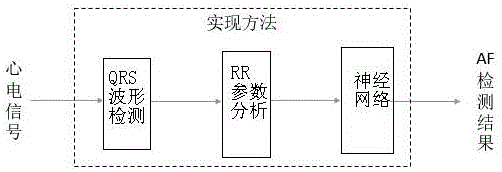
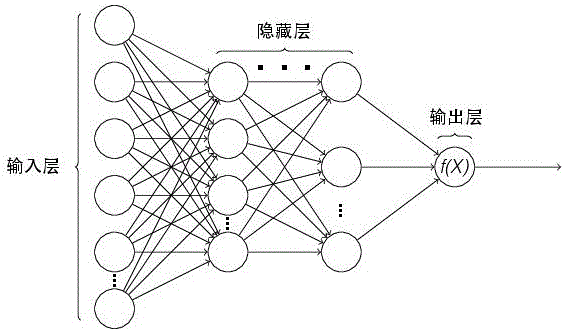
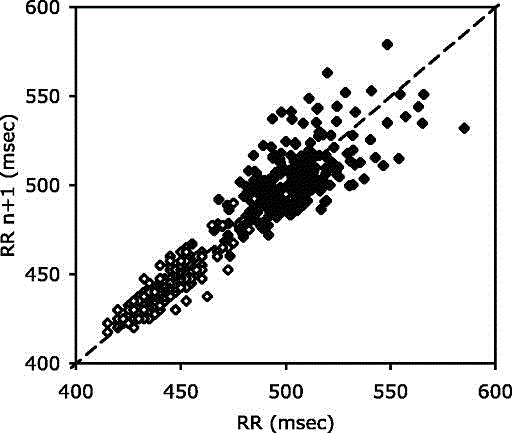
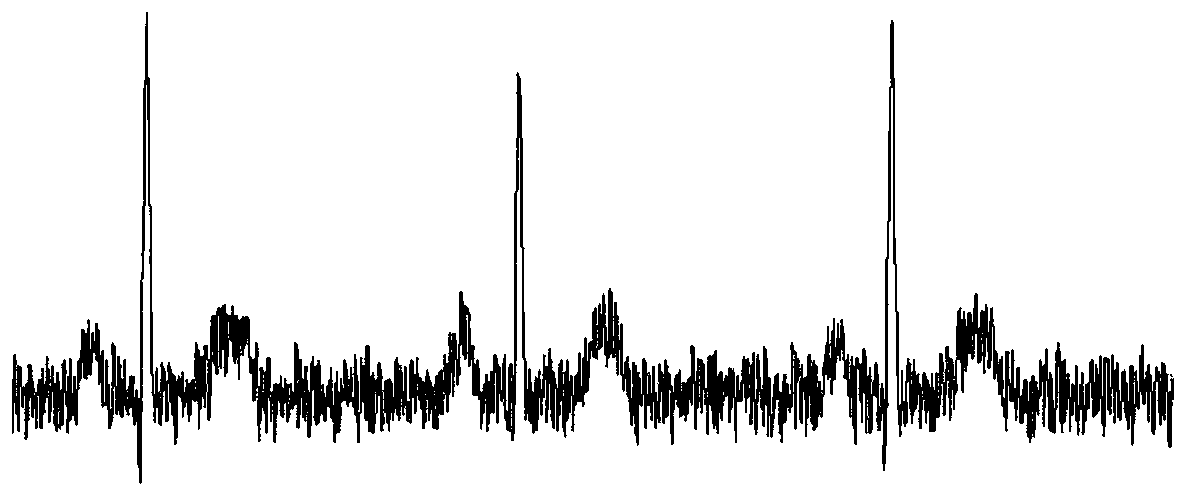
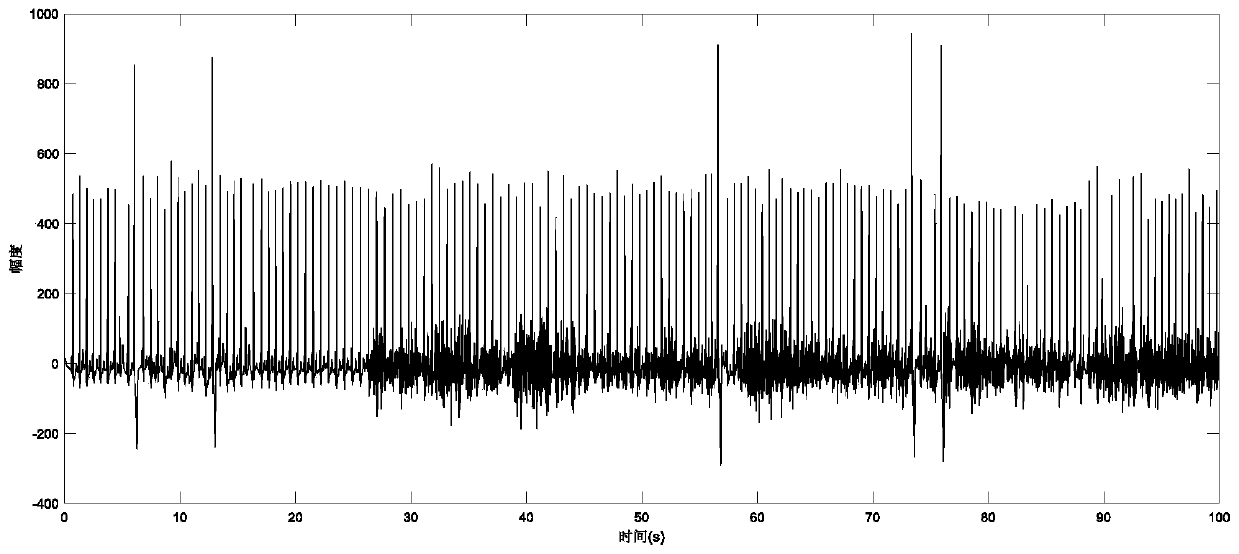
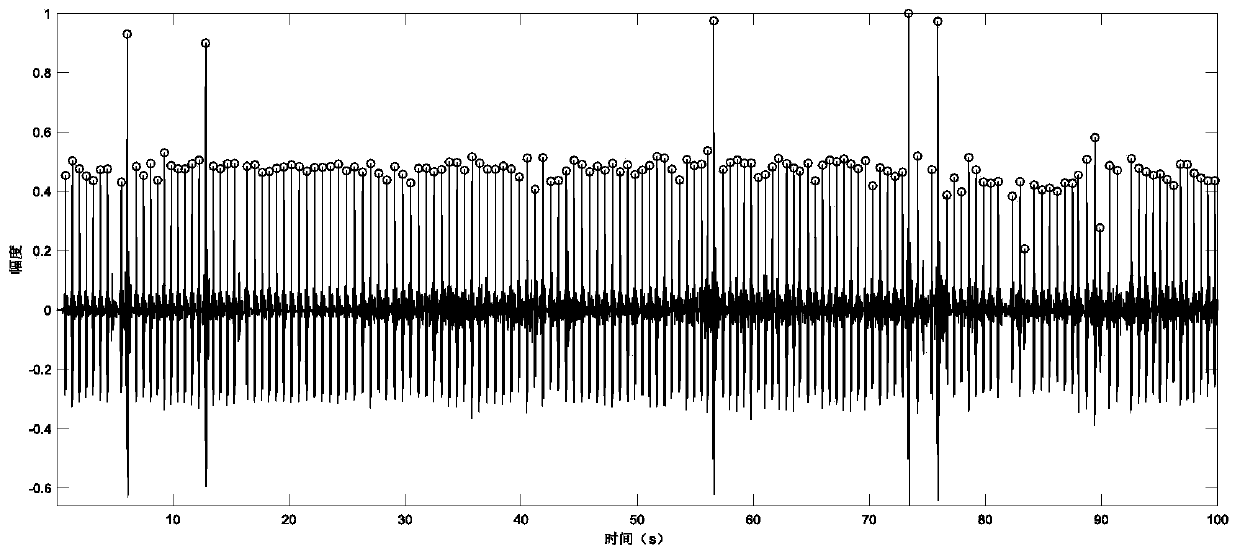
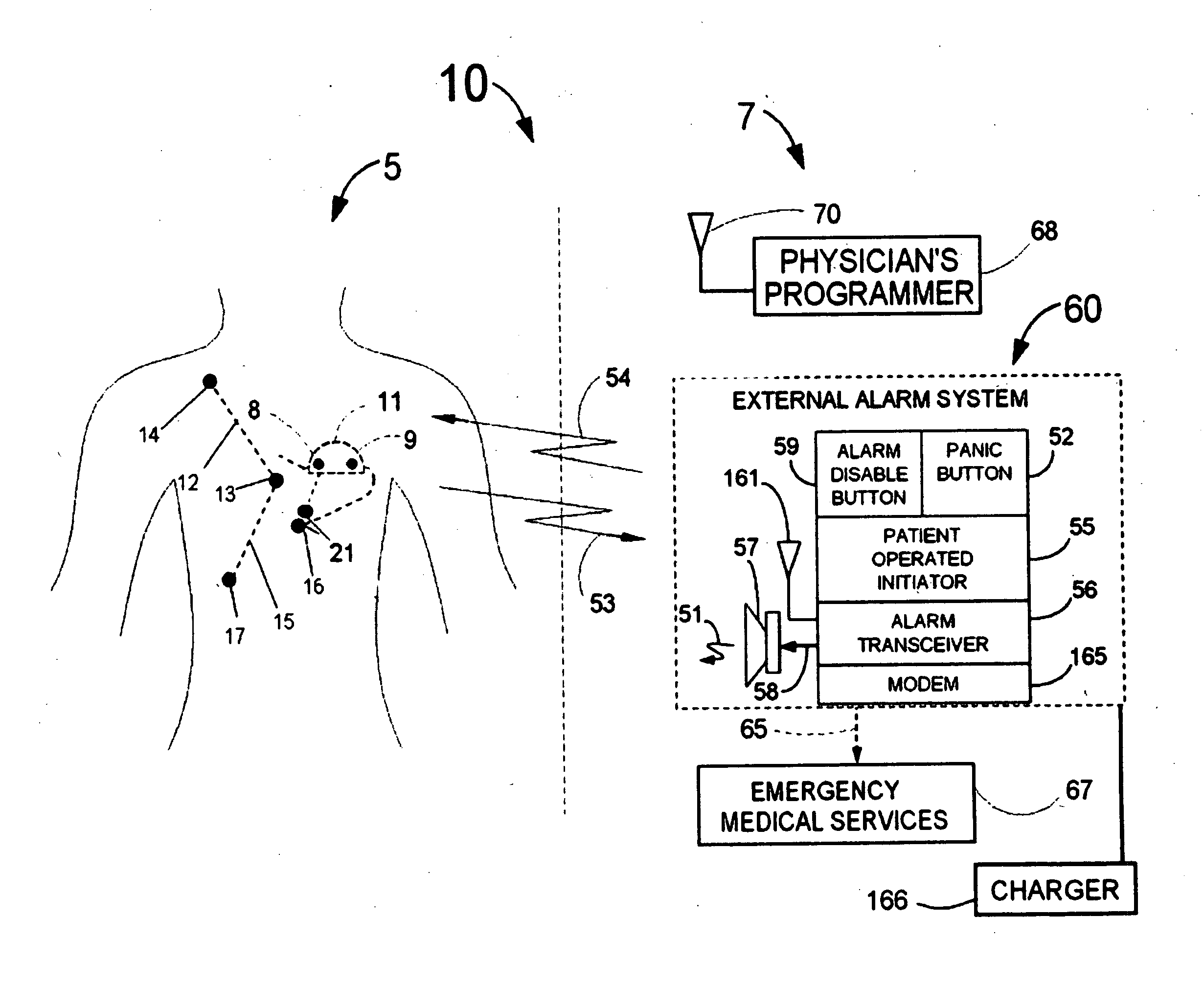
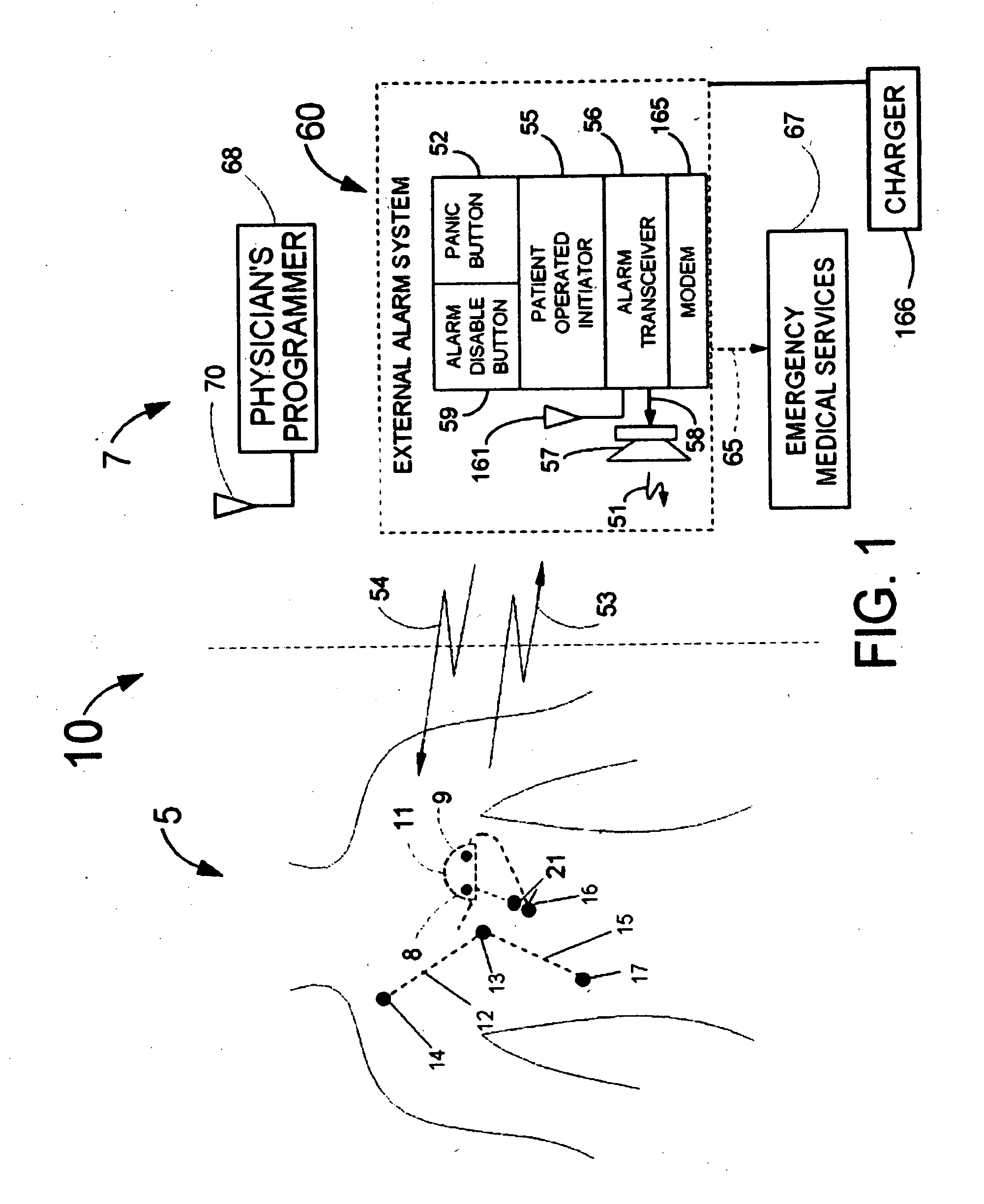
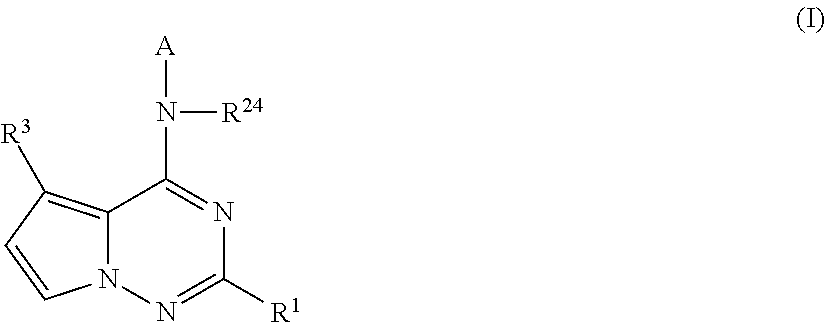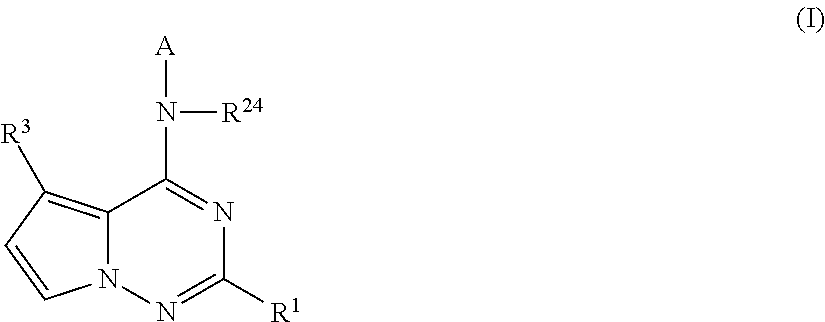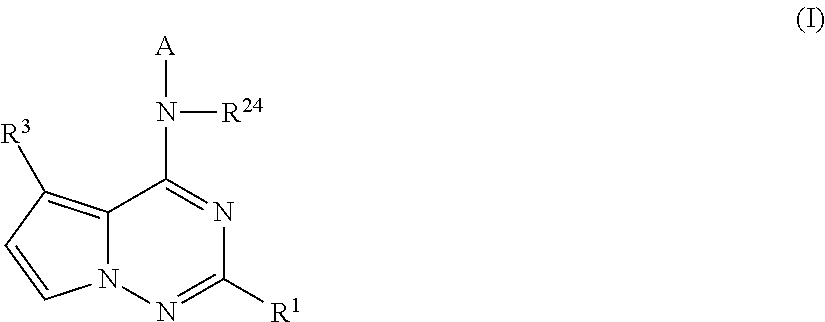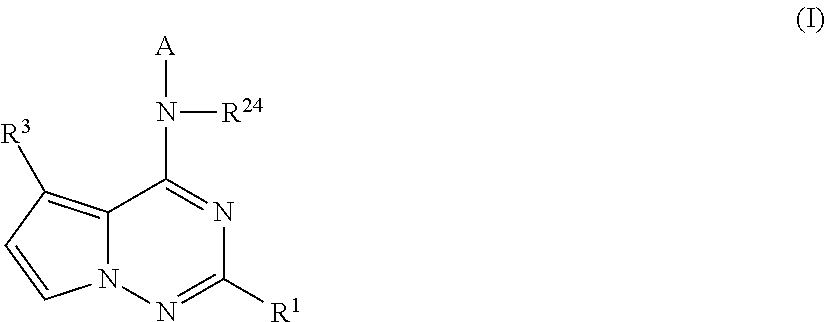Patents
Literature
53 results about "Normal Sinus Rhythm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
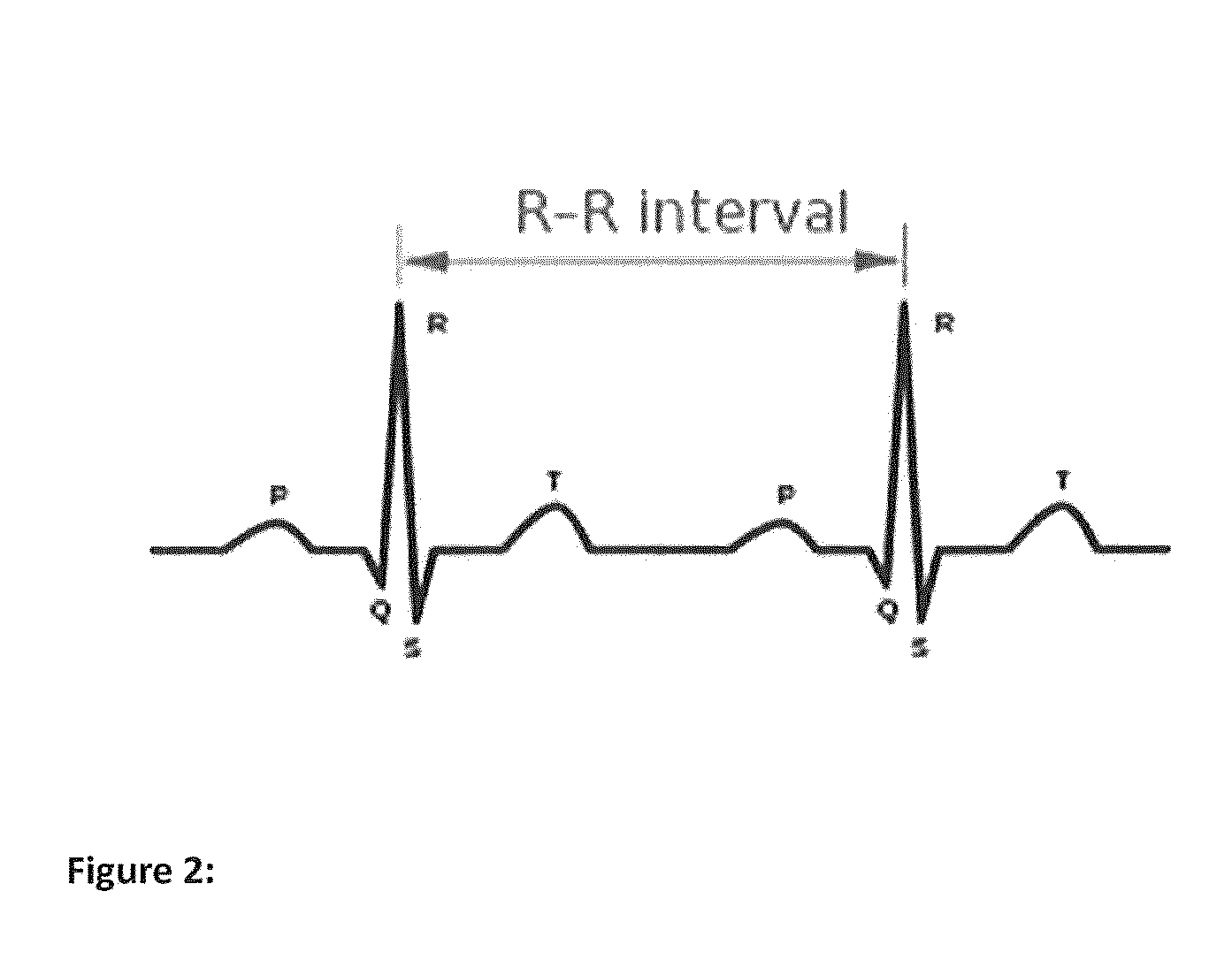
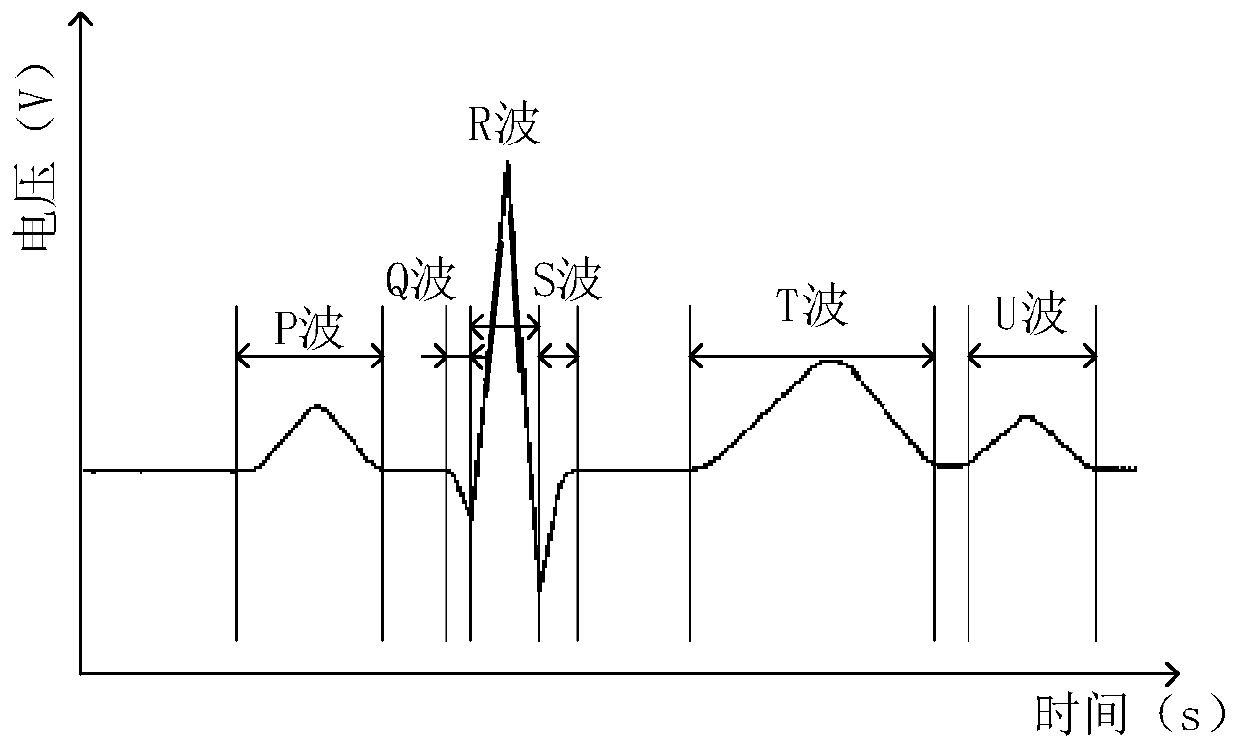
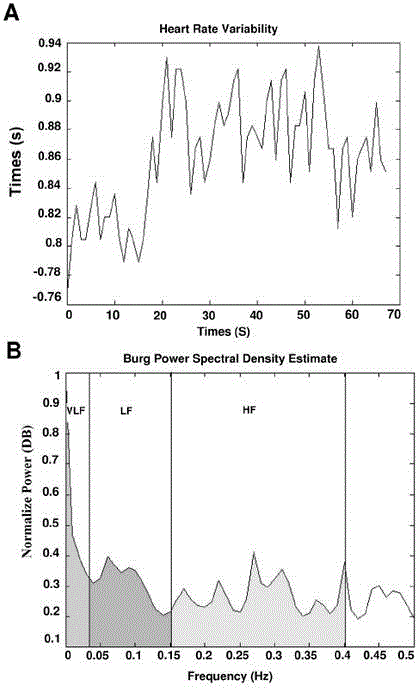
Normal sinus rhythm. Normal sinus rhythm is defined as the rhythm of a healthy heart. It means the electrical impulse from your sinus node is being properly transmitted. In adults, normal sinus rhythm usually accompanies a heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute. However, normal heart rates vary from person to person.
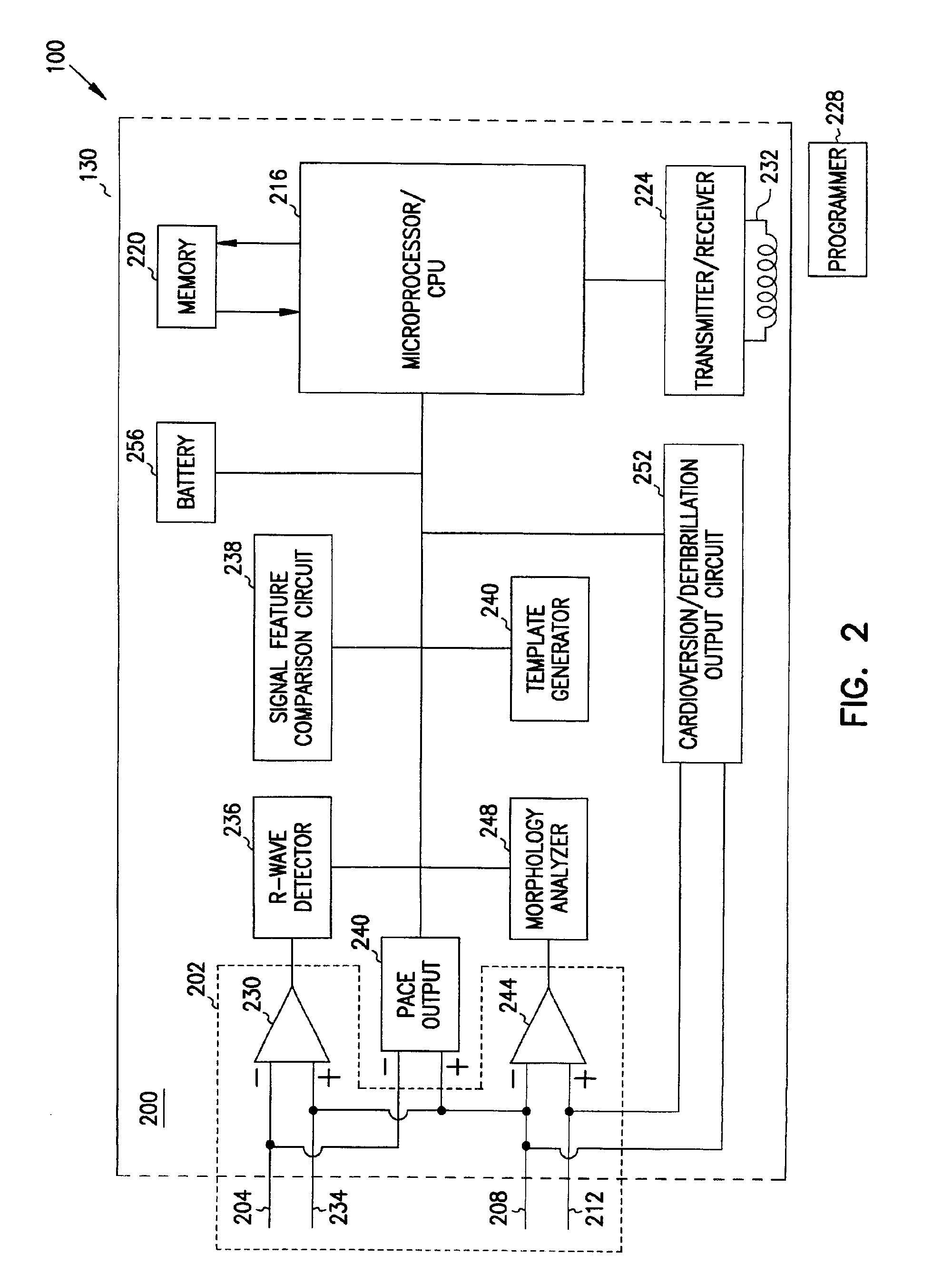
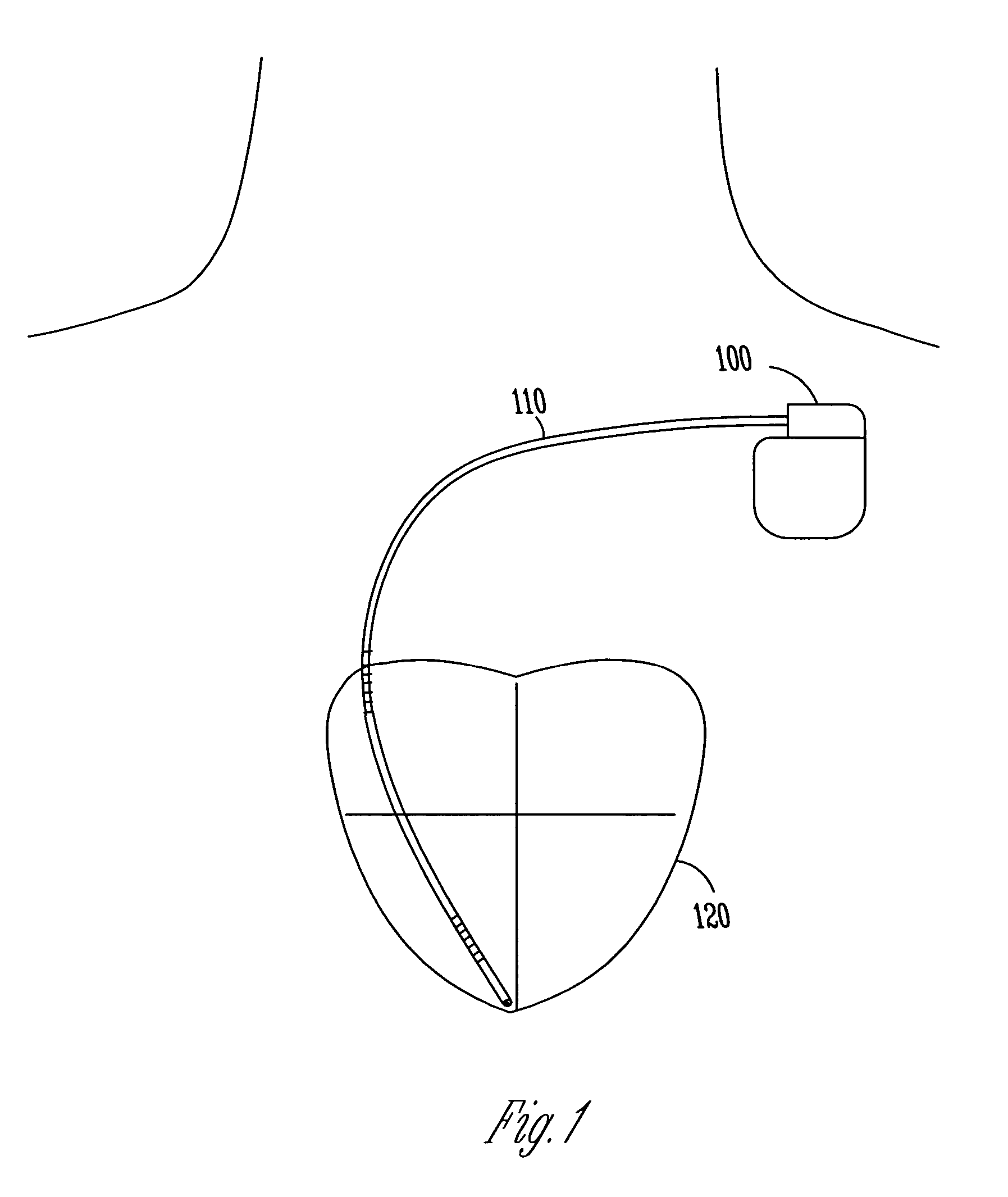
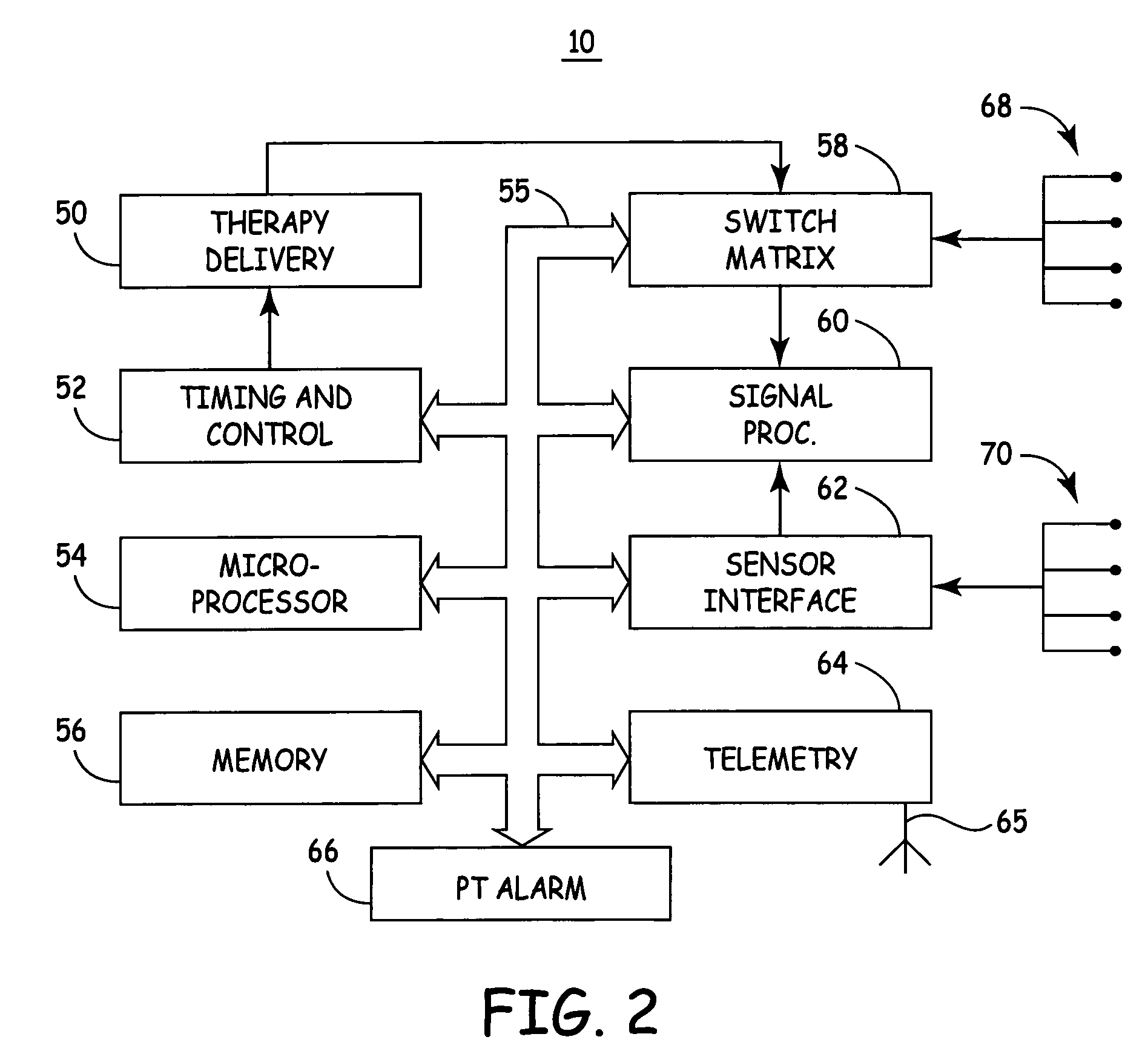
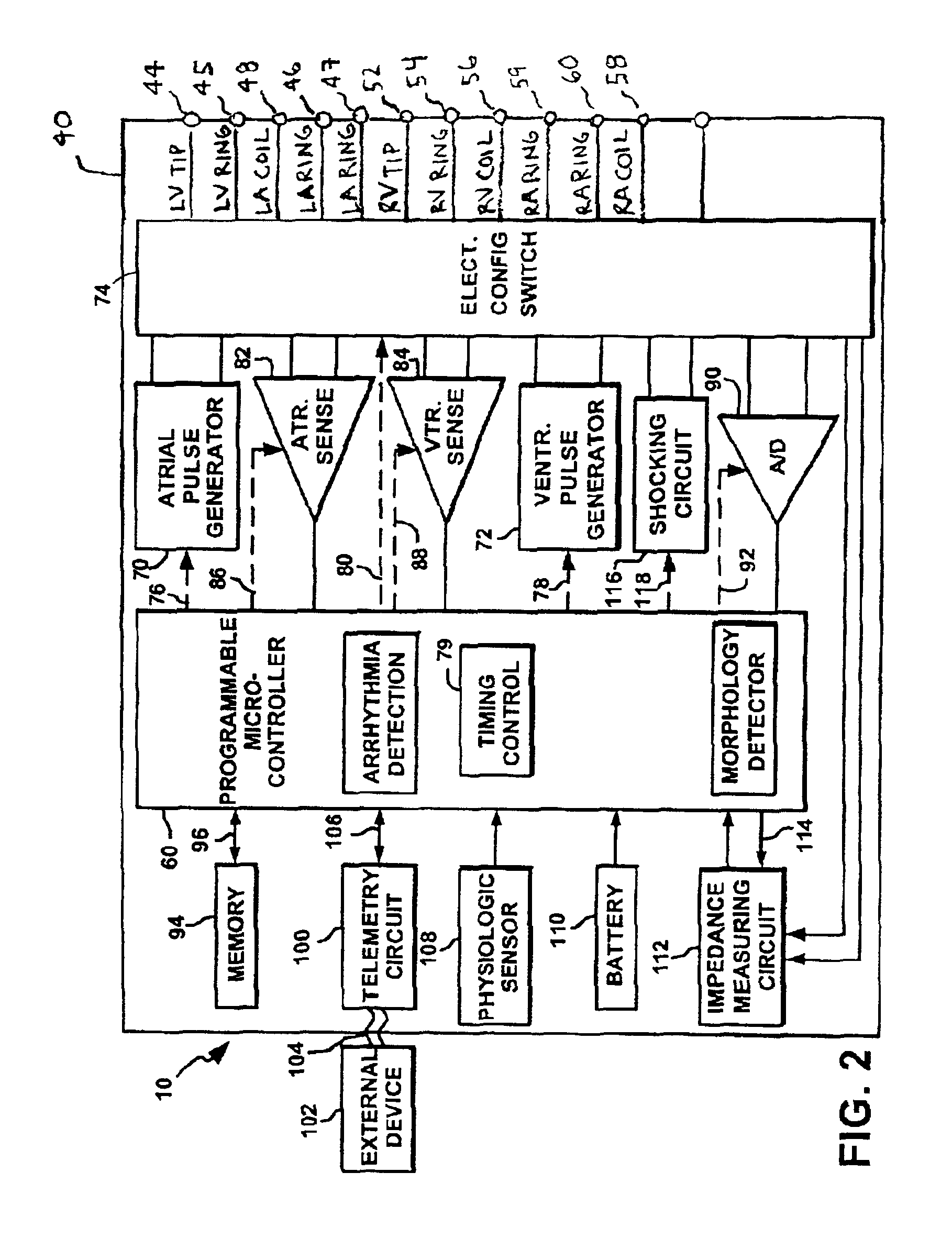
Multi-parameter arrhythmia discrimination
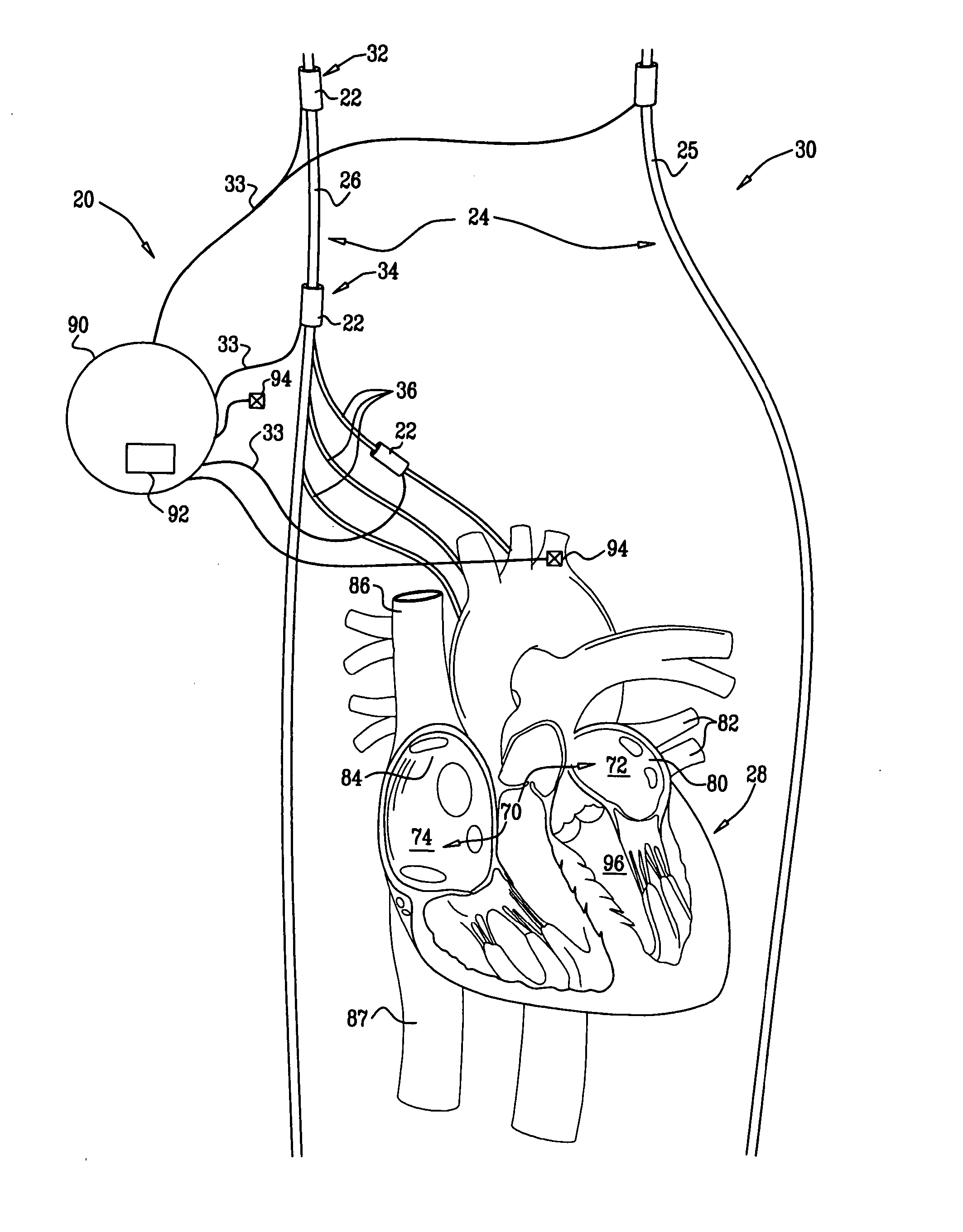
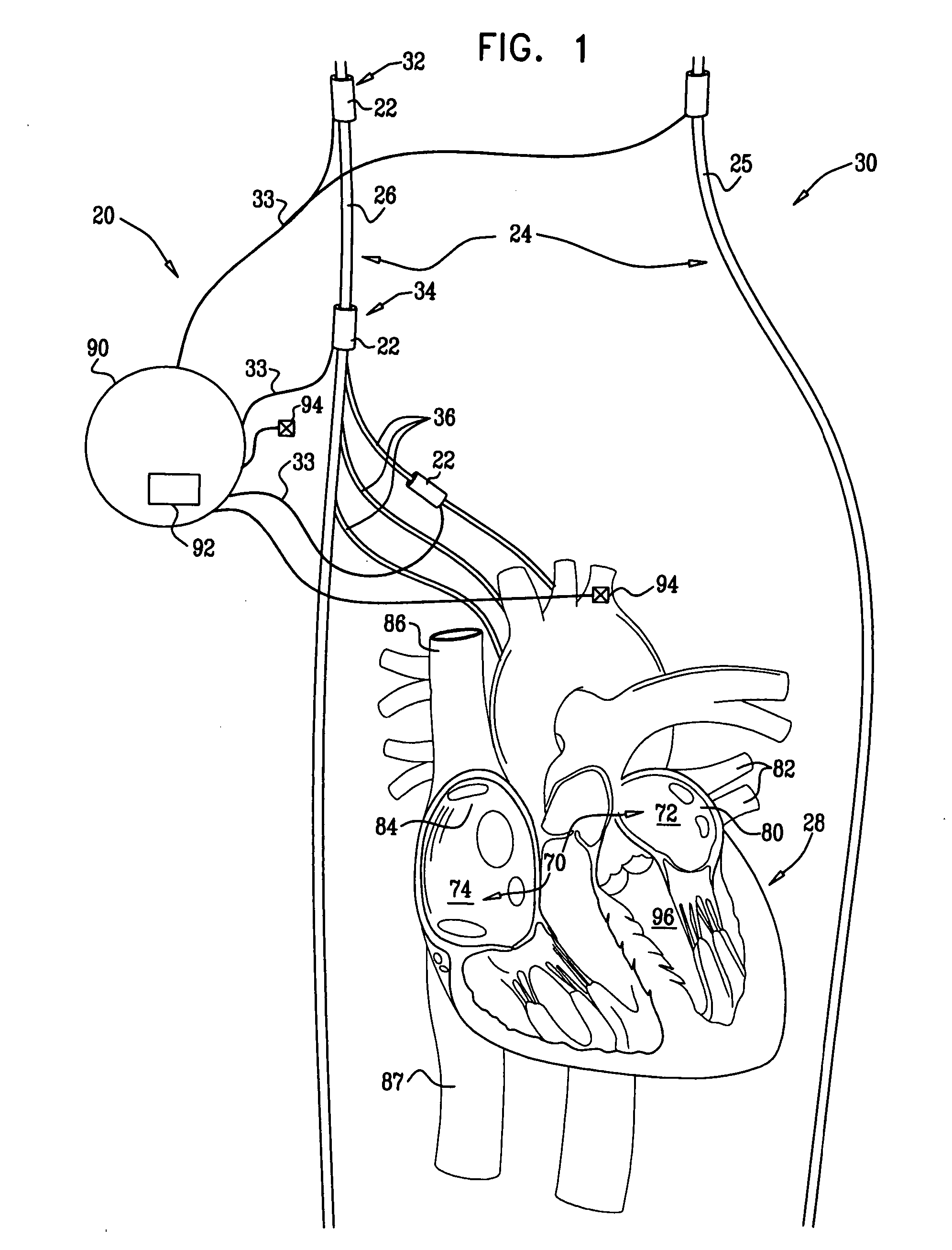
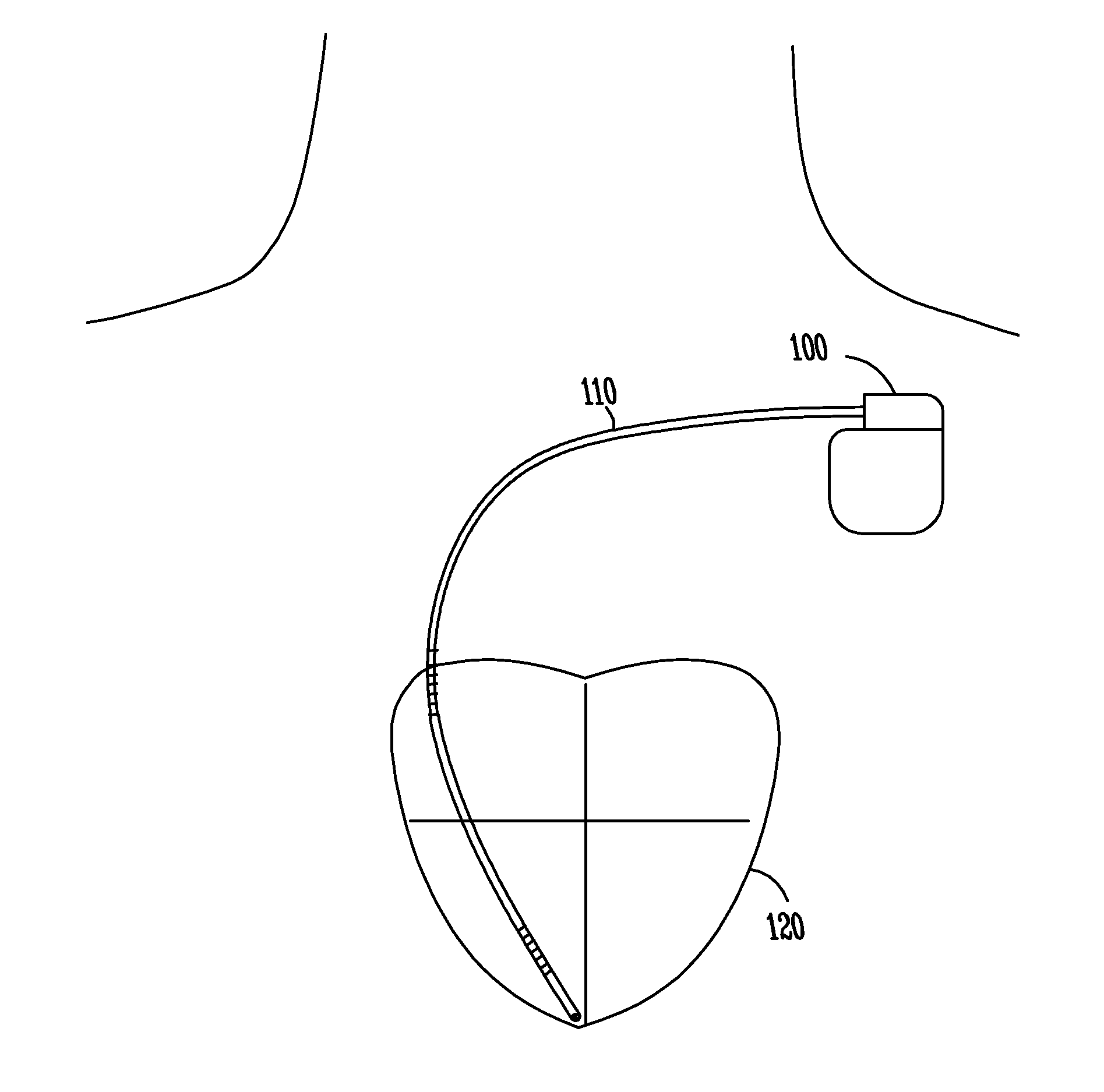
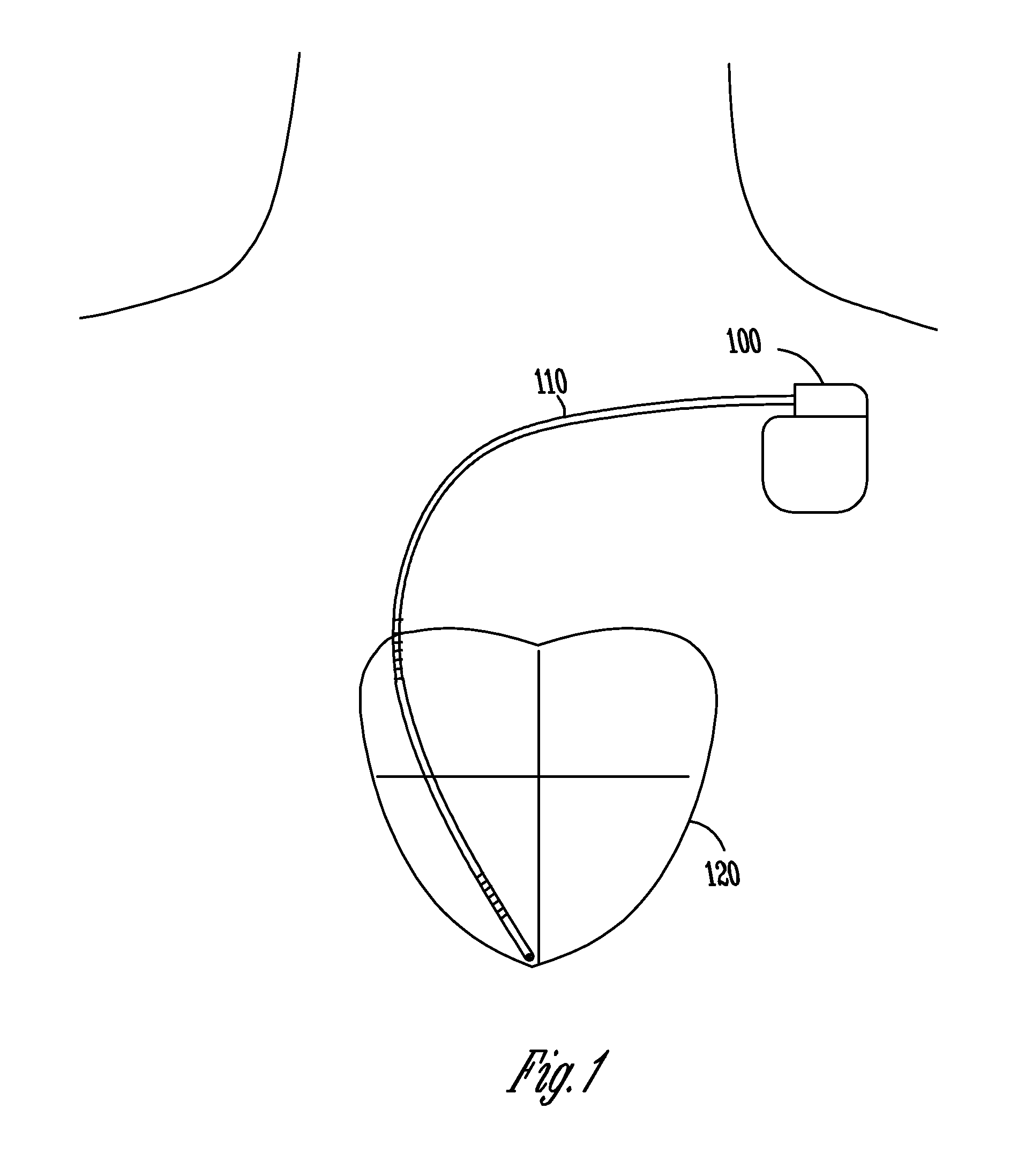
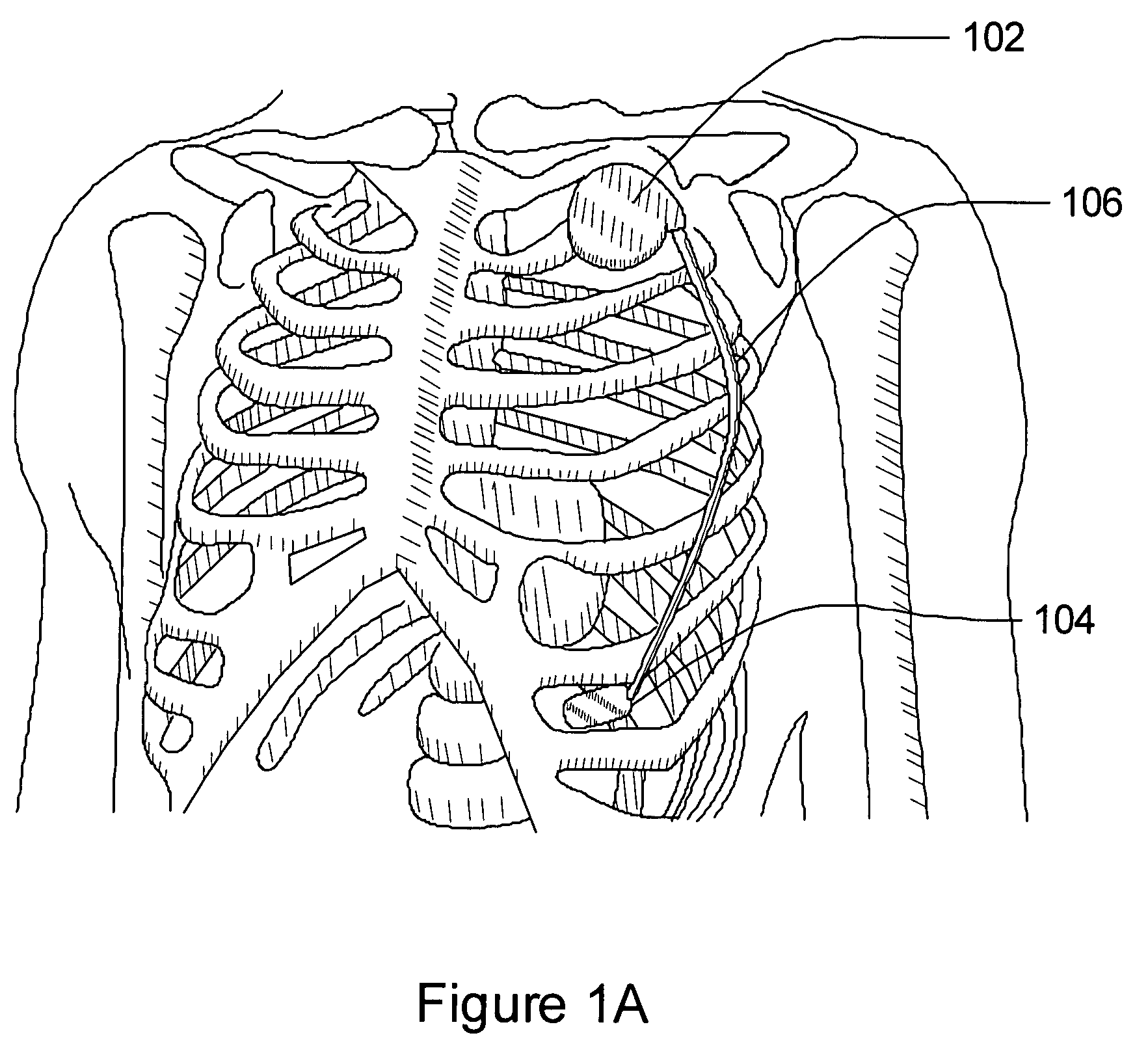
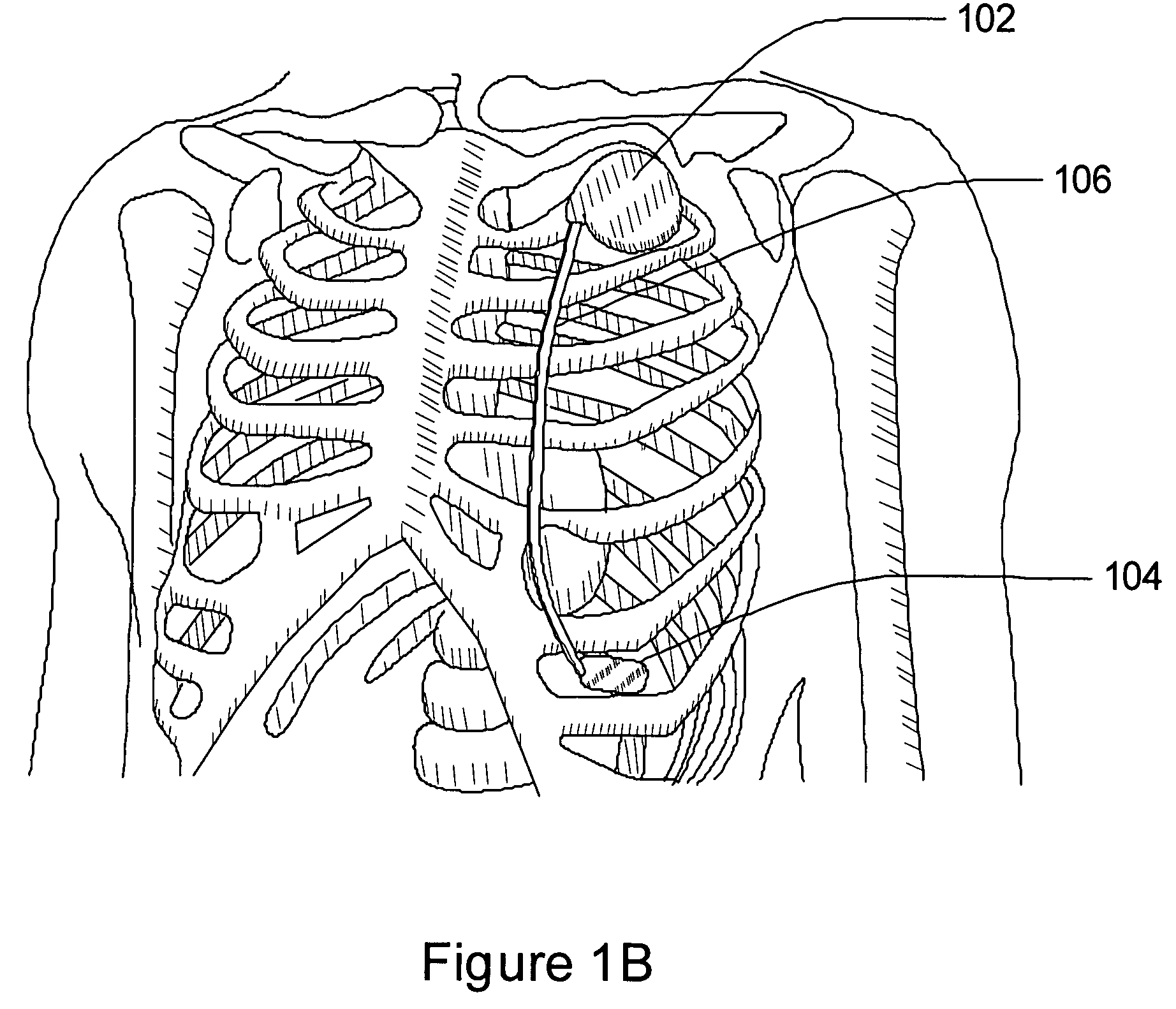
ActiveUS7218966B2Inhibiting therapeutic deliverySurgical needlesHeart defibrillatorsPulse rateNormal Sinus Rhythm
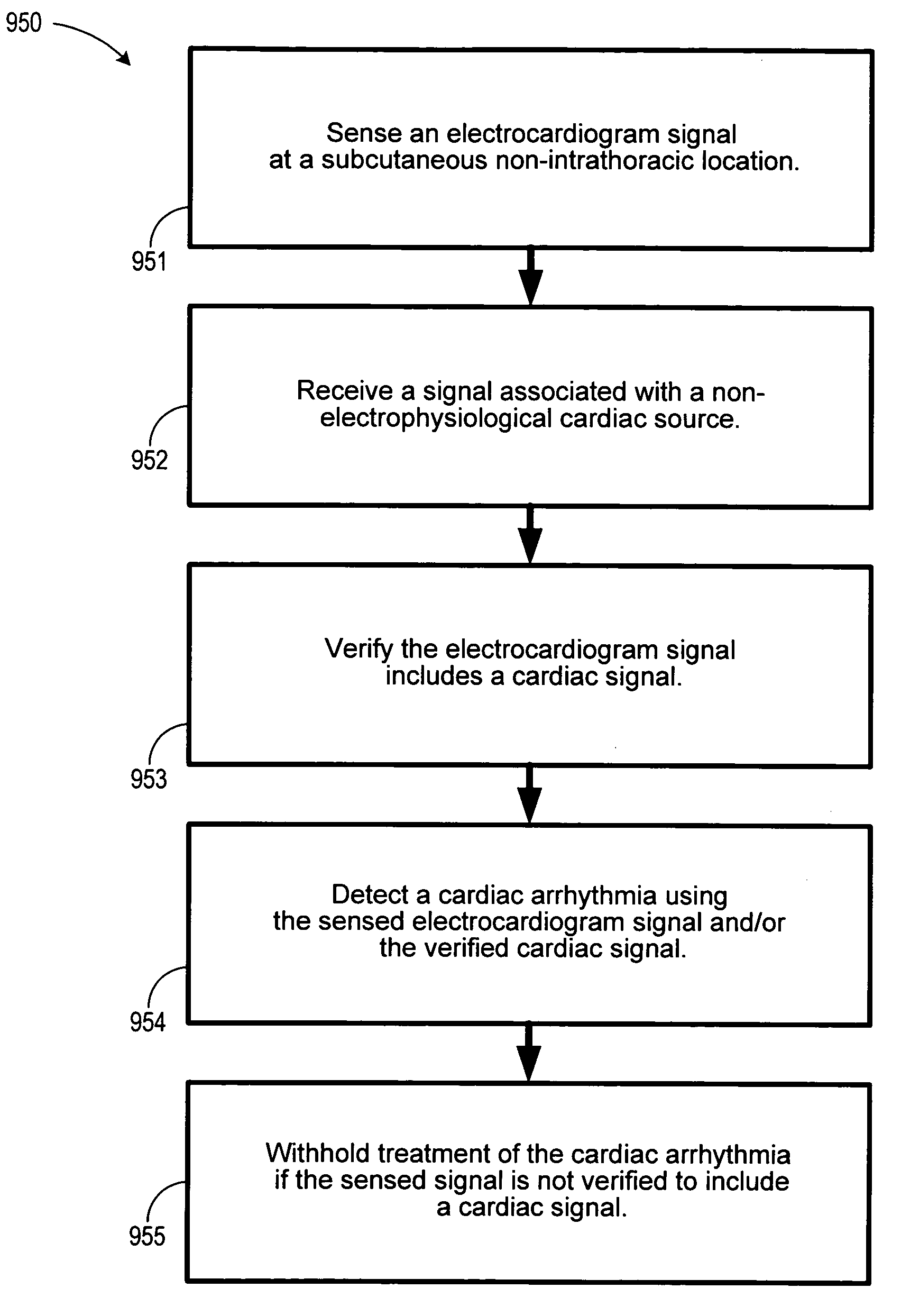
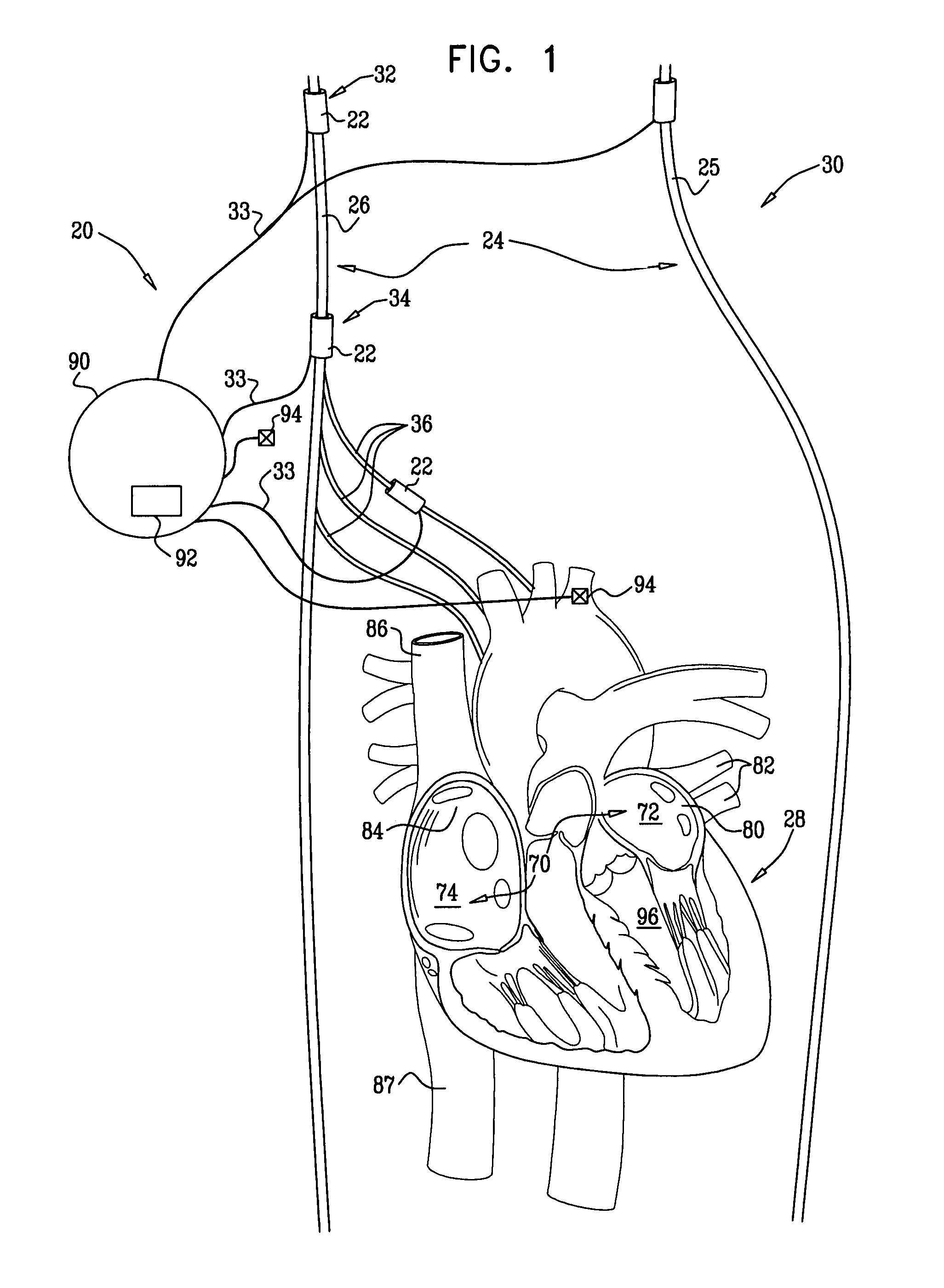
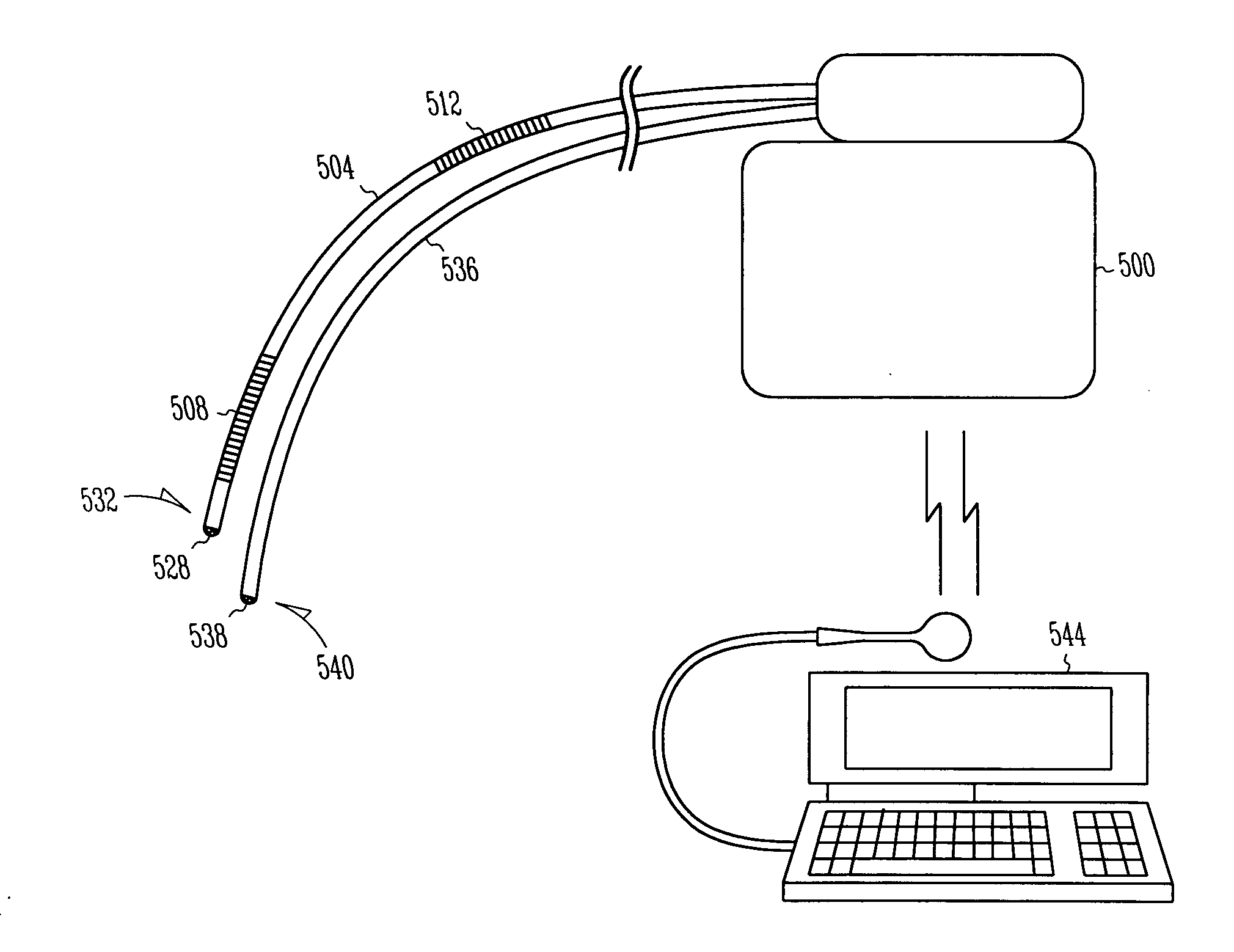
An arrhythmia discrimination device and method involves receiving electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals at subcutaneous locations. Both the electrocardiogram-signals and non-electrophysiologic signals are used to discriminate between normal sinus rhythm and an arrhythmia. An arrhythmia may be detected using electrocardiogram signals, and verified using the non-electrophysiologic signals. A detection window may be initiated in response to receiving the electrocardiogram signal, and used to determine whether the non-electrophysiologic signal is received at a time falling within the detection window. Heart rates may be computed based on both the electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals. The rates may be used to discriminate between normal sinus rhythm and arrhythmia, and used to determining absence of an arrhythmia.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Parasympathetic stimulation for termination of non-sinus atrial tachycardia
InactiveUS8060197B2Avoid stimulationHigh strengthElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMedicineNormal Sinus Rhythm
Apparatus is provided, which includes an electrode device, configured to be coupled to an atrial site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue, and a control unit. The control unit is configured to, responsively to a detection of an episode of non-sinus atrial tachycardia, restore normal sinus rhythm (NSR) of the subject, by driving the electrode device to apply a parasympathetic stimulation signal to the atrial site, and configuring the parasympathetic stimulation signal to activate the parasympathetic nervous tissue sufficiently to restore the NSR. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
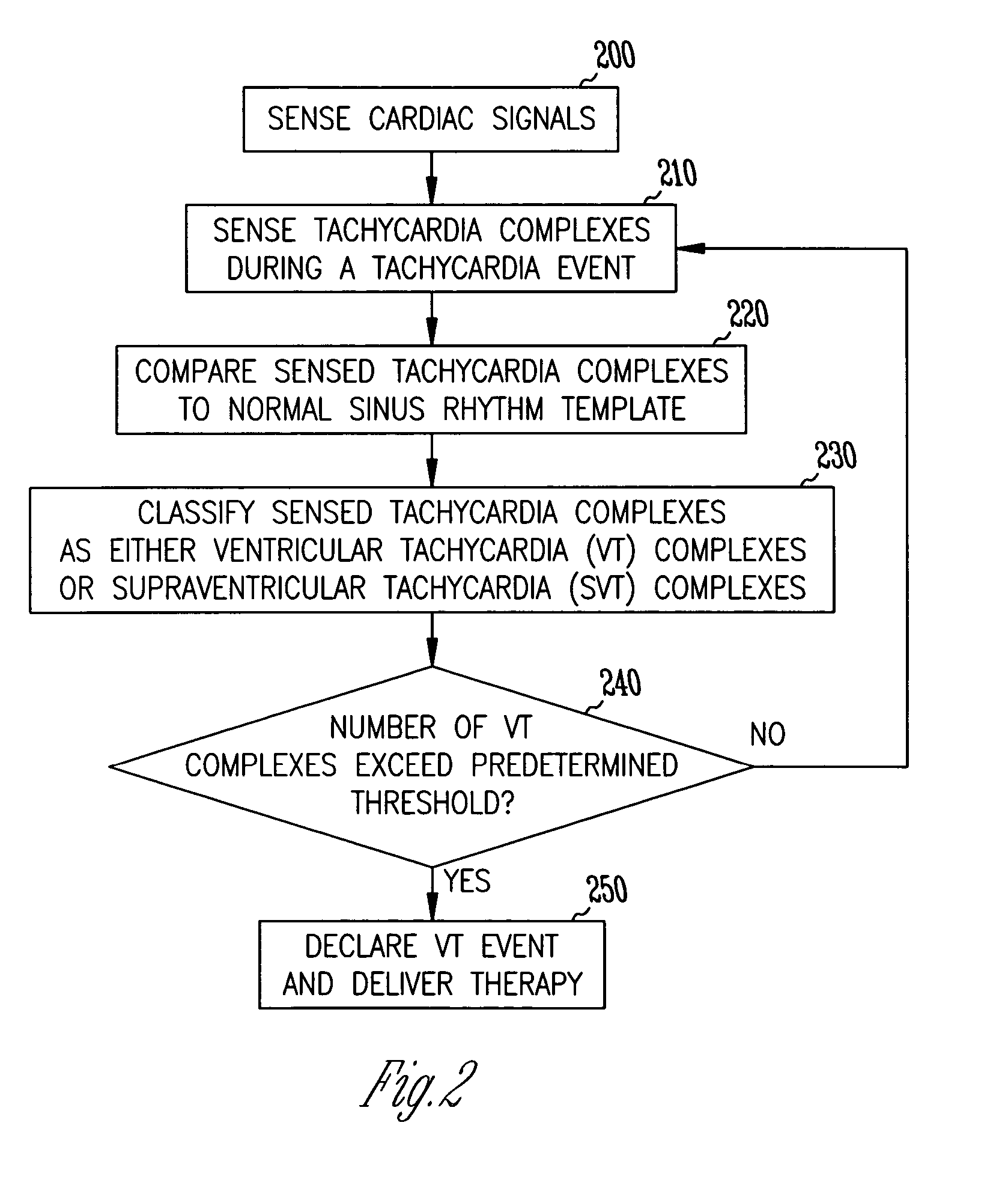
System and method for arrhythmia discrimination
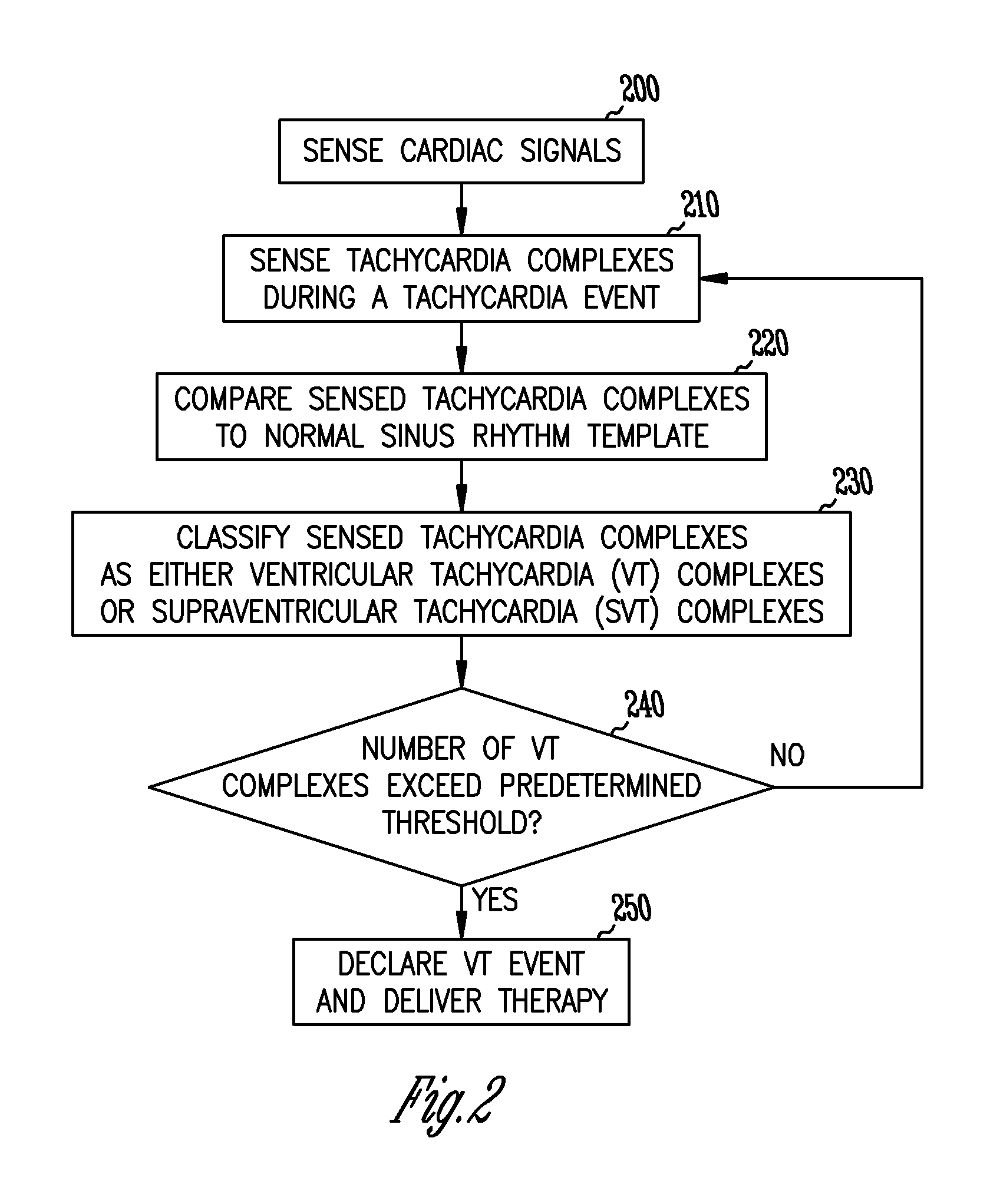
InactiveUS6959212B2Effective treatmentHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular dysrhythmiaVentricular tachycardia
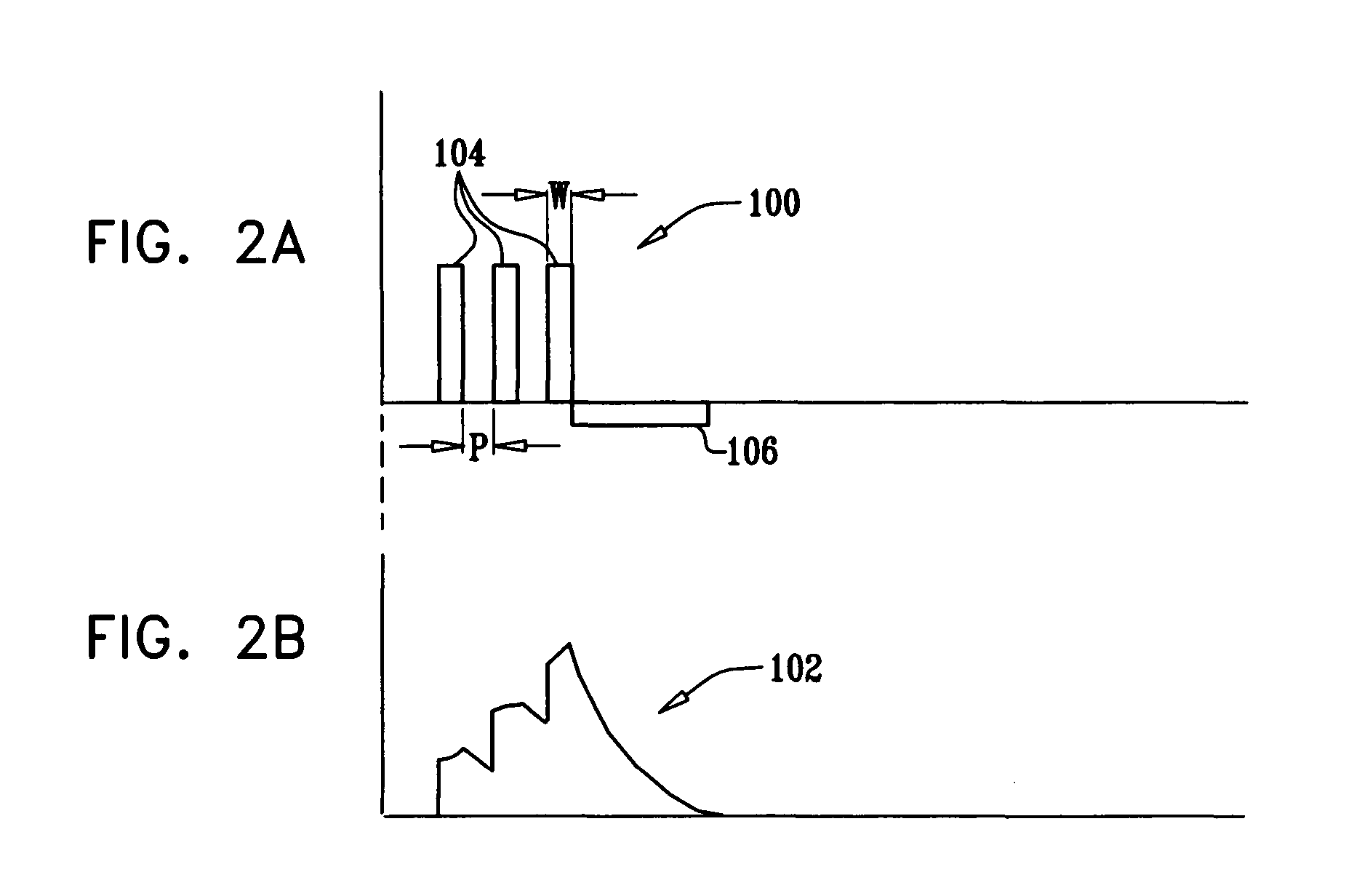
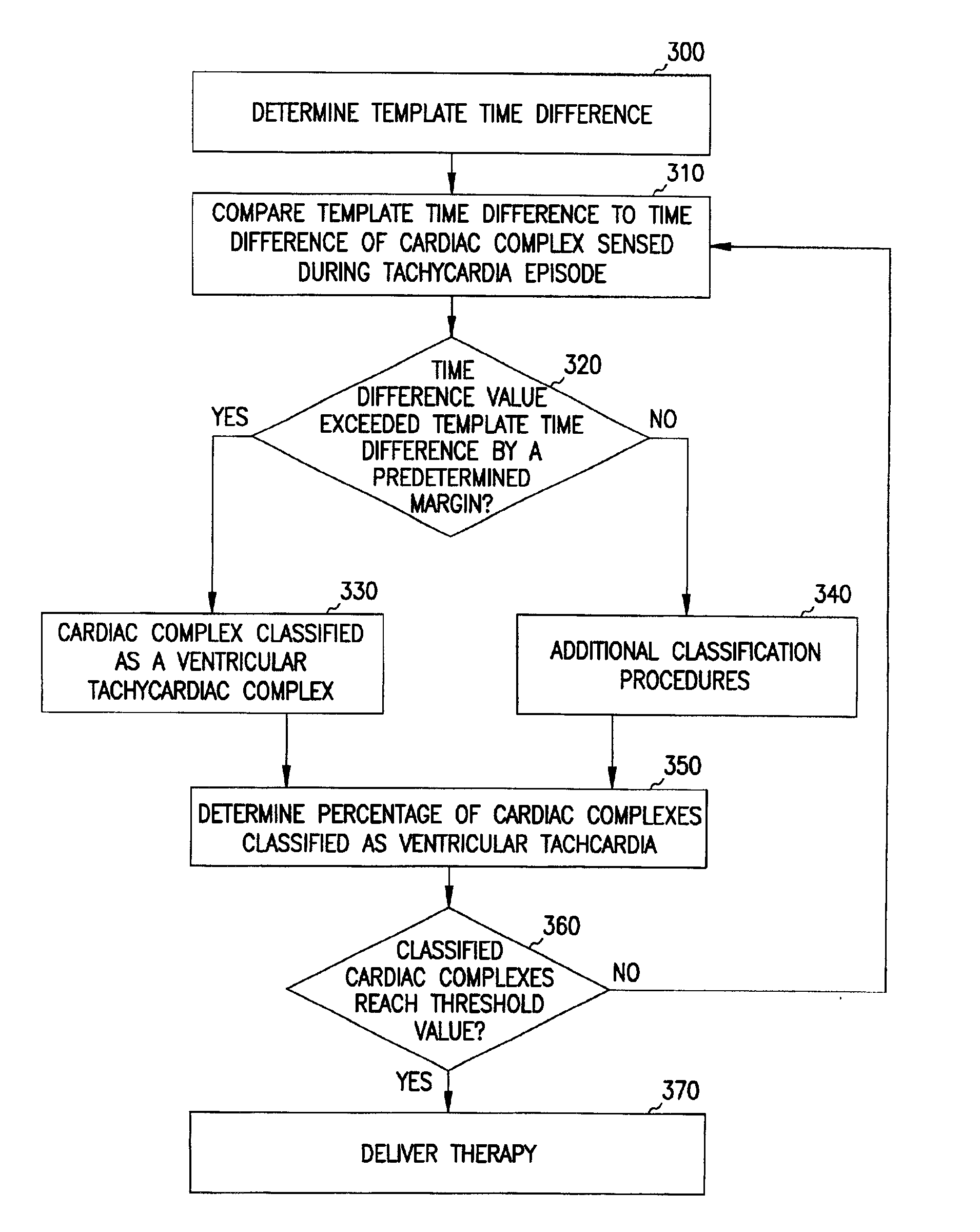
The present invention provides a system and a method for discriminating supraventricular tachyarrhythmias from ventricular arrhythmias during a tachycardia episode. First cardiac signals and second cardiac signals are sampled for cardiac complexes. A first feature on the first cardiac signal and a second feature on the second cardiac signal are utilized to determine an average time difference for a plurality of normal sinus rhythm complexes. A time difference between the first feature and the second feature is then determined for each cardiac complex of a tachycardiac rhythm. The cardiac complex is characterized as a ventricular tachycardia complex if the time difference exceeds the average time difference by a predetermined amount. Otherwise, it is classified as VT if its morphology after alignment is different from that during normal sinus rhythm.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
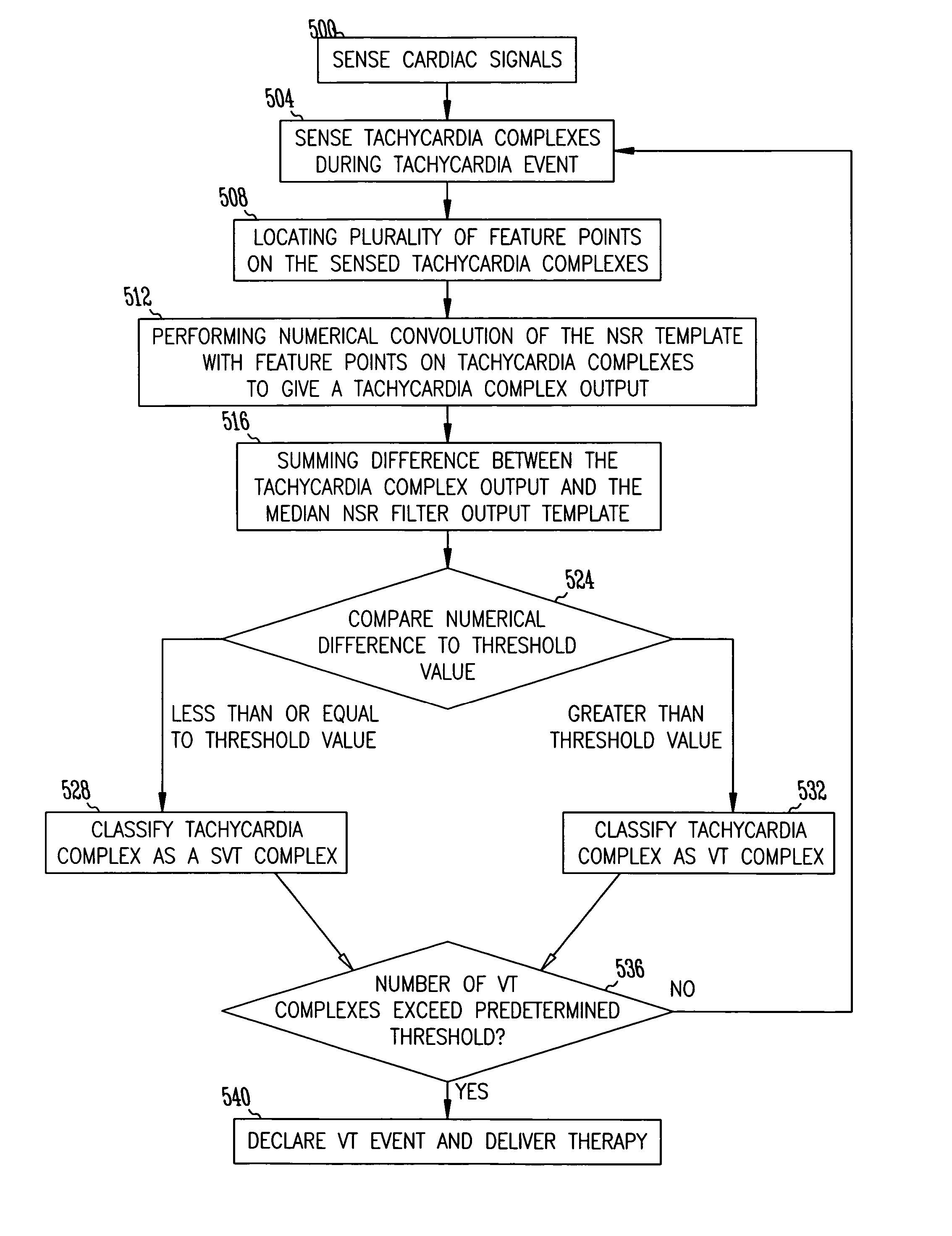
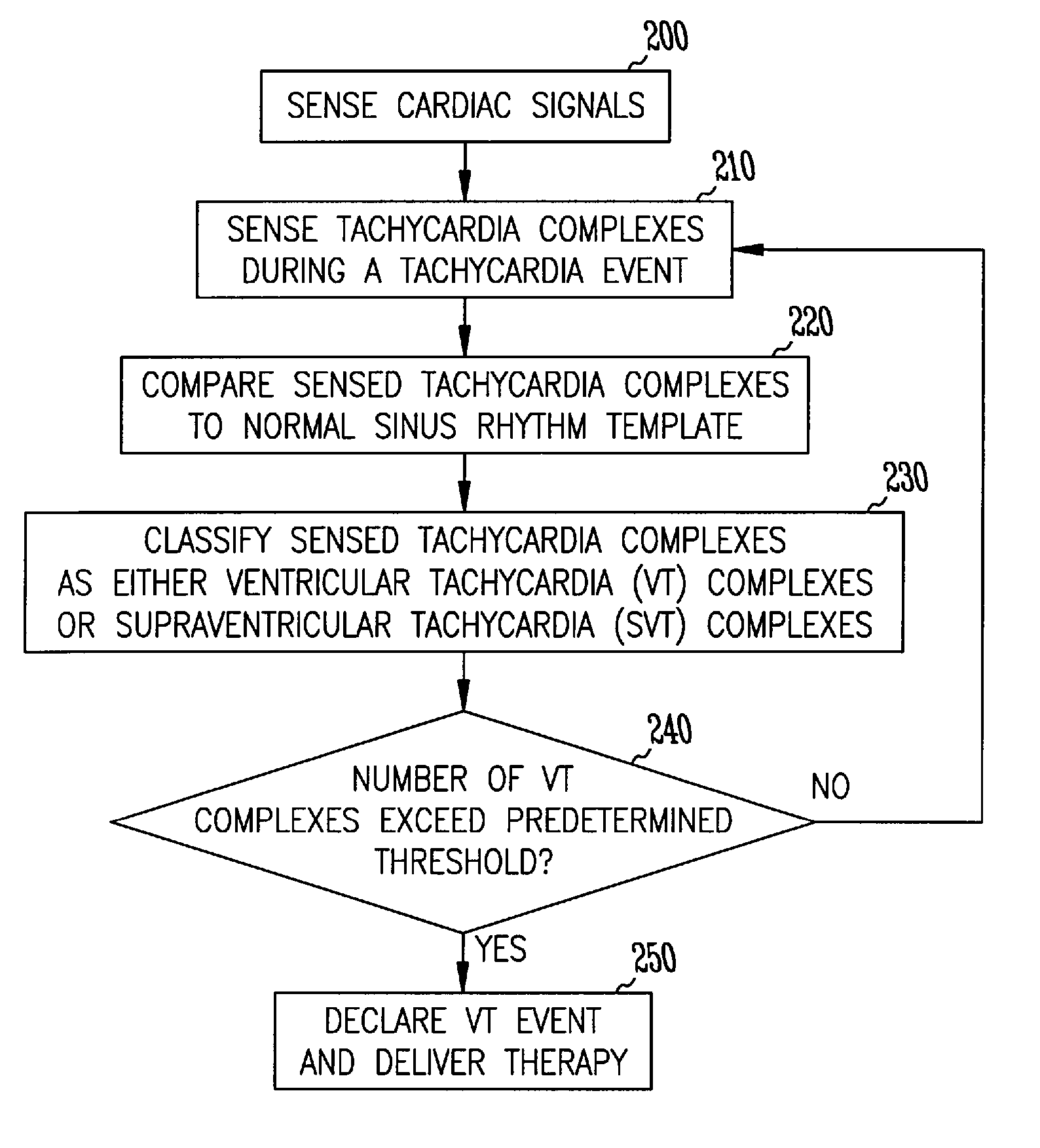
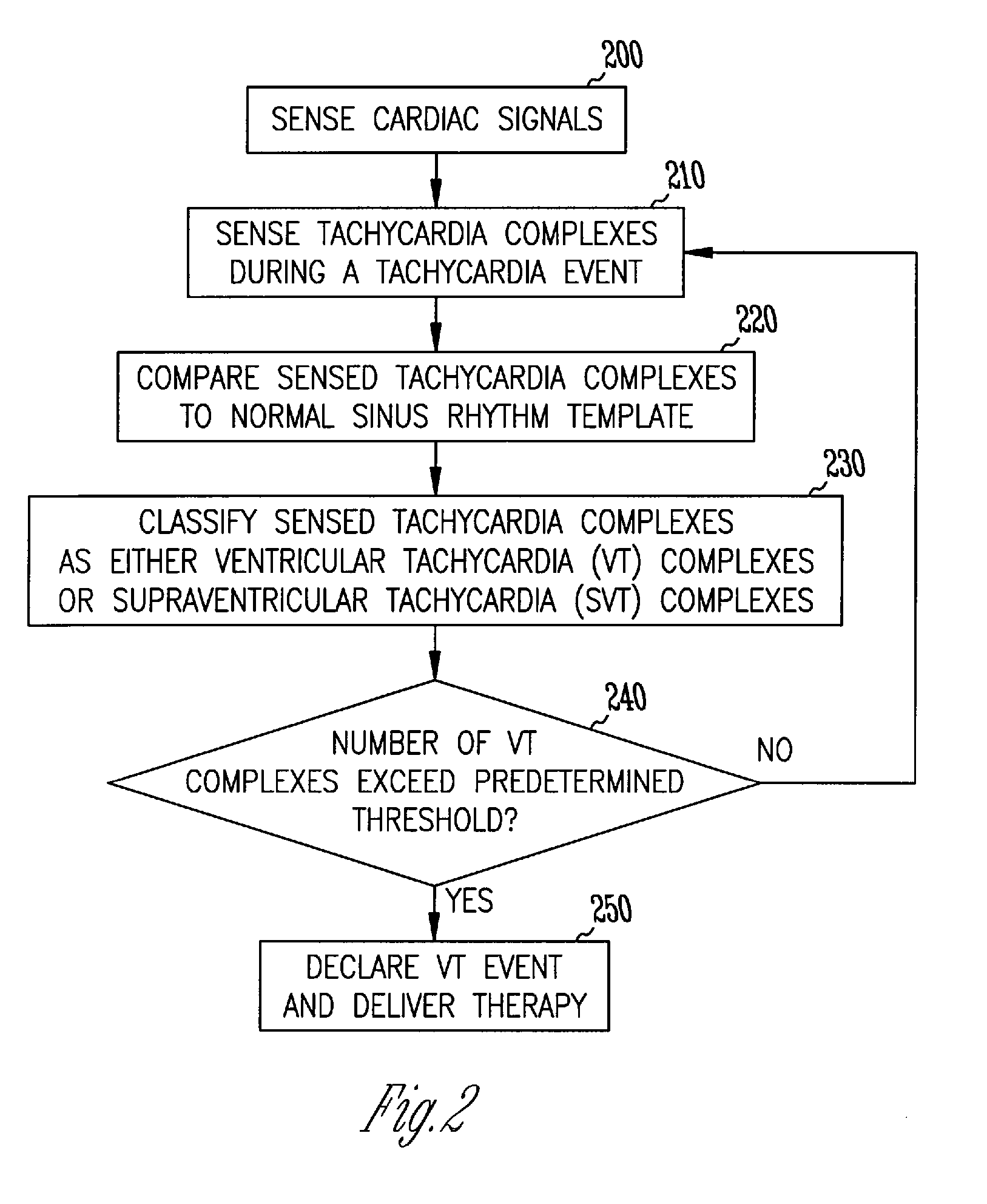
Discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events
InactiveUS7039463B2Reduce in quantityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaNormal Sinus Rhythm
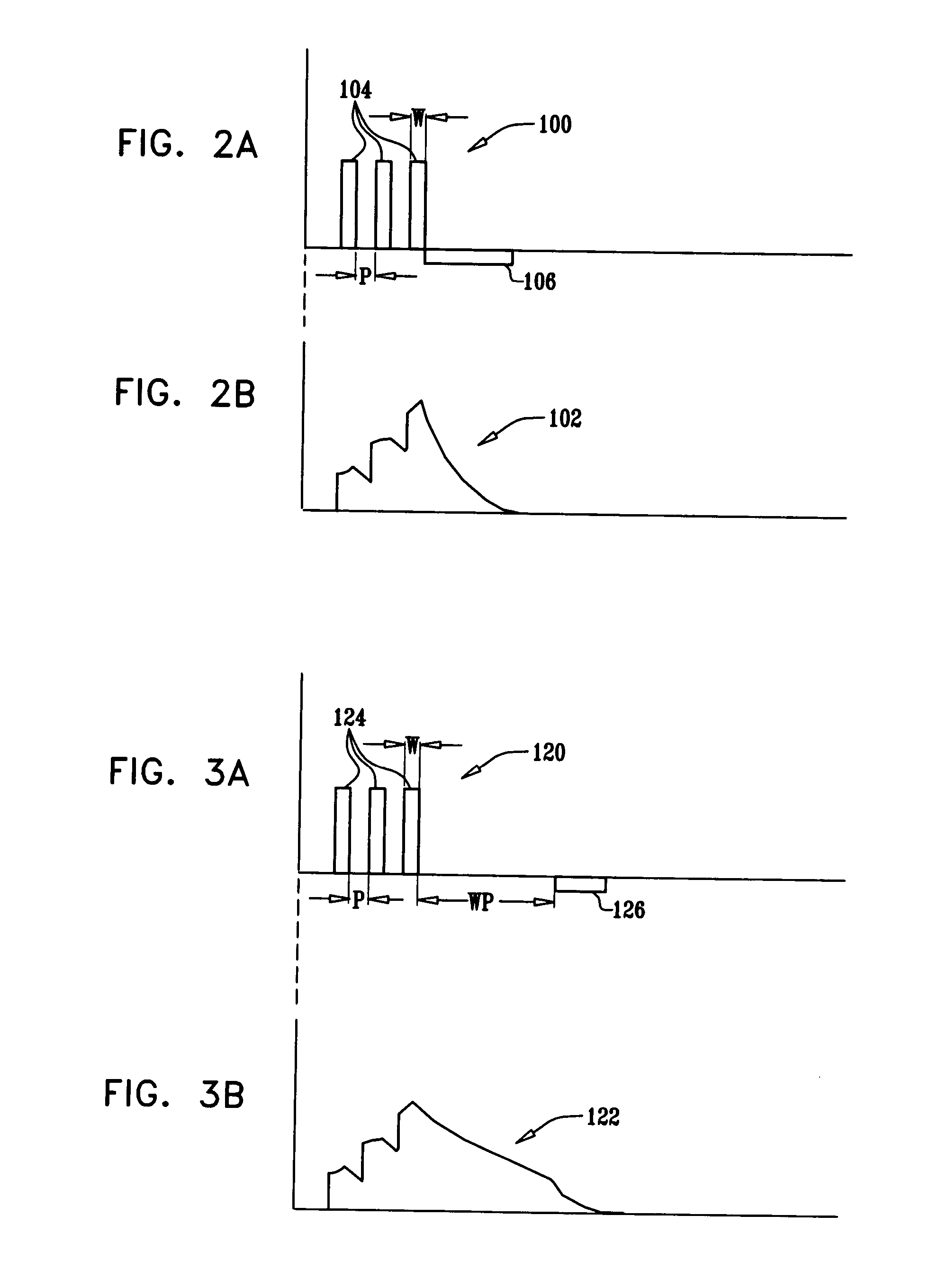
A method and system for discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events. Morphological features points are extracted from normal sinus rhythm (NSR) complexes and used to generate a NSR template. A numerical convolution is performed using the NSR template and the feature points for each sensed NSR to give a NSR filter output. Using a plurality of NSR complexes, a median NSR filter output template is determined, where the median NSR filter output template has a median value for each value in the NSR filter output. The median NSR filter output template is then used during a tachycardia event to distinguish tachycardia events as either ventricular tachycardia events or supraventricular tachycardia events.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Intravascular parasympatheticstimulation for atrial cardioversion
InactiveUS20080046016A1Avoid stimulationHigh strengthInternal electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineNormal Sinus Rhythm
Apparatus is provided, which includes an electrode device, configured to be coupled to an atrial site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue, and a control unit. The control unit is configured to, responsively to a detection of an episode of non-sinus atrial tachycardia, restore normal sinus rhythm (NSR) of the subject, by driving the electrode device to apply a parasympathetic stimulation signal to the atrial site, and configuring the parasympathetic stimulation signal to activate the parasympathetic nervous tissue sufficiently to restore the NSR. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
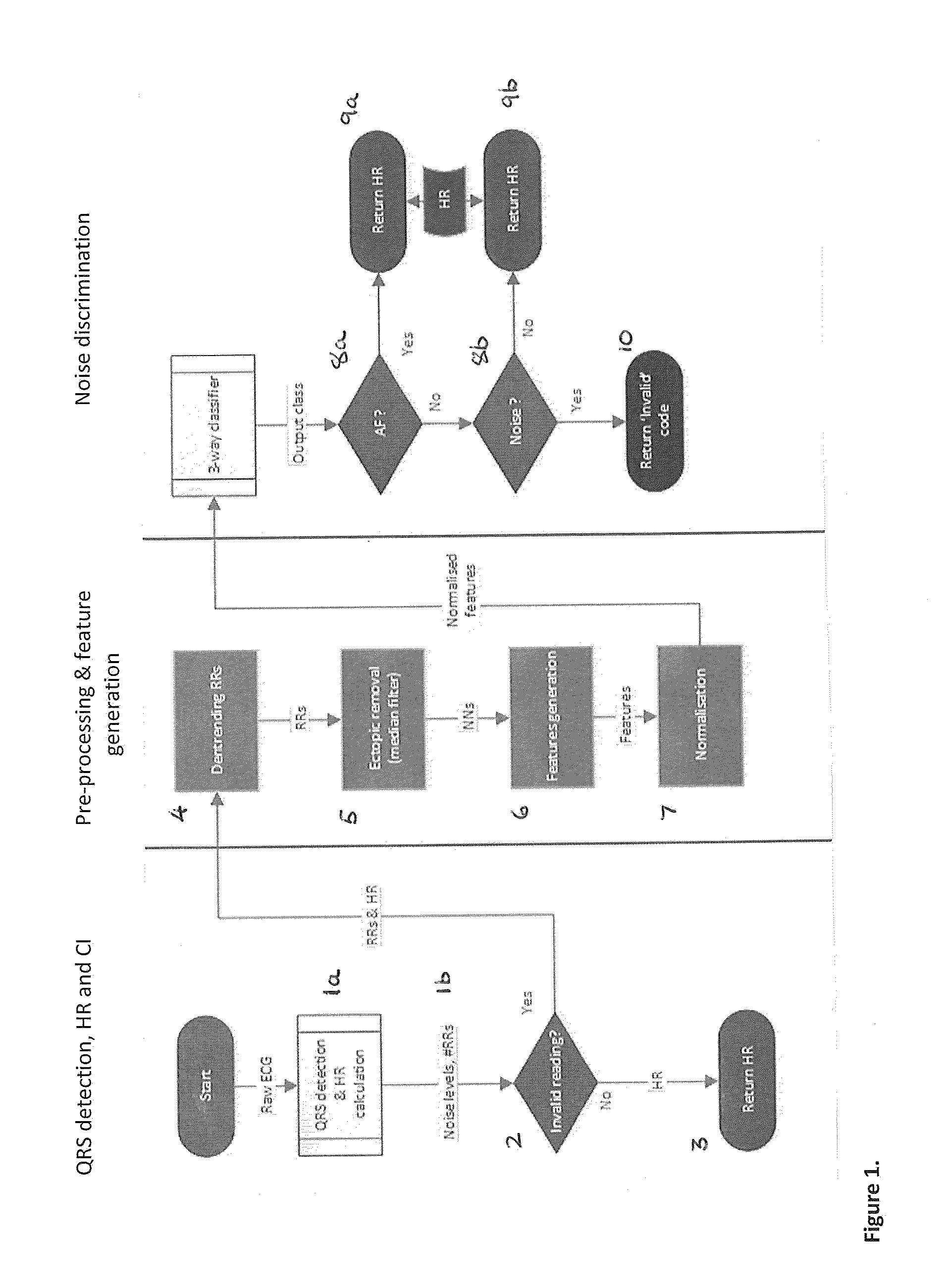
Method for confidence level determination of ambulatory hr algorithm based on a three-way rhythm classifier
ActiveUS20150327781A1Improve monitoring effectLow costElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisEcg signalAmbulatory
A method of determining a confidence level in a heart rate obtained from an ECG signal of a patent comprises determining a heart rate from a segment of an ECG signal, the segment having a pre-determined length, and determining a first confidence level in the determined heart rate. If the first confidence level exceeds a predetermined value, the heart rate is output. Otherwise, the method further comprises determining a set of features from the segment of the ECG signal; and classifying the segment of the ECG signal, based on one or more features selected from the determined set of features and the heart rate, into one of at least three classes: noise, an abnormal sinus rhythm and a normal sinus rhythm.
Owner:SENSIUM HEALTHCARE
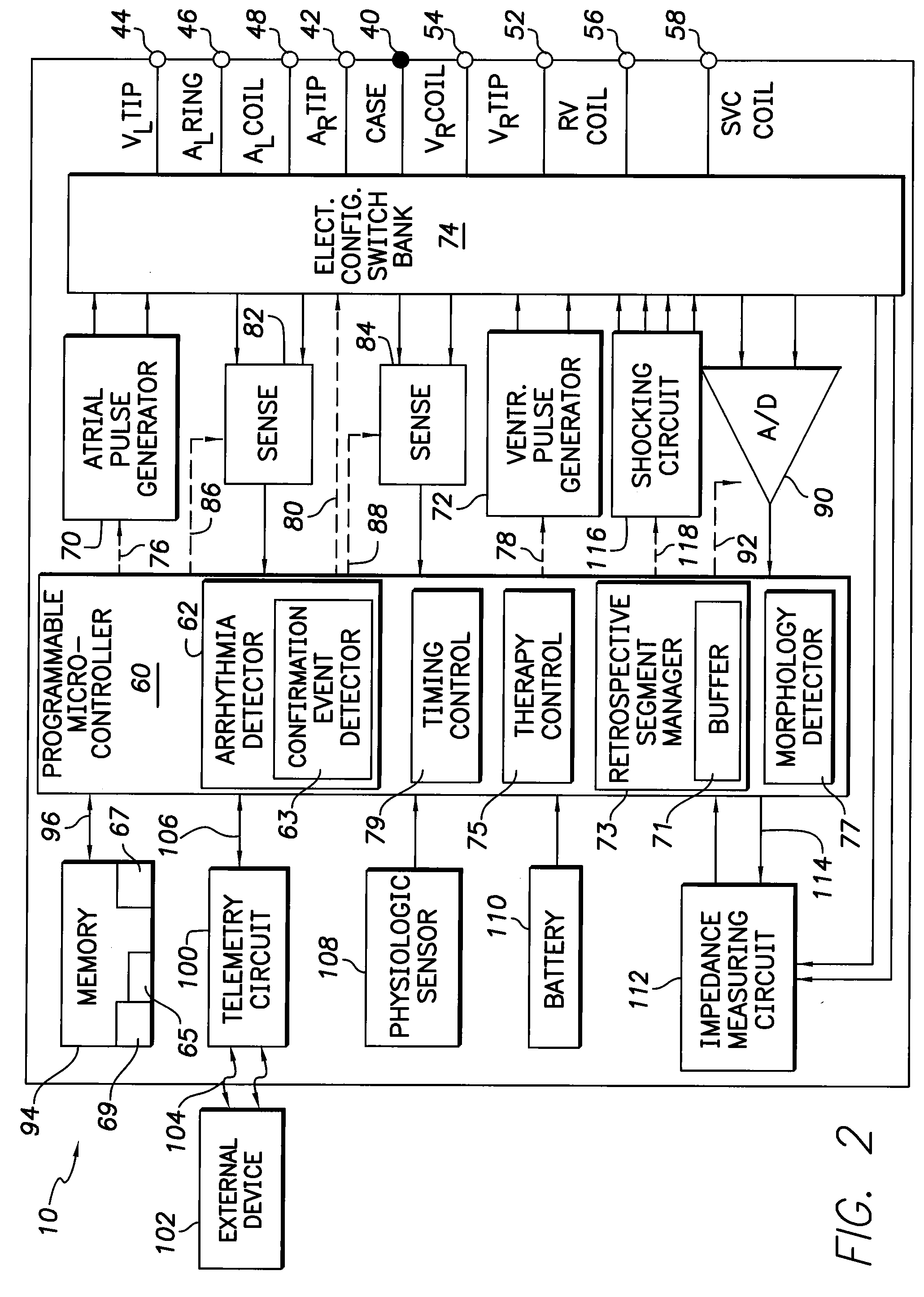
Single chamber implantable medical device for confirming arrhythmia through retrospective cardiac signals
InactiveUS20110125206A1Improve performanceReduce the amplitudeElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsNormal Sinus RhythmSingle chamber
Owner:PACESETTER INC
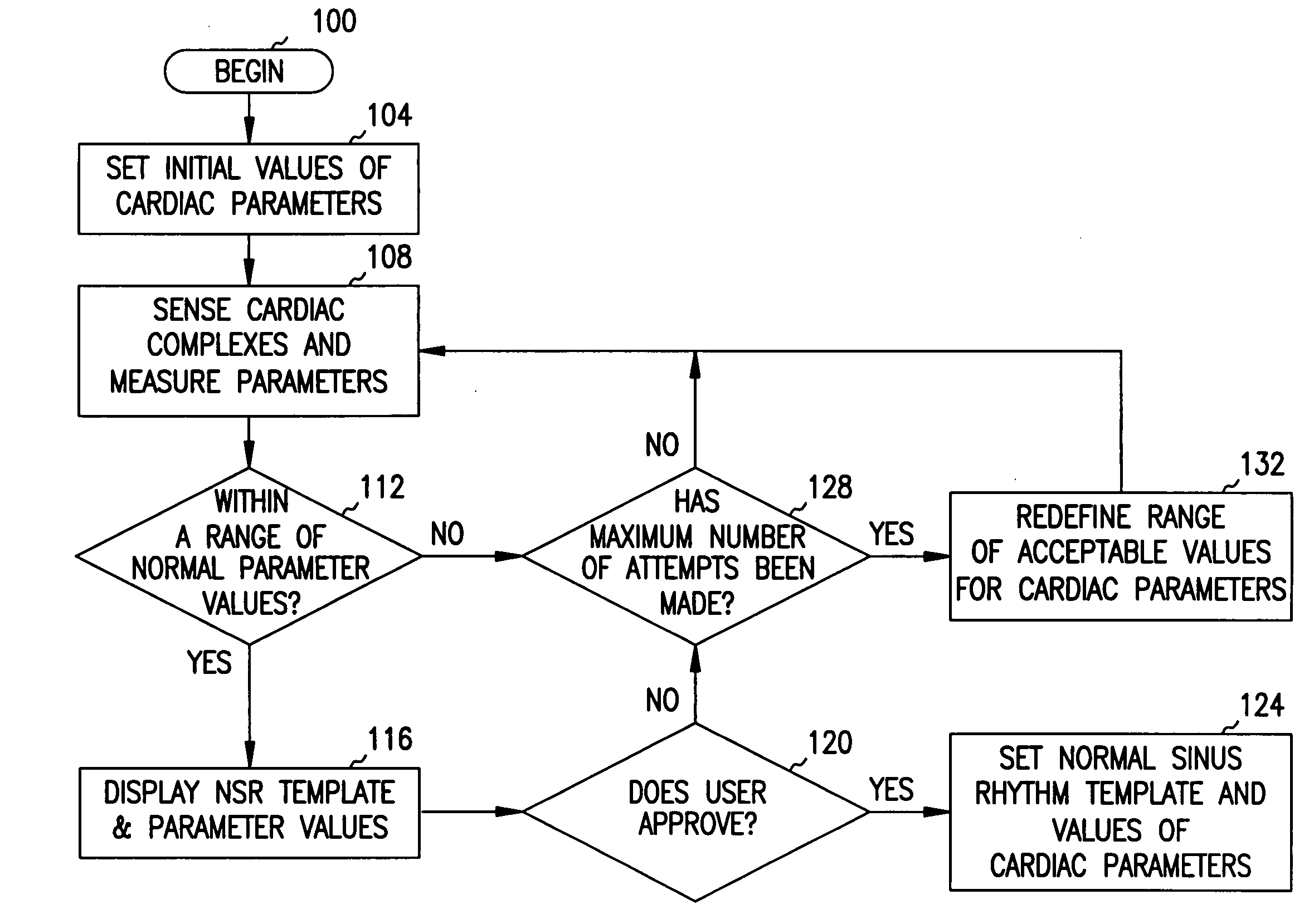
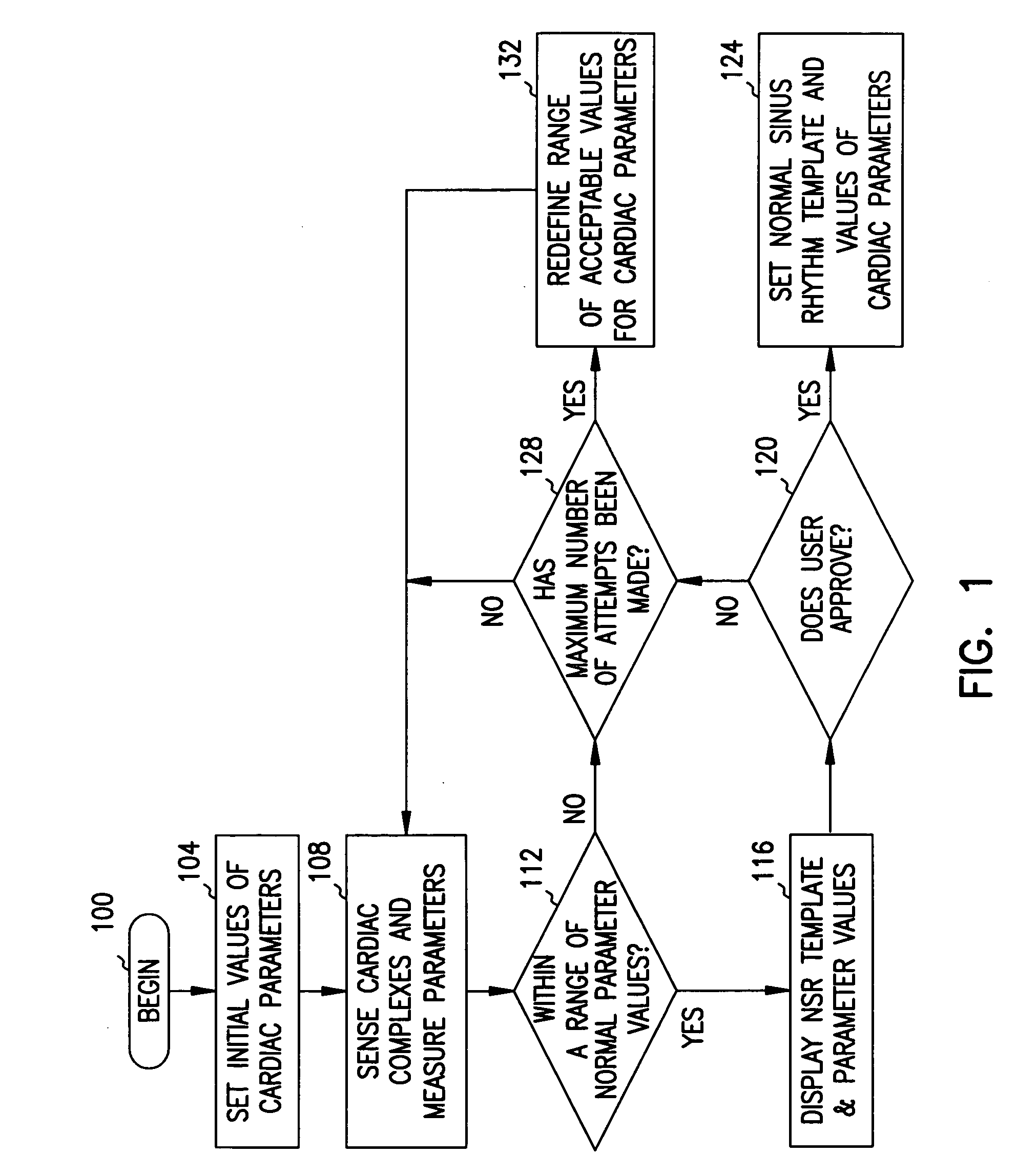
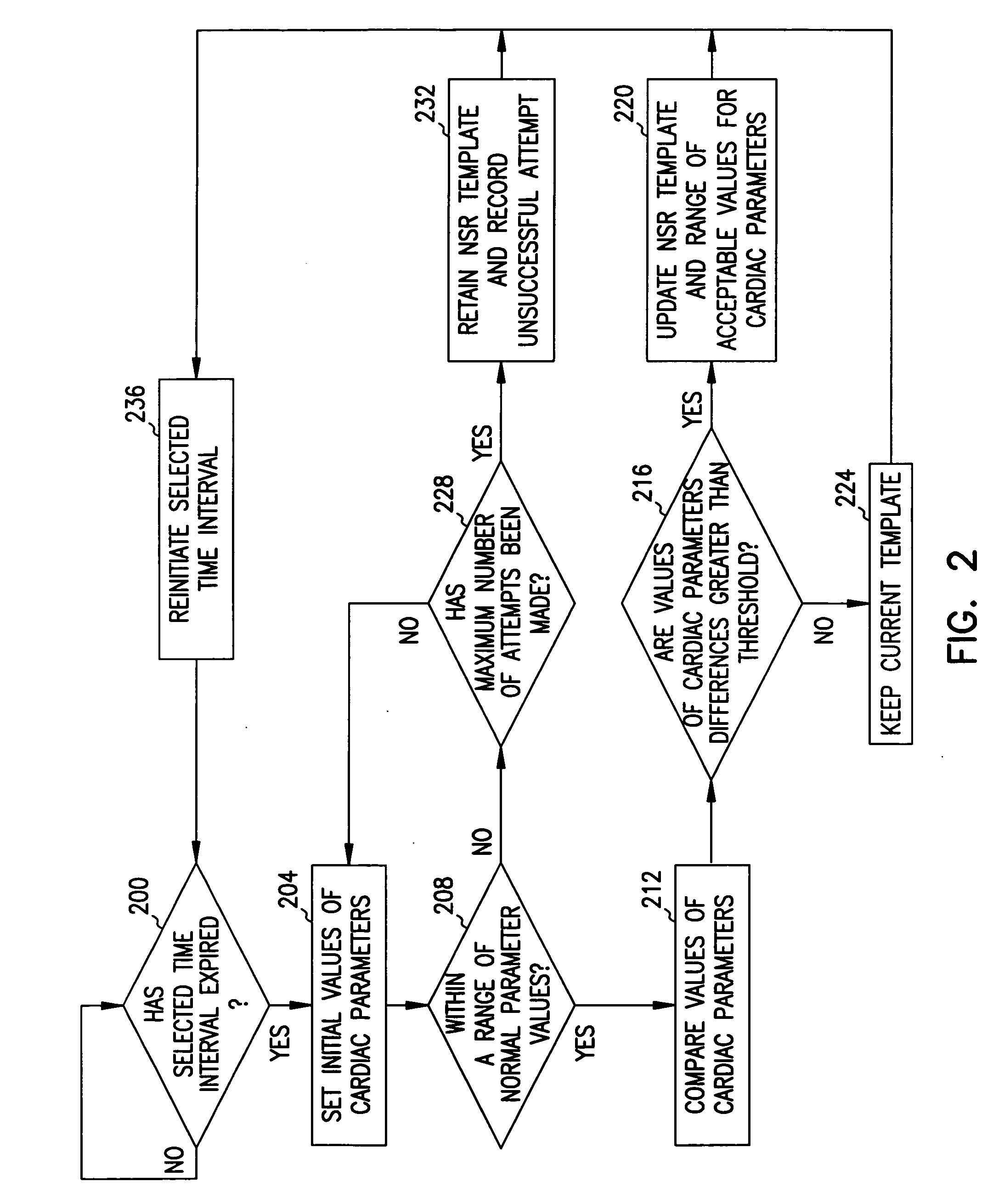
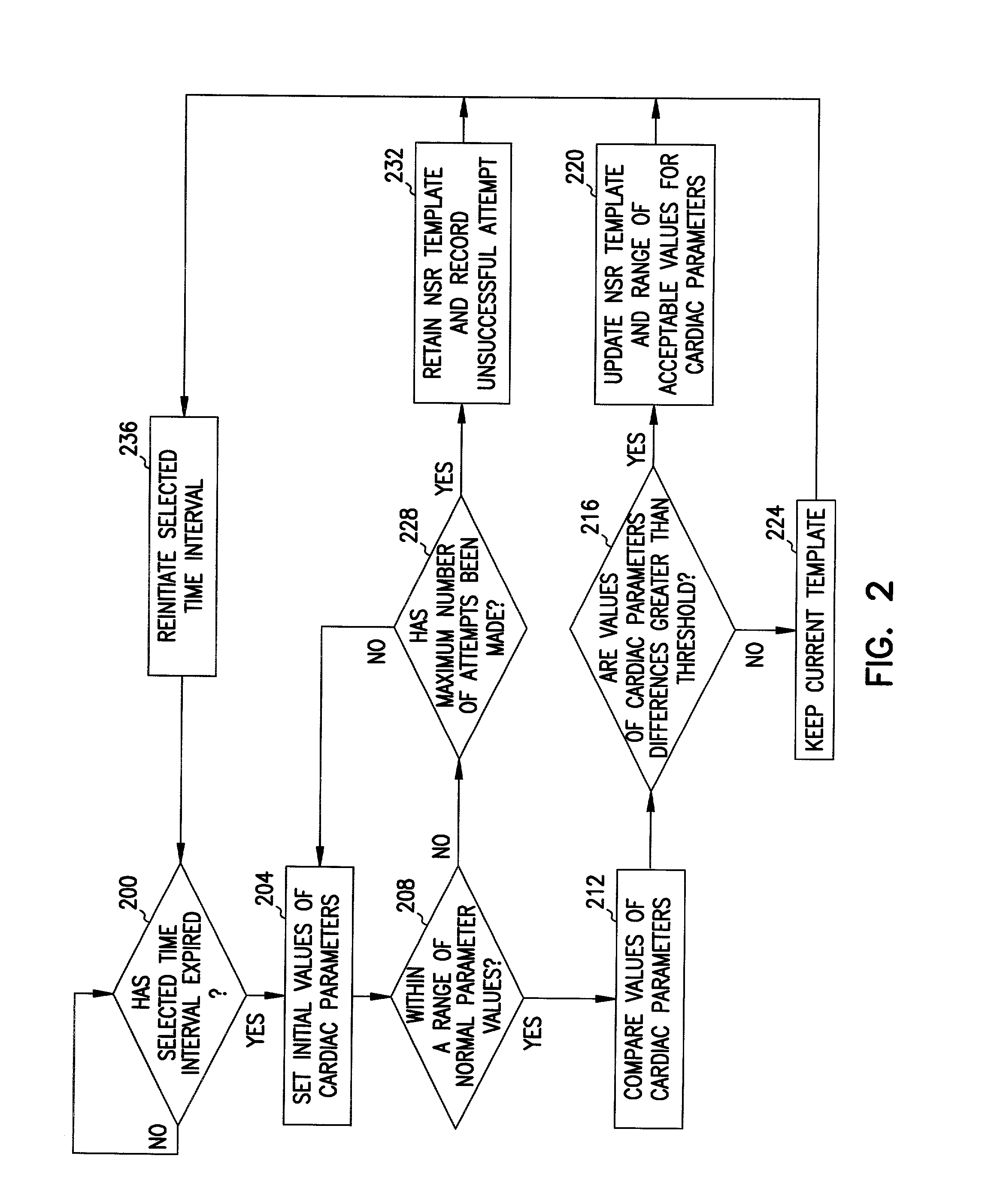
Method and system for verifying the integrity of normal sinus rhythm templates
InactiveUS20060079796A1Classified more accuratelyAccurate classificationElectrocardiographySensorsNormal Sinus RhythmSinus rhythm
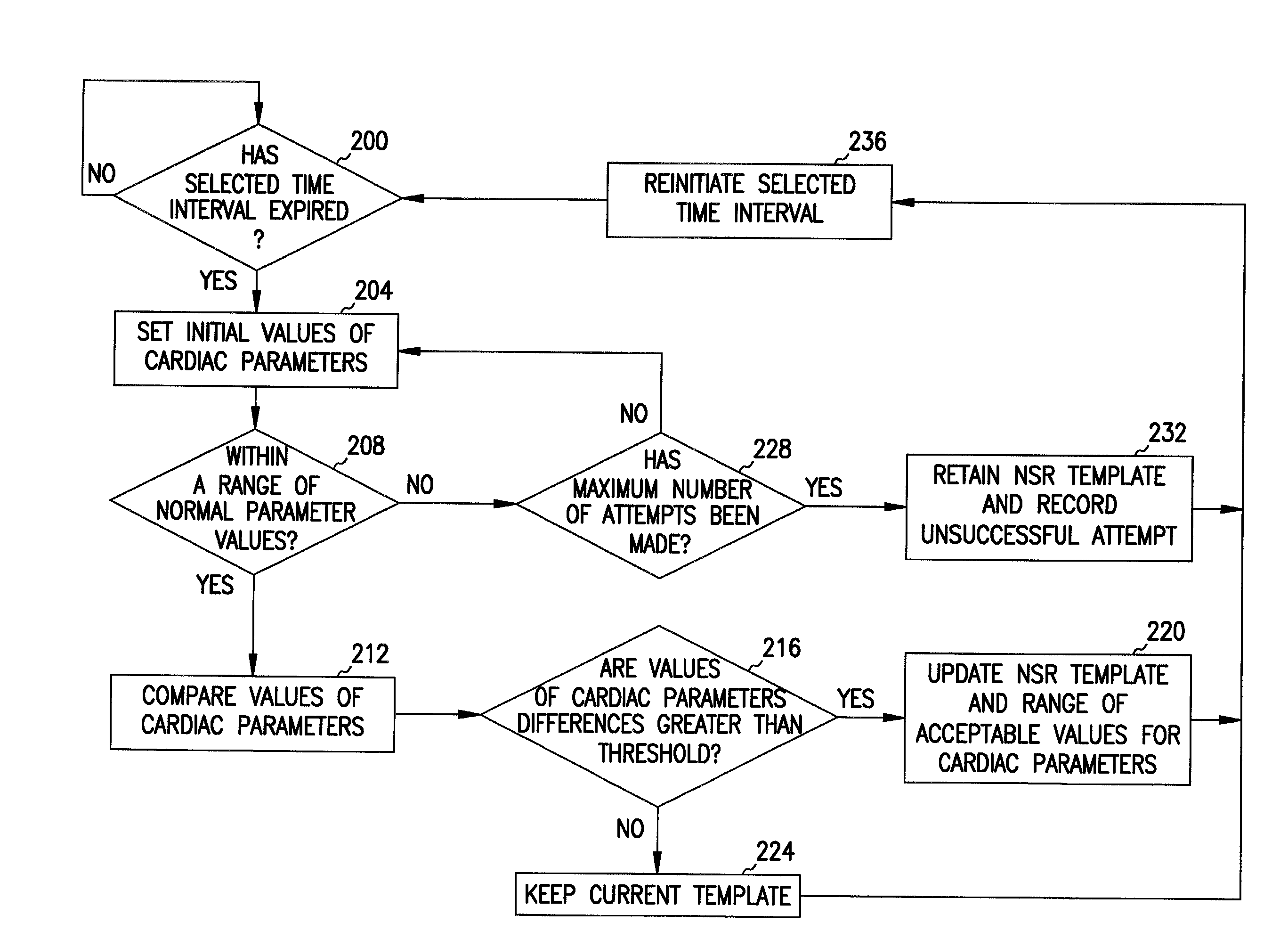
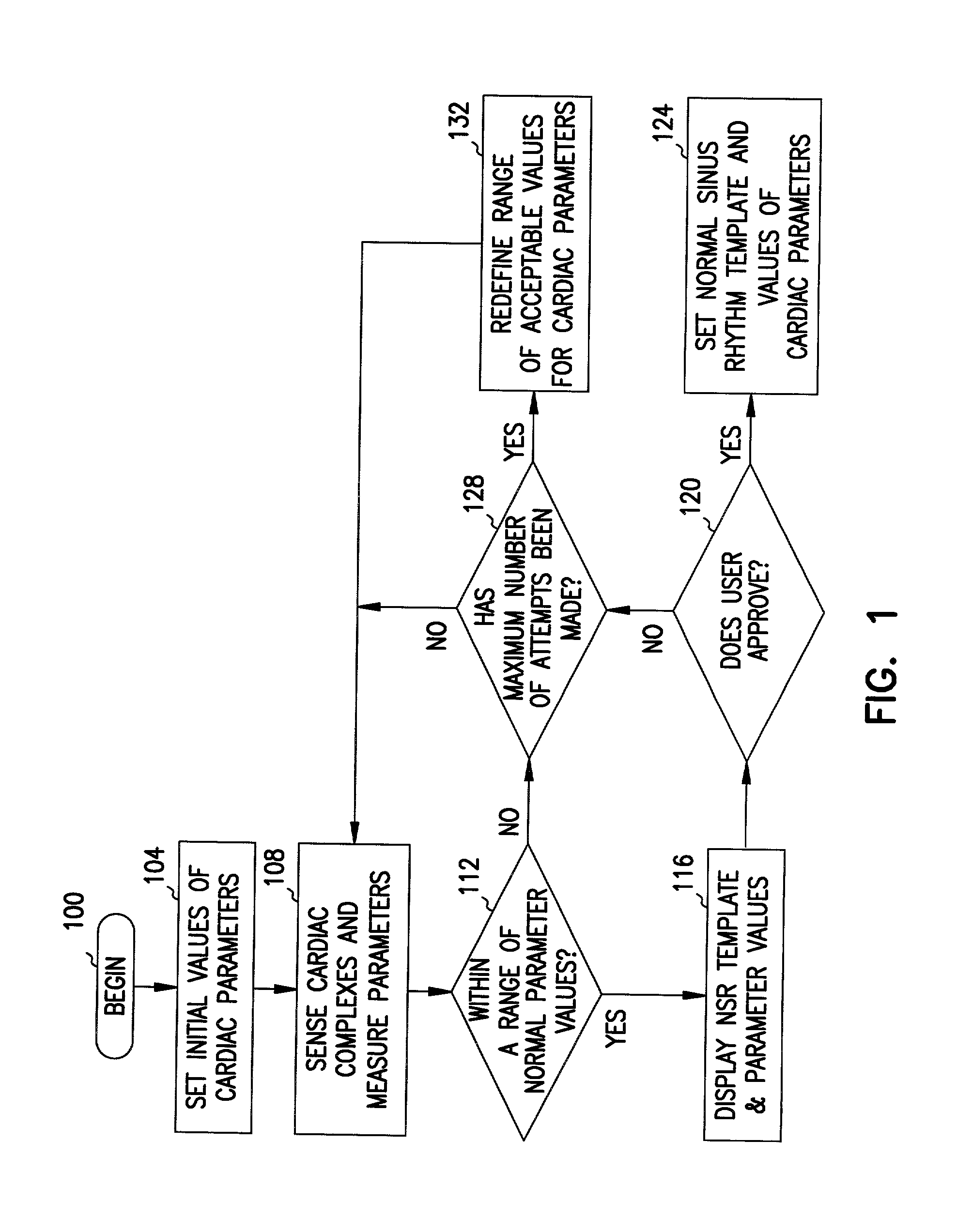
A method and system for verifying the integrity of normal sinus rhythm (NSR) templates and updating the NSR template after selected time intervals. At selected time intervals after establishing a NSR template, cardiac complexes are sensed and values for one or more cardiac parameters are measured. The values of the cardiac parameters are compared to predetermined value ranges for NSR cardiac complexes. When the values of the cardiac parameters fall within the predetermined value ranges, values for the differences between the values of the cardiac parameters for the cardiac complexes and the values for the cardiac parameters of the NSR cardiac complexes are calculated. When the values of the differences are greater than one or more threshold values, the NSR template is updated as a function of the sensed cardiac complexes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
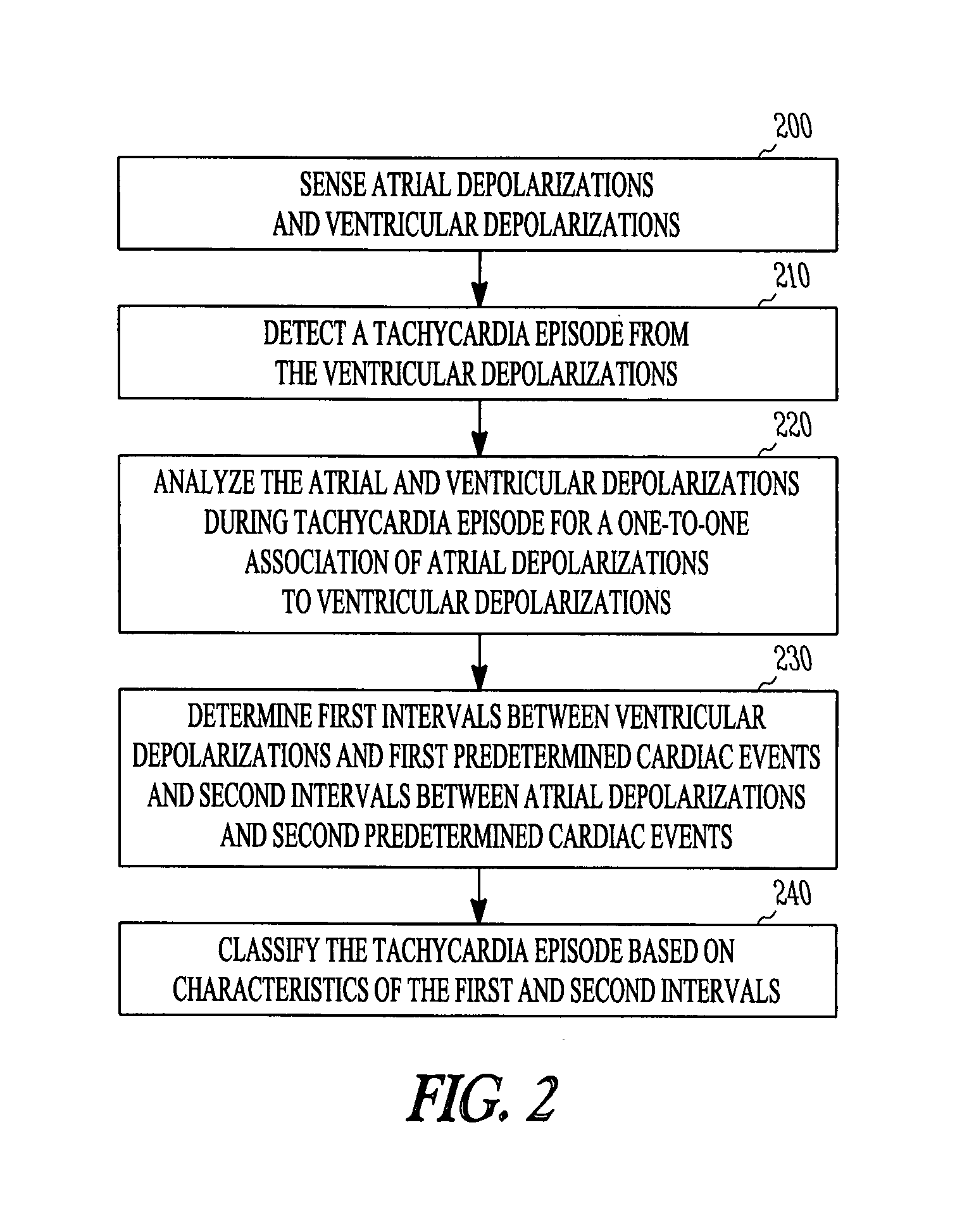
System and method for classifying tachycardia arrhythmias having 1:1 atrial-to-ventricular rhythms
An implantable cardioverter / defibrillator includes a tachycardia detection system that detects one-to-one (1:1) tachycardia, which is a tachycardia with a one-to-one relationship between atrial and ventricular contractions. When the 1:1 tachycardia is detected, the system discriminates ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) based on analysis of a cardiac time interval. Examples of the cardiac time interval include an atrioventricular interval (AVI) and a ventriculoatrial interval (VAI). A template time interval is created during a known normal sinus rhythm. The system measures a tachycardia time interval after detecting the 1:1 tachycardia, and indicates a VT detection if the tachycardia time interval differs from the template time interval by at least a predetermined percentage of the template time interval.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method for realizing automatic recognition of atrial fibrillation on mini dynamic electrocardiogram monitoring equipment
InactiveCN106073755AImprove the detection rateEasy to useDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalHuman body
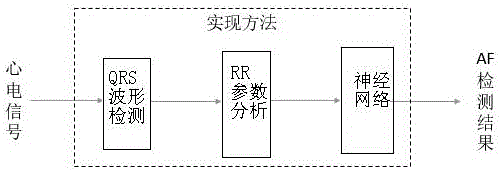
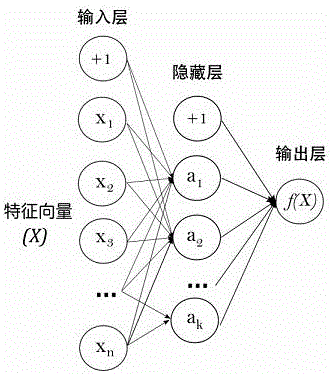
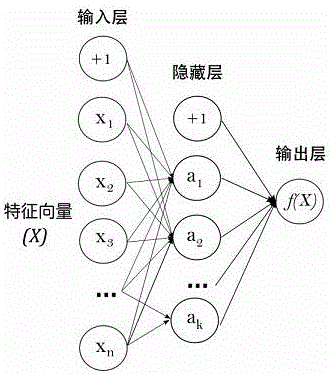
The invention discloses a method for realizing automatic recognition of atrial fibrillation on mini dynamic electrocardiogram monitoring equipment. The method includes: calling an MIT-BIH arrhythmia database, an MIT-BIH normal sinus rhythm database and a long-time atrial fibrillation database as training samples, and introducing an artificial neural network for learning training; setting a weight value for each layer of the artificial neural network, and inputting the training data samples to repeatedly and iteratively correct the weight value of each layer until training errors are less than a certain specified value, through the means, a weight value matrix capable of judging occurrence of atrial fibrillation can be found; utilizing the weight value matrix, and adding the same into an original artificial neural network to build a new artificial neural network; using collected electrocardiosignals of a target human body, processing the electrocardiosignals of the human body, acquiring a target human body feature vector X, and performing prediction operation according to the target human body feature vector X and the new artificial neural network.
Owner:成都信汇聚源科技有限公司
Method and system for verifying the integrity of normal sinus rhythm templates
InactiveUS6996434B2Accurate classificationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyNormal Sinus RhythmCardiology
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events
InactiveUS20060122527A1Reduce in quantityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaNormal Sinus Rhythm
A method and system for discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events. Morphological features points are extracted from normal sinus rhythm (NSR) complexes and used to generate a NSR template. A numerical convolution is performed using the NSR template and the feature points for each sensed NSR to give a NSR filter output. Using a plurality of NSR complexes, a median NSR filter output template is determined, where the median NSR filter output template has a median value for each value in the NSR filter output. The median NSR filter output template is then used during a tachycardia event to distinguish tachycardia events as either ventricular tachycardia events or supraventricular tachycardia events.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Multi-parameter arrhythmia discrimination
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
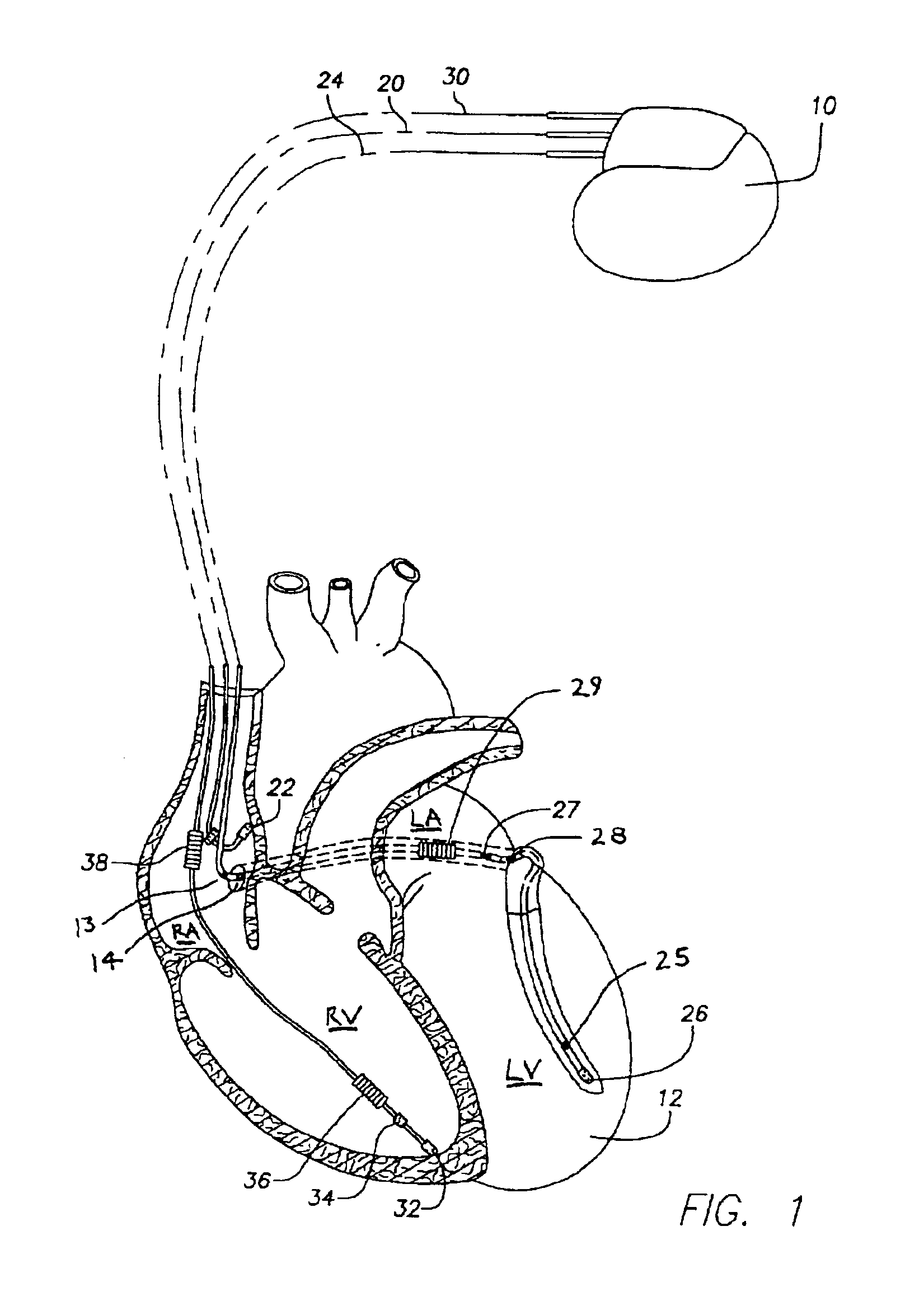
Method and apparatus for discriminating ventricular and supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
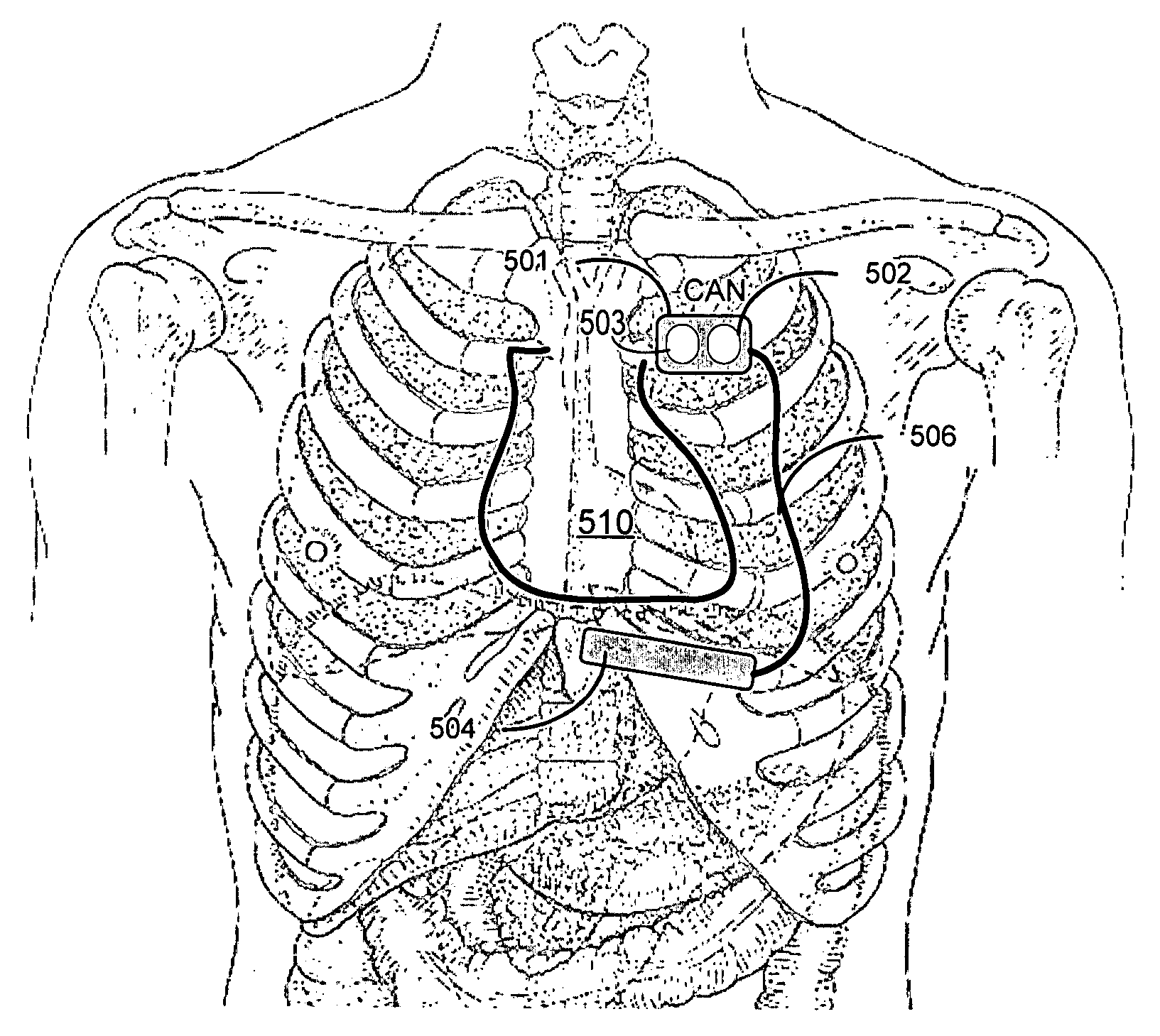
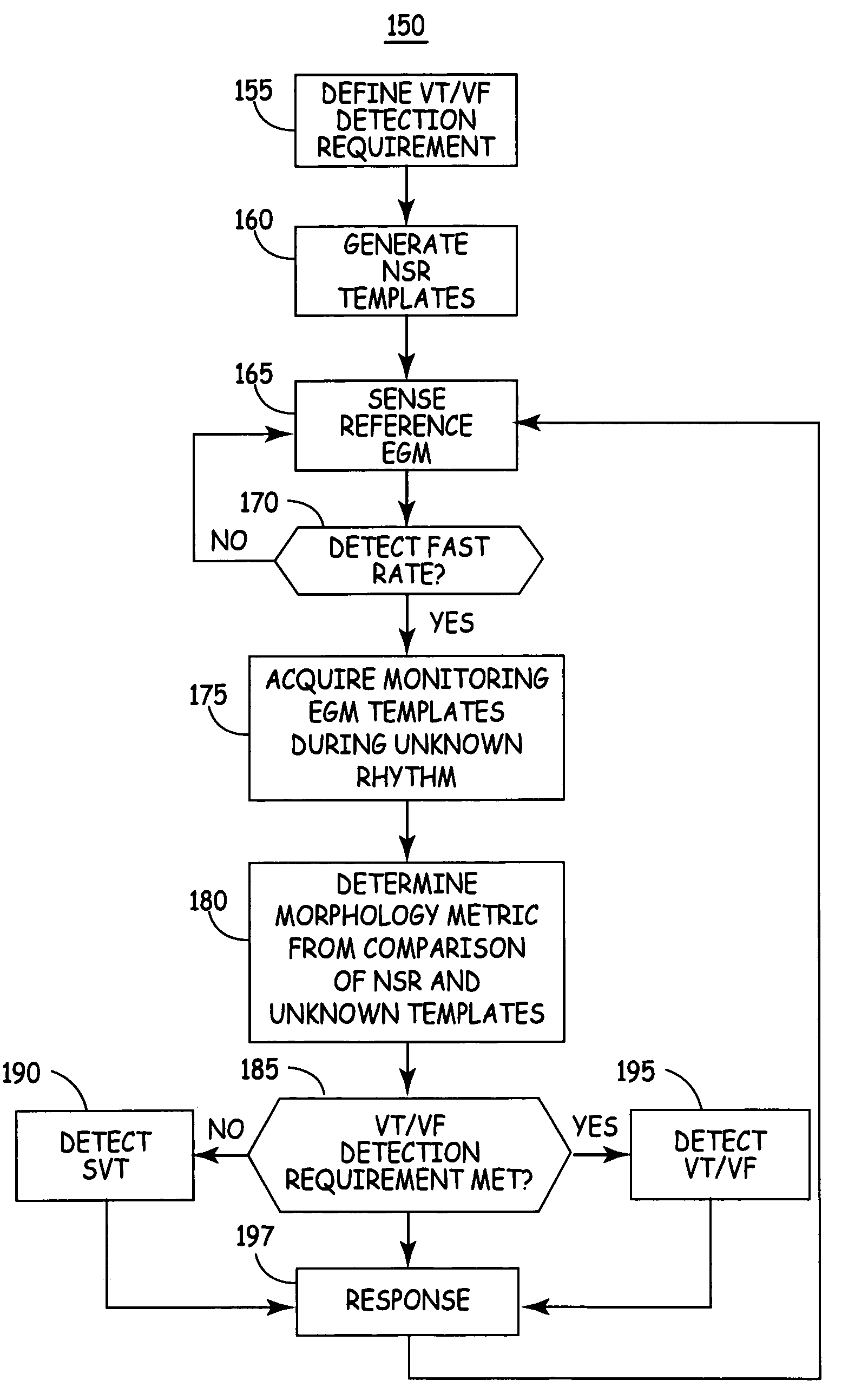
A system and method are provided for discriminating supra-ventricular tachycardia (SVT) from ventricular tachycardia (VT). A monitoring EGM signal is acquired during a sensing window timed according to the time of R-wave detection on a reference EGM signal. A normal sinus rhythm (NSR) template is generated using the monitoring EGM signal during the time-referenced sensing window. During an unknown rhythm, the monitoring EGM signal sensed during the time-referenced sensing window is compared to the NSR template for use in computing a morphology metric. The morphology metric is compared to a VT / VF detection threshold for discriminating SVT from VT / VF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
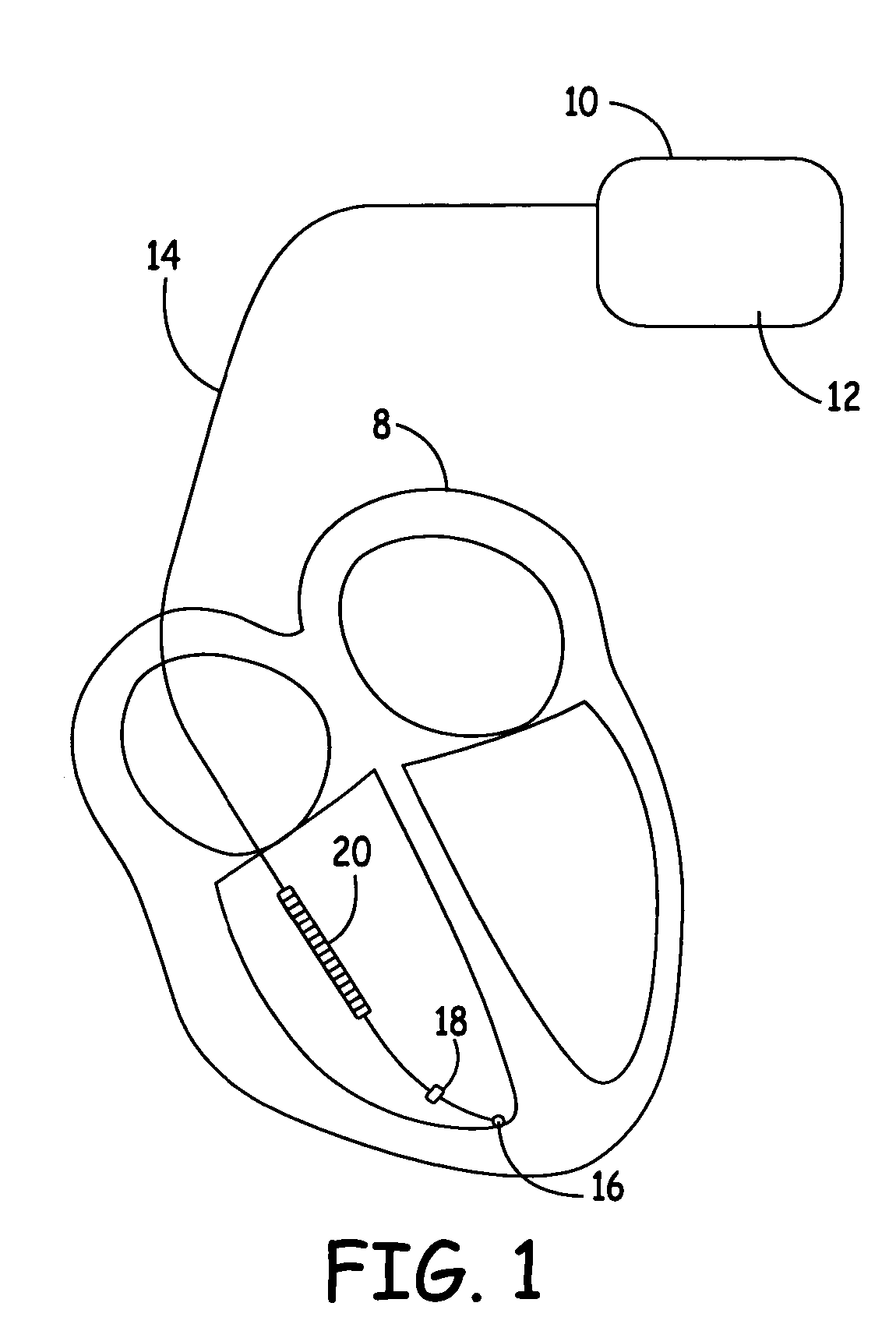
Anti-tachycardia pacing methods and devices
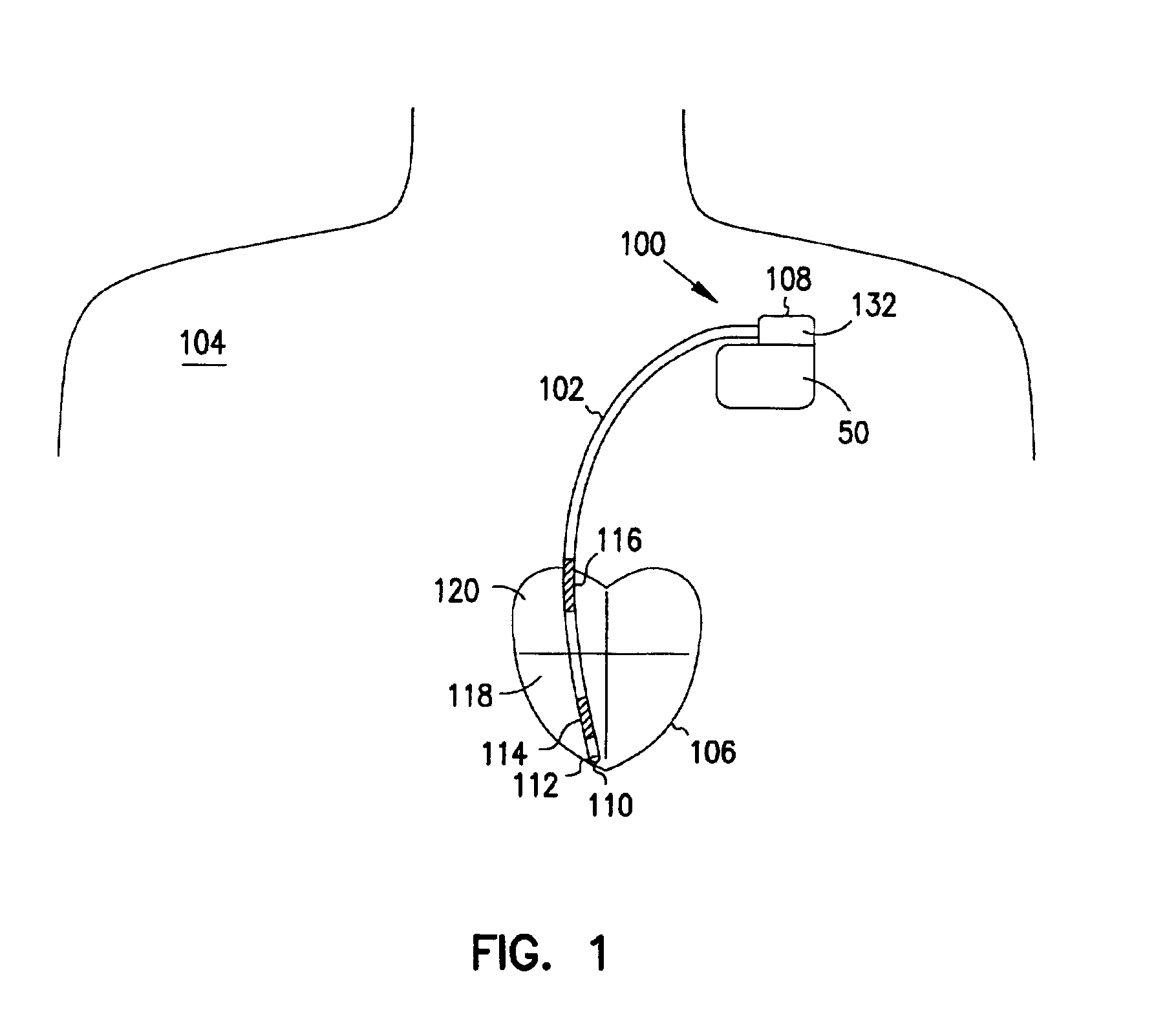
Improved methods and devices perform anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to convert a ventricular tachycardia (VT) to normal sinus rhythm. In one embodiment of the invention bi-ventricular (BV) ATP is employed. In this embodiment the right ventricle and left ventricle of a patient's heart are independently paced based on signals sensed in each chamber.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Pyrrolotriazines as potassium ion channel inhibitors
ActiveUS20140256719A1Treatment effectGood metabolic stabilityBiocideOrganic chemistryPotassium channelIonic Channels
A compound of formula (I)wherein A, R1, R3, and R24 are described herein. The compounds are useful as inhibitors of potassium channel function and in the treatment of arrhythmia, maintaining normal sinus rhythm, IKur-associated disorders, and other disorders mediated by ion channel function.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method for obtaining artificial neural network weighted value matrix for identifying atrial fibrillation
ActiveCN106066933AReal-time automatic detectionSave livesMedical automated diagnosisSpecial data processing applicationsEcg signalNormal Sinus Rhythm
The invention discloses a method for obtaining an artificial neural network weighted value matrix for identifying atrial fibrillation. The method includes the steps of calling an MIT-BIH arrhythmia database, an MIT-BIH normal sinus rhythm database and a long-time atrial fibrillation database as trainning samples, introducing an artificial neural network for learning training, randomly setting the weighted value of each layer of artificial neural network, and inputting training data samples to conduct repeated iteration to correct the weighted value of each layer until the training error is smaller than a designated value. In this way, the weighted value matrix for determining occurrence of atrial fibrillation can be found, the weighted value matrix is added into an original artificial neural network to establish a new artificial neural network, and human electrocardiosignals are processed with the acquired target human electrocardiosignals as data to obtain a target human body characteristic vector X. The prediction operation is carried out according to the target human body characteristic vector X and the new artificial neural network.
Owner:成都信汇聚源科技有限公司
Method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium for electrocardiogram signal detection and classification
ActiveCN110226921AImprove accuracyAbnormal rhythm is accurateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalClassification methods
The invention relates to a method, a device, electronic equipment and a storage medium for electrocardiogram signal detection and classification. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting a signal waveform from an electrocardiogram signal; acquiring a morphological characteristic and a deep characteristic of the signal waveform, wherein the morphological characteristic comprises anyone of a TR wave amplitude difference characteristic, a PR wave quantity ratio characteristic, an ST wave band characteristic and a P wave variation characteristic, and the deep characteristic comprises a depth characteristic and a hierarchy characteristic; inputting the morphological characteristic and the deep characteristic into a classifier; and acquiring a classification result output by theclassifier so as to obtain the signal type of the electrocardiogram signal, wherein the classification result is a result that the classifier performs classification according to the morphological characteristic and the deep characteristic, and the signal type comprises an atrial fibrillation rhythm, a non-atrial fibrillation abnormal rhythm, a normal sinus rhythm and noise. The method can accurately identify various types of abnormal rhythms, avoids the situation that abnormal rhythms of non-atrial fibrillation types such as tachycardia, bradycardia and arrhythmia are classified into atrial fibrillation types in error, and improves the accuracy of classification of electrocardiogram signals.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for obtaining risk predictions of sudden death with weight value matrices of artificial neural network
InactiveCN106021941ATimely measuresLimit detectabilityHealth-index calculationBiological neural network modelsEcg signalNormal Sinus Rhythm
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the weight value matrix of the artificial neural network for sudden death risk prediction. The sudden cardiac death database and the MIT-BIH normal sinus rhythm database are constructed into training data samples and cross-validation samples, and each layer of the artificial neural network is randomly set first. Input training data samples to iteratively correct the weight values of each layer until the training error is less than a specified value, find the weight value matrix that can predict the risk of sudden death, and then use the weight value matrix to add the weight value matrix to the original artificial neural network to construct a new model. The artificial neural network, and then use the collected target human ECG signal as data, process the human ECG signal to obtain the target human feature vector X, and perform prediction calculations according to the target human feature vector X and the new artificial neural network, and finally Get the predicted value.
Owner:成都信汇聚源科技有限公司
Discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events
InactiveUS20110034817A1Reduce in quantityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaNormal Sinus Rhythm
A method and system for discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events. Morphological features points are extracted from normal sinus rhythm (NSR) complexes and used to generate a NSR template. A numerical convolution is performed using the NSR template and the feature points for each sensed NSR to give a NSR filter output. Using a plurality of NSR complexes, a median NSR filter output template is determined, where the median NSR filter output template has a median value for each value in the NSR filter output. The median NSR filter output template is then used during a tachycardia event to distinguish tachycardia events as either ventricular tachycardia events or supraventricular tachycardia events.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Multi-parameter arrhythmia discrimination
An arrhythmia discrimination device and method involves receiving electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals at subcutaneous locations. Both the electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals are used to discriminate between normal sinus rhythm and an arrhythmia. An arrhythmia may be detected using electrocardiogram signals, and verified using the non-electrophysiologic signals. A detection window may be initiated in response to receiving the electrocardiogram signal, and used to determine whether the non-electrophysiologic signal is received at a time falling within the detection window. Heart rates may be computed based on both the electrocardiogram signals and non-electrophysiologic signals. The rates may be used to discriminate between normal sinus rhythm and an arrhythmia, and used to determine absence of an arrhythmia.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method for realizing sudden death risk prediction on mini dynamic electrocardiogram monitoring equipment
InactiveCN106073765AAvoid major dangerAchieving sudden death predictionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFeature vectorHuman body
The invention discloses a method for realizing sudden death risk prediction on mini dynamic electrocardiogram monitoring equipment. The method includes: building a sudden cardiac death data base and an MIT-BIH normal sinus rhythm database into a training data sample and a cross validation sample; randomly setting a weight value for each layer of an artificial neural network, inputting the training data sample to repeatedly and iteratively correct the weight value of each layer until training errors are less than a certain specified value, and finding a weight value matrix capable of predicting sudden death risk; utilizing the weight value matrix, and adding the same into an original artificial neural network to build a new artificial neural network; using collected electrocardiosignals of a target human body, processing the electrocardiosignals of the human body, acquiring a target human body feature vector X, and performing prediction operation according to the target human body feature vector X and the new artificial neural network to finally acquire a prediction value.
Owner:成都信汇聚源科技有限公司
System And Method For Determining The Origin Of A Sensed Beat
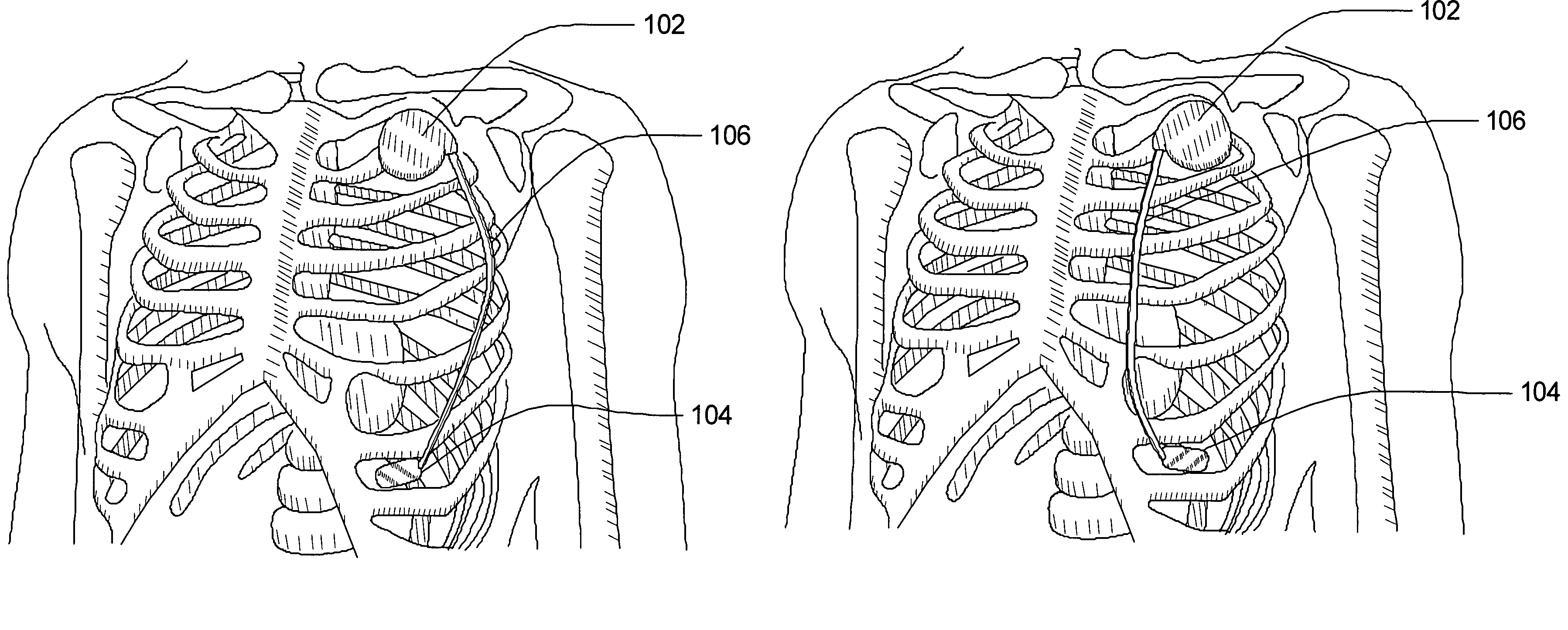
InactiveUS20080281369A1Improve heart functionElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeNormal Sinus Rhythm
A method for monitoring a biological cardiac pacemaker is provided. The method may include stimulating a heart at a region selected for implantation of a biological pacemaker and sensing at least one electrical signal indicative of a cardiac depolarization originating in the region selected for implantation of the biological pacemaker. The method may further include sensing at least one subsequent electrical signal produced by the heart and determining if the subsequent electrical signal originated in the region selected for the biological pacemaker or another region of the heart. In an alternative embodiment, the method may include determining a template time difference between two points on cardiac complexes sensed in two or more different cardiac locations during normal sinus rhythm. The method may further include determining a time difference between two points on a subsequent cardiac complex sensed in two or more different cardiac locations. The time differences may be compared to determine if the subsequently-sensed cardiac complex originates in a left ventricular biological pacemaker site or in another cardiac site.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
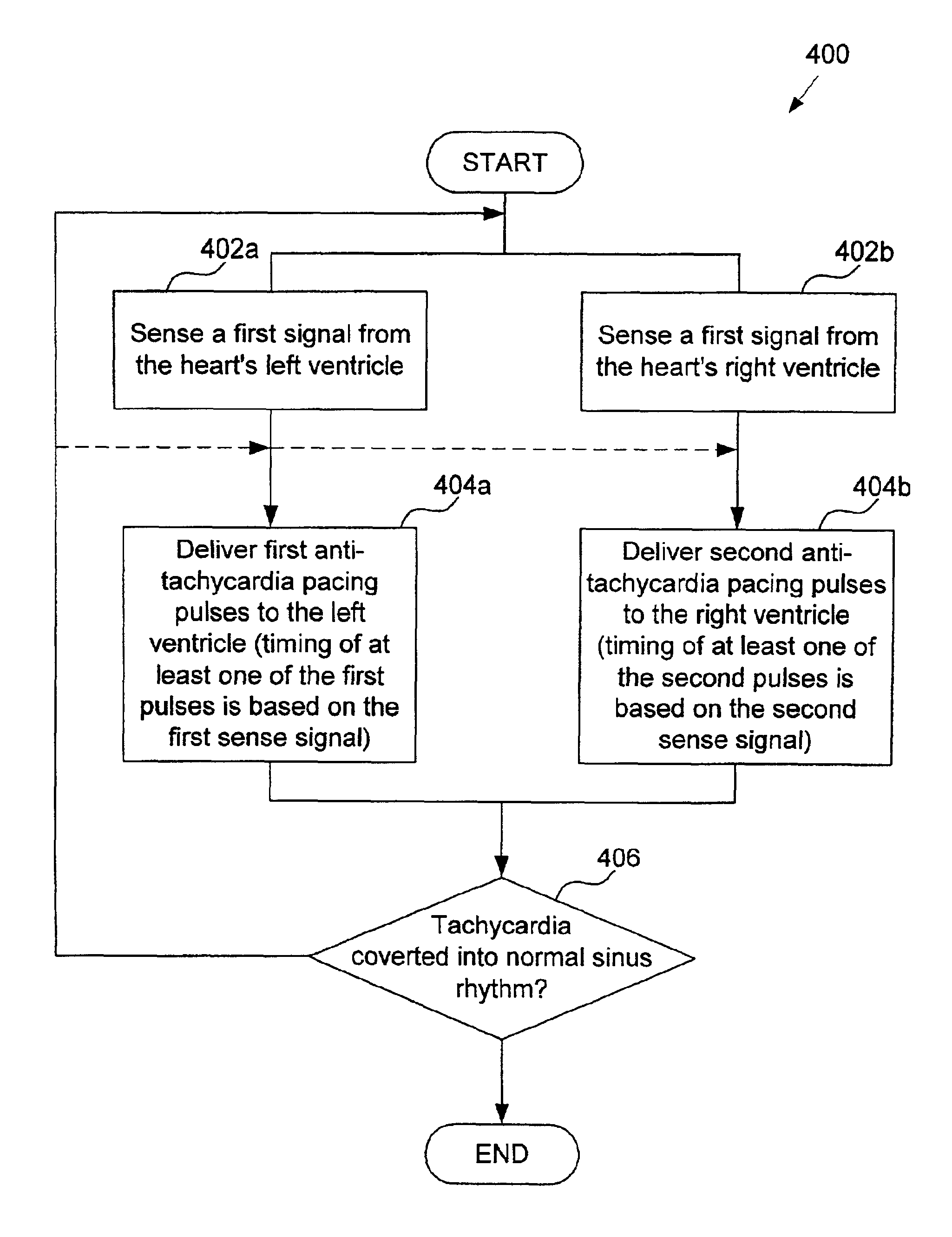
Anti-tachycardia pacing method and apparatus for multi-chamber pacing
Improved methods and devices perform tachycardia detection and anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to convert a tachycardia (e.g., VT or AT) to normal sinus rhythm. According to one embodiment, an anti-tachycardia pacing method includes sensing, during sinus rhythm, first and second cardiac signals at first and second sites, respectively, in a patient's heart. The first and second sites include left and right ventricles or left and right atria, for example. The method further includes sensing third and fourth cardiac signals at the first and second sites, respectively, during a tachycardia (e.g., ventricular tachycardia or atrial tachycardia). The cardiac signals are processed to provide respective values. One or more anti-tachycardia pacing pulses are delivered at the site closest to the reentrant circuit based on a comparison of a first ratio of the first and third values and a second ratio of the second and fourth values. Unipolar sensing of the cardiac signals may be employed by, for example, shorting together pairs of electrodes implanted at each site.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Improved electrocardiosignal quick clustering analysis method
InactiveCN110367969AAvoid the impact of excessive memory usageRun fastDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalMultiple abnormalities
The invention relates to an improved electrocardiosignal quick clustering analysis method. The method includes steps: windowing electrocardiosignal, and preprocessing data in a window to remove interference; capturing a heart beat fragment from the preprocessed data, and performing time domain or frequency domain processing to obtain a new signal sequence; calculating a similarity coefficient of the sequence, comparing with a threshold to further perform heart beat classification, and extracting an average template of each type; moving the window to a next electrocardiosignal section, and repeating the process until the whole electrocardiosignal clustering is completed; subjecting the average templates obtained in each window to secondary clustering to obtain a final heart beat type and the heart beat quantity and the average template of the corresponding type. The method is suitable for short-term or long-term electrocardiosignals and also suitable for single-lead or multi-lead electrocardiosignals and can be used for electrocardiosignal quick clustering of normal sinus rhythm, single abnormal rhythm or various abnormal rhythms. The method can be popularized in electrocardiosignalactivation analysis and relevant quantitative research.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
System and methods for the selective updating of heart signal parameter time series
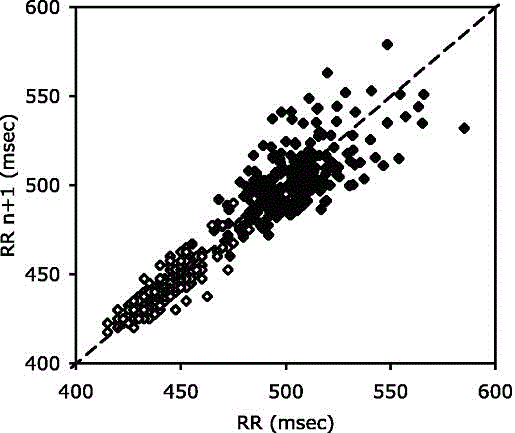
A heart rate monitor is disclosed. The monitor generates an ST deviation time series by employing a recursive filter that is preferably an exponential average filter whose output is a weighted sum of the then existing ST time series value and current ST deviation values of analyzable beats, seats are detected in segments of data. ST deviation is measured for analyzable beats. The ST deviation time series is updated only if certain criteria are met. A first criterion for updating the time series is that at least half of the beats within a segment must be normal sinus rhythm beats: A second criterion for updating the time series is that (i) the average RR interval of the segment is between¾ and 1.5 times the average RR interval of the previous segment; or (ii) both (a) the number of abnormal beats in the current segment is less than 2, and (b) the number of premature ventricular contractions within the current segment is less than 2.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
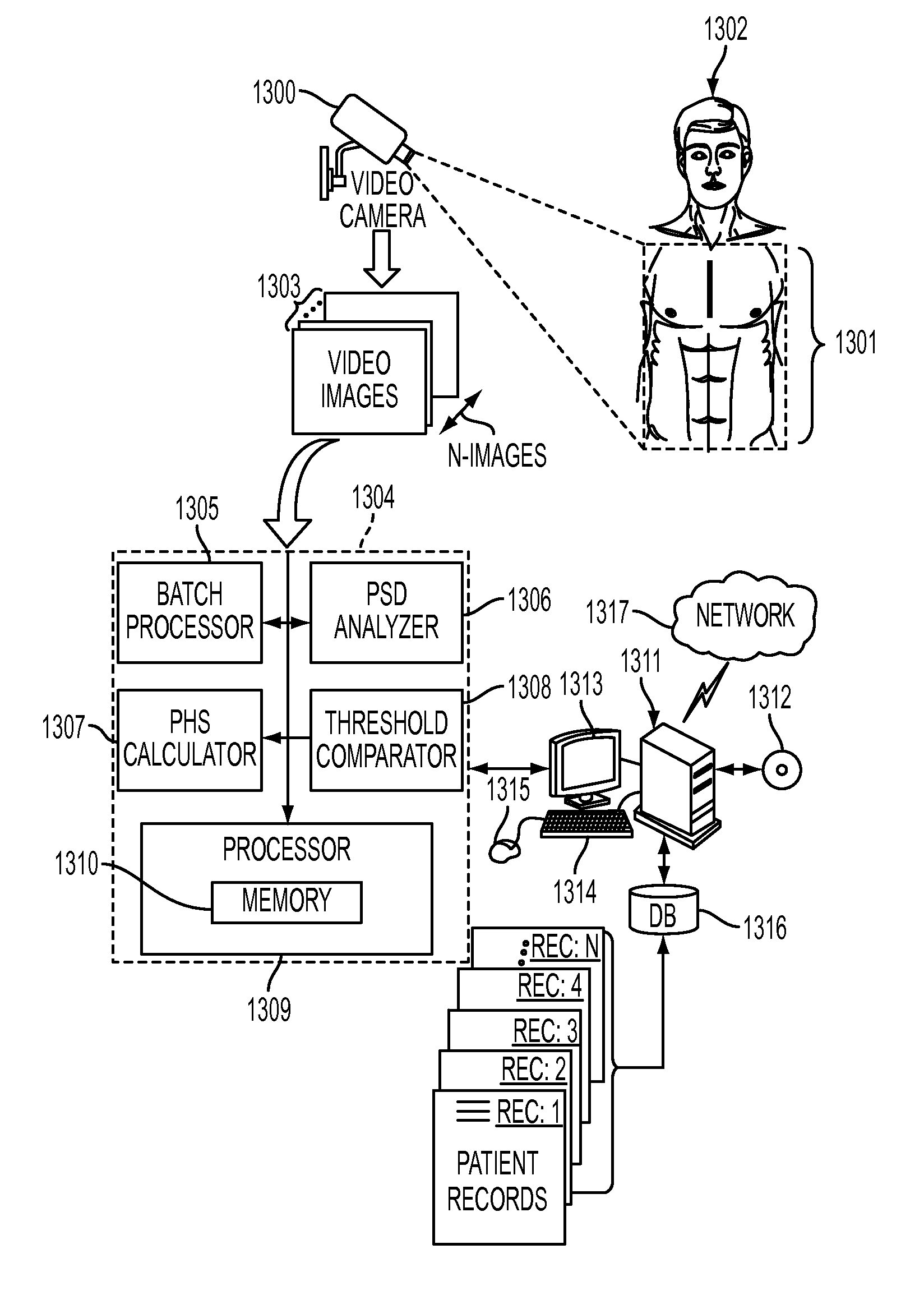
Discriminating between atrial fibrillation and sinus rhythm in physiological signals obtained from video
ActiveUS20150272456A1Effective toolEasy to identifyCatheterSensorsDiscrimination thresholdNormal Sinus Rhythm
What is disclosed is a system and method for determining whether a subject is in atrial fibrillation. A video is received of a region of exposed skin of a subject. The video is acquired of a region where a videoplethysmographic (VPG) signal can be registered by at least one imaging channel of a video imaging device. For each batch of image frames, pixels associated with the region of exposed skin are isolated and processed to obtain a time-series signal. A VPG signal is extracted from the time-series signal. The power spectral density (PSD) is computed across all frequencies within the VPG signal. A pulse harmonic strength (PHS) is calculated for this VPG signal. The pulse harmonic strength is compared to a discrimination threshold, defined herein. A determination is made whether the subject in the video is in atrial fibrillation or in normal sinus rhythm.
Owner:XEROX CORP
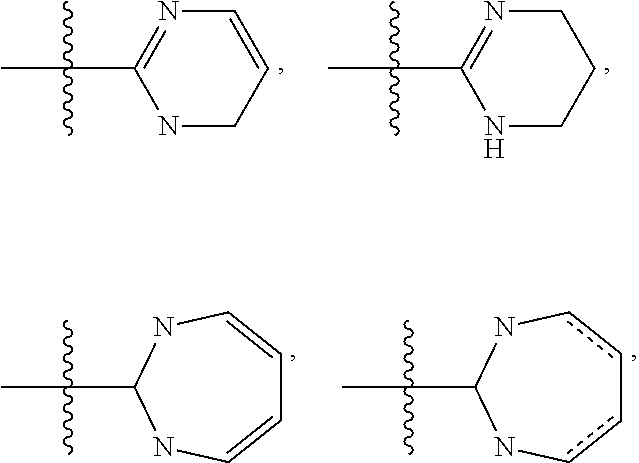
Pyrrolotriazines as potassium ion channel inhibitors
ActiveUS9050345B2Good metabolic stabilityProlong half-life in vivoOrganic chemistryCardiovascular disorderPotassium channelIonic Channels
A compound of formula (I)wherein A, R1, R3, and R24 are described herein. The compounds are useful as inhibitors of potassium channel function and in the treatment of arrhythmia, maintaining normal sinus rhythm, IKur-associated disorders, and other disorders mediated by ion channel function.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Methods of using domperidone to terminate acute episodes of cardiac arrhythmia, to restore normal sinus rhythm or heart rate, to prevent recurrence of cardiac arrhythmia and to maintain normal sinus rhythm or heart rate in mammals
InactiveUS20090143434A1Prevent relapseRestoring normal sinus rhythm or heart rateBiocideAnimal repellantsMetaboliteNormal Sinus Rhythm
Disclosed are methods of terminating acute episodes of cardiac arrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular fibrillation, in a mammal, such as a human, by administering to that mammal an amount of domperidone, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, derivative or metabolite thereof, effective to terminate an acute episode of cardiac arrhythmia and / or restore normal sinus rhythm or heart rate. Also disclosed are methods of maintaining normal sinus rhythm or heart rate in a mammal, such as a human, and preventing a recurrence of an episode of cardiac arrhythmia in a mammal, by administering an amount of domperidone, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, derivative or metabolite thereof, effective to maintain normal sinus rhythm or heart rate in a mammal that has experienced at least one prior episode of cardiac arrhythmia. Pharmaceutical compositions for use in these methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CHANTEST +1
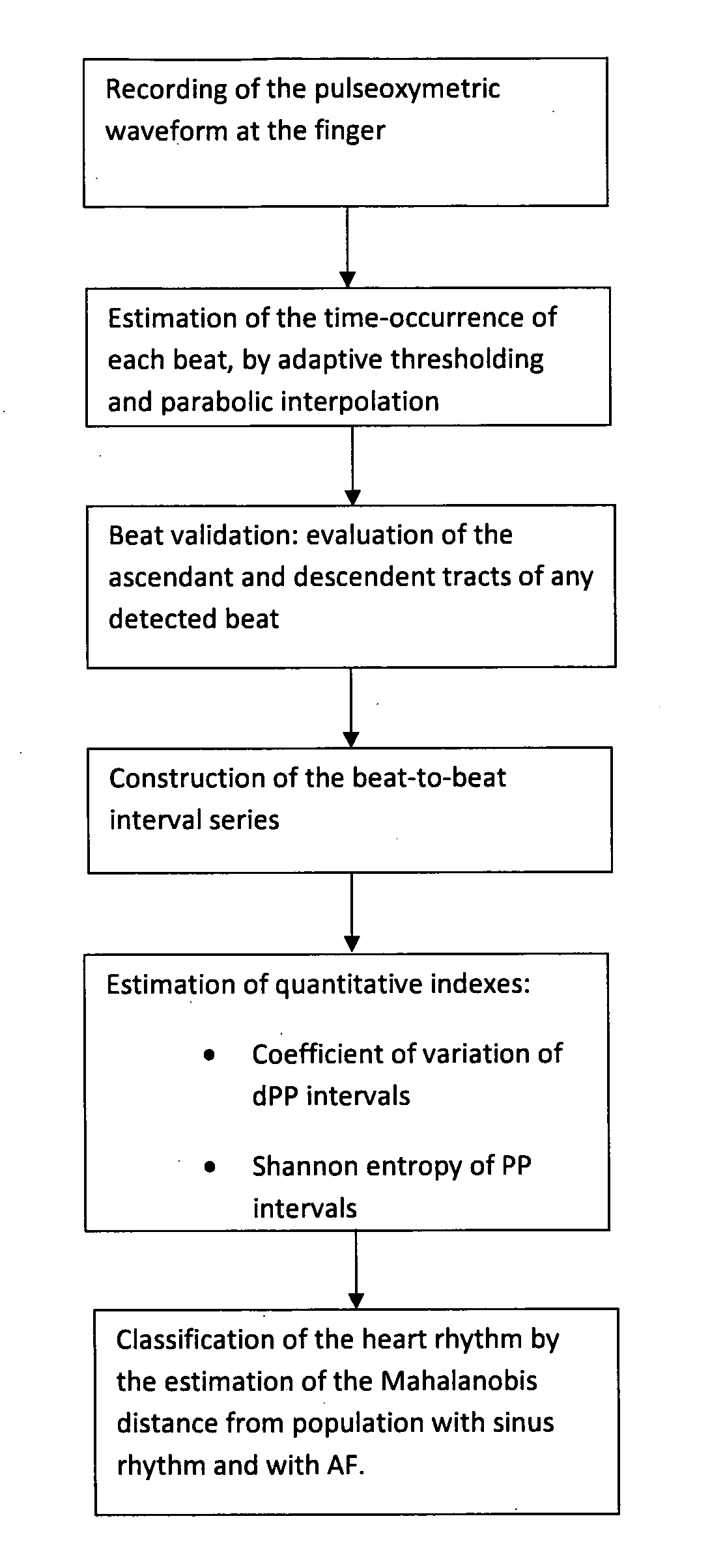
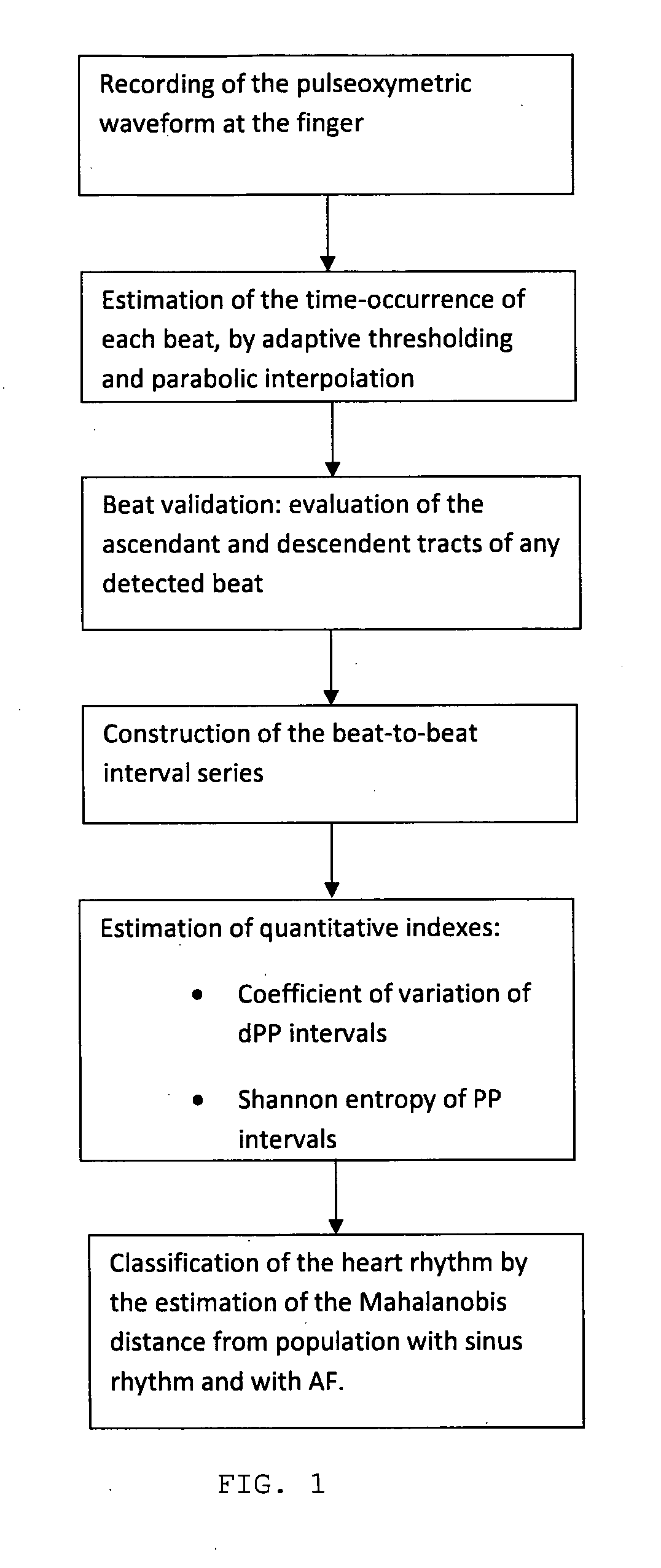
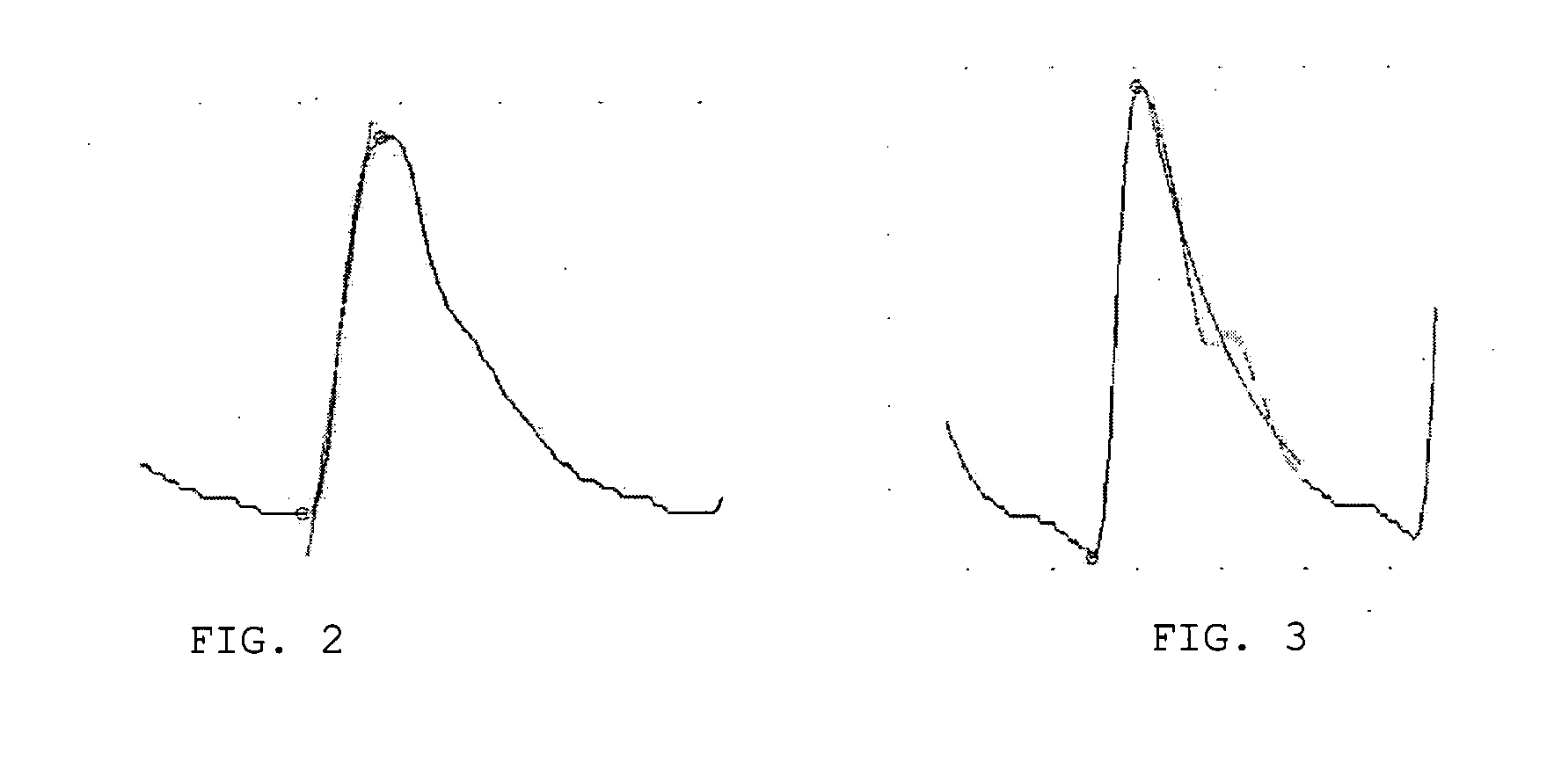
Portable pulseoximeter for a direct and immediate automated evaluation of the cardiac rhythm (regularity) and related method
ActiveUS20130102864A1Medical automated diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringBlood oxygenationPulse oximetry
A method and system of patient monitoring, the system performs short term acquisition of the plethysmographic waveform of a patient from a portable blood oxygenation level monitoring device and establishes whether the patient has an episode of Atrial Fibrillation (AF) or has a Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) or any other not-specific rhythm irregularity. Such classification is implemented directly in the device, suitable for at home use, and the result of the classification is displayed automatically using a three-state, traffic-light indicator.
Owner:M I R SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com