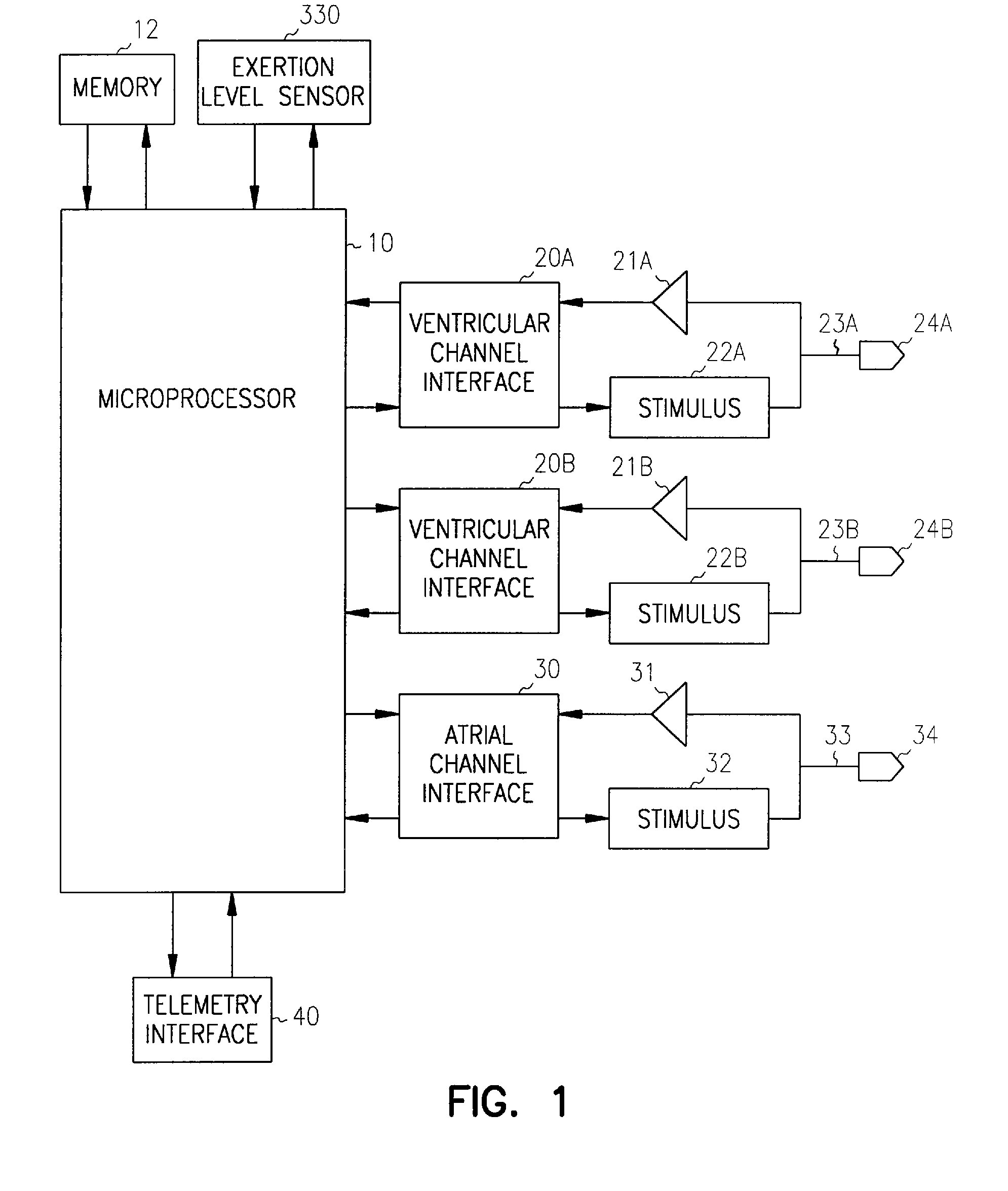
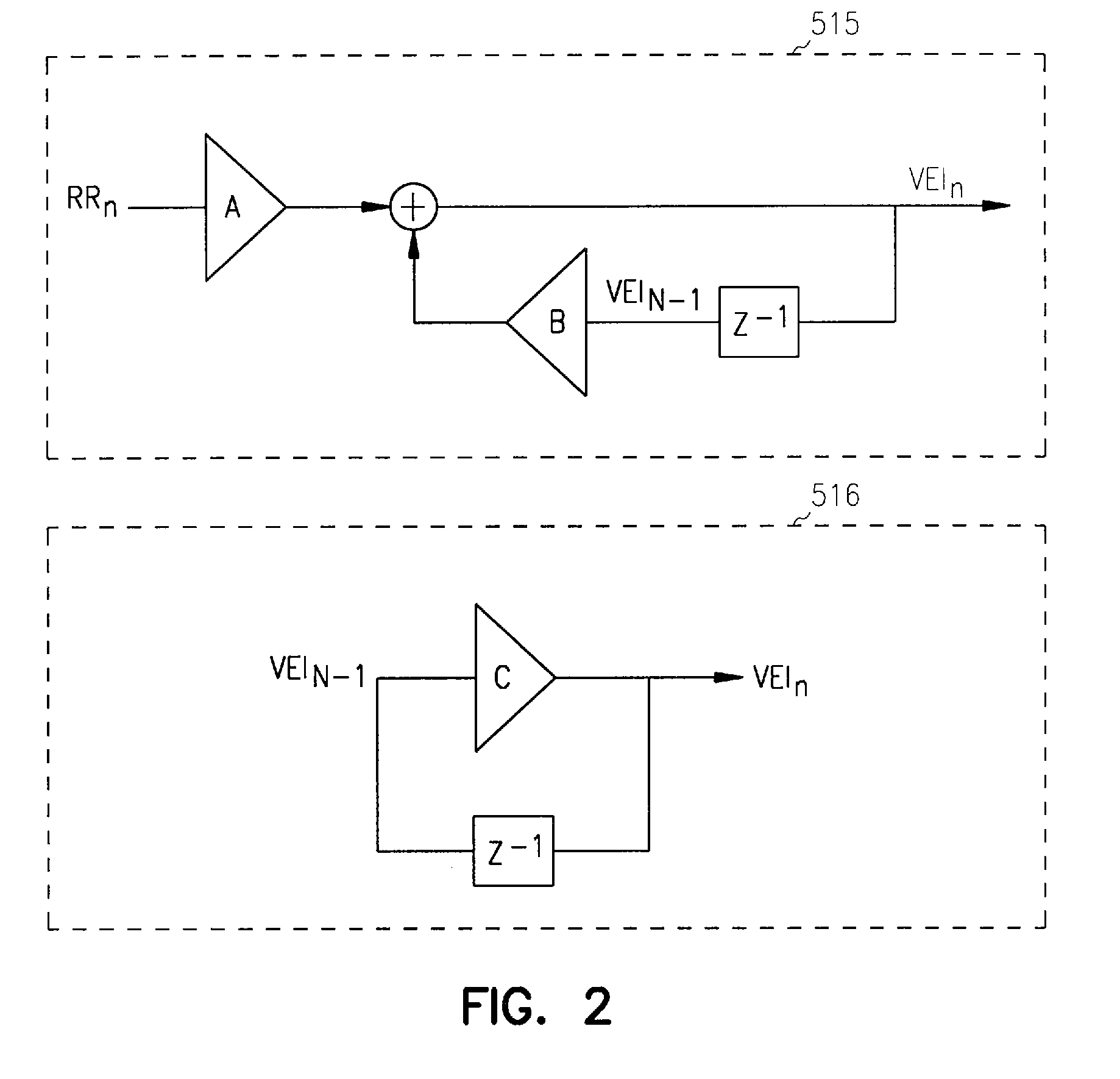
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Atrial tachycardia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm problem in which the heart's electrical impulse comes from an ectopic pacemaker (that is, an abnormally located cardiac pacemaker) in the upper chambers (atria) of the heart, rather than from the sinoatrial node, the normal origin of the heart's electrical activity. Atrial tachycardias can exhibit very regular (consistent) heart rates ranging typically from 140 to 220 beats per minute. As with any other form of tachycardia (rapid heart beat), the underlying mechanism can be either the rapid discharge of an abnormal focus, the presence of a ring of cardiac tissue that gives rise to a circle movement (reentry), or a triggered rapid rhythm due to other pathological circumstances (as would be the case with some drug toxicities, such as digoxin toxicity). Atrial tachycardia is a risk factor for atrial fibrillation, as the rapid rhythm can trigger or degrade into the lack of a rhythm. All atrial tachycardias are by definition supraventricular tachycardias.
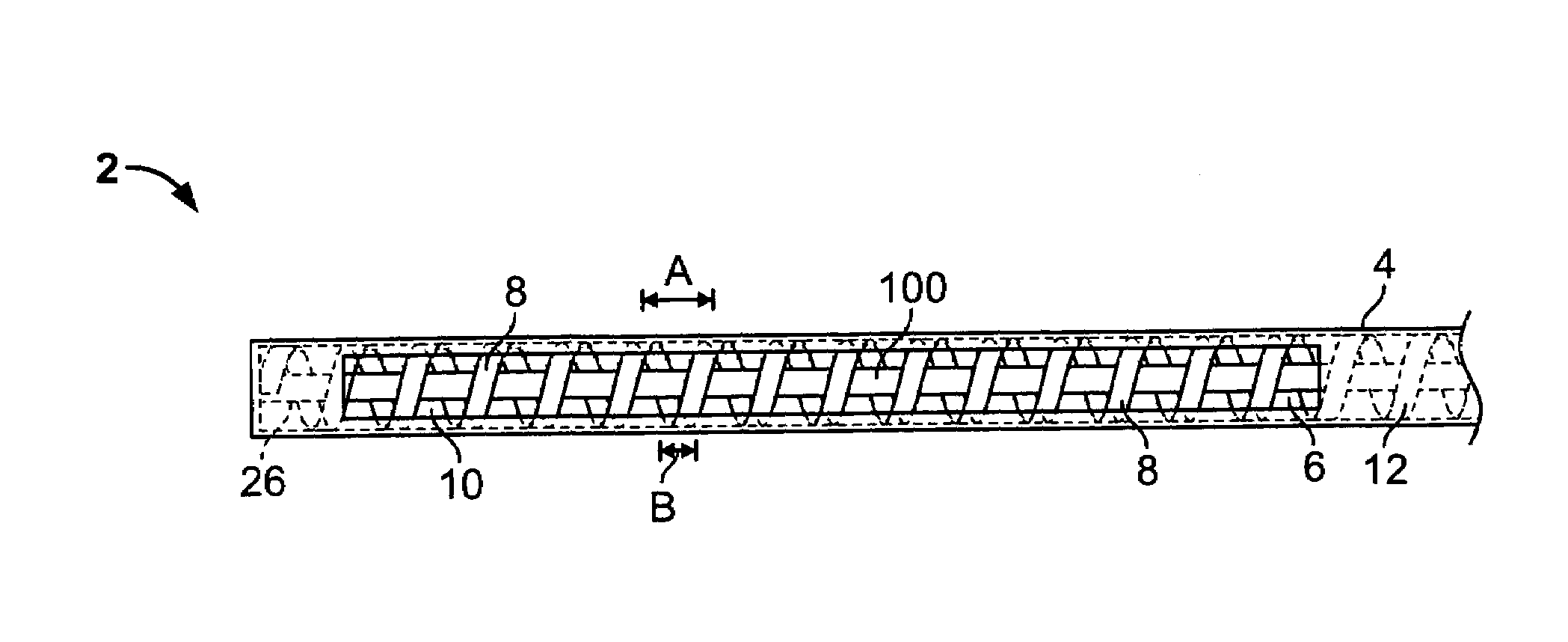
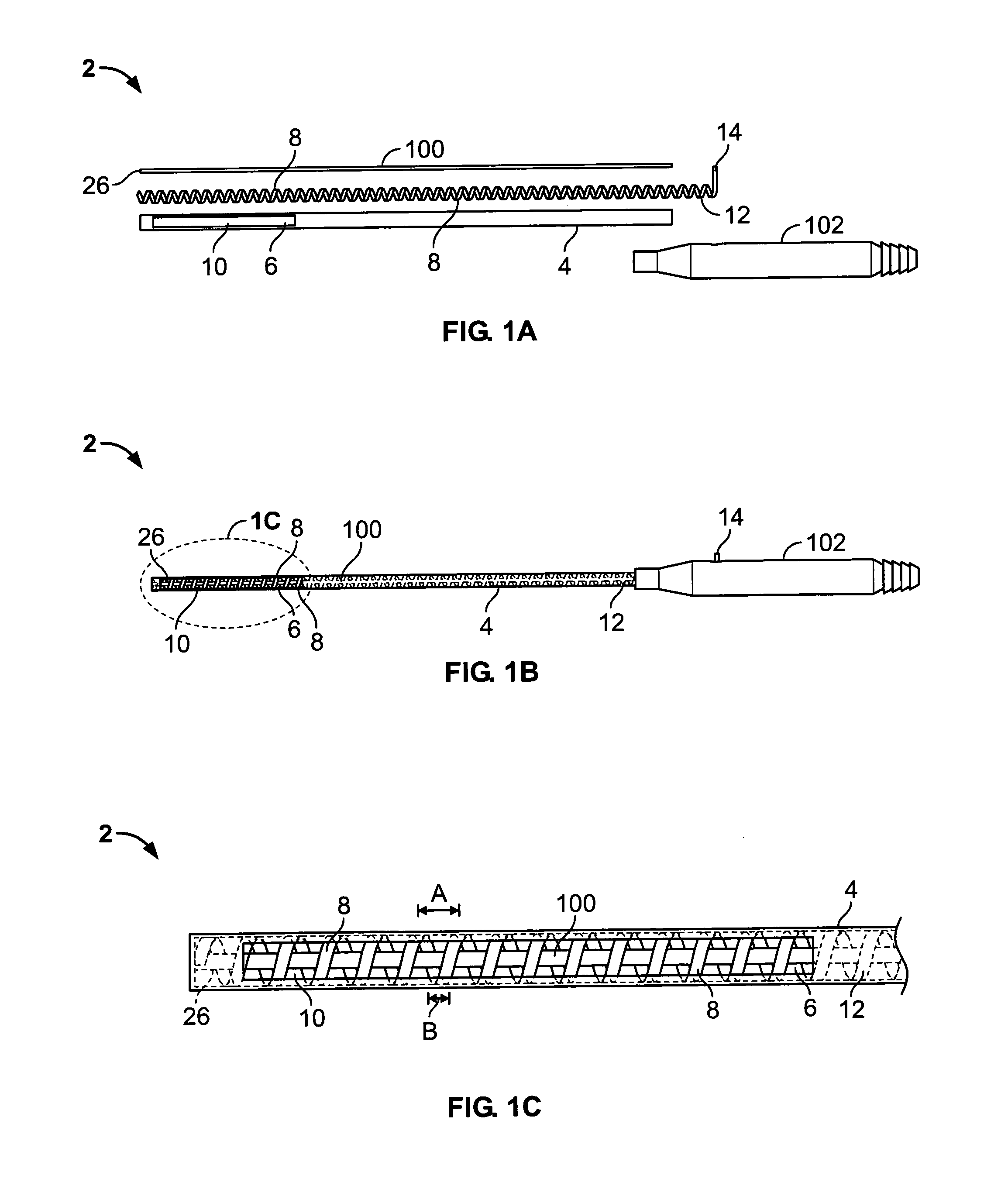
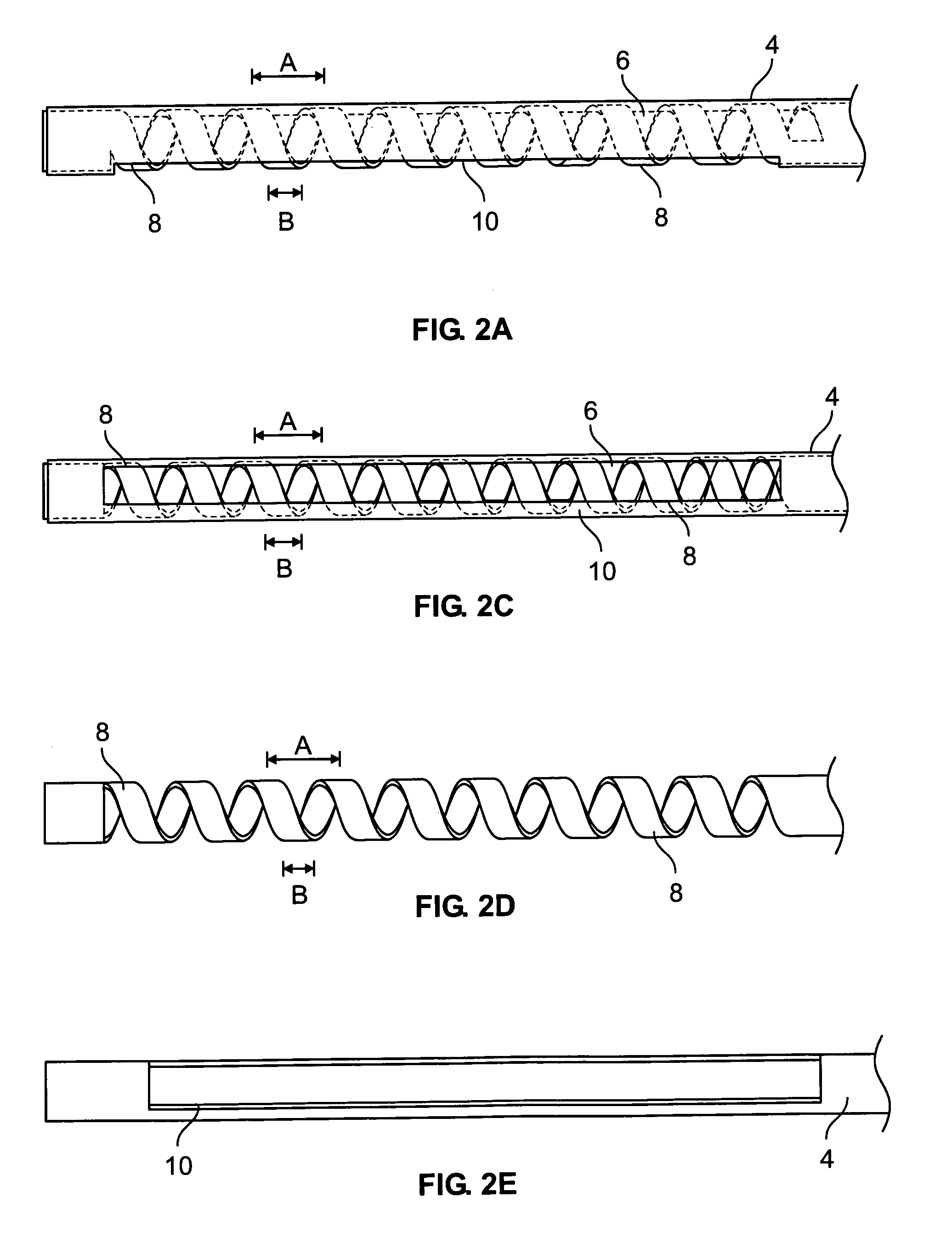
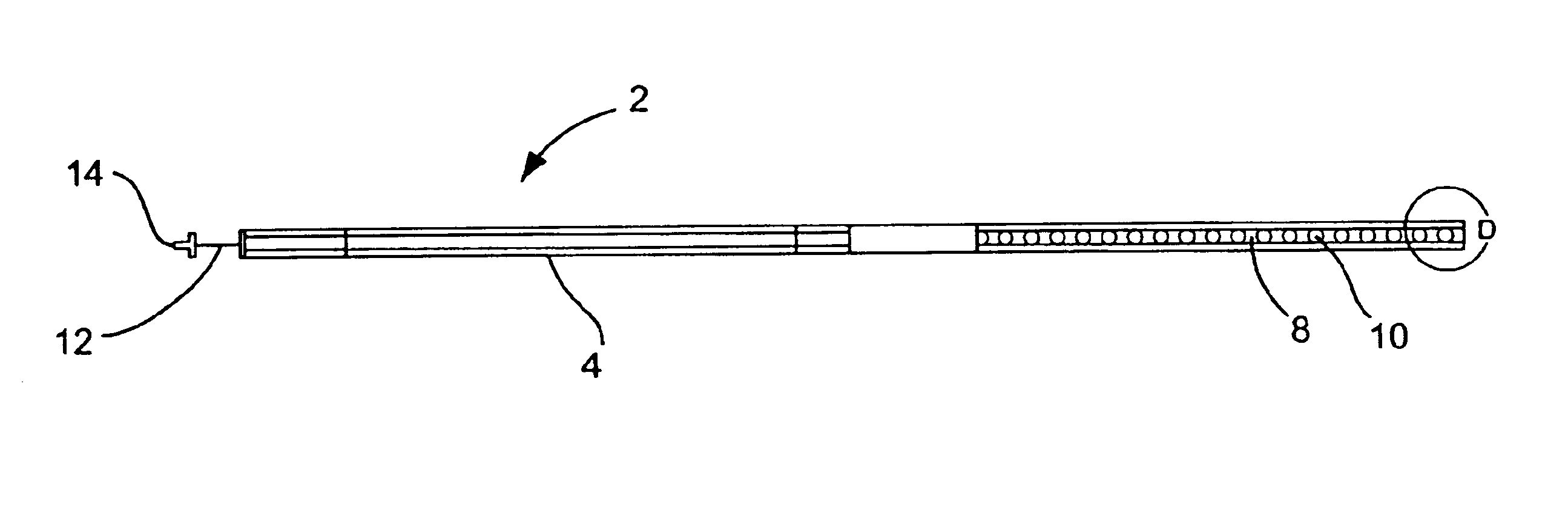
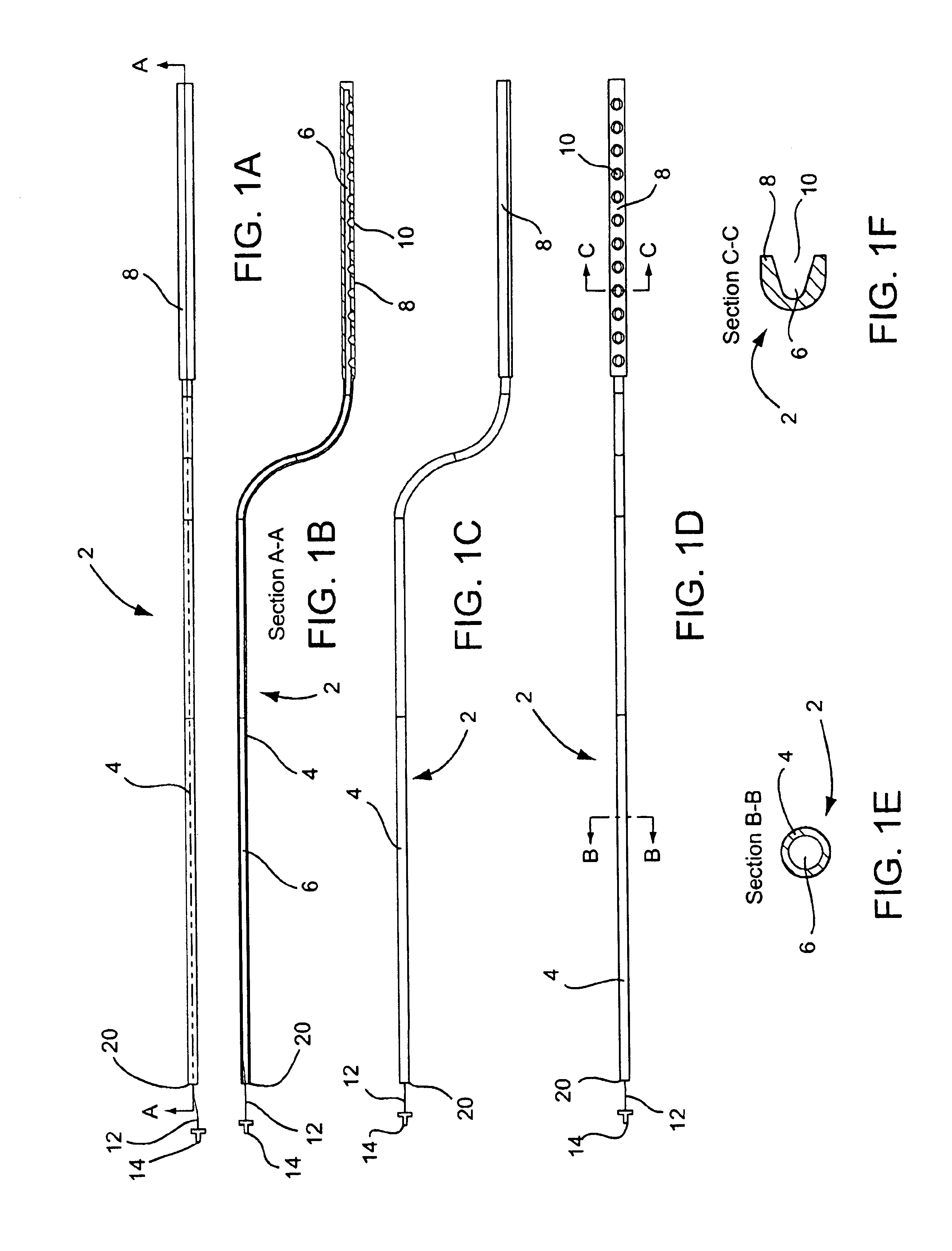
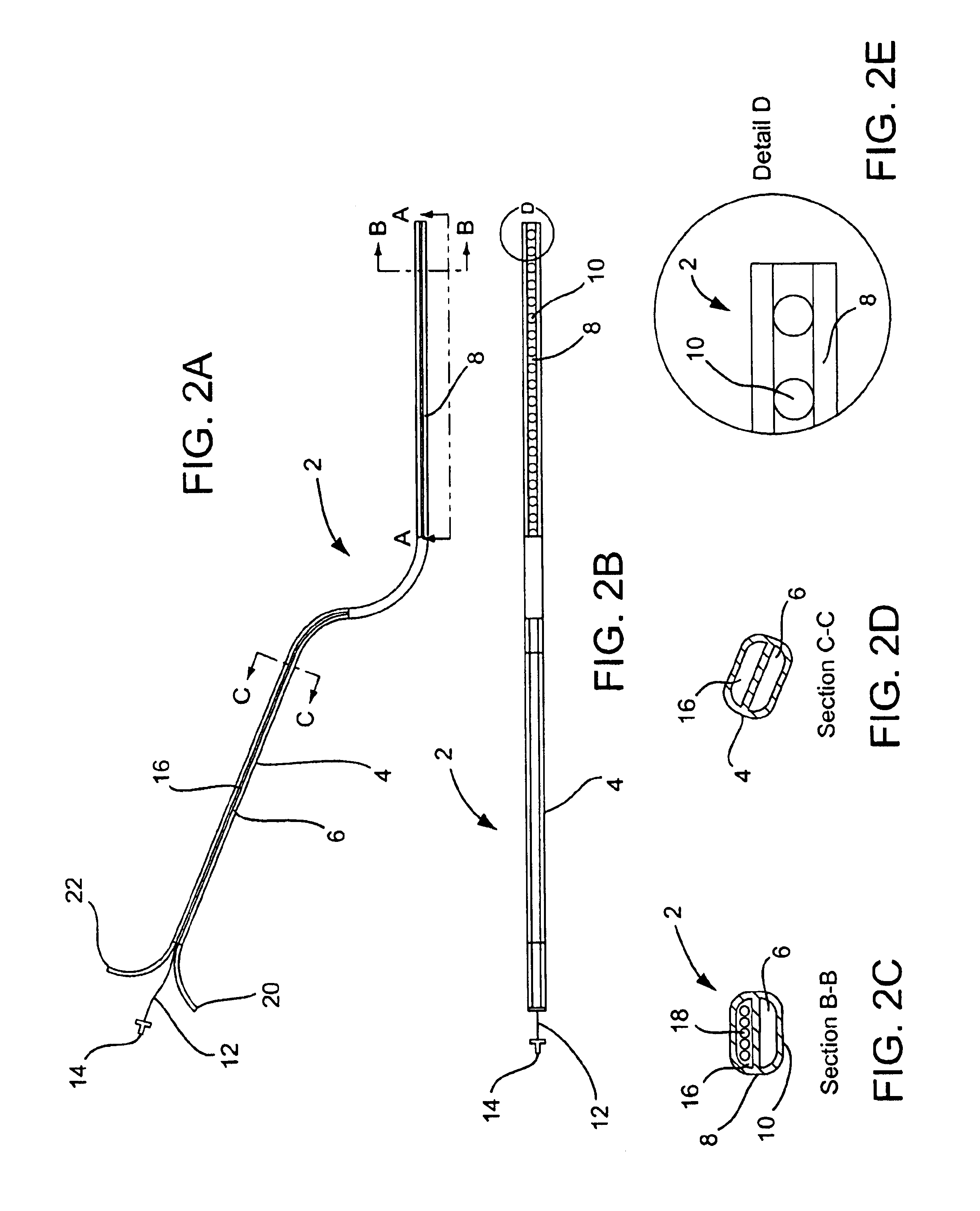
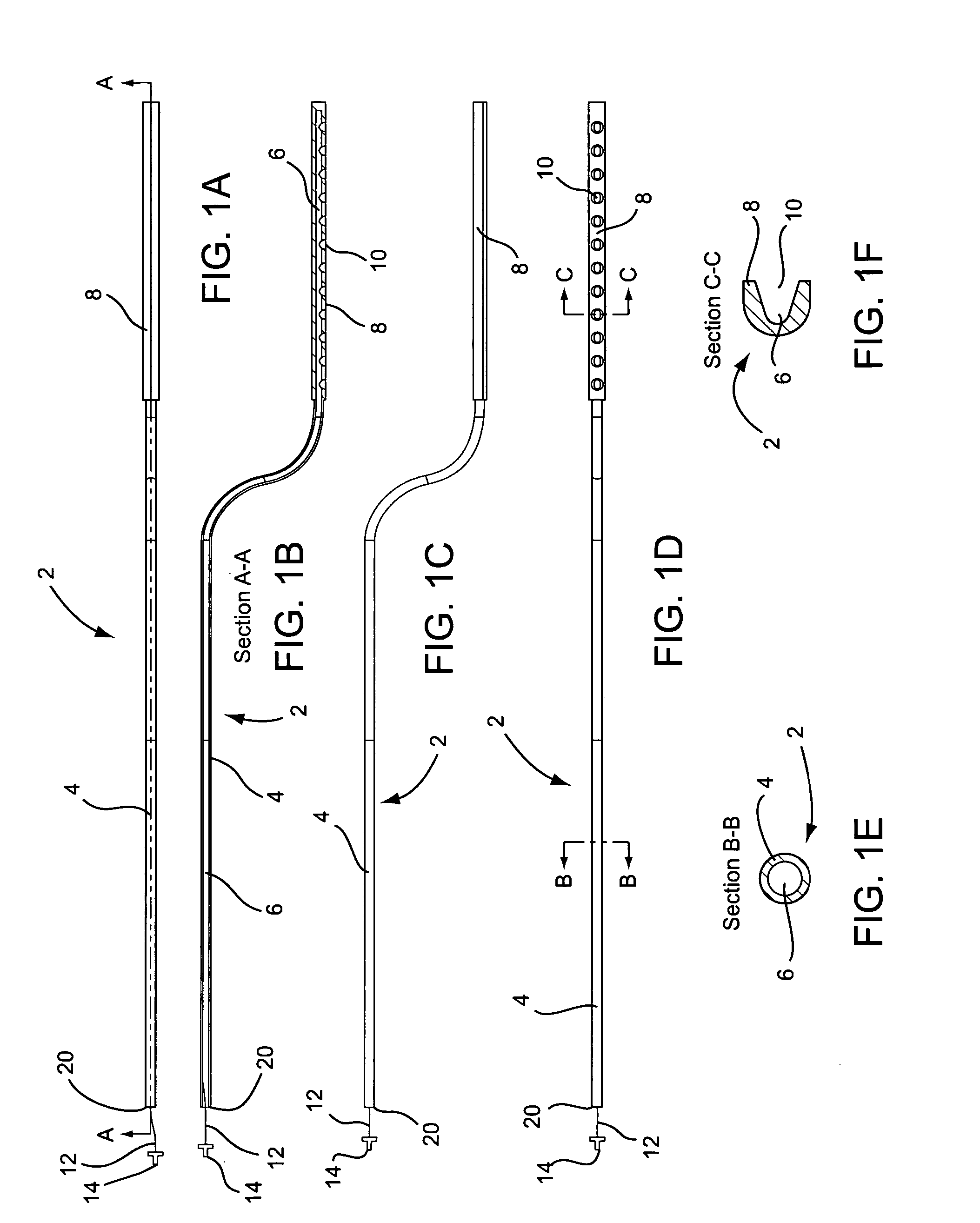
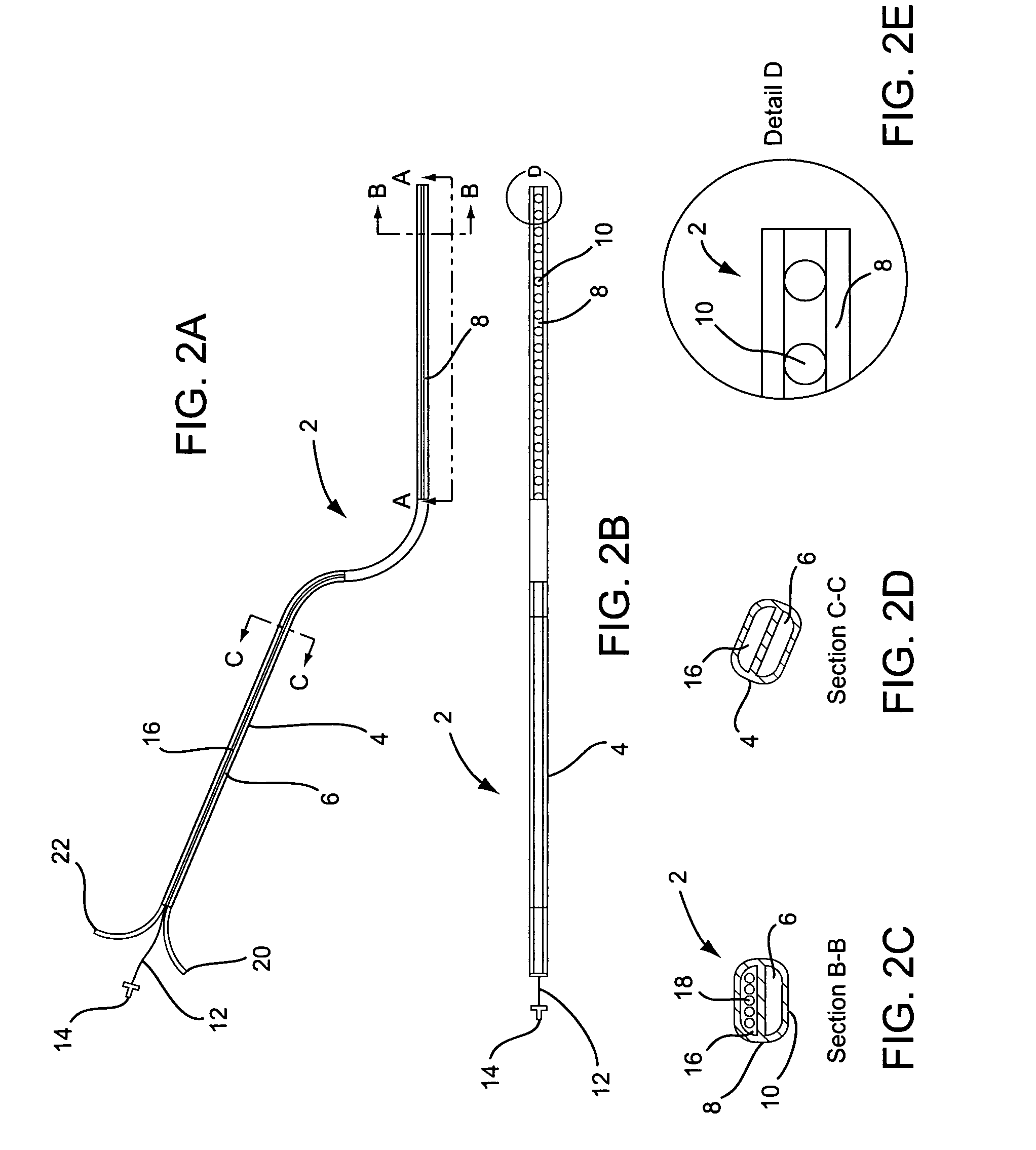
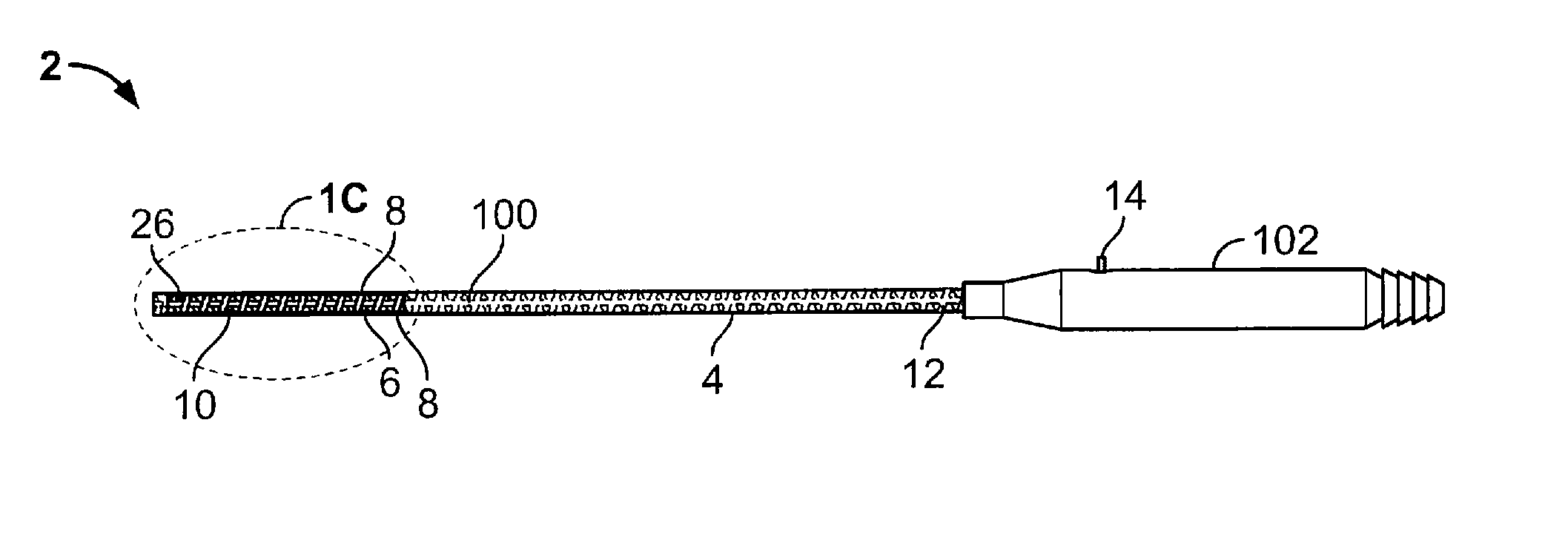
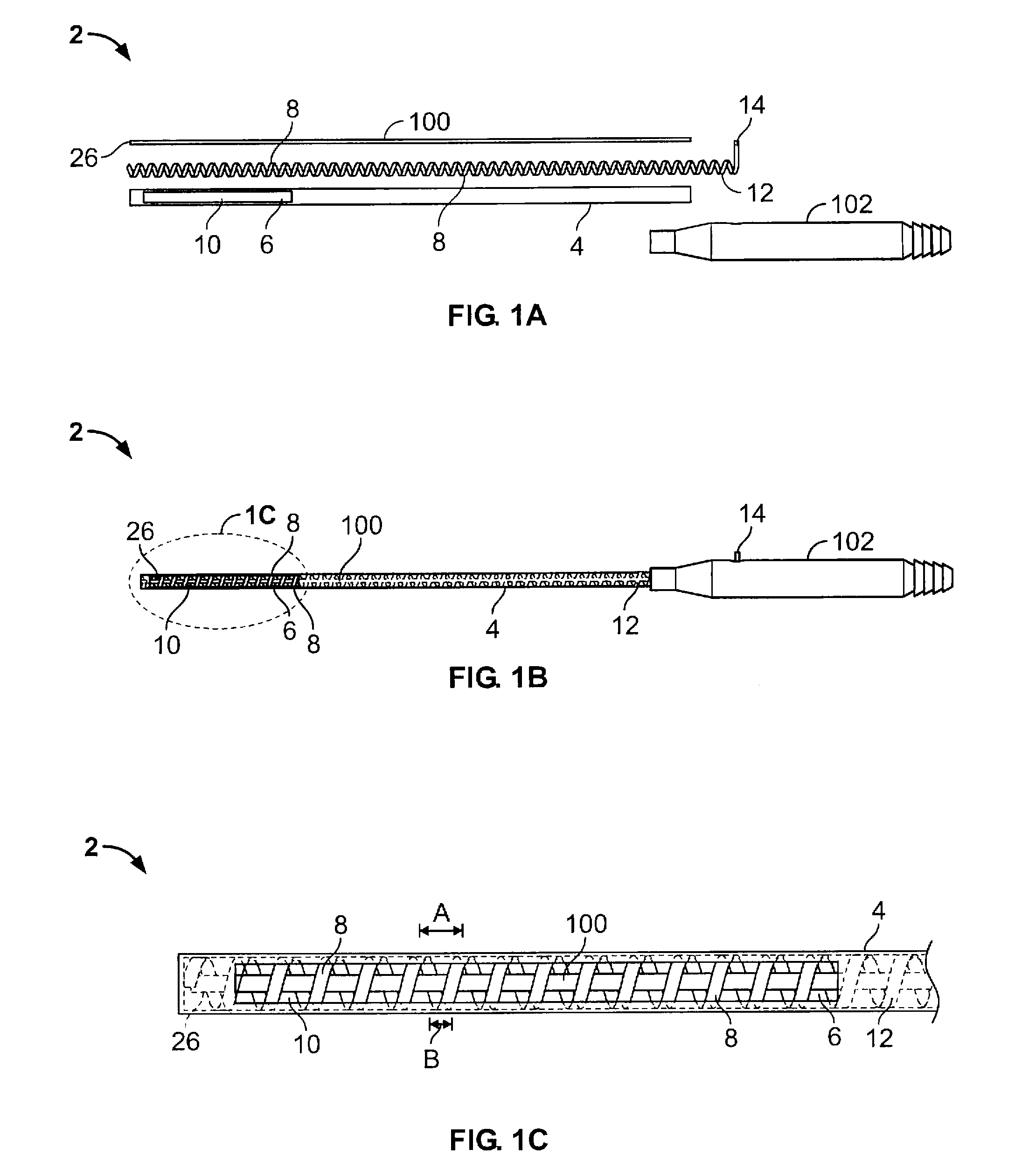
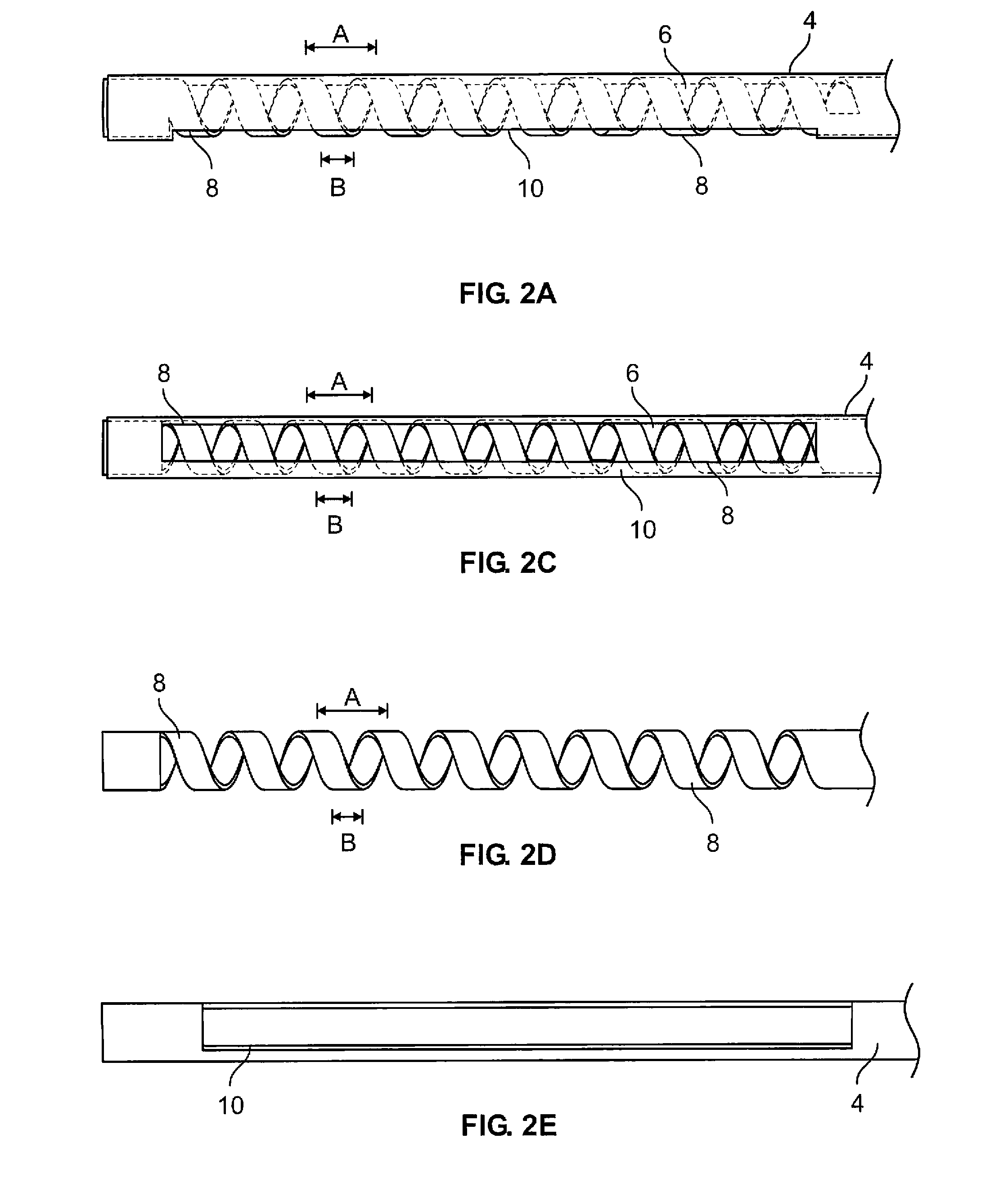
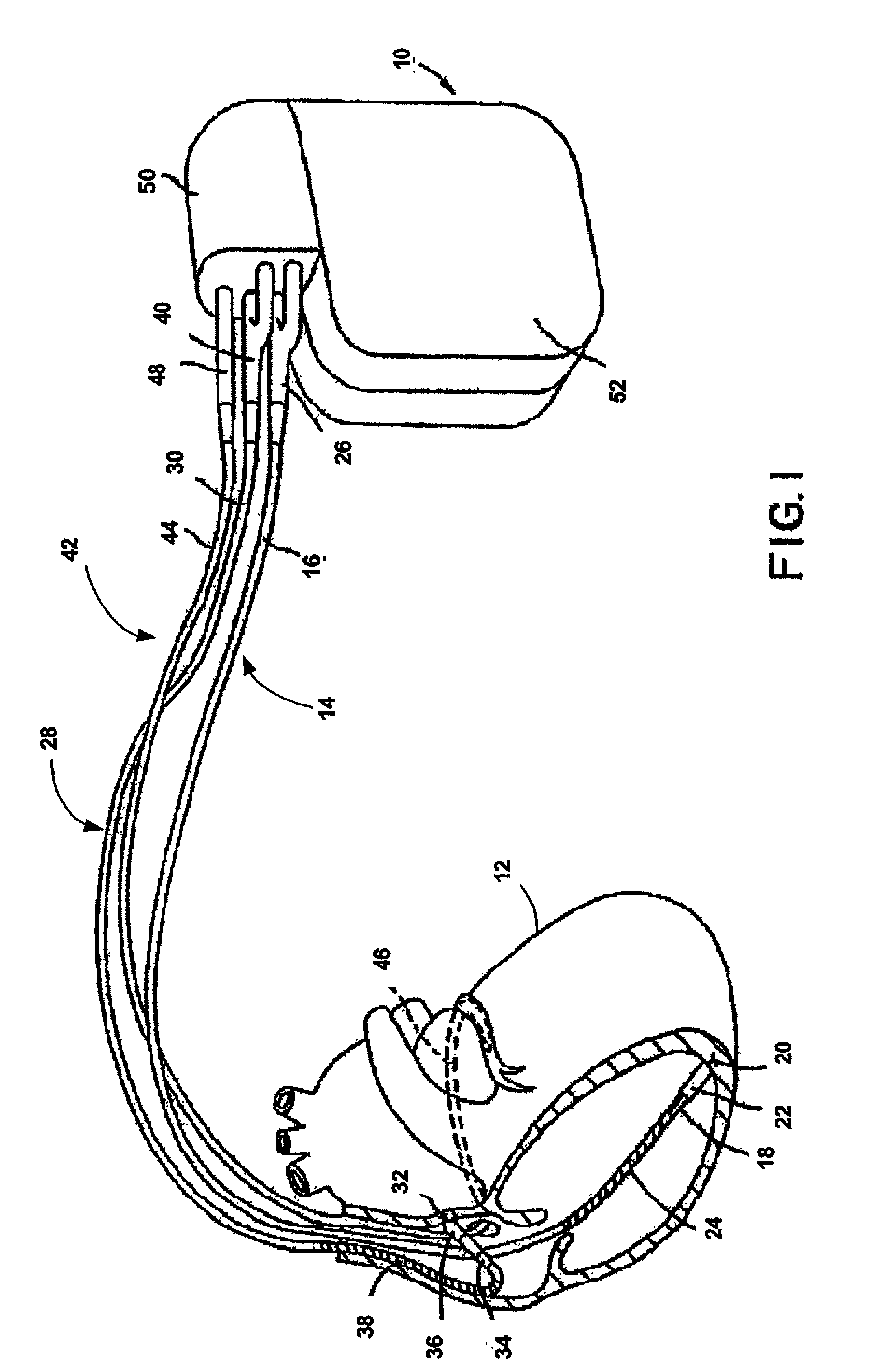
Vacuum coagulation probes
InactiveUS7063698B2Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesRadio frequencyArticular cartilage
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia; tendon or ligament shrinkage; or articular cartilage removal. The surgical device integrates a suction mechanism with the coagulation mechanism improving the lesion creation capabilities of the device. The surgical device comprises an elongate member having an insulative covering attached about conductive elements capable of coagulating soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through the insulative covering expose regions of the conductive elements and are coupled to lumens in the elongate member which are routed to a vacuum source. Suction causes the soft tissue to actively engage the opening thus the integrated, exposed conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, continuous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling mechanisms associated with the conductive elements and coupled to a fluid source to passively transport fluid along the contacted soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
Vacuum coagulation probe for atrial fibrillation treatment
InactiveUS6893442B2Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesLess invasiveRadio frequency
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia. The surgical device can include at least one elongate member comprising conductive elements adapted to coagulate soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through said conductive elements are routed through lumens in the elongate member to a vacuum source to actively engage the soft tissue surface intended to coagulate into intimate contact with the conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, contiguous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling openings positioned near the conductive elements and coupled with a vacuum source or an injection source to transport fluid through the cooling openings causing the soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate features to tunnel between anatomic structures or dissect around the desired tissue surface to coagulate thereby enabling less invasive positioning of the soft tissue coagulating device and ensuring reliable and consistent heating of the soft tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
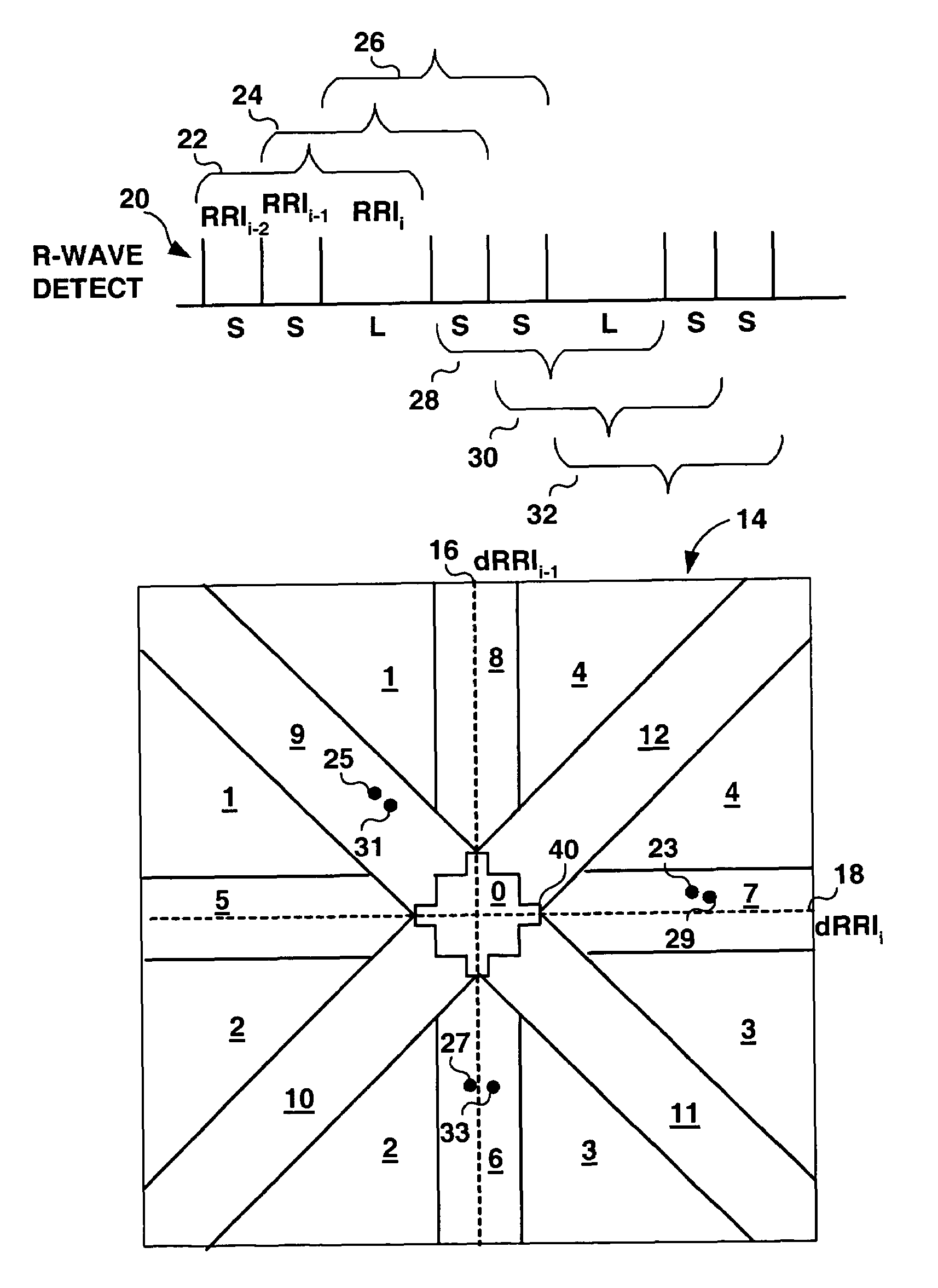
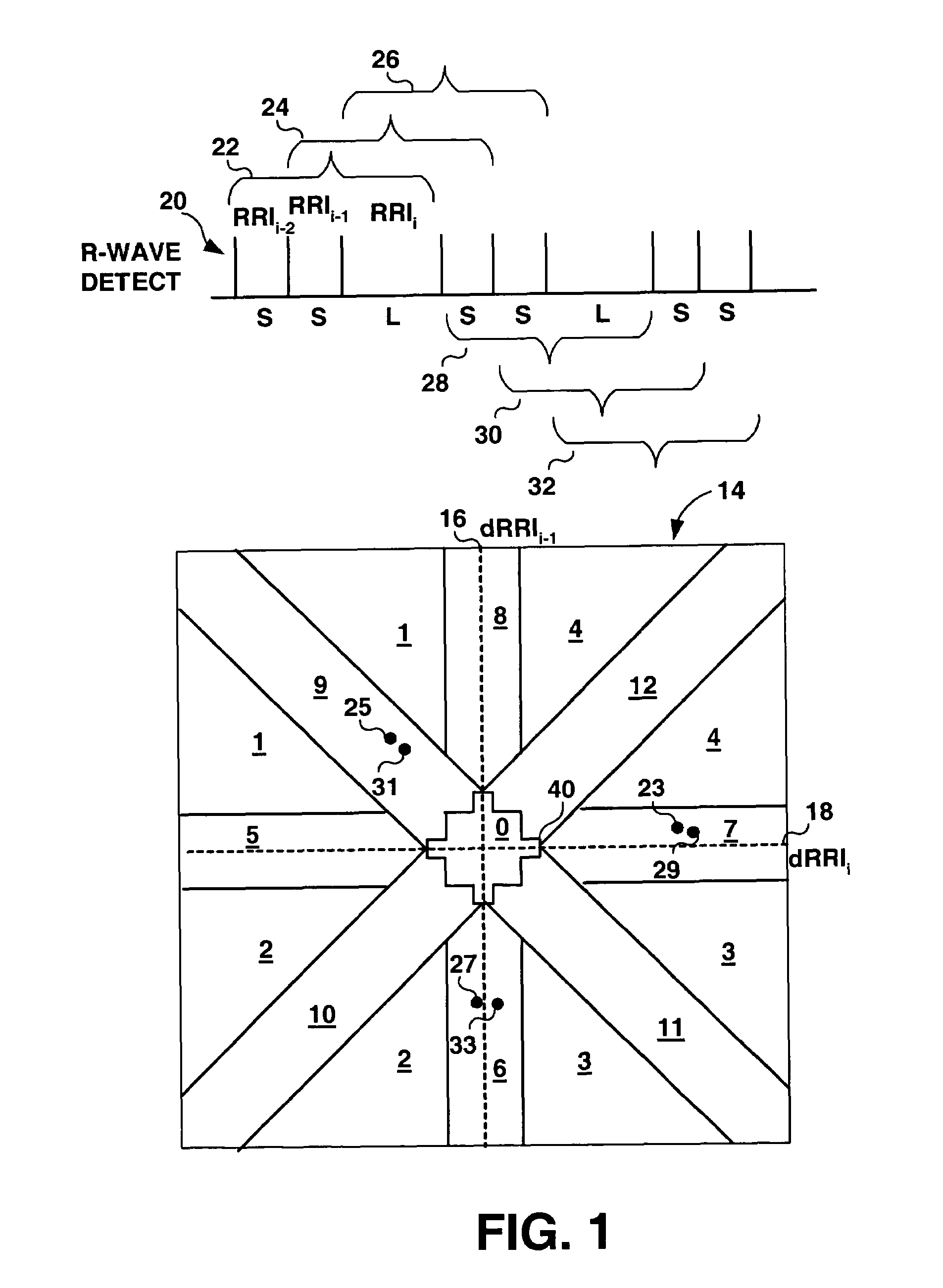
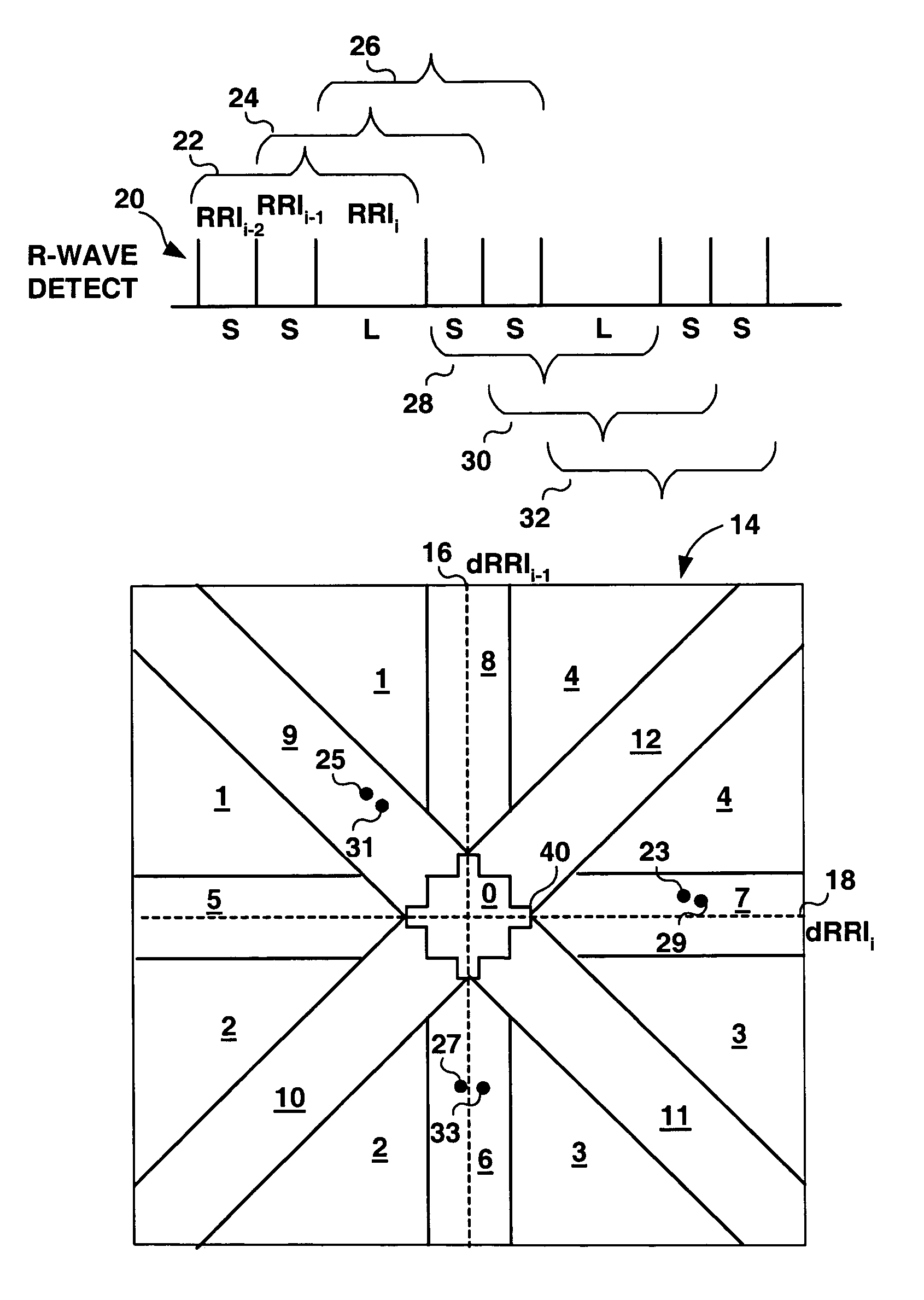
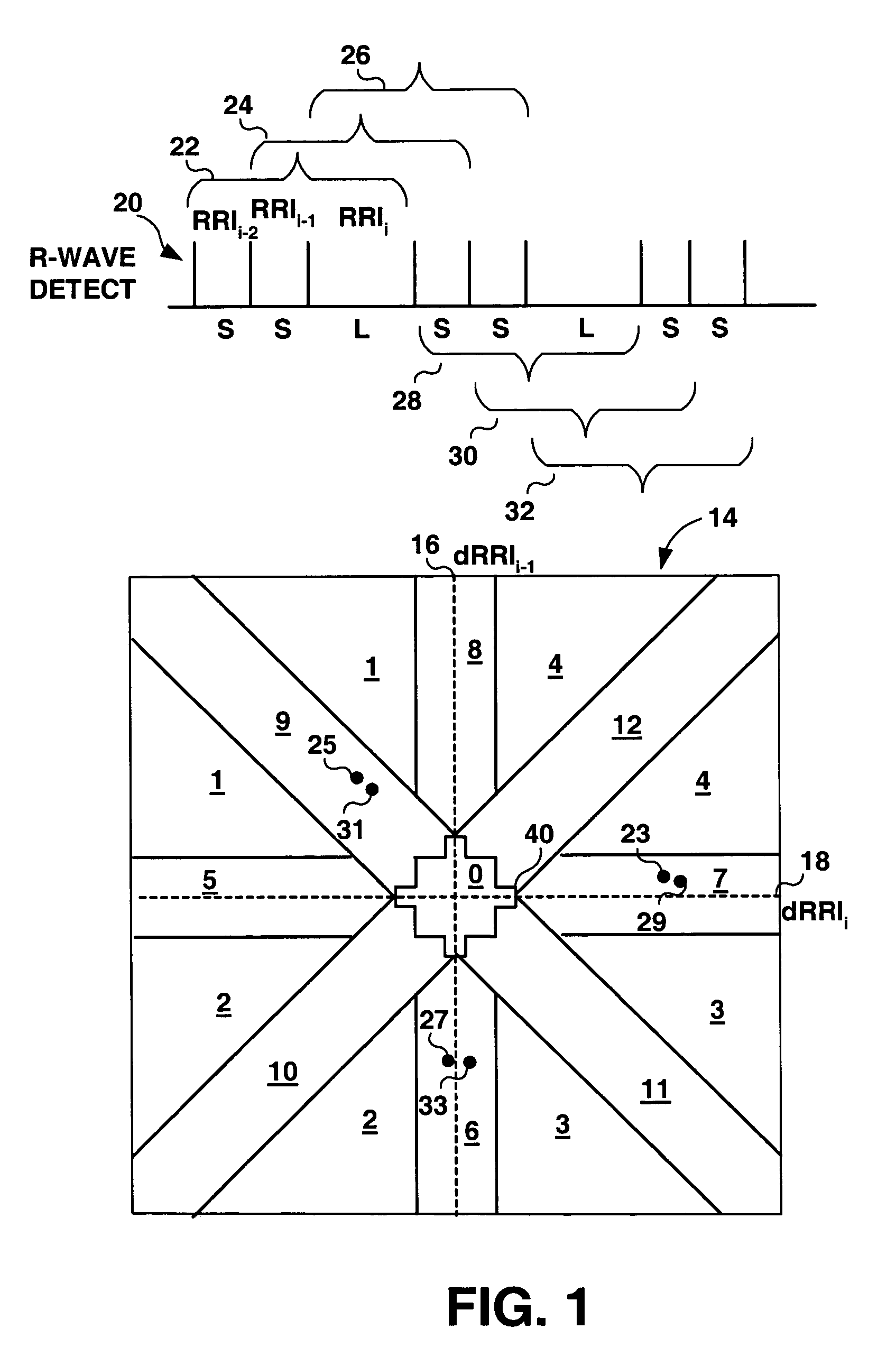
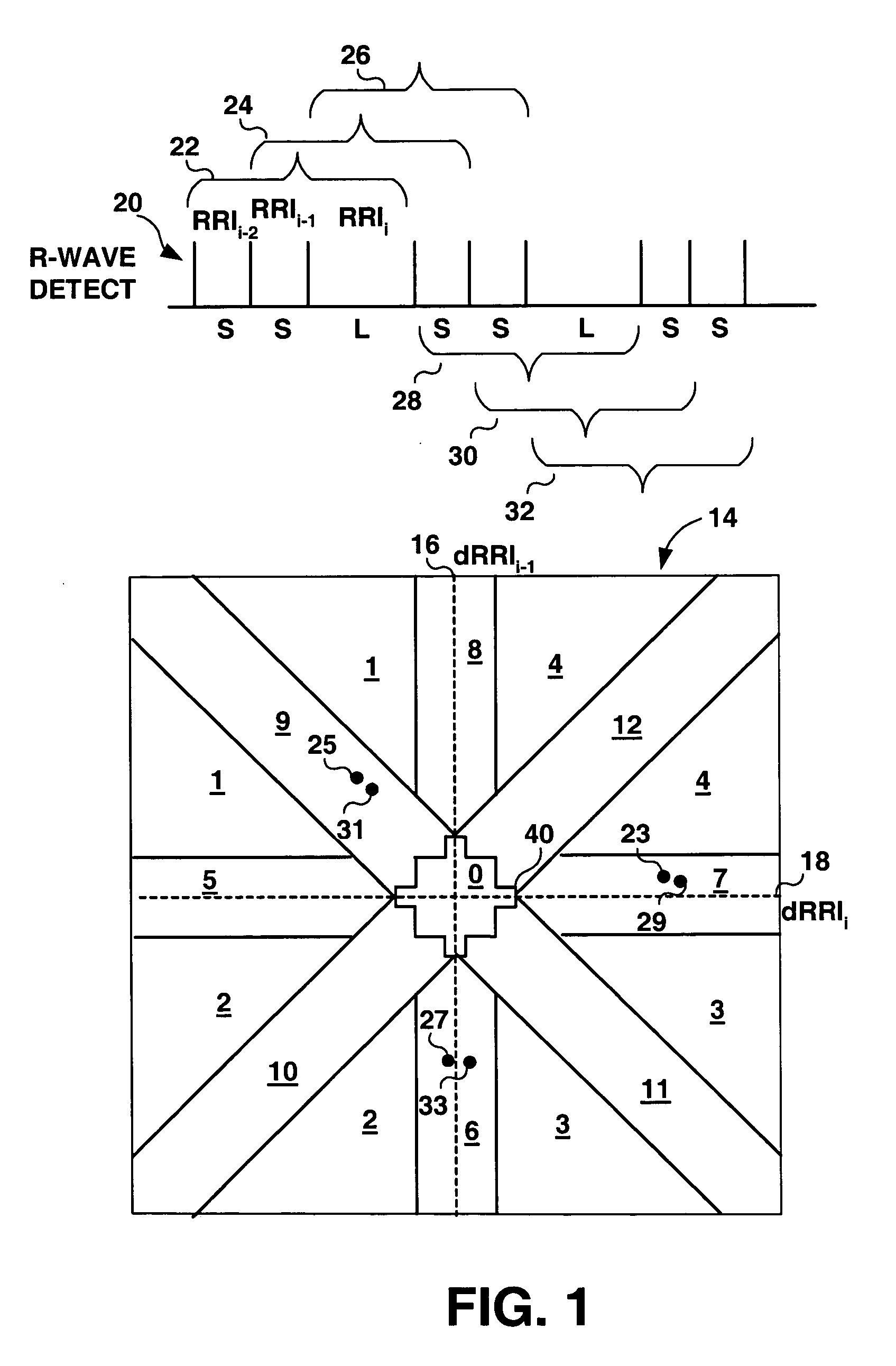
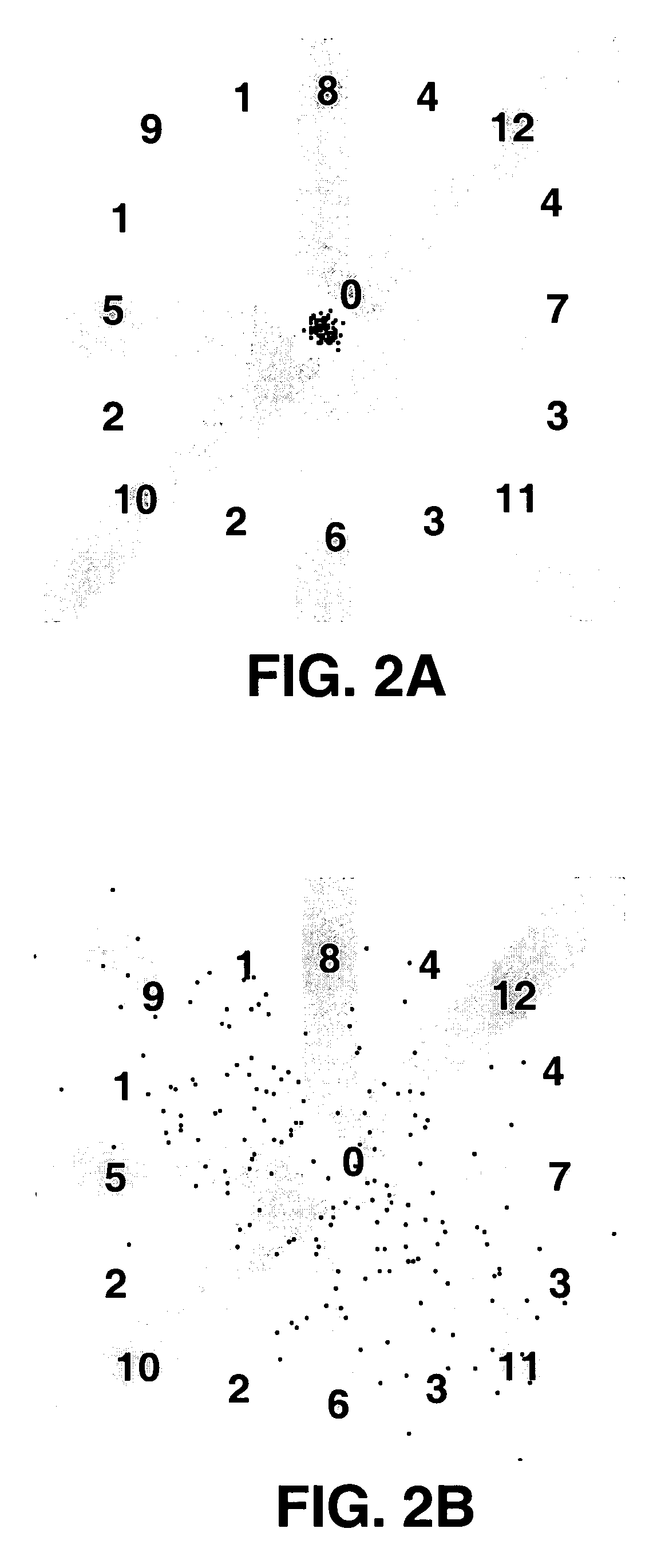
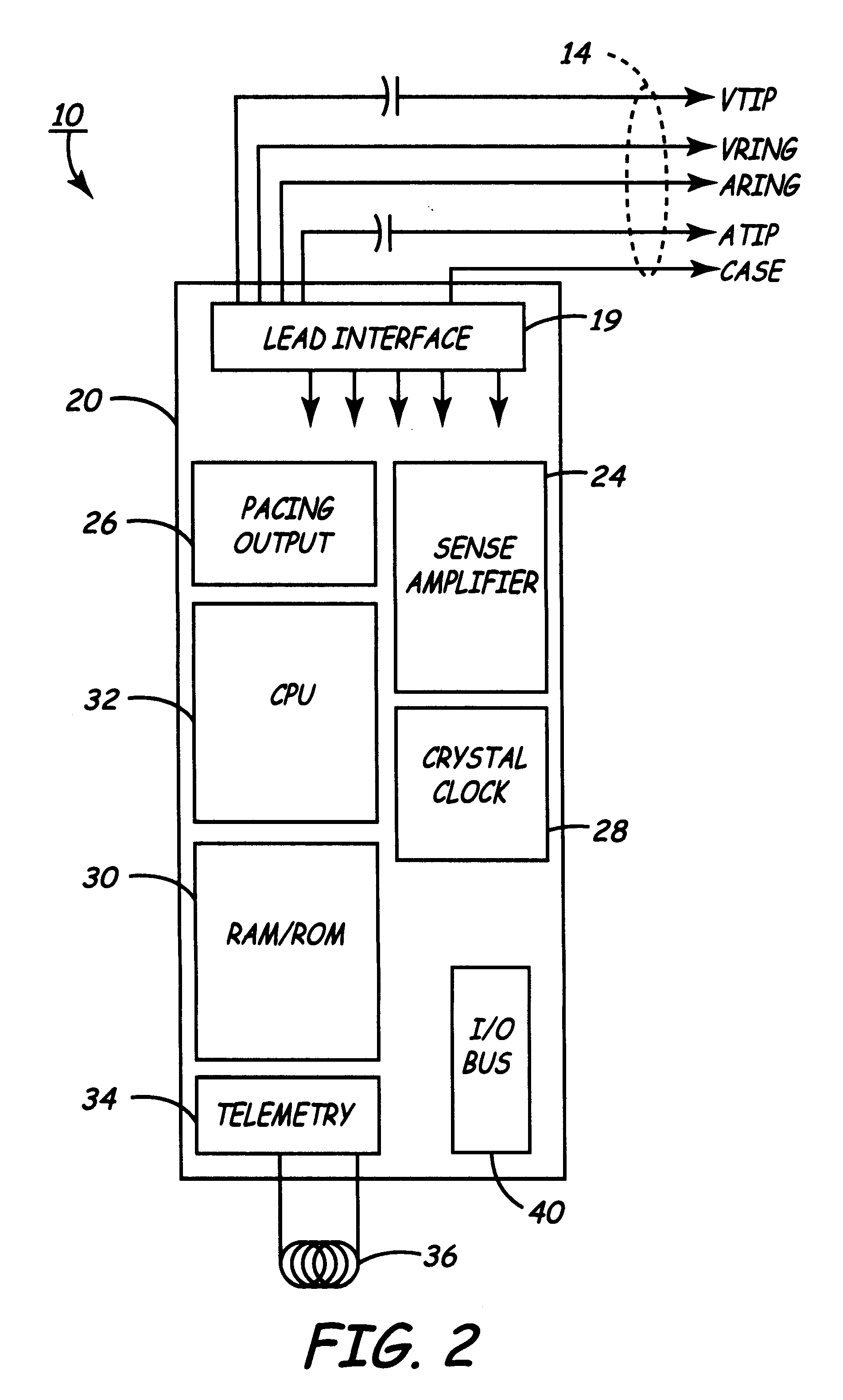
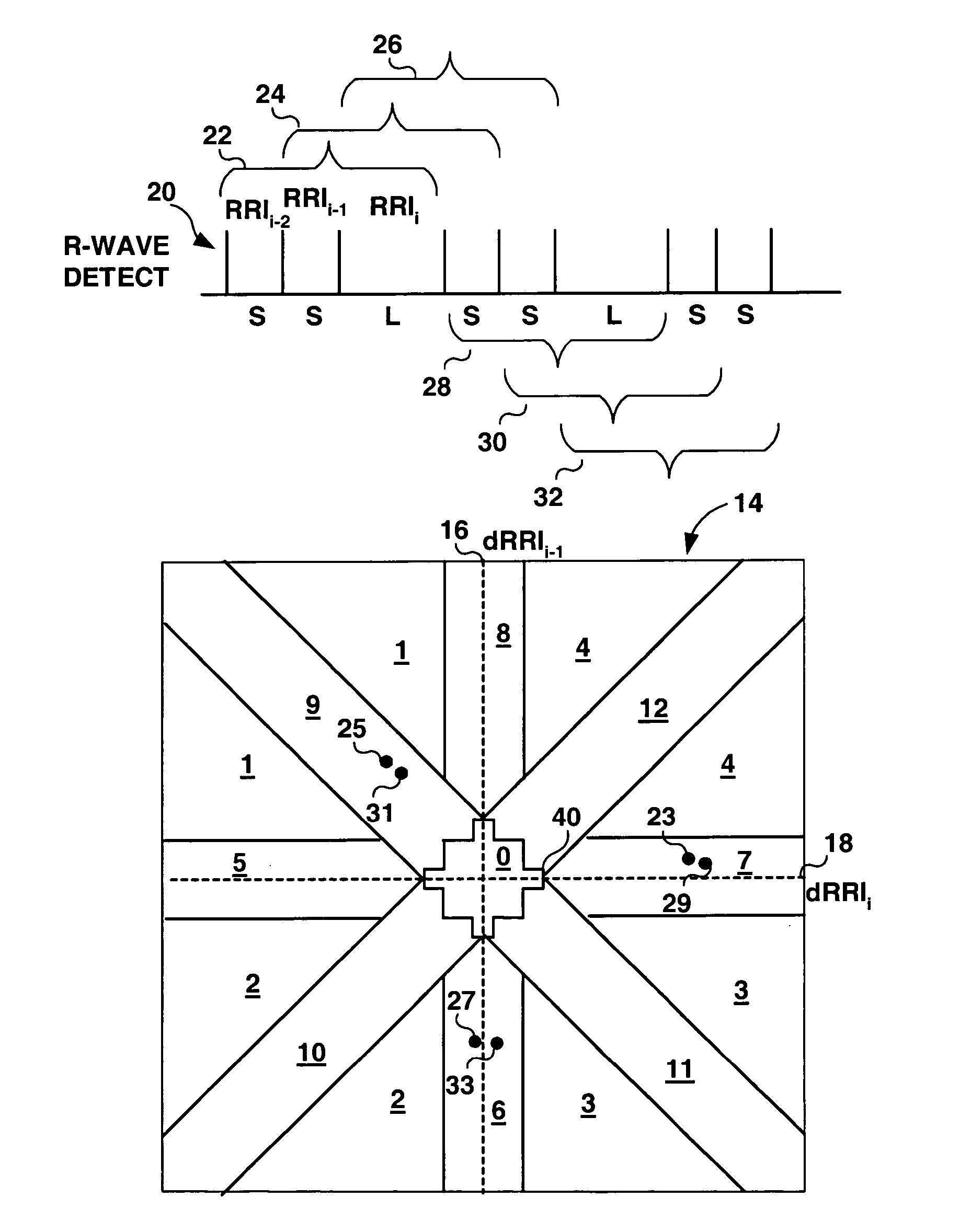
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
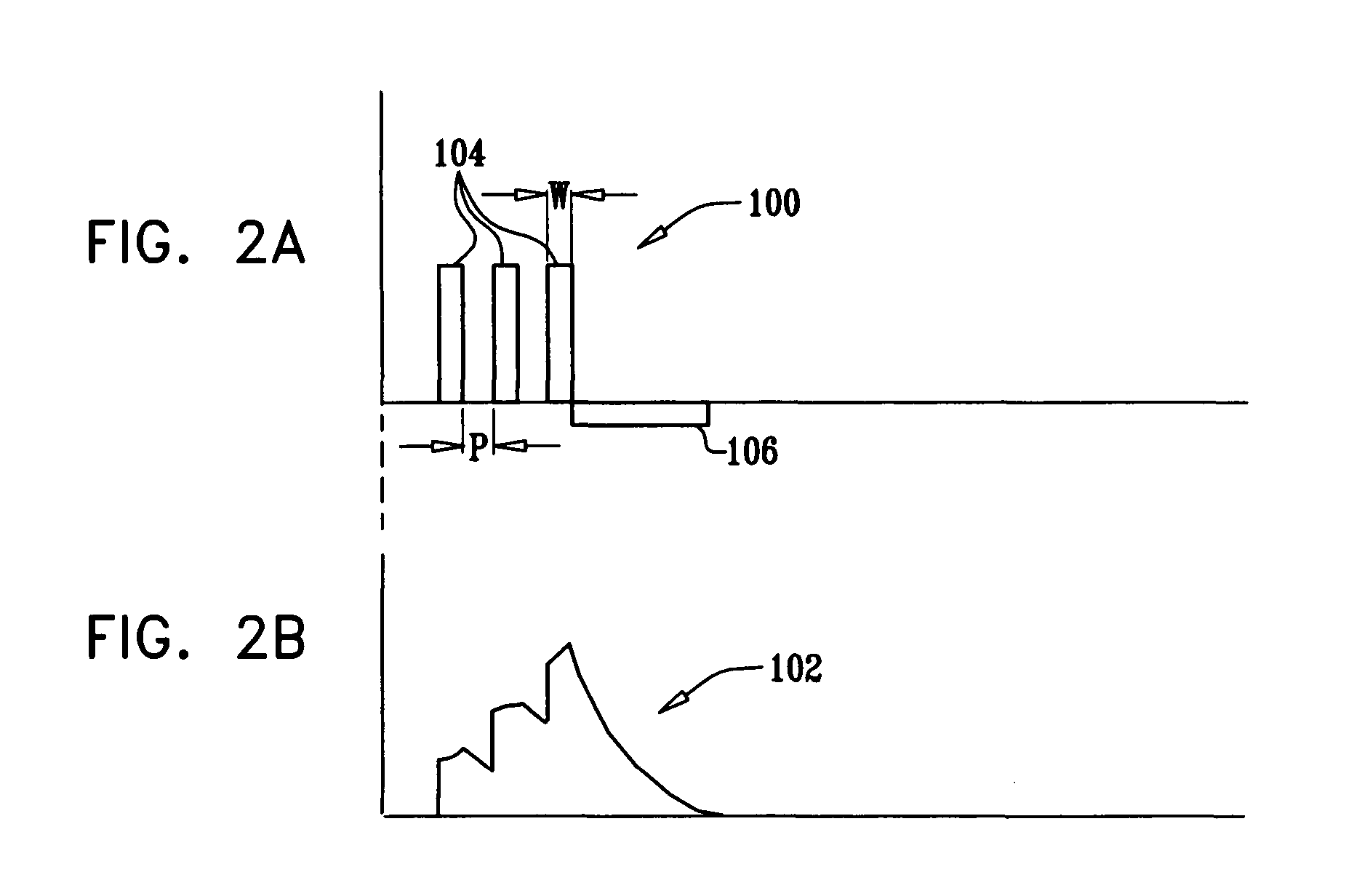
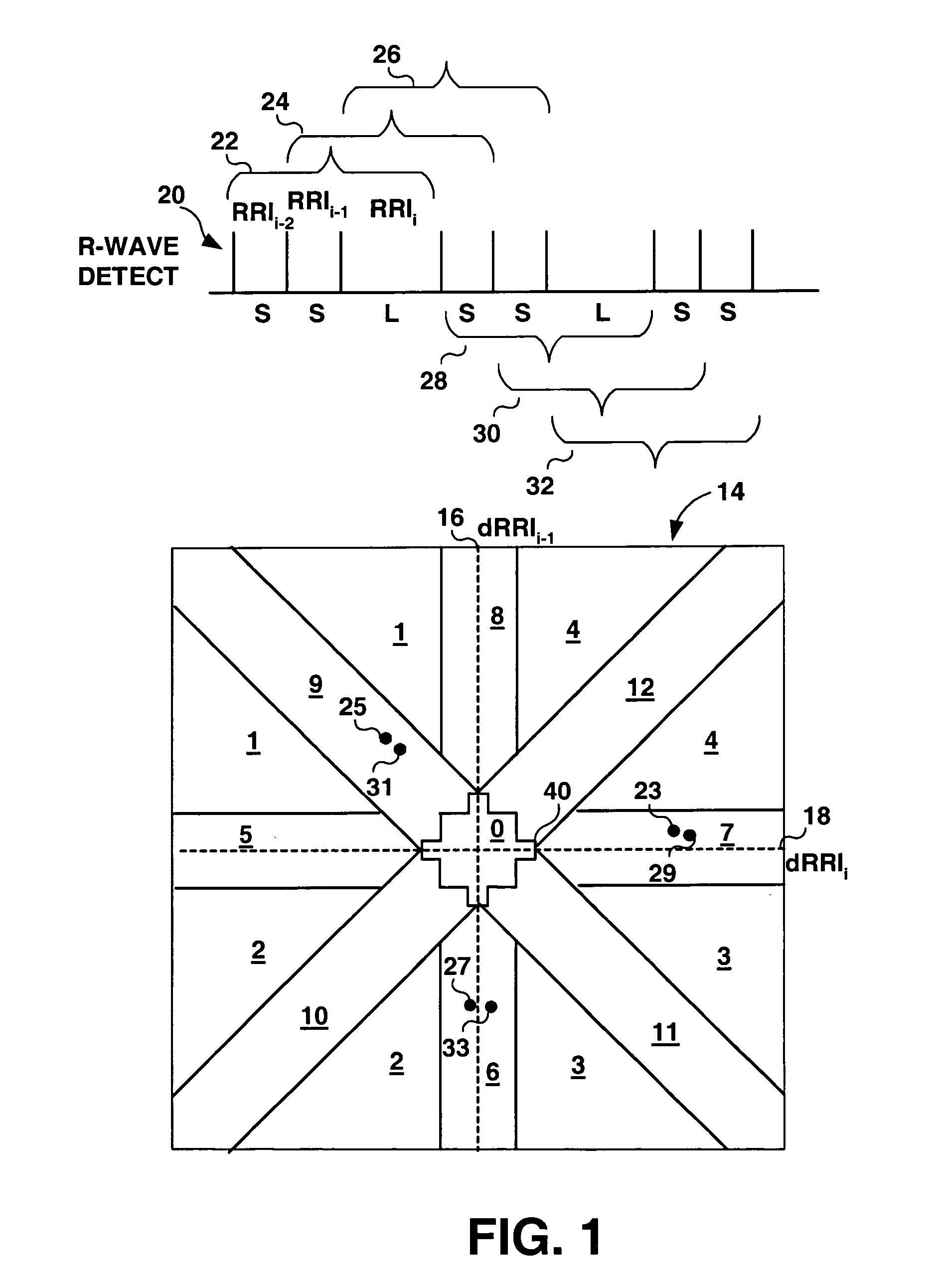
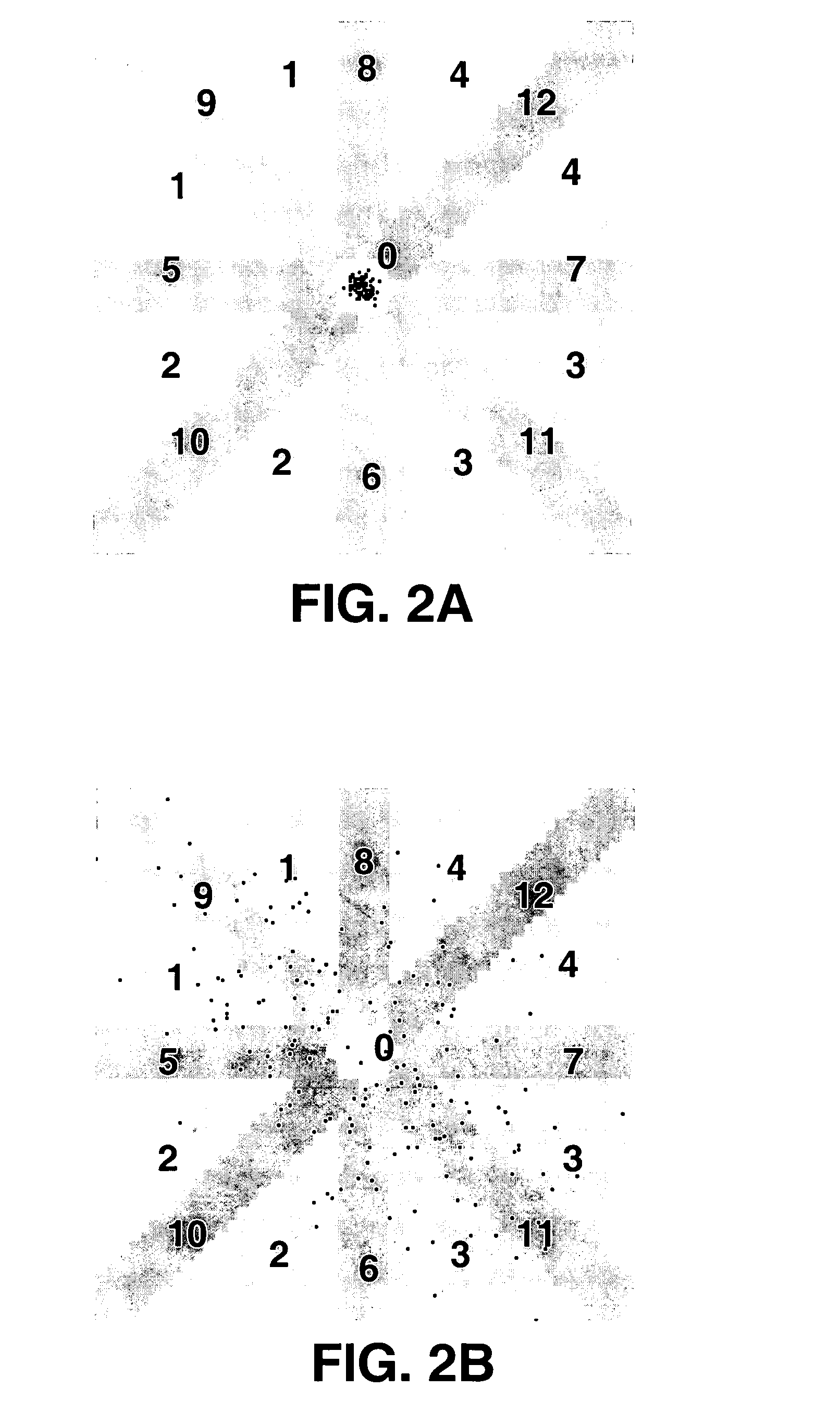
A method and apparatus for detecting atrial arrhythmias and discriminating atrial fibrillation (AF) and organized atrial tachycardia (OAT) that includes defining a threshold detection criteria for a cluster signature evidence metric corresponding to a Lorenz distribution of ventricular cycle lengths representative of AF or OAT. Using a signal containing VCL information, a number of consecutive ventricular cycle lengths are determined during a selected time interval for generating a one-dimensional or a two-dimensional histogram as a numerical representation of a Lorenz plot of VCLs. A number of cluster signature metrics are computed using the stored ventricular cycle length information, and a cluster signature evidence metric is computed from the cluster signature metrics. AF or OAT is detected if a comparative analysis of a corresponding cluster signature evidence metric meets a respective threshold detection criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
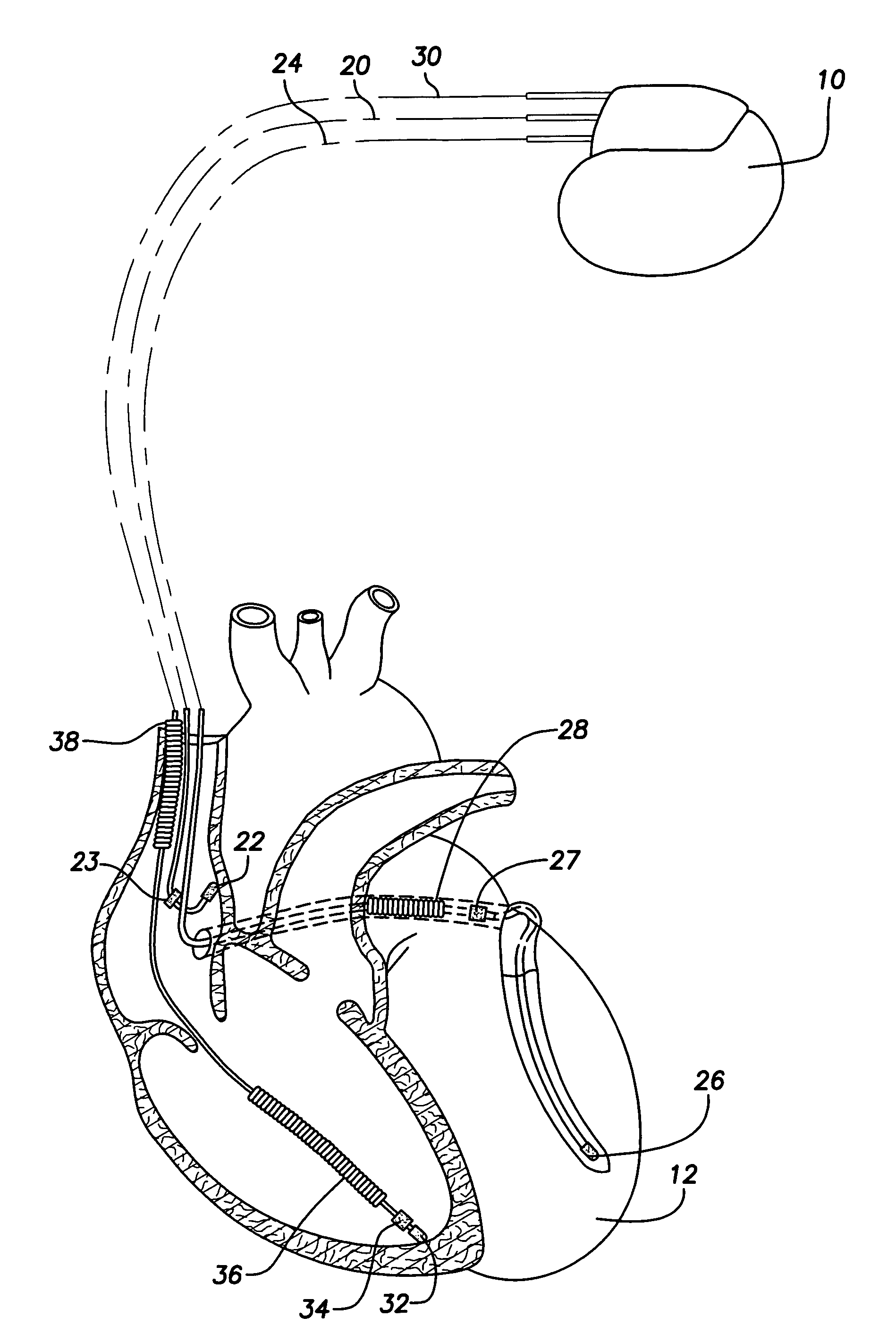
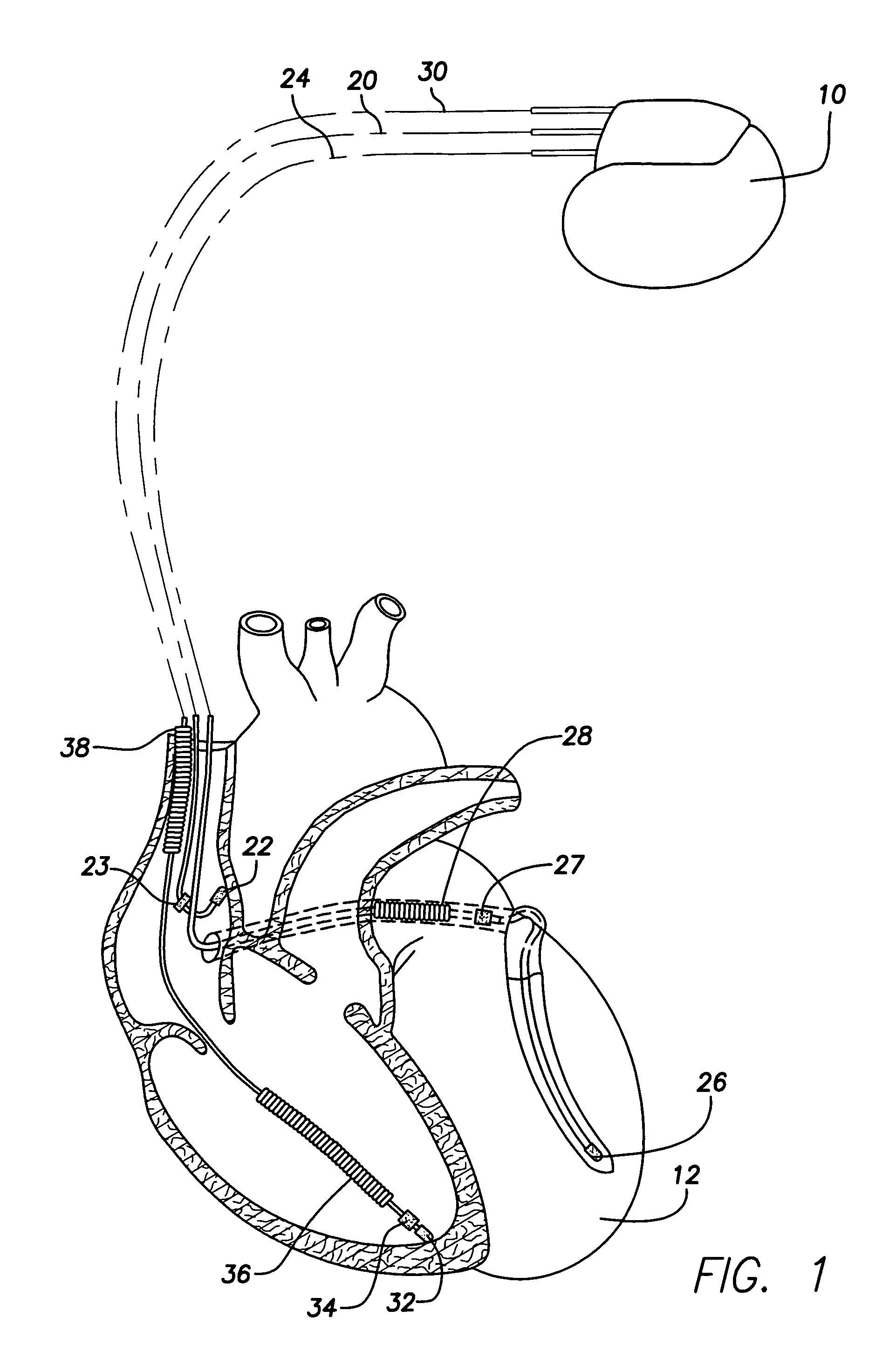
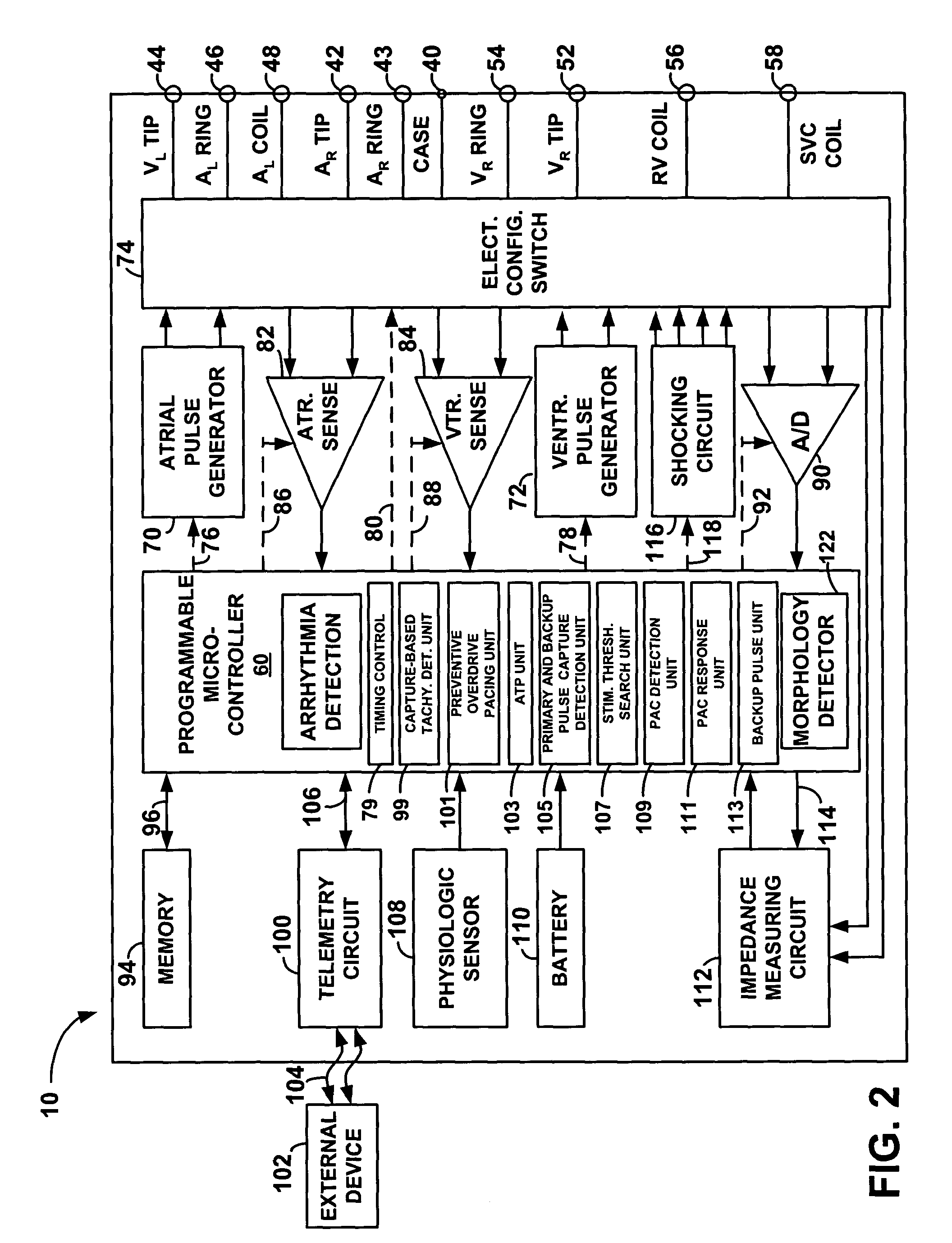
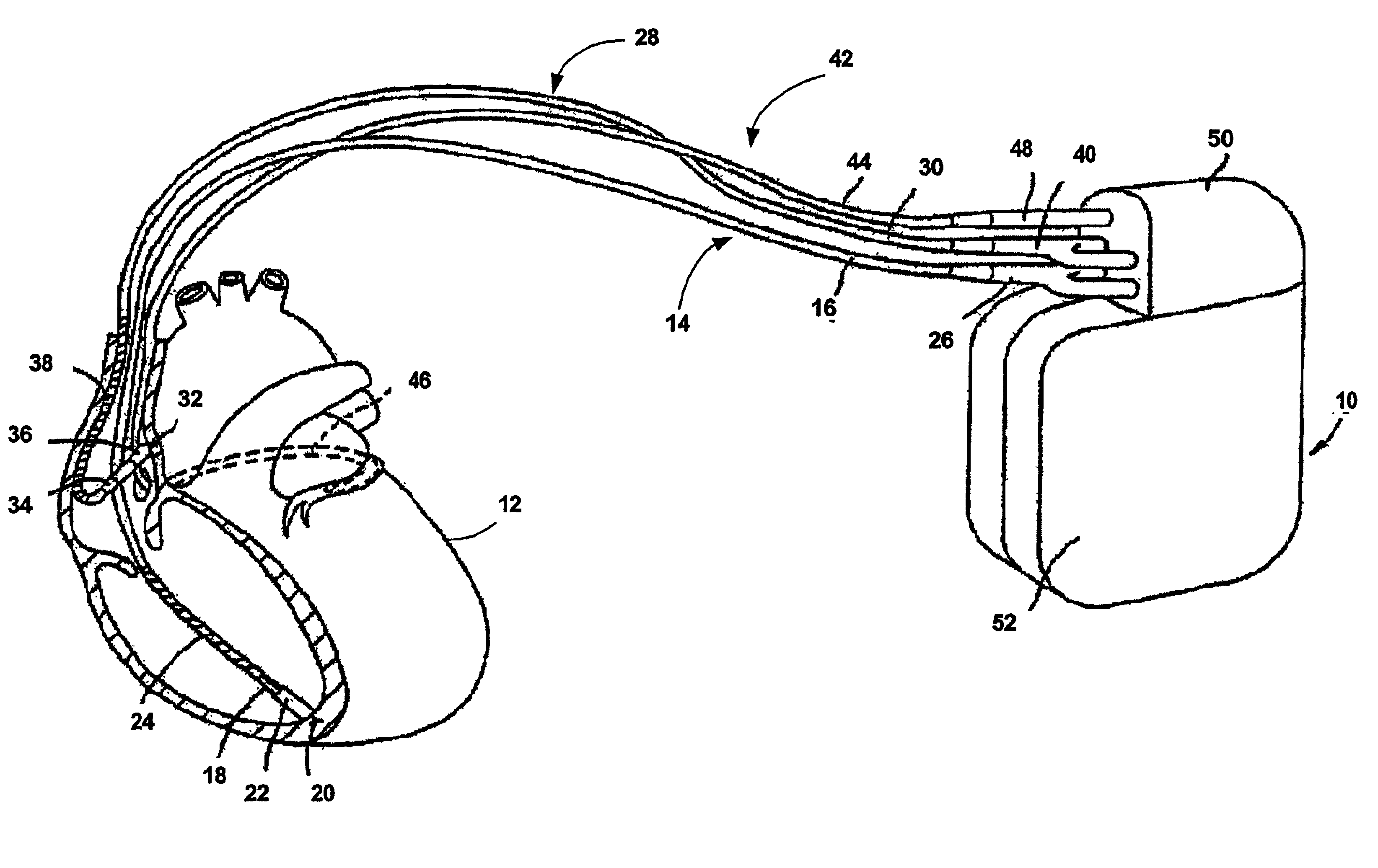
Implantable cardiac stimulation device and method that discriminates between and treats atrial tachycardia and atrial fibrillation
An implantable cardiac stimulation device discriminates and treats accelerated atrial arrhythmias of a patient's heart. The device includes a sensing circuit that senses cardiac activity of one of the patient's atria to provide an atrial activity signal, a detector that detects an accelerated atrial arrhythmia of the patient's heart, and a classifying circuit that measures relative correspondence between successive P waves of the atrial activity signal to classify the detected accelerated atrial arrhythmia as either atrial tachycardia or atrial fibrillation. A therapy circuit provides anti-tachycardia pacing therapy responsive to a classified atrial tachycardia and defibrillation therapy responsive to a classified atrial fibrillation.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Parasympathetic stimulation for termination of non-sinus atrial tachycardia
InactiveUS8060197B2Avoid stimulationHigh strengthElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMedicineNormal Sinus Rhythm
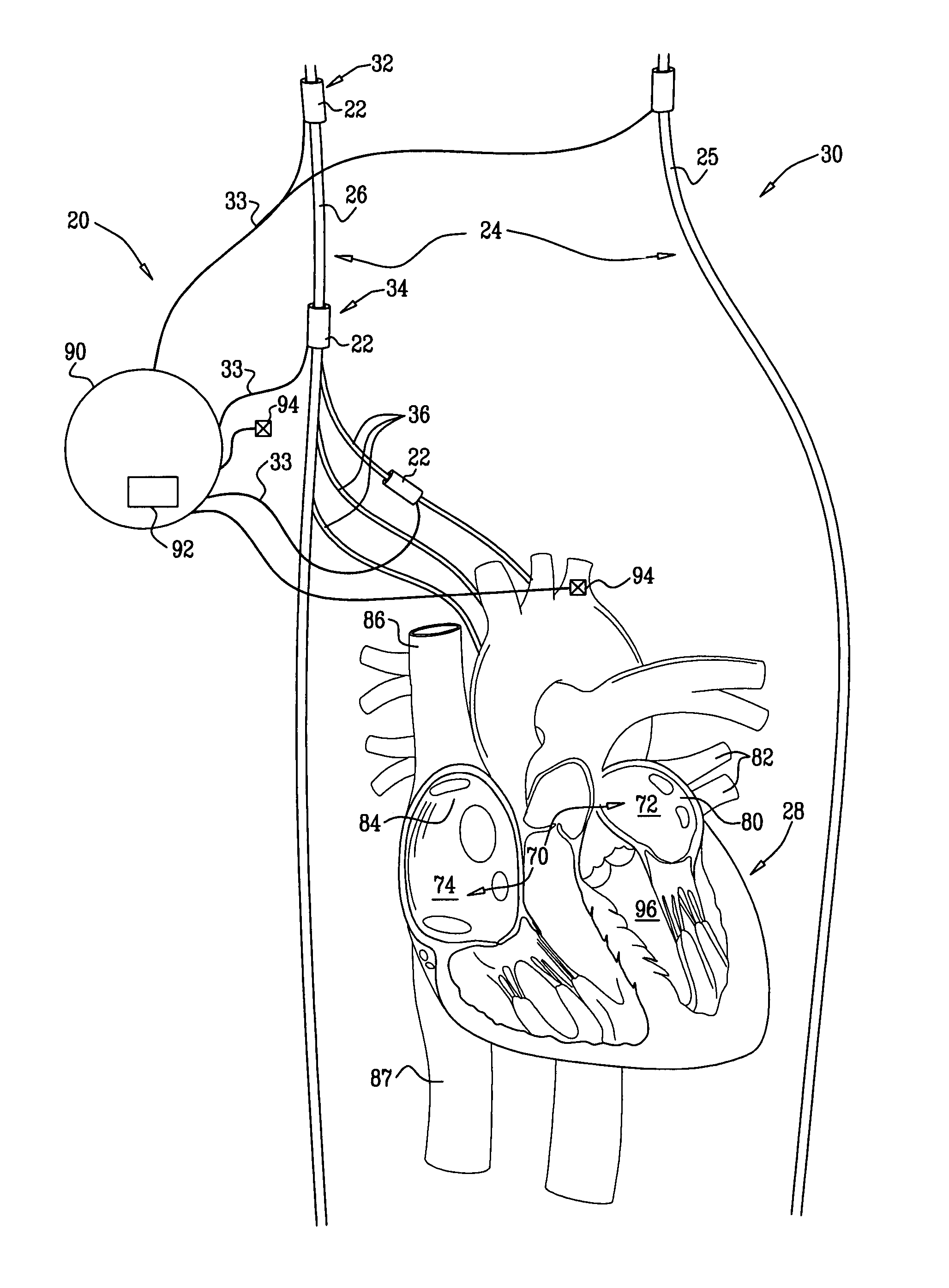
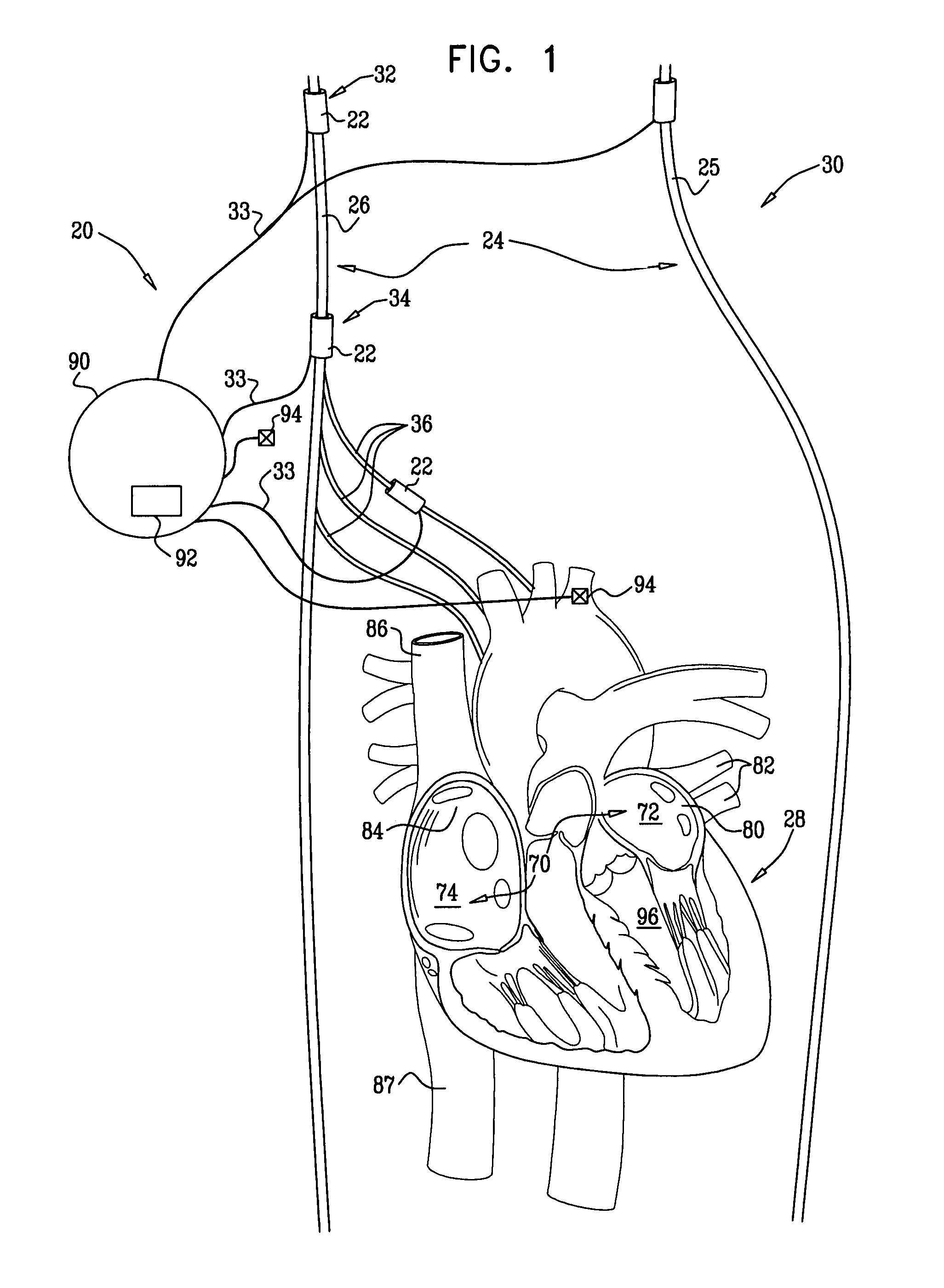
Apparatus is provided, which includes an electrode device, configured to be coupled to an atrial site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue, and a control unit. The control unit is configured to, responsively to a detection of an episode of non-sinus atrial tachycardia, restore normal sinus rhythm (NSR) of the subject, by driving the electrode device to apply a parasympathetic stimulation signal to the atrial site, and configuring the parasympathetic stimulation signal to activate the parasympathetic nervous tissue sufficiently to restore the NSR. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vacuum coagulation probe for atrial fibrillation treatment
InactiveUS20060009762A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesAnatomical structuresLess invasive
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia. The surgical device can include at least one elongate member comprising conductive elements adapted to coagulate soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through said conductive elements are routed through lumens in the elongate member to a vacuum source to actively engage the soft tissue surface intended to coagulate into intimate contact with the conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, contiguous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling openings positioned near the conductive elements and coupled with a vacuum source or an injection source to transport fluid through the cooling openings causing the soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate features to tunnel between anatomic structures or dissect around the desired tissue surface to coagulate thereby enabling less invasive positioning of the soft tissue coagulating device and ensuring reliable and consistent heating of the soft tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A multi-layer method for detecting atrial arrhythmias using ventricular cycle length information that includes performing a base layer algorithm for detecting the onset and offset of an atrial tachyarrhythmia. The multi-layer method further includes one or more higher layer algorithms executed in response to a base layer detection to confirm or reject the base layer detection. The base layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia and the higher layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity and high specificity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
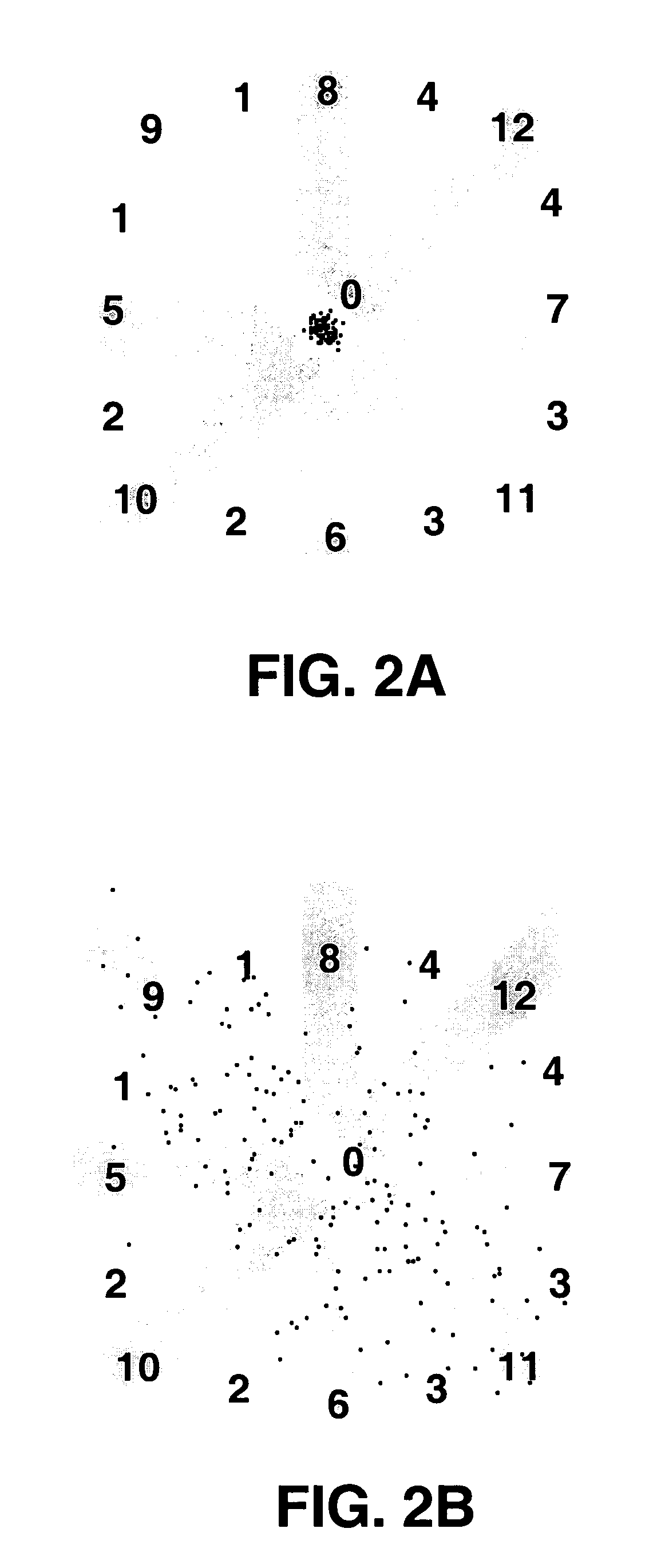
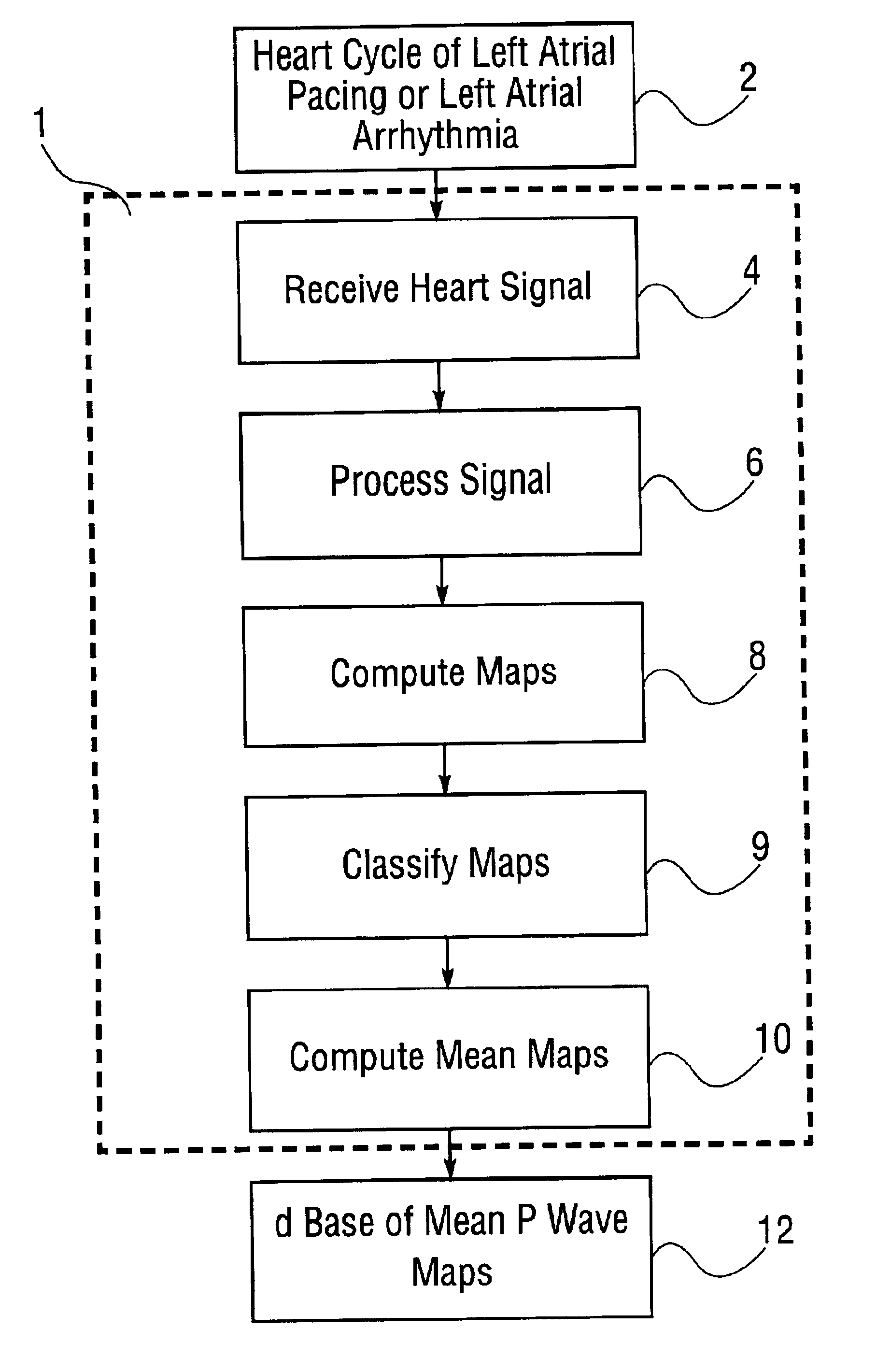
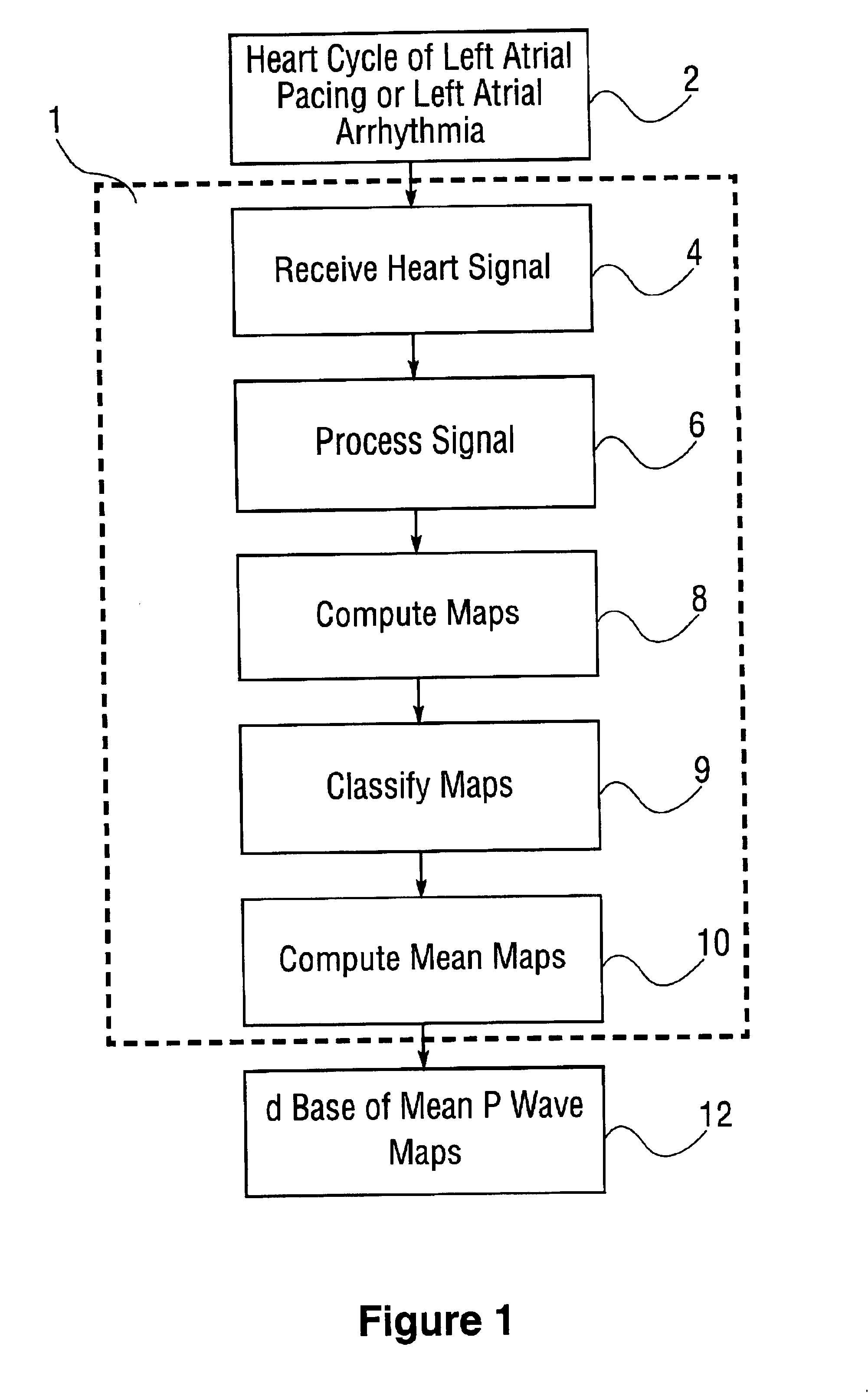
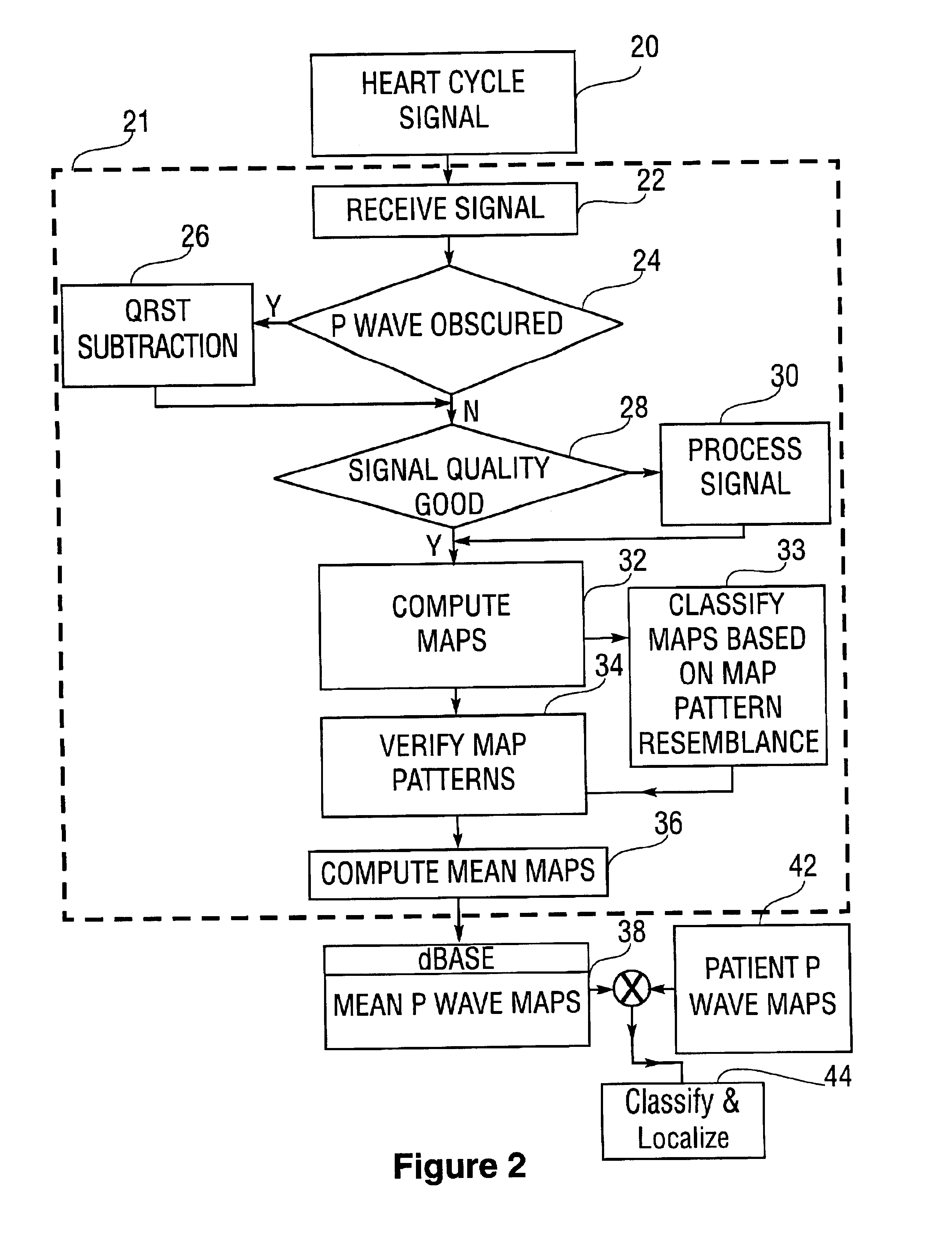
Database of body surface ECG P wave integral maps for localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias
InactiveUS6931273B2ElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyIsorhythmic Atrioventricular DissociationHypsarrhythmia
A system and method are provided for developing a database of body surface ECG P-wave maps for classification and localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias. The system and method include generating and receiving P-wave data in a subject by left atrial pacing or receiving P-wave data in a subject during spontaneously occurring or induced left atrial arrhythmias; computing (e.g. potential or integral) maps of the P-wave data; classifying the maps specific to a left atrial ectopic origin; verifying the classification procedure; averaging the classified maps into mean maps; and storing and accessing the mean maps in the database. The mean maps of the P-wave data in the database can be used to automatically classify and localize P-wave data from a patient obtained during a left atrial arrhythmia such as atrial tachycardia, focal atrial fibrillation, or orthodromic atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Intravascular parasympatheticstimulation for atrial cardioversion
InactiveUS20080046016A1Avoid stimulationHigh strengthInternal electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineNormal Sinus Rhythm
Apparatus is provided, which includes an electrode device, configured to be coupled to an atrial site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue, and a control unit. The control unit is configured to, responsively to a detection of an episode of non-sinus atrial tachycardia, restore normal sinus rhythm (NSR) of the subject, by driving the electrode device to apply a parasympathetic stimulation signal to the atrial site, and configuring the parasympathetic stimulation signal to activate the parasympathetic nervous tissue sufficiently to restore the NSR. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A multi-layer method for detecting atrial arrhythmias using ventricular cycle length information that includes performing a base layer algorithm for detecting the onset and offset of an atrial tachyarrhythmia. The multi-layer method further includes one or more higher layer algorithms executed in response to a base layer detection to confirm or reject the base layer detection. The base layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia and the higher layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity and high specificity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
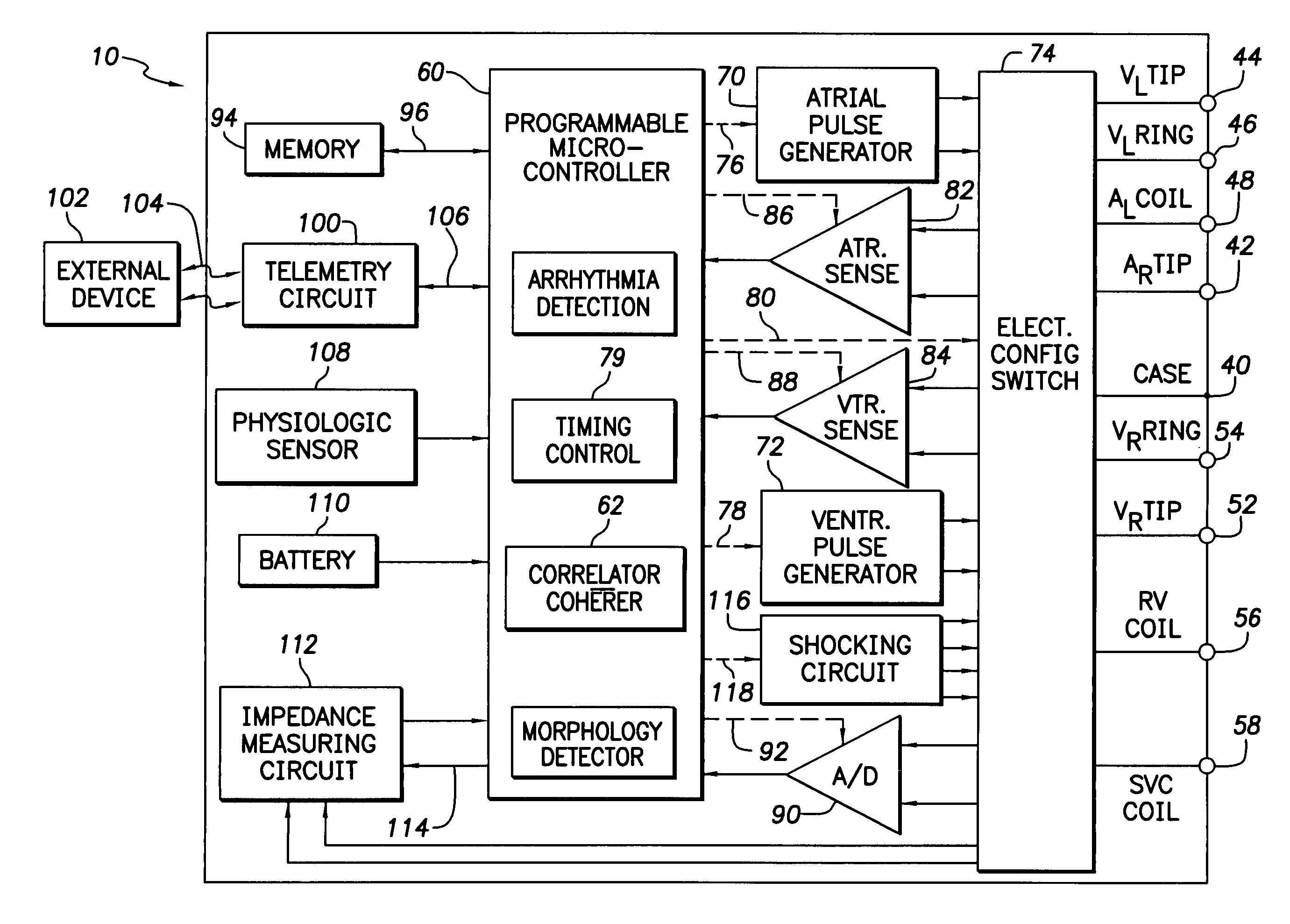
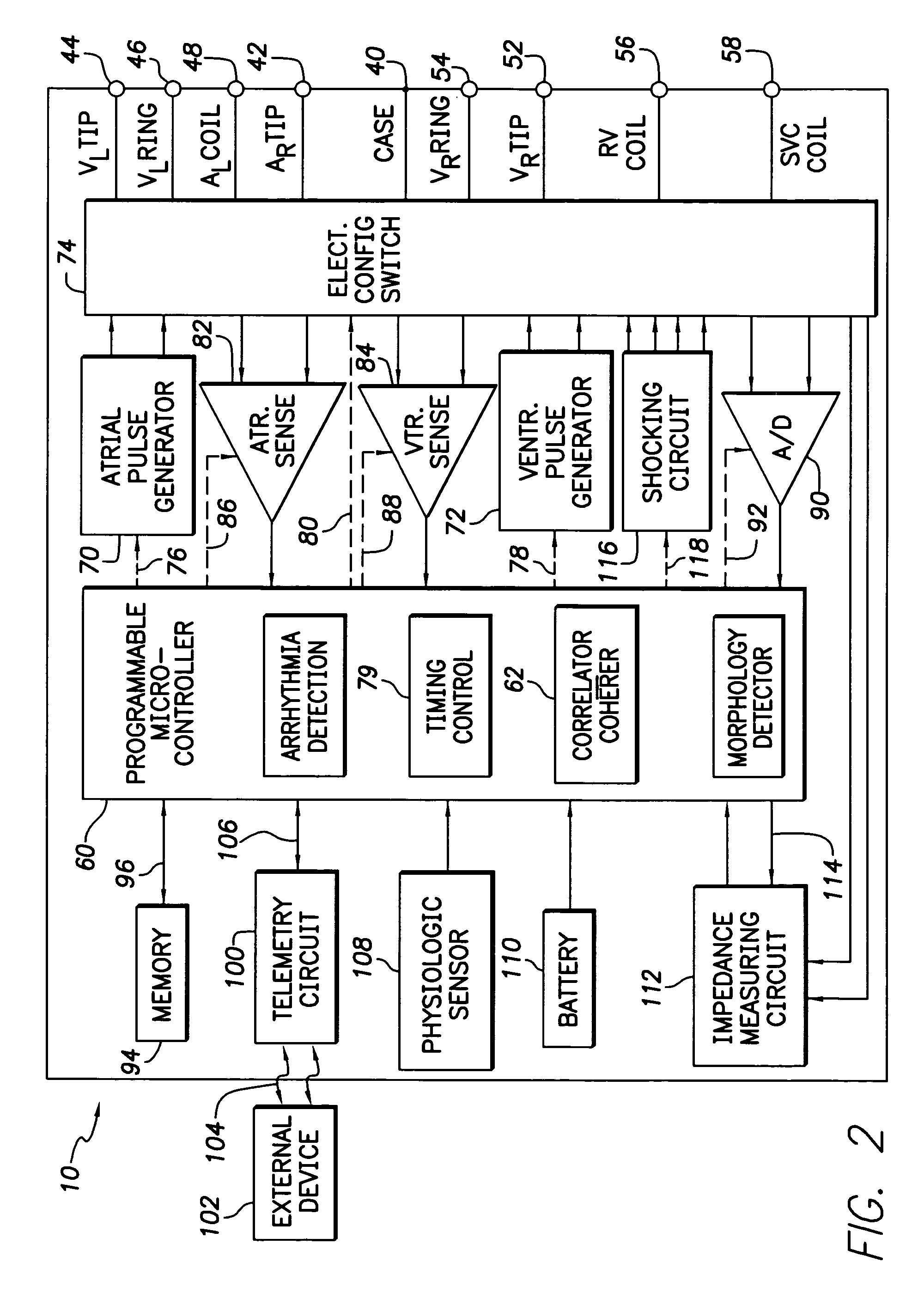
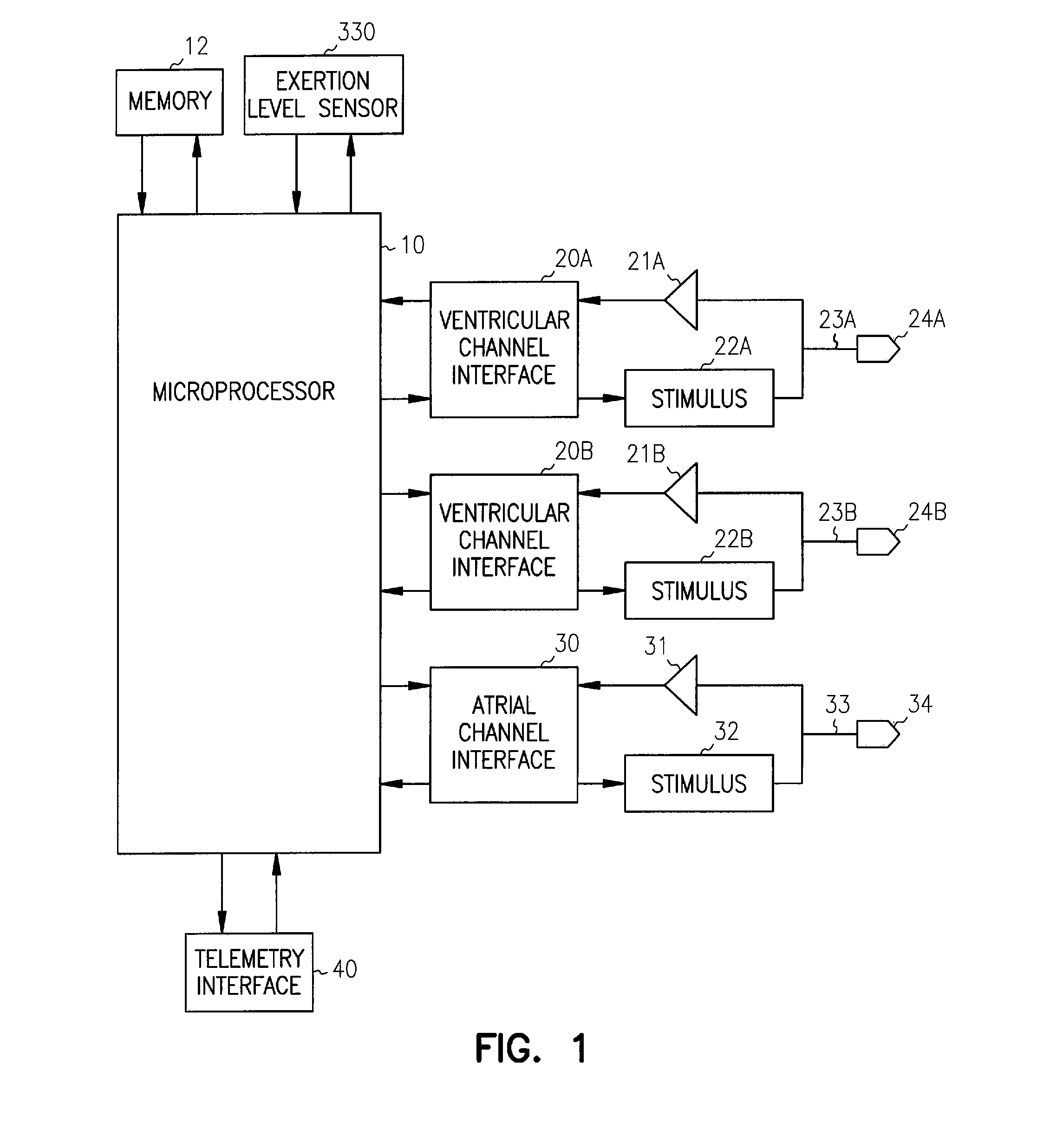
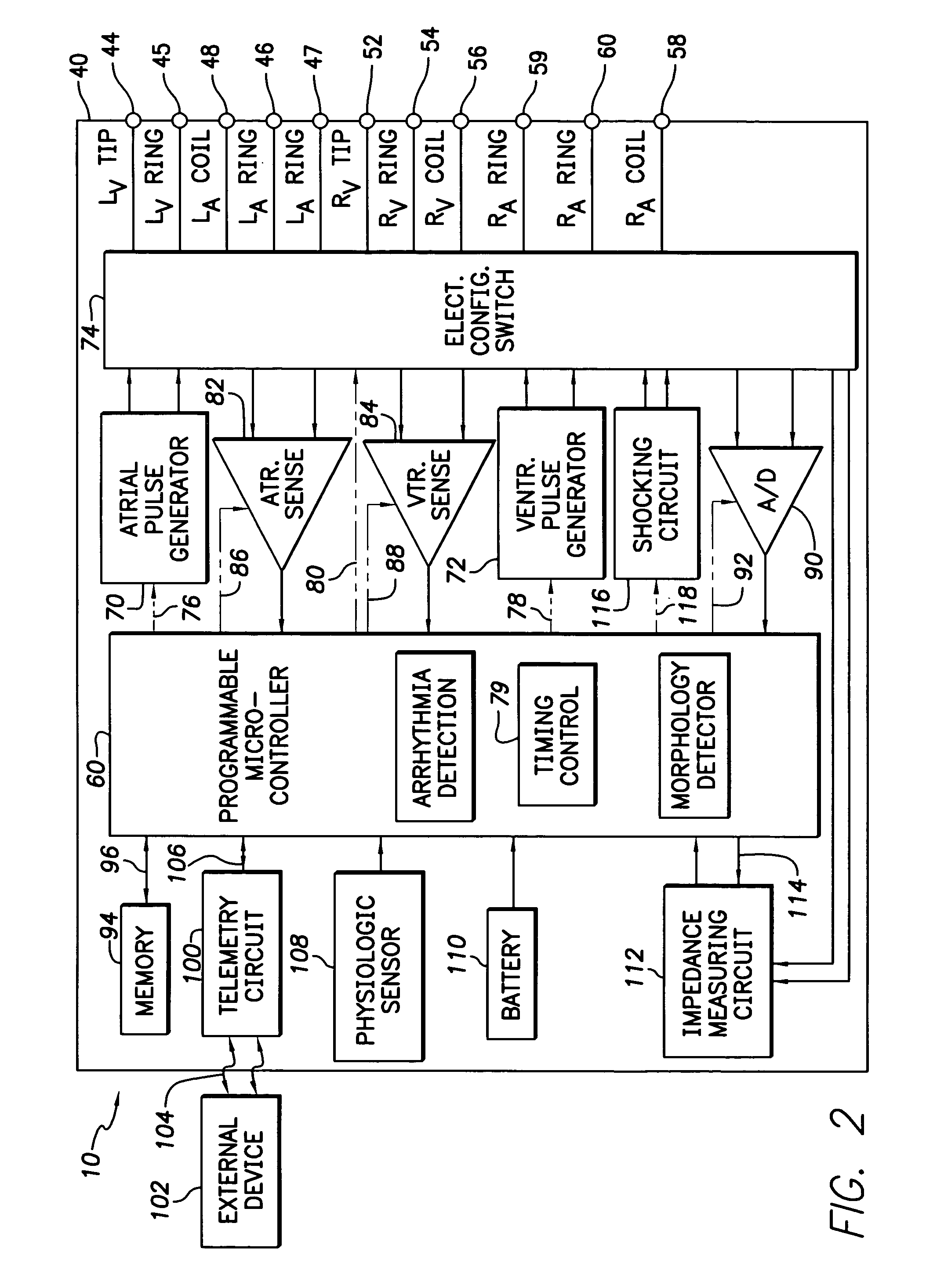
Method and apparatus for displaying information retrieved from an implanted medical device
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods of coagulating tissue
InactiveUS20060206113A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesRadio frequencyLesion
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia; tendon or ligament shrinkage; or articular cartilage removal. The surgical device integrates a suction mechanism with the coagulation mechanism improving the lesion creation capabilities of the device. The surgical device comprises an elongate member having an insulative covering attached about conductive elements capable of coagulating soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through the insulative covering expose regions of the conductive elements and are coupled to lumens in the elongate member which are routed to a vacuum source. Suction causes the soft tissue to actively engage the opening thus the integrated, exposed conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, continuous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling mechanisms associated with the conductive elements and coupled to a fluid source to passively transport fluid along the contacted soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
Vacuum coagulation probes
InactiveUS20060200124A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesArticular cartilageLesion
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia; tendon or ligament shrinkage; or articular cartilage removal. The surgical device integrates a suction mechanism with the coagulation mechanism improving the lesion creation capabilities of the device. The surgical device comprises an elongate member having an insulative covering attached about conductive elements capable of coagulating soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through the insulative covering expose regions of the conductive elements and are coupled to lumens in the elongate member which are routed to a vacuum source. Suction causes the soft tissue to actively engage the opening thus the integrated, exposed conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, continuous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling mechanisms associated with the conductive elements and coupled to a fluid source to passively transport fluid along the contacted soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A method and apparatus for detecting atrial arrhythmias and discriminating atrial fibrillation (AF) and organized atrial tachycardia (OAT) that includes defining a threshold detection criteria for a cluster signature evidence metric corresponding to a Lorenz distribution of ventricular cycle lengths representative of AF or OAT. Using a signal containing VCL information, a number of consecutive ventricular cycle lengths are determined during a selected time interval for generating a one-dimensional or a two-dimensional histogram as a numerical representation of a Lorenz plot of VCLs. A number of cluster signature metrics are computed using the stored ventricular cycle length information, and a cluster signature evidence metric is computed from the cluster signature metrics. AF or OAT is detected if a comparative analysis of a corresponding cluster signature evidence metric meets a respective threshold detection criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
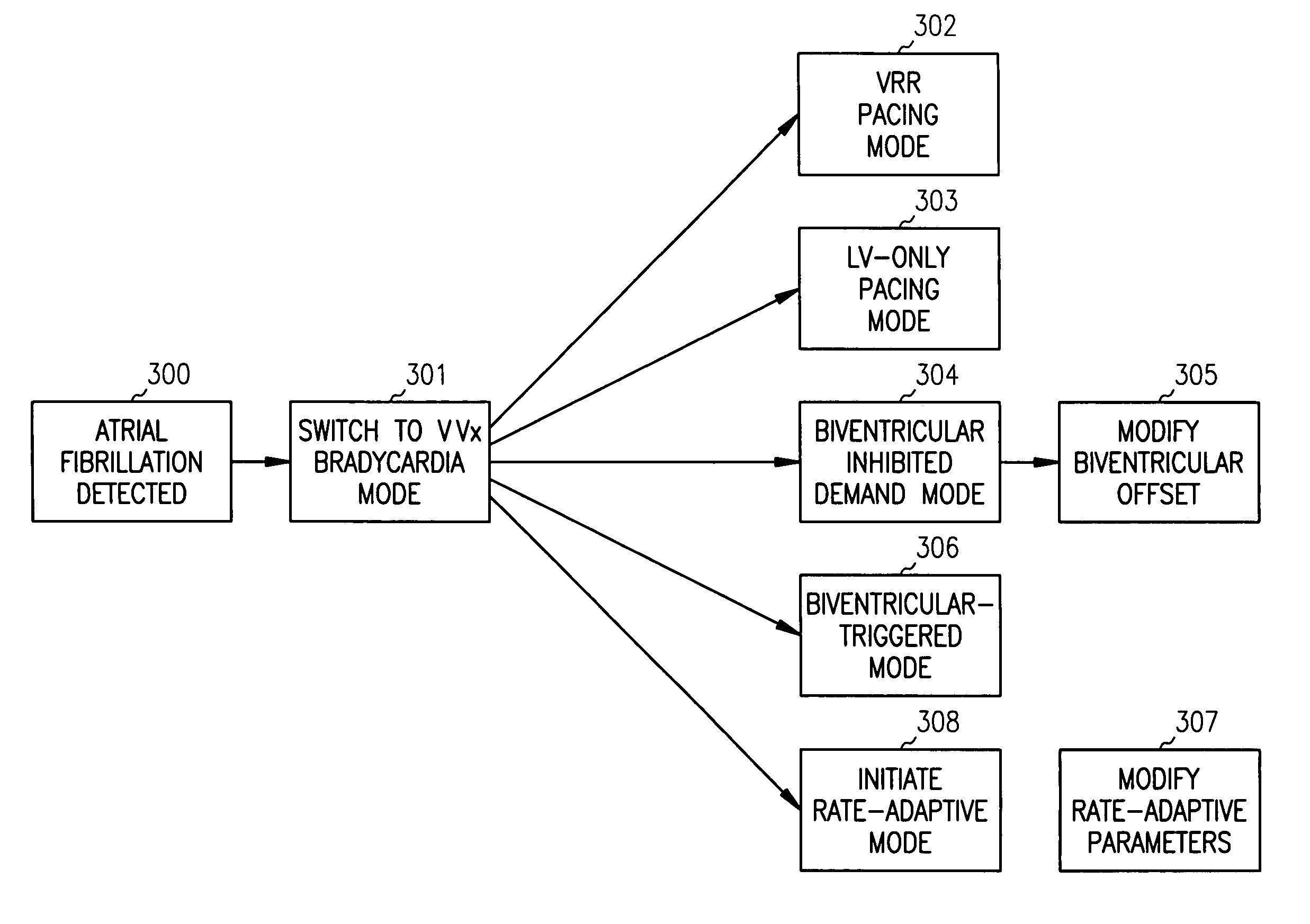
Apparatus and method for pacing mode switching during atrial tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS7142918B2Improve coordinationHigh outputHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCongestive heart failure chf
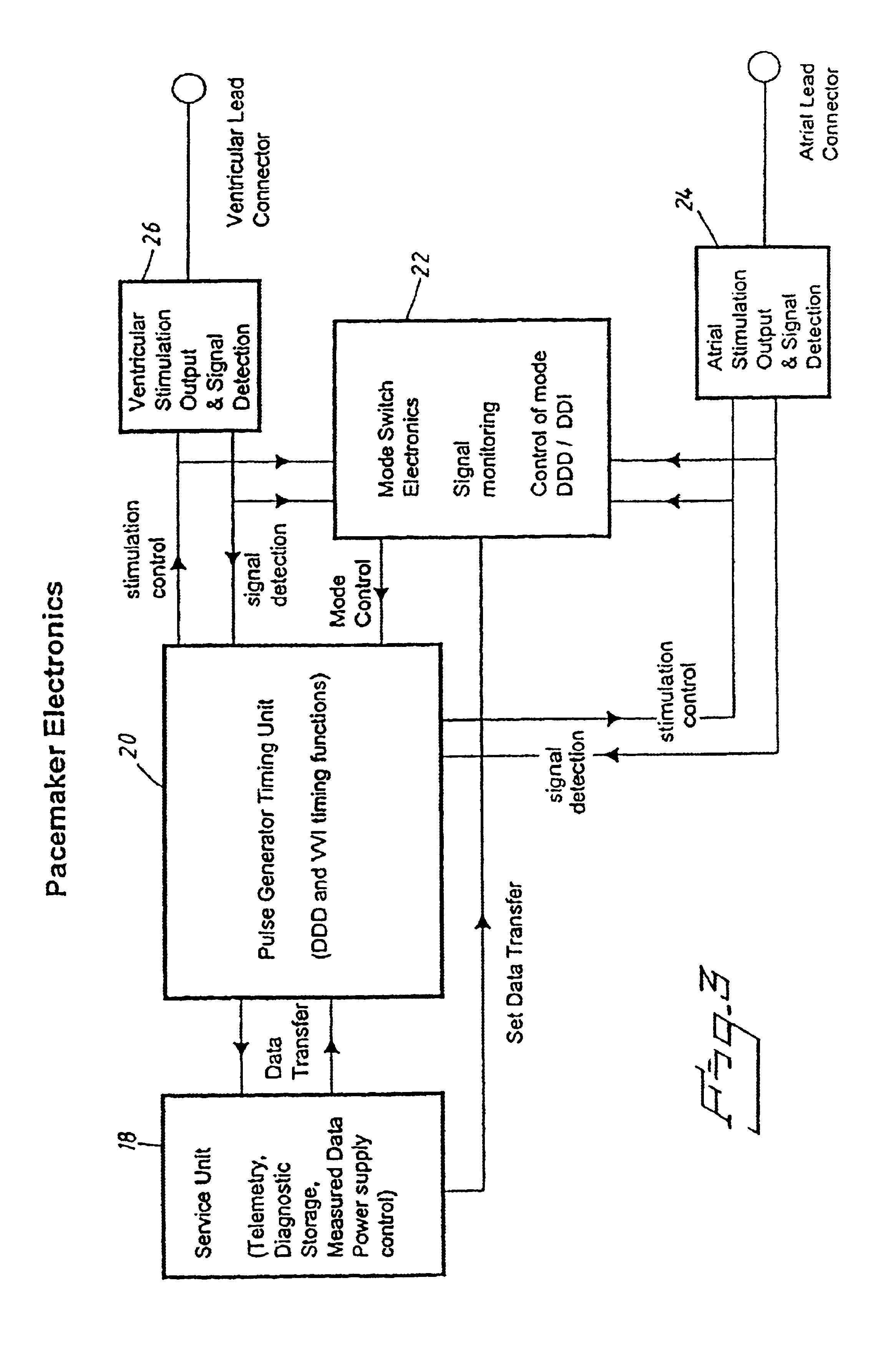
A method for operating a cardiac pacemaker in which the mode of operation of the pacemaker is altered in response to detecting an episode of atrial tachycardia. In accordance with the invention, the pacemaker's pacing mode is altered in a manner that attempts to maintain hemodynamic stability during the atrial tachycardia. Such a mode switch is particularly applicable to pacemaker patients suffering from some degree of congestive heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for providing improved specificity for automatic mode switching within an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7062328B1Avoiding inappropriate mode switchingStrong specificityHeart stimulatorsPacemaker mediated tachycardiaCombined use
Techniques for improving the specificity of automatic mode switching (AMS) are provided to prevent inappropriate mode switching and to ensure that mode switching is performed when needed. In one example, improved techniques for calculating a filtered rate interval (FARI) are provided, which help avoid inappropriate mode switching within devices that employ FARI in connection with the determination of the atrial rate. Also, techniques are provided for detecting atrial tachycardia and for distinguishing between a true tachycardia and a false tachycardia (such as pacemaker mediated tachycardia). The techniques described herein for detecting atrial tachycardia and for distinguishing between true and false tachycardia are advantageously employed in connection with AMS but may be used in other circumstances as well. Techniques employed in conjunction with dynamic atrial overdrive (DAO) pacing are also discussed.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for providing preventive overdrive pacing and antitachycardia pacing using an implantable cardiac stimulation device
InactiveUS7363081B1Easy to detectReliably detecting the onset of an atrial tachycardiaHeart stimulatorsAtrial pacingAntitachycardia Pacing
Techniques for enabling both preventive overdrive pacing and antitachycardia pacing (ATP) within an implantable device are provided. The device gains the benefits of overdrive pacing for preventing the onset of a tachycardia and, if one nevertheless occurs, ATP is employed to terminate the tachycardia. In particular, a technique is provided for promptly detecting the onset of atrial tachycardia during preventive overdrive pacing based on loss of capture of atrial pacing pulses. A technique is also provided for using detection of loss of capture of atrial or ventricular pacing pulses to trigger automatic switching from overdrive pacing to ATP. A setup technique determines whether to enable the automatic switching from overdrive pacing to ATP within a particular patient. Also, techniques are provided for verifying loss of capture of atrial or ventricular backup pacing pulses and for detecting low amplitude ventricular fibrillation based on loss of capture of ventricular backup pacing pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Automated reapplication of atrial pacing therapies
InactiveUS6876880B2Good curative effectReducing atrial tachyarrhythmia burdenHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsAtrial pacingMedical device
The invention relates to the use of atrial pacing therapies to treat atrial tachycardia (AT). When an AT episode is detected, an implantable medical device applies an ATP therapy. If the AT episode persists, the ATP therapy may be automatically reapplied at a later time during the course of the same AT episode. In particular, previously used ATP therapies are reapplied when episodic conditions, such as cycle length or cycle regularity, change. Although a particular ATP therapy initially may be unsuccessful in terminating the AT, it may prove successful when the cycle length or regularity of the atrial rhythm changes. As the rhythm slows down, the AT may be more responsive to ATP therapies that were previously unsuccessful. As a result, potentially efficacious ATP therapies can be reapplied to terminate AT episodes, and reduce the number of episodes that require more aggressive termination by painful, atrial shocks.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and method for pacing mode switching during atrial tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS7212860B2Improve coordinationIncrease cardiac outputHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCongestive heart failure chf
A method for operating a cardiac pacemaker in which the mode of operation of the pacemaker is altered in response to detecting an episode of atrial tachycardia. In accordance with the invention, the pacemaker's pacing mode is altered in a manner that attempts to maintain hemodynamic stability during the atrial tachycardia. Such a mode switch is particularly applicable to pacemaker patients suffering from some degree of congestive heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
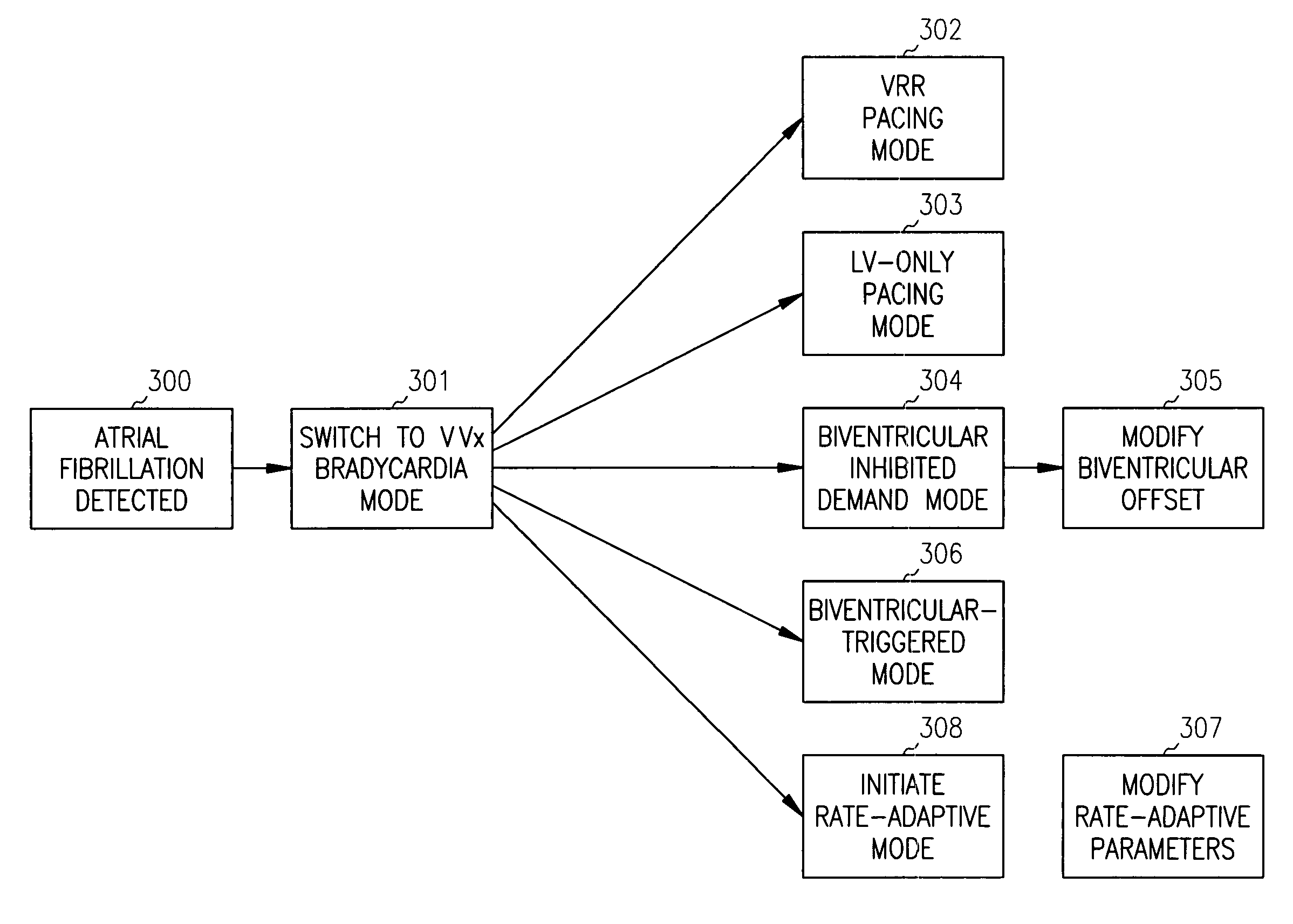
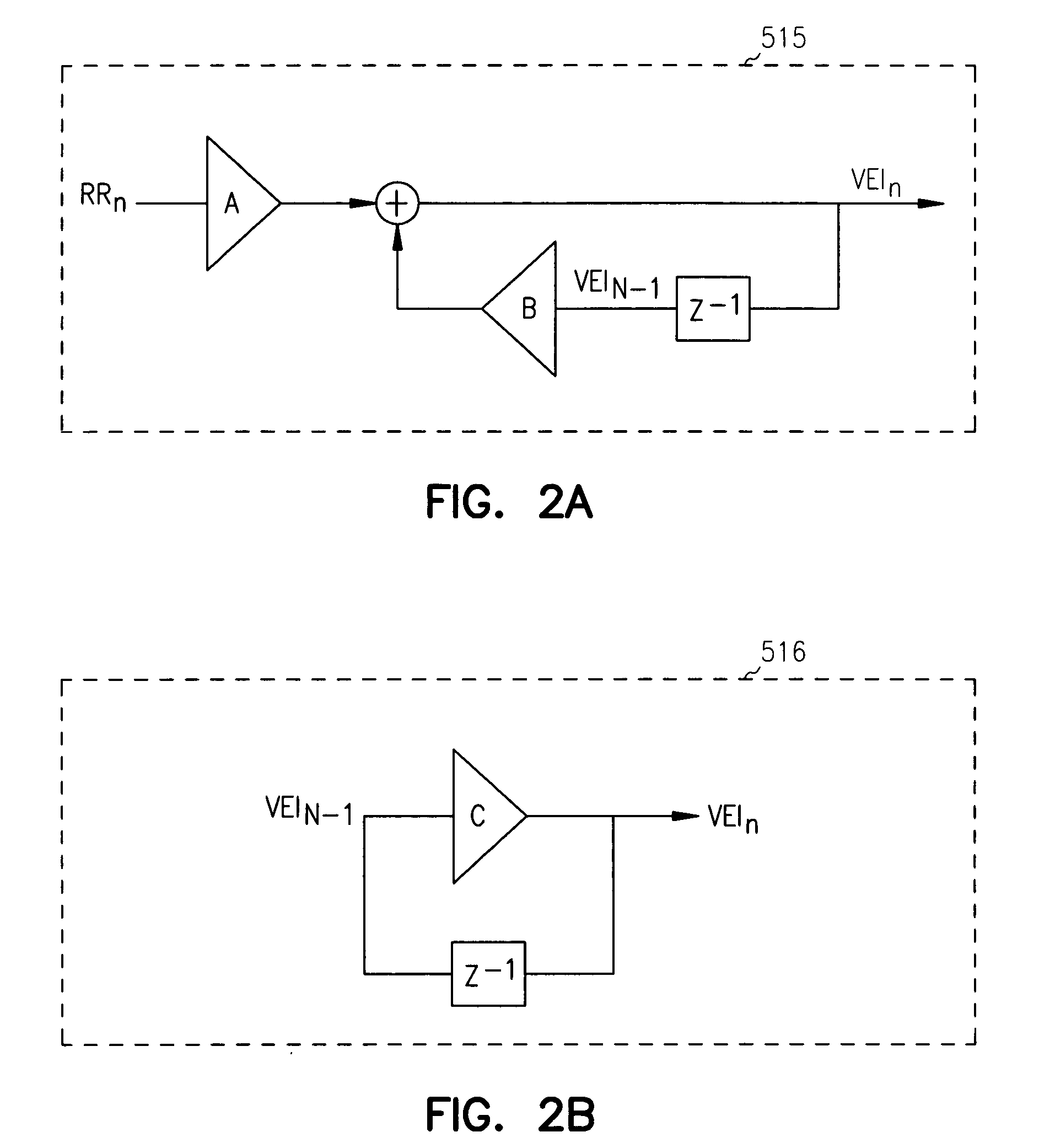
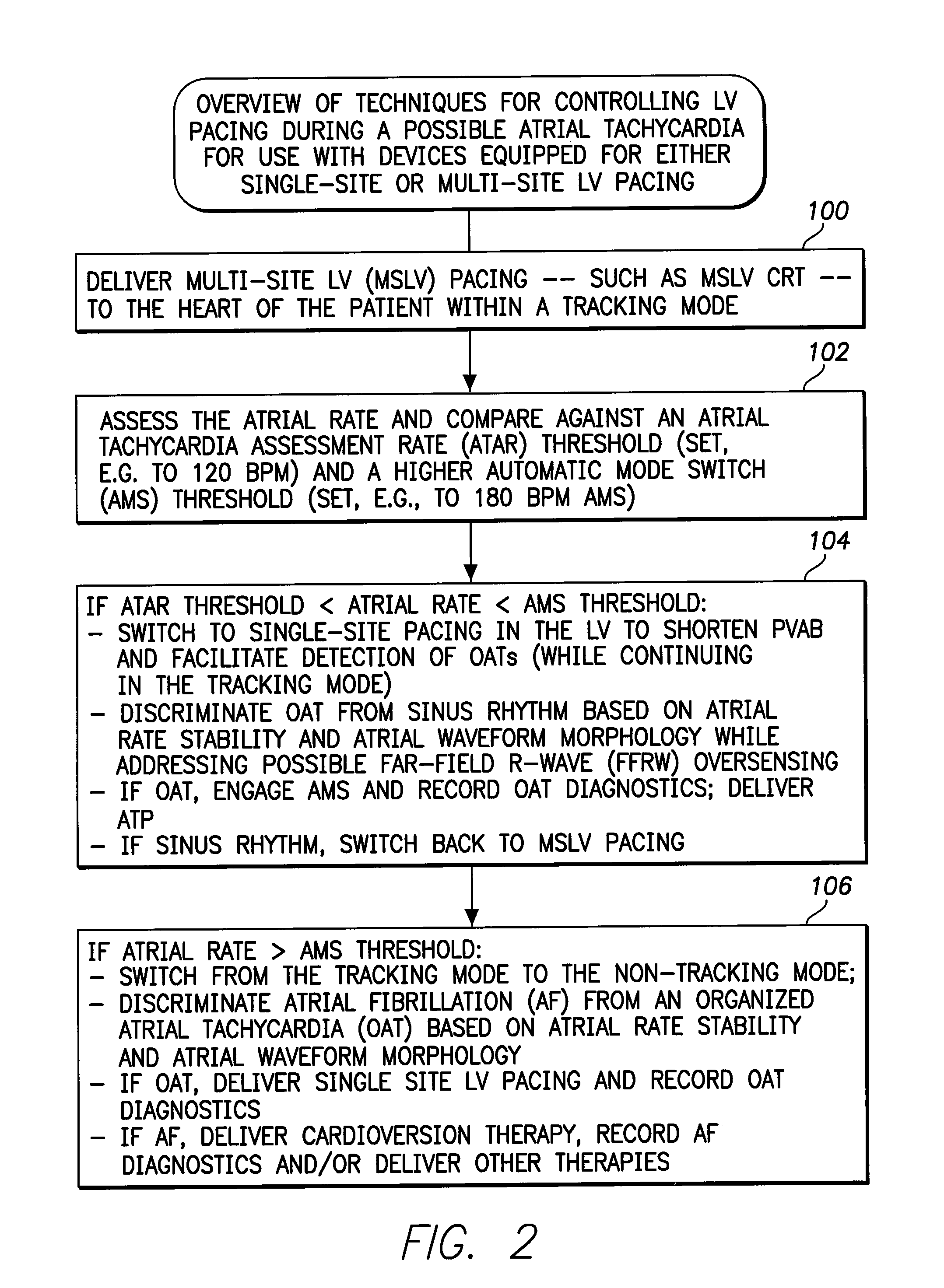
Systems and Methods for Use by an Implantable Medical Device for Controlling Multi-Site CRT Pacing in the Presence of Atrial Tachycardia
Systems and methods are provided for use by implantable medical devices equipped to deliver multi-site left ventricular (MSLV) pacing. MSLV is associated with a relatively long post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) period that might limit the detection of pathologic rapid organized atrial tachycardias (OAT). In one example, MSLV cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) pacing is delivered within a tracking mode. A possible atrial tachycardia is detected based on the atrial rate exceeding an atrial tachycardia assessment rate (ATAR) threshold. The device then switches to single-site LV pacing, thereby effectively shortening the PVAB to detect additional atrial events that might otherwise be obscured, and thereby permitting the device to more reliably distinguish organized atrial tachycardias (such as atrial flutter) from sinus tachycardia. The device may also employ an automatic mode switch (AMS) threshold that is set higher than the ATAR threshold for use in switching from tracking modes to nontracking modes.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Apparatus and method for treating atrial fibrillation and atrial tachycardia
InactiveUS7983748B2Minimize and eliminate useEliminates severe DC shocksElectrotherapyElectrical ProblemAtrial cavity
A method and device for treating an electrical problem in an organ, especially a heart, of a human or animal patient comprises atraumatically blocking the transmission of one or more electrical signals external to the organ. Nerve cell membranes near a cathode are depolarized while nerve cell membranes near an anode are hyperpolarized, inducing a DC conduction block. The method and device are especially suitable for treating atrial tachycardia where unwanted signals from at least one pulmonary vein and / or at least one fat pad are blocked within the construct of the heart.
Owner:HAK CONSULTING
Apparatus and method for pacing mode switching during atrial tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS20070288062A1Improve coordinationHigh outputHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsMedicineCardiac pacemaker electrode
A method for operating a cardiac pacemaker in which the mode of operation of the pacemaker is altered in response to detecting an episode of atrial tachycardia. In accordance with the invention, the pacemaker's pacing mode is altered in a manner that attempts to maintain hemodynamic stability during the atrial tachycardia. Such a mode switch is particularly applicable to pacemaker patients suffering from some degree of congestive heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
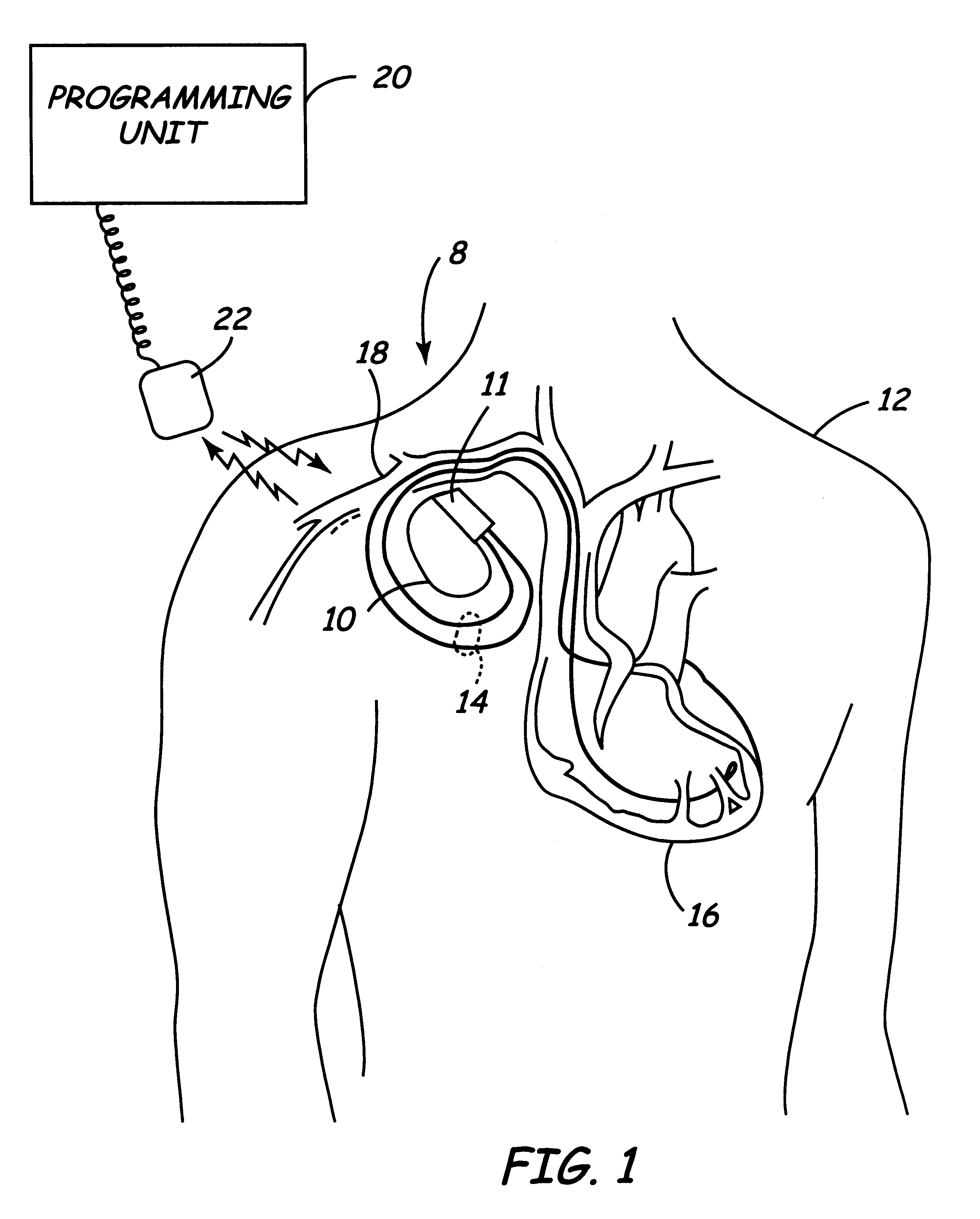
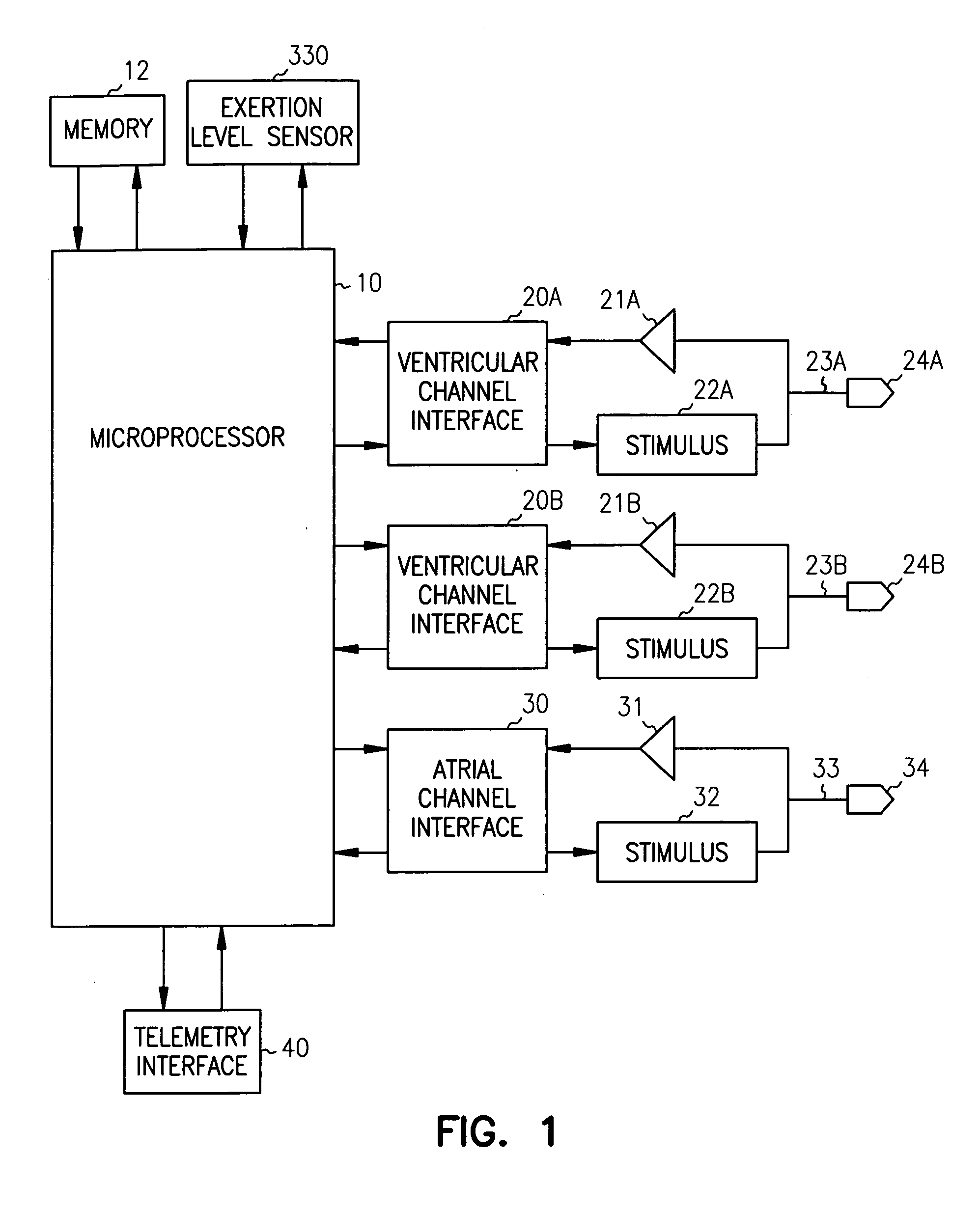
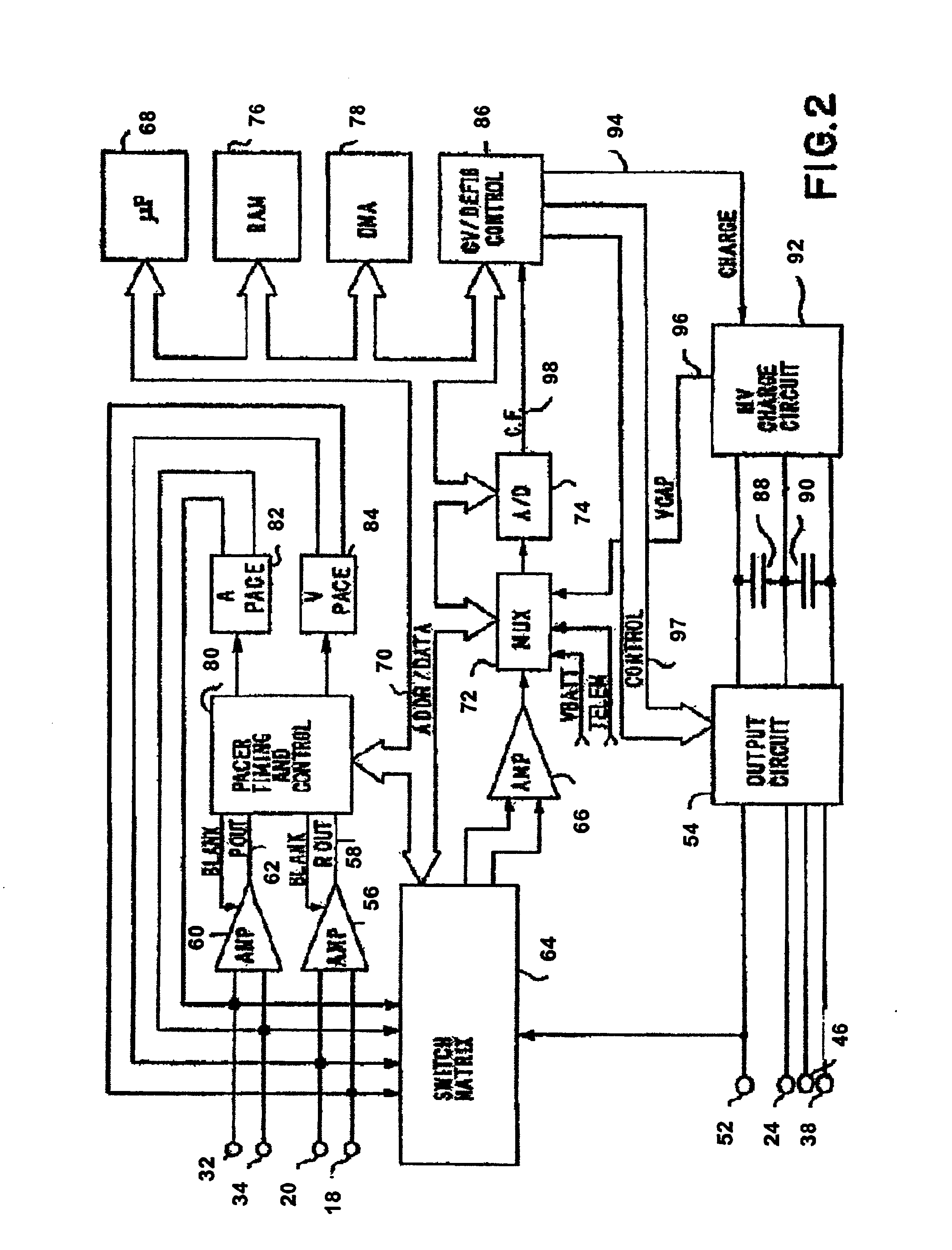
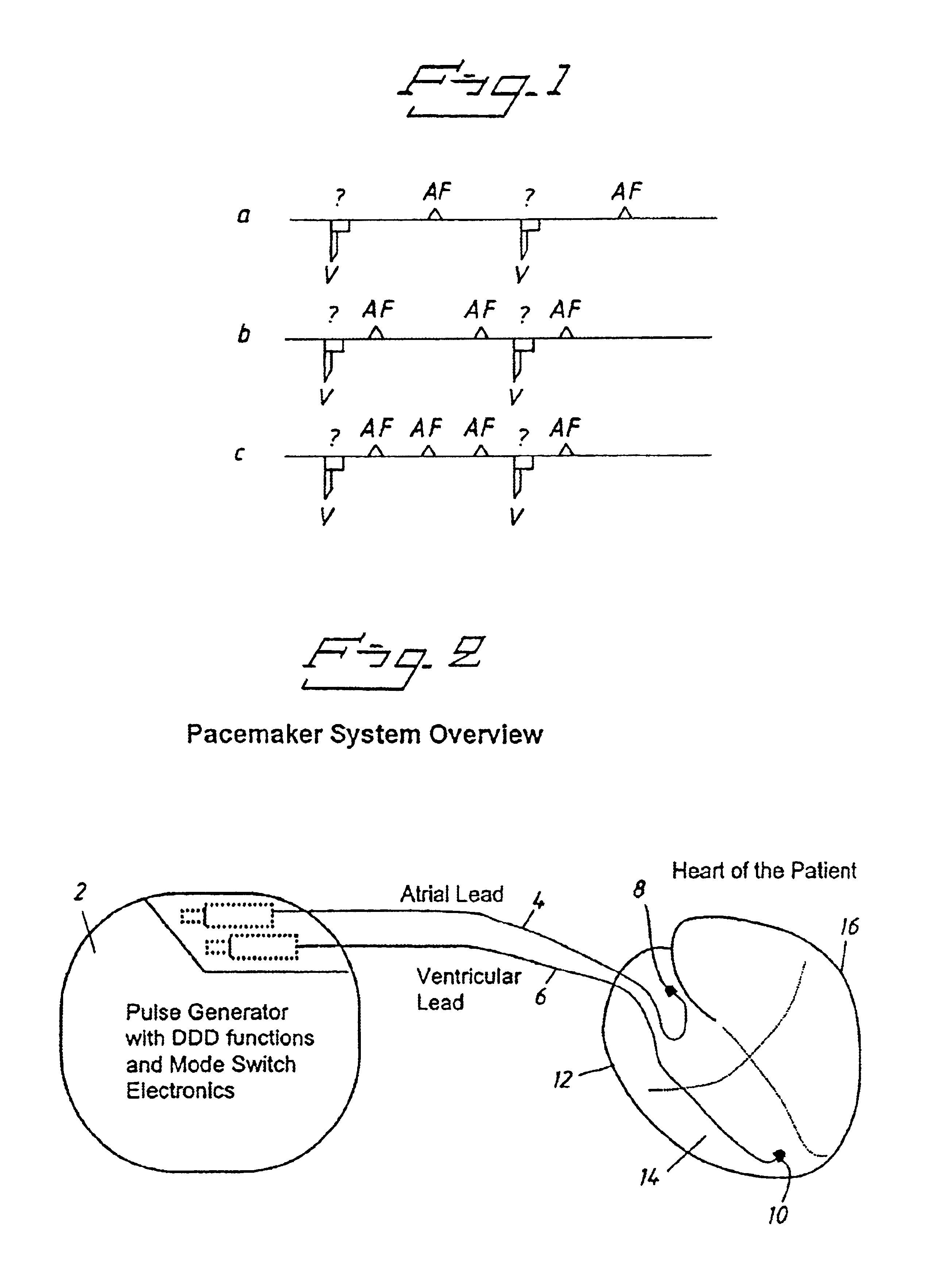
Pacemaker using measured intervals for mode switching
InactiveUS6871097B1Reliable detectionWork lessElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsWave detectionCardiac pacemaker electrode
A pacemaker is operable in a tracking and a non-tracking mode and has an automatic mode switching function for switching the pacemaker into the non-tracking mode of operation in response to the detection of atrial tachycardia. A comparator compares an atrial interval, between detected atrial events, with a predetermined atrial tachycardia limit value and records a tachycardia indication if the interval is less than the atrial tachycardia limit value. The mode switching unit switches the mode of operation to the non-tracking mode if the number of recorded tachycardia indications reaches a predetermined tachycardia count limit. Intervals between other cardiac events detected by the atrial detector or a ventricular detector also are supplied to the comparator wherein they are compared with the atrial tachycardia limit value. The recorded number of tachycardia indications is reduced by one if at least one of these additional intervals, during a pacemaker interval between two consecutive ventricular stimulations or between two consecutive R-wave detections, is longer than the tachycardia limit value.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Apparatus and method for treating atrial fibrillation and atrial tachycardia
InactiveUS20090216290A1Minimize and eliminate useEliminates severe DC shocksHeart stimulatorsElectrical ProblemAtrial cavity
A method and device for treating an electrical problem in an organ, especially a heart, of a human or animal patient comprises atraumatically blocking the transmission of one or more electrical signals external to the organ. Nerve cell membranes near a cathode are depolarized while nerve cell membranes near an anode are hyperpolarized, inducing a DC conduction block. The method and device are especially suitable for treating atrial tachycardia where unwanted signals from at least one pulmonary vein and / or at least one fat pad are blocked within the construct of the heart.
Owner:HAK CONSULTING
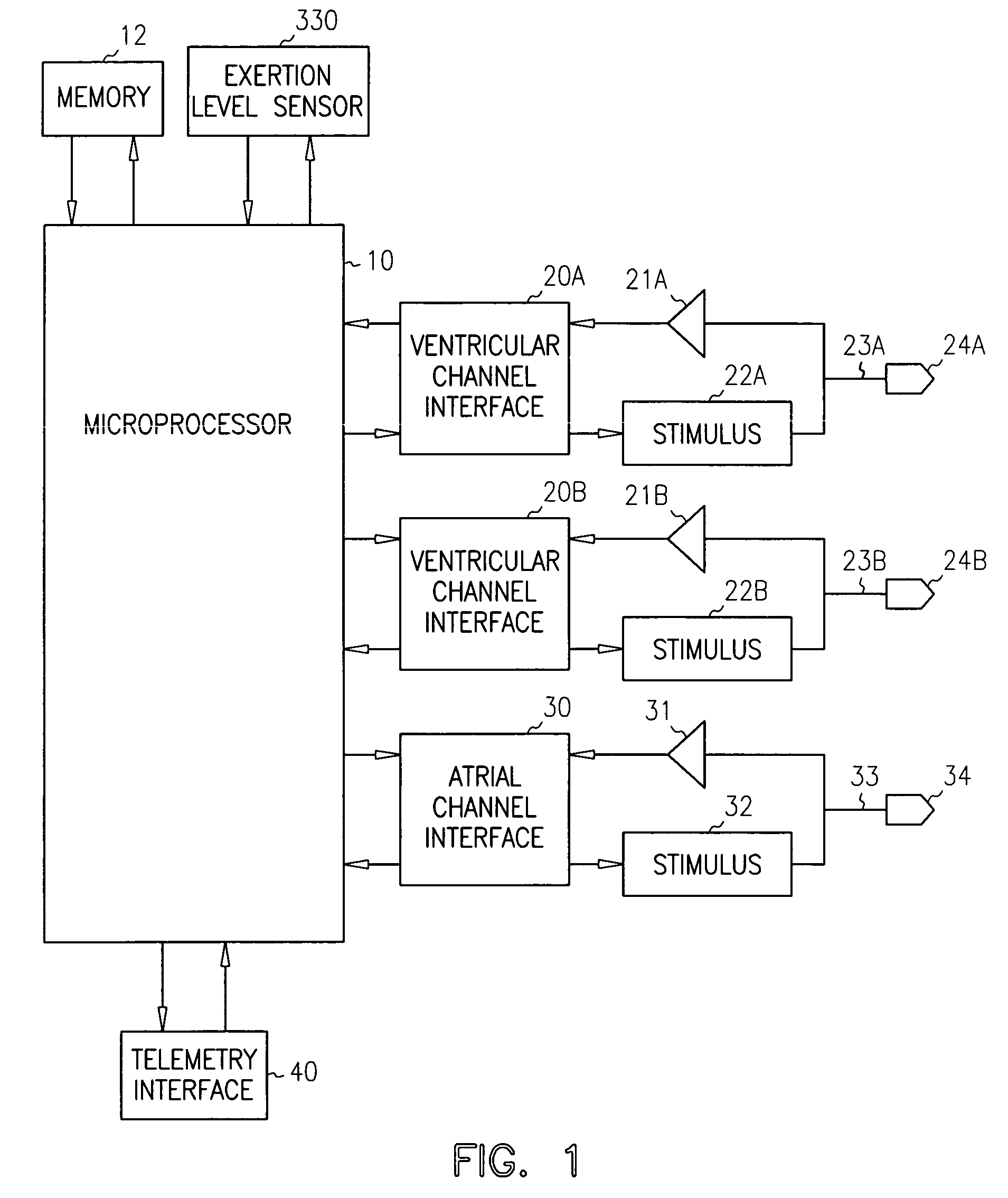
Synchronized atrial anti-tachy pacing system and method
A system and method for an implantable cardiac pacing device provide for delivery of anti-tachycardia pacing of the atrium upon detection of atrial tachycardia combined with automatic re-synchronization of ventricular pacing directly following the last atrial pulse of the anti-tachycardia scheme. At the onset of delivery of the ATP train or like scheme of ATP, an appropriate ventricular pacing interval is calculated to enable asynchronous pacing of the ventricle during the ATP and synchronous delivery of the next ventricular pulse at a delay following the end of the ATP train. Upon determination of AT, an algorithm is used to calculate if a ventricular pacing interval can be found that meets maximum and minimum pacing criteria and also provides that the next ventricular pace pulse following the end of the ATP train will follow the last atrial pulse of the train by a suitable AV delay. If such a suitable pacing interval is found, the ventricular pacing interval is set to a temporary value and the train is delivered. If such a pacing interval cannot be initially determined the system waits for one more atrial sense and then repeats the determination to find such a suitable ventricular pacing interval.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and method for pacing mode switching during atrial tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS7805192B2Improve coordinationHigh outputHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac pacemaker
A method for operating a cardiac pacemaker in which the mode of operation of the pacemaker is altered in response to detecting an episode of atrial tachycardia. In accordance with the invention, the pacemaker's pacing mode is altered in a manner that attempts to maintain hemodynamic stability during the atrial tachycardia. Such a mode switch is particularly applicable to pacemaker patients suffering from some degree of congestive heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Anti-tachycardia pacing method and apparatus for multi-chamber pacing
Improved methods and devices perform tachycardia detection and anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to convert a tachycardia (e.g., VT or AT) to normal sinus rhythm. According to one embodiment, an anti-tachycardia pacing method includes sensing, during sinus rhythm, first and second cardiac signals at first and second sites, respectively, in a patient's heart. The first and second sites include left and right ventricles or left and right atria, for example. The method further includes sensing third and fourth cardiac signals at the first and second sites, respectively, during a tachycardia (e.g., ventricular tachycardia or atrial tachycardia). The cardiac signals are processed to provide respective values. One or more anti-tachycardia pacing pulses are delivered at the site closest to the reentrant circuit based on a comparison of a first ratio of the first and third values and a second ratio of the second and fourth values. Unipolar sensing of the cardiac signals may be employed by, for example, shorting together pairs of electrodes implanted at each site.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
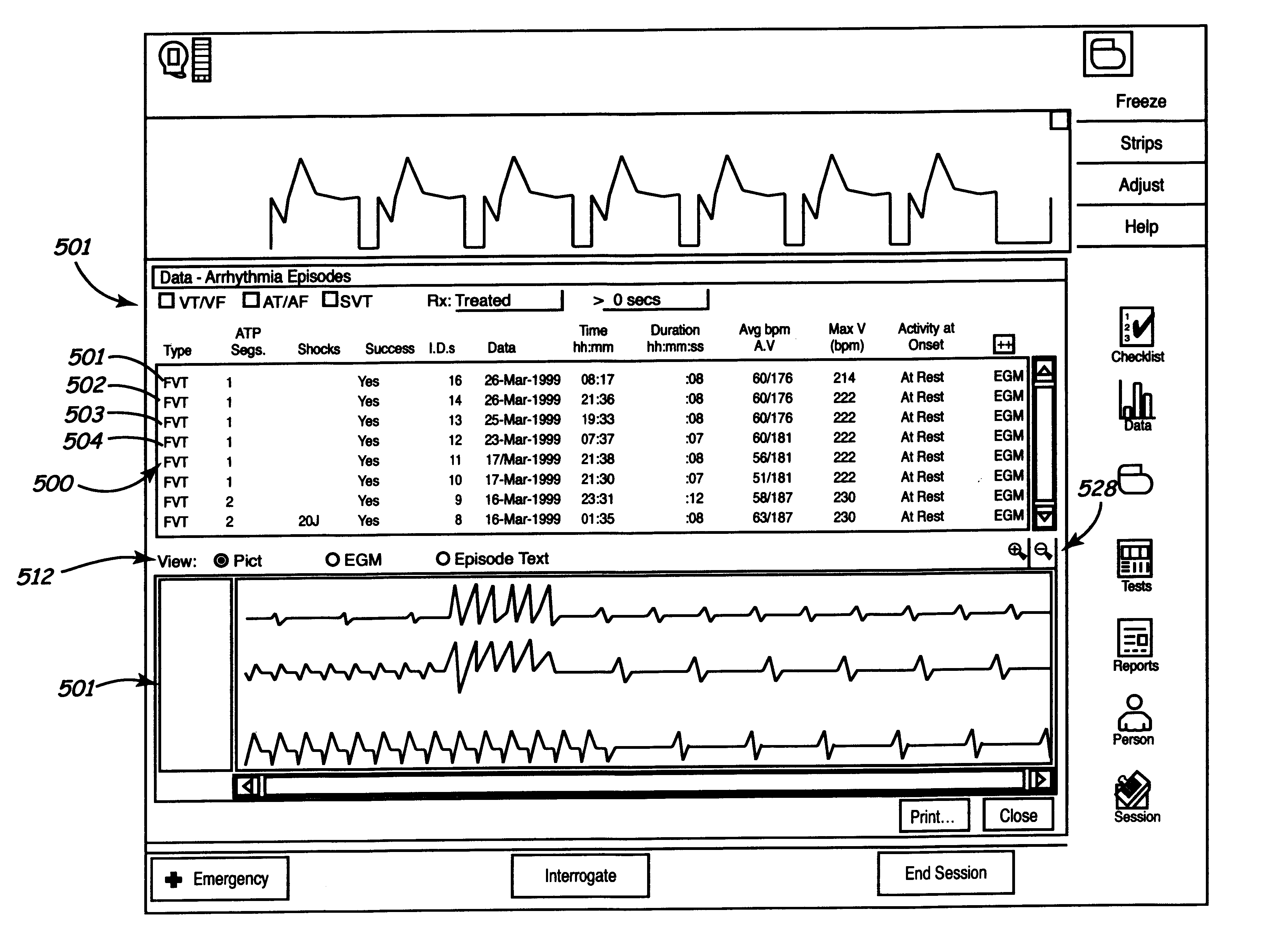
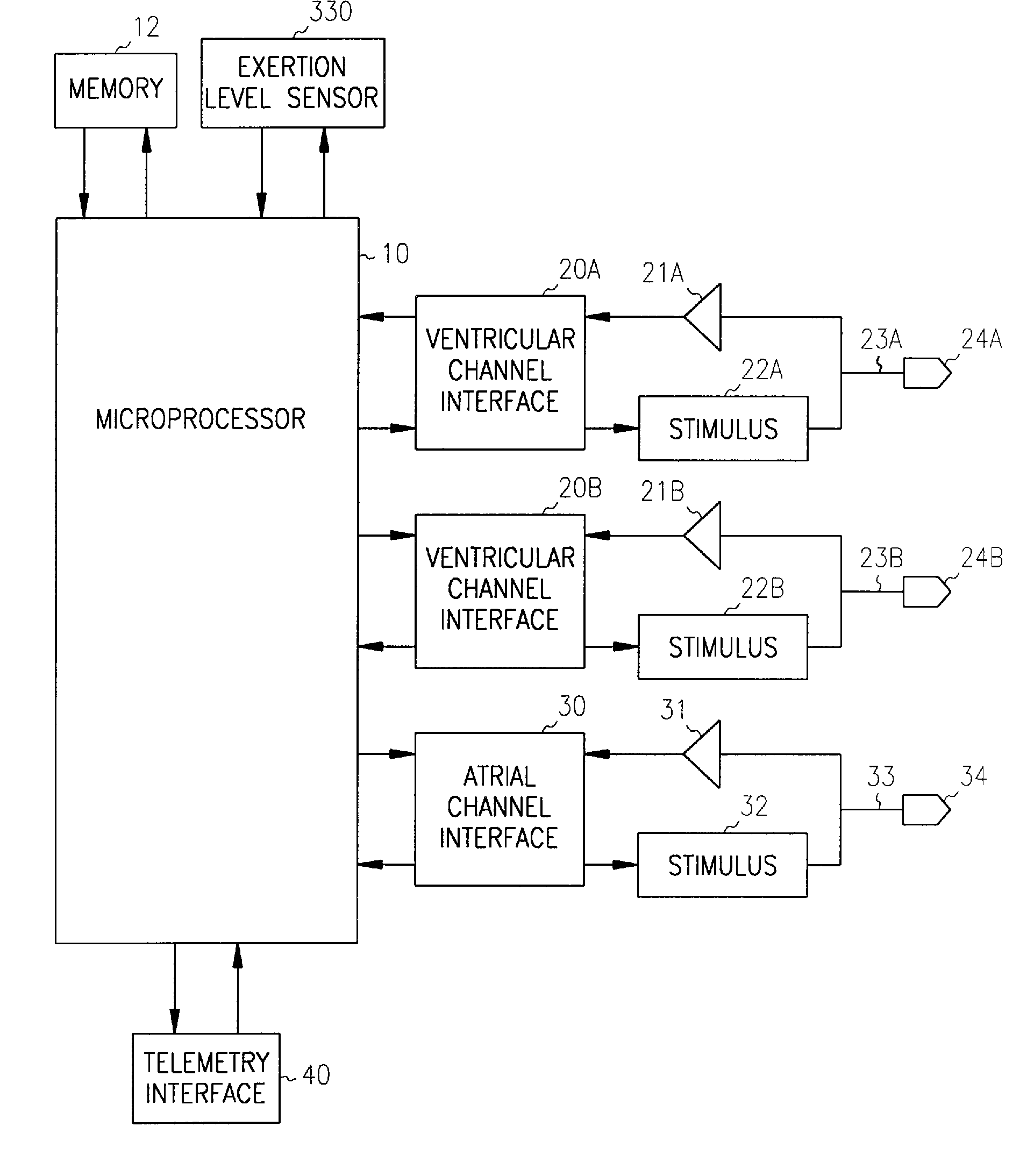
Method and apparatus for displaying information retrieved from an implanted medical device
A graphical user interface is provided controllably displaying information retrieved from an implantable device, such as a pacemaker. The graphical user interface is comprised of a first and second window. The first window is adapted to display data identifying a plurality of episodes recorded by the implantable device, wherein the data is comprised of a plurality of fields. One of the fields may be used to identify a type of episode, such as ventricular tachycardia (VT), atrial and ventricular tachycardia (A&V), atrial fibrillation (AF), atrial flutter (Afl), atrial tachycardia (AT), and premature atrial contraction (PAC). The second window is adapted to display data types, such as VT, A&V, AF, Afl, AT, and PAC, that may be present in the plurality of fields, wherein at least one of the data types may be selected to filter the episodes displayed in the first window and display those episodes having the selected data types.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Intelligent electrocardiogram data classification method based on voting ensemble learning
ActiveCN111000553AGood effectReduce threatDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsClassification methodsTest set
An intelligent electrocardiogram data classification method based on voting ensemble learning in the invention is characterized by being realized through the following steps: a) carrying out data preprocessing; b) establishing a logistic regression model; c) establishing a decision tree model; d) establishing a support vector machine; e) establishing a naive Bayesian model; f) establishing a neuron model; g) establishing a k proximity model; and h) carrying out model integration. Finally, a model with the accuracy of not less than 80% is obtained, and the effect of the model is better than theeffect of the single model established in the steps b) to g). According to the intelligent electrocardiogram data classification method, enough data are firstly acquired from ccdd and are divided into a training set and a test set, then various models are established, and the model with accuracy of not less than 80% is finally obtained, thereby realizing intelligent identification and classification of normal, atrial fibrillation, atrial premature beat, accidental atrial premature beat, frequent atrial premature beat, atrial tachycardia and atrial fibrillation accompanied with rapid ventricular rate, and realizing early discovery and early treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:SHANDONG COMP SCI CENTNAT SUPERCOMP CENT IN JINAN
Apparatus and method for pacing mode switching during atrial tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS20070073348A1Improve coordinationHigh outputHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac pacemaker
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com