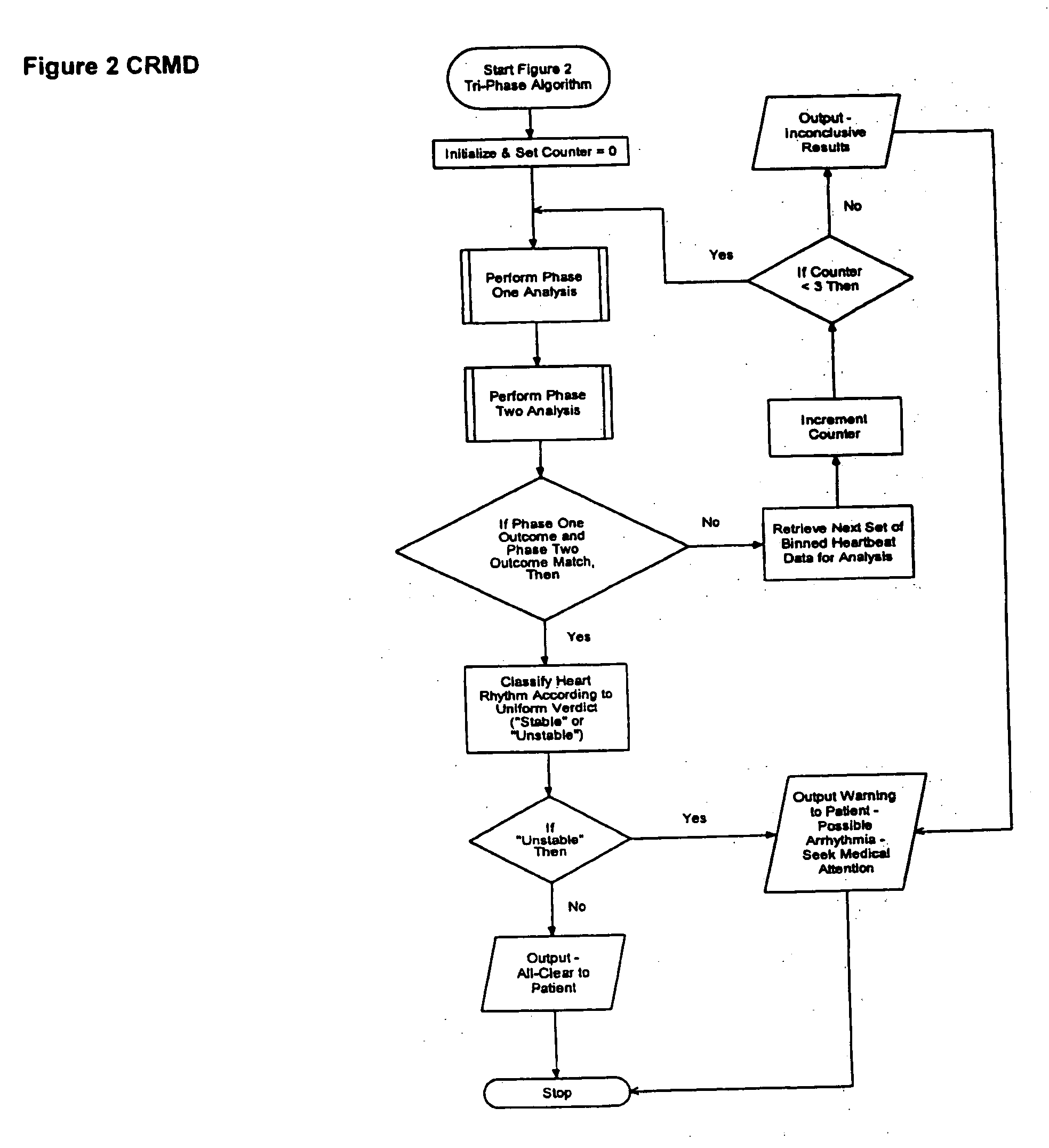
Patents
Literature
120 results about "R-R Interval" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
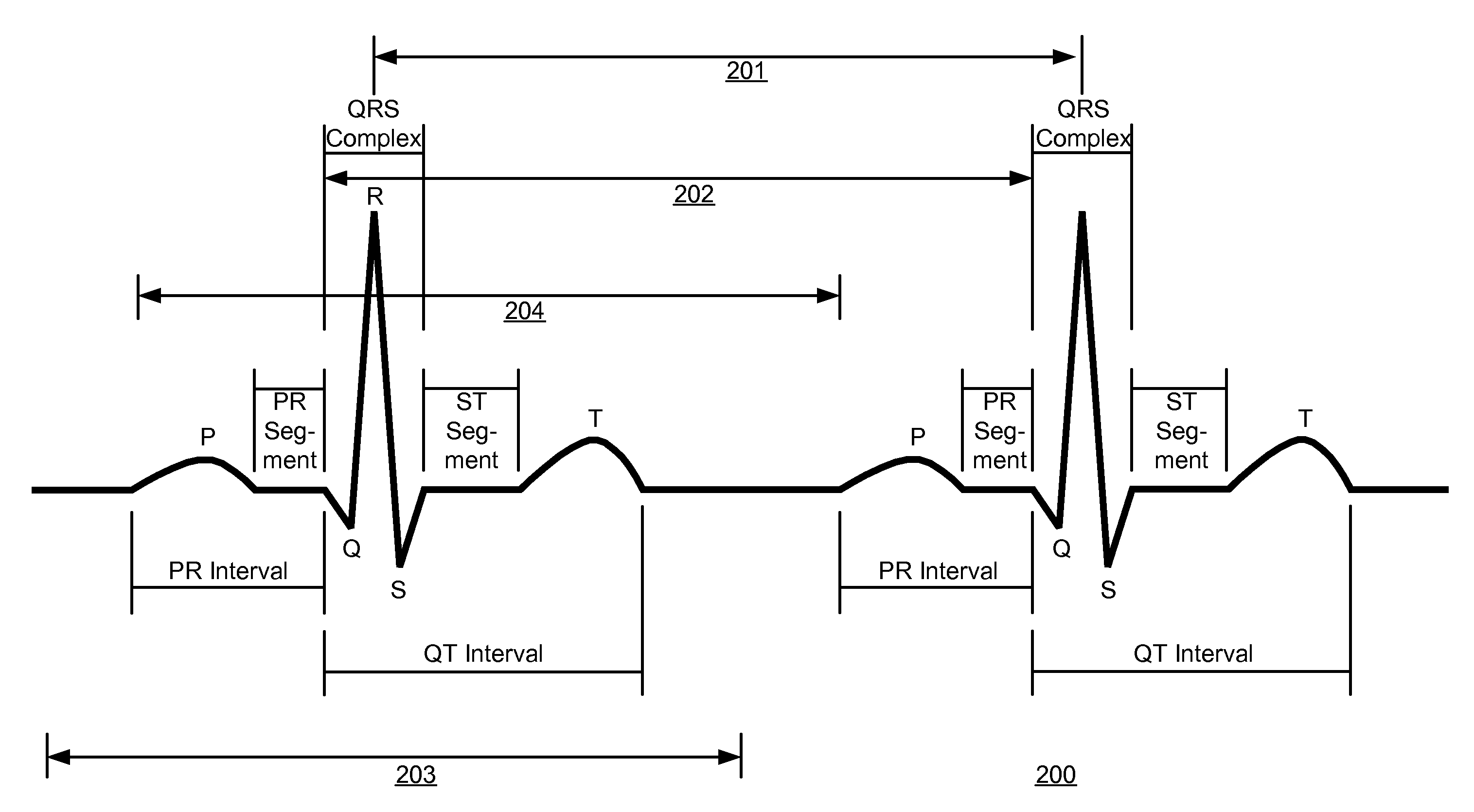
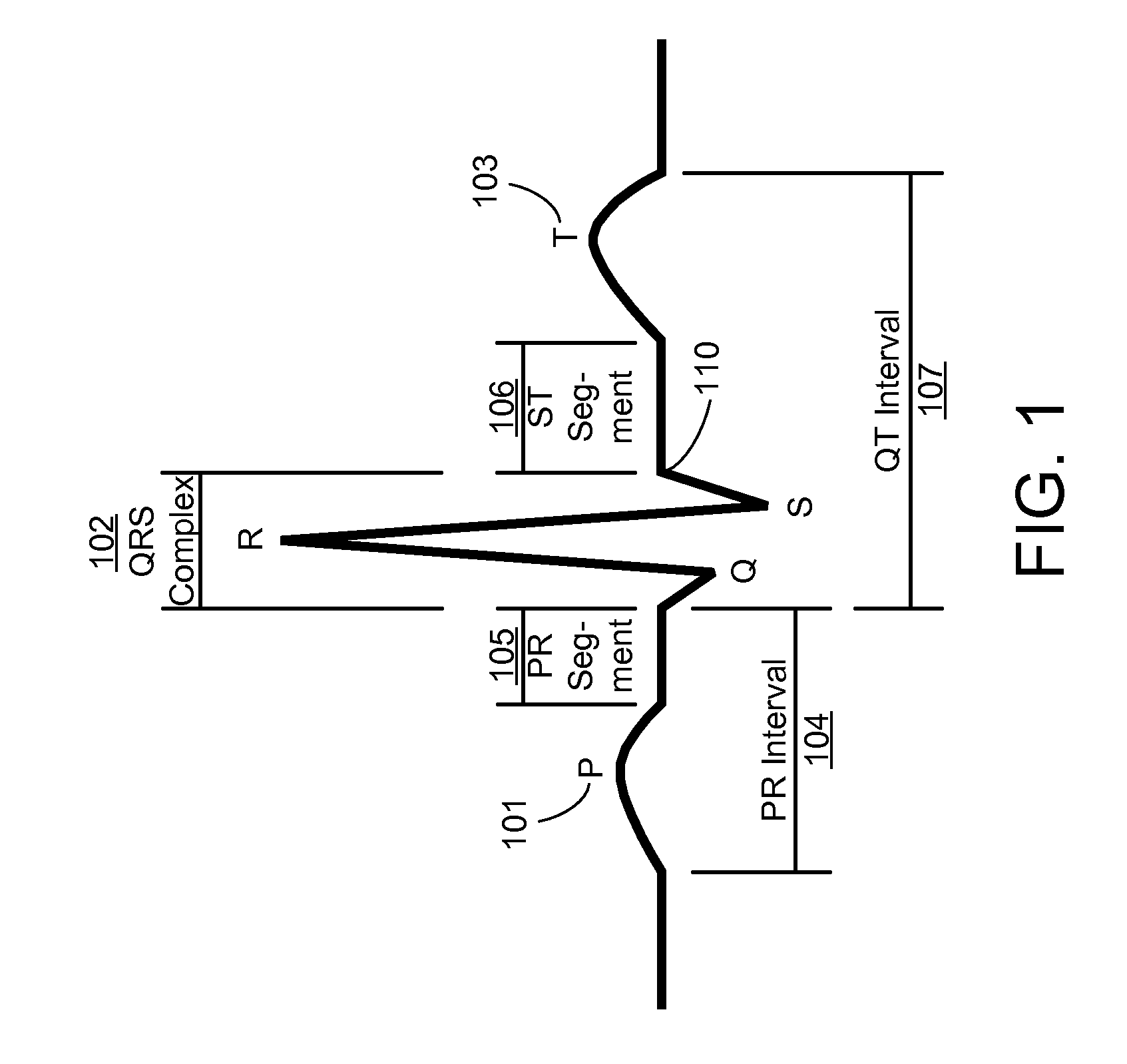
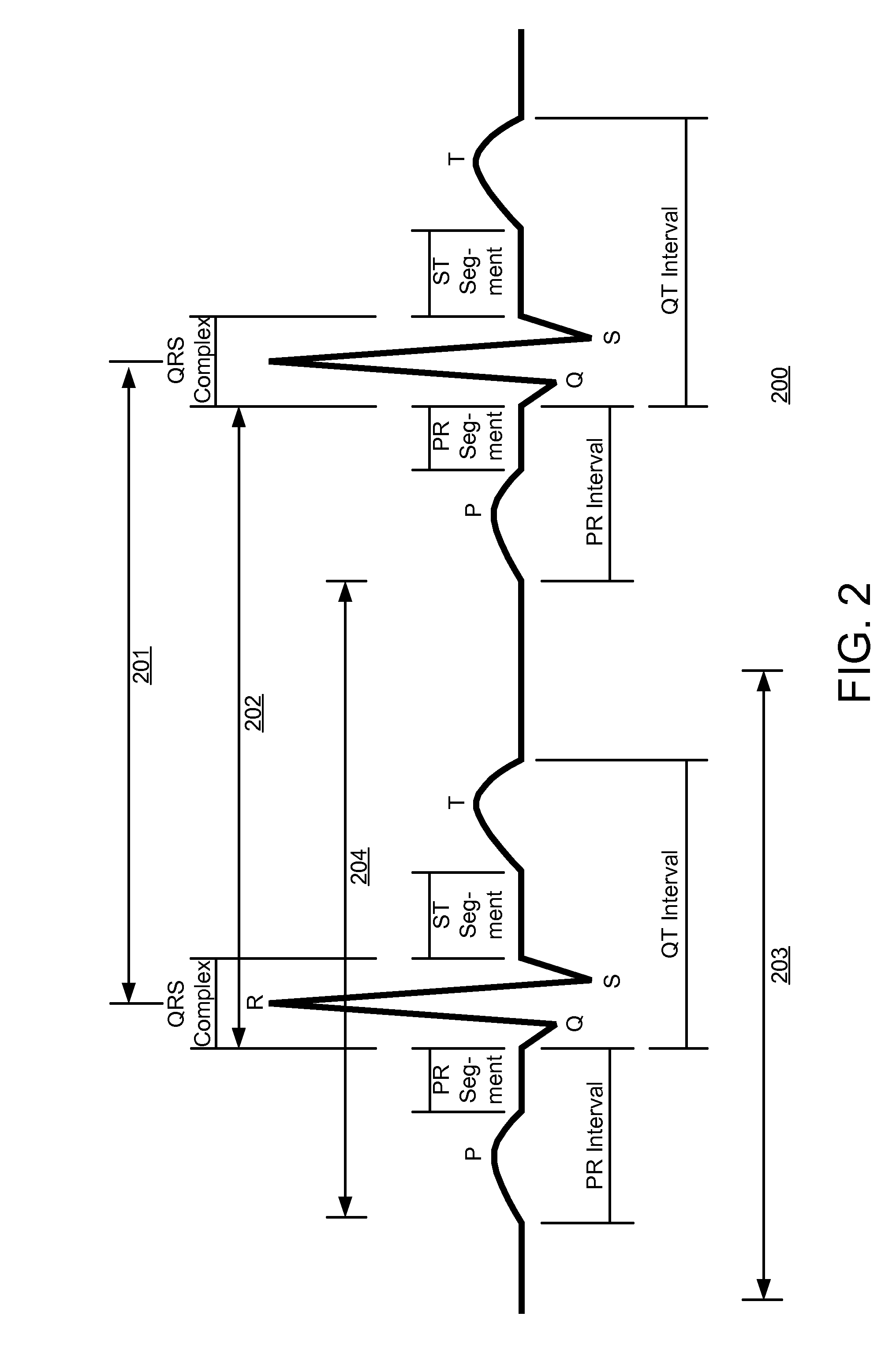
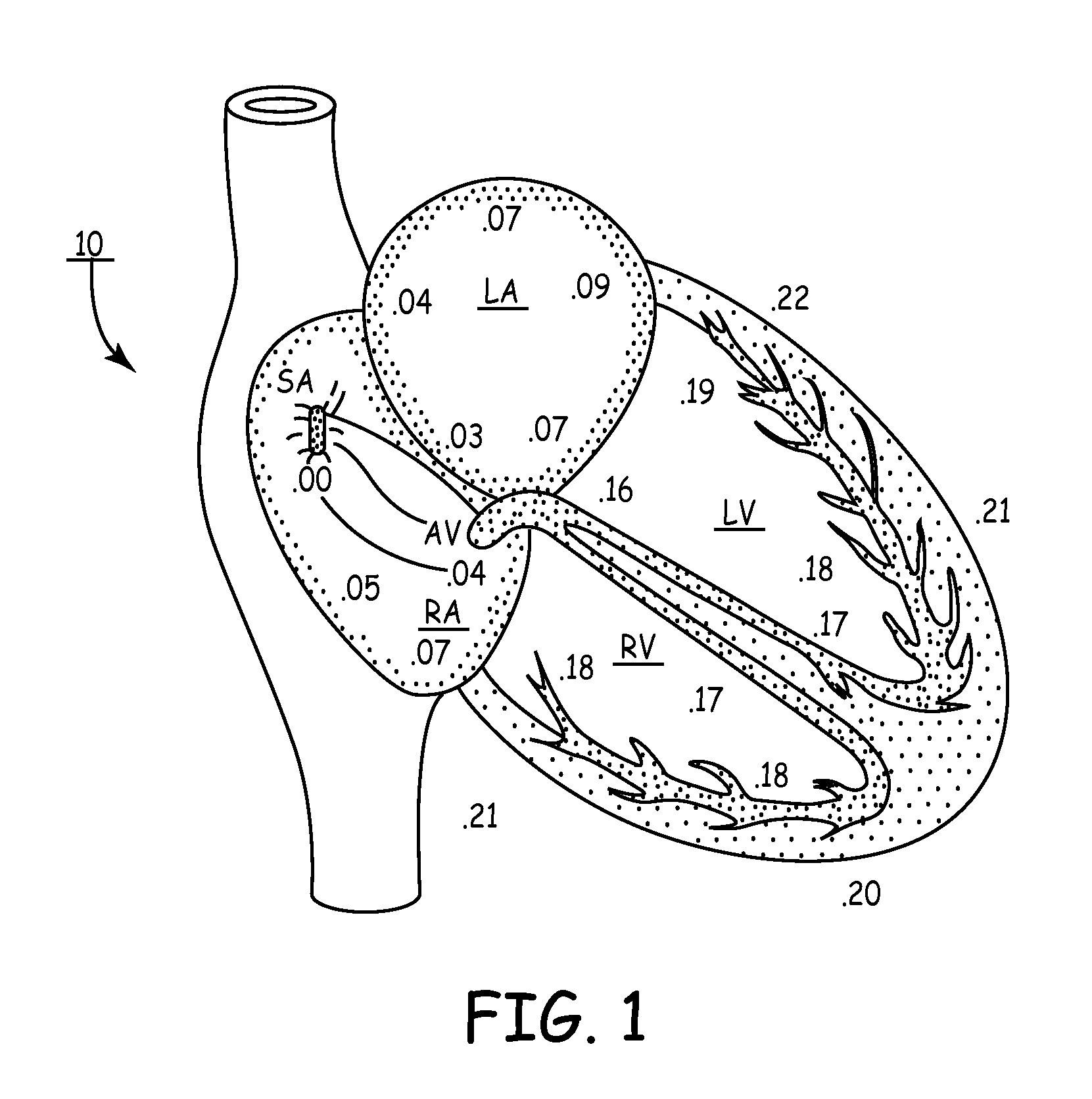
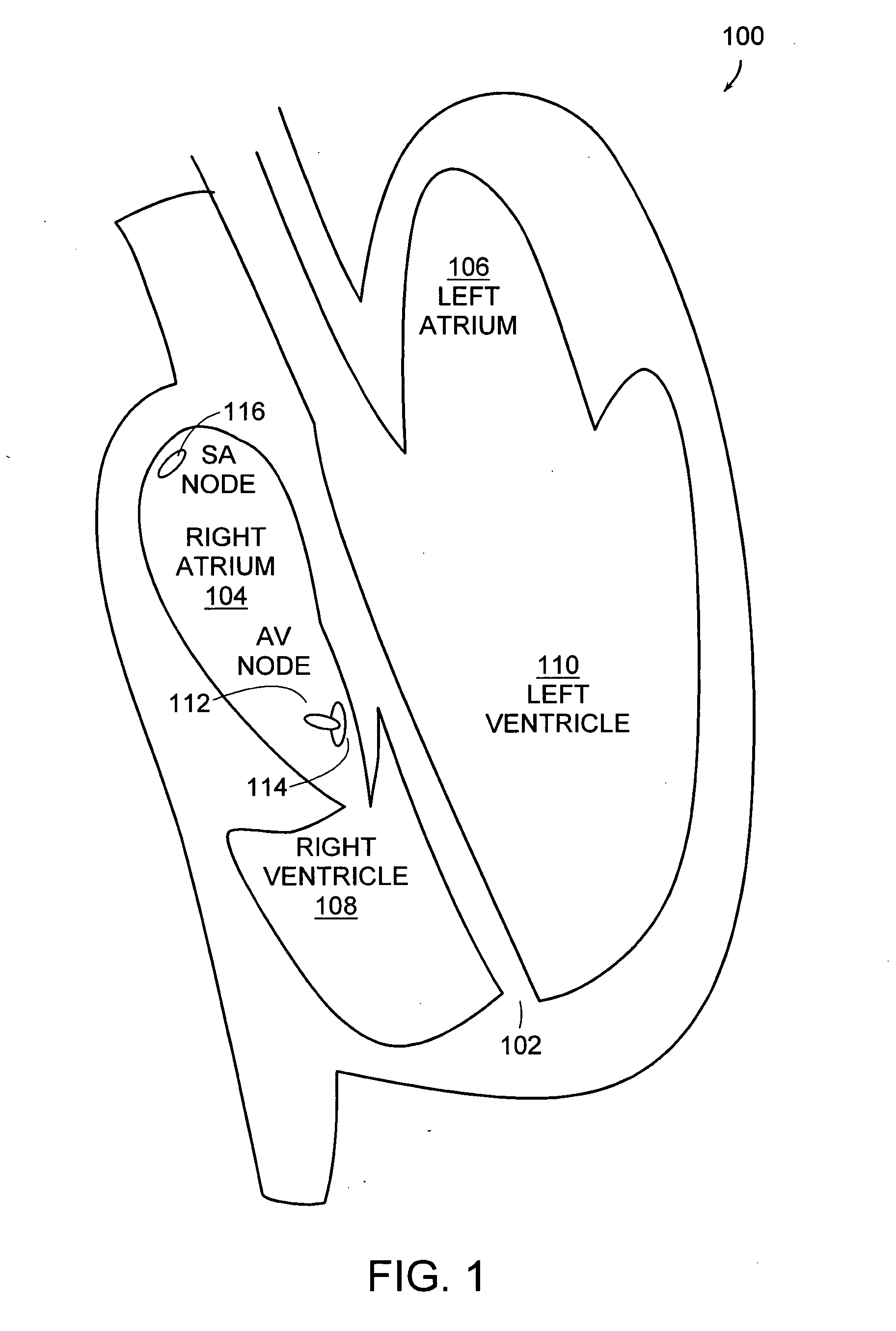
The time measurement between the R wave of successive heartbeats as measured in milliseconds.
Method for analyzing irreversible apneic coma (IAC)
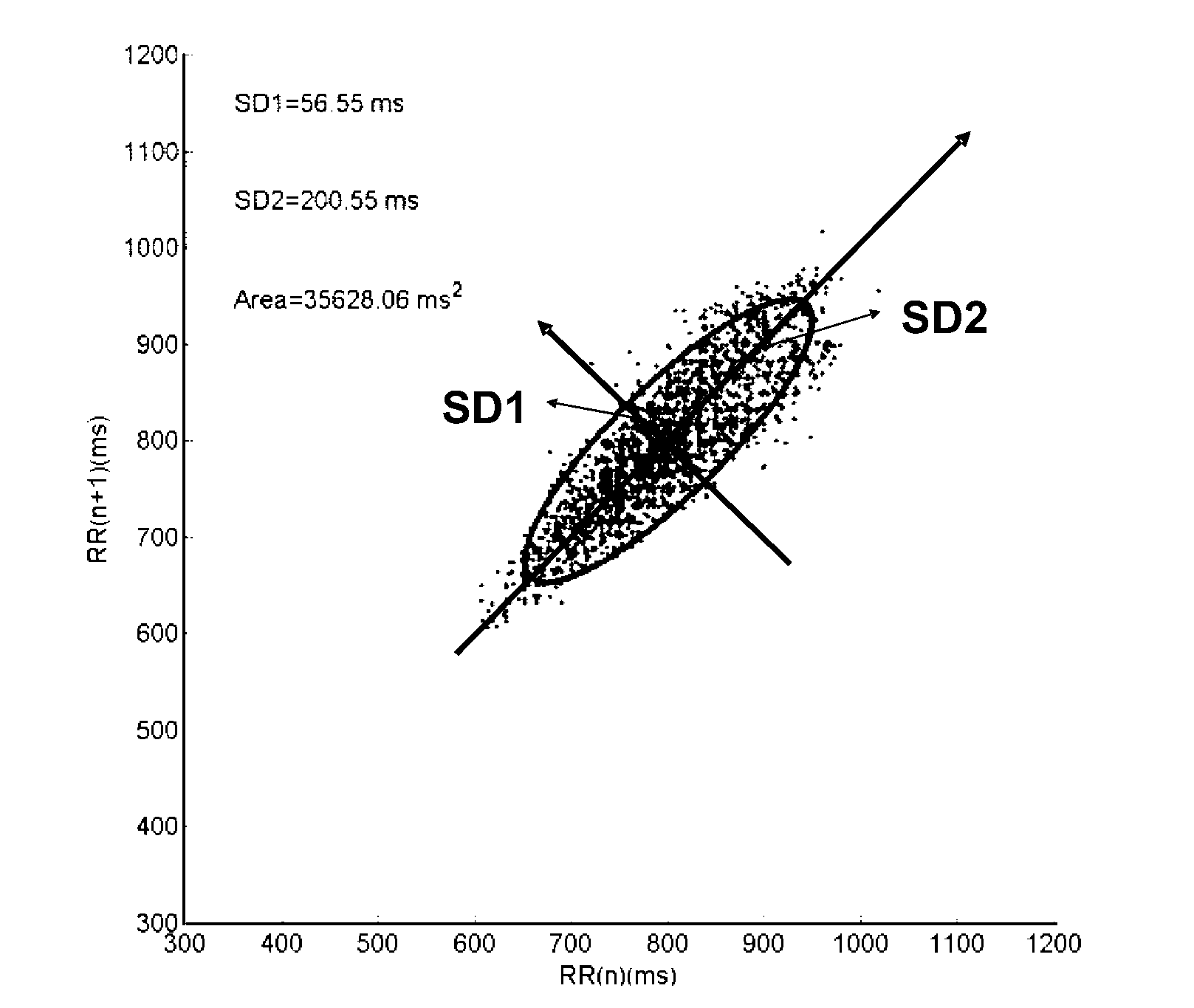
An method for analyzing irreversible apneic coma (IAC) for determining the presence of irreversible apneic coma (IAC) by analyzing the heart rate variability of a brain traumatic patient, thereby providing a physician a reference index to determine whether brain death has occurred. This method includes, at first, recording an electrocardiogram (ECG) from a subject. Then, analyzing R-R interval in said electrocardiogram (ECG), and plotting said R-R interval into Poincaré plot, wherein the X coordinate in said Poincaré plot represents R-R interval(n), and n is a 1˜data number. Y coordinate in said Poincaré plot represents RR(n+1). And, finally, quantifying said Poincaré plot, and obtaining semi-major axis (SD1), semi-minor axis (SD2), and SD1 / SD2 of said Poincaré plot, as well as Poincaré plot area.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
Methods for Detection of Cardiac Arrhythmias
A method for calculating a variability value that is indicative of AF by obtaining a signal sequence of a plurality of RR intervals by monitoring electrical activity of a patient's heart. Each RR interval is converted into an instantaneous heart rate value and sorted into ascending order. The difference between each successive heart rate is calculated, discarding the two largest differences. The variability value is calculated by adding the retained differences.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LTD
Method, apparatus and system for characterizing sleep
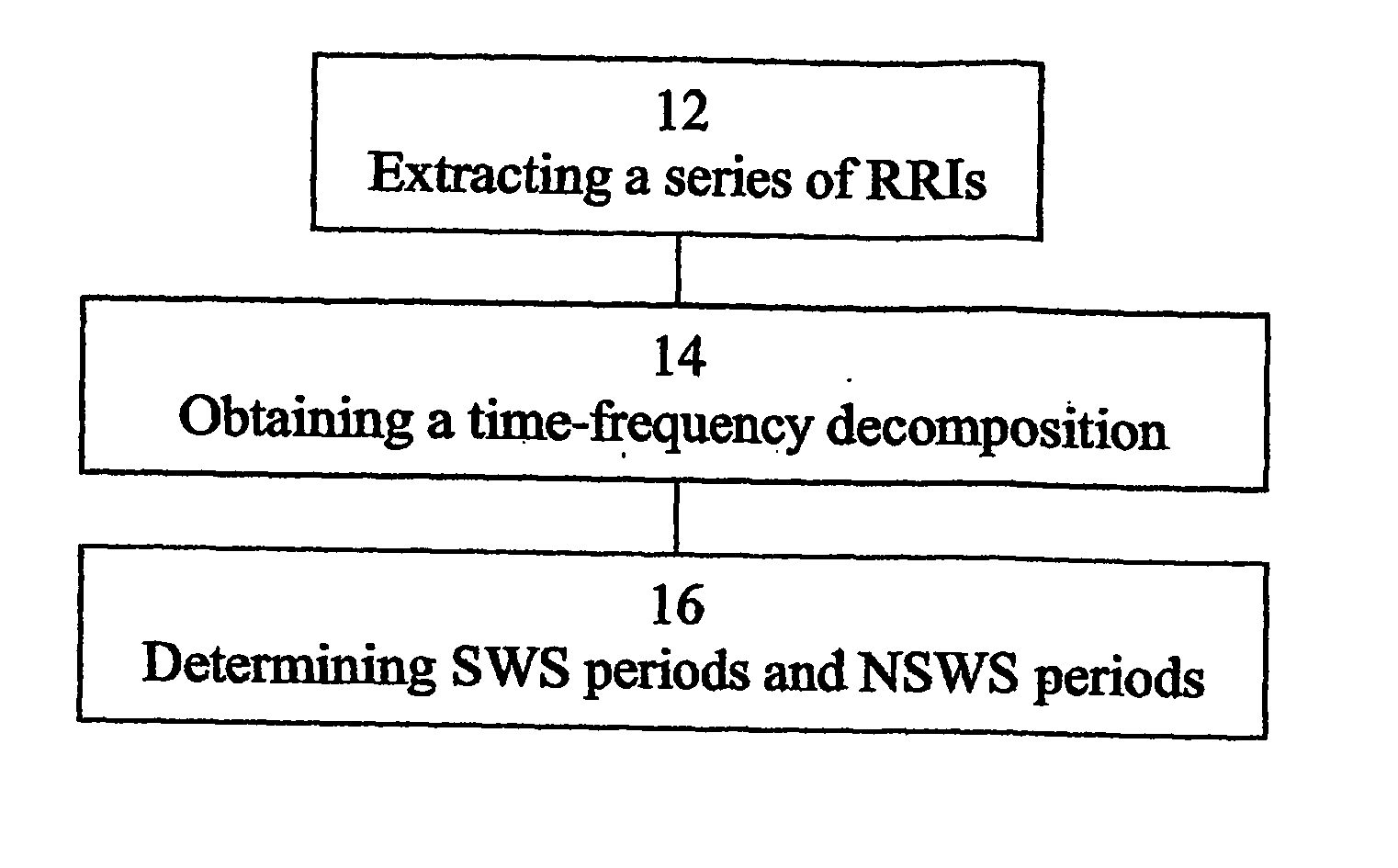
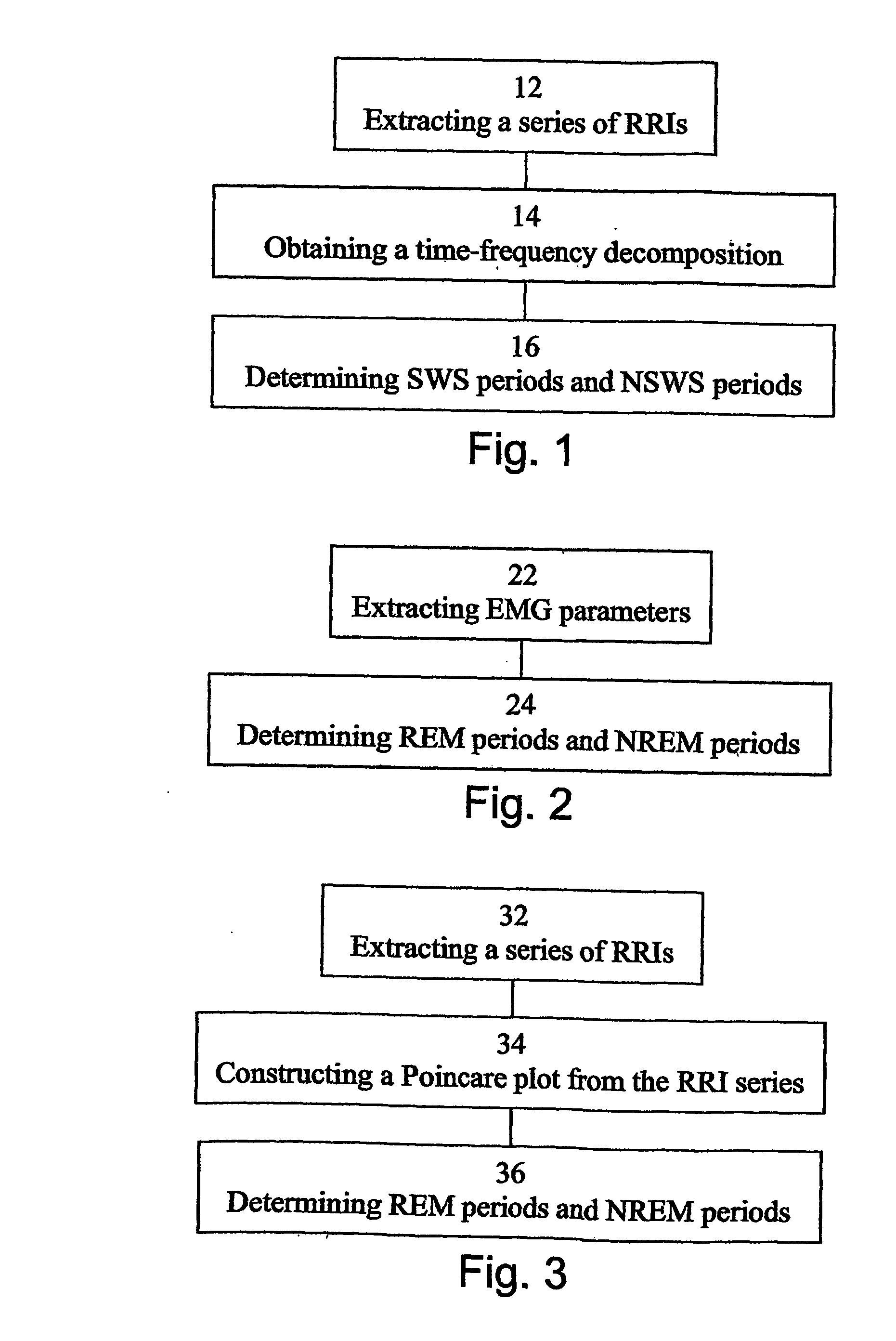
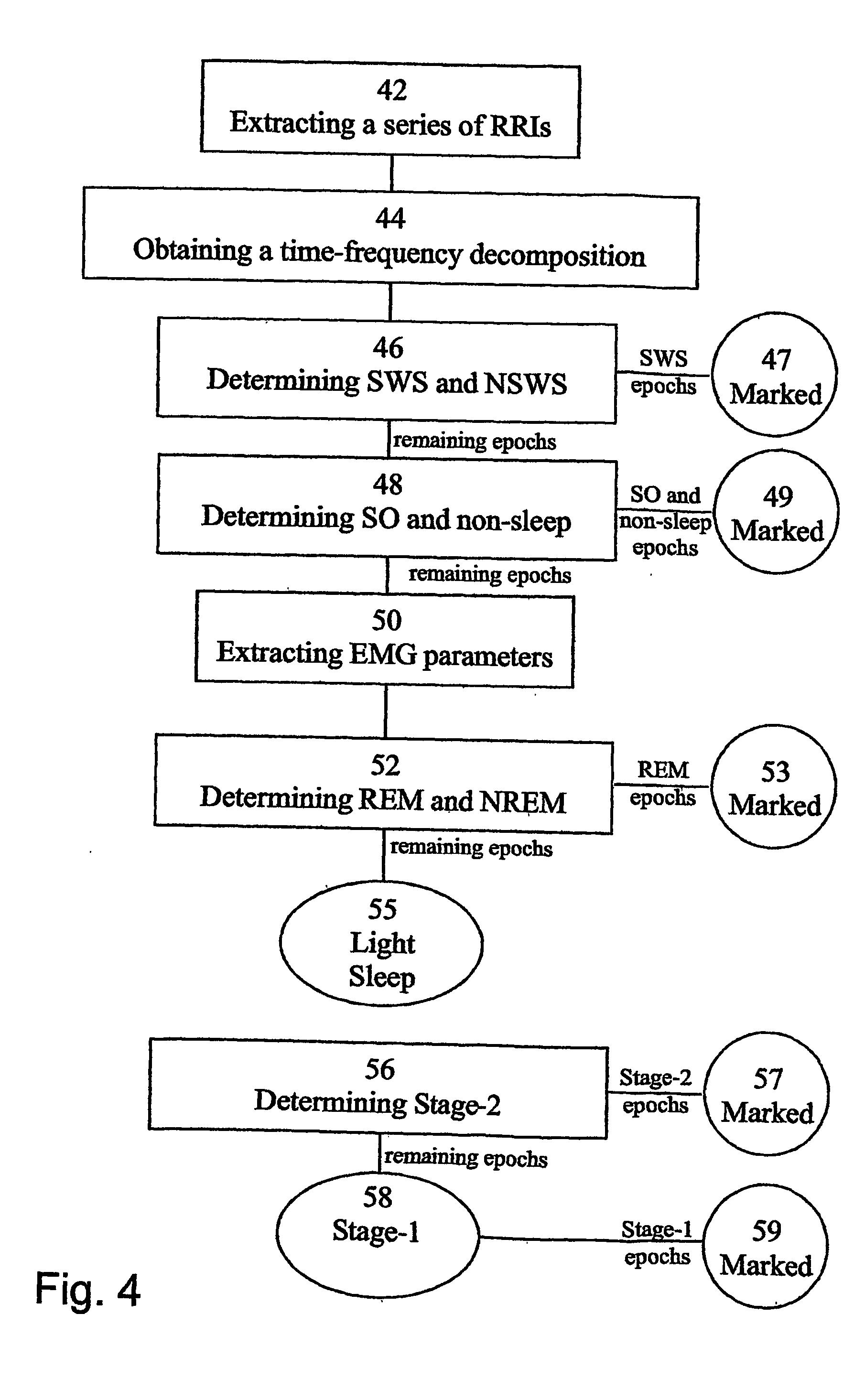
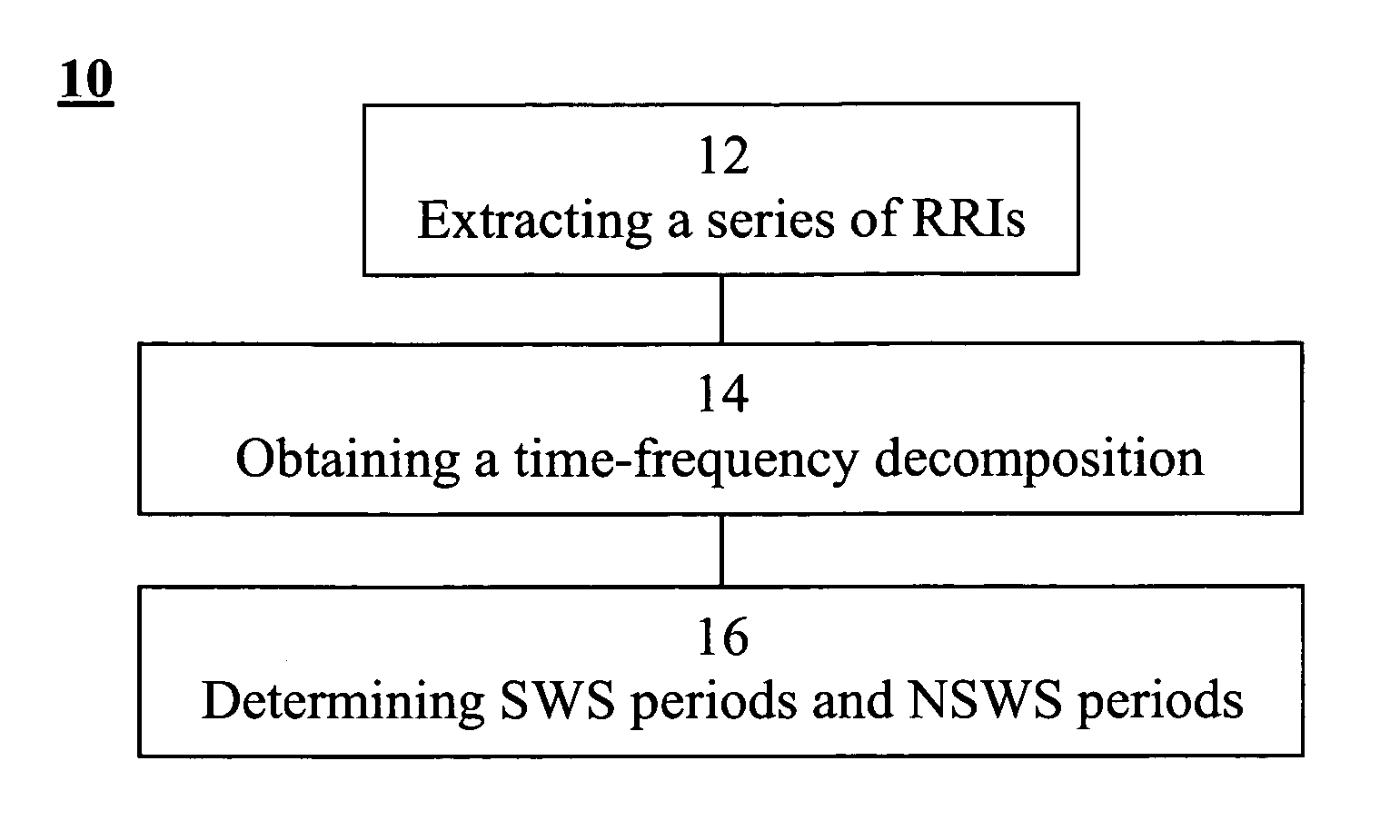
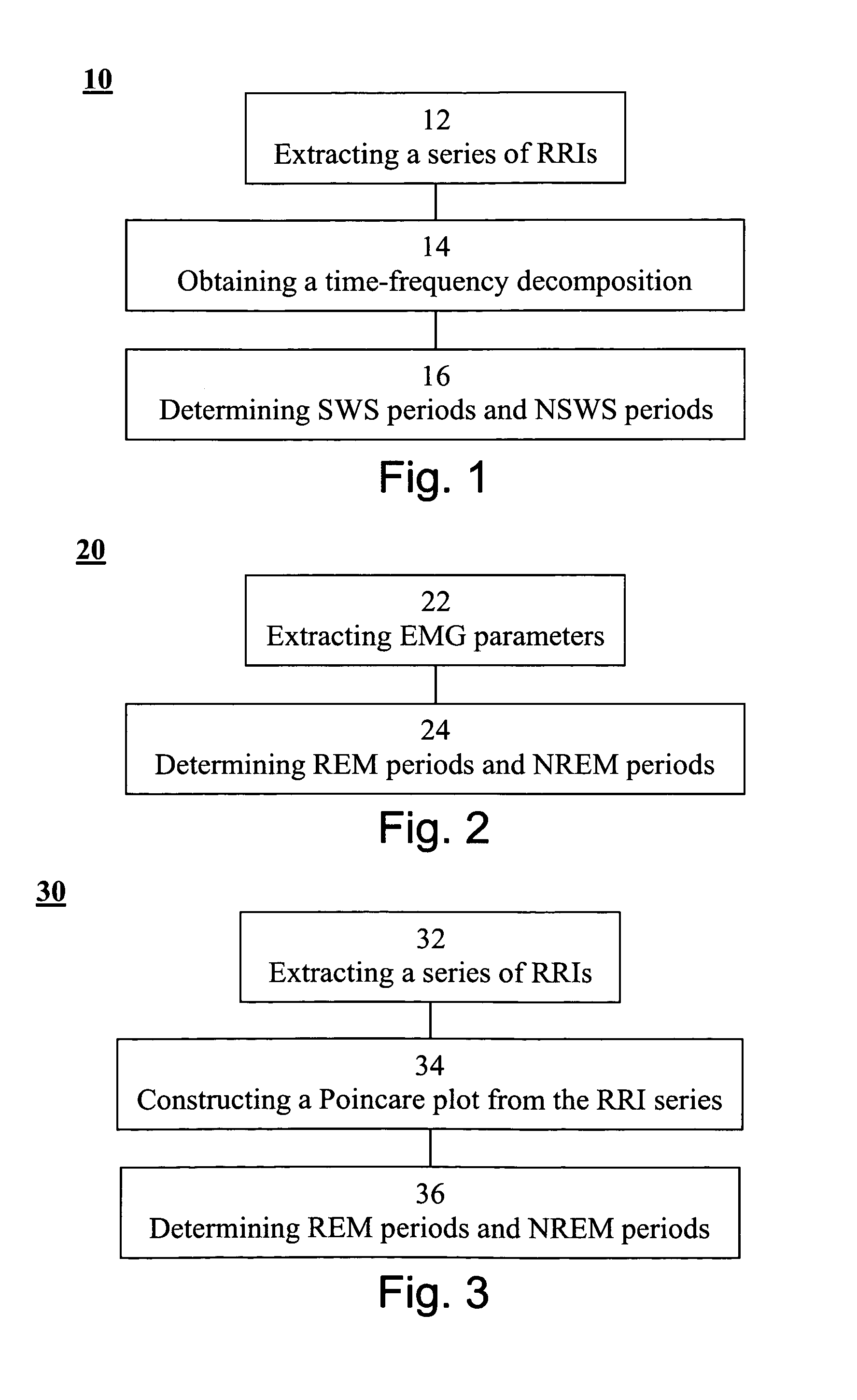
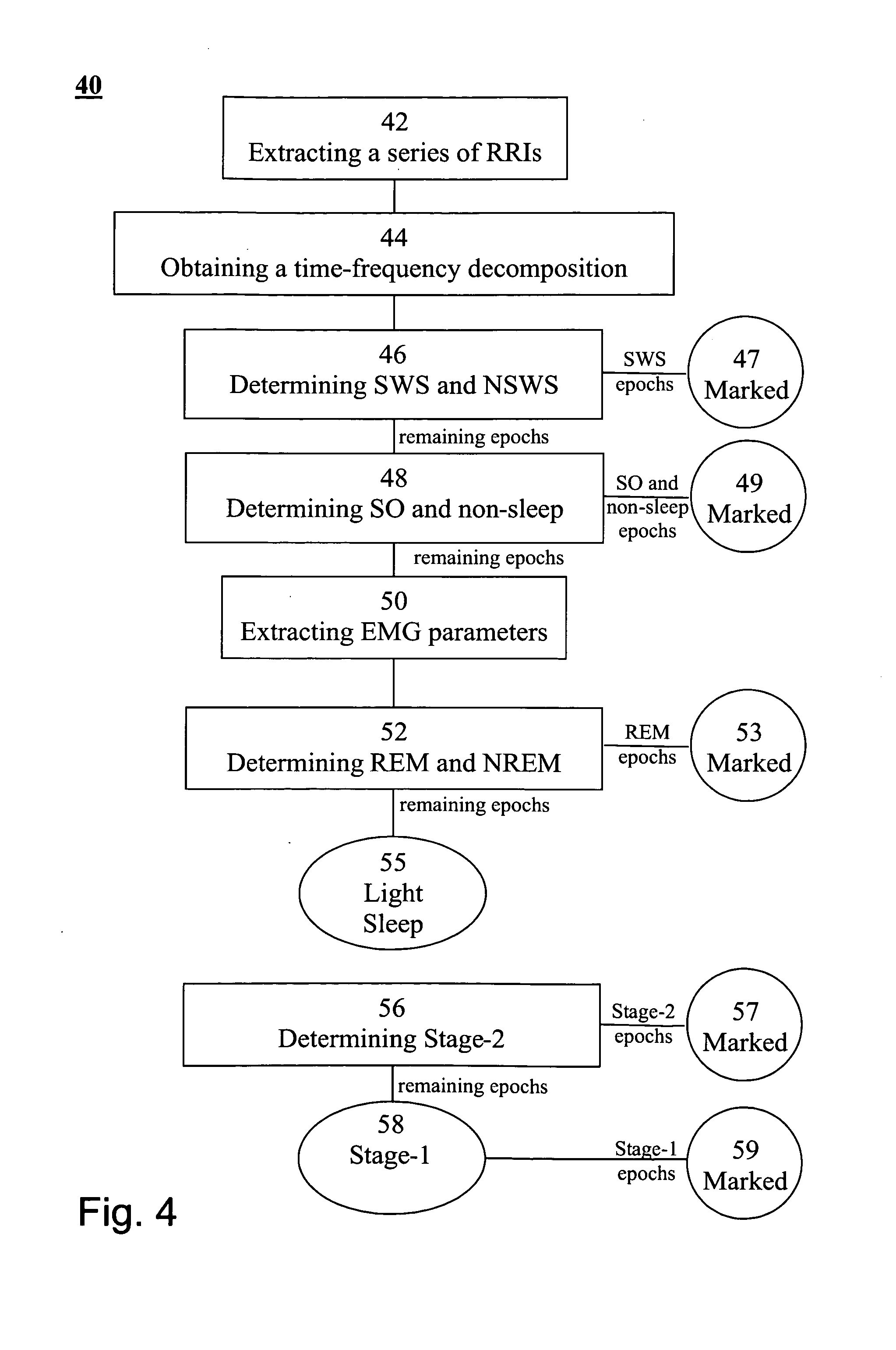
A method of determining sleep stages from signals of electrical activity recorded of a chest of a sleeping subject, the signals being measured over a plurality of epochs. The method comprising: (a) extracting a series of cardiac R-R intervals from the signals and obtaining a time-frequency decomposition from the series of cardiac R-R intervals; (b) using the time-frequency decomposition to determine at least one Slow-Wave-Sleep (SWS) period and at least one Non-SWS (NSWS) period; (c) from the at least one NSWS period, determining at least one sleep-onset (SO) period and a plurality of non-sleep periods; (d) extracting a plurality of electromyogram (EMG) parameters from a portion of the signals, the portion corresponds to a NSWS period other than the at least one SO period and other than the plurality of non-sleep period; (e) using the plurality of EMG parameters to determine at least one REM period thereby also to obtain also at least one light-sleep (LS) period defined as a NSWS period other than the SO periods, other than the non-sleep periods and other than the REM periods; thereby determining the sleep stages of the sleeping subject.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal AV an VV intervals
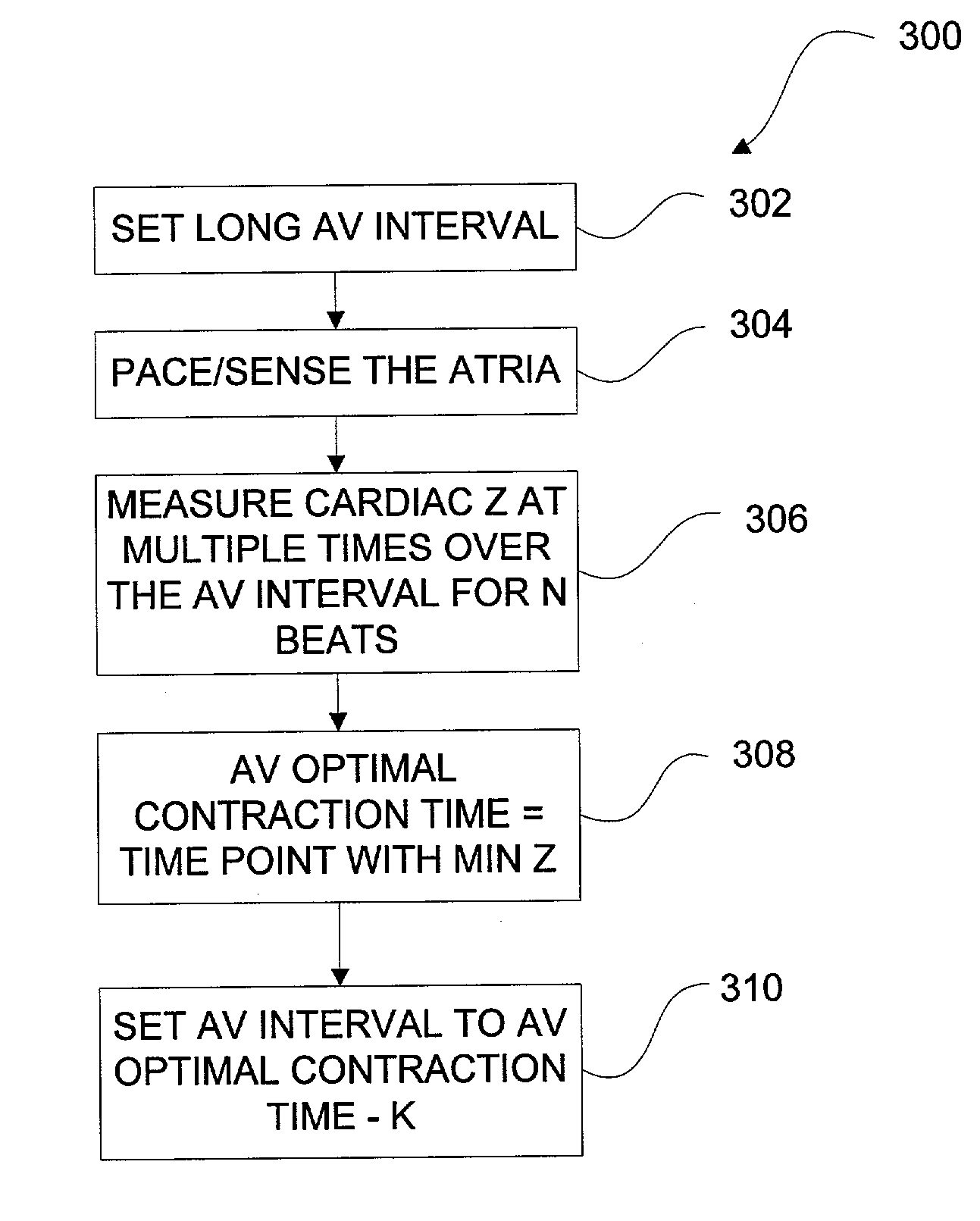
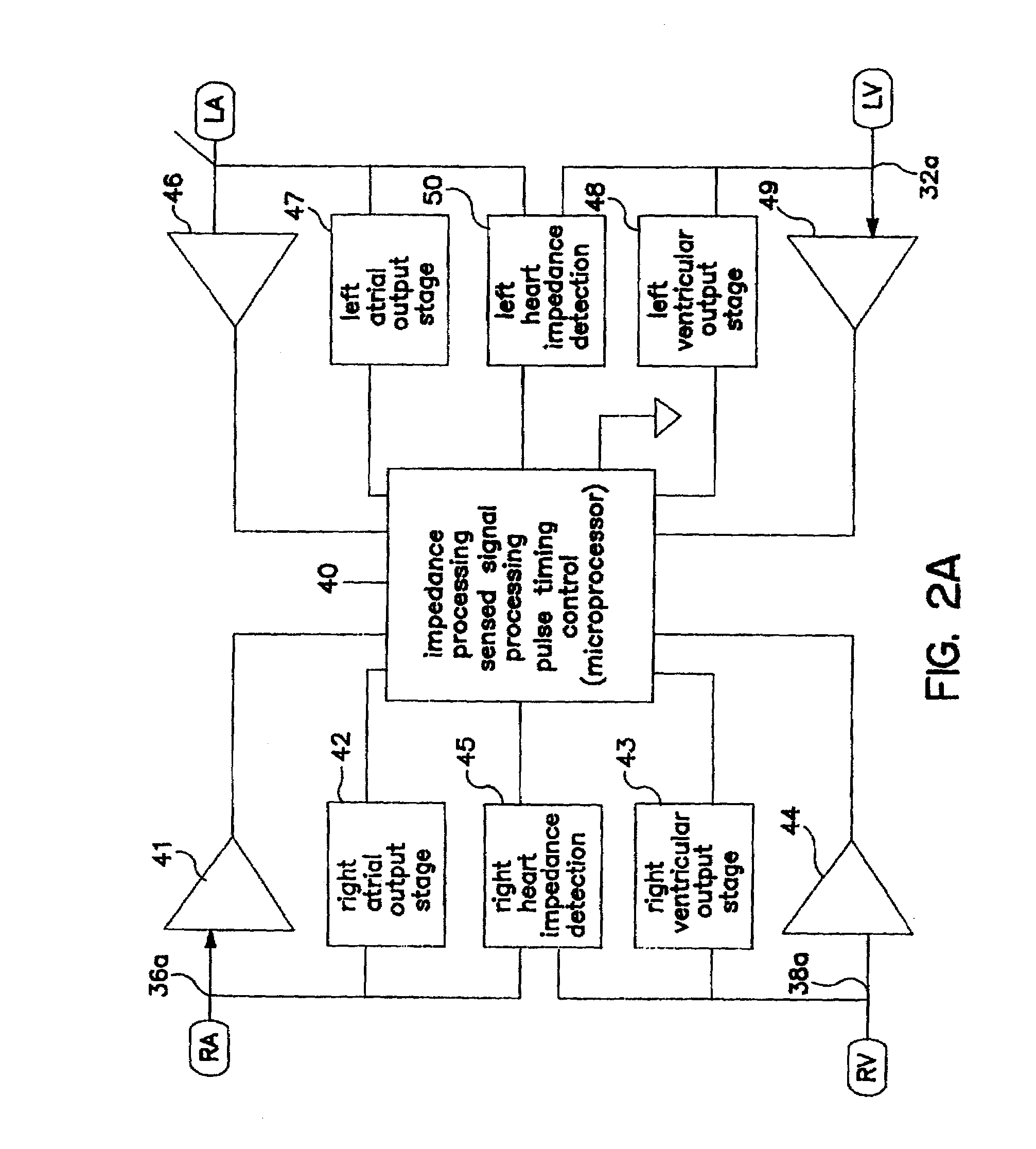
Methods and devices for determining optimal Atrial to Ventricular (AV) pacing intervals and Ventricular to Ventricular (VV) delay intervals in order to optimize cardiac output. Impedance, preferably sub-threshold impedance, is measured across the heart at selected cardiac cycle times as a measure of chamber expansion or contraction. One embodiment measures impedance over a long AV interval to obtain the minimum impedance, indicative of maximum ventricular expansion, in order to set the AV interval. Another embodiment measures impedance change over a cycle and varies the AV pace interval in a binary search to converge on the AV interval causing maximum impedance change indicative of maximum ventricular output. Another method varies the right ventricle to left ventricle (VV) interval to converge on an impedance maximum indicative of minimum cardiac volume at end systole. Another embodiment varies the VV interval to maximize impedance change.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
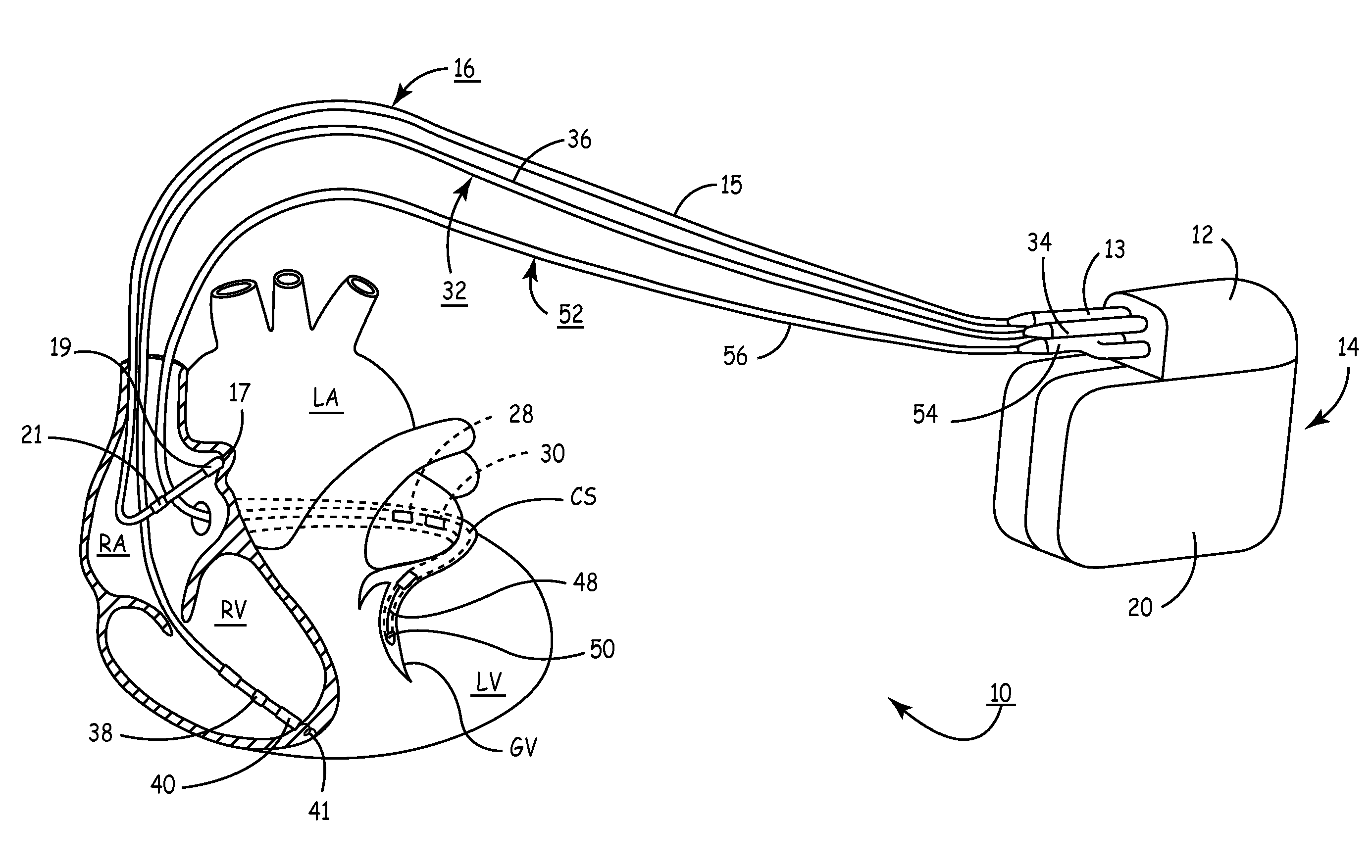
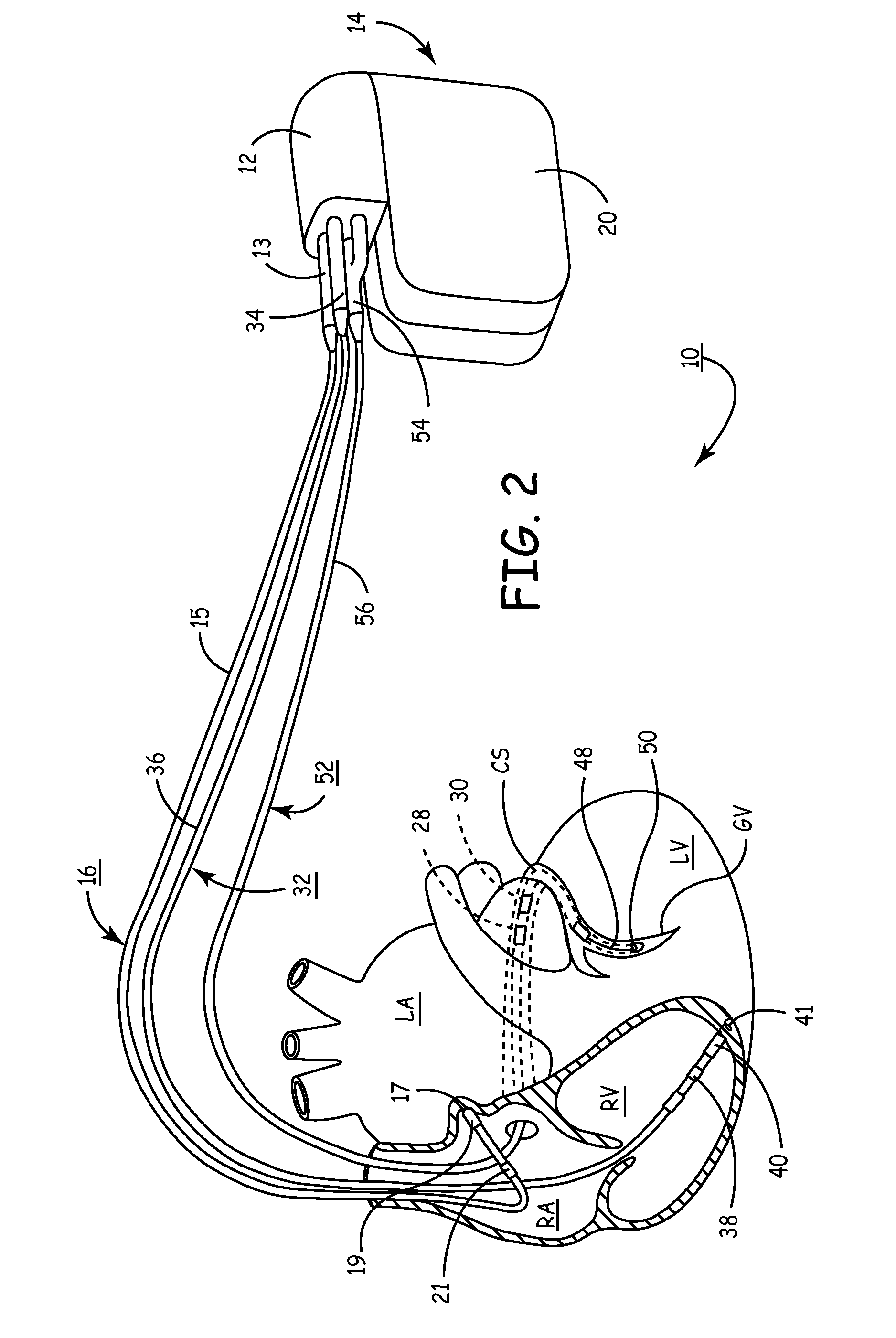
Systems and methods for determining inter-atrial conduction delays using multi-pole left ventricular pacing/sensing leads
Techniques are provided for use by a pacemaker or other implantable medical device for estimating optimal atrio-ventricular pacing delays within a patient. The inter-atrial conduction delays (IACDs) are determined based, at least in part, on atrial far-field (AFF) signals sensed using a multi-pole left ventricular (LV) lead, such as an LV lead implanted via the coronary sinus (CS) with a plurality of electrodes. In one example, for intrinsic atrial events, the IACD is equal to the interval from the beginning of a P-wave detected via a right atrial lead and the end (or peak) of an AFF event detected via a left atrial ring electrode of a CS / LV lead. For paced atrial events, the IACD is instead equal to the interval from the A-pulse to the end (or peak) of the AFF event detected via the CS / LV lead. AV / PV pacing delays are then calculated based on the IACD adjusted by an offset.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
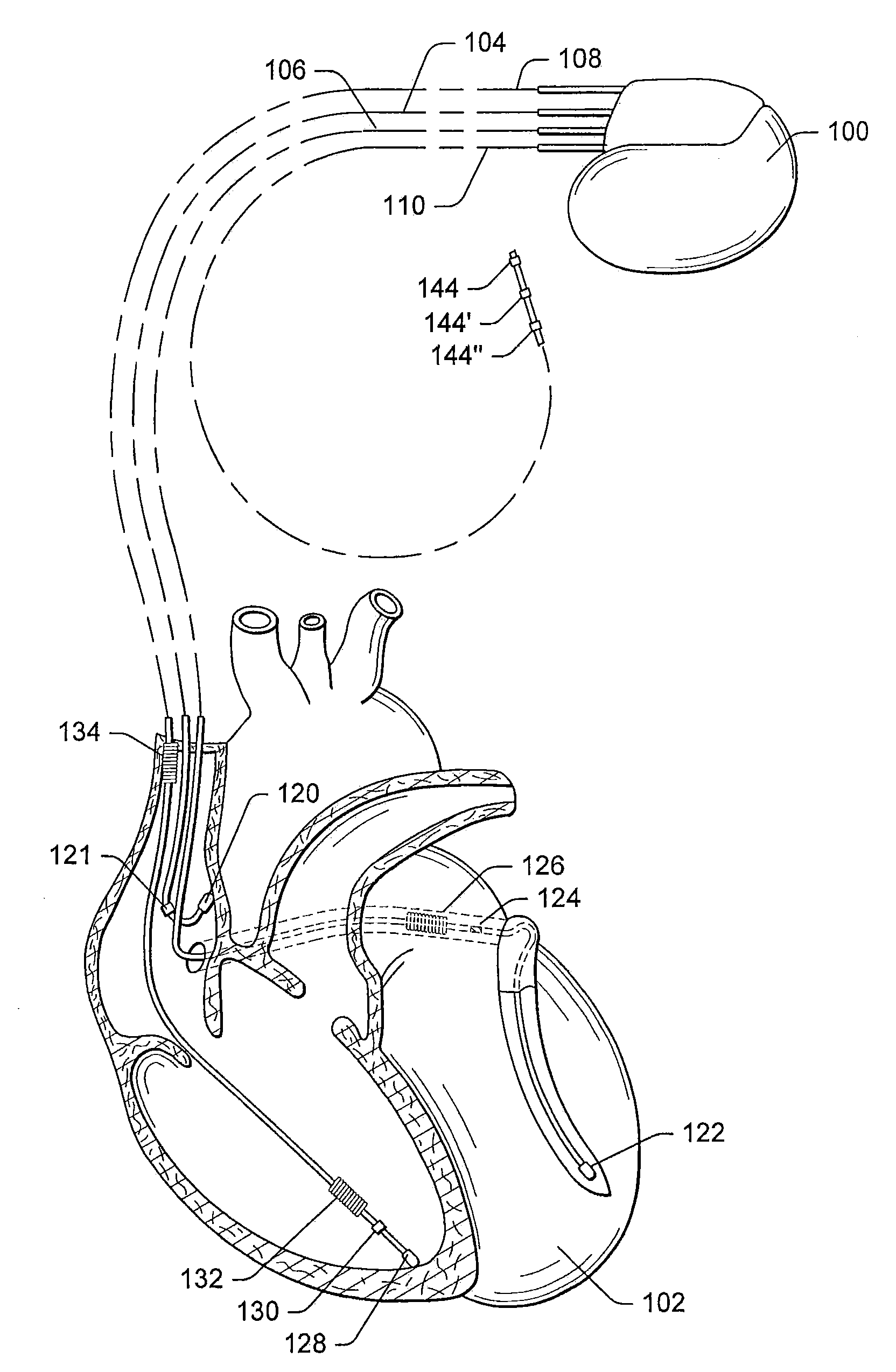
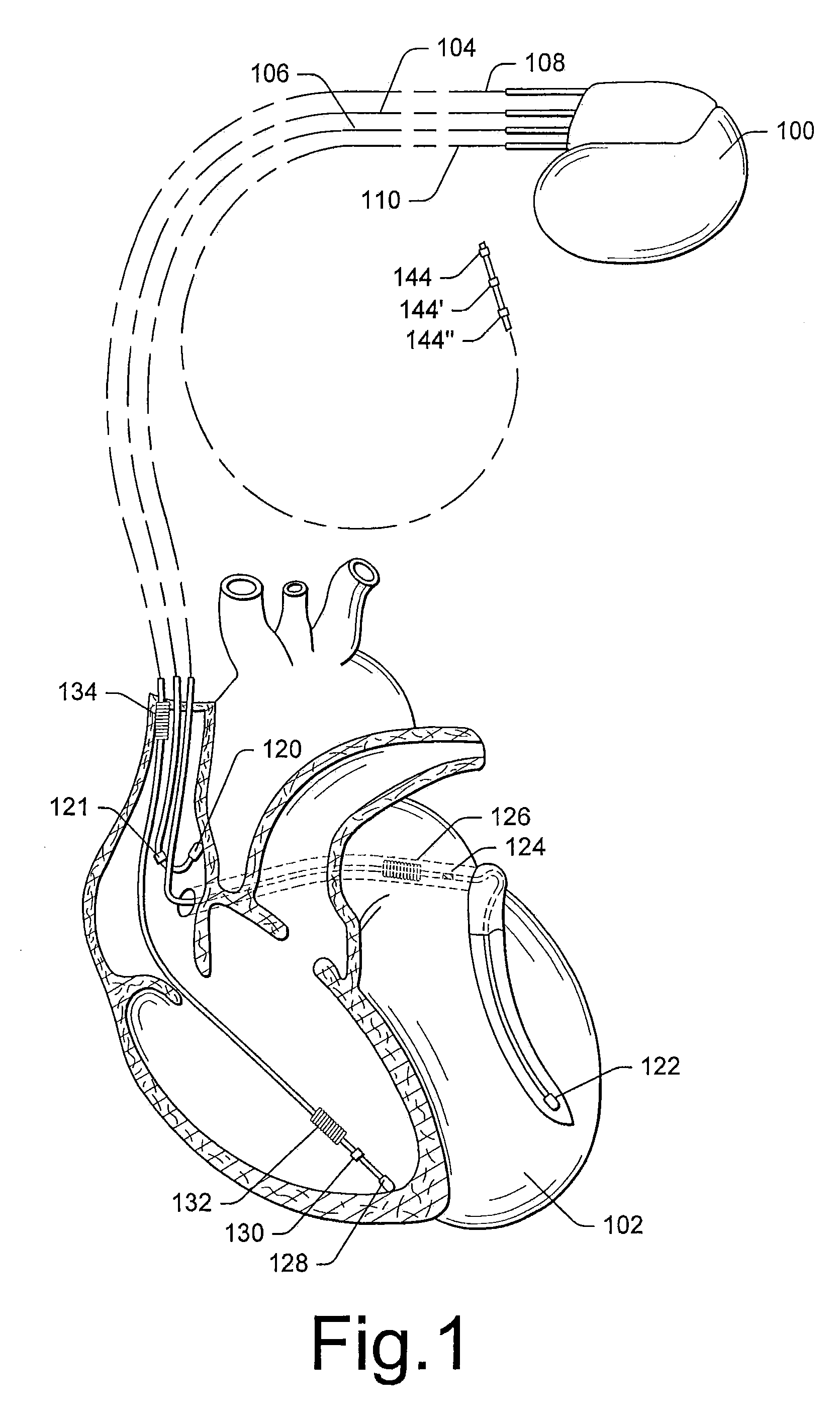
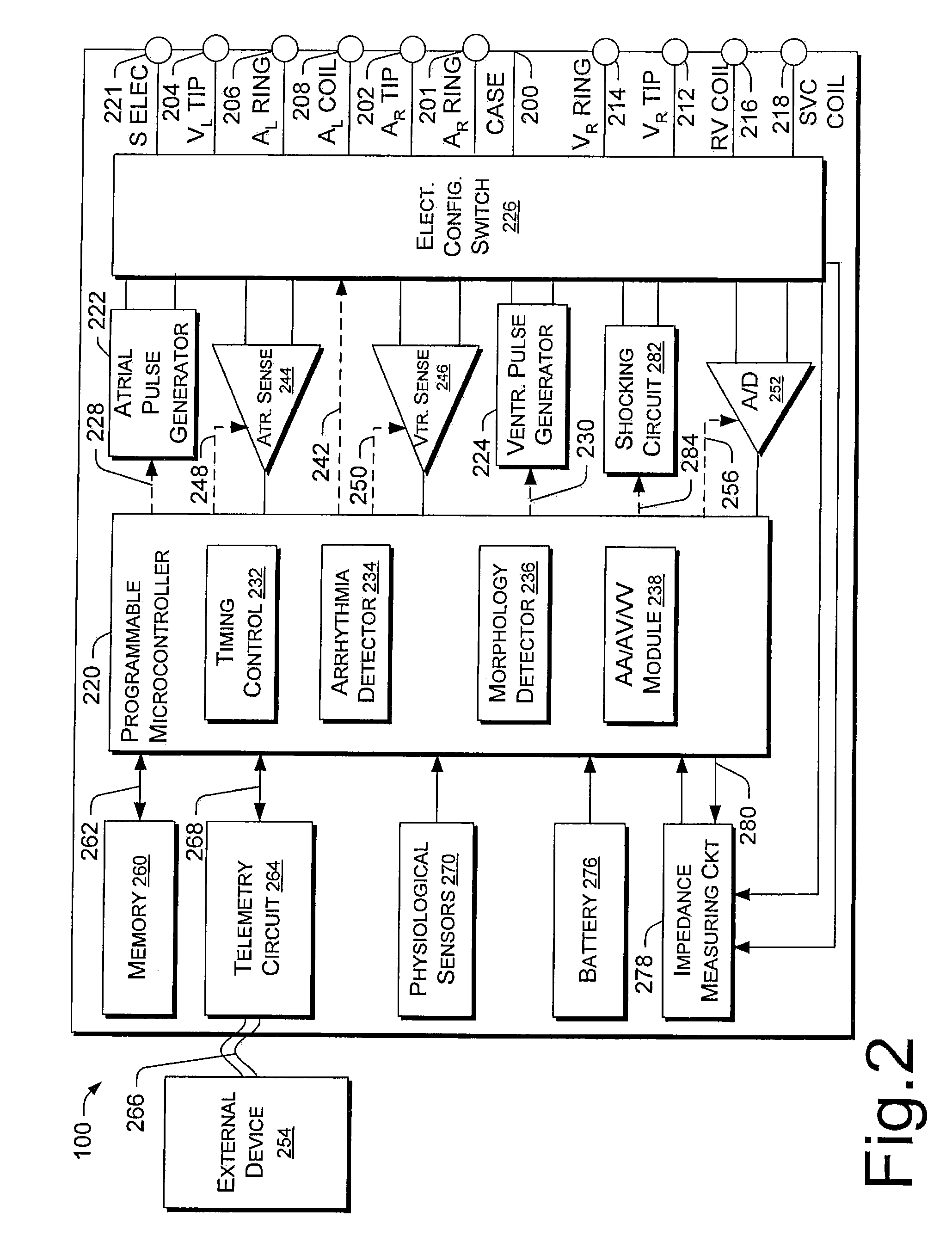
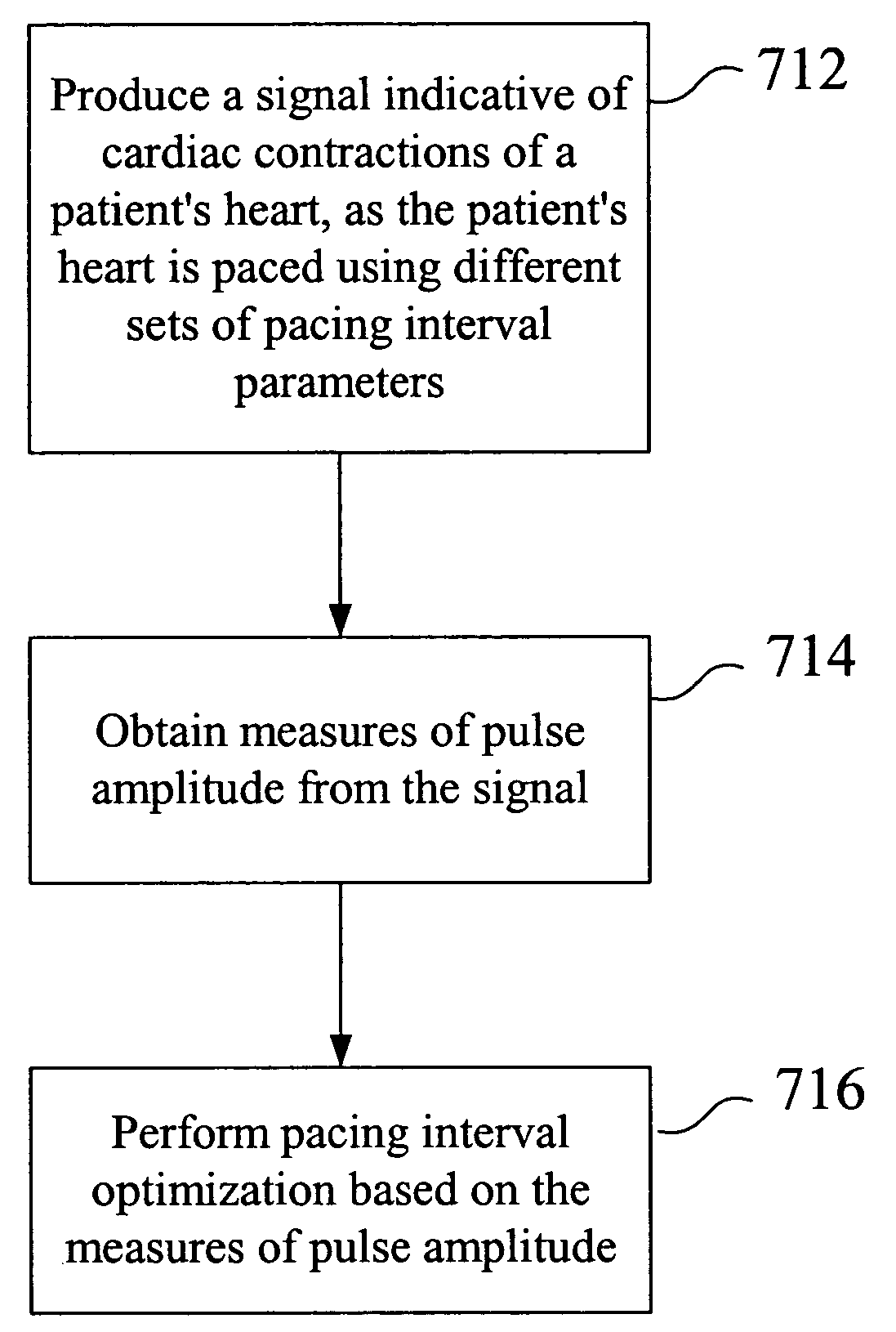
Pacing optimization based on changes in pulse amplitude and pulse amplitude variability
Owner:PACESETTER INC
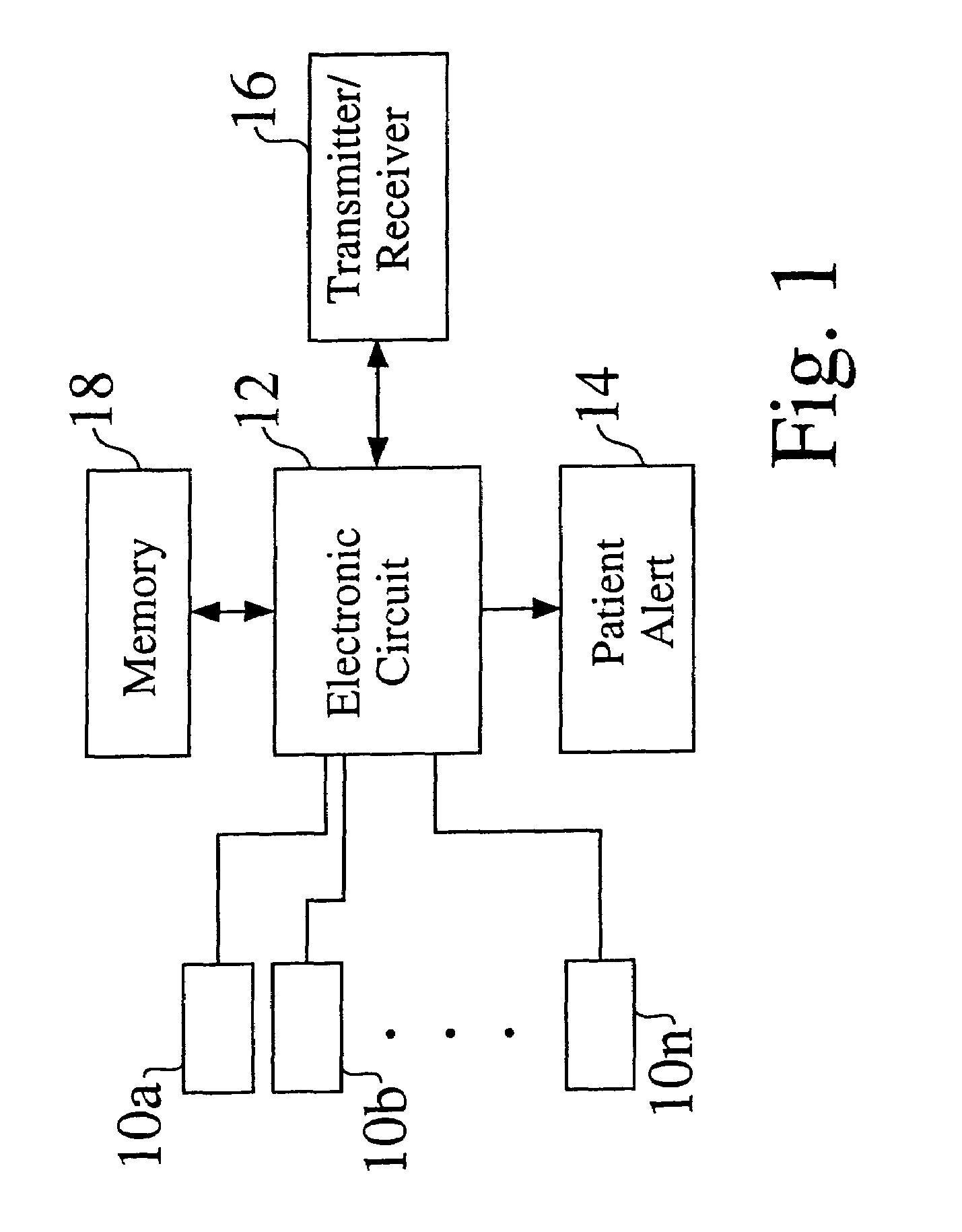
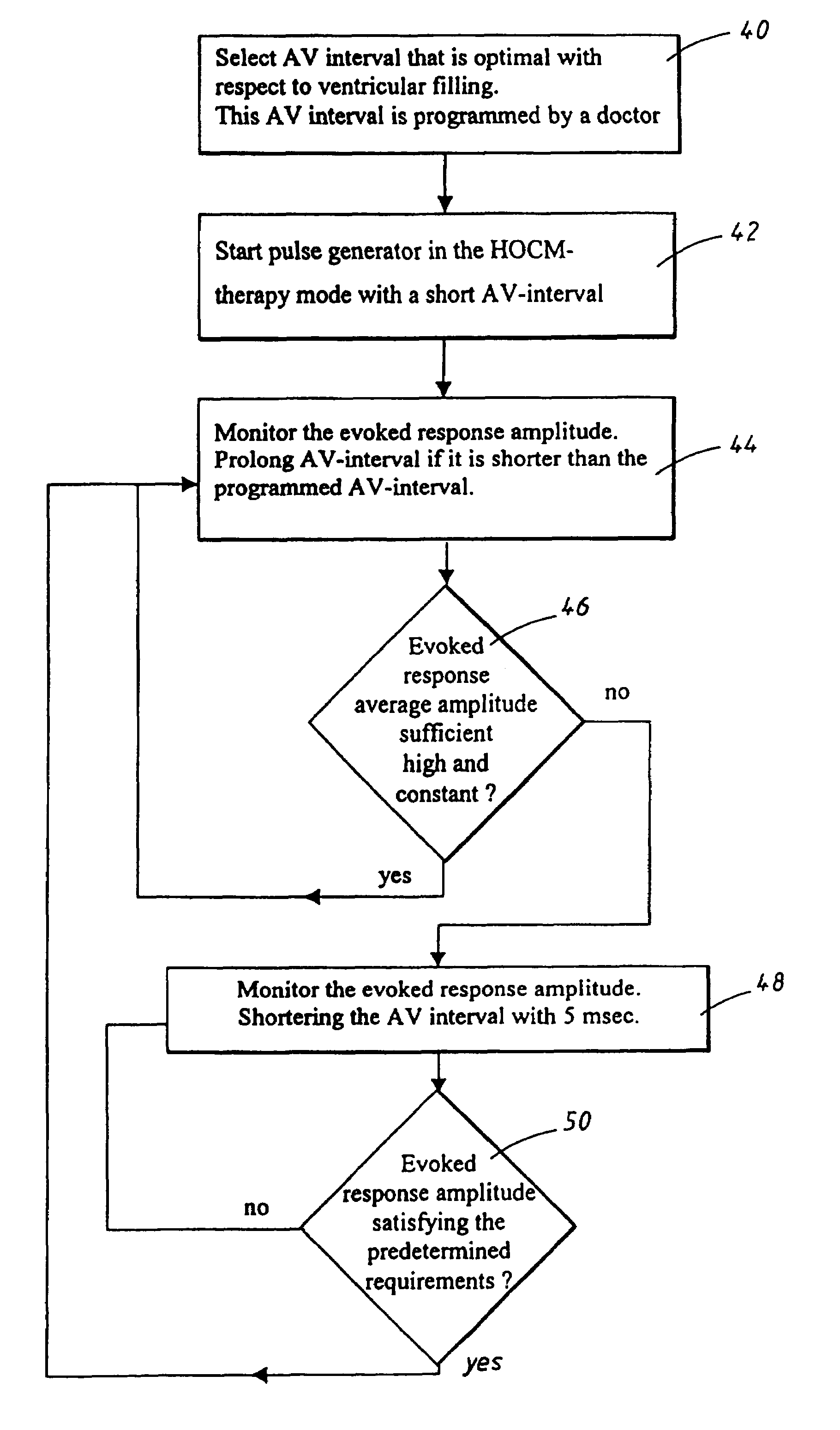
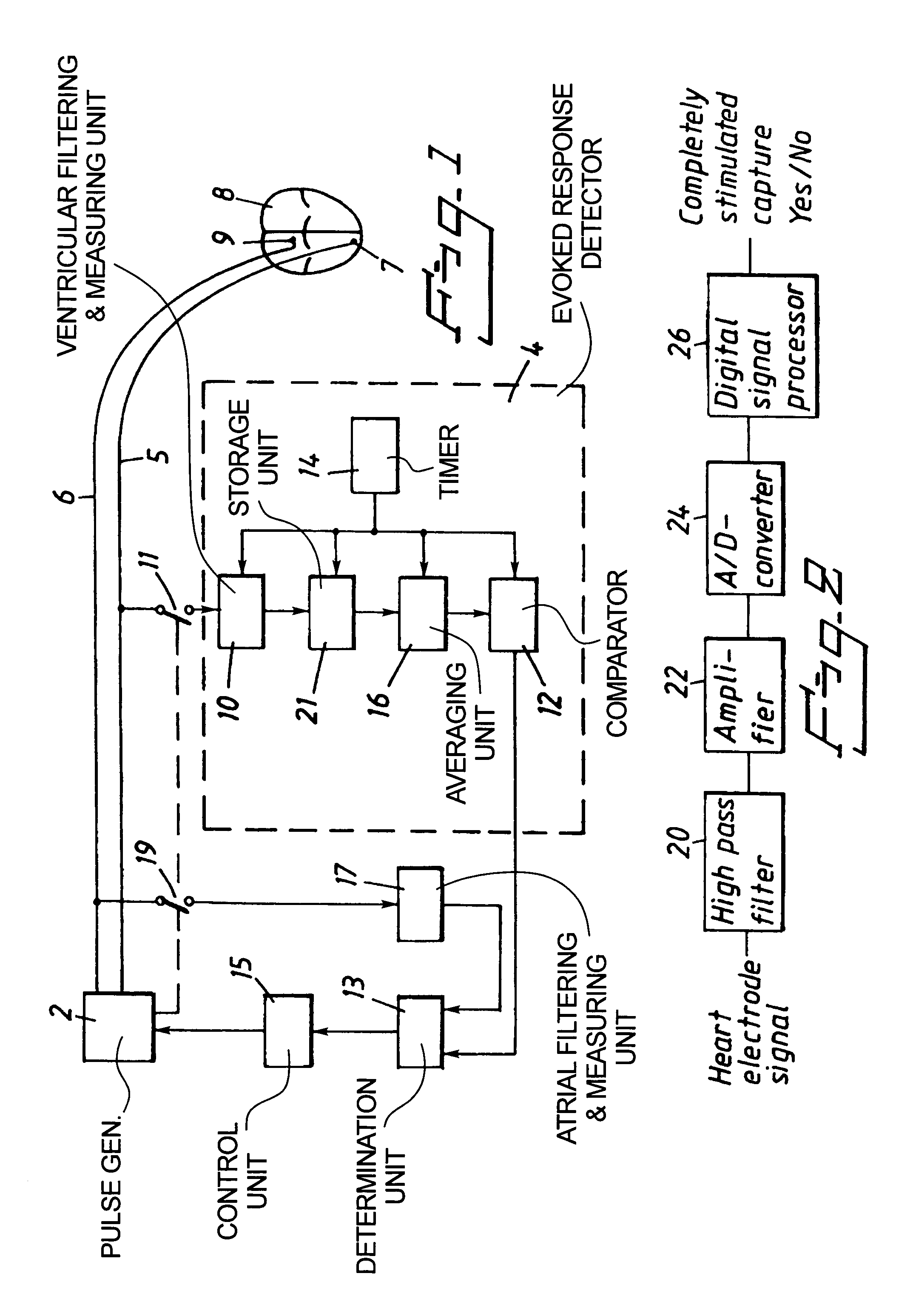
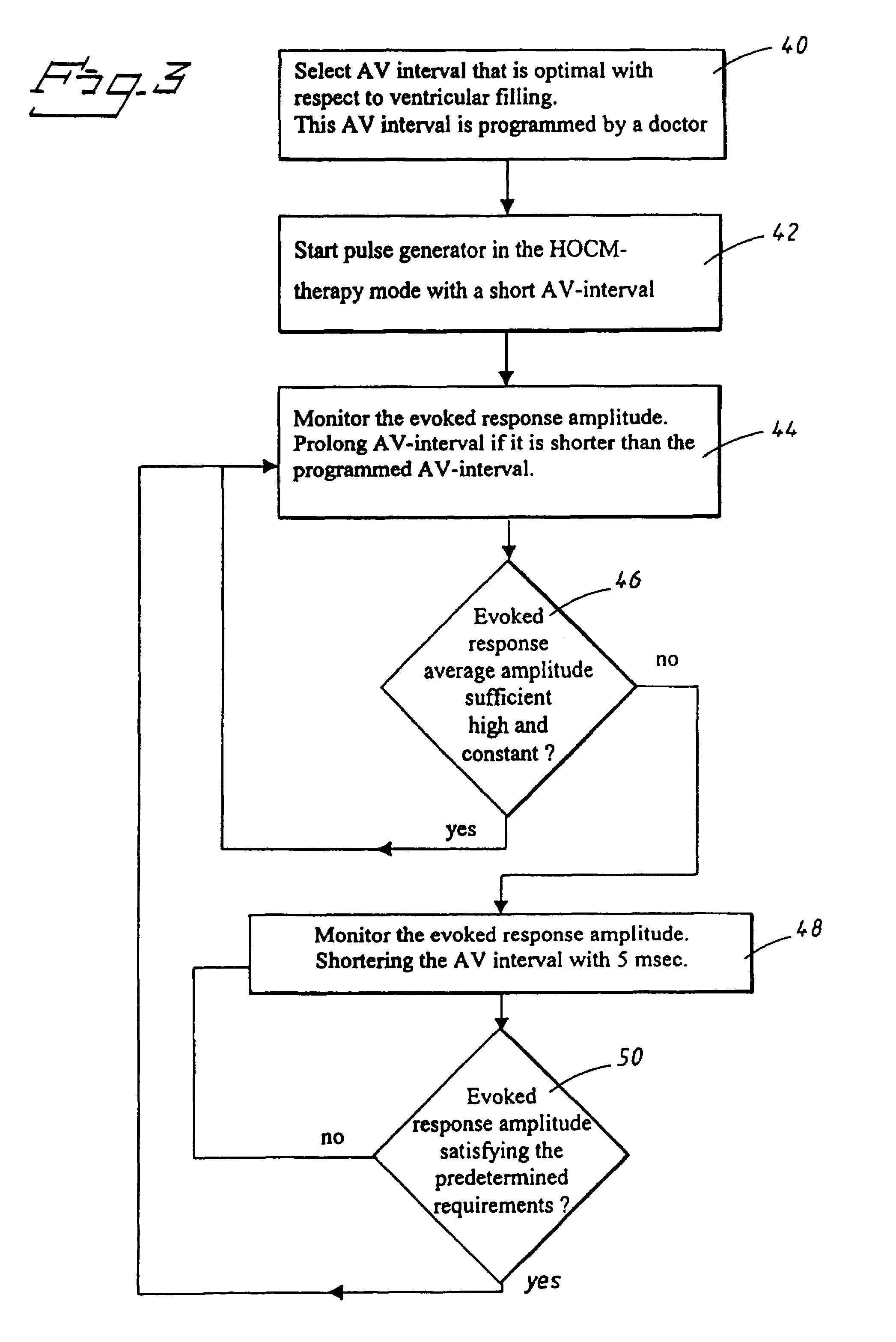
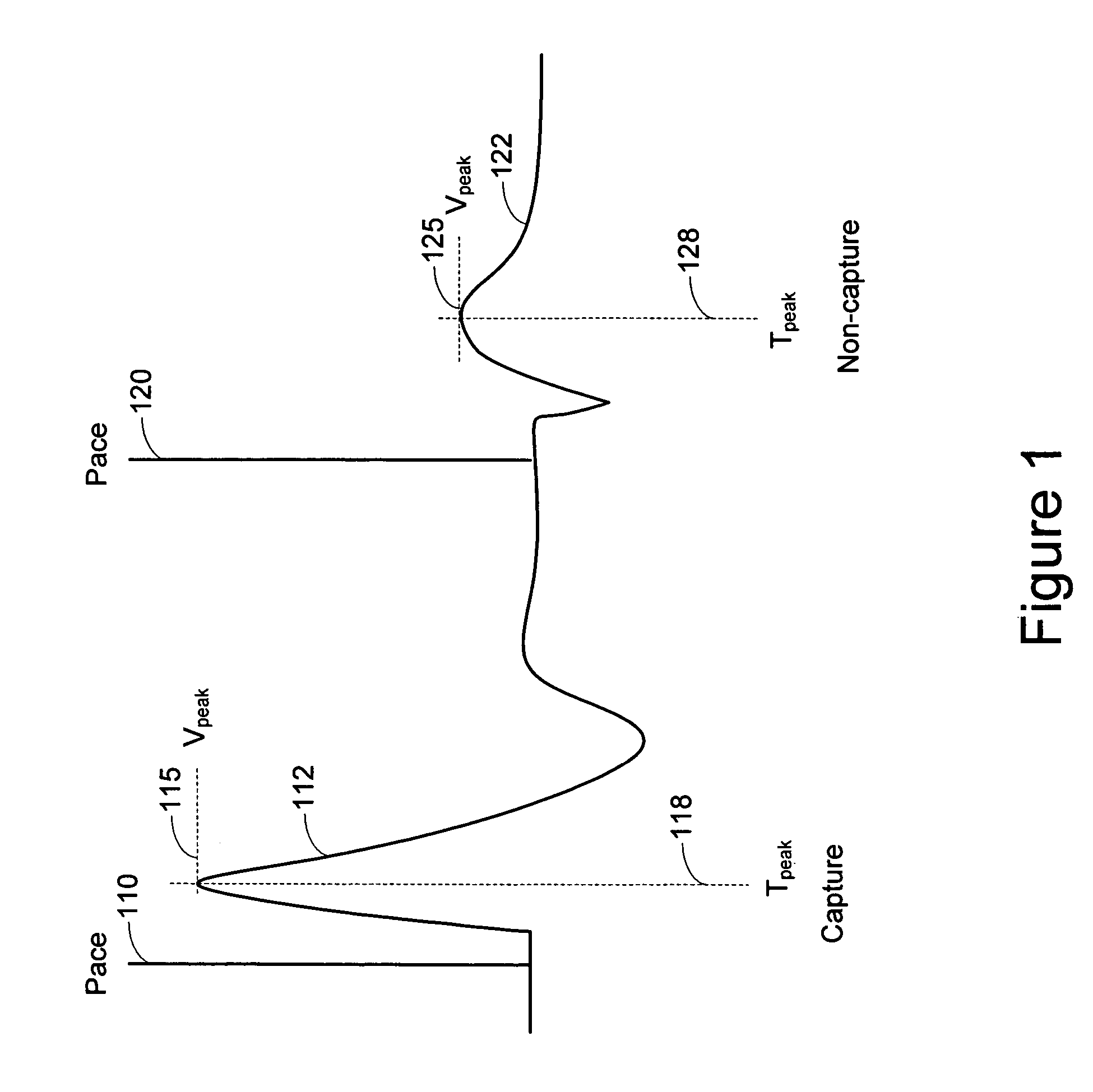
Dual chamber heart stimulator with evoked response detector
InactiveUS7020522B1The method is simple and reliableSimple and reliable processHeart stimulatorsFusion beatCardiac cycle
A heart stimulator has an atrial and ventricular pulse generator for producing atrial and ventricular stimulation pulses, an atrial sensor for sensing atrial signals and an evoked response detector for detecting the occurrence of incipient fusion beats from measured ventricular signals. A determination unit determines an incipient fusion AV-interval from the sensed atrial signals and the detected fusion beats, and a controller controls the pulse generator to deliver stimulation pulses at a controlled AV-interval which is shorter than the incipient fusion AV-interval. The evoked response detector includes an averaging unit which forms an average amplitude value of the measured ventricular signals during a predetermined time window of each cardiac cycle, and a comparator which compares the average value for each cardiac cycle with a predetermined limit criterion, and supplies the result of the comparison to the determination unit for determining a measured ventricular signal resulted from an incipient fusion beat or a completely stimulated capture.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
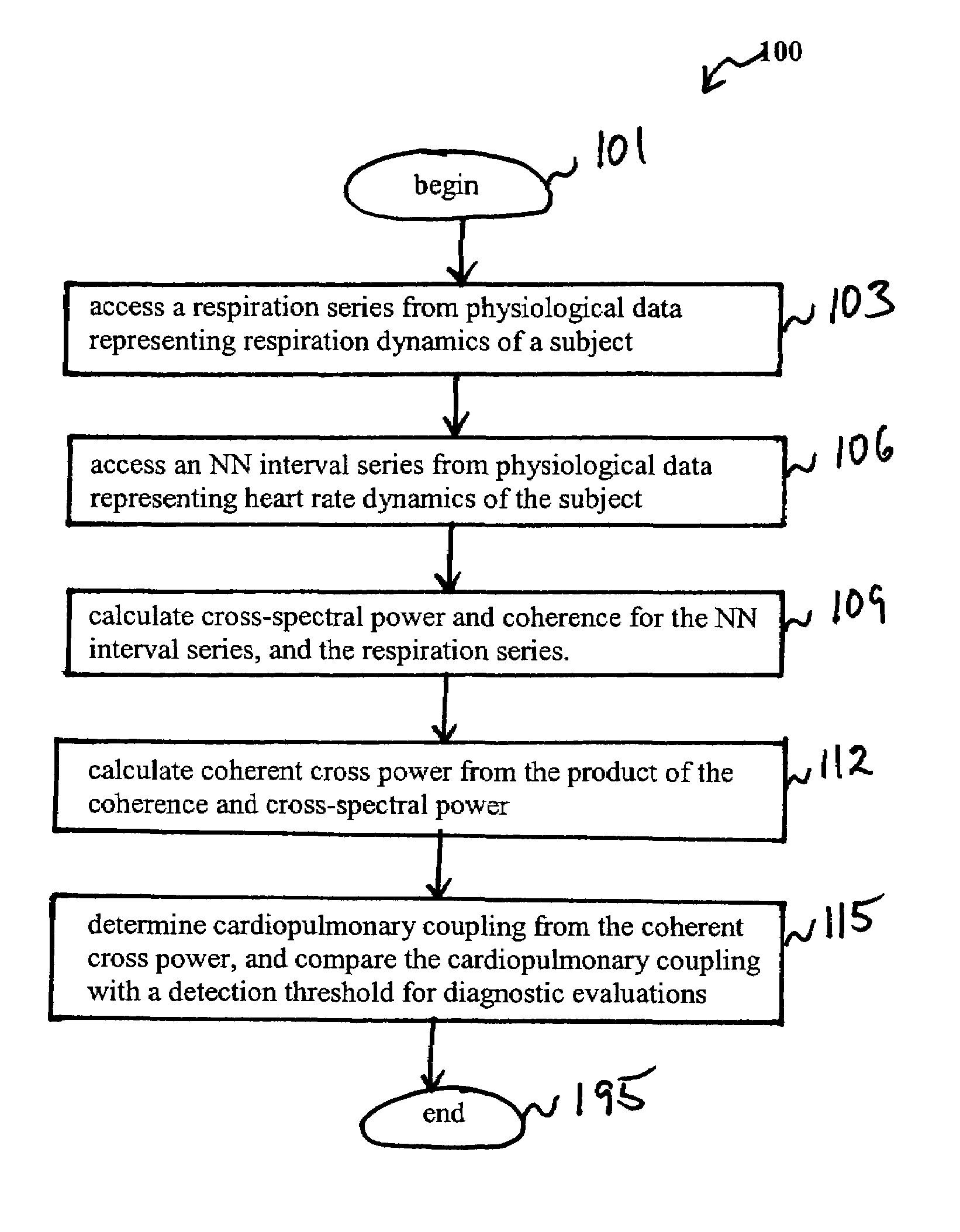
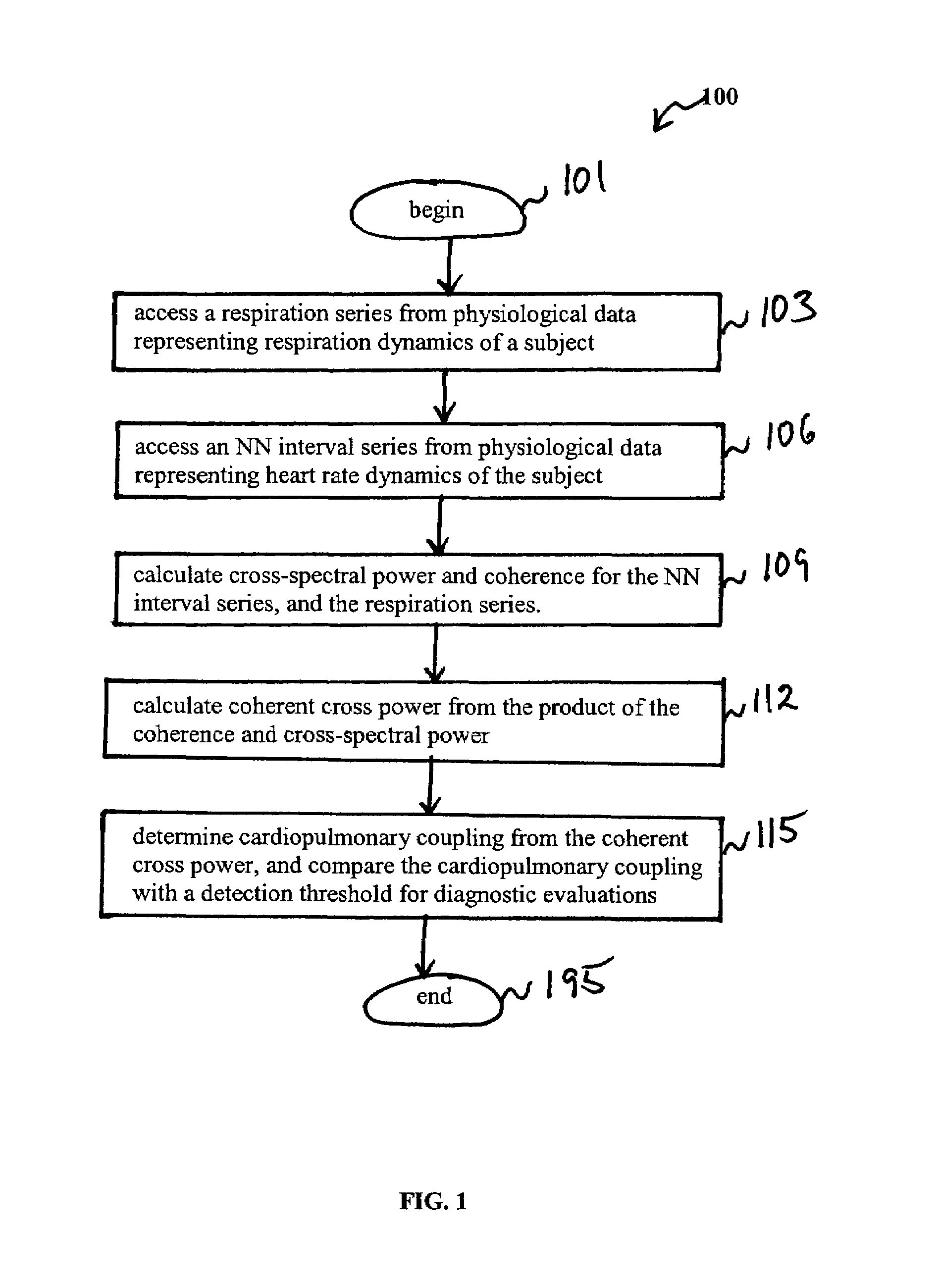
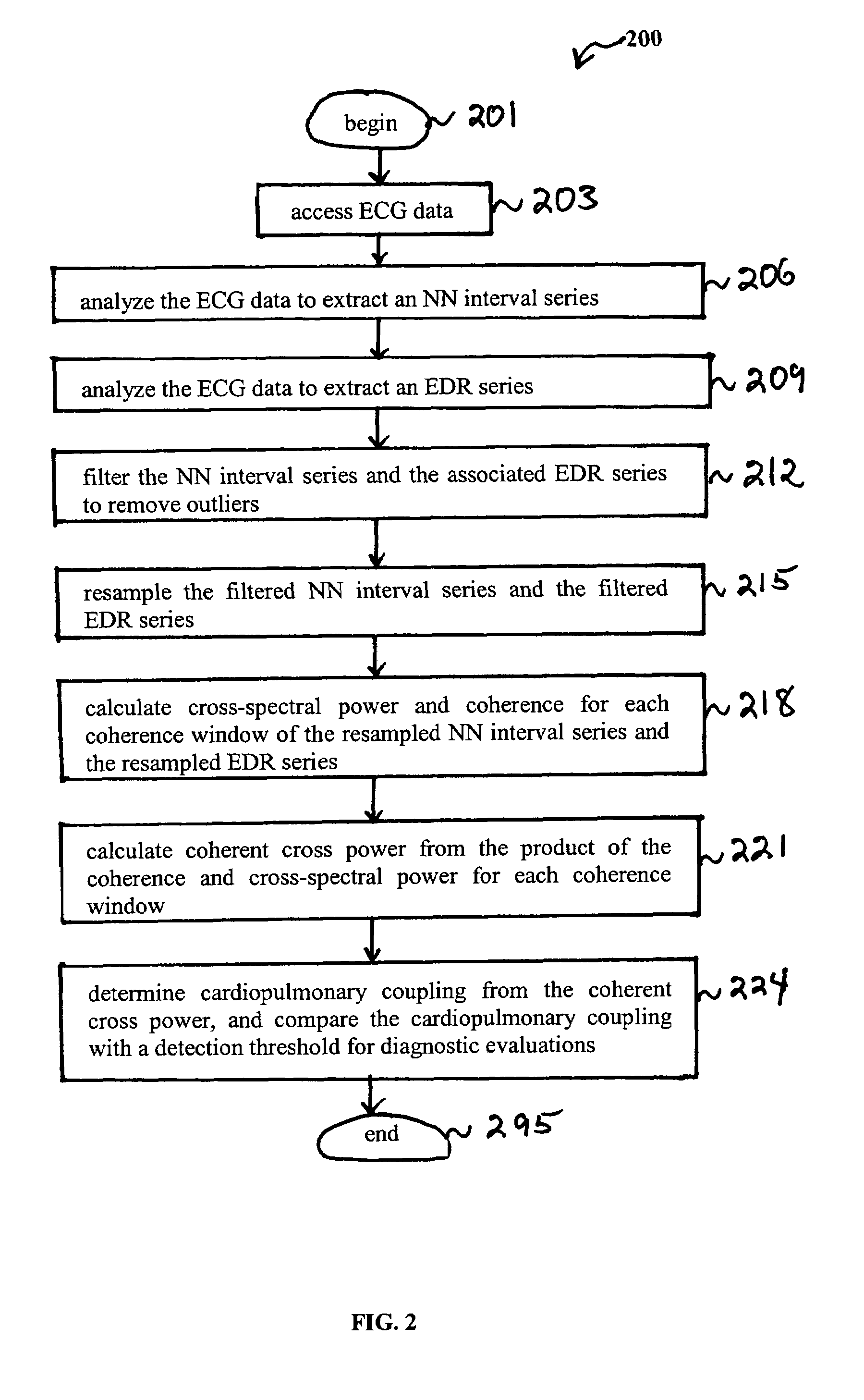
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
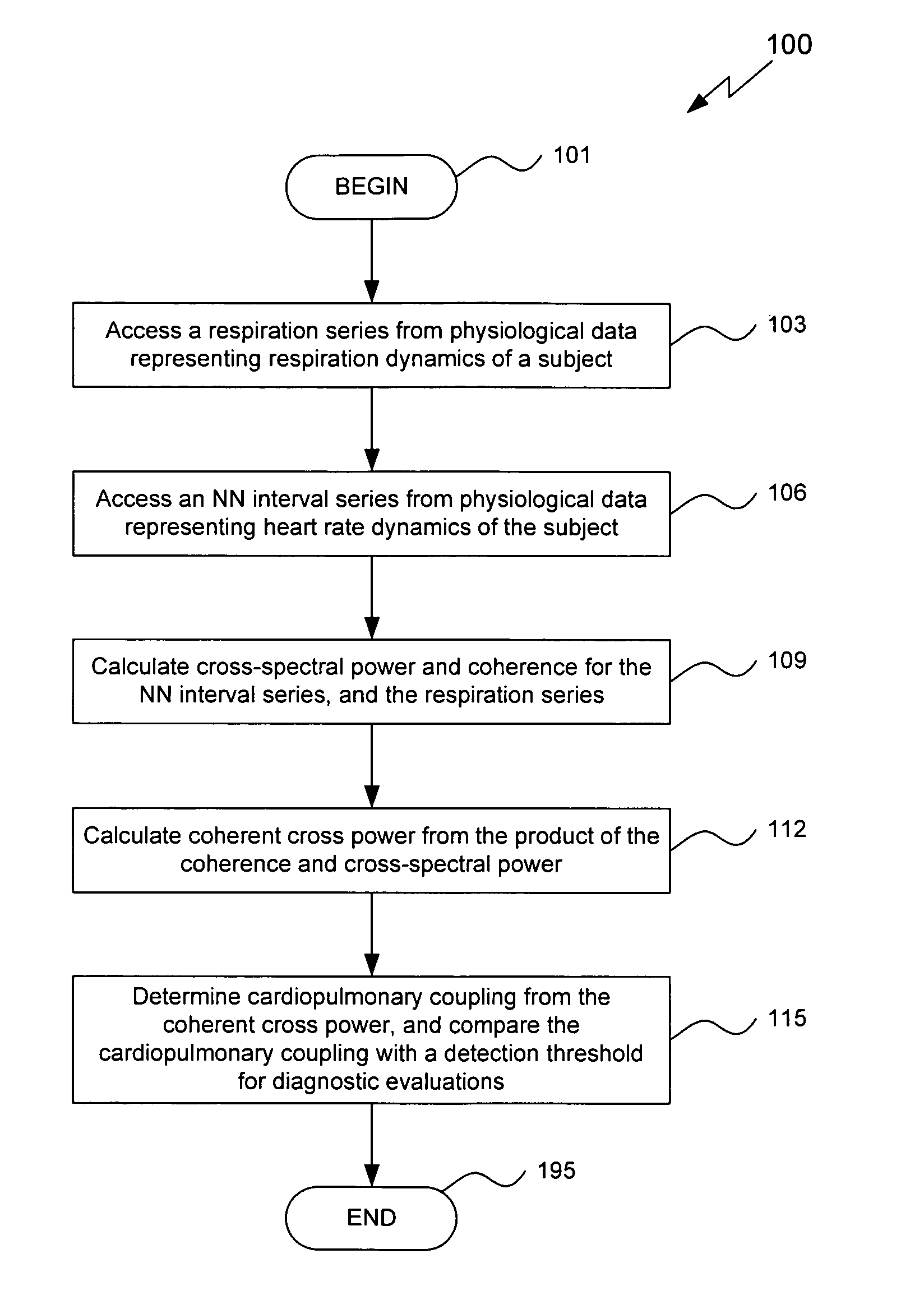
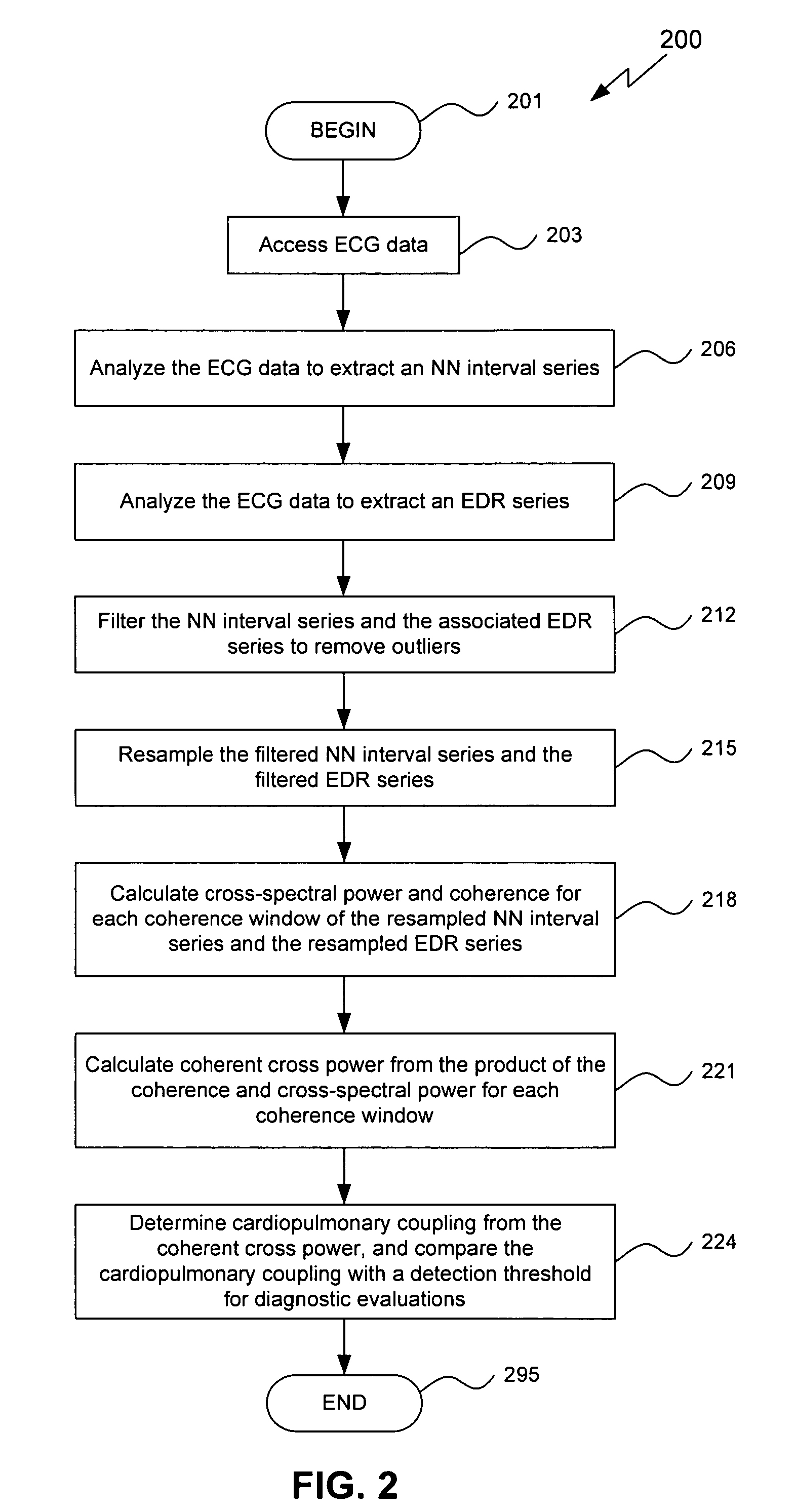
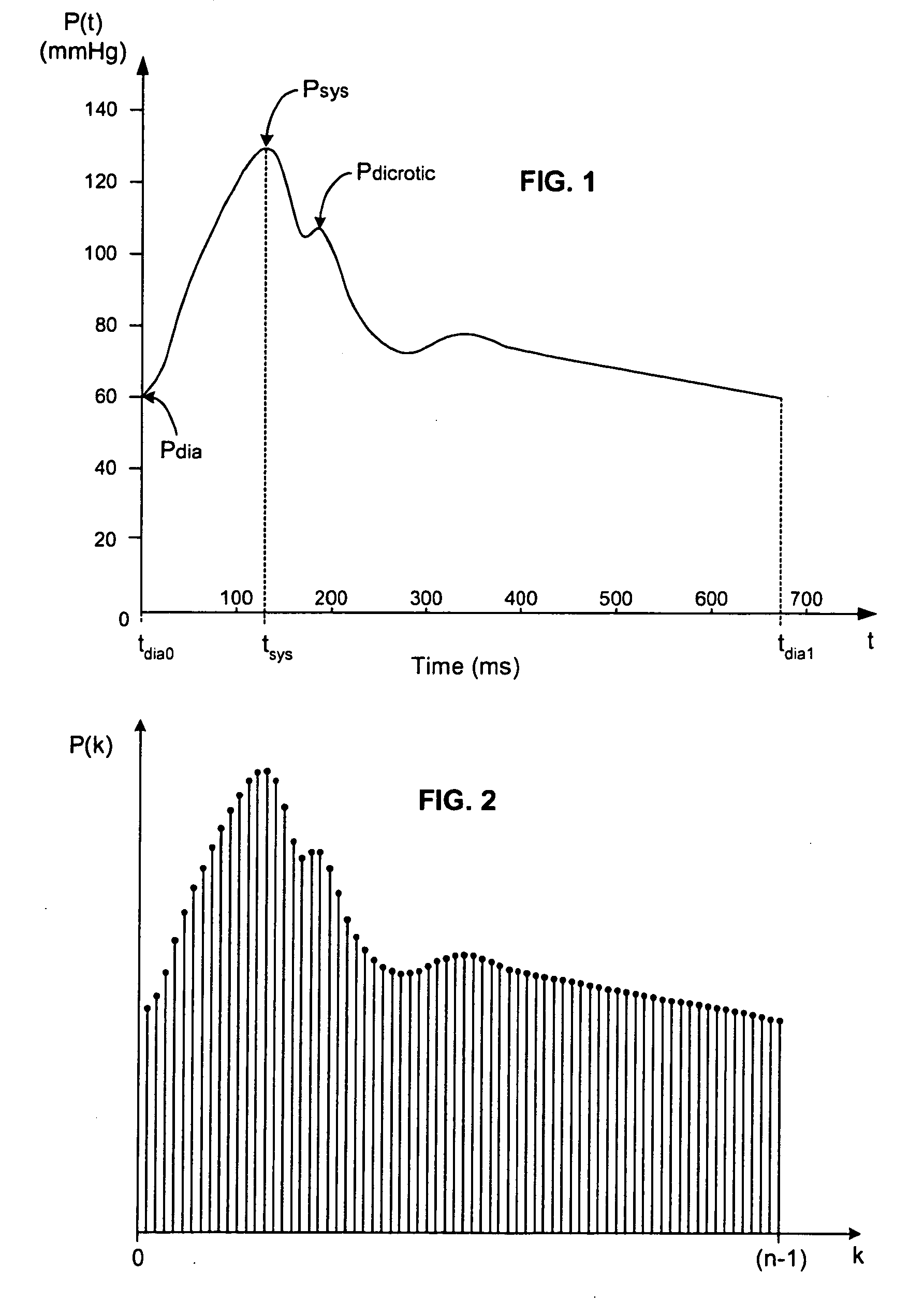
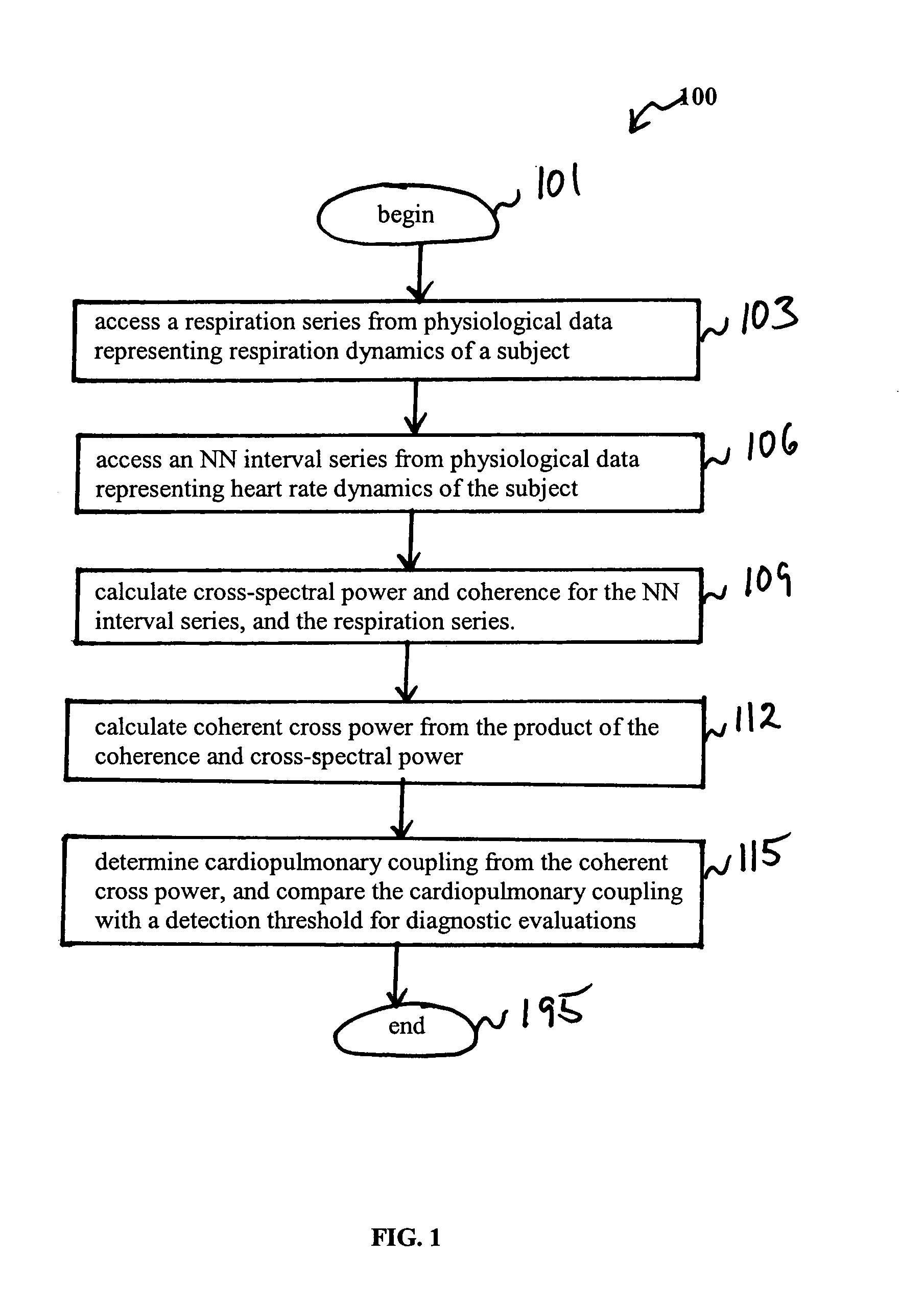
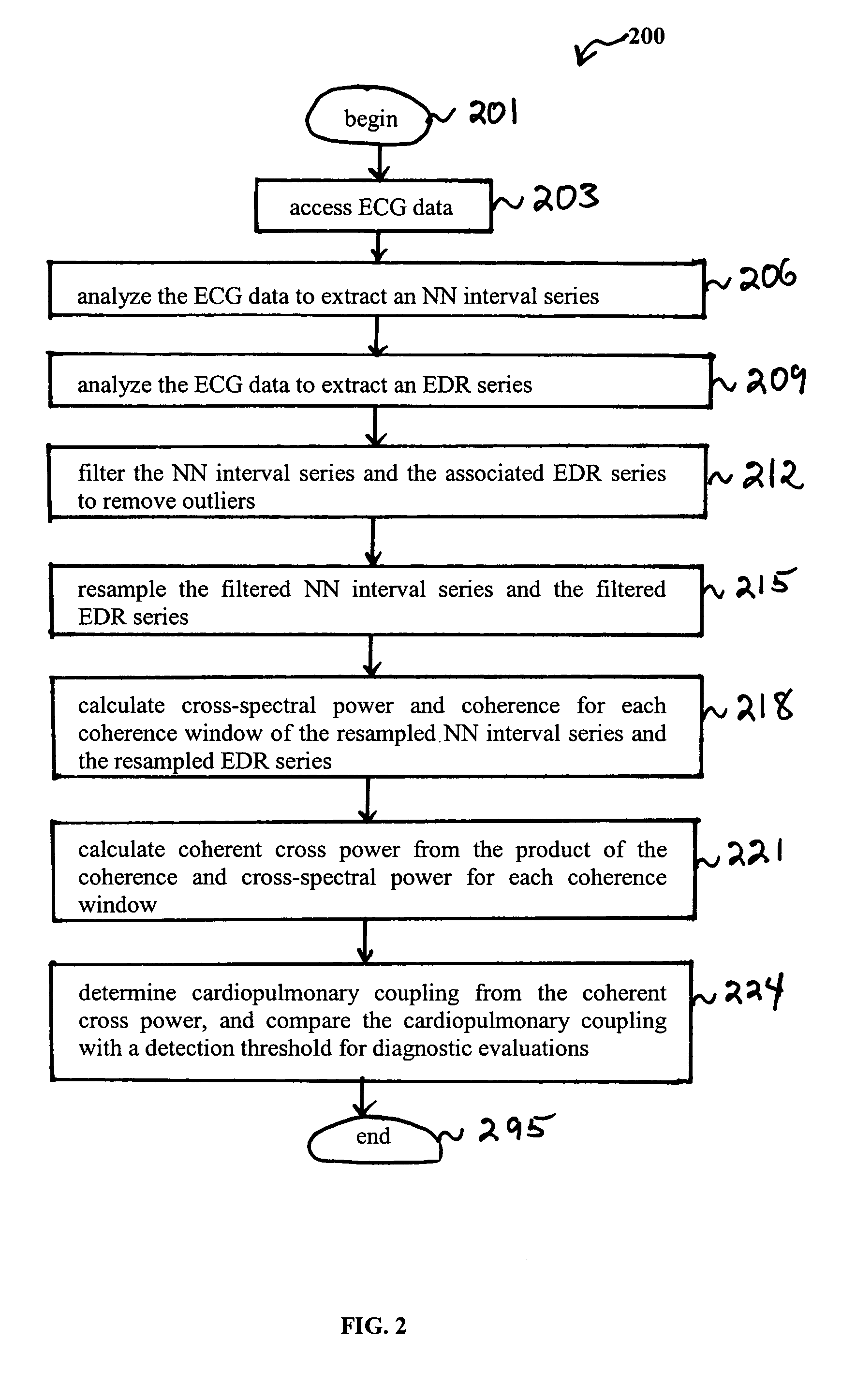
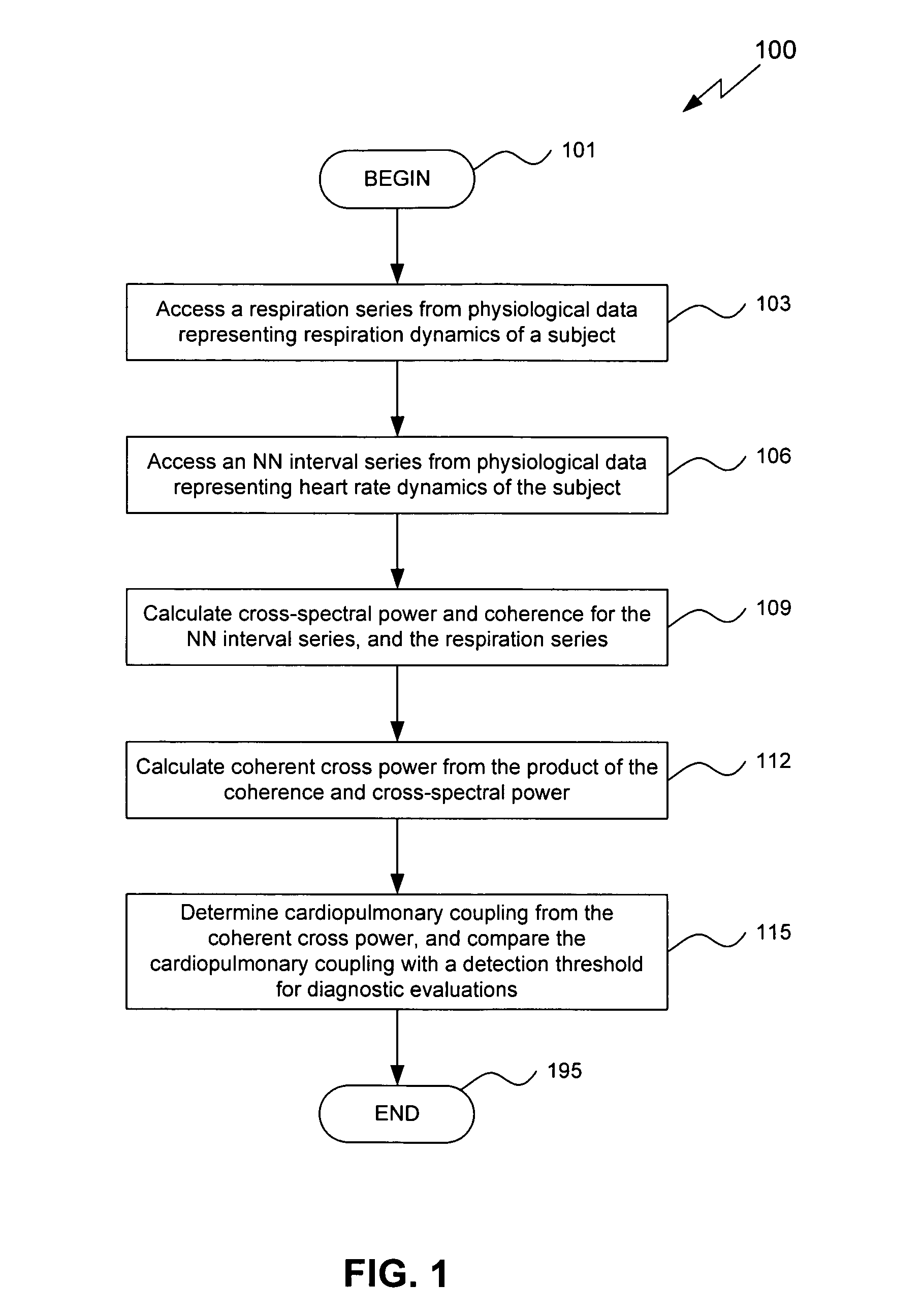
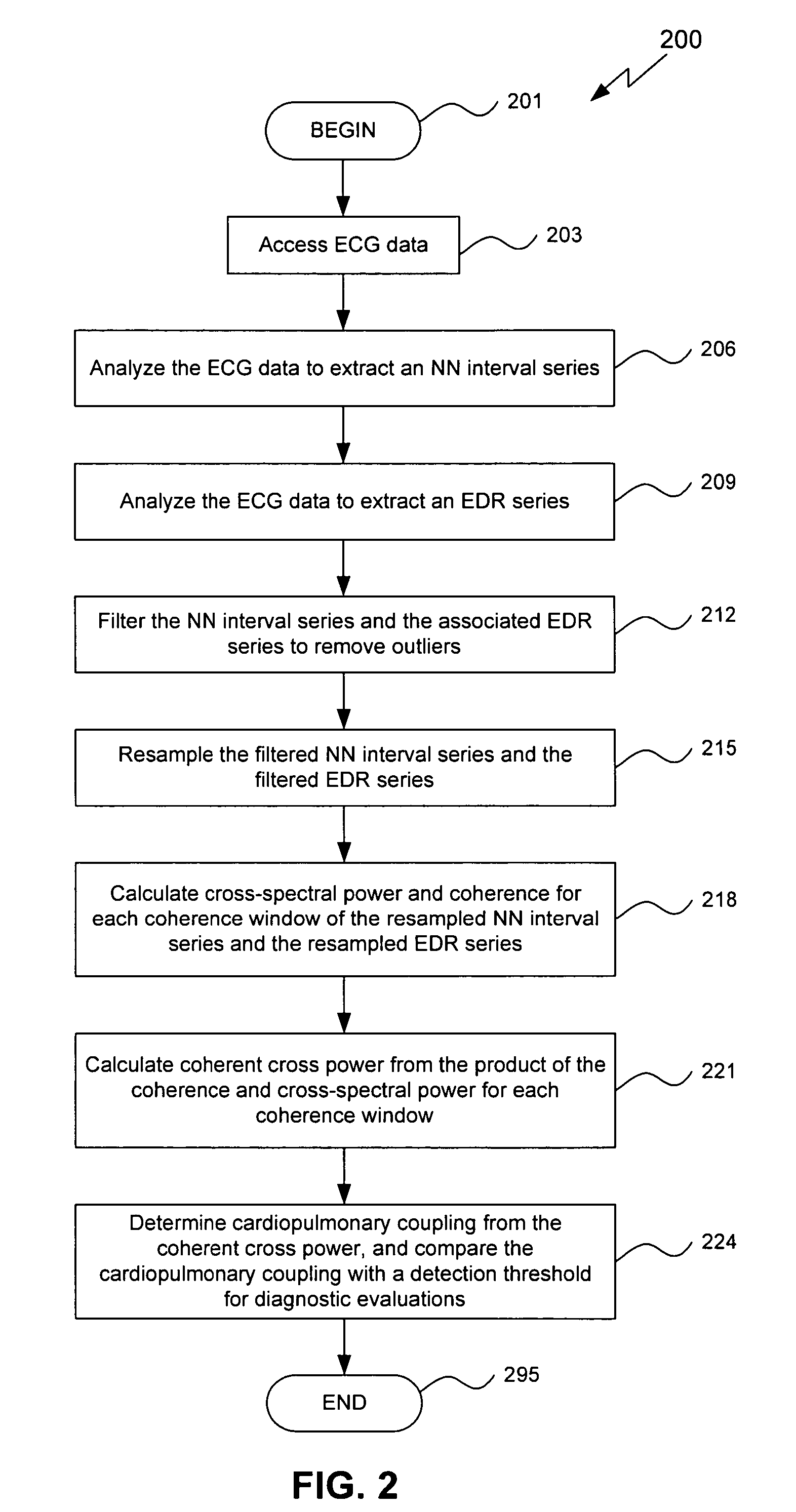
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from the cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. In an embodiment, an R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal (NN) interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract to a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration (EDR)) that is associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
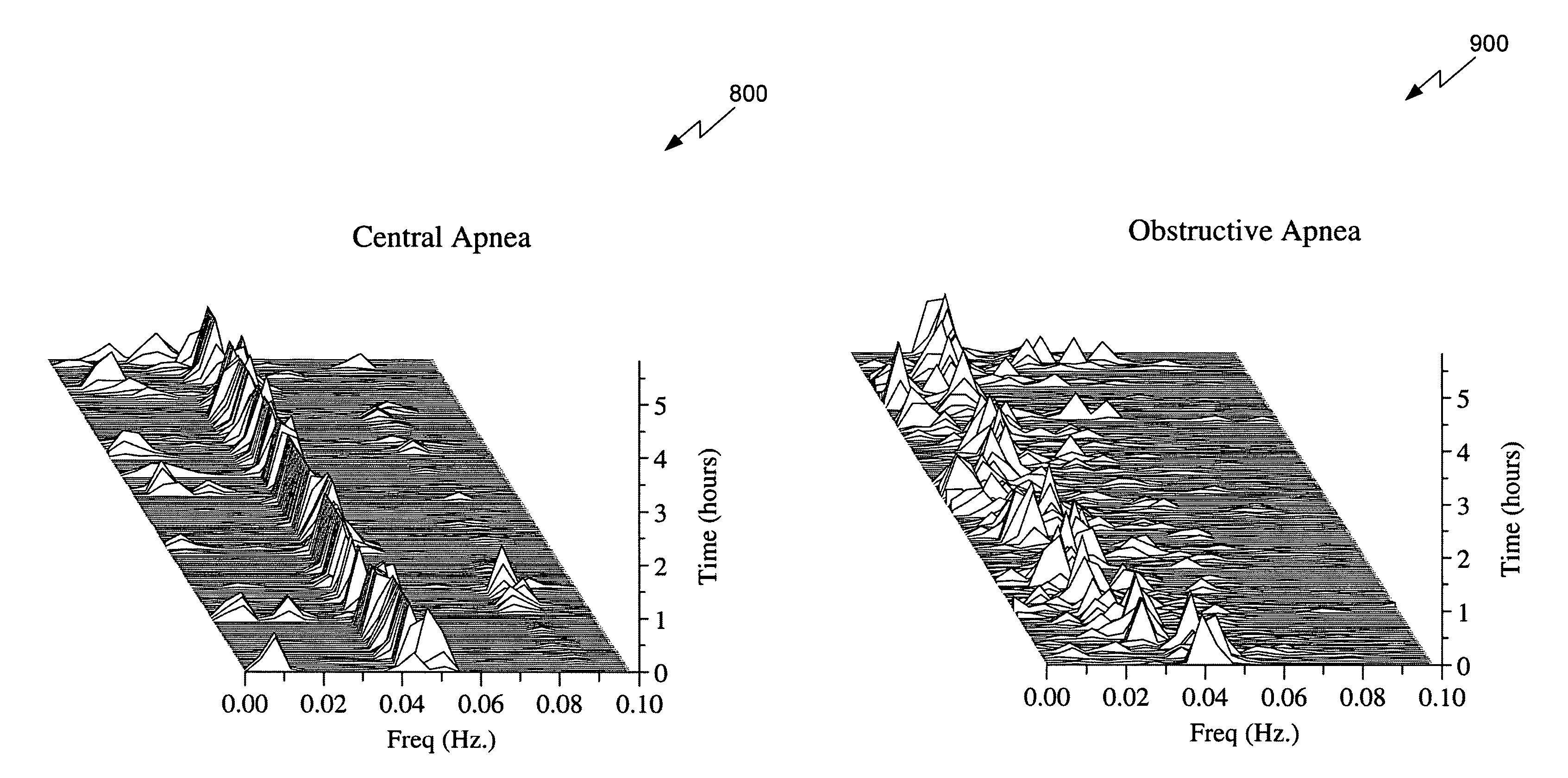
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. An R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration) associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross-power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross-power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined. Coherent cross-power can be applied to differentiate obstructive from non-obstructive disease, and admixtures of the same.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Real-time measurement of ventricular stroke volume variations by continuous arterial pulse contour analysis
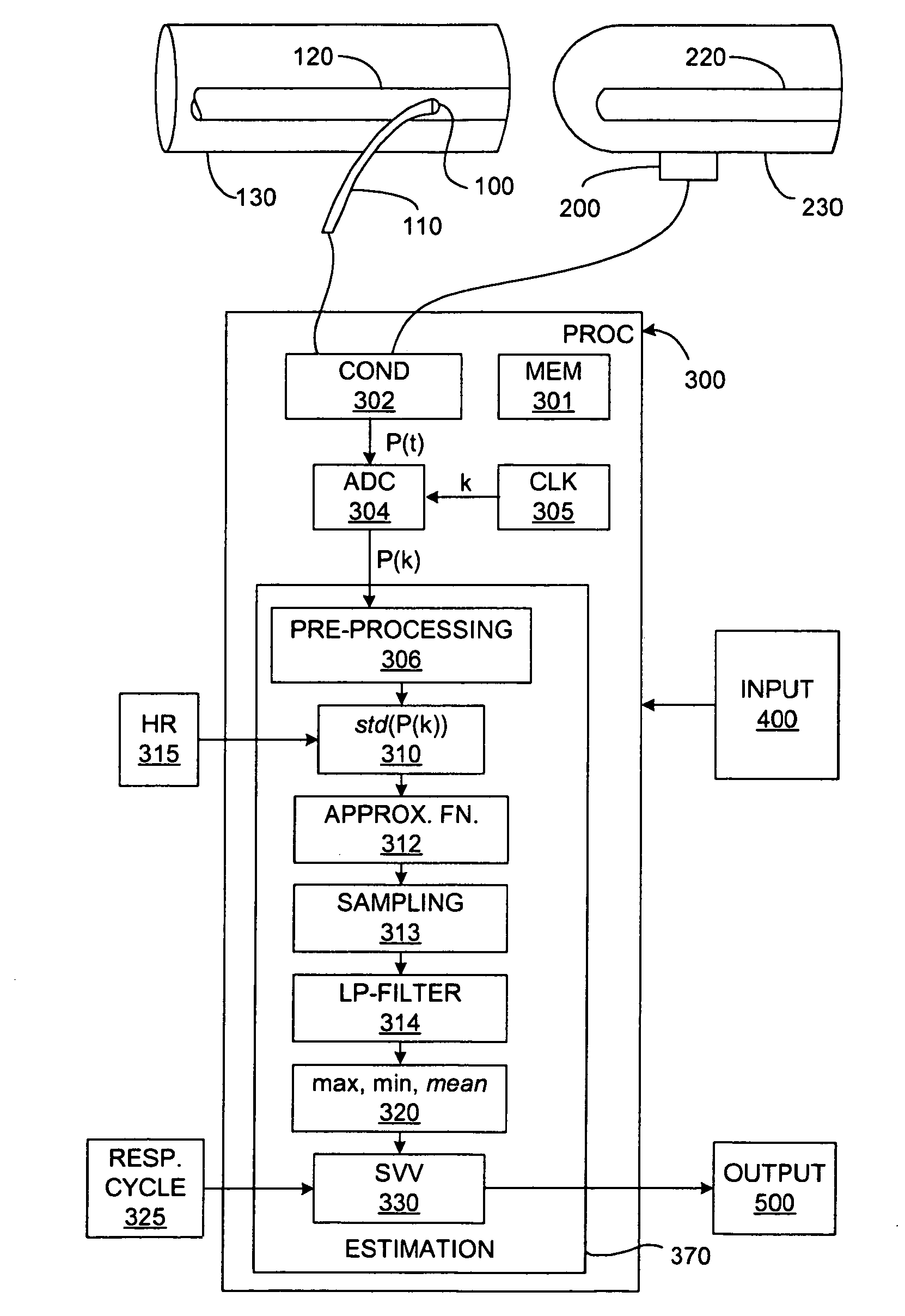
Ventricular stroke volume variation (SVV) is estimated as a function of the standard deviation of arterial blood pressure value measured over each of at least two cardiac cycles, preferably over each of the cardiac cycles in a computation interval covering a full respiratory cycle. In one embodiment, maximum and minimum standard deviation values are determined over the computation interval. SVV is then estimated proportional to the ratio of the difference between the maximum and minimum standard deviation values and the mean of the standard deviation values. In another embodiment, SVV is then estimated proportional to the ratio of the standard deviation of the standard deviation values and the mean standard deviation over the entire computation interval. A pre-processing arrangement for improving reliability of estimates of more general cardiac or hemodynamic parameters is also disclosed and involves smoothing with an approximating function, and sampling and low-pass filtering at an adjustable rate.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from the cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. In an embodiment, an R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal (NN) interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract to a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration (EDR)) that is associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
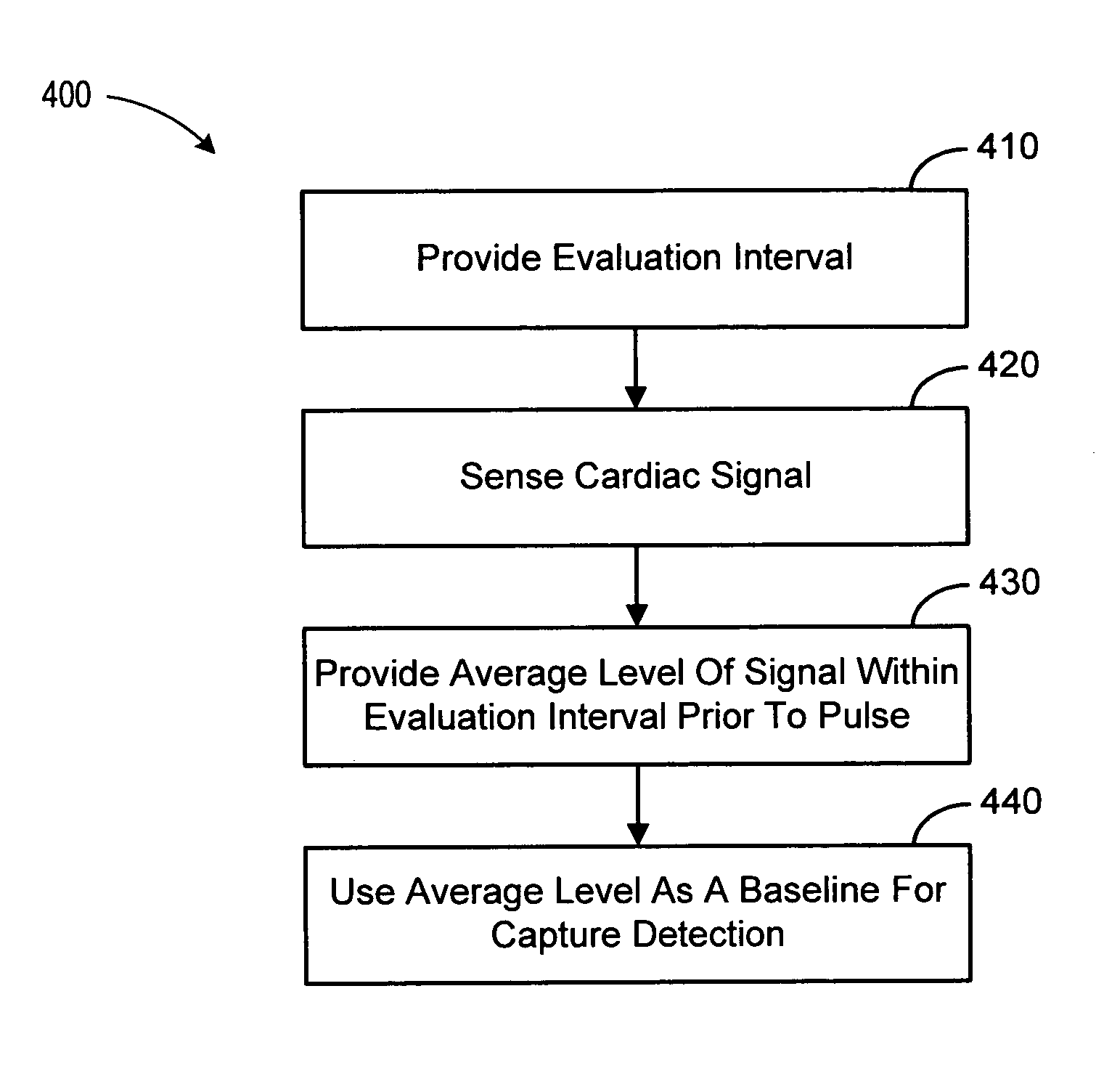
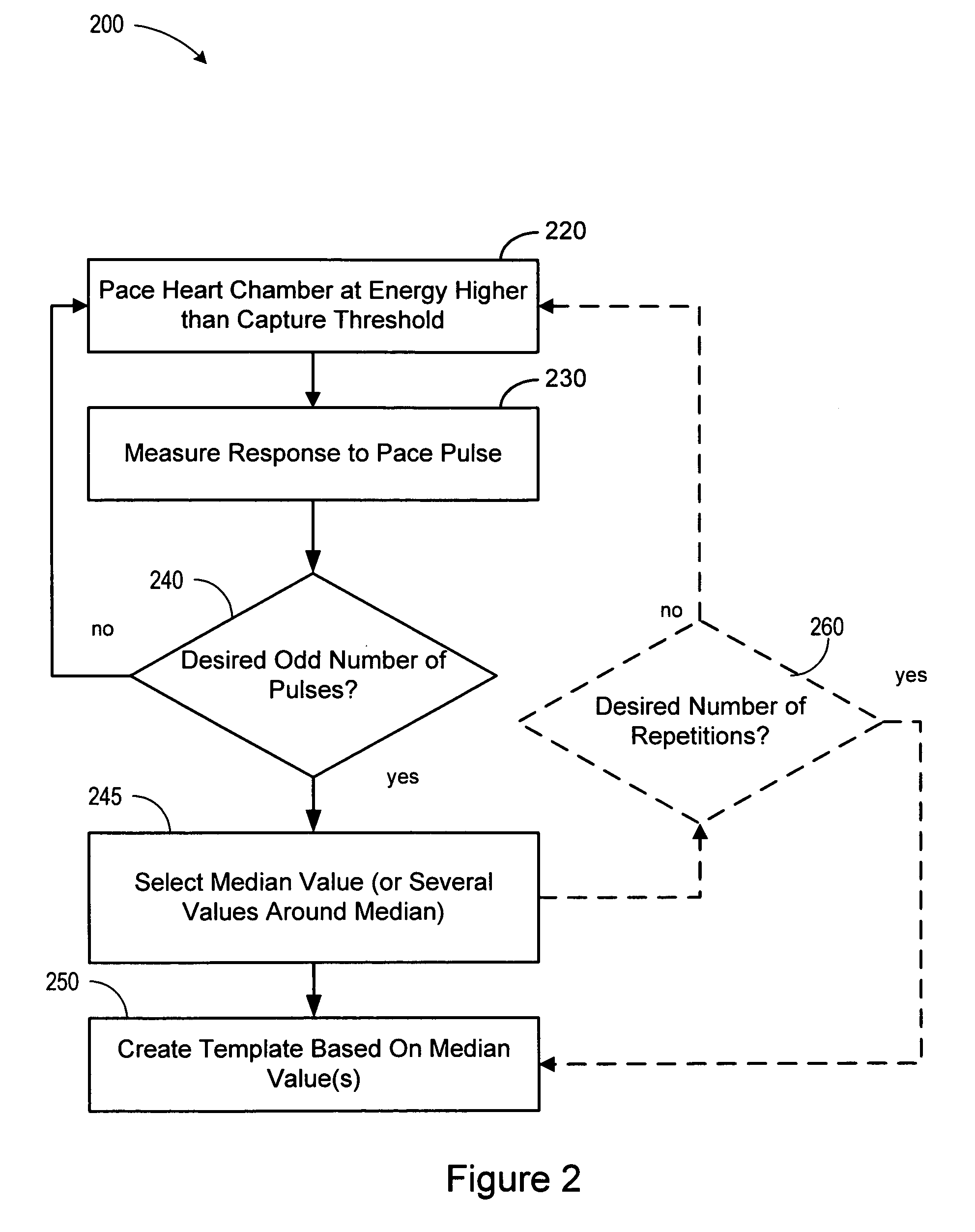
Baseline adaptation for cardiac pacing response classification
ActiveUS7330761B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEvaluation IntervalClassification methods
Methods and devices for establishing and using baseline for cardiac pacing response detection are described. A baseline amplitude of the cardiac signal may be established using data acquired in an evaluation interval prior to the delivery of the pacing pulse. An amplitude of the cardiac signal following delivery of the pacing pulse may be referenced using the baseline amplitude. An evoked response from the pacing pulse is detected using the referenced cardiac signal amplitude.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
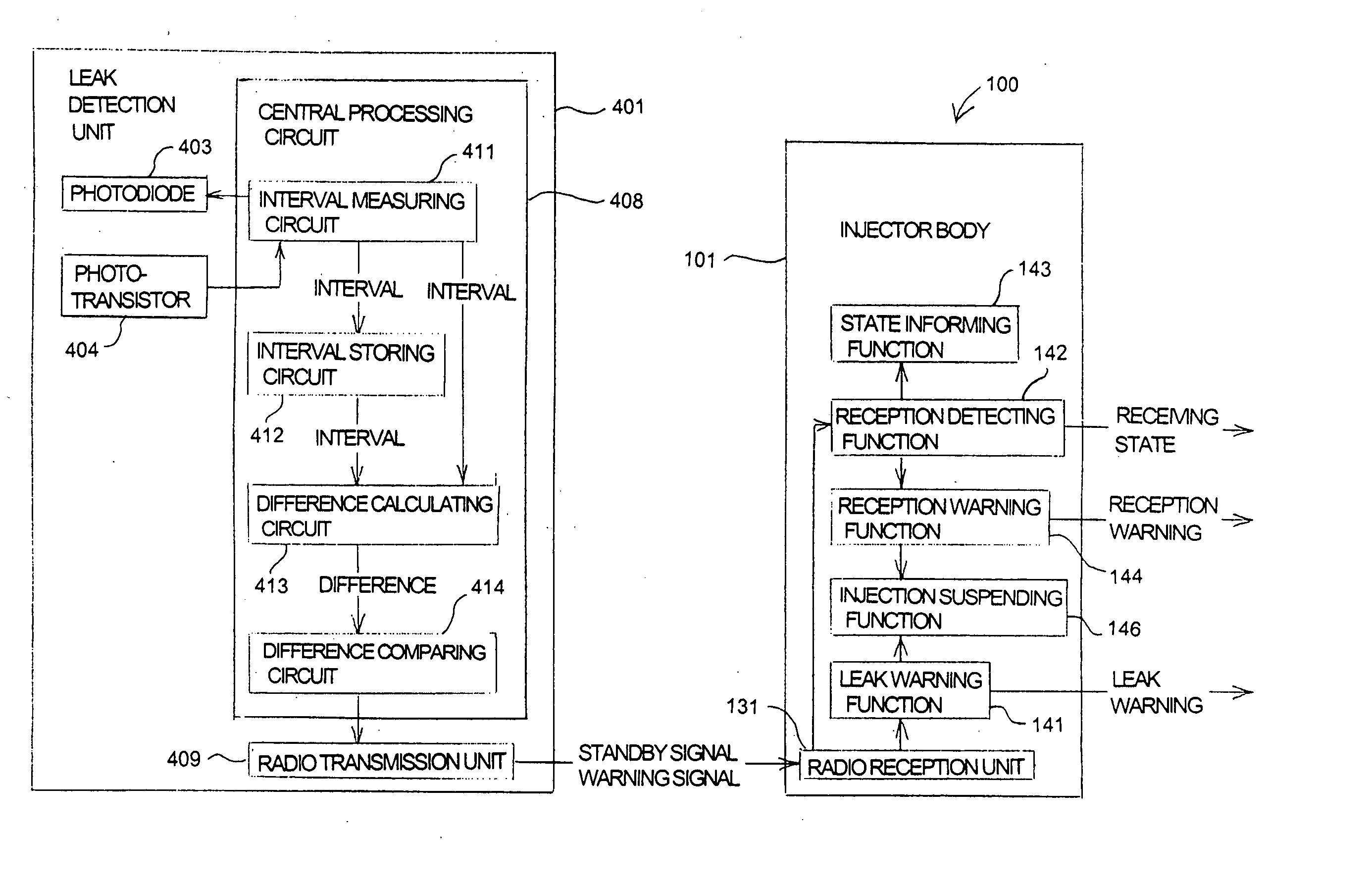
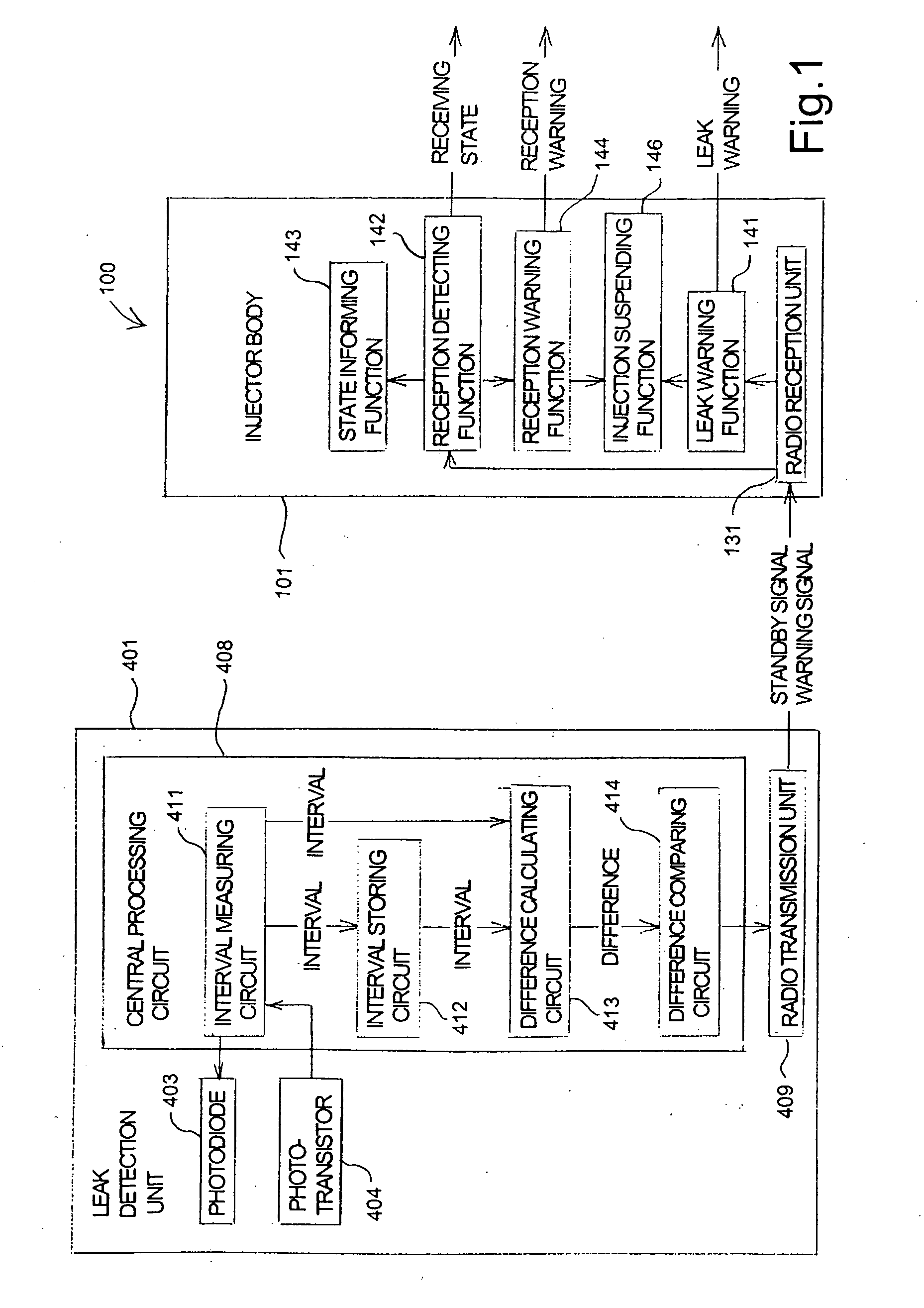
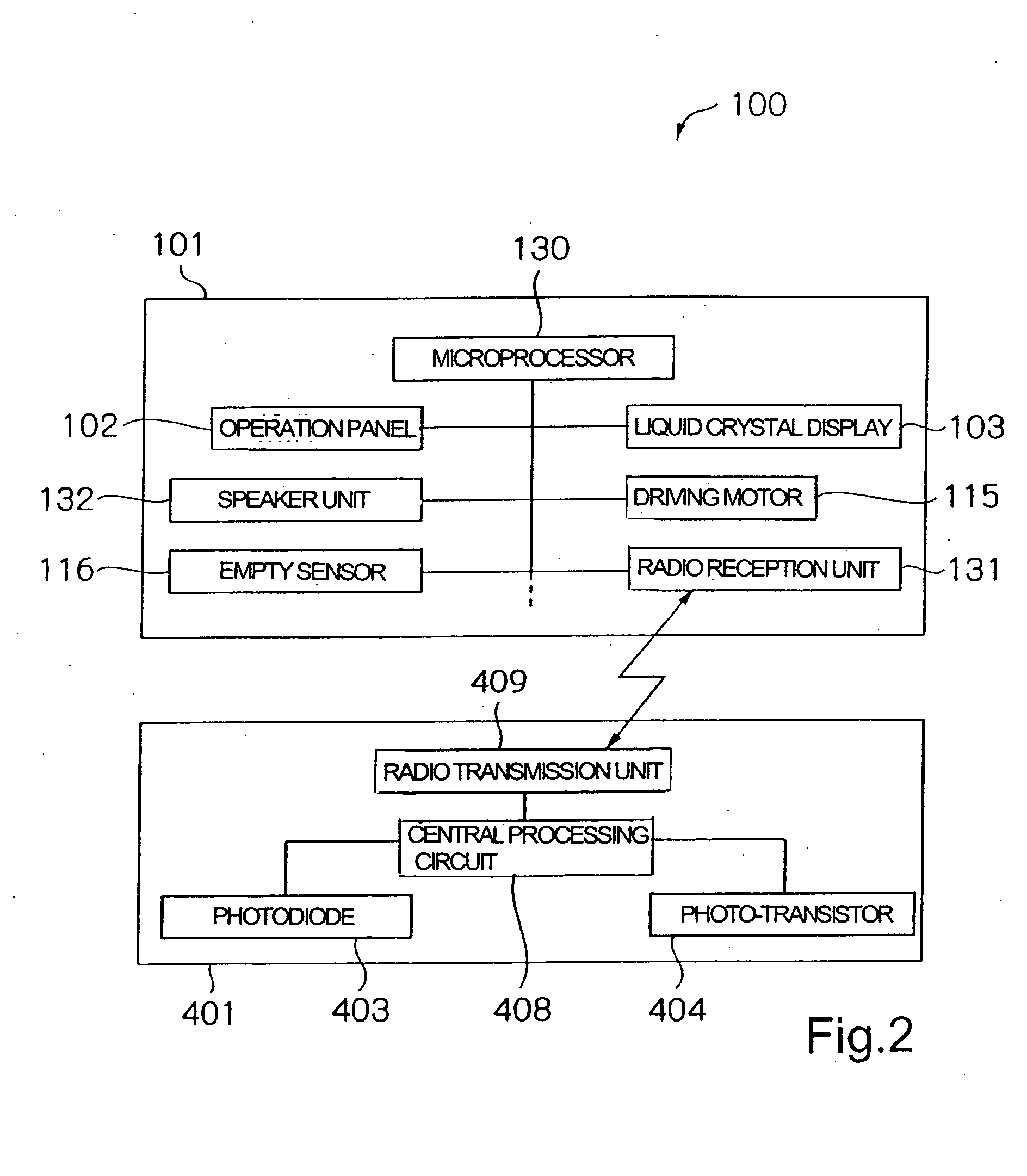
Leak detector for detecting leak of liquid injected into blood vessel using pulse signal
InactiveUS20040225255A1Reduce detection accuracySimple structureCircuit monitoring/indicationVolume/mass flow measurementAcousticsBlood vessel
A leak detector sequentially emits pulse signals toward a human body at a position at which a needle is inserted, detects pulse signals reflected inside of the human body, and measures a time interval between the emission and the detection for each of the pulse signals. Then, the leak detector calculates the difference between the measured interval and a predetermined time interval, and generates a leak warning for notification when the difference exceeds an acceptable range. Since a swelling on the surface of the human body causes a path of the pulse signal to extend, the leak detector can detect, based on the extended signal path, that the needle has come off a blood vessel.
Owner:NEMOTO KYORINDO KK
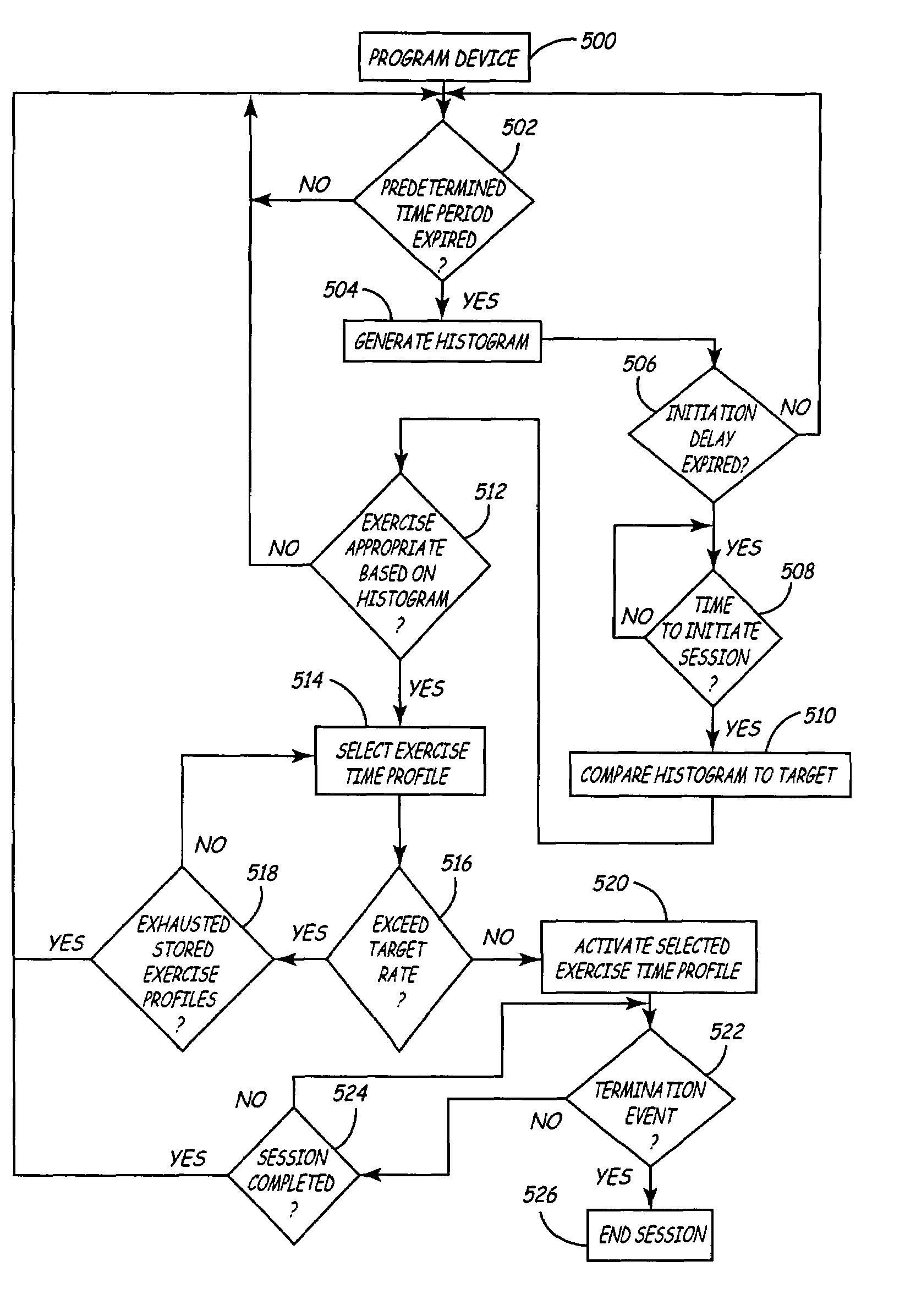
Method and apparatus for temporarily varying a parameter in an implantable medical device
A method and apparatus for varying a parameter in an implantable medical device that includes a plurality of electrodes stimulating heart tissue and sensing cardiac signals, a timing and control device controlling the stimulation of heart tissue by the plurality of electrodes and measuring intervals between the sensed cardiac signals, a storage device storing the measured intervals, and a microprocessor. The microprocessor determines heart rate variability in response to the stored intervals, compares the determined heart rate variability to a predetermined target rate profile, adjusts the parameter from a first setting to a second setting different from the first setting in response to the comparing of the determined heart rate variability and the predetermined target rate profile, and adjusts the parameter from the second setting to a termination setting in response to a termination event or expiration of a first predetermined time period.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for detection of venous pulsation
Methods and systems for detecting venous pulsation are provided. In one embodiment, a metric of the pulse shape of one or more plethysmographic signals is derived and the presence of venous pulsation is detected based on the metric of pulse shape. Examples, of metrics of pulse shape include a skew metric and a ratio of a minima-to-maxima time over a pulse period interval. In an exemplary embodiment, the presence of venous pulsation is detected based on a metric of the pulse shape of one or more plethysmographic signals and on a phase comparison of the plethysmographic signals.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method of and apparatus for detecting atrial fibrillation
A method and apparatus to determine possible atrial fibrillation that includes detecting irregular pulse rhythms from a succession of time intervals each corresponding to a respective interval of time between successive pulse beats of a sequence of the pulse beats; analyzing the detected irregular pulse rhythms to make a determination of possible atrial fibrillation; indicating the possible atrial fibrillation from the determination. If a sphygmomanometer is used, a plurality of pulse beats may be detected with it including the sequence of pulse beats; and respiratory variation in systolic pressure of the pulse beats may be compensated by designating the succession of time intervals to exclude at least an initial one of the plurality of time intervals.
Owner:WIESEL JOSEPH
Apparatus and methods for automatic adjustment of av interval to ensure delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Real-time optimization of right to left ventricular timing sequence in bi-ventricular pacing of heart failure patients
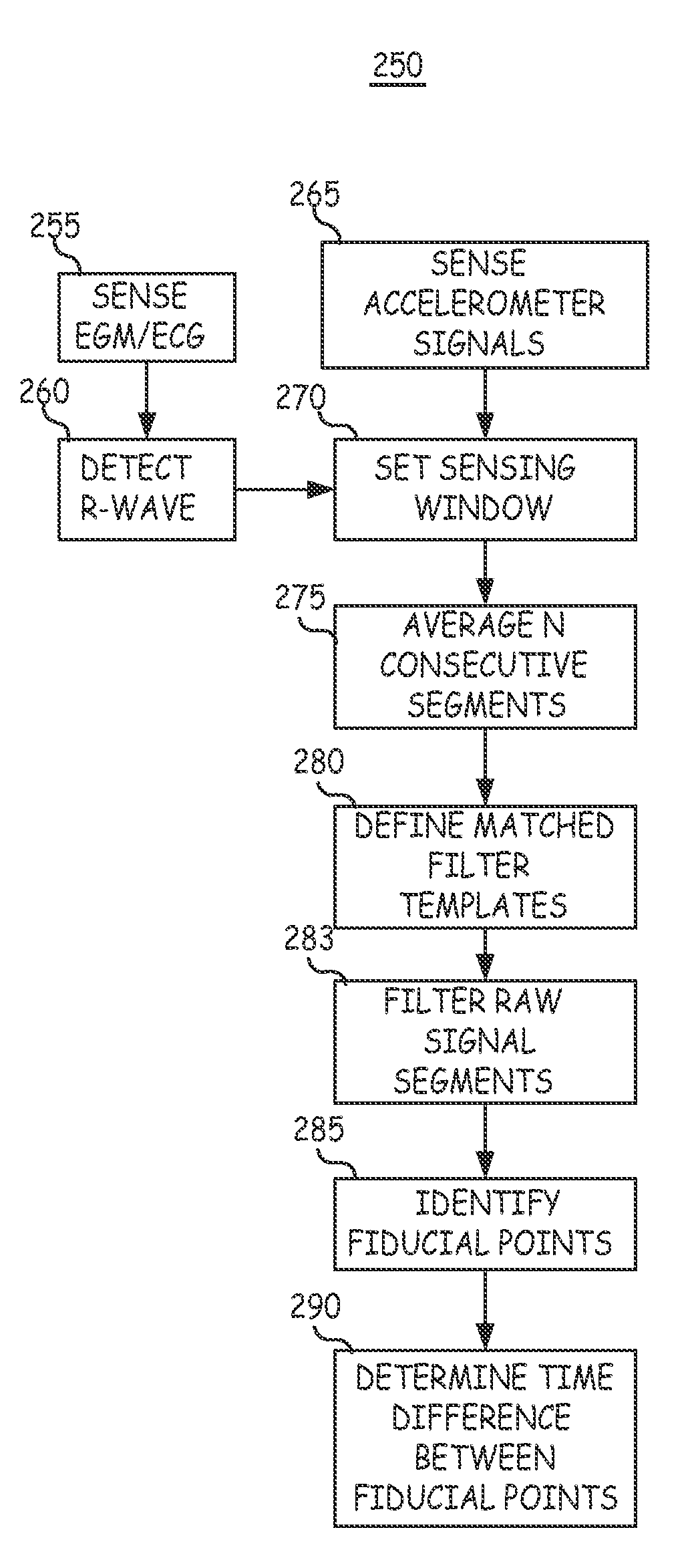
ActiveUS7203541B2Improve performanceHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerWall motion
A system and automated method for assessing ventricular synchrony in ambulatory patients is provided including at least one mechanical sensor (e.g., accelerometer, tensiometric sensor, force transducer, and the like) operatively coupled to a first myocardial location in order to measure a wall motion signal of a first chamber, and a second mechanical sensor operatively coupled to a second myocardial location in order to measure a wall motion signal of a second chamber. The wall motion signals are processed in order to identify the time at which a fiducial (e.g., an inflection point, a threshold crossing, a maximum amplitude, etc.) occurs for each respective signal. The temporal separation between the fiducial points on each respective signal is measured as a metric of ventricular synchrony and can be optionally utilized to adjust pacing therapy timing to improve synchrony.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac rhythm monitoring device
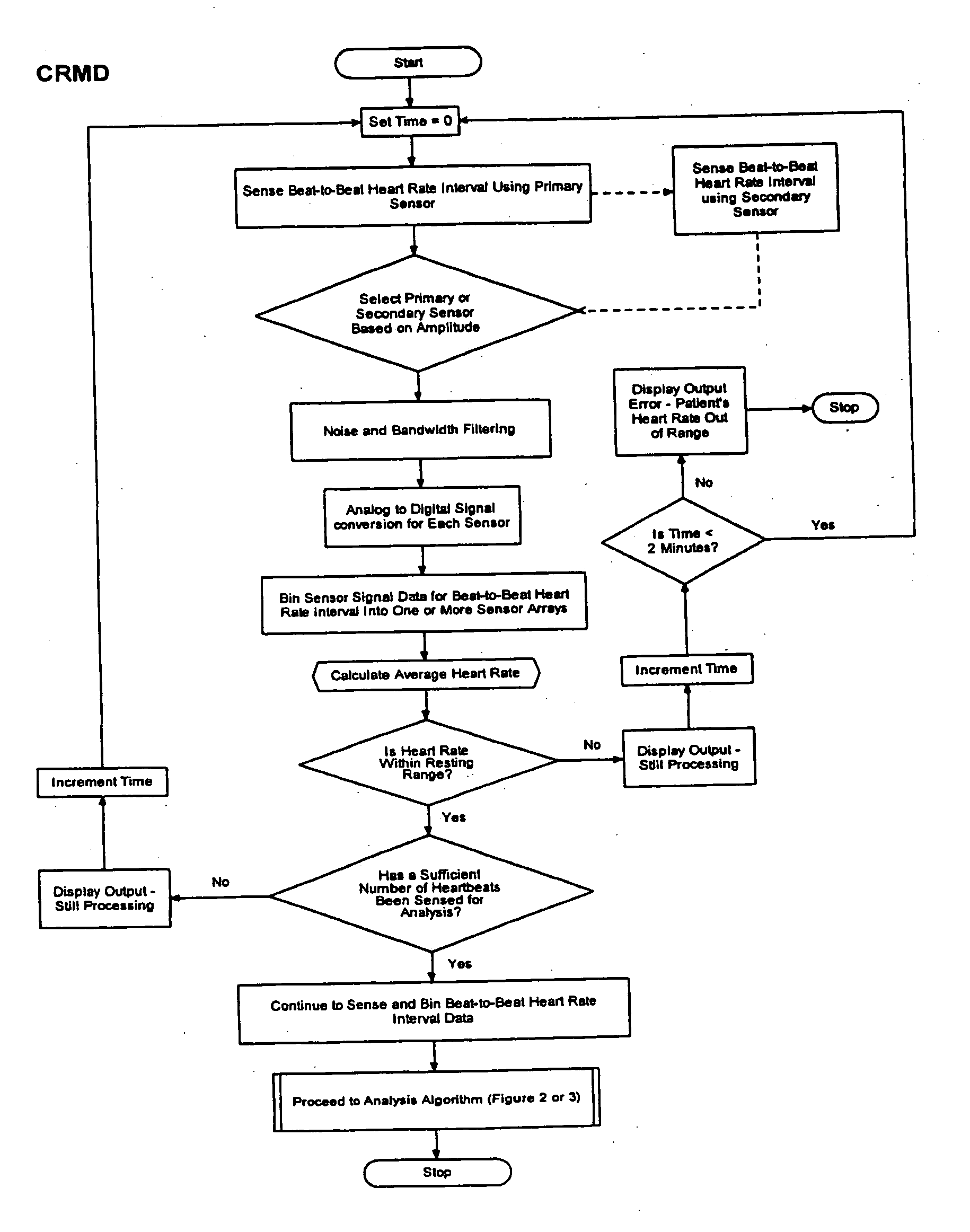
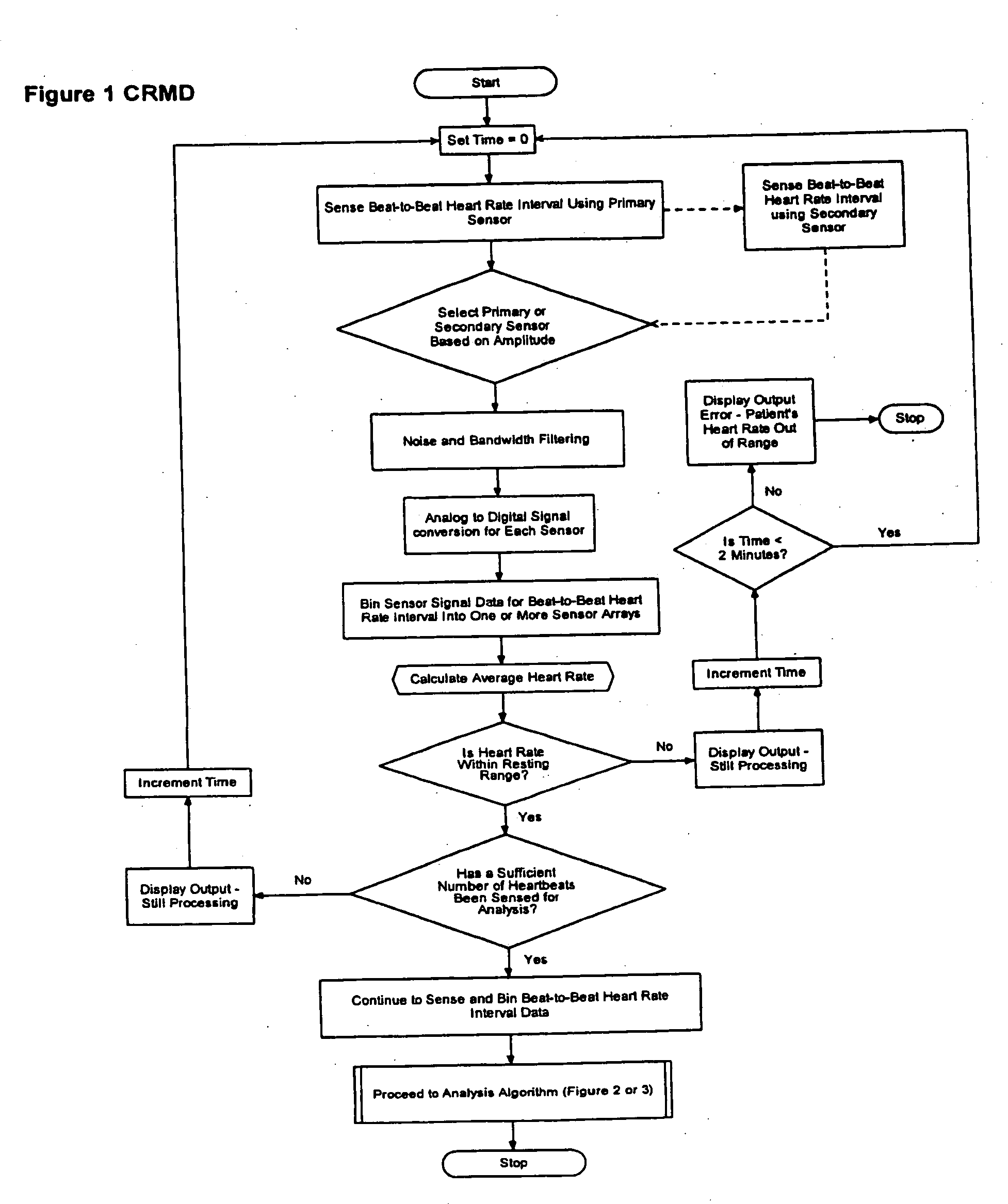
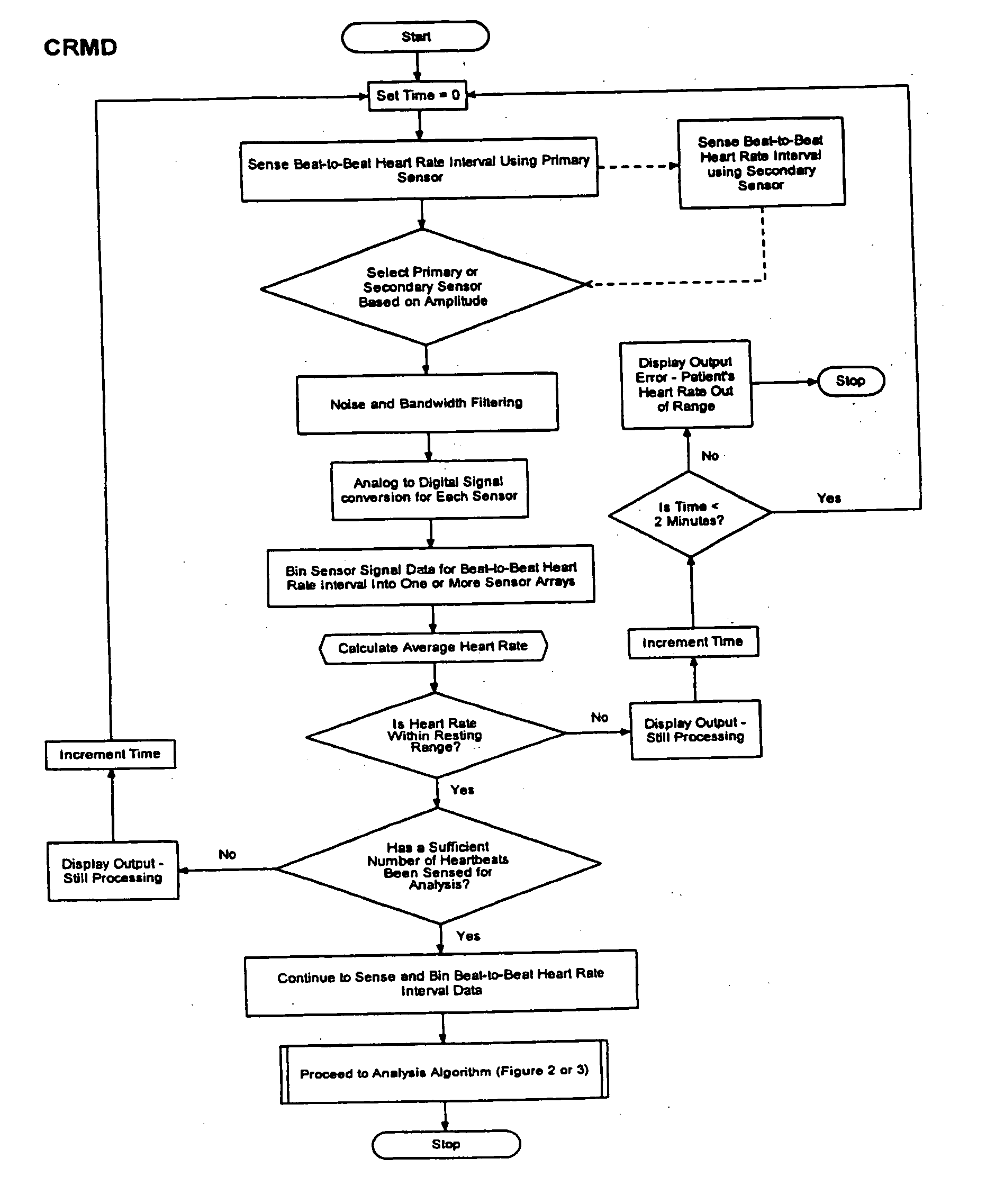
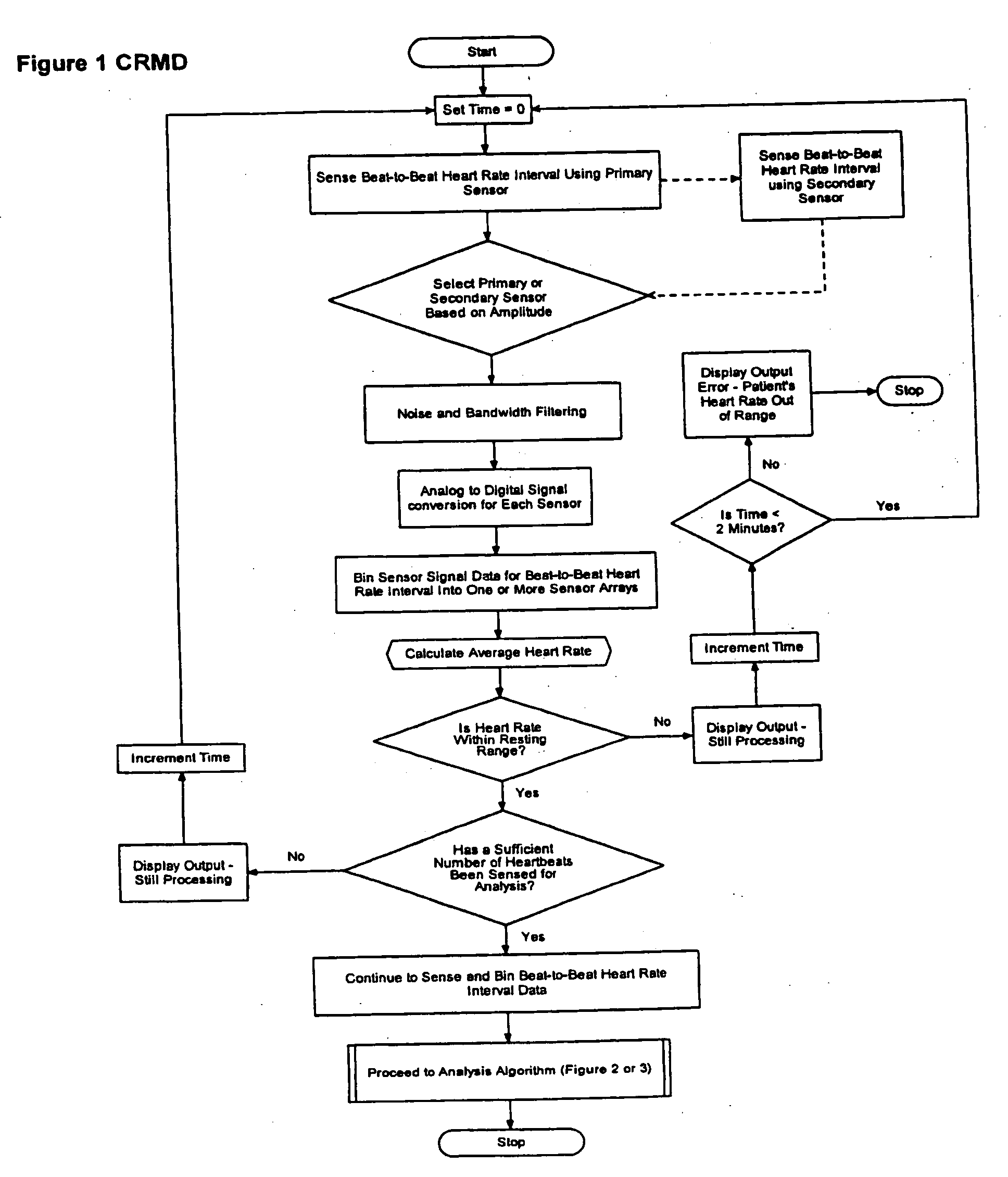
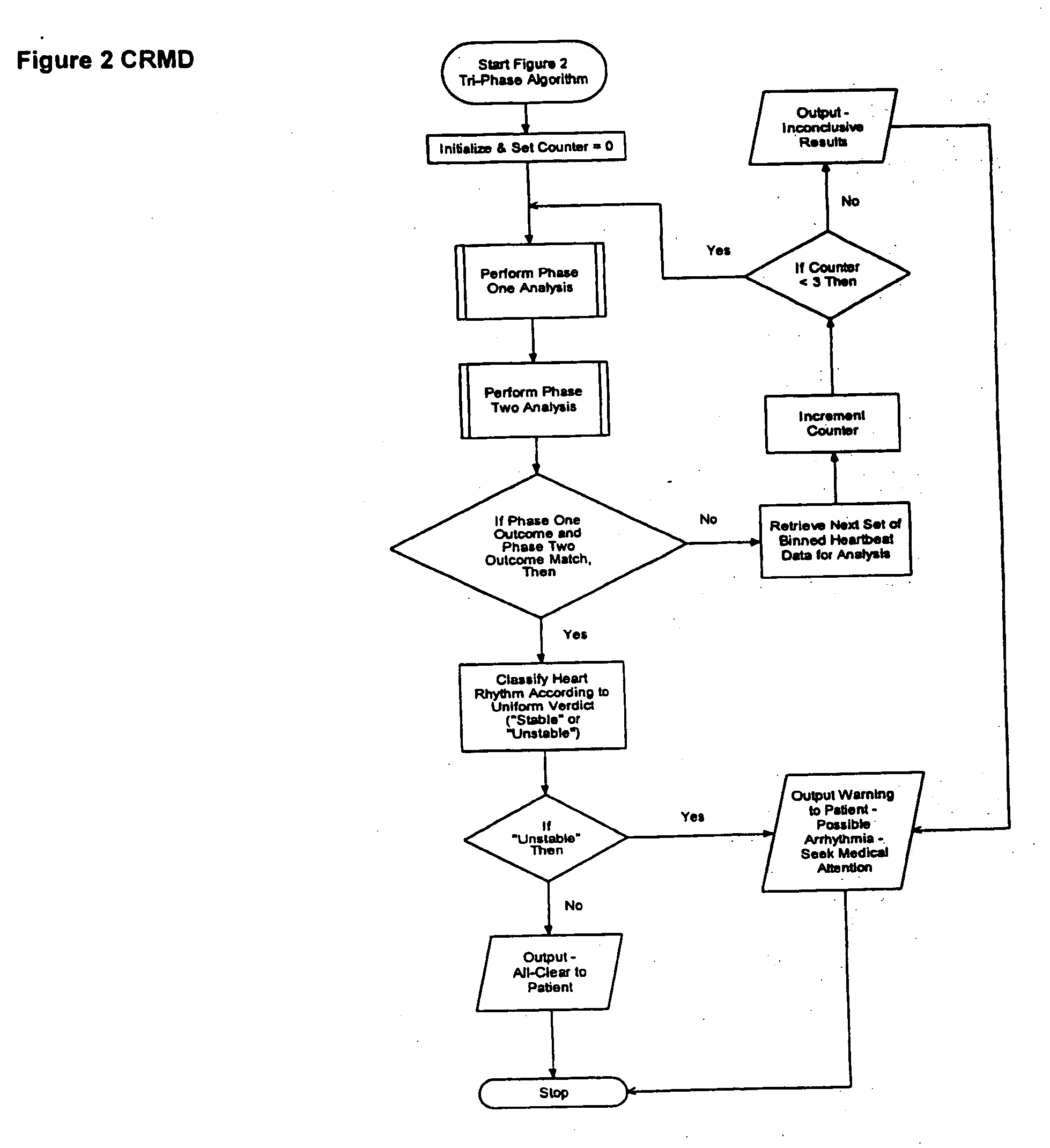
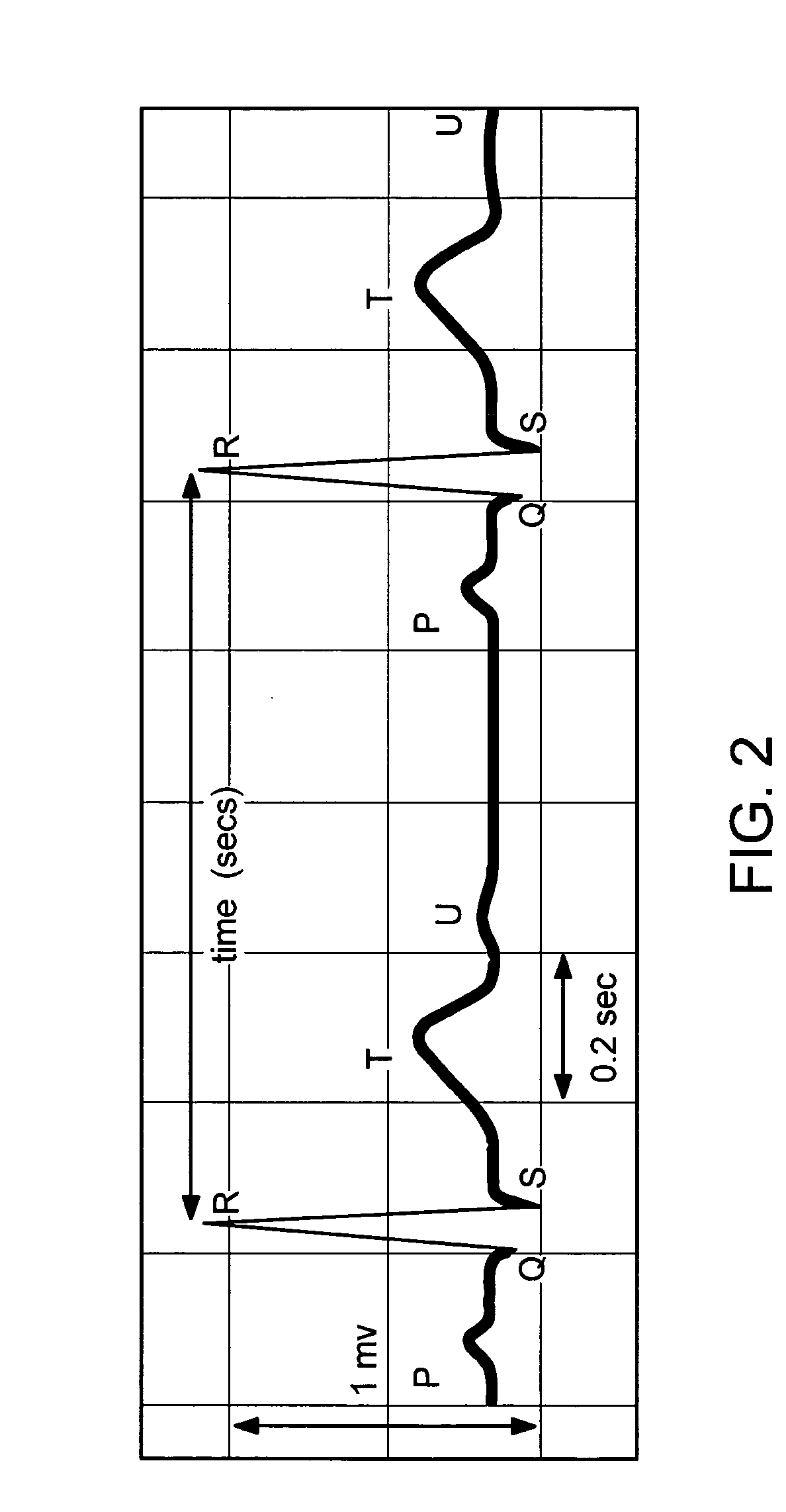
The present invention is a cardiac rhythm-monitoring device, which allows patients to perform a preliminary screening for supraventricular arrhythmia. The device detects beat-to-beat heart rhythms (i.e. the R-R interval between individual heart beats) and performs a screening test to determine if there are indications of arrhythmia. The test looks for variance in the R-R interval that is outside of the normal range, either using a pre-constructed chart based upon general population studies to determine the normal range of variance or using normal distribution analysis of the patient's own heart rhythm to determine the normal range of variance for determining irregular heartbeats, and if there are multiple irregularities within the sensed time frame, the patient is warned of potential supraventricular arrhythmia. By sensing both electrical impulses form the heart and mechanical responses to the heartbeat, the device may augment its analysis.
Owner:BISCHOFF EDWARD T +1
Method and apparatus for measuring blood pressure using relaxed matching criteria
ActiveUS7074192B2ElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsBlood Pressure DeterminationsRR interval
A technique for comparing pressure oscillations obtained during a blood pressure determination wherein two or more sets of matching criteria may be employed. The set of matching criteria to be employed is determined based on the heart rate variability or the presence of heart beat irregularities or arrhythmias as determined by an independent heart monitor, such as an ECG. The selected set of matching criteria may then be employed in determining the acceptability of the time interval between two oscillations and the equivalence of the two oscillations based upon one or more oscillation characteristics, such as peak amplitude. In this manner, non-consecutive oscillations may be matched and used in determining blood pressure.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Cardiac rhythm monitoring device
Owner:BISCHOFF EDWARD T +1
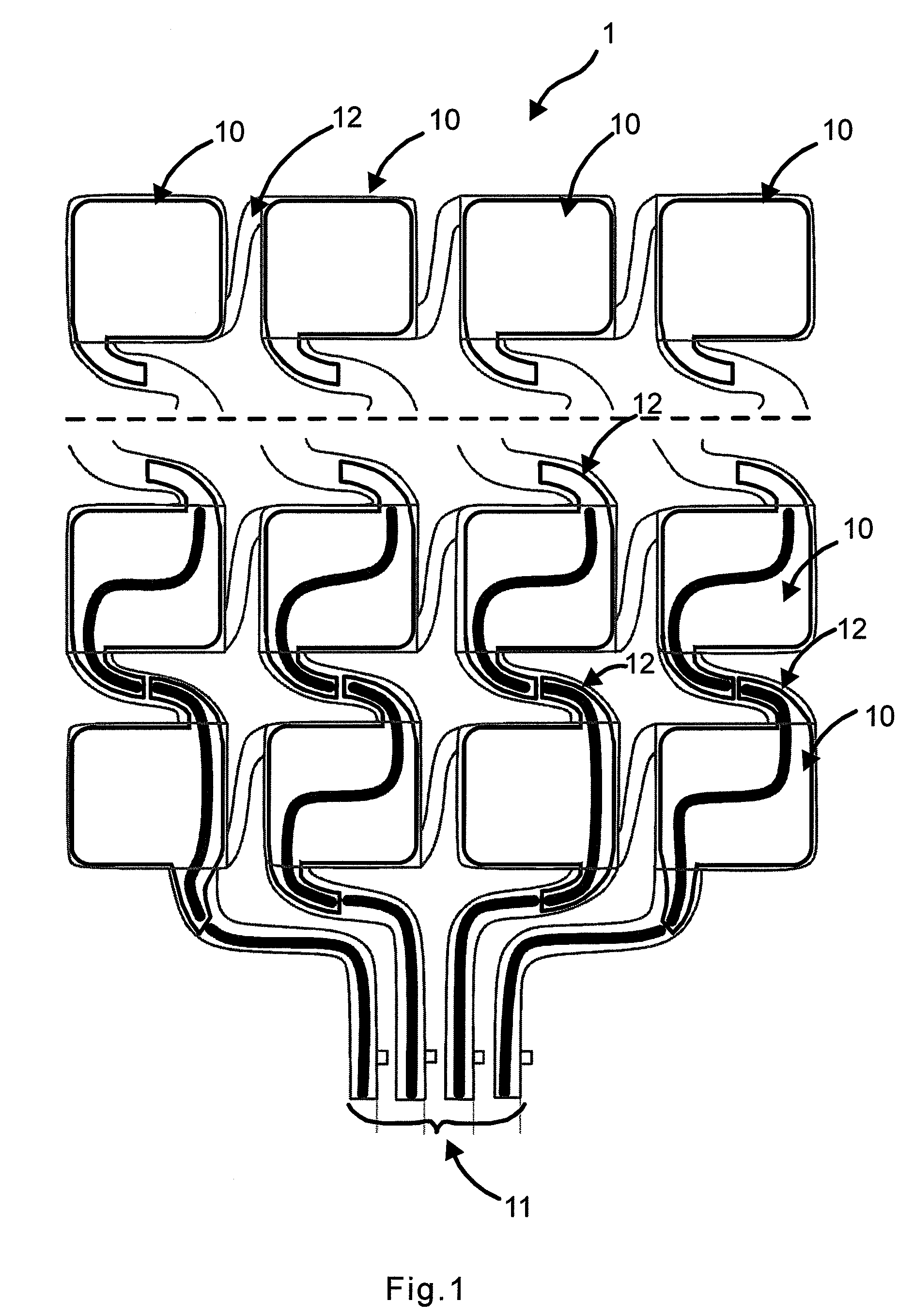
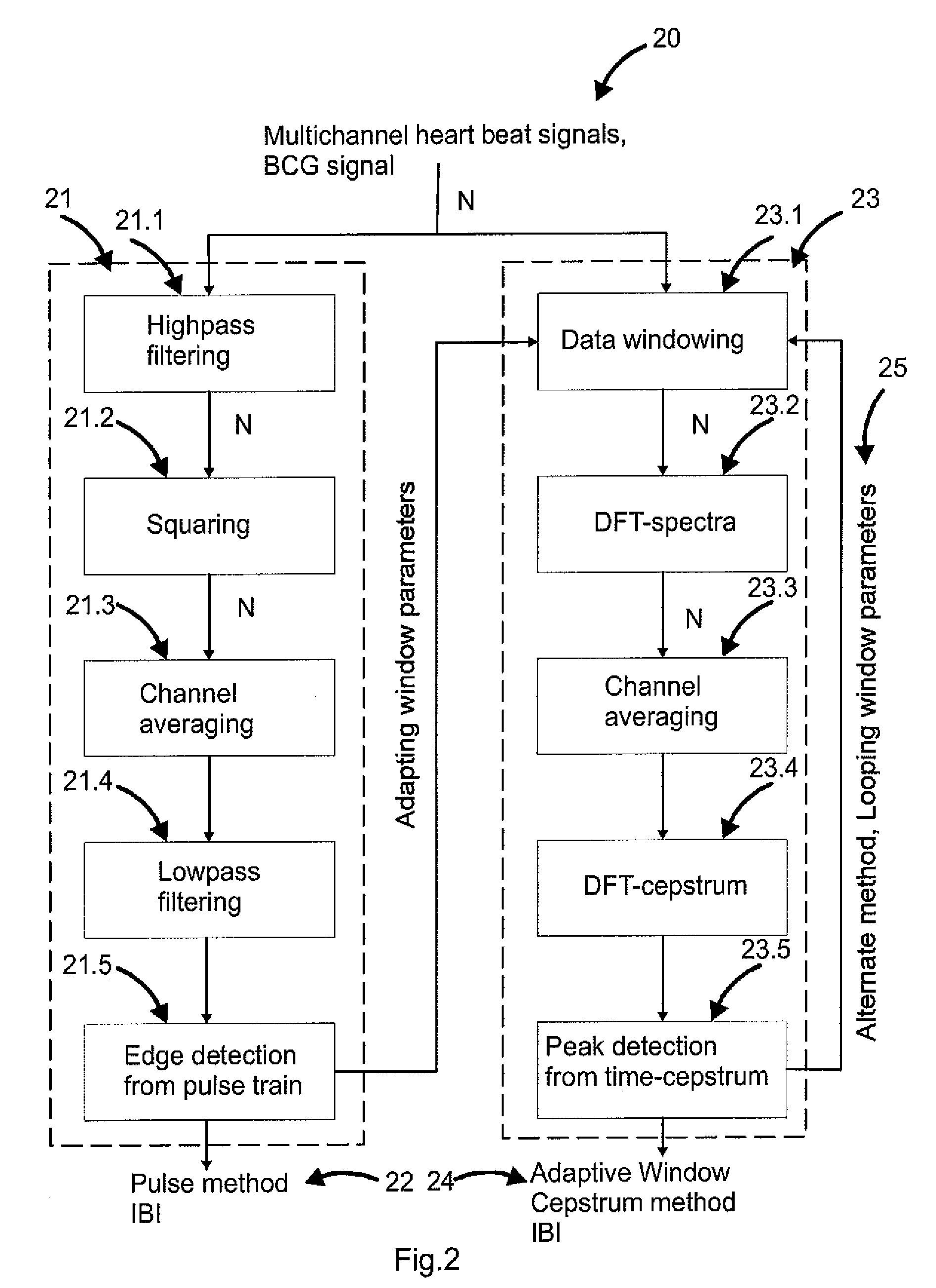
Extraction of heart inter beat interval from multichannel measurements
ActiveUS20100249628A1Accurate and almost unnoticeableImprove measurement qualityCatheterMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateFrequency spectrumPressure sensing
A monitoring apparatus comprising a multichannel pressure sensing sensor for measuring a ballistocardiographic signal of a human body is disclosed. The monitoring apparatus also comprises means for selecting a time window for heart inter beat interval including two consecutive heart beats to be estimated, defining a spectrum for the ballistocardiographic signal averaging between at least two measurement channels of the multichannel pressure sensing sensor, a cepstrum from the logarithm of a spectrum, and a heart inter beat interval. The invention relates to a method for defining a heart inter beat interval, where a ballistocardiographic signal of a body is measured with a multichannel pressure sensing sensor, a time window for heart inter beat interval Including two consecutive heart beats to be estimated is selected, a spectrum for the ballistocardiographic signal averaging between at least two measurement channels of the multichannel pressure sensing sensor, a cepstrum from the logarithm of a spectrum, and a heart inter beat interval are defined.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
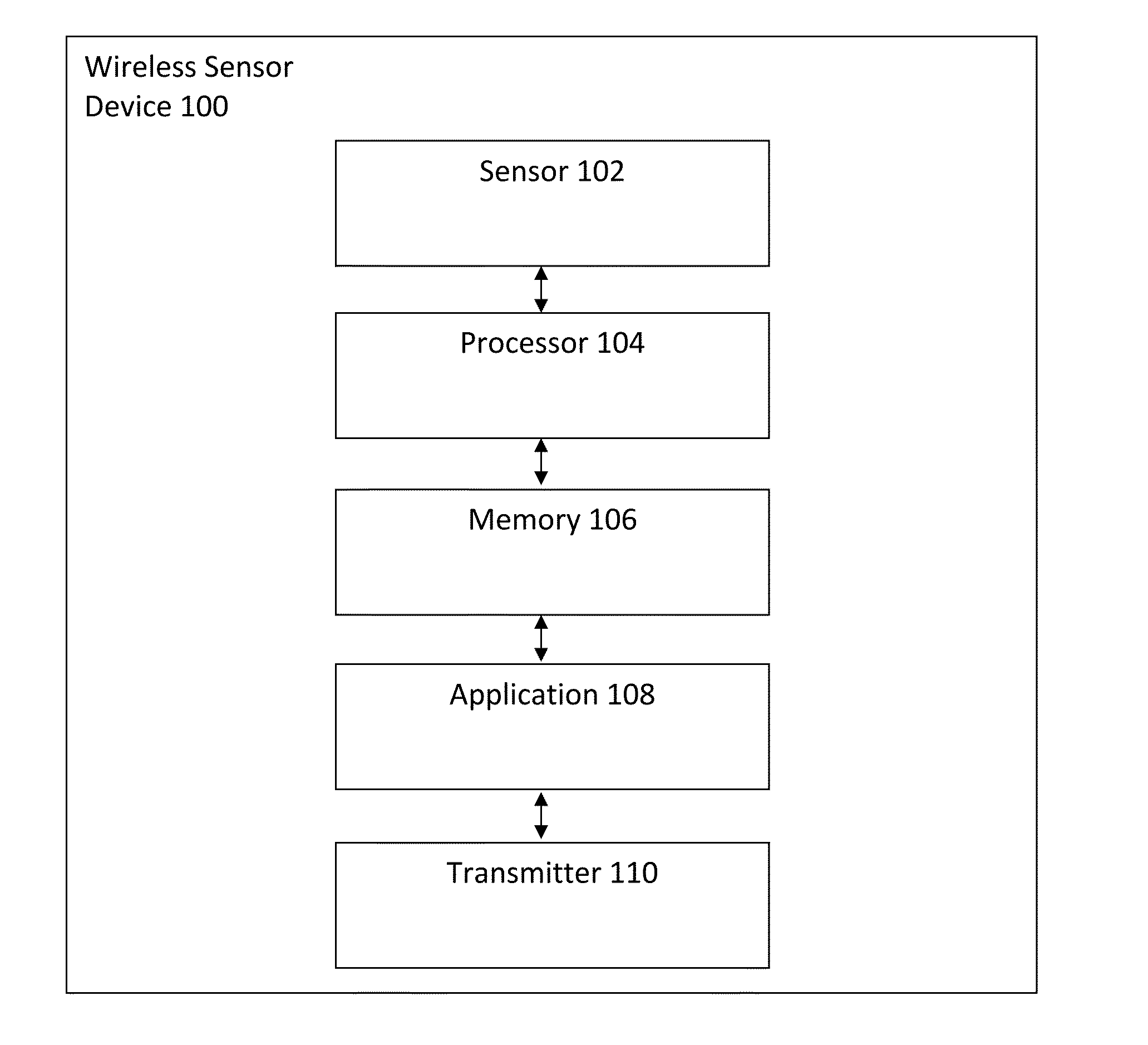
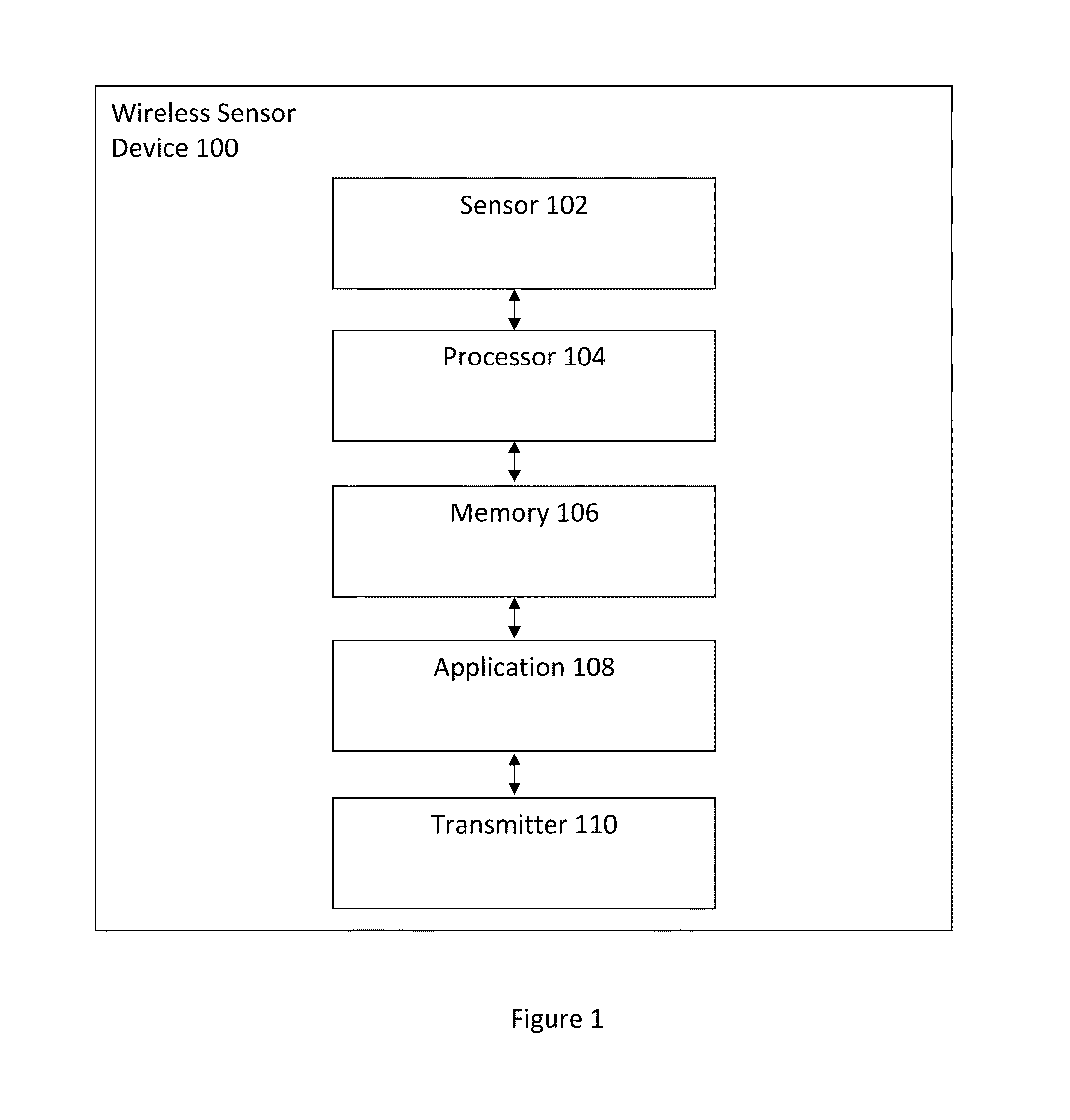
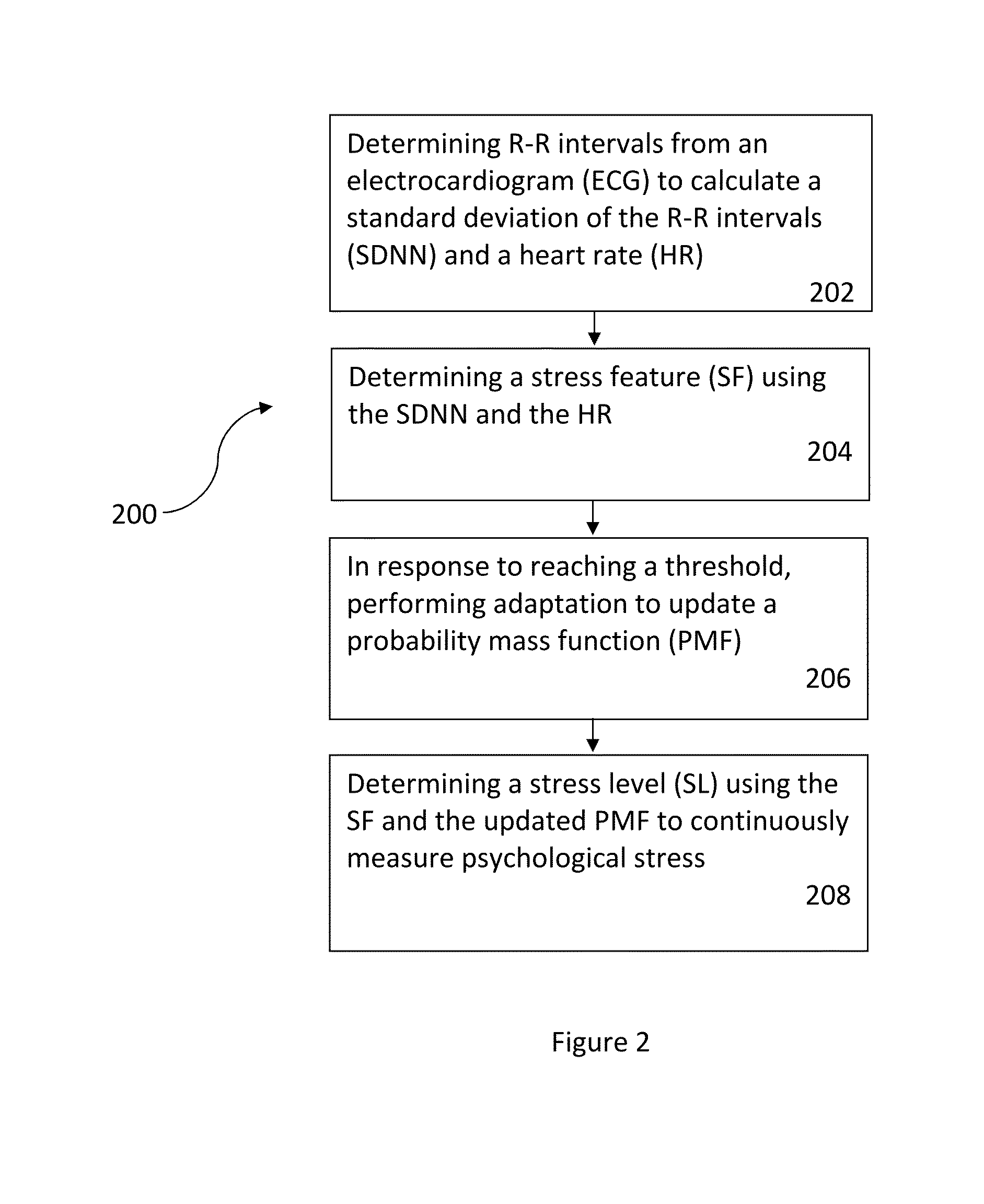
Measuring psychological stress from cardiovascular and activity signals
A method and system for measuring psychological stress disclosed. In a first aspect, the method comprises determining R-R intervals from an electrocardiogram (ECG) to calculate a standard deviation of the R-R intervals (SDNN) and determining a stress feature (SF) using the SDNN. In response to reaching a threshold, the method includes performing adaptation to update a probability mass function (PMF). The method includes determining a stress level (SL) using the SF and the updated PMF to continuously measure the psychological stress. In a second aspect, the system comprises a wireless sensor device coupled to a user via at least one electrode, wherein the wireless sensor device includes a processor and a memory device coupled to the processor, wherein the memory device stores an application which, when executed by the processor, causes the processor to carry out the steps of the method.
Owner:VITAL CONNECT
Assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing based on cardiopulmonary coupling
An assessment of sleep quality and sleep disordered breathing is determined from cardiopulmonary coupling between two physiological data series. An R-R interval series is derived from an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The normal beats from the R-R interval series are extracted to produce a normal-to-normal interval series. The amplitude variations in the QRS complex are used to extract a surrogate respiration signal (i.e., ECG-derived respiration) associated with the NN interval series. The two series are corrected to remove outliers, and resampled. The cross-spectral power and coherence of the two resampled signals are calculated over a plurality of coherence windows. For each coherence window, the product of the coherence and cross-spectral power is used to calculate coherent cross-power. Using the appropriate thresholds for the coherent cross-power, the proportion of sleep spent in CAP, non-CAP, and wake and / or REM are determined. Coherent cross-power can be applied to differentiate obstructive from non-obstructive disease, and admixtures of the same.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Atrial fibrillation detection method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060276716A1Low costReduce skin irritationElectrocardiographySensorsEcg signalSlide window
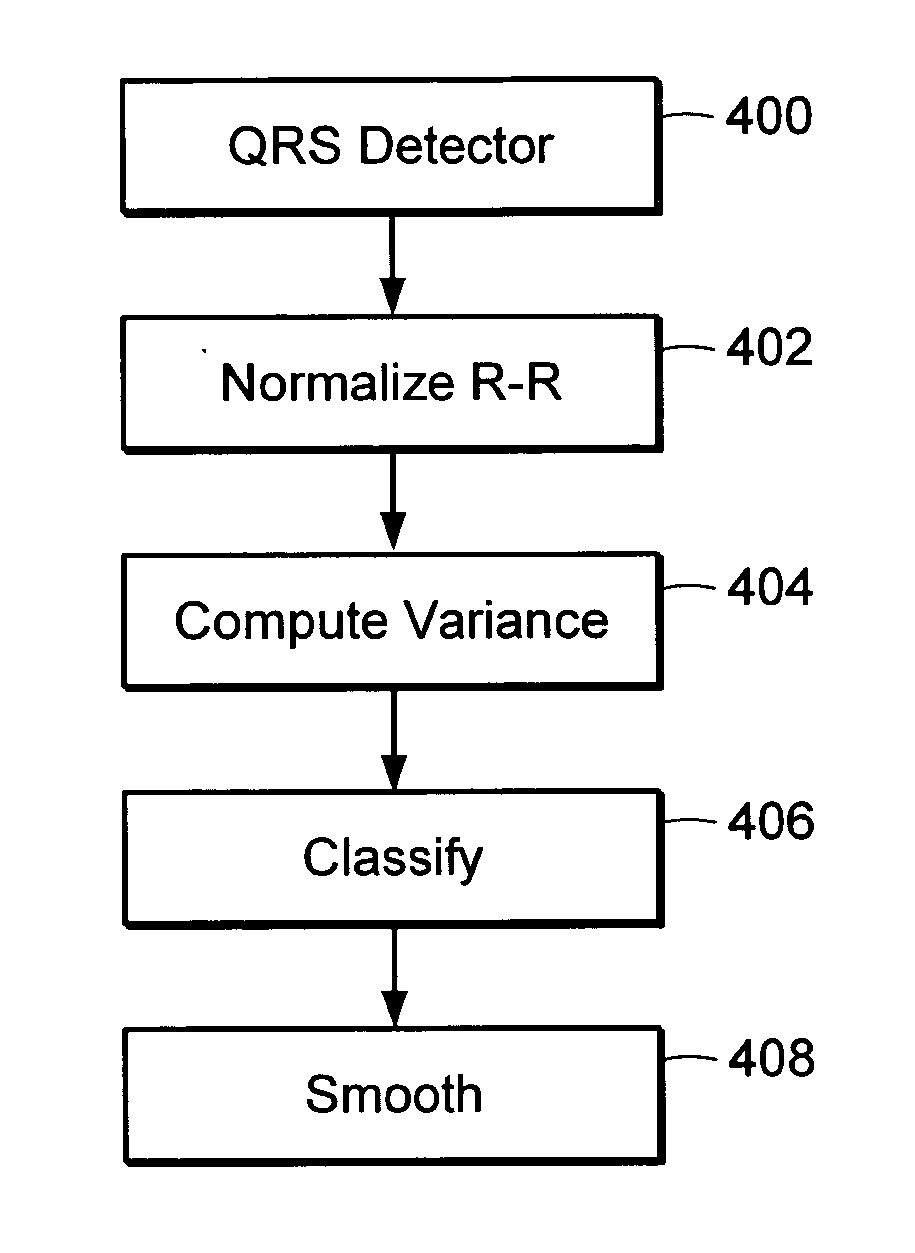
A method for automatically detecting atrial fibrillation in a non-standard ECG signal having changing morphology and containing significant muscle noise generated by an ambulatory subject is provided. A morphology independent QRS detector is used to compute R-R intervals in the ECG signal. The variance of the R-R intervals over a sliding window is normalized and compared with a threshold to determine if atrial fibrillation is present within the window.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
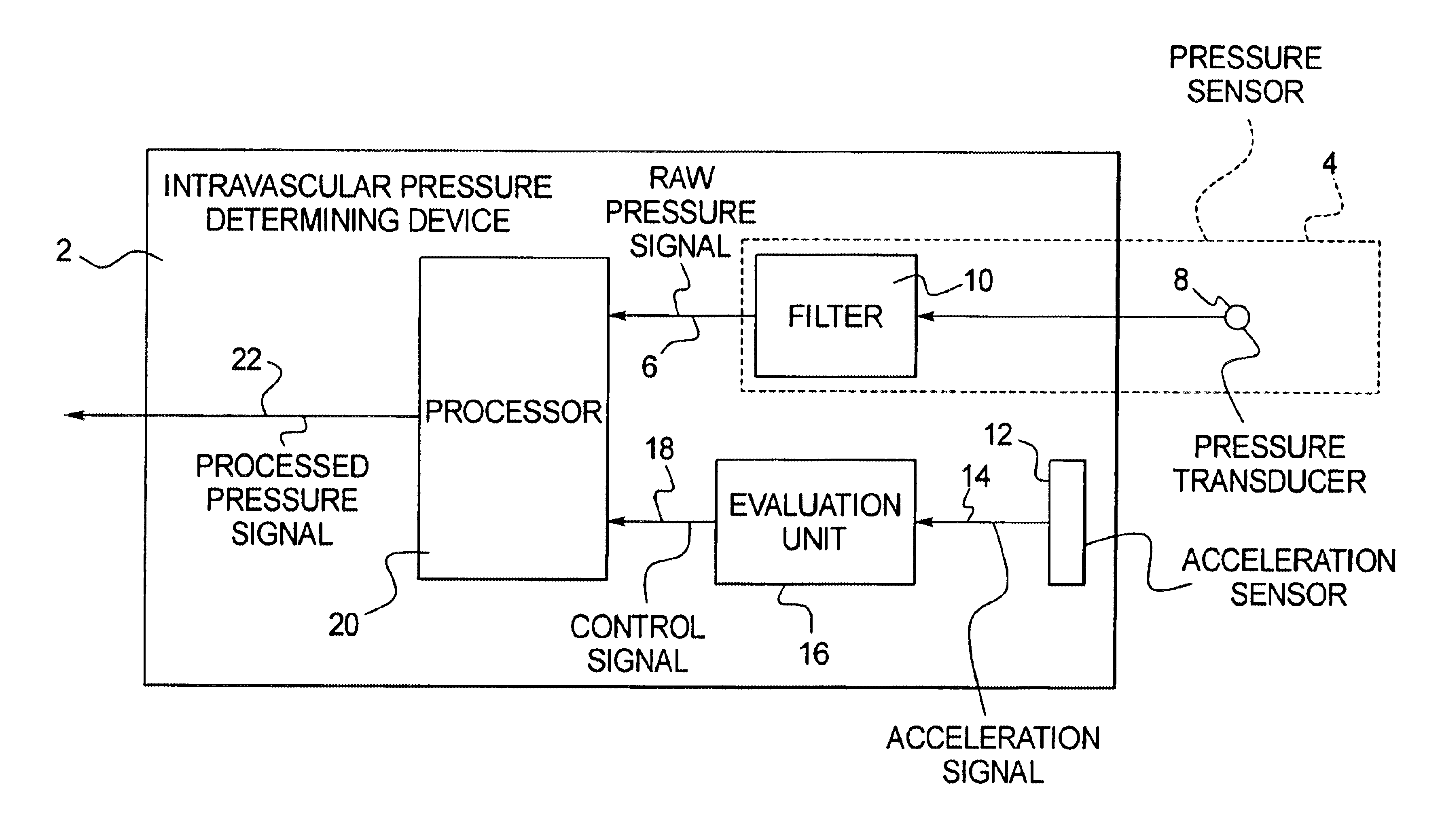
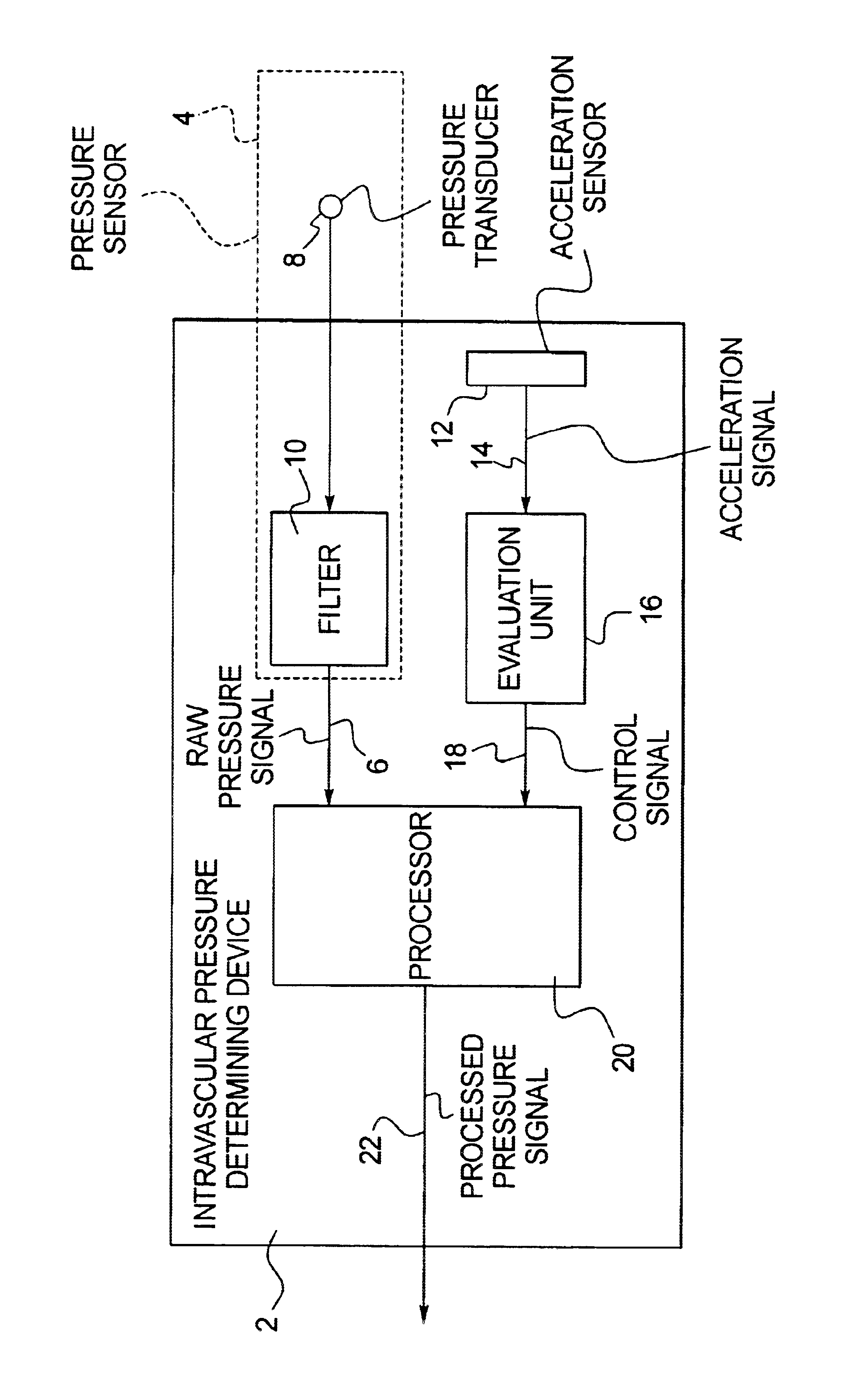
Implantable intravascular pressure determining device and method
InactiveUS6860857B2Improve pressure measurement accuracyImprove accuracyCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationBlood vesselPressure sensor
In an implantable intravascular pressure determining device and method, a pressure sensor generates a raw pressure signal and an acceleration sensor measures acceleration in a patient. Time intervals are identified wherein the raw pressure signal accurately represents the intravascular pressure, these intervals being identified as the time intervals wherein the measured acceleration is below a predetermined threshold. The raw pressure signal is processed, to generate a processed signal which is used as an intravascular pressure signal, only in the aforementioned time intervals.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
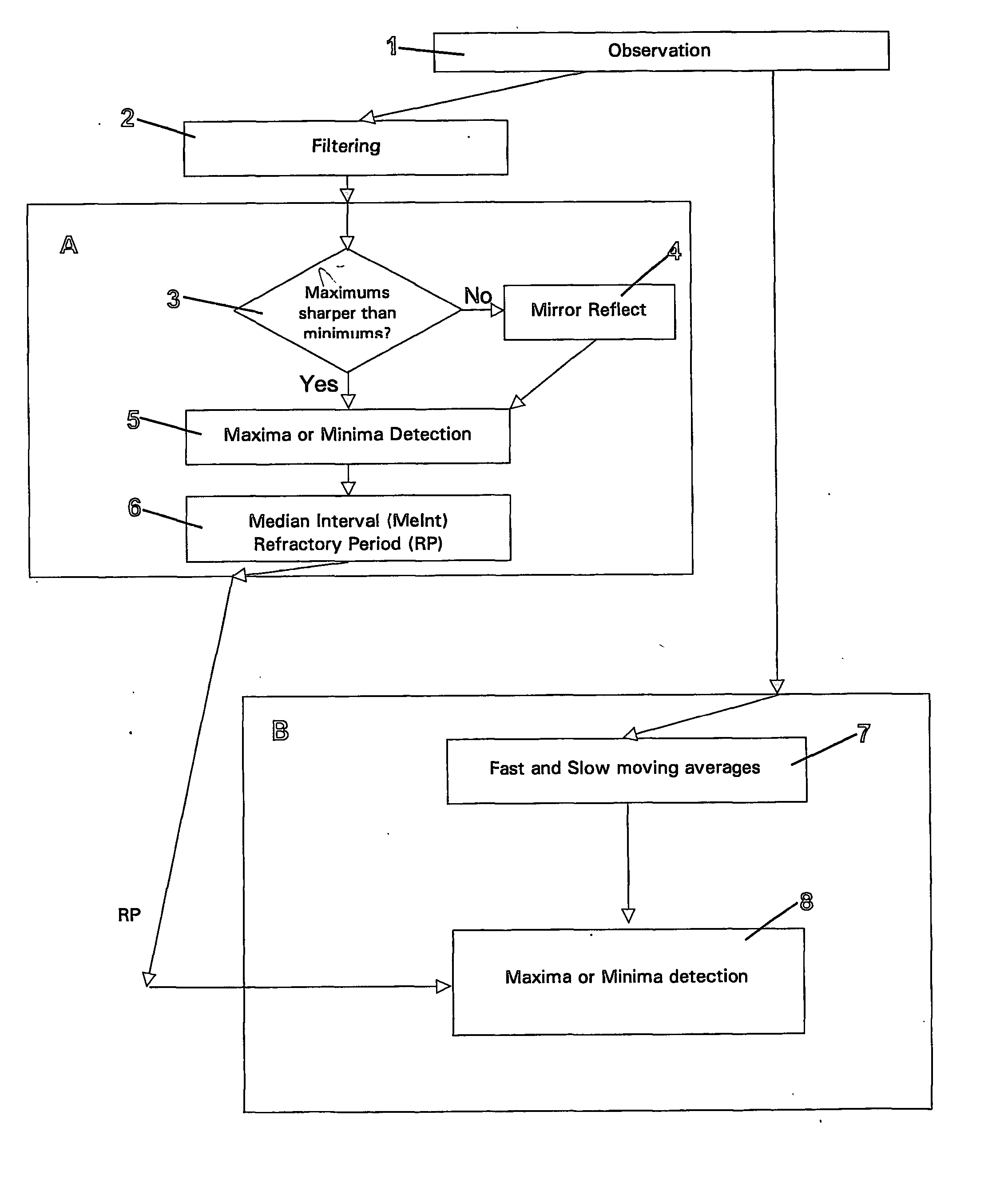
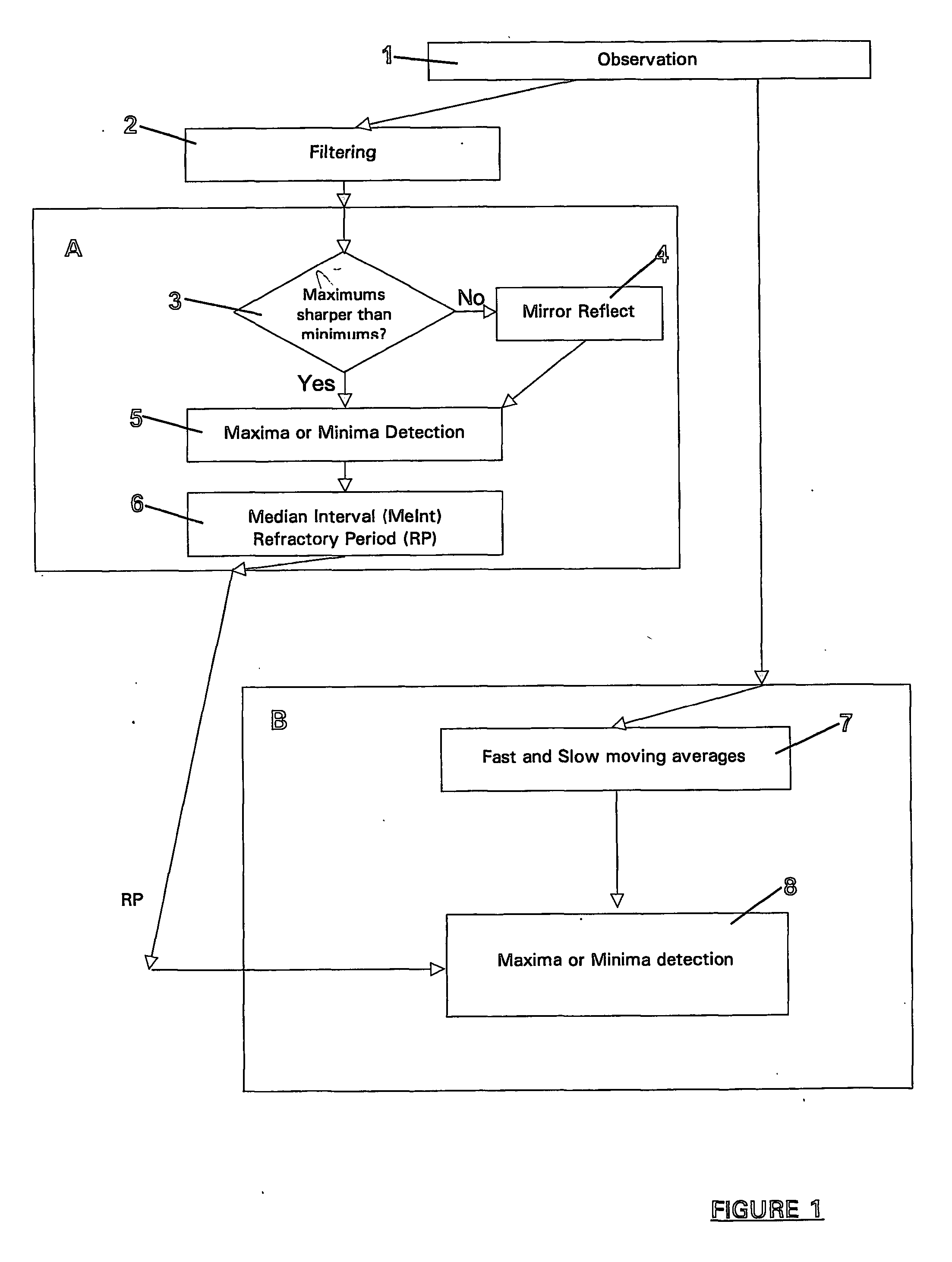
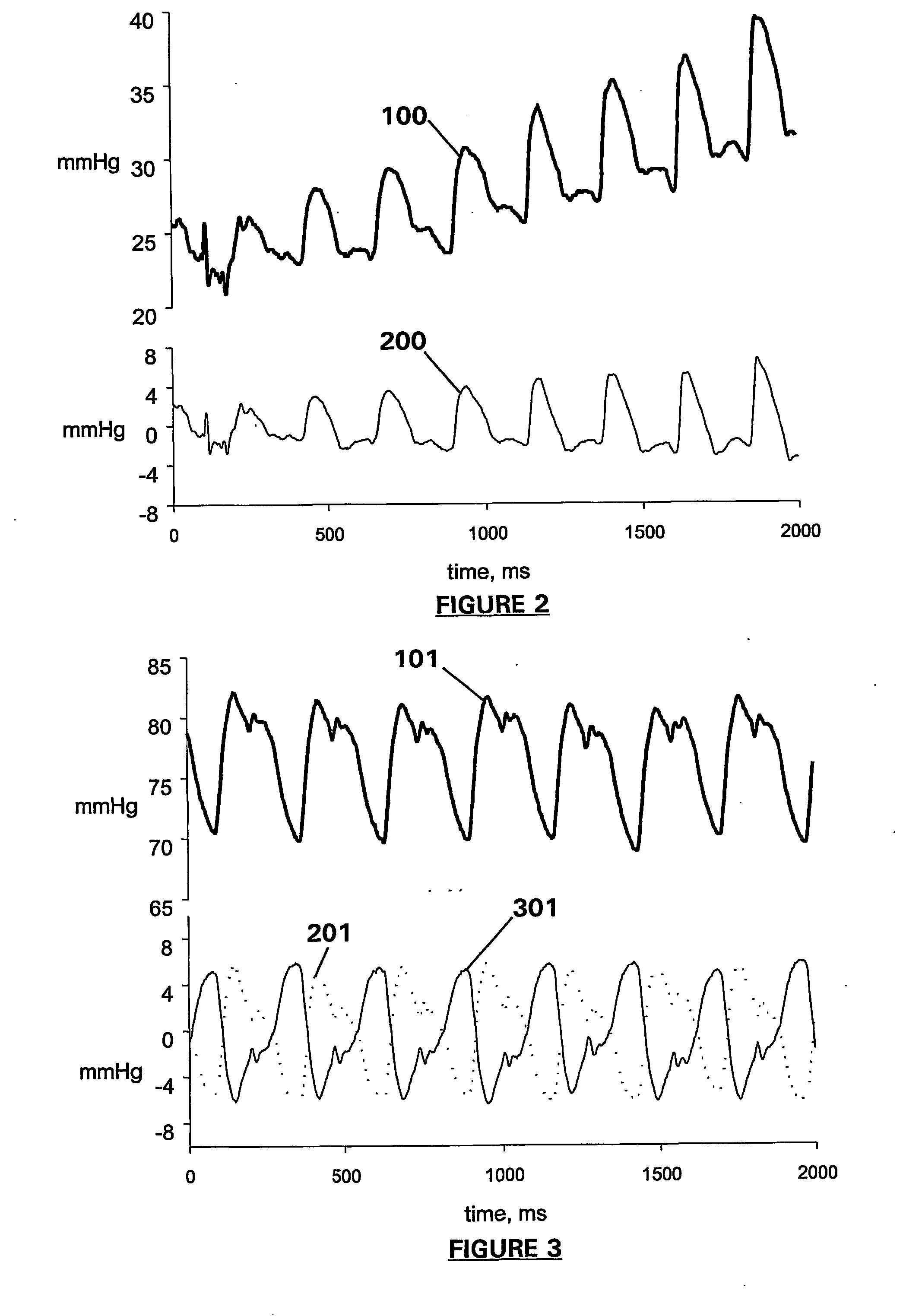
Apparatus and method for detection and quantification of oscillatory signals
A method of determining the location in time of maxima and / or minima of an oscillatory signal. The method may have application to measurement of biological signals, in particular measurement of heart rate from a pulsatile blood signal. The method includes a first stage including the steps of observation over a measurement period, identifying large local maxima or minima and computing an average interval between the identified local maxima or minima. One or more exclusion periods are located in time in the oscillatory signal, having a duration dependent on the average interval, the exclusion periods used to reject false maxima or minima. Maxima or minima may also be detected as an absolute maximum or minimum between crossing points of a fast and a slow moving average of the oscillatory signal. An exclusion period may also be used to reject false maxima or minima when crossing points are used. Apparatus for performing the method is also claimed.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
Method, apparatus and system for characterizing sleep
A method of determining sleep stages from signals of electrical activity recorded of a chest of a sleeping subject, the signals being measured over a plurality of epochs. The method comprising: (a) extracting a series of cardiac R-R intervals from the signals and obtaining a time-frequency decomposition from the series of cardiac R-R intervals; (b) using the time-frequency decomposition to determine at least one Slow-Wave-Sleep (SWS) period and at least one Non-SWS (NSWS) period; (c) from the at least one NSWS period, determining at least one sleep-onset (SO) period and a plurality of non-sleep periods; (d) extracting a plurality of electromyogram (EMG) parameters from a portion of the signals, the portion corresponds to a NSWS period other than the at least one SO period and other than the plurality of non-sleep period; (e) using the plurality of EMG parameters to determine at least one REM period thereby also to obtain also at least one light-sleep (LS) period defined as a NSWS period other than the SO periods, other than the non-sleep periods and other than the REM periods; thereby determining the sleep stages of the sleeping subject.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
False positive reduction in SPO2 atrial fibrillation detection using average heart rate and NIBP
InactiveUS7806832B2Low costElimination of several ECG electrodesCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringOxygen saturationAtrial fibrillation
The method and system includes detecting atrial fibrillation in a patient by monitoring the blood oxygen saturation level over a period of time. The method and system produces a plethysmographic waveform from the monitored blood oxygen saturation level and analyzes the plethysmographic waveform and detected intervals and determines whether the patient is in atrial fibrillation. The method and system is preferably implemented in a software application and may be configured to report to the user on the current state of atrial fibrillation (AFIB) and a current trend.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Implantable medical device with optimization procedure
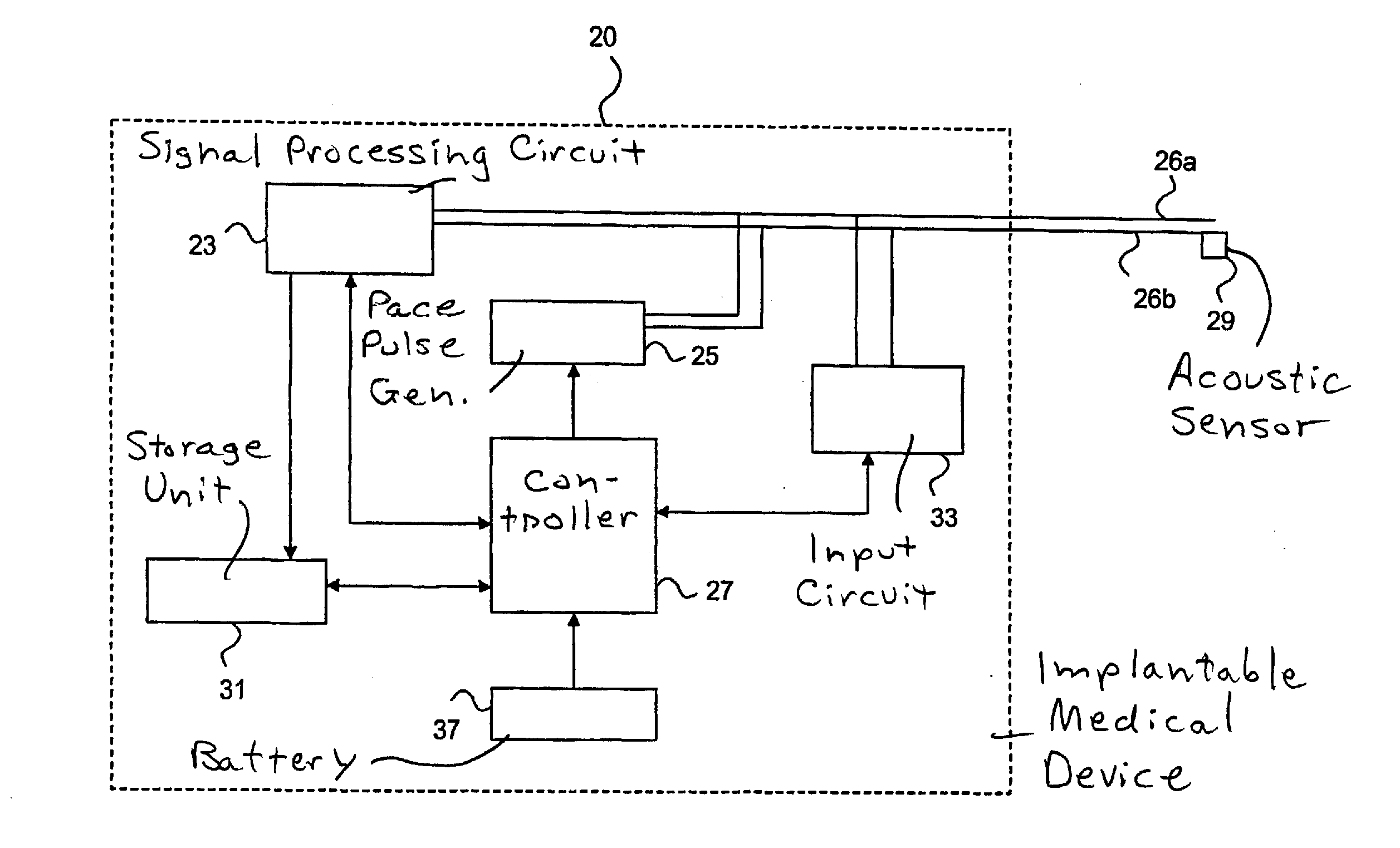
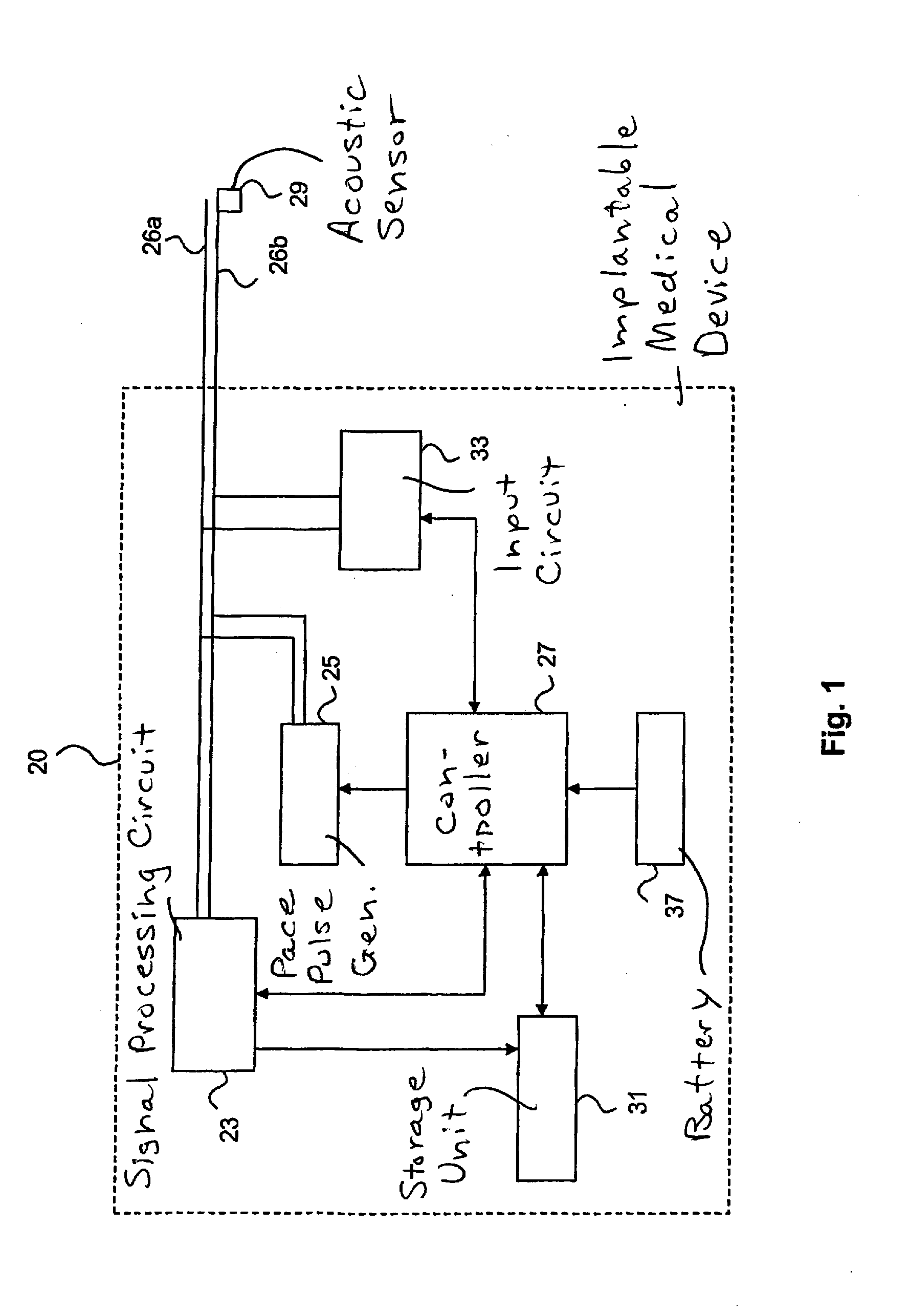
InactiveUS20090254139A1More time to relaxFaster filling timeStethoscopeHeart stimulatorsAcoustic energyCardiac cycle
In an implantable medical device and a method for the operation thereof, acoustic energy is sensed in a subject in whom the device is implanted, and signals indicative of heart sounds of the heart of the patient are produced over predetermined periods of a cardiac cycle, during successive cardiac cycles. A signal corresponding to the second heart sound (S2) is extracted from the sensed signal, and the respective durations of successive second heart sound signals are determined. An optimization procedure is implemented that includes controlling delivery of pacing pulses based on the determined durations of successive second heart sounds, to determined a combination of stimulation intervals, including at least the AV interval and the VV interval, that causes a substantially synchronized closure of the aortic and pulmonary valves.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com