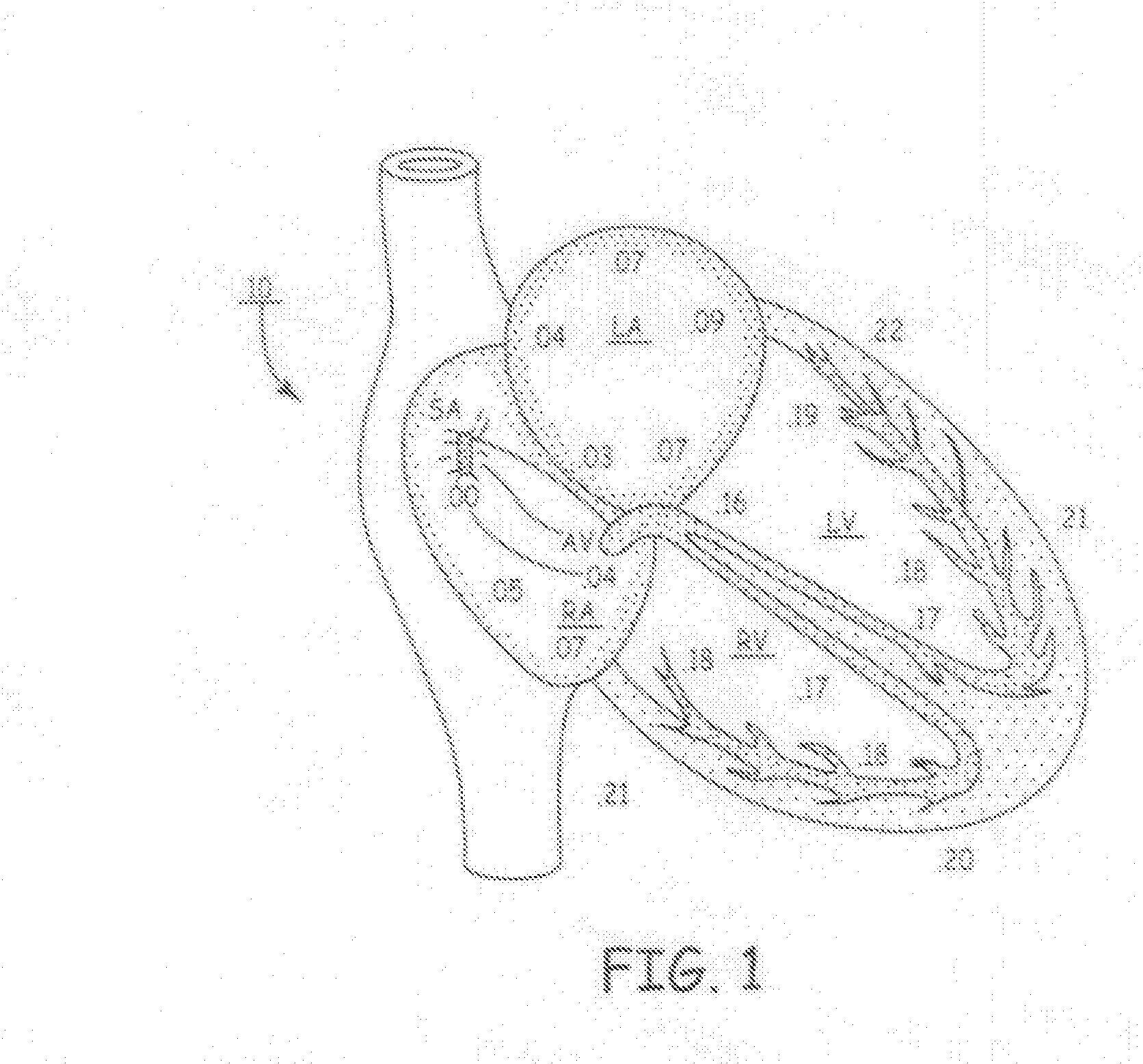
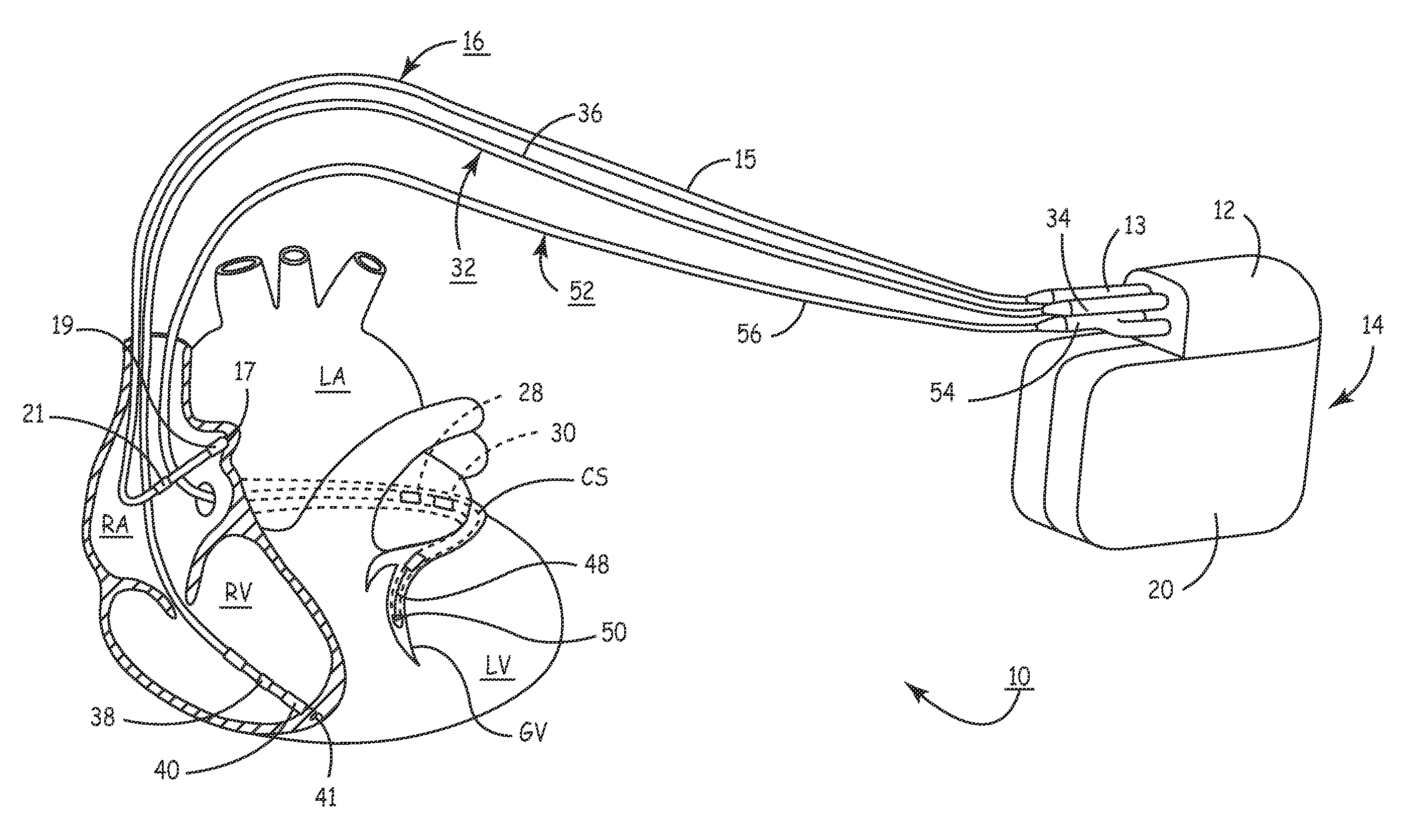
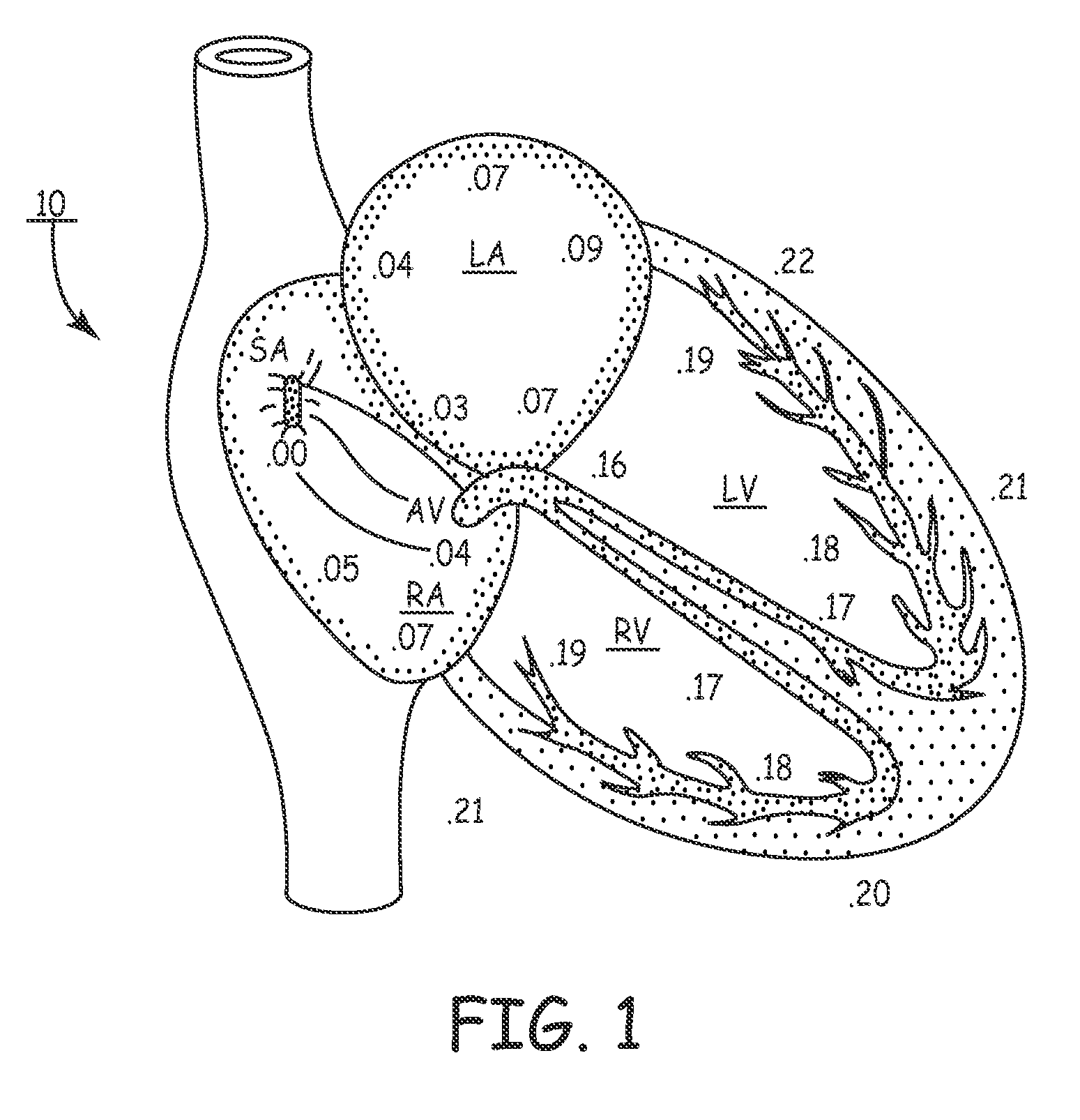
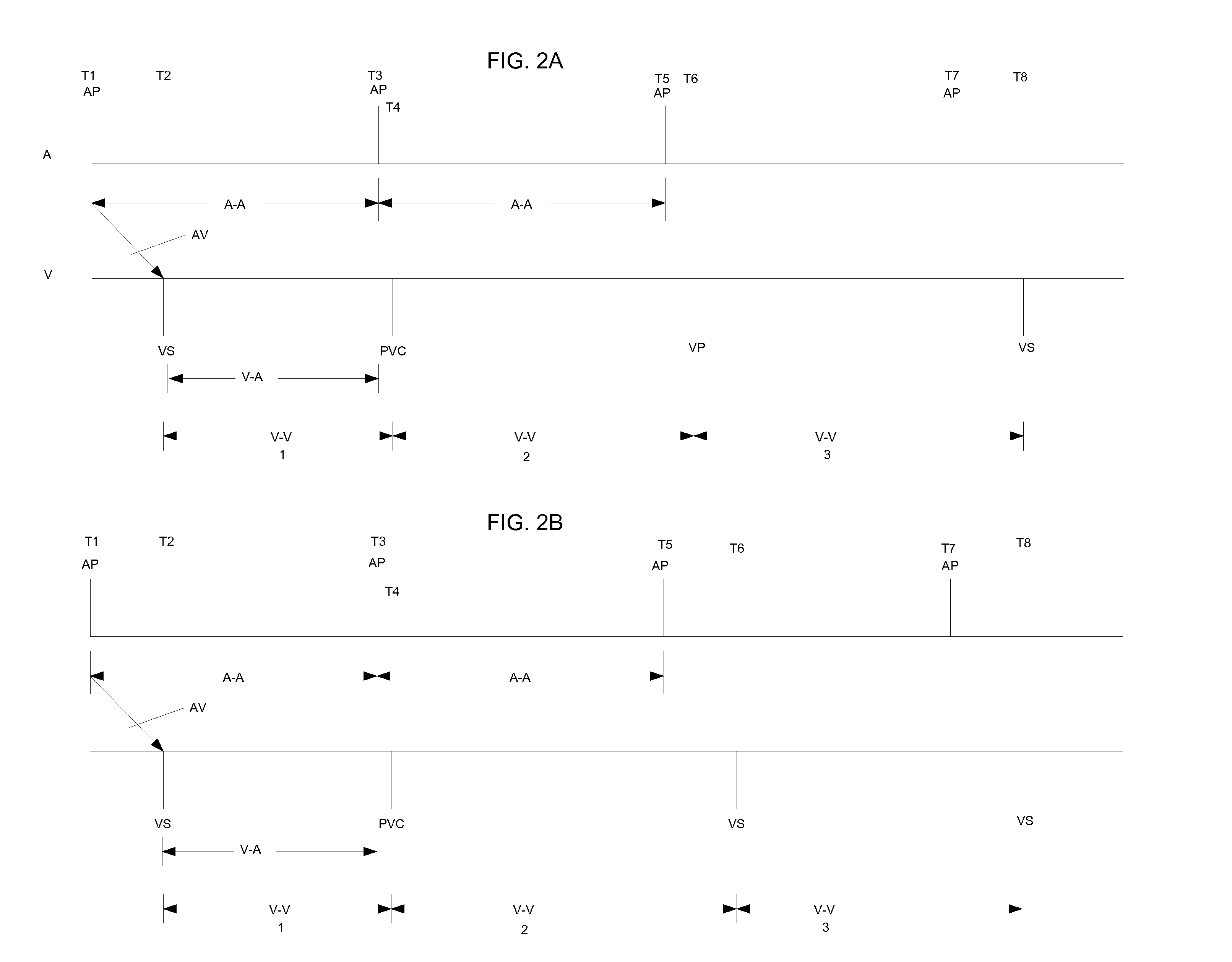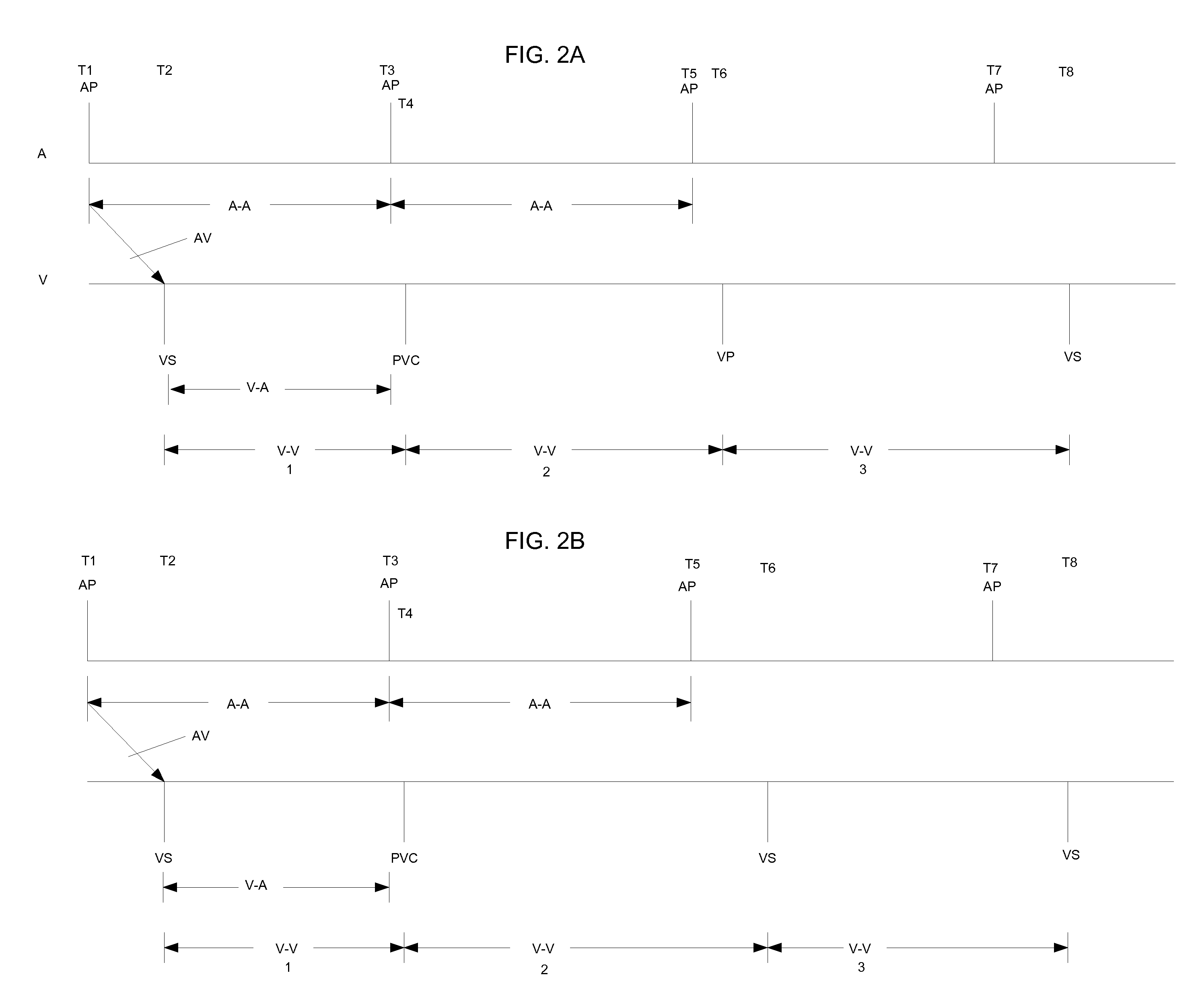Patents
Literature
54 results about "Av interval" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
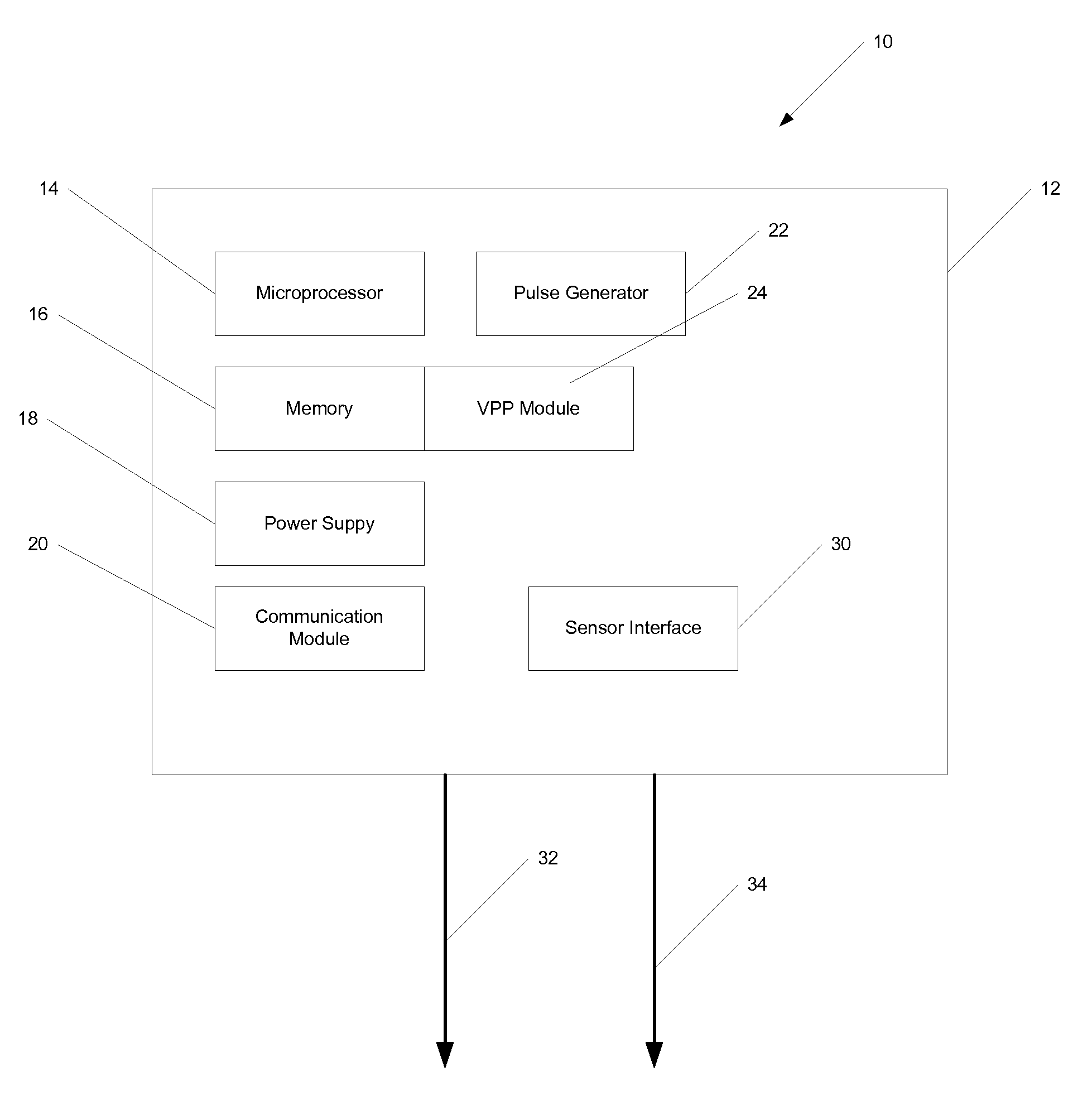
System and Method for Promoting Intrinsic Conduction Through Atrial Timing
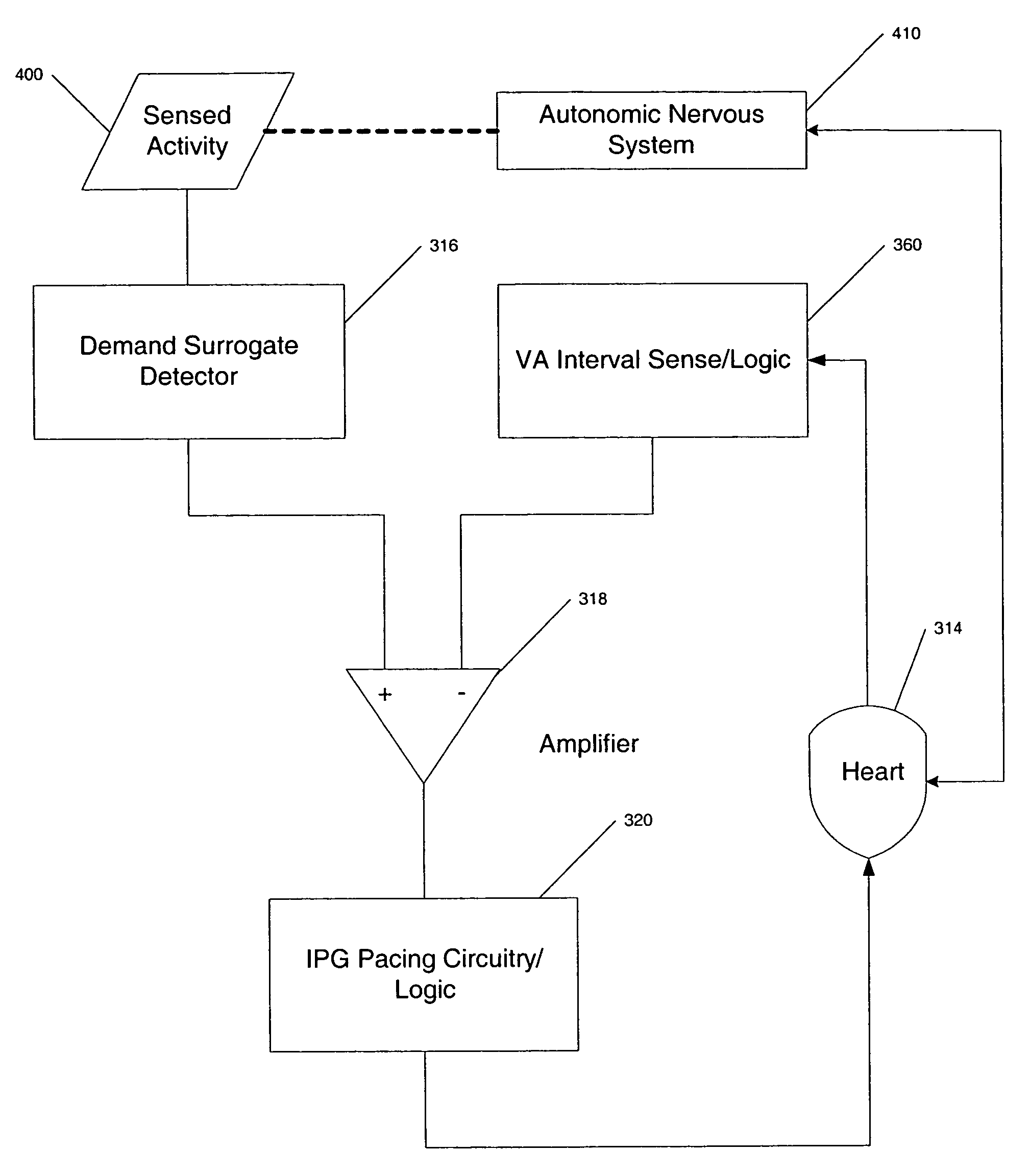
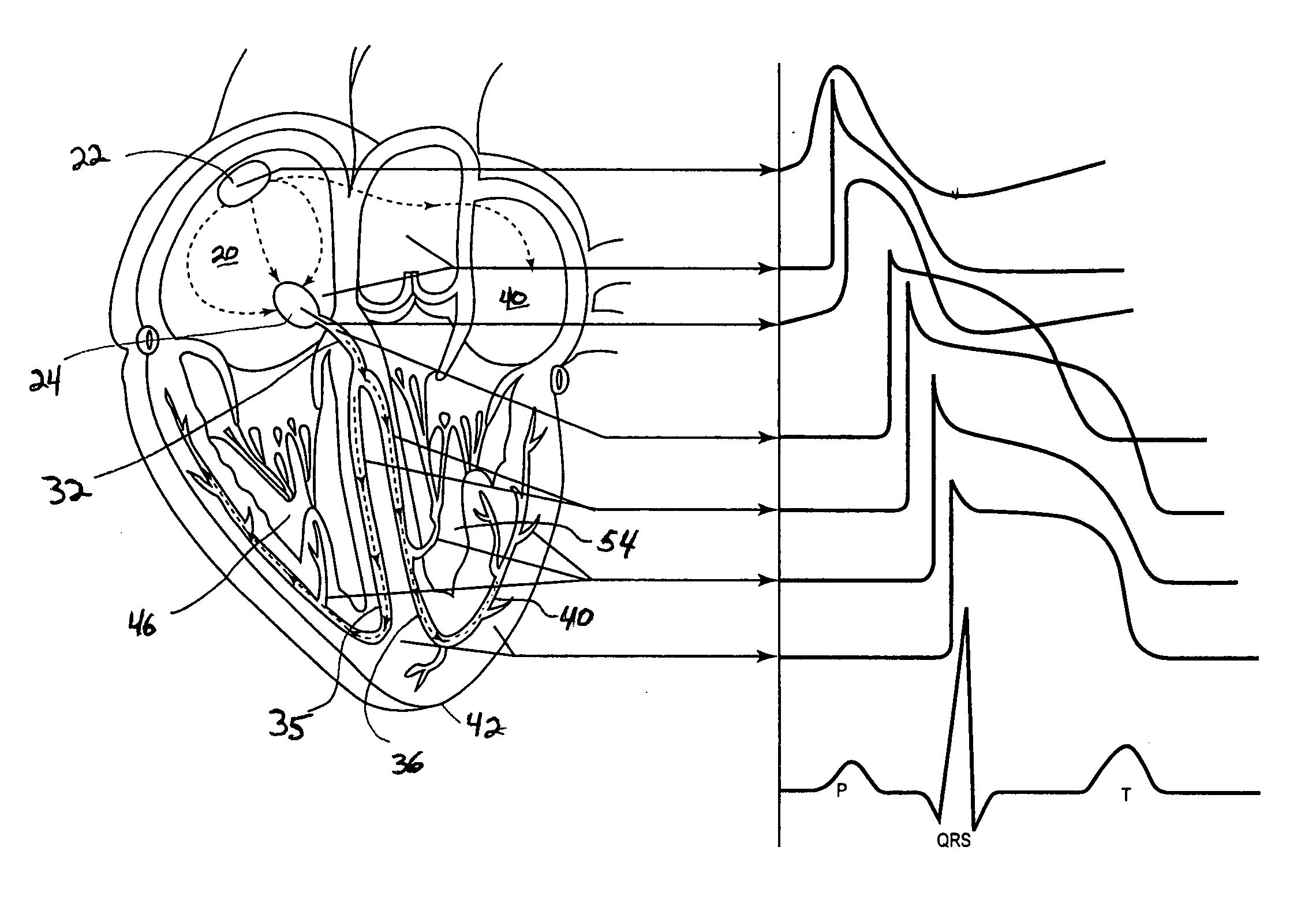
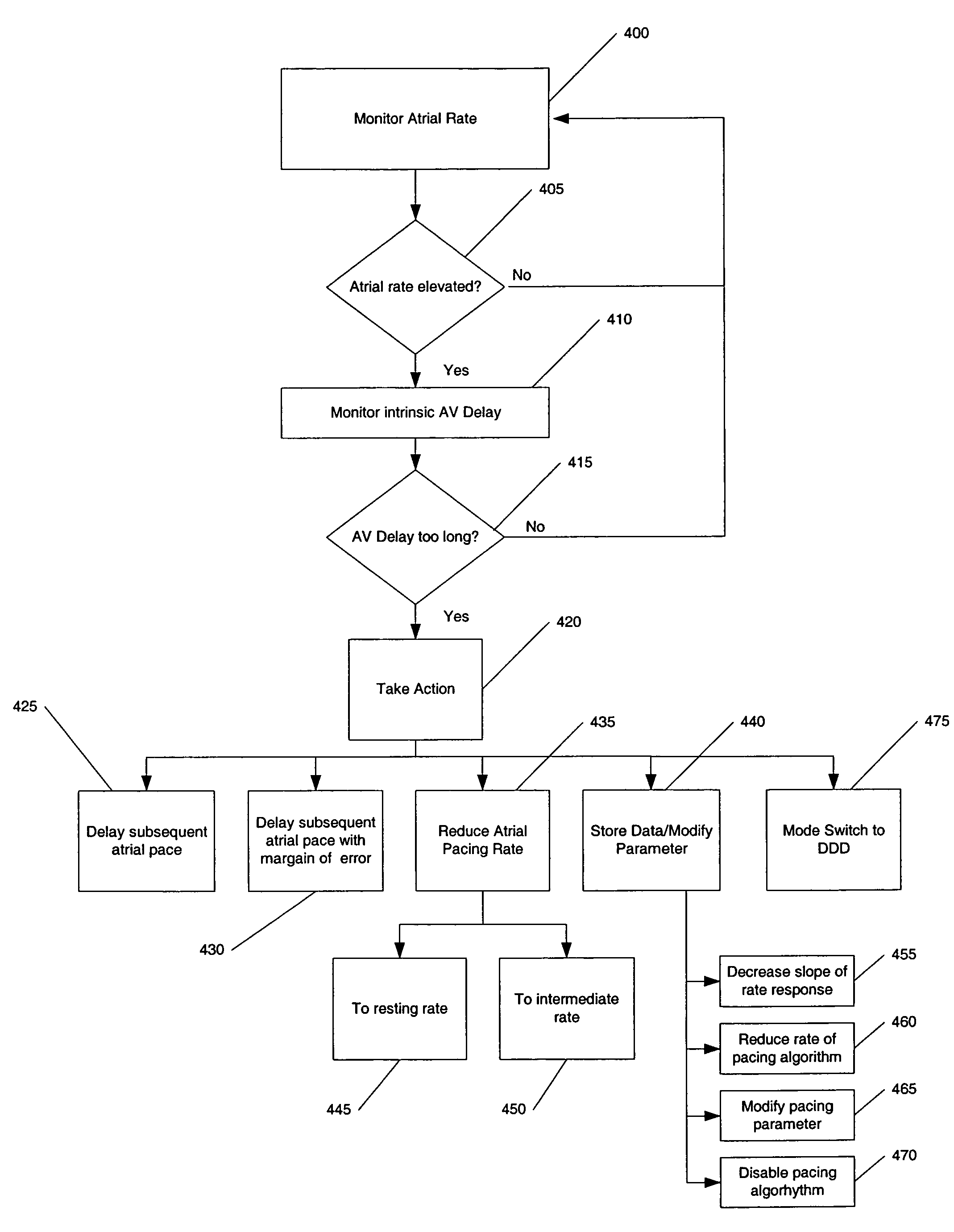
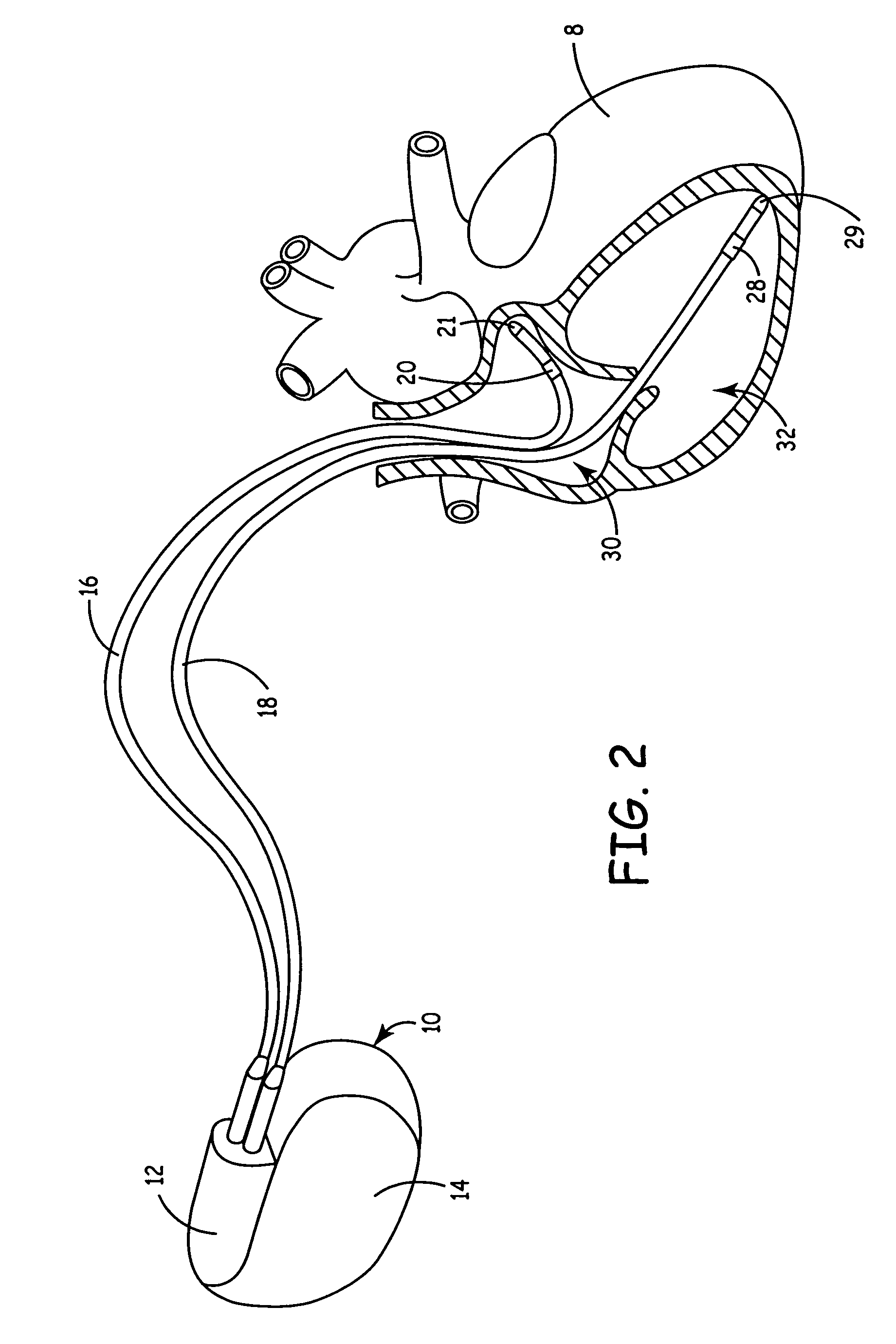
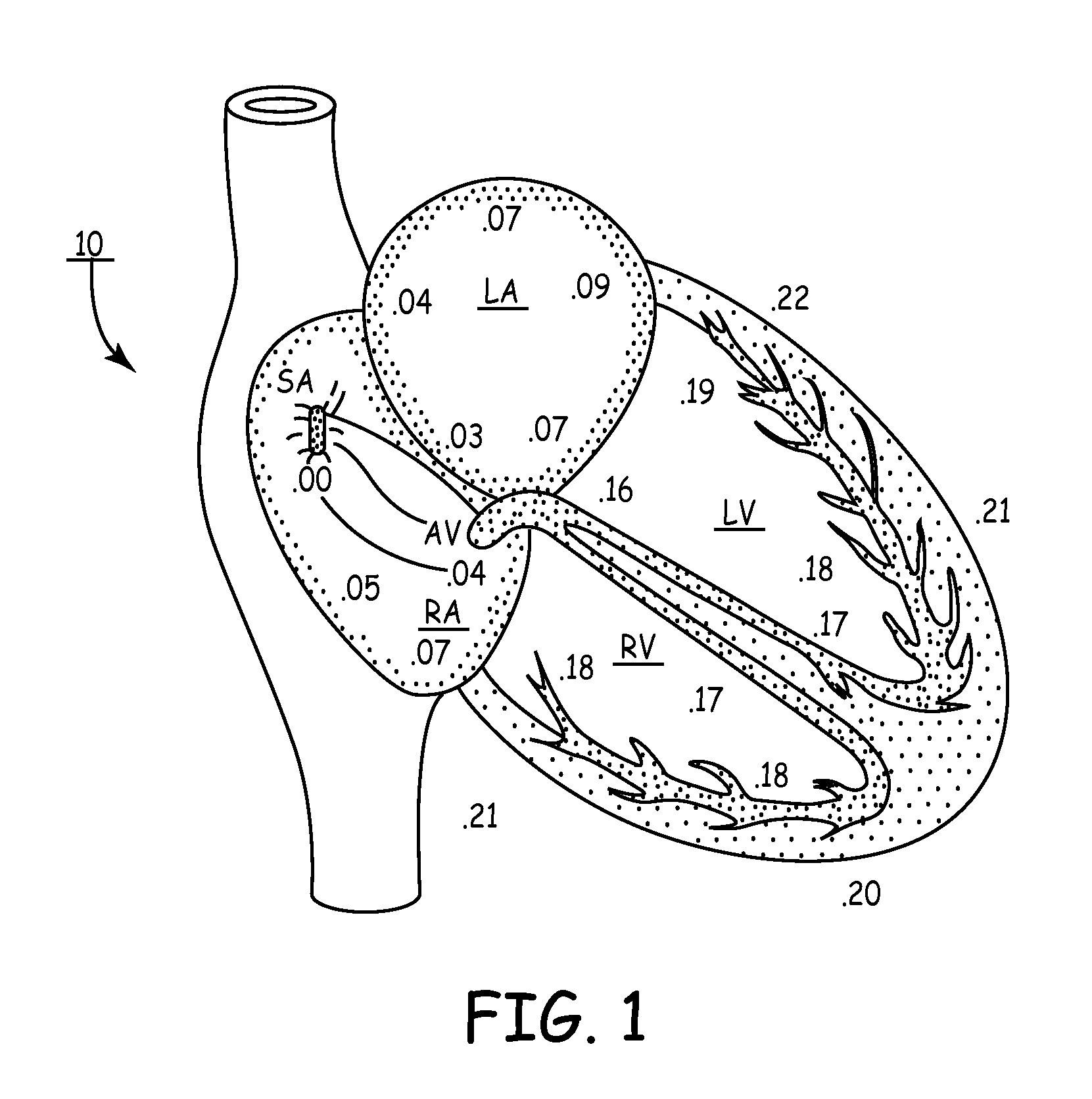
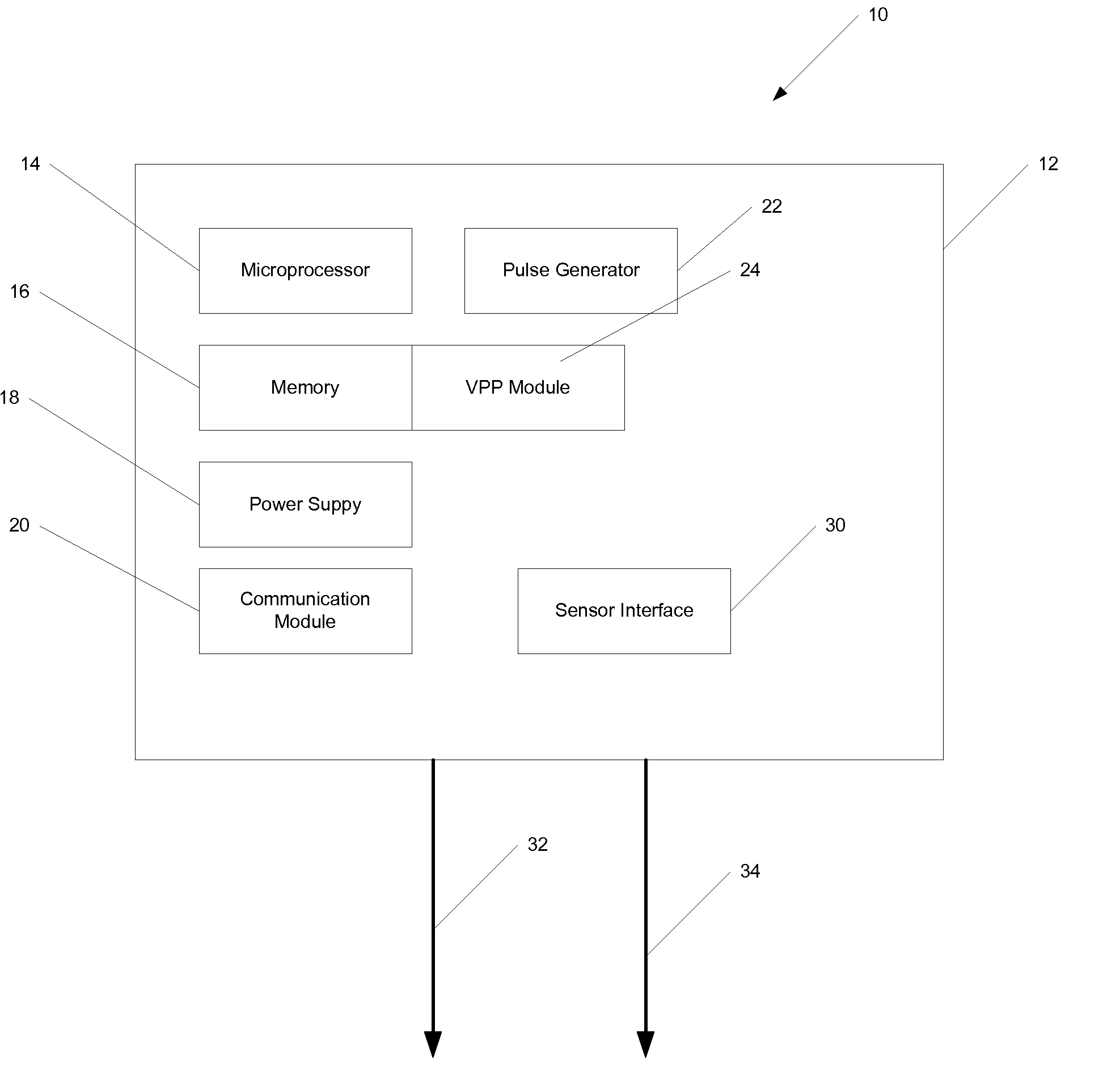
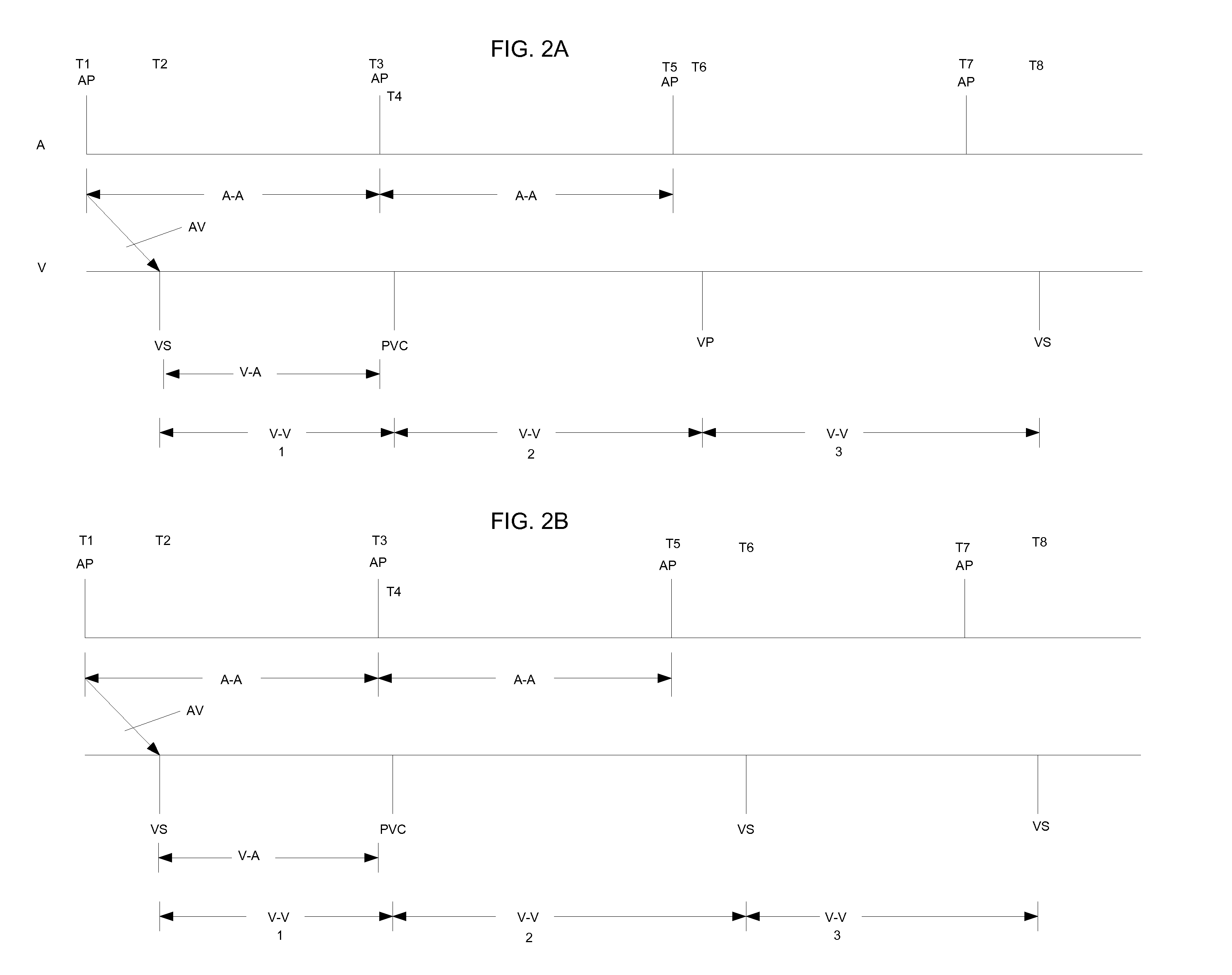
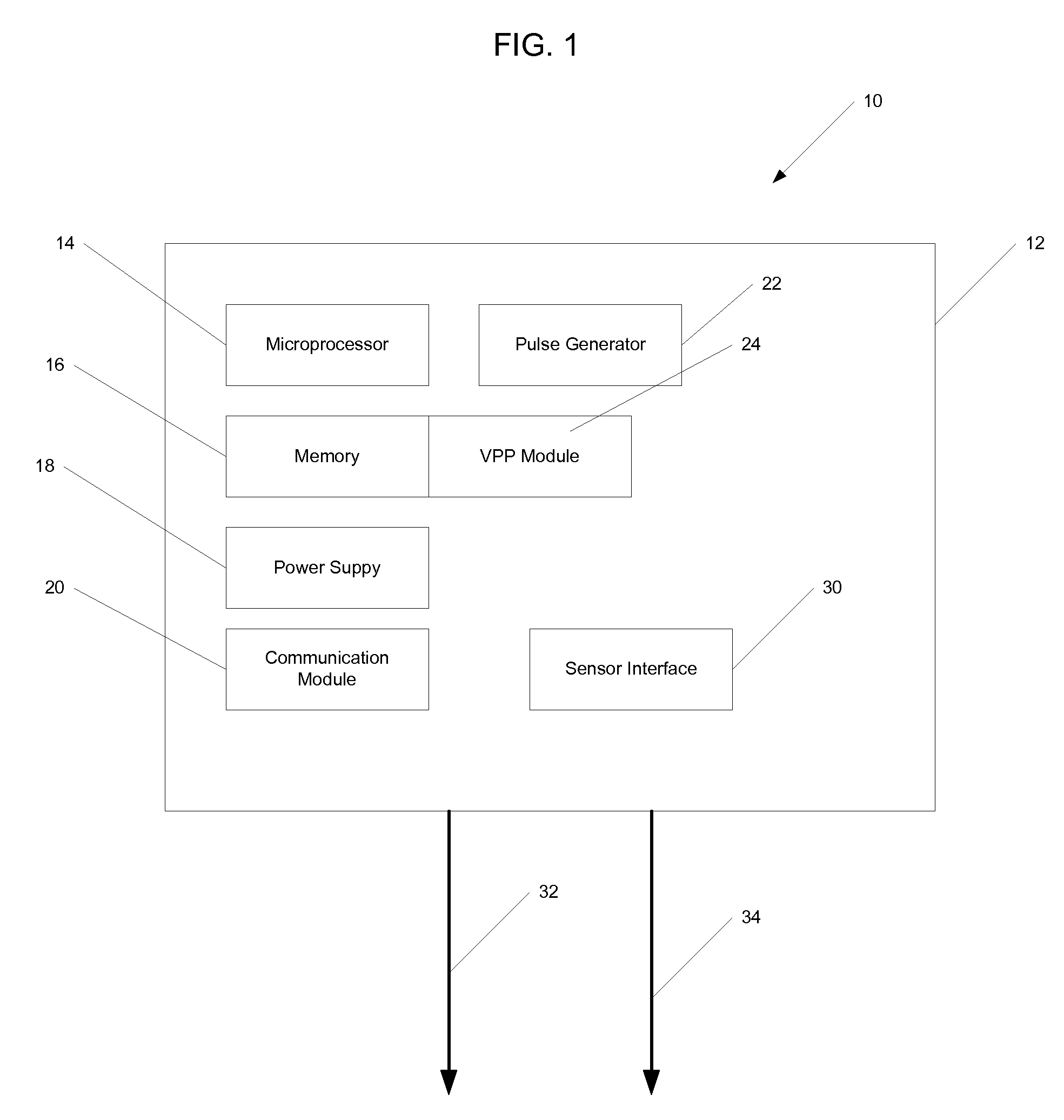
An atrial based pacing protocol promotes intrinsic conduction. An entire cardiac cycle is monitored for ventricular activity and permitted to lapse with ventricular activity. Ventricular pacing is available in a cardiac cycle immediately subsequent to such a skipped beat. When monitoring for intrinsic ventricular events, an event is expected within a given window. If no such event is detected, the cardiac cycle in truncated, leading to a shorter cycle that is devoid of ventricular activity. The subsequent cycle has a high likelihood of a ventricular sensed event and a greater than normal AV interval is provided prior to pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
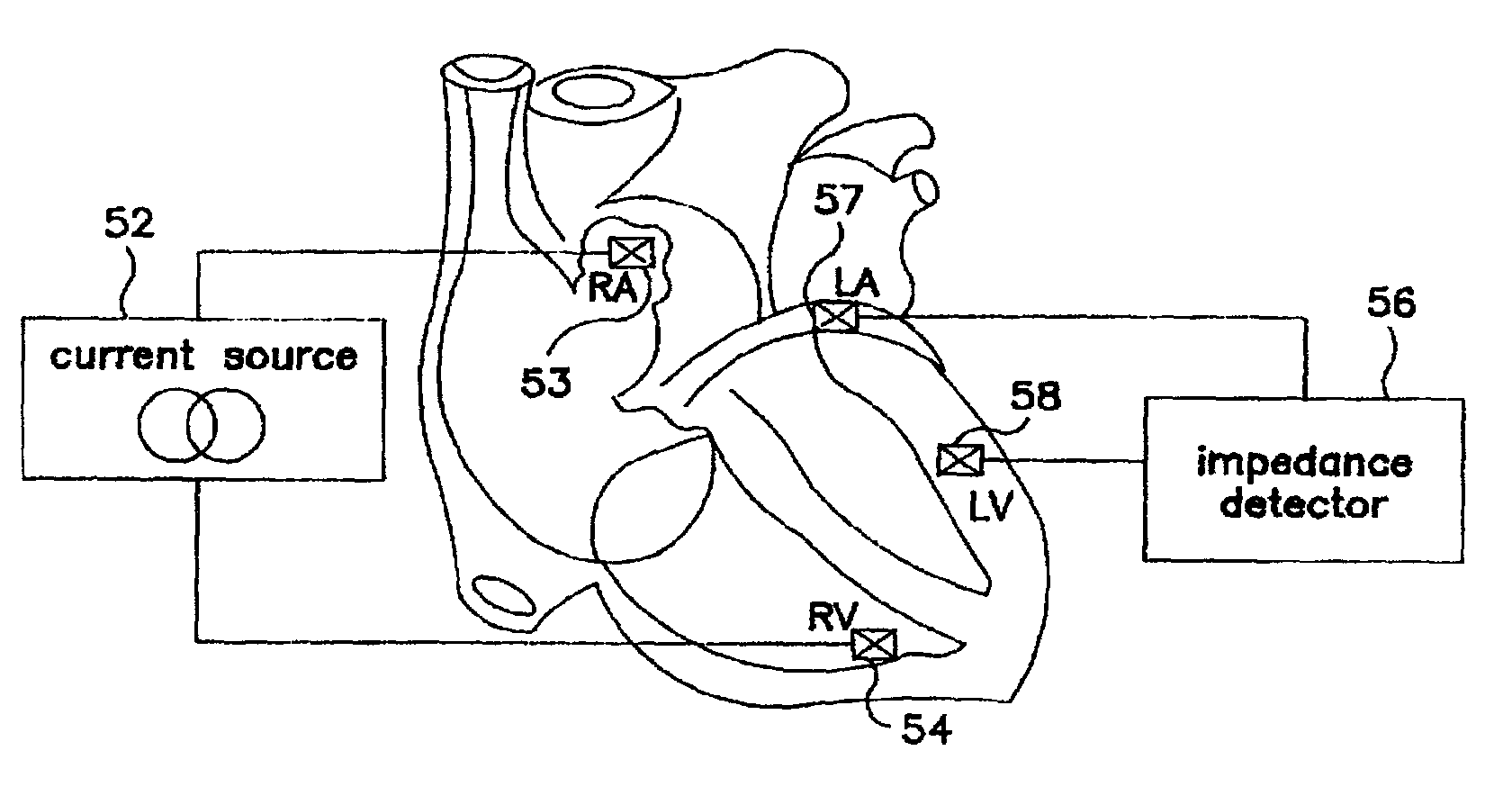
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal AV an VV intervals
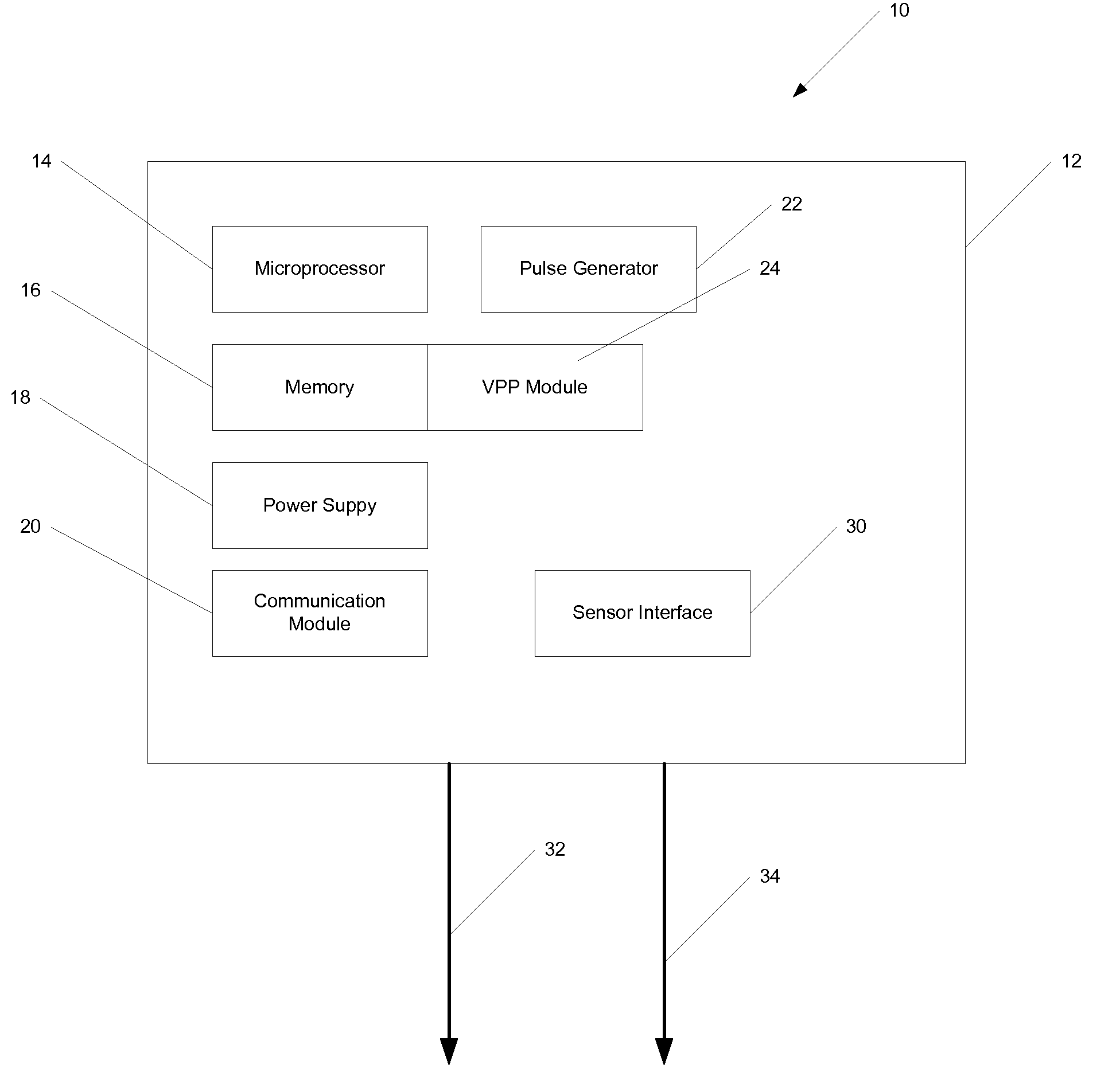
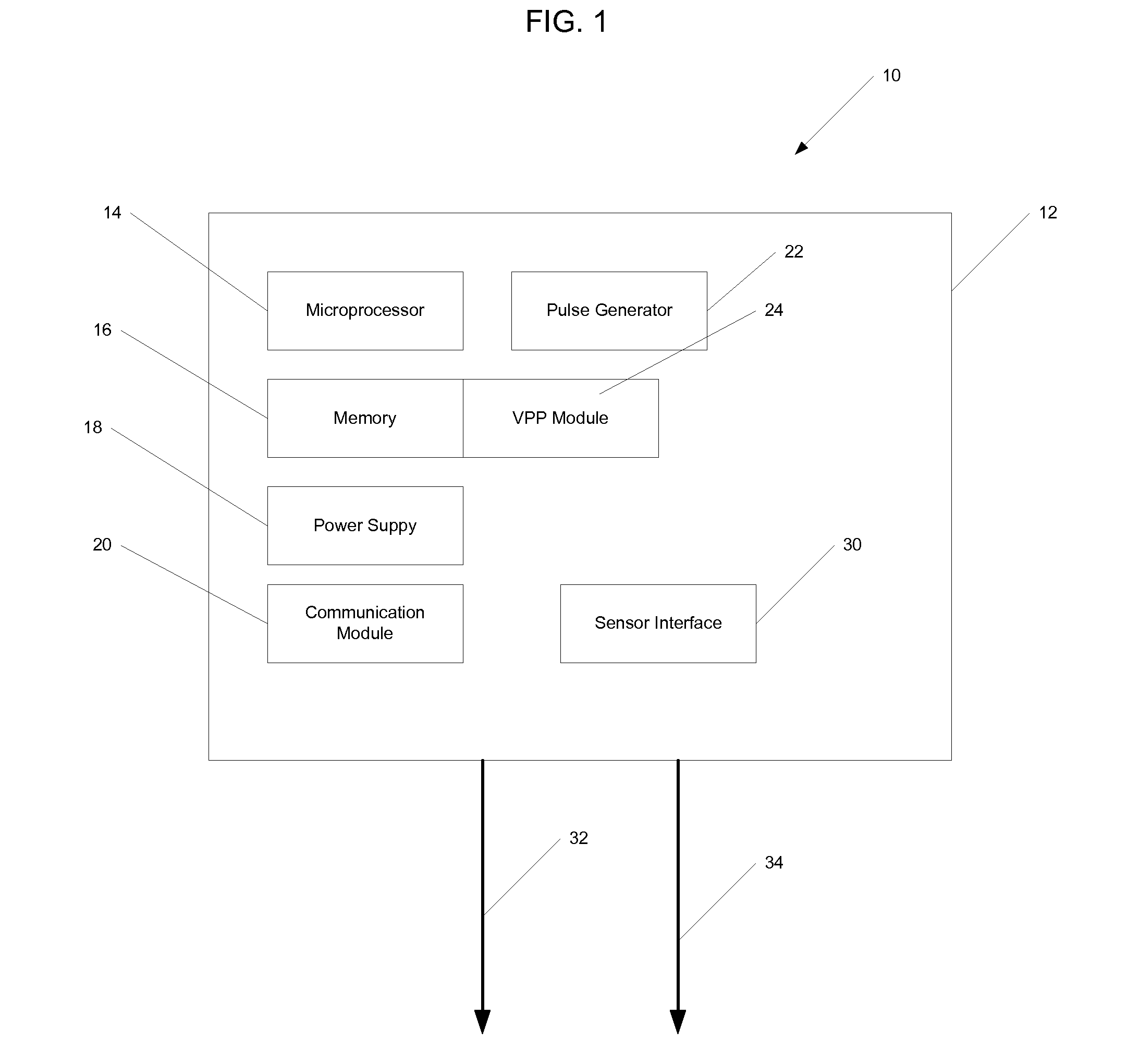
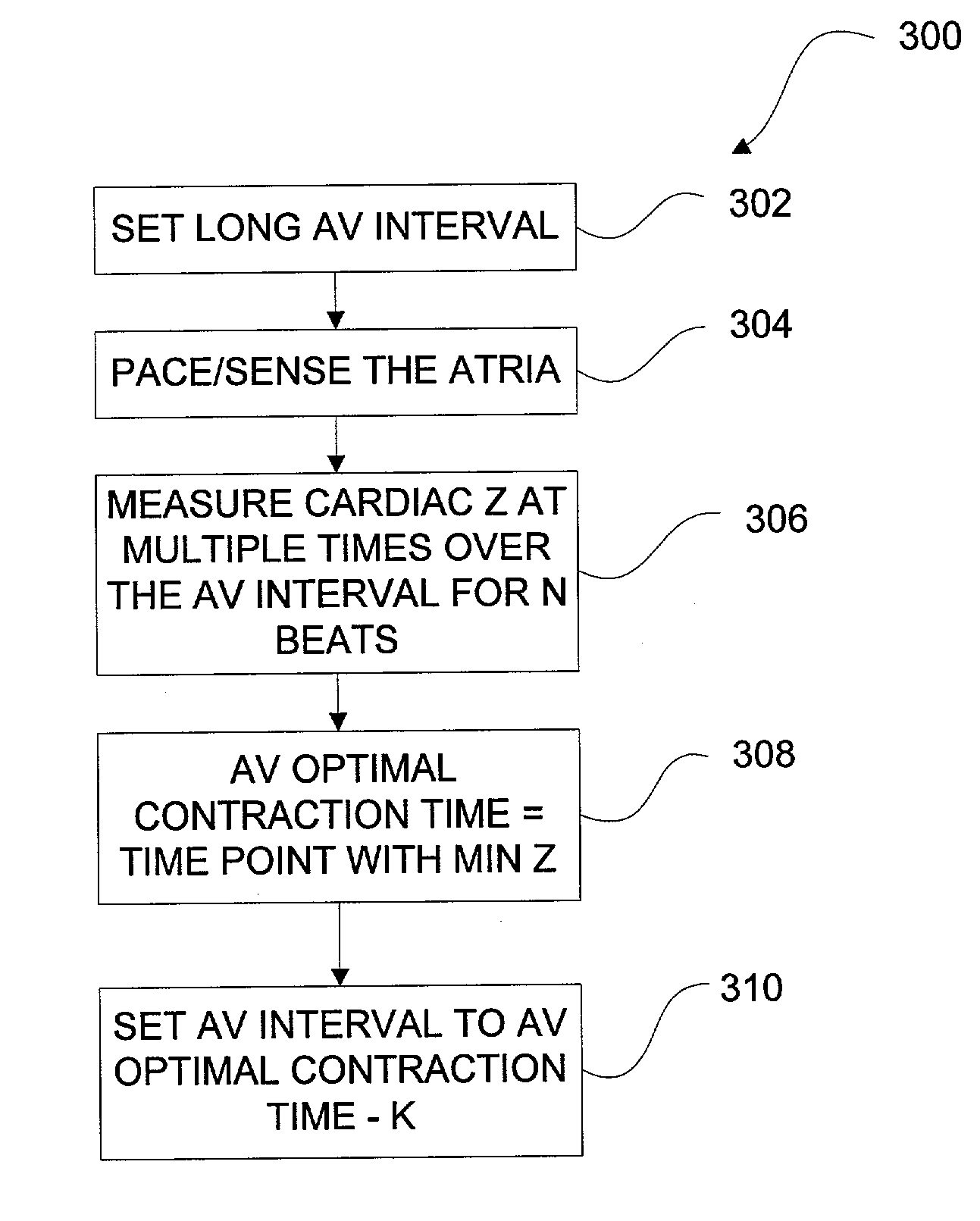
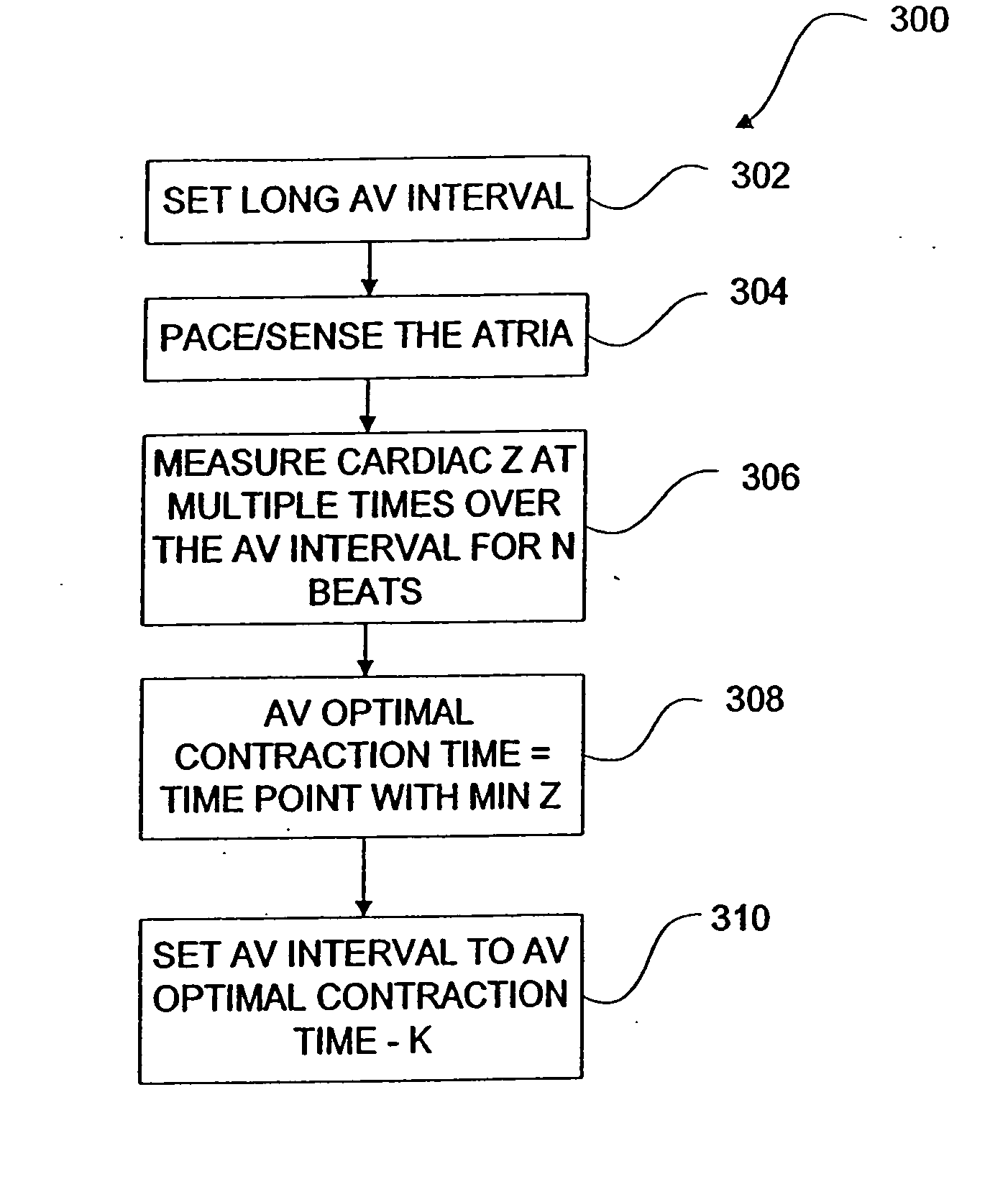
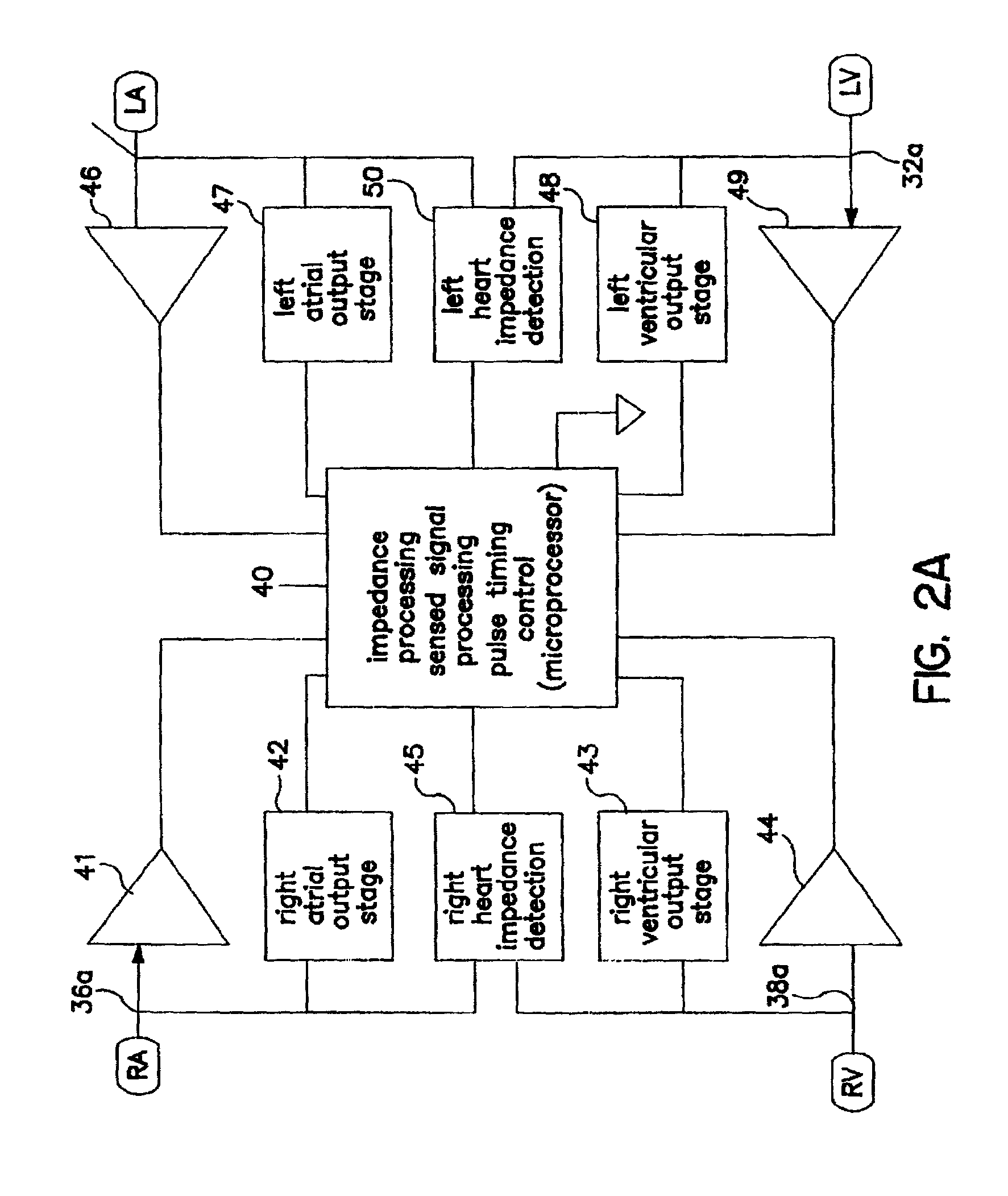
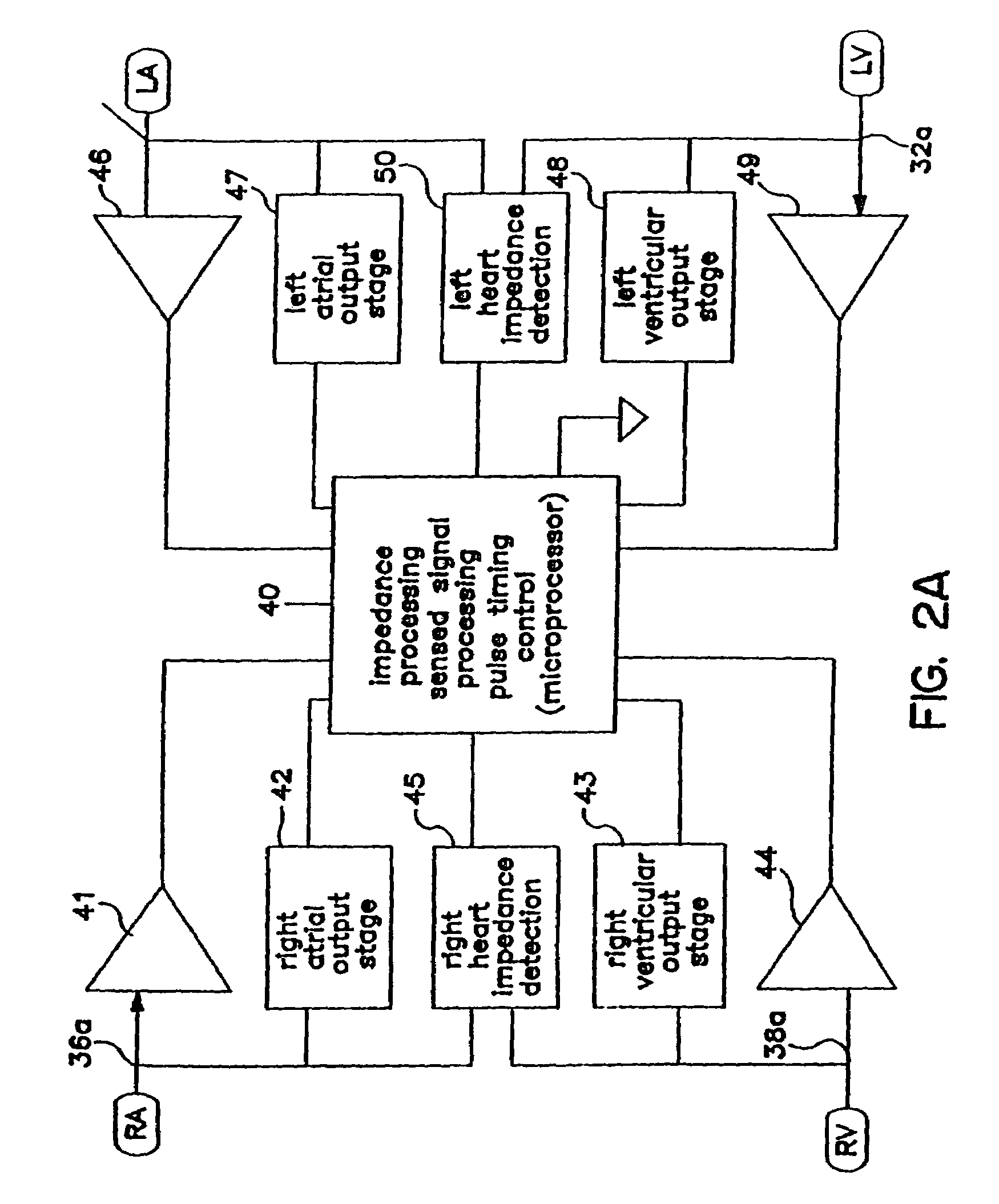
Methods and devices for determining optimal Atrial to Ventricular (AV) pacing intervals and Ventricular to Ventricular (VV) delay intervals in order to optimize cardiac output. Impedance, preferably sub-threshold impedance, is measured across the heart at selected cardiac cycle times as a measure of chamber expansion or contraction. One embodiment measures impedance over a long AV interval to obtain the minimum impedance, indicative of maximum ventricular expansion, in order to set the AV interval. Another embodiment measures impedance change over a cycle and varies the AV pace interval in a binary search to converge on the AV interval causing maximum impedance change indicative of maximum ventricular output. Another method varies the right ventricle to left ventricle (VV) interval to converge on an impedance maximum indicative of minimum cardiac volume at end systole. Another embodiment varies the VV interval to maximize impedance change.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
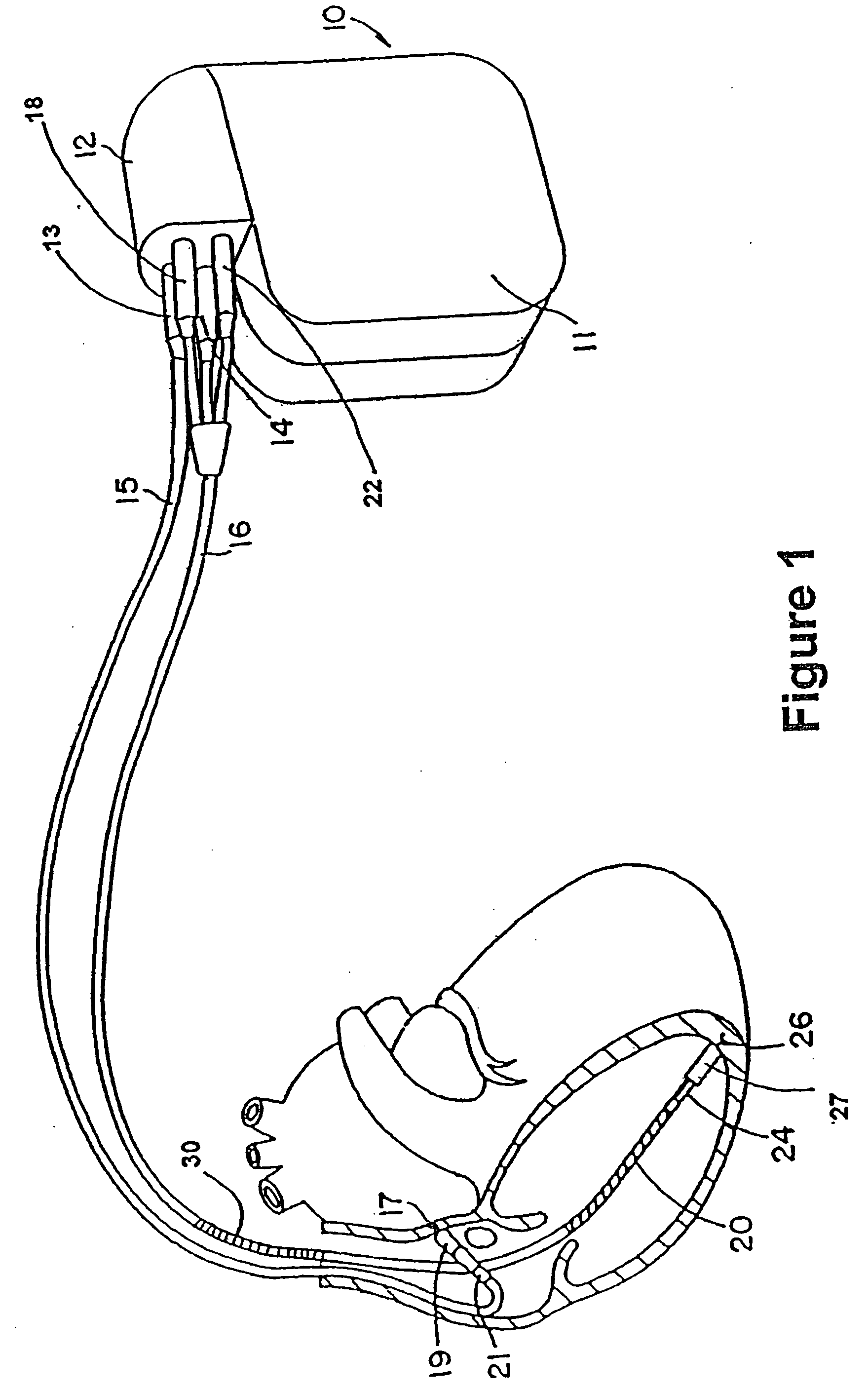
Cardiac stimulating device
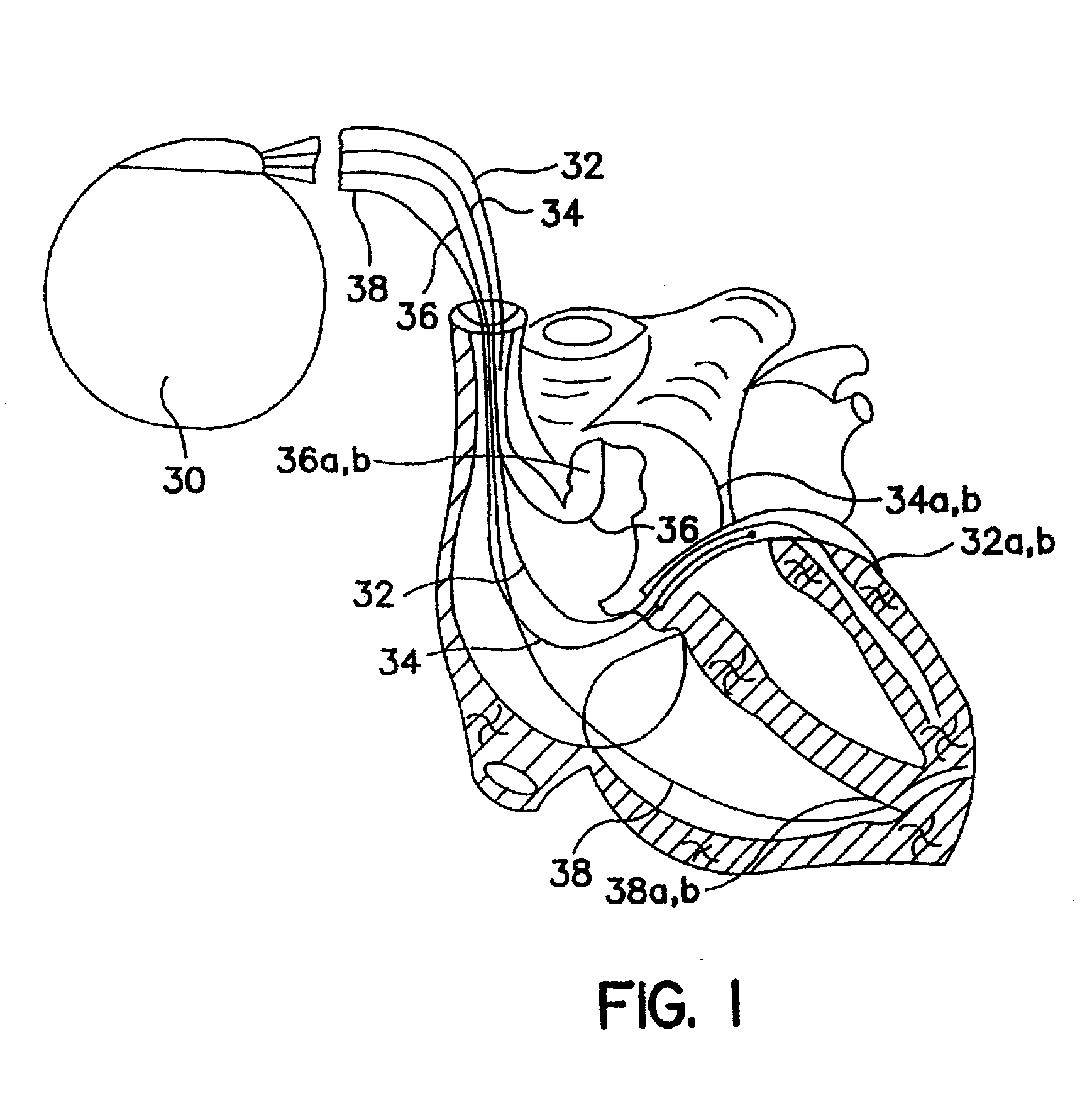
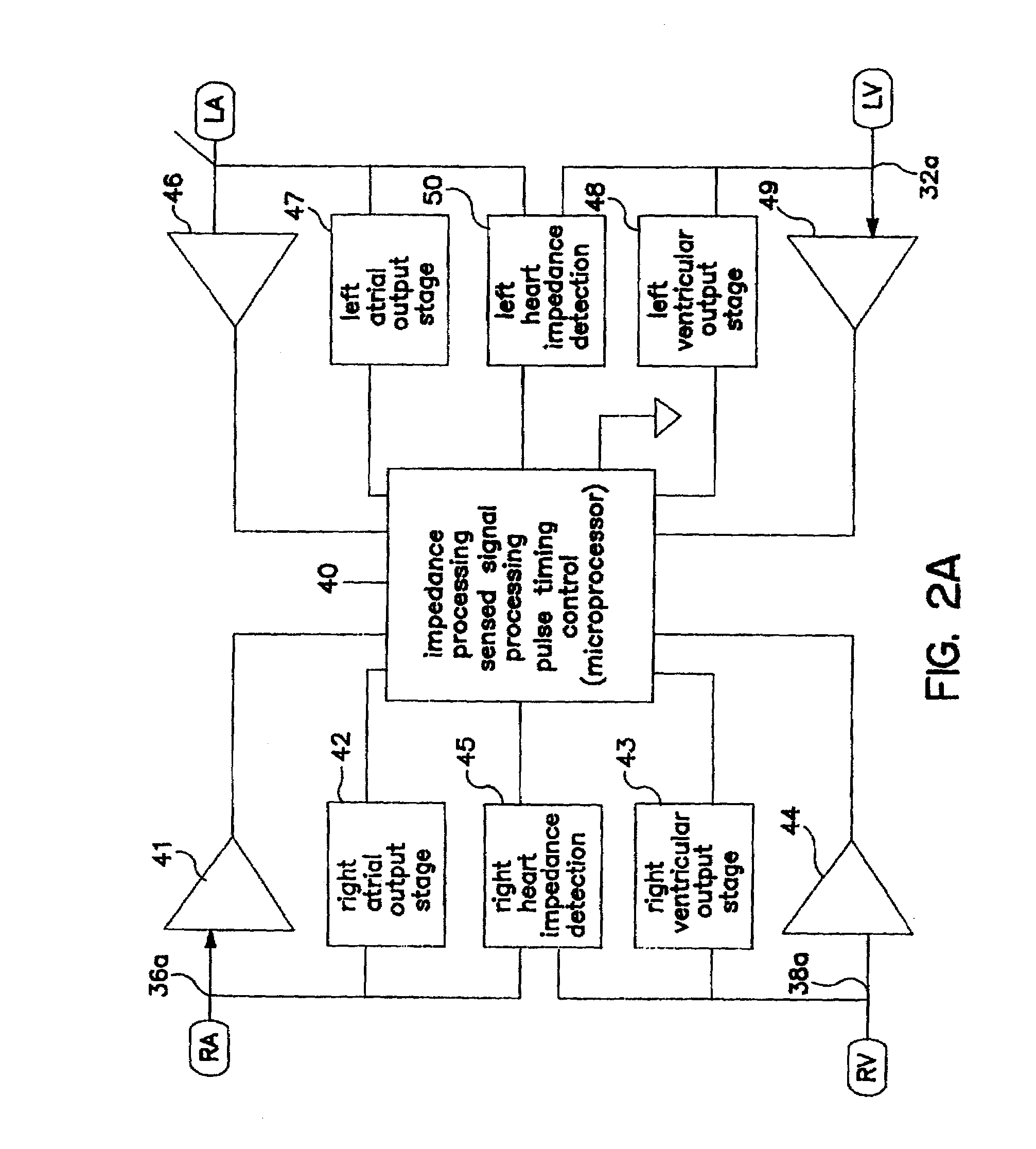
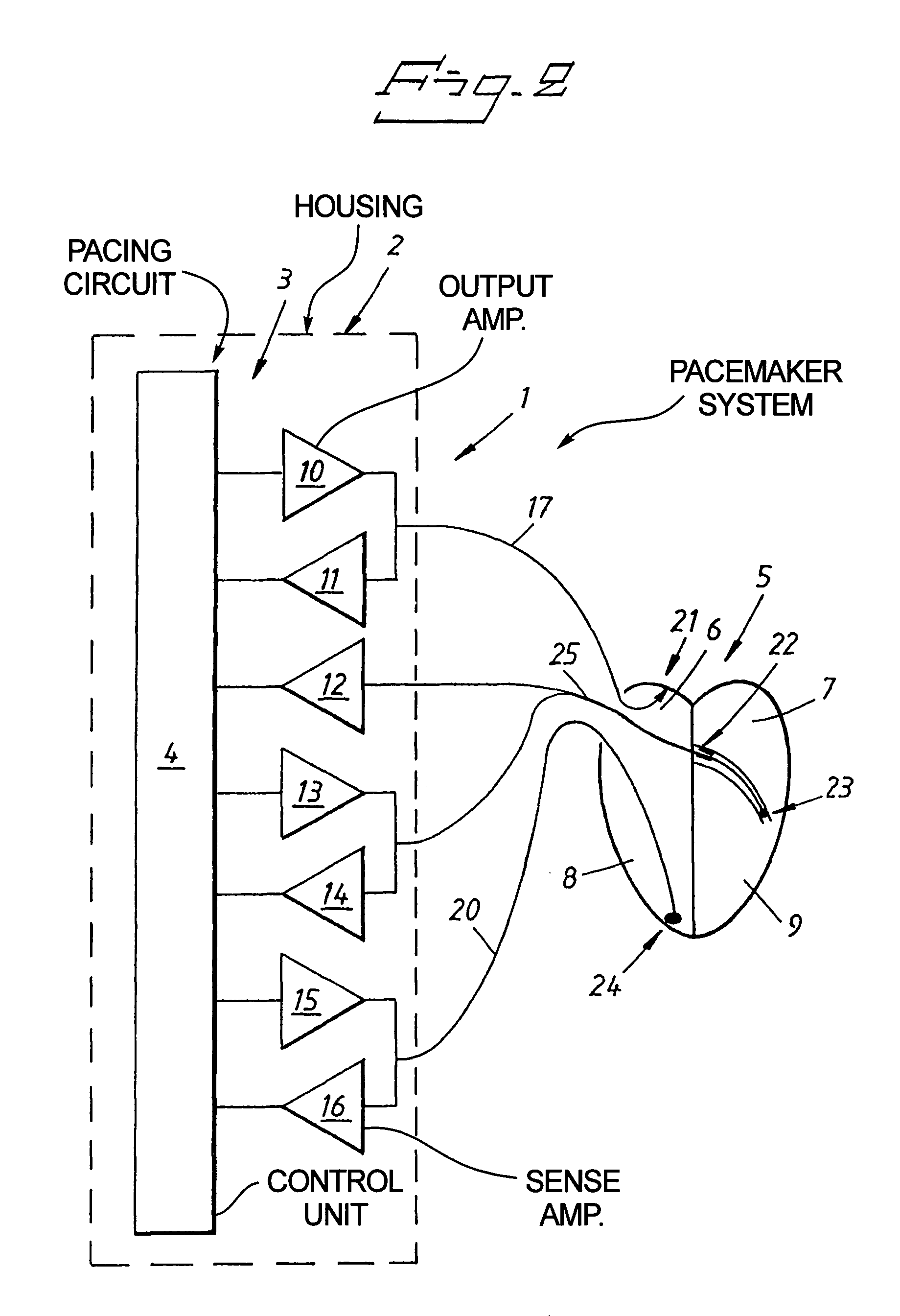
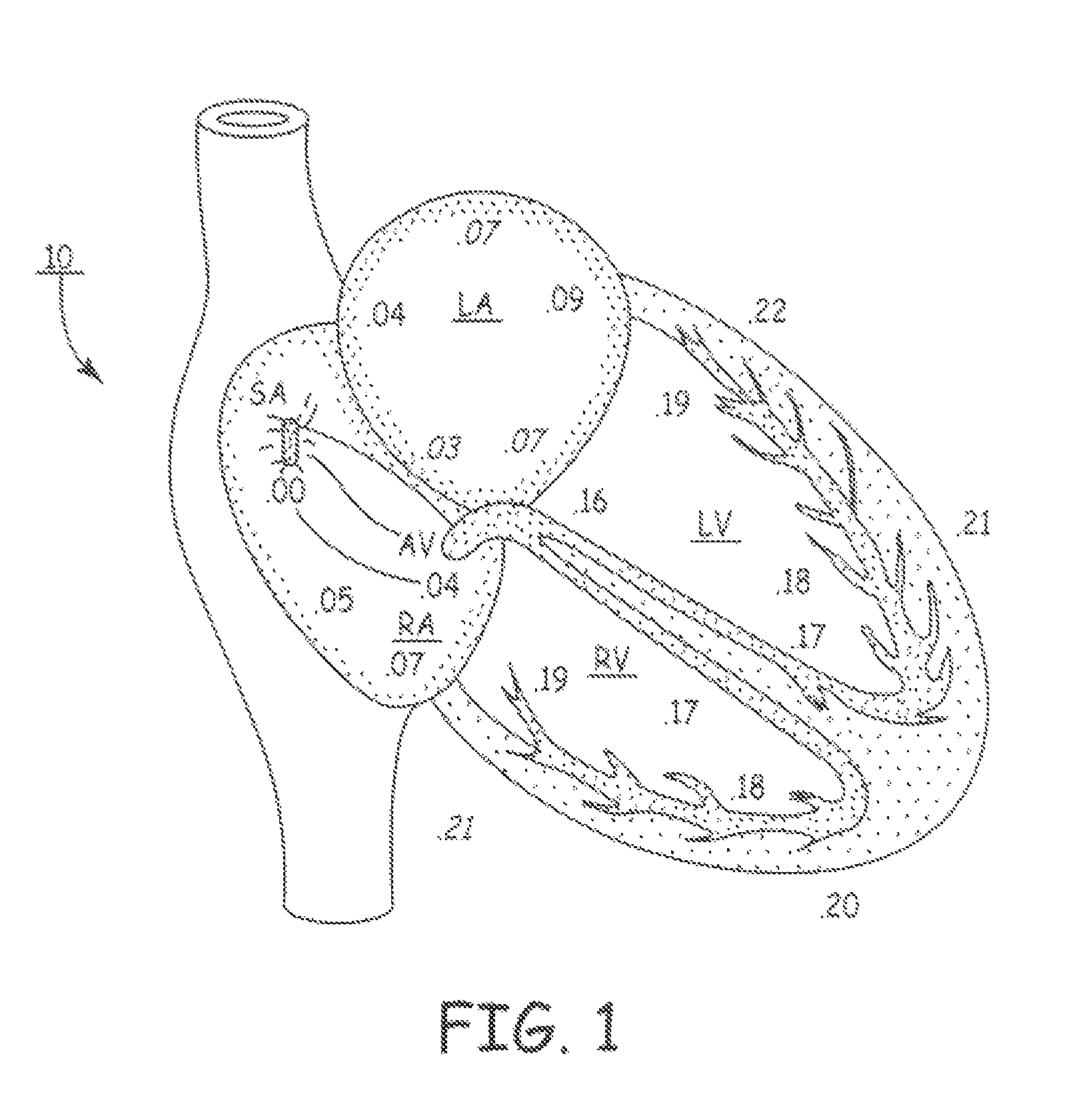
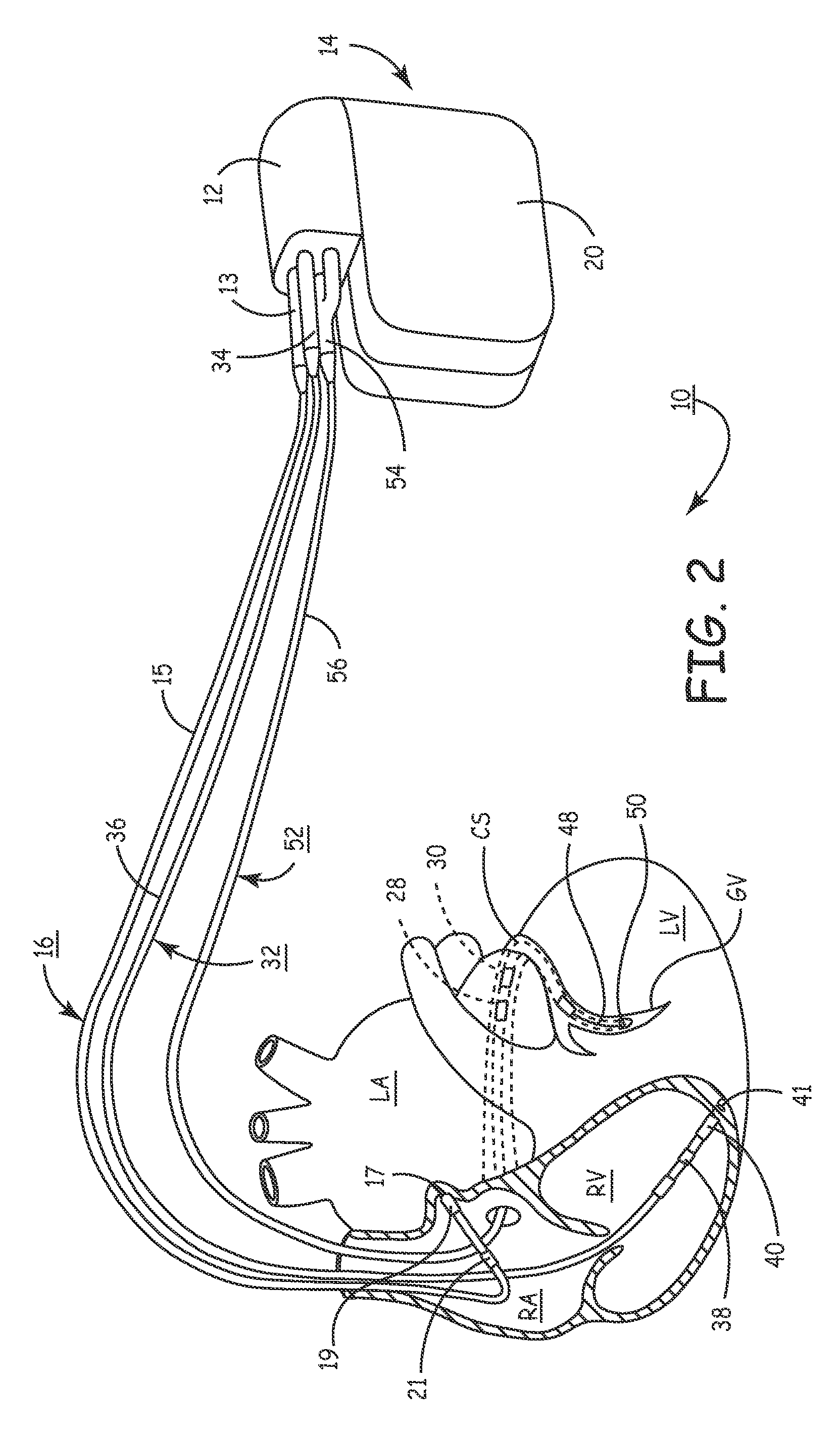
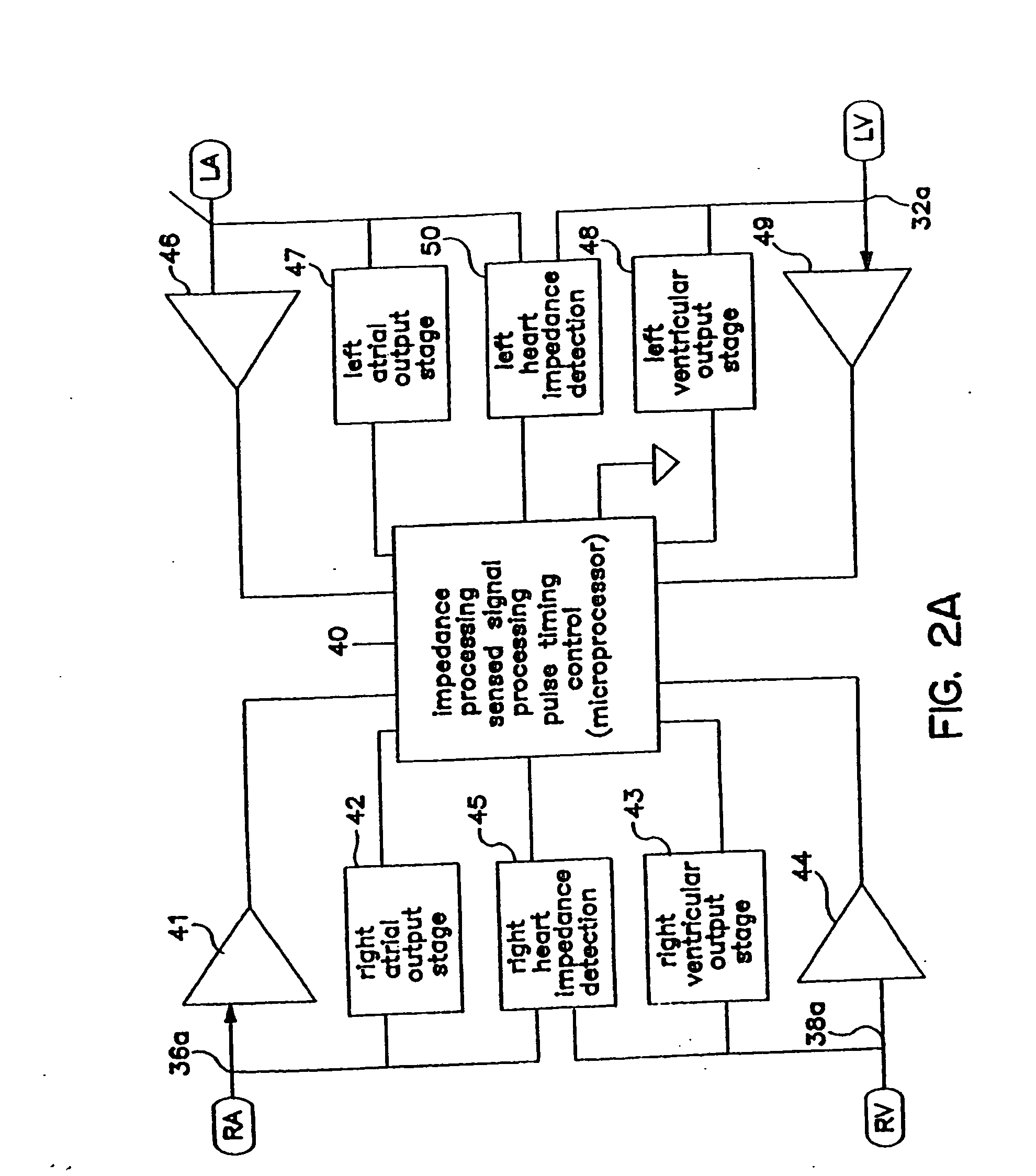
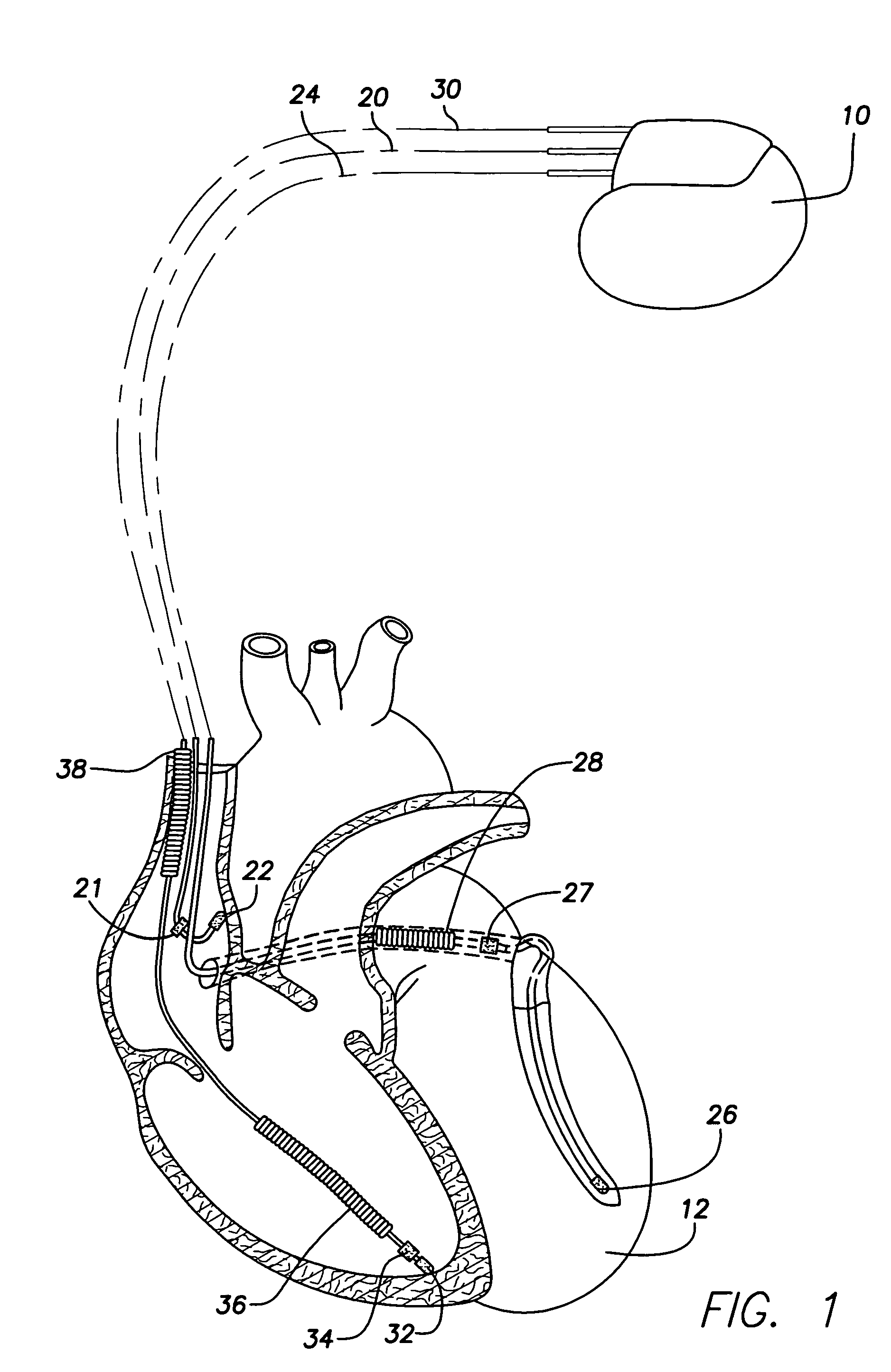
An implantable cardiac stimulating device has a pacing circuit connected via an electrode lead system to a first electrode which stimulates and detects activity in the left ventricle, a second electrode to stimulate and detect activity in the right atrium, and to a third electrode to detect activity in the left atrium. Upon the occurrence of a paced or sensed depolarization of the right atrium, a first AV-delay is started. When the subsequent left atrial depolarization is detected, a new AV-interval is started that is optimized for the left side of the heart. Either the left ventricle only, or both ventricles, is paced at the optimized left side AV-interval.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Optimization of AV intervals in single ventricle fusion pacing through electrogram morphology
ActiveUS20060235478A1Reduce the burden onReduce needHeart stimulatorsAv intervalUltrasonic cardiography
The present invention thus provides a simple and automatic method for determining an optimal AV interval and / or range of AV intervals for, in an exemplary embodiment, LV-only pacing. Such a method provides significant advantages for patients while reducing burdens related to post-implant follow-up by clinicians in that it greatly reduces the need for doing echocardiographic-based AV interval optimization procedures as well as providing a way to dynamically optimize AV intervals as the patient moves about their activities of daily living (ADL).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Self limited rate response
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Optimization of AV intervals in single ventricle fusion pacing through electrogram morphology
ActiveUS8214041B2Reduced magnitudeReduce frequencyHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationPR intervalAv interval
This document provides a simple and automatic method for determining an optimal AV interval and / or range of AV intervals for, in an exemplary embodiment, LV-only pacing. Such a method provides significant advantages for patients while reducing burdens related to post-implant follow-up by clinicians in that it greatly reduces the need for doing echocardiographic-based AV interval optimization procedures as well as providing a way to dynamically optimize AV intervals as the patient moves about their activities of daily living (ADL).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
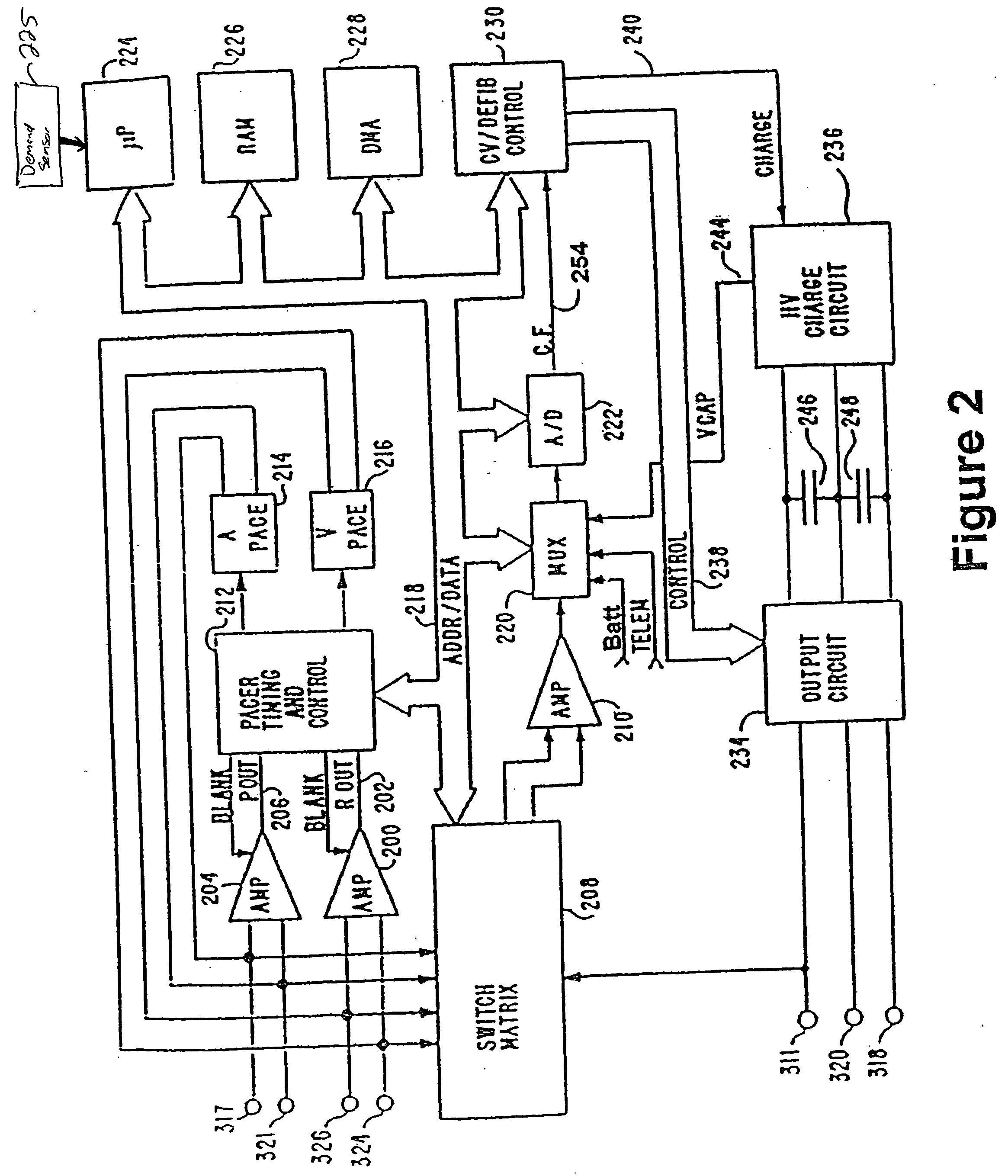
Dual chamber heart stimulator with evoked response detector
InactiveUS7020522B1The method is simple and reliableSimple and reliable processHeart stimulatorsFusion beatCardiac cycle
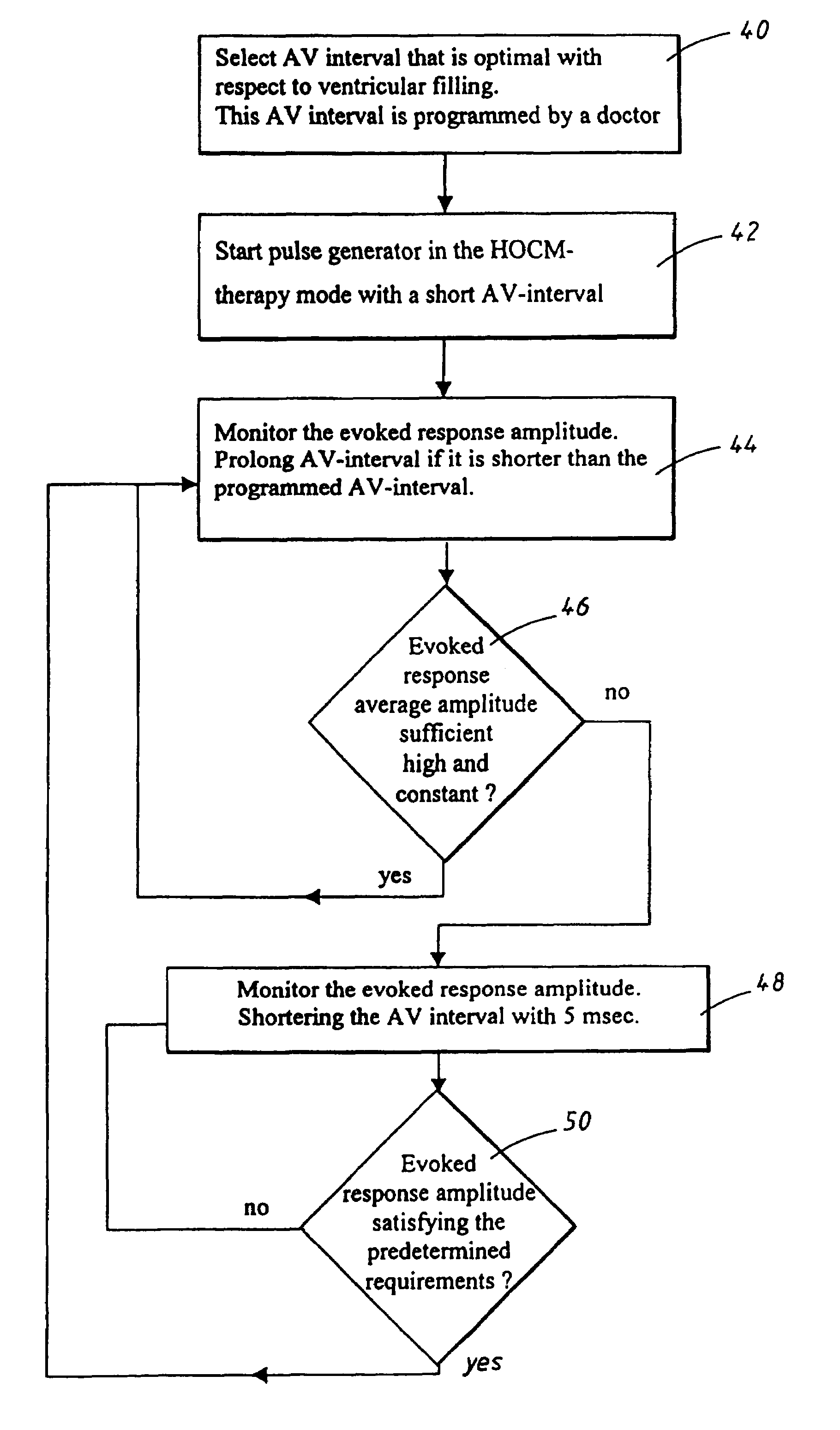
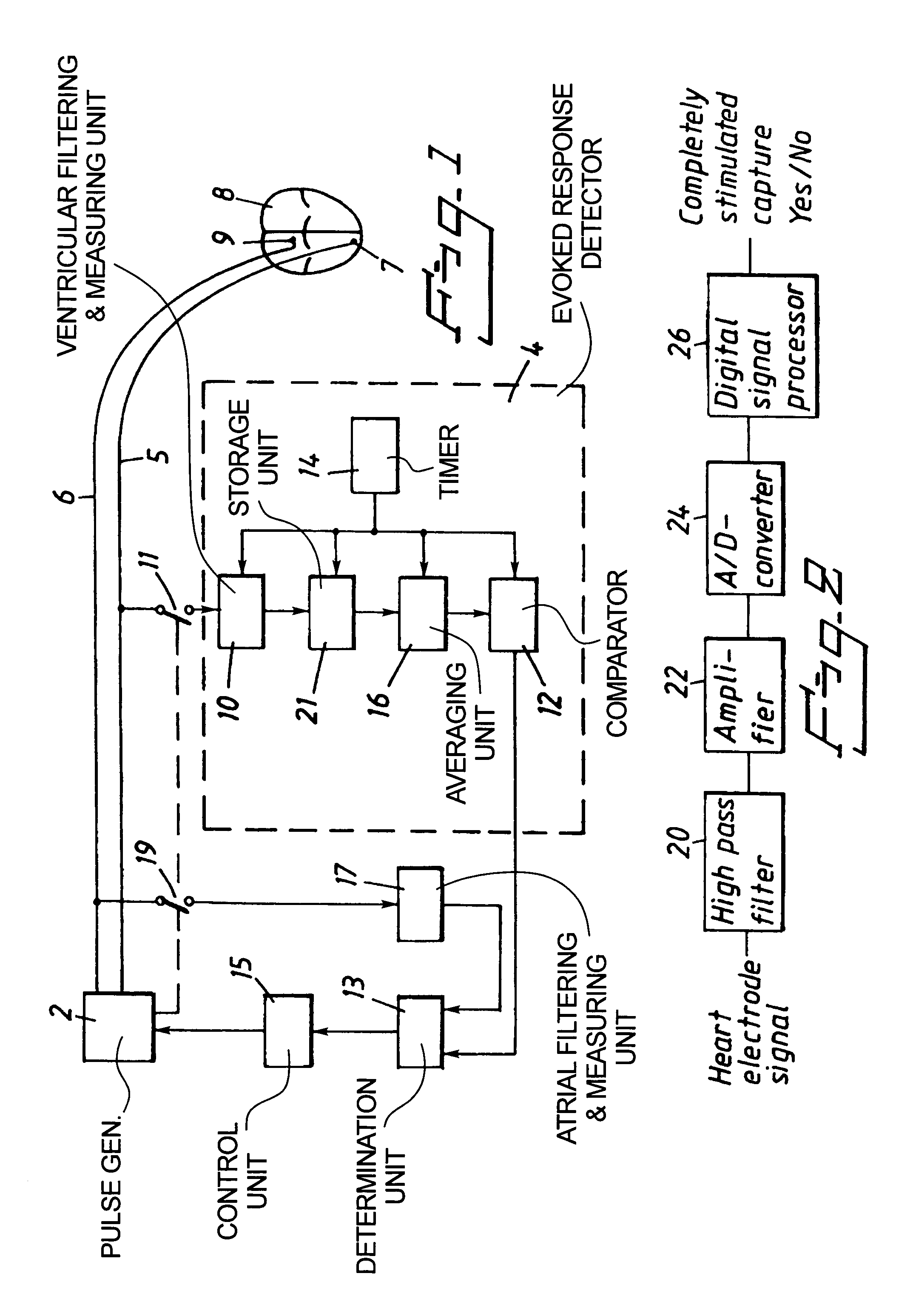
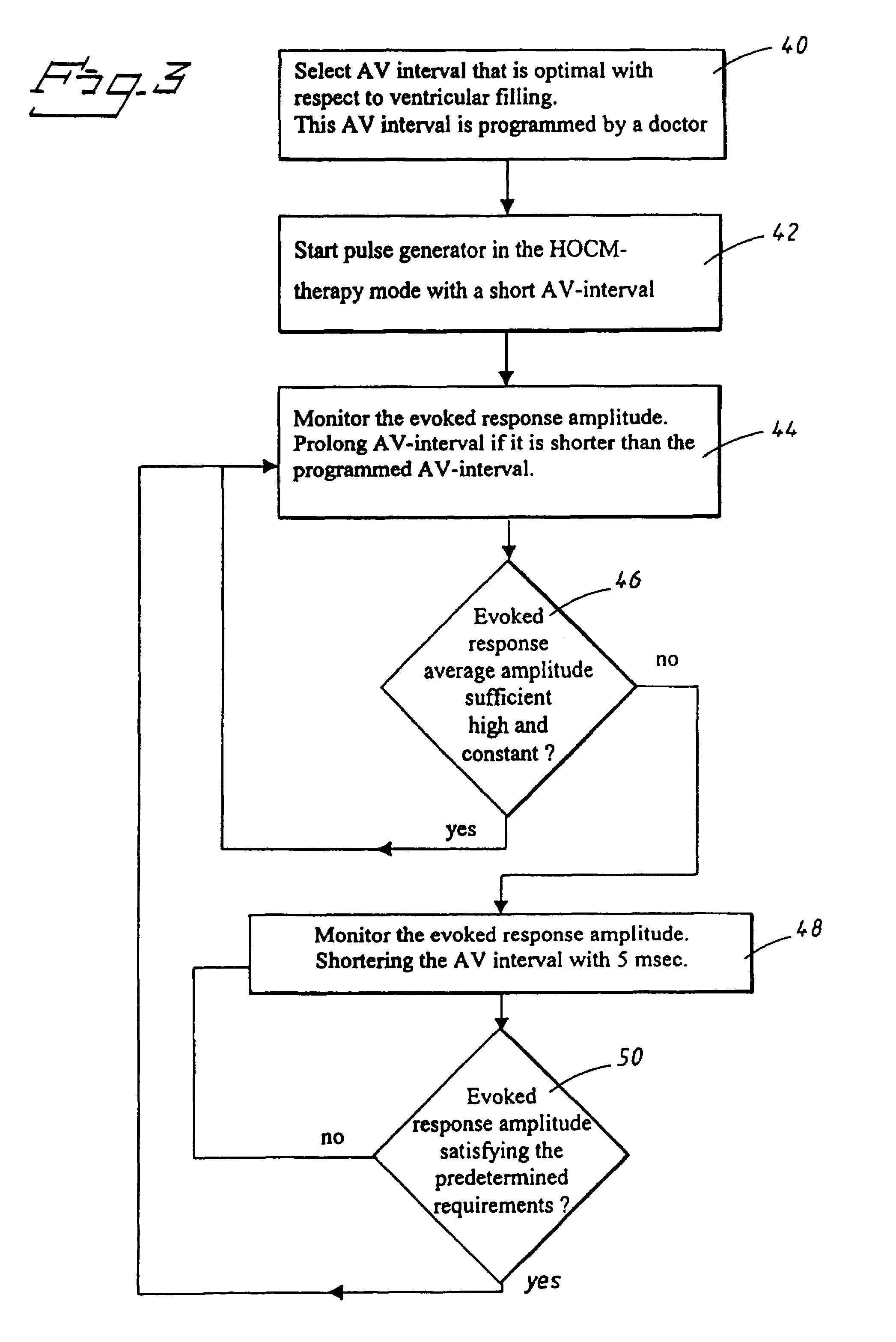
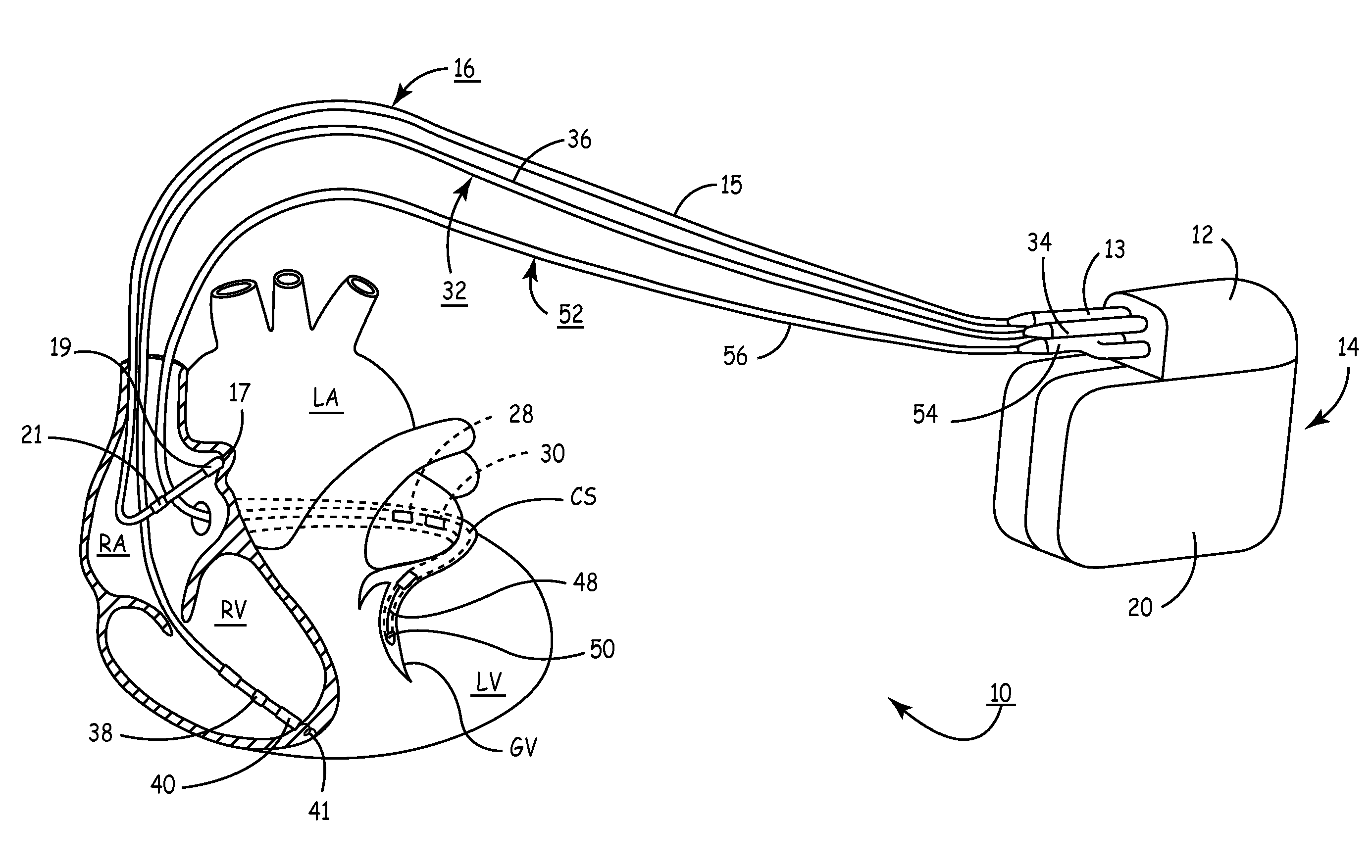
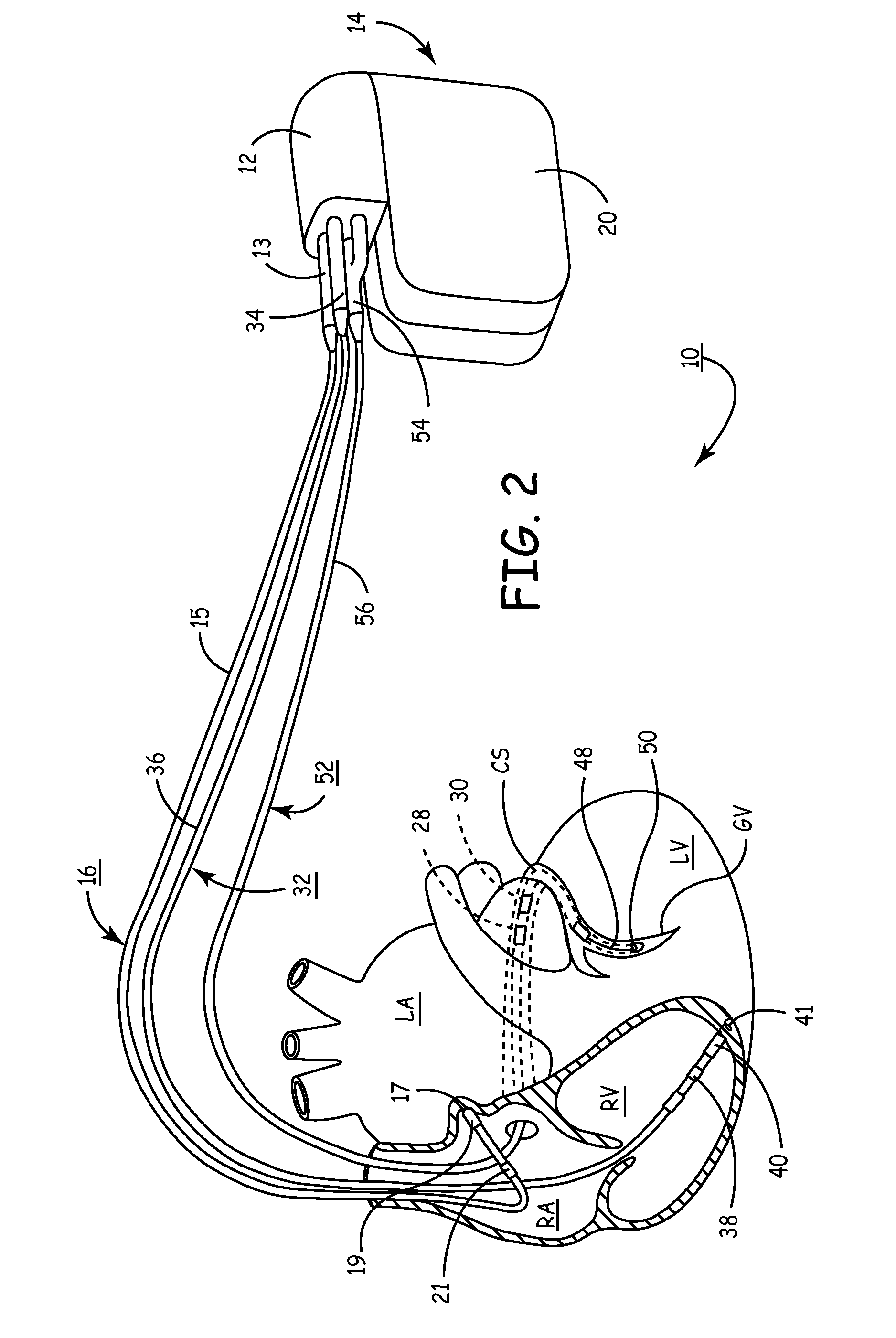
A heart stimulator has an atrial and ventricular pulse generator for producing atrial and ventricular stimulation pulses, an atrial sensor for sensing atrial signals and an evoked response detector for detecting the occurrence of incipient fusion beats from measured ventricular signals. A determination unit determines an incipient fusion AV-interval from the sensed atrial signals and the detected fusion beats, and a controller controls the pulse generator to deliver stimulation pulses at a controlled AV-interval which is shorter than the incipient fusion AV-interval. The evoked response detector includes an averaging unit which forms an average amplitude value of the measured ventricular signals during a predetermined time window of each cardiac cycle, and a comparator which compares the average value for each cardiac cycle with a predetermined limit criterion, and supplies the result of the comparison to the determination unit for determining a measured ventricular signal resulted from an incipient fusion beat or a completely stimulated capture.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Bi-ventricular ventricular capture management in cardiac resyncronization therapy delivery devices
InactiveUS20060155338A1Great likelihoodSignificant comprehensive benefitsHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationVentricular conductionCardiac conduction
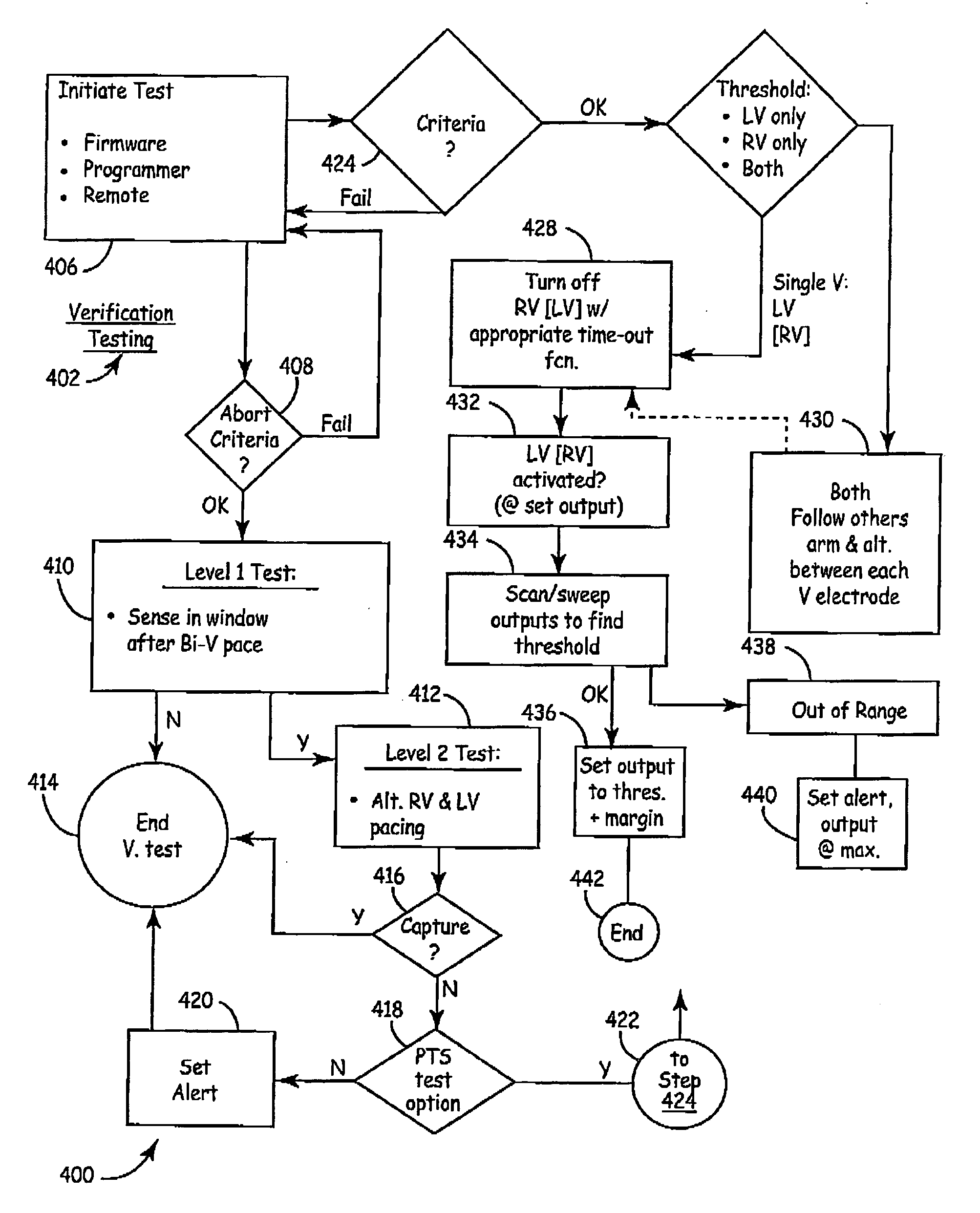
The present invention provides a technique for verifying pacing capture of a ventricular chamber, particularly to ensure desired delivery of a ventricular pacing regime (e.g., “CRT”). The invention also provides ventricular capture management by delivering a single ventricular pacing stimulus and checking inter-ventricular conduction during a temporal window to determine if the stimulus captured. If a loss-of-capture (LOC) signal results from the capture management testing, then the applied pacing pulses are modified and the conduction test repeated. If LOC, an alert message can issue. Other aspects include: use of a trend of A-RV / LV and LV-RV timing intervals to monitor changes in the patient's heart conduction properties; bi-ventricular verification test and search—while still pacing BiV by detecting latent sense; single-V pacing threshold search, use of timing of sense in other V chamber to establish capture and LOC windows; (iv) use of a premature V pace rather than short AV interval if VV cannot be discriminated from AV; (v) option to run a threshold search only if the Bi-ventricular verification test fails.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
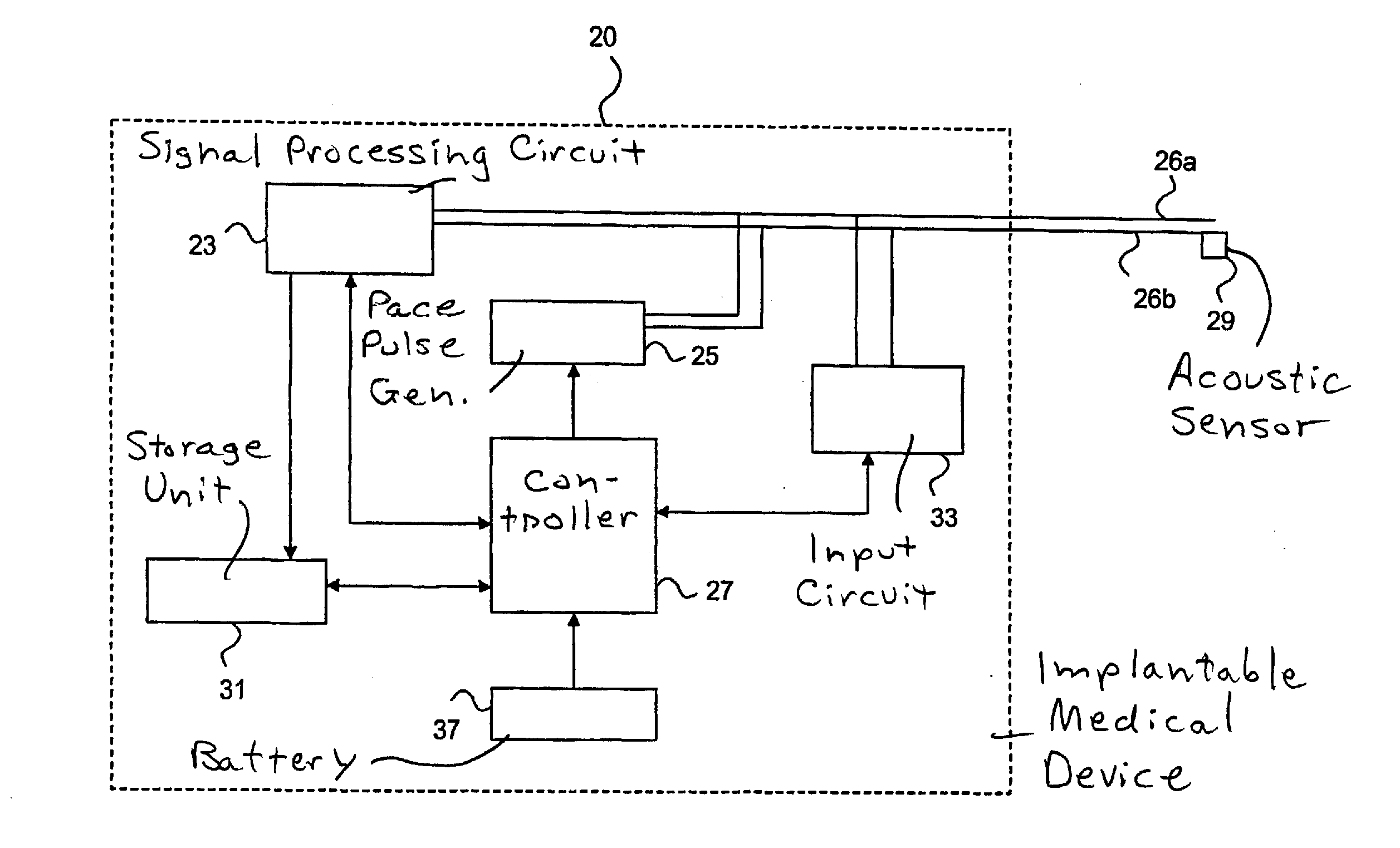
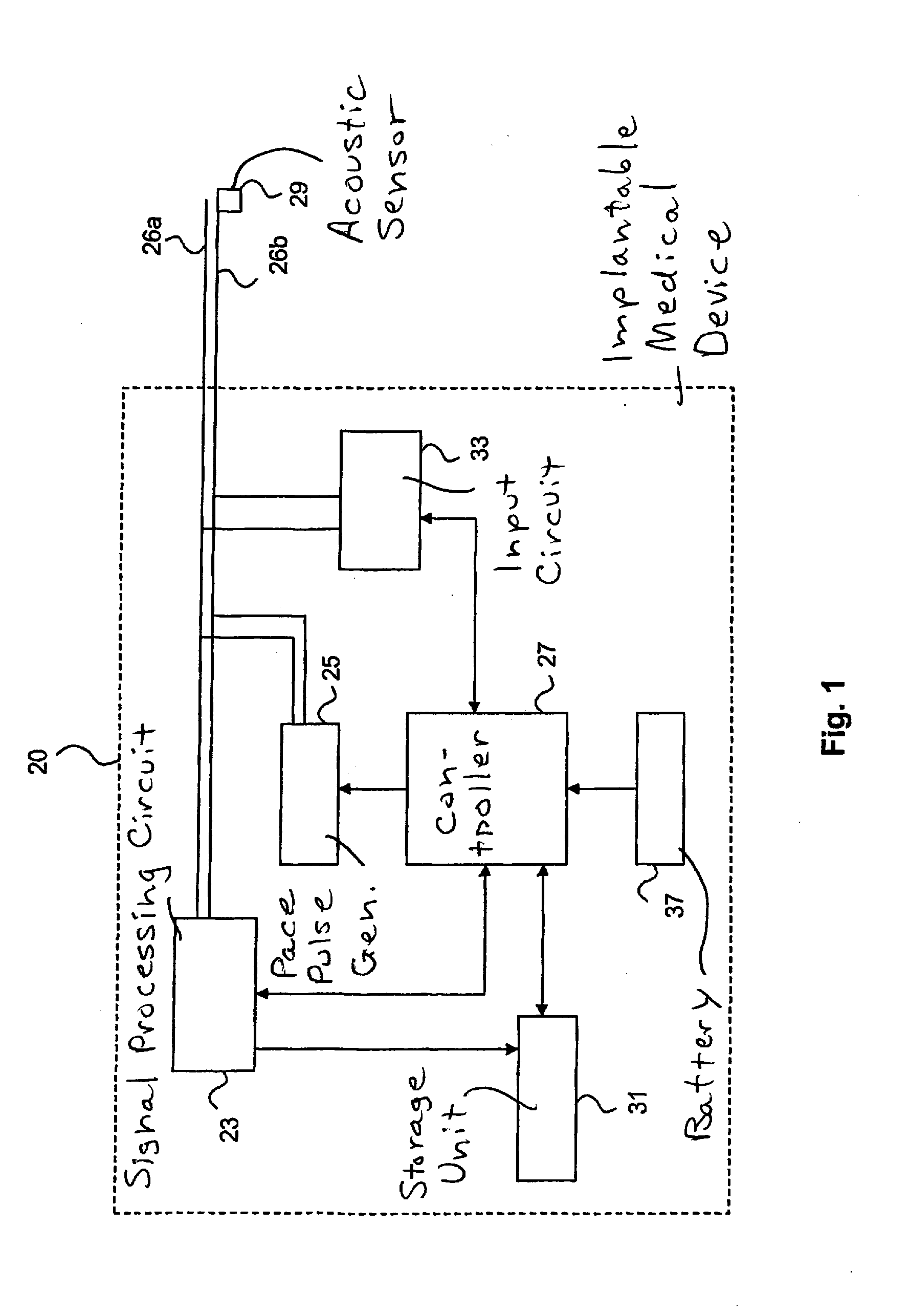
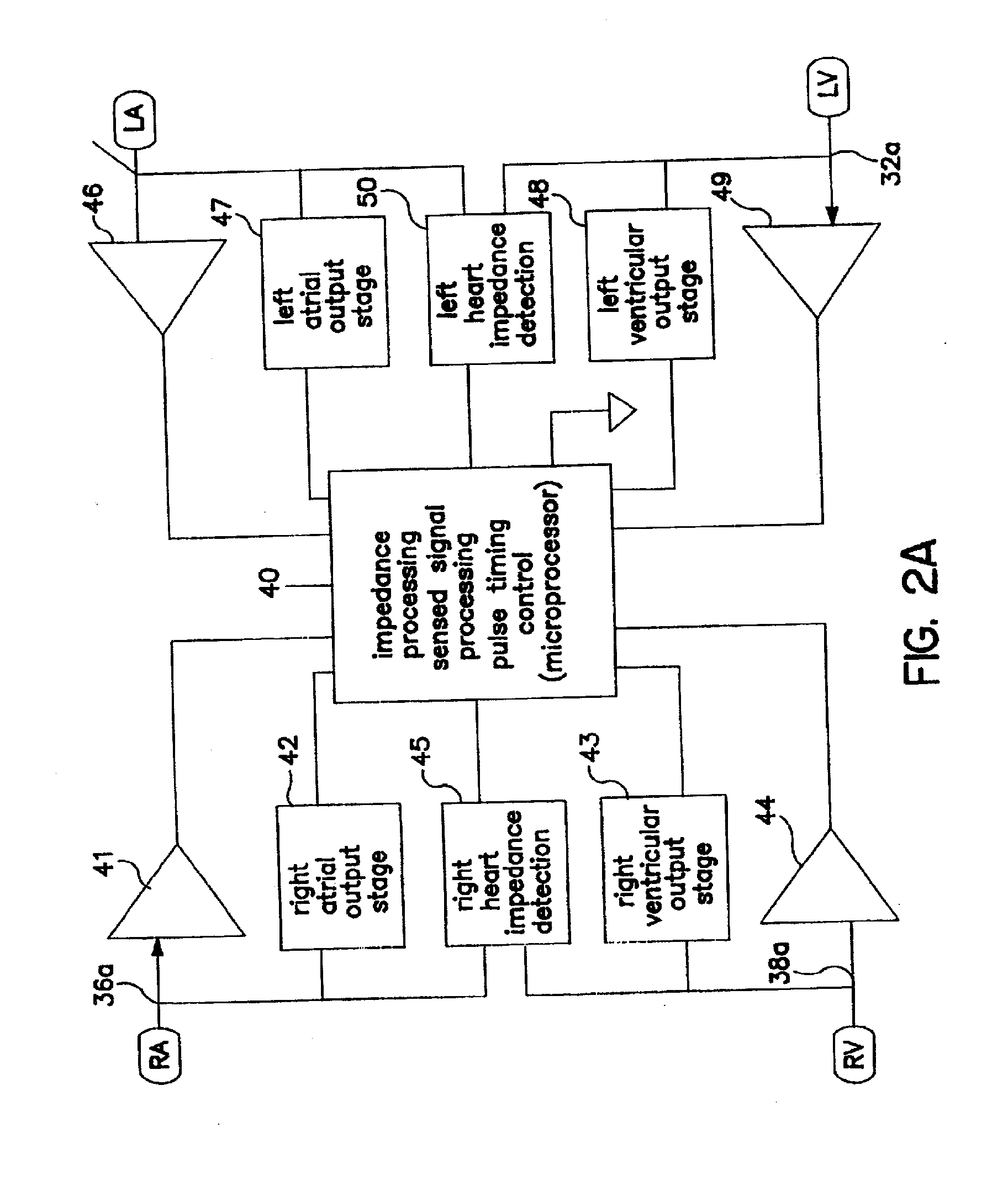
System and method of AV interval selection in an implantable medical device
An implantable medical device provides ventricular pacing capabilities and optimizes AV intervals for multiple purposes. In general, intrinsic conduction is promoted by determining when electromechanical systole (EMS) ends and setting an AV interval accordingly. EMS is determined utilizing various data including QT interval, sensor input, and algorithmic calculations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
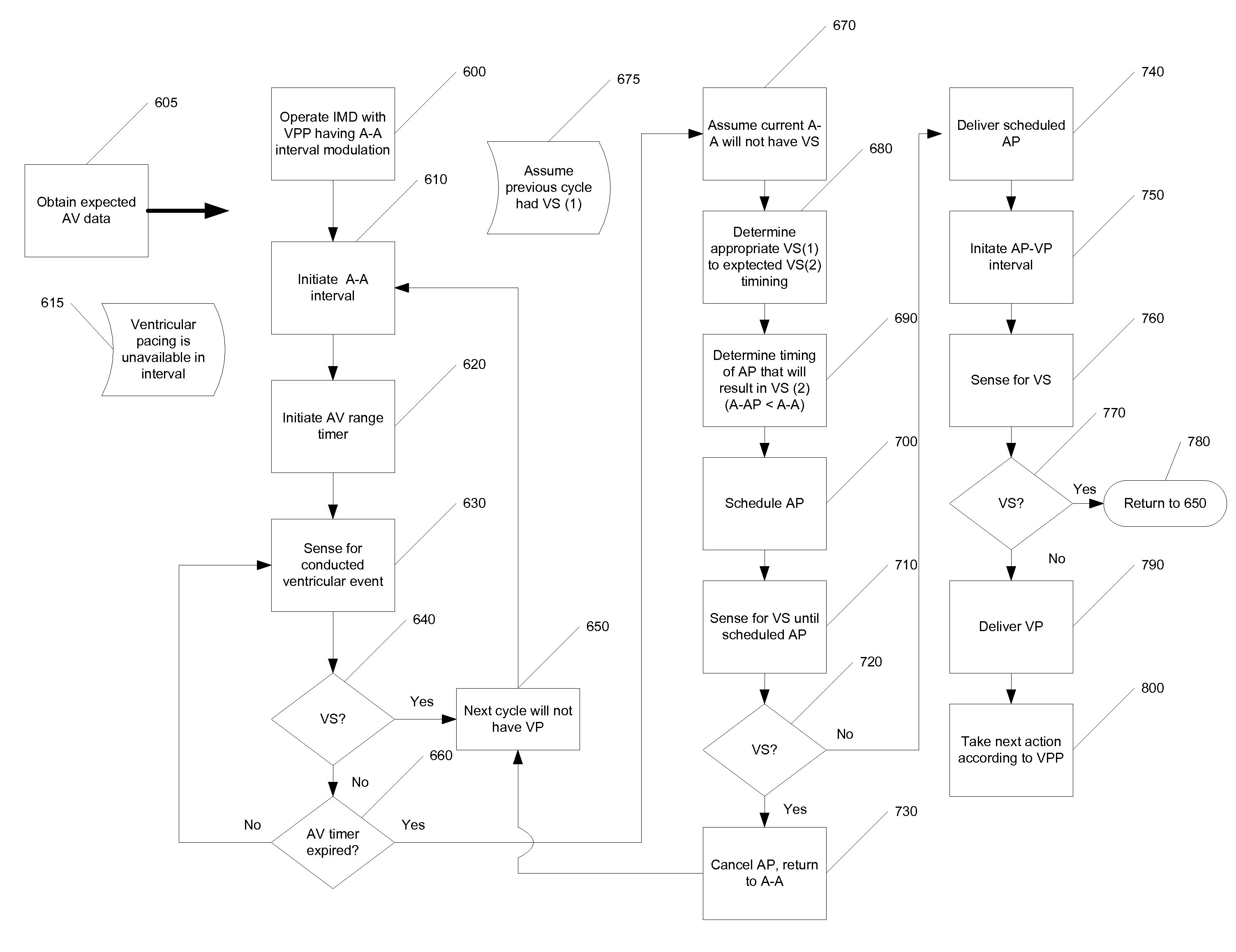
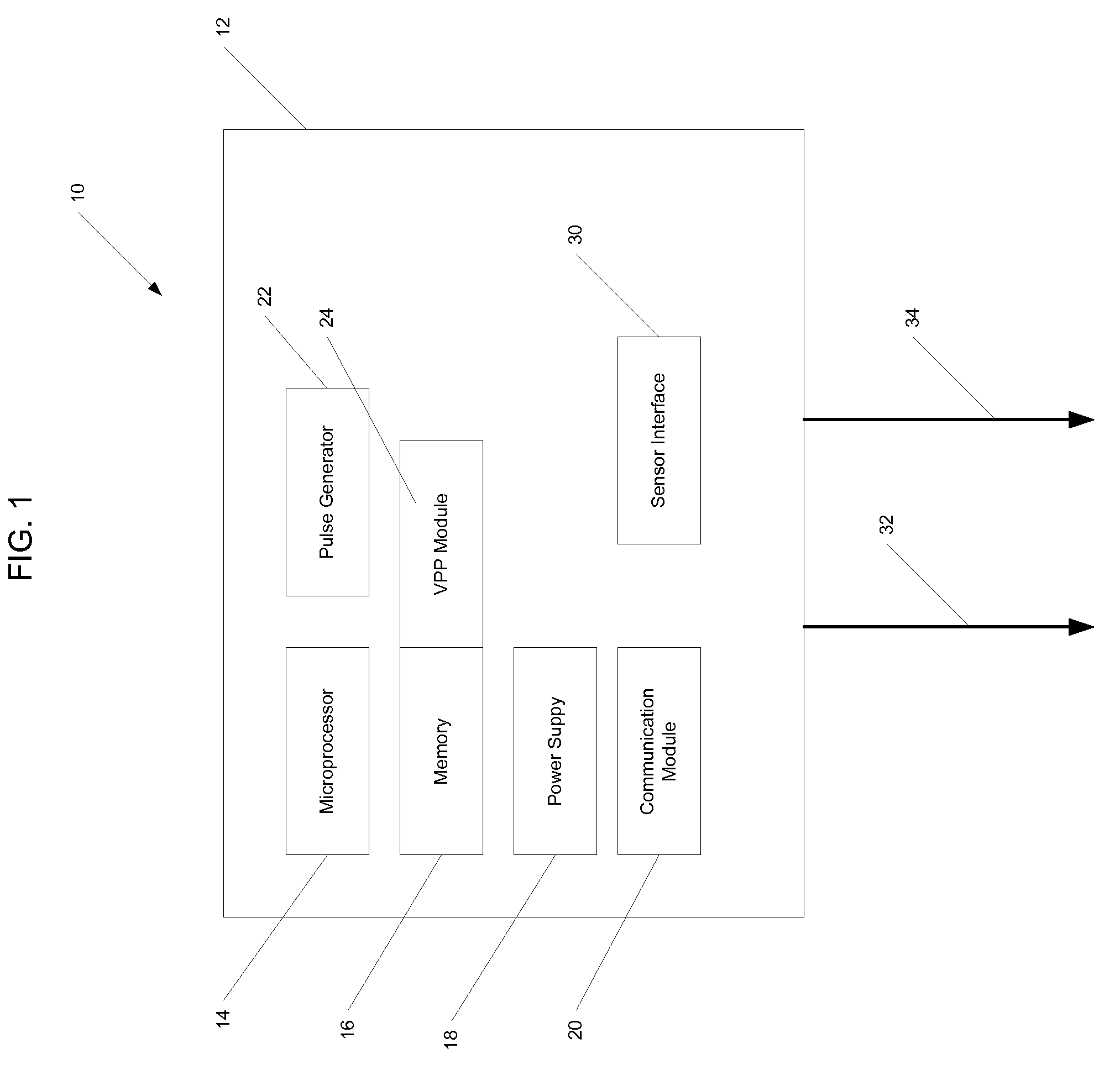
Implantable medical device with ventricular pacing protocol
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
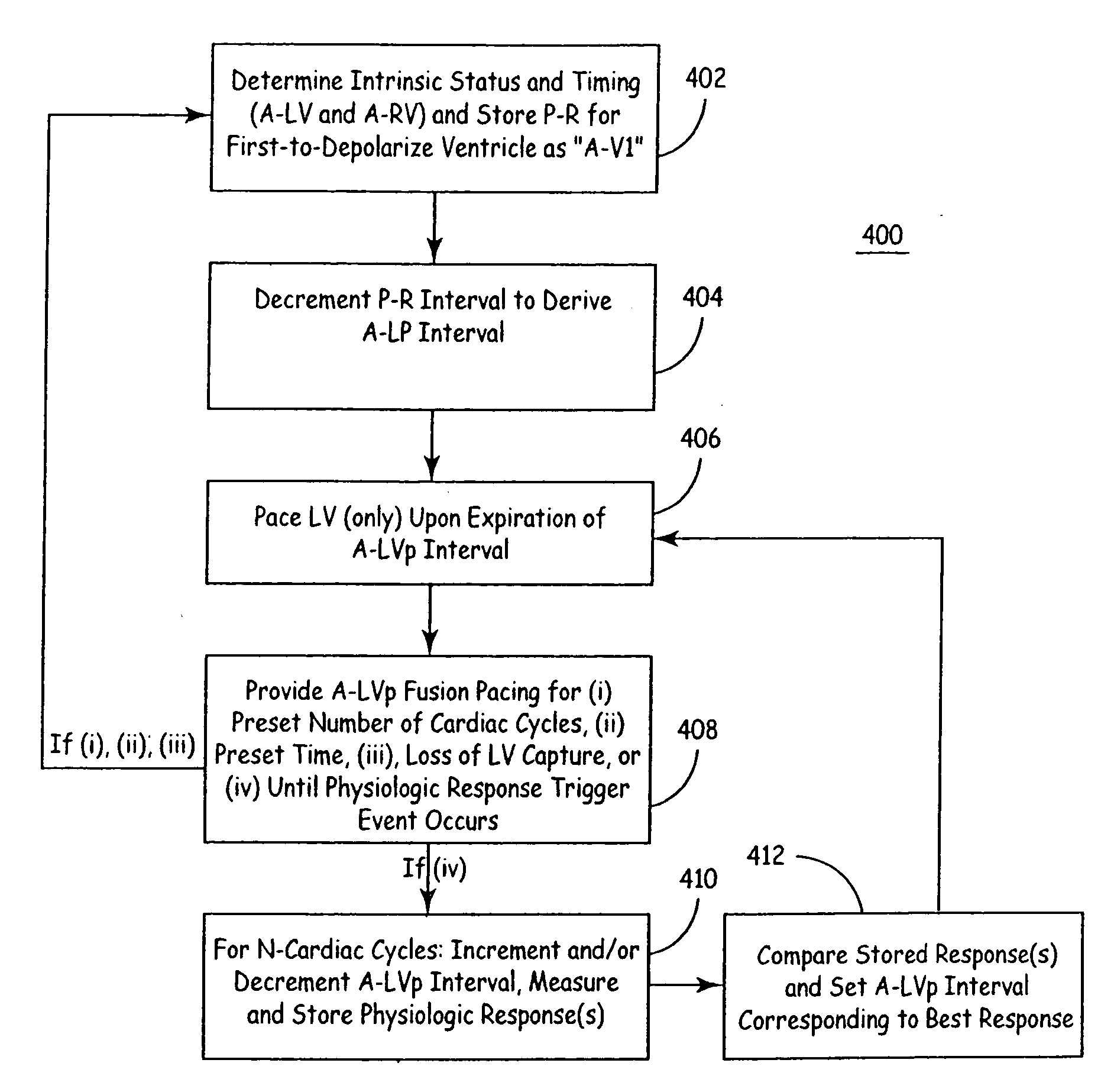
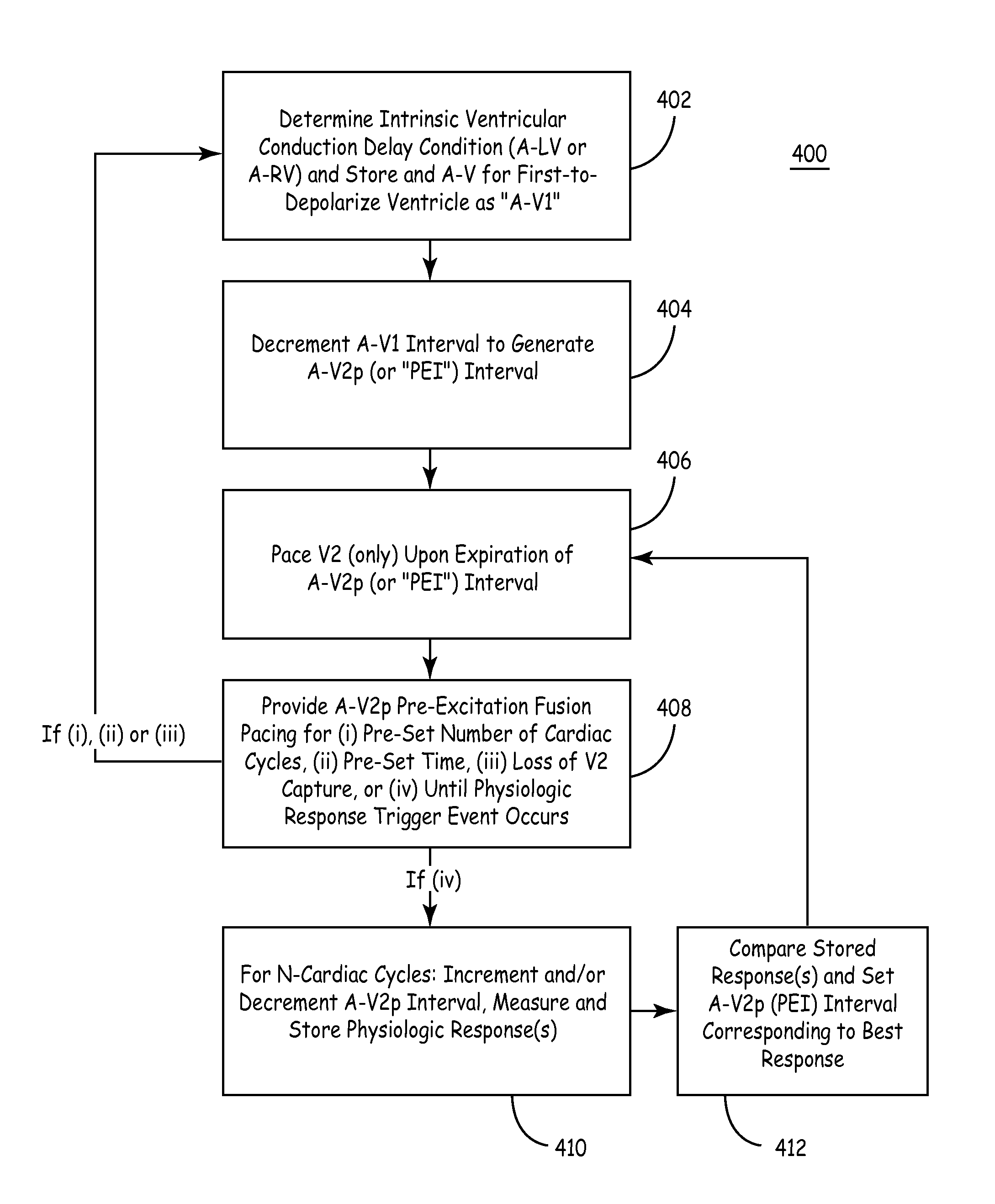
Apparatus and methods for automatic adjustment of av interval to ensure delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy
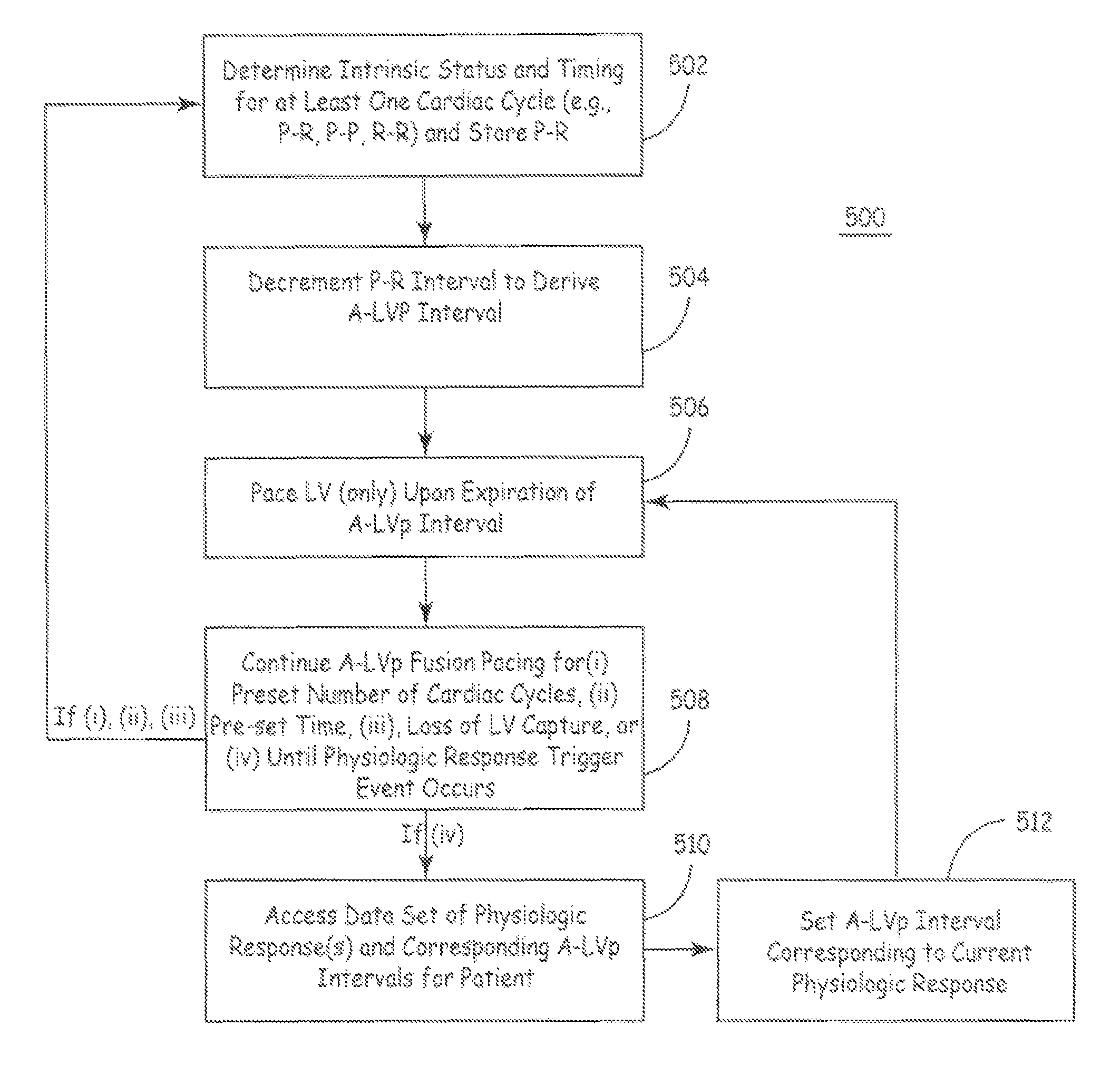
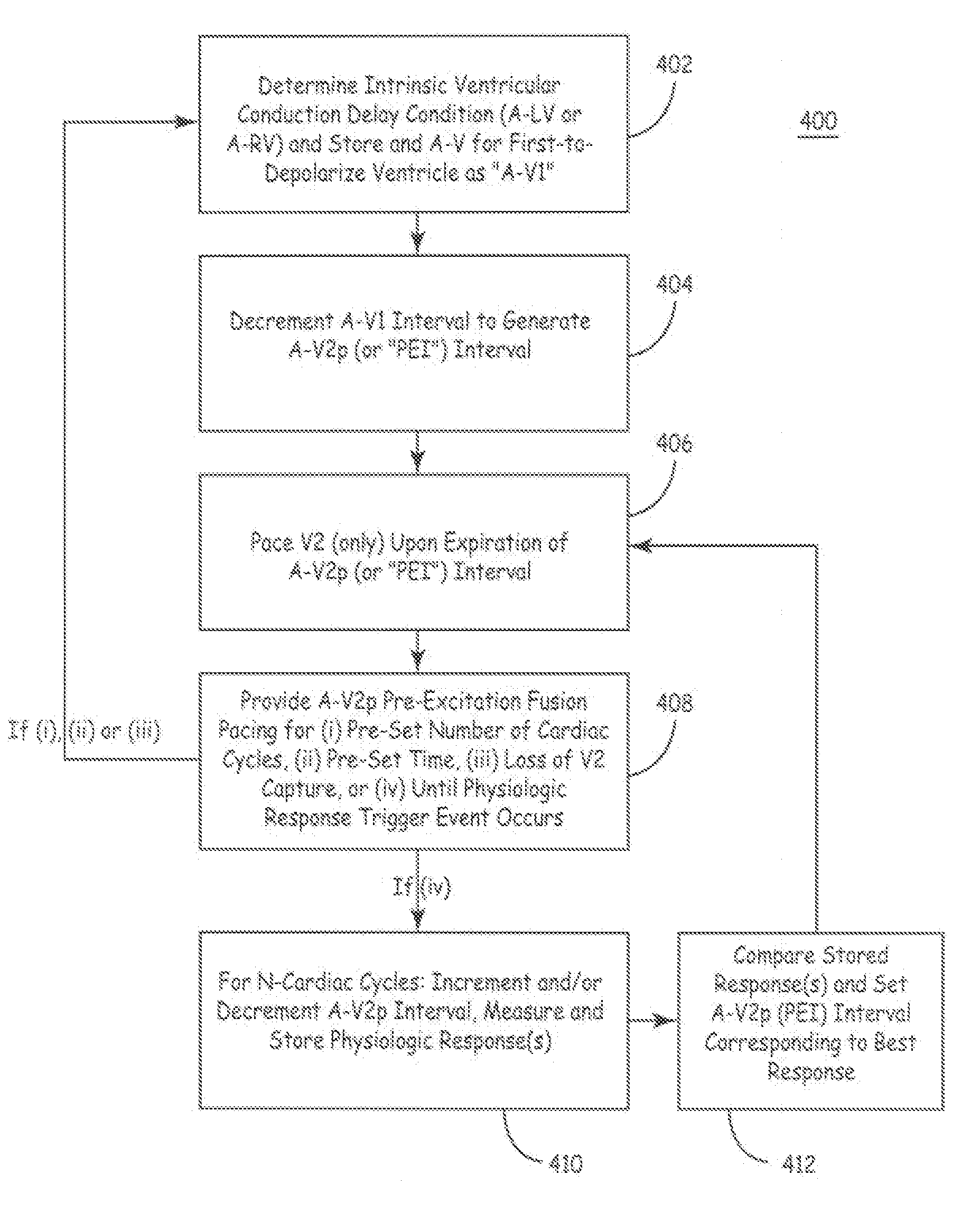
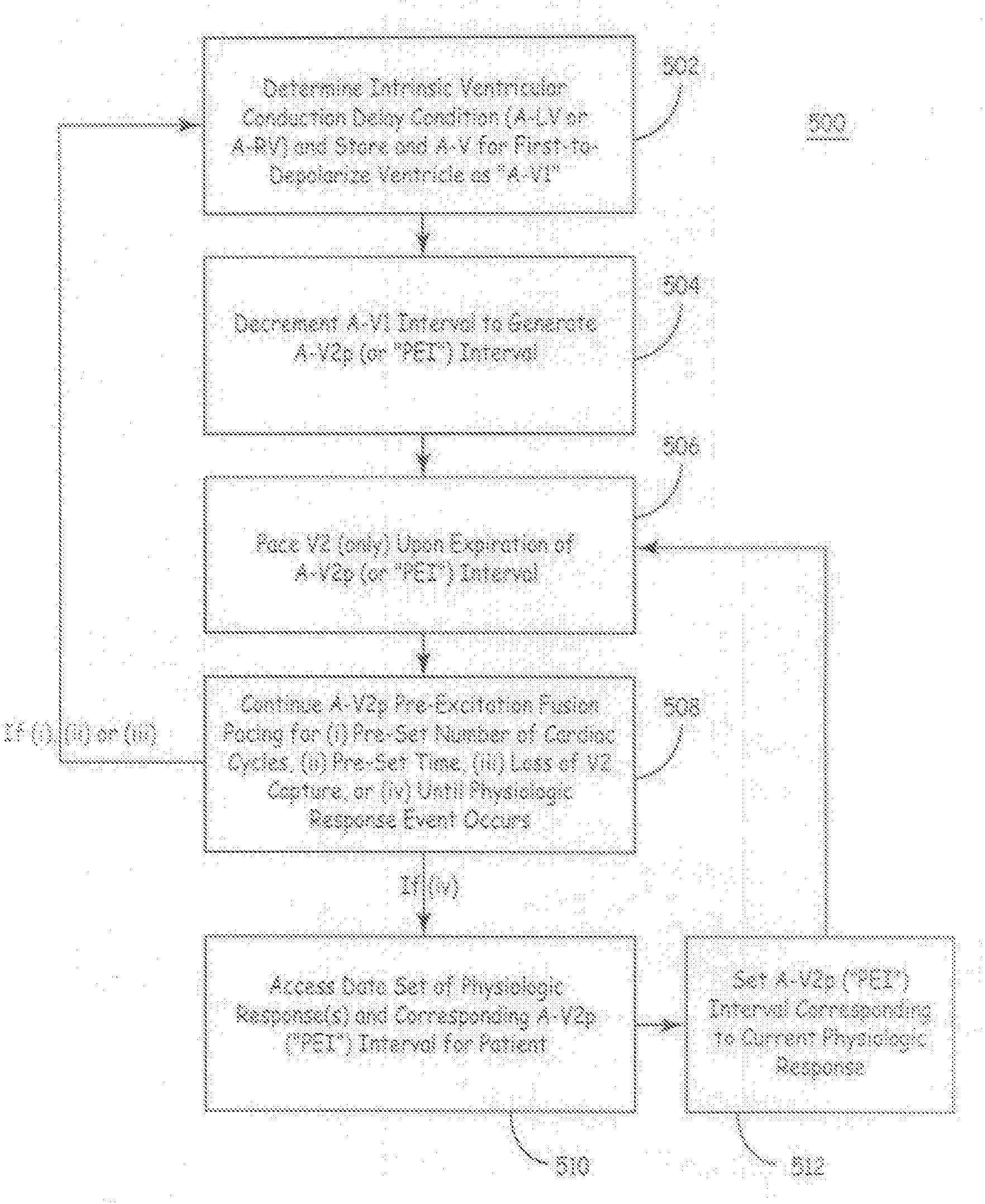
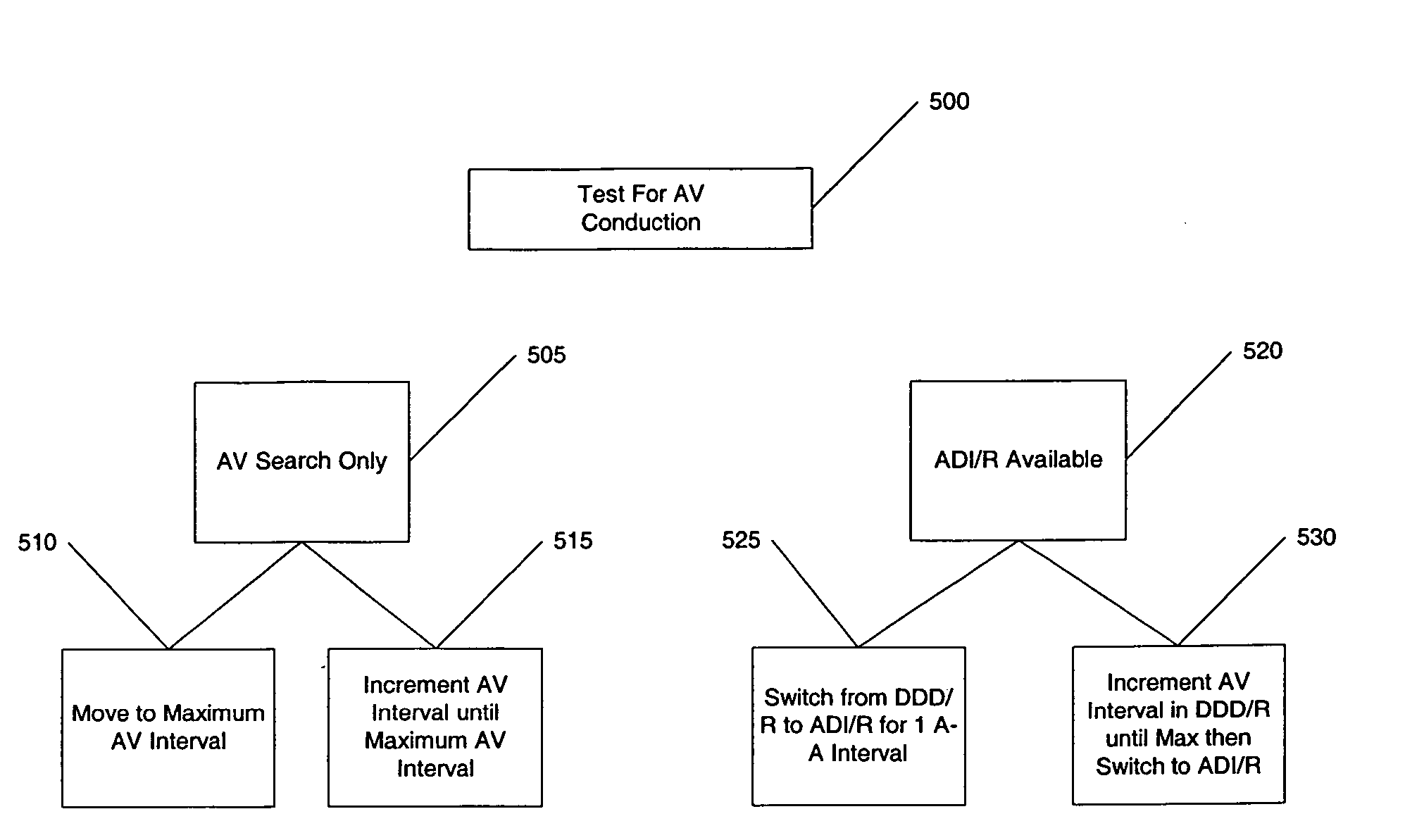
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Fusion Pacing Enhancements
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and methods for automatic adjustment of av interval to ensure delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable medical device with optimization procedure
InactiveUS20090254139A1More time to relaxFaster filling timeStethoscopeHeart stimulatorsAcoustic energyCardiac cycle
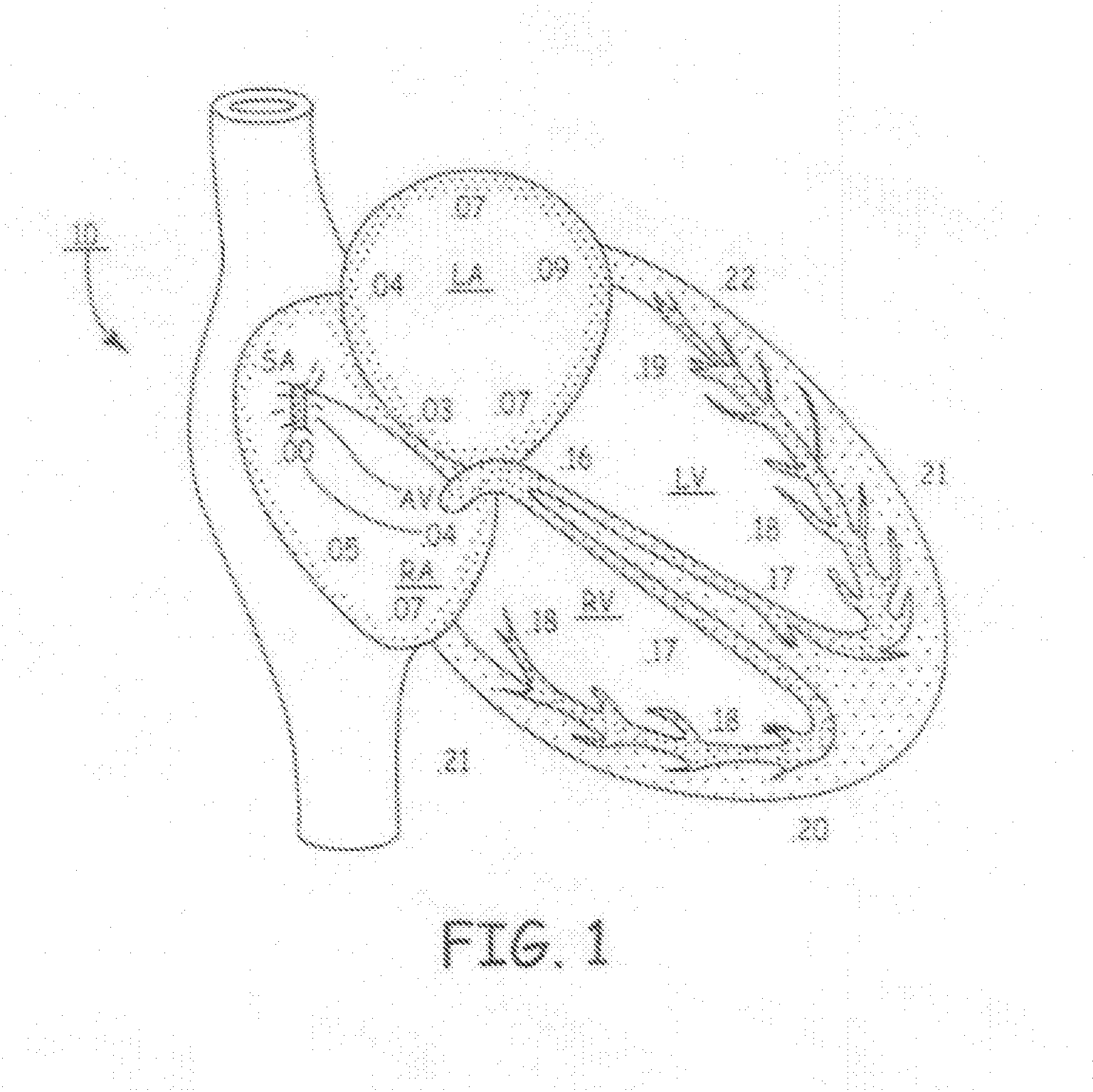
In an implantable medical device and a method for the operation thereof, acoustic energy is sensed in a subject in whom the device is implanted, and signals indicative of heart sounds of the heart of the patient are produced over predetermined periods of a cardiac cycle, during successive cardiac cycles. A signal corresponding to the second heart sound (S2) is extracted from the sensed signal, and the respective durations of successive second heart sound signals are determined. An optimization procedure is implemented that includes controlling delivery of pacing pulses based on the determined durations of successive second heart sounds, to determined a combination of stimulation intervals, including at least the AV interval and the VV interval, that causes a substantially synchronized closure of the aortic and pulmonary valves.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Apparatus and method for hemodynamic-based optimization of cardiac pacing
InactiveUS20050234517A1Improves left ventricular filling pressureOptimal AV-delayHeart defibrillatorsCatheterSonificationLeft ventricular size
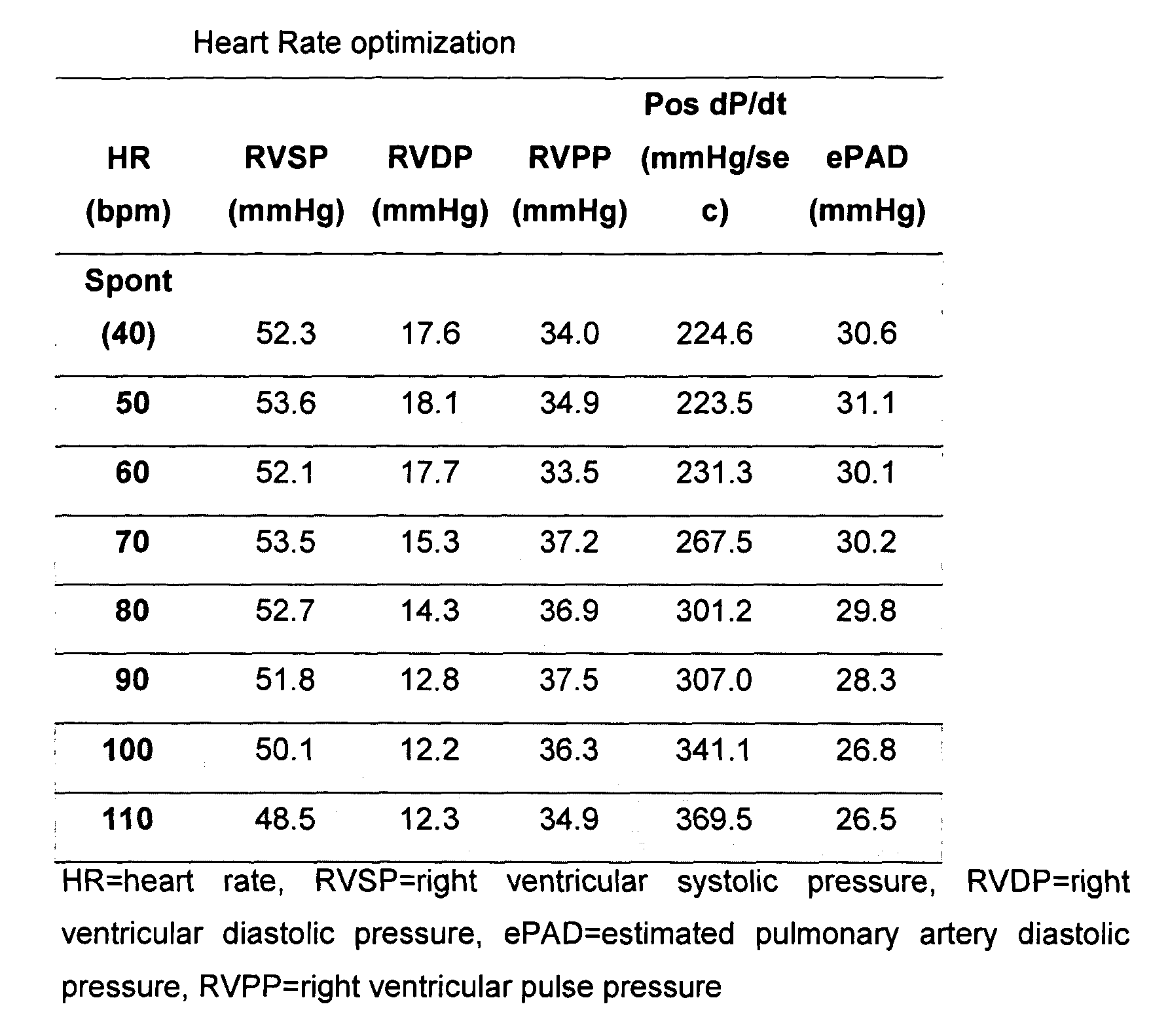
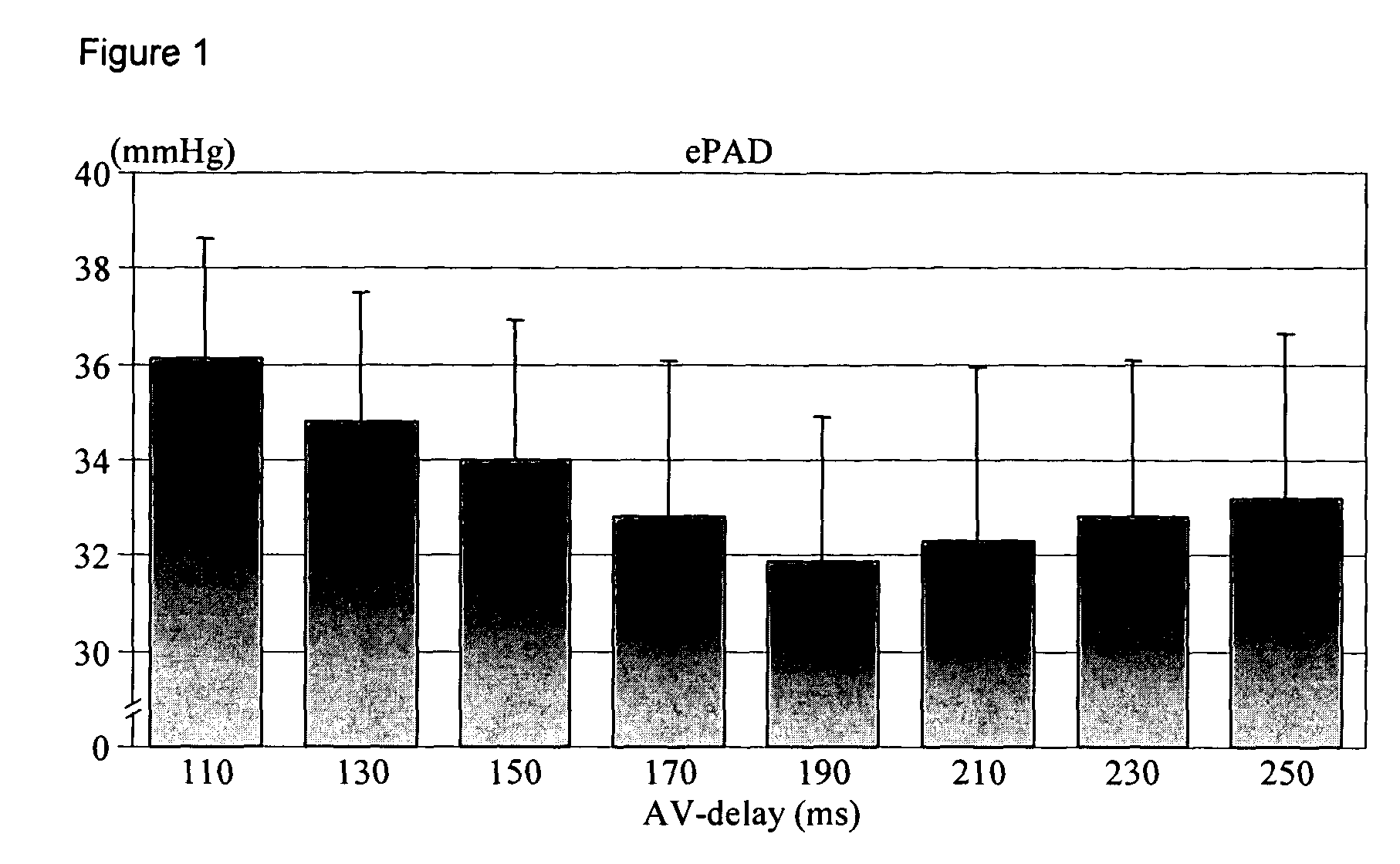
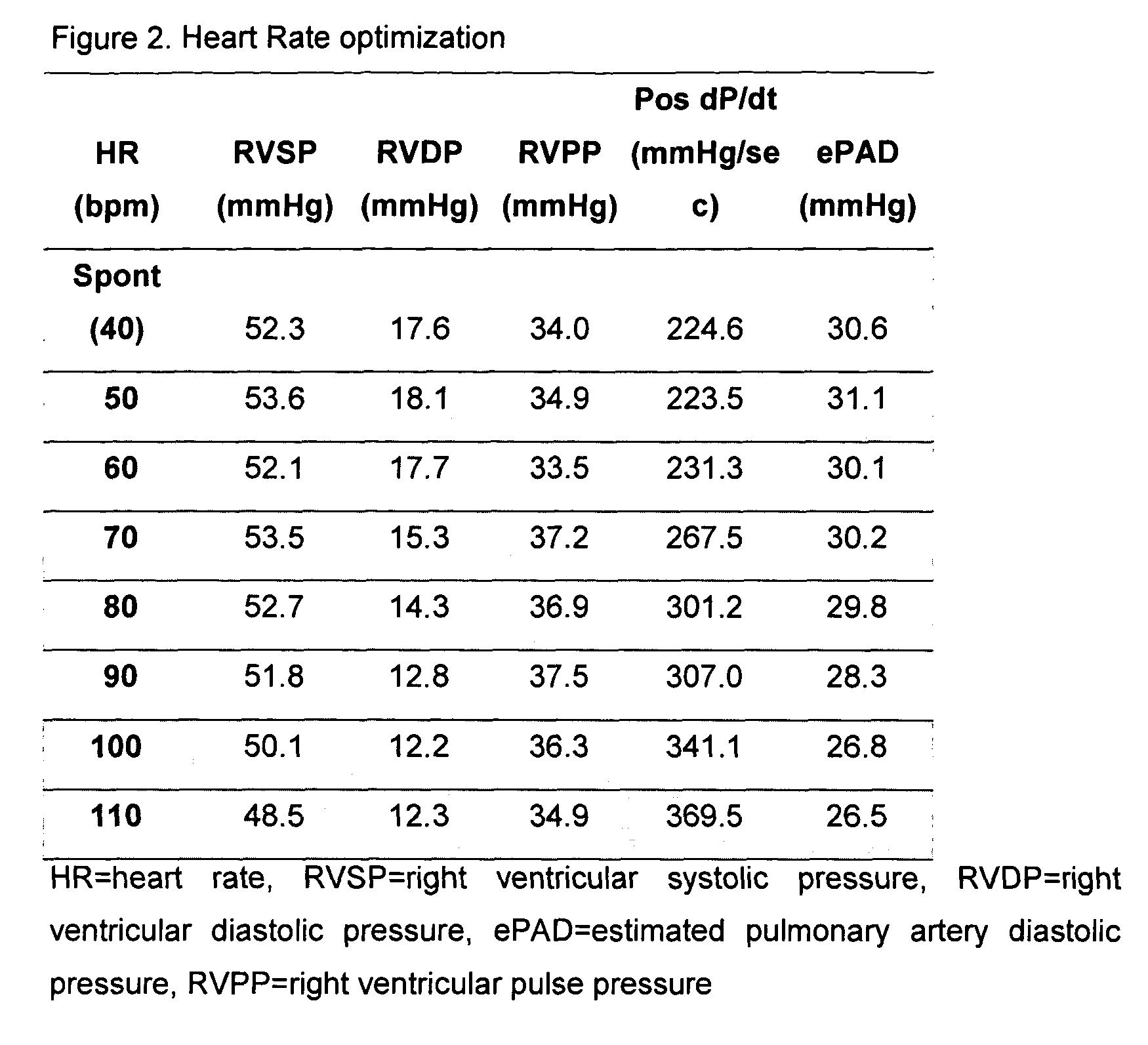
The present invention demonstrates that continuous hemodynamic monitoring can be used to identify the optimal AV-delay in a pacemaker-treated patient with end stage heart failure. The AV-delay determines the timing of late diastolic filling in relation to the onset of ventricular contraction and the duration of diastolic filling. An optimal tuning of the AV-delay improves left ventricular filling pressures in patients with a DDD-programmed pacemaker and is particularly important in the presence of a compromised left ventricular function. It has been discovered that using the lowest ePAD pressure, an indirect parameter of the left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, as an indicator for the optimal AV interval. Importantly, measurements of the ePAD revealed the same optimal AV-delay as echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular diastolic filling by standard echocardiographic methods. Importantly, the HR determined as optimal during the acute hemodynamic test did not turn out to be optimal during daily living activities.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Fusion pacing enhancements
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and methods for automatic adjustment of av interval to ensure delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy
Methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles) and delivering fusion pacing using a decremented value of the intrinsic PR interval.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Bi-ventricular ventricular capture management in cardiac resynchroniziation therapy delivery devices
ActiveUS20130090702A1Great likelihoodSignificant comprehensive benefitsHeart stimulatorsVentricular conductionCRTS
The present invention provides a technique for verifying pacing capture of a ventricular chamber, particularly to ensure desired delivery of a ventricular pacing regime (e.g., “CRT”). The invention also provides ventricular capture management by delivering a single ventricular pacing stimulus and checking inter-ventricular conduction during a temporal window to determine if the stimulus captured. If a loss-of-capture LOC) signal results from the capture management testing, then the applied pacing pulses are modified and the conduction test repeated. If LOC, an alert message can issue. Other aspects include: use of a trend of A-RV / LV and LV-RV timing intervals to monitor changes in the patient's heart conduction properties; bi-ventricular verification test and search—while still pacing BiV by detecting latent sense; single-V pacing threshold search, use of timing of sense in other V chamber to establish capture and LOC windows; (iv) use of a premature V pace rather than short AV interval if VV cannot be discriminated from AV; (v) option to run a threshold search only if the Bi-ventricular verification test fails.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal pacing intervals
InactiveUS20060271117A1Optimize cardiac outputReduce the required powerHeart stimulatorsPacing intervalSub threshold
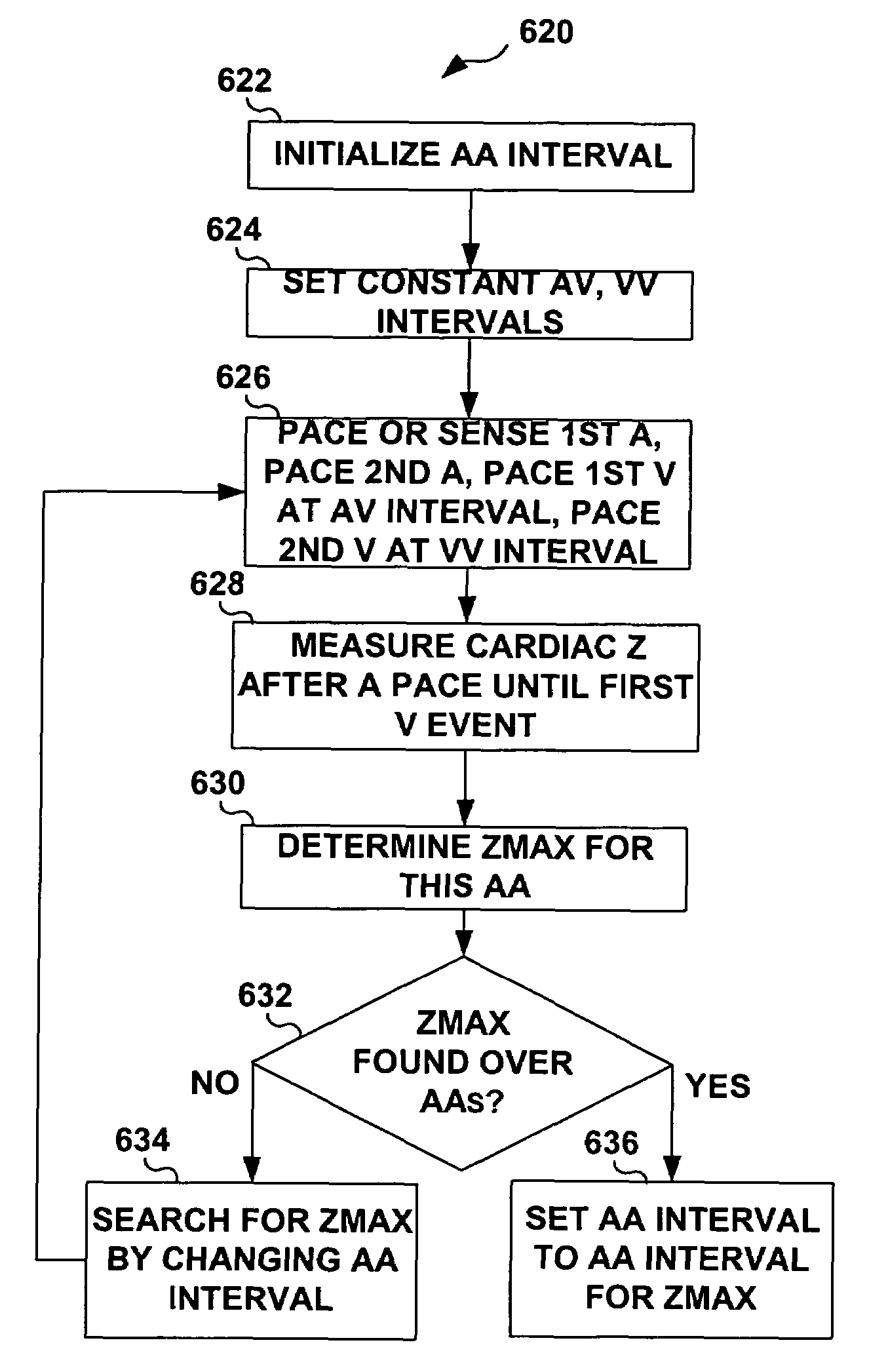
Impedance, e.g. sub-threshold impedance, is measured across the heart at selected cardiac cycle times as a measure of chamber expansion or contraction. One embodiment measures impedance over a long AV interval to obtain the minimum impedance, indicative of maximum ventricular expansion, in order to set the AV interval. Another embodiment measures impedance change over a cycle and varies the AV pace interval in a binary search to converge on the AV interval causing maximum impedance change indicative of maximum ventricular output. Another method varies the right ventricle to left ventricle (VV) interval to converge on an impedance maximum indicative of minimum cardiac volume at end systole. Another embodiment varies the VV interval to maximize impedance change. Other methods vary the AA interval to maximize impedance change over the entire cardiac cycle or during the atrial cycle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and Method for Promoting Instrinsic Conduction Through Atrial Timing Modification and Calculation of Timing Parameters
An atrial based pacing protocol promotes intrinsic conduction. An entire cardiac cycle is monitored for ventricular activity and permitted to lapse with ventricular activity. Ventricular pacing is available in a cardiac cycle immediately subsequent to such a skipped beat. When monitoring for intrinsic ventricular events, an event is expected within a given window. If no such event is detected, the cardiac cycle in truncated, leading to a shorter cycle that is devoid of ventricular activity. The subsequent cycle has a high likelihood of a ventricular sensed event and a greater than normal AV interval is provided prior to pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Self limited rate response
Rate responsive pacing is limited in an atrial based pacing mode by the AV interval in order to avoid or minimize ventricular encroachment of atrial pacing. The AV or VA interval is used to permit rate responsiveness; modulate rate responsiveness or to determine a dynamic upper sensor rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal AV and VV intervals
Methods and devices for determining optimal Atrial to Ventricular (AV) pacing intervals and Ventricular to Ventricular (VV) delay intervals in order to optimize cardiac output. Impedance, preferably sub-threshold impedance, is measured across the heart at selected cardiac cycle times as a measure of chamber expansion or contraction. One embodiment measures impedance over a long AV interval to obtain the minimum impedance, indicative of maximum ventricular expansion, in order to set the AV interval. Another embodiment measures impedance change over a cycle and varies the AV pace interval in a binary search to converge on the AV interval causing maximum impedance change indicative of maximum ventricular output. Another method varies the right ventricle to left ventricle (VV) interval to converge on an impedance maximum indicative of minimum cardiac volume at end systole. Another embodiment varies the VV interval to maximize impedance change.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal pacing intervals
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable medical device with ventricular pacing protocol including progressive conduction search
An implantable medical device operates to promote intrinsic ventricular depolarization according to a pacing protocol. The medical device operates to promote intrinsic conduction by providing elongated AV intervals or operating in an atrial based pacing mode. Conduction checks to determine if AV conduction is present are performed on a graduated or progressive scale to facilitate intrinsic emergence.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and Method for Determining Intrinsic AV Interval Timing
An atrial based pacing protocol promotes intrinsic conduction. An entire cardiac cycle is monitored for ventricular activity and permitted to lapse with ventricular activity. Ventricular pacing is available in a cardiac cycle immediately subsequent to such a skipped beat. When monitoring for intrinsic ventricular events, an event is expected within a given window. If no such event is detected, the cardiac cycle in truncated, leading to a shorter cycle that is devoid of ventricular activity. The subsequent cycle has a high likelihood of a ventricular sensed event and a greater than normal AV interval is provided prior to pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Algorithm for the automatic determination of optimal AV and VV intervals
ActiveUS20070213778A1Reduce the required powerMaximize fillInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsInterval methodCardiac cycle
Methods and devices for determining optimal Atrial to Ventricular (AV) pacing intervals and Ventricular to Ventricular (VV) delay intervals in order to optimize cardiac output. Impedance, preferably sub-threshold impedance, is measured across the heart at selected cardiac cycle times as a measure of chamber expansion or contraction. One embodiment measures impedance over a long AV interval to obtain the minimum impedance, indicative of maximum ventricular expansion, in order to set the AV interval. Another embodiment measures impedance change over a cycle and varies the AV pace interval in a binary search to converge on the AV interval causing maximum impedance change indicative of maximum ventricular output. Another method varies the right ventricle to left ventricle (VV) interval to converge on an impedance maximum indicative of minimum cardiac volume at end systole. Another embodiment varies the VV interval to maximize impedance change.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
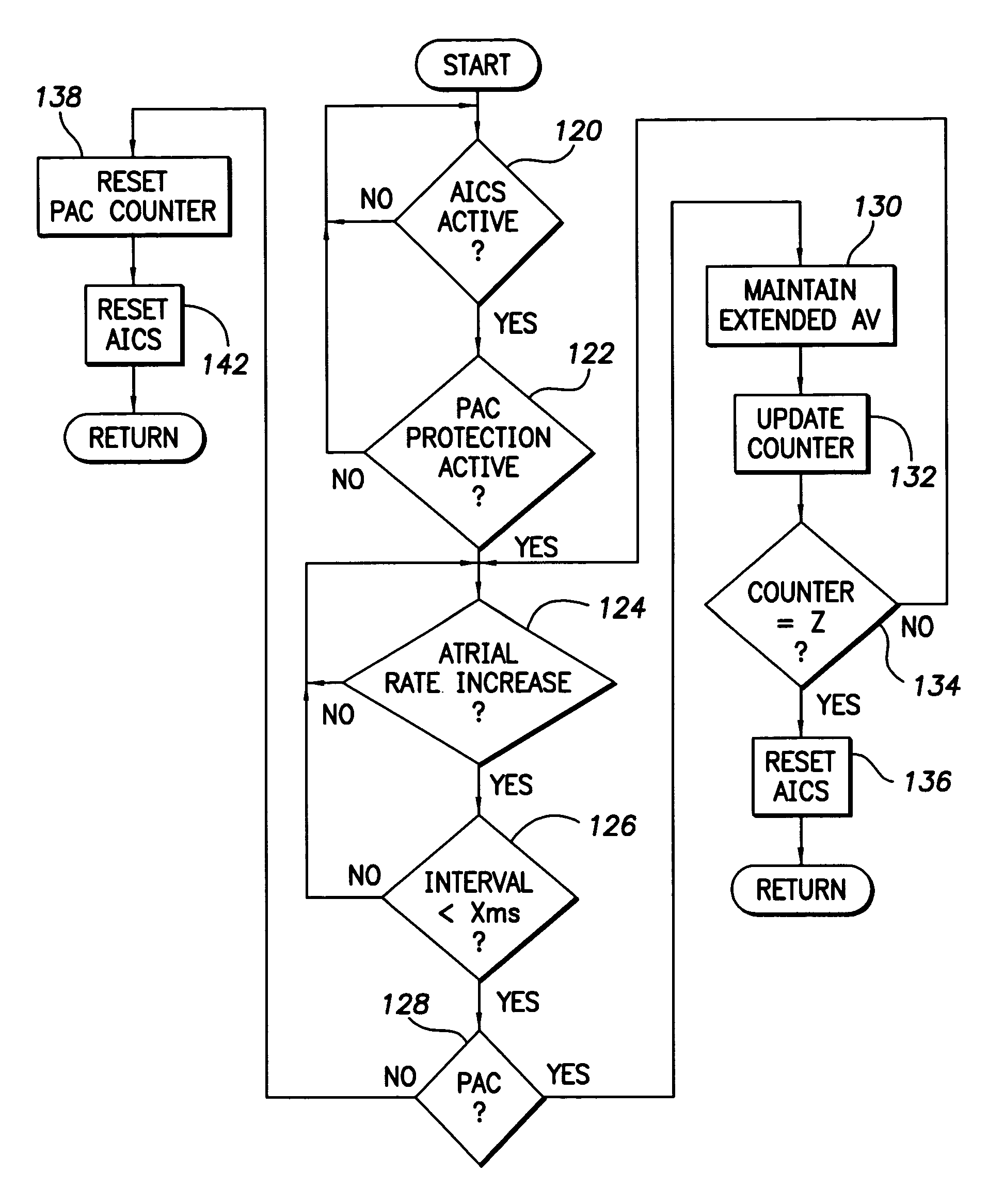
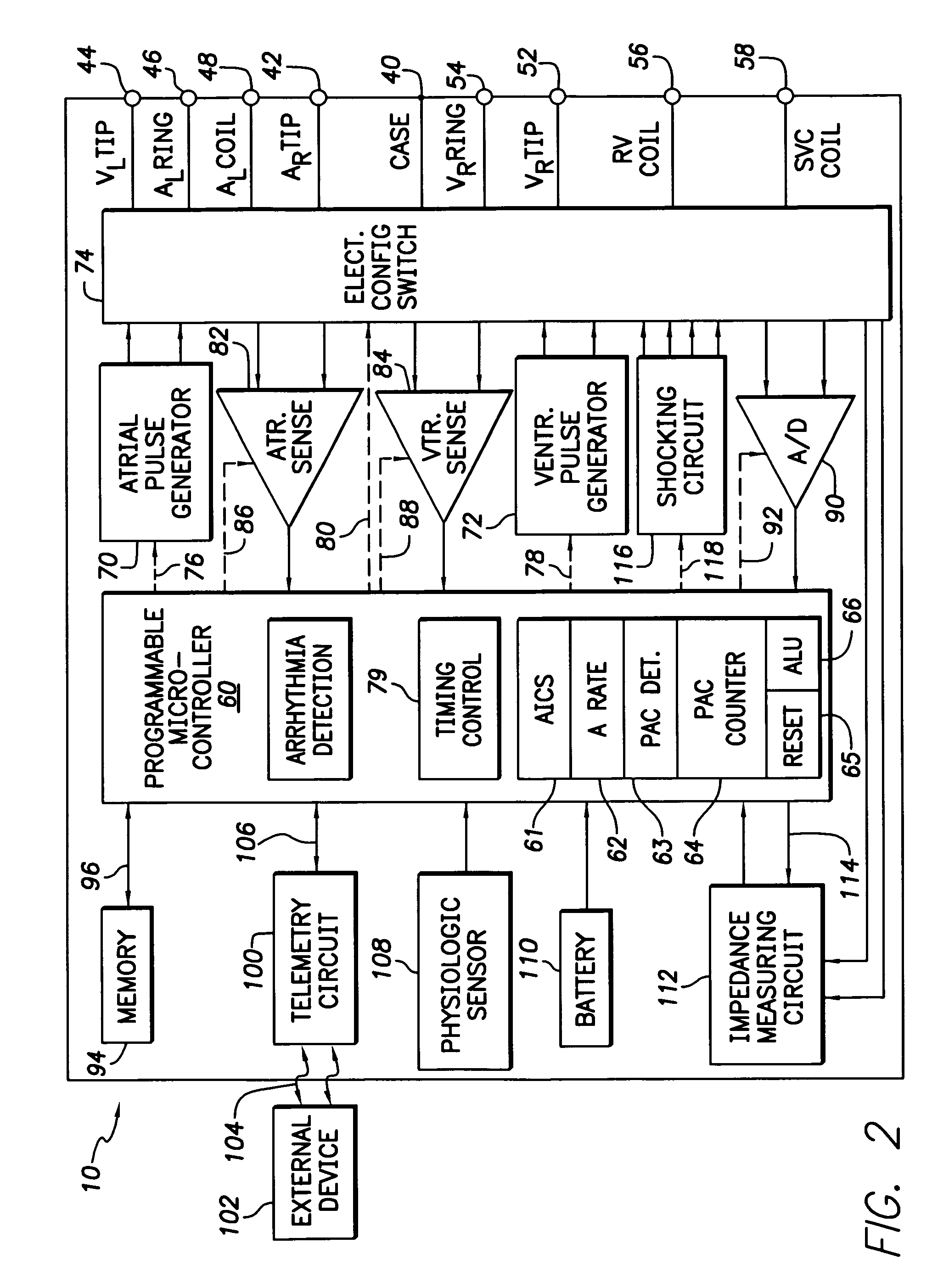
Implantable cardiac device providing intrinsic conduction search with premature atrial contraction protection and method
The extended AV interval of an auto intrinsic conduction search of an implantable cardiac stimulation device has premature atrial contraction protection. A timer times a base AV interval and the extended AV interval. If the heart is paced with the extended AV interval and a premature atrial contraction is detected, the extended AV interval is maintained. Once a predetermined number of consecutive premature atrial contractions are detected, the extended AV interval is reset to the base AV interval.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
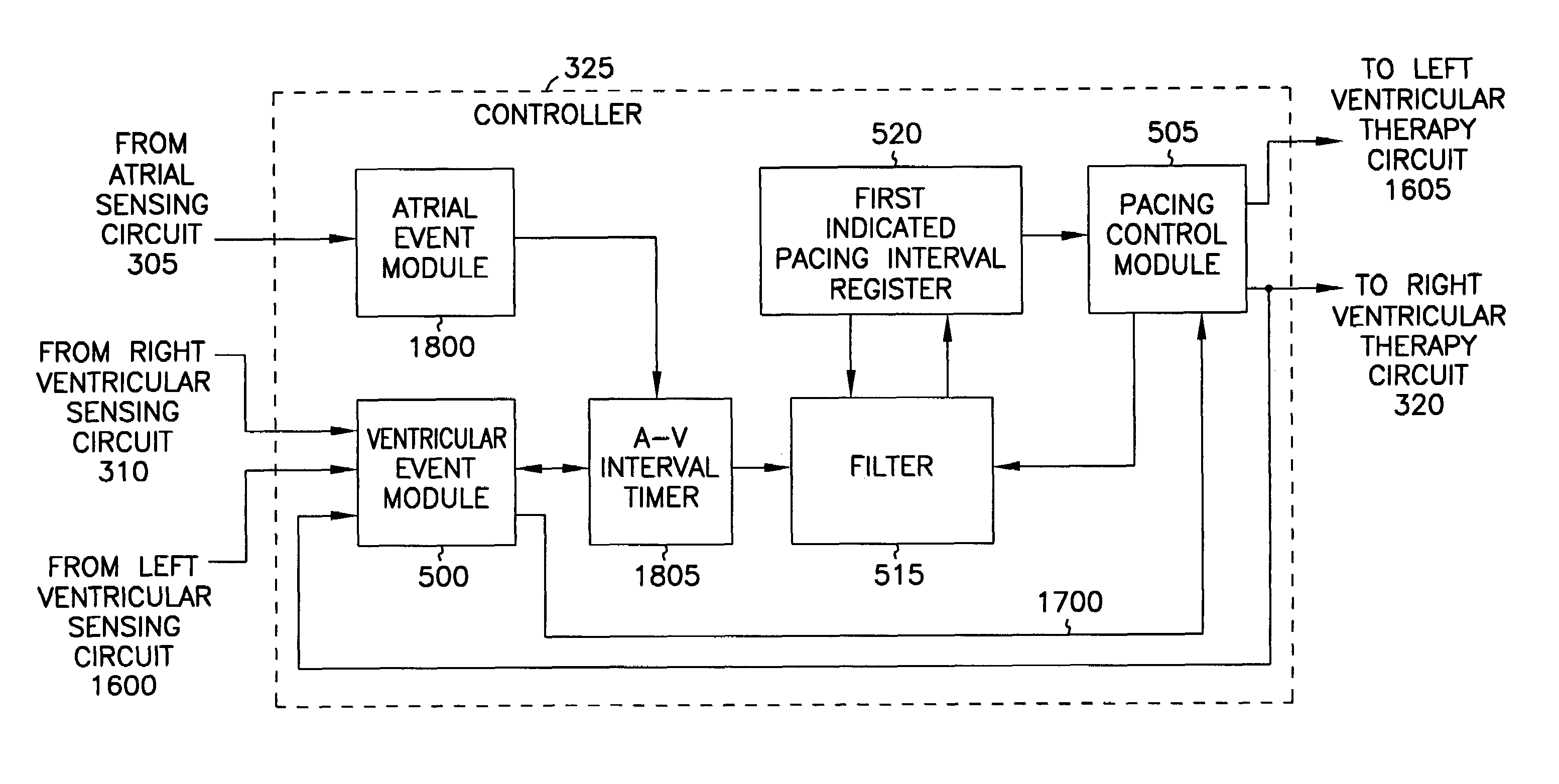
System providing ventricular pacing and biventricular coordination
A cardiac rhythm management system includes techniques for computing an indicated pacing interval, AV delay, or other timing interval. In one embodiment, a variable indicated pacing interval is computed based at least in part on an underlying intrinsic heart rate. The indicated pacing interval is used to time the delivery of biventricular coordination therapy even when ventricular heart rates are irregular, such as in the presence of atrial fibrillation. In another embodiment, a variable filter indicated AV interval is computed based at least in part on an underlying intrinsic AV interval. The indicated AV interval is used to time the delivery of atrial tracking biventricular coordination therapy when atrial heart rhythms are not arrhythmic. Other indicated timing intervals may be similarly determined. The indicated pacing interval, AV delay, or other timing interval can also be used in combination with a sensor indicated rate indicator.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
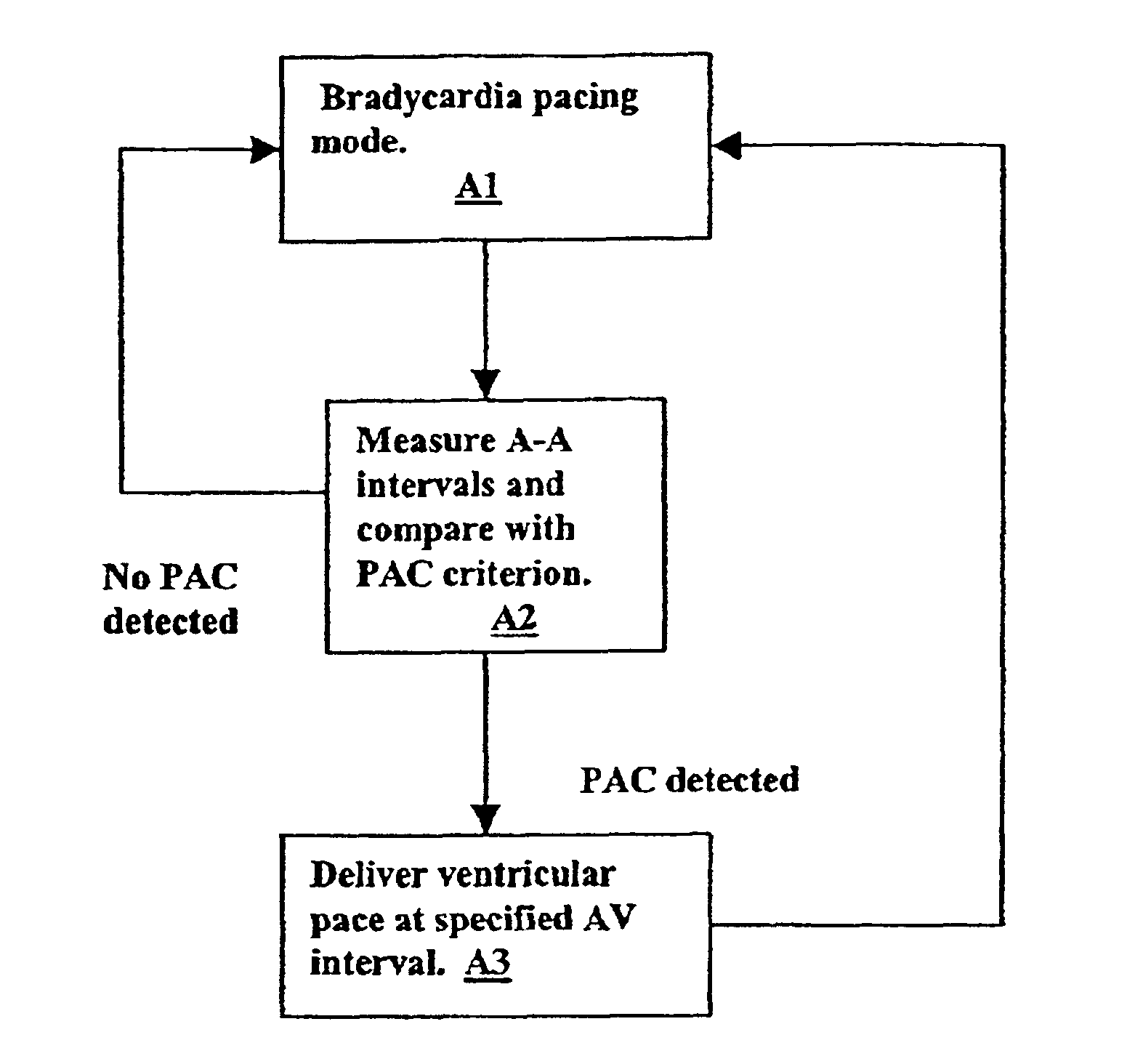
Ventricular pacing for prevention of atrial fibrillation
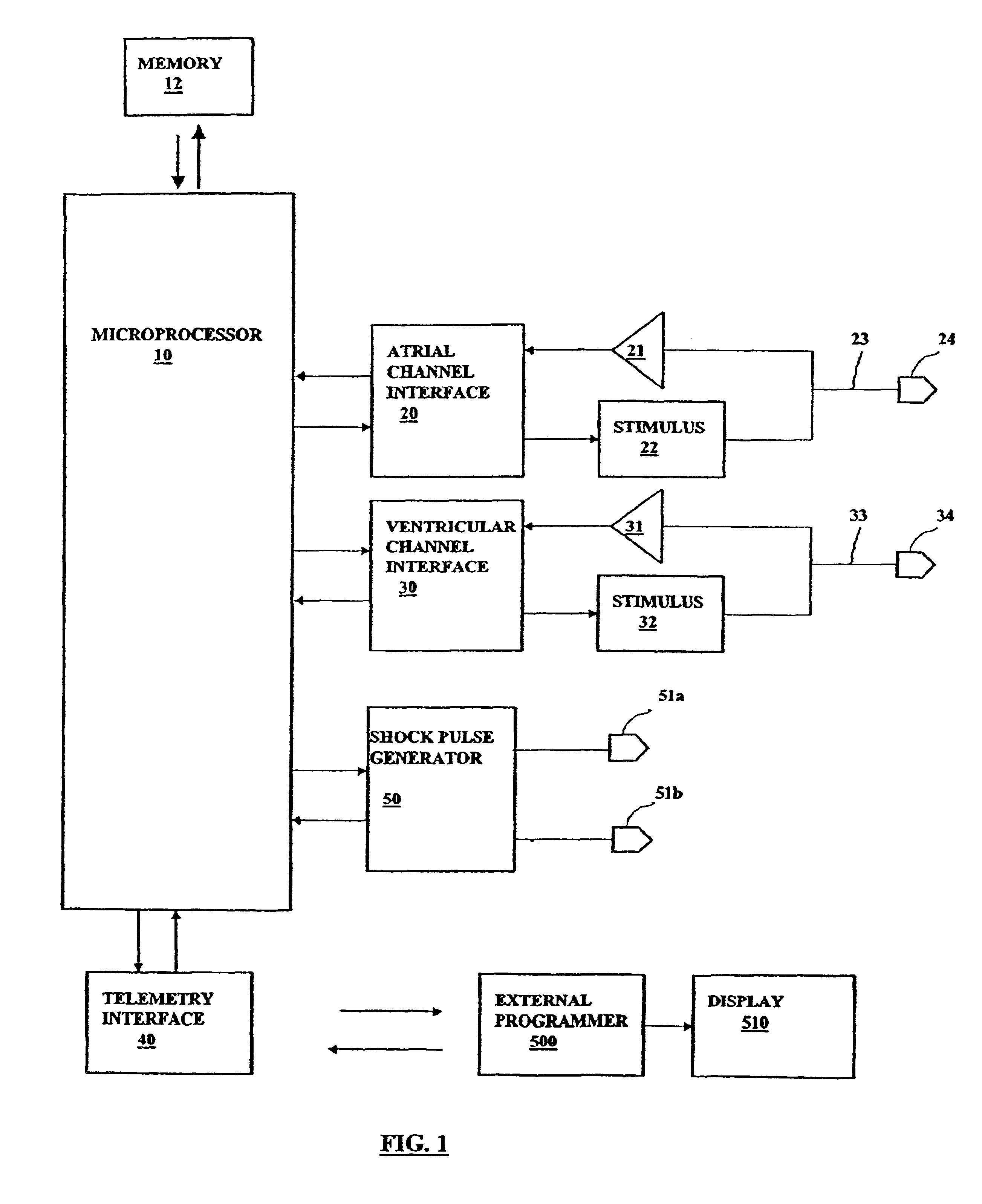
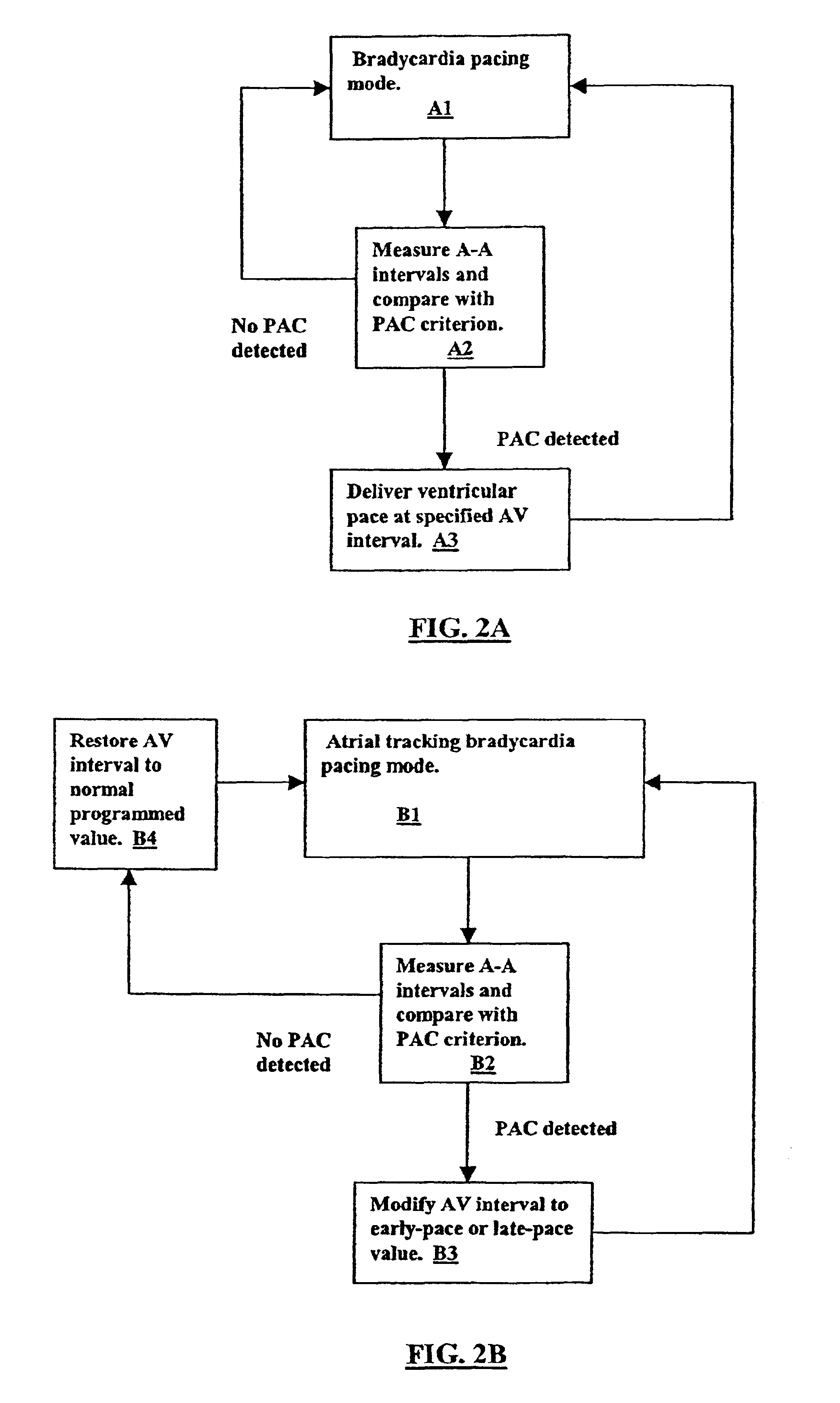
InactiveUS6957104B2Preventing atrial fibrillationAvoid typingHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular depolarizationPremature atrial contraction
A method and apparatus for preventing atrial fibrillation arising from a premature atrial contraction. Upon detection of a premature atrial contraction, a pace is delivered to a ventricle at a specified AV interval selected as either a late-pace or early-pace value. The resulting ventricular depolarization then occurs during a time when the atria are not vulnerable to the triggering of fibrillation.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for promoting intrinsic conduction through atrial timing
An atrial based pacing protocol promotes intrinsic conduction. An entire cardiac cycle is monitored for ventricular activity and permitted to lapse with ventricular activity. Ventricular pacing is available in a cardiac cycle immediately subsequent to such a skipped beat. When monitoring for intrinsic ventricular events, an event is expected within a given window. If no such event is detected, the cardiac cycle in truncated, leading to a shorter cycle that is devoid of ventricular activity. The subsequent cycle has a high likelihood of a ventricular sensed event and a greater than normal AV interval is provided prior to pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com