Patents
Literature
195results about How to "Conveniently obtain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
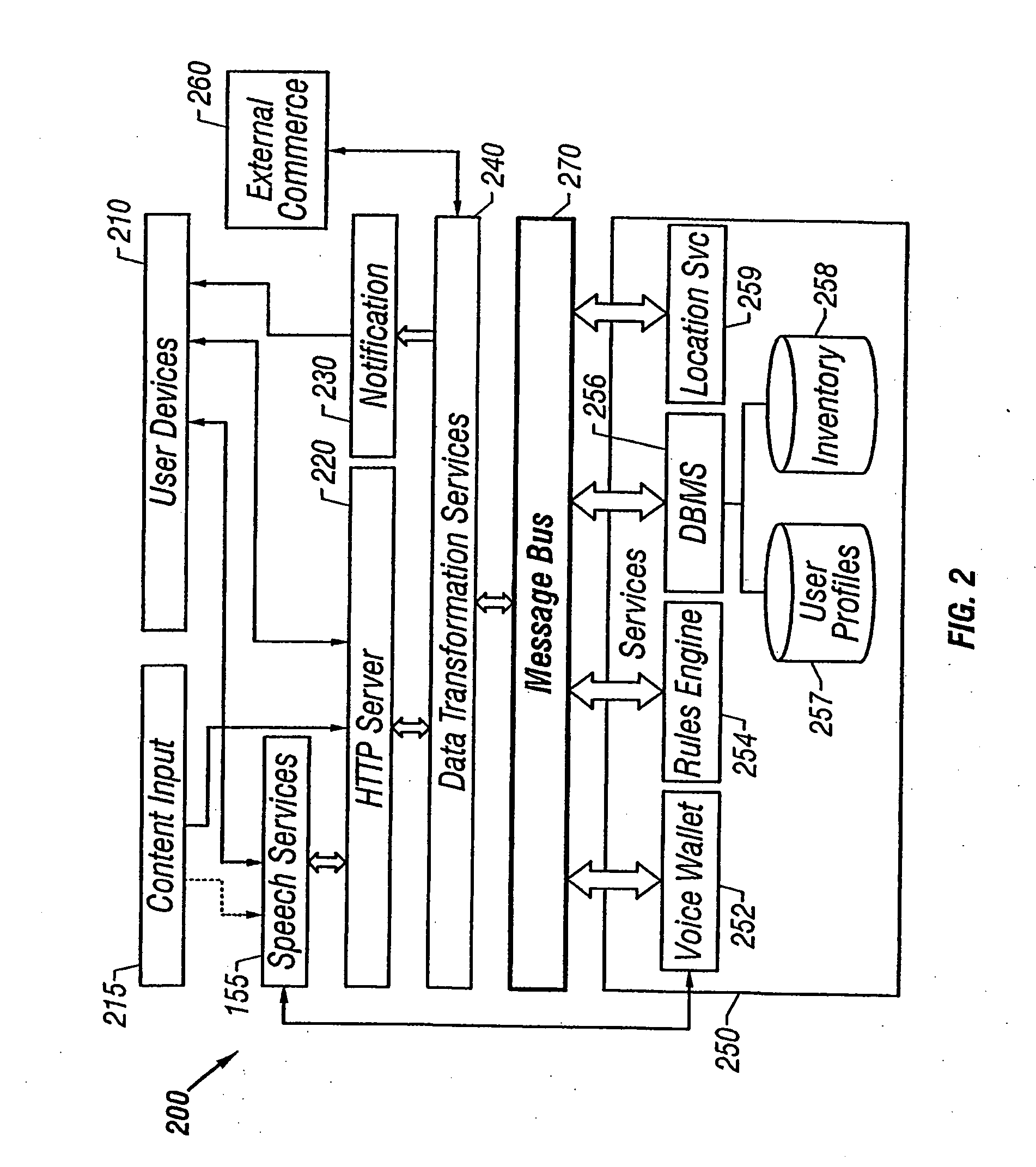
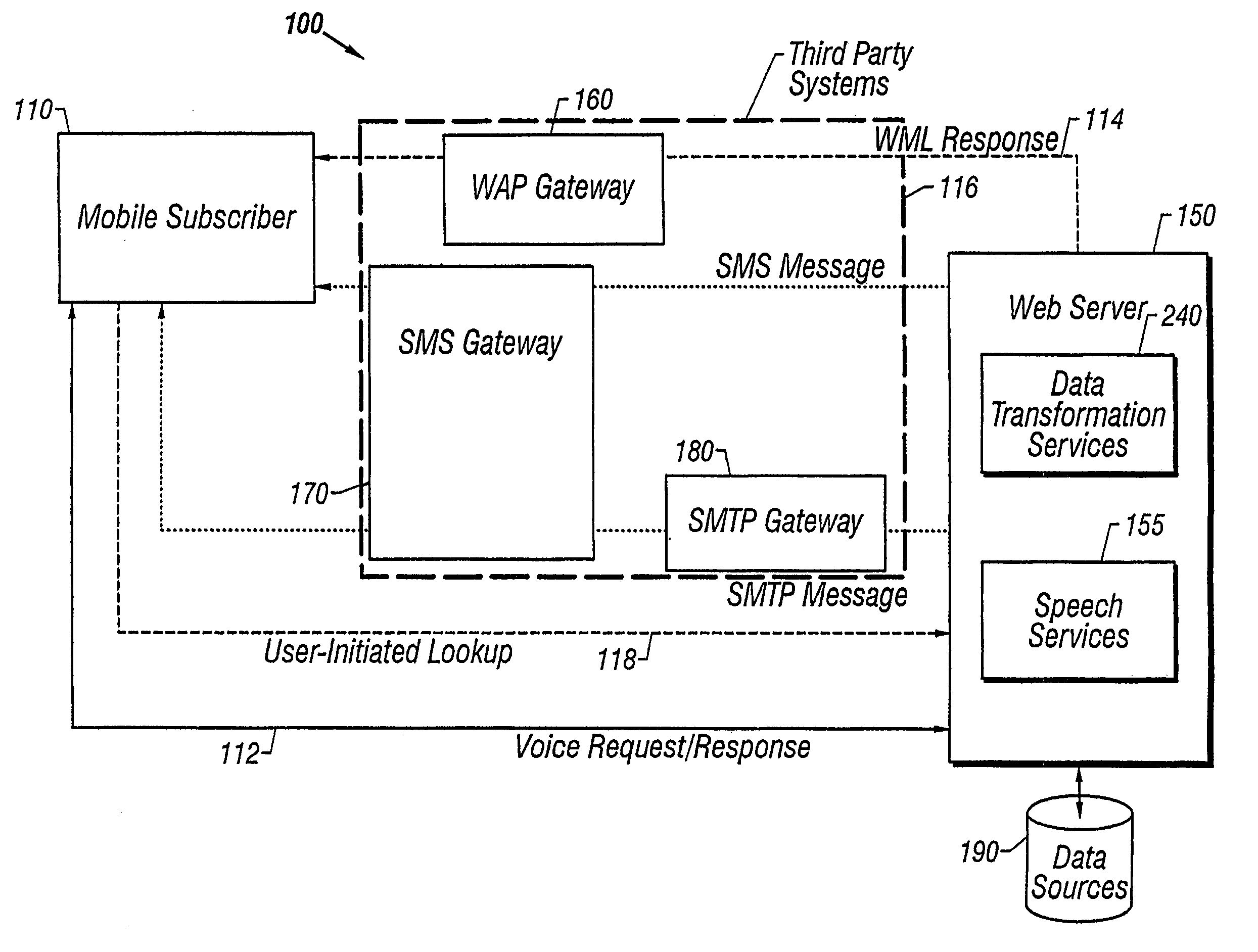
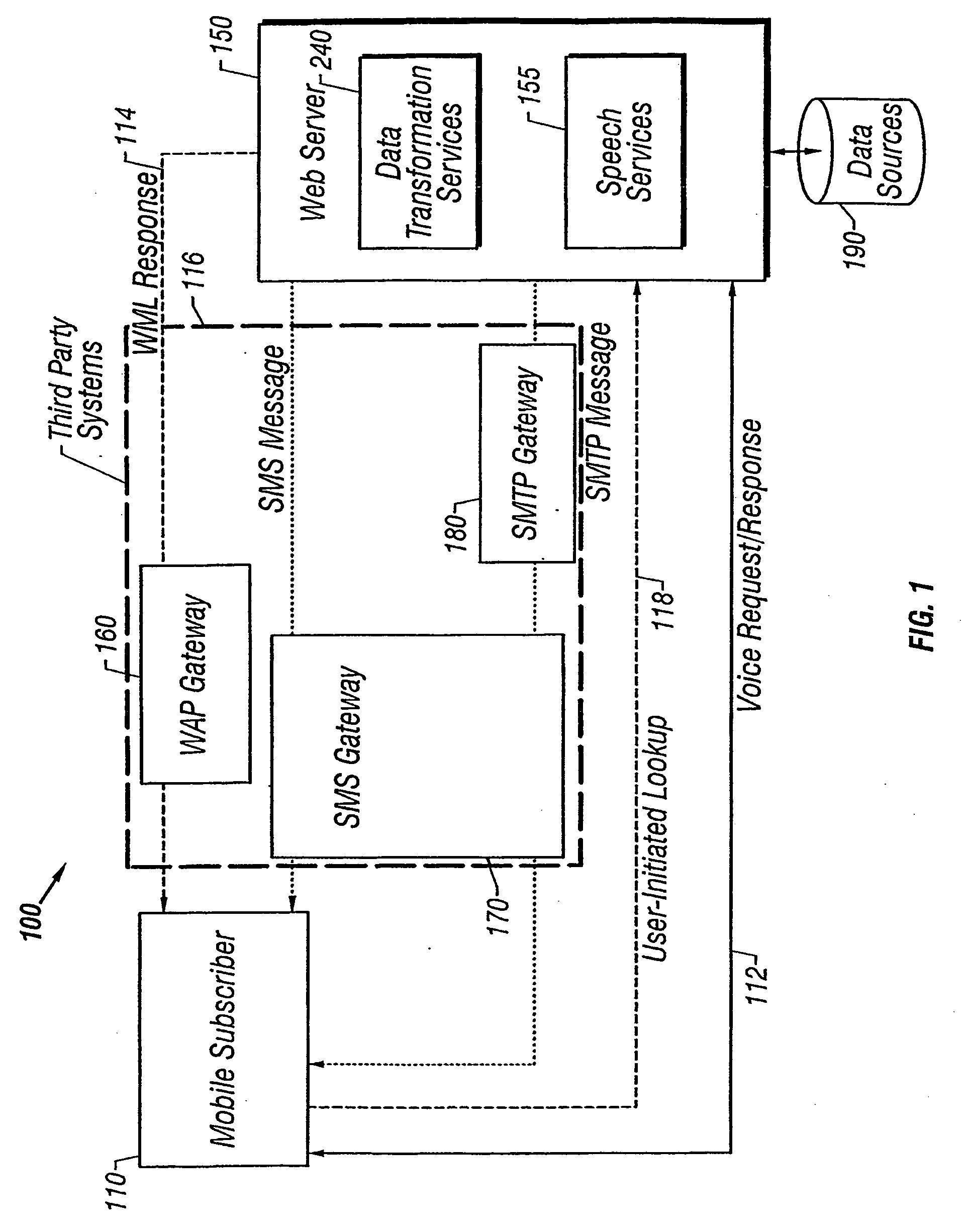
Mixed-mode interaction
InactiveUS6925307B1Information obtainedConveniently obtainUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsThe InternetPurchasing
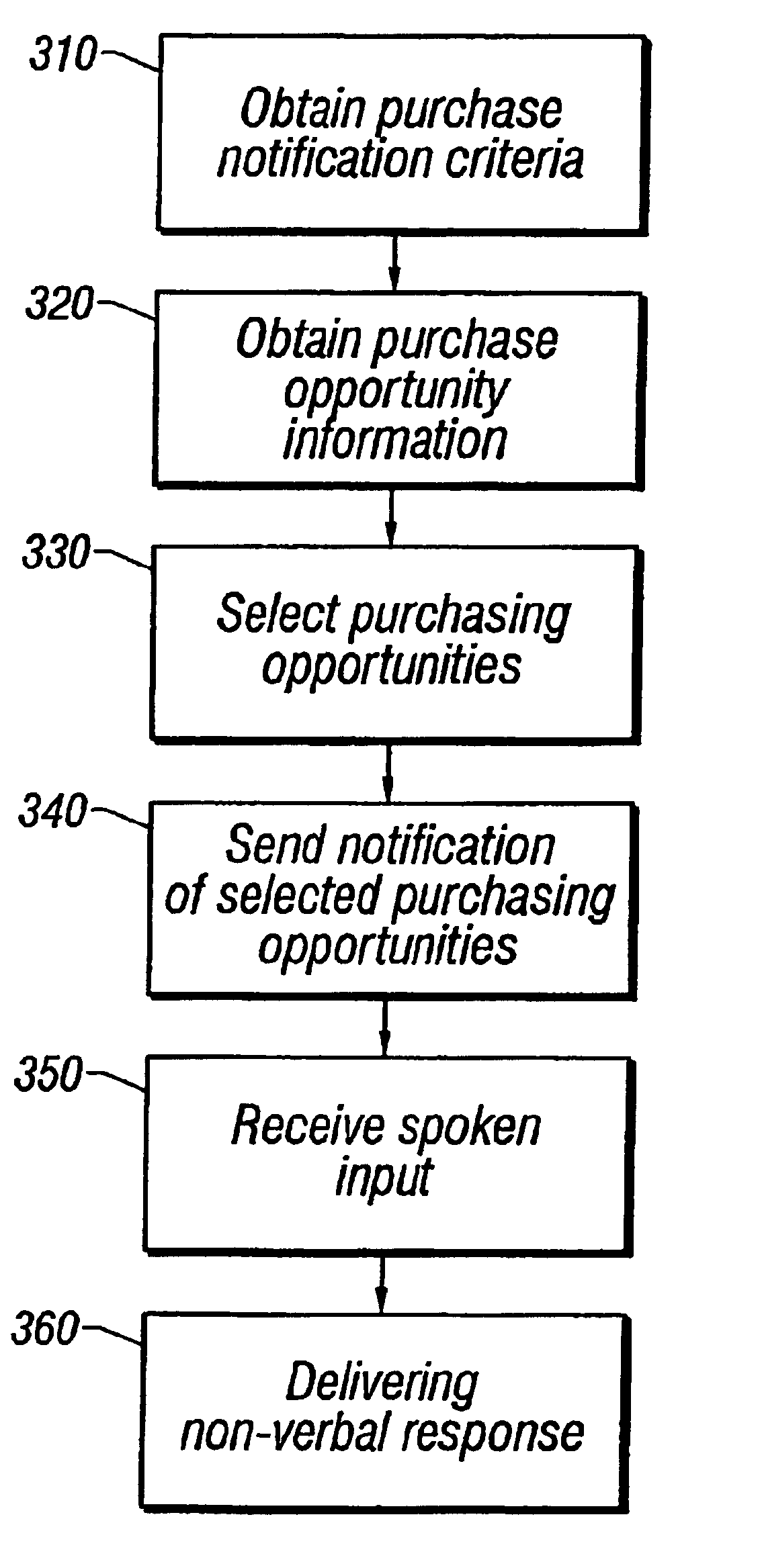
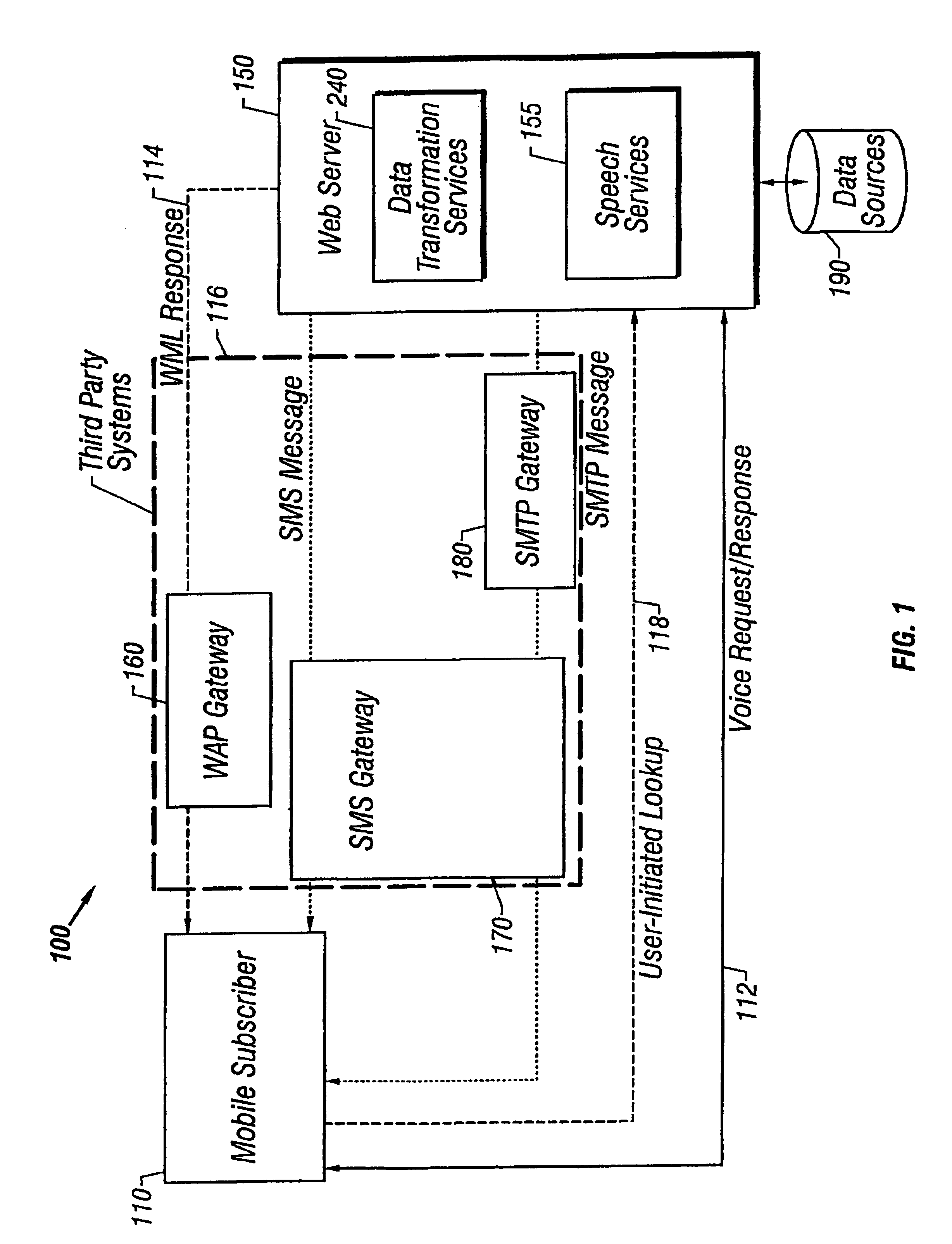
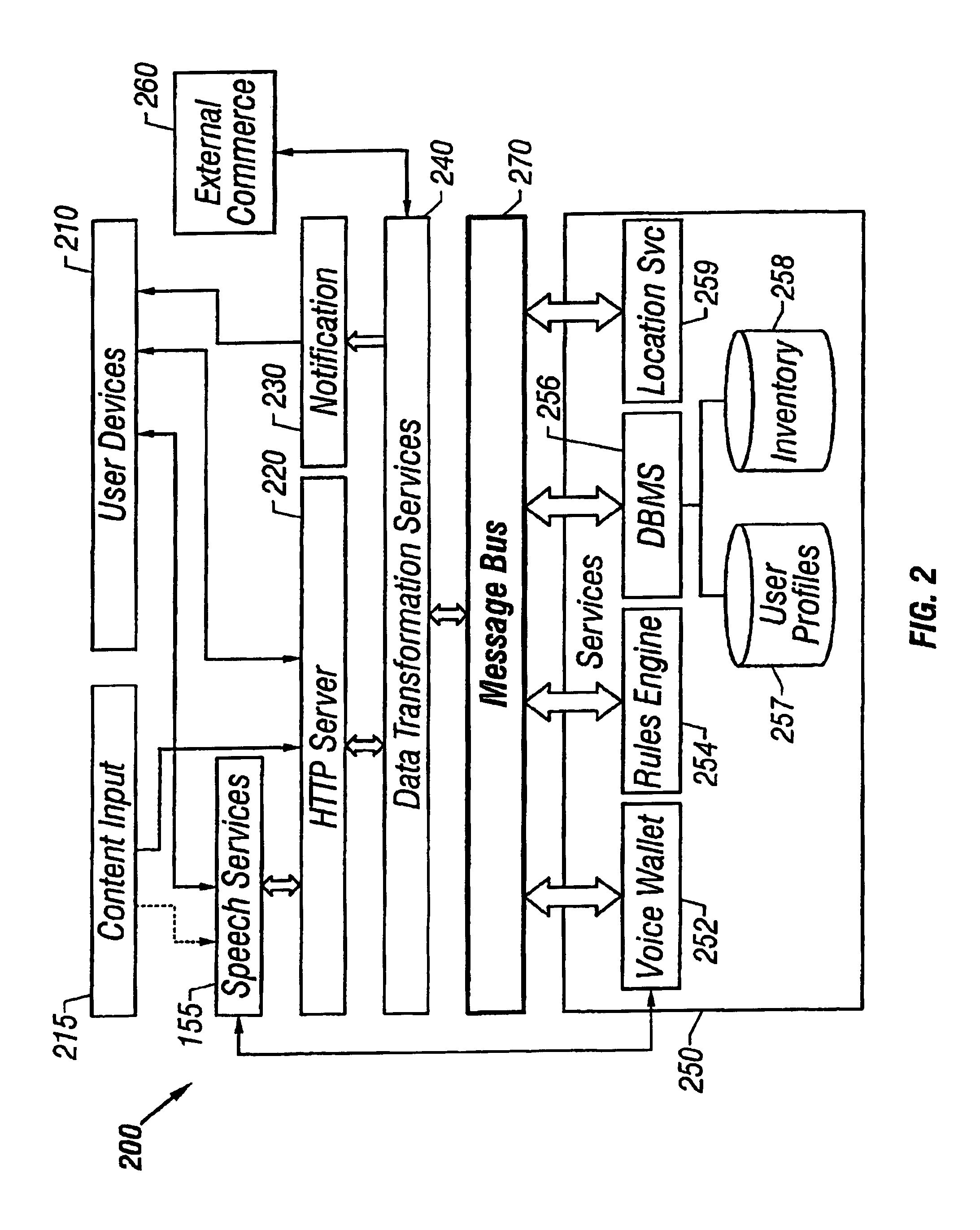
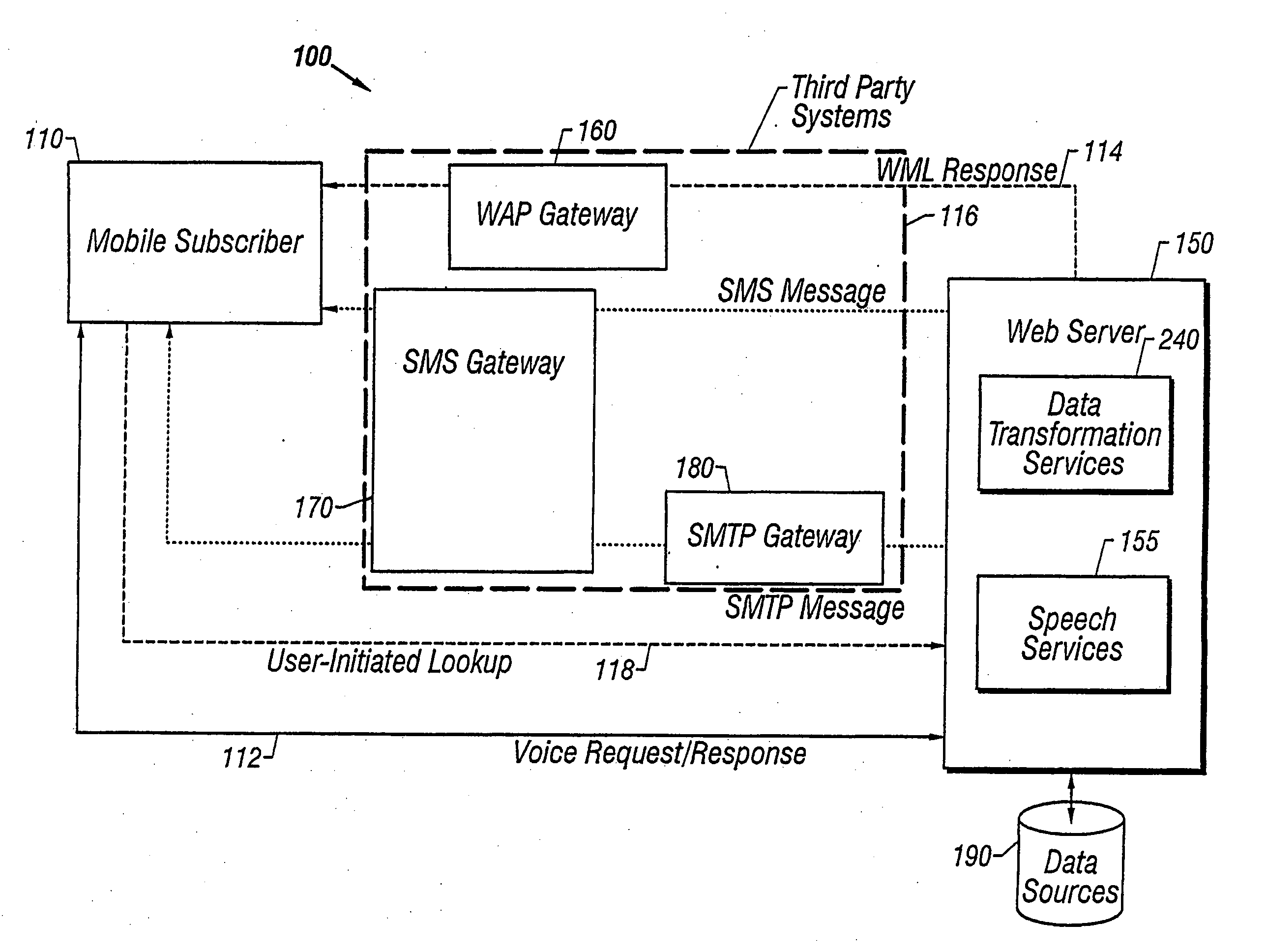
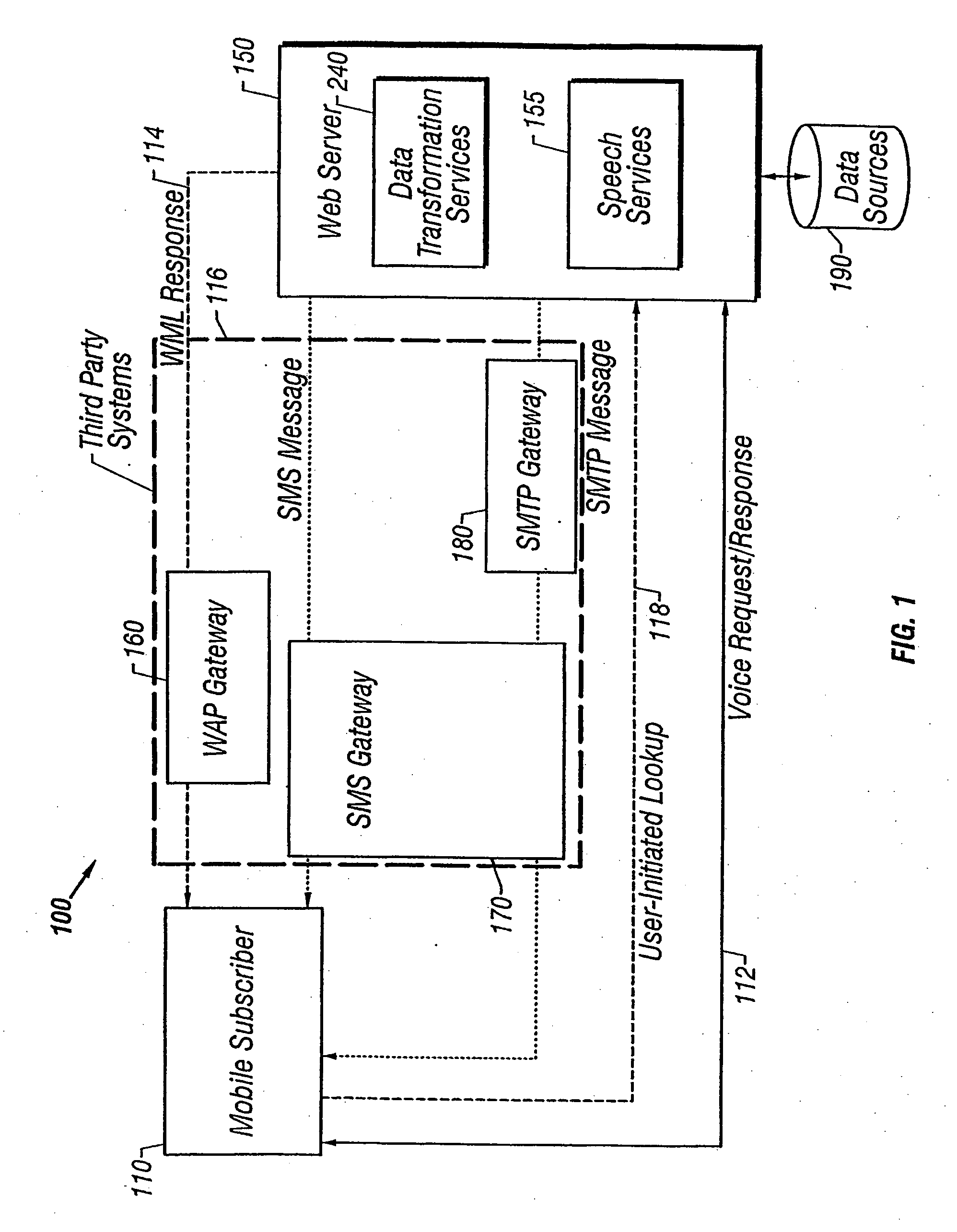
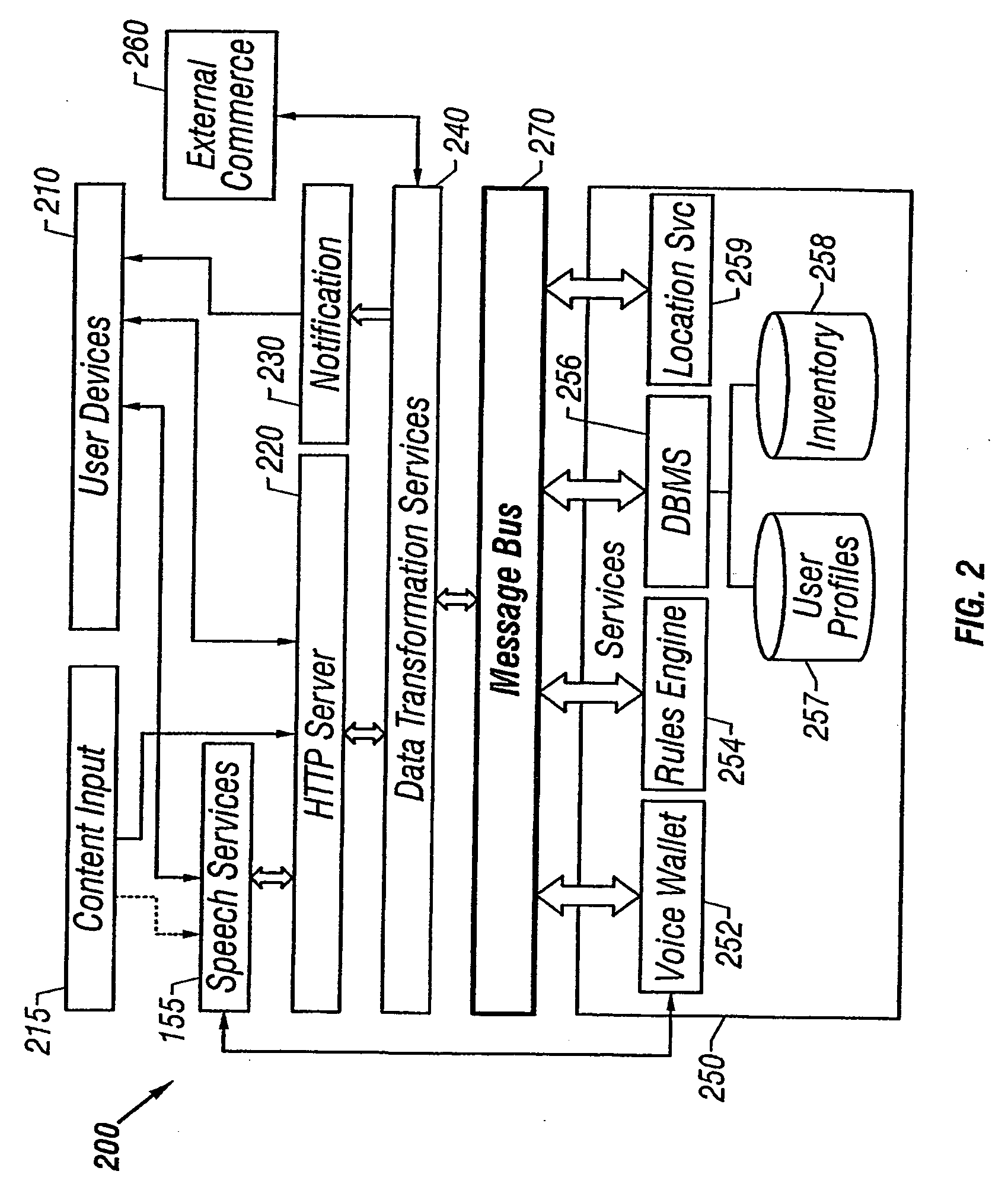
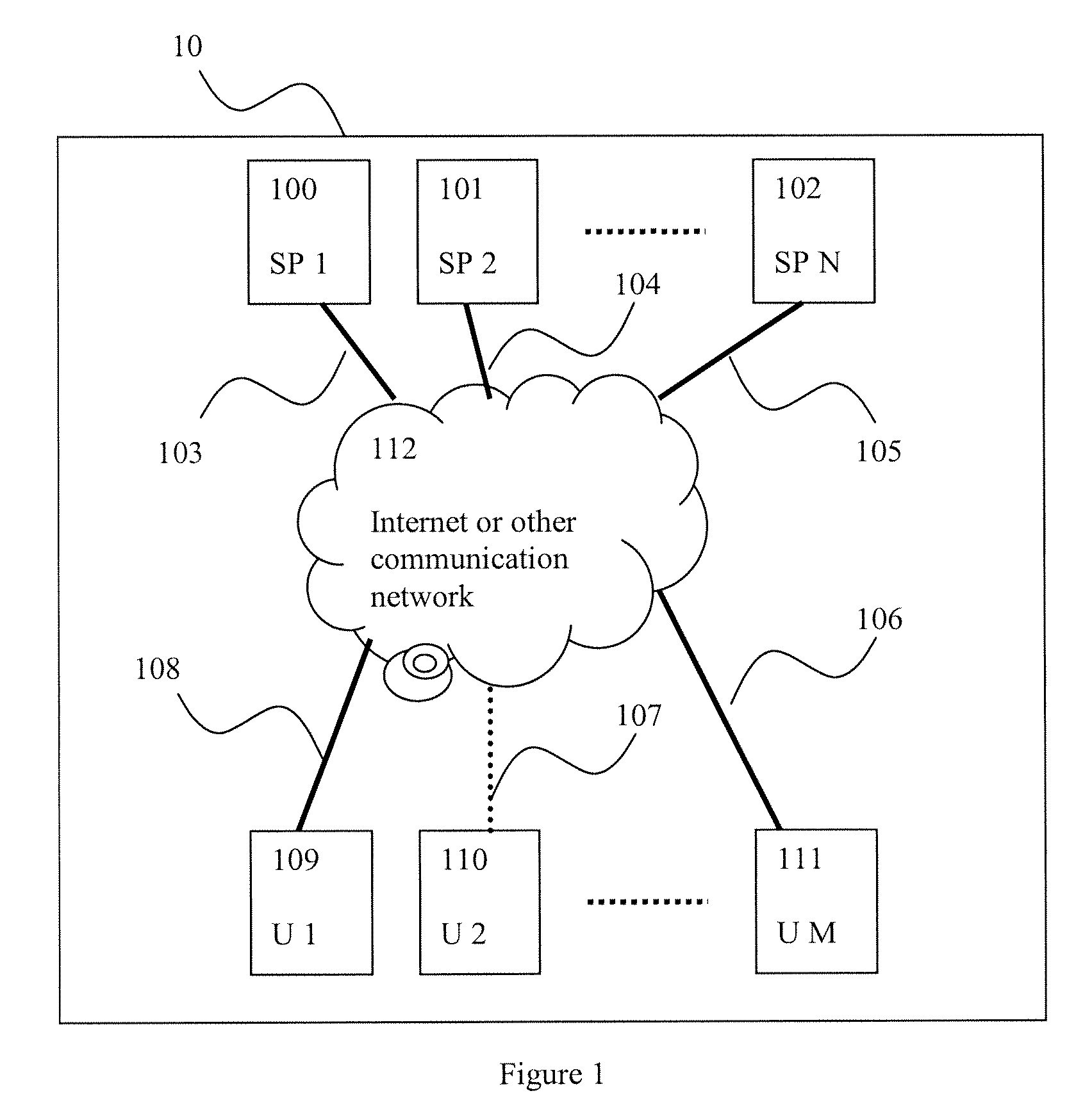
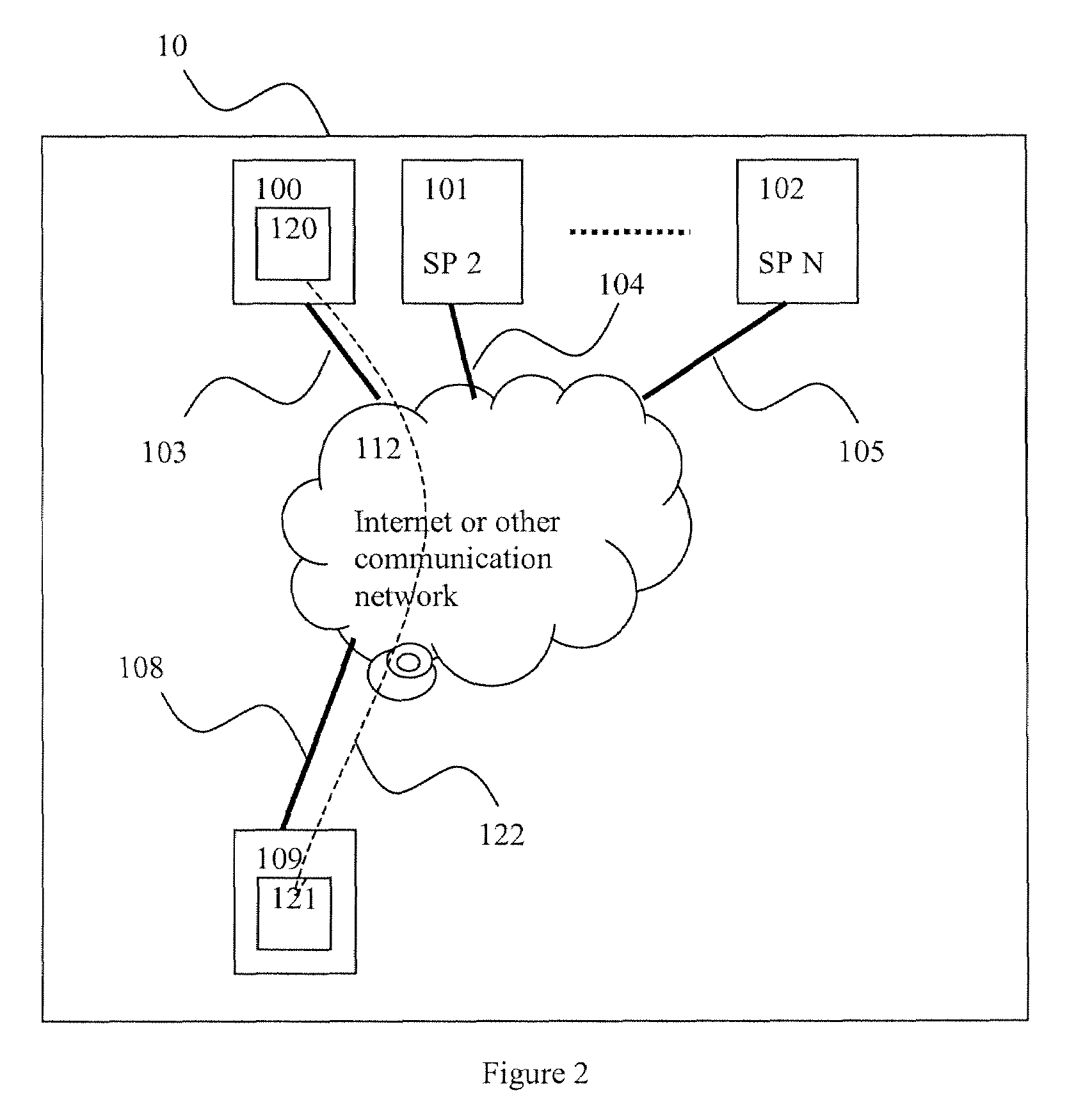
A user of a wireless device, such as a mobile phone, can make purchases or obtain information via a network, such as the Internet, using both voice and non-verbal methods. Users can submit voice queries and receive non-verbal replies, submit non-verbal queries and receive voice replies, or perform similar operations that marry the voice and data capabilities of modern mobile communication devices. The user may provide notification criteria indicating under what conditions a notification should be sent to the user's wireless device. When purchasing opportunities matching the selected notification criteria become available, the user is notified. The user can respond to the notification, and immediately take advantage of the purchasing opportunity if he so desires. Mixed-mode interactions can also be used by sellers to more advantageously control the marketing of distressed, time sensitive, or other merchandise / services.
Owner:AERITAS
Location-based Update of Subscriber Identity Information in a Wireless Device
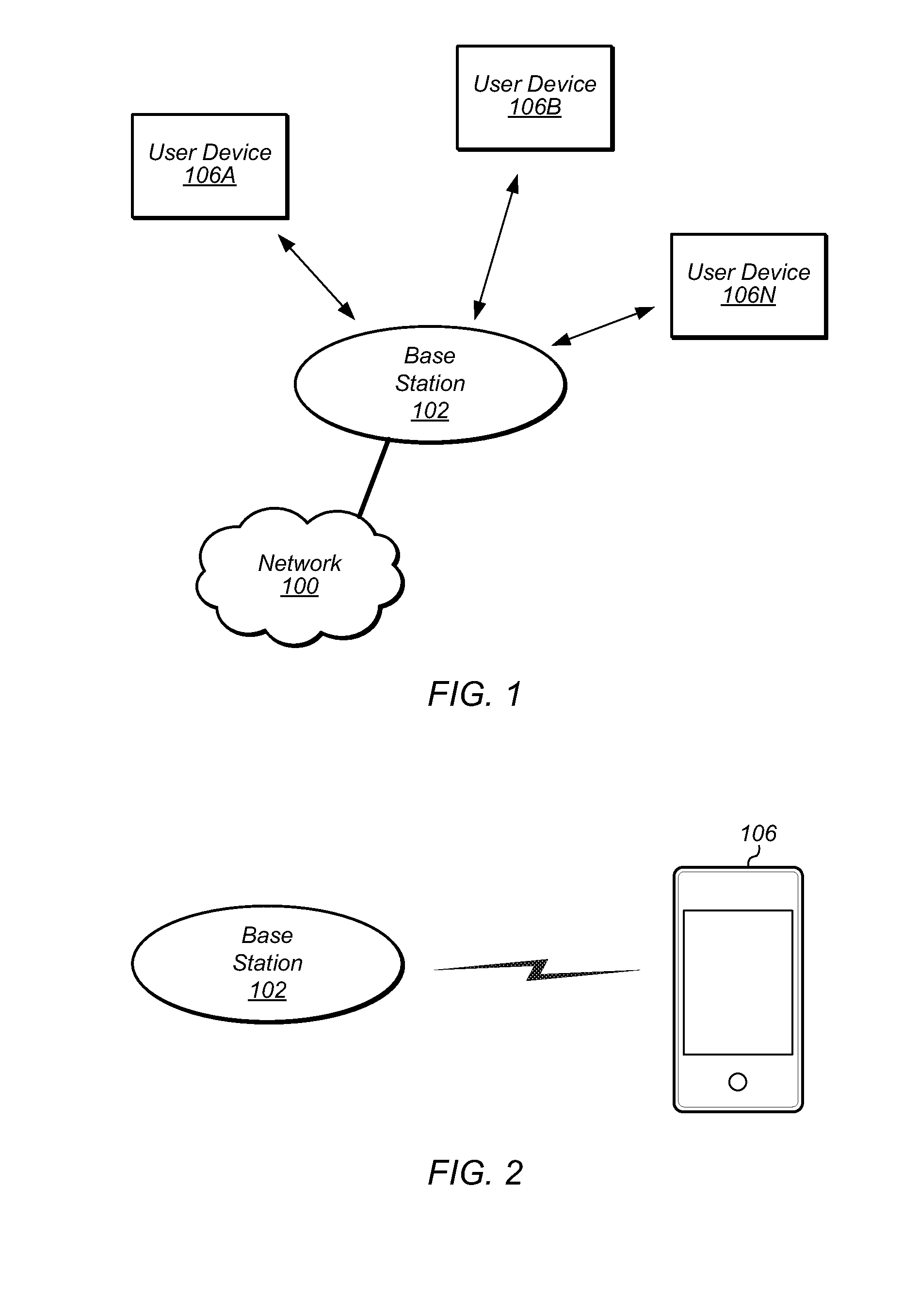
ActiveUS20140099916A1Increase flexibilityEasy to controlAccounting/billing servicesPrepayment with automatic account/card rechargingUser inputUser equipment
Location-based subscriber identity update in a wireless user equipment (UE) device. A location of the UE may be determined. An indication of a plurality of network connectivity options may be provided via a user interface. The plurality of network connectivity options may be provided based on the location of the UE. User input selecting a network connectivity option may be received via the user interface. The UE may be configured according to the selected network connectivity option in response to the user input.
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus and method for identifying optimal PEEP
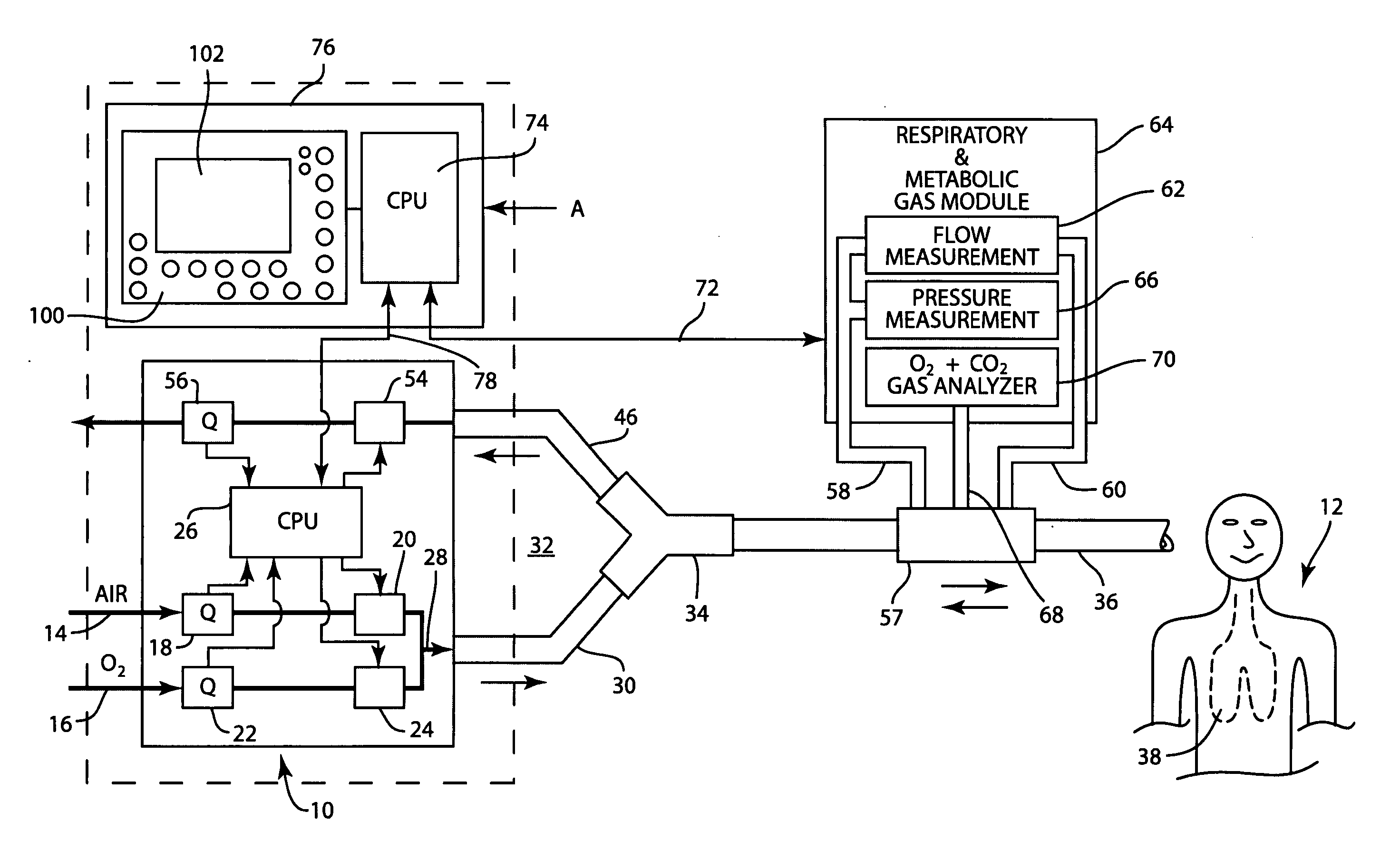
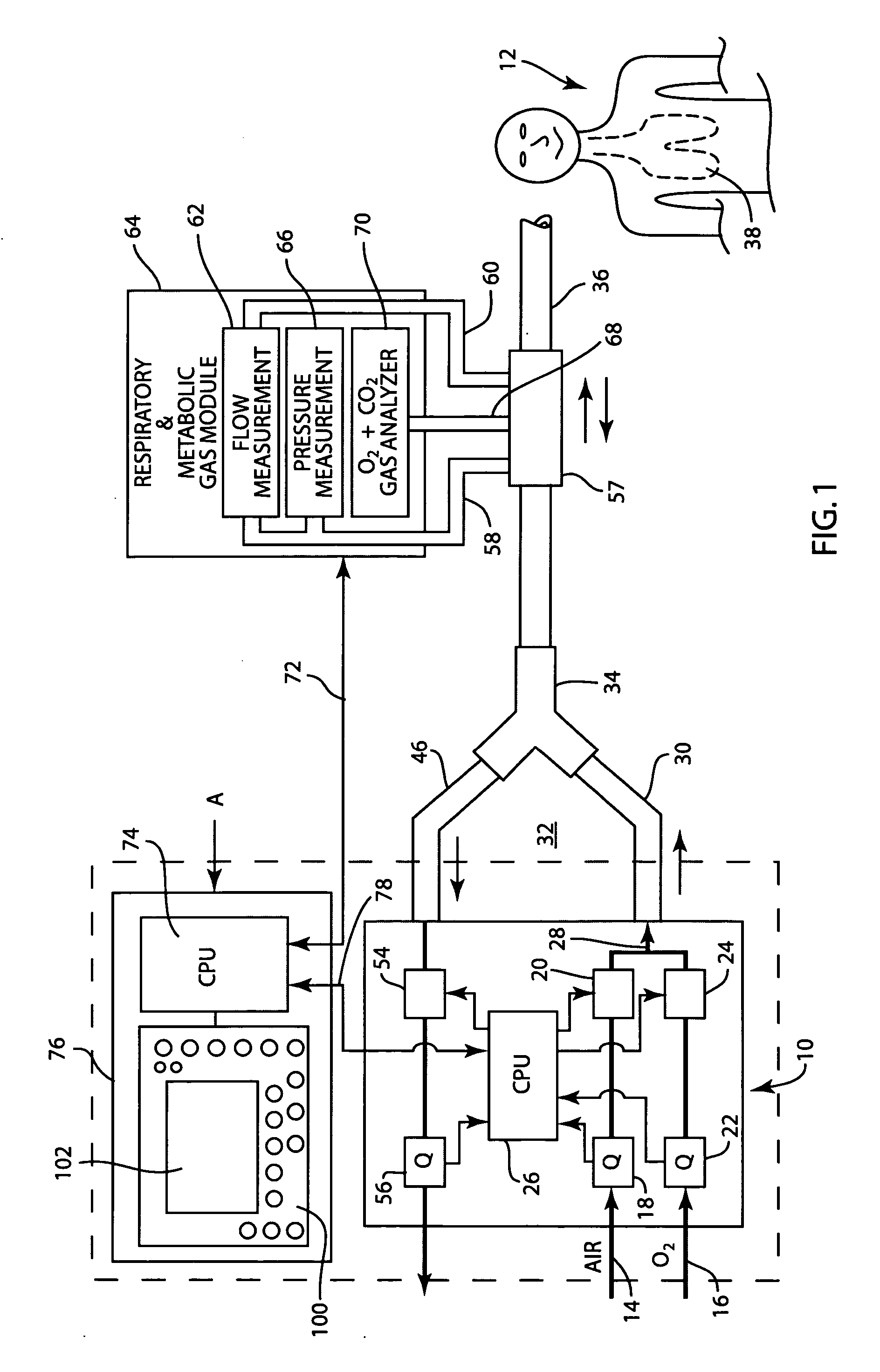
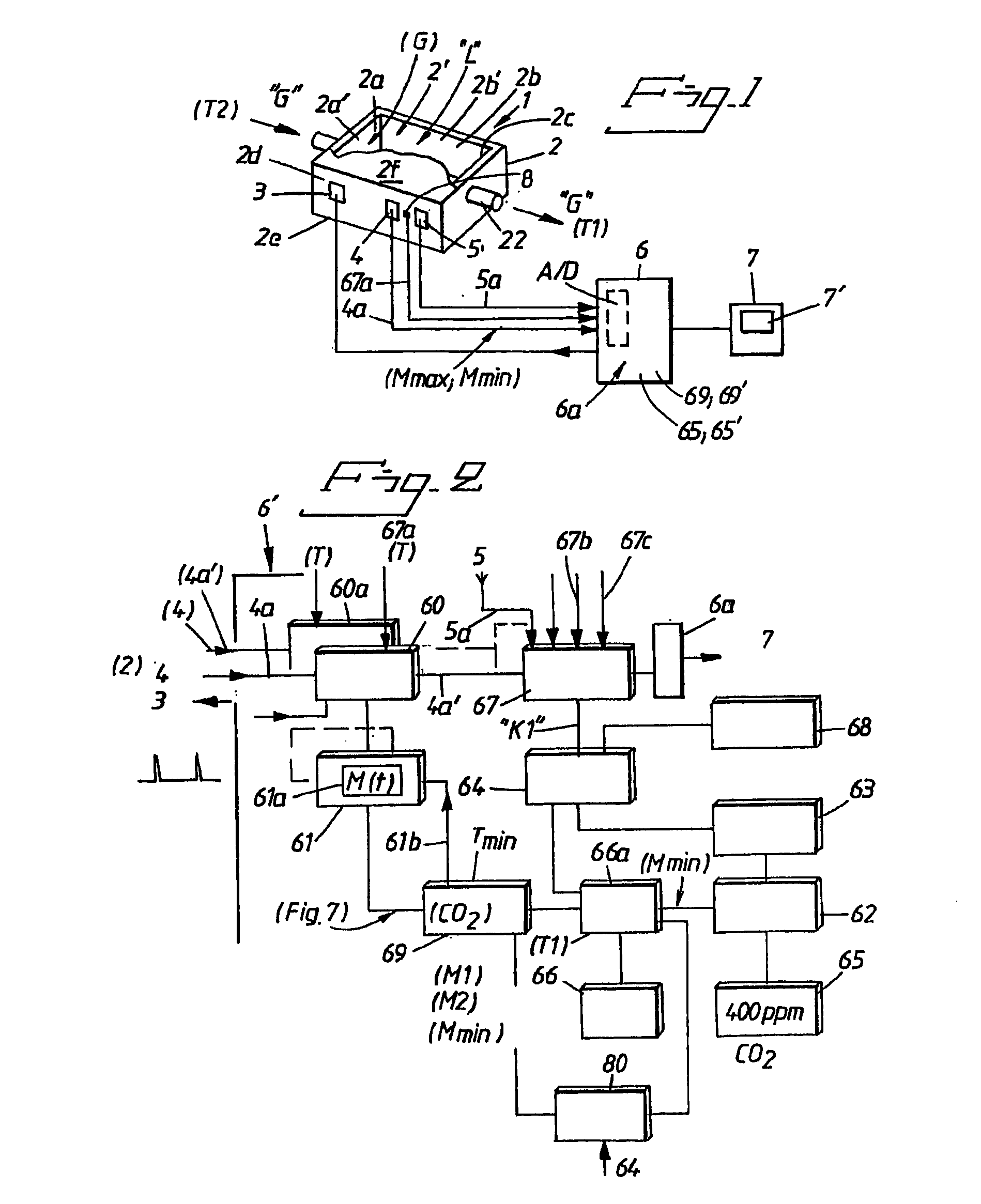
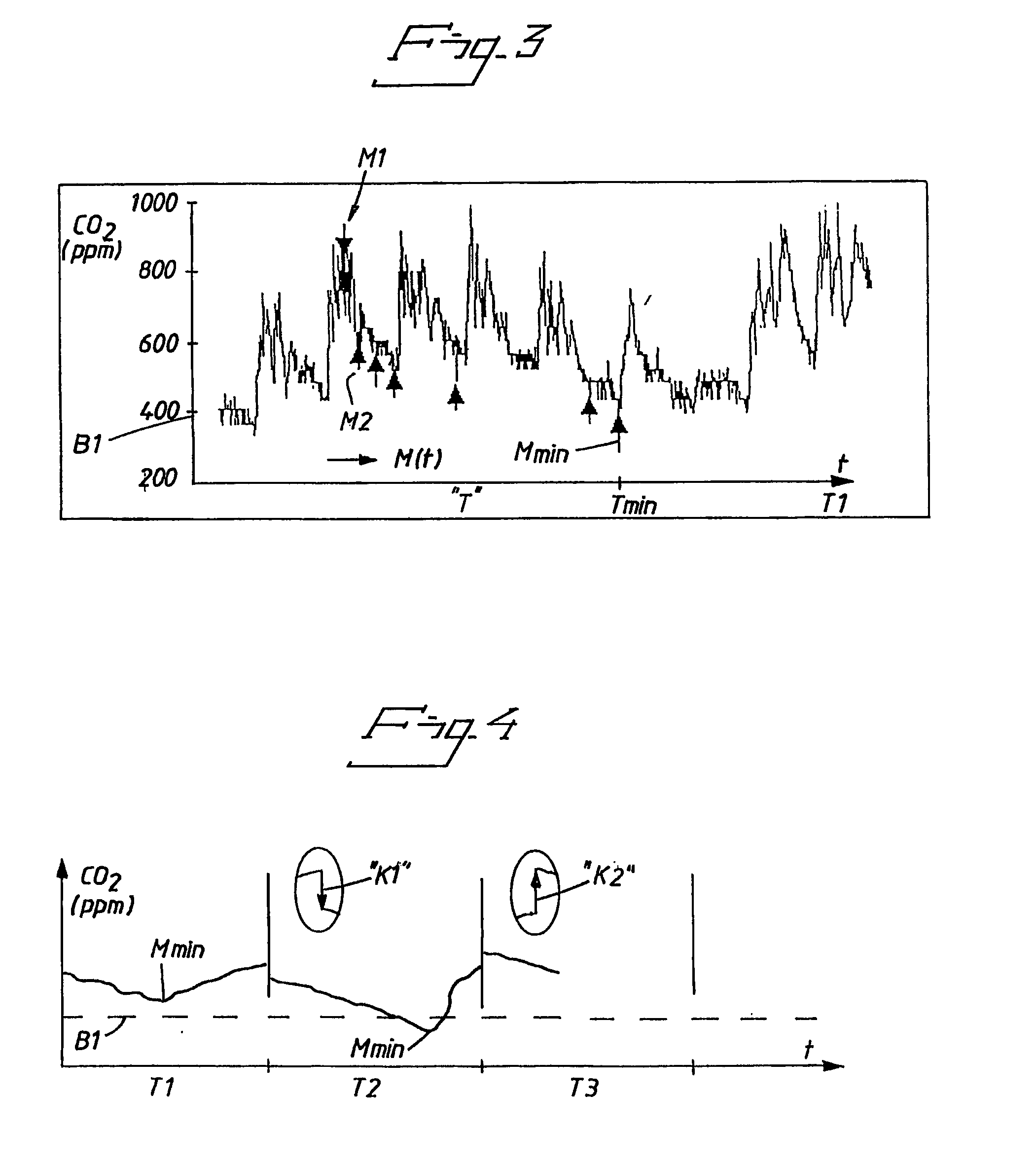
InactiveUS20070062532A1Quickly and easily determineSure easyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesForced expiratory vital capacityRadiology
A ventilator for ventilating a patient also assists a clinician in determining a suitable PEEP for the patient. For this purpose, a graph or tabular display of a series of different value PEEPs and corresponding functional residual capacities of the patient may be provided. Or, the amount of the lung volume recruited / de-recruited at various levels of PEEP may be determined for use in selecting a desired PEEP. To this end, the functional residual capacity of the lungs is determined for a first PEEP level. The PEEP is then altered to a second level and a spirometry dynostatic curve of lung volume and pressure data is obtained. The lung volume on the dynostatic curve at a lung pressure corresponding to the first PEEP value is obtained. The difference between the functional residual capacity of the lungs at the first PEEP level and that determined from the dynostatic curve represents the lung volume recruited / de-recruited when changing between said first and second PEEPs.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
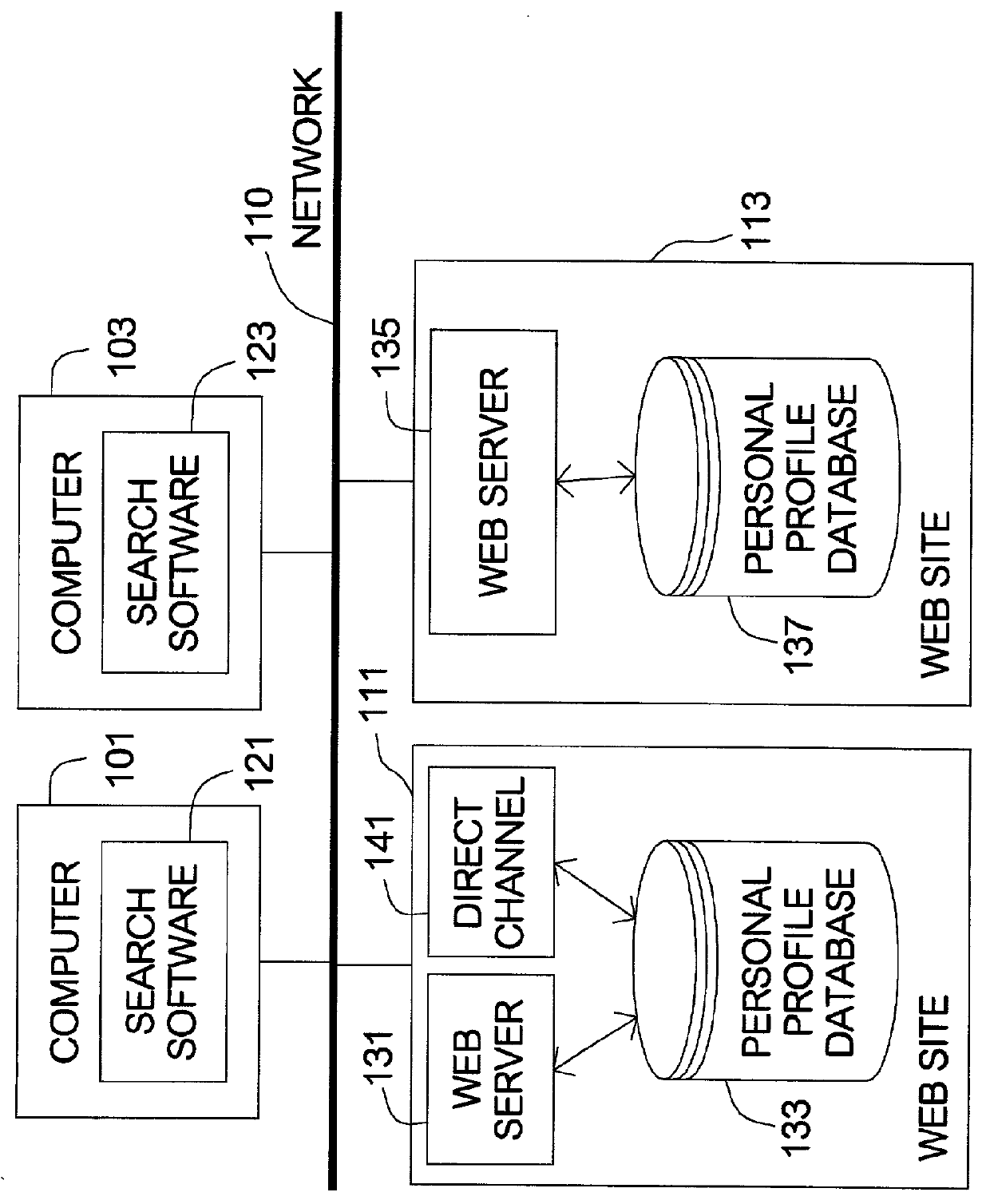
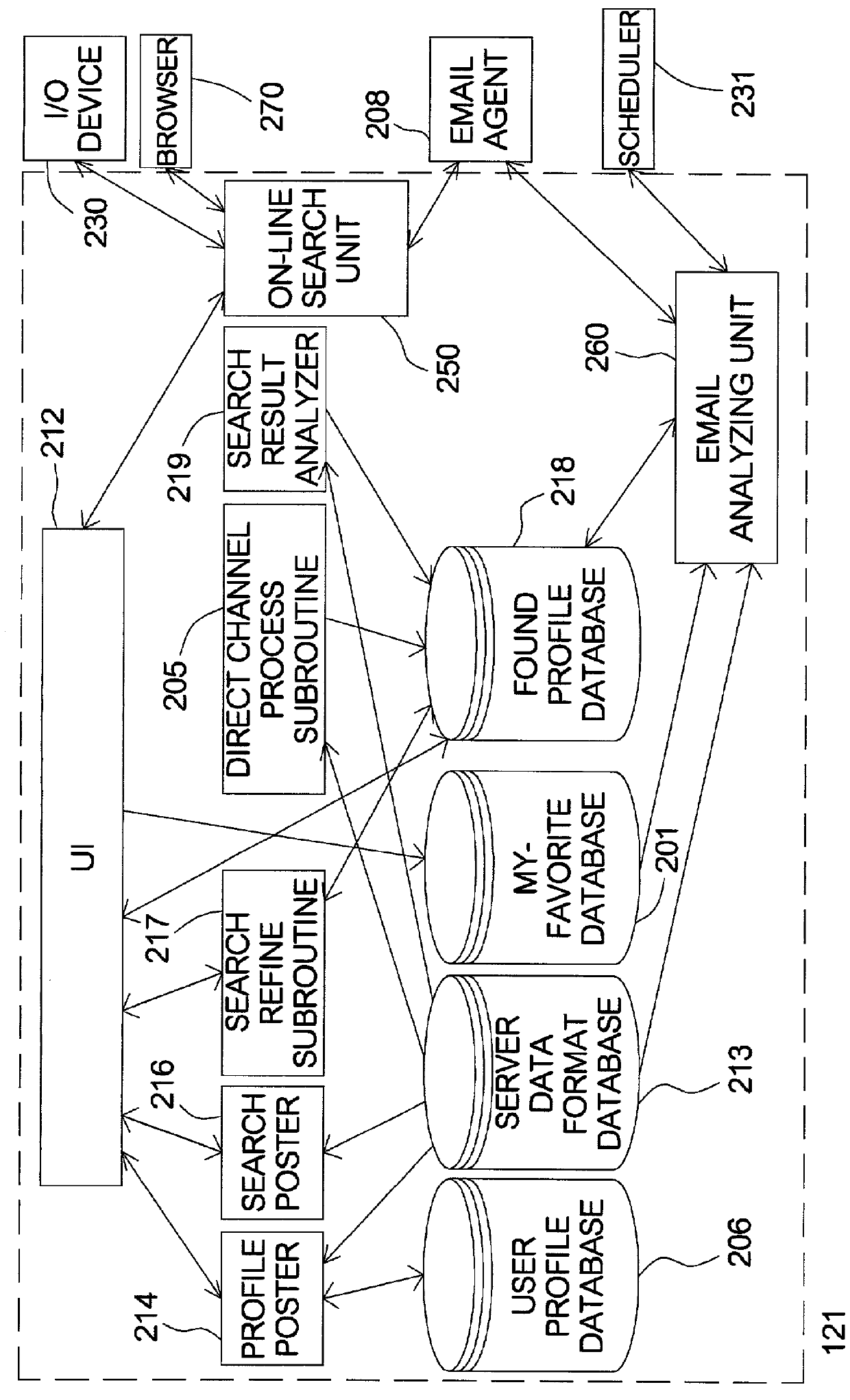
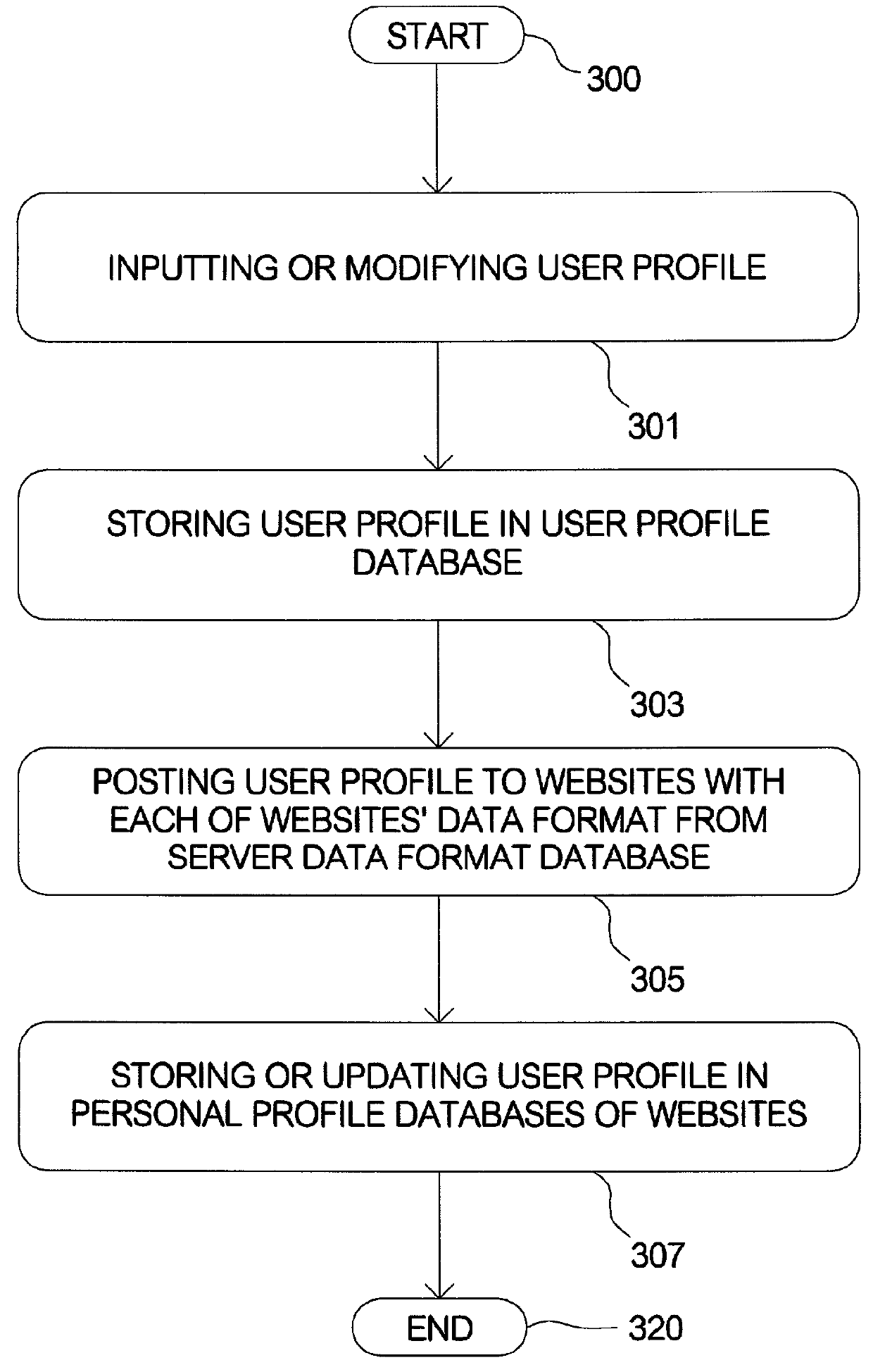
System and method for registering or searching in multiple relationship-searching hosts
InactiveUS20010054041A1Conveniently obtainWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsData formatWorld Wide Web
A method for searching in multiple relationship-searching hosts. The method can be installed in a computer, wherein the computer comprises a user interface (UI) to access search conditions. Firstly the method begins with inputting the search conditions on the UI. Next, the search conditions are transmitted to the hosts with each of the hosts' data format retrieved from a server data format database in the computer. Then the hosts retrieve search results according to the search conditions and transmit the search results to the computer. Next, the search results are stored in a found profile database of the computer. The method makes a user be capable to register and search matched users in the multiple relationship-searching hosts, instead of repeatedly behavior of search in different hosts.
Owner:CHANG LAN
Method and Apparatus for Obtaining Digital Objects in a Communication Network
InactiveUS20110153785A1Conveniently obtainEfficient searchMultimedia data indexingWeb data indexingInternet radioDigital object
A technique for obtaining digital objects (such as songs or video clips) from information providers in data communication networks (such as the Internet); the digital objects being sent through channels (such as Internet radio channels or Internet TV channels) or being otherwise made available. The end-user gains several advantages over techniques supported by the known art. For example, end-users may easily locate desired digital objects, need not be connected during object capture, can be connected through a low speed connection, does not have to have a high capacity computer, can obtain digital objects legally, can receive supplemental information associated with the digital objects, can quickly scan a vast number of digital object having been sent earlier, need not have the required storage space for the digital objects available during object capture, can easily navigate through a multitude of digital object channels, can easily obtain objects with a certain desired quality, can easily obtain objects in a certain desired format, can legally obtain digital objects at no cost and can prove that the digital objects were actually obtained legally.
Owner:MARTINA KASSERI TELECOM L L C
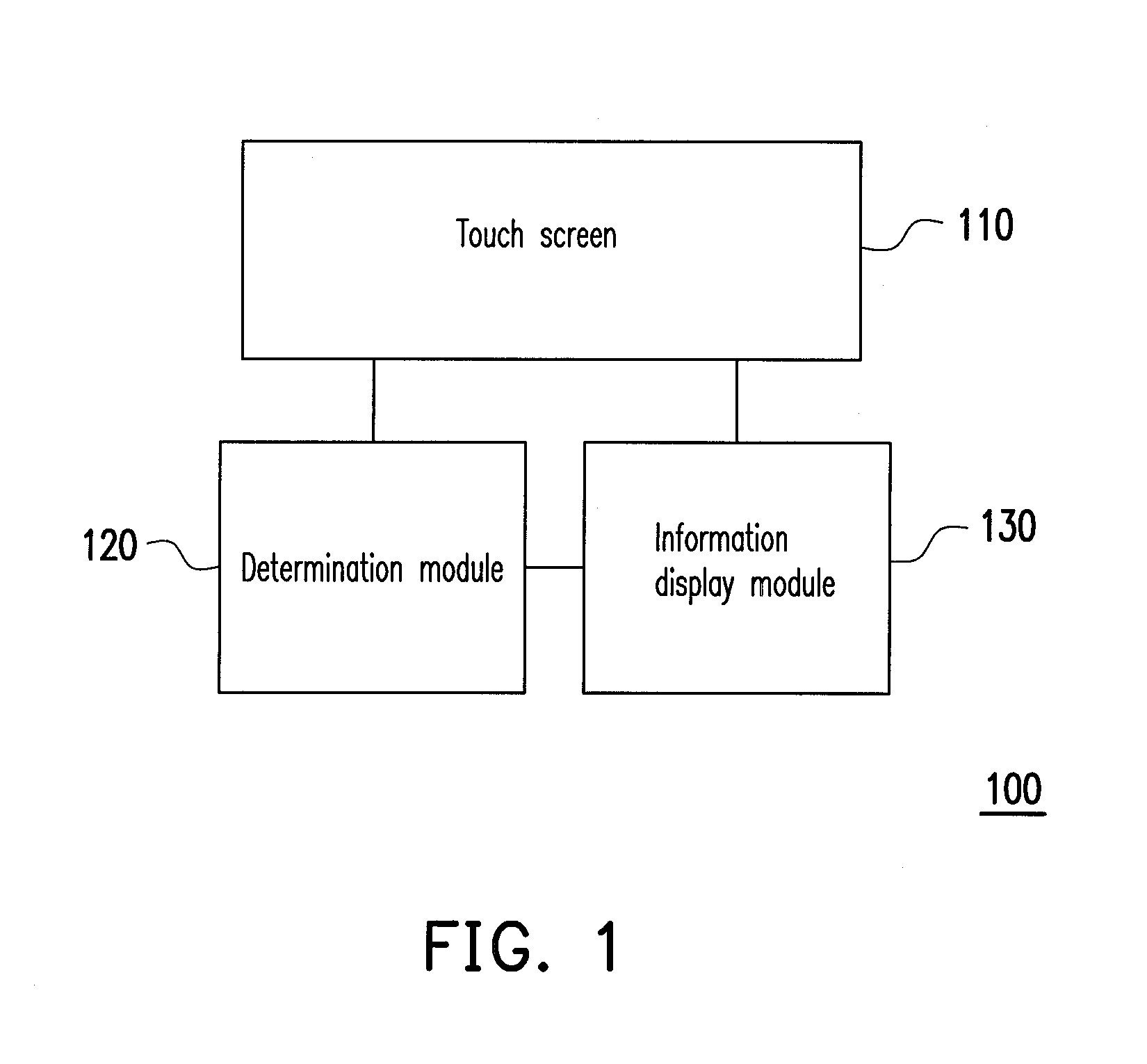
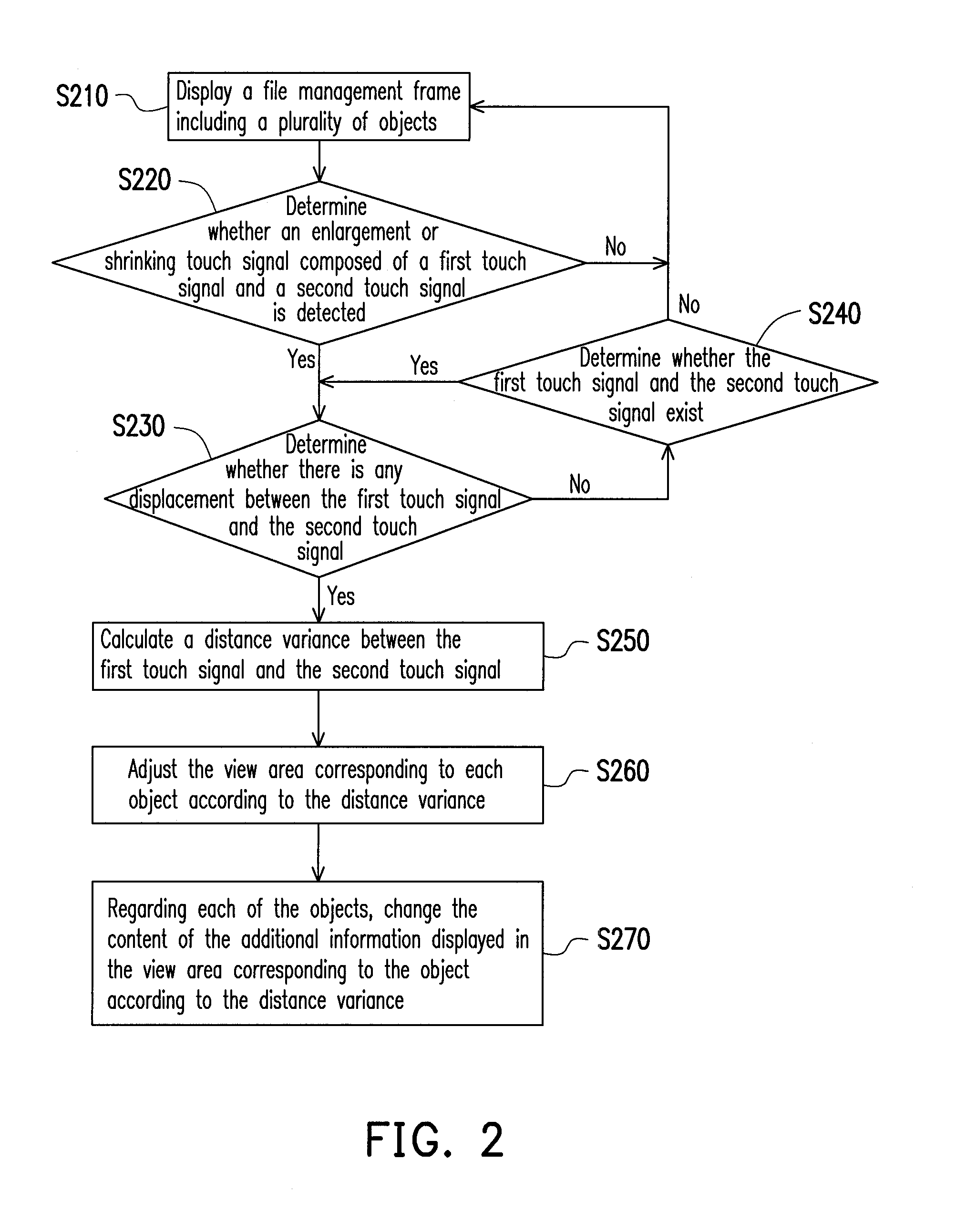
Electronic device and information display method thereof
InactiveUS20120192110A1Conveniently obtainIncrease volumeInput/output processes for data processingPresent methodOn-screen display
An electronic device and an information display method thereof are provided. The electronic device has a screen and is configured to receive signals from a touch input / output interface. The screen displays a file management frame including a plurality of objects, wherein each of the objects is corresponding to a view area within the file management frame and has additional information and / or a preview icon. In the present method, an enlargement or shrinking touch signal is detected via the touch input / output interface. The view area corresponding to each of the objects is adjusted according to the enlargement or shrinking touch signal. Regarding each of the objects, the content of the additional information to be displayed in the view area corresponding to the object is changed according to the enlargement or shrinking touch signal.
Owner:COMPAL ELECTRONICS INC
Method for providing a consumer with information regarding commercial prescription availability and cost
InactiveUS20070250341A1Maximize choiceConveniently obtainDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPharmacyThe Internet
A method is disclosed whereby consumers enrolled in subscribing prescription benefit plans can easily obtain information over the Internet regarding costs and availability of their prescription medications at local and mail-order participating pharmacies of their choice, based on the prescription benefit plans of which they are members. Data on medication dosages, quantities and net costs at a plurality of pharmacies are compiled by the method and presented on-line so that each member of a plan can select the combination of cost and convenience for prescription fulfillment that he or she prefers. The method then allows the user to select prescription fulfillment directly from the selected pharmacy on-line. Other information,.such as general medical, medication and health information can also be made available. Patients, pharmacies, PBMs and plan payers all benefit.
Owner:MEDIMPACT HEALTHCARE SYST
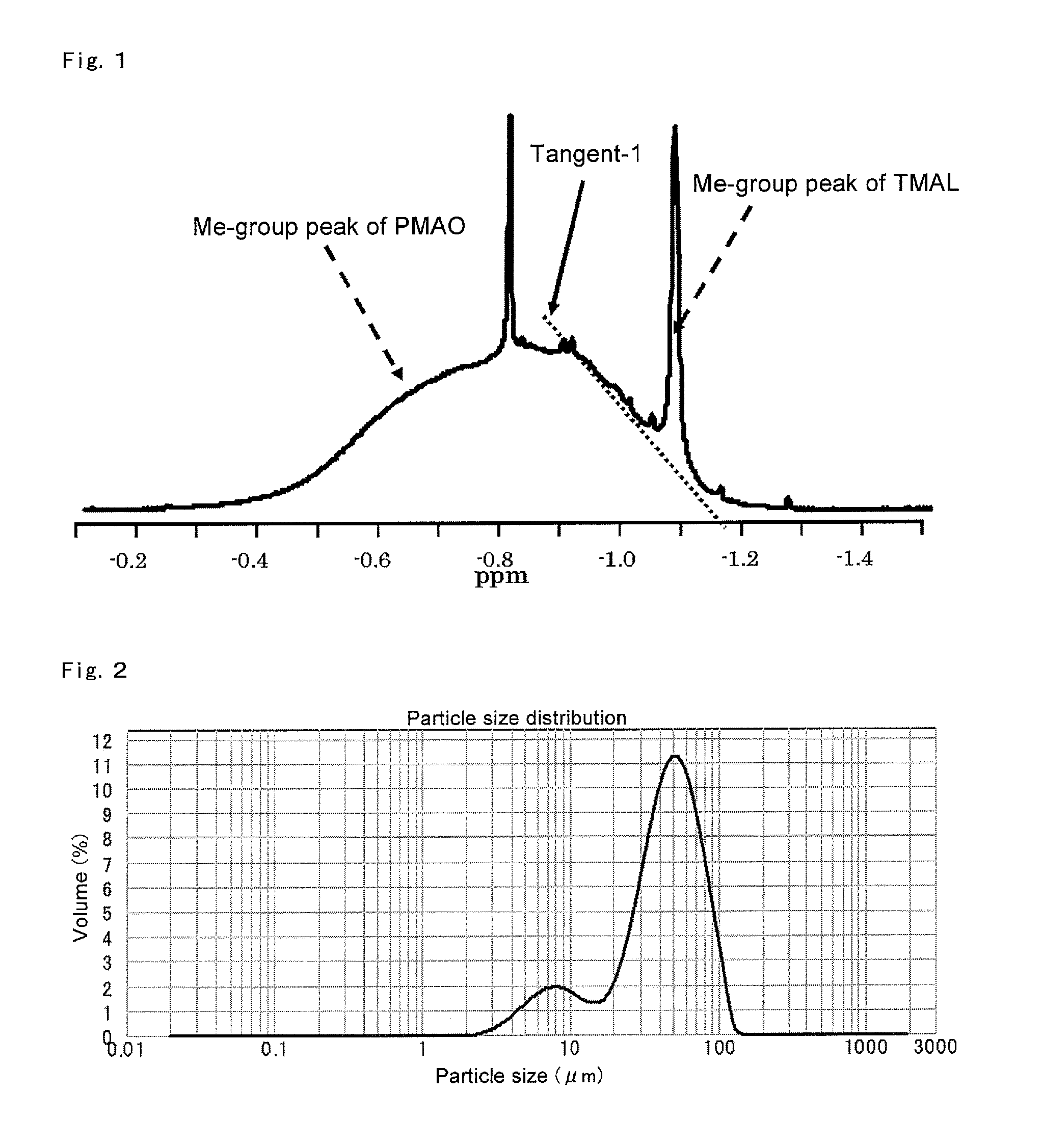
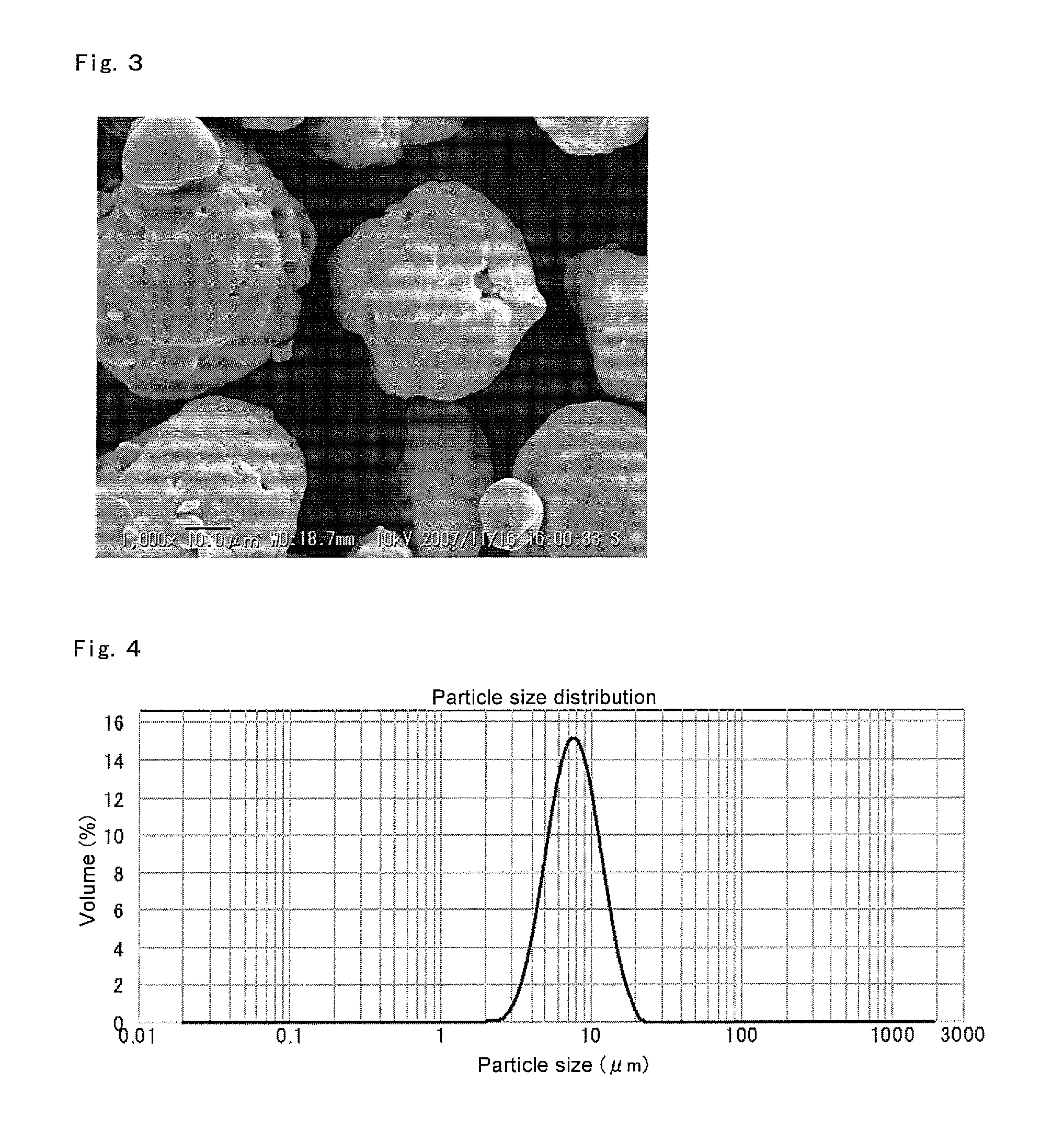
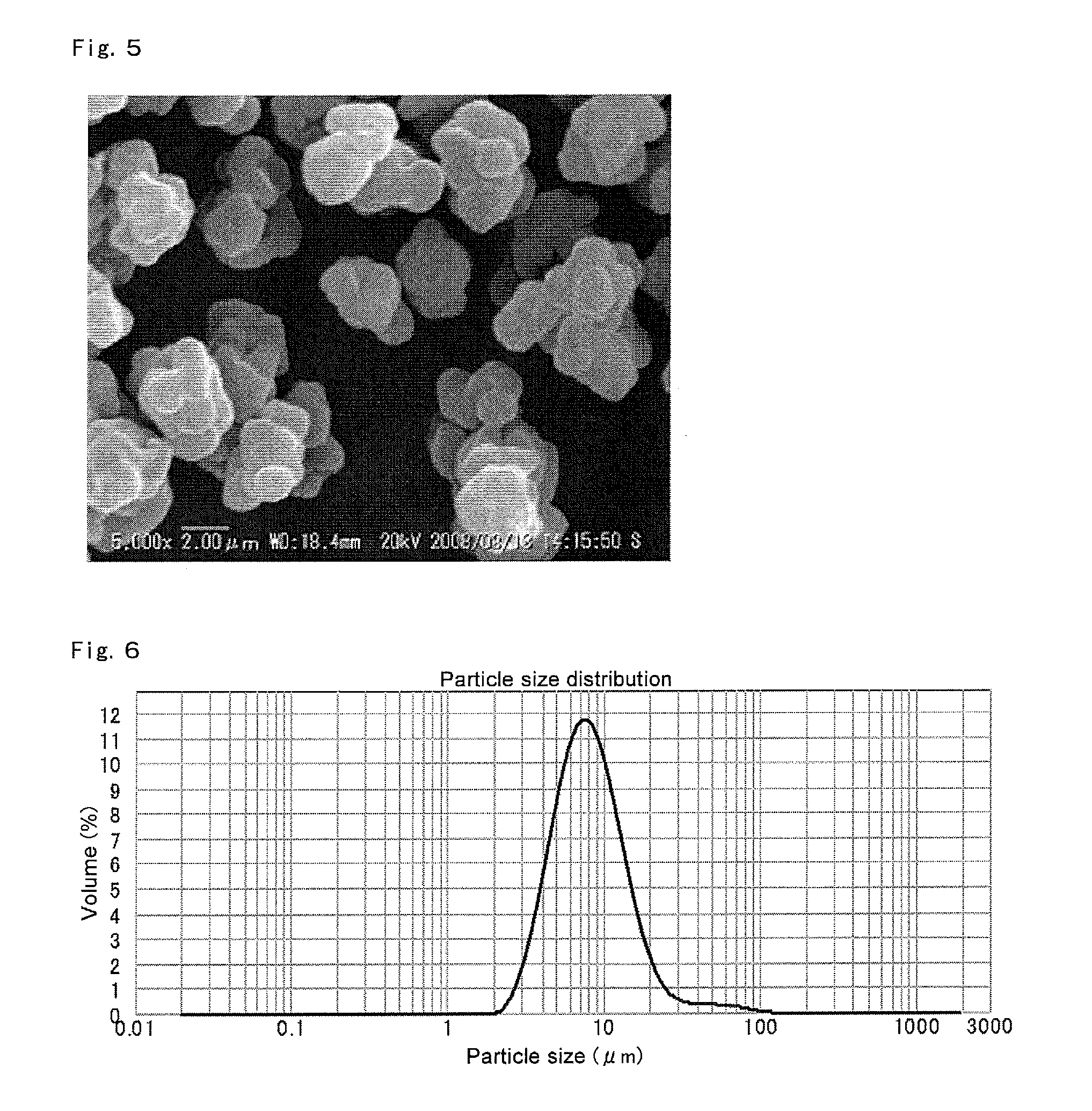
Solid support-polymethylaluminoxane complex, method for producing same, olefin polymerization catalyst, and method for producing polyolefin
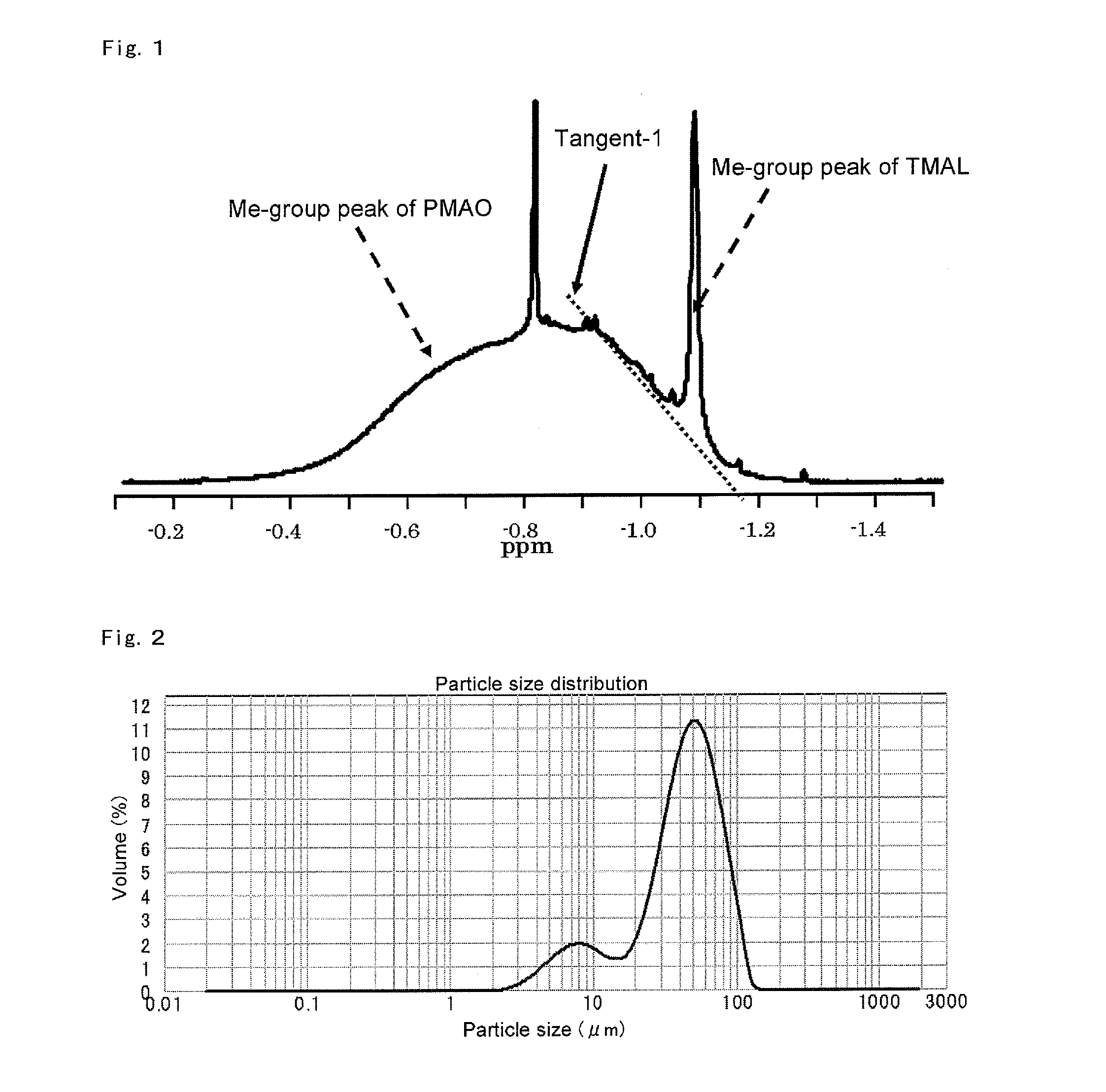
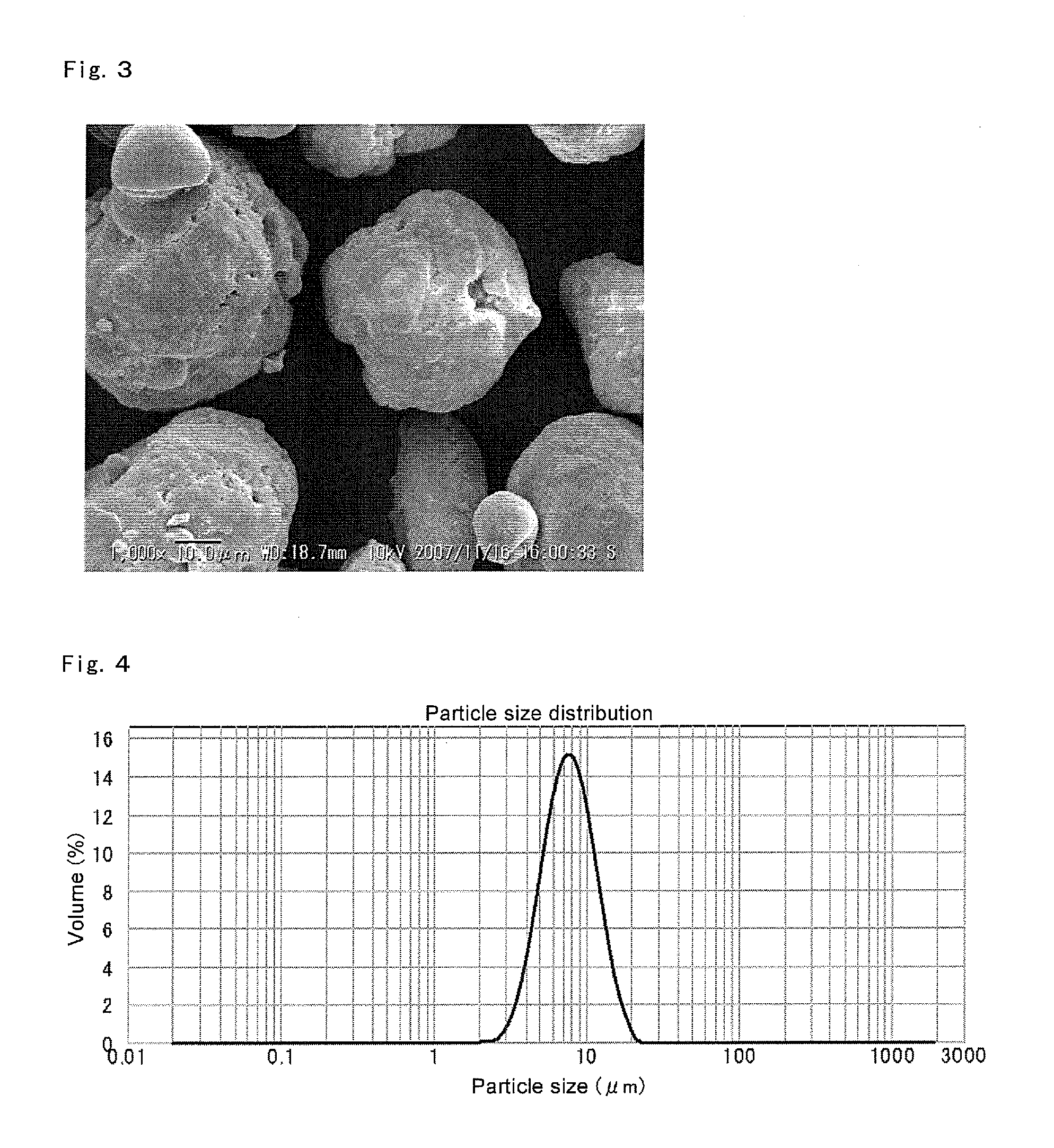
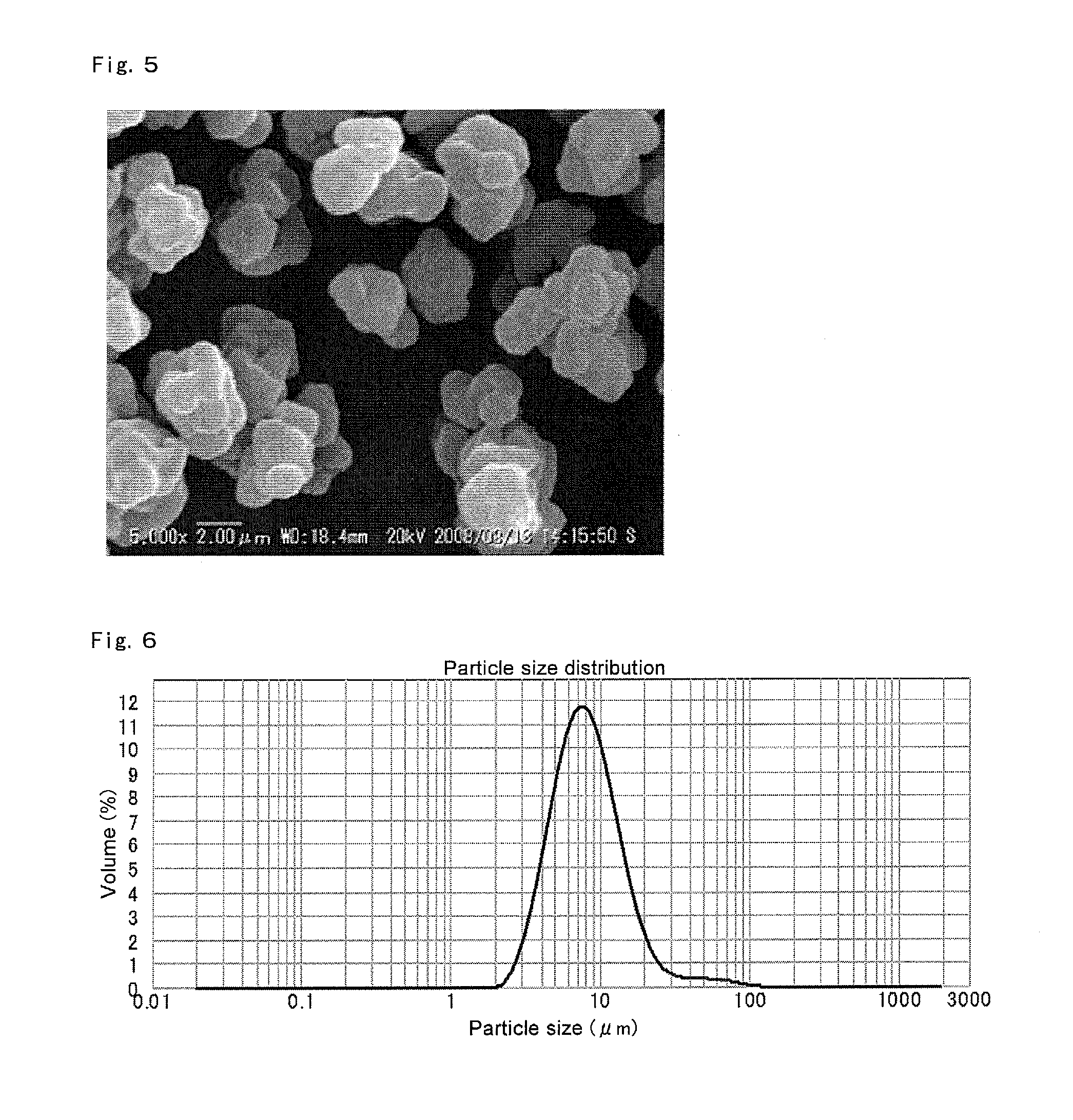
ActiveUS8975209B2Conveniently obtainHigh polymerization activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic chemistry methodsPolyolefinOlefin polymerization
Disclosed is a solid support-polymethylaluminoxane complex exhibiting a higher polymerization activity than a conventional substance and being homogeneous. Also disclosed is a method for producing an olefin-based polymer having a favorable quality using the complex and a transition metal compound. The complex comprises a coating layer containing polymethylaluminoxane and trimethylaluminum on the surface of a solid support. The coating layer comprises a solid polymethylaluminoxane composition in which (i) the content of aluminum is in a range of 36 to 41 mass % and (ii) the molar fraction of methyl groups derived from a trimethylaluminum moiety to the total number of moles of methyl groups is 12 mol % or less. Also disclosed is an olefin polymerization catalyst comprising the complex and a transition metal compound represented by general formula (III): MR5R6R7R8 as catalyst components, and a method for producing a polyolefin comprising polymerizing an olefin using the catalyst.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
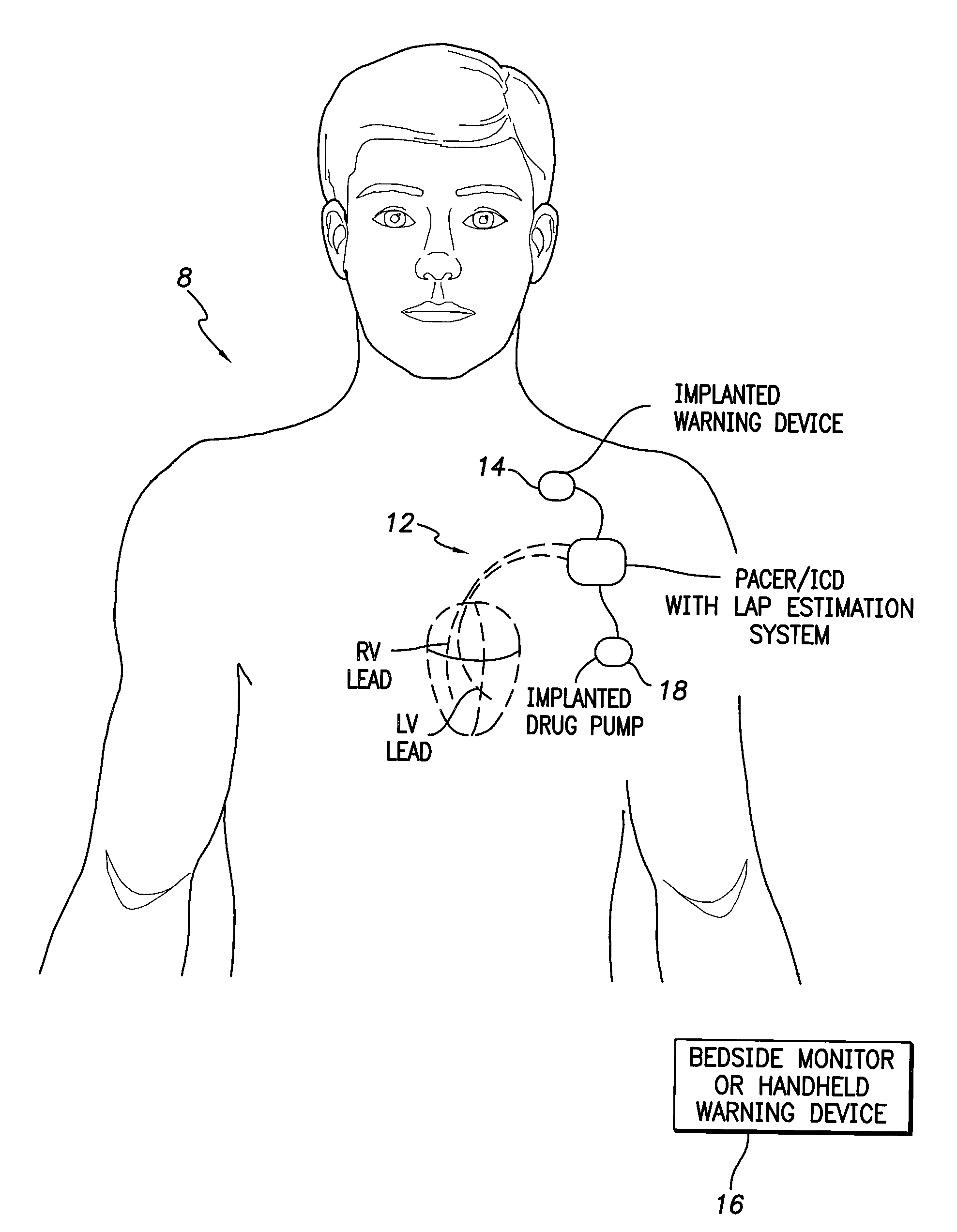
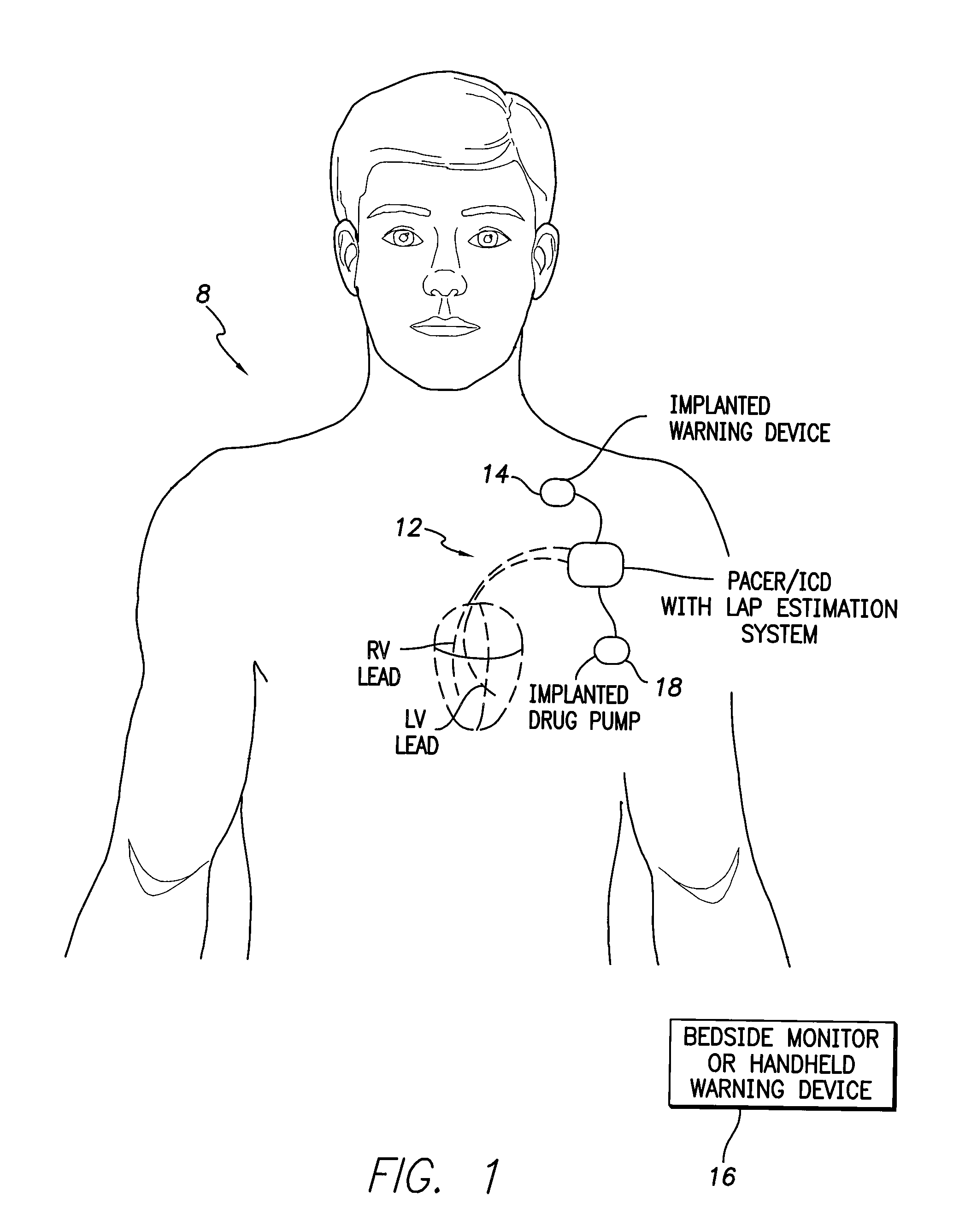
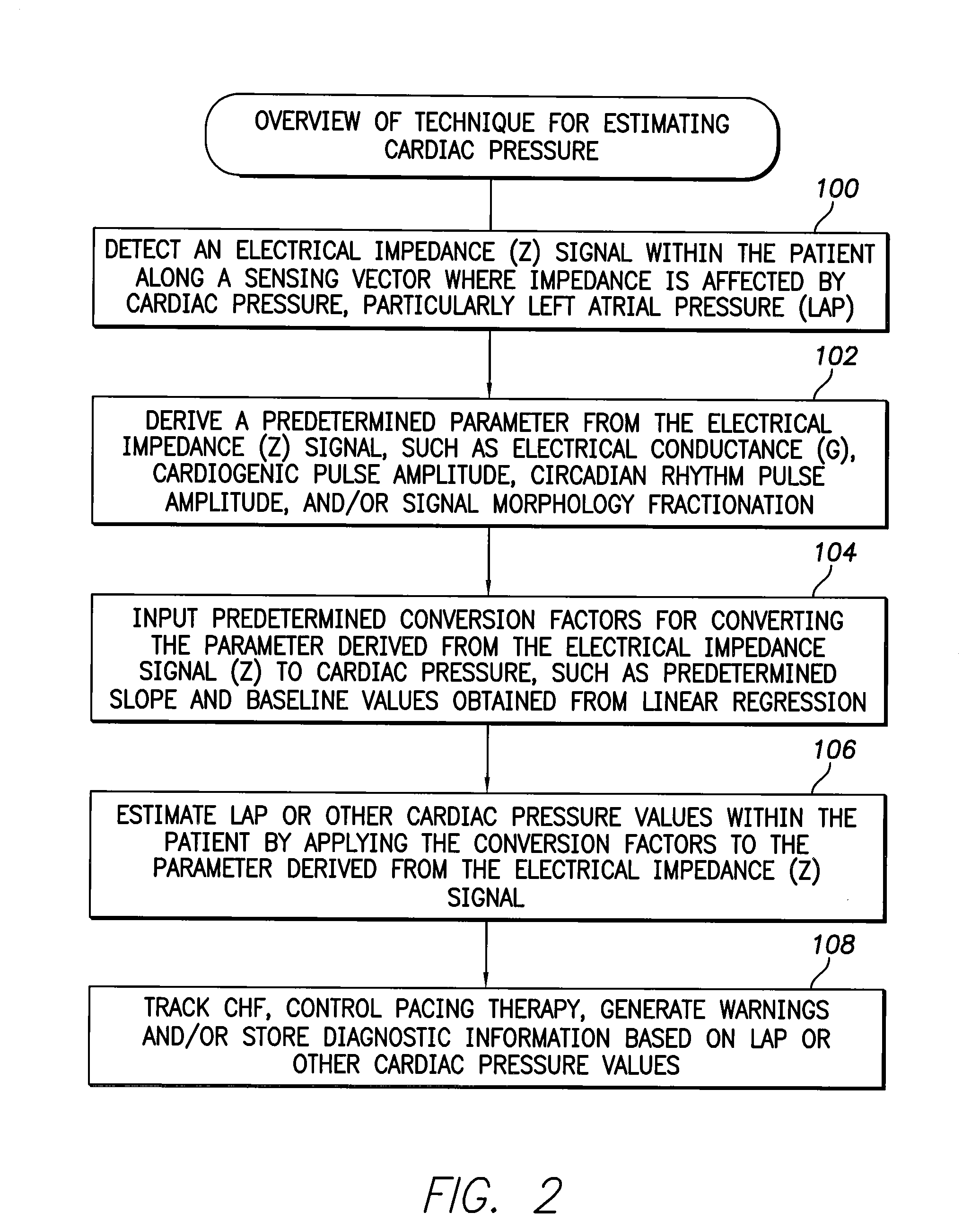
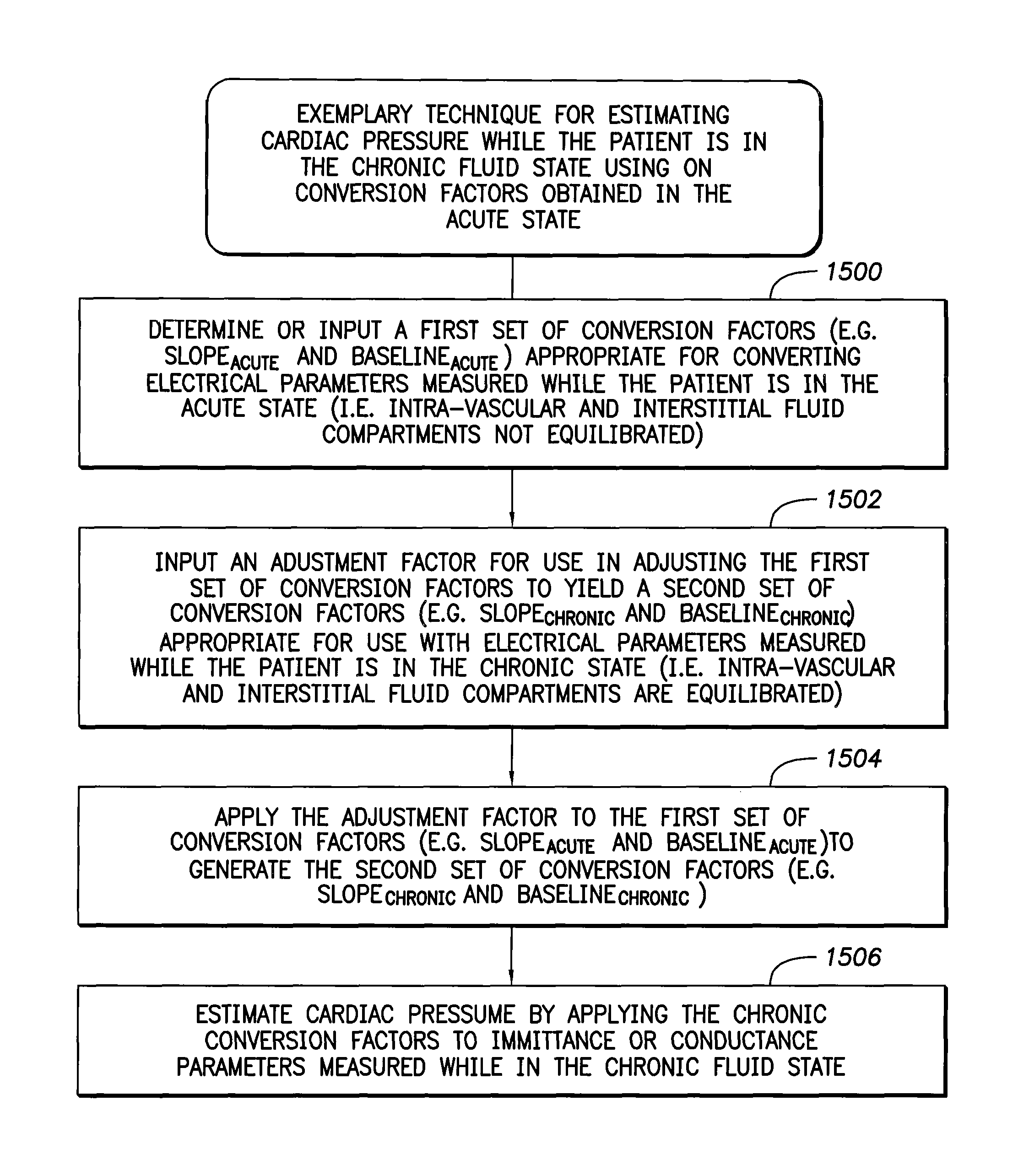
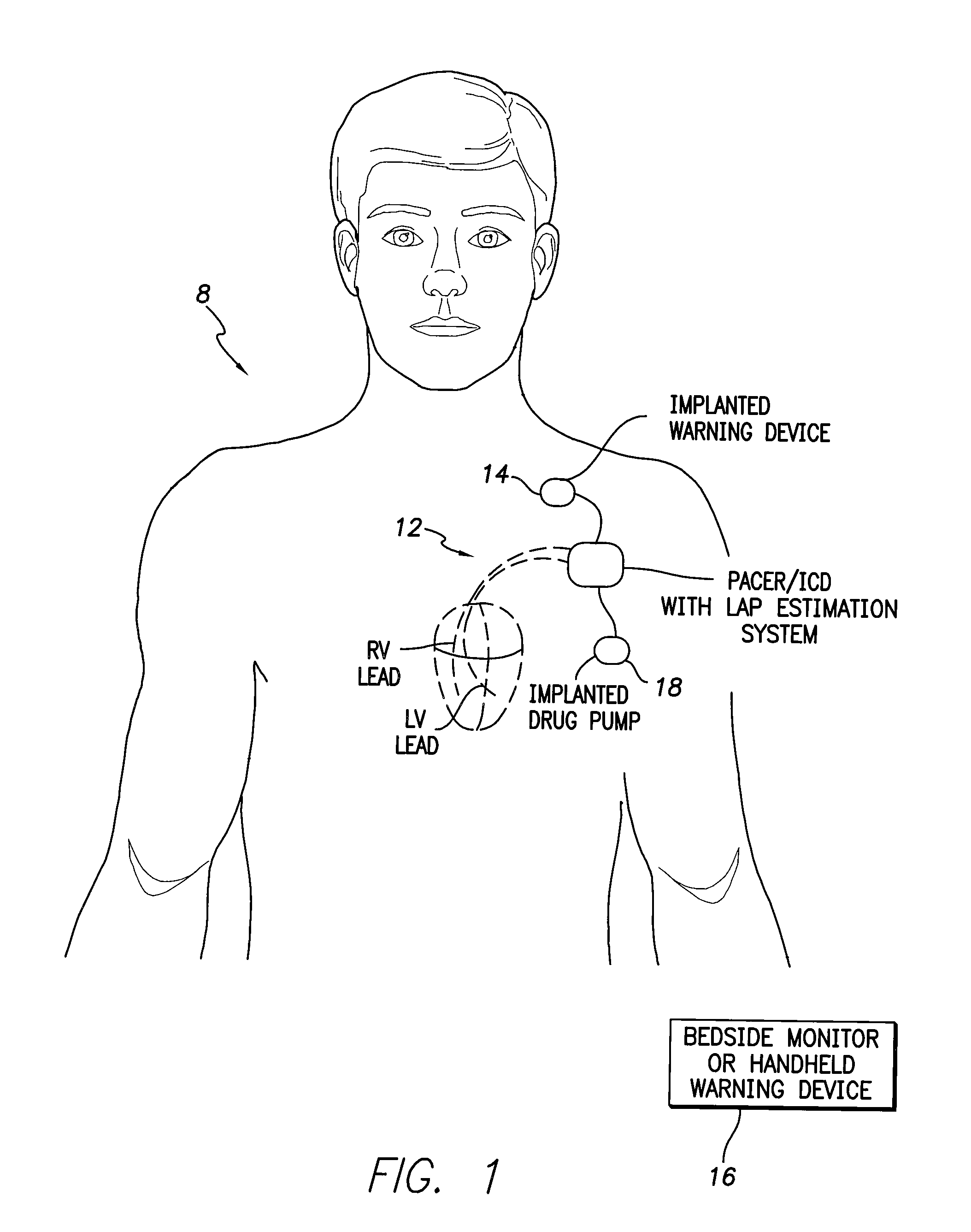
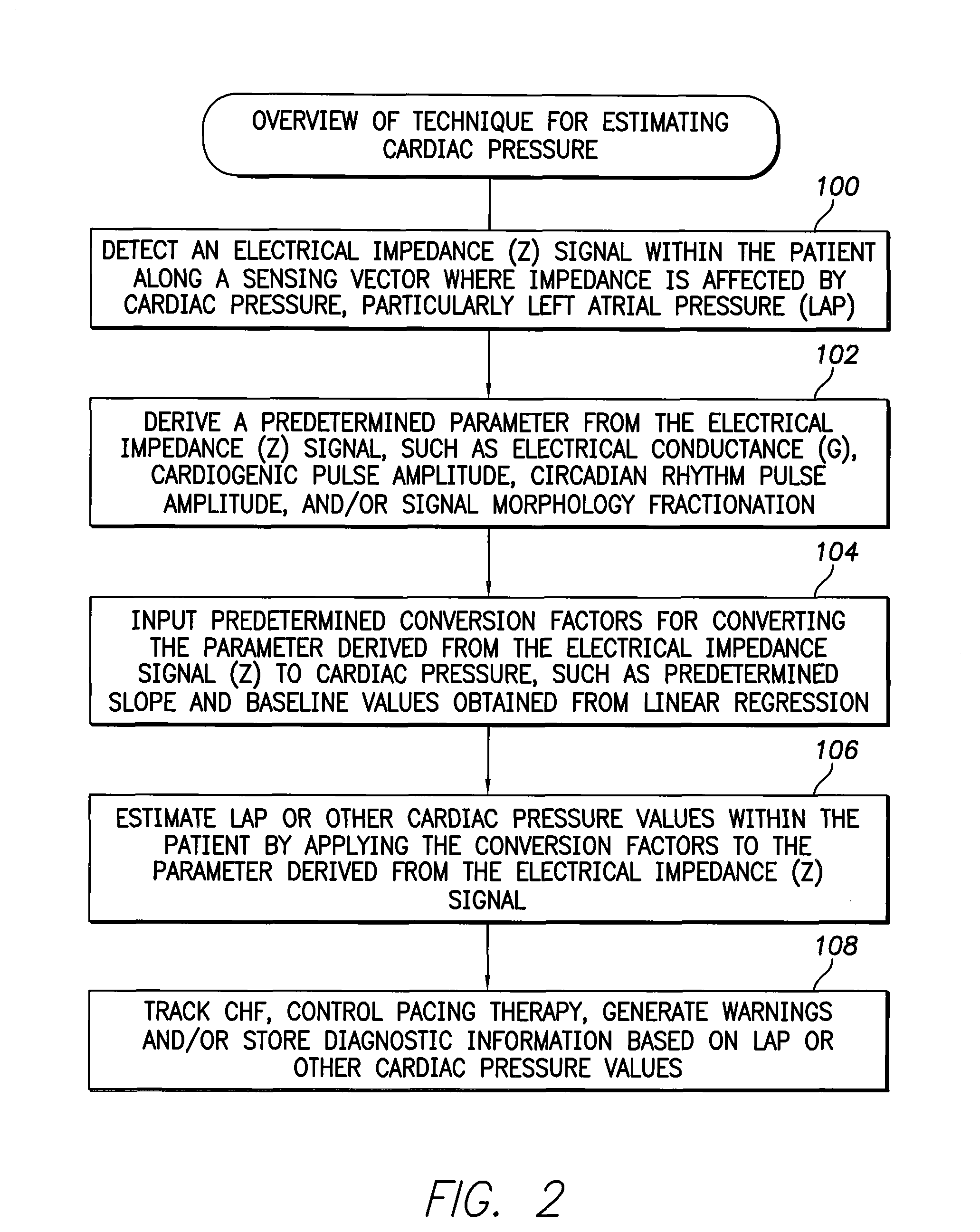
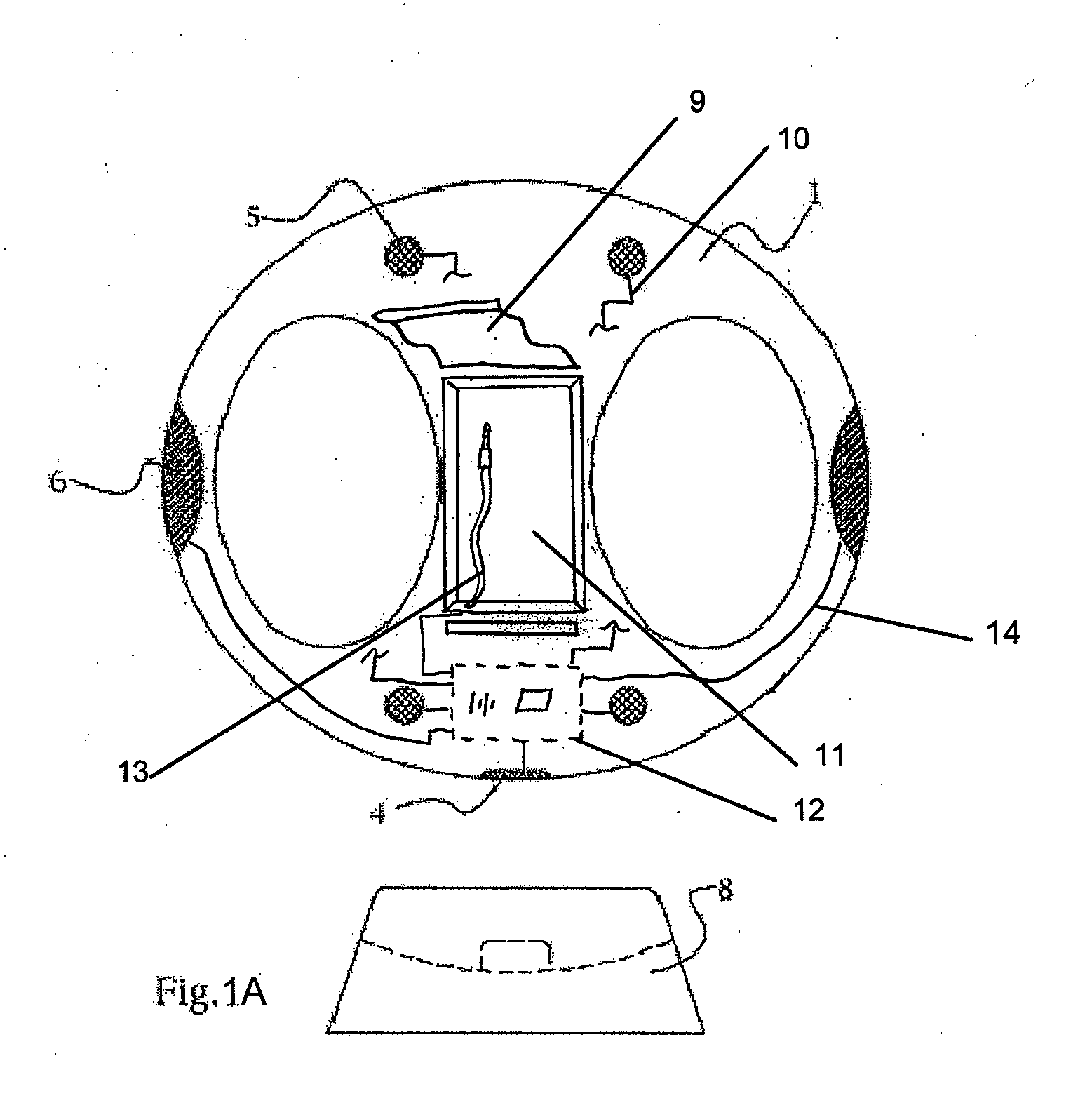
System and method for calibrating cardiac pressure measurements derived from signals detected by an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20080262361A1Accurate CalibrationAccurate slopeElectrotherapyCatheterThoracic FluidLeft atrial pressure
Various techniques are provided for calibrating and estimating left atrial pressure (LAP) using an implantable medical device, based on impedance, admittance or conductance parameters measured within a patient. In one example, default conversion factors are exploited for converting the measured parameters to estimates of LAP. The default conversion factors are derived from populations of patients. In another example, a correlation between individual conversion factors is exploited to allow for more efficient calibration. In yet another example, differences in thoracic fluid states are exploited during calibration. In still yet another example, a multiple stage calibration procedure is described, wherein both invasive and noninvasive calibration techniques are exploited. In a still further example, a therapy control procedure is provided, which exploits day time and night time impedance / admittance measurements.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
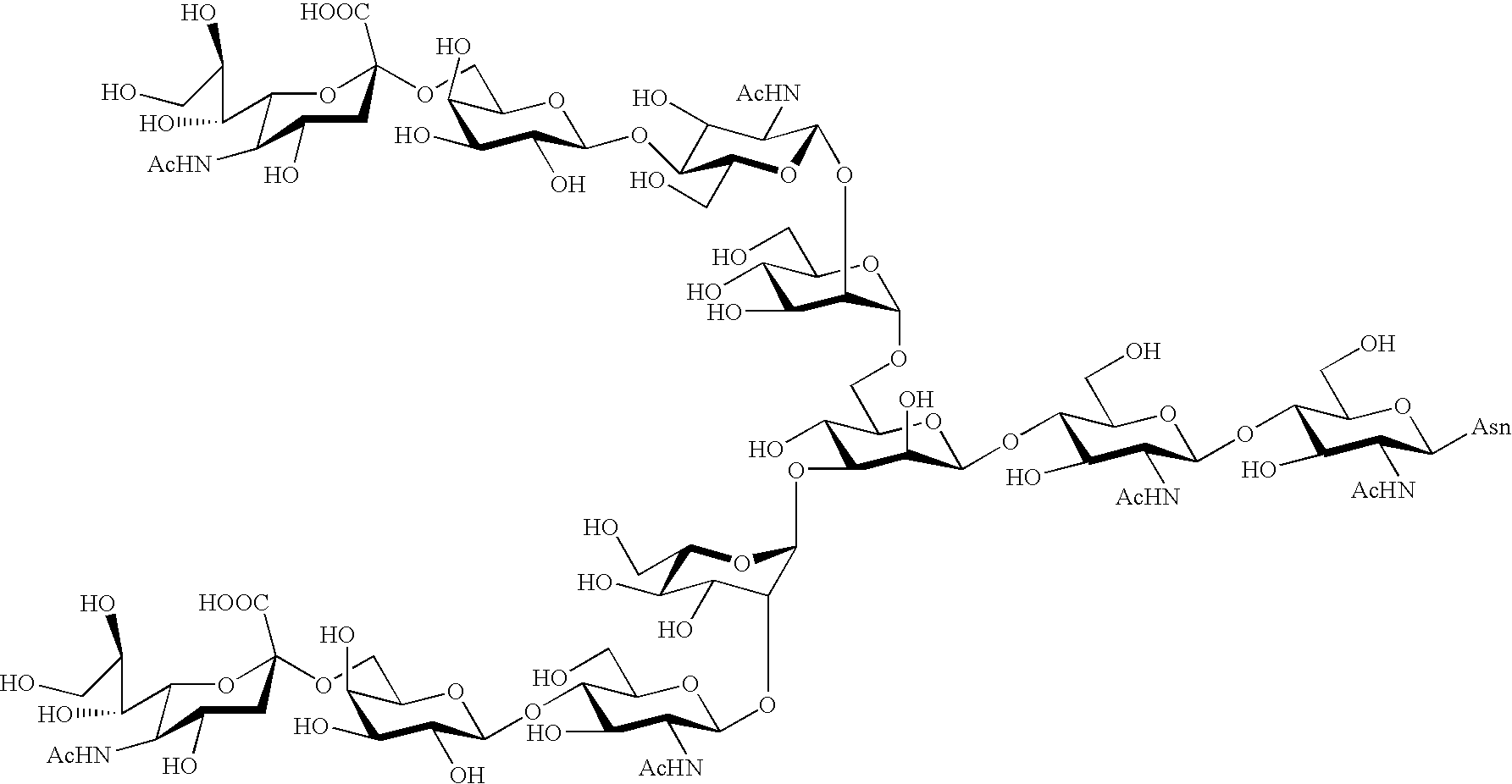
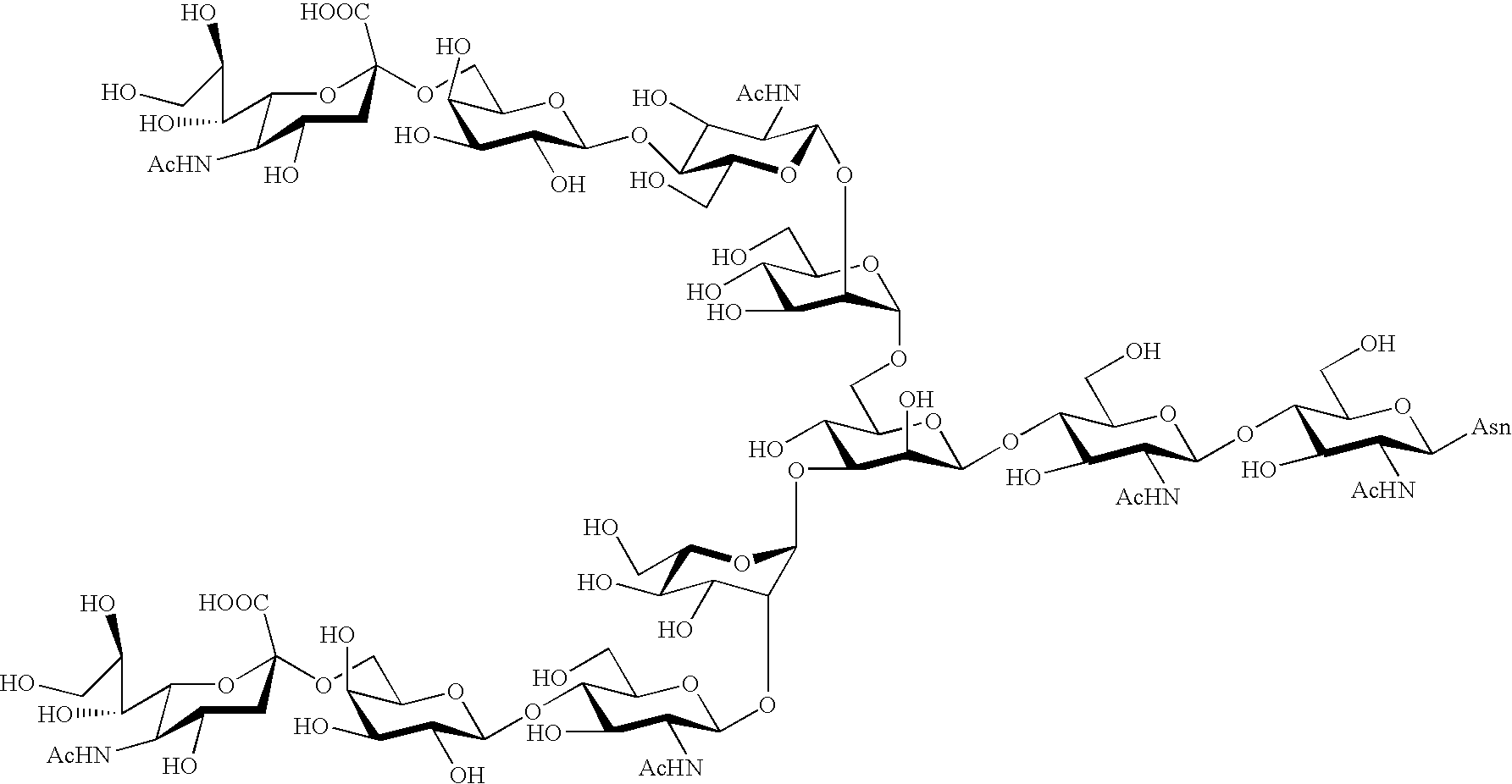
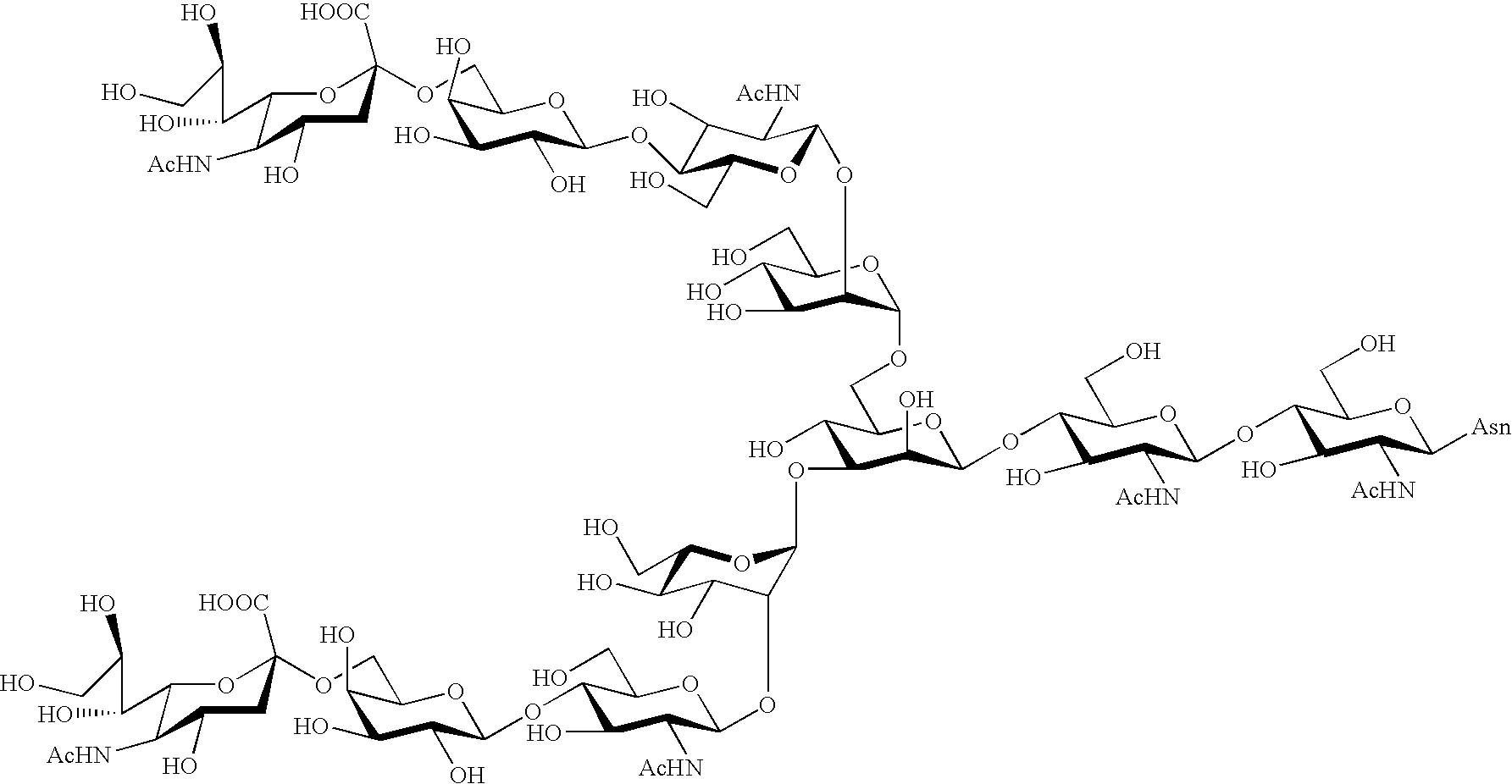
Process for producing sugar chain asparagine derivative
InactiveUS20040181054A1Conveniently obtainEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesSugarMedicinal chemistry
The present invention provides a process for preparing a sugar chain asparagine derivative. According to the process, various isolated sugar chain asparagine derivatives useful in the field of the development of pharmaceuticals and the like can be conveniently obtained in a large amount as compared to that of the prior art. The present invention also provides a process for preparing a sugar chain asparagine and a process for preparing a sugar chain via a step for preparing a sugar chain asparagine derivative. The present invention further provides a novel sugar chain asparagine derivative, a sugar chain asparagine and a sugar chain.
Owner:YASUHIRO KAJIHARA +1
Method of compensating for a measuring error and an electronic arrangement to this end
InactiveUS20060173637A1Sure easyConveniently obtainModulated-carrier systemsColor/spectral properties measurementsComputational physicsControl theory
A method and electronic arrangement for measuring errors with the aid of a gas sensor wherein a plurality of measurement valves occurring instantly during mutual sequential measuring cycles are detected. The electronic circuit arrangement has a plurality of circuit arrangements for compensating measurement errors wherein the measurements are affect with a gas sensor.
Owner:MARTIN HANS EVALD GORAN
Mixed-mode interaction
InactiveUS20080032720A1Information obtainedConveniently obtainSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsThe InternetPurchasing
A user of a wireless device, such as a mobile phone, can make purchases or obtain information via a network, such as the Internet, using both voice and non-verbal methods. Users can submit voice queries and receive non-verbal replies, submit non-verbal queries and receive voice replies, or perform similar operations that marry the voice and data capabilities of modern mobile communication devices. The user may provide notification criteria indicating under what conditions a notification should be sent to the user's wireless device. When purchasing opportunities matching the selected notification criteria become available, the user is notified. The user can respond to the notification, and immediately take advantage of the purchasing opportunity if he so desires. Mixed-mode interactions can also be used by sellers to more advantageously control the marketing of distressed, time sensitive, or other merchandise / services.
Owner:AERITAS
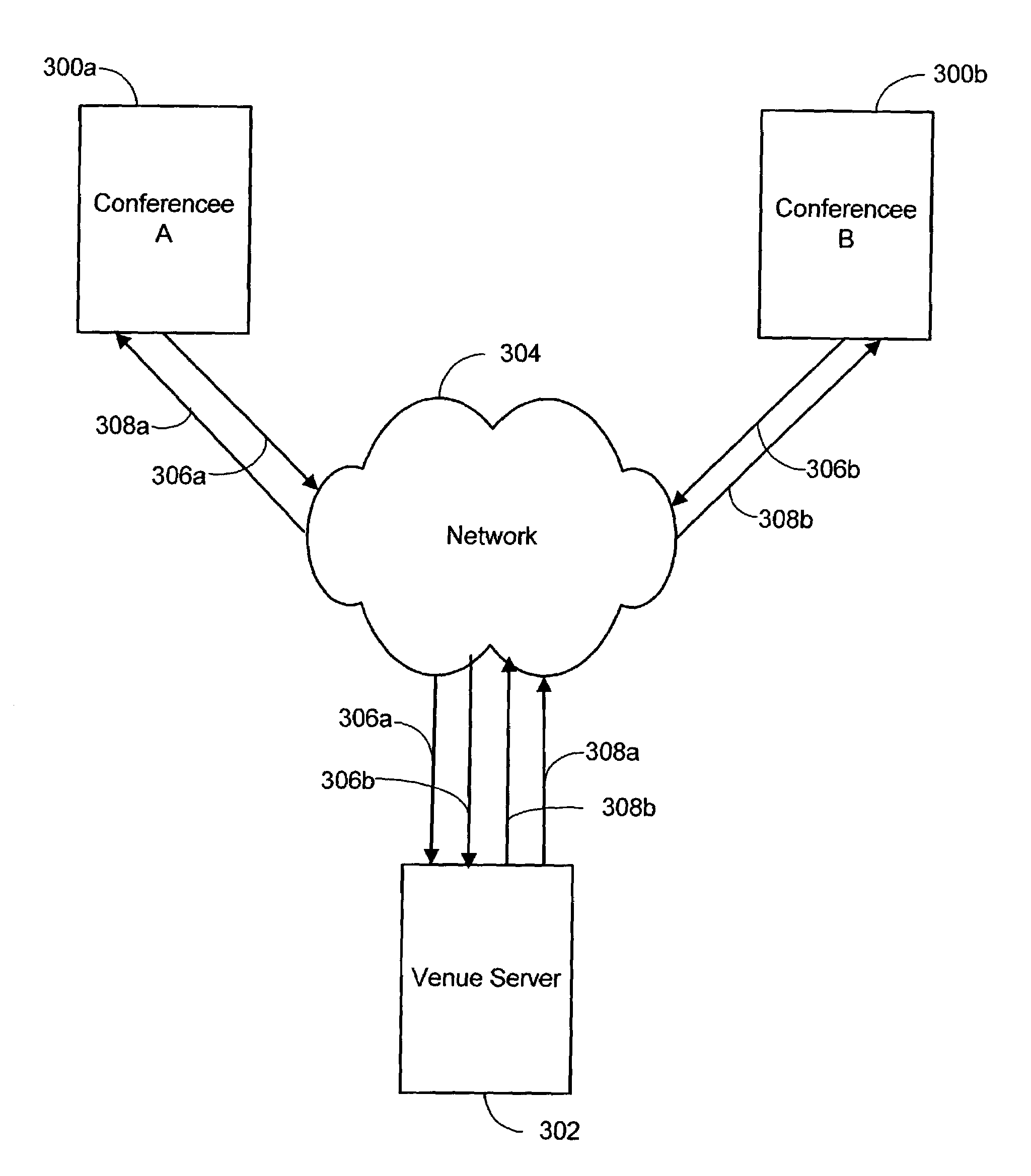
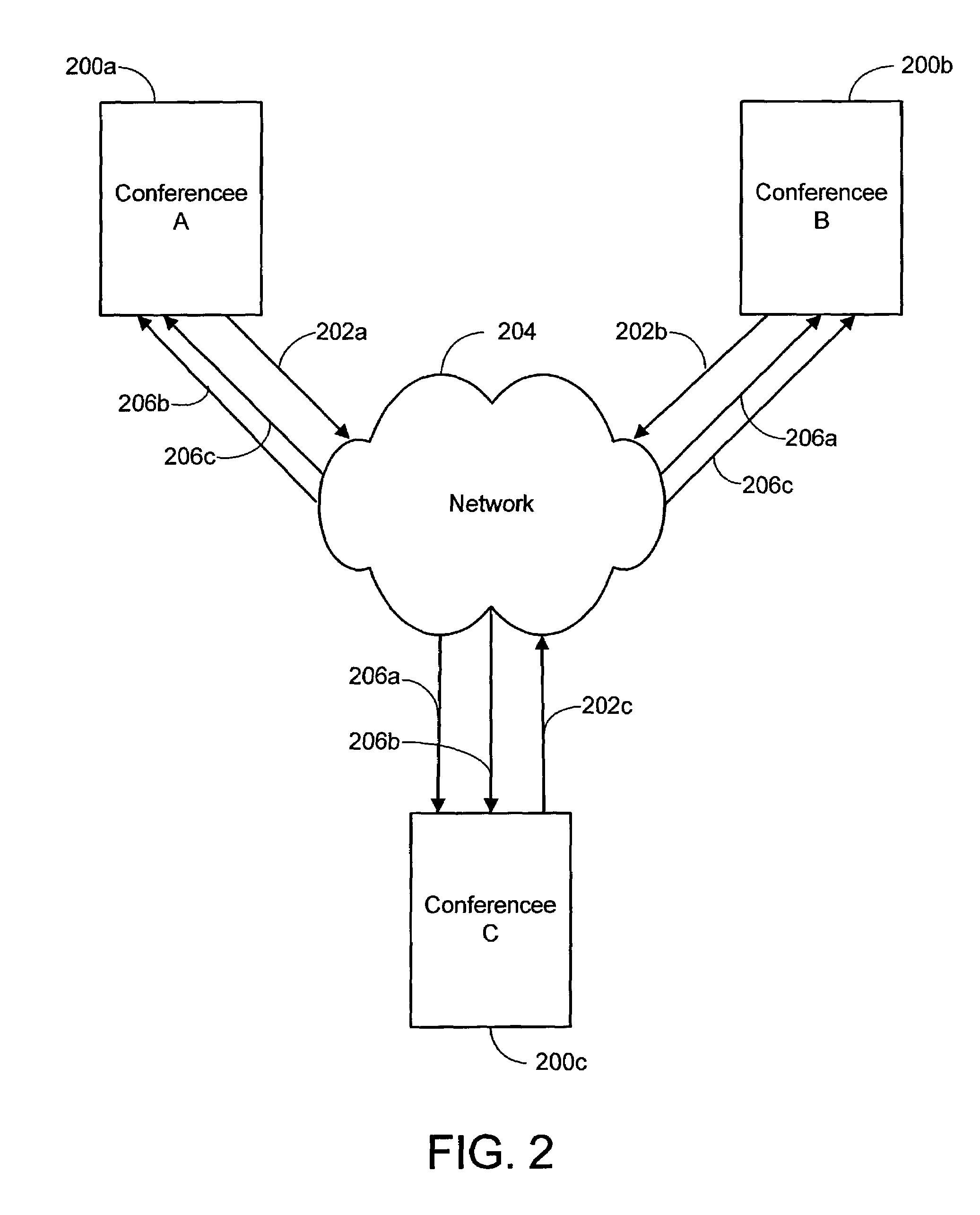
Interactive, computer network-based video conferencing system and process
ActiveUS7487211B2Quality improvementLower latencyTelevision conference systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtual conferenceAudio frequency
A video conferencing system and process is presented that employs a distributed computer network, such as the Internet or a proprietary intranet, to conduct virtual conferences. Each conference has a computer that has access to the network, as well as audio equipment and a video camera for capturing audio and video (A / V) at the conferencee's site. Conducting a conference generally entails each of the conferencee's computers multicasting the A / V data captured at the conferencee's location over the network. At the same time, each conferences subscribes to A / V data multicoated by other conferences participating in the conference. The A / V data received by a conference over the network from the other conferences is rendered and played by the conferencee's computer. In this way, each conference can see and hear the other participating conferences during the conference.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Solid support-polymethylaluminoxane complex, method for producing same, olefin polymerization catalyst, and method for producing polyolefin
ActiveUS20130059990A1High yieldHigh polymerization activityOrganic chemistry methodsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolyolefinOlefin polymerization
Disclosed is a solid support-polymethylaluminoxane complex exhibiting a higher polymerization activity than a conventional substance and being homogeneous. Also disclosed is a method for producing an olefin-based polymer having a favorable quality using the complex and a transition metal compound. The complex comprises a coating layer containing polymethylaluminoxane and trimethylaluminum on the surface of a solid support. The coating layer comprises a solid polymethylaluminoxane composition in which (i) the content of aluminum is in a range of 36 to 41 mass % and (ii) the molar fraction of methyl groups derived from a trimethylaluminum moiety to the total number of moles of methyl groups is 12 mol % or less. Also disclosed is an olefin polymerization catalyst comprising the complex and a transition metal compound represented by general formula (III): MR5R6R7R8 as catalyst components, and a method for producing a polyolefin comprising polymerizing an olefin using the catalyst.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
Co-gasification process for hydrocarbon solids and biomass
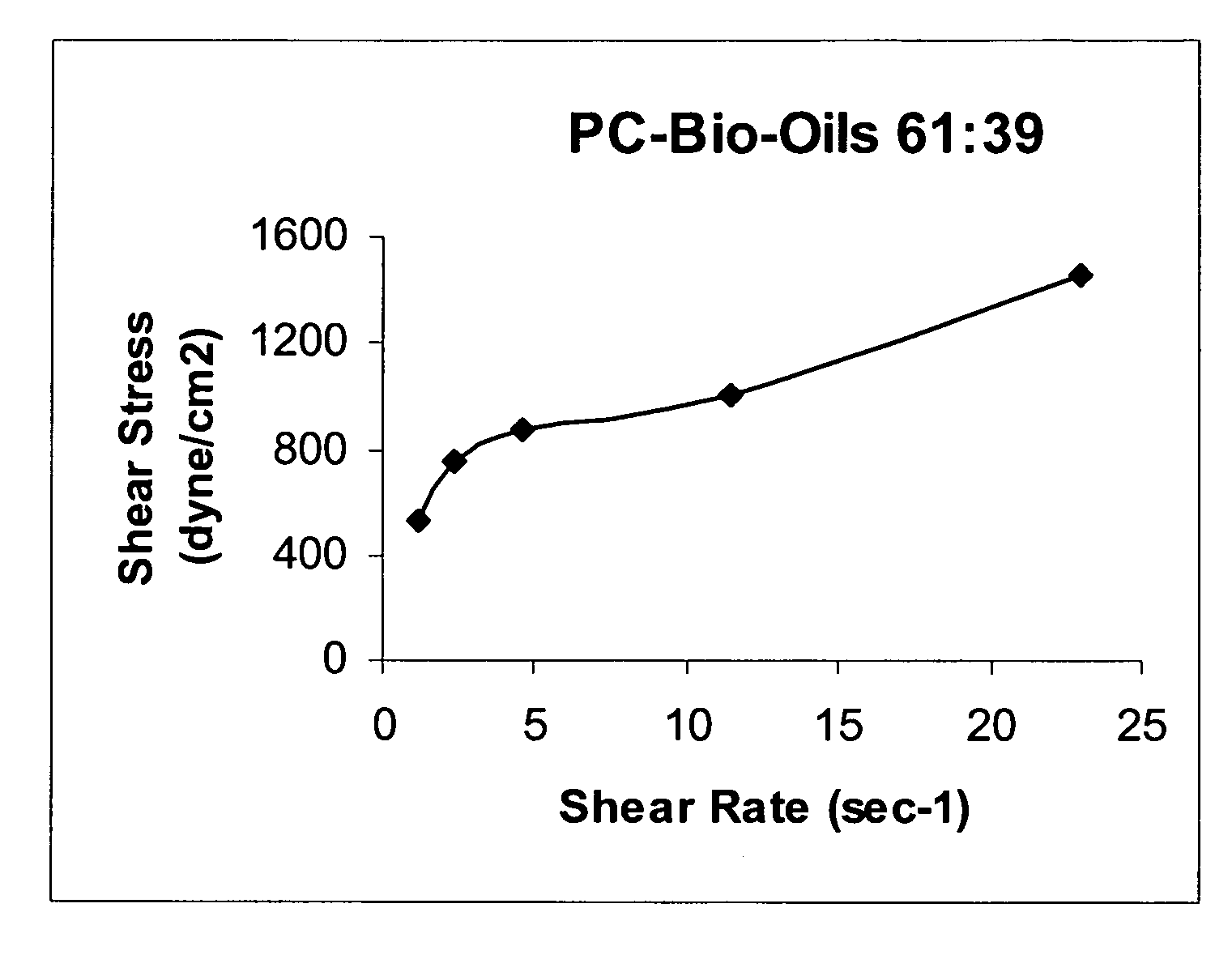
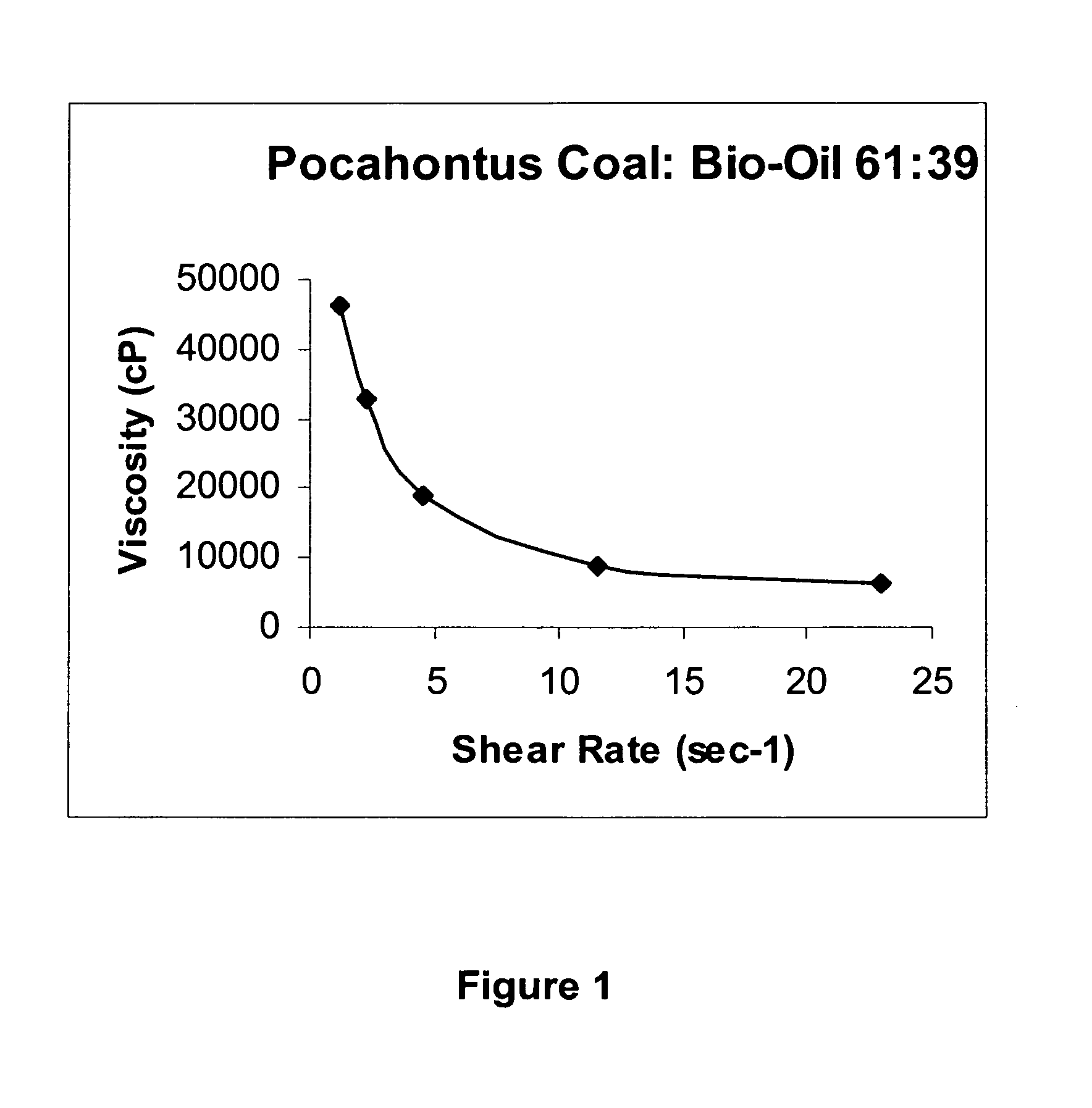
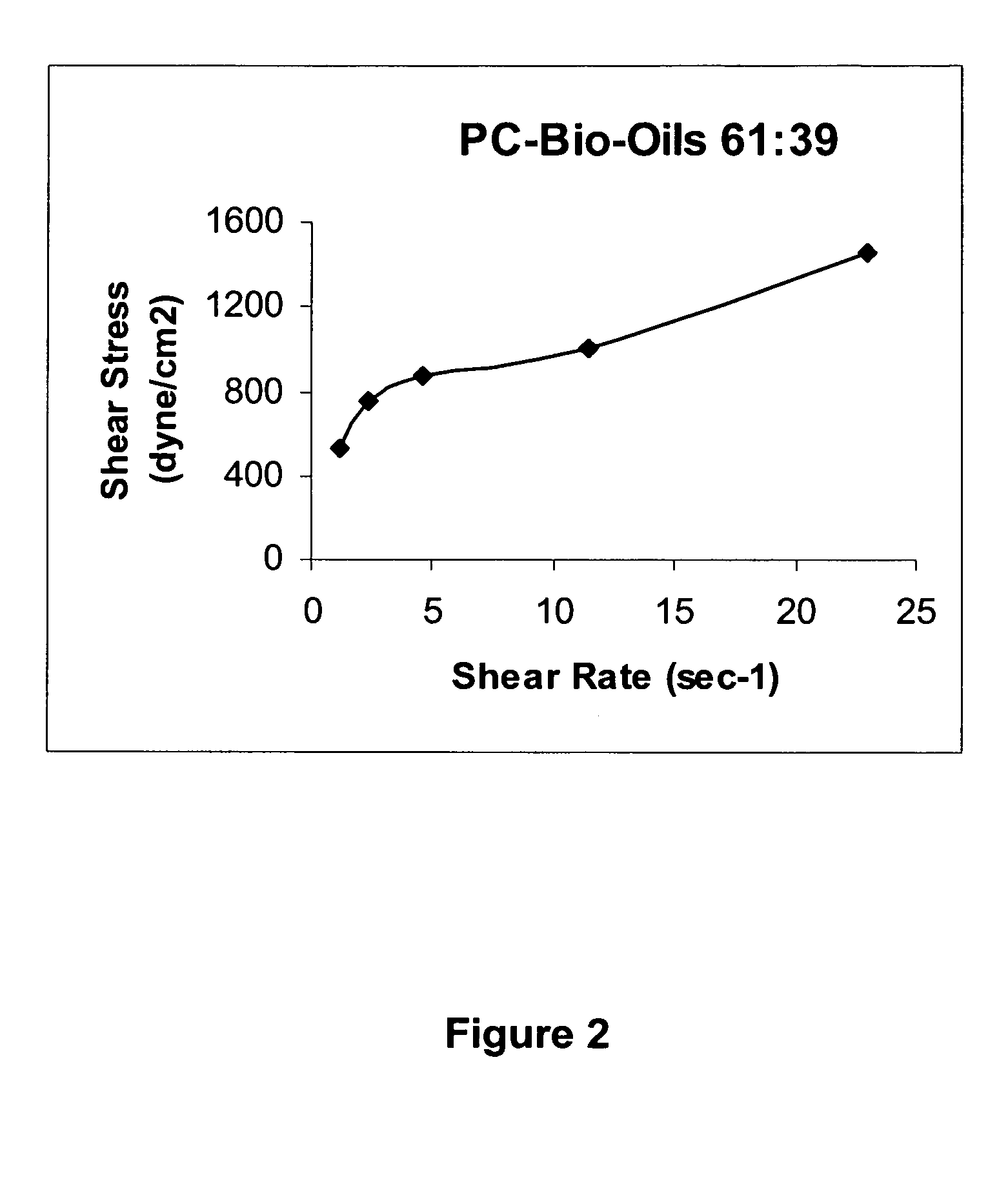
ActiveUS20100083575A1Conveniently obtainBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSlurryEngineering
A process for the co-gasification of carbonaceous solids (coal, coke) and biomass in which the biomass material is pyrolyzed to provide a biomass pyrolysis oil and biomass char or coke which are then mixed with the carbonaceous solid to form a slurry. This slurry is then heated if necessary to achieve a viscosity which can be processed conveniently in the gasifier. The heat required for pyrolyzing the biomass can conveniently be obtained from the heat exchanger used to cool the hot synthesis gas product emerging from the gasifier.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Mixed-mode interaction
InactiveUS20060003780A1Information obtainedConveniently obtainSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsThe InternetPurchasing
A user of a wireless device, such as a mobile phone, can make purchases or obtain information via a network, such as the Internet, using both voice and non-verbal methods. Users can submit voice queries and receive non-verbal replies, submit non-verbal queries and receive voice replies, or perform similar operations that marry the voice and data capabilities of modern mobile communication devices. The user may provide notification criteria indicating under what conditions a notification should be sent to the user's wireless device. When purchasing opportunities matching the selected notification criteria become available, the user is notified. The user can respond to the notification, and immediately take advantage of the purchasing opportunity if he so desires. Mixed-mode interactions can also be used by sellers to more advantageously control the marketing of distressed, time sensitive, or other merchandise / services.
Owner:AERITAS
Aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers in the presence of a partially fluorinated oligomer as an emulsifier
InactiveUS20070004848A1Increase speedSmall particle sizeTransportation and packagingFibre treatmentPolymer scienceOligomer
The present invention relates to a method for making a fluoropolymer comprising an aqueous emulsion polymerization of one or more fluorinated monomers wherein said aqueous emulsion polymerization is carried out in the presence of an oligomer that comprises one or more ionic groups, has a partially fluorinated backbone, a number average molecular weight of not more than 2000 g / mol and that has a combination of repeating units different from that of the fluoropolymer that is being produced by the polymerization of said one or more fluorinated monomers. Since the polymerization of the one or more fluorinated monomers to produce the desired fluoropolymer is carried out in the presence of the oligomer, the resulting dispersion will contain the oligomer in addition to the fluoropolymer. Thus, in a further aspect, the invention relates to an aqueous dispersion of a fluoropolymer comprising the oligomer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Controlled-access database system and method
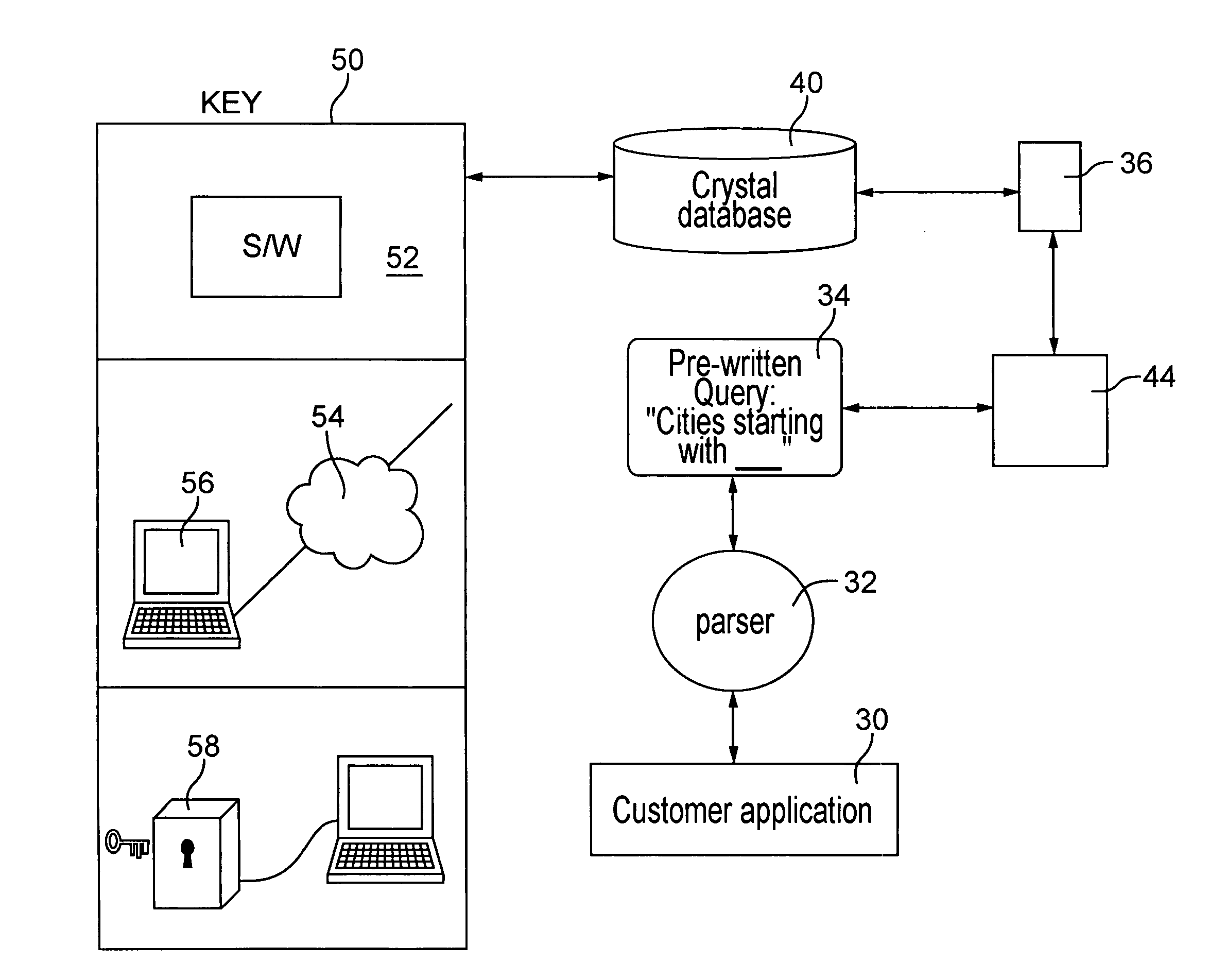
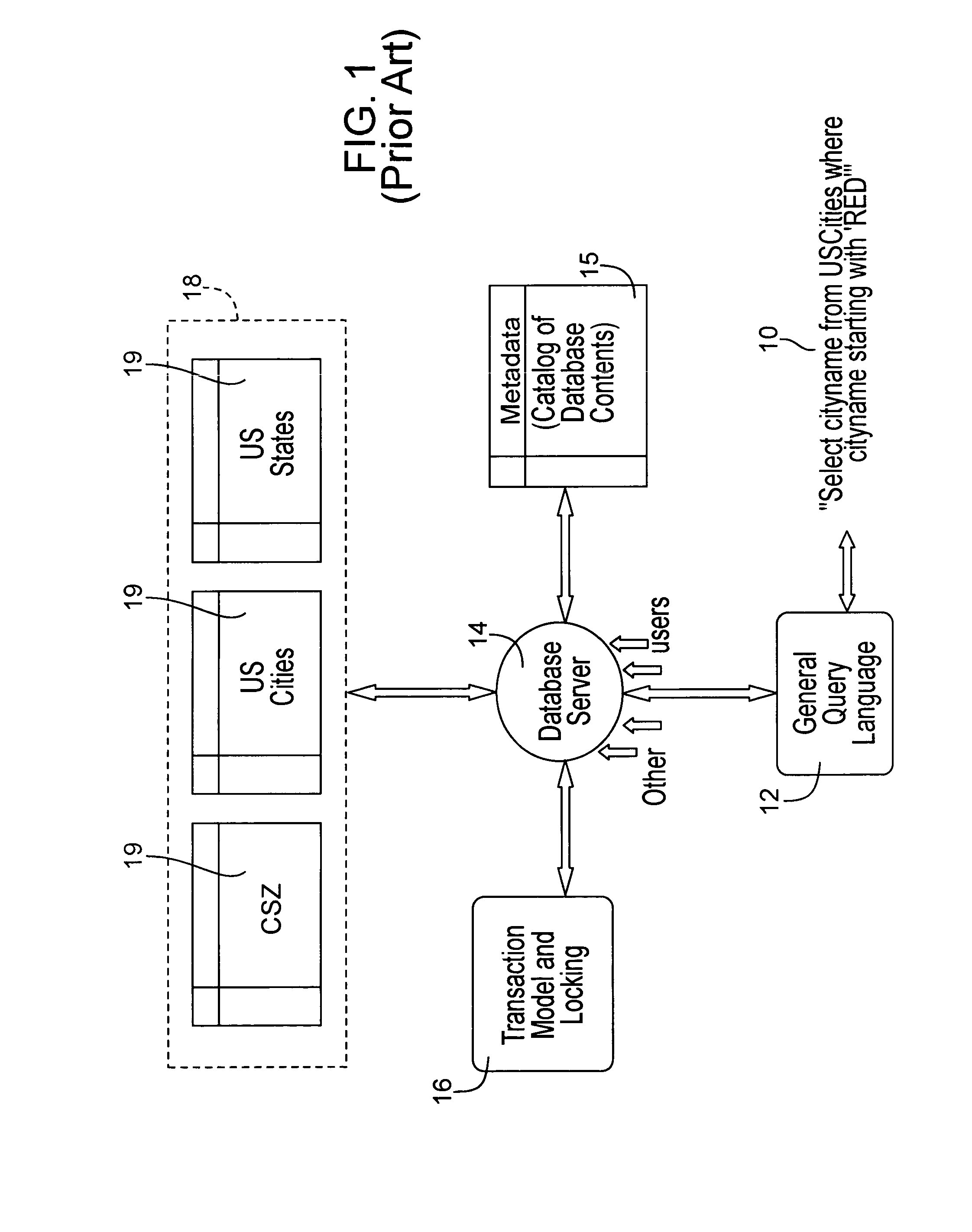
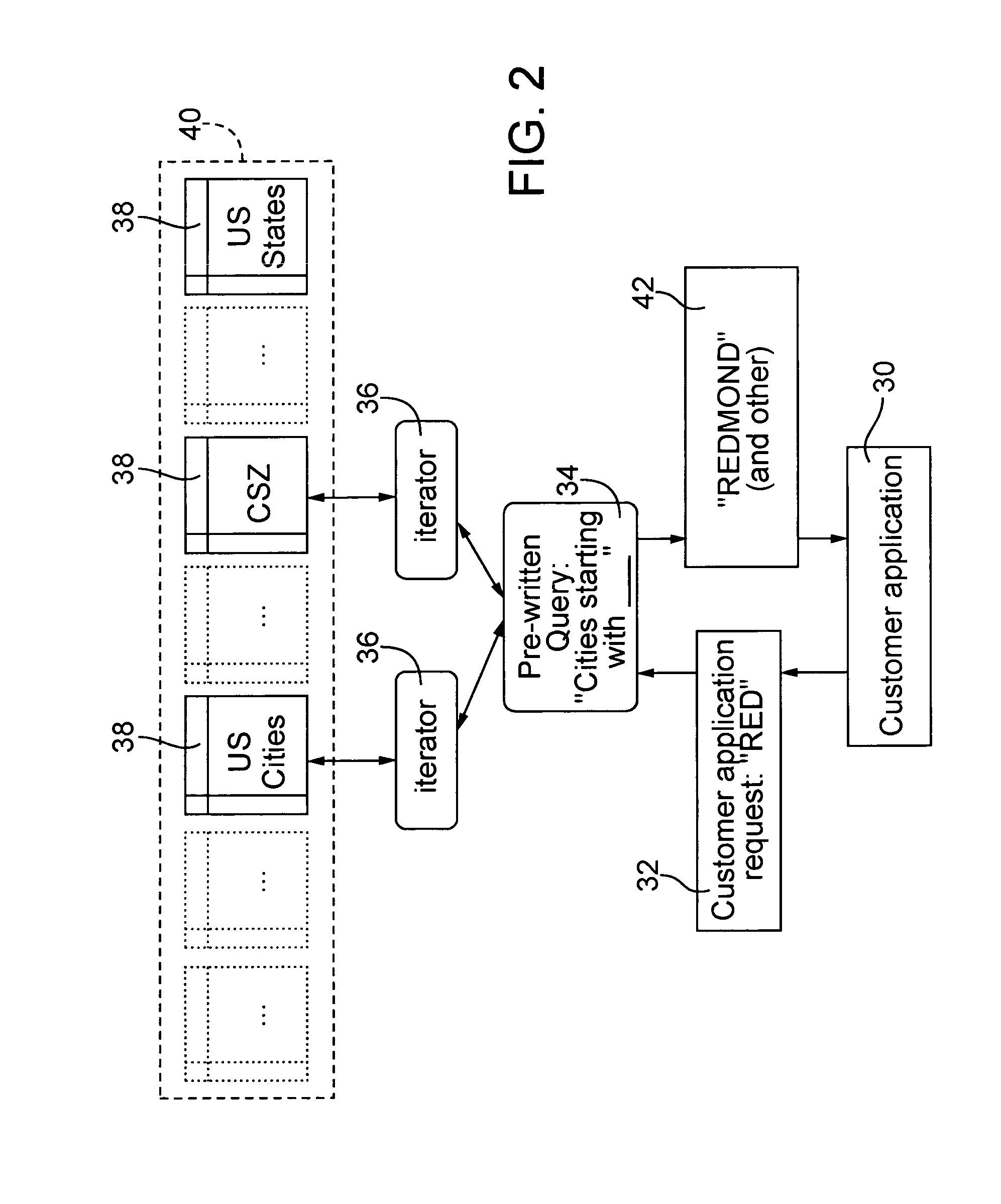
InactiveUS7333987B2Lower requirementEffective mergerData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsLimited accessIterator
A controlled database system is designed for rapid access of data records with reduced memory storage requirements. The database system employs a set of obfuscated data records stored in data crystals that can only be accessed and read by an iterator, which is not directly accessible by the users of the database. The iterator accesses information responsive to a predefined query sent from a customer application. Rather than providing general tools to customers for constructing any possible queries, such as is done in structured query language database systems, database systems embodying the present invention allow only predefined types of queries to be used by customer applications. By restricting the types of queries customer applications can call, valuable data records remain secure from unauthorized reconstruction or duplication while still allowing limited access for specific purposes.
Owner:MATTHEWS INT CORP
Method and system for converting desktop application to web application
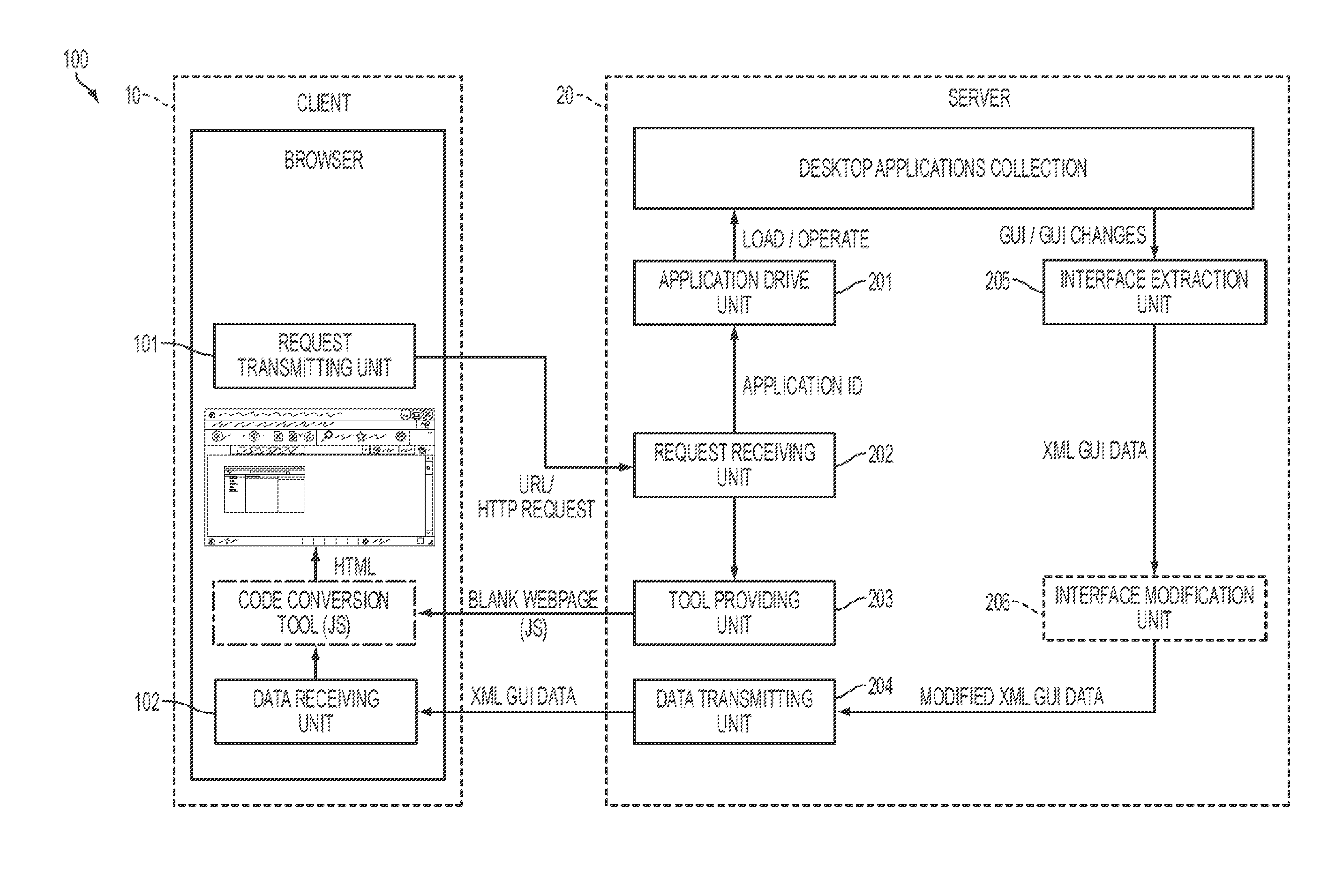
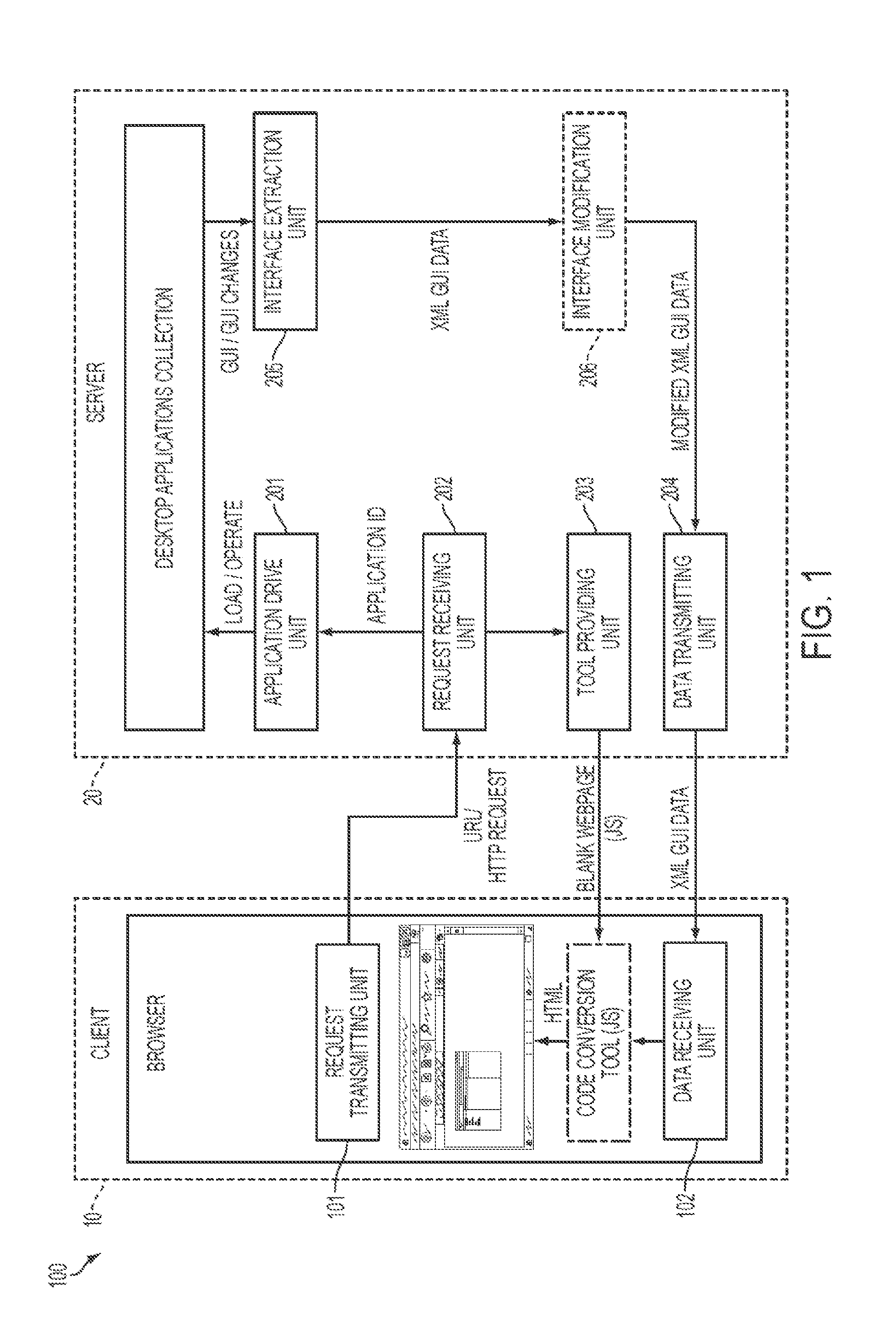
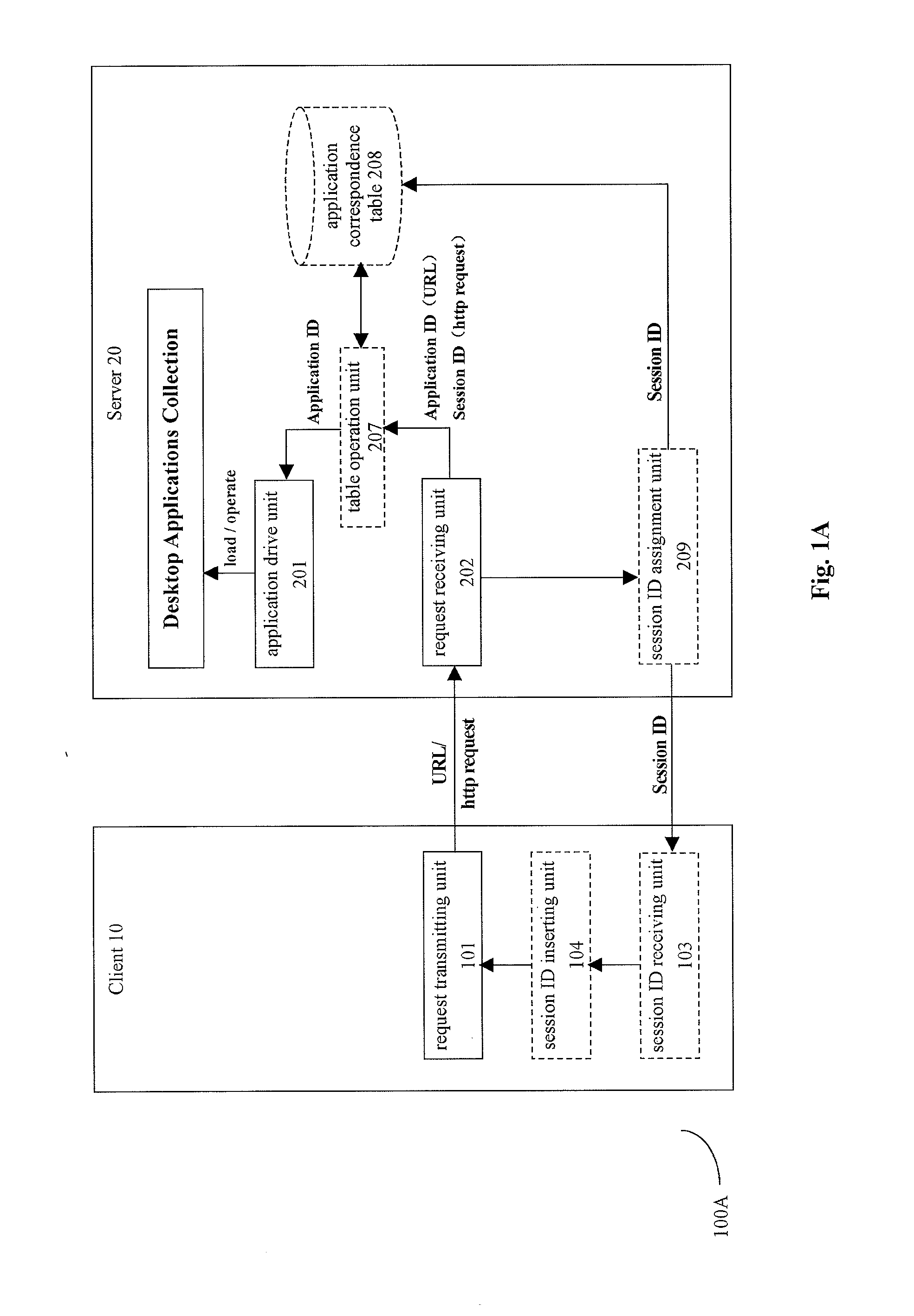
InactiveUS20110035435A1Optimize and update interface (GUI)Conveniently obtainInterprogram communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb applicationClient-side
The present invention provides methods and systems for converting a desktop application to a Web application. The method comprises: inputting, at a client side, URL of a desired desktop application and sending it to a server; the server providing a code conversion tool (e.g. JavaScript code) to the client and loading the desktop application; at the server, extracting interface information of the loaded desktop application, wrapping the interface information to data in an interface descriptive language format (e.g. XML data), and sending the wrapped data back to the client; and at the client, parsing the XML data by utilizing the code conversion tool to generate relevant webpage elements (e.g. HTML data), so as to display the desktop application. In another embodiment, the server can directly run the code conversion tool to implement the code conversion from XML data to HTML webpage elements.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
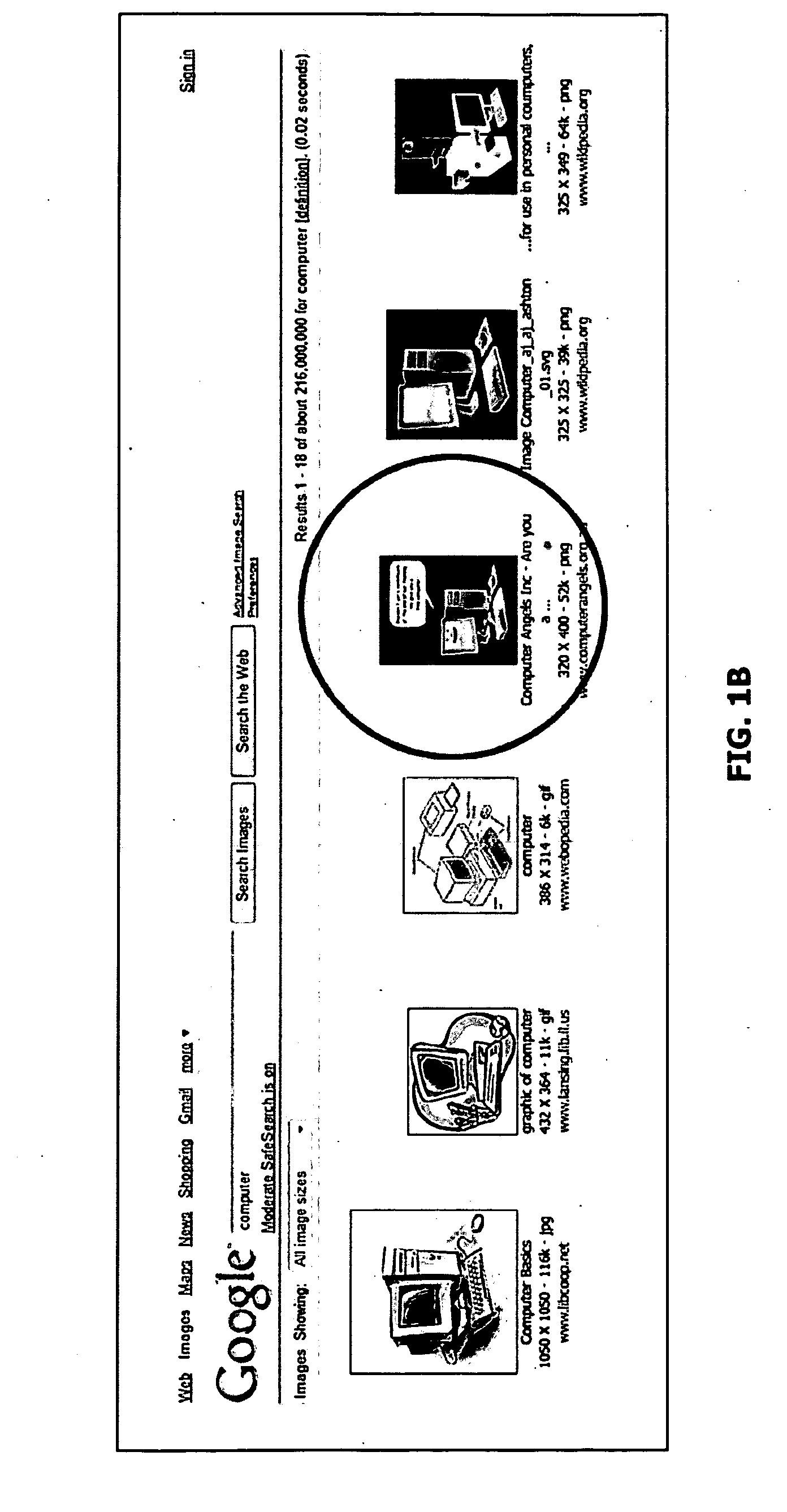
Device for displaying link information and method for displaying the same
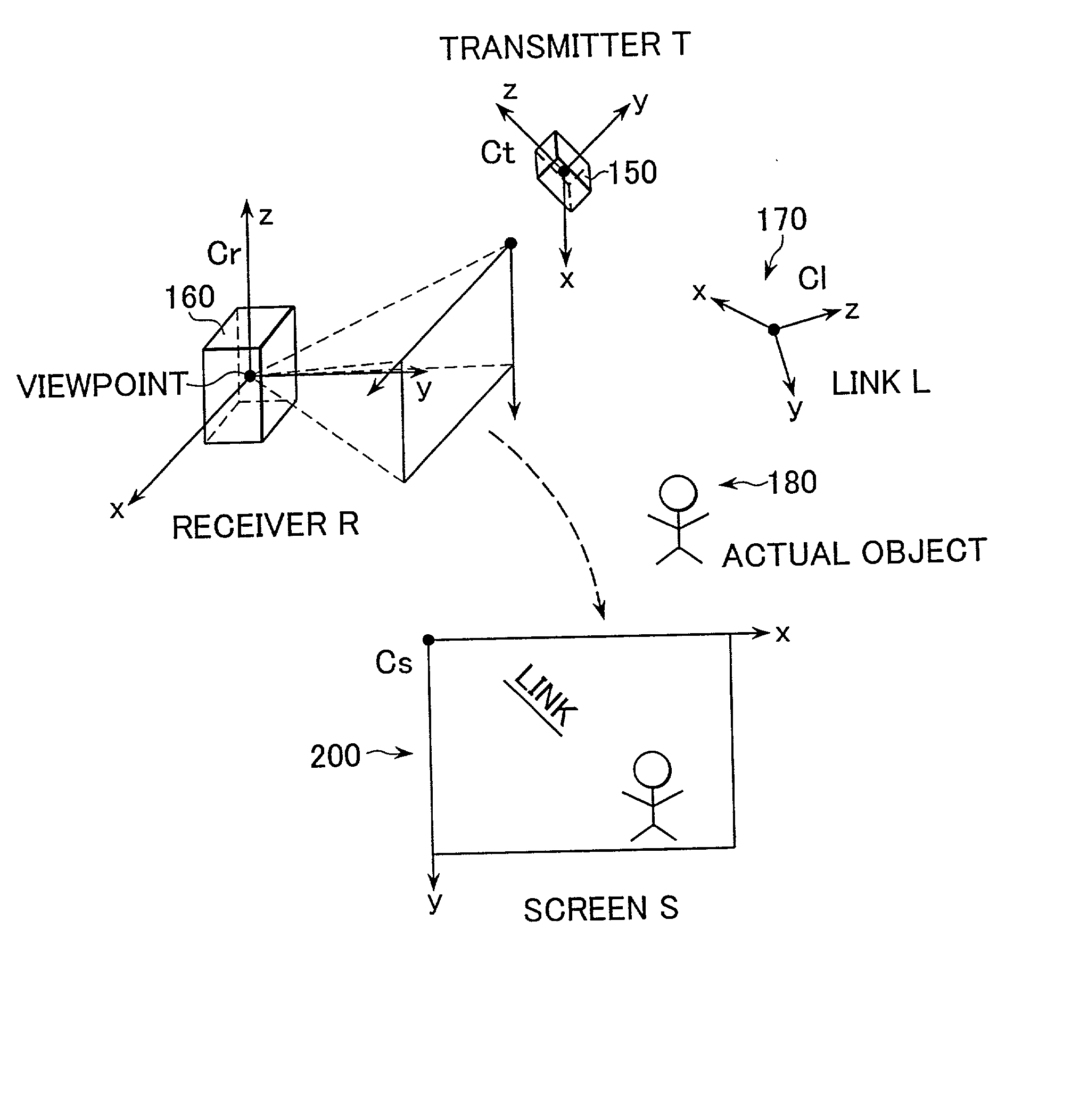
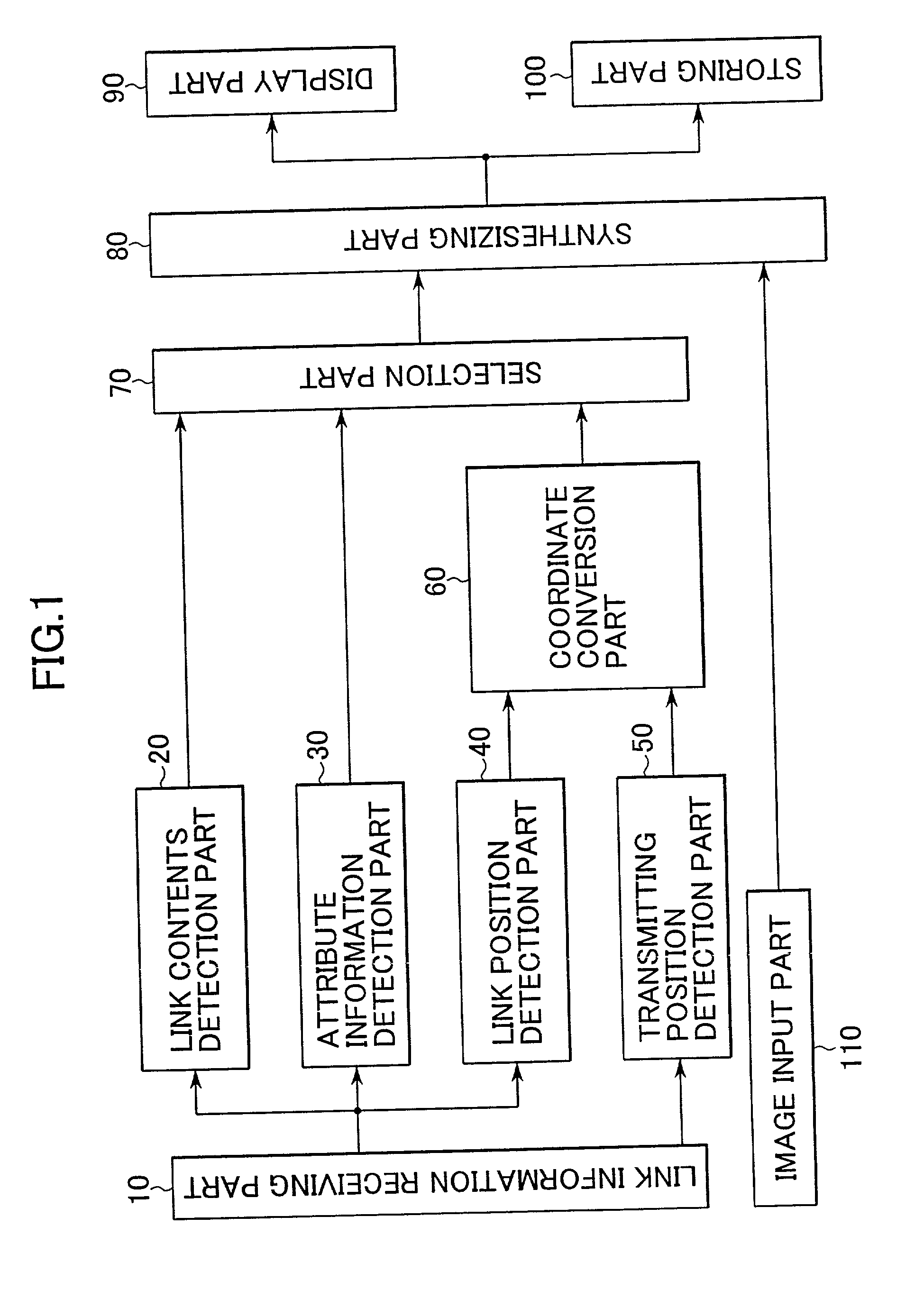
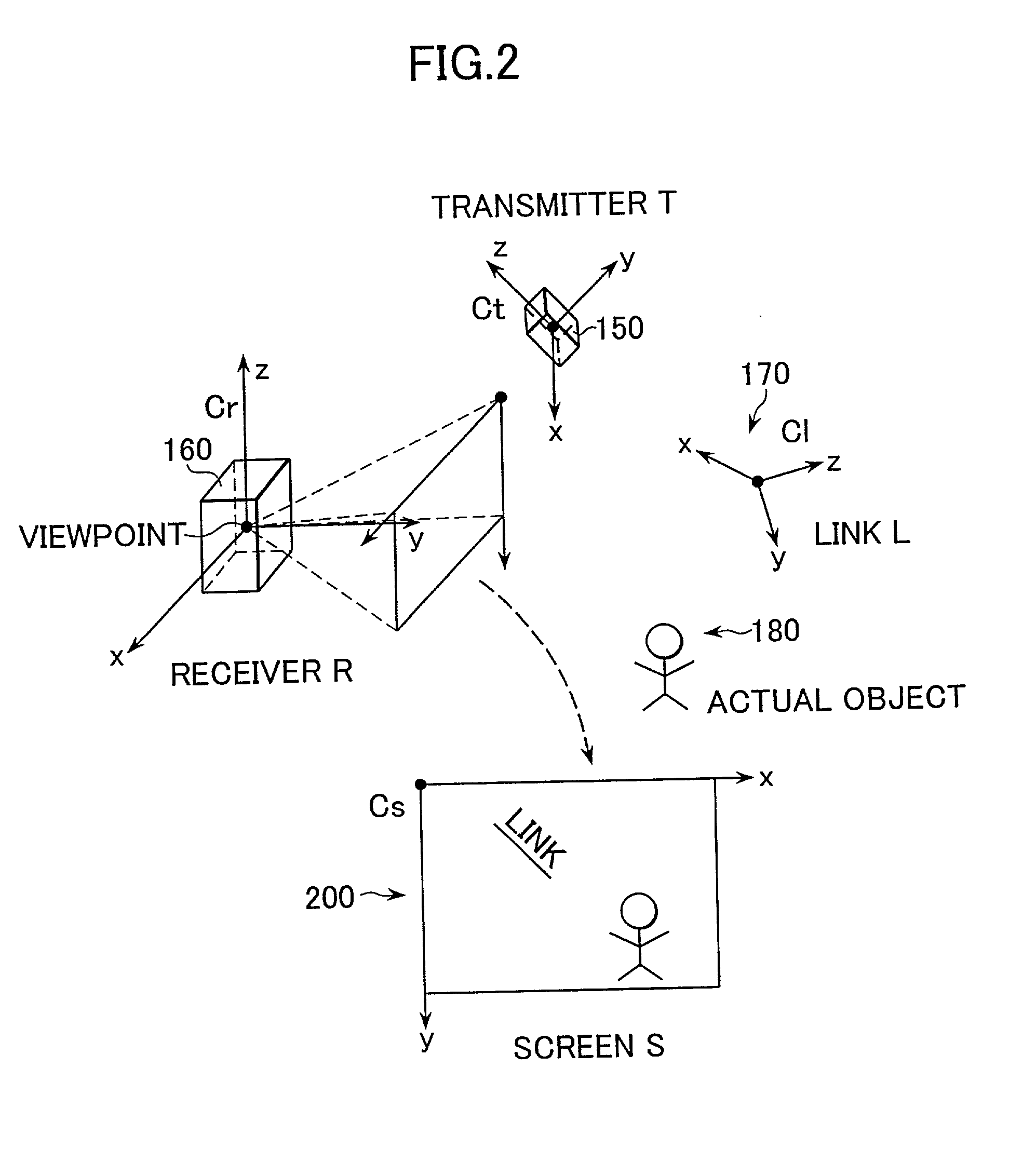
InactiveUS20020044162A1Easy to getConveniently obtainTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Pointing device
There are provided a device for displaying link information and a method for displaying the same which display the image of an actual object superimposed with the label of link information so as to easily obtain information on the actual object and to display a moving link. An image input part obtains the image signal of an actual object. A link information receiving part receives link information transmitted by a transmitter. A link contents detection part detects the link contents. An attribute information detection part detects the attribute. A link position detection part detects the link position. The image signal obtained by a synthesizing part is superimposed with the link contents in the display coordinate of a link label calculated by a coordinate conversion part in accordance with the attribute information. A display part displays the image signal synthesized. The user uses a pointing device to easily obtain the link information on the actual object in accordance with the link label.
Owner:SONY CORP
System and method for calibrating cardiac pressure measurements derived from signals detected by an implantable medical device
ActiveUS8202224B2Easy recalibrationEasy CalibrationElectrotherapyEvaluation of blood vesselsThoracic FluidLeft atrial pressure
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Exercise device integrally incorporating digital capabilities for music, light, video and still imagery, heart rate measurement and caloric consumption
InactiveUS20100190607A1Difficult to performDifficult to describeDumb-bellsClubsHeart rate measurementBluetooth
A fitness device integrally incorporating digital technology can include capabilities for providing music and auditory stimulus that can be heard through a headphone, Bluetooth; or speakers for ambient music. Further capabilities enable the device to record video and still imagery, play video to provide instruction, feedback; or for leisure viewing. Along with sound and video capability, the device can have light emitting capability for a visual dimension in use. For biofeedback, the device can include a heart rate calculator to provide feedback on the level of exercise intensity and caloric consumption. The light emitting capacity allows the user to create patterns in use. Thus, the device can be multi-faceted able to provide ambient music, recording and viewing video, enveloping the user in a “bath” of light, sound, very subtle electromagnetic fields. All of said baths are created at distances from the users body that correspond to the length of the users arms, degree of bend at the elbow joint and chosen pathway for the circular / orbital movements.
Owner:THINKFIT
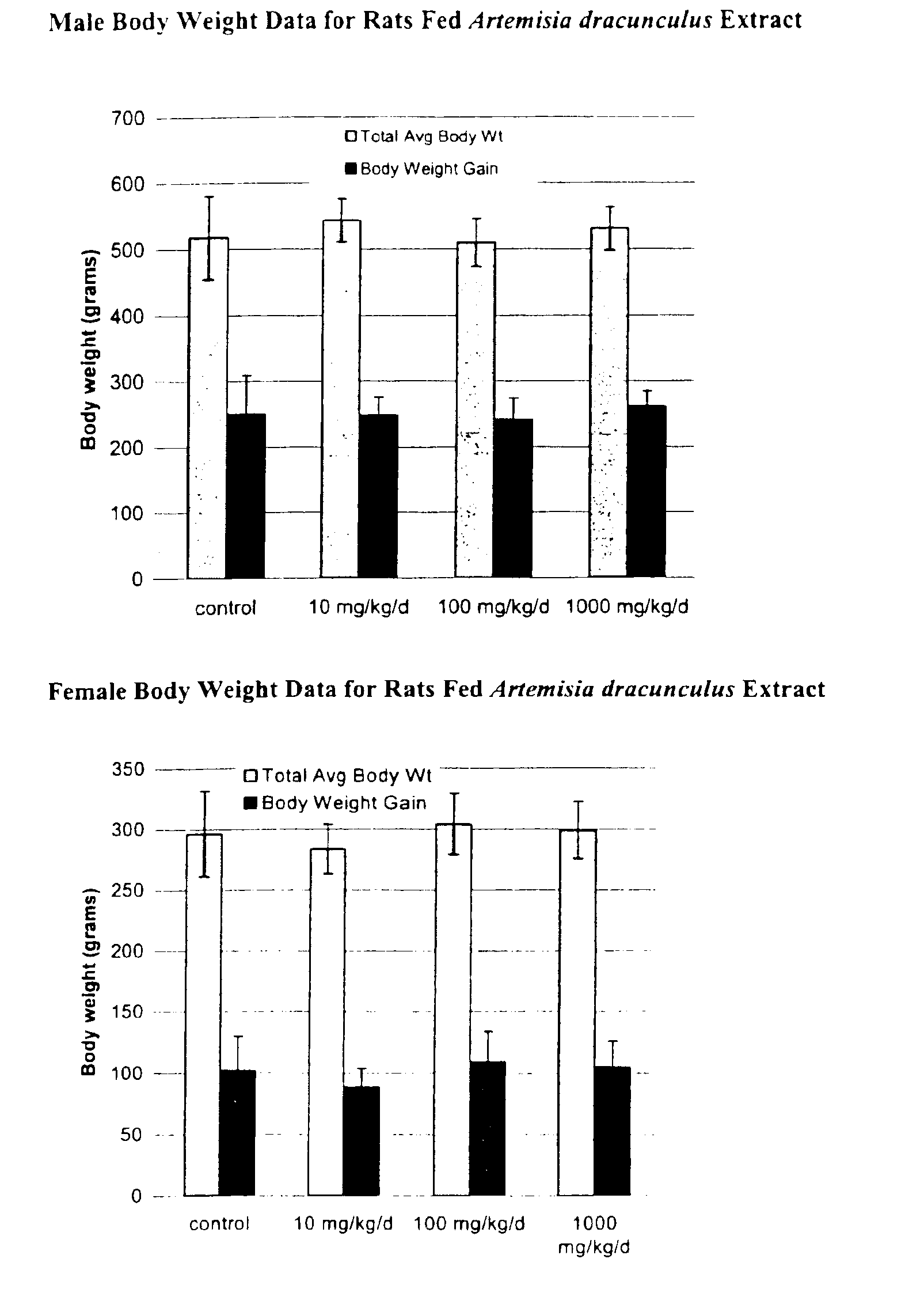
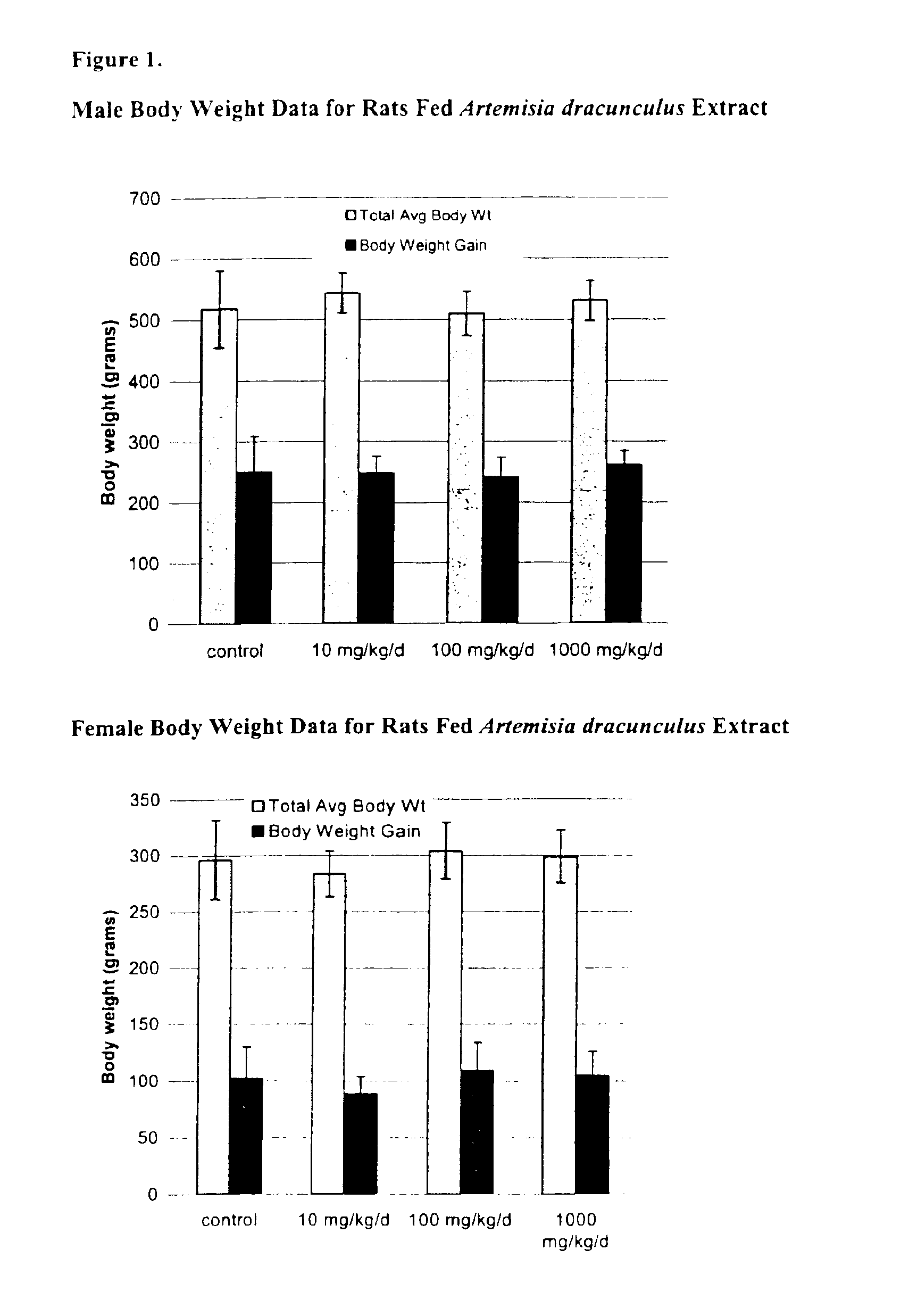
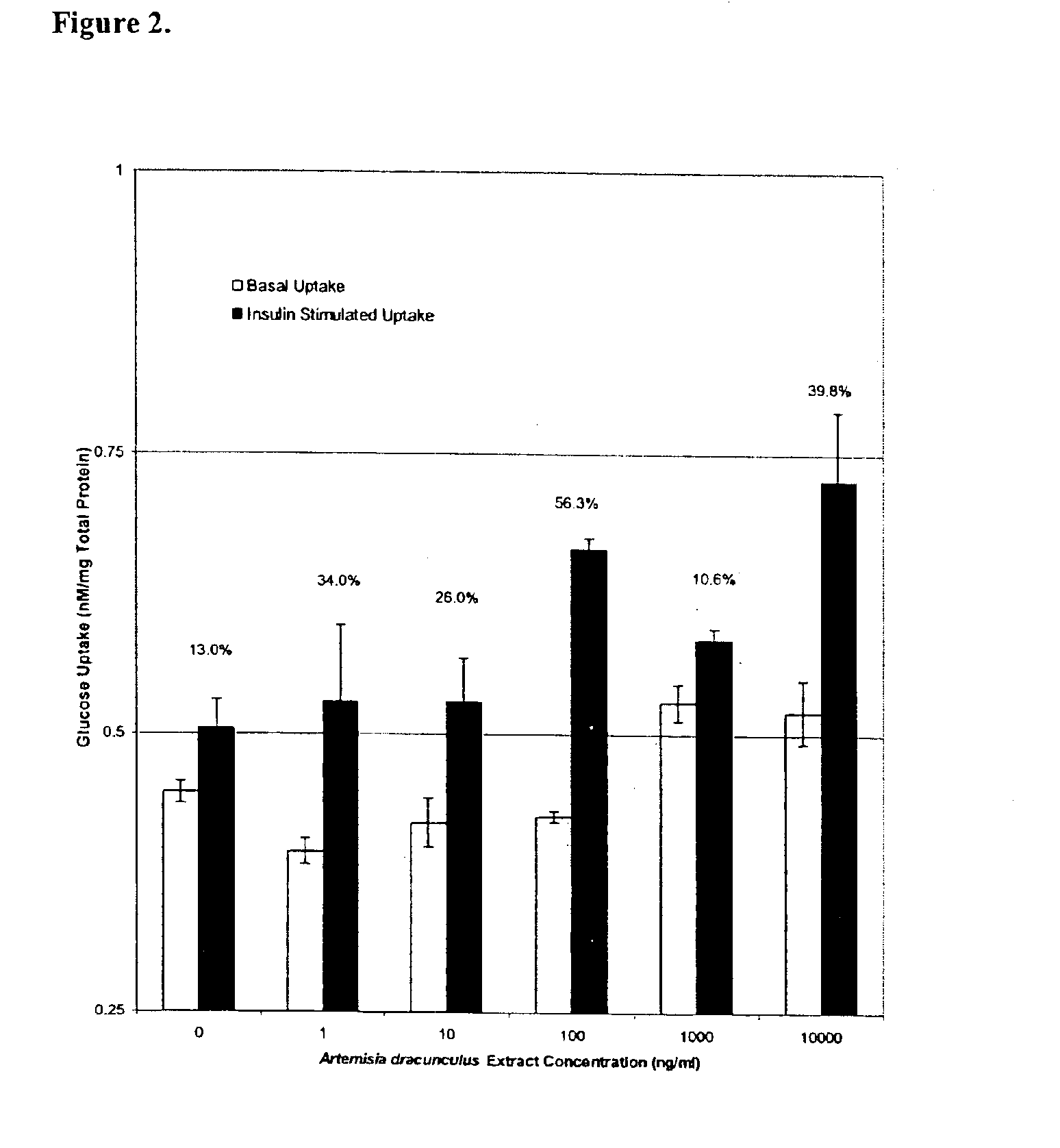
Method for treating type 2 diabetes with an extract of Artemisia
InactiveUS6893627B2Increasing glucose uptakeMethod securityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMammalFractionation
The present invention provides materials and methods relating to mildly polar fluid extracts of plant materials, such as Artemisia plant species, useful in methods for treating diabetes and methods for modulating the activity of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and in methods for modulating phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) activity in a diabetes-specific manner. The extracts are generally non-toxic and non-mutagenic and may be administered to diabetics with beneficial effect on blood glucose levels. The extracts may also be administered to non-diabetics without deleterious effect. The plants are easily grown with a minimum of time, labor, and cost. Extracts are inexpensively and quickly prepared without the need for fractionation to remove potentially deleterious compounds, and the extracts may be administered to mammals such as humans through various routes, in a variety of forms, and at convenient concentrations.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE OF UNIVESITY OF NEW JERSEY
Method and Apparatus For Obtaining Digital Objects In A Communication Network
InactiveUS20080177864A1Easy to useTime-efficient for userTelevision system detailsMultimedia data indexingLow speedInternet radio
A technique for obtaining digital objects (such as songs or video clips) from information providers in data communication networks (such as the Internet); the digital objects being sent through channels (such as Internet radio channels or Internet TV channels) or being otherwise made available. The end-user gains several advantages over techniques supported by the known art. For example, end-users may; easily locate desired digital objects, need not be connected during object capture, can be connected through a low speed connection, does not have to have a high capacity computer, can obtain digital objects legally, can receive supplemental information associated with the digital objects, can quickly scan a vast number of digital object having been sent earlier, need not have the required storage space for the digital objects available during object capture, can easily navigate through a multitude of digital object channels, can easily obtain objects with a certain desired quality, can easily obtain objects in a certain desired format, can legally obtain digital objects at no cost and can prove that the digital objects were actually obtained legally.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Suction plate and cradle for an automobile having the same
InactiveUS20080217826A1Easily dismountedEasy to adjustWork holdersStands/trestlesRelative motionEngineering
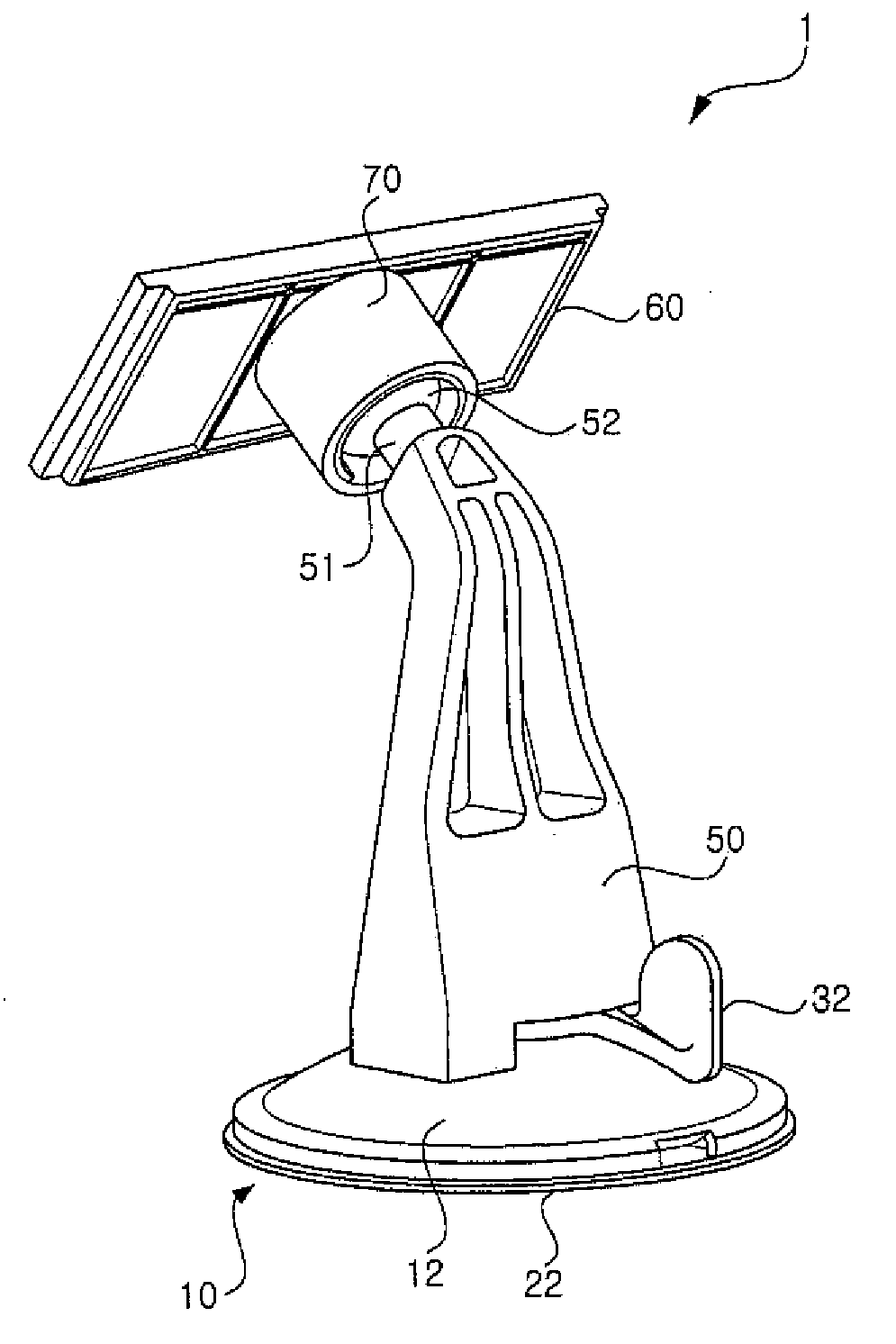
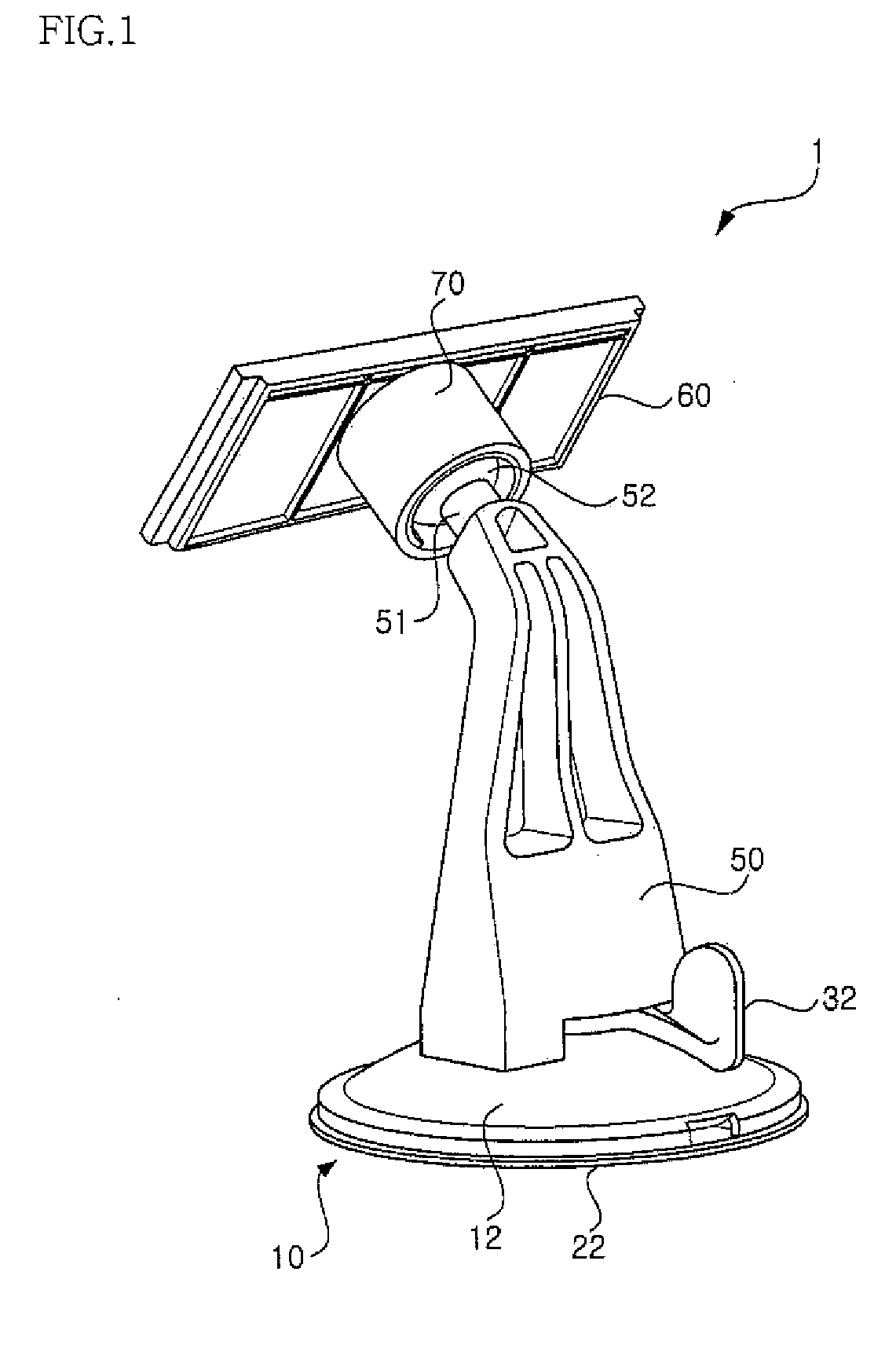
A suction plate and a cradle for an automobile having the same, the suction plate including a housing provided with a boss protruding in one direction, the boss having a through hole formed to pass through a side thereof; a suction member installed at a lower portion of the housing to be moved relative to the housing, the suction member having a central shaft inserted in the boss, the central shaft having a central hole formed thereon to pass through a side thereof; an elastic member provided in an upper portion of the central shaft to provide elastic force in a direction in which the suction member and the housing go away from each other; and an operating lever provided in the housing rotatably within a certain angular range to adjust relative movement of the housing and the suction member.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Apparatus for culturing organism and method of culturing organism
InactiveUS7972840B2More convenientlyConveniently obtainBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyMicrobiology
Owner:PHYTOCULTURE CONTROL CO LTD
Transformant and process for production thereof, and process for production of lactic acid
The present invention relates to a transformant, containing a lactate dehydrogenase gene which is introduced into Schizosaccharomyces pombe as a host, in which a part of a gene cluster encoding a pyruvate decarboxylase in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe host is deleted or inactivated.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
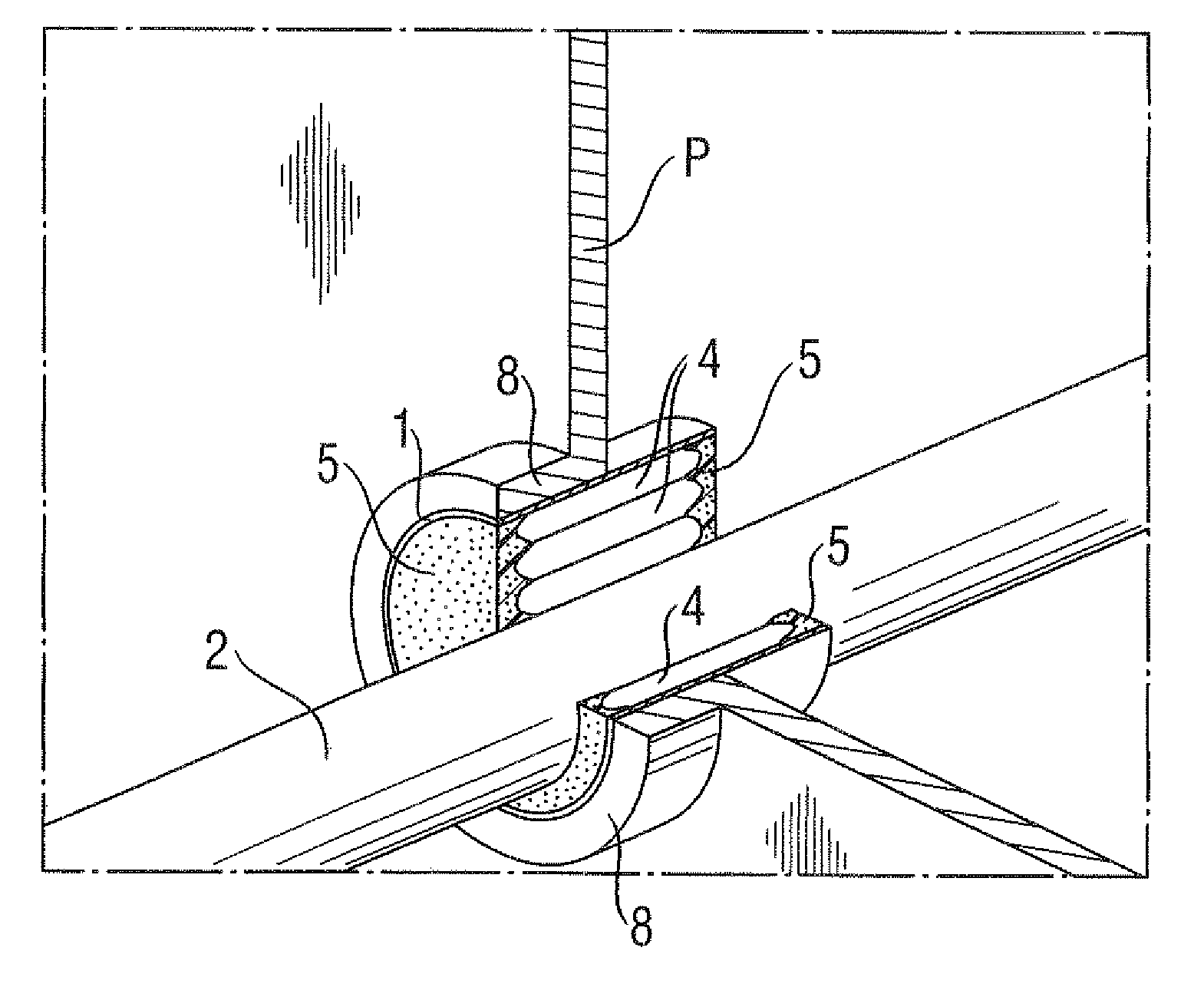
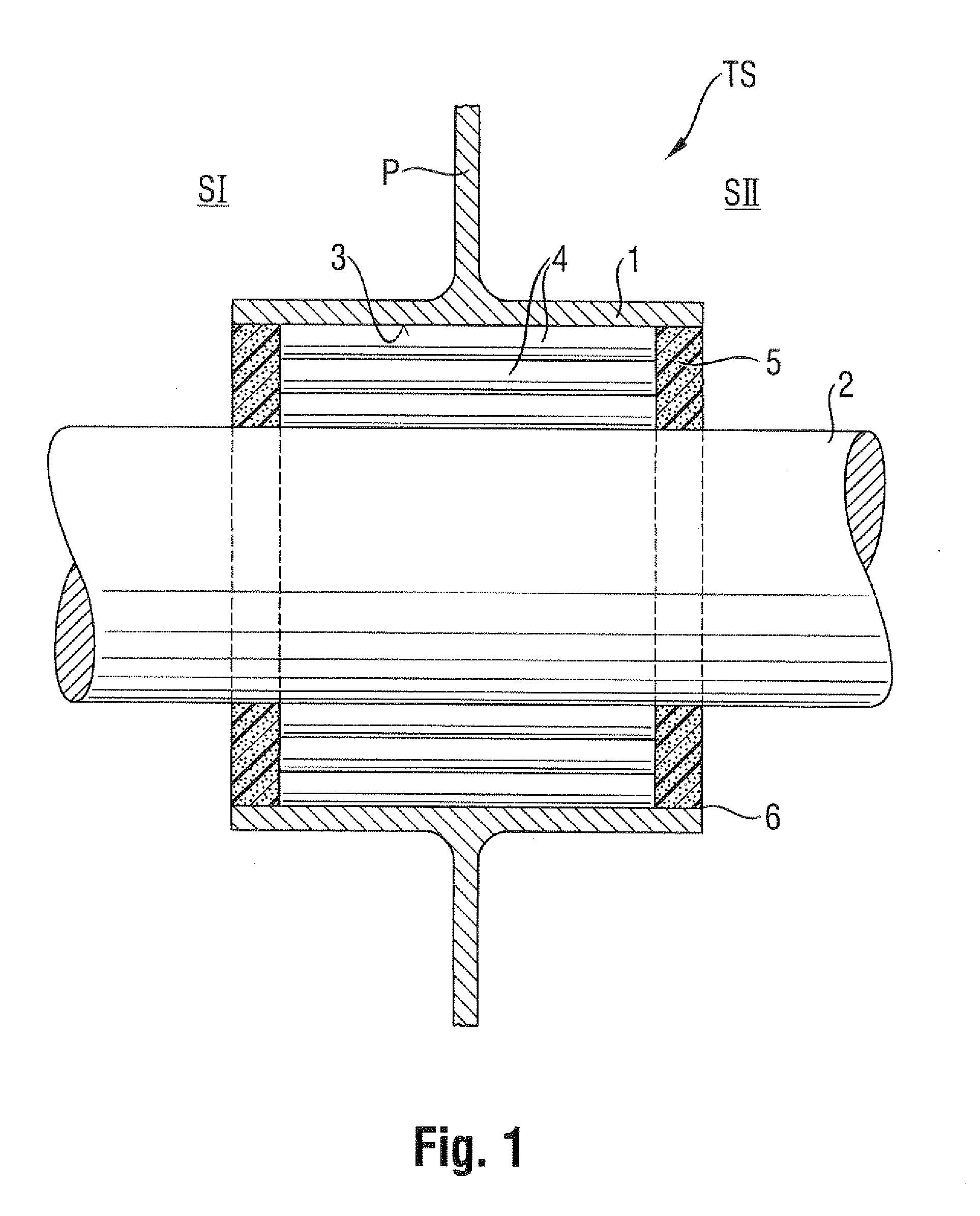
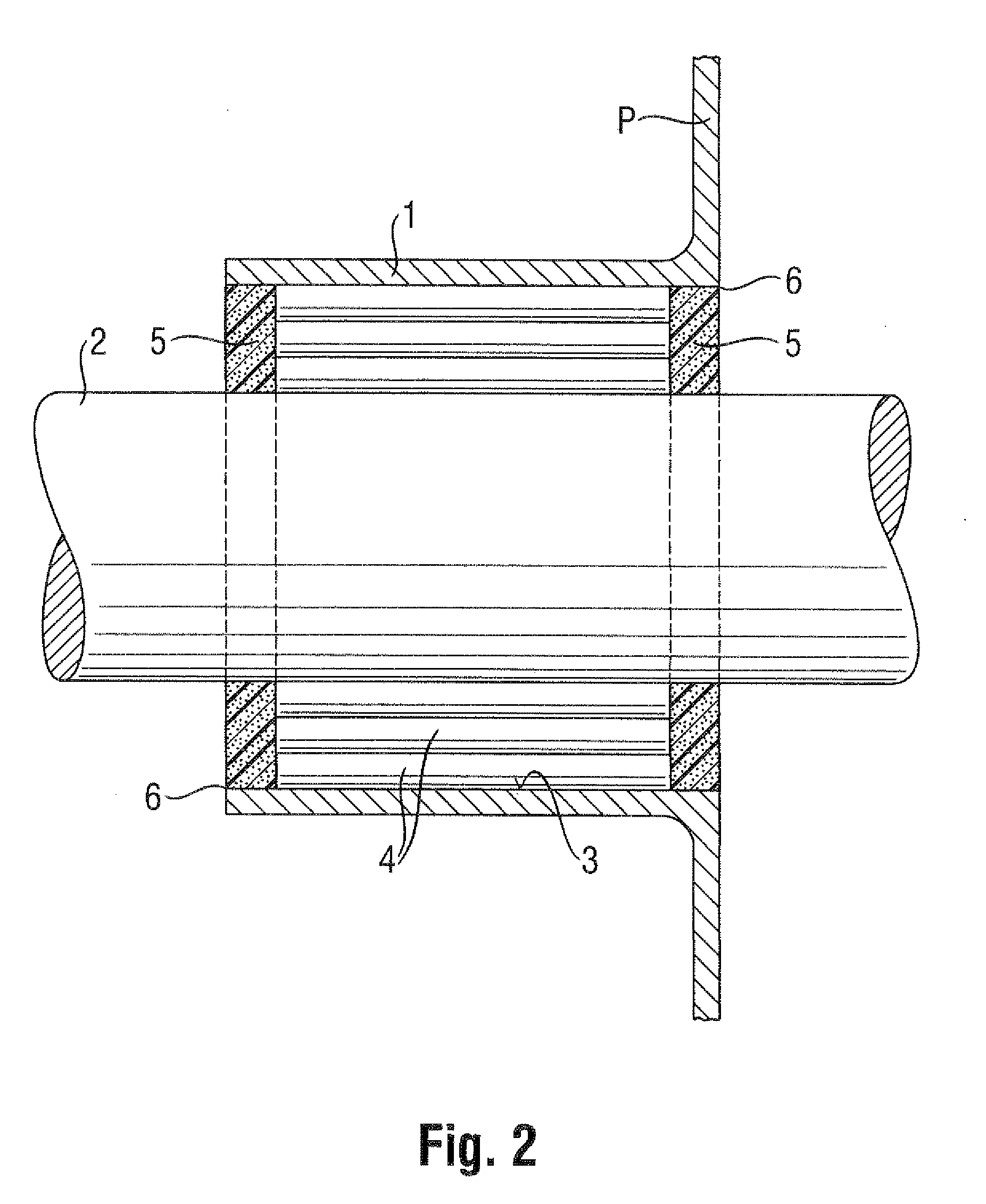
System and method for sealing in a conduit a space between an inner wall of the conduit and at least one pipe or cable extending through the conduit
System for sealing in a conduit a space between an inner wall of the conduit and at least one pipe or cable extending through the conduit, wherein the system comprises: at least one rubber element for providing in the conduit a support-structure which is clampable between the inner wall and the at least one pipe or cable; and a sealant for application against the support-structure and for sealing off at least one end of the conduit between the inner wall and the at least one pipe or cable.
Owner:BEELE ENG
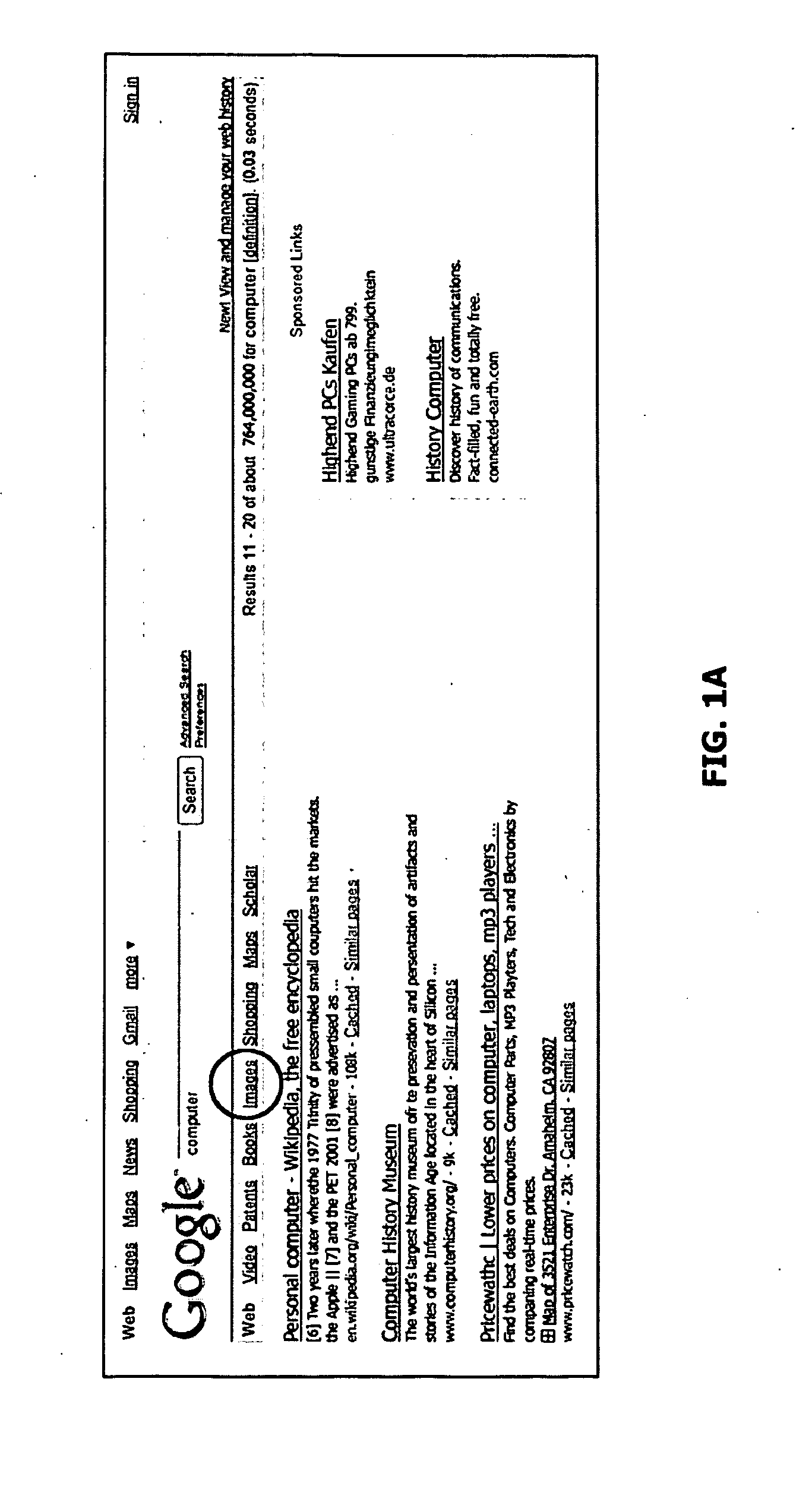
Image-based search system and method
InactiveUS20090112862A1Overcome difficultiesImprove efficiencyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsWeb sitePhysical space
Disclosed-herein is an image-based search system and method. The image-based search system includes at least one user terminal, an information communication network, a search server, and a web server. The user terminal transmits any one or more of a search term entry signal, an image selection signal and an image combination signal to a search server and receives relevant search results from the search server. The information communication network connects the user terminal, the search server and a web server to one another. The search server receives any one or more of the search term entry signal, the image selection signal and the image combination signal from the user terminal, performs searching using attribute information of an image, and transmits search results, including images, to the user terminal. The web server forms a physical space over the information communication network, in which websites, which are objects from which information is gathered by the search server, exist.
Owner:G&G COMMERCE
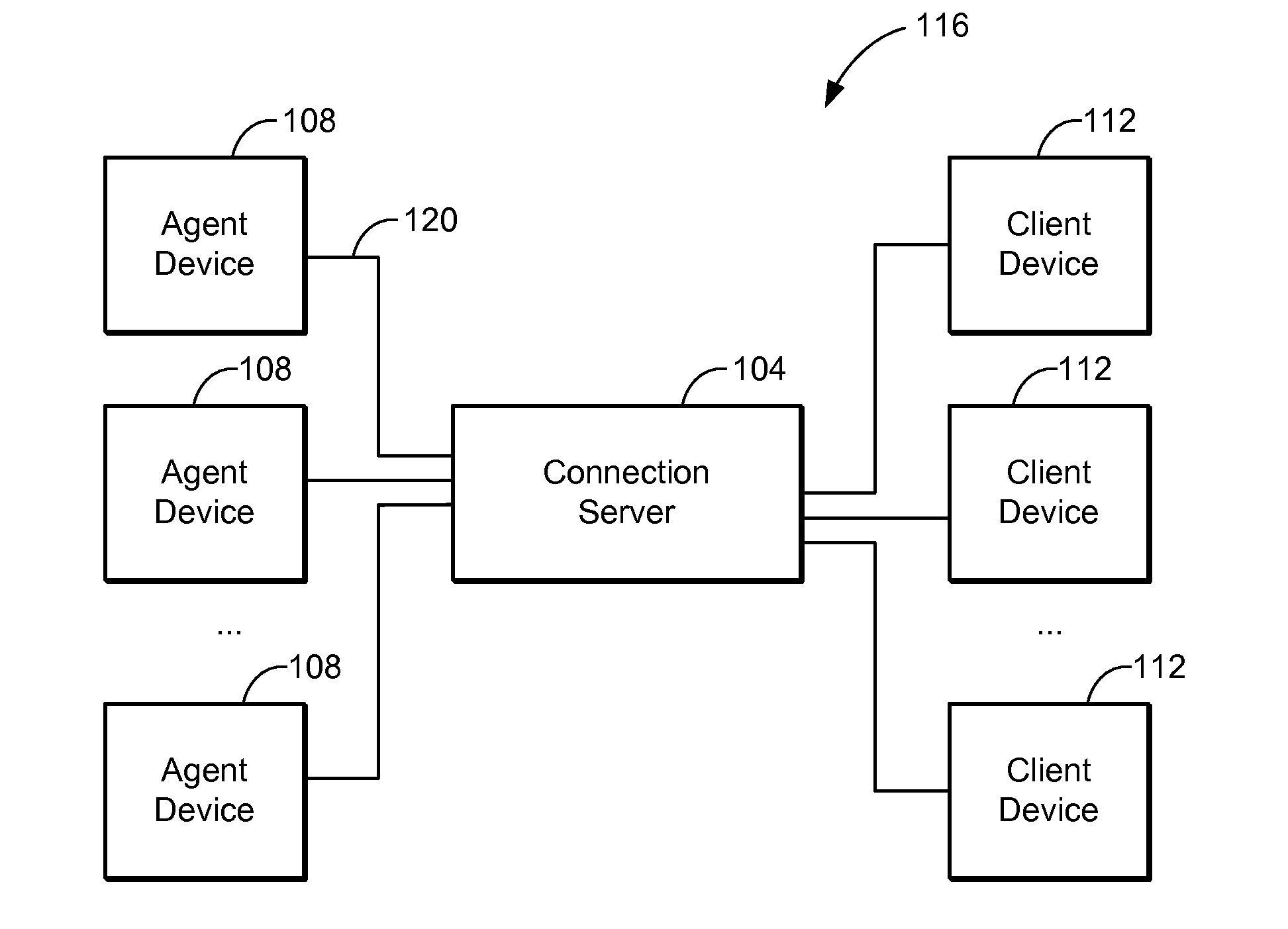
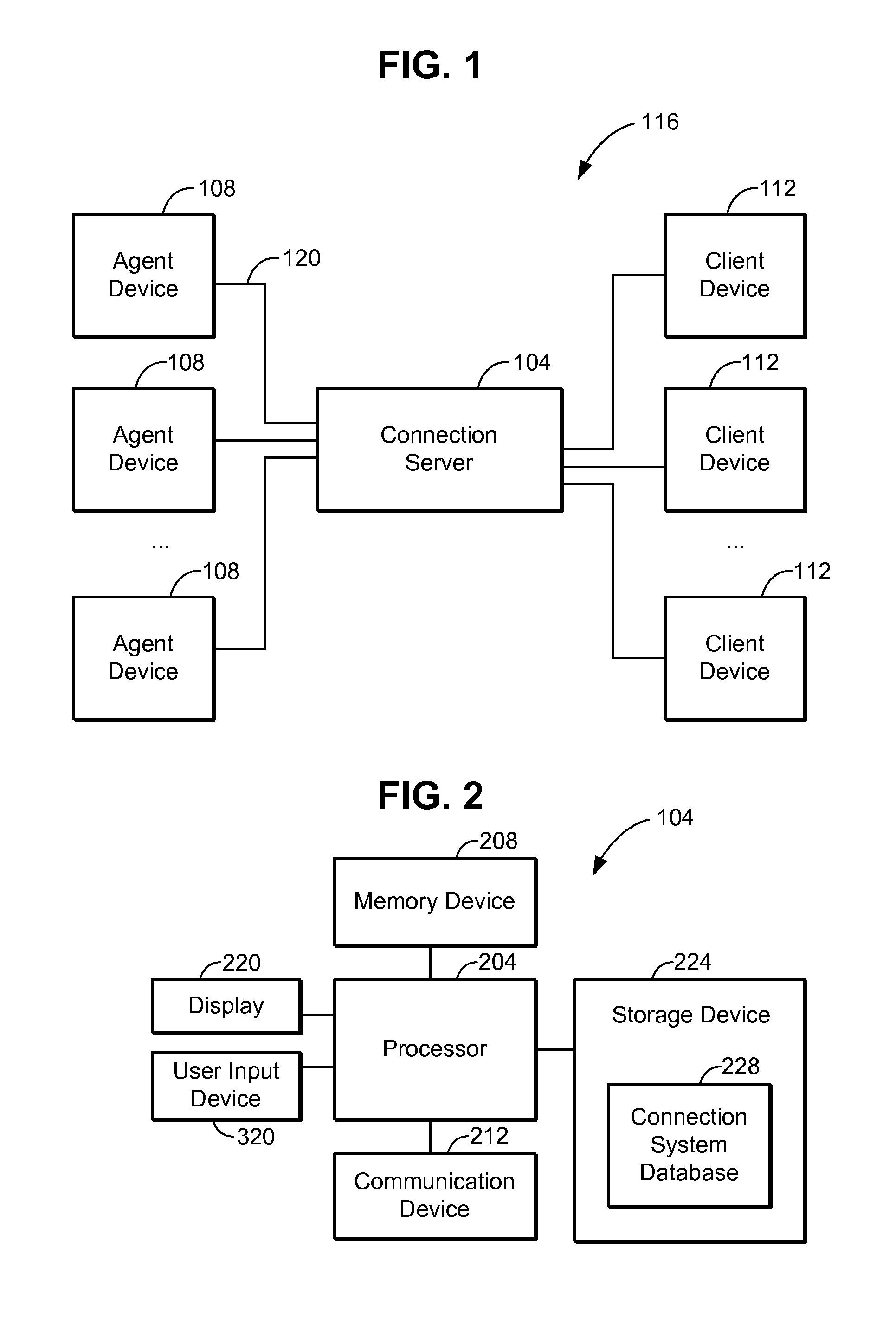
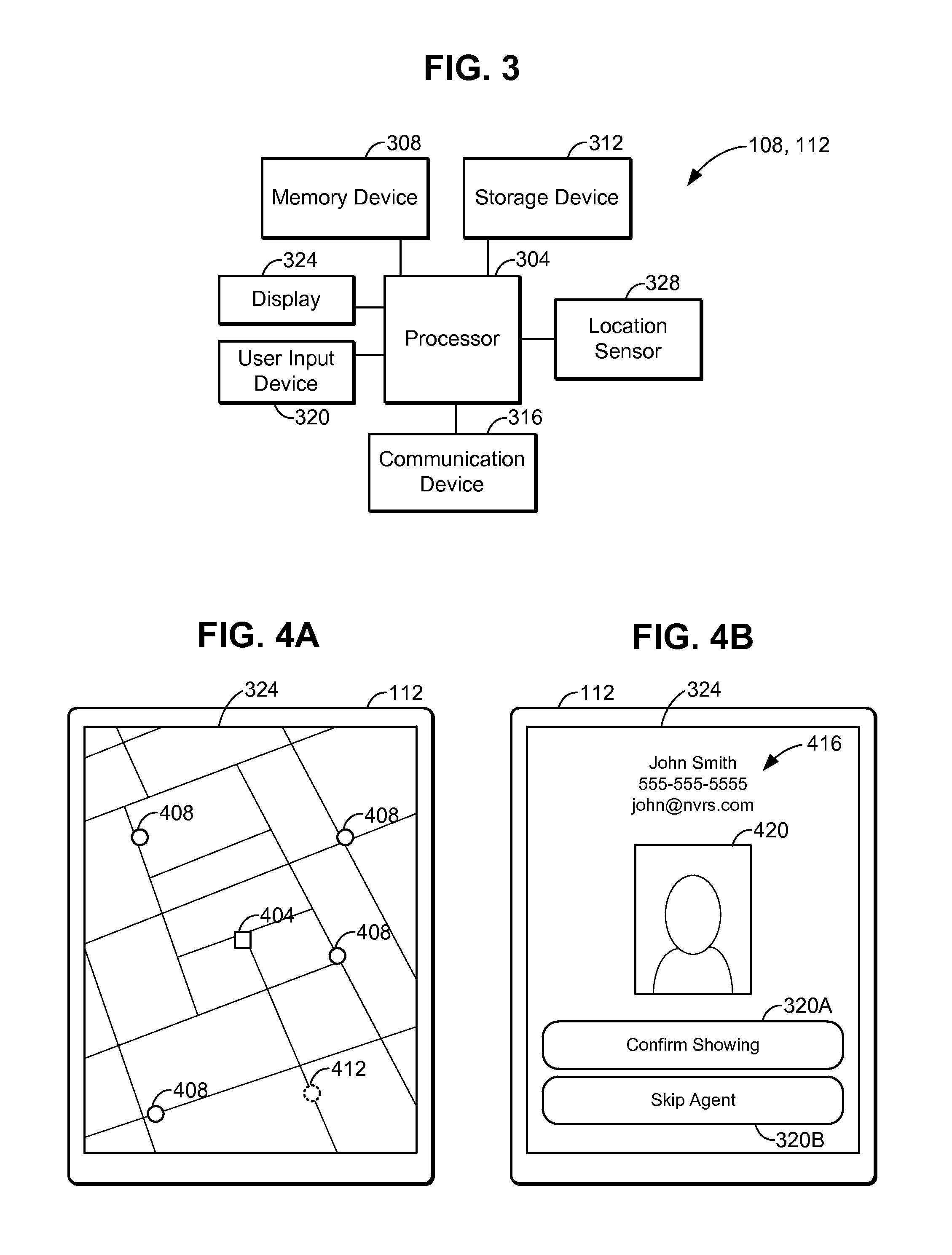
Location-based connection system for real estate agents and clients thereof
InactiveUS20130304657A1Quickly and easily locatedConveniently obtainData processing applicationsClient-sideComputer science
A connection system configured to connect real estate agents and clients based on their relative locations allows rapid deployment of real estate services, such as property viewings. The connection system may include one or more connection servers, agent access devices, and client access devices. A set of nearby agents may be determined based on a client's location. The nearby agents that are available to provide a showing of the client's desired property may be presented to the client for selection. The system may provide identification, biographical, and professional experience information to the client to allow an informed selection. A selected agent may the confirm his or her availability and proceed to show the property to the client.
Owner:MILLER TODD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com