Patents
Literature
172 results about "Internet radio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Internet radio (also web radio, net radio, streaming radio, e-radio, IP radio, online radio) is a digital audio service transmitted via the Internet. Broadcasting on the Internet is usually referred to as webcasting since it is not transmitted broadly through wireless means. It can either be used as a stand-alone device running through the internet, or as a software running through a single computer.
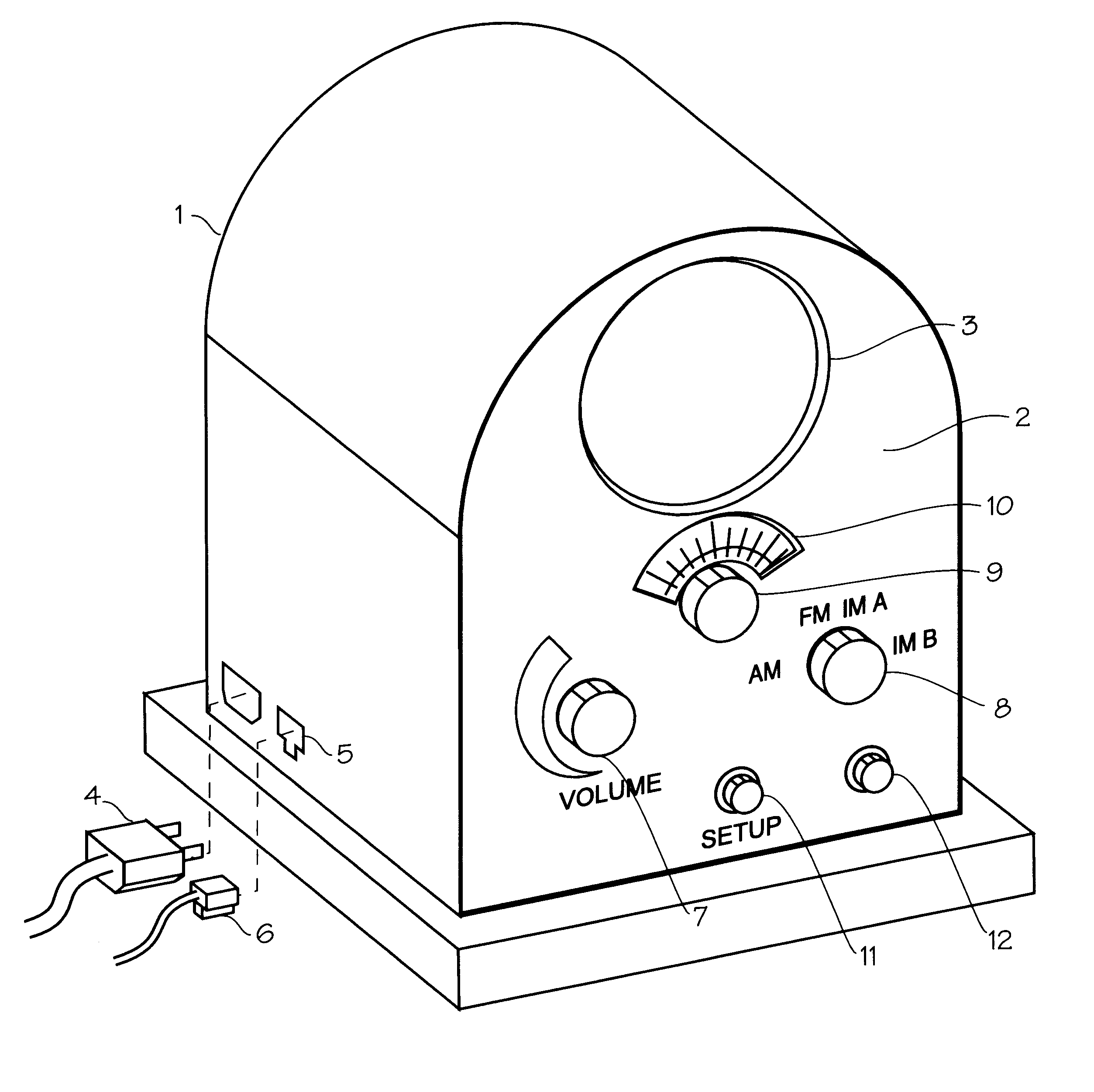
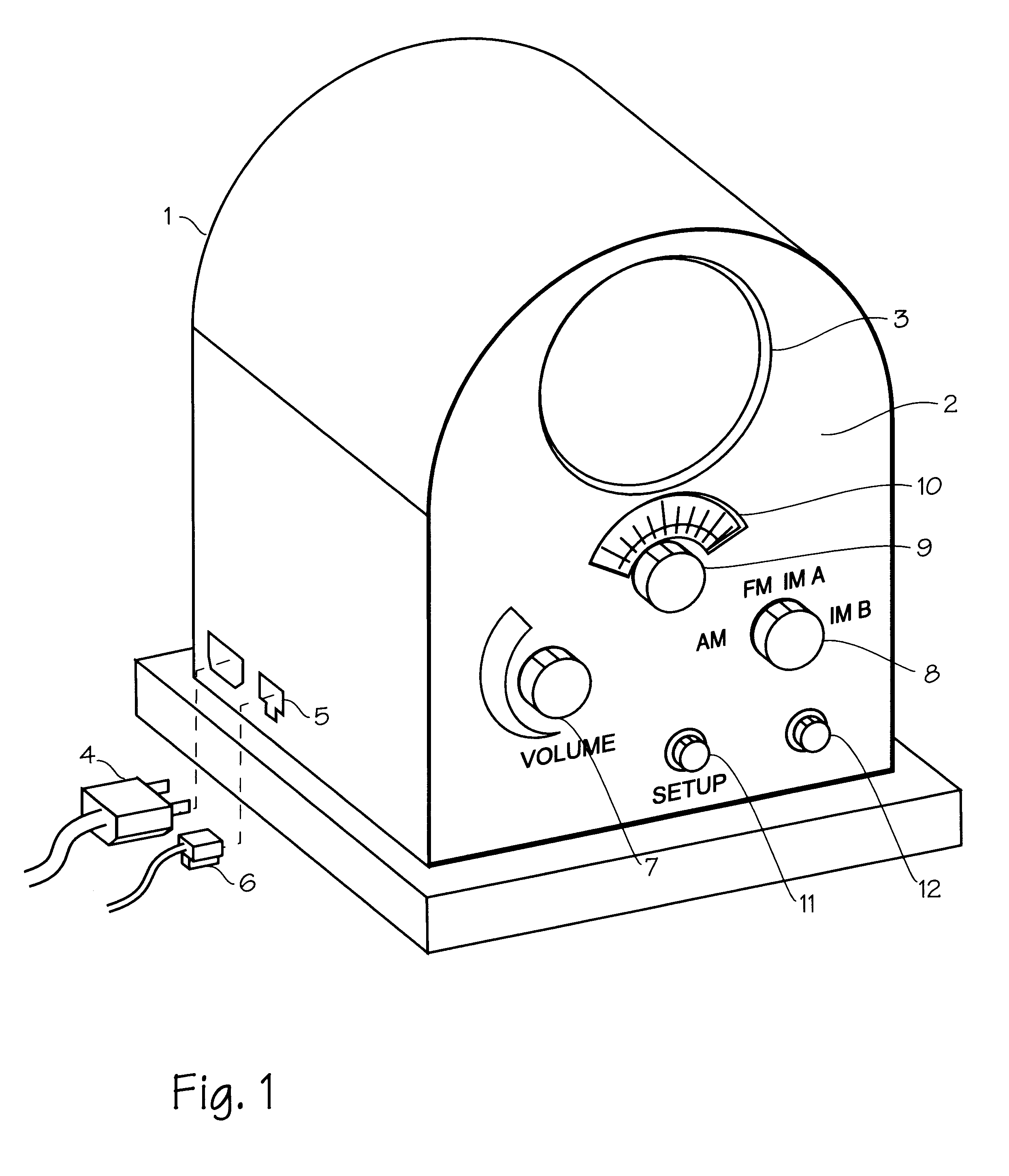
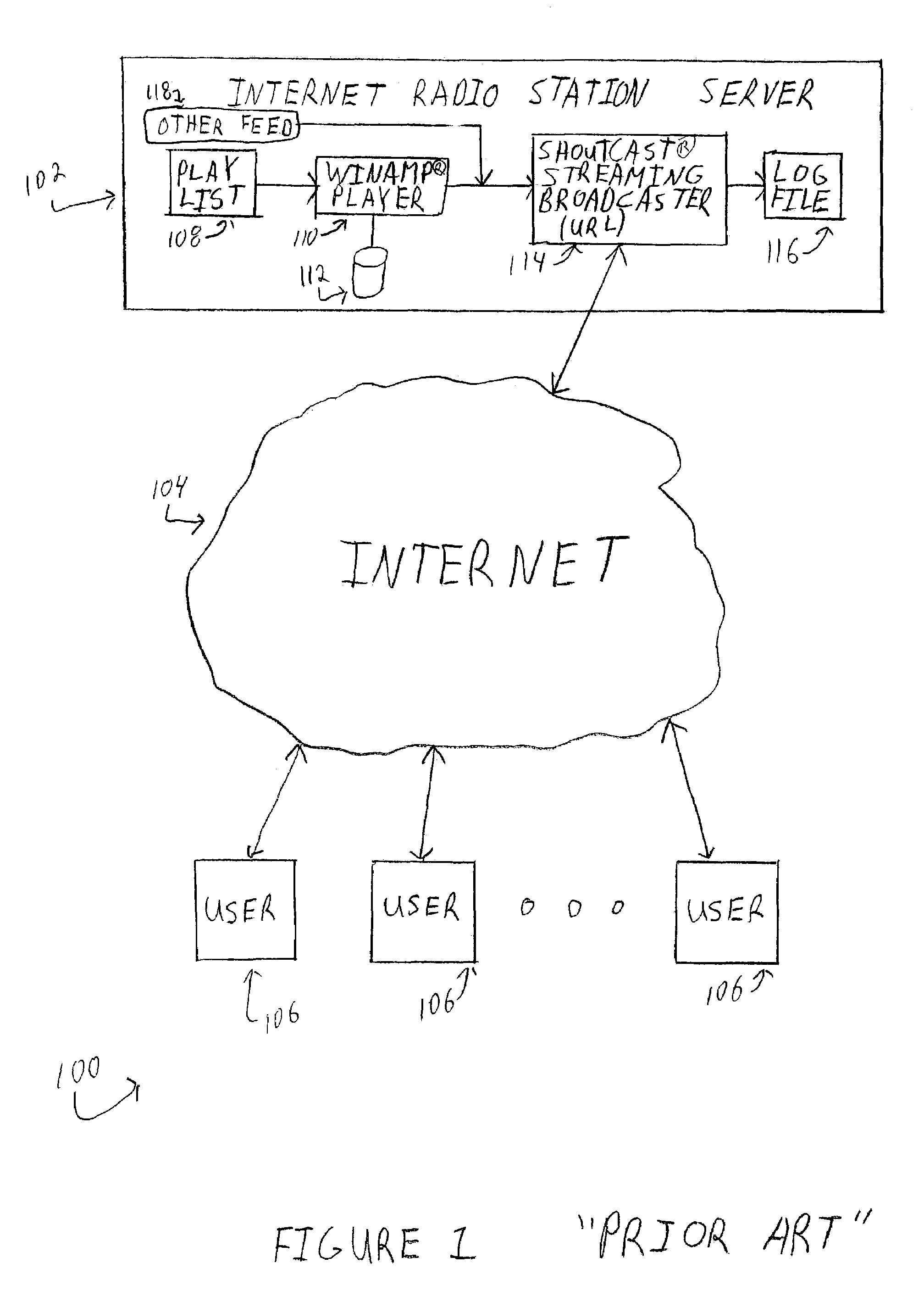
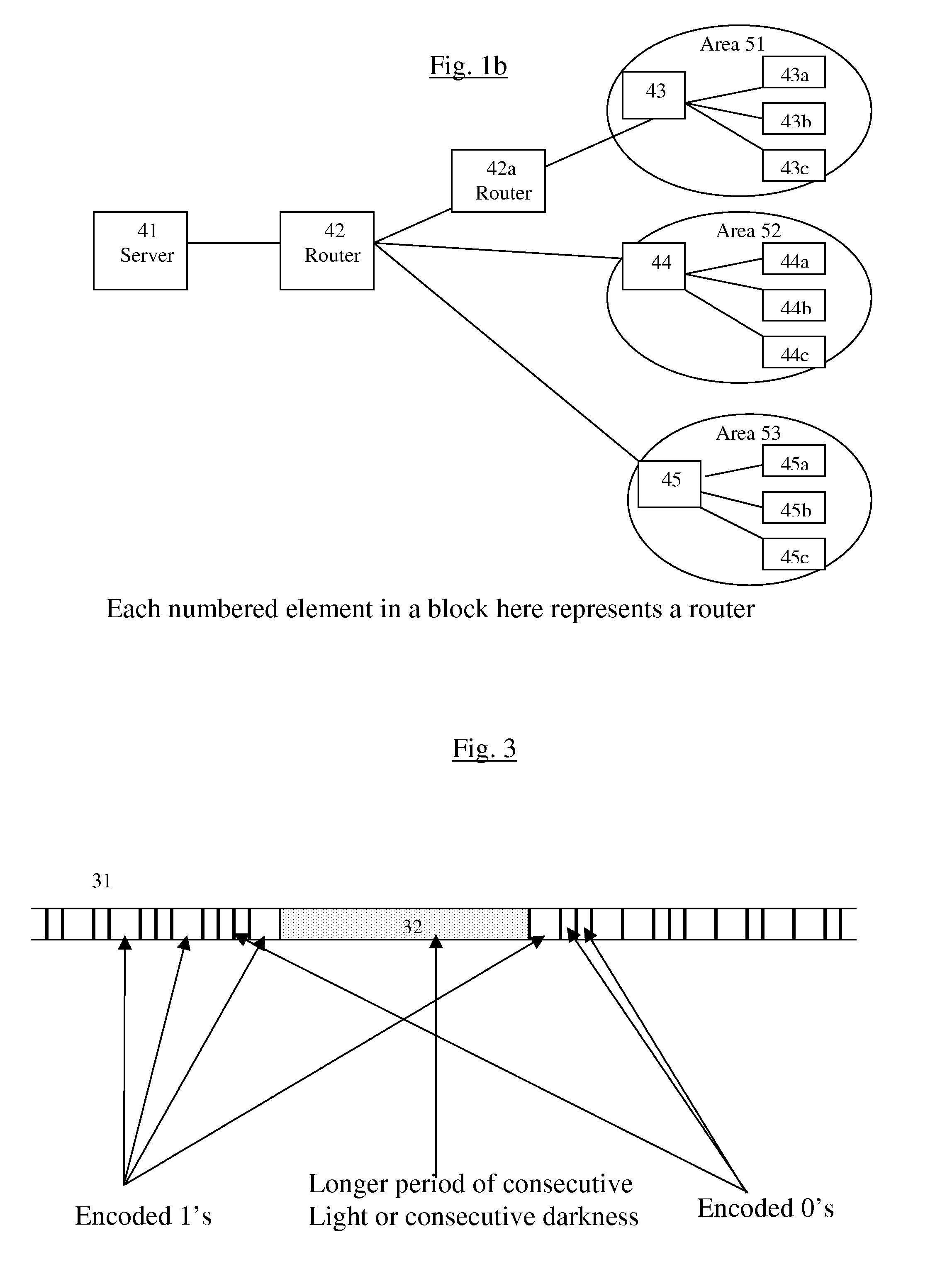
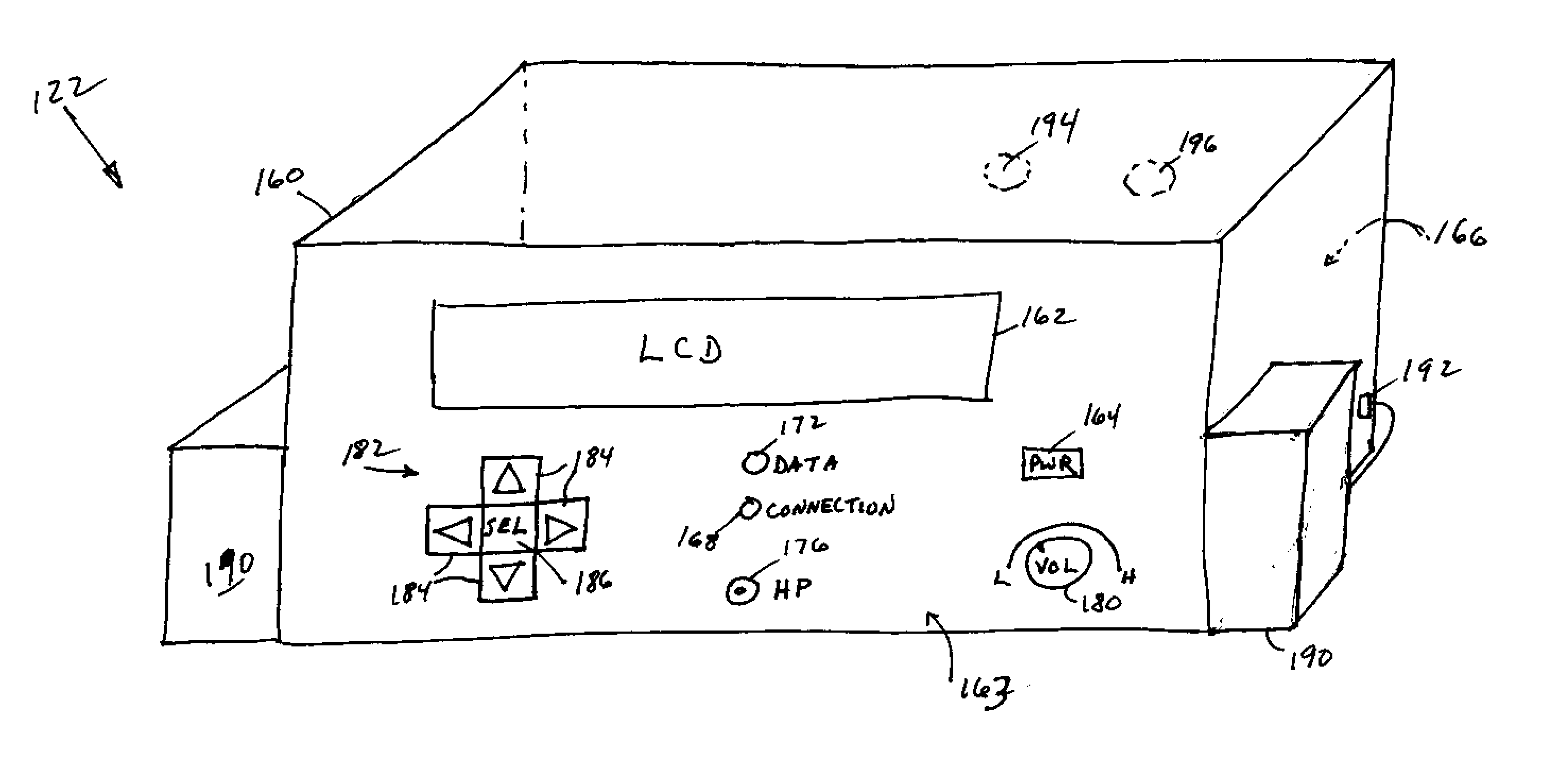
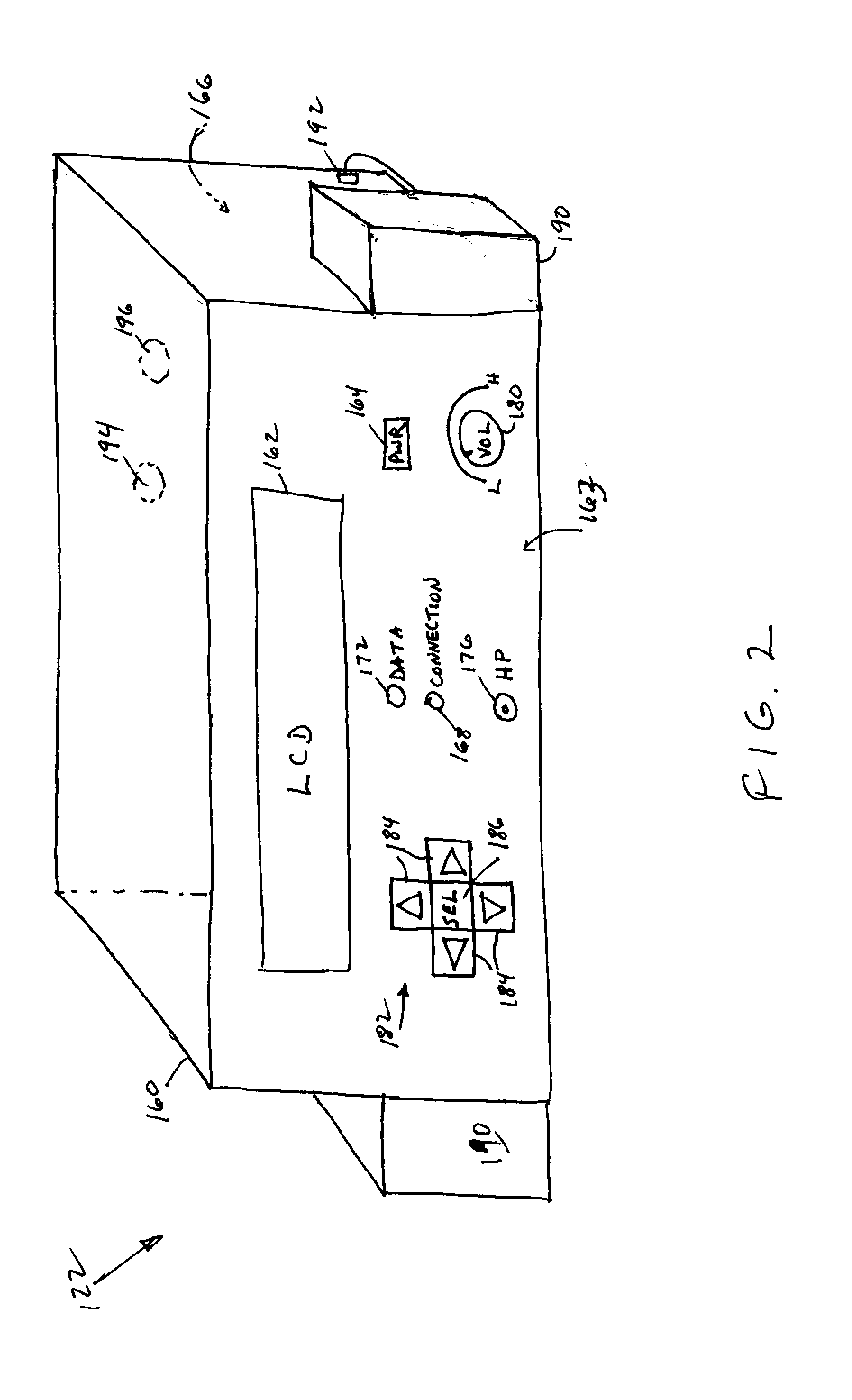
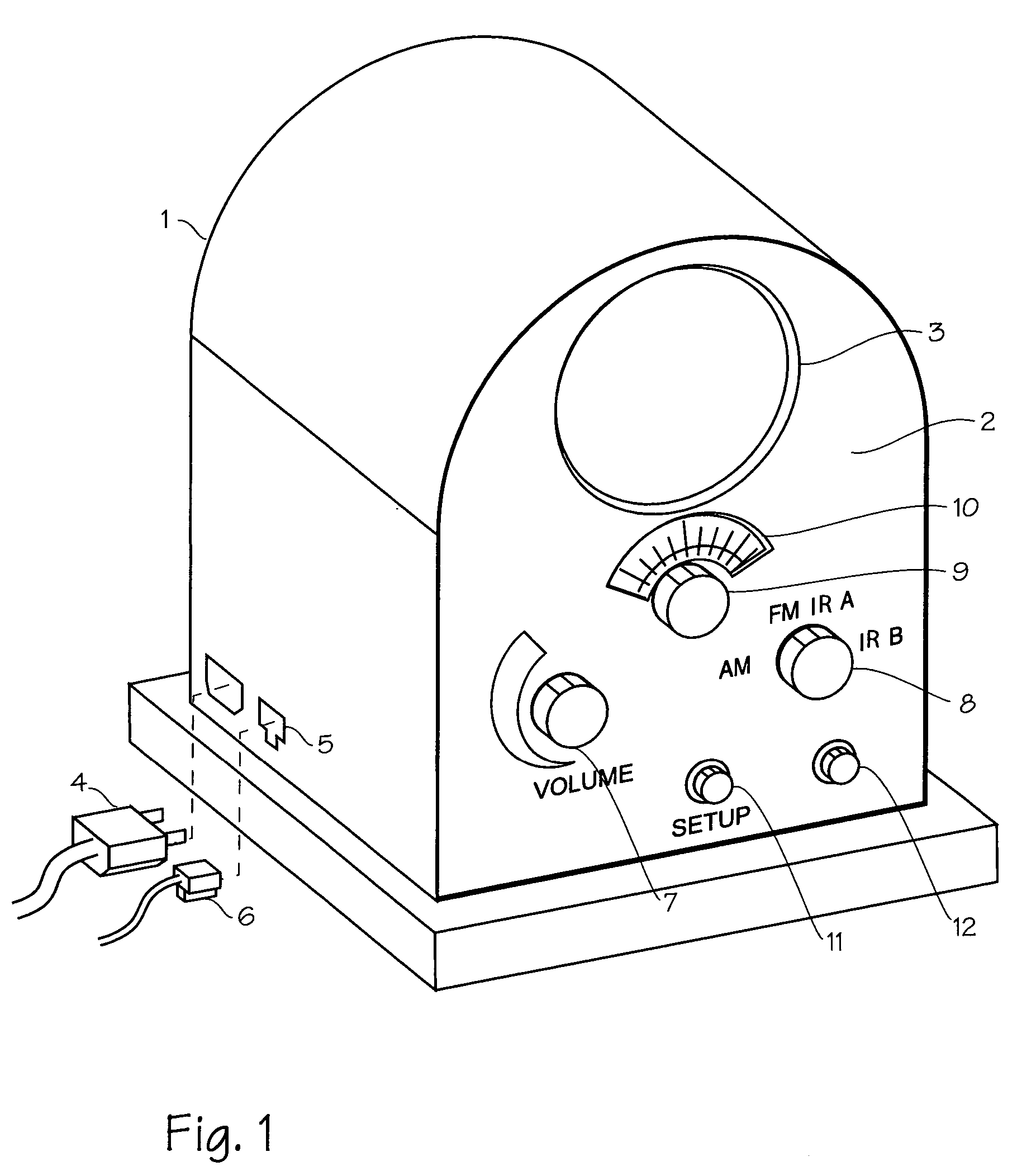
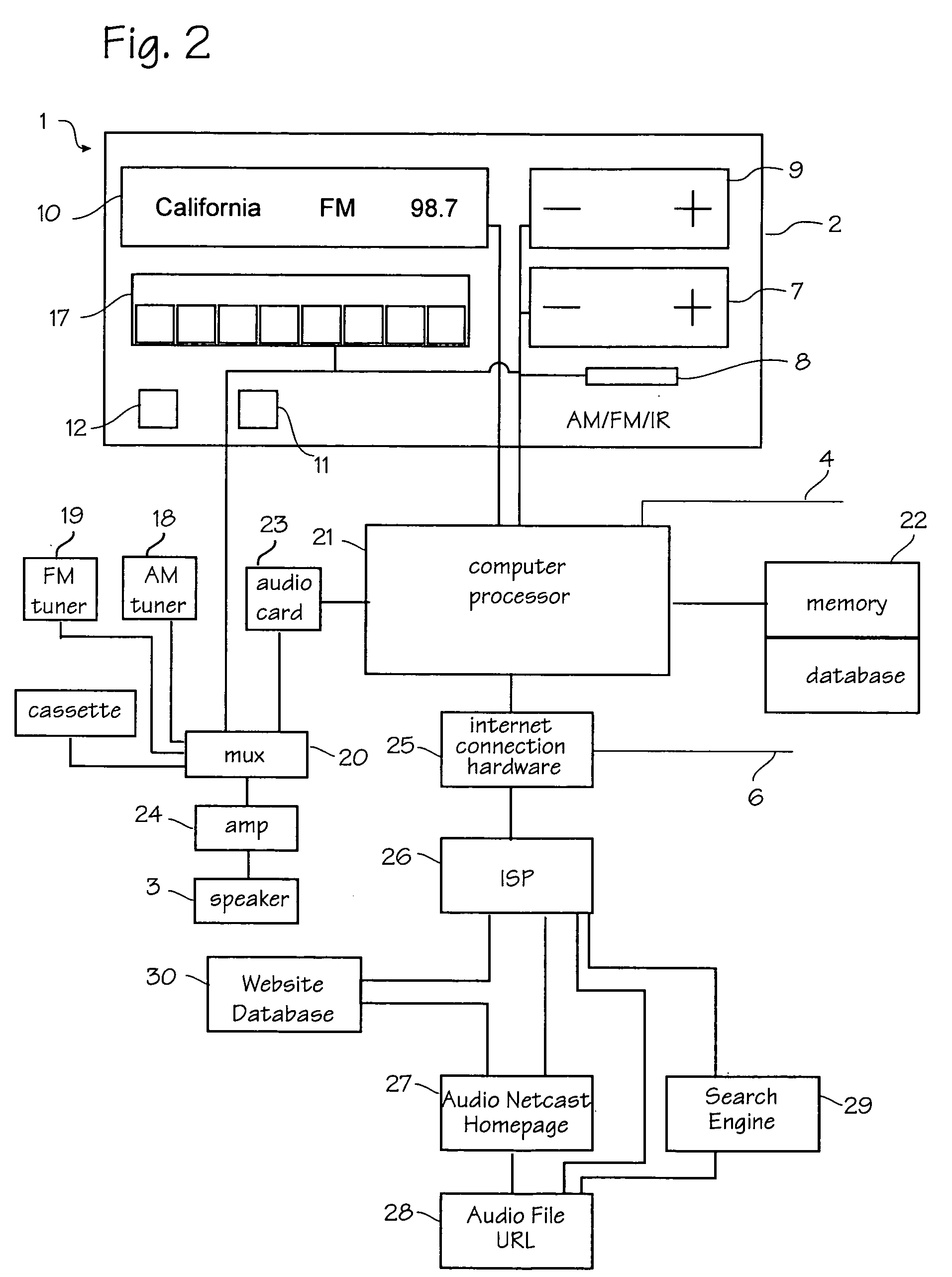
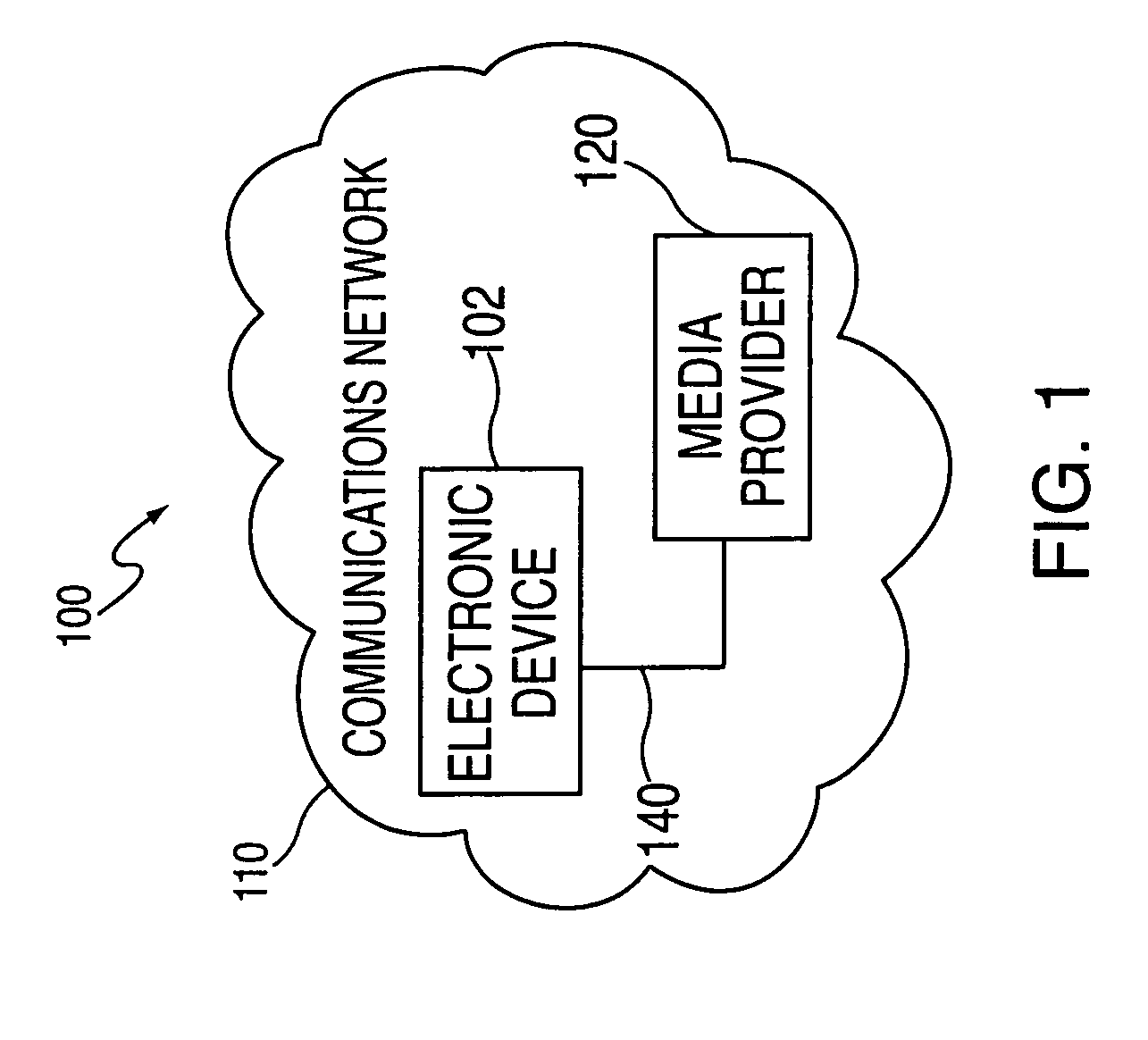
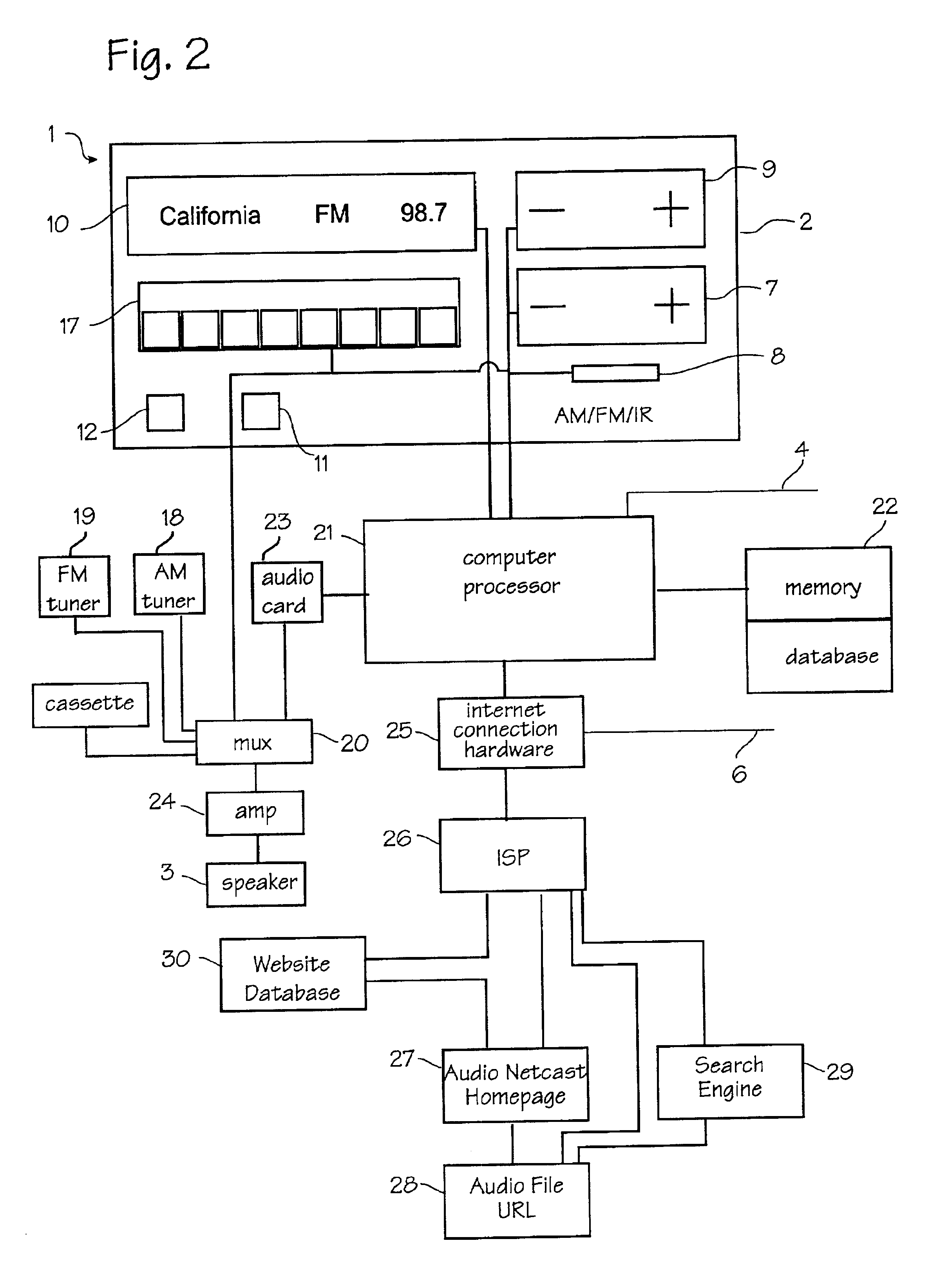
Internet radio receiver having a rotary knob for selecting audio content provider designations and negotiating internet access to URLS associated with the designations
InactiveUS6389463B2Broadcast transmission systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsCable Internet accessTelecommunications
An device for receiving streaming audio or other audio sources netcast in analogous fashion to a radio broadcast, said device providing an interface analogous to a radio receiver, eliminating the necessity of an intervening personal computer system.
Owner:DIGIMEDIA TECH LLC
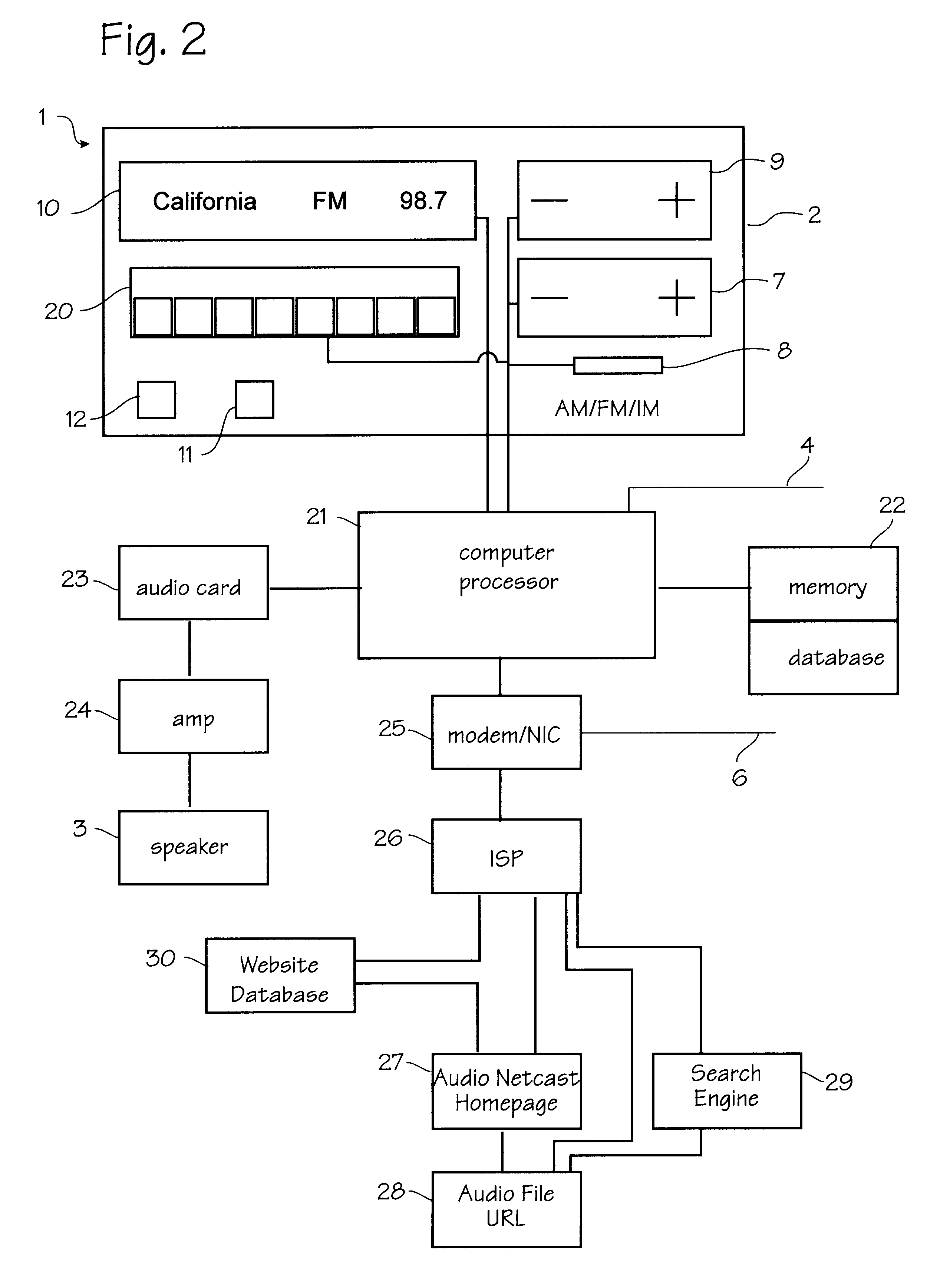
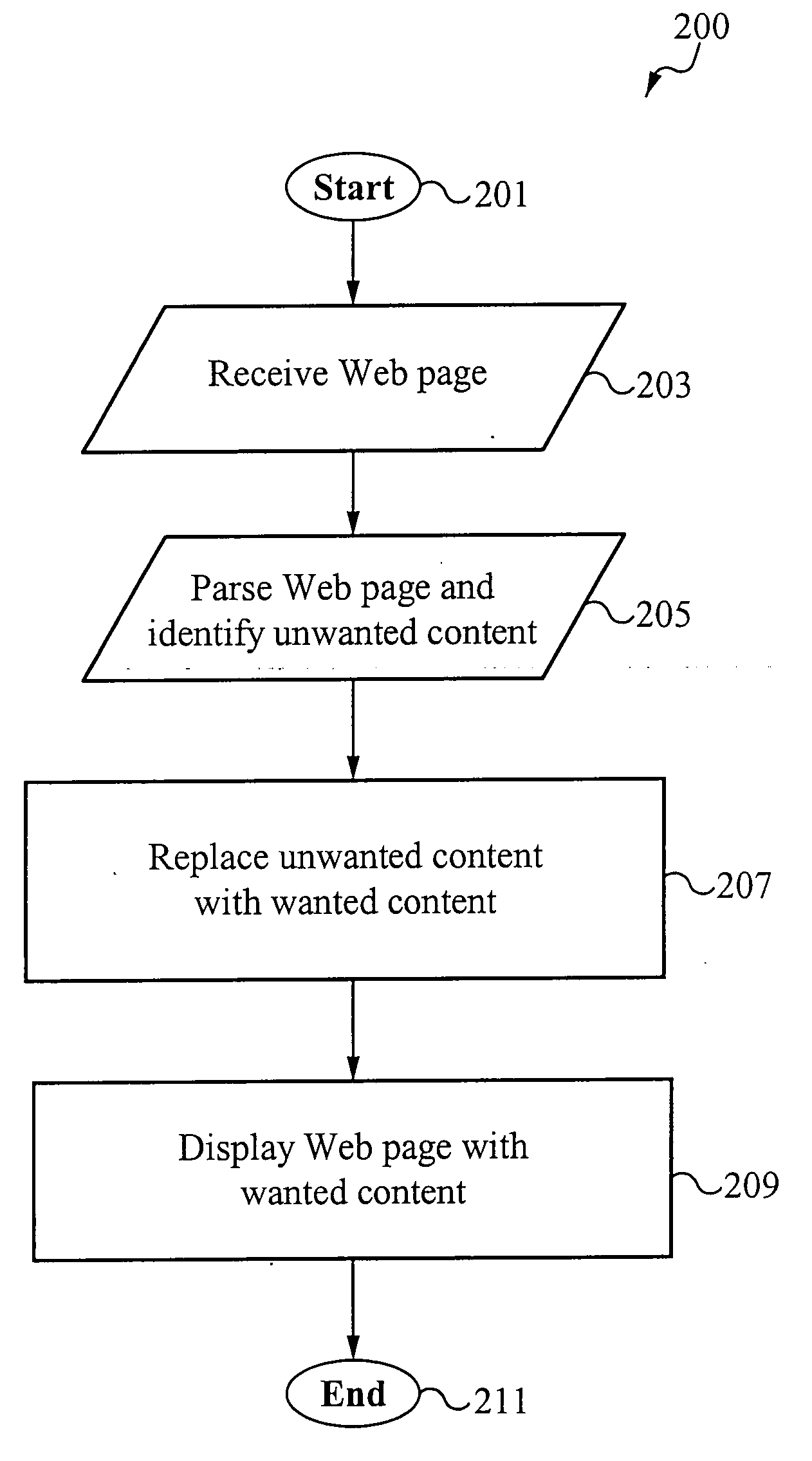
Methods of and systems for personalizing and publishing online content
InactiveUS20070204223A1Digital data information retrievalAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsWeb sitePersonalization
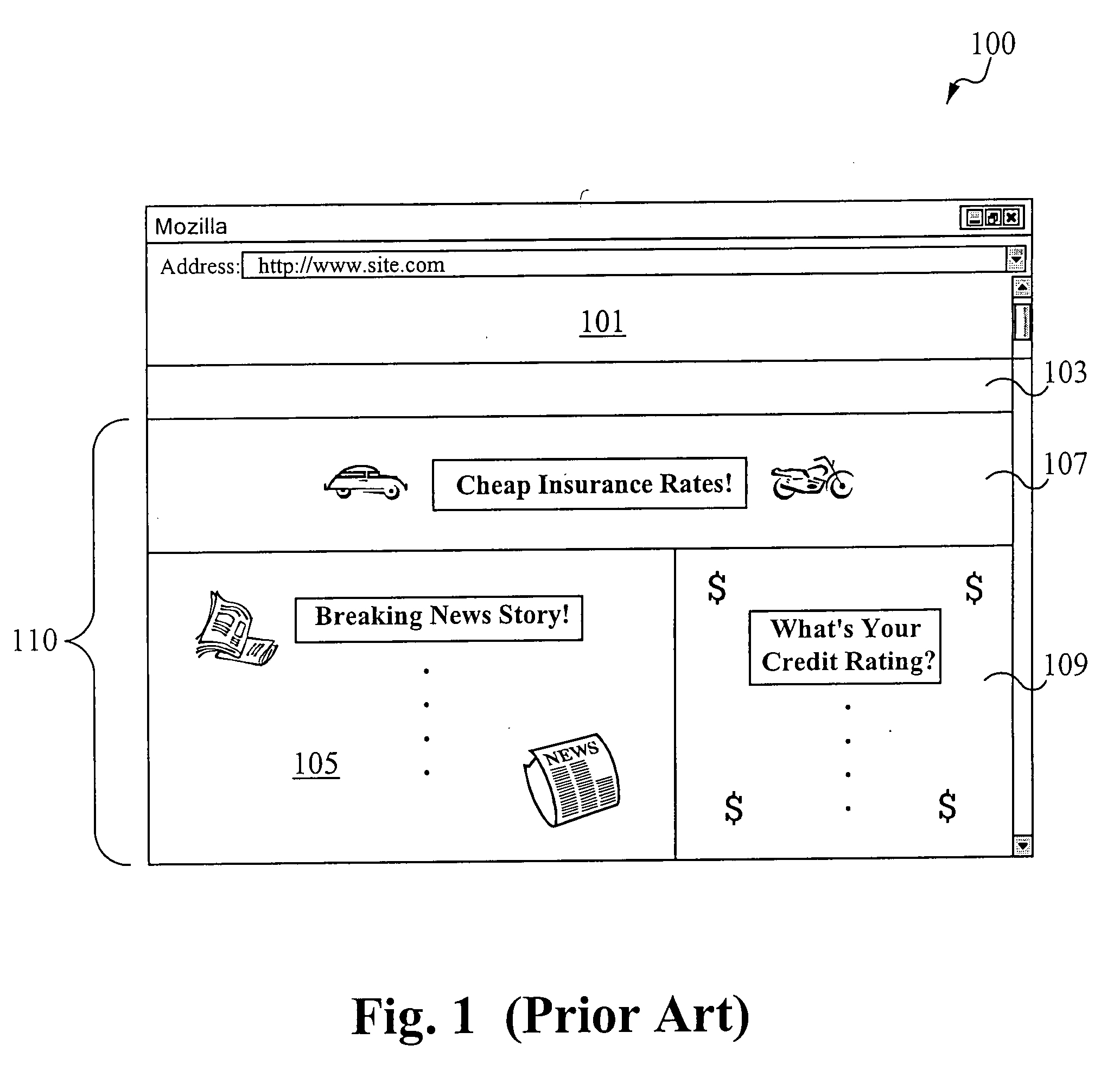
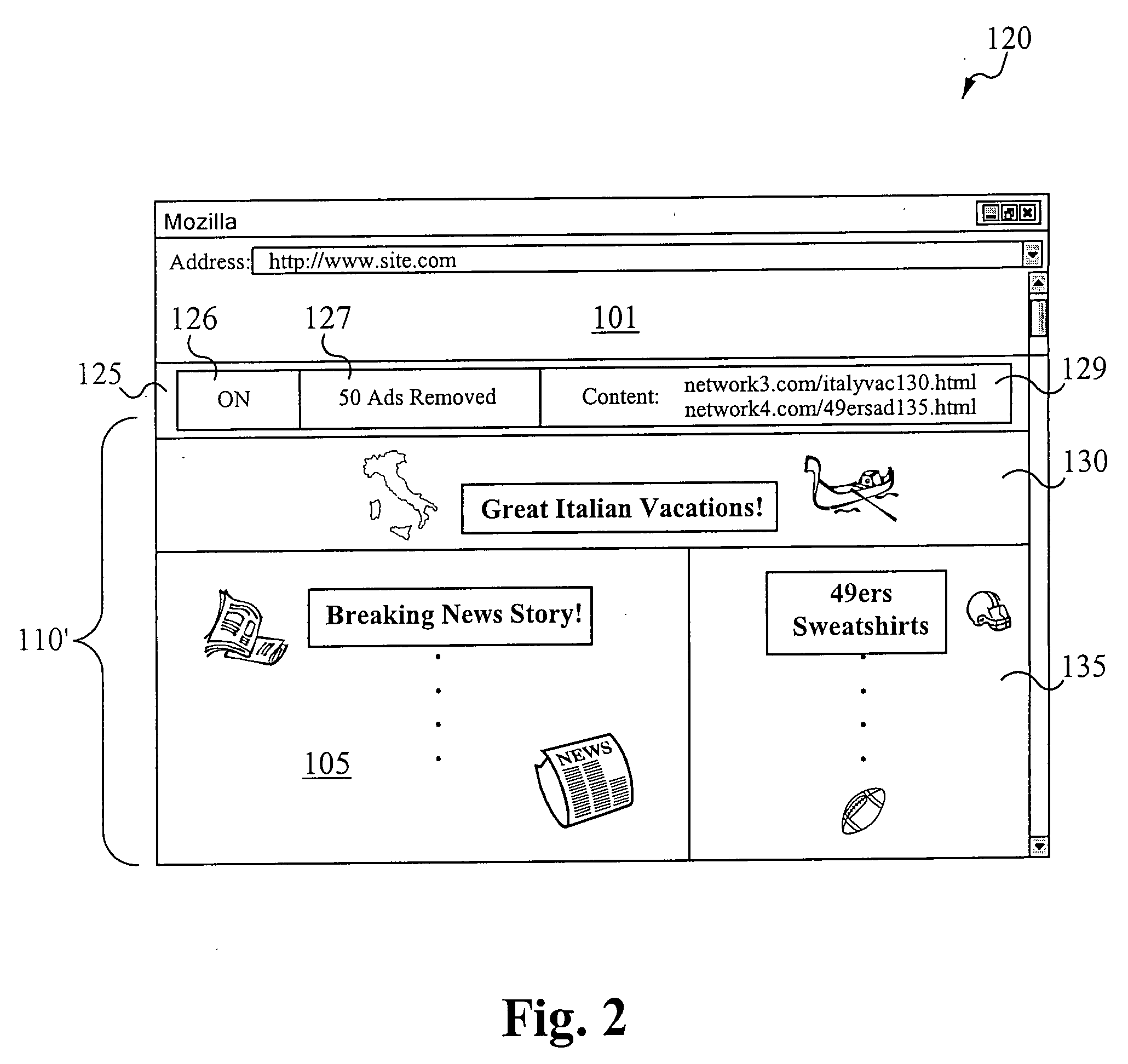
Embodiments of the present invention allow a user to replace unwanted content, such as advertisements, in data distributed over a network with wanted content. Data include Web pages, Internet television broadcasts, Internet radio broadcasts, or any other kind of data that contains content. The data, such as a Web page, is ultimately presented on the user's system, presenting the user with the wanted content. Wanted content includes, among other things, personal photographs, advertisements that the user has expressed interest in, and even advertisements for which the user is compensated for viewing or listening to. In accordance with the present invention, a user opts in to a system that replaces unwanted content with wanted content. The user opts in by providing information that helps determine (a) what content he does not want to see and thus will likely ignore if presented to him and (b) what content he would likely find interesting and thus likely view. This information includes URLs for Web sites; personal information, such as age, income, hobbies, and vacation plans; and work information, such as salary and job title.
Owner:PROWEBSURFER
Integrated vehicle computer system
InactiveUS20090187300A1Easy to useMaintain standardVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesDriver/operatorBroadcasting
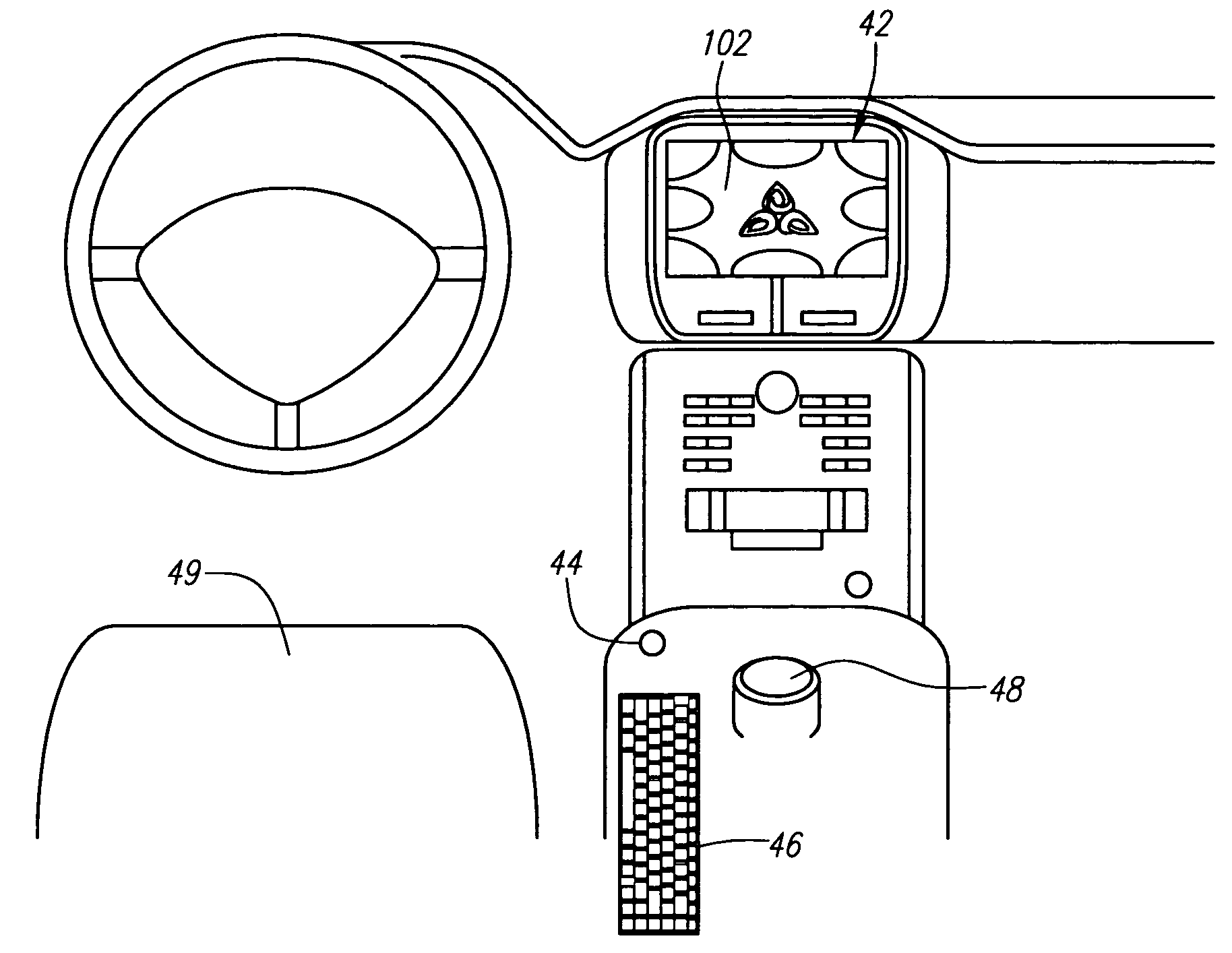
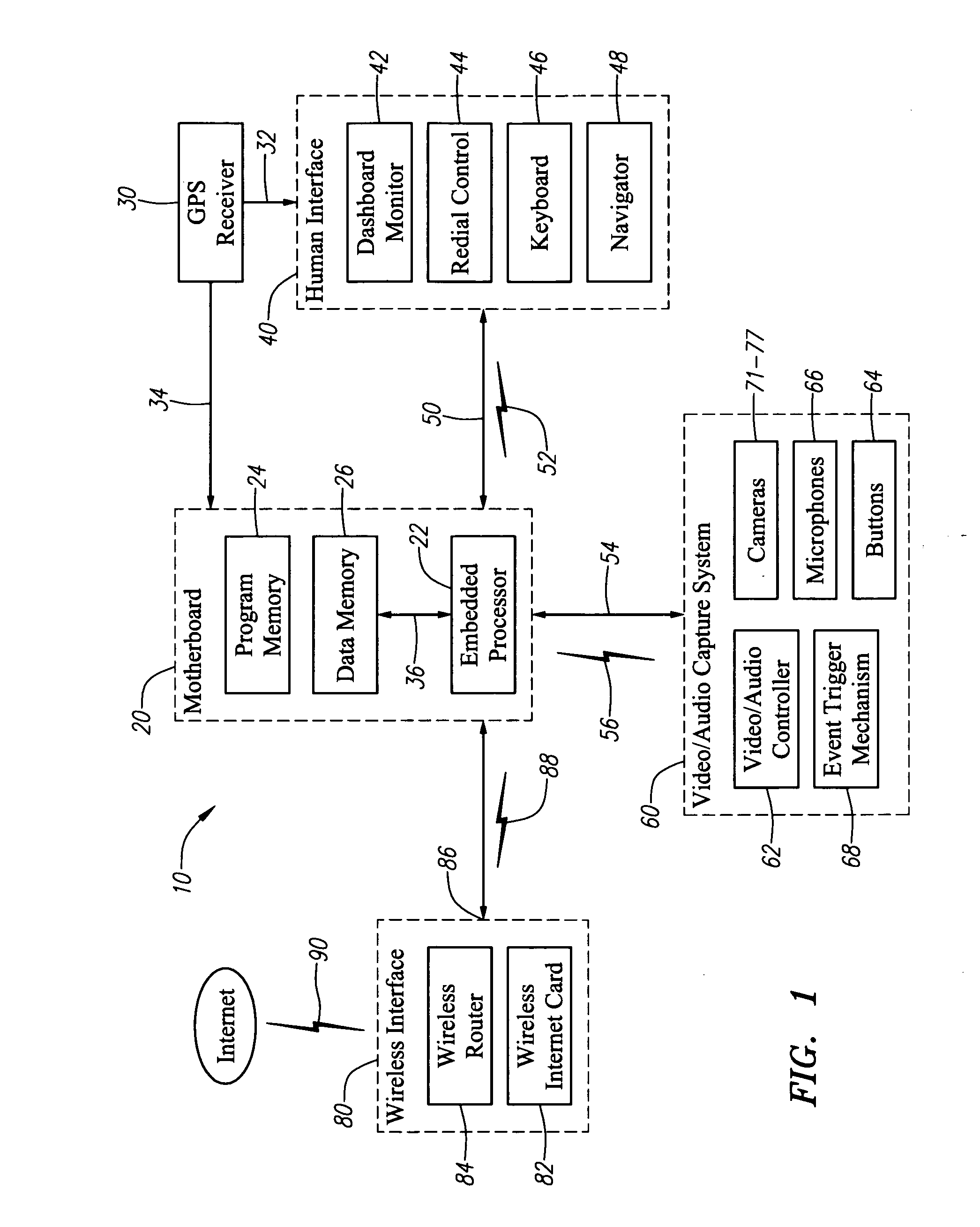
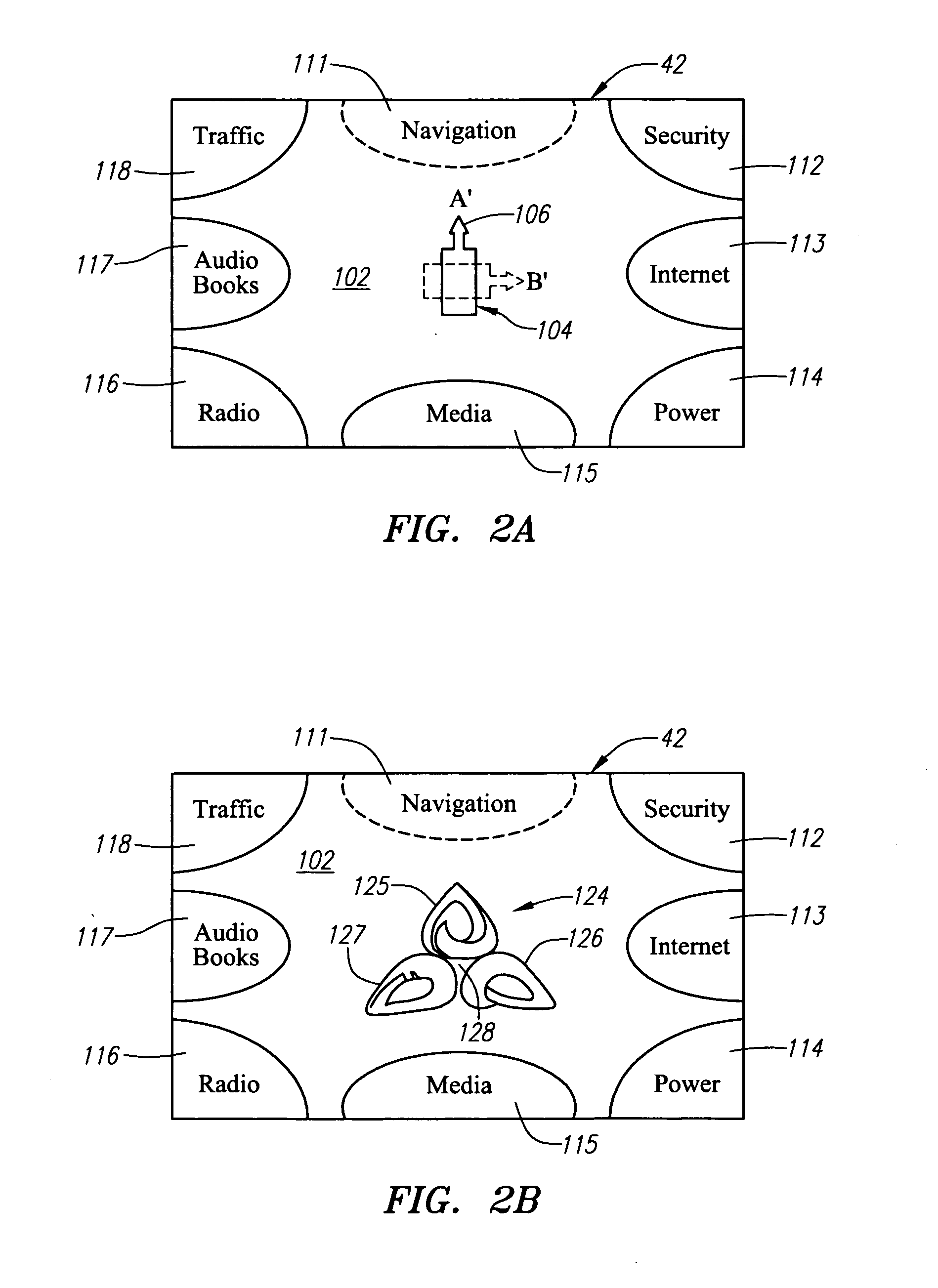
An integrated vehicle computer system is provided. The features of the integrated vehicle computer system include a video based vehicle / driver security system that delivers immediate incident notification, turn-by-turn GPS navigation, live visual traffic grids with links to live freeway cameras, internet access and mobile wireless hub capability, email, internet music service navigation, internet radio station navigation, and MP3 or digital file library selection. One of potential application of the integrated vehicle computer system is to passage vehicles.
Owner:EVERITT DAVID WAYNE +2
Method and Apparatus for Obtaining Digital Objects in a Communication Network
InactiveUS20110153785A1Conveniently obtainEfficient searchMultimedia data indexingWeb data indexingInternet radioDigital object
A technique for obtaining digital objects (such as songs or video clips) from information providers in data communication networks (such as the Internet); the digital objects being sent through channels (such as Internet radio channels or Internet TV channels) or being otherwise made available. The end-user gains several advantages over techniques supported by the known art. For example, end-users may easily locate desired digital objects, need not be connected during object capture, can be connected through a low speed connection, does not have to have a high capacity computer, can obtain digital objects legally, can receive supplemental information associated with the digital objects, can quickly scan a vast number of digital object having been sent earlier, need not have the required storage space for the digital objects available during object capture, can easily navigate through a multitude of digital object channels, can easily obtain objects with a certain desired quality, can easily obtain objects in a certain desired format, can legally obtain digital objects at no cost and can prove that the digital objects were actually obtained legally.
Owner:MARTINA KASSERI TELECOM L L C
Internet radio and broadcast method
InactiveUS20100205166A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsData streamInternet radio
Owner:PANDORA MEDIA
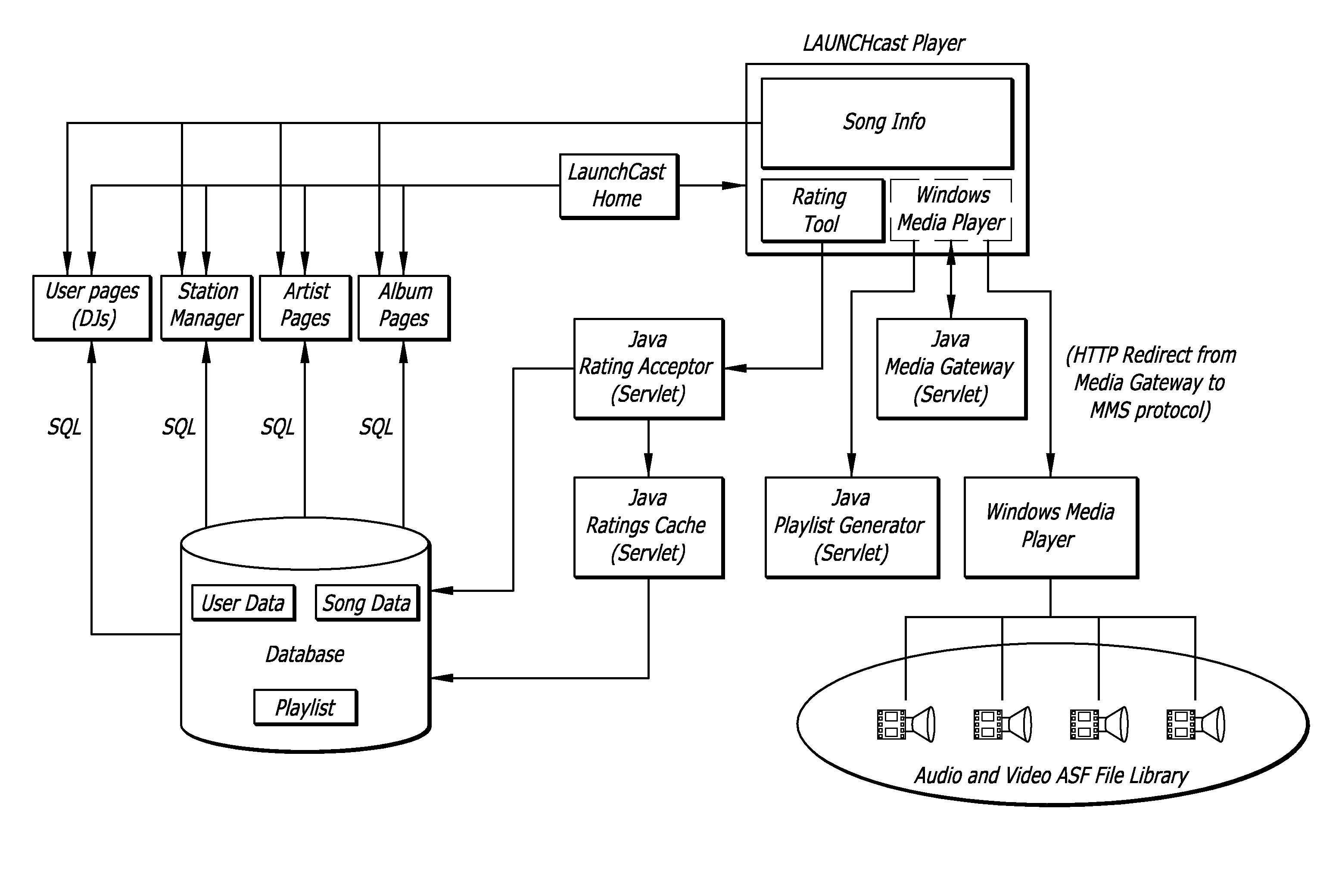
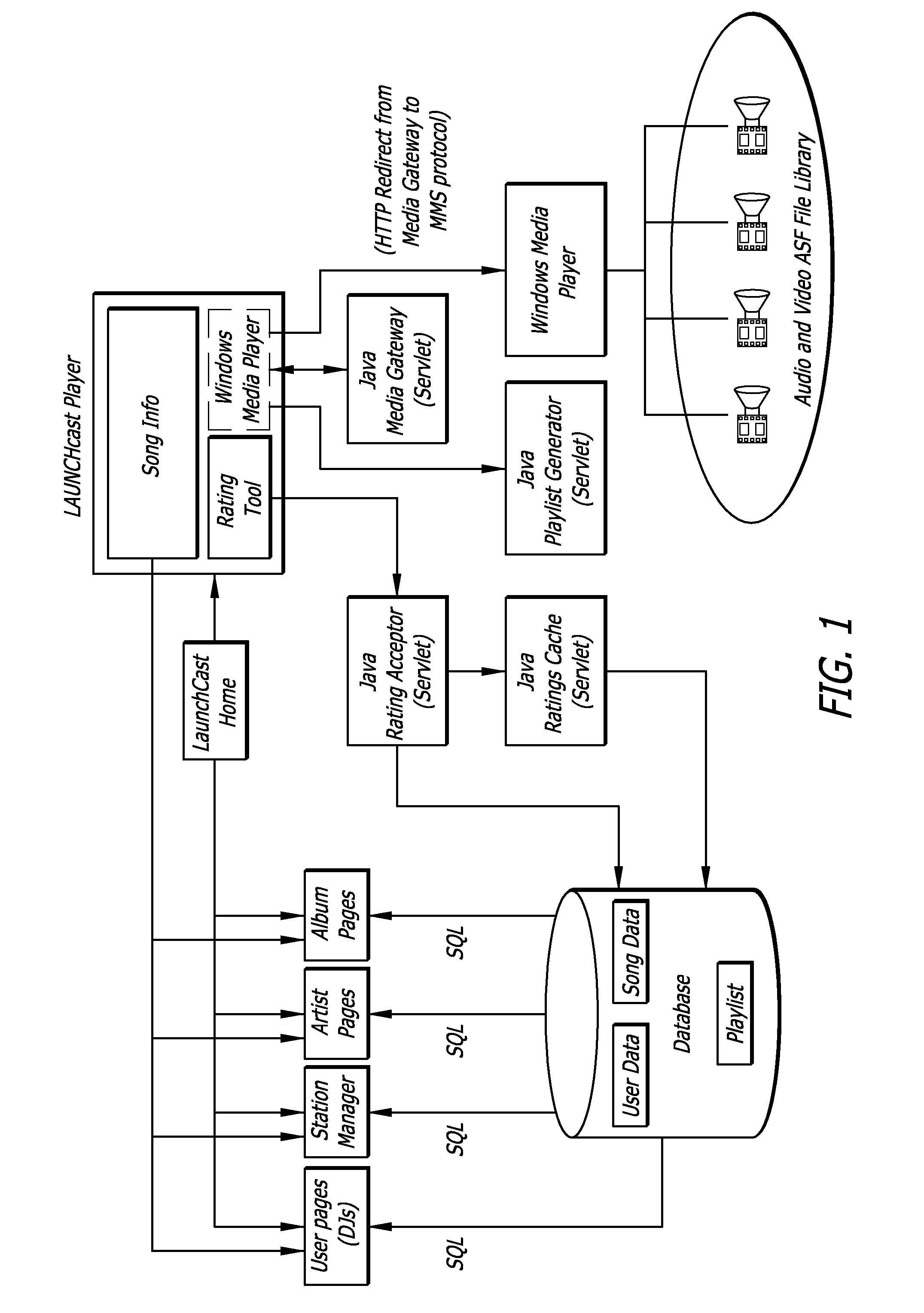
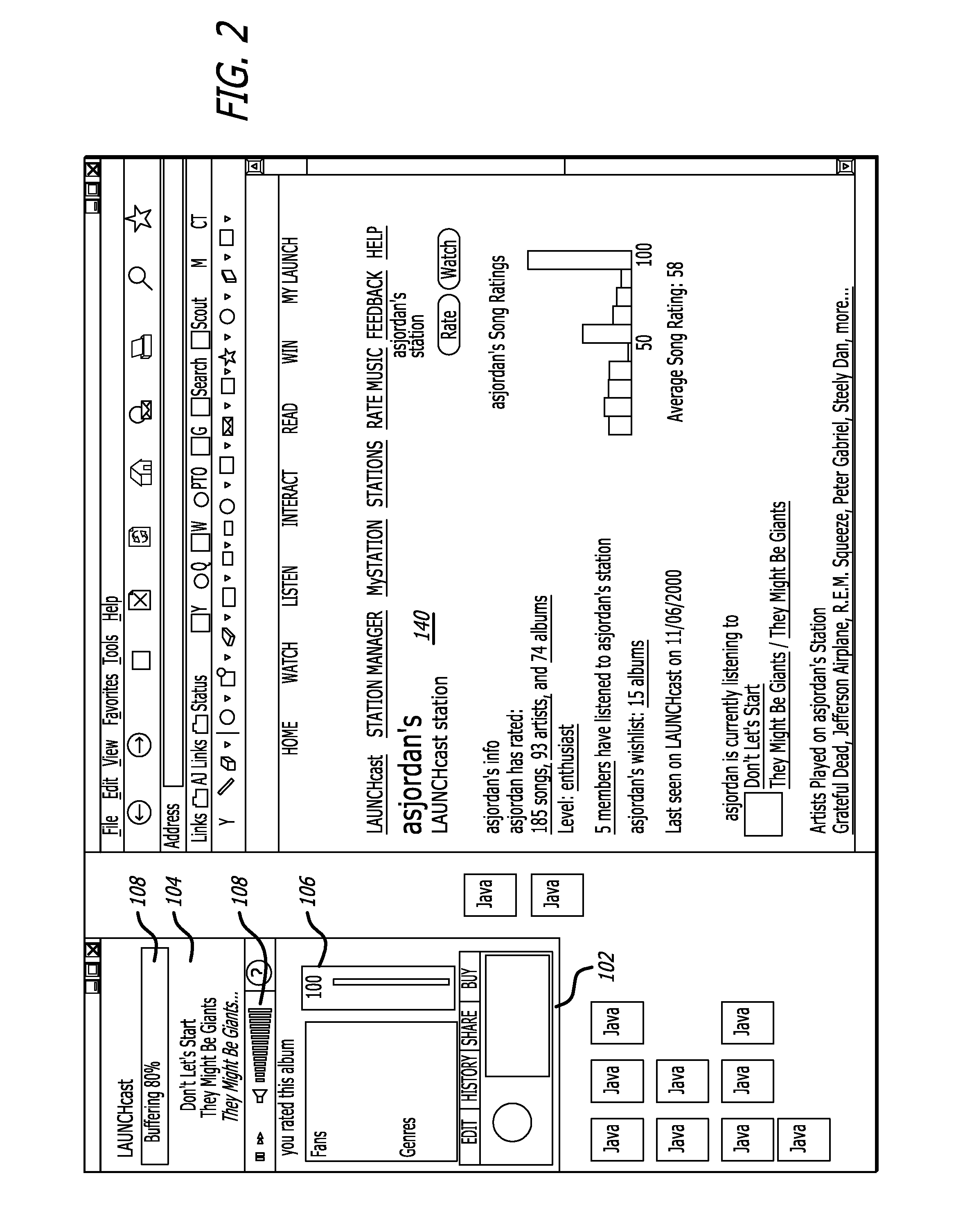
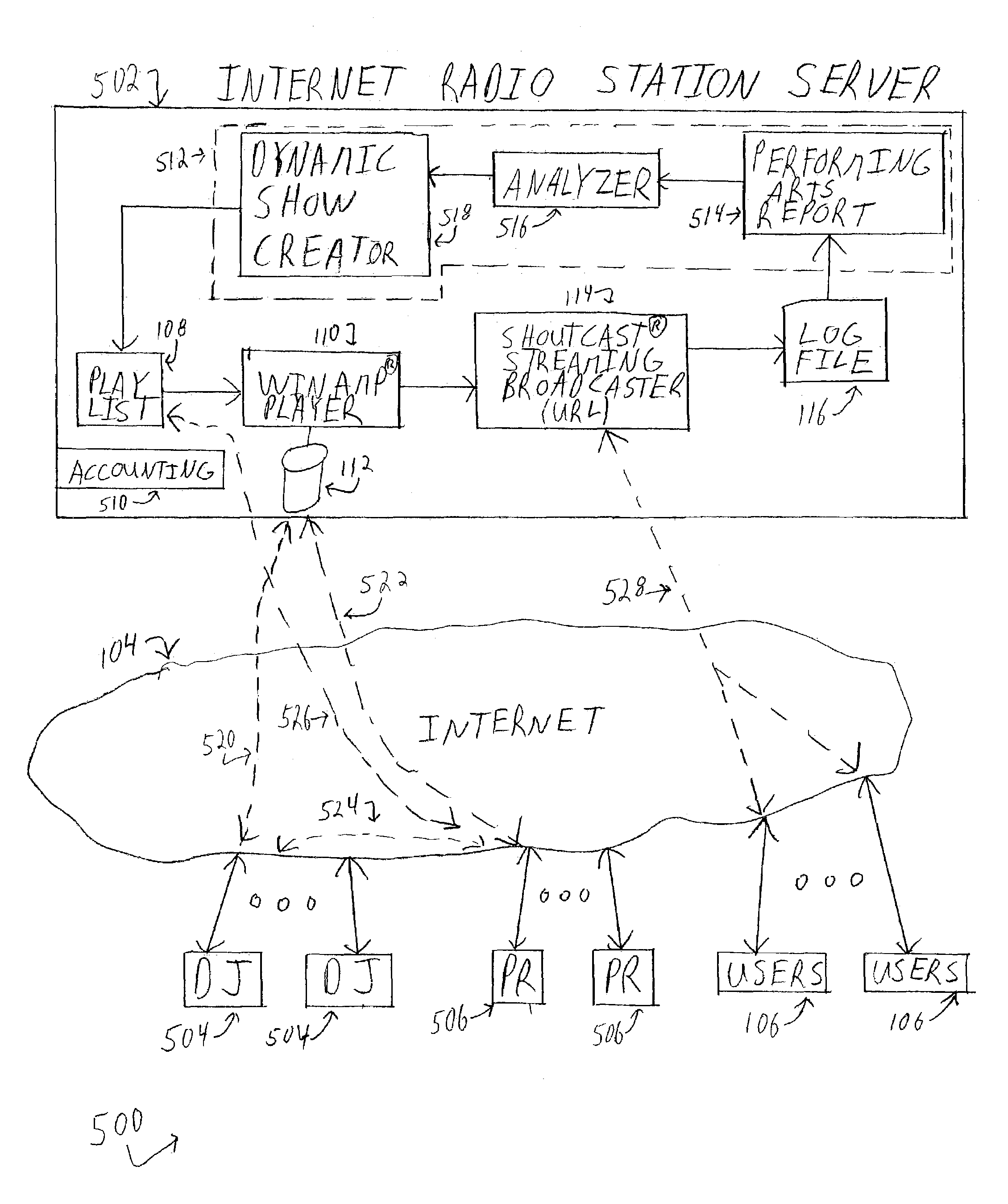
Internet radio station and disc jockey system
InactiveUS7349663B1Easy to use interfaceSpecial service for subscribersBroadcast transmission systemsTelecommunicationsInternet radio
A method for producing a network-based radio show includes transmitting a plurality of segments over a network to a radio station server wherein the plurality of segments contain a plurality of voice tracks and an identification of song tracks located on the radio station server. The plurality of segments are verified and arranged into a play list on the radio station server. The play list is broadcast from the radio station server onto the network to create a network-based radio show, via the network.
Owner:LEAVE A LITTLE ROOM FOUND
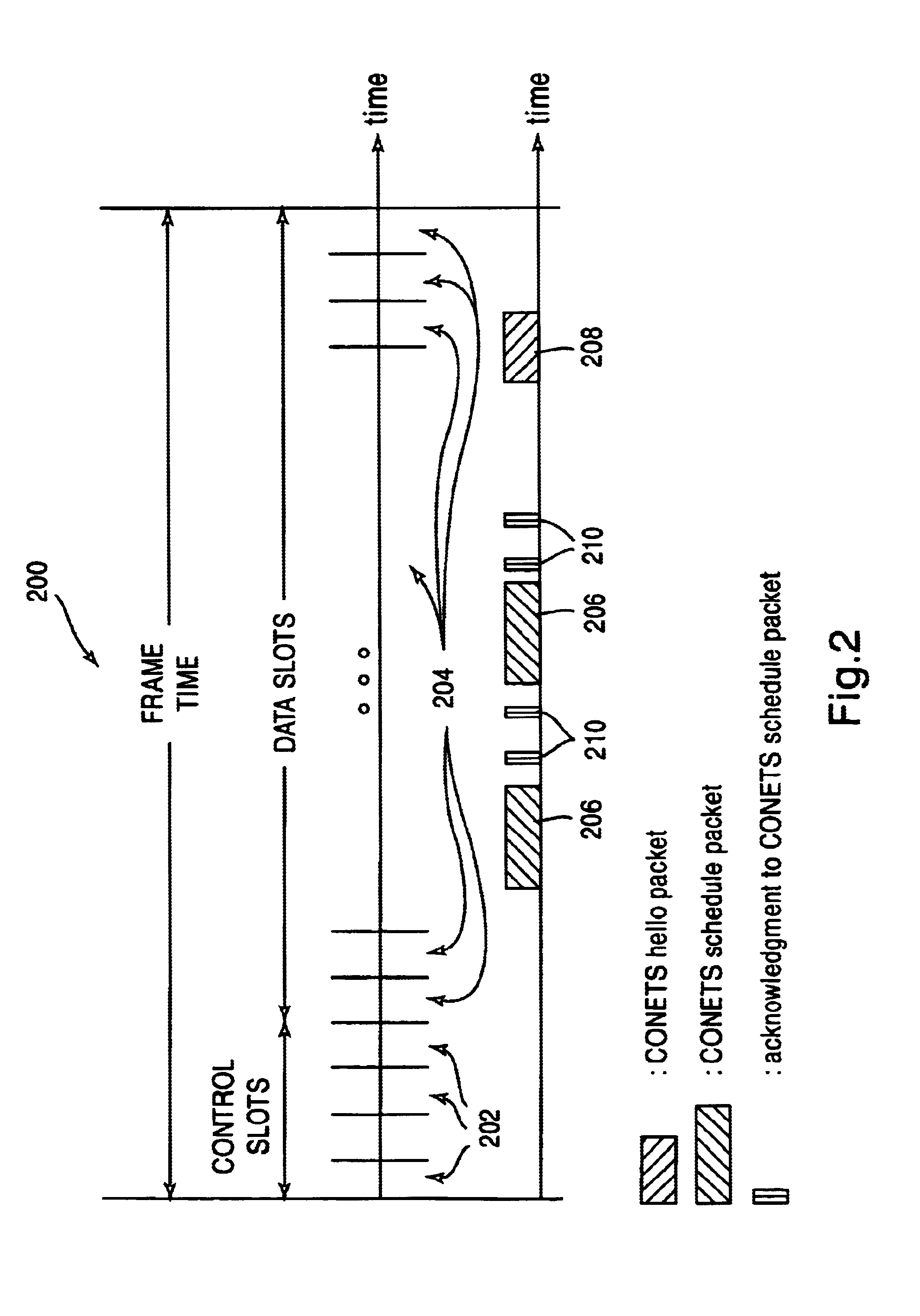
Transmission-scheduling coordination among collocated internet radios
InactiveUS6928061B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork topologiesBroadcast packetComputer network
A method for collocated nodes communicating over a first interface to agree on a conflict-free transmission schedule among themselves, which they can then use to collaborate with neighbors accessed through a second interface, for example through wireless links in order to obtain collision-free transfers of unicast, multicast and broadcast packets over wireless channels, and channel access delay guarantees. The collocated nodes behave as a single virtual node for the purpose of establishing a consistent transmission schedule throughout the nodes of a multihop wireless network.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
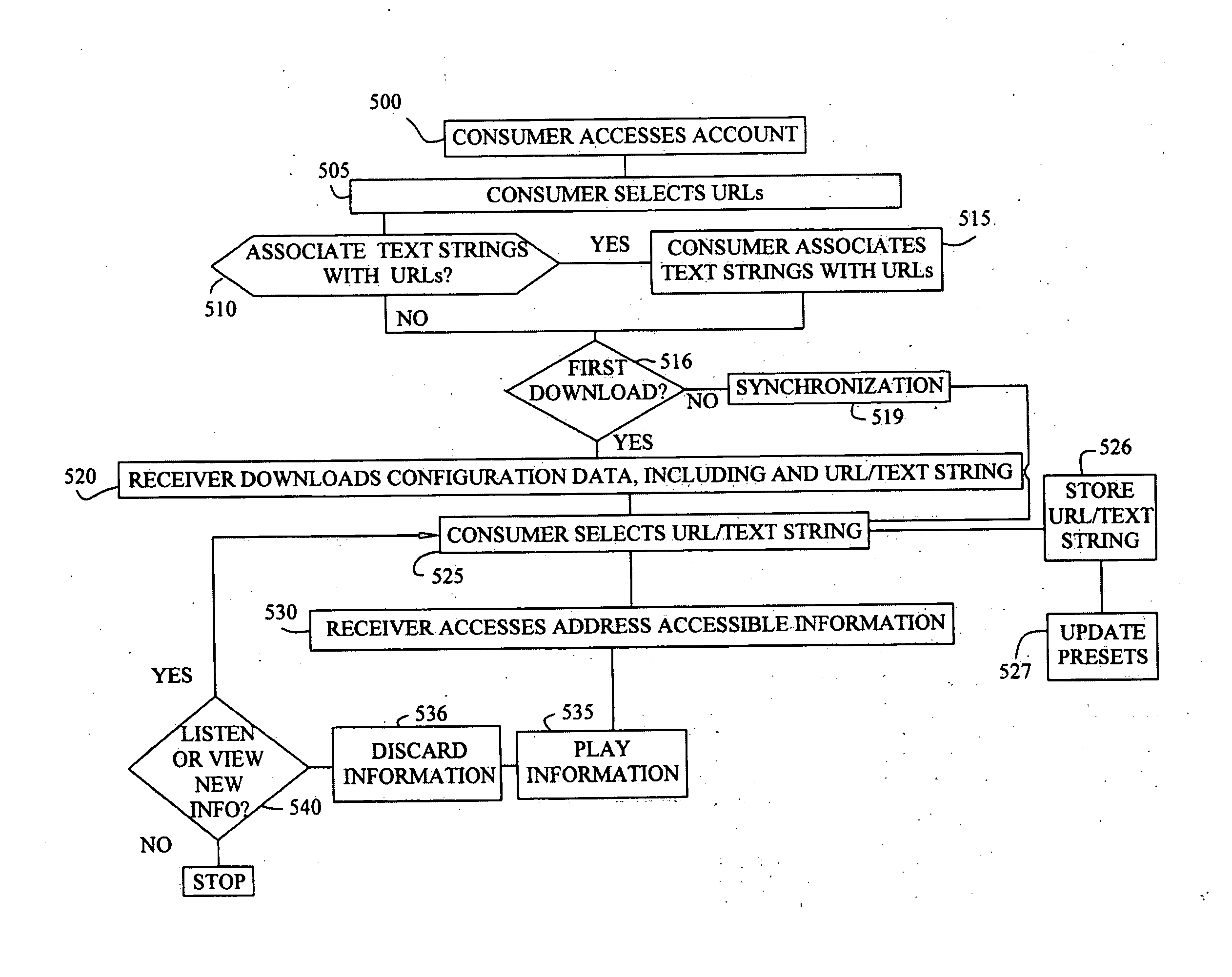
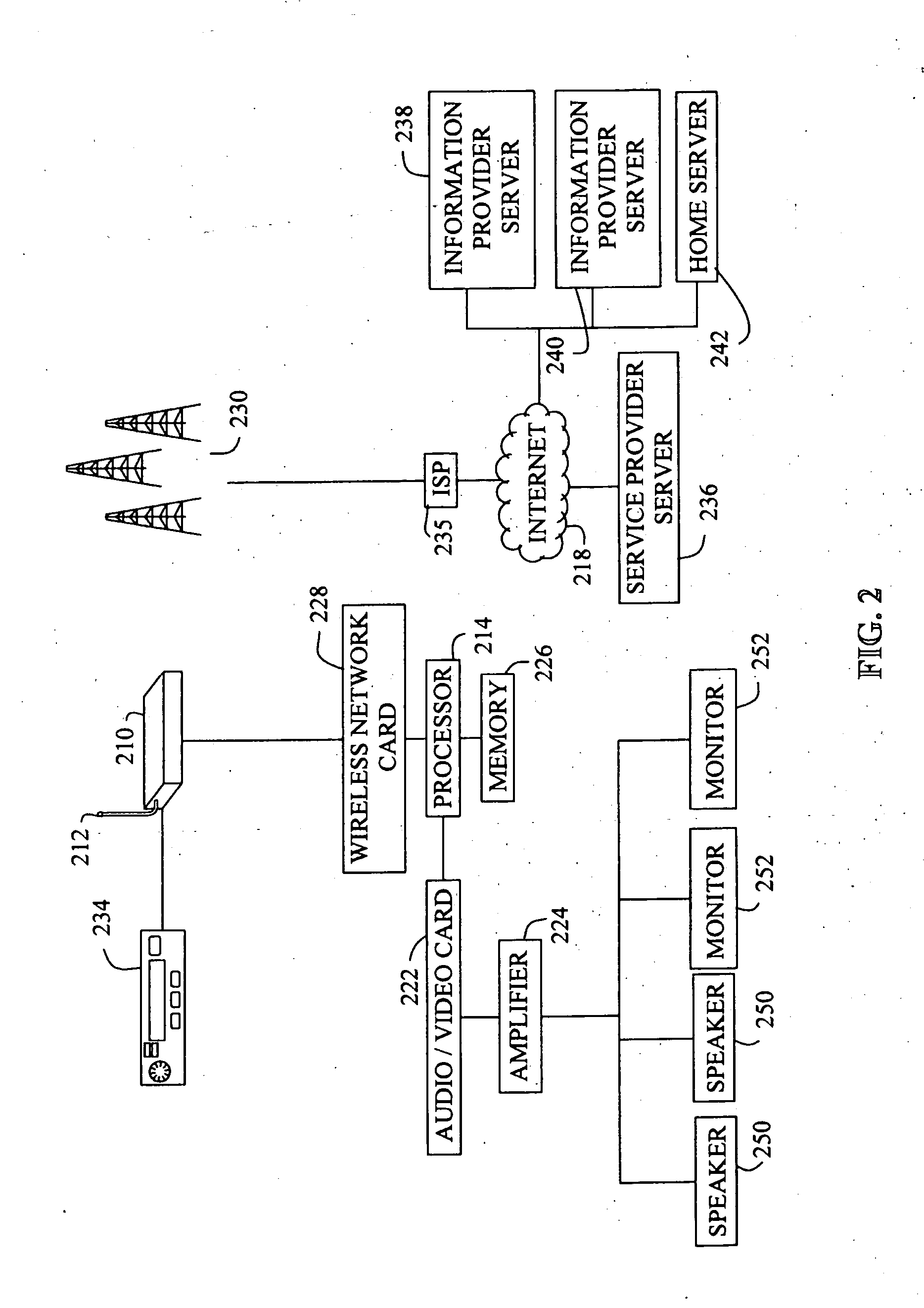
Automotive internet radio system
InactiveUS20040260835A1Broadcast specific applicationsBroadcast transmission systemsInformation transmissionInternet radio
The present invention includes an address accessible information transmission system that enables a vehicle occupant to listen and / or view address accessible information accessible on the Internet through the vehicle's entertainment system. The address accessible information transmission system includes a server capable of obtaining the address accessible information, and a receiver in communication with the server, the receiver capable of utilizing the address to access the address accessible information, and providing the address accessible information to the vehicle's entertainment system. The receiver includes a head unit having an interface that enables the vehicle occupant to select the address accessible information.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Collaborative music network
InactiveUS20090106429A1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet accessMusic player
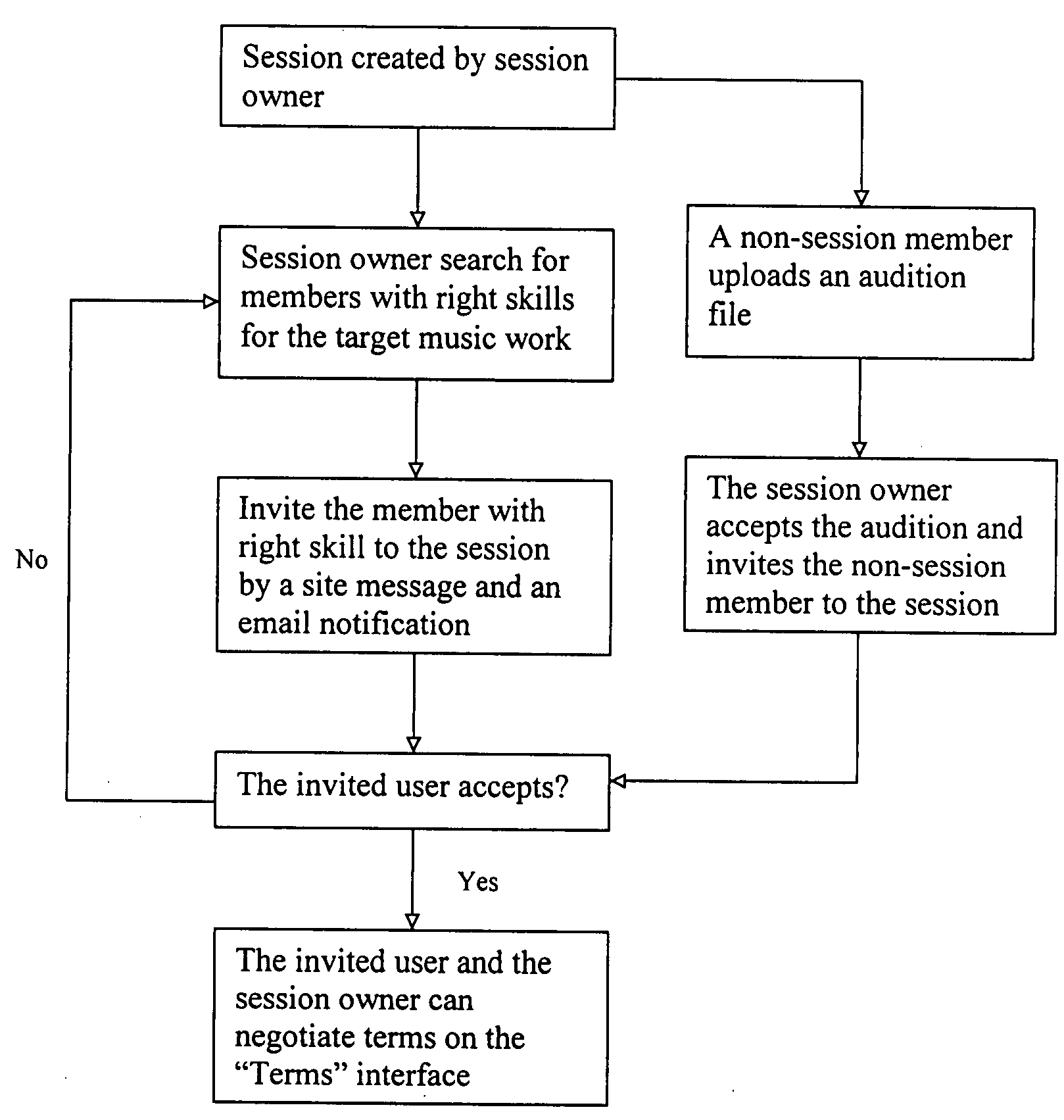
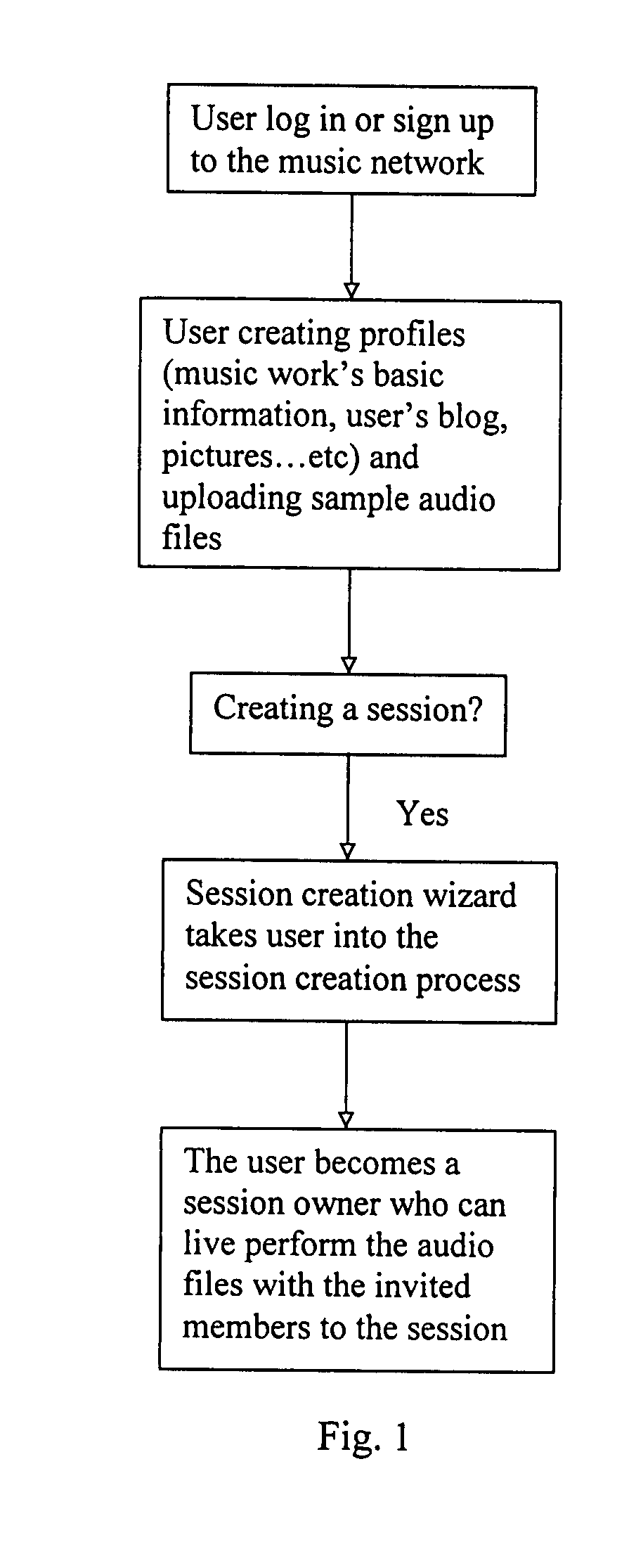
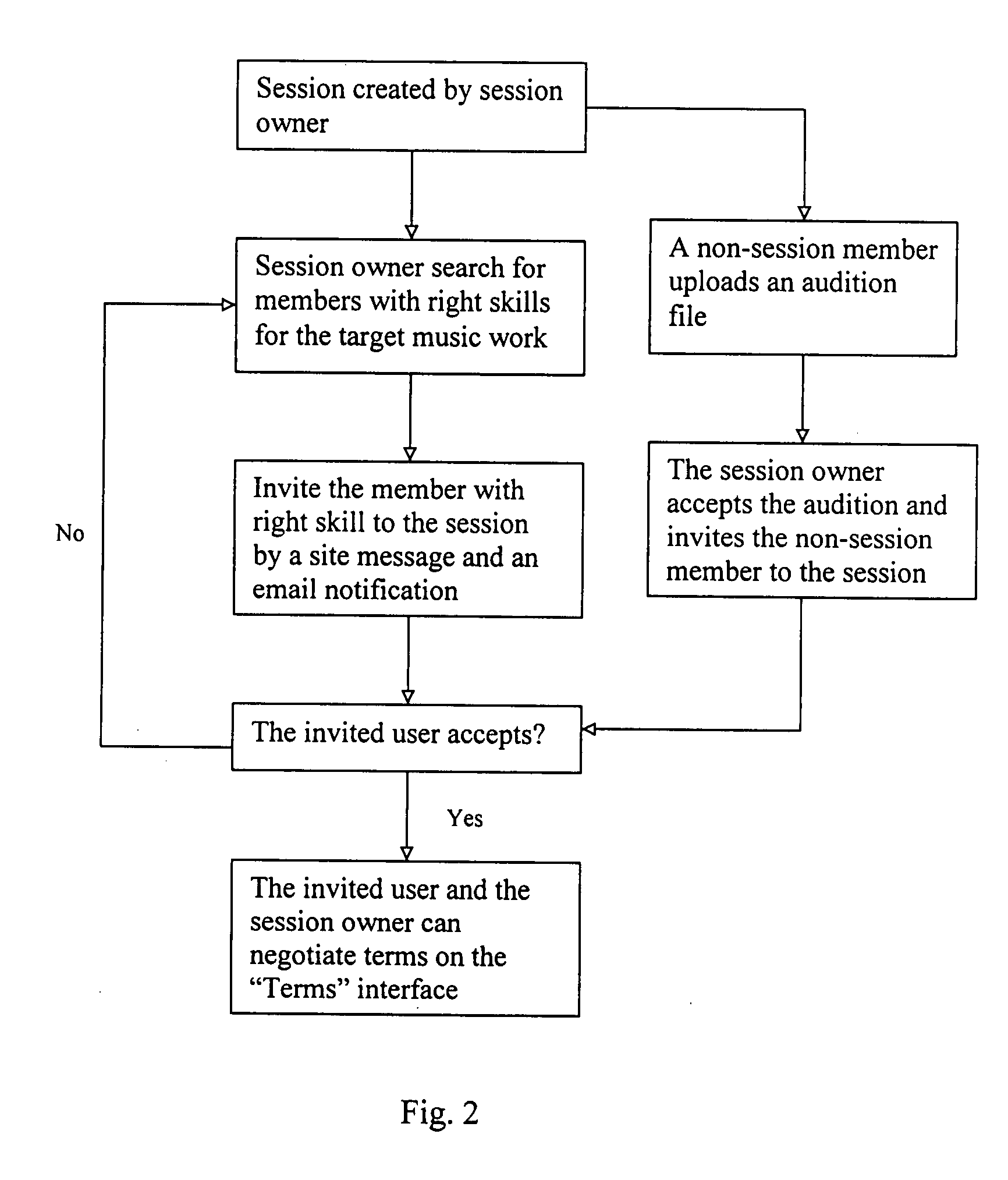
A collaborative music network for collaboratively linking members with each other has a central control center which is adapted for a plurality of members accessing thereto through internet, and a communication center linked to the central control center for interactively networking the members with each other. The music network includes a session for the session-members to edit, mix and record the audio files in the session and save them in the session and the user's own hard drive. The session also provides a live platform for session-members to interact and perform music. Non-session members are able to work on the audio files in the session. The completed music works are played through the network music player and purchased through online music store. The music network also contains an Internet radio to broadcast the audio files selected from member profiles.
Owner:INDABA MEDIA LLC
Internet radio and broadcast method
Owner:PANDORA MEDIA
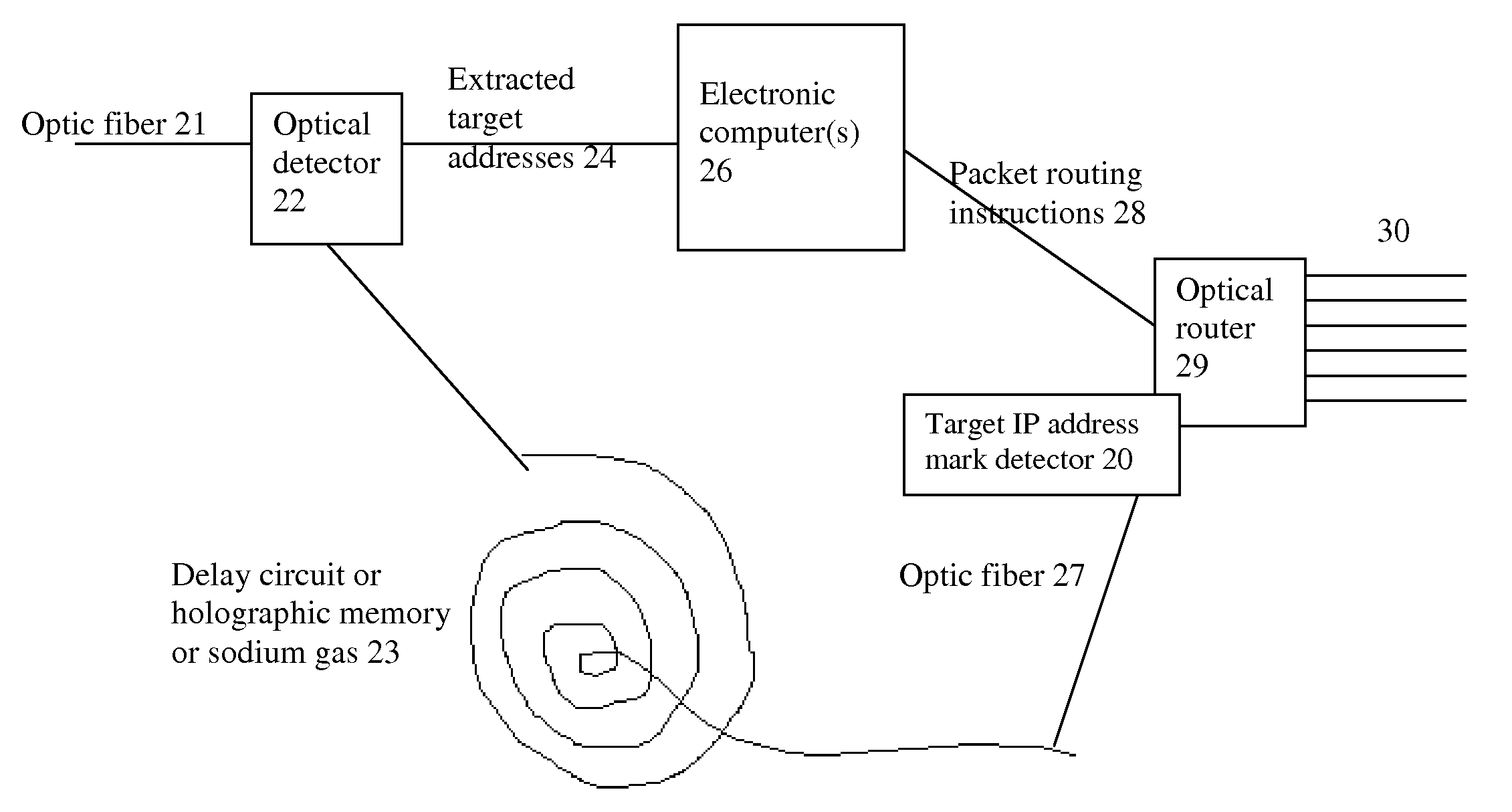
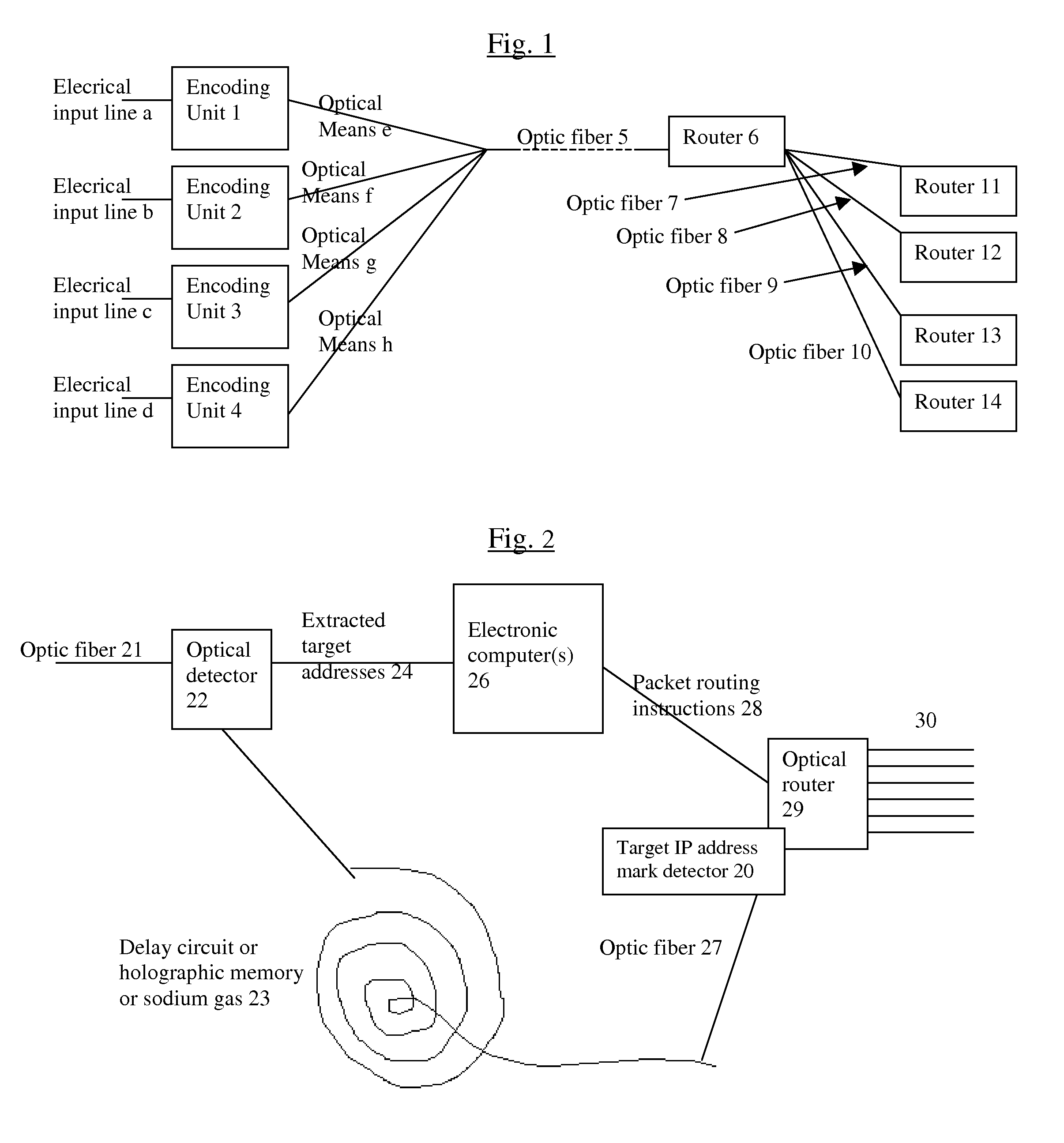
System and method for improving the efficiency of routers on the Internet and/or cellular networks and/or other networks and alleviating bottlenecks and overloads on the network
InactiveUS20080145050A1Simpler and flexible bufferingCheaply and easilyMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical delay lineIndividual data
The biggest bottleneck in the Internet today is caused by the slow speed of routers, compared to the speeds that are achieved by optic fibers with DWDM (Dense Wave Division Multiplexing). Packet switching or something similar to it is needed not just for better utilization of the lines, but also because it is superior to circuit switching in many ways, such as better scalability as the Internet grows, better handling of traffic congestions, and better routing flexibility. But optical routers are currently unable to do packet switching except by translating the data to electronic data and then back, which is very inefficient. The present invention solves this problem by optically marking and detecting the packet headers or parts of them, translating at most only the headers or parts of them to electronics for making packet switching decisions, and keeping the rest of the packets in optical delay lines, and solving response-time problems in the router, so that the crude optical switches can execute the packet switching decisions at fast bit rates. This solution has very high scalability and becomes even more efficient when physical addresses are used. Another optimization described in this invention is improving routing efficiency and bandwidth utilization by grouping together identical data packets from the same source going to the same general area with a multiple list of targets connected to each copy of the data and sent together to the general target area. These grouped packets are then preferably broken down into smaller groups by the routers in the general target area and finally broken down to individual data packets for delivering to the final actual destinations. This optimization works best with Physical addresses, and can be very useful for example for optimizing the access to very popular sites such as for example Yahoo or CNN, and can be used also for example for more efficiently transferring streaming data, such as for example from Internet radio stations, or Internet TV stations which will probably exist in the next years. Another important optimization is a new architecture and principles for routing based on physical geographical IP addresses (such as for example based on GPS), in a way much more efficient than has been previously discussed in the literature that suggested using physical (geographical) addresses. This is preferably based on a hierarchy similar to a hierarchical road system, so that preferably the MAIN routers (and / or intermediary-level routers) are preferably also connected directly and preferably with high-bandwidth as peers between each other, without having to go through lower-level routers in order to reach their peers, so that once a higher-level router (and especially if it's one of the MAIN routers) decides to forward a packet (or a group of packets) to a higher-level peer, preferably the packets don't have to go through lower level routers. However, conversion from the current architecture to the new one can be done very easy, as shown in the description below.
Owner:BARHON MAYER BATYA
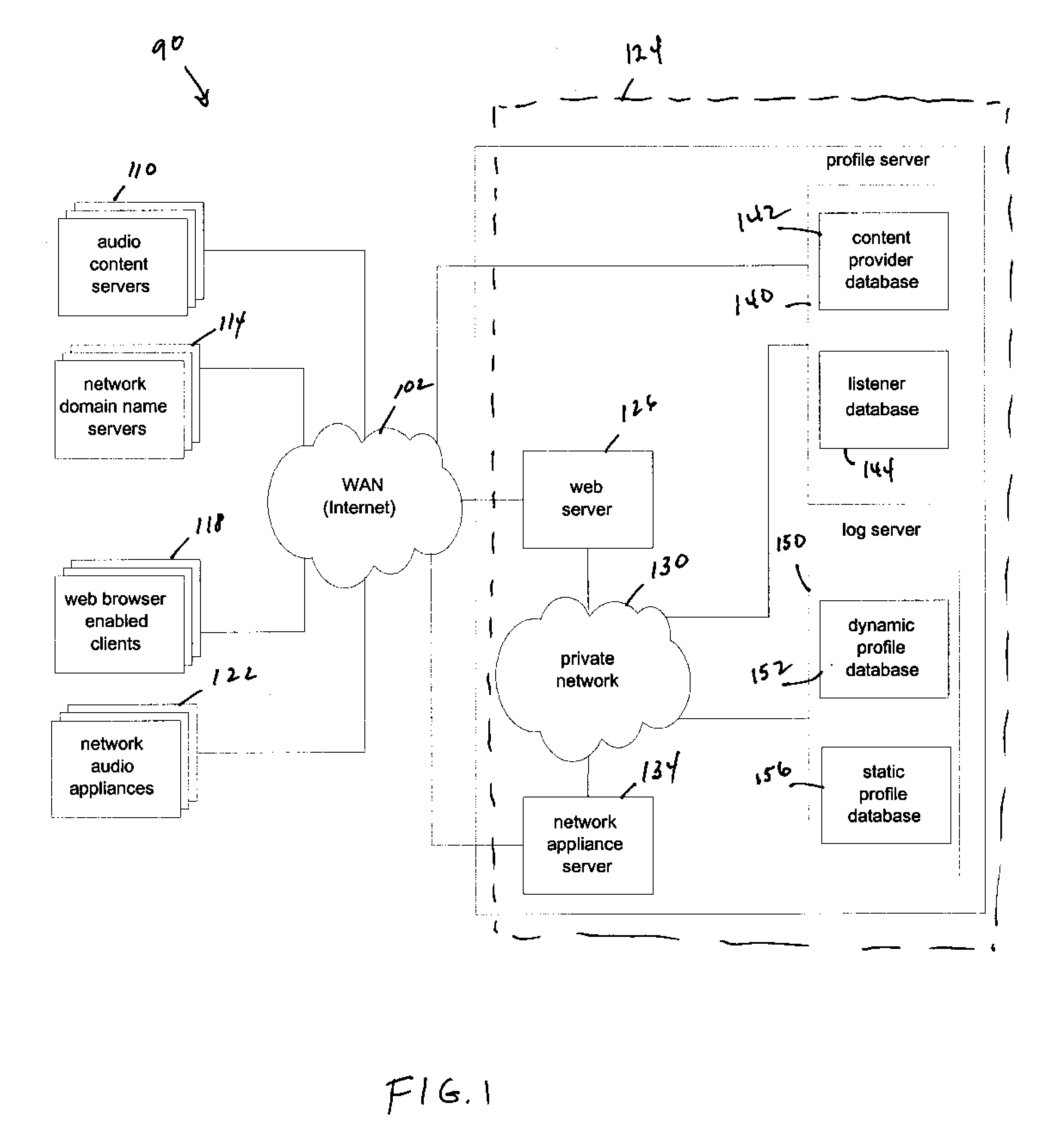
Internet radio and indexing system for managing audio content providers and subscribers
InactiveUS20020091790A1Easy accessBroadcast-related systemsBroadcast transmission systemsInternet radio devicePersonal computer
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> An on-line audio indexing network facilitates listeners to communicate with on-line audio content providers. Preferably, the on-line audio content providers are Internet audio broadcasters and the on-line audio indexing network, listeners and audio content providers are coupled via the Internet. To listen to audio broadcasts, the listeners communicate with the on-line audio content providers and the indexing network via audio appliances, rather than standard personal computers.
Owner:SYNCHTON
Internet radio player
Owner:KARLSGODT STEPHEN
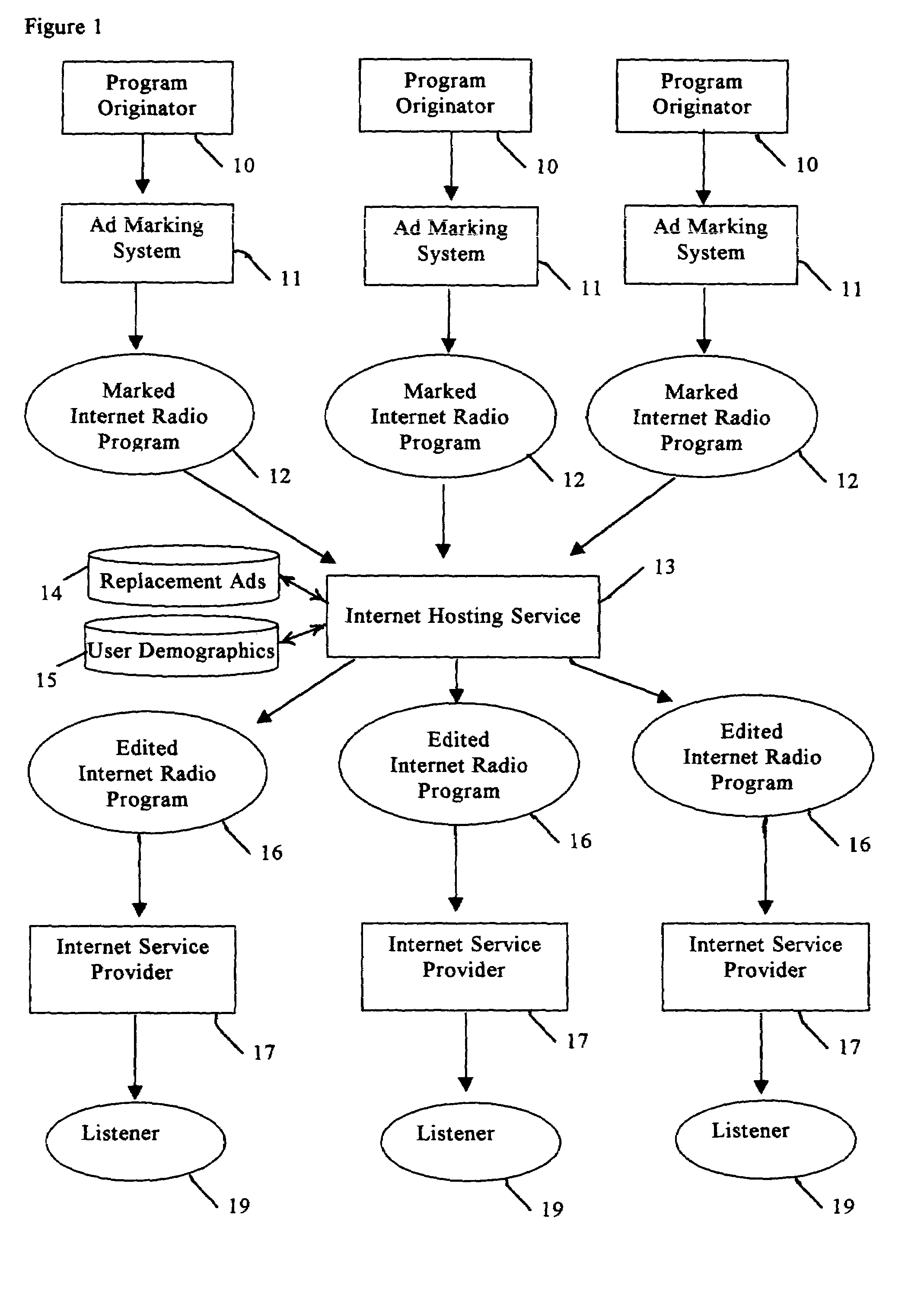
System for modifying and targeting advertising content of internet radio broadcasts
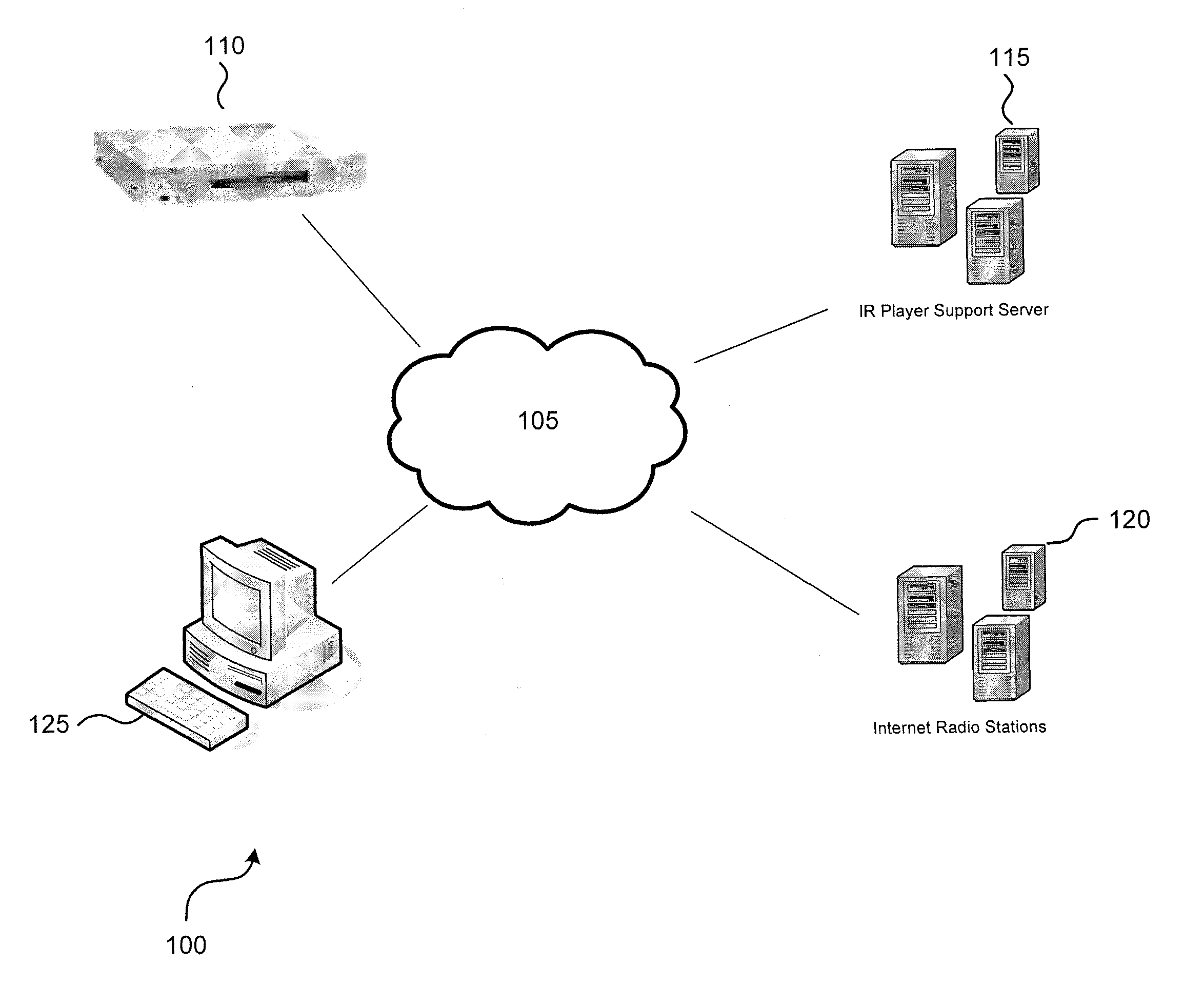
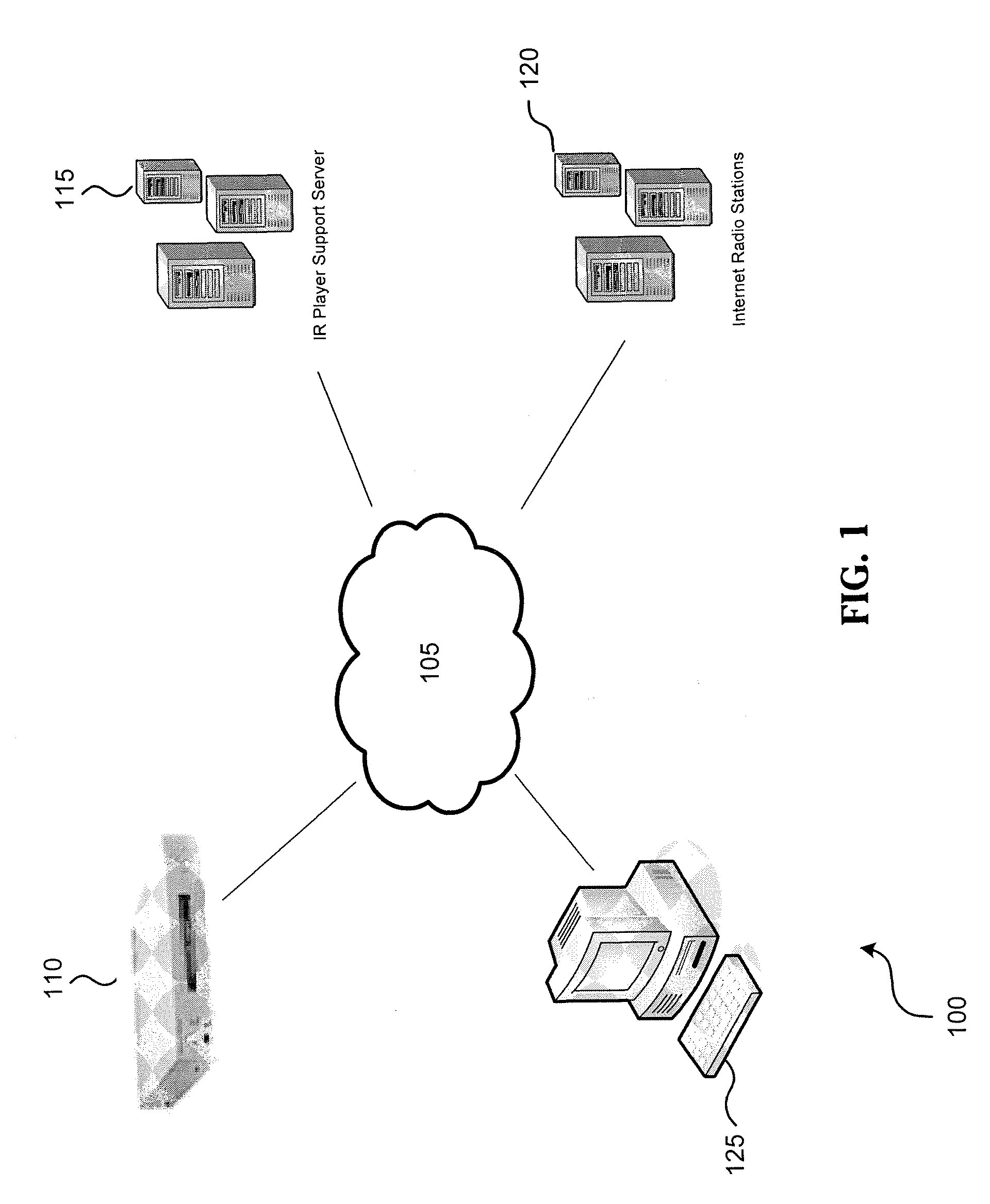
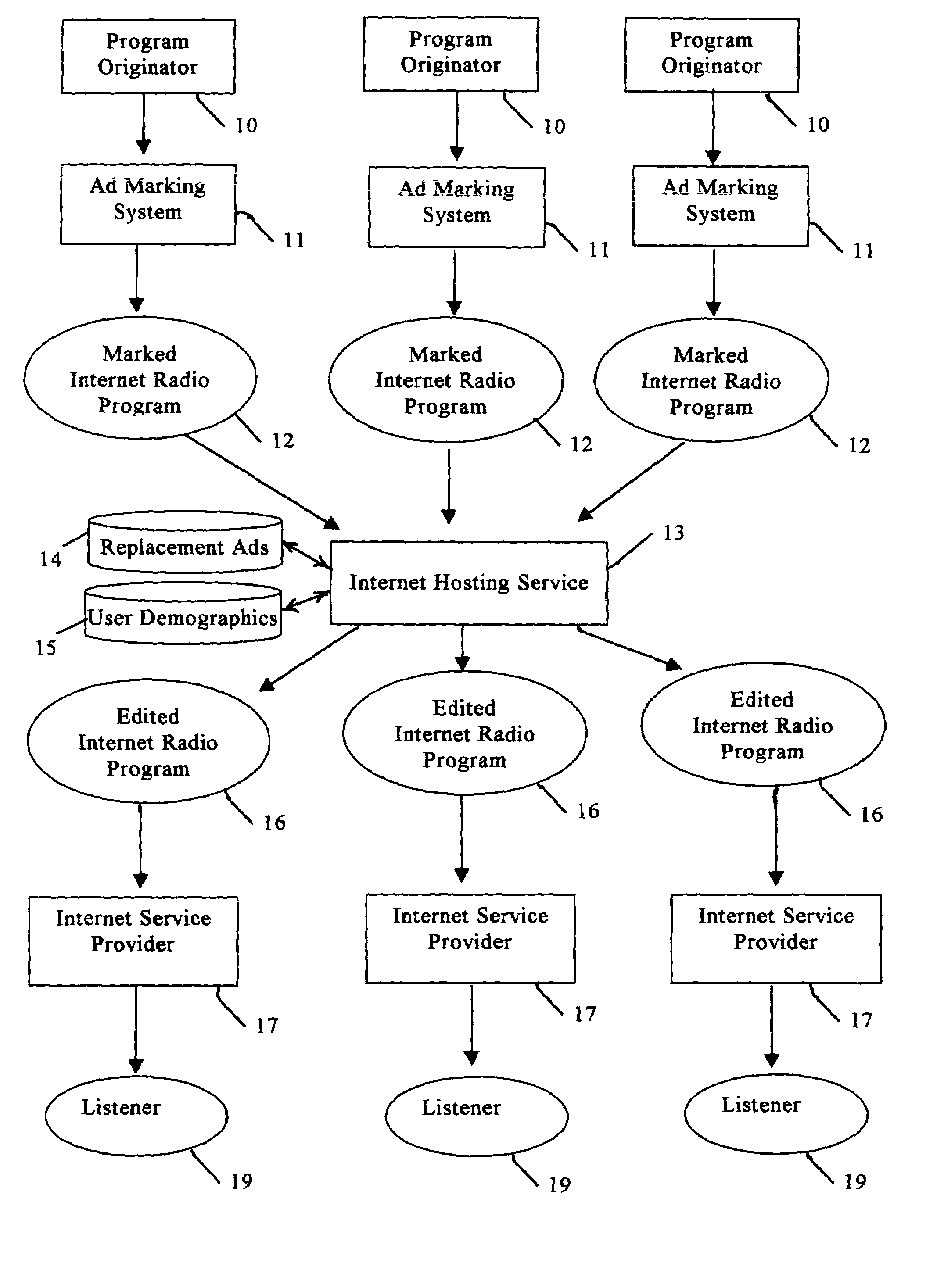
ActiveUS7490053B1Easy to implementGenerate additional revenueBroadcast information switching/replacementBroadcast-related systemsInternet hosting serviceTargeted advertising
A radio station transmits its broadcast audio content, including audible advertisements, to listeners over the Internet via an Internet Hosting Service that provides listener access to radio station content. A computing system at the radio station digitizes the audio, and supplies marking information that identifies the beginning and duration of commercials. The digital marking information is supplied with the radio station's audio to the Internet Hosting Service. The Internet Hosting Service maintains a repository of replacement audio commercials along with information about the commercials including duration. Upon receiving the digital marker indicating the presence of a commercial, the Internet Hosting Service selects a replacement commercial of comparable duration from its repository. The Internet Hosting Service then substitutes the replacement commercial for the original broadcast commercial and produces an edited audio program for delivery to the listeners that carries advertising of higher value than the original advertising.
Owner:WAG ACQUISITION
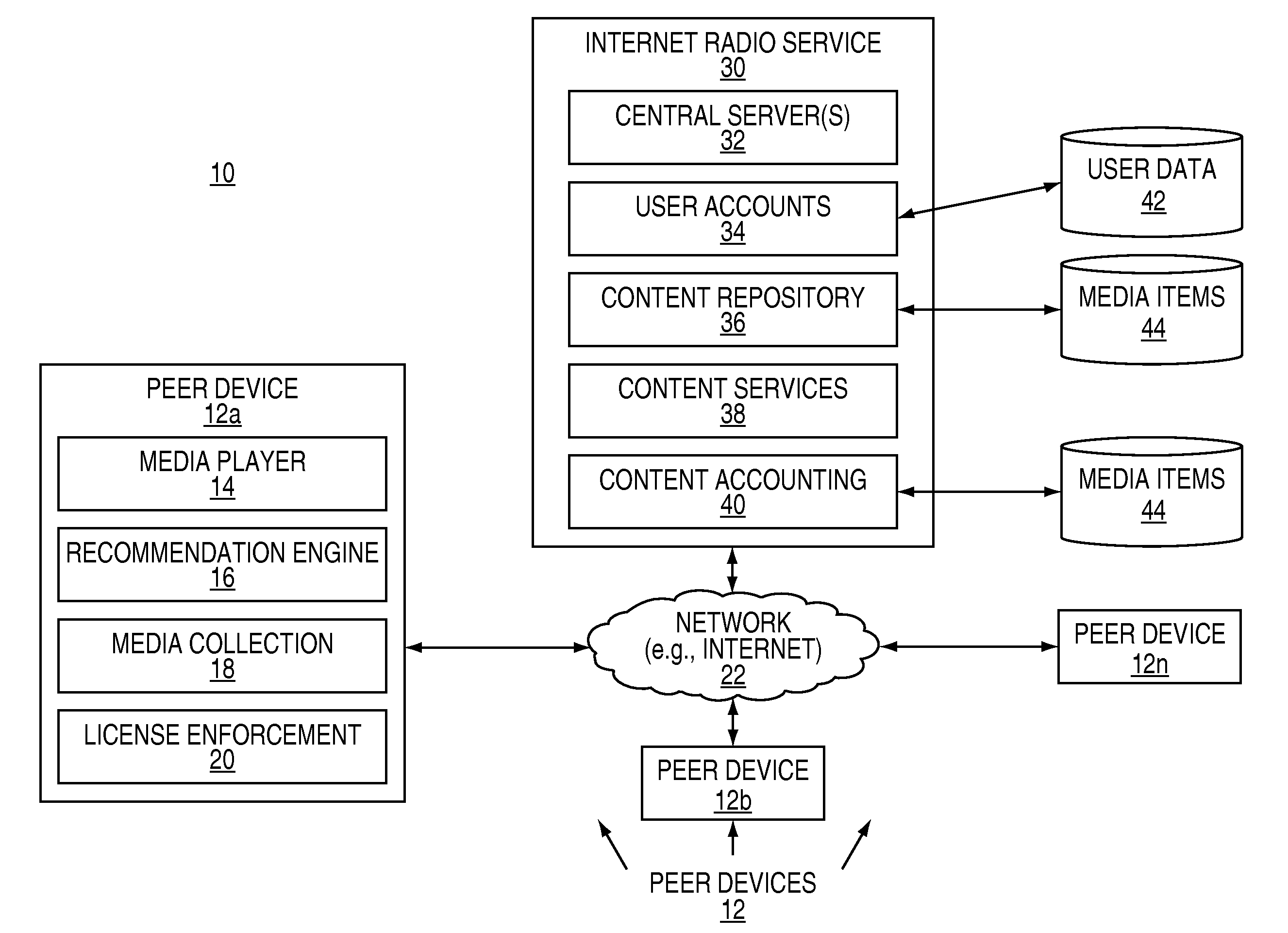
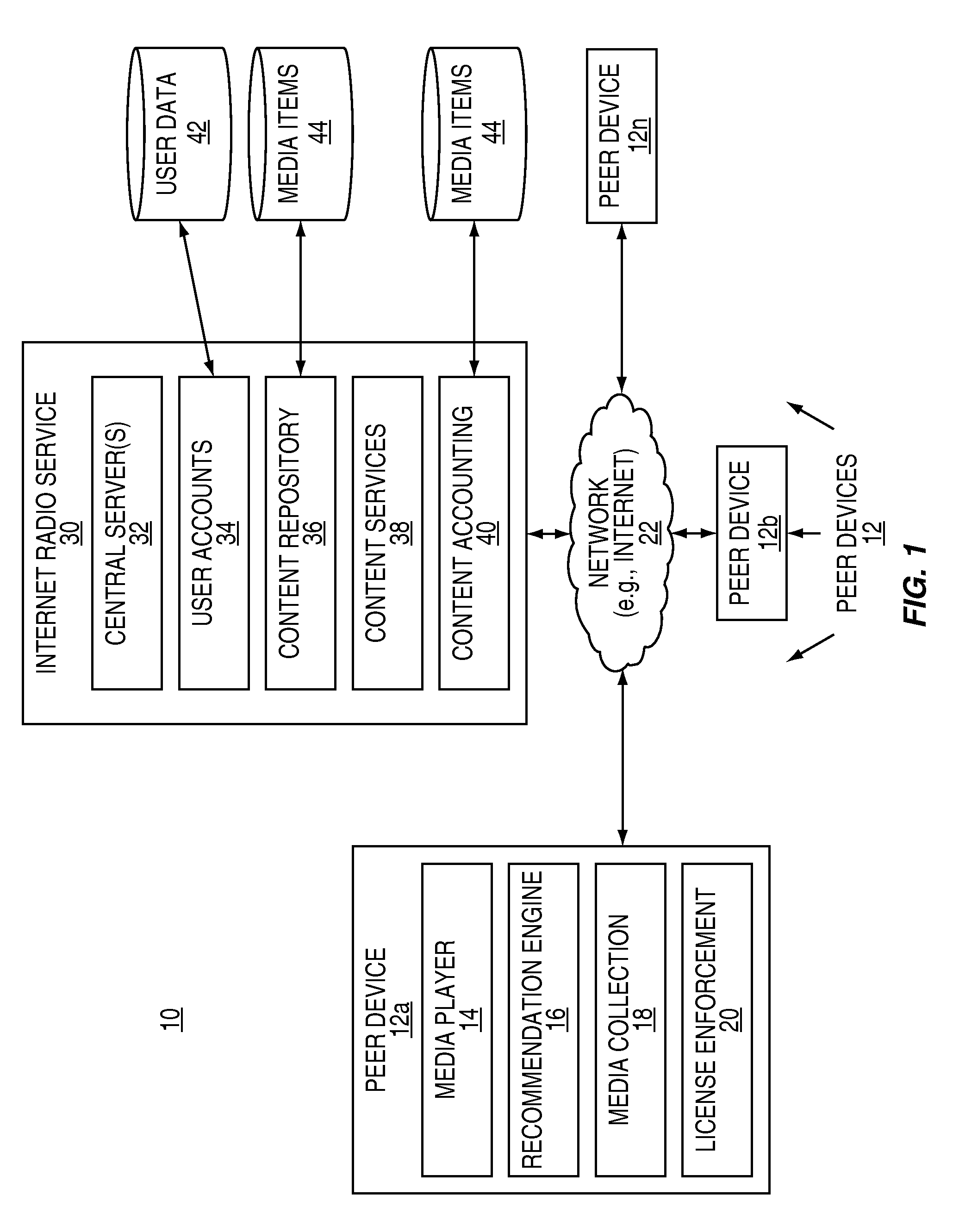
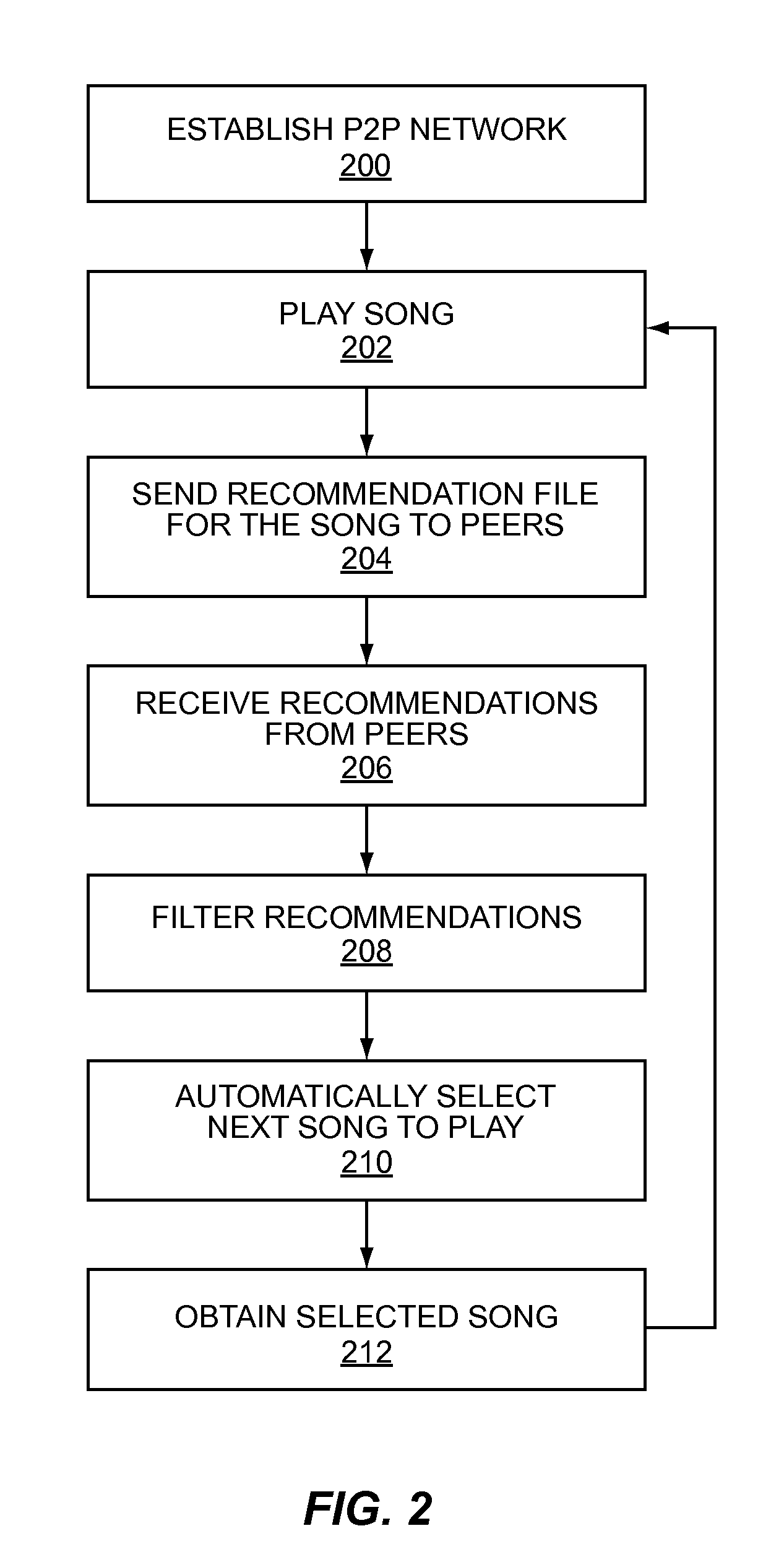
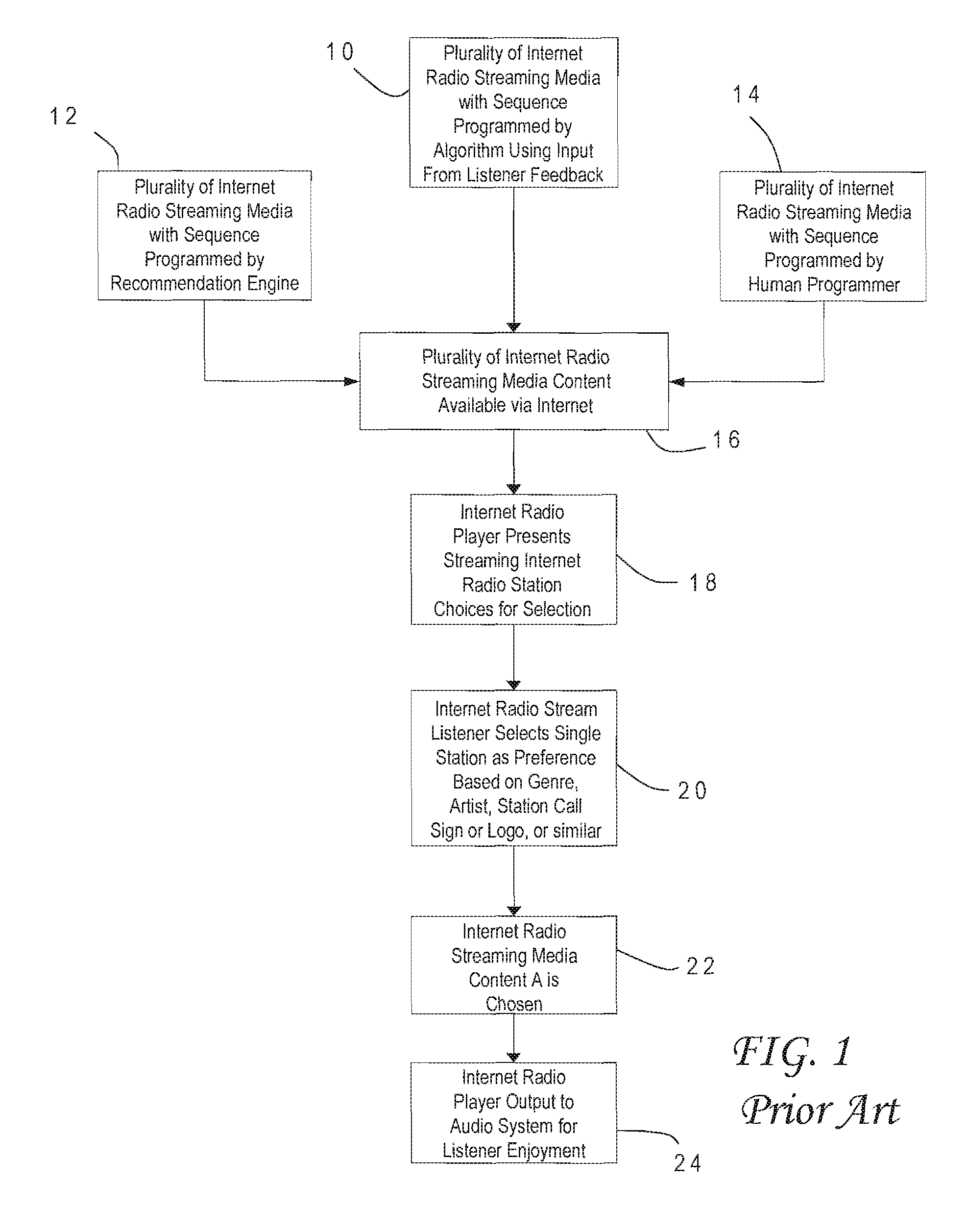
Method and system for populating a content repository for an internet radio service based on a recommendation network
InactiveUS20090164514A1Eliminate needBroadcast-related systemsBroadcast transmission systemsInternet radioWorld Wide Web
A computer-implemented method and system are provided for populating the content repository of the media service based on real-time media recommendation network comprising a plurality of peer devices. Aspects of the method and system include receiving by a server a recommendation from one of the plurality of peer devices for a media item that is intended for a recipient; determining if the media item is present in the content repository; in response to determining that the media item is not present in the content repository, requesting that the peer device upload the media item; and in response to the media item being uploaded, storing the media item in the content repository.
Owner:CONCERT TECH
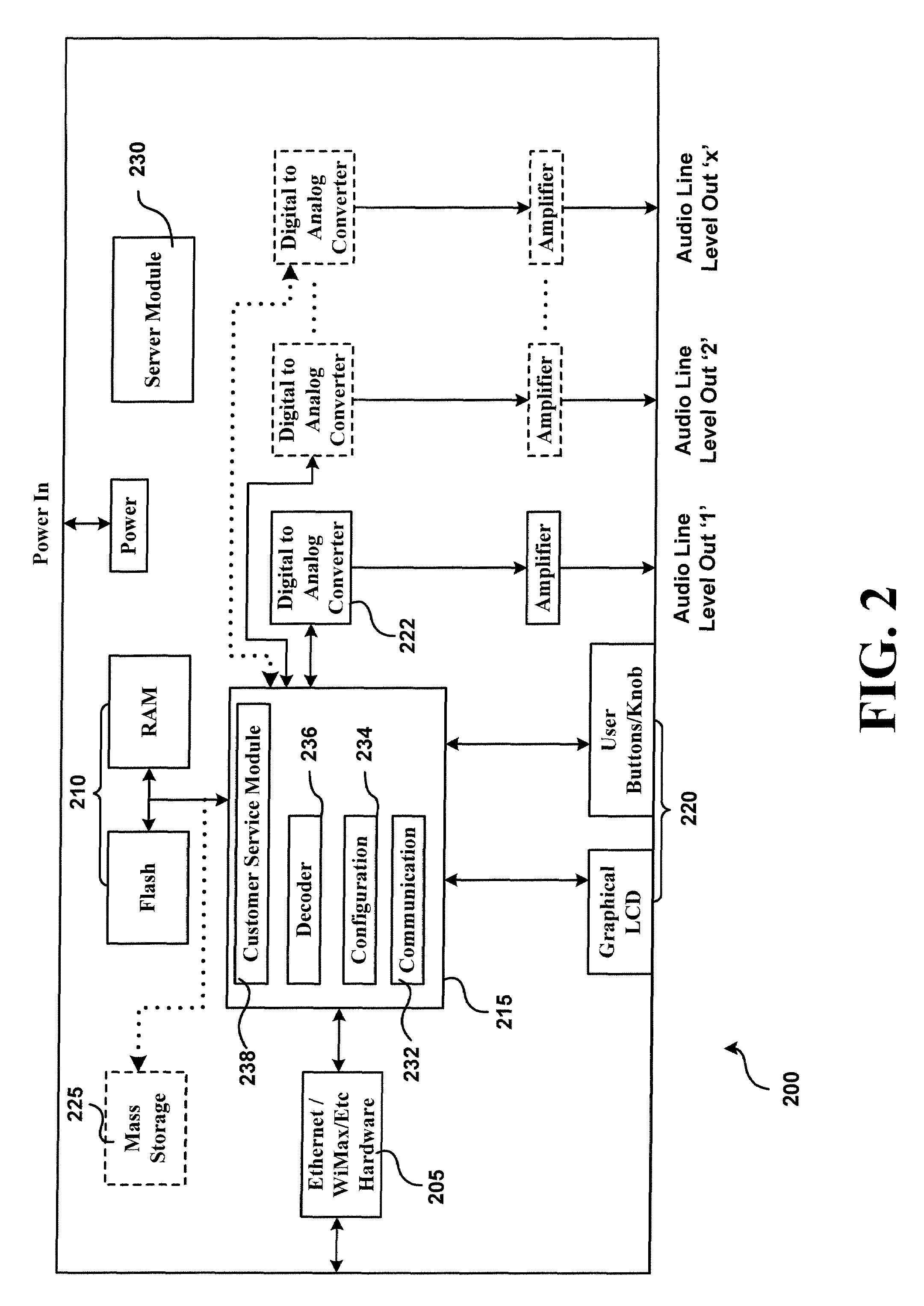
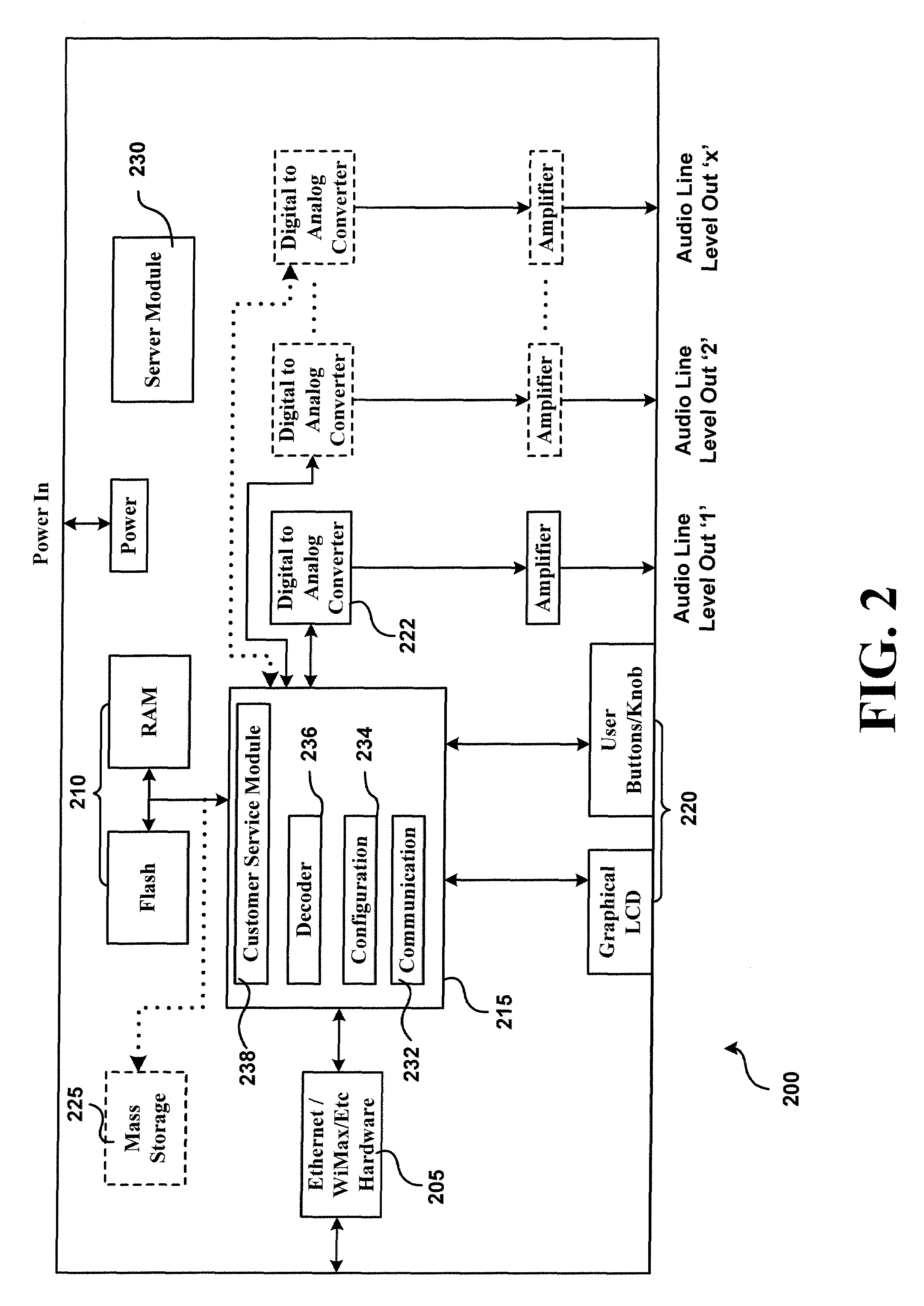
Internet radio player
The present invention provides an apparatus for listening to music on the internet. The apparatus includes a memory unit configured to store a plurality of internet protocol addresses of internet radio stations, a communication unit configured to communicate with one of the internet radio stations using a corresponding IP address stored in the memory, a first logic configured to request a data from one of the internet radio stations, a second logic configured to receive a digital data stream from the internet station and store the received digital data stream in a buffer, a third logic configured to decode the received digital data stream, a fourth logic configured to convert the decoded digital data stream into an analog data stream, and a service module configured to extract information regarding a song from the digital data stream and forward the extracted information to an external device.
Owner:KARLSGODT STEPHEN
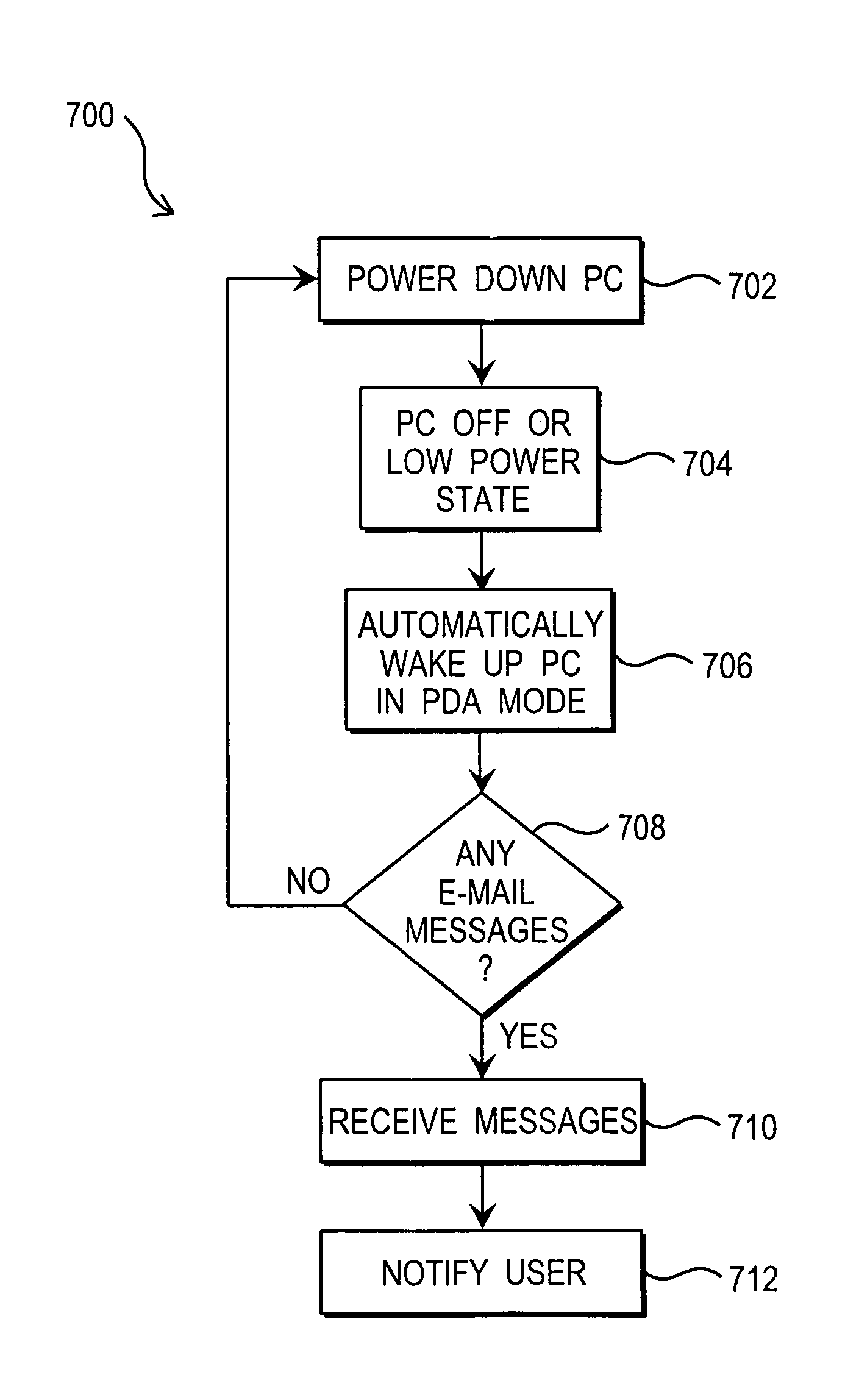
Personal computer integrated with personal digital assistant
A personal computer (PC) adapted to function as a personal digital assistant (PDA) includes: a central processing unit (CPU) responsive to a control signal to load a first operating system or a second operating system, wherein the first operating system is run by the PC in a first PC mode and the second operating system is run by the PC in a second PDA mode. Various software application programs that may be run in PDA mode include Internet auction applications, electronic mail access applications, and Internet radio applications.
Owner:MAISHI ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) LTD
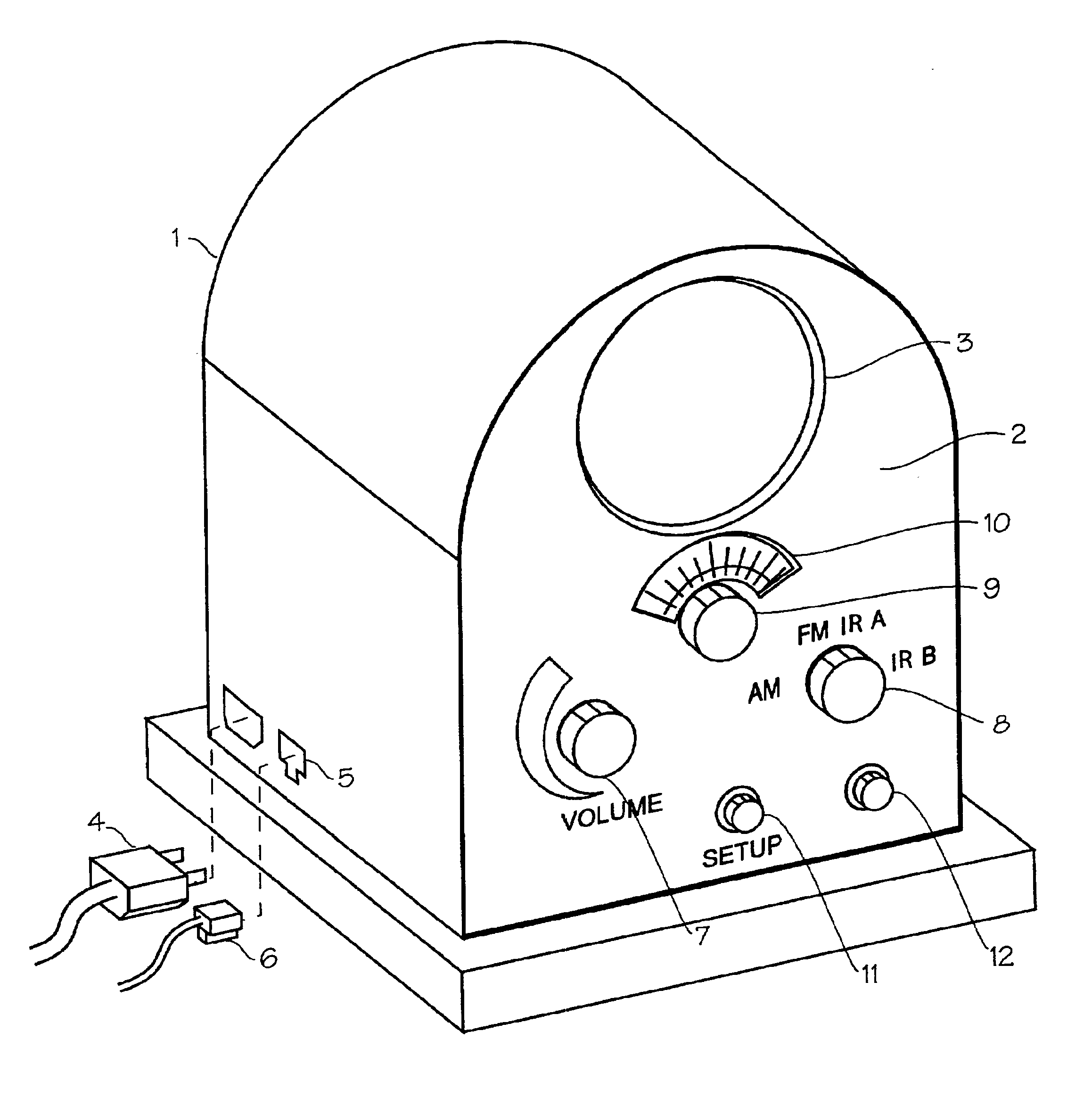
Internet radio receiver with linear tuning interface
InactiveUS20060067304A1Delay of severalEasy to adjustBroadcast transmission systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsRadio receptionIp address
A system for supplying streaming media or other media sources to clients, said system providing for selection of internet based audio content providers based on arbitrarily assigned numbers that function as proxies for the URL or IP address of the audio content providers.
Owner:DIGIMEDIA TECH LLC
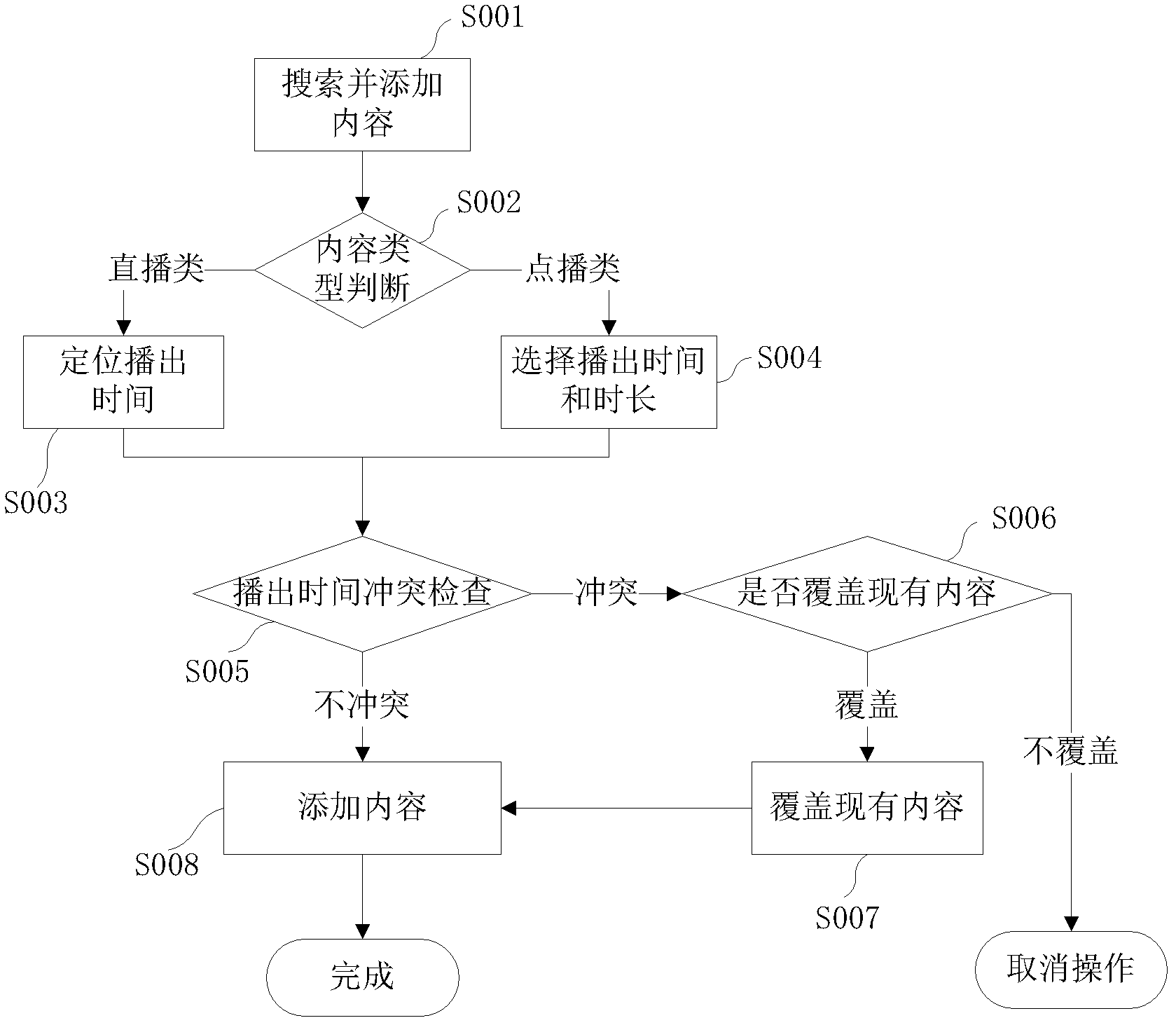
Played content-customizing method and played content-customizing device
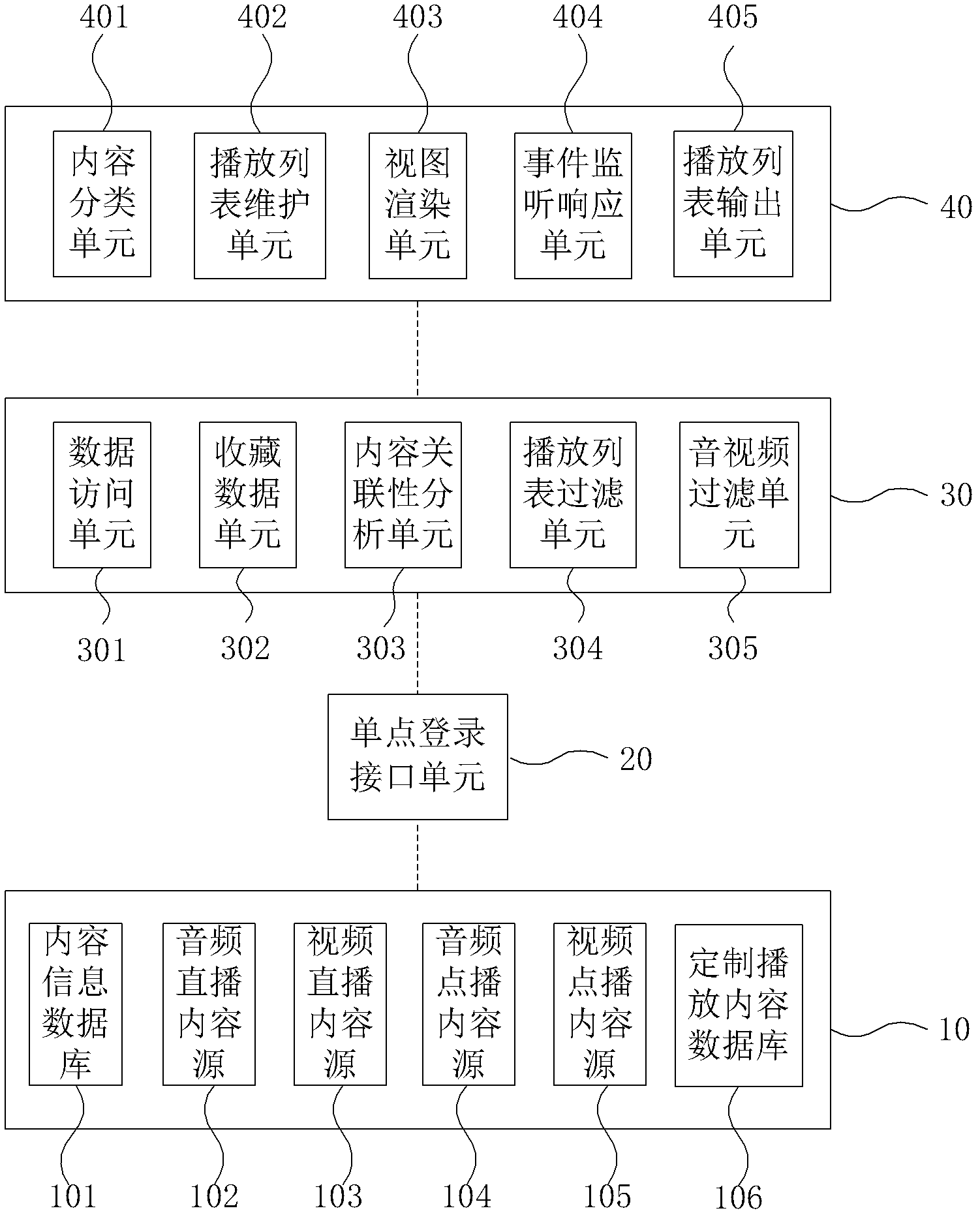
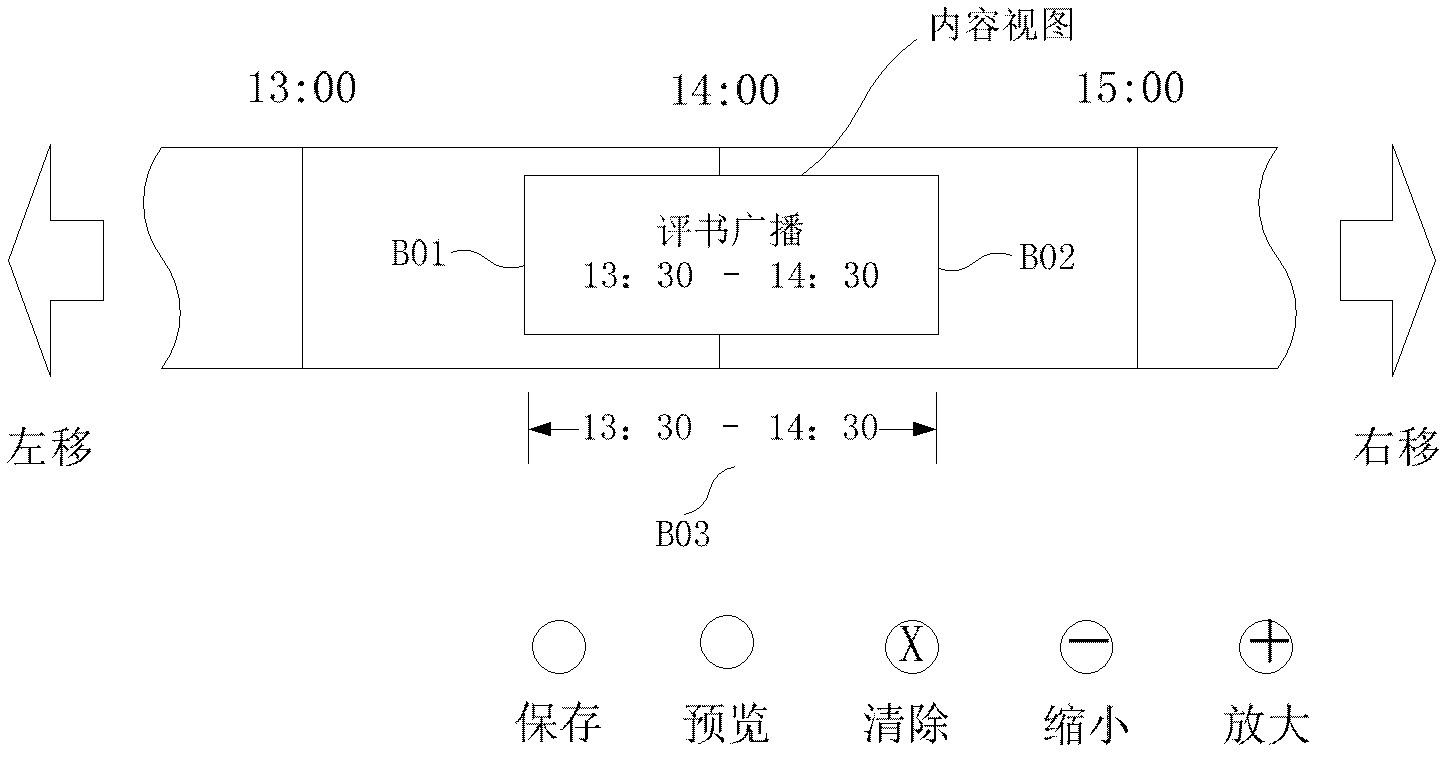
ActiveCN102665129ASimple and intuitive operationRealize mixingSelective content distributionAudio on demandInternet radio
The invention provides a network played content-customizing method, which includes the following steps: building a unified interface for a plurality of different played content sources; according to played contents selected by a user, obtaining the information of the played contents from the different played content sources via the unified interface, the content information including live video, live audio, video on demand, and audio on demand; according to the information of the obtained played contents, determining the locations of the played contents in a content playlist, forming a content playlist view in the timer shaft form, supplying for the user to customize individual played contents, according to the customized content playlist of the user, and a single network player calling the content in the corresponding content source to play through the unified interface. The invention also provides a network played content-customizing device. According to the invention, content information coming from different resources can be mixed in the same content playlist, so that the user can customize, mix and play network radio stations with various types of contents alone.
Owner:北京人民广播电台
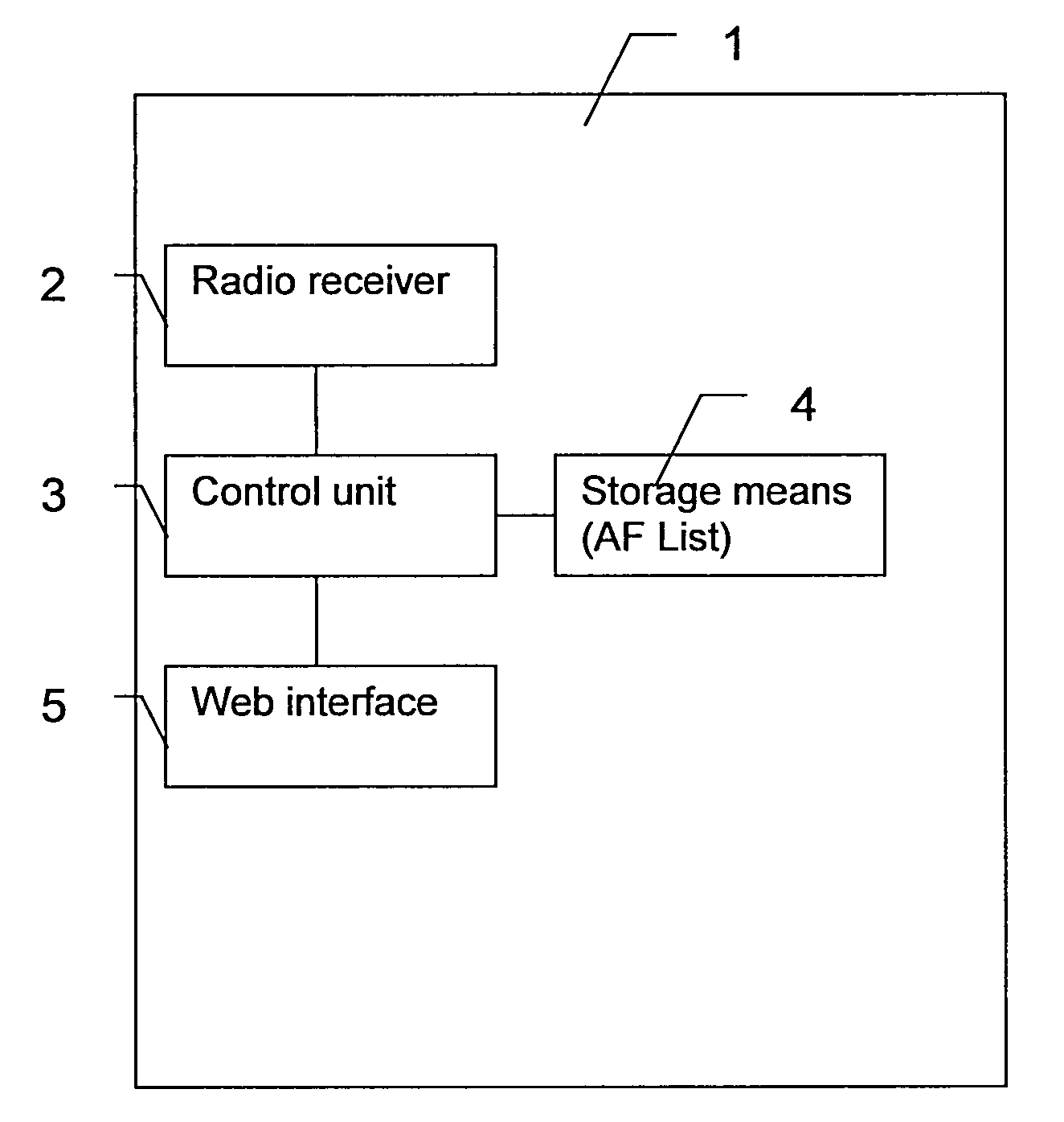
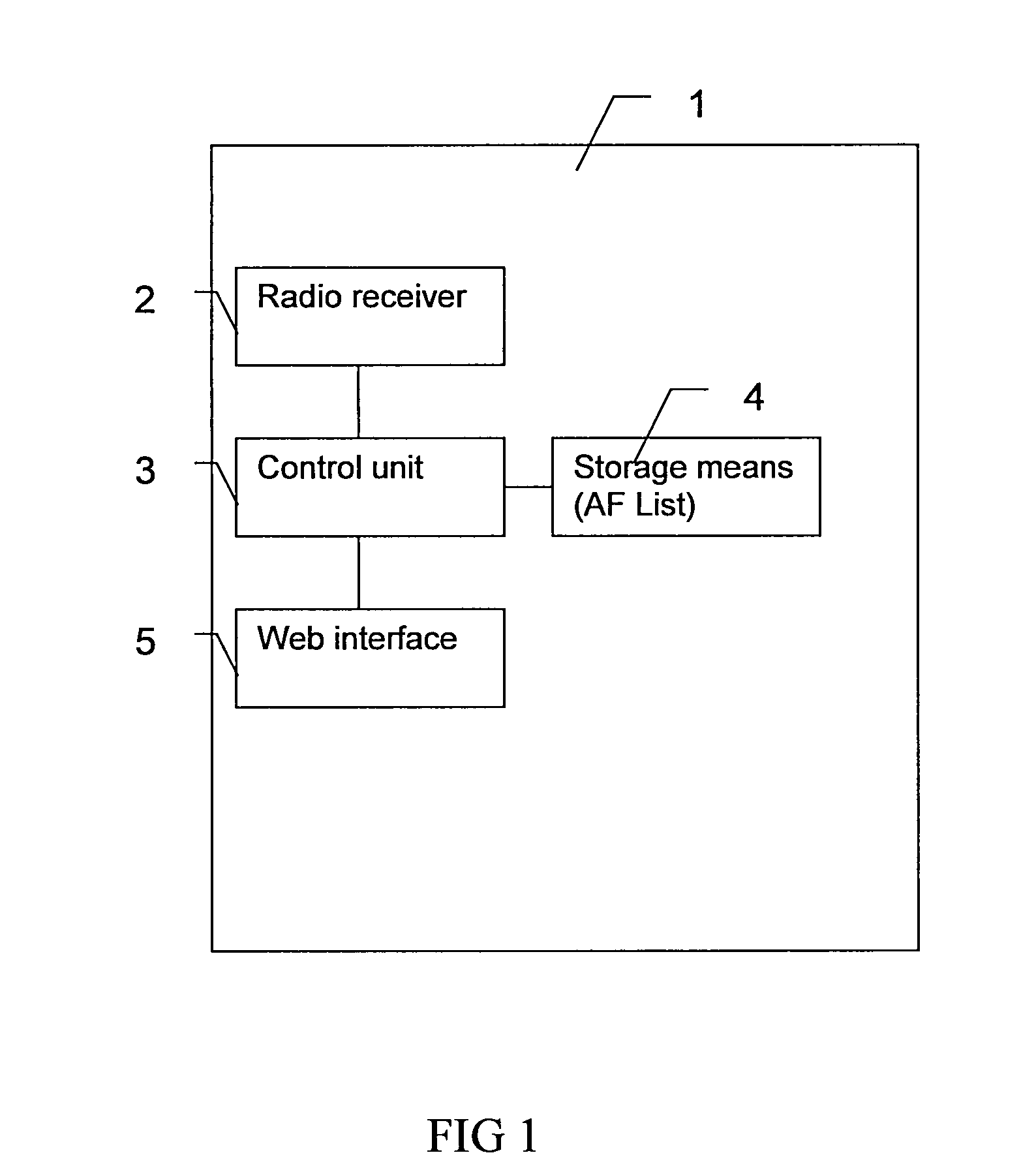
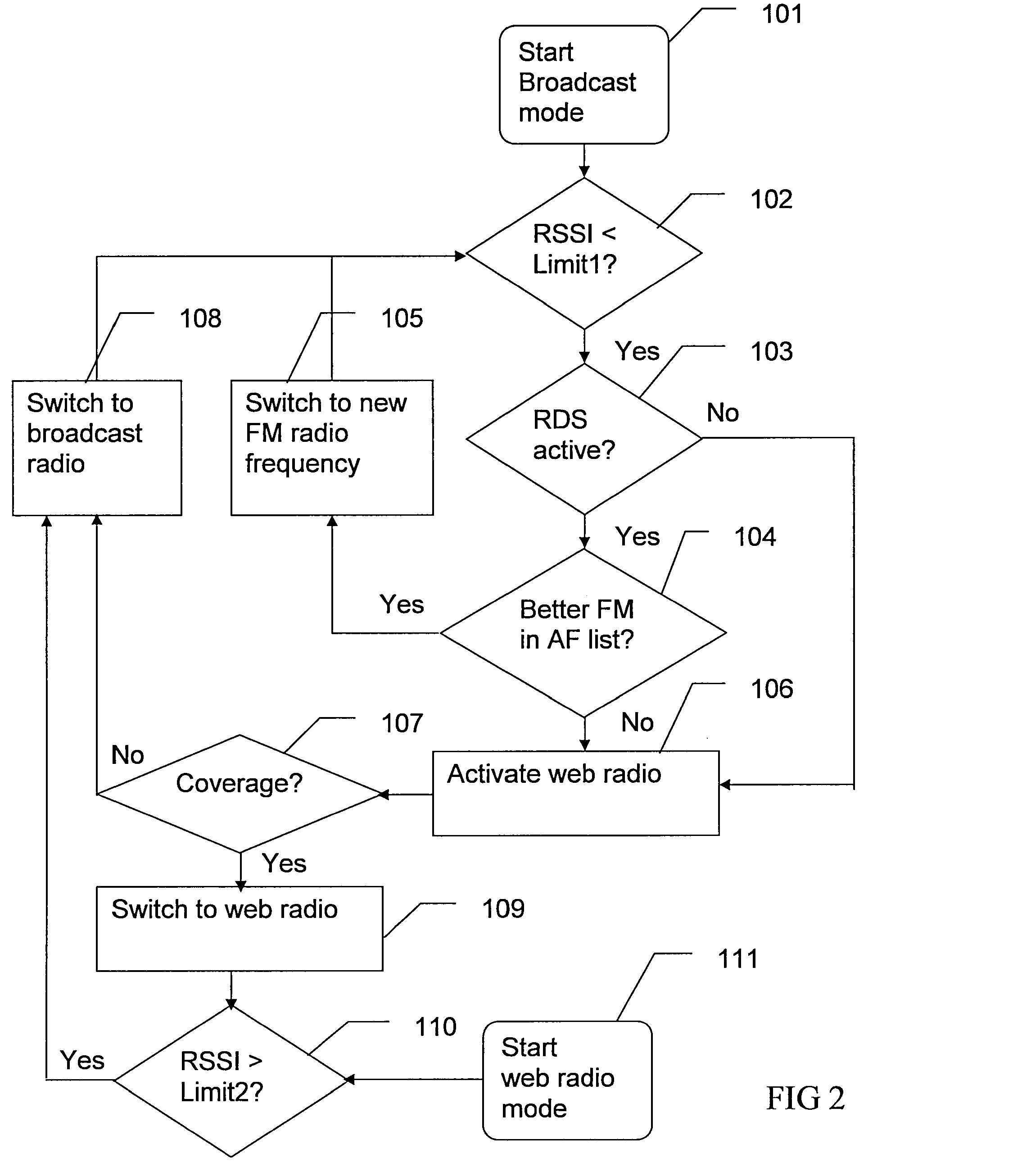
Portable device with combined broadcast and web radio
InactiveUS20080139109A1Broadcast information characterisationBroadcast transmission systemsRadio receptionRadio receiver
The invention relates to a combined broadcast and web radio in a portable device. The device is arranged to switch automatically between broadcast radio and web accessed radio in dependence of received signal strength and quality. The device comprises: a radio receiver tunable to broadcast radio frequencies; a web radio interface adapted to access radio stations through a global communications network; a control unit capable of controlling the radio receiver and the web radio interface and adapted to monitor received signal strength on the radio receiver. The control unit is adapted to switch the device from a broadcast radio reception mode to a web radio reception mode, if the monitored received signal strength of the broadcast radio drops below a first limit.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Remote teaching live broadcast system
InactiveCN105430337AGuaranteed fluencyAchieve interactionTelevision conference systemsClosed circuit television systemsInteraction systemsCollection system
The invention discloses a remote teaching live broadcast system, comprising a main server module, a network broadcast system, an analog on-demand service system, a signal inter cut and short message broadcast system, a video / screen synchronous transmission system, a video collection system and a video interactive system, wherein the network broadcast system broadcasts a video or a network television, an audio signal or an internet radio to a local area network user through a network virtual channel; the video collection system comprises a camera, a noise reduction unit, a central processing unit and a storage device; the video interactive system comprises a memory module and a plurality of display terminal modules. The remote teaching live broadcast system disclosed by the invention is operated by the main server module in the whole course, the user can remotely send a control instruction and realize interaction through the internet communication technology without being limited by the occasion, and no expensive conference facility is needed, so that teaching evaluation activities are more convenient and faster.
Owner:BOZHOU TEACHERS COLLEGE
Media streams and media store
This invention is directed to providing access to one or more media streams in exchange for purchasing articles or items that may be related to at least one of the media streams. In some embodiments, the item purchased may include a media item related to a media item provided as part of a particular media stream. For example, a user may be provided access to an Internet radio station in exchange for purchasing a song. The song may include any song available from a store, a song transmitted by the Internet radio station, or a song related to a song transmitted by the Internet radio station. Each media item purchased may provide the user with a particular amount of media stream credit that may be used to access media streams. In some embodiments, different purchased media items may provide the user with the same or different amounts of credit.
Owner:APPLE INC
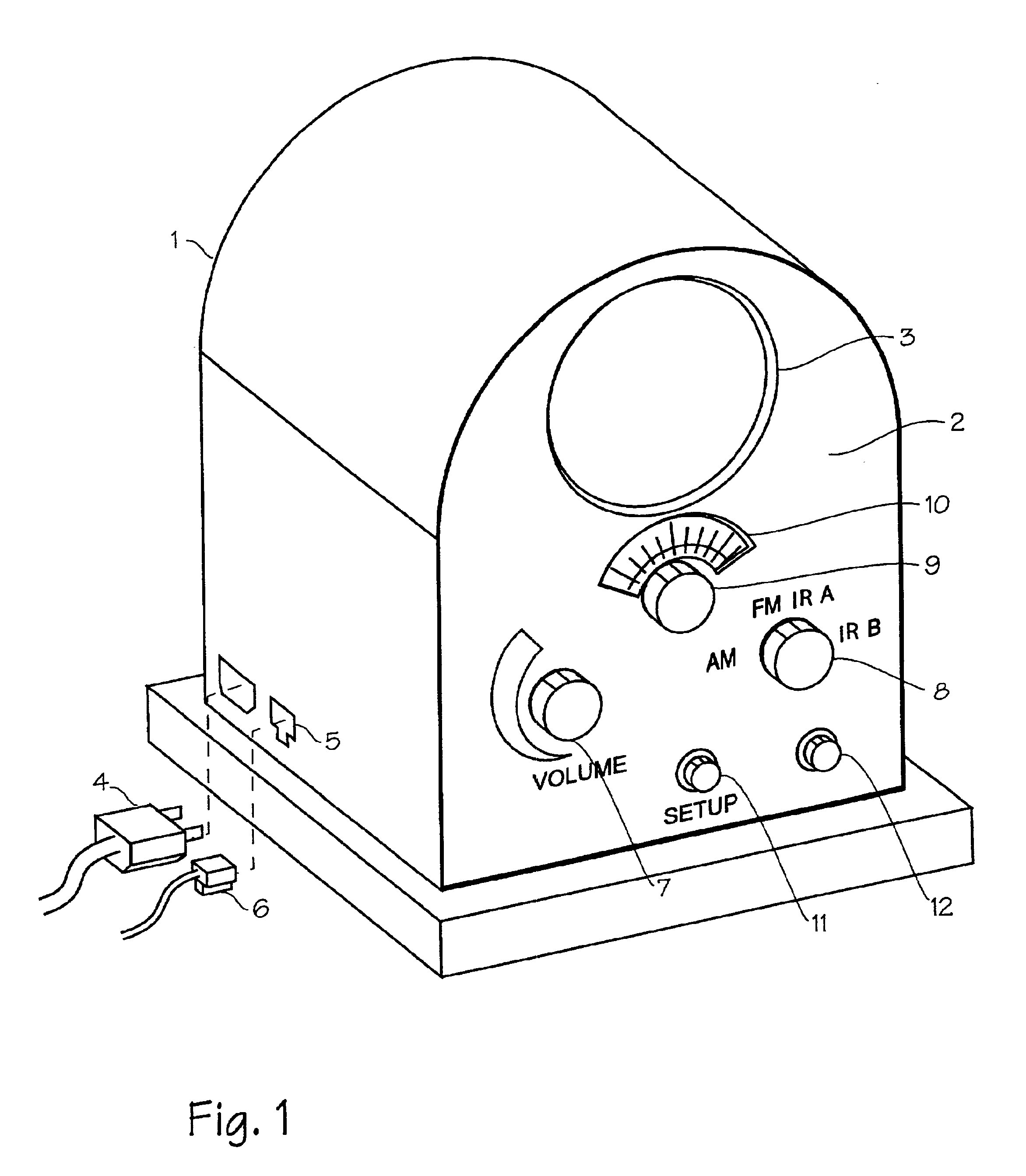
Internet radio receiver with linear tuning interface
InactiveUS6920479B2Delay of severalEasy to adjustBroadcast transmission systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsRadio receptionIp address
A system for supplying streaming media or other media sources to clients, which provides for selection of internet based audio contest providers based on arbitrarily assigned numbers that function as proxies for the URL or IP address of the audio content providers.
Owner:DIGIMEDIA TECH LLC
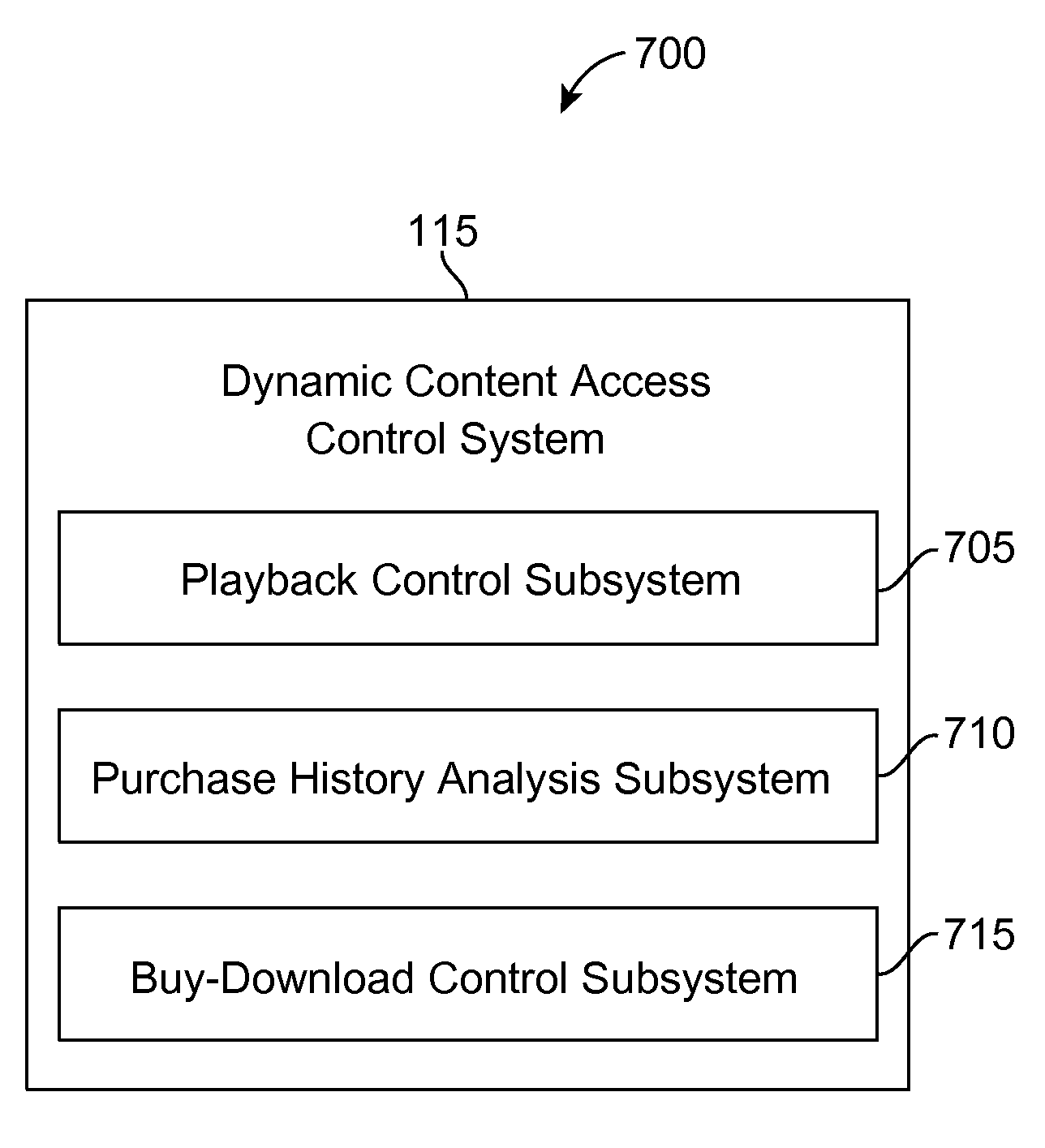
Displaying a buy/download button based on purchase history
ActiveUS9244586B2Easily conveniently useDigital data information retrievalBuying/selling/leasing transactionsComputerized systemInternet radio
Owner:APPLE INC
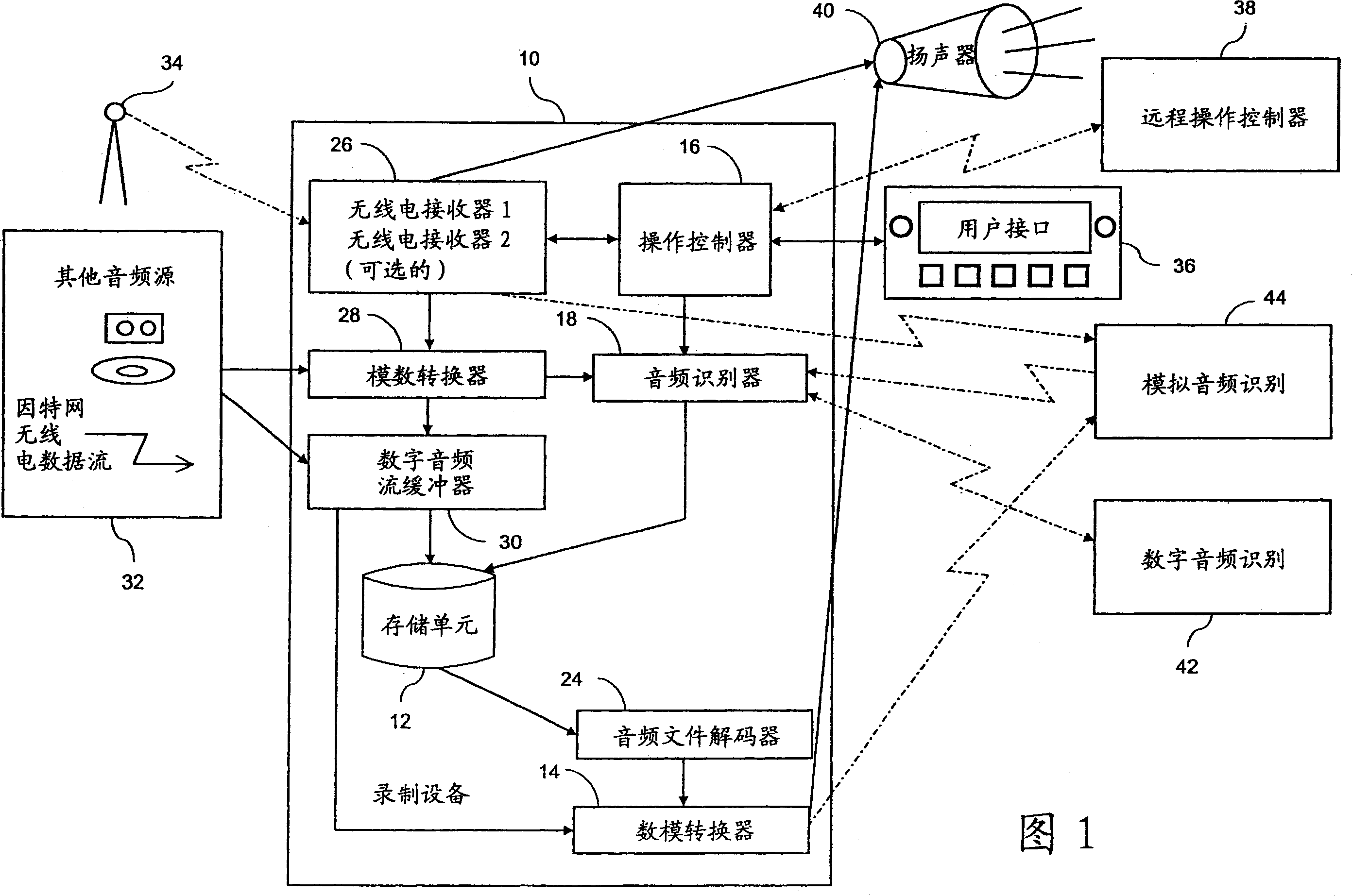
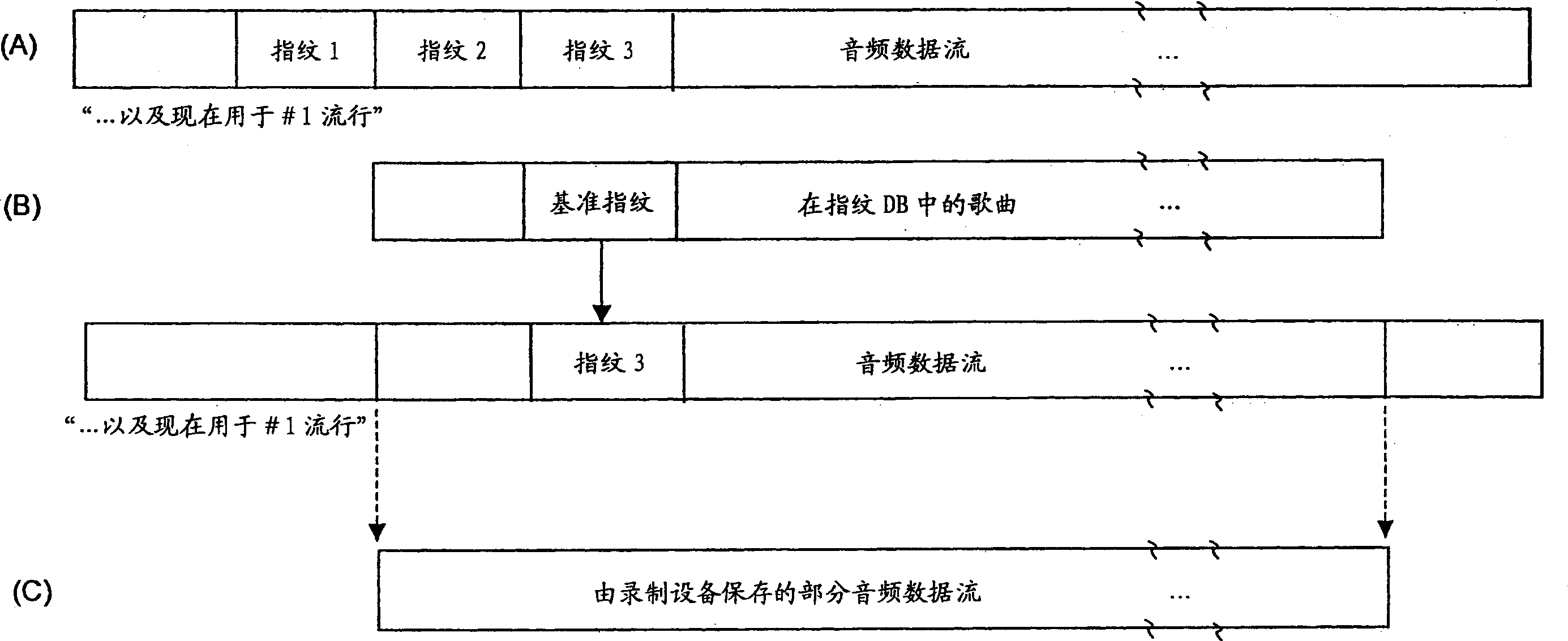
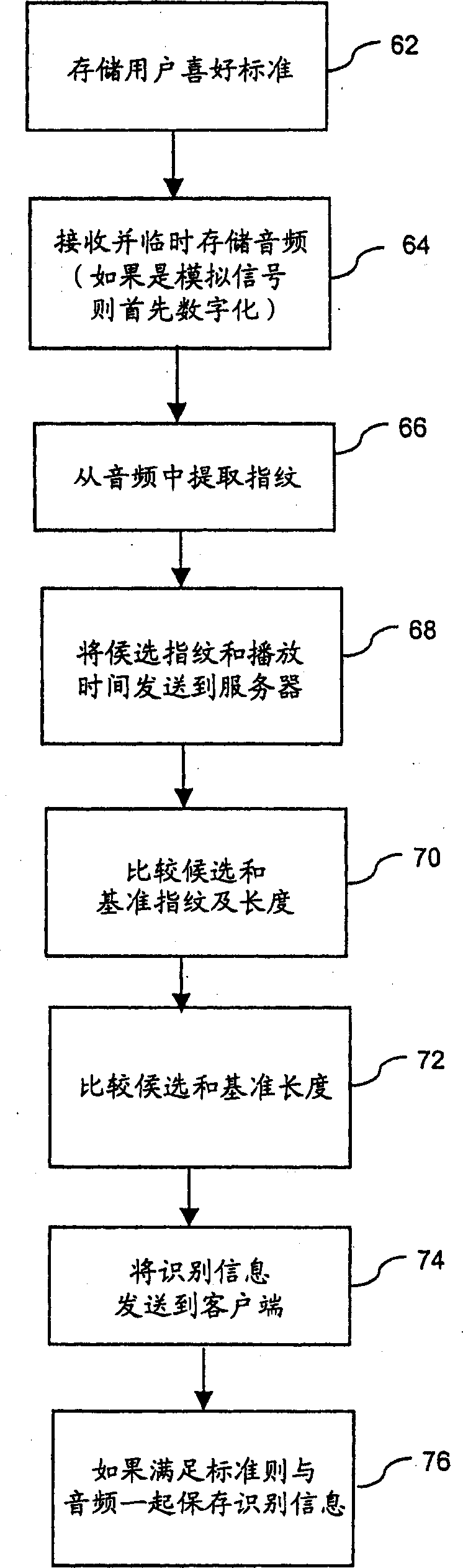
Personal audio recording system
InactiveCN1726489AMetadata audio data retrievalData processing applicationsSignal qualityAdjacent channel
Broadcast music, or other audio that a user wants to hear, is recorded based on criteria obtained from a user. Any of a plurality of techniques may be used to identify the audio, alone or in combination with other identification techniques, including length of song, fingerprint recognition of digital or analog audio, scheduled programming, or metadata transmitted in the same or an adjacent channel or frequency. The criteria used to determine whether to save a recording may be based on attributes included in the identification database, such as artist, genre, popularity, station programming, year, signal quality, etc. The audio selected by a user for listening may be recorded, or a programmable tuner or other input selector may automatically record desired music regardless of whether the music is being output for listening. The audio recorded may be obtained from any source, including analog and digital radio, Internet radio streams and removable pre-recorded media.
Owner:GRACENOTE
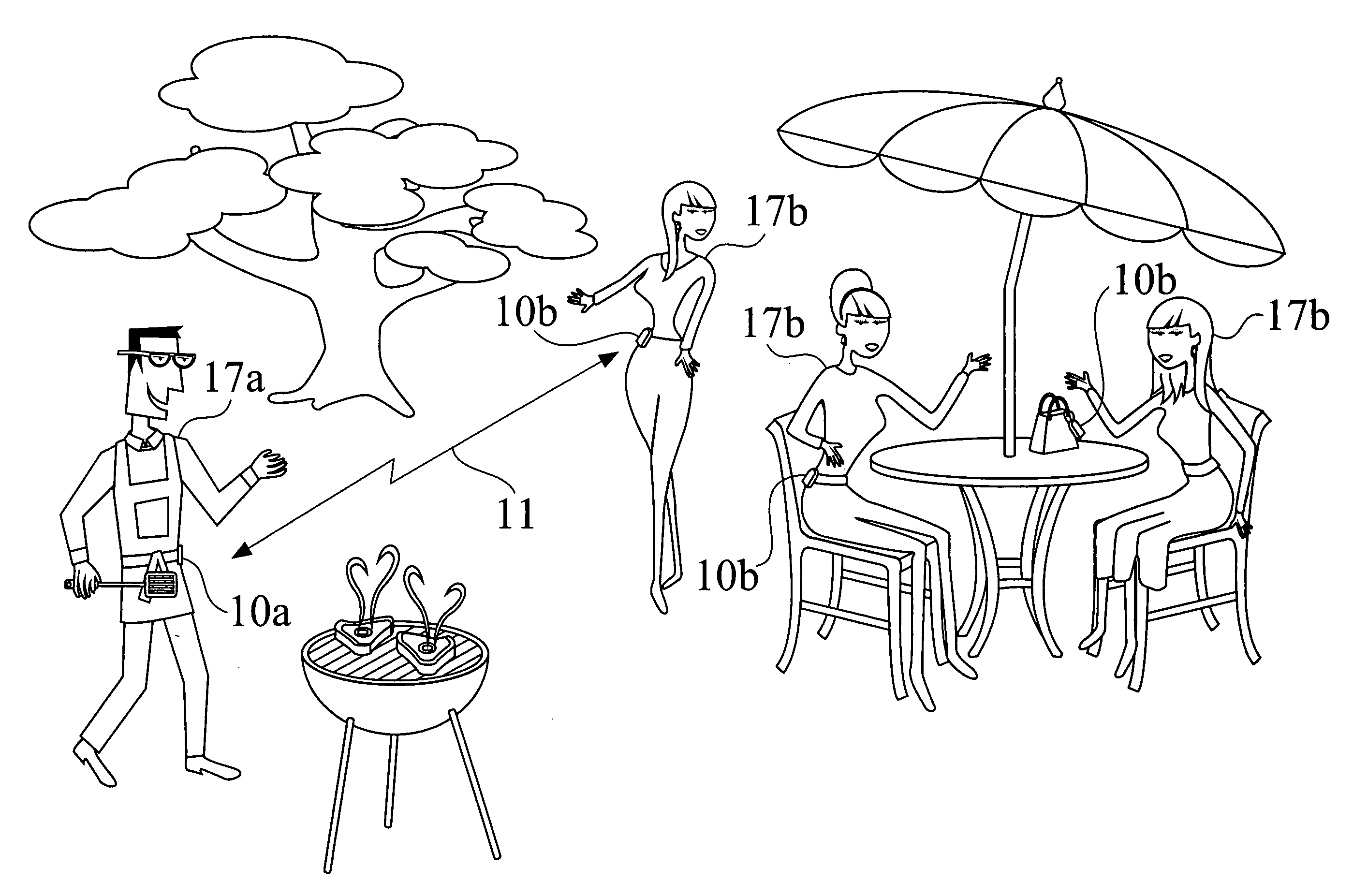
Personal radio location system
InactiveUS20070069890A1Electric signalling detailsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionObject basedRadio location
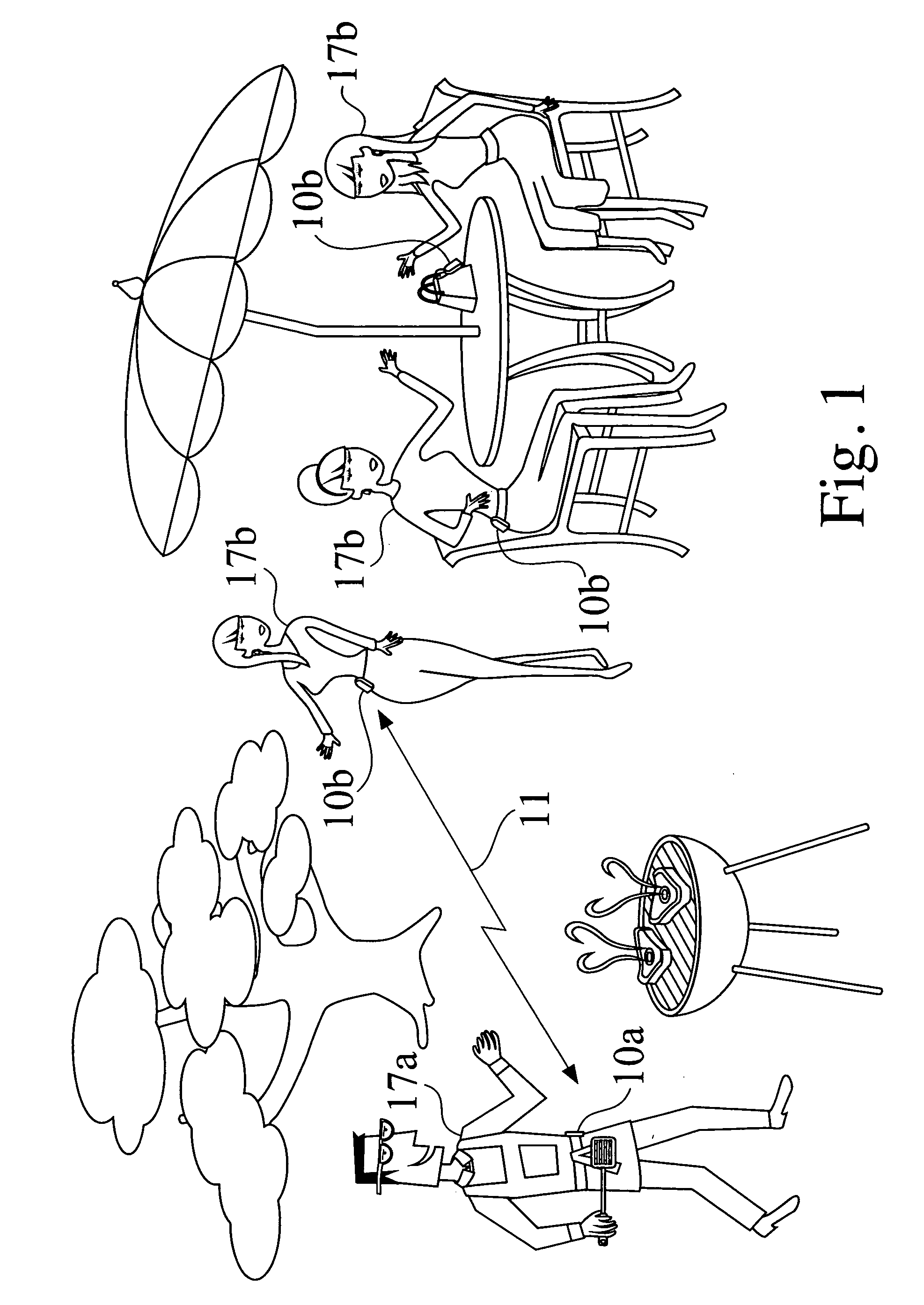
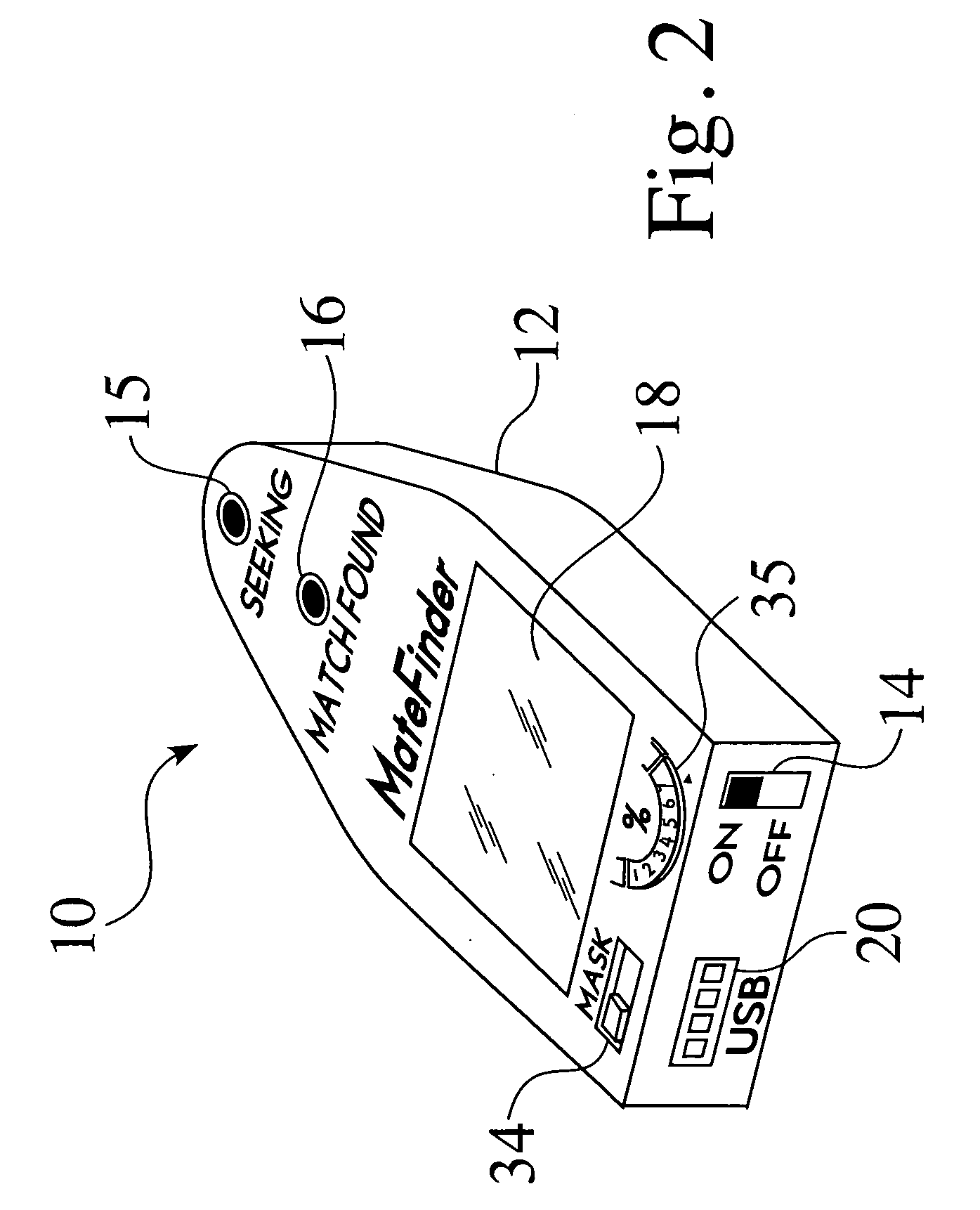
Methods and apparatus for using an energy emanating device to find a person (17a,b) or an object based on preselected attributes (33) stored in the energy emanating device (10) are disclosed. A network radio (52) enables the user of the device to communicate with others over a wireless network (50) via voice calls, text messaging, instant messaging, e-mails and Internet access.
Owner:SOCIAL FABRIC CORP
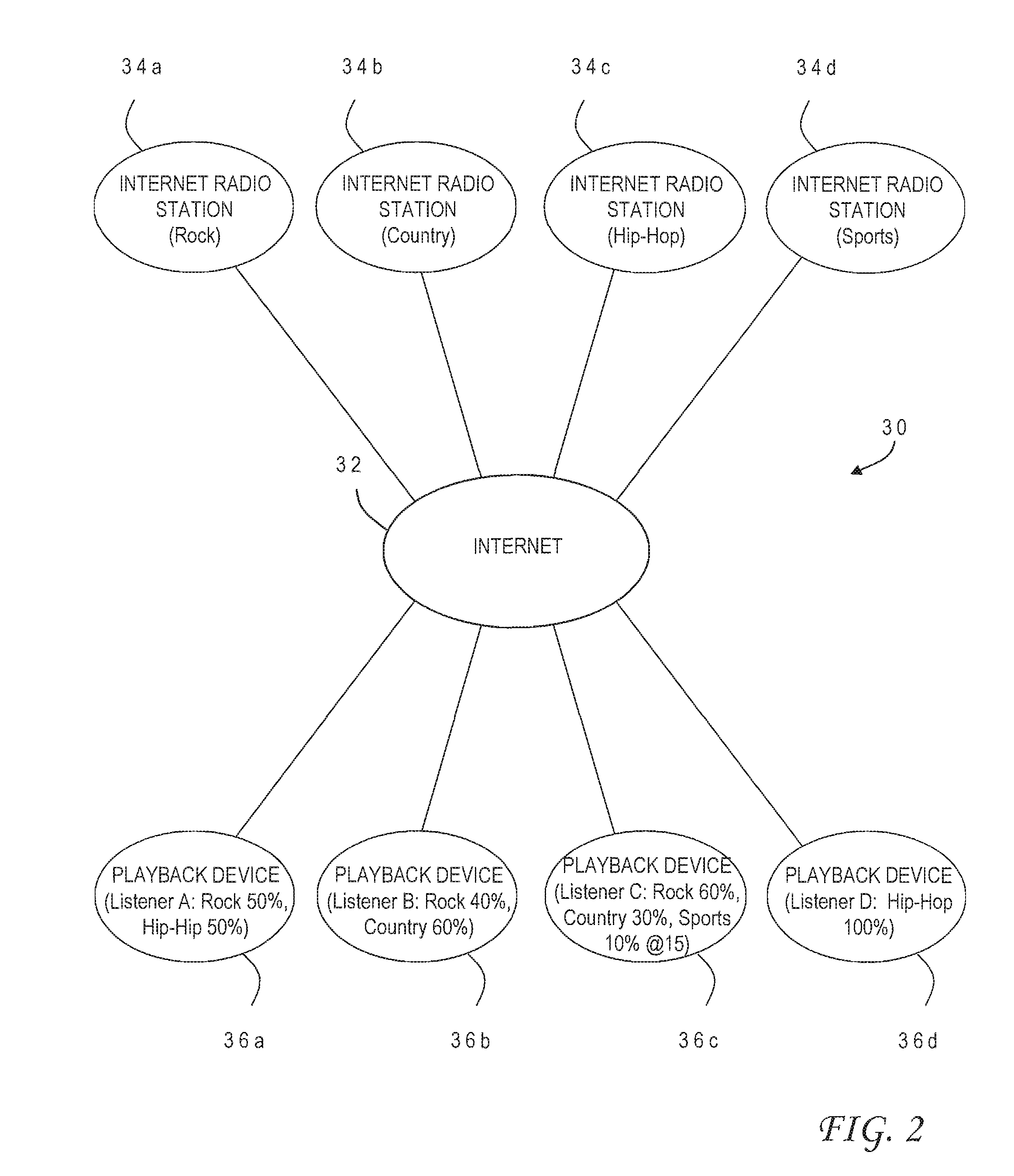
Rules-based user preferences for stream switching in an internet radio player
InactiveUS20110078323A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTelevision systemsPersonalizationClock time
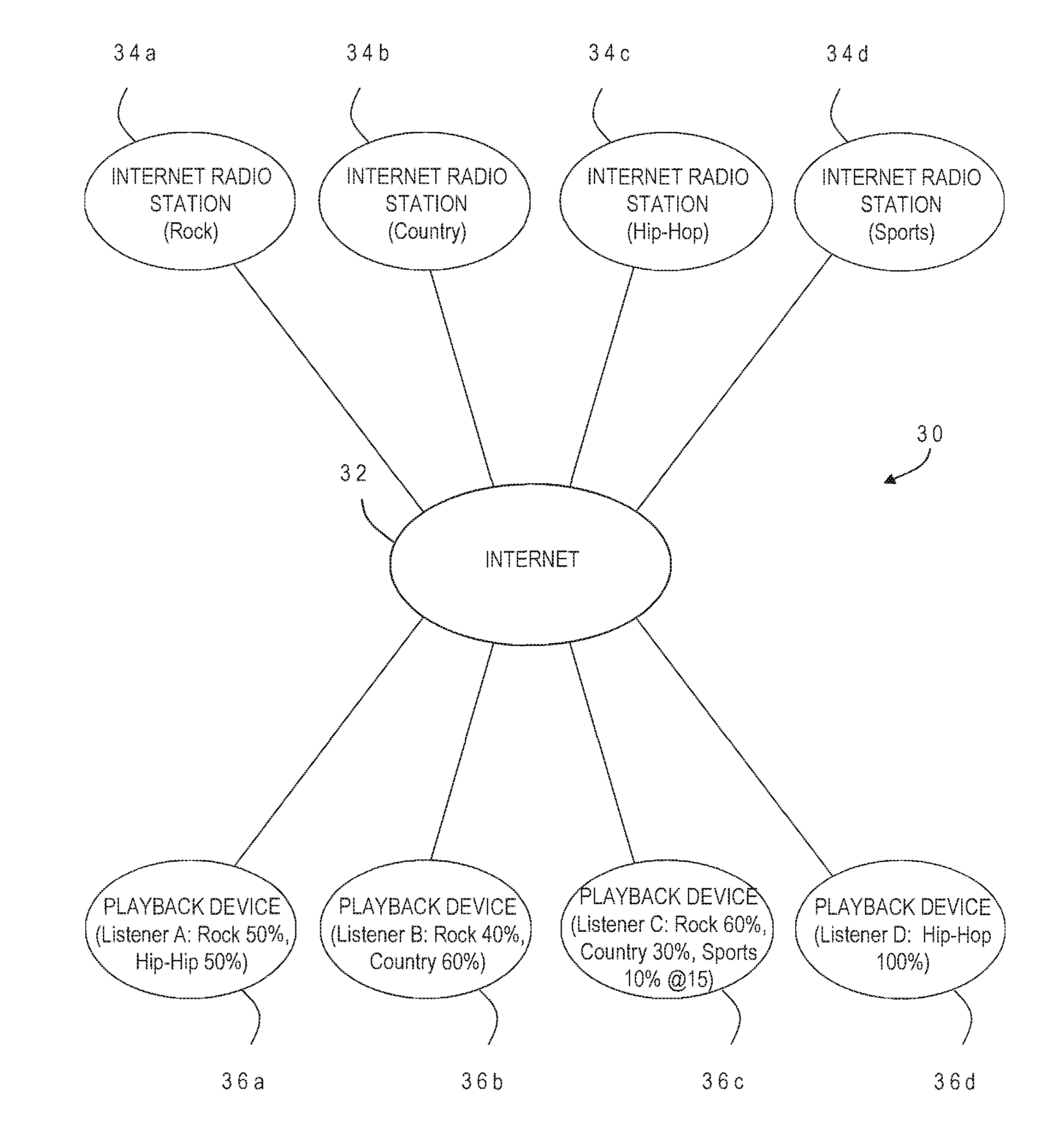
An internet radio player provides more personalized streaming audio content by assigning play amounts to different stream sources, and then playing streams from the different sources at a playback device for play times corresponding to the respective play amounts. The play time for a given stream is calculated as a user-defined percentage for the associated stream source multiplied by an expected listening period. The different stream sources can include different musical genres, news, sports, weather, or traffic. Play amounts are automatically adjusted based on user selection of the currently-playing stream source for increased or decreased play. A particular stream can also be played at a predetermined clock time, and the streams can further be ordered for play according to user preference. The present invention accordingly provides a richer listening experience than that attained by listening to a single internet radio stream, even if the single stream already reflects a user's preferences.
Owner:IHEARTMEDIA MANAGEMENT SERVICES
Method and Apparatus For Obtaining Digital Objects In A Communication Network
InactiveUS20080177864A1Easy to useTime-efficient for userTelevision system detailsMultimedia data indexingLow speedInternet radio
A technique for obtaining digital objects (such as songs or video clips) from information providers in data communication networks (such as the Internet); the digital objects being sent through channels (such as Internet radio channels or Internet TV channels) or being otherwise made available. The end-user gains several advantages over techniques supported by the known art. For example, end-users may; easily locate desired digital objects, need not be connected during object capture, can be connected through a low speed connection, does not have to have a high capacity computer, can obtain digital objects legally, can receive supplemental information associated with the digital objects, can quickly scan a vast number of digital object having been sent earlier, need not have the required storage space for the digital objects available during object capture, can easily navigate through a multitude of digital object channels, can easily obtain objects with a certain desired quality, can easily obtain objects in a certain desired format, can legally obtain digital objects at no cost and can prove that the digital objects were actually obtained legally.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
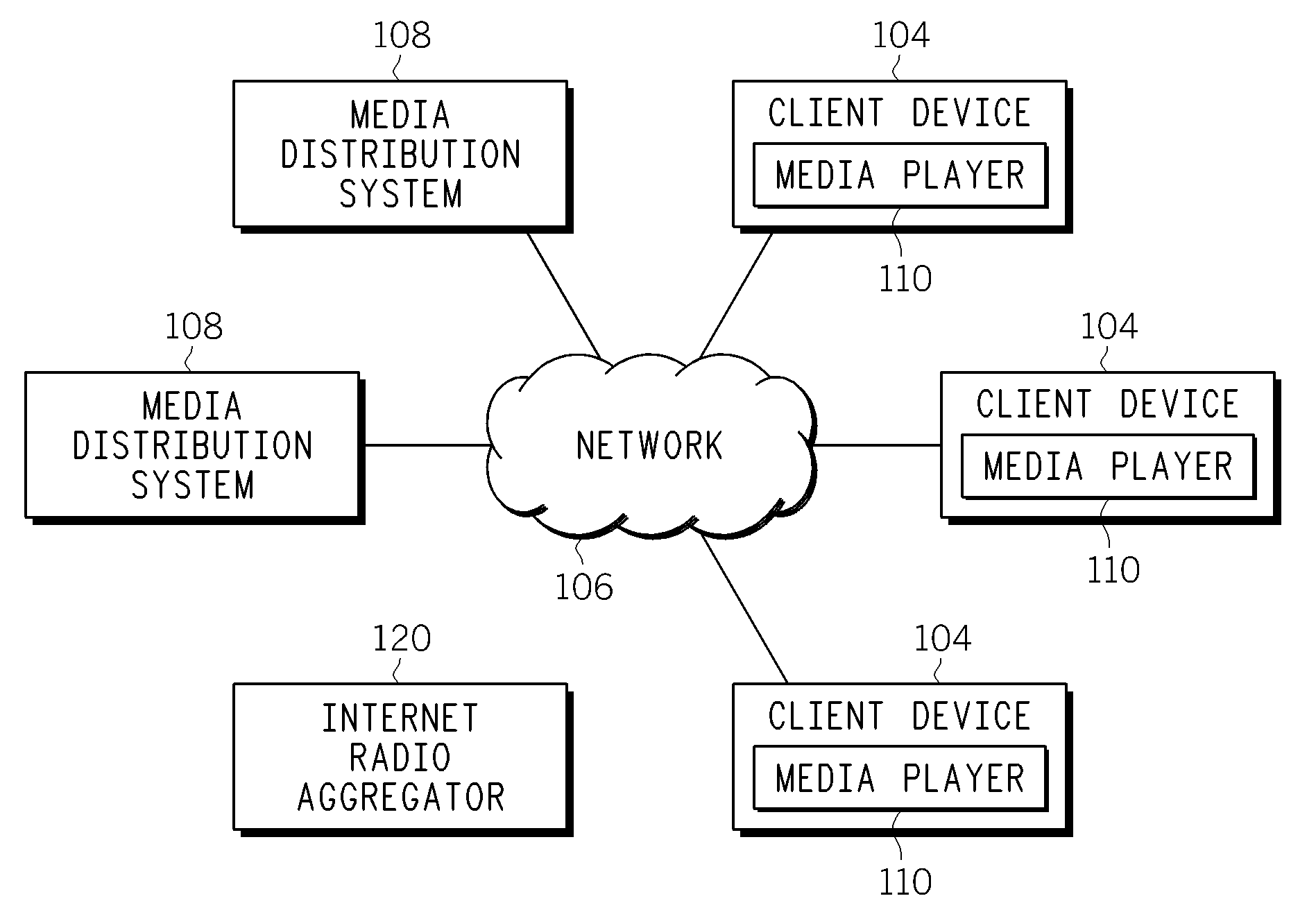
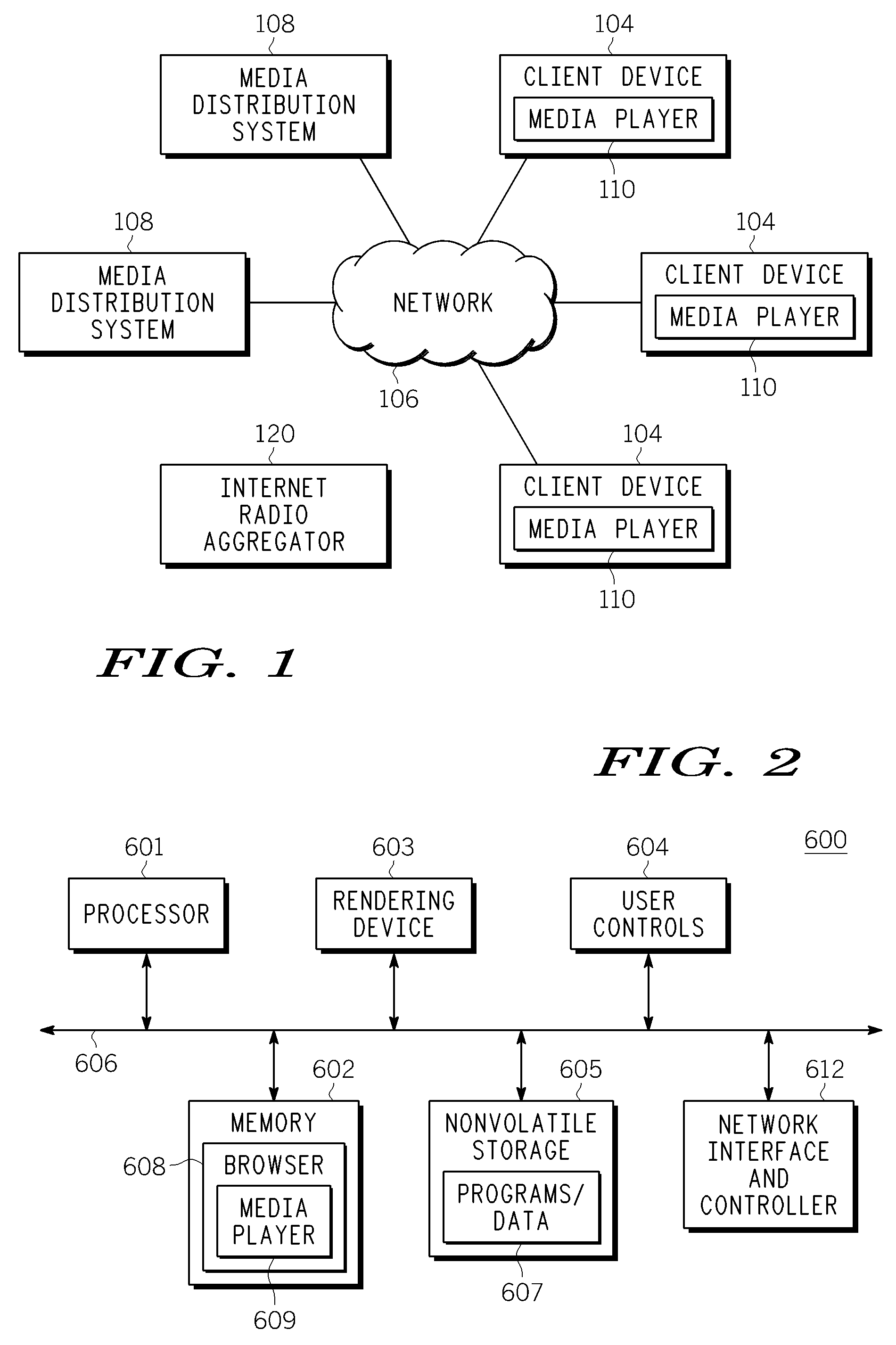
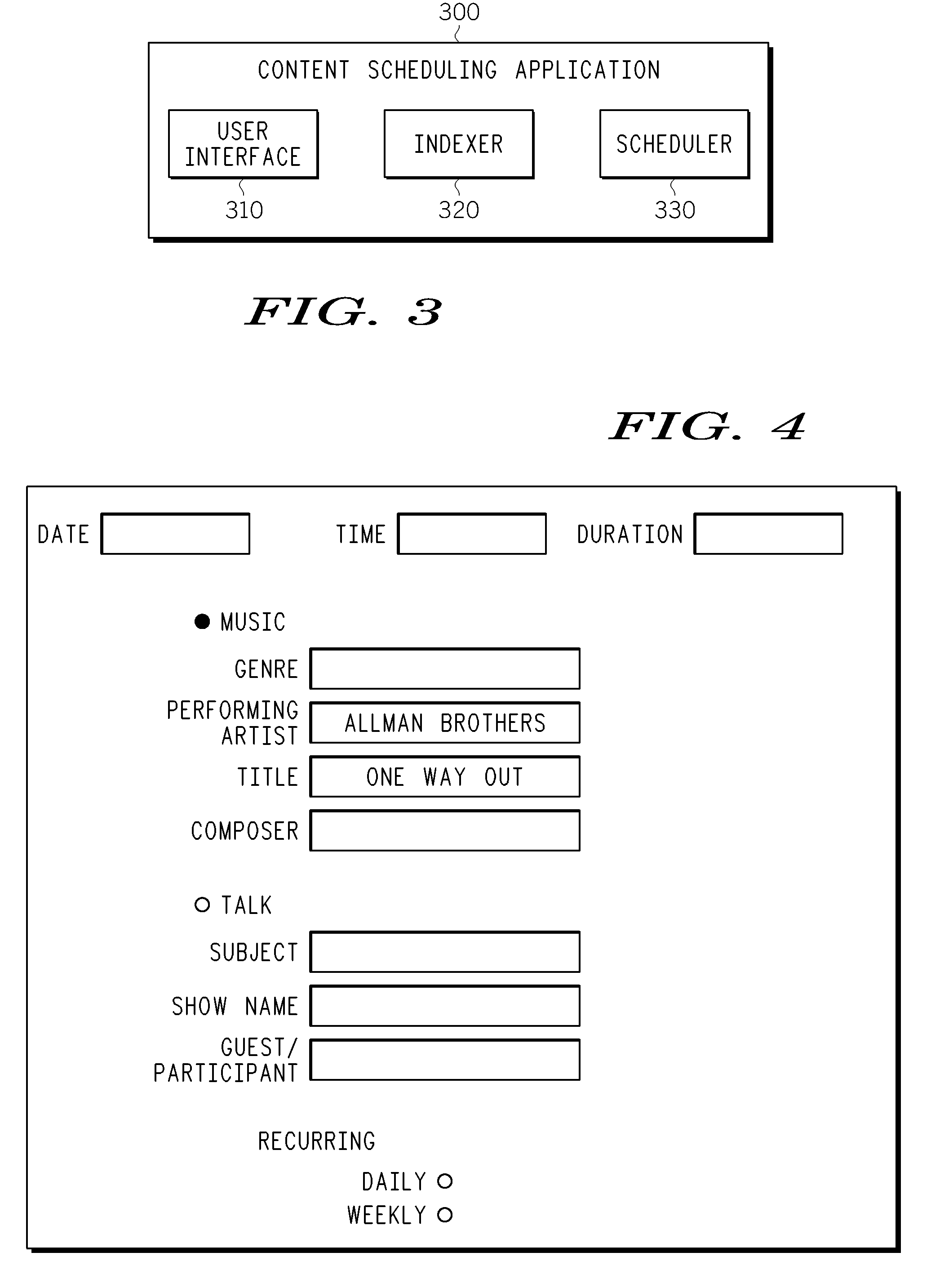
Method and apparatus for identifying and scheduling internet radio programming
InactiveUS20100153572A1Metadata audio data retrievalBroadcast transmission systemsInternet radioClient-side
A client device includes a network interface for receiving media content streamed over a network and a media player for rendering the media content. The client device also includes a content scheduling module configured to identify, schedule and access over the network selected media content items in accordance with a user profile. The content scheduling module is configured to search an online database to identify the selected media content that conforms to the user profile.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
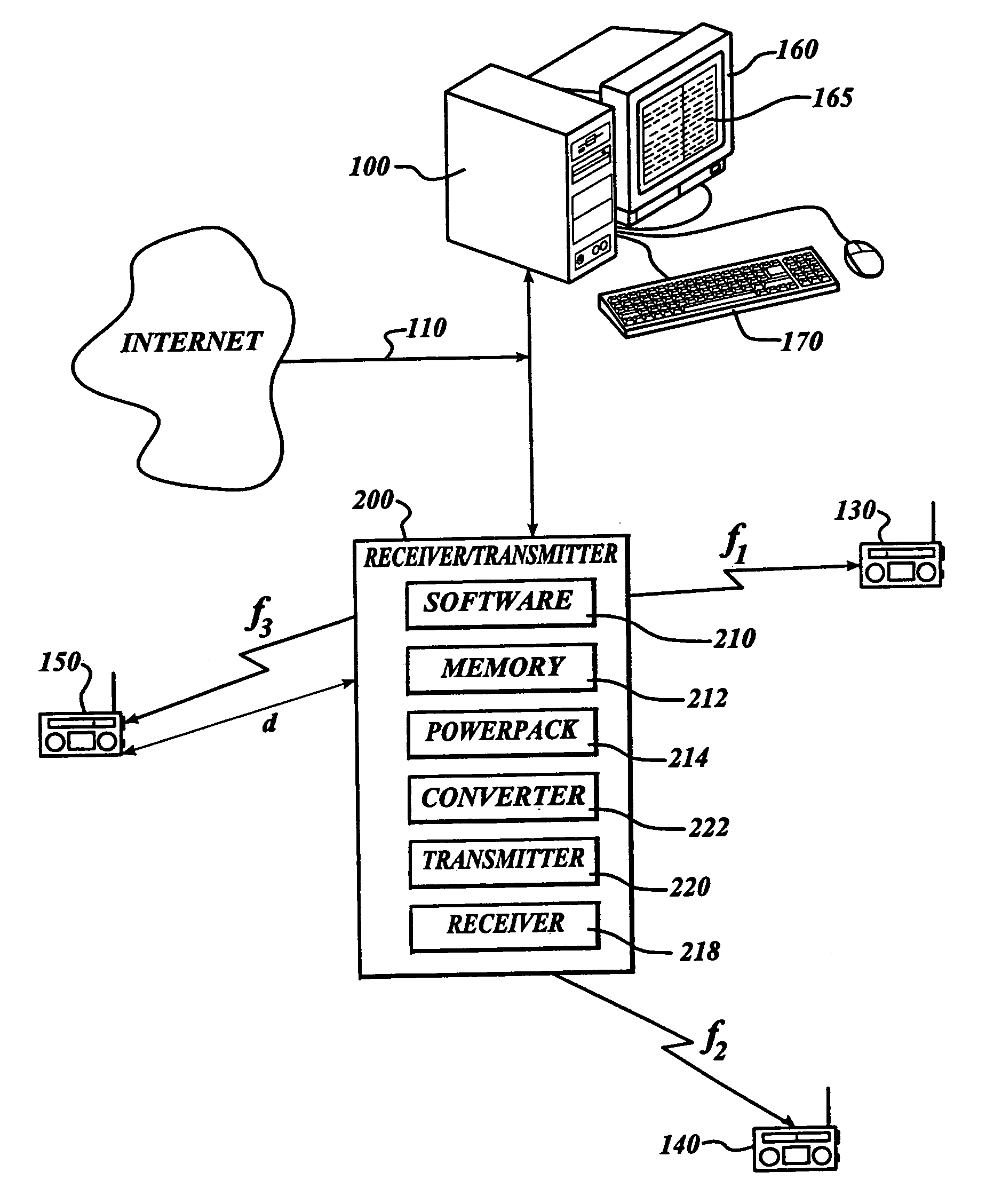
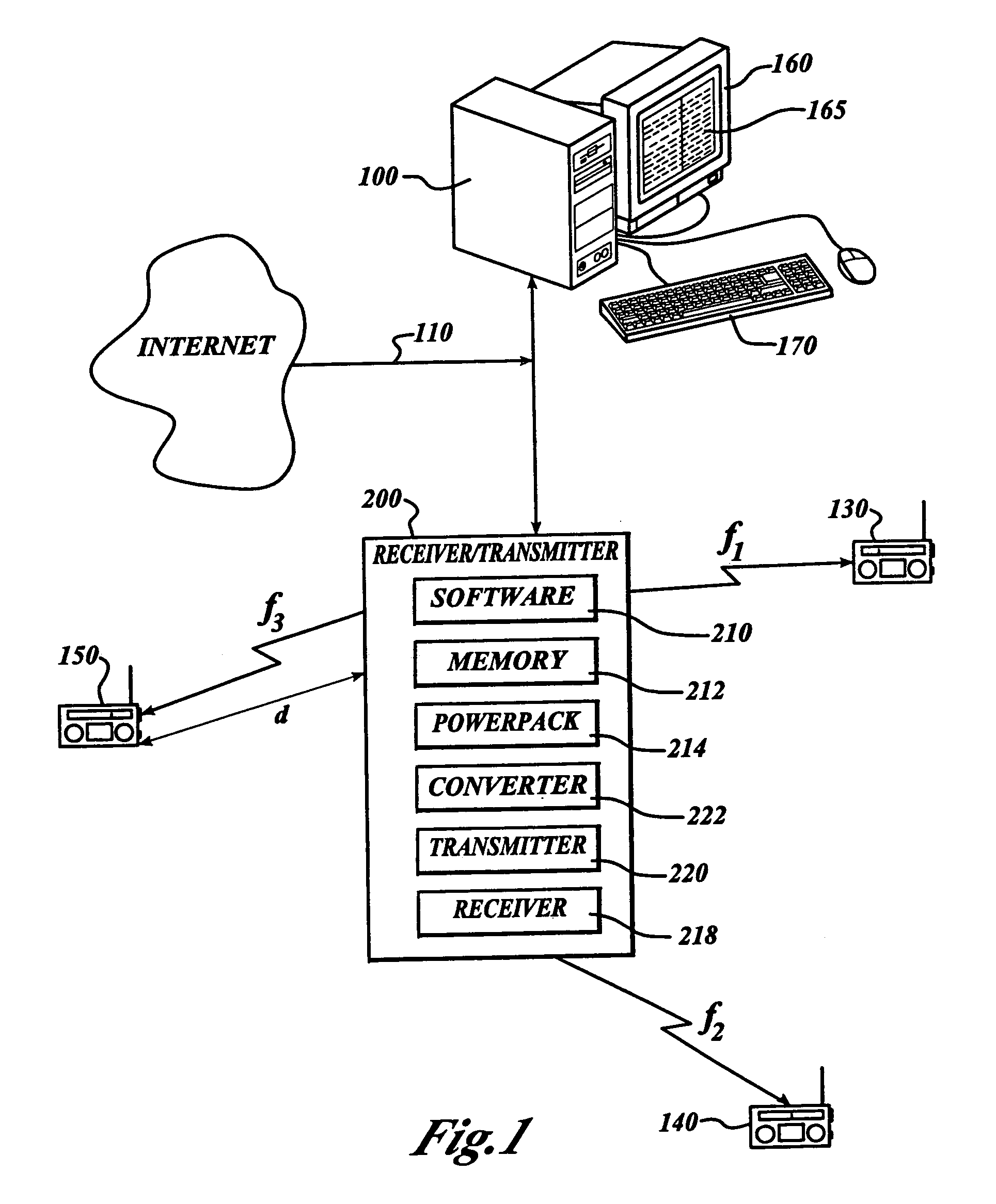
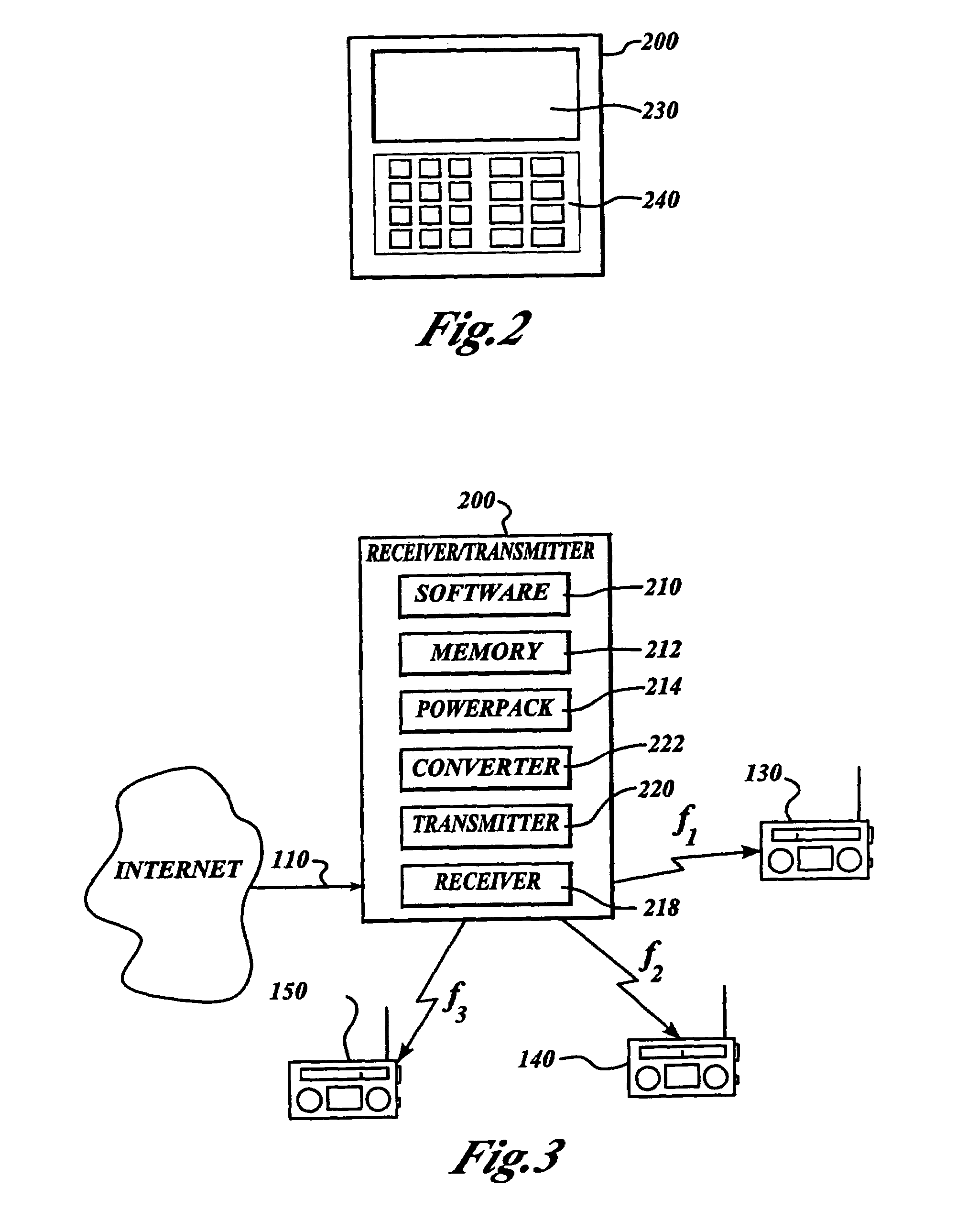
Local area internet radio receiver/transmitter
InactiveUS7110720B1Broadcast specific applicationsBroadcast transmission systemsRadio receptionInternet radio
In accordance with the invention, radio program content or other audio communications and music are transmitted as digital information through the Internet to an Internet radio receiver / transmitter device. The device converts received digital information to analog information and broadcasts the information in the radio frequency band at low power in a localized area for reception by ordinary FM or AM radios. The device is capable of receiving multiple streams of different digital information, and broadcasting each of these on separate radio frequencies, so that each person in a household may hear its own selected programming on its own preselected radio frequency. It is programmable as to at least broadcast commence time, frequency and end time, if desired. Moreover, it may store received information to play at a preprogrammed time, or on demand.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com