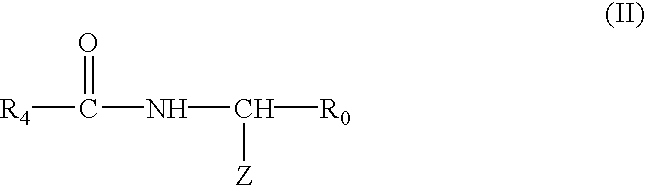Patents
Literature
165results about How to "Improve radiopacity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
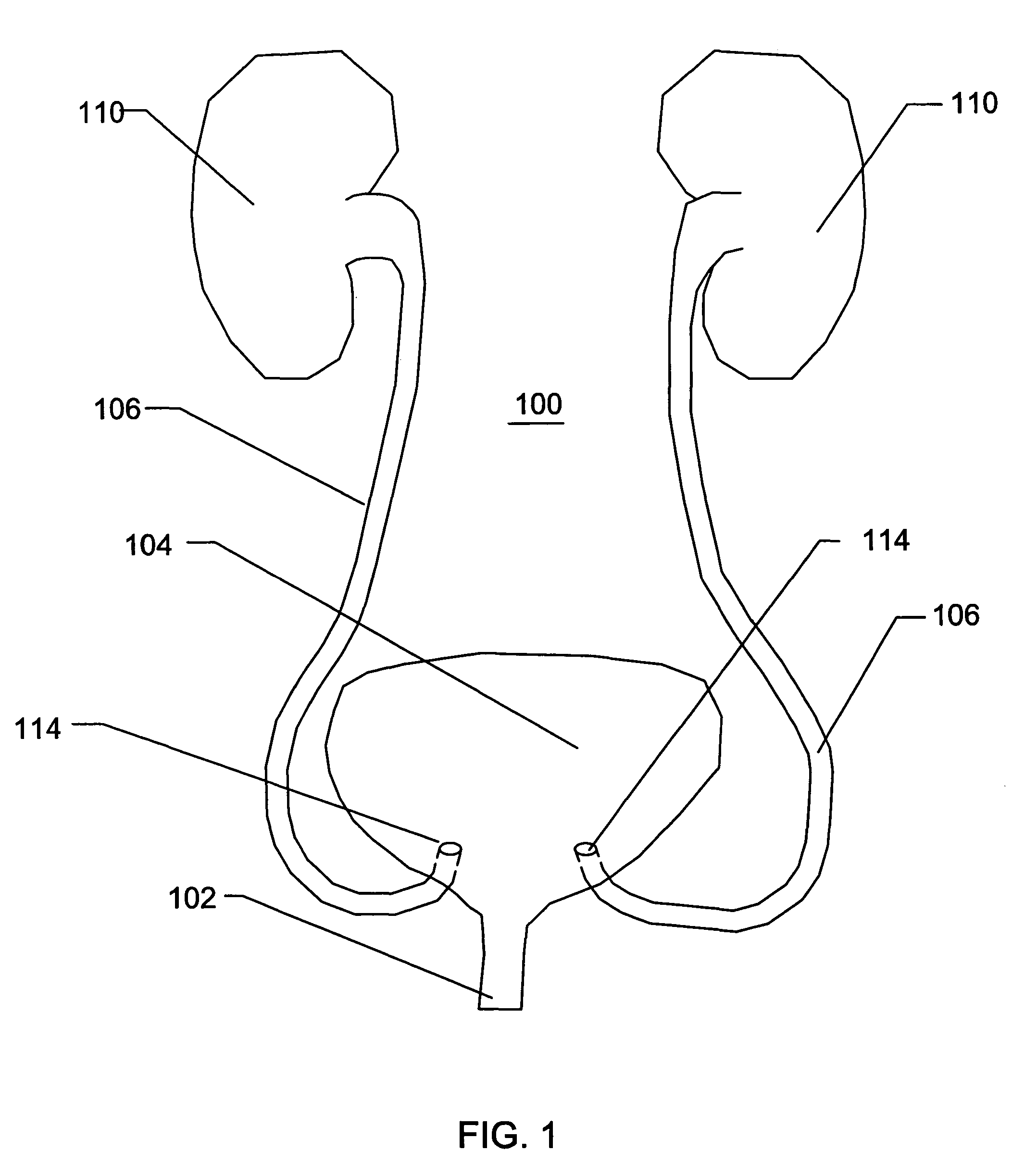
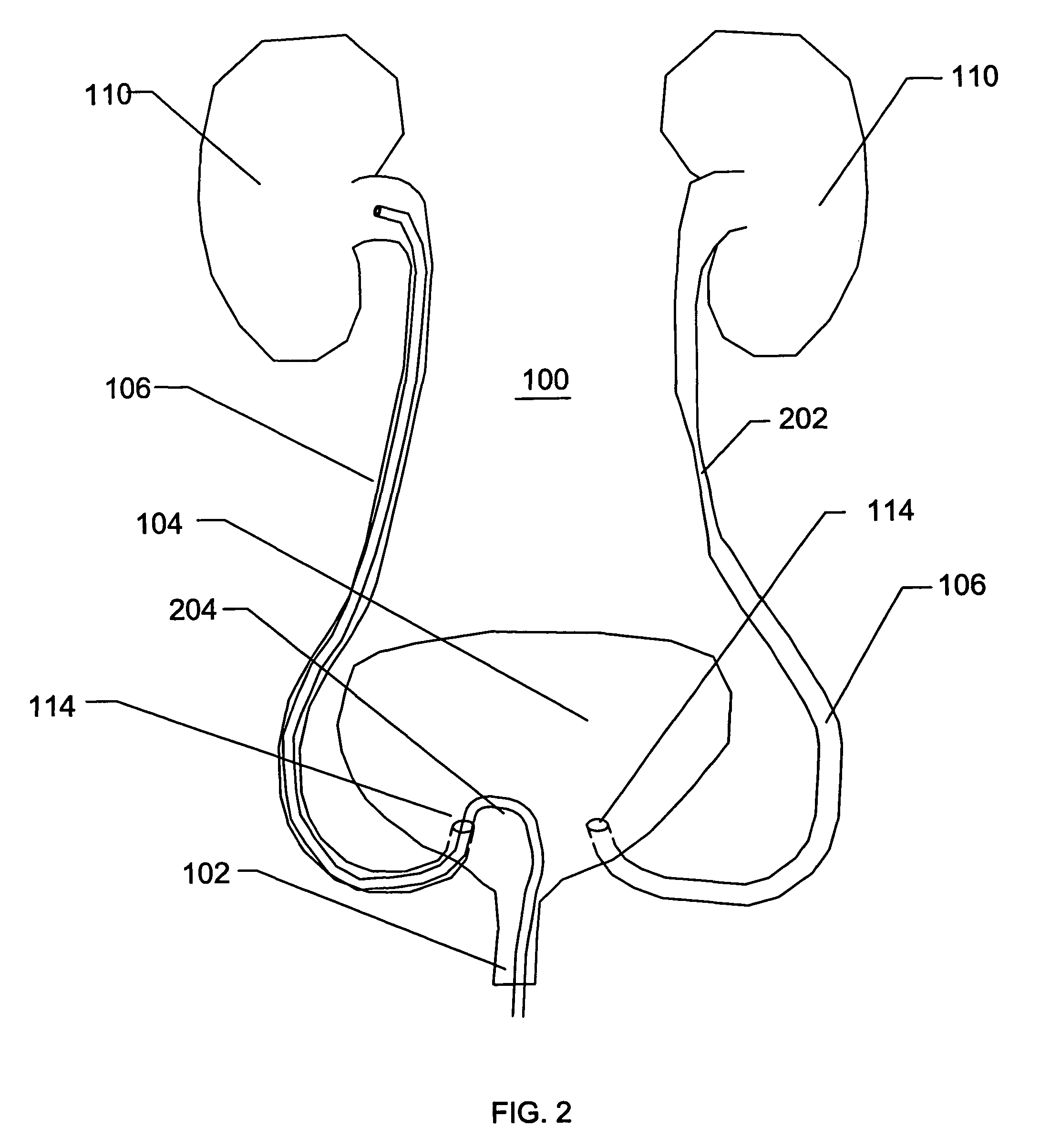
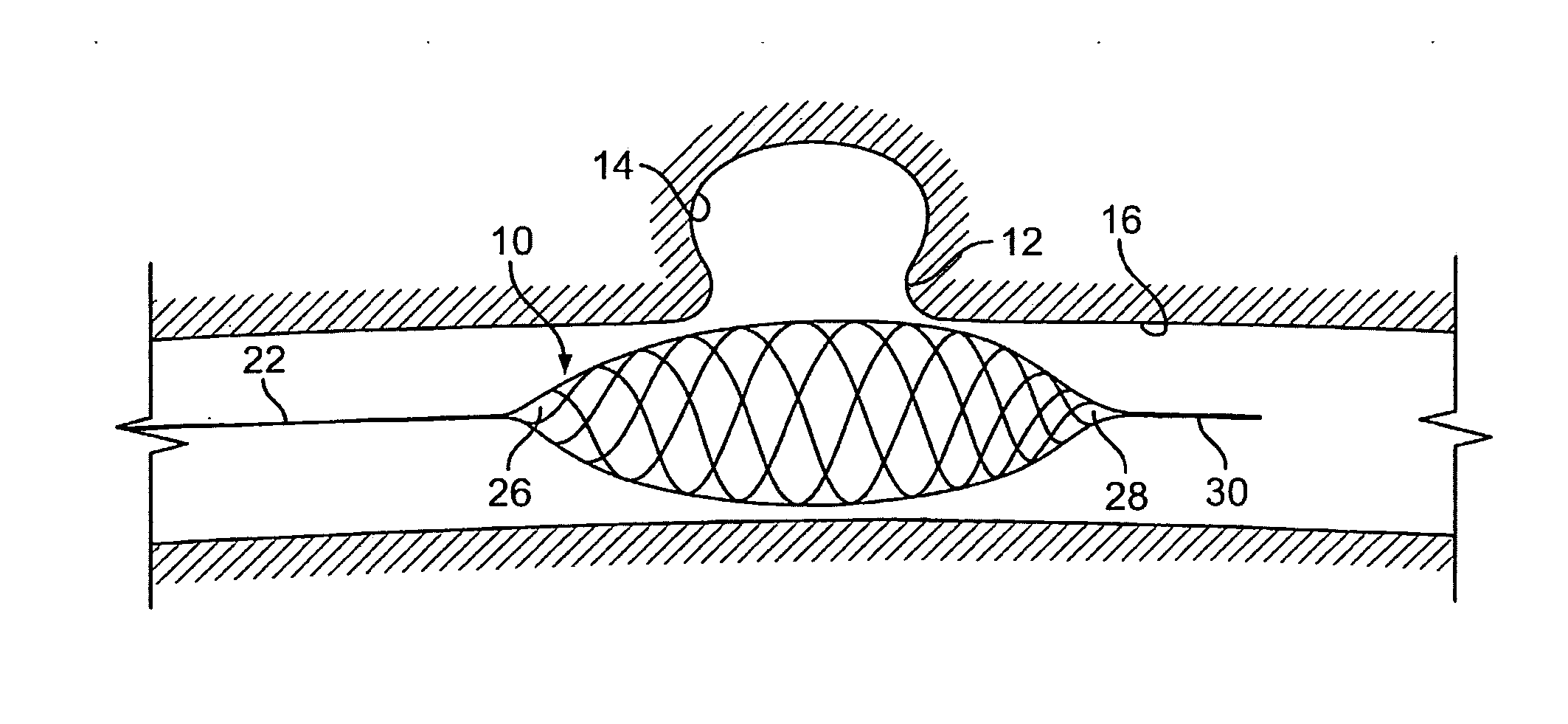
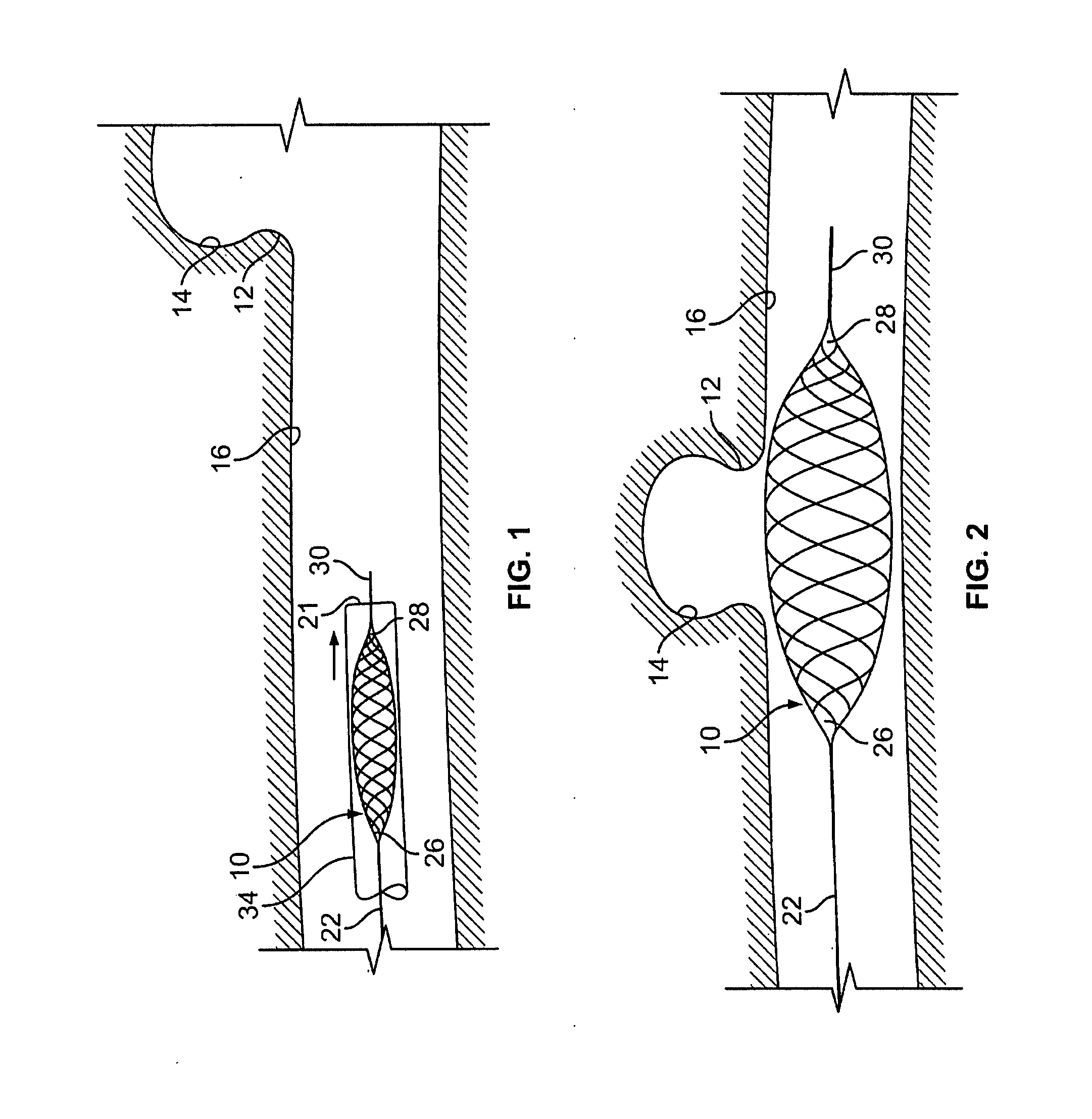
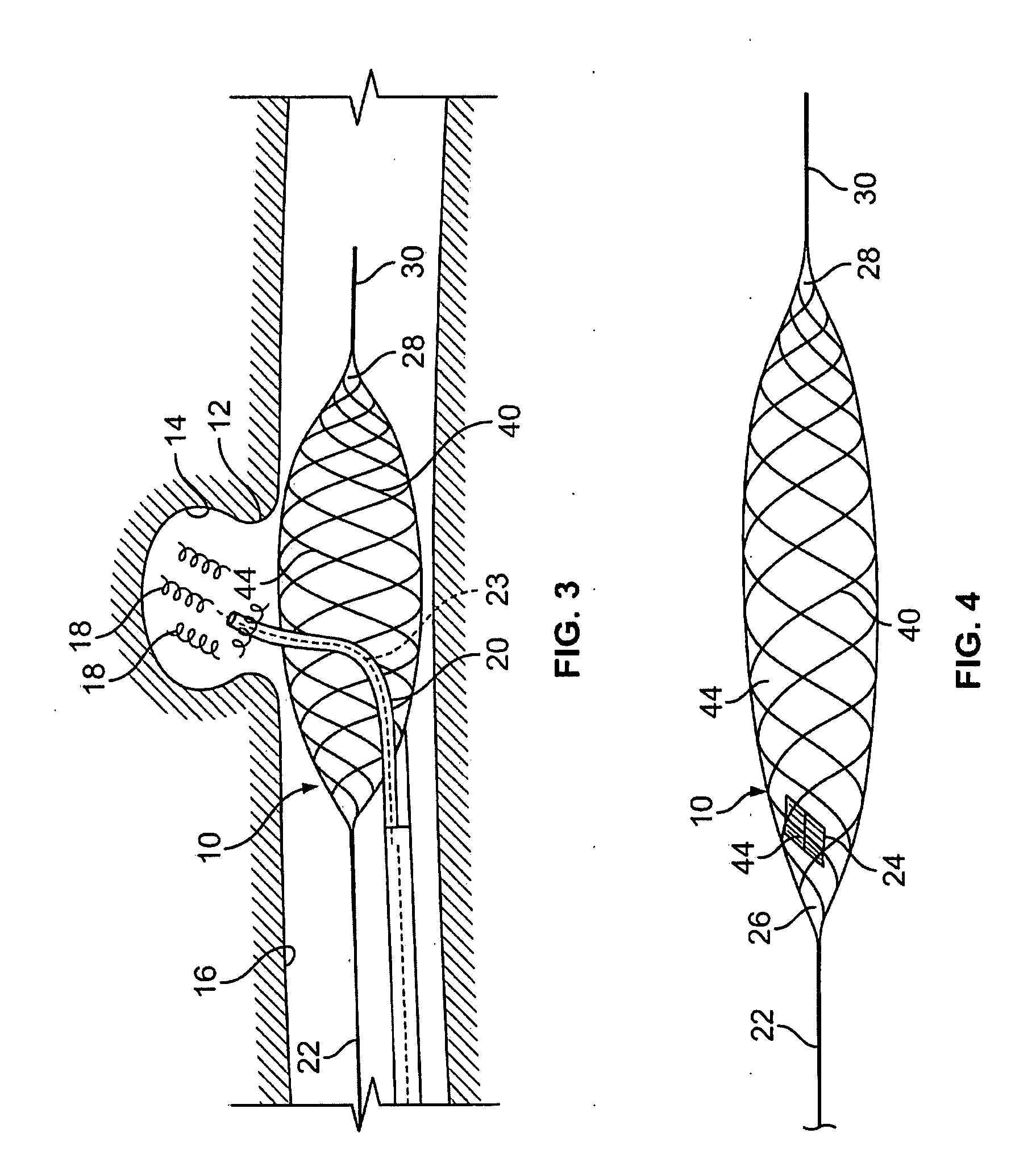
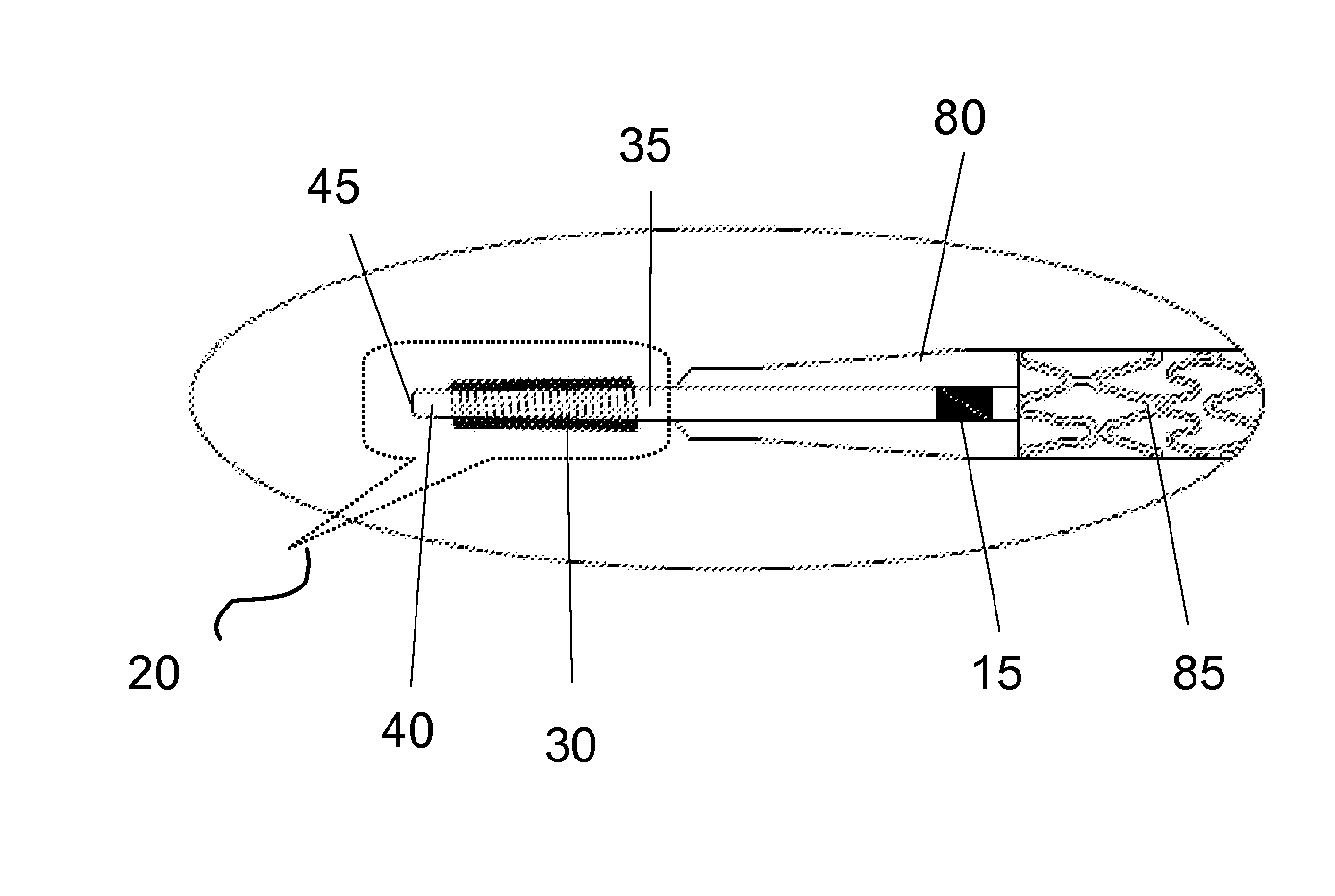
Temporary intraluminal filter guidewire and methods of use
InactiveUS6866677B2Restrict movementPrevent movementDilatorsCatheterRelative displacementEngineering
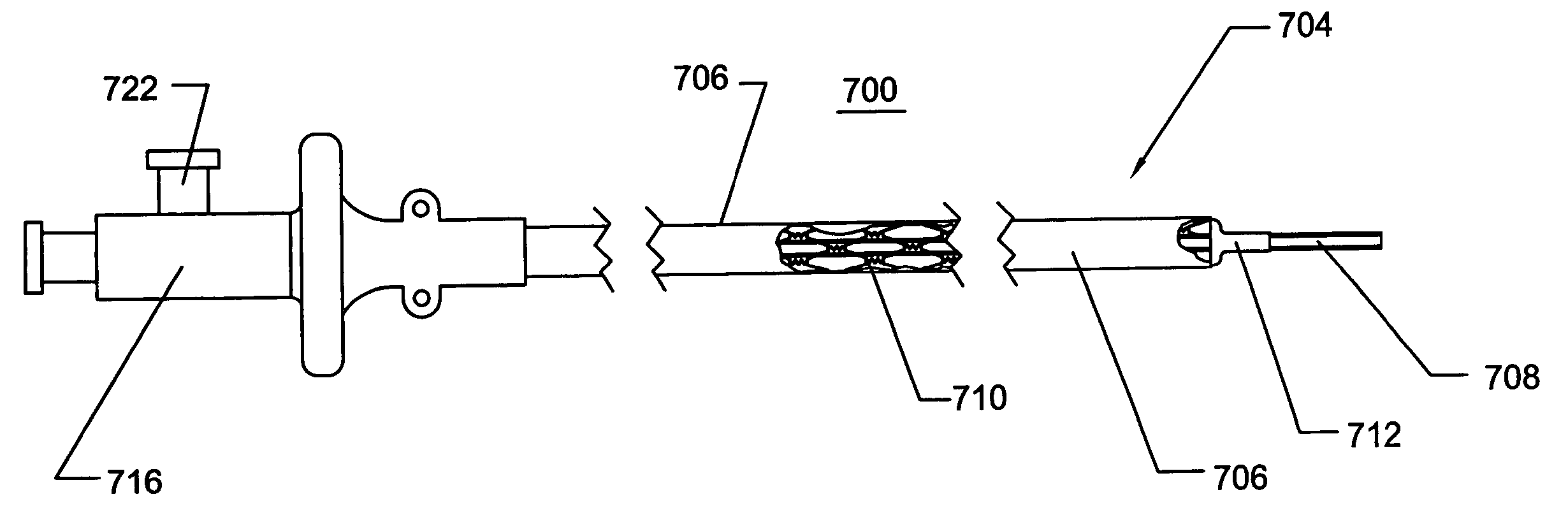
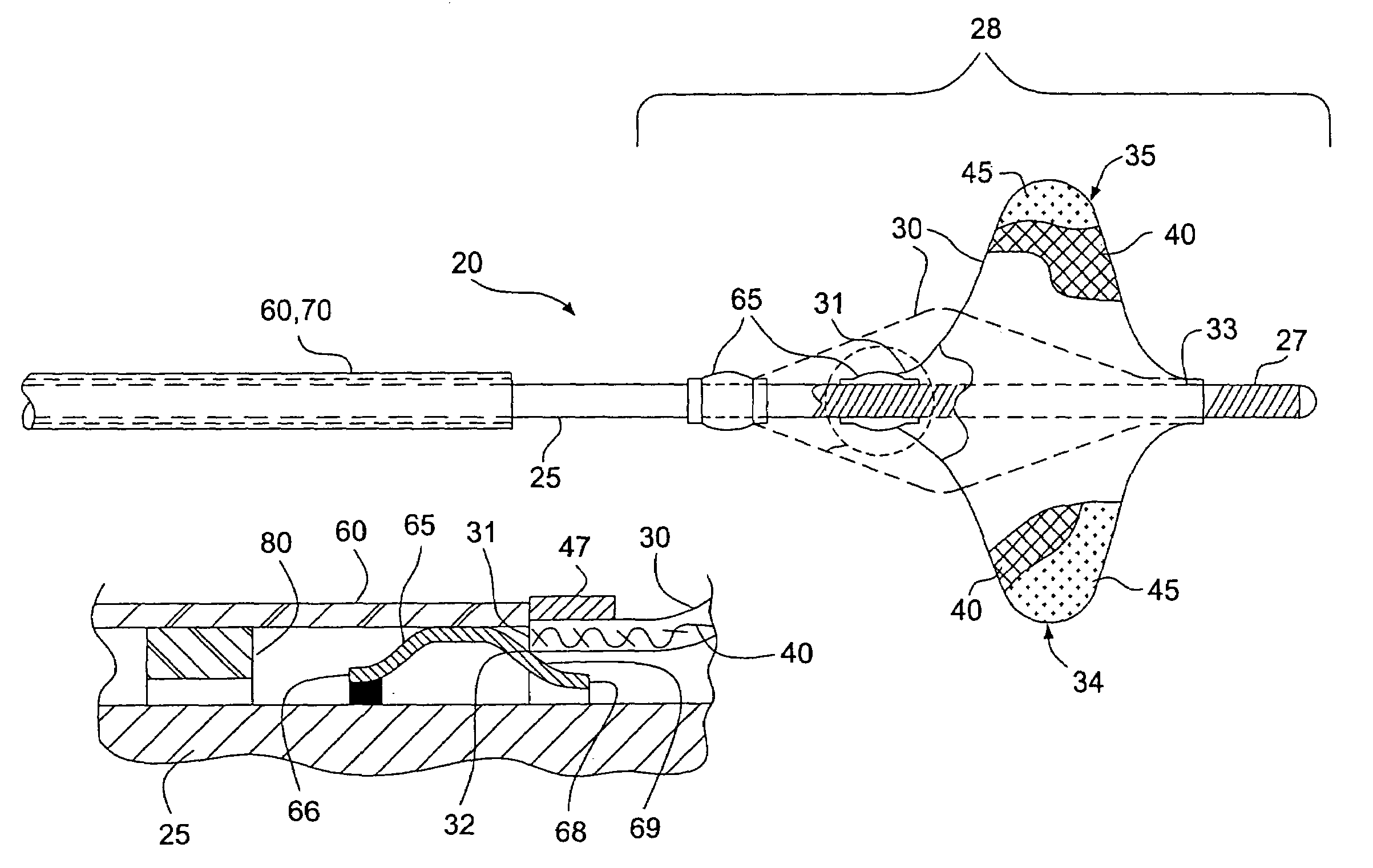
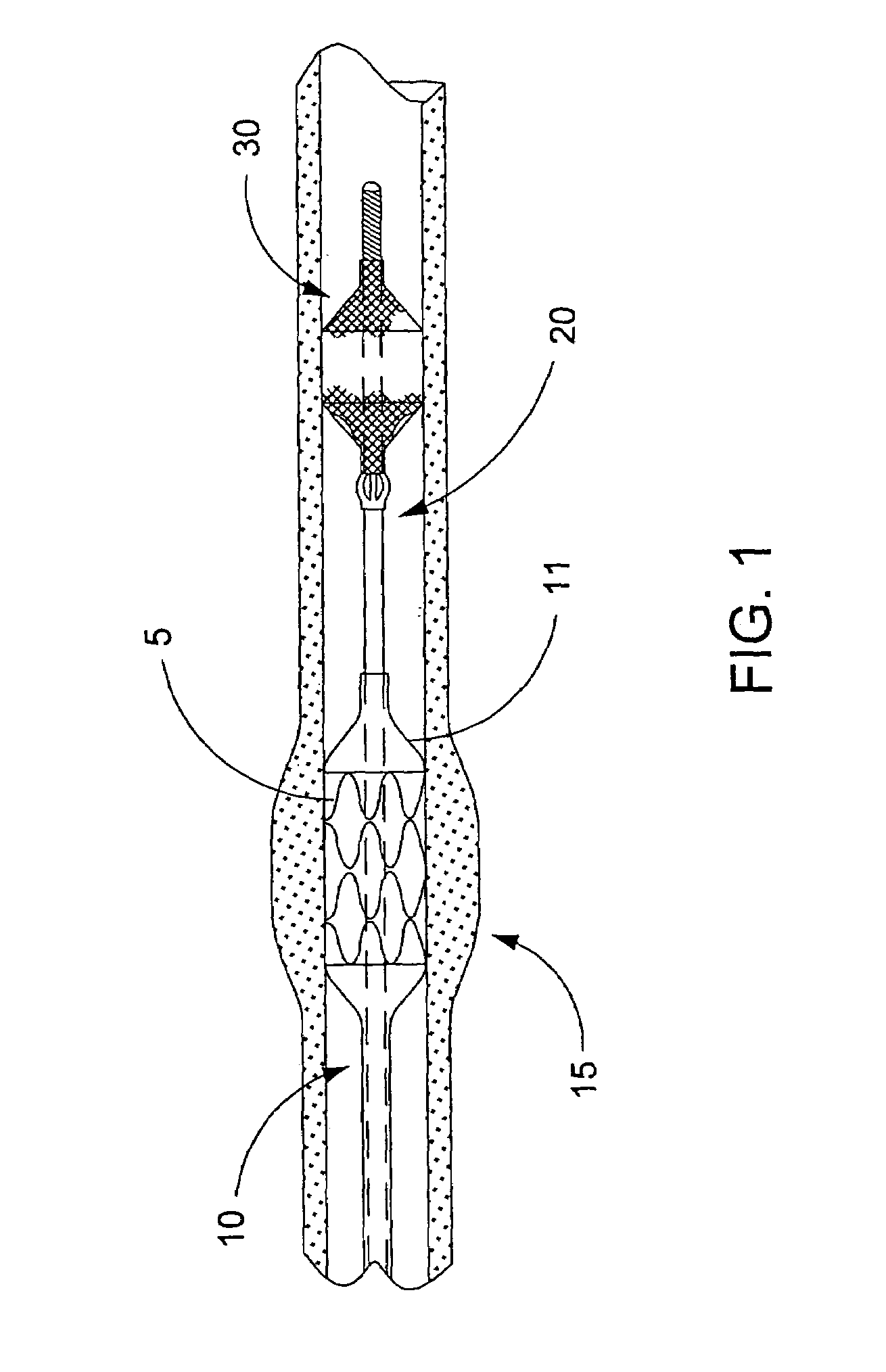
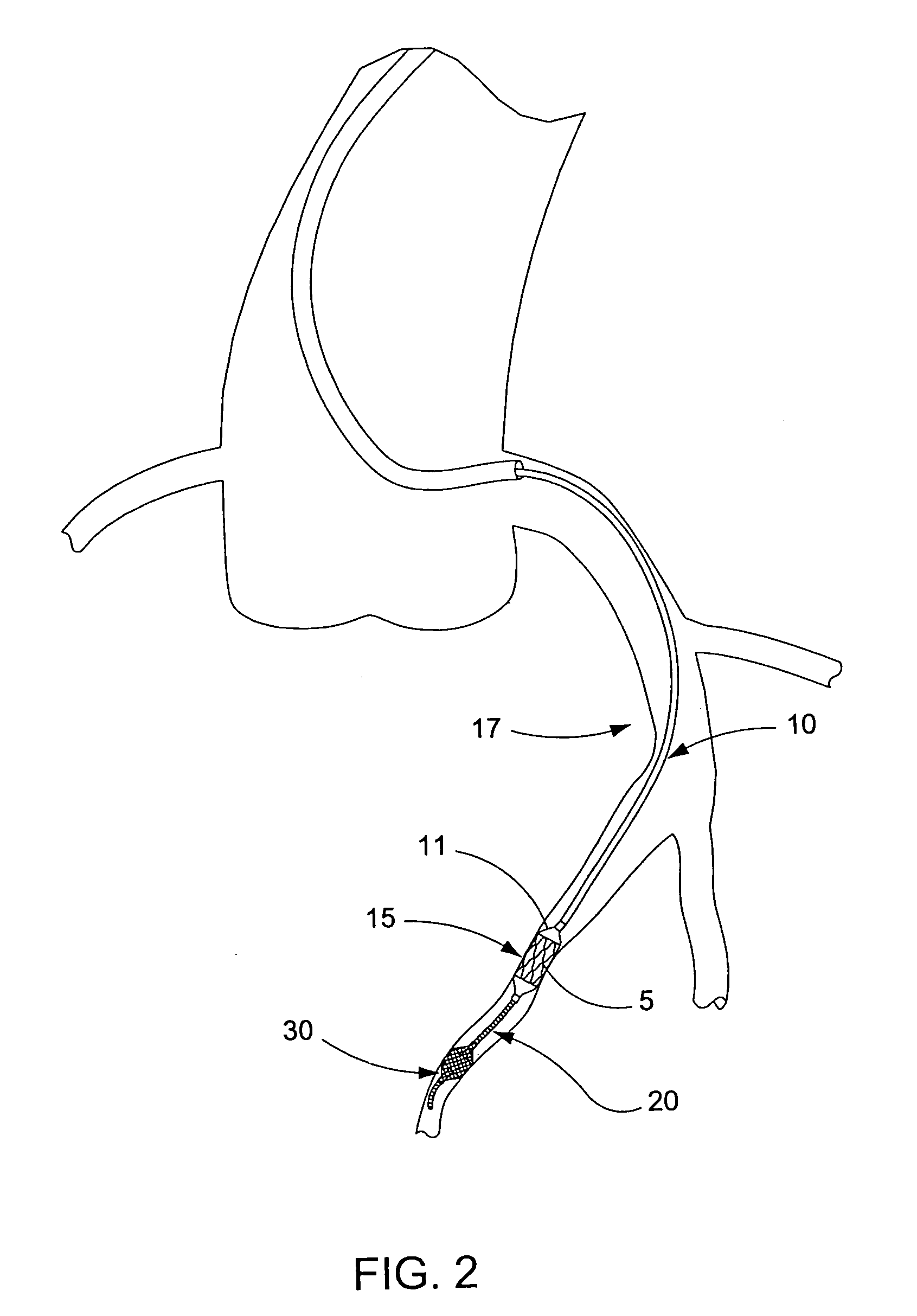
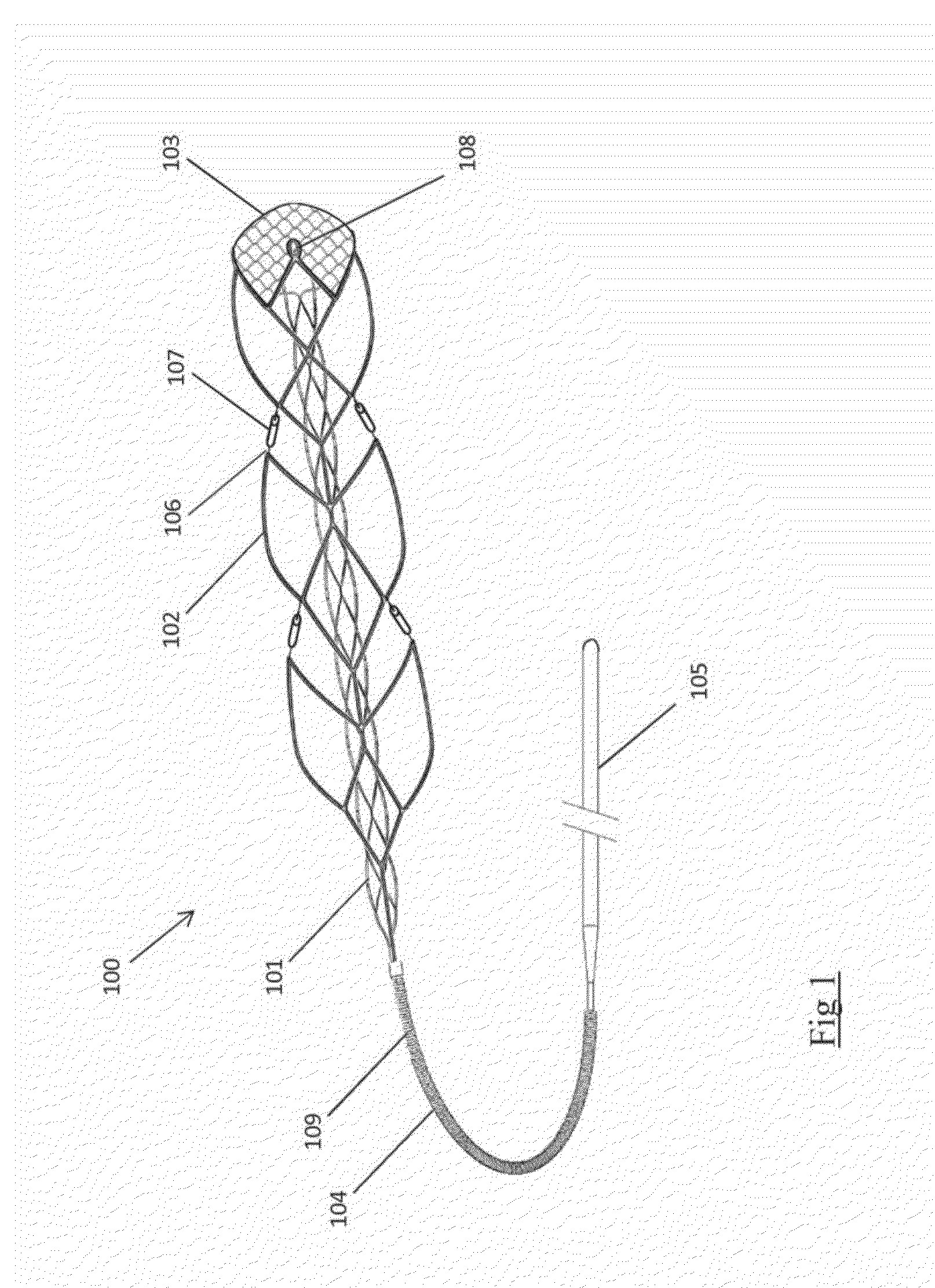
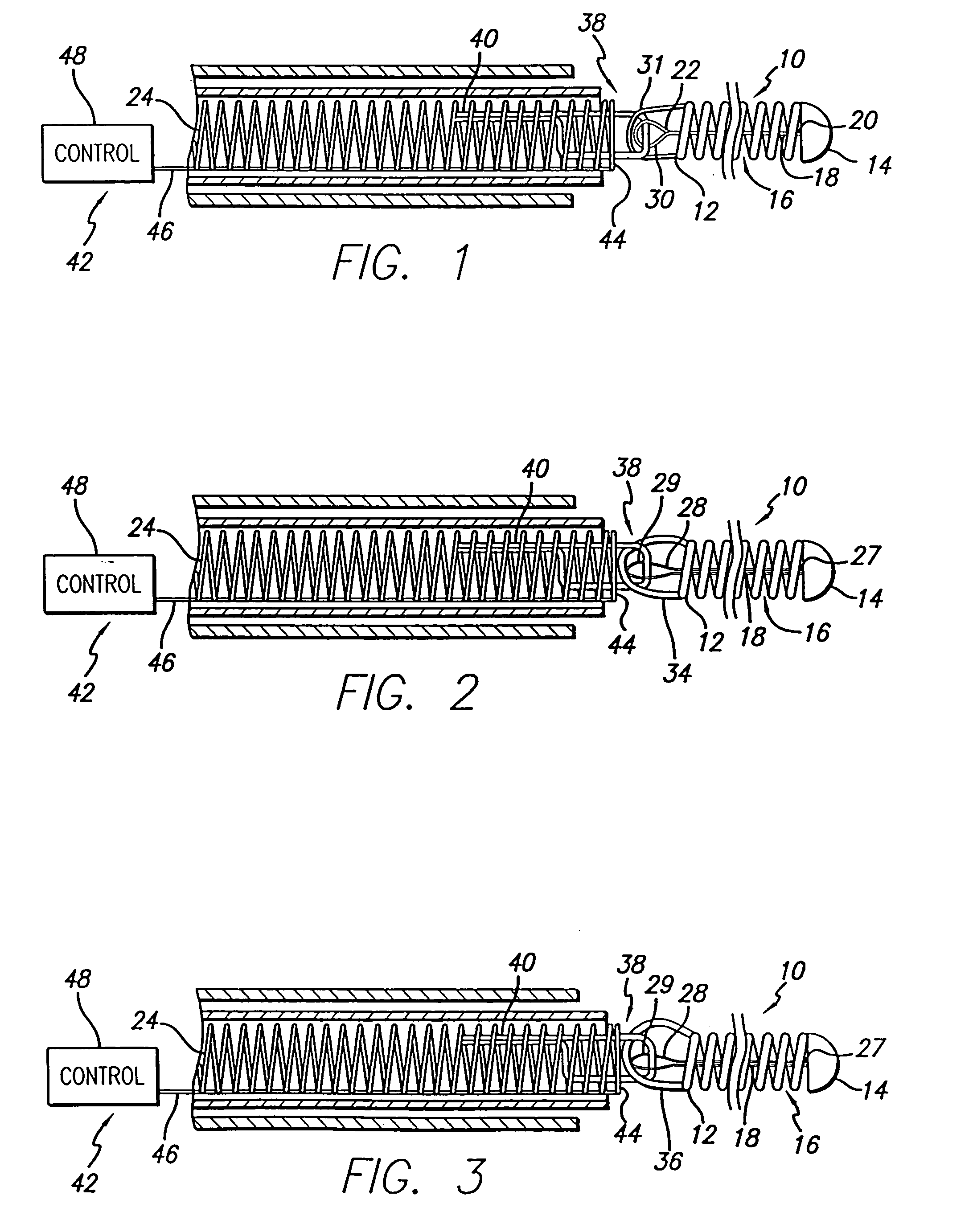
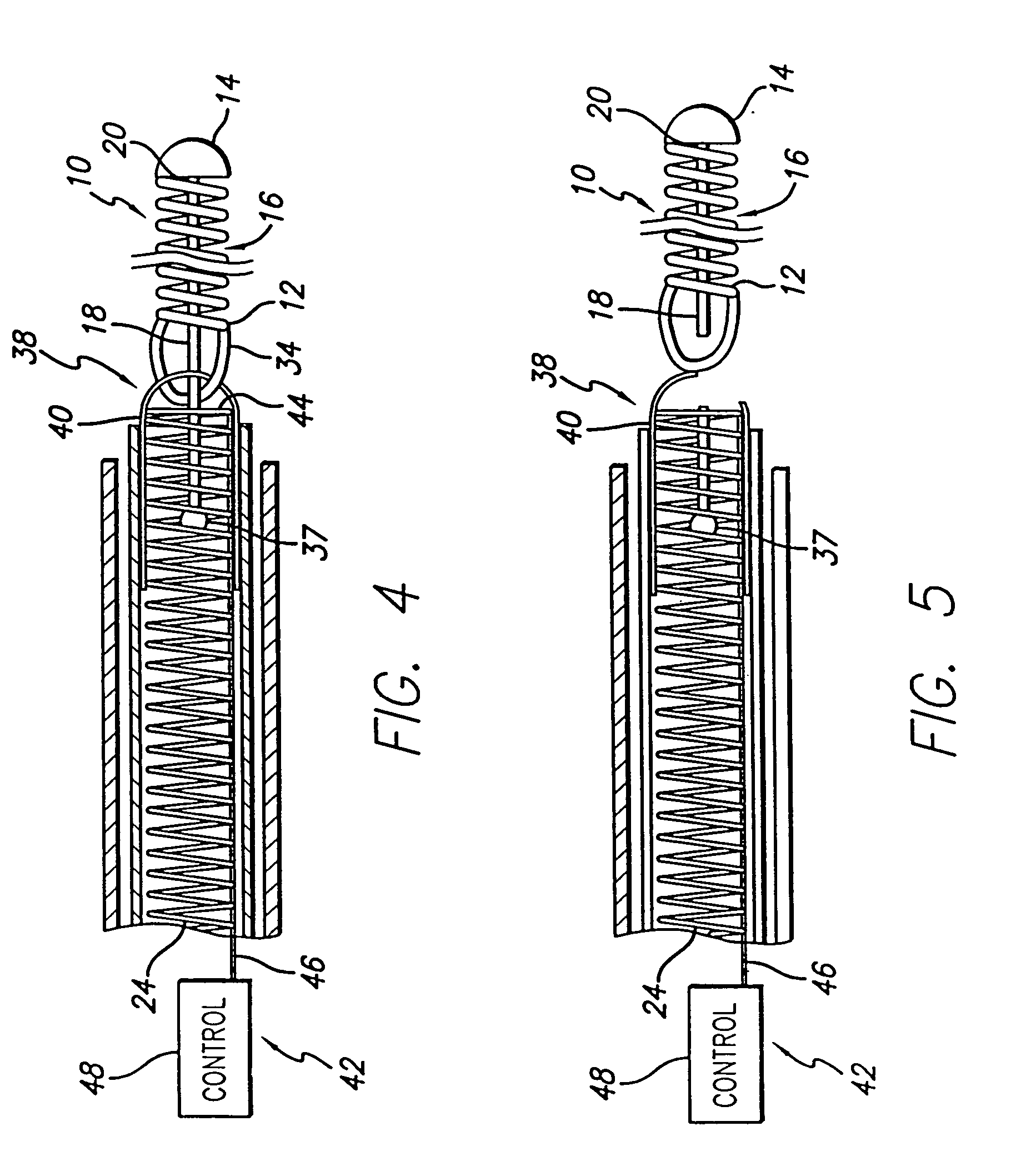
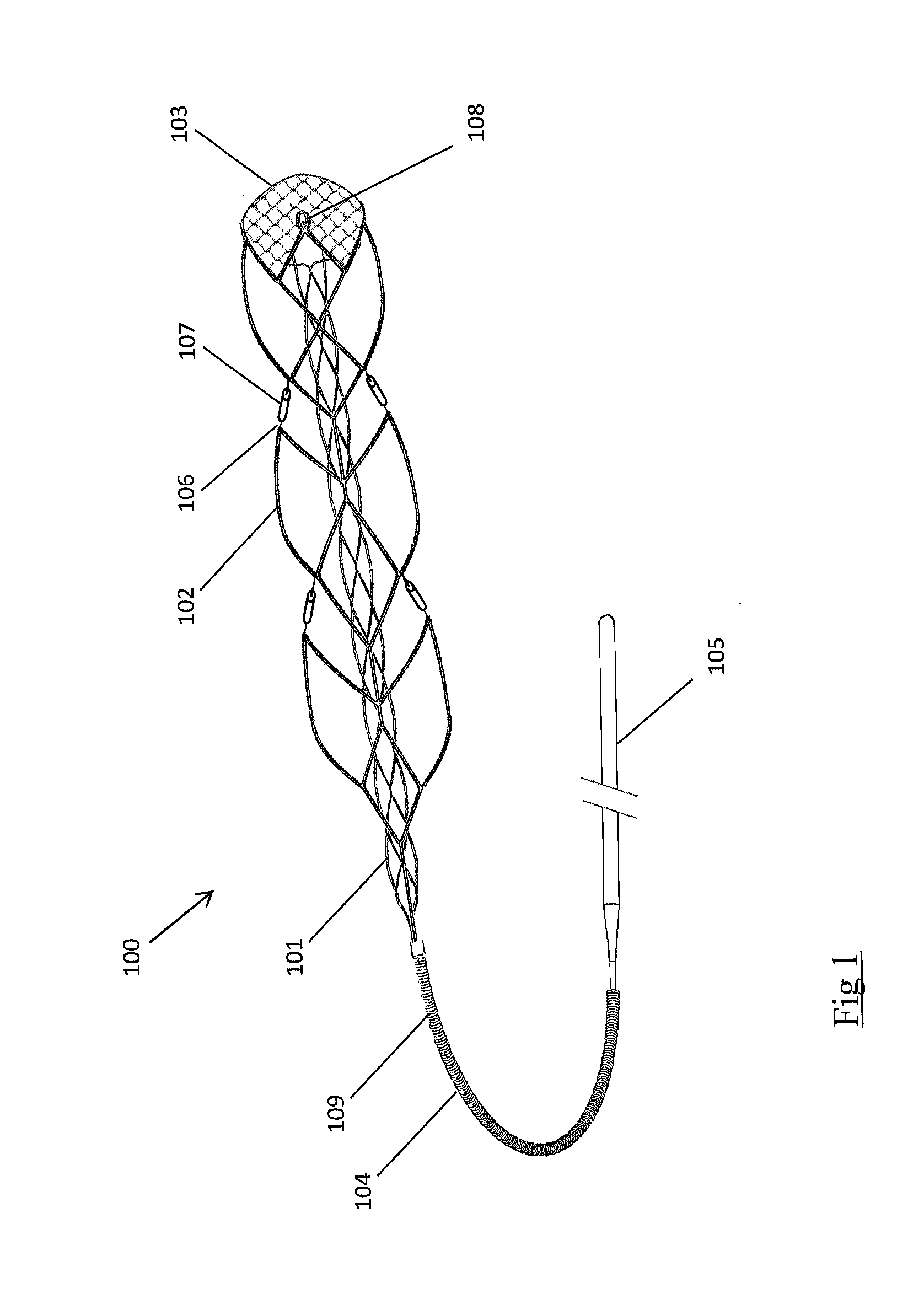
The present invention is a temporary intraluminal filter guidewire for use during interventional procedures, such as angioplasty or stent deployment. A braided filter is mounted near the distal end of a steerable guidewire, which guides a therapeutic catheter. An actuator rod slides over the guidewire and is removably connected to the filter. The rod controls relative displacement of the filter ends, causing transformation of the filter between a deployed configuration and a collapsed configuration. Wire having enhanced radiopacity is included in the filter to provide visualization under fluoroscopy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
Radiopacity intraluminal medical device
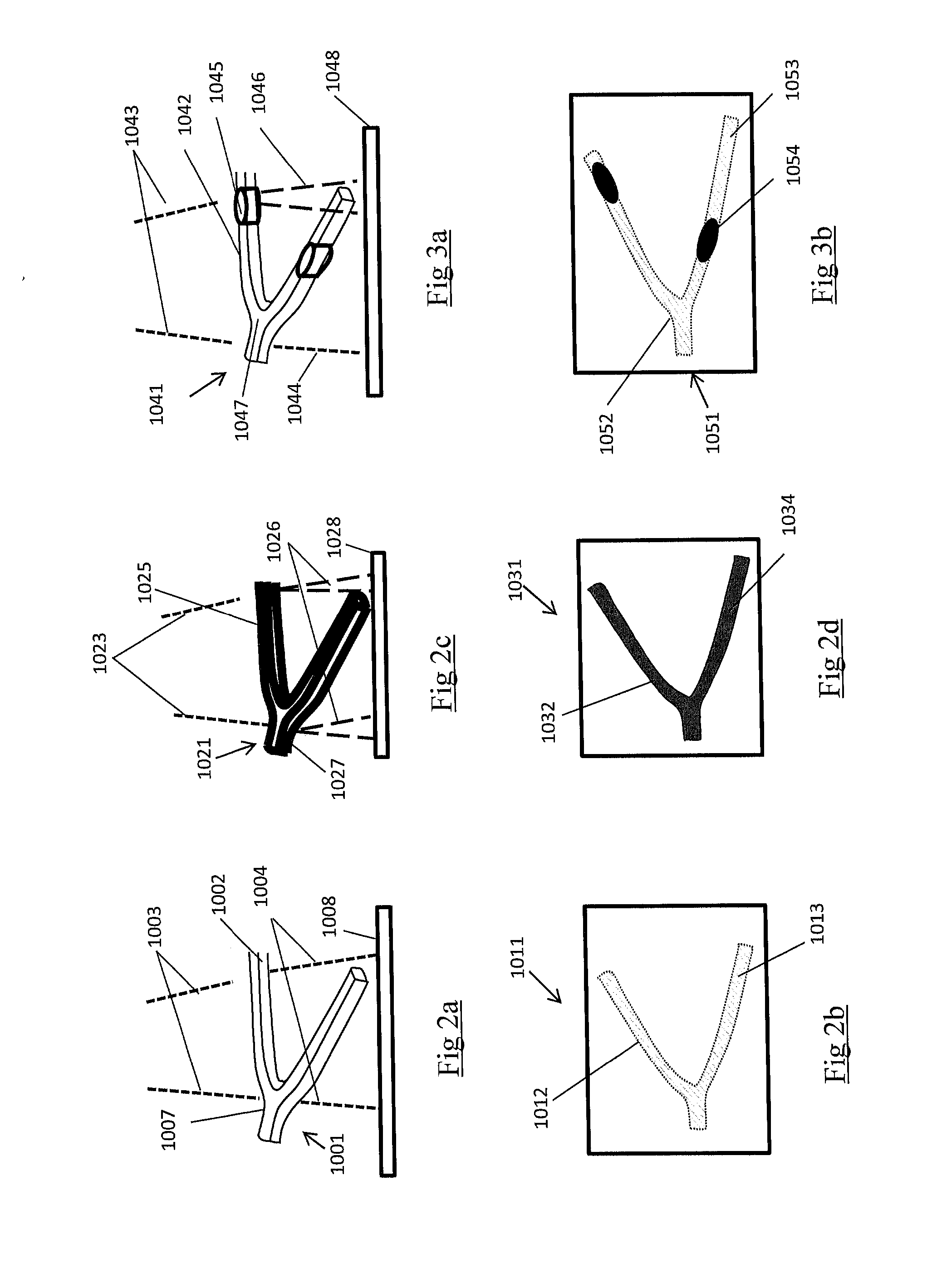
A stent or other intraluminal medical device having markers formed from housings integral with the stent and marker inserts having a higher radiopacity than the stent provides for more precise placement and post-procedural visualization in a vessel, by increasing the radiopacity of the stent under X-ray fluoroscopy. The housings are formed integral to the stent and the marker inserts are made from a material close in the galvanic series to the stent material and sized to substantially minimize the effect of galvanic corrosion.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
Devices and methods for coronary sinus pressure relief
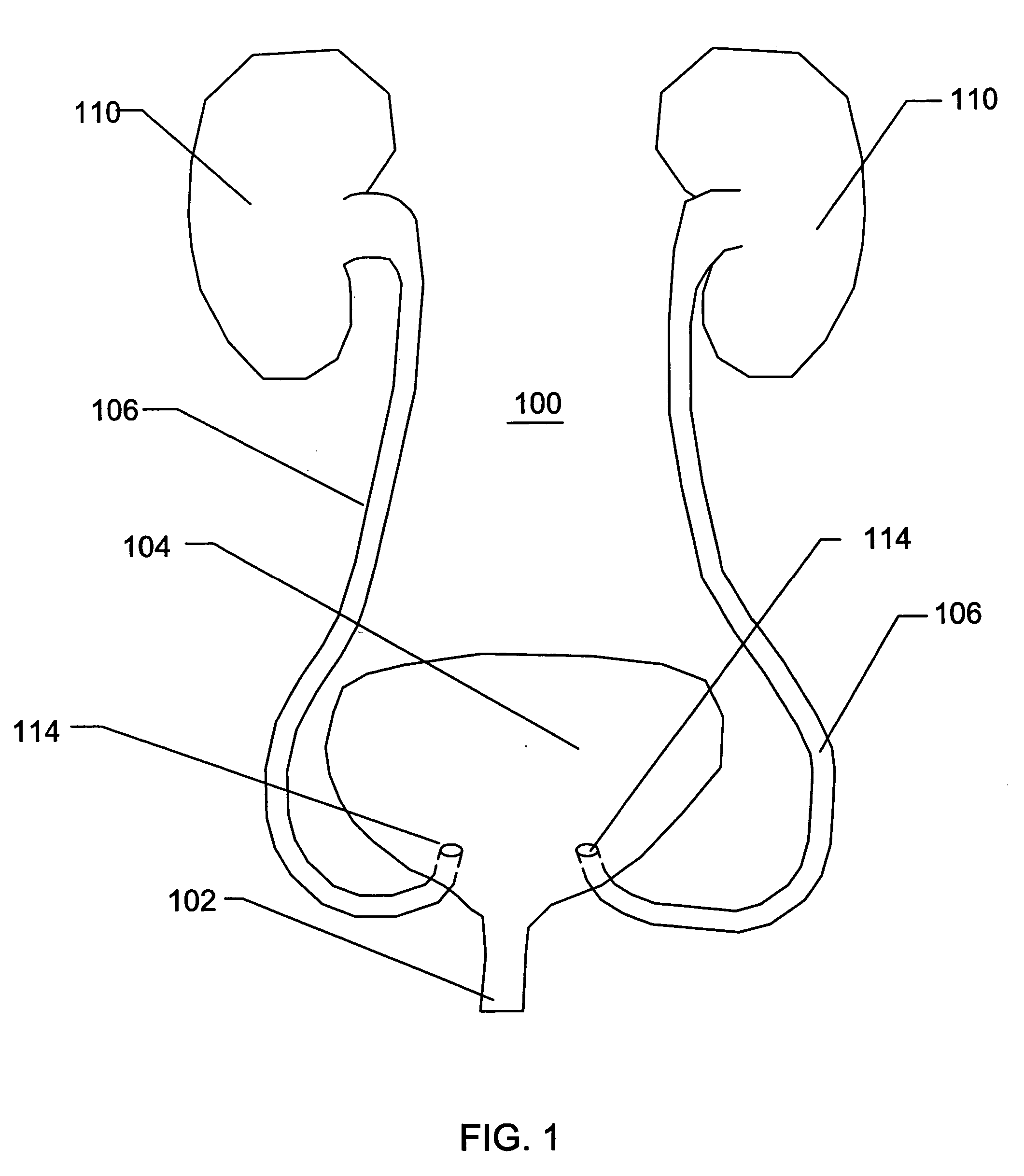
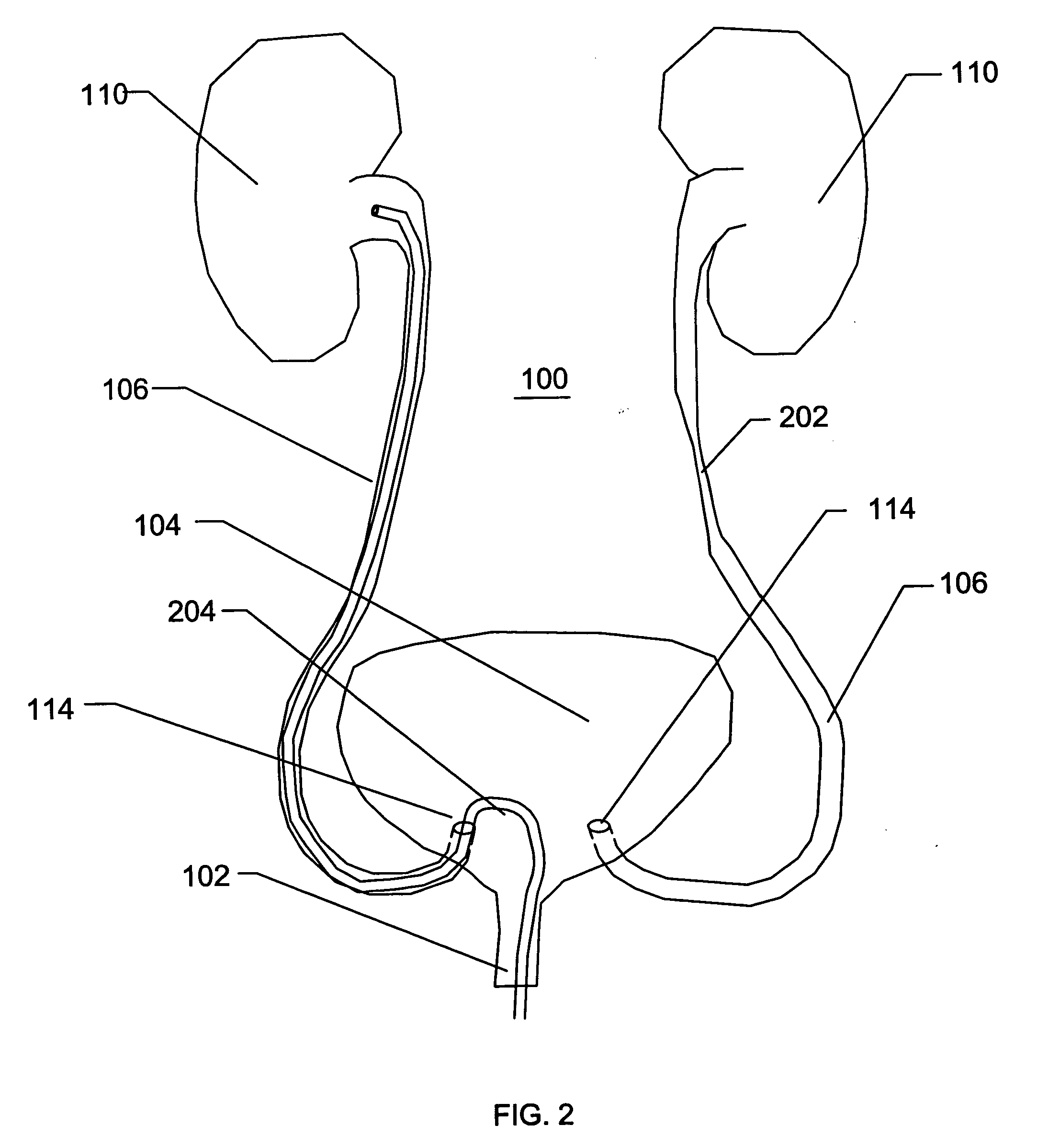
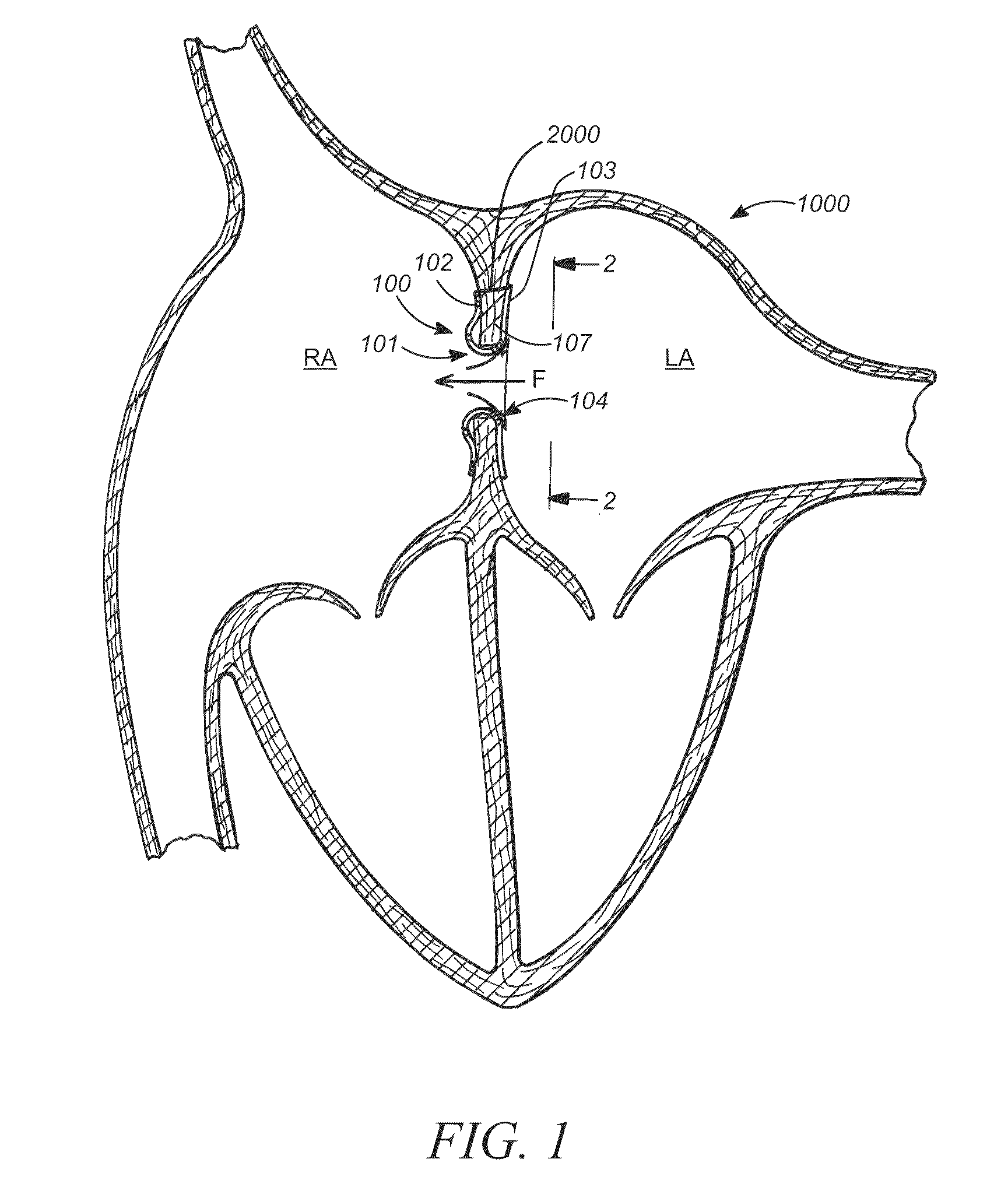
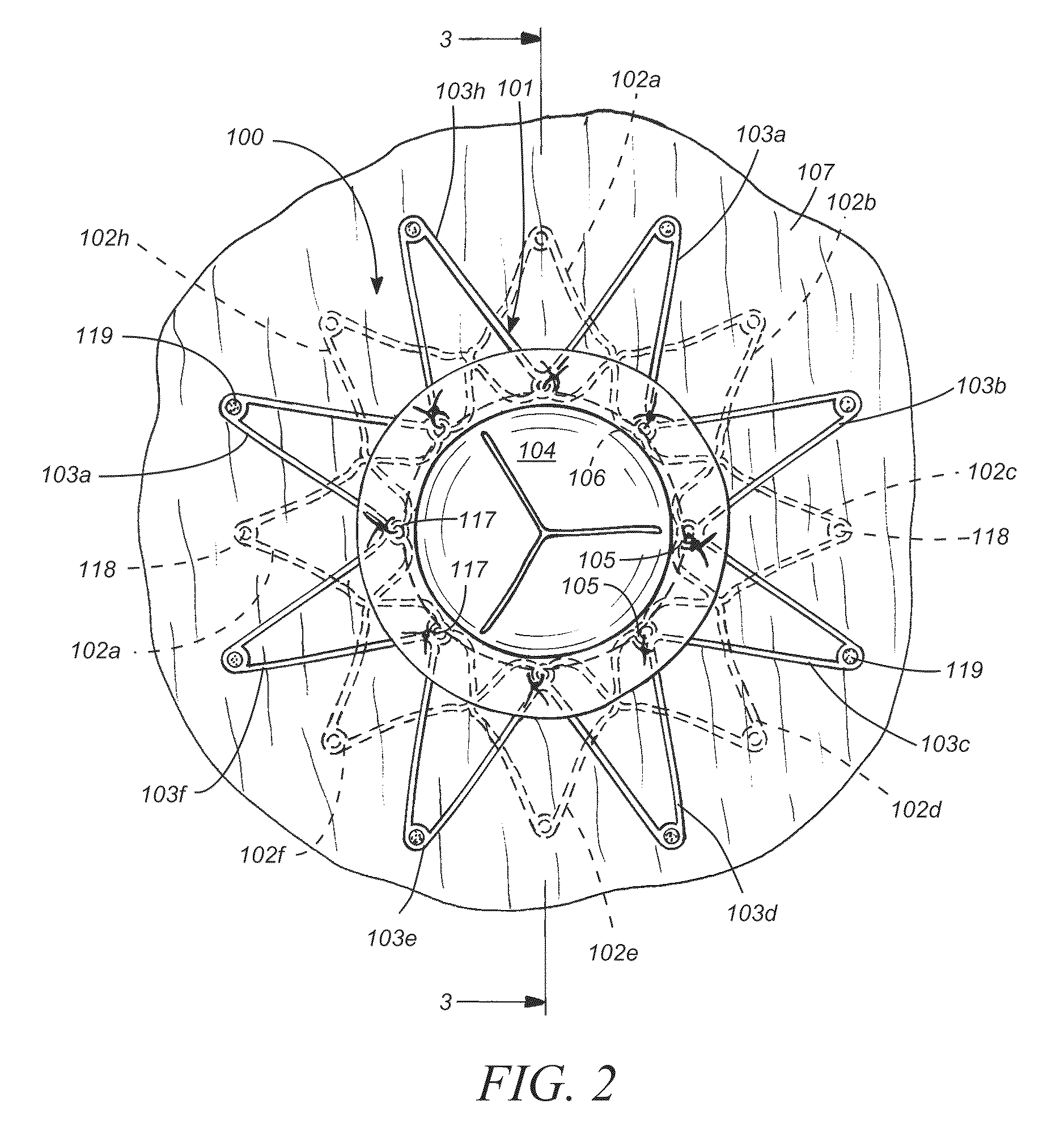
A method and devices for relieving pressure in the left atrium of a patient's heart is disclosed. The method includes using an ablative catheter in a minimally invasive procedure to prepare an opening from the coronary sinus into a left atrium of the patient's heart. Once the opening is prepared, the opening may be enlarged by a technique such as expanding a balloon within the opening. A stent is then placed within the coronary sinus of the patient, with a transverse portion expanding within the opening, allowing blood to flow from the left atrium to the coronary sinus and then to the right atrium. Pressure within the left atrium is thus relieved.
Owner:DC DEVICES
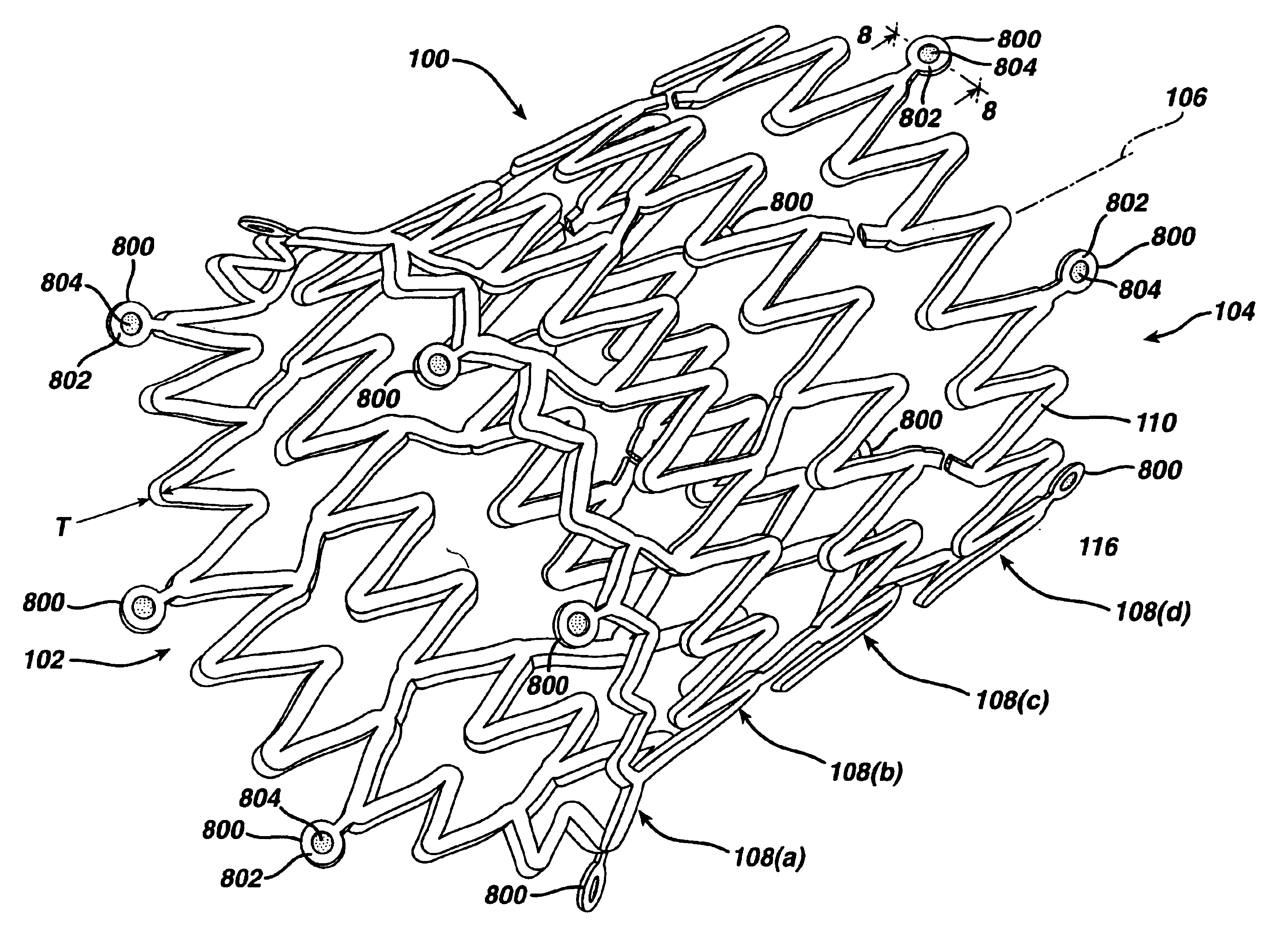
Integrated stent repositioning and retrieval loop
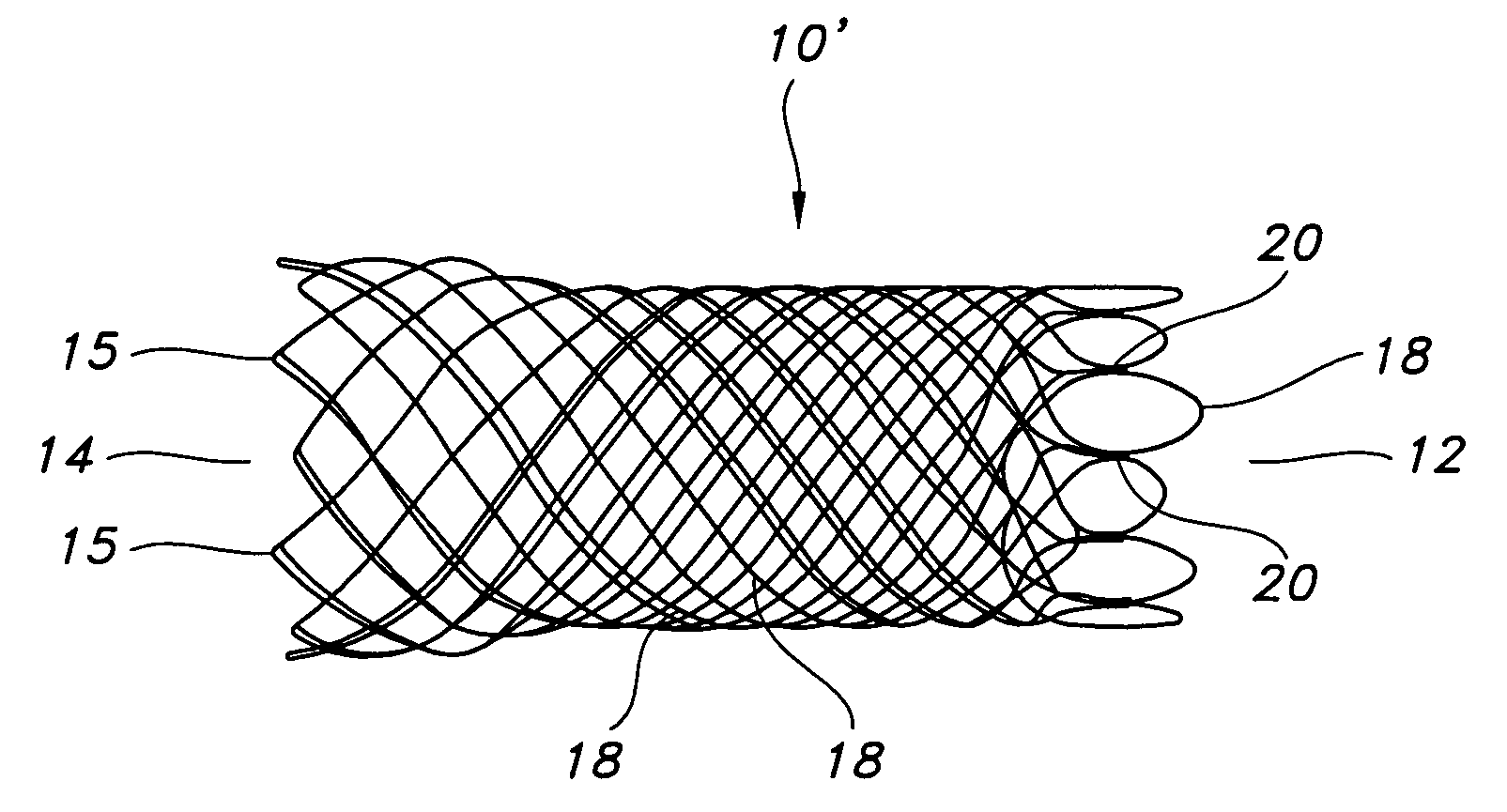
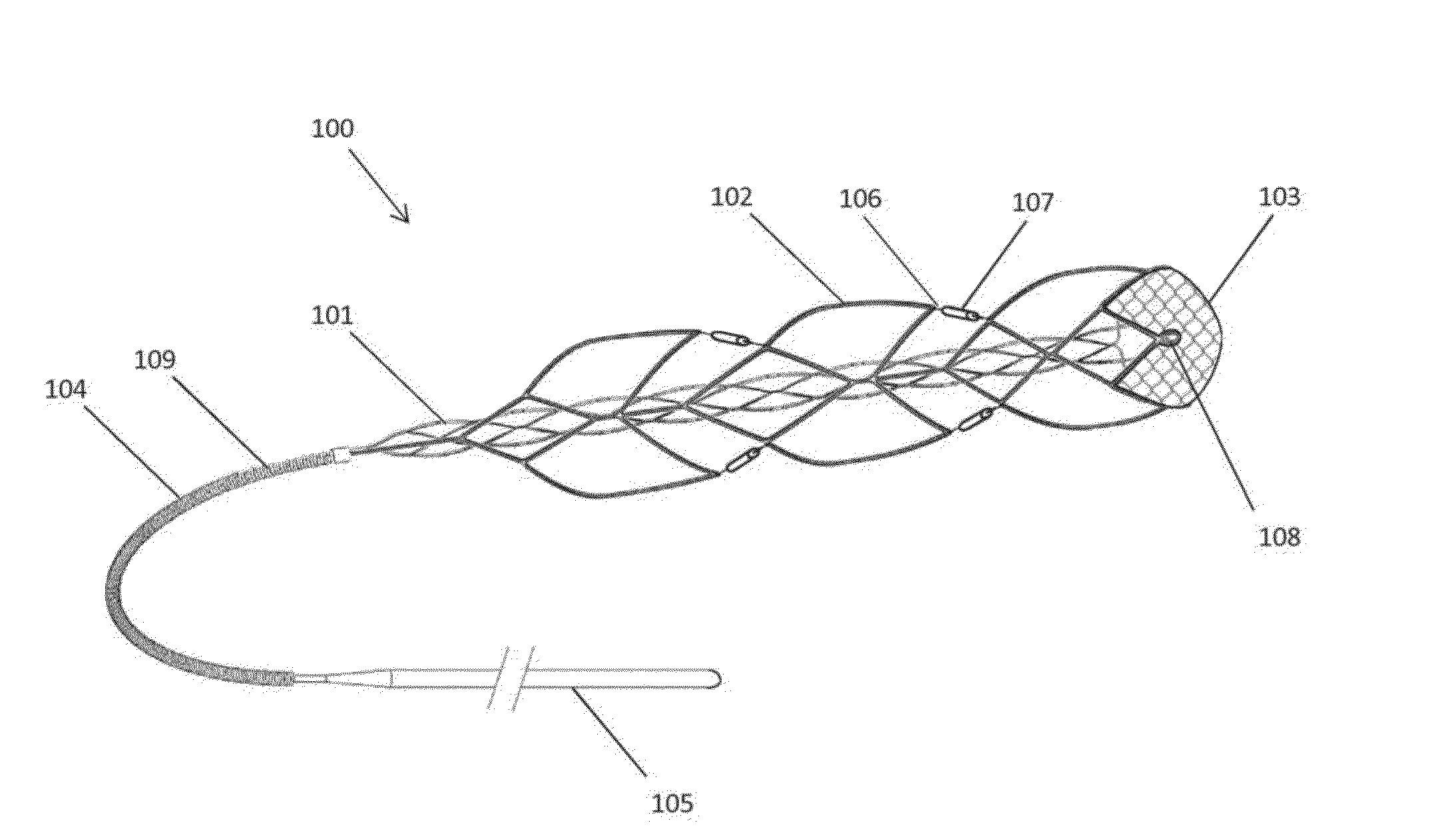
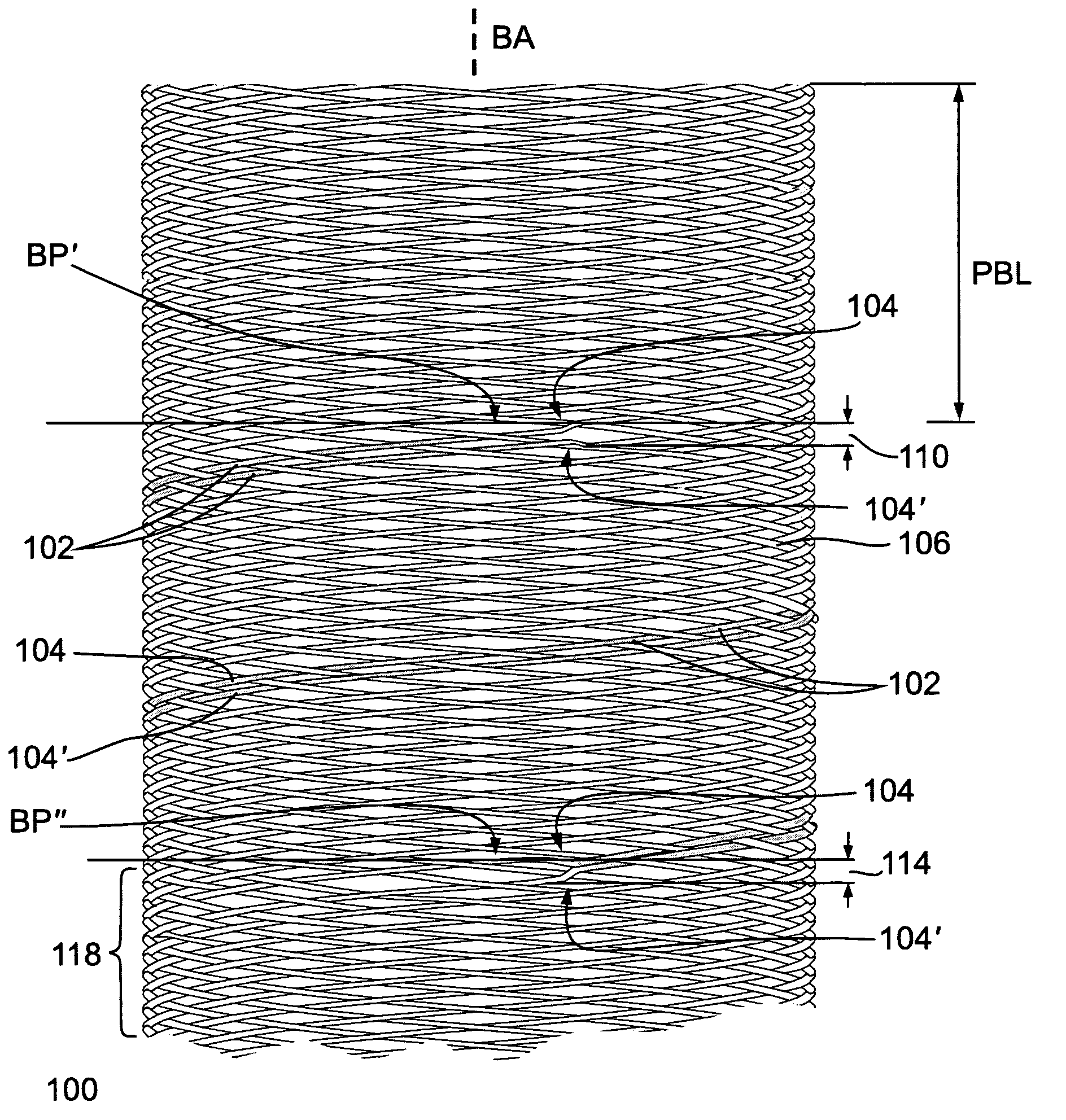
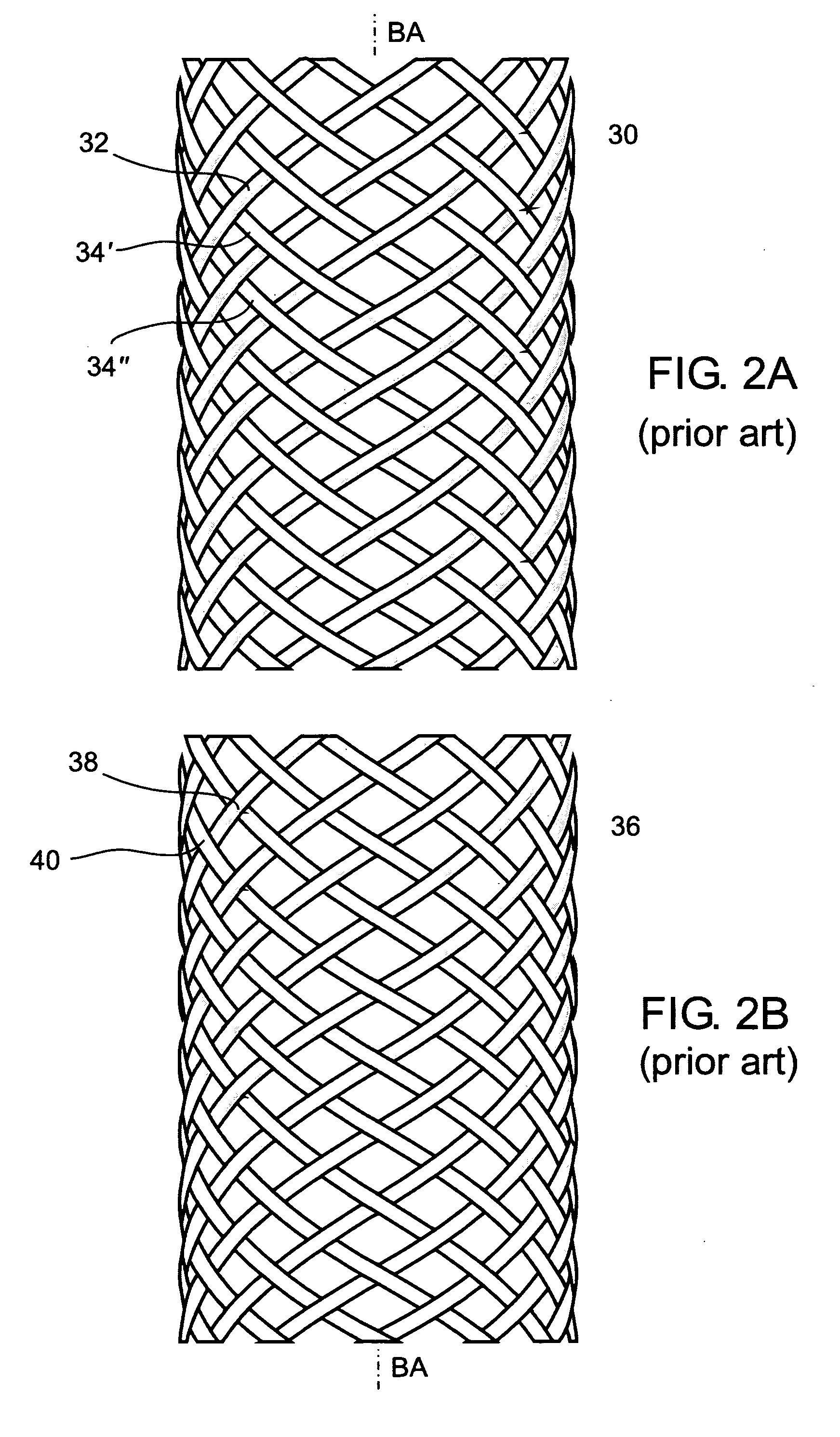
A braided stent having an integral retrieval and / or repositioning loop includes a plurality of wires having first and second ends interbraided in a braided pattern to form a tubular stent having opposed atraumatic first and second open ends with each open end having a circumference; wherein said first and second wires ends are disposed at said second stent open end and said wires are looped at said second stent open end so that none of the first or second wires ends are exposed at the circumference of second stent open end; wherein at least of two of said wires are formed into a repositioning and / or retrieval loop having an elongated portion circumferentially disposed at said first opposed open end; and wherein said reposition and / or retrieval loop comprises two sections which run adjacent to each other prior to crossing to permit grabbing of both sections simultaneously by a practitioner.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Expandable transluminal sheath
ActiveUS20060052750A1Reduce manufacturing costMinimize abrasion and damageGuide needlesStentsStone removalBiomedical engineering
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration and expanded using a radial dilatation device. In an exemplary application, the sheath is utilized to provide access for a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure such as ureteroscopy or stone removal.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Atraumatic stent with reduced deployment force, method for making the same and method and apparatus for deploying and positioning the stent
An implantable stent includes a plurality of elongate wires braided to form a hollow tubular structure having a tubular wall to define an interior surface and an exterior surface and having opposed open first and second ends, wherein the opposed open first and second ends are atraumatic ends The atraumatic ends of the stent are desirably free of any loose wire ends. The wires include composite wires to enhance visibility of the wires to provide improved external imaging of the wires in the body. The elongate composite wires of the stent may be metallic wires having an outer metallic portion including a first metal, such as nitinol, and an inner metallic core portion including a second metal, which is a radiopaque material, such as gold, barium sulfate, ferritic particles, platinum, platinum-tungsten, palladium, platinum-iridium, rhodium, tantalum or combinations thereof.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Stent matrix
InactiveUS20030144725A1Increase anchoring forceAmeliorate degree of traumaStentsSurgeryMedicineUnit structure
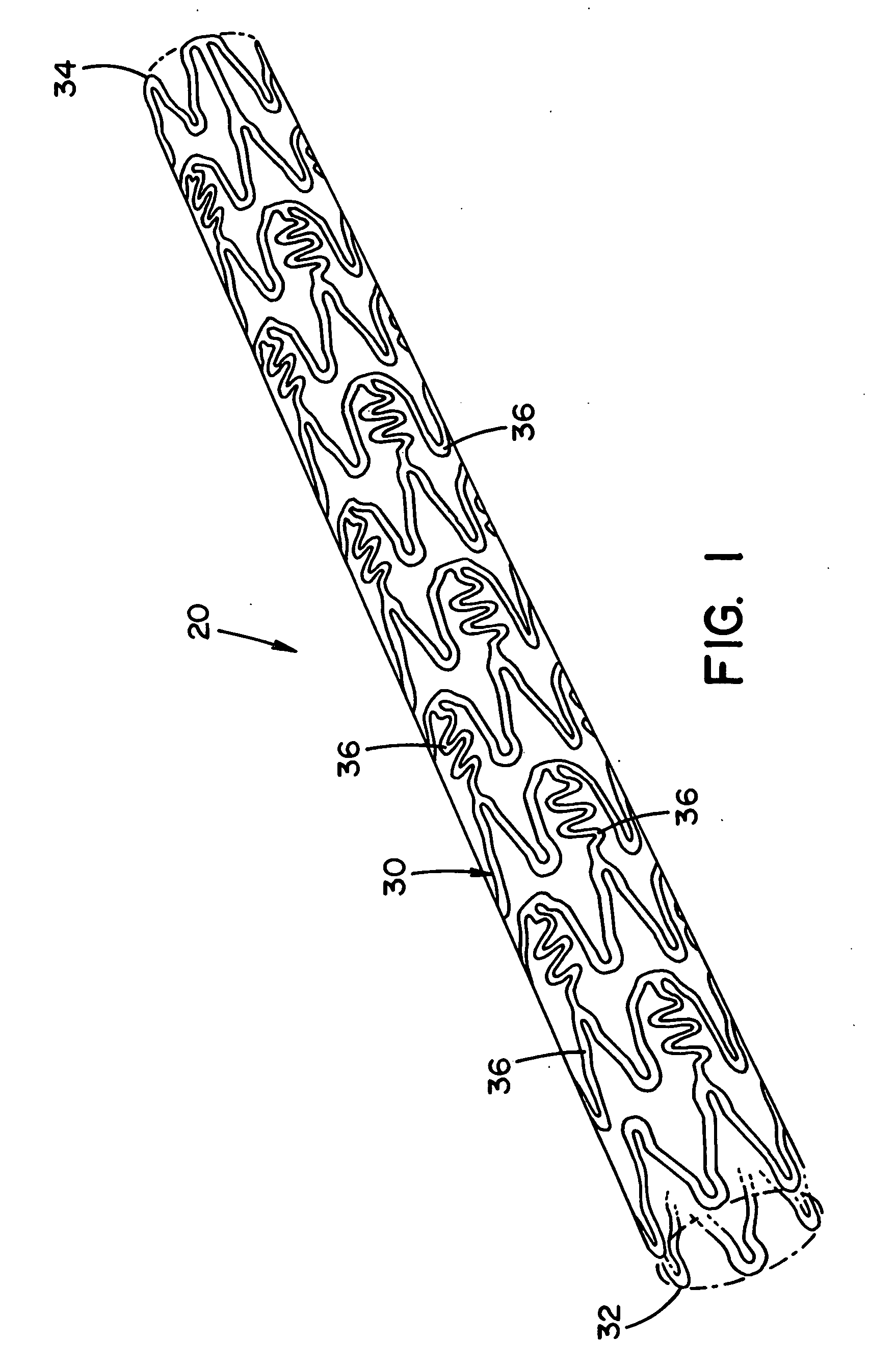
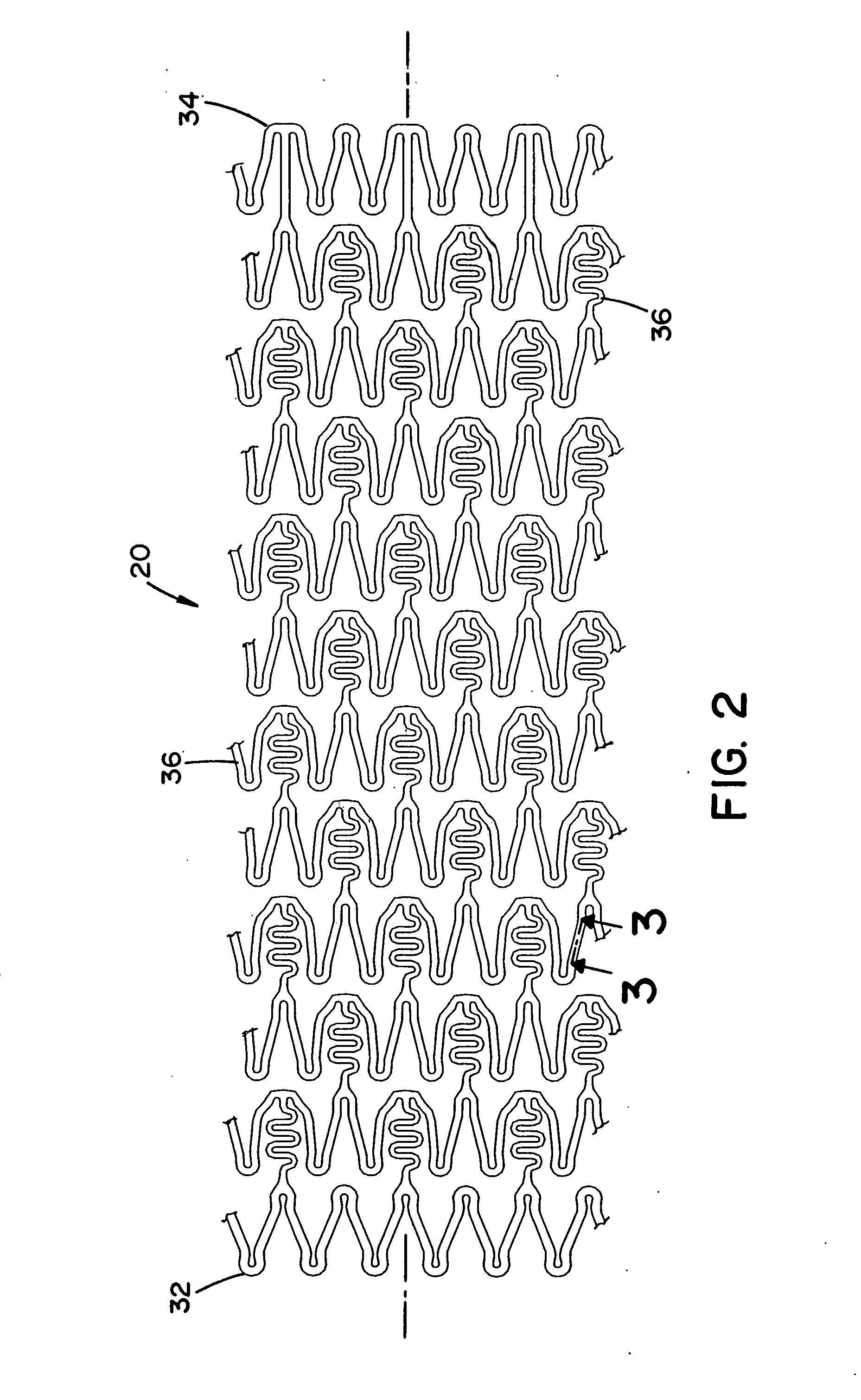
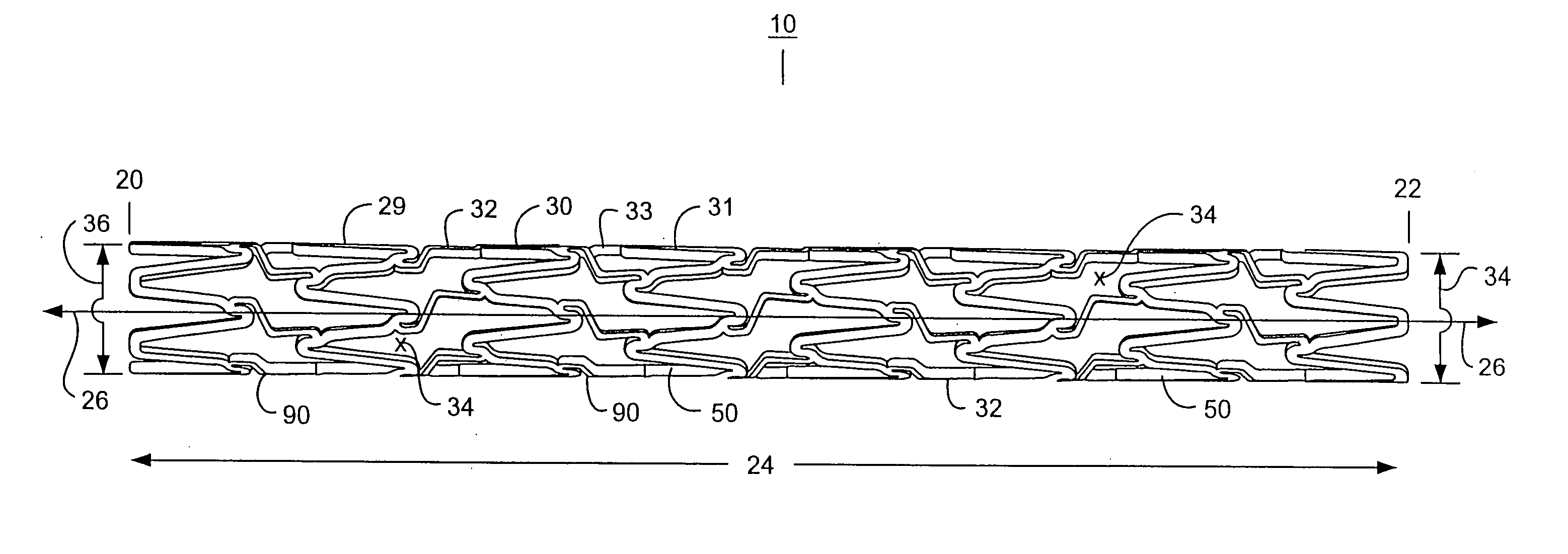
An object of this invention is to provide a radially expandable stent (1) that holds a passageway enlarged by placing the stent (1) into a lumen. The stent (1) comprises a cylindrical frame formed by a plurality of unit structures (11, 12, . . . 16, . . . ); said unit structures (11, 12, . . . 16, . . . ) formed into a closed zig-zag configuration including an endless series of straight sections (111) and joined by bends (112), and arranged face to face into a shape of multistage; connecting members (31, 33, 35, 37 . . . ), which connect said unit structures (11, 12, . . . 16, . . . ); and a mesh (91), which is wrapped around an outside of said frame.
Owner:ANGIOMED GMBH & CO MEDIZINTECHNIK KG
Implantable and lumen-supporting stents and related methods of manufacture and use
InactiveUS20090105809A1Improve expansion propertiesImprove featuresStentsBlood vesselsVisibilityLateral bending
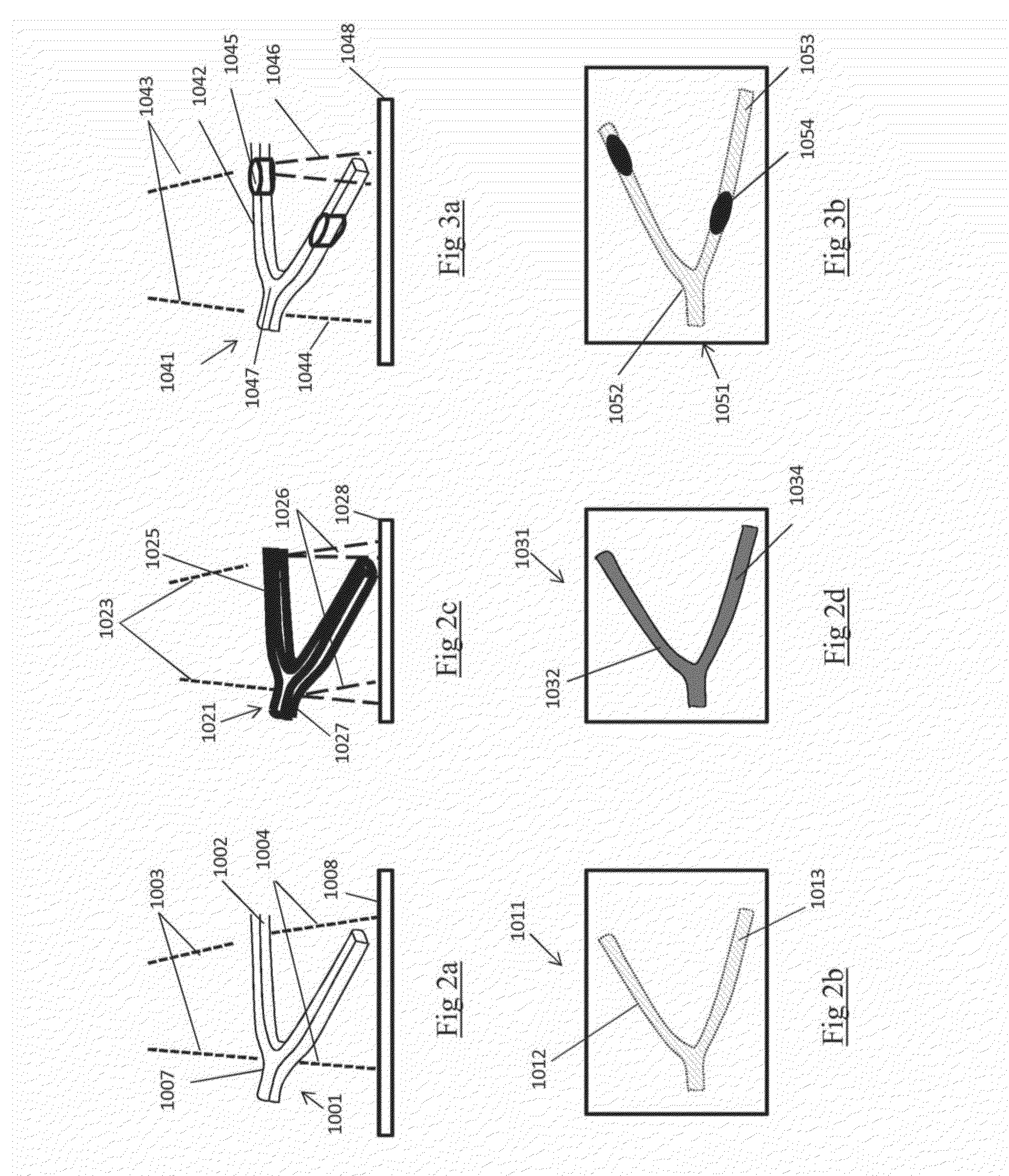
An implantable stent includes multiple circumferential segments that surround a bore and are connected in series along a length to form a tubular wall. Multiple adjacent alternating opposite facing crowns arranged along each segment's circumference are bridged by struts. The struts include a series of staggered arcuate edges with limited flats to provide a limited region of maximum width between significantly extended reducing diameter tapers at either end where they transition into the crowns. Connections between adjacent segments are wider and stiffer than the struts and strut-crown transitions in the segments. The crowns include inner and outer radii with off-set centers along a common axis to provide medial crown peaks along the axis that are wider than the narrowed crown shoulders on either side of the axis and from which the tapered struts extend. Material strain and flexure along the stent during lateral bending is distributed mainly within the segments, e.g. along the struts or crowns, versus at the connections between segments. Material strain and deformation during radial expansion is principally concentrated at the crown shoulders and tapered transition region with the struts. Particular closed-open-closed arrangements along the stent length are disclosed, though with fewer stent connections in the relatively “closed” end-portions along the stent than are provided by other typically “open” cell stents in prior use. Enhanced combinations of performance characteristics are provided regarding visibility, trackability, expansion characteristics, fatigue failures, coating integrity, and local drug delivery from the stent.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
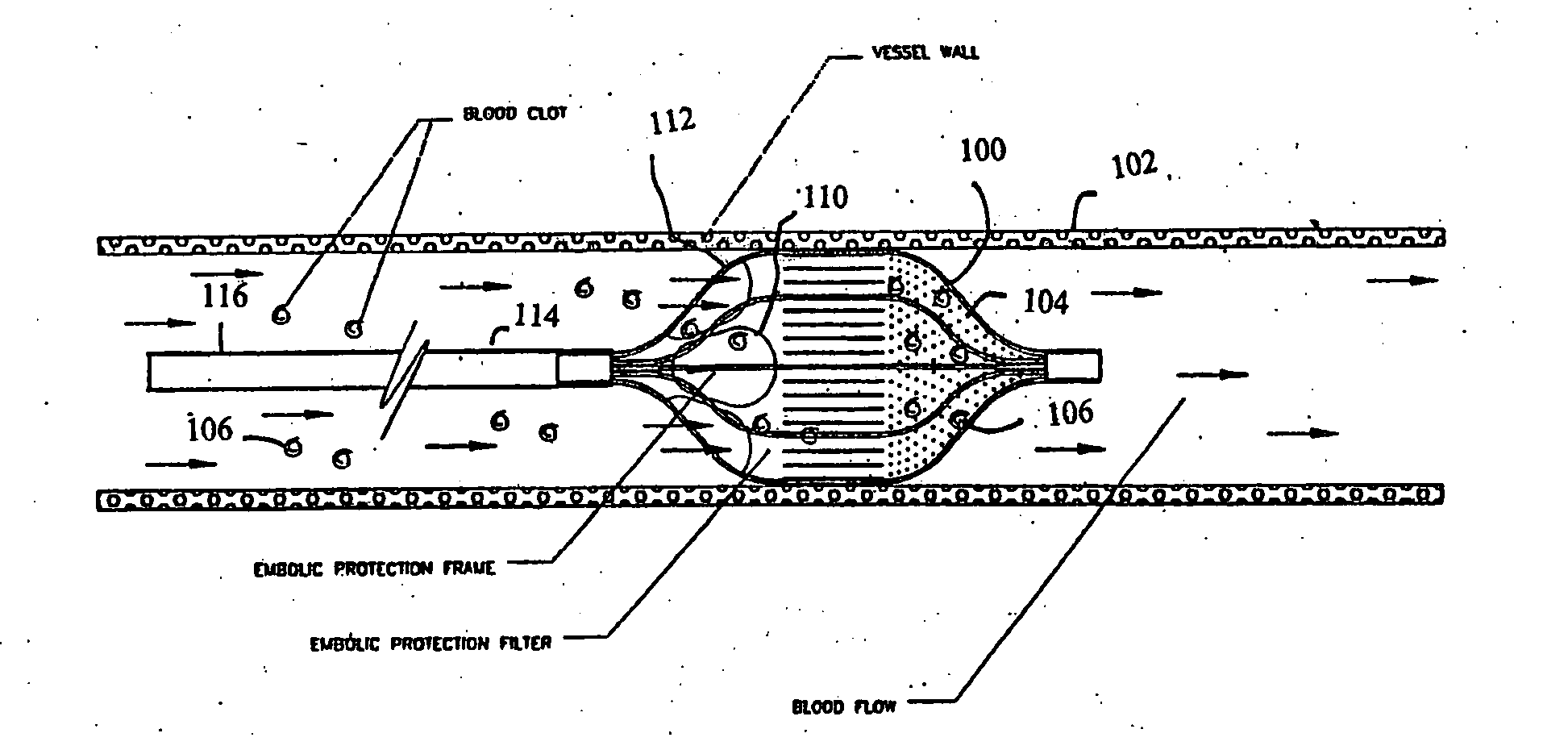
Temporary device for capturing embolic material
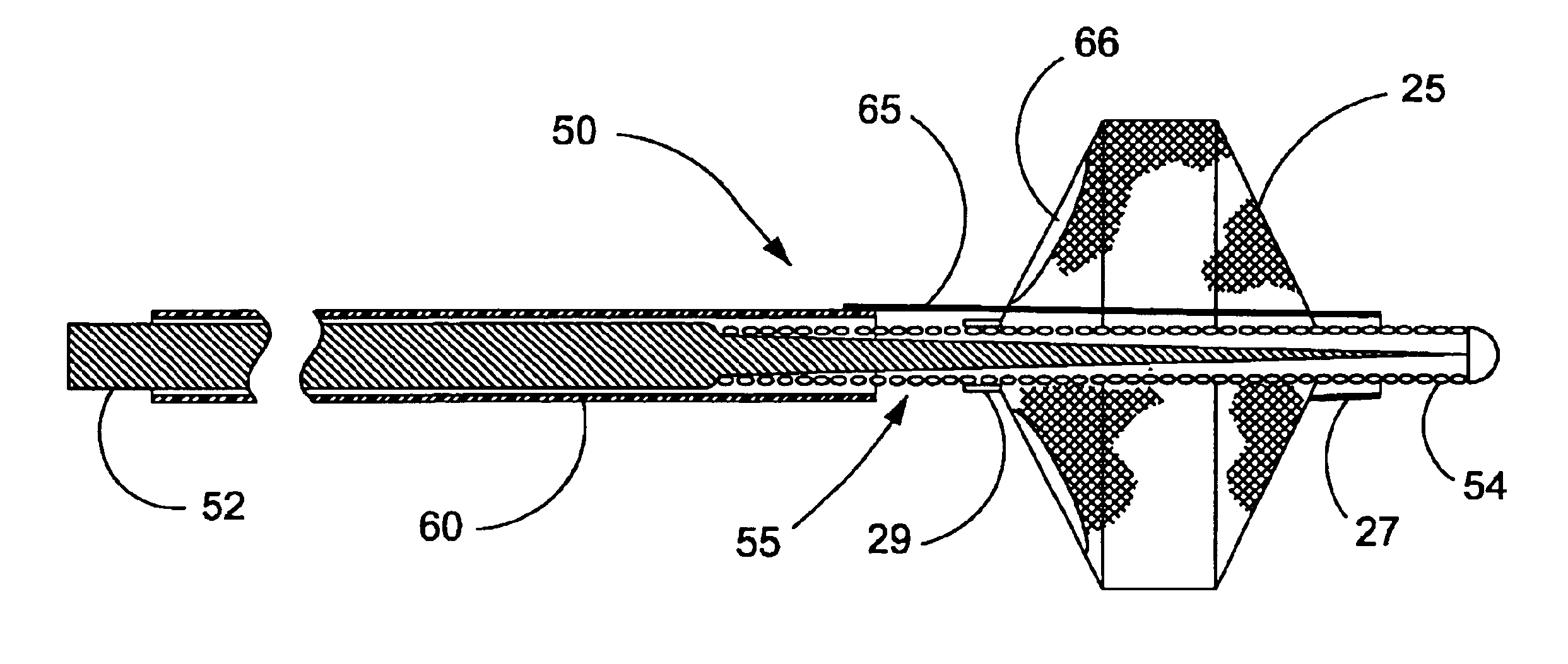
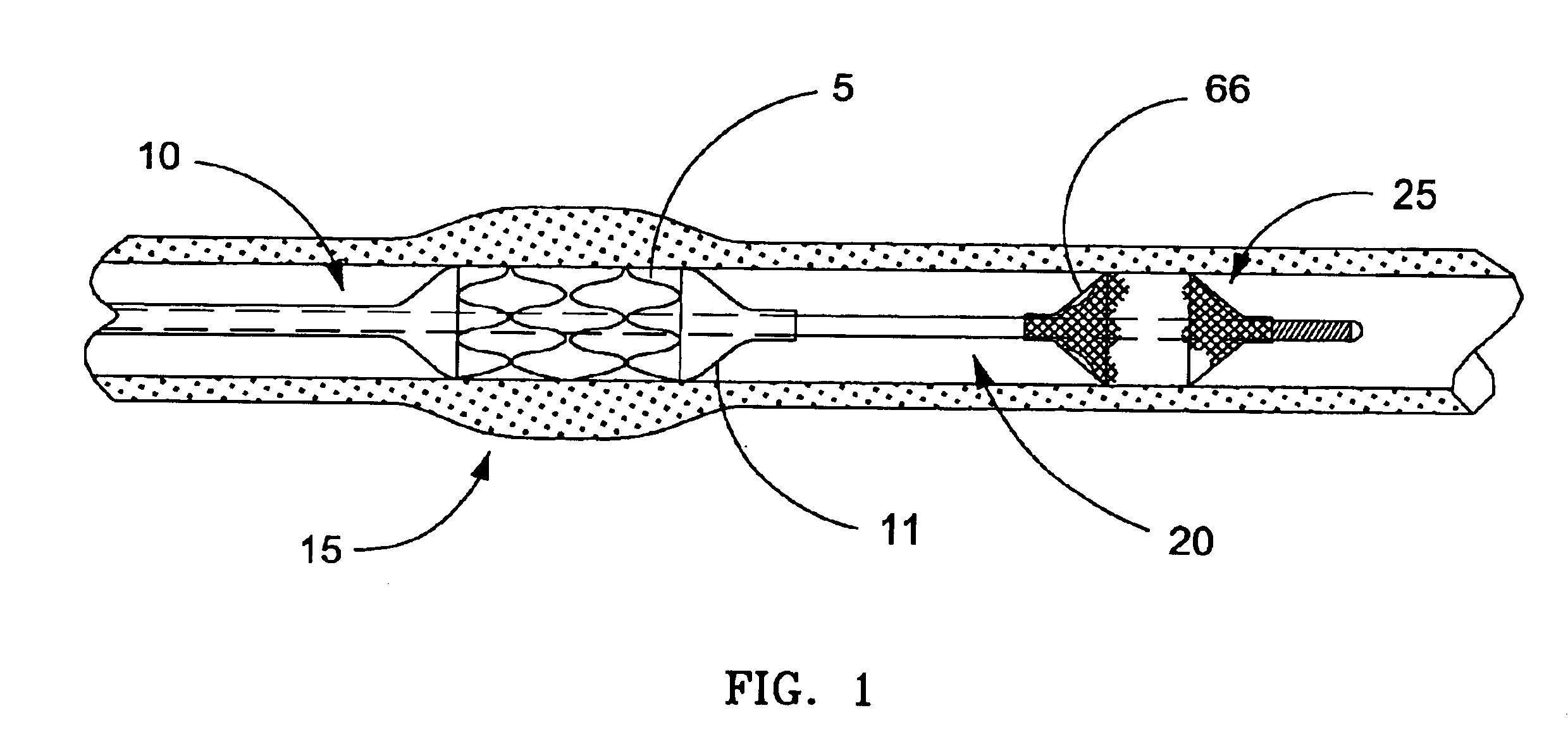
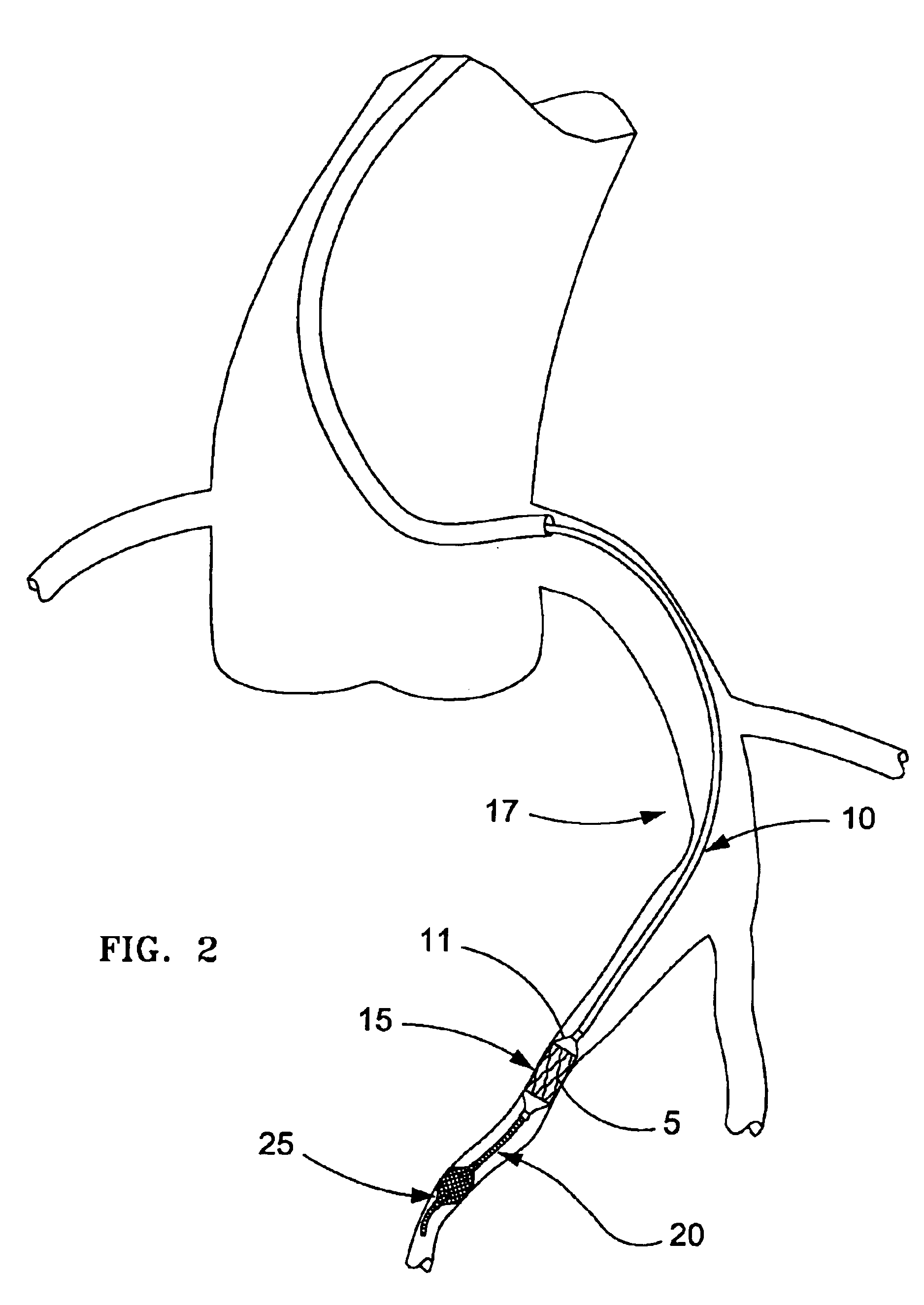
InactiveUS7044958B2Improve radiopacityUndiminished physical performanceSurgeryDilatorsRelative displacementPercutaneous angioplasty
The present invention is a temporary device for capturing and removing embolic material during interventional procedures, such as angioplasty or stent deployment. A self-closing, tubular capture element, which may be either a filter or an occluder, is mounted near the distal end of a guidewire. The guidewire is capable of guiding a therapeutic catheter. Relative displacement of the capture element ends causes transformation of the capture element between a closed configuration and a deployed configuration that spans the vessel to be treated. A latch fixed to the guidewire temporarily retains the capture element in the deployed configuration. A first hollow rod slides over the guidewire to deploy the capture element and engage the capture element proximal end with the latch. A second hollow rod slides over the guidewire to release the latch and close the capture element.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Devices and methods for removal of acute blockages from blood vessels
ActiveUS20160015402A1Maximize visibilityArea maximizationCannulasDiagnosticsBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
Owner:NEURAVI
Bioabsorable medical devices
InactiveUS20060198869A1Facilitate deploymentImprove physical propertiesStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsYttriumMagnesium
Owner:ICON MEDICAL CORP
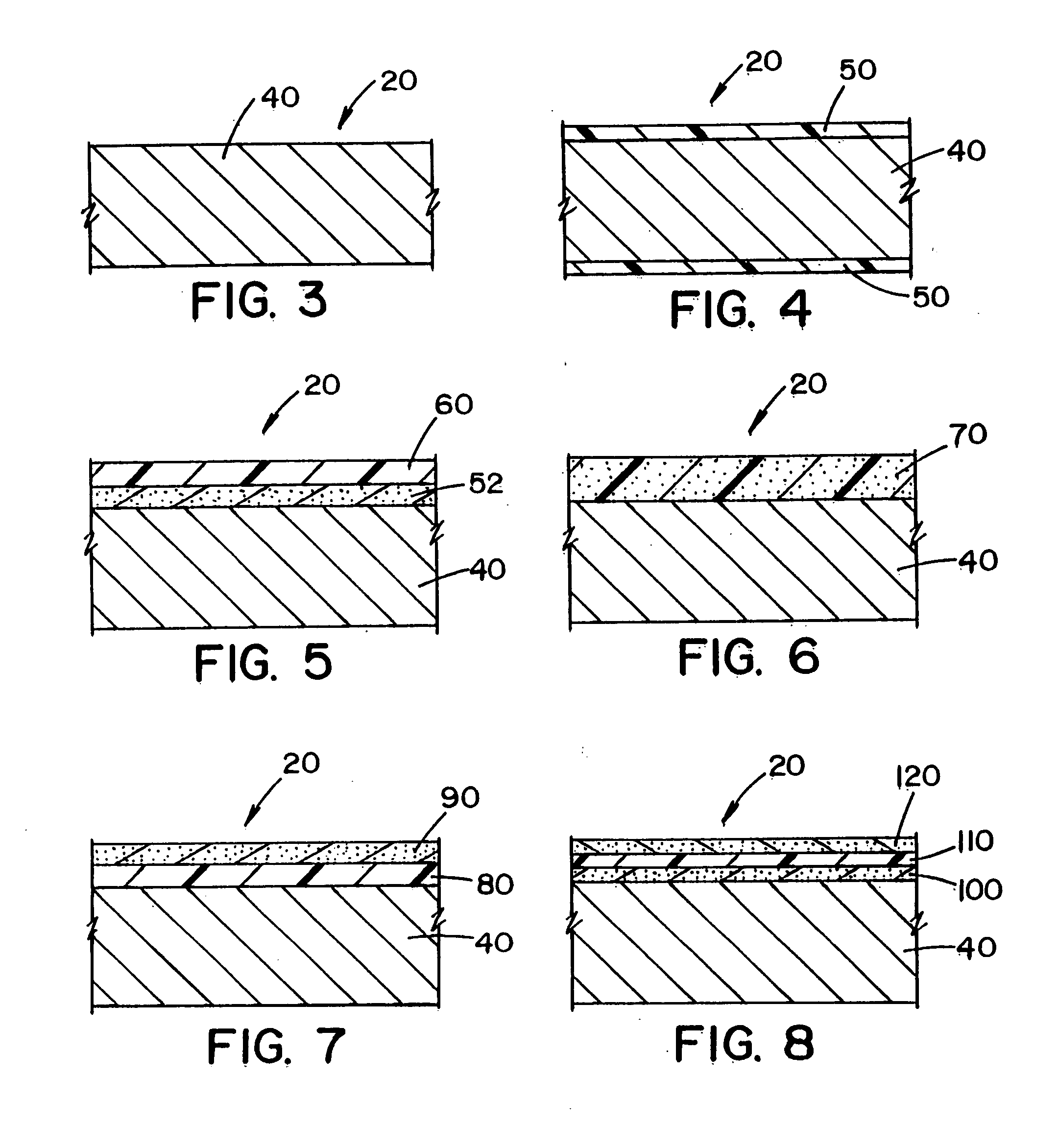
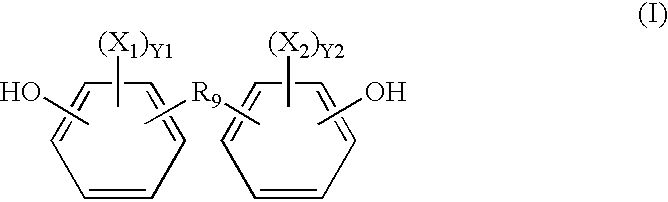
Radio-opaque polymeric biomaterials
InactiveUS6852308B2Improve radiopacityQuality improvementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic chemistryDrug deliveryBiomaterial
Iodinated and / or brominated derivatives of aromatic dihydroxy monomers are prepared and polymerized to form radio-opaque polymers. The monomers may also be copolymerized with other dihydroxy monomers. The iodinated and brominated aromatic dihydroxy monomers can be employed as radio-opacifying, biocompatible non-toxic additives for other polymeric biomaterials. Radio-opaque medical implants and drug delivery devices for implantation prepared from the polymers of the present invention are also disclosed.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Vasoocclusive coil with enhanced therapeutic strand structure
InactiveUS20050043755A1Improve securityProvide stretch resistanceStentsDilatorsMetallic materialsBiomedical engineering
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Bioabsorbable marker having radiopaque constituents and method of using the same
InactiveUS20060004440A1Improve radiopacityImprove locatabilityStentsCatheterProsthesisBiomedical engineering
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
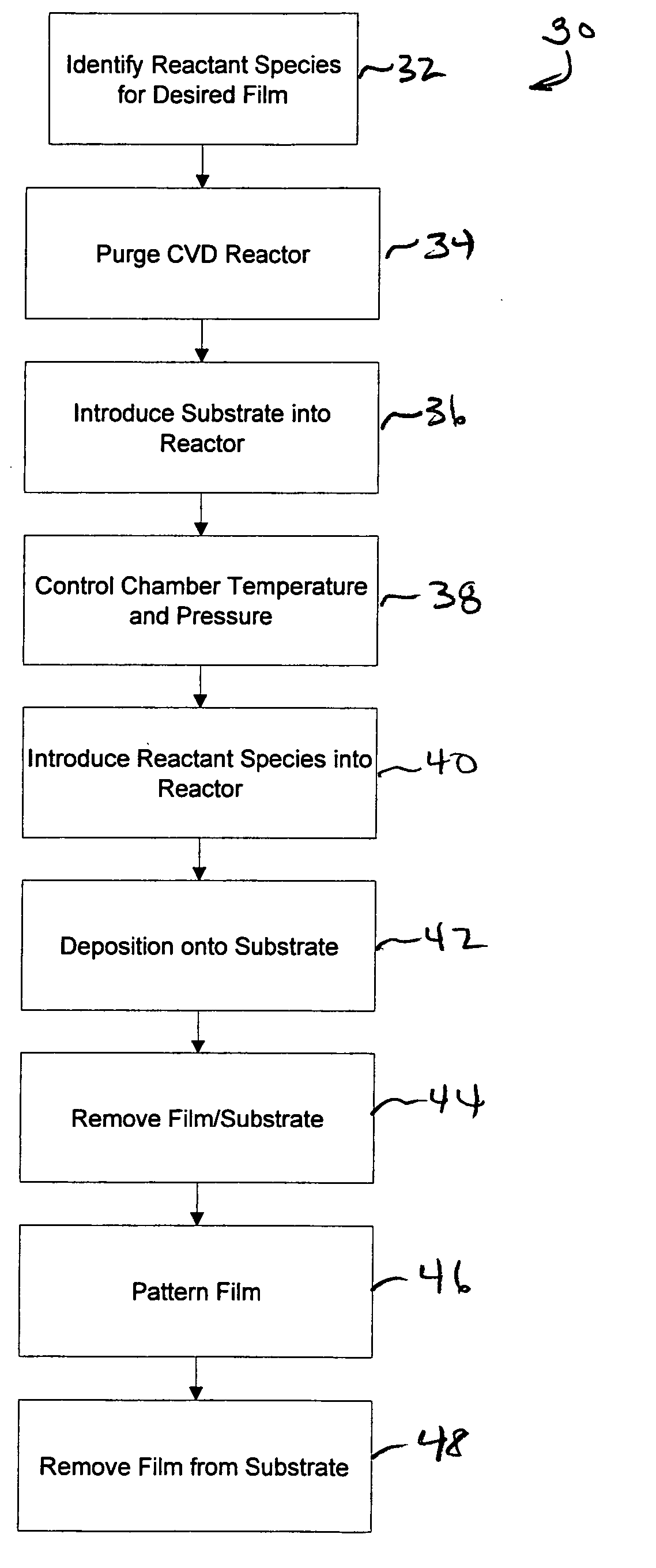
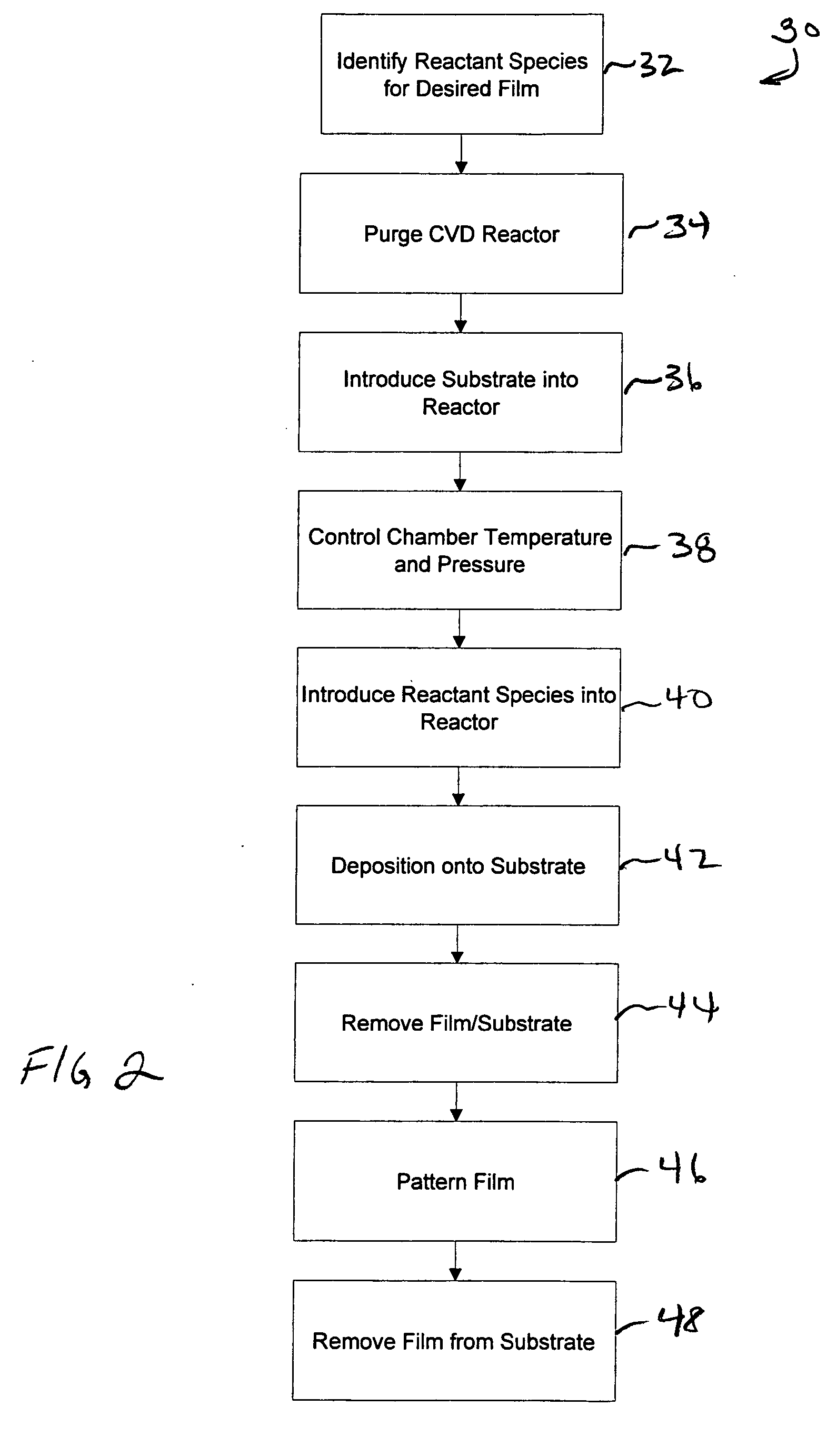
Methods of making shape memory films by chemical vapor deposition and shape memory devices made thereby
A method of depositing shape memory or superelastic thin films by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and medical devices made thereby, including stents, grafts, stent-grafts, stent covers, occlusive and filter membranes and drug-delivery devices. The method entails a thin film is deposited on a substrate surface using a CVD reaction in the production of a film of nickel-titanium shape memory or superelastic alloy. Such nickel-titanium-based shape memory or superelastic alloys may be binary nickel-titanium alloys or may include additional compounds to form ternary, quaternary, or higher level alloys.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Intravascular stent and assembly
InactiveUS20040133271A1Maximum possible flexibility and conformabilityOptimal metal fractionStentsSurgeryVascular lumenIntravascular stent
Various intravascular stents, such as intracoronary stents, include improved expansion and connecting strut designs. Such stents can be both very flexible and fully cover vessel surface inside the vascular lumen, and be well designed for both the delivery phase and the deployed phase of the stent life cycle.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices for retrieving a prosthesis
ActiveUS20110071624A1Reducing pressure necrosisImprove radiopacityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsLeft atrial pressure
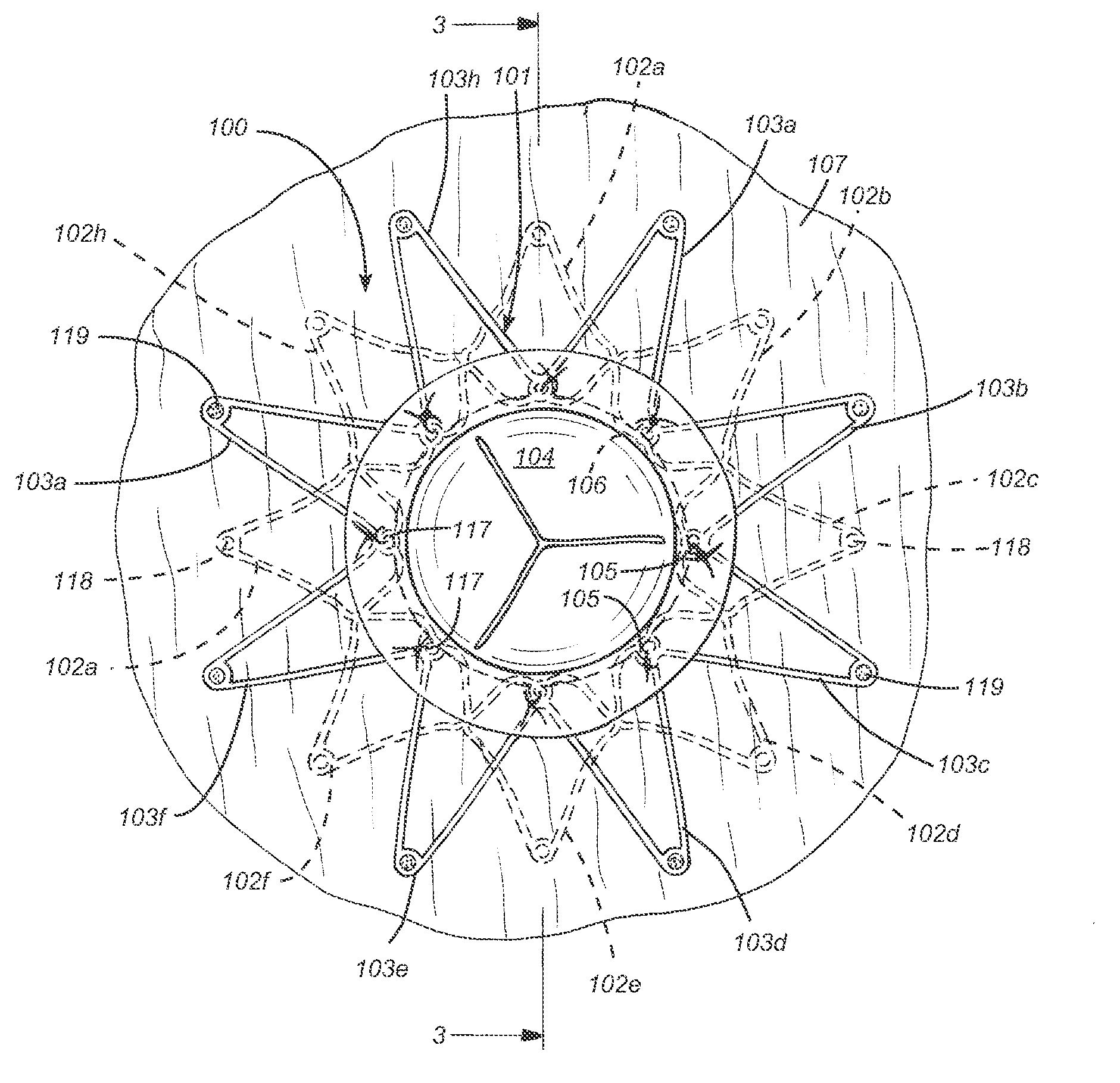
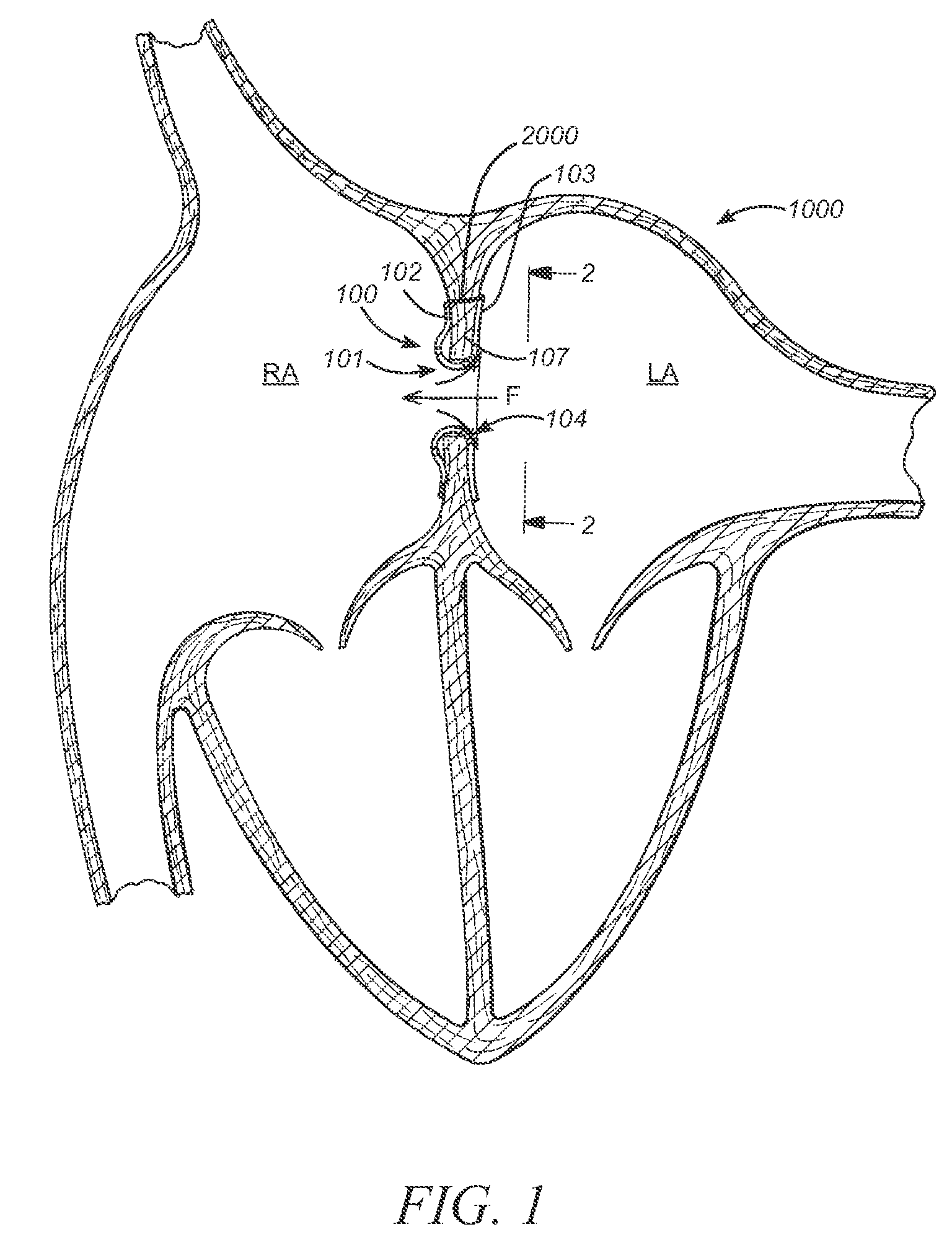
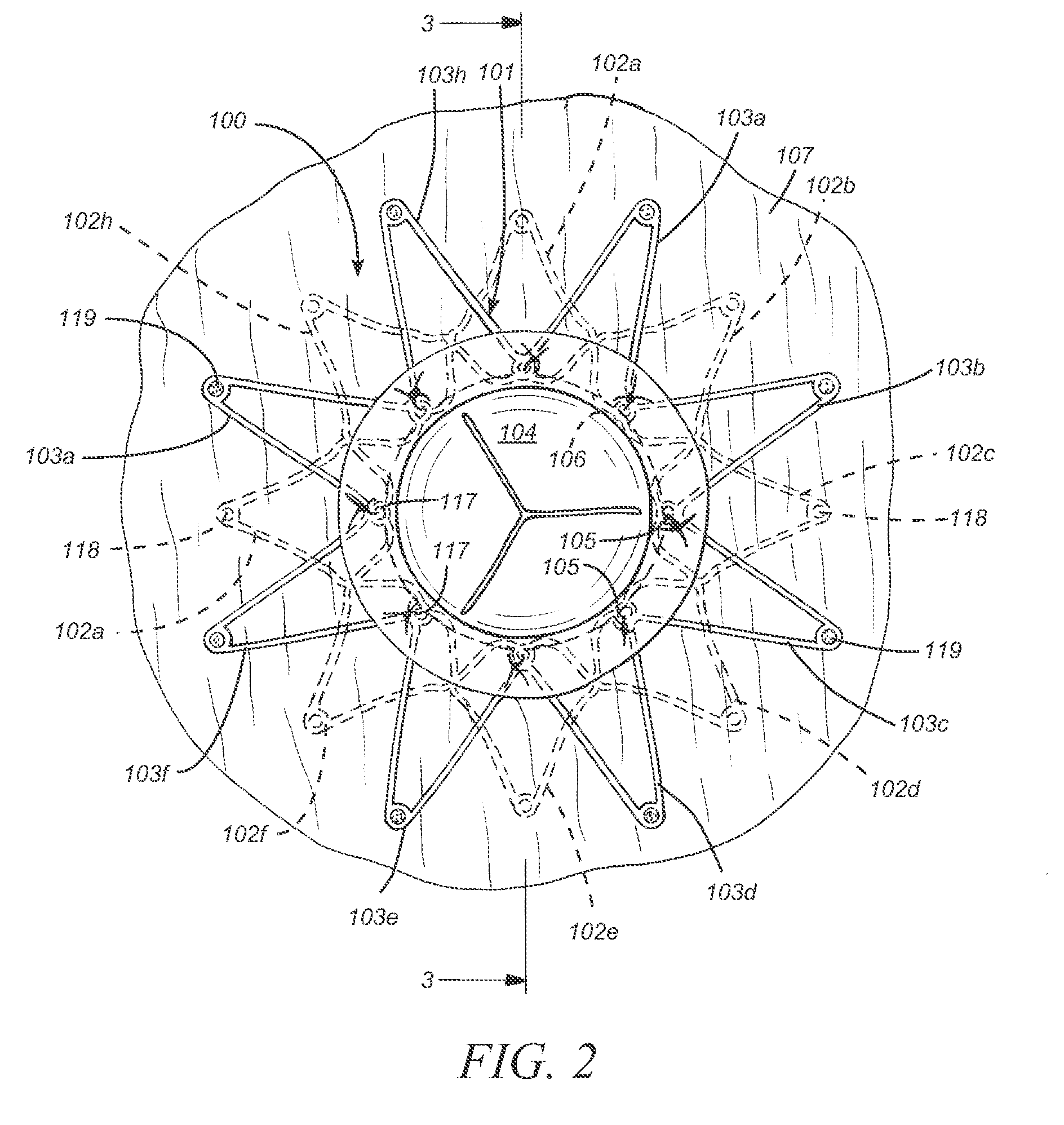
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The disclosure also includes a mounting tool for mounting the prosthesis onto a loading tool, the loading tool useful for loading the prosthesis onto a device for delivering the prosthesis into the patient's heart. Control devices and methods for using these devices are also disclosed. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Striped braided element
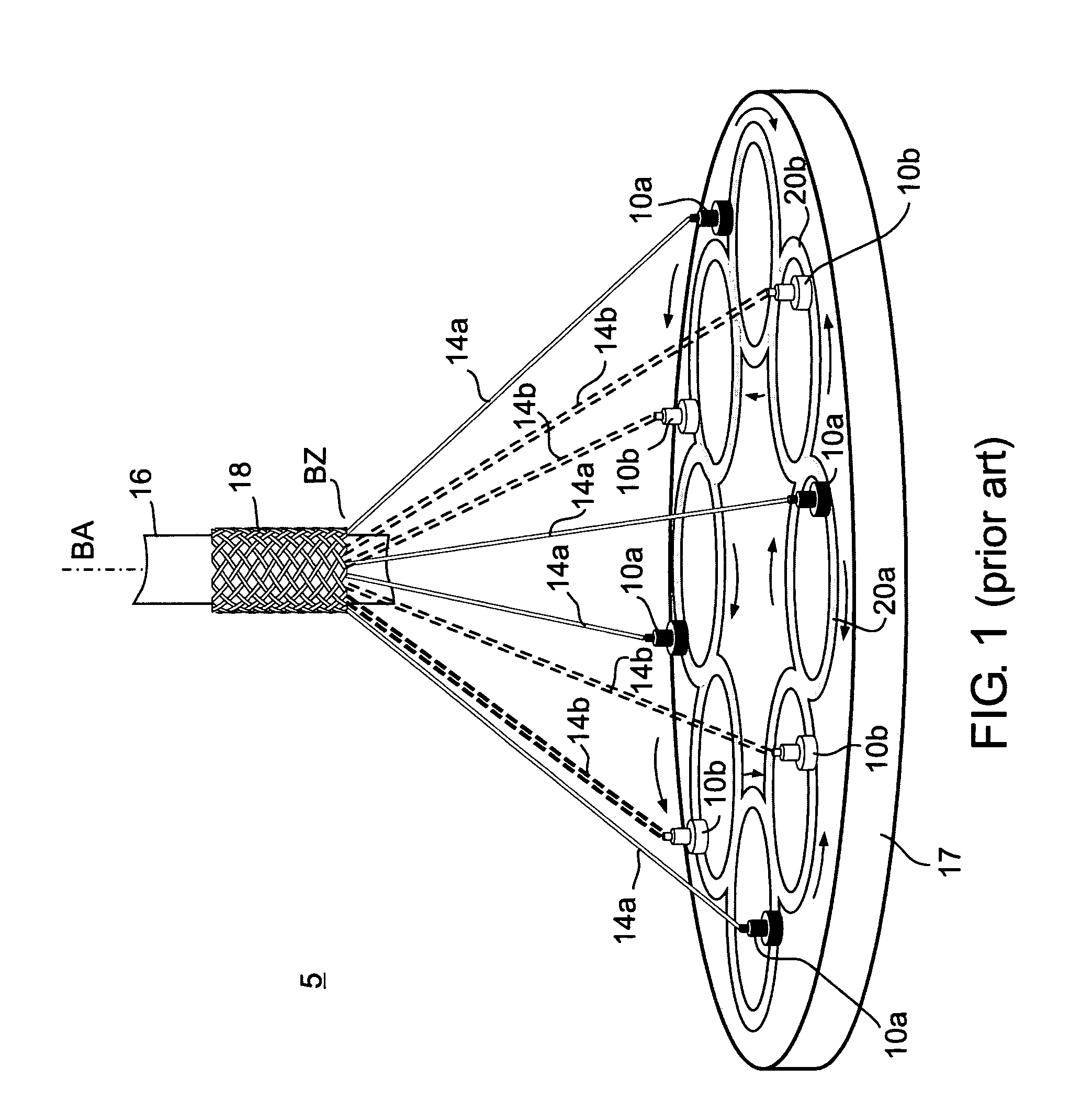
A striped braided element comprising: a first set of members having a common direction of winding, the center axis of said first set of members being axially displaced relative to each other in relation to a common braiding axis; and a second set of members having an opposite direction of winding, the center axis of the second set of members being axially displaced relative to each other in relation to the common braiding axis, the braided element exhibiting a uniform uninterrupted braid pattern and an average uniform distance between the center axis of members having a common direction of winding at a particular circumferential section along the common braiding axis; characterized by having at least one stripe comprising two adjacent members of the same set exhibiting a significantly reduced distance between the center axis of the adjacent members in the particular circumferential section.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Methods for deploying a prosthesis
ActiveUS20110071623A1Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsThrombus
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The disclosure also includes a mounting tool for mounting the prosthesis onto a loading tool, the loading tool useful for loading the prosthesis onto a device for delivering the prosthesis into the patient's heart. Control devices and methods for using these devices are also disclosed. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Radiopaque coatings for polymer substrates
InactiveUS20070178222A1Improve radiopacityImprove adhesionElectric discharge tubesPharmaceutical containersPolymeric surfacePolymer science
Improved radiopaque coatings particularly suitable for polymer substrates are described. A modified ion plasma deposition (IPD) method is used to provide coatings with macroparticle-dense surfaces that have excellent radiopacity. The coatings are particularly adapted to polymer surfaces because of high adherence and resistance to peeling and flaking.
Owner:NANOSURFACE TECH
Expandable transluminal sheath
ActiveUS7892203B2Reduce manufacturing costMinimize abrasion and damageStentsGuide needlesMedicineStone removal
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration and expanded using a radial dilatation device. In an exemplary application, the sheath is utilized to provide access for a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure such as ureteroscopy or stone removal.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
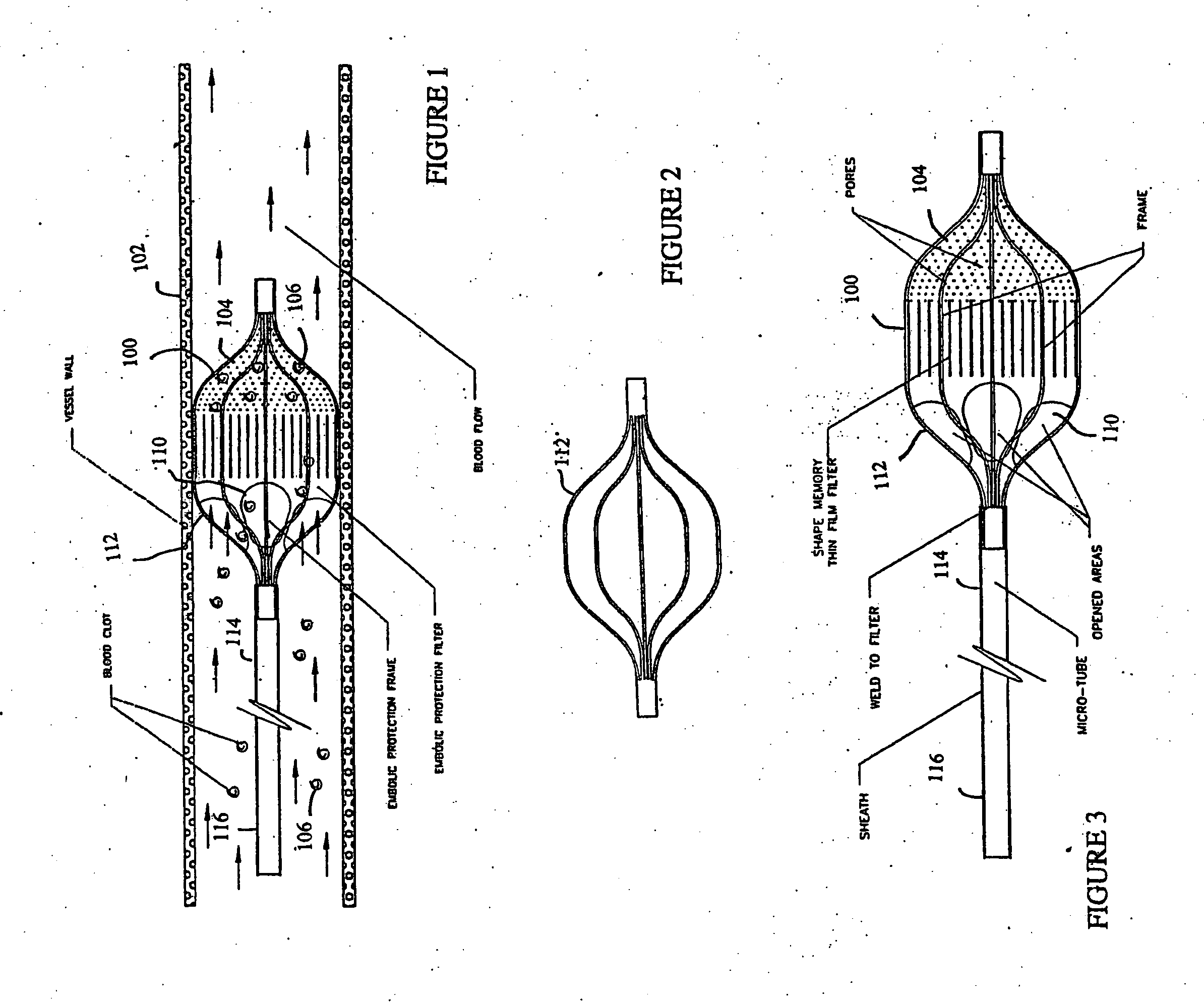
Shape memory thin film embolic protection device with frame
InactiveUS20060100659A1Reducing macroReducing micro-embolizationSurgeryDilatorsContinuous perfusionVascular filter
A removable vascular filter system for capture and retrieval of emboli while allowing continuous perfusion of blood. This system is useful for any percutaneous angioplasty, stenting, thrombolysis or tissue ablation procedure. The system may minimize the incidence of stroke, myocardial infarction or other clinical complications that may be associated with these procedures.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC +1
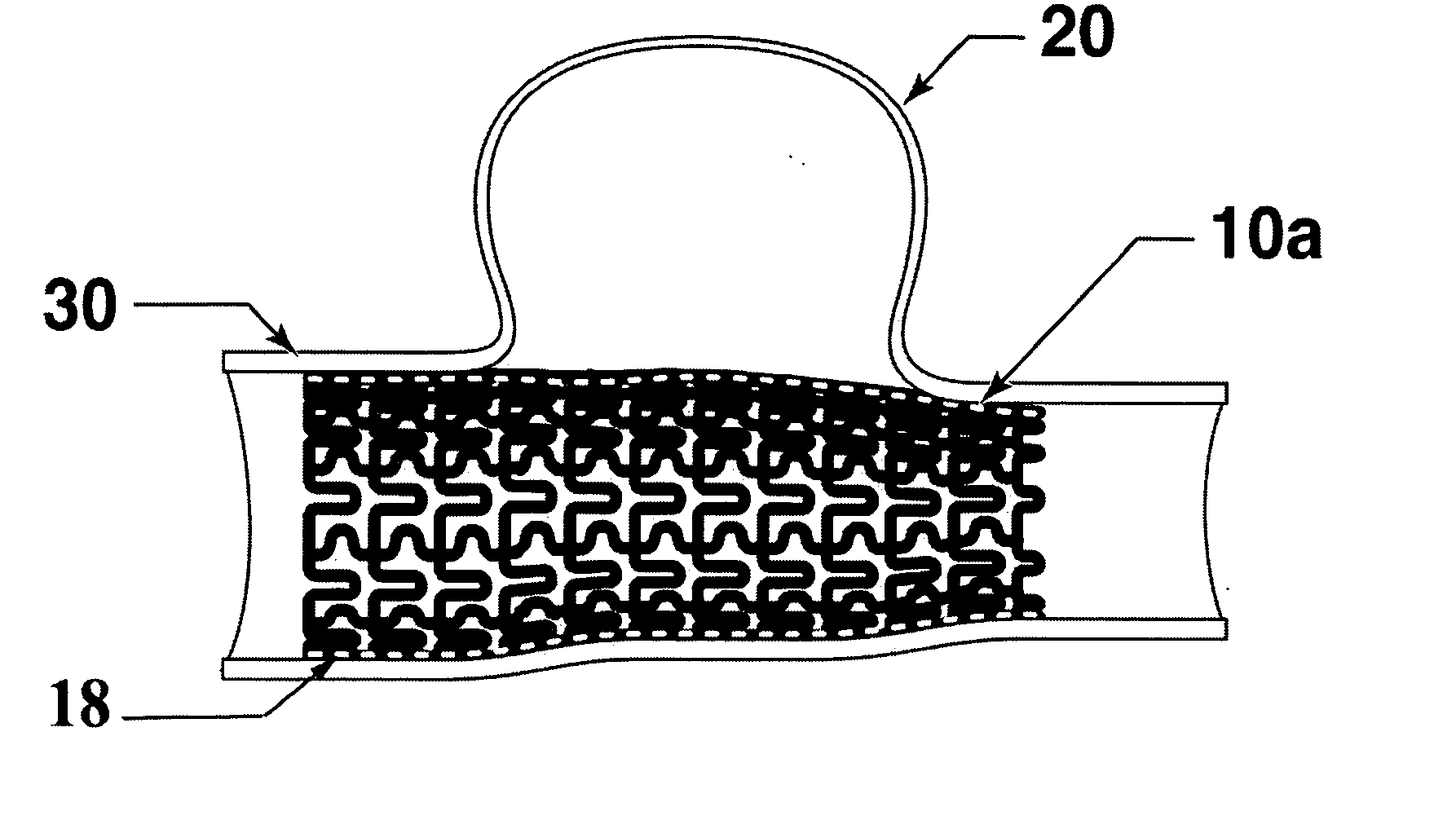
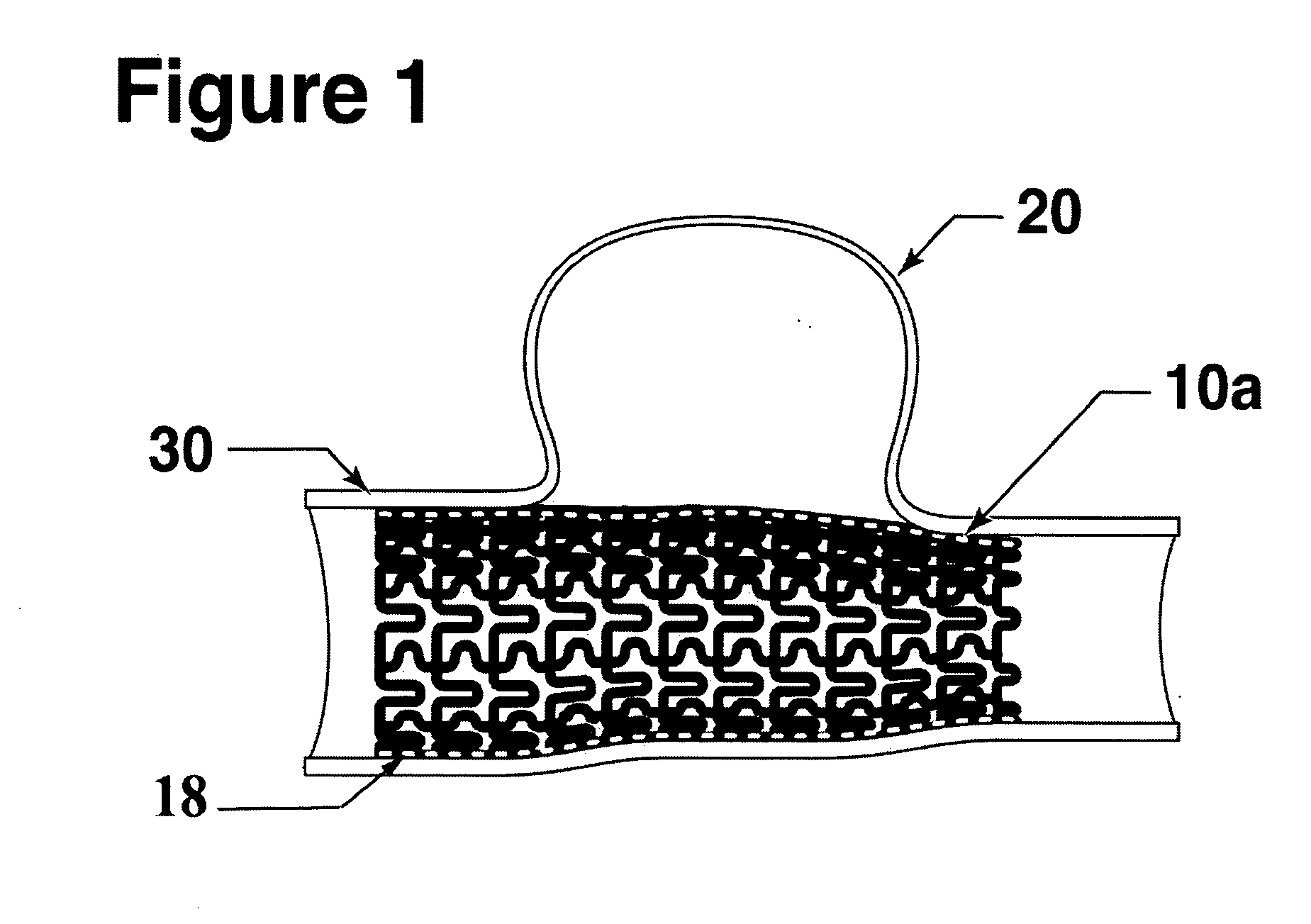
Intravascular device with improved radiopacity
A stent having marker tabs formed from a micro-alloyed combination of materials provides for more precise placement and post-procedural visualization in a vessel, by increasing the radiopacity of the stent under X-ray fluoroscopy. A unique micro-alloying process is utilized to form the tabs, comprising a first alloy and a second alloy, wherein one of these alloys is radiopaque. This substantially eliminates the possibility of galvanic action between the tab and the stent. This process is also applicable to other medical devices.
Owner:DUERIG THOMAS +3
Devices and methods for removal of acute blockages from blood vessels
ActiveUS20140371780A1Overcome limitationsMaximize visibilityDiagnosticsSurgeryEngineeringMechanical engineering
A clot retrieval device may include an elongate shaft and an expandable section. The expandable section may include a framework of interconnected strut elements. The connection region between adjacent strut elements may include crown elements. Additionally, the framework may be formed from a substrate material and at least a portion of a plurality of said strut elements may be coated with a coating material. Further, at least a portion of a plurality of said crown elements may not be coated with said coating material.
Owner:NEURAVI
Micro-pleated stent assembly
InactiveUS20060155367A1Effective treatmentMore longitudinal flexibilityStentsBlood vesselsSolid wallInsertion stent
The present invention is directed to a micro-pleated medical device assembly, preferably a micro-pleated stent assembly, comprising a tube micro-pleated to a delivery diameter suitable for intraluminal delivery. The micro-pleated stent assembly of the present invention is designed to have a substantially solid wall, and is thus particularly suited for the treatment of neurovascular aneurysms, having the ability to block the neck of an aneurysm. Sections of the micro-pleated stent may be selected for expansion to variable diameters in order to optimally fit the configuration of the vessel.
Owner:HINES RICHARD ALLEN
Control devices for deploying a prosthesis
InactiveUS20110295183A1Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsLeft atrial pressure
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The disclosure also includes a mounting tool for mounting the prosthesis onto a loading tool, the loading tool useful for loading the prosthesis onto a device for delivering the prosthesis into the patient's heart. Control devices and methods for using these devices are also disclosed. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Aneurysm buttress arrangement
Owner:NIAGARA GORGE MEDICAL DEVICES
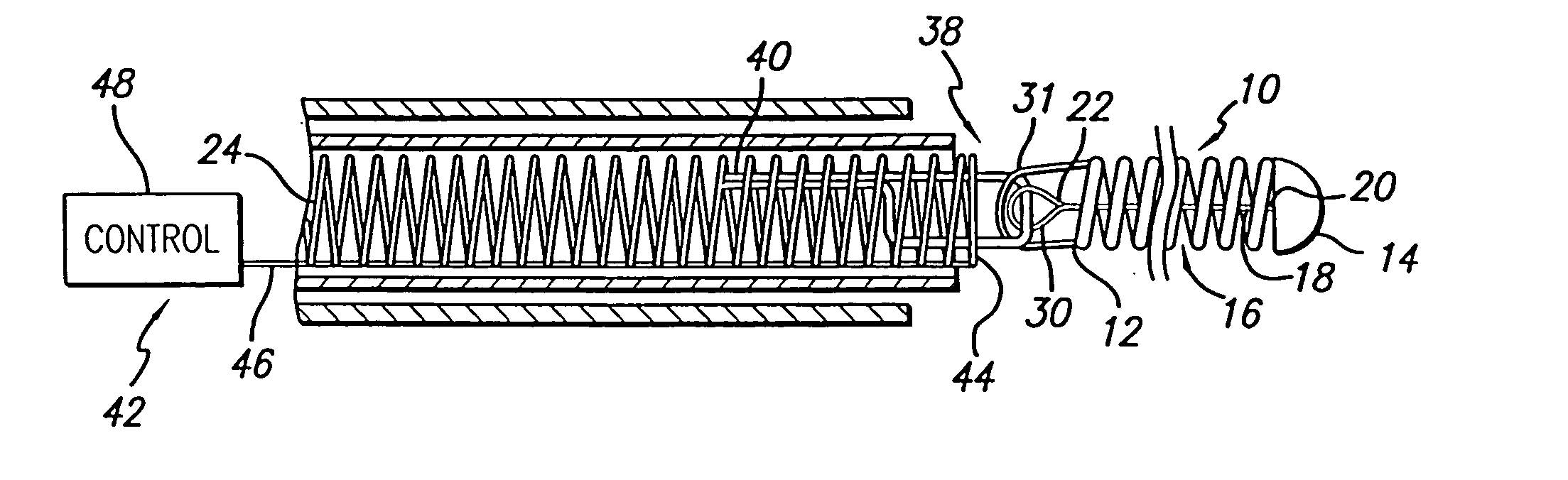
Catheter tip assembled with a spring
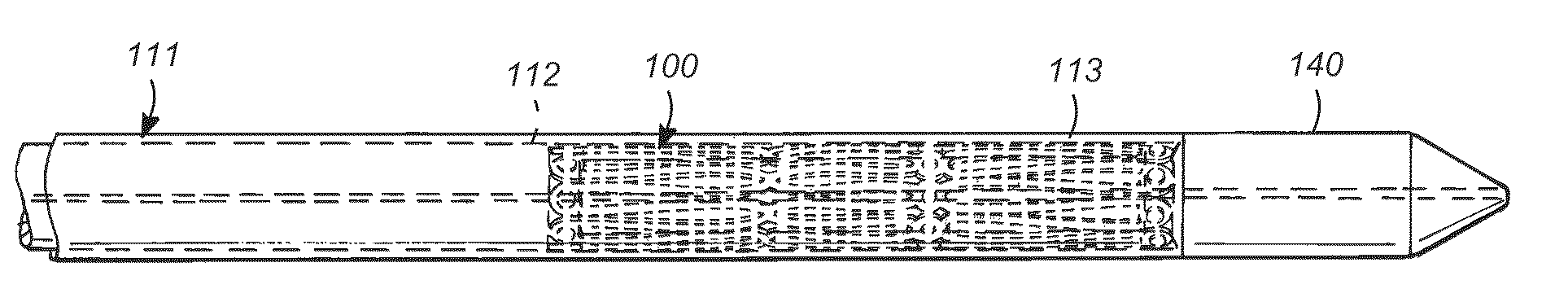
ActiveUS20110196315A1Enhanced deliverability parameterImprove radiopacityBalloon catheterIntravenous devicesCatheterBlood vessel
A catheter tip that provides longitudinal flexibility, pushability and radial rigidity thereby improving deliverability is provided. The catheter tip includes a spring-like element to provide longitudinal flexibility and pushability to the catheter tip. The spring-like element may also provide radial support to the distal edge of the catheter tip. Alternatively, a radially rigid distal end may also be included distal of the spring-like element. The apparatus may be used with any interventional catheter system, but is particularly suitable for use with balloon-expandable stent systems and balloon-angioplasty systems, where flexibility of the catheter tip and minimal flaring of the distal edge of the catheter tip is desirable.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Prosthesis for retrieval and deployment
ActiveUS8740962B2Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsThrombus
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com