Patents
Literature
83 results about "Atrial pacing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
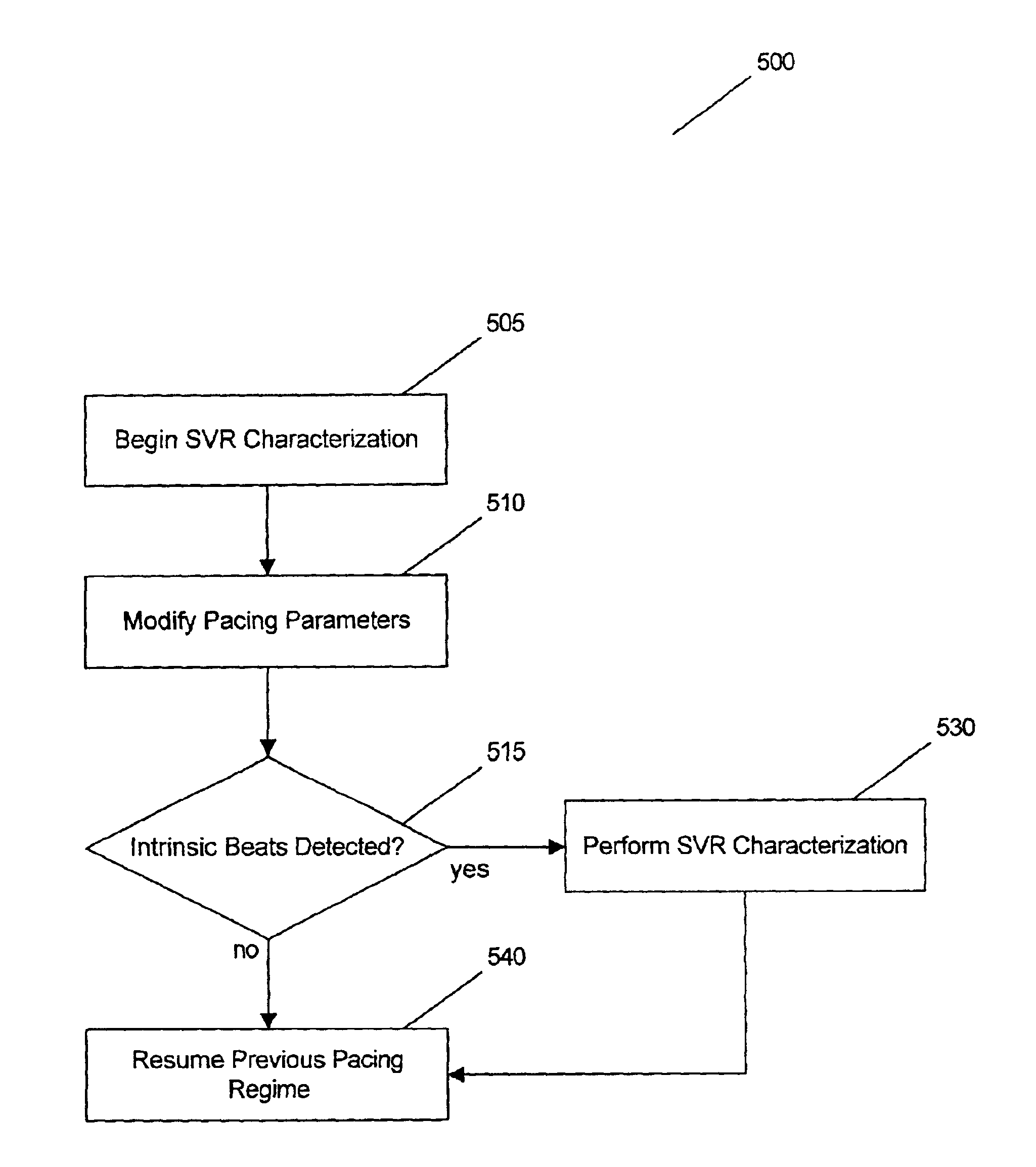
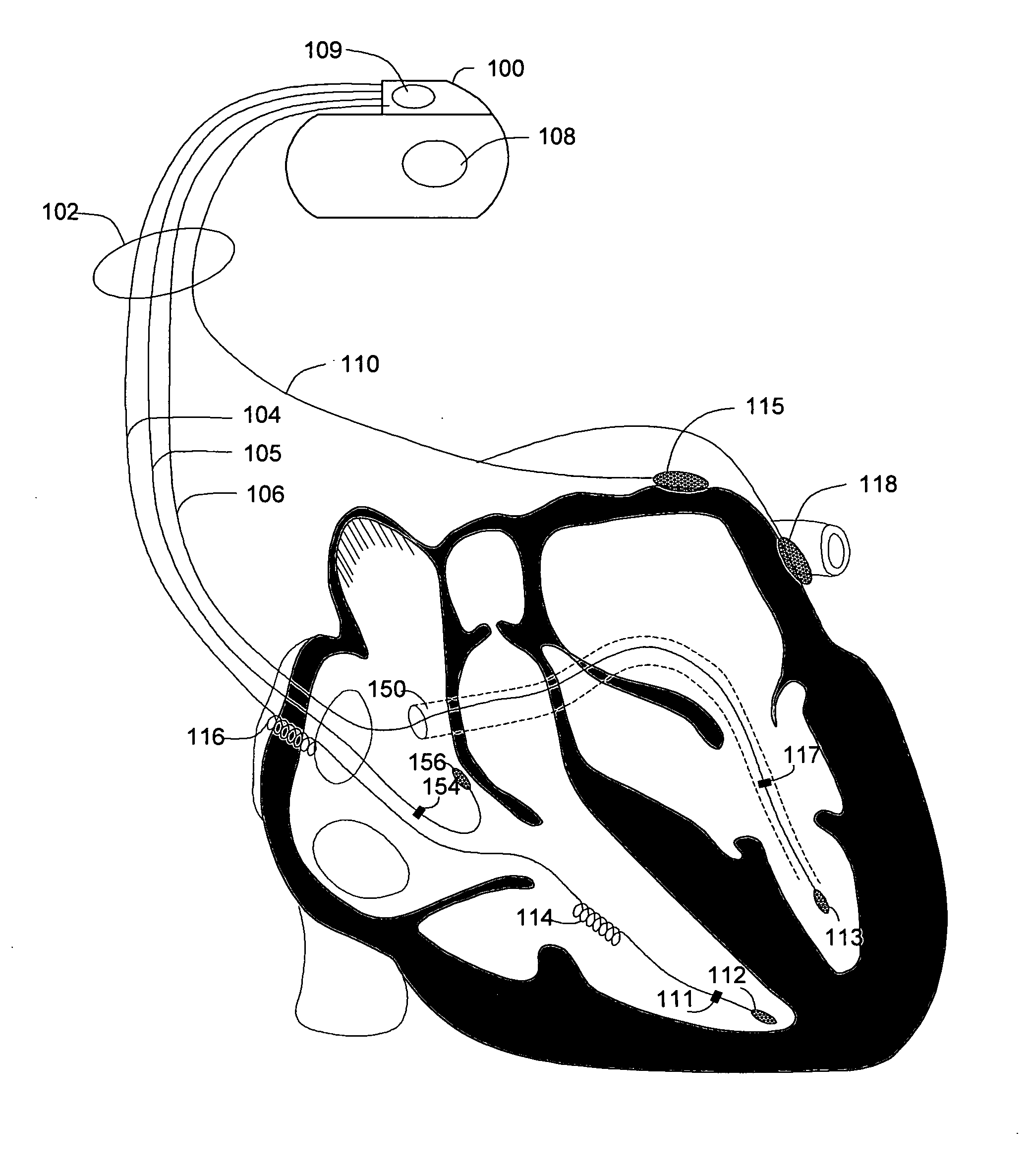
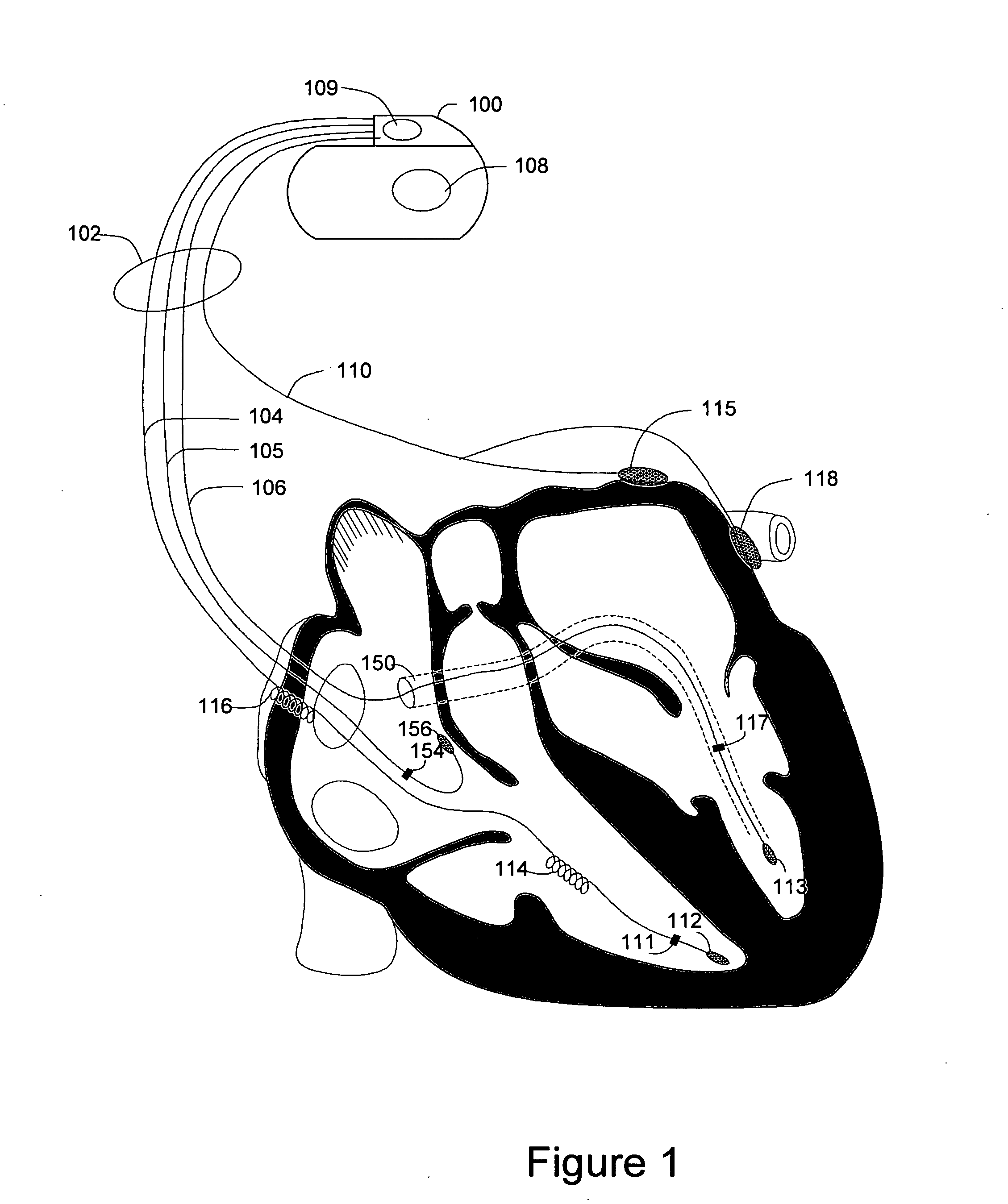
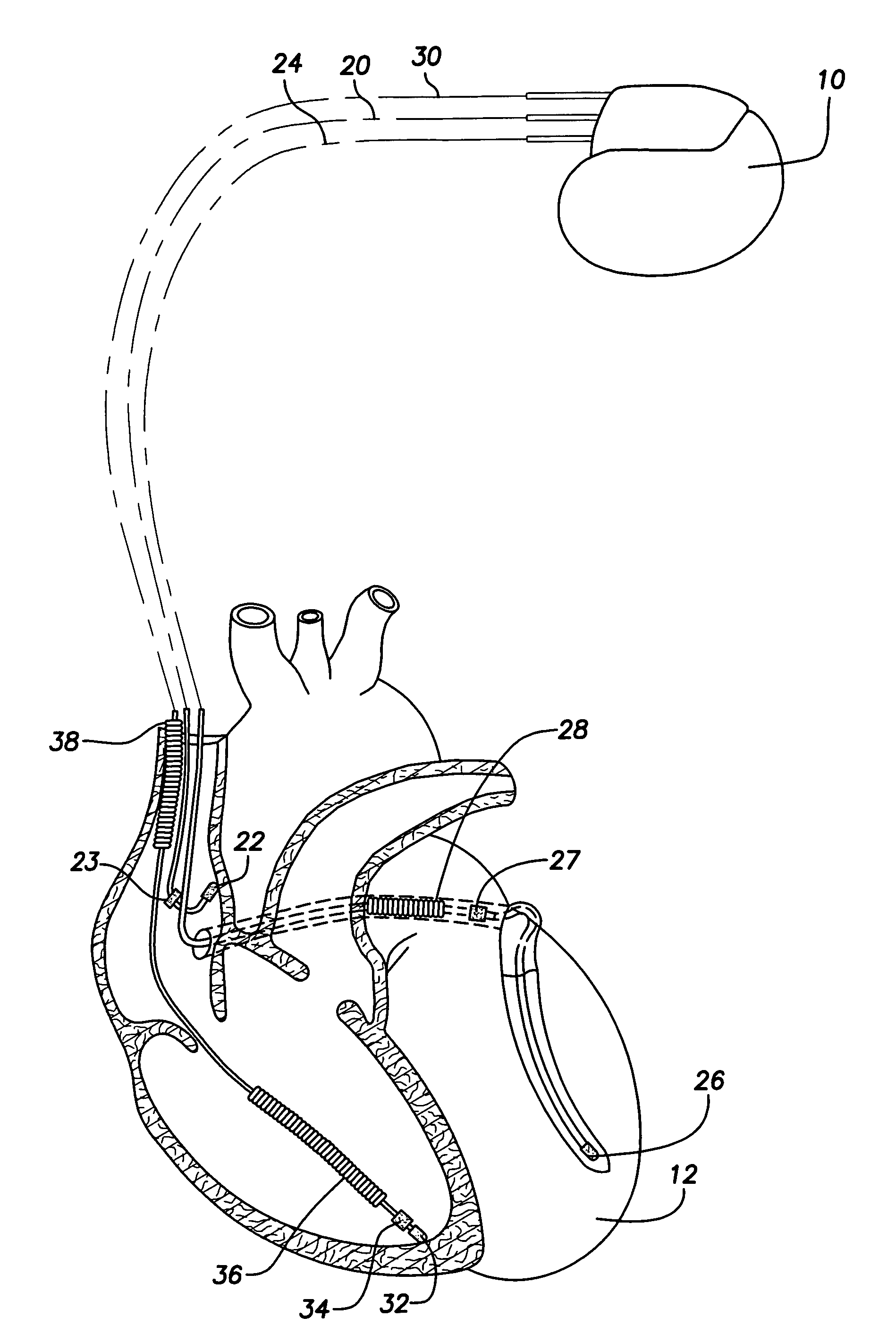
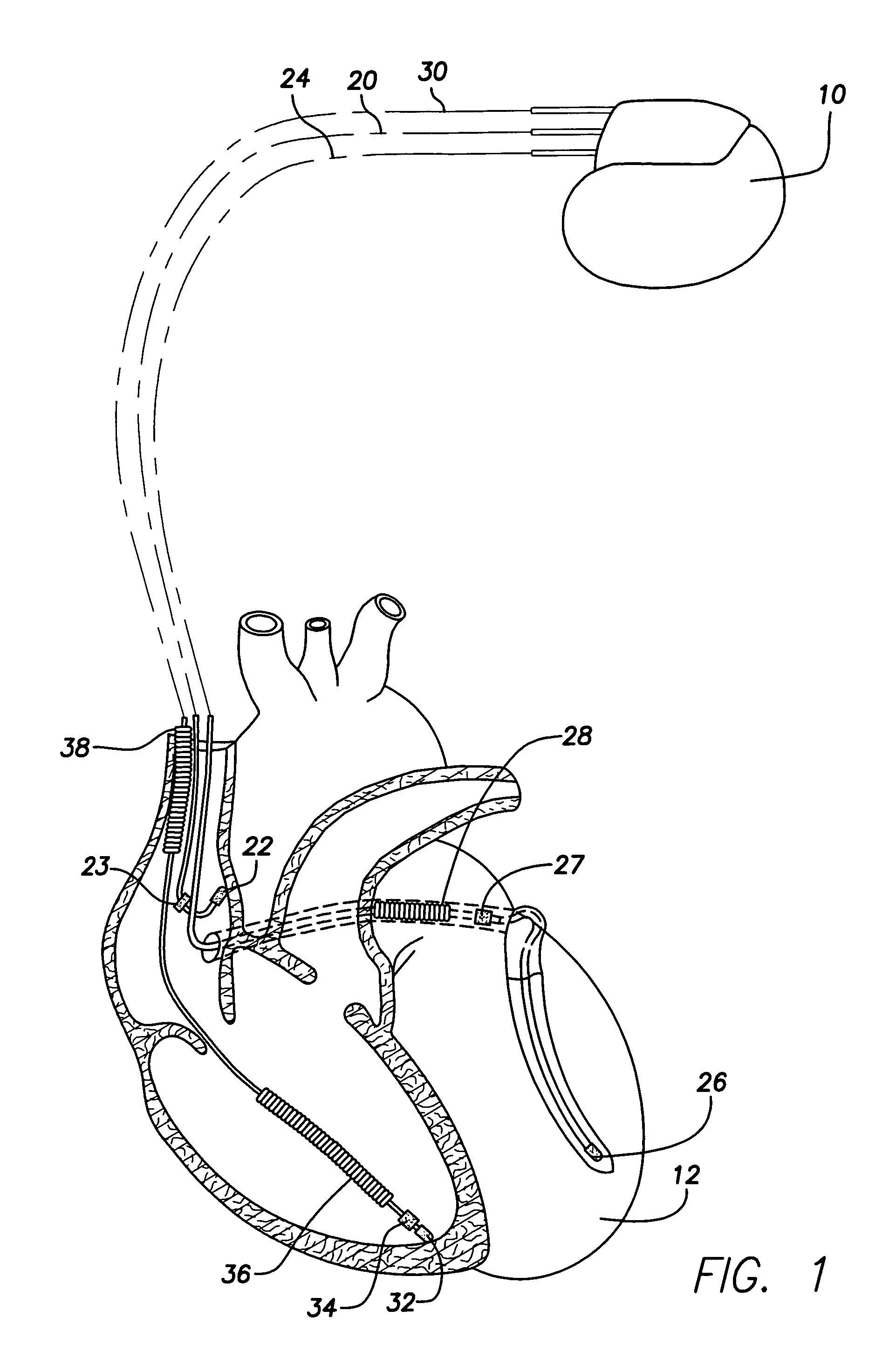
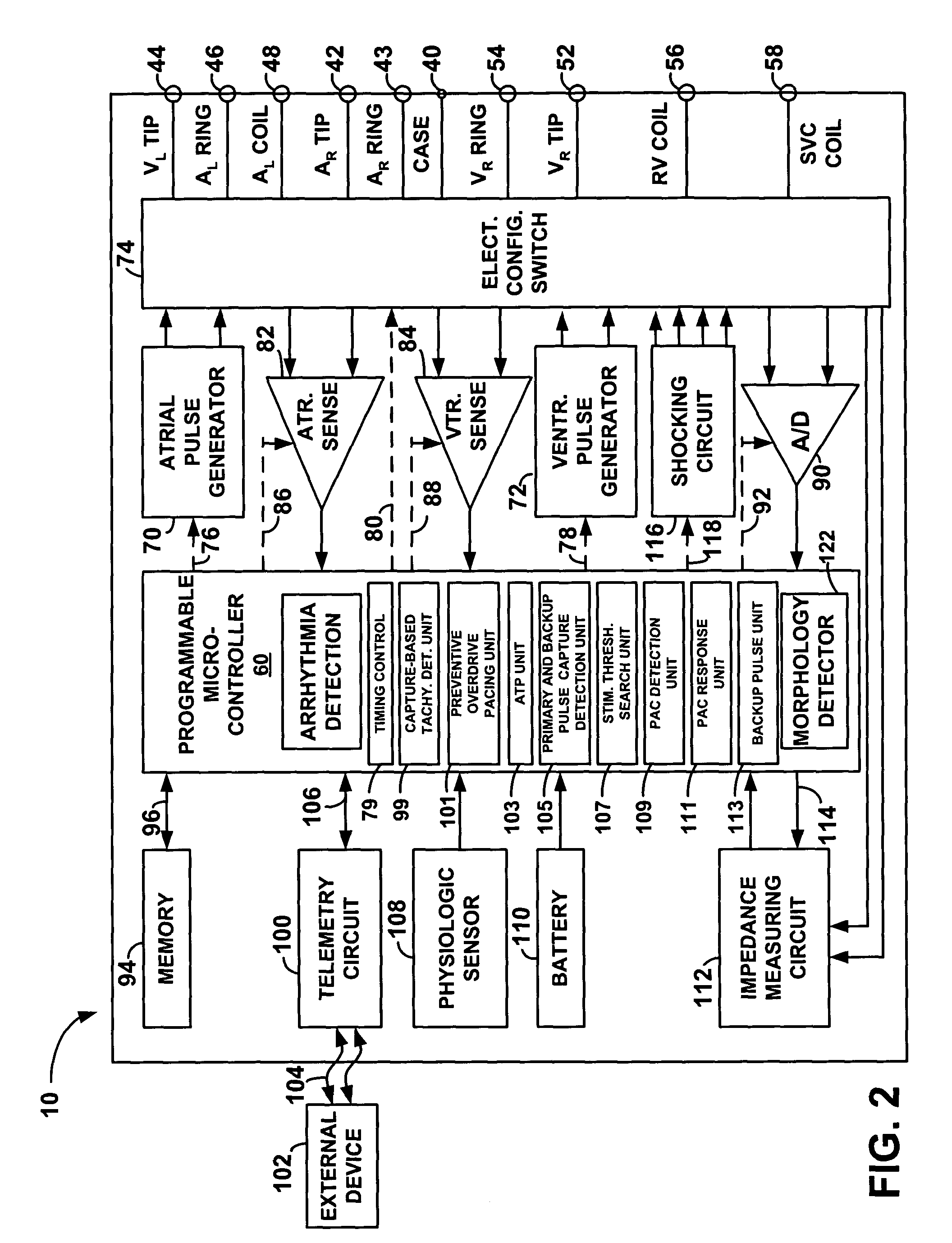
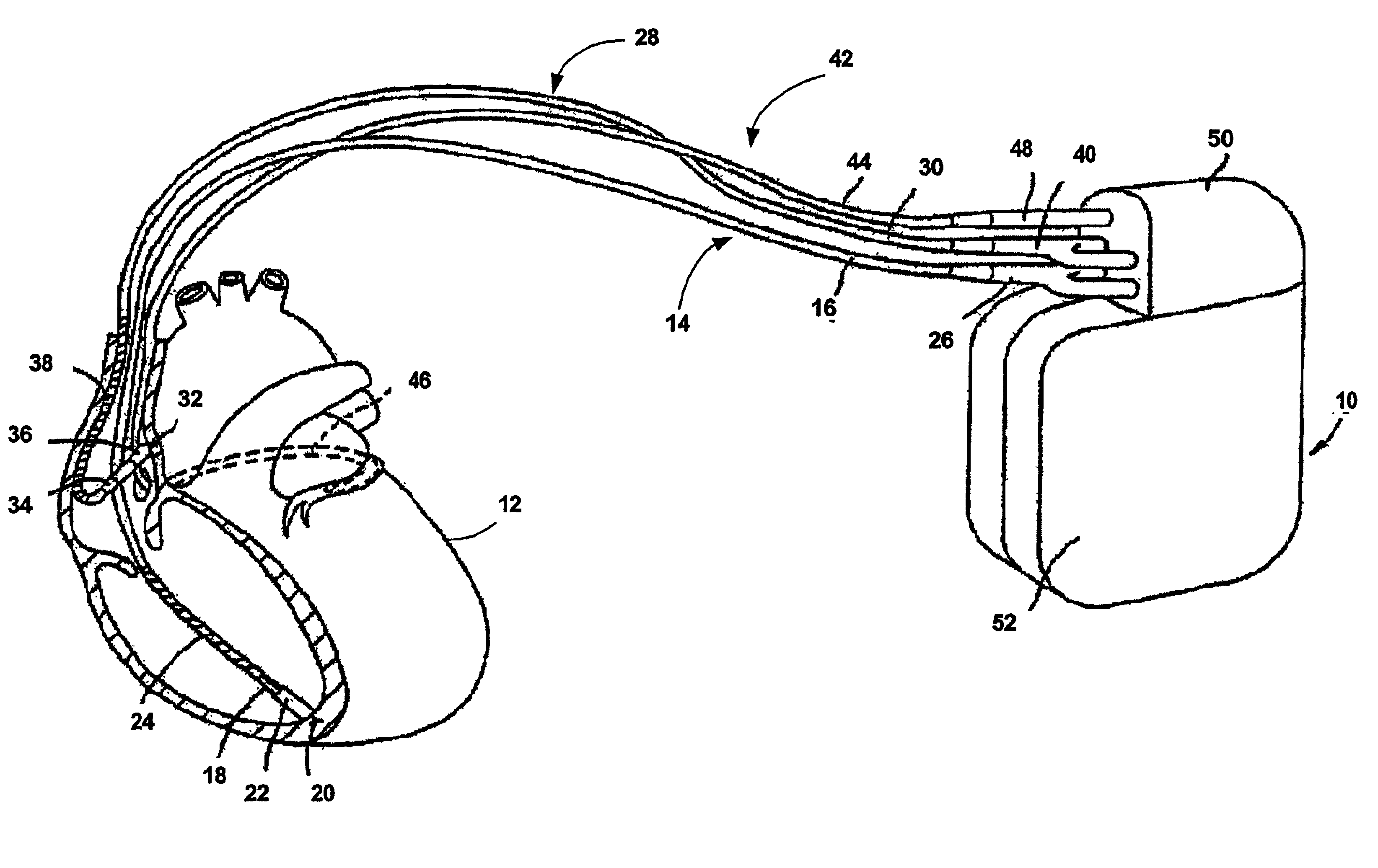
Method and system for characterizing supraventricular rhythm during cardiac pacing
A method and system for generating a characterization of one beat of a patient's supraventricular rhythm (SVR) involves performing such characterization while the heart is being paced. During SVR characterization, various pacing parameters are modified and the patient's supraventricular rhythm is characterized while the pacing parameters are modified. The SVR characterization process is effective in single and multiple chamber pacing modes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC +1
Method and apparatus for enhancing cardiac pacing
ActiveUS7200439B2Realize automatic adjustmentEnhancing cardiac pacingCatheterHeart stimulatorsActuatorHeart wall
Methods, apparatus and systems for enhancing cardiac pacing generally provide for measuring at least one cardiac characteristic, calculating at least one cardiac performance parameter based on the measured characteristic(s), and adjusting at least one functional parameter of a cardiac pacing device. Devices may include at least one catheter (such as a multiplexed catheter with one or more sensors and / or actuators), at least one implant (such as a sensor implantable in a heart wall), or a combination of both. Various cardiac performance parameters and / or pacing device performance parameters may be weighted, and the parameters and their respective weights may be used to determine one or more adjustments to be made to the pacing device. In some instances, the adjustments are made automatically.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
Steerable epicardial pacing catheter system placed via the subxiphoid process
InactiveUS20100241185A1Free from damageEpicardial electrodesDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresThoracic cavity
The epicardial pacing system and related method includes an epicardial catheter configured to be disposed in the middle mediastinum of the thorax of a subject for use in electrical pacing of the heart at one or more locations on the epicardial surface. The epicardial pacing catheter may include at least one electrode whereby the electrode is insulated on at least one side to allow pacing of the heart without damage to adjacent anatomical structures.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
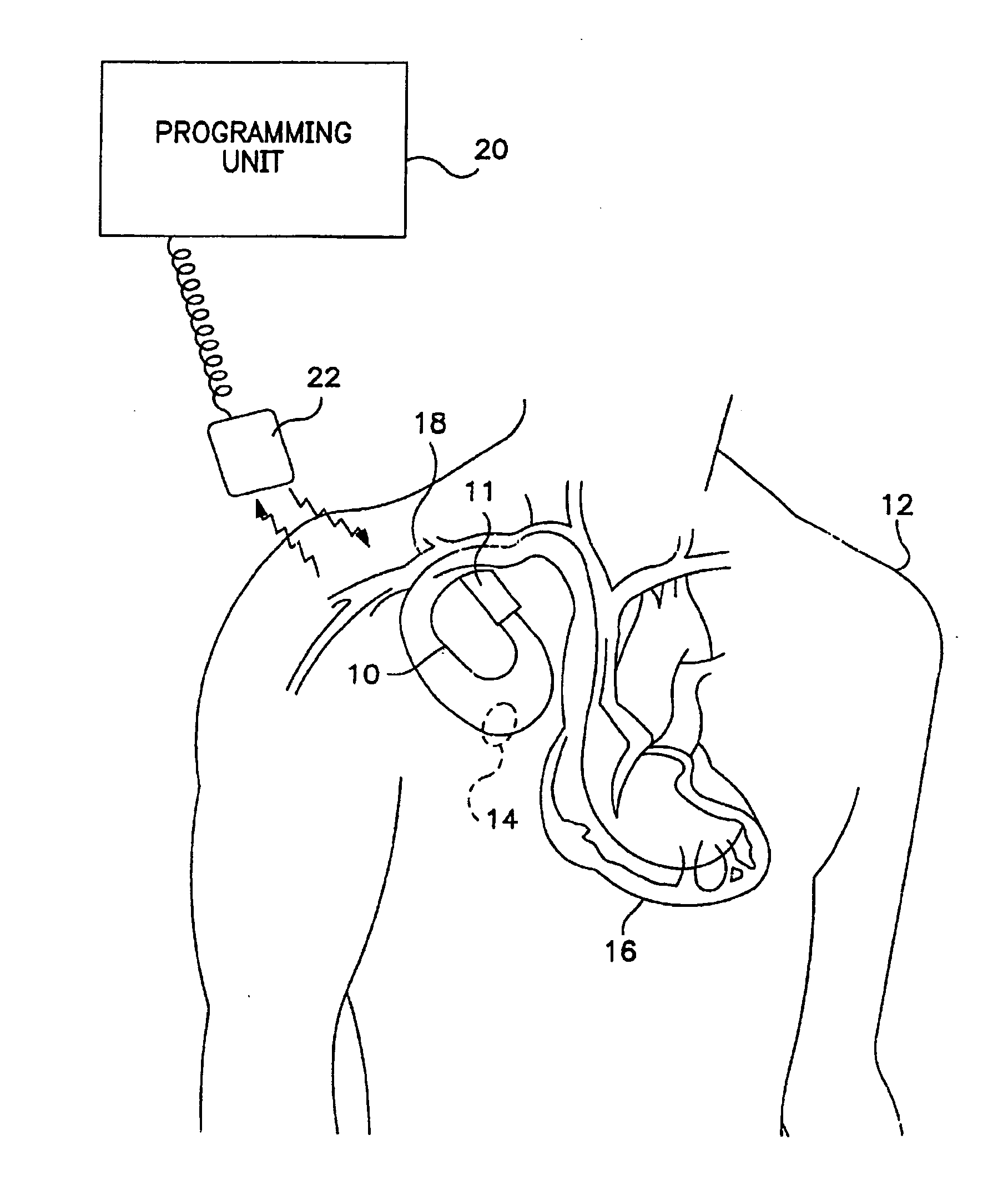
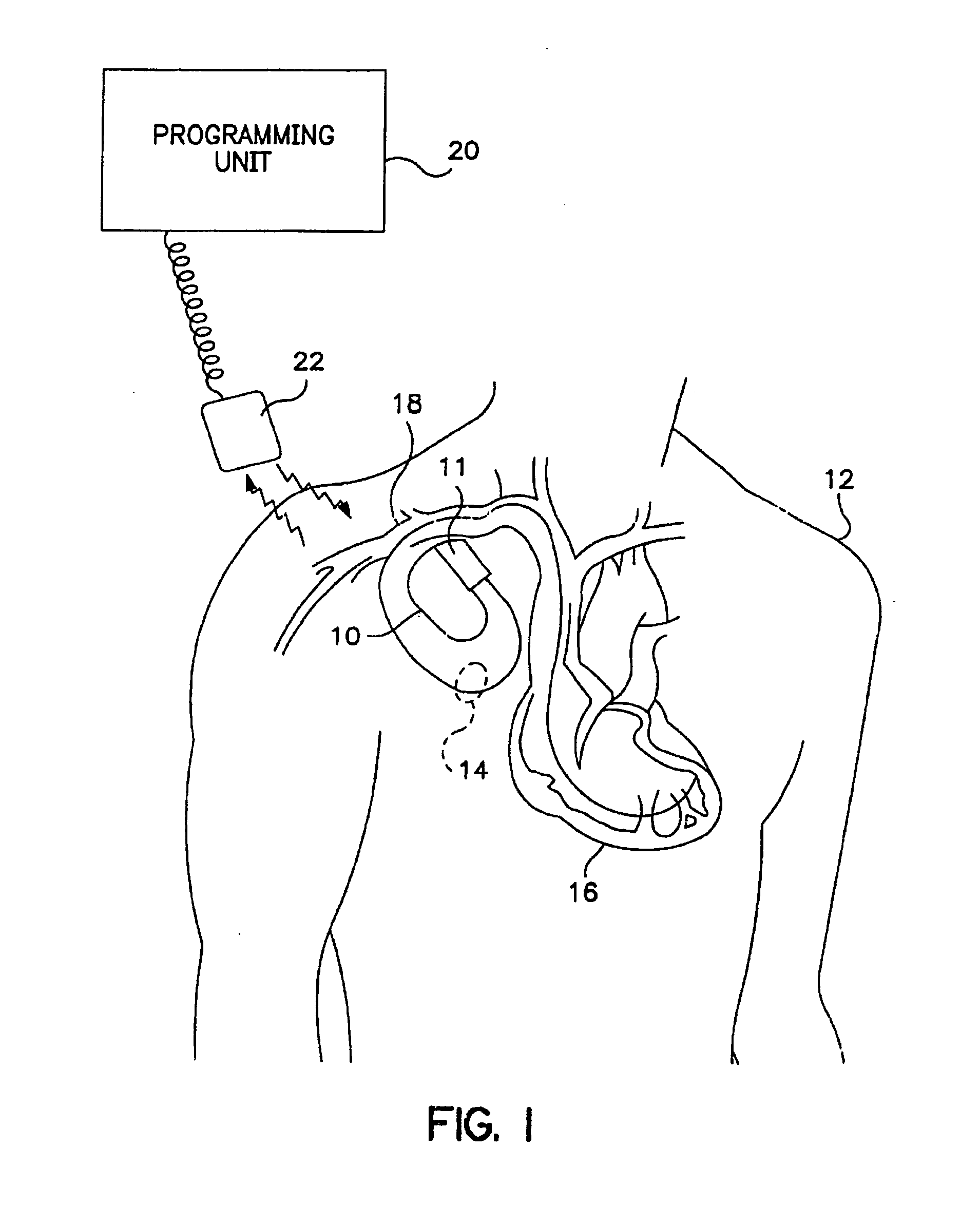
Cardiac pacing using adjustable atrio-ventricular delays
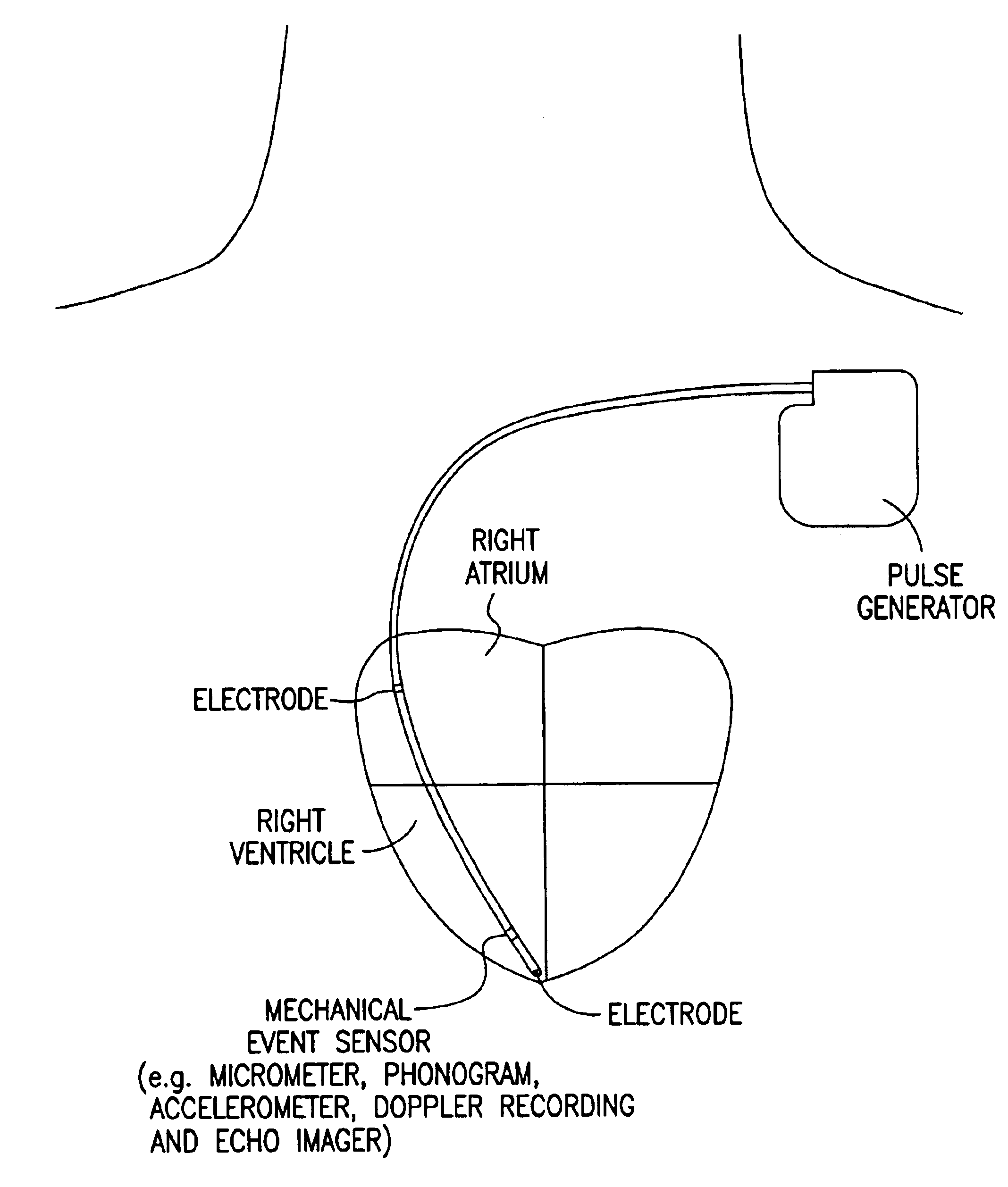
A pacing system for providing optimal hemodynamic cardiac function for parameters such as contractility (peak left ventricle pressure change during systole or LV+dp / dt), or stroke volume (aortic pulse pressure) using system for calculating atrio-ventricular delays for optimal timing of a ventricular pacing pulse. The system providing an option for near optimal pacing of multiple hemodynamic parameters. The system deriving the proper timing using electrical or mechanical events having a predictable relationship with an optimal ventricular pacing timing signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
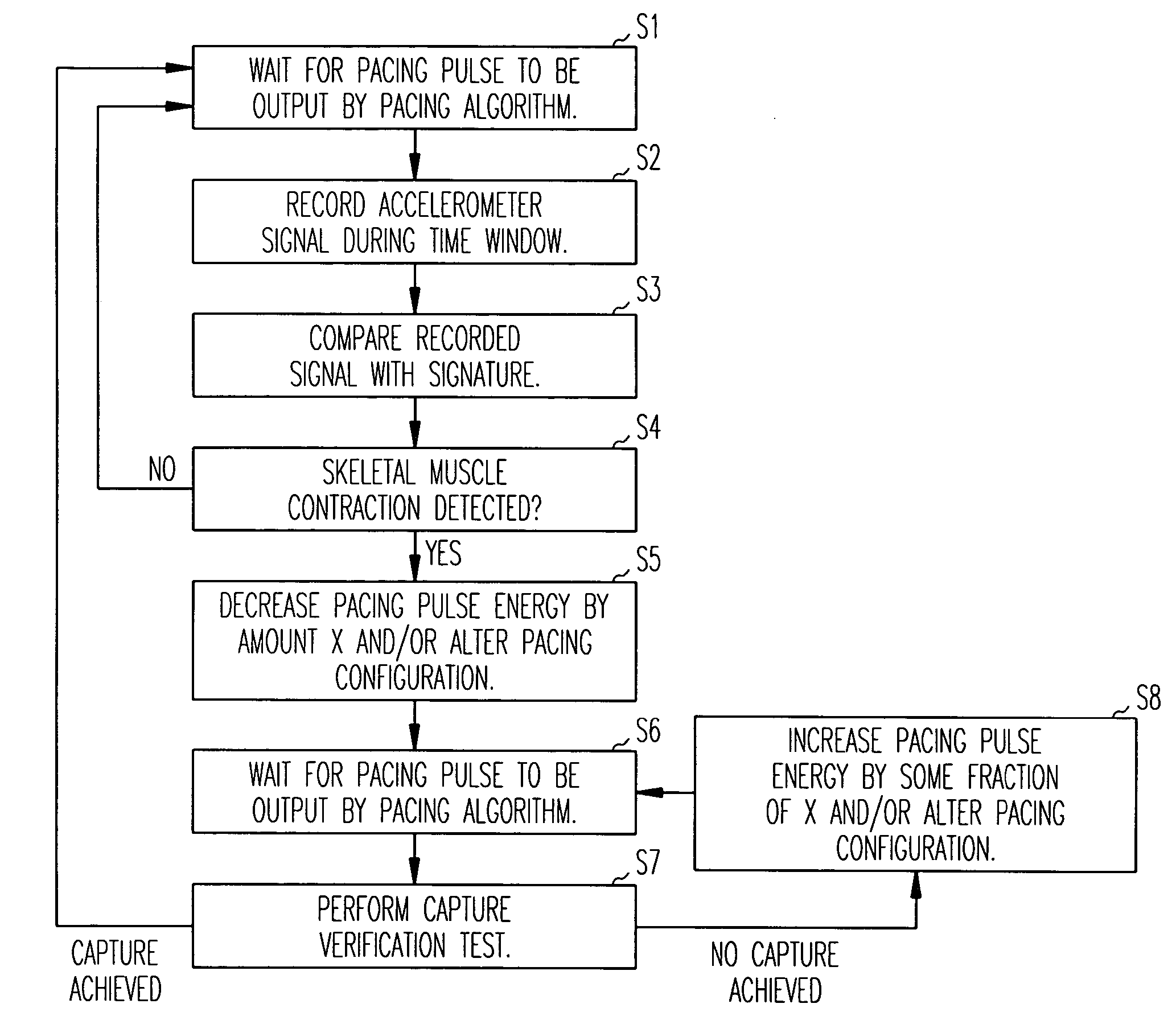
Method and apparatus for avoidance of phrenic nerve stimulation during cardiac pacing
A cardiac rhythm management device in which an accelerometer is used to detect diaphragmatic or other skeletal muscle contraction associated with the output of a pacing pulse. Upon detection of diaphragmatic contraction, the device may be configured to automatically adjust the pacing pulse energy and / or pacing configuration.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Self limited rate response
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
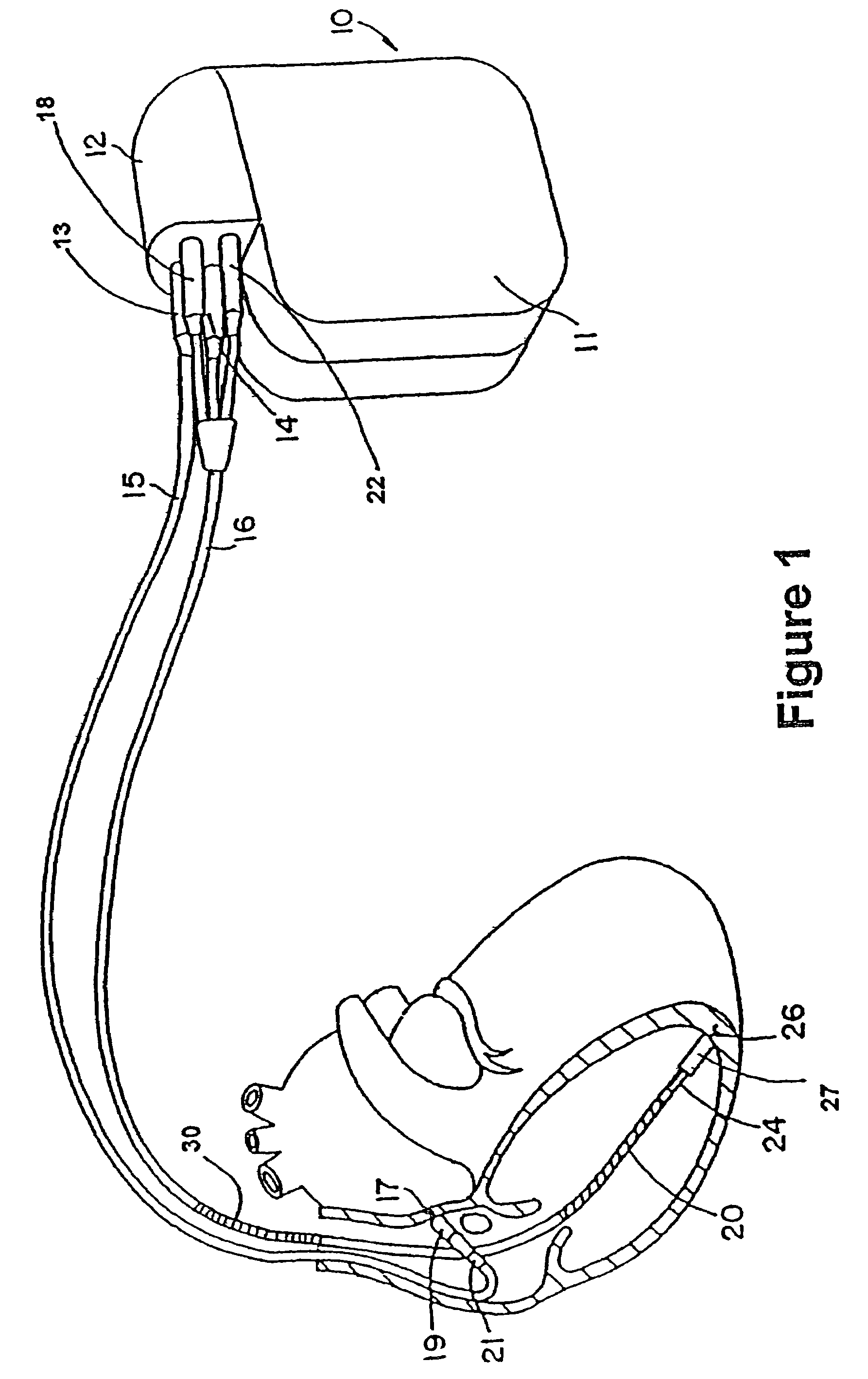
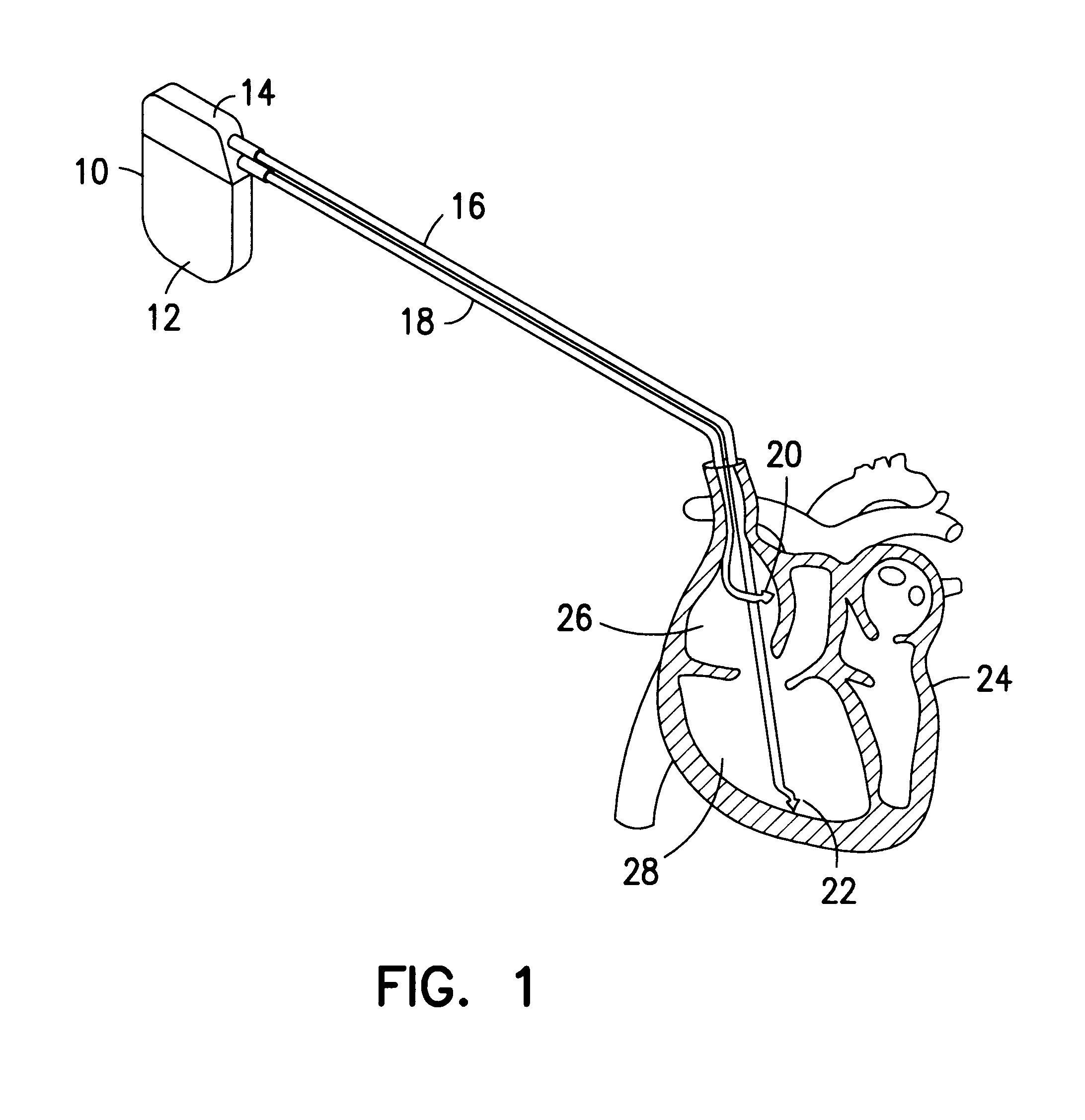
Cardiac stimulating apparatus having a blood clot filter and atrial pacer
InactiveUS6941169B2Formation of blood clots within such atrial appendage is decreased or eliminatedDecrease and eliminate formationHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesAppendageAtrial pacing
An apparatus is provided for reducing the formation and migration of blood clots from an atrial appendage, such as the left atrial appendage, to the blood vessel system of a patient. The apparatus comprises an atrial pacer to treat non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation (NRAF) of an atrial appendage so that the formation blood clots within the atrial appendage is decreased or eliminated. In addition, the apparatus includes a blood clot filter supported by the atrial pacer proximate the atrial appendage and the atrium to reduce the migration of blood clots from the atrial appendage into the blood vessel system of a patient.
Owner:P3 INNOVATIONS LLC
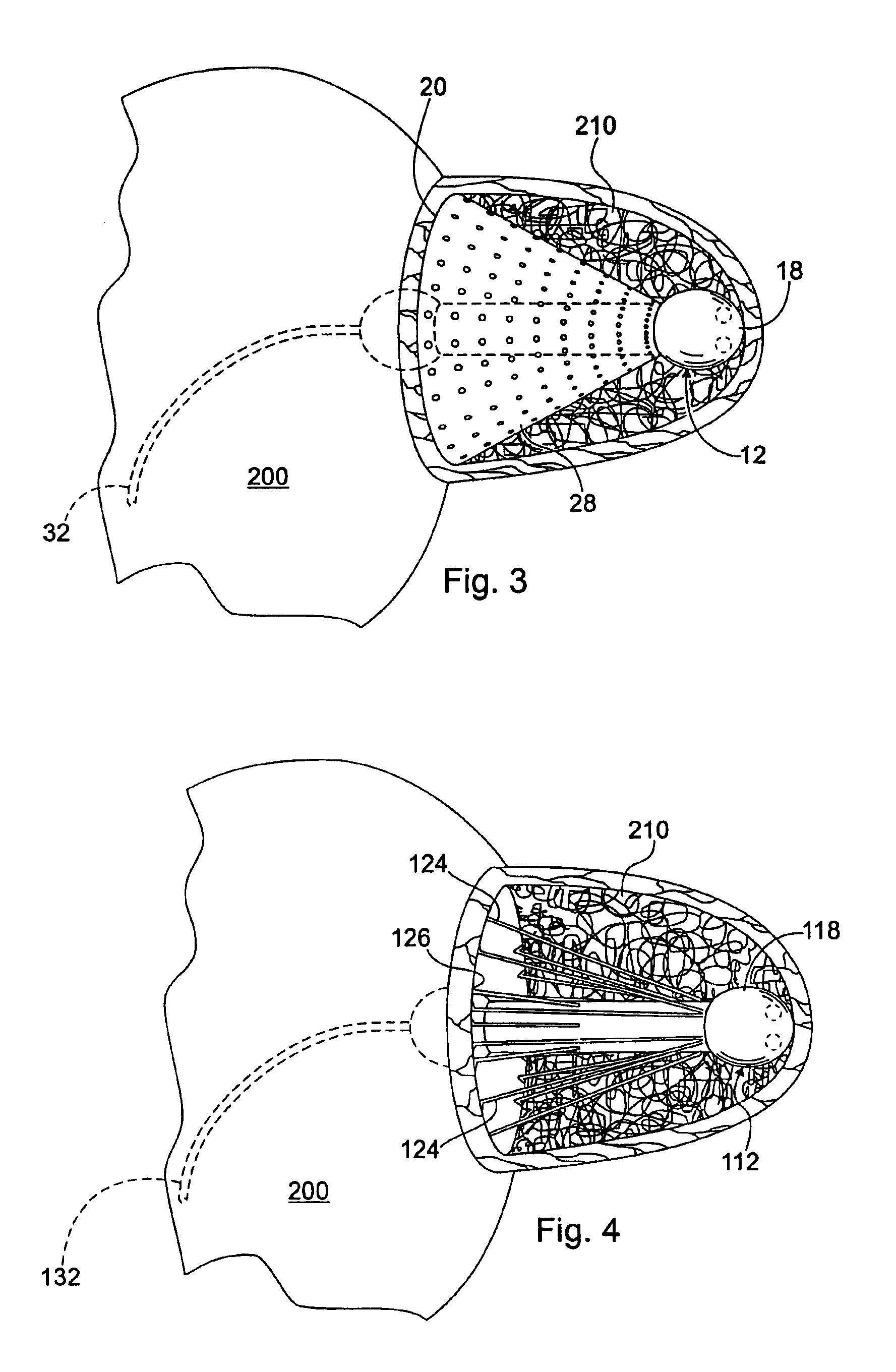
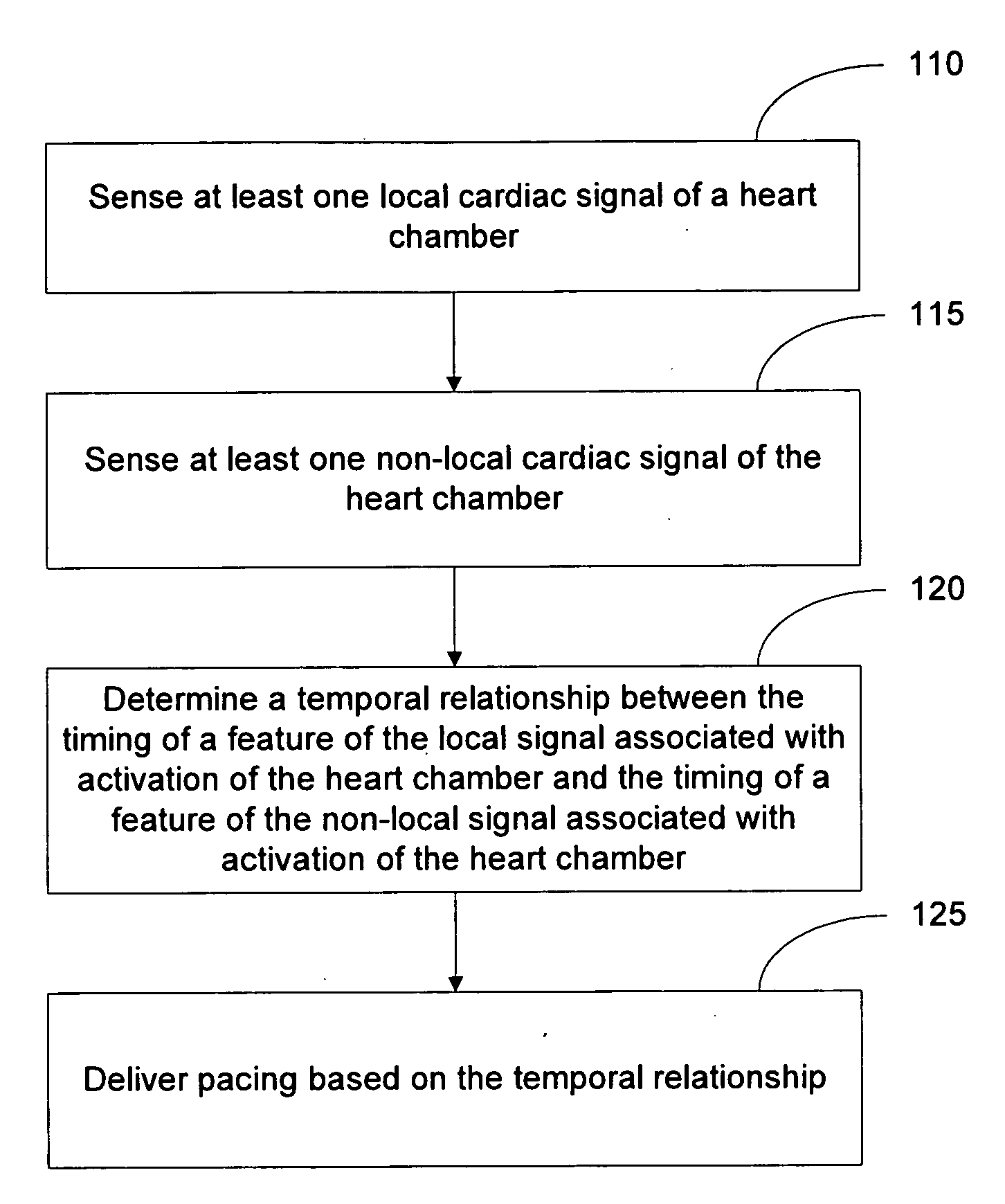
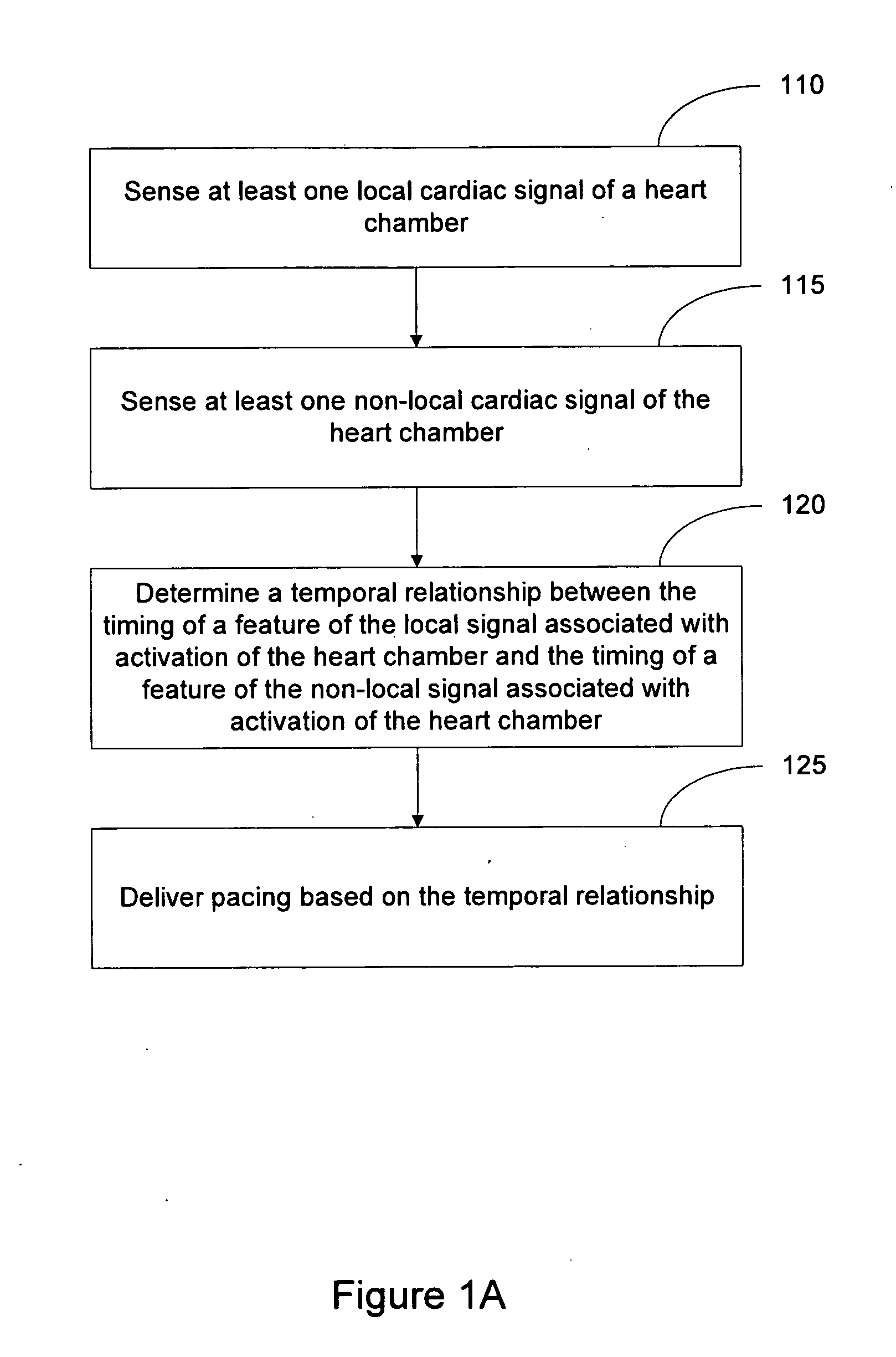
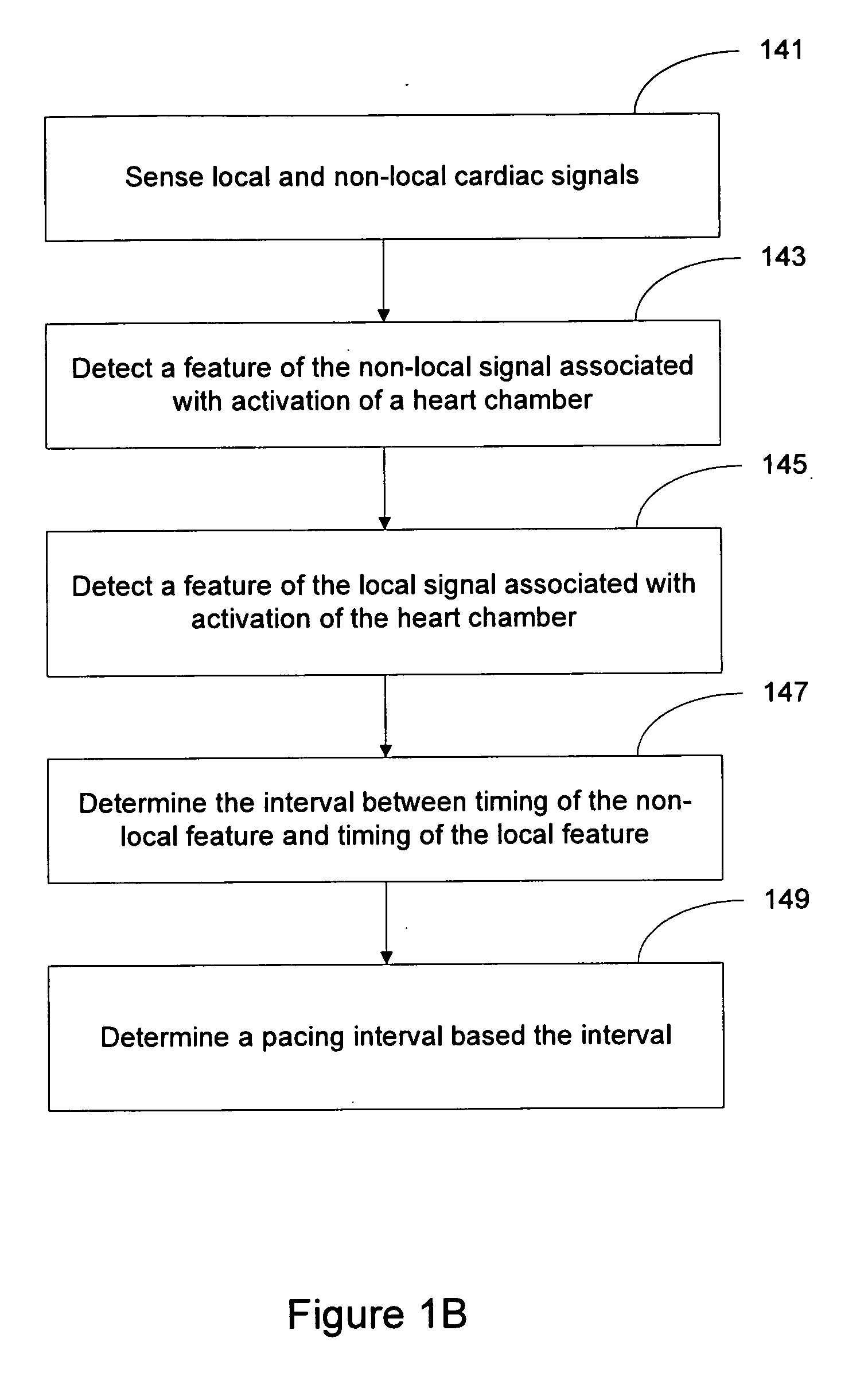
Local and non-local sensing for cardiac pacing
Systems and methods for determining pacing timing intervals based on the temporal relationship between the timing of local and non-local cardiac signal features are described. A device includes a plurality of implantable electrodes electrically coupled to the heart and configured to sense local and non-local cardiac signals. Sense circuitry coupled to first and second electrode pairs senses a local cardiac signal via a first electrode pair and a non-local cardiac signal via a second electrode pair. Detection circuitry is used to detect a feature of the local signal associated with activation of a heart chamber and to detect a feature of the non-local signal associated with activation of the heart chamber. A control processor times delivery of one or more pacing pulses based on a temporal relationship between timing of the local signal feature and timing of the non-local signal feature.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Leadless cardiac pacemaker and system
ActiveCN101578067AEpicardial electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac pacemaker
In a cardiac pacing system, a leadless cardiac pacemaker is configured for implantation in electrical contact with a cardiac chamber and configured for leadless pacing.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL SUPPLIES CO LTD
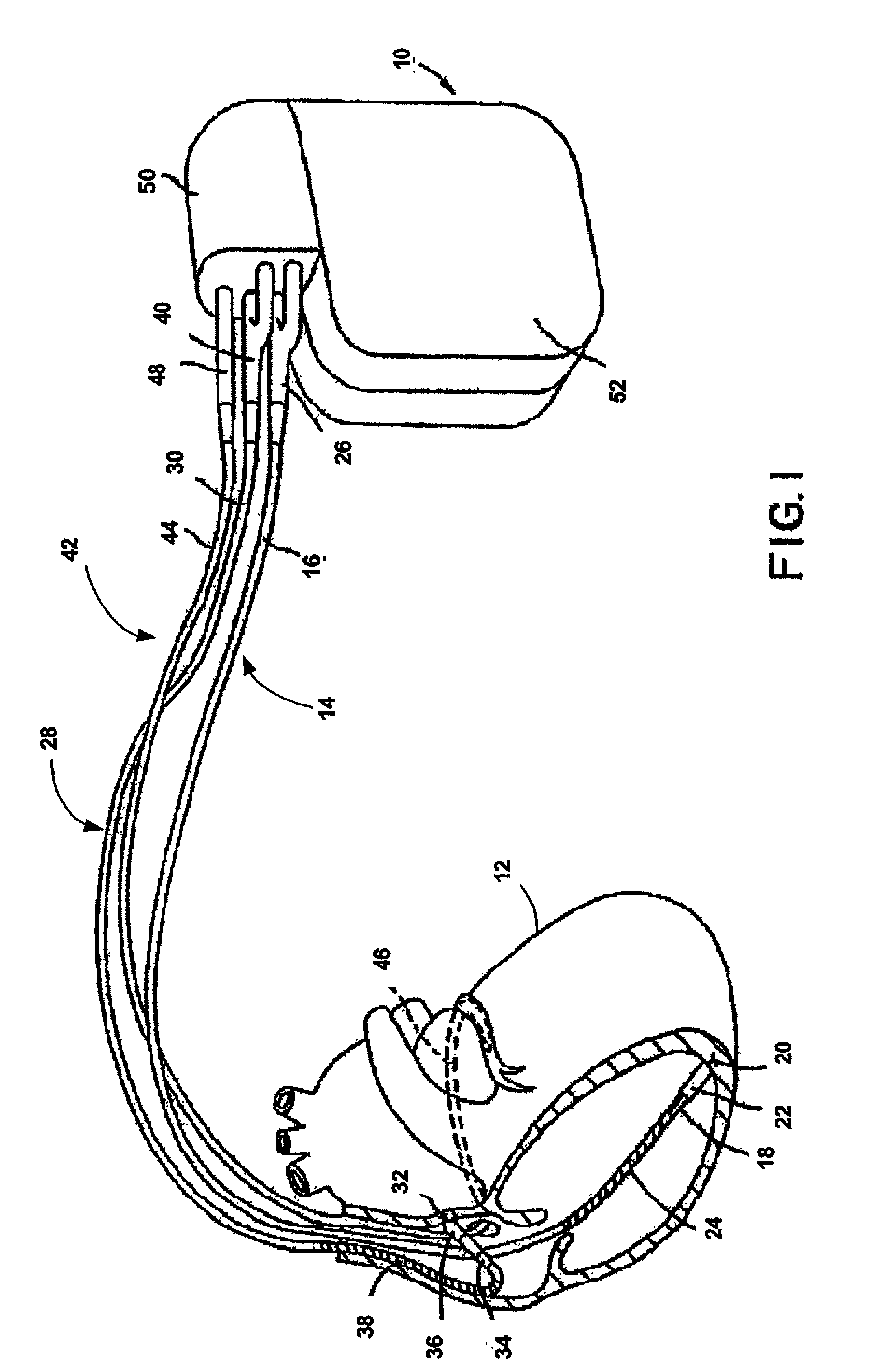
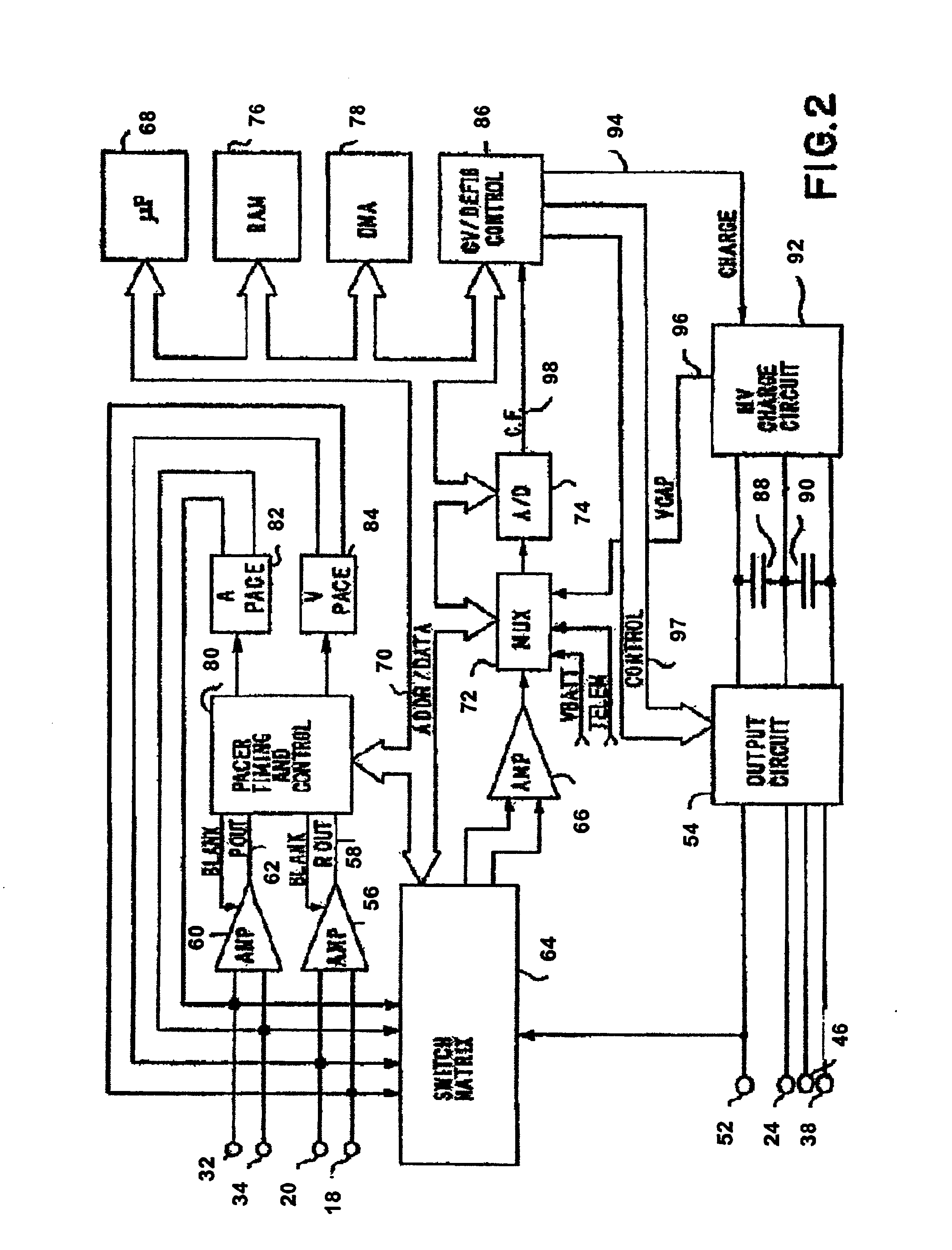
Method and apparatus for affecting atrial defibrillation with bi-atrial pacing
InactiveUS7027861B2Easy to usePreventing atrial fibrillationHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsAtrial cavityCoronary sinus
A method and apparatus for cardioverting the atrium of a human heart that includes insertion of first and second elongated electrodes tranvenously into the heart and associated vessels. One electrode is preferably located in the coronary sinus and great vein of the heart. The other electrode is preferably located in the vicinity of the right atrium of the heart, spaced from the electrode located in the coronary sinus. In response to detection of fibrillation or in response to manual triggering, a defibrillation pulse is applied between the first and second electrodes to effect atrial cardioversion. Further, after delivery of a successful defibrillation shock, the width of intrinsic p-waves are monitored and bi-atrial pacing is temporarily initiated if the width exceeds a preset or programmable threshold.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Automated Assessment Of Atrioventricular And Ventriculoatrial Conduction
ActiveUS20090143832A1Restore normal sinus rhythmHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaInappropriate shock
A method discriminates between ventricular arrhythmia and supraventricular arrhythmia by determining the direction of an electrical signal conducted through the atrioventricular node. An implantable cardiac defibrillator provides atrioventricular and ventriculoatrial pacing bursts to determine if an arrhythmia with a 1:1 atrial to ventricular relationship is due to ventricular tachycardia or supraventricular tachycardia. This discrimination capability reduces the incidence of inappropriate shocks from dual-chamber implantable cardiac defibrillators to near zero and provides a method to differentially diagnose supraventricular tachycardia from ventricular tachycardia.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
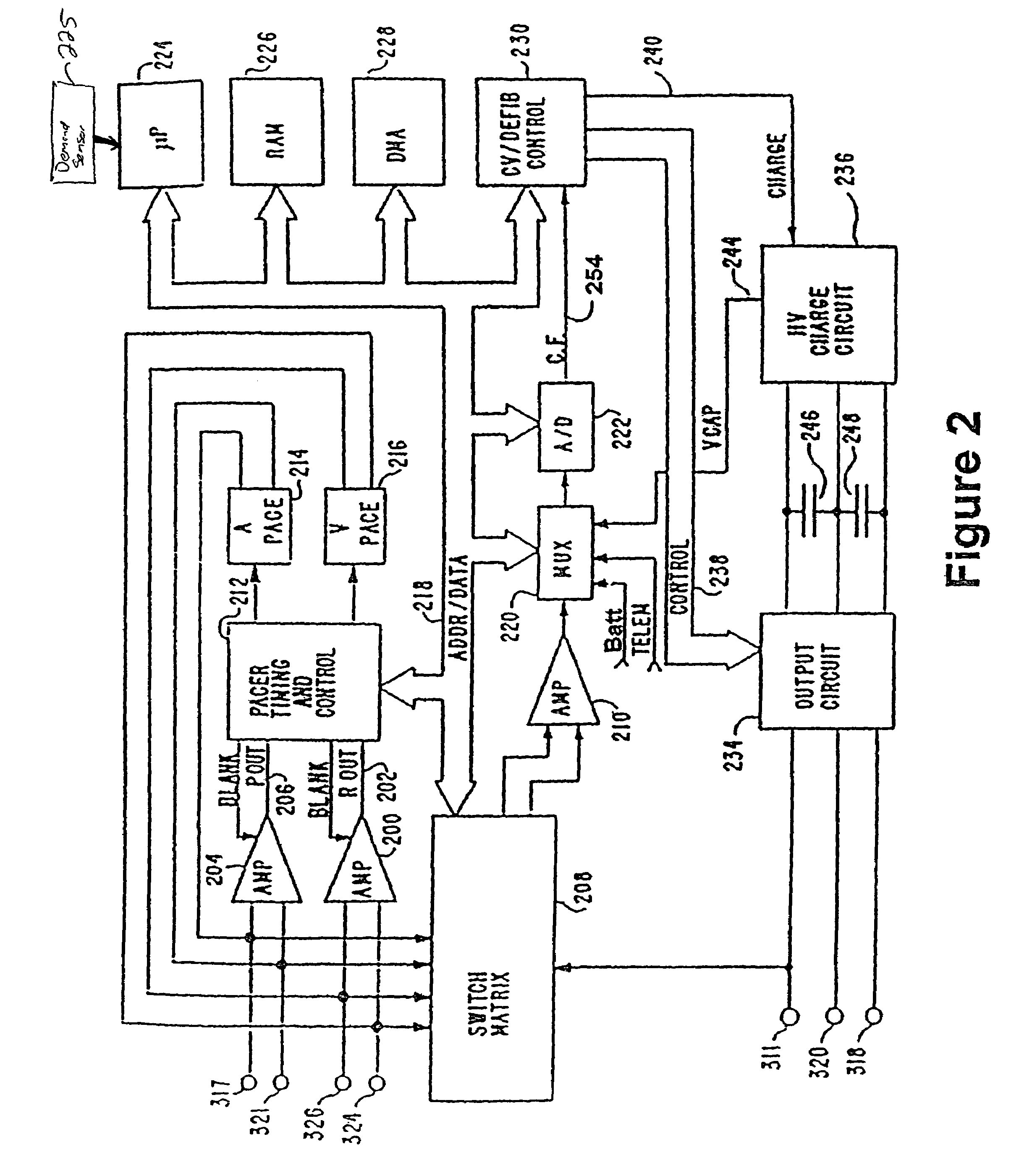
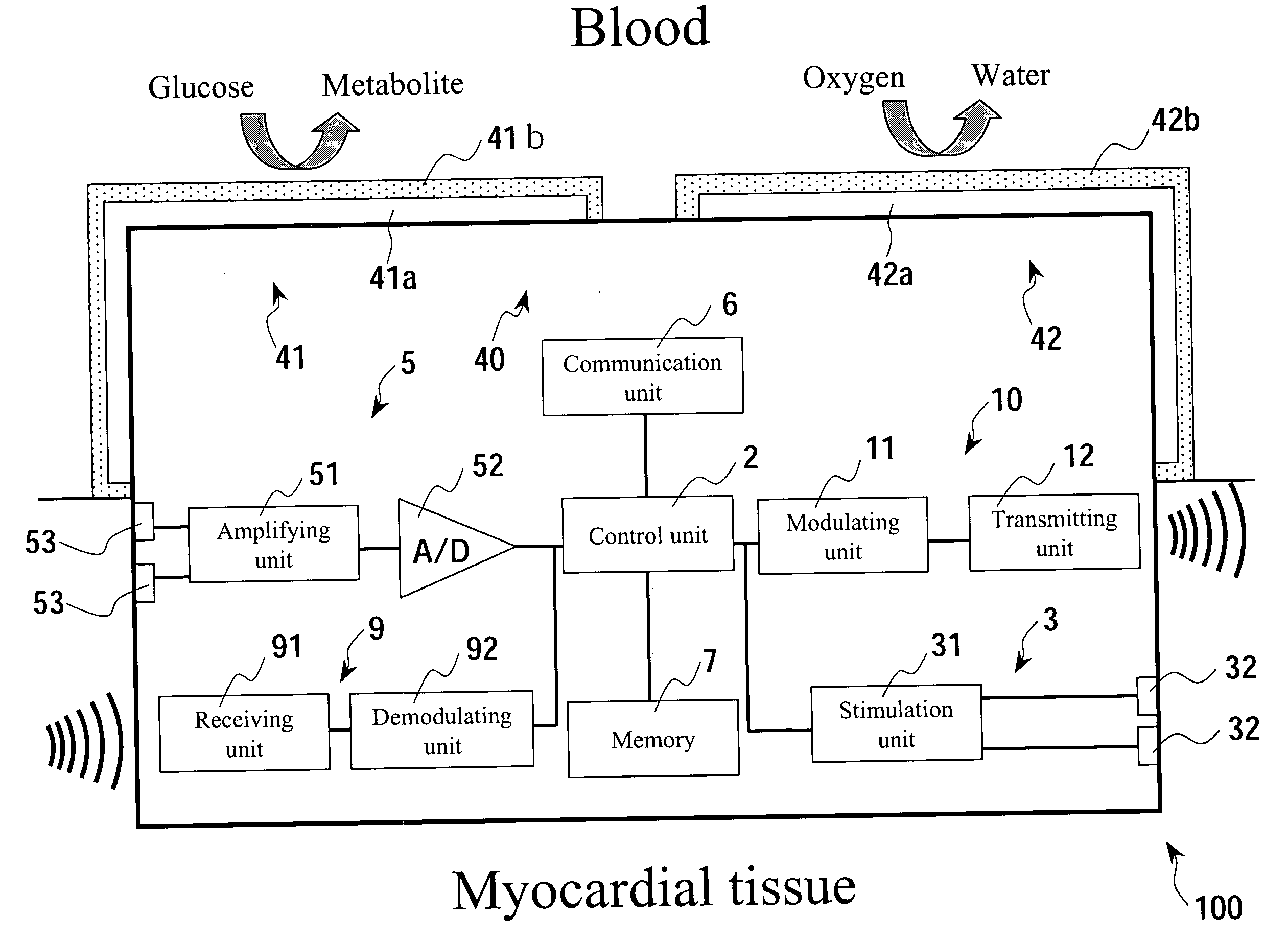
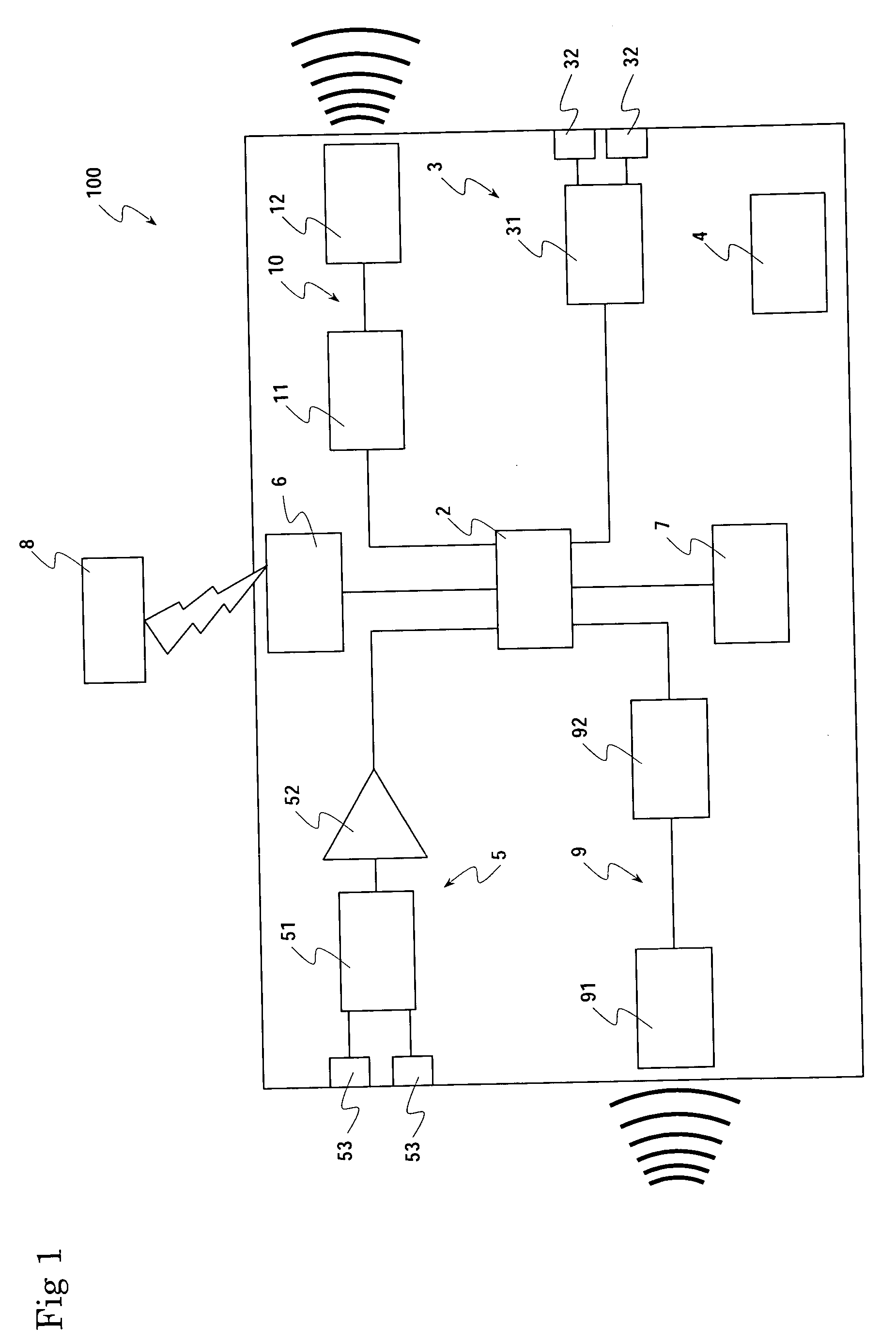
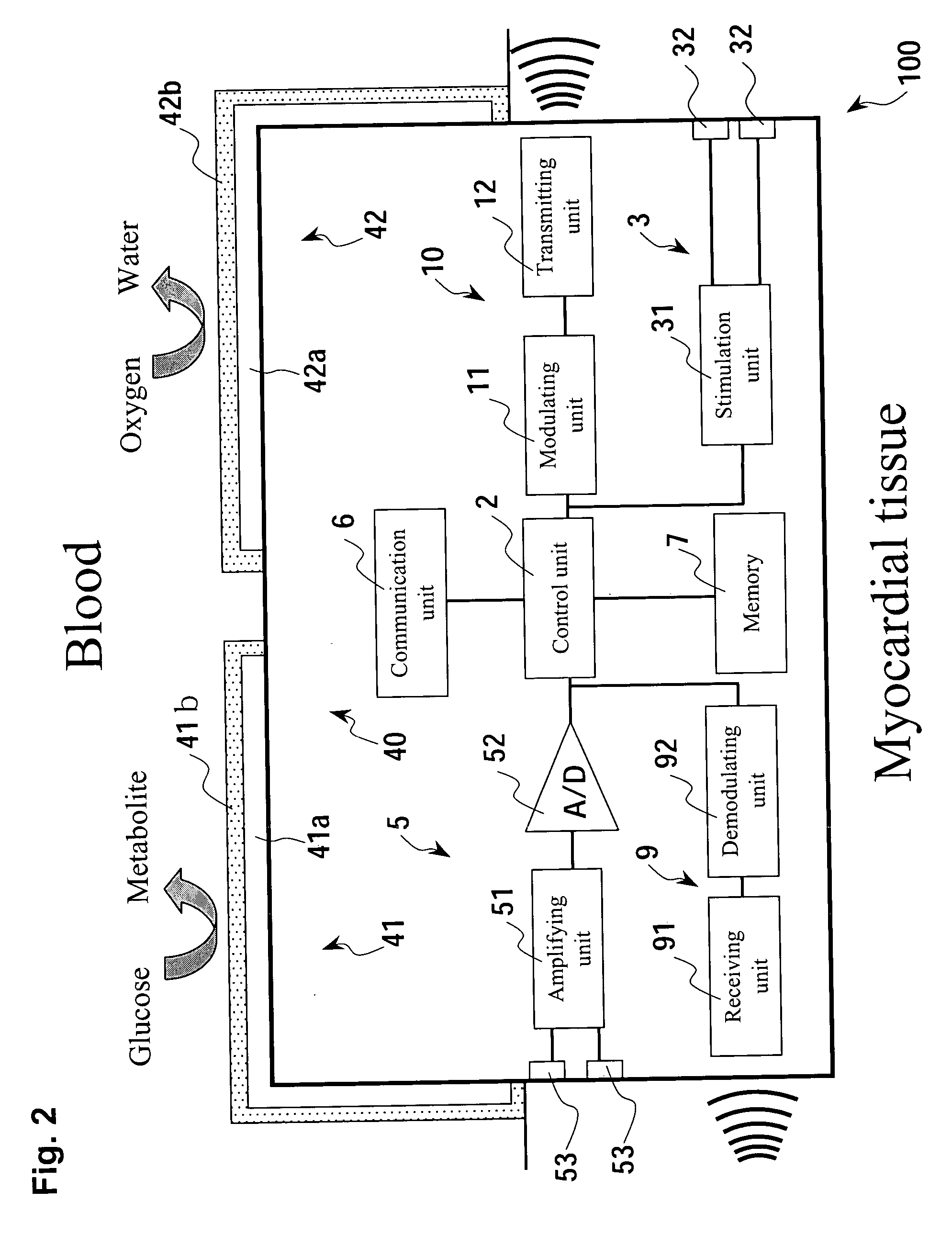
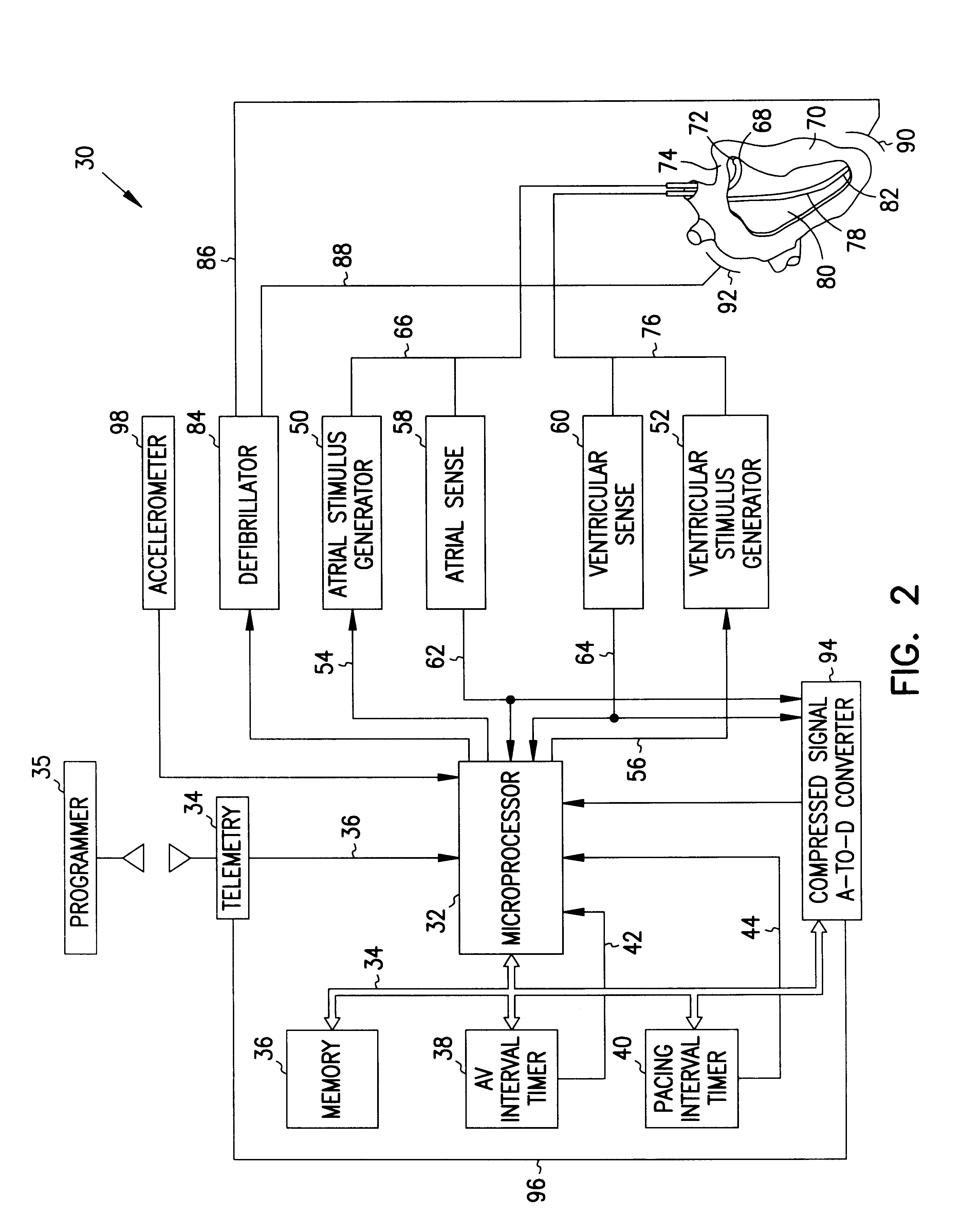
Micro integrated cardiac pacemaker and distributed cardiac pacing system
ActiveUS20050288717A1Suppress generationSuppresses detectionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl signalCardiac pacemaker electrode
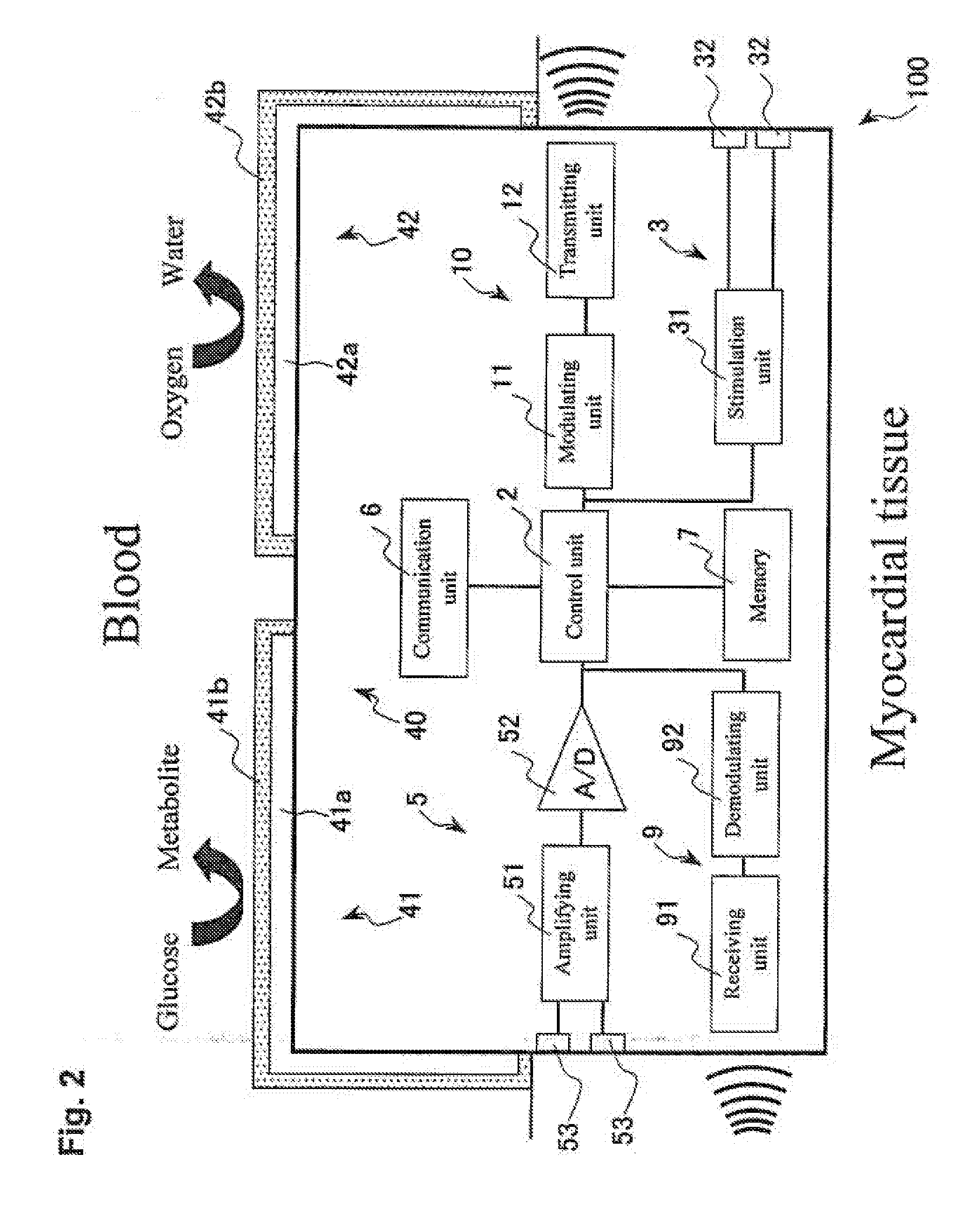
A micro integrated cardiac pacemaker includes a control unit for outputting a control signal according to cardiograph information, heart stimulating means for stimulating heart tissue in response to the control signal, cardiograph information extracting means for extracting cardiograph information and outputting it to the control unit, and a power supply unit for supplying drive power. The power supply unit is a biological fuel cell that takes out electrons by oxidation of a biological fuel. The biological fuel cell includes an anode and a cathode. An oxidase of a biological fuel and a mediator are immobilized on the cathode. Blood and / or body fluid are used as an electrolytic solution, and a biological fuel and oxygen in the blood and / or the fluid are used. The biological fuel cell is attached to the end of a catheter and implanted into the heart, and the catheter is withdrawn, without incising the breast.
Owner:FUJIKIN INC +1
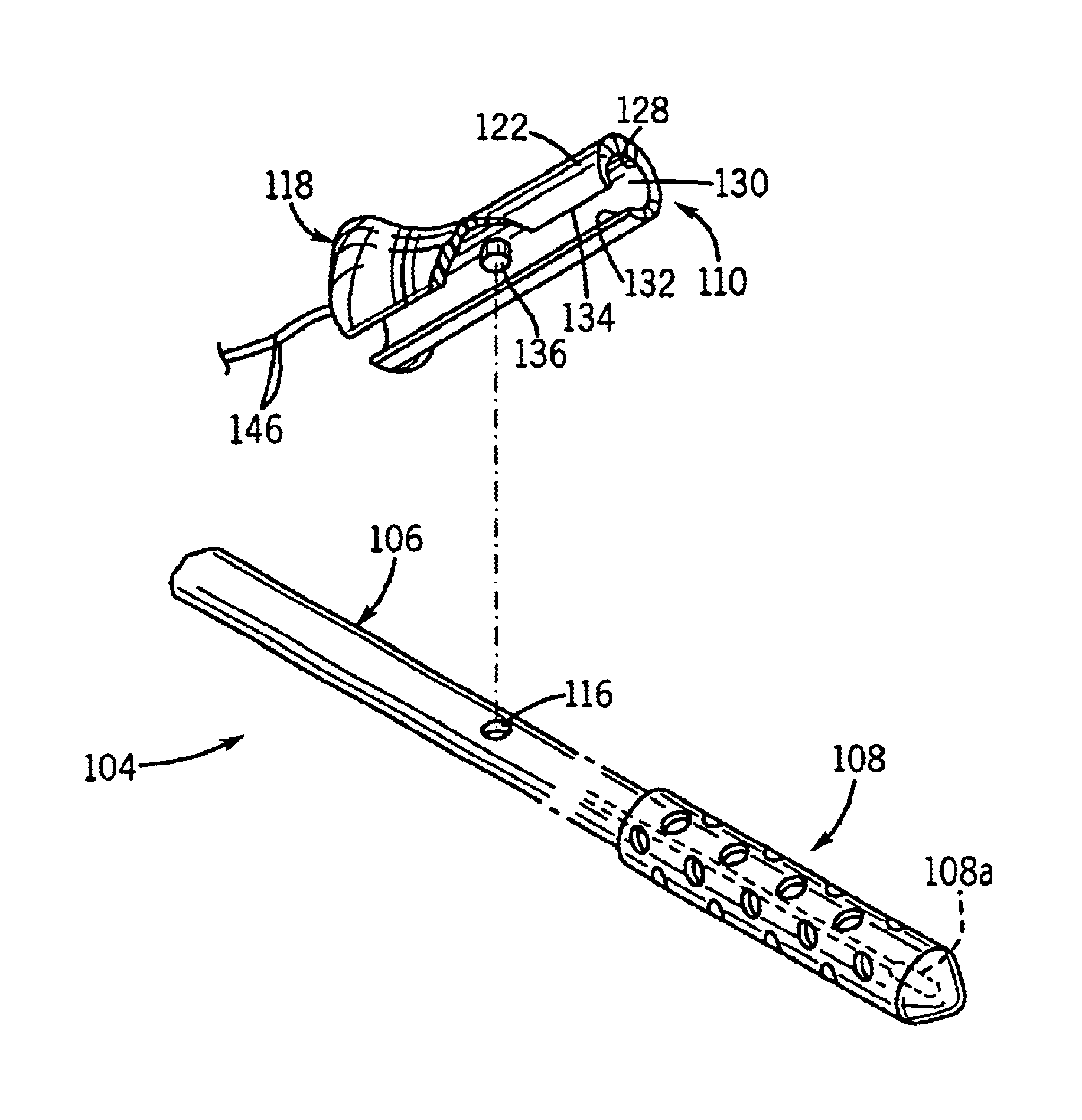
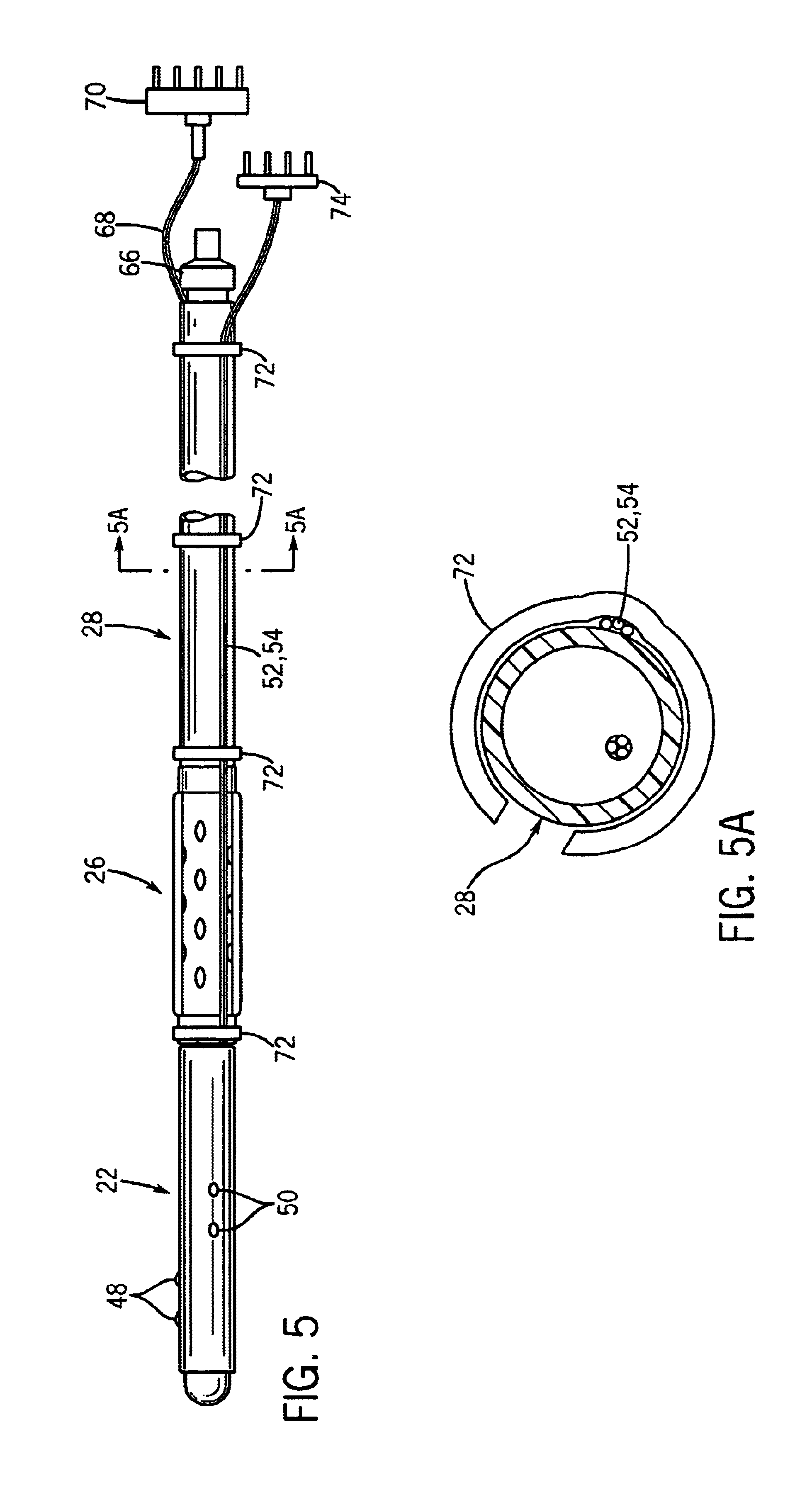
Toolkit for implanting an intracorporeal lead such as for cardiac pacing or sensing
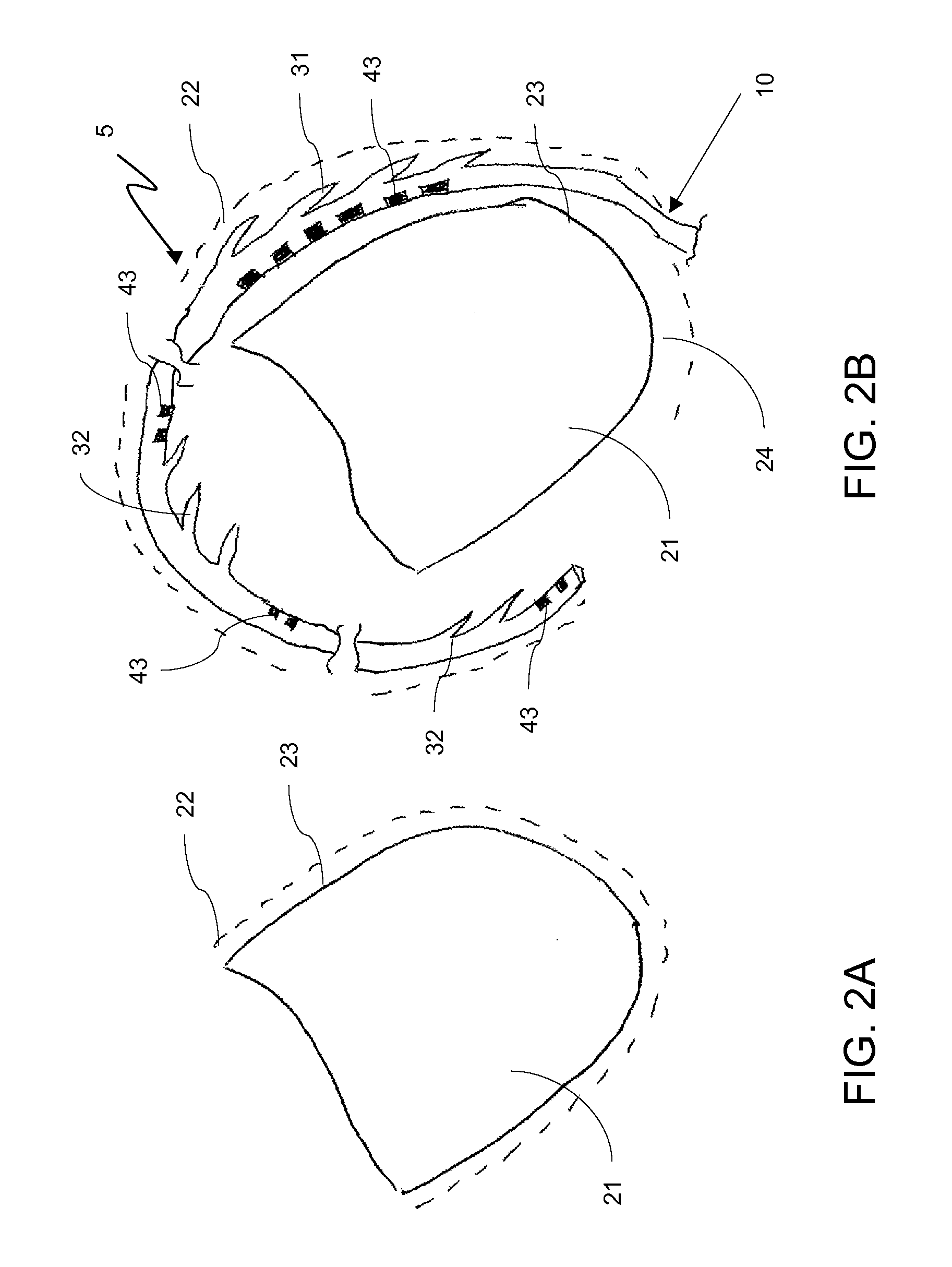
ActiveUS8142446B2Reduce riskRisk minimizationElectrotherapyInfusion syringesExtreme positionAtrial pacing
A toolkit for implanting an intracorporal lead, preferably a cardiac sensing / pacing lead. This toolkit includes a guide-catheter (10), having a sheath (12) with an internal lumen (42) opened at its distal and proximal ends, and cuttable along a generatrix in order to allow extracting of the guide-catheter after use. A hemostatic valve (14) is mounted at the proximal end (40) of the guide-catheter, for selectively filling, or not, the internal lumen of the guide-catheter at its input end. The valve is frangible in at least two parts, each dissociable from the guide-catheter at both sides around a median axial plane. The valve comprising a mobile element sliding on the guide-catheter between two extreme positions, with an opened position where the proximal end (40) of the guide-catheter (10) freely emerges out of the valve so as to allow access to said internal lumen, and a closed position where this proximal end of the guide-catheter is filled in a tight manner.
Owner:SORIN CRM
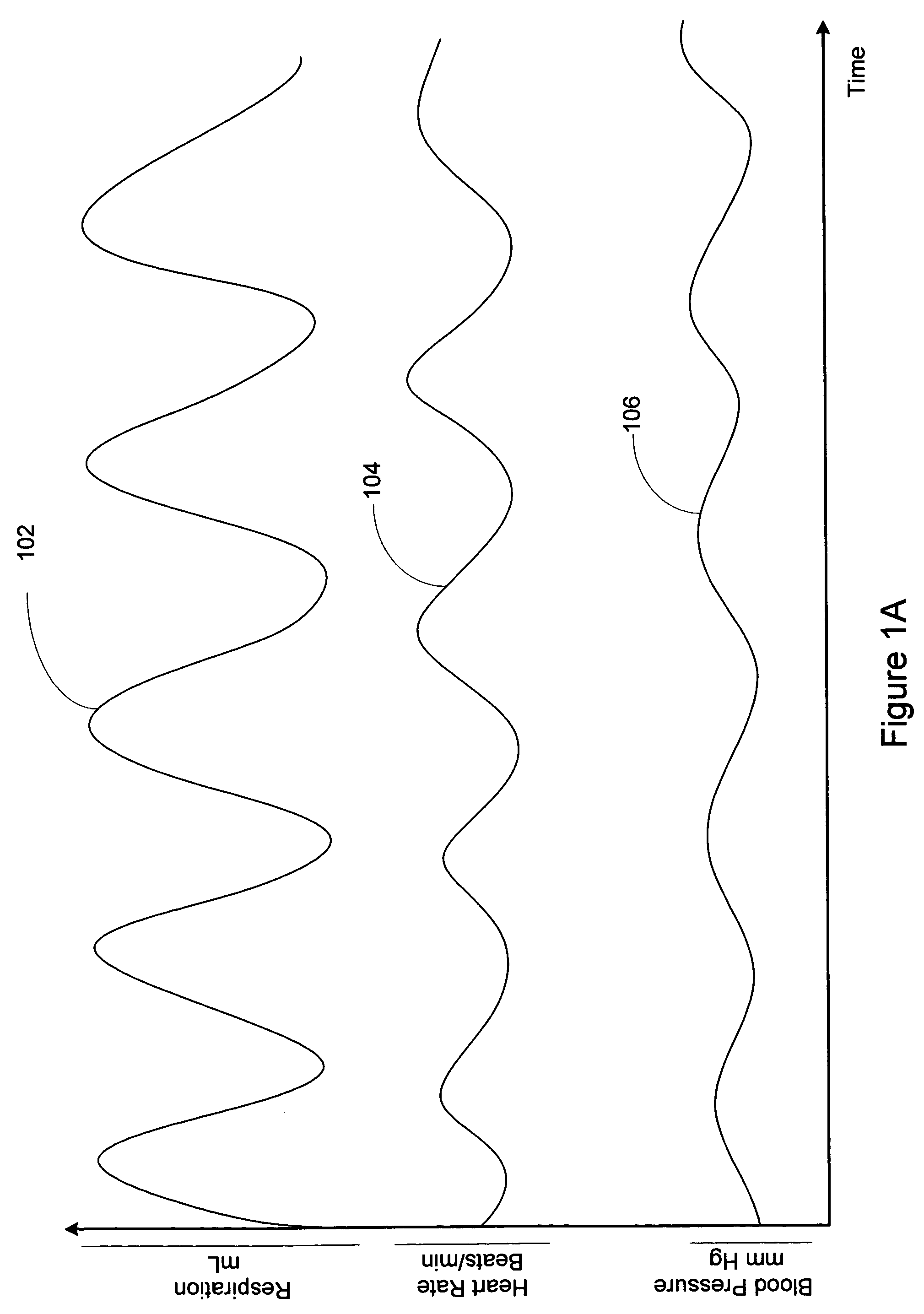
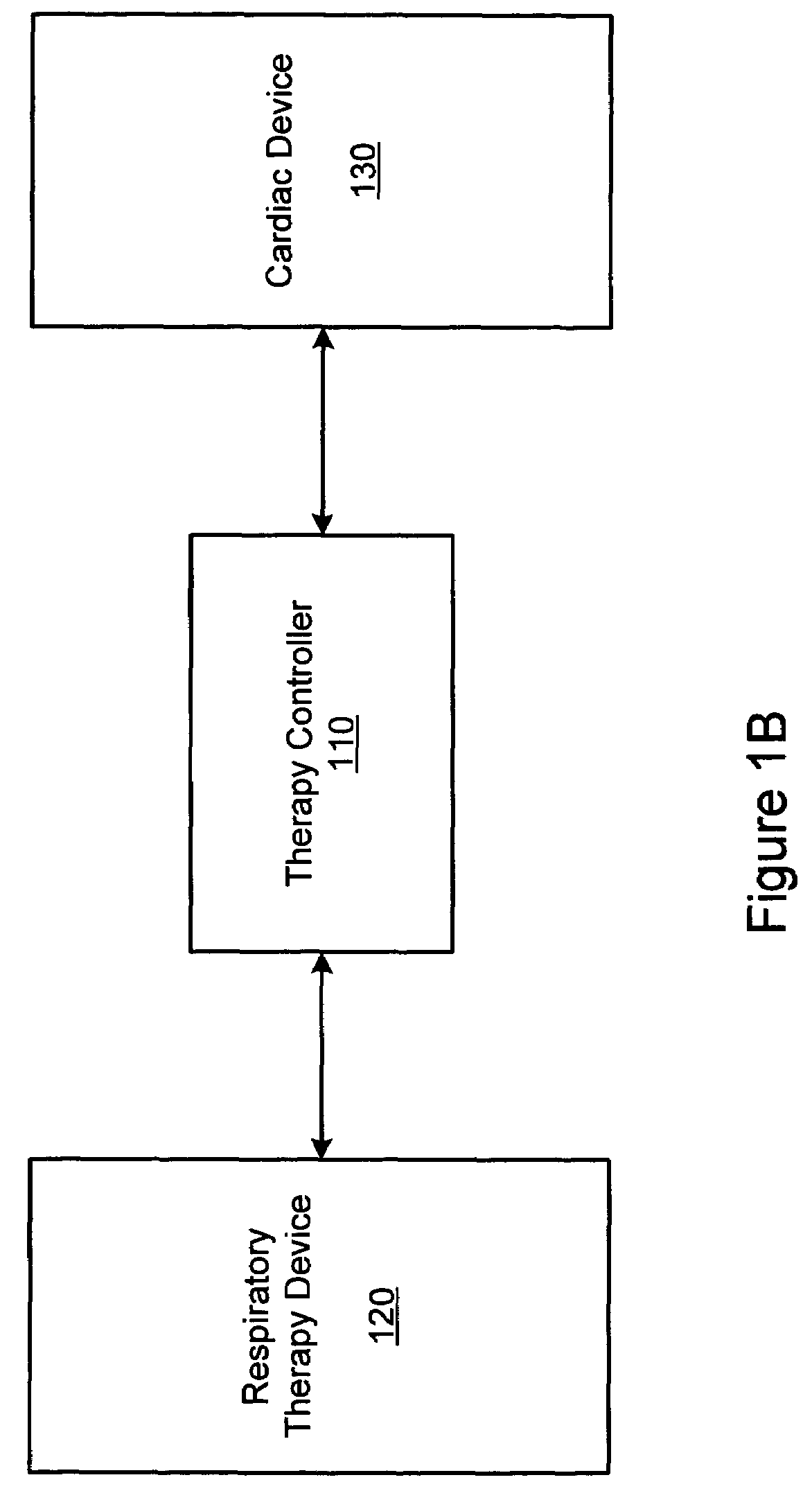
Method and apparatus for mimicking respiratory sinus arrhythmia with cardiac pacing controlled via external respiration therapy device
Methods and systems involve adjusting cardiac pacing based on information acquired via a respiratory therapy device. A medical system includes a respiratory therapy device having one or more sensors and a therapy delivery unit. The one or more sensors are configured to sense respiration cycles. The therapy delivery unit is configured to deliver an external respiratory therapy to the patient. The medical system also includes a pulse generator configured to deliver cardiac pacing pulses to the patient. A controller is coupled to the one or more sensors and the pulse generator. The control unit configured to adjust a cardiac pacing rate based on the patient's respiration cycles.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Cardiac pacing system and distributed cardiac pacing system
InactiveUS20080319502A1Television system detailsColor television detailsCardiac pacemaker electrodeControl signal
A micro integrated cardiac pacemaker includes a control unit for outputting a control signal according to cardiograph information, heart stimulating means for stimulating heart tissue in response to the control signal, cardiograph information extracting means for extracting cardiograph information and outputting it to the control unit, and a power supply unit for supplying drive power. The power supply unit is a biological fuel cell that takes out electrons by oxidation of a biological fuel. The biological fuel cell includes an anode and a cathode. An oxidase of a biological fuel and a mediator are immobilized on the cathode. Blood and / or body fluid are used as an electrolytic solution, and a biological fuel and oxygen in the blood and / or the fluid are used. The biological fuel cell is attached to the end of a catheter and implanted into the heart, and the catheter is withdrawn, without incising the breast.
Owner:FUJIKIN INC +1
Method and system for discriminating captured beats from non-captured beats in a cardiac pacing system
InactiveUS20020116031A1Efficient and accurate means of distinguishing a captured beatAccurate distinctionHeart stimulatorsEngineeringAtrial pacing
A method of discriminating a captured beat is provided. A pulse is transmitted and an evoked response signal is received. The evoked response signal is filtered and the filtered response signal is analyzed for at least one positive signal component. Systems and devices for discriminating a captured beat are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
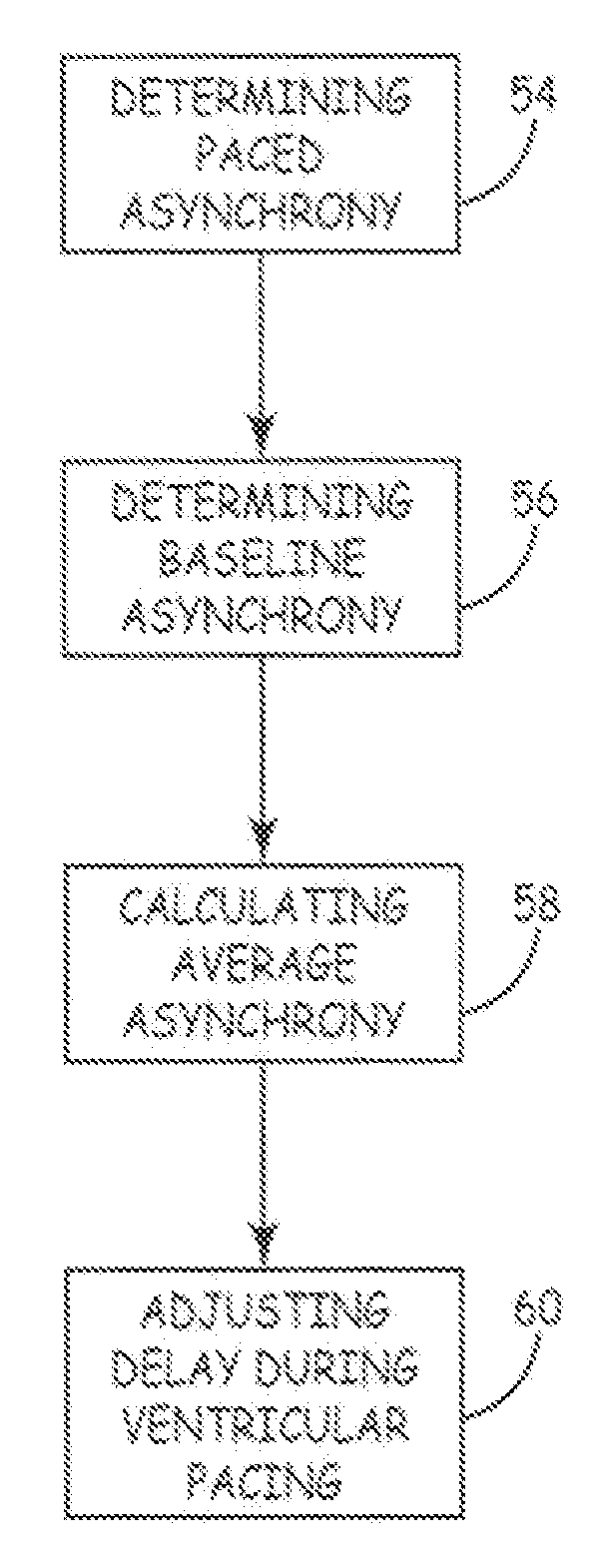
Cardiac pacing for optimal intra-left ventricular resynchronization
Cardiac pacing to treat ventricle dysynchrony for improved cardiac function is performed as follows. Early paced inter-ventricular asynchrony is determined during ventricular pacing. Baseline inter-ventricular asynchrony is determined without pacing. Average inter-ventricular asynchrony is calculated by averaging the early paced inter-ventricular asynchrony and the baseline inter-ventricular asynchrony. Atrio-ventricular delay and ventricular-ventricular delay are adjusted during ventricular pacing to yield the average inter-ventricular asynchrony for optimal intra-left ventricular resynchronization and maximal cardiac function. The elements above can be configured in software contained in an implantable medical device or embodied as a computer software product that includes a medium readable by a processor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Predicting chronic optimal a-v intervals for biventricular pacing via observed inter-atrial delay
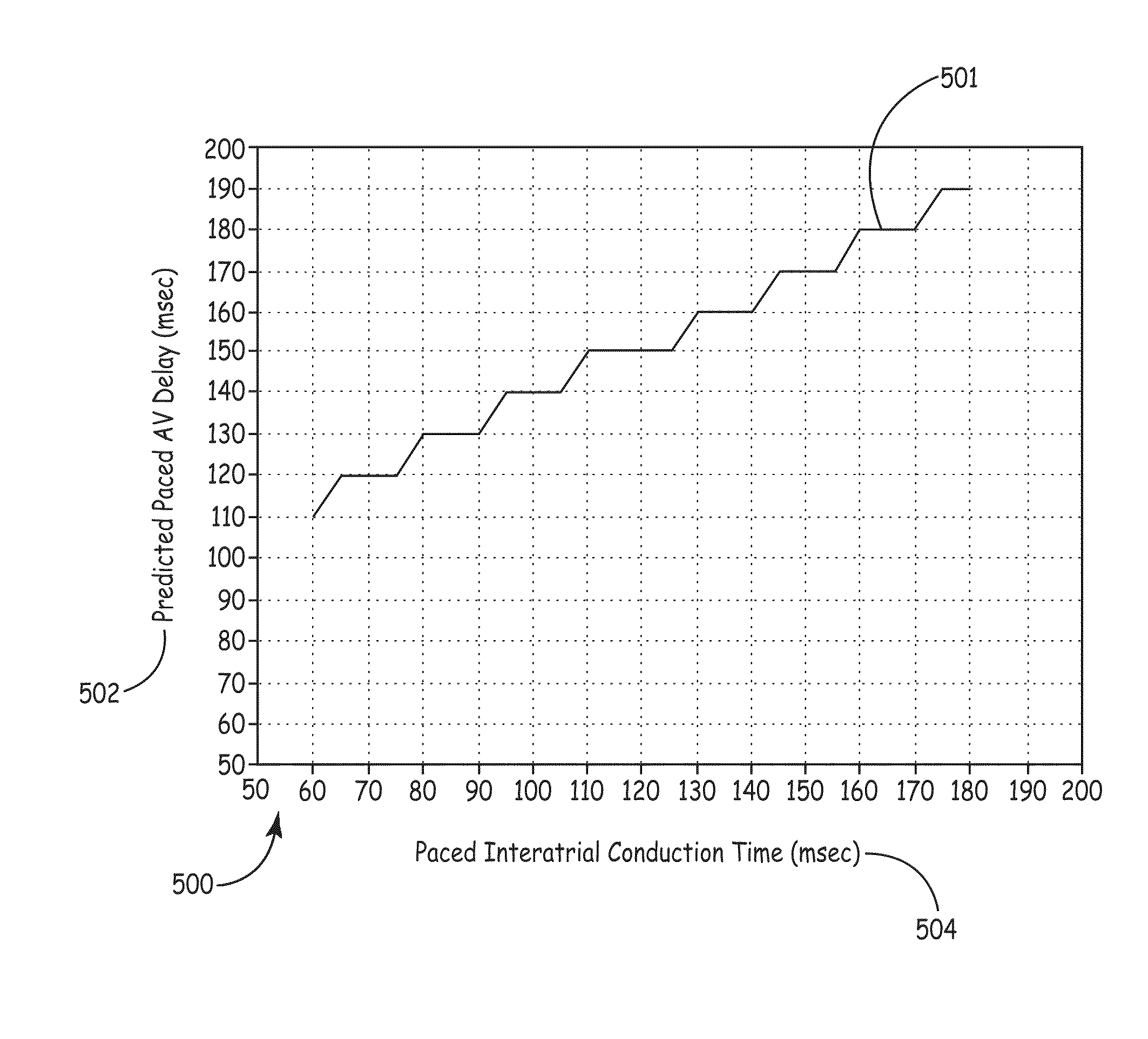
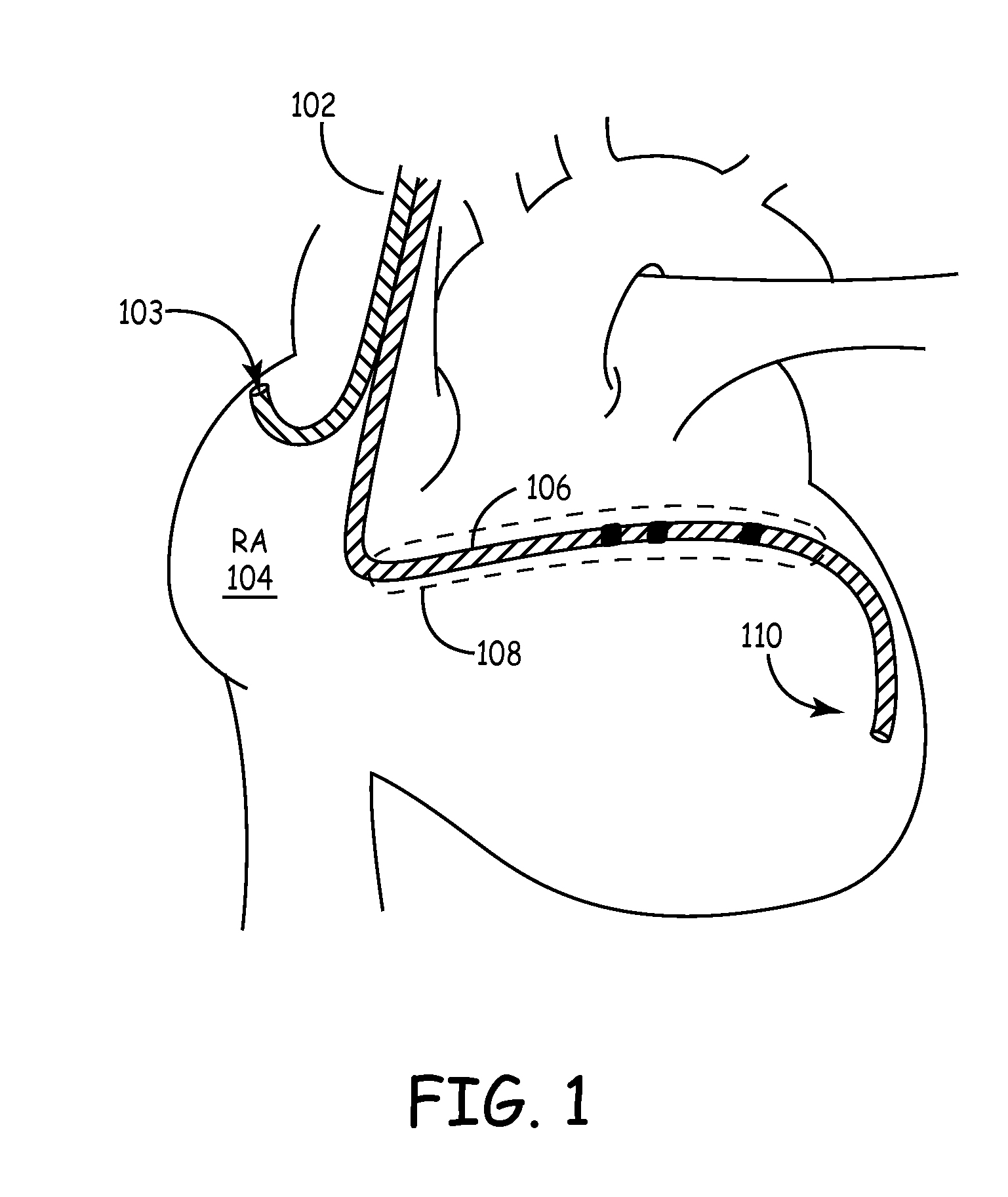
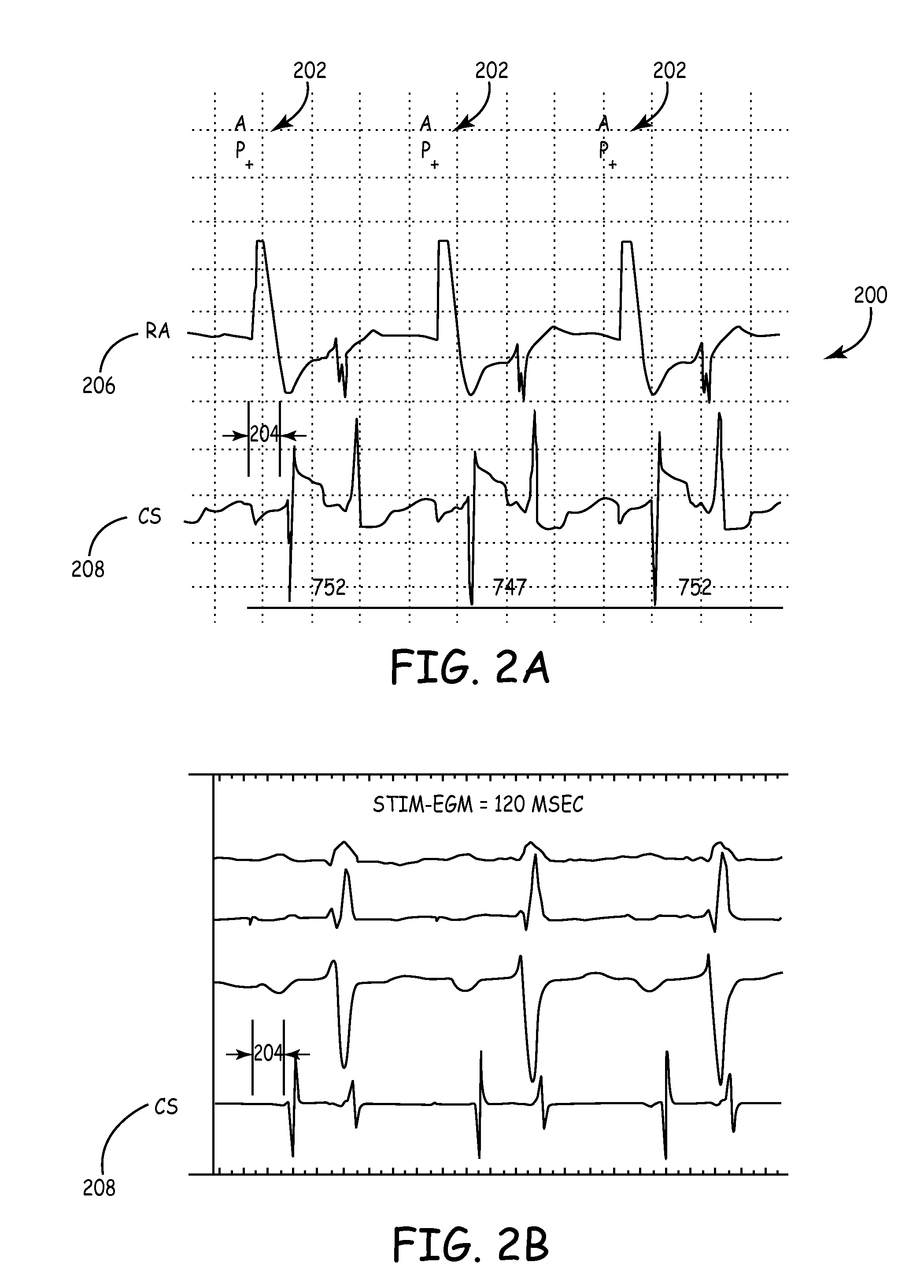
ActiveUS20080027488A1Maximize fillEasy to shrinkElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesAtrial cavityLeft ventricular size
Herein provided are methods for optimizing the atrio-ventricular (A-V) delay for efficacious delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy. The A-V delay is set such that pacing-induced left ventricular contraction occurs following completion of left atrial (LA) contraction. This maximizes left ventricular filling (preload) which theoretically results in optimal LV contraction via the Frank-Starling mechanism. In CRT devices, the programmed A-V delay starts with detection of electrical activity in the right atrium (RA). Thus, a major component of the A-V delay is the time required for inter-atrial conduction time (IACT) from the RA to the LA. This IACT can be measured during implantation as the time from the atrial lead stimulation artifact to local electrograms in a coronary sinus (CS) catheter. Assuming that the beginning of LA contraction closely corresponds with the beginning of LA electrical activity, the optimal AV delay should be related to the time between the start of RA electrical activity and the start of LA electrical activity plus the duration of LA atrial contraction. Thus the inventors hypothesized that during atrial pacing the IACT measured at implantation correlated with the echocardiographically defined optimal paced AV delay (PAV).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of optimizing mechanical heart rate during delivery of coupled or paired pacing
InactiveUS7286873B2Maximize their opportunityOptimize heart rateHeart stimulatorsVentricular ratePulse rate
A method of operating a cardiac pacing device that optimizes the mechanical heart rate using coordinated potentiation therapy while maximizing the opportunity for intrinsic AV conduction to occur. The method may include adjusting the timing of extra stimulus intervals during coupled or paired pacing to promote AV conduction and to effect changes in rate according to certain embodiments of the invention. Other embodiments may include adjusting the atrial pacing rate to achieve a desired target rate consistent with AV conduction. A mode switch to a dual-chamber pacing mode may be provided according to certain embodiments of the invention to ensure a ventricular rate that meets or exceeds a minimum mechanical rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
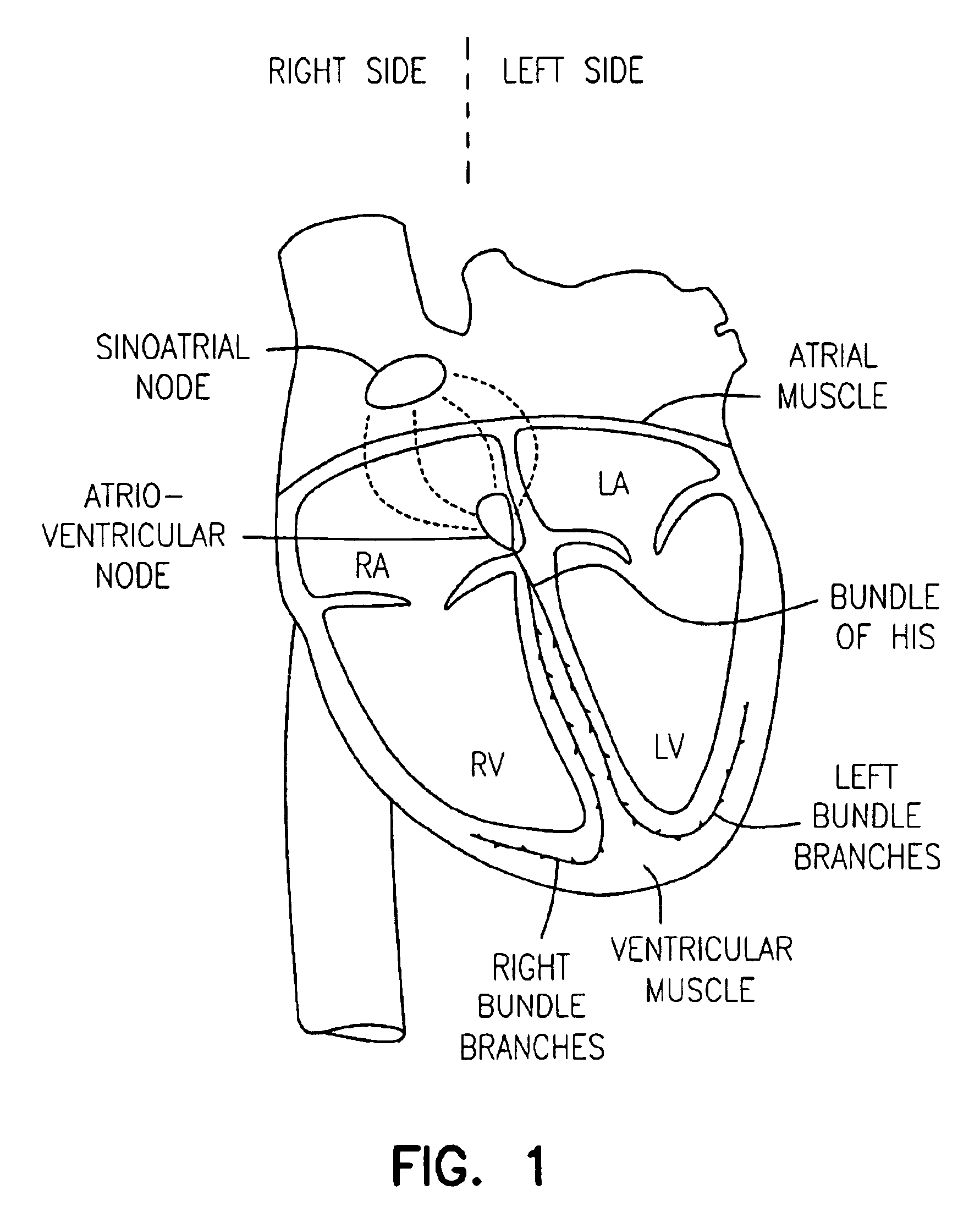
Cardiac pacing using the inferior nodal extension
A device and method for providing stimulation to an inferior nodal extension of a heart. The method includes providing a lead comprising an electrode, positioning the electrode proximate an inferior nodal extension of a heart, and effecting at least one of activation, deactivation, or modulation of the electrode to provide stimulation to the inferior nodal extension.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Methods and apparatus for overdrive pacing multiple atrial sites using an implantable cardiac stimulation device
InactiveUS7006867B1Convenient treatmentPrevent and terminate arrhythmiaHeart stimulatorsAtrial cavityAtrial pacing
Methods and apparatus are disclosed herein that advantageously combine beneficial aspects of overdrive pacing and multi-site atrial pacing in order to provide an improved treatment for atrial fibrillation. The methods and apparatus include sensing of atrial activity at multiple sites within the atria at an overdrive pacing rate to detect intrinsic atrial depolarization, and delivery of pacing pulses to multiple sites within the atria to prevent or terminate arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
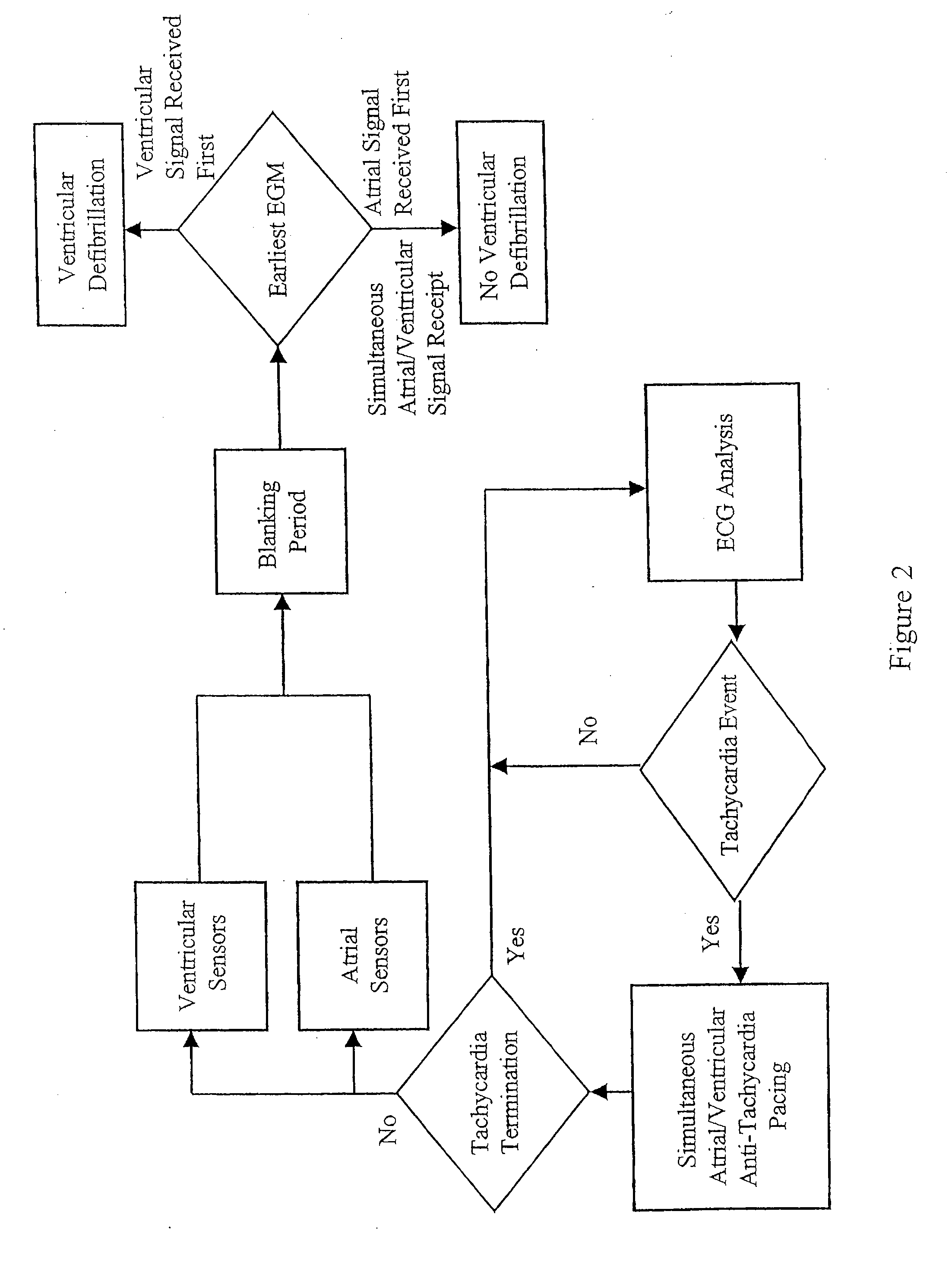
Methods and apparatus for tachycardia rate hysteresis for dual-chamber cardiac stimulators
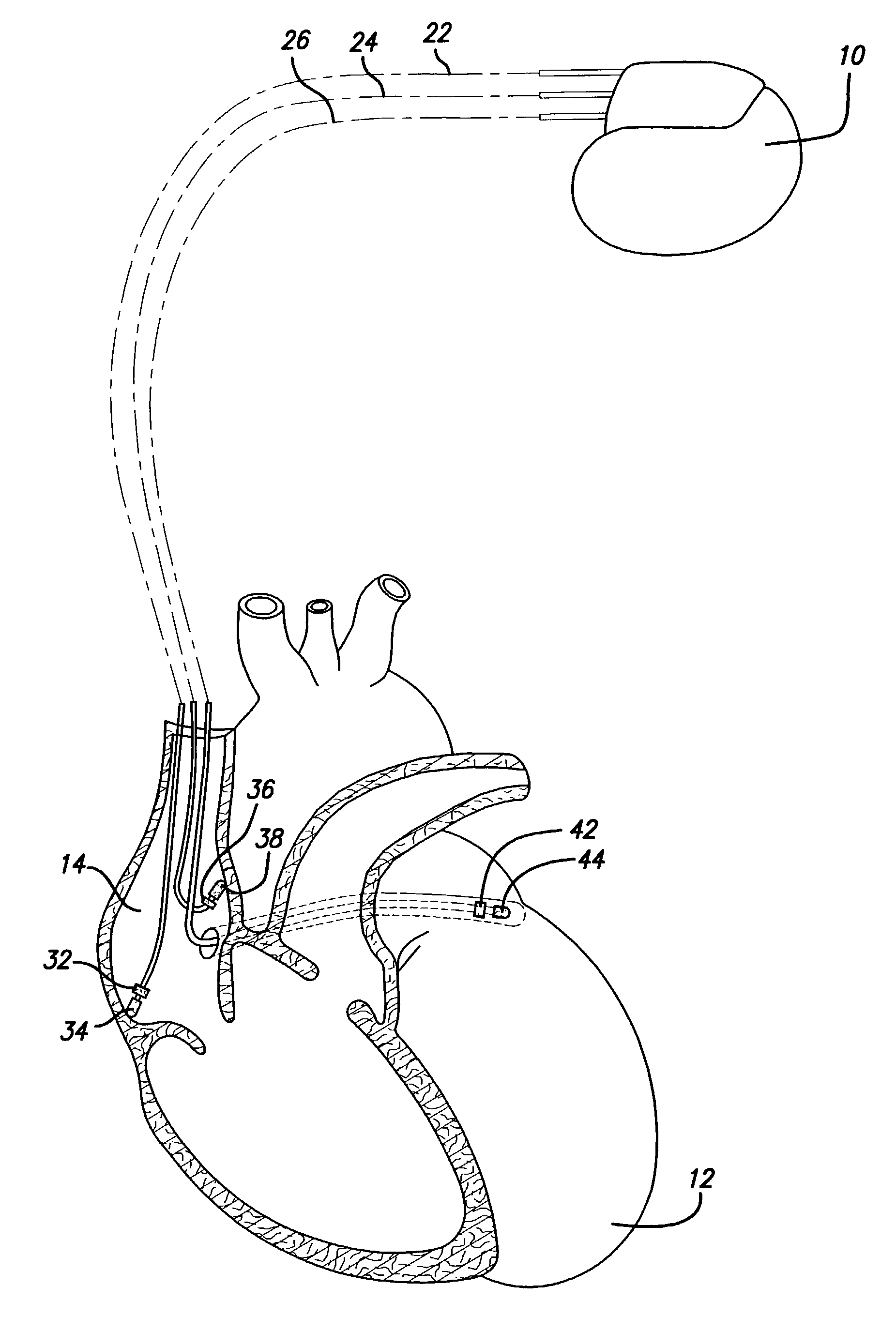
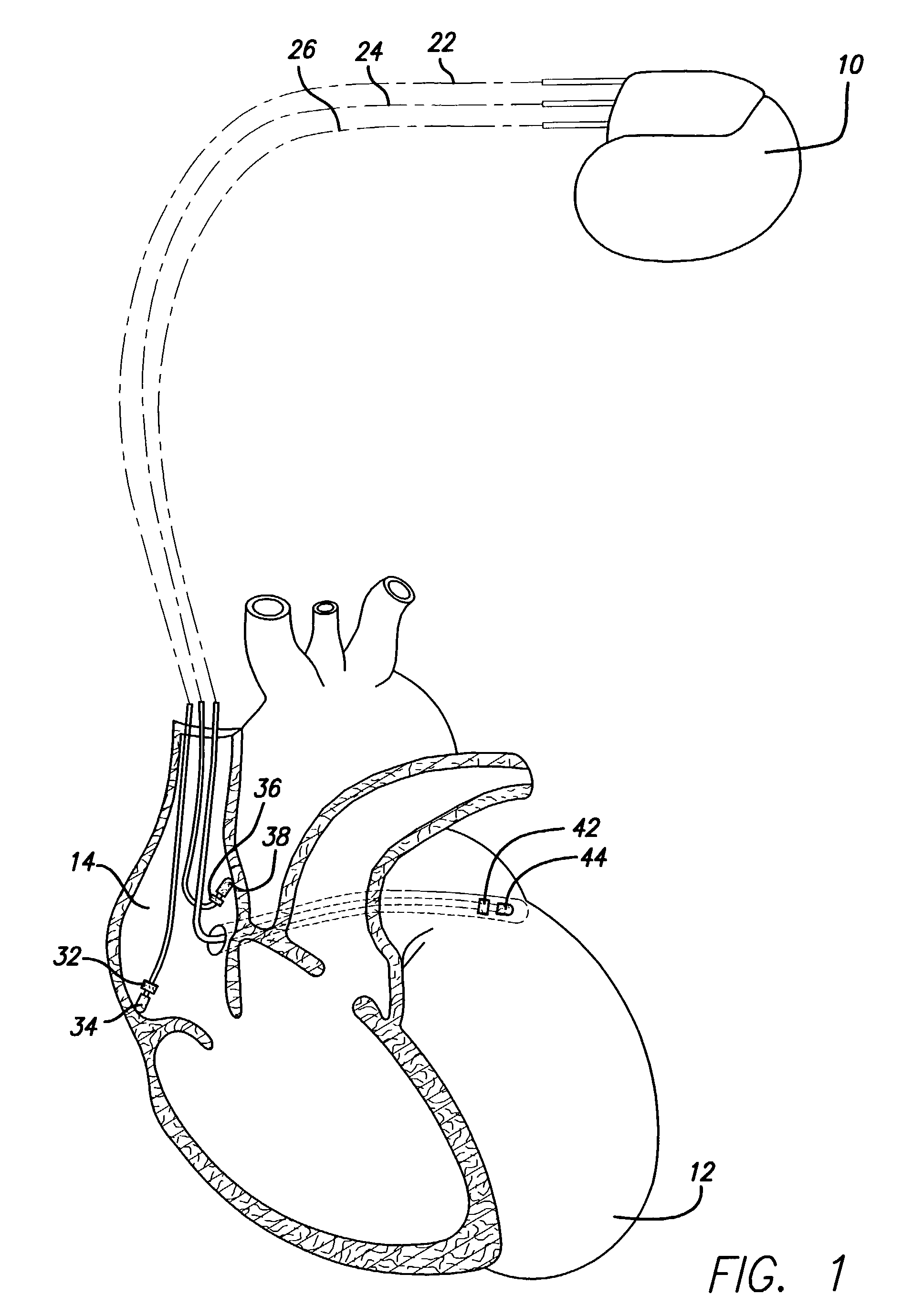
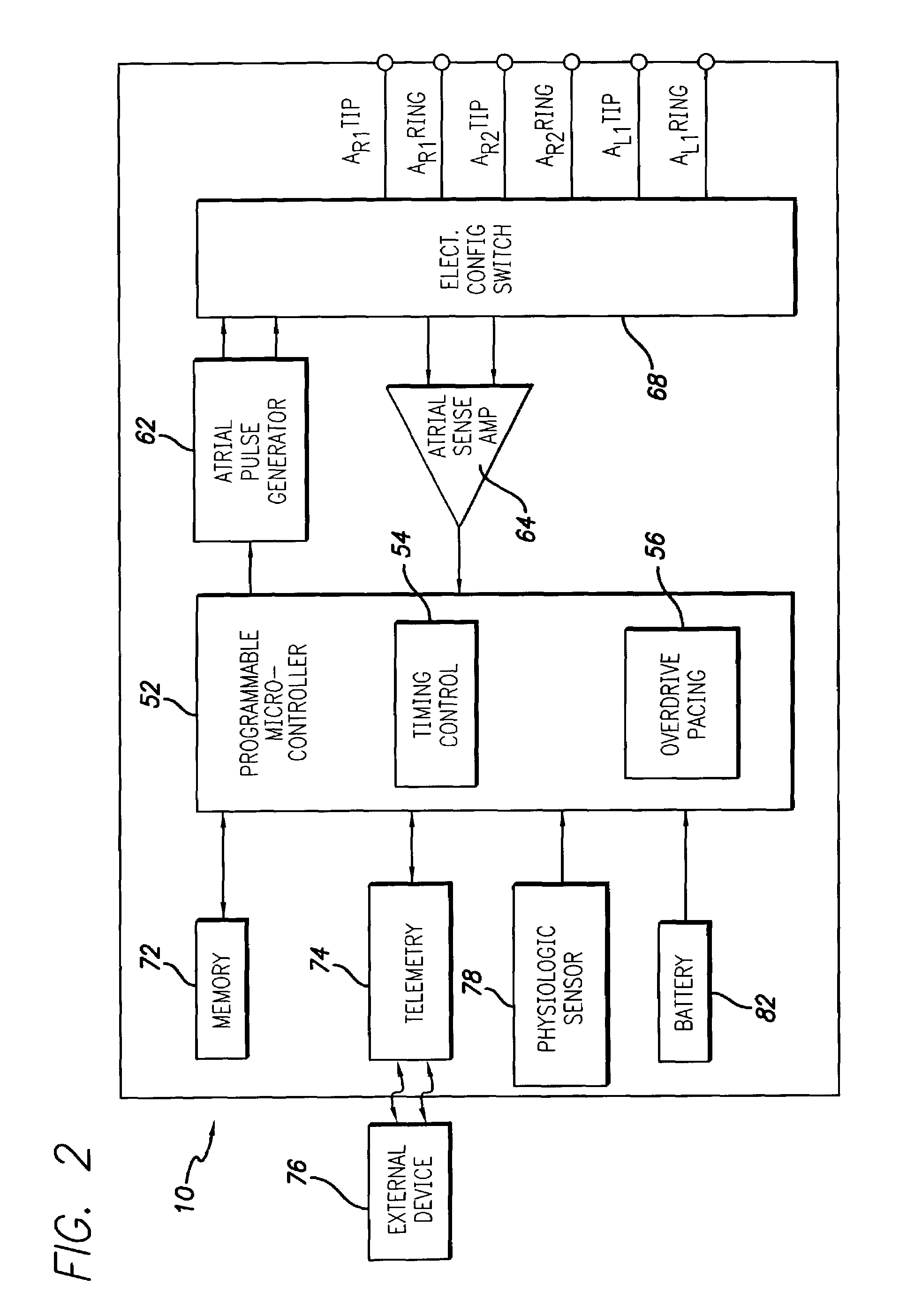
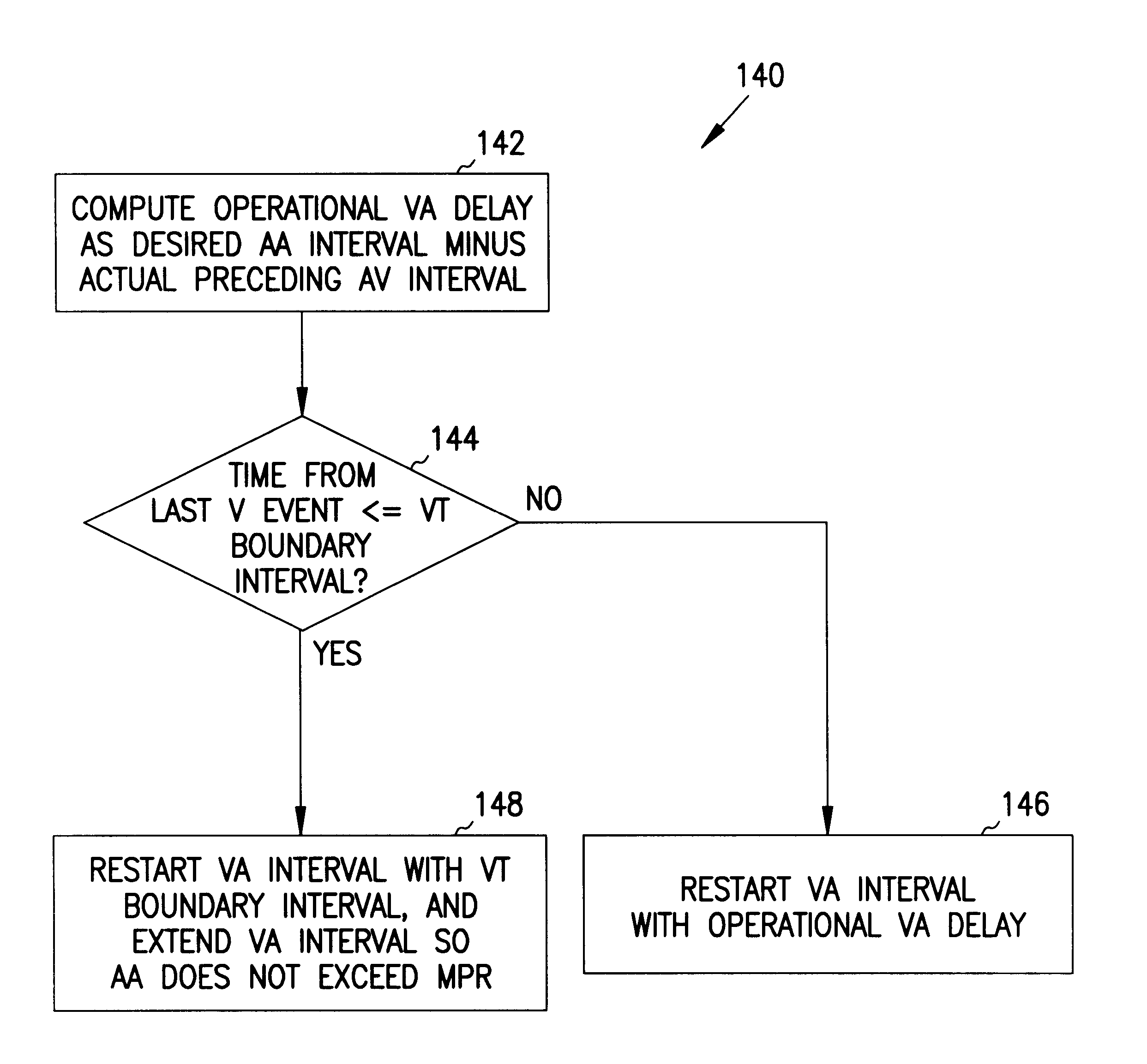
It has been determined that certain dual-chambered cardiac stimulators may operate in a region in which an atrial pacing event may obscure the detection of a ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Various exemplary techniques may be used to improve the ability of dual-chamber cardiac stimulators to detect such ventricular events. In accordance with one technique, it is determined whether a ventricular event should be classified as a ventricular tachyarrhythmia. If not, the VA interval is restarted as usual. However, if the ventricular event may be classified as a ventricular tachyarrhythmia, it is determined whether the ventricular event falls within the region in which an atrial pacing event may obscure its detection. If not, then the VA interval is restarted as usual. However, if the ventricular event falls within this region, the VA interval is restarted with the VT rate detection boundary. This has the effect of lengthening the VA interval and the AA interval in this region so that atrial pacing events will not obscure the sensing and treatment of ventricular tachyarrhythmias in the region.
Owner:INTERMEDICS
Esophageal stethoscope with carrier members for cardiac pacing and oximetry
InactiveUS6855116B2Maximum flexibilityReduce complexityElectrocardiographyStethoscopeMedicineSensing applications
An esophageal stethoscope includes a tubular flexible body having an acoustic input region. A carrier member, which is separate from the tubular flexible body, is selectively engageable with the tubular flexible body either proximally or distally of the acoustic input region. The carrier member carries one or more devices for providing esophageal recording, monitoring or stimulation functions. For transesophageal cardiac pacing, electrodes are mounted to the carrier member such that engagement of the carrier member with the tubular flexible body functions to convert the esophageal stethoscope to a pacing stethoscope. To carry out a sensing, recording or monitoring function, such as esophageal oximetry, one or more oximetry probes are mounted to the carrier member such that engagement of the carrier member with the esophageal stethoscope converts the stethoscope for use in an oximetry sensing application. A “universal” stethoscope includes engagement structures at predetermined locations along the length of the tubular flexible body, for use in engaging a stimulation carrier and / or a recording / monitoring carrier with the esophageal stethoscope.
Owner:ESO TECH
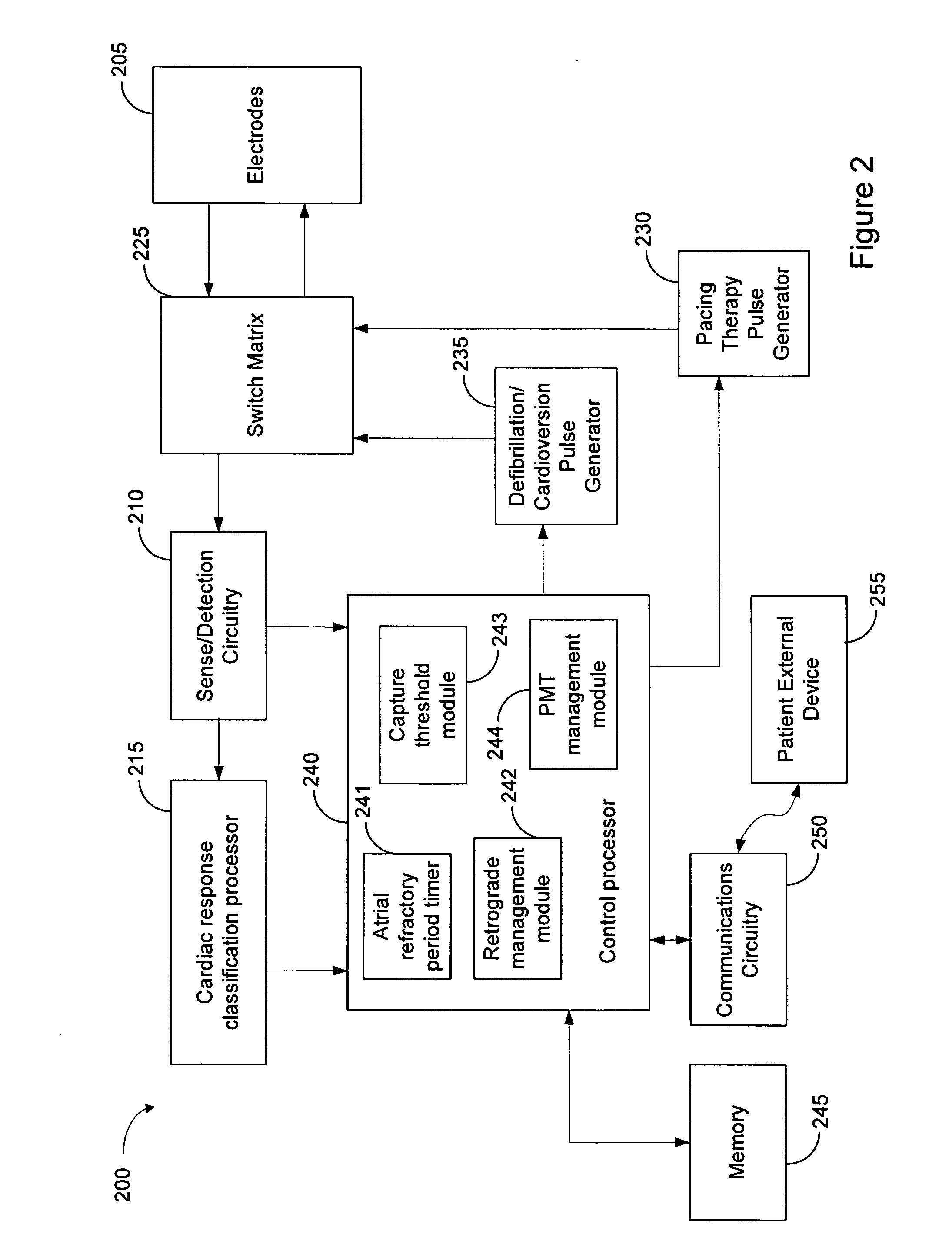
Methods and systems for management of atrial retrograde conduction and pacemaker mediated tachyarrhythmia threshold
Methods and systems for classifying cardiac responses to pacing stimulation and managing retrograde conduction and pacemaker mediated tachyarrhythmia are described. An atrial pacing pulse and a ventricular pacing pulse are delivered during a paced cardiac cycle. A post ventricular atrial refractory period (PVARP) is timed following the ventricular pacing pulse. The system determines if the atrial pacing pulse captures the atrium. An atrial depolarization occurring after the paced cardiac cycle is sensed. Retrograde management is initiated if the atrial pacing pulse did not capture the atrium and the atrial depolarization occurred during the PVARP. Pacemaker mediated tachyarrhythmia (PMT) is initiated if the atrial pacing pulse did not capture the atrium and the atrial depolarization did not occur during the PVARP.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Predicting chronic optimal A-V intervals for biventricular pacing via observed inter-atrial delay
Methods for optimizing the atrio-ventricular (A-V) delay for efficacious delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy. In CRT devices, the programmed A-V delay starts with detection of electrical activity in the right atrium (RA). Thus, a major component of the A-V delay is the time required for inter-atrial conduction time (IACT) from the RA to the LA. This IACT can be measured during implantation as the time from the atrial lead stimulation artifact to local electrograms in a coronary sinus (CS) catheter. Assuming that the beginning of LA contraction closely corresponds with the beginning of LA electrical activity, the optimal AV delay should be related to the time between the start of RA electrical activity and the start of LA electrical activity plus the duration of LA atrial contraction. Thus ‘during atrial pacing’ the IACT measured at implantation is correlated with the echocardiographically defined optimal paced AV delay (PAV).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
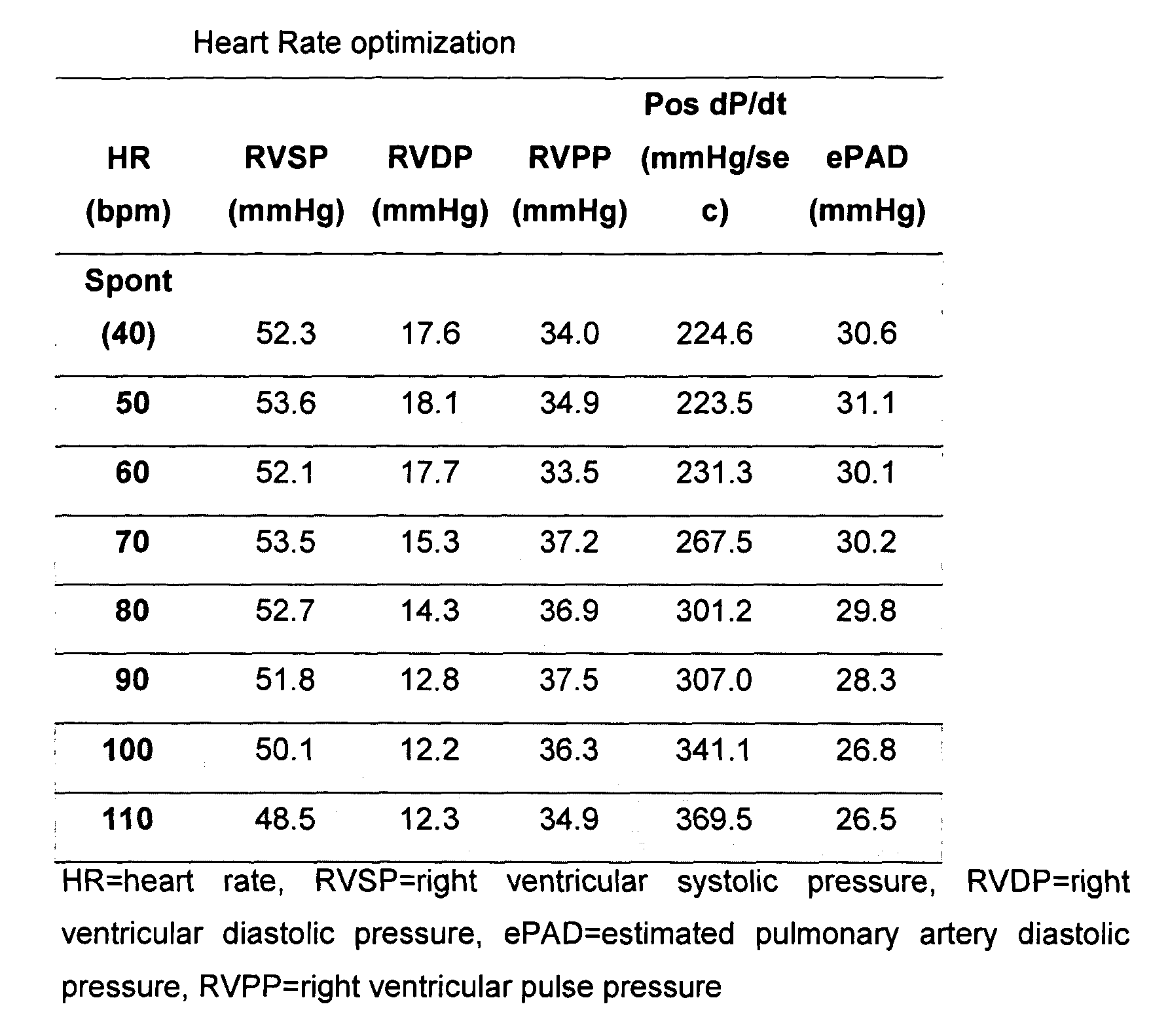
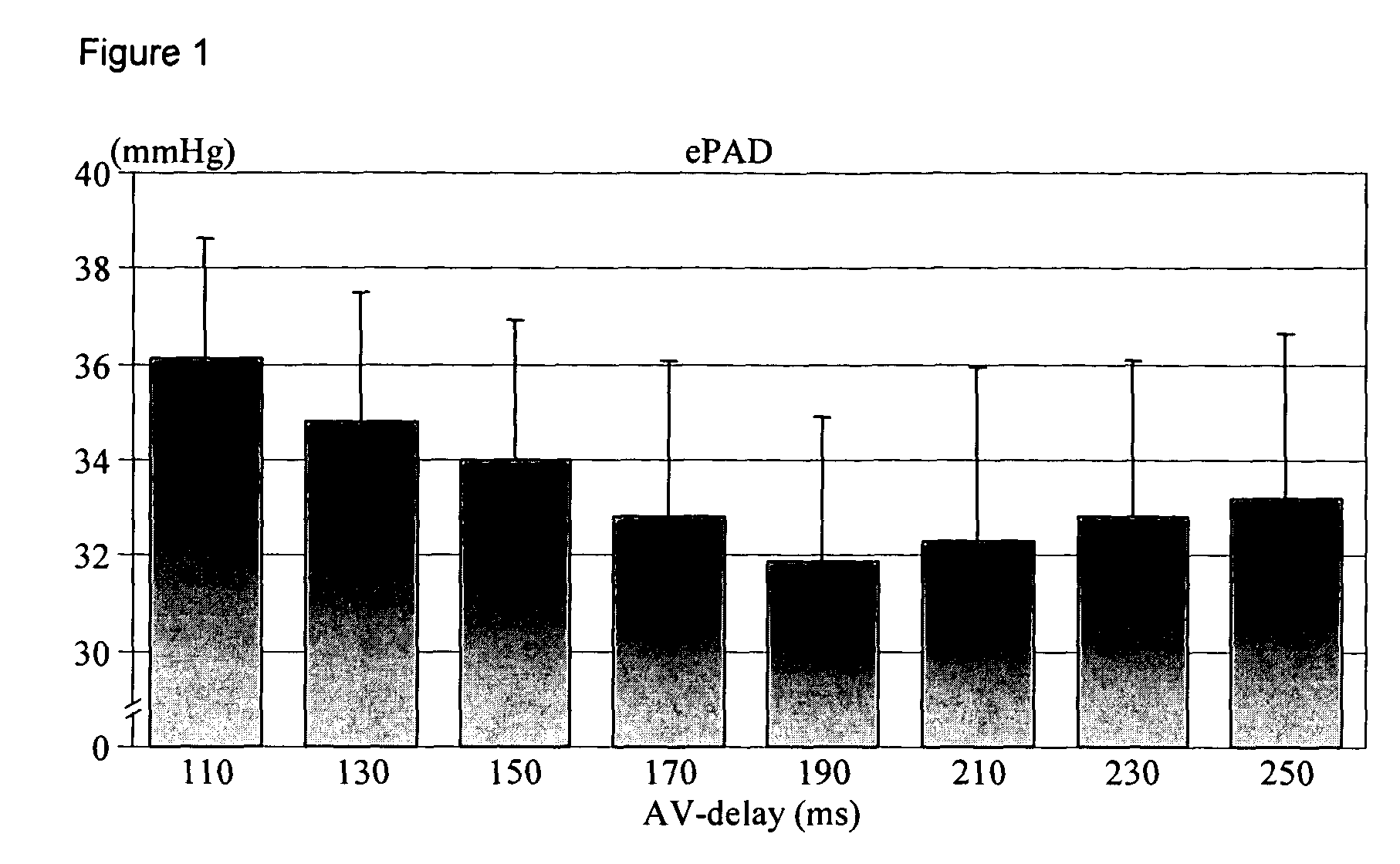
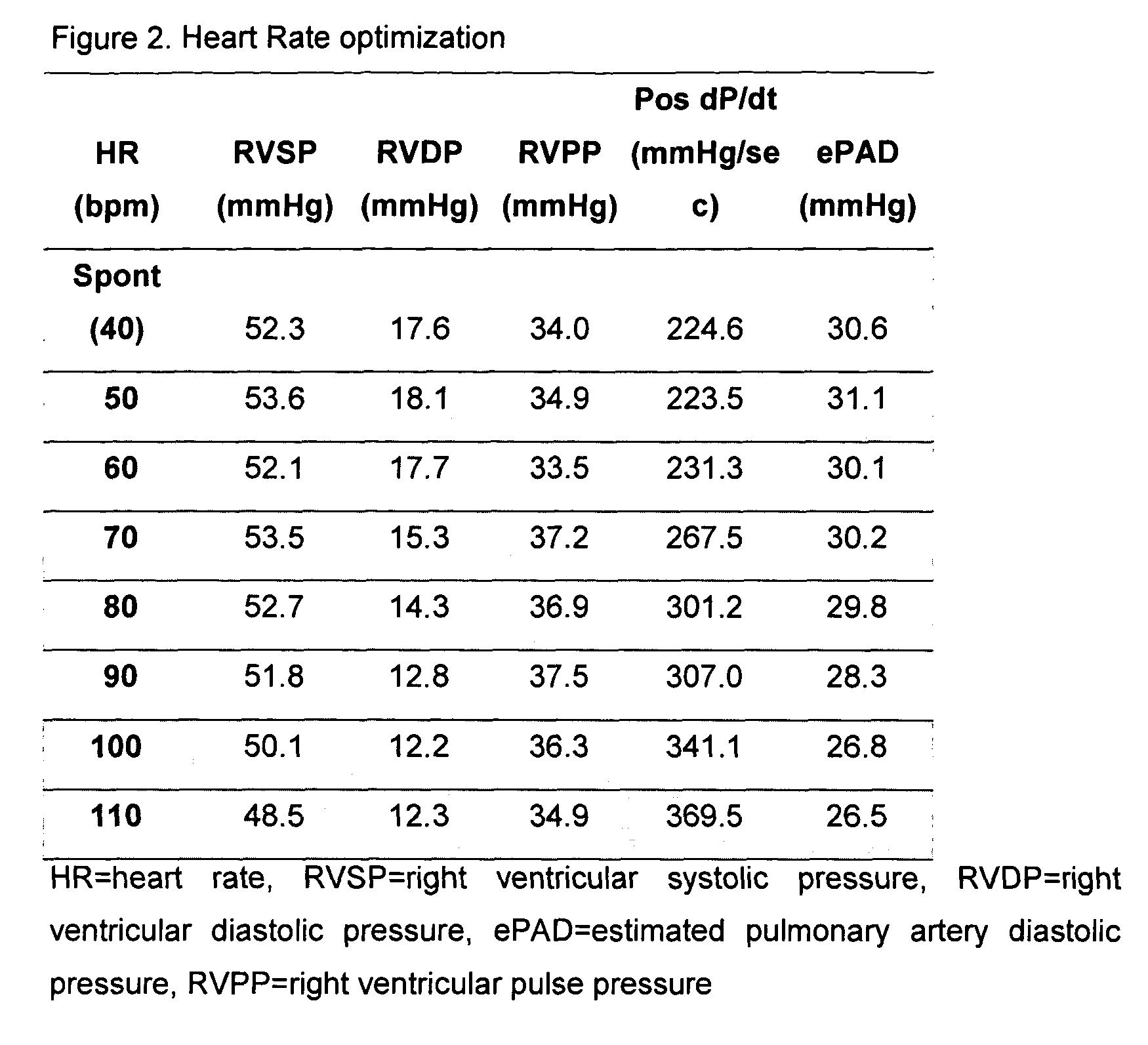
Apparatus and method for hemodynamic-based optimization of cardiac pacing
InactiveUS20050234517A1Improves left ventricular filling pressureOptimal AV-delayHeart defibrillatorsCatheterSonificationLeft ventricular size
The present invention demonstrates that continuous hemodynamic monitoring can be used to identify the optimal AV-delay in a pacemaker-treated patient with end stage heart failure. The AV-delay determines the timing of late diastolic filling in relation to the onset of ventricular contraction and the duration of diastolic filling. An optimal tuning of the AV-delay improves left ventricular filling pressures in patients with a DDD-programmed pacemaker and is particularly important in the presence of a compromised left ventricular function. It has been discovered that using the lowest ePAD pressure, an indirect parameter of the left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, as an indicator for the optimal AV interval. Importantly, measurements of the ePAD revealed the same optimal AV-delay as echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular diastolic filling by standard echocardiographic methods. Importantly, the HR determined as optimal during the acute hemodynamic test did not turn out to be optimal during daily living activities.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of optimizing mechanical heart rate during delivery of coupled or paired pacing
InactiveUS20060224197A1Optimize mechanical heart rateMinimum rateHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateAtrial pacing
A method of operating a cardiac pacing device that optimizes the mechanical heart rate using coordinated potentiation therapy while maximizing the opportunity for intrinsic AV conduction to occur. The method may include adjusting the timing of extra stimulus intervals during coupled or paired pacing to promote AV conduction and to effect changes in rate according to certain embodiments of the invention. Other embodiments may include adjusting the atrial pacing rate to achieve a desired target rate consistent with AV conduction. A mode switch to a dual-chamber pacing mode may be provided according to certain embodiments of the invention to ensure a ventricular rate that meets or exceeds a minimum mechanical rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
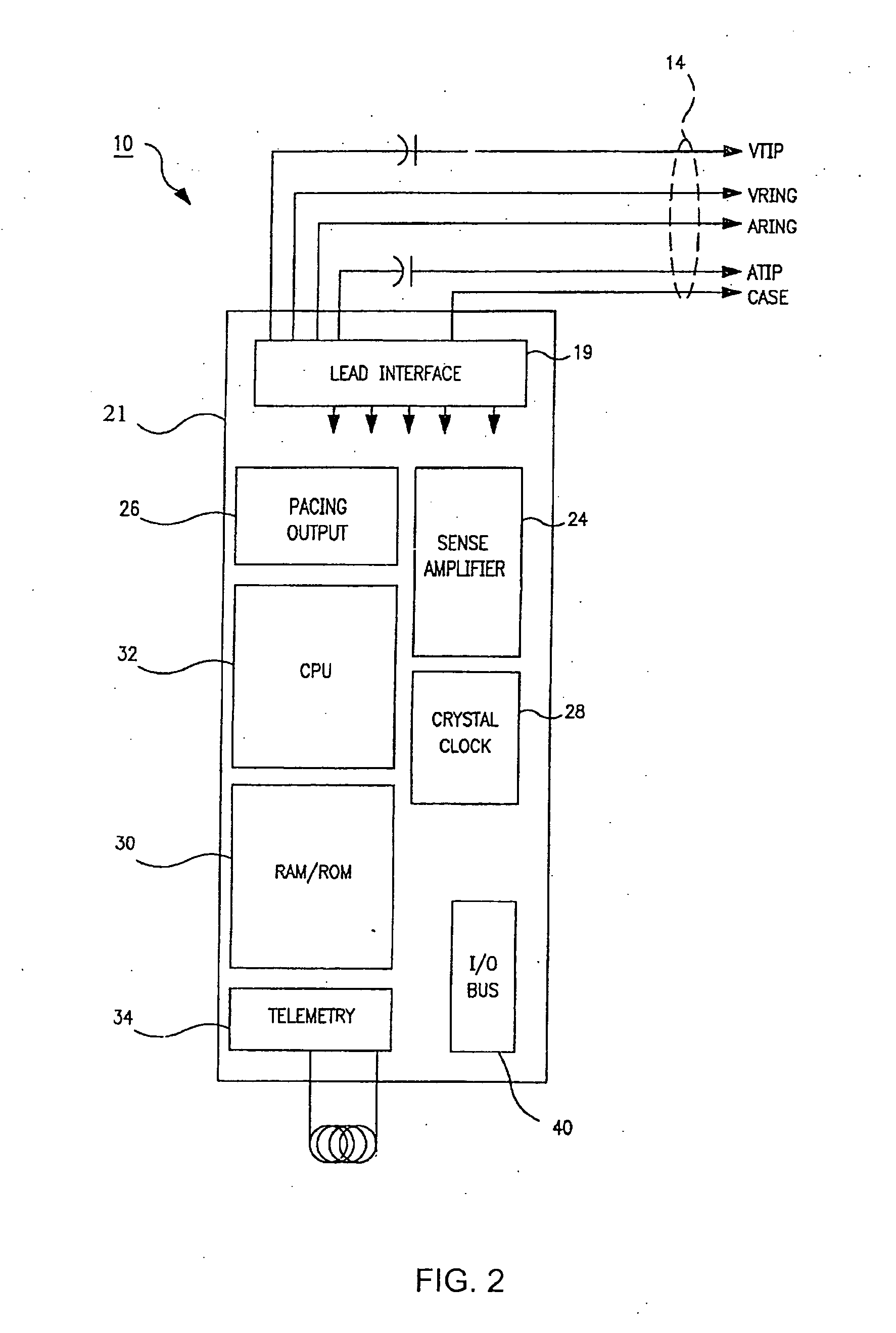
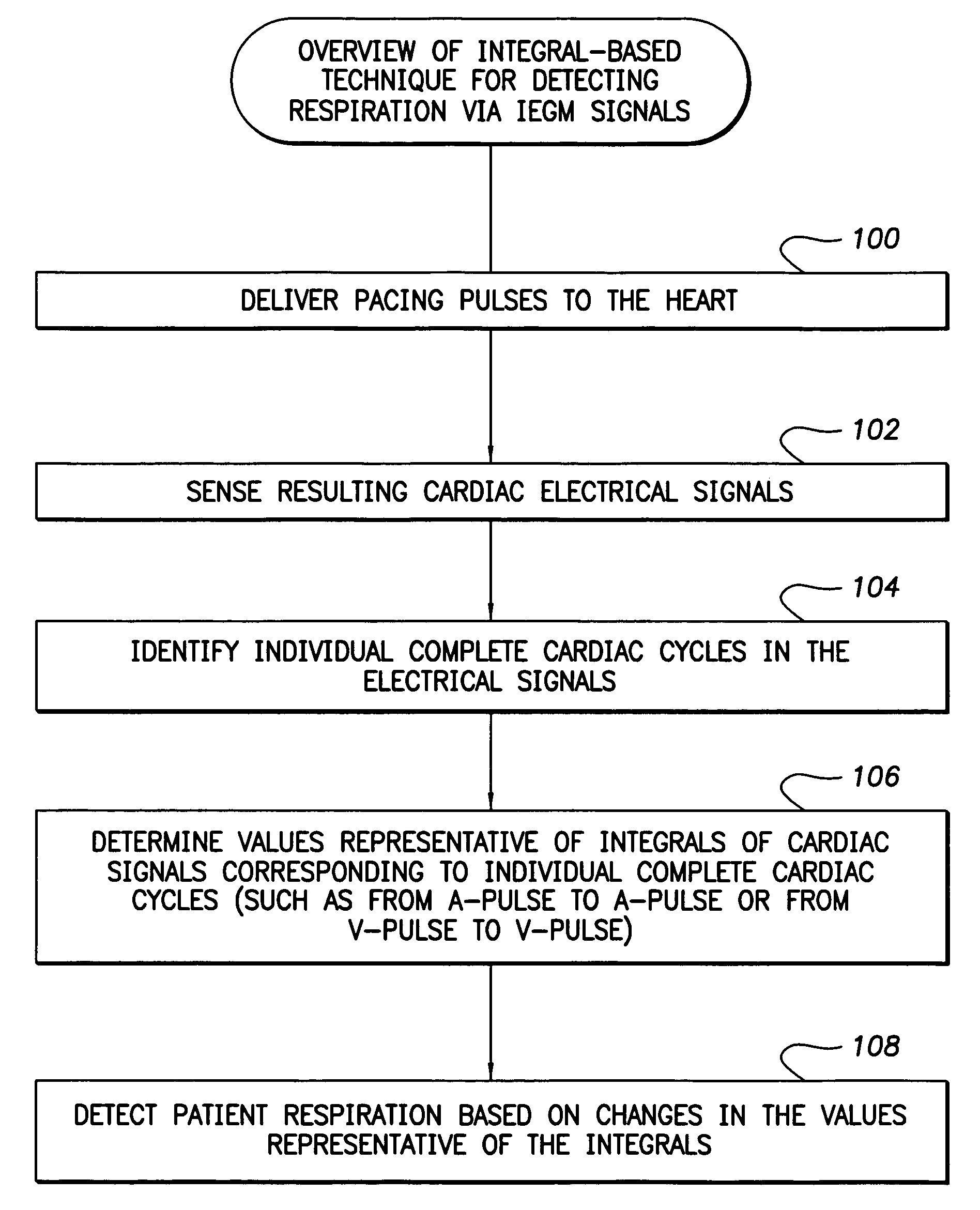
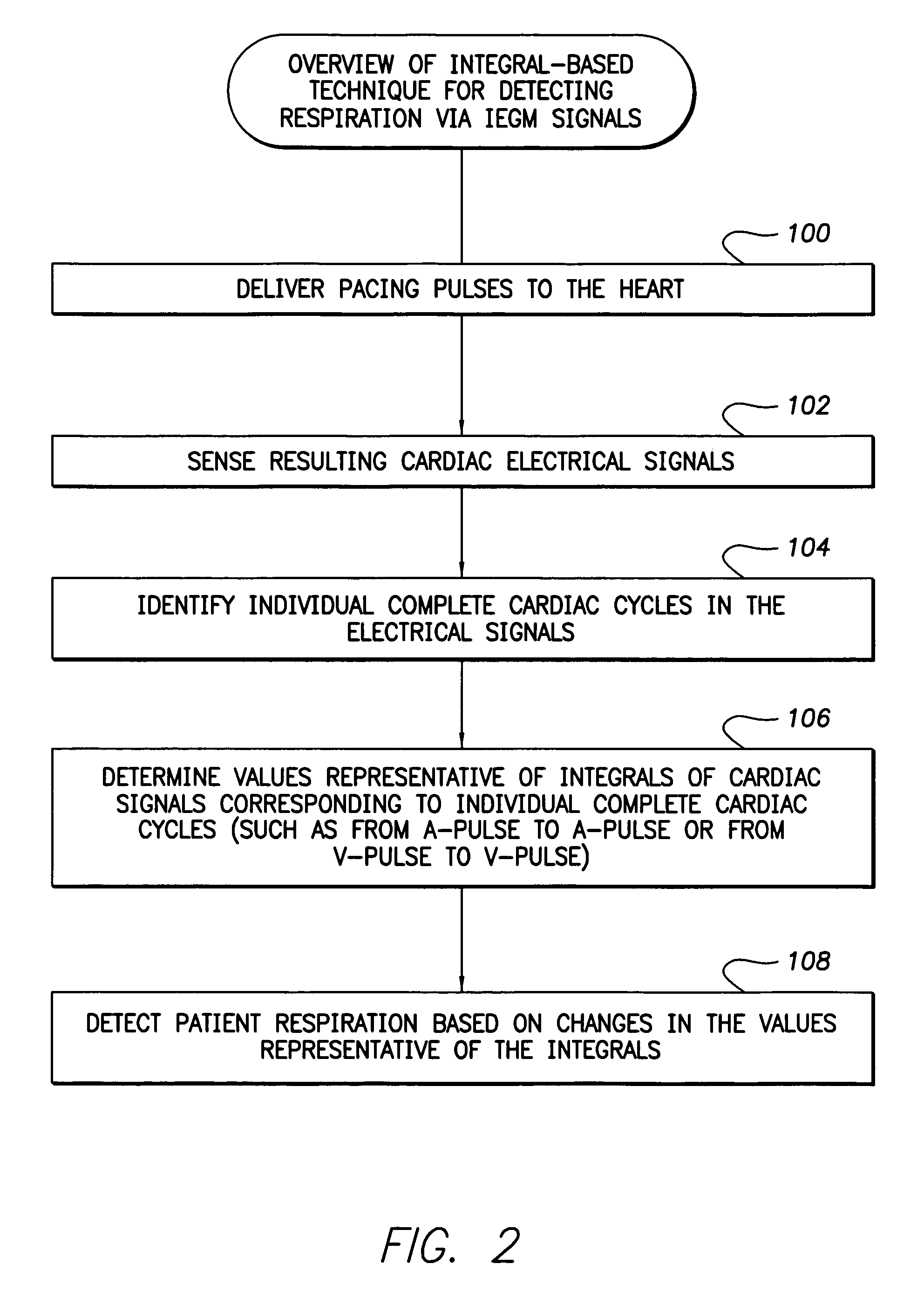
System and method for detection of respiration patterns via integration of intracardiac electrogram signals
Techniques are provided for tracking patient respiration based upon intracardiac electrogram signals or other electrical cardiac signals. Briefly, respiration patterns are detected by integrating cardiac electrical signals corresponding to individual paced cardiac cycles. The integrals may be obtained between consecutive pairs of ventricular pacing pulses or between consecutive pairs of atrial pacing pulses. In either case, cyclical changes in the integrals of the individual cardiac cycles are tracked. The cyclical changes are representative of respiration. Once respiration patterns have been identified, episodes of abnormal respiration, such as apnea, hyperpnea, nocturnal asthma, or the like, may be detected and therapy automatically delivered.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for providing preventive overdrive pacing and antitachycardia pacing using an implantable cardiac stimulation device
InactiveUS7363081B1Easy to detectReliably detecting the onset of an atrial tachycardiaHeart stimulatorsAtrial pacingAntitachycardia Pacing
Techniques for enabling both preventive overdrive pacing and antitachycardia pacing (ATP) within an implantable device are provided. The device gains the benefits of overdrive pacing for preventing the onset of a tachycardia and, if one nevertheless occurs, ATP is employed to terminate the tachycardia. In particular, a technique is provided for promptly detecting the onset of atrial tachycardia during preventive overdrive pacing based on loss of capture of atrial pacing pulses. A technique is also provided for using detection of loss of capture of atrial or ventricular pacing pulses to trigger automatic switching from overdrive pacing to ATP. A setup technique determines whether to enable the automatic switching from overdrive pacing to ATP within a particular patient. Also, techniques are provided for verifying loss of capture of atrial or ventricular backup pacing pulses and for detecting low amplitude ventricular fibrillation based on loss of capture of ventricular backup pacing pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Automated reapplication of atrial pacing therapies
InactiveUS6876880B2Good curative effectReducing atrial tachyarrhythmia burdenHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsAtrial pacingMedical device
The invention relates to the use of atrial pacing therapies to treat atrial tachycardia (AT). When an AT episode is detected, an implantable medical device applies an ATP therapy. If the AT episode persists, the ATP therapy may be automatically reapplied at a later time during the course of the same AT episode. In particular, previously used ATP therapies are reapplied when episodic conditions, such as cycle length or cycle regularity, change. Although a particular ATP therapy initially may be unsuccessful in terminating the AT, it may prove successful when the cycle length or regularity of the atrial rhythm changes. As the rhythm slows down, the AT may be more responsive to ATP therapies that were previously unsuccessful. As a result, potentially efficacious ATP therapies can be reapplied to terminate AT episodes, and reduce the number of episodes that require more aggressive termination by painful, atrial shocks.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com