to a temperature fluctuation, stray light, or contamination. Responsive to the fluctuating condition, energy can transfer among individual modes in a plurality of aligned longitudinal modes. Modes shifting towards a state of misalignment with the DWDM coordinate can attenuate, while modes shifting towards a state of alignment can gain energy. Fabrication processes and systems and light management, such as beam steering, epoxy scaffolds, spectral adjustments, mode matching, thermal expansion control, alignment technology, etc. can facilitate nano-scale control of device parameters and can support low-cost fabrication.
Owner:CIRREX SYST
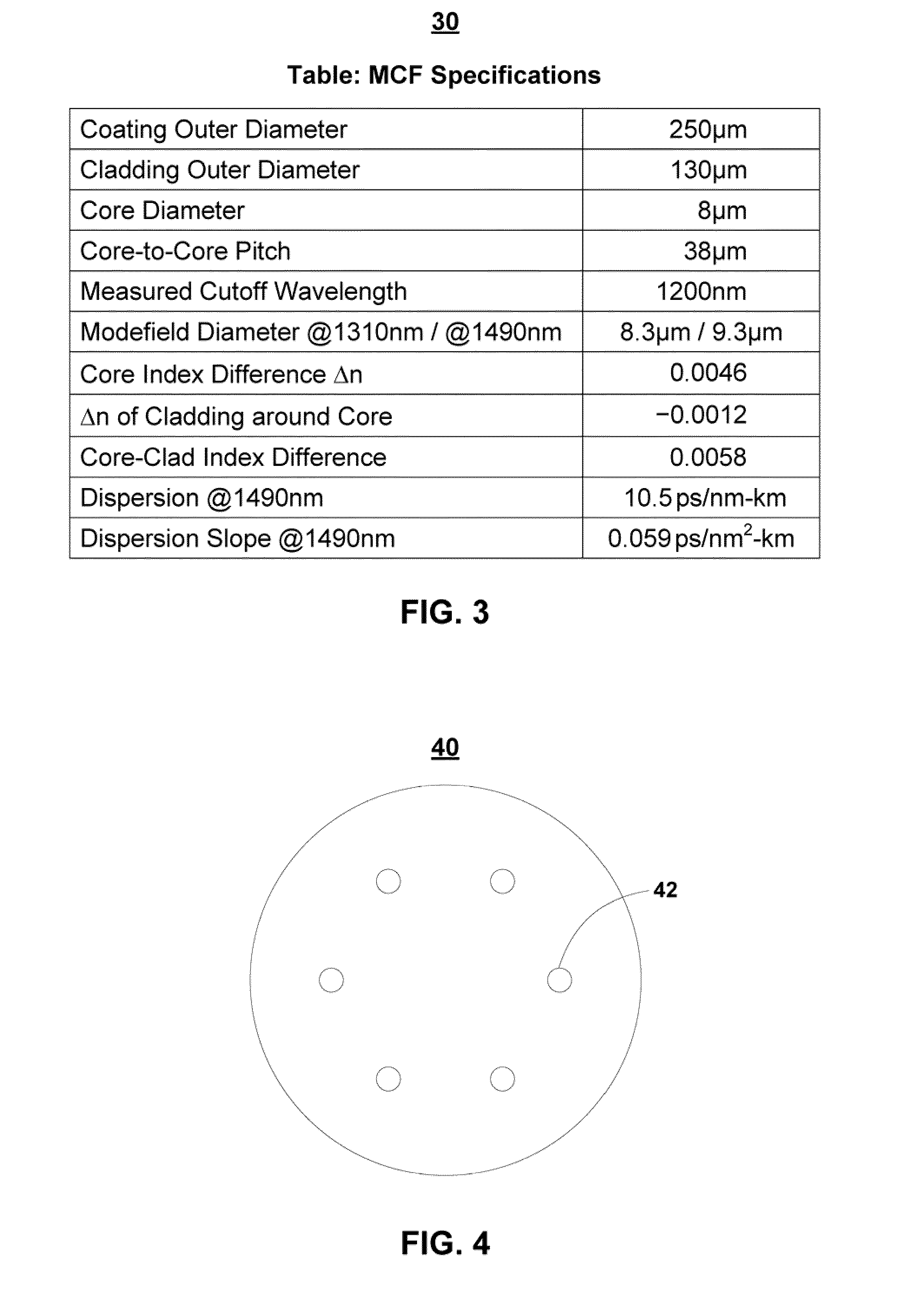
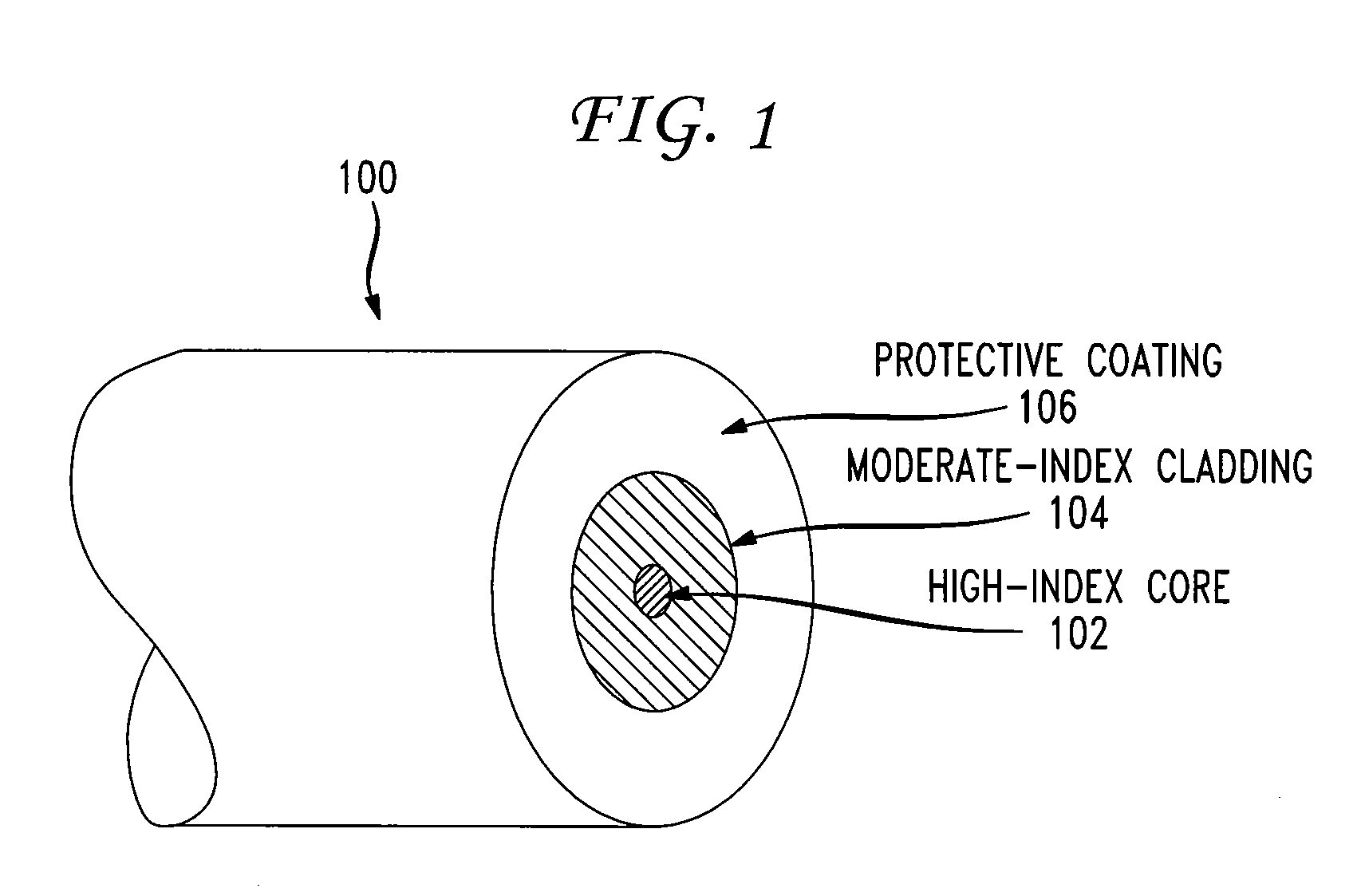
Multicore fibers and associated structures and techniques
ActiveUS20110274398A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexEngineering
A multicore fiber comprises a plurality of cores extending along the length of a fiber body. Each of the cores is surrounded by a cladding. The plurality of cores and surrounding cladding provide respective index variations, so as to form a respective plurality of waveguides for conducting parallel data transmissions from a first end of the fiber to a second end. The plurality of cores has a cross-sectional geometry in which the plurality of cores is configured in a polygonal array, in which at least some of the cores are positioned at the vertices of the array. The polygonal array is configured such that neighboring cores in the array are separated from each other by a distance that is sufficient to prevent crosstalk therebetween.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
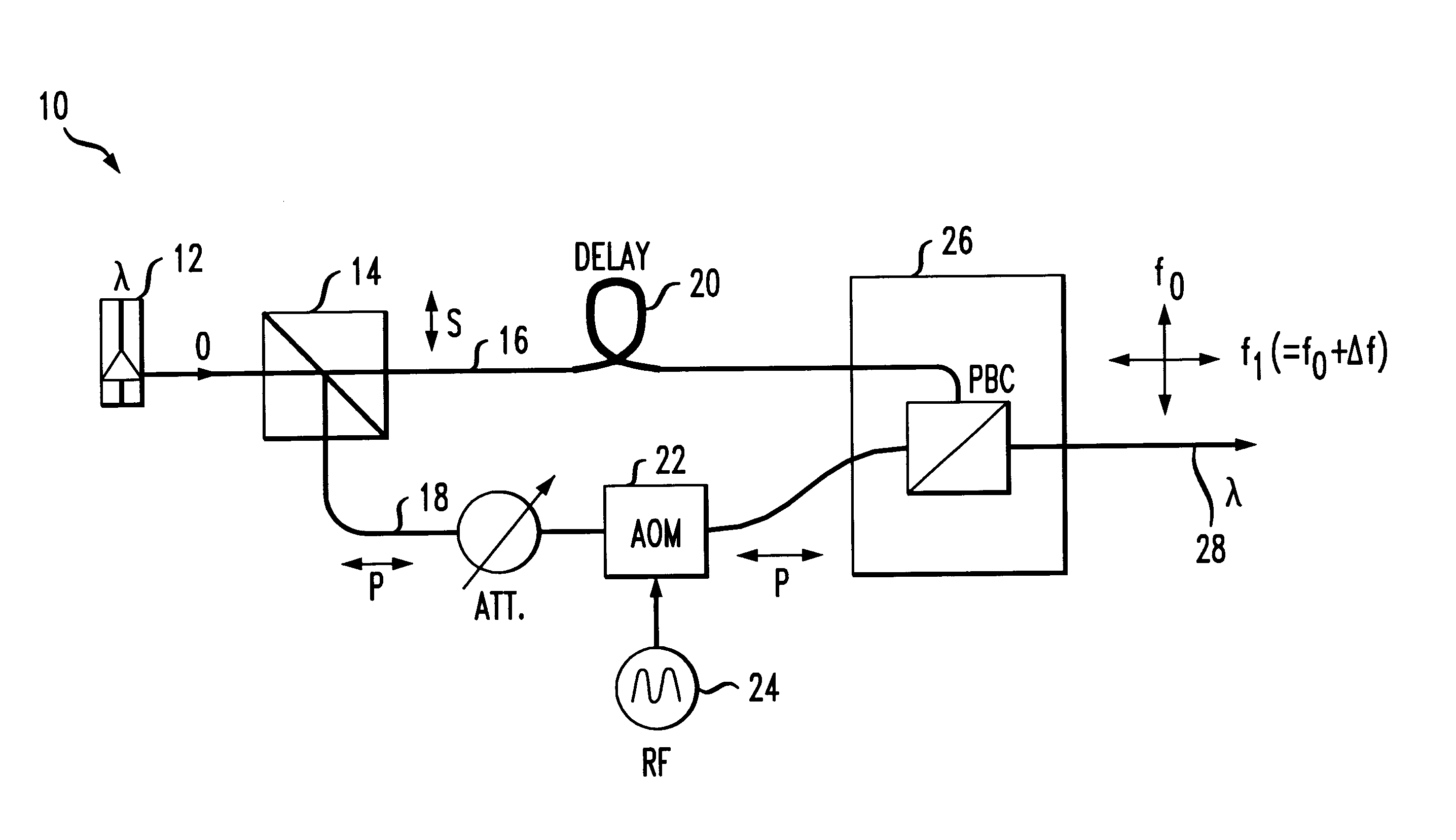
Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmission System, Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmitter, and Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Receiver
InactiveUS20120134676A1Preventing signal quality degradationReliable polarizationPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsDigital signal processingPolarization diversity
There is a need to prevent two receivers from converging on a state of receiving the same polarization state, fast start receivers, and ensure highly reliable operations. A polarization-multiplexed transmitter previously applies frequency shifts of frequencies +Δf and −Δf to X-polarization and Y-polarization digital information signals to be transmitted. Optical field modulators modulate and polarization-multiplex the signals. As a result, a frequency difference of 2Δf is supplied to X-polarization and Y-polarization components. A polarization diversity coherent optical receiver 215 receives the signal. A frequency estimation portion in a digital signal processing circuit detects a frequency difference signal in both polarization components. This signal is used to a polarization splitting circuit in the digital signal processing circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Antenna array based oam wireless communication
Systems and methods for orbital angular momentum (OAM)-based multidimensional wireless communication. The OAM-based multidimensional wireless communication is preformed with a transmitter for generating an RF modulated signal carrying a data sequence. Further included is an OAM antenna array including OAM antenna elements, each of which includes an azimuthal phase shifter and an antenna element. The azimuthal phase shifter shifts an azimuthal phase term of a wavefront generated by the antenna element such that the OAM antenna element imposes the multidimensional modulated signal on a pre-determined OAM mode of a carrier signal corresponding to the azimuthal phase term.
Owner:NEC CORP
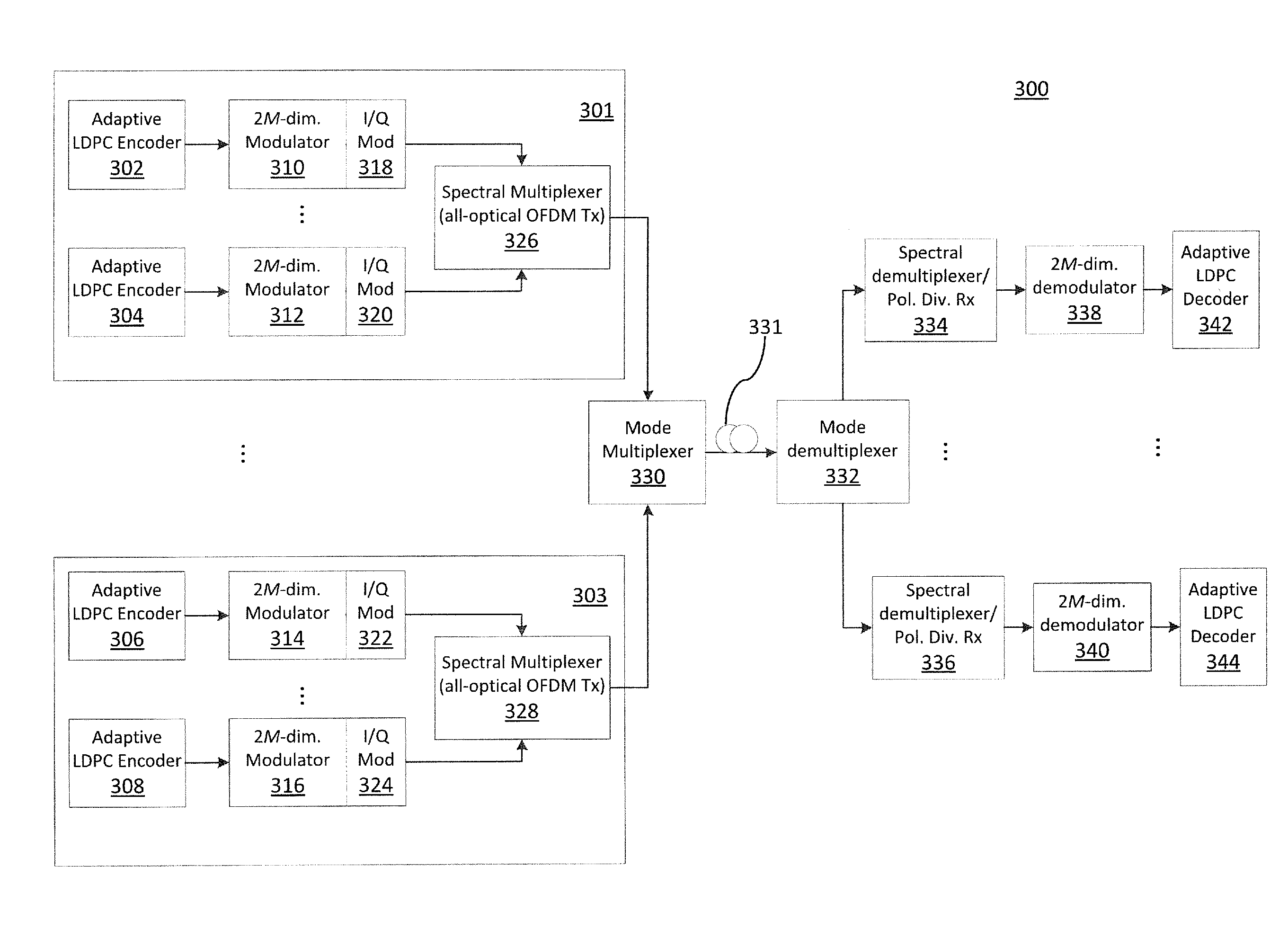
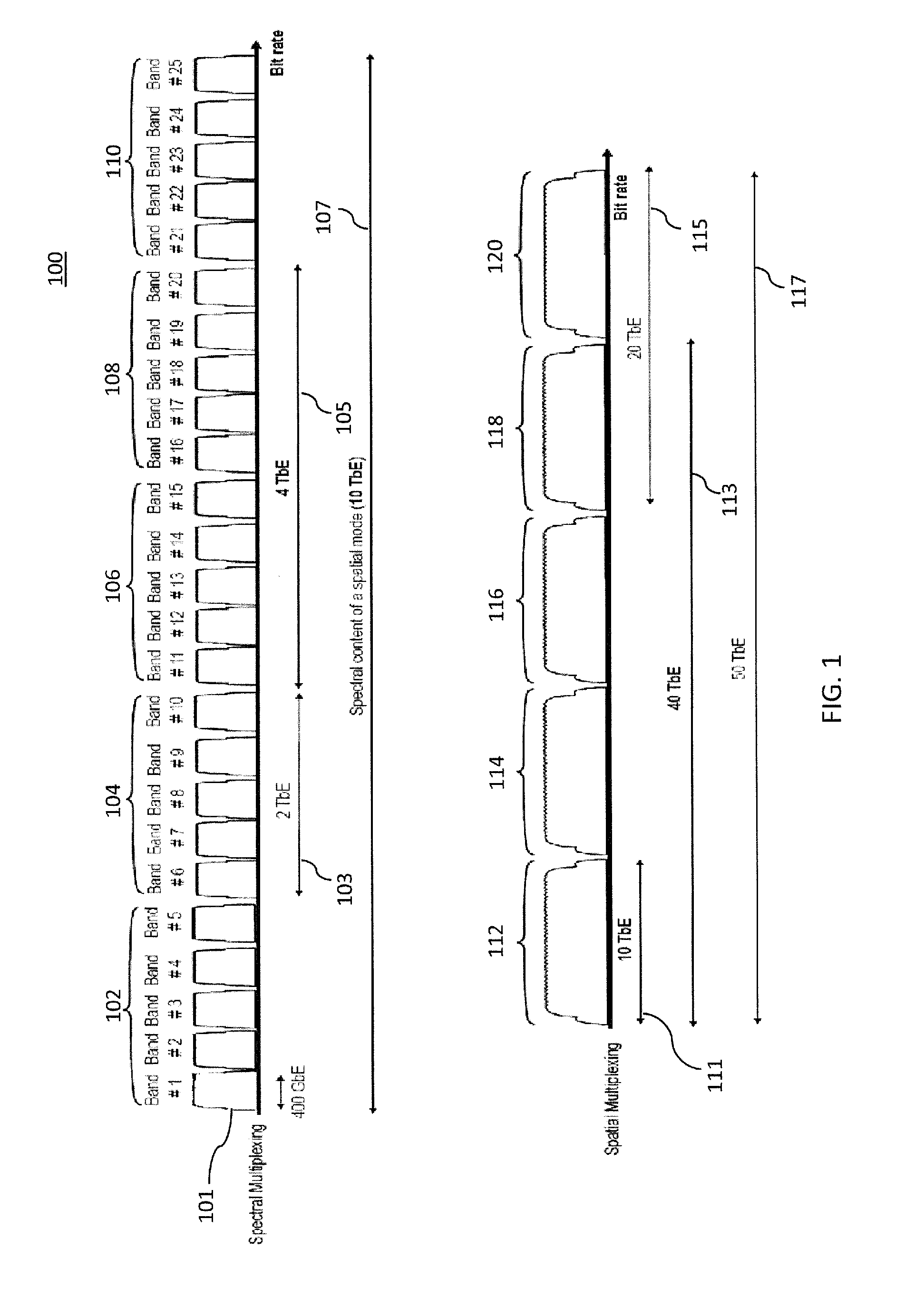
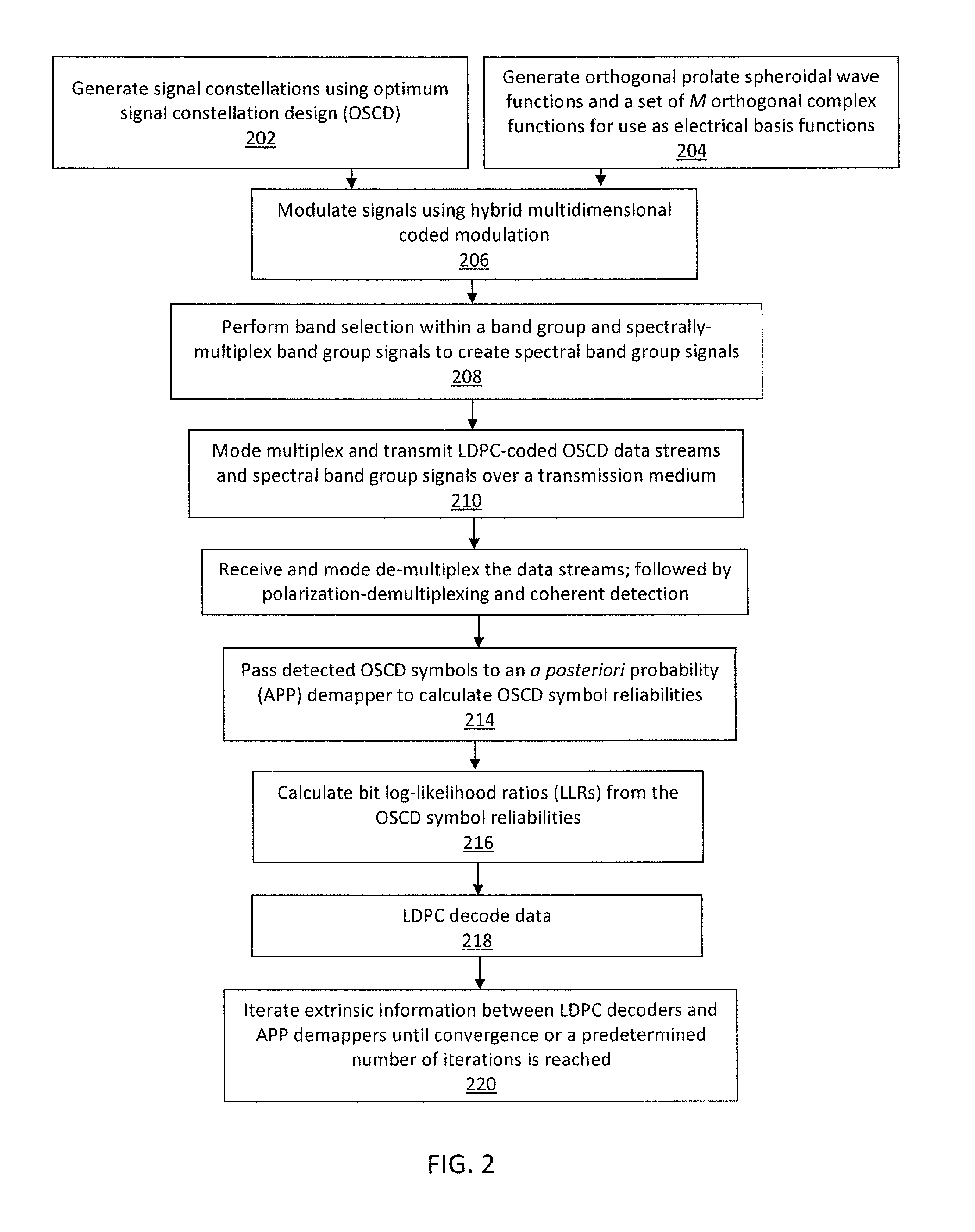
Ultra-high-speed optical transport based on adaptive ldpc-coded multidimensional spatial-spectral scheme and orthogonal prolate spheroidal wave functions
ActiveUS20140270759A1Polarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsSpectral bandsMultidimensional scaling
Systems and methods for transmitting data, including encoding one or more streams of input data using one or more adaptive Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) encoders, wherein the encoders generate one or more signal constellations; modulate one or more signals using hybrid multidimensional coded modulation; apply orthogonal prolate spheroidal wave functions as electrical basis functions; generate one or more spectral band group signals by selecting and combining two or more spectral band groups with center frequencies that are orthogonal to each other; and spectral-mode-multiplex and transmit the one or more adaptive LDPC-coded data streams including the one or more spectral band group signals combined into corresponding spatial modes over a transmission medium.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical fiber transmission system with polarization multiplexing to reduce stimulated brillouin scattering
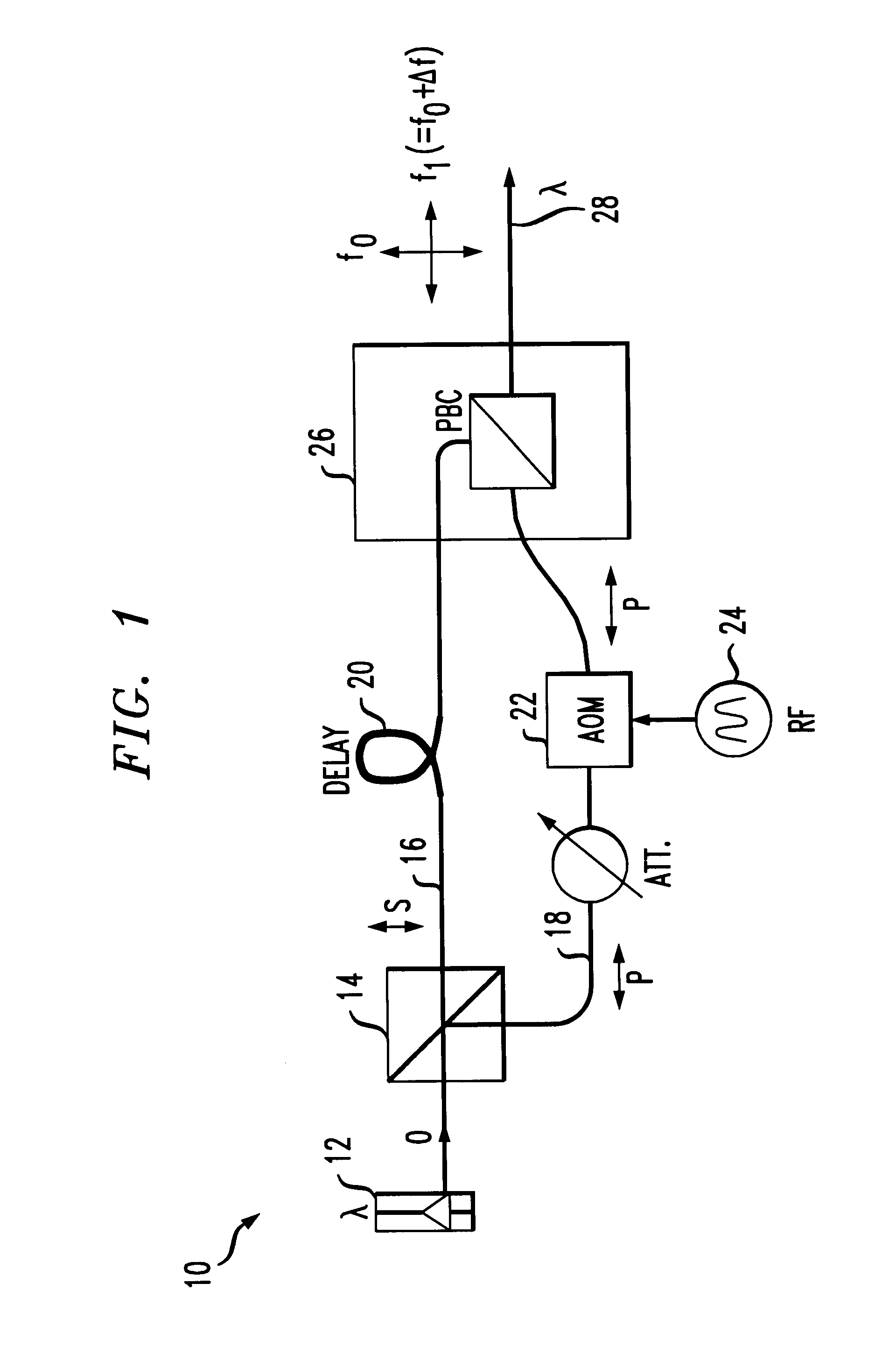
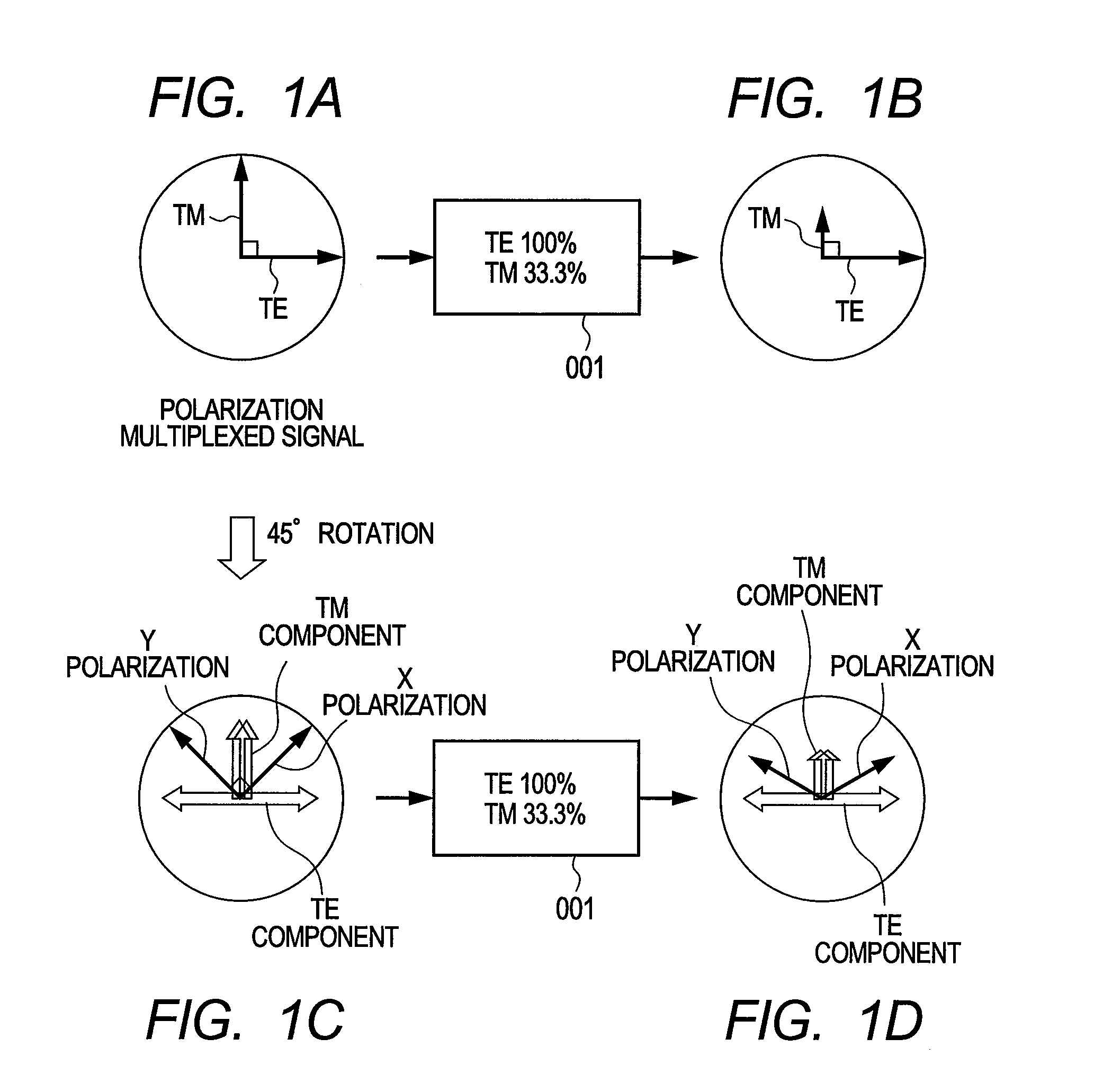
InactiveUS6850712B1Lower Level RequirementsReduce impactLaser detailsPolarisation multiplex systemsLine widthTime delays
A technique for suppressing stimulated Brillouin scattering SBS along an optical fiber signal path utilizes polarization modulation at the transmitter to split the launched power into orthogonal polarization states. By reducing the power along each polarization, SBS will be reduced. Linewidth broadening of the optical source is achieved by introducing: (1) a incoherence between the polarization states (using a time delay along the signal path of one polarization state); and (2) a frequency shift between the polarization states (using an acousto-optic modulator along the signal path of the remaining polarization state).
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
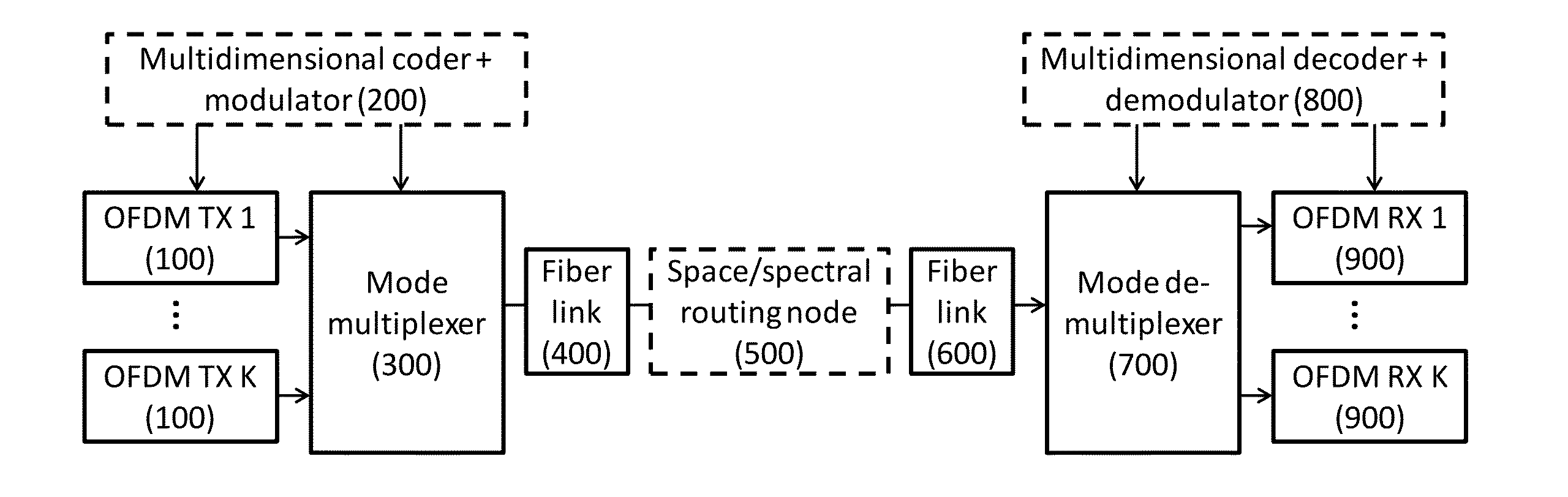
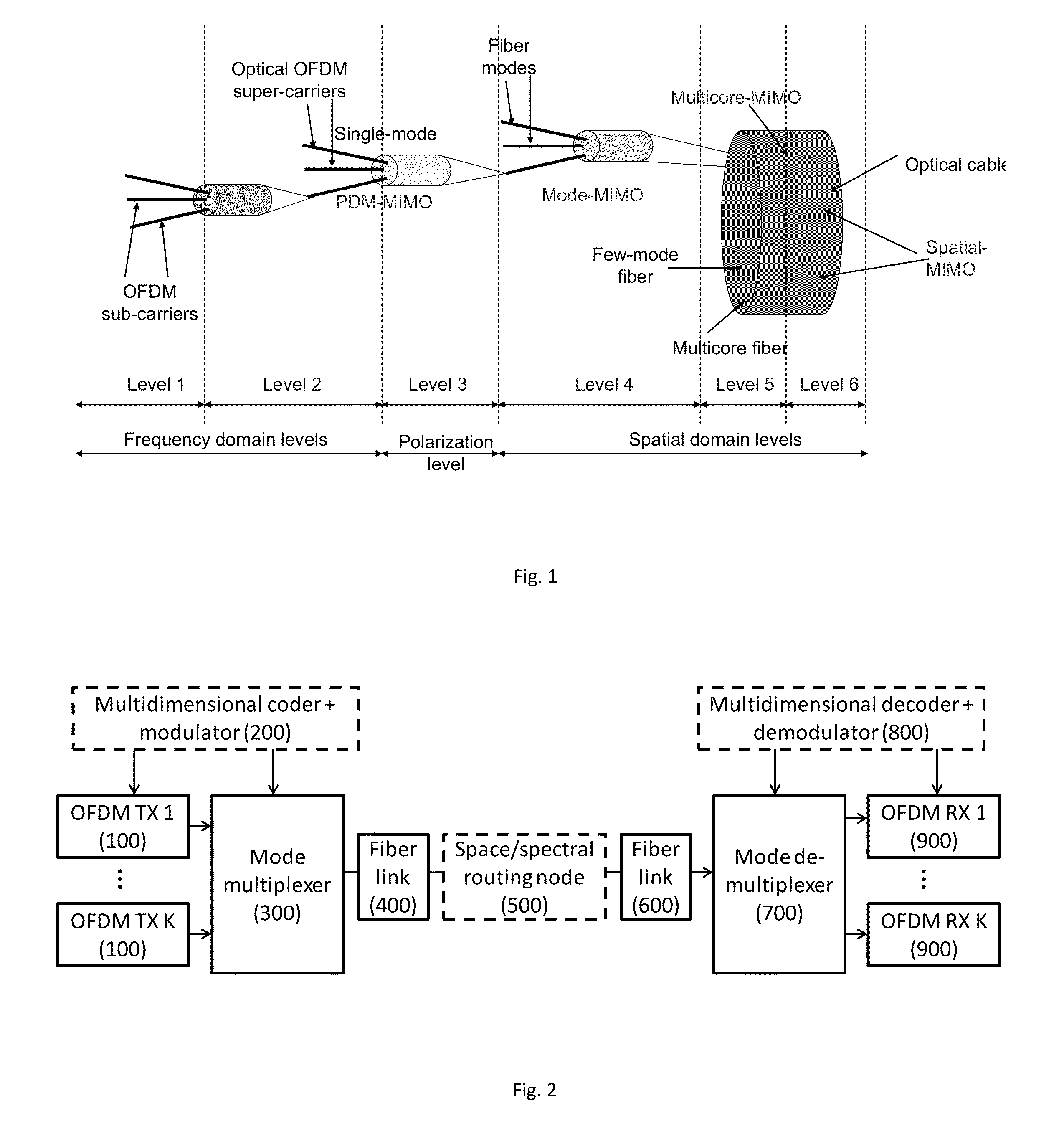
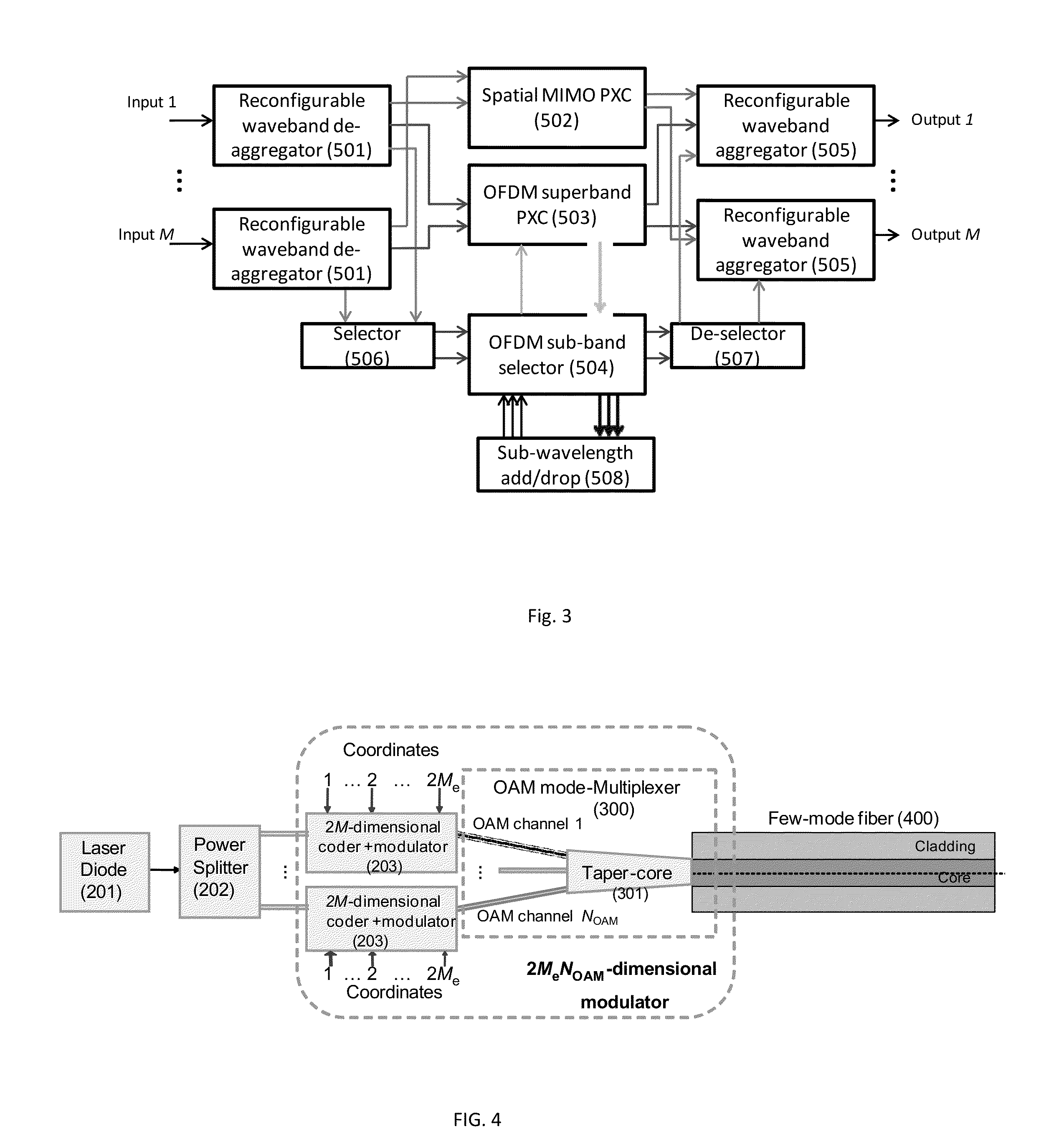
Dynamic Multidimensional Optical Networking Based on Spatial and Spectral Processing
An optical network includes a multidimensional coder and modulator for handling multiple-in-multiple-out MIMO spatial lightpath properties and content of any specific supercarrier, a spatial mode multiplexer responsive to orthogonal frequency division multiplexing OFDM transmissions and the multidimensional coder, a spatial-spectral routing node coupled over a fiber link to the spatial mode multiplexer for performing switching granularity by a spatial mode reconnection, a multidimensional decoder and demodulator; and a spatial mode demultiplexer coupled over a fiber link to the spatial-spectral routing node and responsive to the multidimensional decoder and demodulator.
Owner:NEC CORP
Fiber communication systems and methods
ActiveUS20170294966A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsInjection lockedFiber
An injection locked transmitter for an optical communication network includes a master seed laser source input substantially confined to a single longitudinal mode, an input data stream, and a laser injected modulator including at least one slave laser having a resonator frequency that is injection locked to a frequency of the single longitudinal mode of the master seed laser source. The laser injected modulator is configured to receive the master seed laser source input and the input data stream, and output a laser modulated data stream.
Owner:CABLE TELEVISION LAB
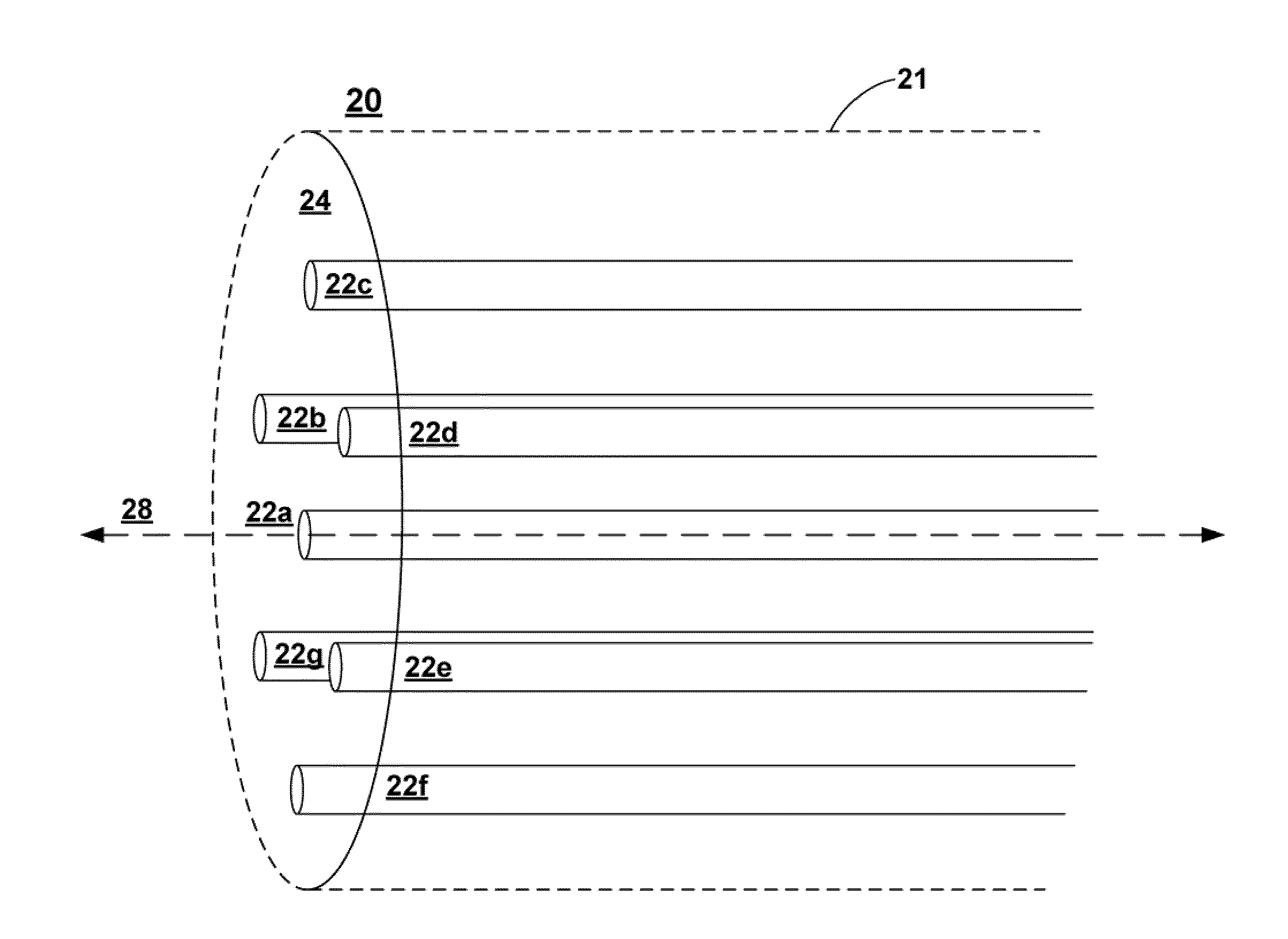
Multicore Optical Fiber with Reduced Inter-Core Crosstalk
ActiveUS20130136404A1Reducing inter-core crosstalkOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexOptical fiber cable
Various apparatus and methods for reducing inter-core crosstalk in a multicore optical fiber are disclosed. A multicore optical fiber may include a plurality of cores capable of transmitting optical signals, and a cladding surrounding the cores, the cladding having a heterogeneous refractive index such that the optical signals propagate at different velocities in different ones of the cores. A multicore optical fiber may include a first length including cores having heterogeneous modal velocities and a second length, adjacent to the first length, including cores having heterogeneous modal velocities, and the cores in the first length are aligned with cores in the second length having a different modal velocity. Inter-core cross talk in a multicore optical fiber may also be reduced by transmitting optical signals through cores of a multicore optical fiber and pumping light into the cores to create unequal modal velocities in the cores.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
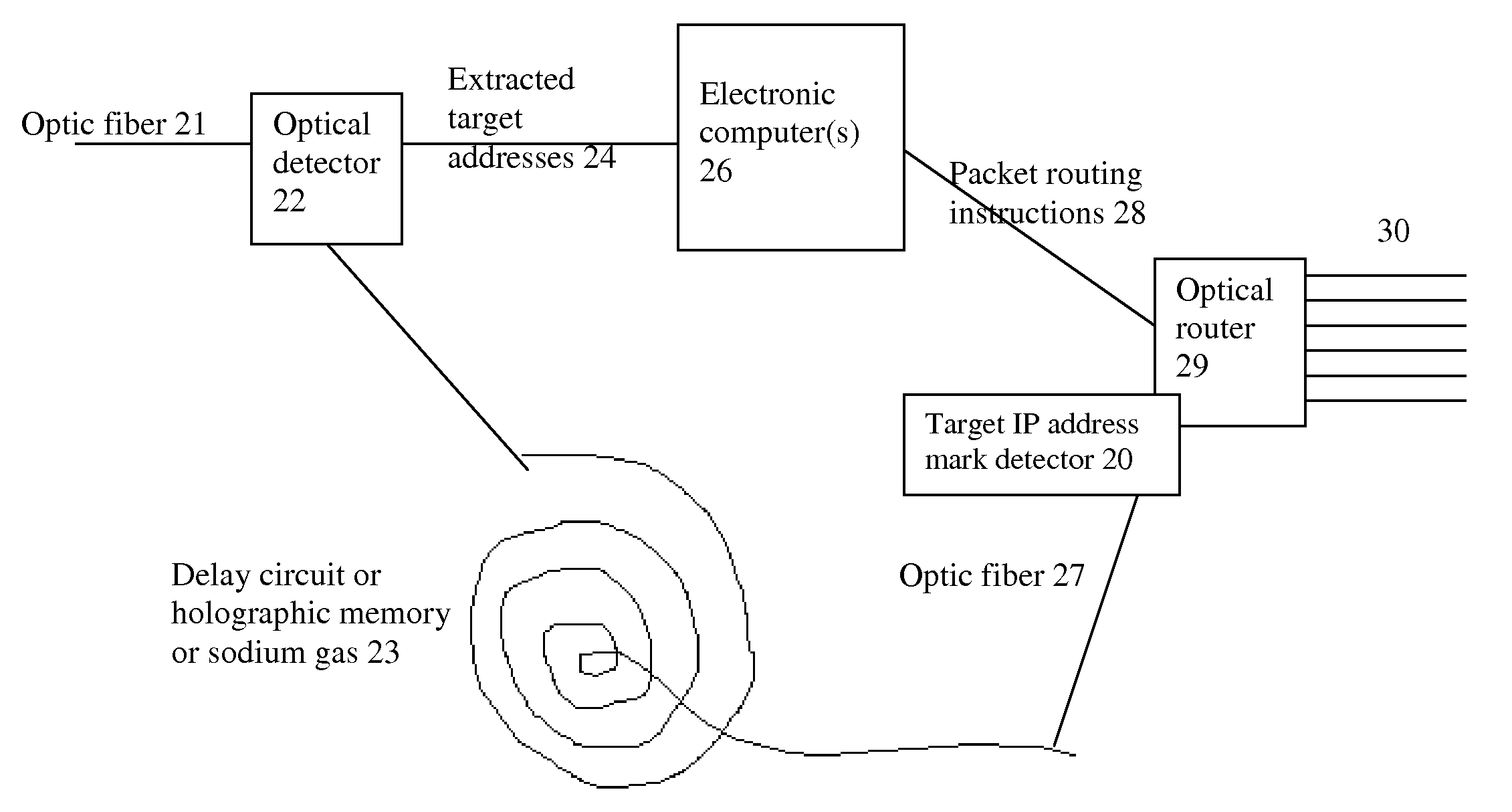
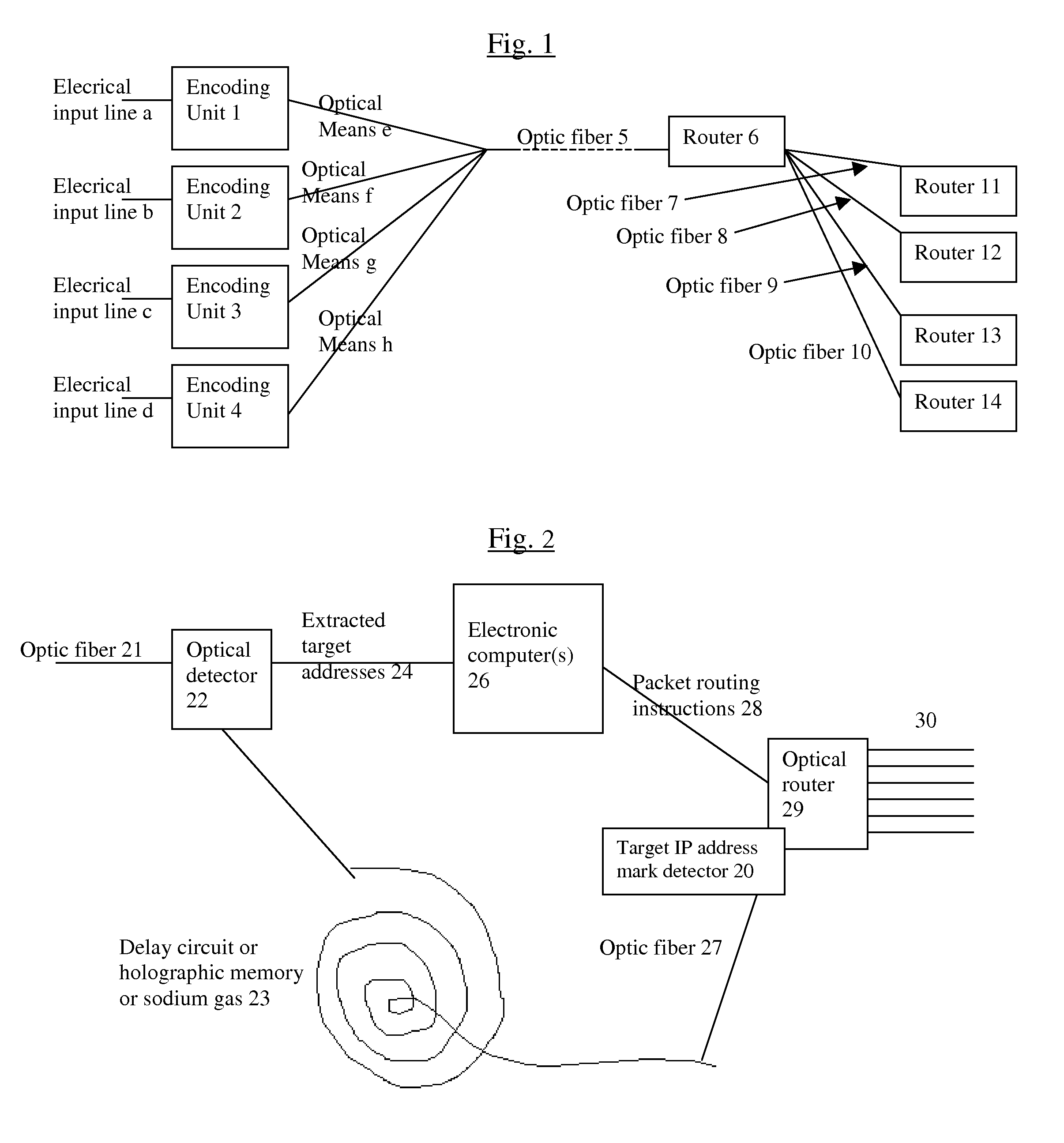
System and method for improving the efficiency of routers on the Internet and/or cellular networks and/or other networks and alleviating bottlenecks and overloads on the network
InactiveUS20080145050A1Simpler and flexible bufferingCheaply and easilyMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical delay lineIndividual data
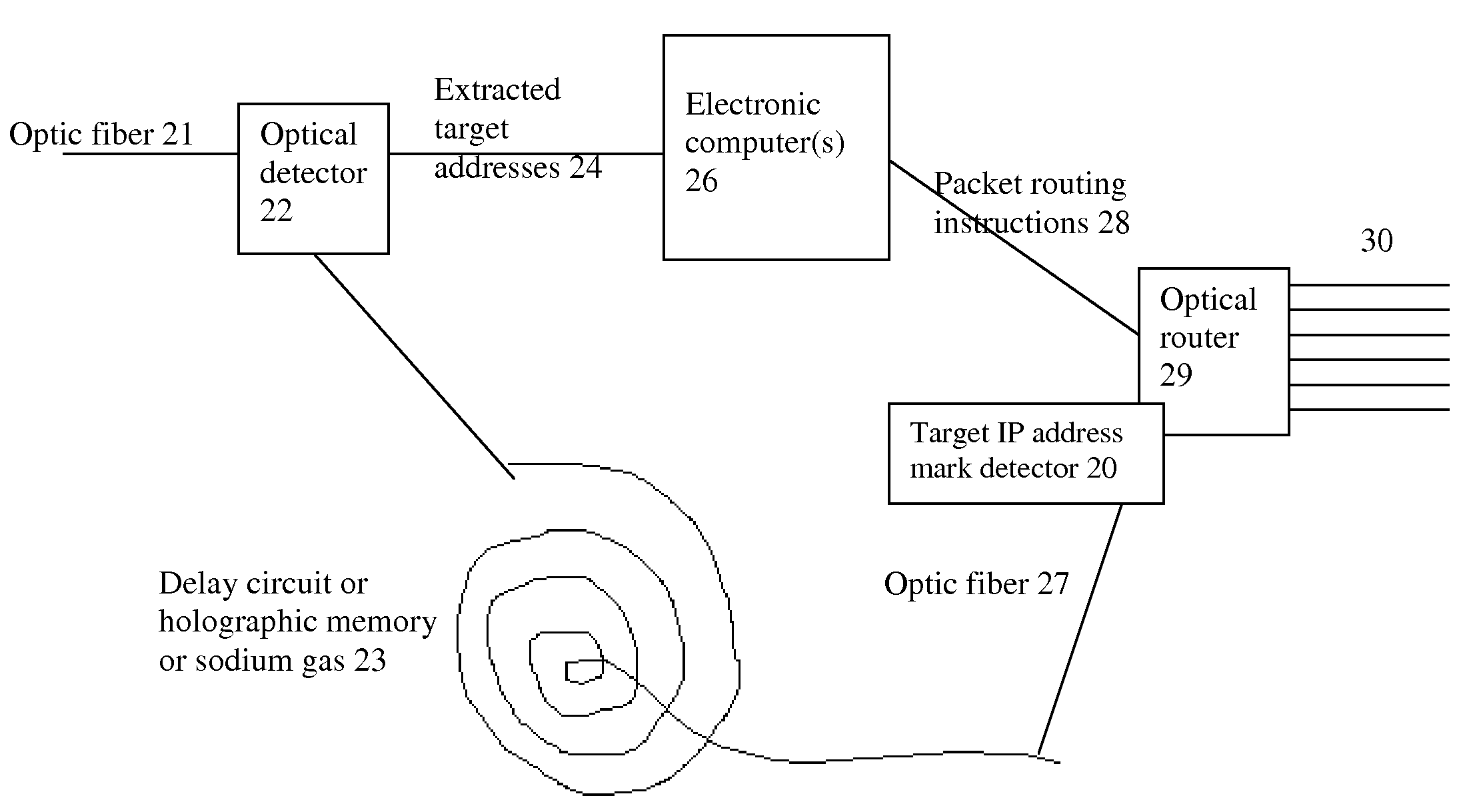
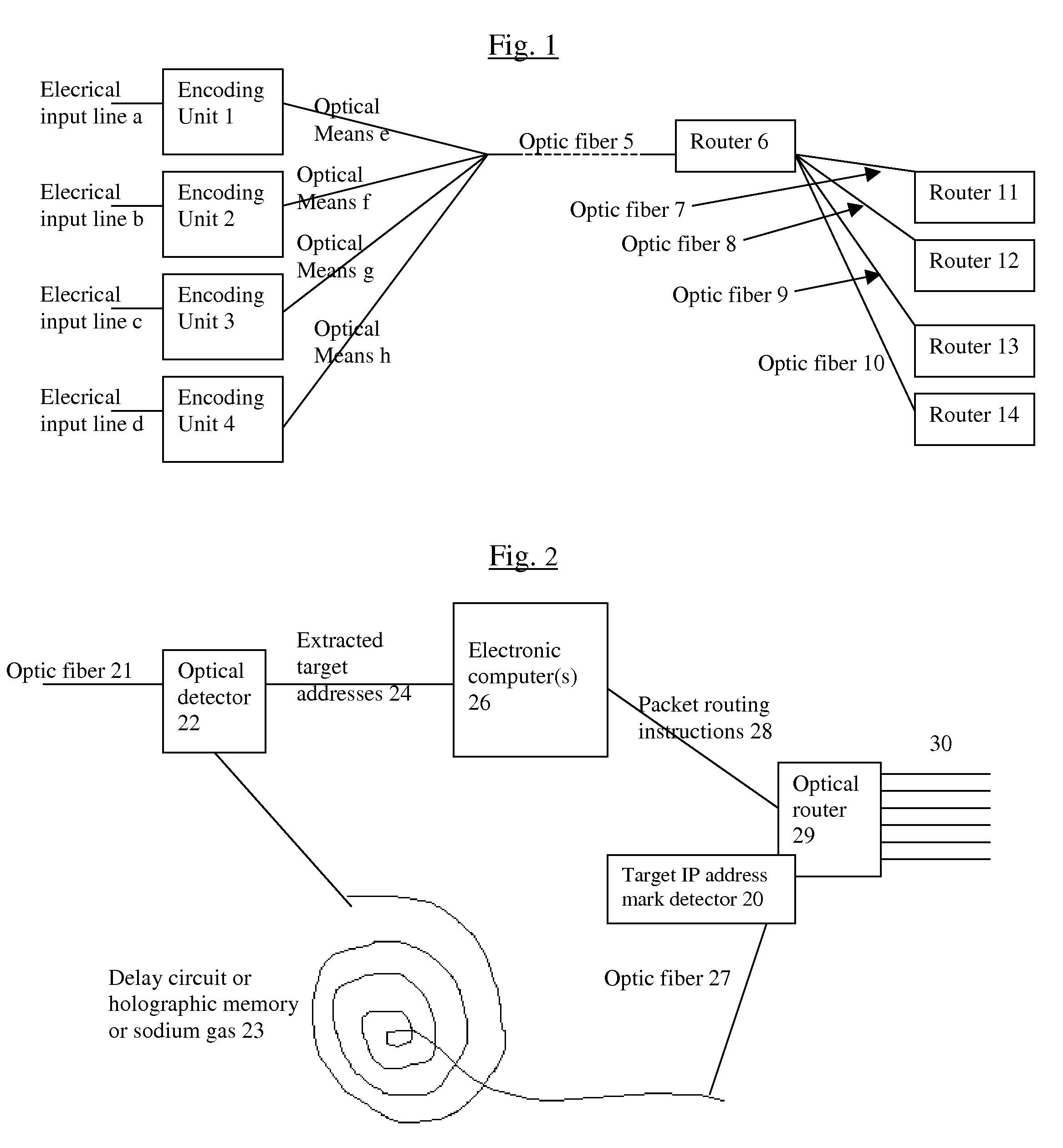
The biggest bottleneck in the Internet today is caused by the slow speed of routers, compared to the speeds that are achieved by optic fibers with DWDM (Dense Wave Division Multiplexing). Packet switching or something similar to it is needed not just for better utilization of the lines, but also because it is superior to circuit switching in many ways, such as better scalability as the Internet grows, better handling of traffic congestions, and better routing flexibility. But optical routers are currently unable to do packet switching except by translating the data to electronic data and then back, which is very inefficient. The present invention solves this problem by optically marking and detecting the packet headers or parts of them, translating at most only the headers or parts of them to electronics for making packet switching decisions, and keeping the rest of the packets in optical delay lines, and solving response-time problems in the router, so that the crude optical switches can execute the packet switching decisions at fast bit rates. This solution has very high scalability and becomes even more efficient when physical addresses are used. Another optimization described in this invention is improving routing efficiency and bandwidth utilization by grouping together identical data packets from the same source going to the same general area with a multiple list of targets connected to each copy of the data and sent together to the general target area. These grouped packets are then preferably broken down into smaller groups by the routers in the general target area and finally broken down to individual data packets for delivering to the final actual destinations. This optimization works best with Physical addresses, and can be very useful for example for optimizing the access to very popular sites such as for example Yahoo or CNN, and can be used also for example for more efficiently transferring streaming data, such as for example from Internet radio stations, or Internet TV stations which will probably exist in the next years. Another important optimization is a new architecture and principles for routing based on physical geographical IP addresses (such as for example based on GPS), in a way much more efficient than has been previously discussed in the literature that suggested using physical (geographical) addresses. This is preferably based on a hierarchy similar to a hierarchical road system, so that preferably the MAIN routers (and / or intermediary-level routers) are preferably also connected directly and preferably with high-bandwidth as peers between each other, without having to go through lower-level routers in order to reach their peers, so that once a higher-level router (and especially if it's one of the MAIN routers) decides to forward a packet (or a group of packets) to a higher-level peer, preferably the packets don't have to go through lower level routers. However, conversion from the current architecture to the new one can be done very easy, as shown in the description below.
Owner:BARHON MAYER BATYA
Optical CDMA system using sub-band coding
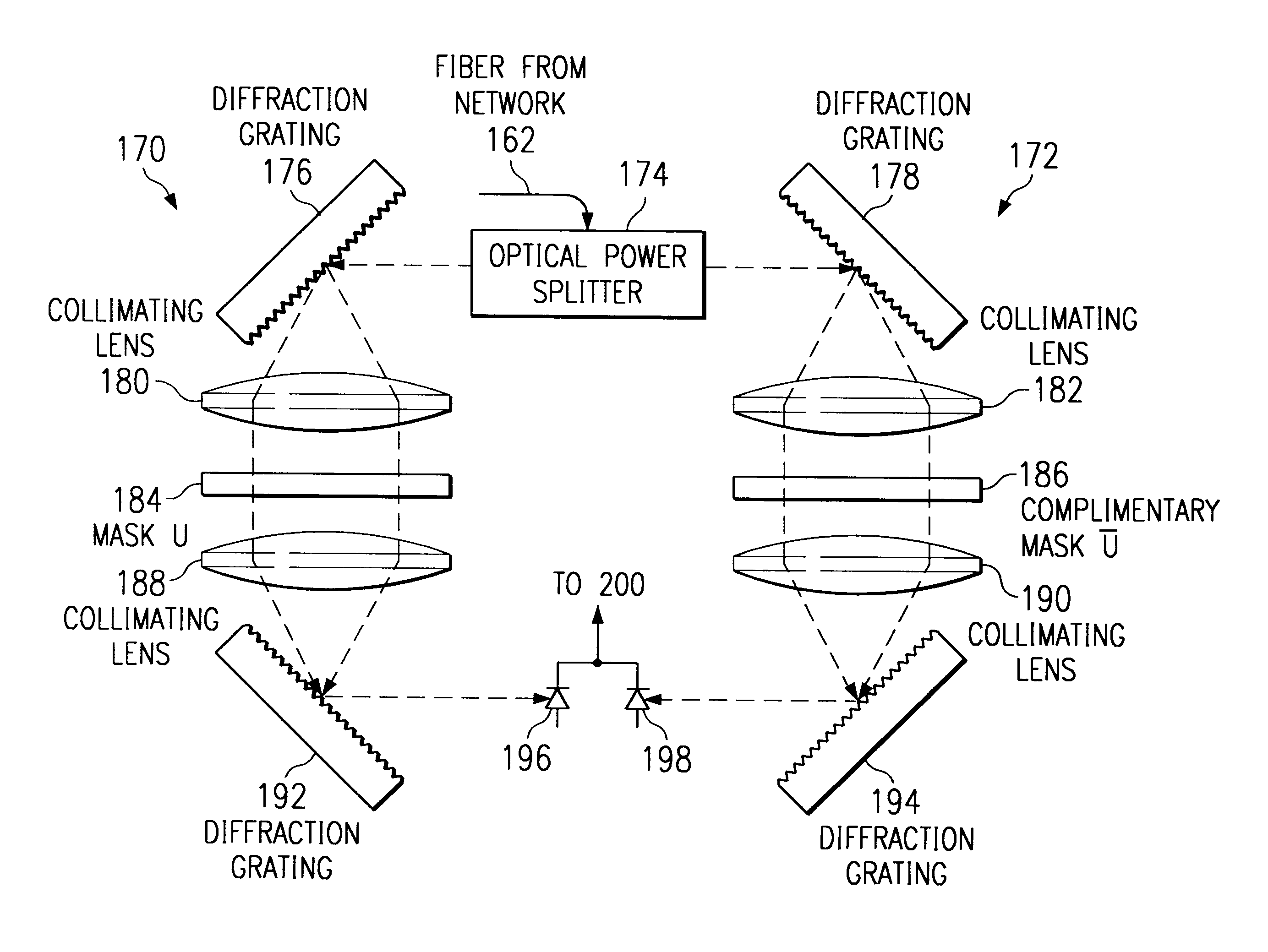
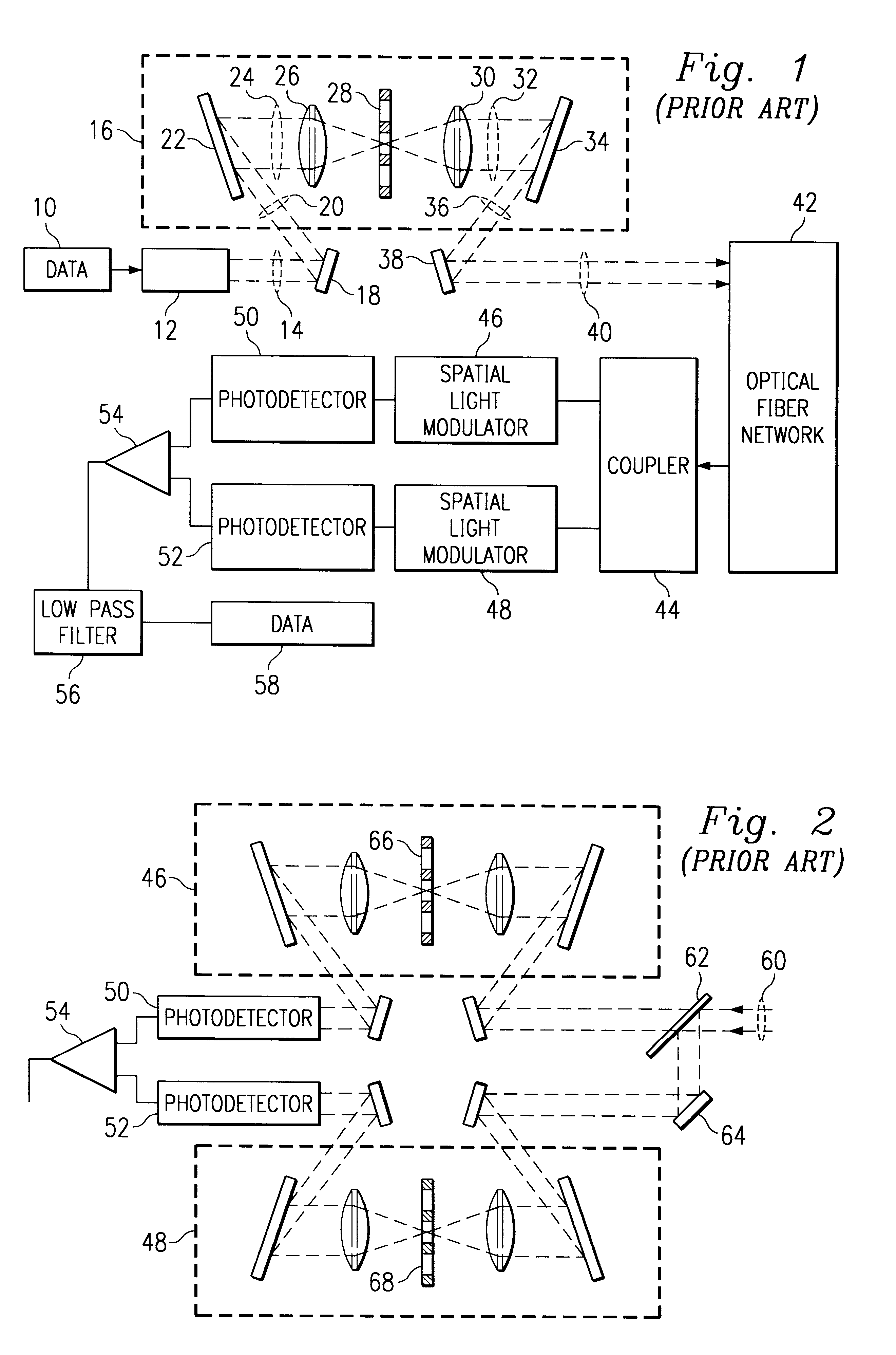
InactiveUS6236483B1Polarisation multiplex systemsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical cdmaCommunications system
An optical fiber communications system using spread spectrum code division multiple access techniques to achieve better bandwidth utilization. A transmitting user in the system encodes the optical signal using a first coding mask, and a receiving user decodes the received signal using two decoding masks, all of the masks having lengths N. The first mask is divided into two sections of lengths N / 2 each, one of the sections defining a first sub-code of length N / 2, while the other section blocks light. Each of the second and third masks is also divided into two sections, which correspond to the two sections of the first mask. The section of the second mask corresponding to the coded section of the first mask has a second code that is identical to the first code, and the section of the second mask corresponding to the blocked section of the first mask is also blocked. The section of the third mask corresponding to coded section of the first mask has a third code that is complementary to the first code, and the section of the third mask corresponding to the blocked section of the first mask is also blocked. Some users on the system have masks in which the first of the two sections are blocked and the second of the two sections are coded, while other users have masks in which the second of the two sections are blocked and the first of the two sections are coded. The first codes used to code the encoding masks are selected from a set of unipolar codes that are derived from a set of balanced bipolar orthogonal codes.
Owner:CODESTREAM TECH CORP
Method And Apparatus For Space-Division Multiplexing Systems
ActiveUS20130236175A1Reducing performance variationImprove system performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFew mode fiberSignal on
A space division multiplexed (SDM) transmission system that includes at least two segments of transmission media in which a spatial assignment of the two segments is different is provided. For example, the SDM transmission may include a first segment of transmission media having a first spatial assignment and a second segment of transmission media having a second spatial assignment, wherein the first spatial assignment differs from the second spatial assignment. An example method obtains an optical signal on a first segment of transmission media having a first spatial assignment and forwards the optical signal on a second segment of transmission media with a different spatial assignment. The transmission media may be a multi-core fiber (MCF), a multi-mode fiber (MMF), a few-mode fiber (FMF), or a ribbon cable comprising nominally uncoupled single-mode fiber (SMF).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method of and system for detecting skew between parallel signals
ActiveUS20120020660A1Simple receiver structureSimple codingChannel dividing arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsData streamPolarization multiplexed
A method is provided for detecting the skew between parallel light signals generated from a serial data stream. The method can be used with polarization multiplexed signal, as well as with wavelength division multiplexed signals, spatial division multiplexed signals, phase modulated signals, or intensity modulated signals. The method can be used with direct detection schemes as well as with coherent detection schemes. The method is provided with: imprinting dips between a fixed number of transmitted symbols of the parallel signals; detecting an electrical signal related to the dips for each parallel signal; and comparing the electrical signals in delay.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of and system for detecting skew between parallel signals
ActiveUS8971723B2Simple methodHigh precisionChannel dividing arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsData streamPolarization multiplexed
A method is provided for detecting the skew between parallel light signals generated from a serial data stream. The method can be used with polarization multiplexed signal, as well as with wavelength division multiplexed signals, spatial division multiplexed signals, phase modulated signals, or intensity modulated signals. The method can be used with direct detection schemes as well as with coherent detection schemes. The method is provided with: imprinting dips between a fixed number of transmitted symbols of the parallel signals; detecting an electrical signal related to the dips for each parallel signal; and comparing the electrical signals in delay.
Owner:NEC CORP
Photonic Lantern Spatial Multiplexers with mode selectivity
ActiveUS20150086157A1Reduce lossMode selectivityOptical mode multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesSingle-mode optical fiberMultiplexer
A photonic lantern spatial multiplexer that provides mode selectivity includes a multimode optical waveguide and a plurality of single mode optical waveguides. The single mode cores of the single mode optical waveguides merge with the multimode core of the multimode optical waveguide. At least two of the single mode cores have different respective single mode effective refractive indexes.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
System and method for transmitting optical signal over multiple channels
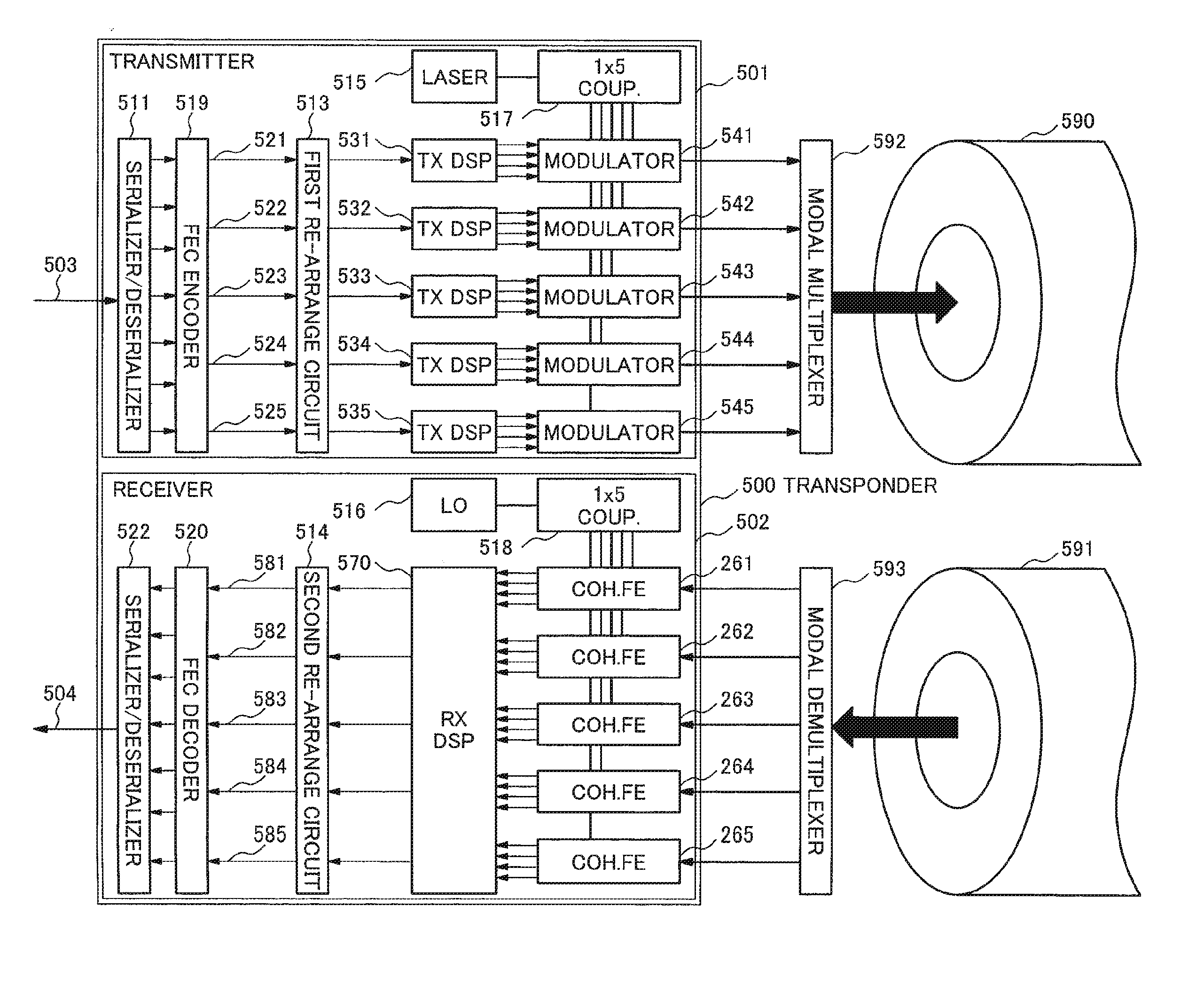
ActiveUS20150229438A1Improve system marginReduce outage rateError preventionWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignal qualityEngineering
Since it is difficult to transmit optical signal over multiple channels with an improved received signal quality, better system margins, and reduced system outages, a method for transmitting optical signal over multiple channels according to an exemplary aspect of the invention includes: (a) firstly rearranging a plurality of tributaries of data to be transmitted in order to scramble the data among the plurality of tributaries; (b) transmitting optical signals modulated with rearranged data generated in step (a) over the multiple channels; (c) receiving the optical signals through the multiple channels; (d) demodulating the optical signals into a plurality of tributaries of the rearranged data; (e) secondly rearranging the plurality of tributaries of the rearranged data in order to recover the plurality of tributaries of data before step (a); and wherein, the number of tributaries of the rearranged data is equal to or more than two and is less than or equal to the number of the multiple channels.
Owner:NEC CORP
Secure Data Transmission Using Spatial Multiplexing
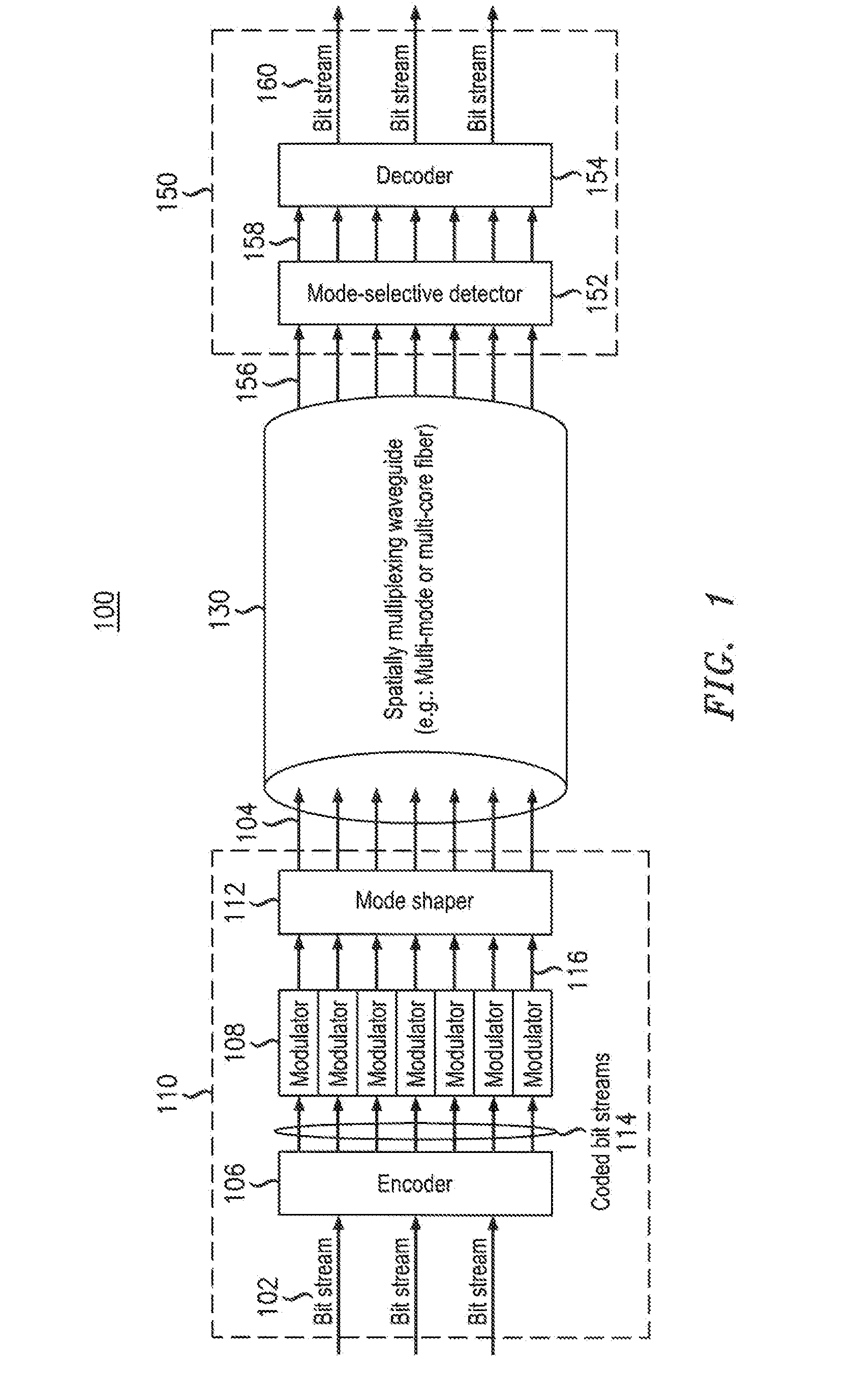
InactiveUS20120177065A1Secure transmissionProhibits detectionModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation multiplex systemsMultiplexerWaveguide
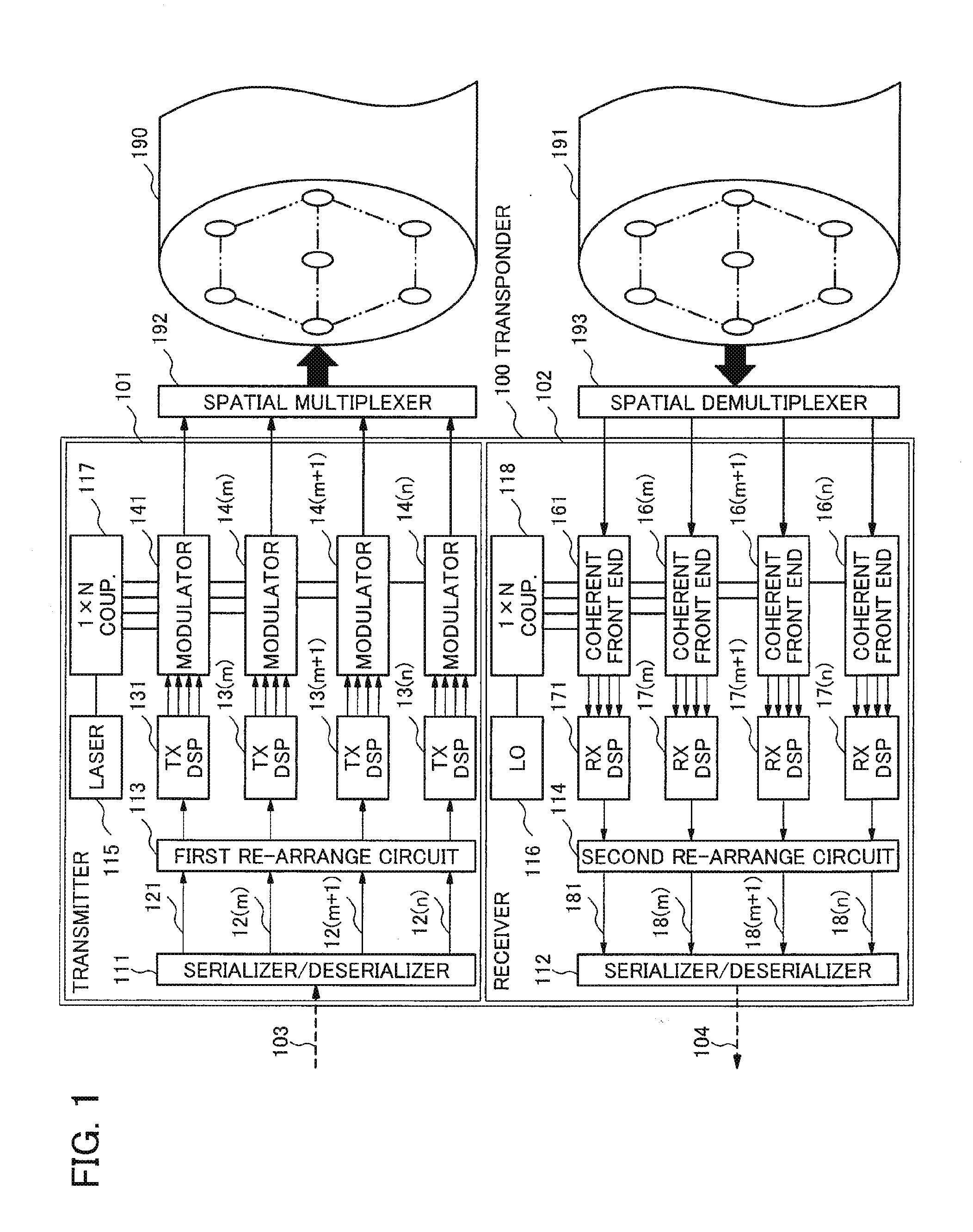
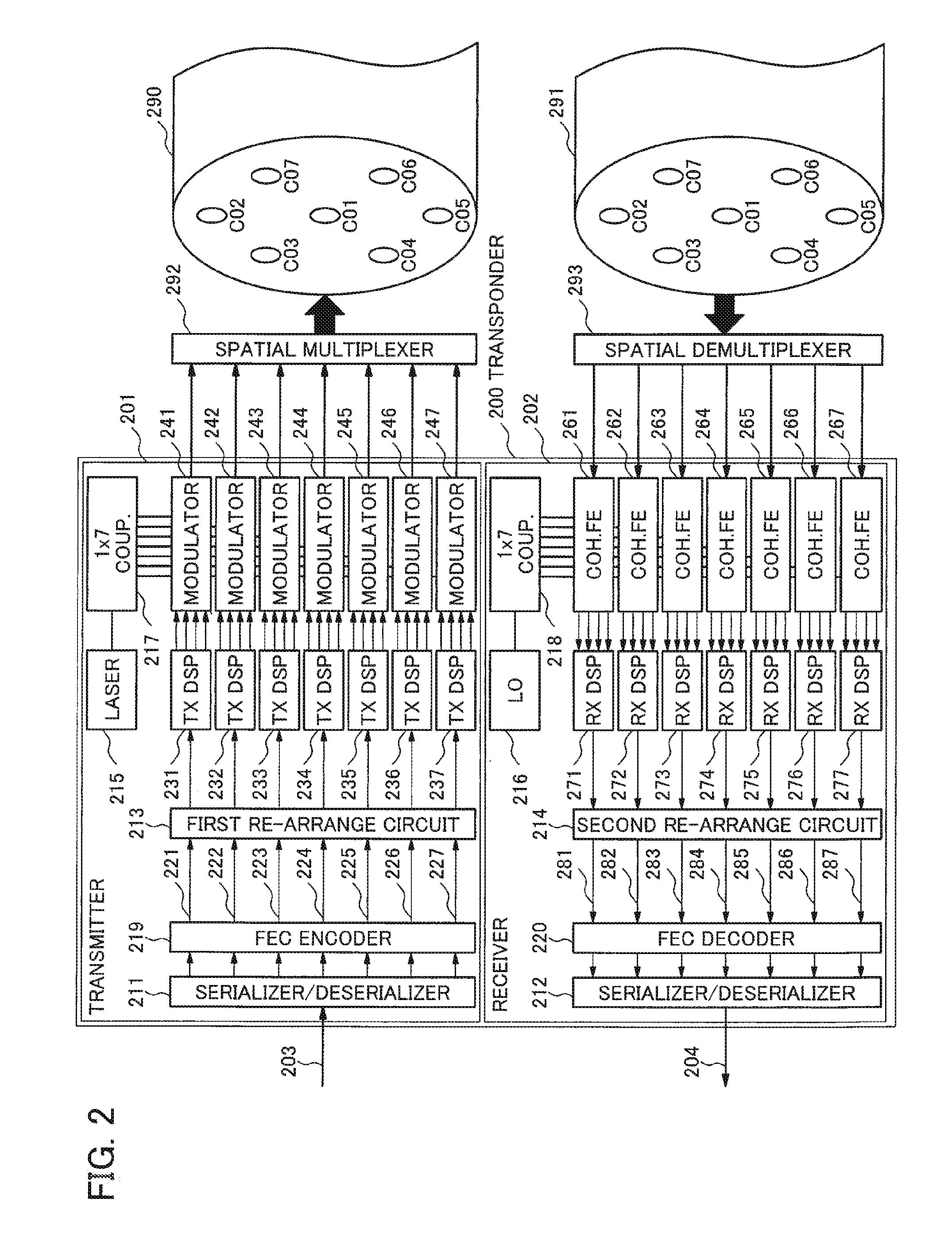
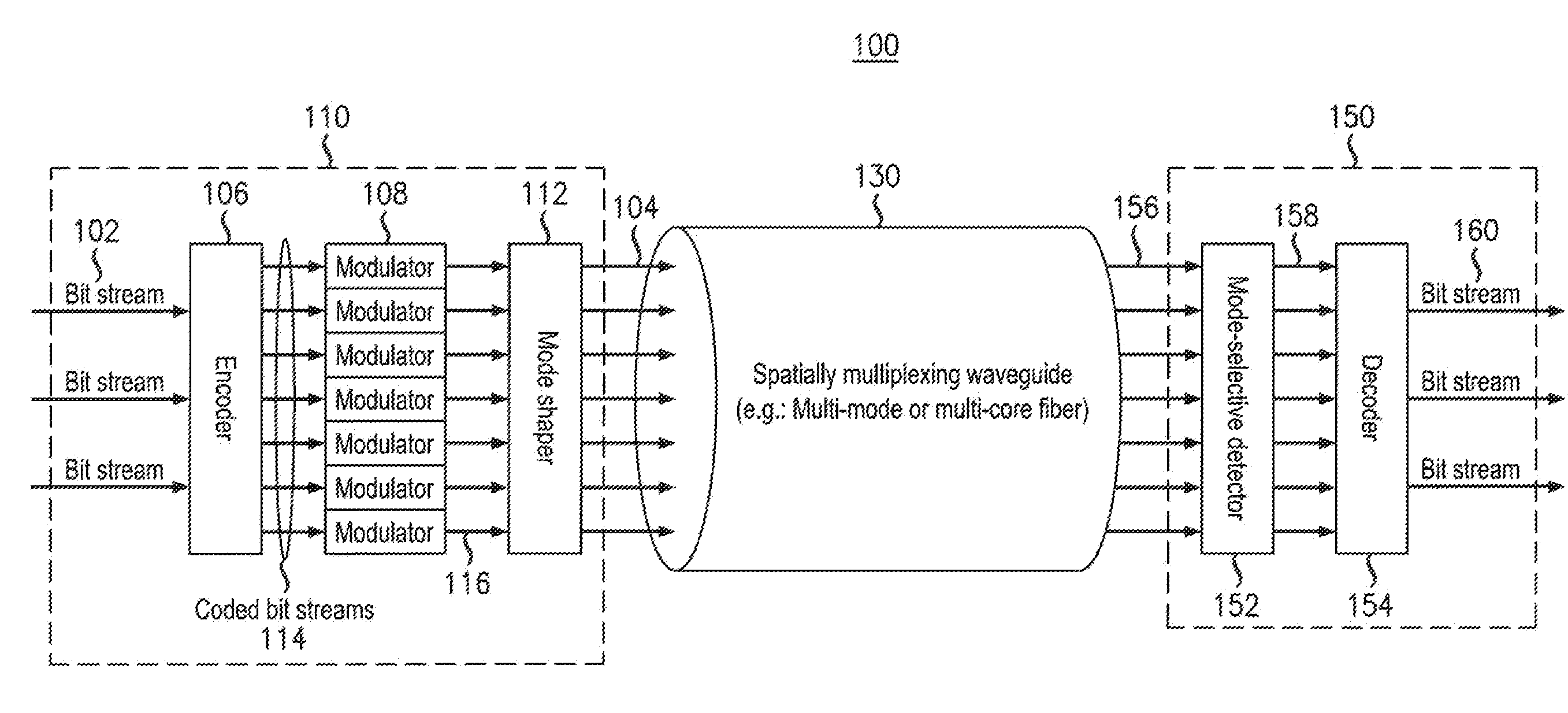
An example transmitter includes an encoder, a plurality of modulators and a spatial multiplexer. The encoder is configured to encode one or more input bit streams into a plurality of coded bit streams which are provided as output. Each modulator is configured to receive and modulate a respective one of the plurality of coded bit streams and to provide a modulated output signal. The spatial multiplexer is configured to spatially multiplex the plurality of modulated output signals for insertion on a spatially multiplexing waveguide. A modulated output signal(s) may be inserted onto a mode of a multi-mode fiber or onto a core of a multi-core fiber. In one embodiment, a subset of the plurality of spatially multiplexed modulated output signals which correspond to the one or more input bit streams must be simultaneously and spatially selectively detected in order to recover a first input bit stream.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
System and method for improving the efficiency of routers on the internet and/or cellular networks and/or other networks and alleviating bottlenecks and overloads on the network
InactiveUS8073327B2Improving routing efficiency and bandwidth utilization efficiencyEfficient transferMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsIp addressThe Internet
Owner:BARHON MAYER BATYA
Optical communication system, lighting equipment and terminal equipment used therein
InactiveUS20070008258A1Reliable communicationSignal redundancy is increasedLaser detailsPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemLight equipment
A communication system has lighting equipment that has transmitter comprising multiple light-emitting elements that each emit light of different wavelengths and terminal equipment that has light-receiver comprising multiple light-receiving elements that receive optical signals for each of the different wavelengths.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Optical transmission system
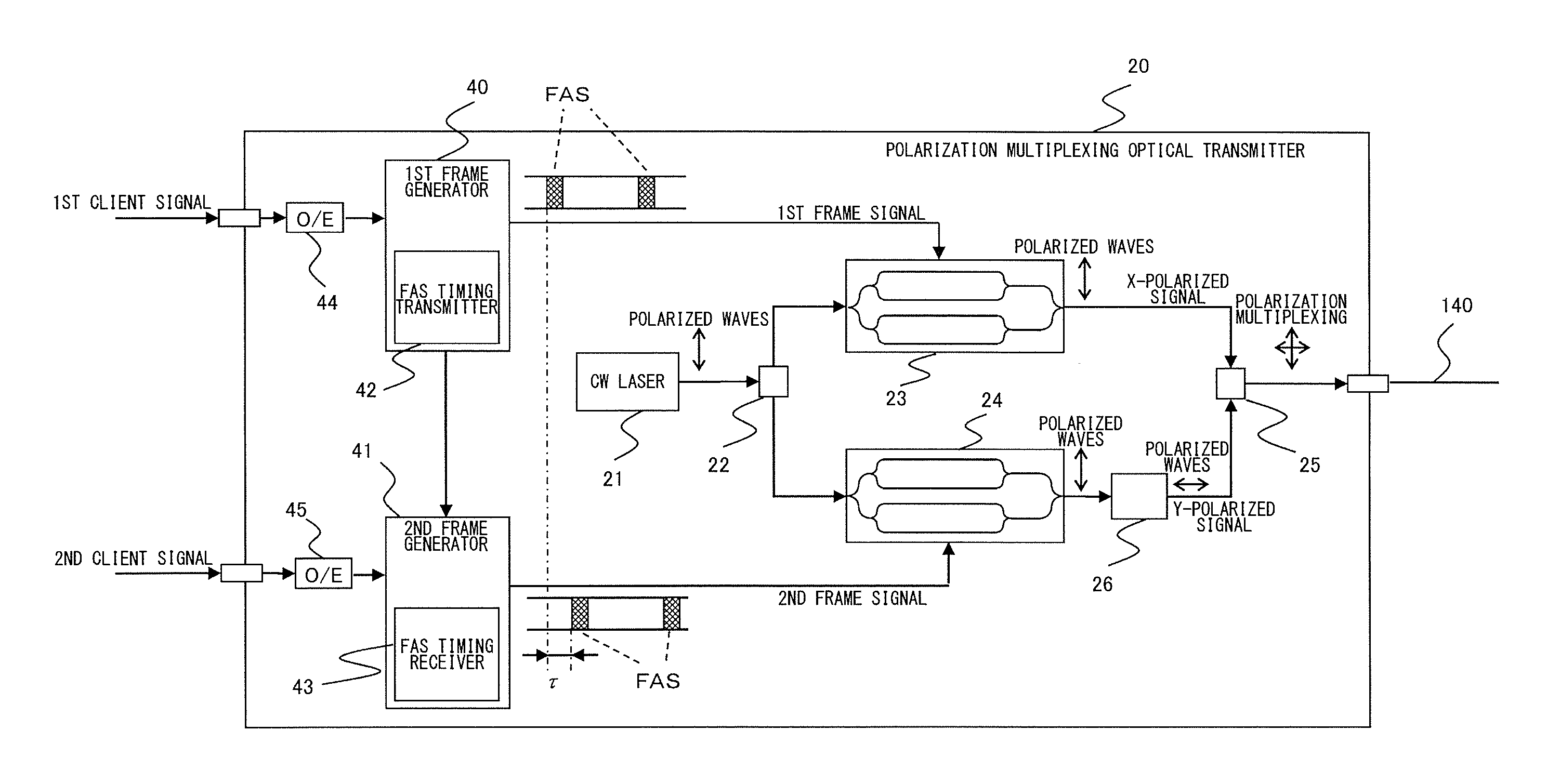
InactiveUS20110217040A1Accurate distinctionPolarisation multiplex systemsTime-division optical multiplex systemsPolarization multiplexedDelayed time
An optical transmission system includes a polarization multiplexing optical transmitter for transmitting an optical signal, where an X-polarized signal and a Y-polarized signal each having a having predetermined frame structure are polarization-multiplexed, to an optical fiber transmission path, and a polarization multiplexing receiver for receiving the optical signal that has propagated through the optical transmission path. The polarization multiplexing optical transmitter delays a frame assignment signal (FAS) in the Y-polarized signal, by a predetermined delay time τ, relative to FAS in the X-polarized signal. The polarization multiplexing optical receiver includes a polarization splitter for splitting the received optical signal into two branches of polarized signals which are orthogonal to each other, a time difference detector for detecting a time difference of FASs between the two polarized signals, and a polarization identifying unit for identifying which of the two polarized signals is the X-polarized signal or Y-polarized signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical communication system using wdma and CDMA
InactiveUS20100158527A1Avoid signalingInterference componentMultiplex system selection arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemResource information
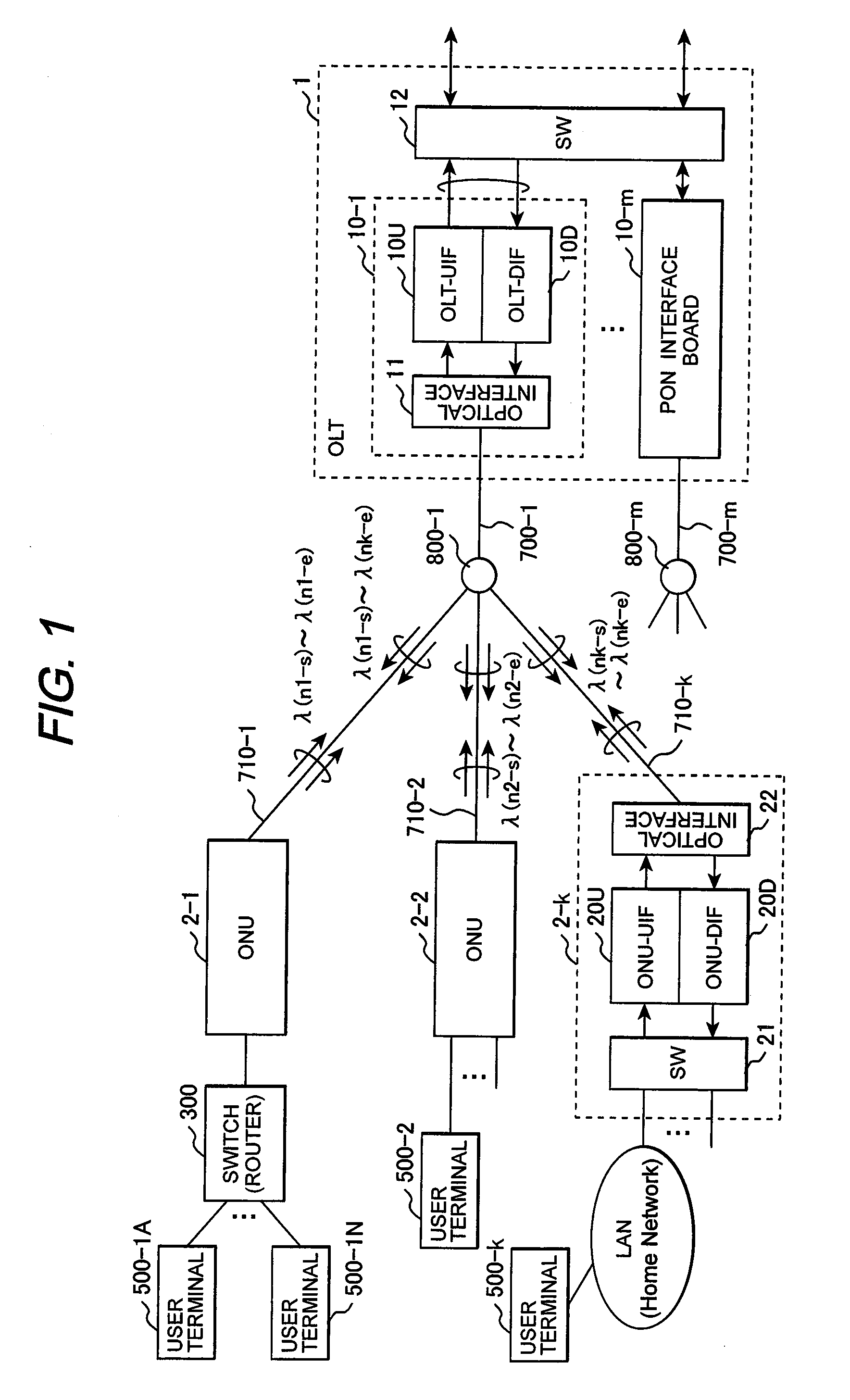
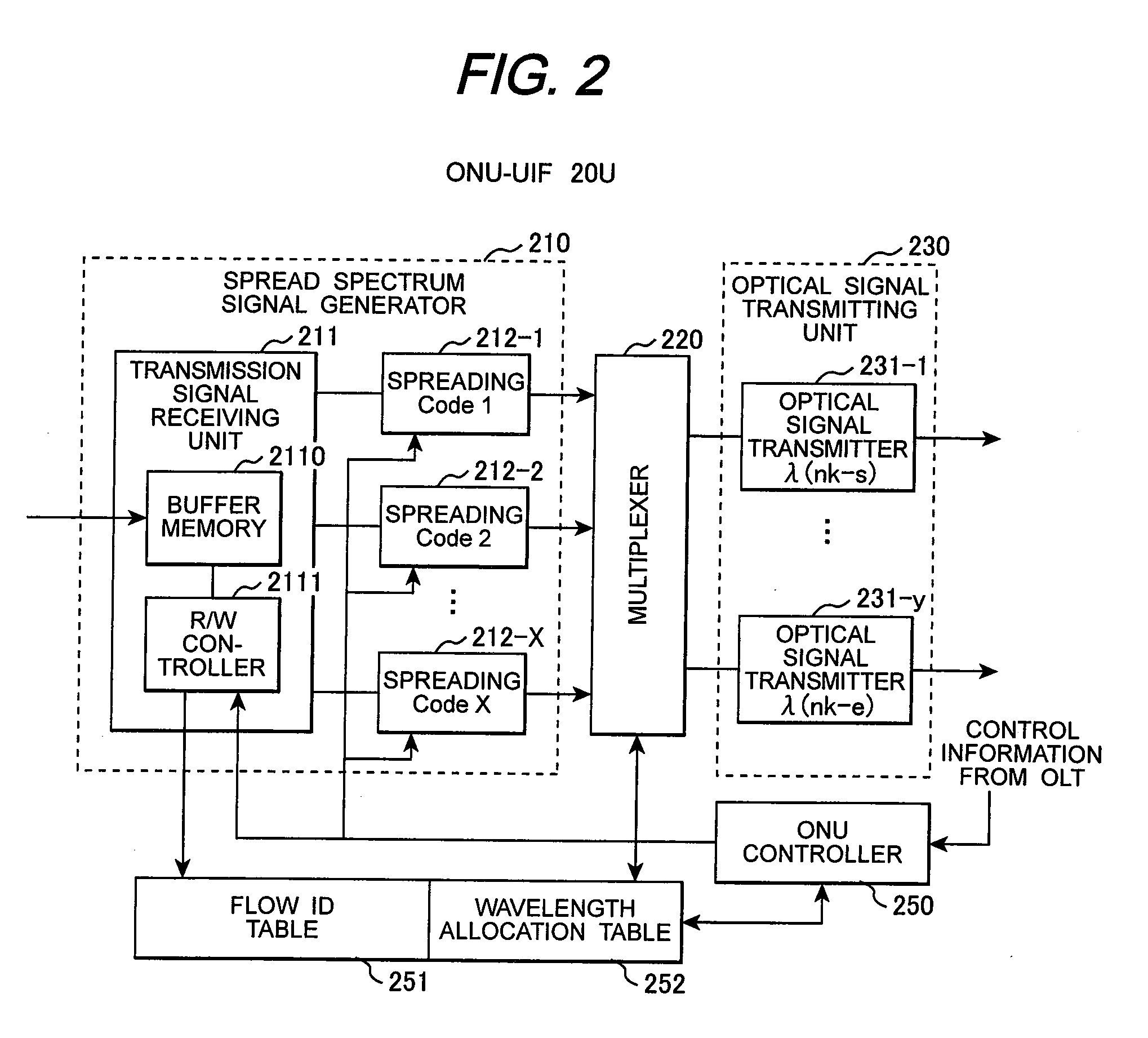
In a PON system, an OLT periodically transmits a channel resource information block specifying a carrier wavelength and a spreading code on a first downstream channel to which a spread-spectrum spreader having a first spreading code is applied; one of ONUs receives the channel resource information block with a spread-spectrum despreader having the first spreading code and transmits a connection request to the OLT, using the carrier wavelength and the spreading code specified by the channel resource information block; the OLT having received the connection request transmits a new channel resource information block specifying a carrier wavelength and a spreading code to be used on an upstream data channel to the requester ONU through the first channel; and the requester ONU transmits data, using the carrier wavelength and the spreading code specified by the new channel resource information block.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Polarization multiplexing transmitter and transmission system
InactiveUS20110170869A1Reduce equipment costsSmall sizePolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsTransfer systemMultiplexer
A polarization multiplexing transmitter which generates polarization-multiplexed signals which are arbitrarily polarization-scrambled at high speed, without adding a polarization modulator and a polarization scrambler. In the transmitter, an orthogonally polarized signal generator includes two optical modulators which modulate the electric fields of optical signals and generate two optical signals with mutually orthogonal polarized waves. The transmitter includes electric field mappers which convert two data strings into electric field signals, polarization mappers which give different polarized waves to the two signals, polarization rotators which rotate the polarized waves of the signals uniformly, a polarization multiplexer which multiplexes the two polarization-rotated signals, a polarization demultiplexer which demultiplexes the multiplexed signal into polarized wave components of optical signals generated by the orthogonally polarized signal generator, and a driver. The optical modulators are driven to make the two demultiplexed electric field signals consistent with the electric fields of optical signals modulated by the modulators.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com