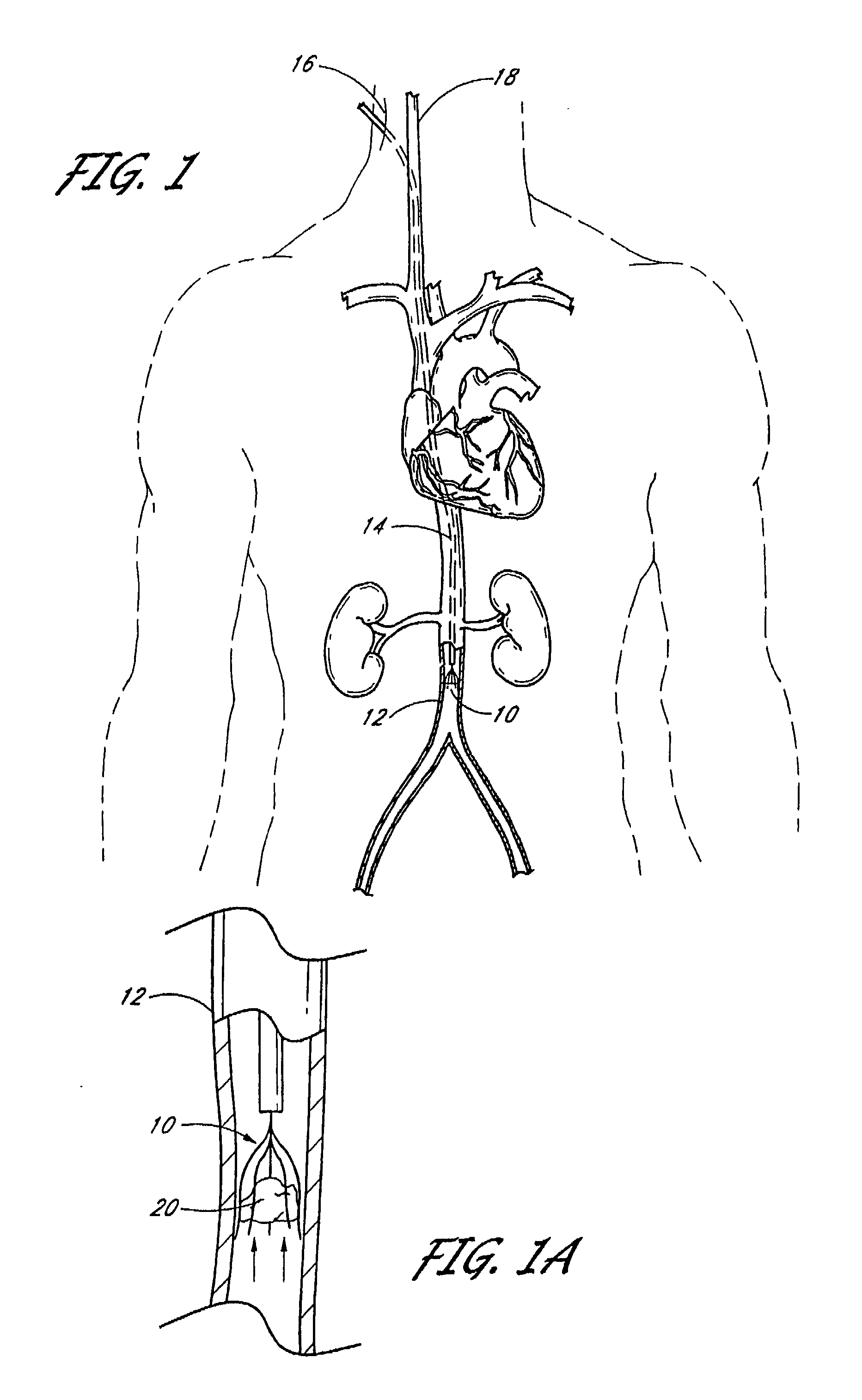Patents
Literature
109 results about "Vascular filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An inferior vena cava filter (IVC filter) is a type of vascular filter, a medical device that is implanted by interventional radiologists or vascular surgeons into the inferior vena cava to presumably prevent life-threatening pulmonary emboli (PEs).
Everted filter device
ActiveUS20050283186A1Effective coverageProvide protectionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesVascular filterThrombus
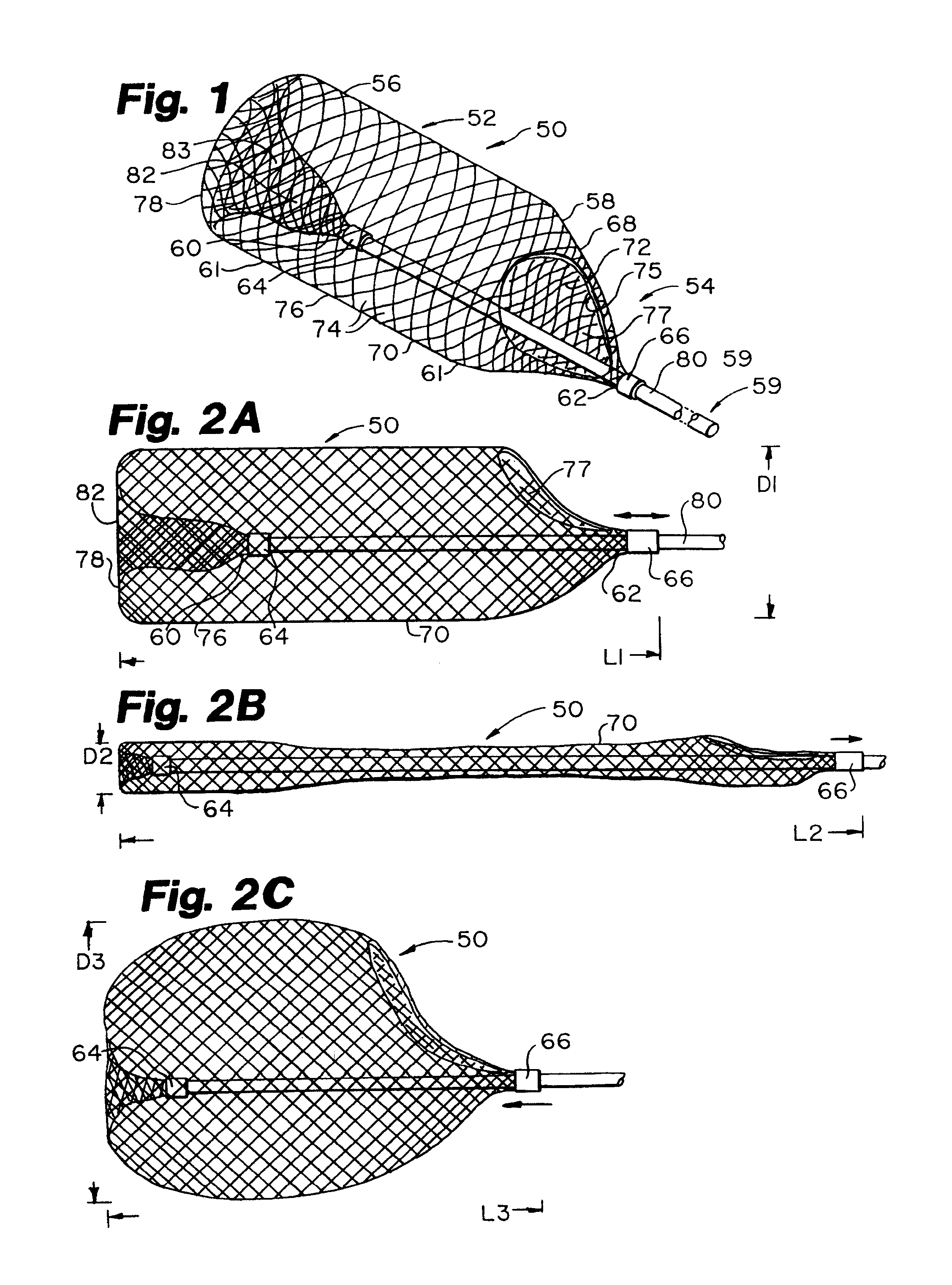
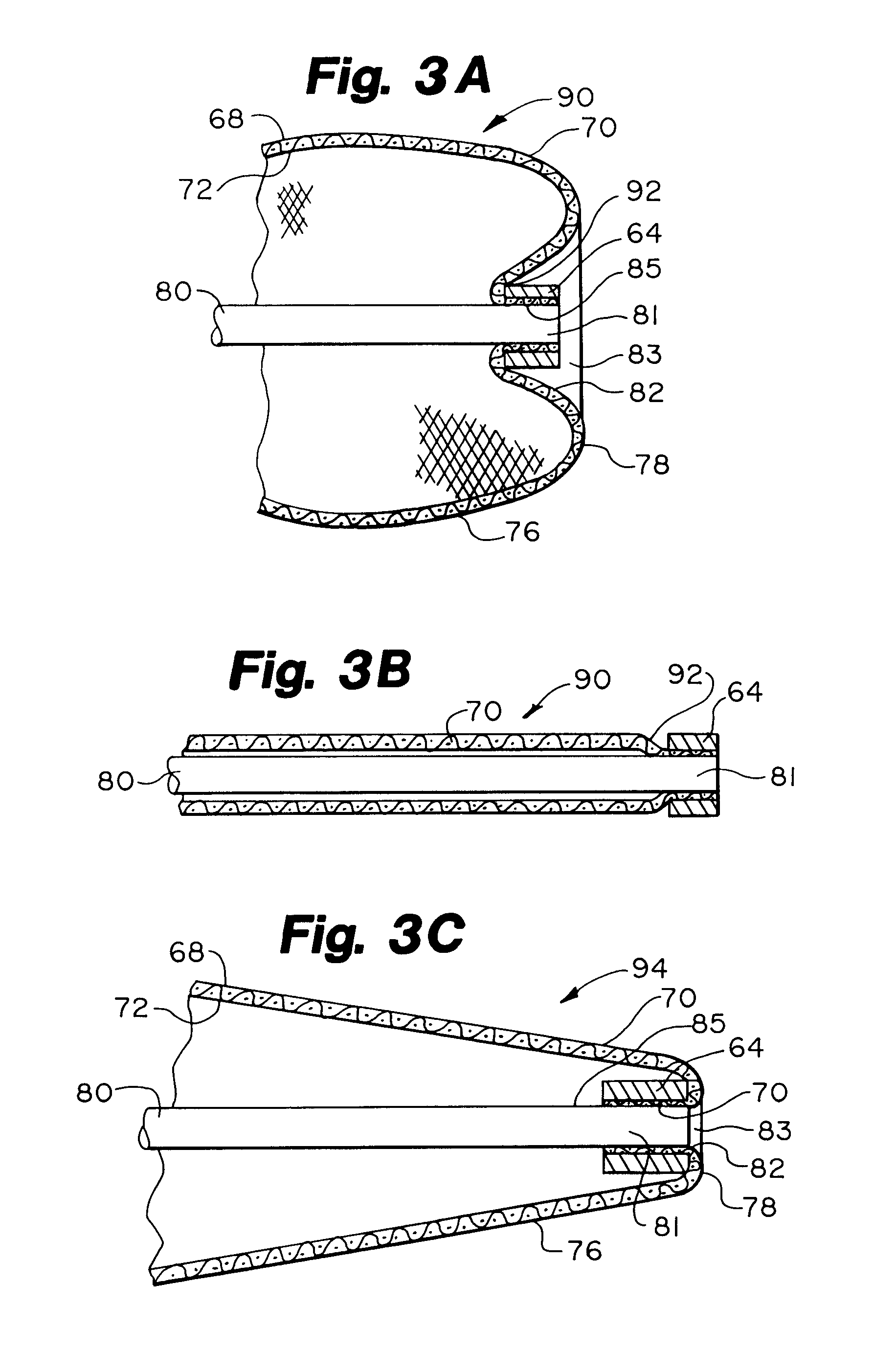
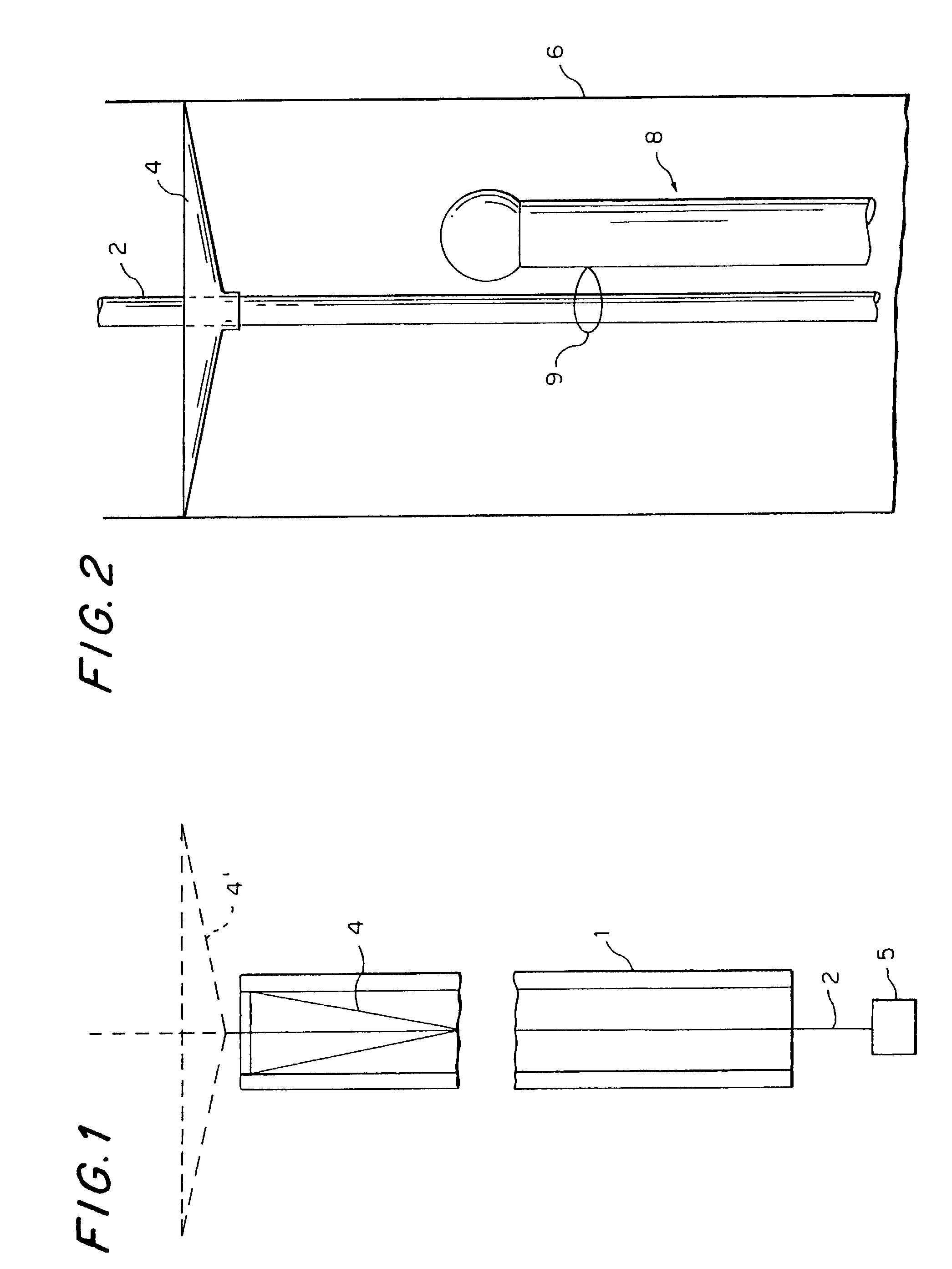
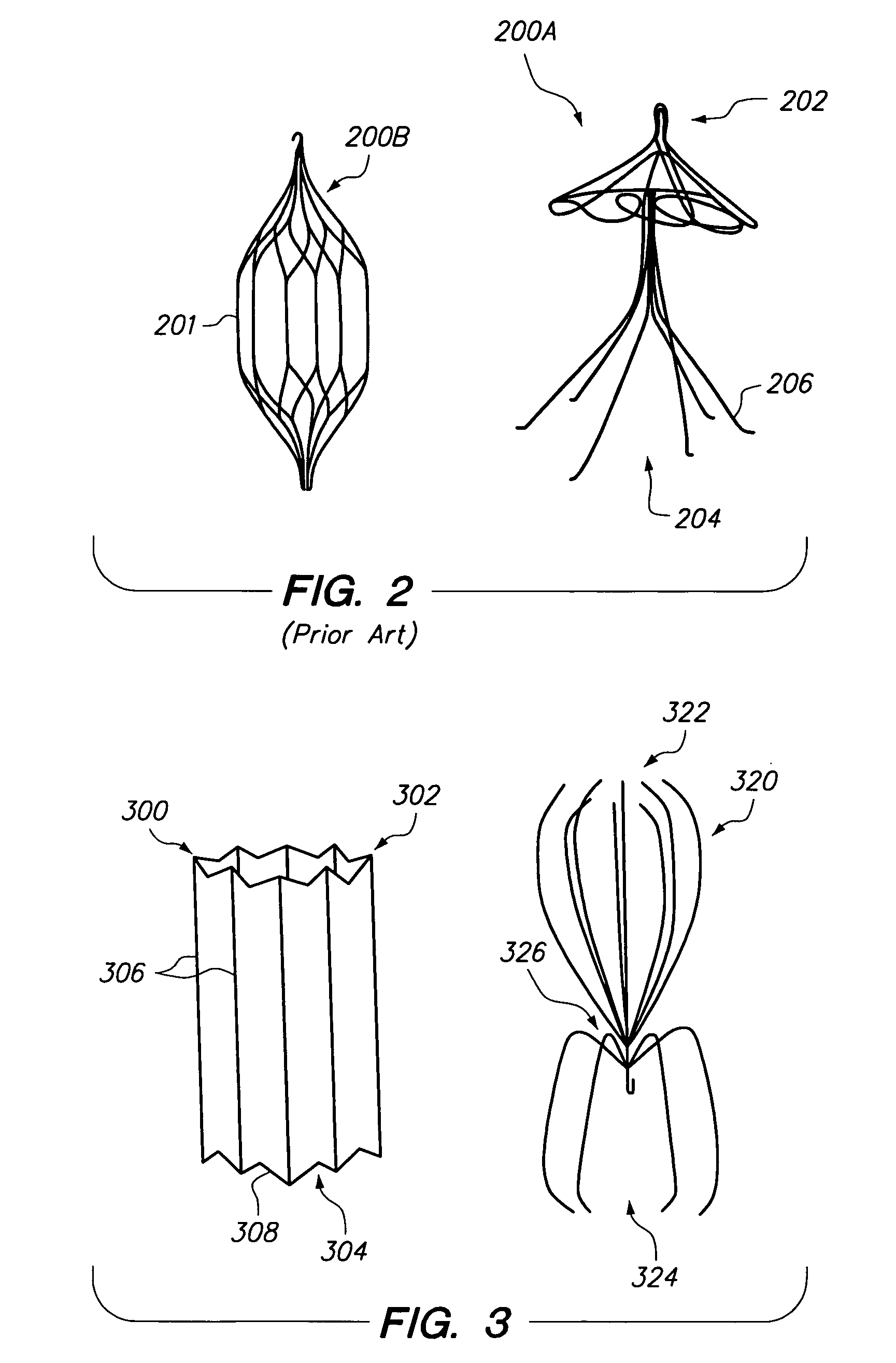
Everting filter devices and methods for using the devices, including using the devices as intra-vascular filters to filter thrombus, emboli, and plaque fragments from blood vessels. The filter devices include a filter body nominally tubular in shape and having a large proximal opening. The filter body can extend from a proximal first end region distally over the non-everted exterior surface of the filter, further extending distally to a distal-most region, then converging inwardly and extending proximally toward the filter second end region, forming a distal everted cavity. The degree of eversion of the filter can be controlled by varying the distance between the filter first end region near the proximal opening and the closed second end region. Bringing the filter first and second end regions closer together can bring filter material previously on the non-everted filter exterior to occupy the distal-most region. The everting process can also bring filter material previously in the distal-most position further into the distal everted cavity. The filter devices can be used to remove filtrate from body vessels, with the filtrate eventually occluding the distal-most region. The filter can then be further everted, bringing fresh, unoccluded filter material into place to provide additional filter capacity. Some everting filters have the capability of switching between occluding and filtering modes of operation, thereby allowing a treating physician to postpone the decision to use filtering or occluding devices until well after insertion of the device into the patient's body.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Devices and methods for aspirating from filters
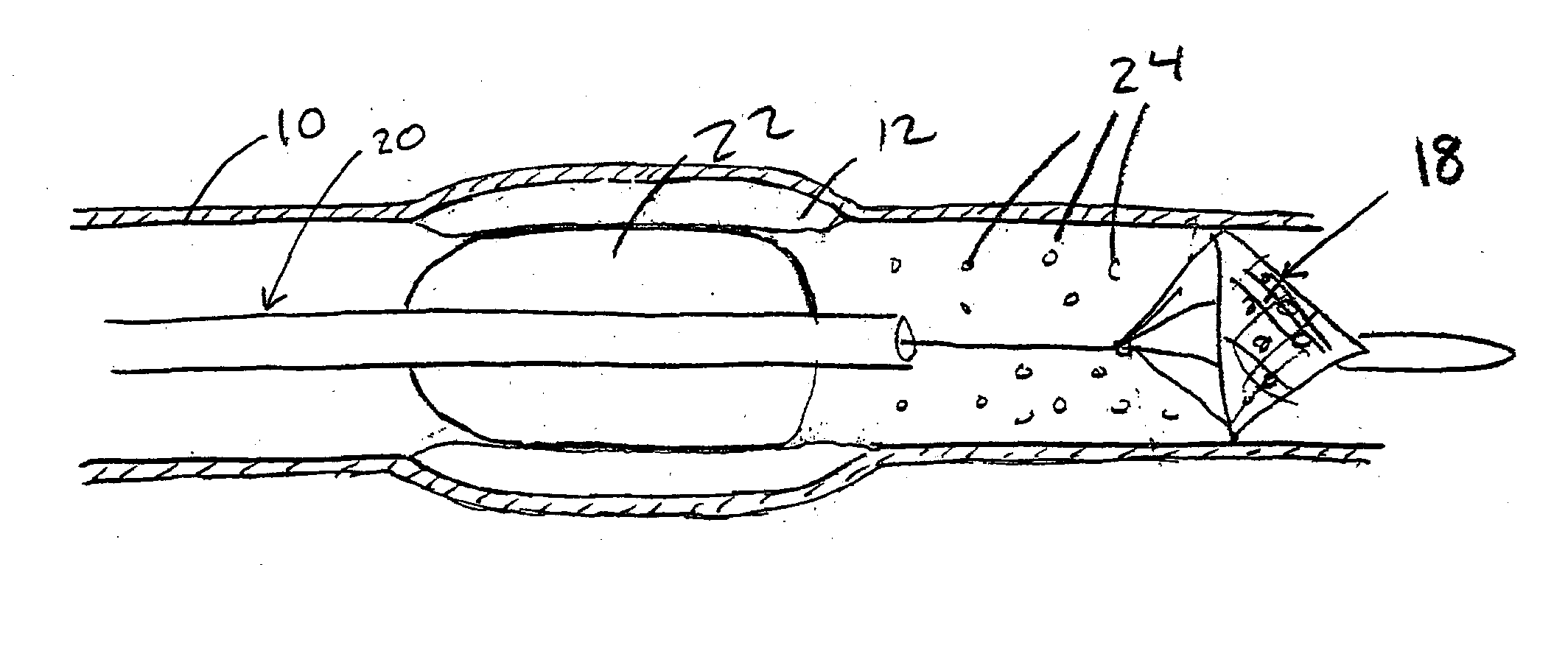
A method and apparatus for aspirating emboli and other particles from a vascular filter within a patient's vasculature. The aspiration catheter comprises an elongate body with an aspiration lumen having an aspiration port at the distal end and a guidewire lumen for receiving a guidewire. The aspiration lumen extends substantially beyond the distal end of the guidewire lumen such that the aspiration port may be,inserted into the interior volume of a filter. Accordingly, embolic particles may be aspirated from the interior volume of the filter. The aspiration port may have an oblique shape for increasing aspiration efficiency. The aspiration catheter may also have a therapy device mounted thereon, such as, for example, an inflatable balloon.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Slideable vascular filter
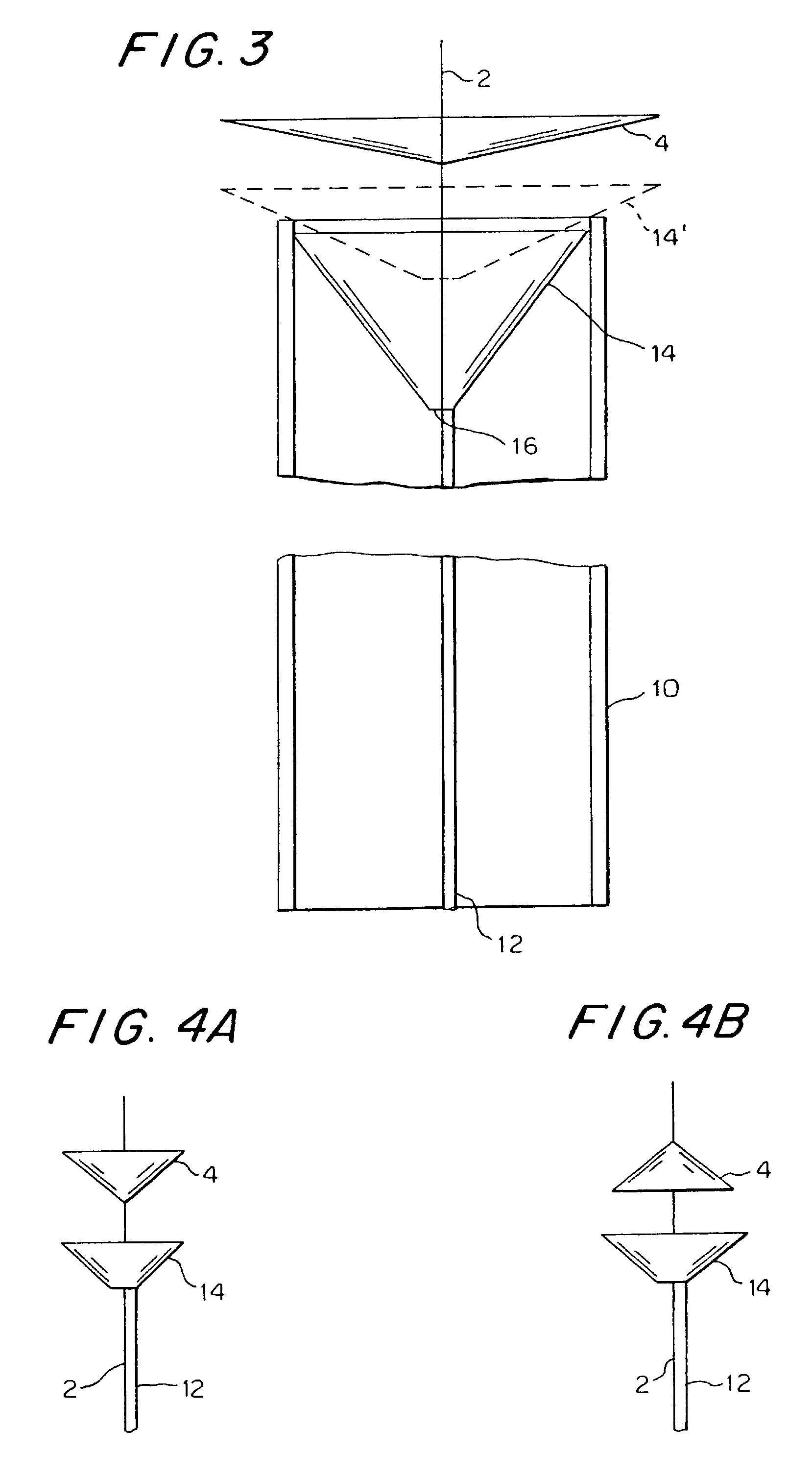
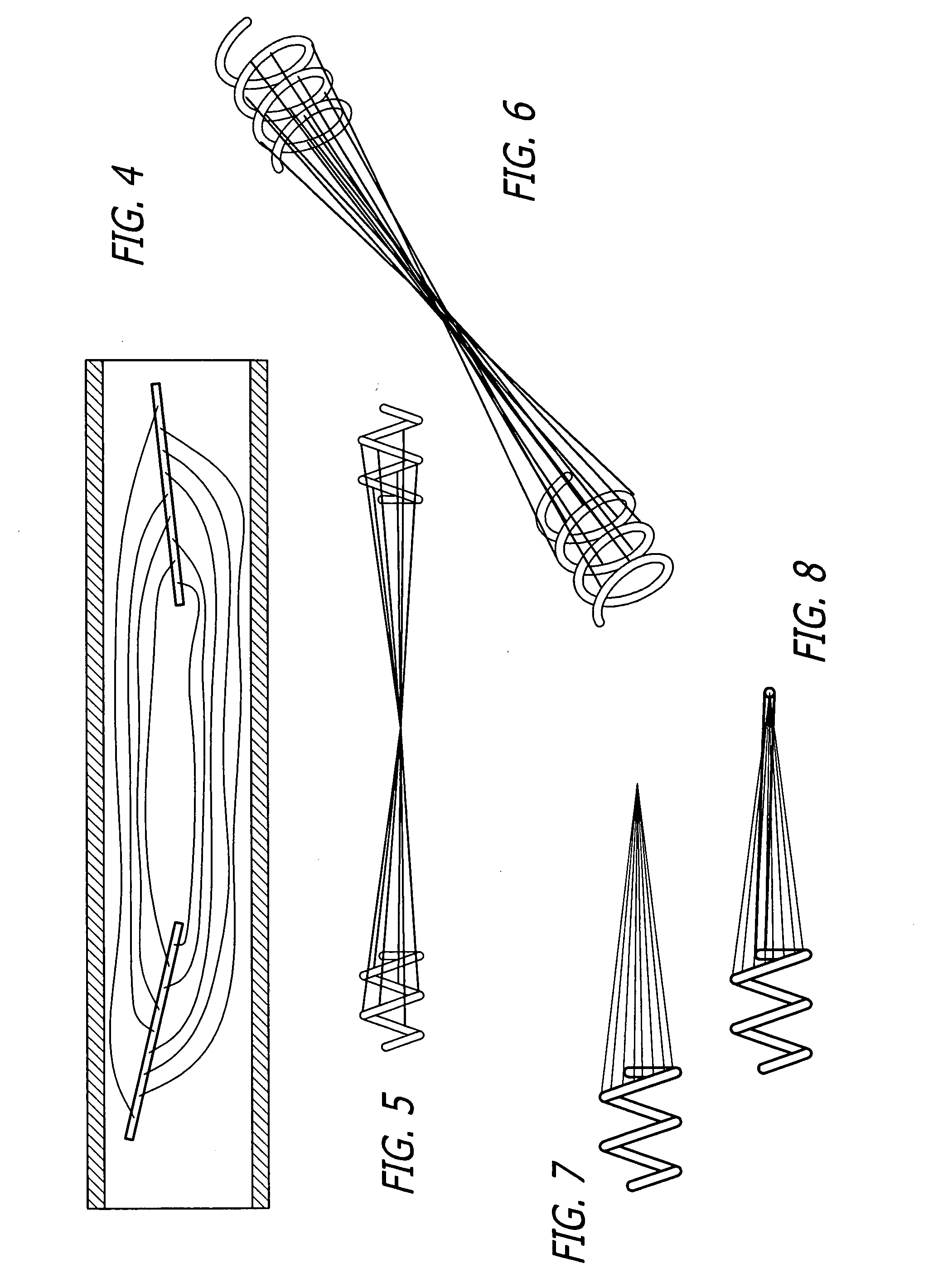
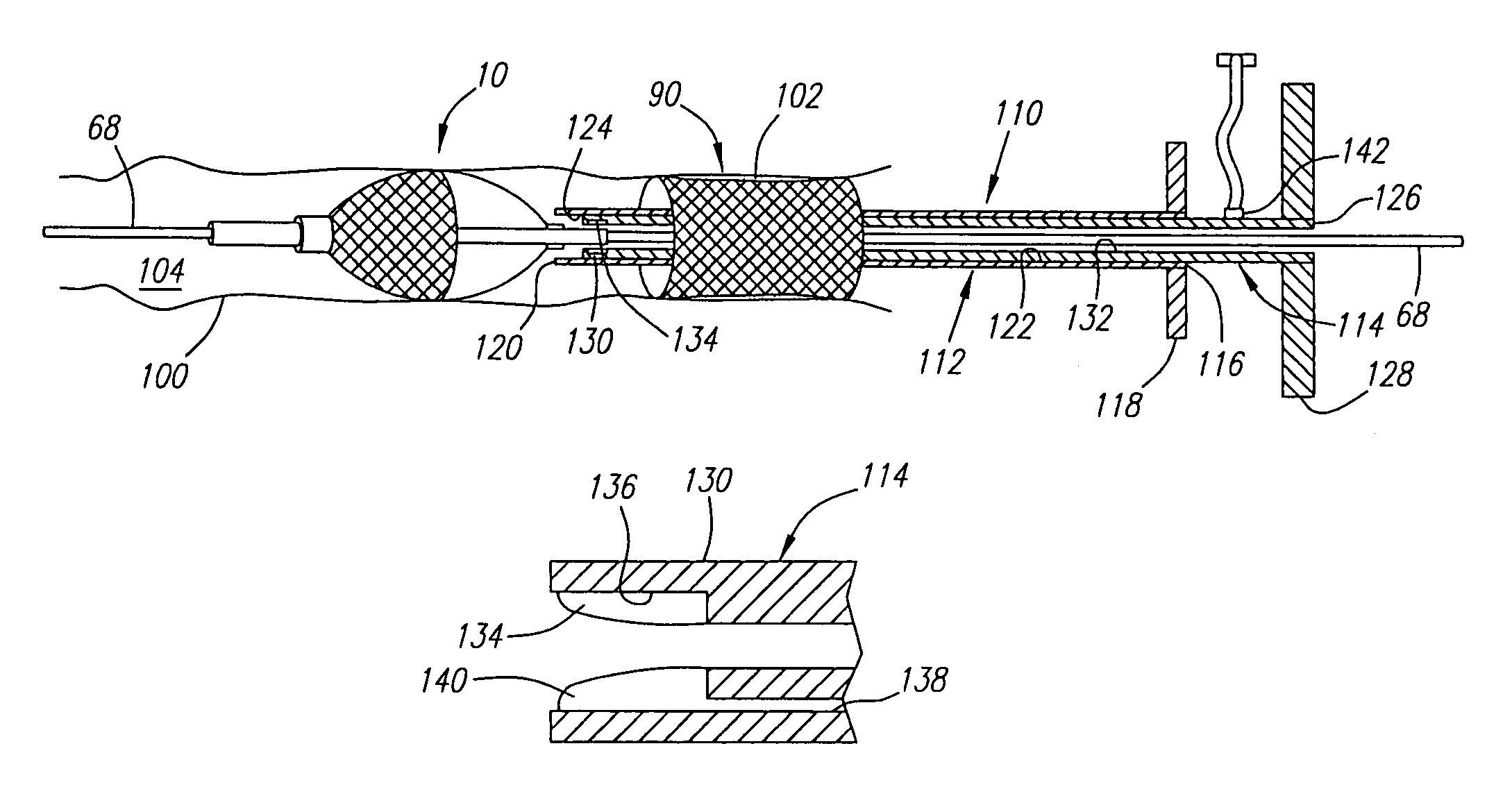
A collapsible medical device for use, e.g., as a vascular filter. The device includes a mandrel having a distal end and a stop spaced proximally of the distal end. A proximal length of the mandrel extends proximally of the stop and a distal length of the mandrel extends distally of the stop. A functional element (e.g., a vascular filter) has a radially expandable body and includes a proximal slider and a distal slider. The proximal and distal sliders are slidable along the mandrel independently of one another such that the distance between the proximal slider and distal slider can be varied to effect different configurations of the functional element. In one method of using such a device, the functional element is urged distally to a treatment site by urging the mandrel distally. This causes the stop to exert a distal biasing force on the distal slider, which acts against a restorative force of the functional element to axially elongate the functional element and reduce friction between the functional element and a wall of the vessel.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
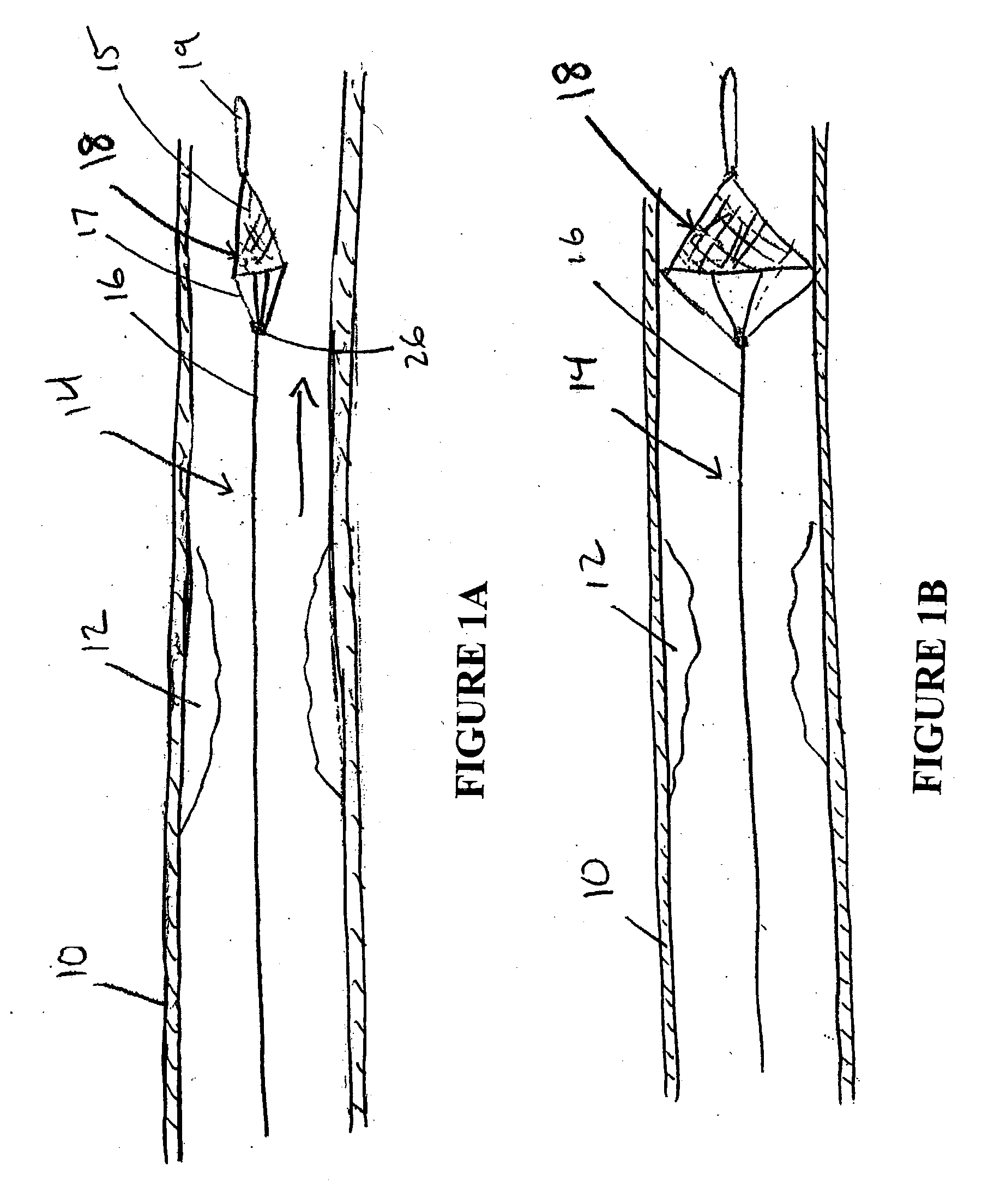
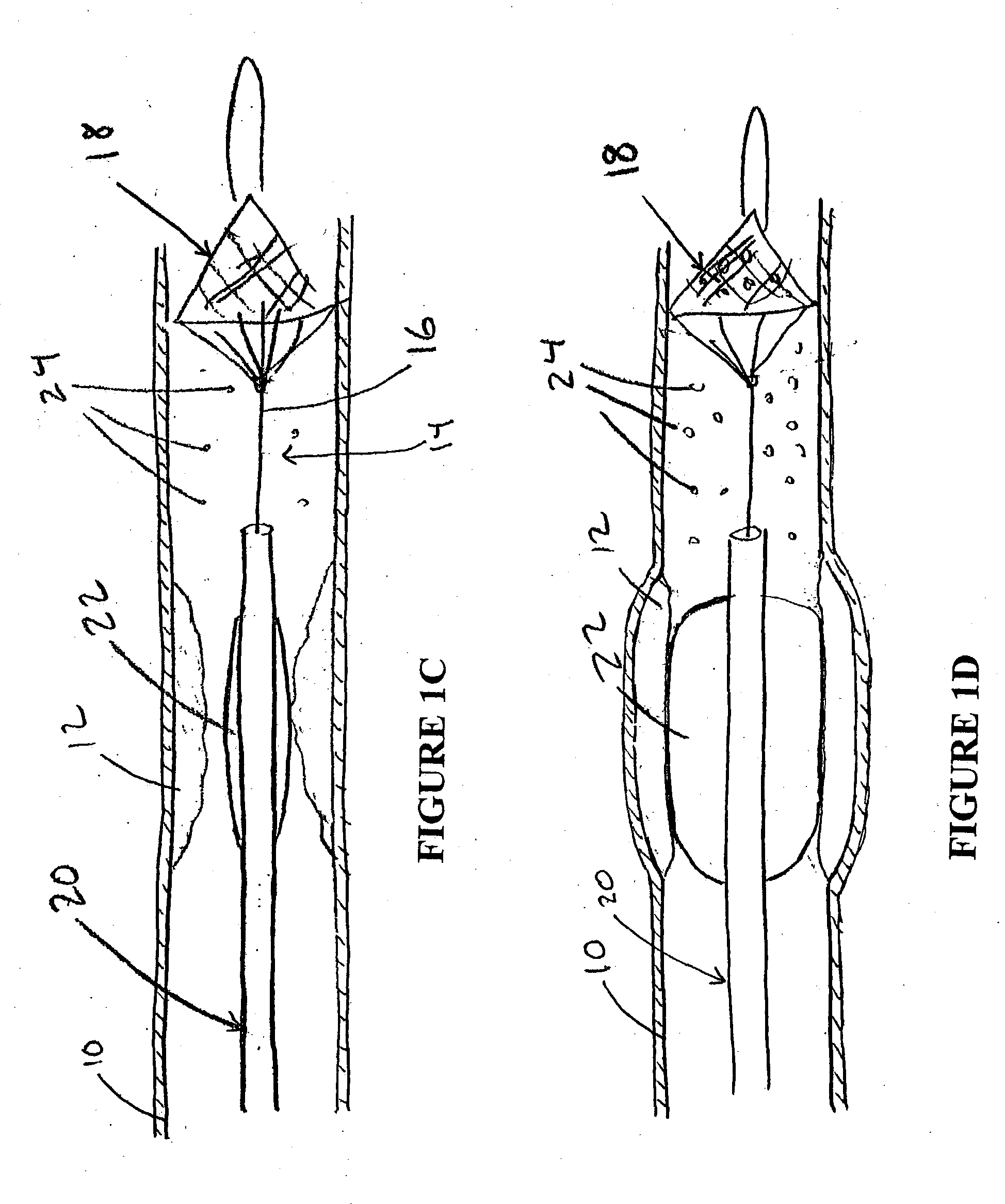
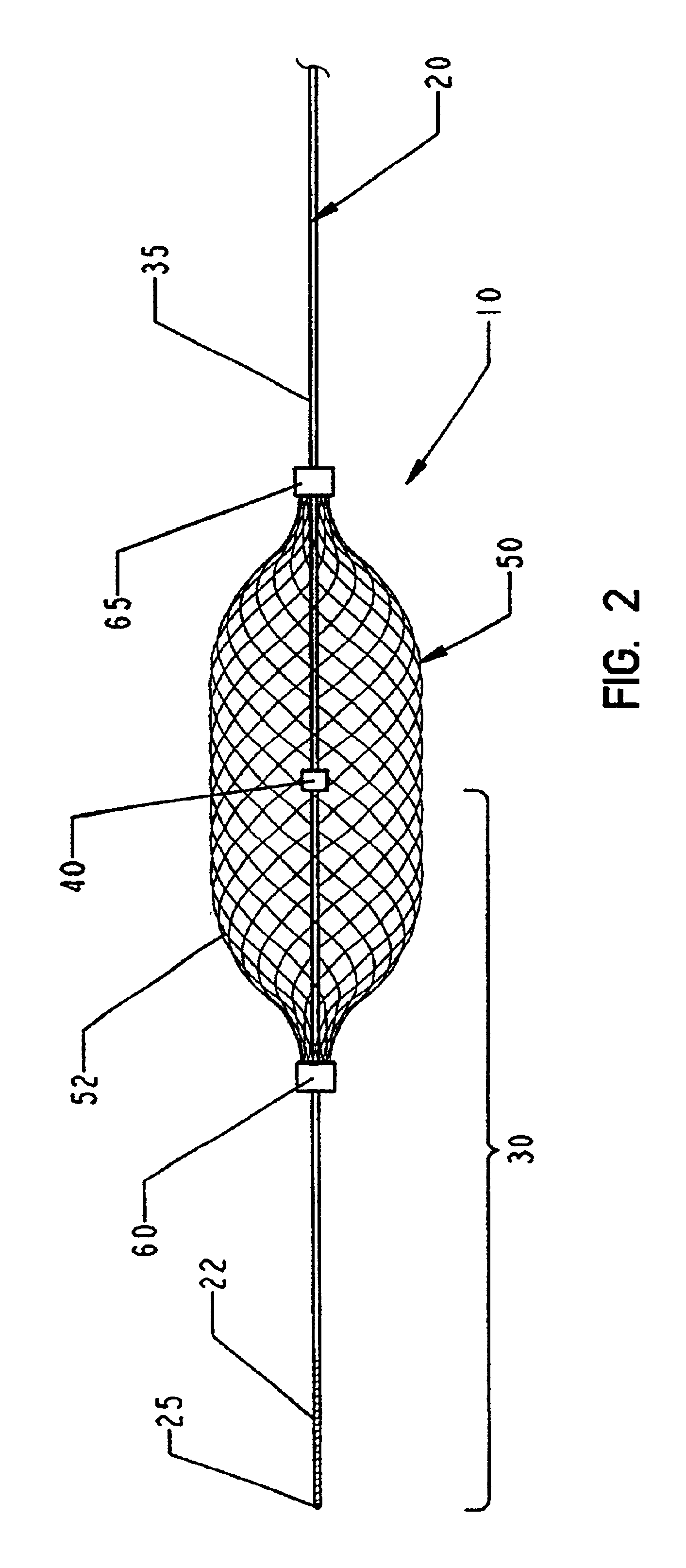
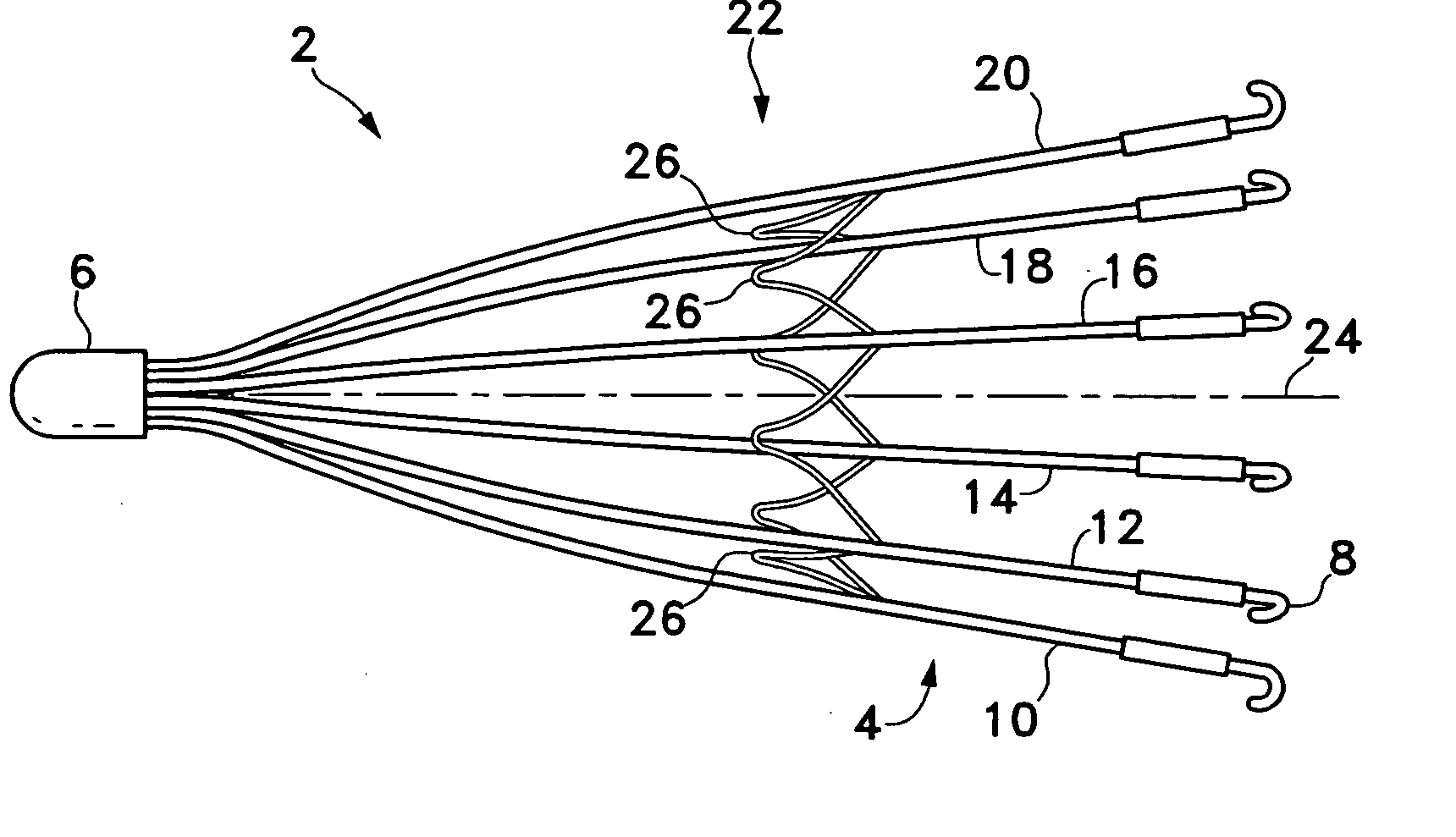
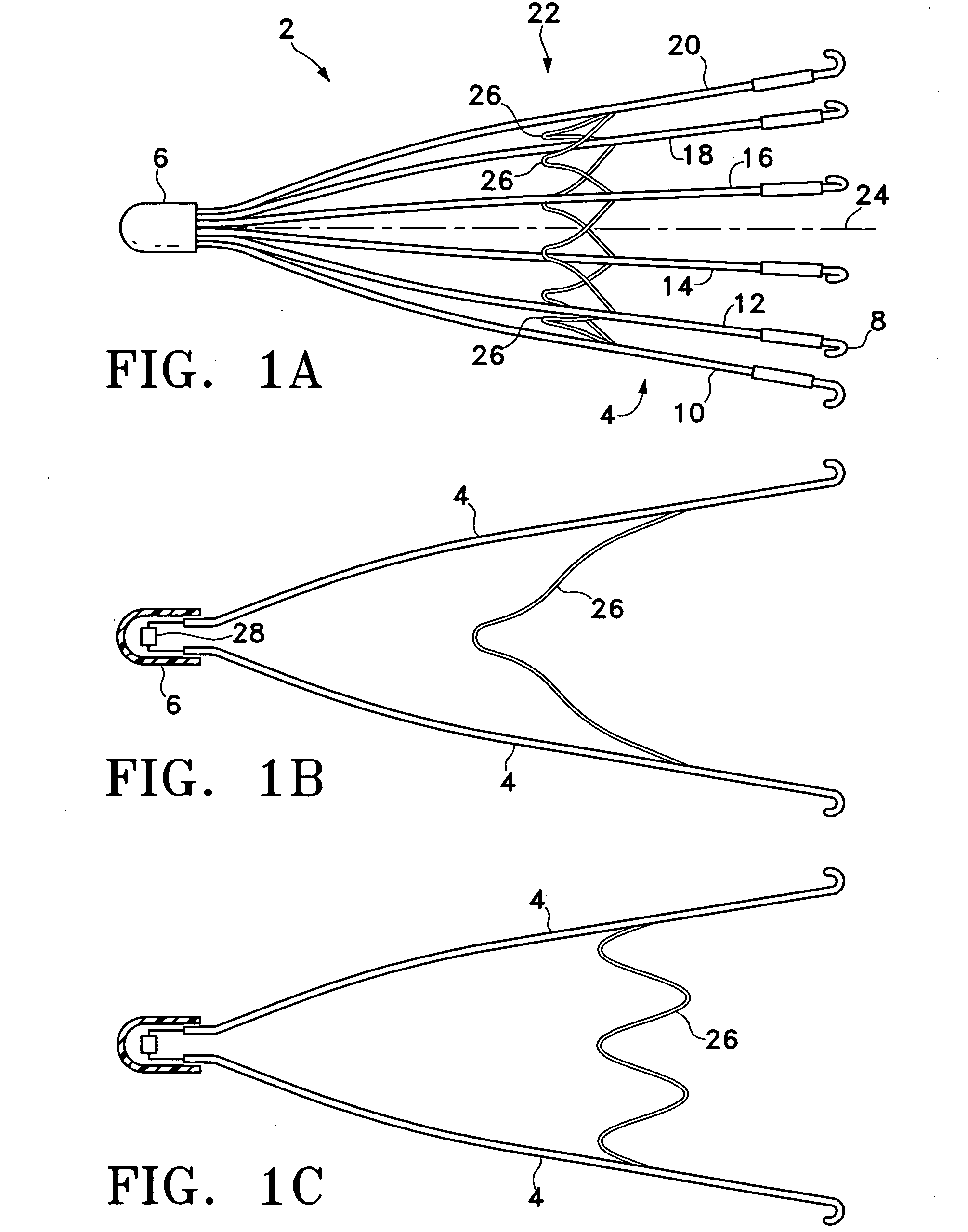
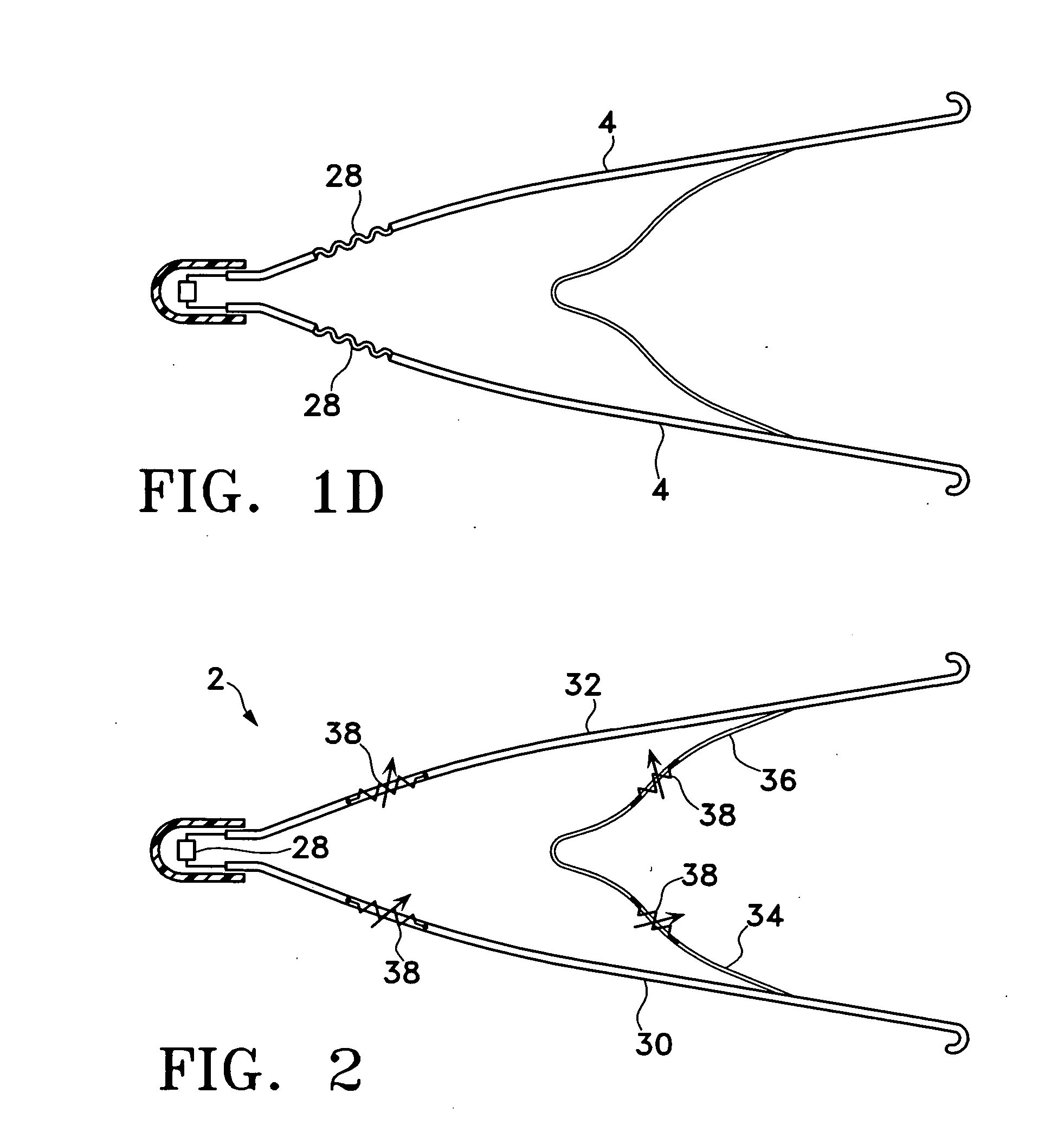
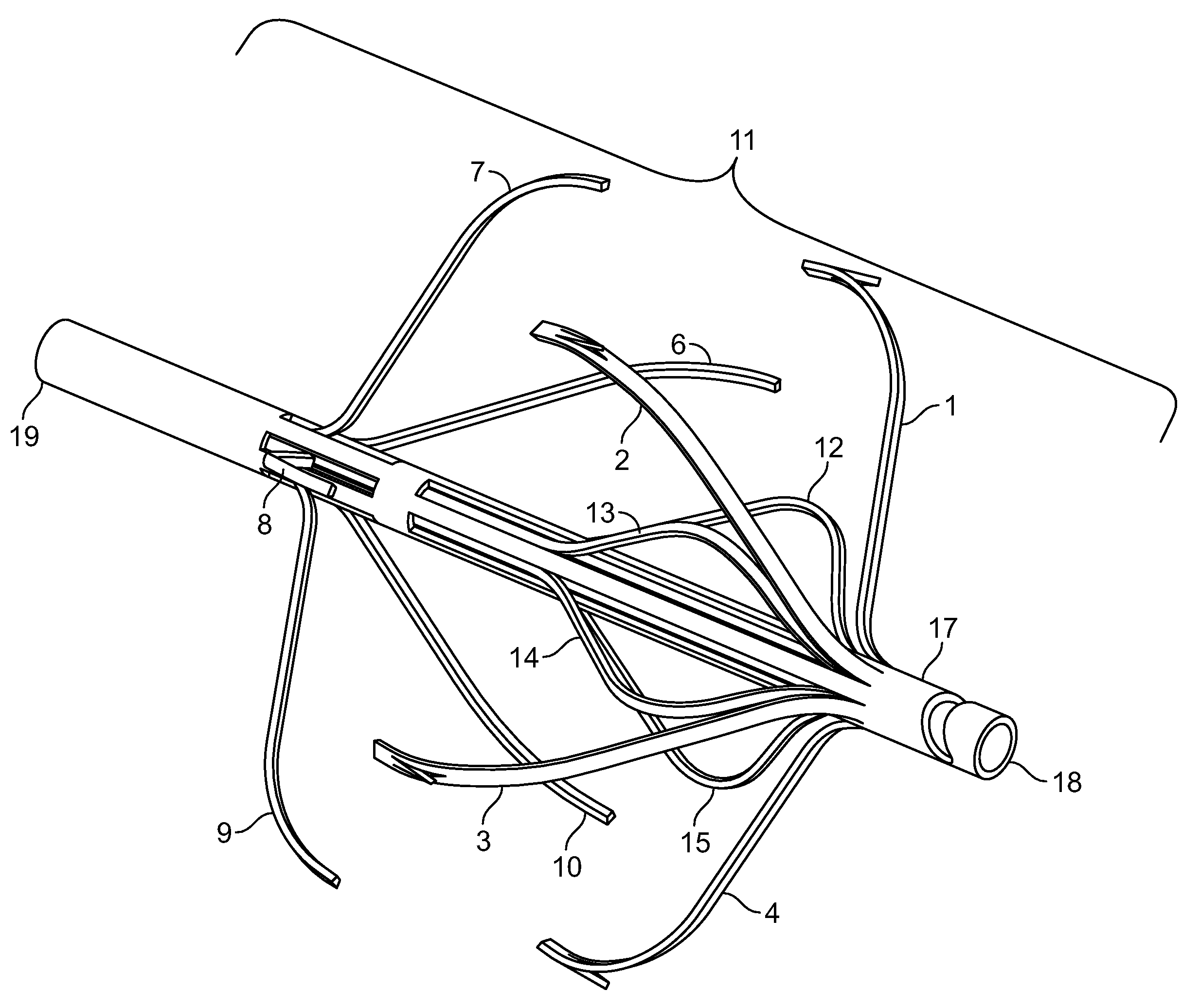
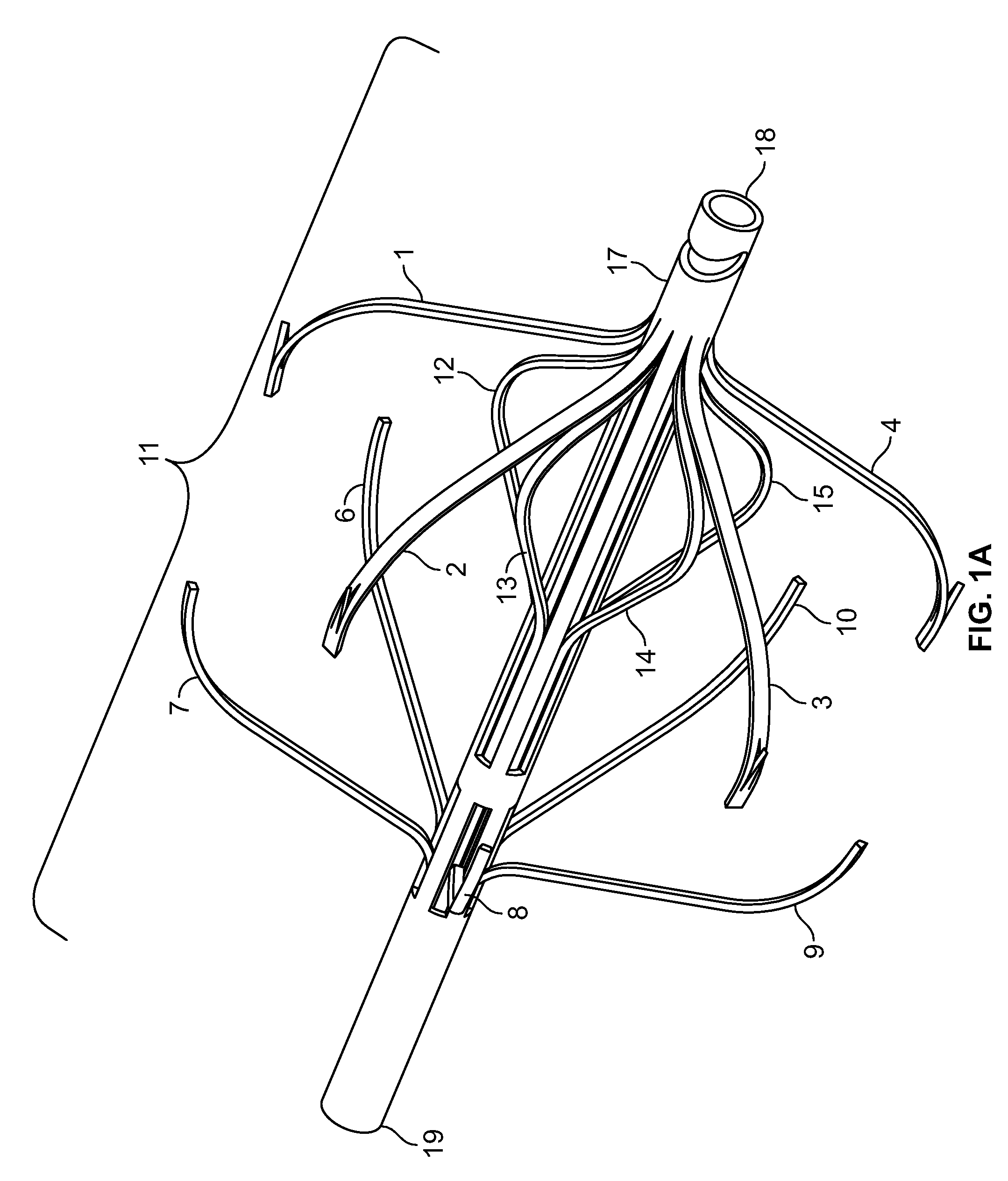
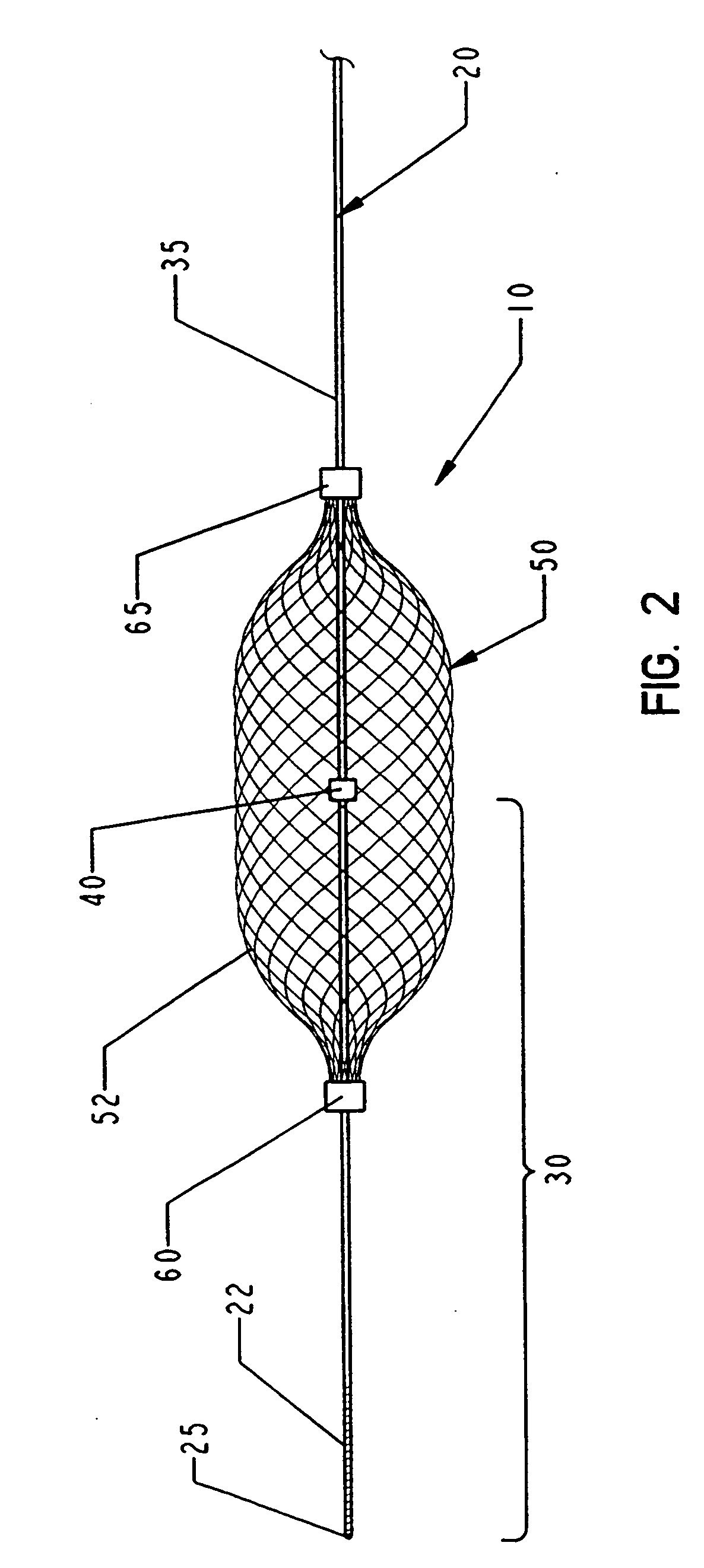
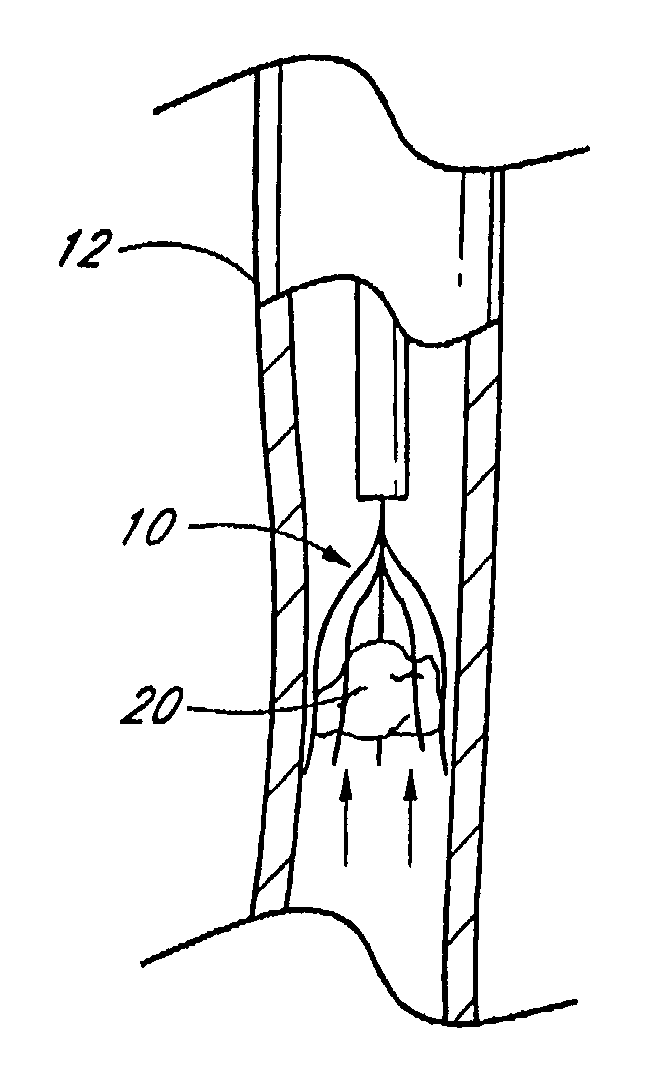
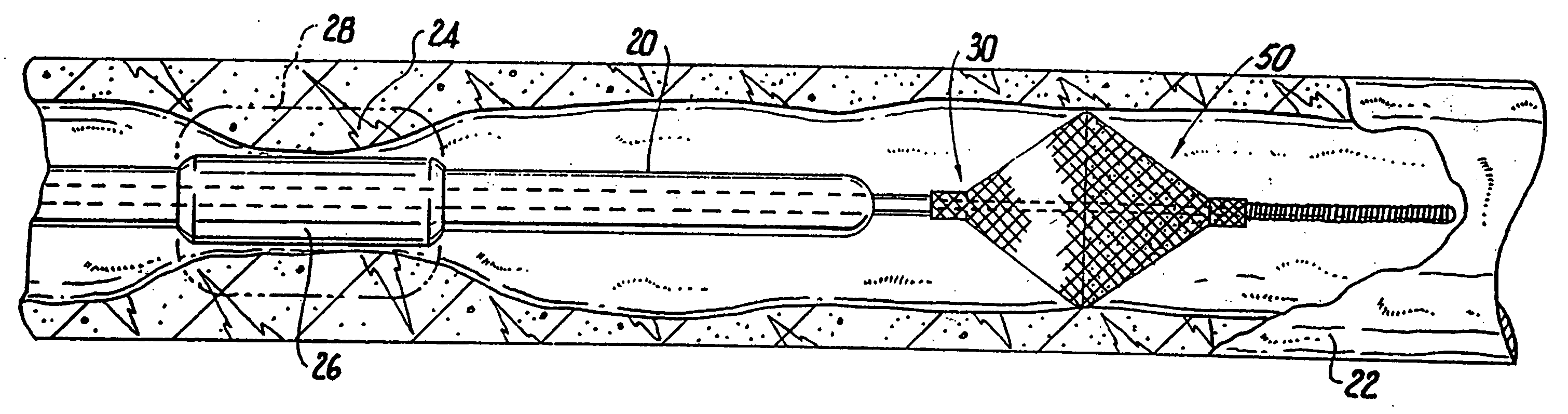
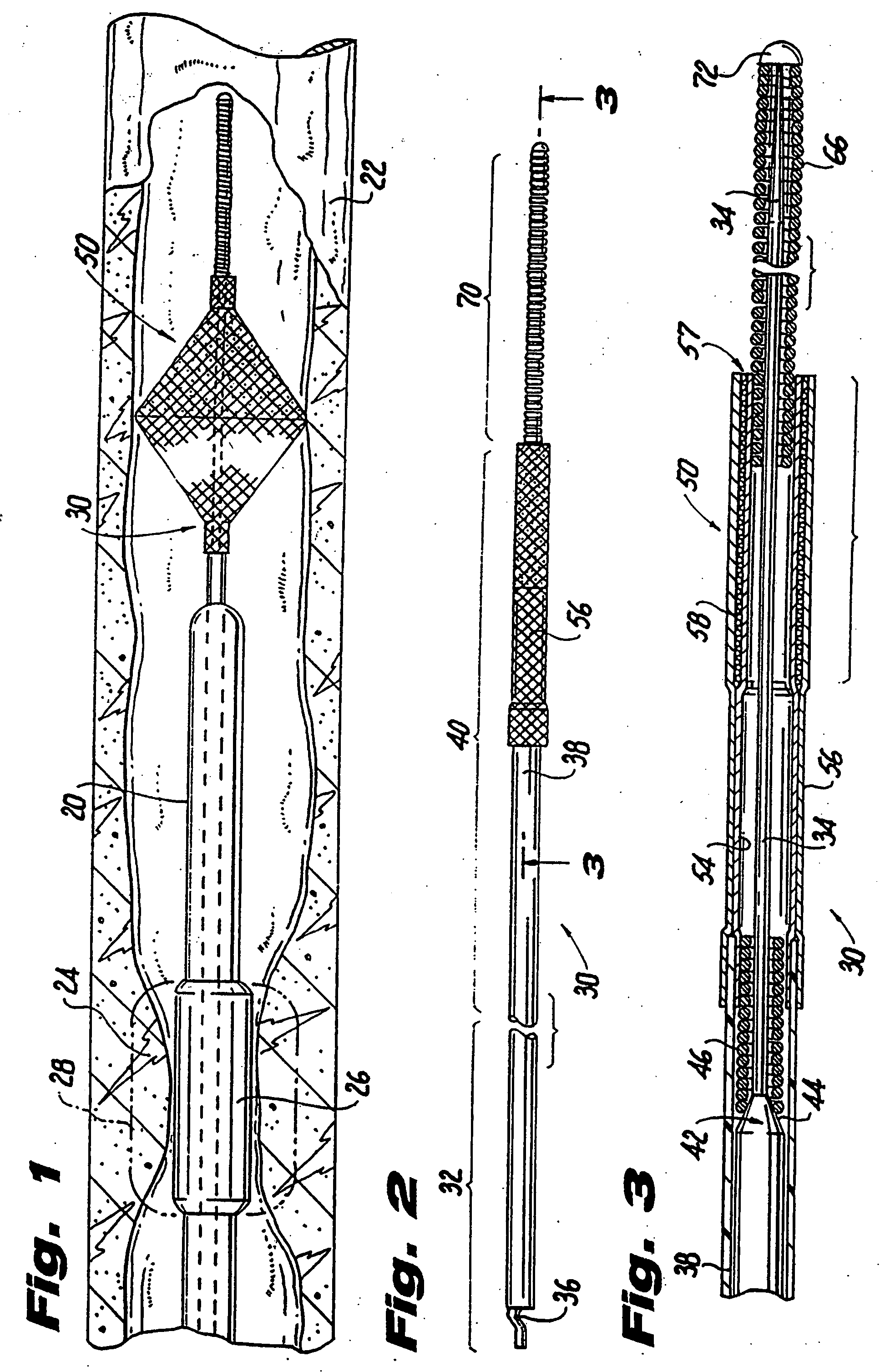
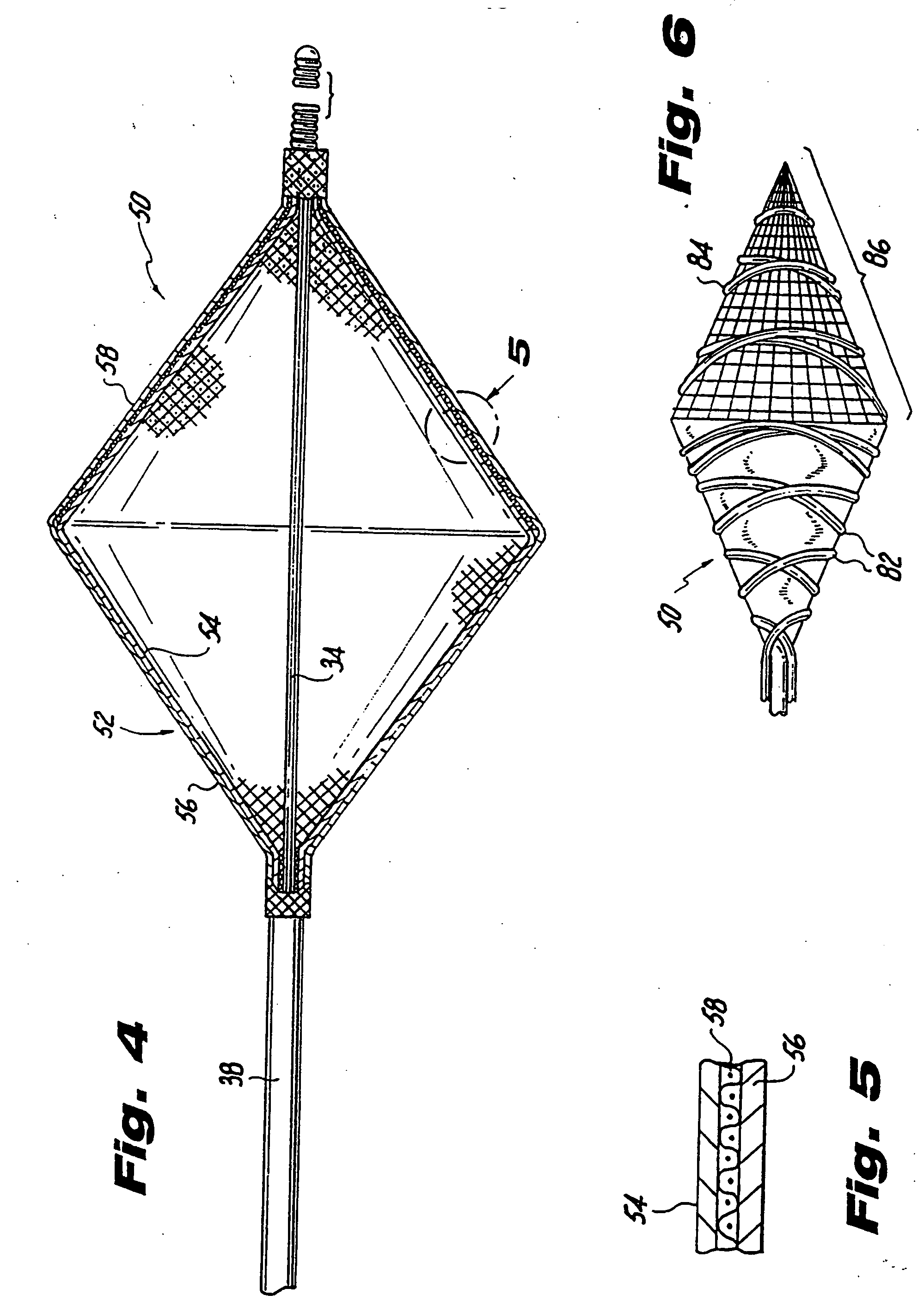
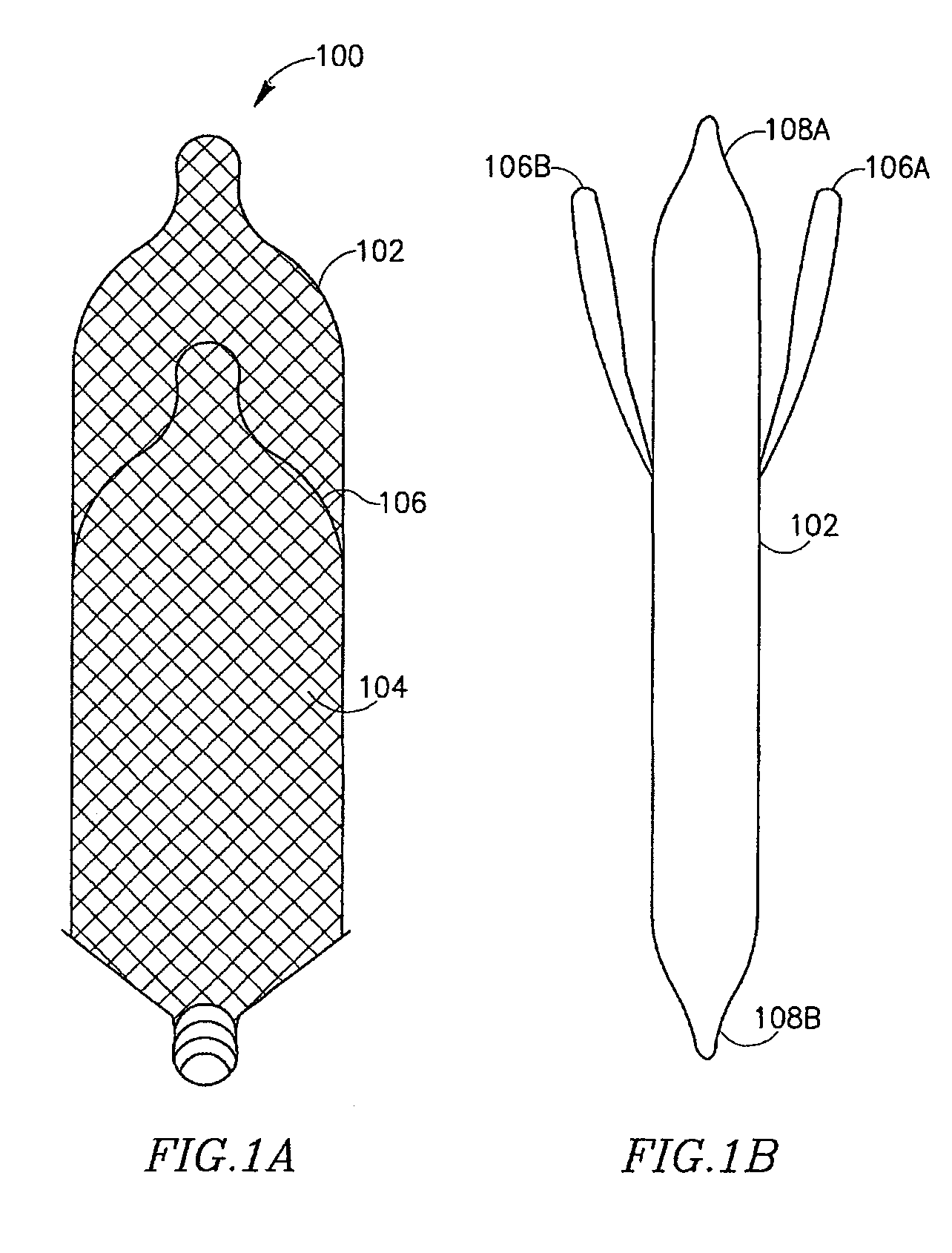
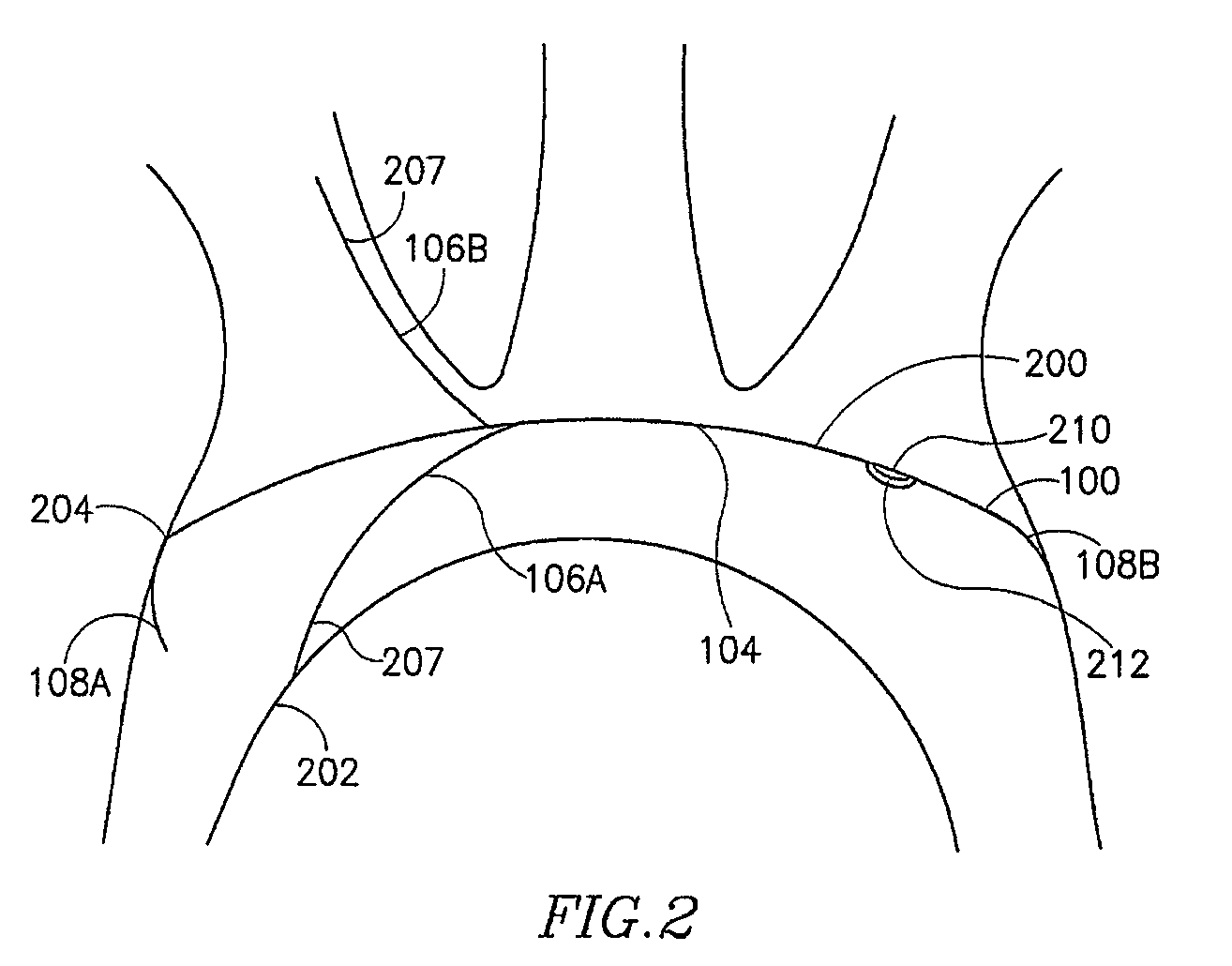
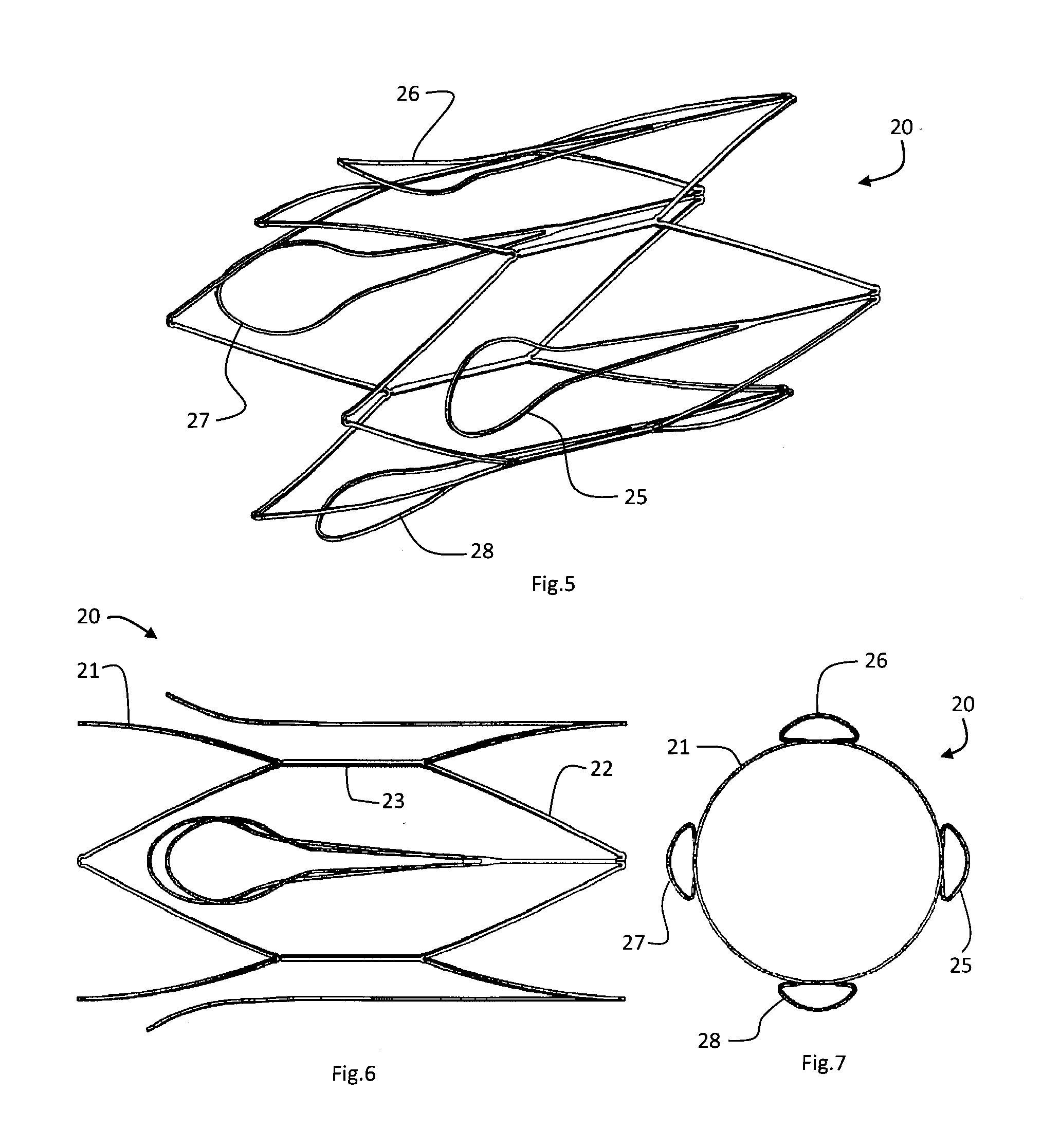
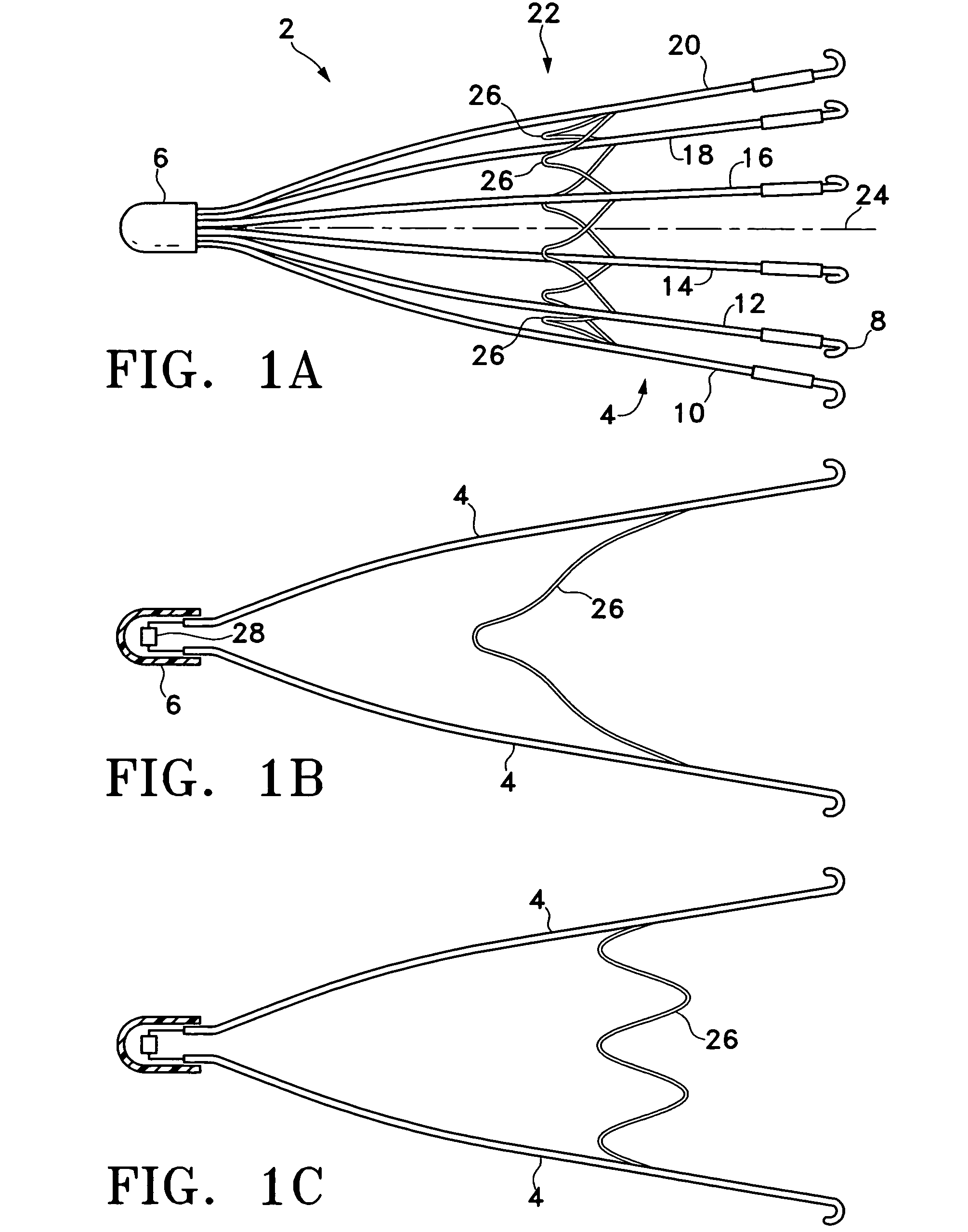
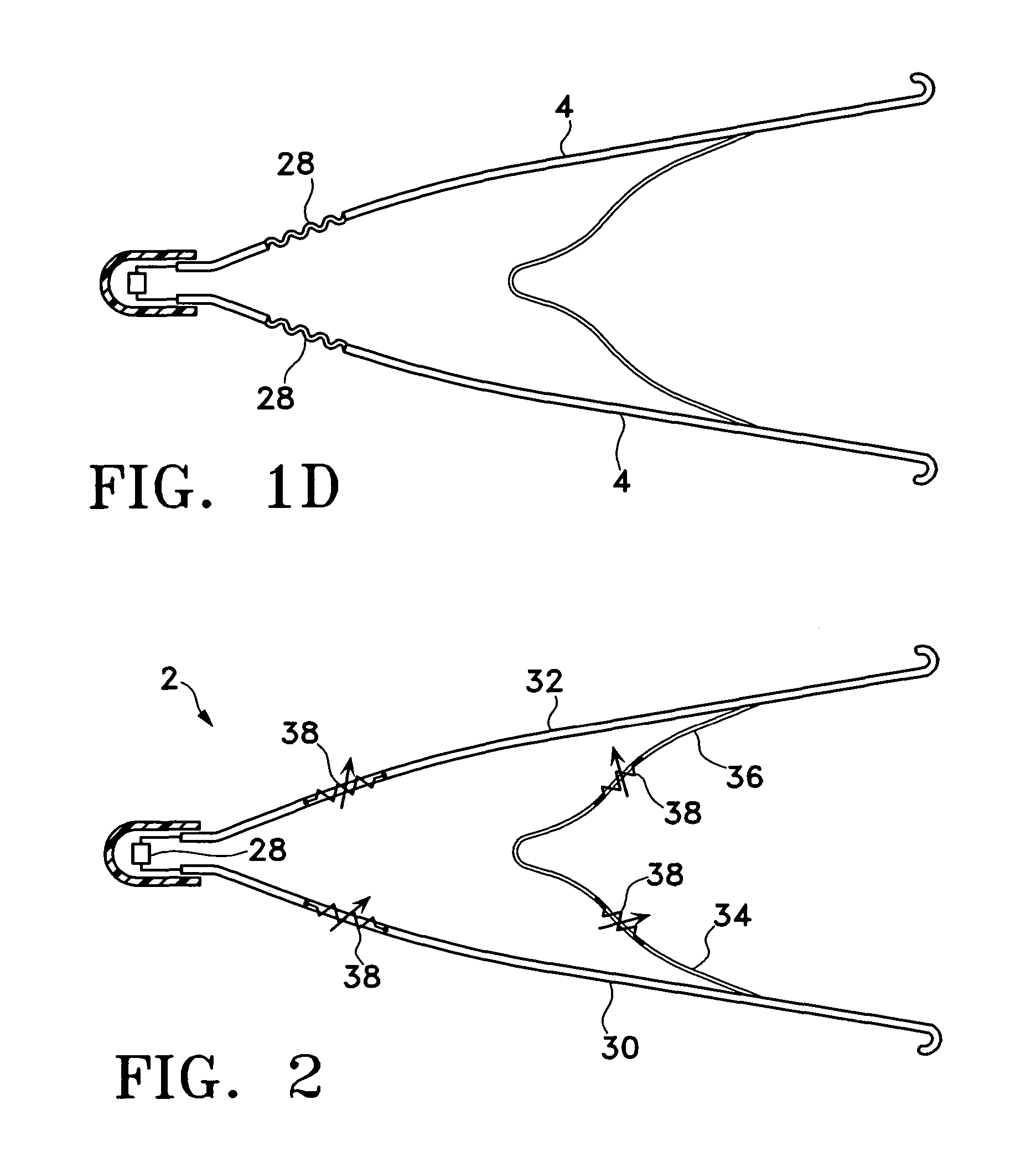
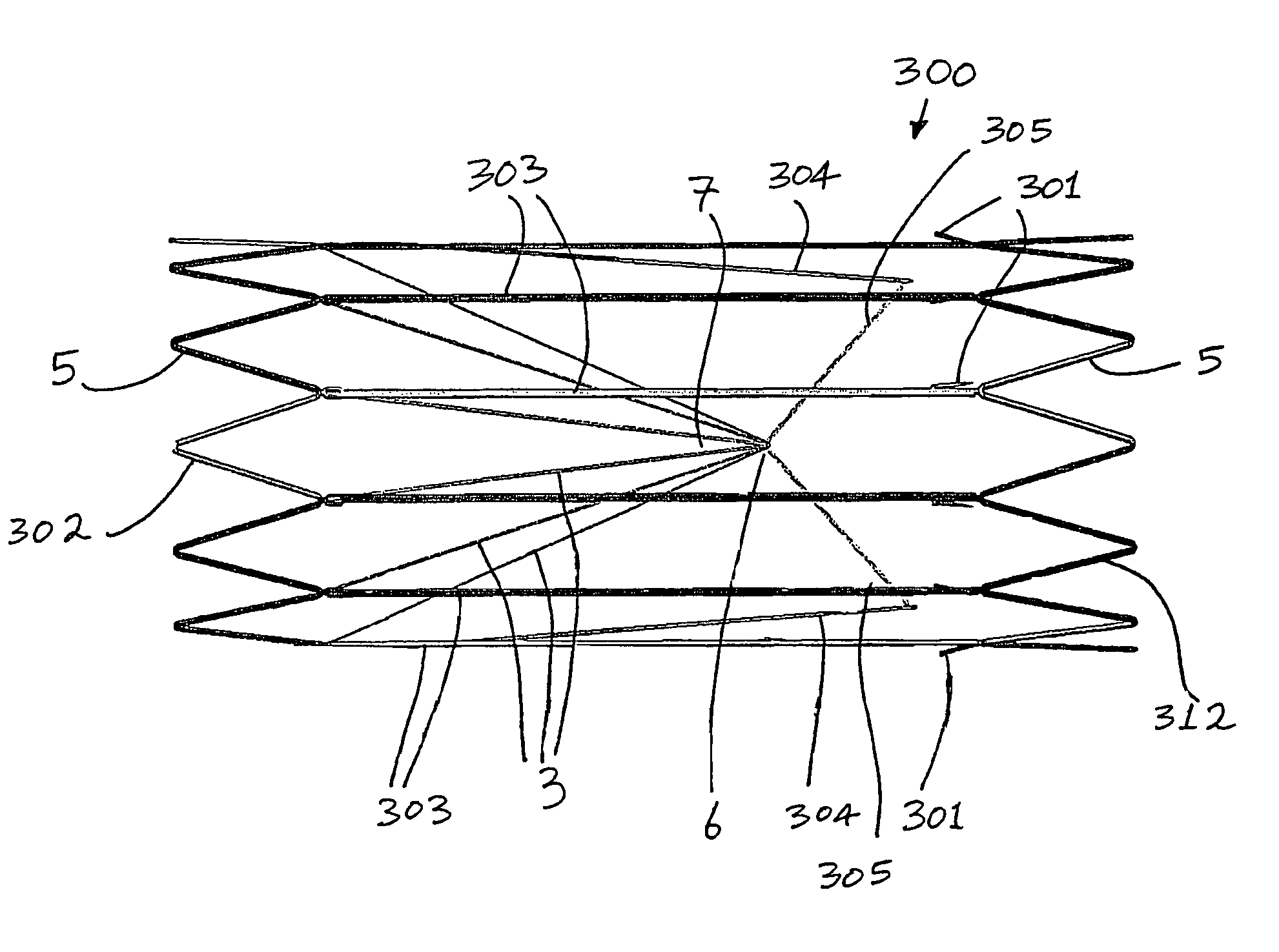
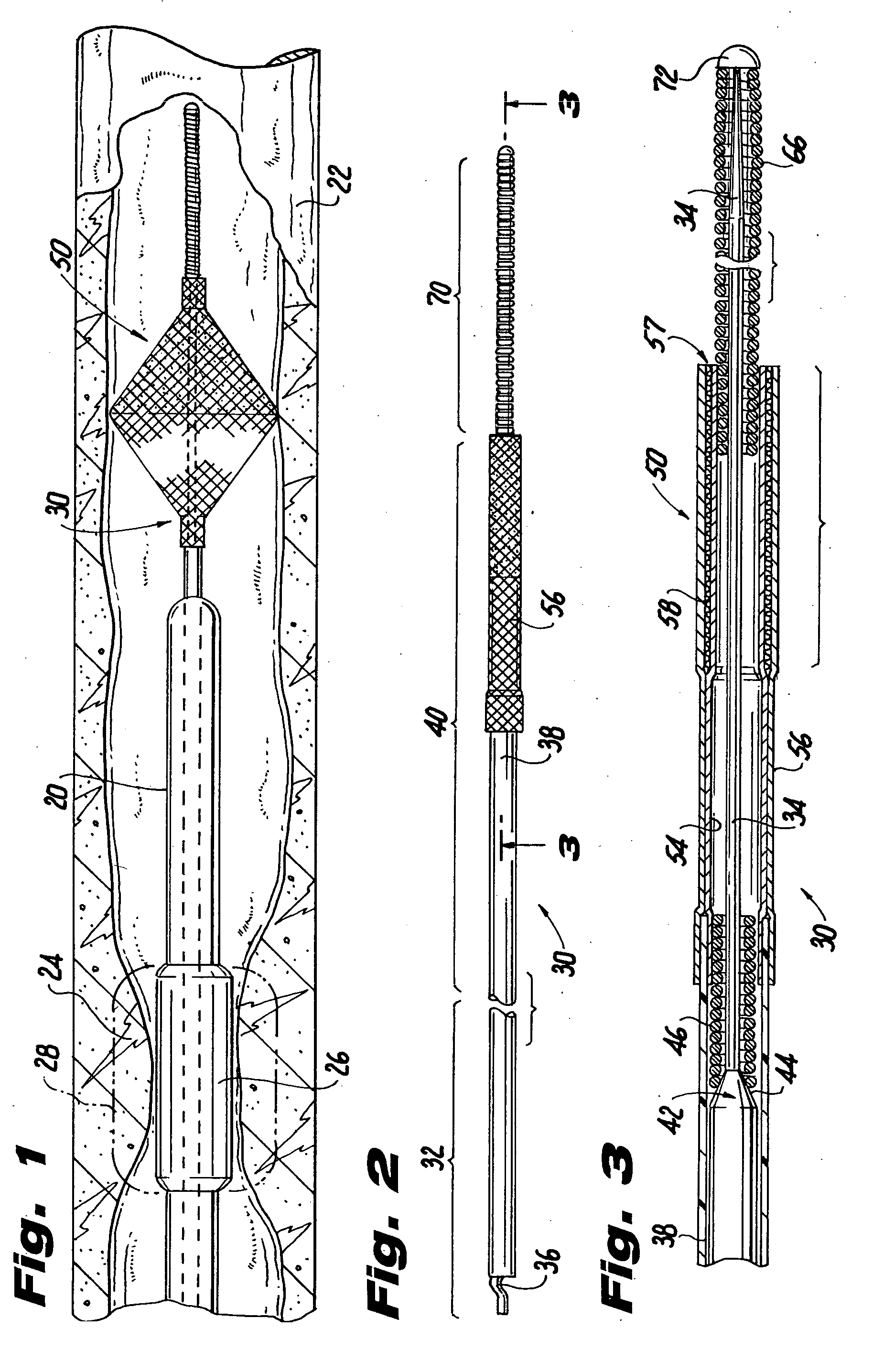
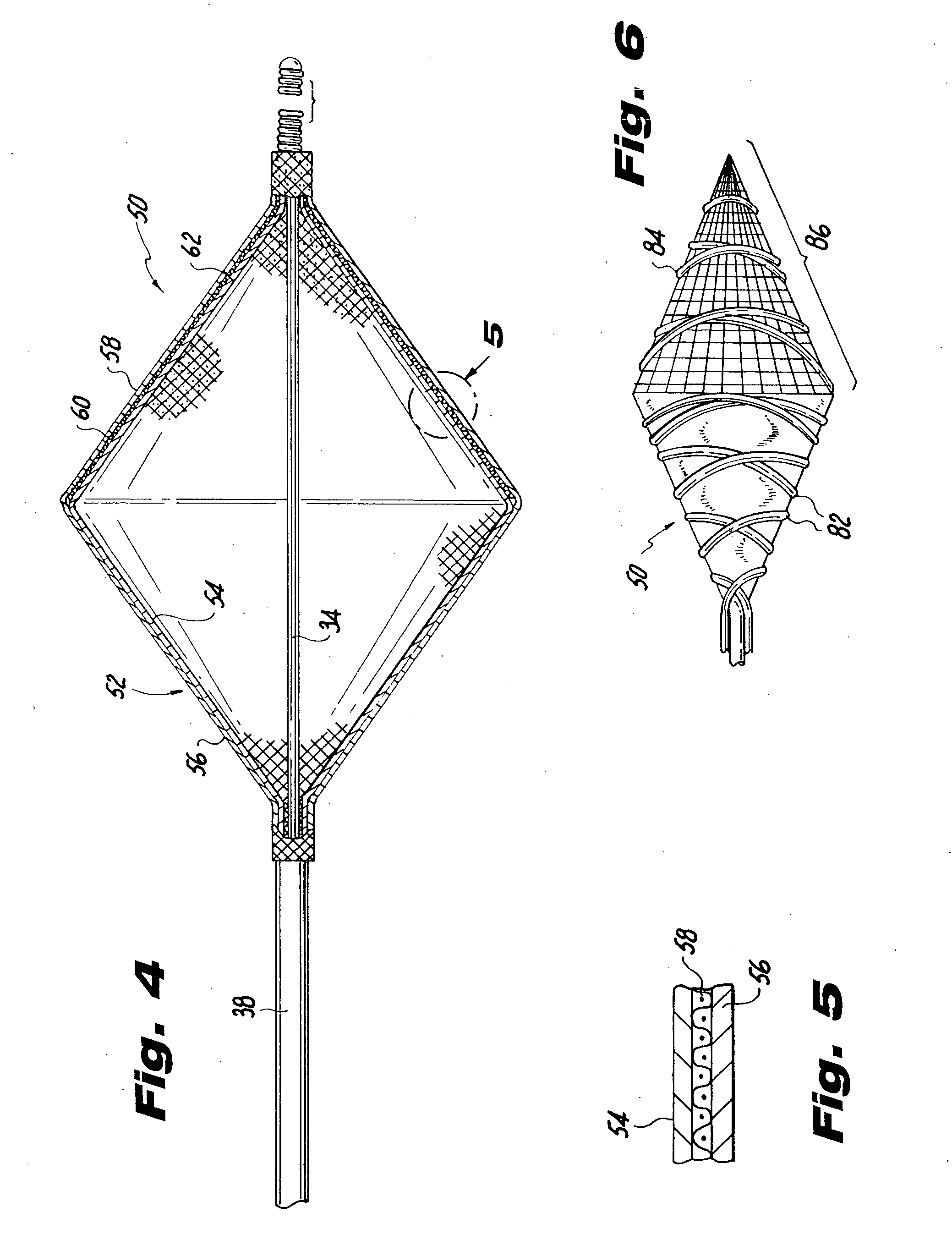
Vascular filter
An inferior vena cava filter (340) for use in the inferior vena cava (4) to capture thrombus (8) passing through the inferior vena cava (4) towards the heart and lungs to prevent pulmonary embolism comprises a proximal support hoop (302), a distal support hoop (312) and a plurality of support struts (303) extending between the proximal support hoop (302) and the distal support hoop (312). The filter (340) also comprises a plurality of capture arms (121) which are movable from a capturing configuration to an open configuration. The capture arms (121) are biased towards the open configuration. A biodegradable suture holds the capture arms (121) in the capturing configuration.
Owner:COVIDIEN GROUP +1
Low profile vascular filter system
InactiveUS6991641B2Easy accessMaintain positionGuide wiresSurgeryContinuous perfusionVascular filter
A removable, low profile, vascular filter system for capture and retrieval of emboli while allowing continuous perfusion of blood, comprising a guidewire having proximal and distal markers, a filter delivery and deployment system, having an outer member and an inner member, and a filter removably attached near the distal end of the inner member. The filter comprises proximal and distal basket sleeves which position the filter between the proximal and distal markers on the guidewire, after the guidewire is in position past the vessel occlusion. The guidewire placement prior to filter delivery may facilitate access to the interventional site, especially through tortuous anatomy. Also, retrievability of the filter from the wire may avoid loss of guidewire position, which may occur following removal of filters permanently attached to guidewires.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Everted filter device
Everting filter devices and methods for using the devices, including using the devices as intra-vascular filters to filter thrombus, emboli, and plaque fragments from blood vessels. The filter devices include a filter body nominally tubular in shape and having a large proximal opening. The filter body can extend from a proximal first end region distally over the non-everted exterior surface of the filter, further extending distally to a distal-most region, then converging inwardly and extending proximally toward the filter second end region, forming a distal everted cavity. The degree of eversion of the filter can be controlled by varying the distance between the filter first end region near the proximal opening and the closed second end region. Bringing the filter first and second end regions closer together can bring filter material previously on the non-everted filter exterior to occupy the distal-most region. The everting process can also bring filter material previously in the distal-most position further into the distal everted cavity. The filter devices can be used to remove filtrate from body vessels, with the filtrate eventually occluding the distal-most region. The filter can then be further everted, bringing fresh, unoccluded filter material into place to provide additional filter capacity. Some everting filters have the capability of switching between occluding and filtering modes of operation, thereby allowing a treating physician to postpone the decision to use filtering or occluding devices until well after insertion of the device into the patient's body.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Vascular filter system
A removable vascular filter system for capture and retrieval of emboli while allowing continuous perfusion of blood, comprising a porous filter membrane and a filter membrane support structure. This system is useful for any percutaneous angioplasty, stenting, thrombolysis or tissue ablation procedure. The system may minimize the incidence of stroke, myocardial infarction or other clinical complications that may be associated with these procedures.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
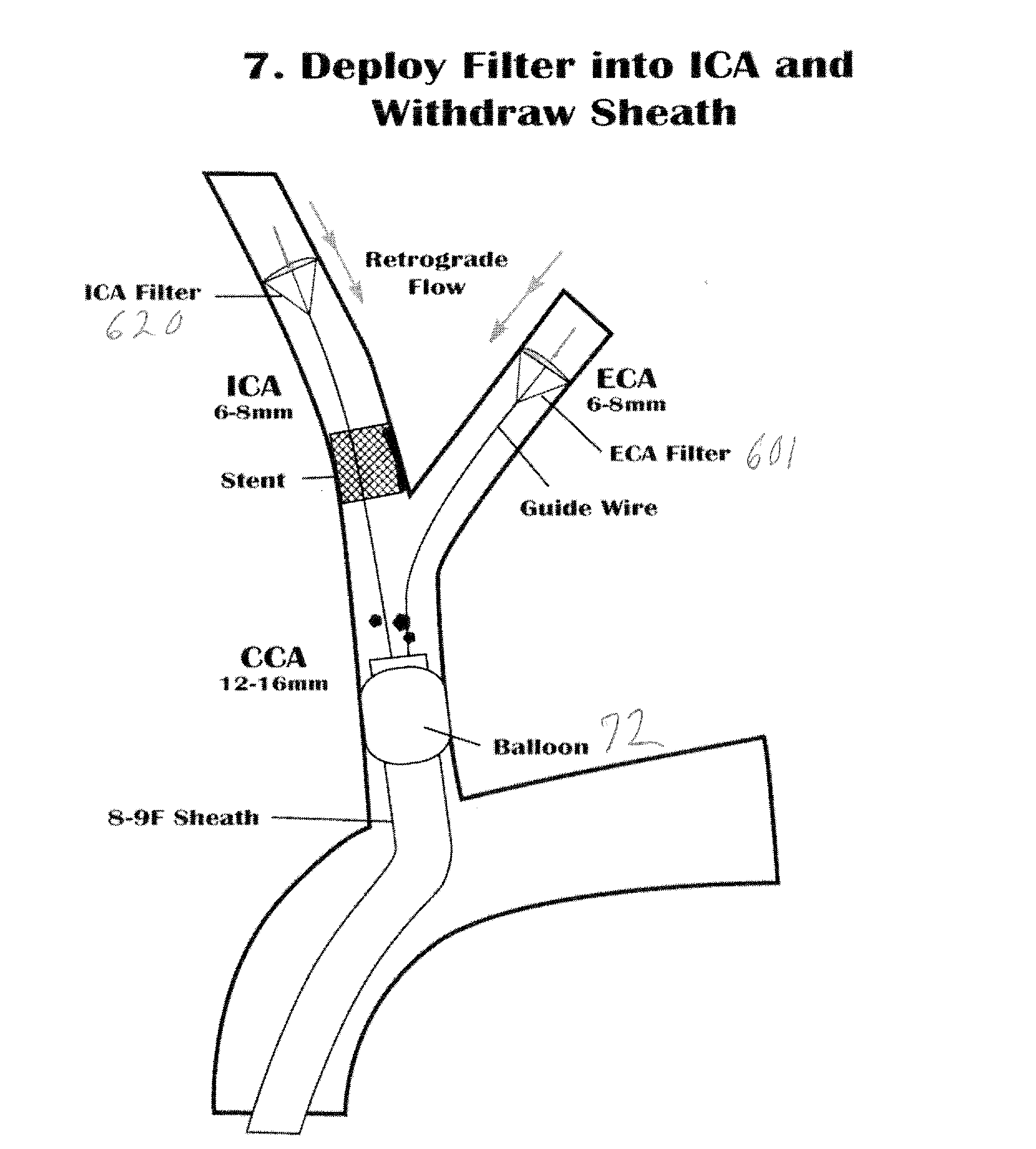
Vascular filter with sensing capability
An implantable vessel filter having an integrated sensing capability for monitoring the condition of the vessel filter. In one variation, the vessel filter comprises a plurality of legs that would themselves perform as a sensor device for detecting distention, which would indicate the presence of a clot or thrombus therein. A passive electrical circuit may be implemented on the vessel filter to receive electromagnetic energy and transmit signals indicative of the condition of the implanted vessel filter. In another variation, a miniaturized sensor is adapted for measuring the strain and / or other physical parameters of the filter legs.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Percutaneous permanent retrievable vascular filter
Retrievable vena cava filters for the temporary or permanent prevention of Pulmonary embolism (PE) are disclosed. A filter in accordance with the present invention has a tube-within-tube structure with overlapping semi-spheres. The semi-spheres comprise a plurality of expandable legs. The first tube may have a first set of expandable legs and a plurality of slots allowing for deployment of a second or third set of expandable legs on the second tube. The free end of each leg in the first set of expandable legs is oriented in a direction opposite to the free end of each leg in the second set forming a cage which comprises legs from the first and second sets of expandable legs. The filter of the present invention may be retrieved by a catheter and snare. The third set of expandable legs conveys the vector force from the closing of the first set to the second set to cause it to collapse.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
Vascular filter with improved strength and flexibility
A medical device, such as a vascular filter, composed of: a reinforced membrane unit composed of: a thin filter membrane; and fibers of reinforcement material embedded in the membrane to strengthen the filter and securely attach the fibers to the membrane.A method of fabricating the filter by the steps of: providing a mold that can be melted, dissolved, or deformed without damaging membrane material; covering the mold with an intermediate material that is easily separated from the membrane material; covering the intermediate material with the membrane material; placing the fibers in contact with the membrane material that covers the intermediate material; covering the fibers with additional membrane material to form the membrane with embedded fibers; removing the mold by melting, dissolving, or deforming the mold; and removing the intermediate material from the membrane.
Owner:DON MICHAEL INT
Removable vascular filter and method of filter placement
A vascular filter system and method for implanting the same are disclosed. The filter system generally includes a filter housing and a filter element where the element is suspended within the housing by a plurality of filter holding members. The housing is held in place in a vein by a plurality of securing barbs which generally extend outward from the housing. The housing and its holding members may be bioabsorbable. In these embodiments, the filter element may include at least one filter barb to secure the element after the housing has been bioabsorbed. The filter system may be implanted by accessing a vein and inserting a deployment sheath containing the filter system. The deployment sheath is advanced to the proper location and a deployment member is used to release the filter system as the sheath is retracted. The deployment member and sheath may be removed.
Owner:BATISTE STANLEY
Emboli removal system with oxygenated flow
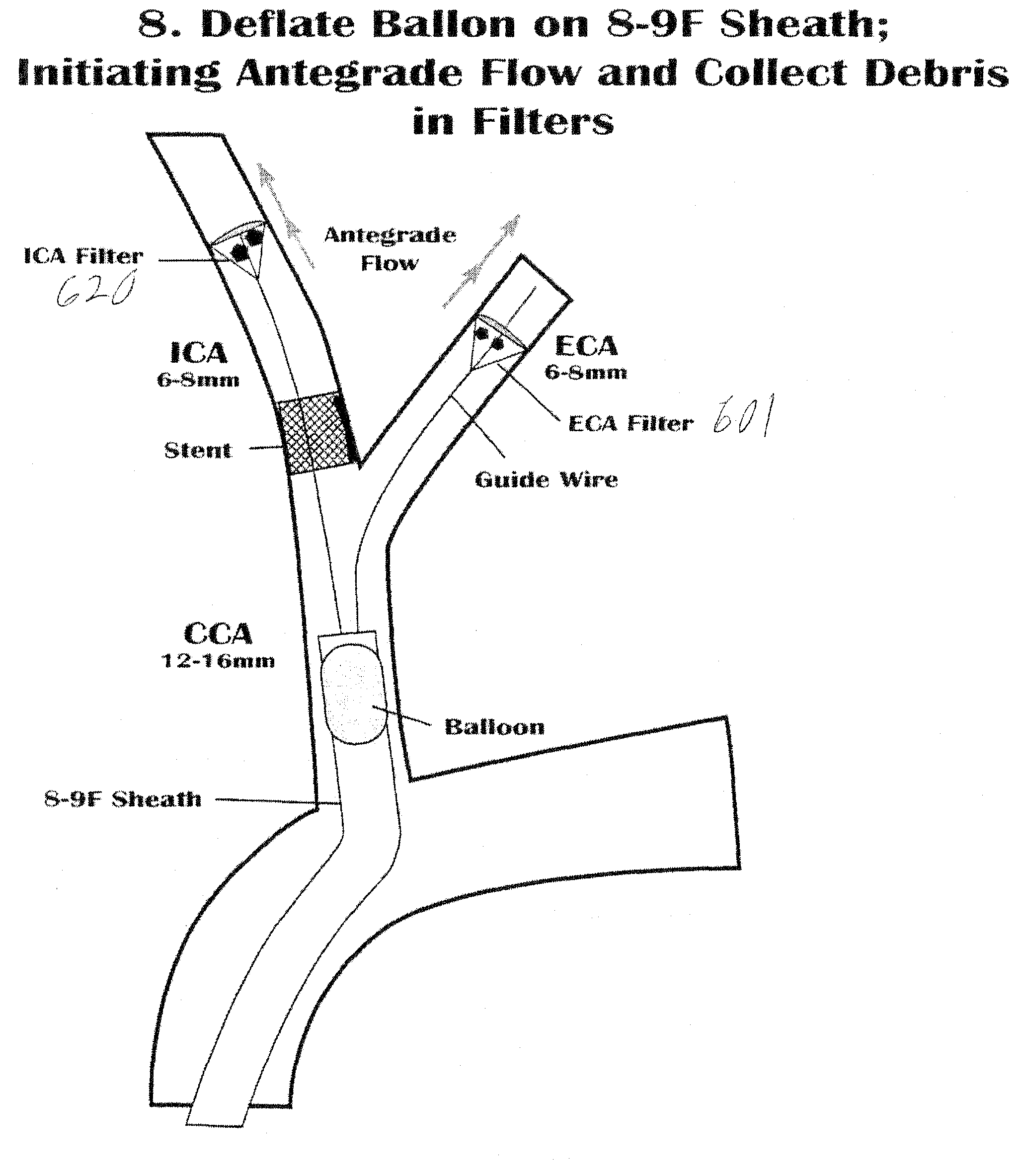
Medical treatment systems incorporate inflow catheters to delivery oxygenated blood into a blood vessel. Devices suitable for the removal of emboli can be used with the inflow catheters. Suitable emboli removal structures include, for example, aspiration catheters and / or vascular filters. Blood removed with aspiration catheters can be filtered and returned to the patient through the inflow catheter.
Owner:LUMEN BIOMEDICAL
Temporary vascular filters
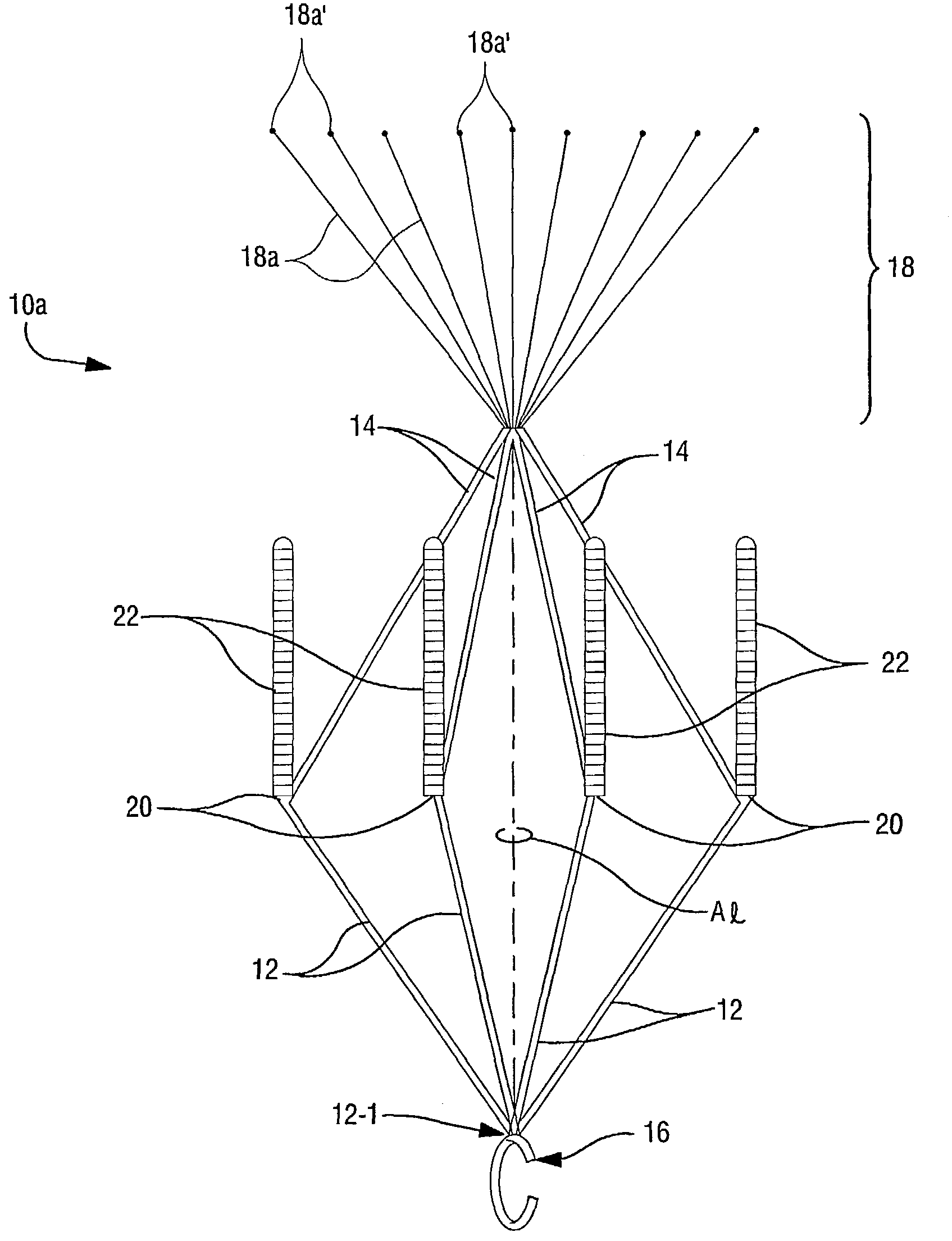
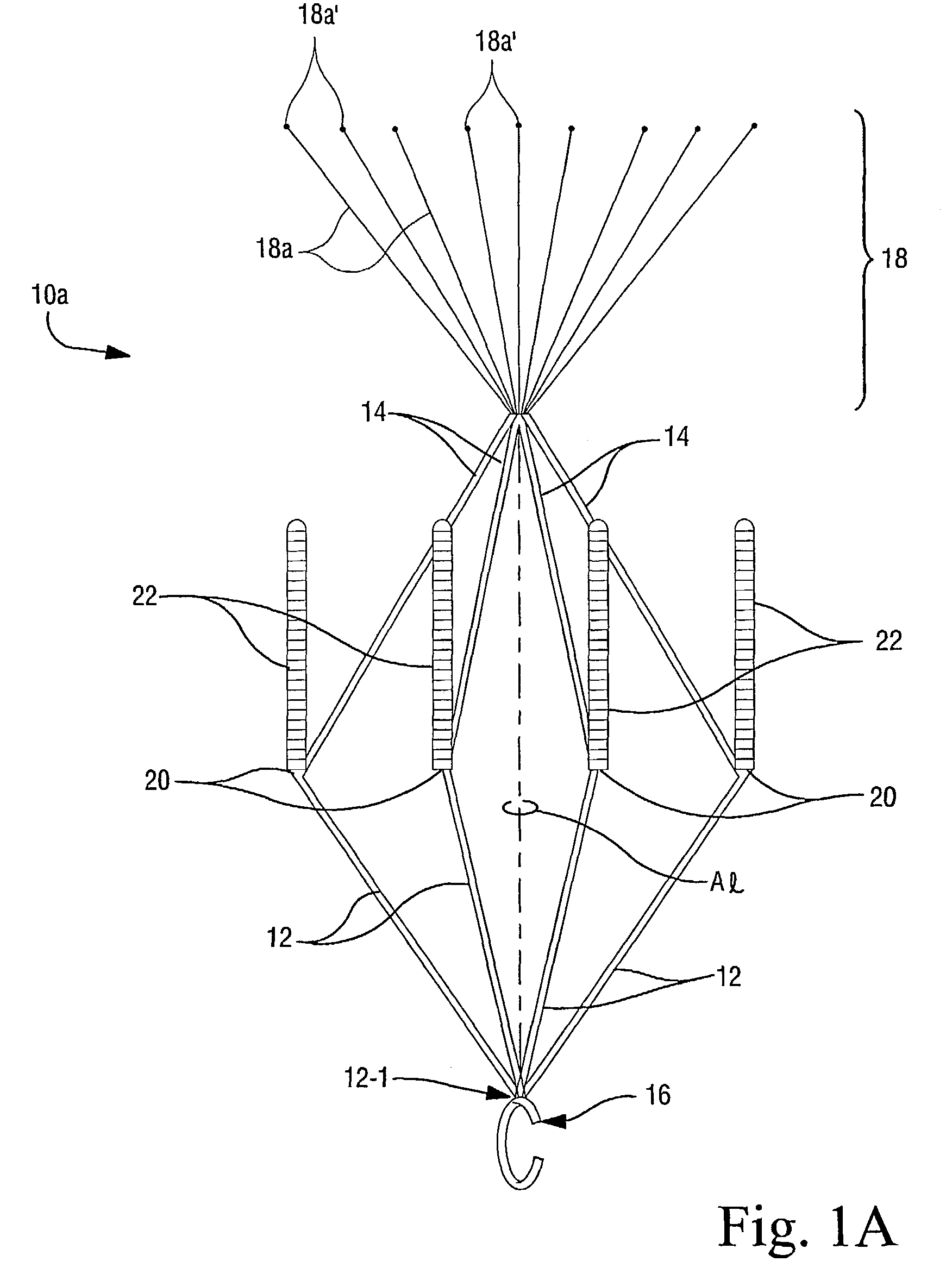
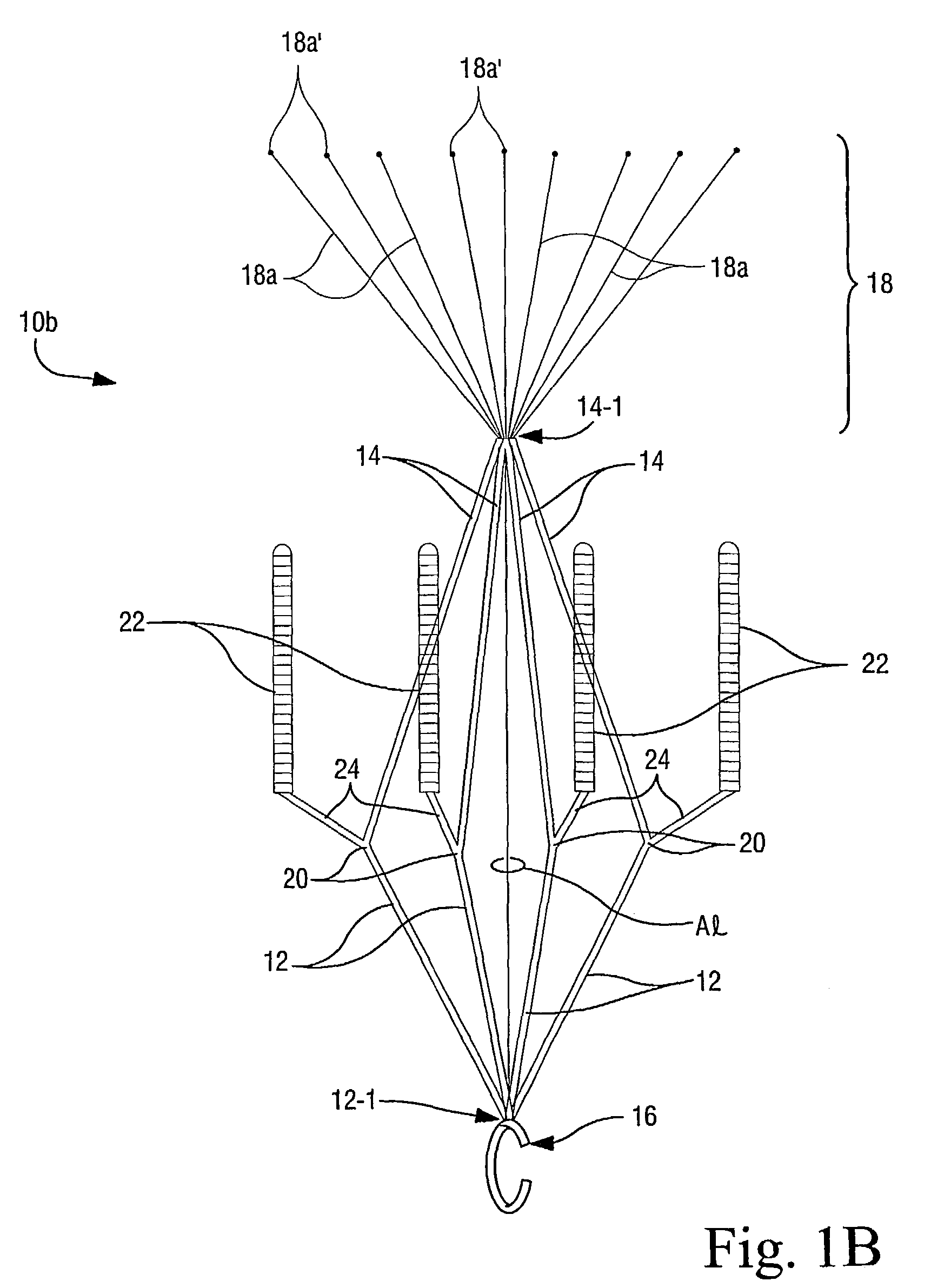
InactiveUS7147649B2Easily and safely removableEasily and safely removedStentsSurgeryVascular filterVascular endothelium
Blood filters (10a, 10b) sized and configured to be positioned within a vascular vessel include a plurality of anchoring arms (22) having a removable sleeve (22-2) for temporarily anchoring the blood filter to a vessel wall. In especially preferred embodiments, the removable sleeve (22-2) is formed of bioabsorbable material. When the filter (10a, 10b) is deployed, it is this removable sleeve (22-2) which comes into contact with the inner tissue wall of the patient's blood vessel (typically the inferior vena cava). When it is desired to remove the filter, endothelization of the sleeve (22-2) has typically occurred but since the sleeves are a removable (separable) component part of the anchoring arms (22), the entire filter device (10a, 10b) can be retrieved thereby leaving the endothelized sleeves (22-2) remaining in place on the interior wall of the patient's vascular vesse. However, such sleeves (22-2) will be absorbed over time (preferably by means of hydrolysis) since they are formed of a bioabsorbable polymeric material. In such a manner, the filters (10a, 10b) of the present invention allow relatively easy retrieval while minimizing (if not preventing entirely) harm to the vascular endothelium.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Vascular filter with improved strength and flexibility
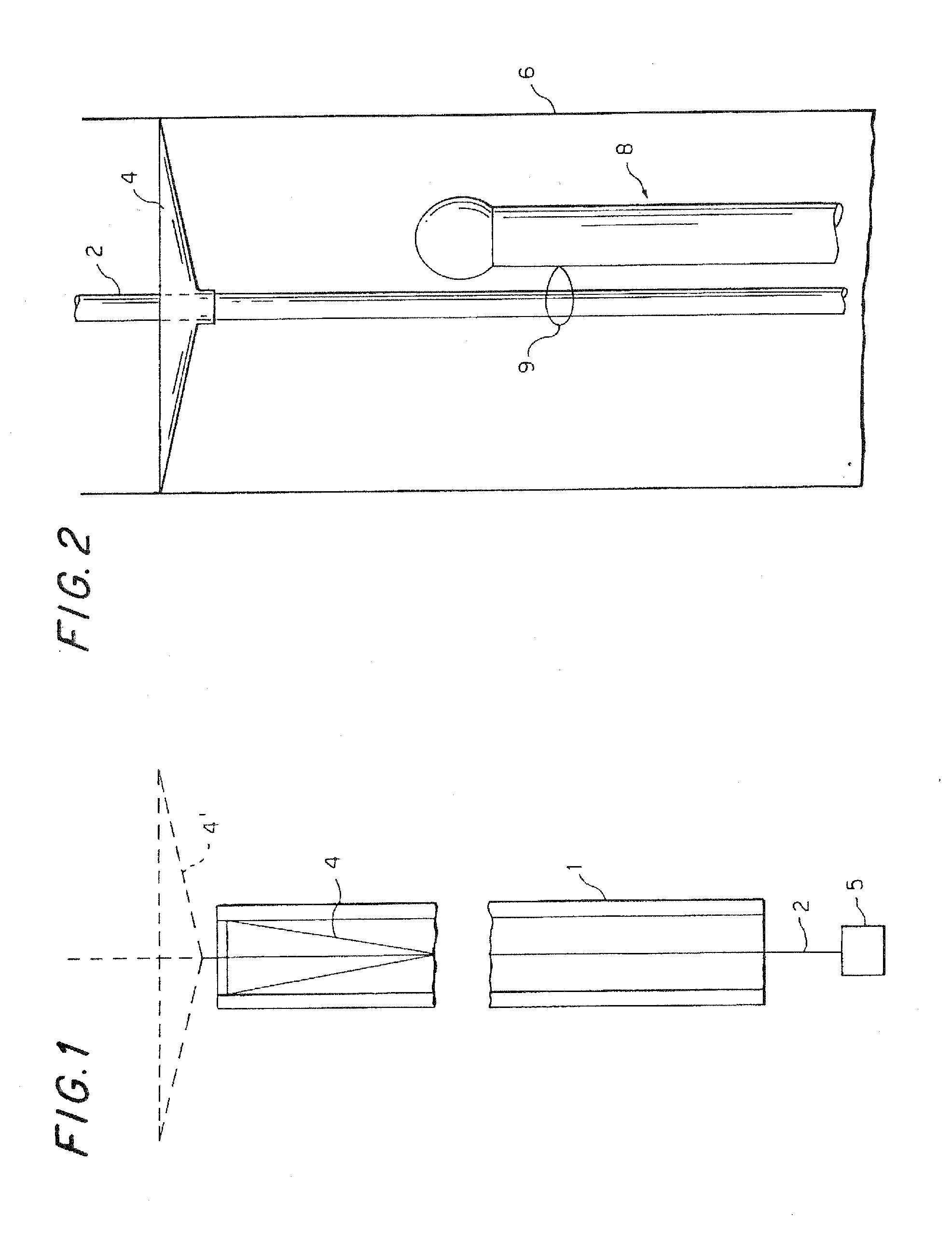
A method and apparatus for treating a patient having an obstruction in a first blood vessel through which blood normally flows in a given direction, at a location downstream of a branch point where the first blood vessel and, a second blood vessel branch off from a main blood vessel, by: blocking blood flow in the main blood vessel at a point upstream of the branch point; inserting into the second blood vessel a first filter adapted to pass blood while trapping debris resulting from removal of the obstruction; inserting an obstruction removal assembly into the first blood vessel and operating the assembly to at least partially break up the obstruction and produce debris; withdrawing the obstruction removal assembly from the patient's body; and then inserting into the first blood vessel a filter adapted to pass blood while trapping debris; then restoring blood flow in the main blood vessel.
Owner:DON MICHAEL INT
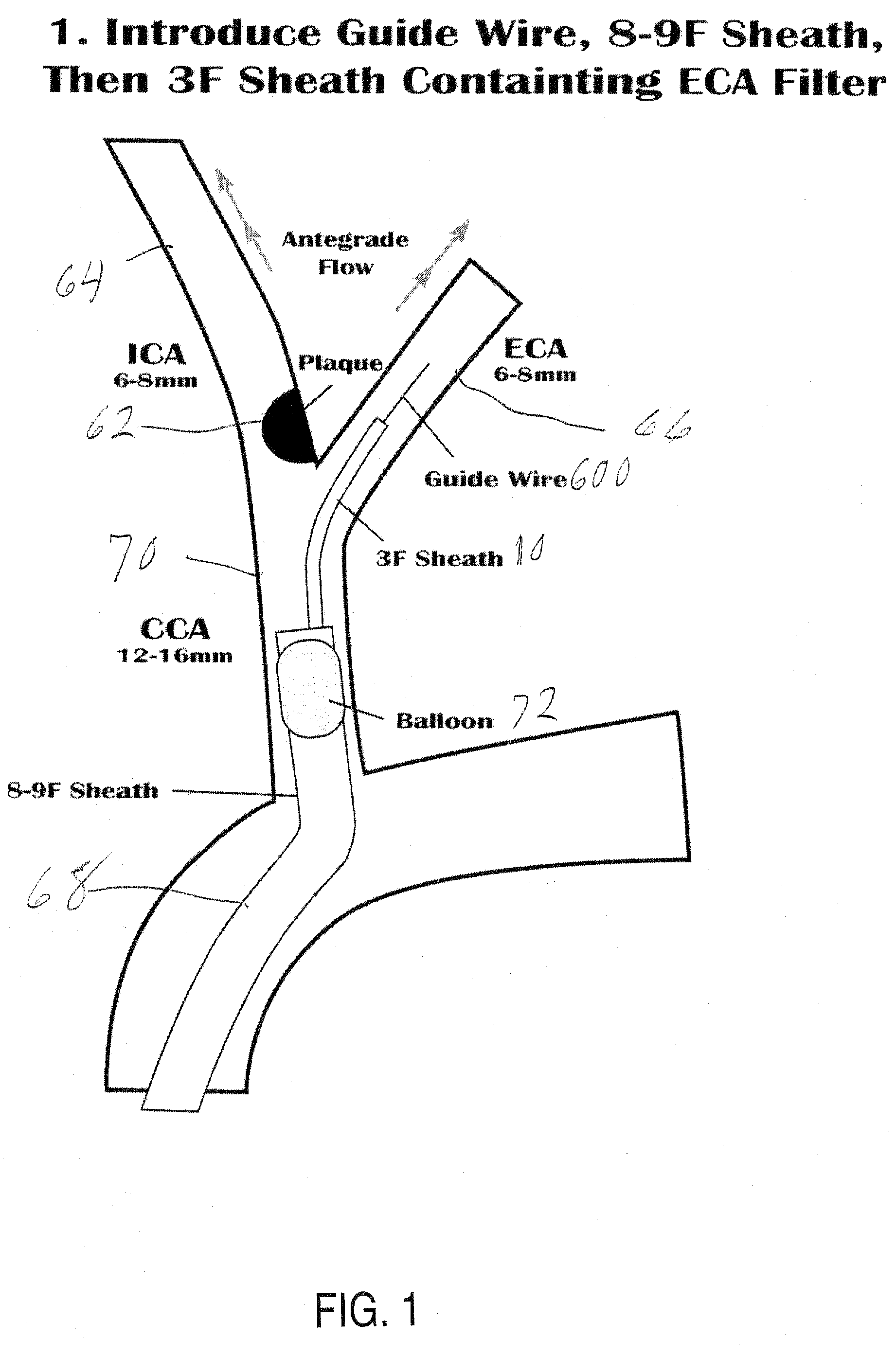
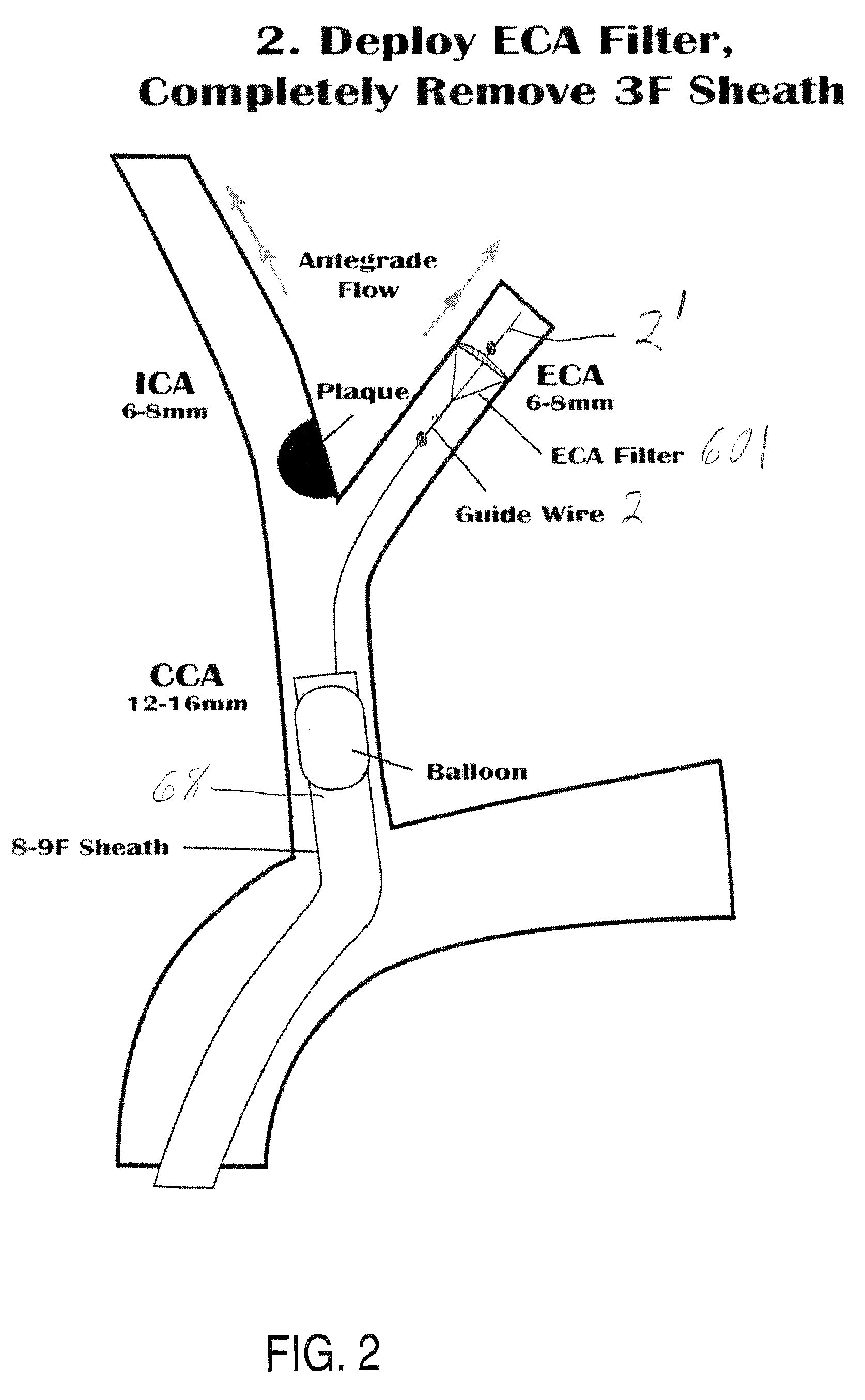
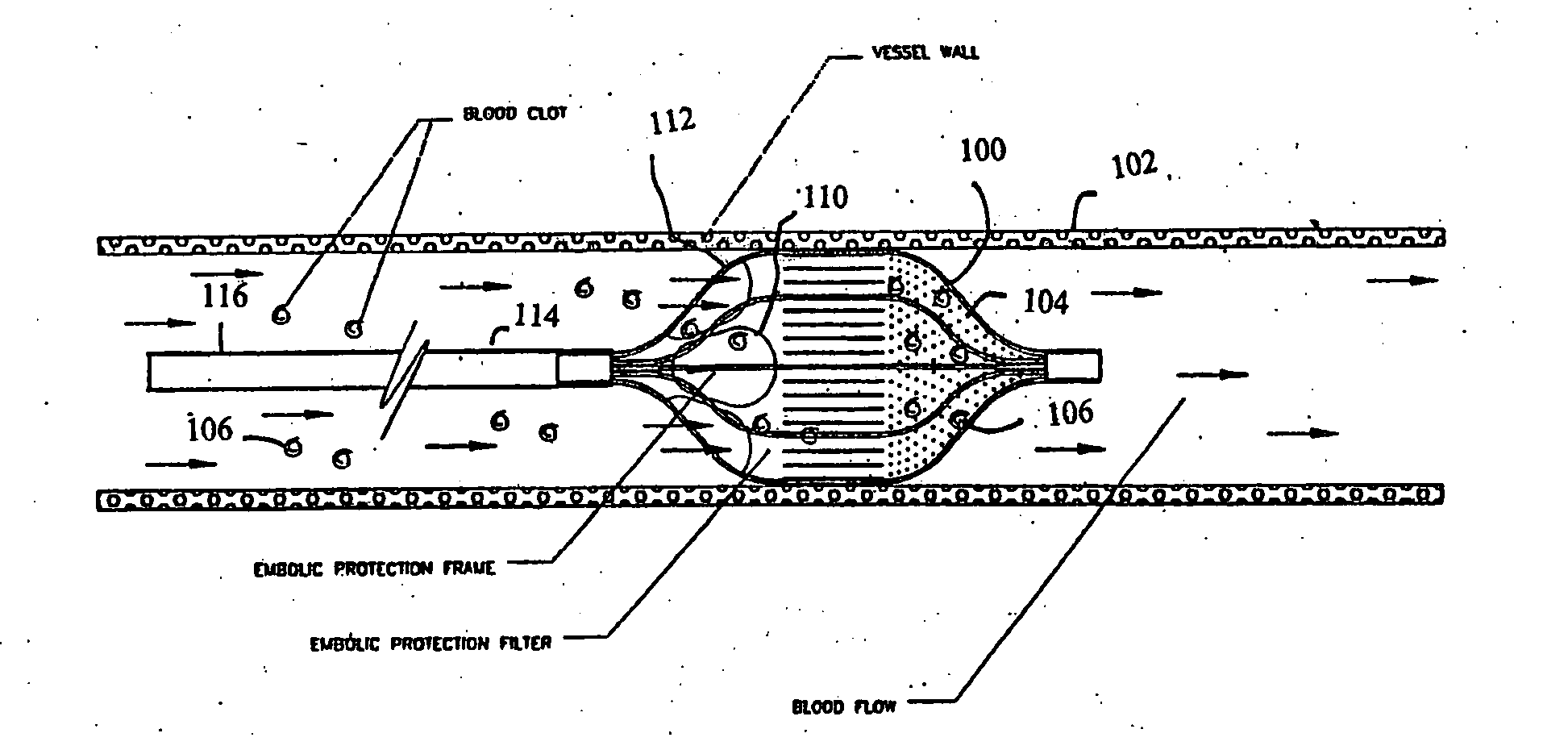
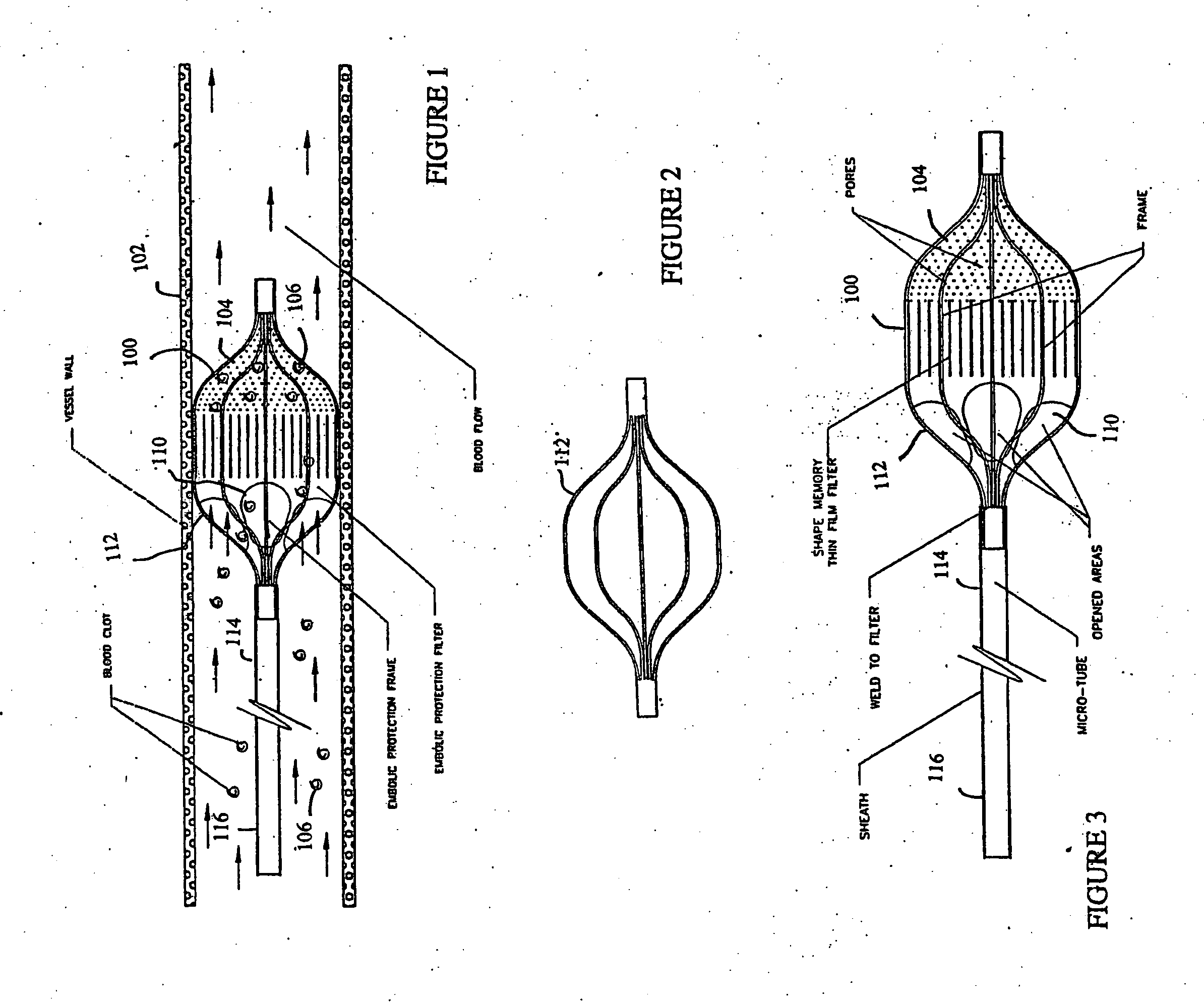
Shape memory thin film embolic protection device with frame
InactiveUS20060100659A1Reducing macroReducing micro-embolizationSurgeryDilatorsContinuous perfusionVascular filter
A removable vascular filter system for capture and retrieval of emboli while allowing continuous perfusion of blood. This system is useful for any percutaneous angioplasty, stenting, thrombolysis or tissue ablation procedure. The system may minimize the incidence of stroke, myocardial infarction or other clinical complications that may be associated with these procedures.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC +1
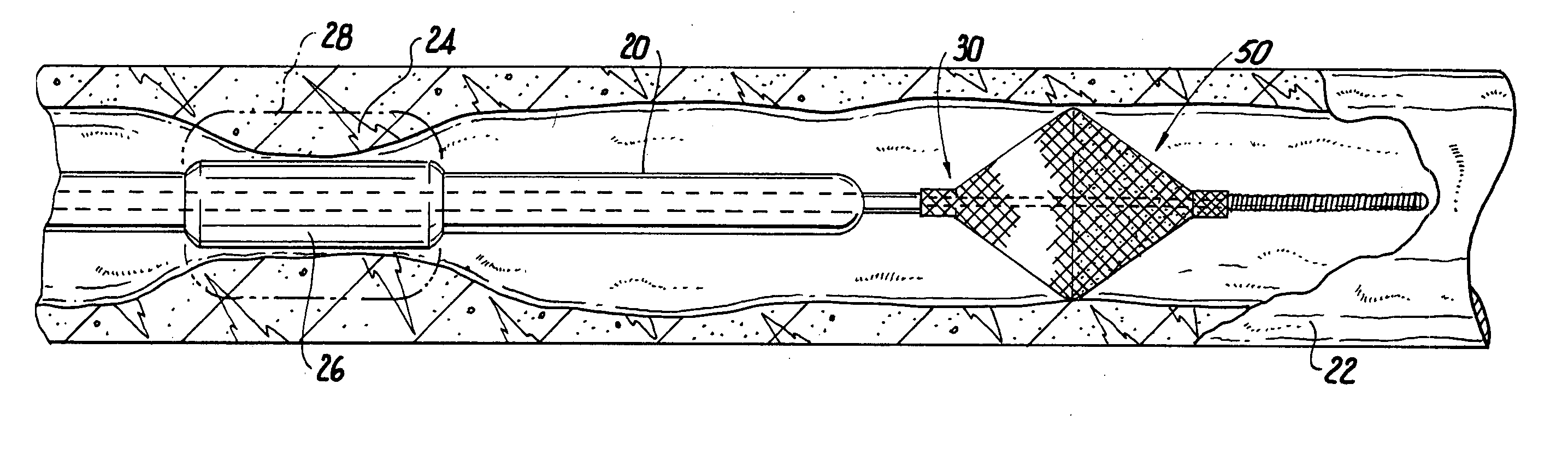
Intravenous deep vein thrombosis filter and method of filter placement
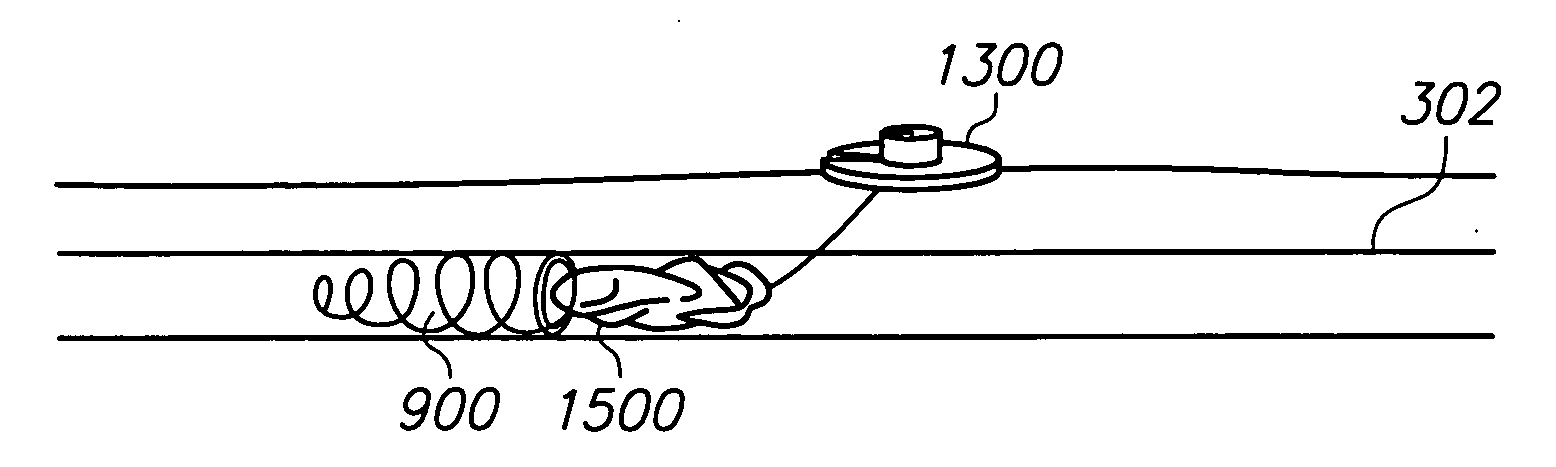
A vascular filter system and method are disclosed. In one embodiment, the filter system comprises a dispensing needle releasably attached to a filter dispenser which stores a length of filter wire. The filter wire dispenser has a guide tube which guides the filter wire into the needle and then into a vein during surgical implantation. The filter wire is configured to coil into a predetermined shape as it is deployed from the needle. The shape of the filter wire captures blood clots in the blood stream. Once the filter wire is deployed, the needle may be removed and a portion of the filter wire may be left protruding from the patient's skin surface to allow the filter wire to be secured by a fixation device. A syringe may be used to draw blood to confirm that the needle is properly positioned within a vein before the filter wire is deployed.
Owner:BATISTE STANLEY
Vascular filter system for cardiopulmonary bypass
InactiveUS7229463B2Other blood circulation devicesSurgeryExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
A removable vascular filter system for capture and retrieval of emboli while allowing continuous perfusion of blood during a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure, comprising a porous filter membrane with variable diameter holes, and a filter membrane support structure. The system may minimize the incidence of stroke, myocardial infarction or other clinical complications that may be associated with cardiopulmonary bypass procedures.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Slideable vascular filter
A collapsible medical device for use, e.g., as a vascular filter. The device includes a mandrel having a distal end and a stop spaced proximally of the distal end. A proximal length of the mandrel extends proximally of the stop and a distal length of the mandrel extends distally of the stop. A functional element (e.g., a vascular filter) has a radially expandable body and includes a proximal slider and a distal slider. The proximal and distal sliders are slidable along the mandrel independently of one another such that the distance between the proximal slider and distal slider can be varied to effect different configurations of the functional element. In one method of using such a device, the functional element is urged distally to a treatment site by urging the mandrel distally. This causes the stop to exert a distal biasing force on the distal slider, which acts against a restorative force of the functional element to axially elongate the functional element and reduce friction between the functional element and a wall of the vessel.
Owner:KUSLEIKA RICHARD S +1
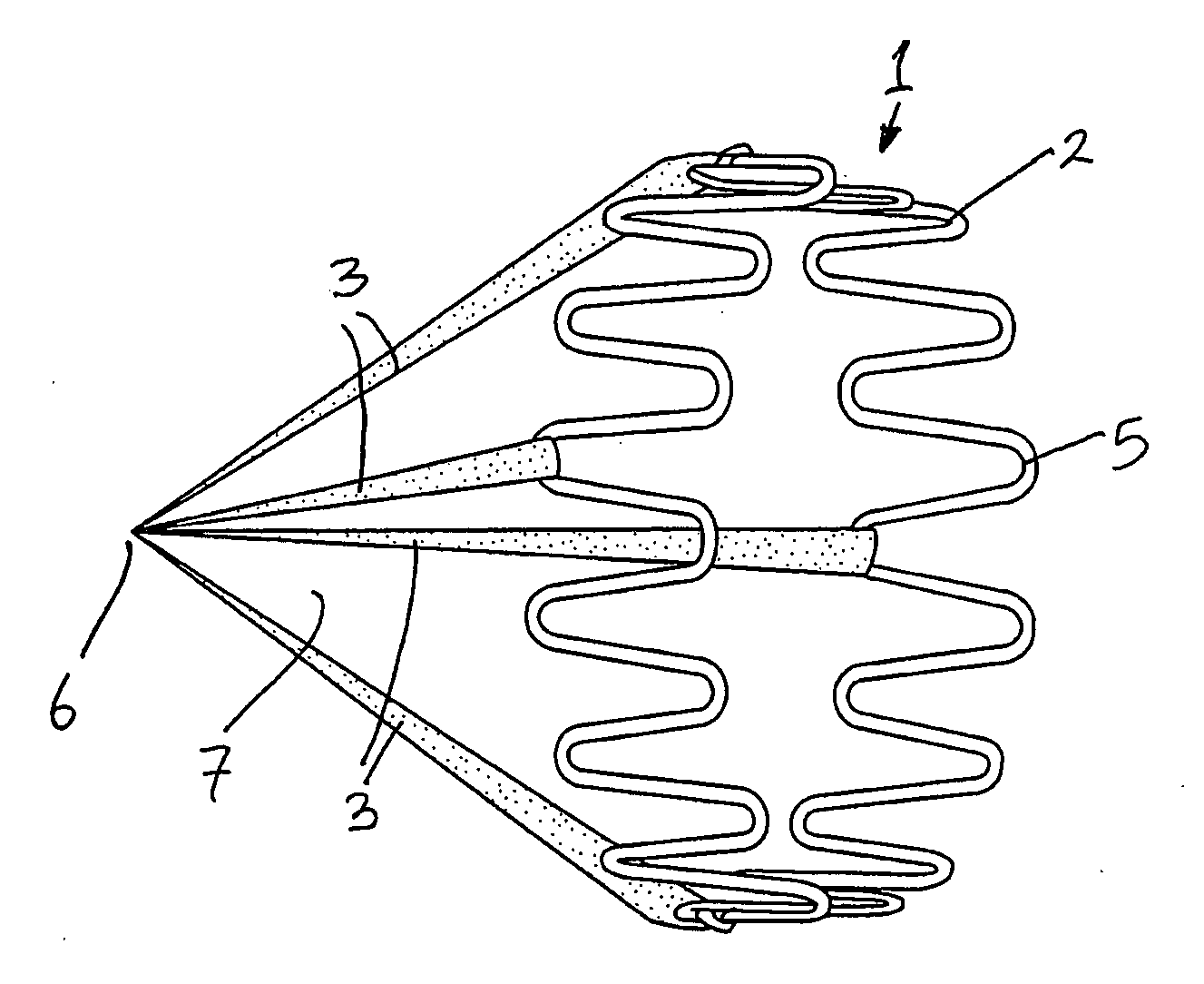
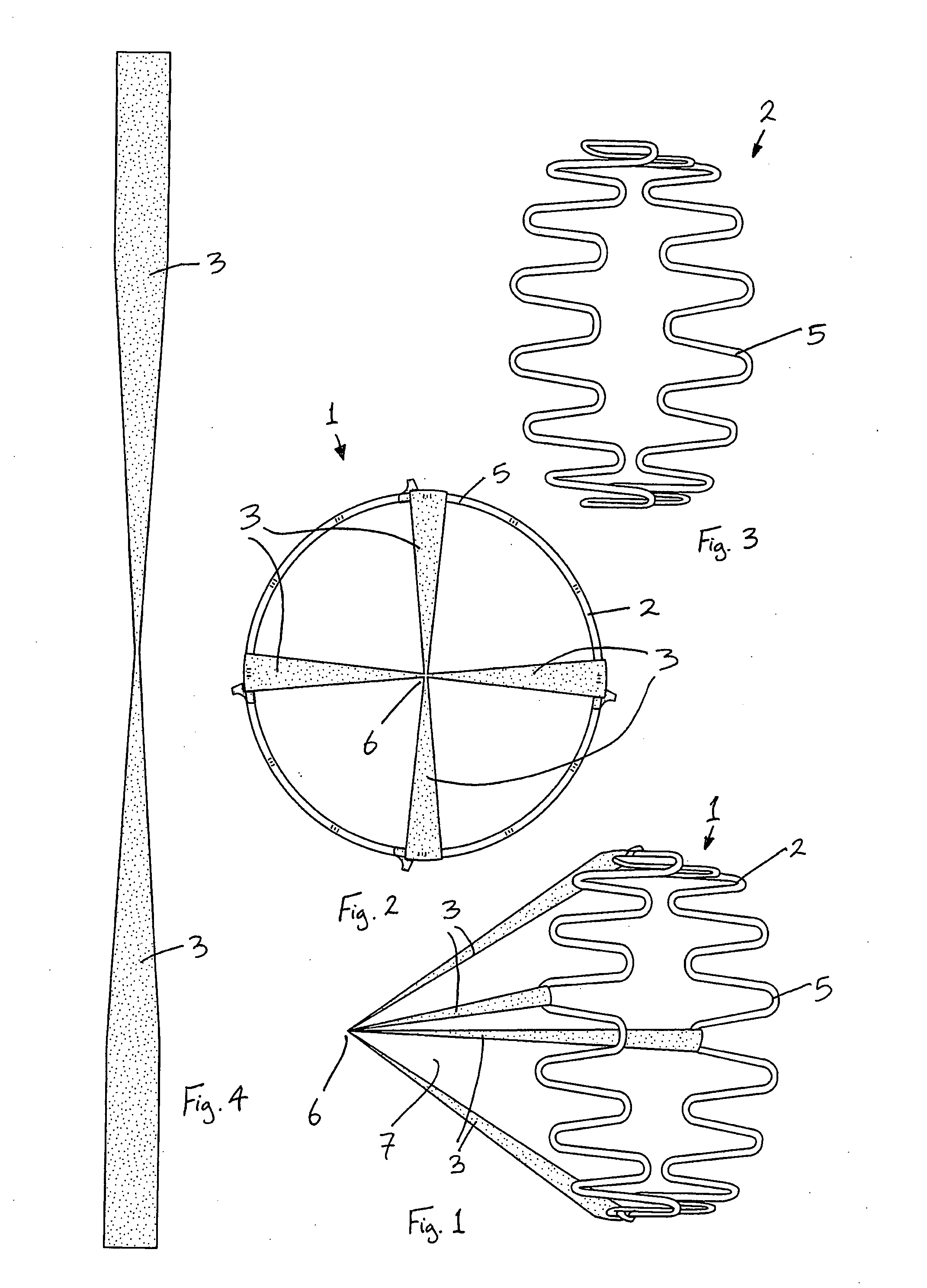
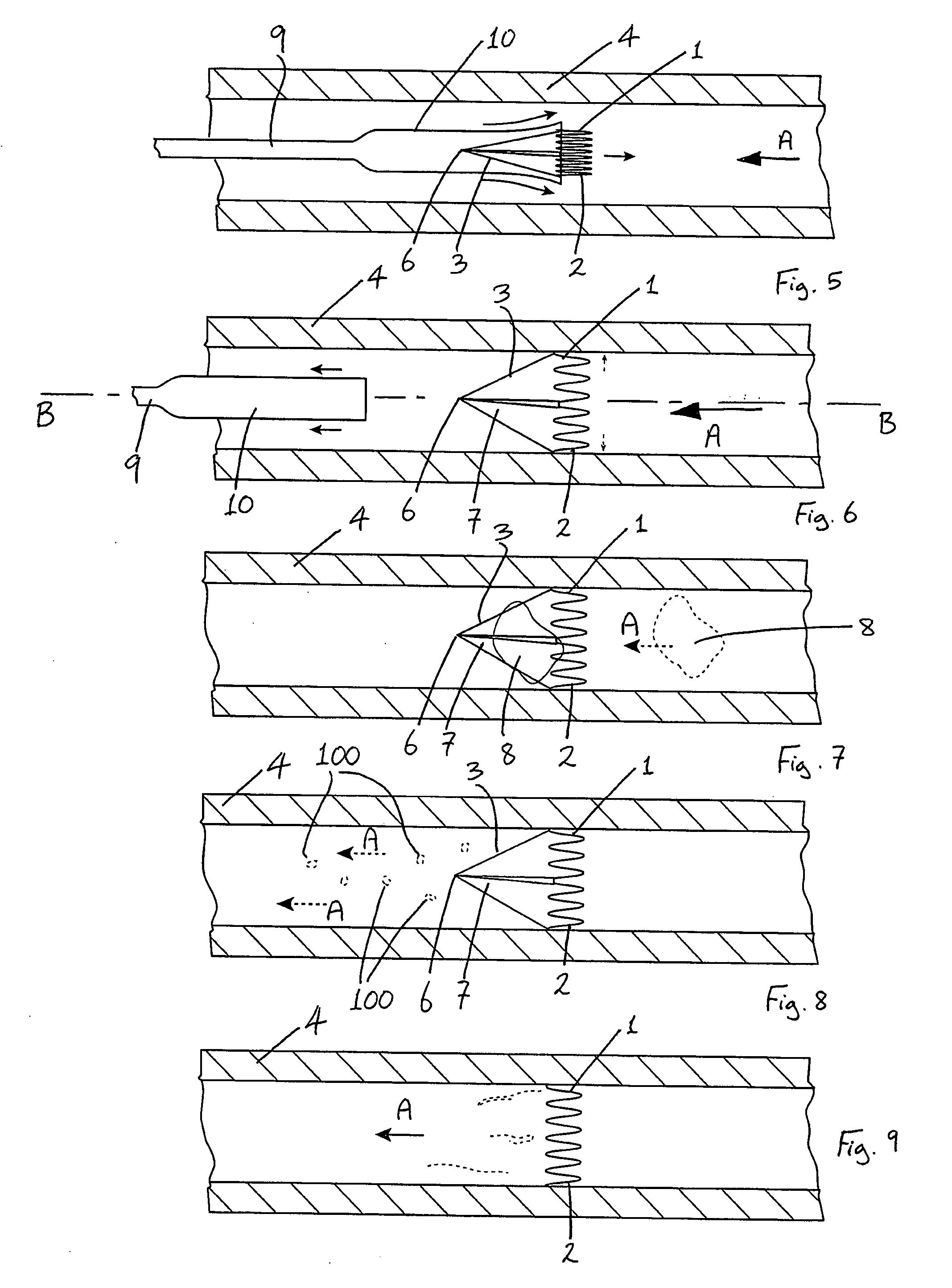
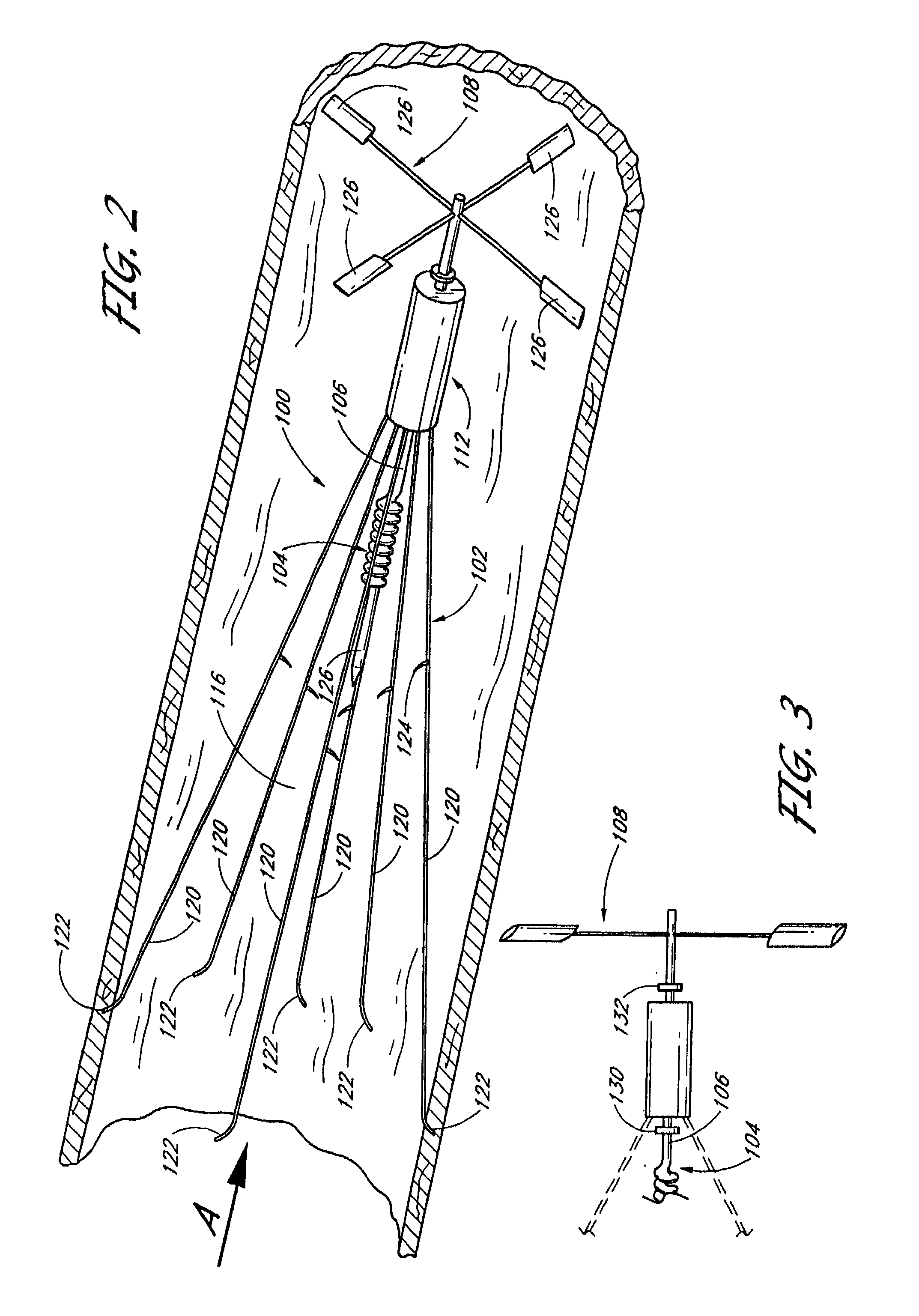
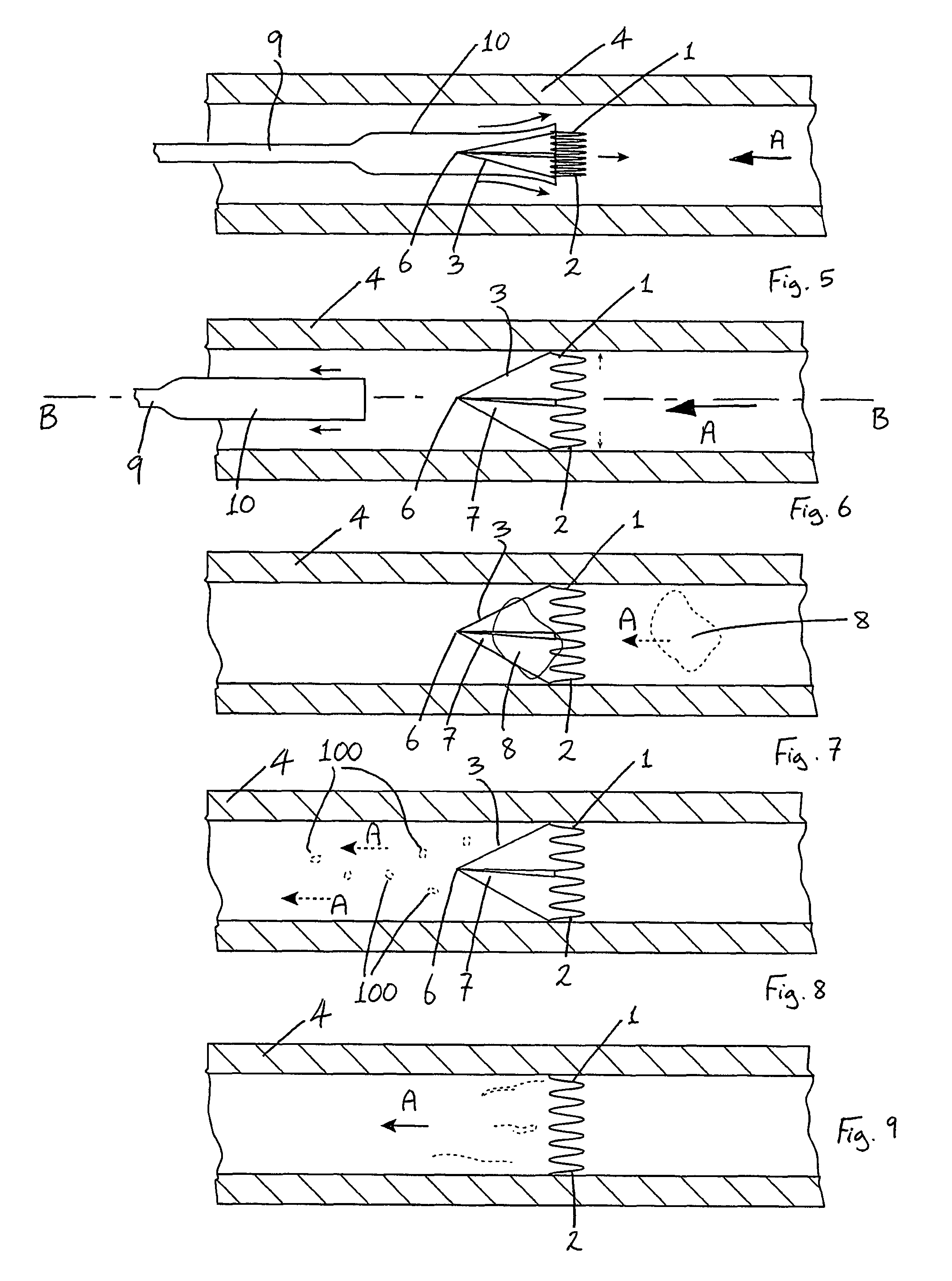
Vascular Filter Device
InactiveUS20070208370A1High dissolution rateReduce the possibilityDilatorsExcision instrumentsVascular filterDissolution
A vascular filter for capturing and breaking apart particles in the blood. The vascular filter includes a filter body and an agitation member disposed within the filter body. Movement of the agitation member acts on particles trapped within the filter body for enhancing the dissolution of the particles, thereby reducing the likelihood of filter occlusion and improving the flow of blood through the vessel. The vascular filter is preferably collapsible for percutaneous delivery to a treatment site. The agitation member is preferably rotatably coupled to the filter body and a flow receiving member is provided for causing the agitation member to rotate. A clutch mechanism may be provided such that the agitation member only rotates when a particle, such as a blood clot, is trapped within the filter body.
Owner:INARI MEDICAL INC
Temporary vascular filter, guide wire
A vascular filter guide wire is disclosed for directing precision placement of a catheter proximate a blood vessel lesion and filtering particulate matter dislodged by treatment of the vessel. The guide wire includes an actuating mechanism, an elongated flexible core wire having a proximal end mounted to the actuating mechanism and a distal end for insertion through a vasculature to a position downstream of the restriction. A tubular flexible shaft is slidably disposed telescopically along the core wire and includes a proximal portion affixed to the actuating mechanism in movable relation to the core wire. The guide wire includes a collapsible filter at its proximal end to the distal portion of the shaft and, at its distal end, to the core wire. The filter deploys radially in response to axial movement of the core wire relative to the shaft so that it can trap particulate matter arising from treatment of the lesion.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Device and method for vascular filter
A device implantable into a blood vessel having a filter to prevent particles from passing into a blood vessel, and having bows extending from a horizontal plain of the device, such bows to hold such device in place in a blood vessel.
Owner:KEYSTONE HEART
Vascular filter device
A vascular filter device comprises a support; and a filter comprising one or more filter elements configured to capture thrombus passing through a blood vessel. A holder holds the filter in a closed filtering state and releases to convert the filter to an open state after a period of time. The filter is adapted to retain thrombus after said conversion. In one case the filter elements are arranged to remain in a closed state after release by the holder, because they are blocked by a retained clot from opening fully, and the filter elements are biased to the open state with a bias level which is counter balanced by force exerted by a retained clot under action of blood flow.
Owner:COVIDIEN GROUP +1
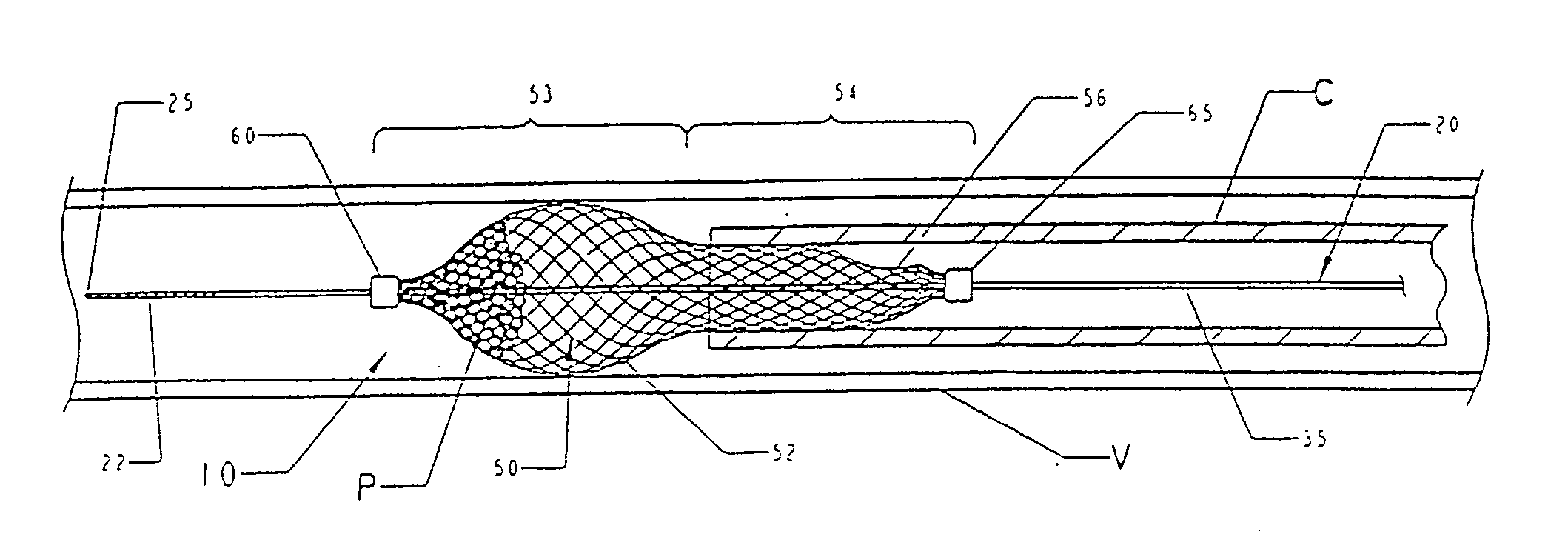
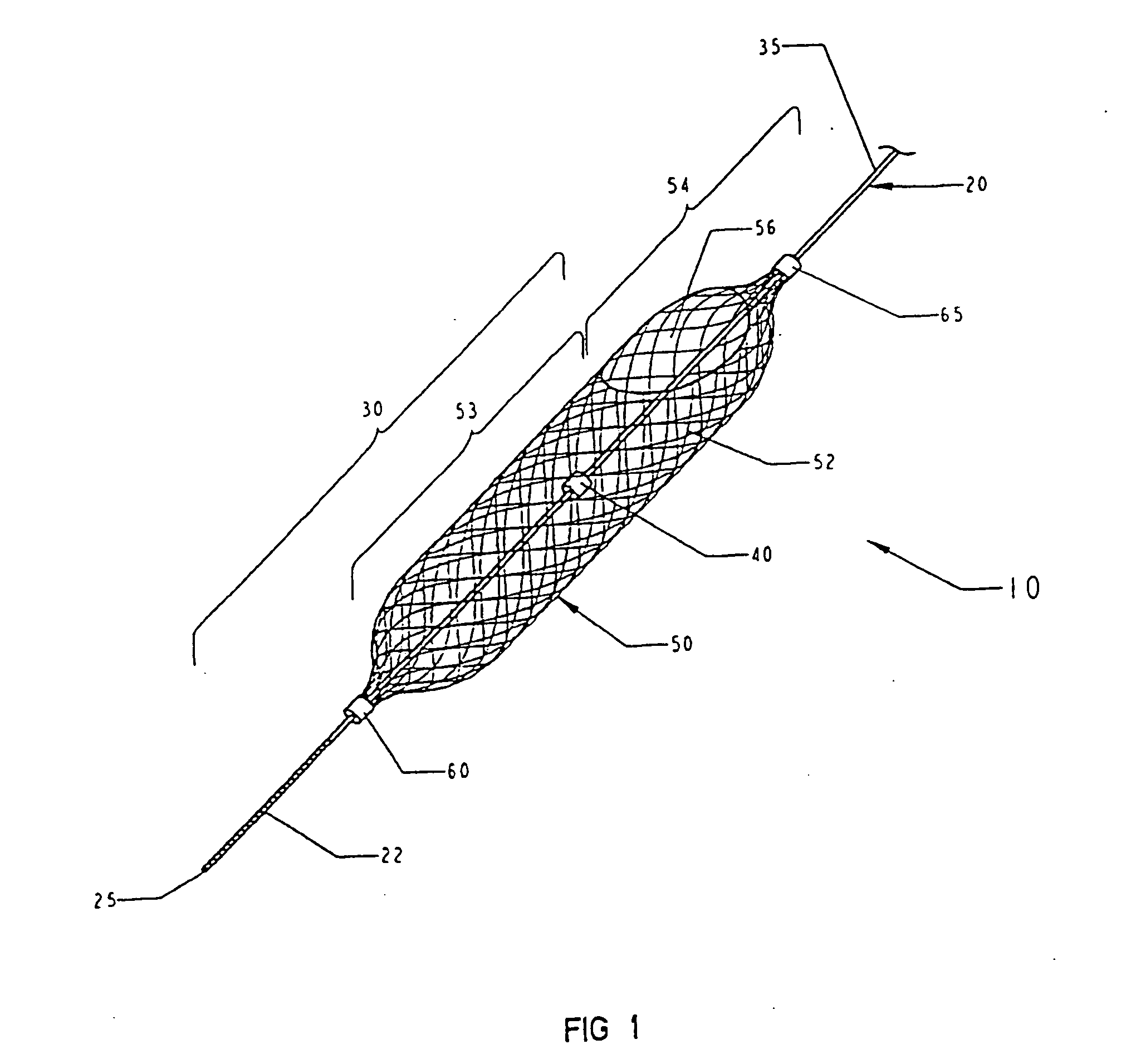
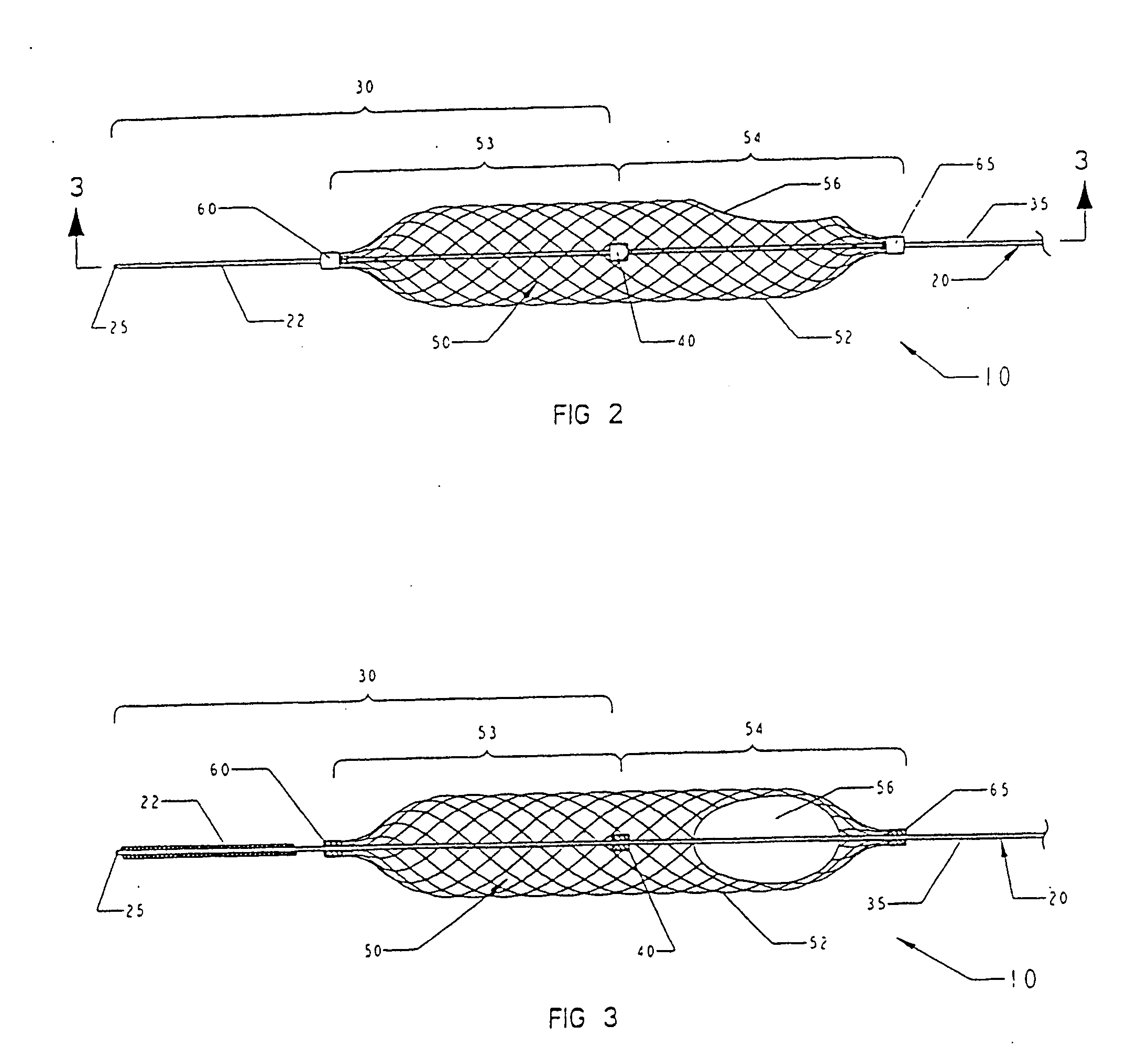
Temporary vascular filter
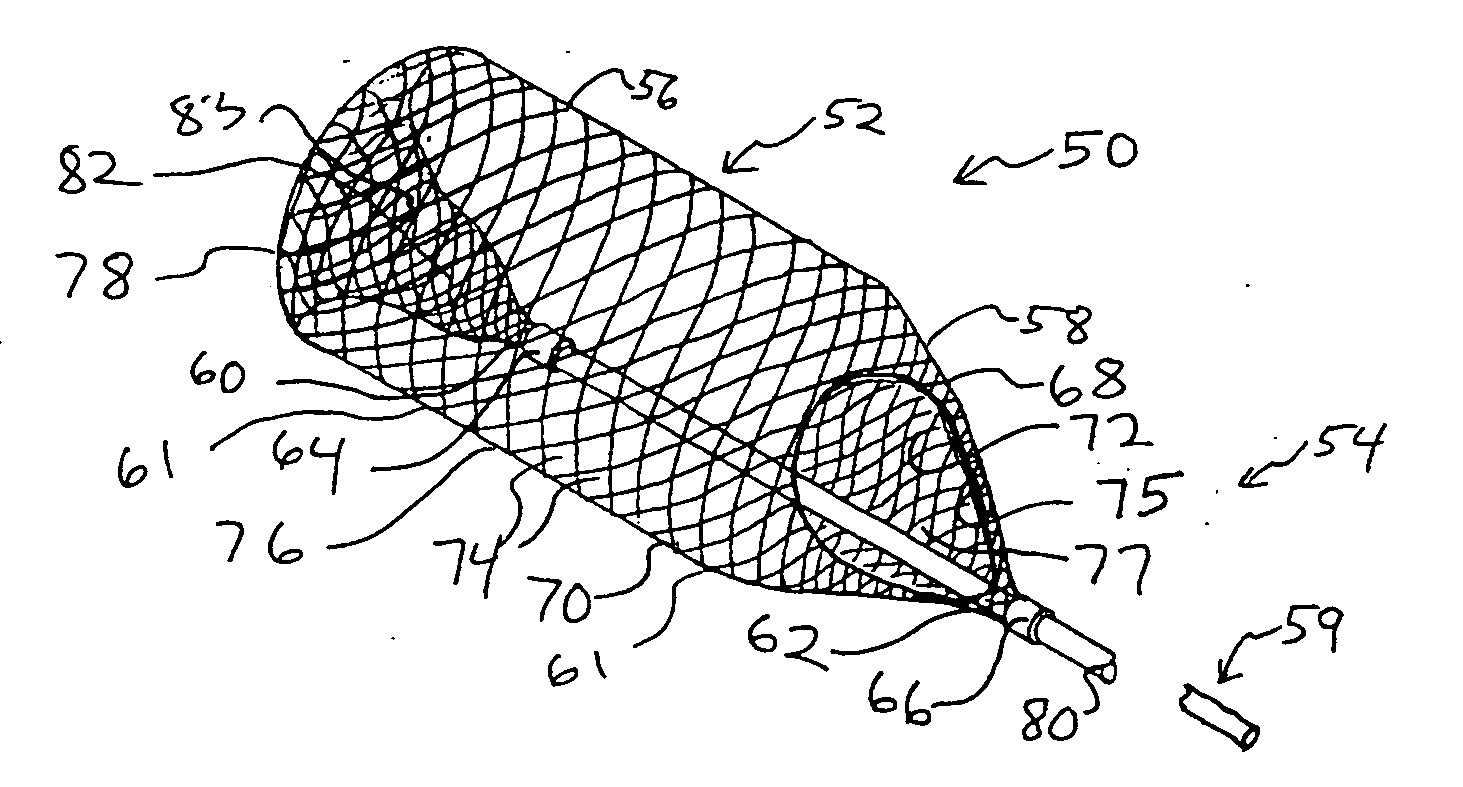
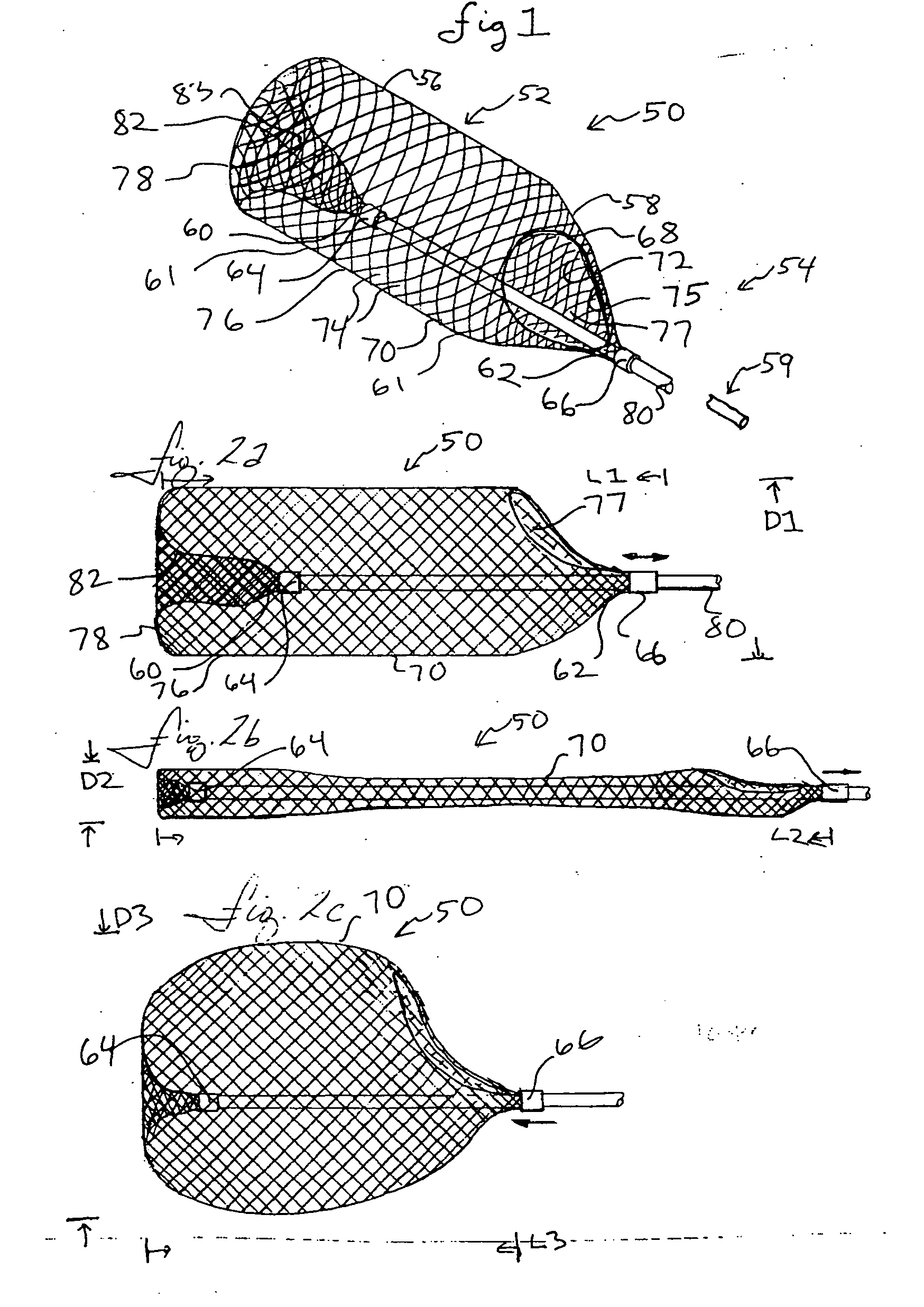
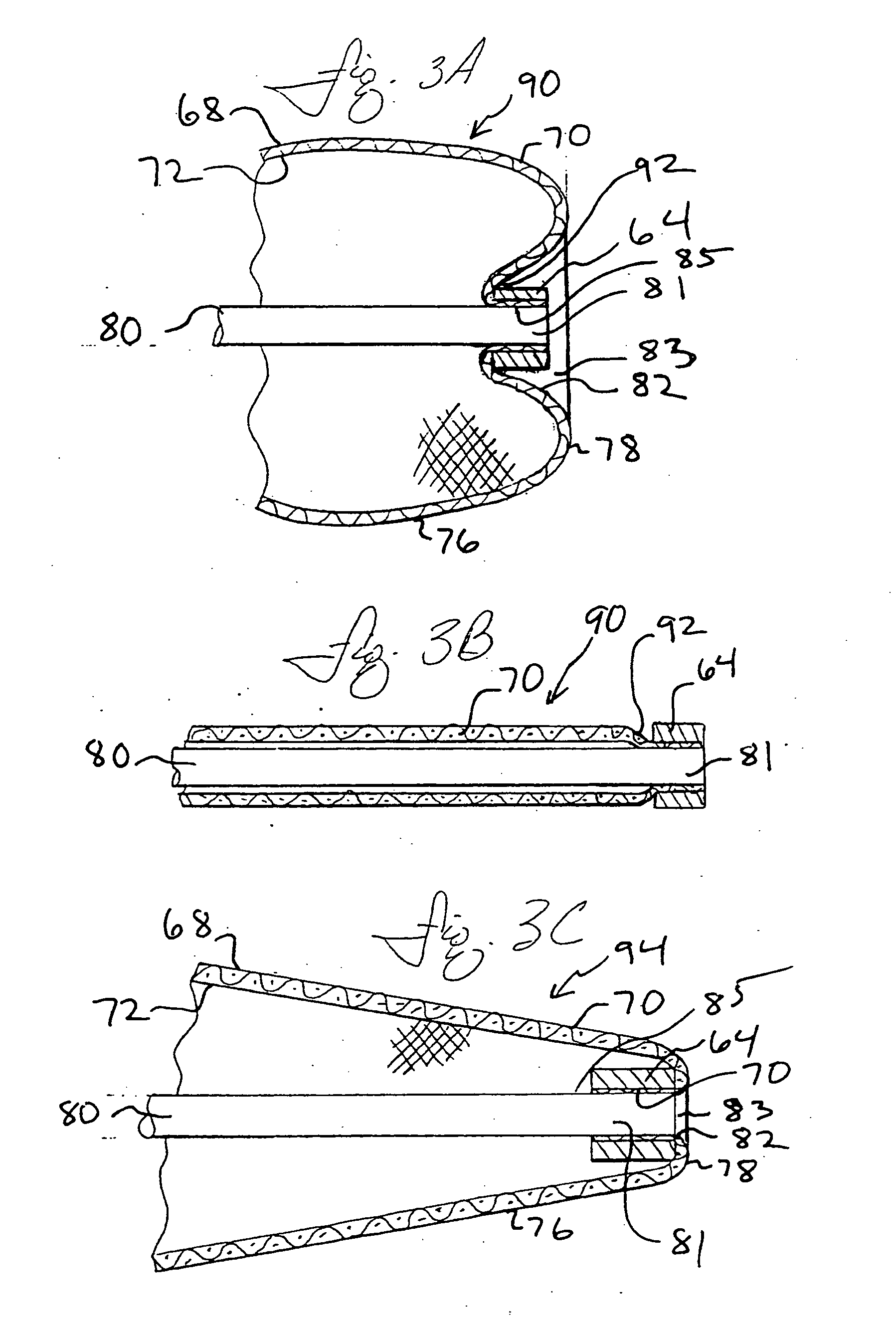
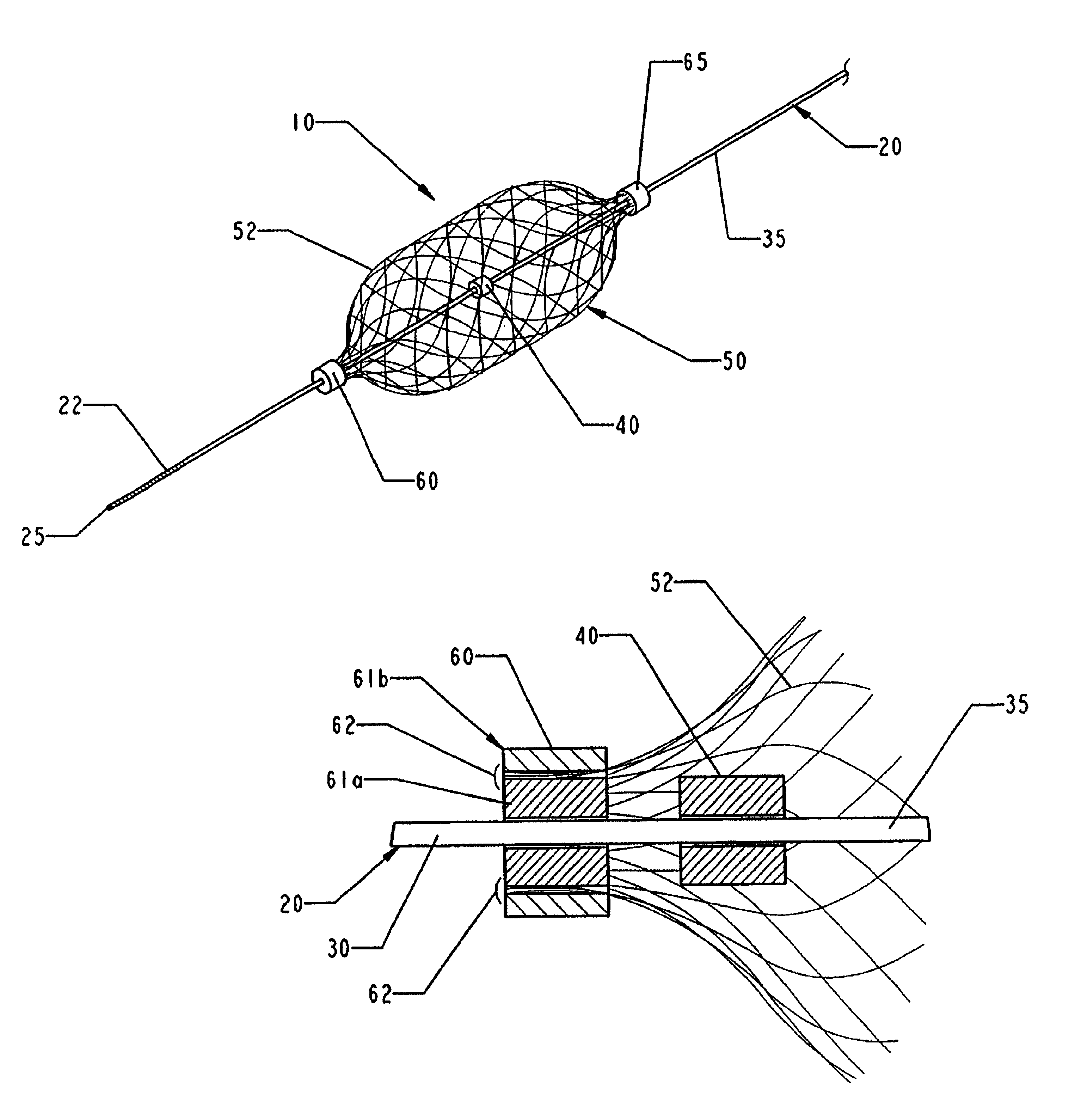
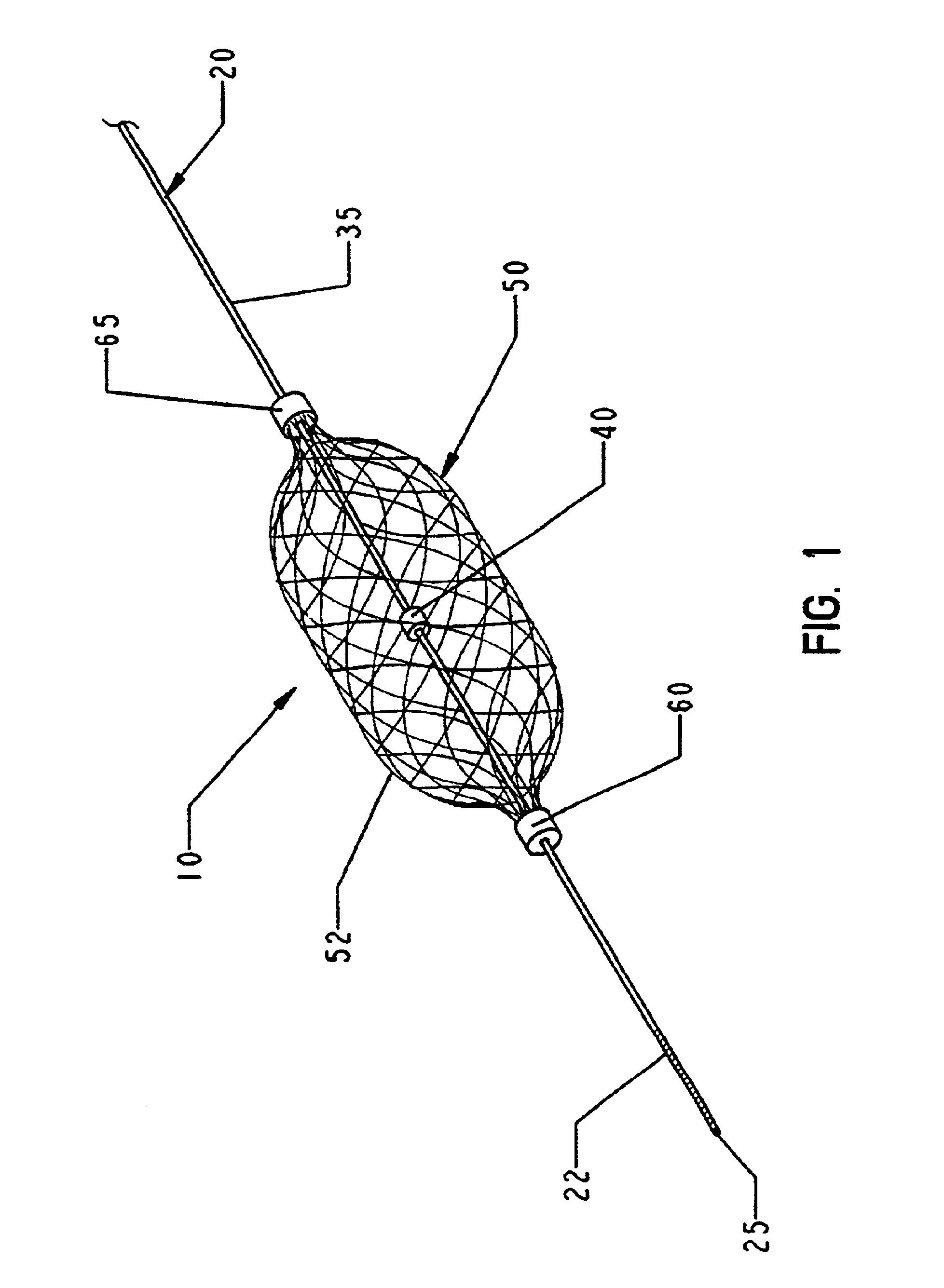
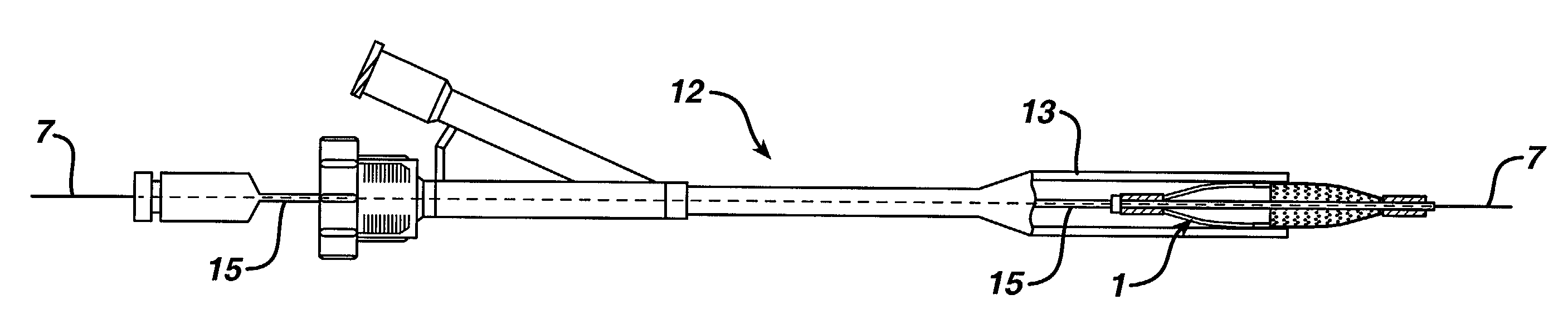
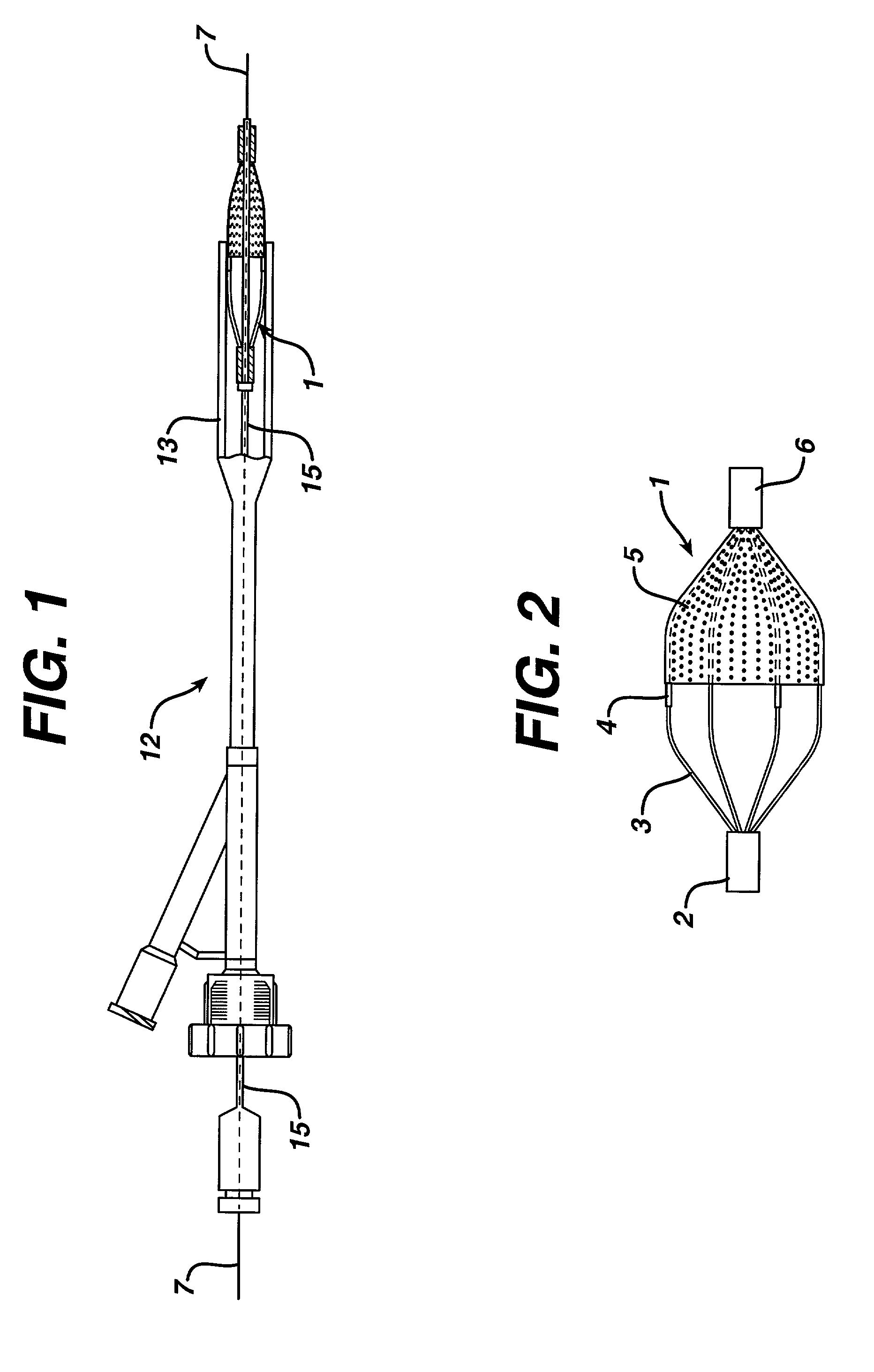
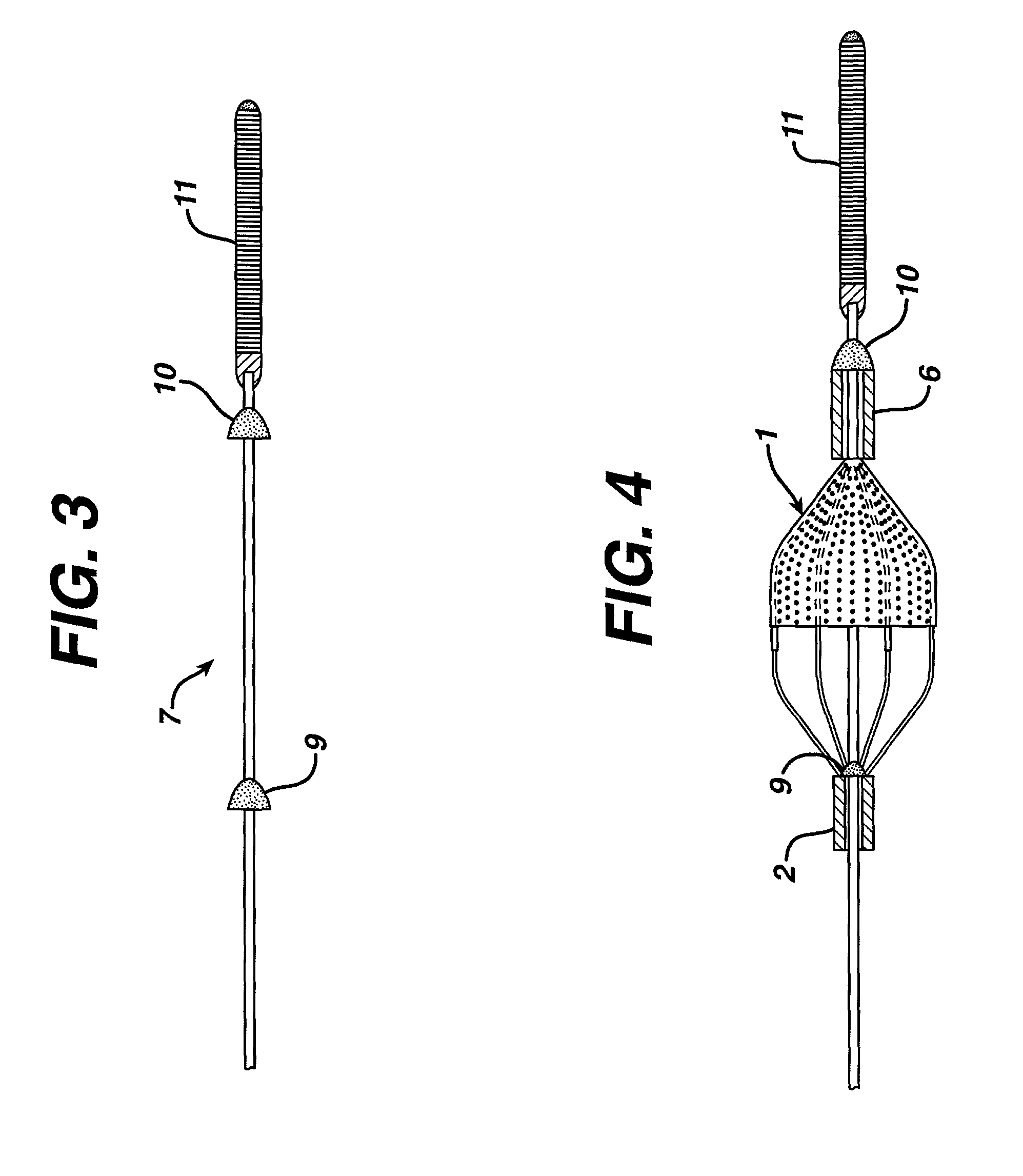
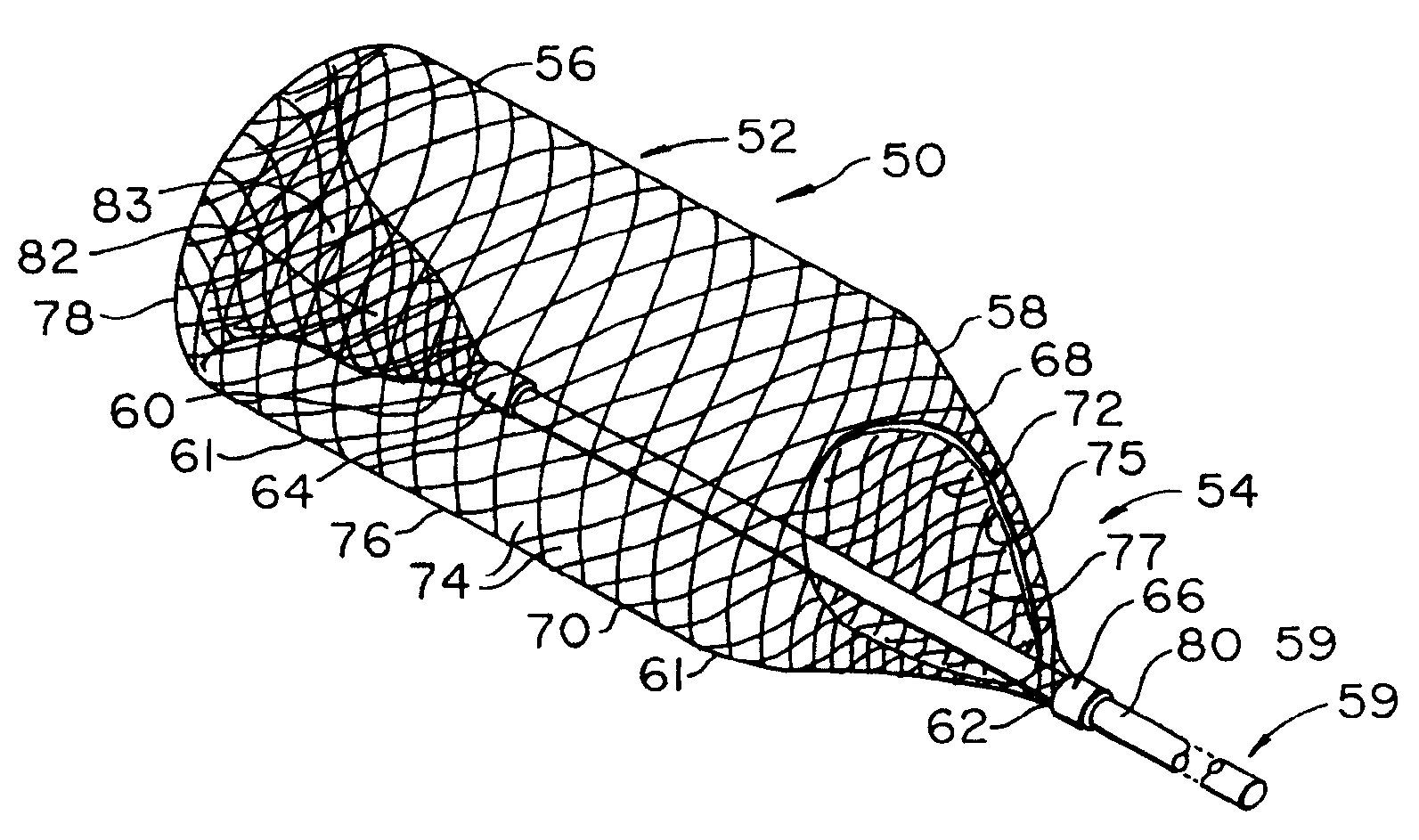
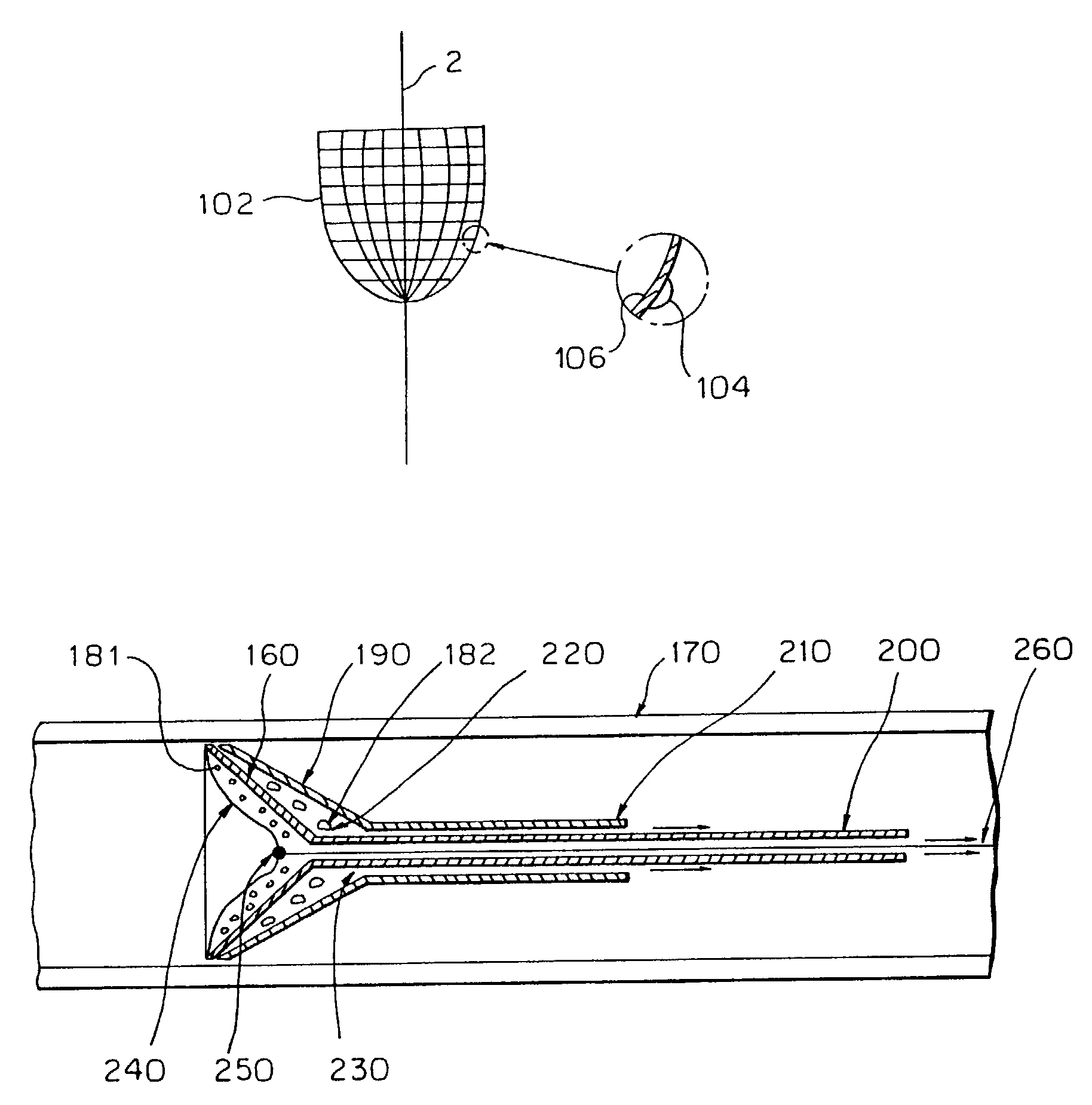
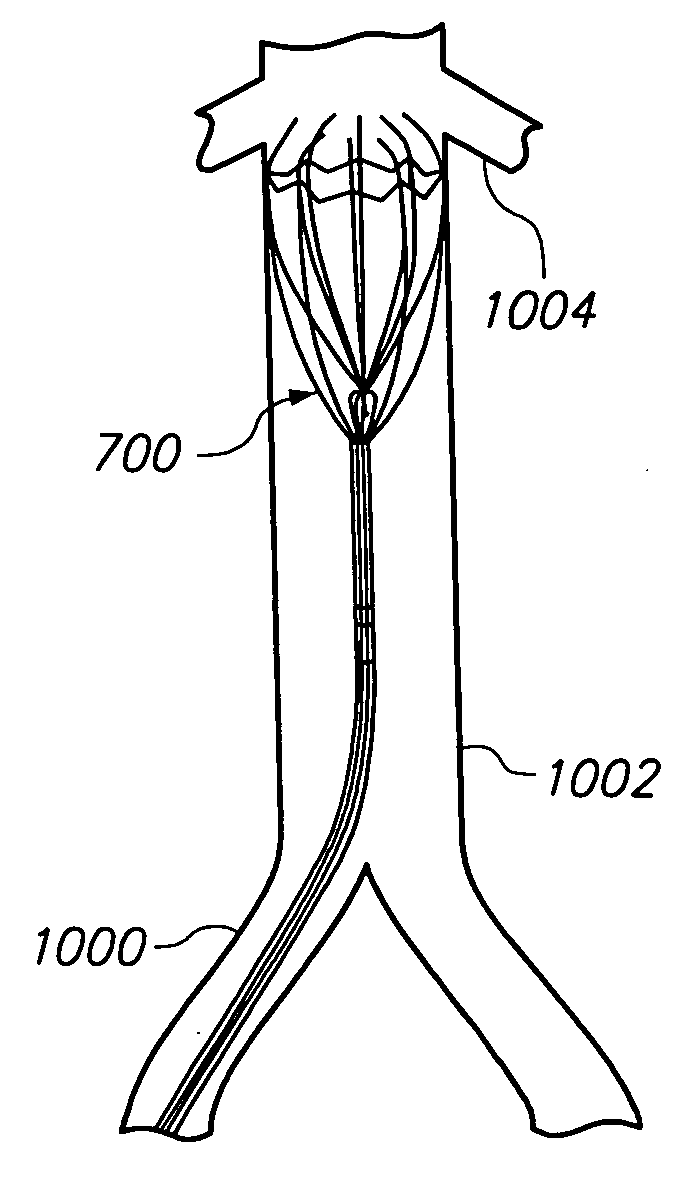
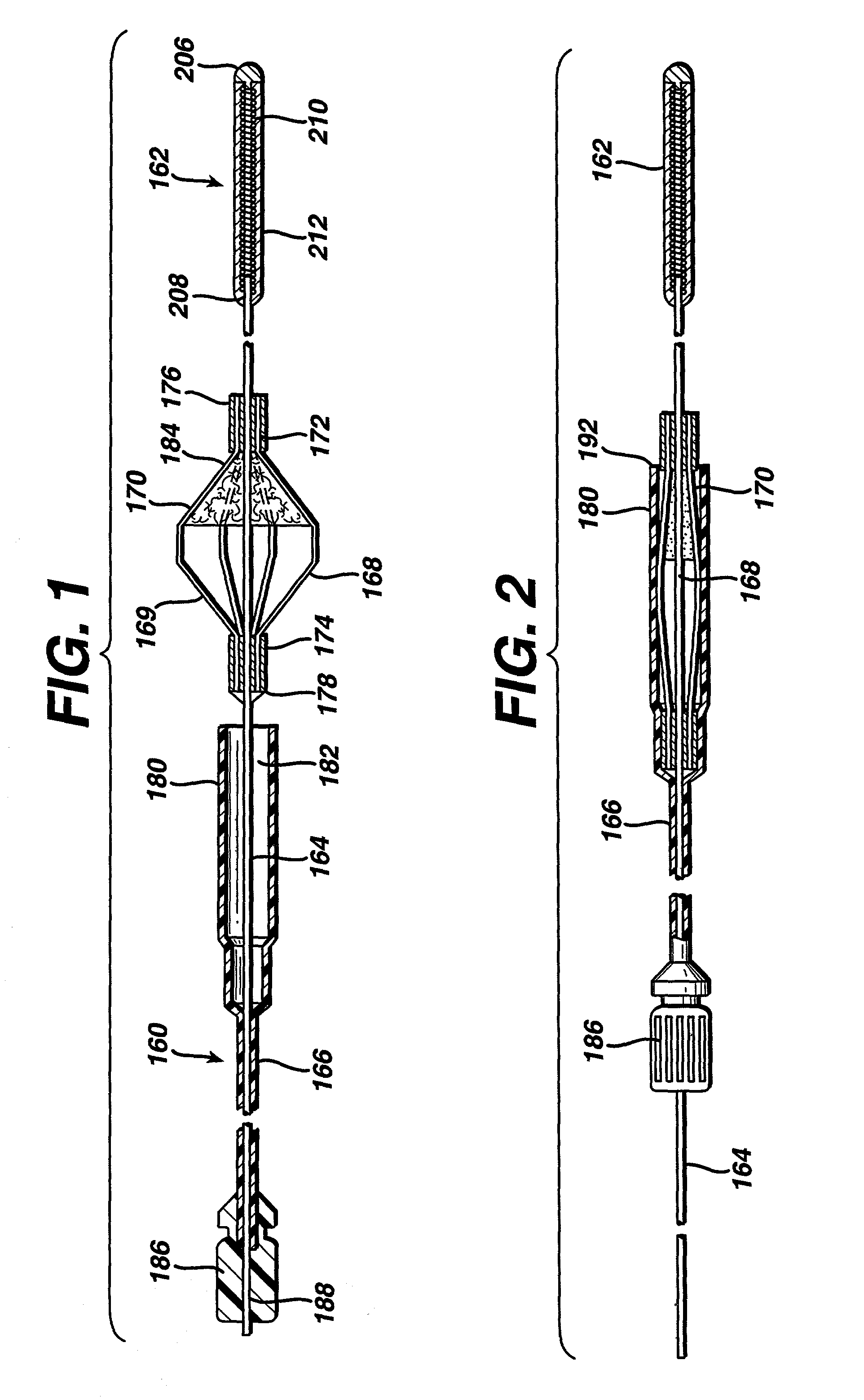
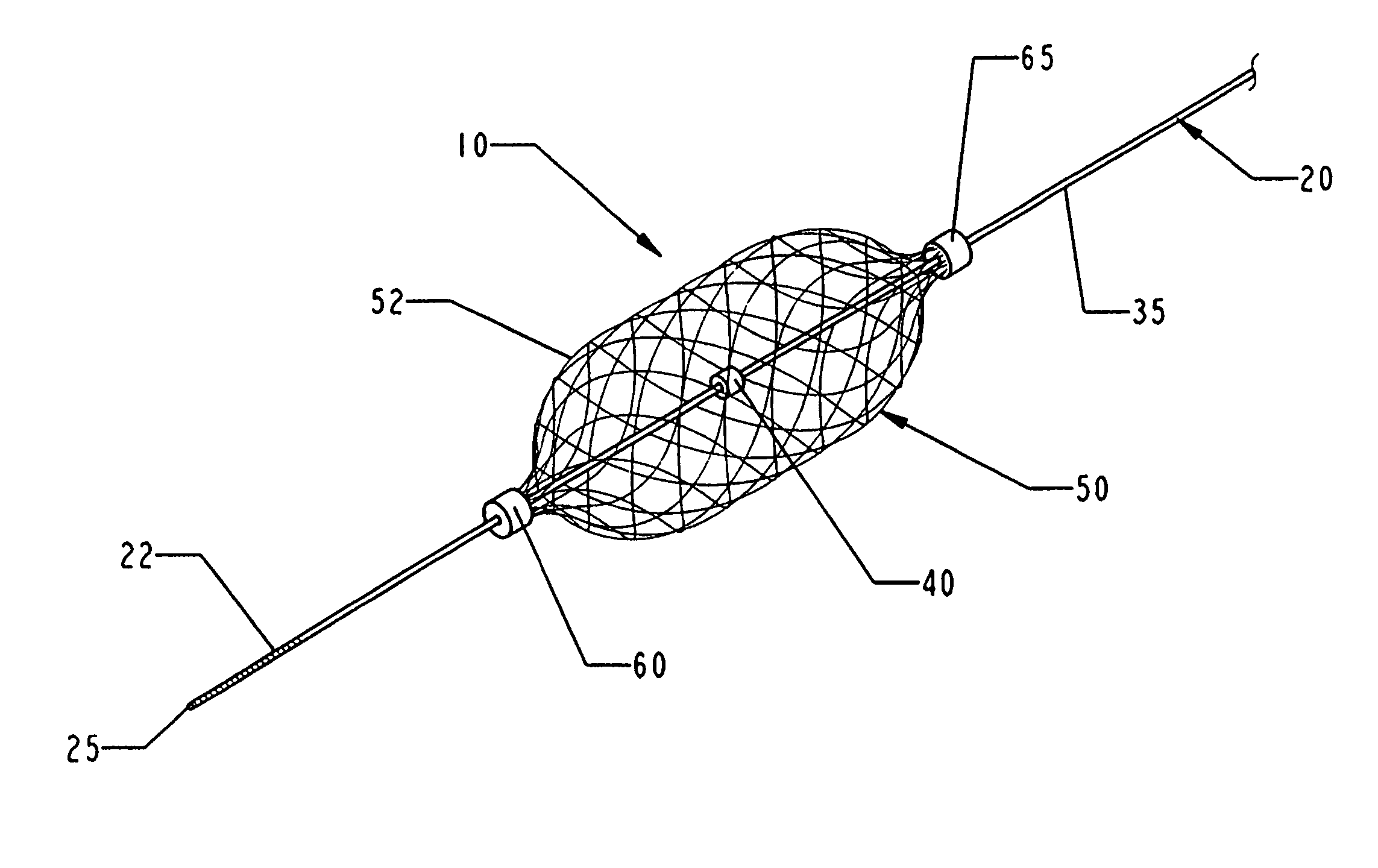
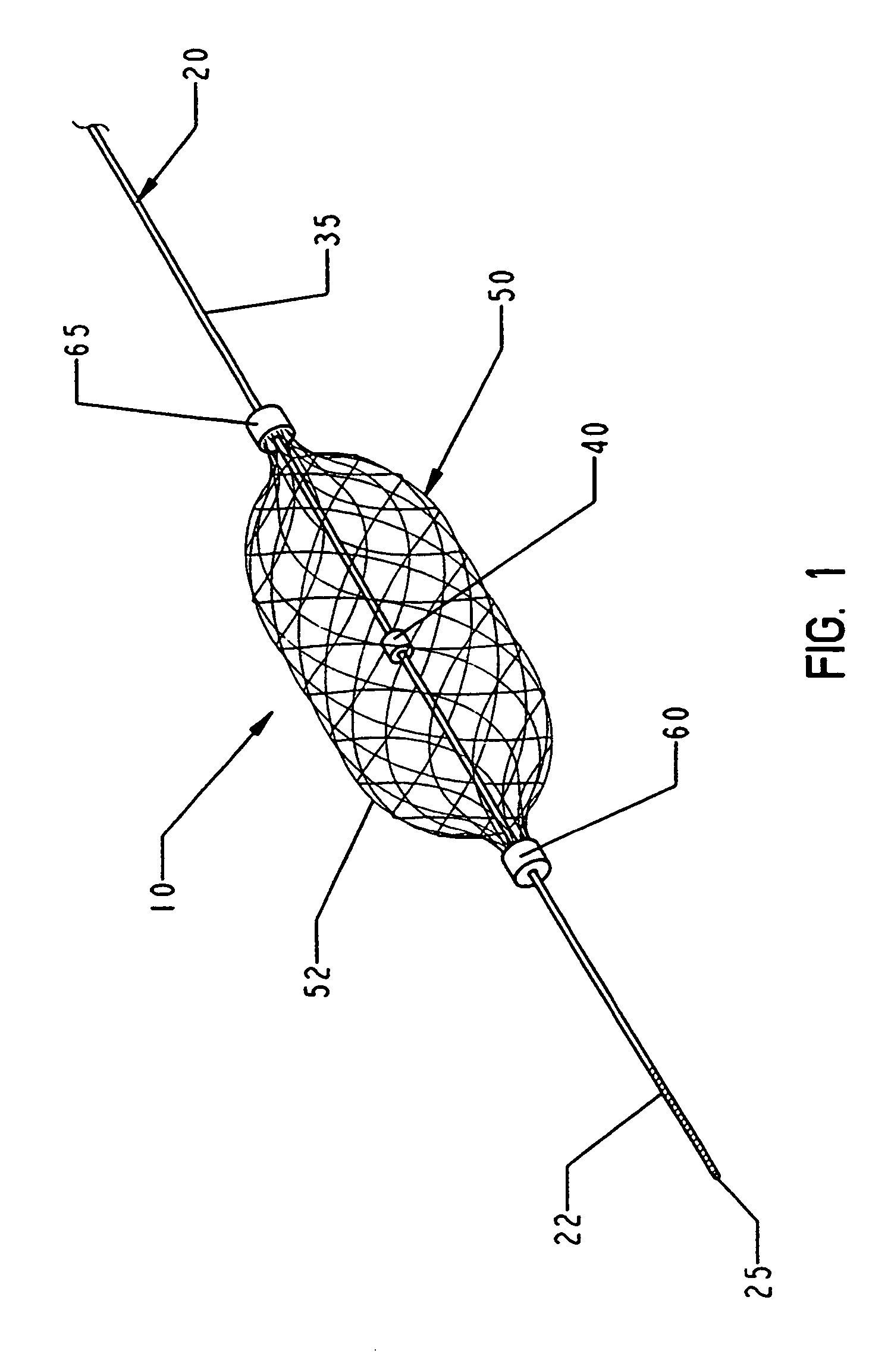
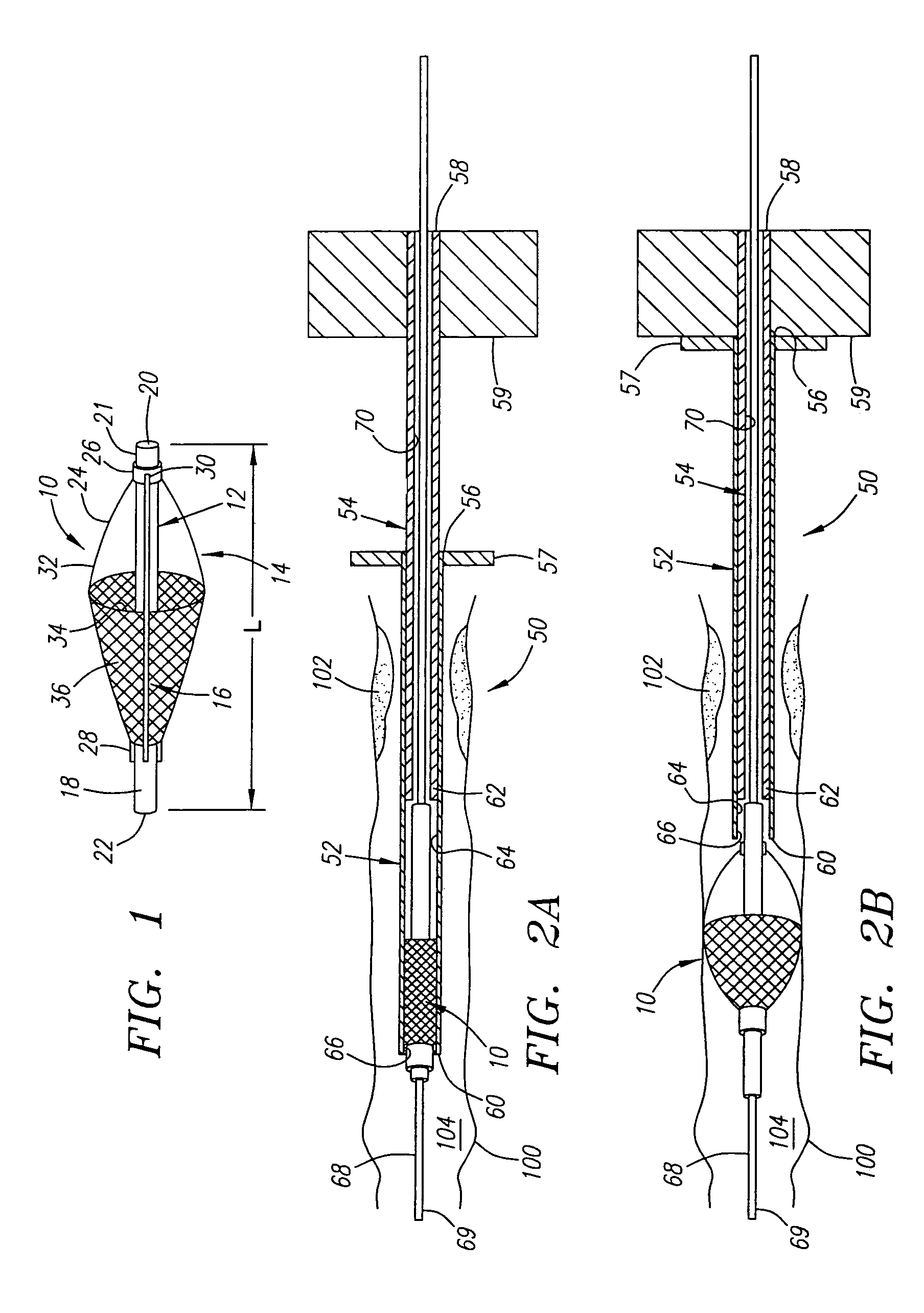
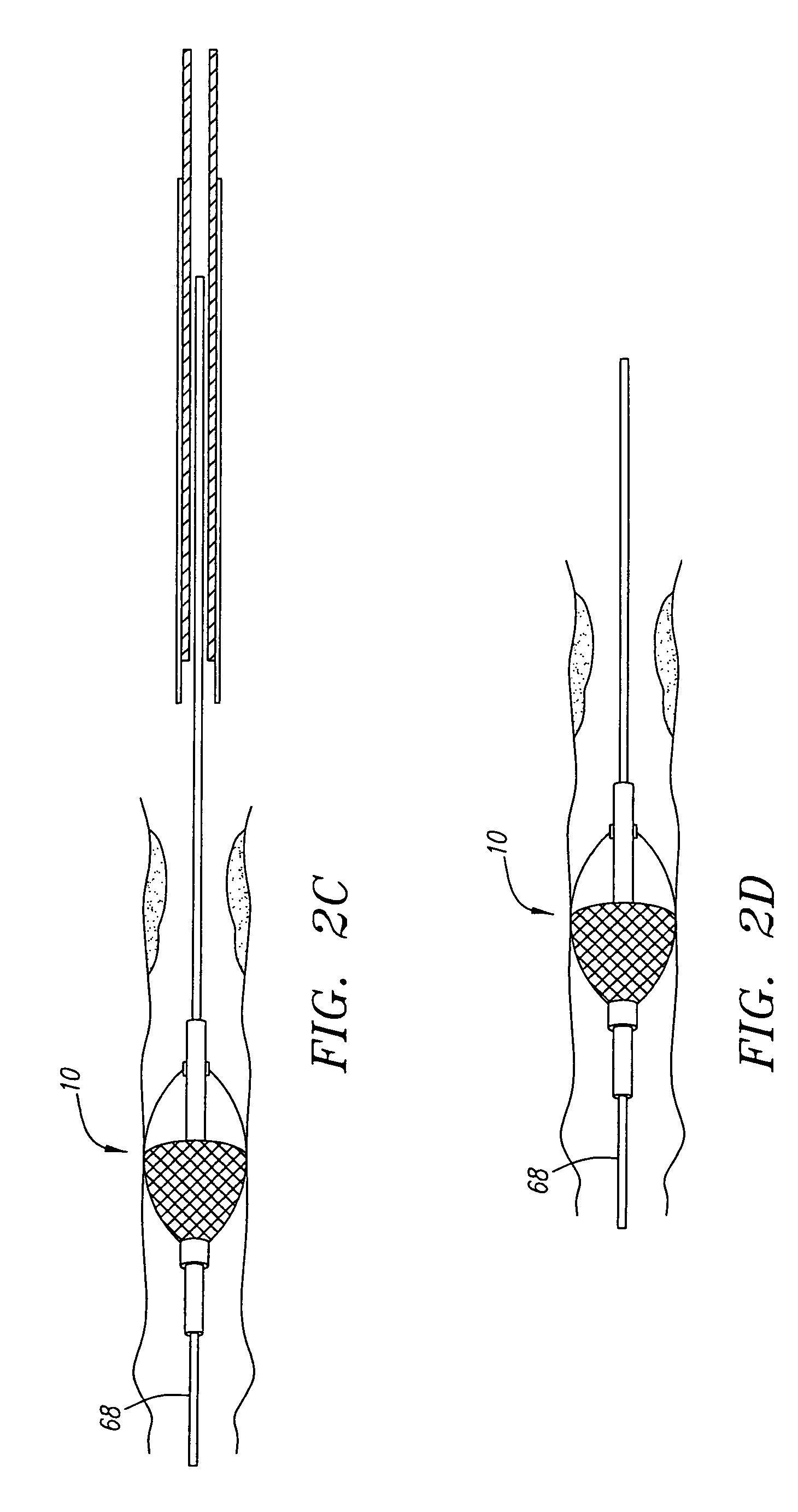
The present invention provides a method of deploying a medical filter within a channel in a patient's body and filter systems which can be used in such a method. Such a filter may include a radially expandable body 52 having an opening 56 in a proximal length thereof. In one method, the filter is urged along a length of the channel with the filter body in a radially reduced configuration. This body is expanded to substantially fill the lumen of the vessel and orient the opening in the body proximally. Body fluid is permitted to enter the filter body through the proximally oriented opening and pass distally through the distal length of the body so that the distal length of the body filters from the body fluid particulate material entrained therein. The proximal length of the body can be drawn into the retrieval catheter, thereby effectively closing the proximally oriented opening within the catheter to retain the particulate material within the enclosure. In a preferred embodiment, the filter body 52 is formed of a porous, resilient fabric having pores therein and the proximal opening 56 is at least five times the size of such pores.
Owner:EV3
Inferior vena cava filter
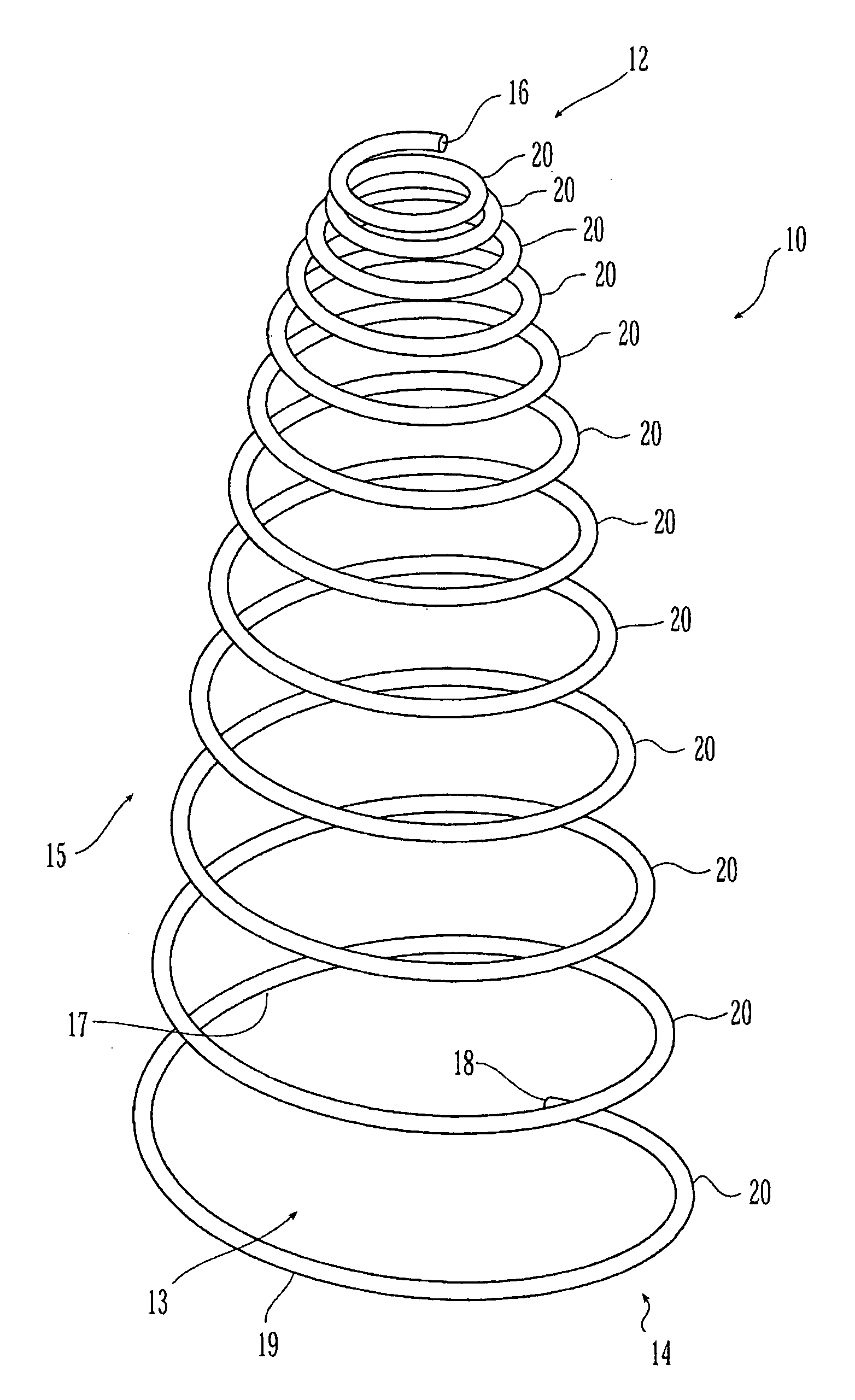
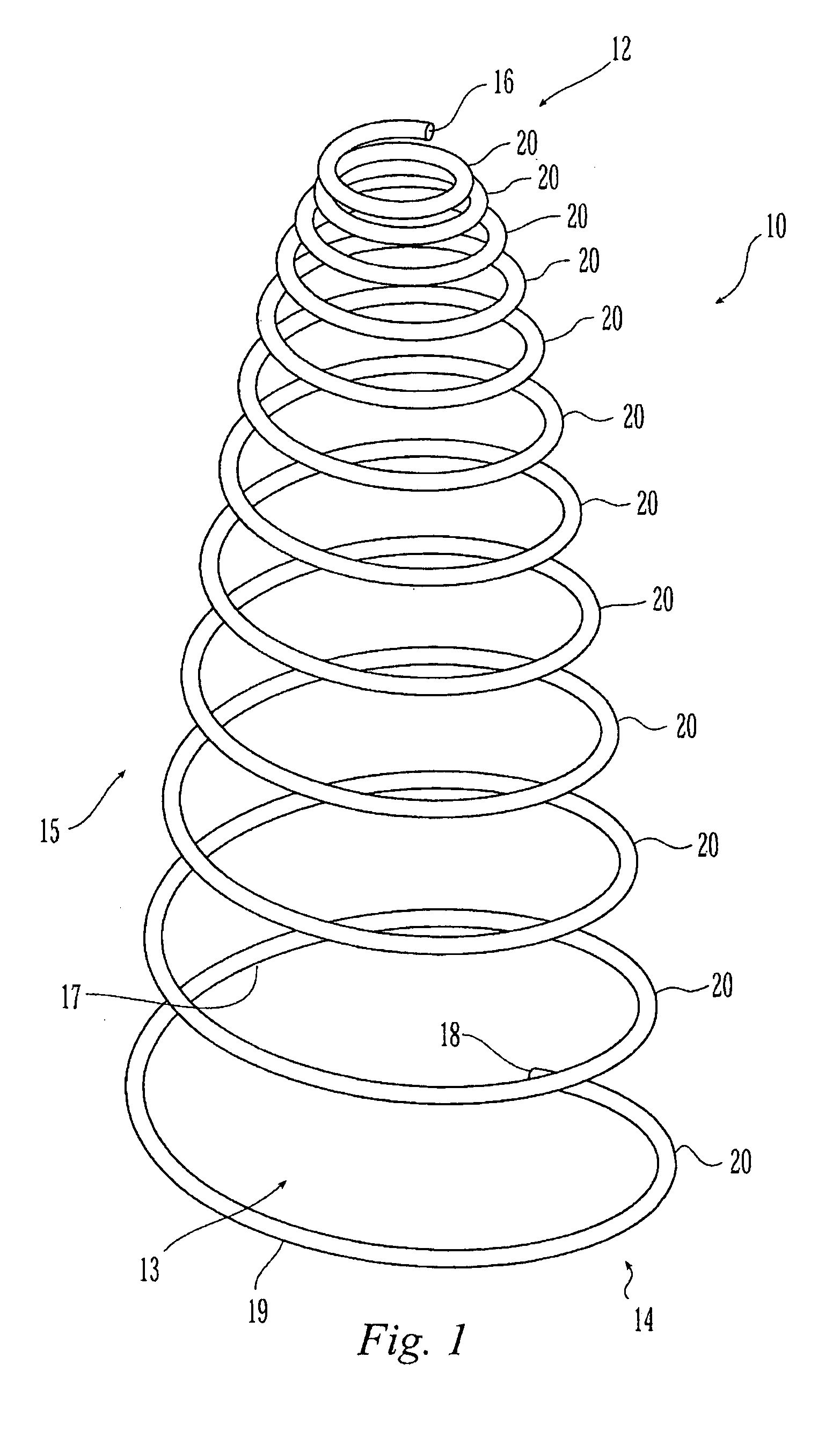
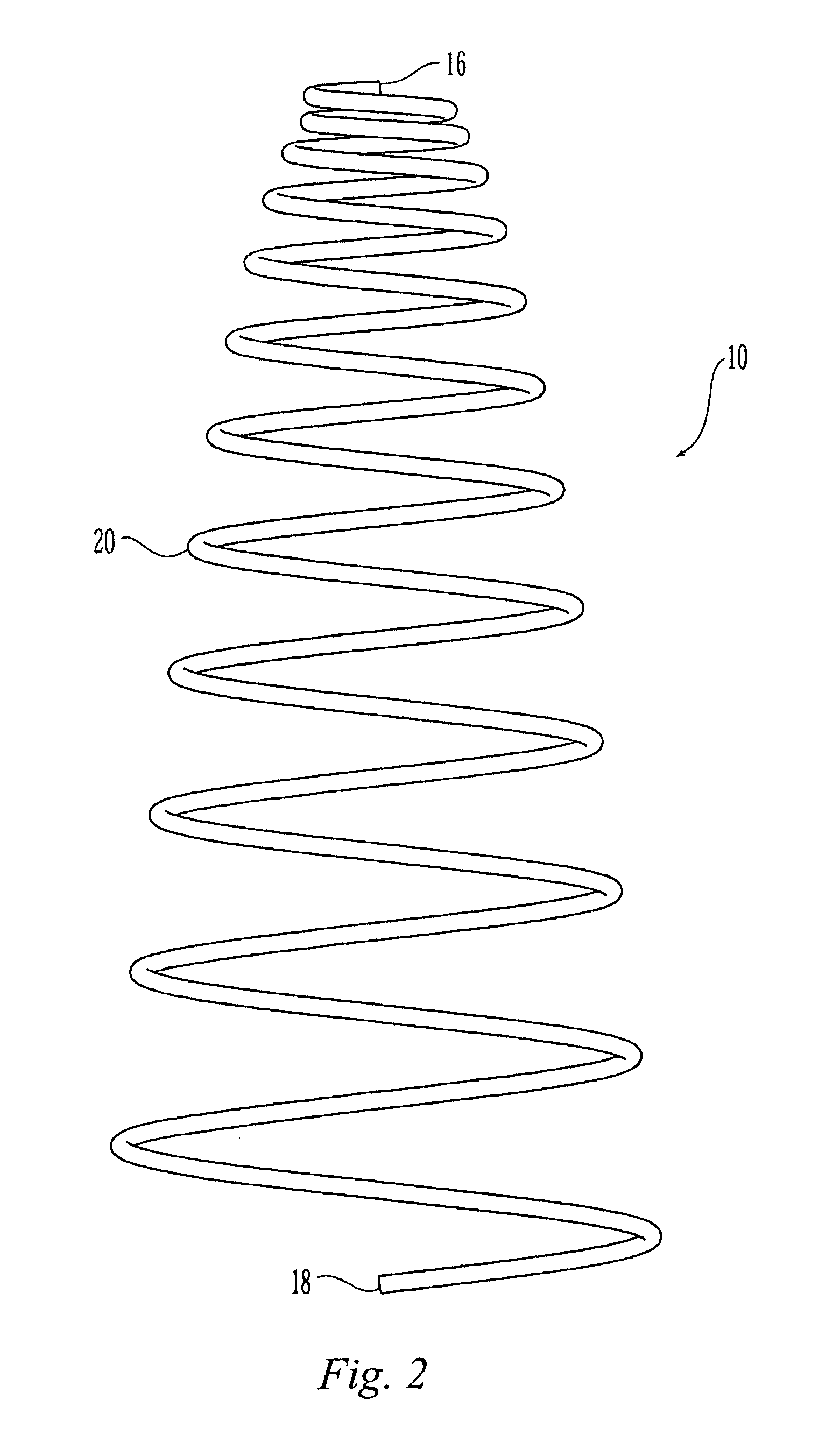
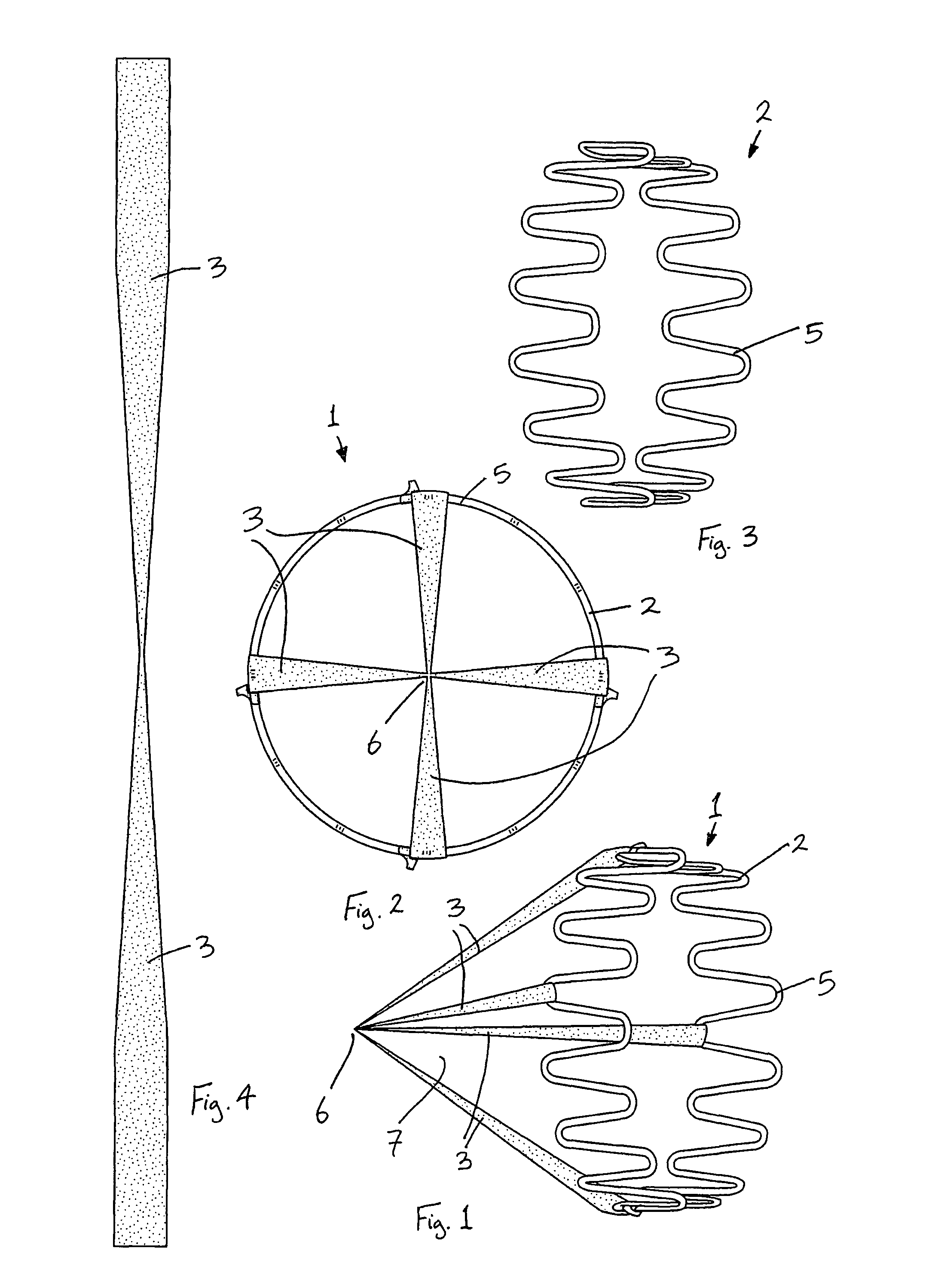
The present invention relates to a vascular filter including a coiled wire formed of a shape memory material for implantation into a vessel. The vascular filter captures particulates within the blood flow in the vessel, without substantially interfering with the normal blood flow. Prior to implantation, the coiled wire is generally elongated and thereafter it reverts to a predetermined shape that is suitable for filtering the blood flow. The predetermined shape of the vascular filter includes a plurality of loops coaxially disposed about a longitudinal axis and has a conical portion and a cylindrical portion.
Owner:JAYARAMAN SWAMINATHAN
Vascular filter with sensing capability
An implantable vessel filter having an integrated sensing capability for monitoring the condition of the vessel filter. In one variation, the vessel filter comprises a plurality of legs that would themselves perform as a sensor device for detecting distention, which would indicate the presence of a clot or thrombus therein. A passive electrical circuit may be implemented on the vessel filter to receive electromagnetic energy and transmit signals indicative of the condition of the implanted vessel filter. In another variation, a miniaturized sensor is adapted for measuring the strain and / or other physical parameters of the filter legs.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Biodegradable vascular filter
InactiveUS20070112372A1Preventing recurrent pulmonary embolismEfficient trappingStentsSurgeryVascular filterInsertion stent
Novel enhanced products and processes for trapping emboli utilize self-expanding skeletons and biodegradable polymer systems, for example stent-like Nitinol® elements and PLGA, to address longstanding issues related to thrombus capture without deleterious impacts on the vasculature or other negative artifacts of the procedure by at least partial post-use dissolution in situ. Drug coating and elution technologies are included as would be known to those skilled in the art.
Owner:COVIDIEN GROUP +1
Deployable recoverable vascular filter and methods for use
InactiveUS7077854B2Reduce risk of damageEasy to introduceStentsSurgeryVascular filterFilter material
A vascular filter is provided that includes a tubular member having proximal and distal ends, and a guidewire lumen. An expandable frame is attached to the tubular member capable of assuming collapsed and enlarged conditions, and filter material is attached to the frame, the filter material having an open proximal end when the frame assumes its enlarged condition. An apparatus for recovering a vascular filter from a blood vessel is also provided that includes a sheath and a retrieval member deployable from the sheath. The retrieval member includes a connector on its distal end for securing the tubular member, such as an expandable member within a recess for receiving the tubular member. The vascular filter may be constrained in its collapsed condition in a sheath, and the tubular member advanced over a guidewire to a location downstream of a treatment site. The vascular filter is deployed and expanded to its enlarged condition across the blood vessel, the guidewire remaining in place. A procedure is performed at the treatment site, the vascular filter capturing released emboli. The retrieval device is advanced over the guidewire, the vascular filter is secured to the retrieval member, and the vascular filter and retrieval device are withdrawn from the blood vessel.
Owner:ENDOTEX INTERVENTIONAL SYST
Vascular filter
ActiveUS8162970B2Avoid passingPromote crashStentsSemi-permeable membranesVascular filterInferior vena cava filter
An inferior vena cava filter (340) for use in the inferior vena cava (4) to capture thrombus (8) passing through the inferior vena cava (4) towards the heart and lungs to prevent pulmonary embolism comprises a proximal support hoop (302), a distal support hoop (312) and a plurality of support struts (303) extending between the proximal support hoop (302) and the distal support hoop (312). The filter (340) also comprises a plurality of capture arms (121) which are movable from a capturing configuration to an open configuration. The capture arms (121) are biased towards the open configuration. A biodegradable suture holds the capture arms (121) in the capturing configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD +1
Temporary vascular filter guide wire
A vascular filter guide wire including a collapsible filter that deploys radially in response to axial movement of a core wire relative to a shaft to trap particulate matter arising from treatment of a lesion.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Vascular filter with improved strength and flexibilty
InactiveUS20090024153A1High strengthIncrease flexibilityCannulasDilatorsVascular filterUltimate tensile strength
Owner:DON MICHAEL INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com