Patents
Literature
70 results about "Septal wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
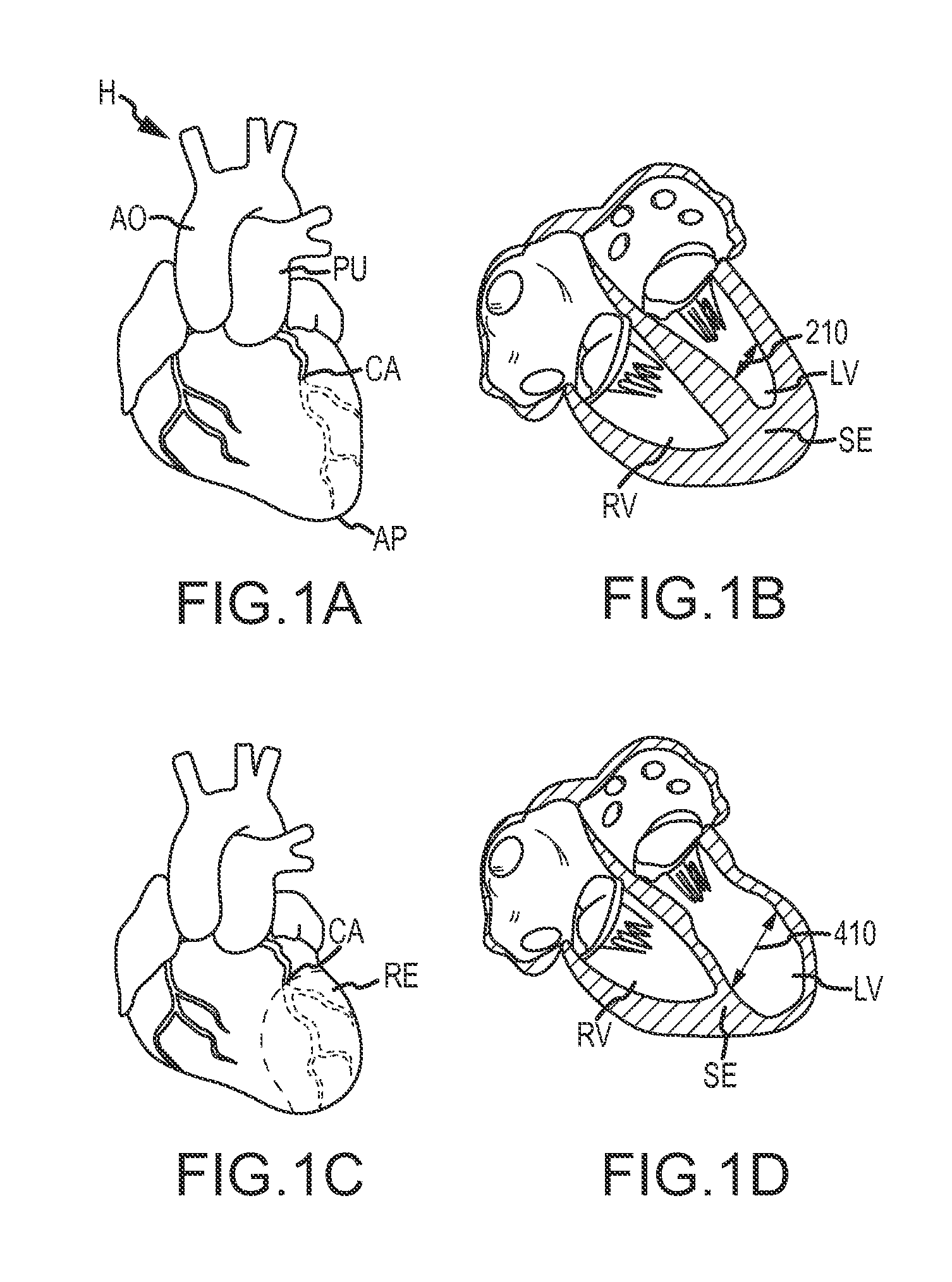
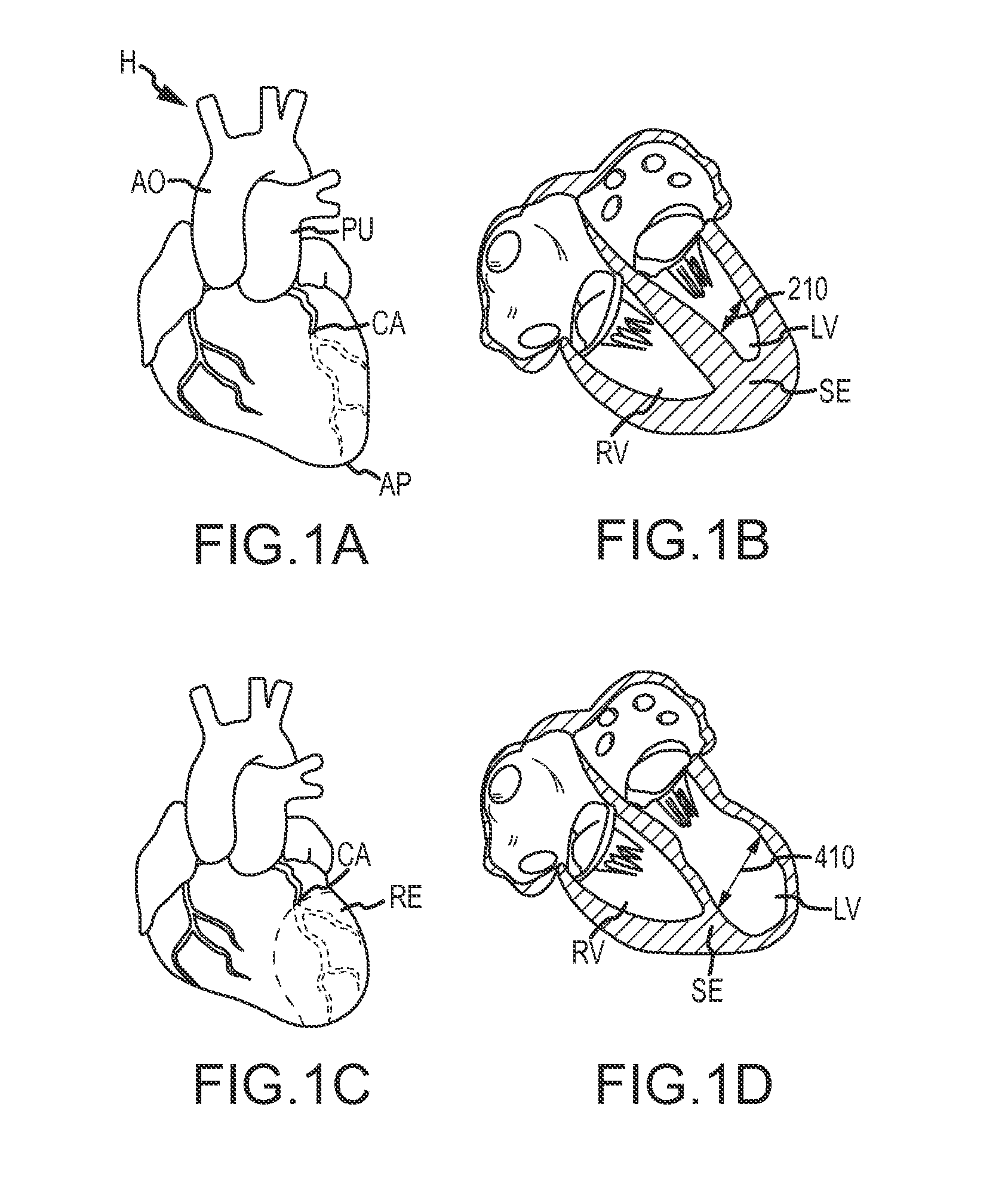
Septal infarct is a patch of dead, dying, or decaying tissue on the septum. The septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right ventricle of your heart from the left ventricle.
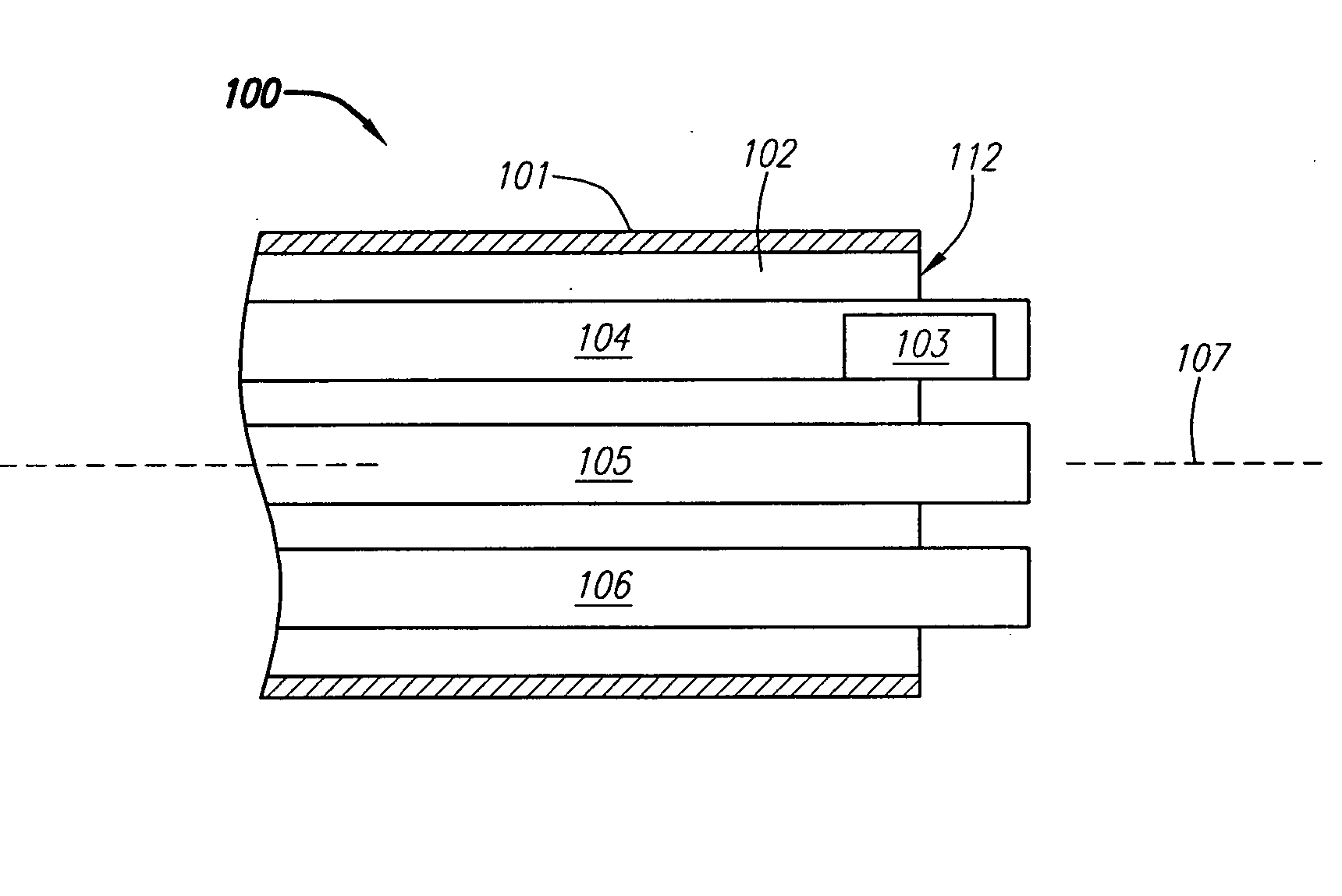
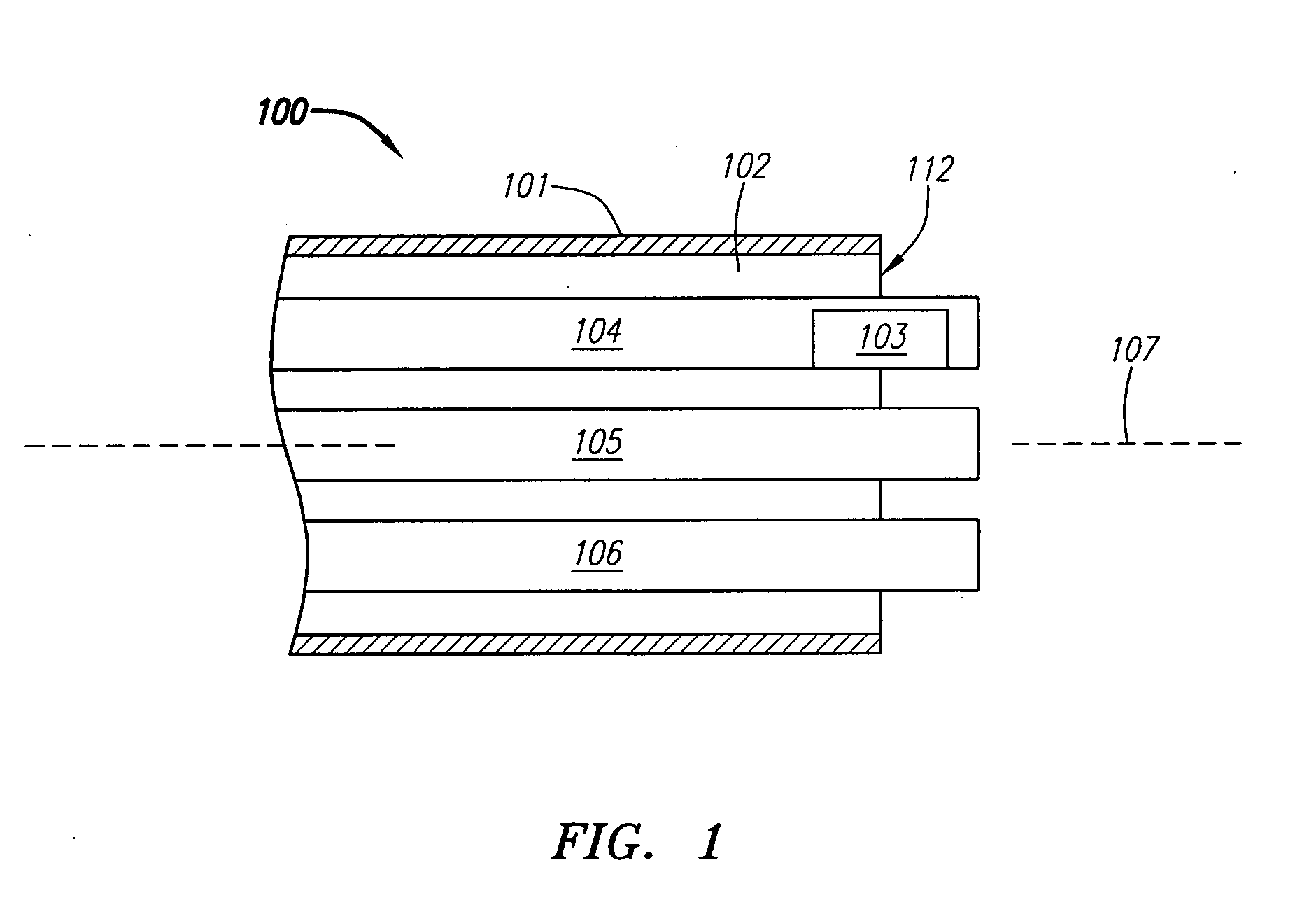
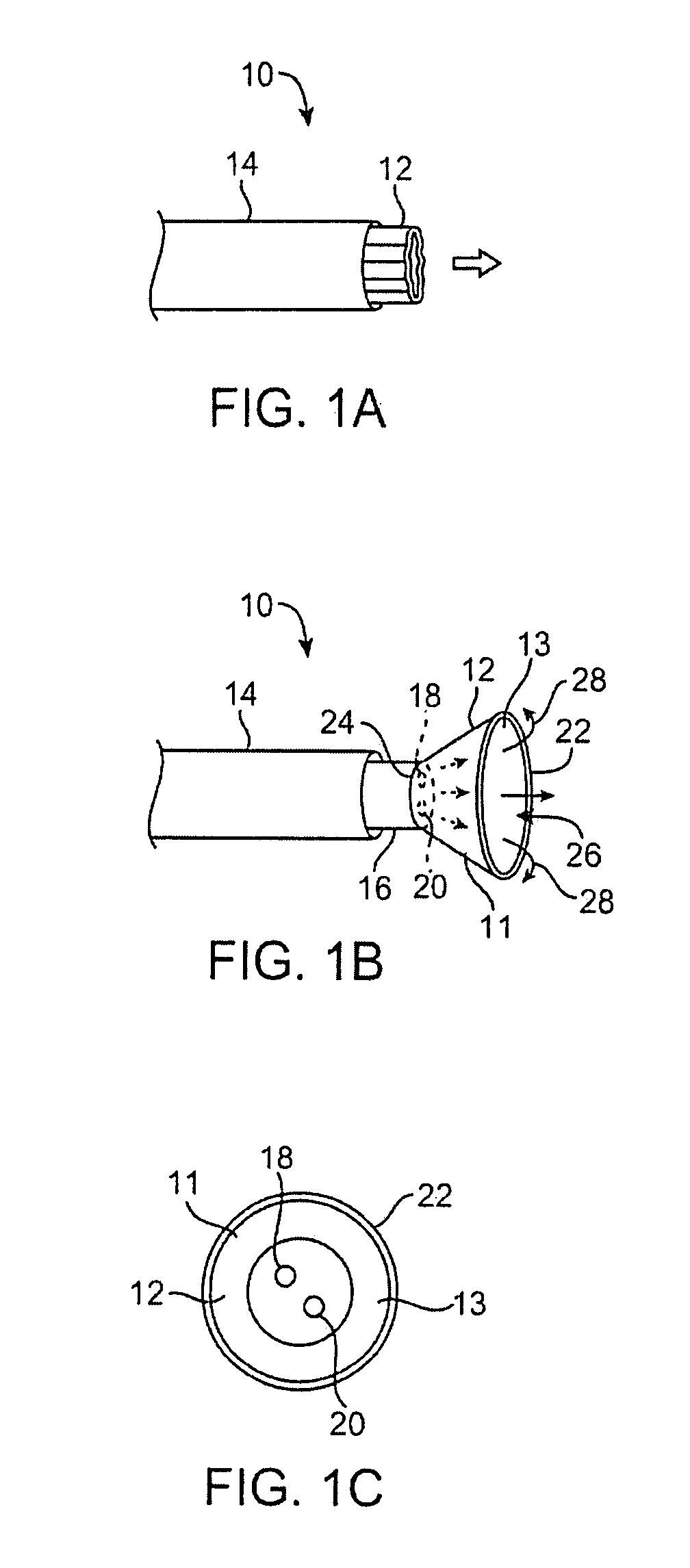
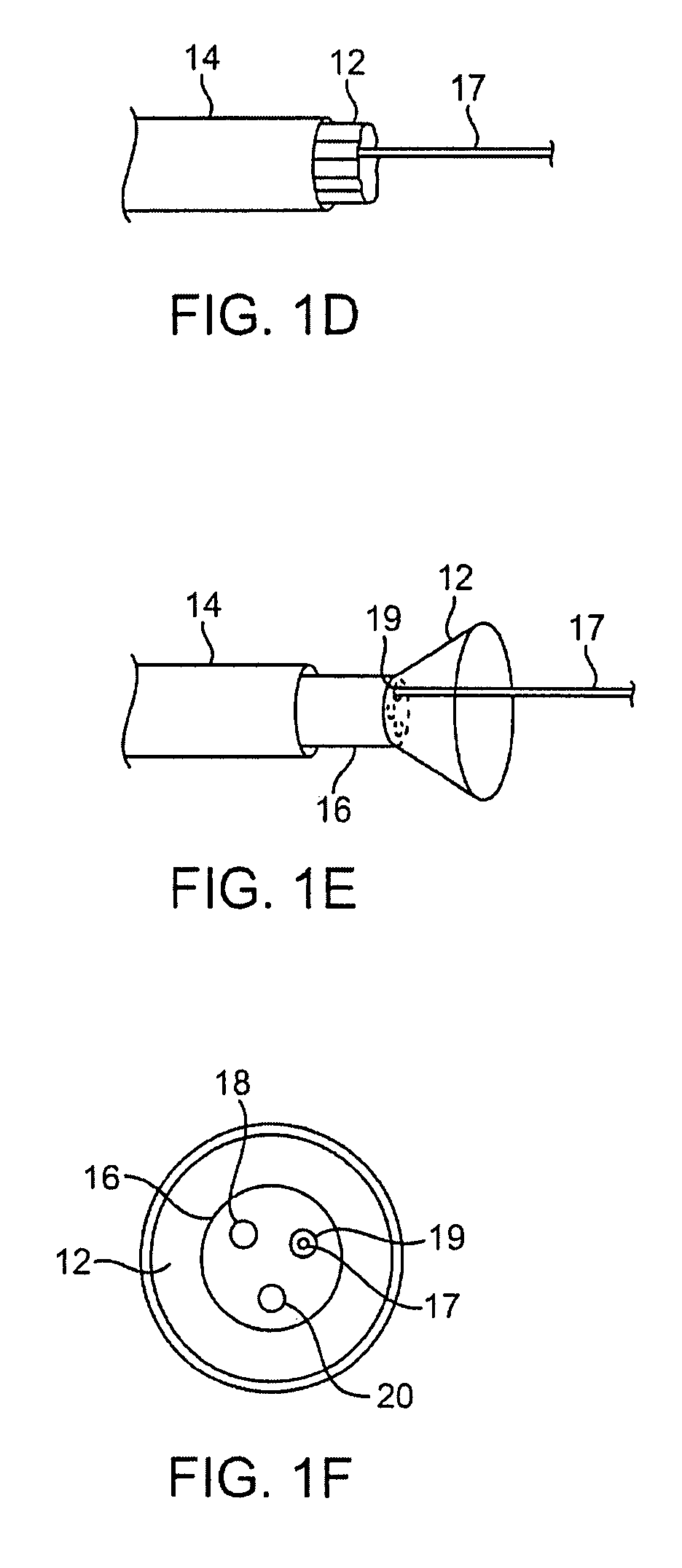
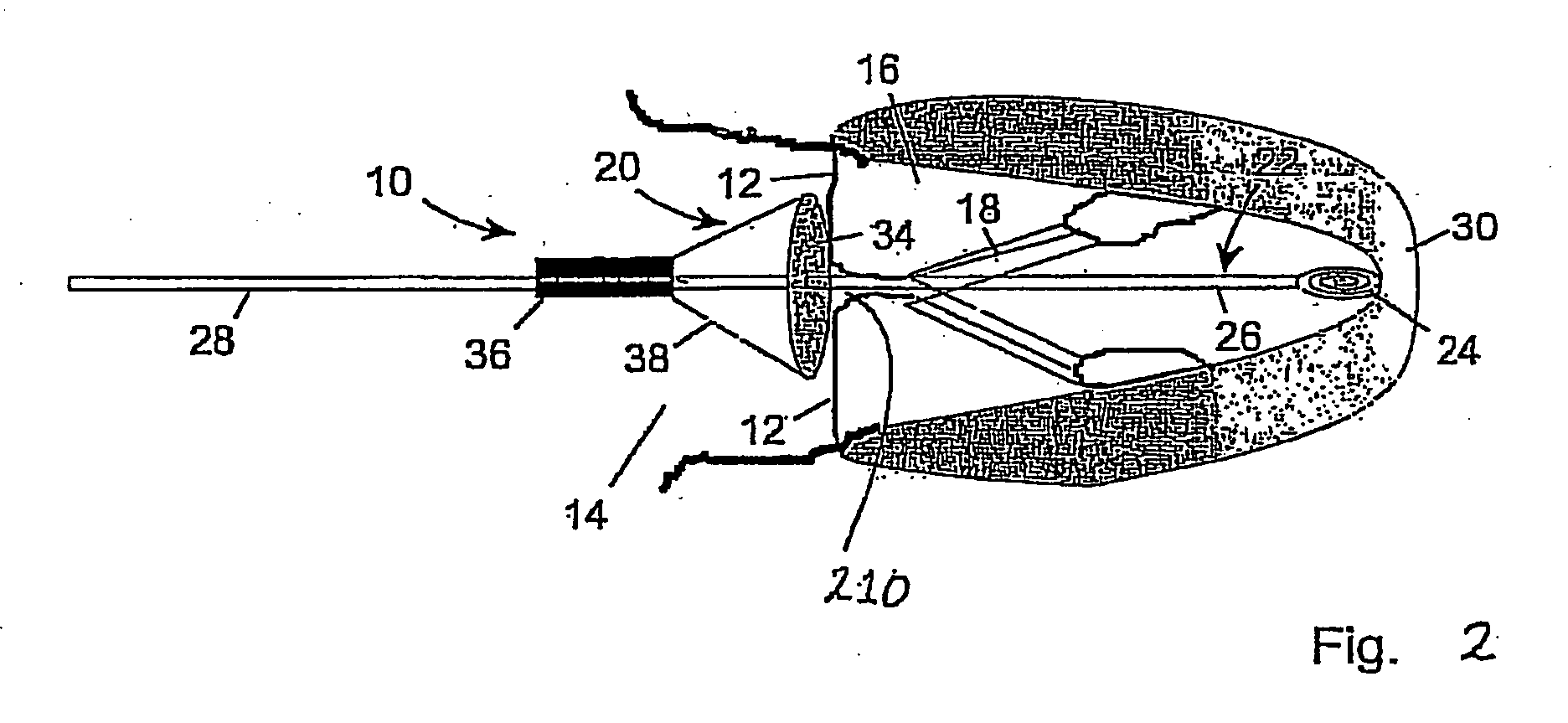
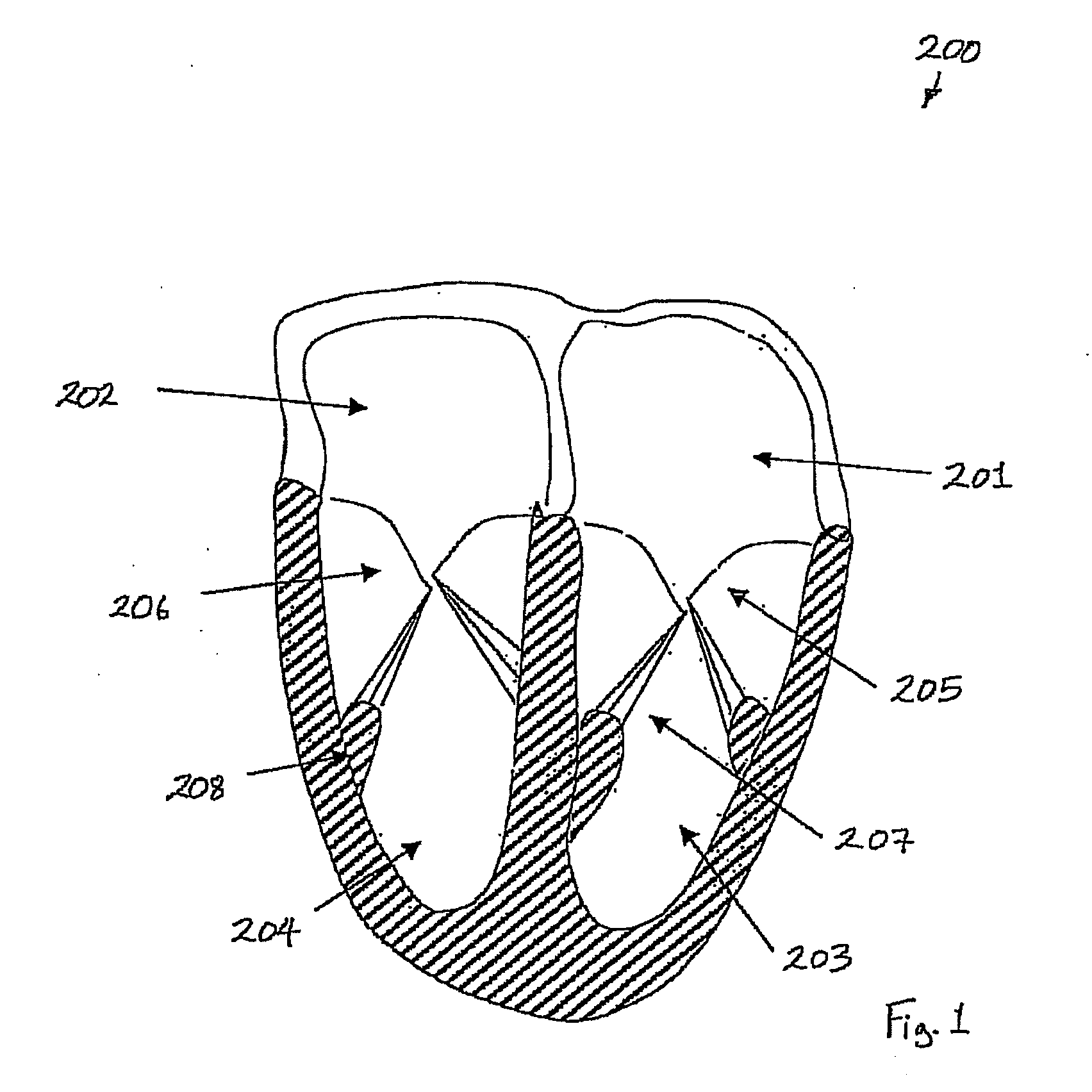
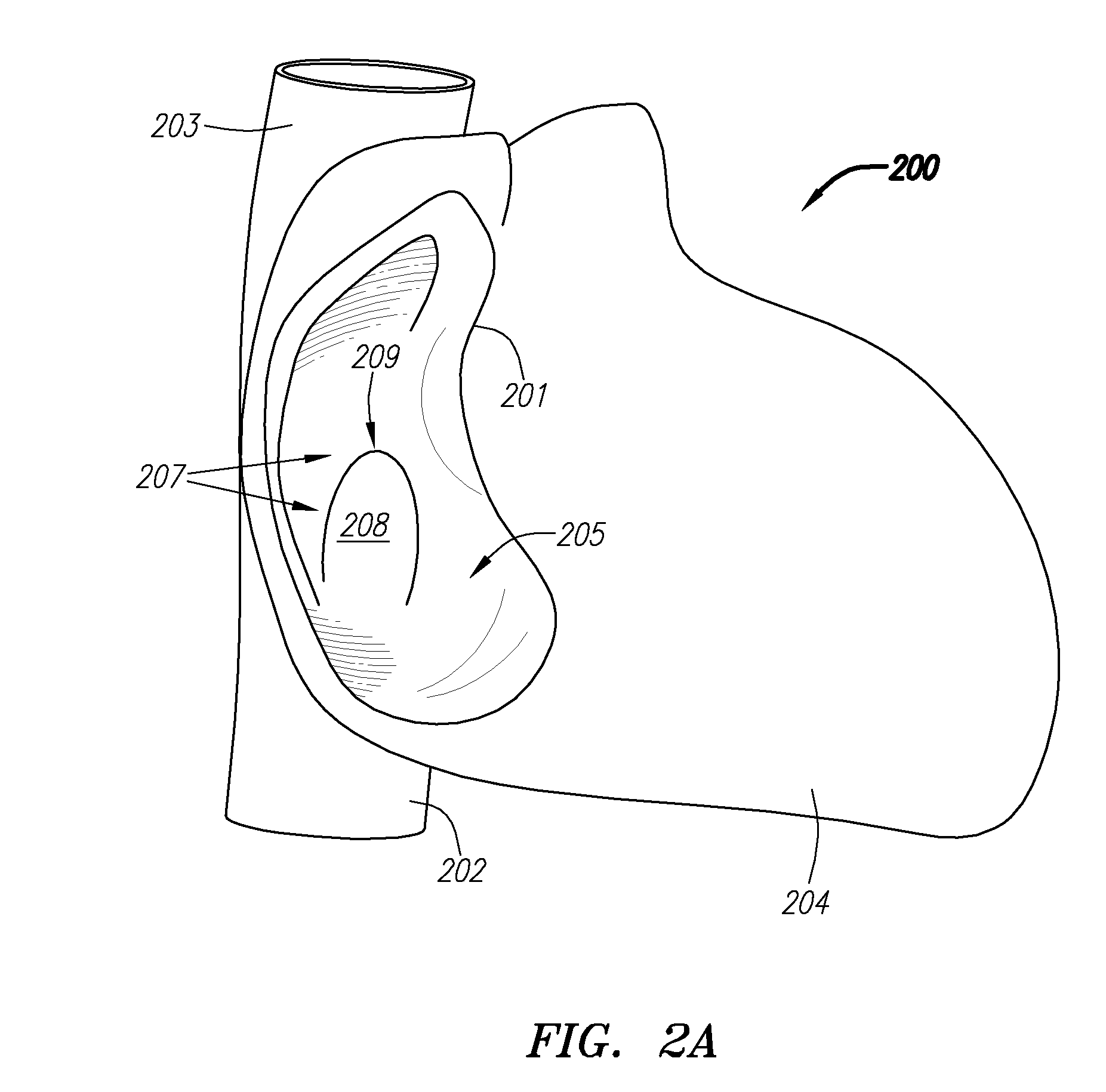
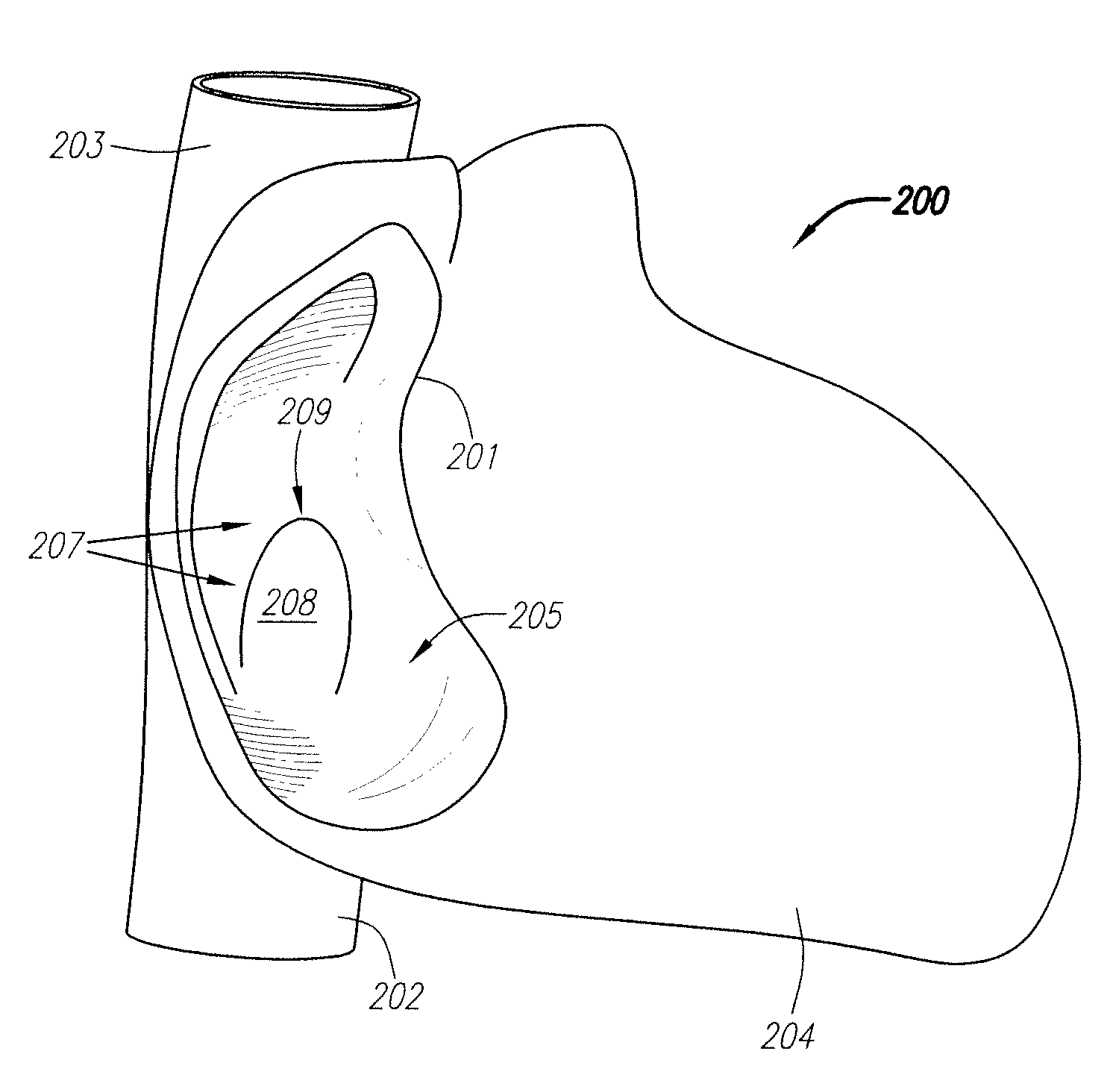
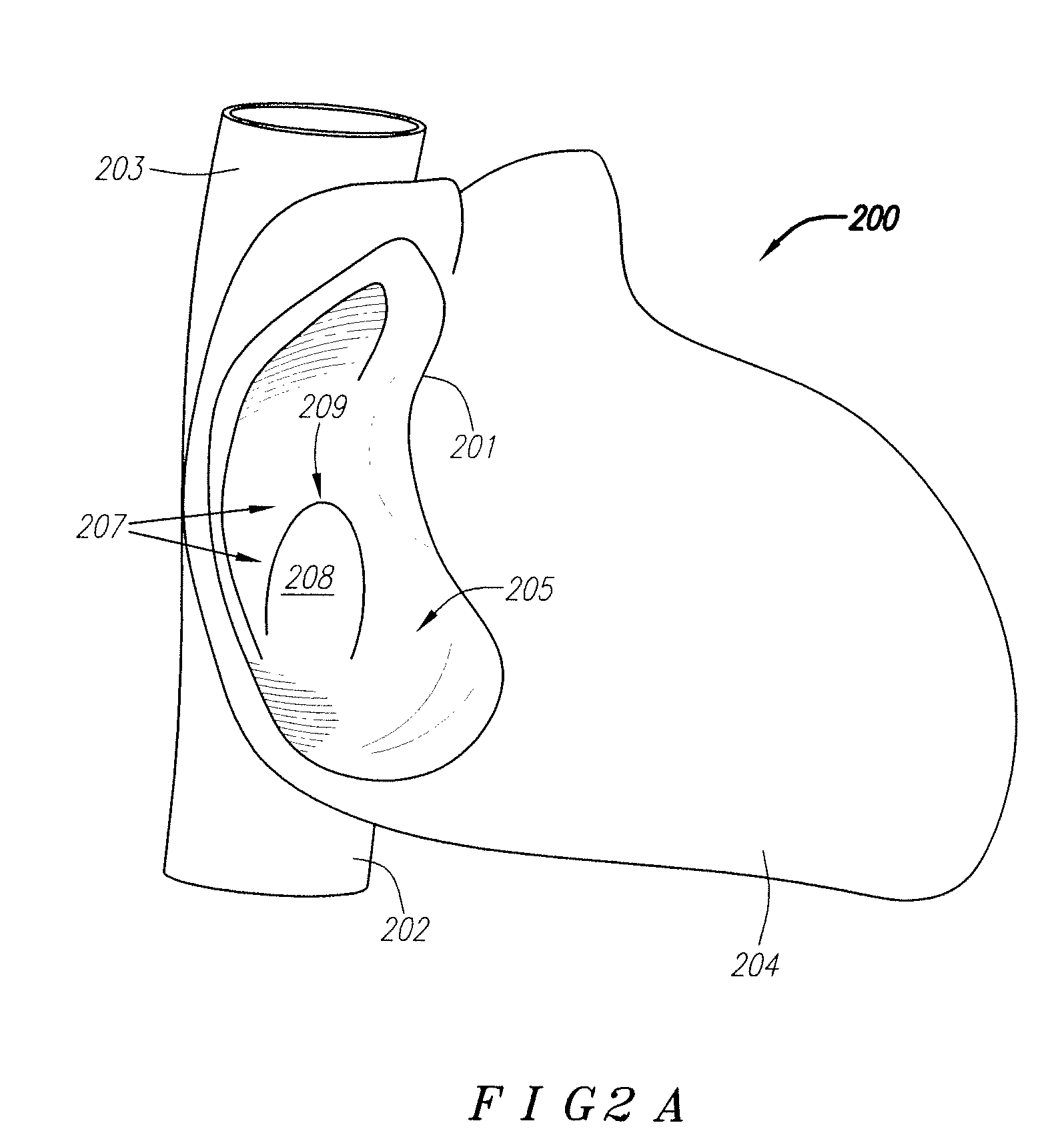
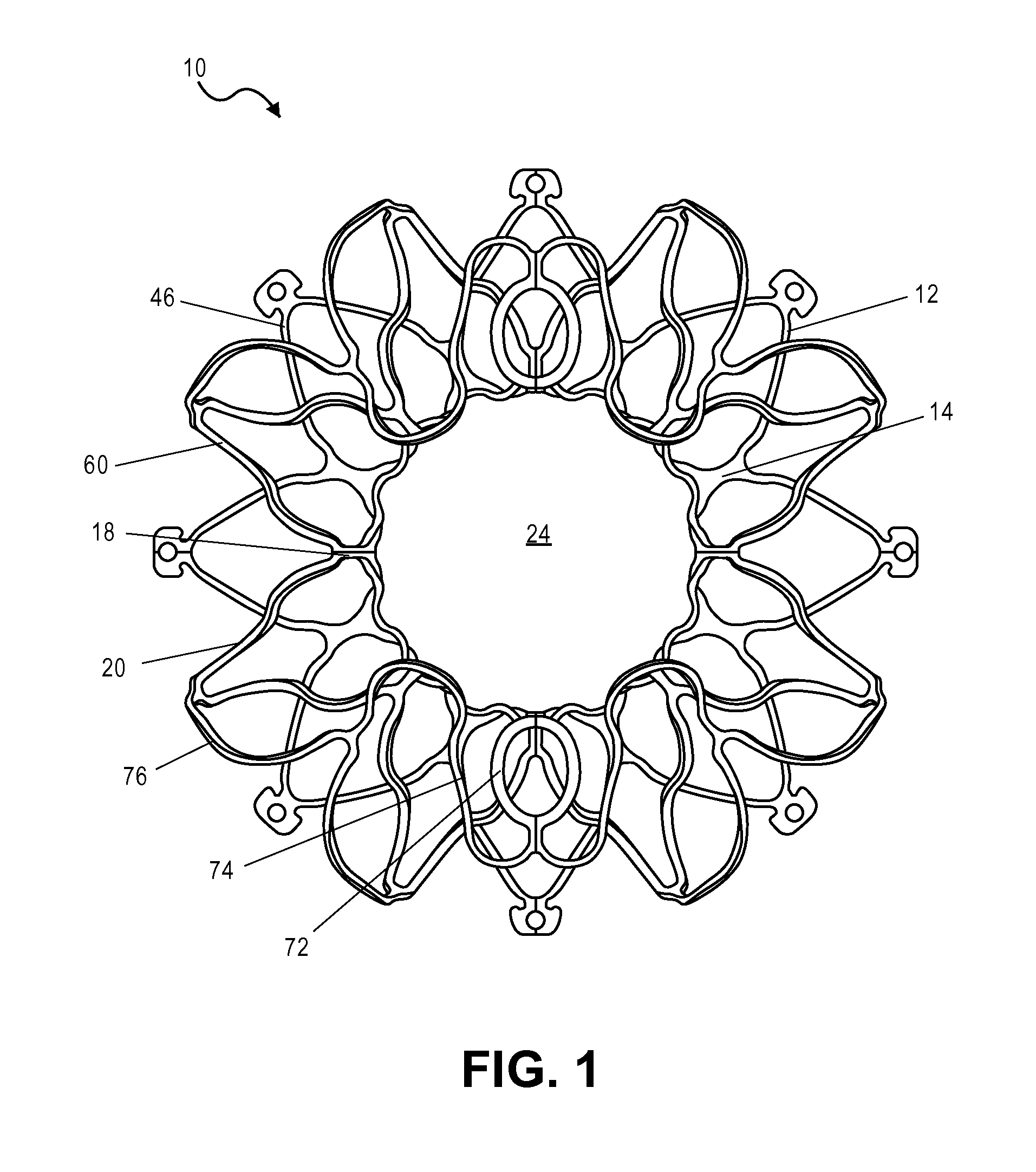
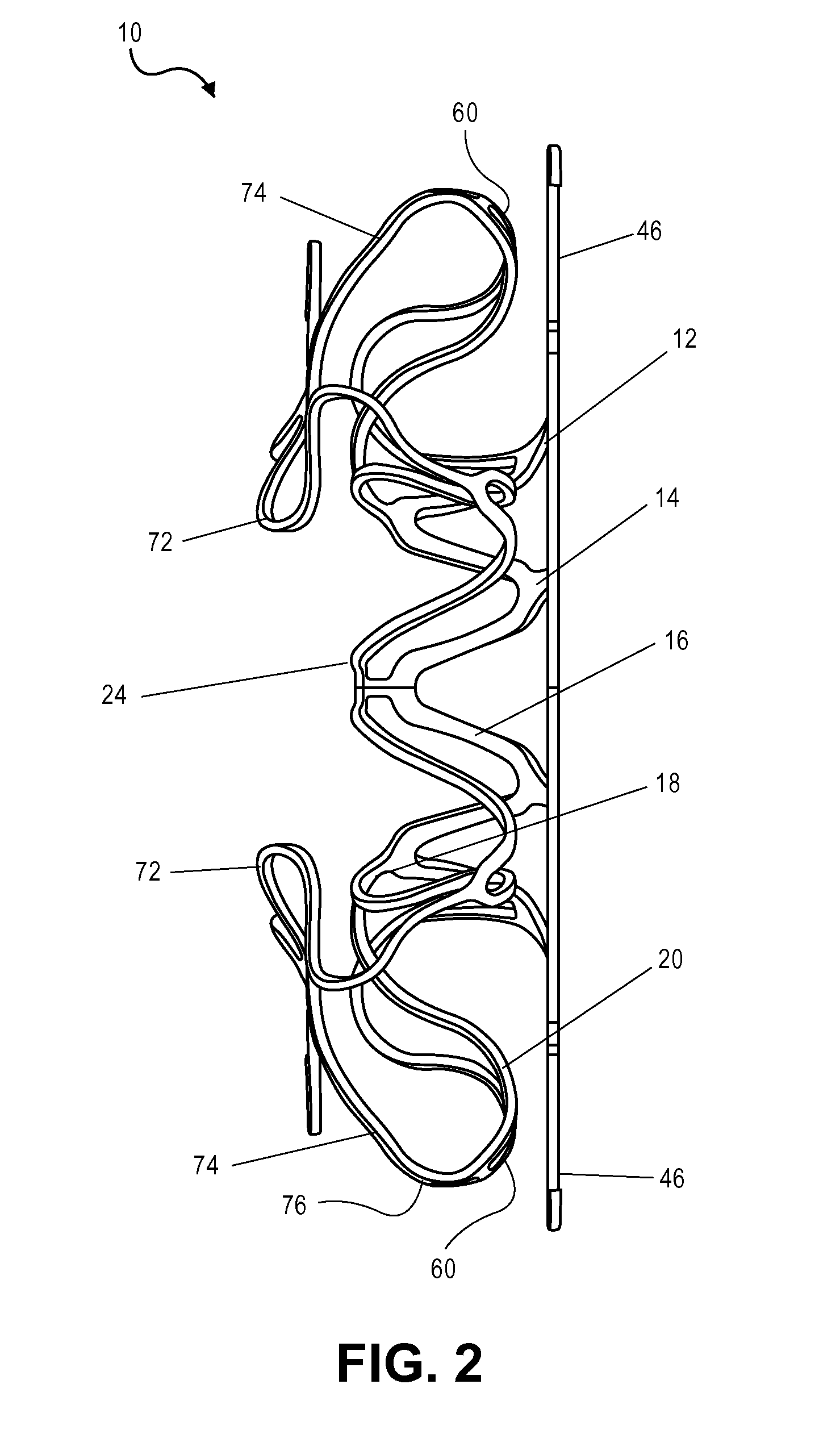
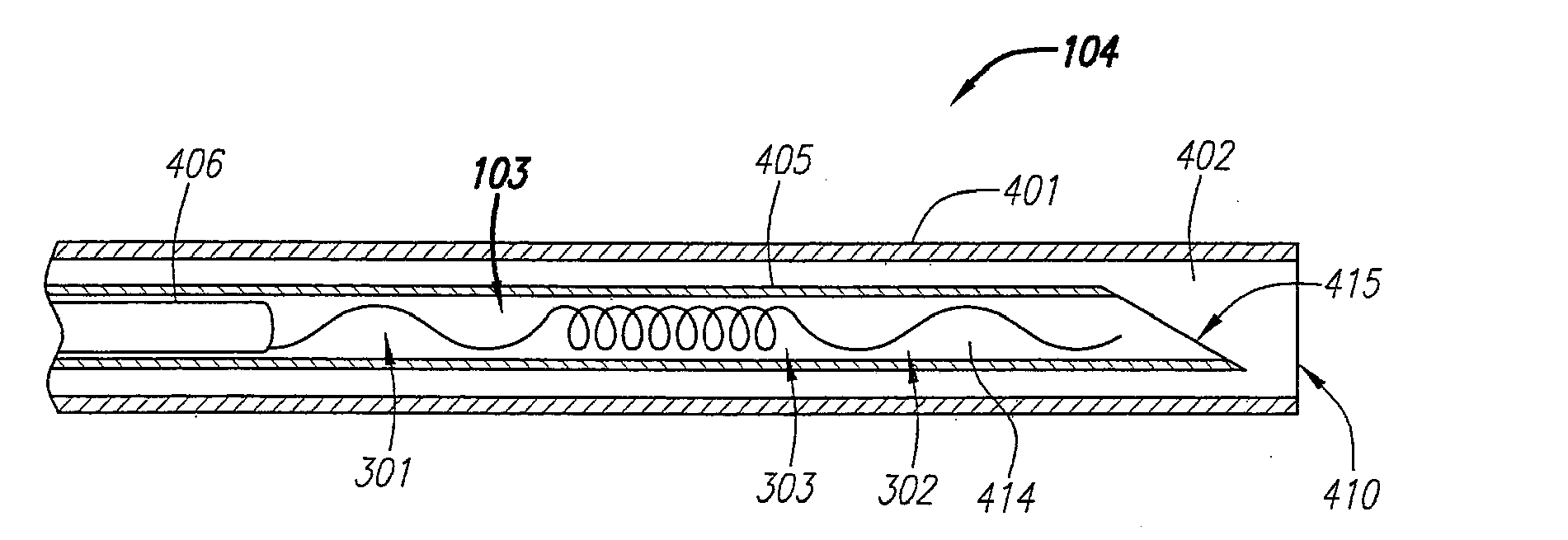
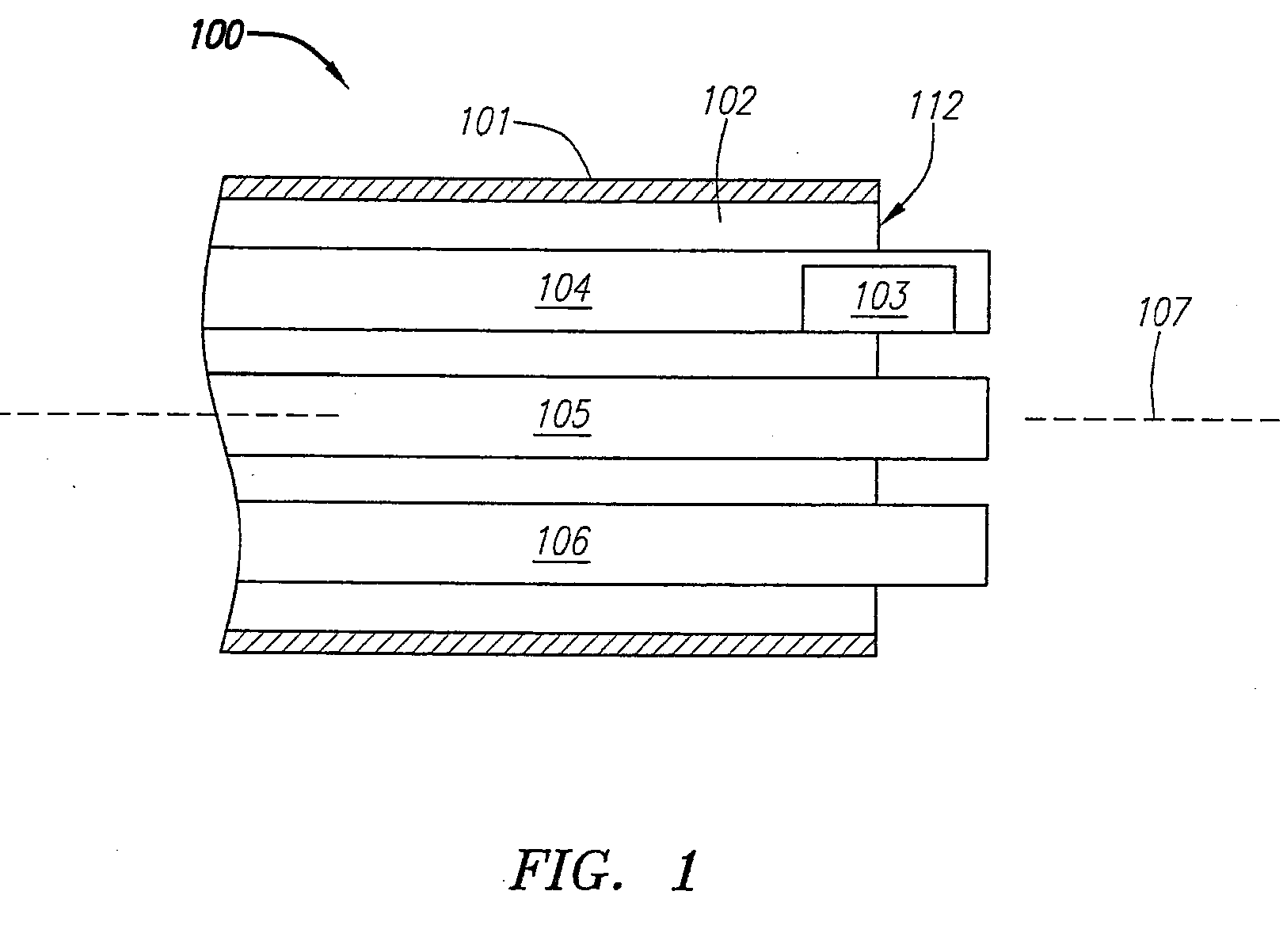
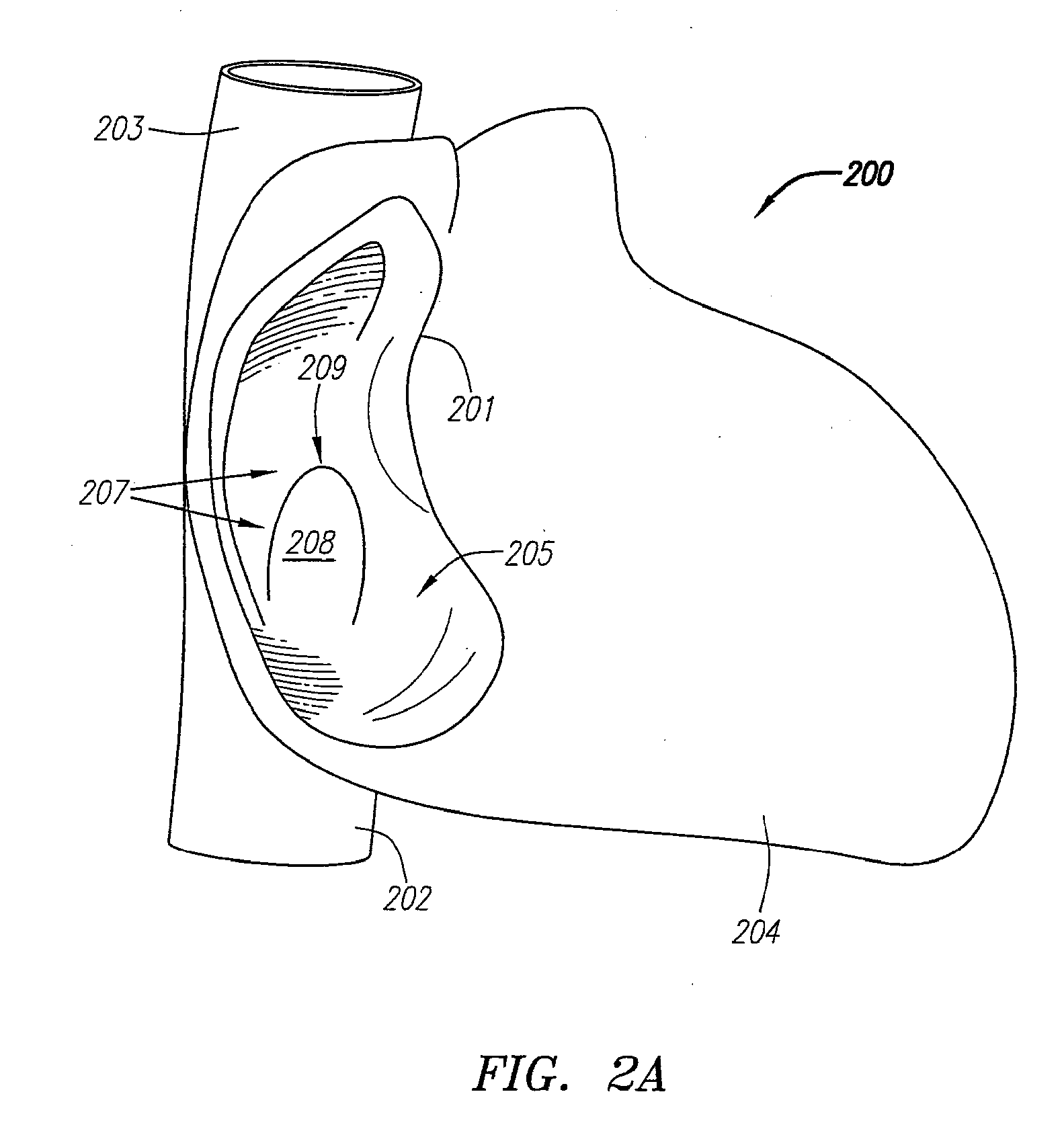
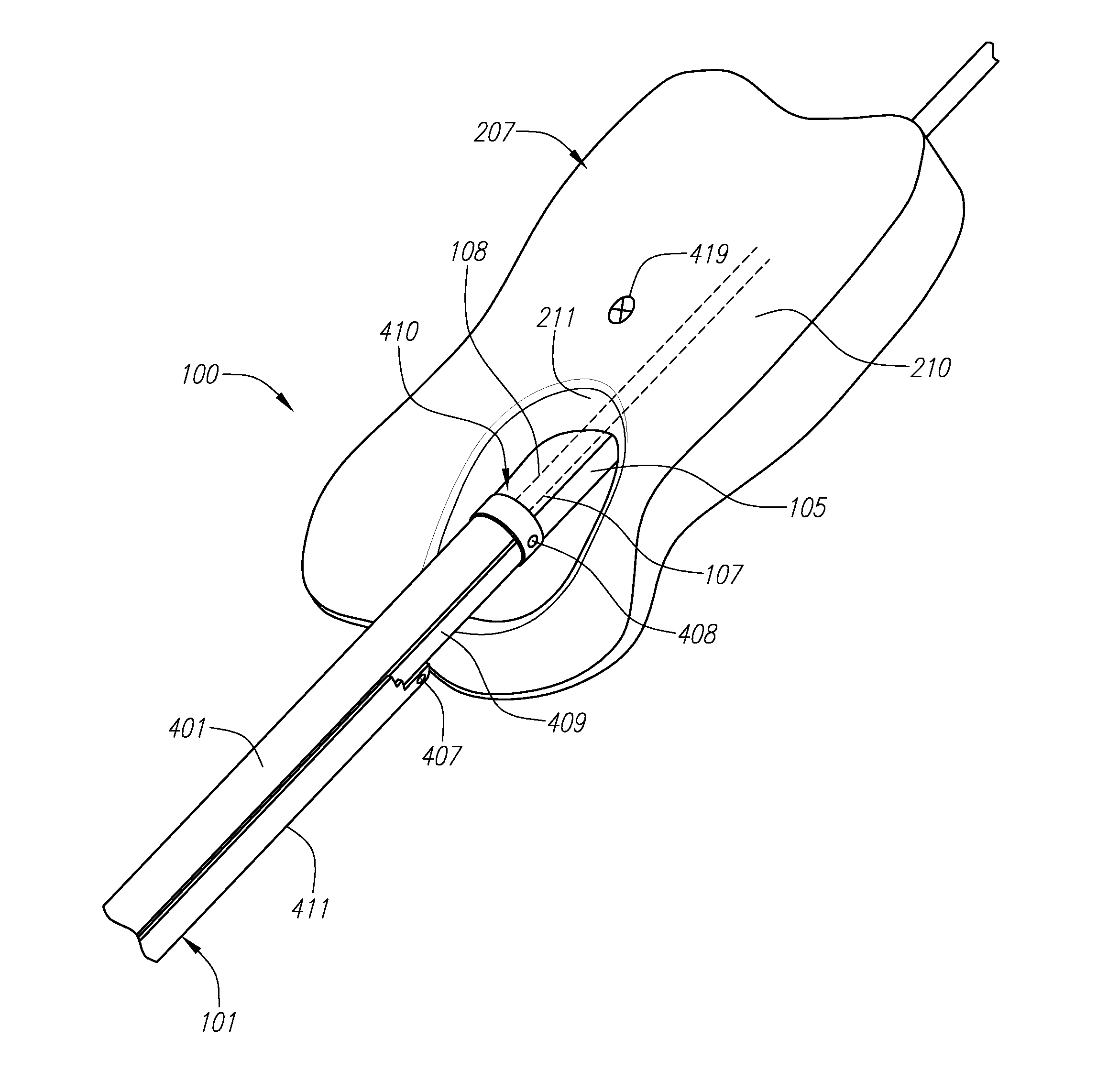
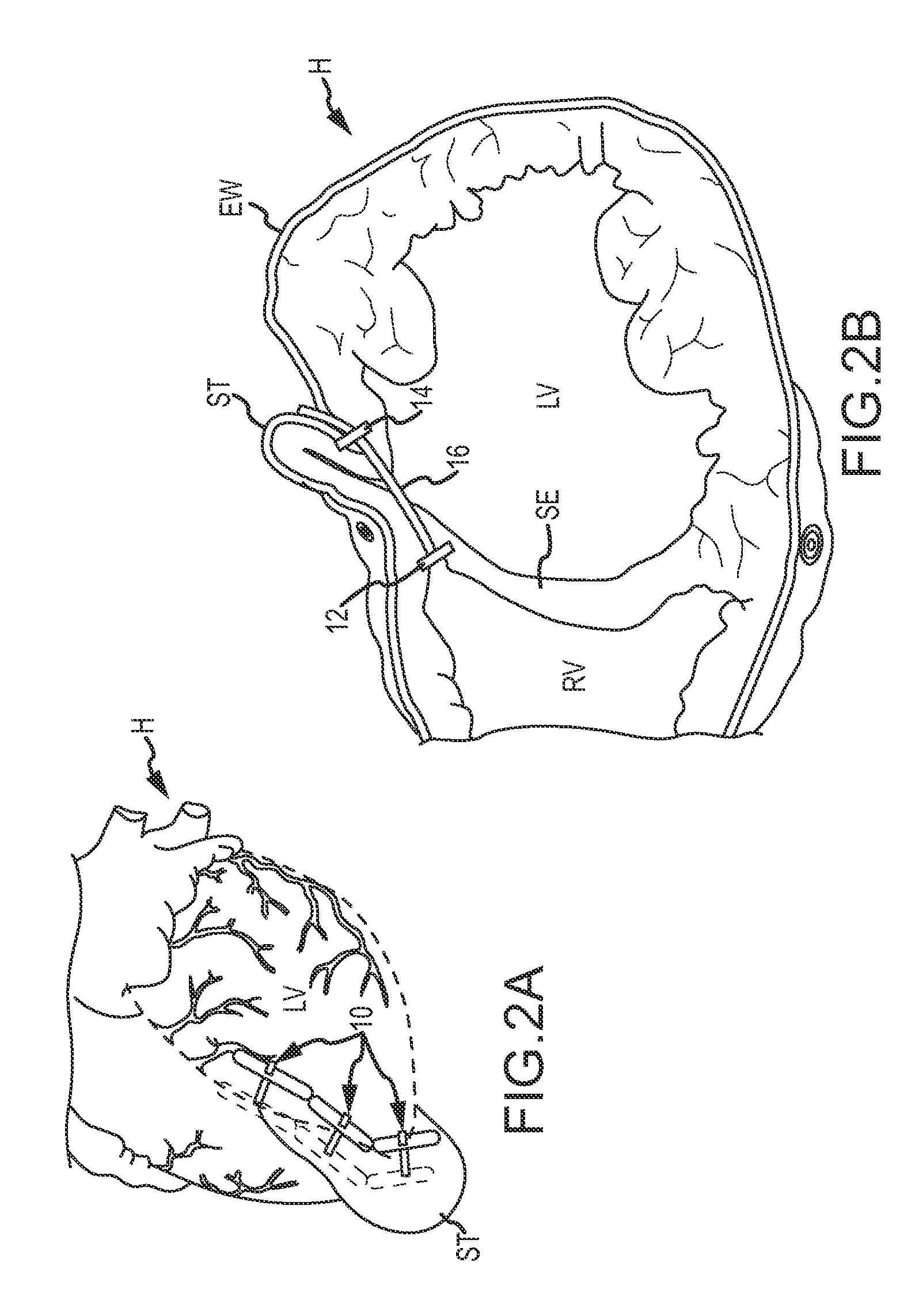
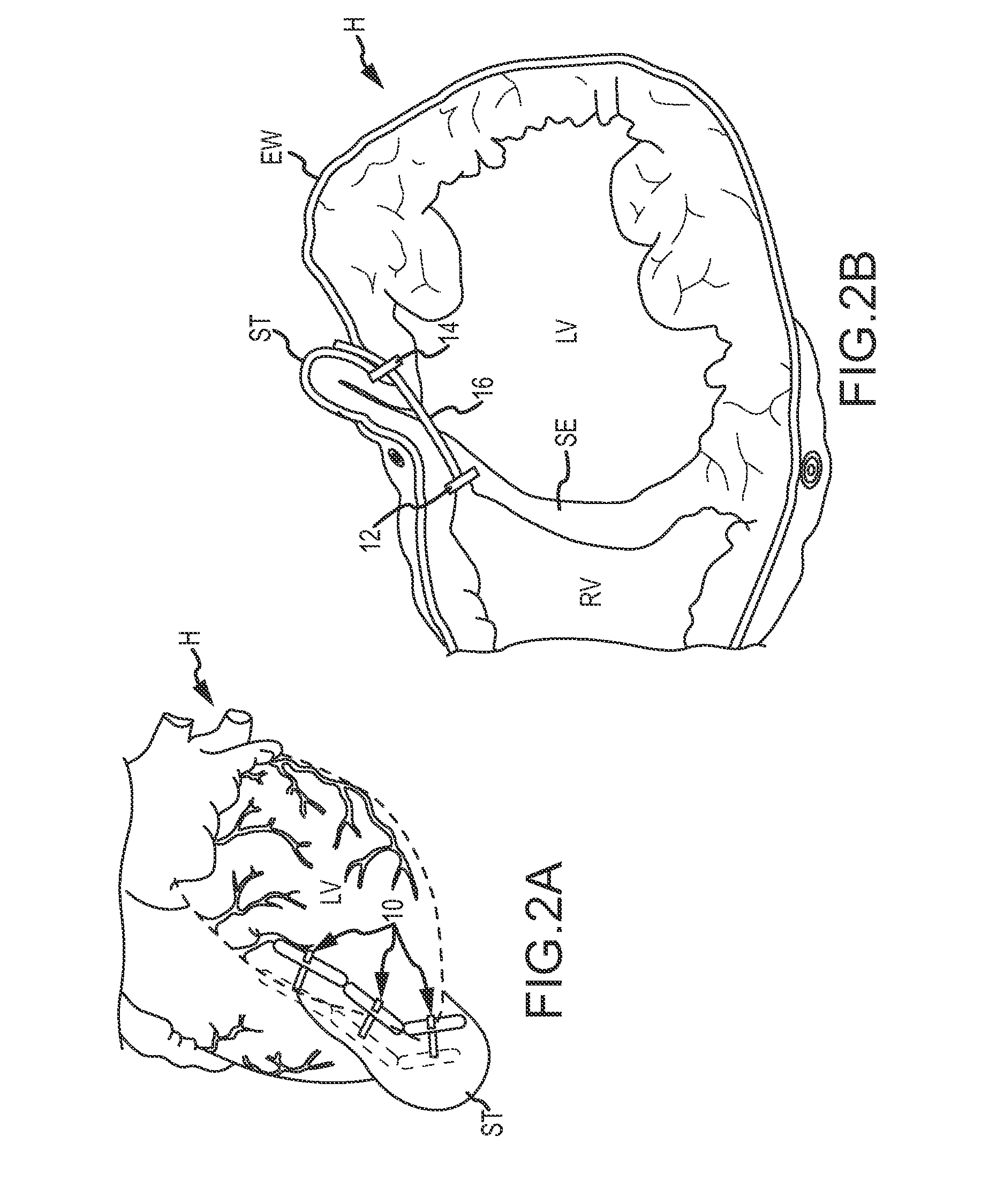
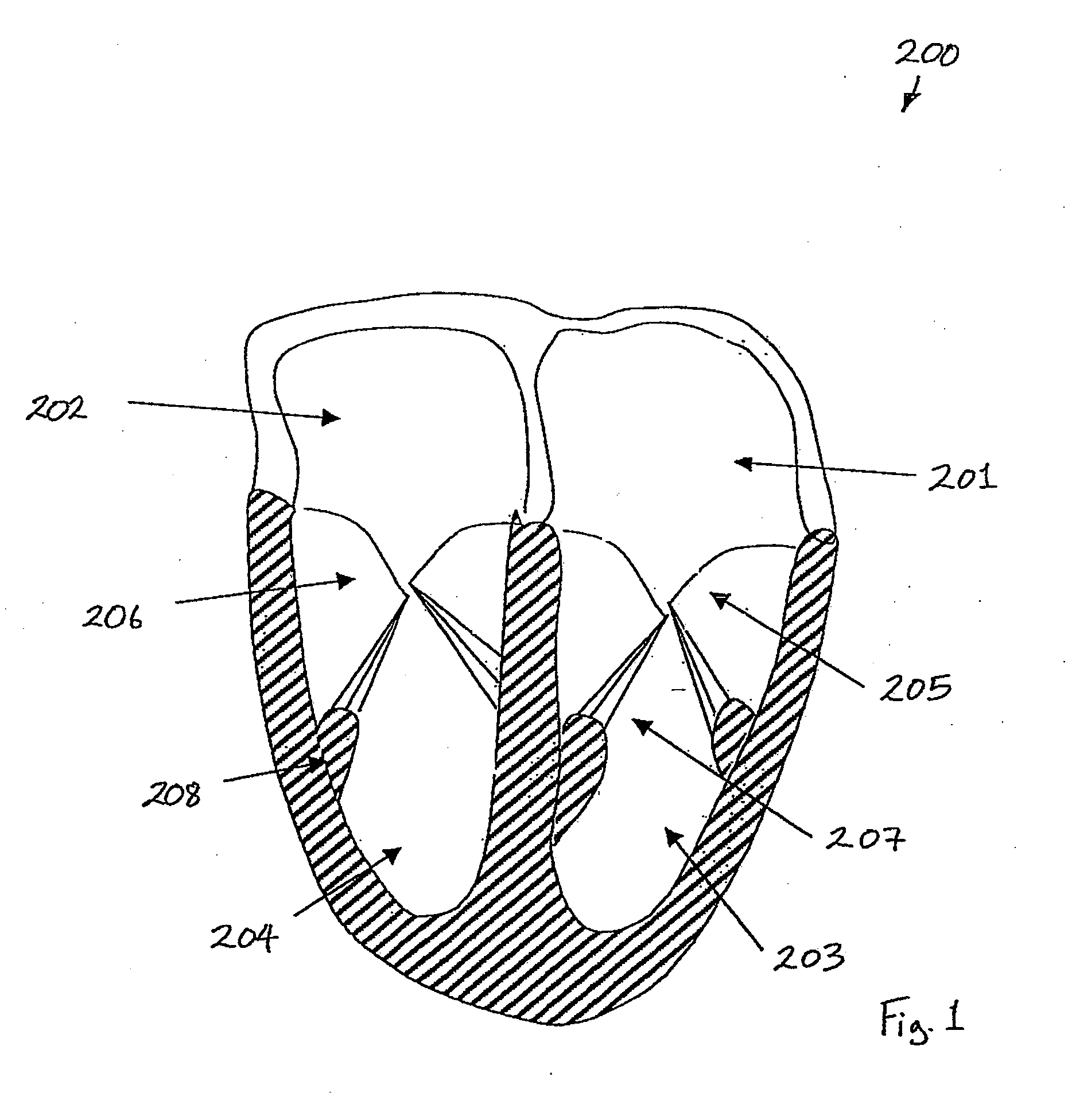
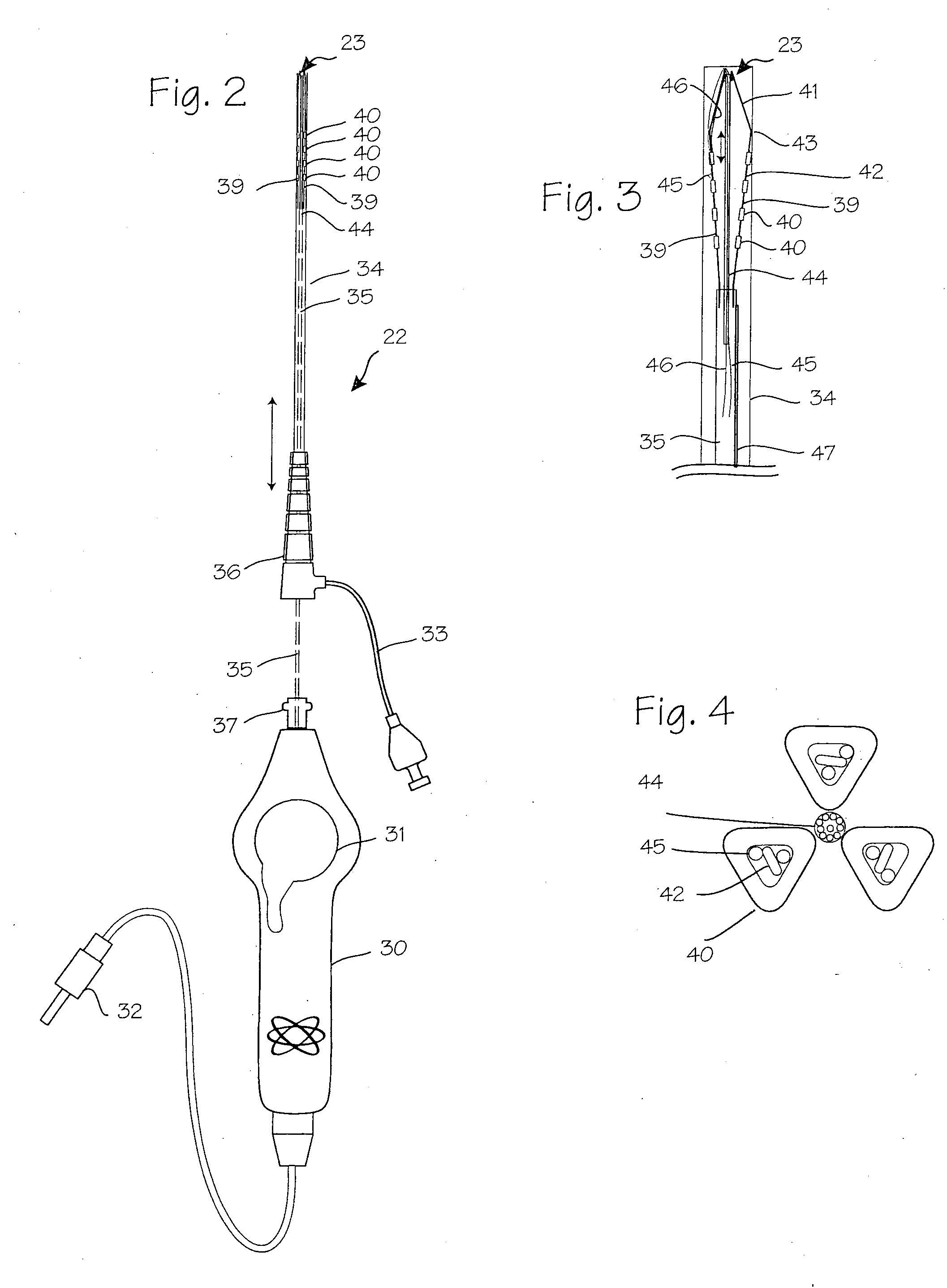
Suture-based systems and methods for treating septal defects
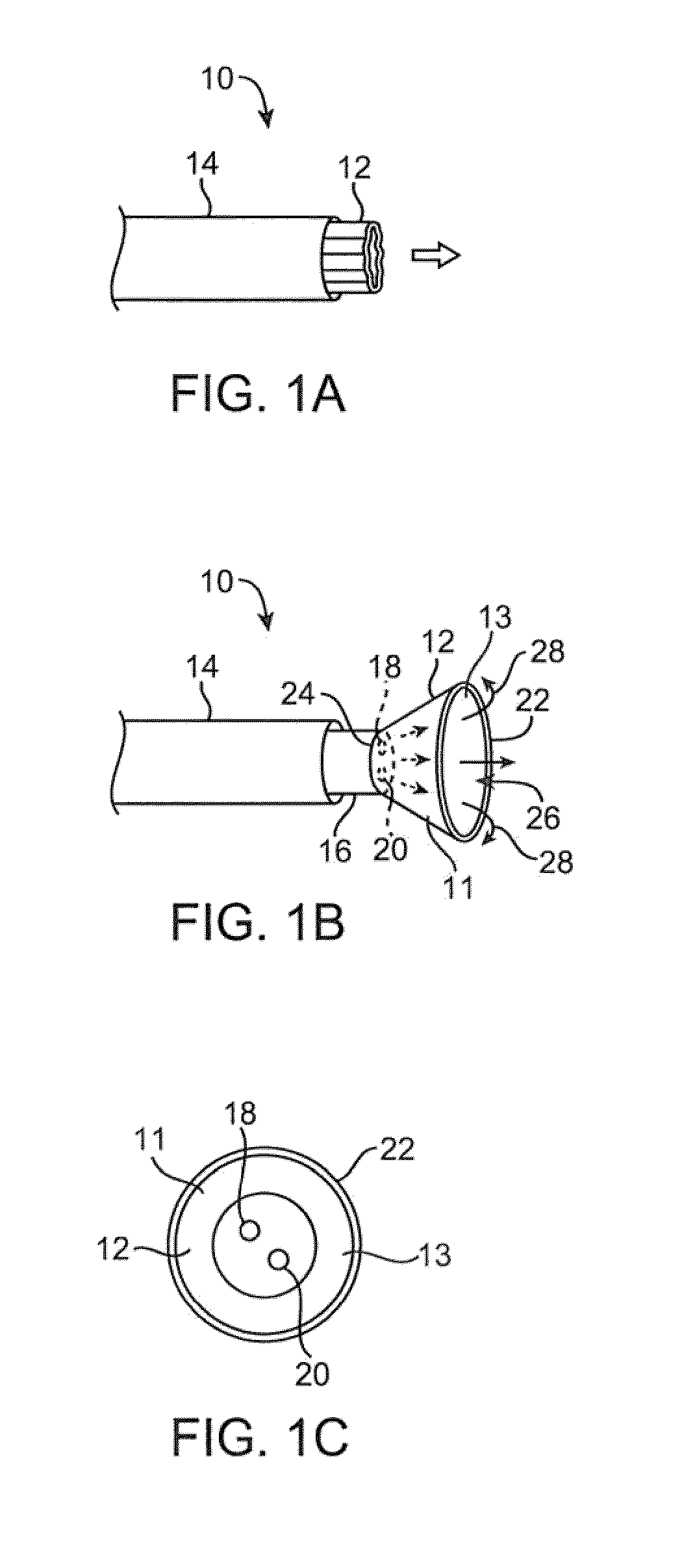
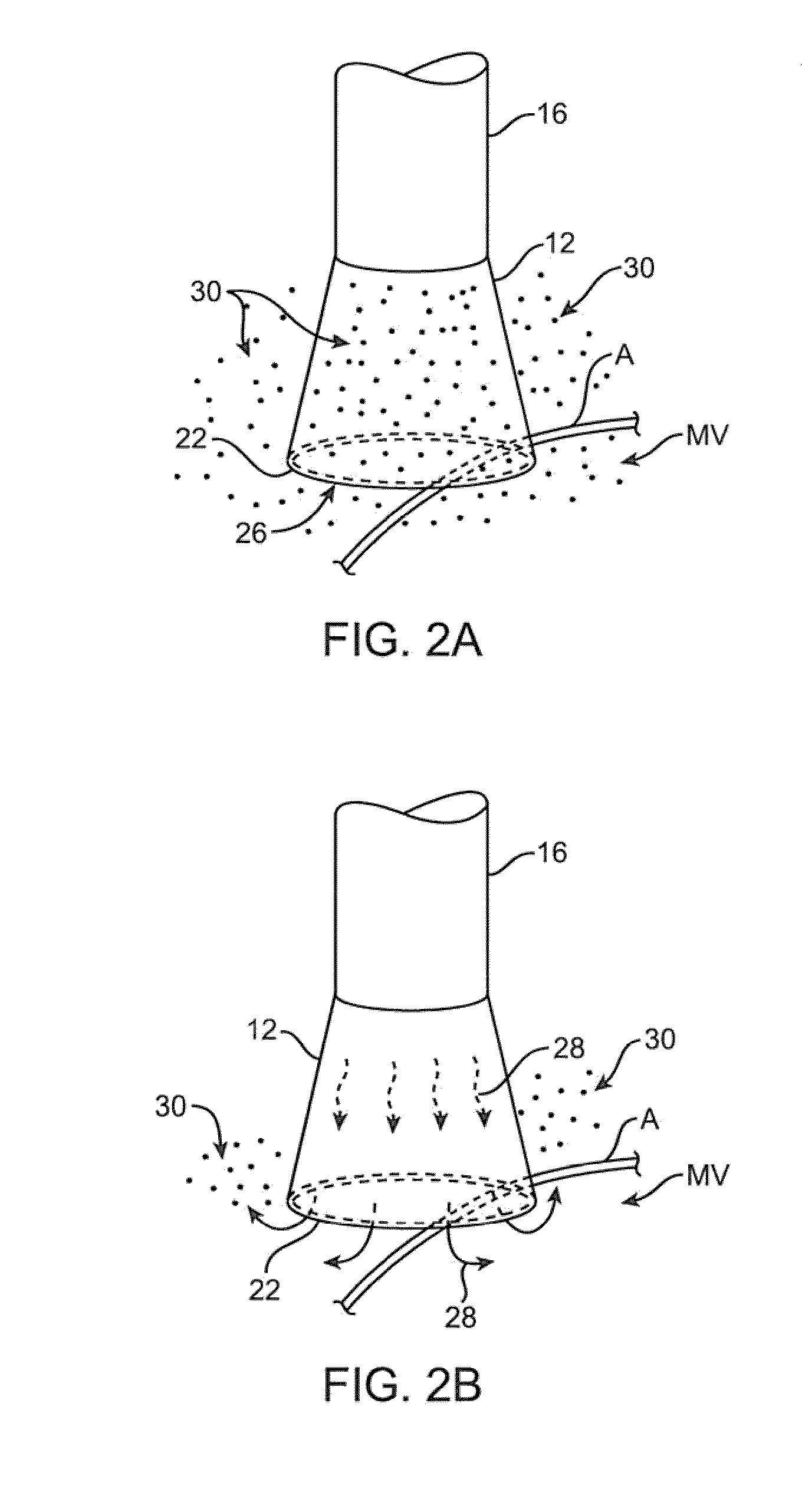
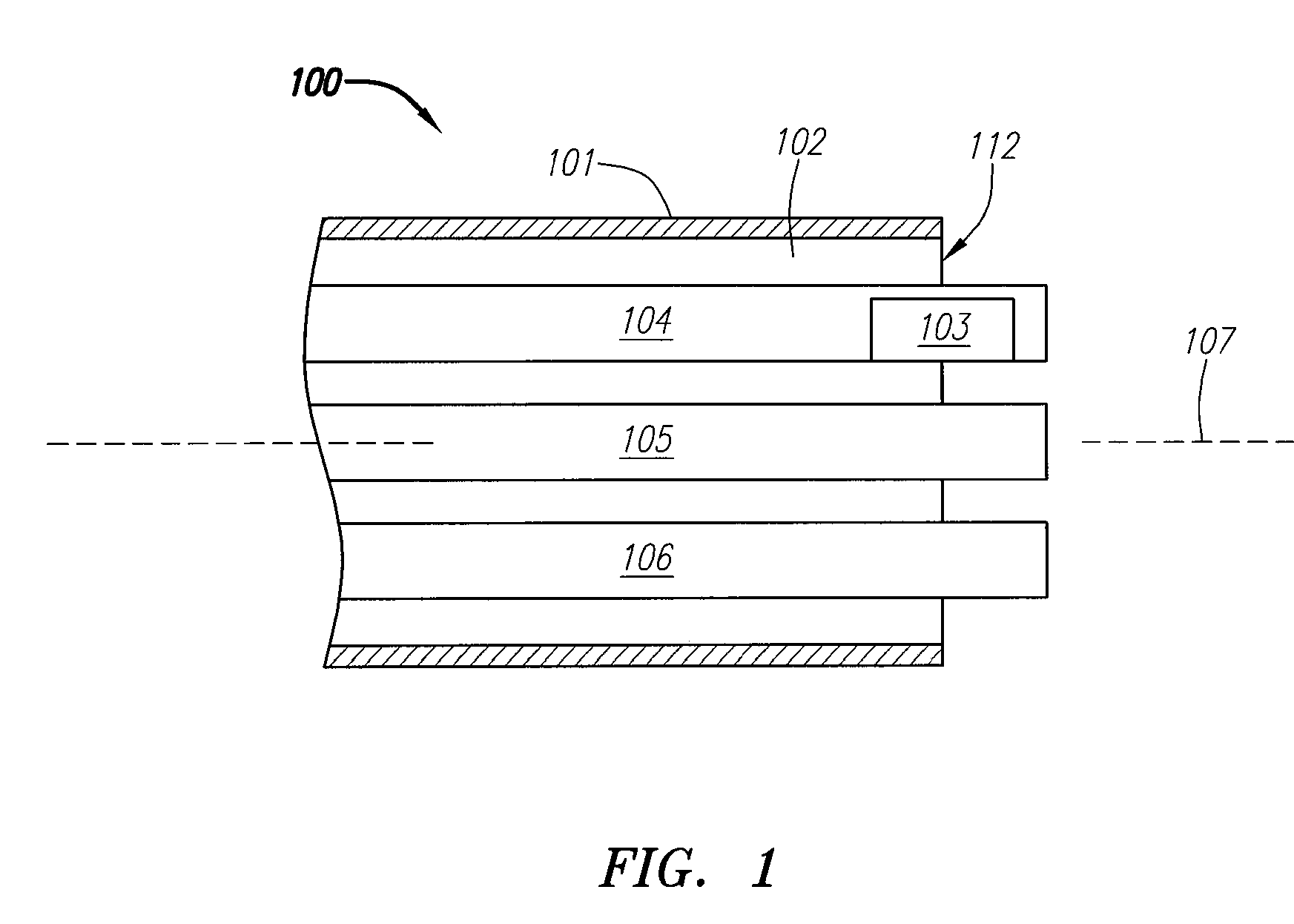
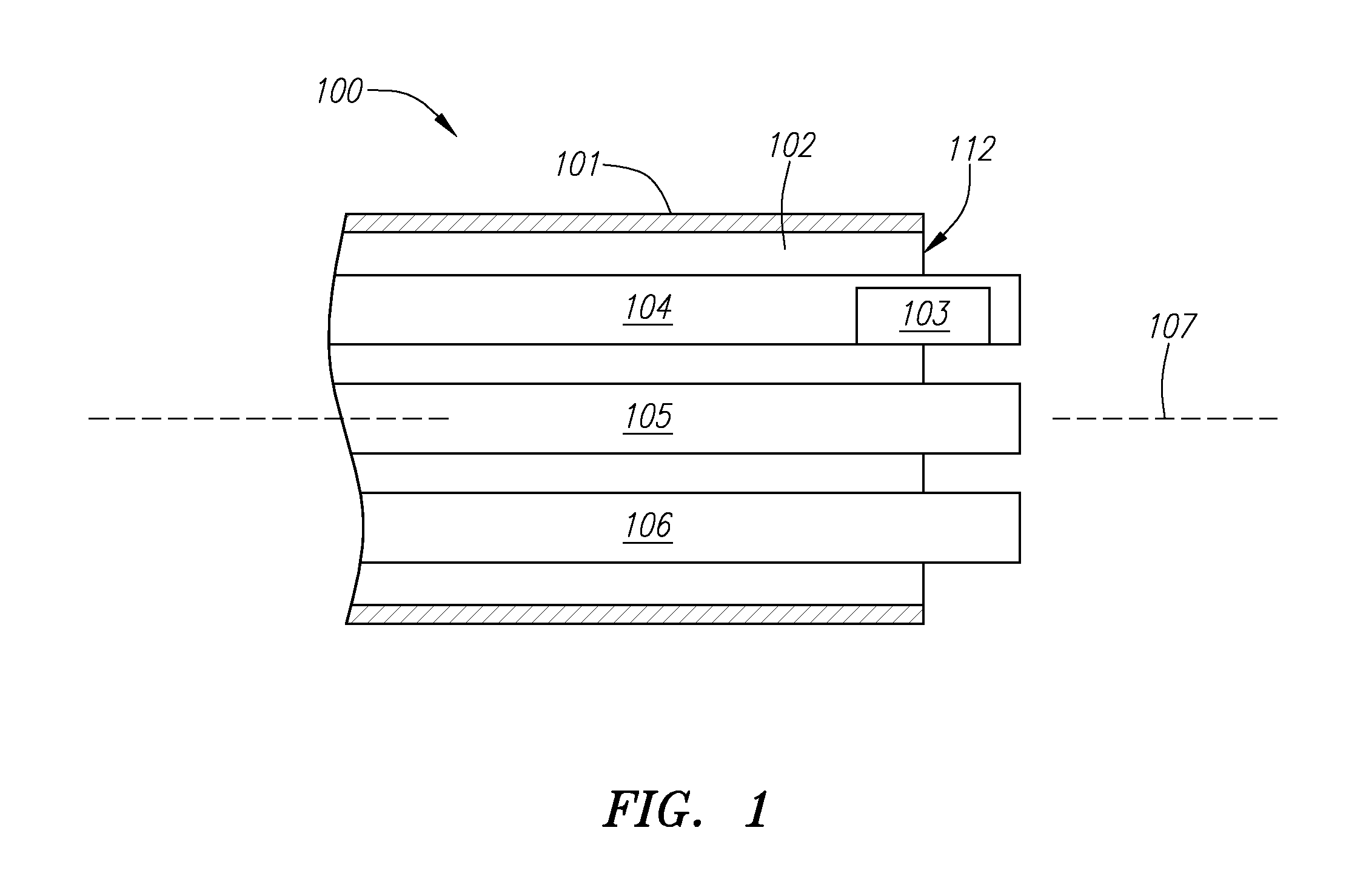
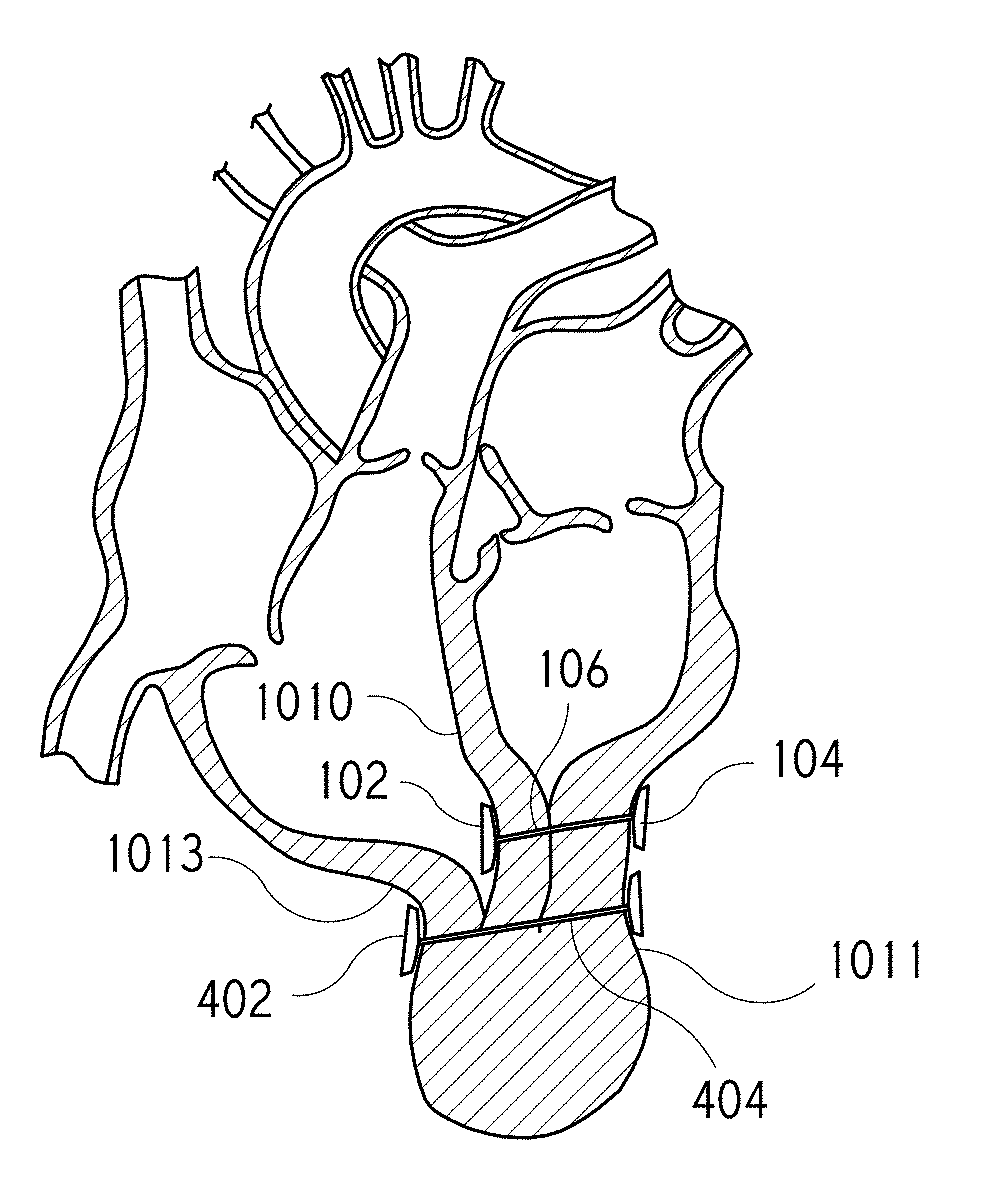
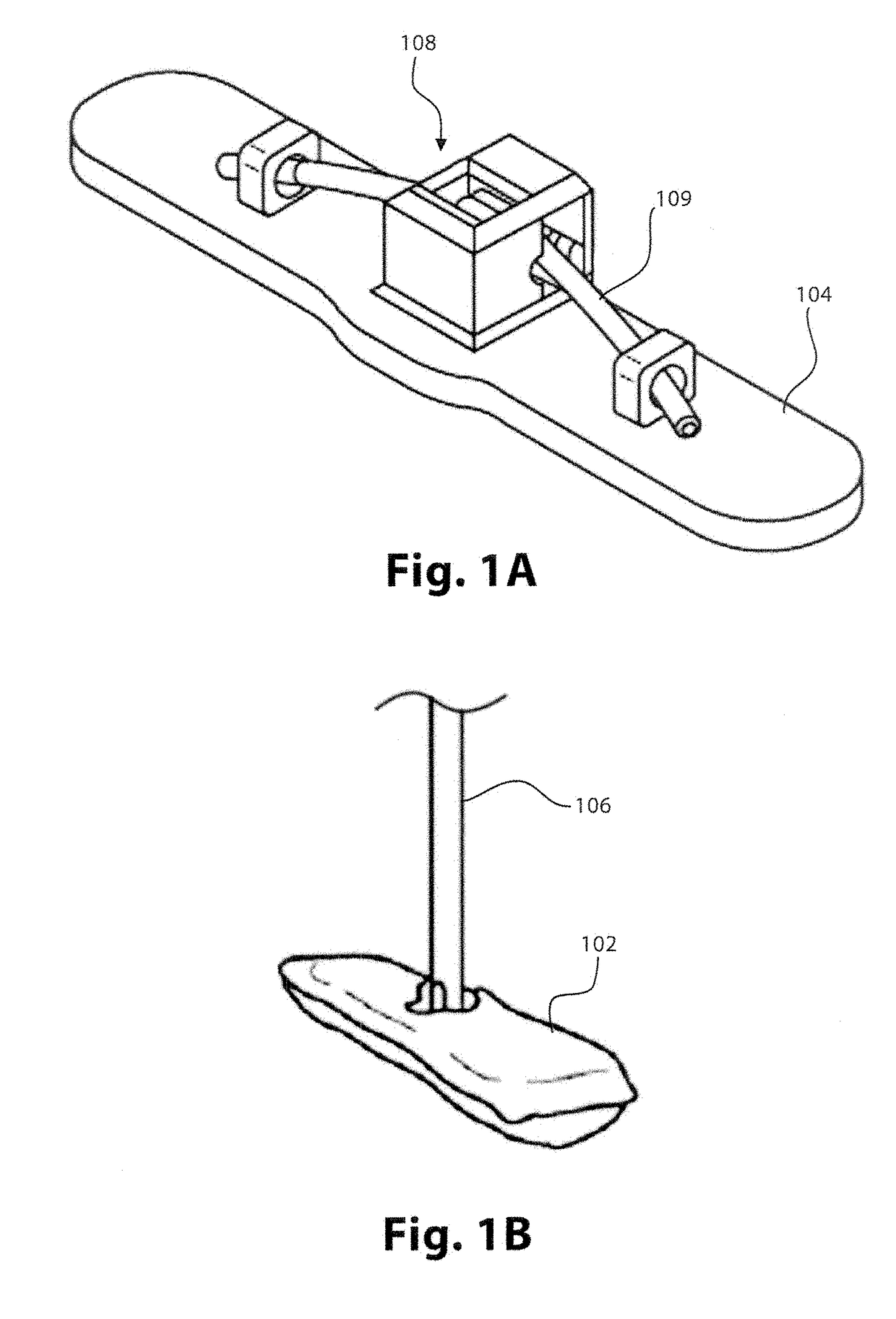
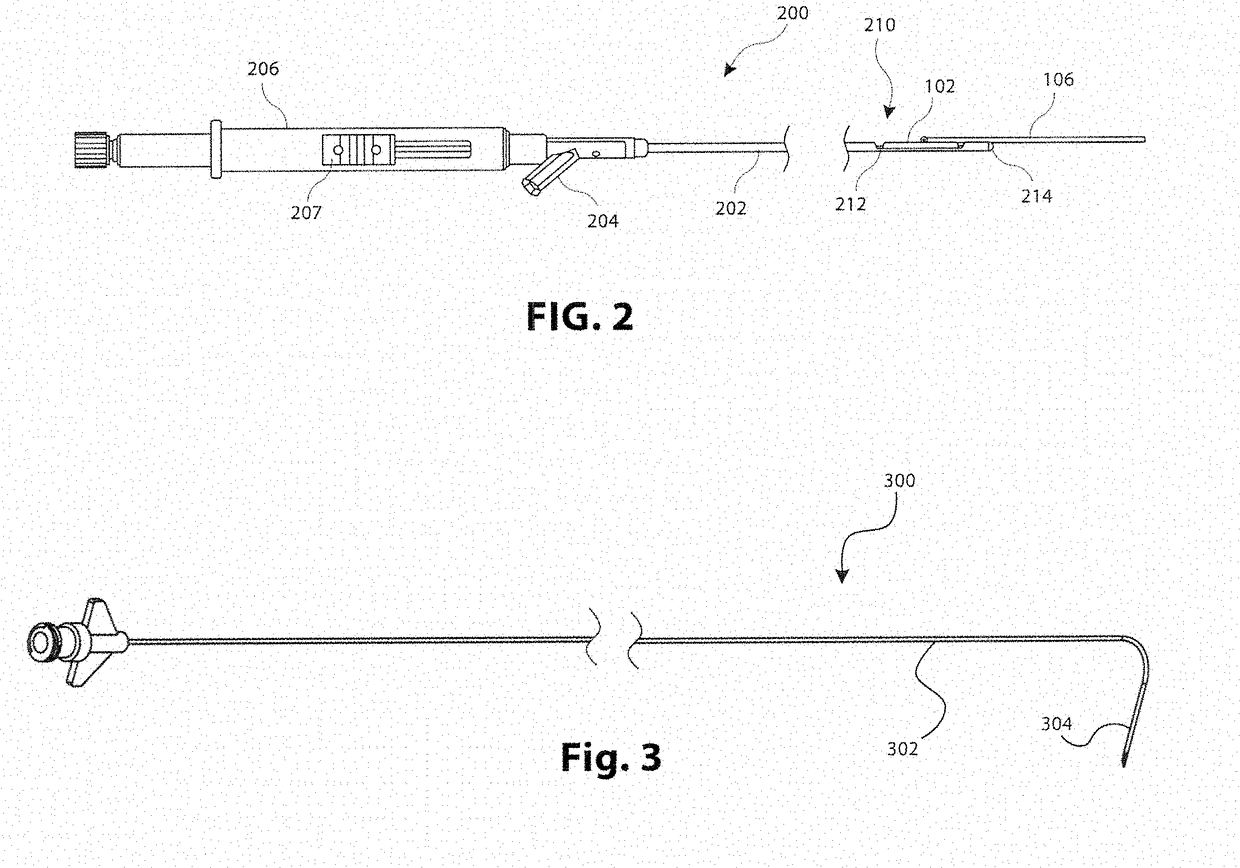
A system for treating a septal defect having a suture-like implantable treatment apparatus and devices for delivering the implantable treatment apparatus and methods for treating a septal defect are provided. The suture-like apparatus is preferably implantable through a septal wall or portion thereof. The treatment system can include a flexible elongate body member, a delivery device configured to deliver the suture-like apparatus, a stabilization device configured to stabilize the delivery device and a positioning device configured to position the delivery device in a desired location. The suture-like device can include a suture body coupled with one or more lock devices or anchor devices.
Owner:PROMED
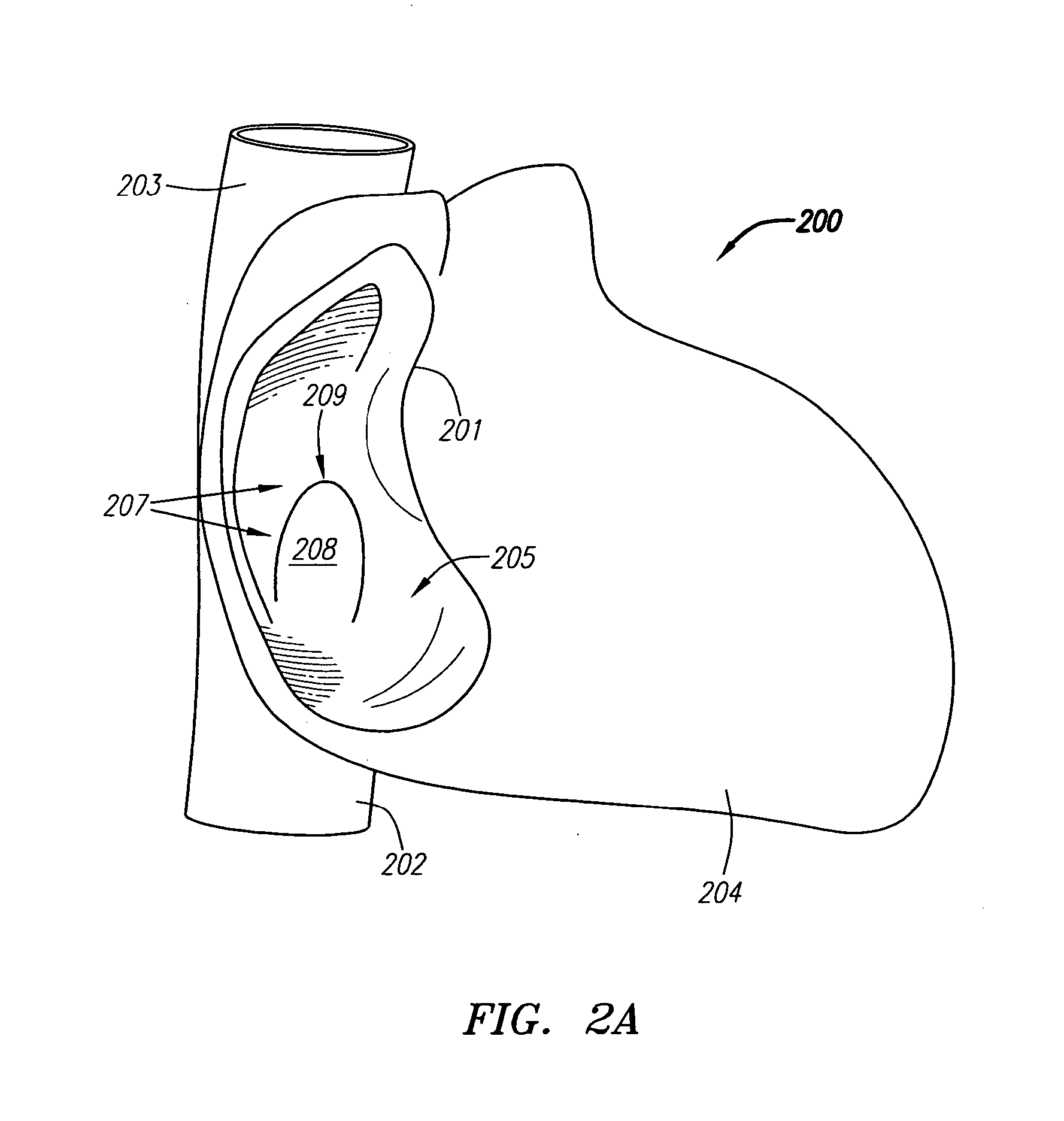
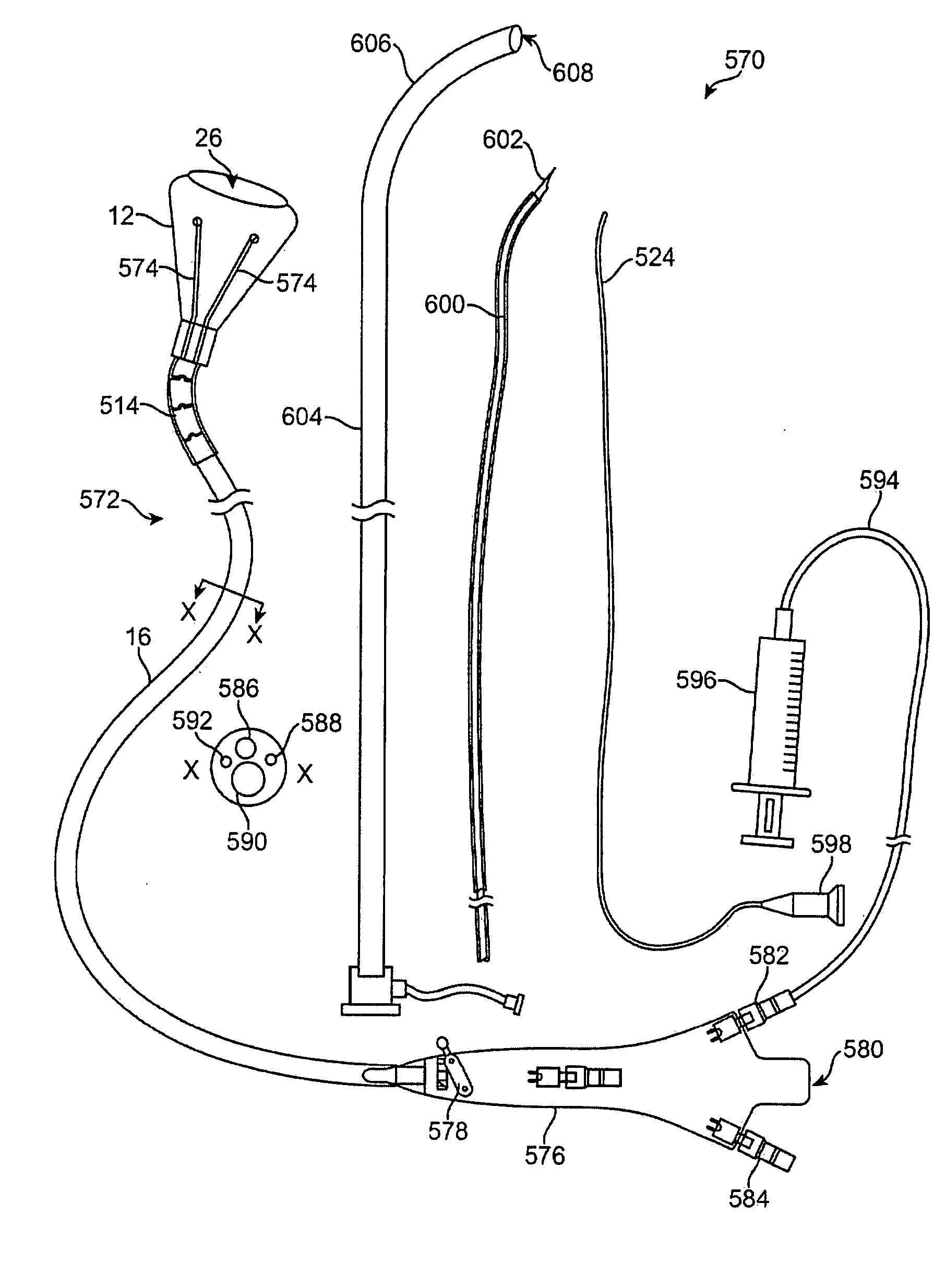
Visualization apparatus for transseptal access
ActiveUS20070293724A1Easy to identify visuallyDifficult to identifyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySeptal wallVia device
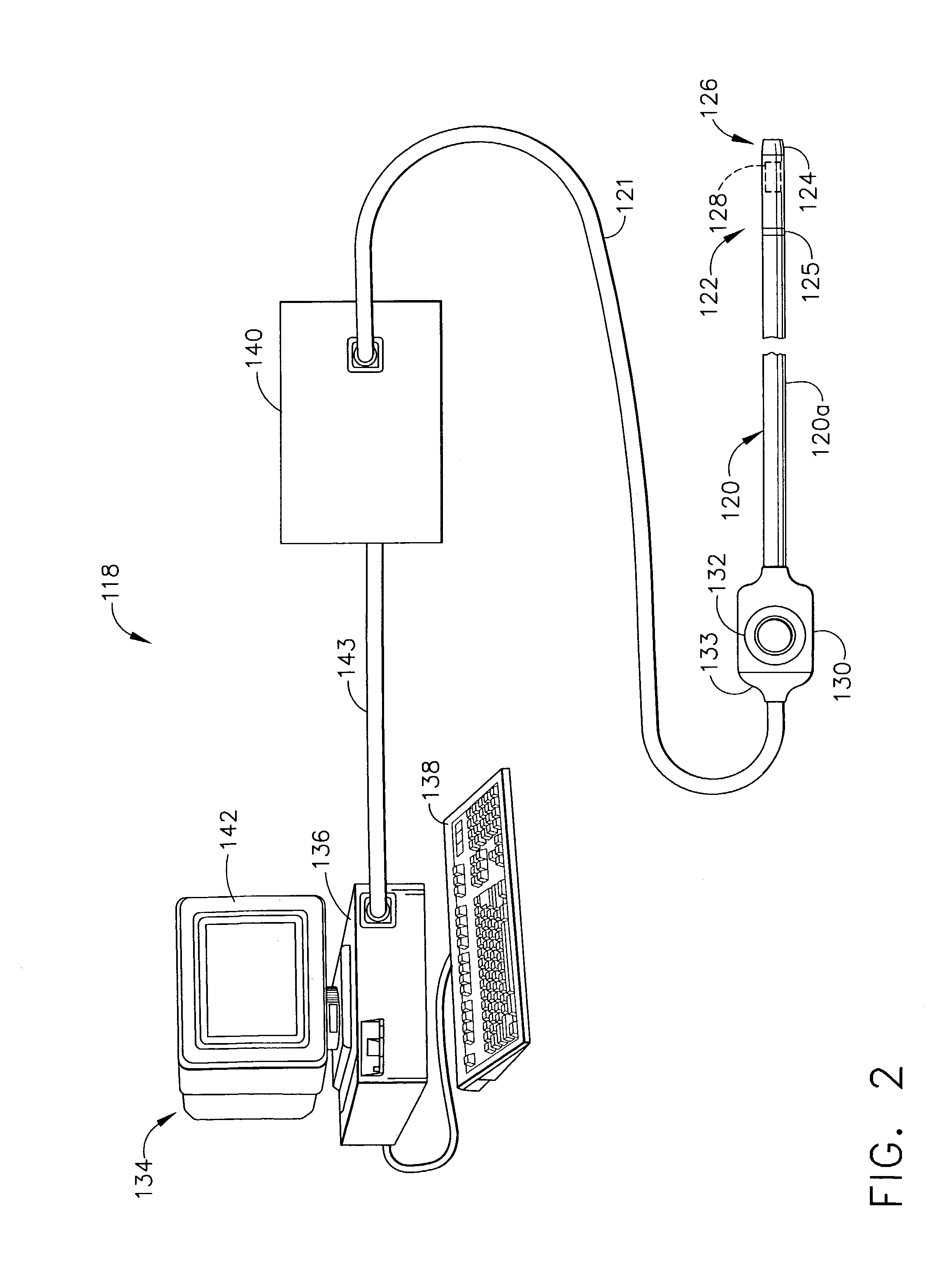
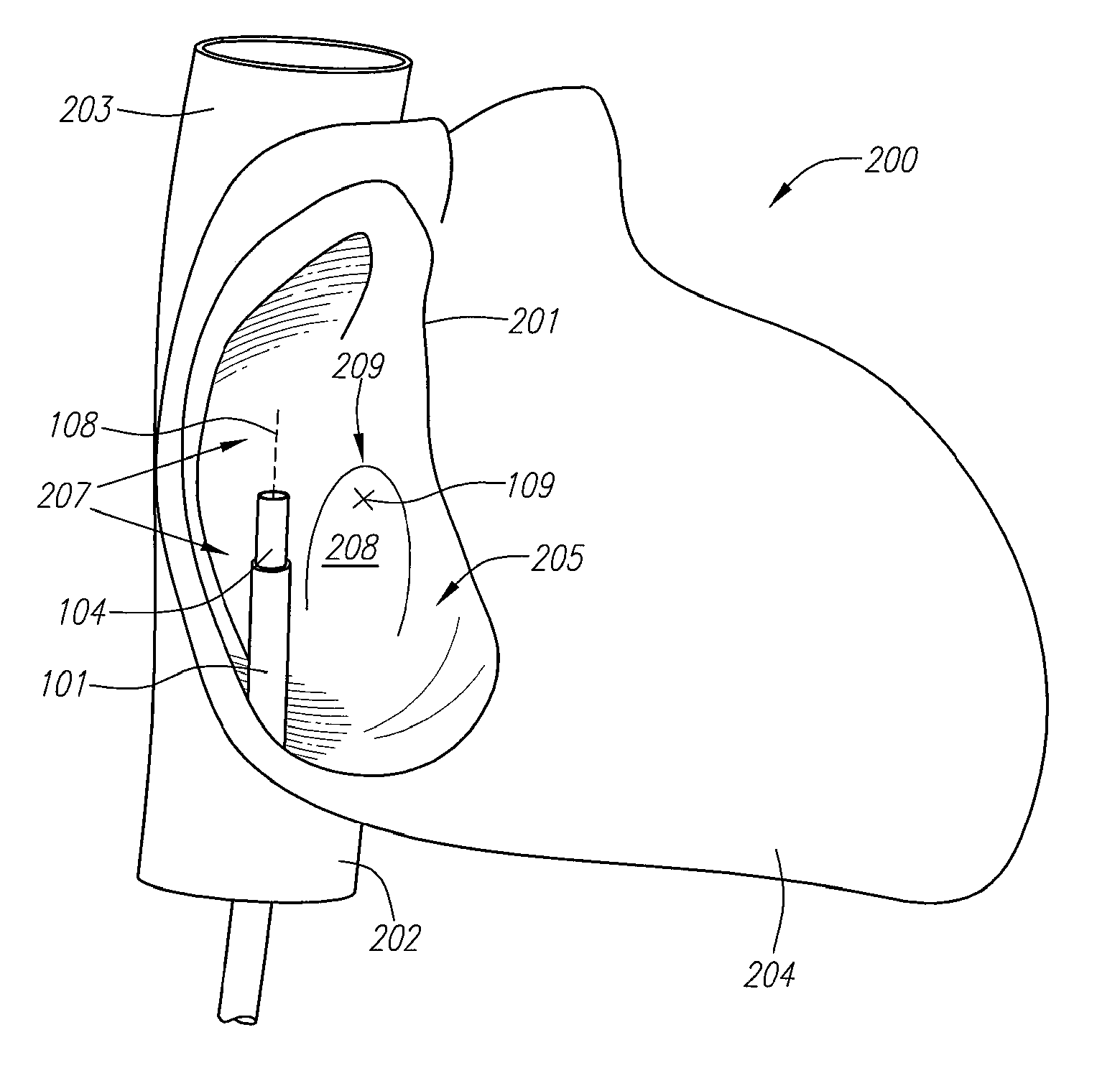
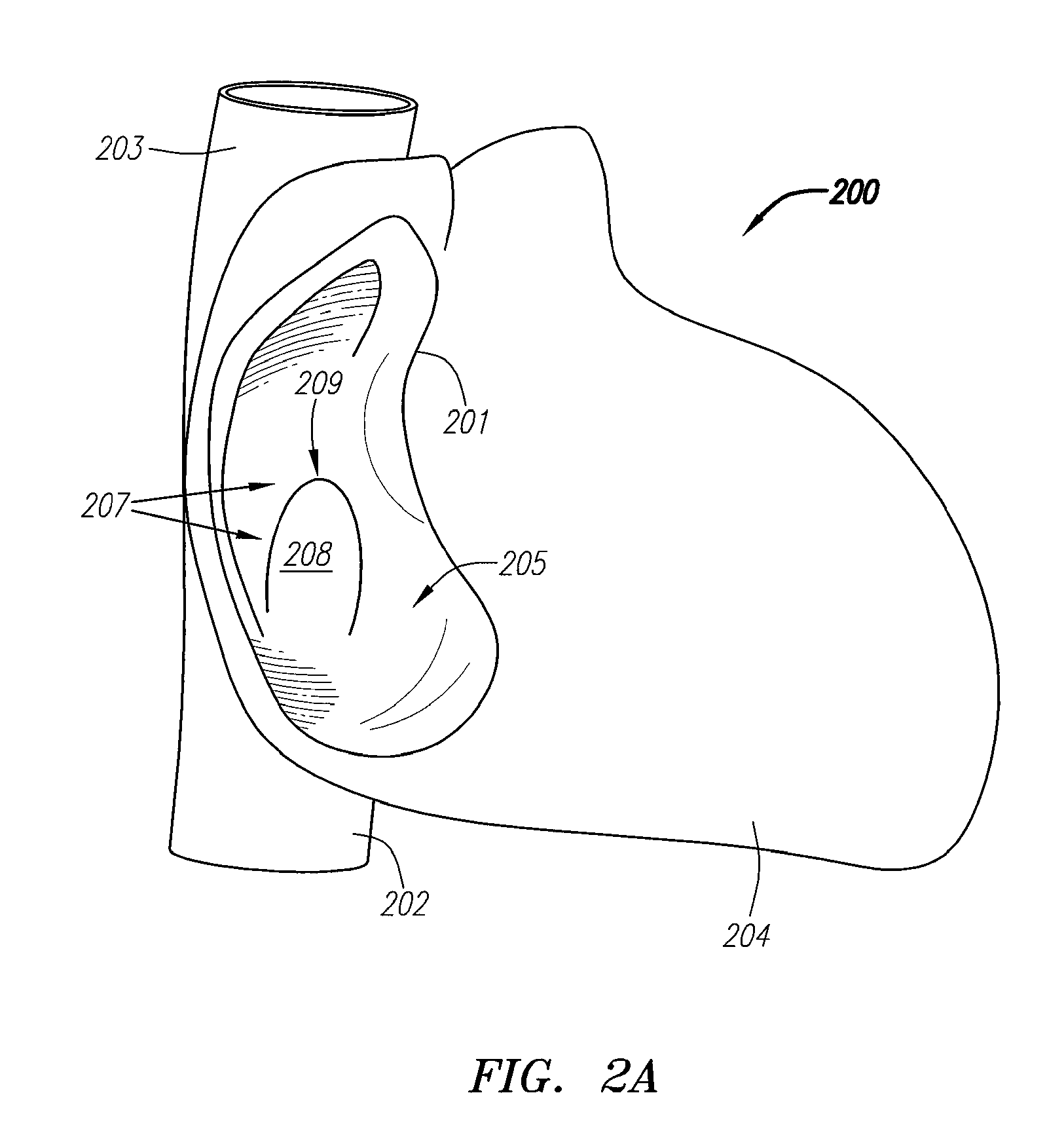
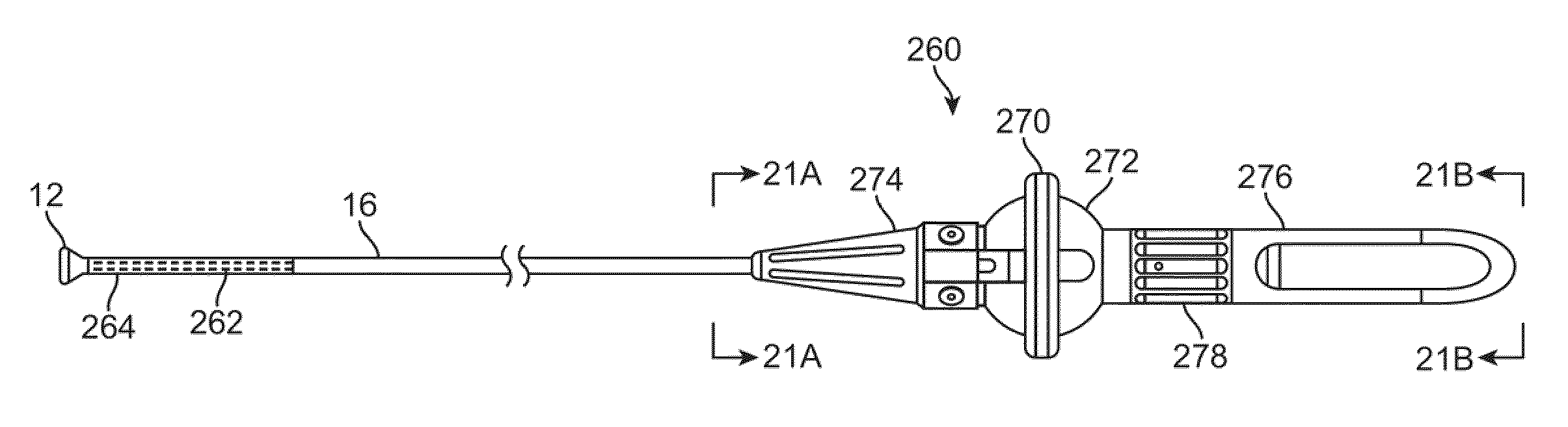
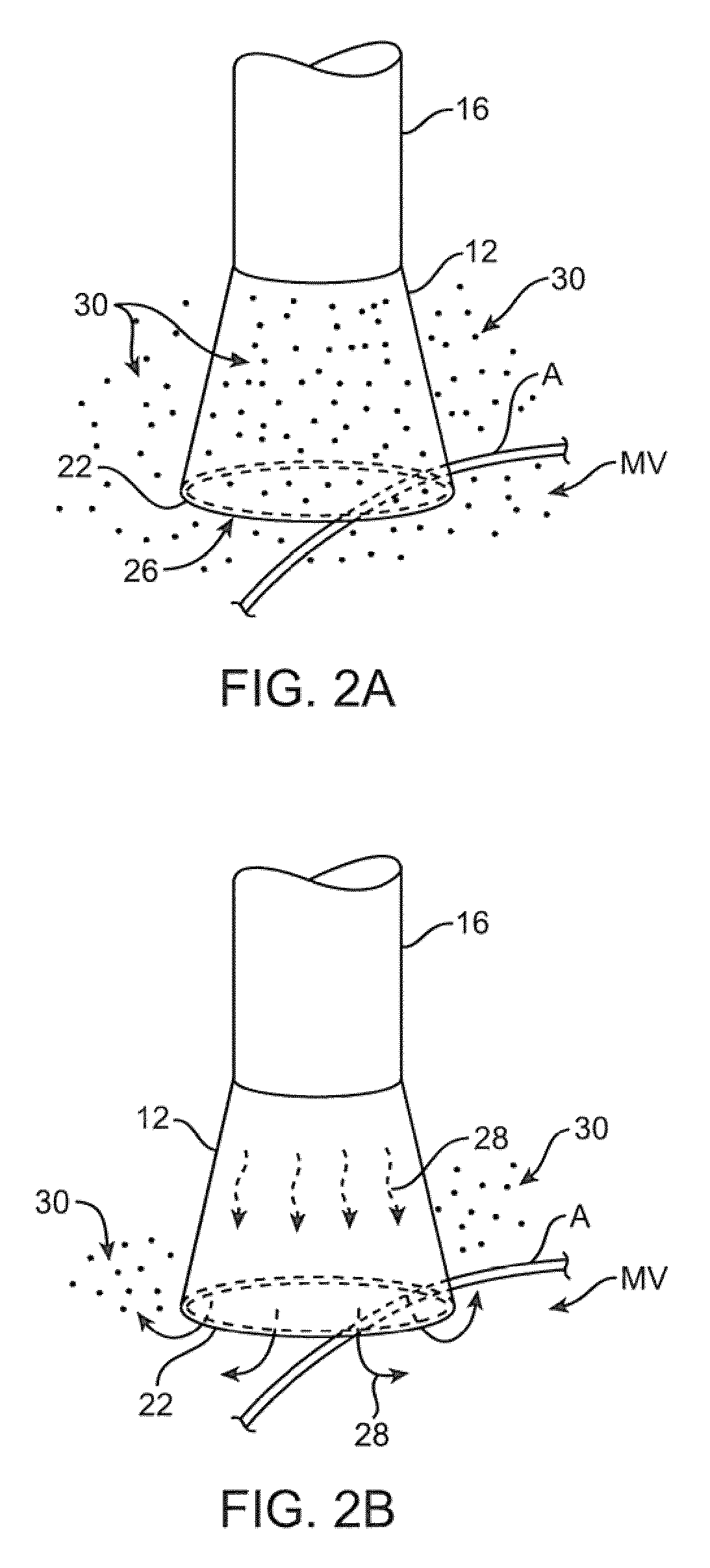
Visualization apparatus and methods for transseptal access are described herein where intravascular access across a septal wall is facilitated via devices which provide for direct visual viewing of tissue area. Such a system may include a deployment catheter and an attached imaging hood deployable into an expanded configuration. In use, the imaging hood is placed against or adjacent to the tissue to be imaged in a body lumen that is normally filled with an opaque bodily fluid such as blood. A translucent or transparent fluid can be pumped into the imaging hood until the fluid displaces any blood leaving a clear region of tissue to be imaged via an imaging element in the deployment catheter. Any number of therapeutic tools or a guidewire can be passed through the catheter and into the imaging hood for crossing the septal wall and passing the guidewire or instruments therethrough.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Medical device suitable for use in treatment of a valve
InactiveUS20060178700A1Prevent leakageProfound clinical consequencesSuture equipmentsHeart valvesSeptal wallMedical device
A medical device (1210) comprises a generally cylindrical treatment element (1220) for location between a pair of valve leaflets (1212) situated between an atrium (1214) and a ventricle (1216) of a heart. The treatment element (1220) supports the valve leaflets (1212) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212) and occludes the valve opening to resist fluid flow in the retrograde direction through the valve opening. The device (1210) comprises a support (1222) to support the treatment element (1210) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212). The support has an anchor (1224) and a tether (1226), the tether (1226) being provided at the end of a guide wire (1228) which is initially utilised in the percutaneous insertion of the treatment element (1220). The anchor (1224) is secured, in use, to a septal wall (1230), while the guide wire (1228) exits the atrium (1214) through a vein adjacent a rear wall (1224) thereof. The treatment element (1220) includes a remotely actuatable clamp therein, in order to allow the treatment element (1220) to be secured to the guide wire (1228) or the tether (1226).
Owner:MEDNUA
Systems and methods for treating septal defects
InactiveUS20060052821A1Reduce deliverySurgical pincettesSurgical veterinaryTherapeutic DevicesTreatment interval
A system for treating a septal defect having an implantable treatment apparatus and devices for delivering the implantable treatment apparatus and methods for treating a septal defect are provided. The implantable treatment apparatus is preferably implantable through a septal wall or portion thereof. The treatment system can include a flexible elongate body member, a delivery device configured to deliver the implantable apparatus, a stabilization device configured to stabilize the body member and a positioning device configured to position the delivery device in a desired location.
Owner:OVALIS
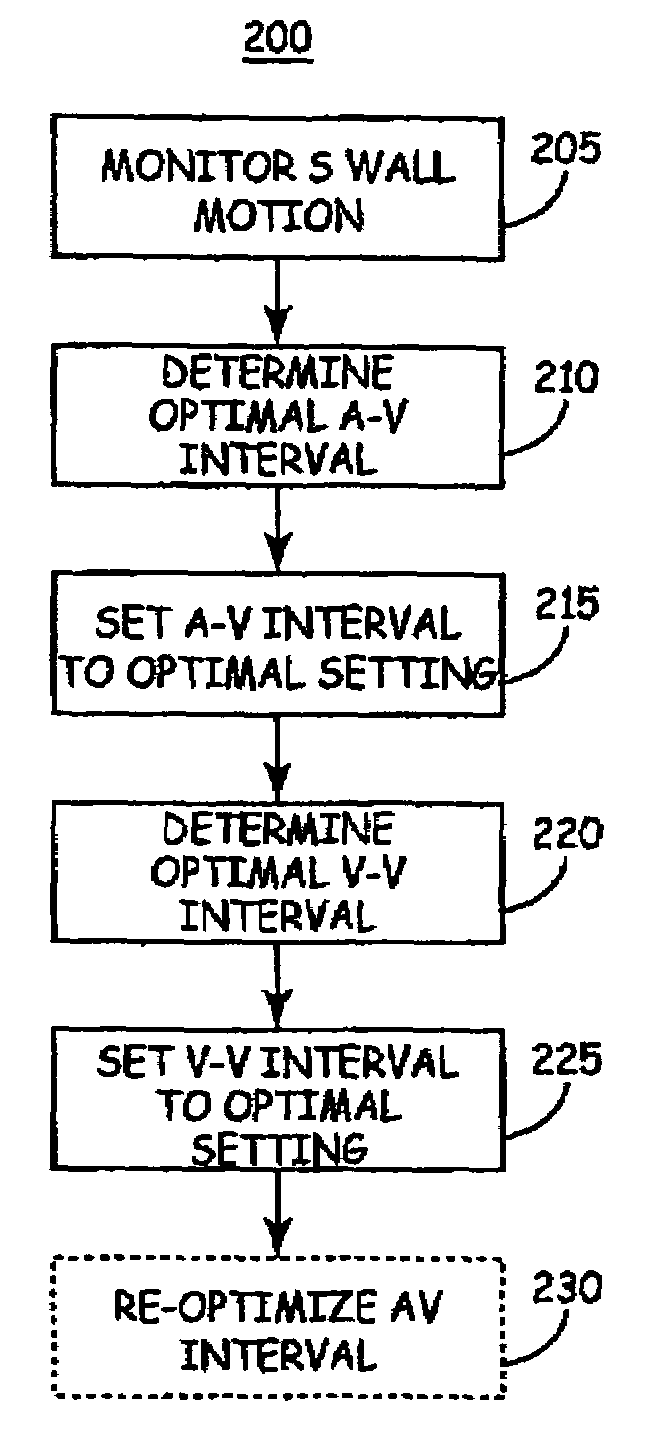
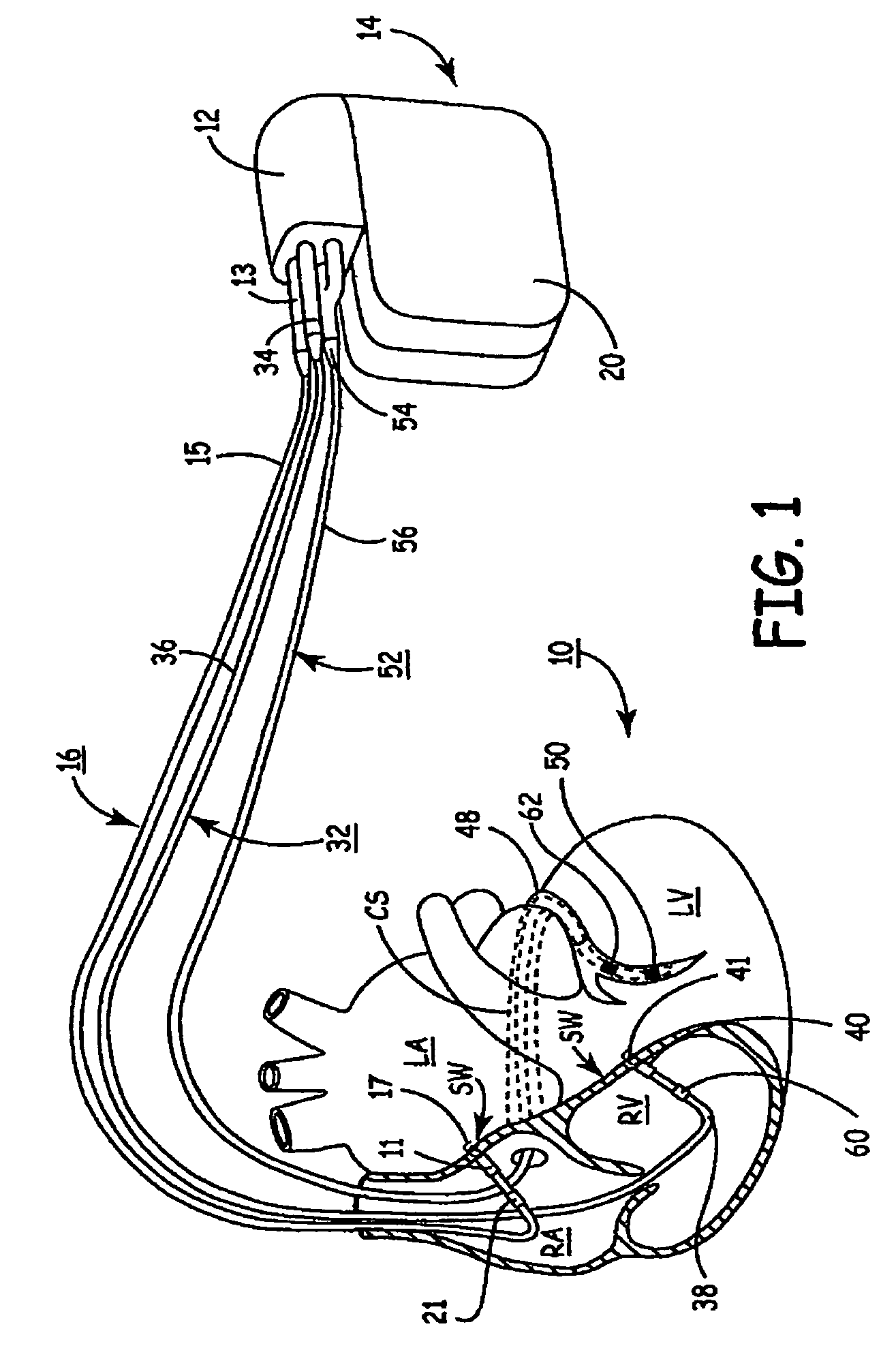
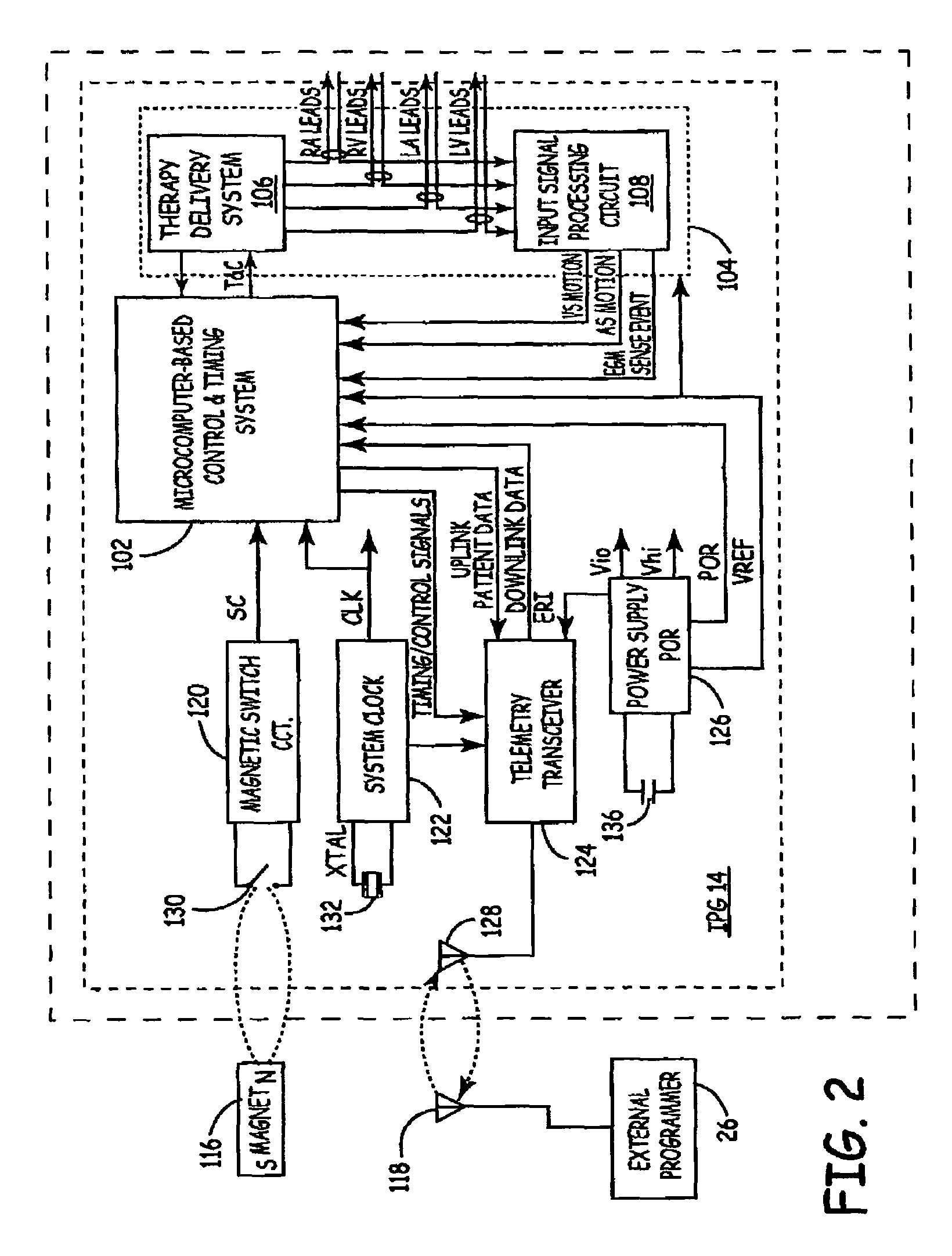
Method of optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy using sensor signals of septal wall motion
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and Methods for Treating Septal Defects
A system for treating a septal defect having an implantable treatment apparatus and devices for delivering the implantable treatment apparatus, devices for controlling delivery of the treatment apparatus and methods for treating a septal defect are provided. The implantable treatment apparatus is preferably implantable through a septal wall or portion thereof. The treatment system can include a flexible elongate body member, a delivery device configured to deliver the implantable apparatus, a stabilization device configured to stabilize the body member, a positioning device configured to position the delivery device in a desired location, and a proximal control device for controlling delivery of the implantable apparatus.
Owner:OVALIS
Method and device for transseptal facilitation based on injury patterns
ActiveUS6994094B2Accurate identificationImprove permeabilityElectrocardiographySurgical needlesSeptal wallSurgery
A method for performing a procedure at the fossa ovalis in the septal wall of the heart includes the steps of providing a sheath having a body wherein the body has a lumen extending therethrough and an open end at the distal end of the body. The body also has at least one electrode and a position sensor at the distal end of the body. The position sensor generates signals indicative of the location of the distal end of the body. The sheath is navigated to the septal wall using the position sensor and the fossa ovalis in the septal wall is identified using the at least one electrode of the sheath.
Owner:BIOSENSE
Catheter control systems
ActiveUS20100004633A1Guaranteed simulation effectEfficiently controlling the hood positionSurgeryEndoscopesControl systemSeptal wall
Catheter control systems which facilitate the tracking of an angle of deflection of a catheter distal end can be used for any number of procedures where catheter orientation relative to the body is desirable, e.g., in transseptal access procedures where an accurate angle of puncture of the septal wall is desirable. Such control systems may comprise a steerable handle which is oriented relative to the catheter steerable section to provide for consistent catheter articulation upon corresponding manipulation of the steering ring. Another variation may utilize an orientation indicator to track the deflectable distal end. For instance, an orientation marker as visualized through an imaging hood on the distal end may correspond to identical orientation markers on the control handle such that articulation of a steering mechanism in a direction relative to the orientation markers deflects the catheter distal end in a corresponding direction relative to the visualized orientation markers.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
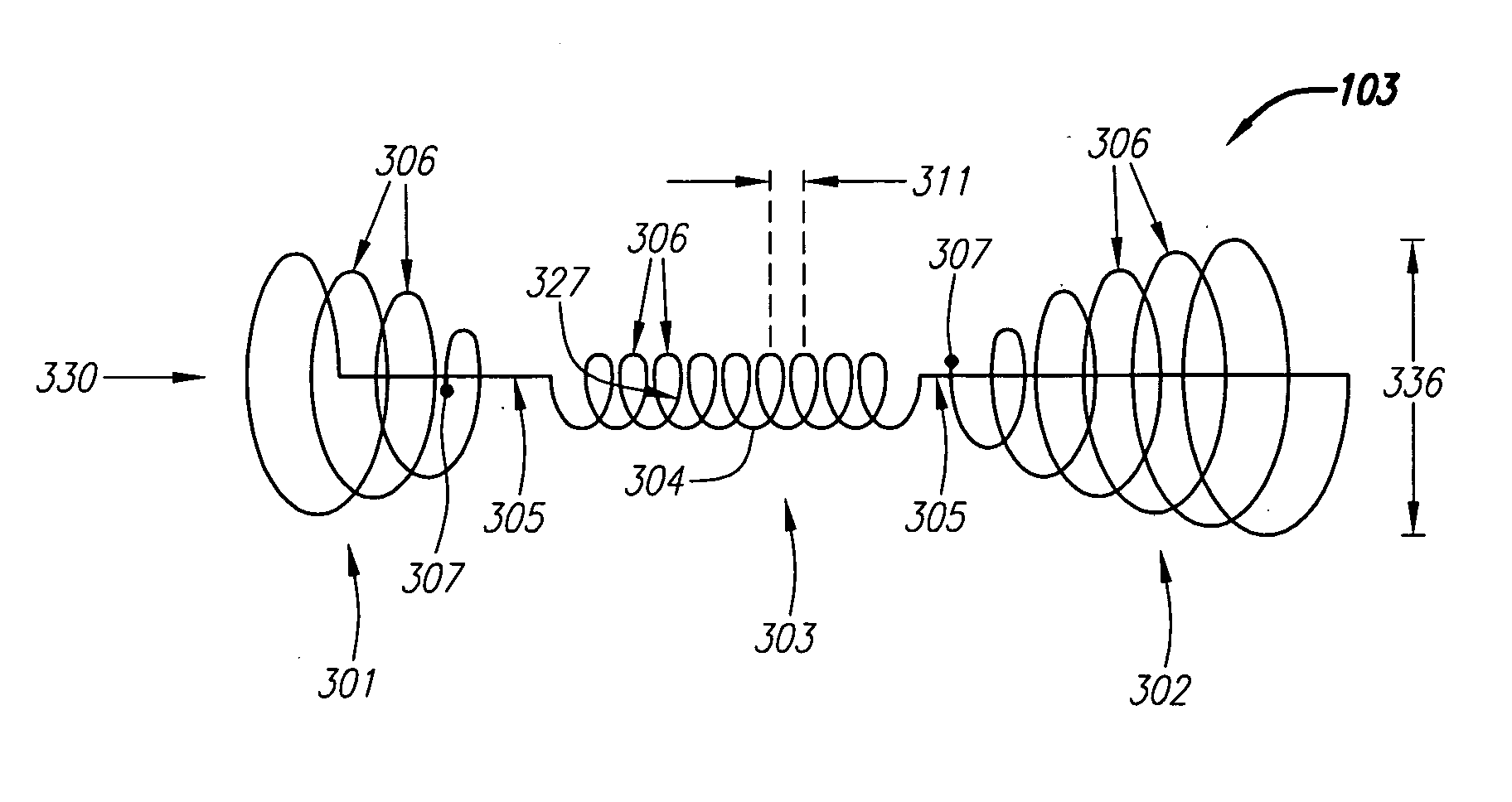
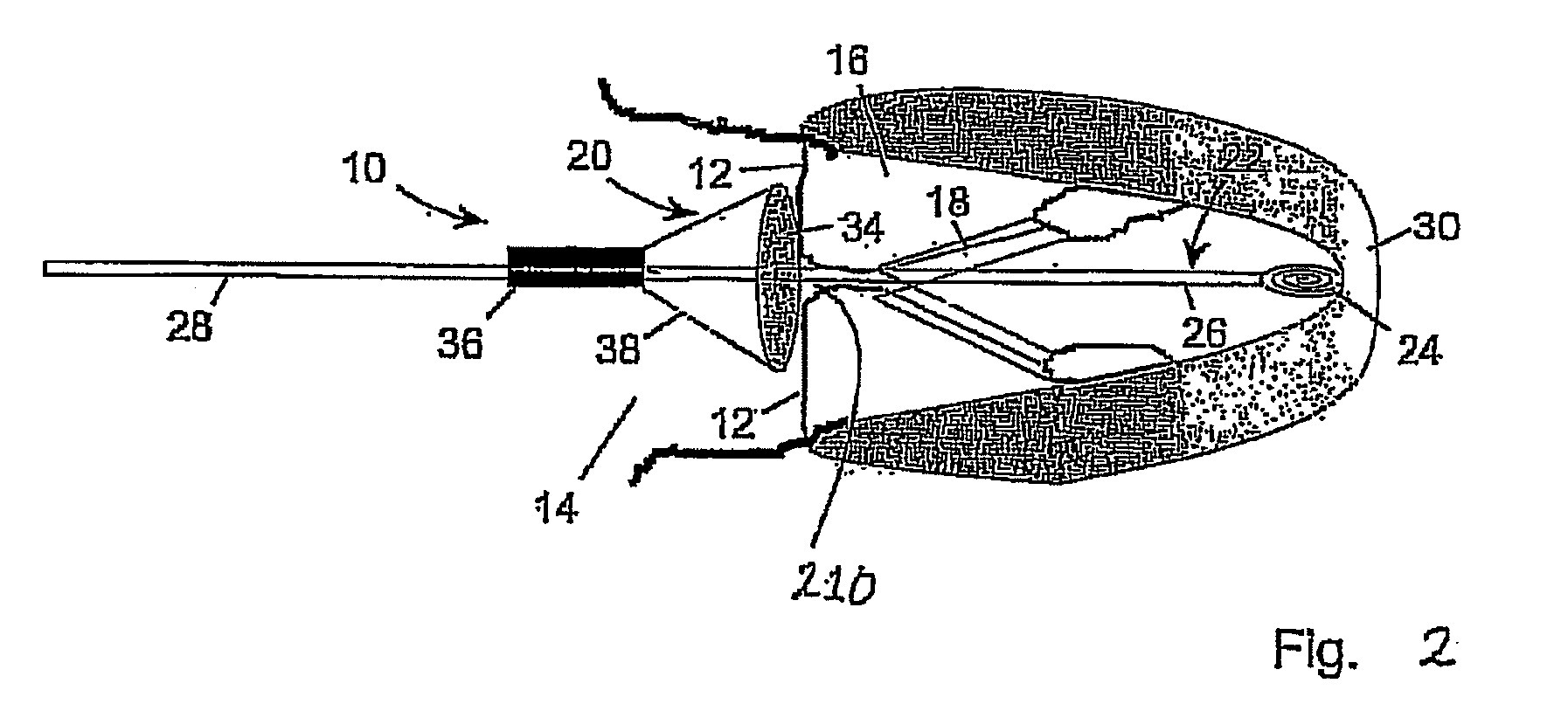
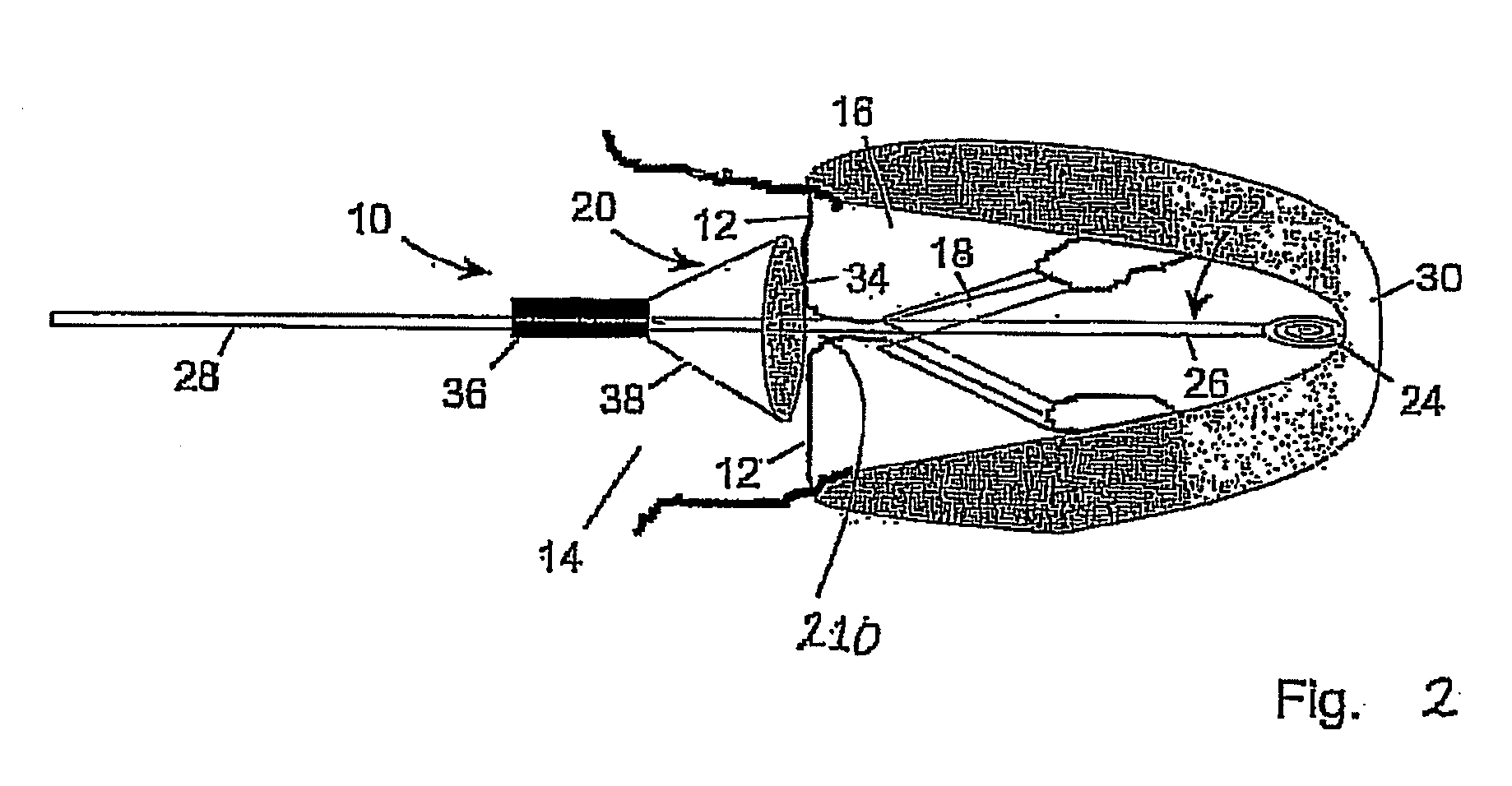
Catheter-based tissue remodeling devices and methods
Methods and systems for closing an opening or defect in tissue, closing a lumen or tubular structure, cinching or remodeling a cavity or repairing a valve preferably utilizing a purse string or elastic device. The preferred devices and methods are directed toward catheter-based percutaneous, transvascular techniques used to facilitate placement of the devices within lumens, such as blood vessels, or on or within the heart to perform structural defect repair, such as valvular or ventricular remodeling. In some methods, the catheter is positioned within the right ventricle, wherein the myocardial wall or left ventricle may be accessed through the septal wall to position a device configured to permit reshaping of the ventricle. The device may include a line or a plurality of anchors interconnected by a line. In one arrangement, the line is a coiled member.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Medical device suitable for use in treatment of a valve
InactiveUS20090076600A1Profound clinical consequencesIncrease pressureSuture equipmentsHeart valvesSeptal wallSurgery
A medical device (1210) comprises a generally cylindrical treatment element (1220) for location between a pair of valve leaflets (1212) situated between an atrium (1214) and a ventricle (1216) of a heart. The treatment element (1220) supports the valve leaflets (1212) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212) and occludes the valve opening to resist fluid flow in the retrograde direction through the valve opening. The device (1210) comprises a support (1222) to support the treatment element (1210) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212). The support has an anchor (1224) and a tether (1226), the tether (1226) being provided at the end of a guide wire (1228) which is initially utilised in the percutaneous insertion of the treatment element (1220). The anchor (1224) is secured, in use, to a septal wall (1230), while the guide wire (1228) exits the atrium (1214) through a vein adjacent a rear wall (1224) thereof. The treatment element (1220) includes a remotely actuatable clamp therein, in order to allow the treatment element (1220) to be secured to the guide wire (1228) or the tether (1226).
Owner:MEDNUA
Systems and Methods for Treating Septal Defects with Capture Devices and Other Devices
InactiveUS20080154286A1Convenient treatmentSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesTissue defectSeptal wall
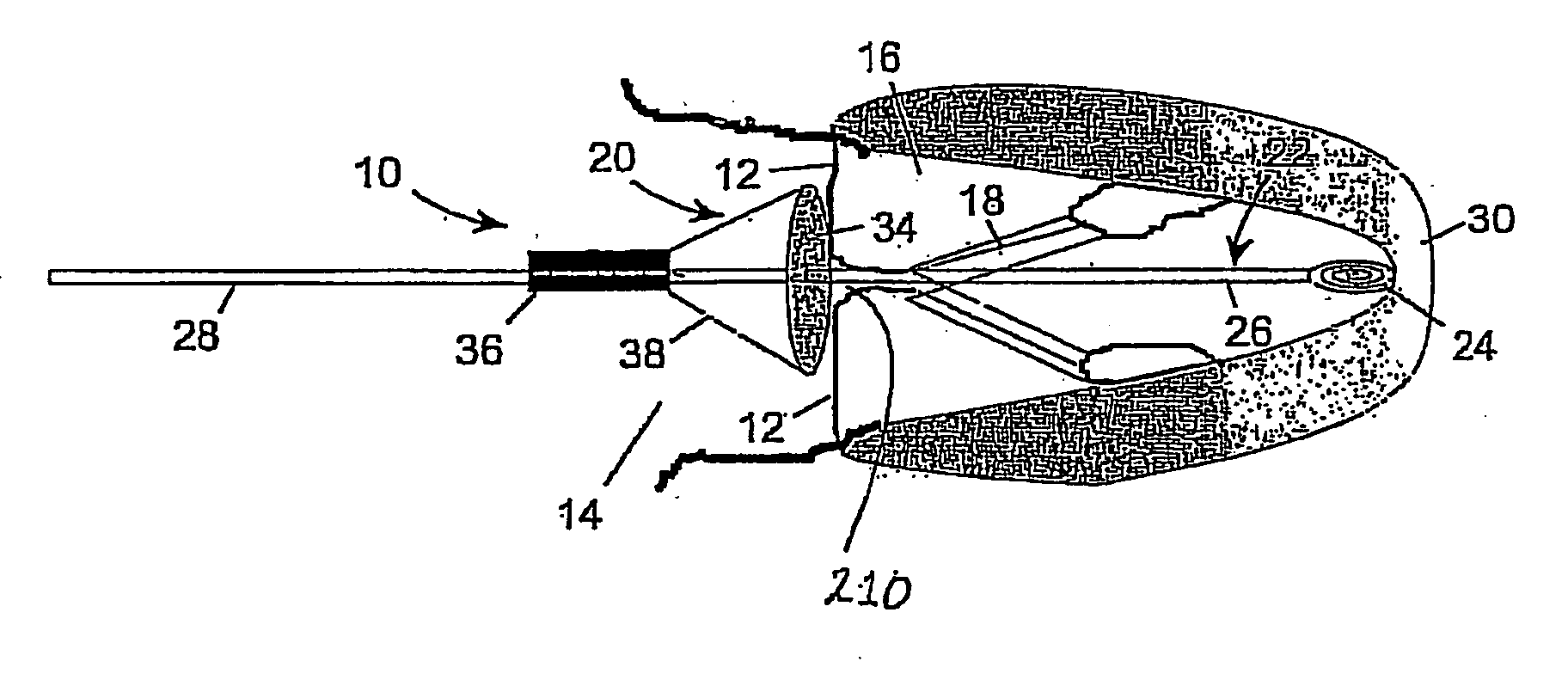
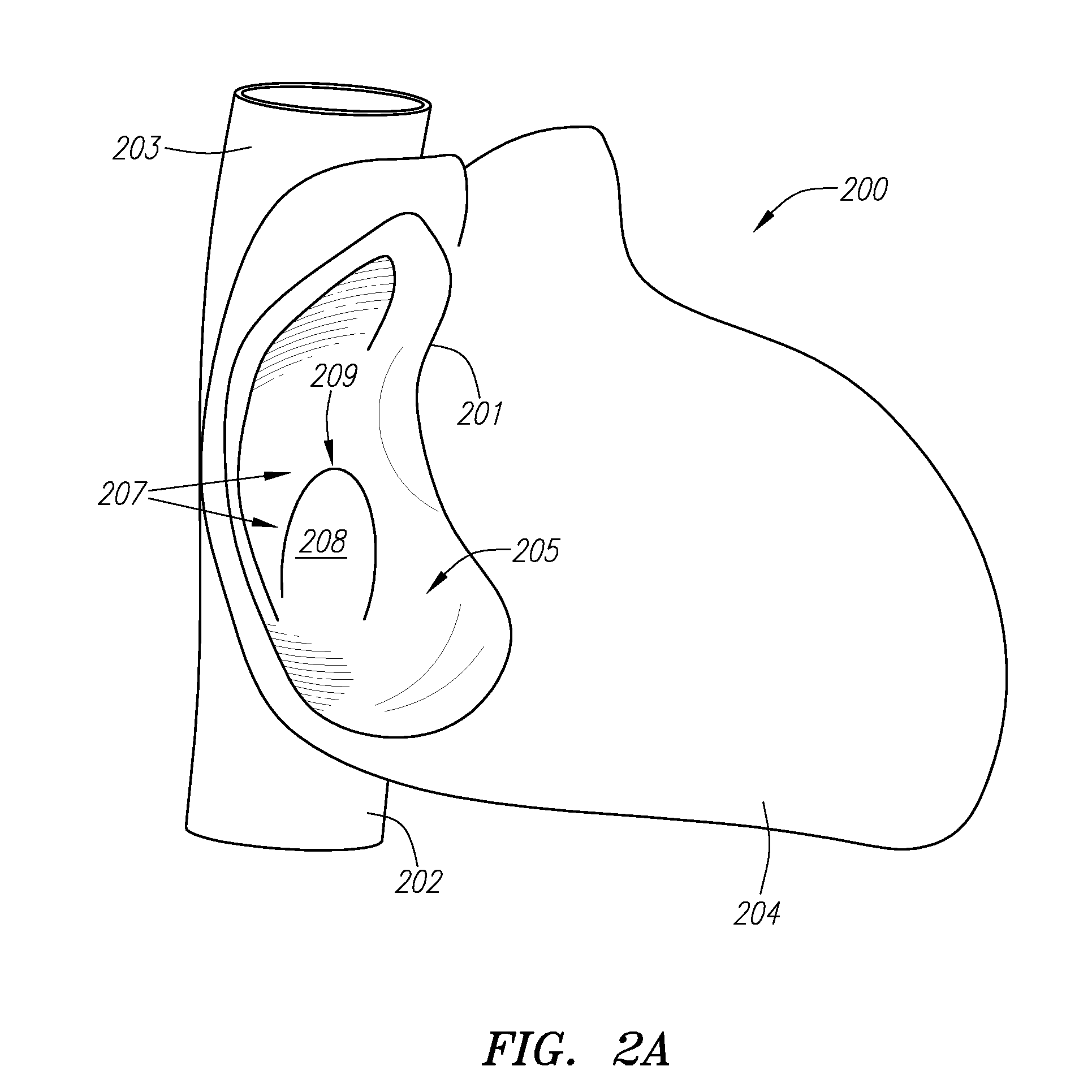
Systems, devices and methods for treating internal tissue defects, such as septal defects, are provided. An exemplary method of treating an internal tissue defect, specifically a method of closing a patent foramen ovale (PFO), can include passing a closure element from a right atrium through a septal wall in a first location and into the left atrium. A capture device, which can be configured as a snare-like device, can be used to capture the closure element in the left atrium and pull the closure element back through the septal wall in a different, second location, such that the closure element is routed over the PFO. The closure element can then be anchored and / or locked against the septal wall such that the PFO is at least partially closed.
Owner:OVALIS
Systems and Methods for Treating Septal Defects
InactiveUS20090054912A1Enhanced interactionEasy to operateStentsDiagnosticsSeptal wallImplanted device
A system for treating a septal defect having an implantable treatment apparatus and devices for delivering the implantable treatment apparatus, devices for controlling delivery of the treatment apparatus and methods for treating a septal defect are provided. The implantable treatment apparatus is preferably implantable through a septal wall or portion thereof. The treatment system can include a flexible elongate body member, a delivery device configured to deliver the implantable apparatus, and a proximal control device for controlling delivery of the implantable apparatus, among others.
Owner:OVALIS
Systems and Methods for Treating Septal Defects
InactiveUS20080015633A1Enhanced interactionEasy to operateSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsTherapeutic DevicesSeptal wall
A system for treating a septal defect having an implantable treatment apparatus and devices for delivering the implantable treatment apparatus, devices for controlling delivery of the treatment apparatus and methods for treating a septal defect are provided. The implantable treatment apparatus is preferably implantable through a septal wall or portion thereof. The treatment system can include a flexible elongate body member, a delivery device configured to deliver the implantable apparatus, and a proximal control device for controlling delivery of the implantable apparatus, among others.
Owner:OVALIS
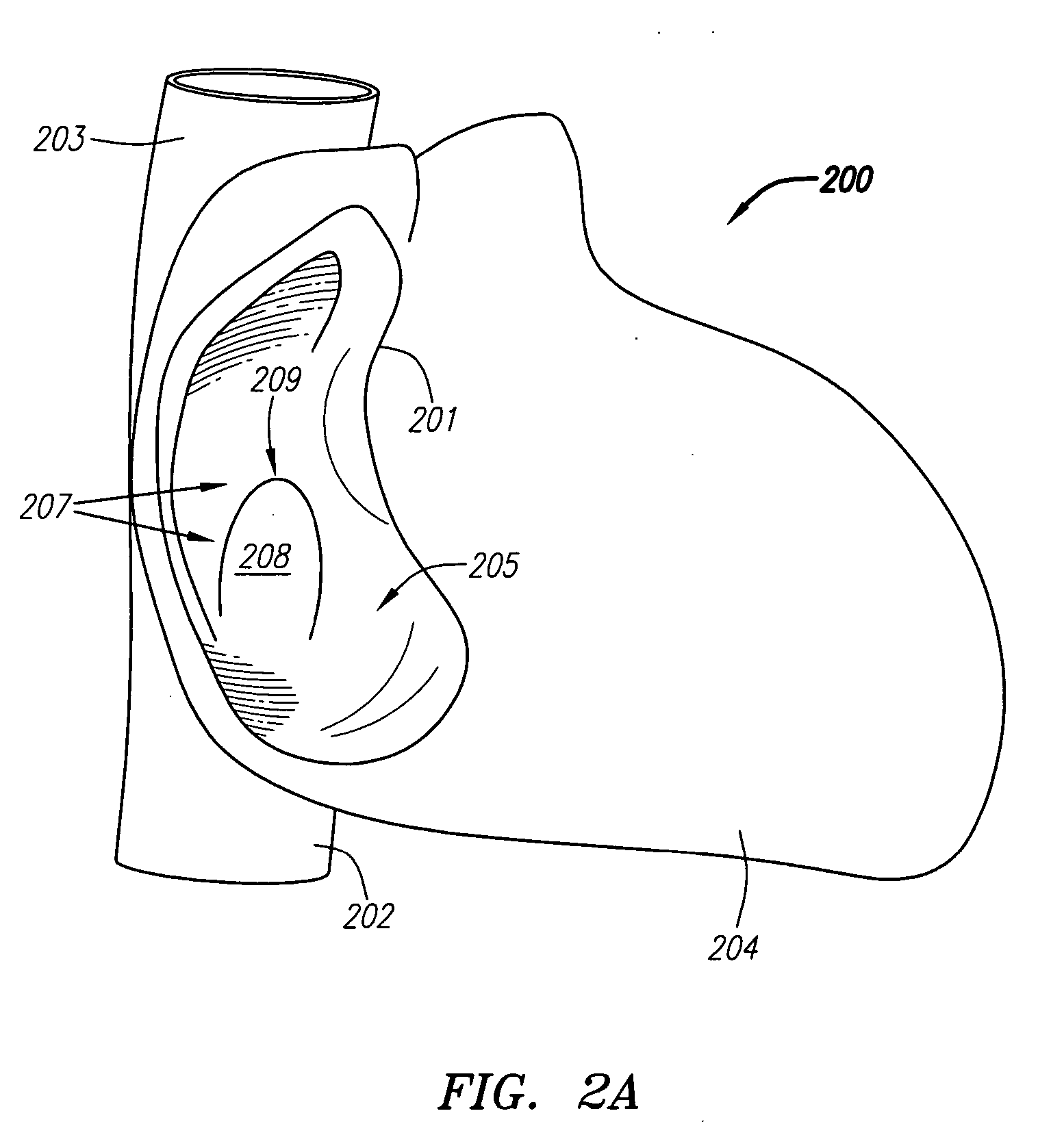
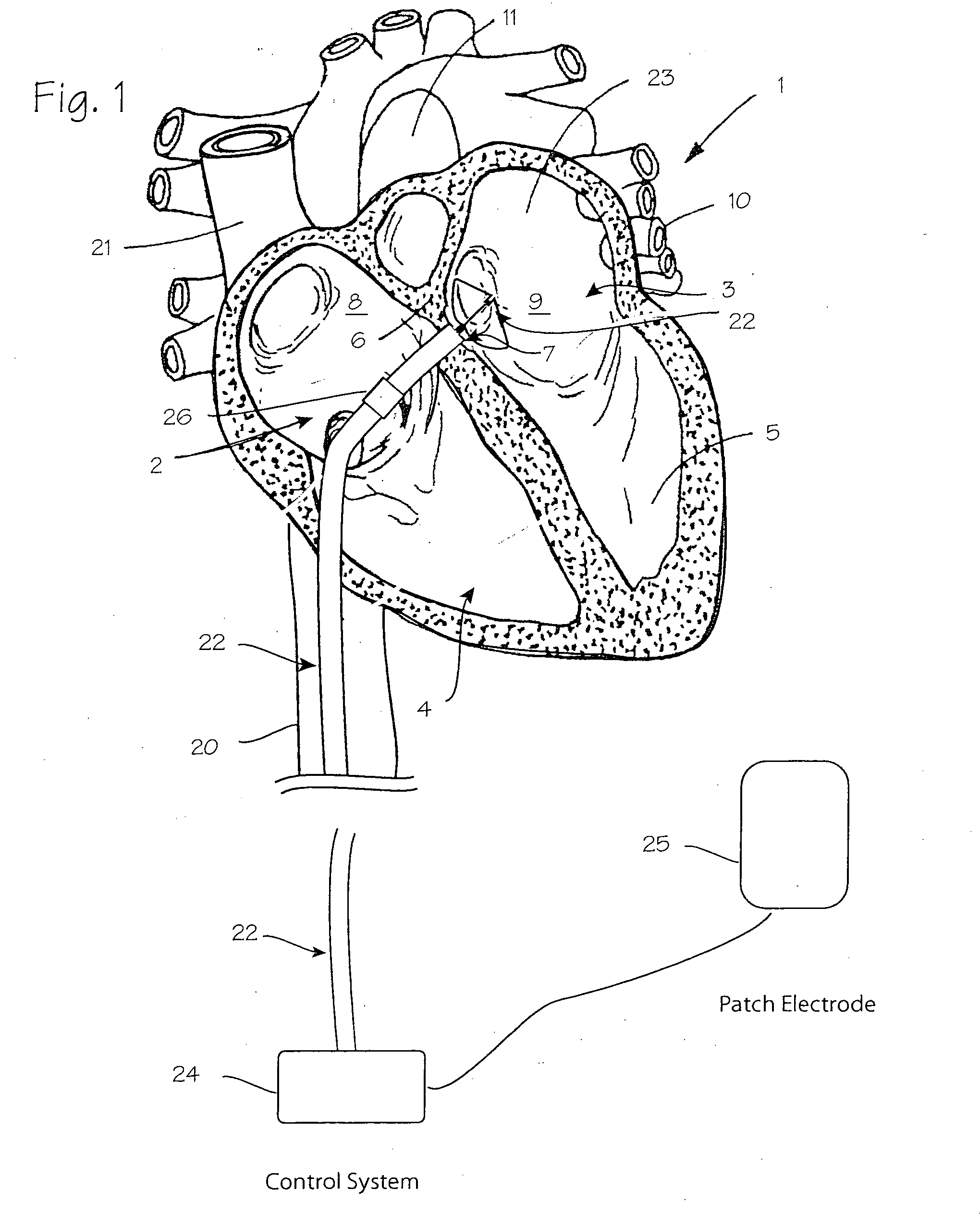
Devices and methods for treating heart failure
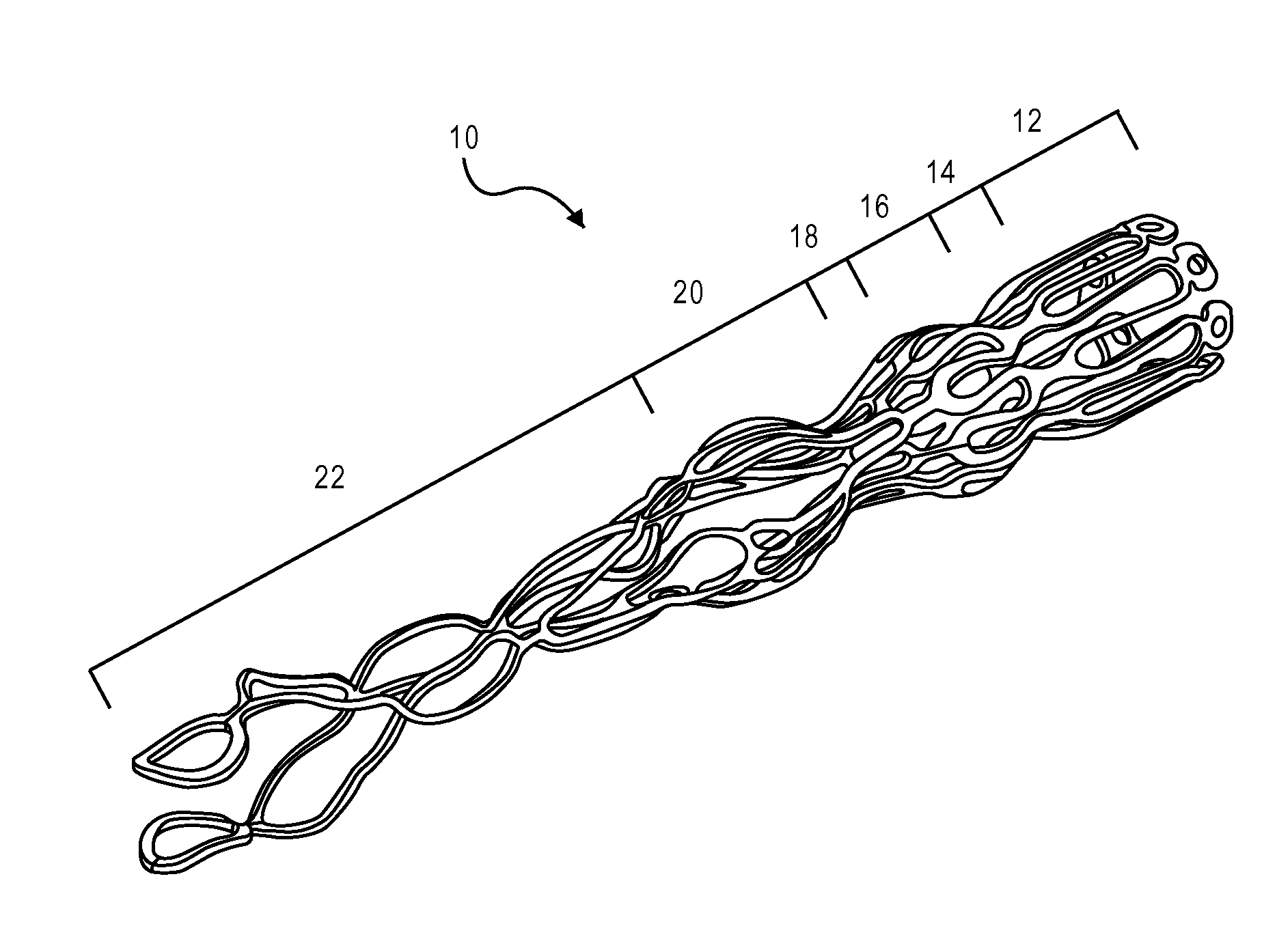
A device for implanting into an atrial septum of a patient. In some embodiments, the device has a core region to be disposed in an opening in the atrial septum; a distal retention region adapted to engage tissue on a left atrial side of the septal wall; a proximal retention region adapted to engage tissue on a right atrial side of the septal wall; and a retrieval region comprising a plurality of retrieval members, each retrieval member comprising a connector at a proximal end, the connector being adapted to connect to a delivery system. The device has a delivery configuration and a deployed configuration, the core region, distal retention region and proximal retention region each having a smaller diameter in the delivery configuration than in the deployed configuration, the retrieval member connectors being disposed proximal to and radially outward from the opening in the deployed configuration.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
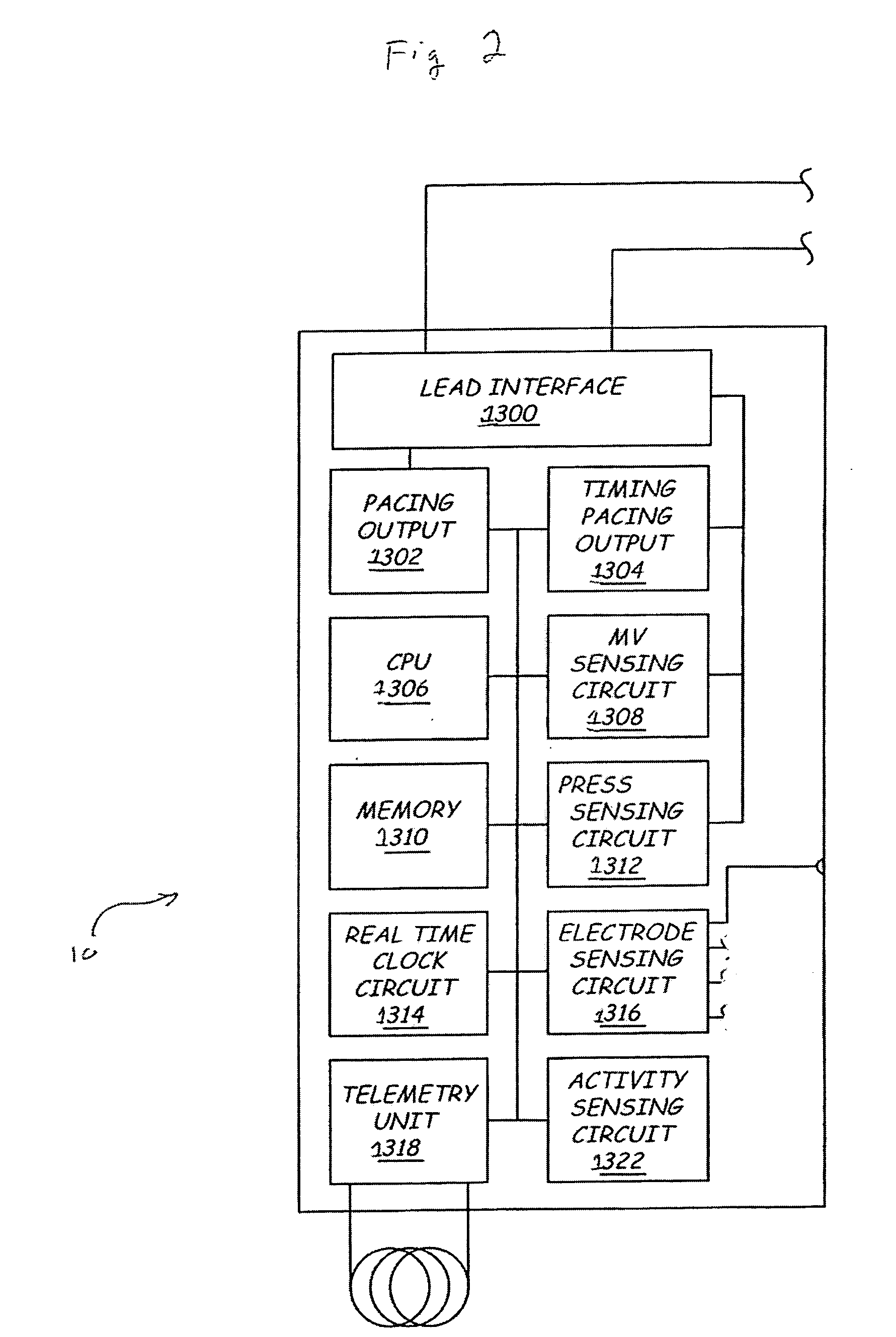
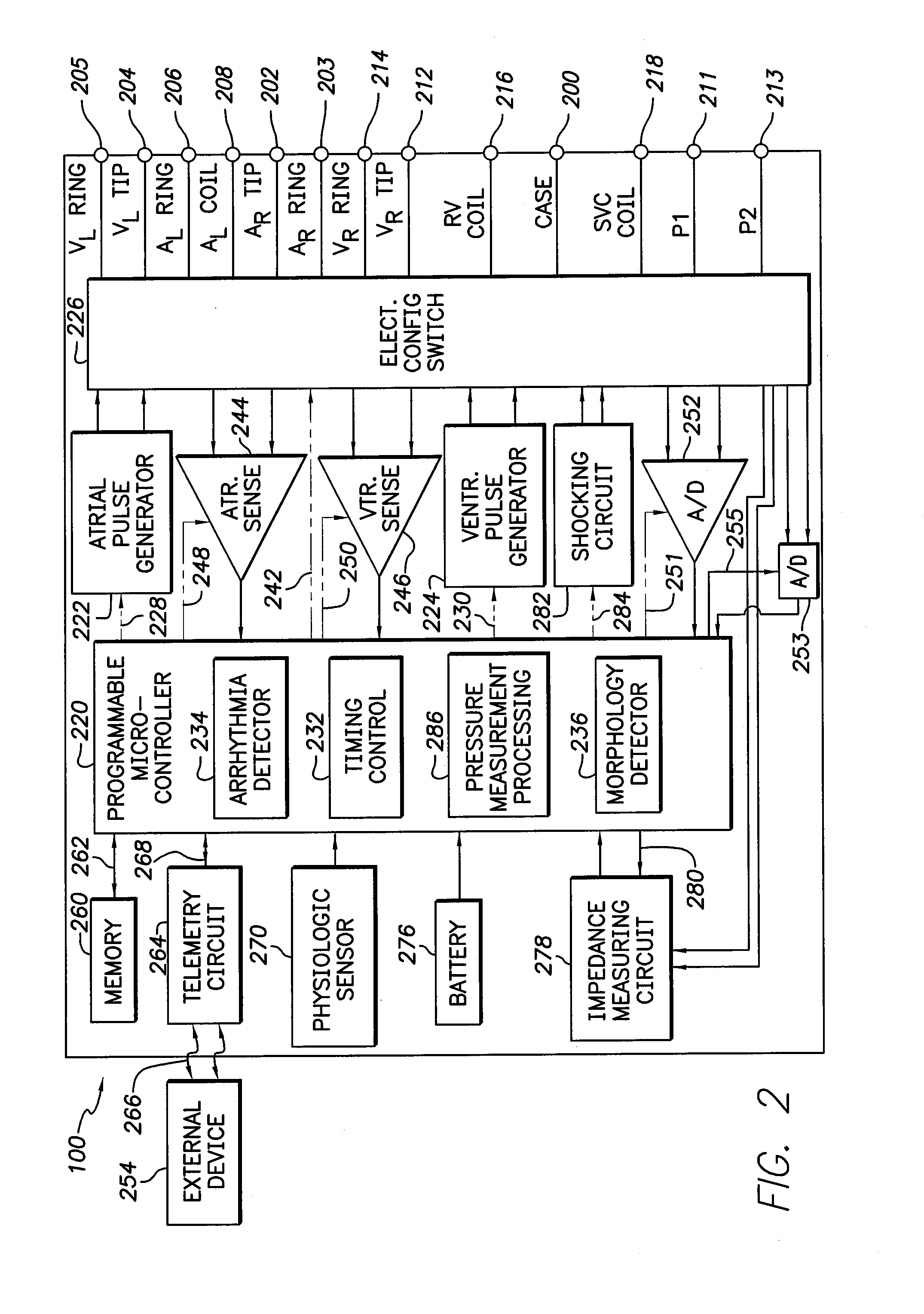
Trans-septal pressure sensor
InactiveUS20070049980A1ElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesSeptal wallEngineering
A pressure sensor, in one embodiment, is passed through the atrial septal wall. Pivoting anchors secure the pressure sensor within the right atrium and flexible tines secure the pressure sensor from within the left atrium. Selectively pivoting the anchors permits adjustment of the radial span of the anchors, which may act as an electrode; thus, operable positioning of the electrode is adjustable.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Atrial ablation catheter adapted for treatment of septal wall arrhythmogenic foci and method of use
InactiveUS20060111702A1Improve efficacyImproved outcomeSurgical instruments for heatingSeptal wallElectrode array
An atrial ablation catheter with an electrode array particularly adapted to locate and ablate foci of arrhythmia which are required for sustained atrial fibrillation is provided. The array is easily deployed and retracted from the catheter, and presents a proximally oriented electrode array that can be pulled against the septal wall of the left atrium to engage the septal wall.
Owner:ABLATION FRONTIERS
Systems and Methods for Treating Septal Defects
InactiveUS20060212047A1Reduce deliverySurgical pincettesSurgical staplesTherapeutic DevicesSeptal wall
A system for treating a septal defect having an implantable treatment apparatus and devices for delivering the implantable treatment apparatus and methods for treating a septal defect are provided. The implantable treatment apparatus is preferably implantable through a septal wall or portion thereof. The treatment system can include a flexible elongate body member, a delivery device configured to deliver the implantable apparatus, a stabilization device configured to stabilize the body member and a positioning device configured to position the delivery device in a desired location.
Owner:ABBOTT RYAN +6
Systems and methods for treating septal defects
InactiveUS20110093007A1Reduce deliveryEasy to operateStentsSurgical needlesSeptal wallBiomedical engineering
A system for treating a septal defect having an implantable treatment apparatus and devices for delivering the implantable treatment apparatus, devices for controlling delivery of the treatment apparatus and methods for treating a septal defect are provided. The implantable treatment apparatus is preferably implantable through a septal wall or portion thereof. The treatment system can include a flexible elongate body member, a delivery device configured to deliver the implantable apparatus, and a proximal control device for controlling delivery of the implantable apparatus, among others.
Owner:PROMED
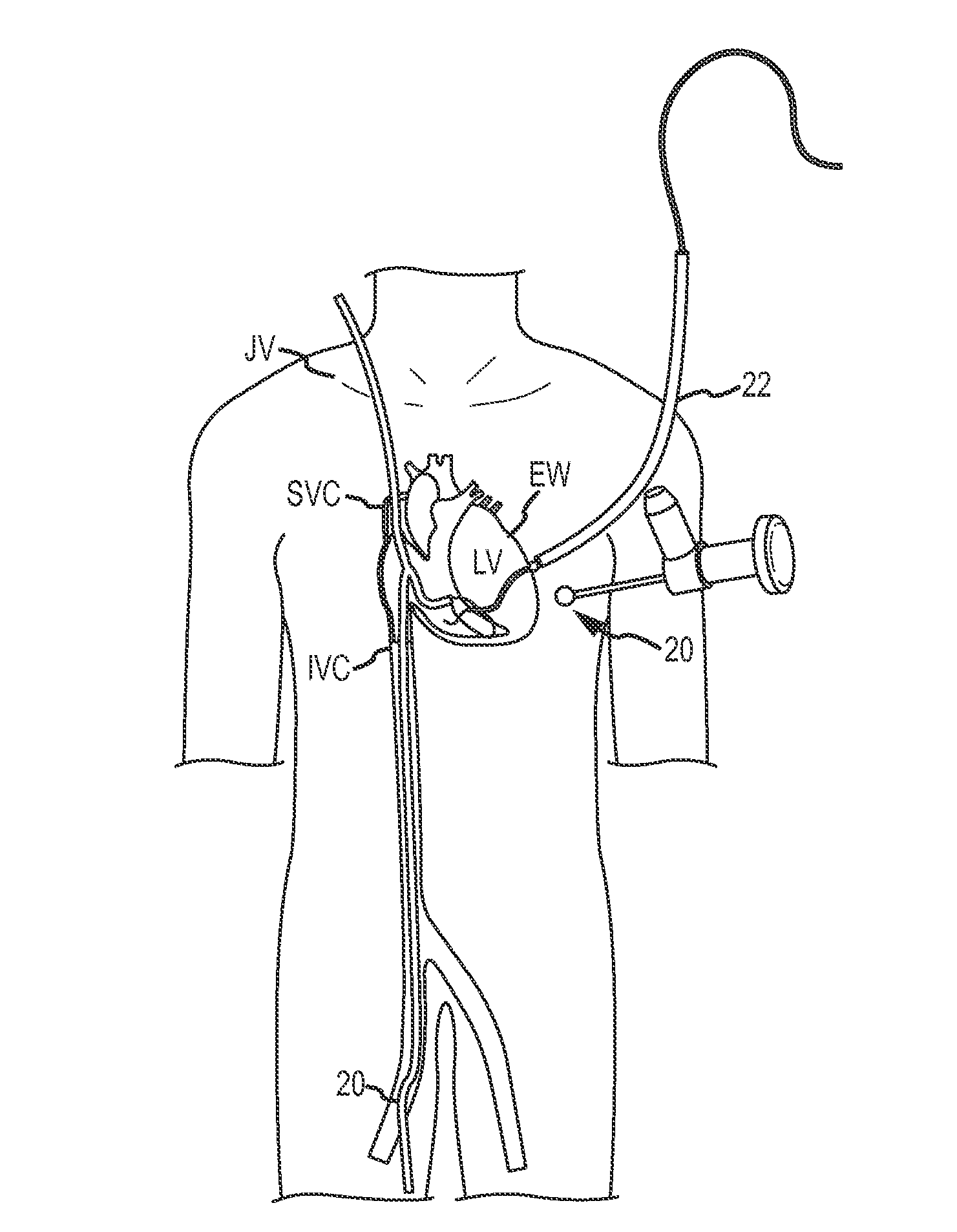
Over-the-wire cardiac implant delivery system for treatment of chf and other conditions
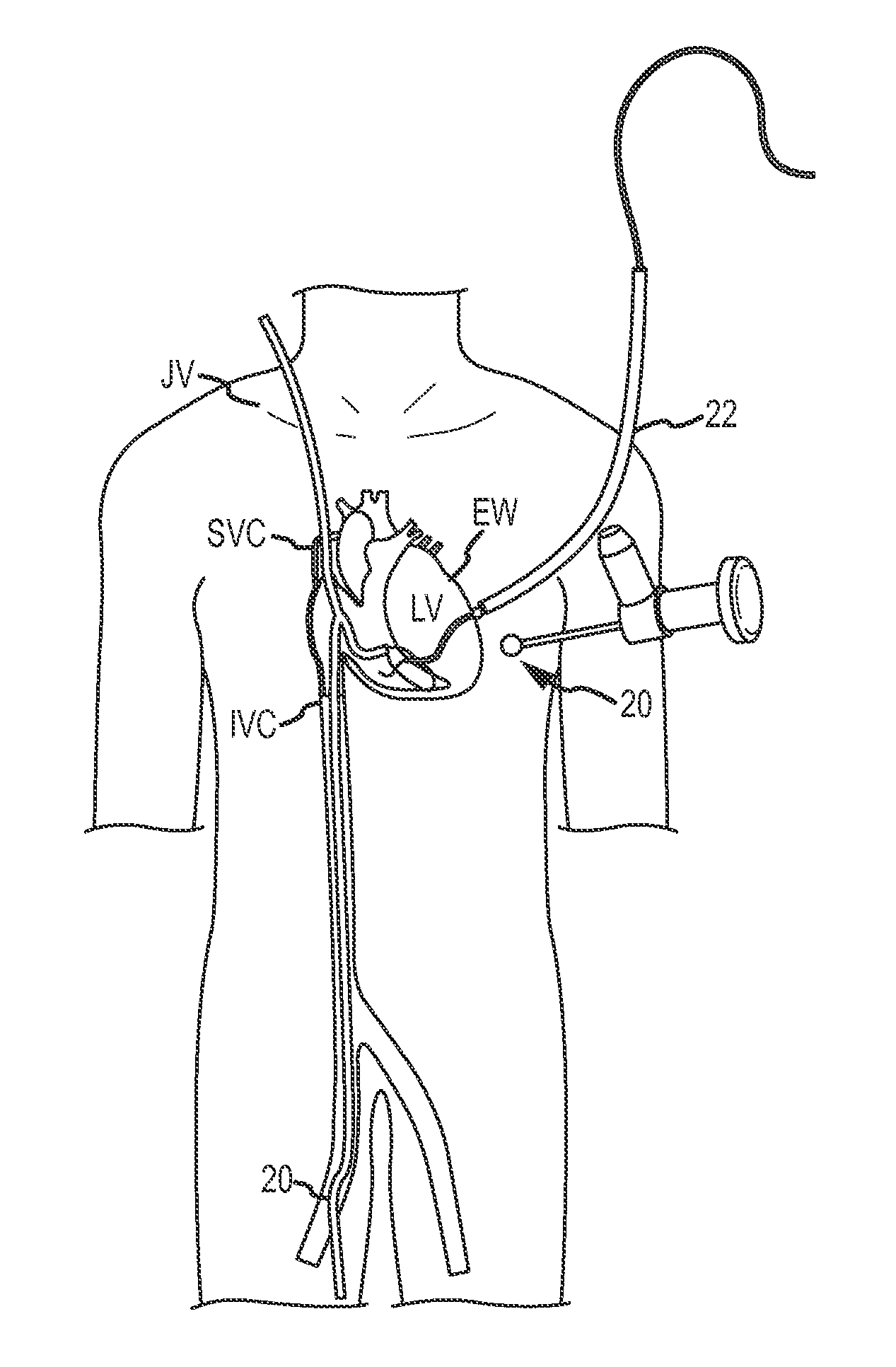
Medical devices, systems, and methods reduce the distance between two locations in tissue in a minimally invasive manner, often for treatment of congestive heart failure. In one embodiment, an anchor of an implant system may, when the implant system is fully deployed, reside within the right ventricle in engagement with the ventricular septum. A tension member may extend from that anchor through the septum and an exterior wall of the left ventricle to a second anchor disposed along an epicardial surface of the heart. Deployment of the anchor within the right ventricle may be performed by inserting a guidewire through the septal wall into the right ventricle. The anchor may be inserted into the right ventricle over the guidewire and through a lumen of a delivery catheter. Delivering the anchor over the guidewire may provide improved control in the delivery and placement of the anchor within the right ventricle.
Owner:BIOVENTRIX A CHF TECH
Cardiac implant migration inhibiting systems
ActiveUS20130090672A1Reduce distanceEasy to controlSuture equipmentsHeart valvesSeptal wallCongestive heart failure chf
Medical devices, systems, and methods reduce the distance between two locations in tissue, often for treatment of congestive heart failure. In one embodiment an anchor of an implant system may reside within the right ventricle in engagement with the ventricular septum. A tension member may extend from that anchor through the septum and an exterior wall of the left ventricle to a second anchor disposed along an epicardial surface. Deployment of the anchor within the right ventricle may be performed by inserting a guidewire through the septal wall into the right ventricle. The anchor may be inserted into the right ventricle over the guidewire and through a lumen of a catheter. An anchor force may be applied within a desired range to secure the anchors about the septum and epicardial surface. The anchor force may inhibit migration of the anchors relative to the septum and epicardial surface.
Owner:BIOVENTRIX A CHF TECH
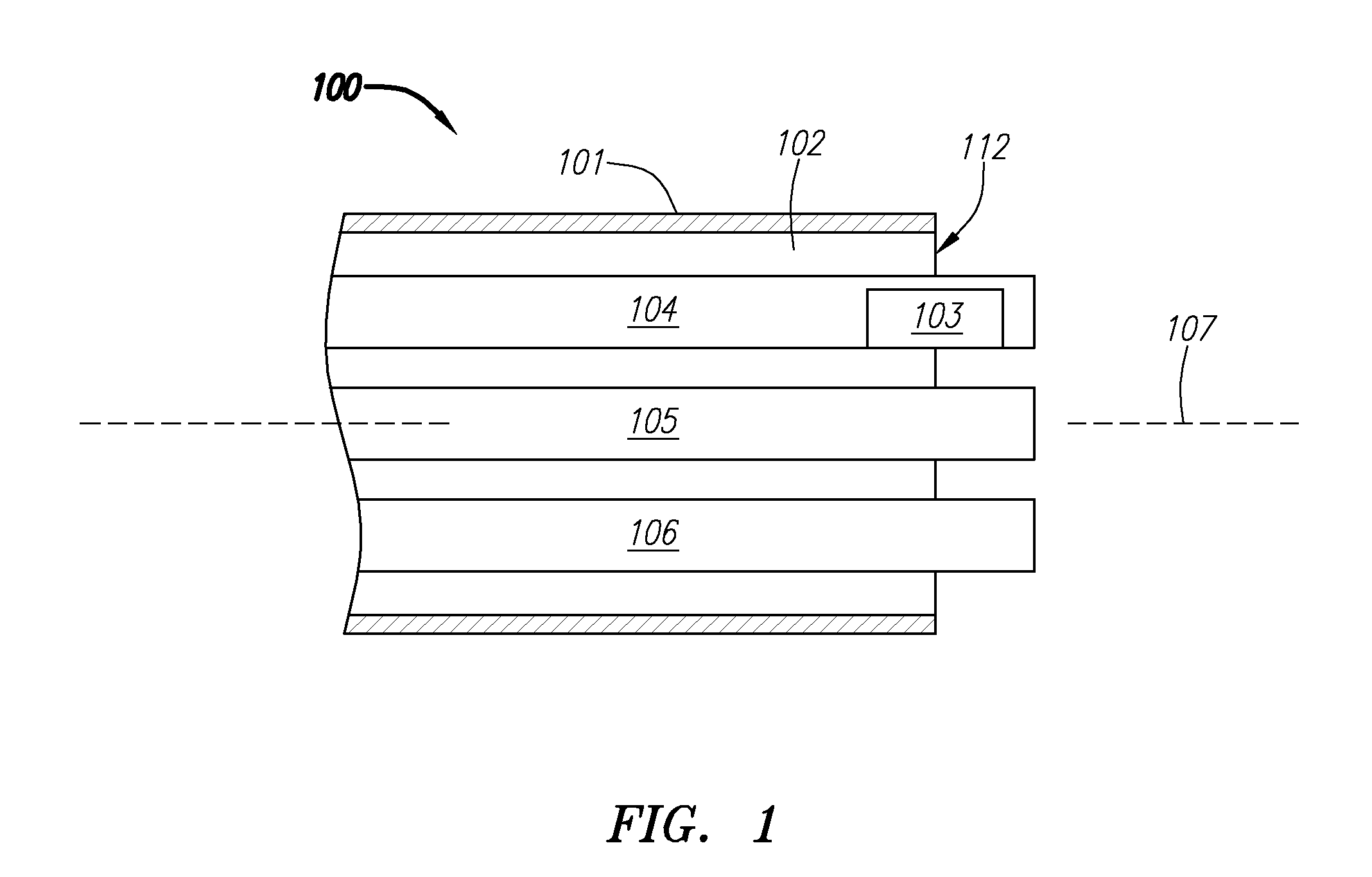
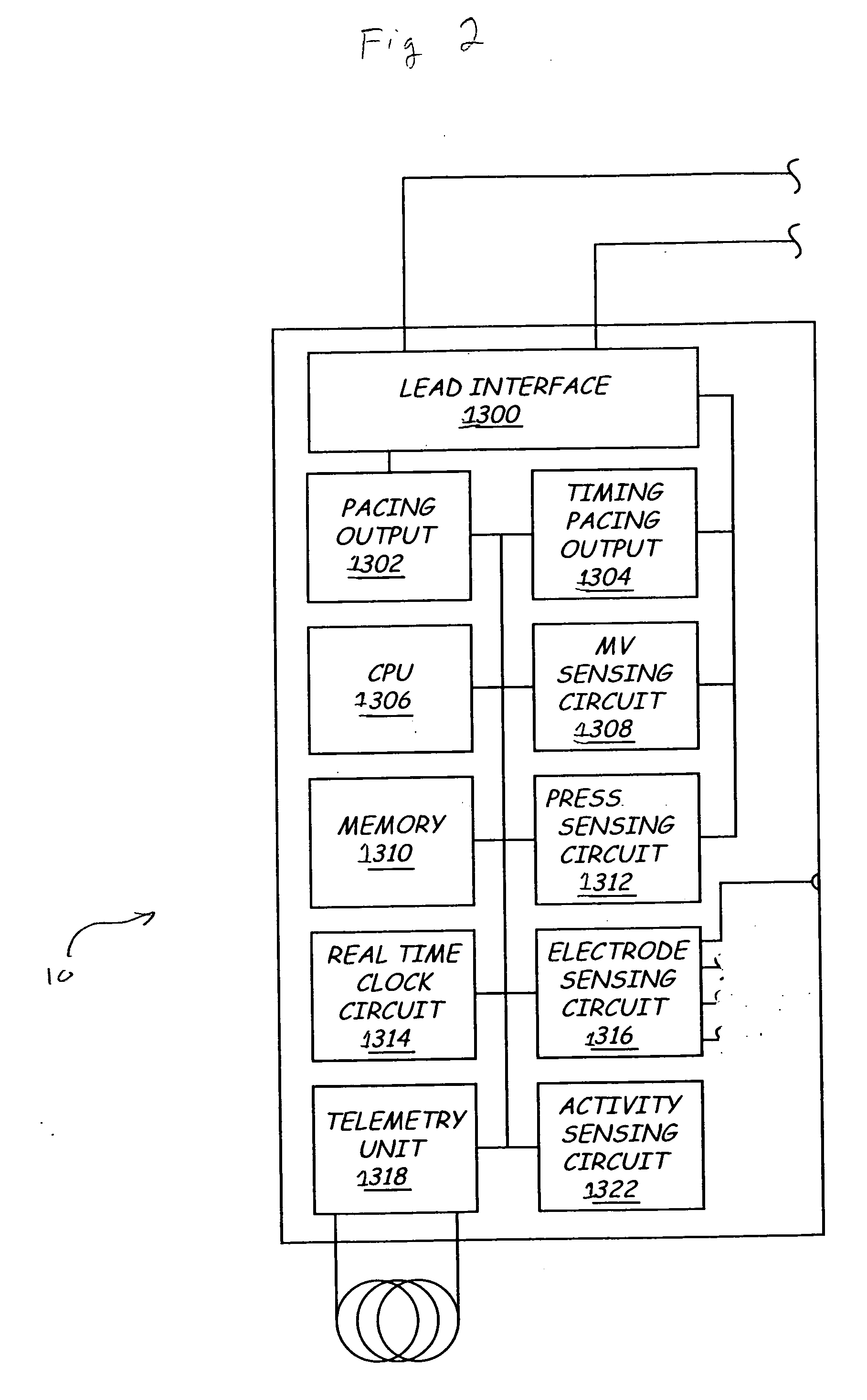
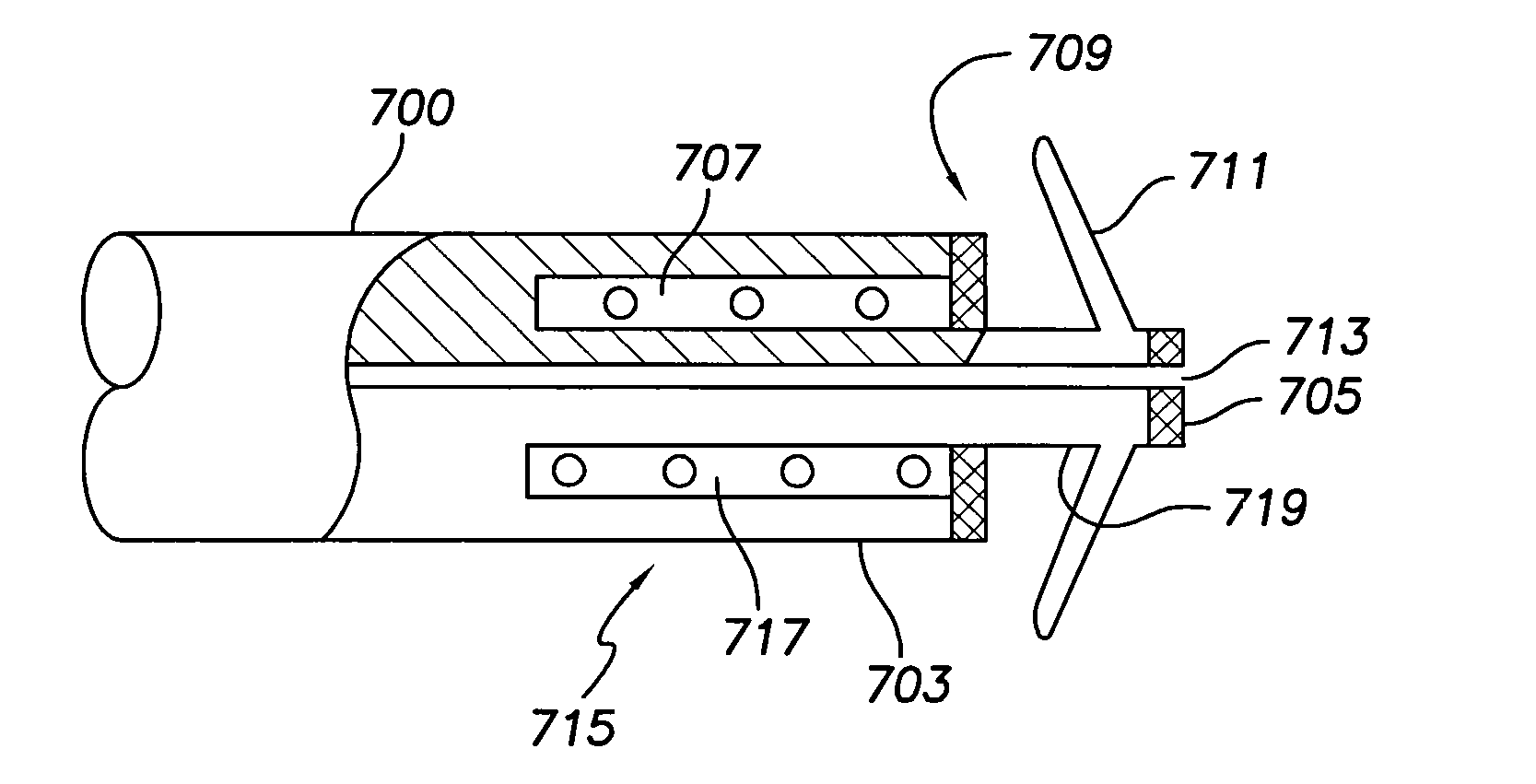
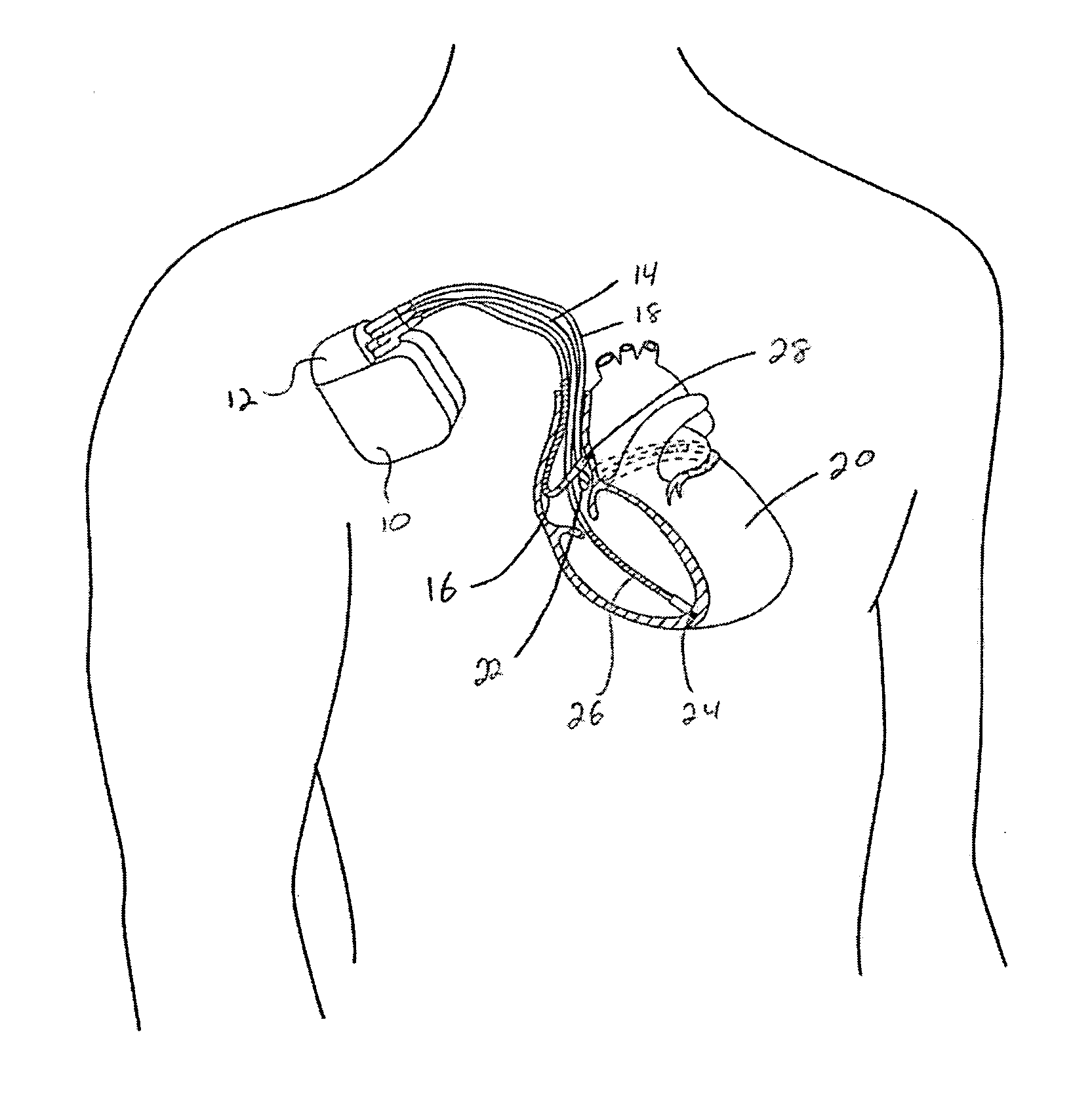
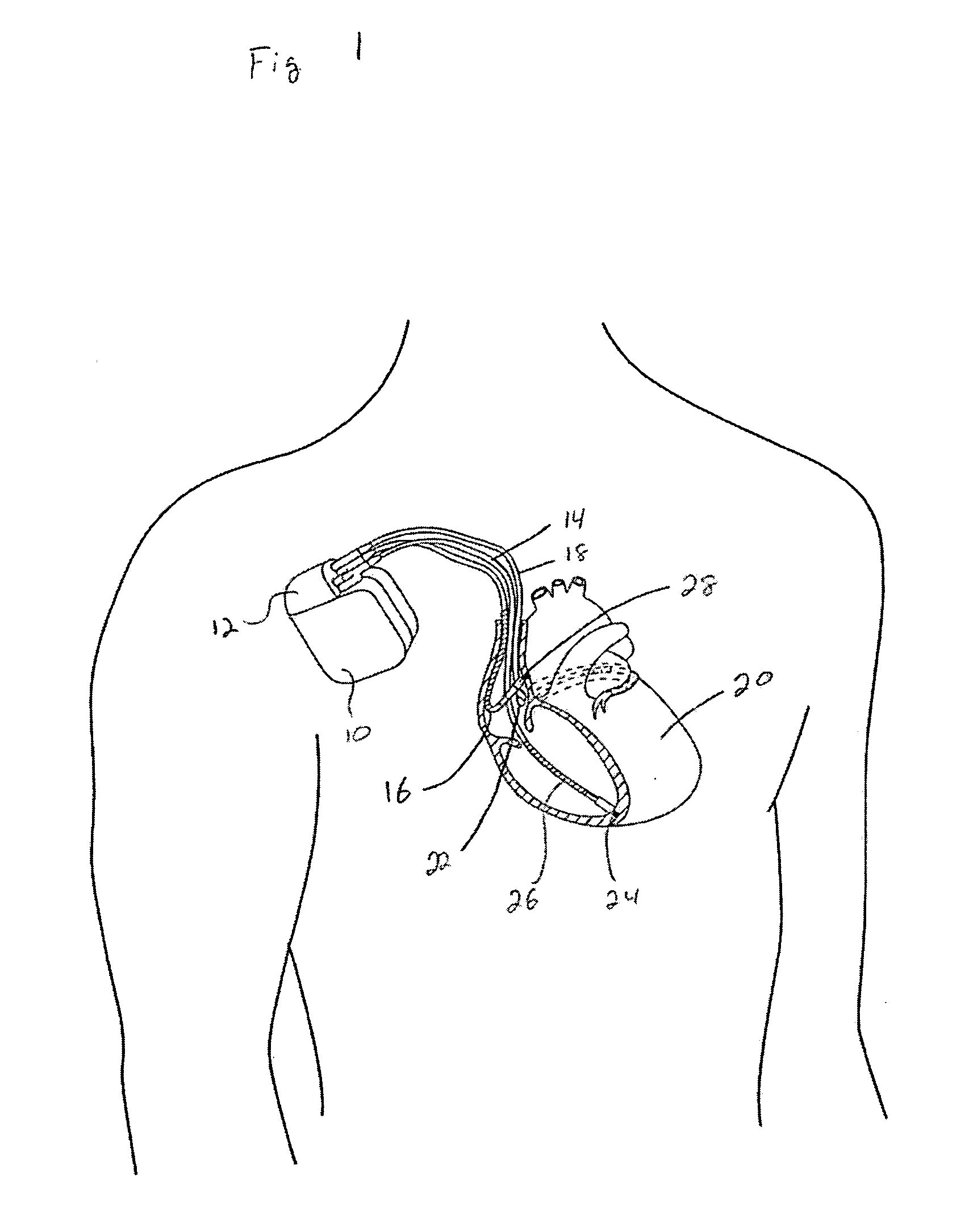
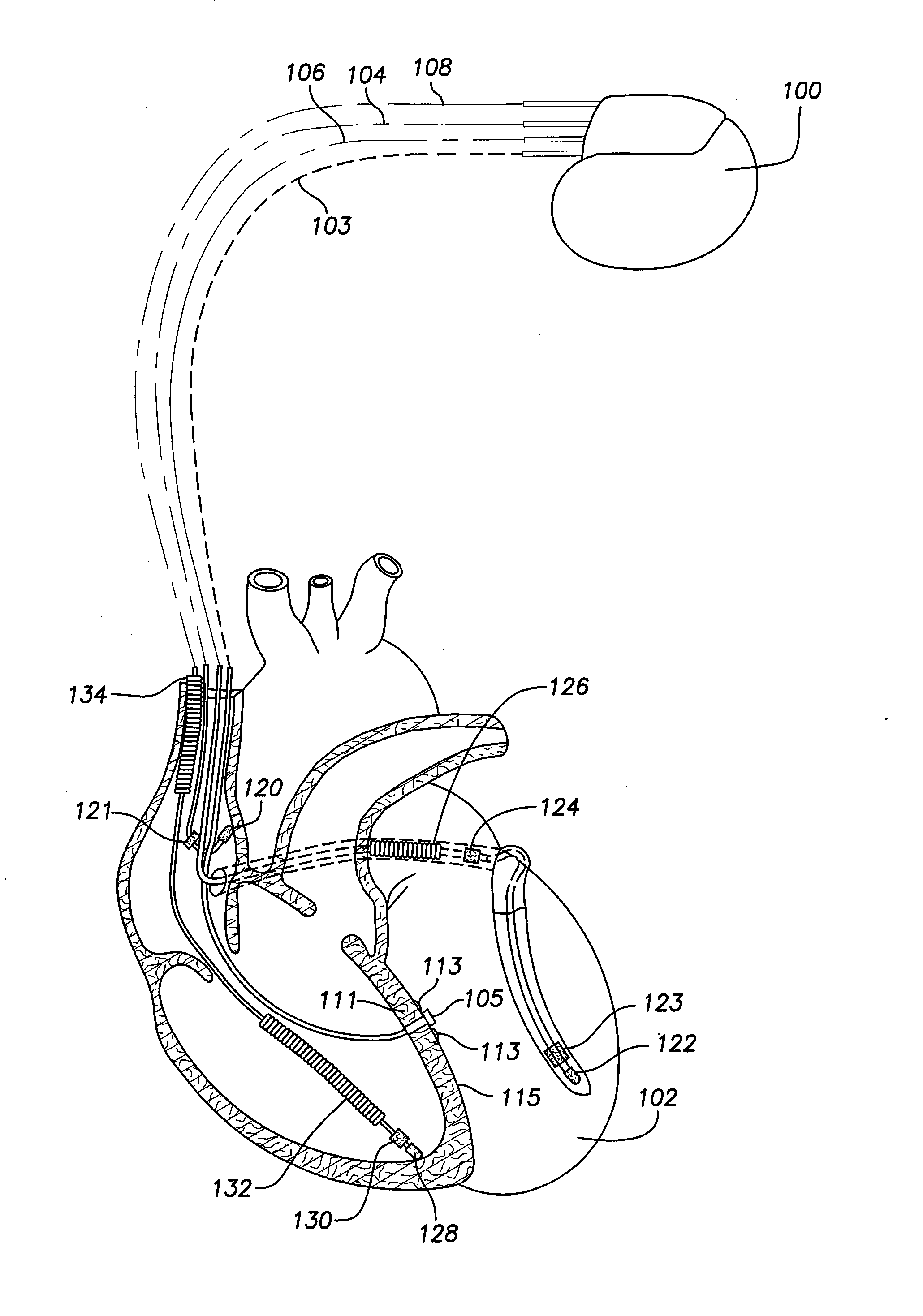
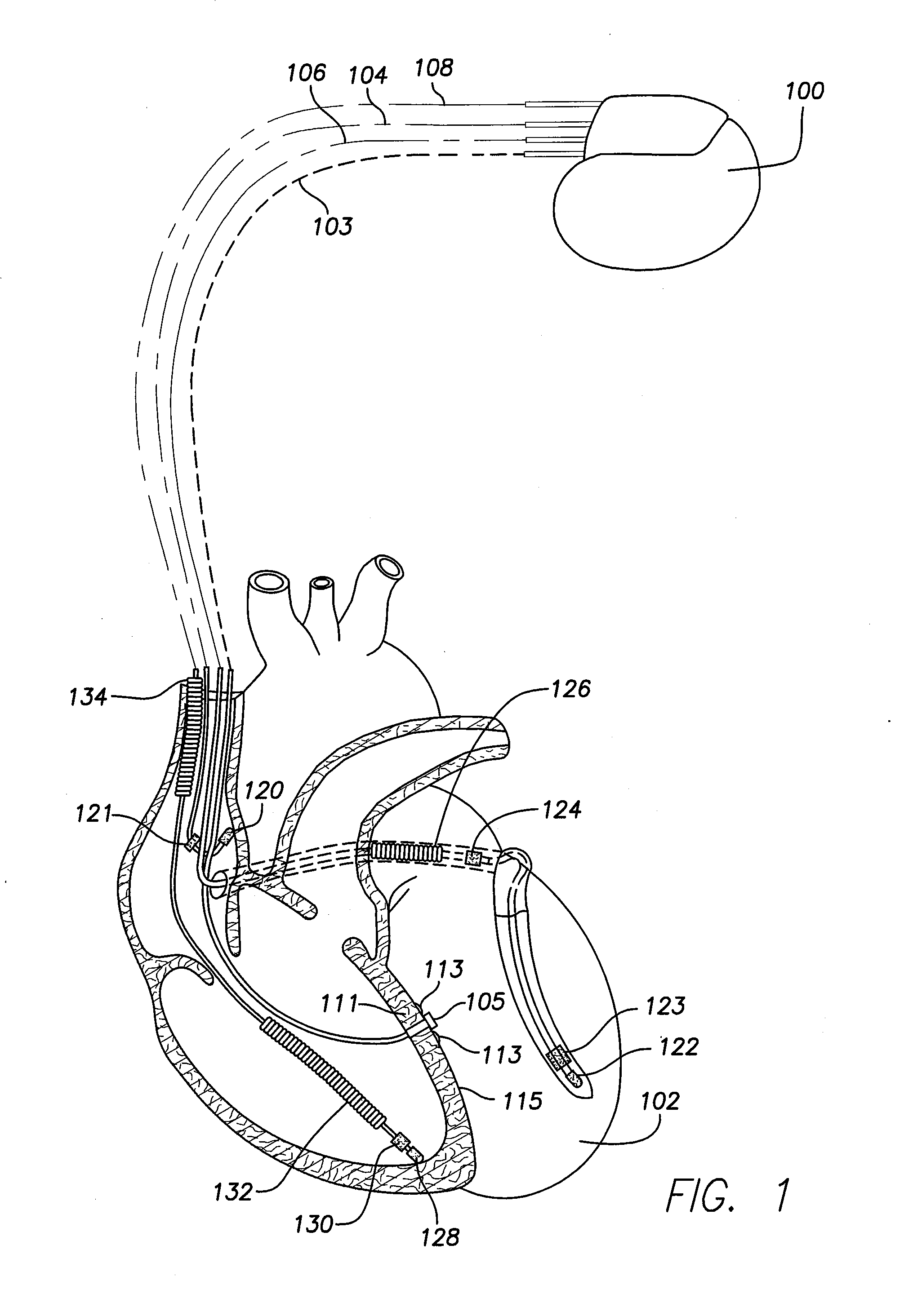
Left chamber pressure sensor lead delivery system
An apparatus for and method of measuring pressure through a septum in a patient's heart. A lead inserted into the right side of a heart is routed through the septum to gain access to the left side of the heart. The lead includes a mounting mechanism that secures the lead to one or both sides of the septal walls. The lead also includes one or more sensors for measuring cardiac pressure on the left side of the heart and, as necessary, the right side of the heart.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Medical device suitable for use in treatment of a valve
InactiveUS20090149949A1Profound clinical consequencesIncrease pressureSuture equipmentsHeart valvesSeptal wallSurgery
A medical device (1210) comprises a generally cylindrical treatment element (1220) for location between a pair of valve leaflets (1212) situated between an atrium (1214) and a ventricle (1216) of a heart. The treatment element (1220) supports the valve leaflets (1212) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212) and occludes the valve opening to resist fluid flow in the retrograde direction through the valve opening. The device (1210) comprises a support (1222) to support the treatment element (1210) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212). The support has an anchor (1224) and a tether (1226), the tether (1226) being provided at the end of a guide wire (1228) which is initially utilised in the percutaneous insertion of the treatment element (1220). The anchor (1224) is secured, in use, to a septal wall (1230), while the guide wire (1228) exits the atrium (1214) through a vein adjacent a rear wall (1224) thereof. The treatment element (1220) includes a remotely actuatable clamp therein, in order to allow the treatment element (1220) to be secured to the guide wire (1228) or the tether (1226).
Owner:MEDNUA
Atrial ablation catheter adapted for treatment of septal wall arrhythmogenic foci and method of use
InactiveUS20060111701A1Improve efficacyImproved outcomeElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingSeptal wallElectrode array
An atrial ablation catheter with an electrode array particularly adapted to locate and ablate foci of arrhythmia which are required for sustained atrial fibrillation is provided. The array is easily deployed and retracted from the catheter, and presents a proximally oriented electrode array that can be pulled against the septal wall of the left atrium to engage the septal wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
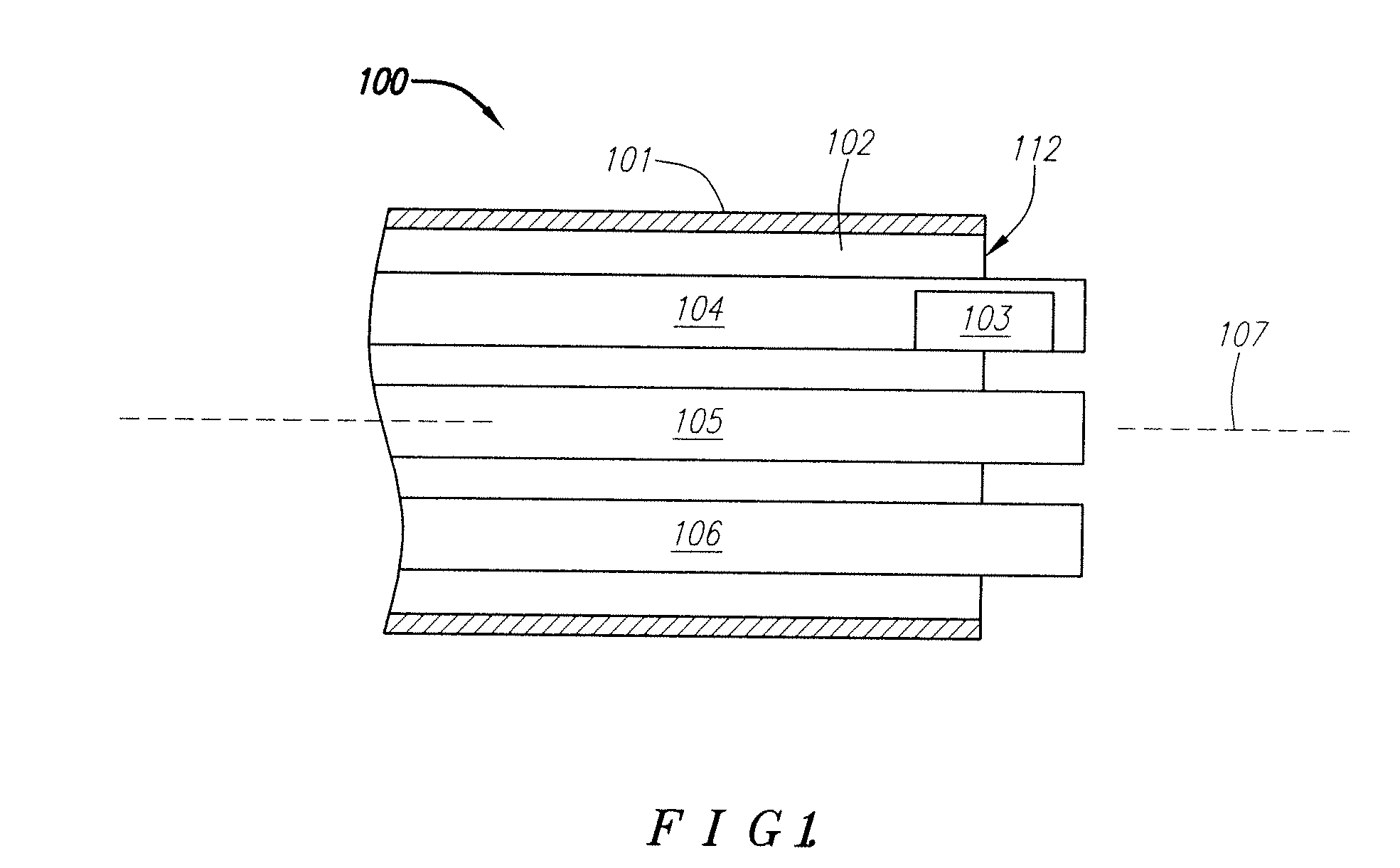
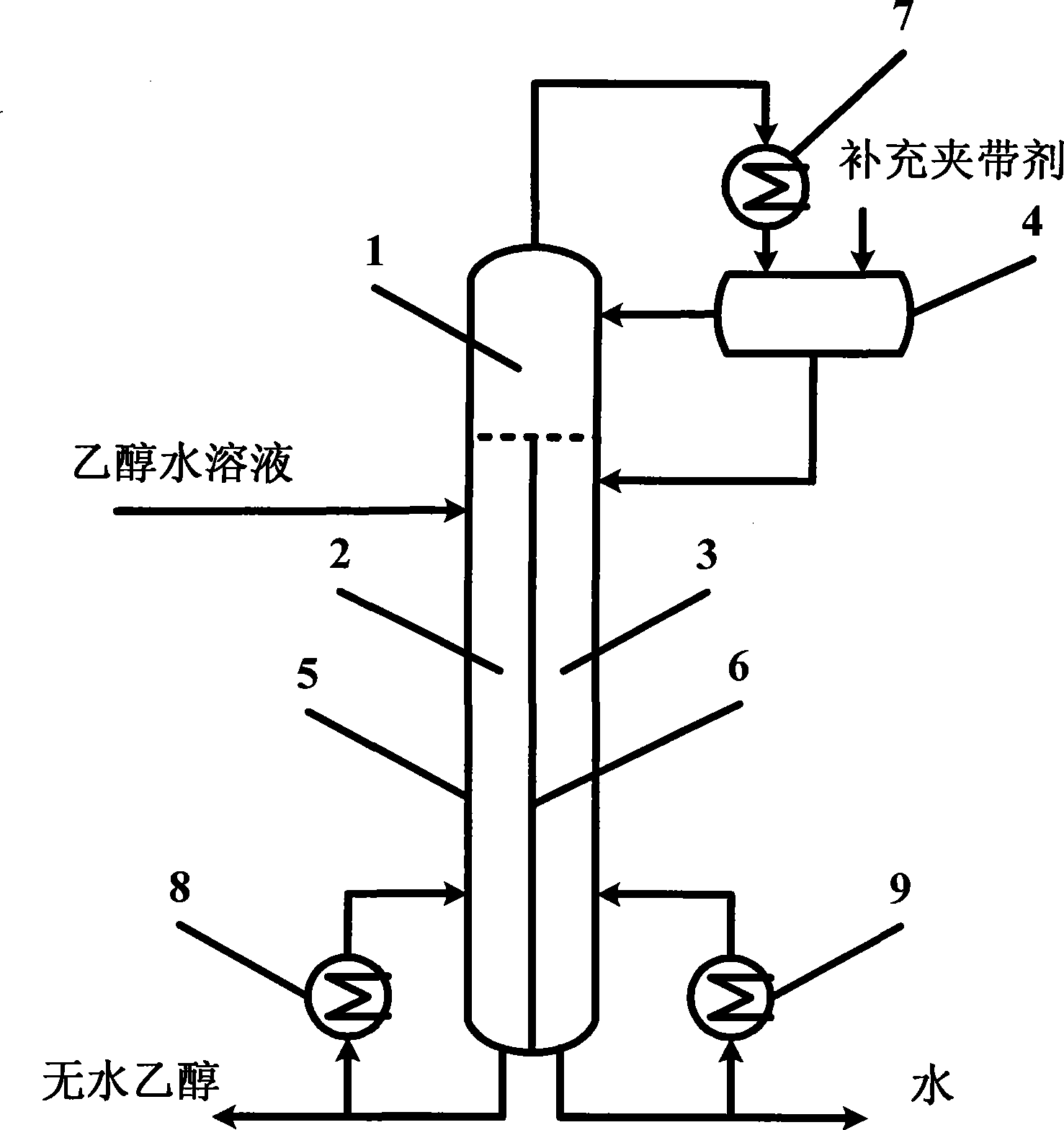
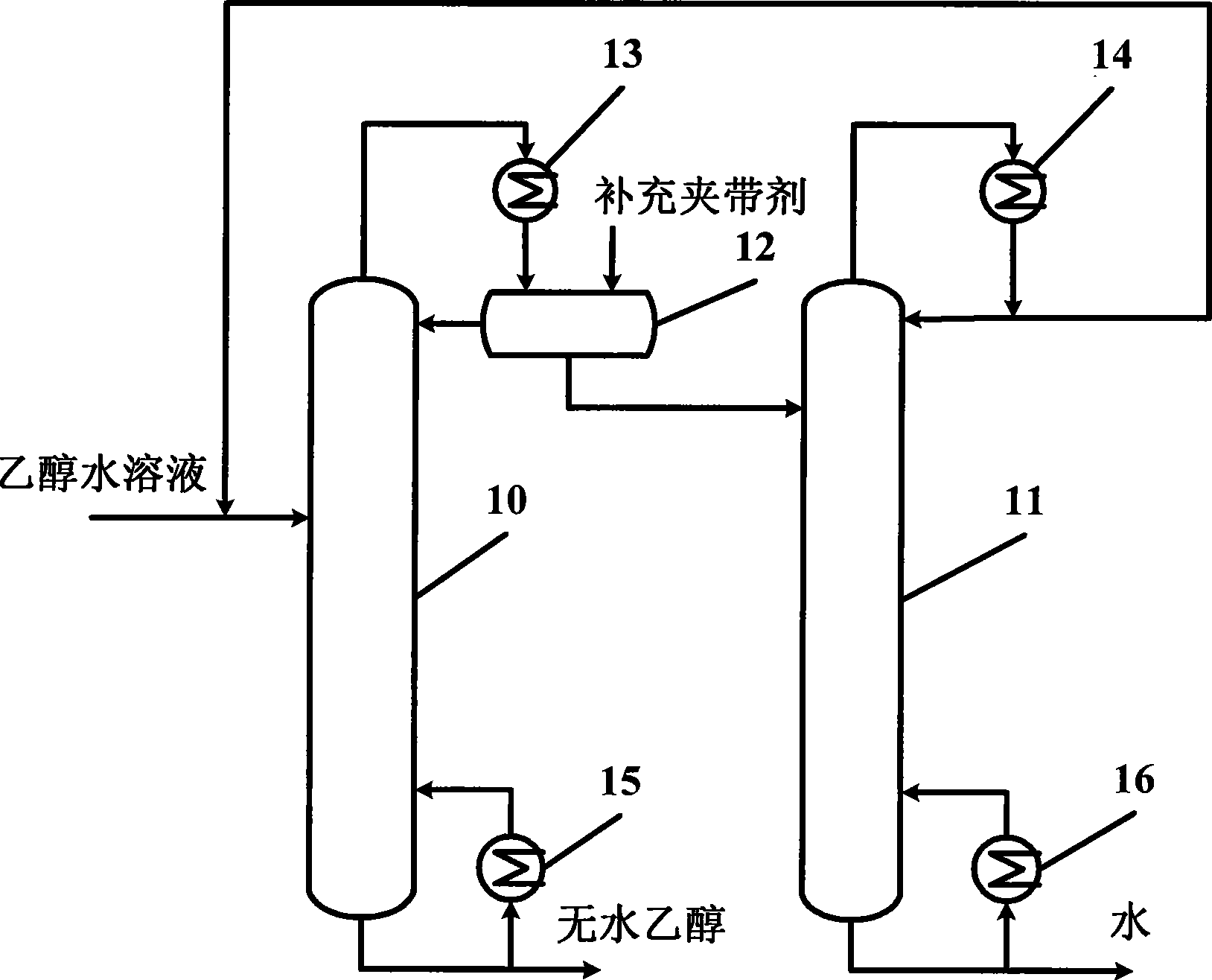
Process and apparatus for preparing absolute ethyl alcohol
InactiveCN101367710ALess investmentSimplify the conventional azeotropic distillation processOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAlcoholPhase splitter
The invention relates to a novel azeotropic distillation process method and a device thereof, in particular to a process method which use a septal azeotropic distillation column (5) to produce absolute alcohol, and a device thereof. The septal azeotropic distillation column (5) is achieved by arranging a septal wall (6) in the azeotropic distillation column in the vertical direction, and the septal wall (6) divides the space of the azeotropic distillation column into three areas with different functions; a public distillation part (1), a dehydration part (2) and a side stripper part (3). The alcohol solution to be separated is filled to the azeotropic distillation column from the upper part of the dehydration part (2), and the absolute alcohol is obtained at the bottom of the dehydration part (2); ternary azeotrope is steamed out of the top of the column, and condensed by a condenser (7) and then splitted into light phase solution and heavy phase solution in a phase splitter; the light phase solution (entrainer) reflows and the heavy phase solution is the feed stock in the side stripper part (3), and little water containing alcohol is obtained at the bottom of the side stripper part (3). The device and the process method of the invention can produce the absolute alcohol, and can simplify the process, reduce the energy consumption and the cost of the divices.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
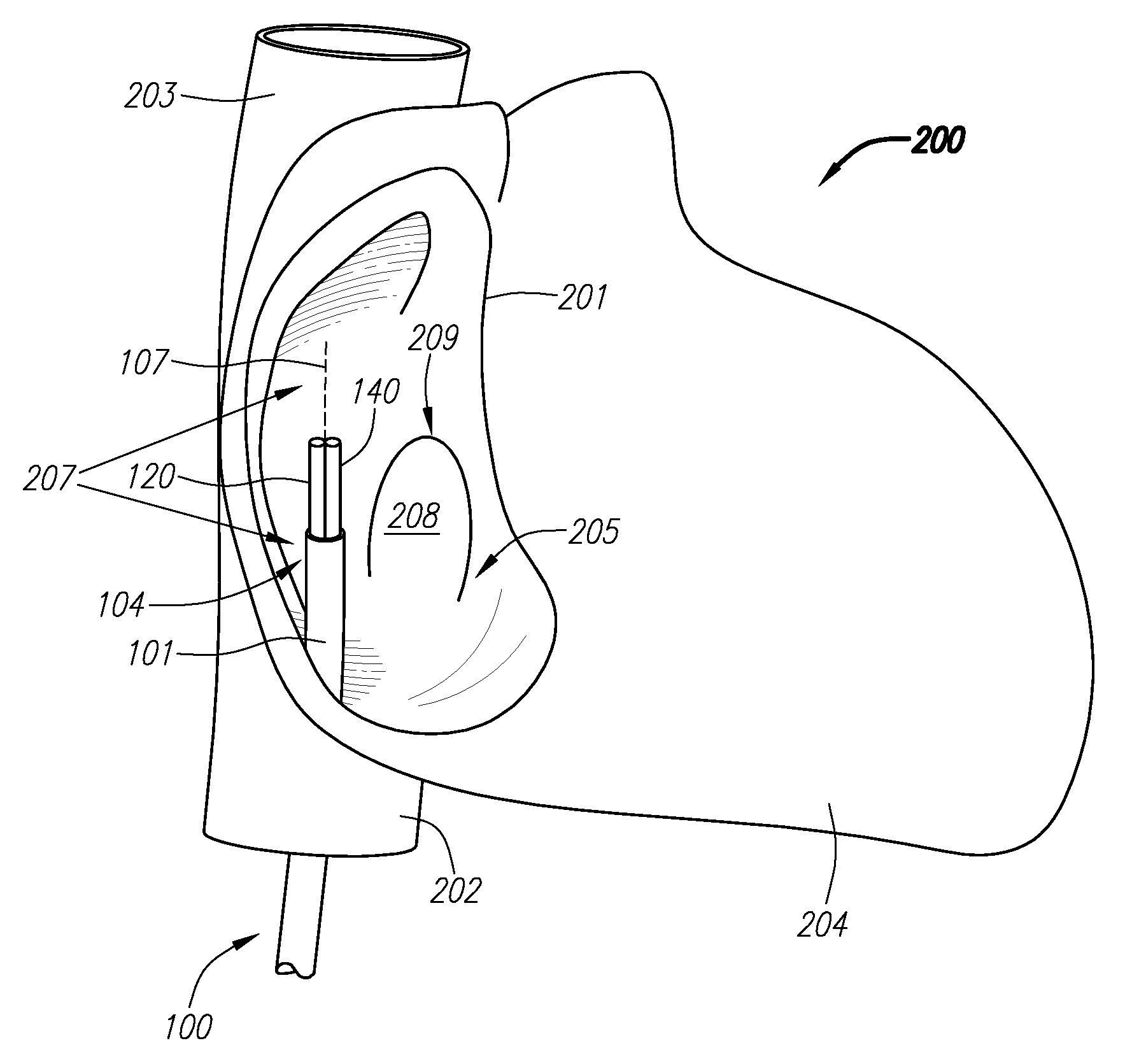
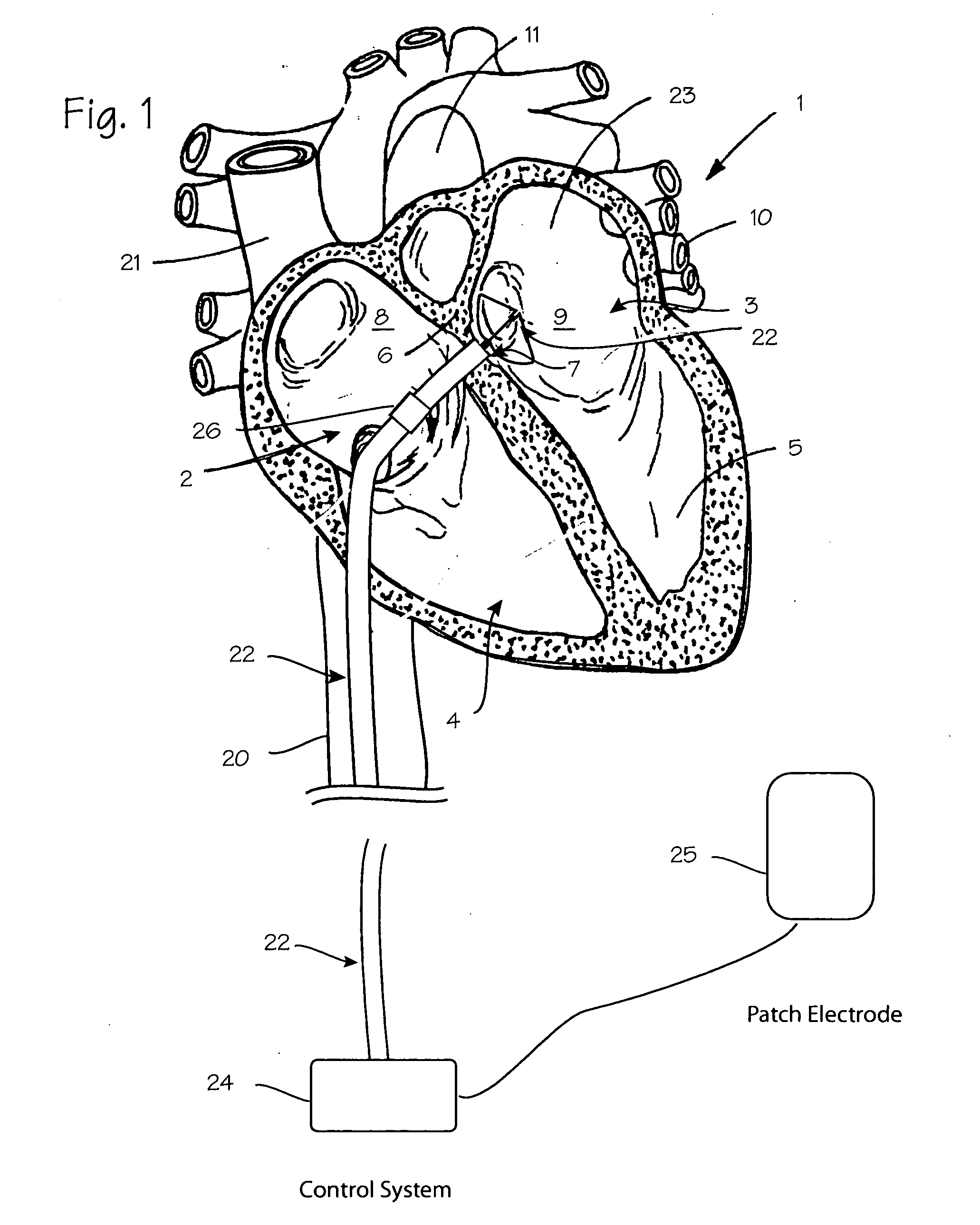
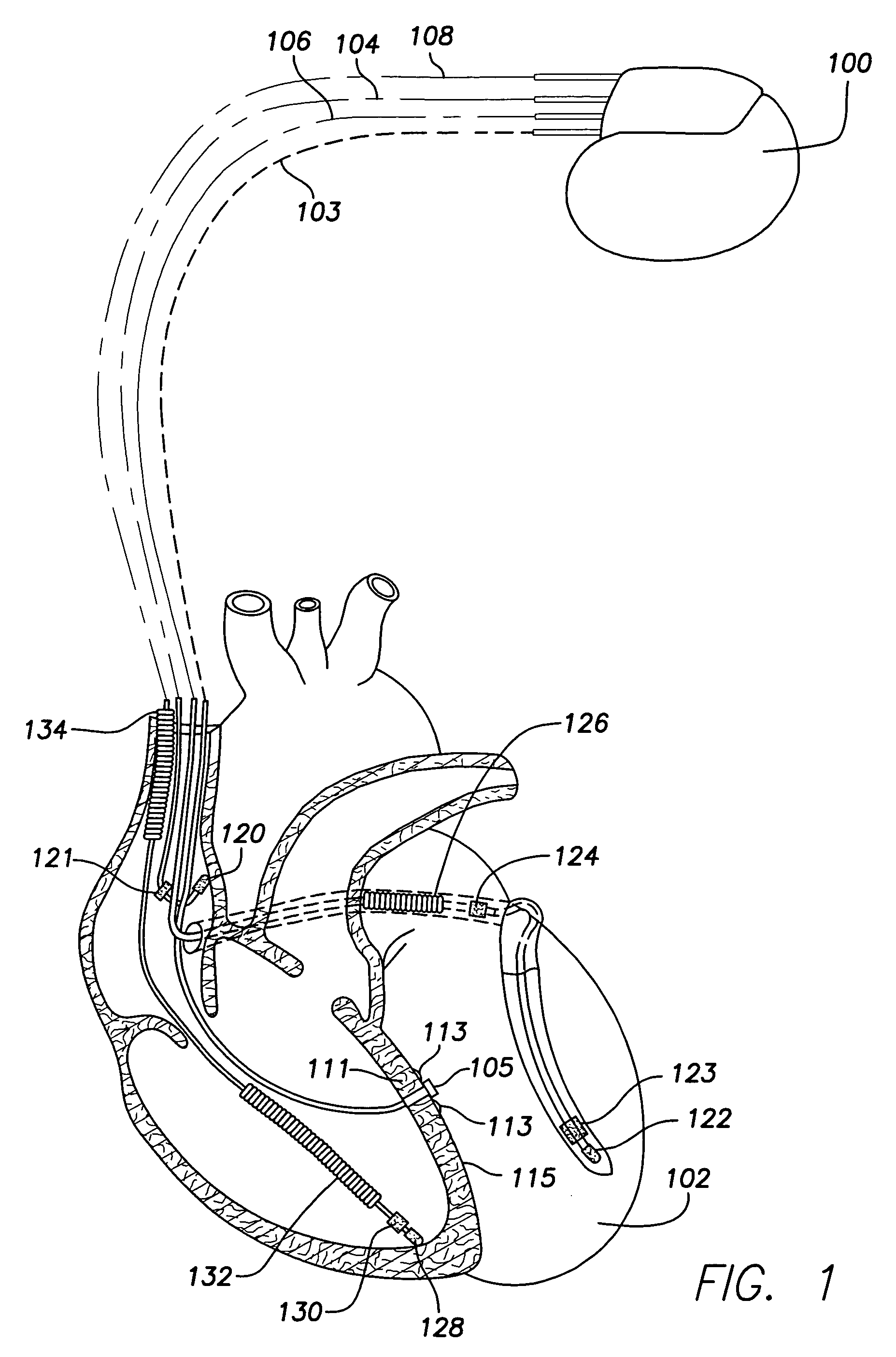
Trans-septal anchoring system and method
A pressure sensor, in one embodiment, is passed through the atrial septal wall. A plurality of anchors is disposed on each side of the septal wall and secure the position of the pressure sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
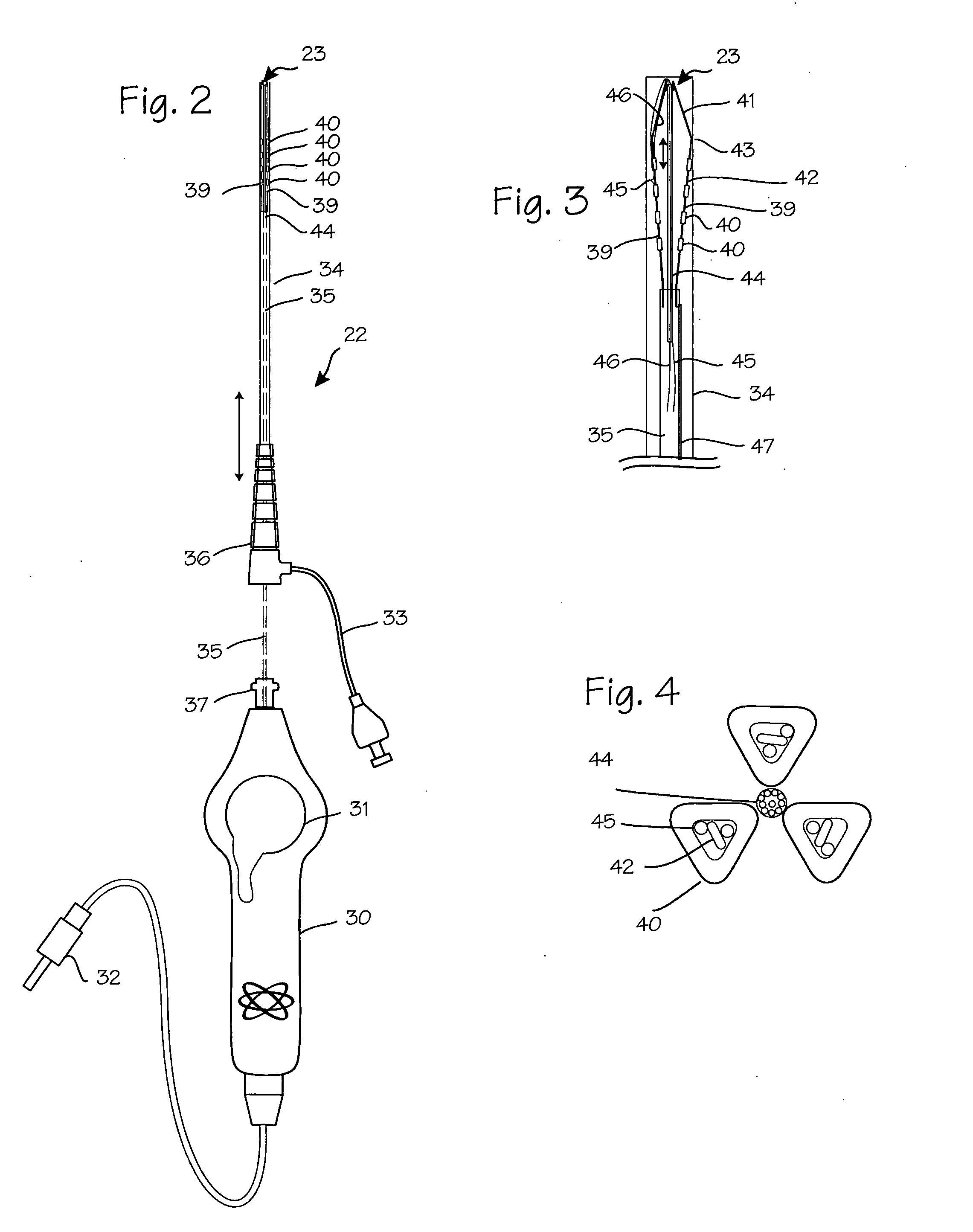
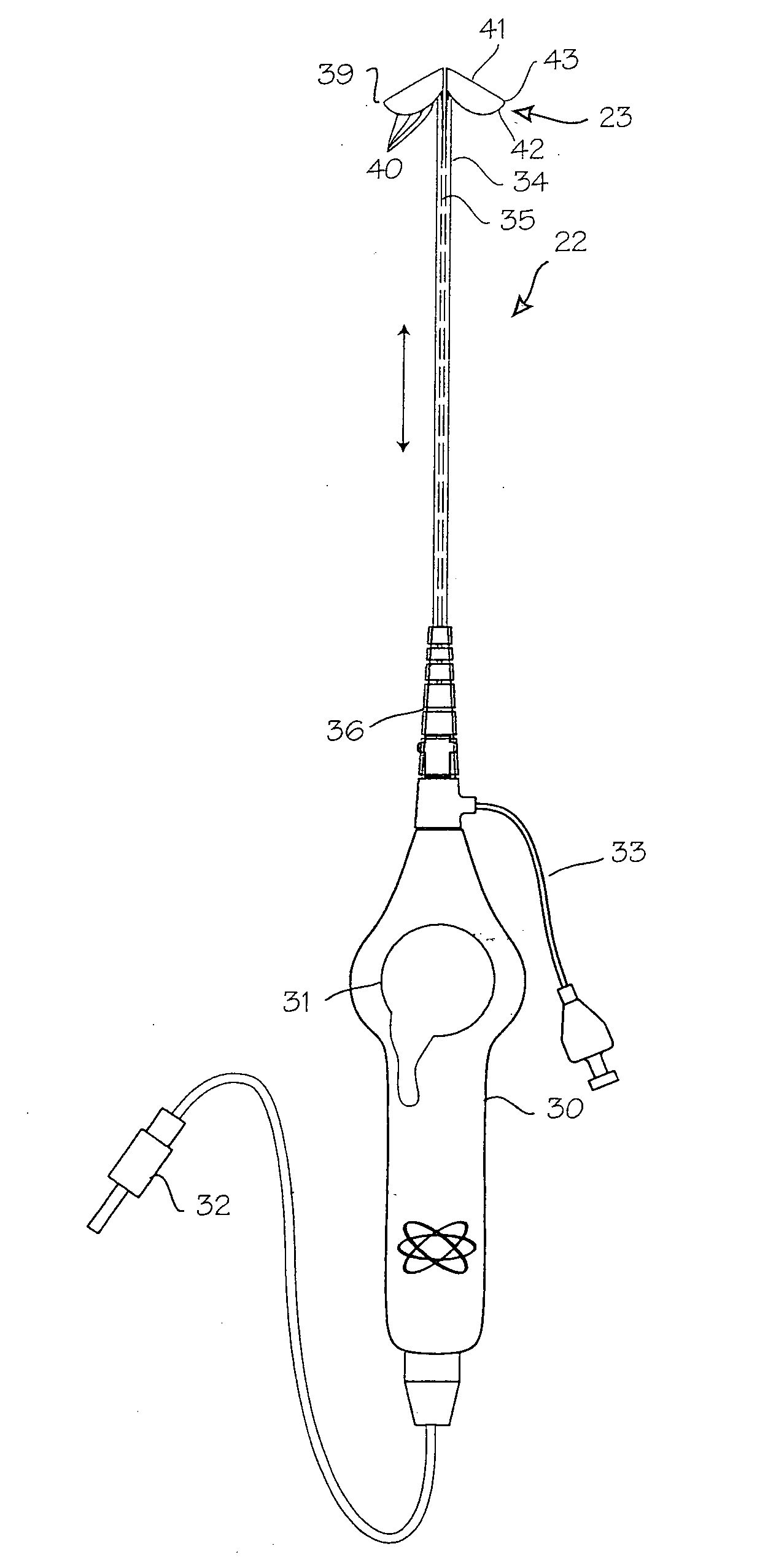
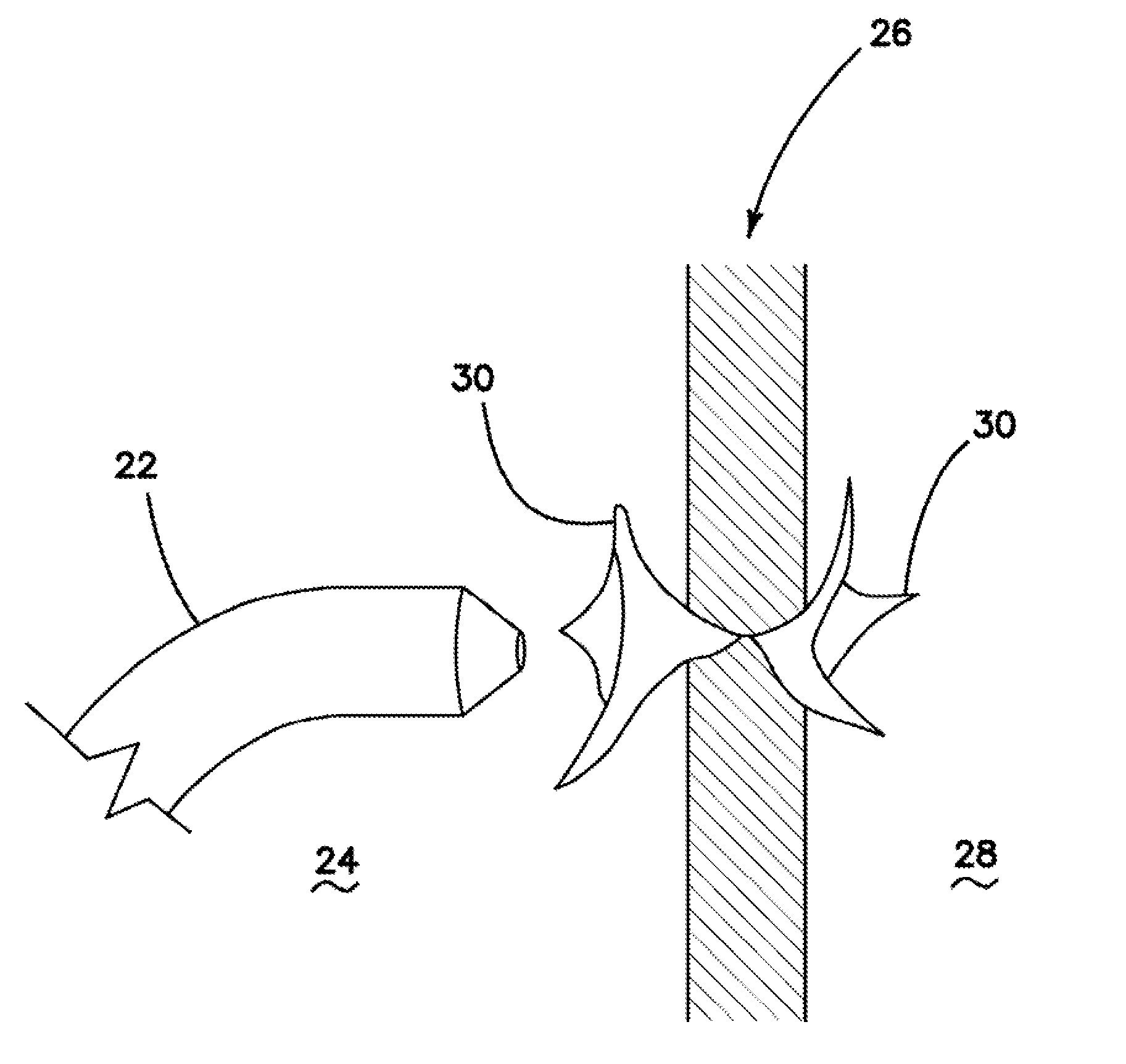
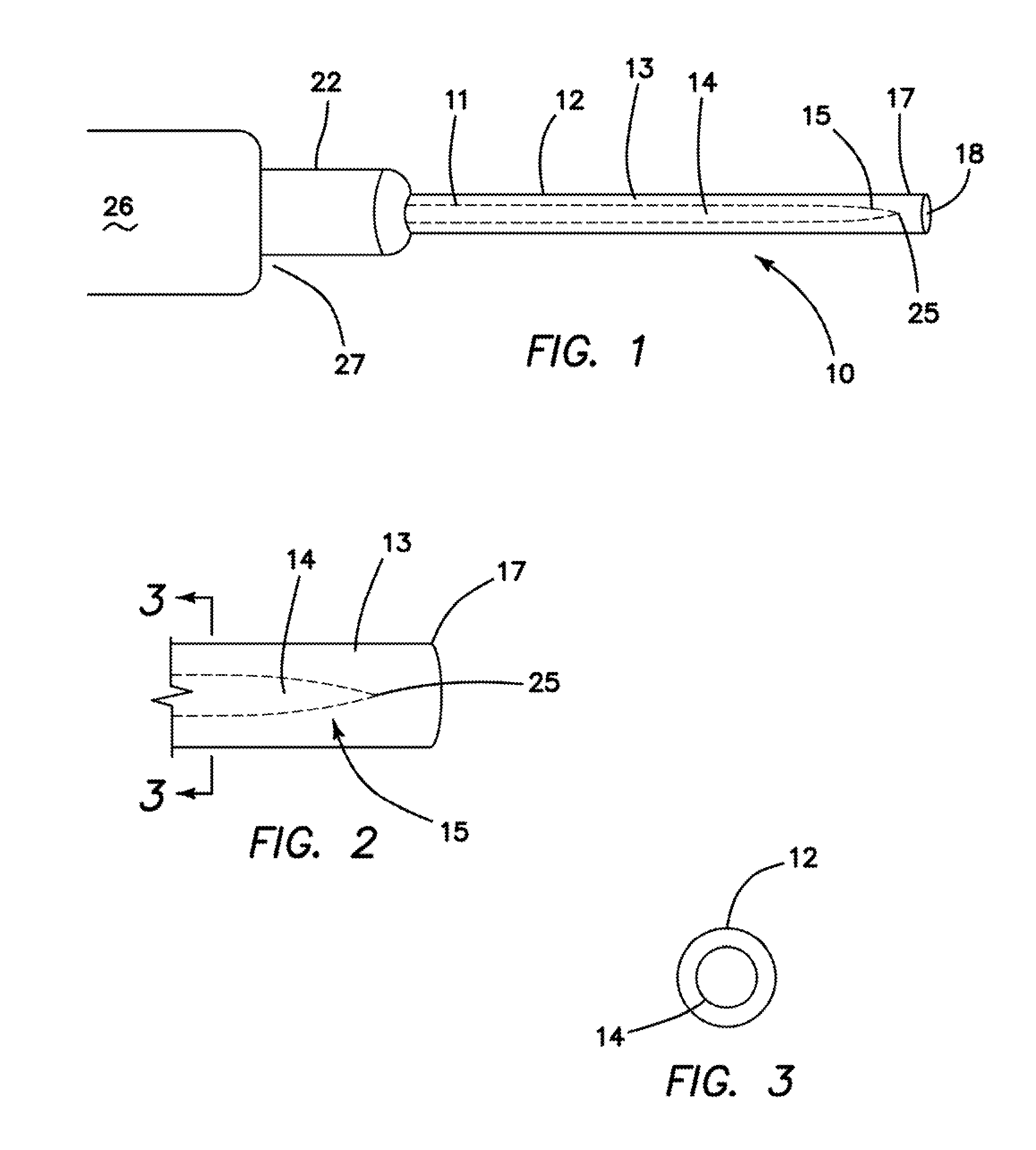
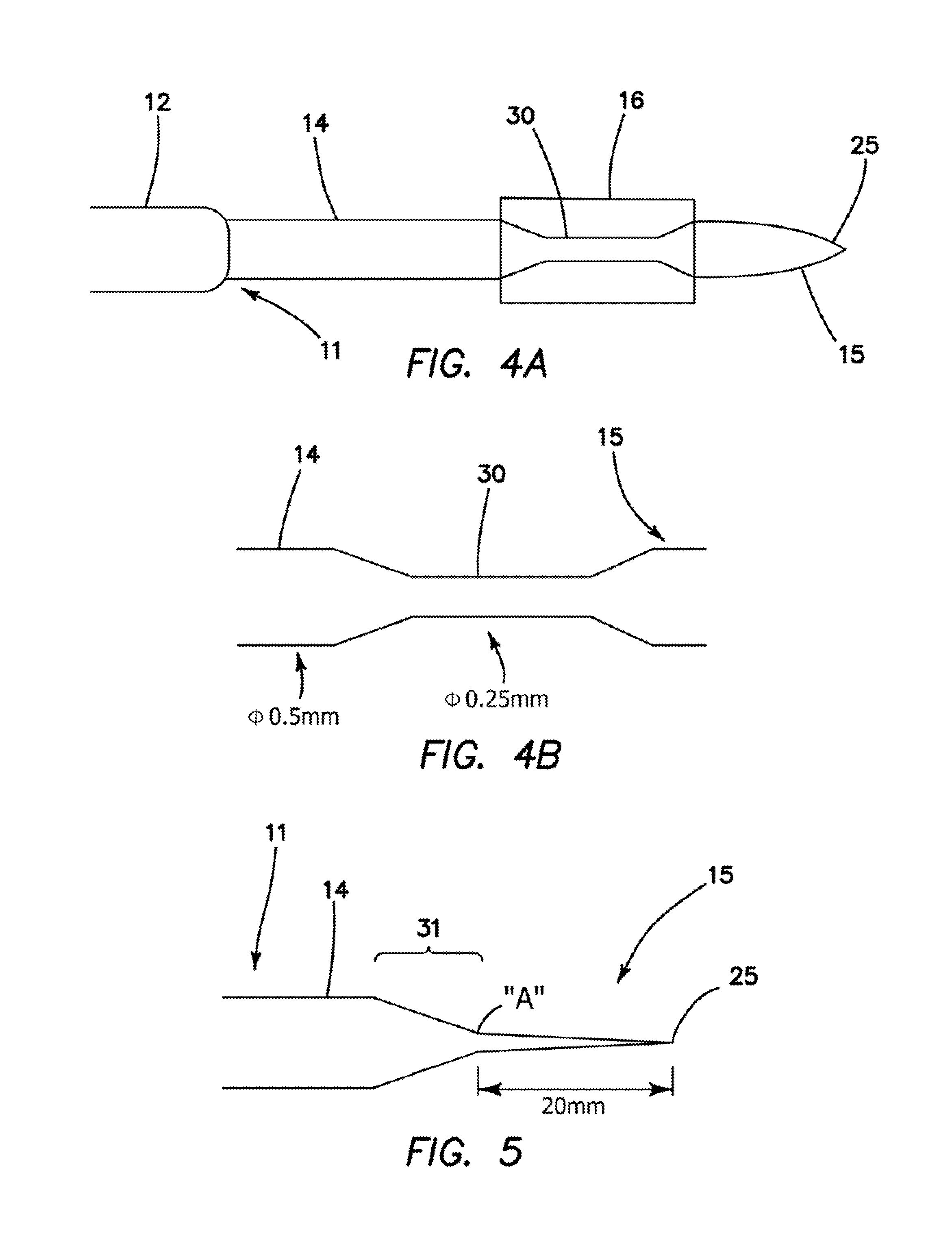
Transseptal puncture apparatus and method for using the same
Devices and methods for performing a transseptal puncture procedure using a device which includes either an untapered or tapered blunt end cannula disposed in an introducer carrying a sharp guidewire disposed longitudinally through the lumen of the blunt cannula, and a blunt end dilator wherein the guidewire is flexible and has an atraumatic shape at its tip. The cannula gives the more flexible introducer a defined shape and steerabilty allowing an ordinarily skilled physician to easily access a selected location on the septal wall of the heart for transseptal puncture and introducer placement thereacross without employing an exposed sharp end needle during the procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Catheter control systems
ActiveUS9101735B2Guaranteed simulation effectEfficiently controlling the hood positionSurgeryEndoscopesControl systemSeptal wall
Catheter control systems which facilitate the tracking of an angle of deflection of a catheter distal end can be used for any number of procedures where catheter orientation relative to the body is desirable, e.g., in transseptal access procedures where an accurate angle of puncture of the septal wall is desirable. Such control systems may comprise a steerable handle which is oriented relative to the catheter steerable section to provide for consistent catheter articulation upon corresponding manipulation of the steering ring. Another variation may utilize an orientation indicator to track the deflectable distal end. For instance, an orientation marker as visualized through an imaging hood on the distal end may correspond to identical orientation markers on the control handle such that articulation of a steering mechanism in a direction relative to the orientation markers deflects the catheter distal end in a corresponding direction relative to the visualized orientation markers.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Percutaneous arterial access to position trans-myocardial implant devices and methods
A system for treating a heart includes a catheter that is advanceable into a chamber of the heart and that is repositionable within the chamber between a septal wall and an external wall to enable penetration of the septal and external walls via a needle that is disposed within a lumen of the catheter. A first guidewire is deliverable through the penetration of the septal wall so that a distal end of the first guidewire is disposed within another chamber of the heart. A second guidewire is deliverable through the penetration of the external wall so that a distal end of the second guidewire is disposed externally of the external wall. The first guidewire is connectable to the second guidewire to join or form a path within the chamber that extends between the septal wall and the external wall.
Owner:BIOVENTRIX A CHF TECH
Left chamber pressure sensor lead delivery system
An apparatus for and method of measuring pressure through a septum in a patient's heart. A lead inserted into the right side of a heart is routed through the septum to gain access to the left side of the heart. The lead includes a mounting mechanism that secures the lead to one or both sides of the septal walls. The lead also includes one or more sensors for measuring cardiac pressure on the left side of the heart and, as necessary, the right side of the heart.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
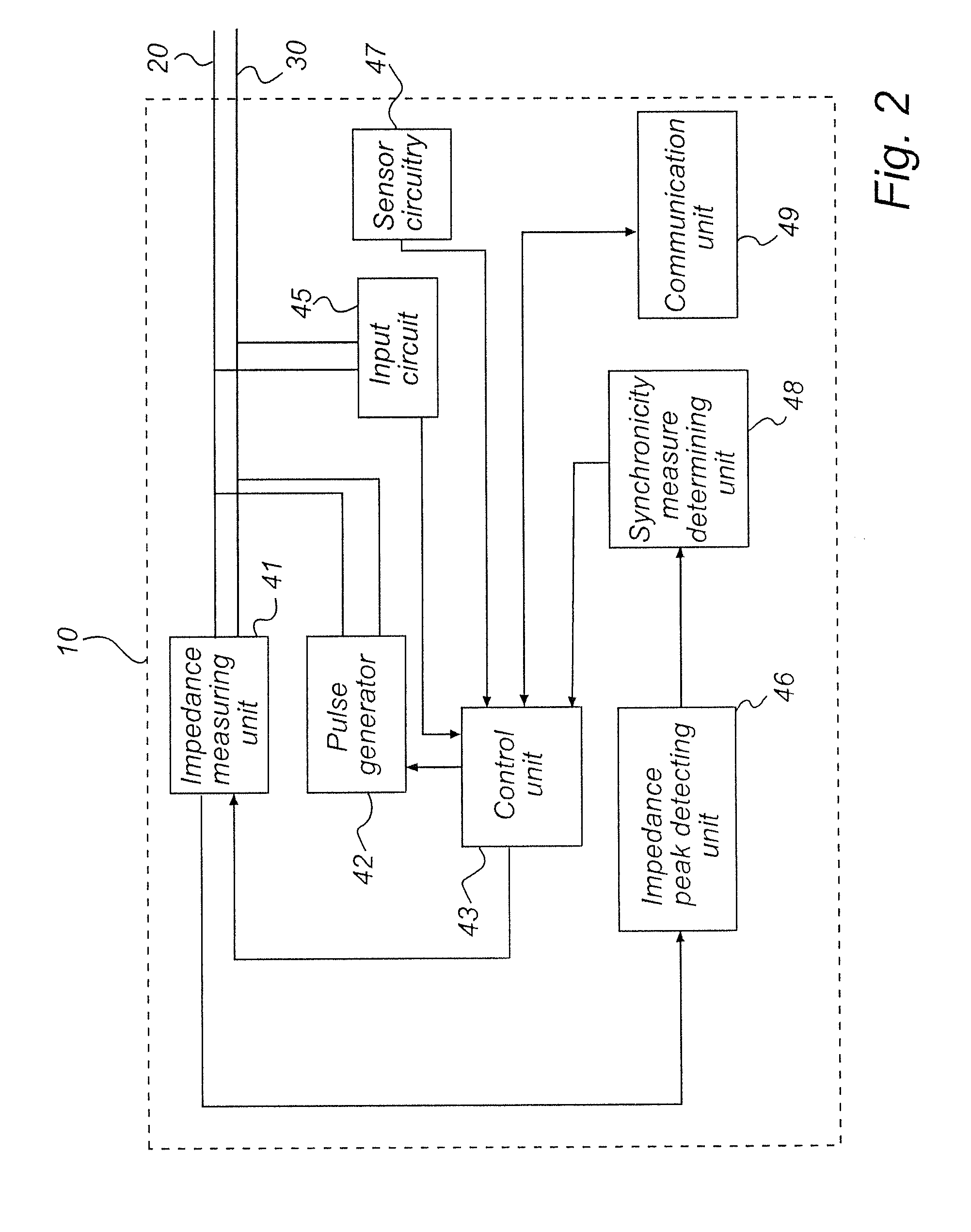
Implantable medical device and method for monitoring synchronicity of the ventricles of a heart
InactiveUS20110257696A1Accurate and reliable mannerAccurate and reliable wayHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac cycleVentricular contraction
In an implantable medical device and a method for monitoring ventricular synchronicity of a heart, impedance signals are measured that reflect septal wall movements and impedance amplitude peaks in the impedance signal are detected. A synchronicity index indicating a degree of synchronicity is determined based on detected impedance peaks, with at least two impedance peaks detected within a predetermined time window including a cardiac cycle or a part of a cardiac cycle indicating an increased dyssynchronicity in the ventricular contractions.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com