Patents
Literature
636 results about "Heart atrium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
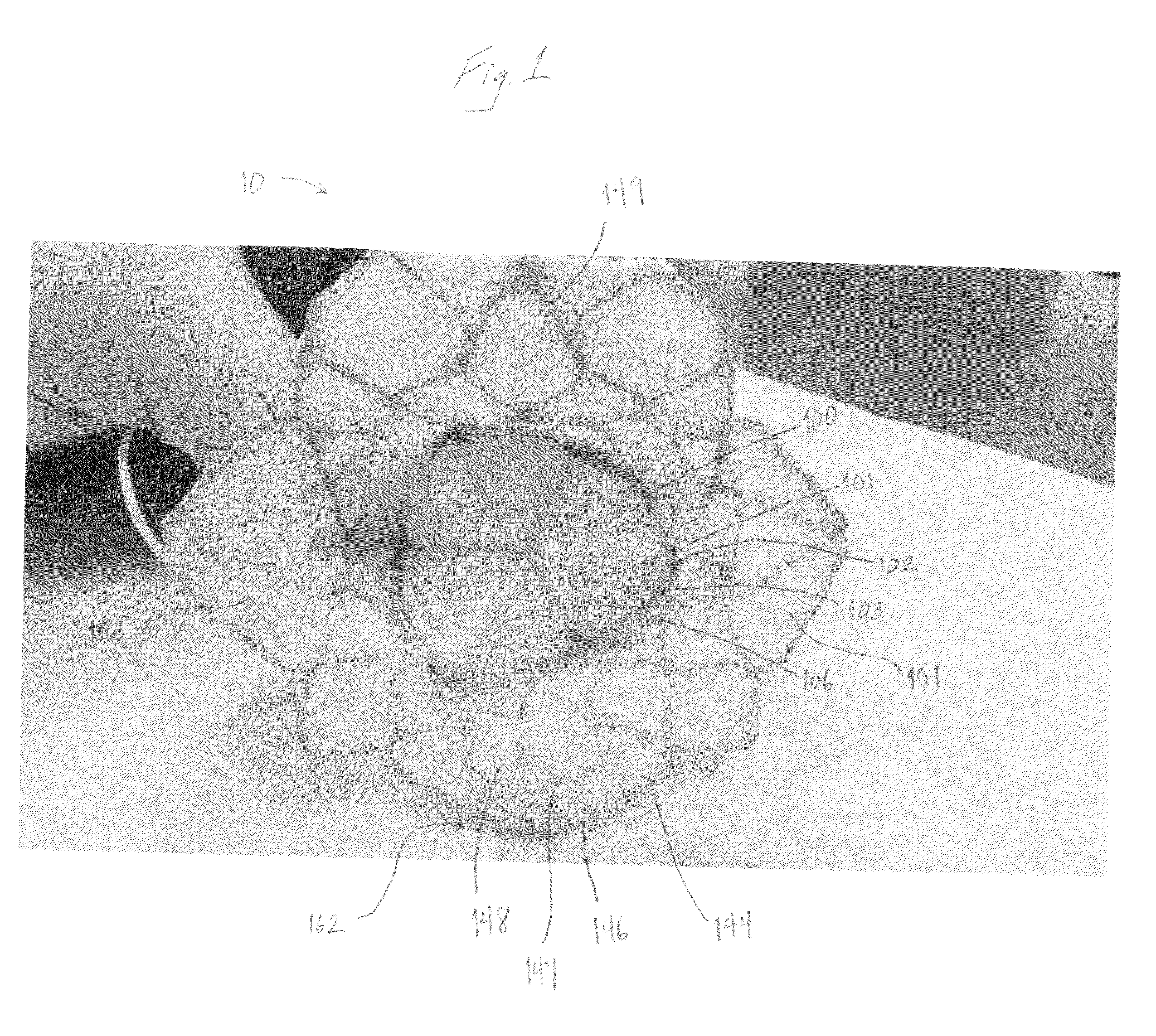
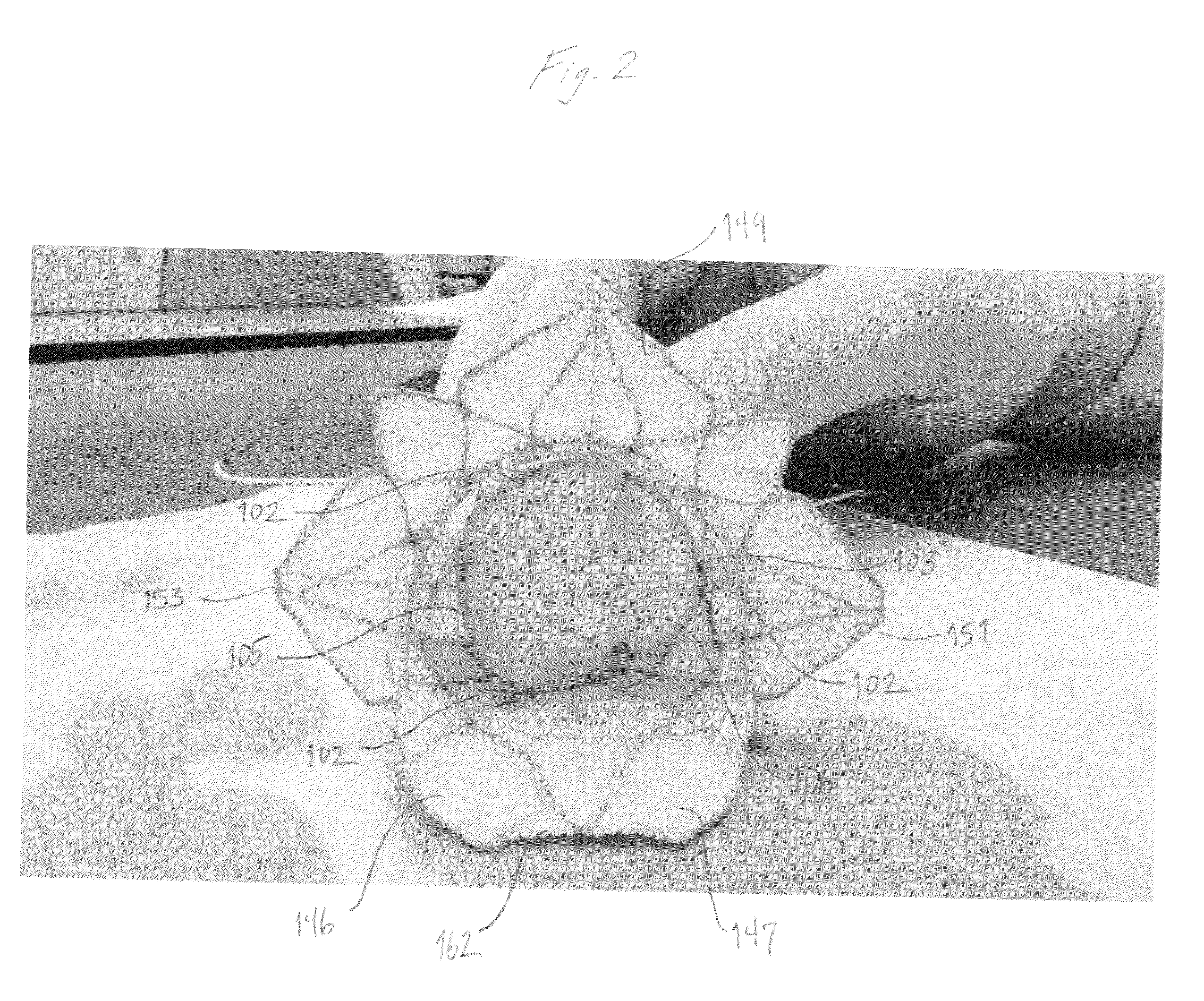
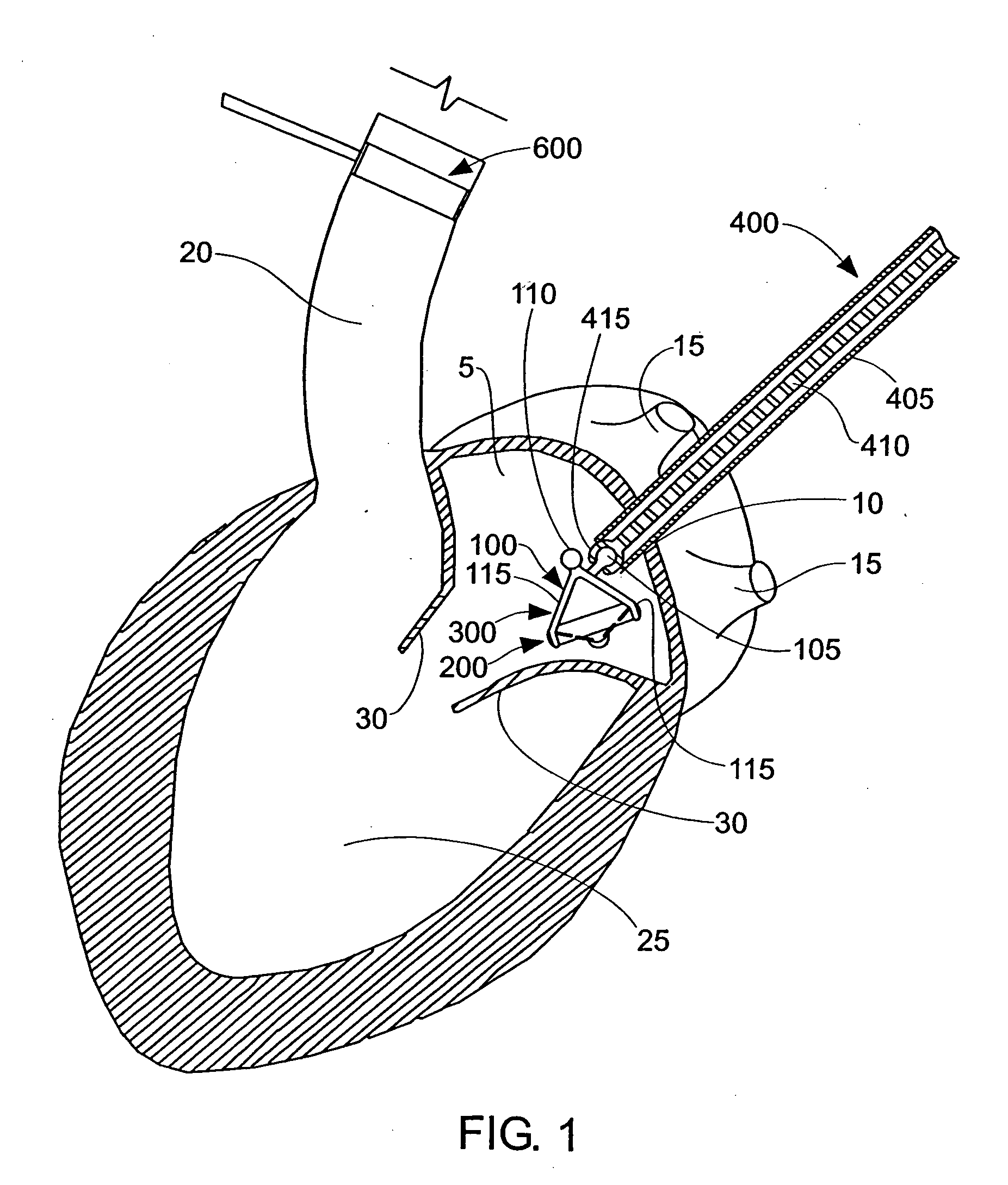
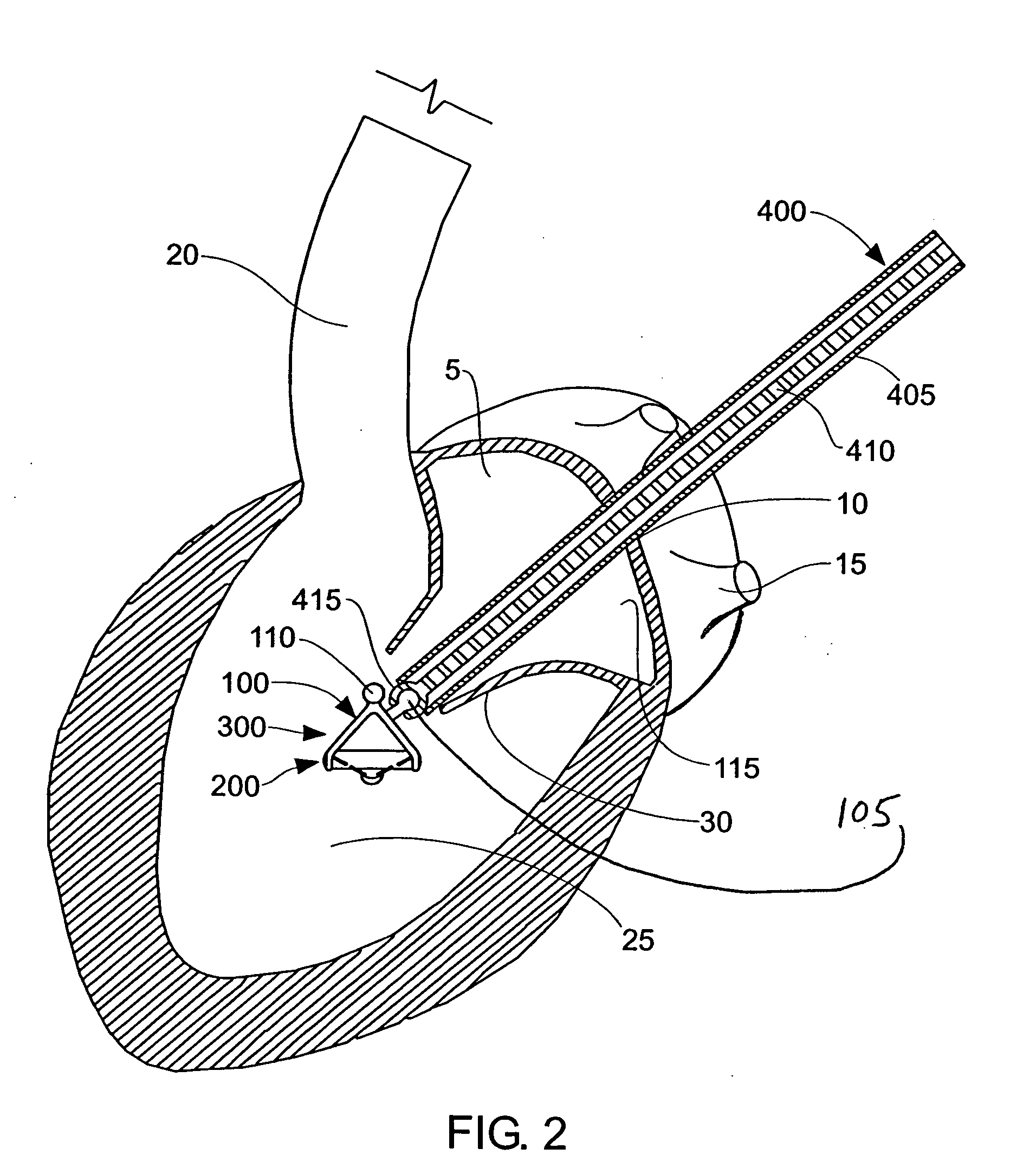
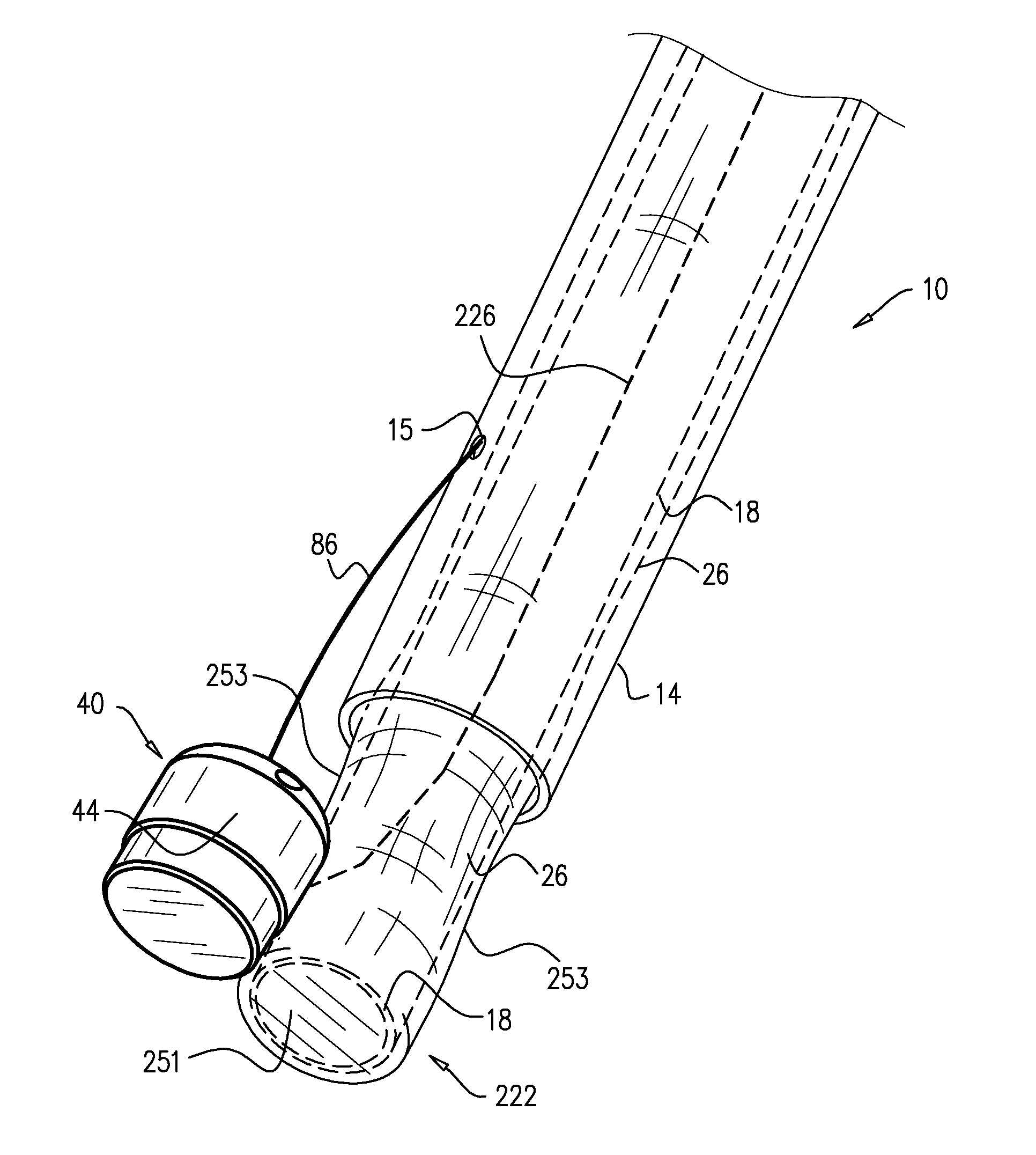
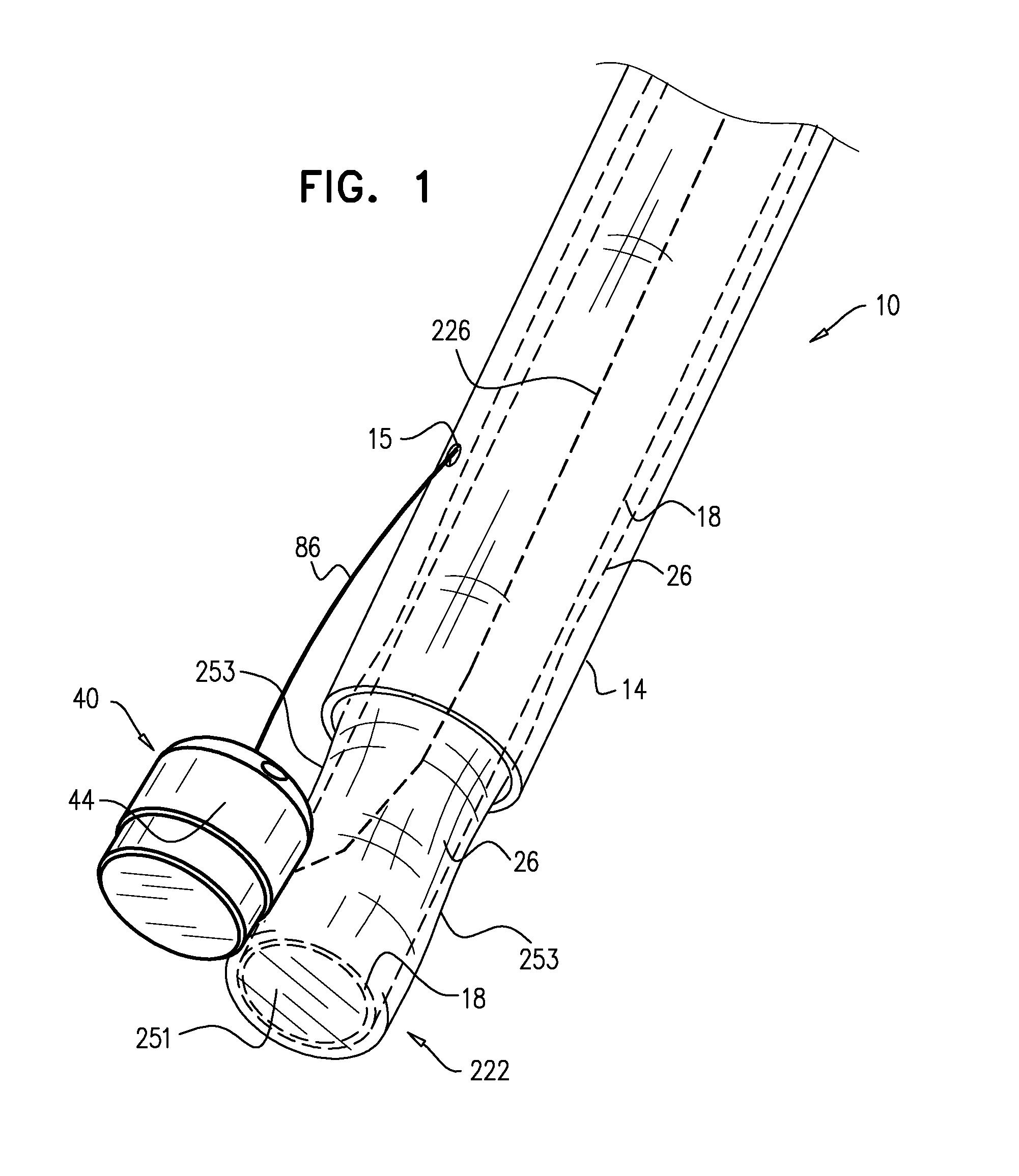
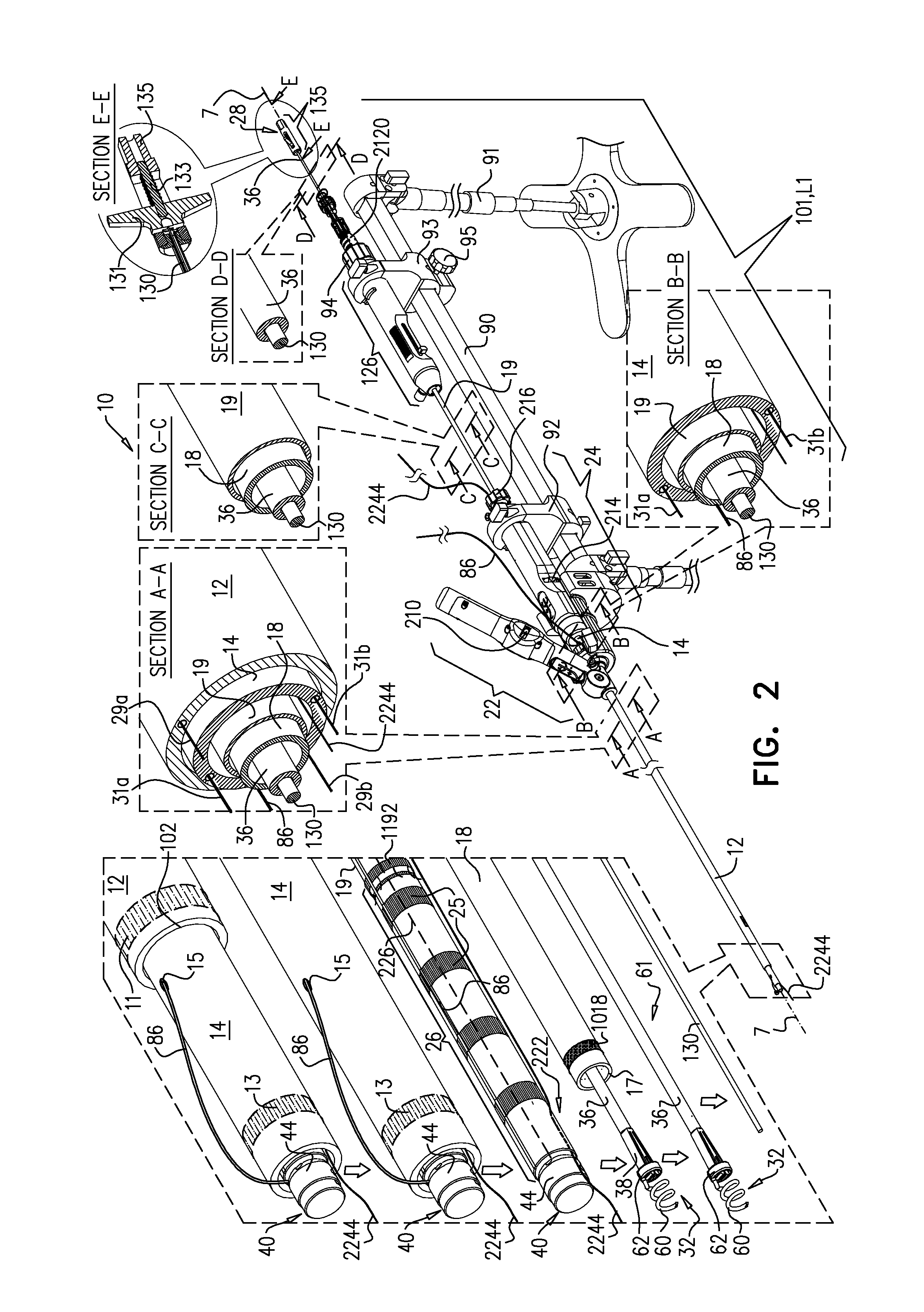
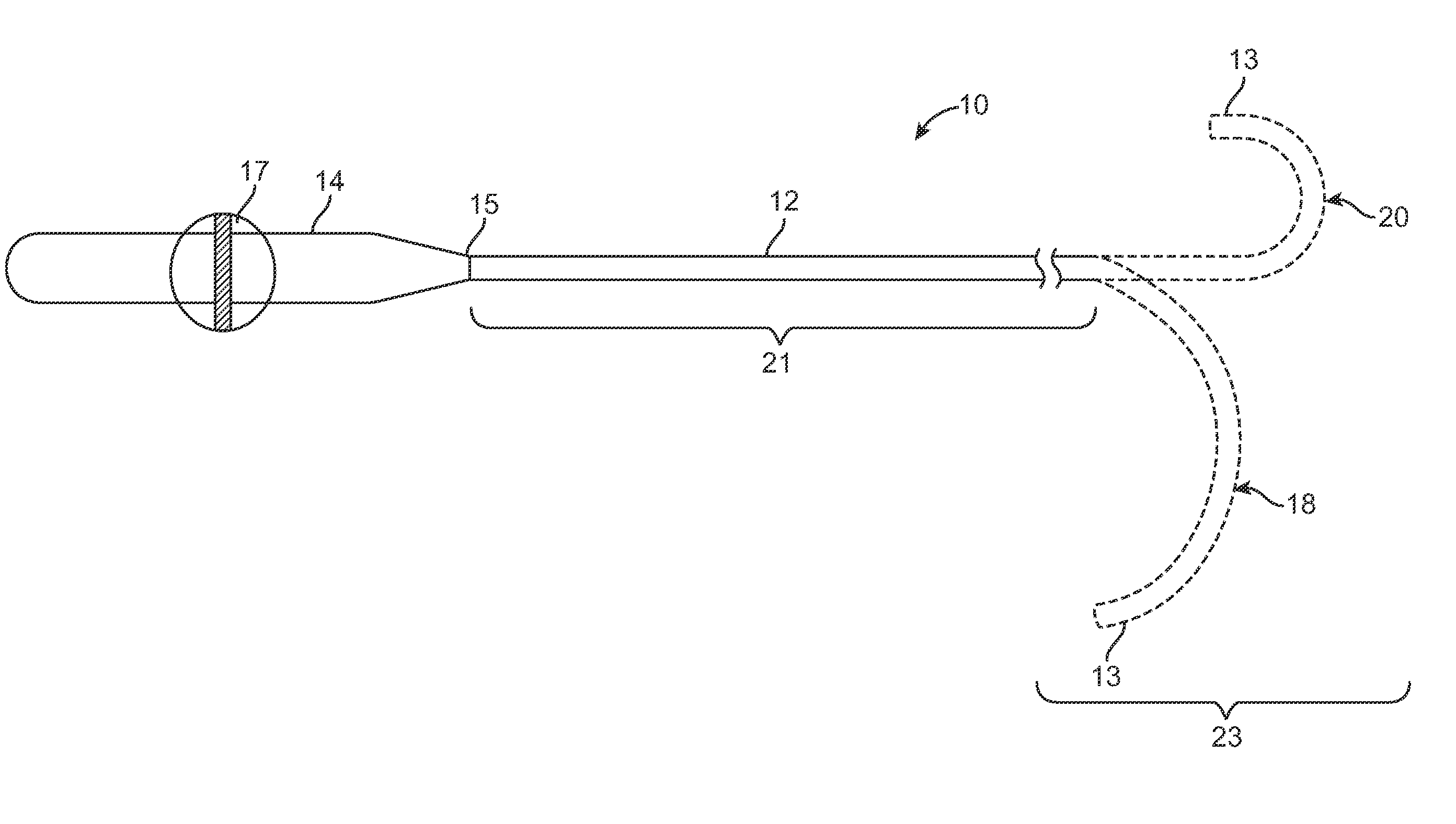
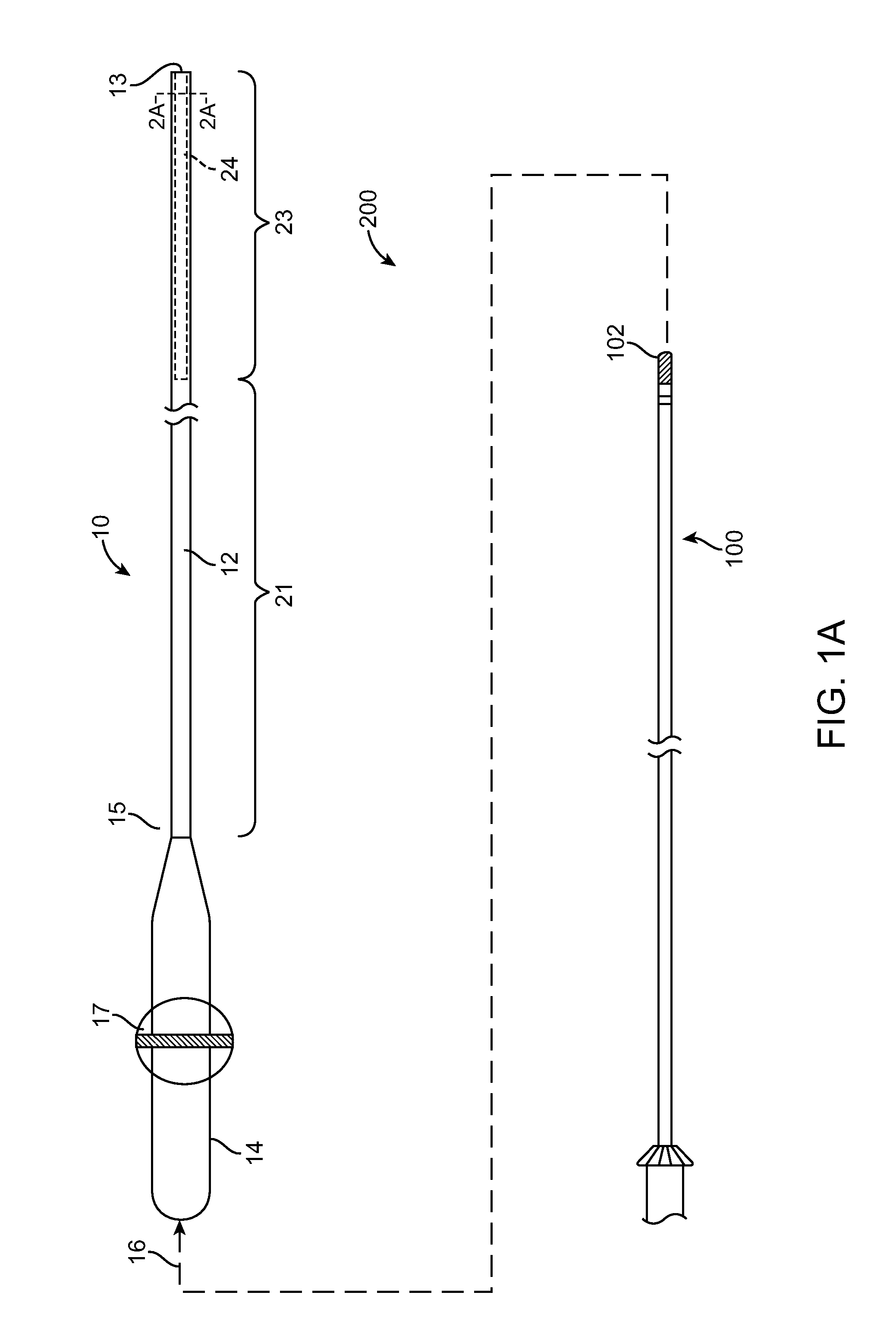
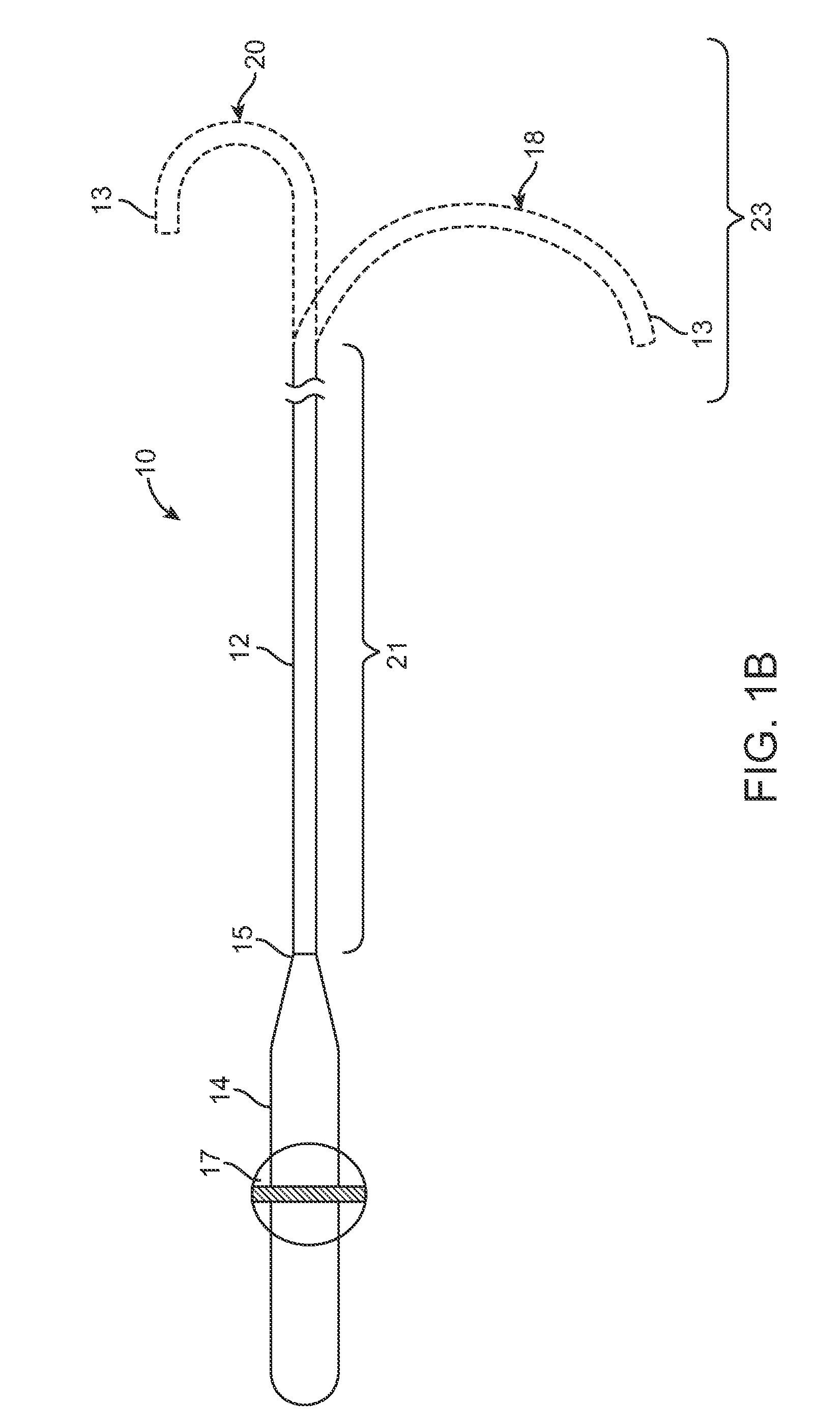
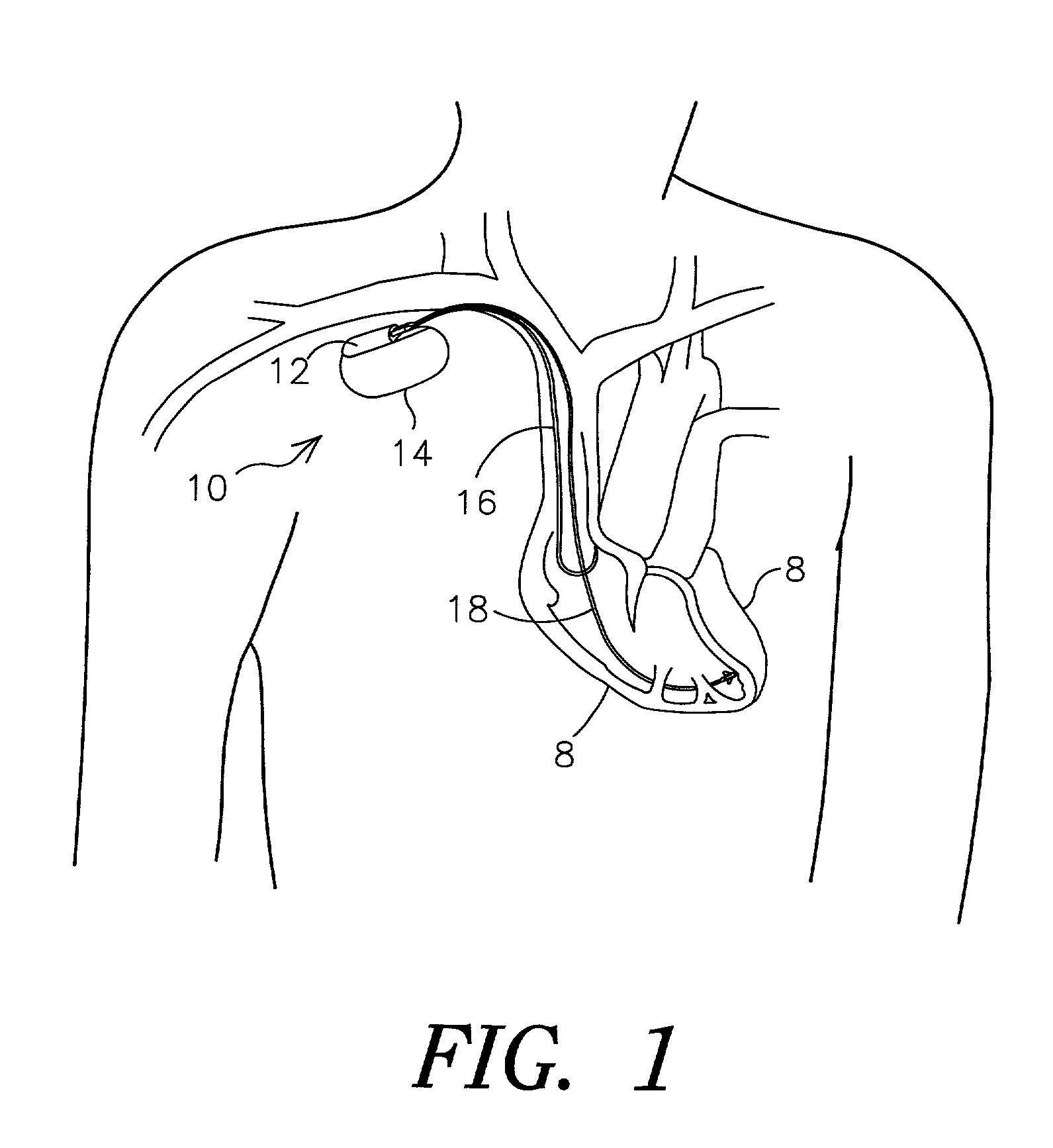
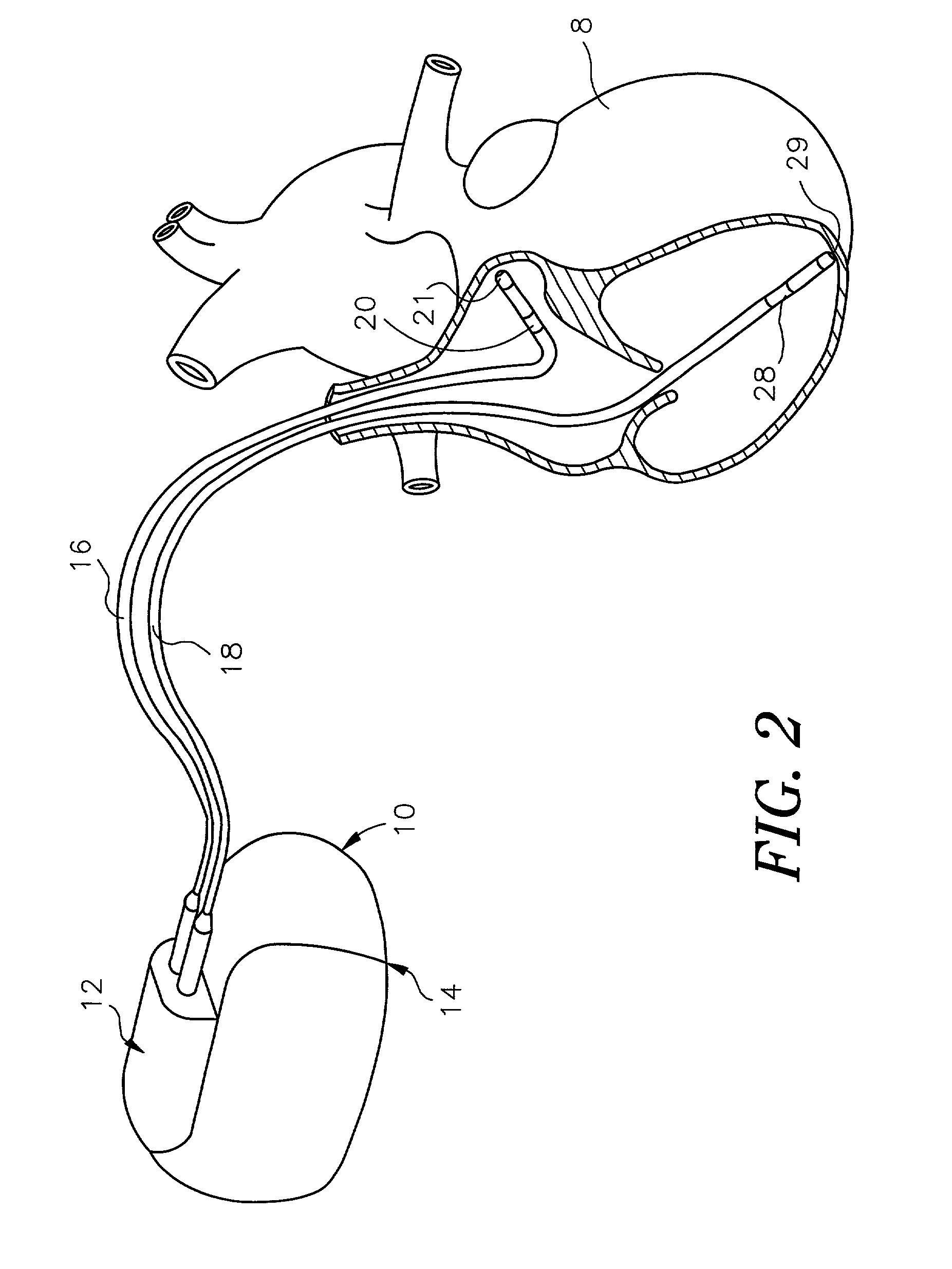
Devices, systems, and methods for reshaping a heart valve annulus
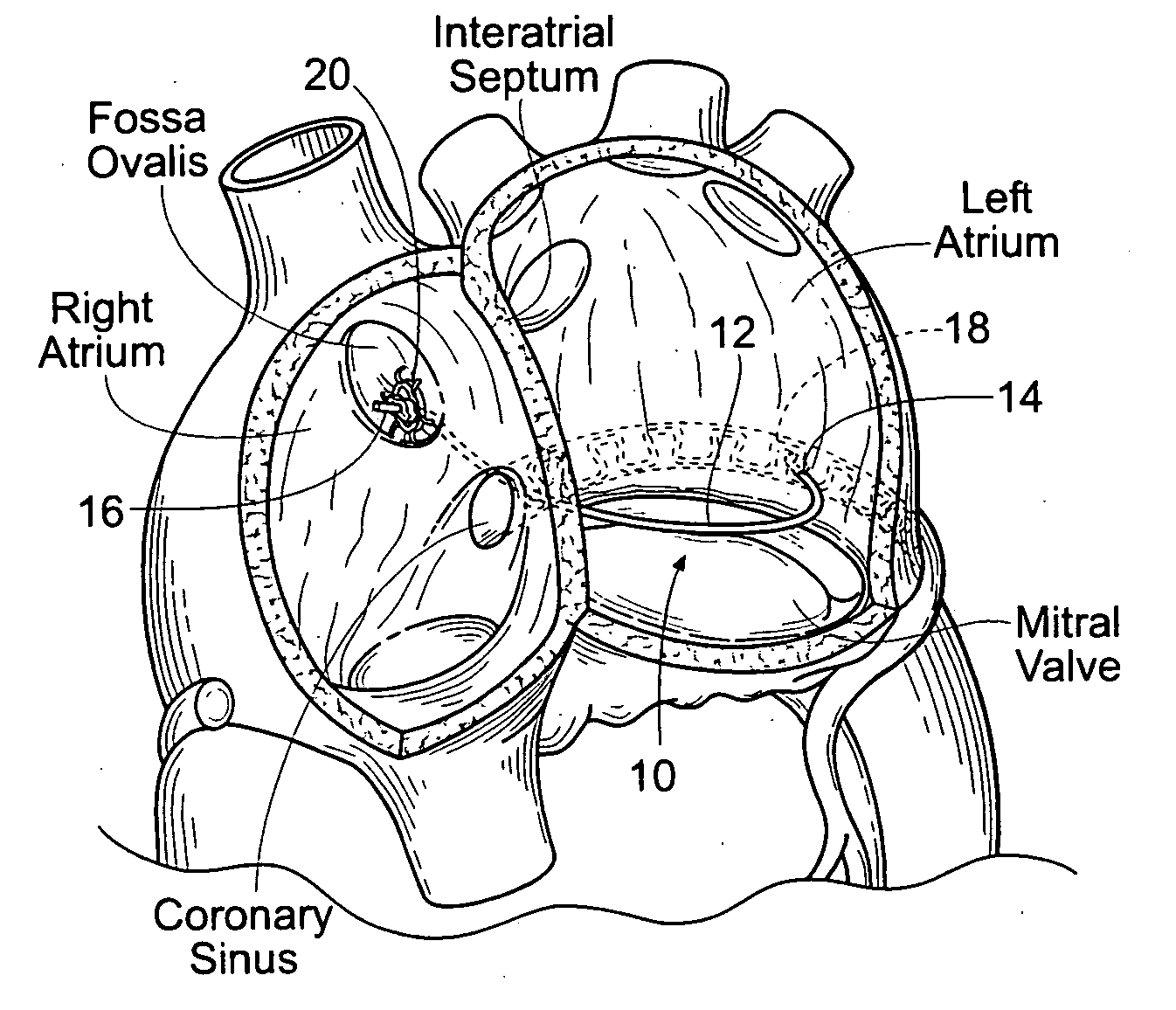
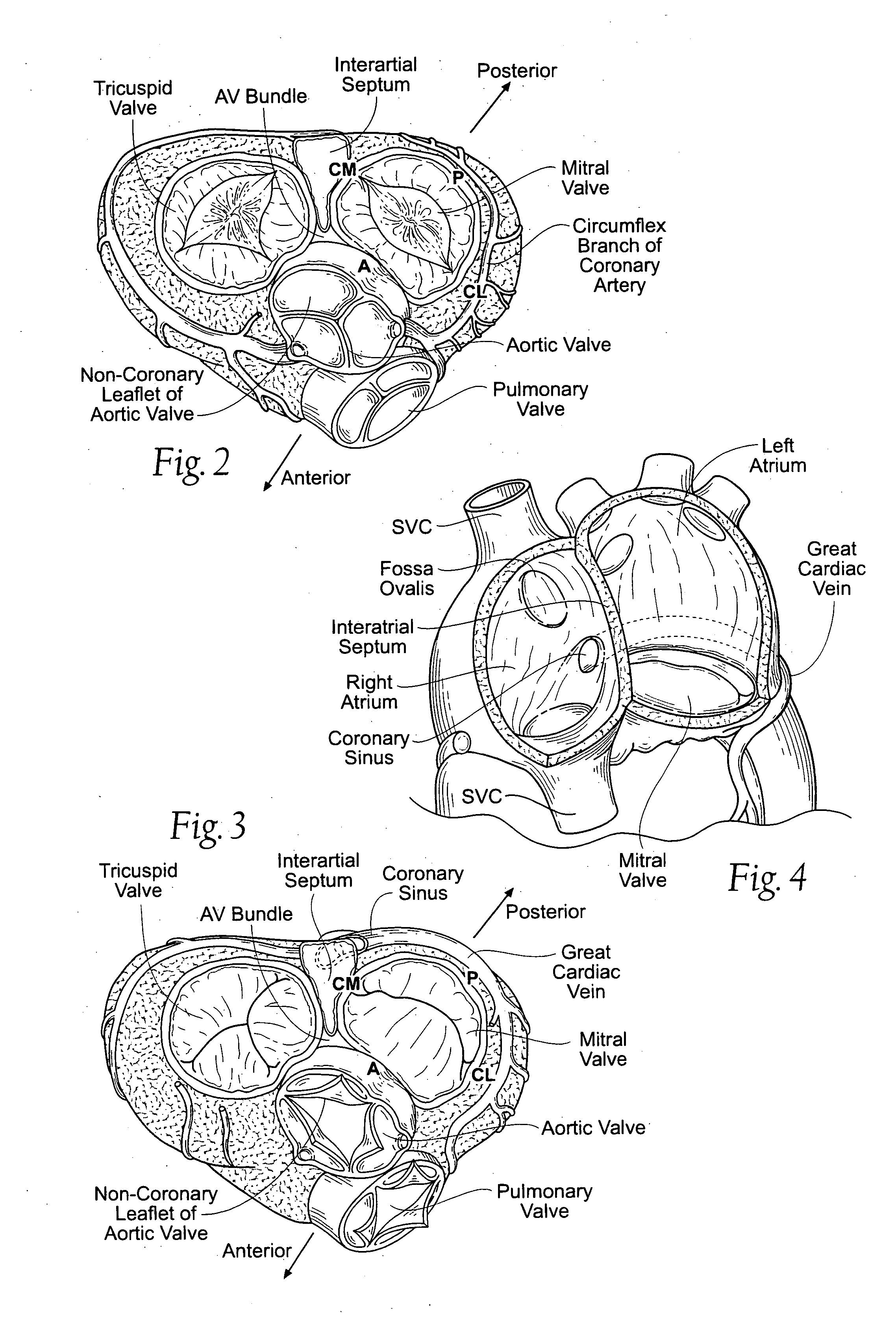
ActiveUS20050055089A1Improve septal-to-lateral dimensionImproved leaflet coaptionSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsMitral valve leafletLeft atrium
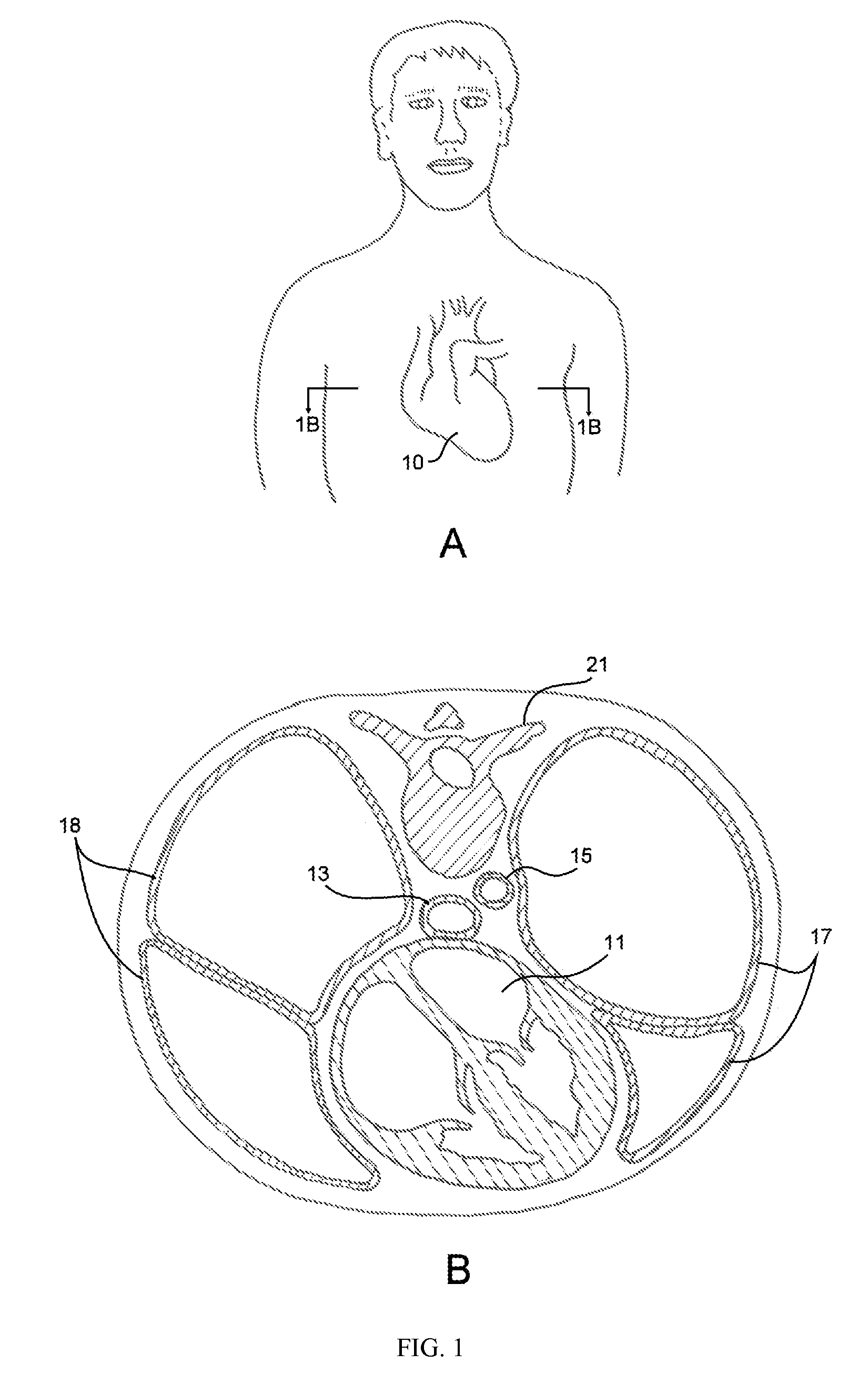
Implants or systems of implants apply a selected force vector or a selected combination of force vectors within or across the left atrium, which allow mitral valve leaflets to better coapt. The implants or systems of implants make possible rapid deployment, facile endovascular delivery, and full intra-atrial retrievability. The implants or systems of implants also make use of strong fluoroscopic landmarks.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
Method and apparatus for resecting and replacing an aortic valve
InactiveUS20050131438A1Minimize riskRisk minimizationEar treatmentCannulasAortic valveNeoaortic valve
A method and apparatus for delivering a device to a given location within a heart, the method and apparatus being adapted for: passing a first catheter through the left atrium of the heart, through the mitral valve and into the left ventrical, and passing a second catheter through the aorta toward the heart, one or the other of the first catheter and the second catheter, with the device attached thereo, forming a device-carrying assembly for engagement with the remaining catheter; causing the device-carrying assembly and the remaining catheter to engage one another so as to form a connection therebetween; and retracting one of the device-carrying assembly and the remaining catheter in a direction opposite to the other of the device-carrying assembly and the remaining catheter so as to position the device relative to the given location within the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
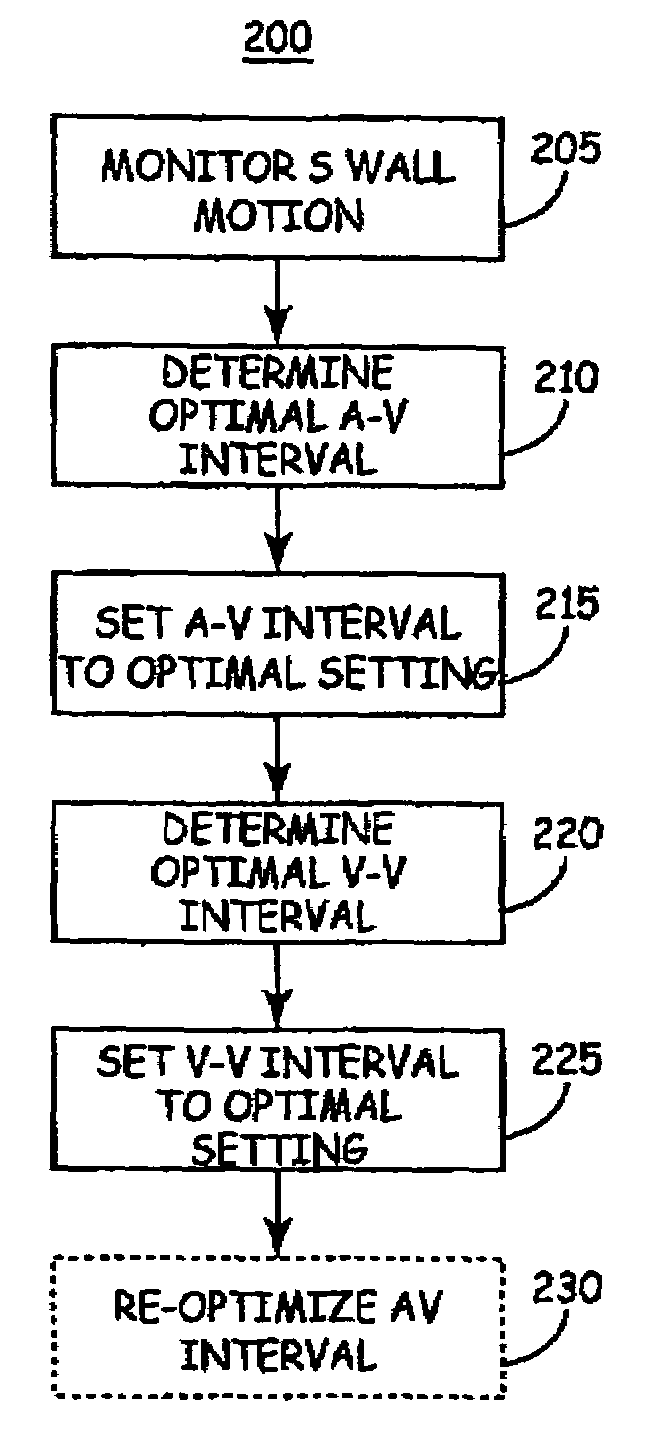
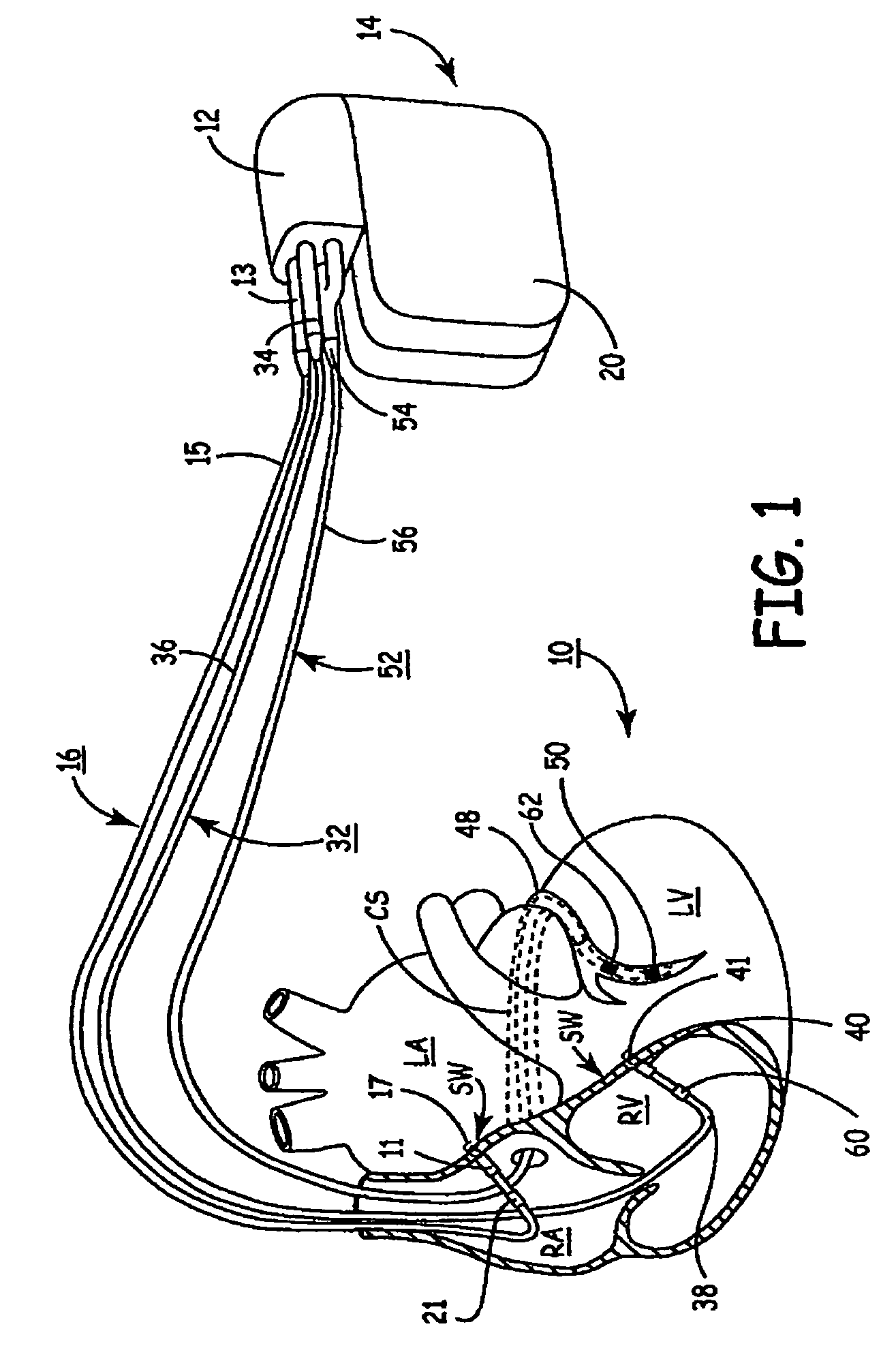
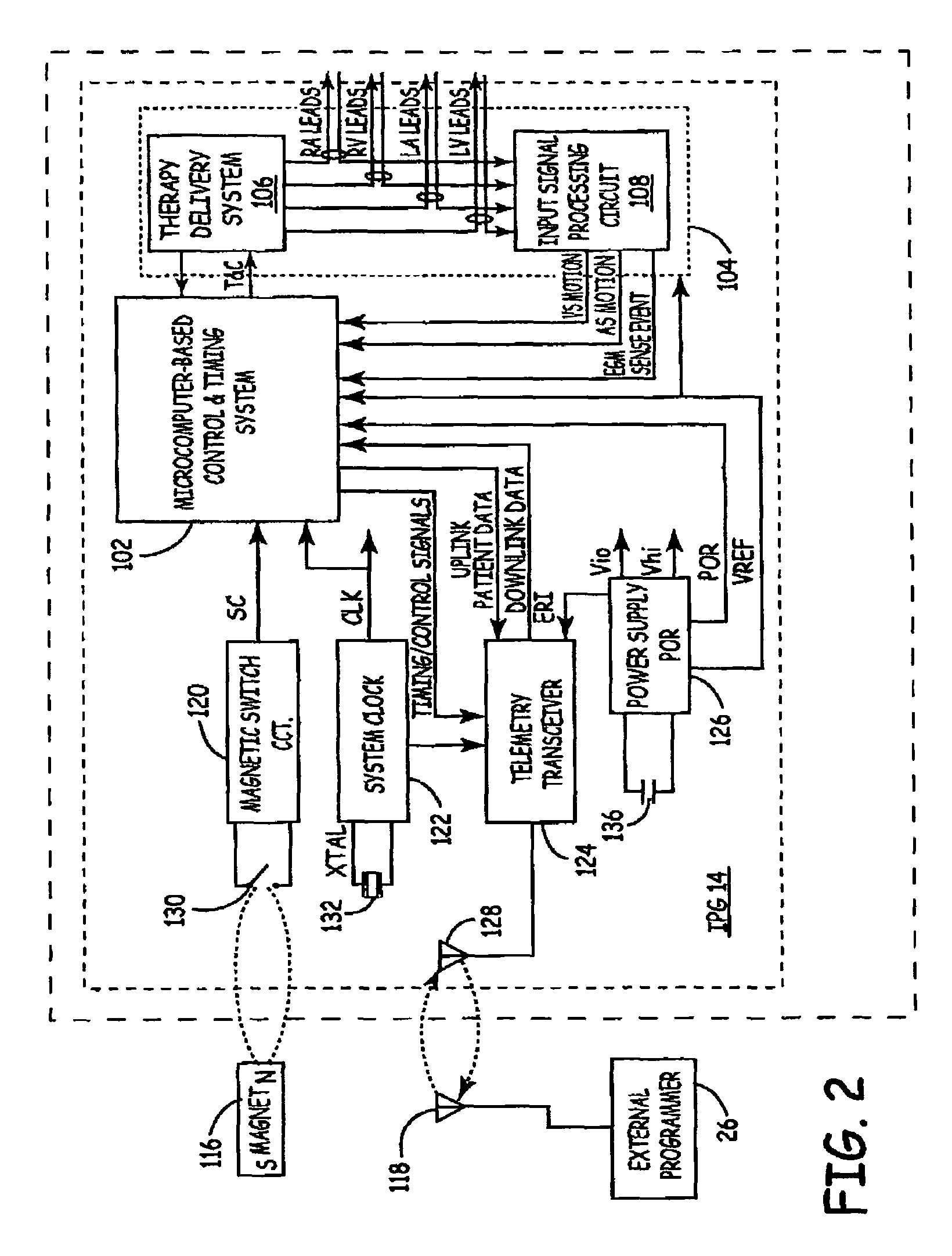
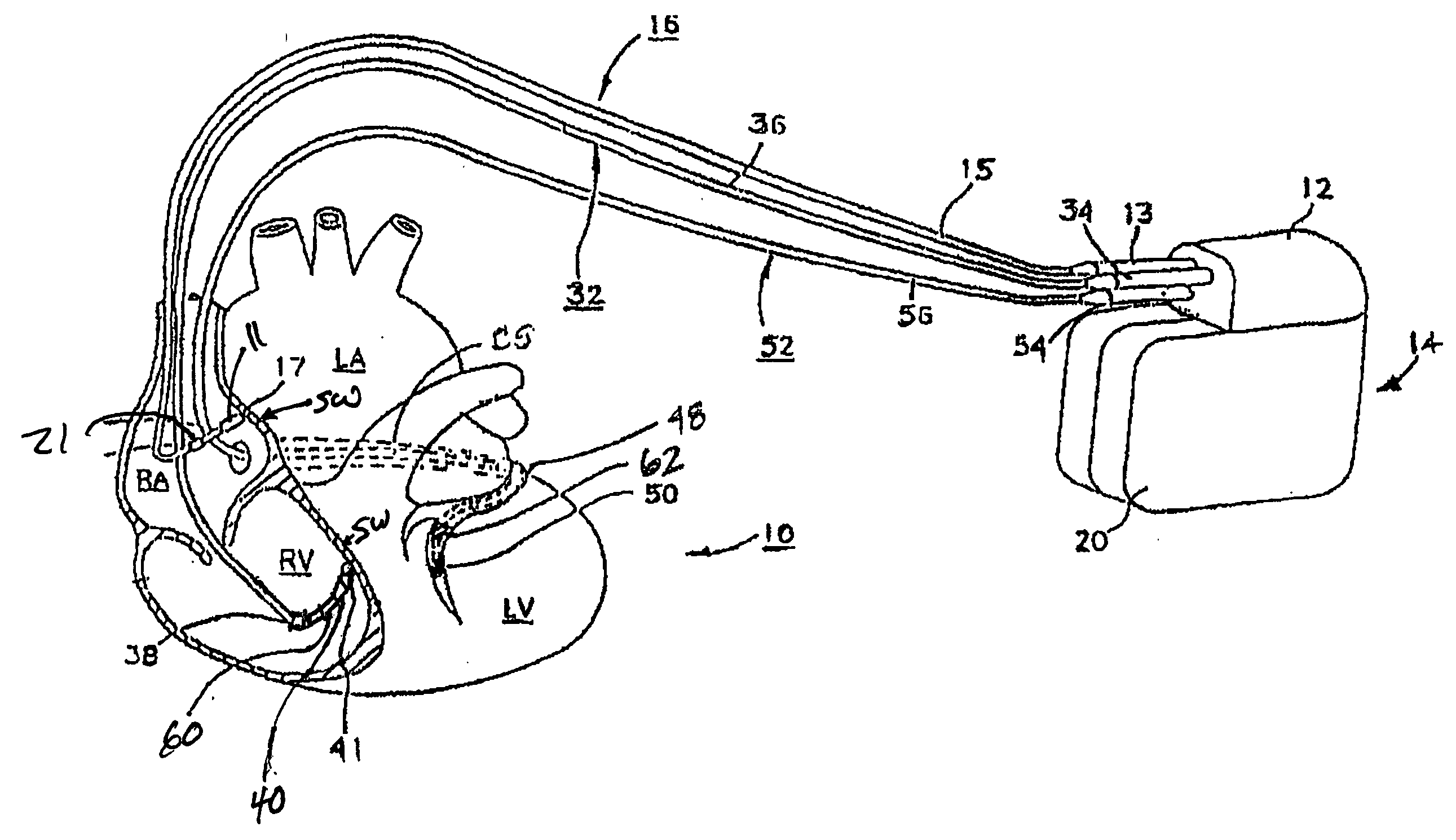
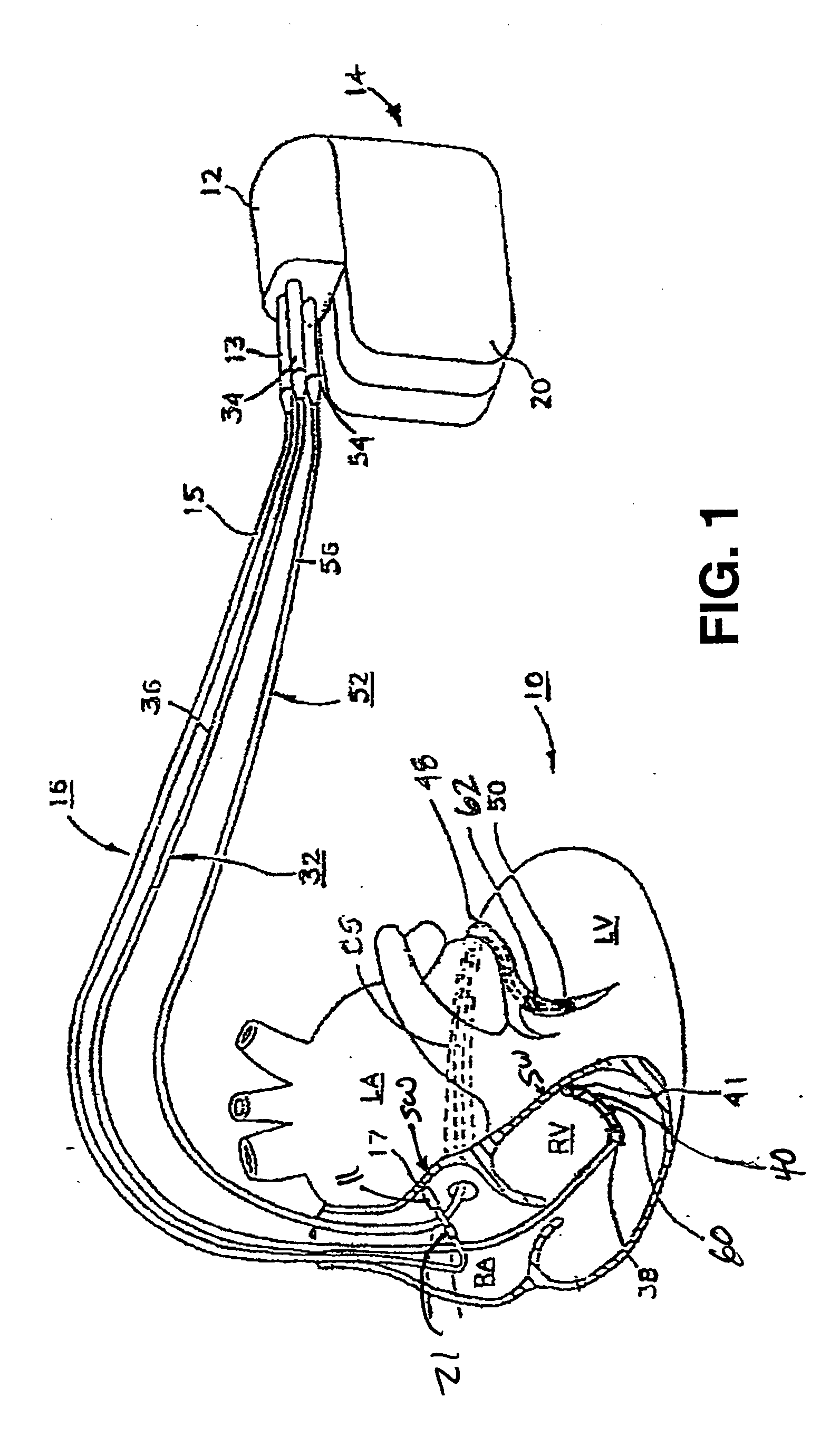
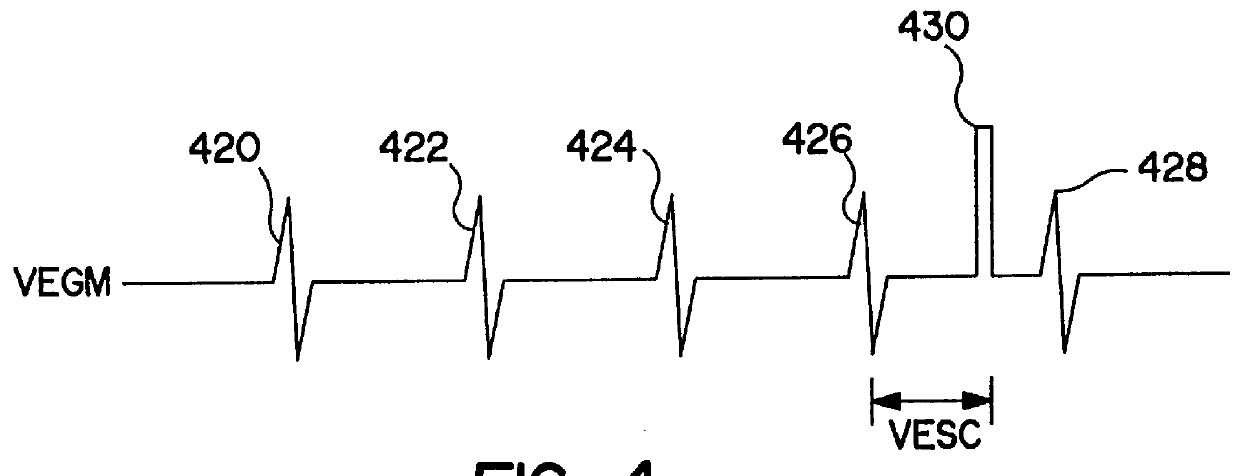
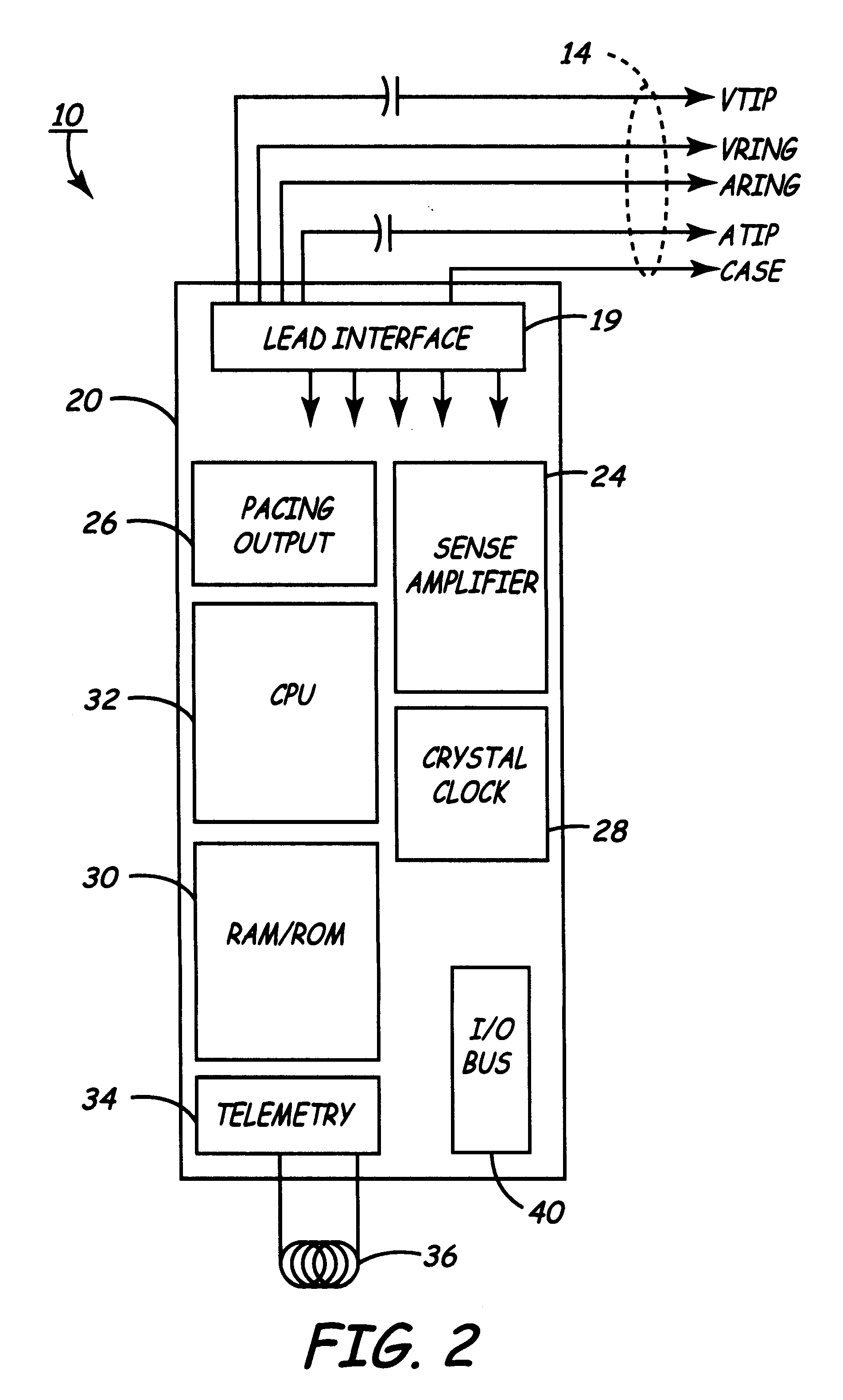
Method of optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy using sensor signals of septal wall motion
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Devices and methods for the treatment of heart failure
ActiveUS20100057192A1Reduce atrial pressureReduce pressureStentsAnnuloplasty ringsAtrial septumHeart failure
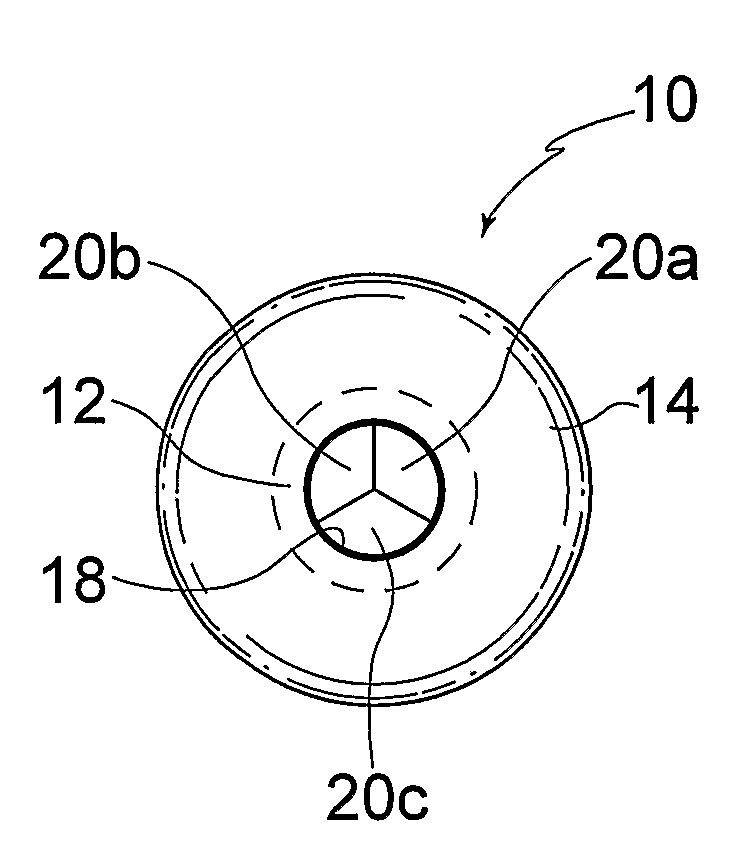
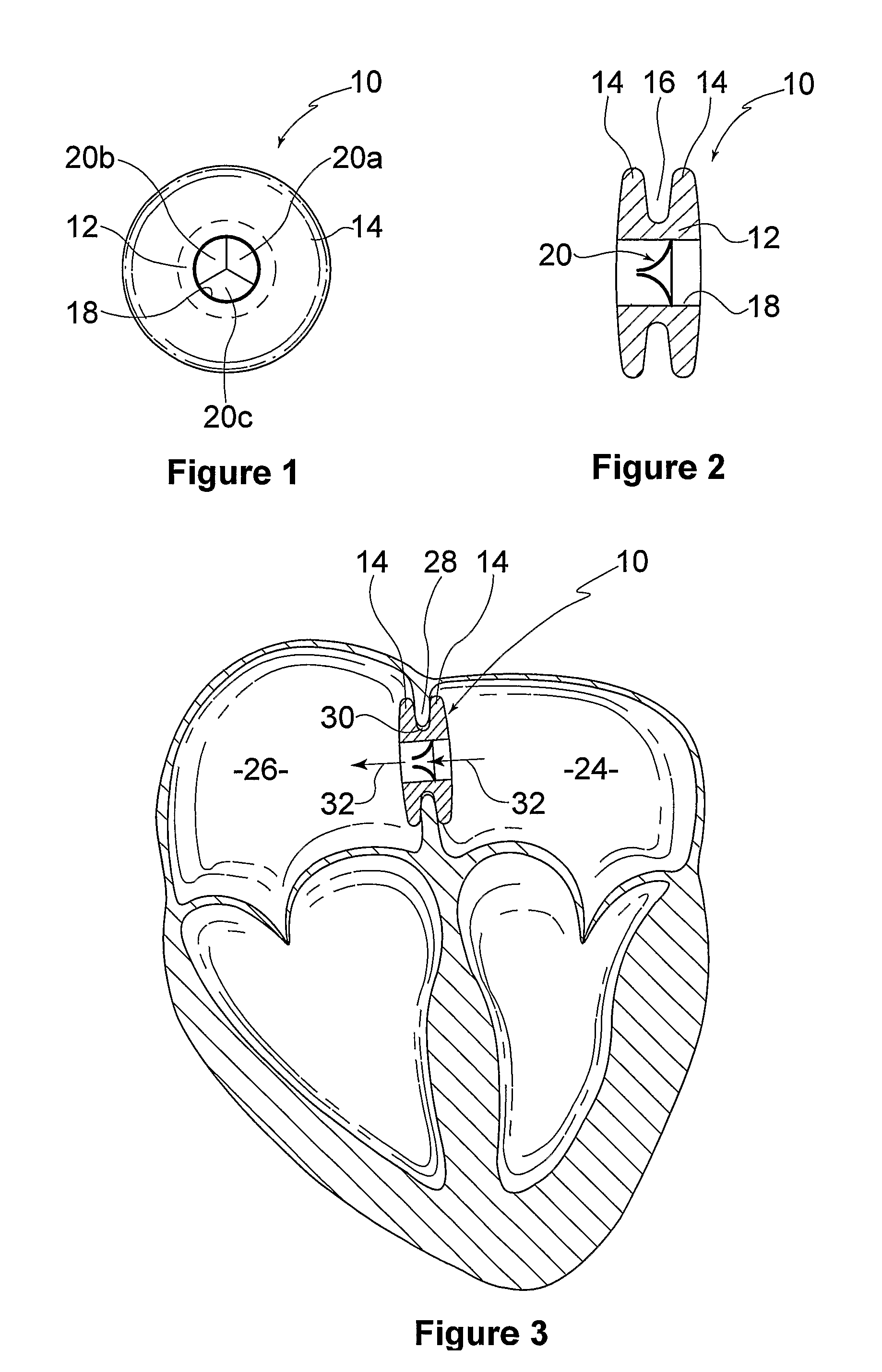
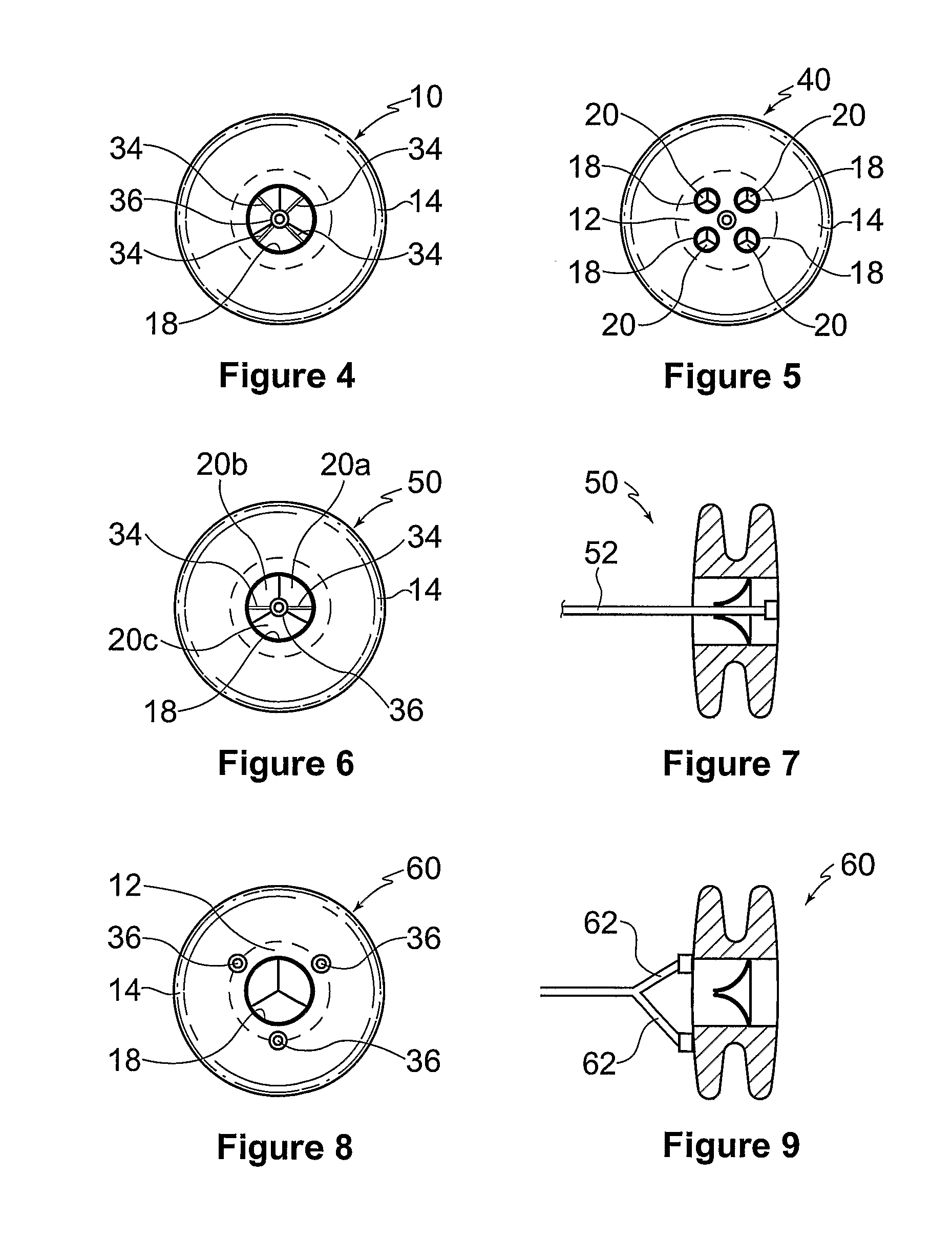
A device (10) for treating heart failure in a patient. The device (10) comprising a body (12), at least one passage (18) through the body (12), at least one one way valve (20) in the passage (18) and a mounting means (14) adapted for mounting the body (12) in an opening provided in the patient's atrial septum. In use, the device (10) is oriented such that, when the patient's left atrial pressure exceeds the patient's right atrial pressure by a predetermined amount, the one way valve(s) (20) opens to allow blood flow through the passage(s) from the left atrium to the right atrium to thereby reduce the left atrial pressure.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Atrial Thrombogenic Sealing Pockets for Prosthetic Mitral Valves
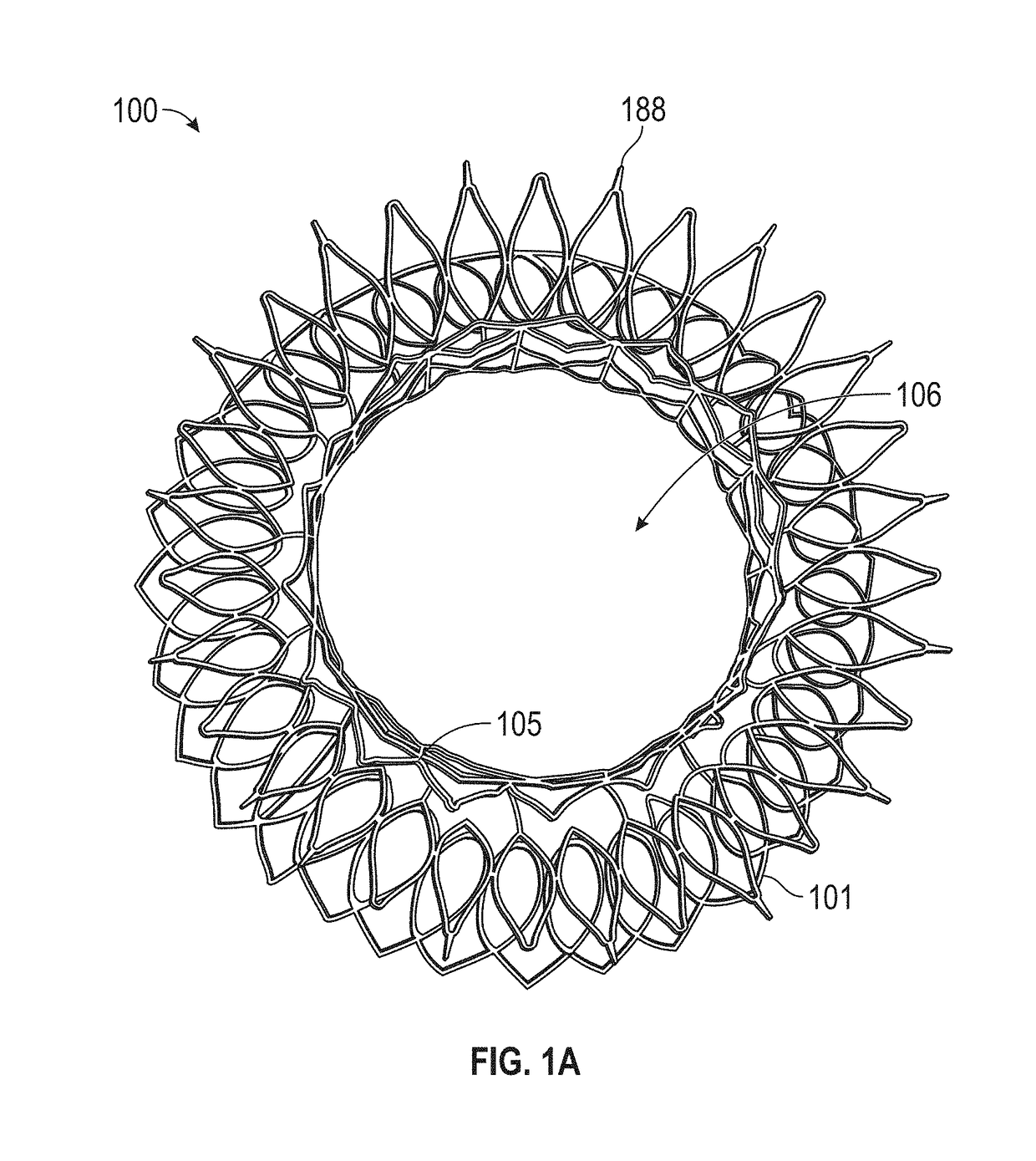
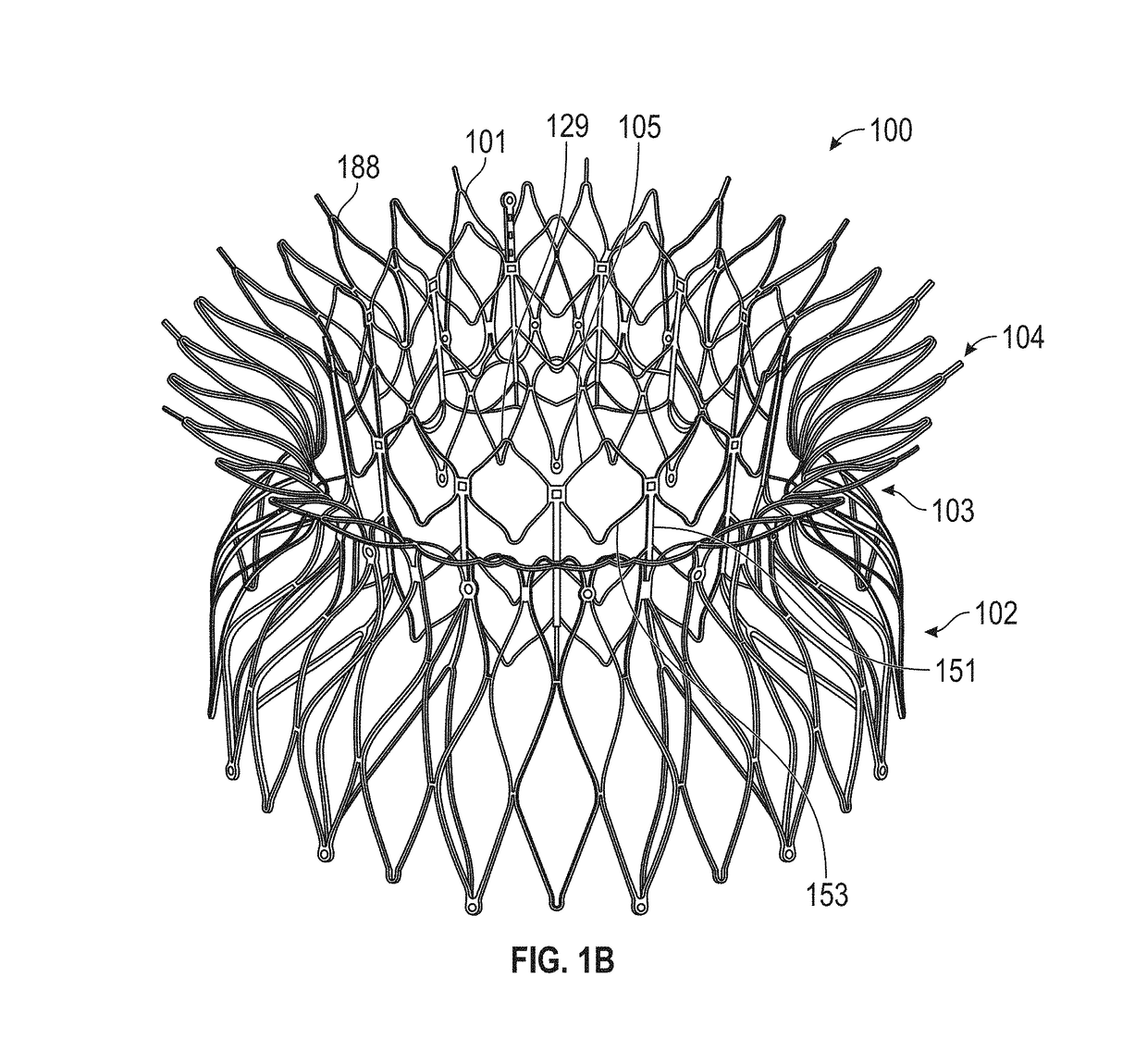
This invention relates to a self-expanding pre-configured compressible transcatheter prosthetic cardiovascular valve that comprises atrial thrombogenic sealing pocket cover mounted on a self-expanding inner wire frame having a leaflet structure comprised of articulating leaflets that define a valve function, said inner wire frame is disposed within a self-expanding annular tissue-covered outer wire frame, said outer wire frame having an articulating collar, forming a multi-component prosthetic valve assembly for anchoring within the mitral valve or triscuspid valve of the heart, and methods for deploying such a valve for treatment of a patient in need thereof.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Method of optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy using sensor signals of septal wall motion
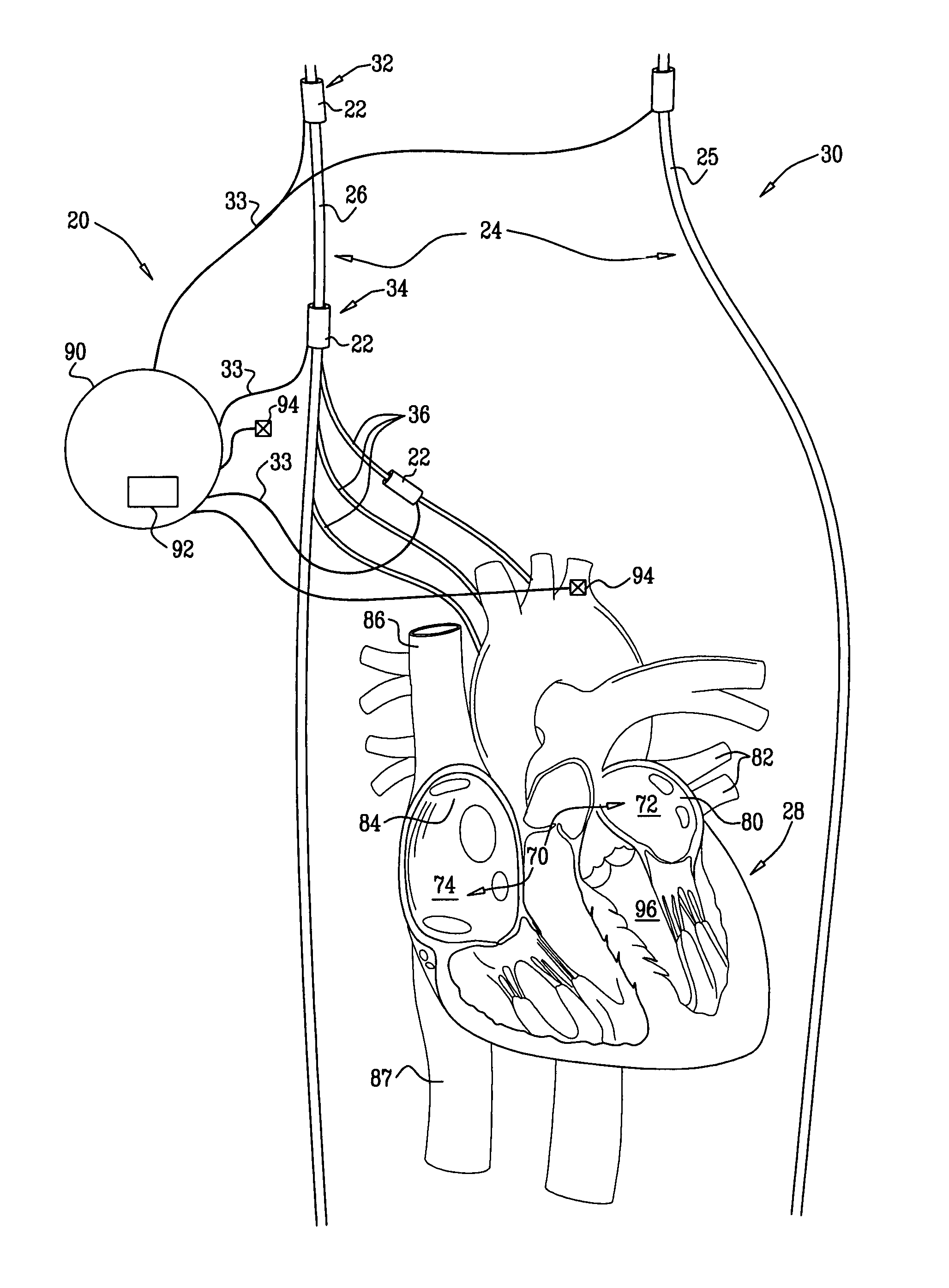
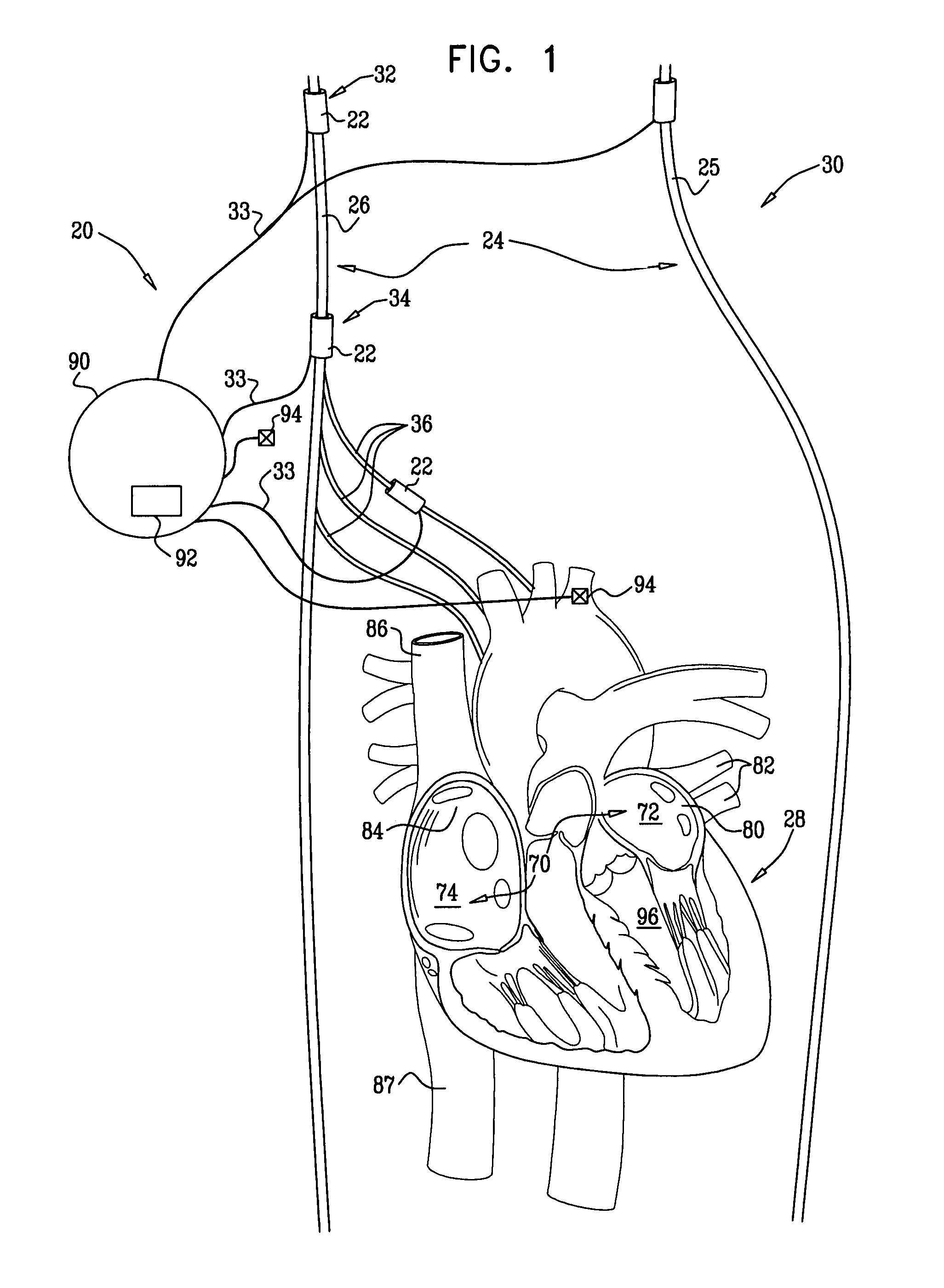
The present invention relates to monitoring septal wall motion of the atrial and / or ventricular chambers of a heart for optimizing cardiac pacing intervals based on signals derived from said wall motion. At least one lead of medical device is equipped with a motion sensor adapted to couple to septal tissue. The device receives and may post-process (e.g., suitably filter, rectify and / or integrate) motion signals to determine acceleration, velocity or displacement. During pacing interval optimization the wall motion is measured for many pacing intervals and the pacing interval setting(s) that produce minimal wall motion are implemented for therapy delivery. In addition, the present invention provides methods for periodically determining whether to cease or resume delivery of a bi-ventricular pacing therapy to a patient that may have experienced beneficial reverse remodeling of the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and a method for altering the geometry of the heart
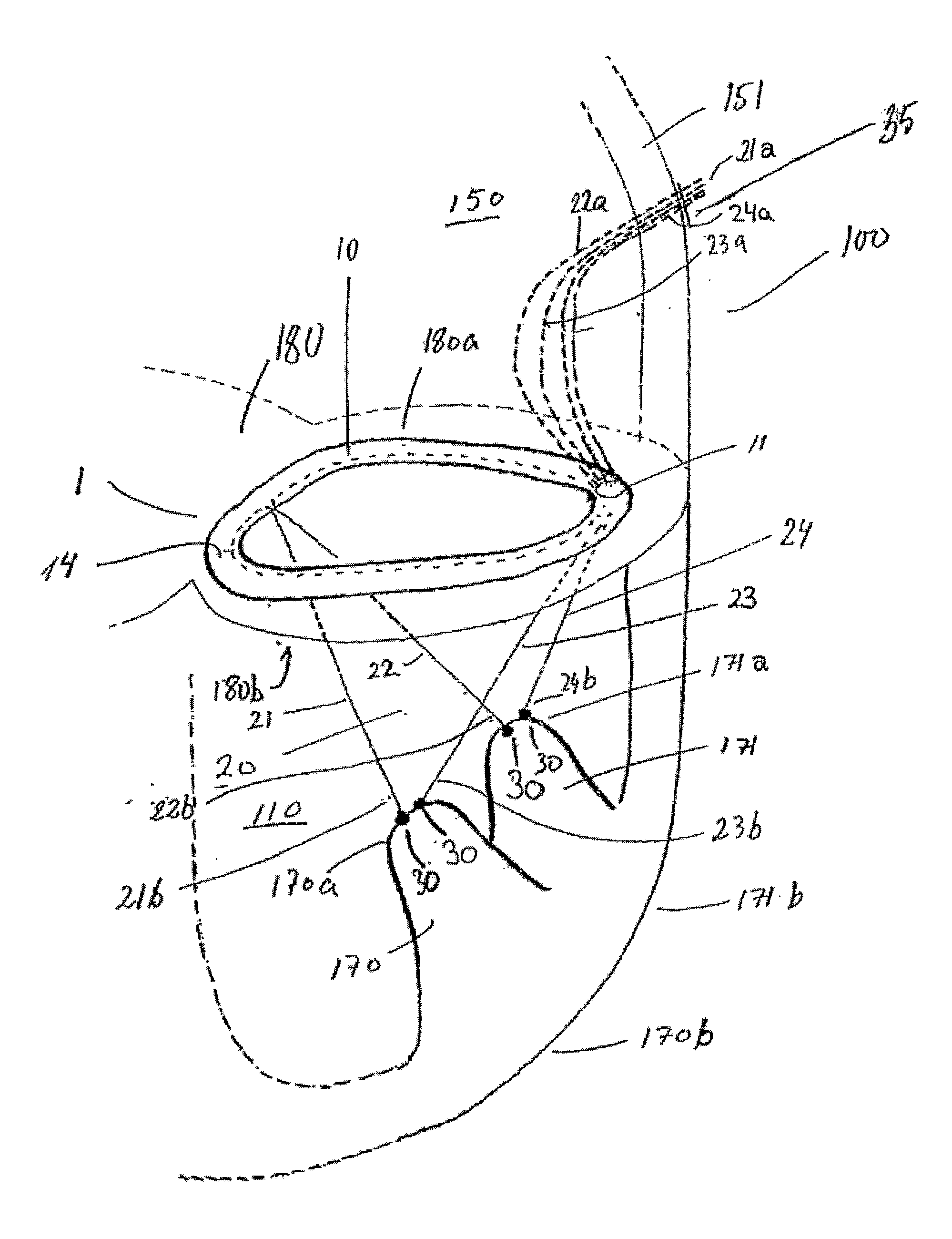
ActiveUS20100063586A1Improve approachReduced stabilitySuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsPapillary muscleEngineering
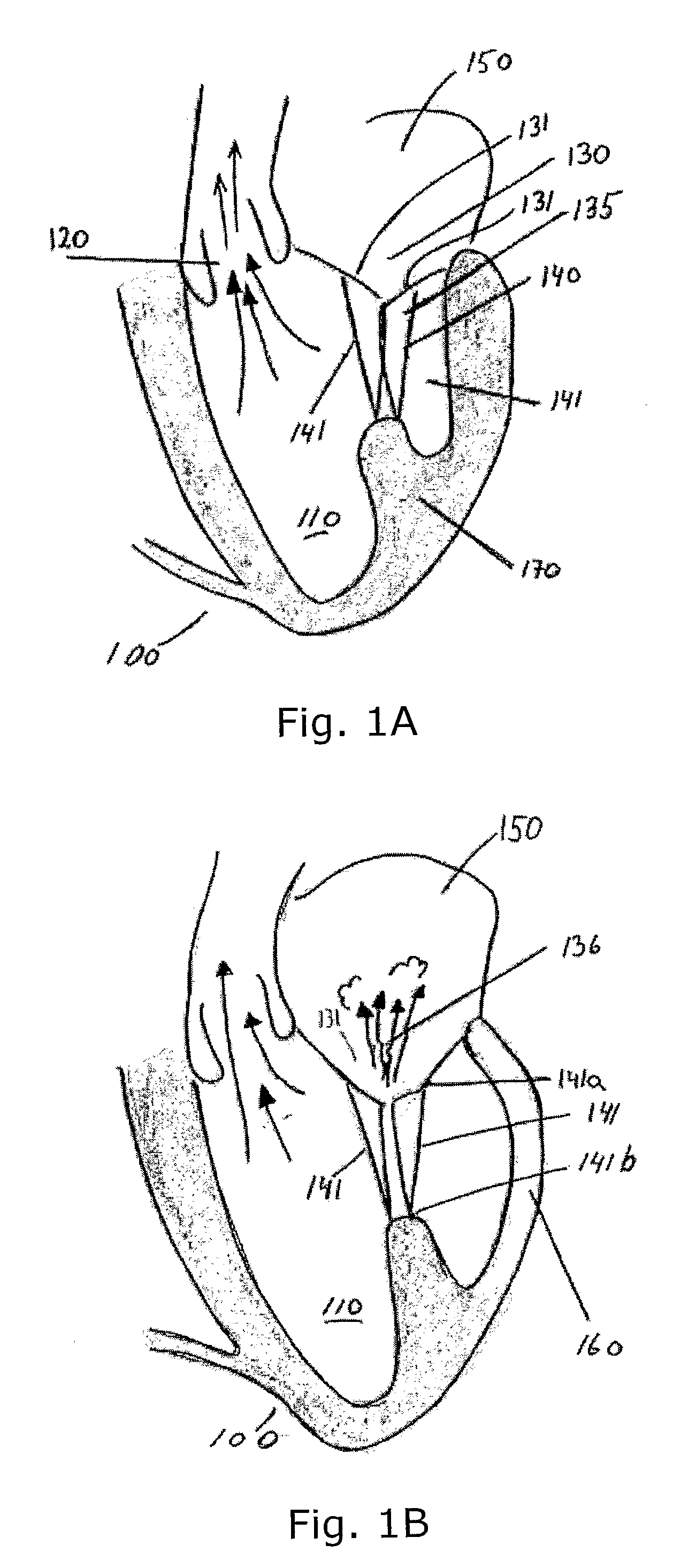
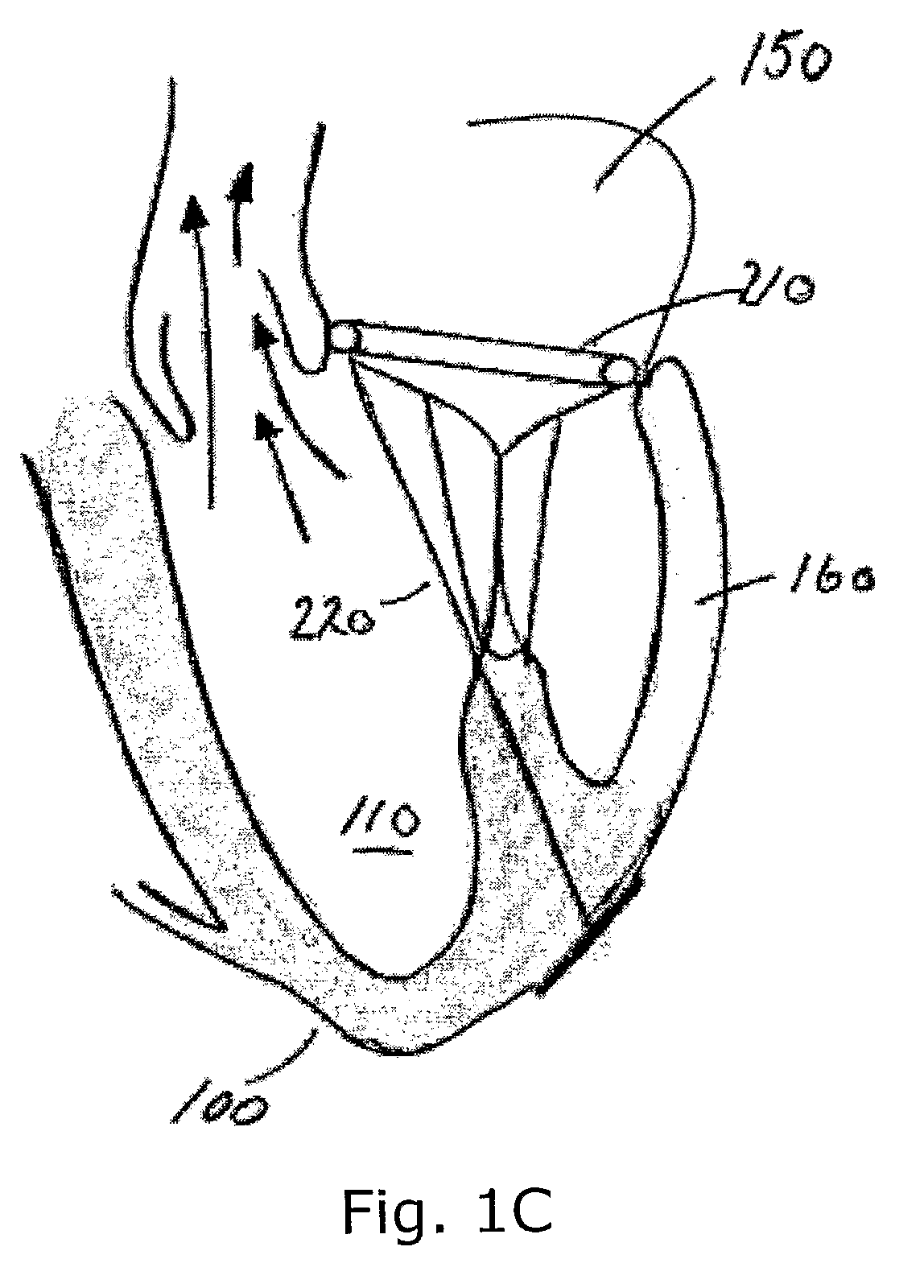
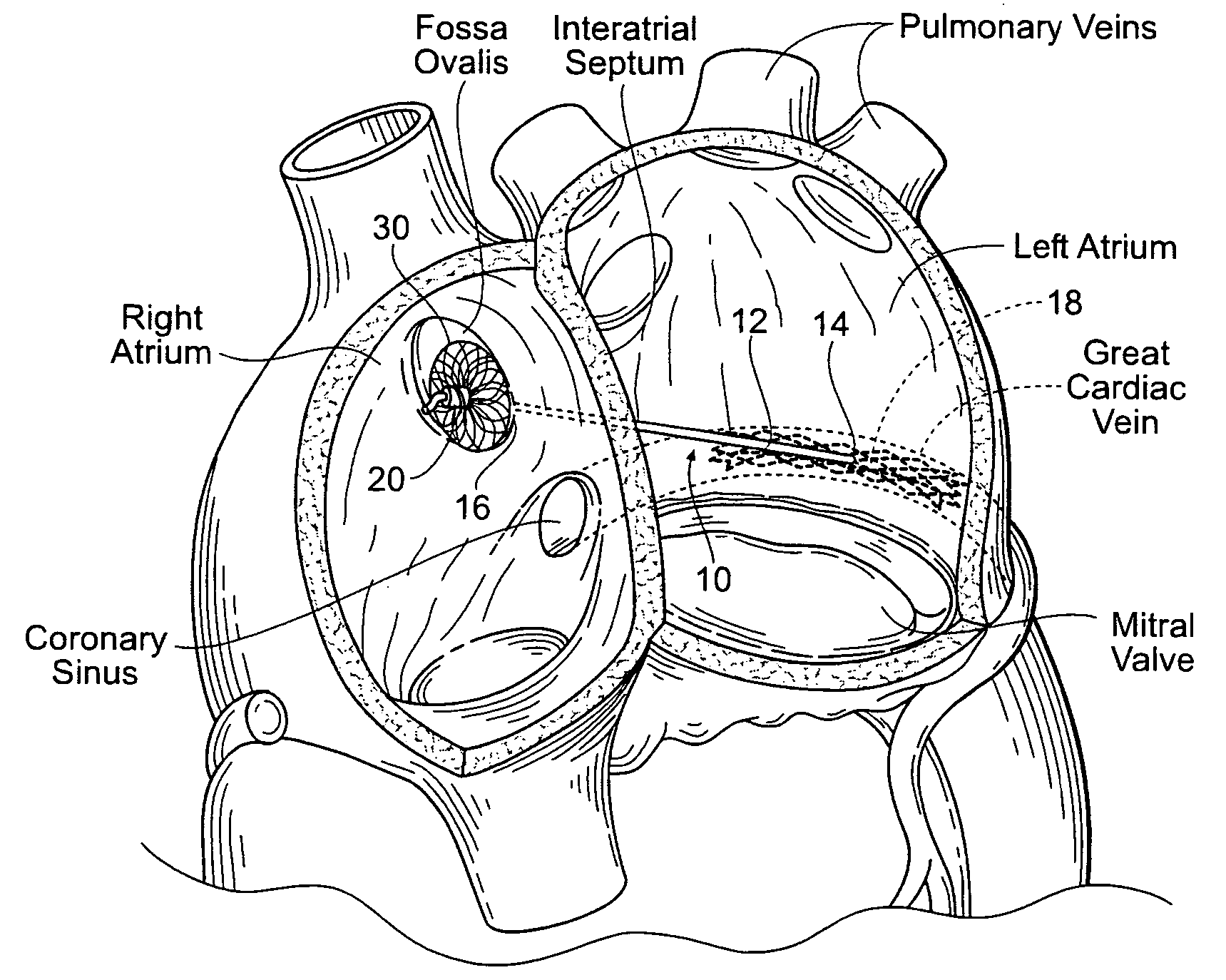
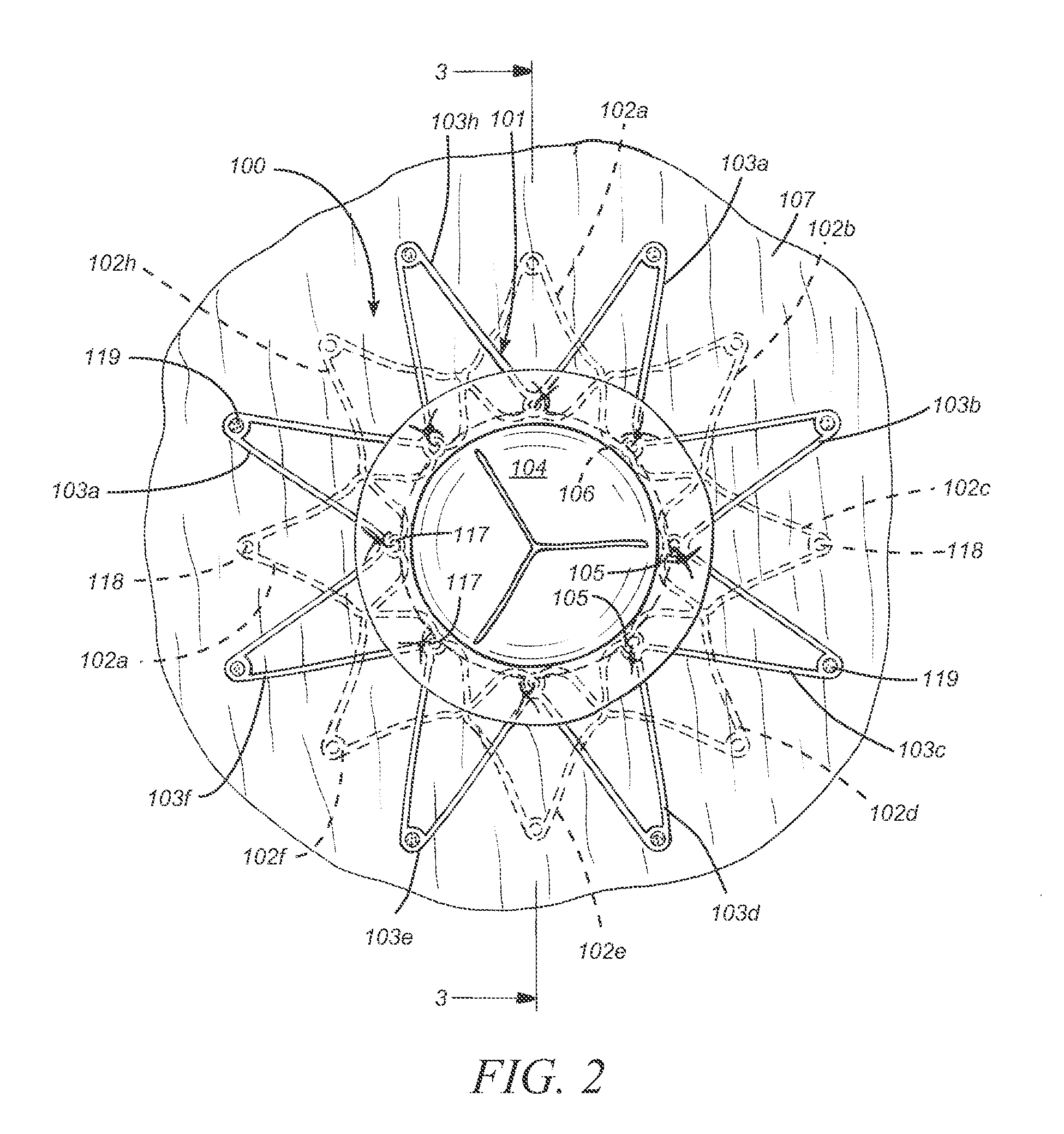
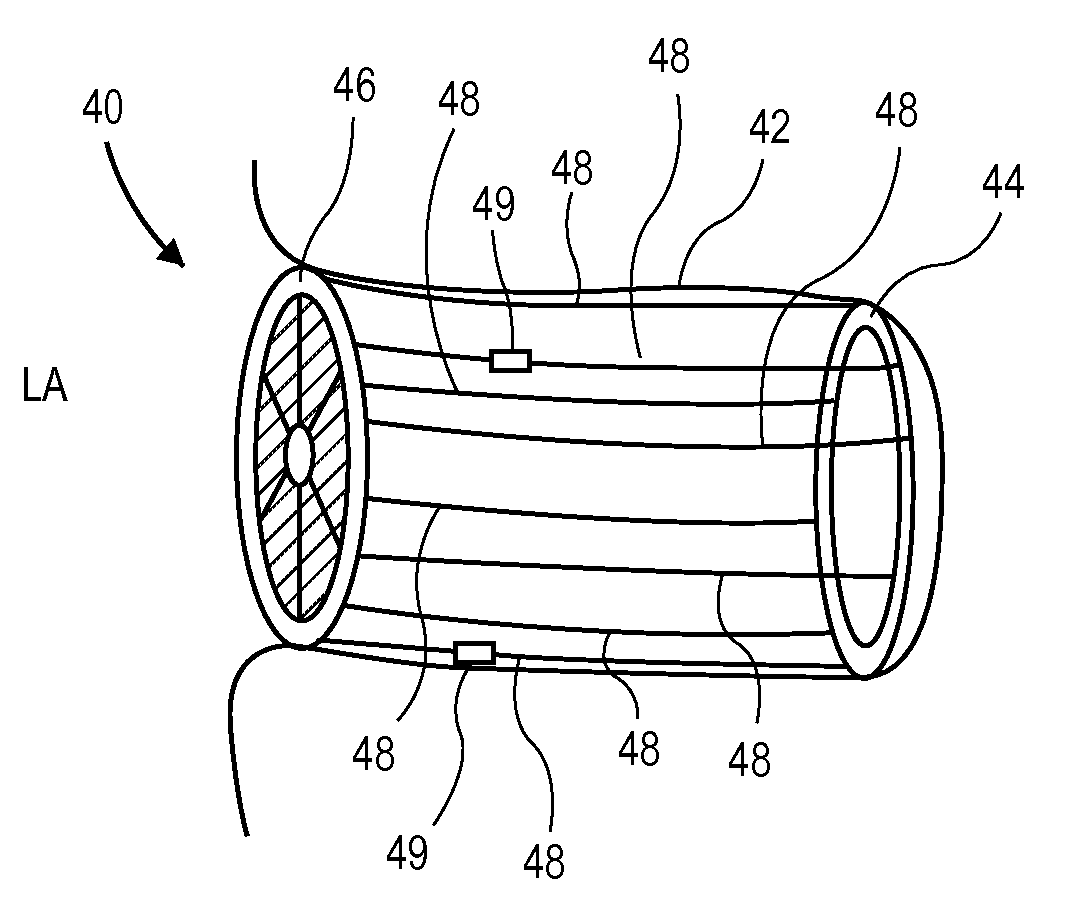
A system (1) for altering the geometry of a heart (100), comprising an annuloplasty ring; a set of elongate annulus-papillary tension members (21, 22, 23, 24), each of which tension members are adapted for forming a link between said ring (10) and a papillary muscle, each of said tension members (21, 22, 23, 24) having a first end (21b, 22b, 23b, 24b) and a second end (21a, 22a, 23a, 24a); and a first set of papillary anchors (30) for connecting each of the first ends (21b, 22b, 23b, 24b) of said tension members (21, 22, 23, 24) to said muscle; and where said annuloplasty ring (10) has at least one aperture (12, 13); where each of said annulus-papillary tension members (21, 22, 23, 24) are extendable through said ring (10) through said apertures (11, 12, 13), and through an atrium to an exterior side of said atrium, such that the distance of each link between the annulus and the muscles is adjustable from a position exterior to the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Device and method for esophageal cooling
InactiveUS20070055328A1Equally distributedDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsOesophageal injuryPreventing injury
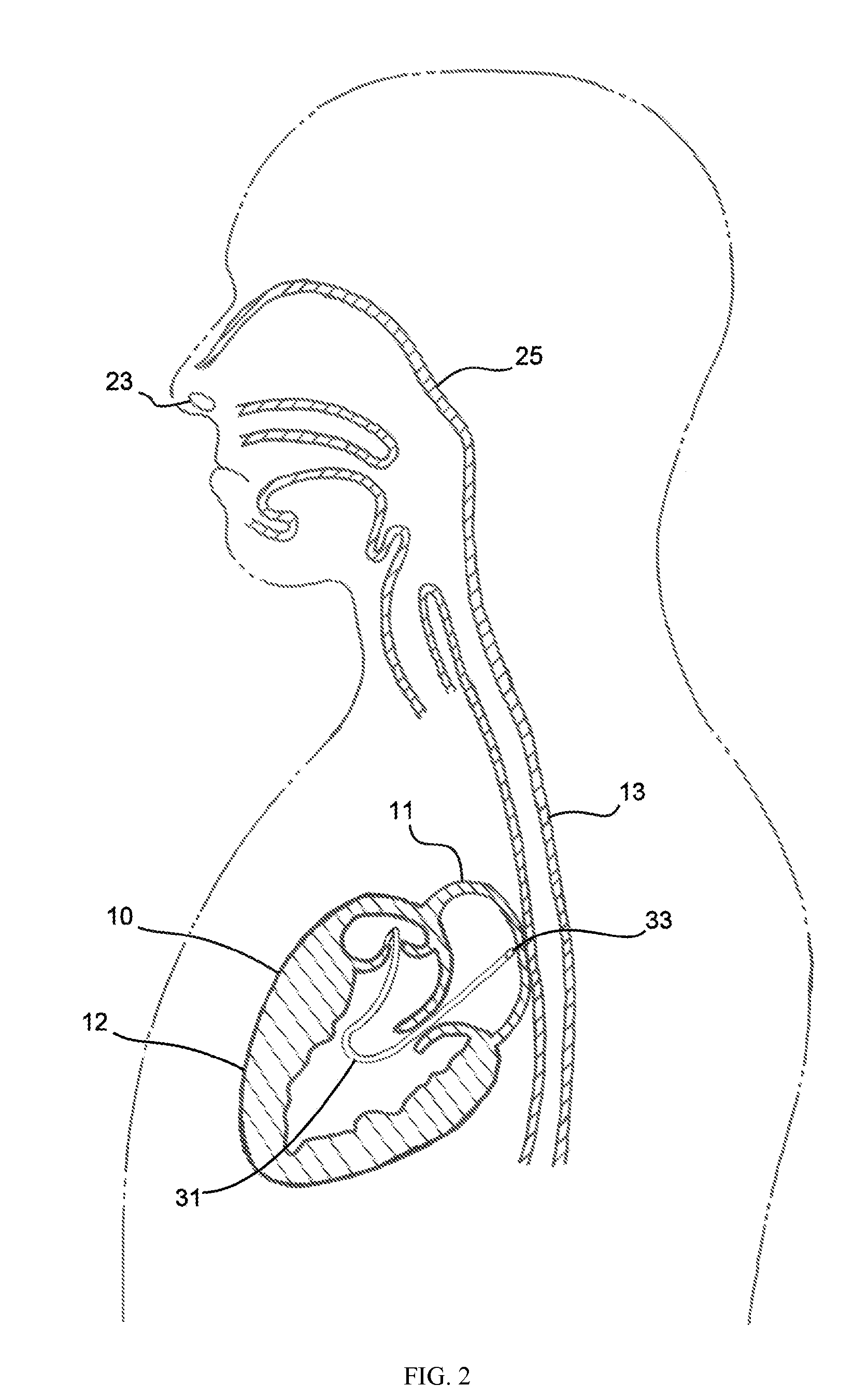
The present invention includes a device and a method for preventing injury of the esophagus during thermal ablation of the left atrium. The device has an esophageal probe with a balloon tip for insertion into the esophagus of a patient. During usage, coolant passes into the esophageal probe and then fills its balloon. The coolant, when circulating through the balloon and an external cooling machine, protects the esophageal tissue in contact with the esophageal probe from thermal damage during ablation of the posterior wall of the left atrium of the heart, or other procedure.
Owner:MAYSE MARTIN L +1
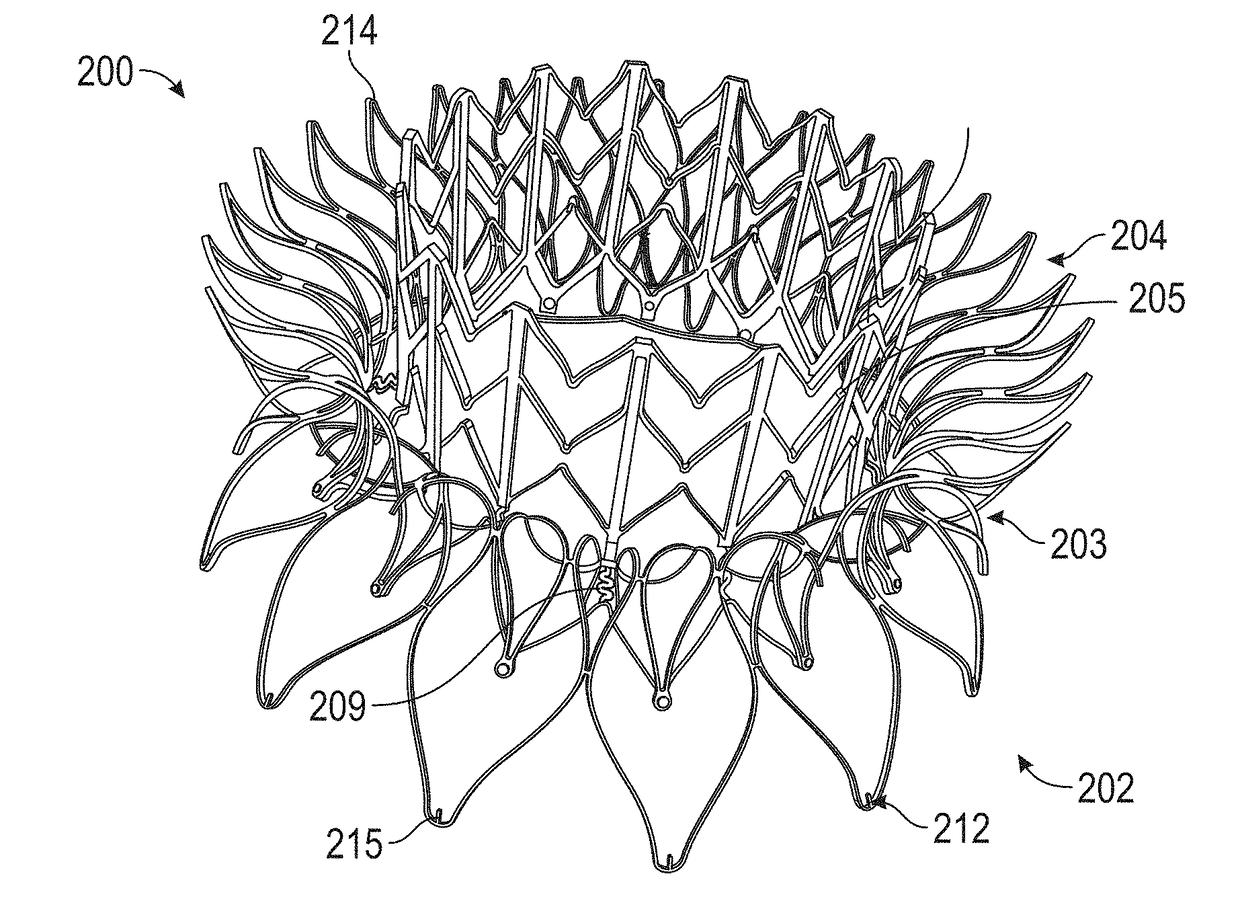
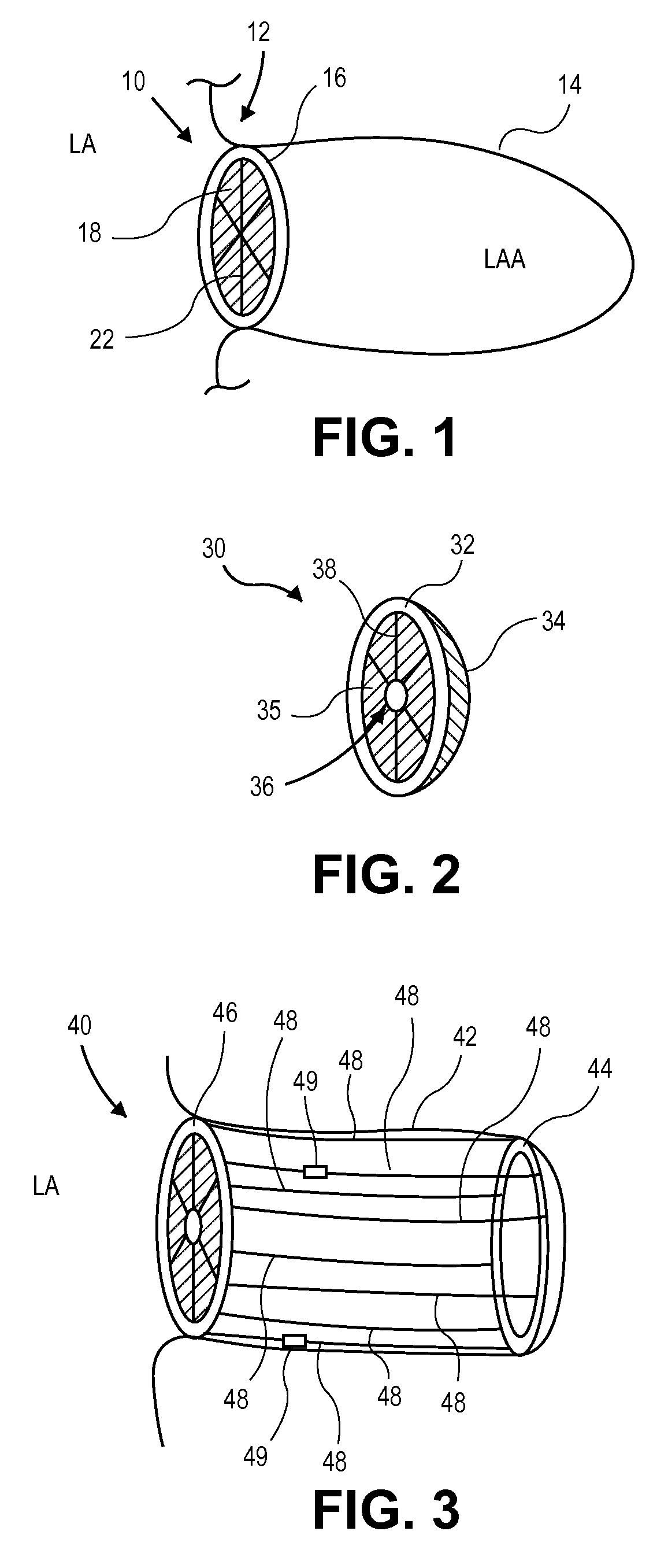
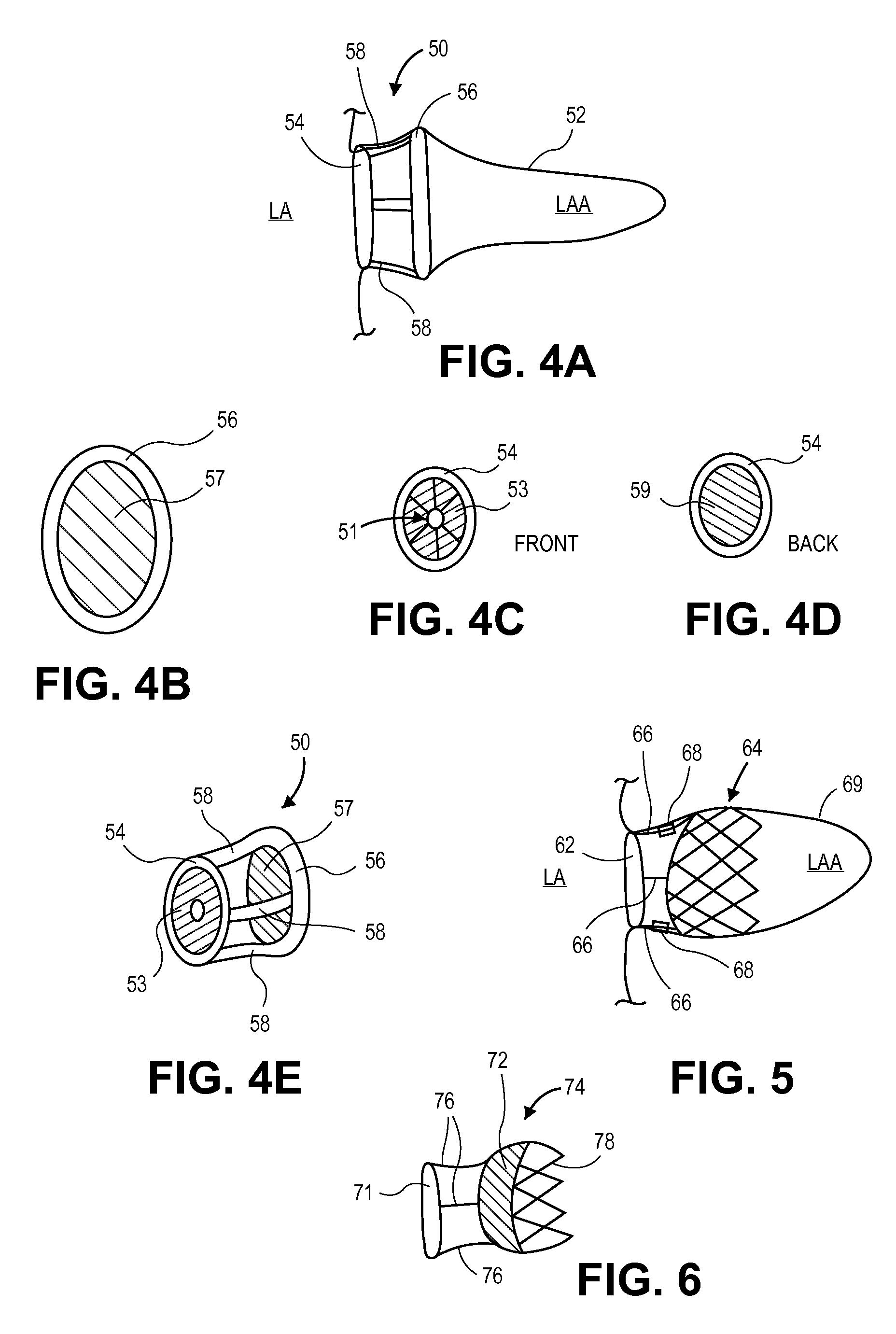
Devices, systems, and methods for reshaping a heart valve annulus, including the use of a bridge implant having an adjustable bridge stop
Implants or systems of implants and methods apply a selected force vector or a selected combination of force vectors within or across the left atrium, which allow mitral valve leaflets to better coapt. The implants or systems of implants and methods make possible rapid deployment, facile endovascular delivery, and full intra-atrial adjustability and retrievability years after implant. The implants or systems of implants and methods also make use of strong fluoroscopic landmarks. The implants or systems of implants and methods make use of an adjustable implant and a fixed length implant. The implants or systems of implants and methods may also utilize an adjustable bridge stop to secure the implant, and the methods of implantation employ various tools.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
Signal Analysis System for Heart Condition Determination
InactiveUS20120232417A1Easy to detectFast and slow atrial rotor activityElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisTime domainSignal processing
A system for heart performance characterization and abnormality detection includes an interface for receiving sampled data representing an electrical signal indicating electrical activity of a patient heart over multiple heart beat cycles. A signal processor automatically, decomposes the received sampled data to multiple different subcomponent signals in the time domain. The signal processor associates individual decomposed subcomponents with corresponding different cardiac rotors and determined characteristics of the subcomponents indicating relative significance of the rotors in a cardiac atrial condition. A reproduction device provides data indicating the subcomponent characteristics indicating relative significance of the rotors in a cardiac atrial condition.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
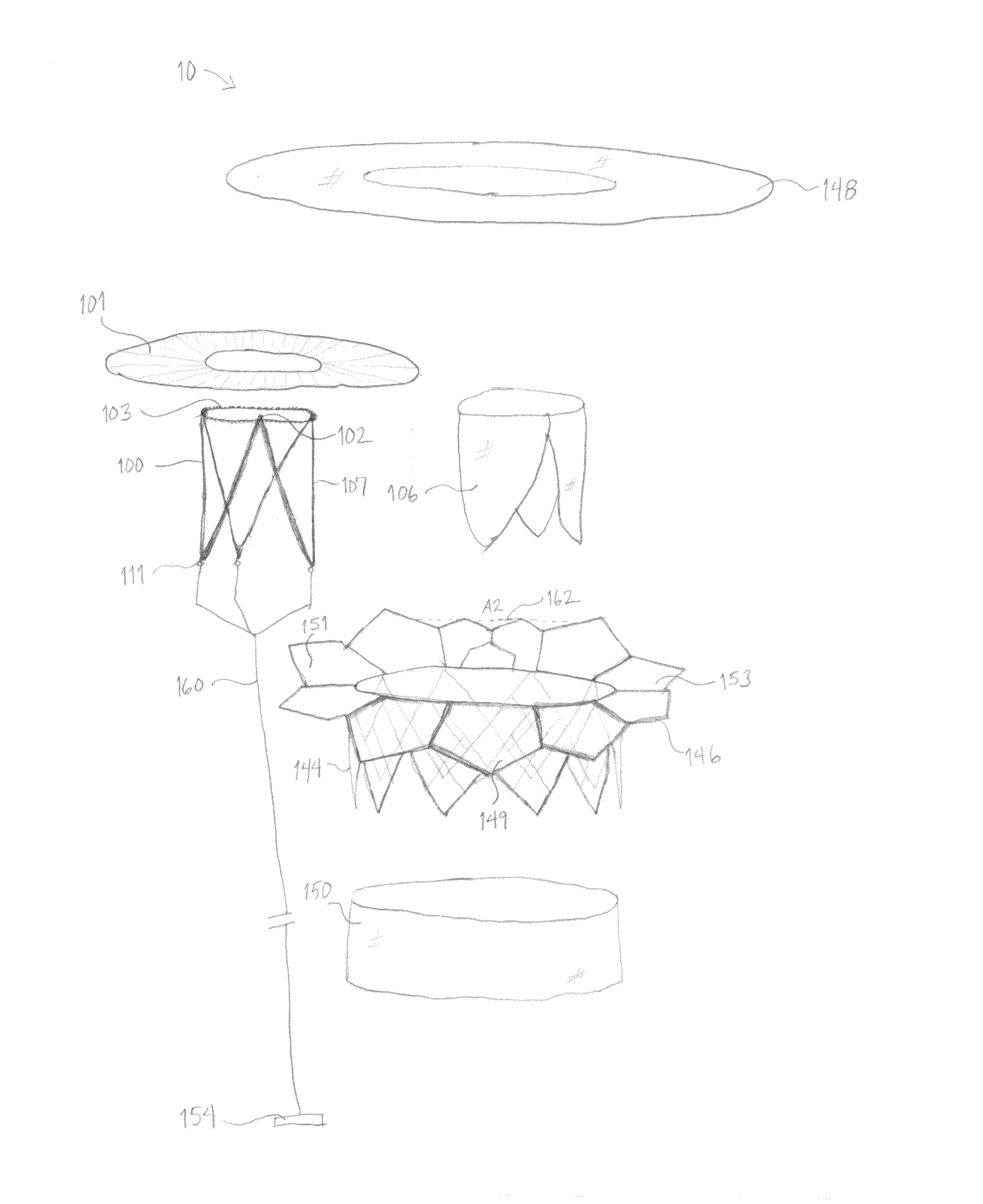
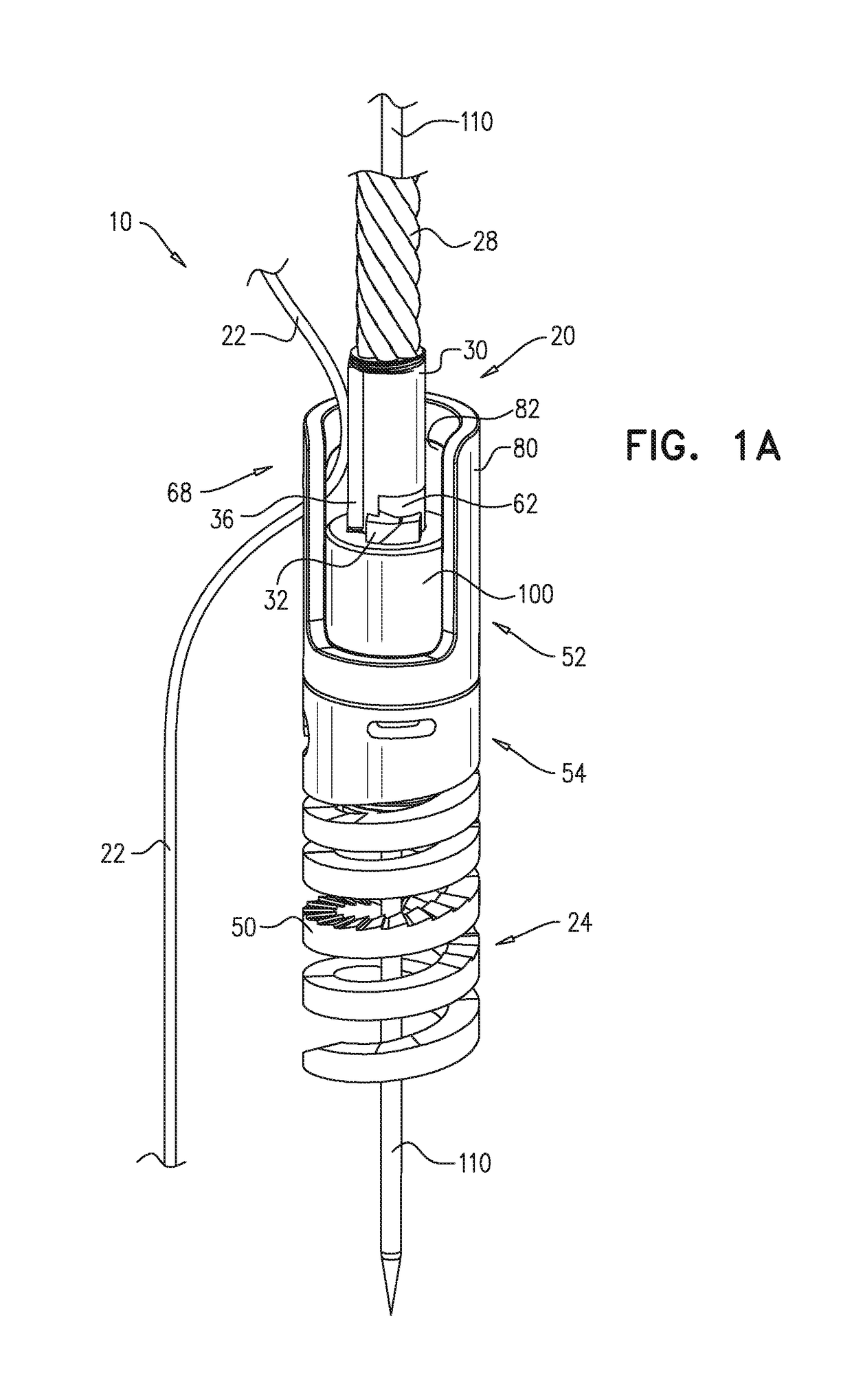
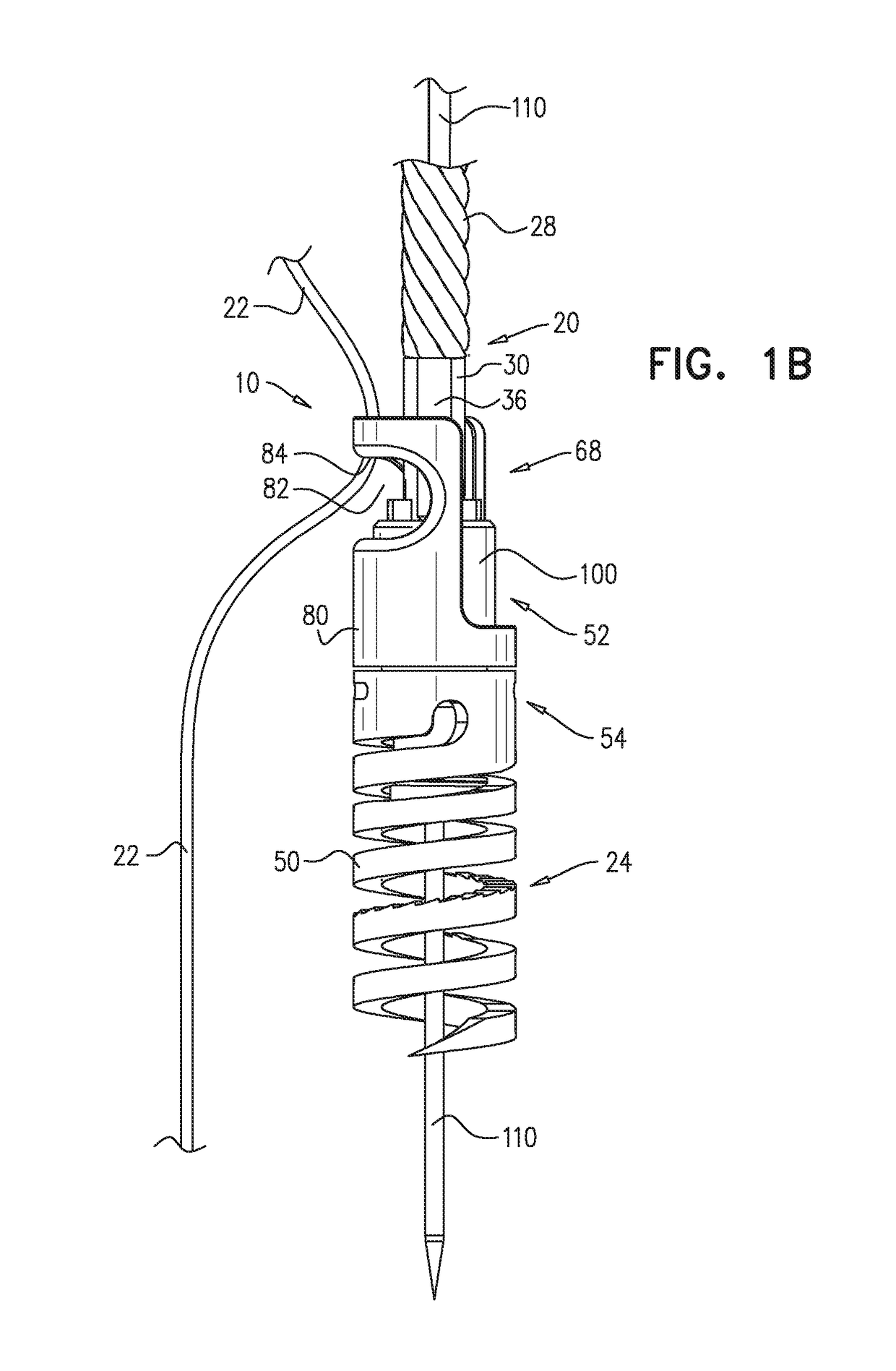
Implantation of flexible implant
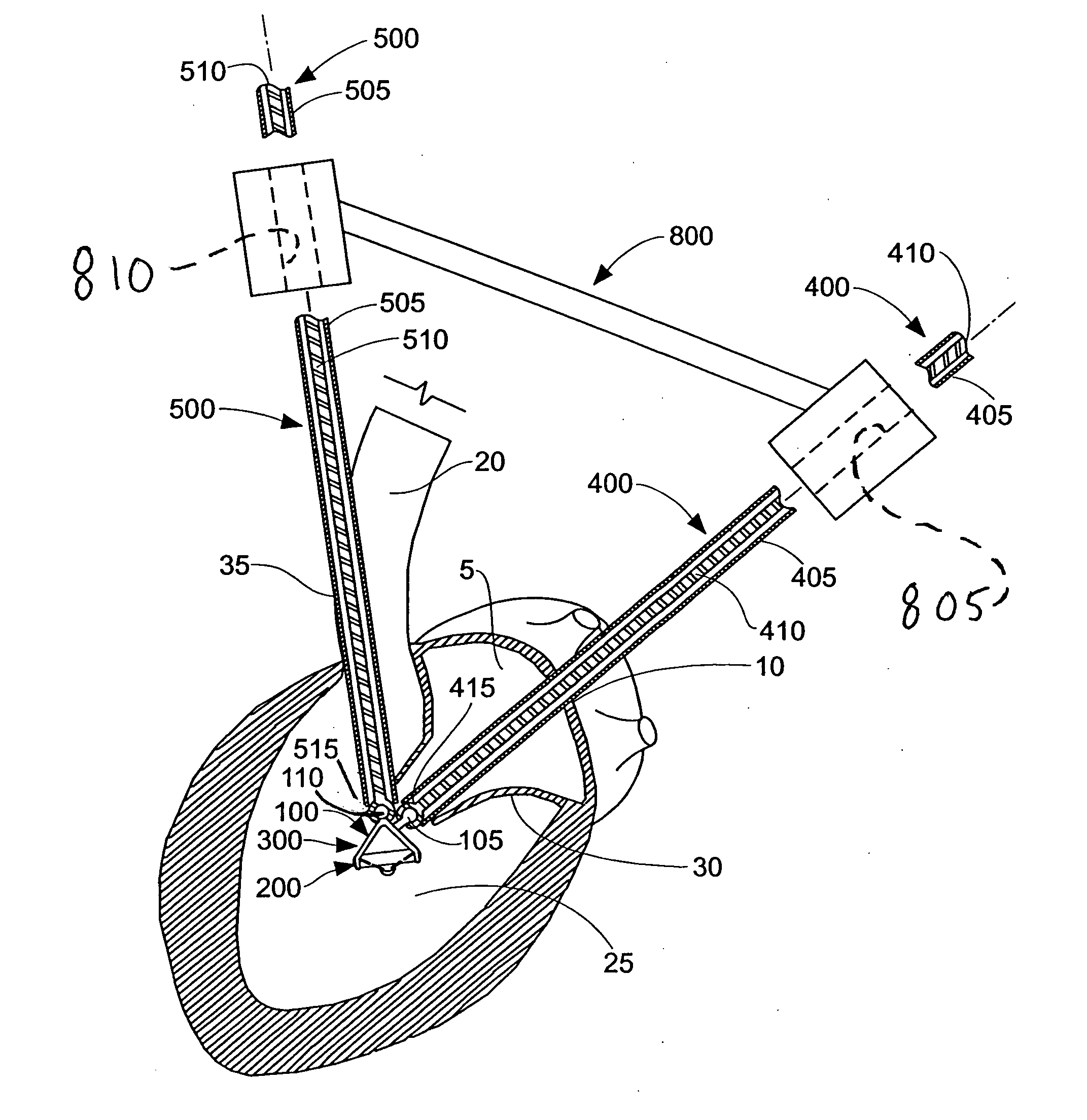
A method is provided, including introducing into a heart atrium, an annuloplasty structure having a sleeve with an elongated tubular side wall and at least one distal end wall having a surface substantially transverse to a lateral surface of the tubular side wall. A first tissue anchor is deployed through the surface of the end wall of the sleeve and into a first portion of annulus tissue. A second tissue anchor is deployed through a portion of the tubular side wall and into a second portion of annulus tissue, such that the first tissue anchor and the second tissue anchor are both deployed consecutively, to extend in a substantially same direction and into a common, substantially planar surface of a valve annulus, the common, substantially planar surface including the first and second portions of the annulus tissue. Other applications are also described.
Owner:VALTECH CARDIO LTD
Asymmetric dual directional steerable catheter sheath
ActiveUS20100217261A1Shorten travel distanceImprove usabilityMedical devicesCatheterDistal portionBiomedical engineering
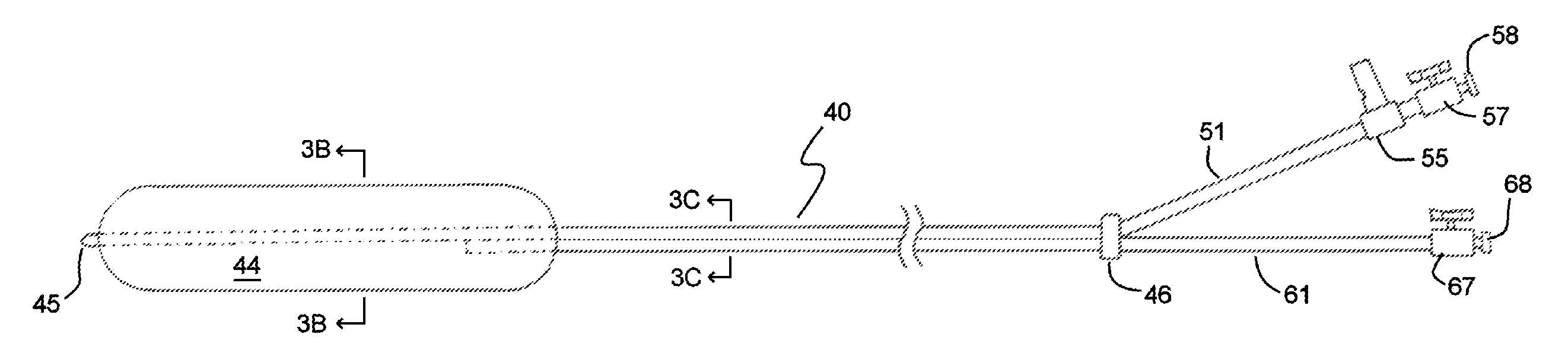
A steerable catheter sheath for use in directing a catheter into a desired position is provided. The sheath includes an elongated member configured to receive the catheter therein. The distal end of the elongated member is steerable in two directions, each direction having a different bent configuration, e.g., a sharp curve in one direction and an open arching curve in the other direction. A resilient structure having different bending properties in each of its lateral sides is carried in the distal portion of the elongated member and causes the asymmetric bending. In one embodiment, the resilient structure includes a hypotube with a plurality of notches and slits in the sides. In another embodiment, the resilient structure is covered in an outer coating having different durometer portions. The sheath is particularly useful for accessing left and right pulmonary veins when a transeptal entry approach is used into the left atrium.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Prosthesis for reducing intra-cardiac pressure having an embolic filter
ActiveUS20120053686A1Reducing pressure necrosisImprove radiopacityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsProsthesis
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Parasympathetic stimulation for termination of non-sinus atrial tachycardia
InactiveUS8060197B2Avoid stimulationHigh strengthElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMedicineNormal Sinus Rhythm
Apparatus is provided, which includes an electrode device, configured to be coupled to an atrial site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue, and a control unit. The control unit is configured to, responsively to a detection of an episode of non-sinus atrial tachycardia, restore normal sinus rhythm (NSR) of the subject, by driving the electrode device to apply a parasympathetic stimulation signal to the atrial site, and configuring the parasympathetic stimulation signal to activate the parasympathetic nervous tissue sufficiently to restore the NSR. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
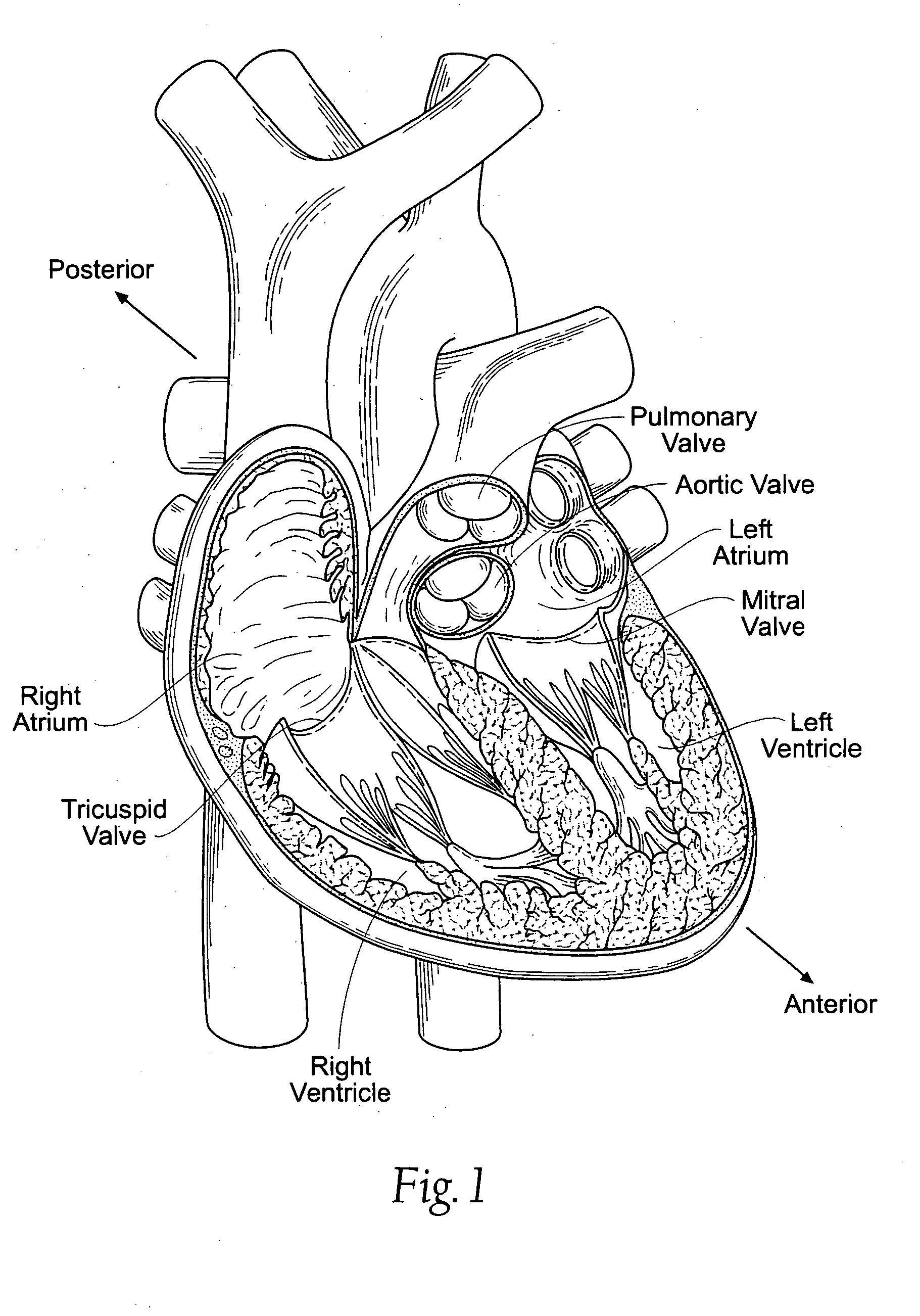
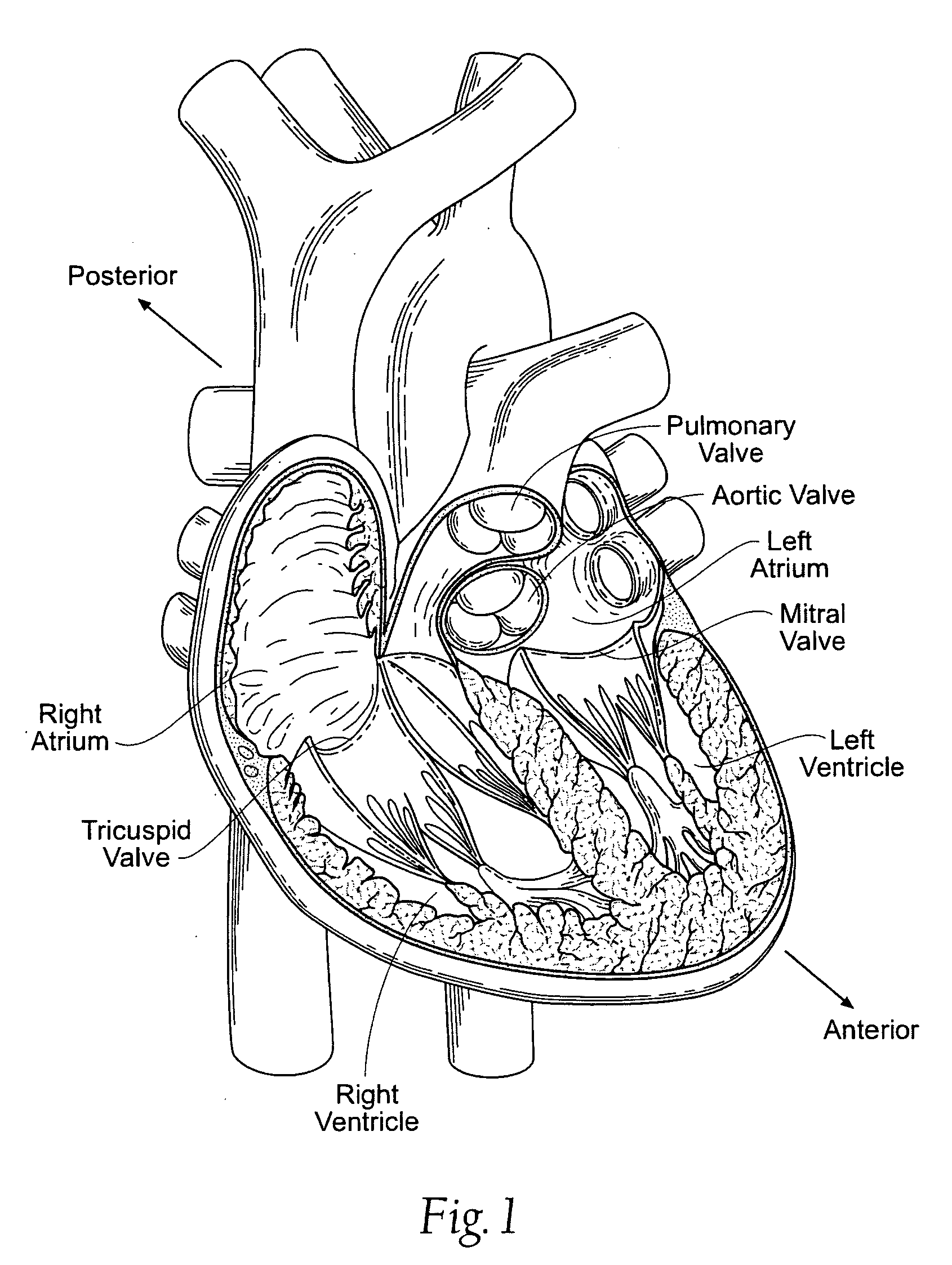
Replacement mitral valves
A prosthetic mitral valve includes an anchor assembly, a strut frame, and a plurality of replacement leaflets secured to the annular strut frame. The anchor assembly includes a ventricular anchor, an atrial anchor, and a central portion therebetween. The ventricular anchor and the atrial anchor are configured to flare radially outwards relative to the central portion. The annular strut frame is disposed radially within the anchor assembly and is attached to the anchor assembly. The central portion is configured to align with a native valve orifice and the ventricular anchor and the atrial anchor are configured to compress native cardiac tissue therebetween.
Owner:CEPHEA VALVE TECH
Atrial Appendage Occlusion and Arrhythmia Treatment
InactiveUS20120283585A1Prevent blood clotPrevent blood clotsElectrotherapySurgeryCardiac arrhythmiaHeart atrium
Owner:VENTRIMEND INC
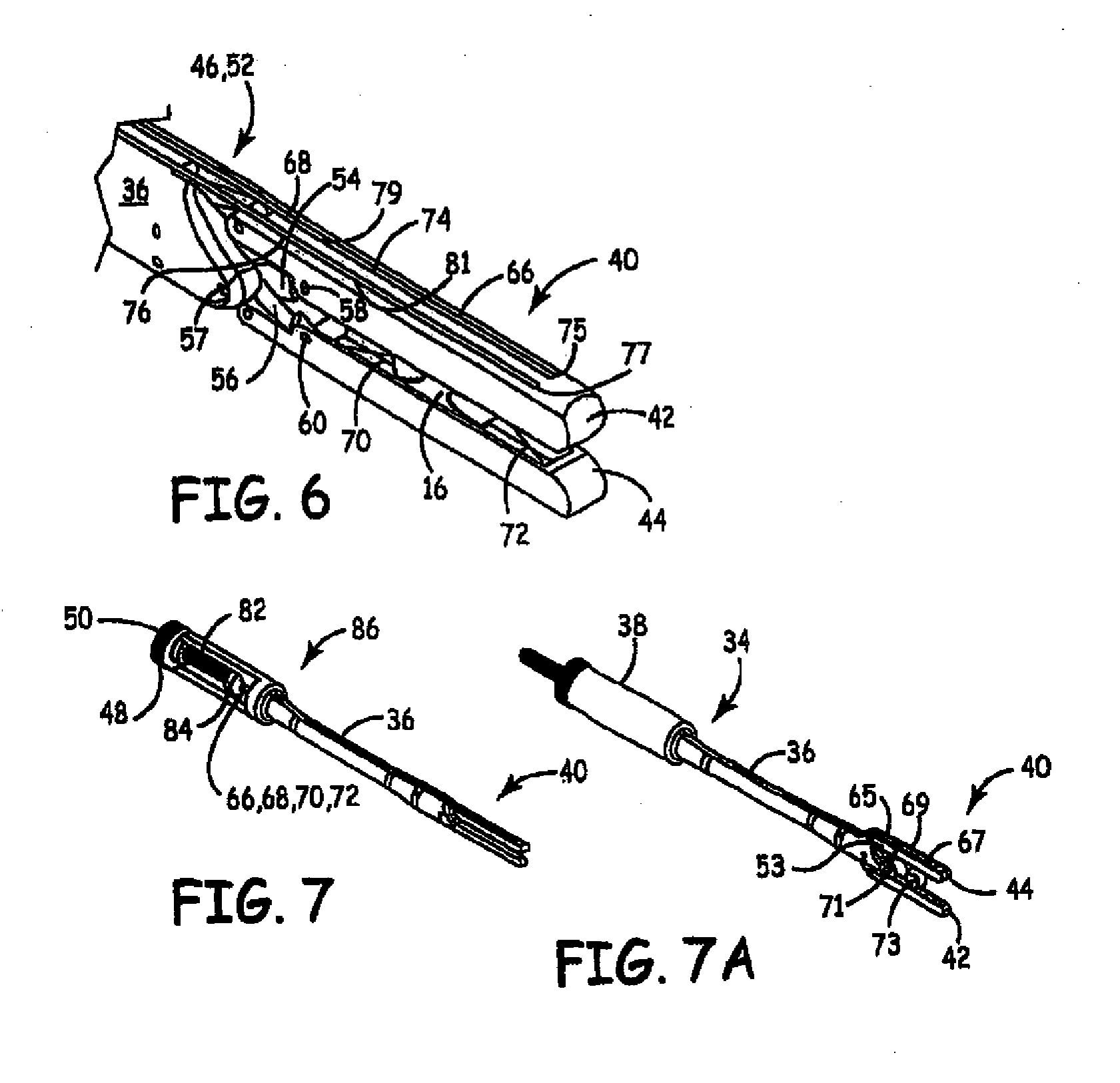
Method and apparatus for synchronization of atrial defibrillation pulses
A method and apparatus for detecting and treating atrial fibrillation. In response to detecting atrial fibrillation, the device derives an escape interval based on one or more preceding intervals between ventricular depolarizations. The escape interval is initiated in response to a ventricular depolarization, and in response to the expiration of the escape interval, an atrial cardioversion pulse is delivered. In one embodiment of the invention, the cardioverting pulse is delivered immediately upon expiration of the derived escape interval. In a second embodiment of the invention, a ventricular pacing pulse is delivered on expiration of the escape interval, with an atrial cardioversion pulse following after a short delay.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
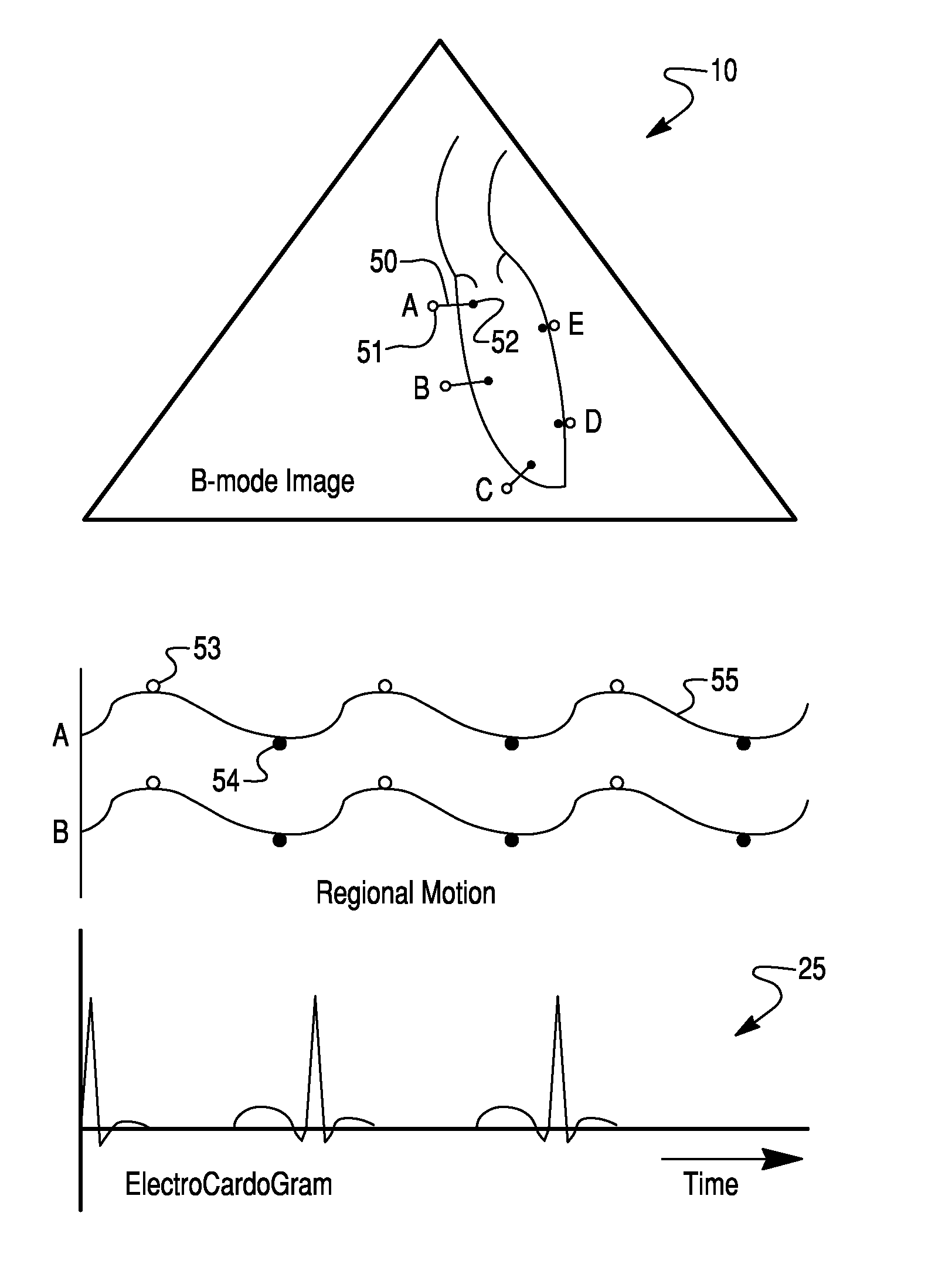
Method and System For Estimating Cardiac Ejection Volume And Placing Pacemaker Electrodes Using Speckle Tracking
InactiveUS20070167809A1Eliminate error of inputReduce duplicationBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsEcg signalSystole
A method and system for estimating the volume of blood ejected from a cardiac ventricle or atrium uses ultrasound to track speckle patterns in the heart. The process utilizes the M-mode to estimate volume differences in a view of the ventricle or atrium over time using speckle pattern motion to estimate volume differences between systole and diastole. Alternatively, the ultrasound speckle tracking method may be used in combination with Doppler processing techniques or to obtain temporal flow profiles across flow cross-sectional areas, from which the flow volume is computed. The method can also measure the phase delay of motion of sites on the cardiac wall relative to each other or relative to an ECG signal.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Cardiac tissue cinching
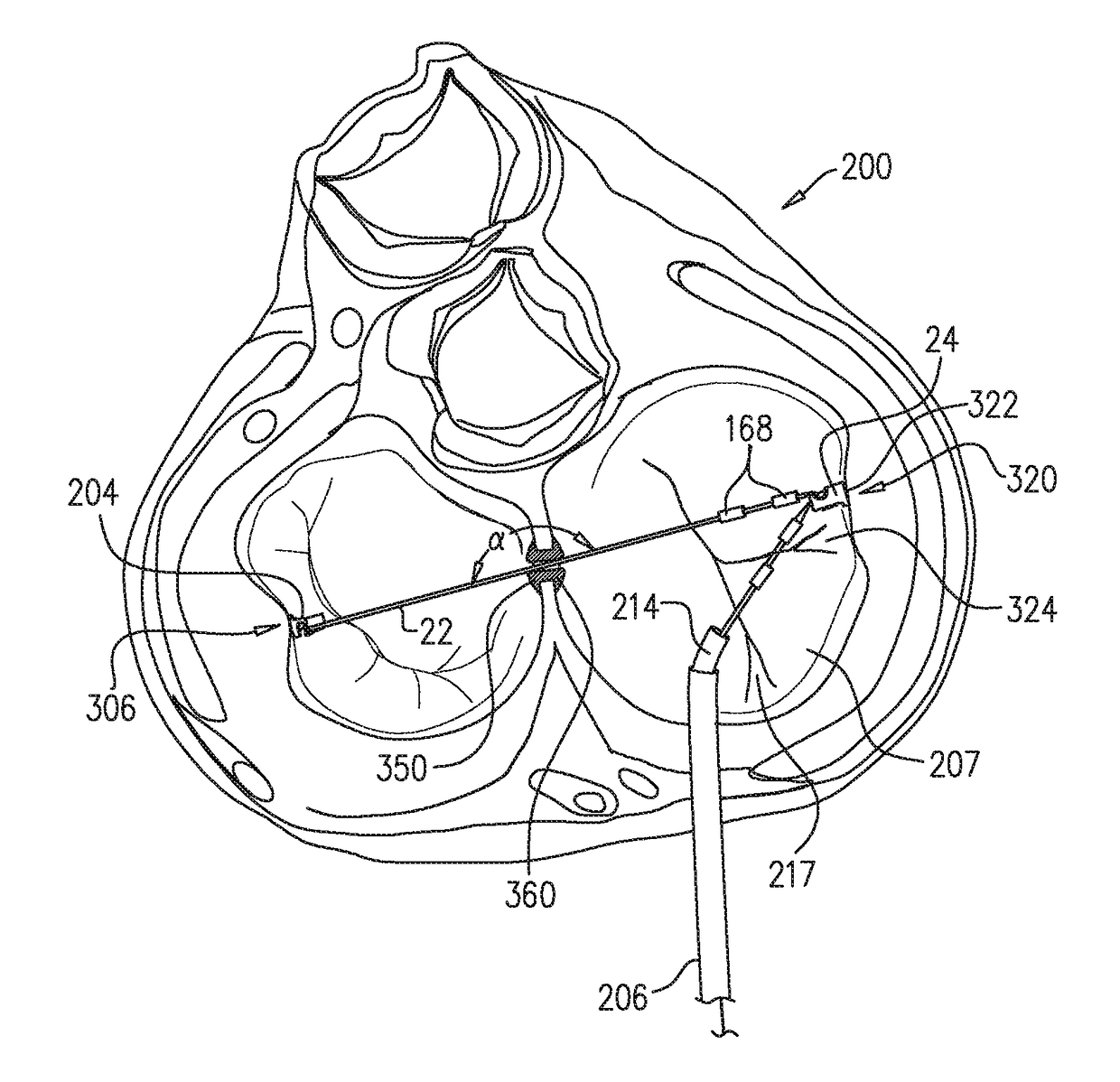
ActiveUS9801720B2Enhanced couplingPrevent slidingSuture equipmentsHeart valvesAtrial cavityRight atrium
A method is provided including making an opening (300) through an atrial septum (302) at a septal site (304) at least 5 mm from a fossa ovalis (330). A first tissue anchor (204) is endovascularly advanced to a left-atrial site (306) on an annulus of a mitral valve (310) or a wall of a left atrium (308) above the annulus. The first tissue anchor (204) is implanted at the left-atrial site (306). A second tissue anchor (24) is endovascularly advanced to a right-atrial site (320) on an annulus of a tricuspid valve (207) or a wall of a right atrium (200) above the annulus. The second tissue (24) anchor is implanted at the right-atrial site (320). The left-atrial site (306) and the right-atrial site (320) are approximated by tensioning a tether (22) that passes through the opening (300) of the atrial septum (302) and connects the first and the second tissue anchors (204, 24). Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:4TECH INC OXO CAPITAL
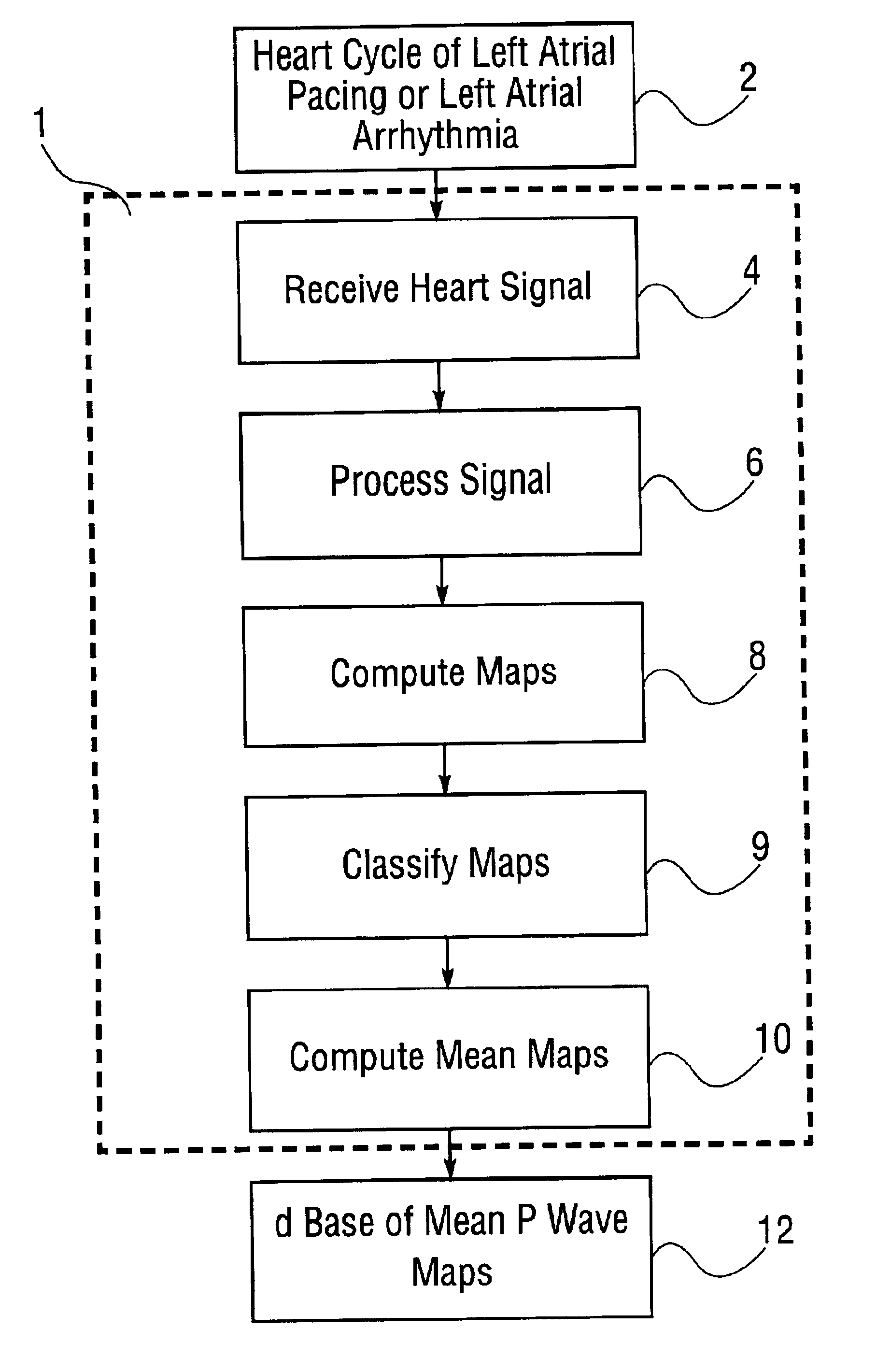
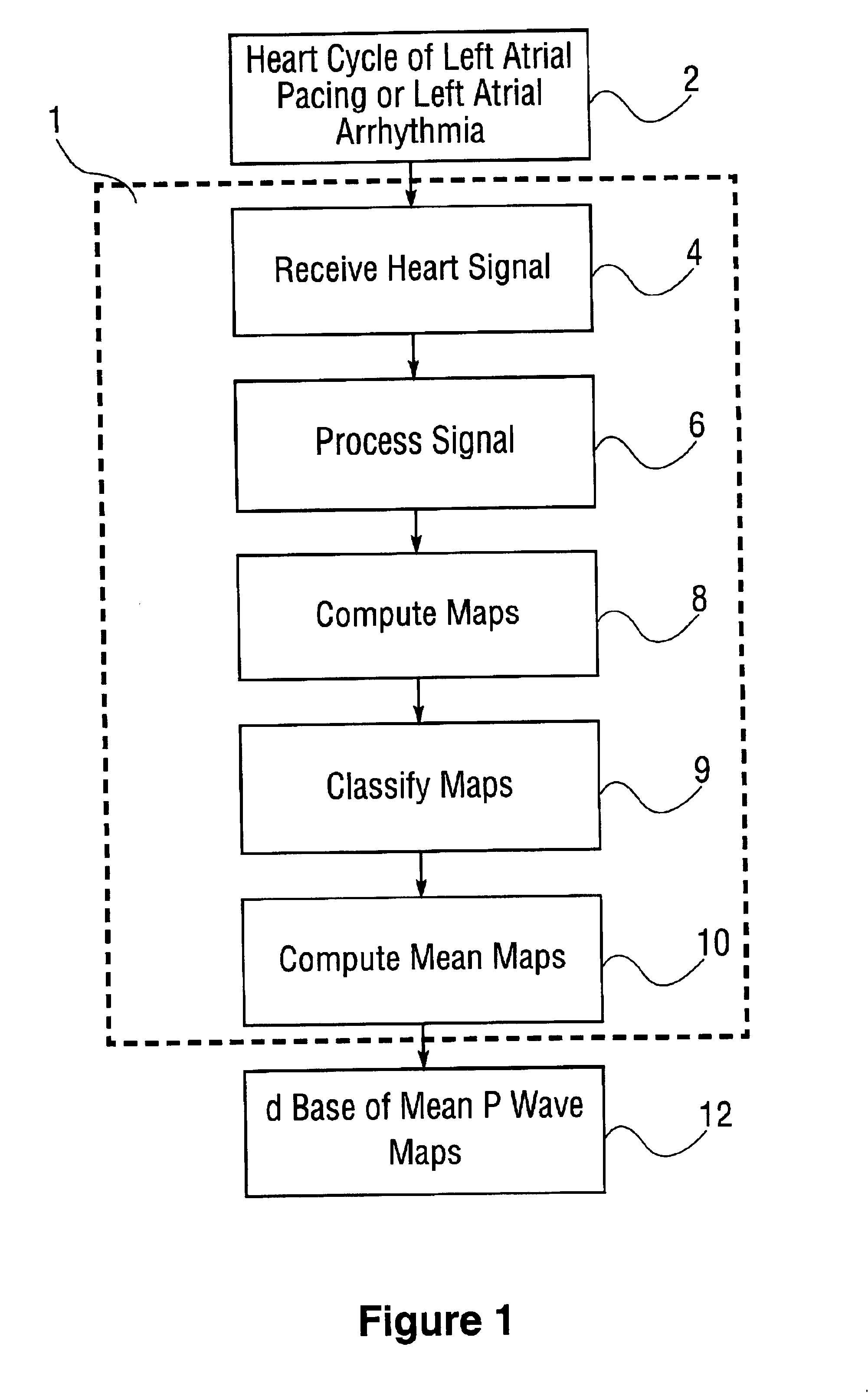
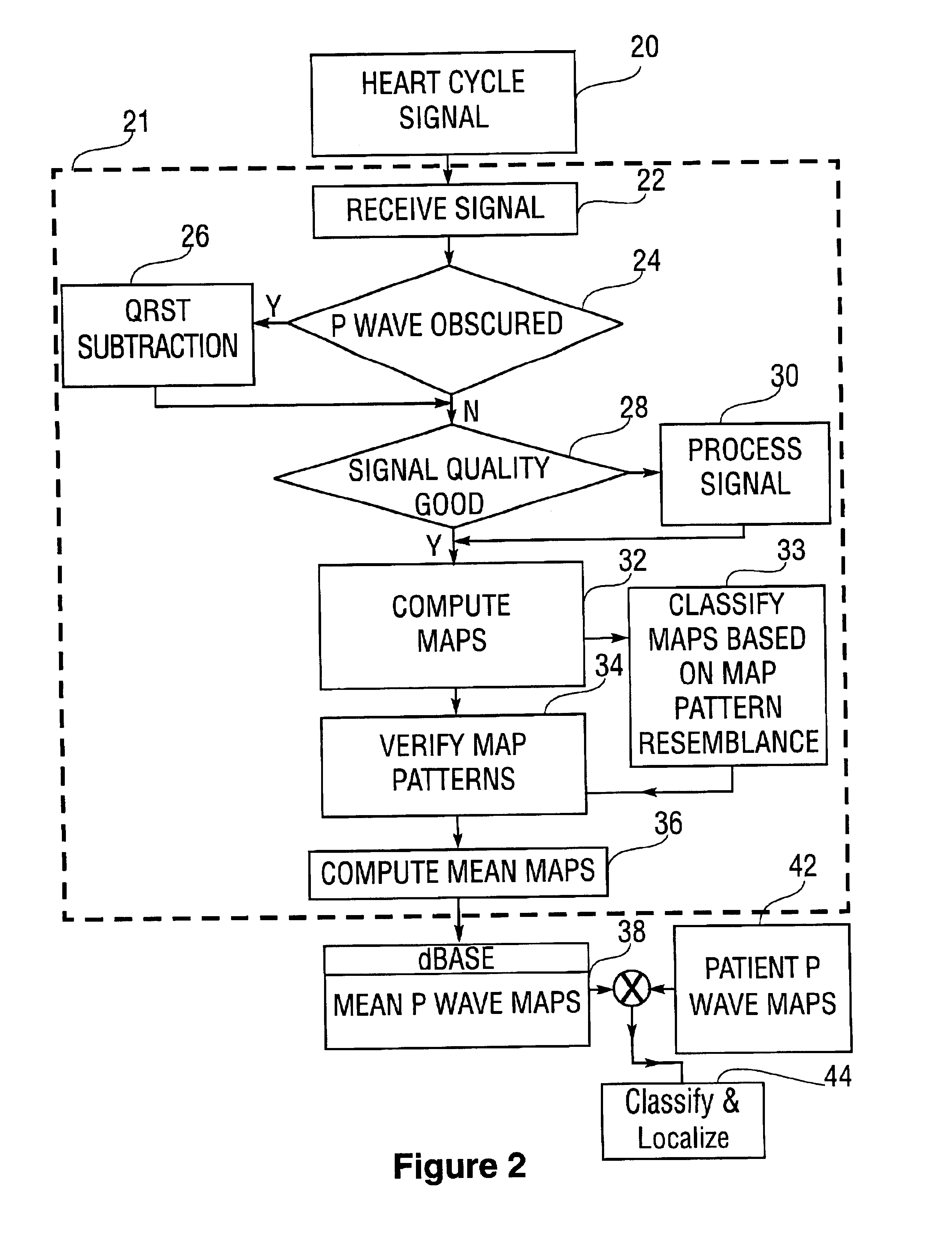
Database of body surface ECG P wave integral maps for localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias
InactiveUS6931273B2ElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyIsorhythmic Atrioventricular DissociationHypsarrhythmia
A system and method are provided for developing a database of body surface ECG P-wave maps for classification and localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias. The system and method include generating and receiving P-wave data in a subject by left atrial pacing or receiving P-wave data in a subject during spontaneously occurring or induced left atrial arrhythmias; computing (e.g. potential or integral) maps of the P-wave data; classifying the maps specific to a left atrial ectopic origin; verifying the classification procedure; averaging the classified maps into mean maps; and storing and accessing the mean maps in the database. The mean maps of the P-wave data in the database can be used to automatically classify and localize P-wave data from a patient obtained during a left atrial arrhythmia such as atrial tachycardia, focal atrial fibrillation, or orthodromic atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
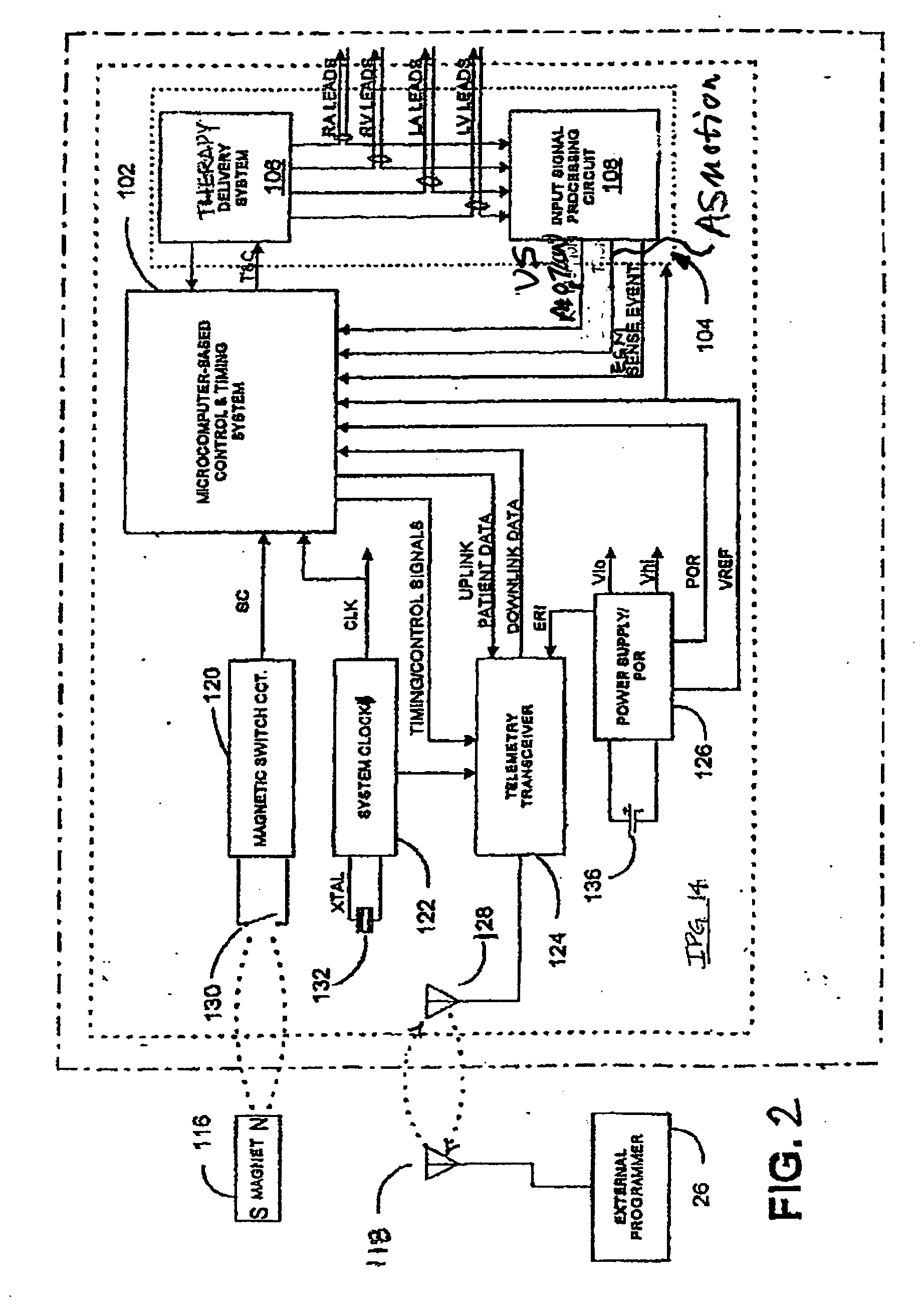
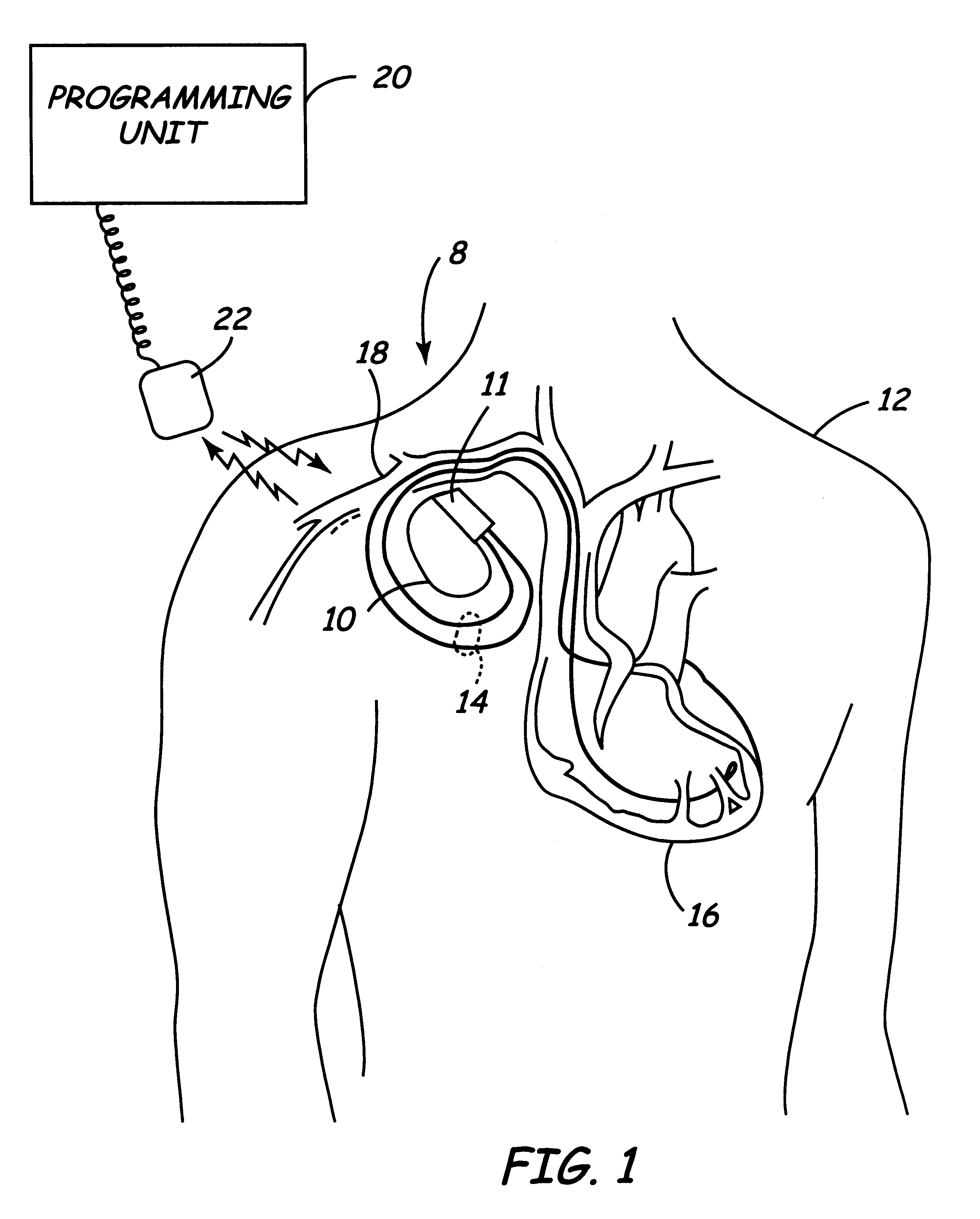
Method and apparatus for displaying information retrieved from an implanted medical device
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vacuum coagulation probes
InactiveUS20060200124A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesArticular cartilageLesion
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia; tendon or ligament shrinkage; or articular cartilage removal. The surgical device integrates a suction mechanism with the coagulation mechanism improving the lesion creation capabilities of the device. The surgical device comprises an elongate member having an insulative covering attached about conductive elements capable of coagulating soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through the insulative covering expose regions of the conductive elements and are coupled to lumens in the elongate member which are routed to a vacuum source. Suction causes the soft tissue to actively engage the opening thus the integrated, exposed conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, continuous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling mechanisms associated with the conductive elements and coupled to a fluid source to passively transport fluid along the contacted soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
Automatic LV/RV capture verification and diagnostics
ActiveUS7555336B2Significant comprehensive benefitsPrecise deliveryHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular conductionRat heart
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
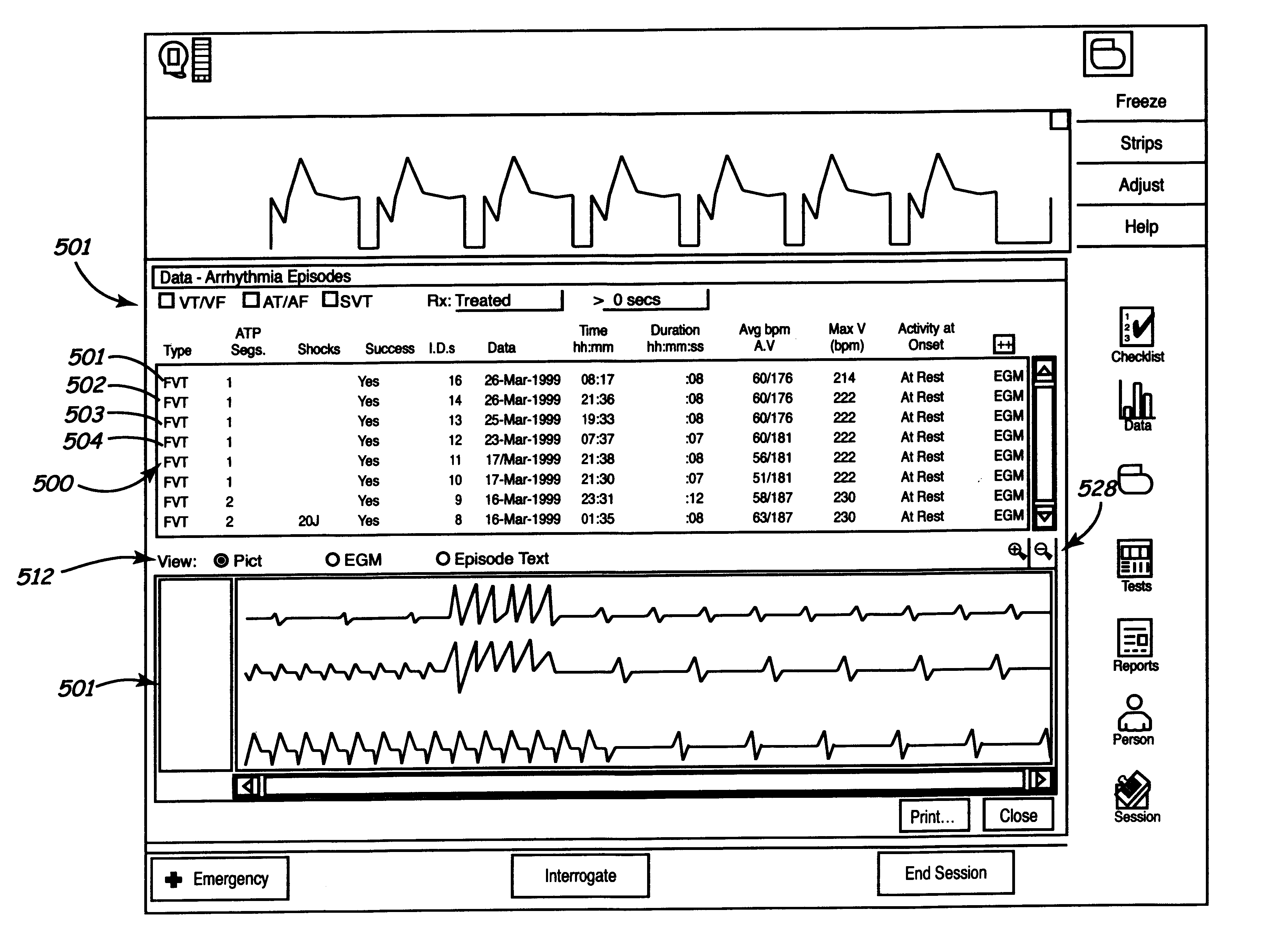
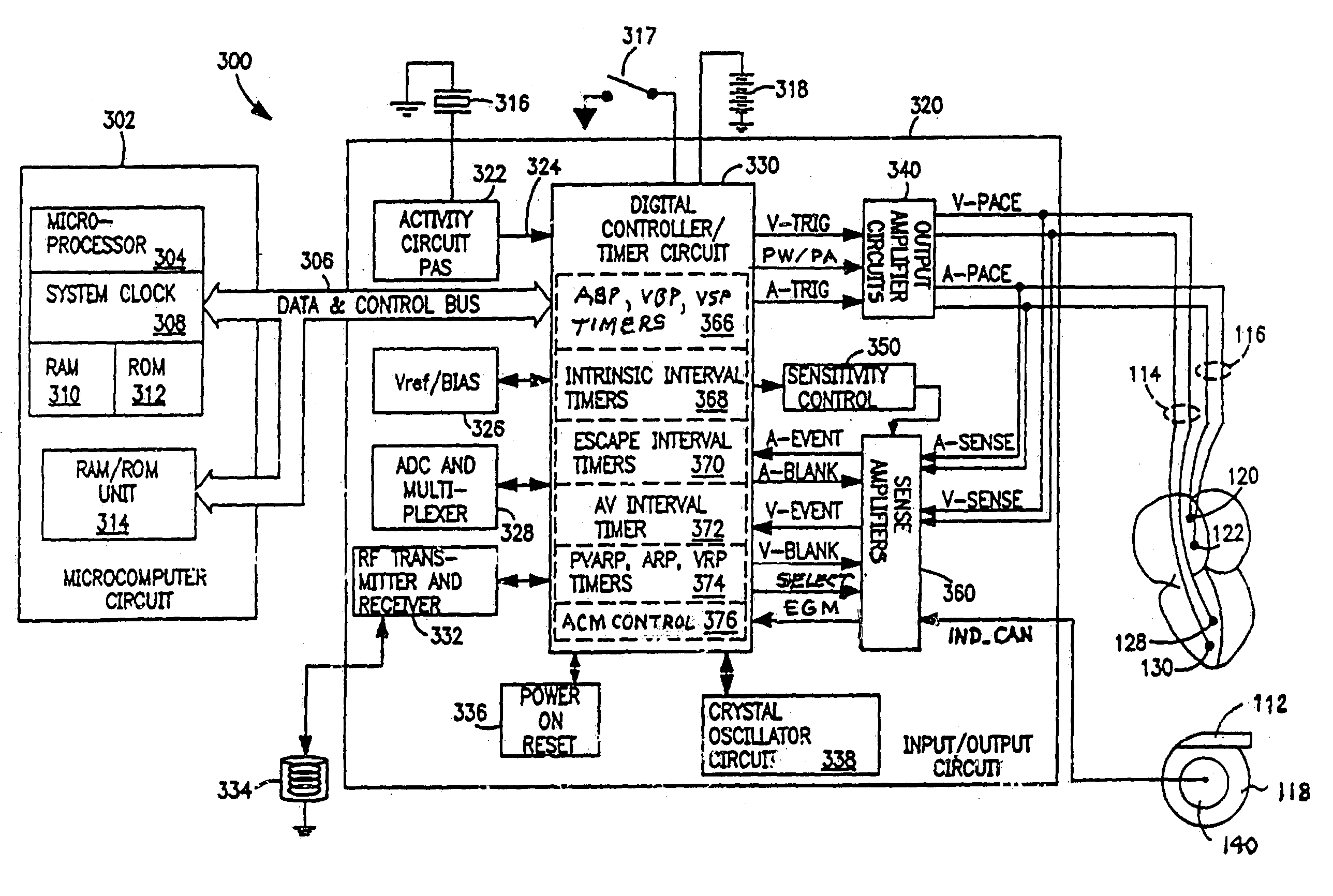
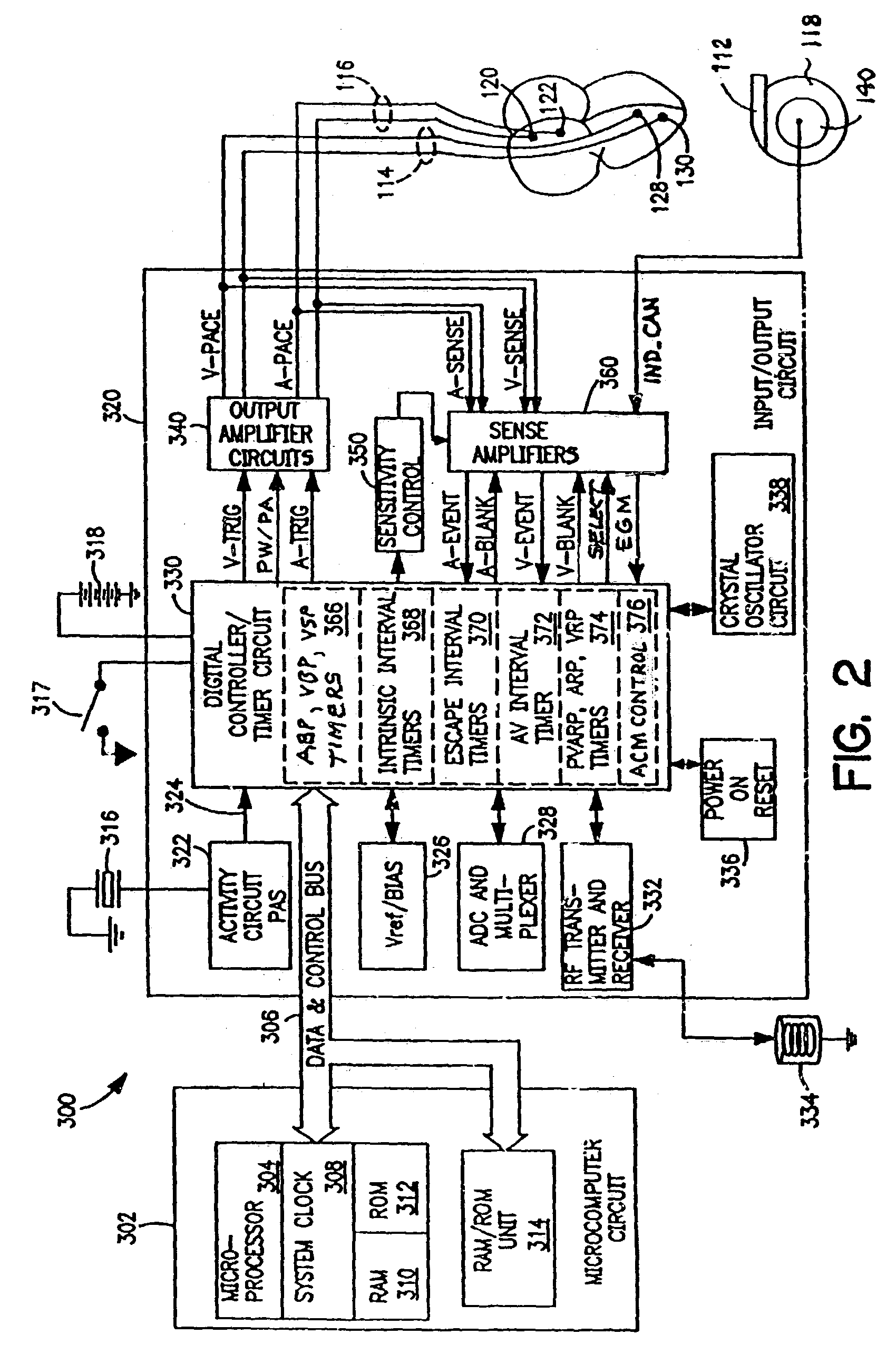
Diagnostic features in biatrial and biventricular pacing systems
InactiveUS7058443B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac pacemaker electrodeVentricular pacing
A biatrial and / or biventricular pacing system is used in a diagnostic context. By placing a pacing / sensing lead in three or four chambers of the heart, various conduction sequences can be determined and the originating chamber of various arrhythmias can be identified. This information is stored temporarily in the pacemaker until it is extracted for analysis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
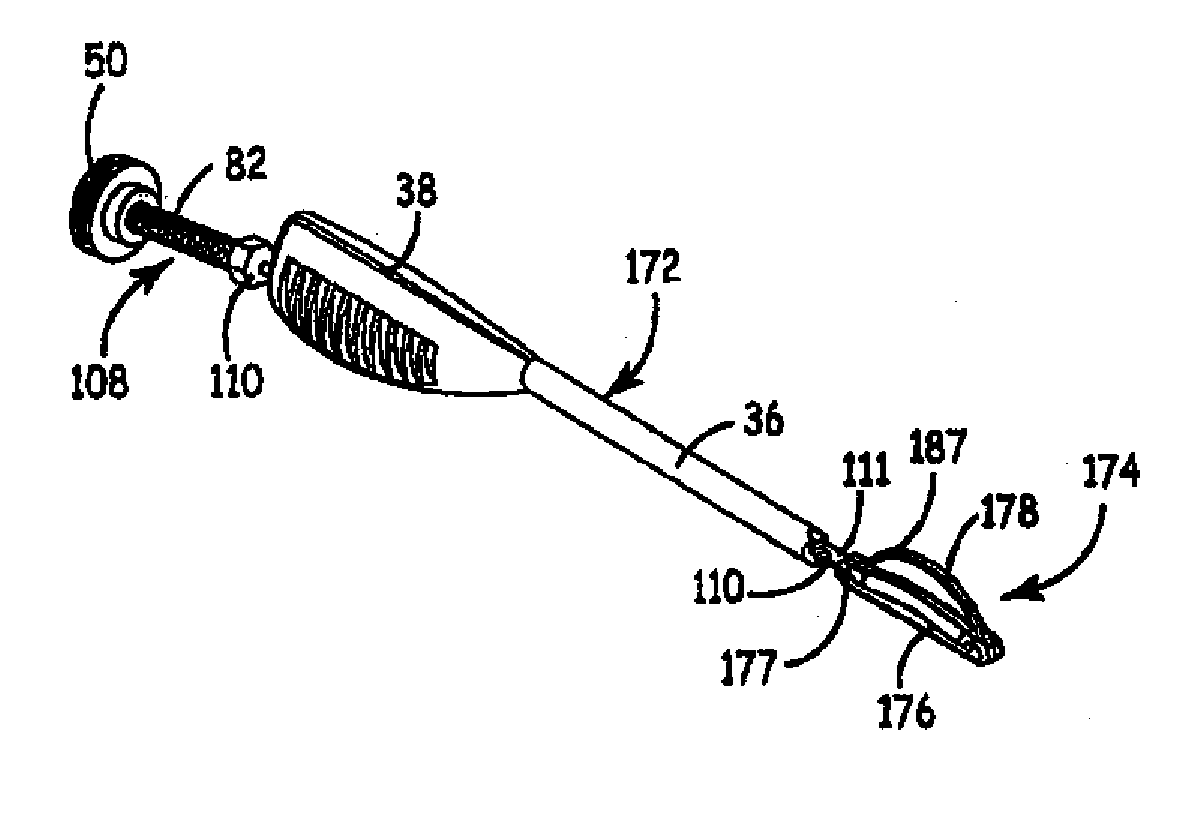
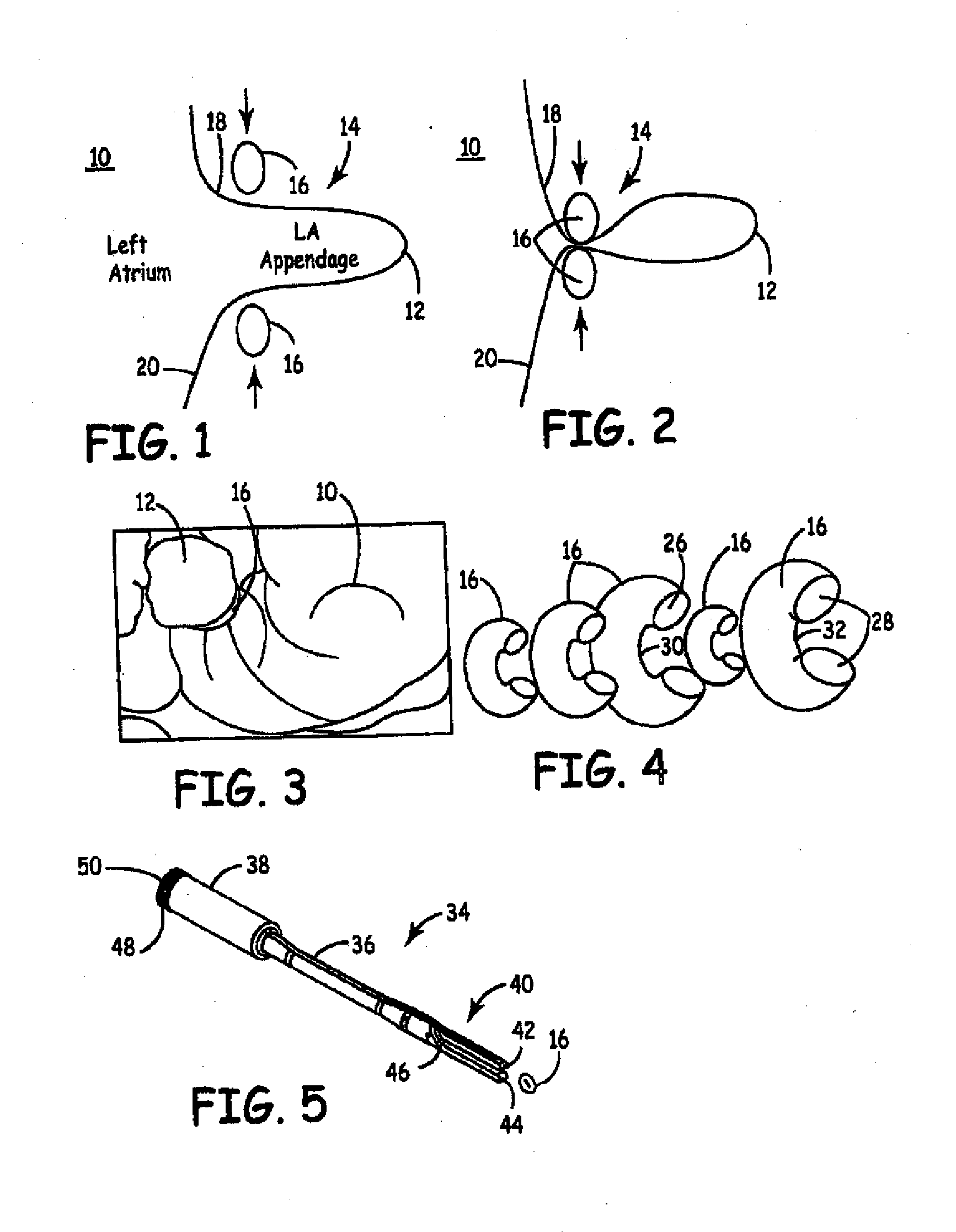
Methods and devices for occlusion of an atrial appendage
Some embodiments of the invention provide a system for occluding a left atrial appendage of a patient. Some embodiments of the system can include a ring occluder that can be positioned around the left atrial appendage and a ring applicator to position the ring occluder with respect to the left atrial appendage. One embodiment discloses a method of accessing endocardial surfaces of the heart through the atrial appendage. Additional embodiments of the invention provide a clip occluder that can be positioned around the left atrial appendage. A clip applicator can position the clip occluder with respect to the left atrial appendage.
Owner:STEWART MARK T +13
Atrial capture management during atrial and ventricular pacing
In an atrial pacing system, the A-PACE pulse energy, defined by the pulse width and pulse amplitude, sufficient to reliably capture the atrium without being wasteful of battery energy is periodically determined in accordance with atrial capture management (ACM) algorithms. The ACM algorithms allow a slow intrinsic atrial heart rate that is suppressed by delivered A-PACE pulses resulting in A-CAPTURE and that occurs when delivered test A-PACE pulses result in ALOC to be detected. ALOC is declared if an A-EVENT of the slow intrinsic atrial heart rate is detected either during an ACM test window timed from the last delivered test A-PACE pulse or during delivery of a sequence of test A-PACE pulses delivered within or defining the ACM test window correlated to the slow intrinsic atrial heart rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
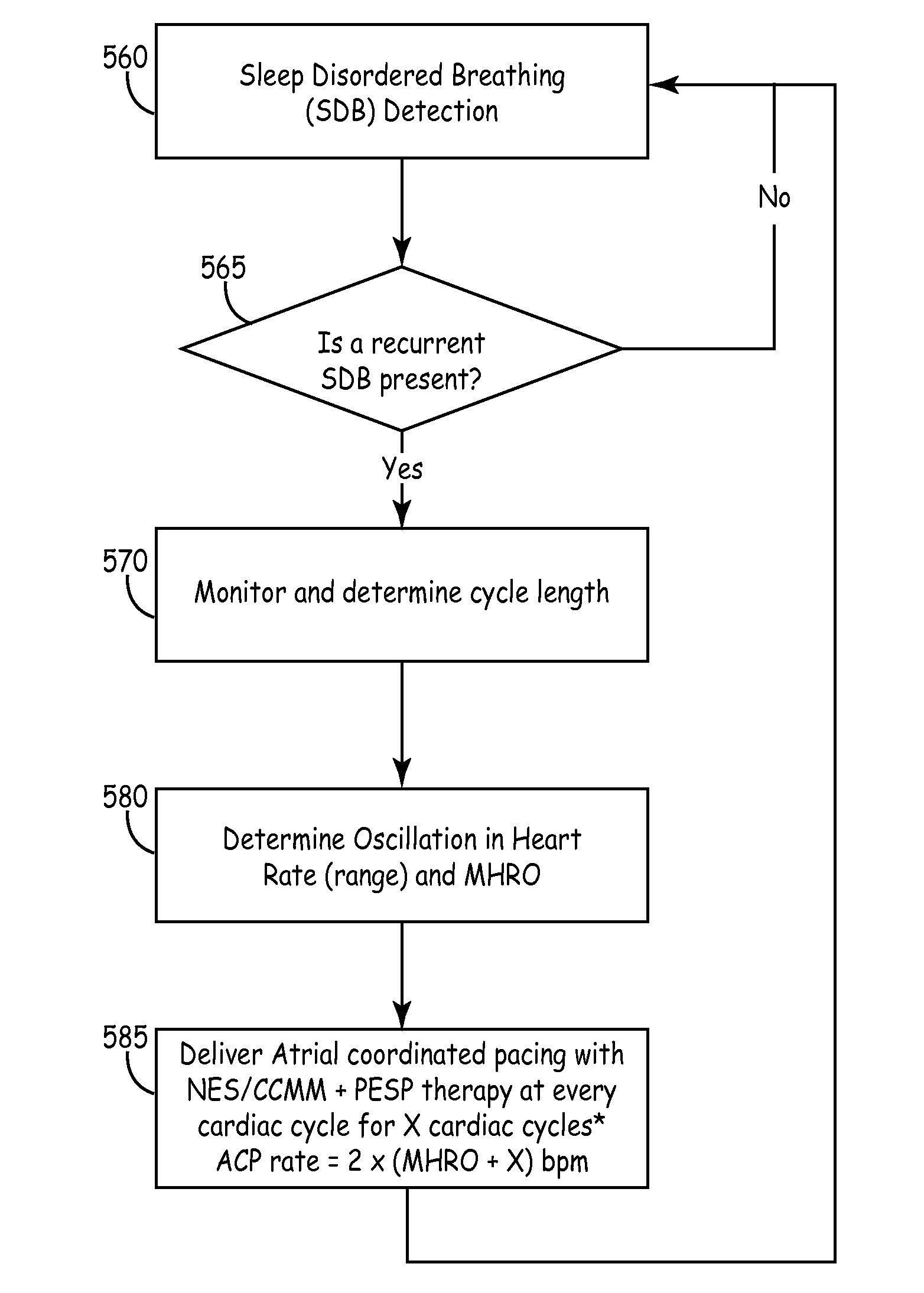
Implantable medical device and method for delivering therapy for sleep-disordered breathing
InactiveUS7130687B2CatheterRespiratory organ evaluationSleep disordered breathingElectrical stimulations
An implantable medical device delivers augmentation therapy to intervene in a pattern of sleep-disordered breathing. Augmentation therapy includes the delivery of electrical stimulation to cardiac tissue above and / or below a capture threshold. PESP and NES / CCM are possible augmentation therapies that are used alone or in combination. In addition, augmentation therapies can be used with other pacing therapies such as atrial overdrive pacing and atrial coordinated pacing as a therapy for sleep-disordered breathing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
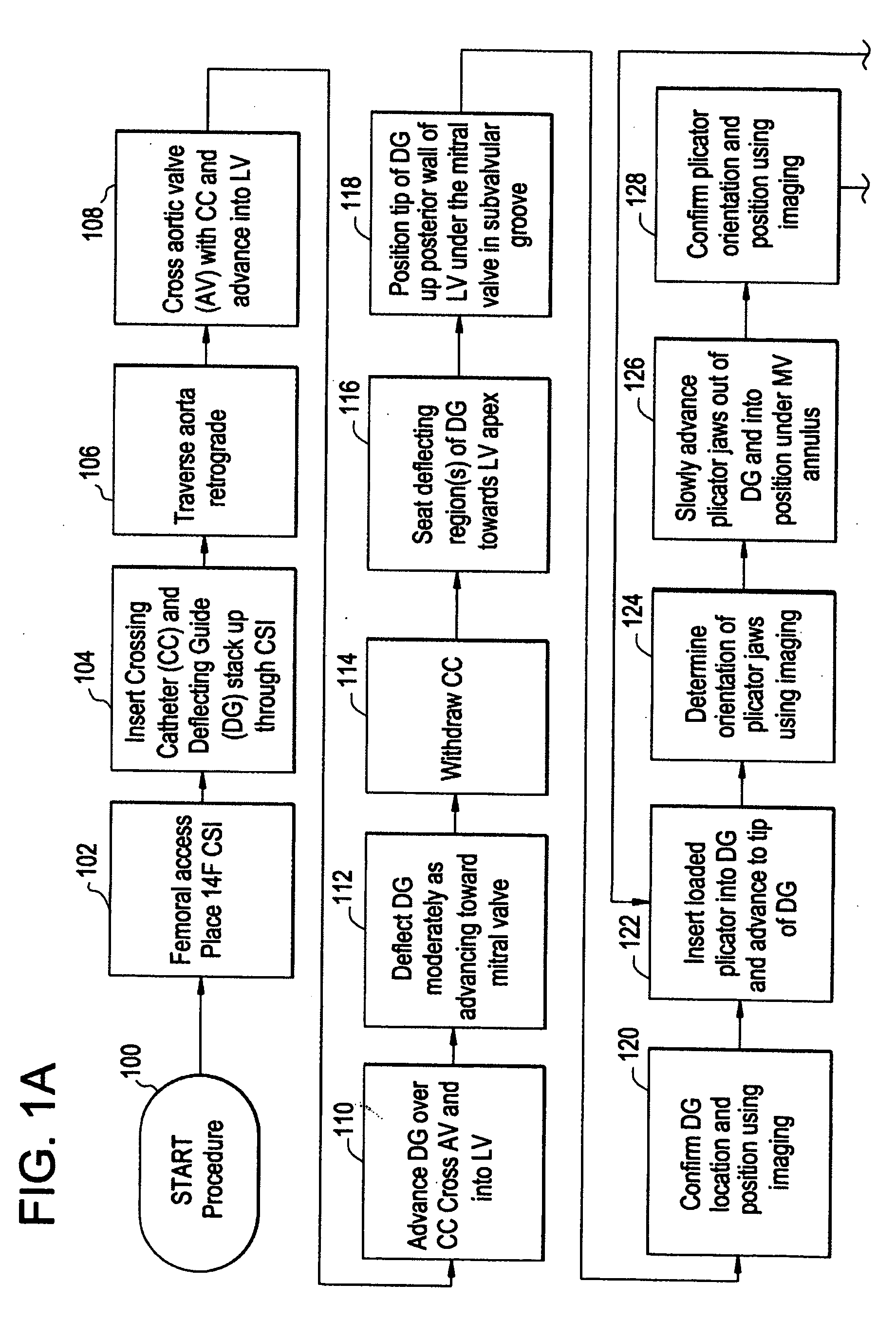
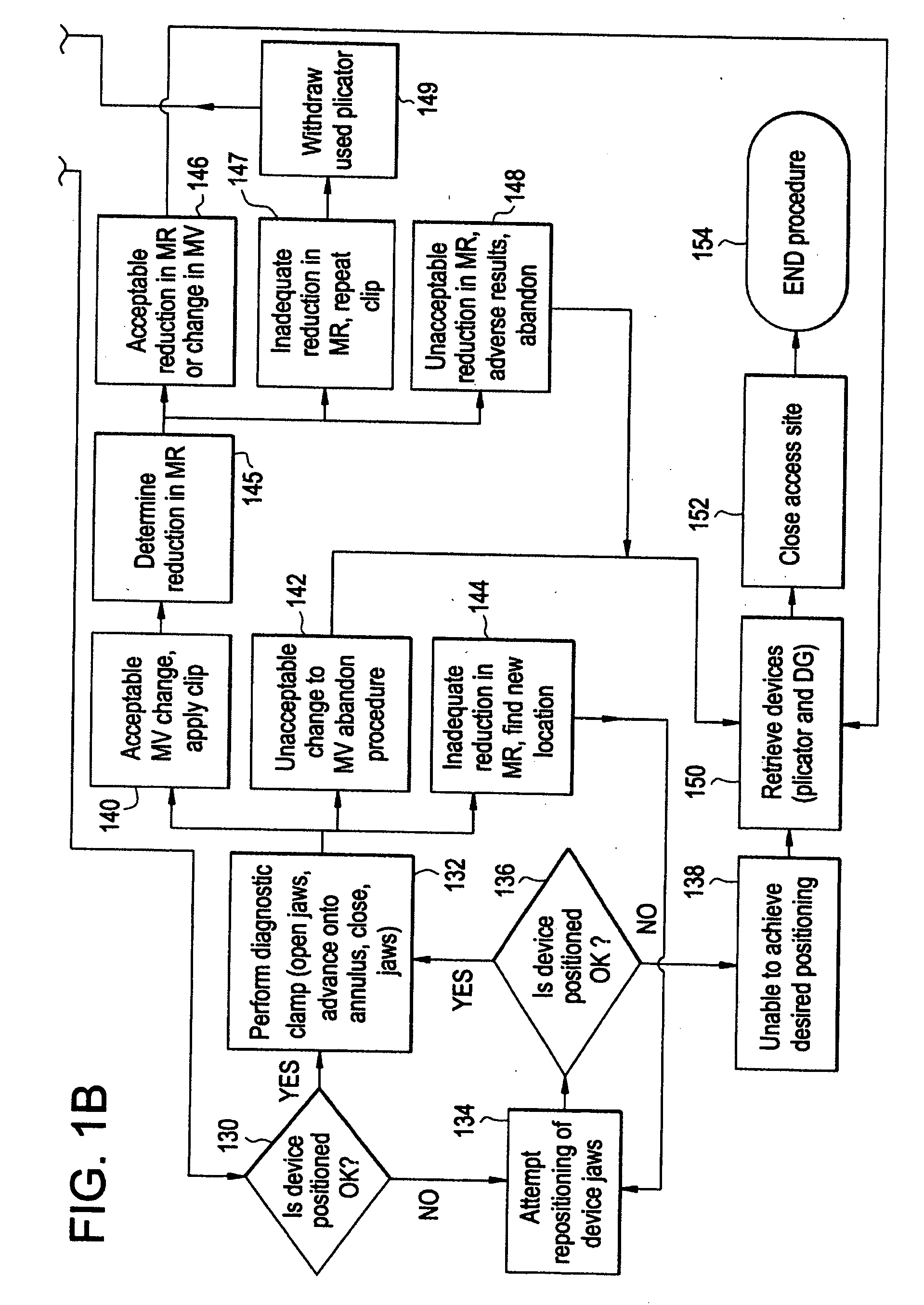
Method and system for plicating tissue in a minimally invasive medical procedure for the treatment of mitral valve regurgitation
ActiveUS20090105814A1Increase pressureInhibit sheddingHeart valvesBone implantMitral valve leafletMedical treatment
A system and method for the treatment of mitral valve regurgitation by reshaping the mitral valve annulus using one or more plications of annular or adjacent tissue each fixed by a retainer is described. The system includes four devices to achieve such percutaneous direct plication annuloplasty. The first is a crossing catheter having a prolapseable or curved tip. Second, a deflecting guide catheter is used to provide a means for guiding the plication device into proper position at the subvalvular region of the mitral valve annulus. Third, the plication device is then used to make plications in the subvalvular region of the mitral valve annulus. Fourth, a “C” shaped retainer with deformable ends is deployed by the plication device in order to retain the plicated tissue in the plicated form. A transseptal approach may be used to plicate and retain tissue on the atrial side of the mitral valve to achieve a reduction in mitral valve regurgitation.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
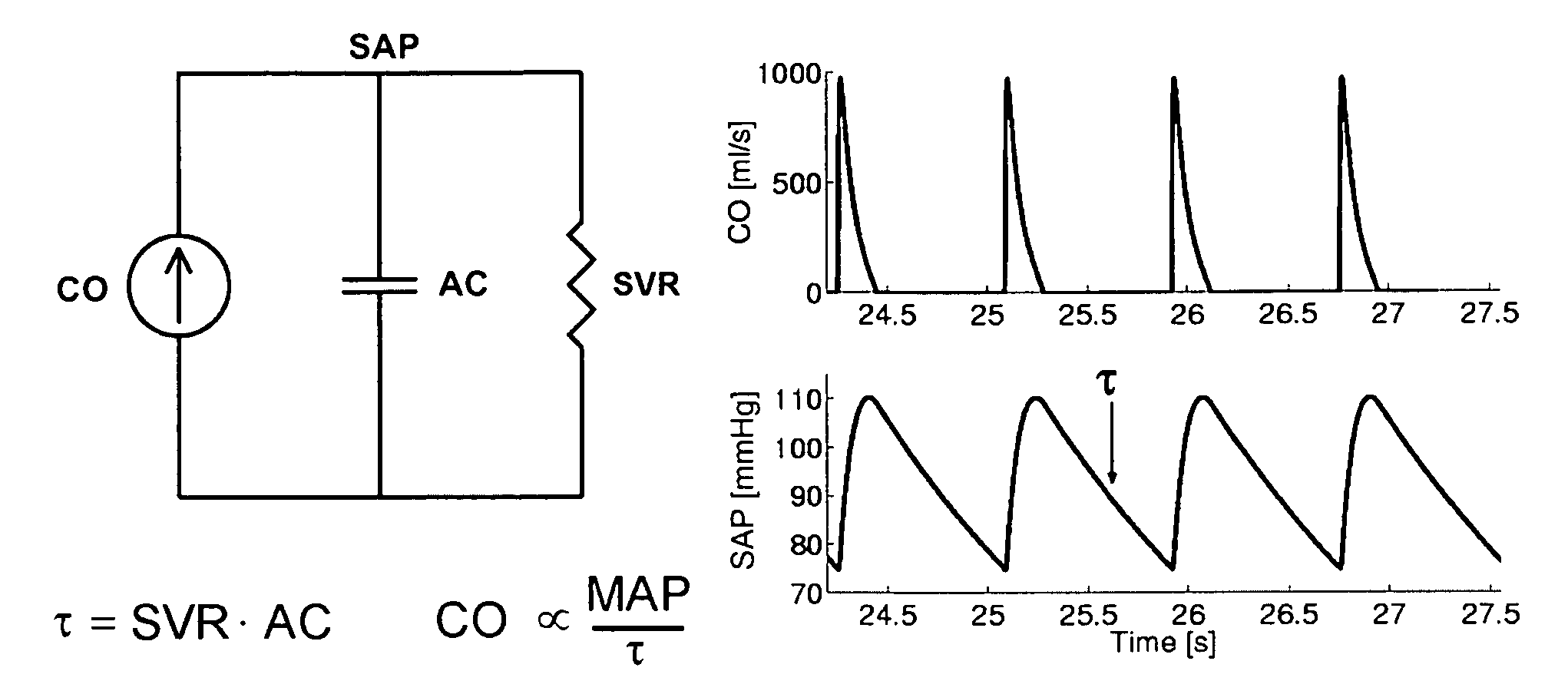
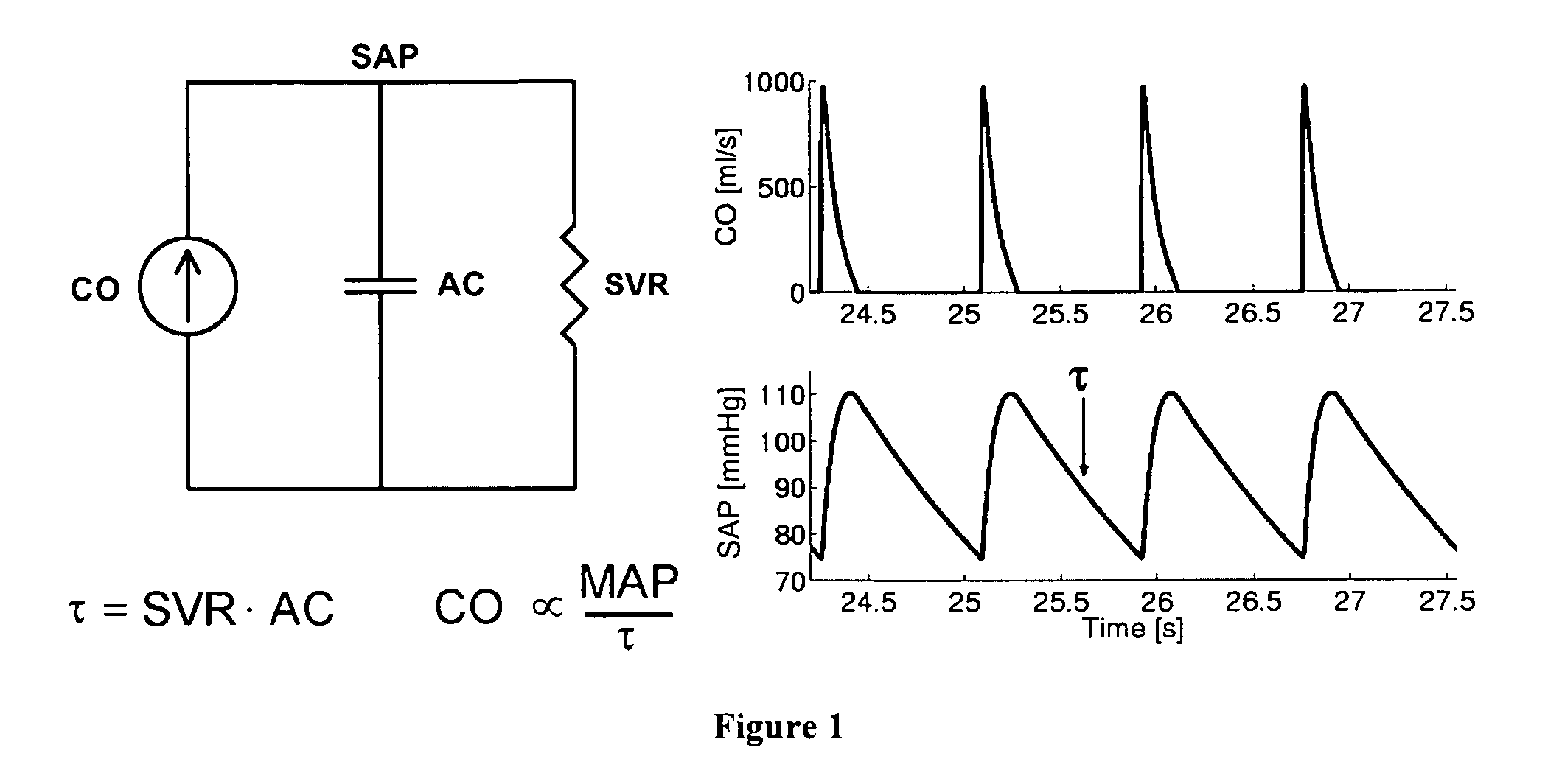
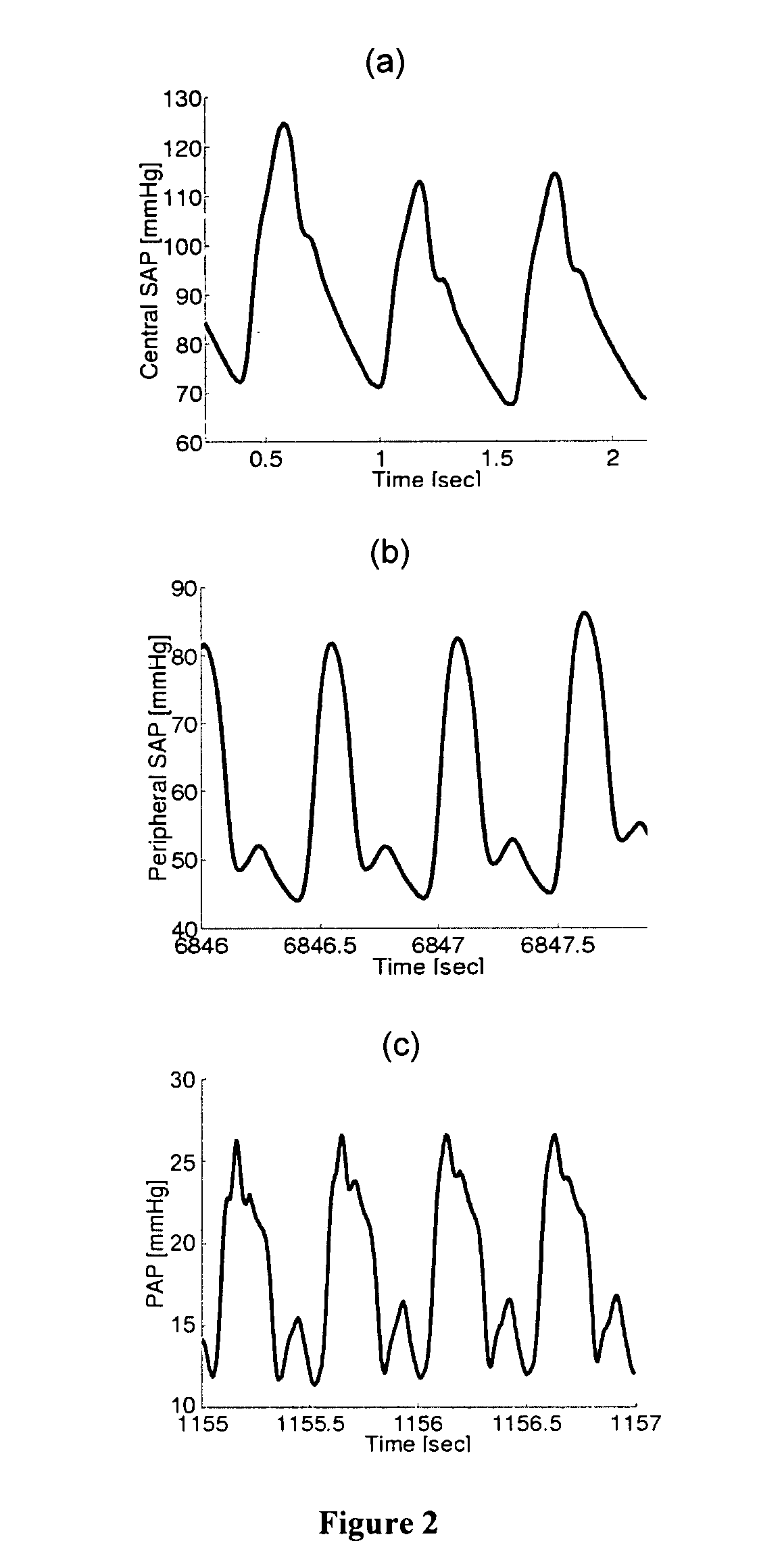
Methods and apparatus for determining cardiac output and left atrial pressure
Method and apparatus are introduced for determining proportional cardiac output (CO), absolute left atrial pressure (LAP), and / or other important hemodynamic variables from a contour of a circulatory pressure waveform or related signal. Certain embodiments of the invention provided herein include the mathematical analysis of a pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) waveform or a right ventricular pressure (RVP) waveform in order to determine beat-to-beat or time-averaged proportional CO, proportional pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), and / or LAP. The invention permits continuous and automatic monitoring of critical hemodynamic variables with a level of invasiveness suitable for routine clinical application. The invention may be utilized, for example, to continuously monitor critically ill patients with pulmonary artery catheters installed and chronically monitor heart failure patients instrumented with implanted devices for measuring RVP.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
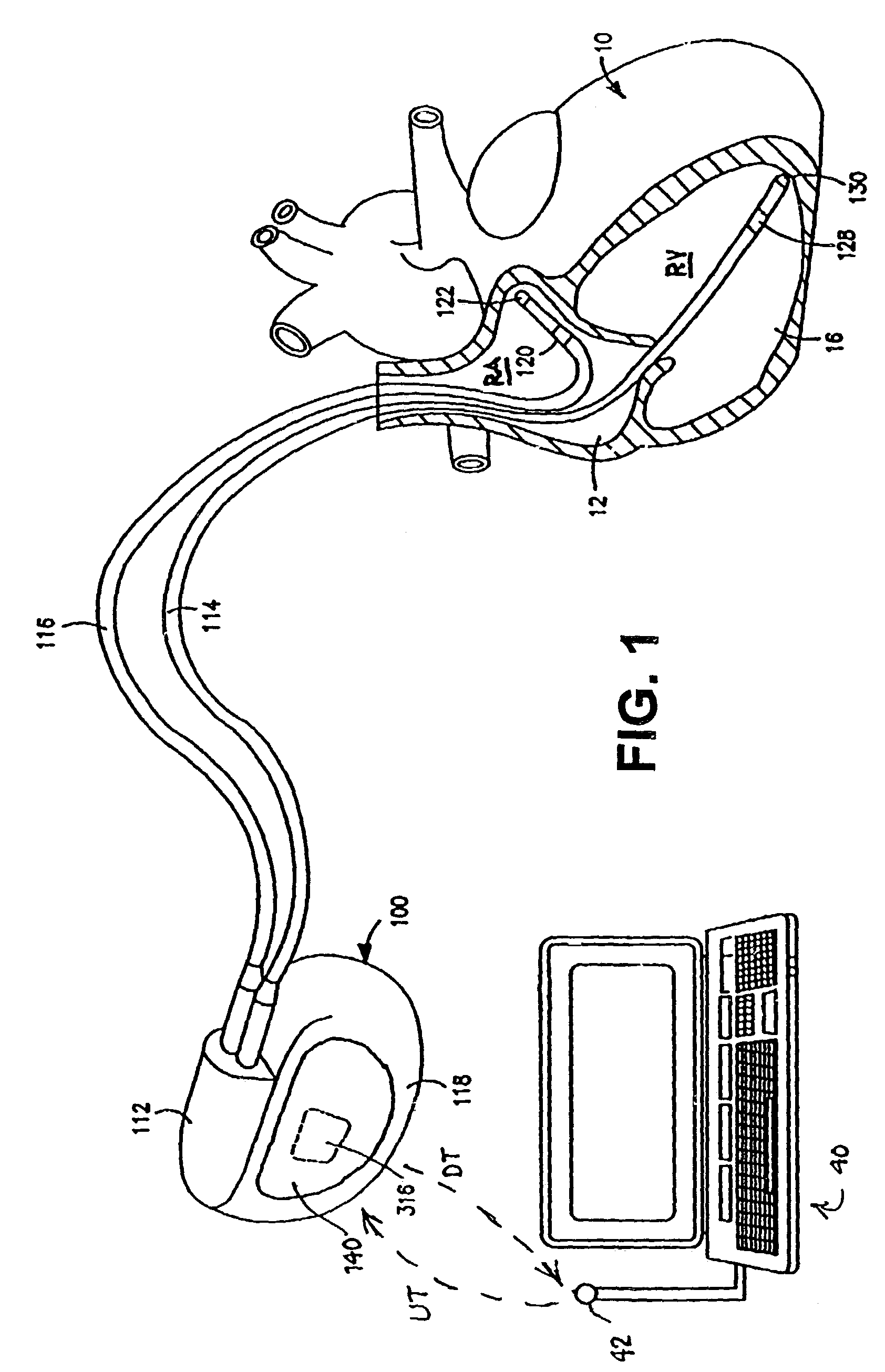
Shunt for redistributing atrial blood volume
A shunt for regulating blood pressure between a patient's left atrium and right atrium comprises an anchor comprising a neck region, first and second end regions, and a conduit affixed with the anchor that formed of a biocompatible material that is resistant to transmural and translation tissue ingrowth and that reduces a risk of paradoxical embolism.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com