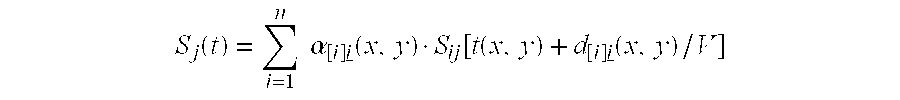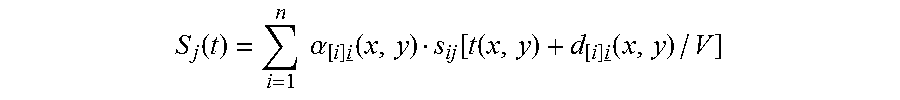Patents
Literature
48 results about "Heart contractility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
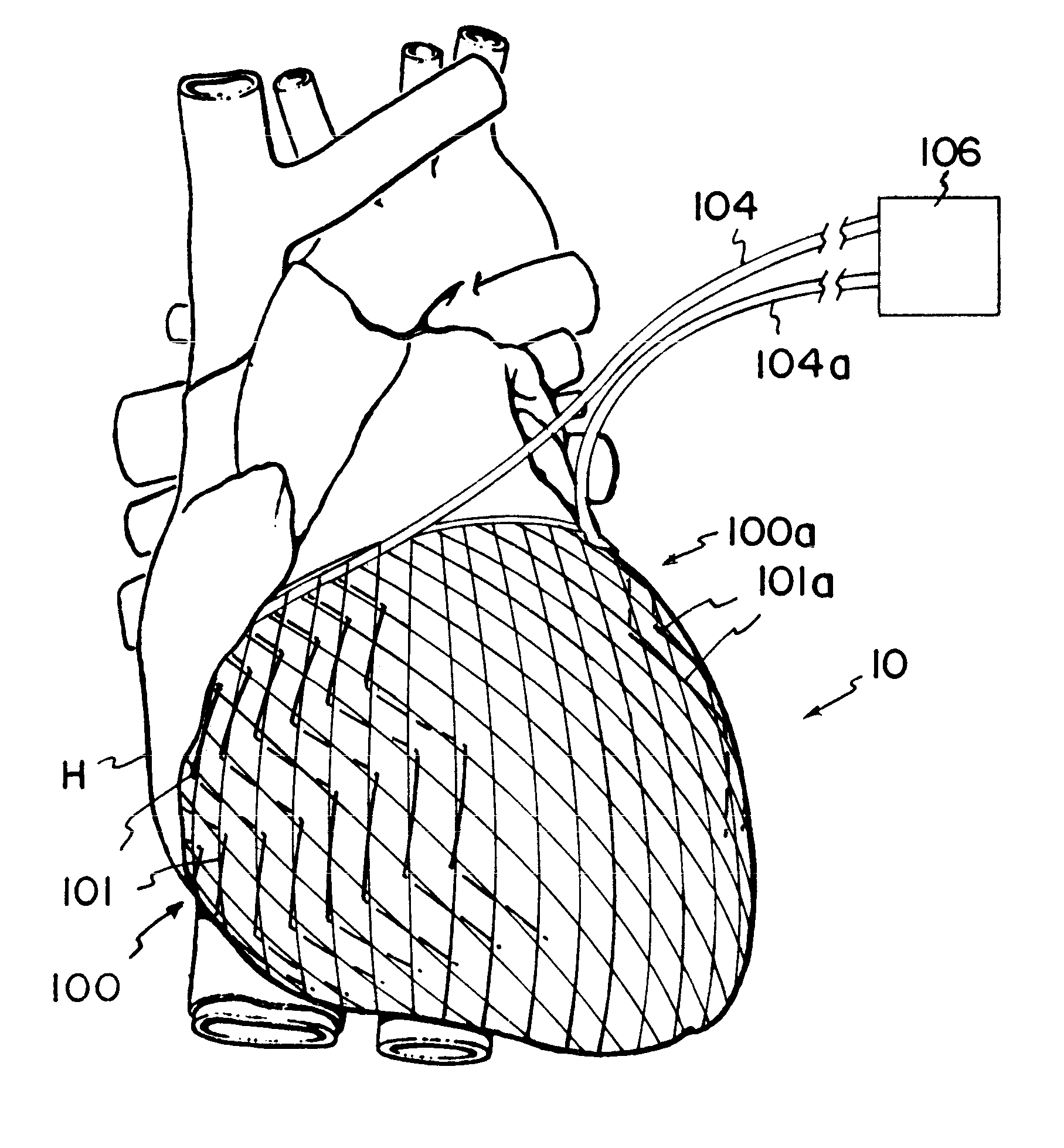
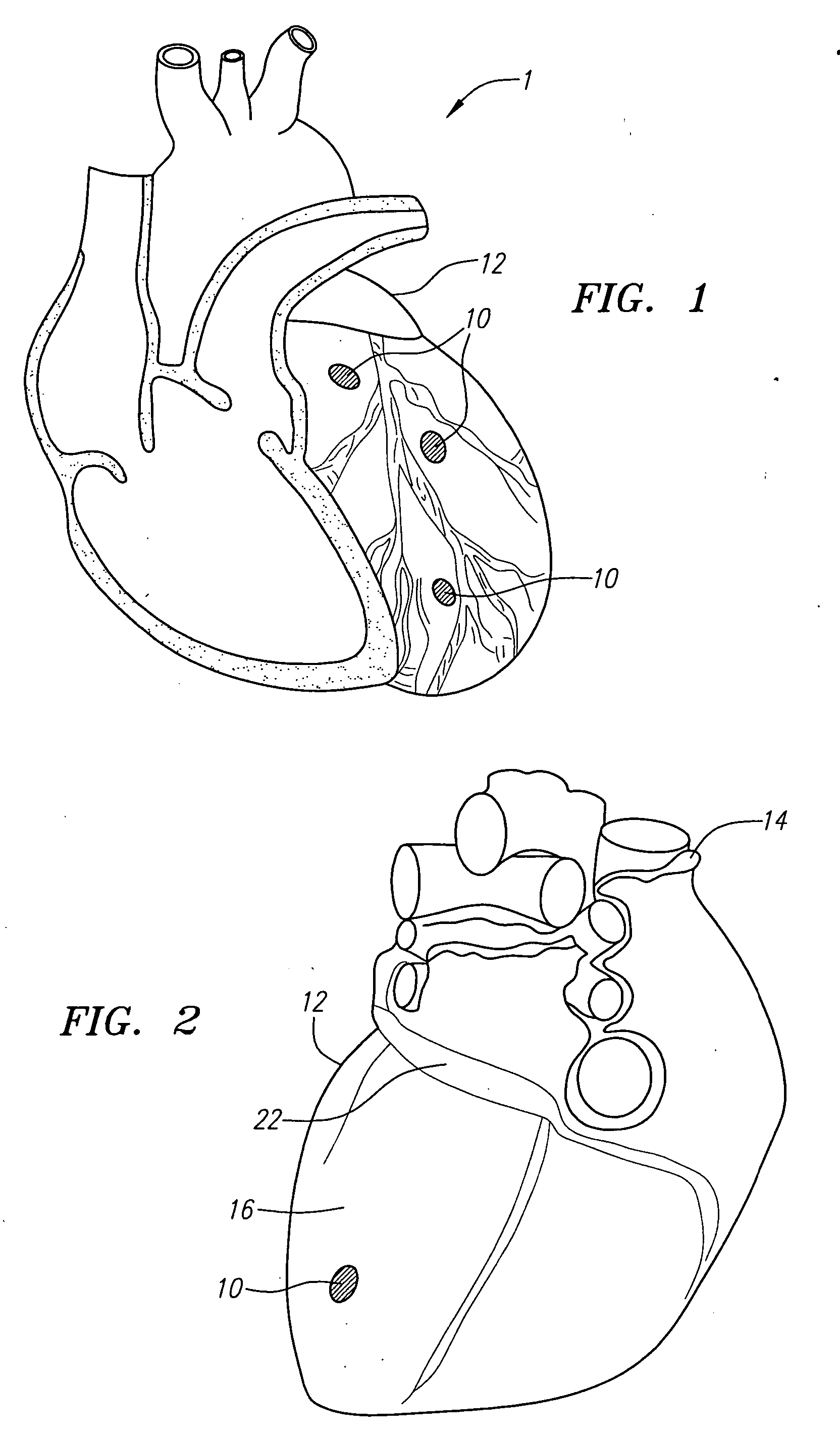
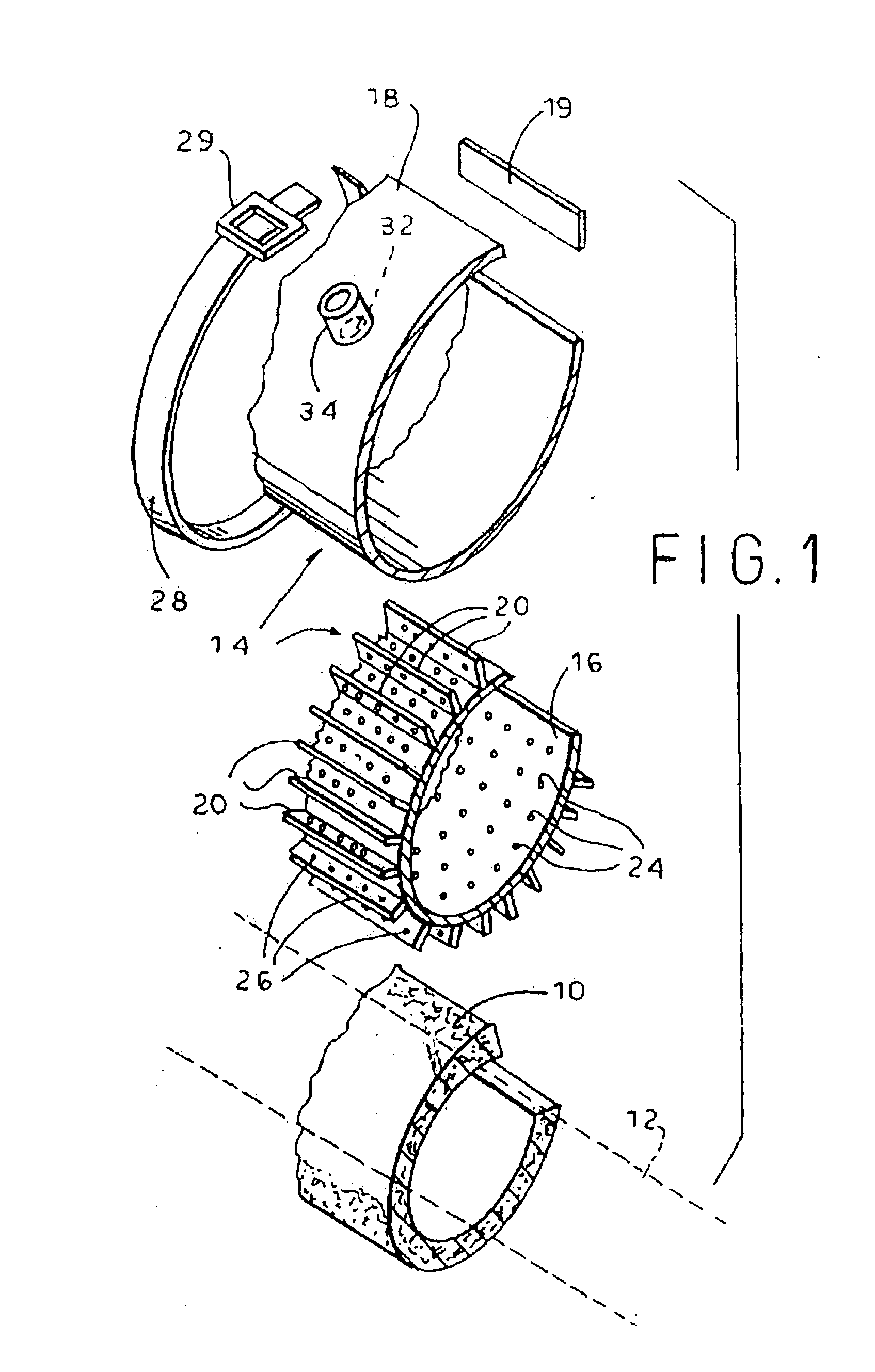
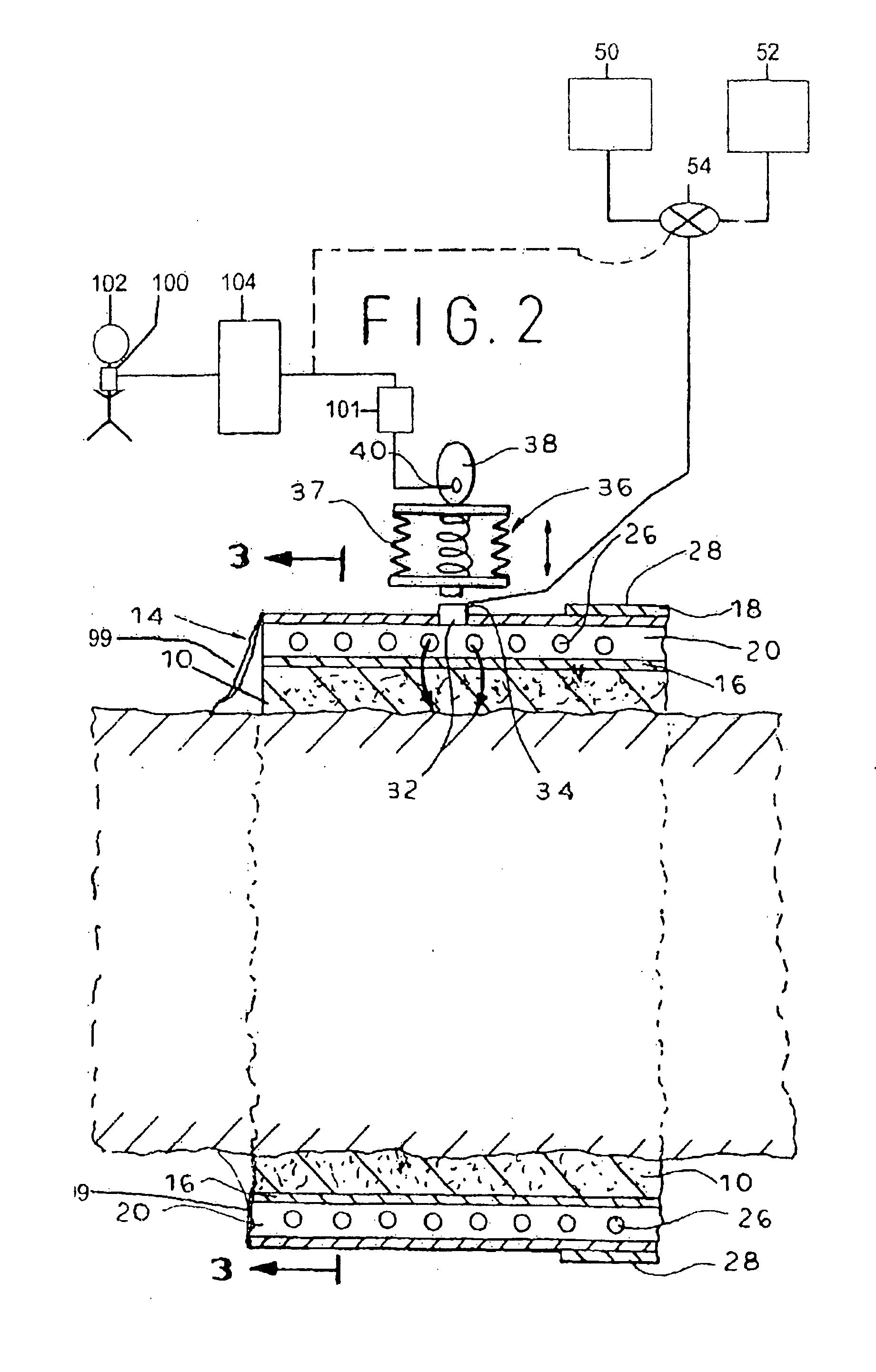
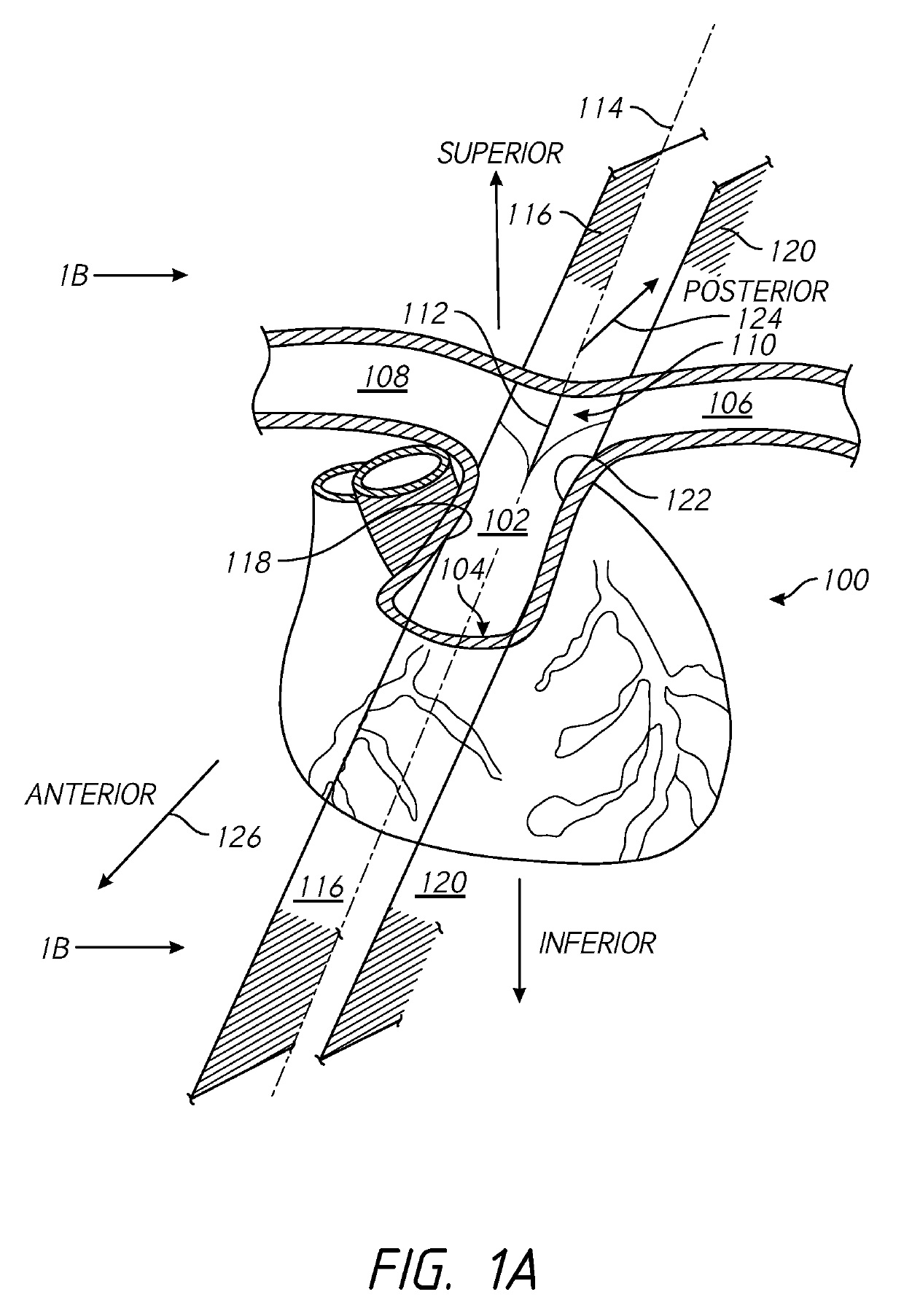
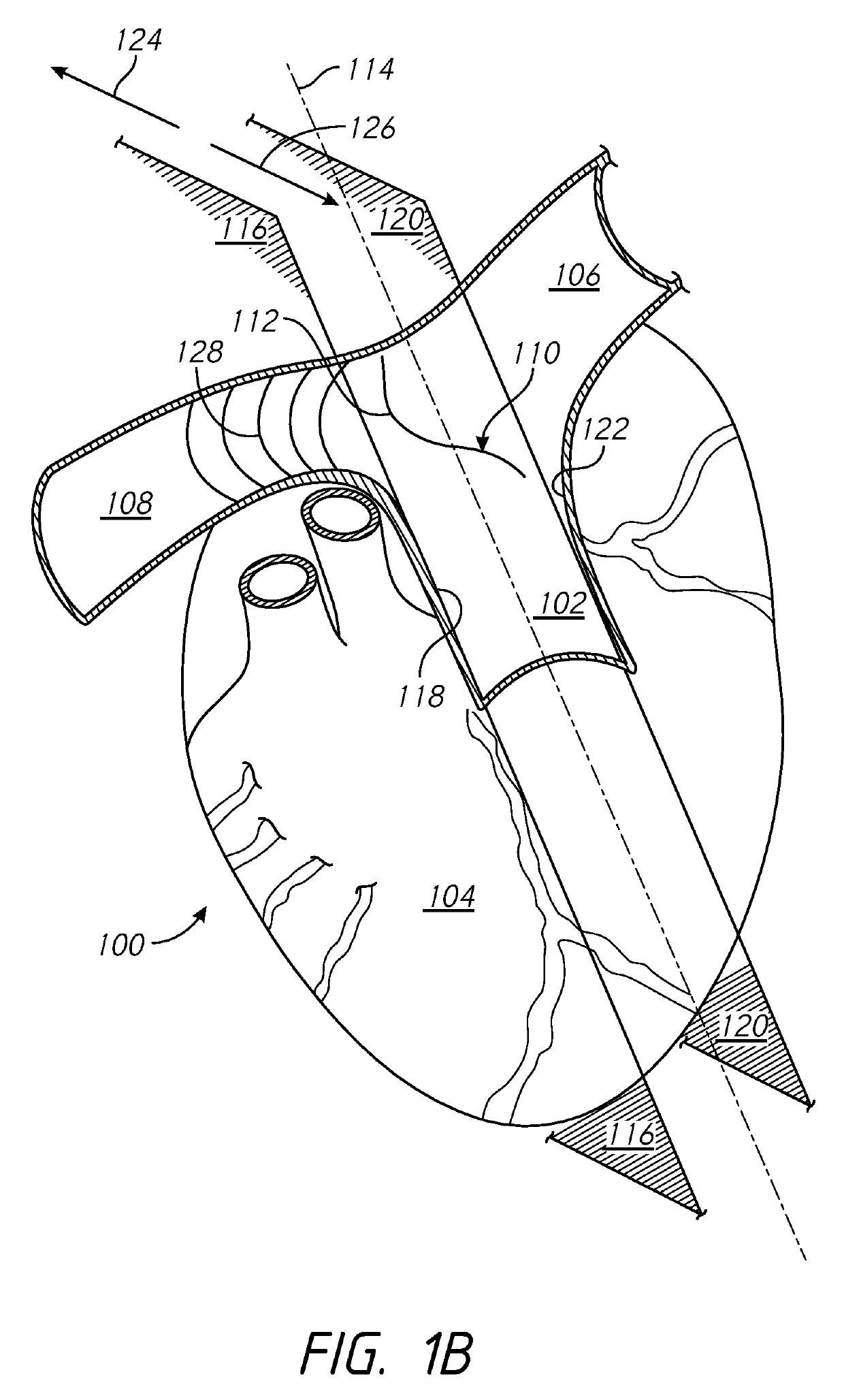
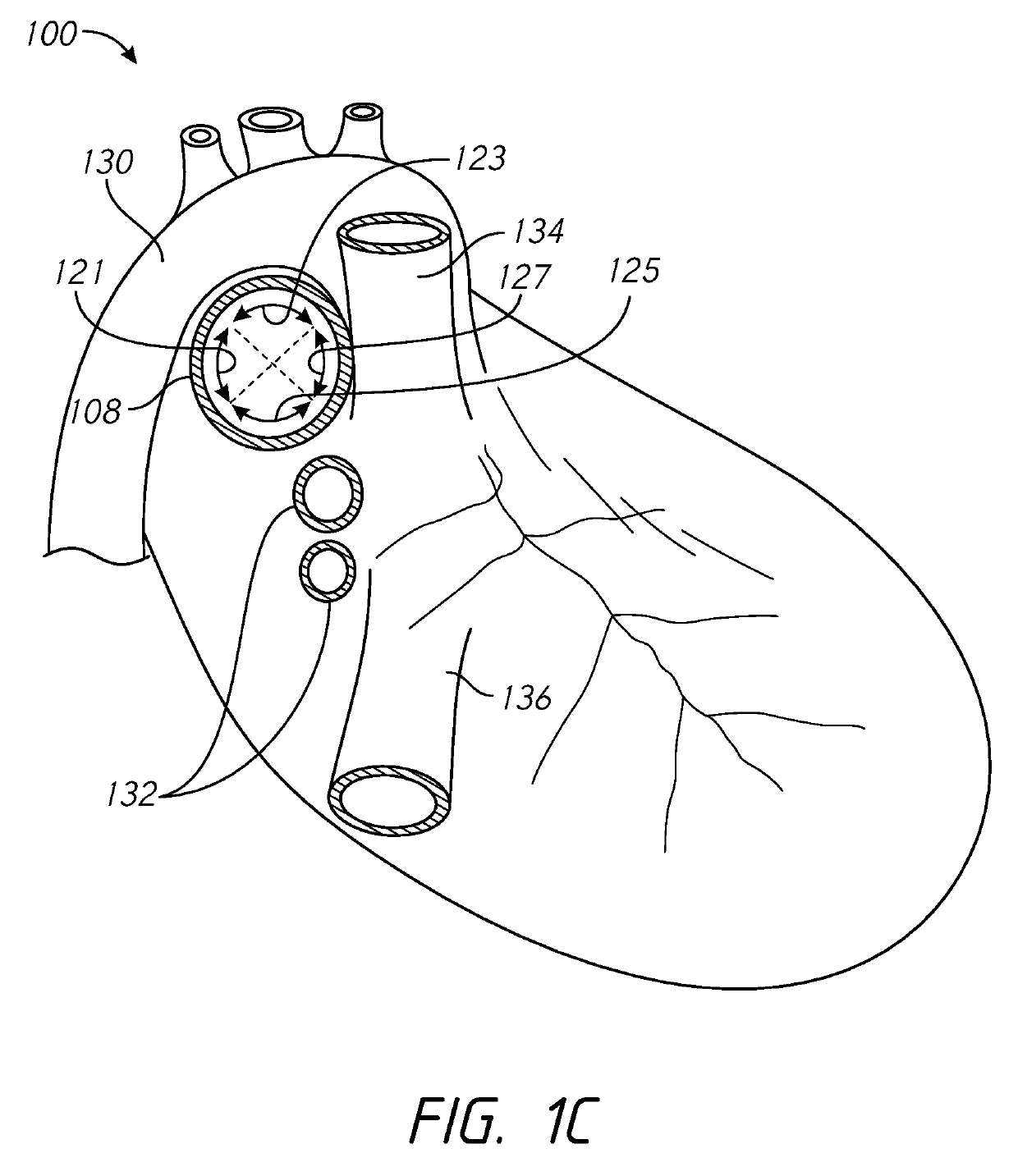
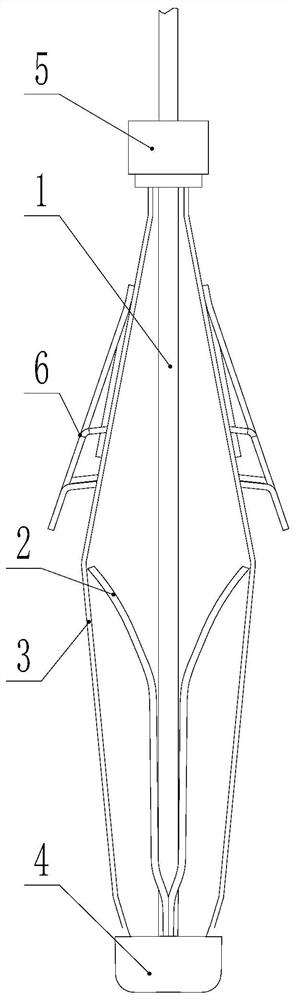
Defibrillating cardiac constraint
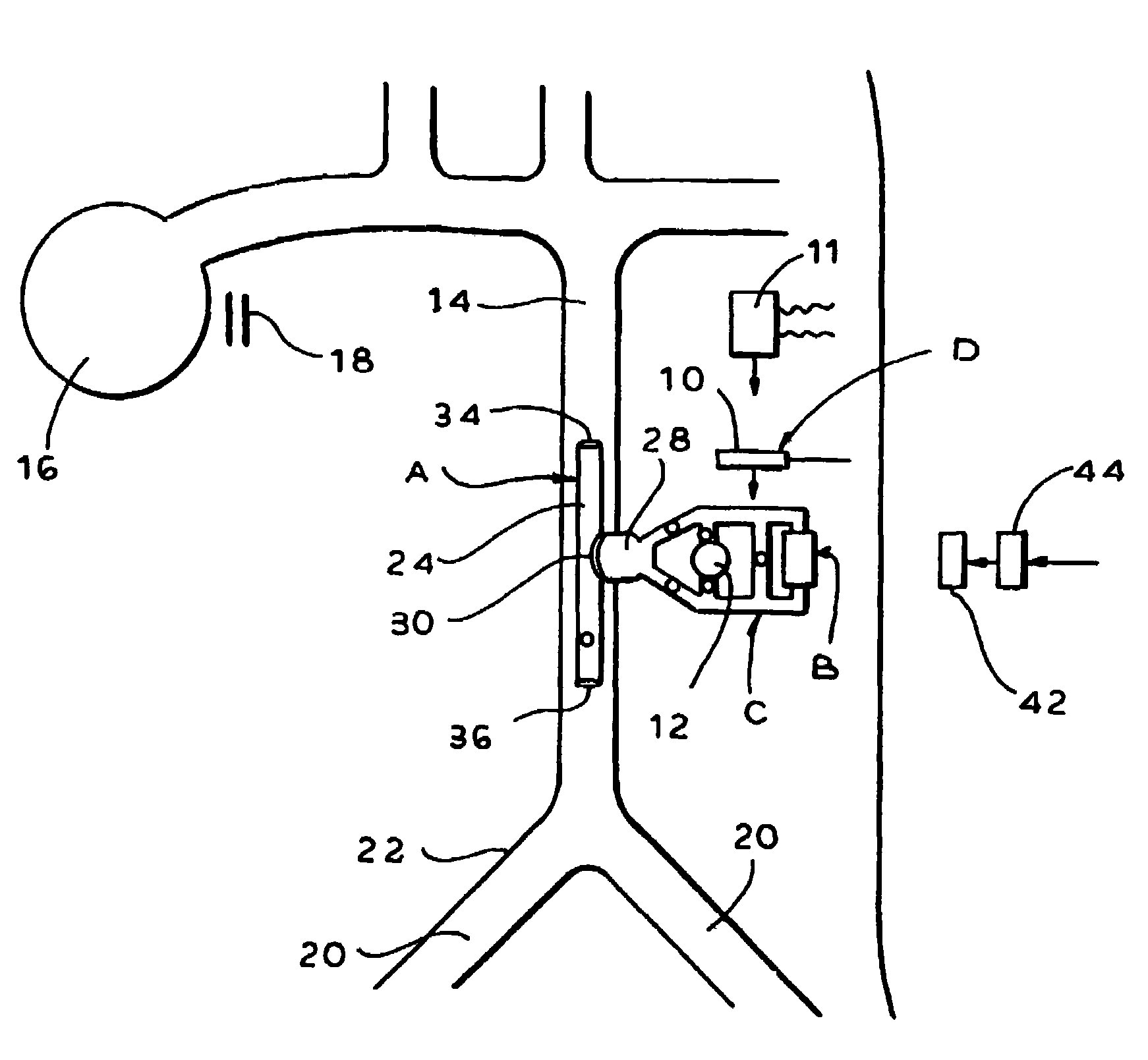
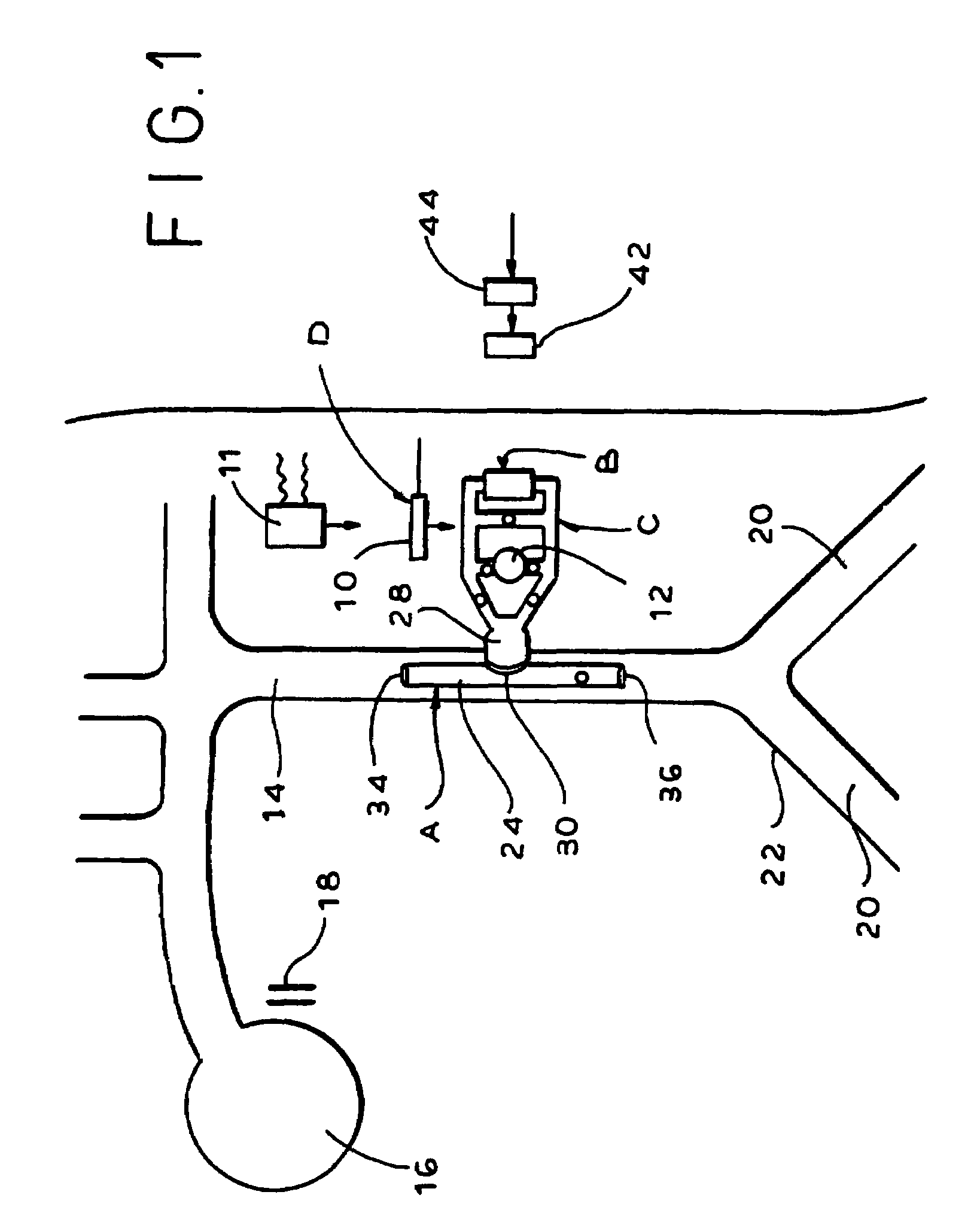
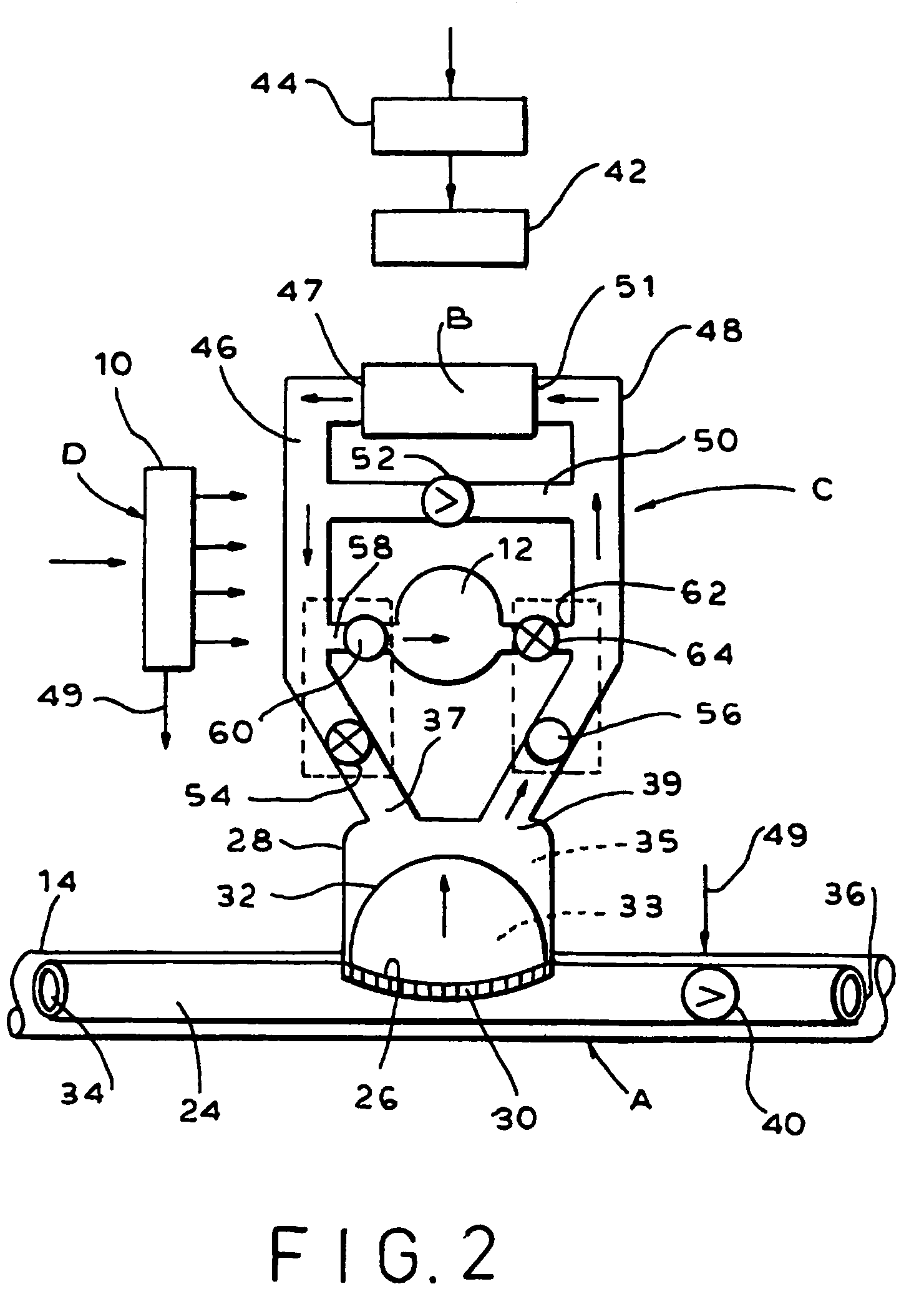
A device for treating cardiac disease of a heart includes a jacket of flexible material defining a volume between an open upper end and a lower end. The jacket is dimensioned for an apex of the heart to be inserted into the volume through the open upper end and for the jacket to be slipped over the heart. The jacket is adapted to be secured to the heart with the jacket having portions disposed on opposite sides of the heart. The jacket is adjustable to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and to constrain circumferential expansion of the heart during diastole and permit substantially unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole. A first and a second grid of electrodes are carried on the jacket. The grids are disposed to be in overlying relation to individual ones of the opposite sides of the heart when the jacket is secured to the heart. The first and second grids are connectable to a source of a defibrillating waveform.
Owner:MARDIL
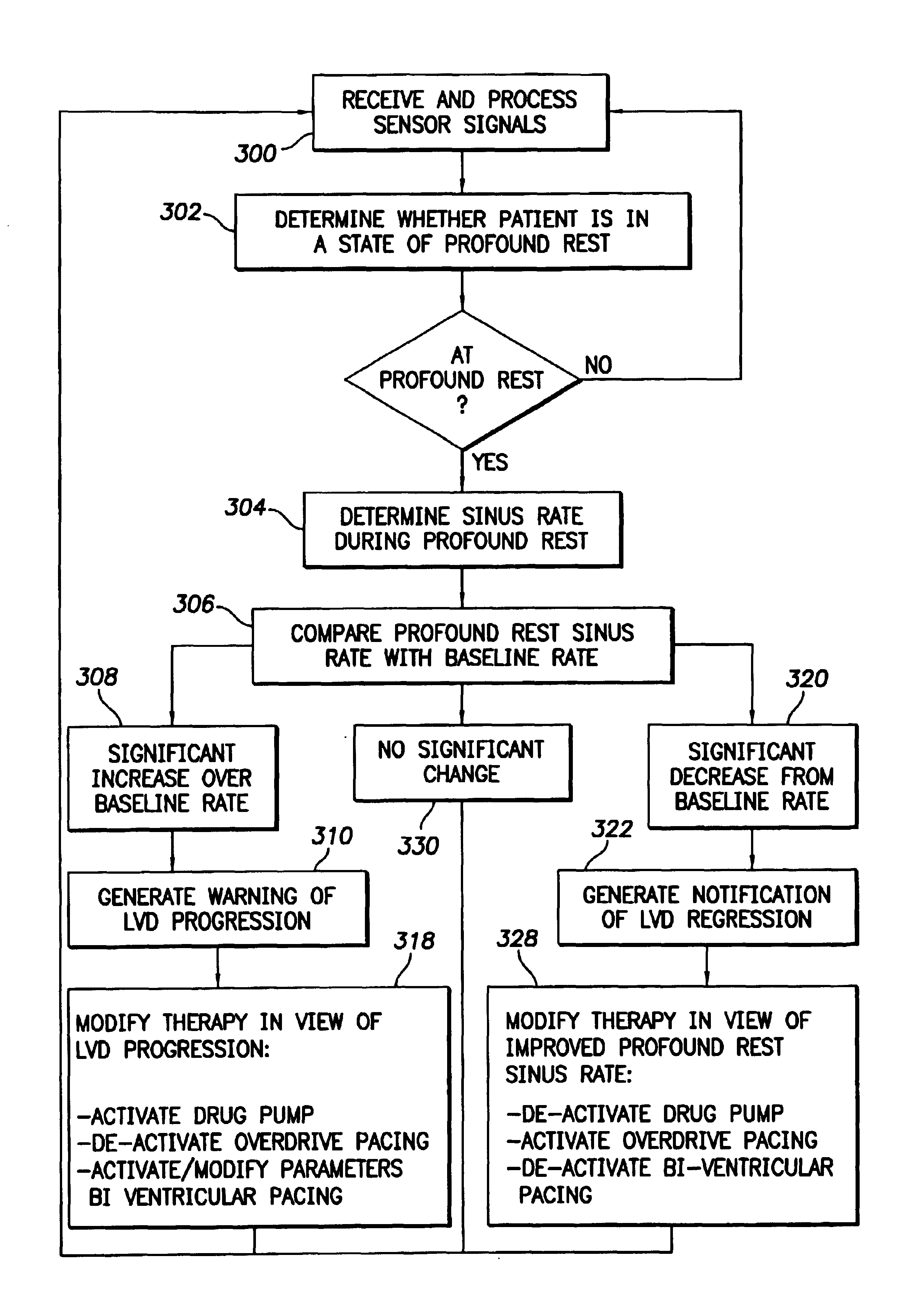
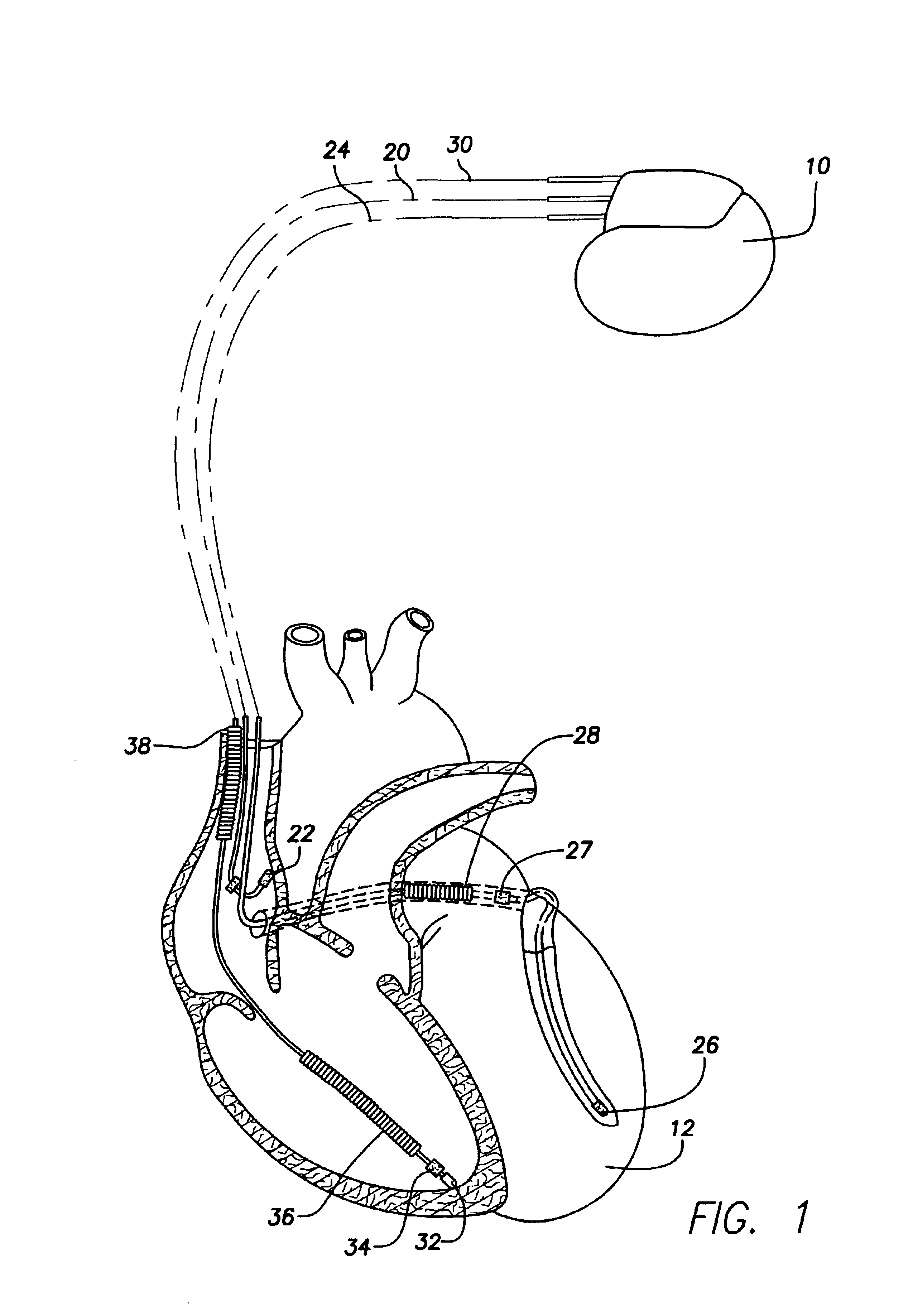
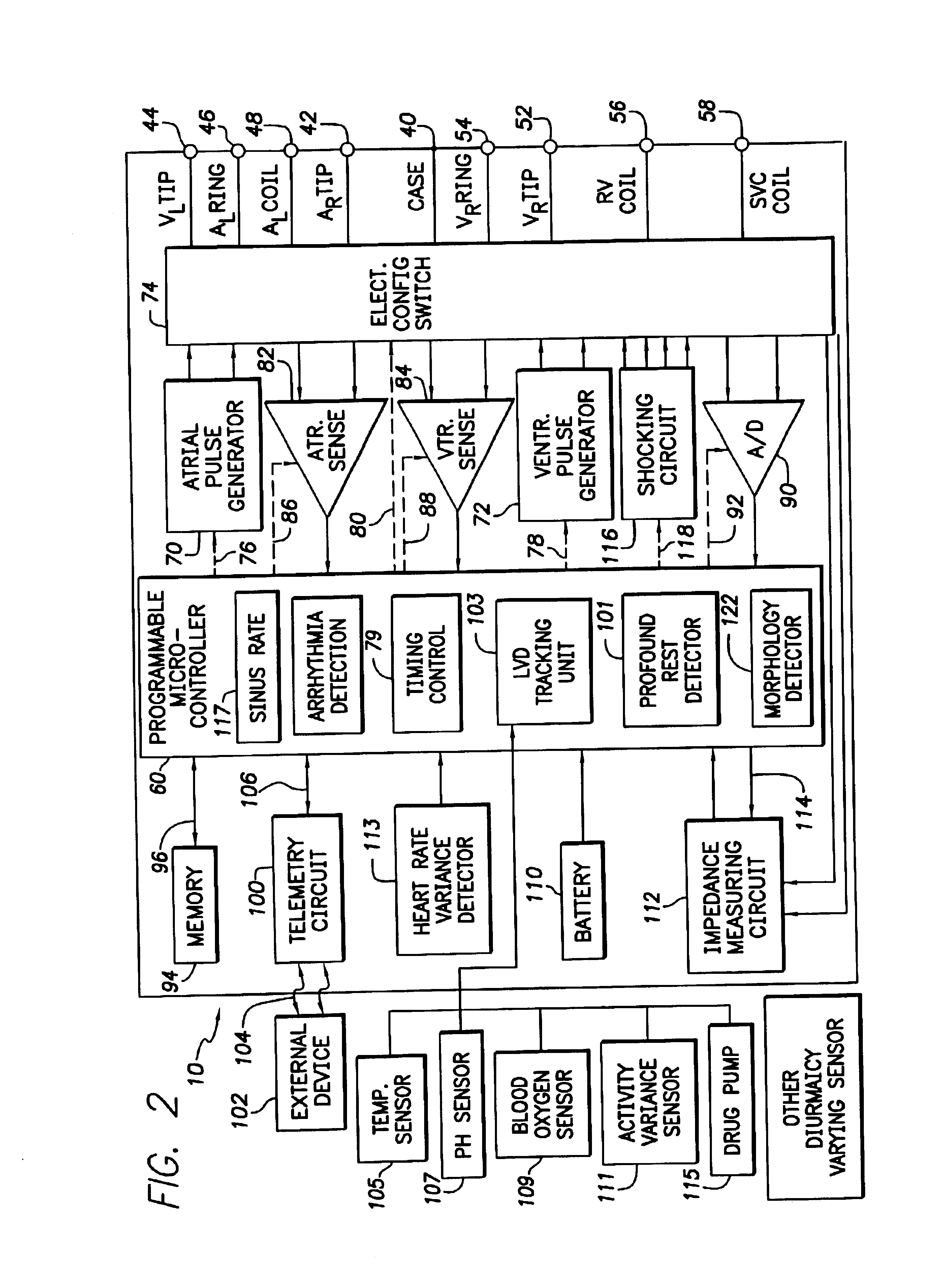
System and method for tracking progression of left ventricular dysfunction using implantable cardiac stimulation device
InactiveUS6922587B2Accurate and reliable assessmentAlter heart contractilityHeart stimulatorsPost extrasystolic potentiationCardiac pacemaker electrode
The progression or regression of left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) is automatically evaluated by a pacemaker or other implantable cardiac stimulation device by tracking changes in the resting sinus rate of the patient in which the device is implanted. The resting sinus rate is detected by first determining whether the patient is in a state of profound rest, such as sleep, then measuring the actual sinus rate during profound rest. Profound rest may be detected by using an activity variance sensor. An increase in the profound rest sinus rate over a period of several months indicates progression of LVD; whereas a decrease indicates regression. Appropriate LVD diagnostic information is recorded for subsequent review by a physician. Based on the progression or regression of LVD, the physician may then modify LVD drug therapy administered to the patient or may adjust control parameters of the pacemaker, such as overdrive pacing control parameters or control parameters affecting heart contractility via post-extrasystolic potentiation. If a drug pump is implanted within the patient for automatically delivering LVD drug therapy, the pacemaker controls the drug pump in view of any detected progression or regression of LVD. The technique may also be used to verify the efficacy of LVD drug therapy administered to the patient, whether delivered via an implanted drug pump or otherwise. Processing may be primarily performed within the implanted device itself or with an external programmer in communication with the implanted device. Activity state-based LVD tracking techniques are also set forth.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Wireless sensing devices for evaluating heart performance
InactiveUS20050288727A1Evaluate performanceInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsWireless transmitterHeart contractility
A system for monitoring heart performance comprises a plurality of sensing devices configured to attach to a patient's heart tissue and a controller. Each sensing device comprises a sensor configured to detect physiological data relating to heart contractility and a wireless transmitter configured to transmit data detected by the sensor. The controller comprises a receiver configured to receive the detected data transmitted by the plurality of sensing devices and a processor configured to analyze the received data.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
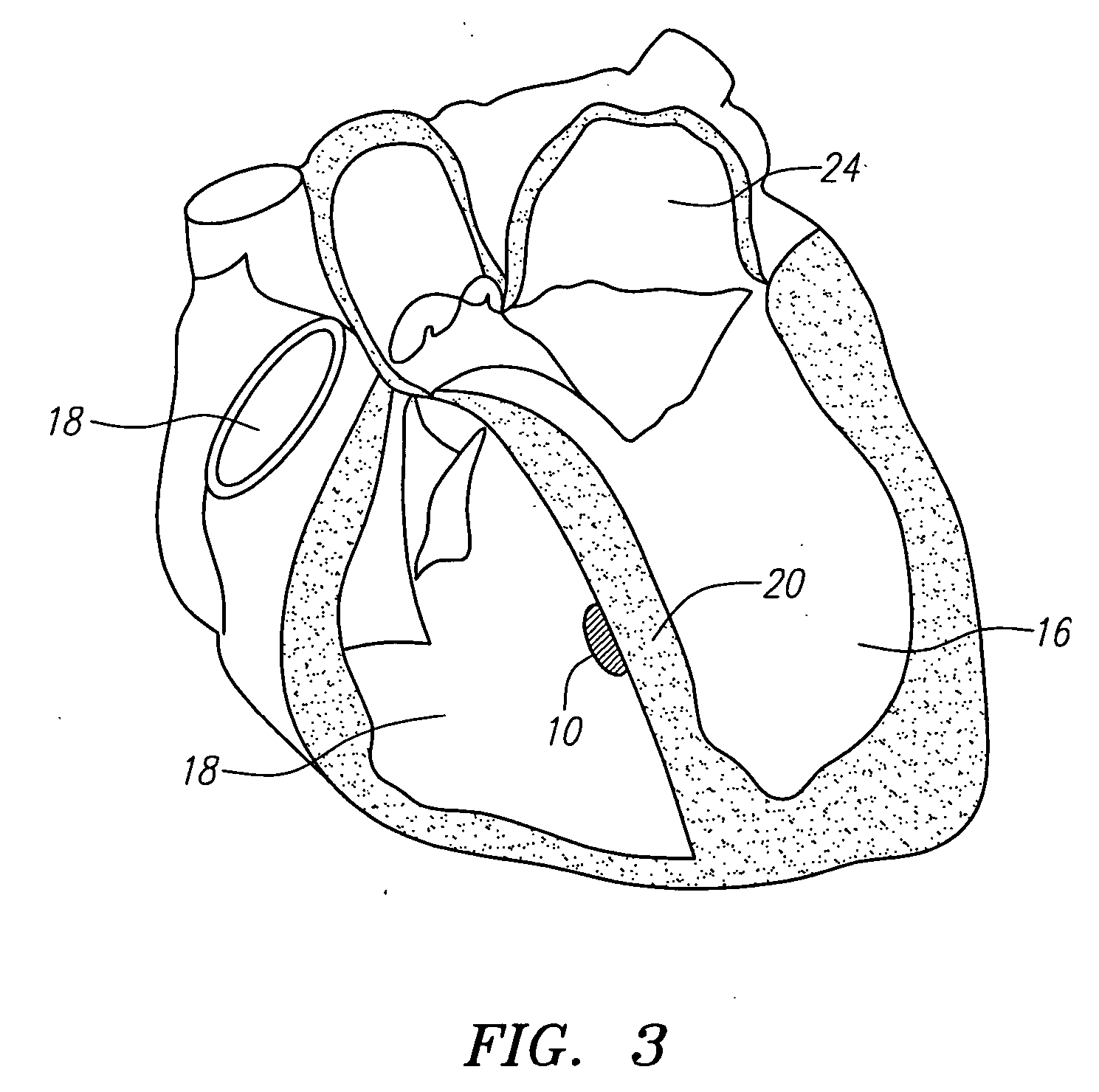
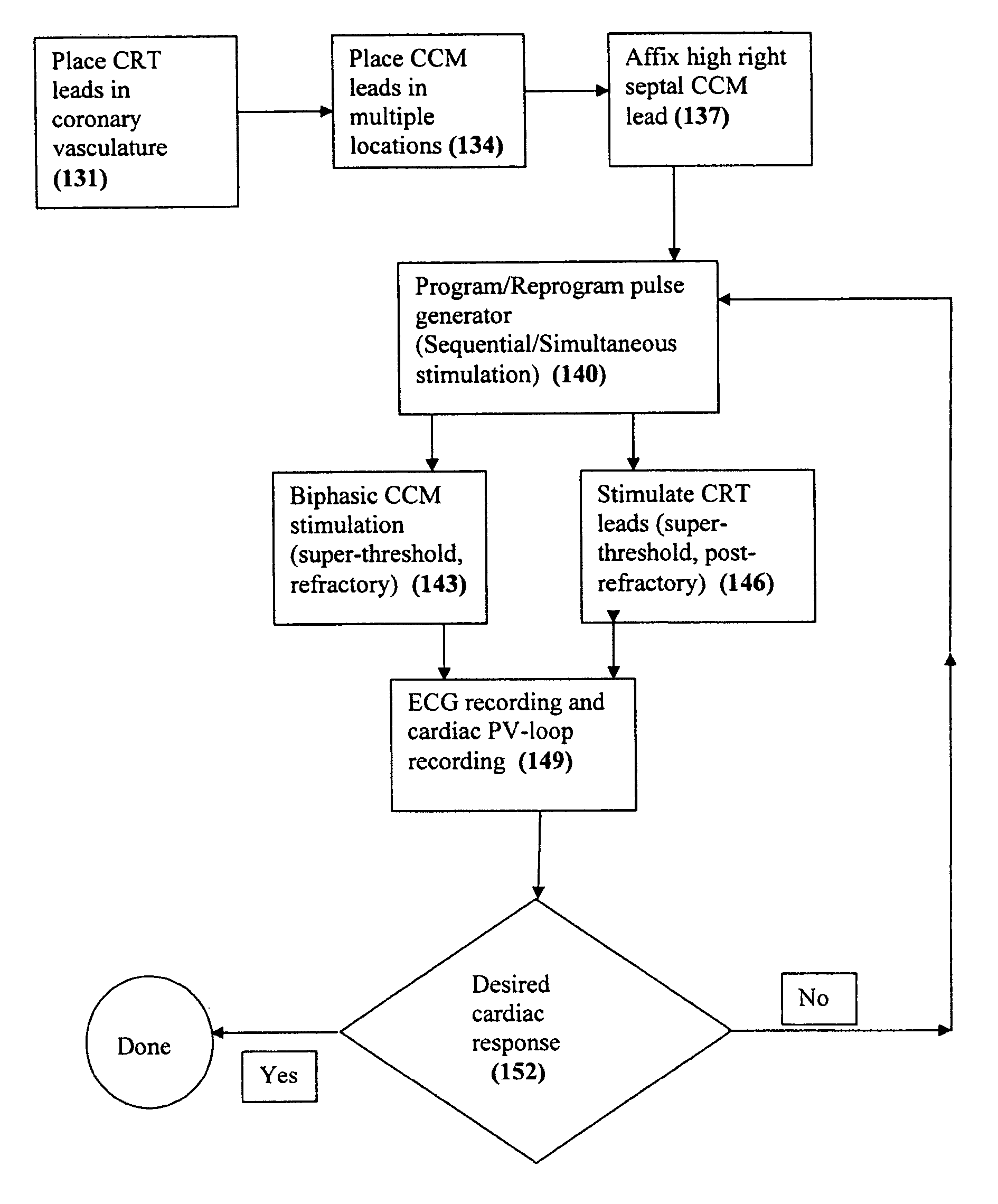
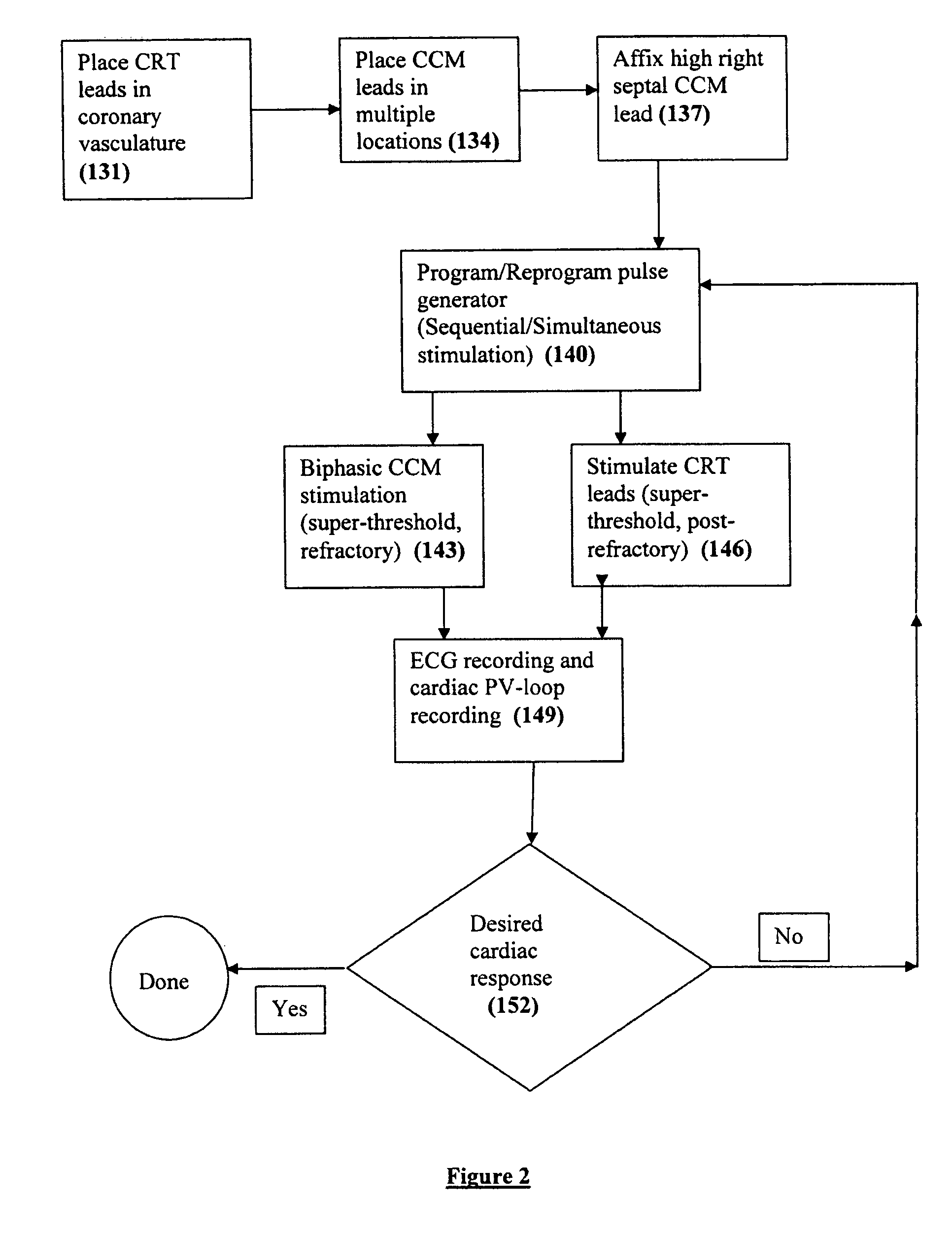
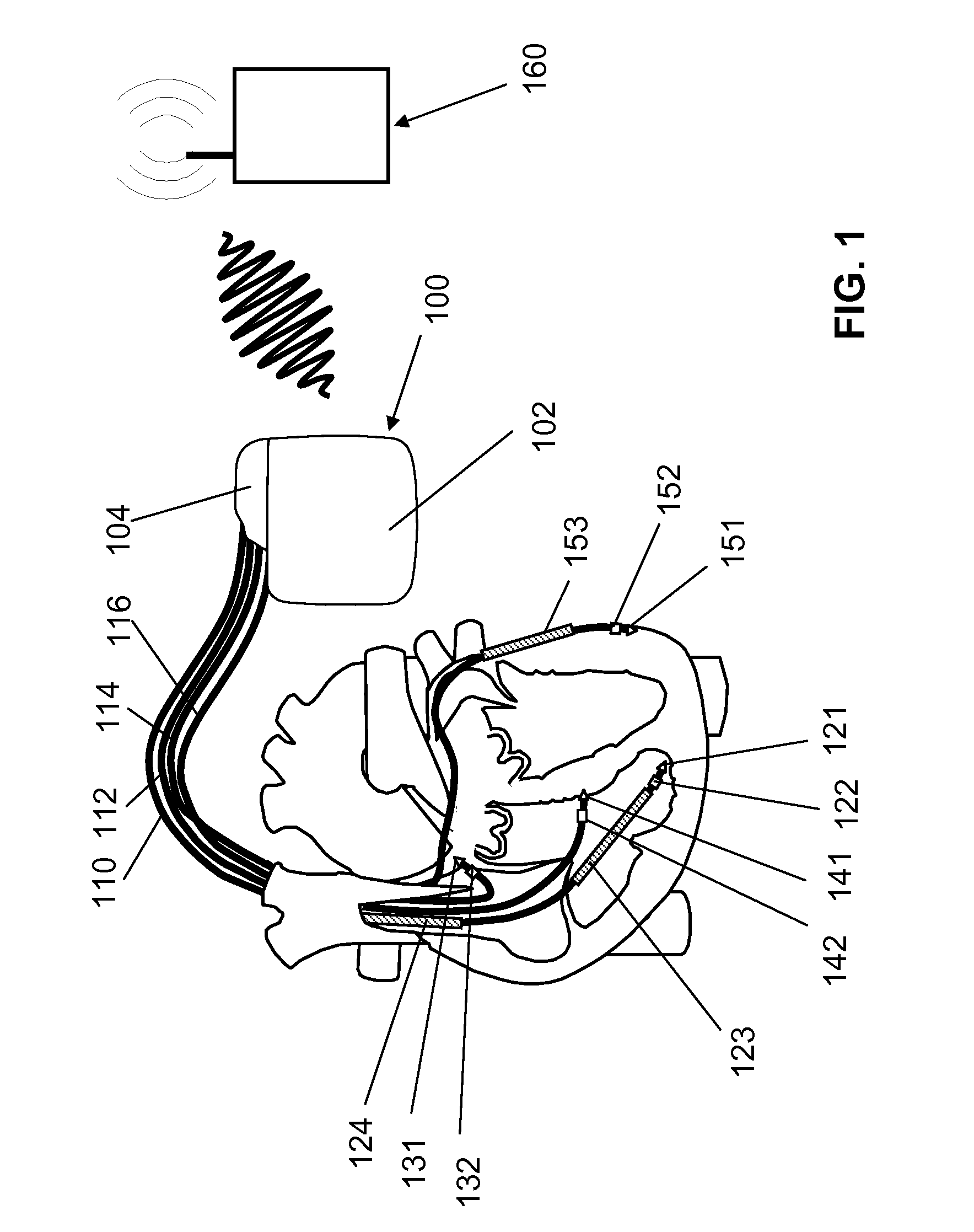
Apparatus and methods for cardiac resynchronization therapy and cardiac contractility modulation
A method of placing and testing placement of a plurality of pacing and stimulation leads for cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) employs cardiac contractility modulation (CCM), using a plurality of cardiac contractility modulation leads placed at a plurality of sites.
Owner:PAPPONE CARLO
Apparatus and method for delivering electrical signals to a heart
ActiveUS7966067B2Increased effective sensing rangeLong distanceElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsEcg signalVentricular dysrhythmia
Devices, systems and methods for controlling (inhibiting or enabling) the delivery of electrotherapeutic signals to a heart using sensing of local and / or global ECG signals to detect ventricular arrhythmia or indication of possible ventricular arrhythmia in the heart. The devices, systems and methods process the sensed signals and are capable of delivering electroptherapeutic signals to the heart in the presence of a supra-ventricular arrhythmia such as atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, while inhibiting the delivering electroptherapeutic signals in the presence of PVCs and / or extopic beats, and / or ventricular arrhythmia. The electrotherapeutic signals may include, among others, pacing signals and cardiac contractility modulating signals.
Owner:IMPULSE DYNAMICS NV
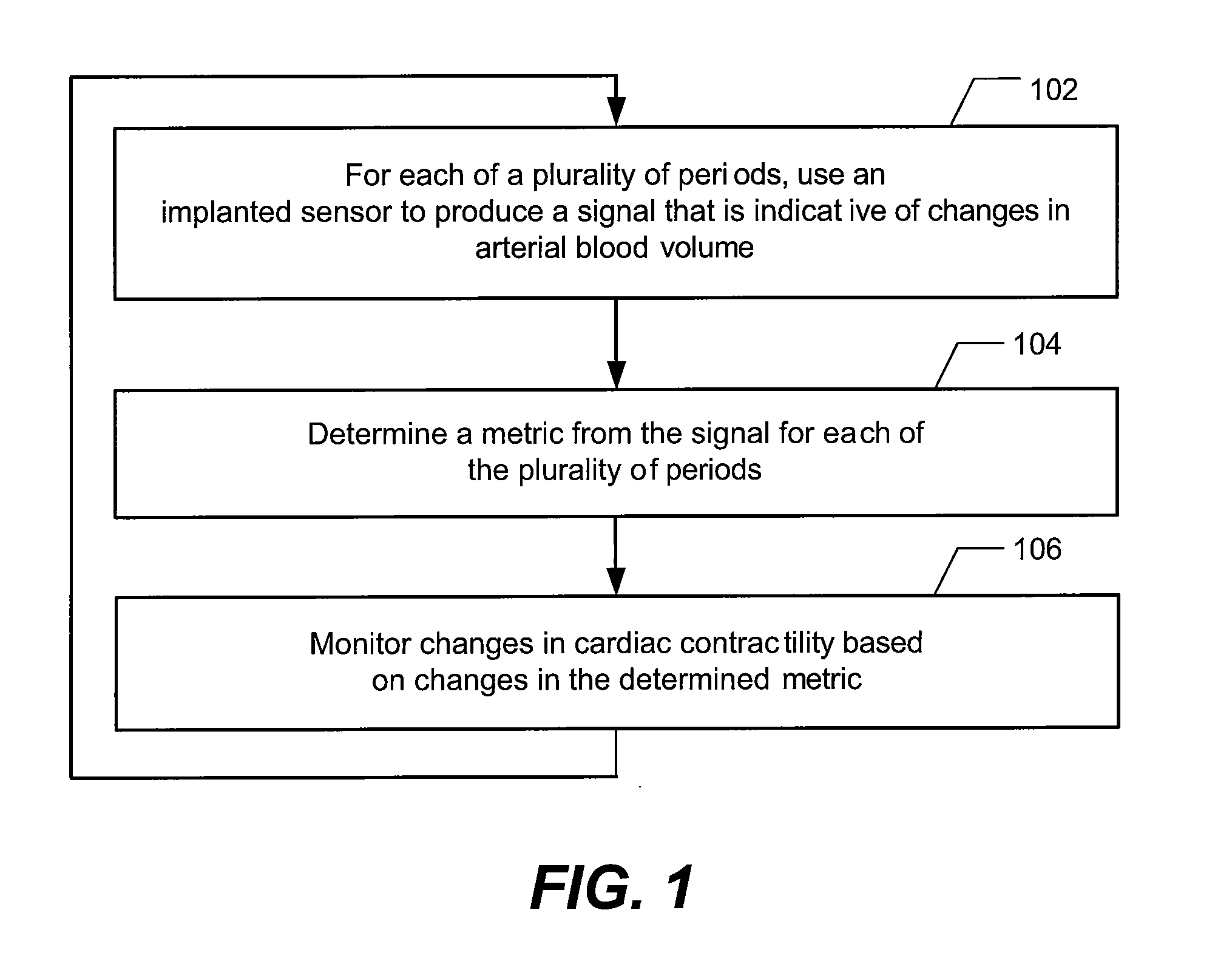
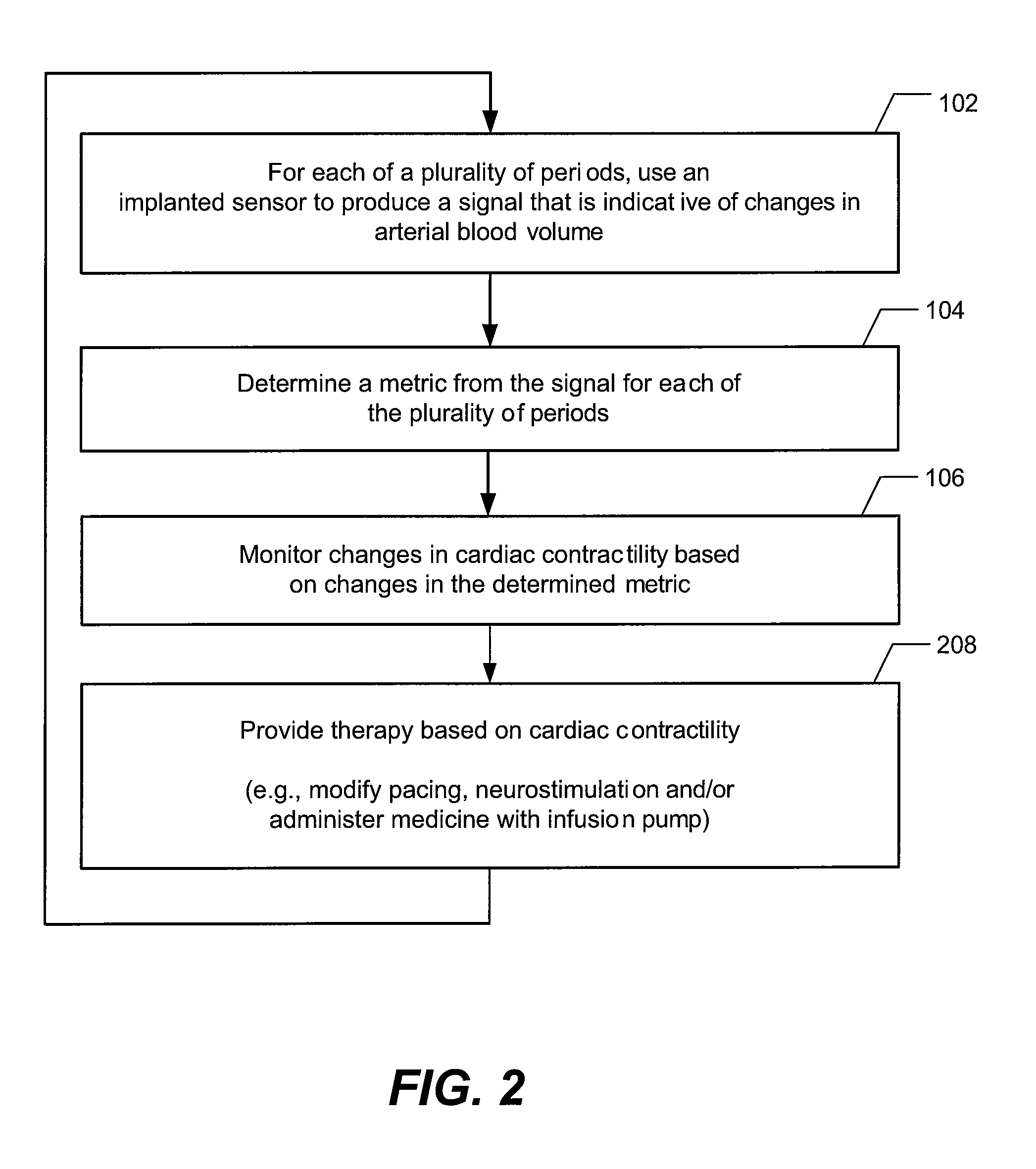
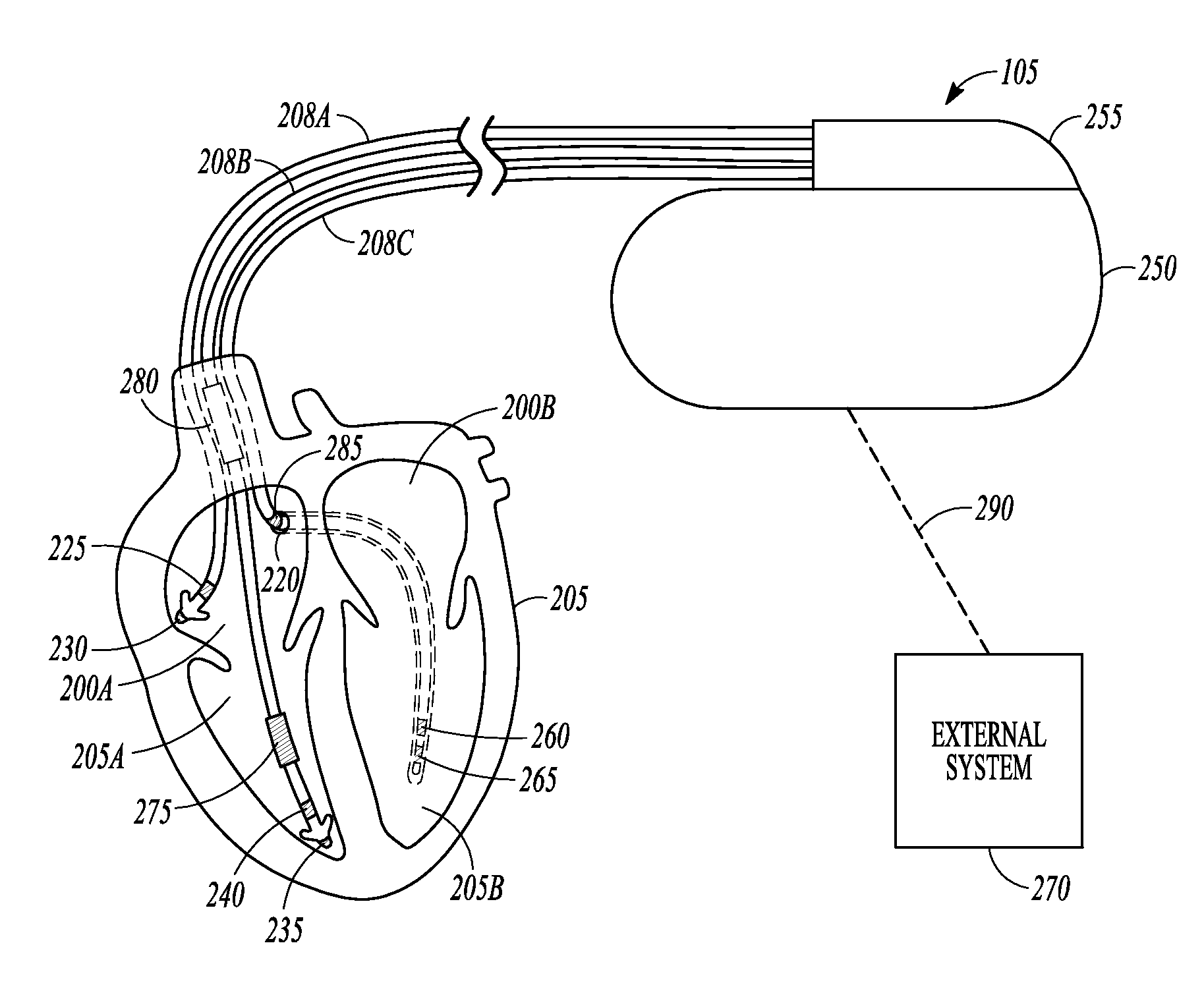
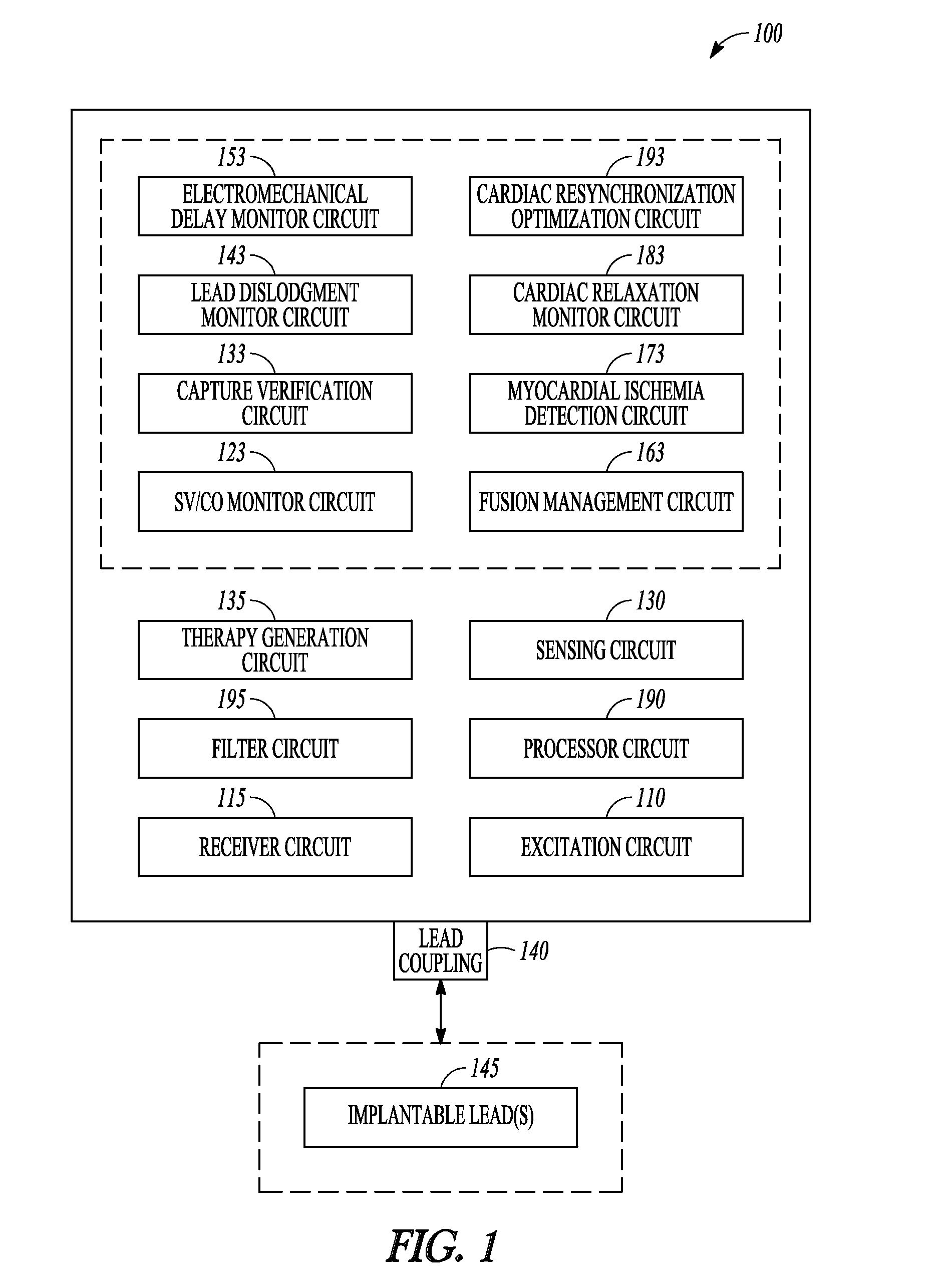
Methods and systems to monitor cardiac contractility
InactiveUS20110125208A1Increase cardiac contractilityDecrease cardiac contractilityCatheterHeart stimulatorsArteryContractility
An implanted sensor produces a signal that is indicative of changes in arterial blood volume, such as a photoplethysmography signal or an impedance plethysmography signal. A metric is determined from the signal for each of the plurality of periods. Changes in cardiac contractility are monitored based on changes in the determined metric.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac contraction detection using information indicative of lead motion
Systems and methods for cardiac contraction detection using information indicative of lead motion are described. In an example, an implantable medical device can include a receiver circuit configured to be electrically coupled to conductor comprising a portion of an implantable lead and be configured to obtain information indicative of a movement of the implantable lead due at least in part to a motion of a heart. The device can include a processor circuit configured to determine whether a cardiac mechanical contraction occurred during a specified interval included in the obtained information indicative of the movement of the implantable lead. The processor circuit can be configured to determine information about the cardiac mechanical contraction using the obtained information indicative of the movement of the implantable lead.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and system to correct contractility based on non-heart failure factors
ActiveUS20120239104A1Remove non-HF effectElectrocardiographySurgeryHeart contractilityCardiac Volume
Owner:PACESETTER INC
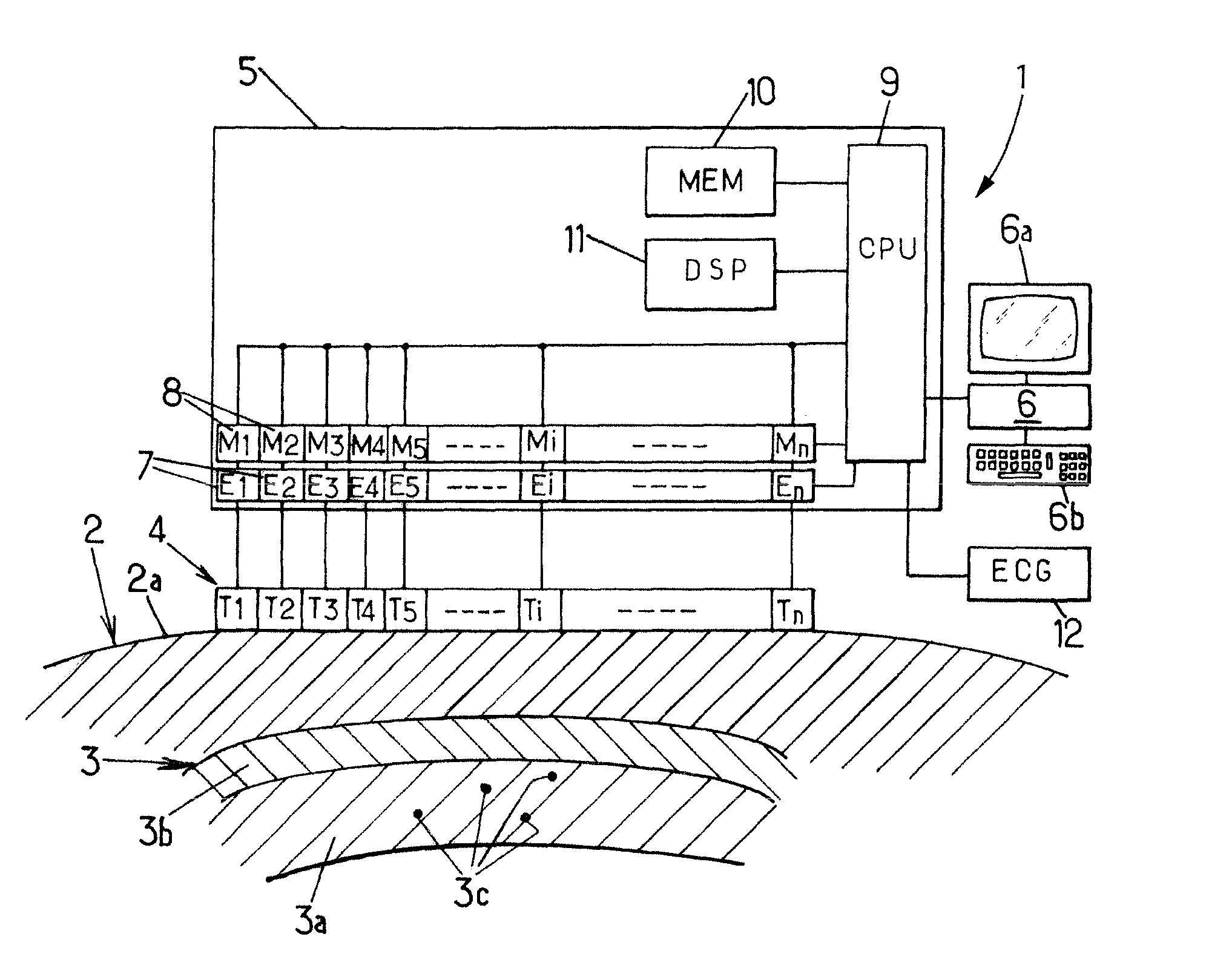
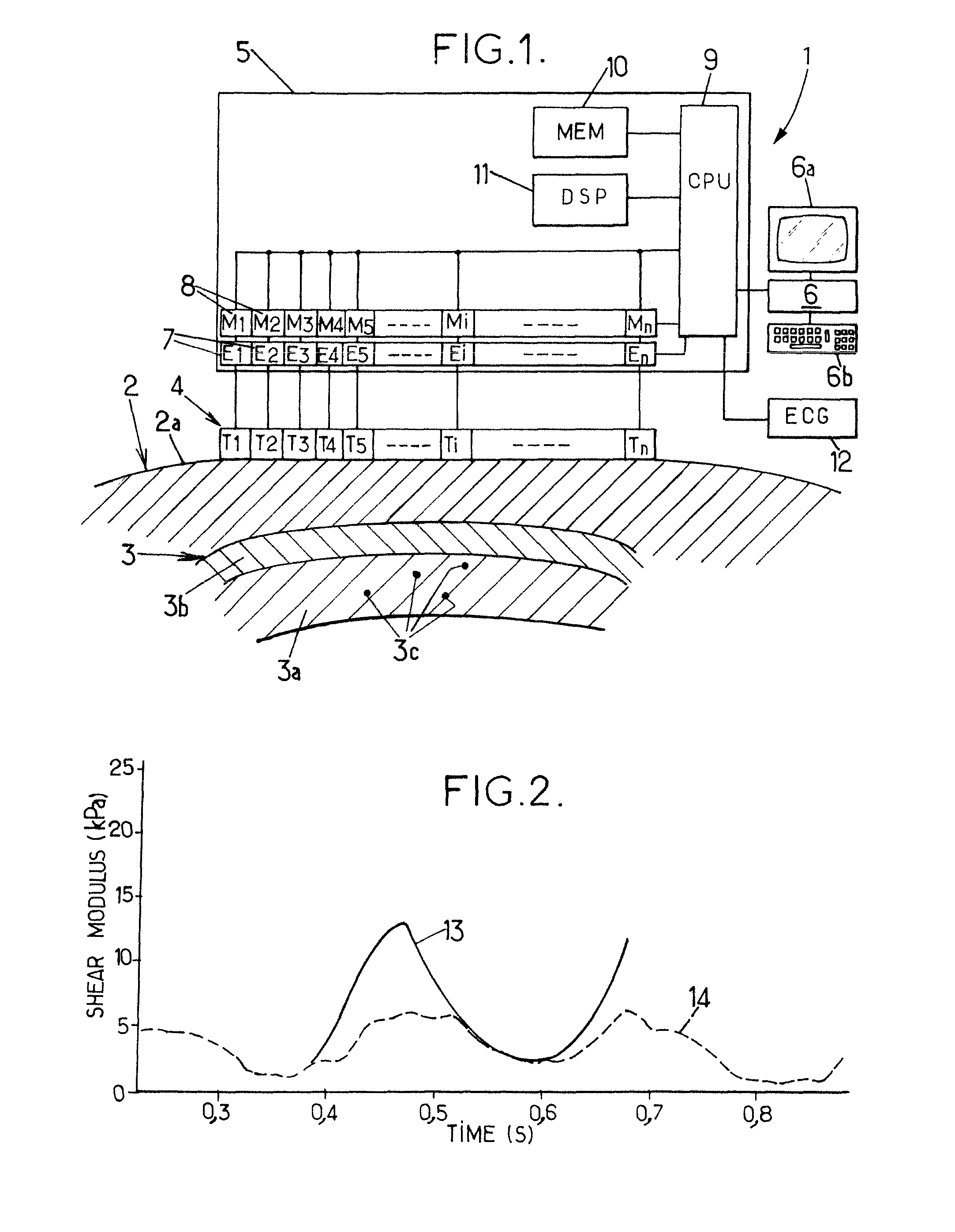
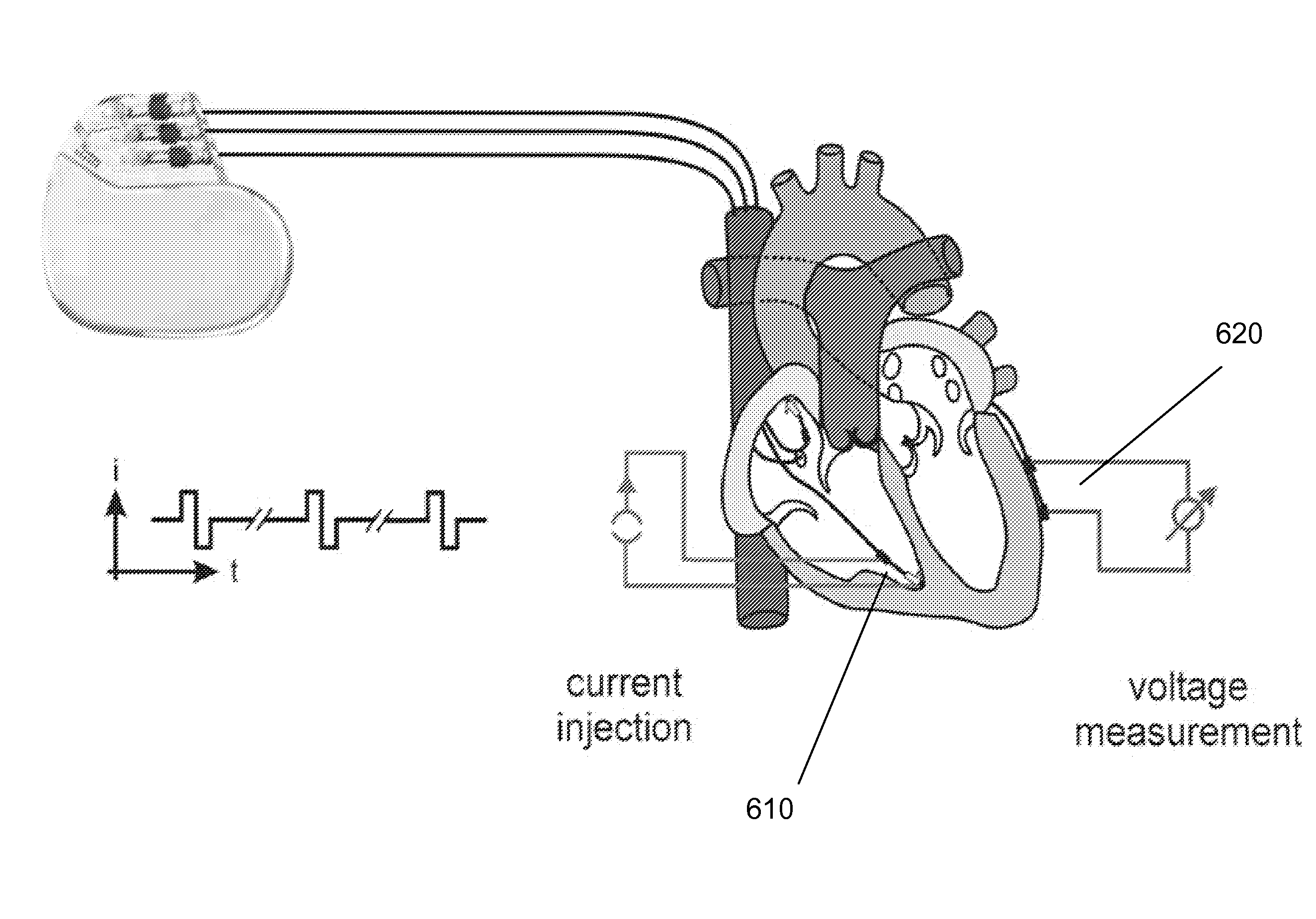
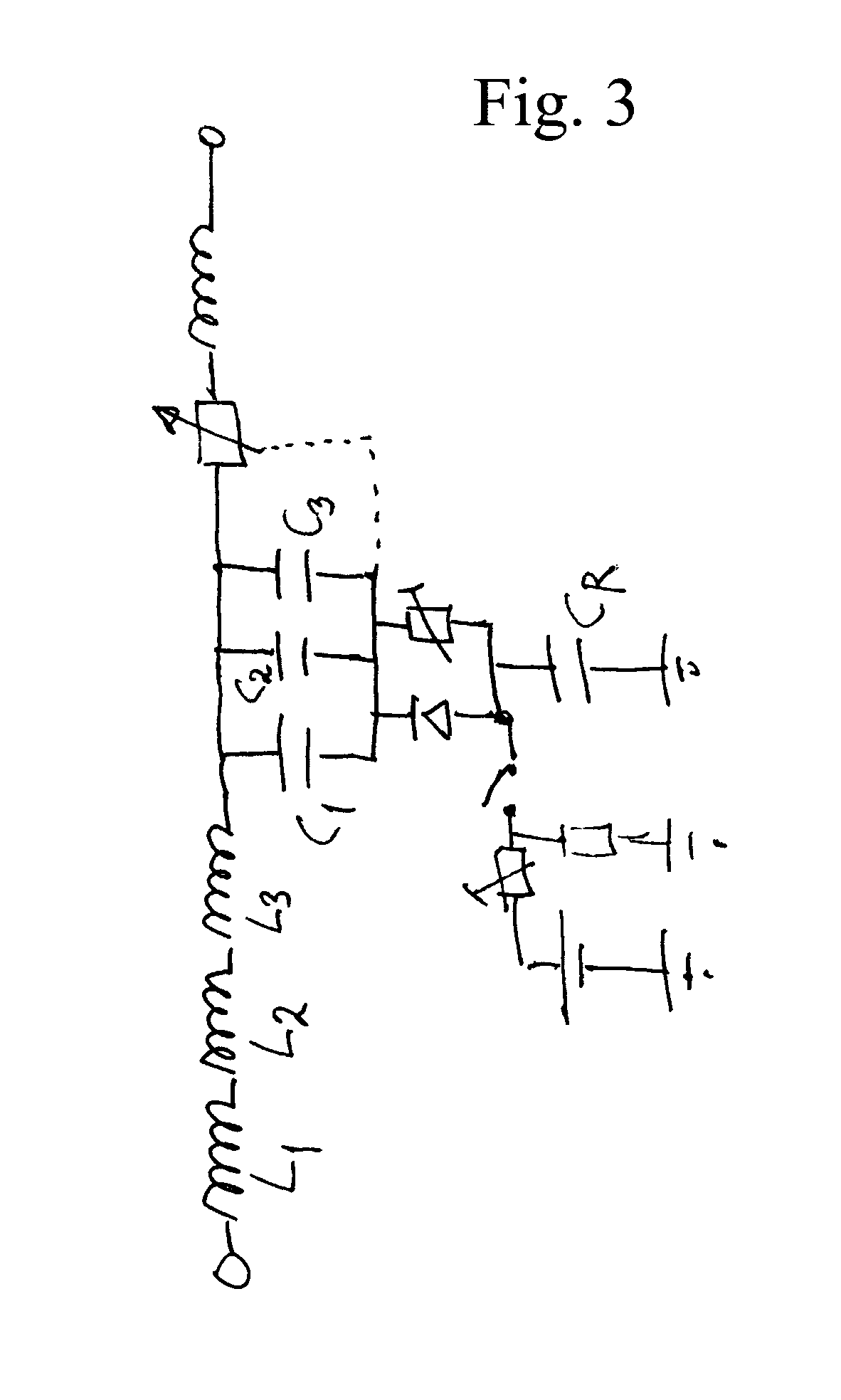
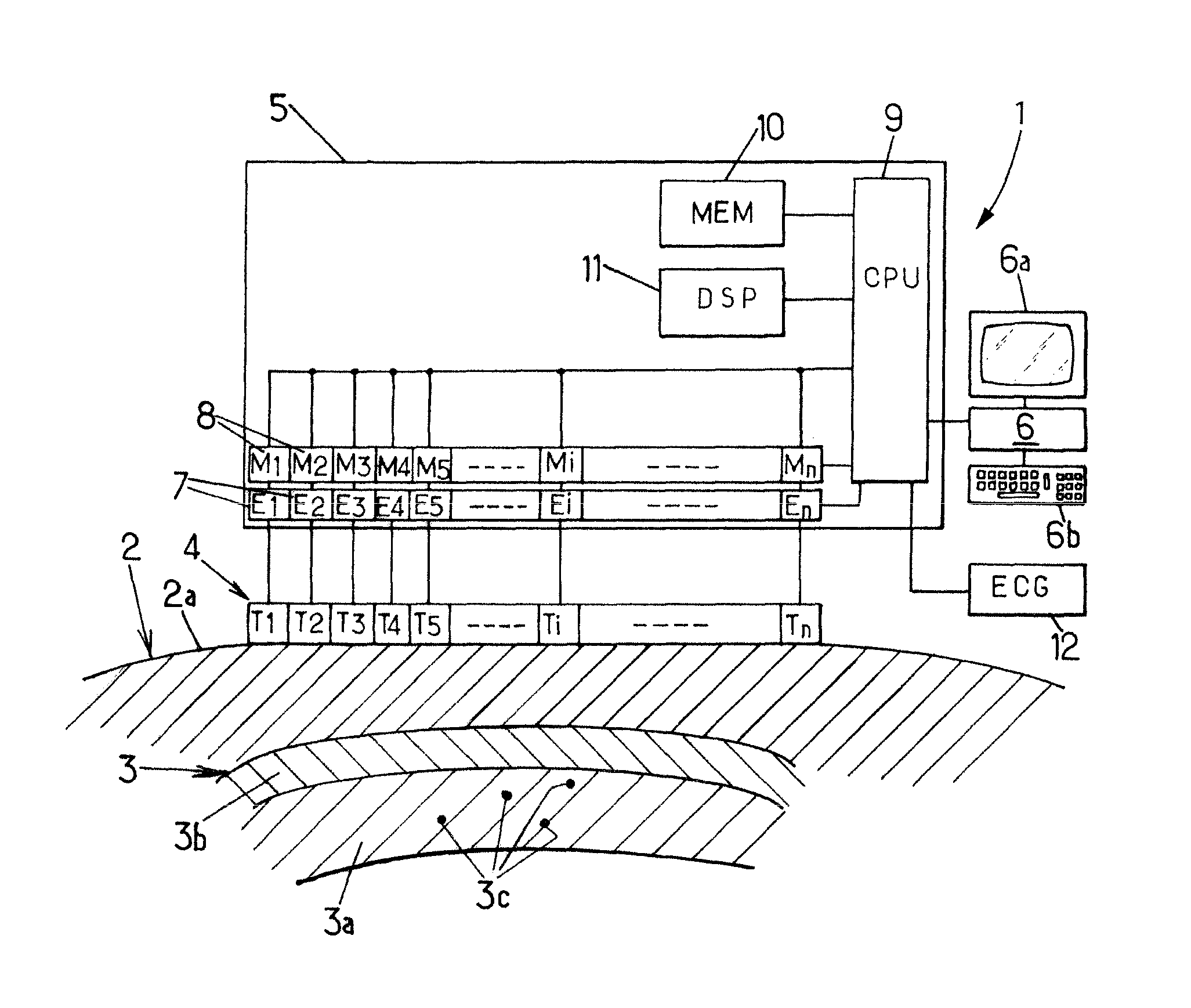
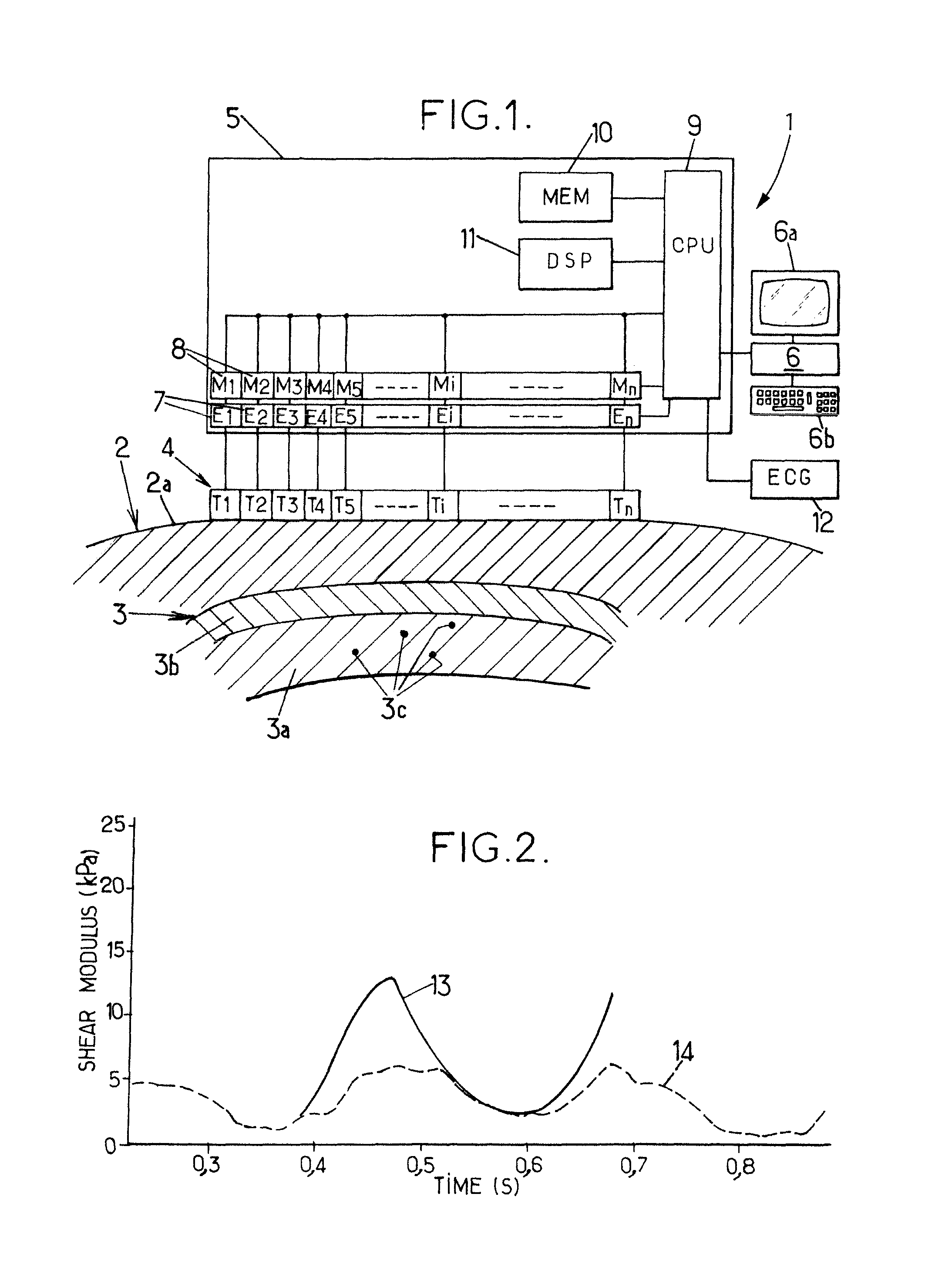
Method and Apparatus for Measuring Heart Contractility
ActiveUS20100312116A1Determined precisely, quickly and non-invasivelyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave based measurement systemsSystoleMedicine
A Method for measuring heart contractility of a patient, in which a mechanical shear wave is propagated through the heart and observation of the propagation leads to determine a shear wave propagation parameter representative of the elasticity of the heart is disclosed. The value of the propagation parameter at the end of a systole is sampled, which leads to a parameter representative of the end systolic elastance.
Owner:SUPER SONIC IMAGINE +1
External left ventricular assist device for treatment of congestive heart failure
InactiveUS20080045866A1Lower blood pressureAvoid excessive volumeElectrotherapyPneumatic massageLeft ventricular sizeCongestive heart failure chf
The invention provides a treatment for congestive heart failure (CHF) in a patient. At least one pressure applicator is arranged externally around a body segment of the patient. Negative pressure, relative to atmospheric pressure, is applied to the body segment of the patient during cardiac systole using the pressure applicator, thereby reducing ventricular afterload in the patient. The negative pressure to the body segment of the patient is removed during cardiac diastole.
Owner:RASTEGAR JAHANGIR +1
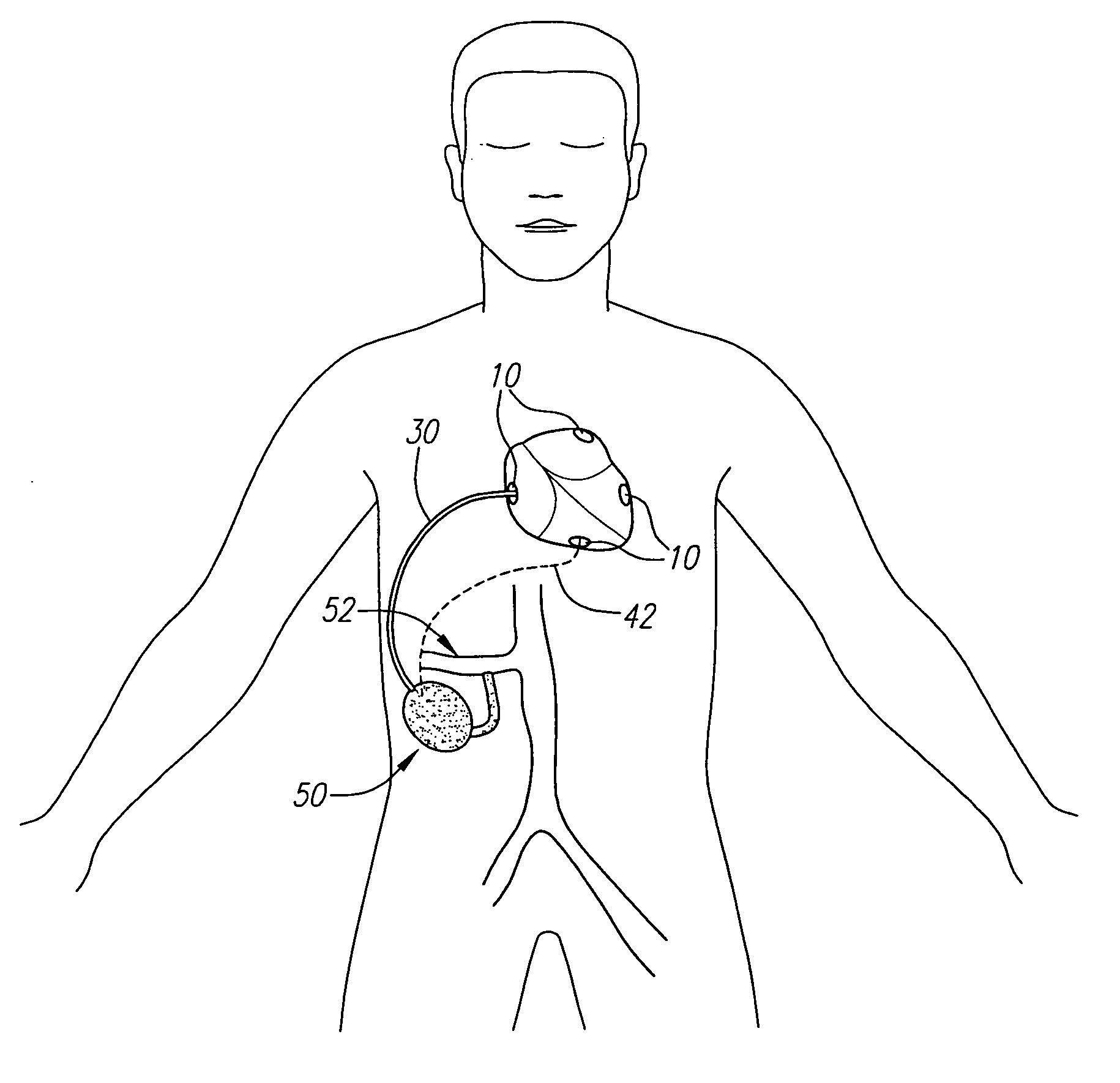
Method and System for Treating Acute Heart Failure by Neuromodulation
Methods and systems of treating acute heart failure by applying a therapy signal at least one sympathetic cardiopulmonary fiber surrounding the pulmonary trunk that affects heart contractility more than heart rate. Methods and systems also include adjusting the signal to effectuate treatment.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Electromagnetic cardiac pulse assisting device
PendingCN112933396AEasy to shrinkEasy to relaxBlood pumpsMedical devicesSurgical operationCardiac surface
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, in particular to an electromagnetic cardiac pulse assisting device. The electromagnetic cardiac pulse assisting device comprises an inner membrane, an outer membrane supporting body, two permanent magnets, electromagnets, a power source and a controller. The inner membrane covers the surface of the heart, and the outer membrane supporting body covers the outer side of the inner membrane. The two permanent magnets are fixed to the outer side of the inner membrane and correspond to the left ventricle and the right ventricle respectively. The two electromagnets are fixed to the inner side of the outer membrane supporting body and are opposite to the permanent magnets. The power source and the controller are used for supplying power to the electromagnets and adjusting the magnitude and the direction of current, so that the electromagnets can apply repulsive force or attractive force to the permanent magnets, and then the heart is driven to contract or relax. The device has the advantages of being capable of assisting the heart of the human body to beat, high in controllability, capable of improving the heart failure symptom and prolonging the service life of a patient, simple in structure, small and exquisite in size, capable of being implanted only through surgical operation, convenient to replace, low in manufacturing and using cost, long in service life and easy to accept by doctors and patients.
Owner:深圳脉腾医学技术有限公司 +1
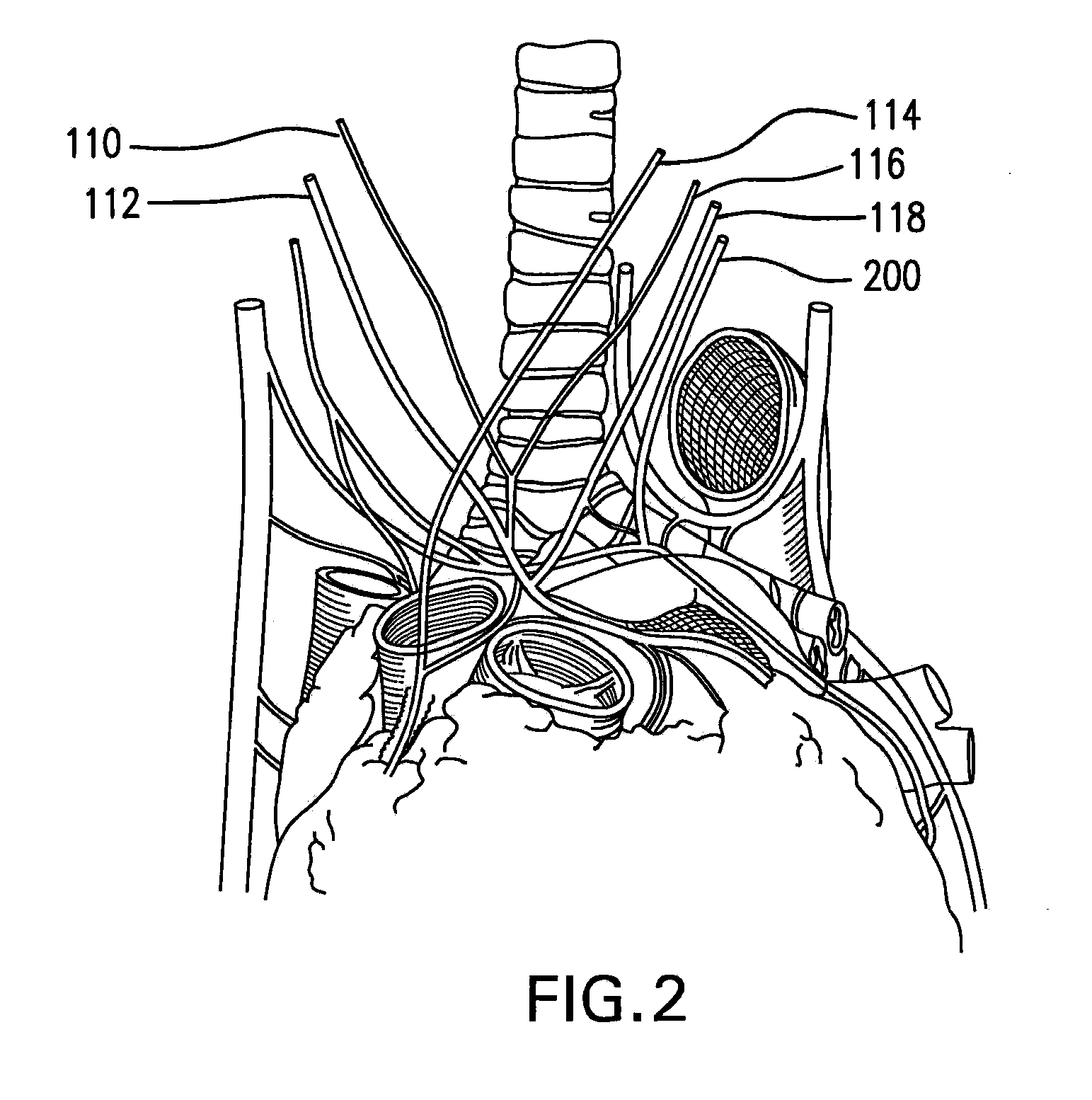
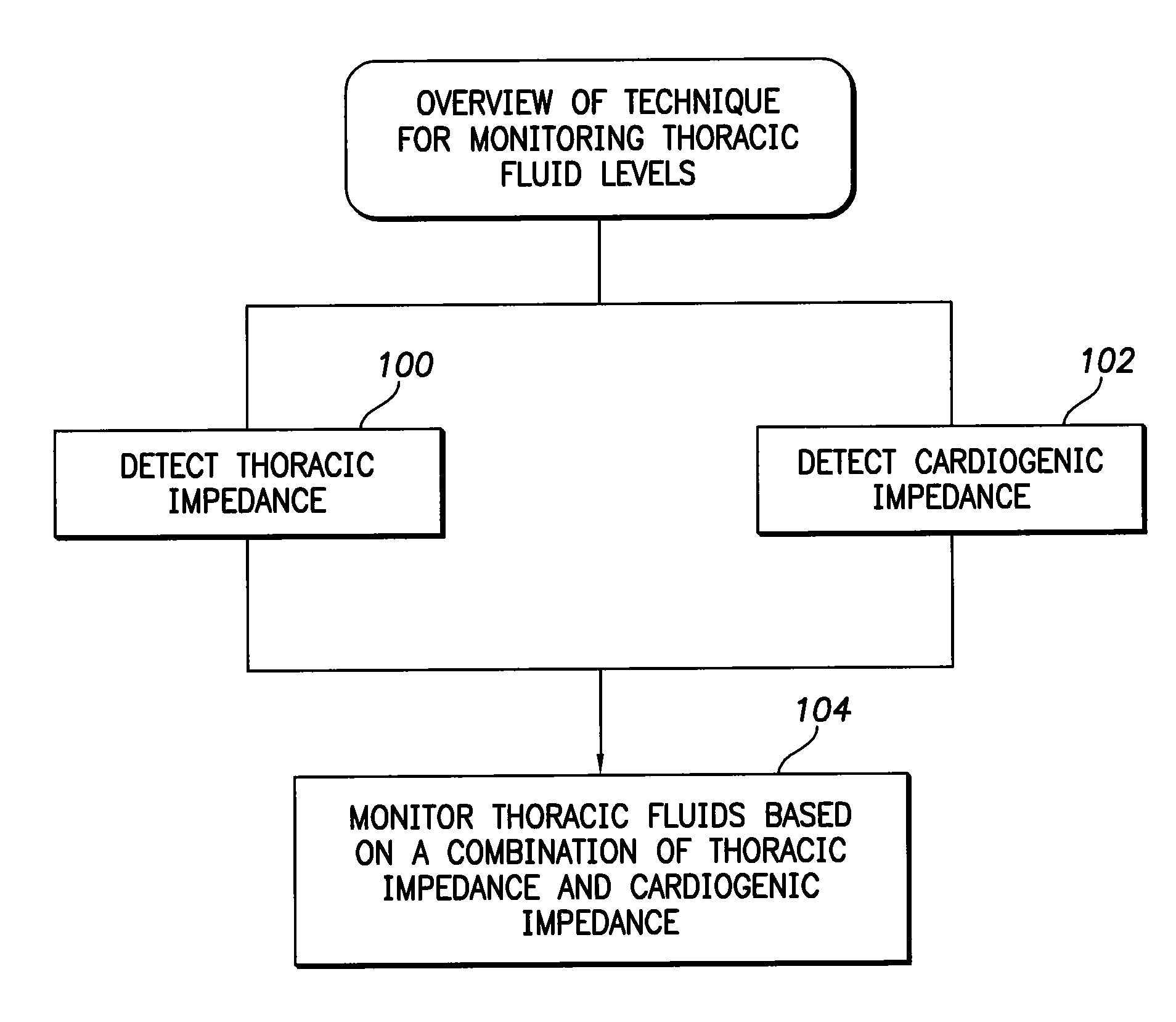
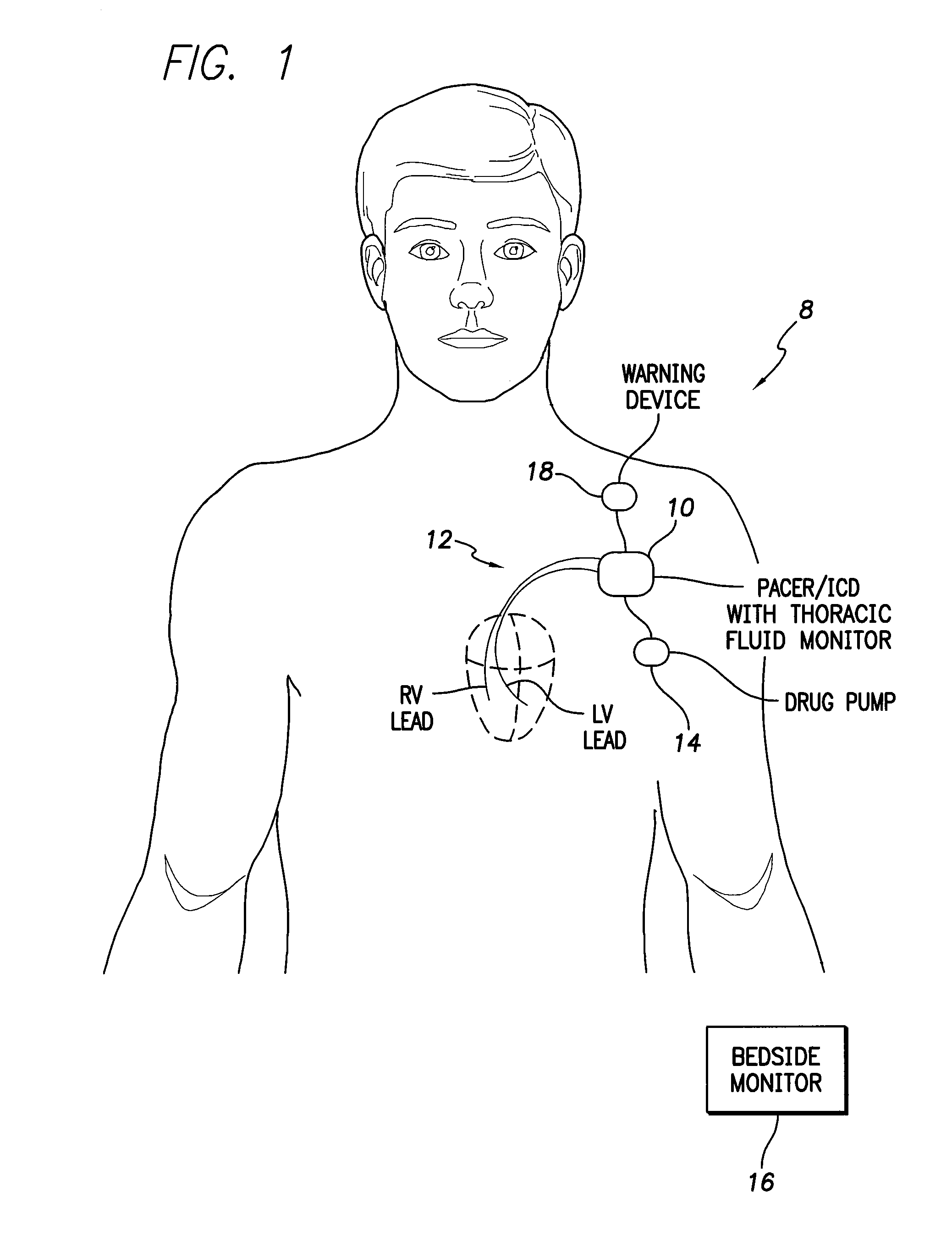
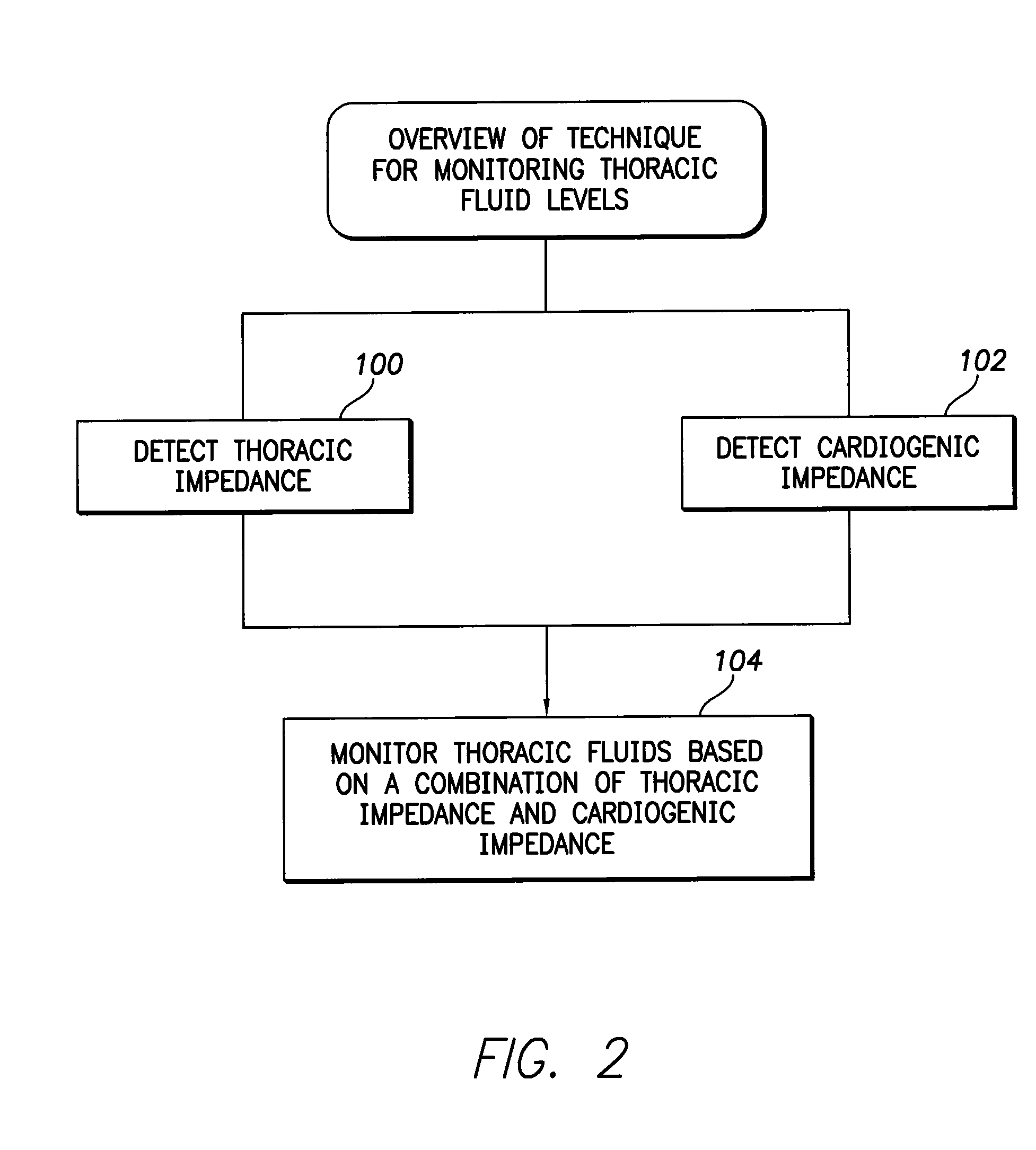
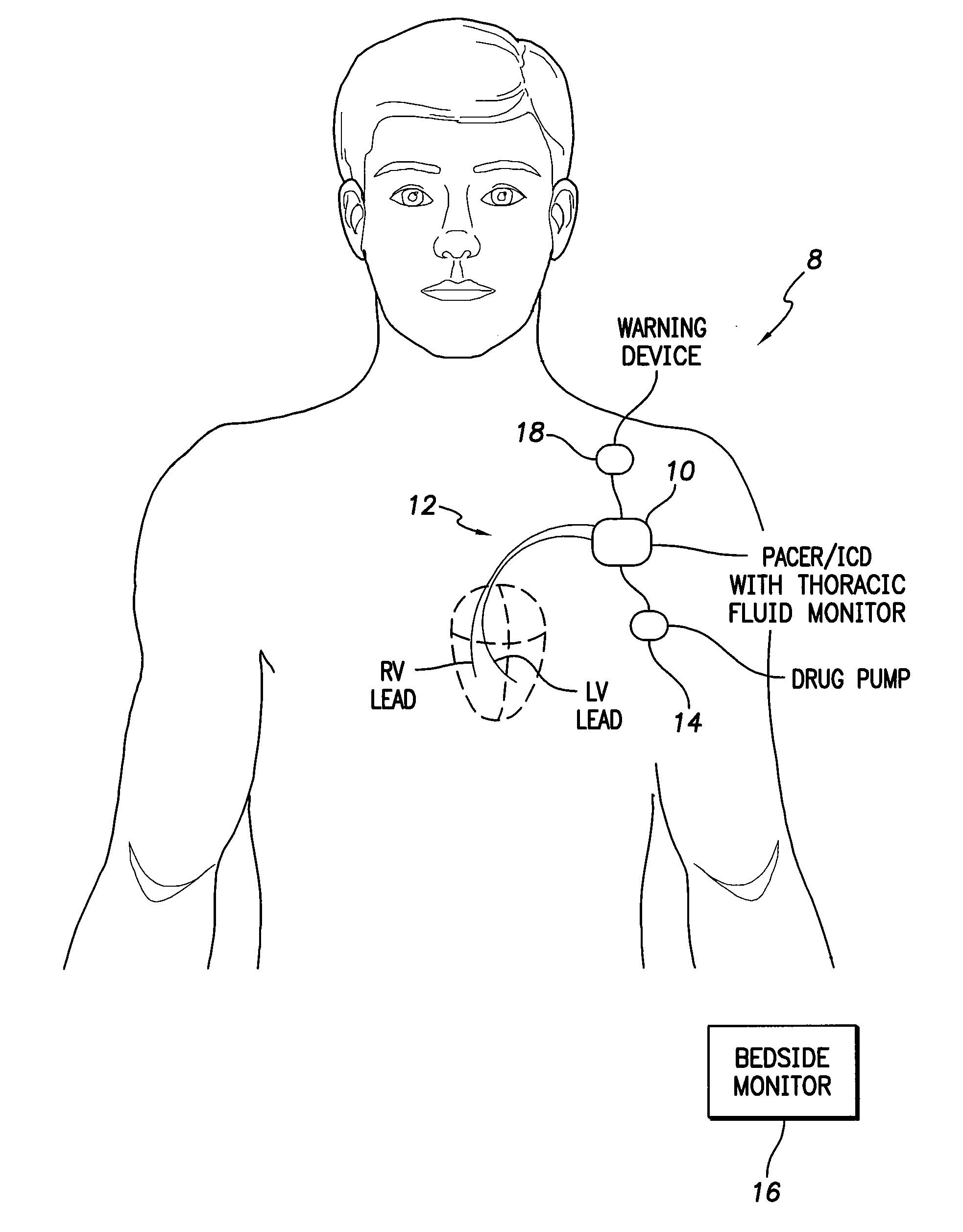
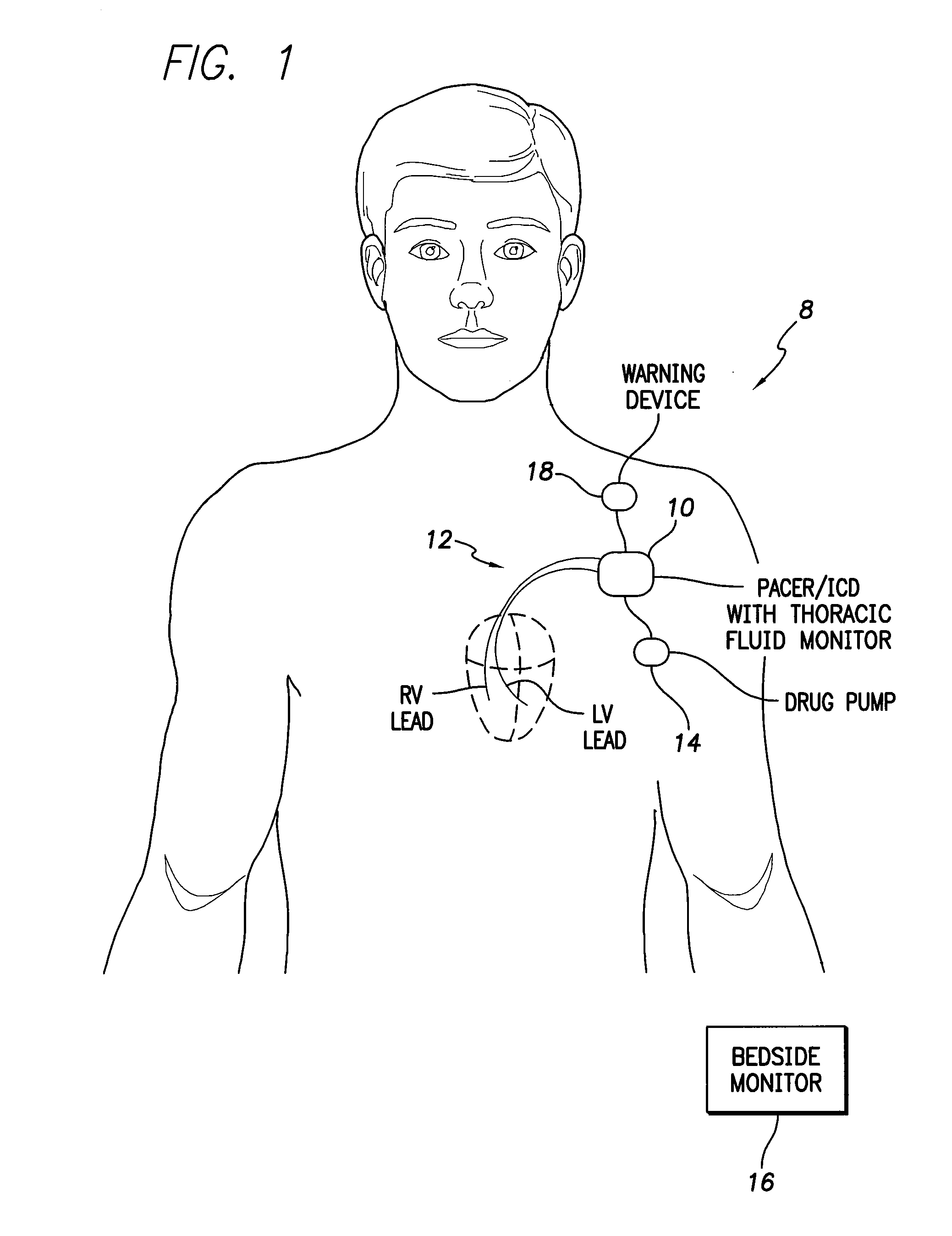
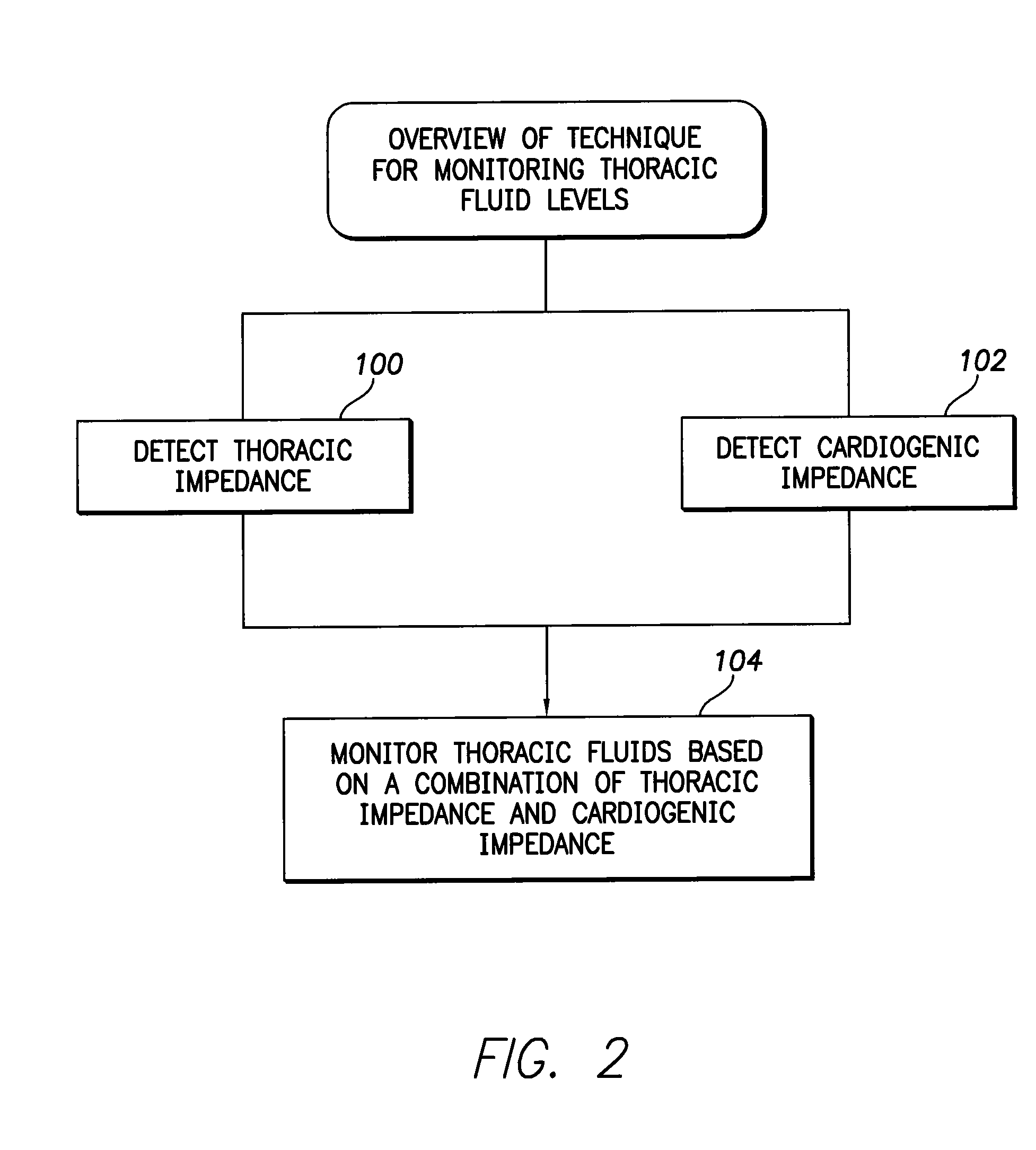
System and method for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on impedance using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS8032212B2Monitored more effectivelyEffective monitoringElectrotherapyCatheterThoracic FluidThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on thoracic impedance (ZT) and cardiogenic impedance (ZC). In one example, the implantable device tracks the maximum time rate of change in cardiogenic impedance (i.e. max(dZC / dt)) to detect trends toward hypervolemic or hypovolemic states within the patient based on changes in heart contractility. The detection of these trends in combination with trends in thoracic impedance allows for a determination of whether the thoracic cavity of the patient is generally “too wet” or “too dry,” and thus allows for the titration of diuretics to avoid such extremes. In particular, a decrease in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too wet” (i.e. a fluid overload). Conversely, an increase in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too dry” (i.e. a fluid underload).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac stimulator for delivery of cardiac contractility modulation therapy
ActiveUS20130006318A1Current consumptionImprove energy consumptionHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular volumeSub threshold
A cardiac stimulator having at least one stimulation unit which is connected or connectable to one or more stimulation electrodes, and is configured to deliver at least sub-threshold stimulation pulses for cardiac contraction modulation therapy, an impedance detection unit which is connectable to one or more electrodes, and is configured to detect a voltage or current intensity that occurs as the result of a particular sub-threshold stimulation pulse, and to determine a particular impedance value, an impedance evaluation unit, configured to determine at least one value based on ventricular volume, and / or a value based on minute ventilation, and a control unit connected to the stimulation unit and the cardiac rhythm detection unit, and is configured to control a delivery of a stimulation pulse via the stimulation unit such that the cardiac stimulator can deliver sub-threshold stimulation pulses for cardiac contraction modulation therapy.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Methods and systems for treating acute heart failure by neuromodulation
ActiveUS20130172953A1Internal electrodesSurgical instrument detailsPulmonary arteryHeart contractility
Methods of treating acute heart failure in a patient in need thereof. Methods include inserting a therapy delivery device into a pulmonary artery of the patient and applying a therapy signal to autonomic cardiopulmonary fibers surrounding the pulmonary artery. The therapy signal affects heart contractility more than heart rate. Specifically, the application of the therapy signal increases heart contractility and treats the acute heart failure in the patient. The therapy signal can include electrical or chemical modulation.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
System and method for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on impedance using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20100069778A1Avoid problemsExcellent stateElectrotherapyCatheterThoracic FluidThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for monitoring thoracic fluid levels based on thoracic impedance (ZT) and cardiogenic impedance (ZC). In one example, the implantable device tracks the maximum time rate of change in cardiogenic impedance (i.e. max(dZC / dt)) to detect trends toward hypervolemic or hypovolemic states within the patient based on changes in heart contractility. The detection of these trends in combination with trends in thoracic impedance allows for a determination of whether the thoracic cavity of the patient is generally “too wet” or “too dry,” and thus allows for the titration of diuretics to avoid such extremes. In particular, a decrease in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too wet” (i.e. a fluid overload). Conversely, an increase in thoracic impedance (ZT) in combination with a decrease in max (dZC / dt) is indicative of the thorax being “too dry” (i.e. a fluid underload).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac modulation facilitation methods and systems
ActiveUS20180050206A1Increase in myocardium consumptionIncreased oxygen consumptionElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectricityPulmonary artery
A method of facilitating therapeutic neuromodulation of a heart of a patient includes positioning an electrode in a pulmonary artery, positioning a sensor in vasculature, delivering via a stimulation system first and second electrical signals of a series of electrical signals to the electrode. The second electrical signal differs from the first electrical signal by a magnitude of a first parameter of a plurality of parameters. The method includes determining via the sensor, sensor data indicative of one or more heart activity properties in response to the delivery of the series of electrical signals, and delivering a therapeutic neuromodulation signal to the pulmonary artery using selected electrical parameters. The selected electrical parameters include a selected magnitude of the first parameter. The selected magnitude of the first parameter is based at least partially on the sensor data. The therapeutic neuromodulation signal increases heart contractility.
Owner:CARDIONOMIC
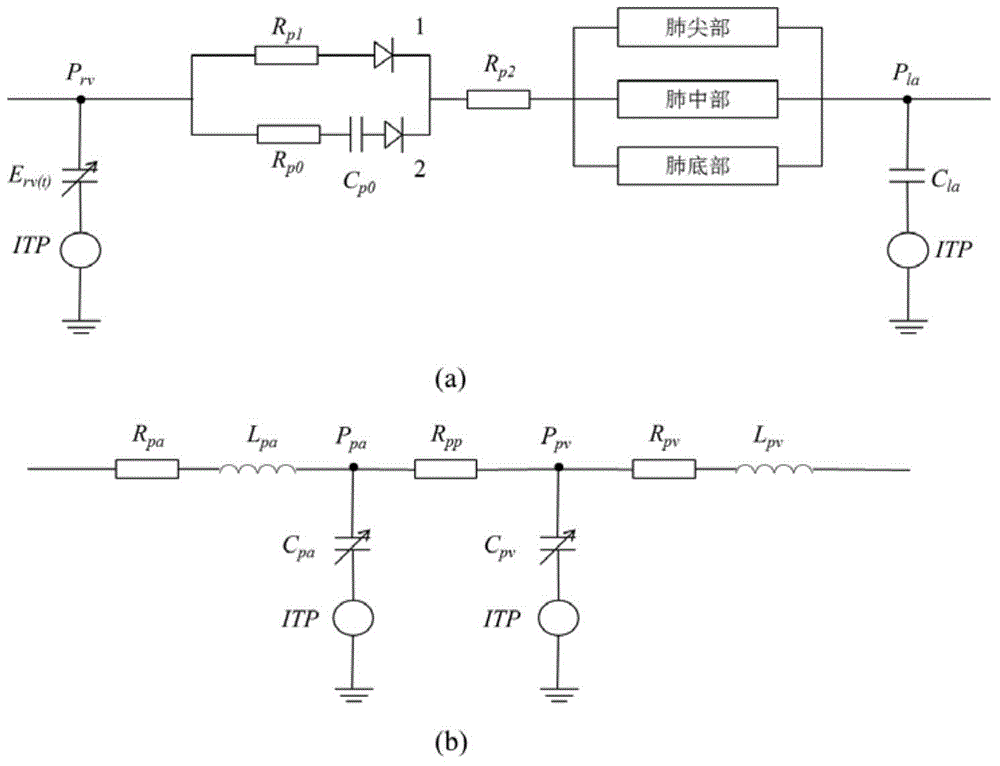
Distributed-type cardiovascular system simulation model
InactiveCN104794973AIncrease reflectionIn-depth analysisEducational modelsPulmonary vasculatureModel system
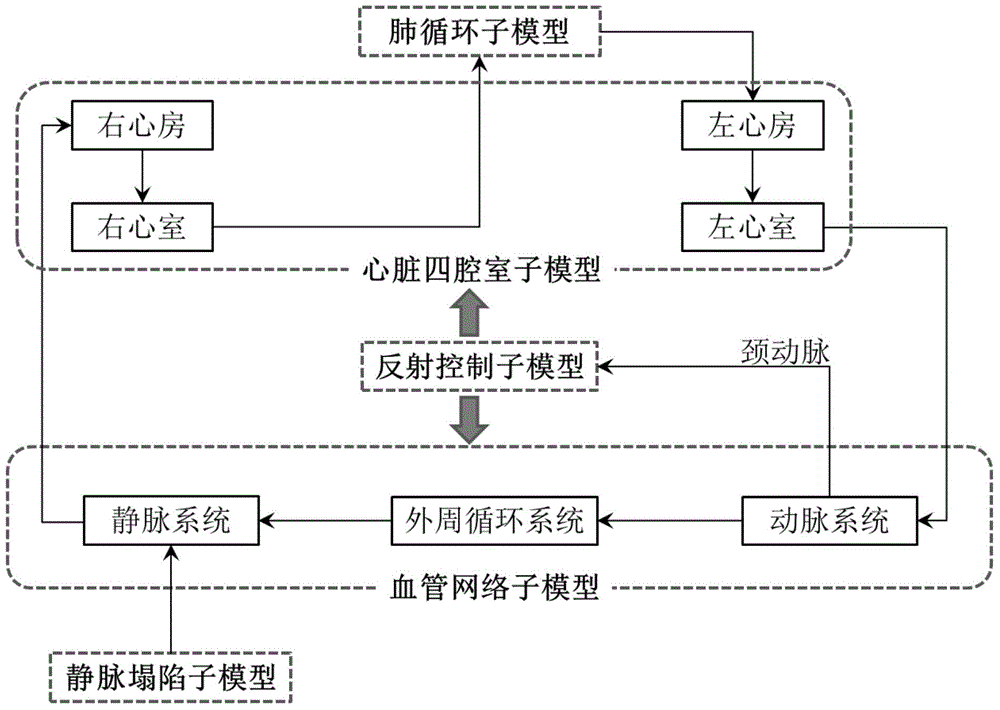
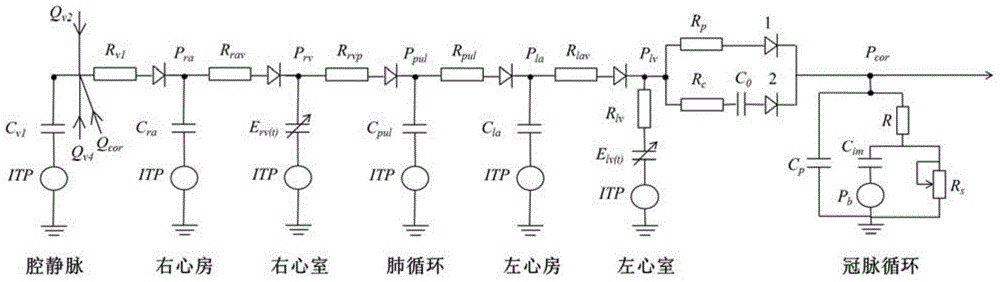
The invention discloses a distributed-type cardiovascular system simulation model. The distributed-type cardiovascular system simulation model is characterized by comprising a cardiac four-cavity sub-model, a pulmonary circulation sub-model, a blood vessel network sub-model, a reflection control sub-model and a vein collapse sub-model, the cardiac cavity sub-model is provided with a left ventricle connected with a left atrium and a right ventricle connected with a right atrium, the left ventricle and the right ventricle drive systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation, the blood vessel network sub-model comprises an arterial system, a peripheral circulation system and a venous system which are connected sequentially, an input end of the arterial system is connected with an output end of the left ventricle, an output end of the venous system is connected with an input end of the right ventricle, the vein collapse sub-model is connected with another input end of the venous system, an output end of the arterial system is connected with the reflection control sub-model through a carotid artery, and the reflection control sub-model controls blood pressure fluctuation of a model system through heart rate and heart contractility effectors arranged on the cardiac four-cavity model and arterial resistance, venous volume and vascular tone effectors arranged in the blood vessel network model.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Cardiac modulation facilitation methods and systems
ActiveUS10493278B2Increase contractilityIncrease consumptionElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectricityPulmonary artery
A method of facilitating therapeutic neuromodulation of a heart of a patient includes positioning an electrode in a pulmonary artery, positioning a sensor in vasculature, delivering via a stimulation system first and second electrical signals of a series of electrical signals to the electrode. The second electrical signal differs from the first electrical signal by a magnitude of a first parameter of a plurality of parameters. The method includes determining, via the sensor, sensor data indicative of one or more heart activity properties in response to the delivery of the series of electrical signals, and delivering a therapeutic neuromodulation signal to the pulmonary artery using selected electrical parameters. The selected electrical parameters include a selected magnitude of the first parameter. The selected magnitude of the first parameter is based at least partially on the sensor data. The therapeutic neuromodulation signal increases heart contractility.
Owner:CARDIONOMIC
Cardiac stimulator for cardiac contractility modulation
InactiveUS20130218222A1Lowering proarrhythmic riskEliminate potentially proarrhythmic effectHeart stimulatorsEvaluation resultCardiac contractility modulation
At least one embodiment of the invention relates to a cardiac stimulator comprising at least one stimulation unit to deliver subthreshold stimulation pulses for a cardiac contractility modulation therapy via at least two stimulation electrode poles, and at least one sensing unit to detect cardiac electrical or mechanical actions. The at least one sensing unit detects signals characteristic of cardiac action and comprises, or is connected to, an evaluation unit that evaluates signals detected by the sensing unit and supplies a corresponding evaluation result signal. The cardiac stimulator further comprises a therapy control unit to control a respective cardiac contractility modulation therapy depending on a respective evaluation result signal. A respective cardiac contractility modulation therapy is activated / deactivated depending on a stimulation success / failure of a suprathreshold stimulation, and / or therapy parameters of a respective cardiac contractility modulation therapy are selected and / or adjusted depending on the respective evaluation result signal.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Neurostimulation systems and methods for affecting cardiac contractility
ActiveUS20200206511A1Increase contractilityIncrease consumptionTransvascular endocardial electrodesEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterRat heart
A method of detecting catheter movement includes positioning a first sensor in a first body cavity, monitoring a first parameter profile of the first body cavity, positioning a second sensor in a second body cavity, monitoring a second parameter profile of the second body cavity, the second parameter profile different than the first parameter profile at a first time, and, when the second parameter profile is the same as the first parameter profile at a second time after the first time, taking a catheter movement action.
Owner:CARDIONOMIC
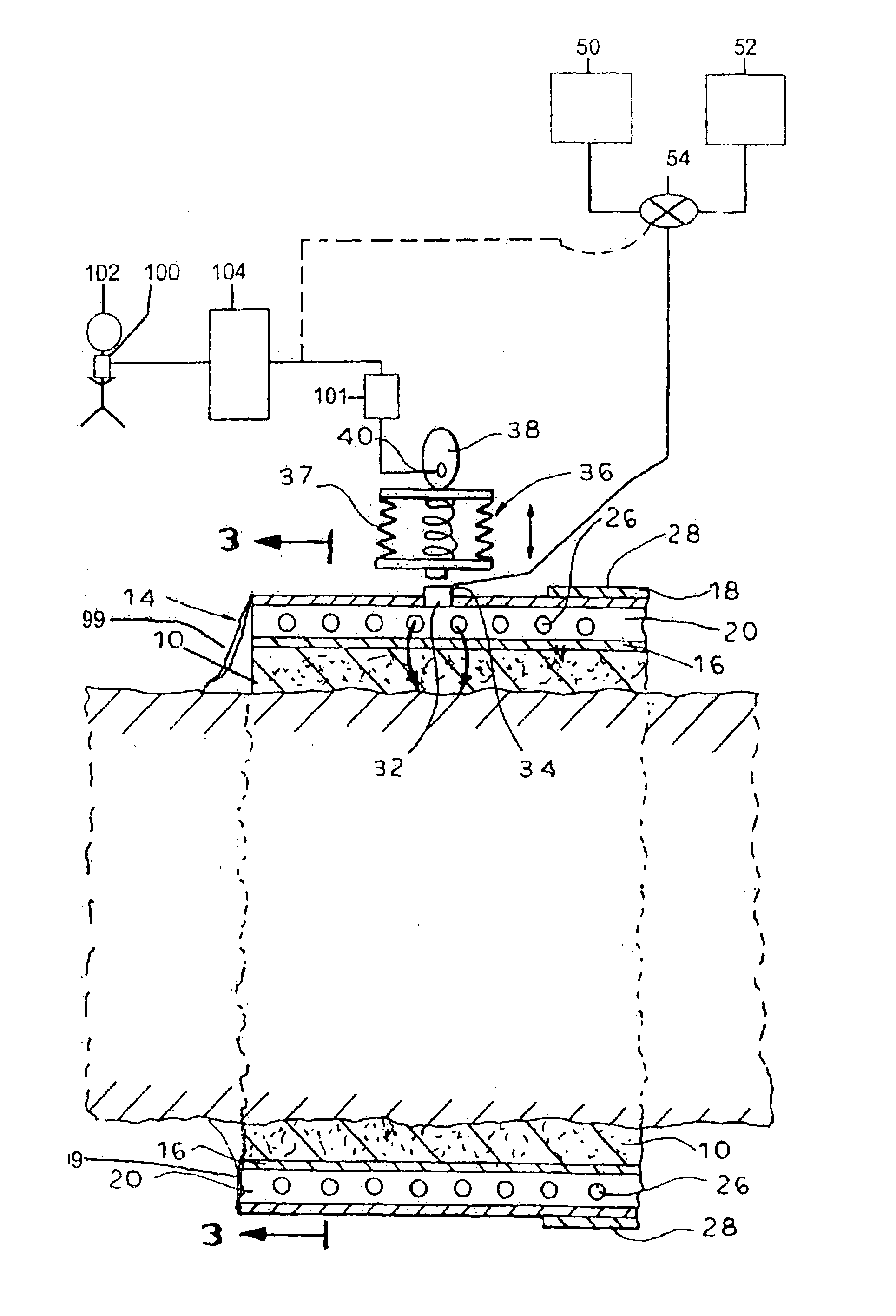
Afterload device for a beating heart during examination thereof
ActiveUS10405756B2Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate onePharmaceutical containersMedical devicesSystoleAfterload
An examination device for a heart. An afterload device connected to the aorta provides a counter-pressure by an annular space delimited between a rigid cylinder and an elastic tube inserted in the rigid cylinder. The annular space comprises a compressible medium, such as air, nitrogen gas or carbon dioxide and is connected to a reservoir providing a predetermined pressure corresponding to a diastolic pressure. The reservoir is connected to the annular space via a restriction and a back-flow valve. During diastole, the annular space is inflated by the reservoir and provides a diastolic counter pressure for providing coronary flow. During systole, the ejected fluid from the heart ventricle displaces the medium inside the annular space through the restriction to the reservoir, thereby removing energy from the fluid. The compressible medium forms a compliance. Also, there is a preload device comprising a vertical collapsible tube for preload of the atrium.
Owner:XVIVO PERFUSION
Health care cold noodle containing Sauropus rostratus Miq powder and its production method
InactiveCN103392999AChange the shortcomings of single taste and simple compositionGreat tasteFood preparationNervous systemStructural composition
The invention provides a health care cold noodle containing Sauropus rostratus Miq powder and its production method. The health care cold noodle is made from 65-75 of flour, 8-10 of Sauropus rostratus Miq, 0.7-1.2 of tea polyphenols, 0.8-1.3 of sodium citrate, 1-1.5 of a peanut shell aqueous extract, 1-1.3 of carrageenan, 1.5-2.5 of Salvia Miltiorrhiza, 1.5-2.5 of Fructus Aurantii Immaturus, 1-1.5 of Polygonatum, 1-1.2 of lucid ganoderma, 0.6-1 of Prunus humilis Bunge leaf, 4-6 of hawthorn nuclear powder, 2-4 of pineapples, 2-3 of white sugar, 2-3 of table salt, and a proper amount of edible oil. The cold noodle produced in the invention changes the defects of unique taste and simple structural composition of traditional cold noodles. The Sauropus rostratus Miq powder added in the main materials not only improves the flavor, but also can clear away lung heat. The Salvia Miltiorrhiza added in the auxiliary materials can strengthen cardiac contractility, improve heart functions, increase myocardial blood flow, expand peripheral vessels, and lower blood pressure. The lucid ganoderma has an inhibitory effect on the nervous system, and has blood pressure lowering and heart contractility strengthening effects on the circulatory system. The Fructus Aurantii Immaturus, Polygonatum and the like all have certain blood pressure lowering efficacy. Long-term eating of the product provided in the invention is beneficial to the body health.
Owner:安徽省枞阳县金腾食品有限公司
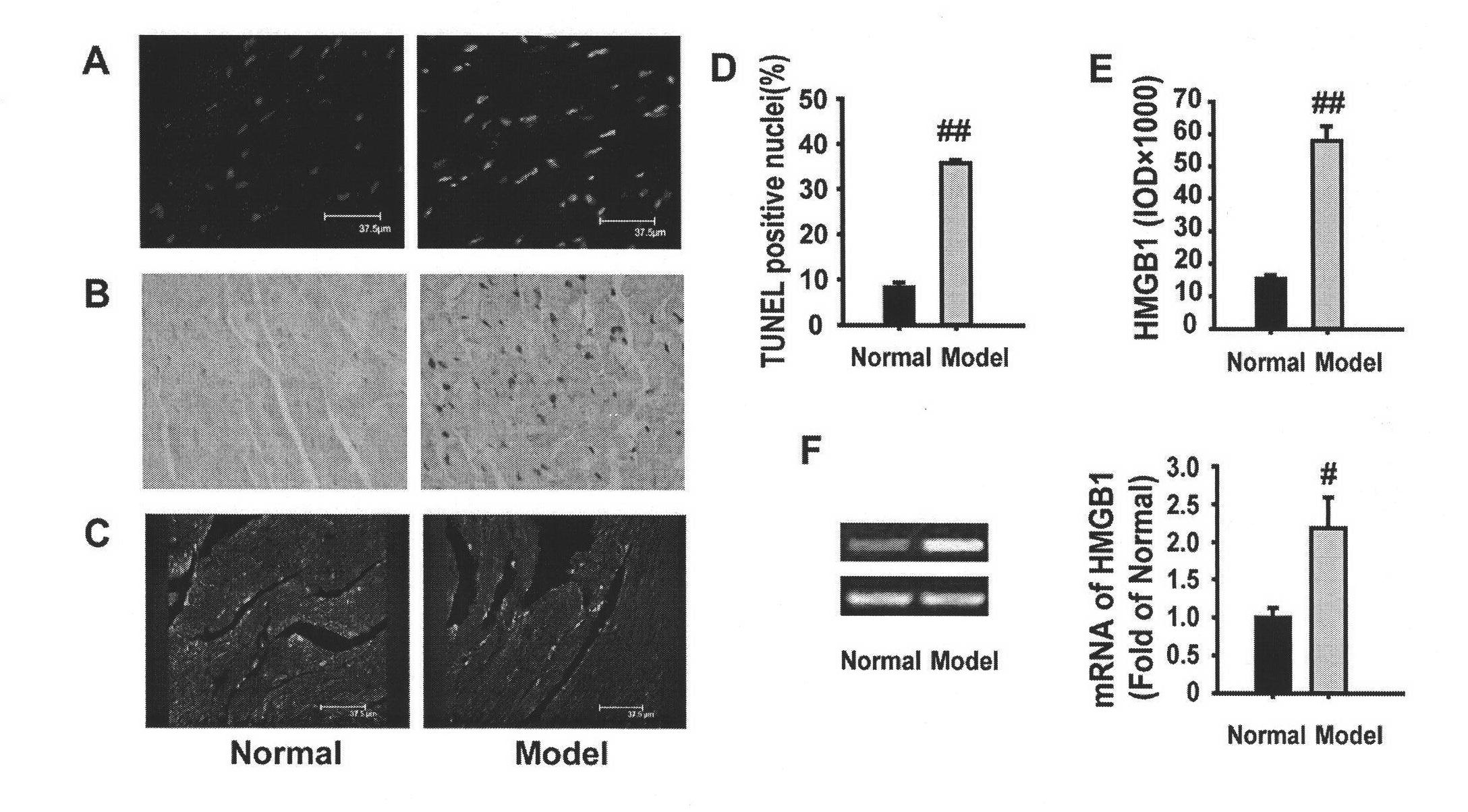
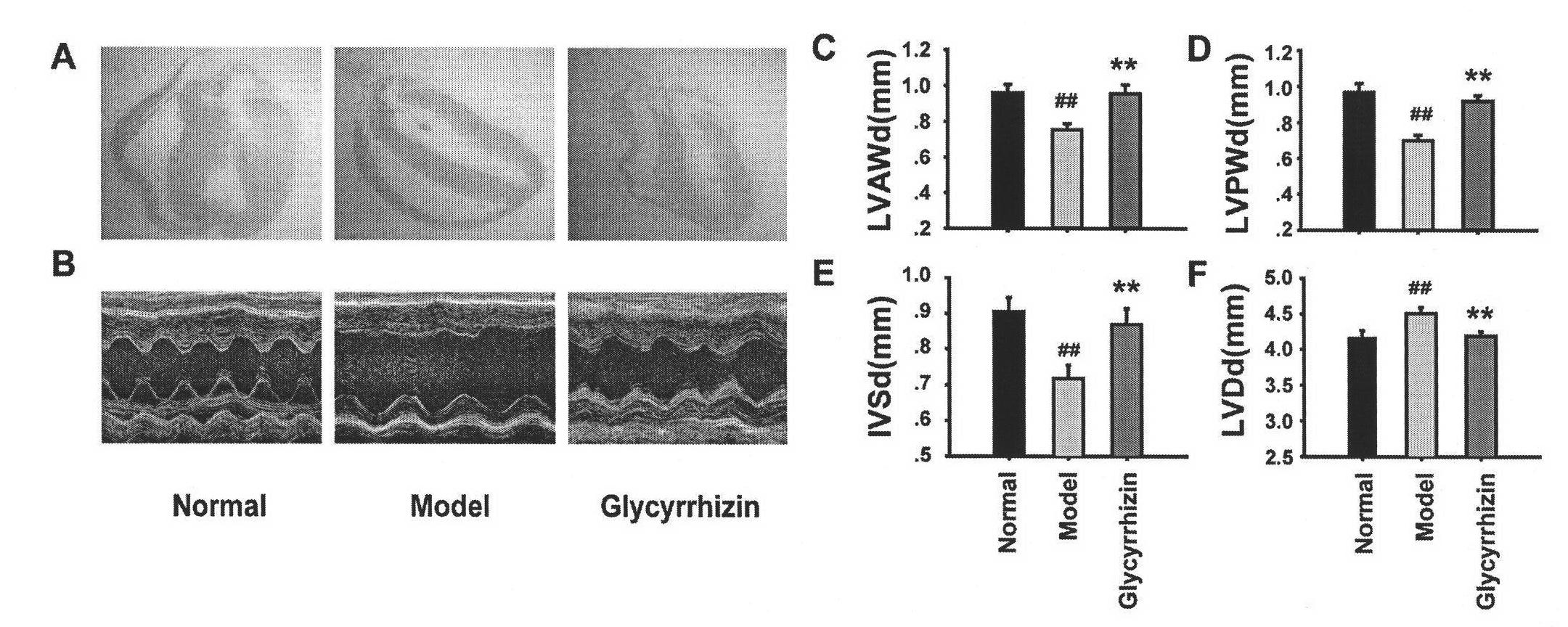
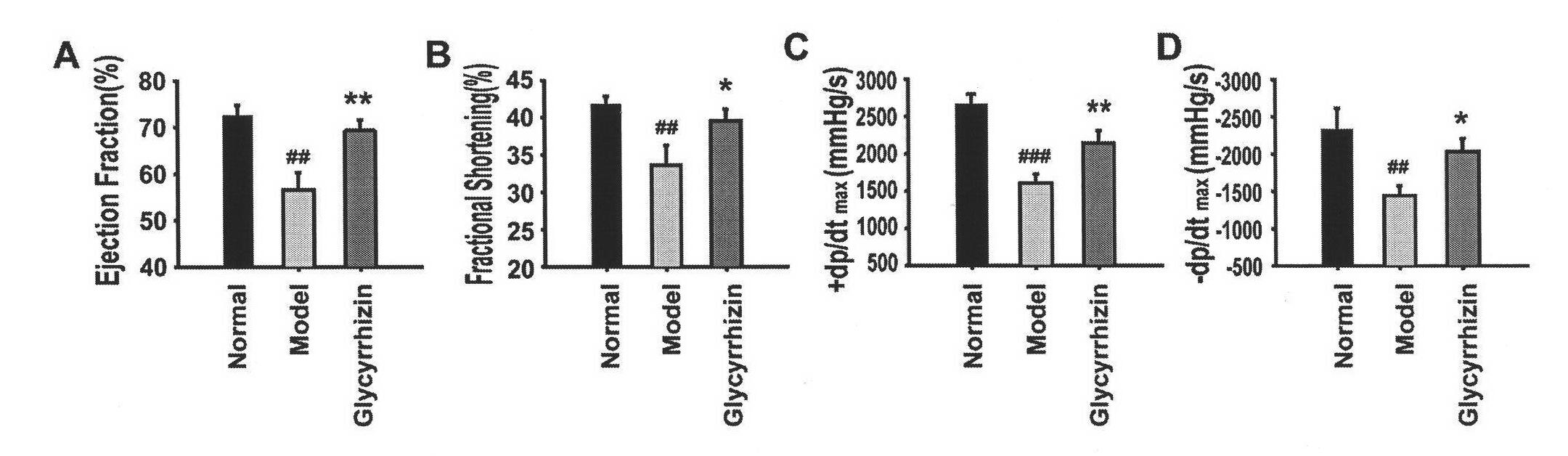
Application of glycyrrhizic acid on treating dilated cardiomyopathy cardiac remodeling and cardiac dysfunction
InactiveCN102247392ARelieve cardiomyopathyOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderFunctional disturbanceCardiac dysfunction
The invention discloses an application of glycyrrhizic acid on preventing, curing and alleviating dilated cardiomyopathy, comprising the steps of inhibiting cardiac abnormal remodeling, improving cardiac dysfunction and improving heart tissue fibrosis of dilated cardiomyopathy patients, wherein the step of inhibiting cardiac abnormal remodeling comprises the steps of inhibiting the ventricular dilatation of dilated cardiomyopathy patients, especially the abnormal dilatation of the ventriculus sinister or bilateral sinister; and the step of improving cardiac dysfunction means the operation of improving systolic and diastolic function obstacles of the dilated cardiomyopathy patients.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Cardiac arrhythmia treatment methods and biological pacemaker
InactiveUS20110286931A1Effective therapyGuaranteed functionOrganic active ingredientsMedical devicesCardiac cellCardiac arrhythmia
Disclosed are methods of preventing or treating cardiac arrhythmia. In one embodiment, the methods include administering to an amount of at least one polynucleotide that modulates an electrical property of the heart. The methods have a wide variety of important uses including treating cardiac arrhythmia. Also disclosed are methods and systems for modulating electrical behavior of cardiac cells. Preferred methods include administering a polynucleotide or cell-based composition that can modulate cardiac contraction to desired levels, e.g., the administered composition functions as a biological pacemaker.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Myoblast treatment of diseased or weakened organs
InactiveUS20070009499A1Increase blood flowImprove bindingBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeterograftsWeakness
Bioengineering the regenerative heart or other body organ in need of greater muscle mass or improved blood perfusion provides a novel treatment for organ weakness or failure. In the case of cardiac failure treatment, on May 14, 2002, a 55-year-old man suffering ischemic myocardial infarction received 25 injections carrying 465 million cGMP-produced pure myoblasts into his myocardium after coronary artery bypass grafting. Three myogenesis mechanisms were elucidated with 17 human / porcine xenografts using cyclosporine as immunosuppressant. Some myoblasts developed to become cardiomyocytes. Others transferred their nuclei into host cardiomyocytes through natural cell fusion. As yet others formed skeletal myofibers with satellite cells. De novo production of contractile filaments augmented heart contractility. Human myoblasts transduced with VEGF165 gene produced six times more capillaries in porcine myocardium than placebo. Xenograft rejection was not observed for up to 20 weeks despite cyclosporine discontinuation at 6 weeks.
Owner:LAW PETER
Valve clamping device
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments, in particular to a valve clamping device. The valve clamping device comprises a control rod, a first supporting piece, a clamping piece, at least one pair of folding pieces and at least one pair of closing pieces. The folding pieces are arranged on the two sides of the control rod respectively and correspond to the closing pieces. One end of the folding piece is rotationally connected with the control rod, the other end of the folding piece is movably connected with the first supporting piece, and the first supporting piece slides on the control rod; the closing piece is connected with the folding piece; and the clamping piece is arranged between the folding piece and the control rod. The opening and closing degree, namely the opening and closing degree of the valve, of the clamping device is adjusted by automatically adjusting the opening and closing angle through blood pressure driving; therefore, the effects of reducing blood regurgitation during cardiac contraction and reducing the resistance of blood passing through the valve during cardiac diastole are achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG PULSE MEDICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring heart contractility
ActiveUS9168021B2Determined precisely, quickly and non-invasivelyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave based measurement systemsSystoleMedicine
A Method for measuring heart contractility of a patient, in which a mechanical shear wave is propagated through the heart and observation of the propagation leads to determine a shear wave propagation parameter representative of the elasticity of the heart is disclosed. The value of the propagation parameter at the end of a systole is sampled, which leads to a parameter representative of the end systolic elastance.
Owner:SUPERSONIC IMAGINE SA +1
Implantable counterpulsation cardiac assist device
InactiveUS7481760B2Increase coronary blood flowPromotes perfusionBlood pumpsMedical devicesPerfusionMechanical failure
A hollow tubular element is inserted in the descending aorta. The caudad end contains a pressure sensitive passive or preferably, hydraulically or electrically activated, unidirectional valve. A flexible diaphragm situated in a rigid shell affixed over an opening in the element wall divides the shell interior into first and second variable volume chambers. The first chamber opens to the artery. A continuously operating electrical pump is connected to the second chamber through a closed hydraulic system including a multi-valve chamber. The valves regulate fluid flow to the second chamber in accordance with electrical signals from the heart. Fluid flow is directed to the second chamber during cardiac diastole and away from the second chamber during cardiac systole, causing the device to function in a counterpulsation mode. The work of the heart is decreased and coronary blood flow is increased to promote the formation of new coronary collateral channels and the perfusion of the heart itself. In the event of mechanical failure, pre-implantation heart function is not impeded.
Owner:PPTT
Automatic diagnosis system for human body dilated cardiomyopathy
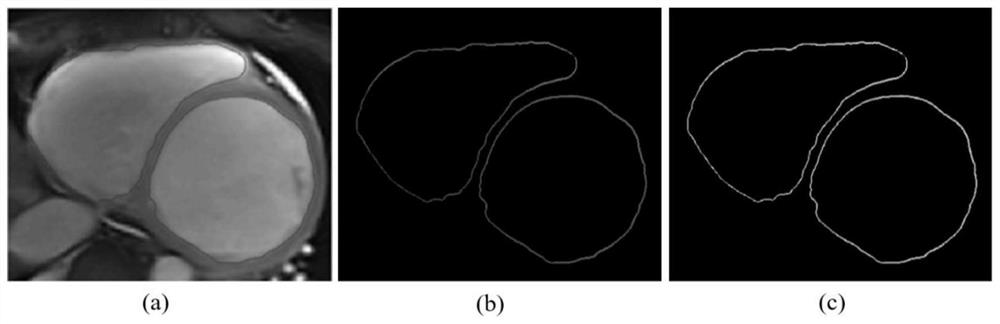
ActiveCN113112473AAvoid errorsReduce manual involvementImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyOriginal data
The invention relates to the technical field of diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), in particular to an automatic diagnosis system for human dilated cardiomyopathy. The system provided by the invention can realize the following diagnosis process: a heart image in a heart cycle is used as original data to be input, and a computer program can judge an end diastole image and an end systole image from the original data to segment a left ventricle and a right ventricle; and then heart parameters capable of reflecting the strain information of the left ventricle, the right ventricle and the ventricular muscle wall are calculated. After heart parameters are obtained, features of the heart parameters are input into a classifier, and DCM patients and non-DCM patients can be distinguished. The end-to-end full-automatic DCM diagnosis is realized, and compared with manual or semi-automatic diagnosis, the end-to-end full-automatic DCM diagnosis method has a good application prospect.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com