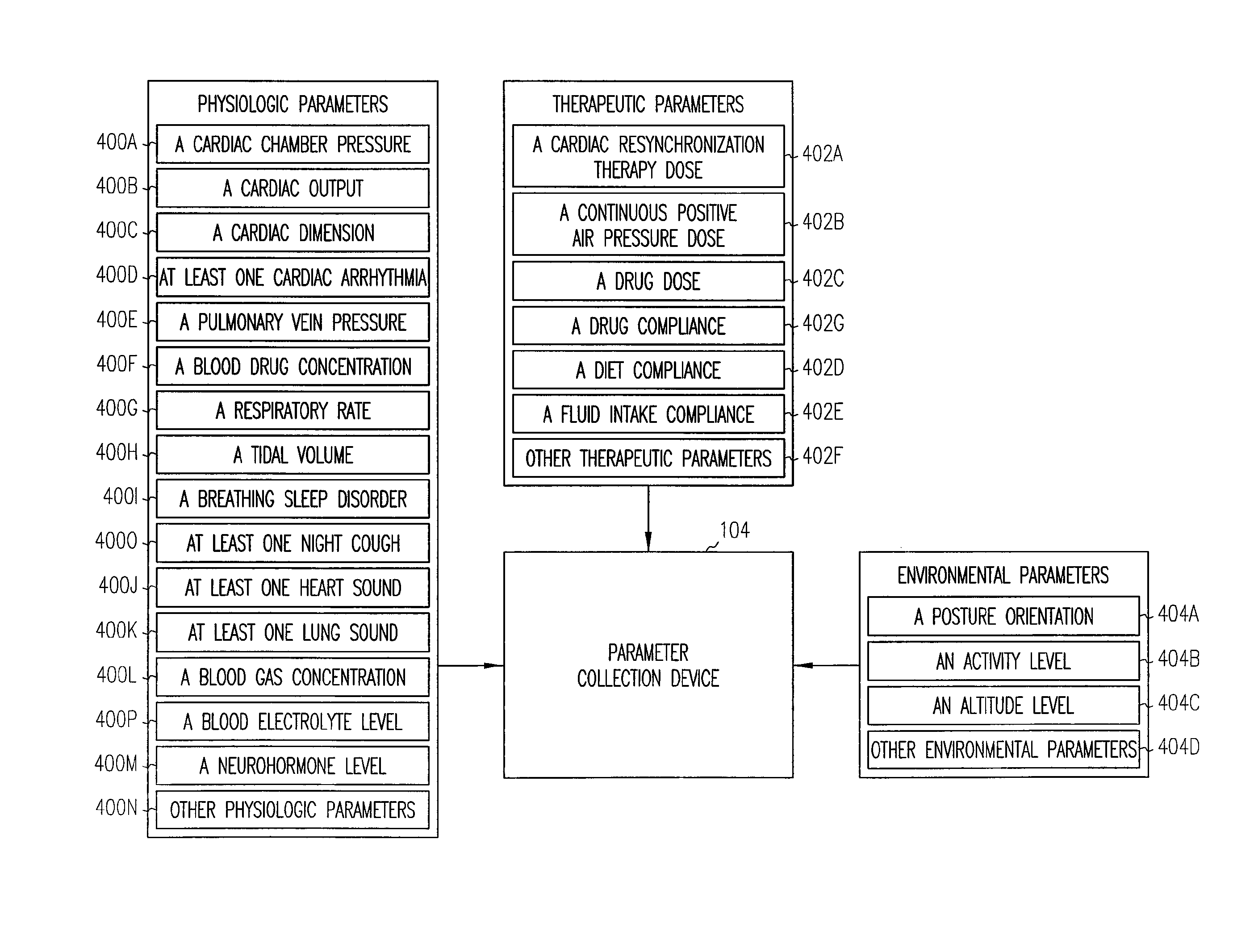
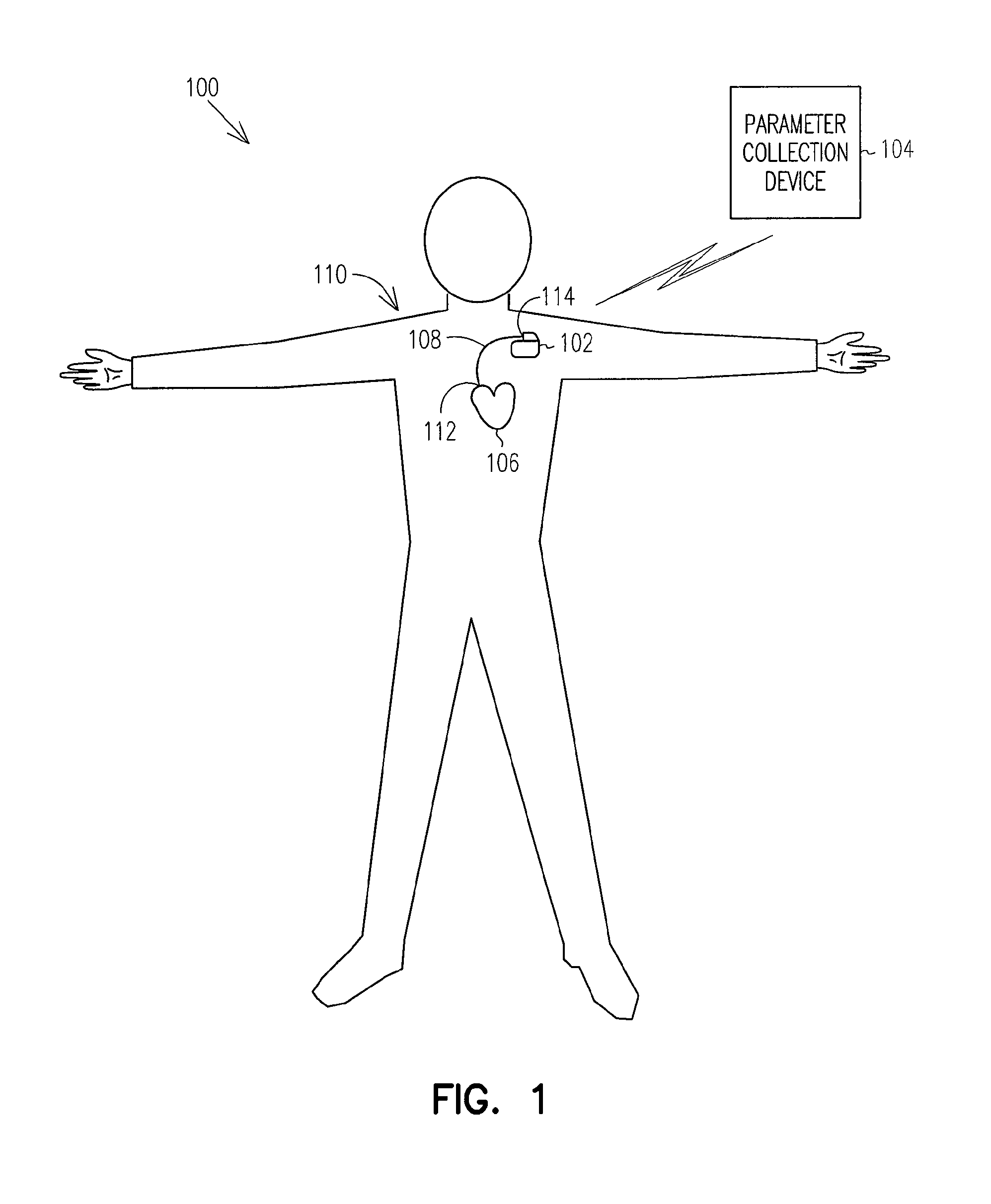
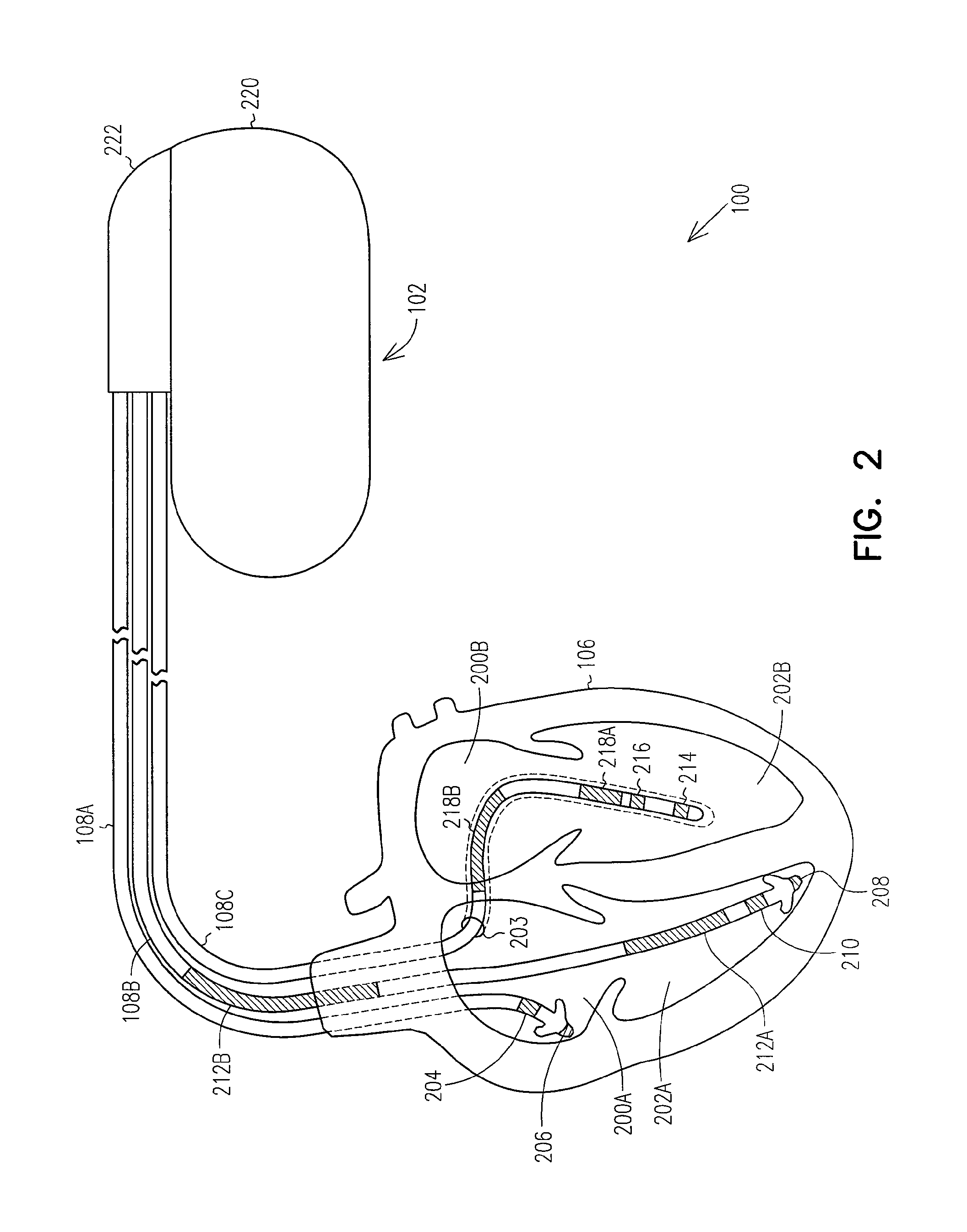
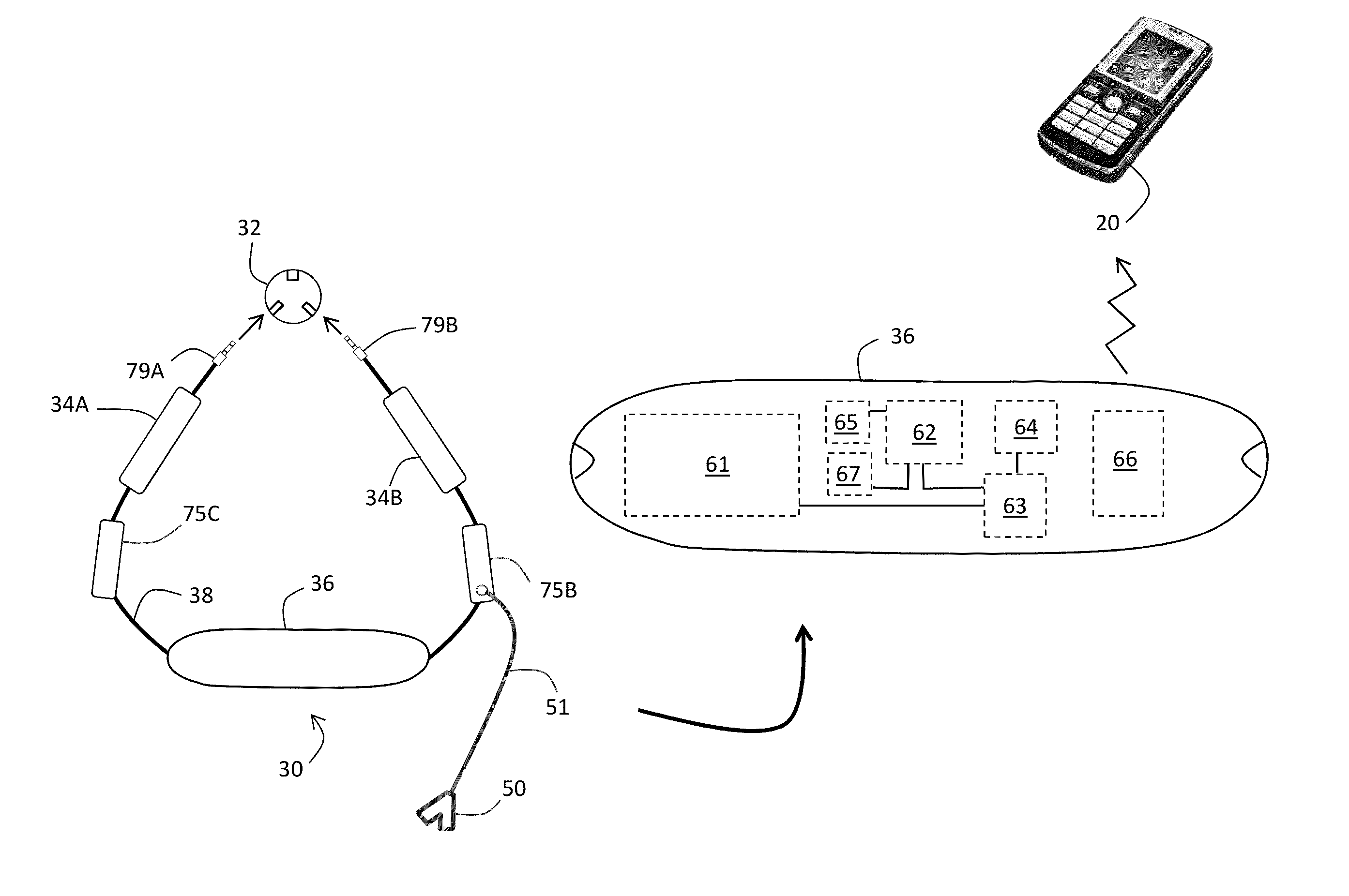
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Thoracic Fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluid that is present in the thoracic cavity.
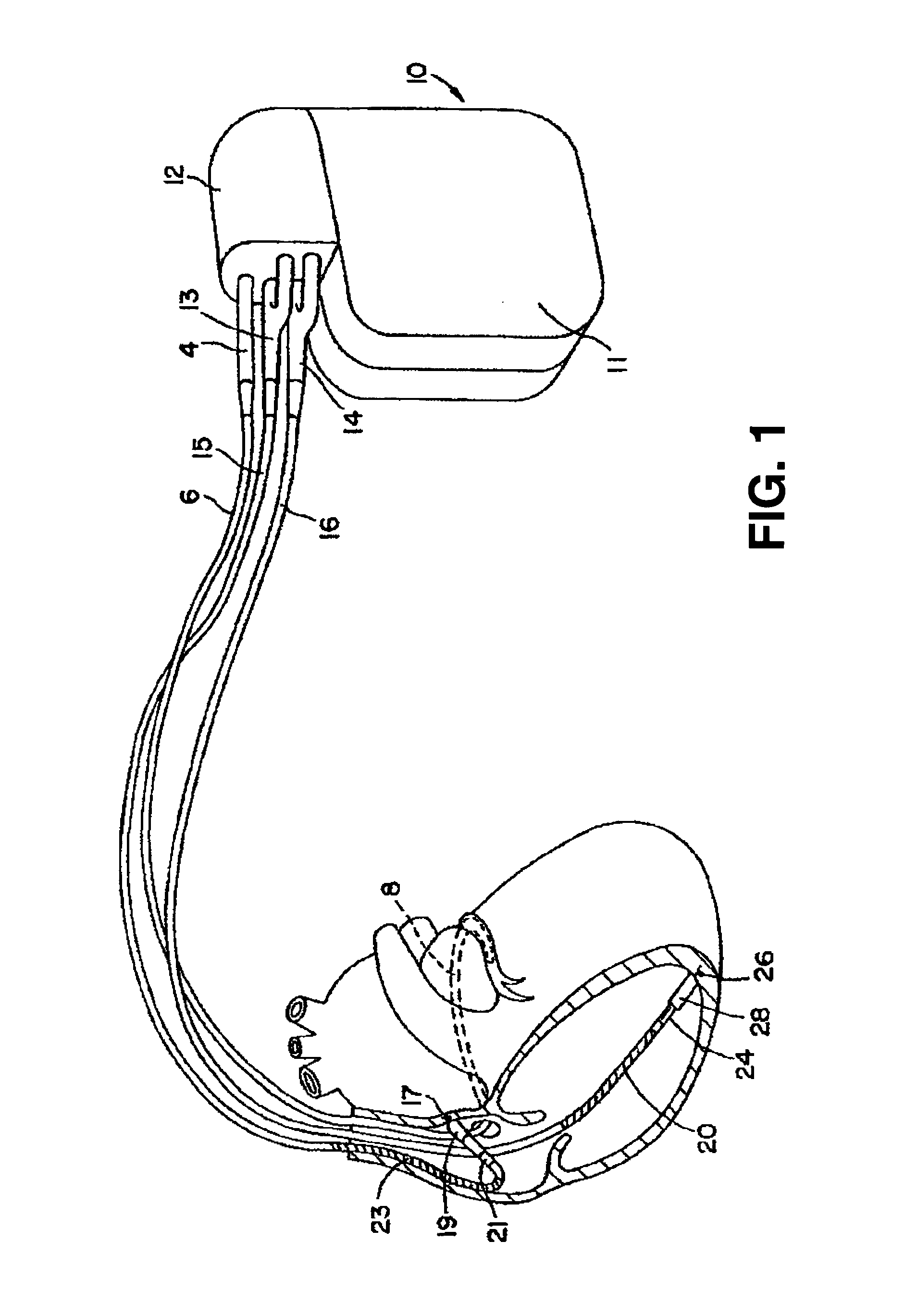
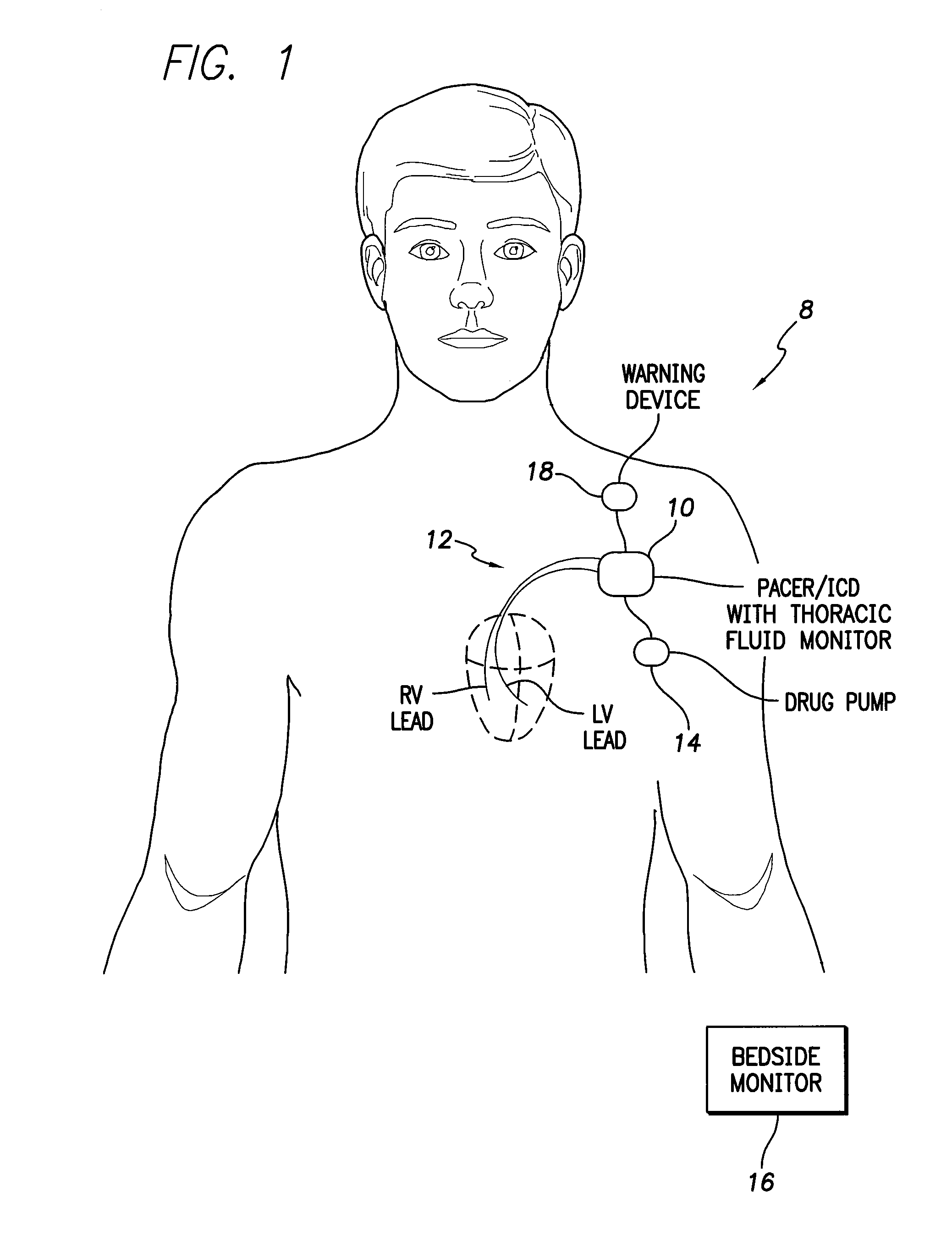
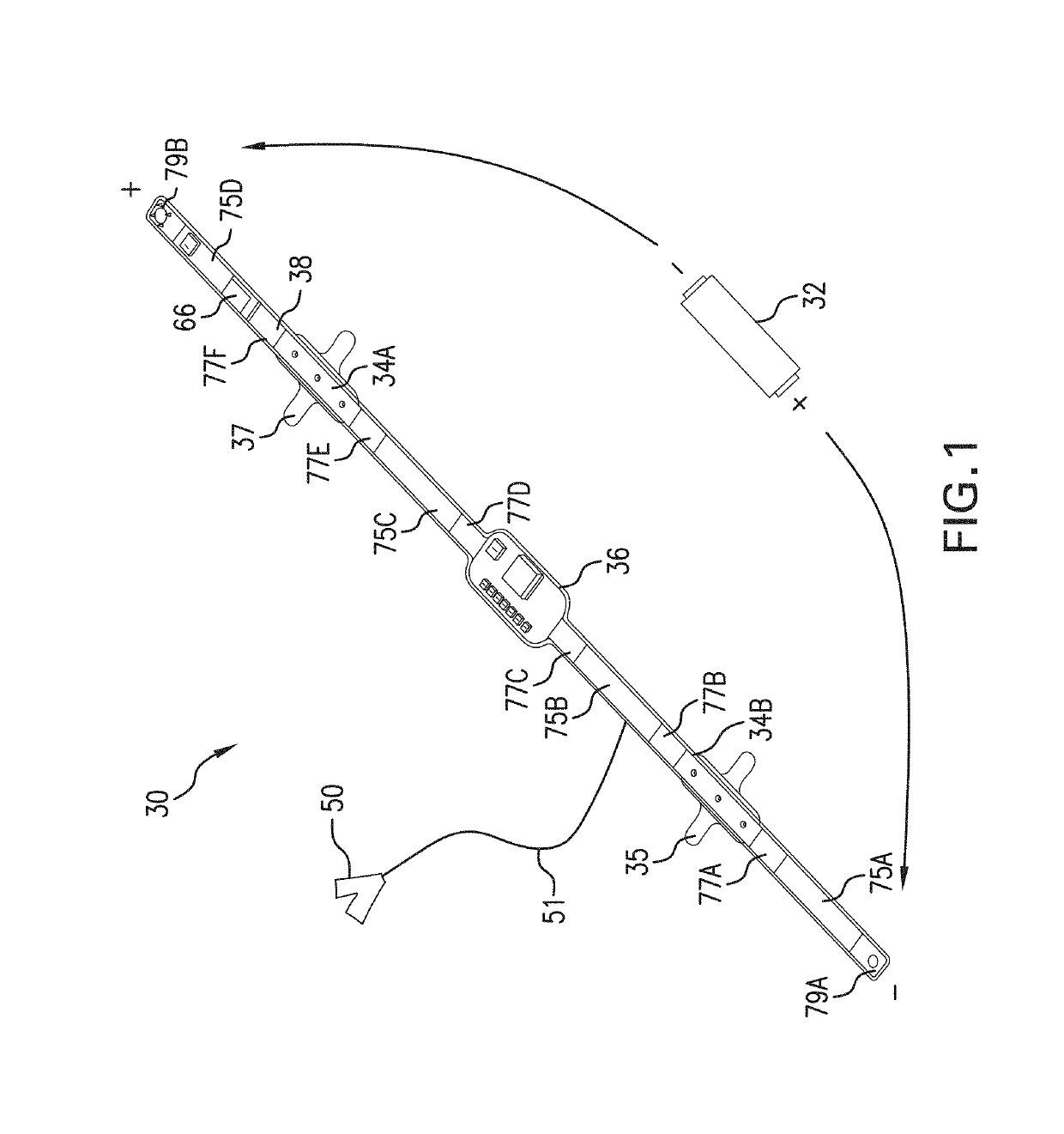
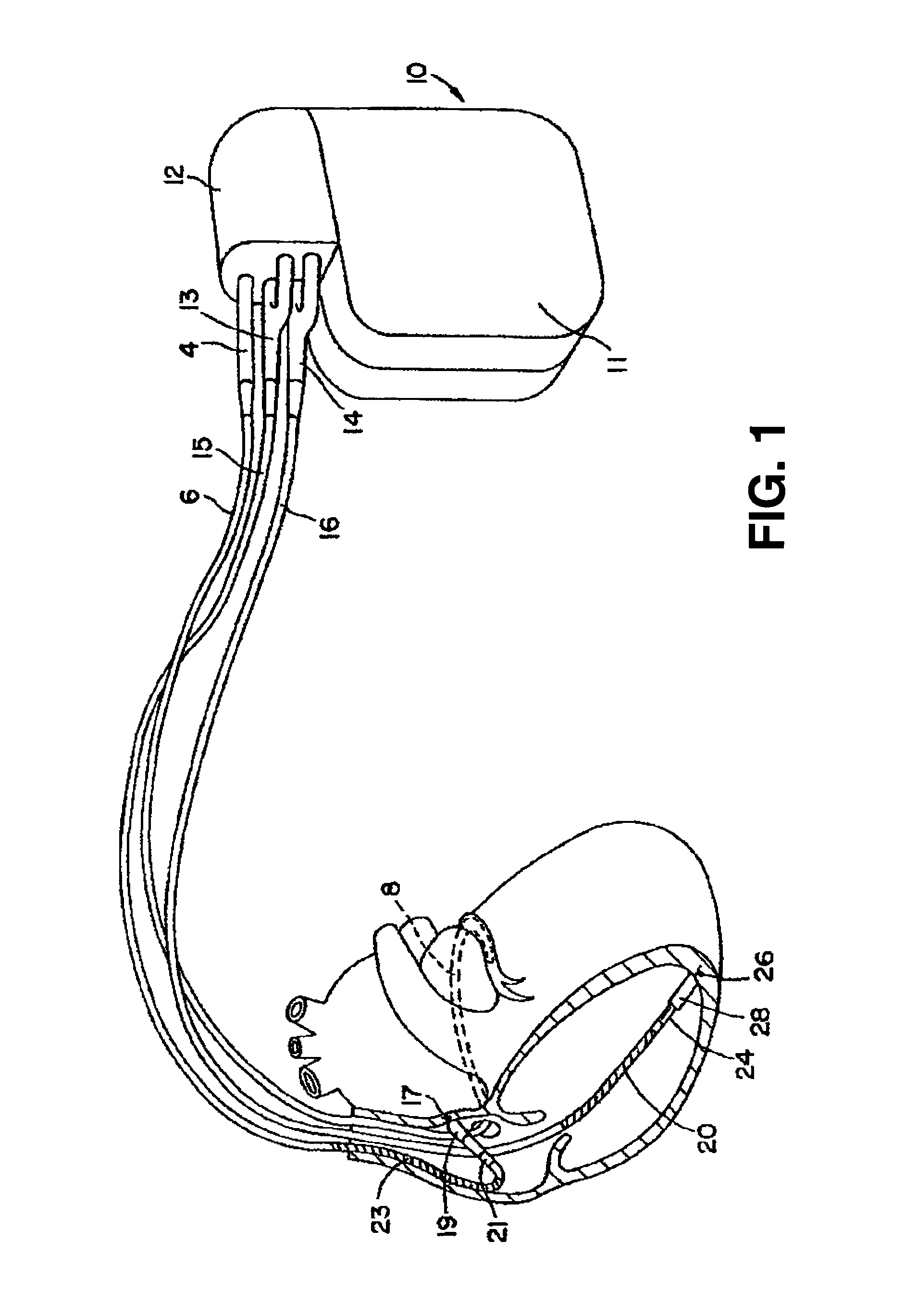
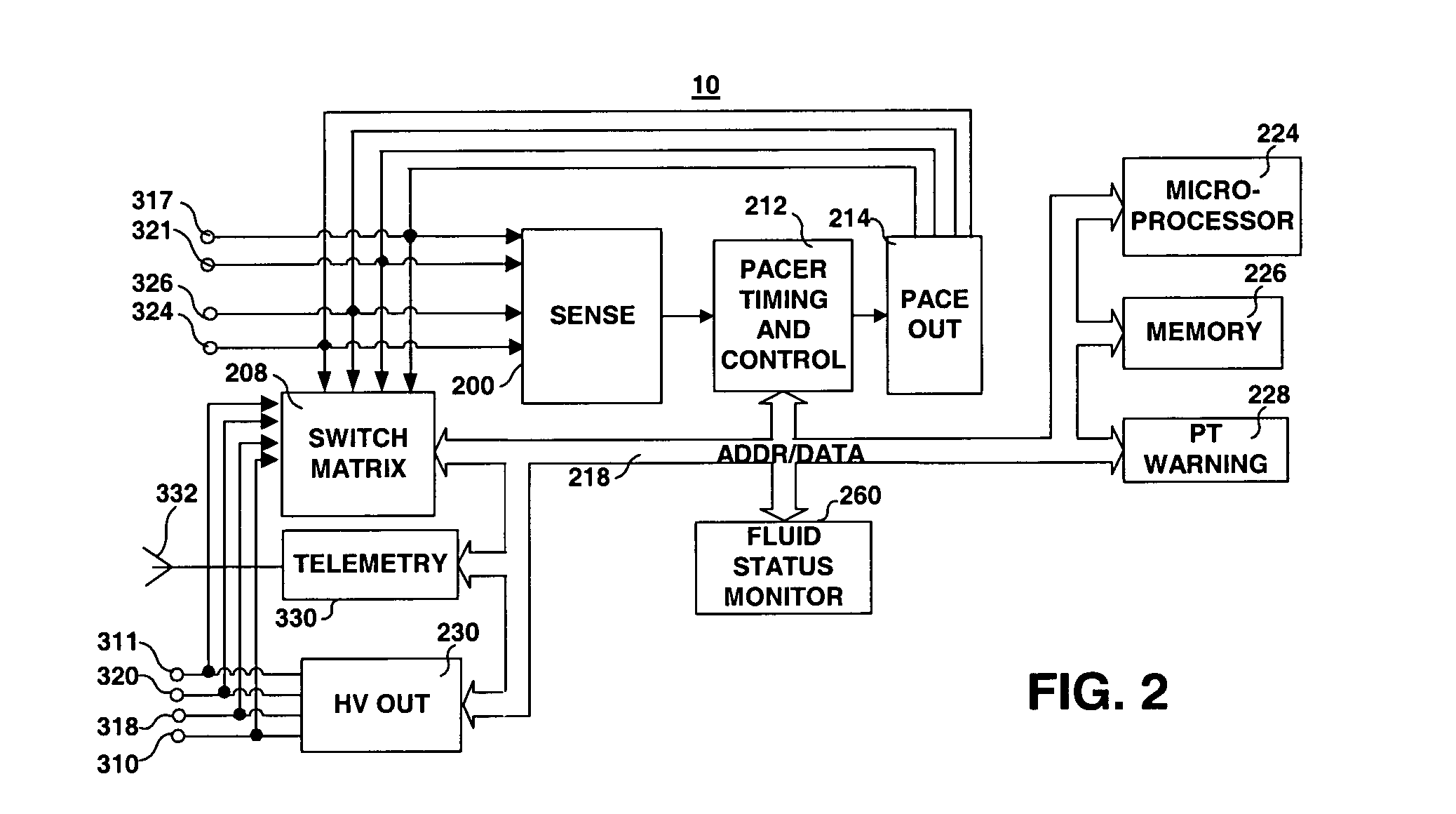
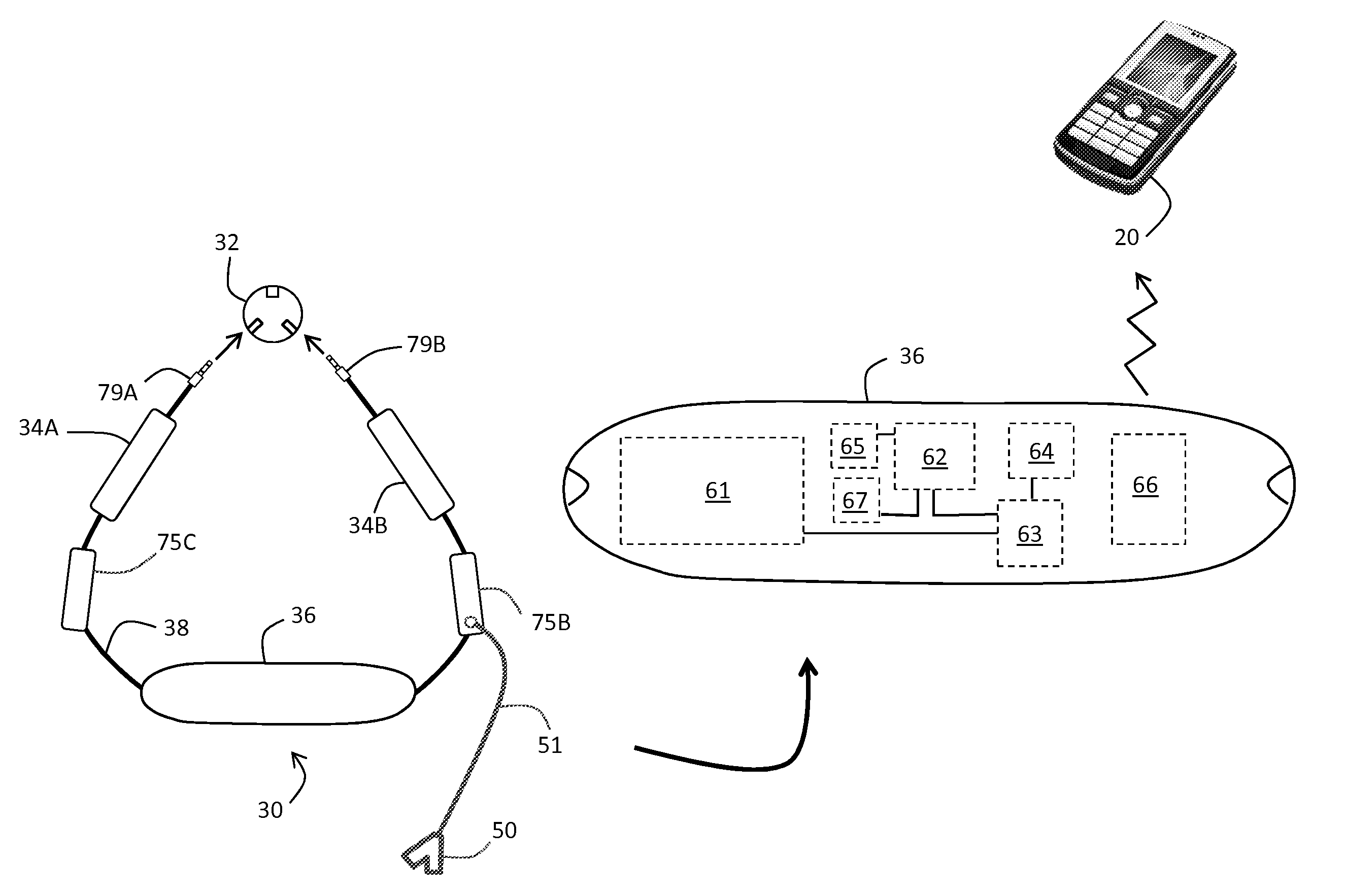
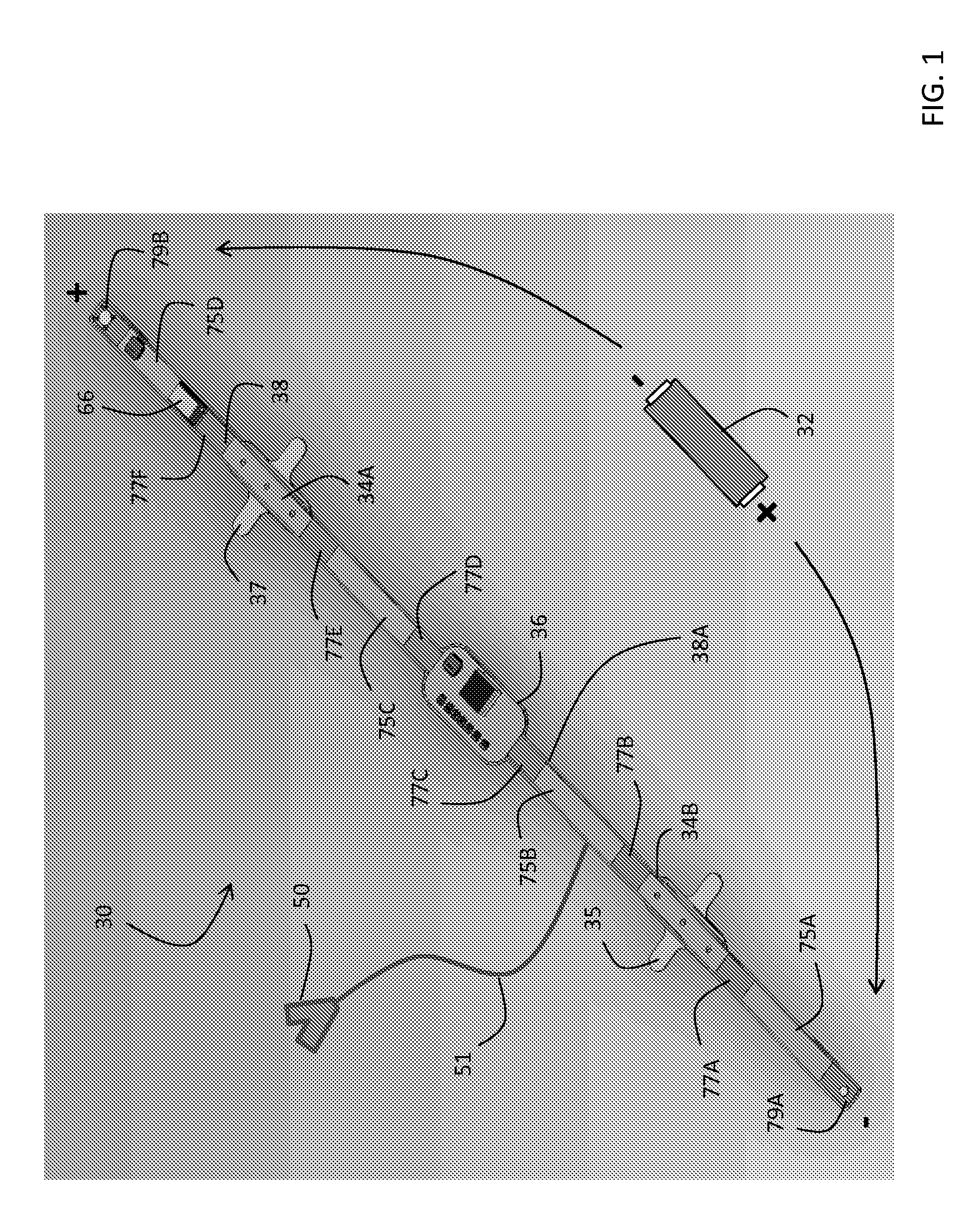
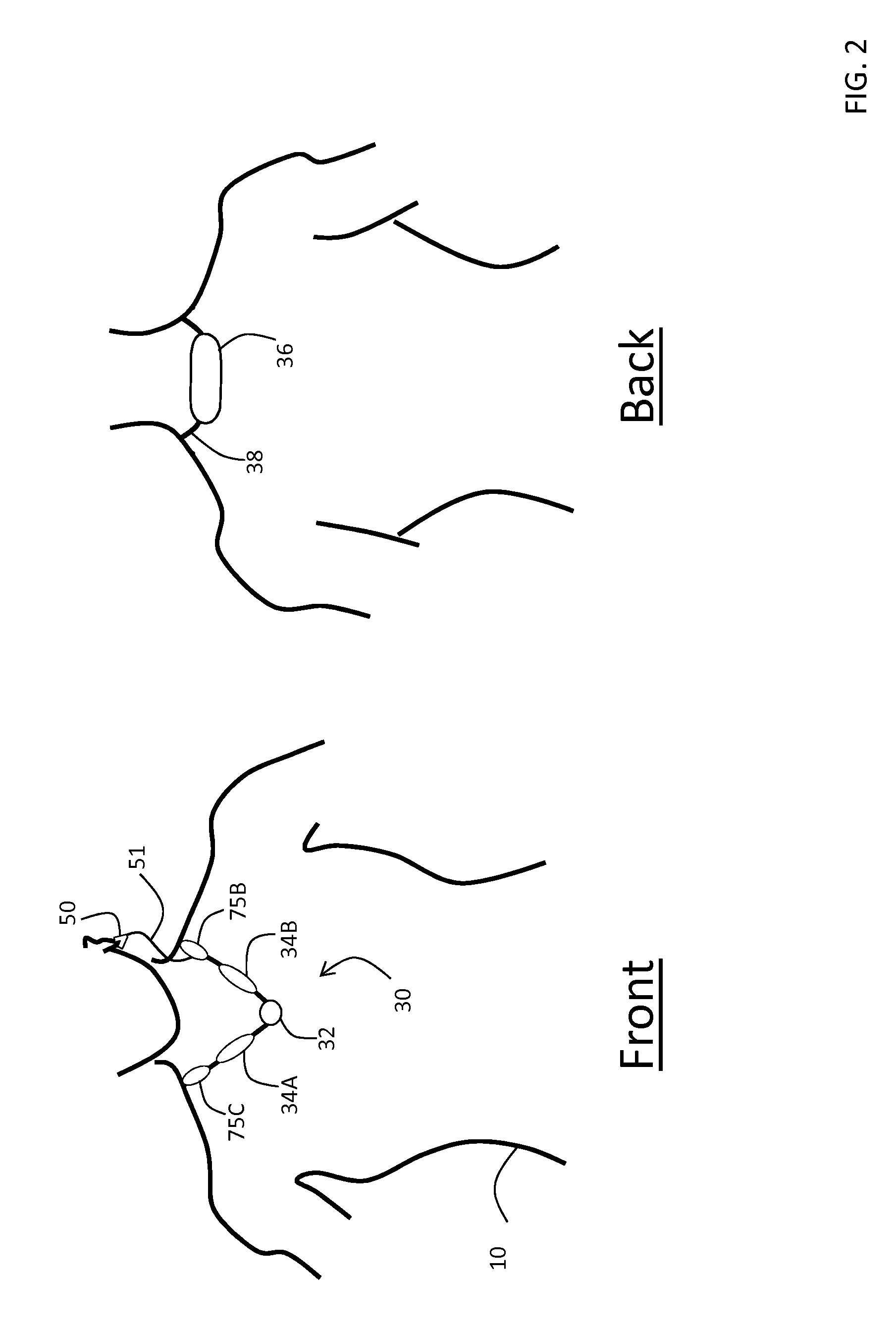
Thoracic impedance monitor and electrode array and method of use
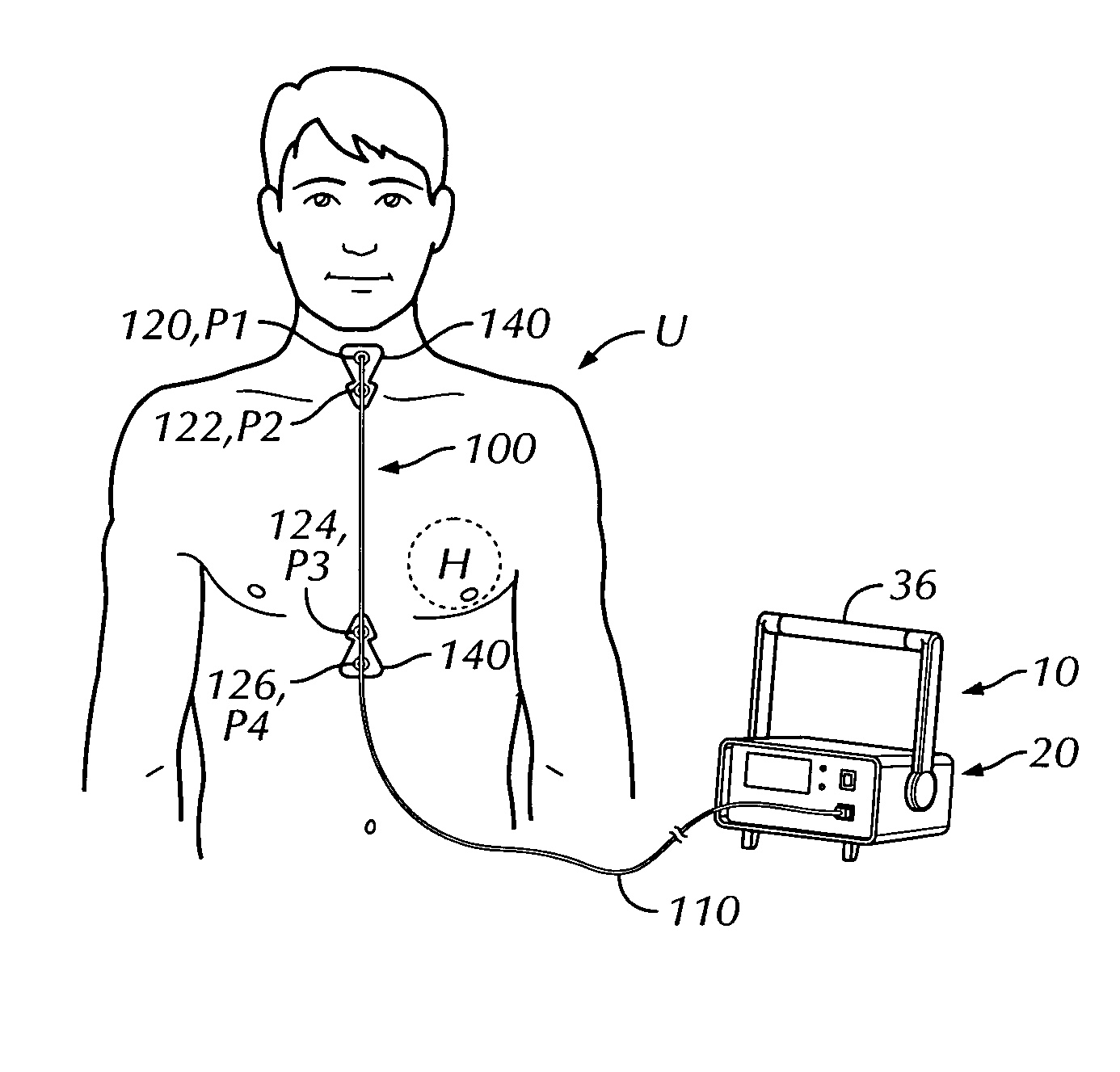
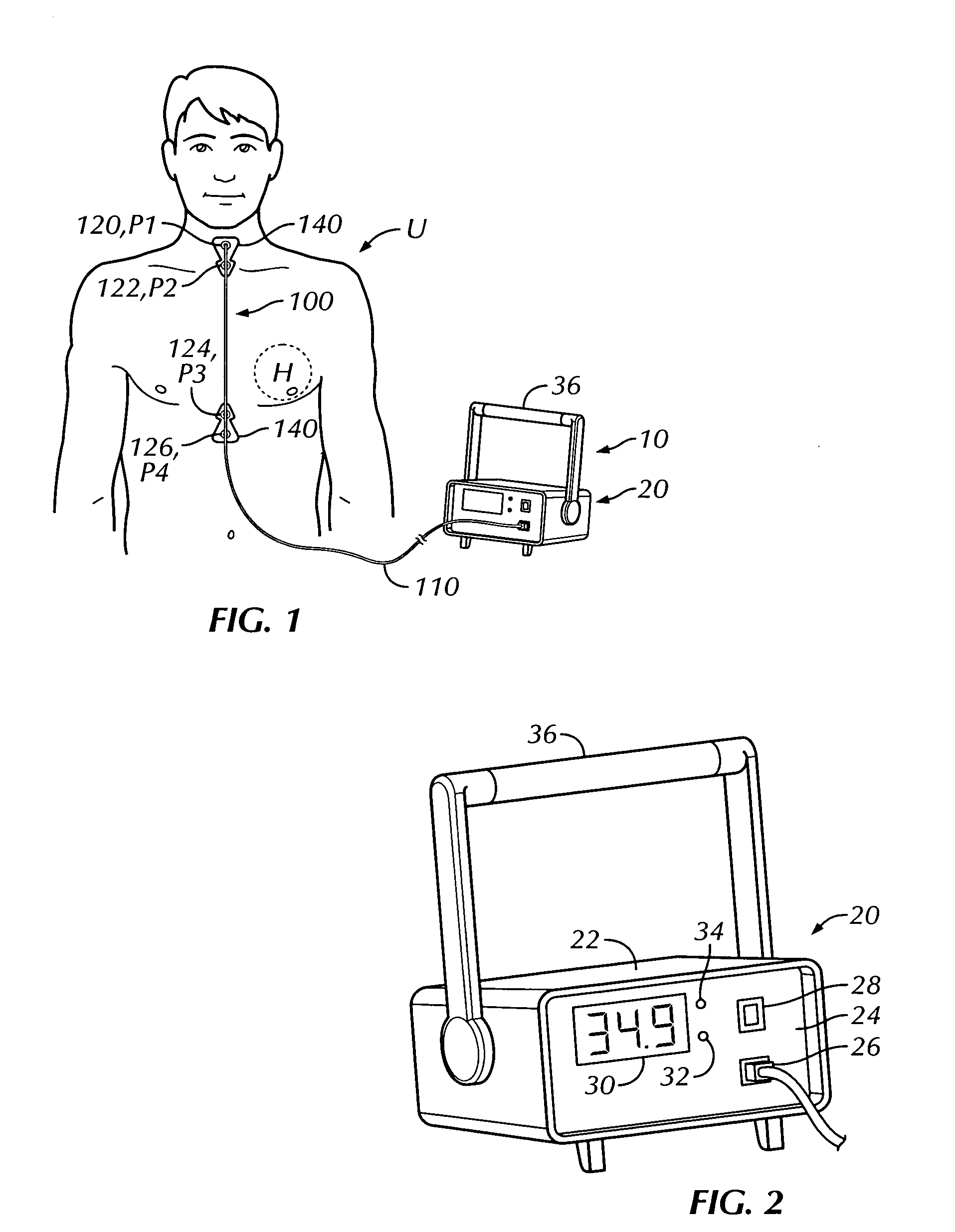
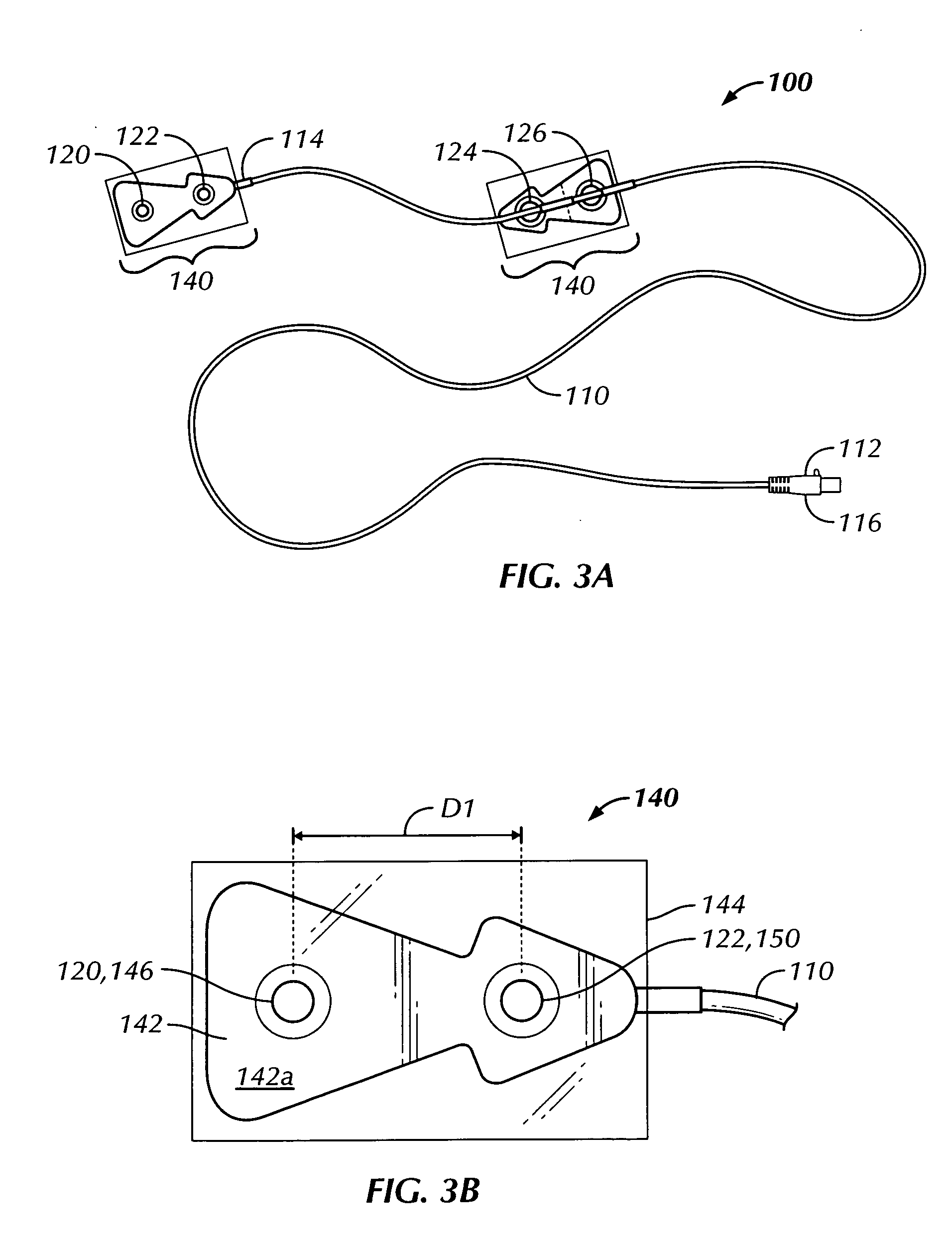
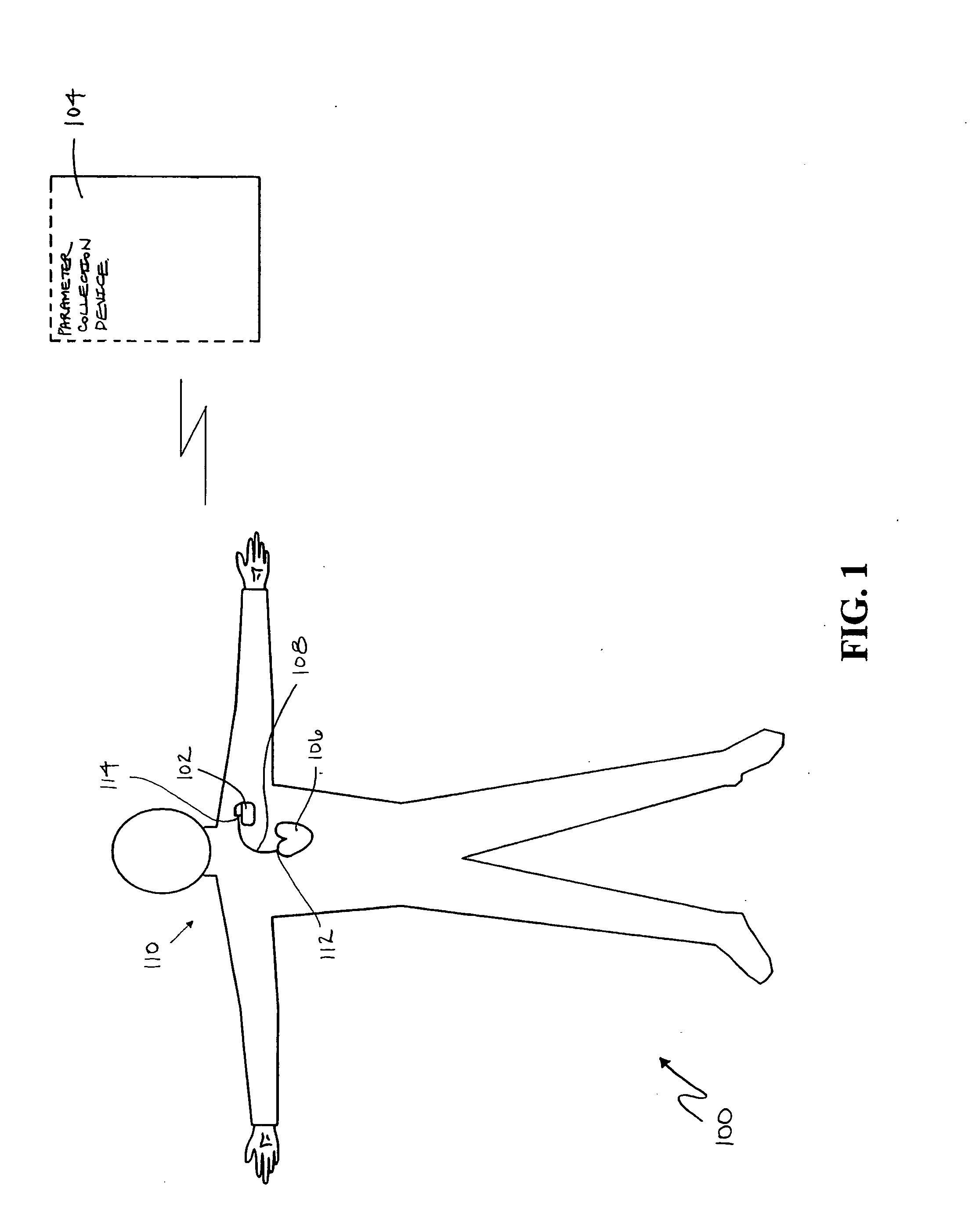
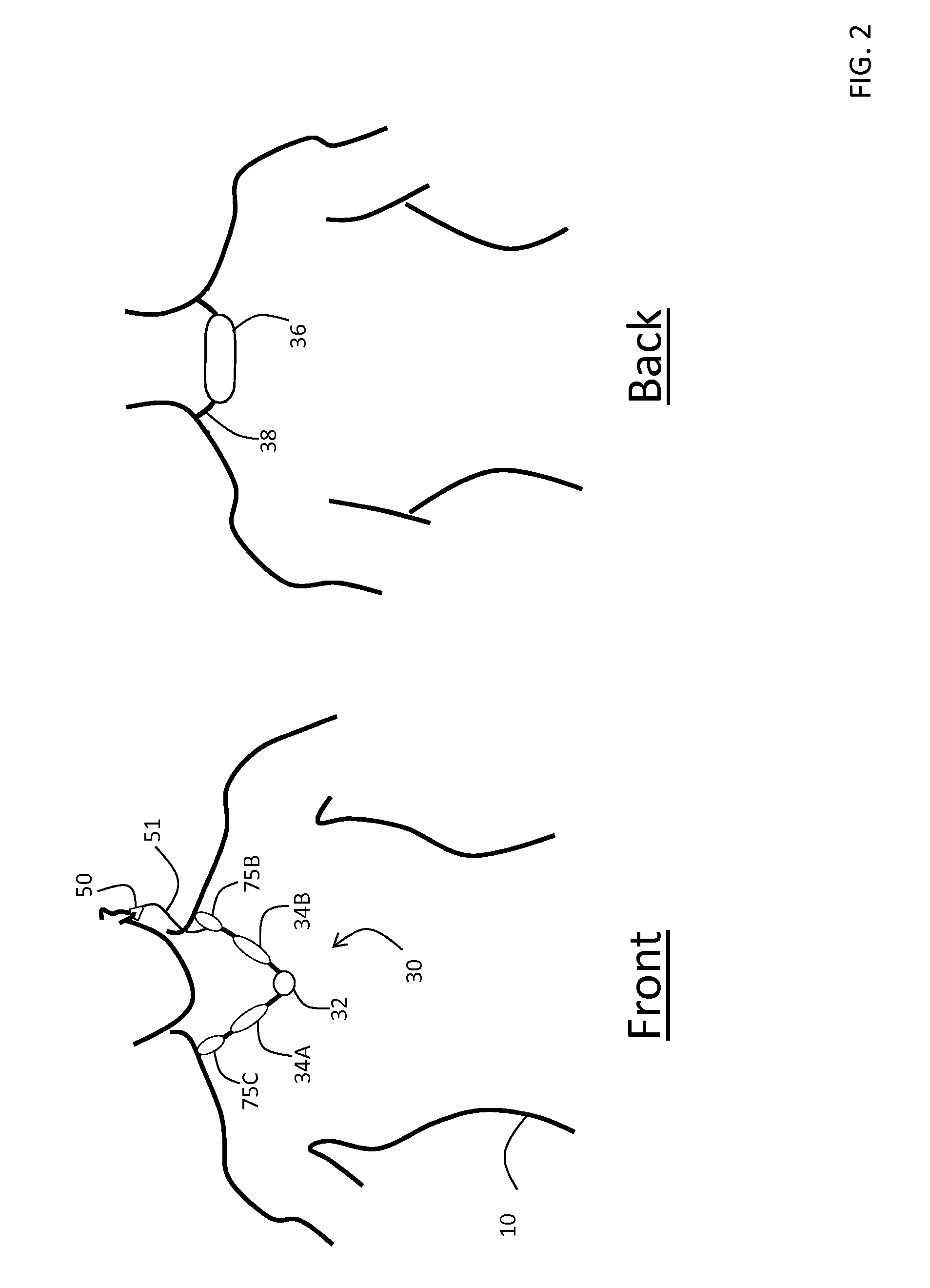
A portable thoracic impedance monitor for monitoring thoracic fluid levels, an electrode array assembly having a single linear electrode array lead with first, second, third, and fourth electrodes arranged sequentially and axially along the linear electrode array lead, and a method of use of the thoracic impedance monitor. A measurement of the user's thoracic impedance is obtained by connecting the second electrode to the user's body at the junction of the clavicles, superior to the sternum, the third electrode to the user's body at the xyphiod-sternal junction, and the first and fourth electrodes to the user's body substantially along a centerline of the user's sternum respectively at a first pre-determined distance above the second electrode and a second predetermined distance below the third electrode, followed by initiating operation of the monitor.
Owner:CALDWELL SIMPSON LLC
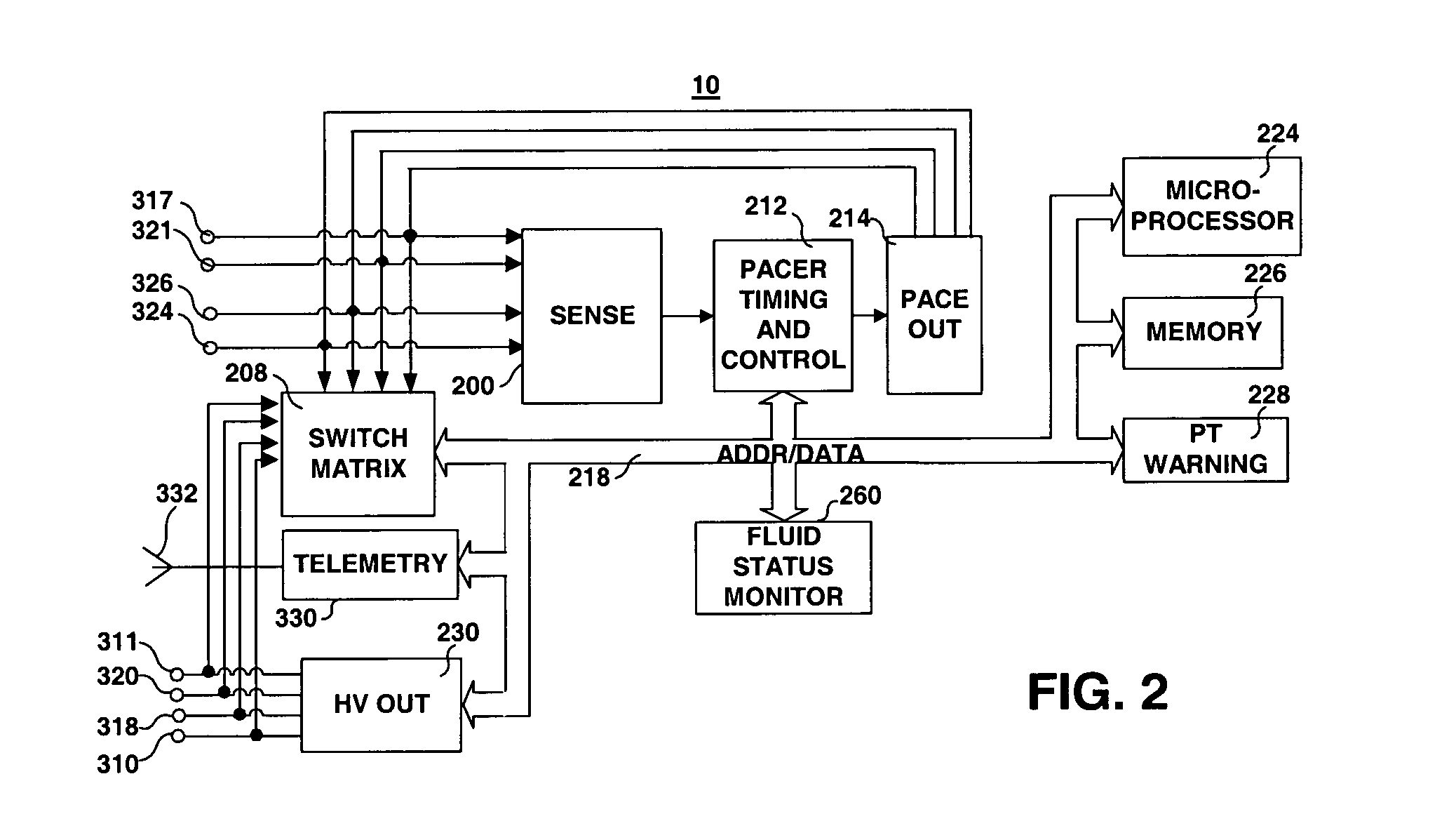
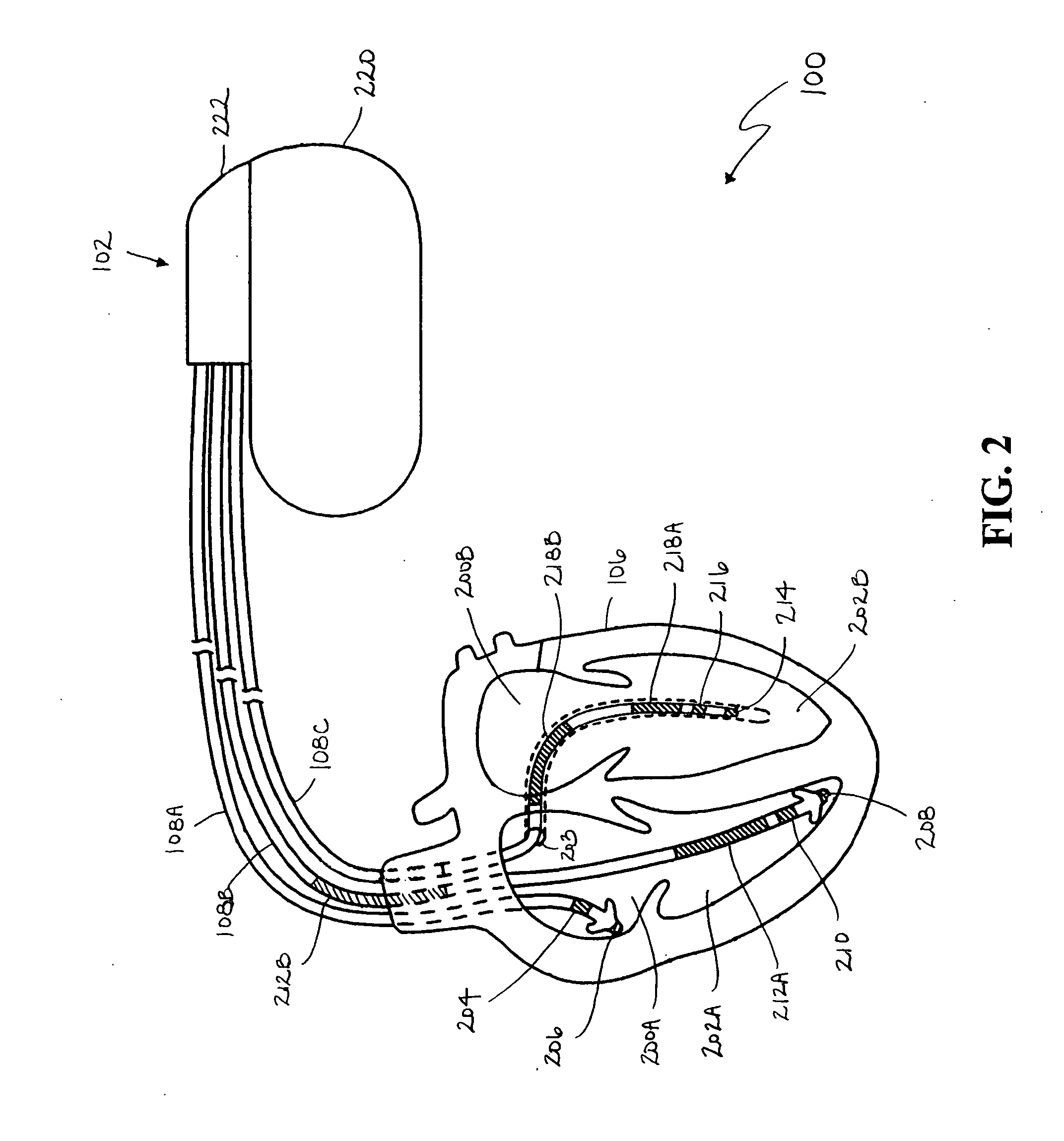
Method and apparatus for monitoring tissue fluid content for use in an implantable cardiac device
ActiveUS20050080460A1Easy to implementCancel noiseHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsThoracic FluidTissue fluid
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Detection of pleural effusion using transthoracic impedance
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Detection of pleural effusion using transthoracic impedance
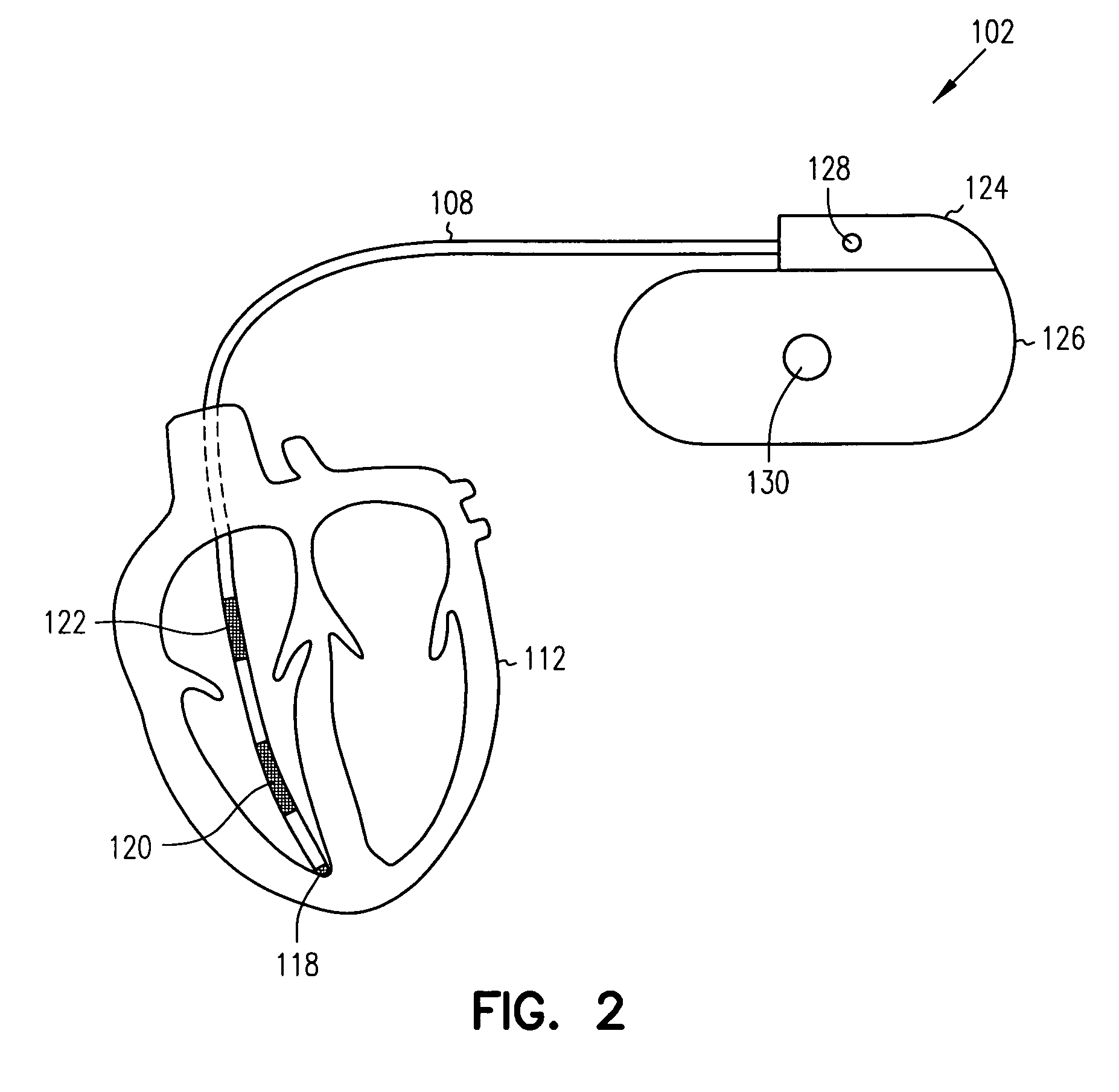
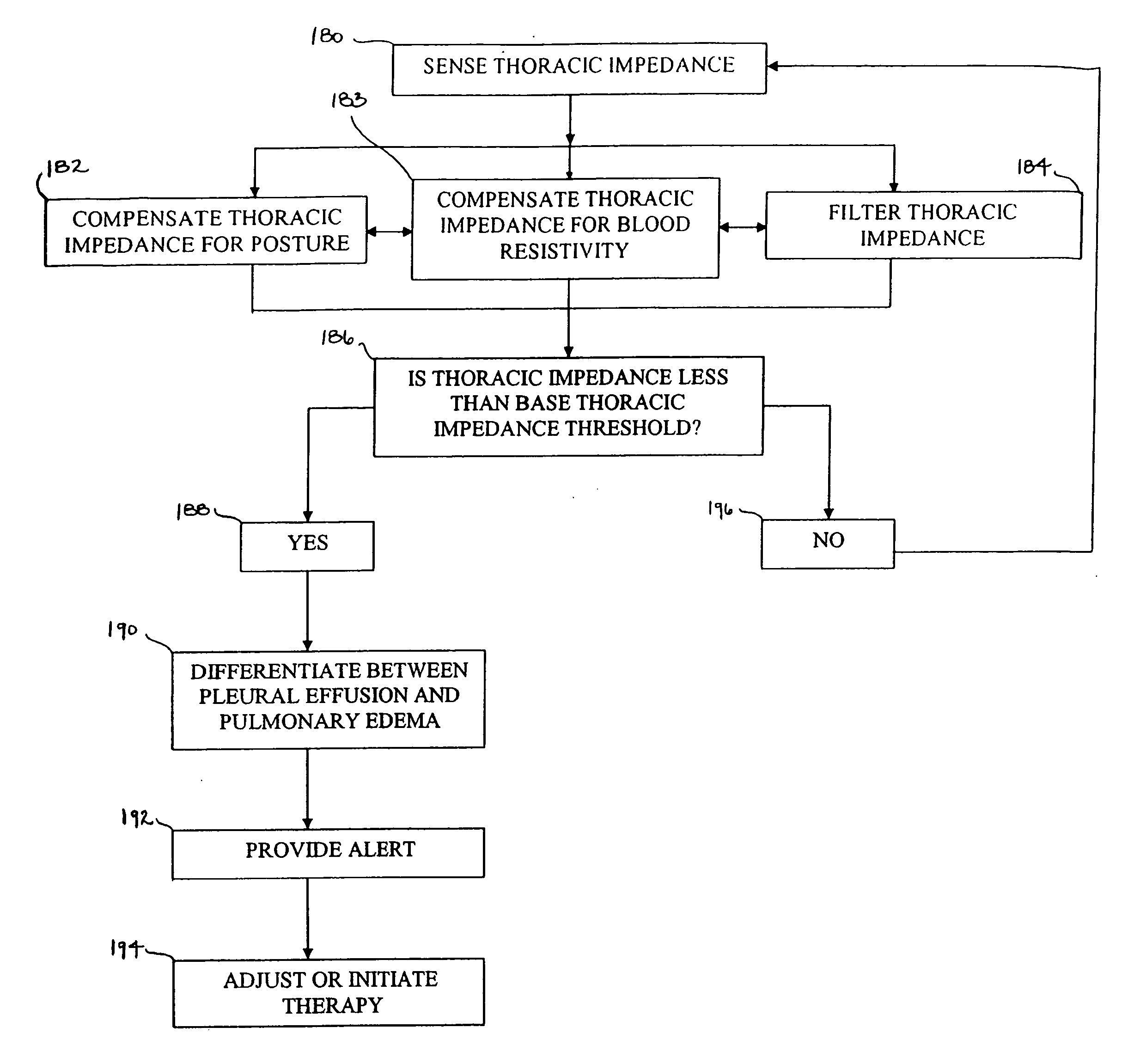
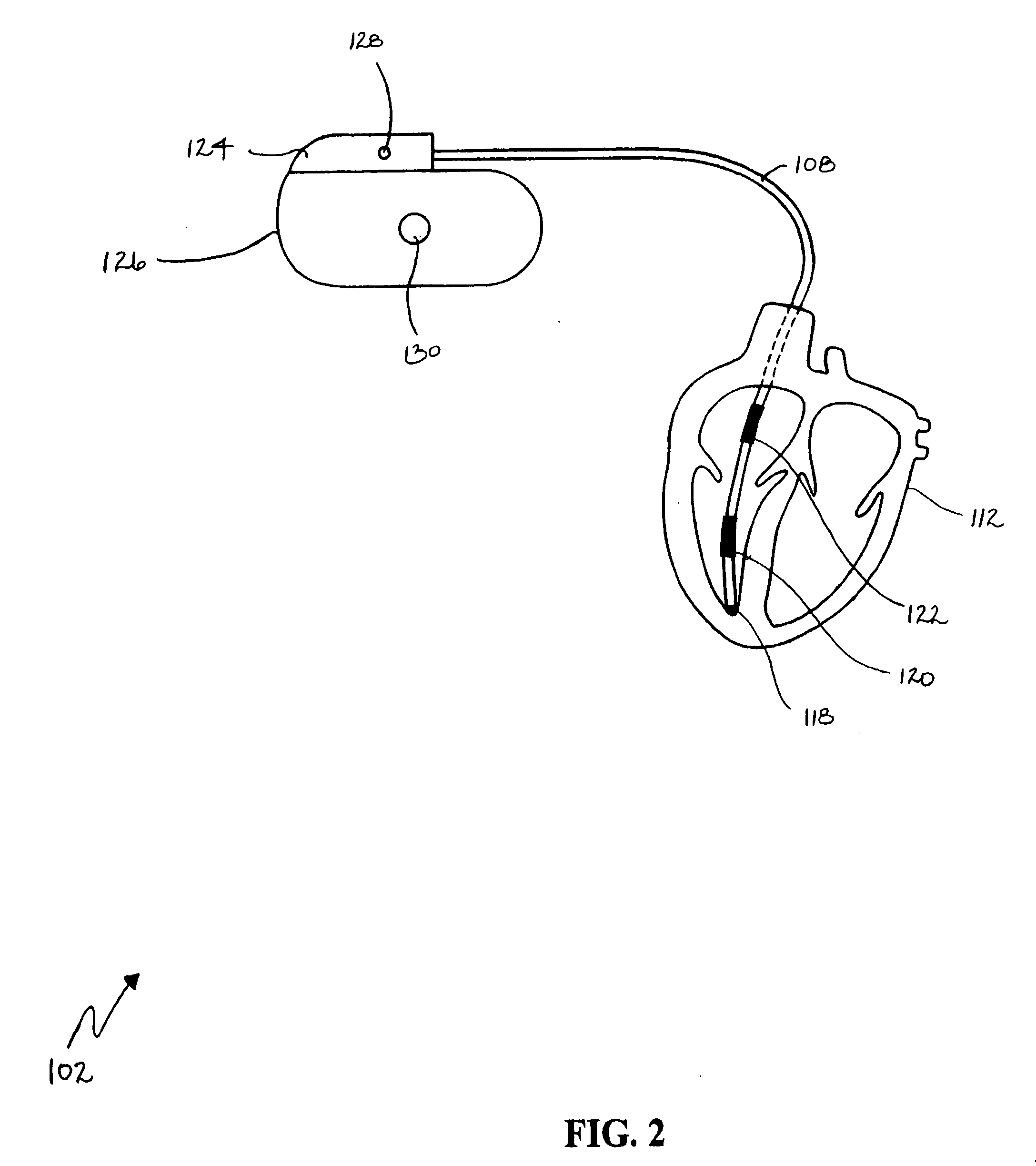
This patent document discusses systems, devices, and methods for increasing a sensitivity or specificity of thoracic fluid detection in a subject and differentiating between pleural effusion and pulmonary edema. In one example, a thoracic impedance measurement circuit senses a thoracic impedance signal. In another example, a processor receives the thoracic impedance signal and determines whether such thoracic impedance signal is “significant.” A significant thoracic impedance signal indicates the presence of thoracic fluid and may be recognized by comparing the thoracic impedance signal (or variation thereof) to a thoracic impedance threshold. When a significant thoracic impedance signal is recognized, the processor is adapted to detect one or both of: a pleural effusion indication and a pulmonary edema indication using one or a combination of: physiologic information, patient symptom information, and posture information. In another example, the thoracic impedance threshold is adjusted using such physiologic, patient symptom, or posture information.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
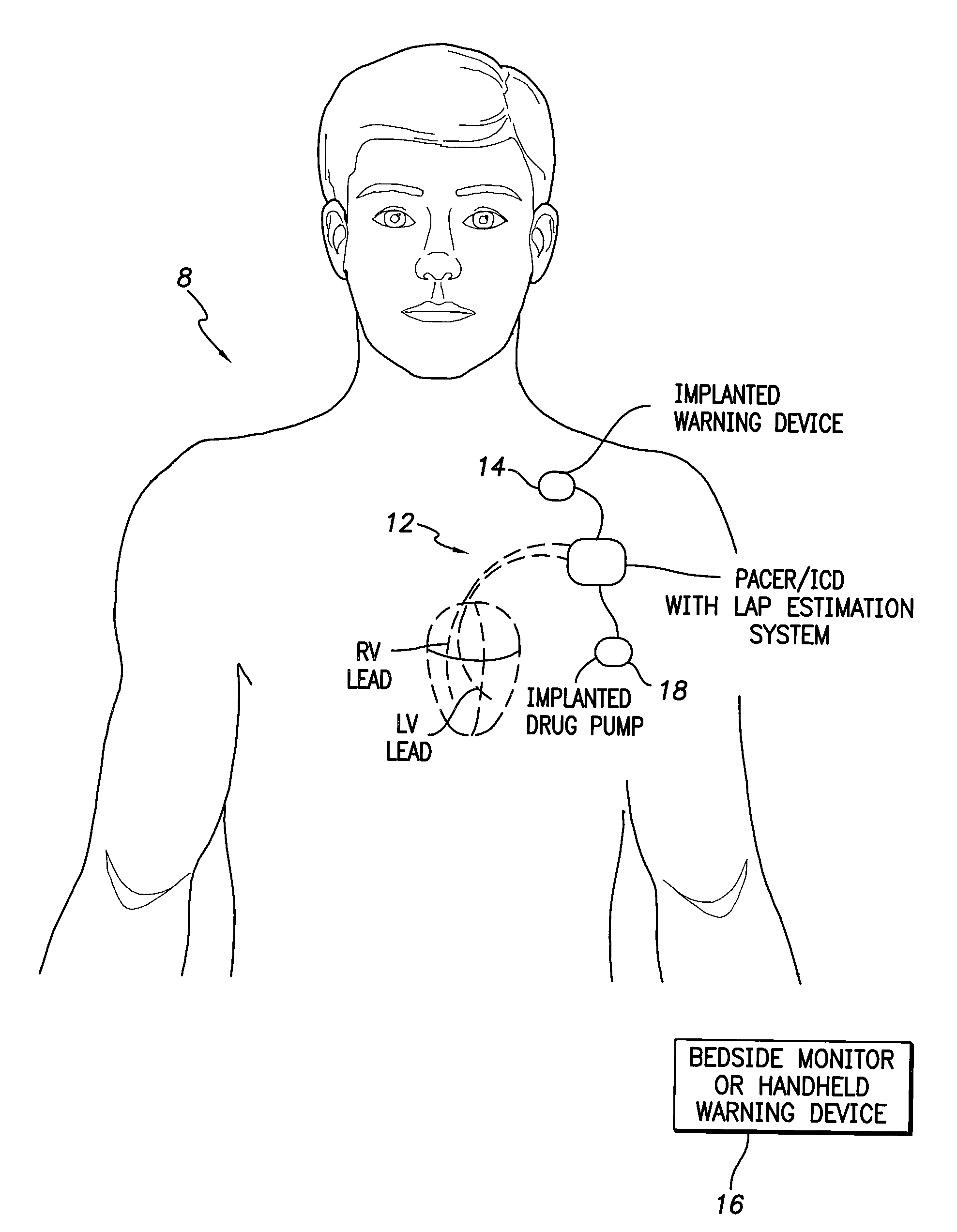
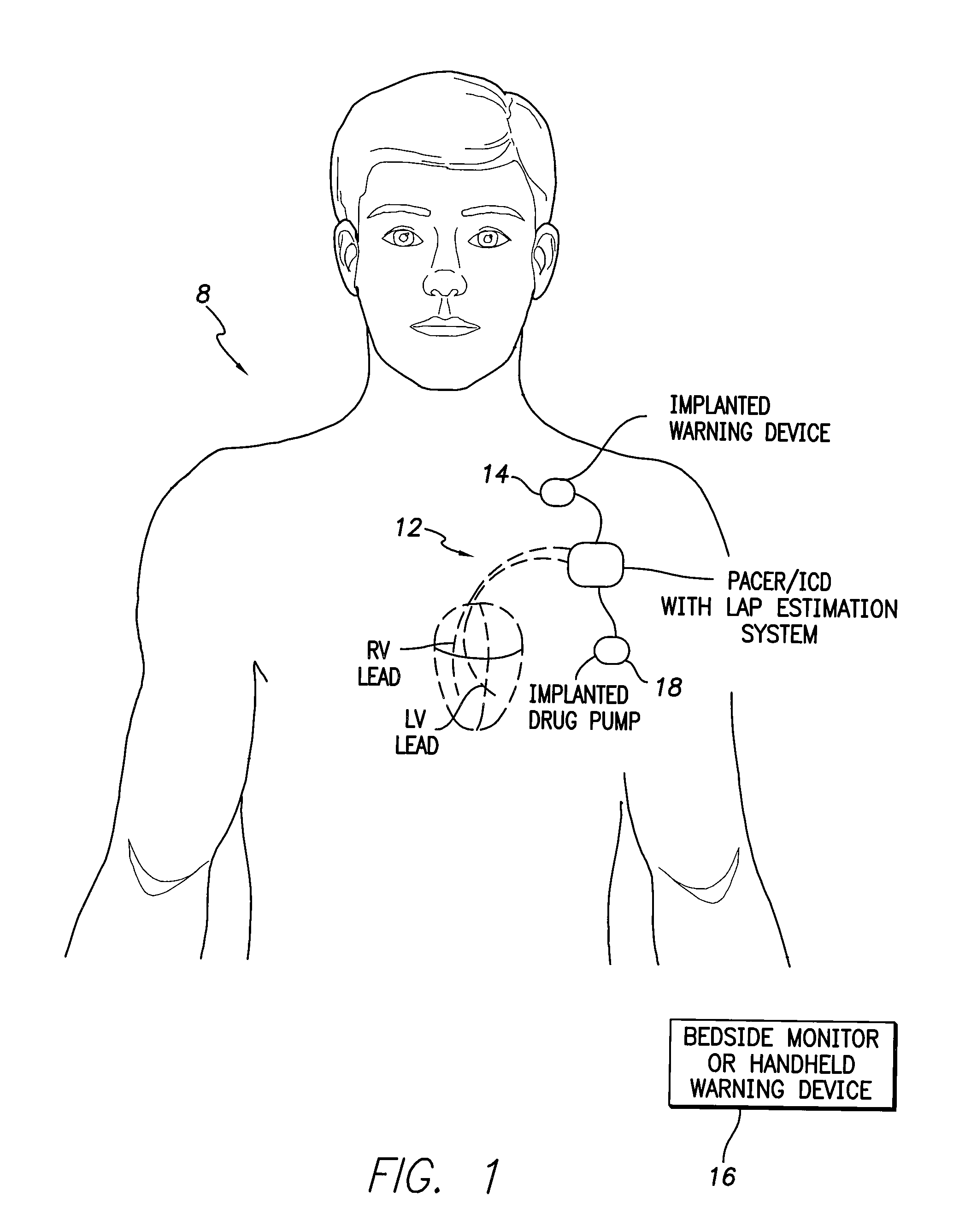
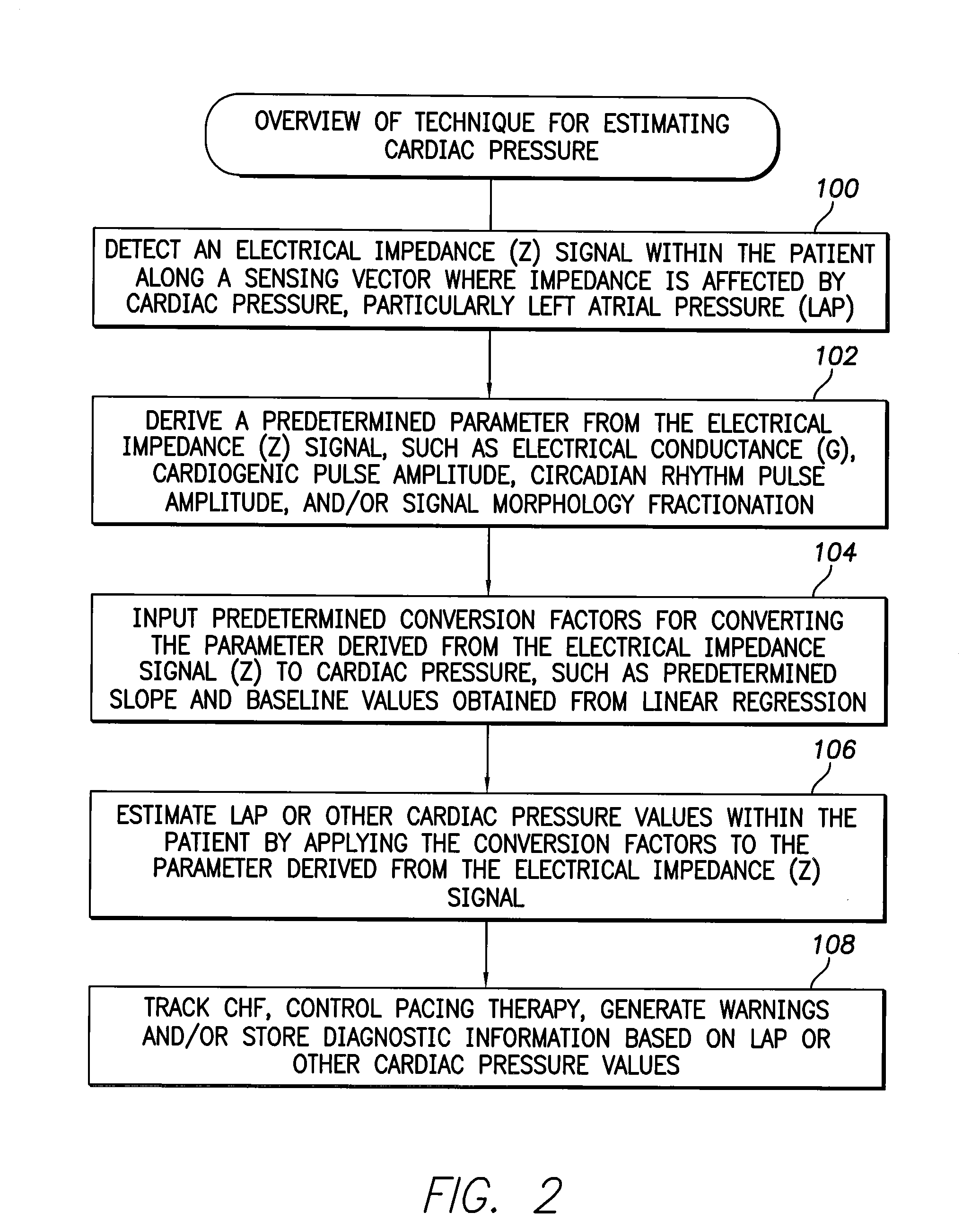
System and method for calibrating cardiac pressure measurements derived from signals detected by an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20080262361A1Accurate CalibrationAccurate slopeElectrotherapyCatheterThoracic FluidLeft atrial pressure
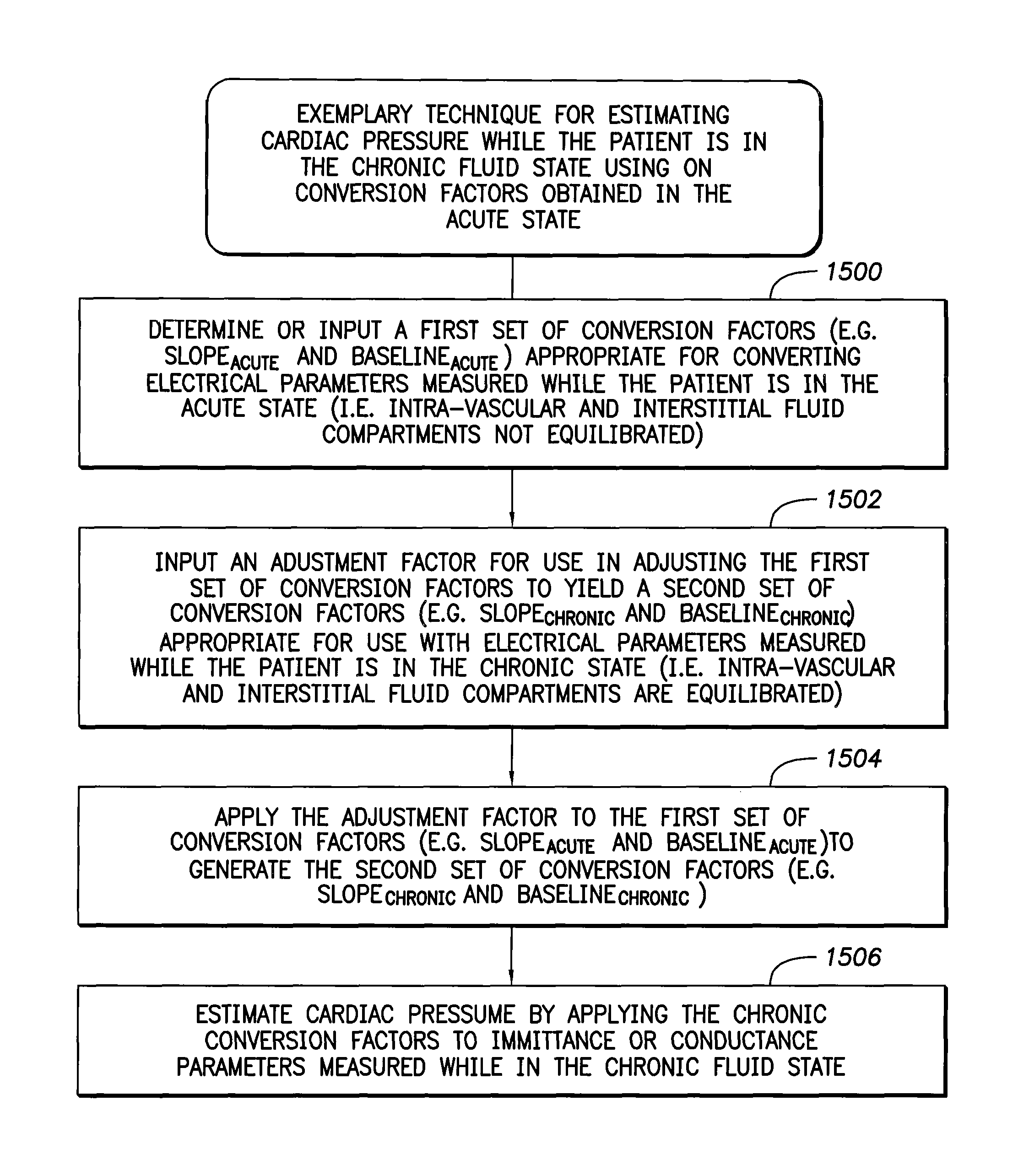
Various techniques are provided for calibrating and estimating left atrial pressure (LAP) using an implantable medical device, based on impedance, admittance or conductance parameters measured within a patient. In one example, default conversion factors are exploited for converting the measured parameters to estimates of LAP. The default conversion factors are derived from populations of patients. In another example, a correlation between individual conversion factors is exploited to allow for more efficient calibration. In yet another example, differences in thoracic fluid states are exploited during calibration. In still yet another example, a multiple stage calibration procedure is described, wherein both invasive and noninvasive calibration techniques are exploited. In a still further example, a therapy control procedure is provided, which exploits day time and night time impedance / admittance measurements.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
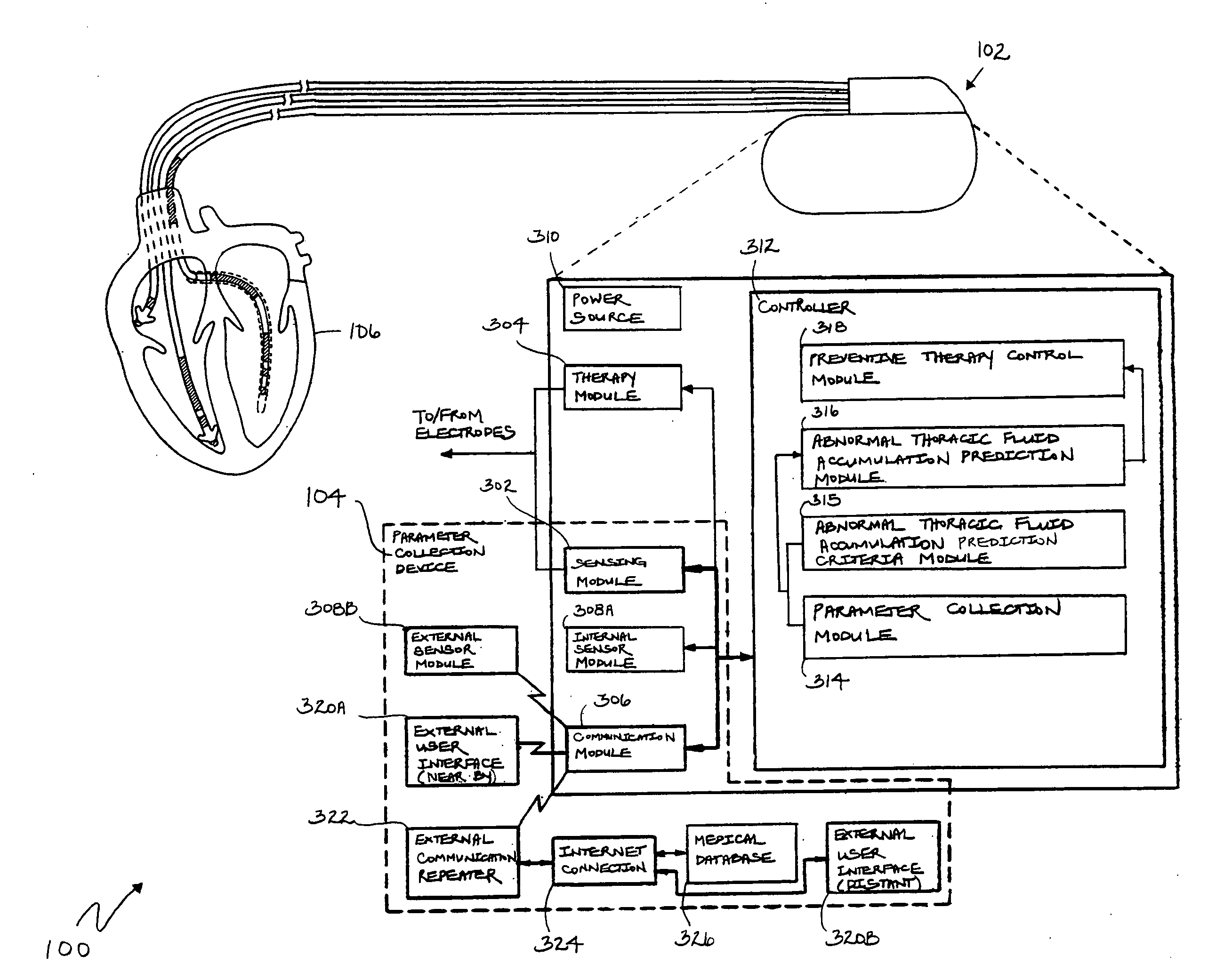
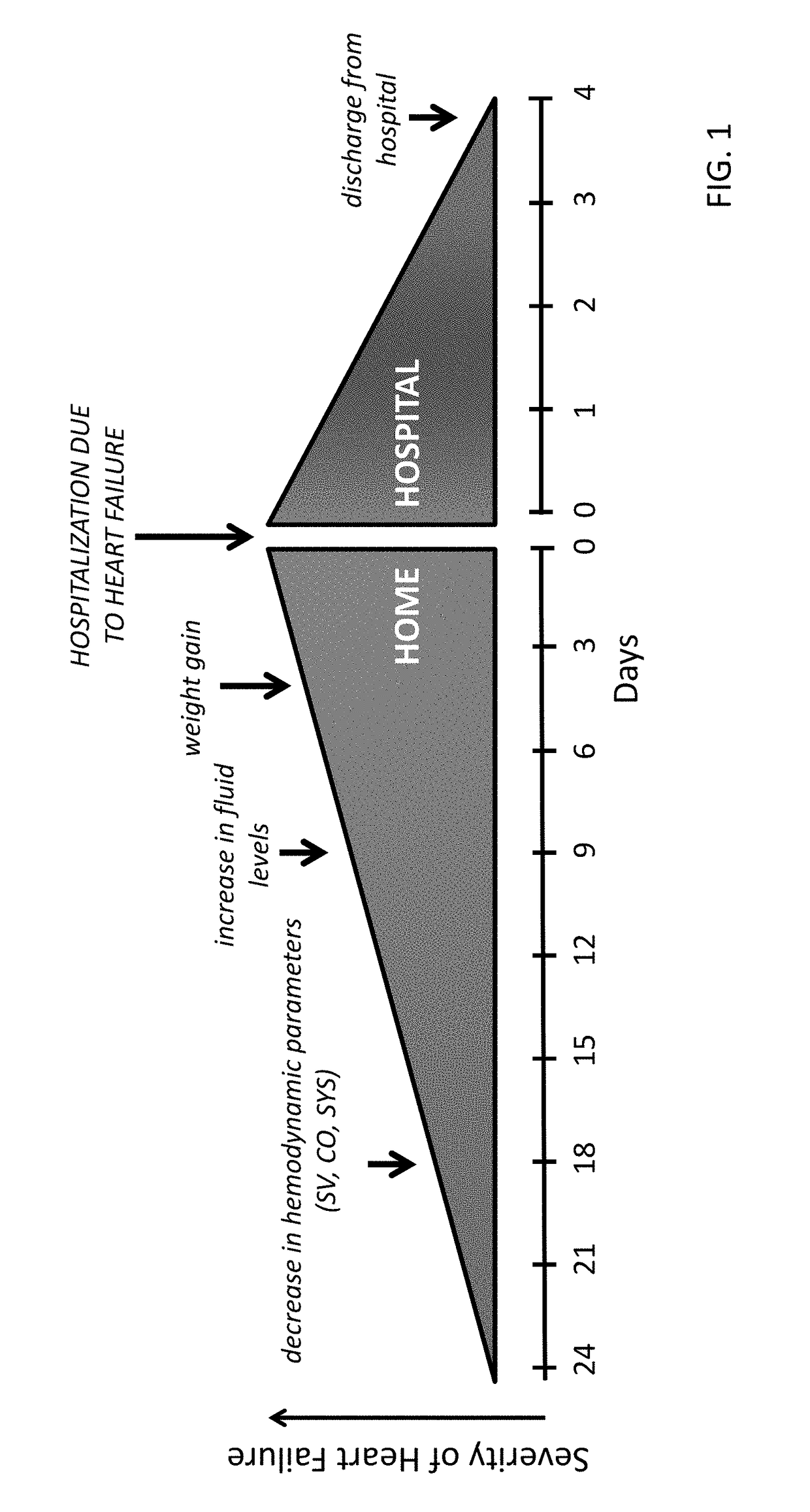
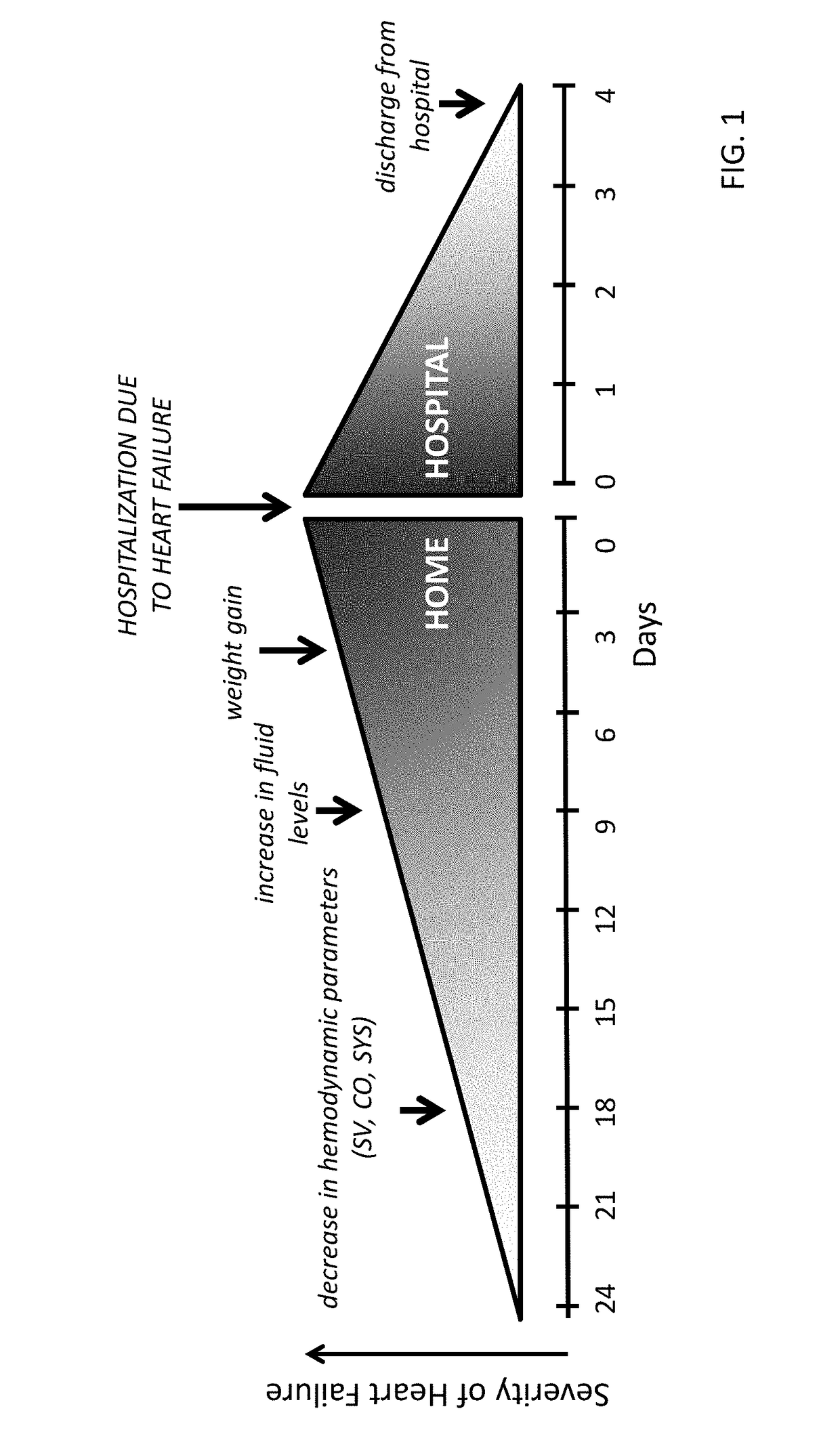
Prediction of thoracic fluid accumulation
ActiveUS20060271116A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsThoracic FluidThoracic cavity
This patent document discusses, among other things, systems, devices, and methods for predicting an occurrence of impending thoracic fluid accumulation and in one example, invoking a responsive therapy, such as to prevent or minimize the consequences of the impending thoracic fluid accumulation. One example of the present systems, devices, and methods senses or receives at least one parameter that is statistically associated with impending thoracic fluid accumulation from a subject. Using such parameter(s), a probability of impending thoracic fluid accumulation is estimated. A list of parameters determines which values are recurrently sensed or received at various desired time intervals. Another example of the present systems, devices, and methods weights the sensed or received parameter value(s) to compute the probability estimate of impending thoracic fluid accumulation. A responsive preventive thoracic fluid accumulation therapy or other therapy is selected and activated using the probability estimate of impending thoracic fluid accumulation.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
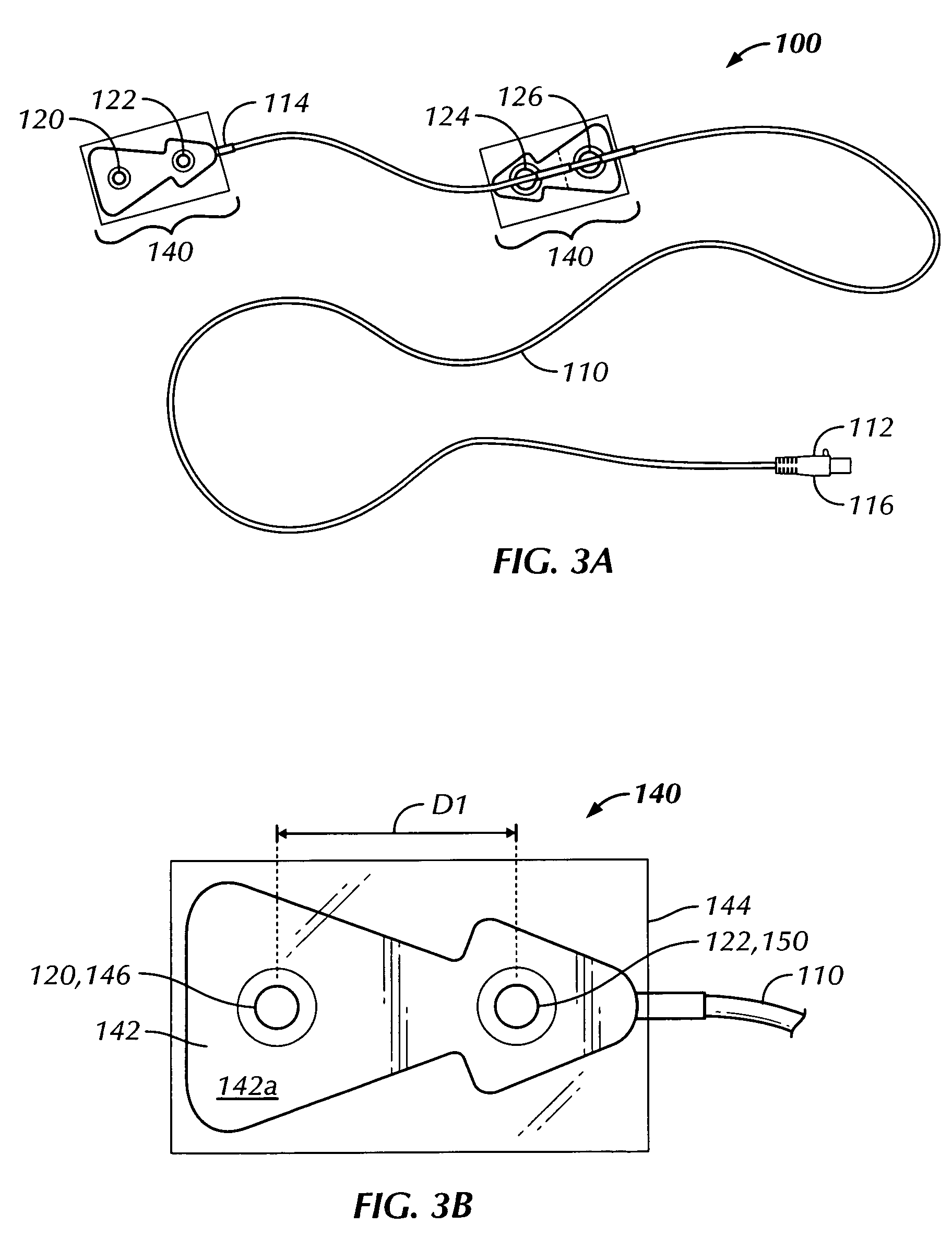
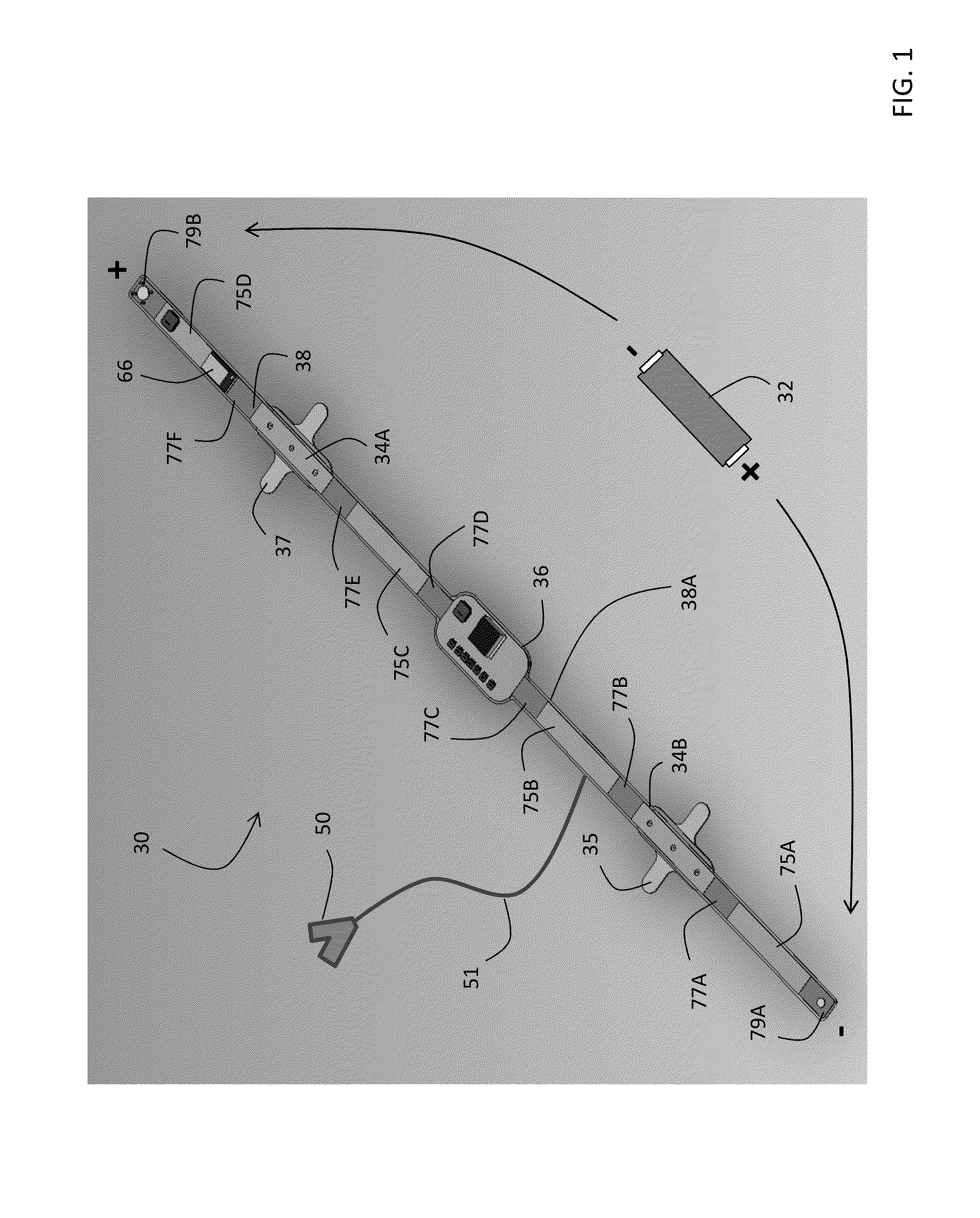
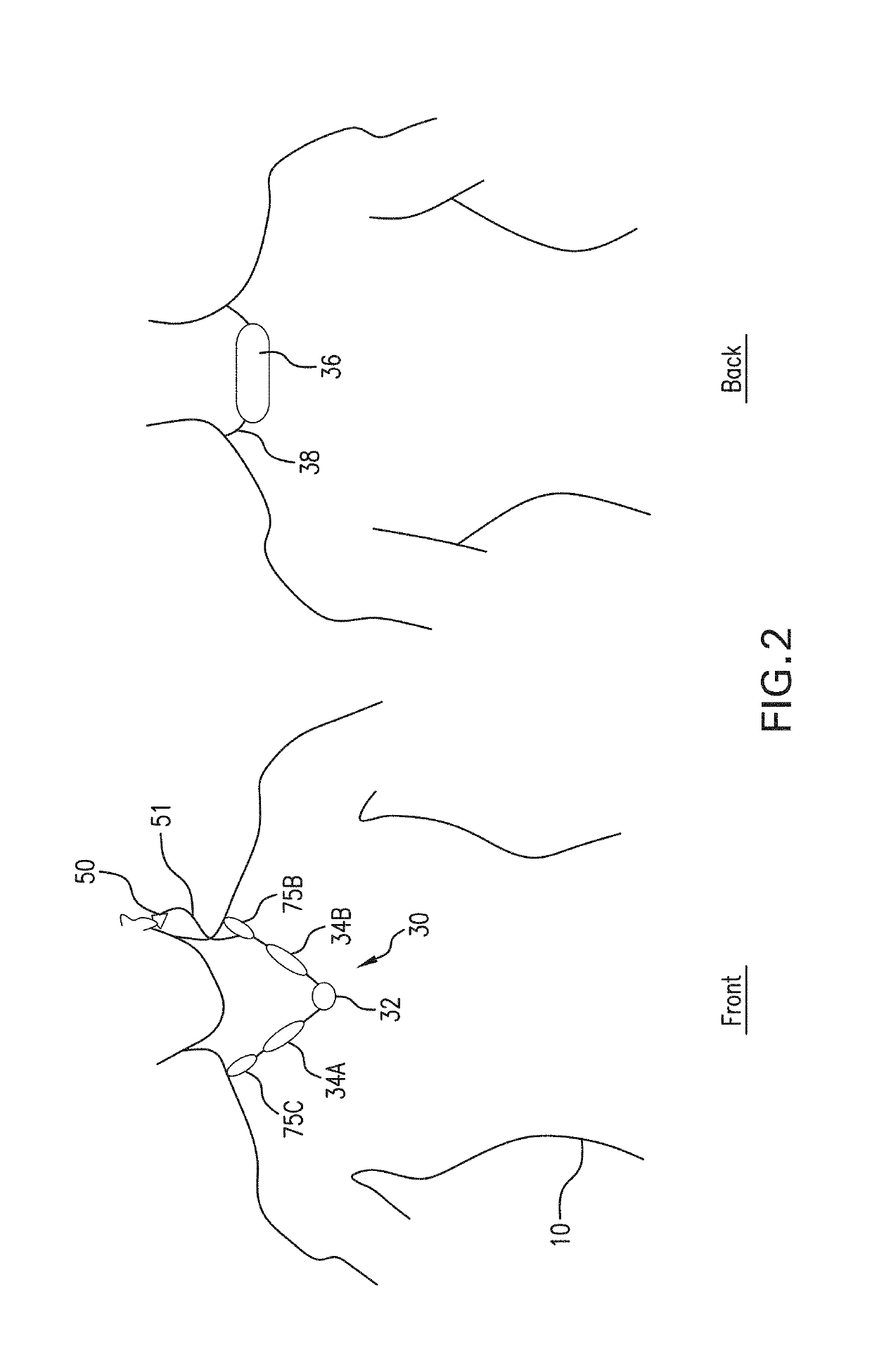
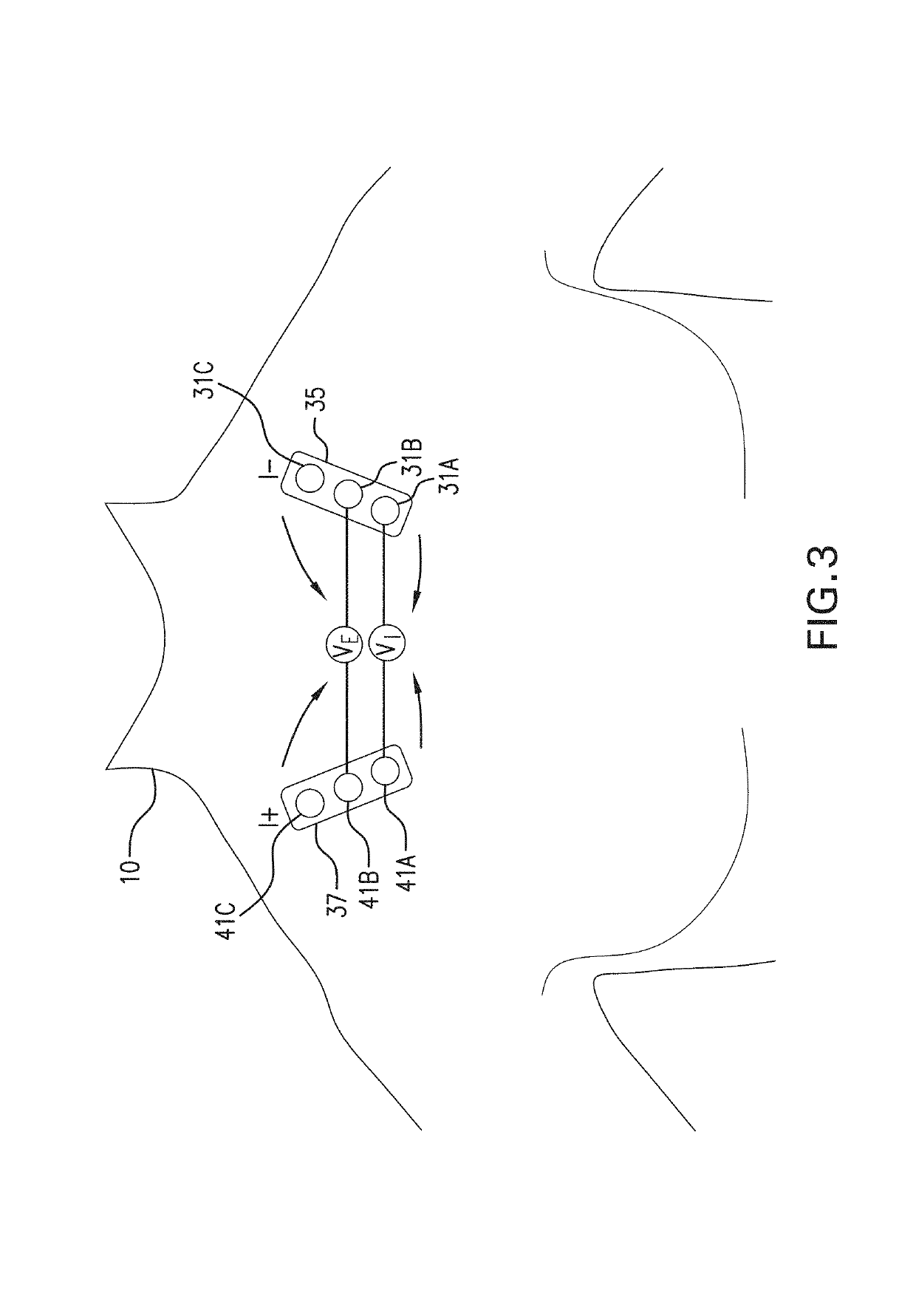
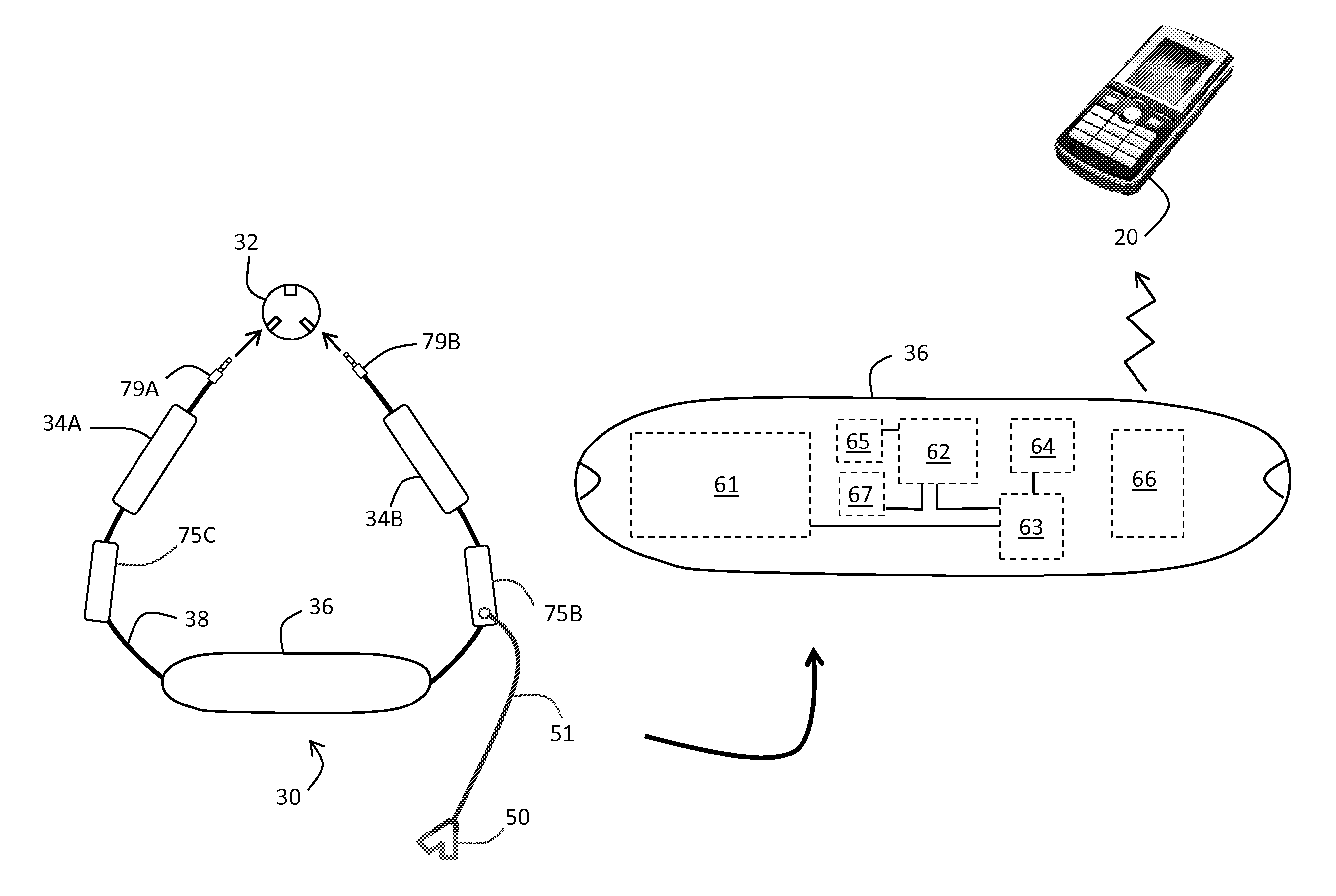
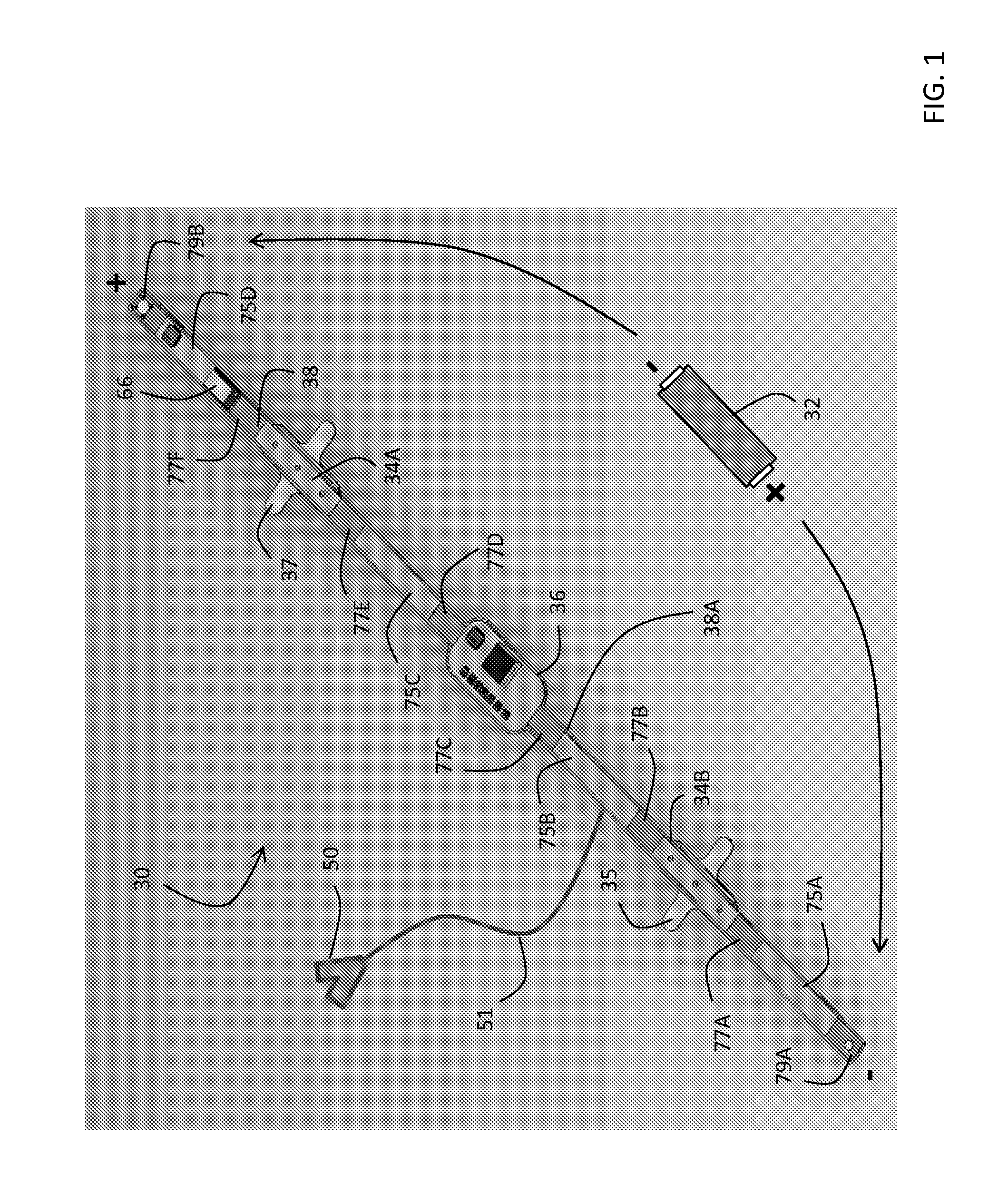
Thoracic impedance monitor and electrode array and method of use
A portable thoracic impedance monitor for monitoring thoracic fluid levels, an electrode array assembly having a single linear electrode array lead with first, second, third, and fourth electrodes arranged sequentially and axially along the linear electrode array lead, and a method of use of the thoracic impedance monitor. A measurement of the user's thoracic impedance is obtained by connecting the second electrode to the user's body at the junction of the clavicles, superior to the sternum, the third electrode to the user's body at the xiphoid-sternal junction, and the first and fourth electrodes to the user's body substantially along a centerline of the user's sternum respectively at a first pre-determined distance above the second electrode and a second predetermined distance below the third electrode, followed by initiating operation of the monitor.
Owner:CALDWELL SIMPSON LLC
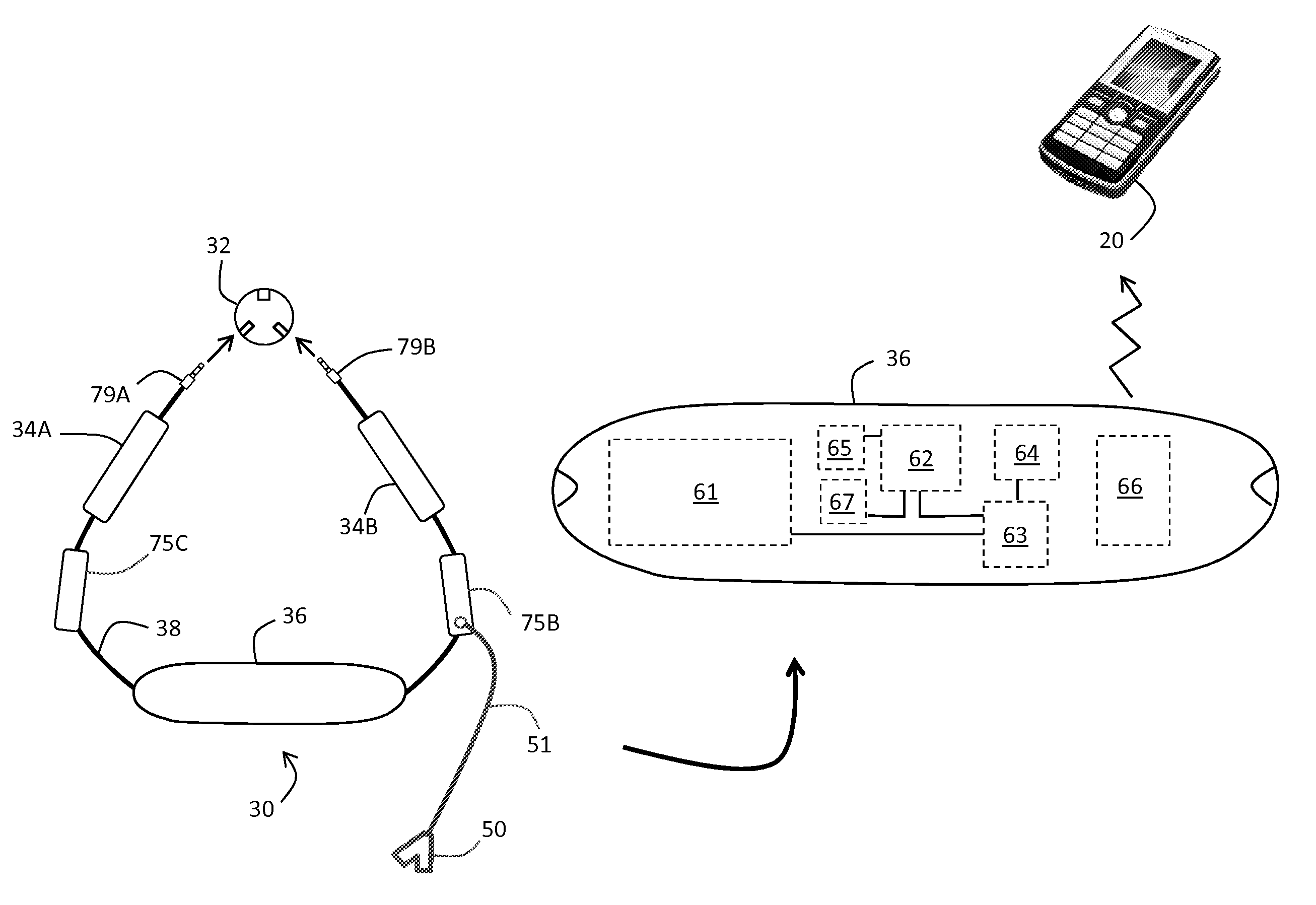
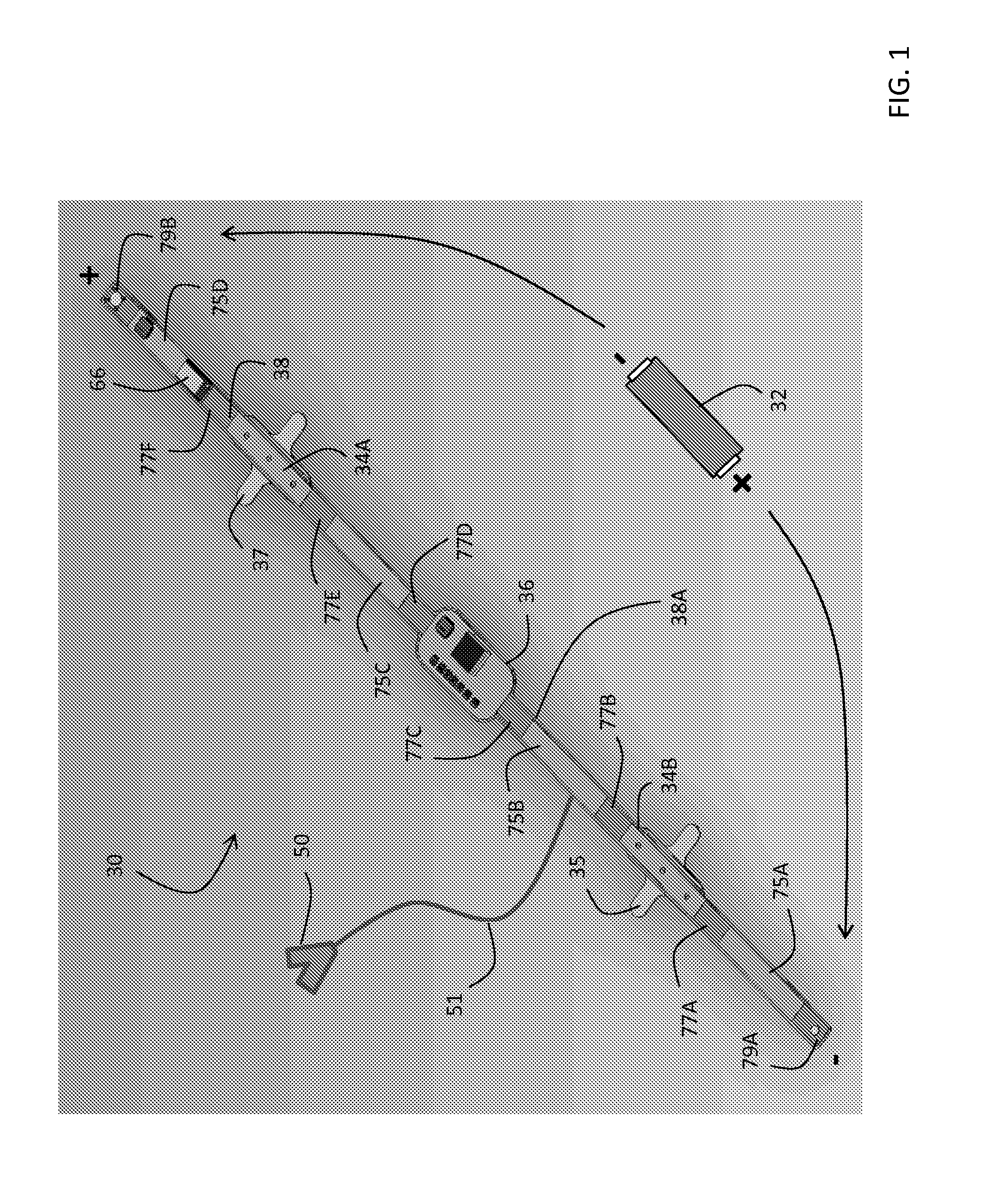
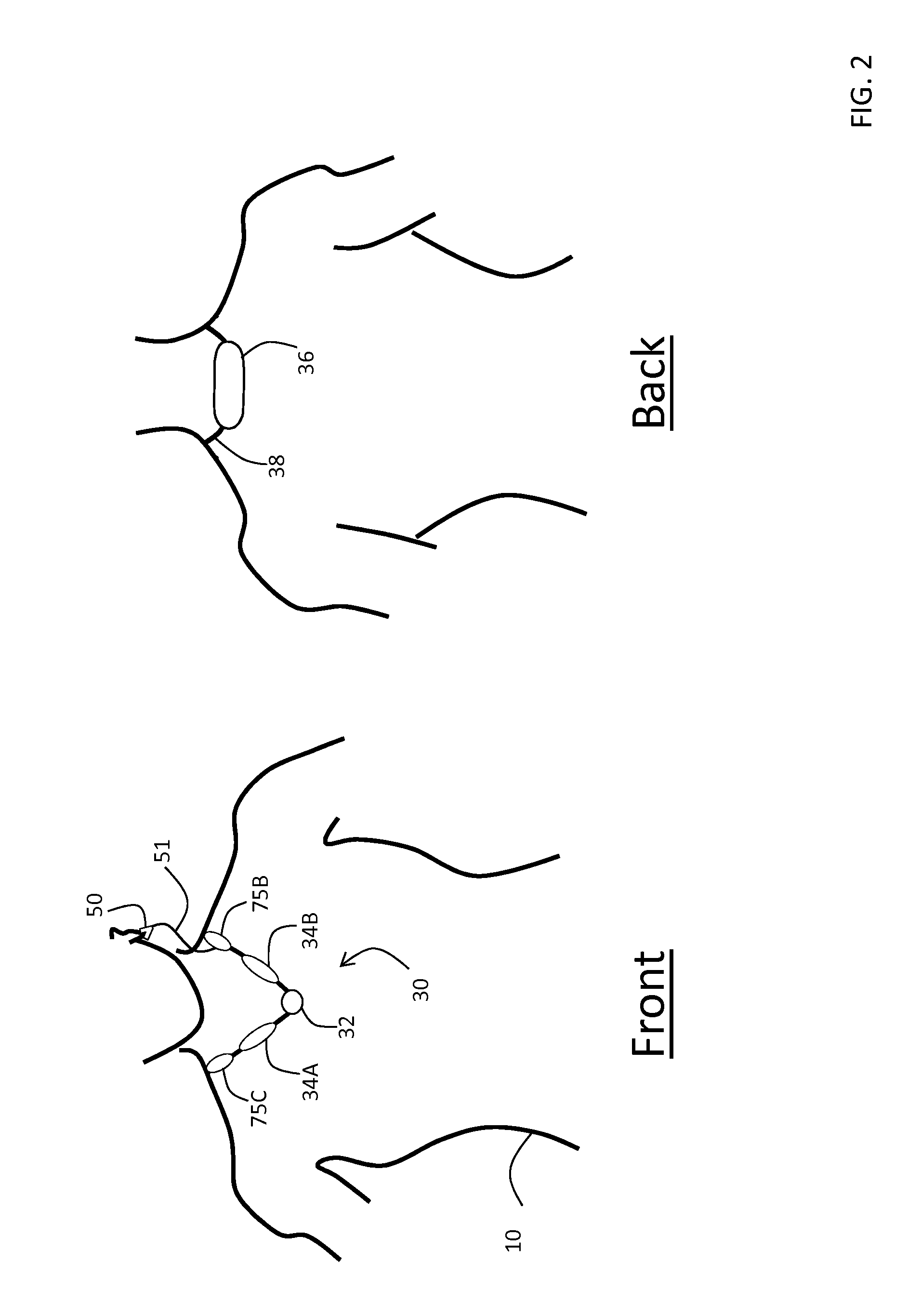
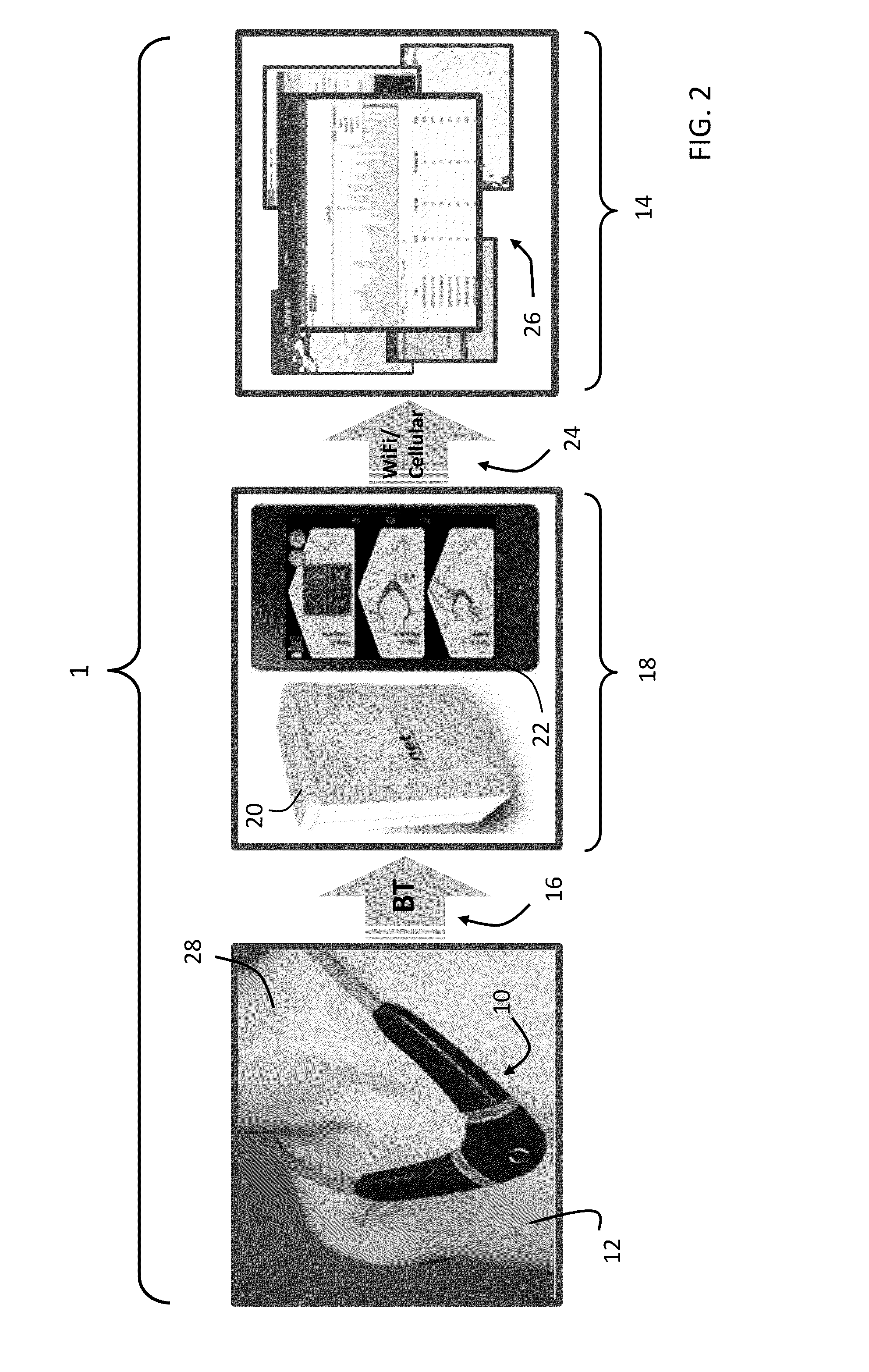
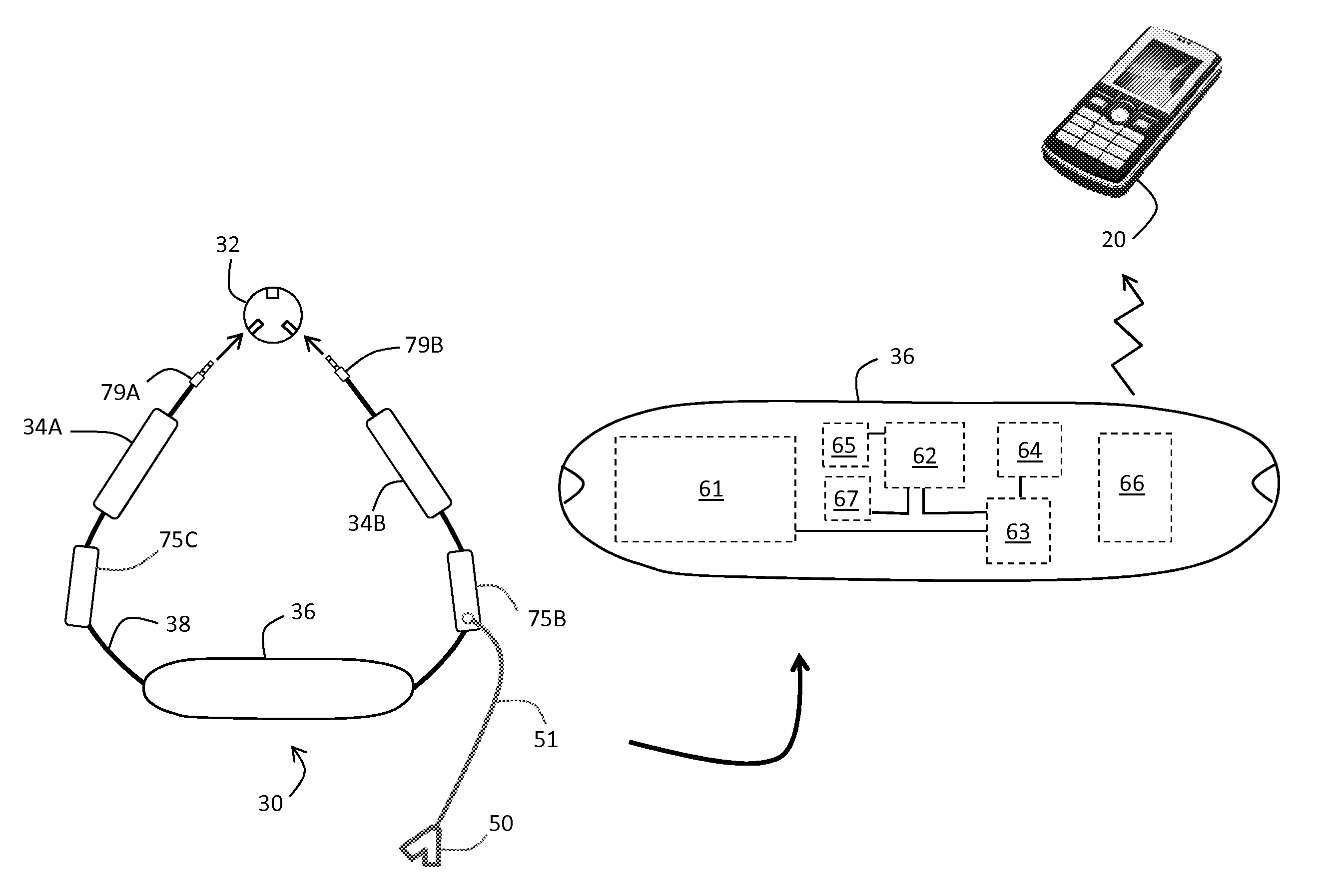
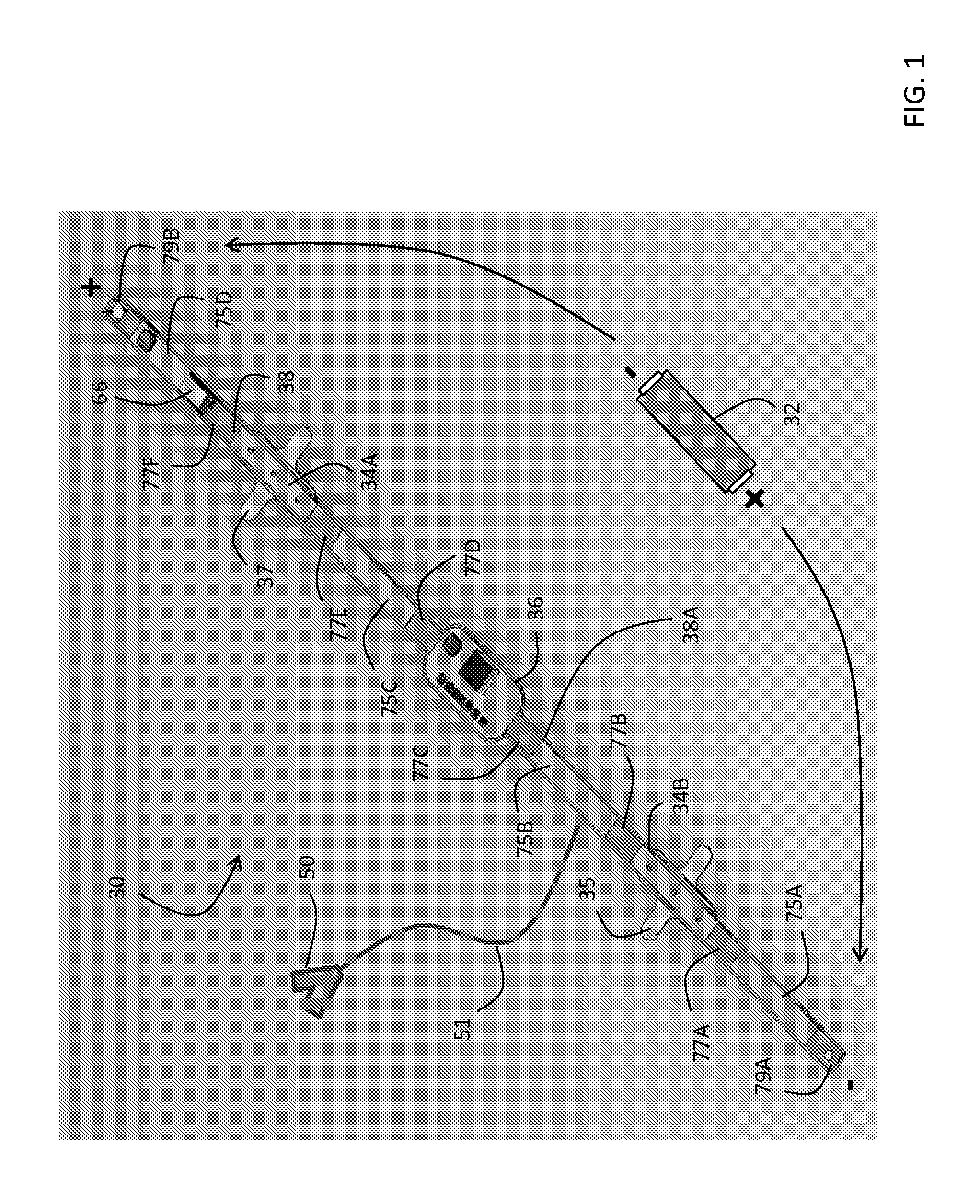
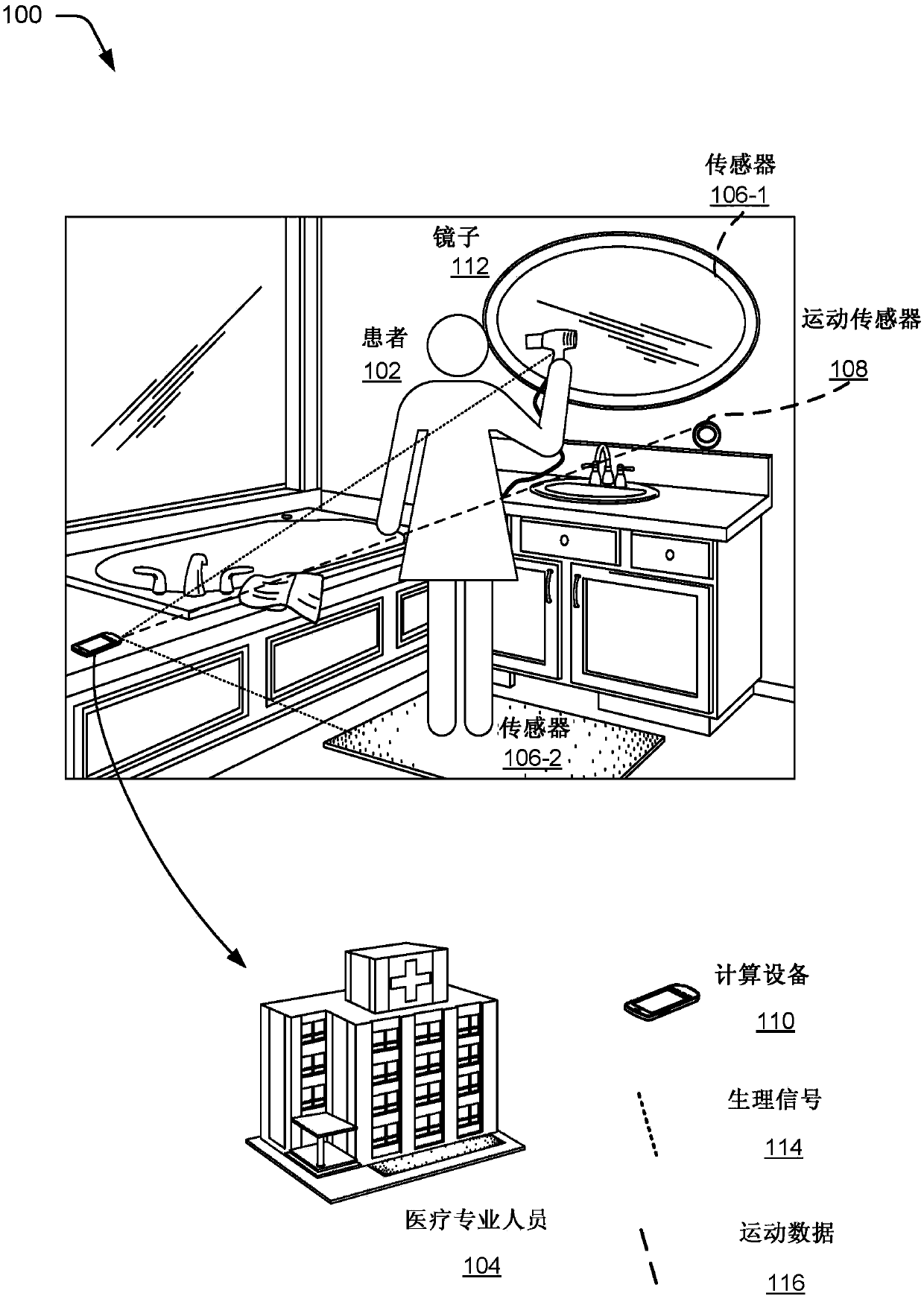
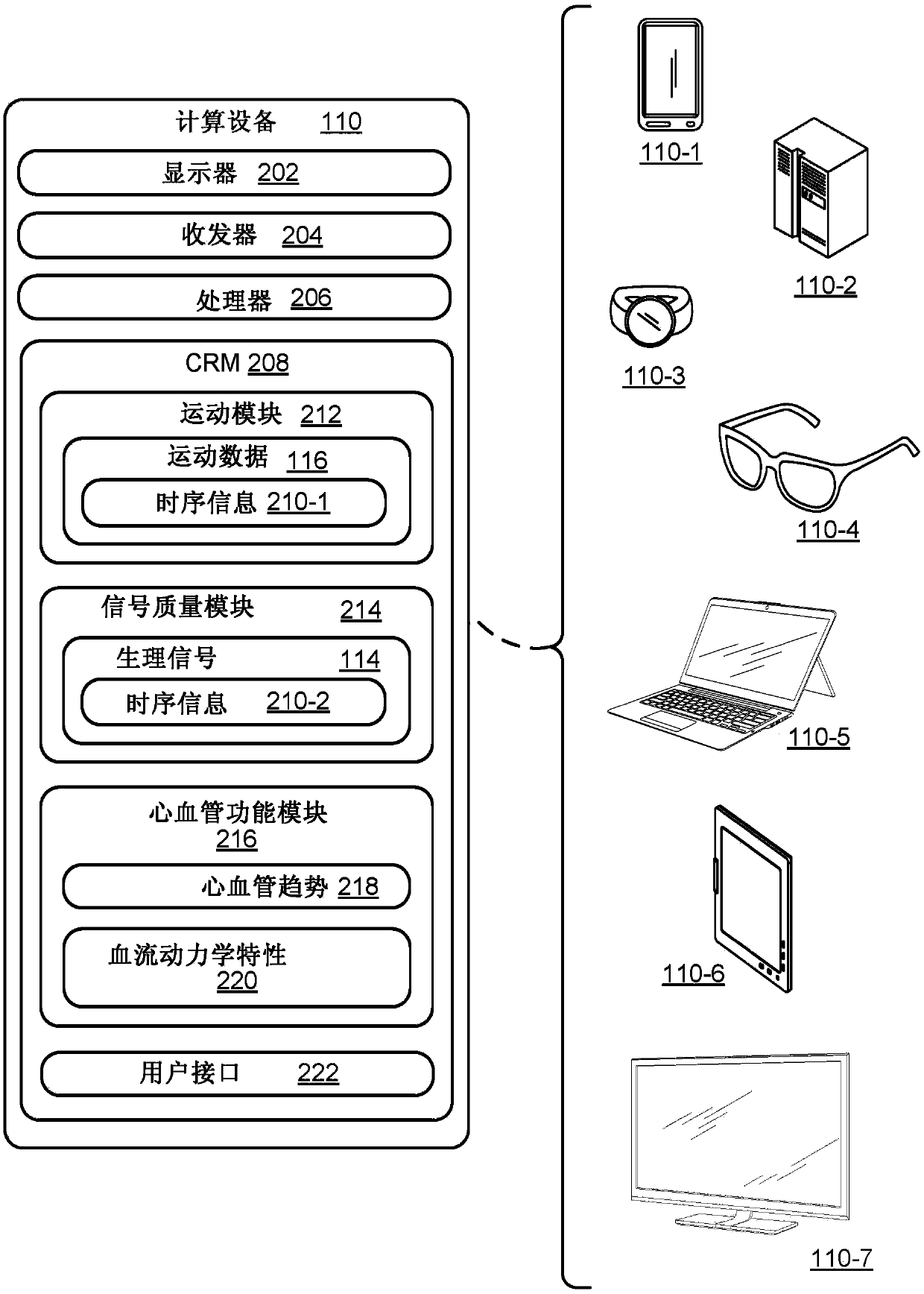
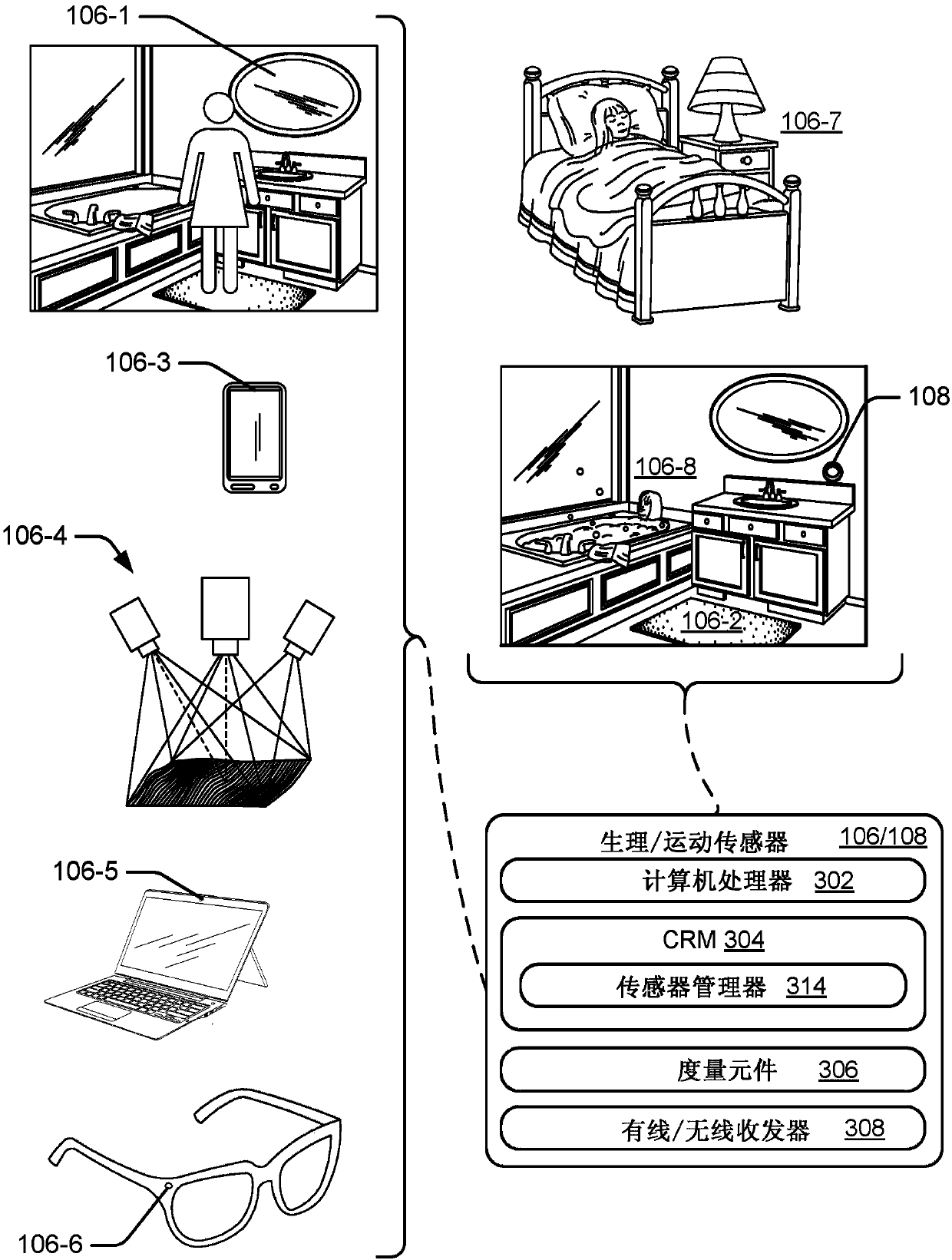
Necklace-shaped physiological monitor
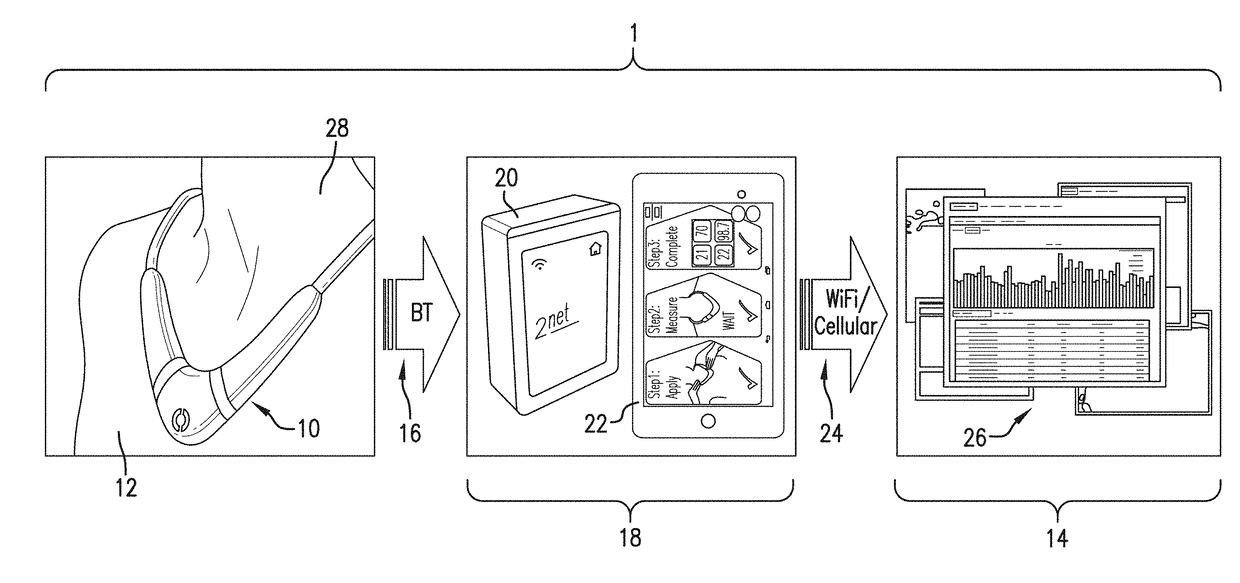
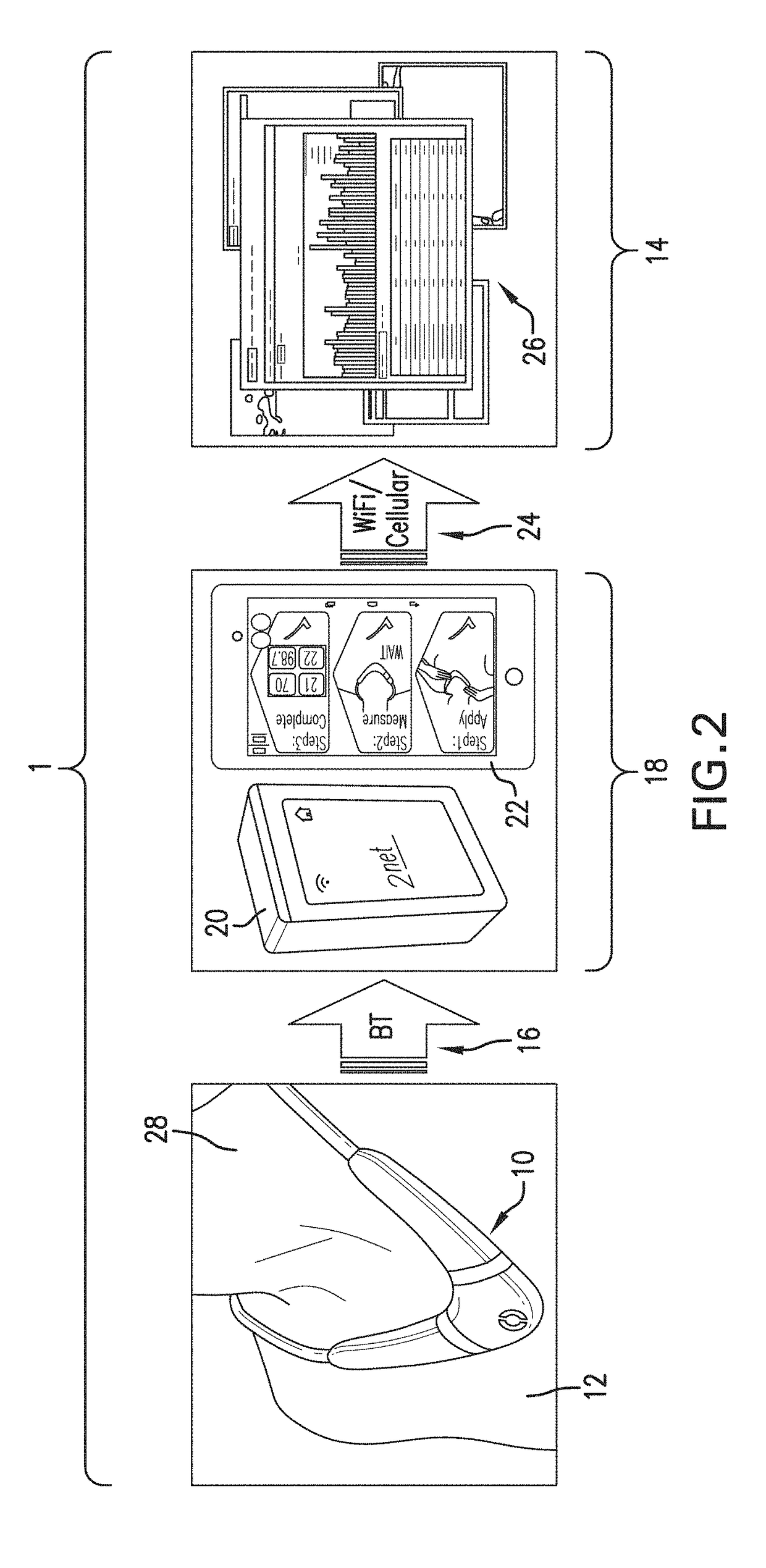
InactiveUS20140236037A1Improve calculation accuracyReduce artifactsRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsThoracic FluidAccelerometer
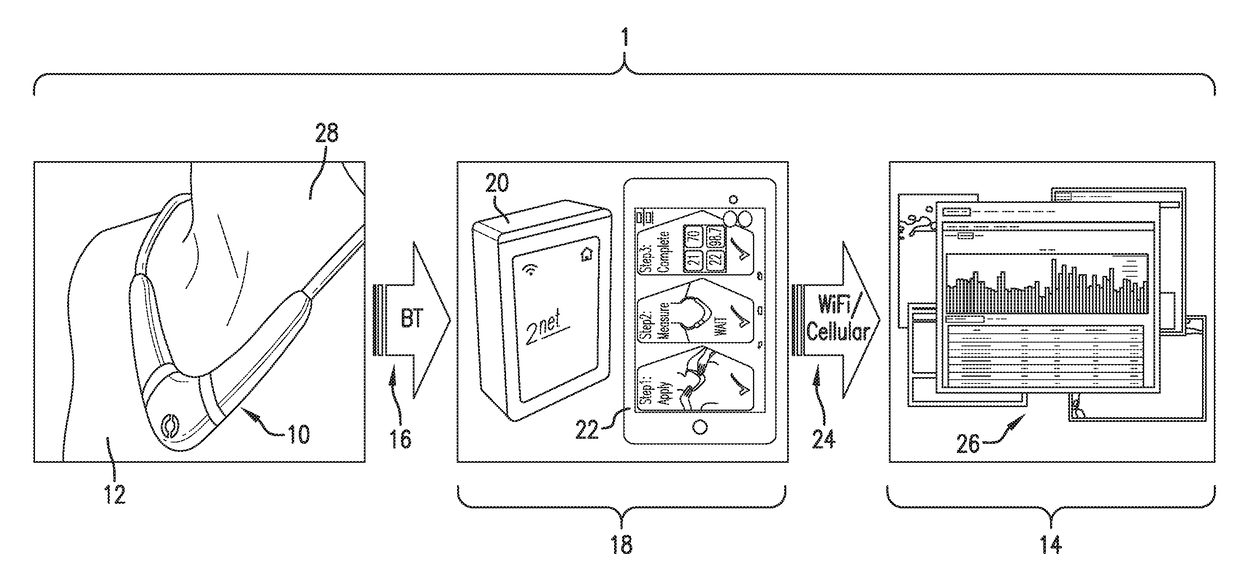
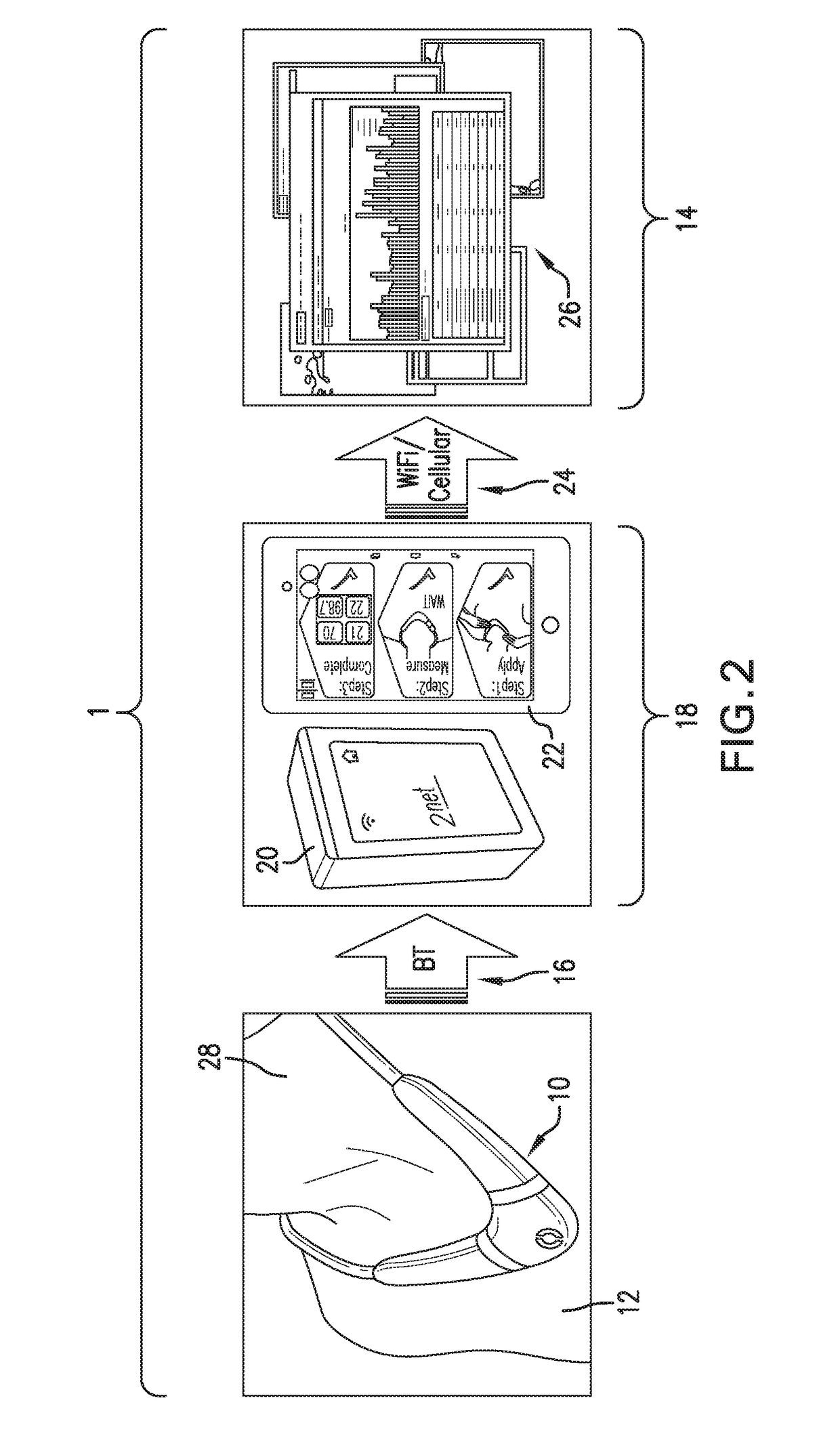
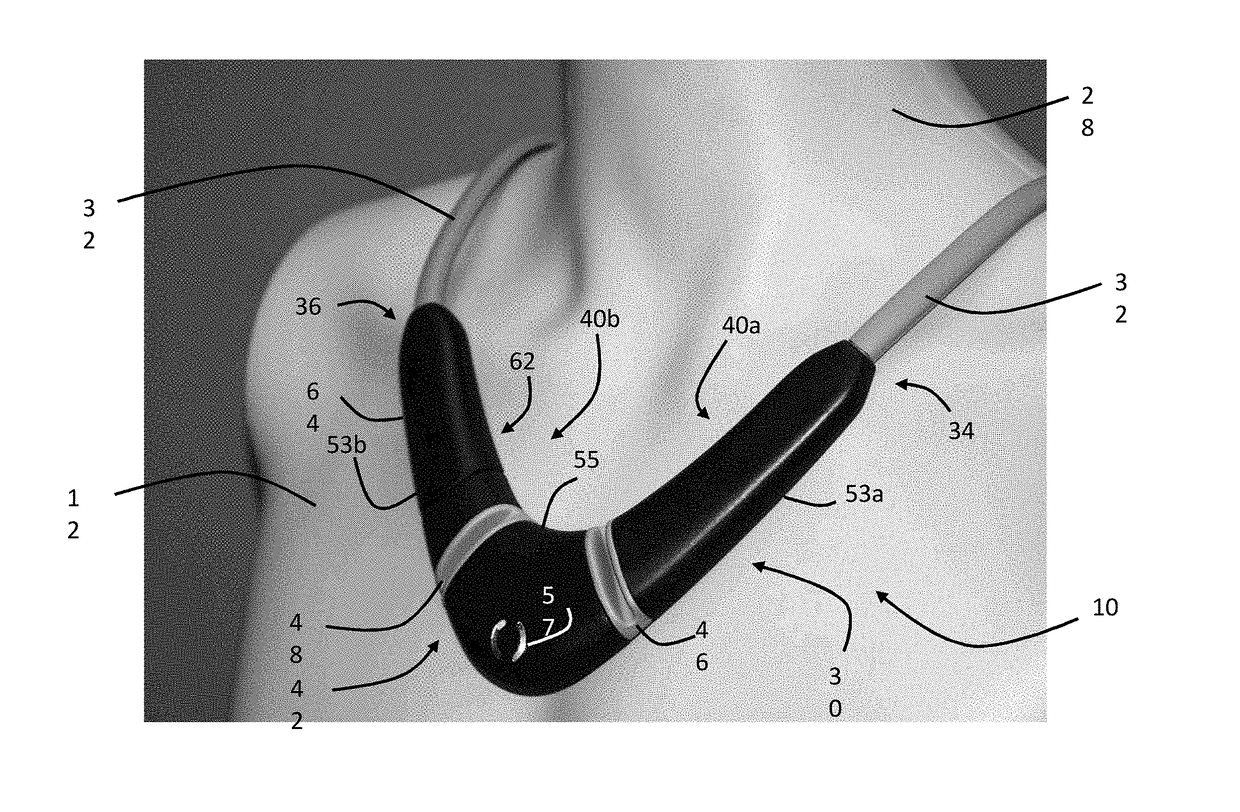
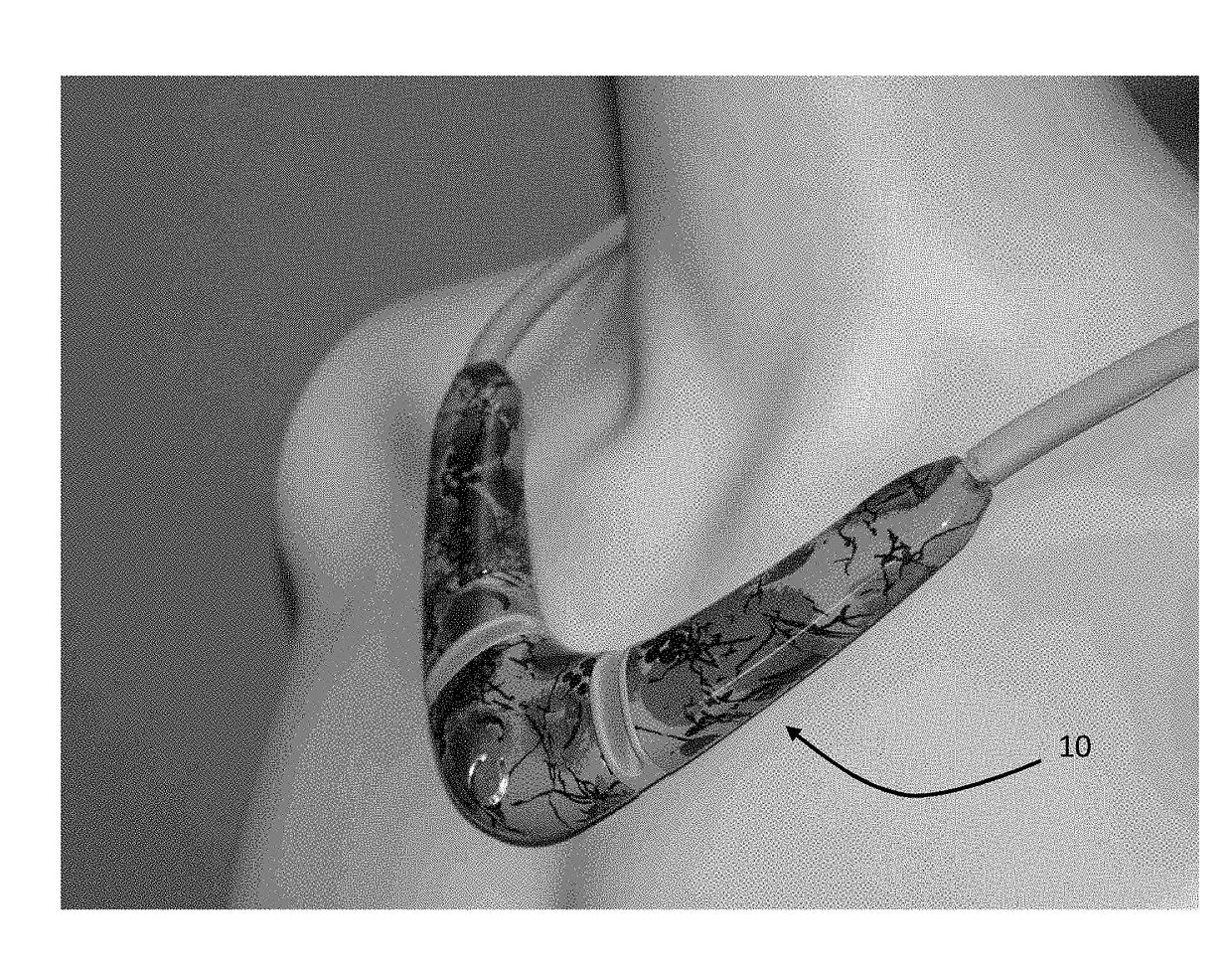
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor (referred to herein as the ‘necklace’) that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the necklace can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:TOSENSE
System and method for calibrating cardiac pressure measurements derived from signals detected by an implantable medical device
ActiveUS8202224B2Easy recalibrationEasy CalibrationElectrotherapyEvaluation of blood vesselsThoracic FluidLeft atrial pressure
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Neck-worn physiological monitor
ActiveUS20160106366A1Patient compliance is goodGood repeatabilityElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsThoracic FluidAccelerometer
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the sensor can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
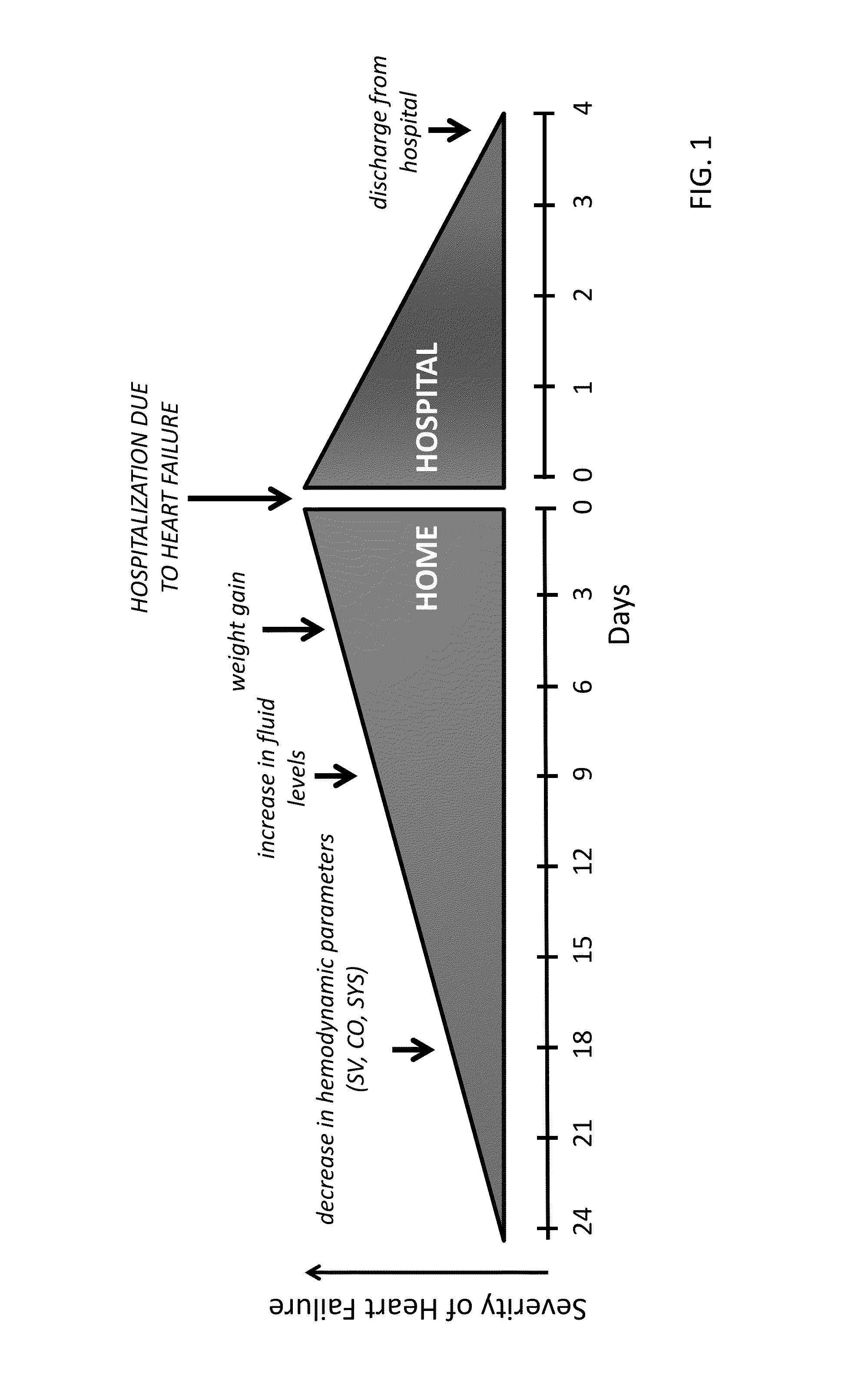
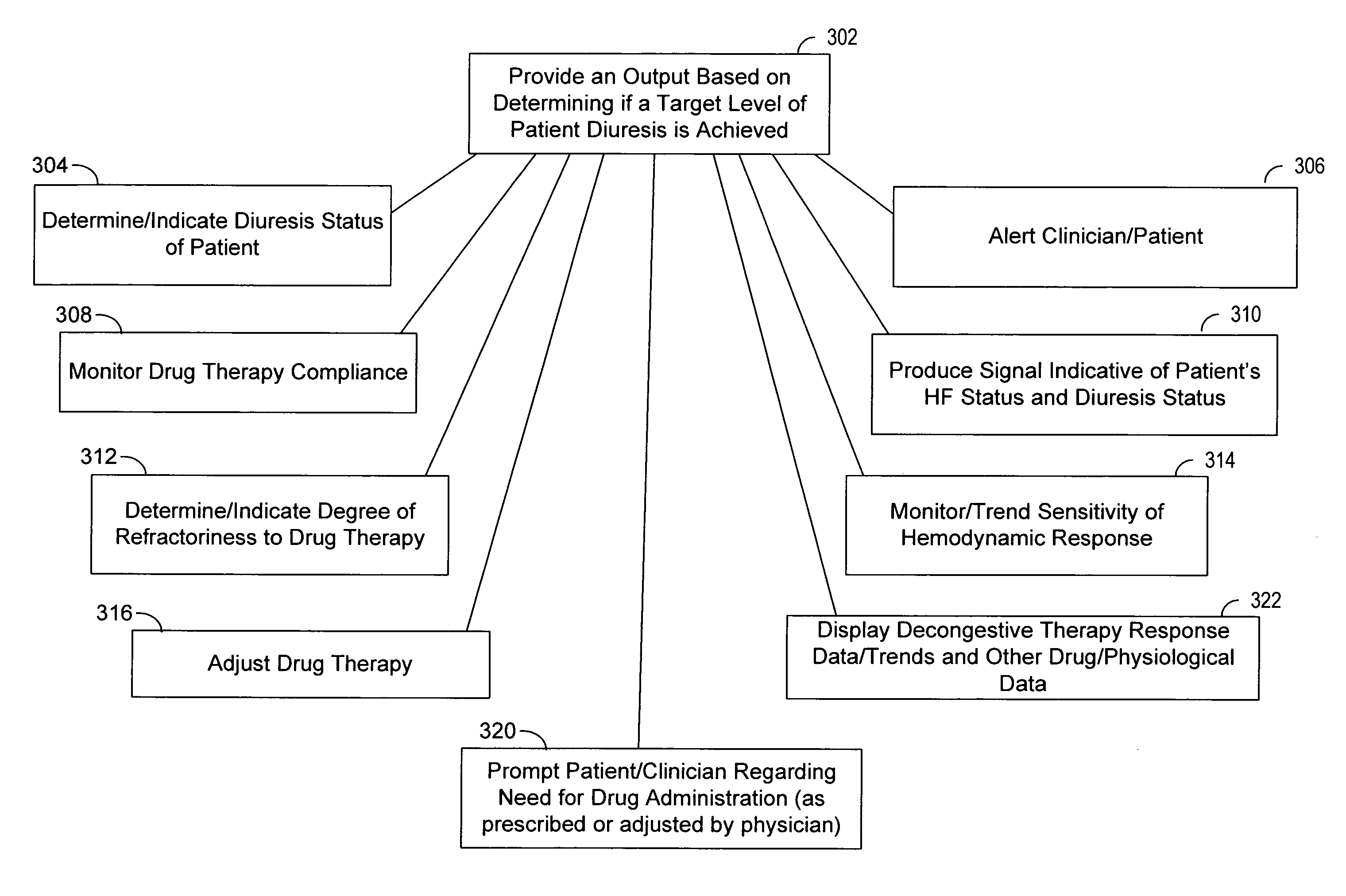
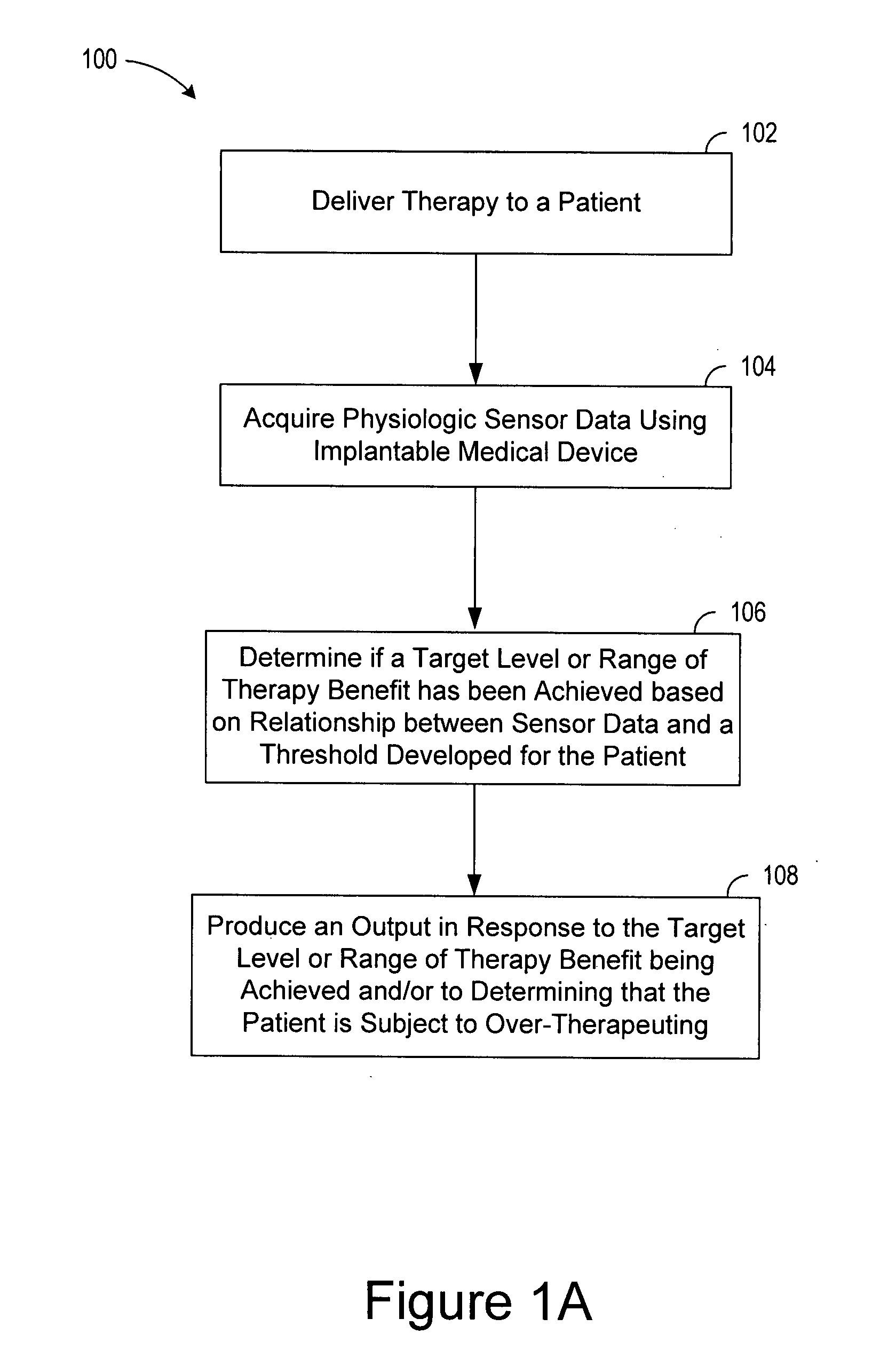
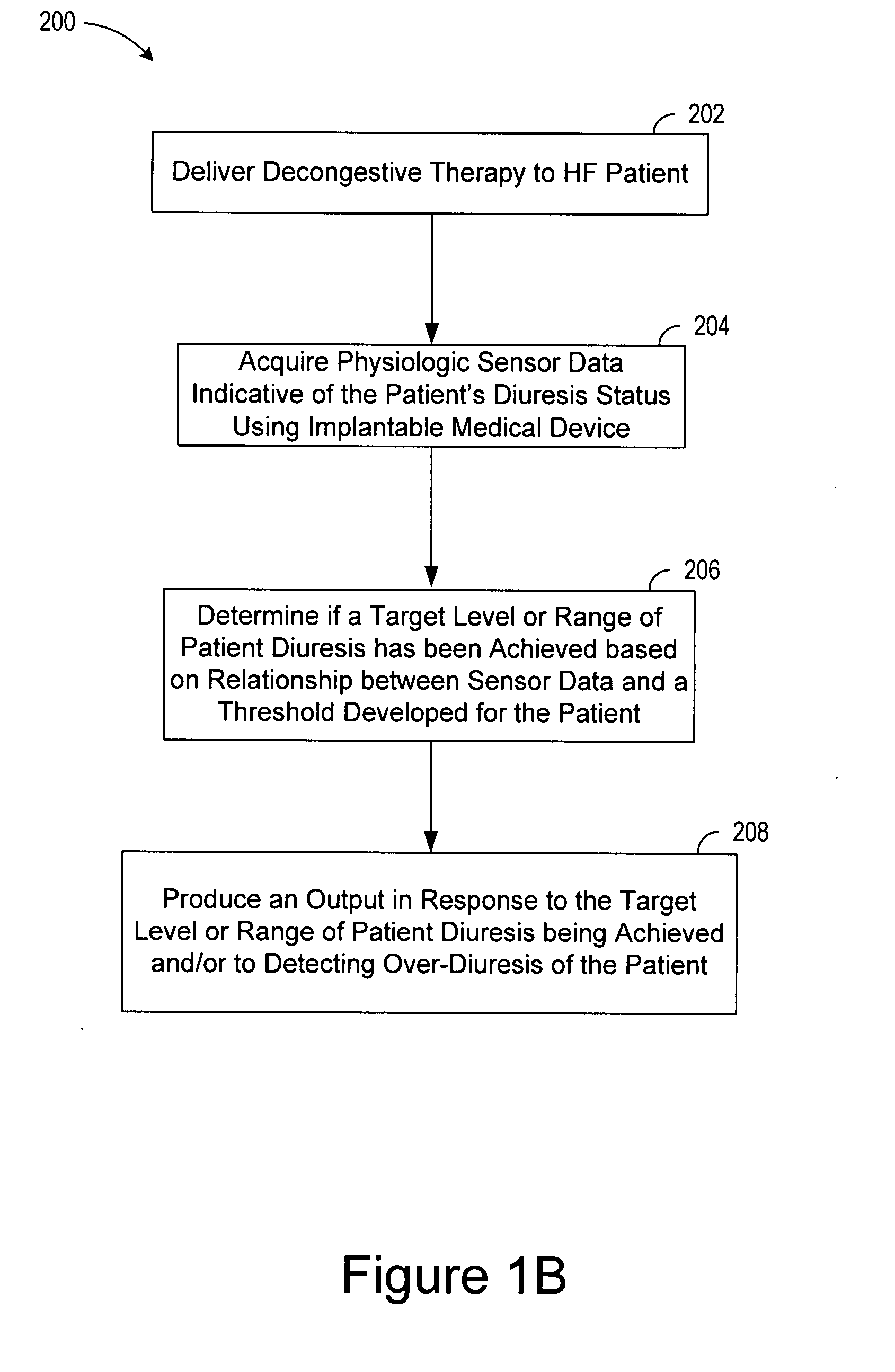
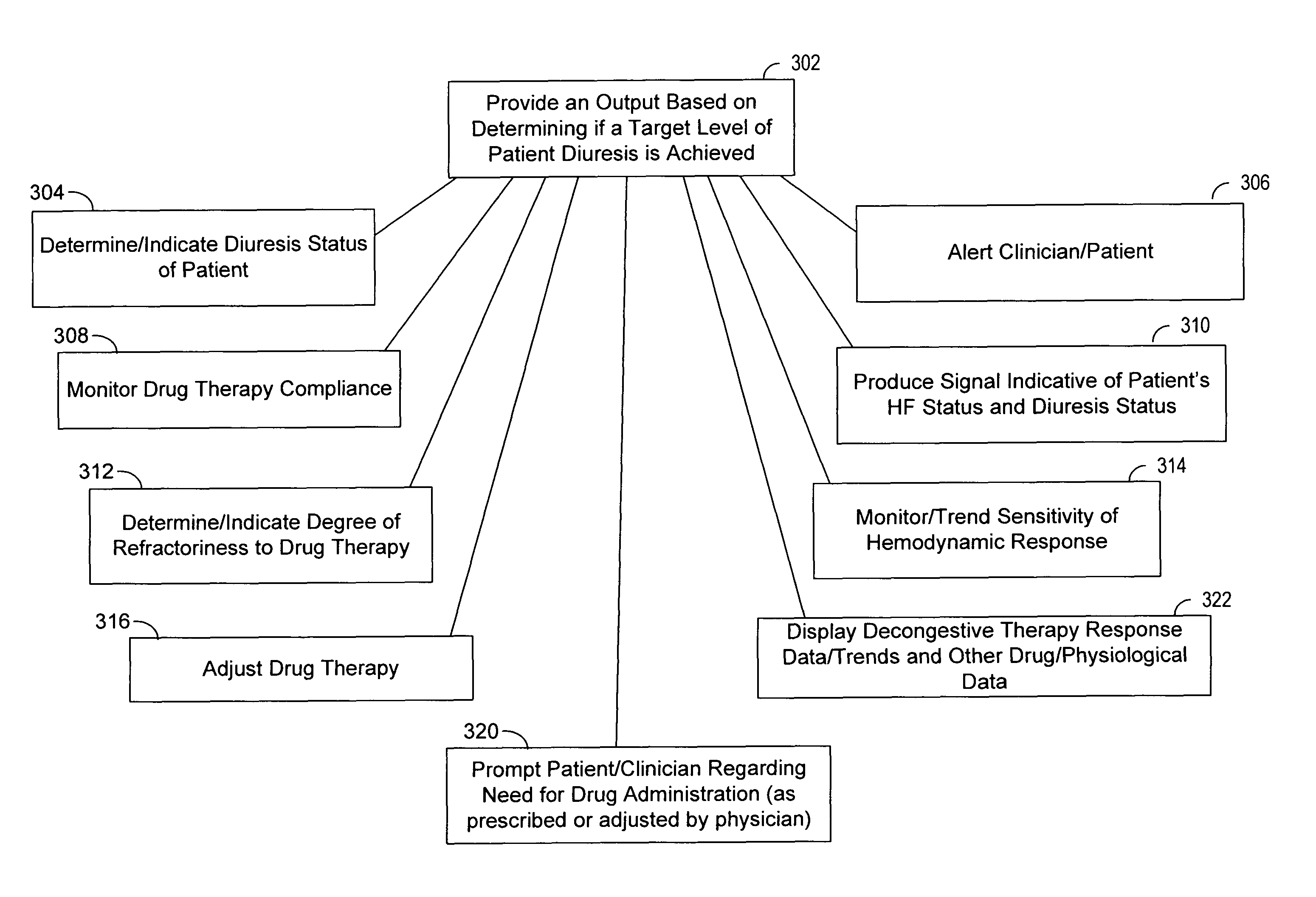
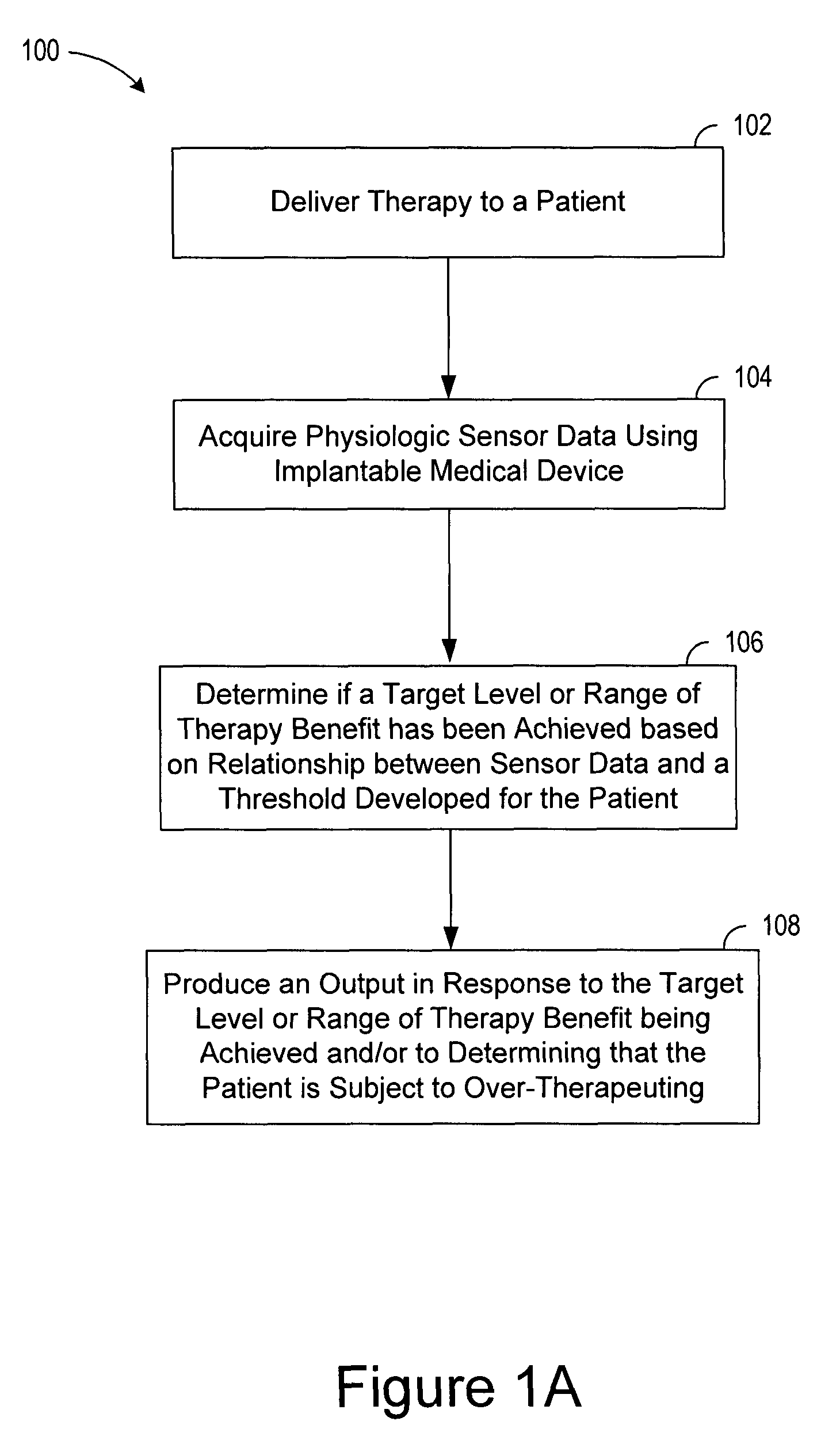
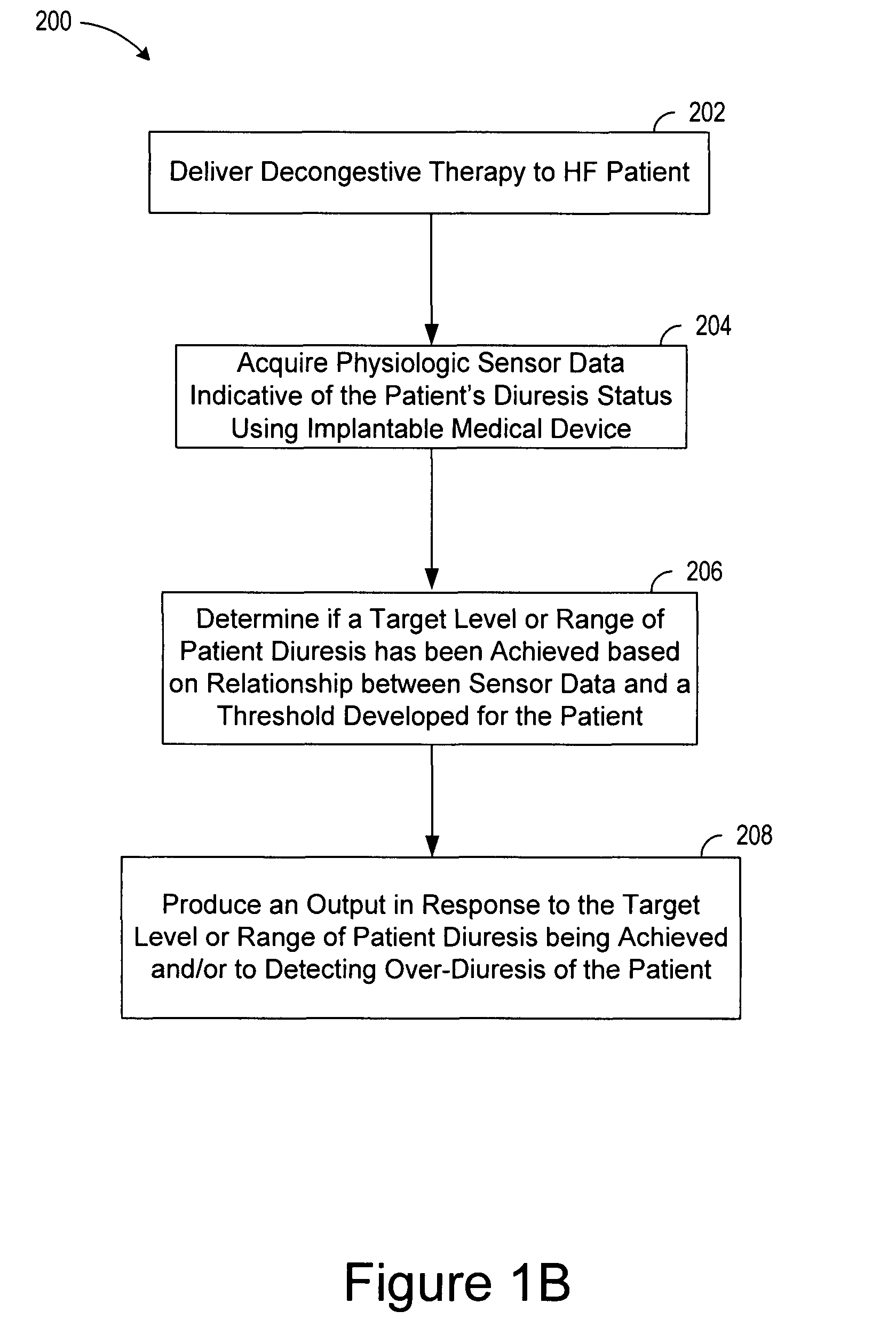
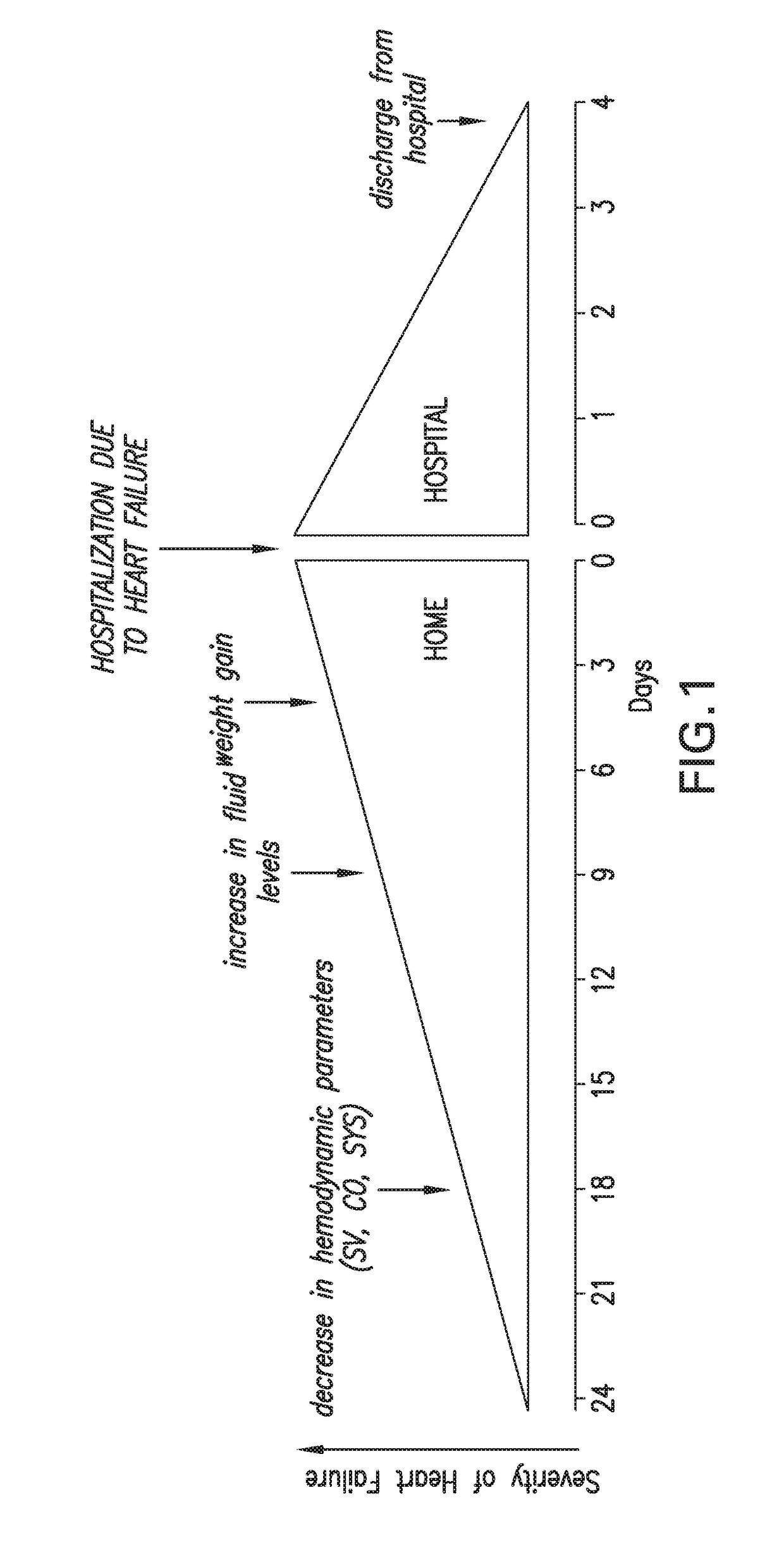
Decongestive therapy titration for heart failure patients using implantable sensor
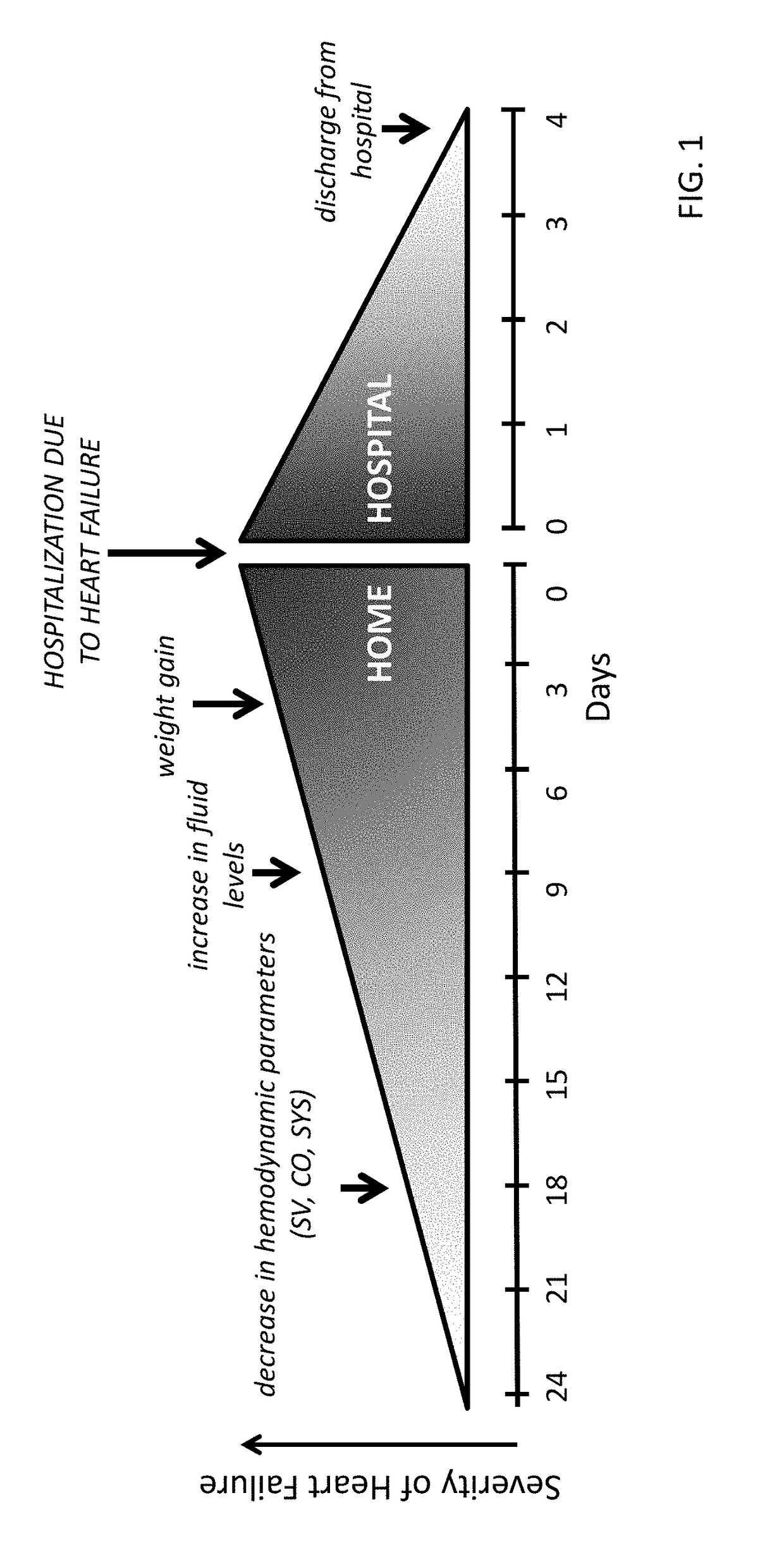
ActiveUS20080294209A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDrug and medicationsThoracic FluidDiuresis
Assessing decongestive therapy delivered to a heart failure patient involves use of an implantable sensor configured to sense a physiologic parameter indicative of the patient's diuresis status and a processor coupled to the implantable sensor. The sensor may comprise a thoracic fluid sensor, a heart sounds sensor, a cardiac chamber or arterial pressure sensor, a respiration sensor, or a blood chemistry sensor, for example. The processor is configured to determine if a target level of patient diuresis has been achieved based on a relationship between the sensed physiologic parameter and a threshold developed for the patient, and to produce an output in response to determining that the target level of patient diuresis has been achieved. The processor may be disposed in an implantable housing, in a patient-external housing, or in a network server system.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Neck-worn physiological monitor
ActiveUS20180214079A1Easy to monitorGood repeatabilityElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsThoracic FluidAccelerometer
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the sensor can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
System and method for identifying a potential cause of pulmonary edema
A method of identifying a potential cause of pulmonary edema is provided. The method includes obtaining one or more impedance vectors between predetermined combinations of the electrodes positioned proximate the heart. At least one of the impedance vectors is representative of a thoracic fluid level. The method also includes applying a stimulation pulse to the heart and sensing cardiac signals of the heart that are representative of an electrophysiological response to the stimulation pulse. The method further includes monitoring the cardiac signals and at least one of the impedance vectors with respect to time to identify the potential cause of pulmonary edema.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
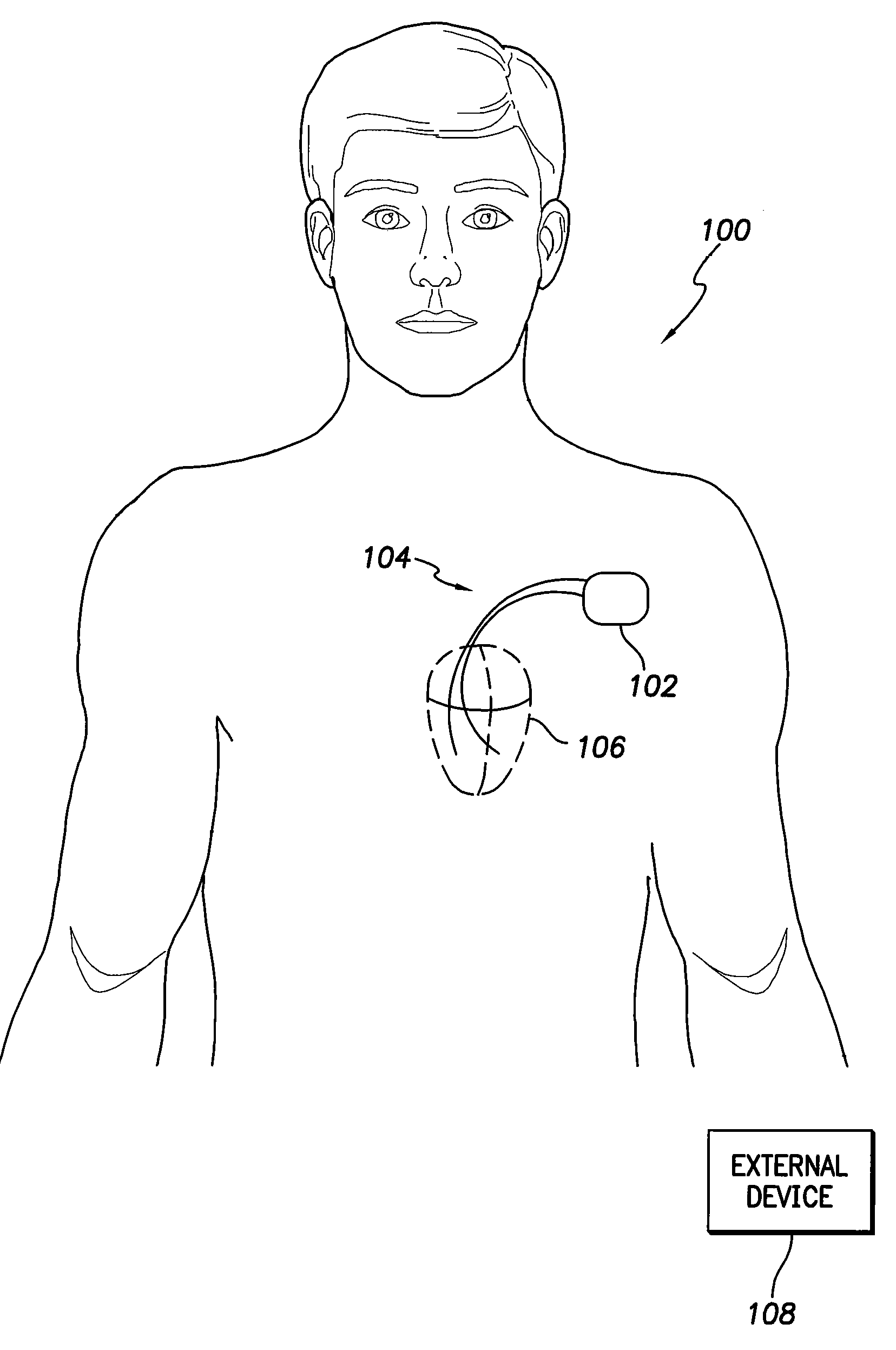
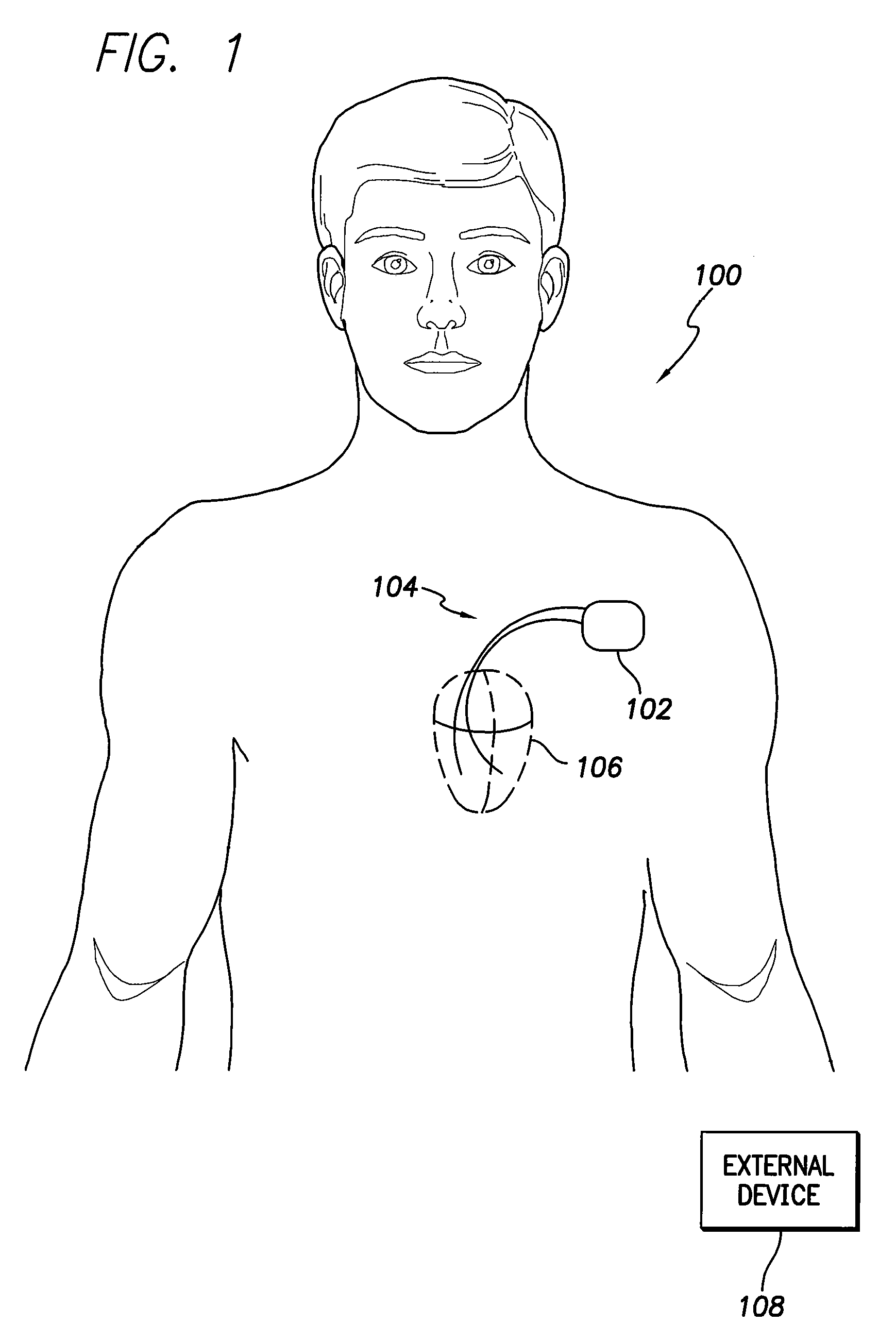
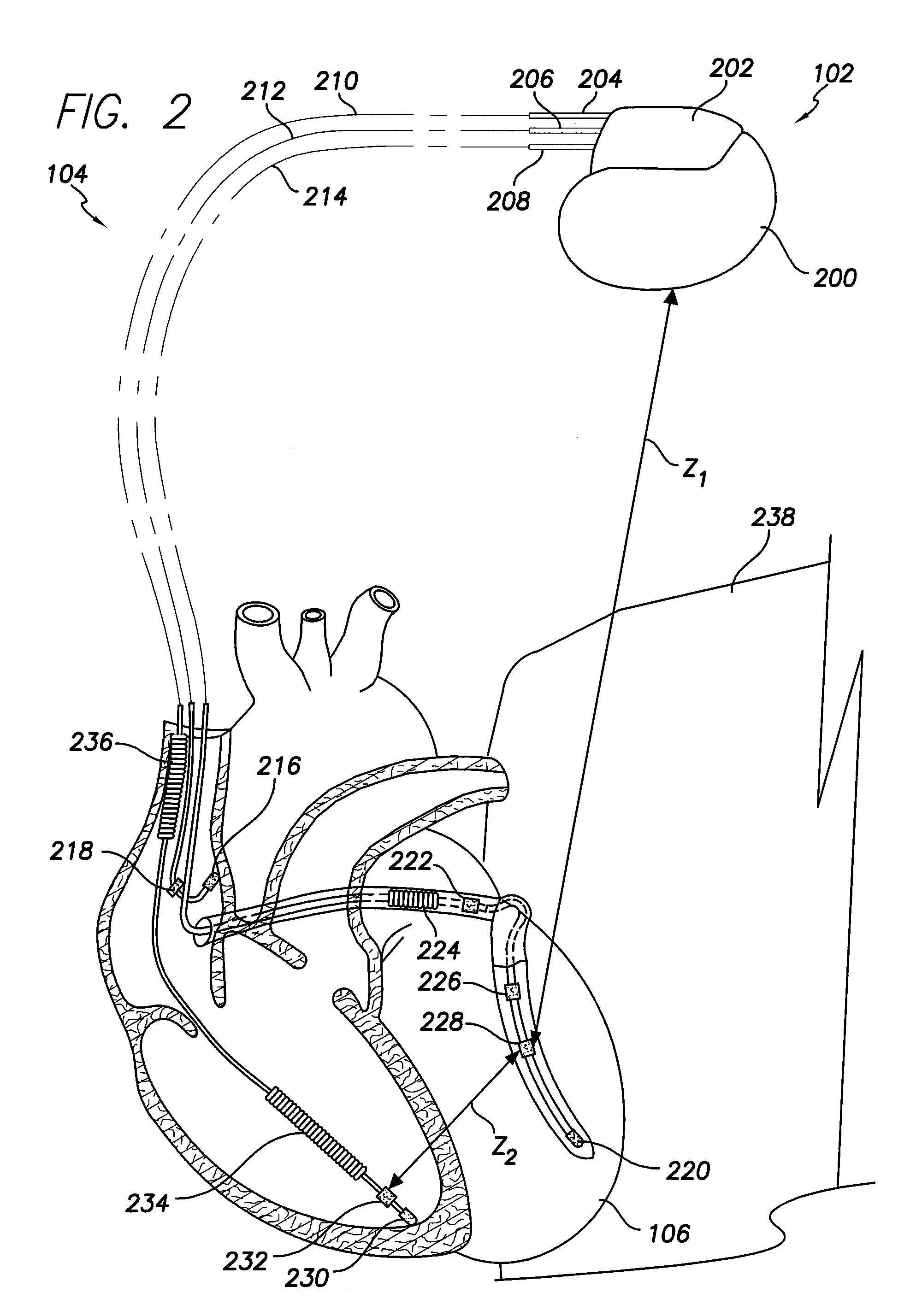
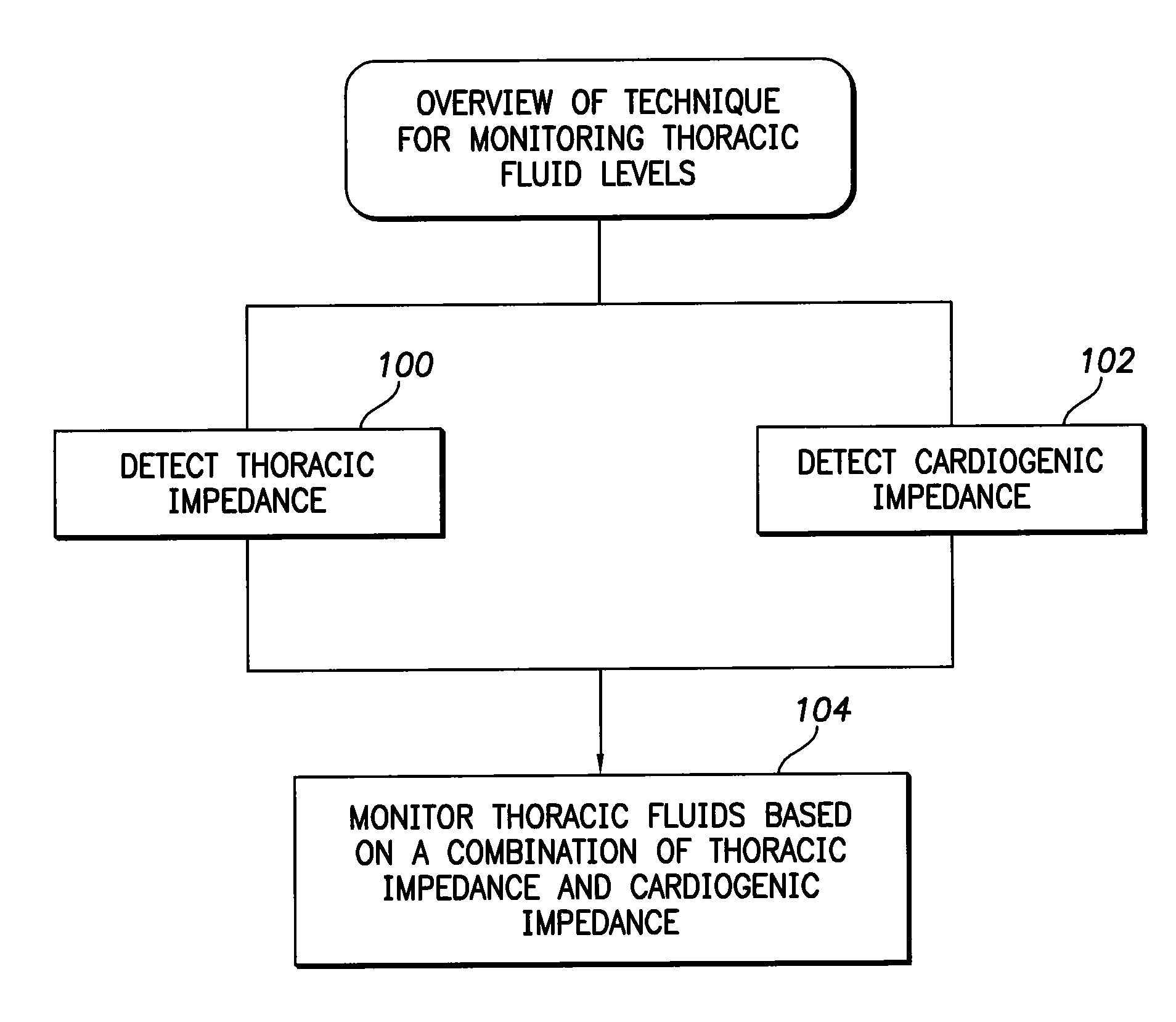
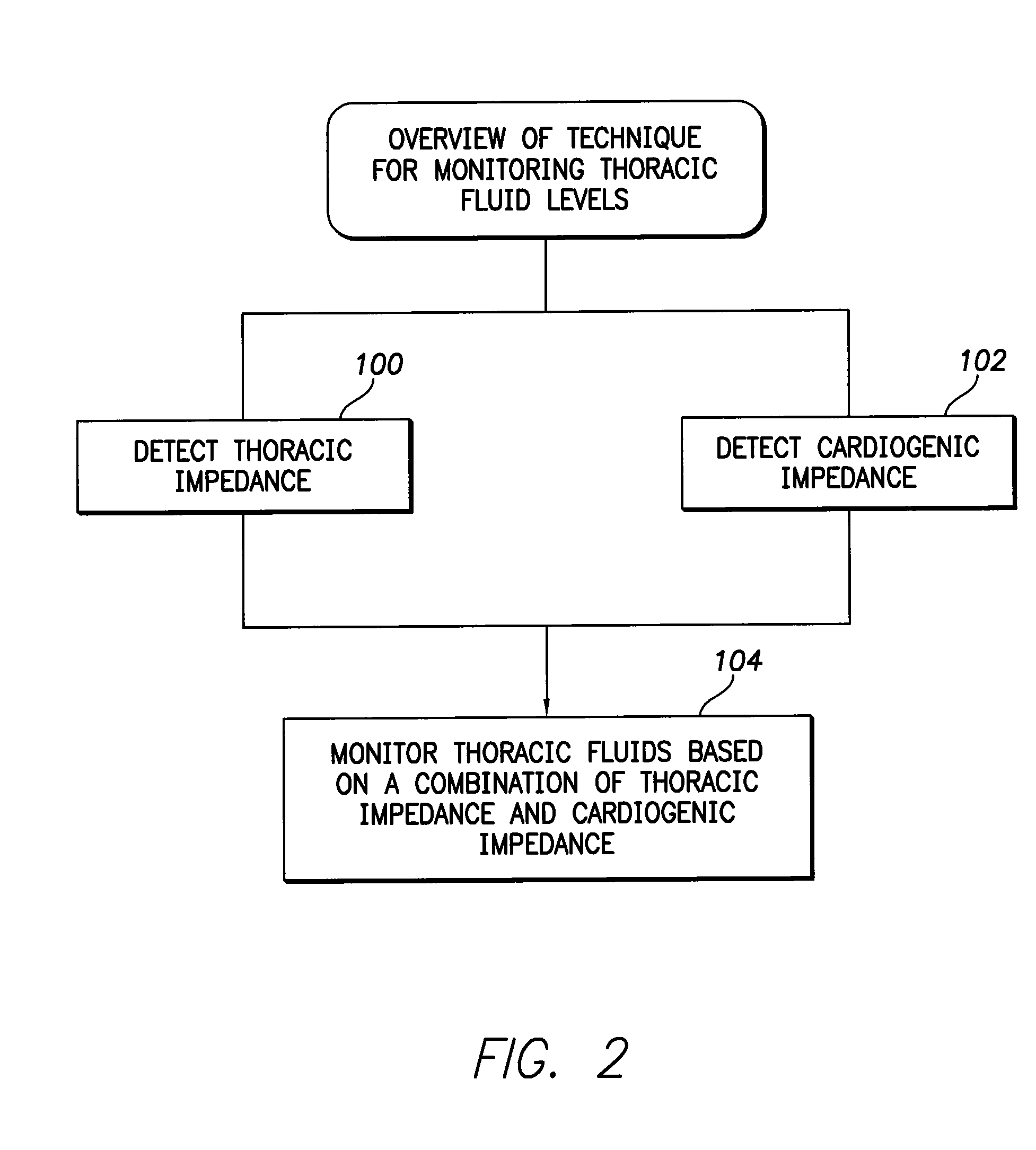
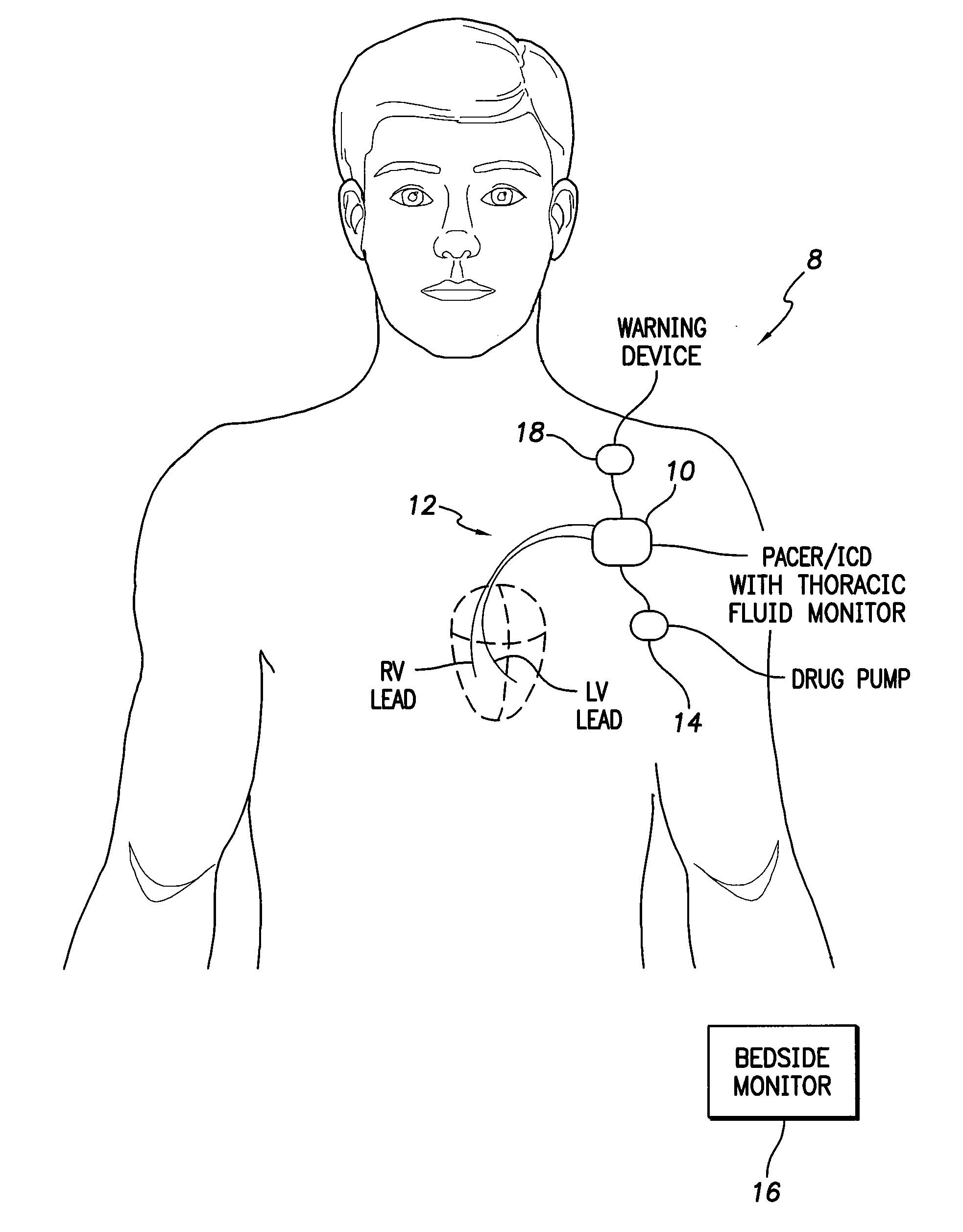
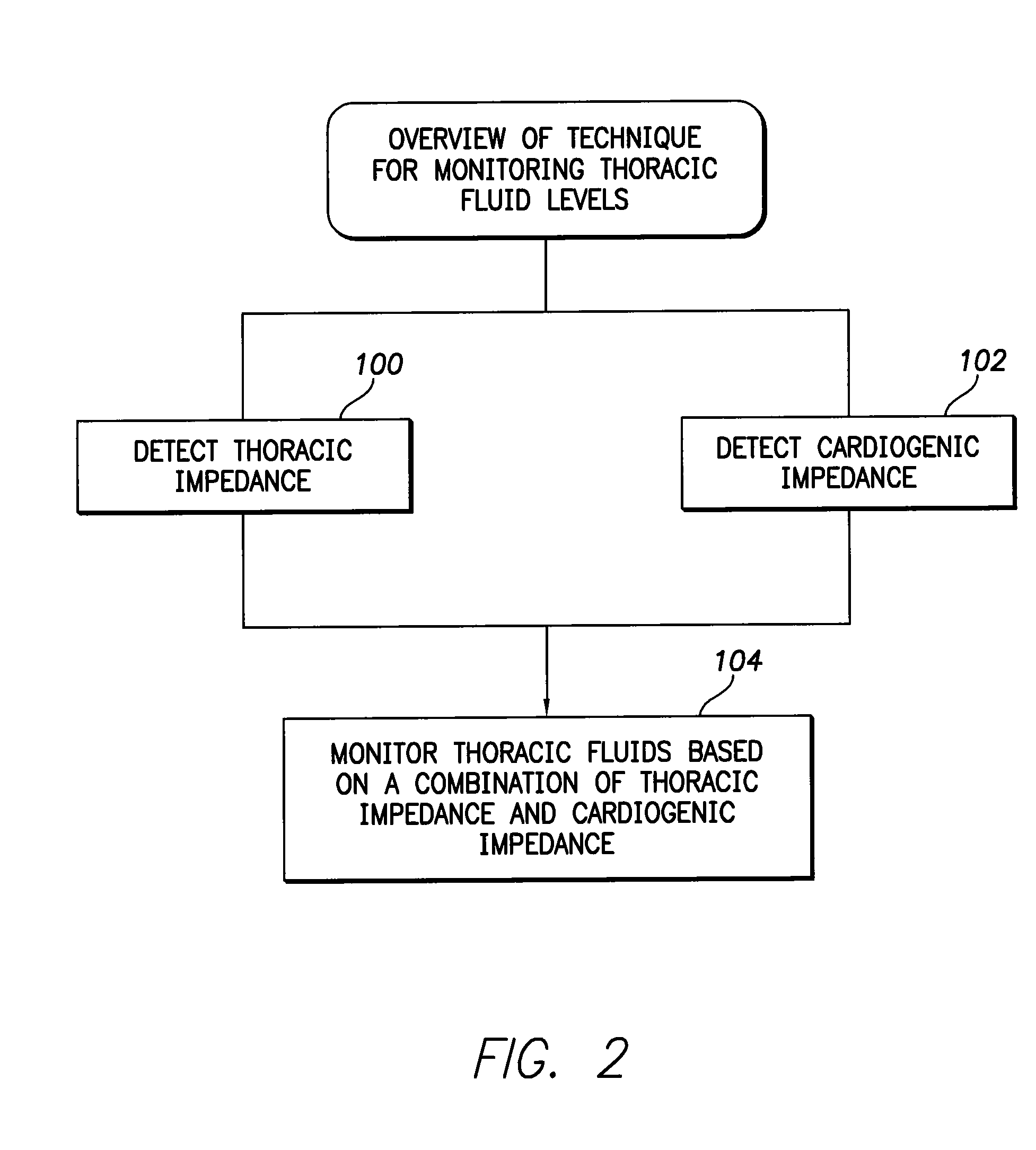
System and method for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on impedance using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS8032212B2Monitored more effectivelyEffective monitoringElectrotherapyCatheterThoracic FluidThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on thoracic impedance (ZT) and cardiogenic impedance (ZC). In one example, the implantable device tracks the maximum time rate of change in cardiogenic impedance (i.e. max(dZC / dt)) to detect trends toward hypervolemic or hypovolemic states within the patient based on changes in heart contractility. The detection of these trends in combination with trends in thoracic impedance allows for a determination of whether the thoracic cavity of the patient is generally “too wet” or “too dry,” and thus allows for the titration of diuretics to avoid such extremes. In particular, a decrease in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too wet” (i.e. a fluid overload). Conversely, an increase in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too dry” (i.e. a fluid underload).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Necklace-shaped physiological monitor
InactiveUS20140235979A1Patient compliance is goodEasy to wearCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationAccelerometerThoracic Fluid
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor (referred to herein as the ‘necklace’) that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the necklace can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:TOSENSE
System and method for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on impedance using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20100069778A1Avoid problemsExcellent stateElectrotherapyCatheterThoracic FluidThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on thoracic impedance (ZT) and cardiogenic impedance (ZC). In one example, the implantable device tracks the maximum time rate of change in cardiogenic impedance (i.e. max(dZC / dt)) to detect trends toward hypervolemic or hypovolemic states within the patient based on changes in heart contractility. The detection of these trends in combination with trends in thoracic impedance allows for a determination of whether the thoracic cavity of the patient is generally “too wet” or “too dry,” and thus allows for the titration of diuretics to avoid such extremes. In particular, a decrease in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too wet” (i.e. a fluid overload). Conversely, an increase in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too dry” (i.e. a fluid underload).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Prediction of thoracic fluid accumulation
This patent document discusses, among other things, systems, devices, and methods for predicting an occurrence of impending thoracic fluid accumulation and in one example, invoking a responsive therapy, such as to prevent or minimize the consequences of the impending thoracic fluid accumulation. One example of the present systems, devices, and methods senses or receives at least one parameter that is statistically associated with impending thoracic fluid accumulation from a subject. Using such parameter(s), a probability of impending thoracic fluid accumulation is estimated. A list of parameters determines which values are recurrently sensed or received at various desired time intervals. Another example of the present systems, devices, and methods weights the sensed or received parameter value(s) to compute the probability estimate of impending thoracic fluid accumulation. A responsive preventive thoracic fluid accumulation therapy or other therapy is selected and activated using the probability estimate of impending thoracic fluid accumulation.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Necklace-shaped physiological monitor
ActiveUS9211073B2Improve calculation accuracyReduce artifactsEvaluation of blood vesselsRespiratory organ evaluationThoracic FluidAccelerometer
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Decongestive therapy titration for heart failure patients using implantable sensor
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Neck-worn physiological monitor
ActiveUS20170172515A1Patient compliance is goodGood repeatabilityElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisAccelerometerThoracic Fluid
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the sensor can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Altering physiological signals based on patient movement
InactiveCN107743374AGood for healthEvaluation of blood vesselsRespiratory organ evaluationThoracic FluidBlood vessel
This document describes ways in which to alter physiological signals to address corrupt, noisy, or otherwise faulty data. By so doing, accuracy and robustness in sensing and assessing a patient's cardiovascular health can be improved. These improved assessments permit better measures of health, such as relevant hemodynamics understood by heart rates, heart rate variability, cardiac arrhythmias, blood pressures, pulse-wave velocities, arterial stiffness, cardiac valve timing, thoracic fluids, ballistocardiogram force, photo-plethysmograms, blood oxygenation, and pressure-volume loops.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Necklace-shaped physiological monitor
ActiveUS10314496B2Improve calculation accuracyReduce artifactsElectrocardiographyCatheterAccelerometerThoracic Fluid
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor (referred to herein as the ‘necklace’) that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the necklace can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Necklace-shaped physiological monitor
InactiveUS20140236027A1Patient compliance is goodEasy to wearCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationAccelerometerThoracic Fluid
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor (referred to herein as the ‘necklace’) that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the necklace can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:TOSENSE
Neck-worn physiological monitor
InactiveUS20170172427A1Patient compliance is goodGood repeatabilityElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationAccelerometerThoracic Fluid
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the sensor can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Neck-worn physiological monitor
ActiveUS20170172517A1Patient compliance is goodGood repeatabilityElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationThoracic FluidAccelerometer
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the sensor can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Neck-worn physiological monitor
InactiveUS20170172423A1Patient compliance is goodGood repeatabilityPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationAccelerometerThoracic Fluid
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the sensor can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:TOSENSE
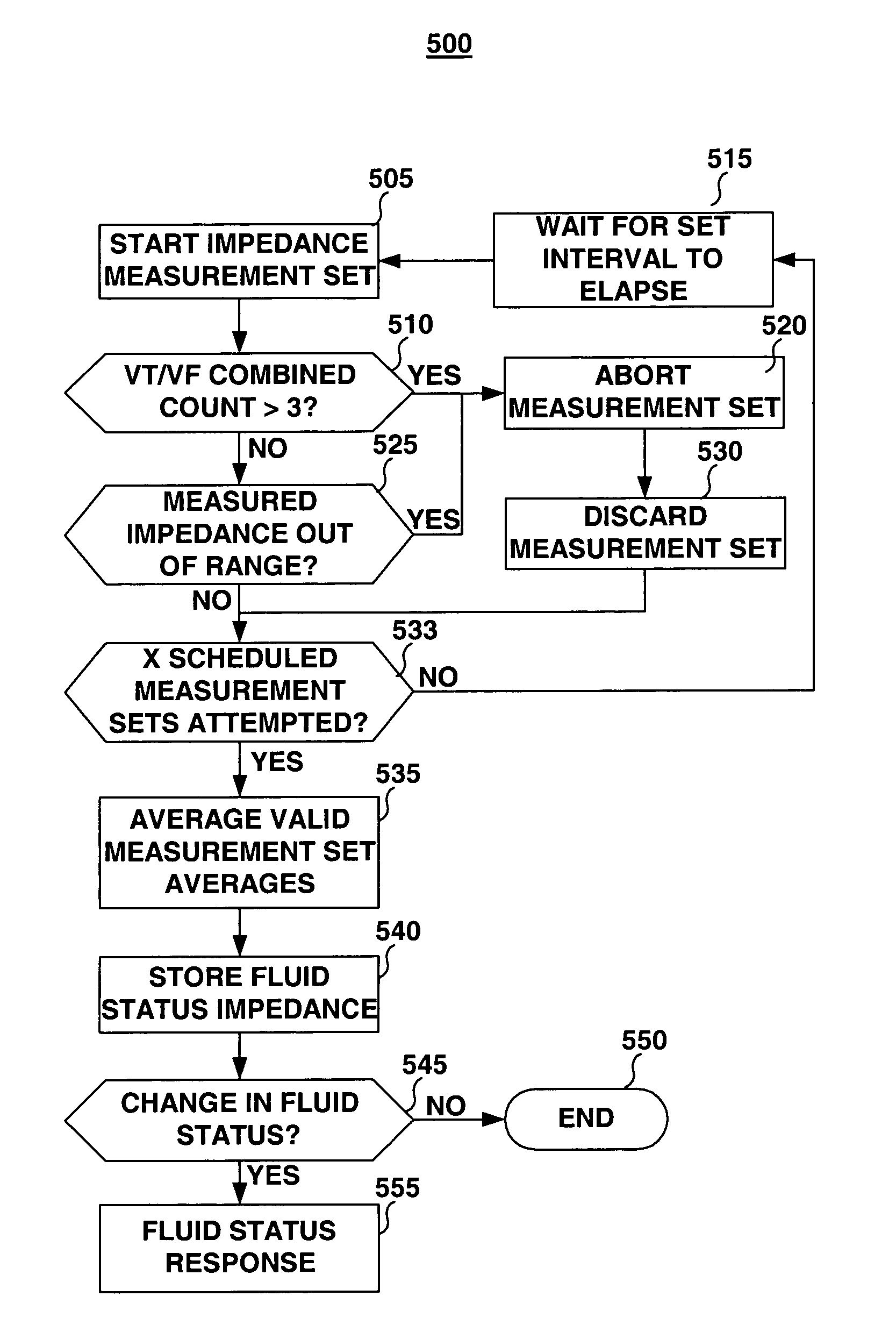
Method and apparatus for monitoring tissue fluid content for use in an implantable cardiac device
ActiveUS8428717B2Easy to implementHigh resolutionHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsThoracic FluidTissue fluid
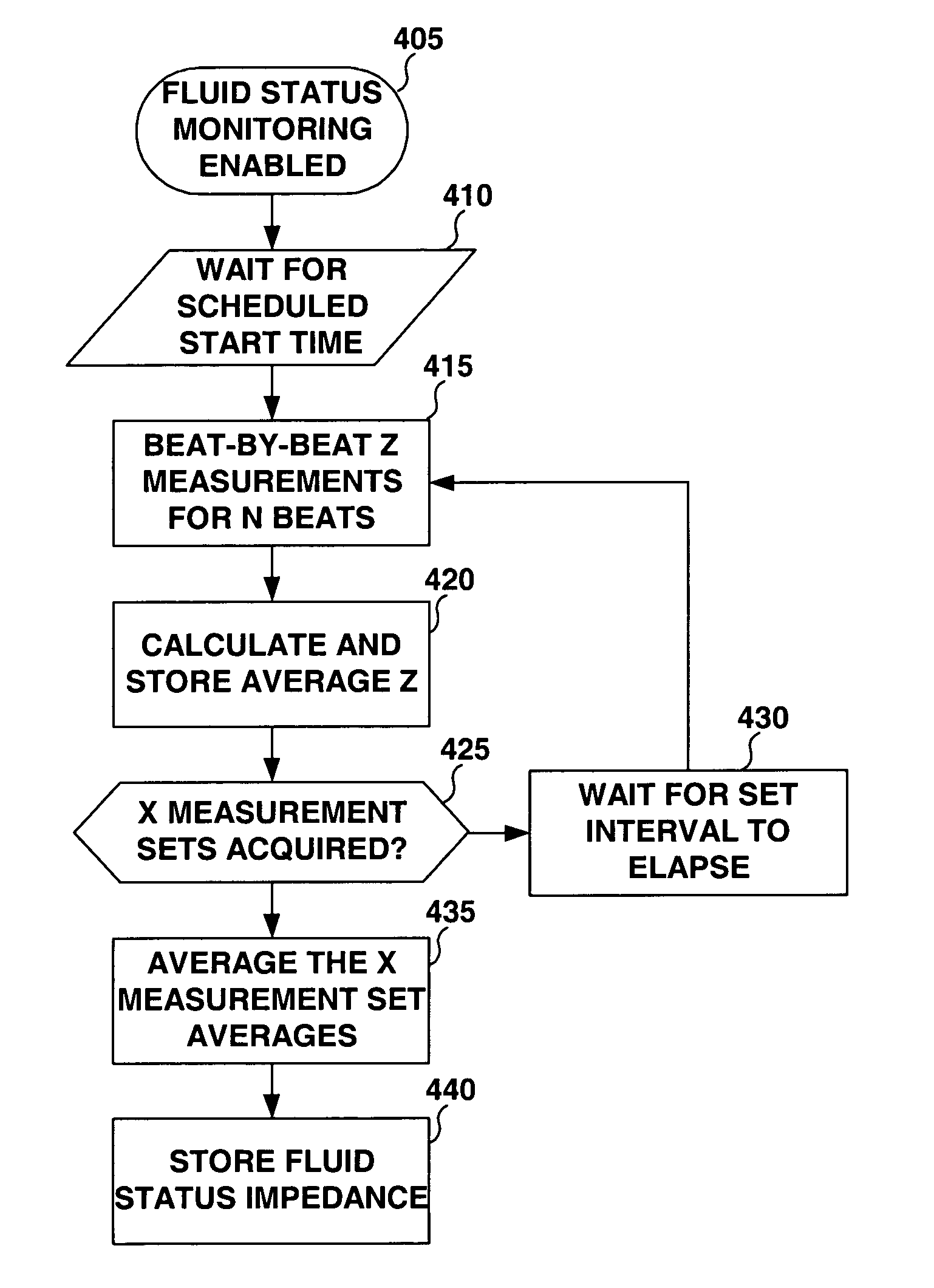
A fluid status monitoring system for use in implantable cardiac stimulation or monitoring devices is provided for monitoring changes in thoracic fluid content. A fluid status monitor includes excitation pulse generating and control circuitry, and voltage and current measurement and control circuitry for performing a series of cardiac-gated, intra-thoracic impedance measurements. The cardiac-gated measurements are filtered or time-averaged to provide a fluid status impedance value, with respiratory noise removed. Based on comparative analysis of the fluid status impedance value, a clinically relevant trend in fluid status may be tentatively diagnosed and a fluid status response provided. Cross-check intra-thoracic impedance measurements performed using the same or a different excitation pathway and a different measurement pathway than the primary intra-thoracic impedance measurement configuration may be used to verify a tentative diagnosis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
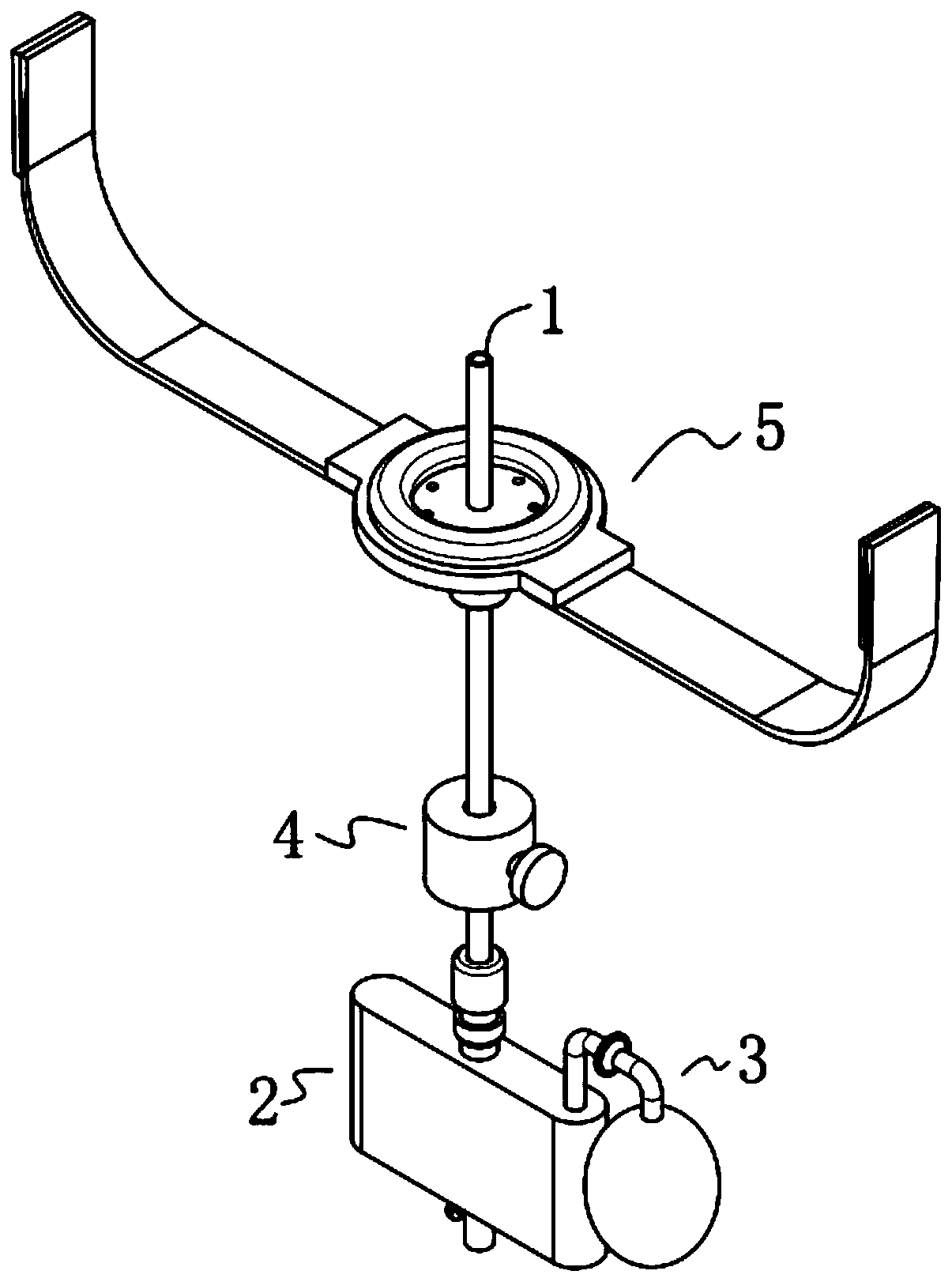
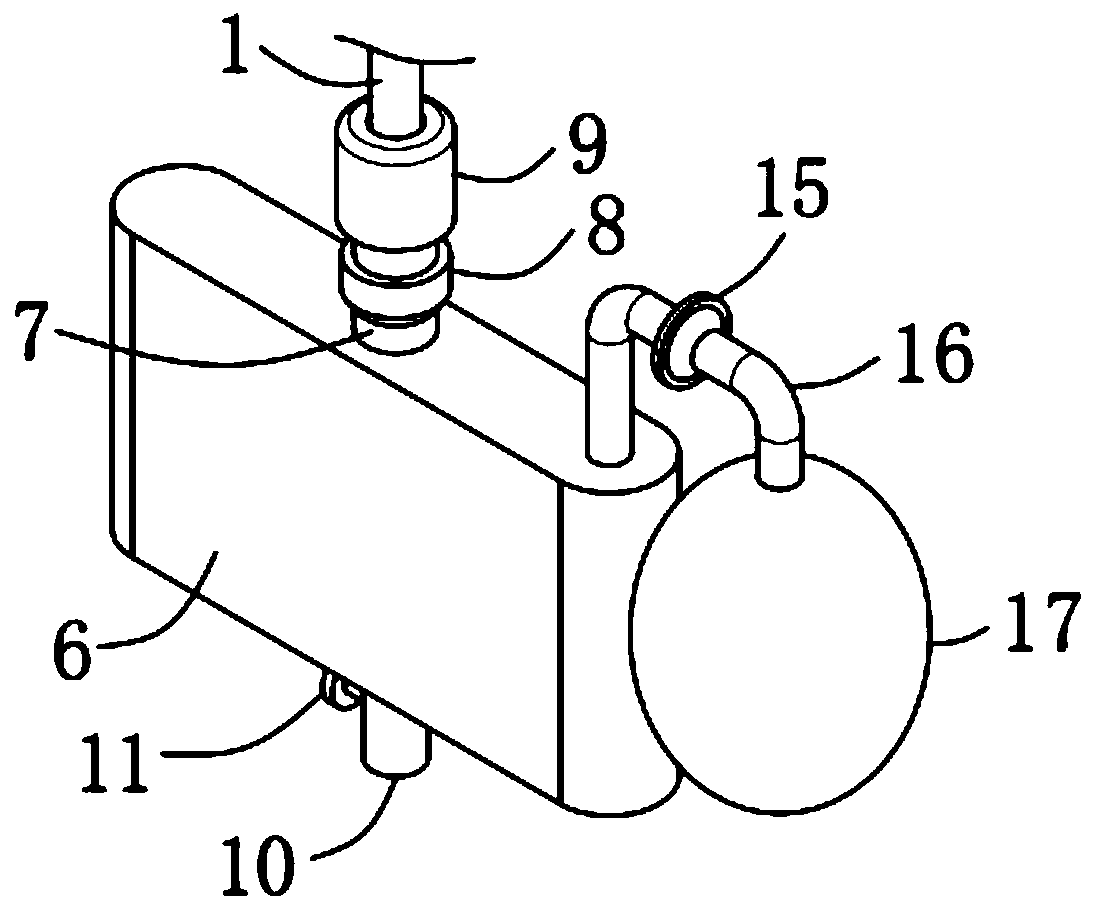
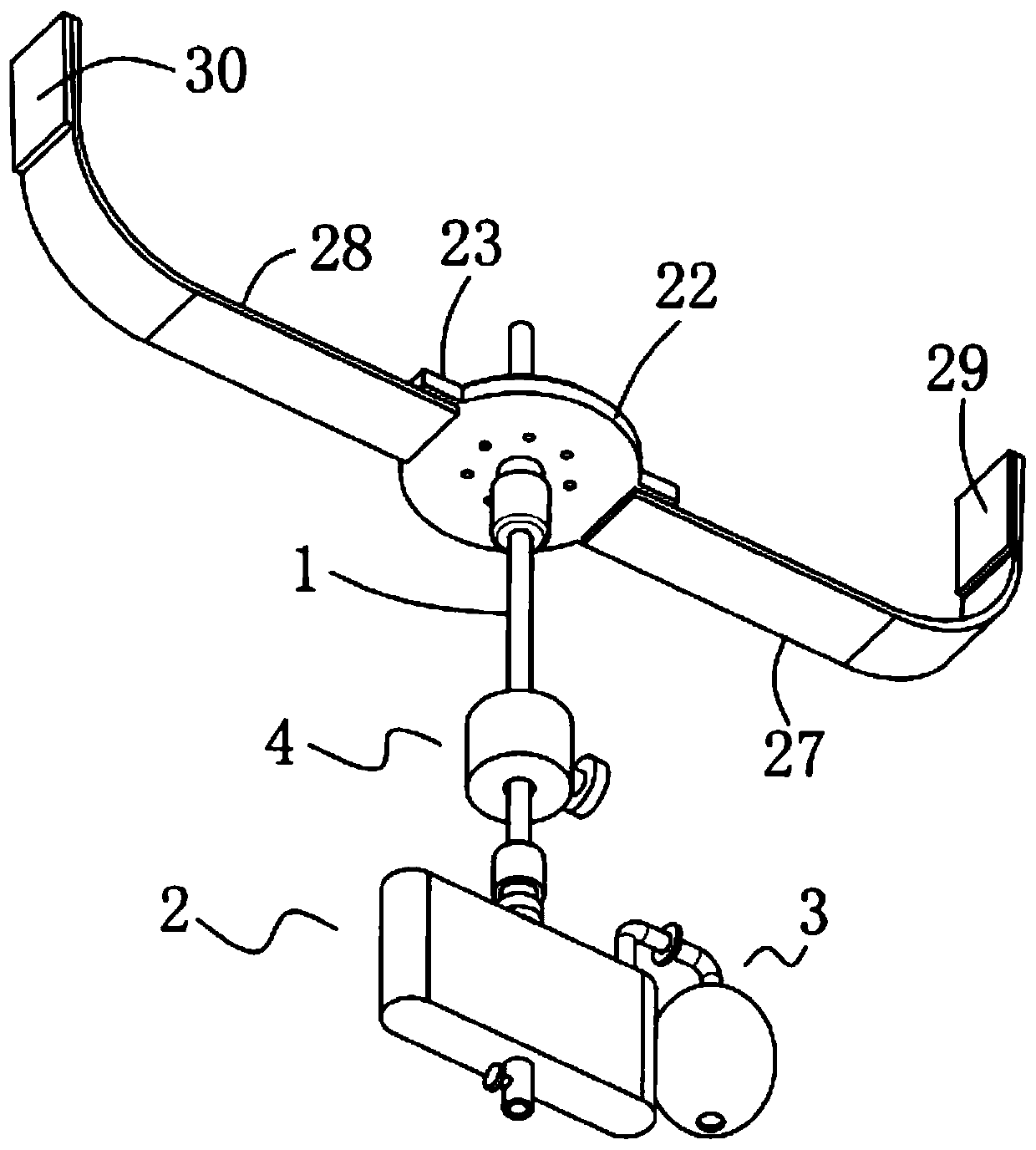
Thin-catheter closed type chest fluid drainage device
InactiveCN110772674AInhibit sheddingGuarantee the safety of lifeAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesThoracic FluidCatheter
The invention discloses a thin-catheter closed type chest fluid drainage device, which comprises a drainage thin catheter, a fluid storage unit, a negative pressure generation unit, a catheter switchand a fixing unit, wherein two ends of the drainage thin catheter are both opening ends; the fluid storage unit is in communication installation on one end of the drainage thin catheter; the negativepressure generation unit and the fluid storage unit are in communication connection; the catheter switch and the fixing unit are both sheathed out of the drainage thin catheter; in addition, the catheter switch is positioned between the fixing unit and the fluid storage unit; and one end, which is far away from the fluid storage unit, of the drainage thin catheter is a free end. By use of the thin-catheter closed type chest fluid drainage device, negative pressure suction is used so as to be favorable for successfully draining and discharging hydrops in the chest of a patient, a drainage effect is good, a treatment effect is effectively guaranteed, the drainage thin catheter can be prevented from falling from the chest of the patient, the life safety of the patient is effectively guaranteed, a prepared protection layer can avoid a situation that a great quantity of bacteria is bred on the inner surface and the outer surface of a fluid storage bottle to generate peculiar smells, and a use sanitary condition is good.
Owner:THE FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF CHANGZHOU
Necklace-shaped physiological monitor
ActiveUS20140235978A1Patient compliance is goodEasy to wearDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsThoracic FluidAccelerometer
The invention provides a neck-worn sensor (referred to herein as the ‘necklace’) that is a single, body-worn system that measures the following parameters from an ambulatory patient: heart rate, pulse rate, pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, thoracic fluid levels, stroke volume, cardiac output, and a parameter sensitive to blood pressure called pulse transit time. From stroke volume, a first algorithm employing a linear model can estimate the patient's pulse pressure. And from pulse pressure and pulse transit time, a second algorithm, also employing a linear algorithm, can estimate systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, the necklace can measure all five vital signs along with hemodynamic parameters. It also includes a motion-detecting accelerometer, from which it can determine motion-related parameters such as posture, degree of motion, activity level, respiratory-induced heaving of the chest, and falls.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
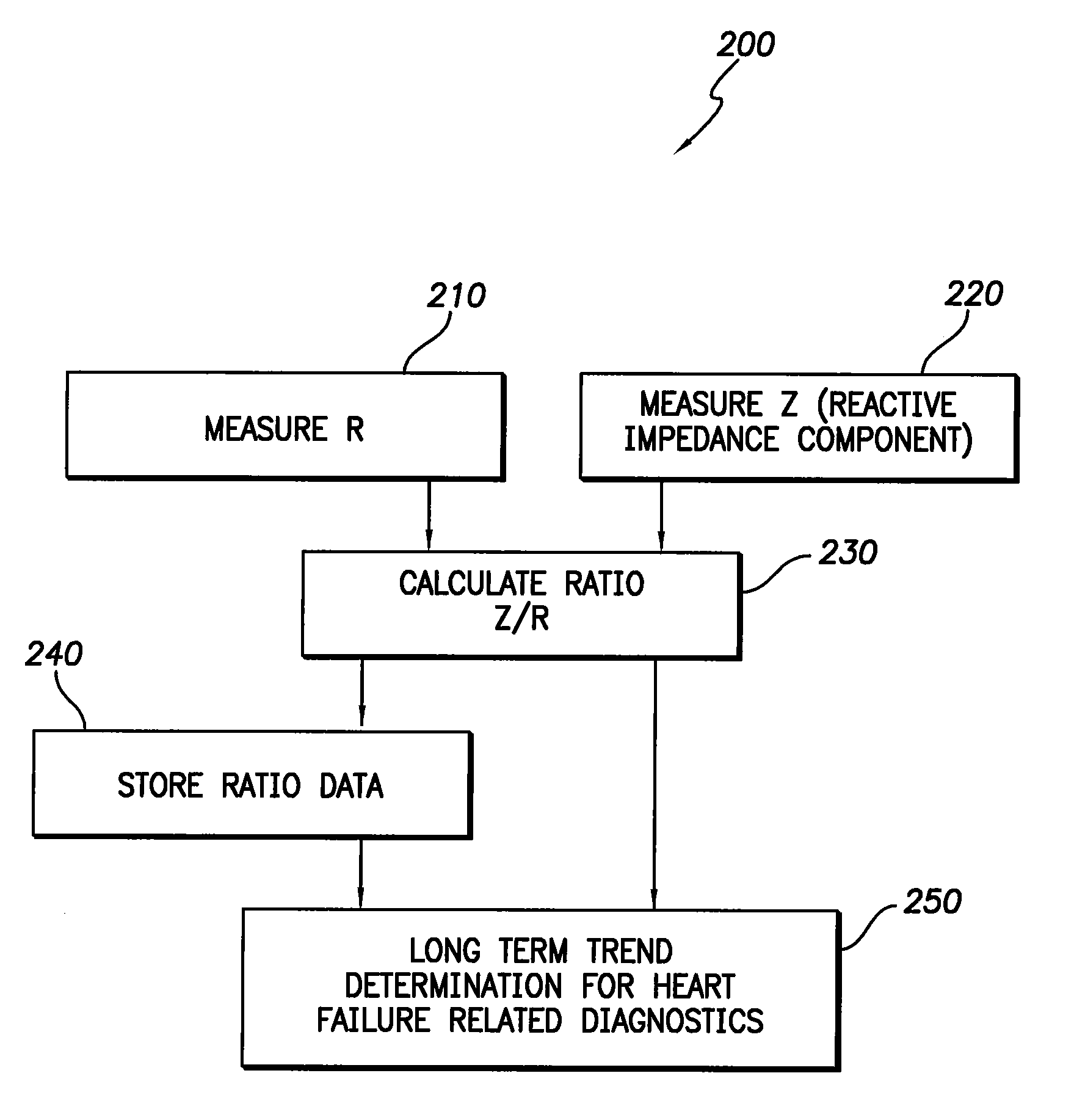
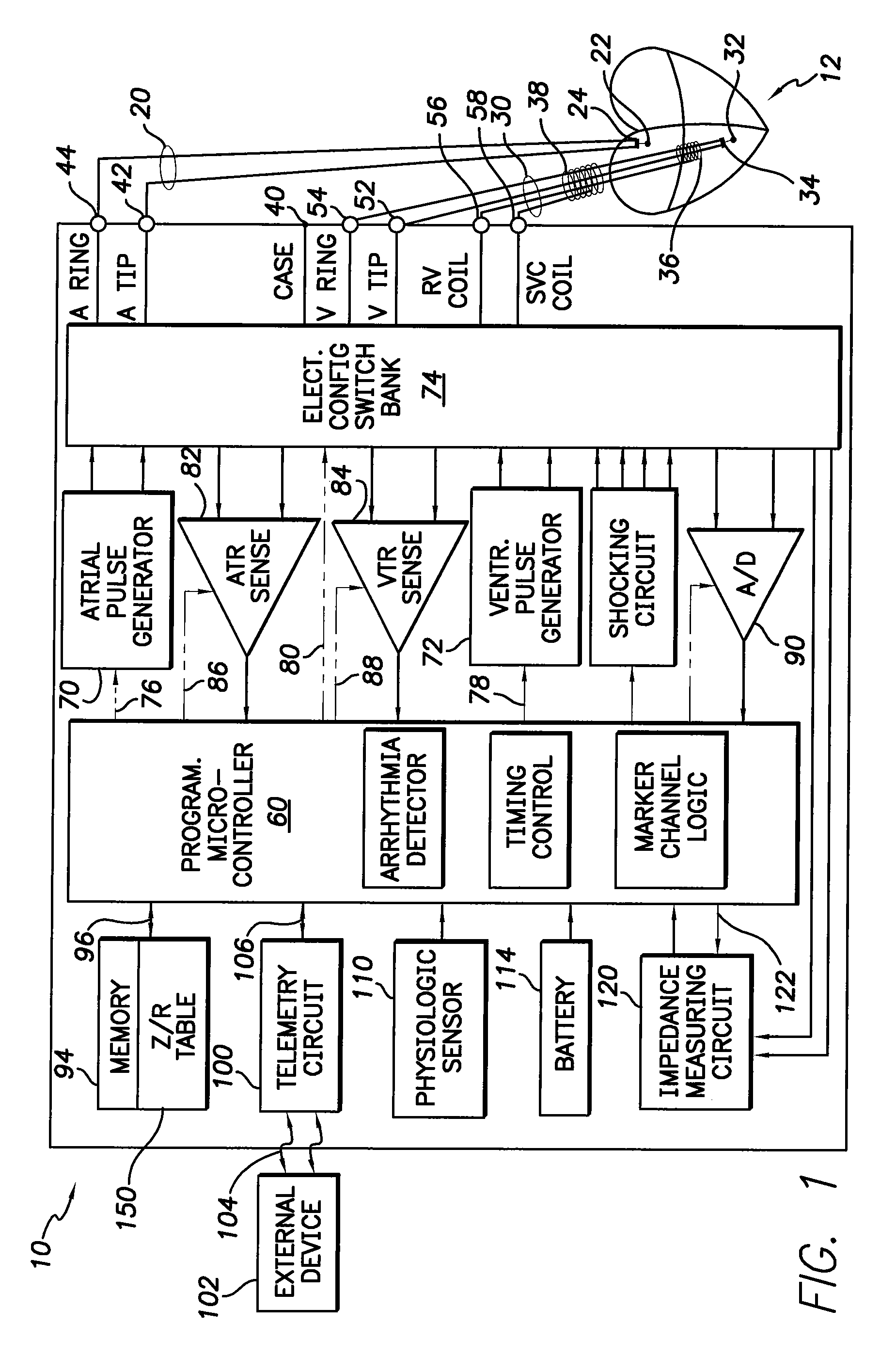
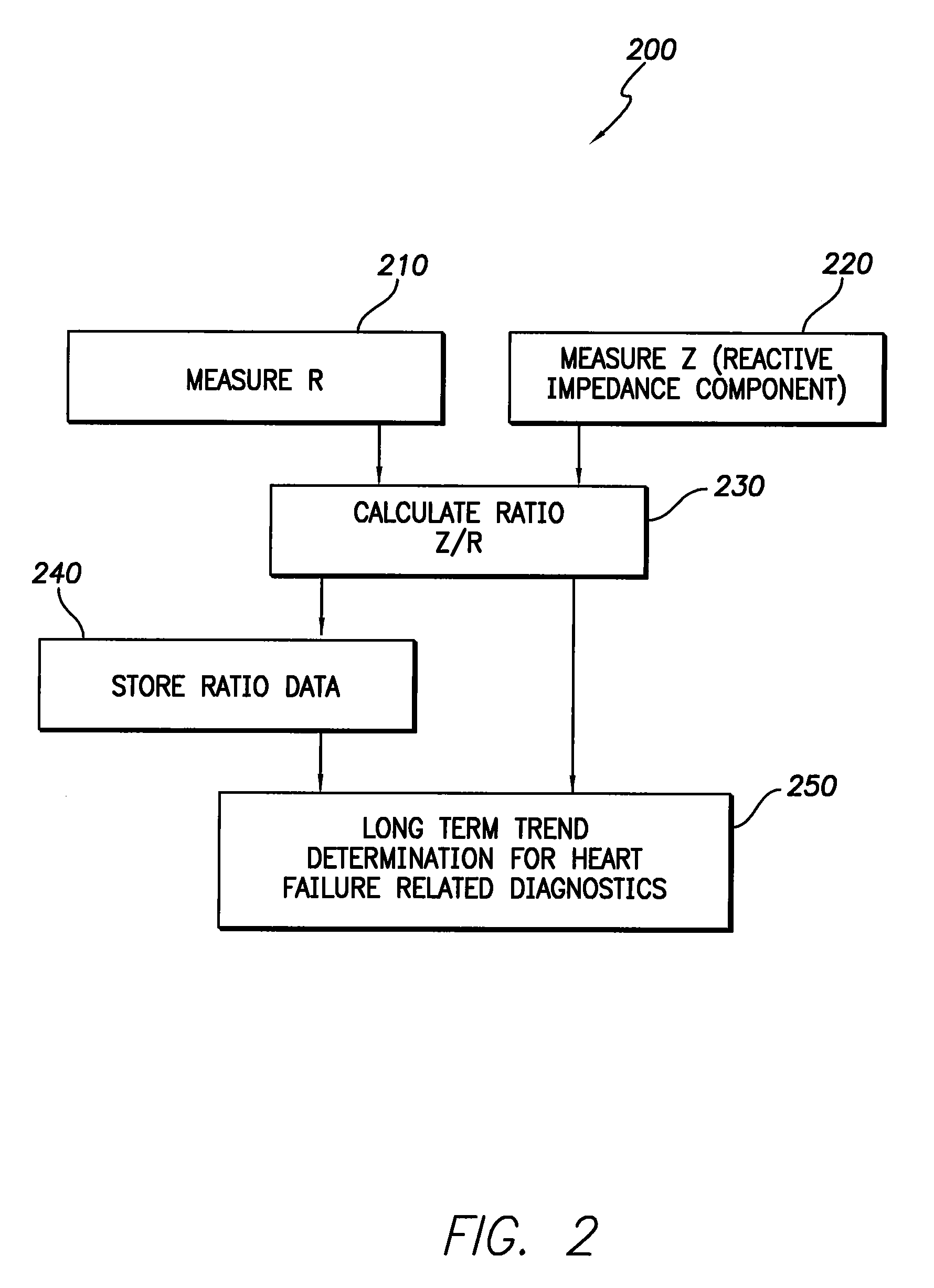
Apparatus and method for two-component bioelectrical impedance ratio measuring and monitoring
InactiveUS7596411B1Reduce and eliminate negative impactRemove Motion ArtifactsElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical resistance and conductanceMicrocontroller
An implantable cardiac stimulation and rhythm management device includes an impedance measuring circuit which determines a patient's intra-thoracic impedance and the resistance and reactance components of the impedance. The device includes a microcontroller which calculates a ratio (Z / R) which equals the reactance (Z) divided by the resistance (R). The microcontroller is configured to use the calculated ratios to establish a baseline intra-thoracic fluid level, an upper bound relative to the baseline, and a lower bound relative to the baseline, and to monitor the Z / R ratio relative to the baseline and upper and lower bounds. When the Z / R ratios are outside of the established bounds, operating parameters of the stimulation and rhythm management may be altered by the microcontroller.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com