Patents
Literature
51 results about "End systole" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
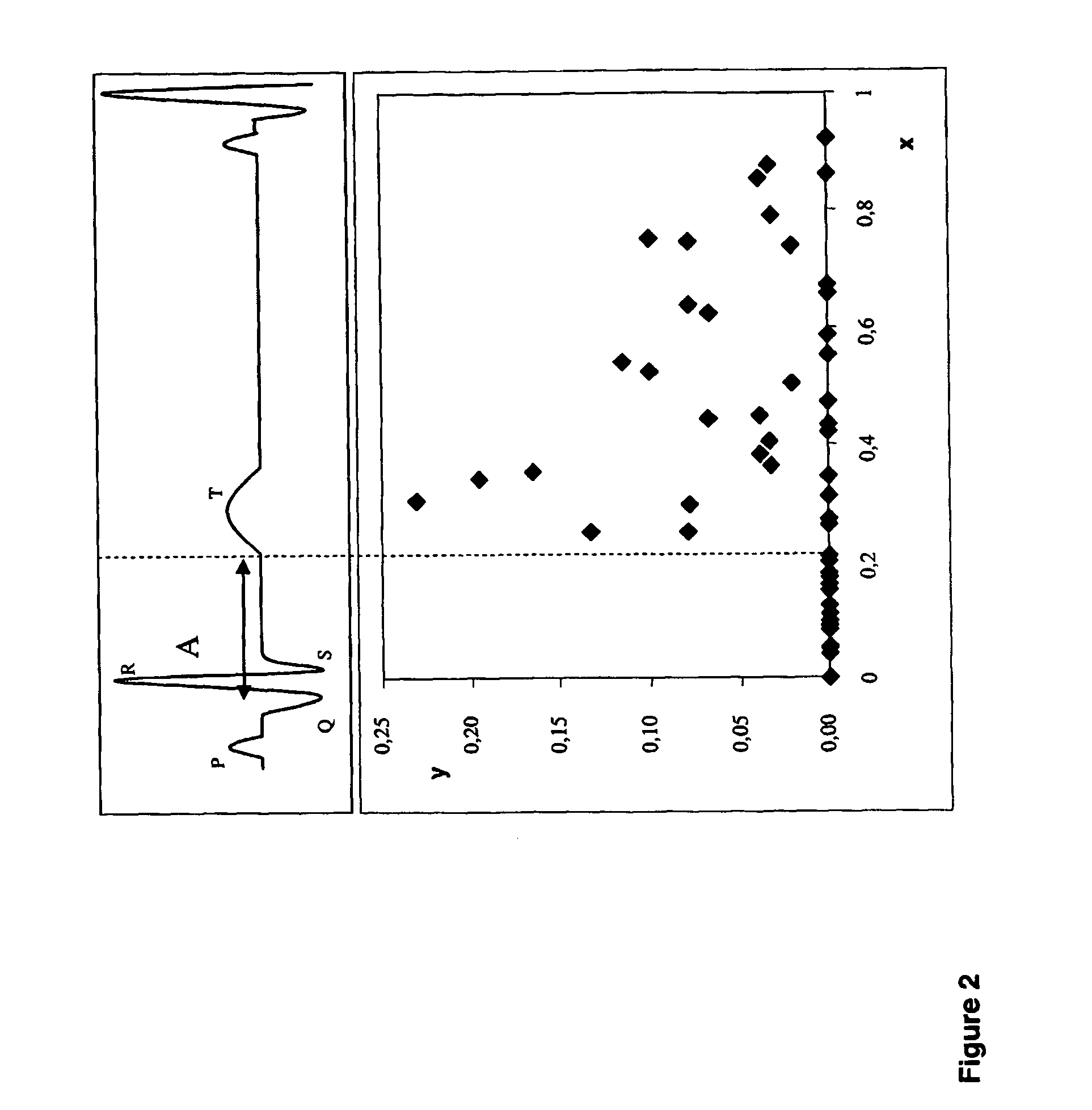
End-systolic volume (ESV) is the volume of blood in a ventricle at the end of contraction, or systole, and the beginning of filling, or diastole. ESV is the lowest volume of blood in the ventricle at any point in the cardiac cycle.
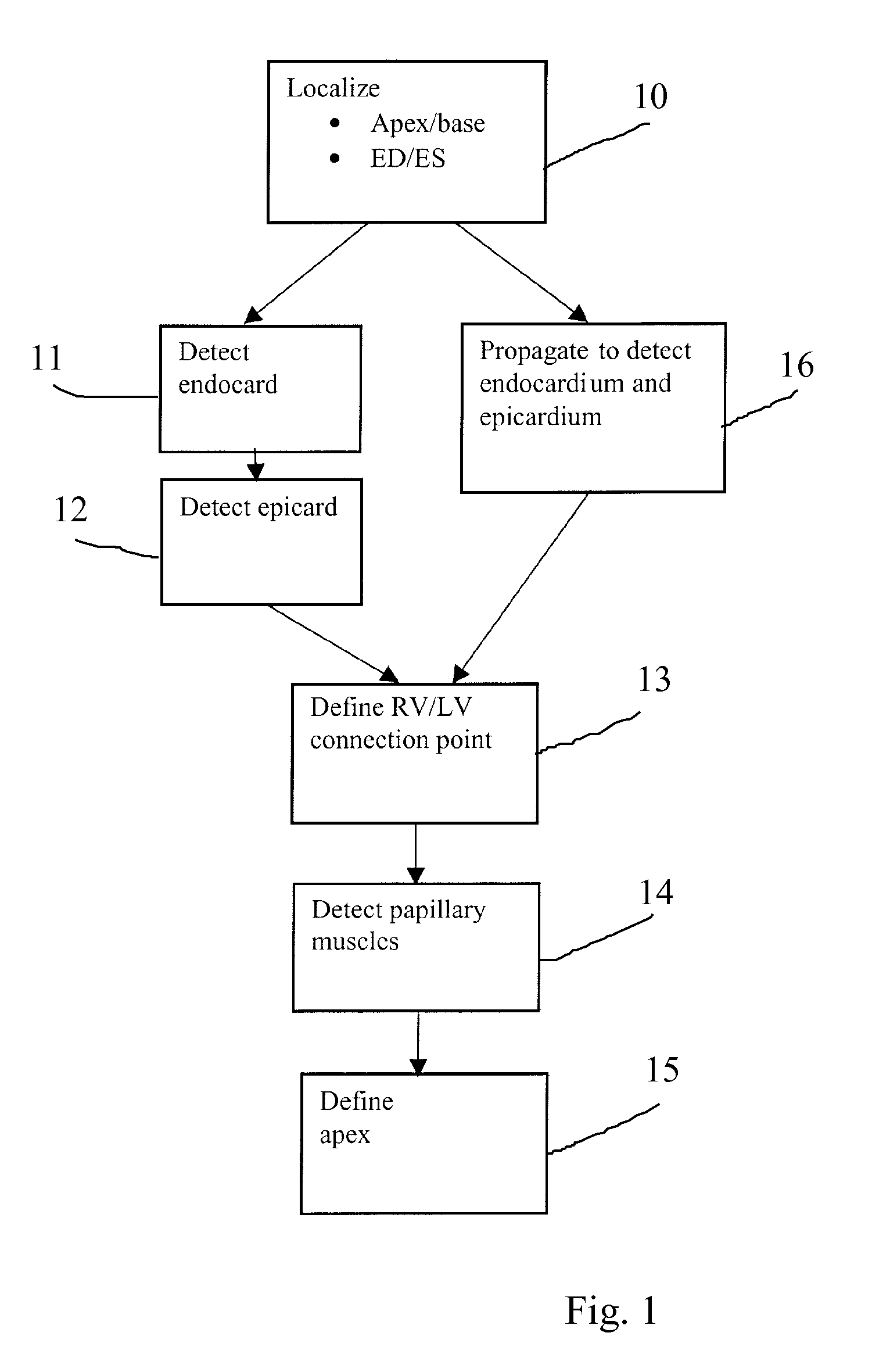
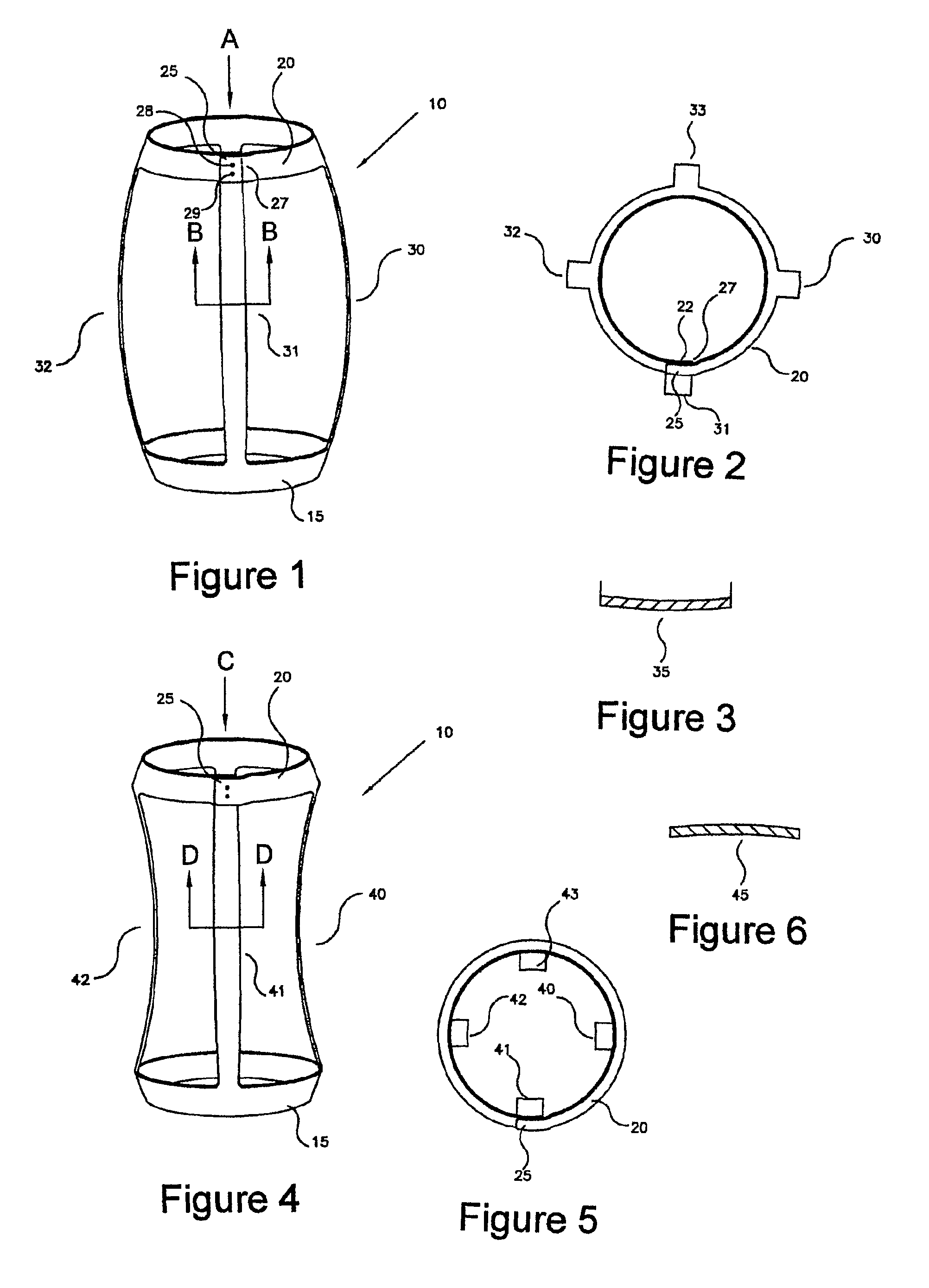
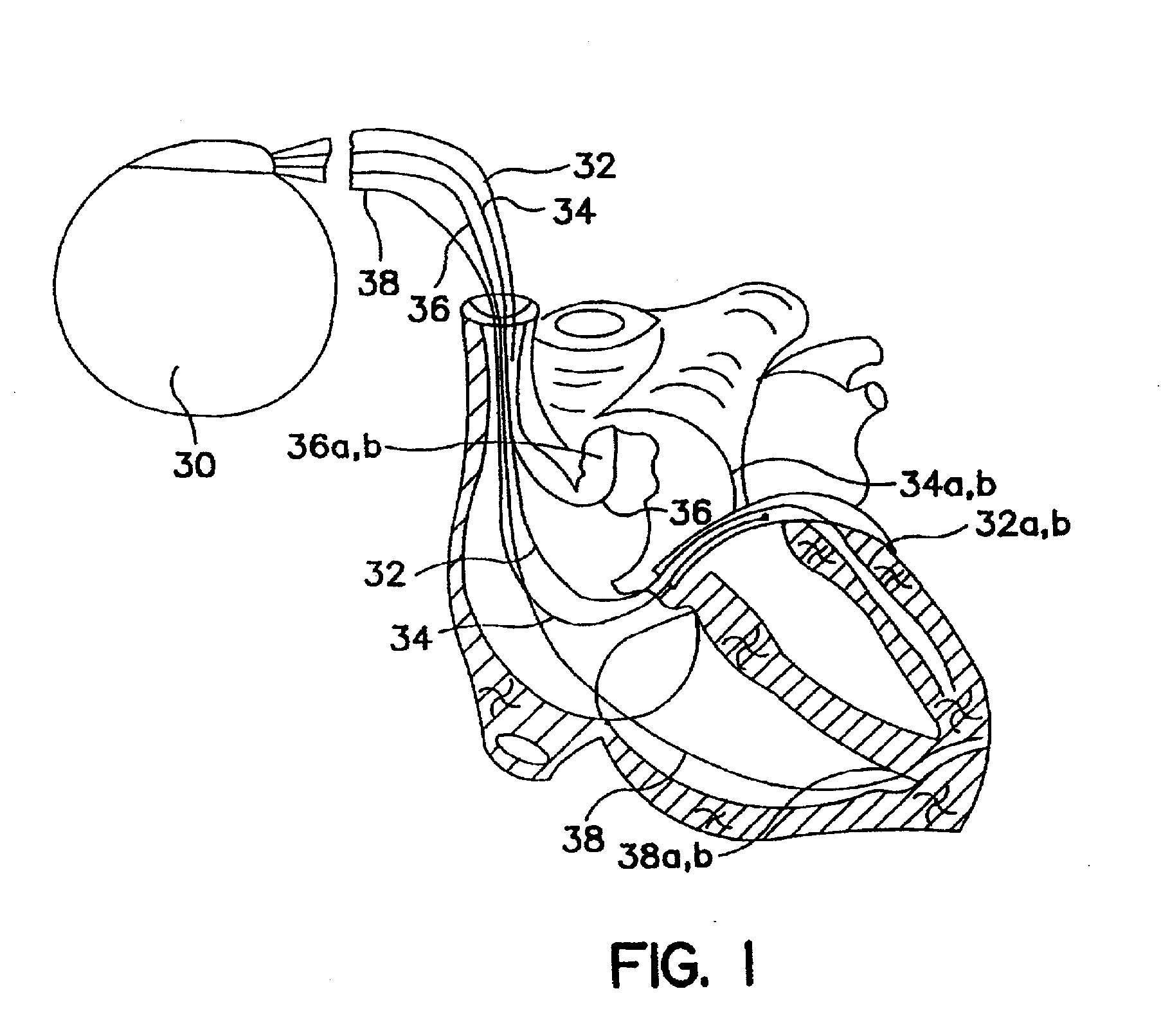
Autonomous boundary detection system for echocardiographic images
InactiveUS6716175B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationEndocardial border
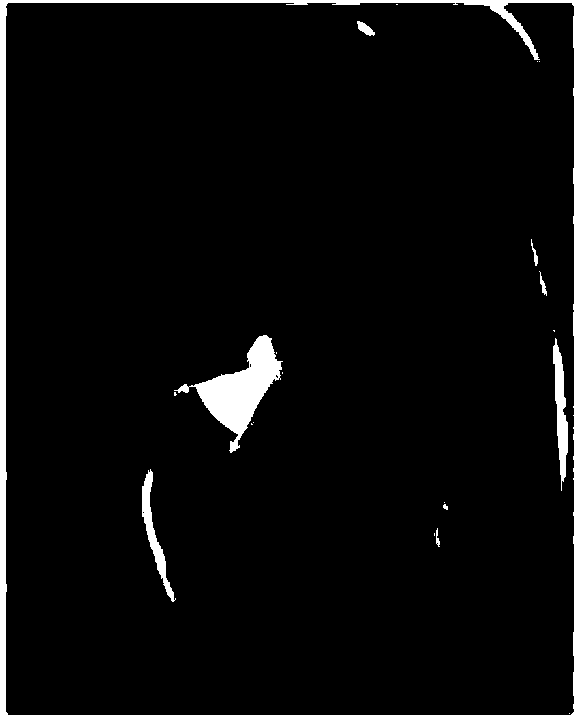
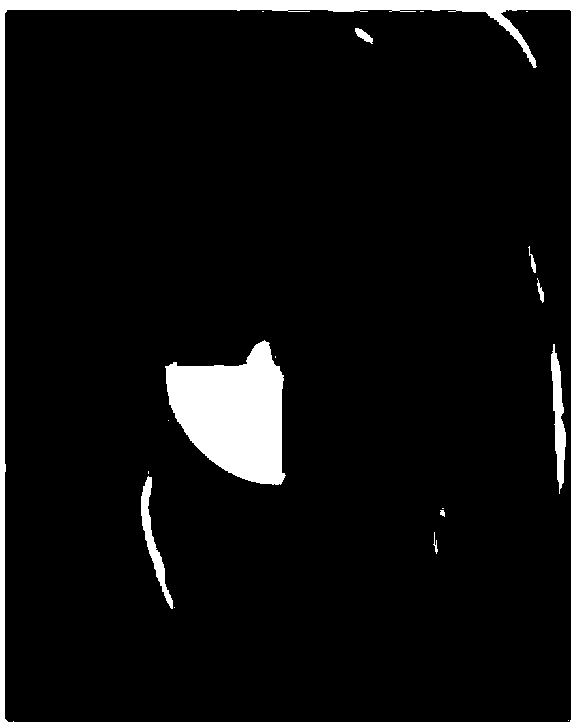
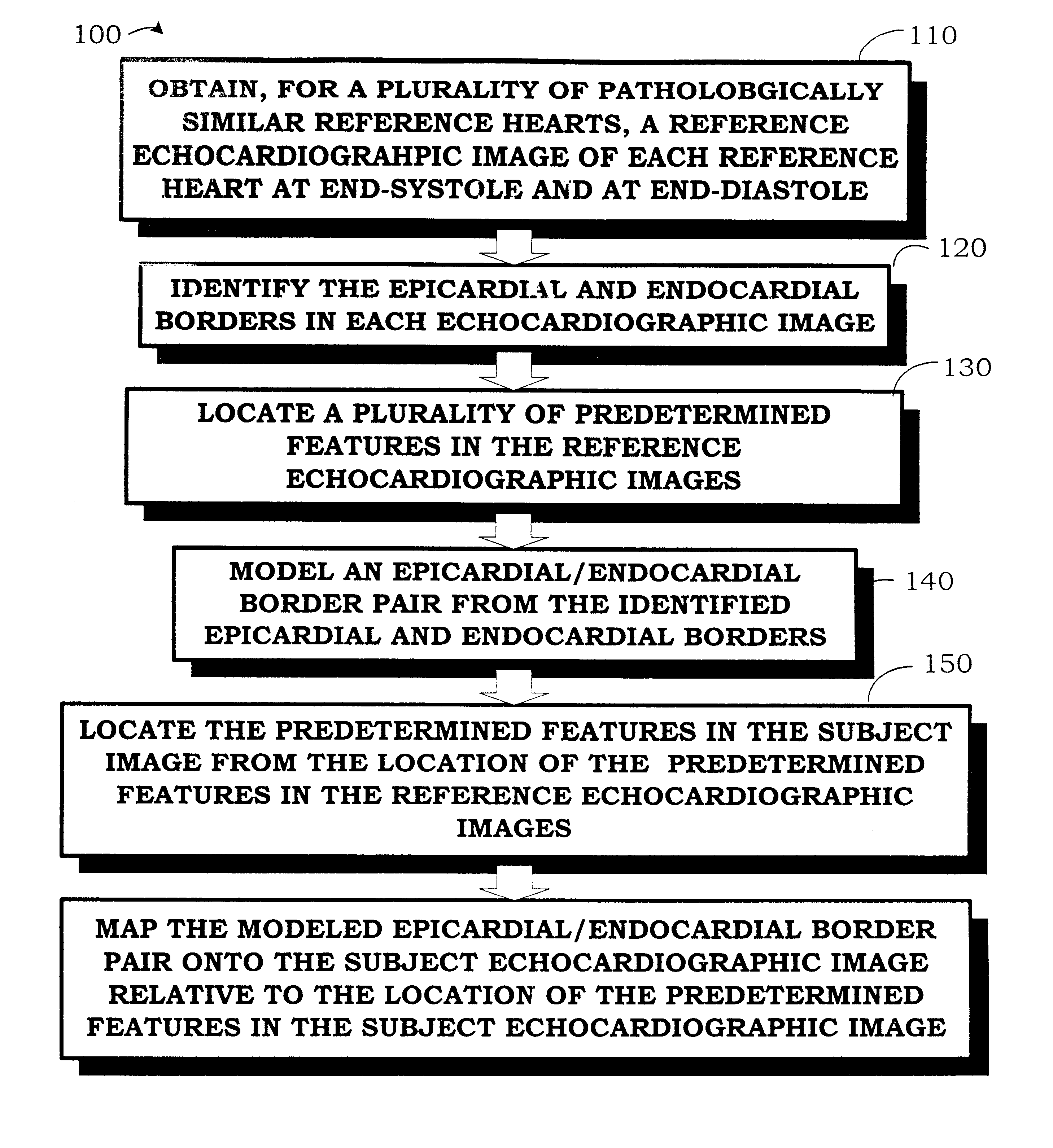
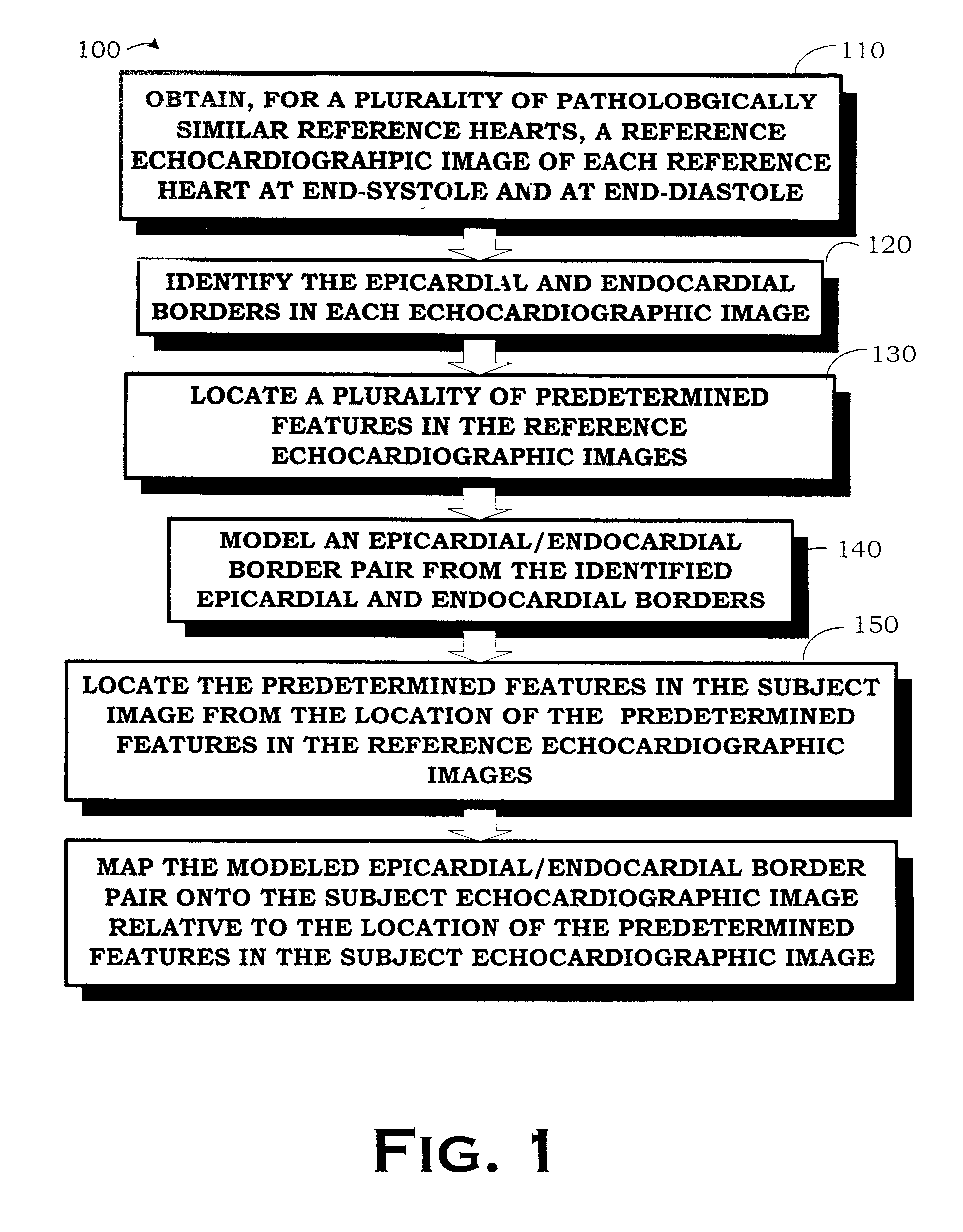
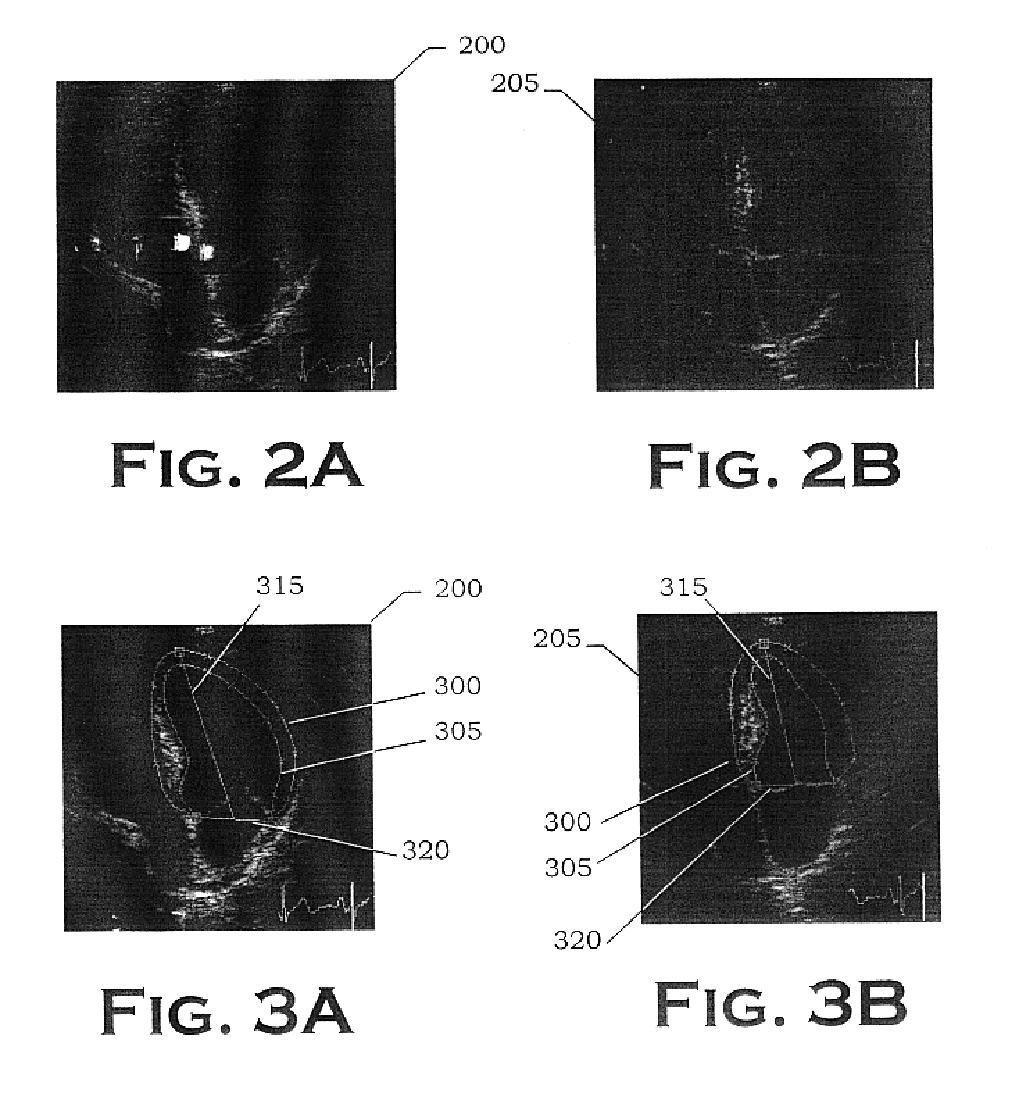
The invention comprises a method and apparatus for generating a synthetic echocardiographic image. The method comprises first obtaining, for a plurality of pathologically similar reference hearts, a reference echocardiographic image of each reference heart at end-systole and at end-diastole. Next, the coupled epicardial and endocardial borders are identified in each echocardiographic image. An epicardial / endocardial border pair is then modeled from the identified borders. The method then locates a plurality of predetermined features in the reference echocardiographic images. The predetermined features are then located in the subject echocardiographic image from the location of the predetermined features in the reference echocardiographic images. The modeled epicardial / endocardial border pair is then mapped onto the subject echocardiographic image relative to the location of the predetermined features in the subject echocardiographic image. The apparatus generally comprises an echocardiographic machine for obtaining the echocardiographic images that are then processed by a computing system. In one aspect of the invention, the invention comprises such a computing system programmed to perform the autonomous portions of the method. In another aspect, the invention comprises a program storage medium encoded with instructions that perform the autonomous portions of the method when executed by a computer.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal AV an VV intervals
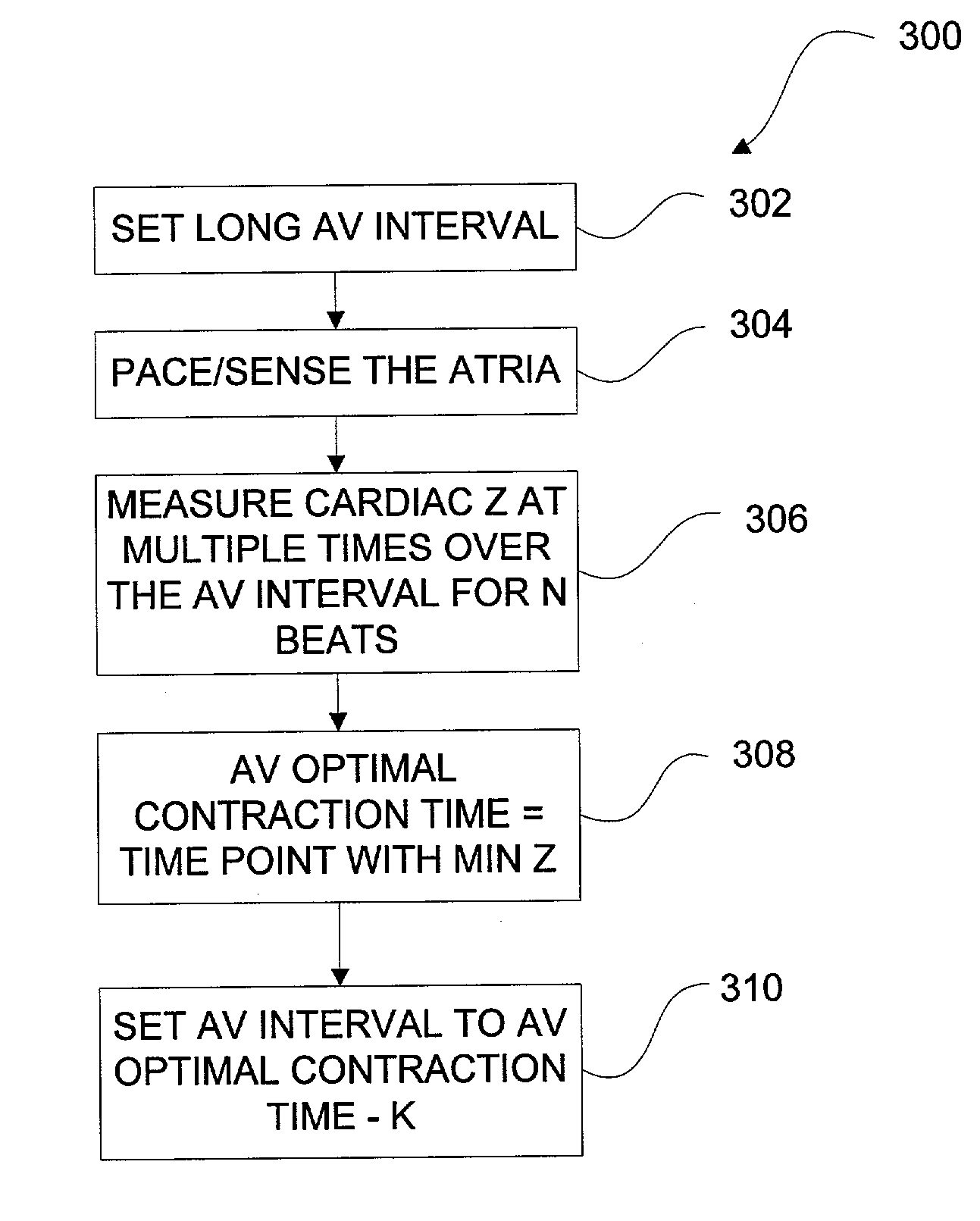
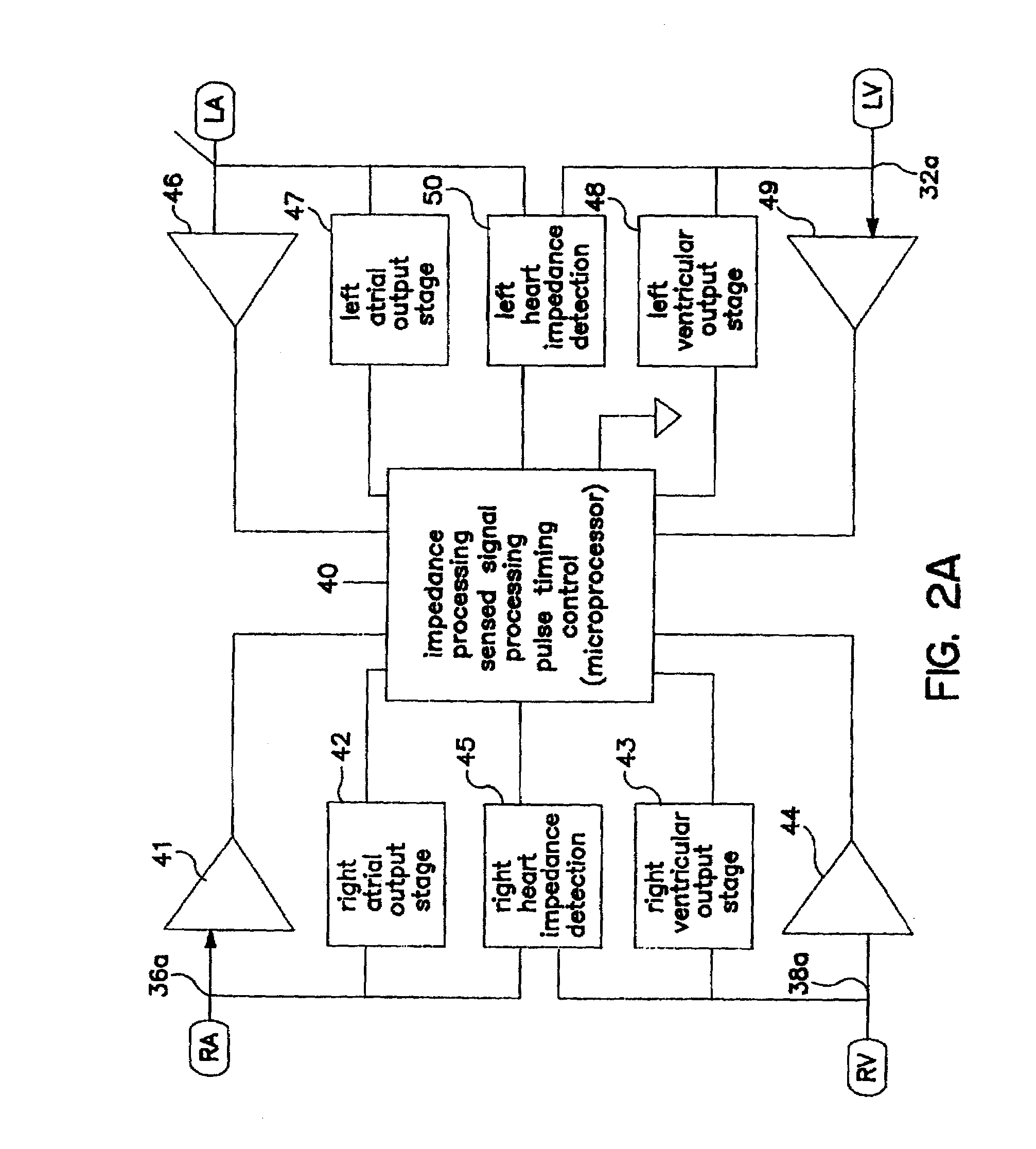
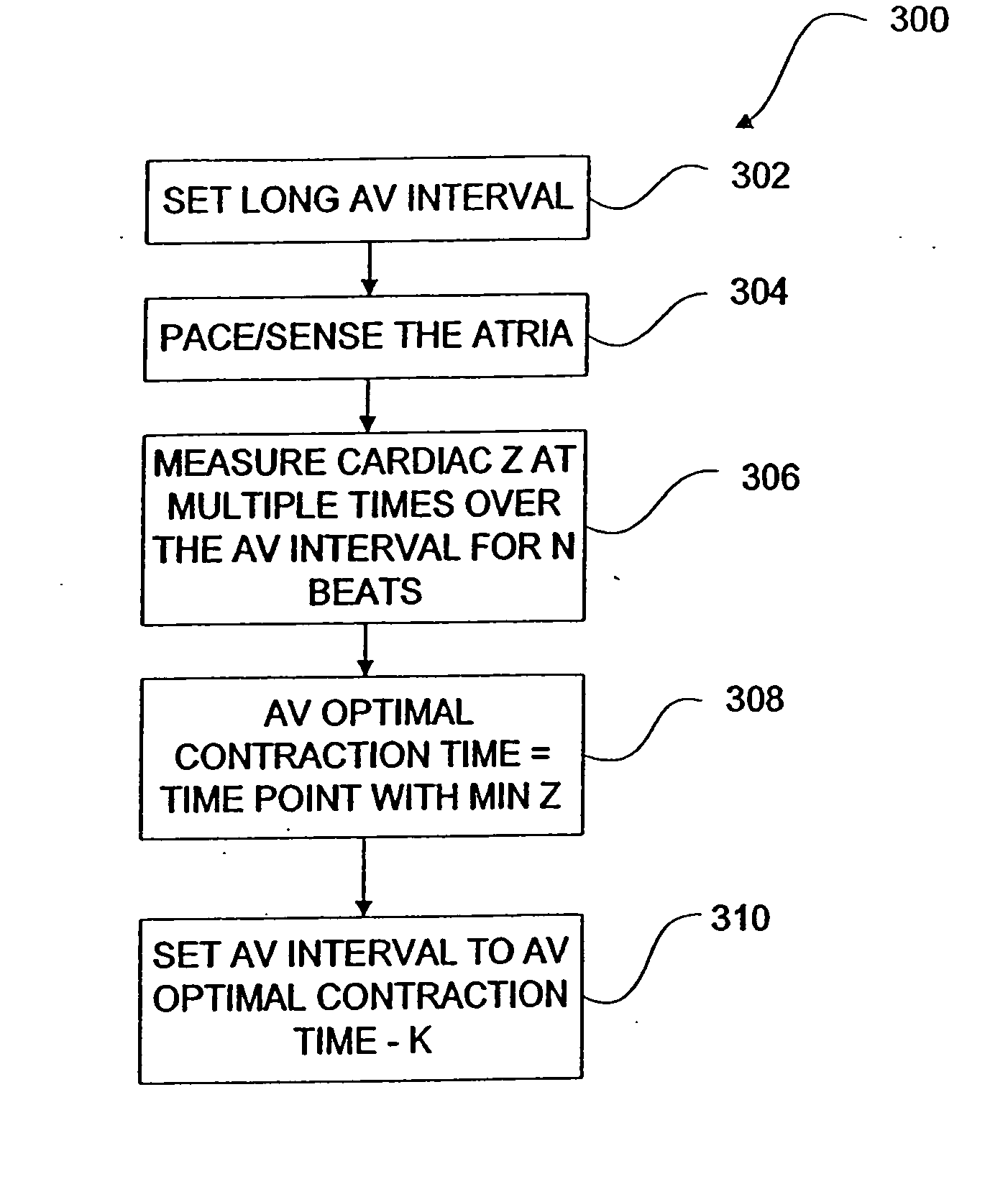
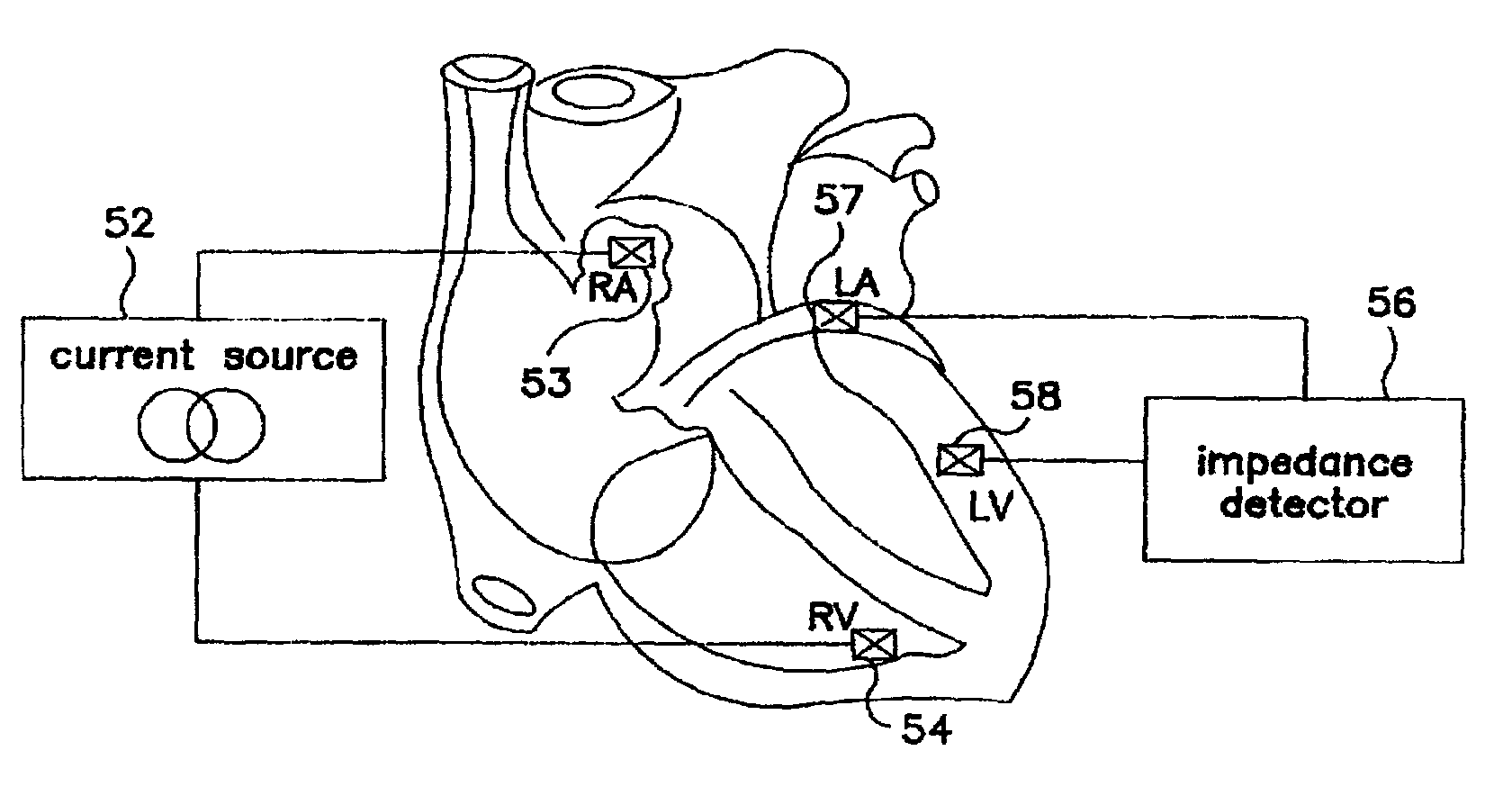
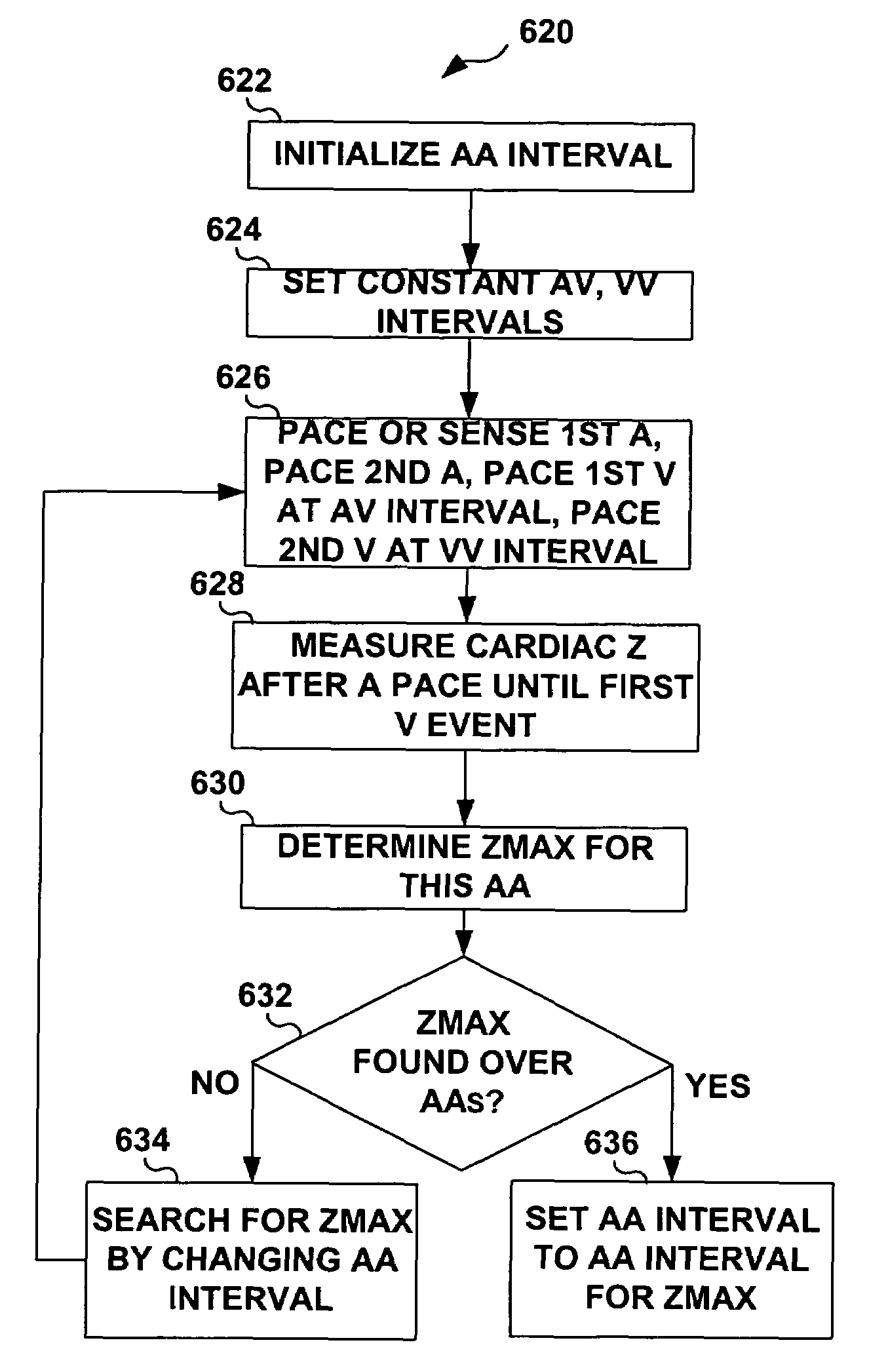
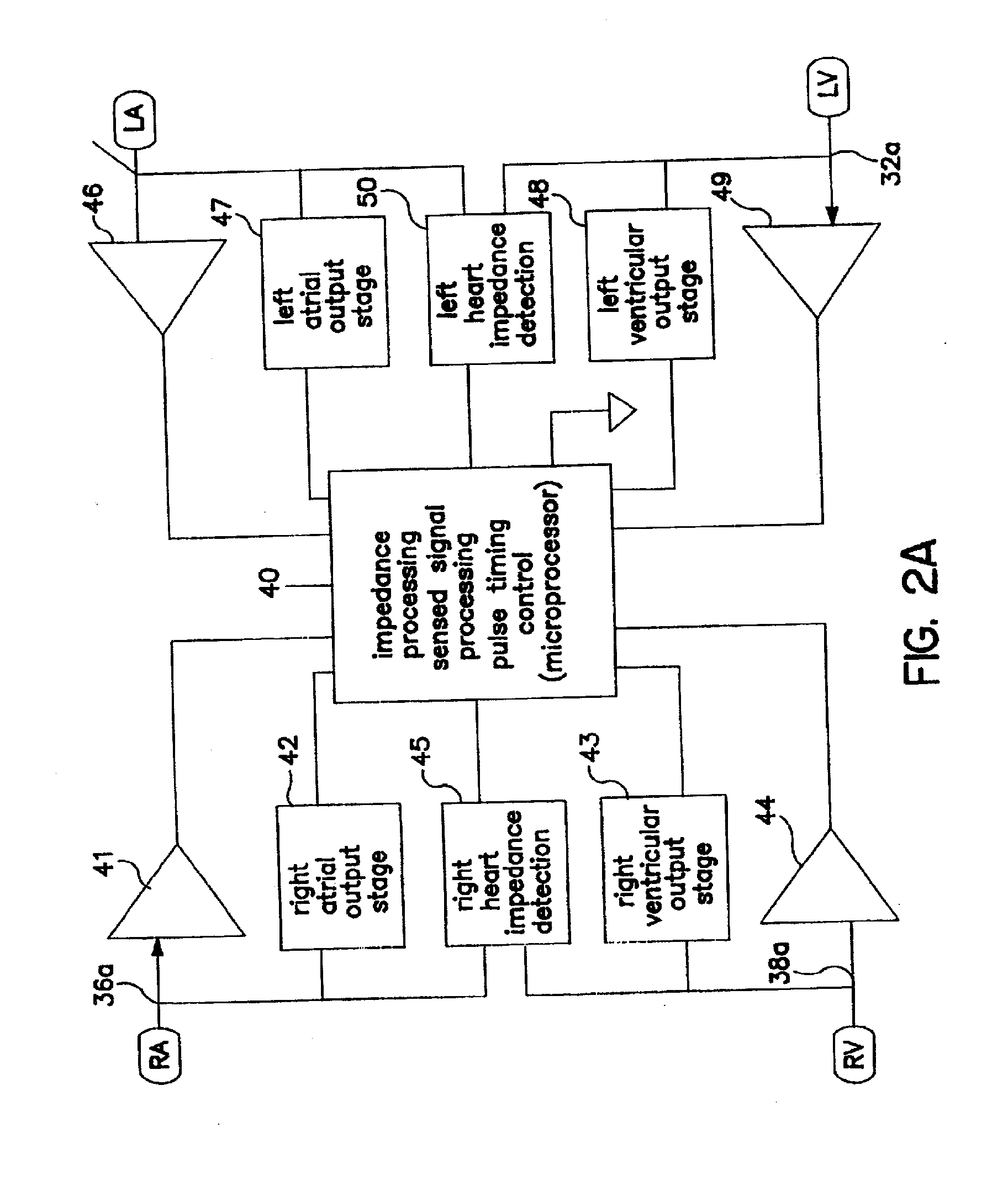
Methods and devices for determining optimal Atrial to Ventricular (AV) pacing intervals and Ventricular to Ventricular (VV) delay intervals in order to optimize cardiac output. Impedance, preferably sub-threshold impedance, is measured across the heart at selected cardiac cycle times as a measure of chamber expansion or contraction. One embodiment measures impedance over a long AV interval to obtain the minimum impedance, indicative of maximum ventricular expansion, in order to set the AV interval. Another embodiment measures impedance change over a cycle and varies the AV pace interval in a binary search to converge on the AV interval causing maximum impedance change indicative of maximum ventricular output. Another method varies the right ventricle to left ventricle (VV) interval to converge on an impedance maximum indicative of minimum cardiac volume at end systole. Another embodiment varies the VV interval to maximize impedance change.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
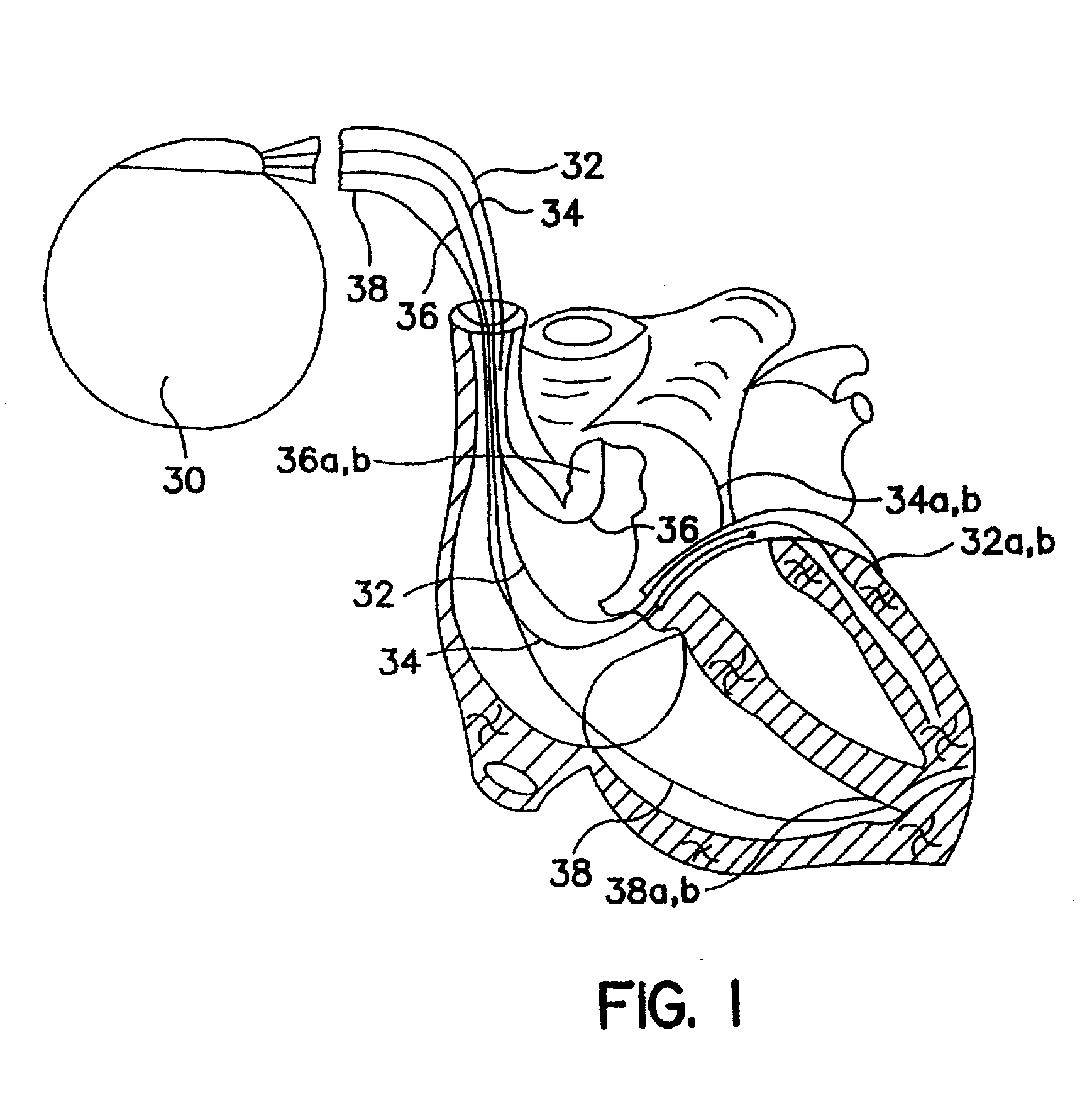
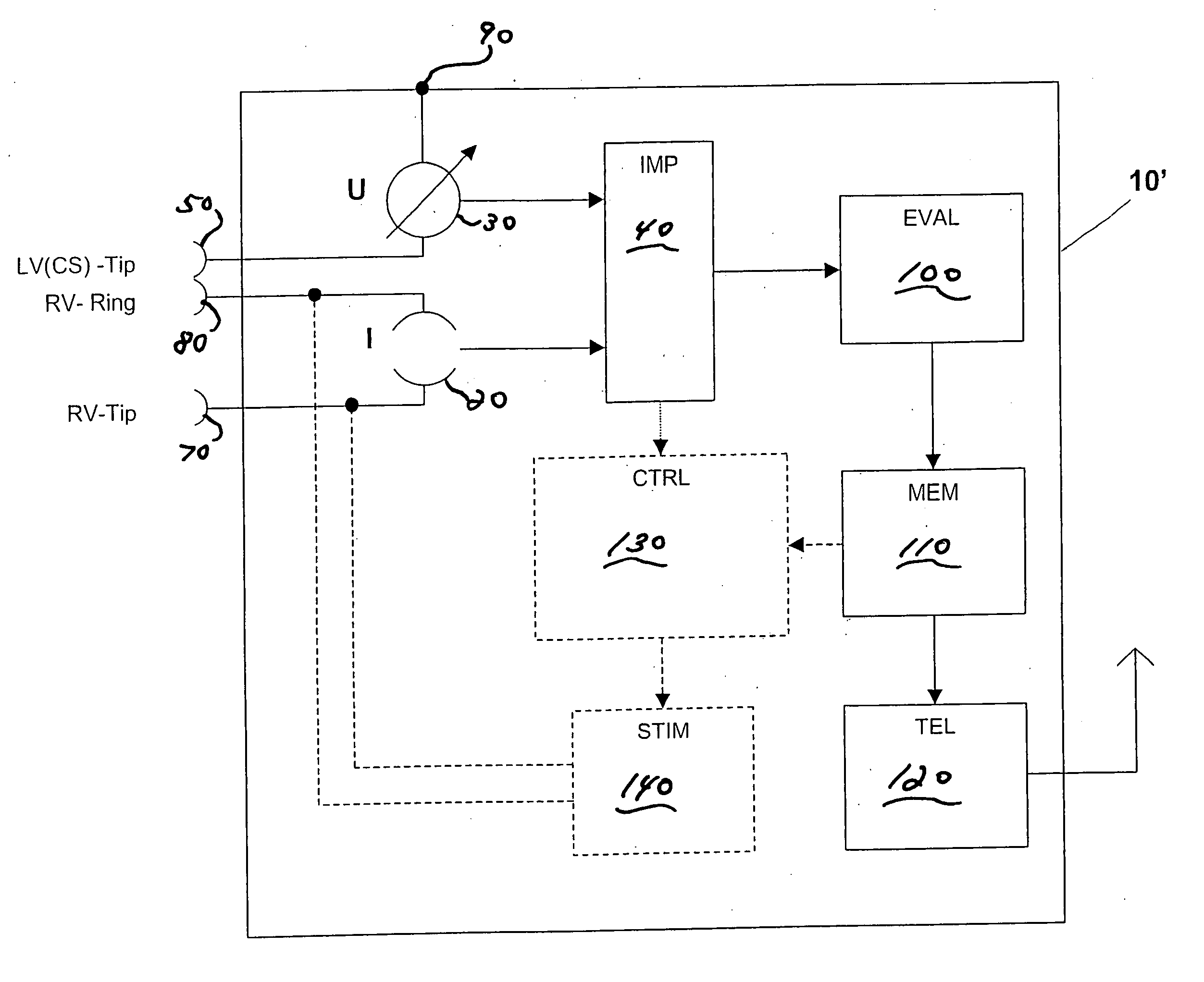
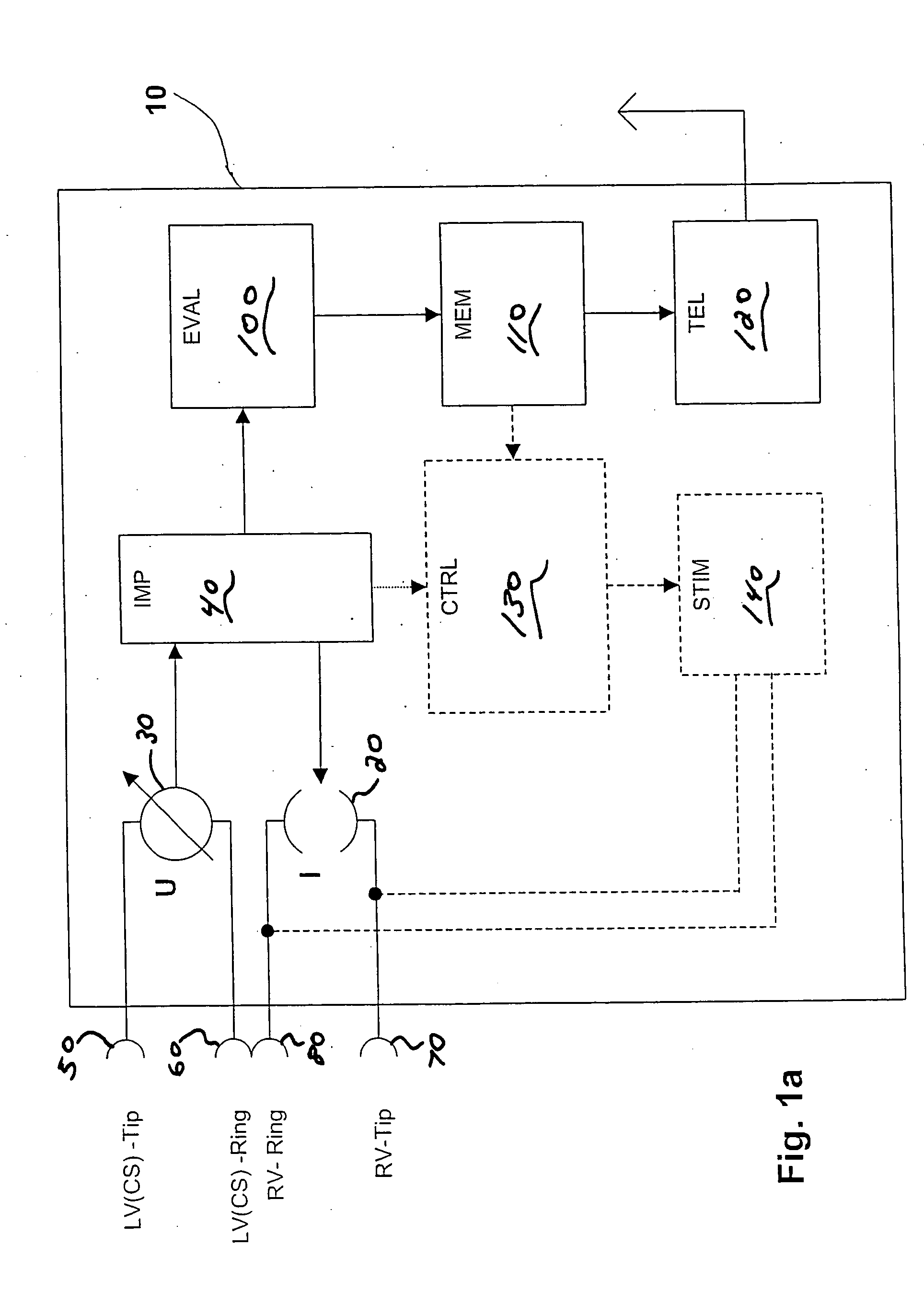
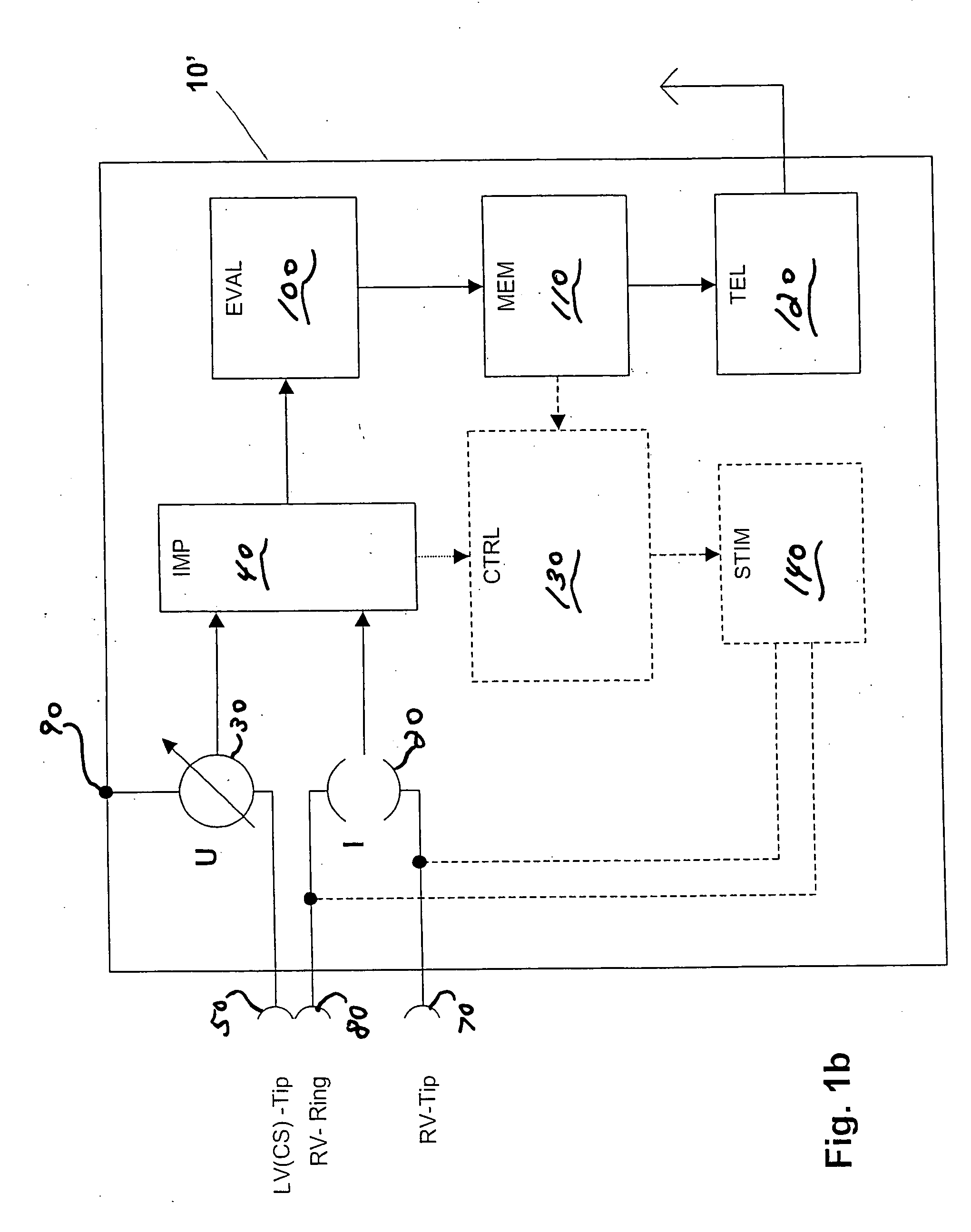
Intracardial impedance measuring arrangement
Certain embodiments of the present invention disclose an implant with electrode line connections for the connection of intracardial and / or epicardial electrode lines, wherein the electrode line connections have together at least three electrical contacts of which at least one is associated with a right-ventricular electrode and another is associated with a left-ventricular electrode, an impedance determining unit (IMP) which has a current or voltage source (I) and a measuring device (U) for a corresponding voltage or current measurement operation, which is connected to the electrical contacts and possibly a housing electrode of the implant, in such a way as to afford a tri- or quadrupolar impedance measuring arrangement which includes exclusively ventricular electrodes and in addition possibly the housing electrode, wherein the impedance measuring arrangement produces impedance measurement values and is connected to an evaluation unit (EVAL) and the evaluation unit (EVAL) is adapted to ascertain a minimum of the impedance measurement values within a first time window (defined relative to a ventricular event) as end-diastolic impedance (EDZ) and a maximum of the impedance measurement values within a second time window as end-systolic impedance (ESZ).
Owner:BIOTRONIK
System and method to measure cardiac ejection fraction
InactiveUS20080249414A1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsCardiac cycleLeft ventricle wall
A system and method to acquire 3D ultrasound-based images during the end-systole and end-diastole time points of a cardiac cycle to allow determination of the change and percentage change in left ventricle volume at the time points.
Owner:VERATHON
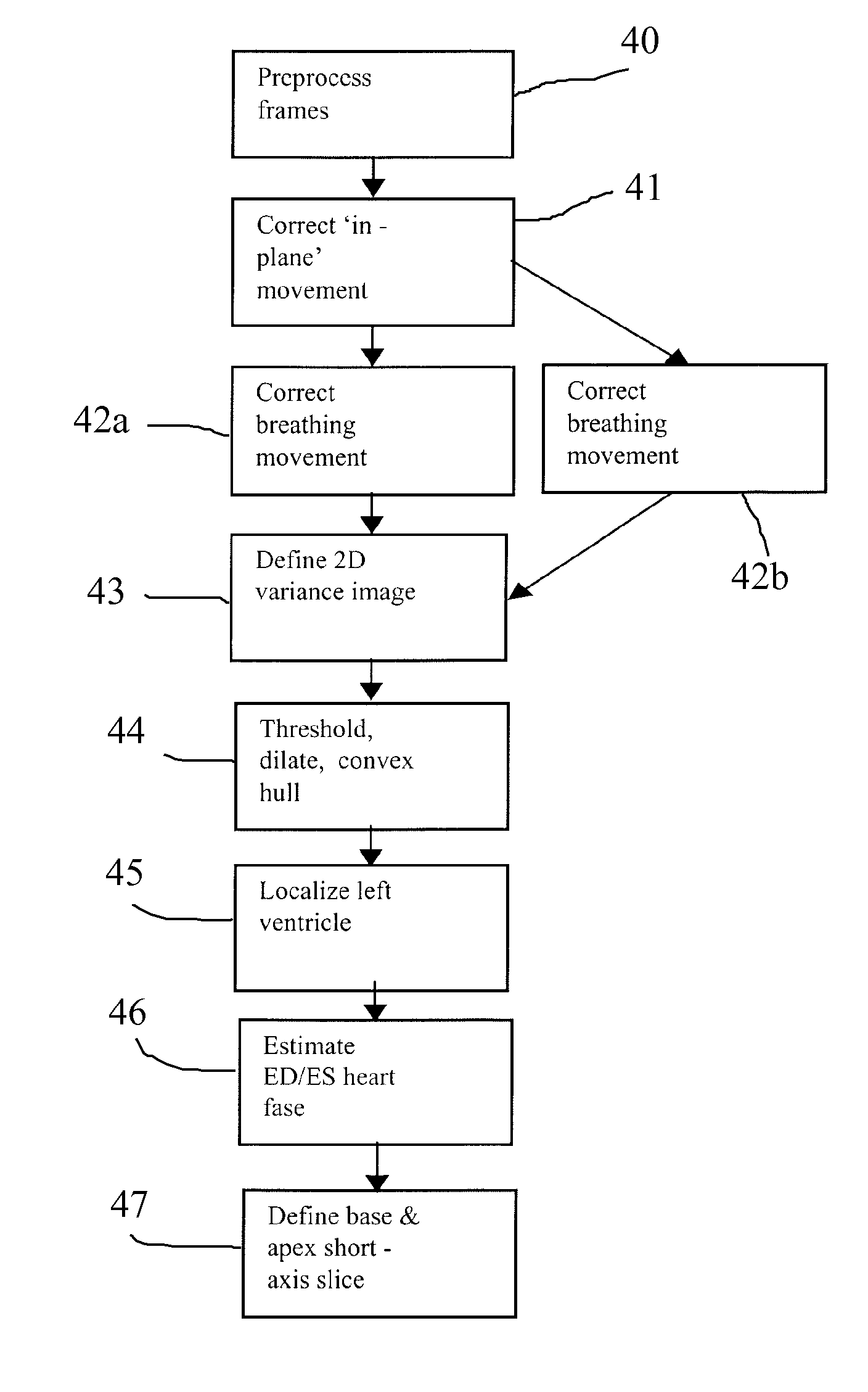
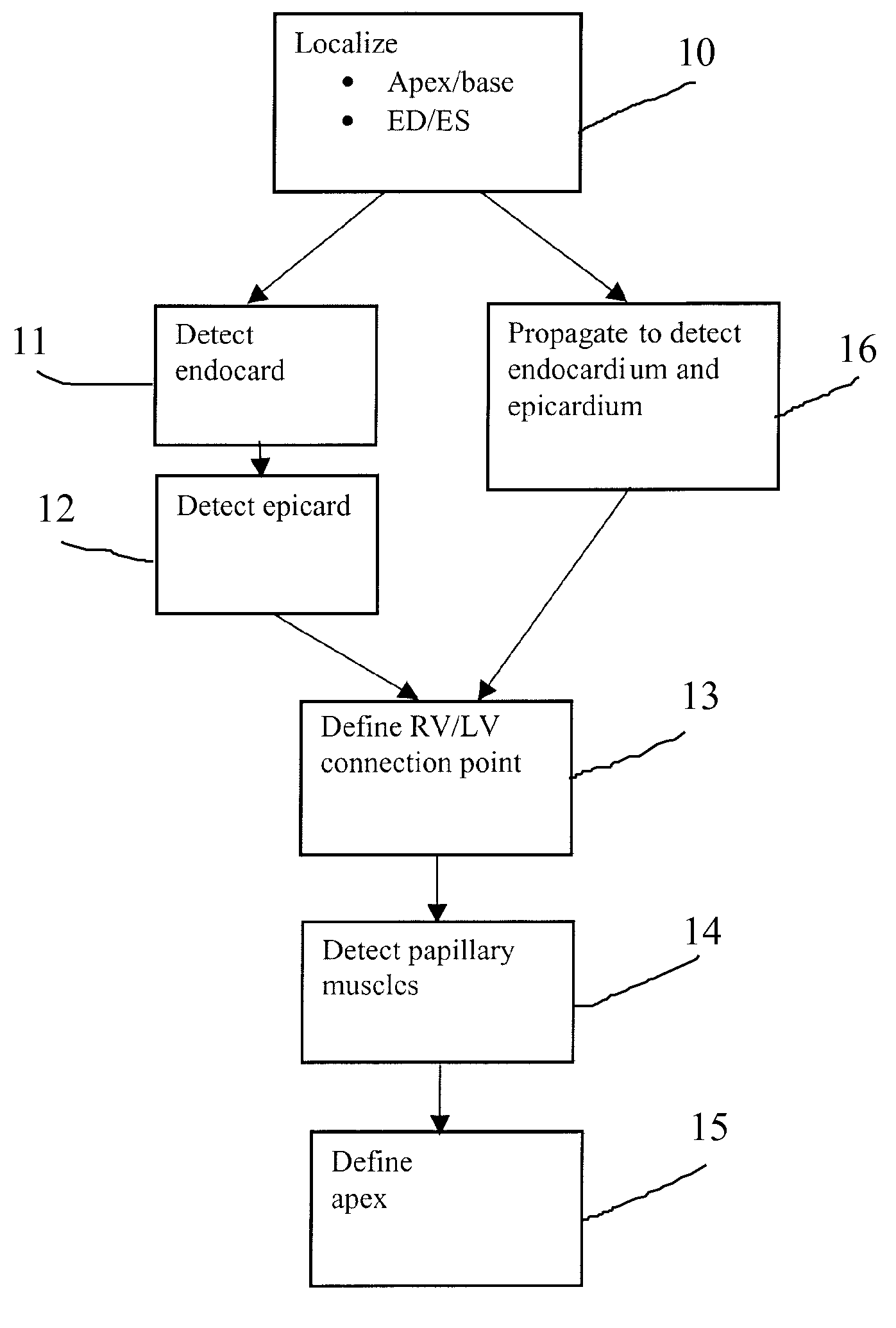
Method, Apparatus and Computer Program Product for Automatic Segmenting of Cardiac Chambers
ActiveUS20070253609A1Improve accuracyGood reproducibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementData setResonance
A method, apparatus and computer program product for machine-based segmentation of the cardiac chambers in a four-dimensional magnetic resonance image data that contains at least short-axis cine sequences. The segmenting is based on temporal variations in the data set and on features extracted from the image data. In particular, the method and apparatus process the image data to automatically segment an endocard based on fuzzy object extraction and to automatically segment an epicard through finding a radial minimum cost with dynamic sign definition and tissue classification. In addition, image data is preferably preprocessed to eliminate high local image variances and inhomogeneity. The image data is also preferably processed to identify positions of a base slice, an apex slice, an end-diastole, an end-systole and an LVRV connection.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
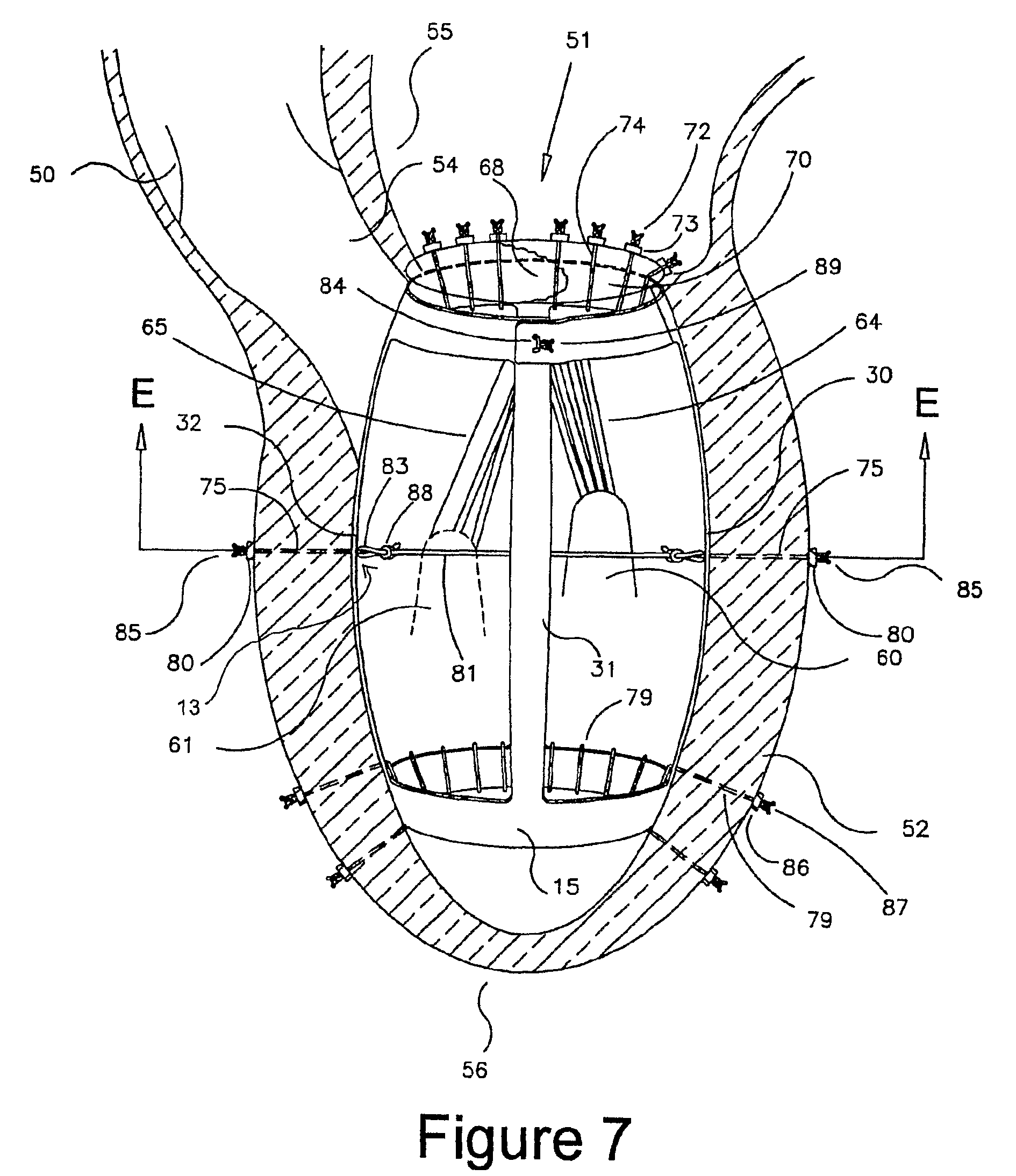
Method and apparatus for the surgical treatment of congestive heart failure
ActiveUS7758491B2Effective of treatingReduce manufacturing costSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsSurgical treatmentSystole
An apparatus implantable in a heart ventricle includes a frame configured to engage an inner circumferential periphery of the ventricle and to expand and contract between an expanded state corresponding to a desired end diastolic diameter of the ventricle and a contracted state corresponding to a desired end systolic diameter of the ventricle. A bistable structure is operatively associated with the frame. The bistable structure mechanically assists movement of the ventricle toward both an end systolic diameter during systole and an end diastolic diameter during diastole. The bistable structure may be integrally formed of the frame. A method of implanting the apparatus in a heart ventricle includes surgically accessing a ventricle, inserting the apparatus in the ventricle and attaching the device to a portion of myocardium defining an inner circumferential periphery of the ventricle.
Owner:GENESEE BIOMEDICAL
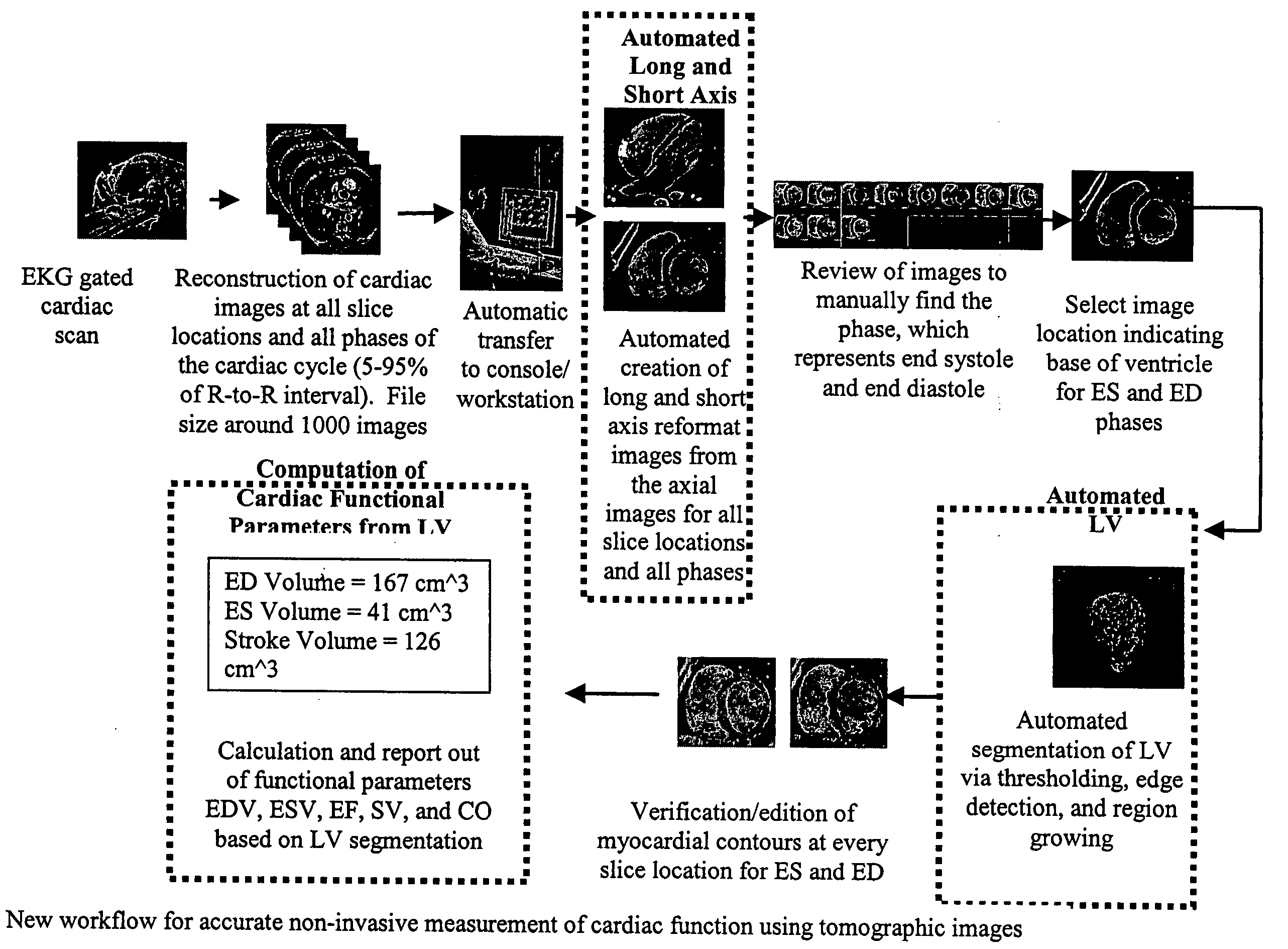
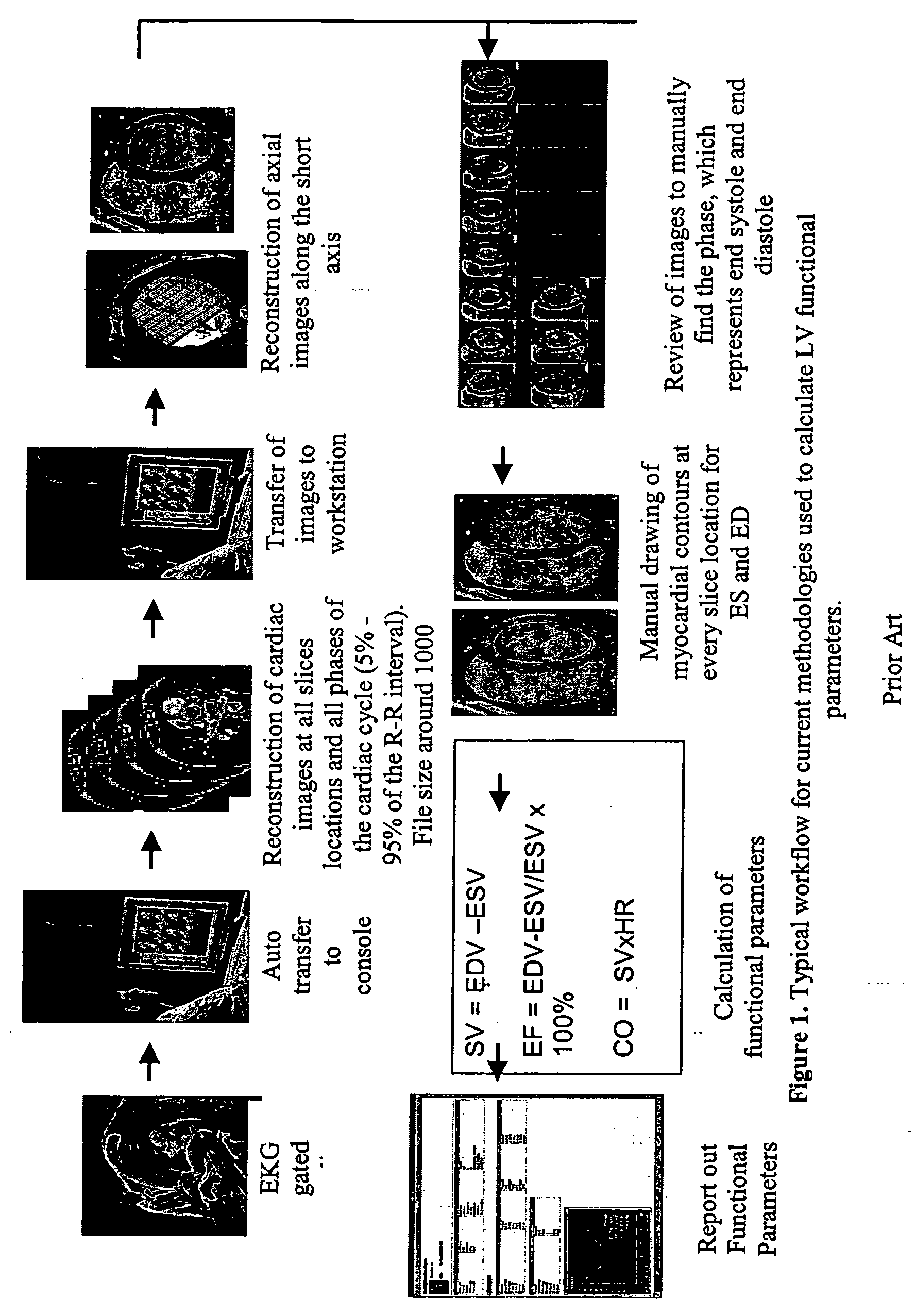
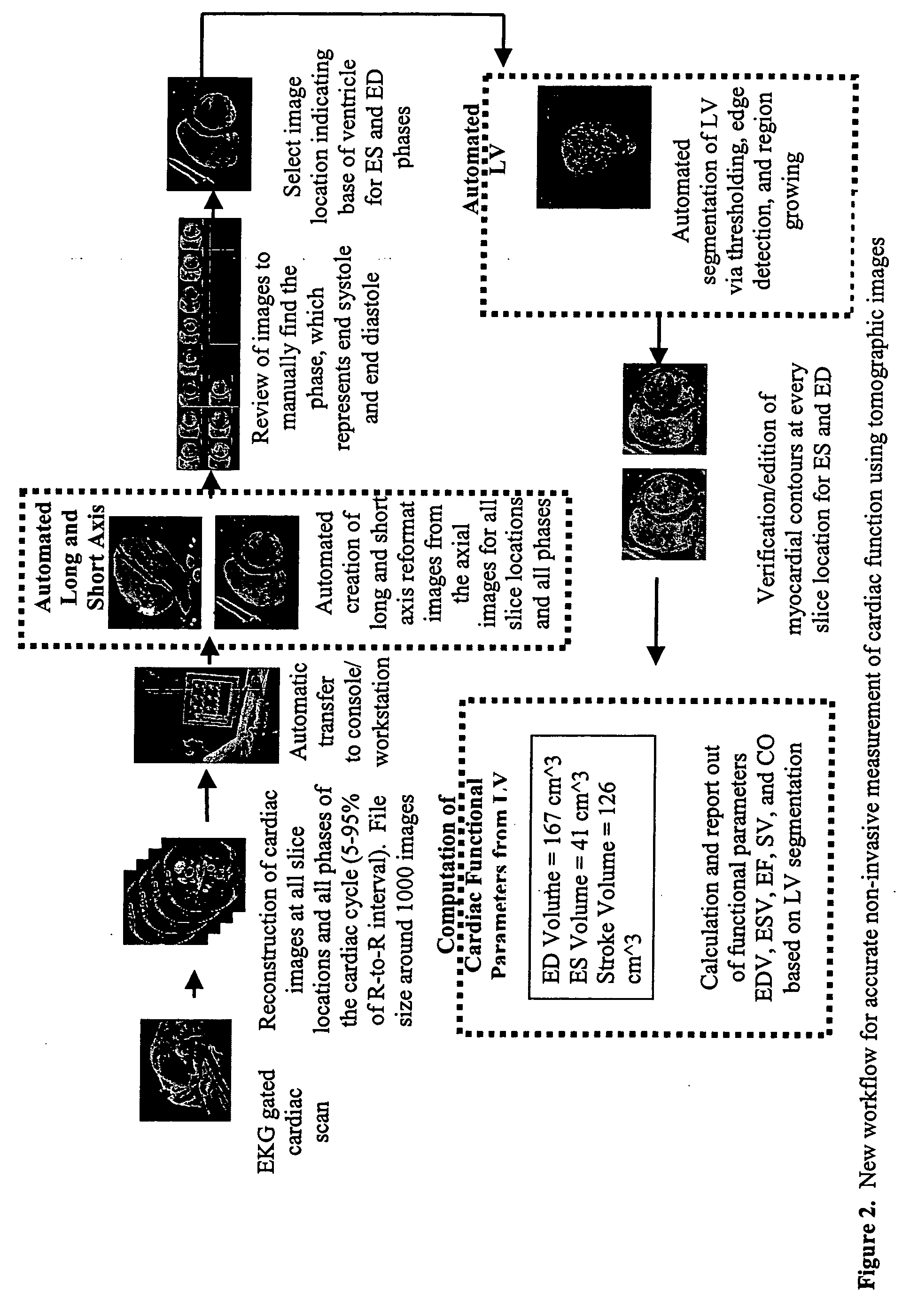
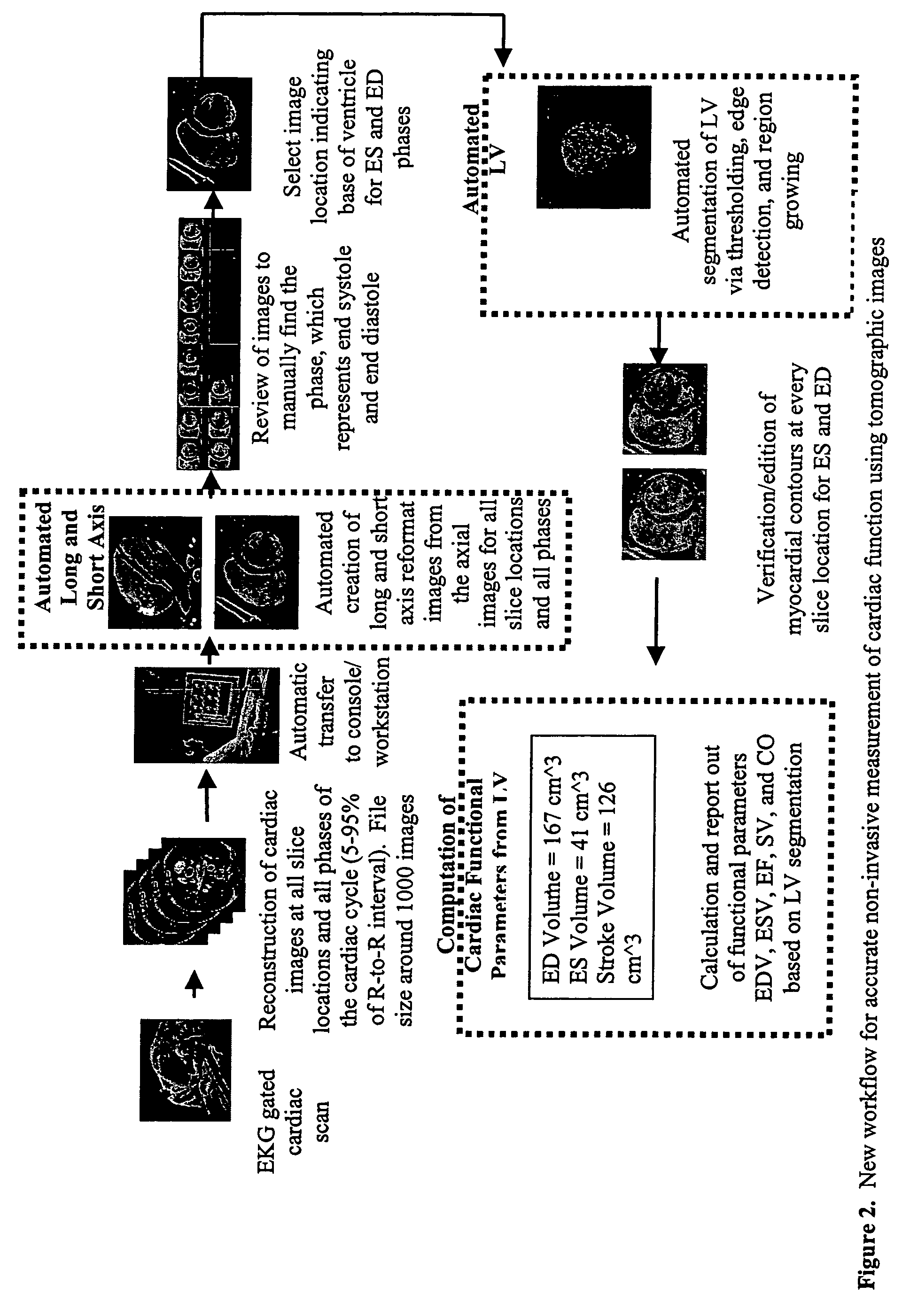
Cardiac display methods and apparatus
A method includes receiving a multi-phase axial cardiac dataset, receiving a selection of a phase from a user, when the received selection is systole, generating an endocardial volume of a left ventricle at an end systole phase without further user intervention, and when the received selection is diastole, generating an endocardial volume of the left ventricle at an end diastole phase without further user intervention.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
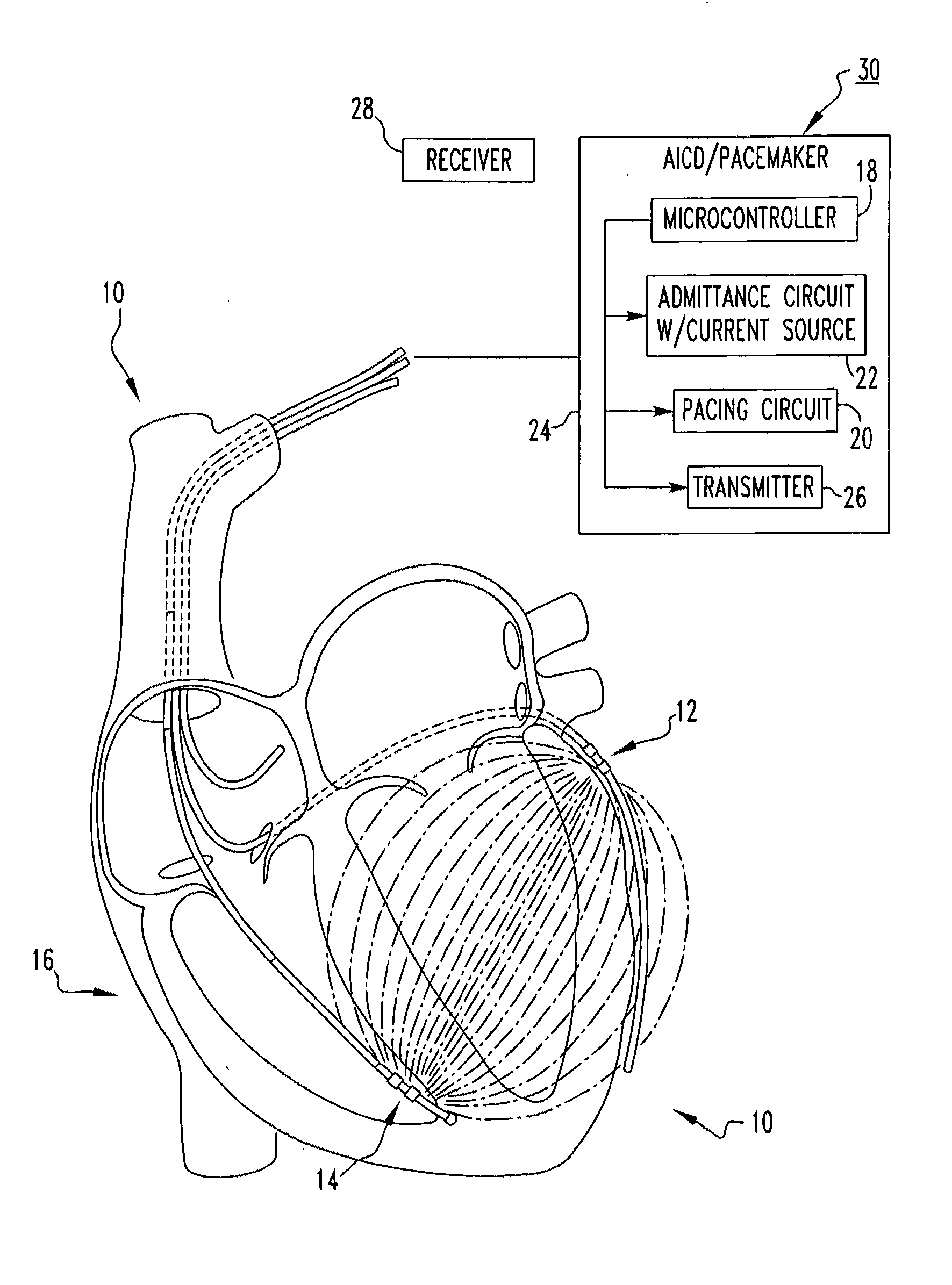
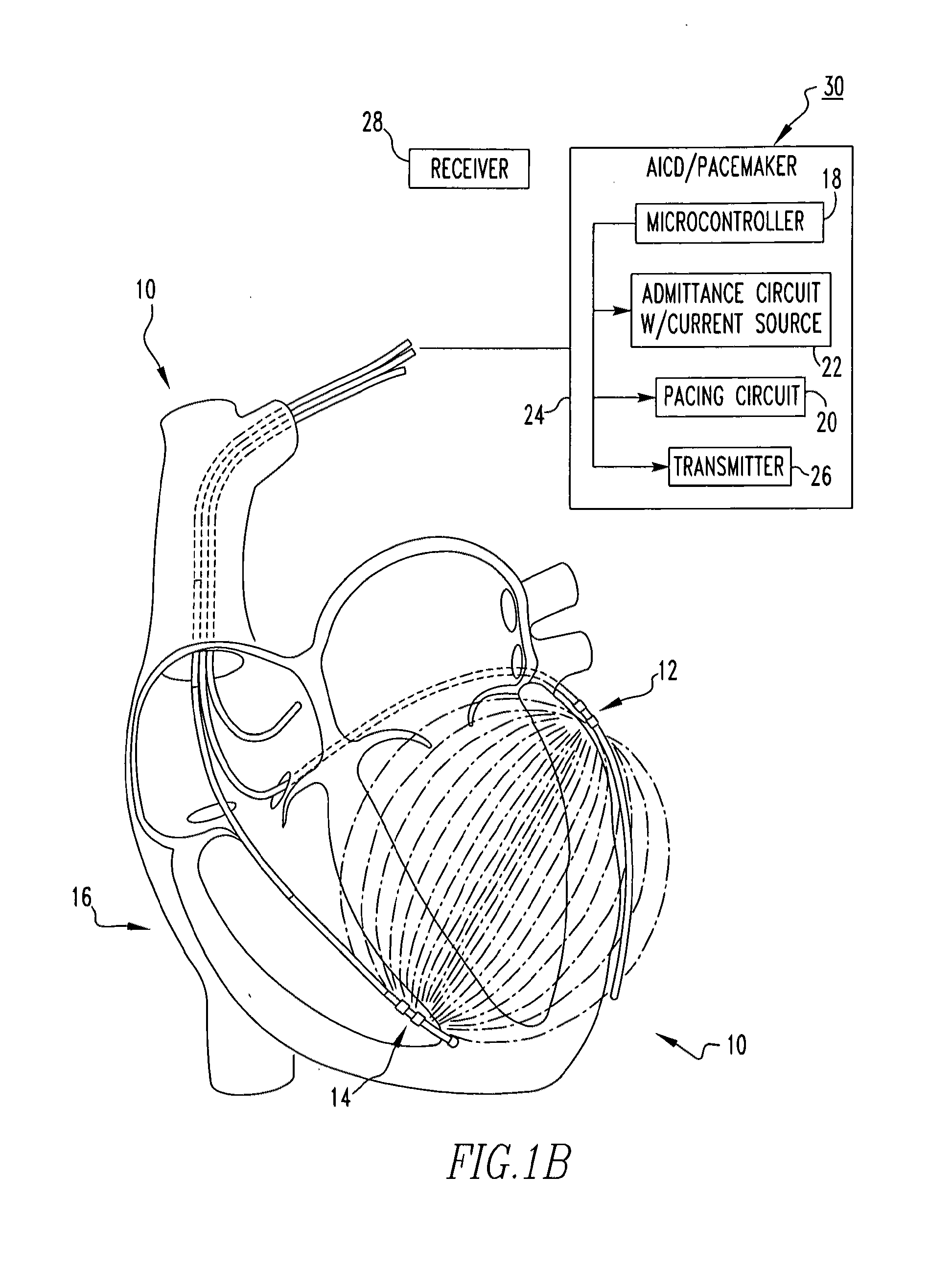
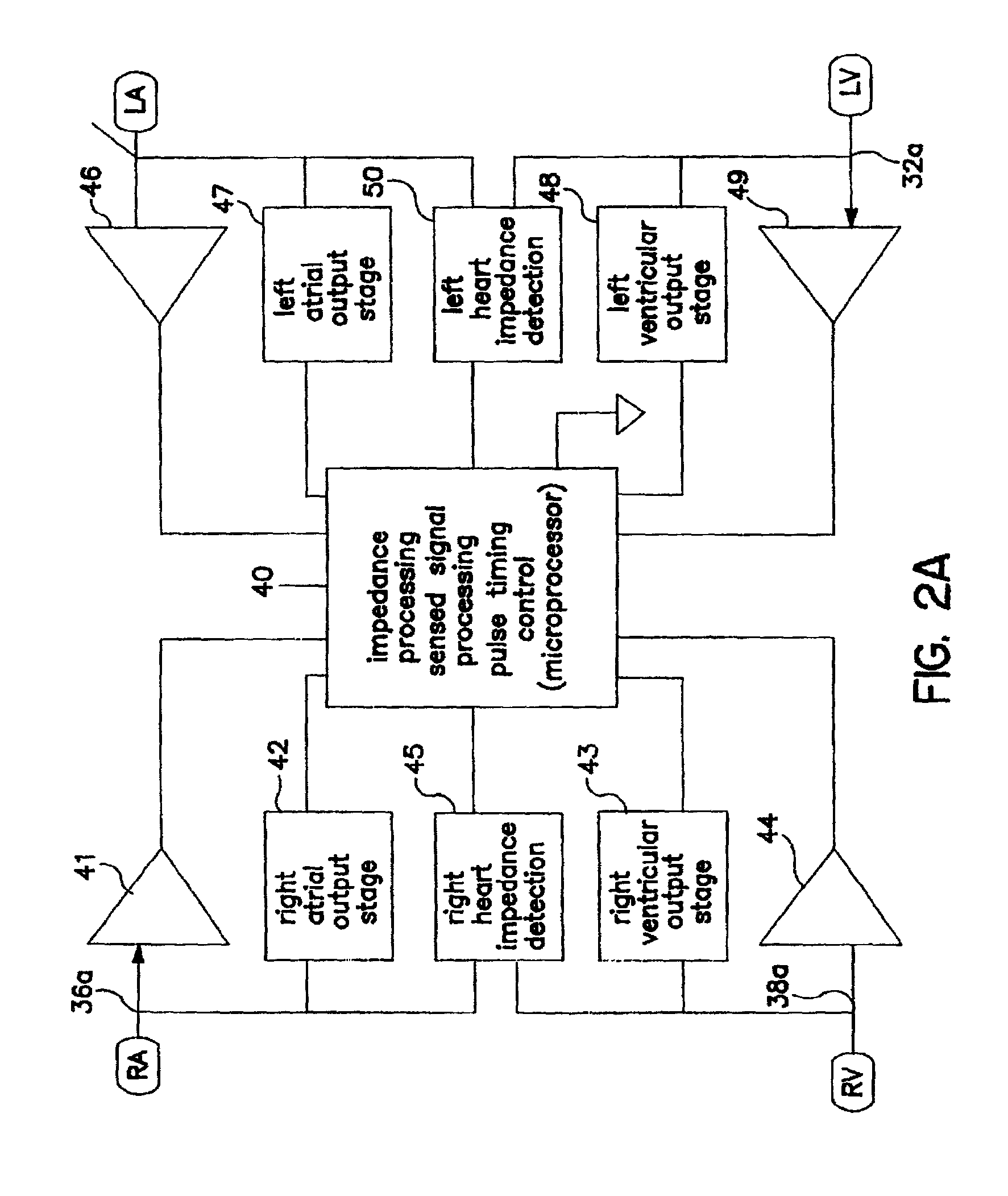
Admittance measurement for tuning bi-ventricular pacemakers
ActiveUS20120150252A1Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerCardiac pacemaker electrode
An apparatus for treating a heart of a patient includes a first lead and at least a second lead for pacing the heart adapted to be in electrical communication with the heart. The apparatus includes a microcontroller in communication with the first and second leads which triggers the first lead at either different times or the same time from when the microcontroller triggers the second lead. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a microcontroller in communication with the first and second leads that determines heart volume, including stroke volume, end-systolic volume, and calculated values including ejection fraction, from admittance from signals from the first and second leads and uses the admittance as feedback to control heart volume ejected, as measured by stroke volume, calculated values such as ejection fraction, and control end-systolic volume, with respect to the first and second leads. A method for treating the heart of a patient.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
System and method to measure cardiac ejection fraction
InactiveUS20060025689A1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsCardiac cycleLeft ventricle wall
A system and method to acquire 3D ultrasound-based images during the end-systole and end end-diastole time points of a cardiac cycle to allow determination of the change and percentage change in left ventricle volume at the time points.
Owner:VERATHON
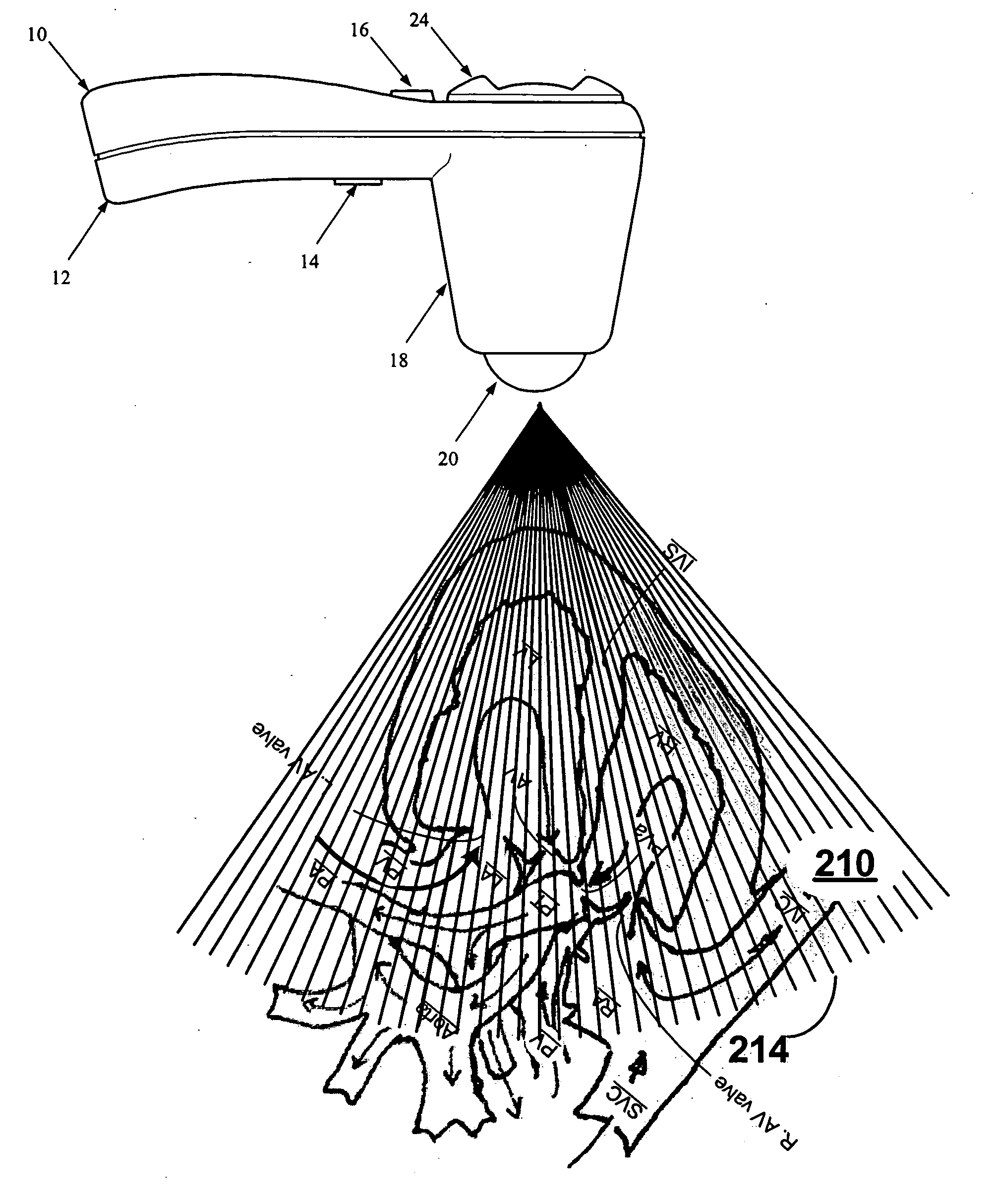
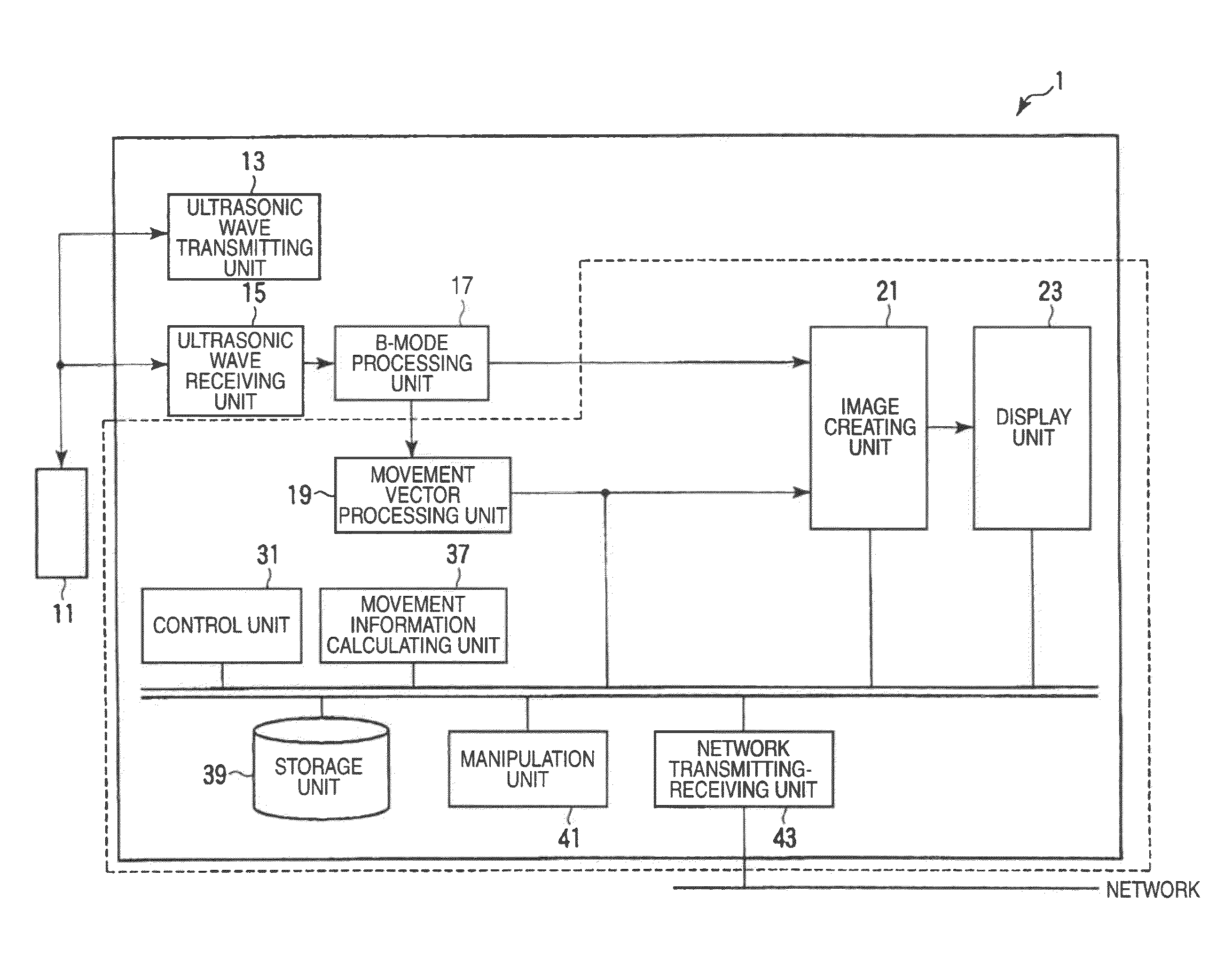
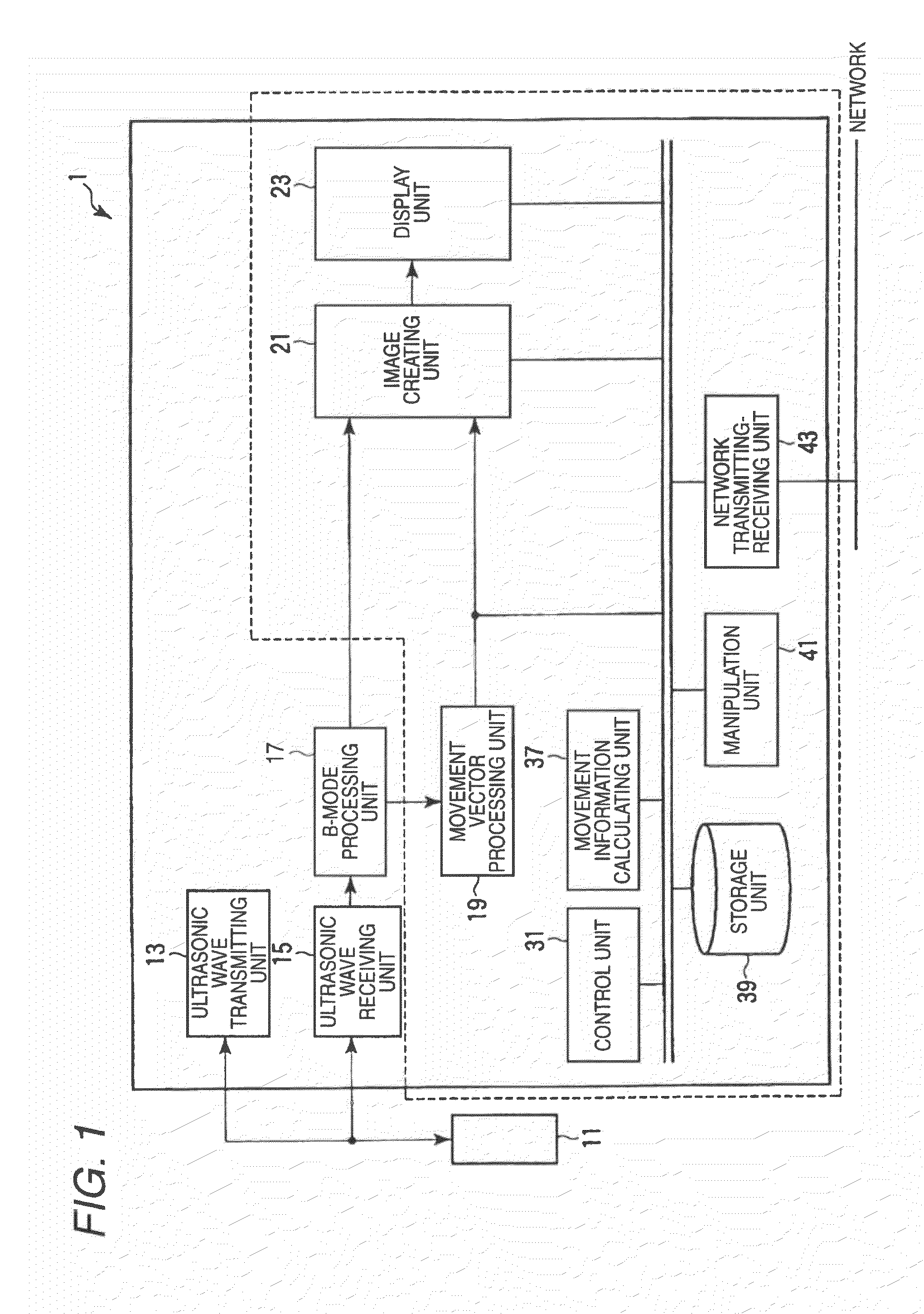
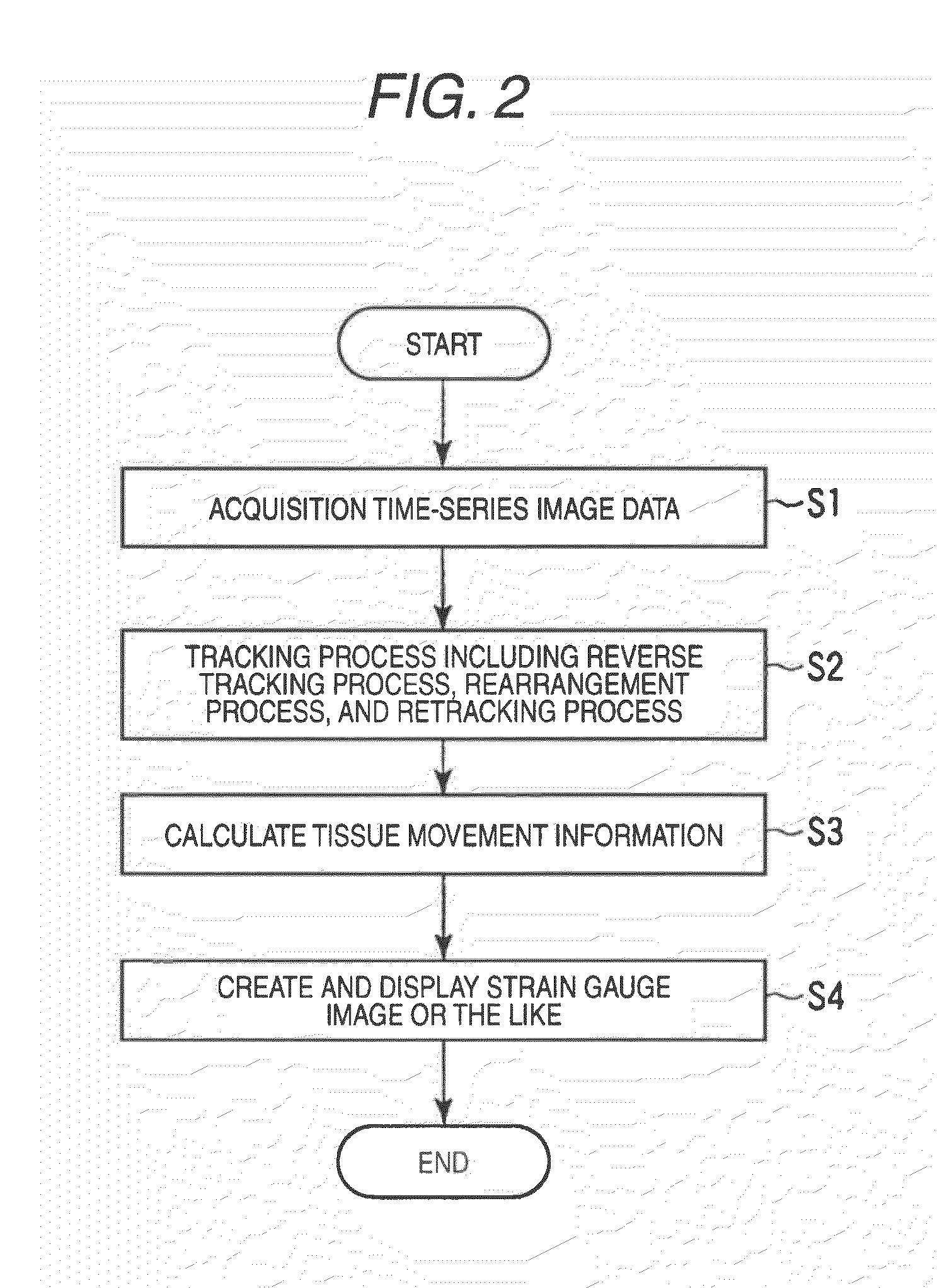
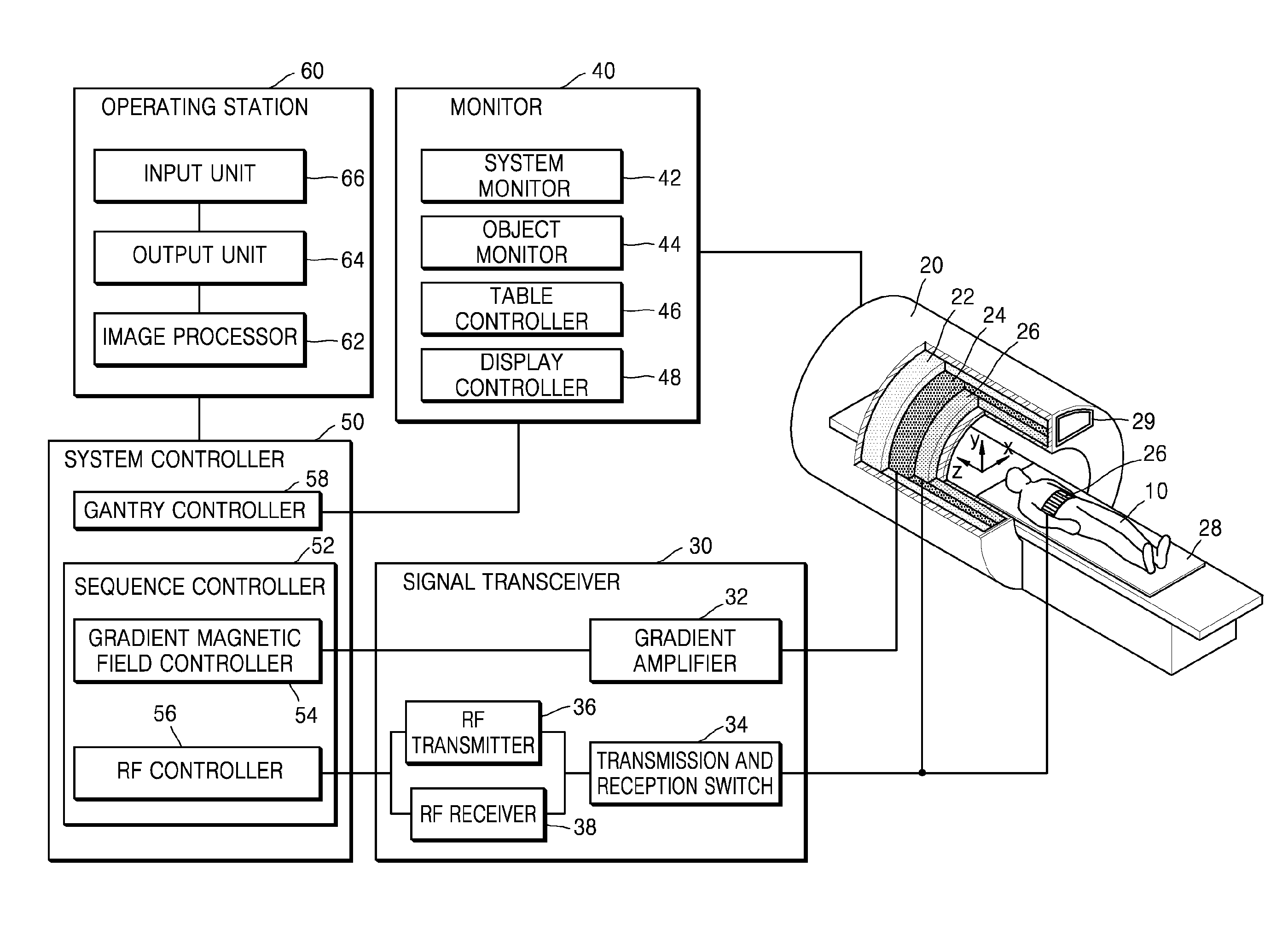
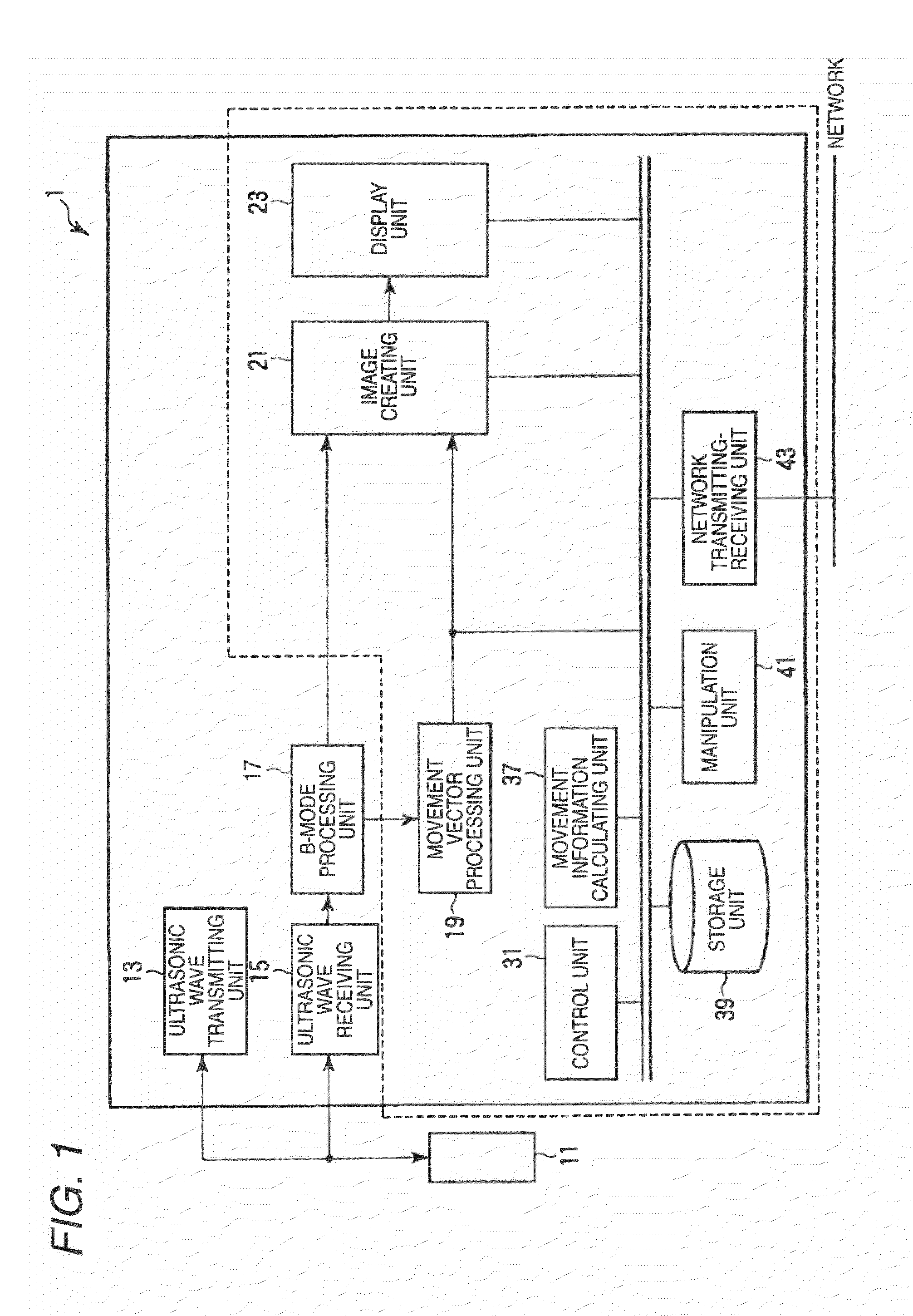
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus, ultrasonic image processing apparatus, medical image diagnostic apparatus, medical image processing apparatus, ultrasonic image processing method, and medical image processing method
ActiveUS20100198072A1Accurate assessmentOrgan movement/changes detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionCardiac wallImaging diagnostic
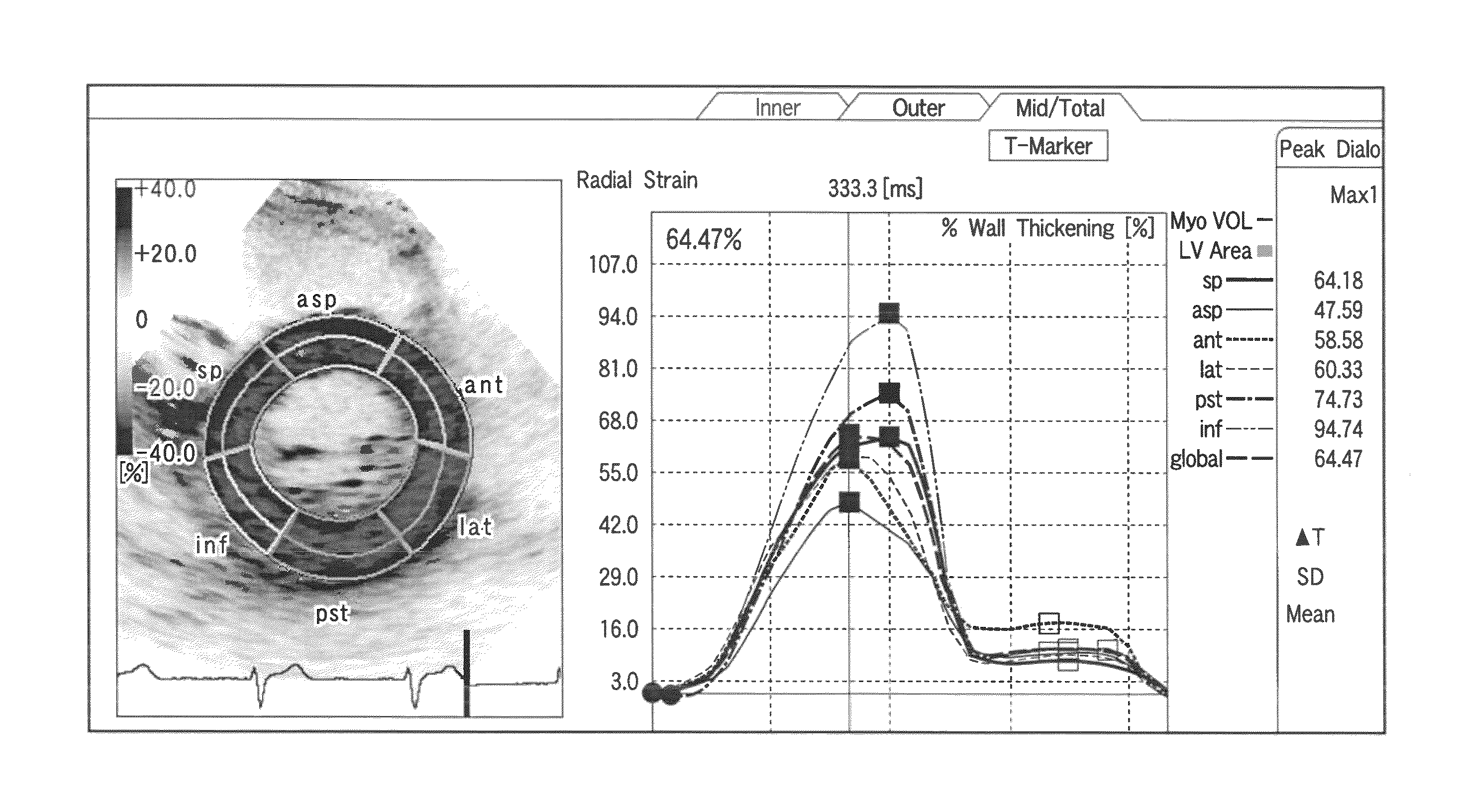
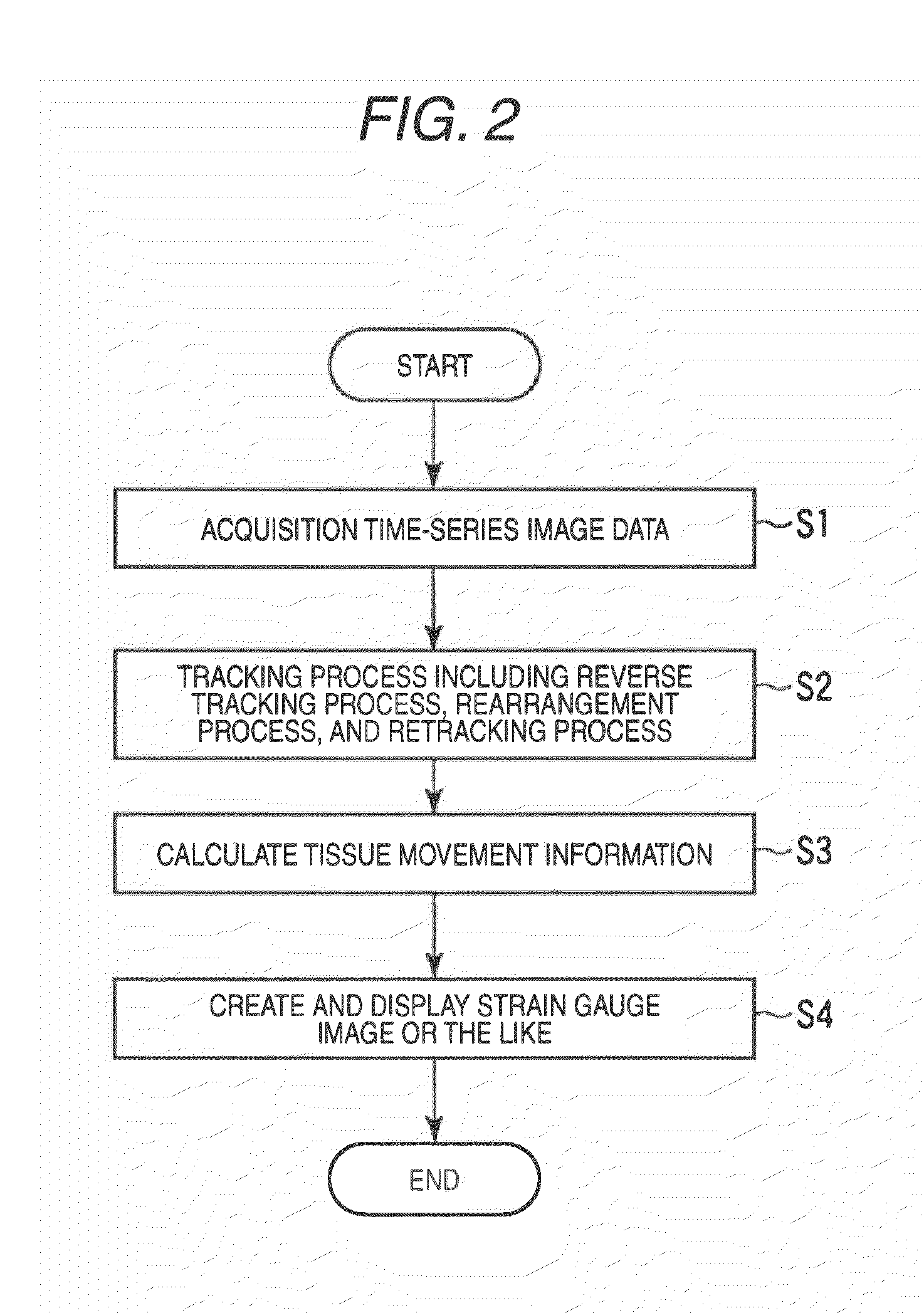
In the case where a tracking process of a moving tissue performing a contraction movement and an expansion movement and represented by a cardiac wall is performed for one heartbeat from the ED1 to the ED2, a contour position (tracking point) initially set at the ES (End-Systole) is tracked until ED1 in accordance with movement information, the tracking point is rearranged and a position of a middle layer is set at the ED (End-Diastole), the rearranged tracking point including the position of the middle layer is tracked in accordance with the movement information already obtained, and then the tracking point is further tracked in the normal direction until the ED2. Alternatively, an initial reverse tracking process is performed from the ES to the ED1 by using plural middle layer path candidates, and a path passing through the tracking point existing on the middle layer or contours of inner and outer layers and rearranged at the ED1 is searched, thereby accurately creating and evaluating movement information of each of an endocardium and an epicardium of a cardiac wall.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Ultrasonic diagnostic stystem and system and method for ultrasonic imaging
ActiveUS20060122512A1High time accuracyOperability is insufficientImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationUltrasonic imaging
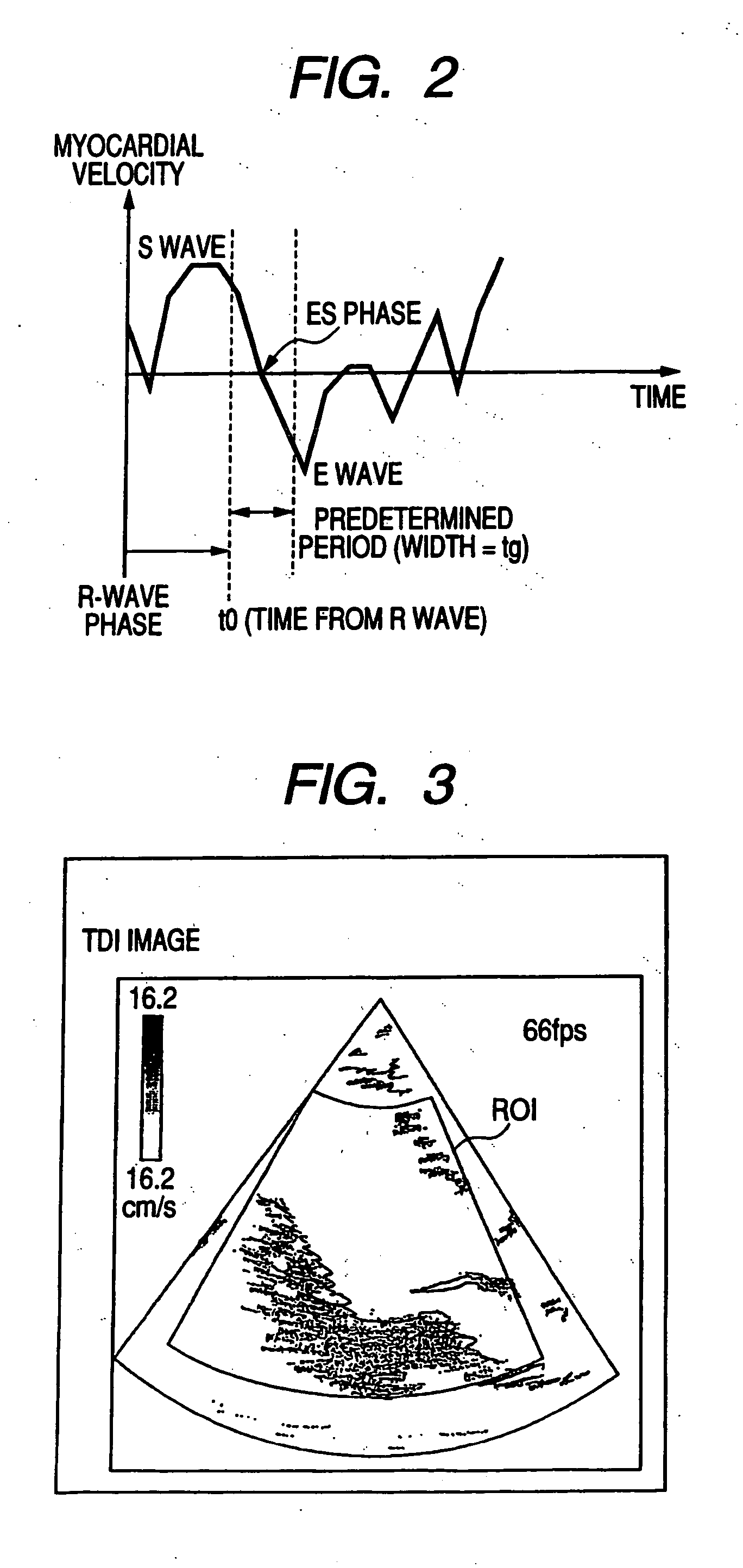
The ultrasonic diagnostic system estimates a desired time phase or one cycle period of a moving region (e.g., a heart) that repeats contraction and relaxation cyclically and which can be specified by a presystole, an end systole, a prediastole, an end diastole, and other clinical characteristics for one cycle of the moving region on the basis of the velocity information on multiple positions of the moving region which is obtained for each time phase. More specifically, assuming that, for example, the end systole phase=a time phase in which the myocardial velocity comes to zero or close to zero, the system calculates |myocardial velocity| for each time phase in a predetermined period, and estimates a time phase in which this value comes closest to zero as an end systole phase.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method, apparatus and computer program product for automatic segmenting of cardiac chambers
ActiveUS7864997B2Improve accuracyGood reproducibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementData setFuzzy object
A method, apparatus and computer program product for machine-based segmentation of the cardiac chambers in a four-dimensional magnetic resonance image data that contains at least short-axis cine sequences. The segmenting is based on temporal variations in the data set and on features extracted from the image data. In particular, the method and apparatus process the image data to automatically segment an endocard based on fuzzy object extraction and to automatically segment an epicard through finding a radial minimum cost with dynamic sign definition and tissue classification. In addition, image data is preferably preprocessed to eliminate high local image variances and inhomogeneity. The image data is also preferably processed to identify positions of a base slice, an apex slice, an end-diastole, an end-systole and an LVRV connection.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
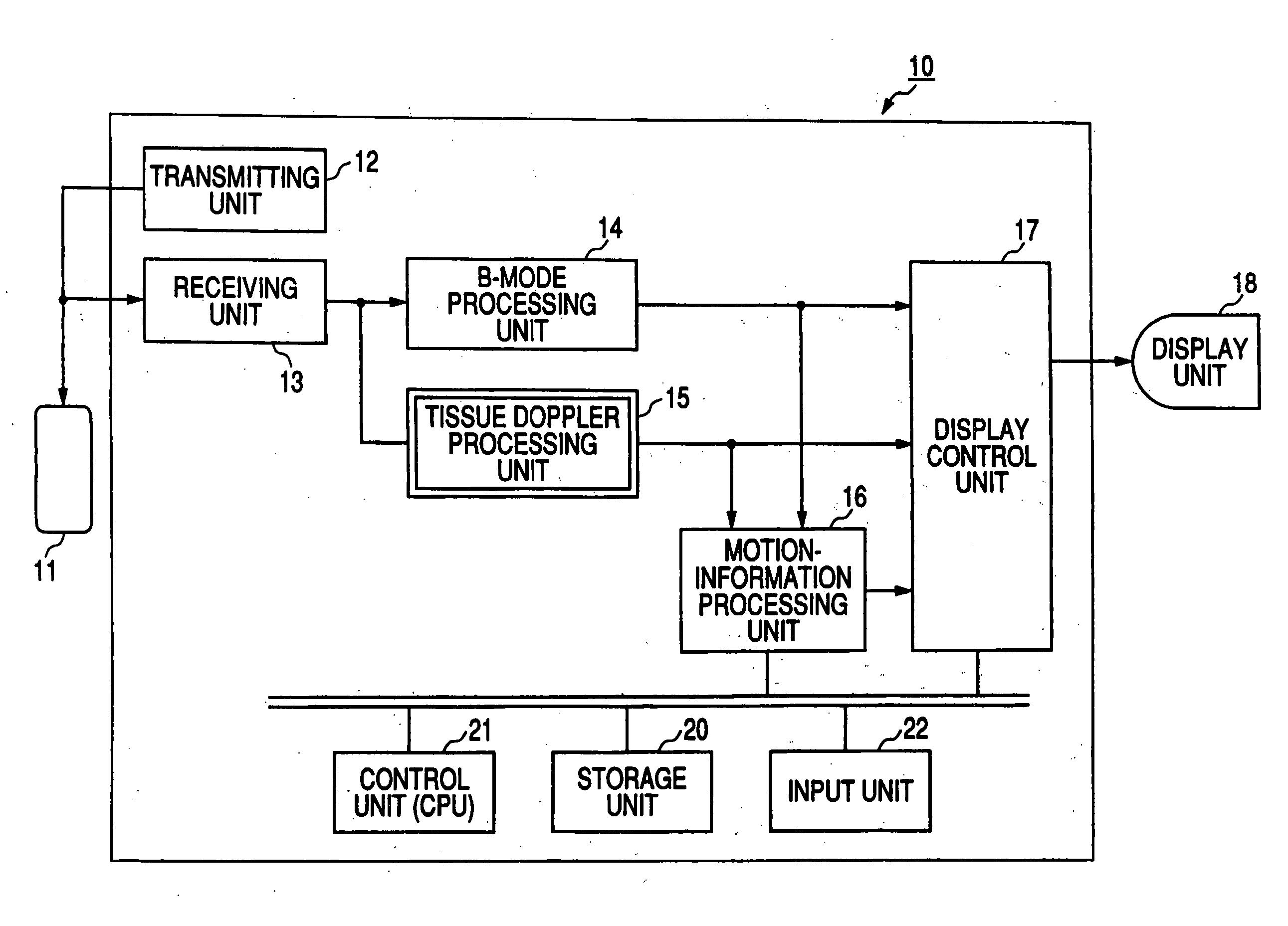
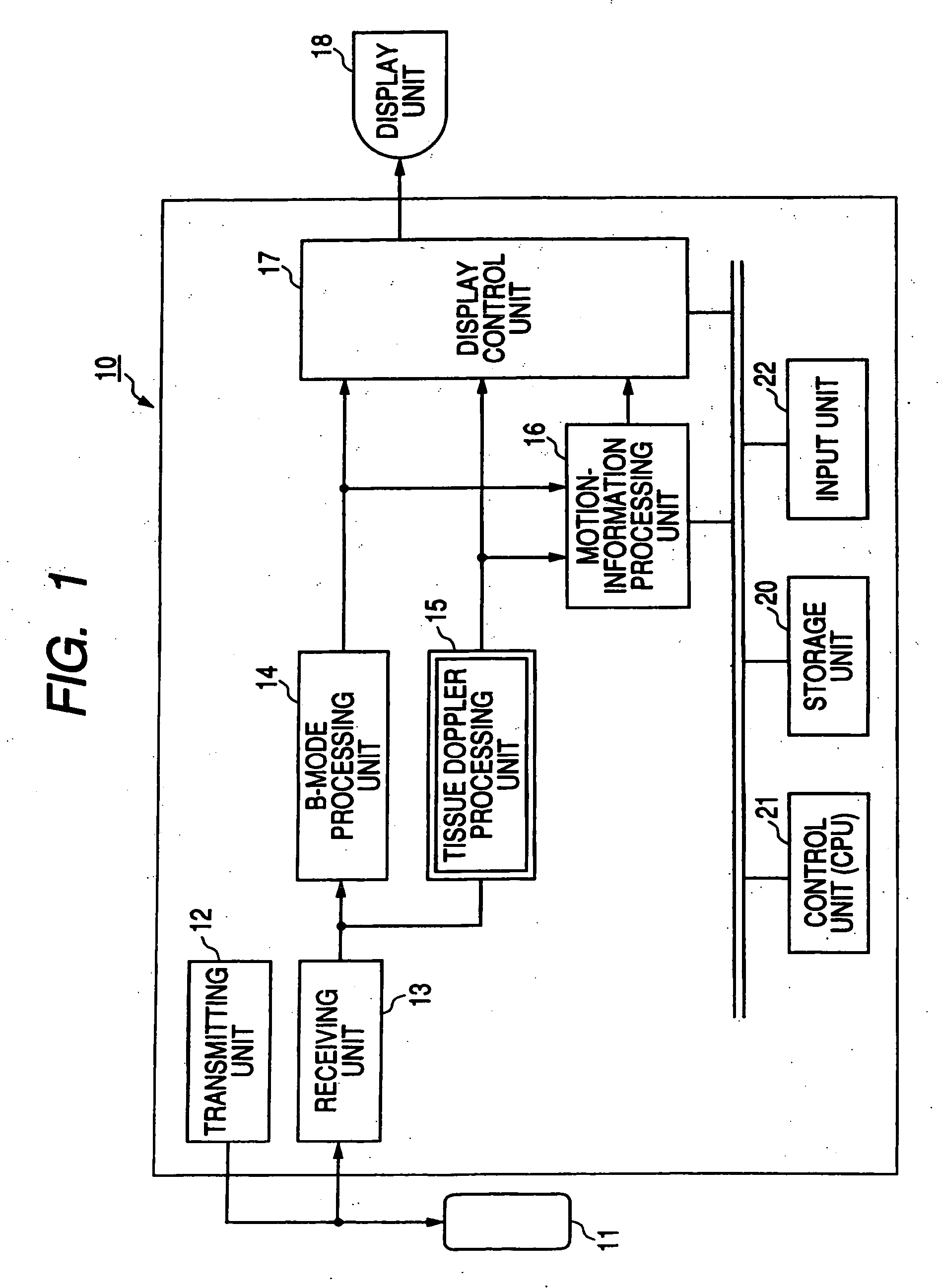
Ultrasound diagnosis apparatus
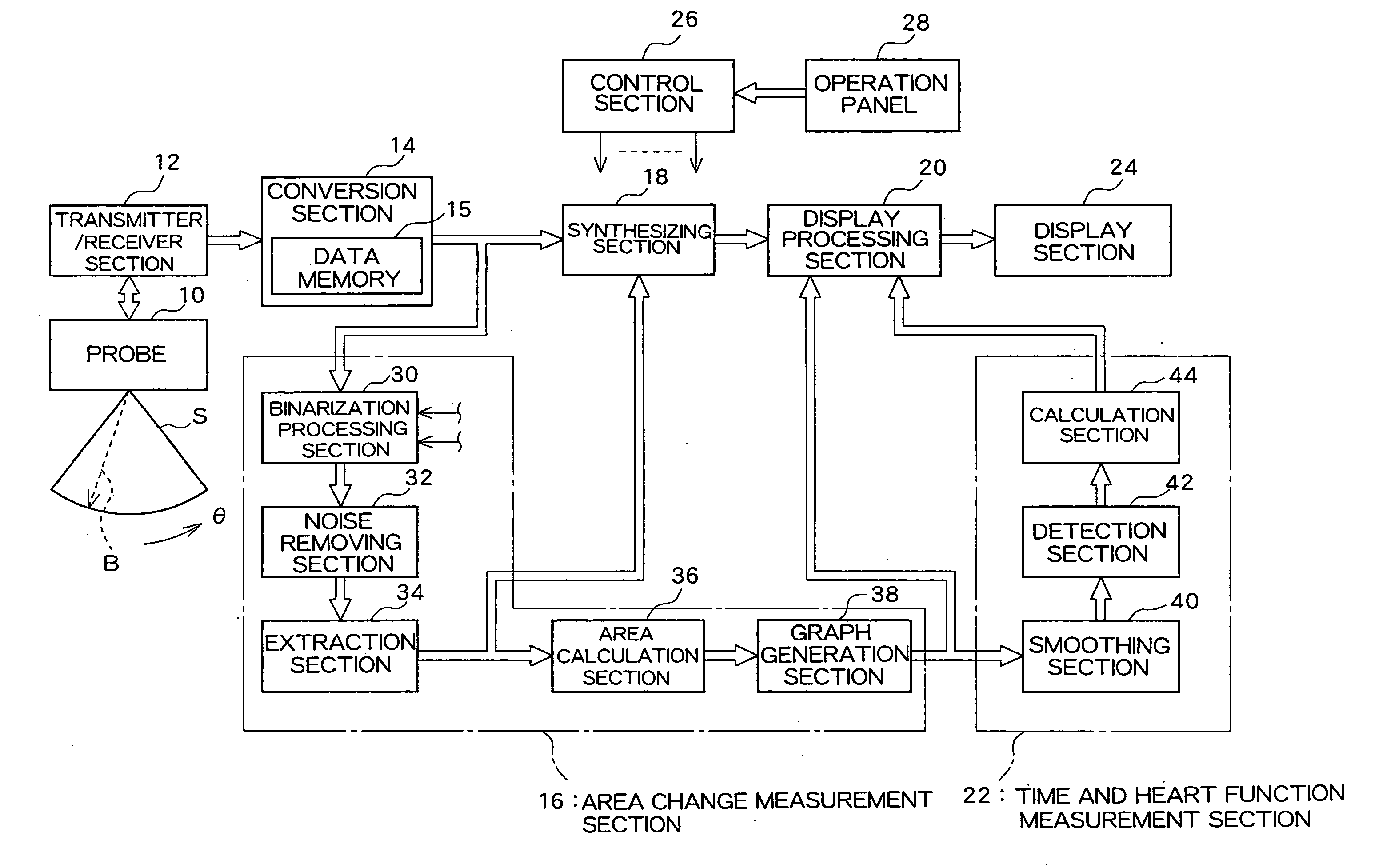
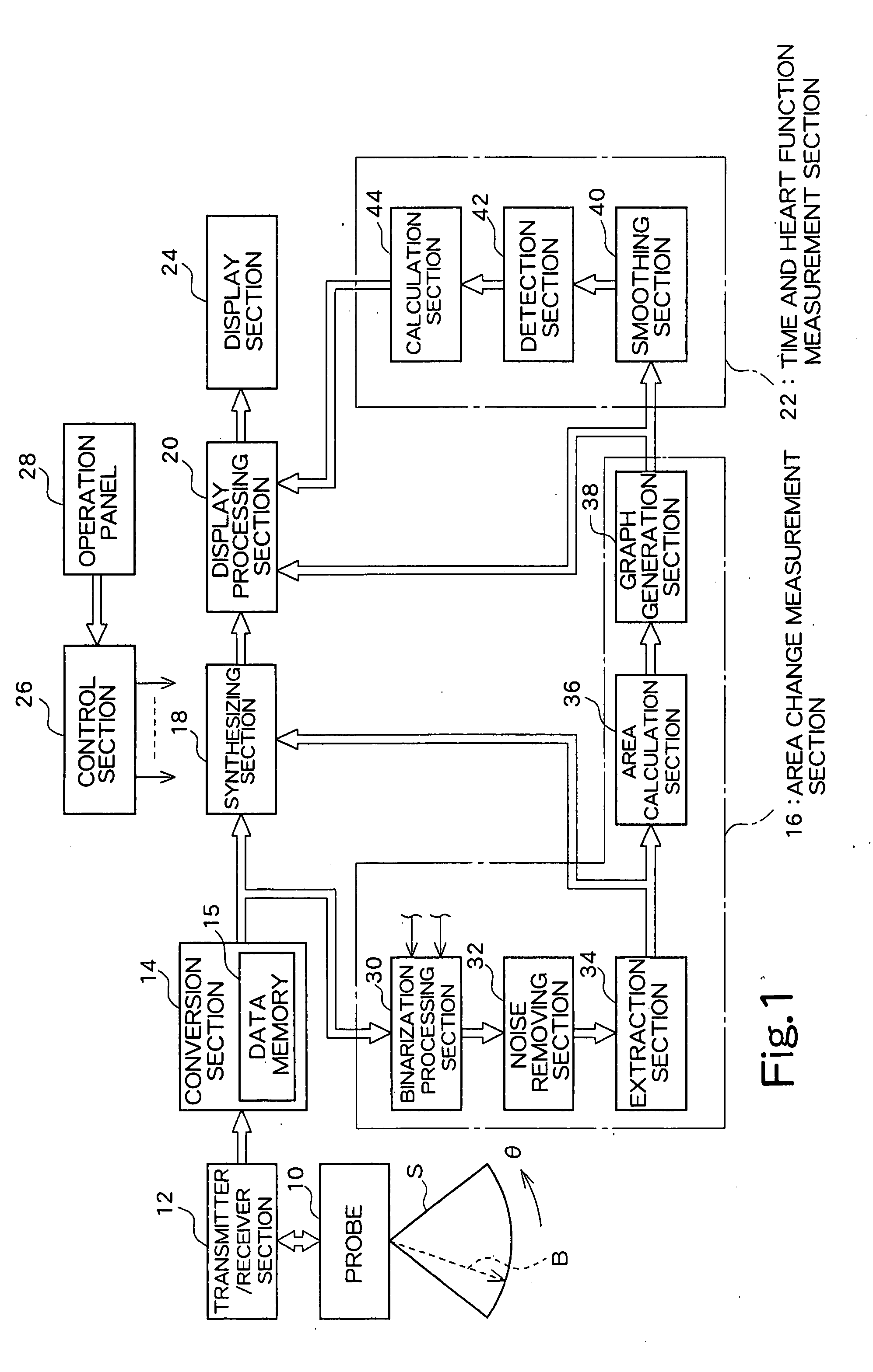
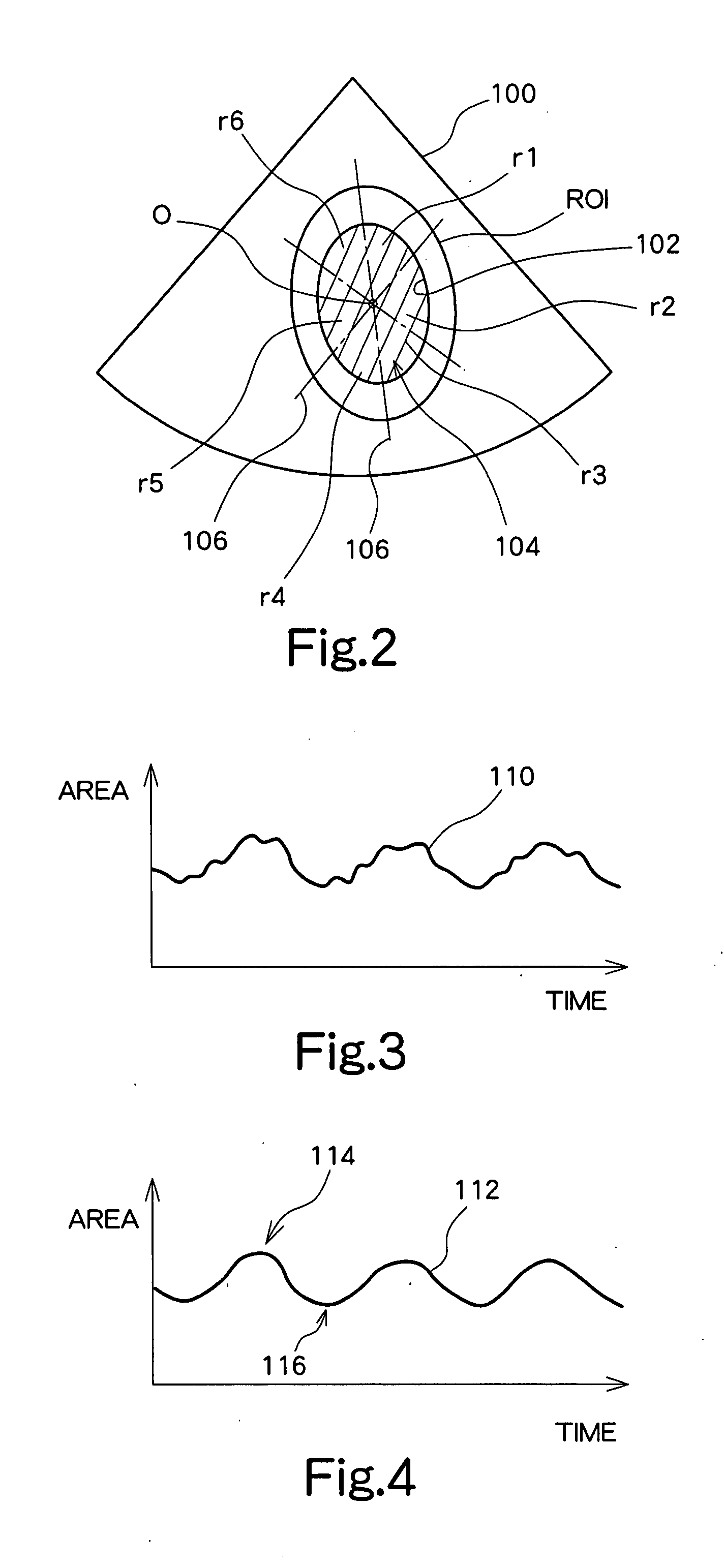
An ultrasound diagnosis apparatus which performs ultrasonic diagnosis with respect of a fetal heart. An area change measurement section calculates an area of a specific heart chamber (left ventricle) in the fetal heart in frame units. Further, the area change measurement section generates a graph representing the area which is calculated in frame units. The maximum value and the minimum value are specified in the graph to thereby specify end-diastole and end-systole. Based on this information, a heart rate and a cardiac cycle with regard to the fetal heart are calculated. Further, an ejection fraction is also calculated from an end-diastolic area and an end-systolic area.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal pacing intervals
InactiveUS20060271117A1Optimize cardiac outputReduce the required powerHeart stimulatorsPacing intervalSub threshold
Impedance, e.g. sub-threshold impedance, is measured across the heart at selected cardiac cycle times as a measure of chamber expansion or contraction. One embodiment measures impedance over a long AV interval to obtain the minimum impedance, indicative of maximum ventricular expansion, in order to set the AV interval. Another embodiment measures impedance change over a cycle and varies the AV pace interval in a binary search to converge on the AV interval causing maximum impedance change indicative of maximum ventricular output. Another method varies the right ventricle to left ventricle (VV) interval to converge on an impedance maximum indicative of minimum cardiac volume at end systole. Another embodiment varies the VV interval to maximize impedance change. Other methods vary the AA interval to maximize impedance change over the entire cardiac cycle or during the atrial cycle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac display methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7689261B2Image analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTunica intimaMulti phase
A method includes receiving a multi-phase axial cardiac dataset, receiving a selection of a phase from a user, when the received selection is systole, generating an endocardial volume of a left ventricle at an end systole phase without further user intervention, and when the received selection is diastole, generating an endocardial volume of the left ventricle at an end diastole phase without further user intervention.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal AV and VV intervals
Methods and devices for determining optimal Atrial to Ventricular (AV) pacing intervals and Ventricular to Ventricular (VV) delay intervals in order to optimize cardiac output. Impedance, preferably sub-threshold impedance, is measured across the heart at selected cardiac cycle times as a measure of chamber expansion or contraction. One embodiment measures impedance over a long AV interval to obtain the minimum impedance, indicative of maximum ventricular expansion, in order to set the AV interval. Another embodiment measures impedance change over a cycle and varies the AV pace interval in a binary search to converge on the AV interval causing maximum impedance change indicative of maximum ventricular output. Another method varies the right ventricle to left ventricle (VV) interval to converge on an impedance maximum indicative of minimum cardiac volume at end systole. Another embodiment varies the VV interval to maximize impedance change.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal pacing intervals
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal AV and VV intervals
ActiveUS20070213778A1Reduce the required powerMaximize fillInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsInterval methodCardiac cycle
Methods and devices for determining optimal Atrial to Ventricular (AV) pacing intervals and Ventricular to Ventricular (VV) delay intervals in order to optimize cardiac output. Impedance, preferably sub-threshold impedance, is measured across the heart at selected cardiac cycle times as a measure of chamber expansion or contraction. One embodiment measures impedance over a long AV interval to obtain the minimum impedance, indicative of maximum ventricular expansion, in order to set the AV interval. Another embodiment measures impedance change over a cycle and varies the AV pace interval in a binary search to converge on the AV interval causing maximum impedance change indicative of maximum ventricular output. Another method varies the right ventricle to left ventricle (VV) interval to converge on an impedance maximum indicative of minimum cardiac volume at end systole. Another embodiment varies the VV interval to maximize impedance change.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
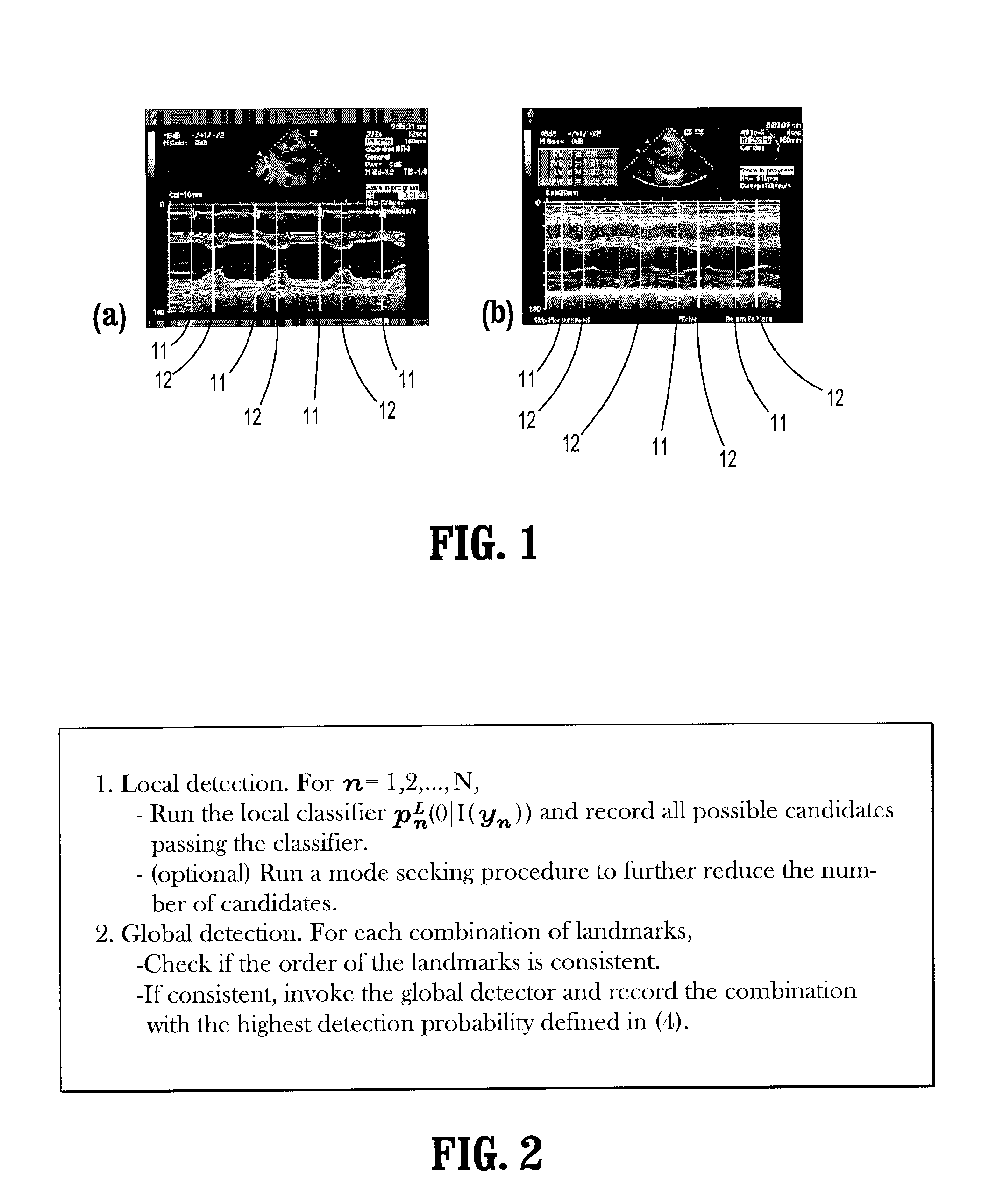
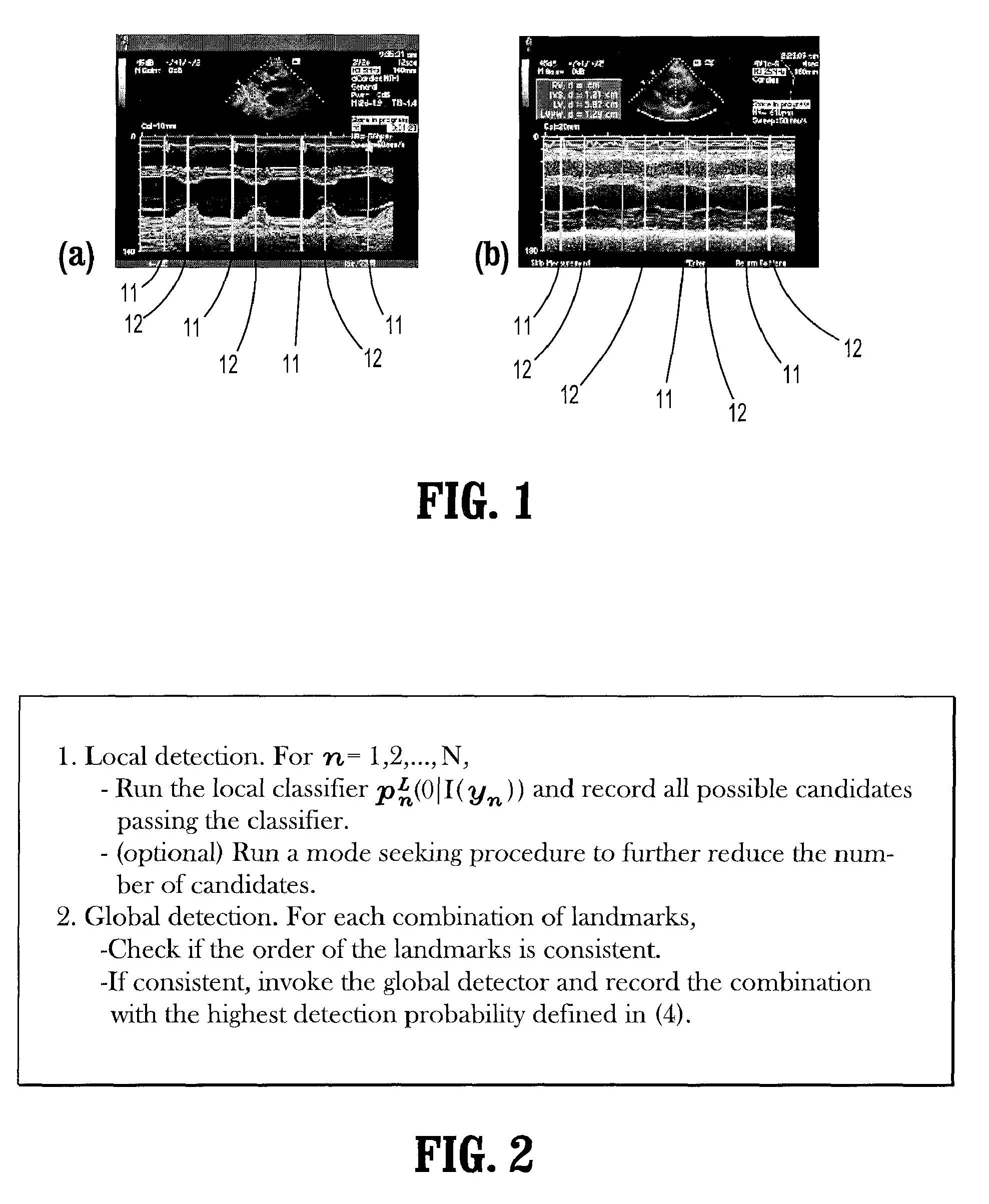
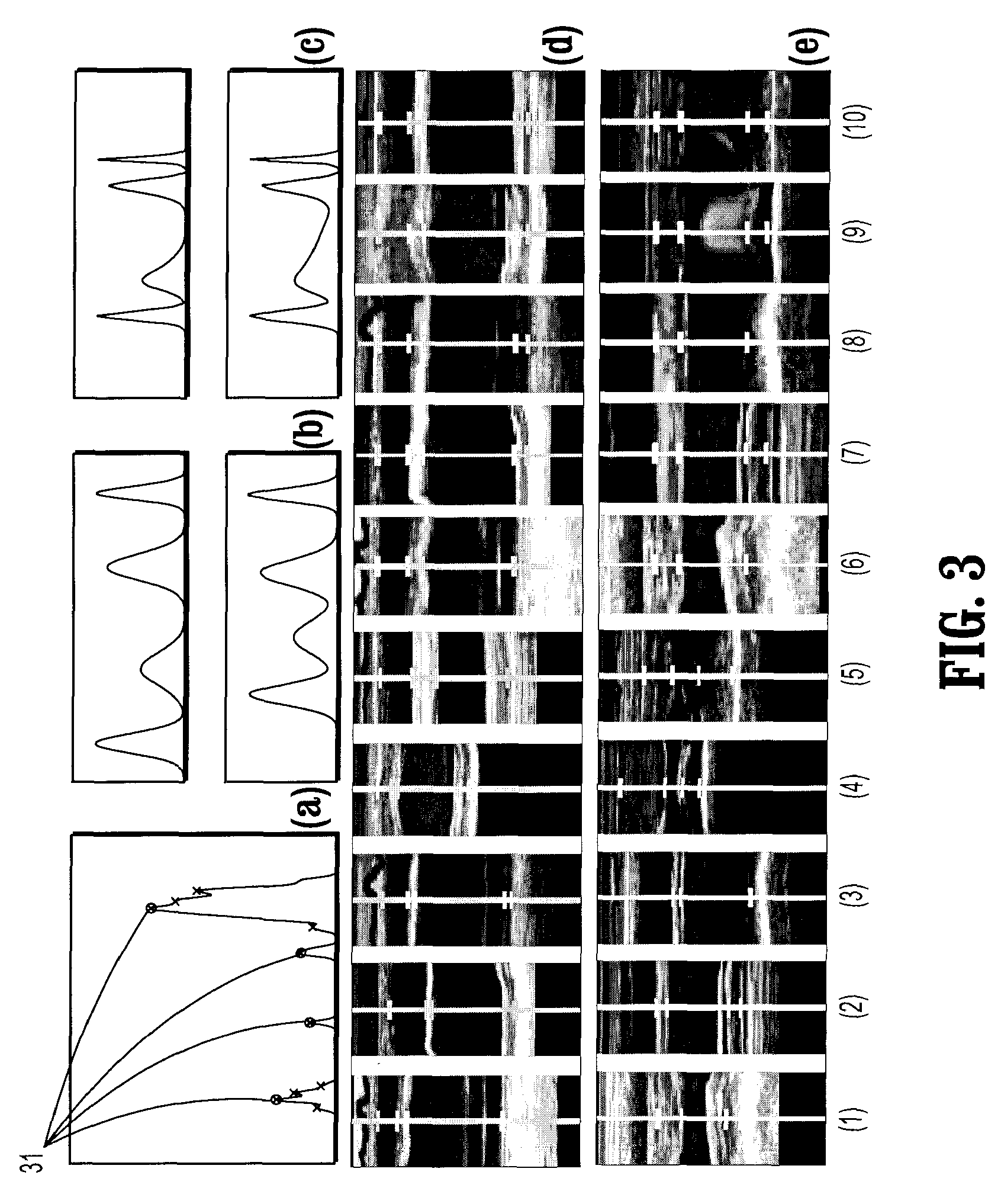
System and Method for Quasi-Real-Time Ventricular Measurements From M-Mode EchoCardiogram
ActiveUS20080281203A1Fast and accurate derivationEfficiently exploreMedical data miningImage analysisSonificationComputer science
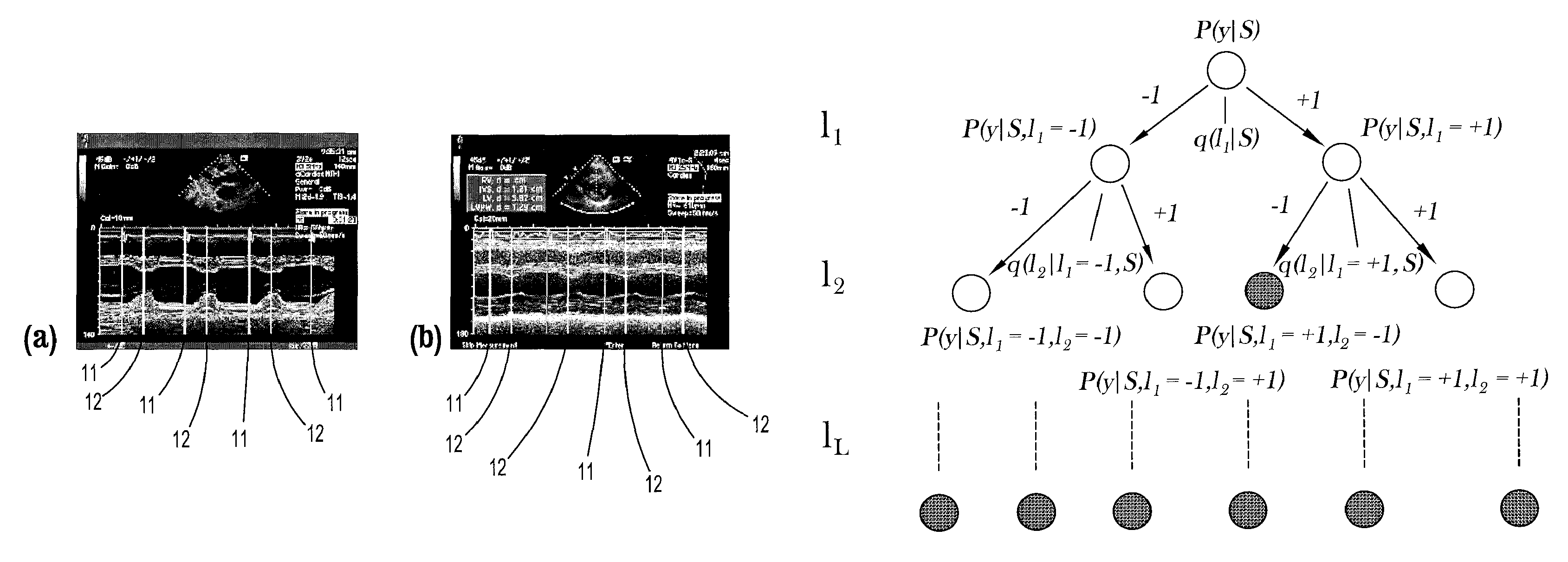
A method for measuring ventricular dimensions from M-mode echocardiograms, includes providing a digitized M-mode echocardiogram image, running a plurality of local classifiers, where each local classifier trained to detect a landmark on either an end-diastole (ED) line or an end-systole (ES) line in the image, recording all possible landmarks detected by the classifiers, where a search range in an N-dimensional parameter space defined by the landmarks for each dimension is reduced to a union of subsets, where each dimension of the parameter space corresponds a landmark, for each combination of possible landmarks, checking if an order of the landmarks is consistent with a known ordering of the landmarks, and if the order is consistent, running a global detector on each consistent combination of landmarks to find a landmark combination with a highest detection probability as a confirmed landmark detection, where the landmarks are used for measuring ventricular dimensions.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method and system for processing heart real-time film imaged picture
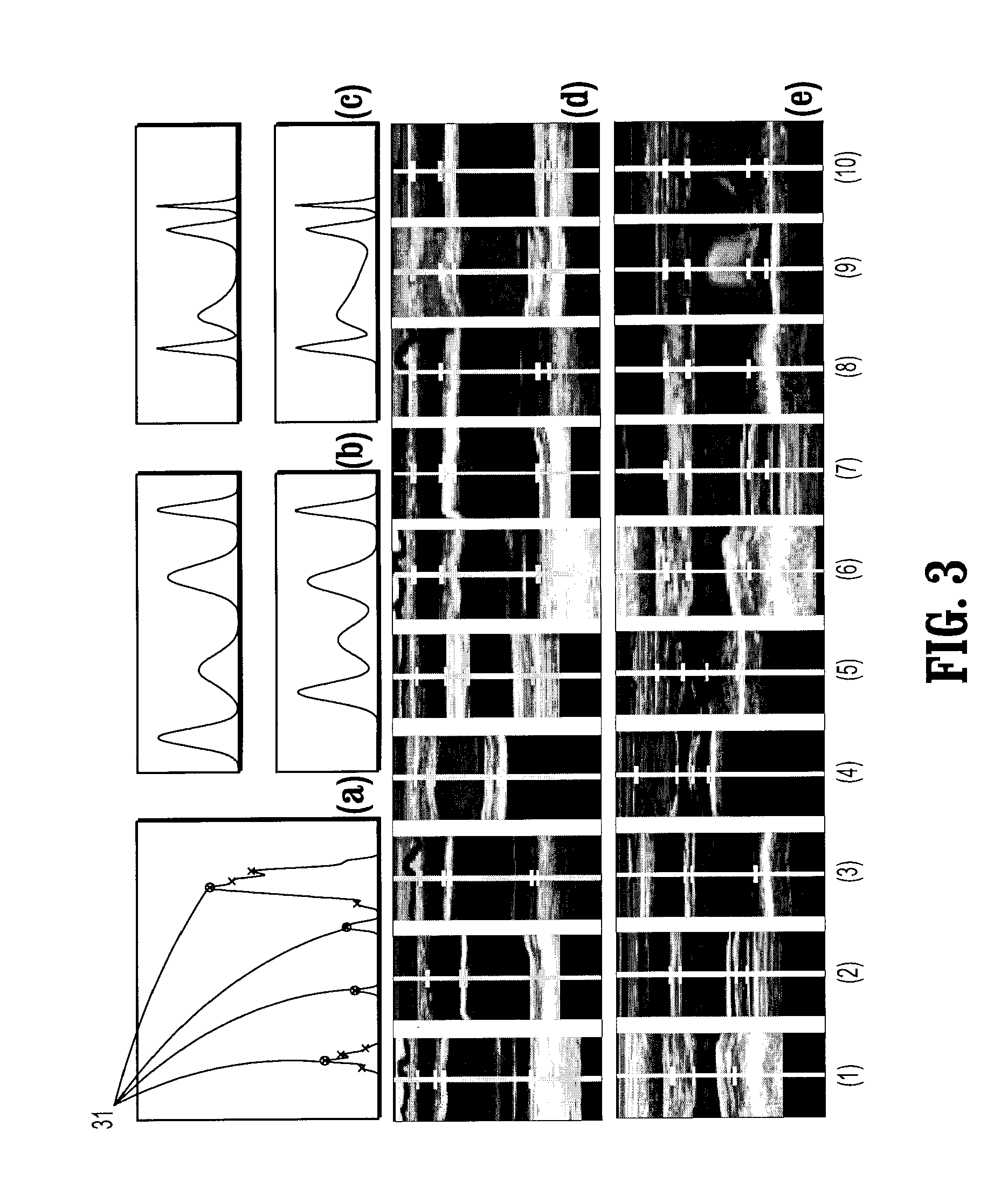
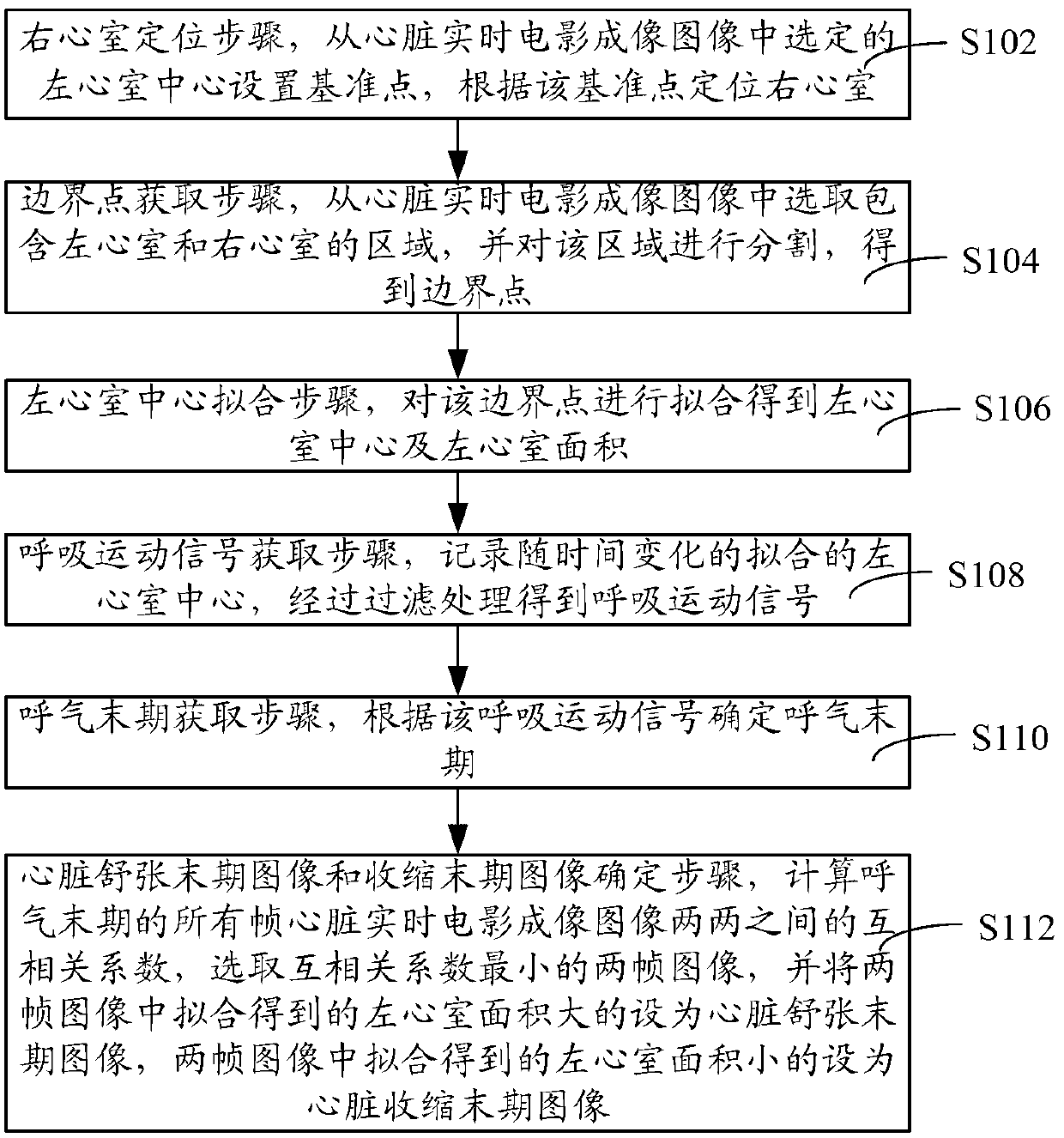
ActiveCN103340628AImprove processing efficiencyEasy to operateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCorrelation coefficientRadiology
The invention relates to a method and system for processing a heart real-time film imaged picture. The method comprises the steps that the center of the left ventricle is selected from the heart real-time film imaged picture so that a datum point can be arranged and the right ventricle can be located according to the datum point; a region is selected from the heart real-time film imaged picture and is divided so that a boundary point can be obtained; fitting is conducted on the boundary point so that the center of the left ventricle and the area of the left ventricle can be obtained; the fitted center, changing along with the time, of the left ventricle is recorded so that a breathing movement signal can be obtained and an end expiration period can be determined; a cross correlation coefficient between every two frame pictures in the expiration rear period is calculated, the two frames of pictures with the smallest correlation coefficient are selected, the picture of the left ventricle with the large area obtained through fitting serves as an end diastolic picture and the picture of the left ventricle with the small area obtained through fitting serves as an end-systole picture. According to the method and system for processing the heart real-time film imaged picture, operation is simple, time is saved, and the cardiac function can be analyzed conveniently, rapidly and reliably.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Ultrasound triggering method
InactiveUS20060155192A1Affects efficacyBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsEnd systoleSonification
The invention relates to a triggered ultrasound imaging method for imaging of the myocardium, minimizing the risk of eliciting cardiac arrhythmia. Particularly, the invention is directed to a method of assessing cardiac perfusion. Destruction pulses are triggered such that they fall within the refractory period of the heart, while imaging pulses are triggered at any given time of the ECG cycle, preferably during end-systole.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
Medical imaging apparatus and method of processing medical image
A medical imaging apparatus includes: an output unit configured to display a magnetic resonance (MR) image matrix in which MR images, obtained by performing magnetic resonance imaging on a heart, are arranged in columns and rows; and an image processor configured to display at least one first indicator which indicates a column of the MR image matrix corresponding to at least one of end diastole and end systole and display at least one second indicator which indicates a row of the MR image matrix corresponding to at least one of an apex and a base of the heart, wherein the columns of the MR image matrix are arranged according to time when MR images included in the columns are captured, and the rows of the MR image matrix are arranged according to a position on a longitudinal axis of the heart corresponding to MR images included in the rows.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cardiovascular index estimation methods
InactiveUS20120259189A1Reduce estimated instantaneous aortic blood flowUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEvaluation of blood vesselsEstimation methodsPulse pressure
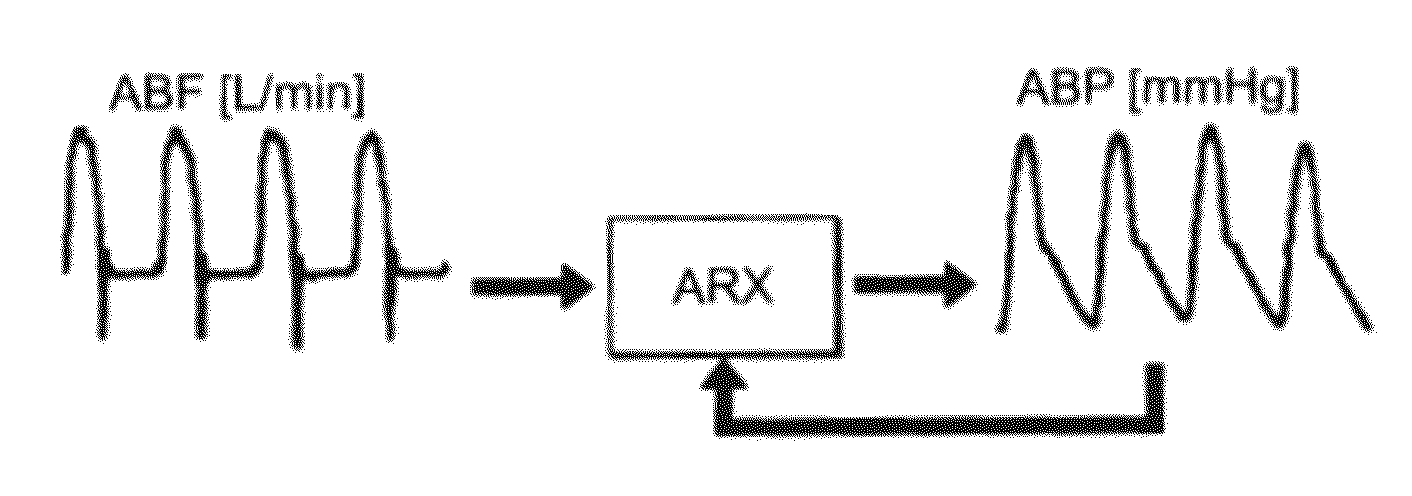
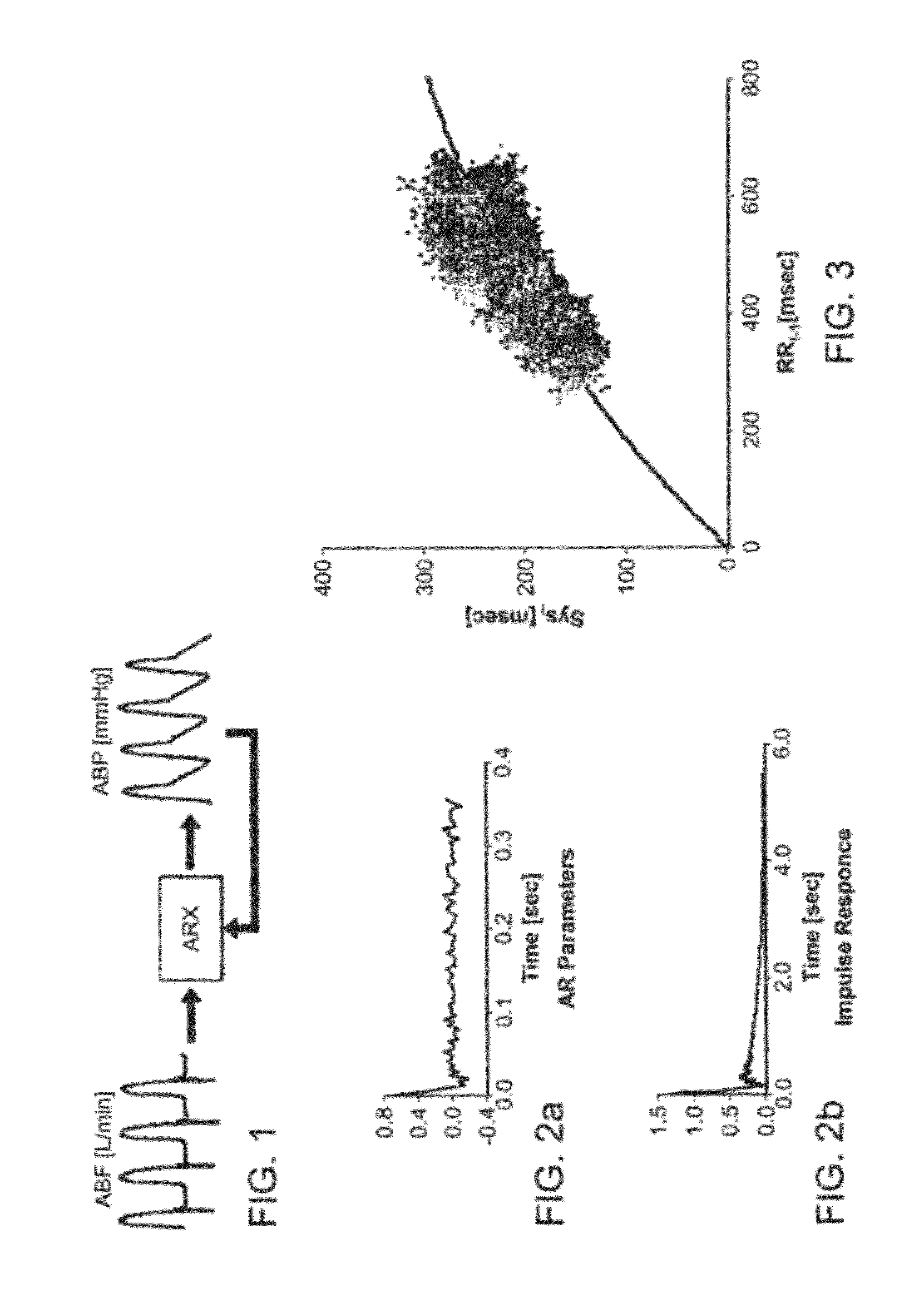
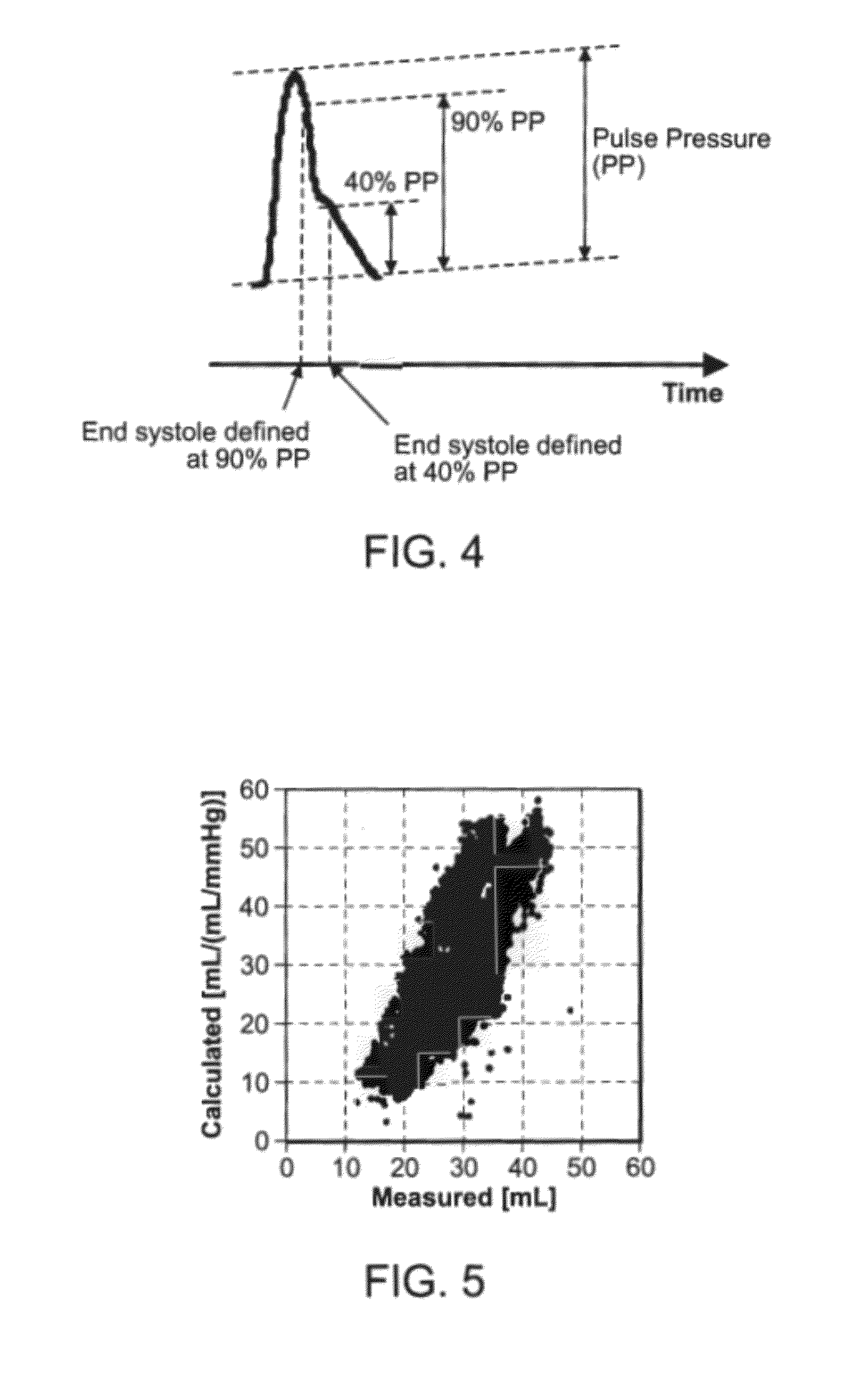
New algorithms to estimate cardiovascular indices by analysis of the arterial blood pressure (ABP) signal. The invention comprises recording and identification of cardiovascular descriptors (including ABP signal, diastolic pressure, systolic pressure, pulse pressure, and end systole), calculation of cardiovascular system parameters, and calculation of aortic blood flow, stroke volume, cardiac output, total peripheral resistance, and characteristic time constant.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for quasi-real-time ventricular measurements from M-mode echocardiogram
ActiveUS8396531B2Fast and accurate derivationEfficiently exploreMedical data miningImage analysisSonificationComputer science
A method for measuring ventricular dimensions from M-mode echocardiograms, includes providing a digitized M-mode echocardiogram image, running a plurality of local classifiers, where each local classifier trained to detect a landmark on either an end-diastole (ED) line or an end-systole (ES) line in the image, recording all possible landmarks detected by the classifiers, where a search range in an N-dimensional parameter space defined by the landmarks for each dimension is reduced to a union of subsets, where each dimension of the parameter space corresponds a landmark, for each combination of possible landmarks, checking if an order of the landmarks is consistent with a known ordering of the landmarks, and if the order is consistent, running a global detector on each consistent combination of landmarks to find a landmark combination with a highest detection probability as a confirmed landmark detection, where the landmarks are used for measuring ventricular dimensions.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
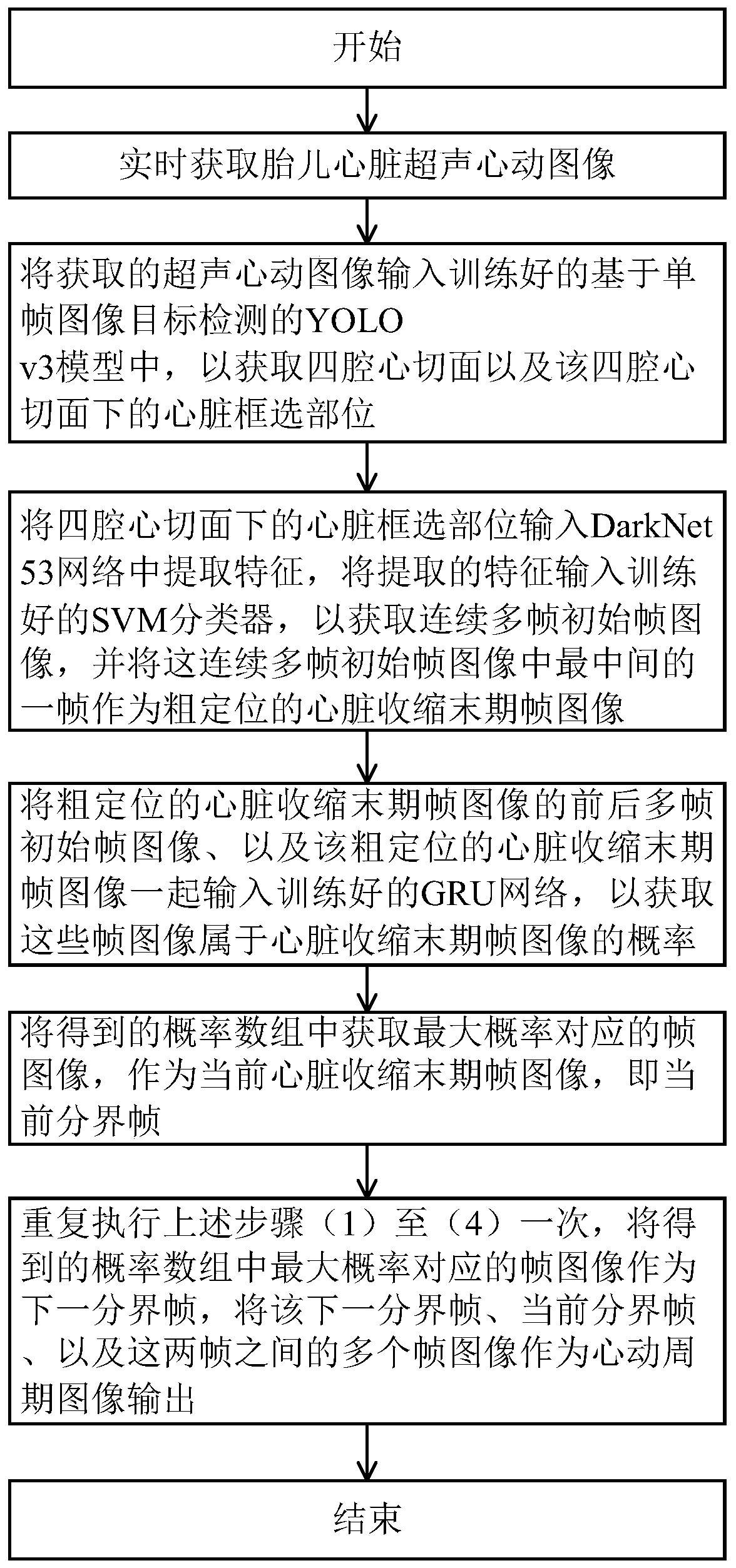
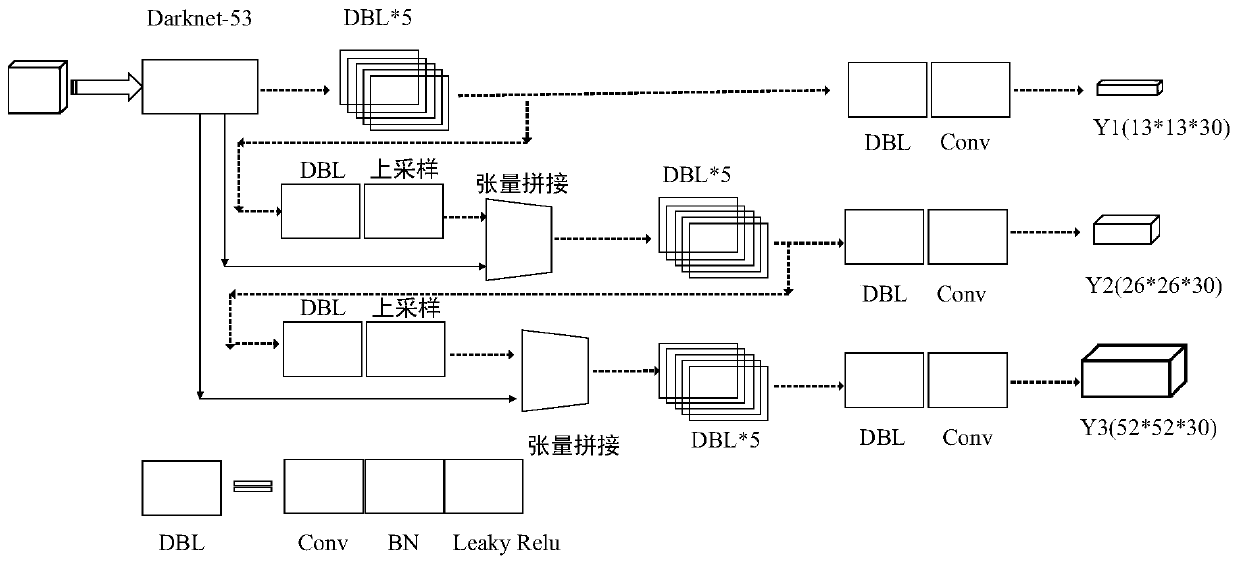
Method for obtaining fetal cardiac cycle images intelligently based on ultrasonic four-chamber views
ActiveCN110604597AFacilitate standardized collectionSolve technical problems with poor universalityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationCardiac cycle
The invention discloses a method for obtaining fetal cardiac cycle images intelligently based on ultrasonic four-chamber views. The method includes the steps that a ultrasonic cardiac video containingthe fetal four-chamber views with a plurality of cycles is collected in real time; the four-chamber heart views in ultrasonic cardiac video frames identified by a trained YOLO v3 model based on single-frame image target detection are used for assisting a sonographer in determining a standard view, and an SVM is used for distinguishing end-systole frames; next, front and rear frames of the preliminarily positioned end-systole frames are input in a GRU module for further optimization selection, and then more accurate and reasonable frames corresponding to end-systoles of the four-chamber viewsare obtained; and in this way, all frames of every two adjacent end-systoles and the intermediate end-systole are a cardiac cycle, and even extraction of the four to five frames is final output. The method aims at using computers to automatically intercept fetal ultrasonic cardiac cycles to facilitate subsequent automatic auxiliary diagnosis.
Owner:深圳蓝湘智影科技有限公司
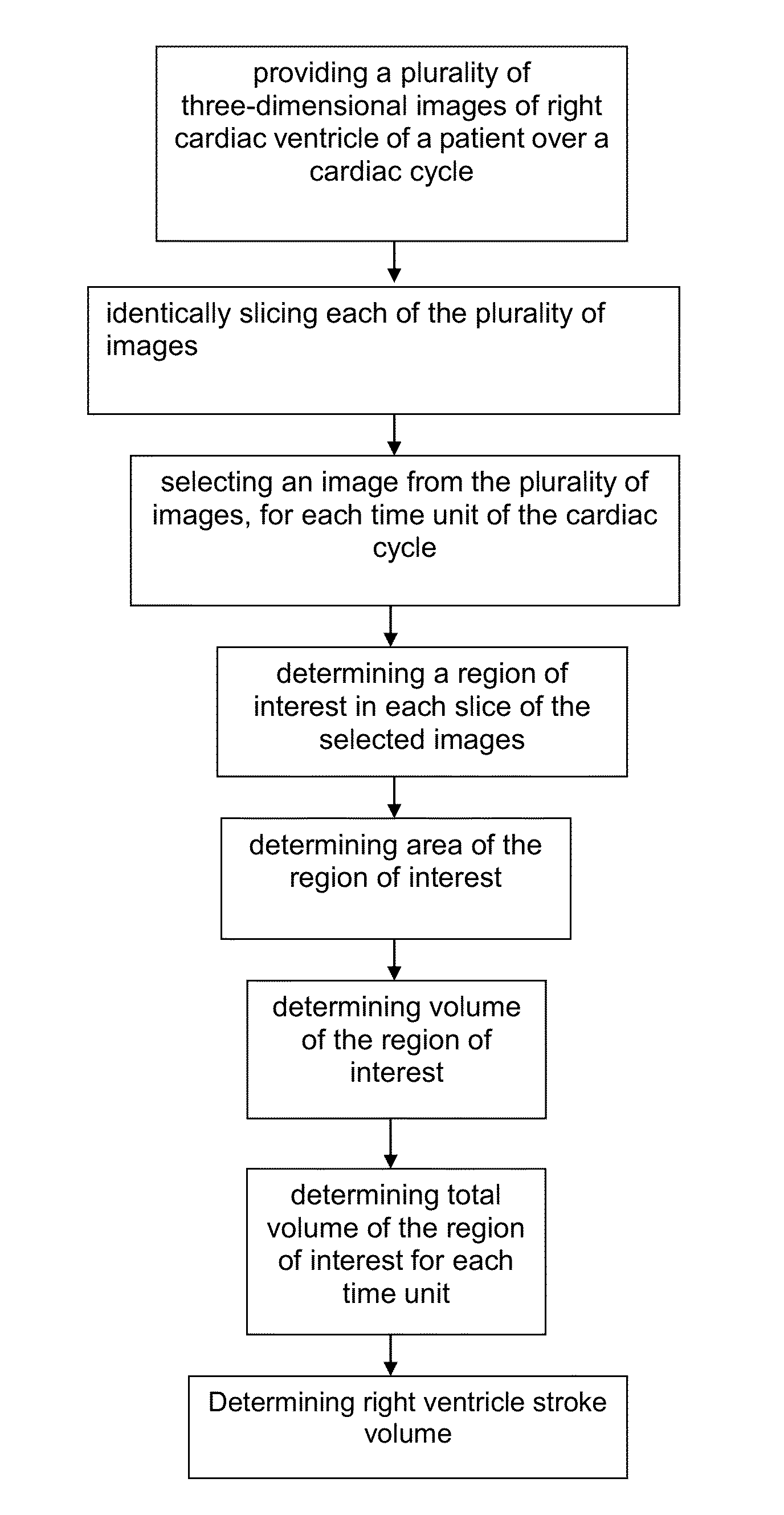
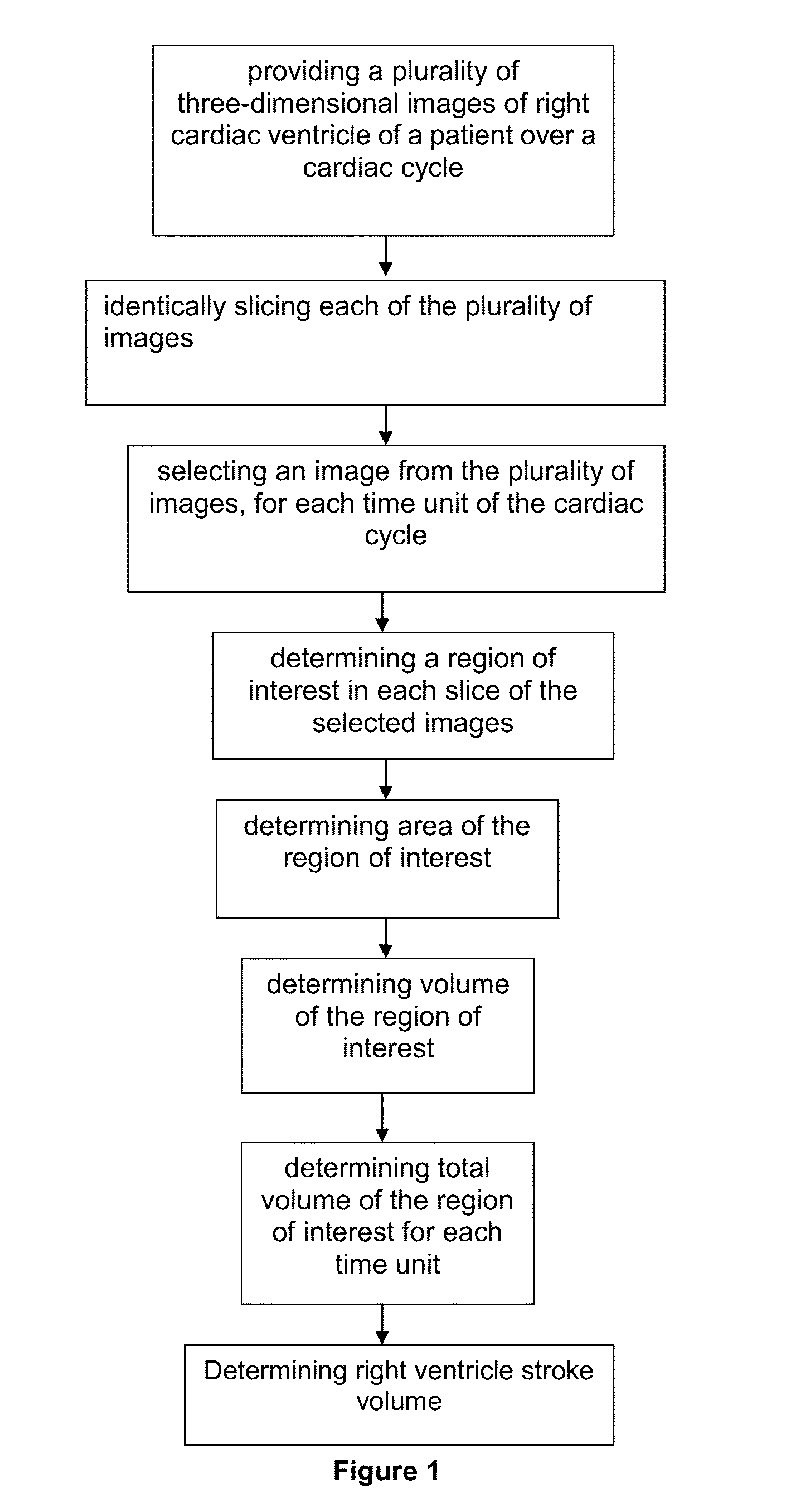
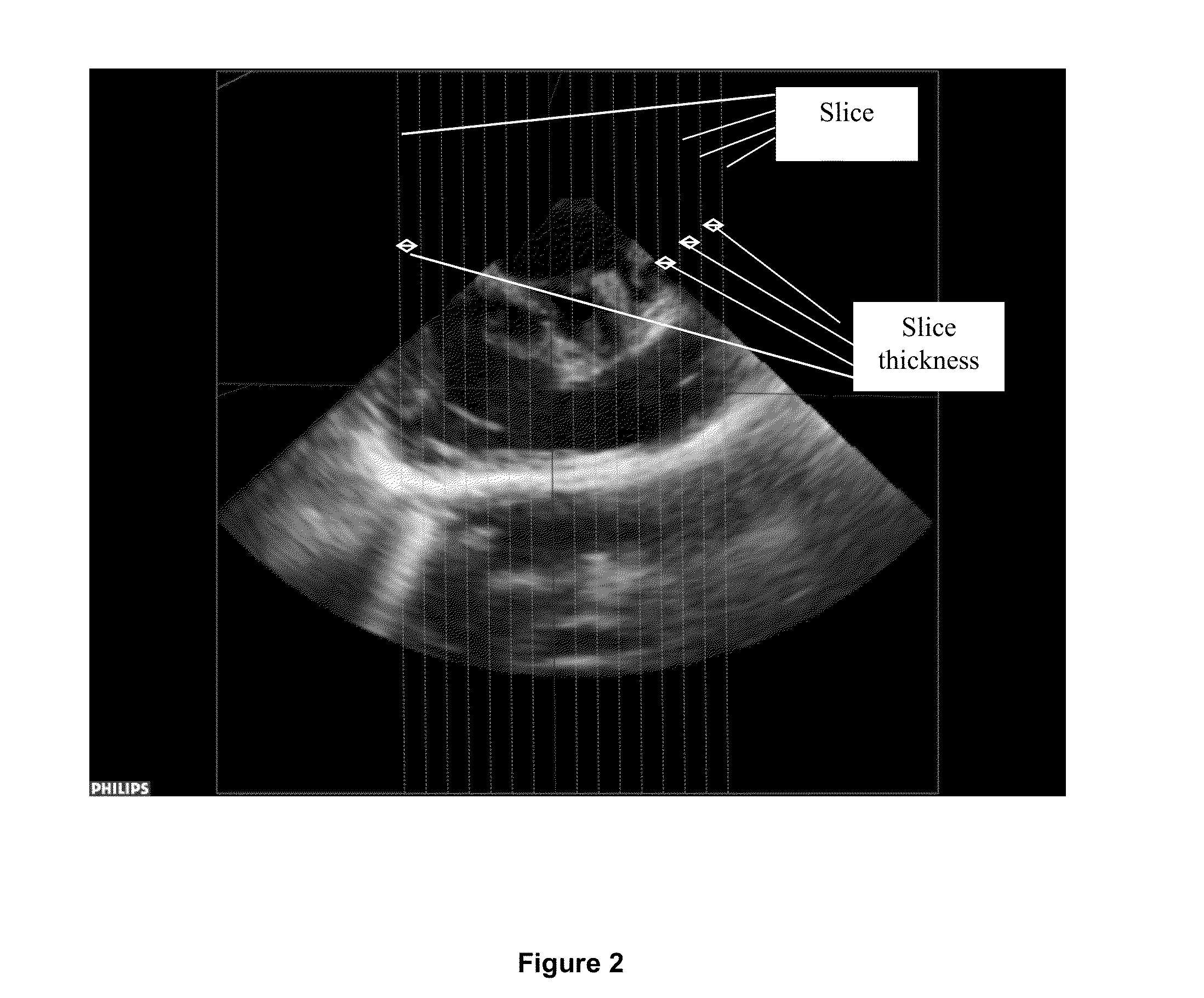
Method for Determining Right Ventricle Stroke Volume
InactiveUS20150078638A1Minimal manual manipulationMinimal correctionImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac cycleEnd-systolic volume
The present invention relates to a method for determining right ventricle stroke volume comprising the steps of: providing a plurality of three-dimensional images of right cardiac ventricle of a patient over a cardiac cycle; identically slicing each of the plurality of images; selecting an image from the plurality of images, for each time unit of the cardiac cycle; determining a region of interest in each slice of the selected images, wherein the region of interest shows the right ventricle of the patient; determining area of the region of interest; determining volume of the region of interest; determining total volume of the region of interest for each time unit, wherein the maximum total volume is end diastolic volume and the minimum total volume is end systolic volume; and determining the right ventricle stroke volume using an equation:Right Ventricle Stroke Volume=end diastolic volume−end systolic volume (3).
Owner:UNIVERSITI PUTRA MALAYSIA
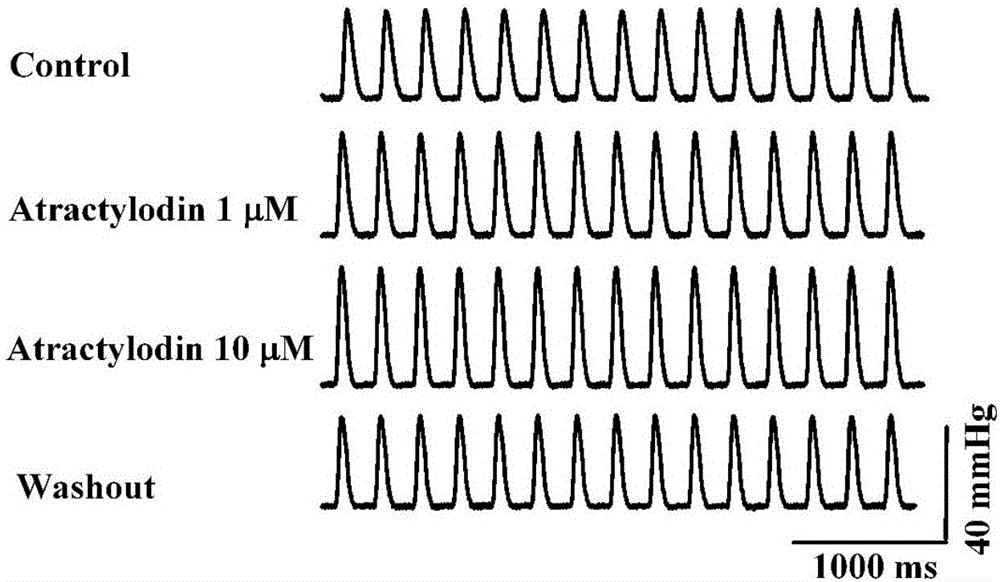
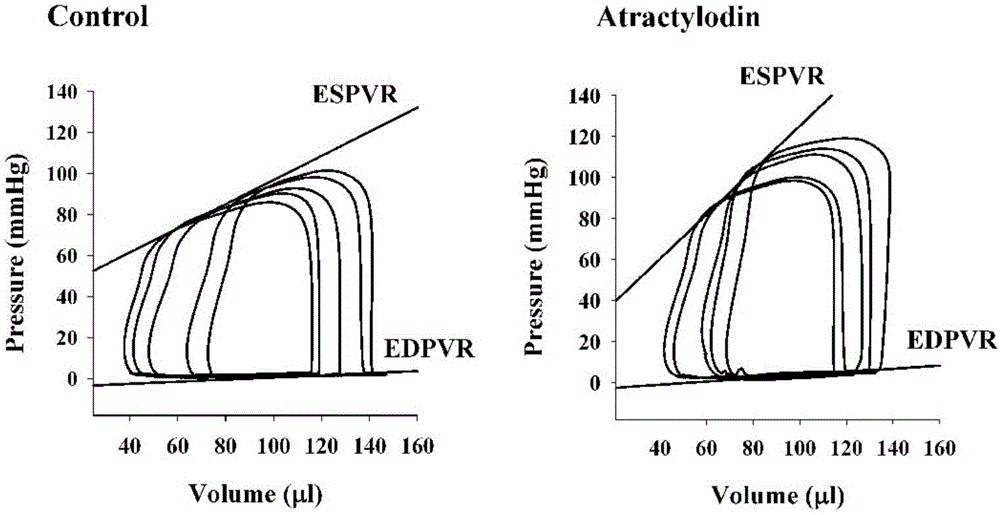
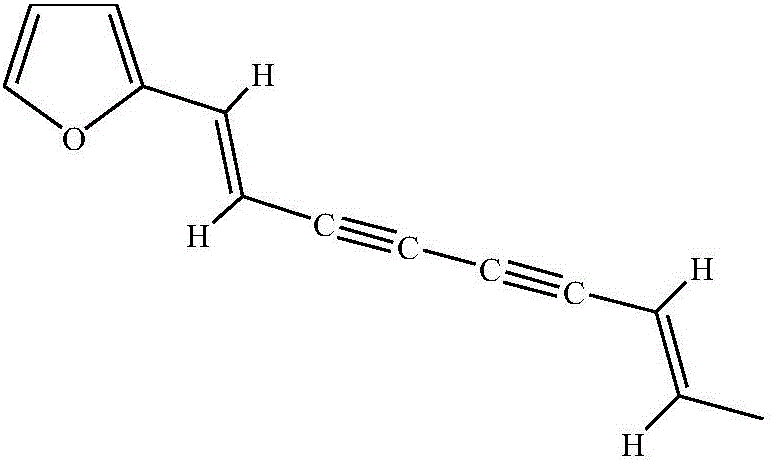
Application of atractylodin in pharmacy
InactiveCN106727487APositive inotropic effectOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderIncreased heart rateLeft ventricular size
The invention discloses application of atractylodin in the preparation of drugs for treating and preventing heart failure, and belongs to the field of medicine. Atractylodin can significantly increase maximum rising speed of left ventricular developed pressure and left ventricular pressure of rat isolated heart, is dependent on concentration, causes no significant effect on heart rate, and is free of adverse effect causing arrhythmia. It is indicated that atractylodin has positive inotropic action and is not dependent on neurohumor. Atractylodin can significantly increase a normal rat's end-systolic volume, end-systolic pressure, stroke volume, ejection fraction, cardiac output, left ventricular pressure maximum rising speed, stroke work, and slope of end-systolic pressure-volume relational curve. It is indicated that atractylodin has positive inotropic action without increasing heart rate.
Owner:泰州中国医药城中医药研究院
Ultrasound imaging system and method
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Ultrasound imaging system and method
ActiveUS20210196228A1Permit trackingImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac cycle3D ultrasound
An ultrasound imaging system is for determining stroke volume and / or cardiac output. The imaging system may include a transducer unit for acquiring ultrasound data of a heart of a subject (or an input for receiving the acquired ultrasound data), and a controller. The controller is adapted to implement a two-step procedure, the first step being an initial assessment step, and the second being an imaging step having two possible modes depending upon the outcome of the assessment. In the initial assessment procedure, it is determined whether regurgitant ventricular flow is present. This is performed using Doppler processing techniques applied to an initial ultrasound data set. If regurgitant flow does not exist, stroke volume is determined using segmentation of 3D ultrasound image data to identify and measure the volume of the left or right ventricle at each of end systole and end-diastole, the difference between them giving a measure of stroke volume. If regurgitant flow does exist, stroke volume is determined using Doppler techniques applied to ultrasound data continuously collected throughout a cardiac cycle.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com