Patents
Literature
213 results about "Vena cava filters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
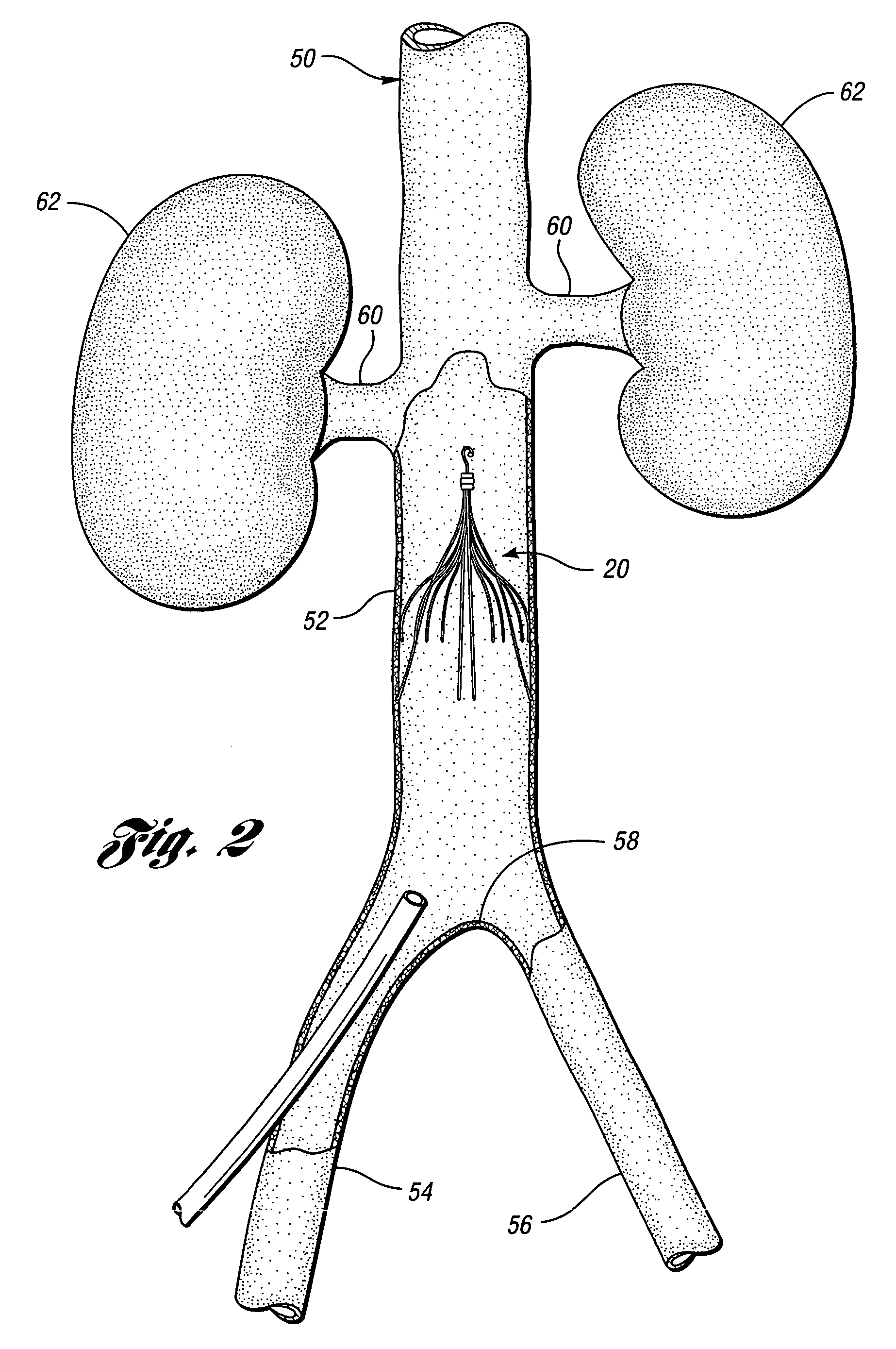
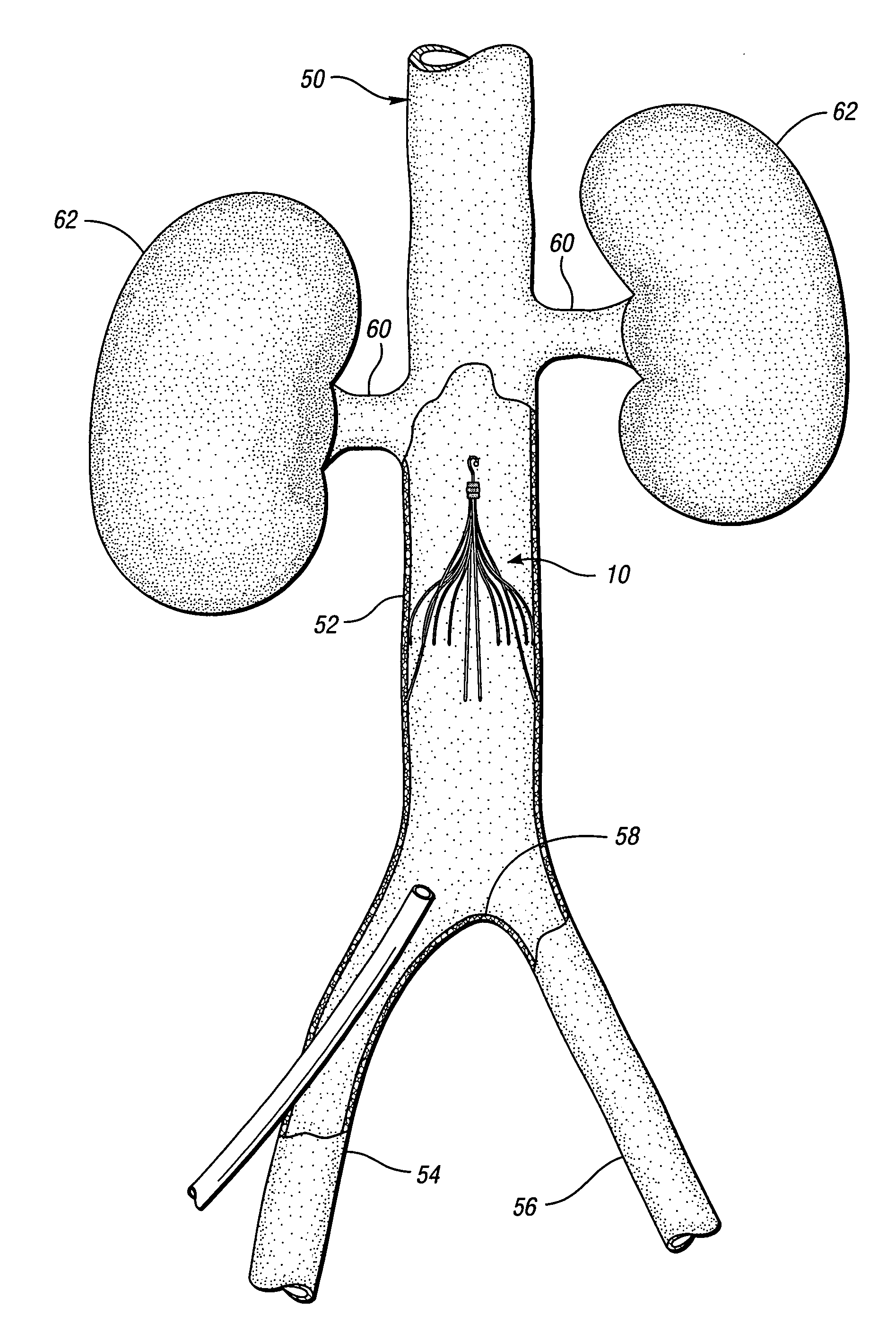
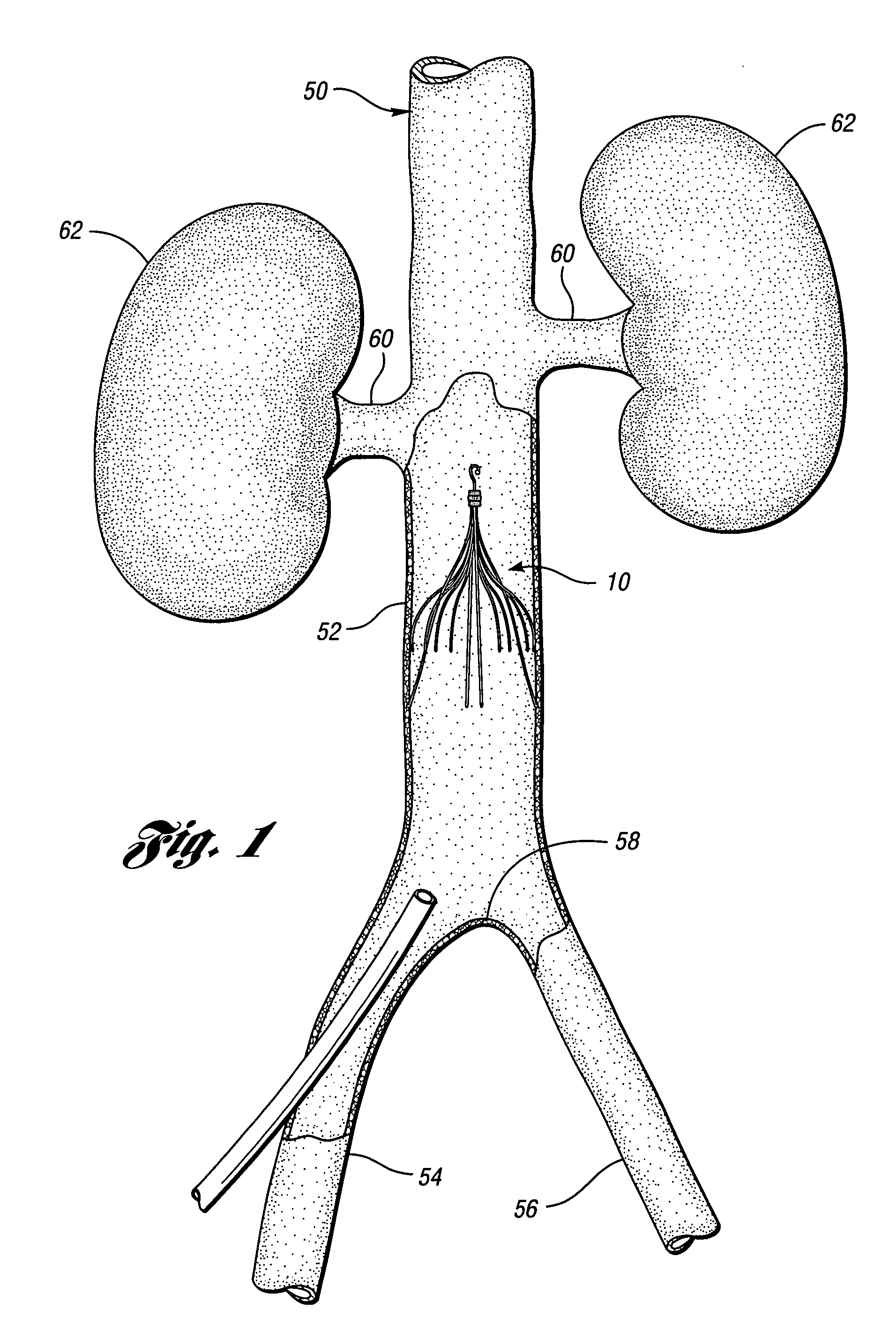
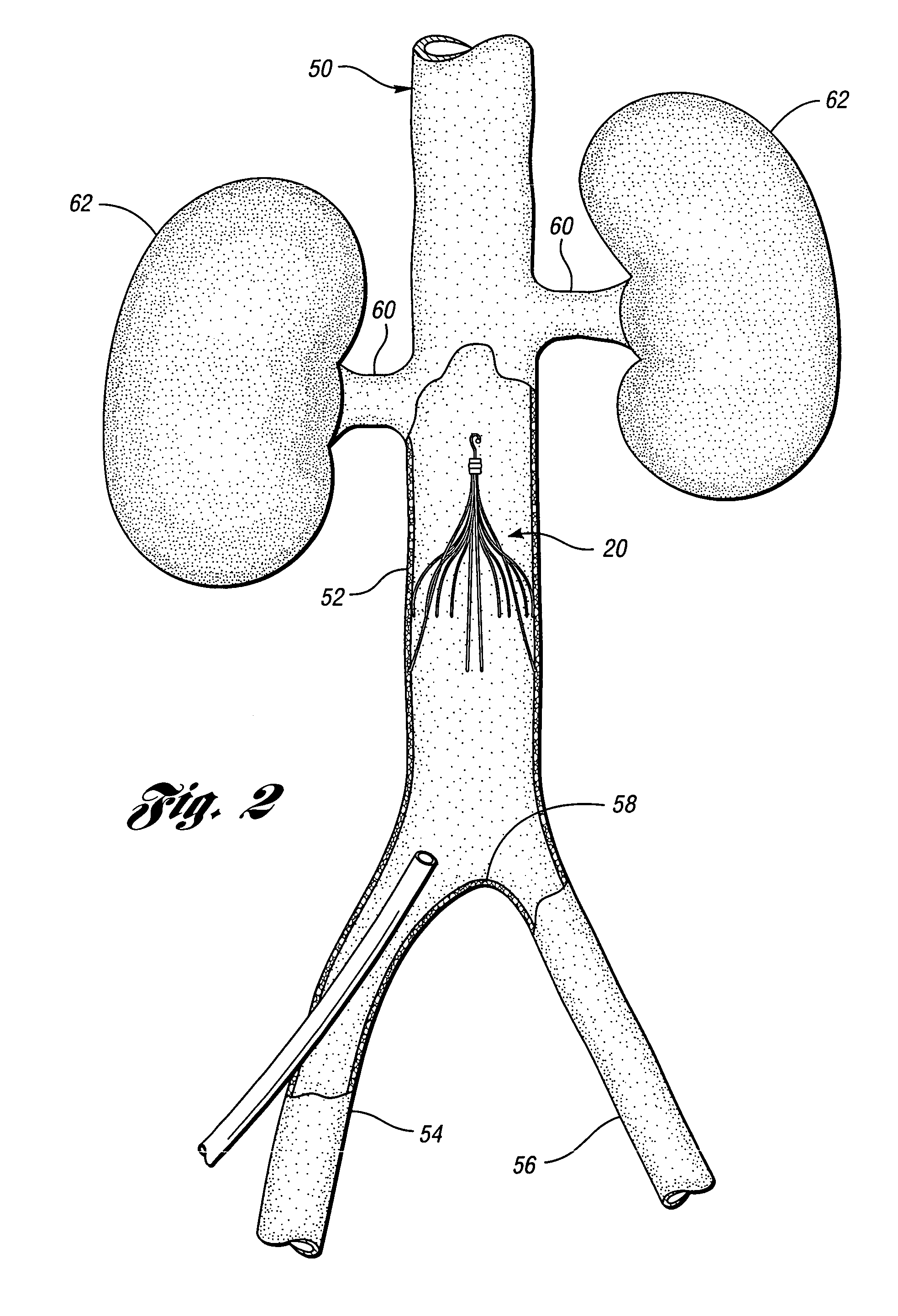
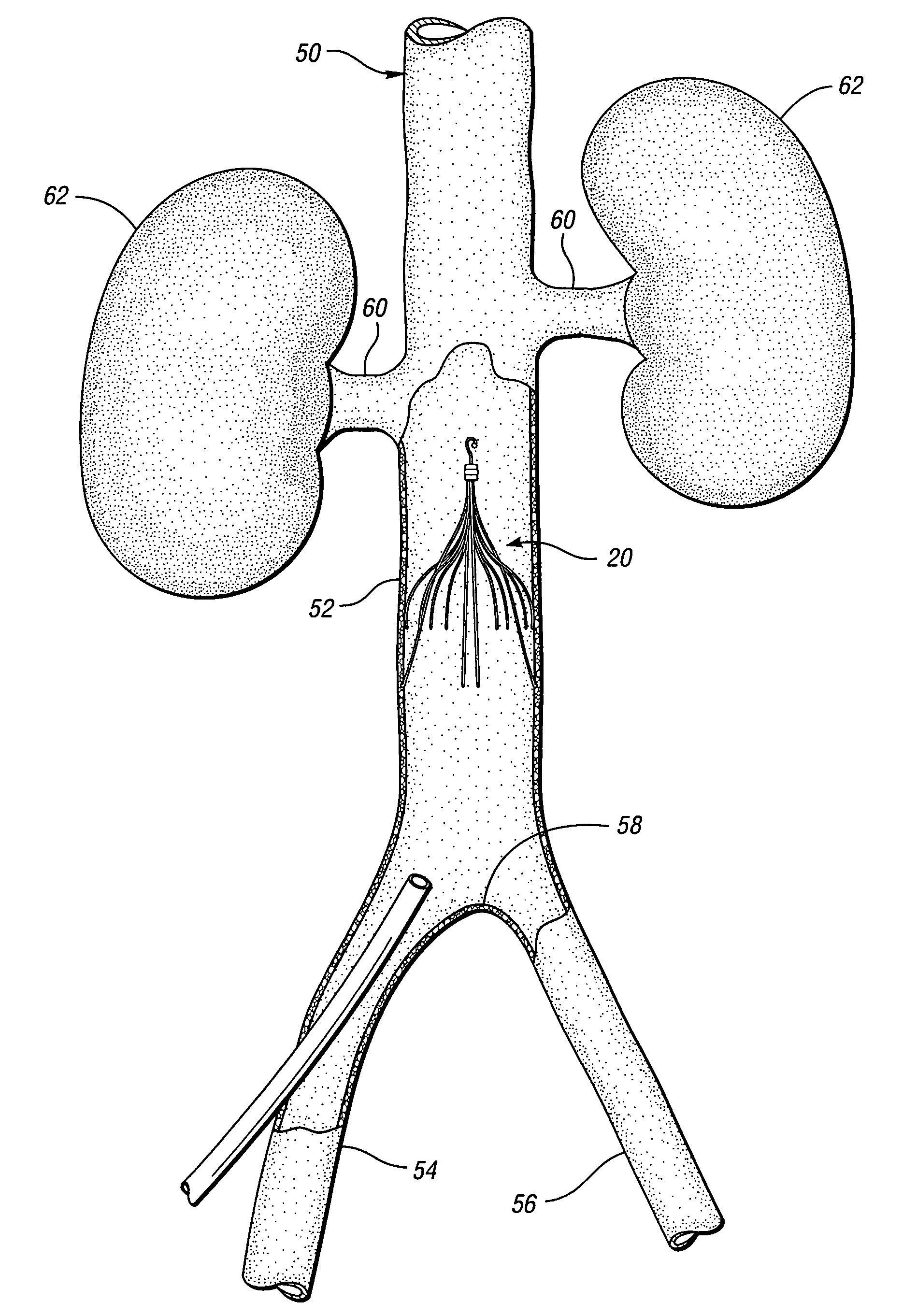
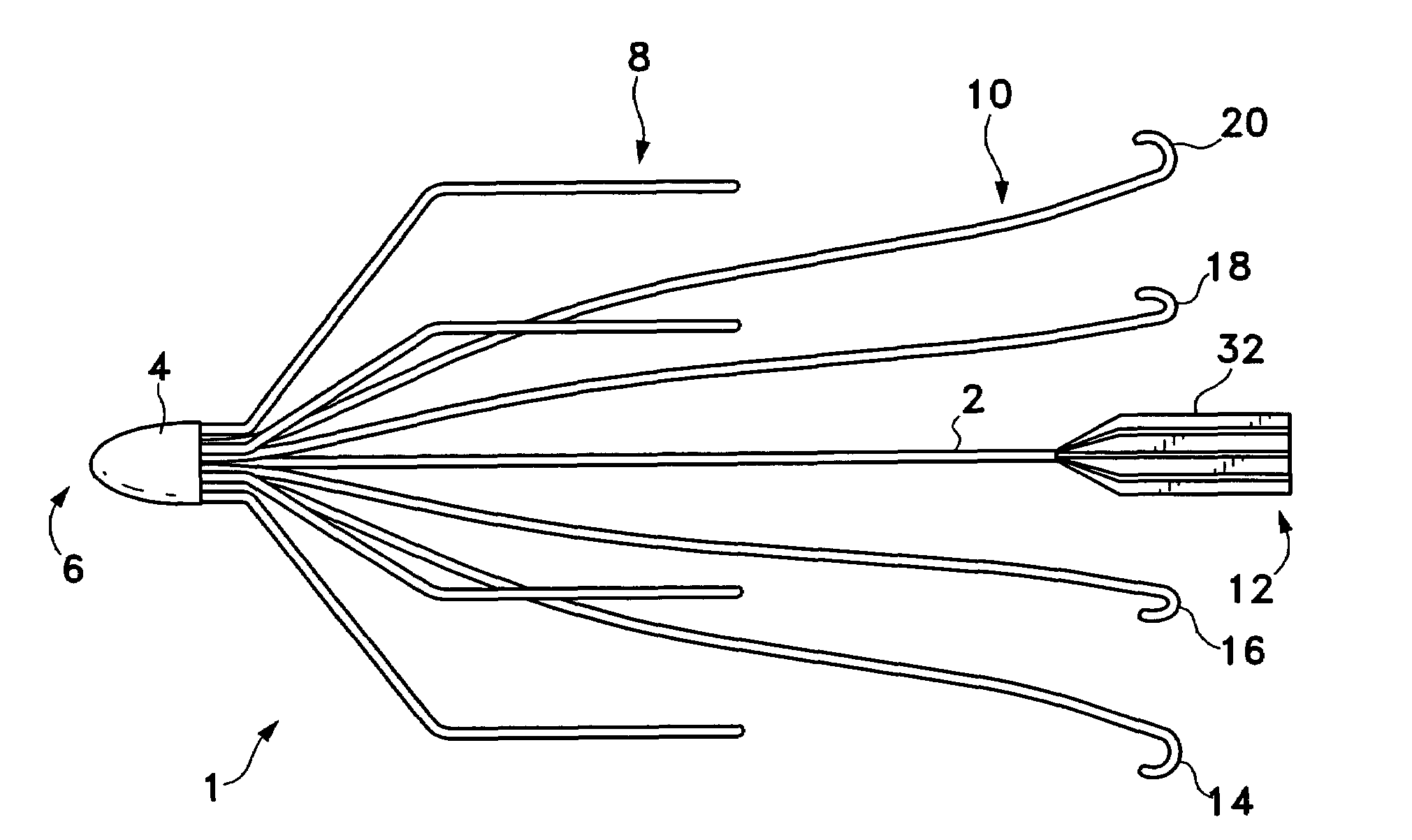
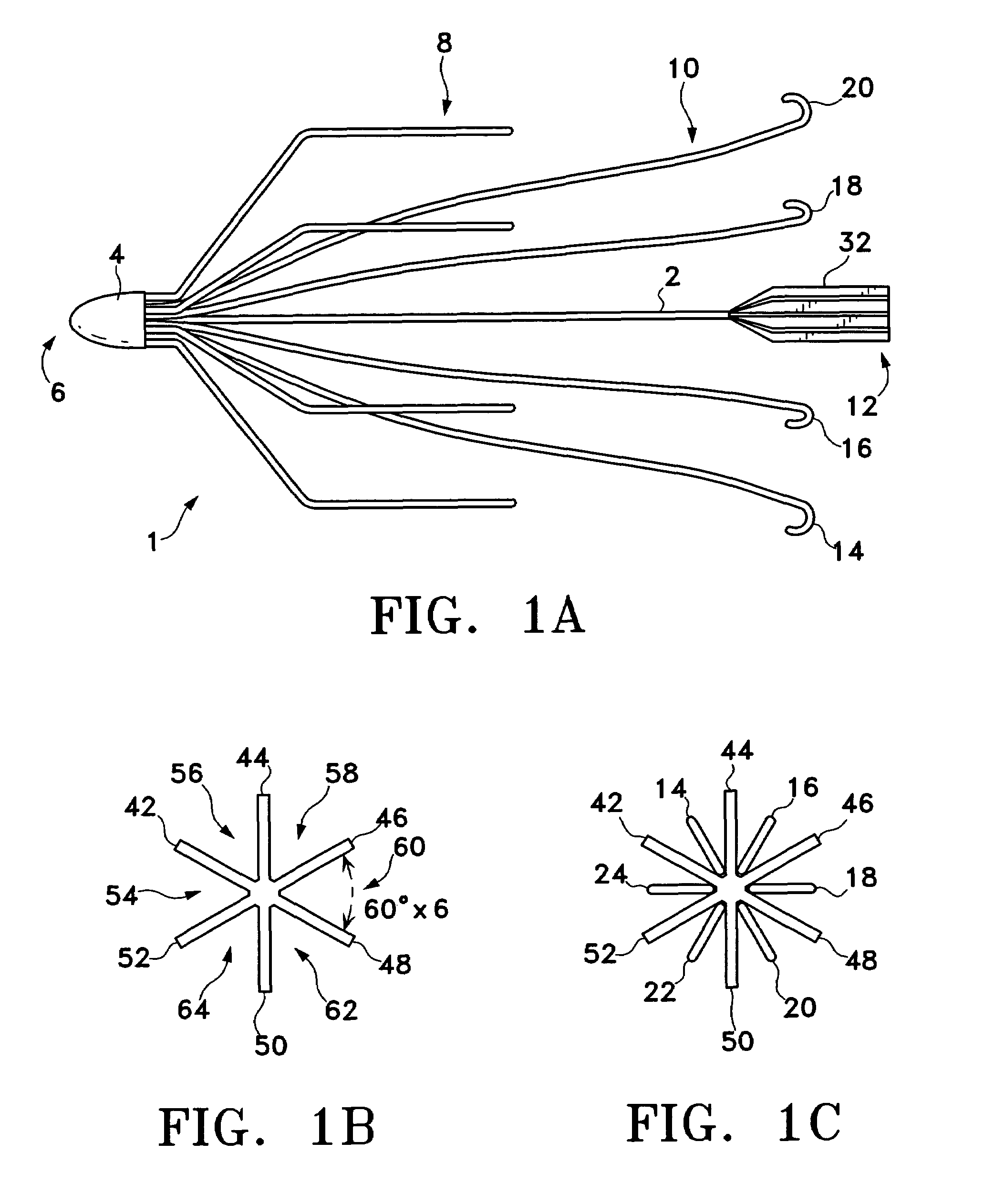
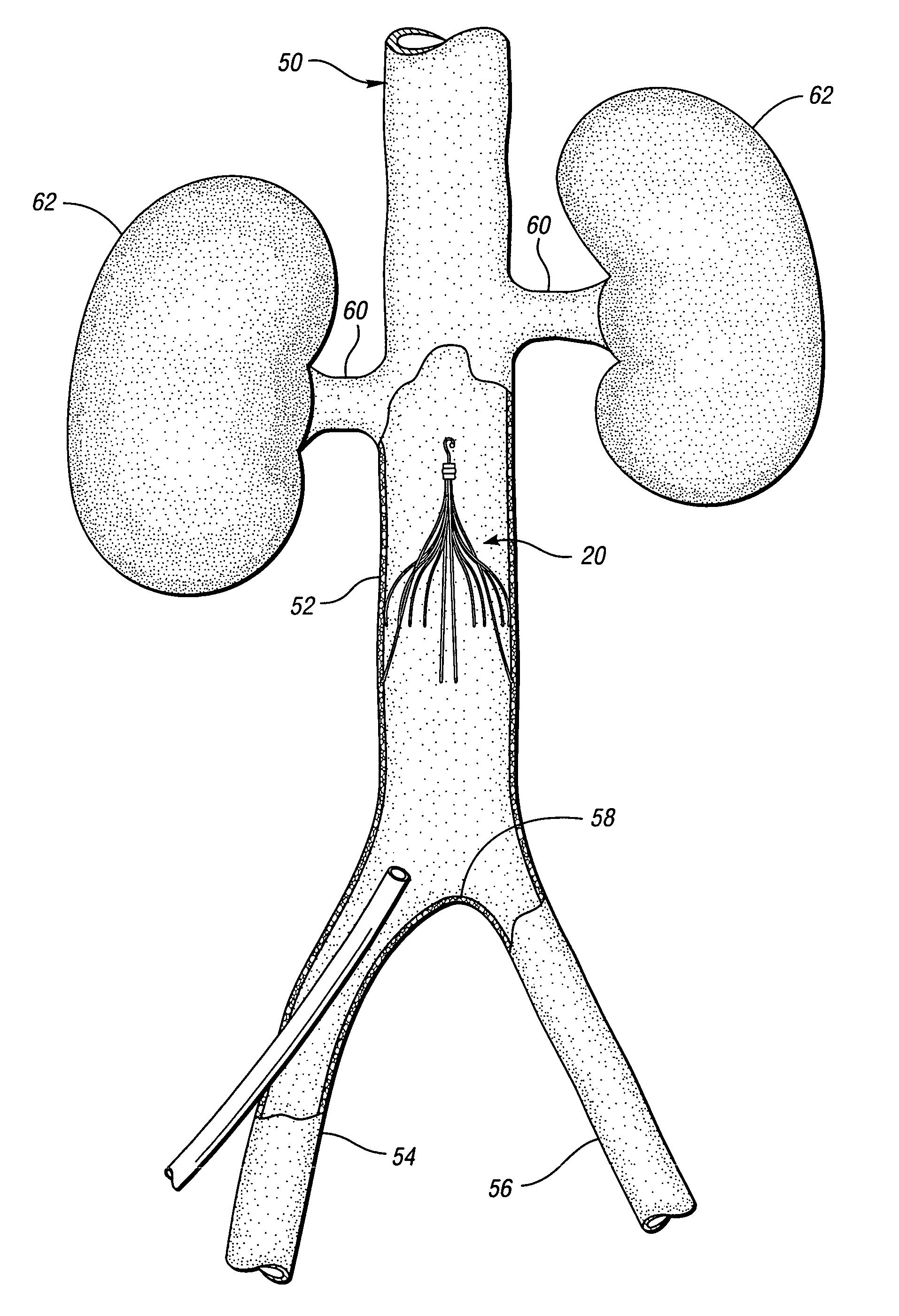
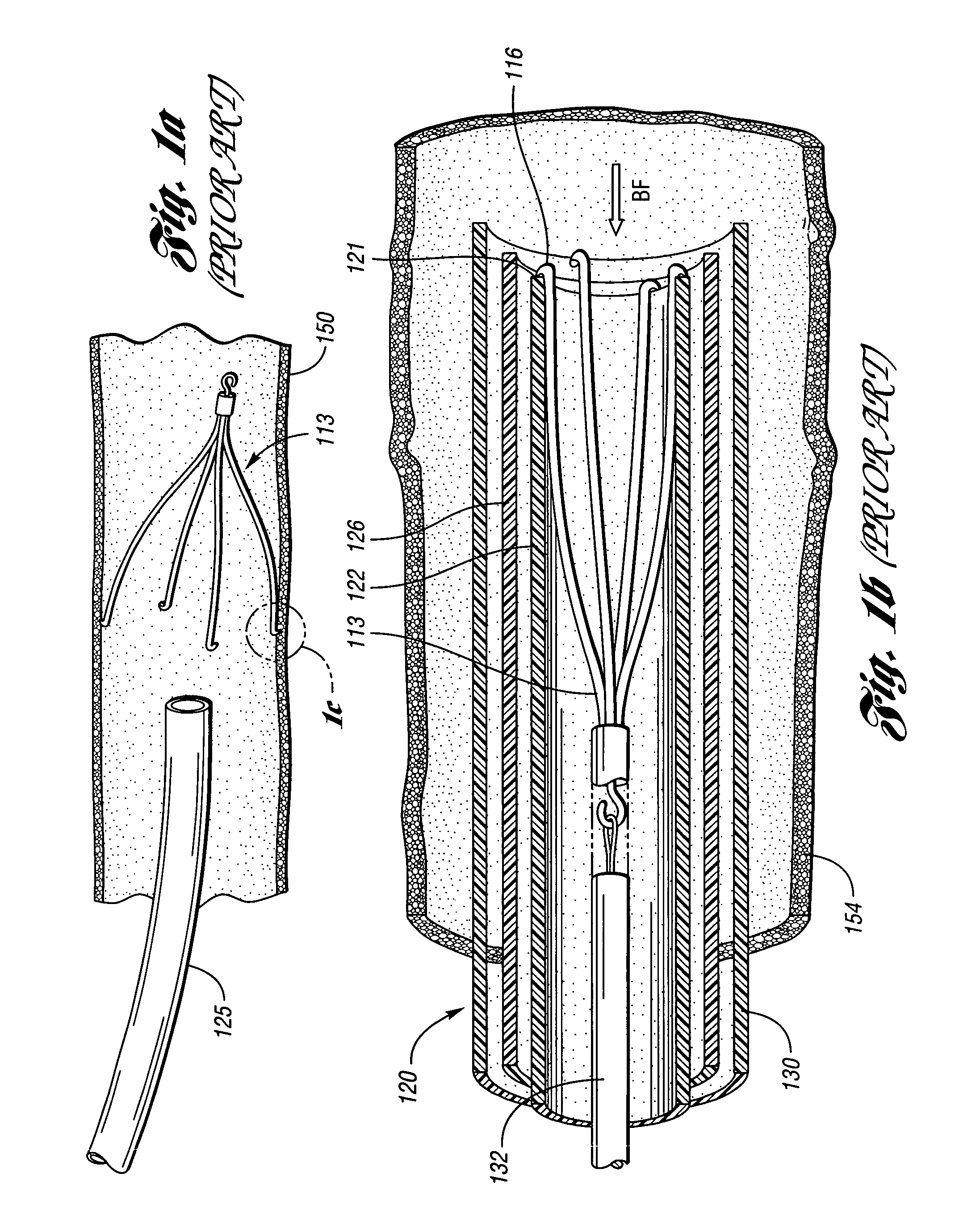
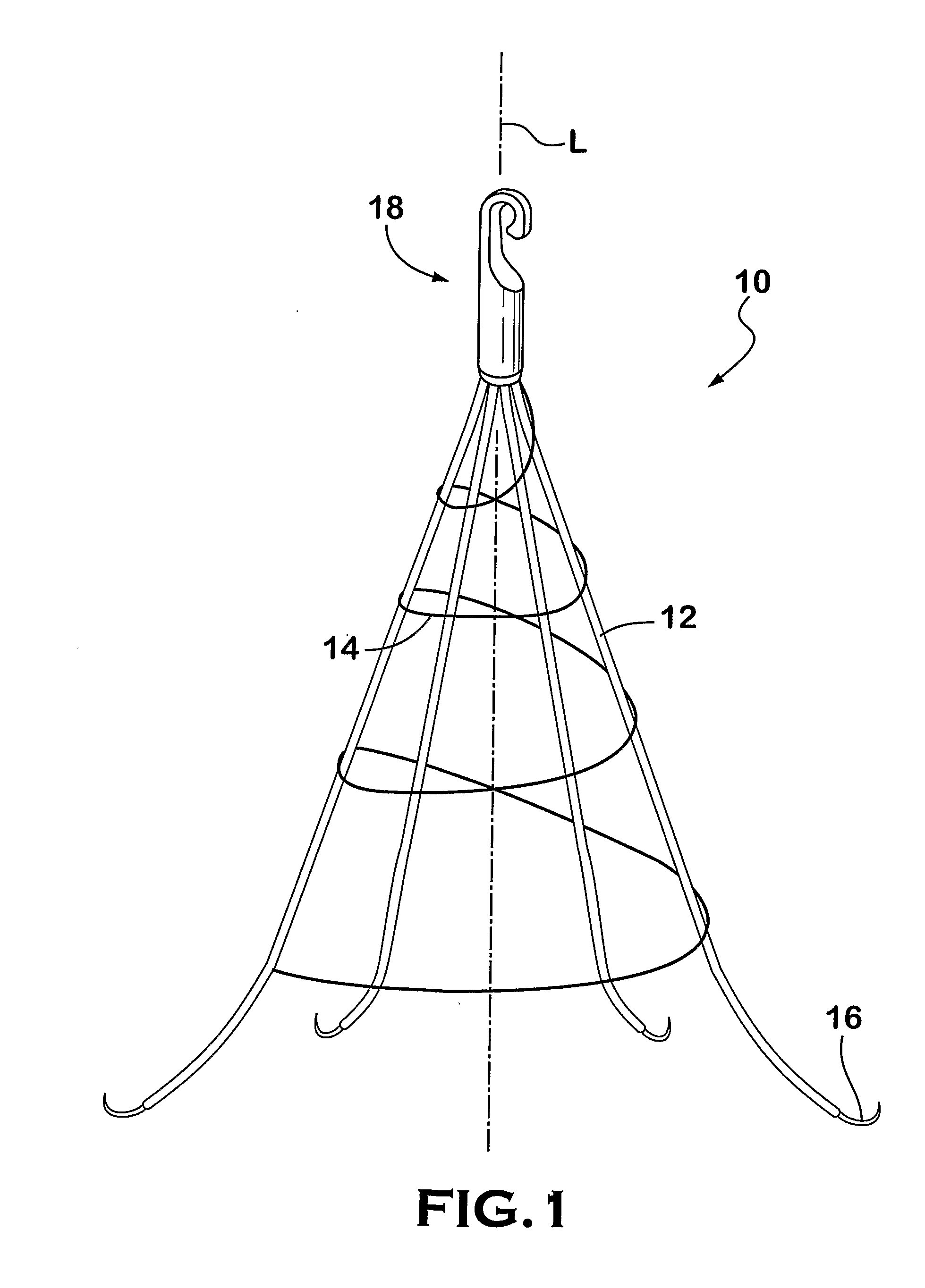
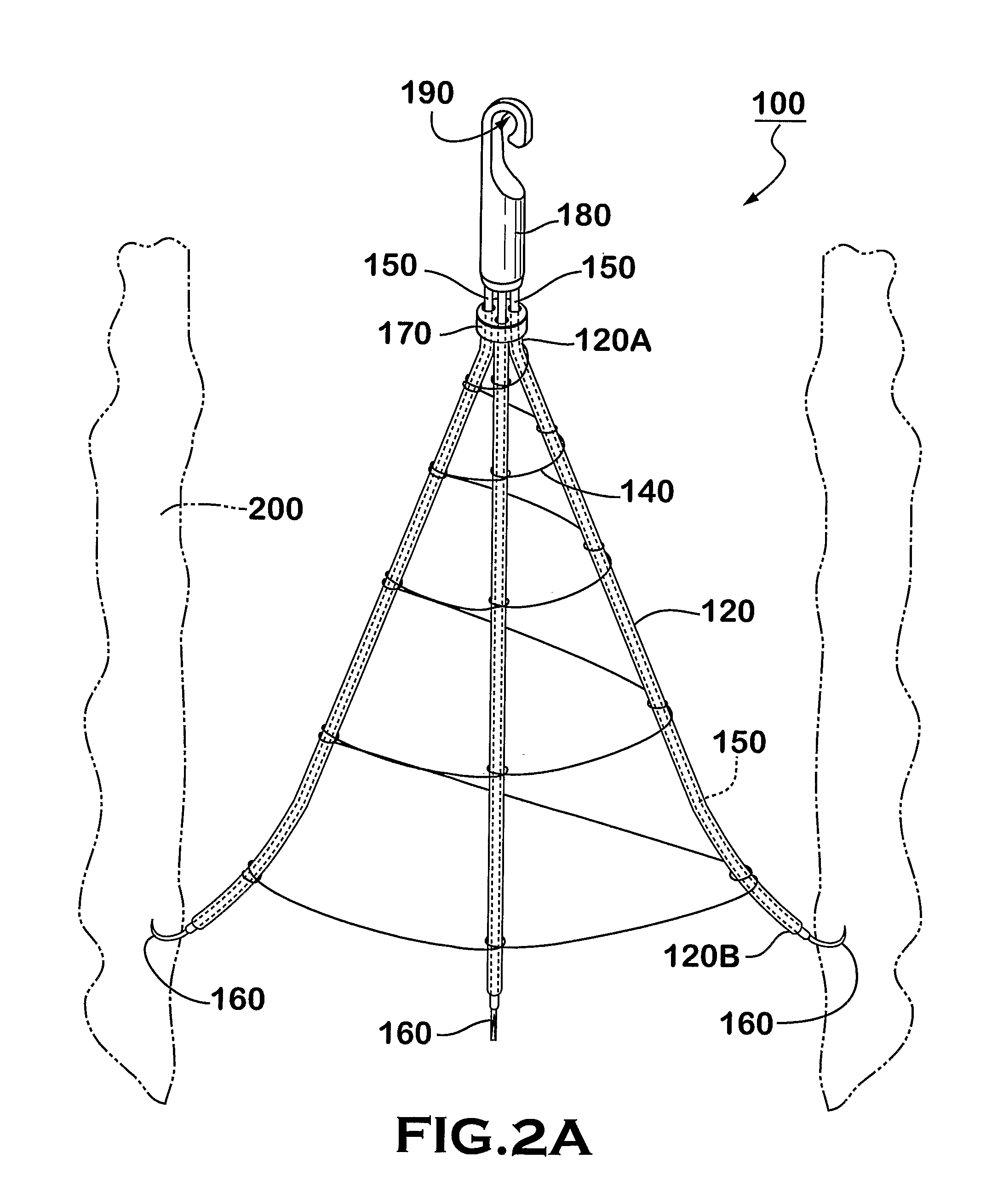
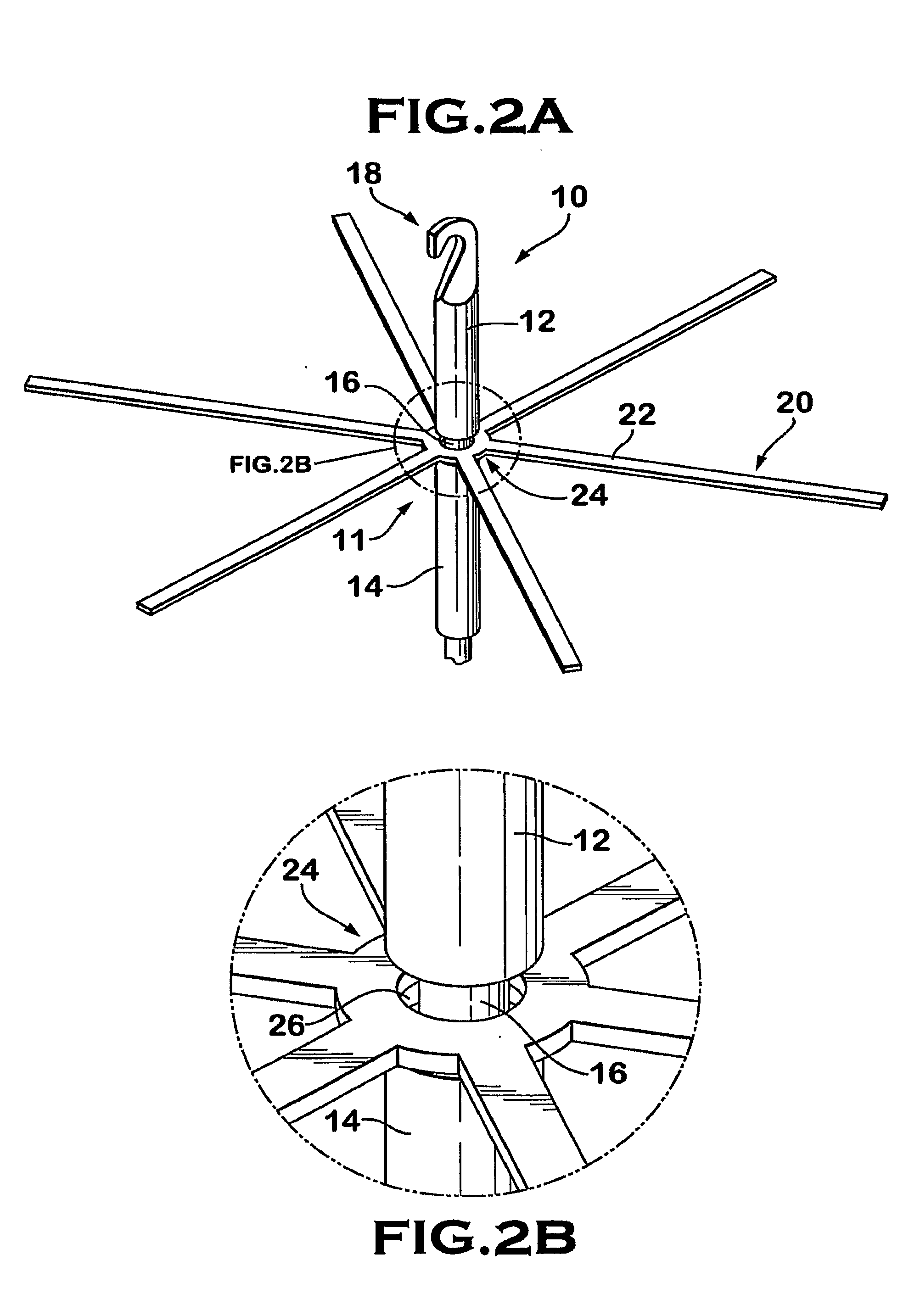
An inferior vena cava filter (IVC filter) is a type of vascular filter, a medical device that is implanted by interventional radiologists or vascular surgeons into the inferior vena cava to presumably prevent life-threatening pulmonary emboli (PEs).
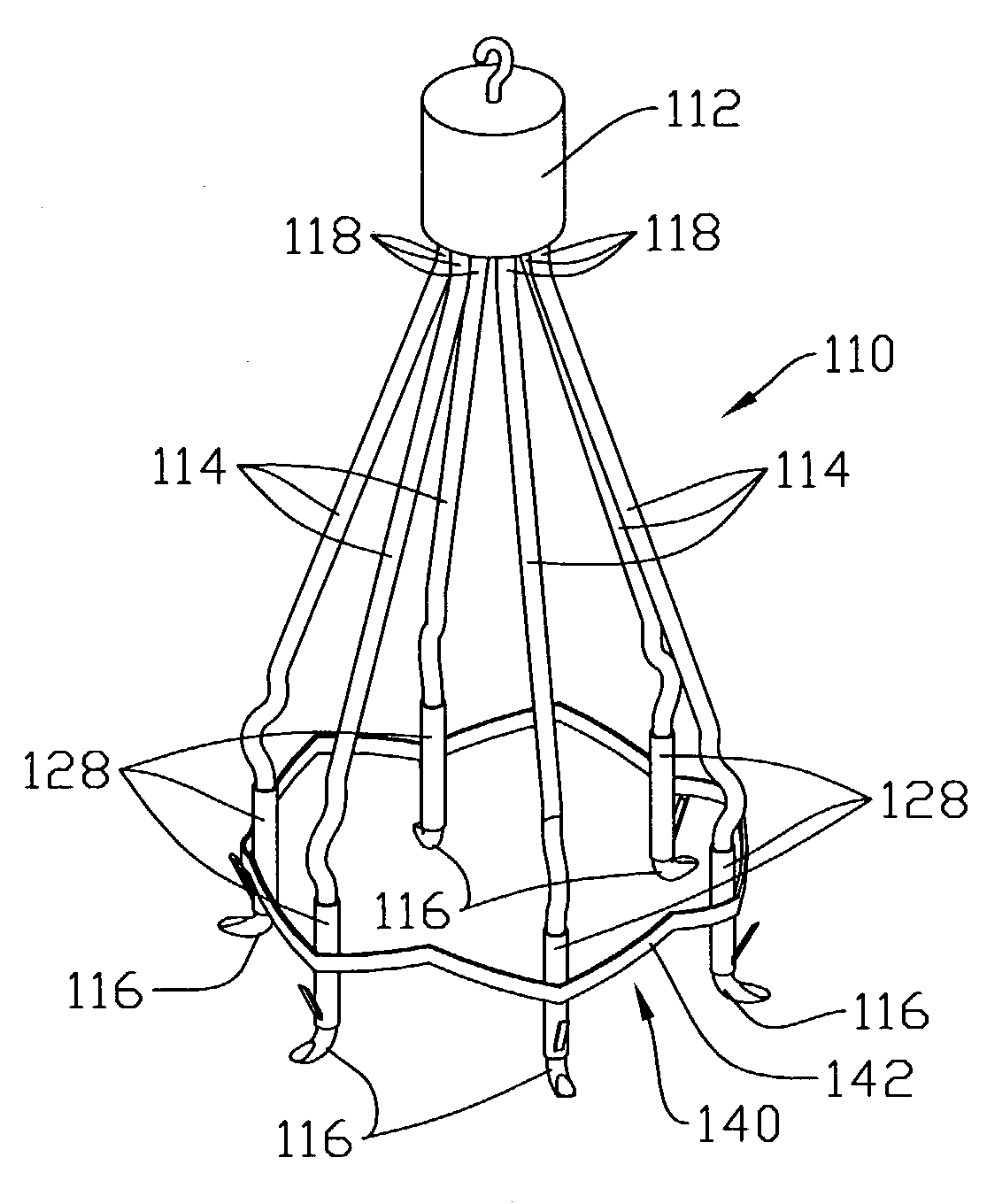
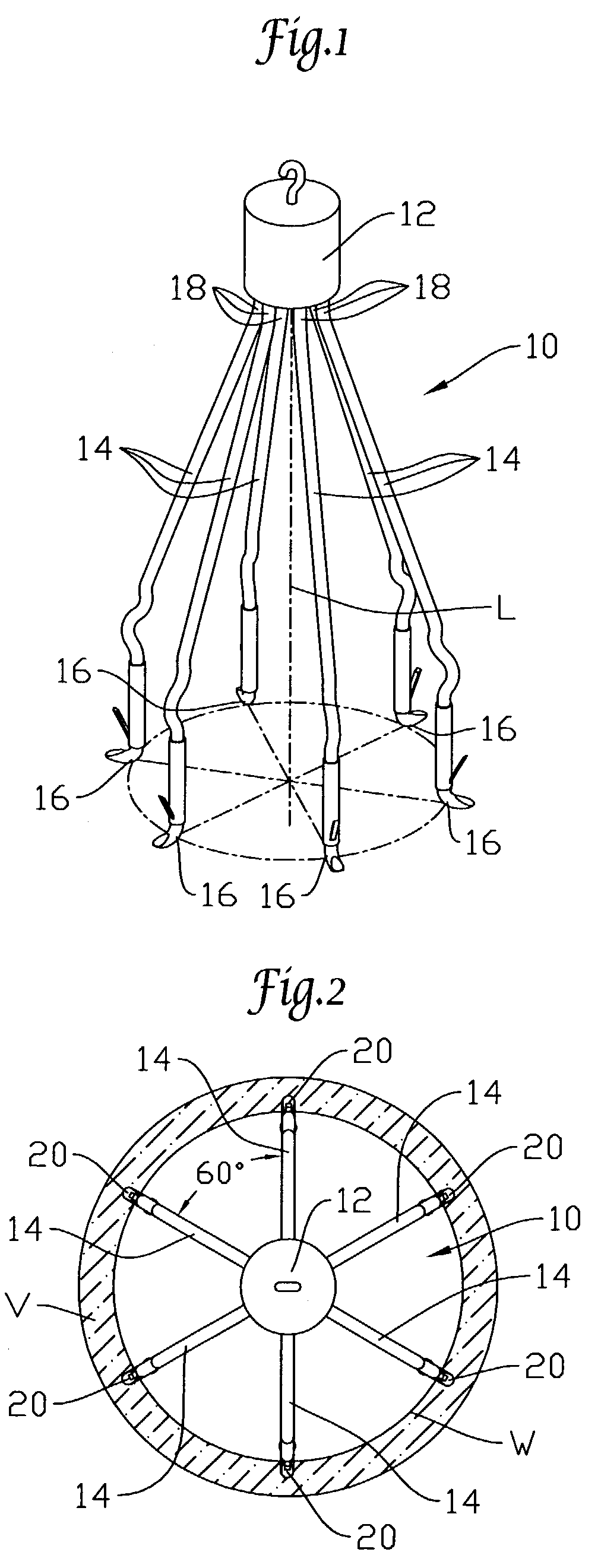
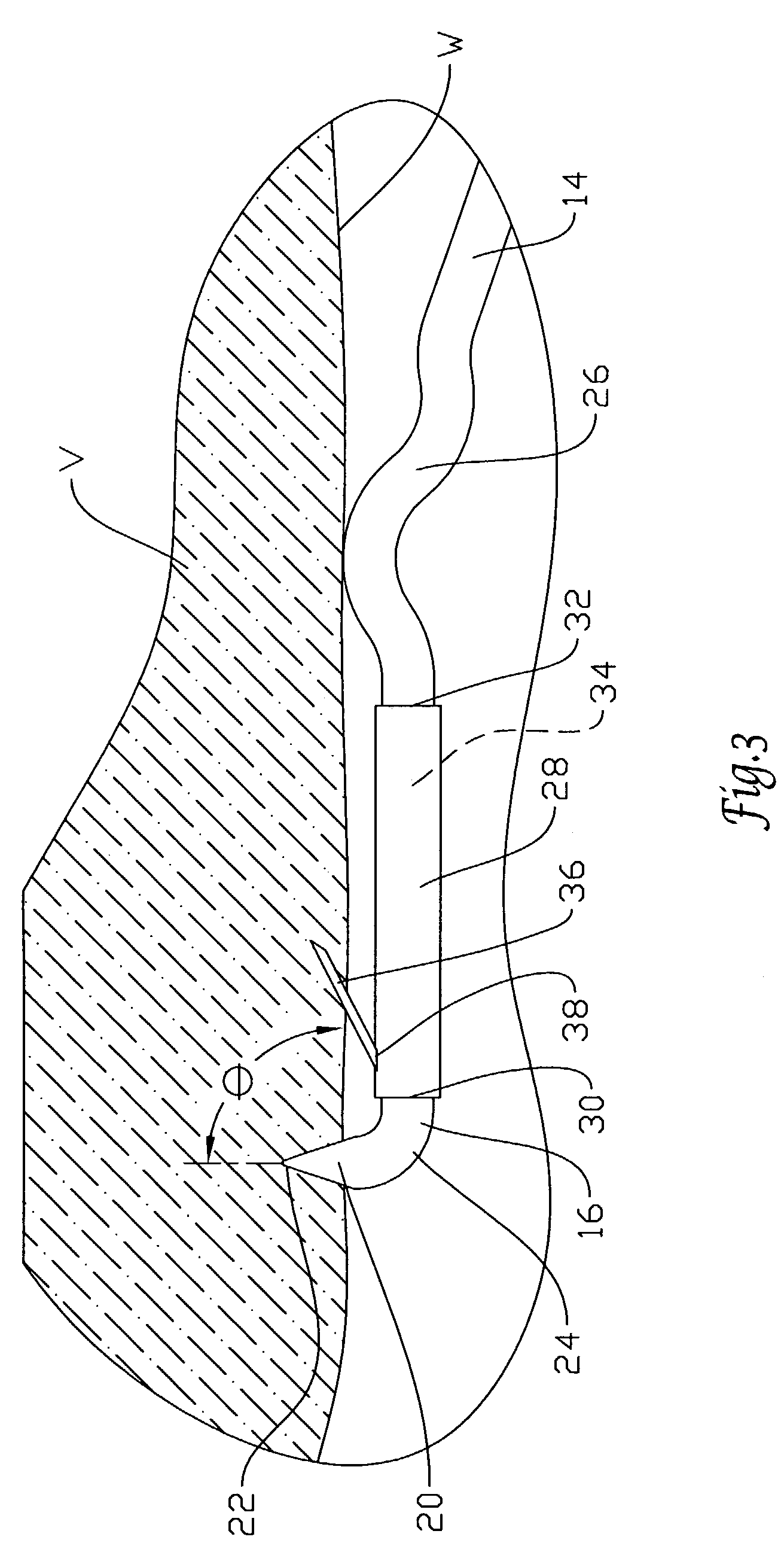
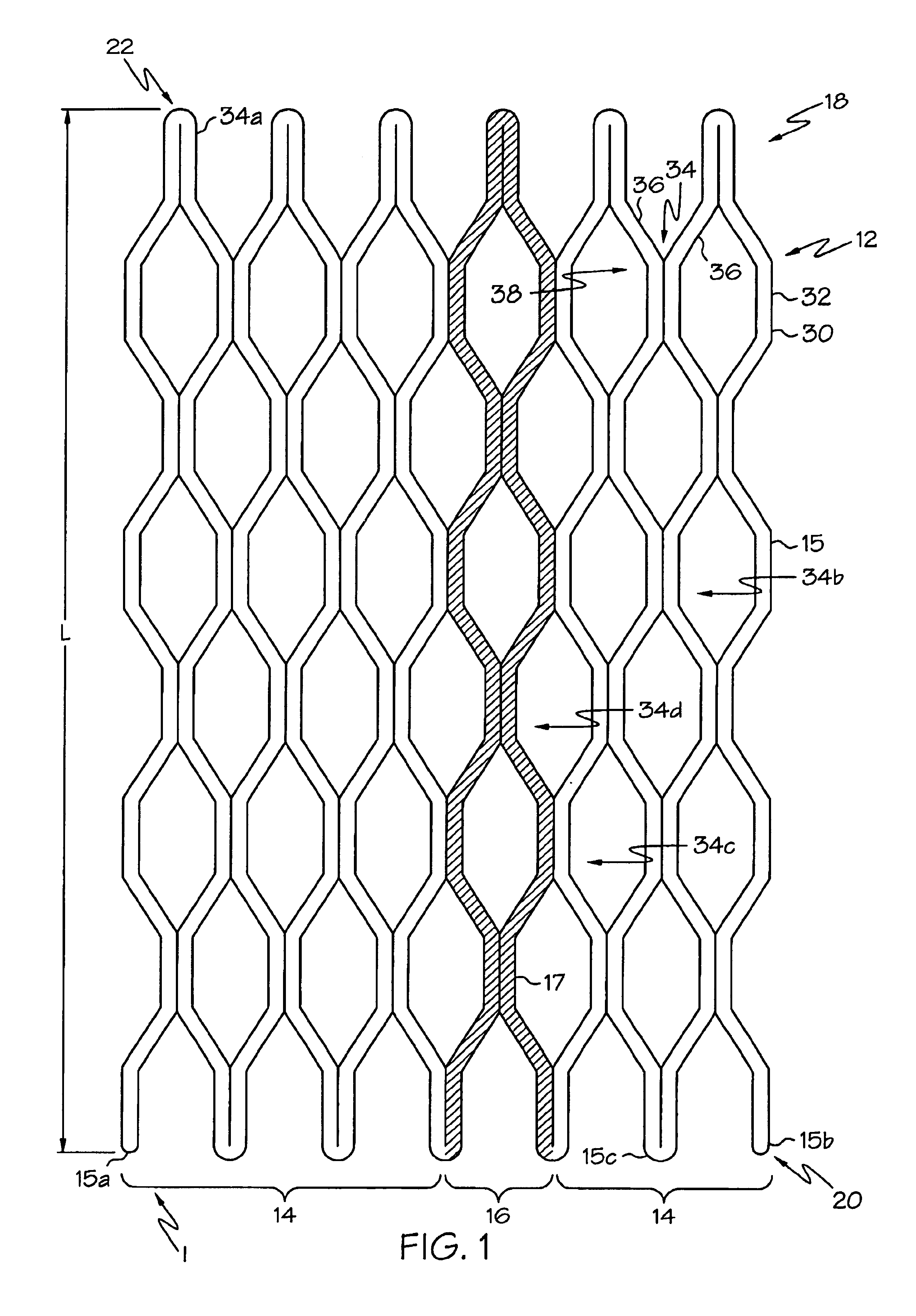
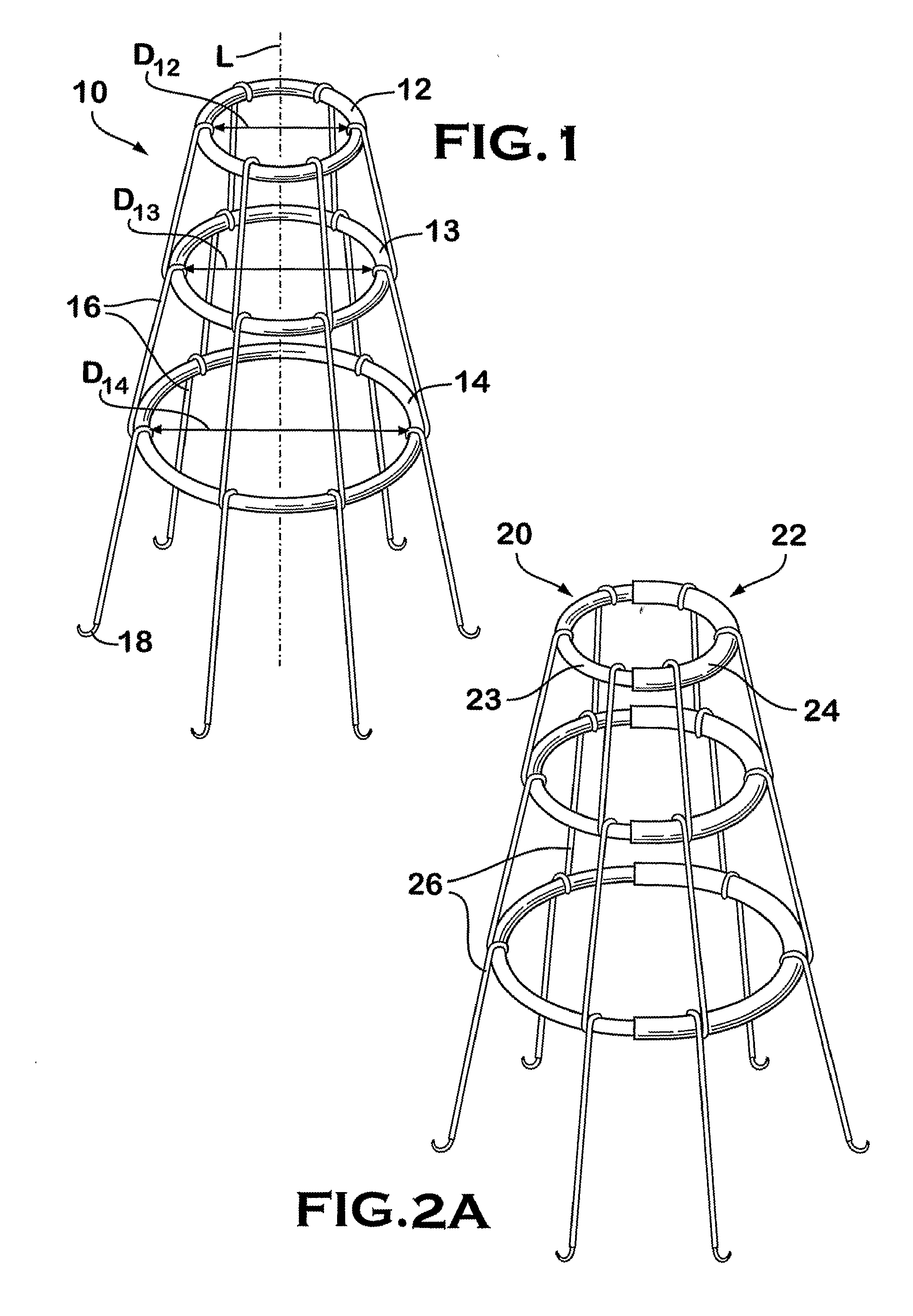
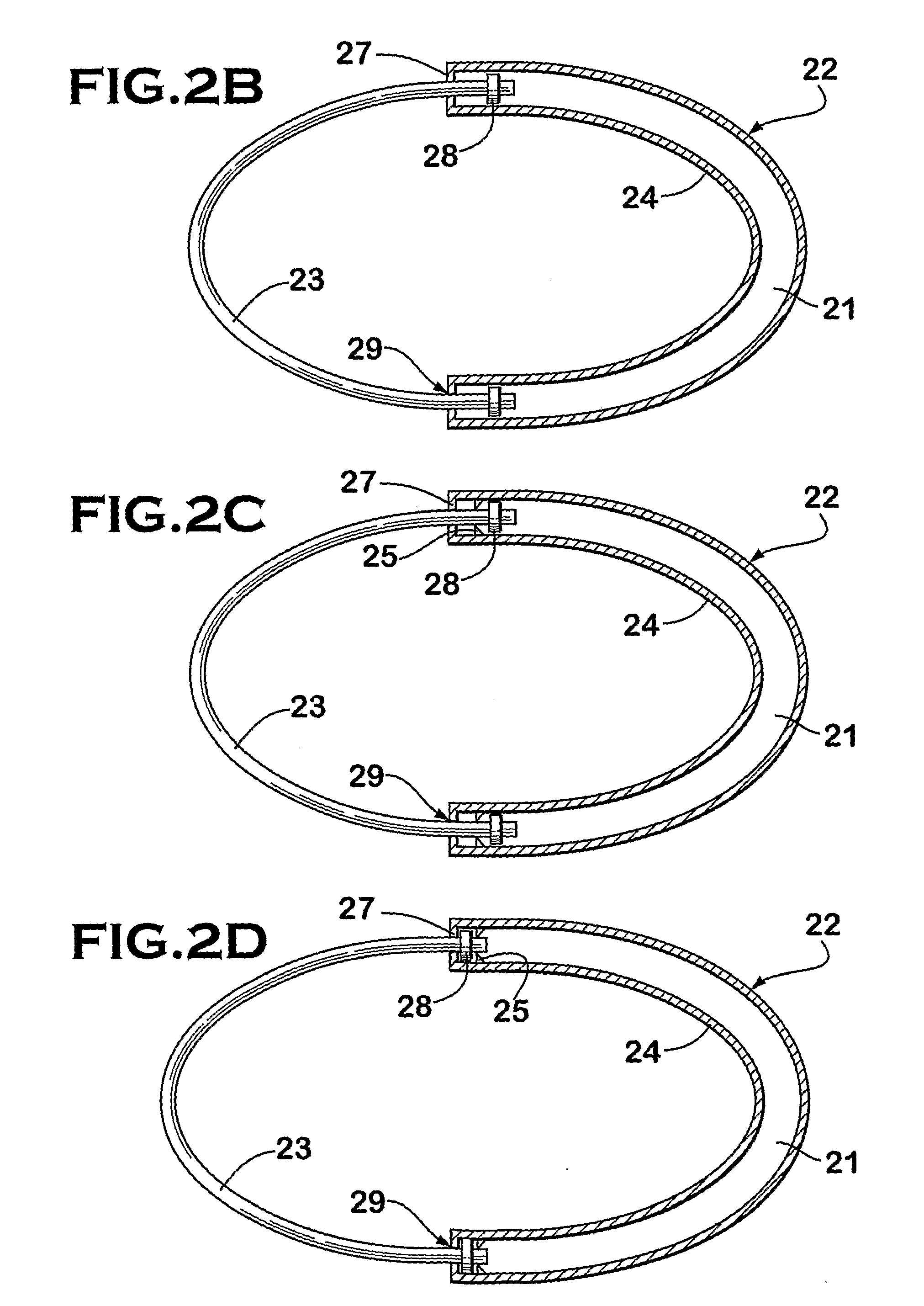
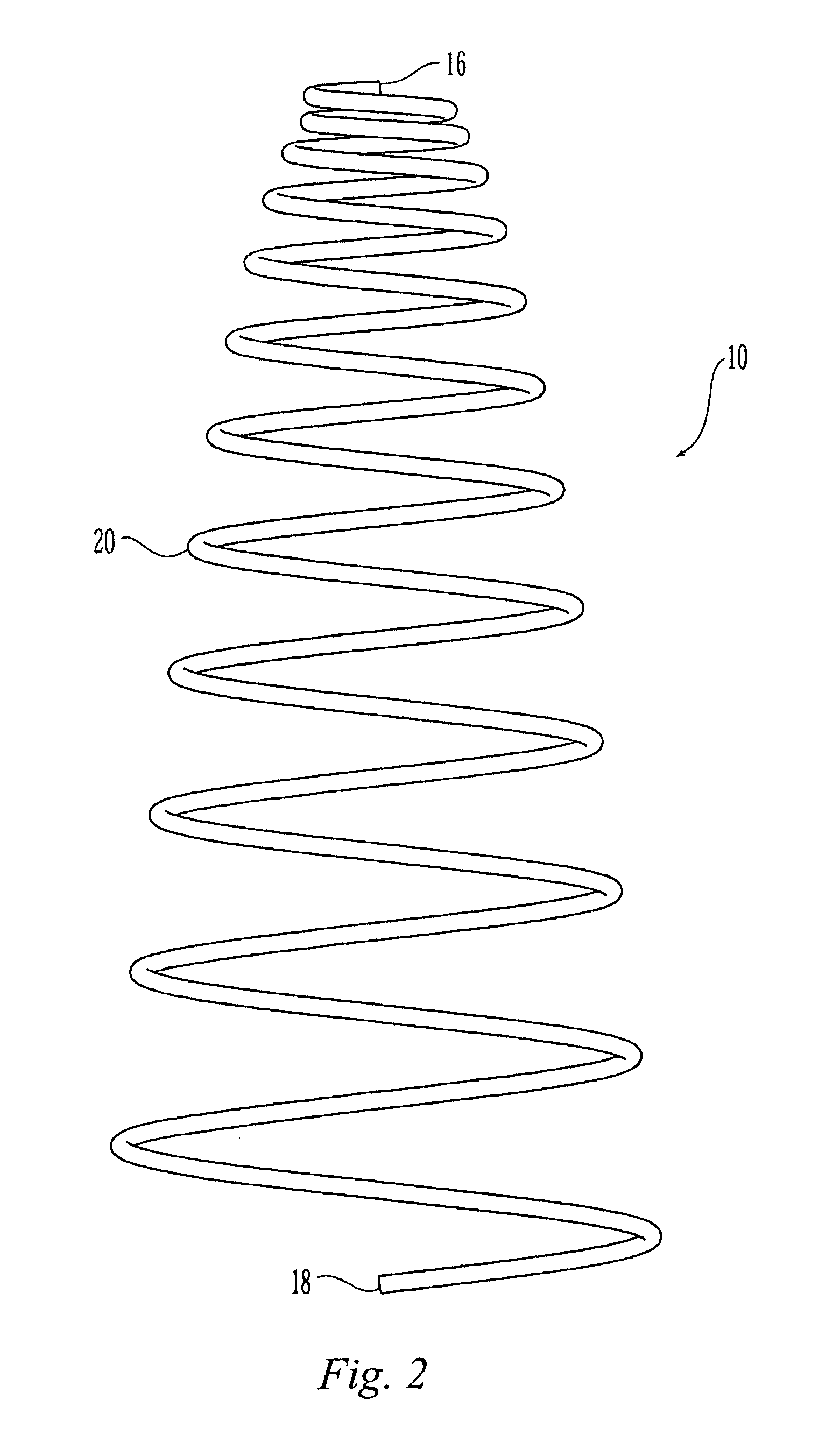
Delivery system and method for deployment of foreshortening endoluminal devices
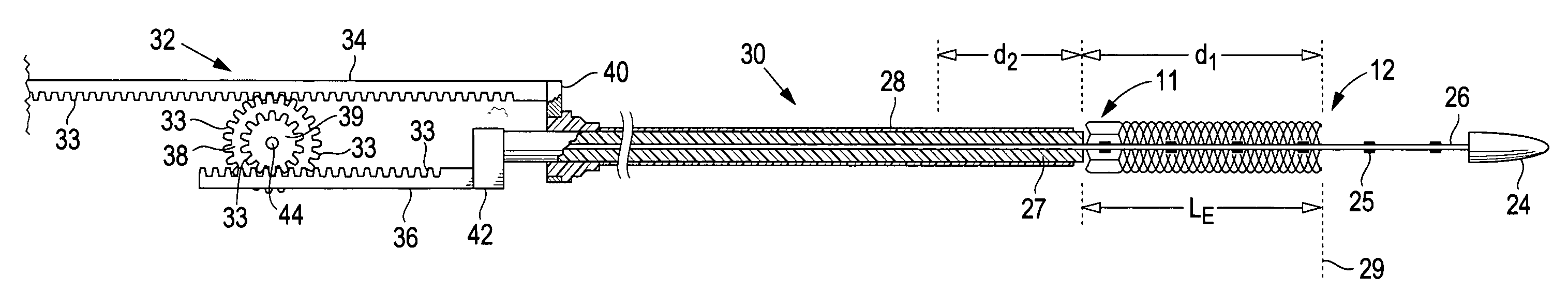
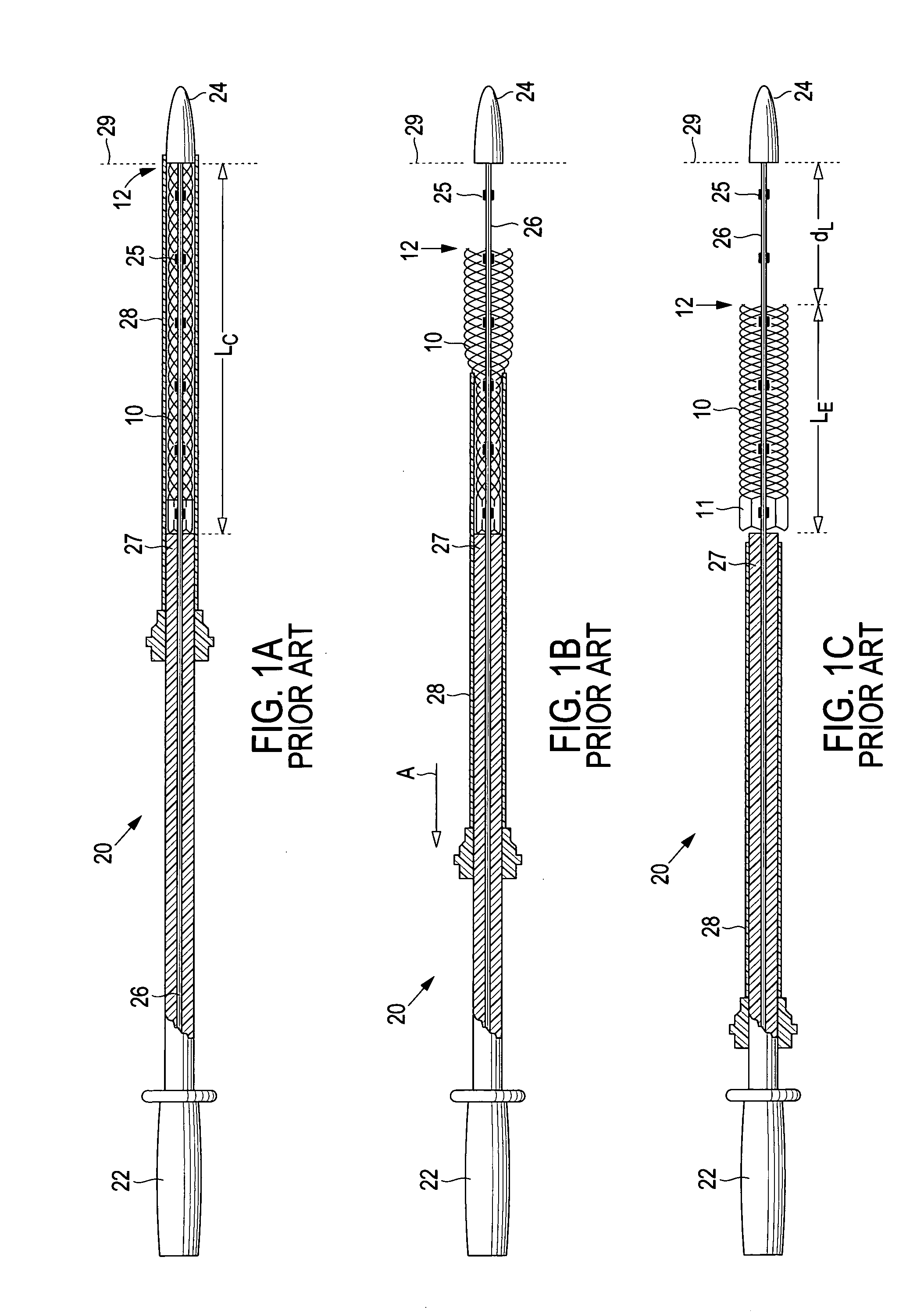
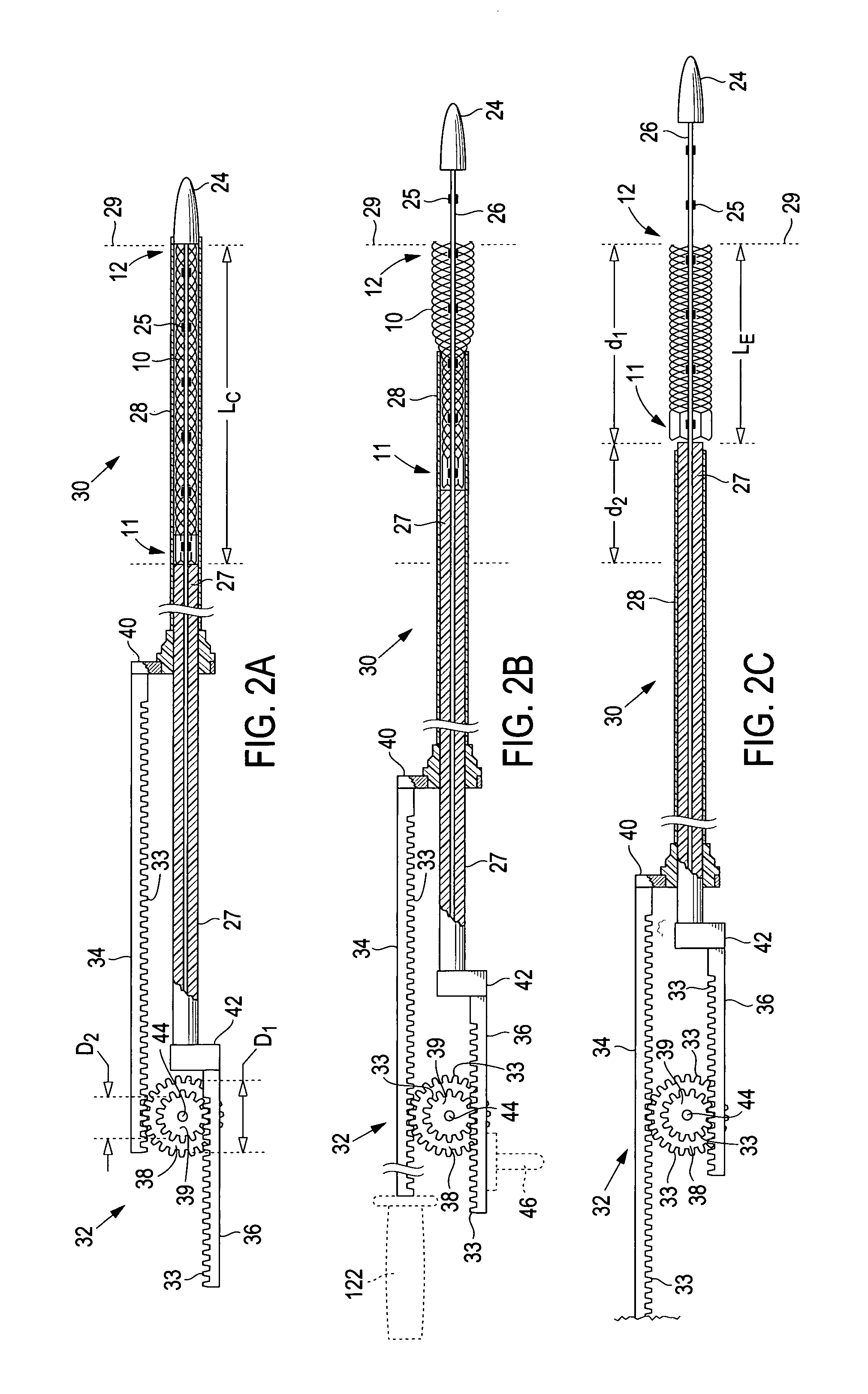
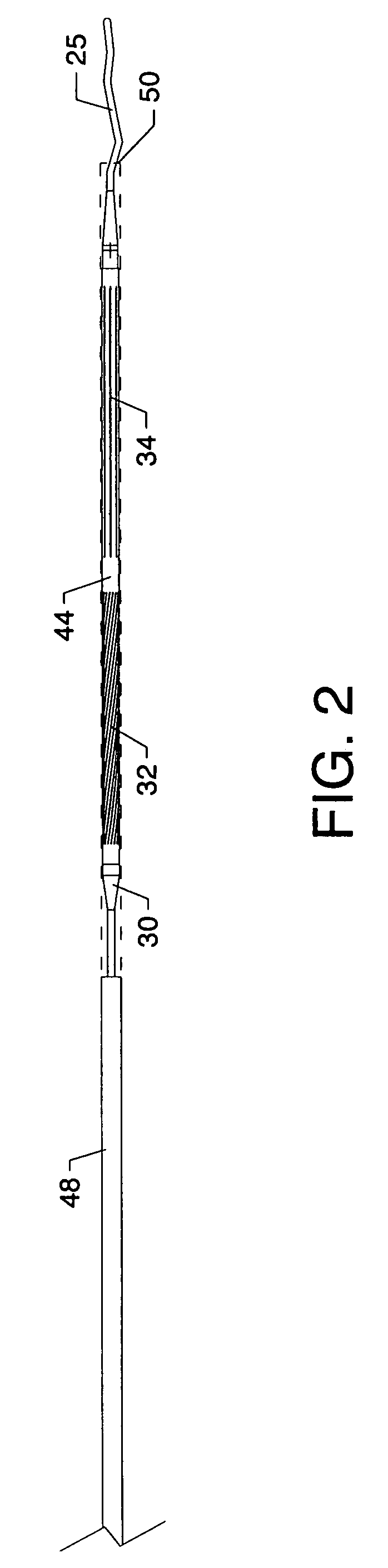
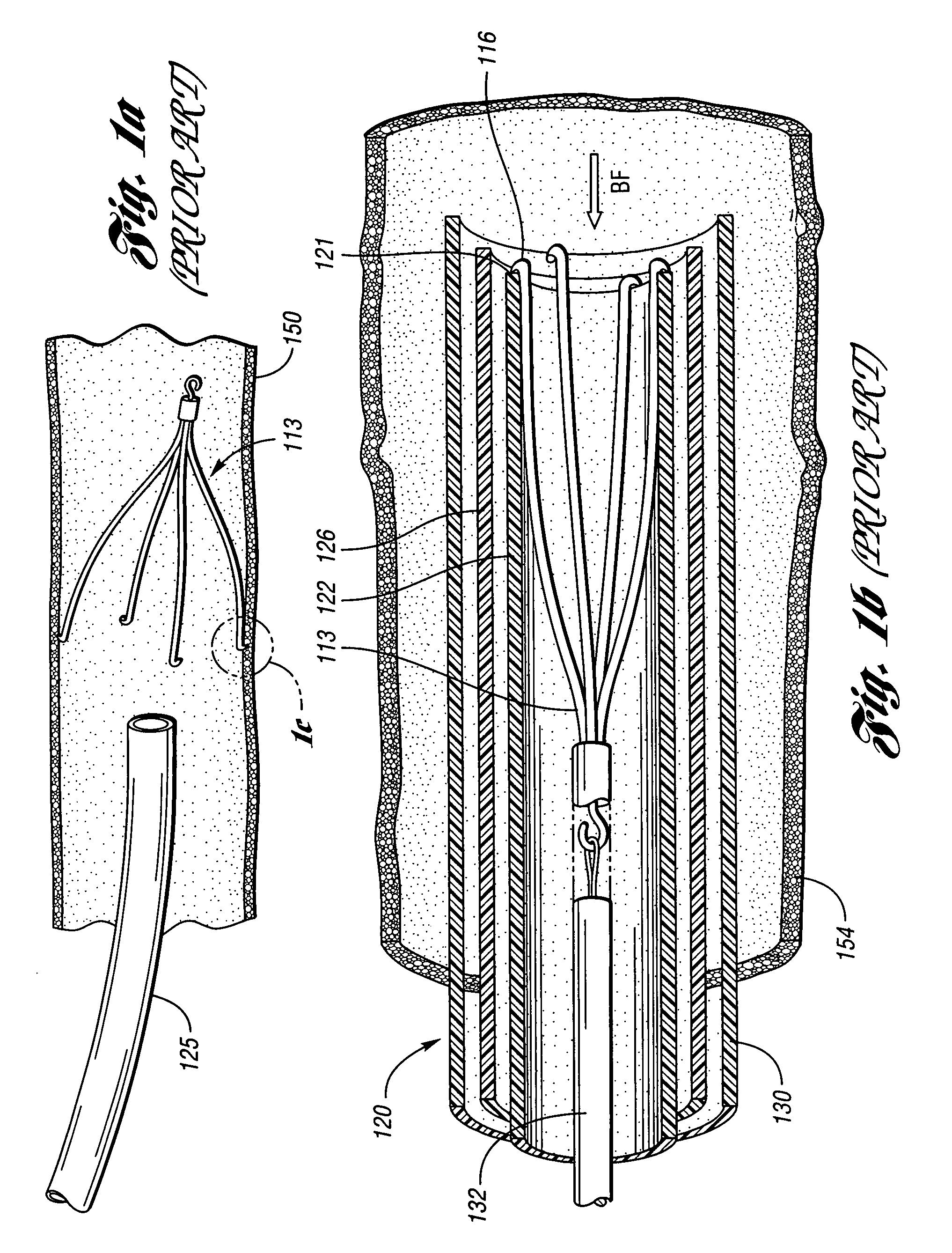
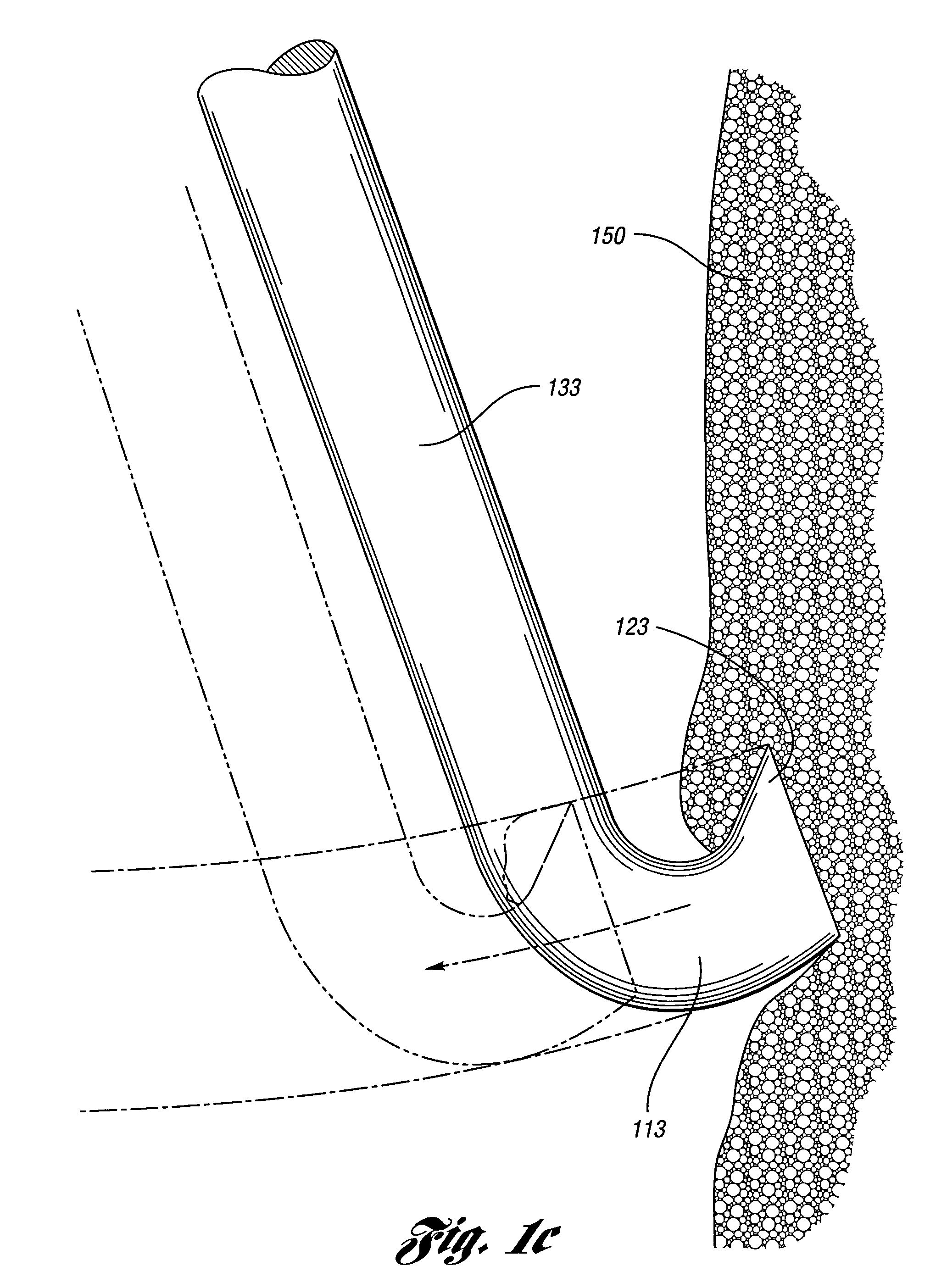
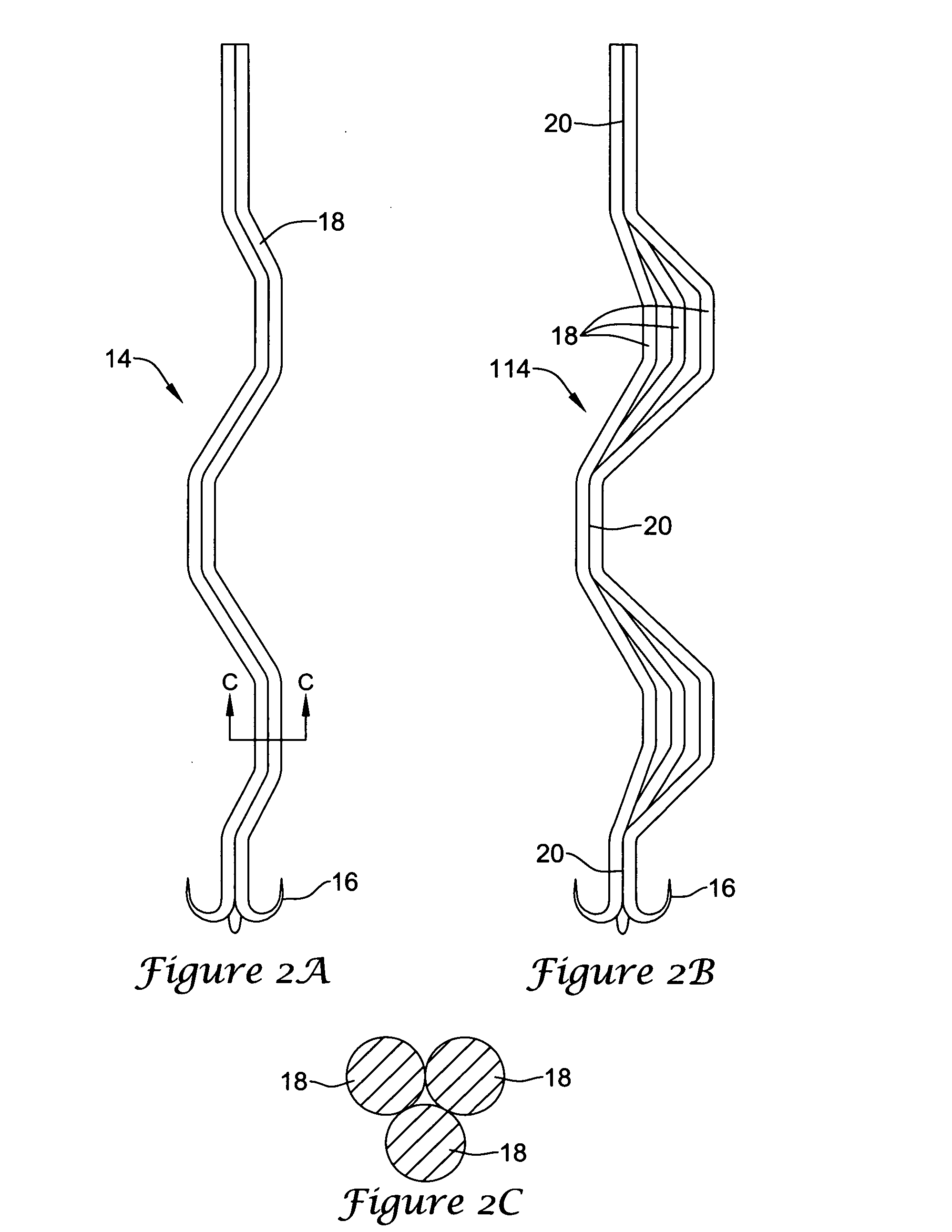
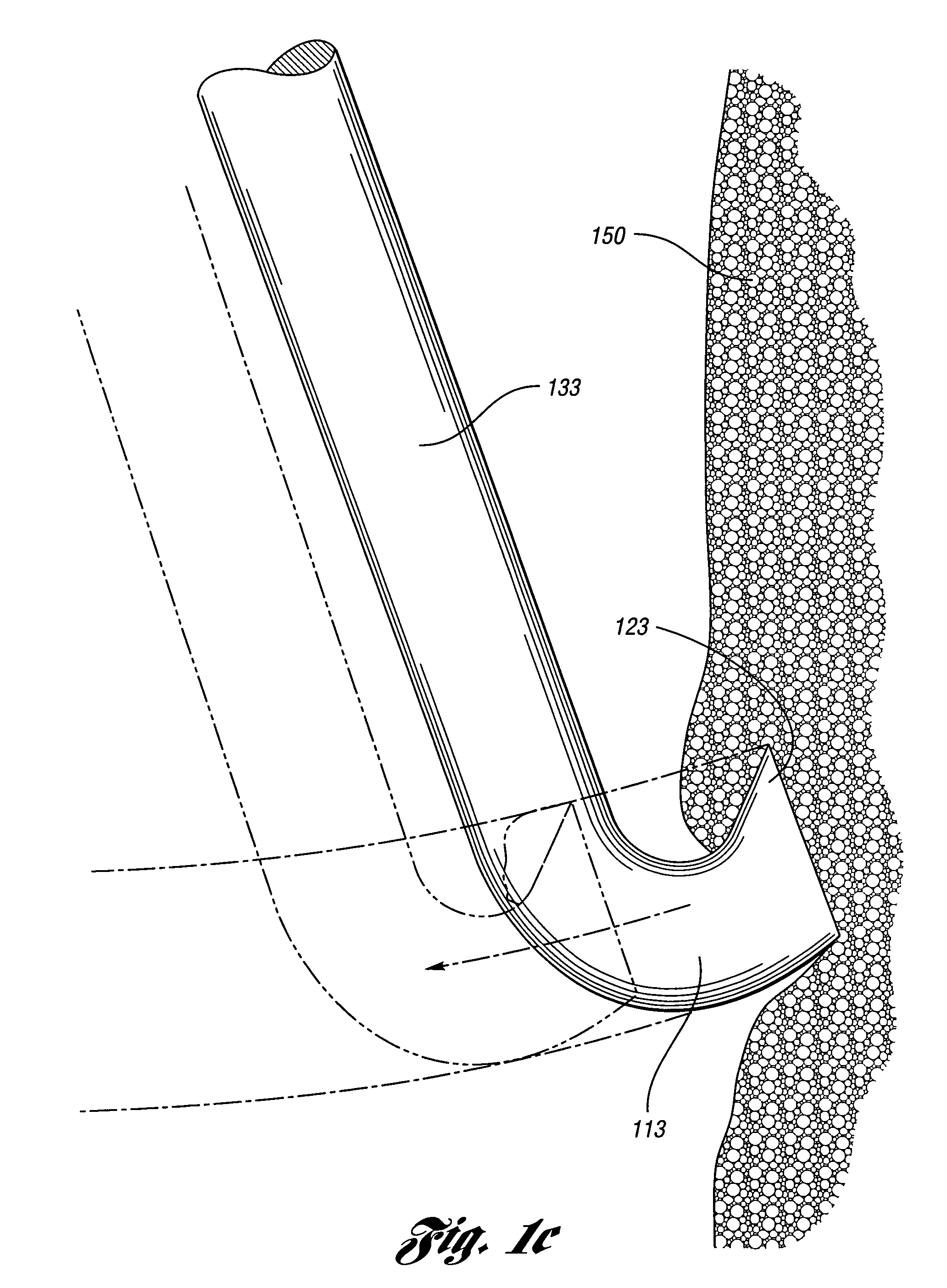
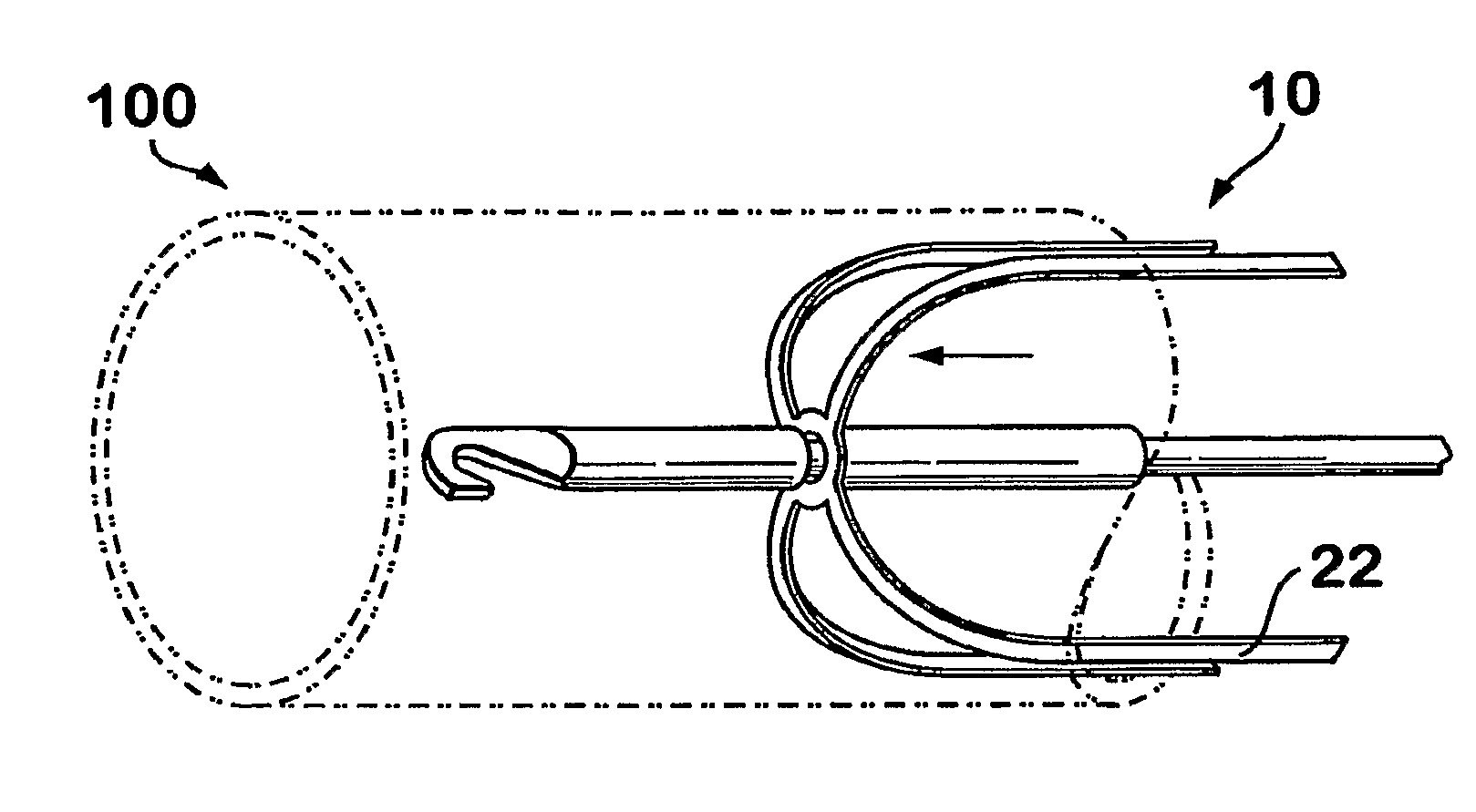
A delivery system comprising an endoluminal device, an outer sheath that radially surrounds the endoluminal device, a pusher positioned at one end of the endoluminal device, and a linkage between the pusher and the outer sheath that coordinates movement of the outer sheath in a first direction with simultaneous movement of the pusher in a second direction opposite the first direction. This delivery system is particularly useful for endoluminal devices that foreshorten, and may comprise the outer sheath moving a first distance (d1) and the pusher moving a second distance (d2), where d2 / d1 is approximately equal to the foreshortening ratio. The delivery system of this invention enables a foreshortening device, such as a vena cava filter, or stent, graft, or combination thereof, to be deployed with its end in a precise deployment location without foreshortening causing the end to move from the deployment location as the stent expands.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
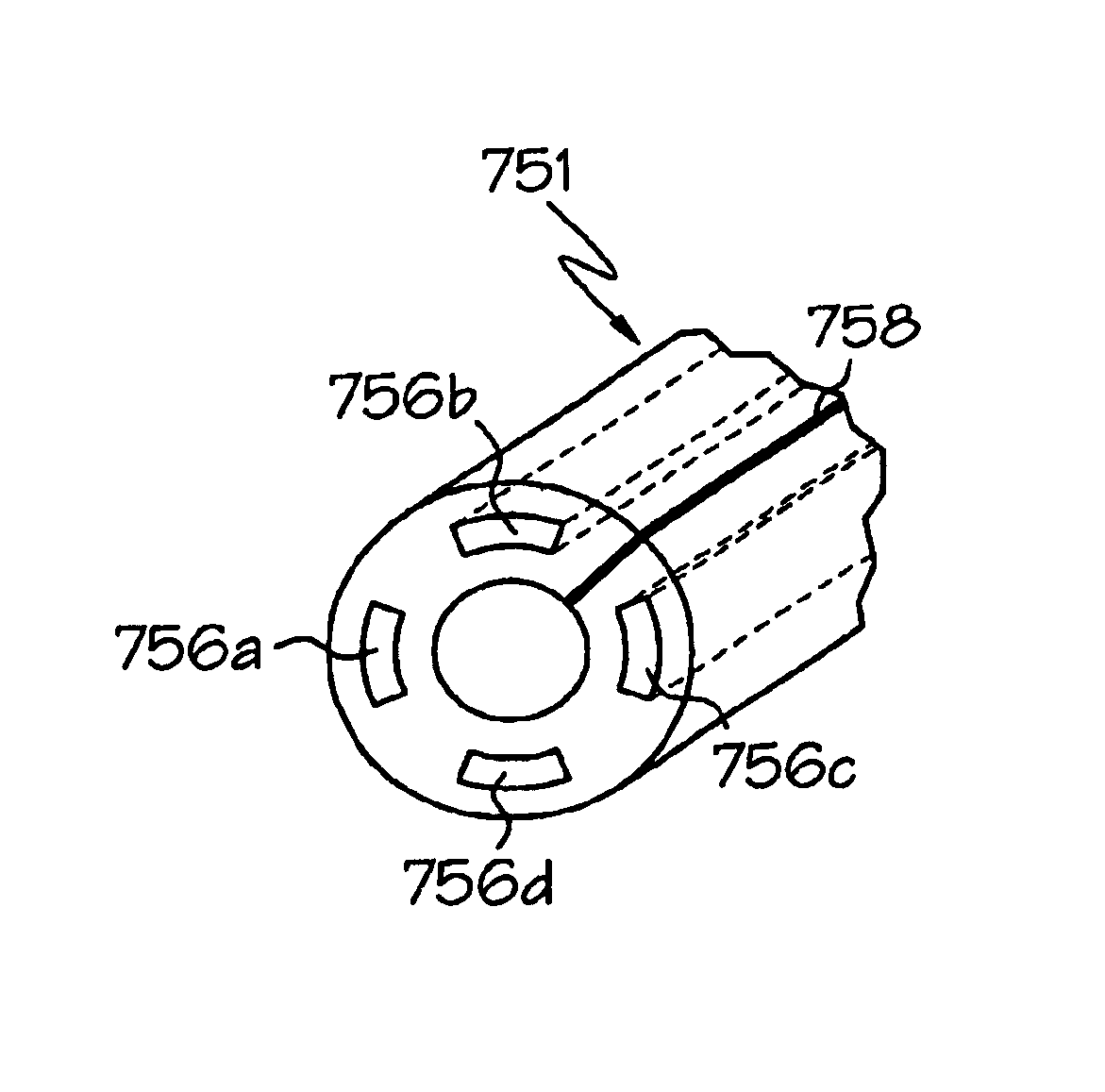
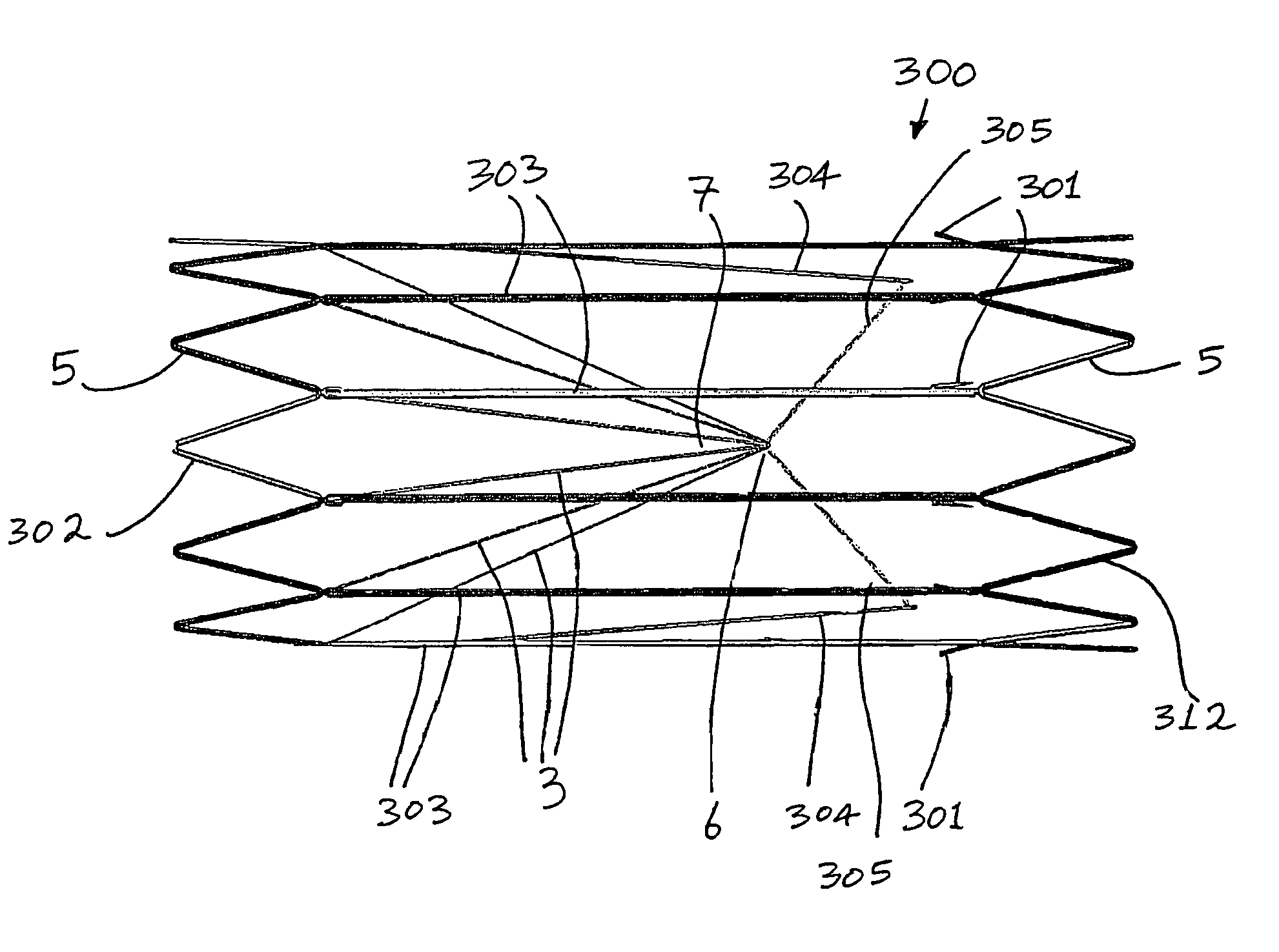
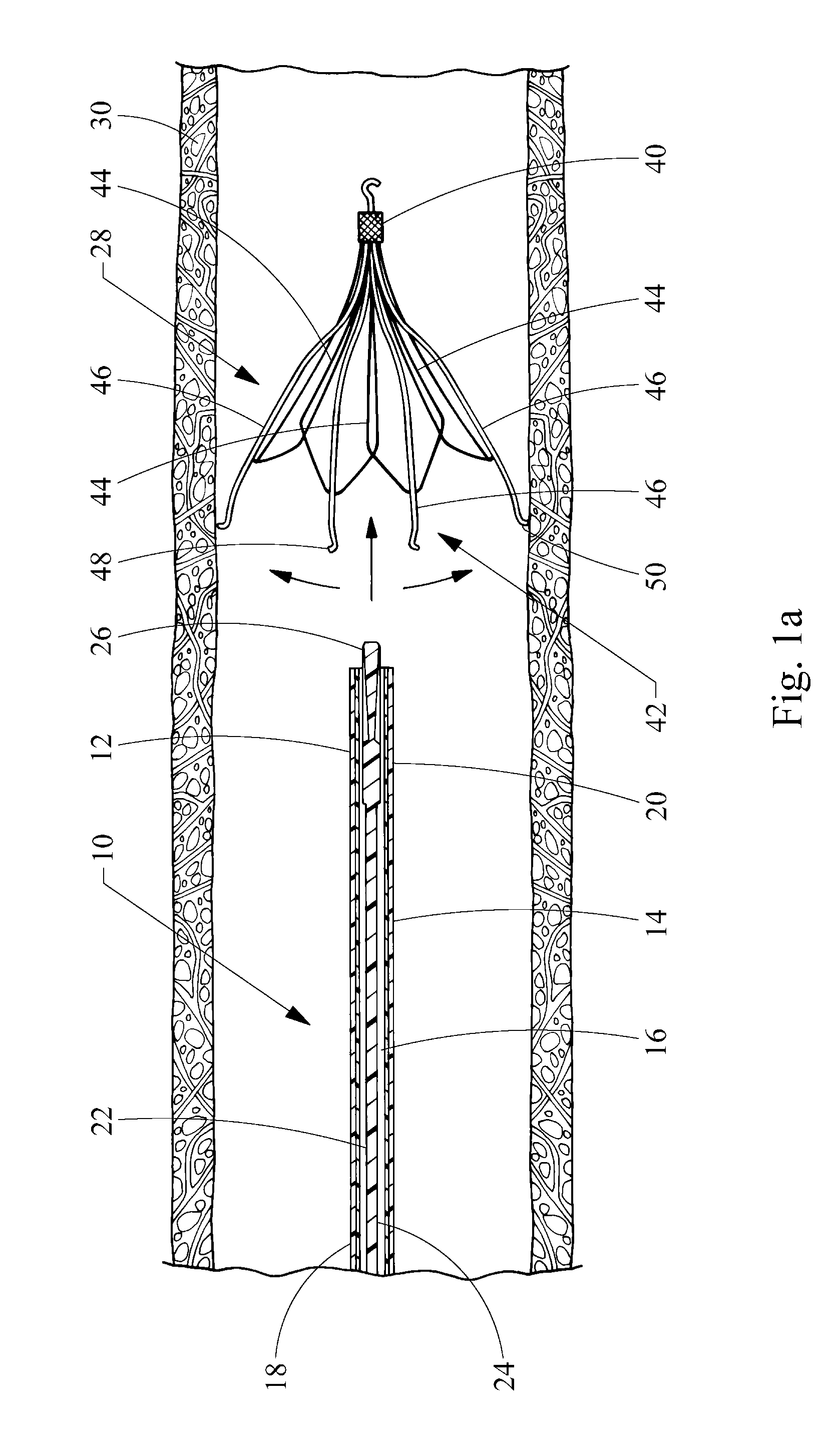
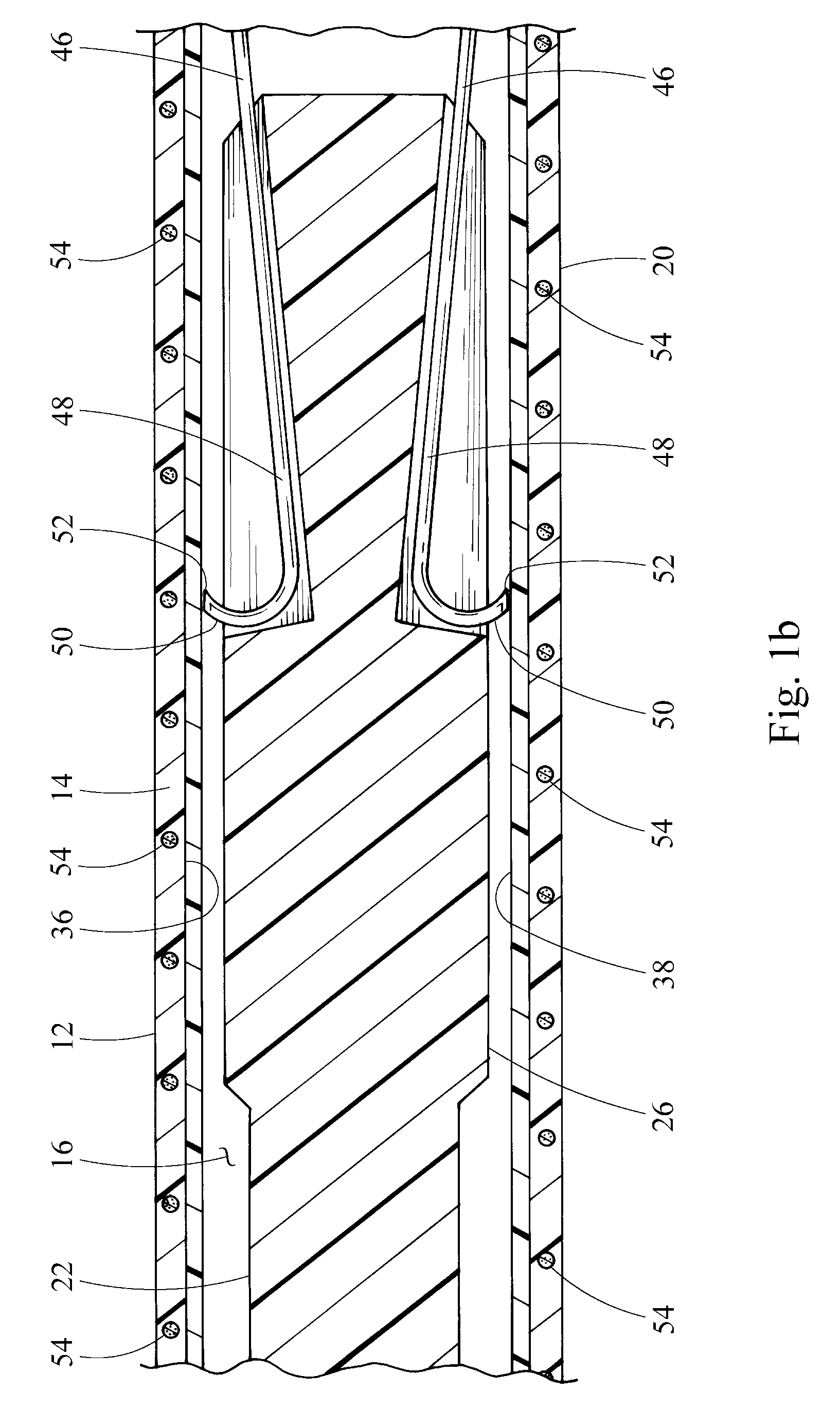
Vascular filter
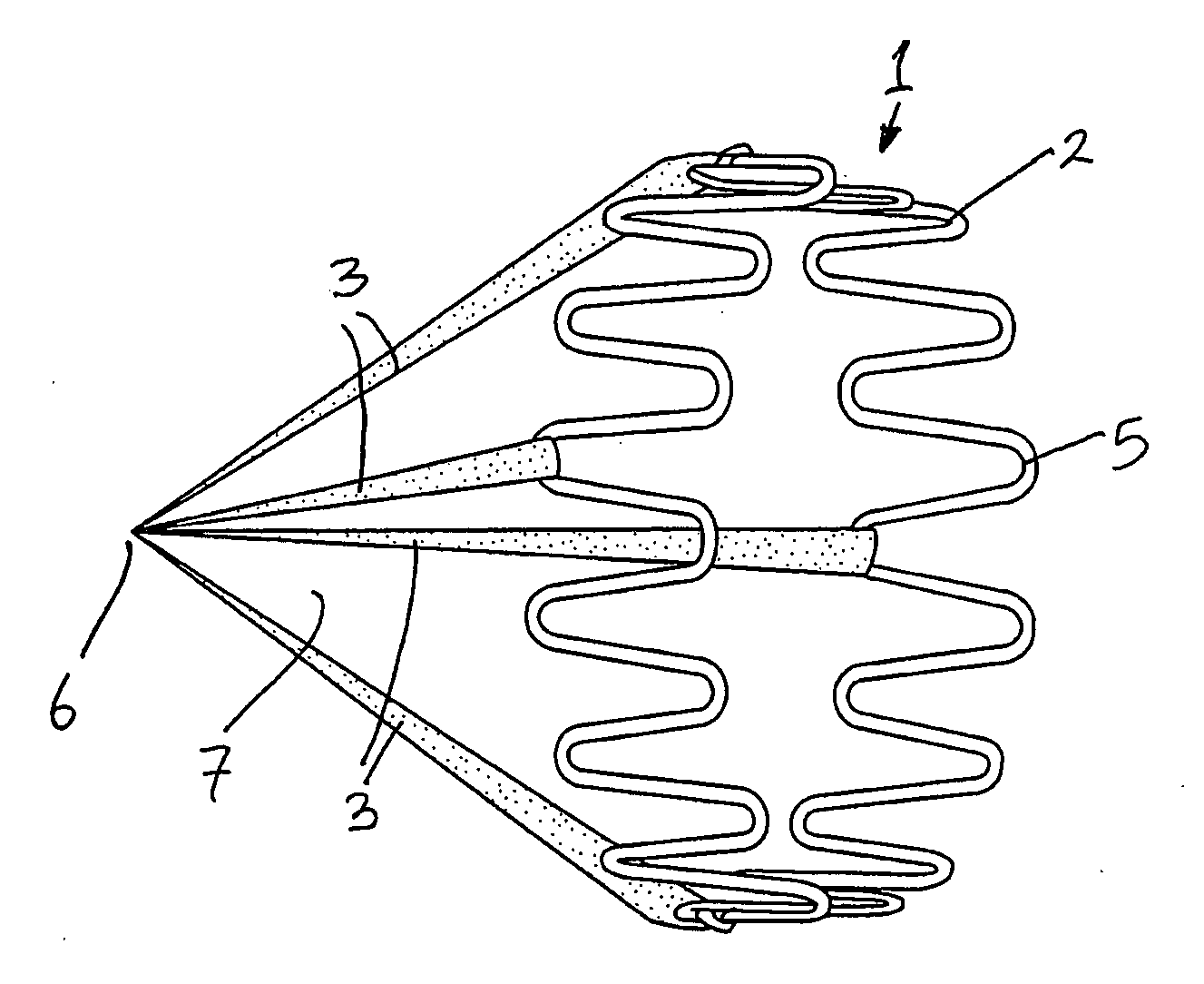
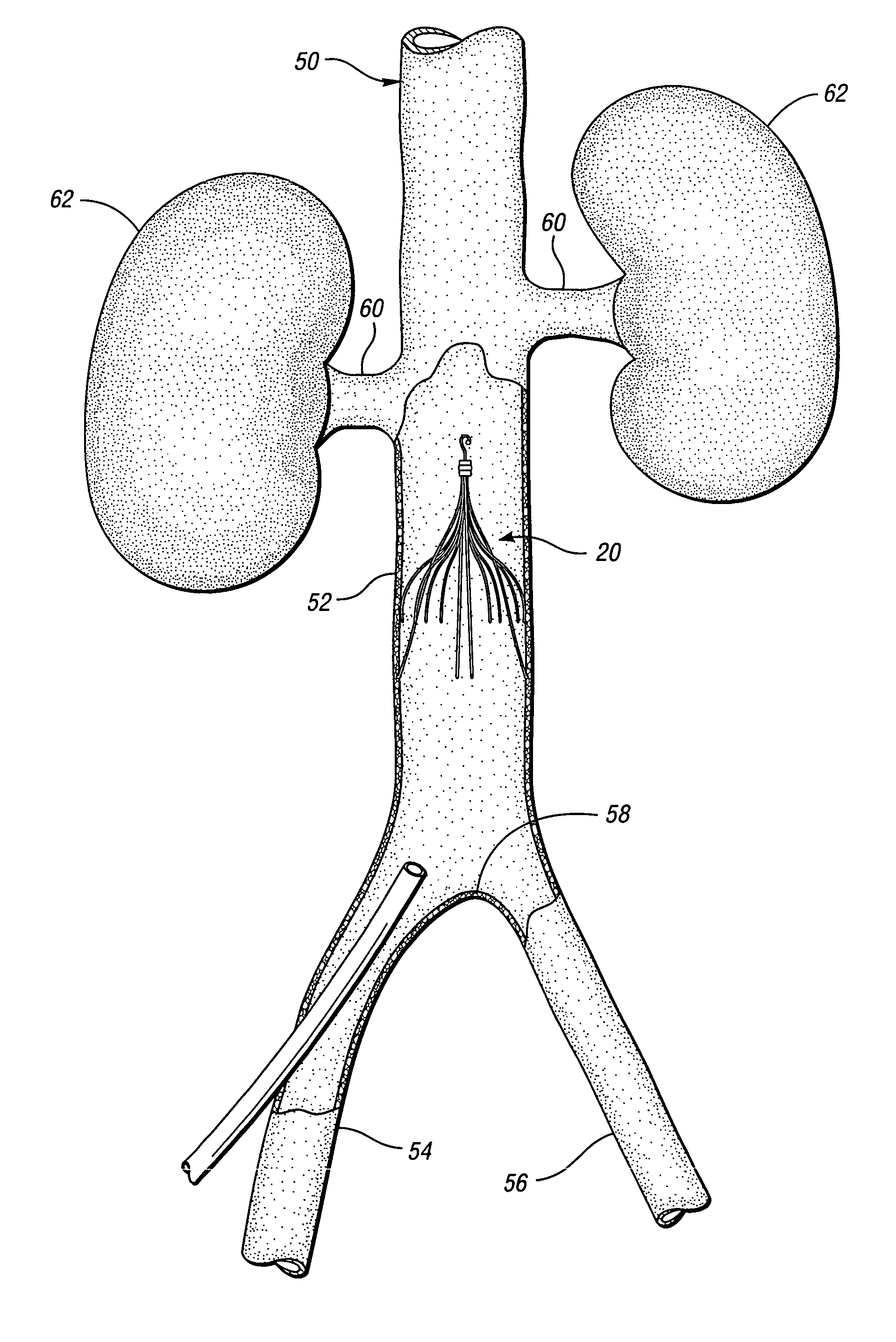
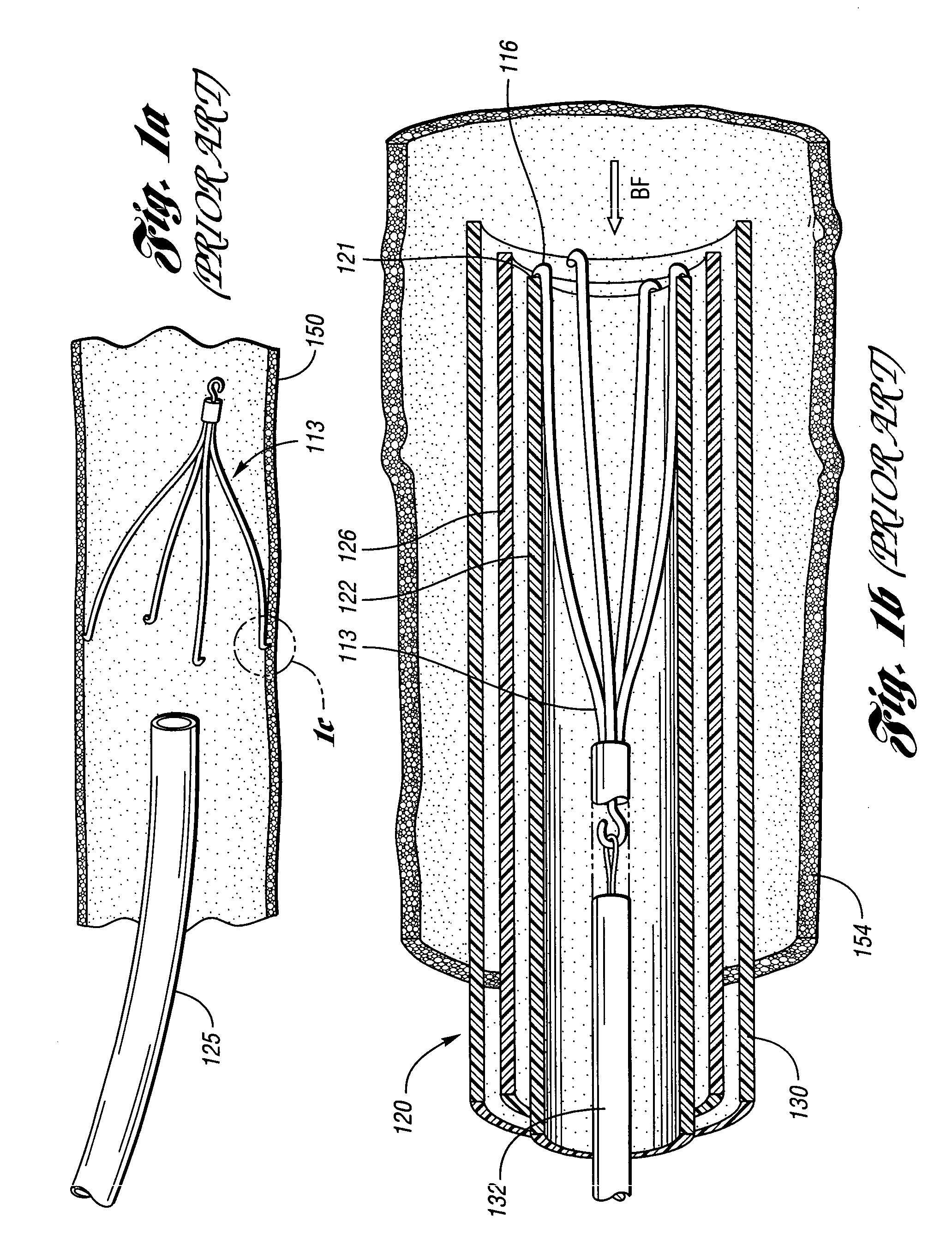
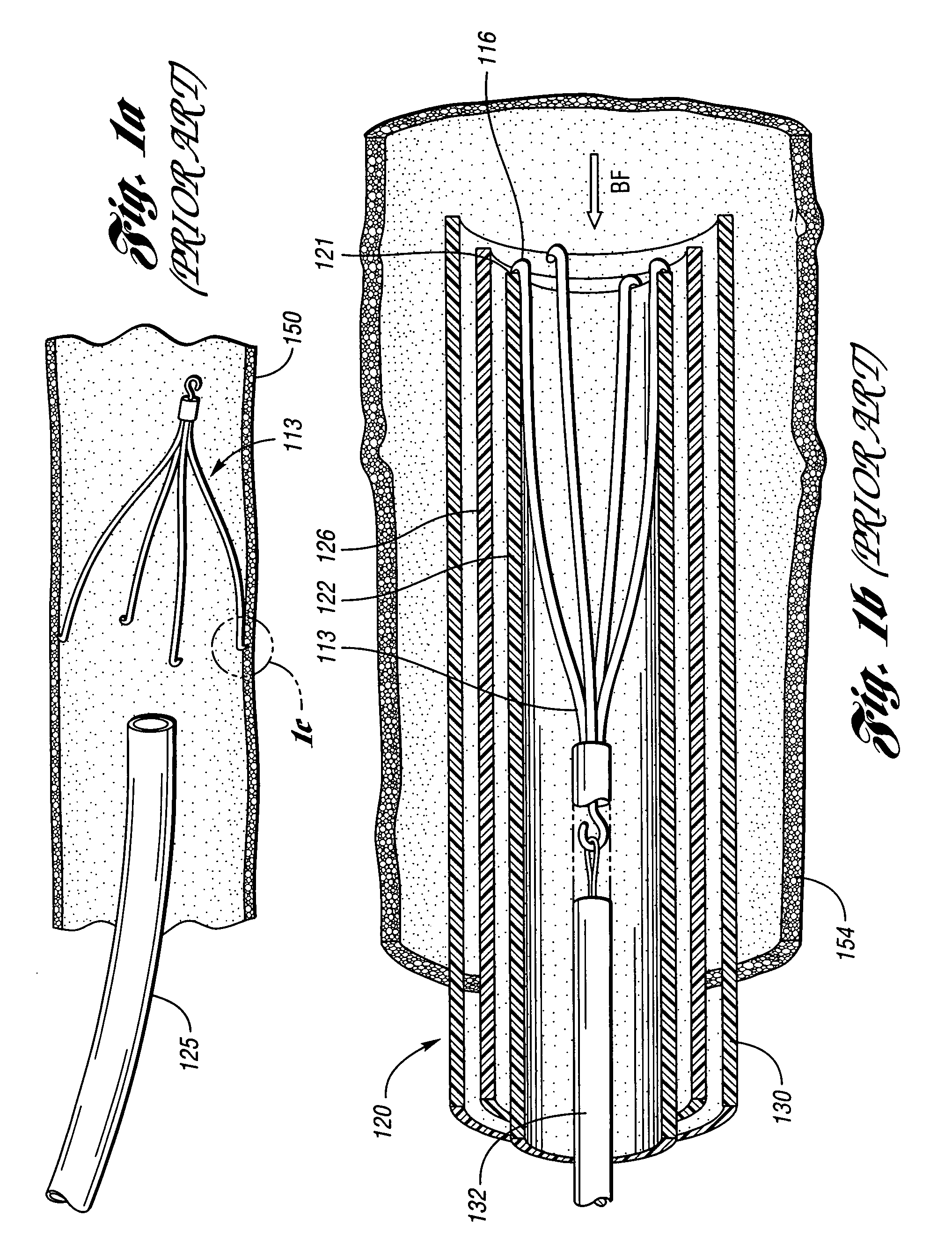
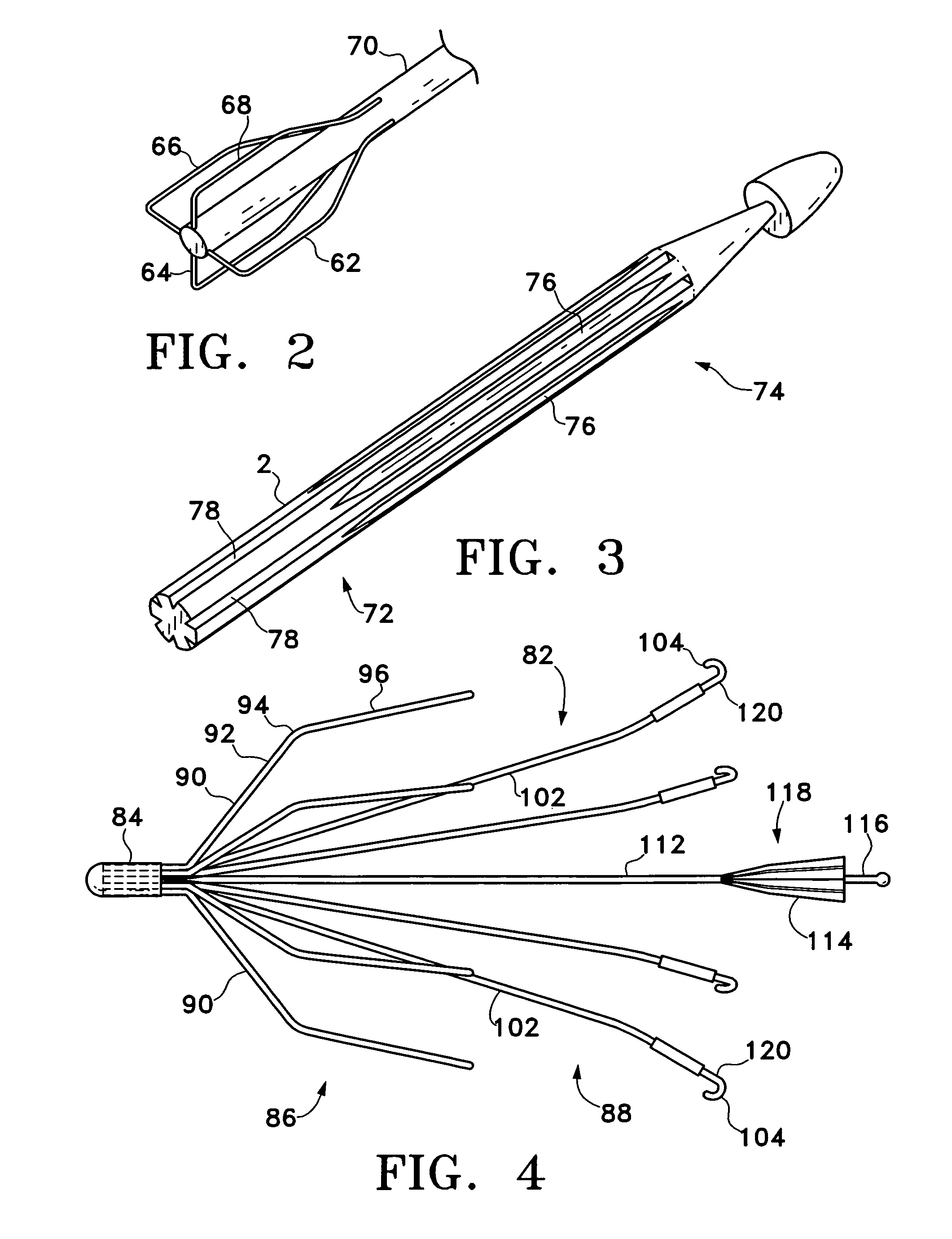
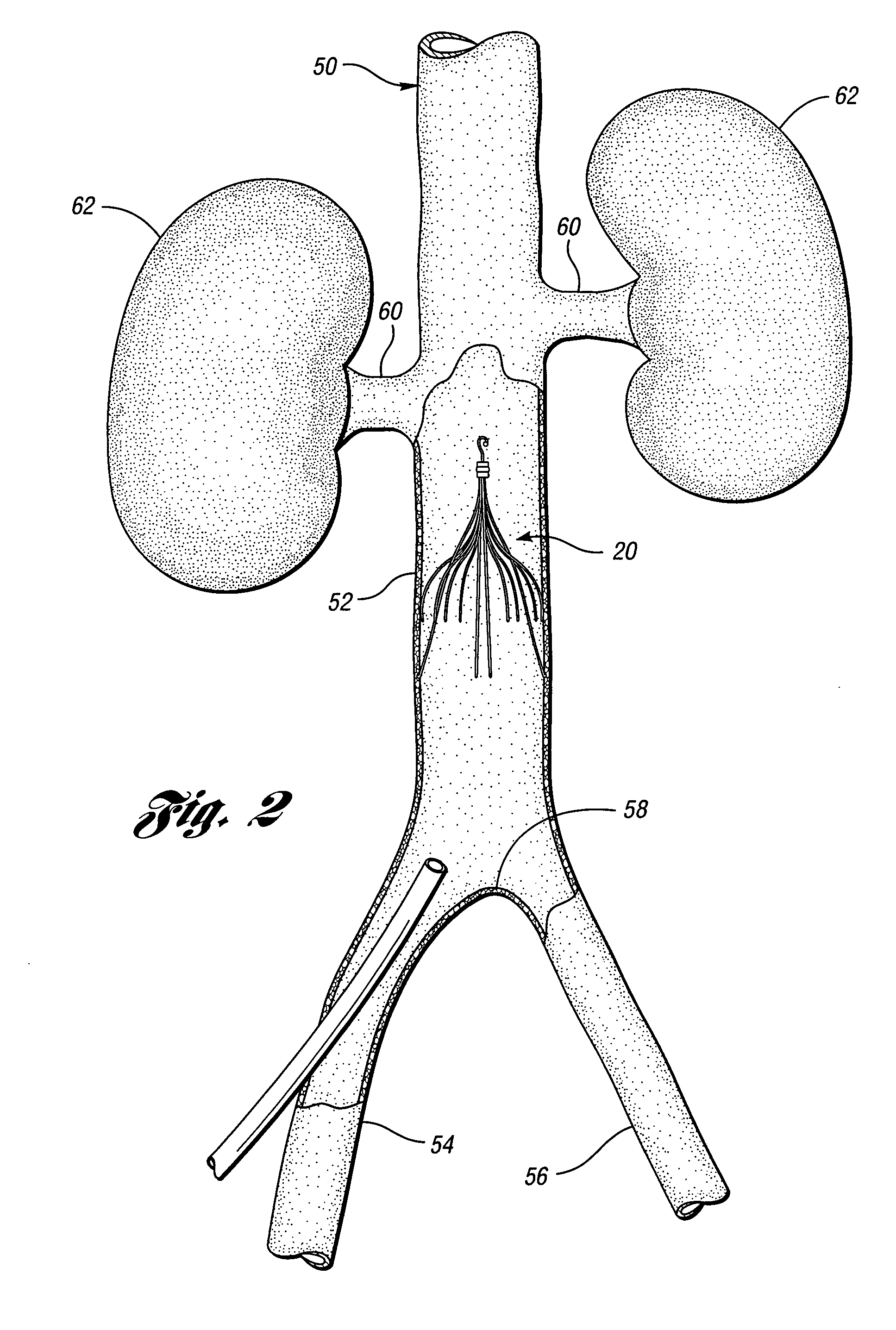
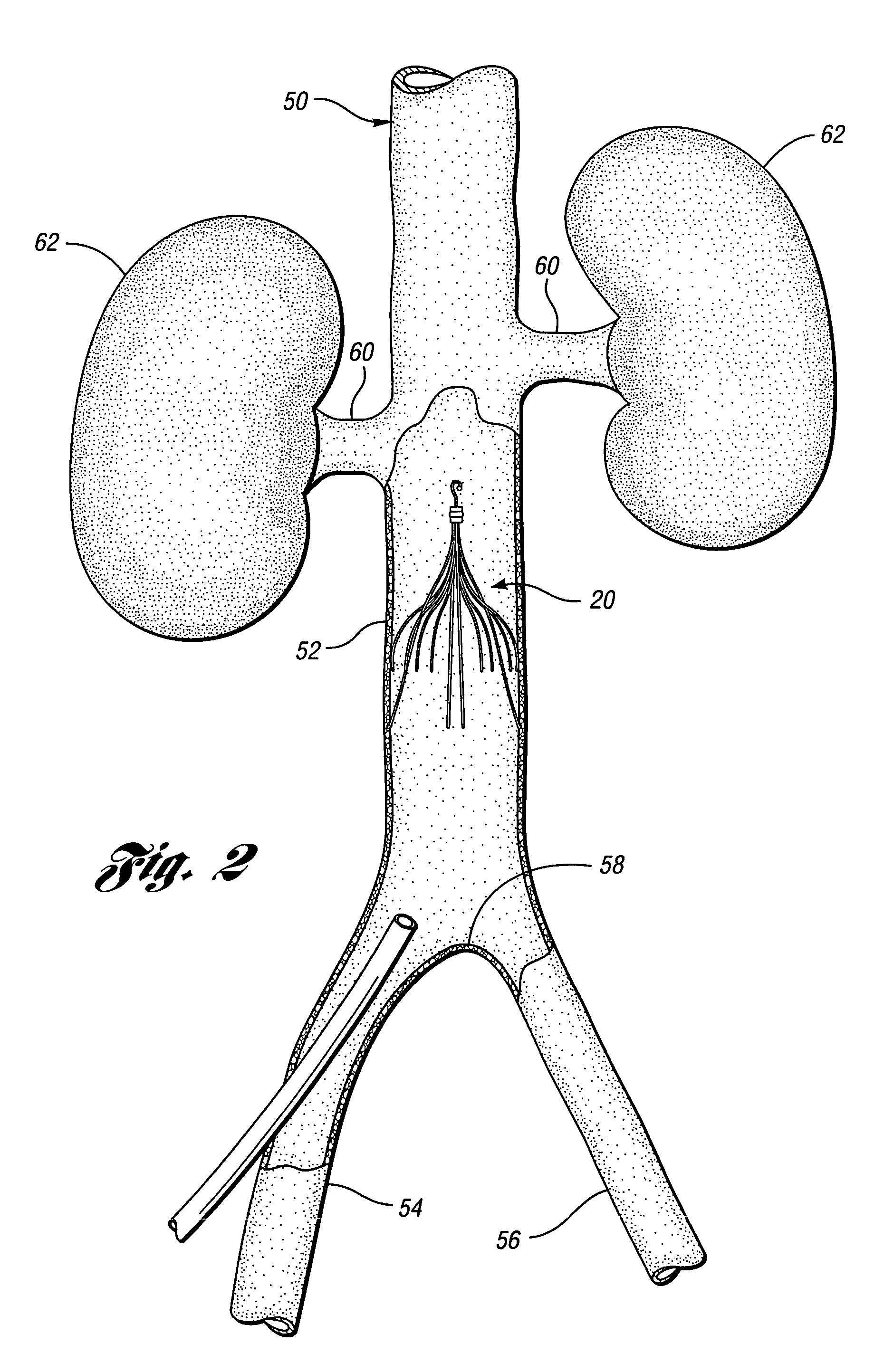
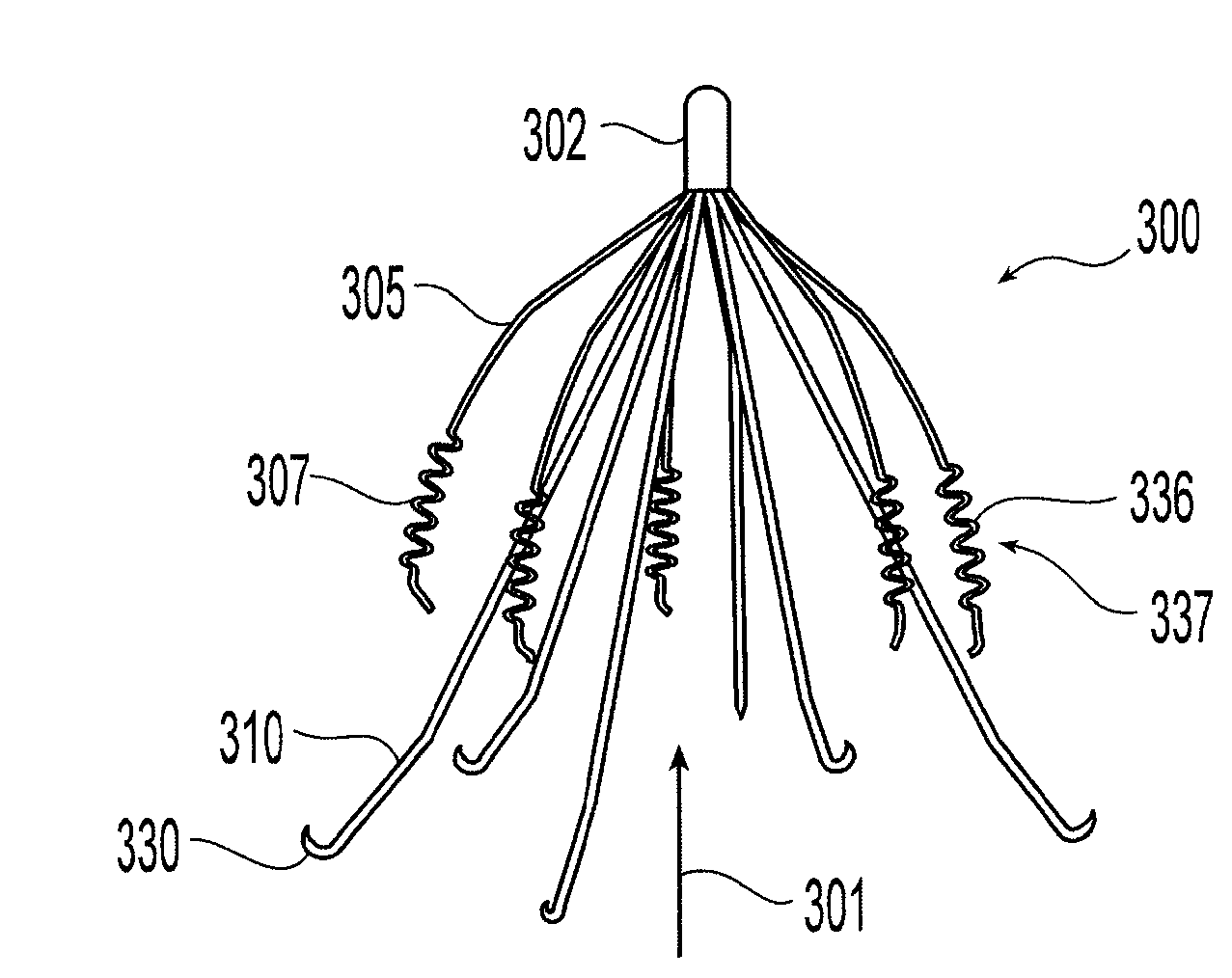
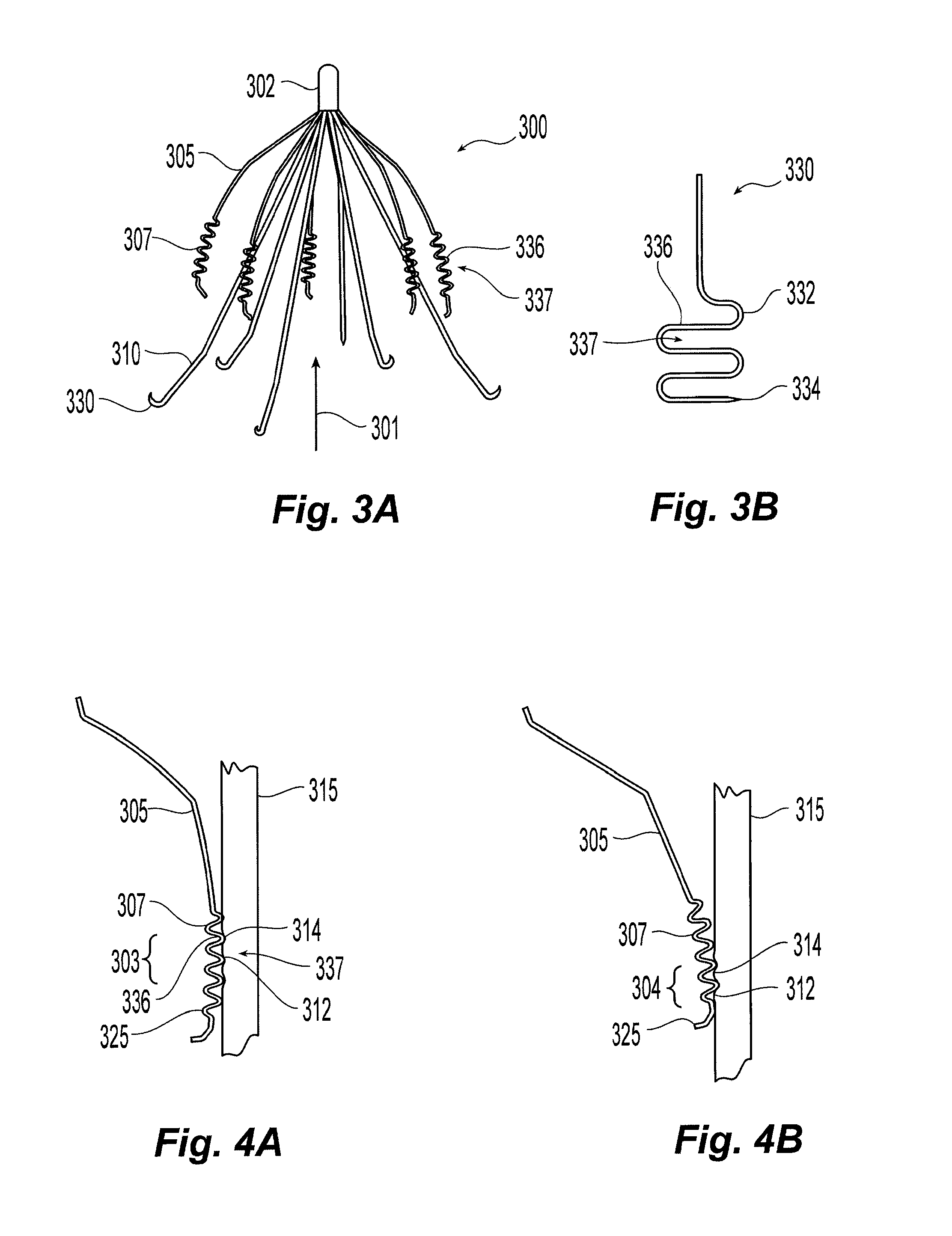
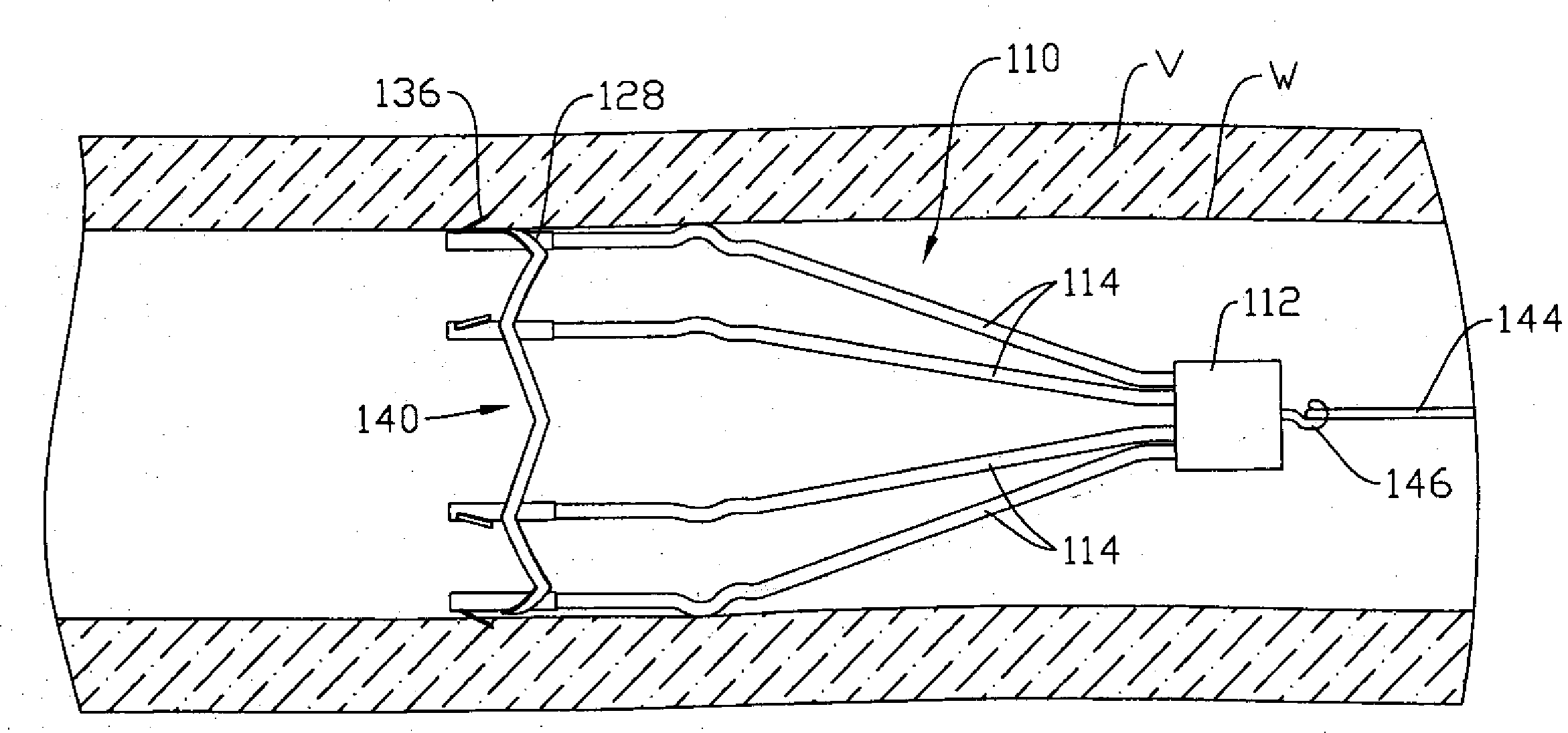
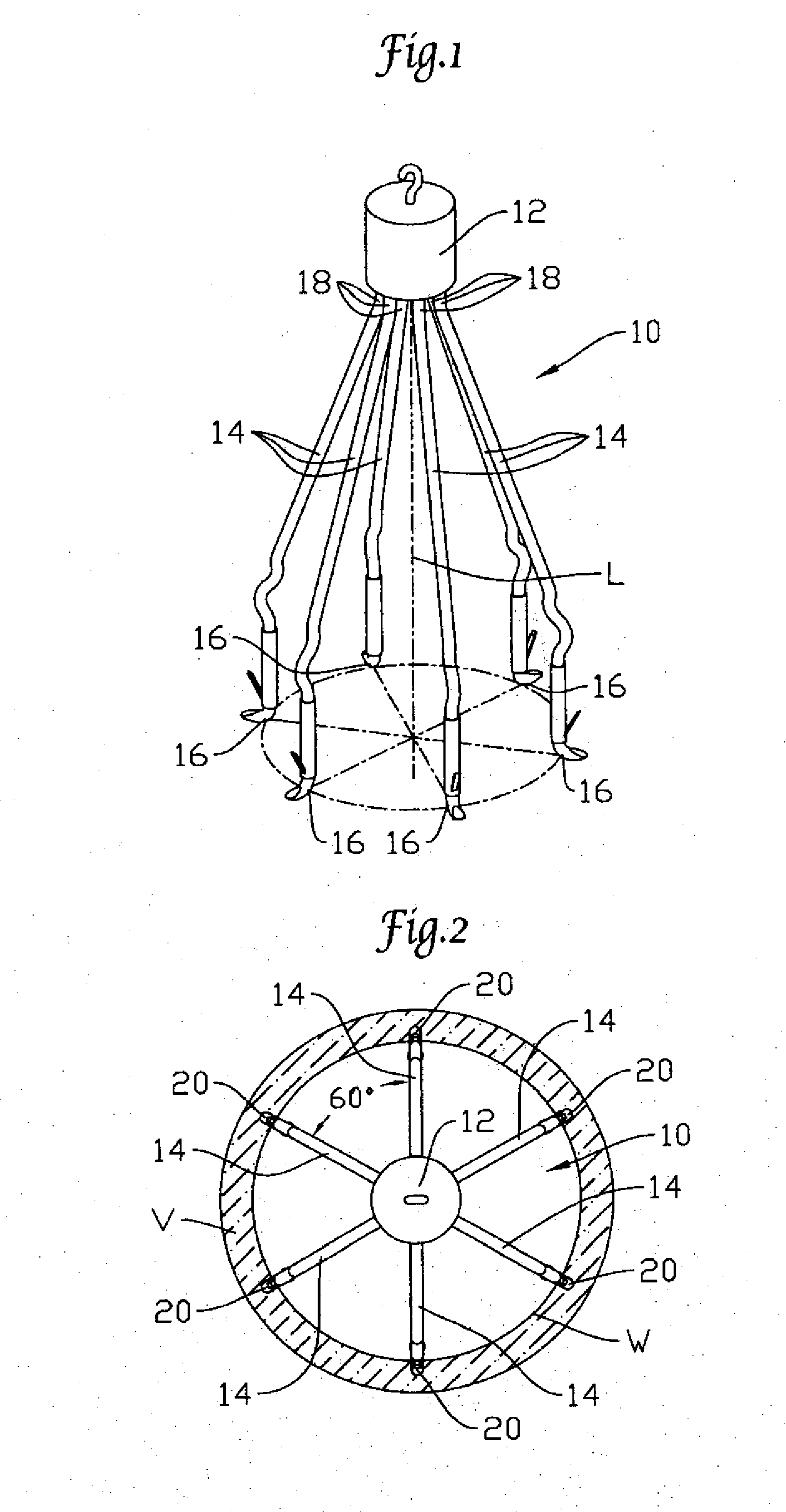
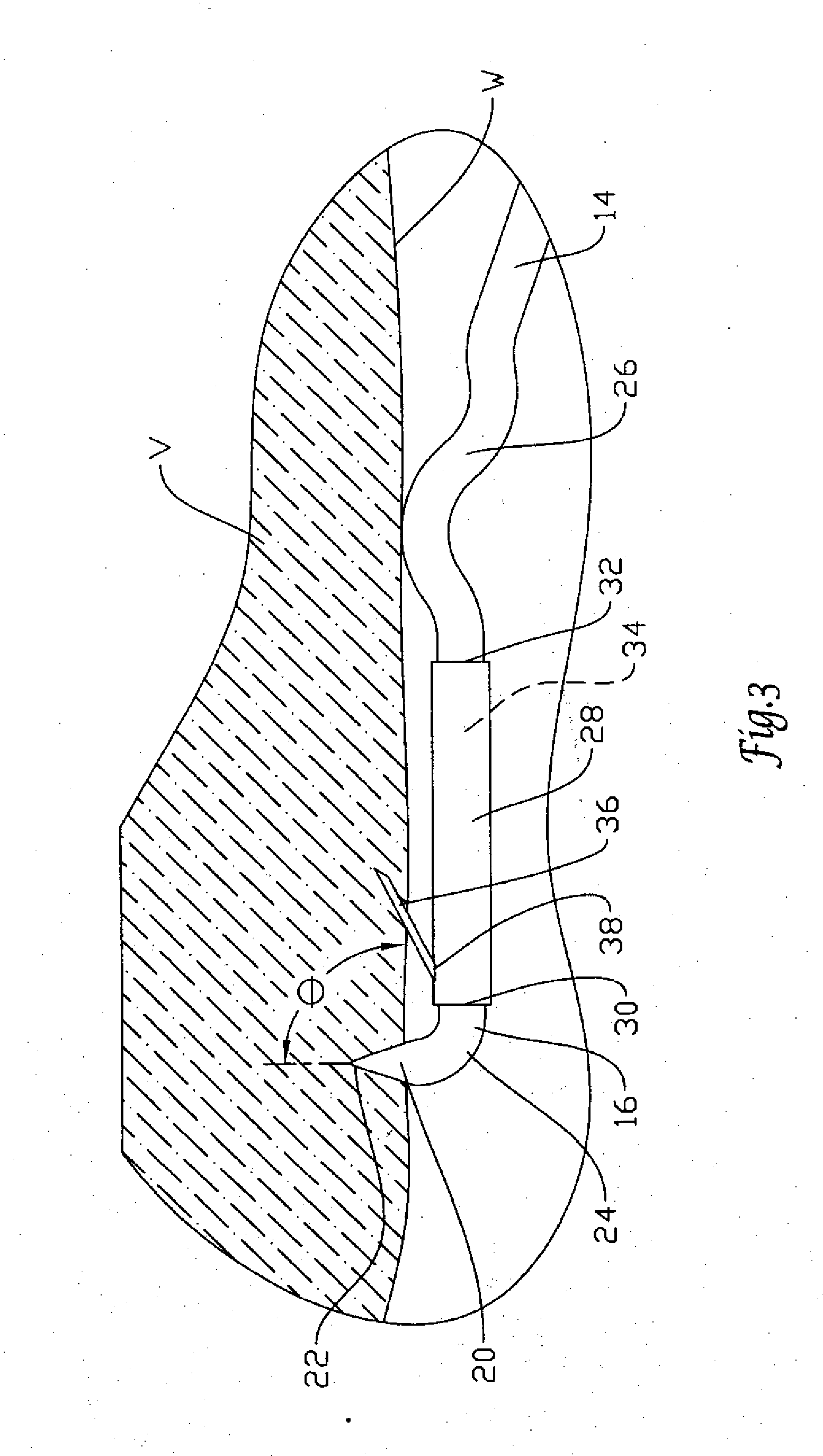
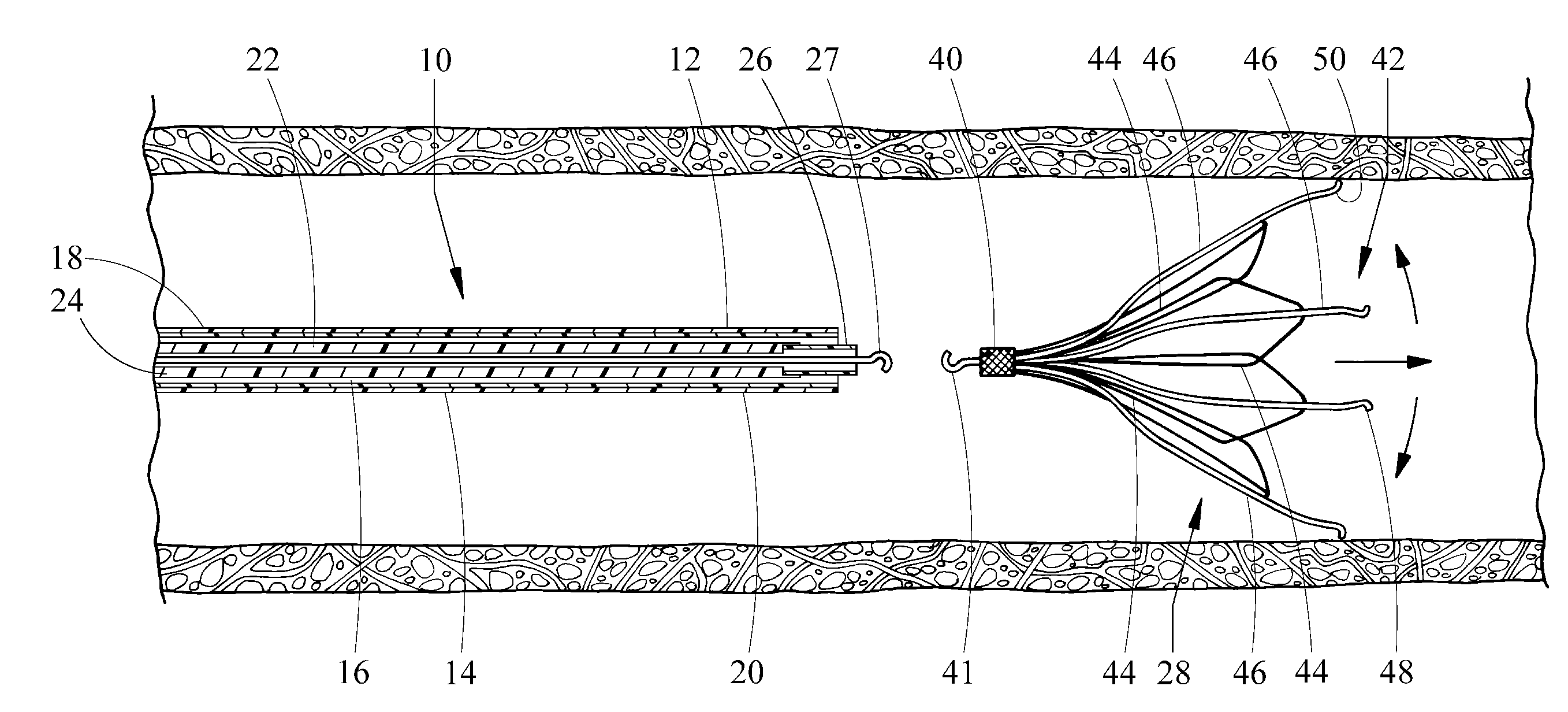
An inferior vena cava filter (340) for use in the inferior vena cava (4) to capture thrombus (8) passing through the inferior vena cava (4) towards the heart and lungs to prevent pulmonary embolism comprises a proximal support hoop (302), a distal support hoop (312) and a plurality of support struts (303) extending between the proximal support hoop (302) and the distal support hoop (312). The filter (340) also comprises a plurality of capture arms (121) which are movable from a capturing configuration to an open configuration. The capture arms (121) are biased towards the open configuration. A biodegradable suture holds the capture arms (121) in the capturing configuration.
Owner:COVIDIEN GROUP +1
Inferior vena cava filter on guidewire
InactiveUS20080234722A1Ease of initial deploymentEasy to disassembleSurgeryDilatorsVeinPulmonary artery embolism
A temporary inferior vena cava filter including a guidewire and a doublet cage filter distally located on the guidewire. The doublet cage filter has a proximal cage filter and a distal cage filter, both of resilient and biased toward their expanded or deployed state. The proximal and distal cage filters may be collapsed by actuation, preferably with a sheath. A method of protecting from pulmonary embolism during treatment of a deep vein thrombosis is disclosed. The doublet cage provides stability when deployed in the inferior vena cava, is readily retrieved and readily manufactured. A method of manufacturing the doublet cage filter assembly is also disclosed and involves a nitinol tube with plural cuts to form struts which are heat treated in an expanded state.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
Vena Cava Filter with Stent
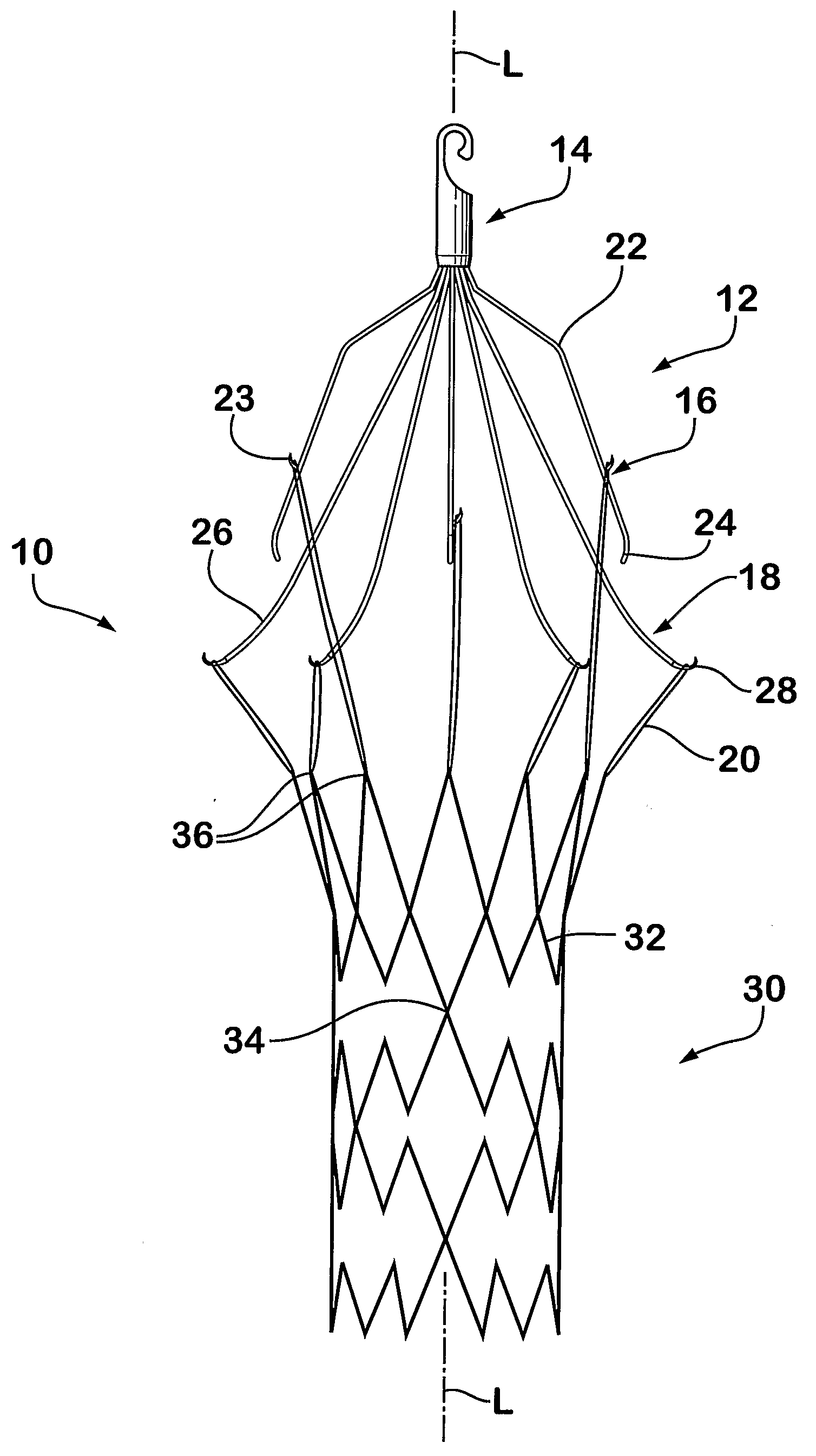
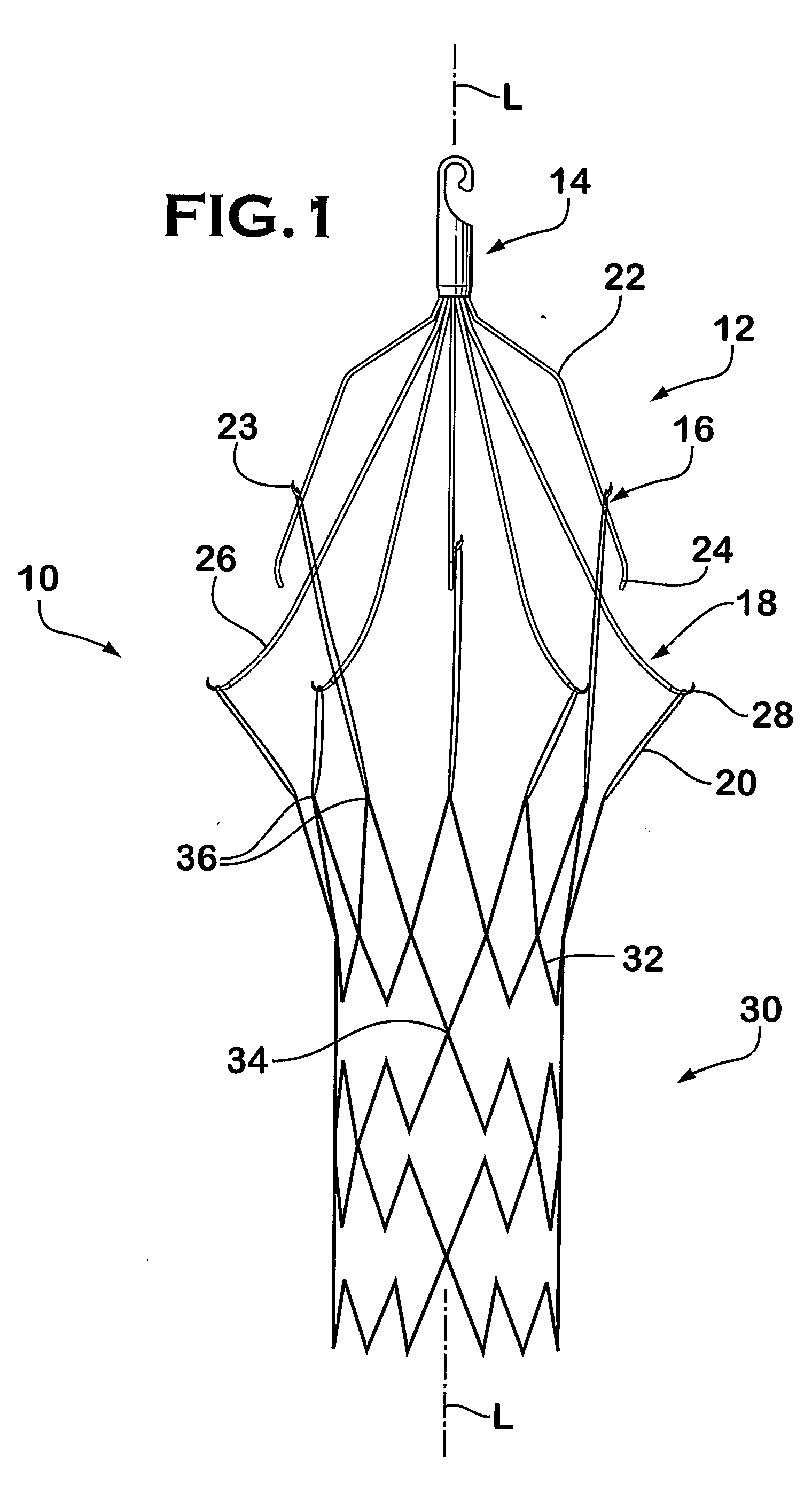
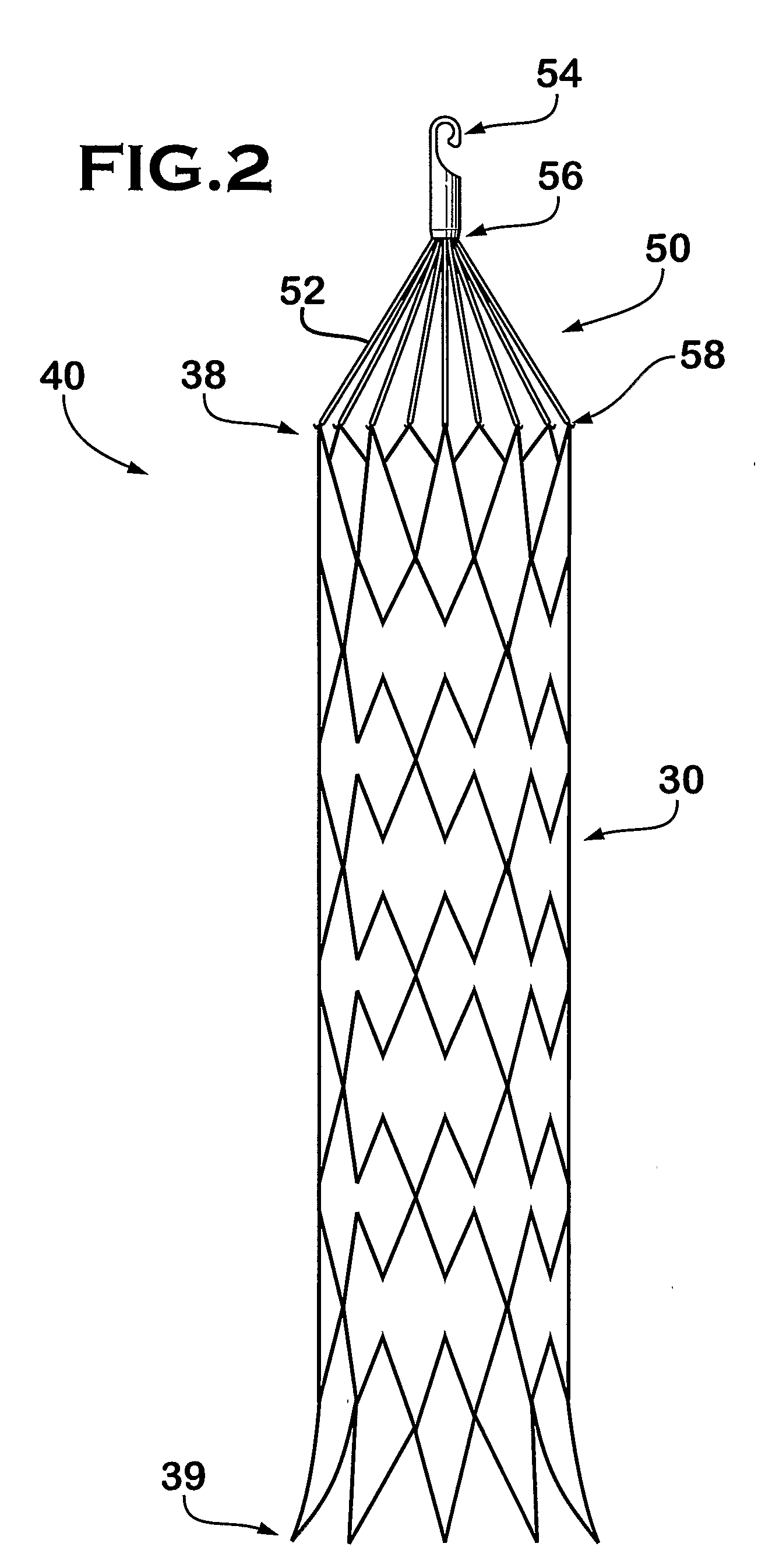
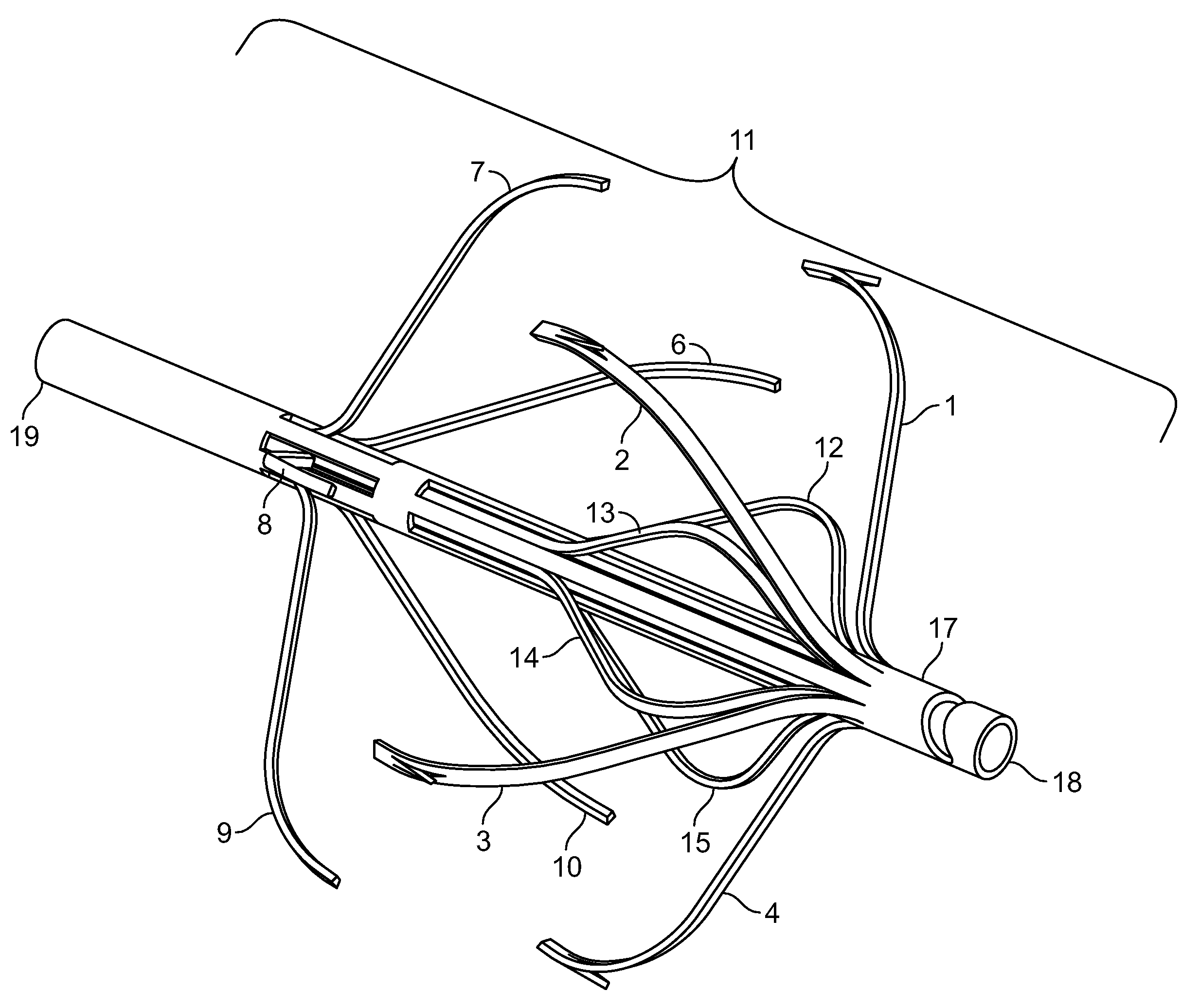
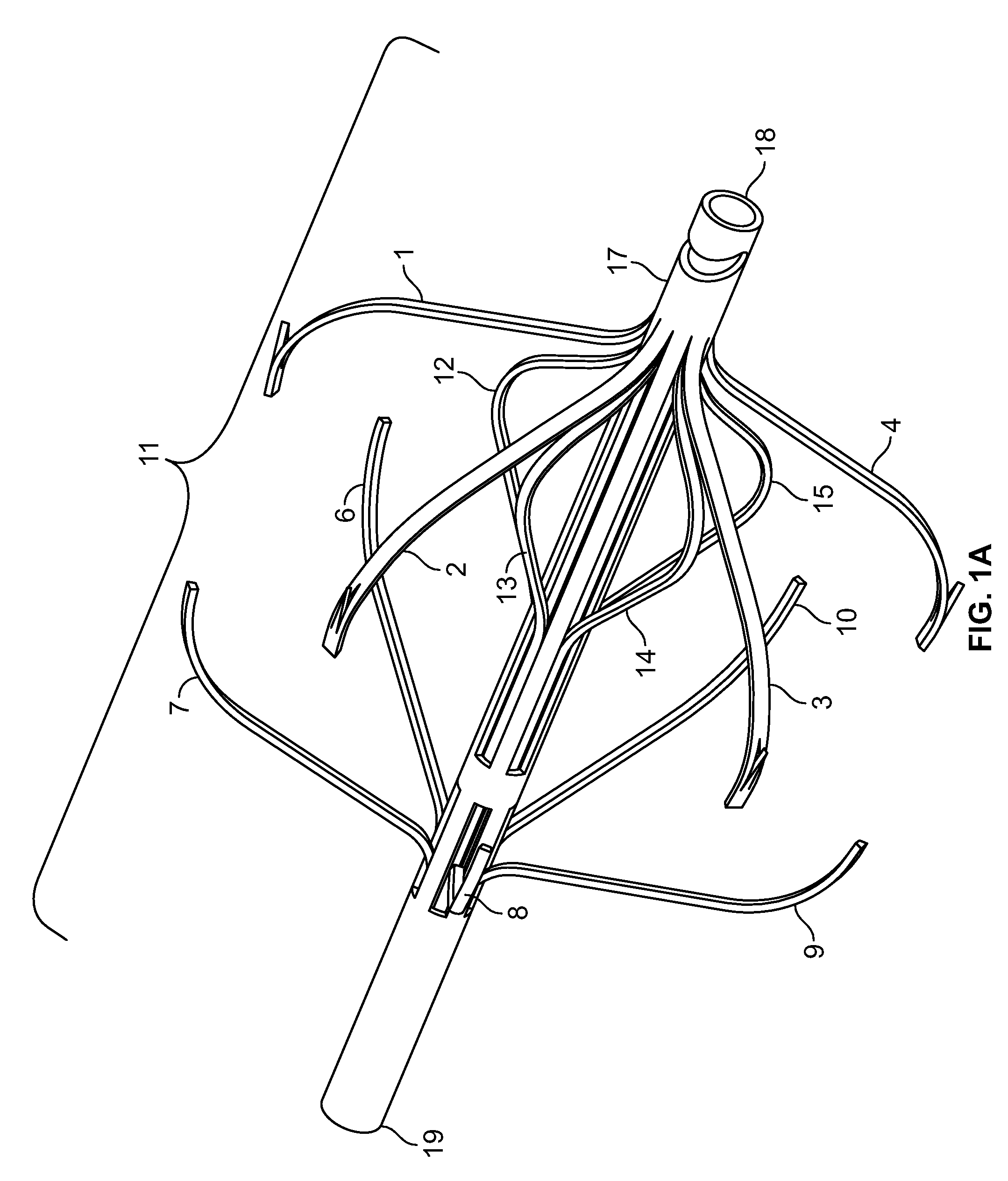
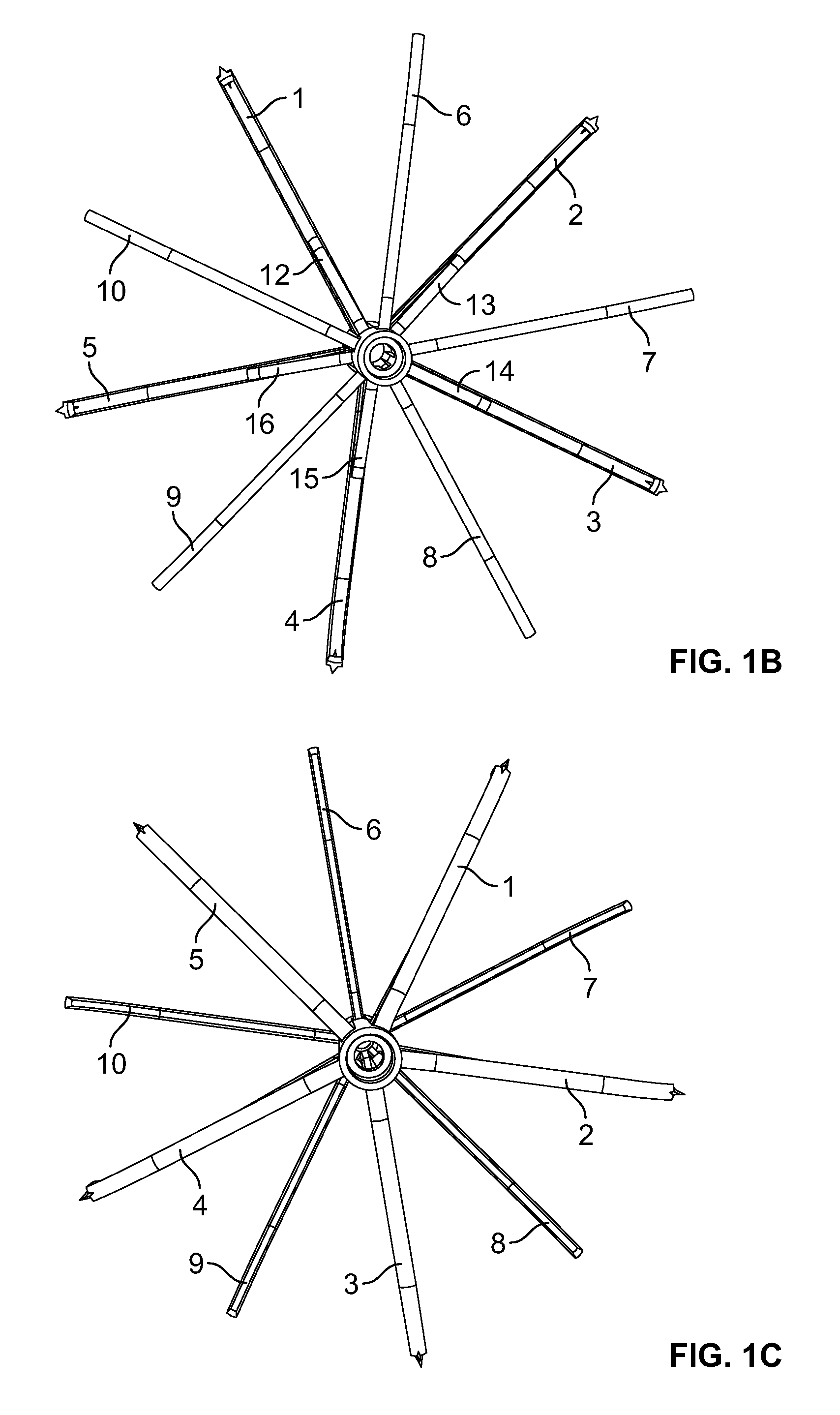
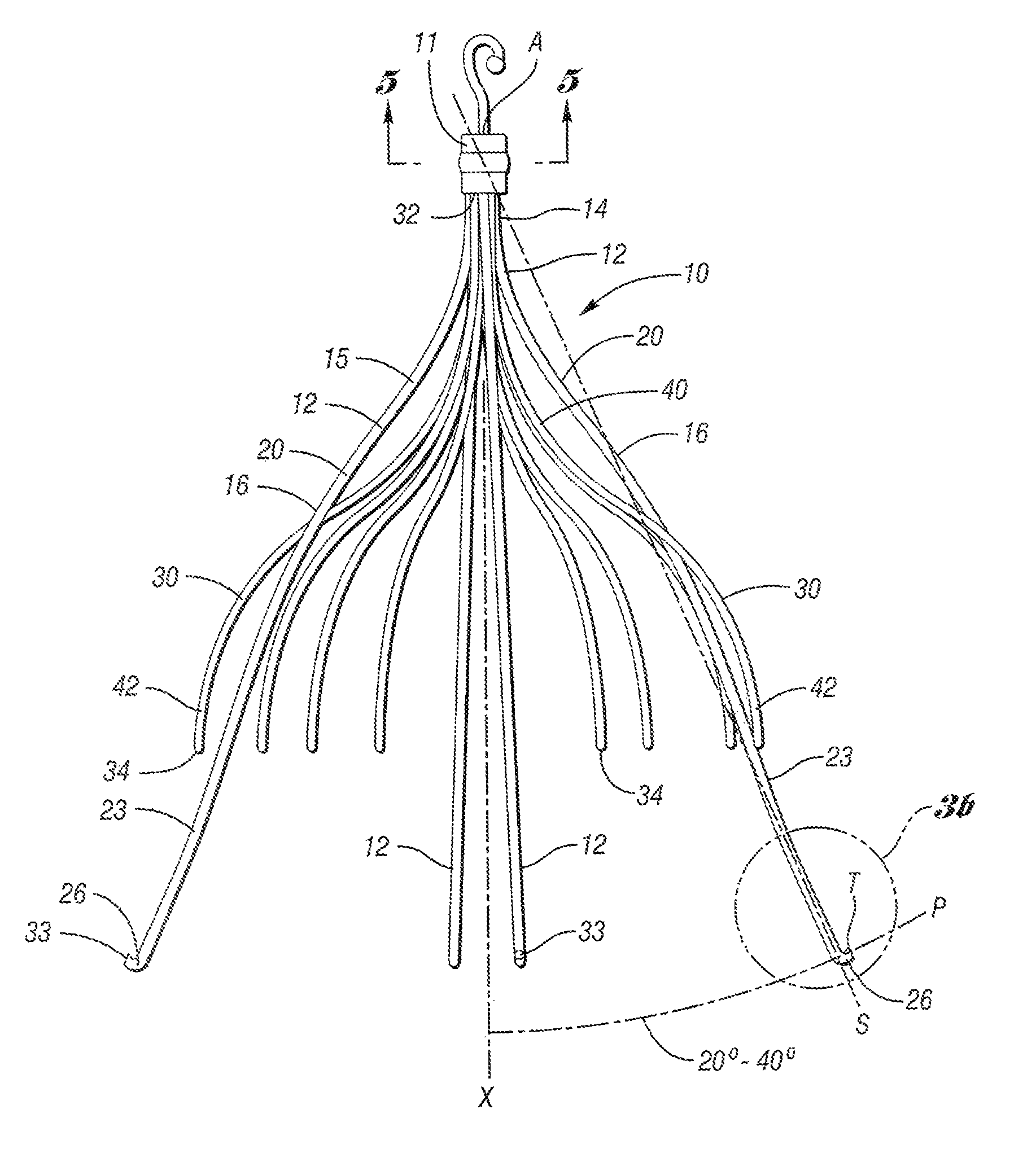
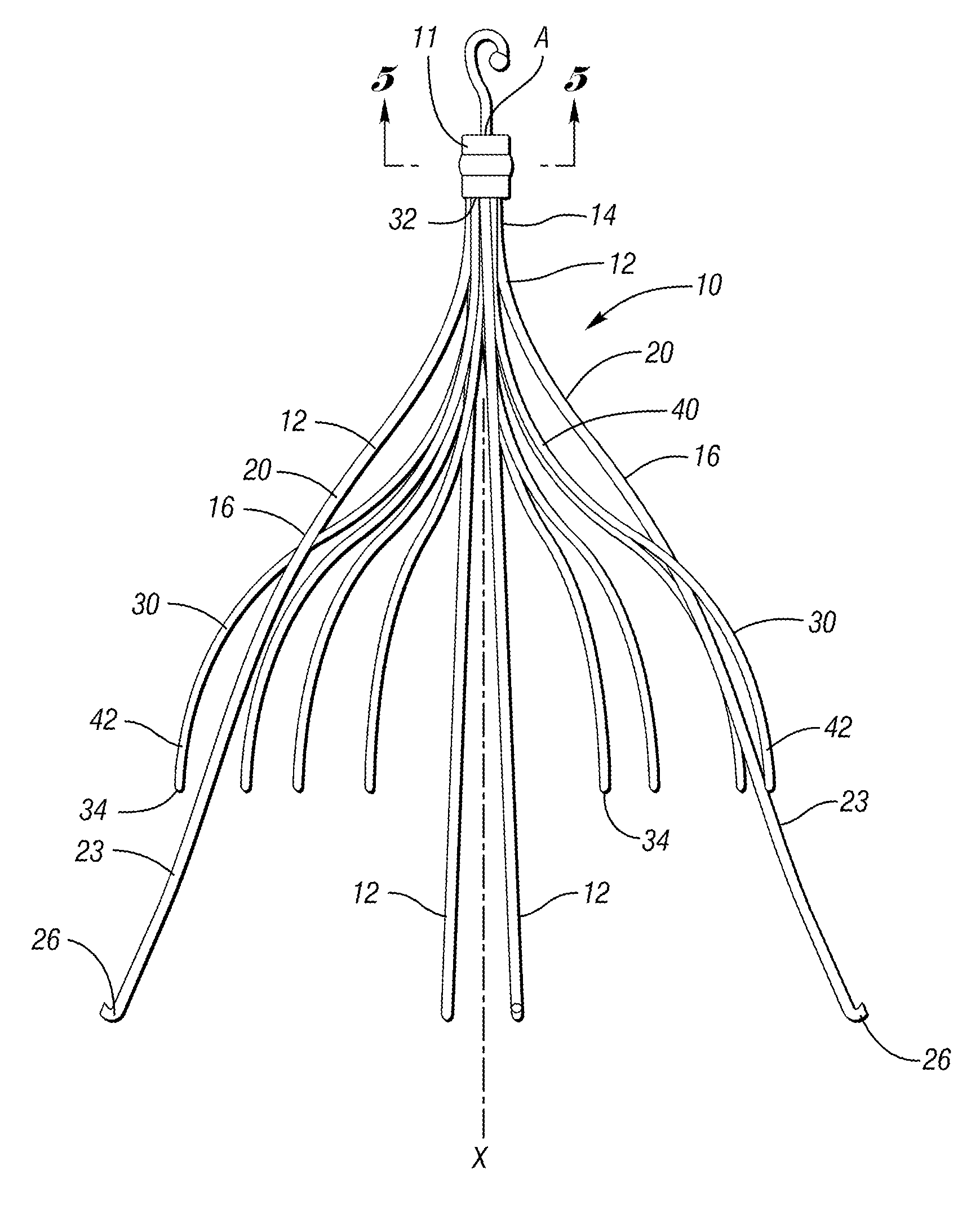
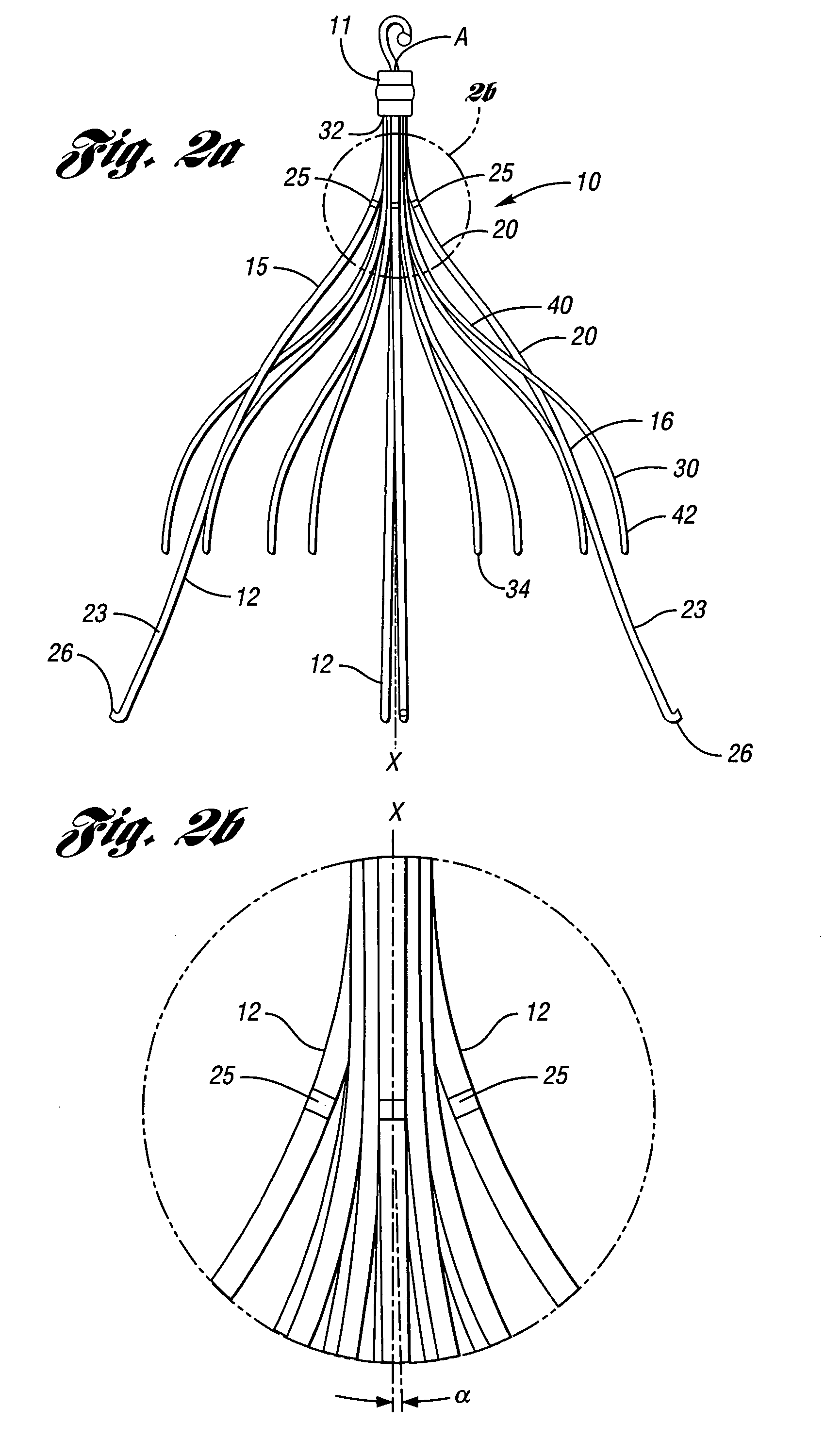
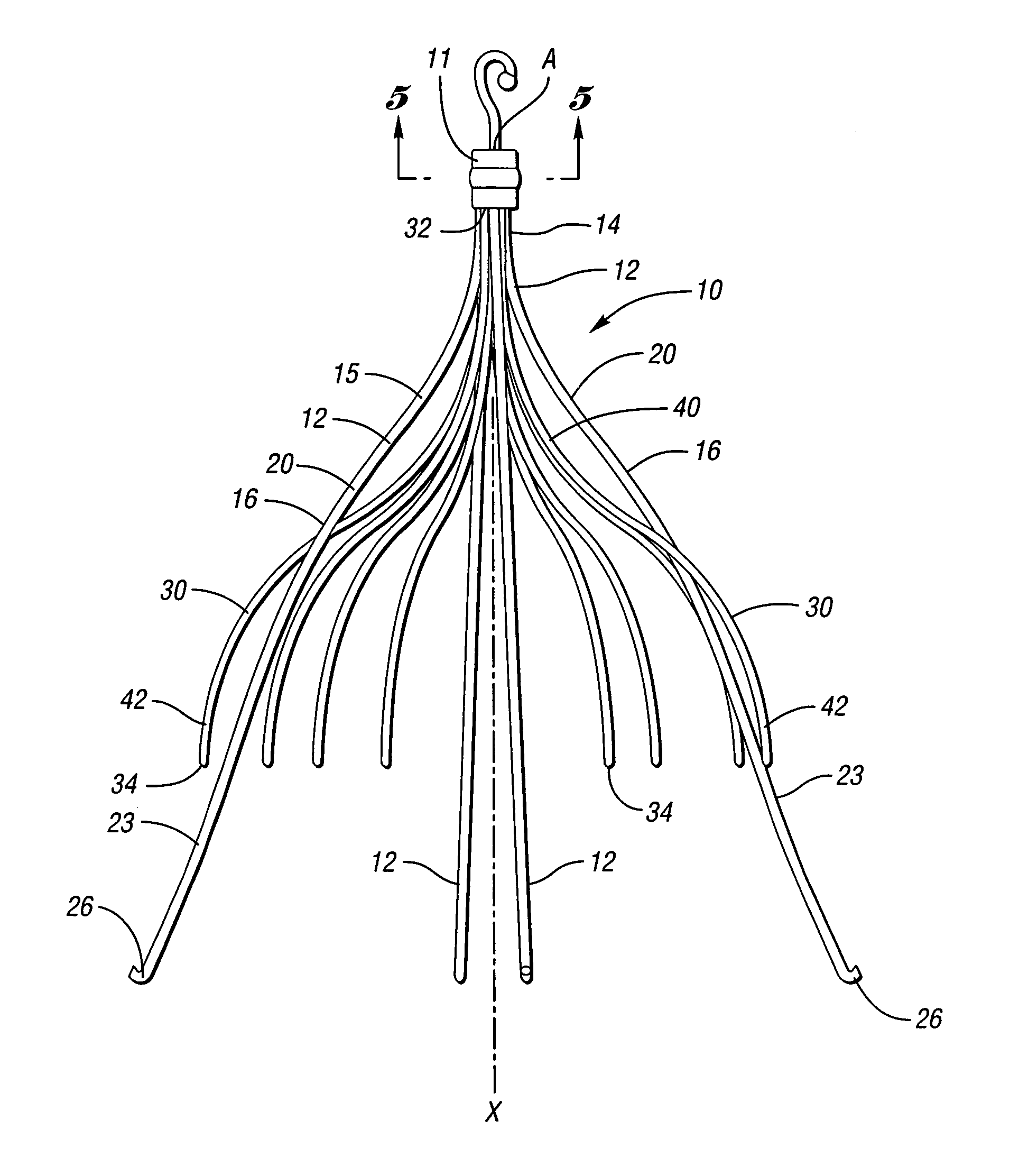
An implantable medical device is described, including a filtering element and radially expandable structure. In one variation, the filtering element may include a pluralit of filaments attached to the structure, the filaments being joined together at a proximal en thereof. The filtering element may include strut members and a hub attached to the proxima end of the filaments. The filaments may be made of suture material. In another variation, the filtering element may include a filter with a plurality of legs, the filter being attached to the support structure via a plurality of filaments.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Retrievable IVC filter
Retrievable vena cava filters for filtering blood clots within a vessel are disclosed. A retrievable vena cava filter in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention may include a plurality of elongated filter legs each having a hook portion configured to engage the vessel wall, and an expandable member releasably connected to the filter. In certain embodiments, the expandable member may comprise a bendable member and several tubular members, or a coiled wire.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
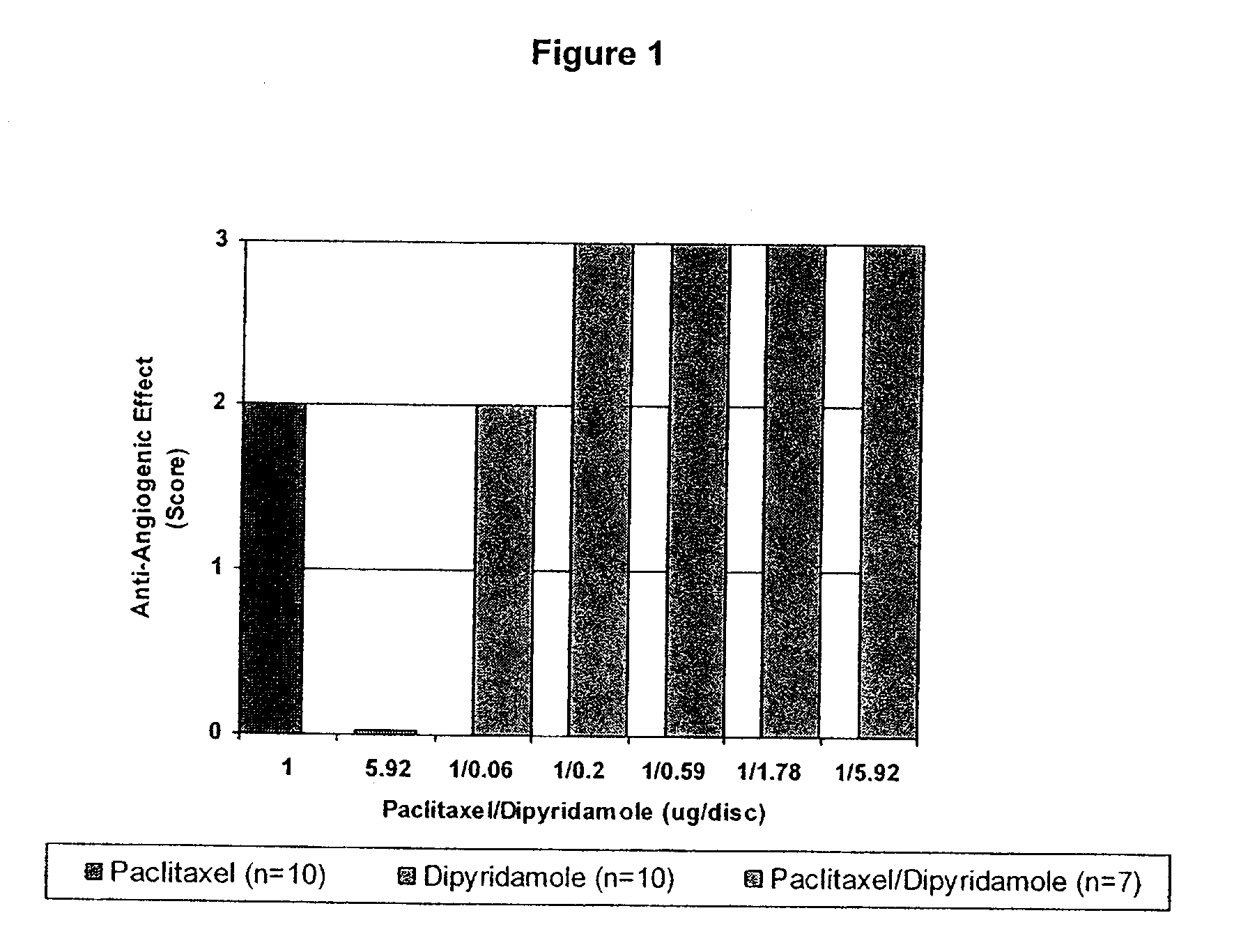
Medical implants with a combination of compounds
InactiveUS20100074934A1Minimize formationImprove biological effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDipyridamoleFibrosis
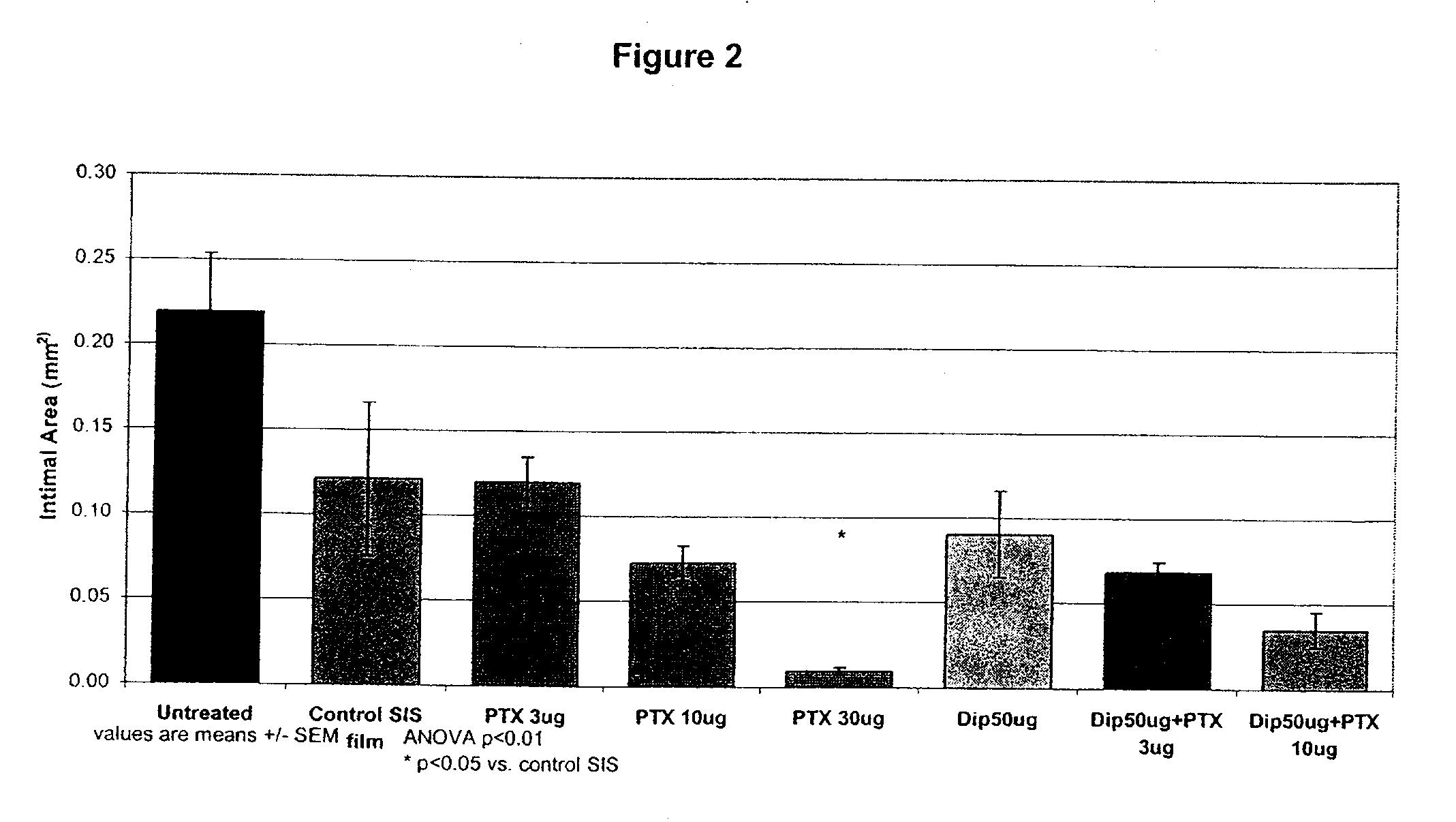
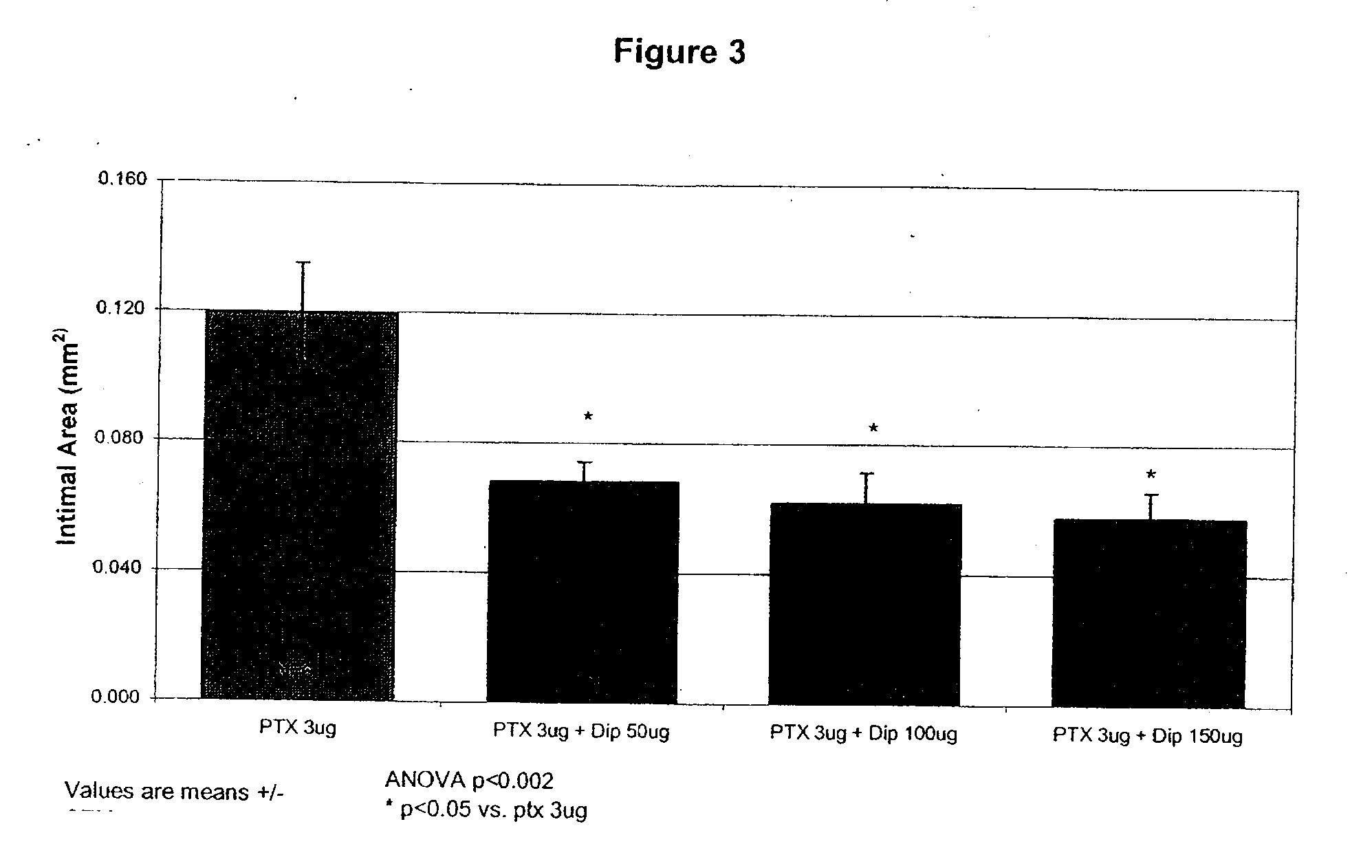
Implants are associated with a combination of paclitaxel or derivatives and dipyridamole or derivatives in order to inhibit fibrosis that may otherwise occur when the implant is placed within an animal. Exemplary implants include intravascular implants (e.g., coronary and peripheral vascular stents, catheters, balloons), non-vascular stents, pumps and sensors, vascular grafts, perivascular devices, implants for hemodialysis access, vena cava filters, implants for providing an anastomotic connection, electrical devices, intraocular implants, and soft tissue implants and fillers.
Owner:ANGIOTECH PHARMA INC
Combination self-expandable, balloon-expandable endoluminal device
An endoluminal device, such as a stent or a vena cava filter, comprising at least one superelastic section and at least one plastically deformable section. The superelastic section may comprise, for example, a superelastic grade of nitinol, whereas the plastically deformable section may comprise, for example, gold, platinum, tantalum, titanium, stainless steel, tungsten, a nickel alloy, a cobalt ally, a titanium alloy, or a combination thereof. Each plastically deformable section may merely comprise a constrained portion of the superelastic section comprising a plastically deformable material, such as gold. The device enables deployment by a method comprising introducing the device into a body lumen with the device radially constrained in a first configuration having a first diameter; allowing the device to self-expand into a second configuration having a second diameter less than or equal to a fully-self-expanded diameter; and then optionally “fine-tuning” the device by forcibly expanding the device into a third configuration having a third diameter in a range between the second diameter and less than or equal to a fully-forcibly-expanded diameter. The superelastic and plastically deformable sections may be tubular sections placed end-to-end, such that the plastically deformable section can be conformed to fit a tapered section of a lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Removable vena cava filter having inwardly positioned anchoring hooks in collapsed configuration
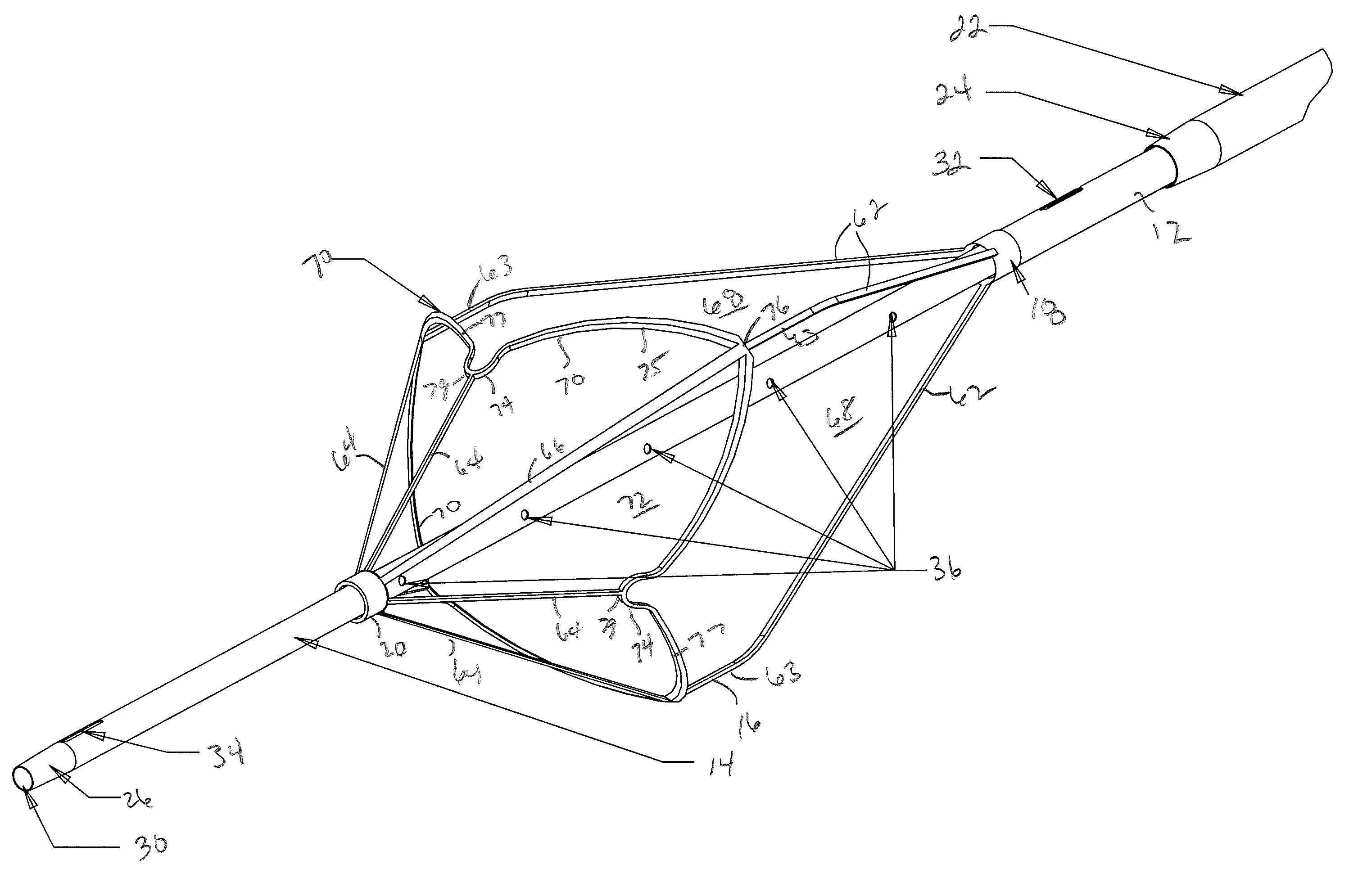
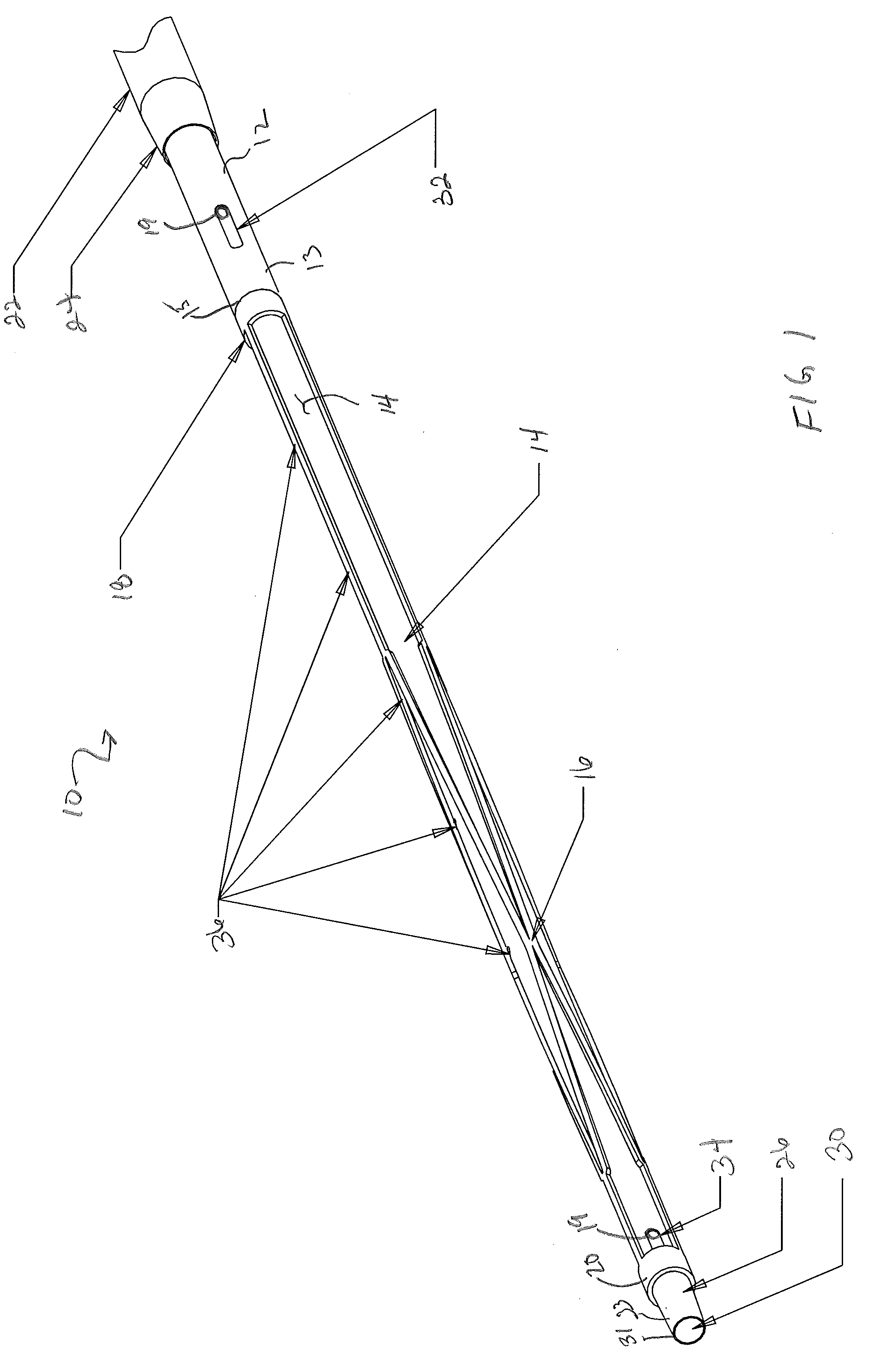
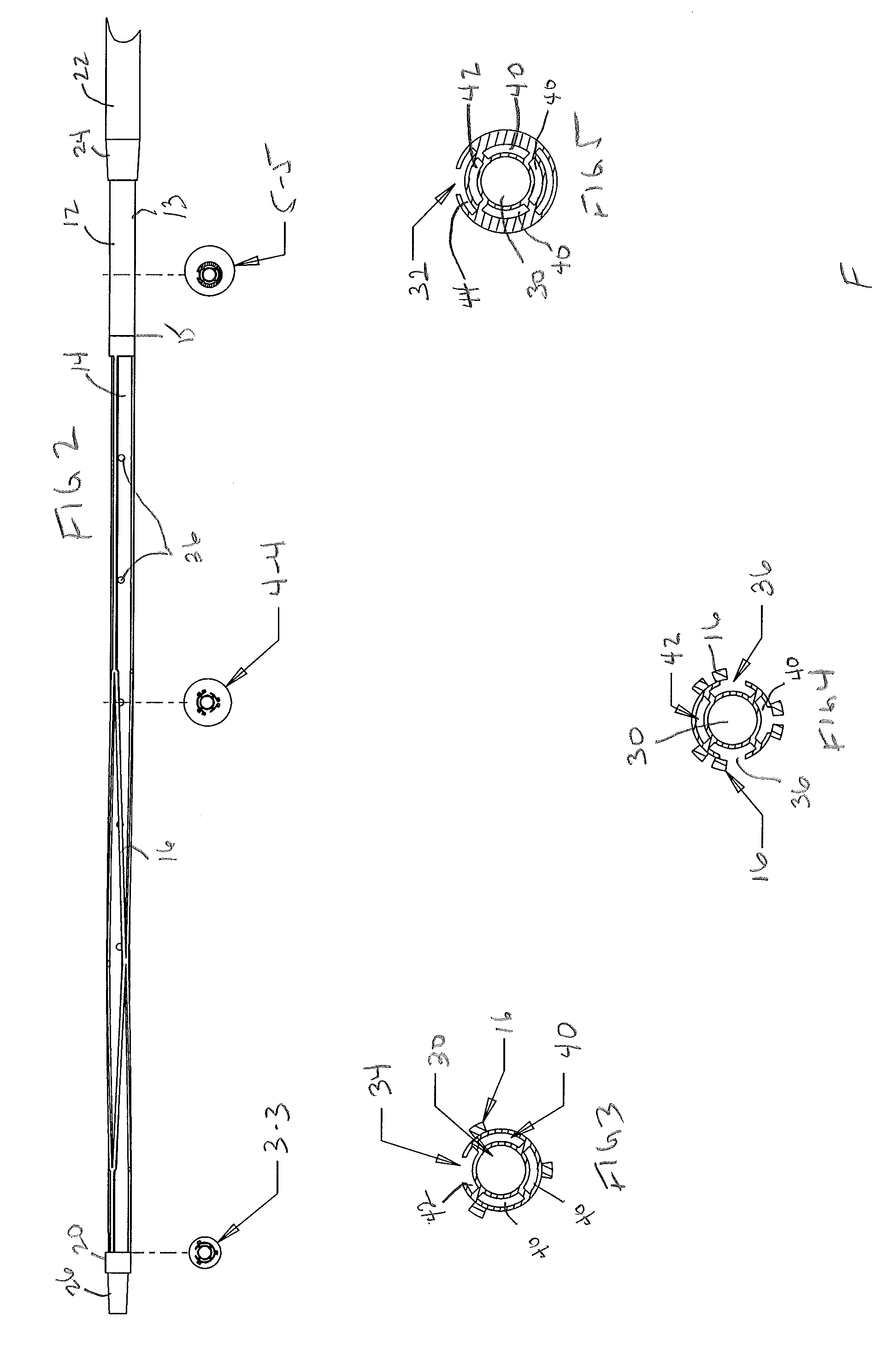
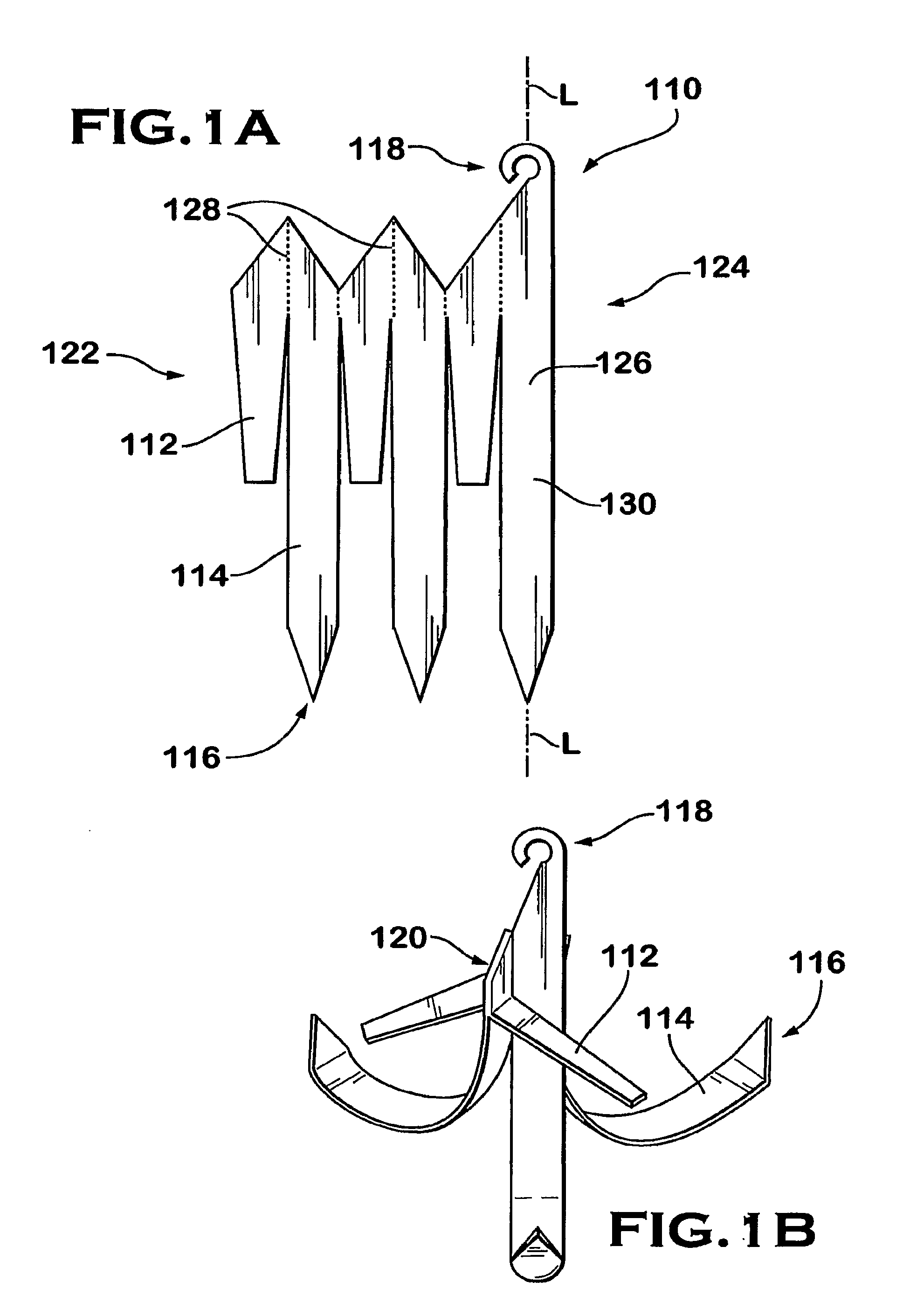
The present invention involves a removable filter for capturing thrombi in a blood vessel. The filter comprises a plurality of primary struts and a plurality of secondary struts. The plurality of primary struts has first ends attached together along a longitudinal axis. Each primary strut has an arcuate segment extending from the first end to an anchoring hook. The primary struts are configured to move between an expanded state for engaging the anchoring hooks with the blood vessel and a collapsed state for filter retrieval or delivery. Each primary strut is configured to cross another primary strut along the longitudinal axis in the collapsed state such that each anchoring hook faces the longitudinal axis away from the blood vessel for filter retrieval or delivery. The plurality of secondary struts has connected ends attached together along the longitudinal axis. The secondary struts extend therefrom to free ends to centralize the filter in the expanded in the blood vessel.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Percutaneous permanent retrievable vascular filter
Retrievable vena cava filters for the temporary or permanent prevention of Pulmonary embolism (PE) are disclosed. A filter in accordance with the present invention has a tube-within-tube structure with overlapping semi-spheres. The semi-spheres comprise a plurality of expandable legs. The first tube may have a first set of expandable legs and a plurality of slots allowing for deployment of a second or third set of expandable legs on the second tube. The free end of each leg in the first set of expandable legs is oriented in a direction opposite to the free end of each leg in the second set forming a cage which comprises legs from the first and second sets of expandable legs. The filter of the present invention may be retrieved by a catheter and snare. The third set of expandable legs conveys the vector force from the closing of the first set to the second set to cause it to collapse.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
Removable vena cava filter with anchoring feature for reduced trauma
The present invention involves a removable filter for capturing thrombi in a blood vessel. The filter comprises a plurality of struts having first ends attached together along a longitudinal axis of the filter. Each strut has a body member extending from the first end along the longitudinal axis to an anchoring hook defining a strut axis. Each strut is configured to move along a strut path relative to the longitudinal axis between an expanded state for engaging with the blood vessel and a collapsed state for filter delivery or retrieval. Each anchoring hook has an angle of up to about 90 degrees relative to the strut axis.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Retrievable vena cava filter
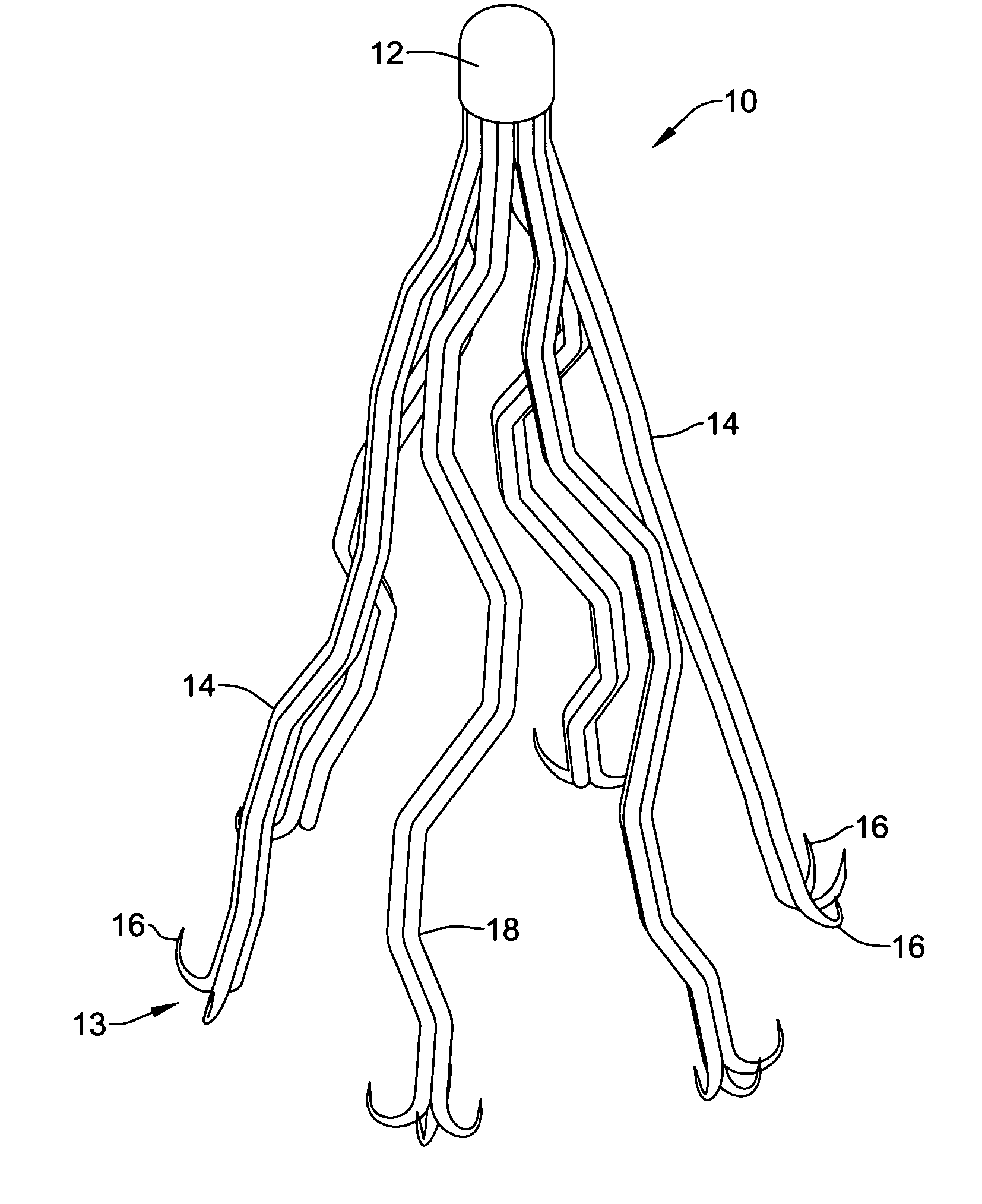
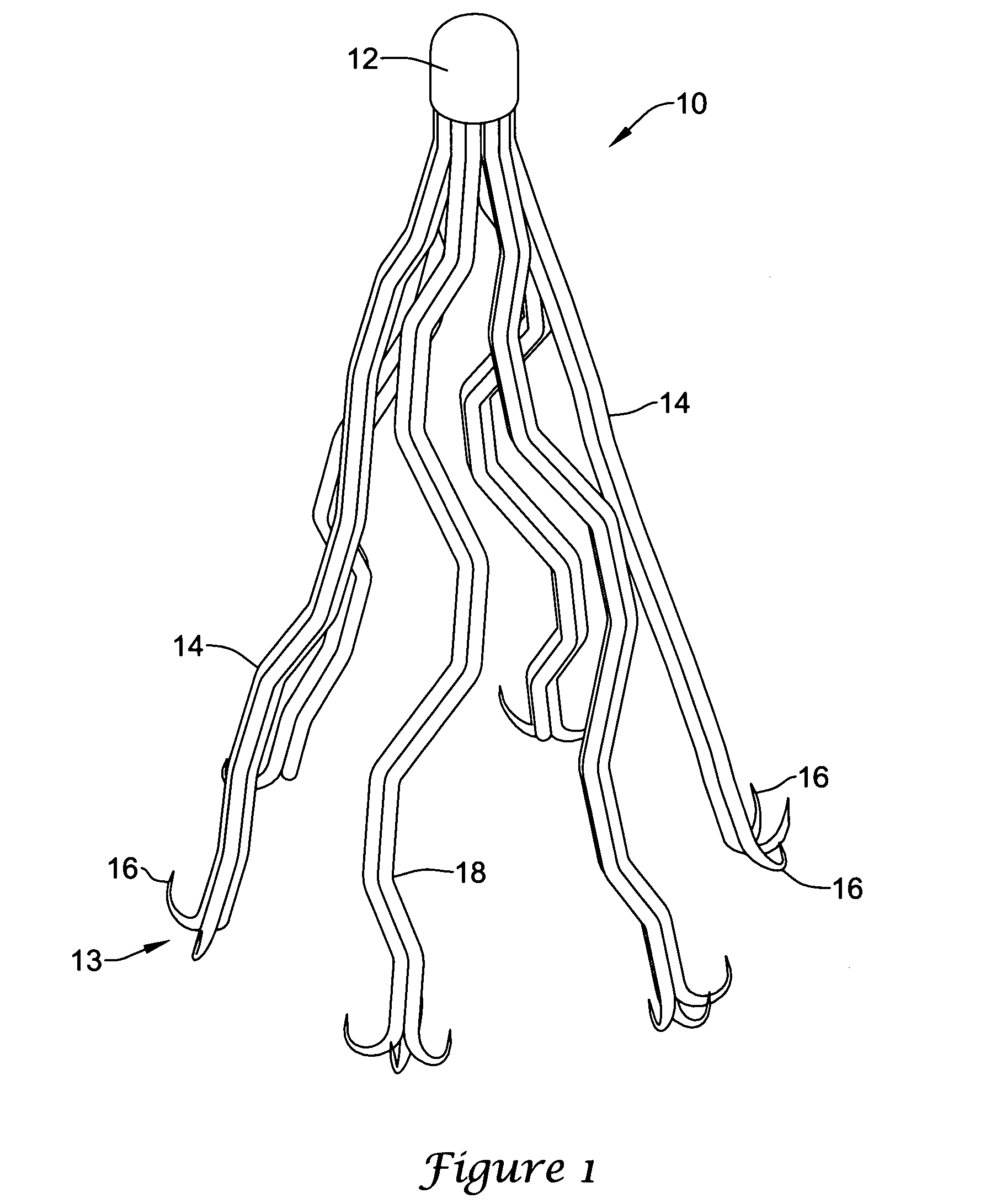
A filter device positionable within a blood vessel for trapping emboli in the vessel, the filter device having a head and a plurality of divergent legs each secured at a first end to the head; each leg having one or more hooks at a second end. The hooks can include an expandable and contractible sleeve or hook that provides securing means for the legs and which also allows for easy removal of the filter device.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
Removable vena cava filter
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Removable vena cava filter comprising struts having axial bends
ActiveUS20060069406A1Simple deliveryMinimizes entanglementSurgeryDilatorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A removable vena cava filter configured for simplified delivery to and retrieval from the vena cava of a patient is disclosed. The filter includes struts configured to be arranged in consistent orientation together between expanded (opened) and collapsed (closed) configurations, thereby minimizing entanglement of the struts. Each of the struts has a circumferential bend relative to the longitudinal axis of the filter. The circumferential bends allow for consistent orientation of the struts when moved between the expanded and collapsed configurations and when placed in the closed configuration of the filter.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Removable vena cava filter
The present invention provides a removable vena cava filter for capturing thrombi in a blood vessel. The filter comprises a plurality of primary struts having first ends attached together along a longitudinal axis. Each primary strut includes an arcuate segment having a first tensile strength. The arcuate segment extends from the first end to an anchoring hook. The anchoring hook is integral with the arcuate segment and having the first thickness and first tensile strength. The filter further comprises a plurality of secondary struts freely spaced between the primary struts and having connected ends attached together along the longitudinal axis. Each secondary strut freely extends from the connected end to a free end avoiding contact with other secondary struts and primary struts. Each secondary strut has a second tensile strength.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Removable vena cava filter with anchoring feature for reduced trauma
The present invention involves a removable filter for capturing thrombi in a blood vessel. The filter comprises a plurality of struts having first ends attached together along a longitudinal axis of the filter. Each strut has a body member extending from the first end along the longitudinal axis to an anchoring hook defining a strut axis. Each strut is configured to move along a strut path relative to the longitudinal axis between an expanded state for engaging with the blood vessel and a collapsed state for filter delivery or retrieval. Each anchoring hook has an angle of up to about 90 degrees relative to the strut axis.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
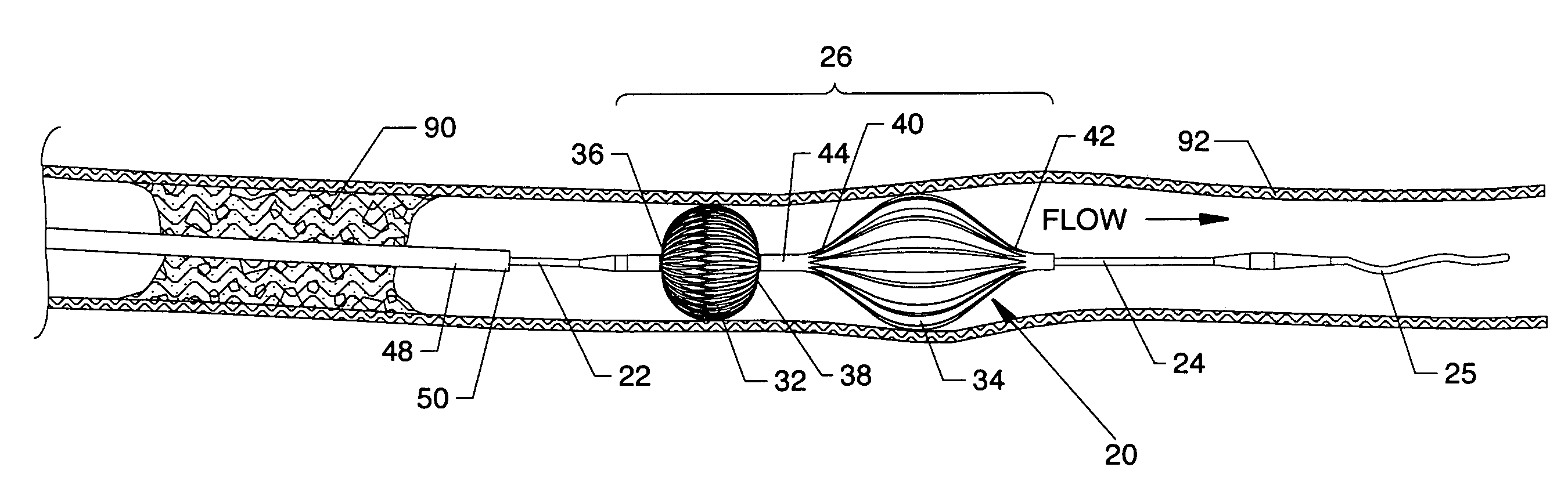
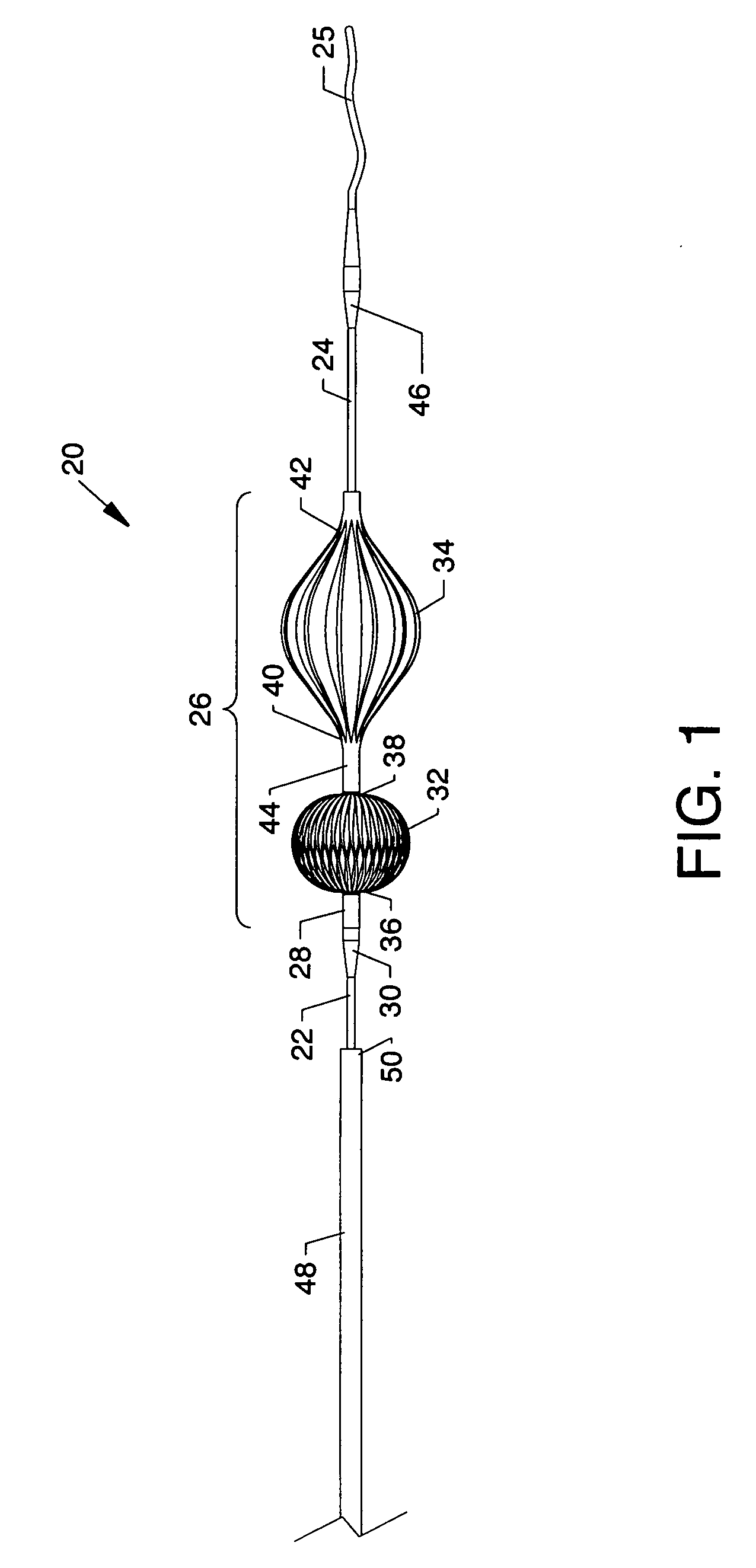
Multi-lumen central access vena cava filter apparatus and method of using same
ActiveUS20090062840A1Increase ratingsComplicate upper extremityMulti-lumen catheterSurgeryVeinFluid infusion
A combined multi-lumen central access catheter and an embolic filter including ports proximal and distal the filter for fluid infusion and / or pressure sensing and infusion ports in the catheter to permit infusion of bioactive agents, flushing agents and / or contrast agents. The embolic filter may be removably coupled to the multi-lumen catheter for temporary placement and retrieval under recommended indications.
Owner:BIO2MEDICAL
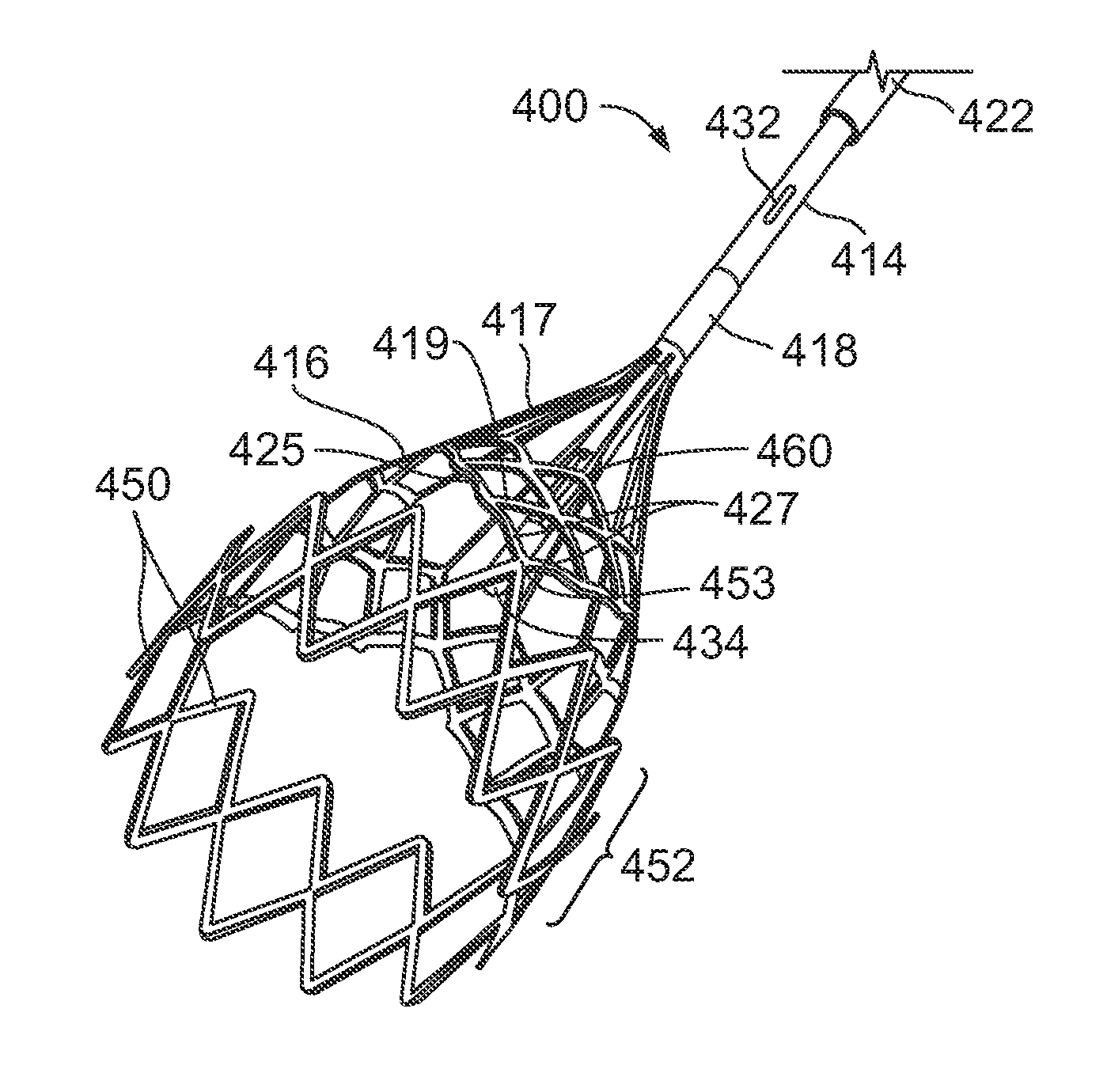
Non-entangling vena cava filter
An implantable vessel filter device having a plurality of radially expandable legs with hooks, and a center-post configured to prevent entanglement of the radially expandable legs when they are compressed against the center-post. In one variation, the filter device includes a first set of legs, forming a first filter basket in the expanded position, and a second set of legs, forming a second filter basket distal to the first filter in the expanded position. Hooks may be provided on the second set of legs to prevent migration of the filter along the vessel after the filter is deployed. Grooves may be provided along the shaft of the center-post to receive the hooks and prevent the hooks from interlocking when the legs of the filter are compressed along the center-post.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Removable vena cava filter for reduced trauma in collapsed configuration
The present invention provides a removable vena cava filter for capturing thrombi in a blood vessel. The filter comprises a plurality of primary struts having first ends attached together along a longitudinal axis. Each primary strut has an arcuate segment extending from the first end to an anchoring hook. The primary struts are configured to move between an expanded state for engaging the anchoring hooks with the blood vessel and a collapsed state for filter retrieval or delivery. Each primary strut are configured to cross another primary strut along the longitudinal axis in the collapsed state such that the arcuate segments occupy a first diameter greater than a second diameter occupied by the anchoring hooks in the collapsed state for filter retrieval or delivery.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Removable vena cava filter having primary struts for enhanced retrieval and delivery
A removable filter having a collapsed state and an expanded state for capturing thrombi in a blood vessel is disclosed. The filter comprises a plurality of primary struts and a plurality of secondary struts. Each primary strut in the expanded state extends from a primary strut first end to an anchoring hook. Each primary strut extends arcuately along a longitudinal axis and linearly radially. The plurality of primary strut first ends are attached together along the longitudinal axis. Each secondary strut in the expanded state extends from a secondary strut first end to a free end. Each secondary strut extends arcuately along the longitudinal axis and linearly radially. The plurality of secondary struts are attached together along the longitudinal axis. The plurality of secondary struts centralize the filter in the expanded state in the blood vessel.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Removable vena cava filter for reduced trauma in collapsed configuration
The present invention provides a removable vena cava filter for capturing thrombi in a blood vessel. The filter comprises a plurality of primary struts having first ends attached together along a longitudinal axis. Each primary strut has an arcuate segment extending from the first end to an anchoring hook. The primary struts are configured to move between an expanded state for engaging the anchoring hooks with the blood vessel and a collapsed state for filter retrieval or delivery. Each primary strut are configured to cross another primary strut along the longitudinal axis in the collapsed state such that the arcuate segments occupy a first diameter greater than a second diameter occupied by the anchoring hooks in the collapsed state for filter retrieval or delivery.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Inferior vena cava filter with stability features
ActiveUS20100049238A1Easy to disassembleTotal force per axial-load-resisting contact point is reducedSurgeryDilatorsInferior vena cava filterEngineering
A filter having a first set of members and a second set of members defining a trap sized to fit into a blood vessel. Each of the first and second members are configured to resiliently extend from the trap. At least one of the first set of members includes a first surface for engaging the vessel wall such that the at least one of the first set of members resists downstream movement within the vessel. At least one of the second set of members includes a second surface for engaging the vessel wall such that the at least one second member resists upstream movement within the vessel.
Owner:CR BARD INC
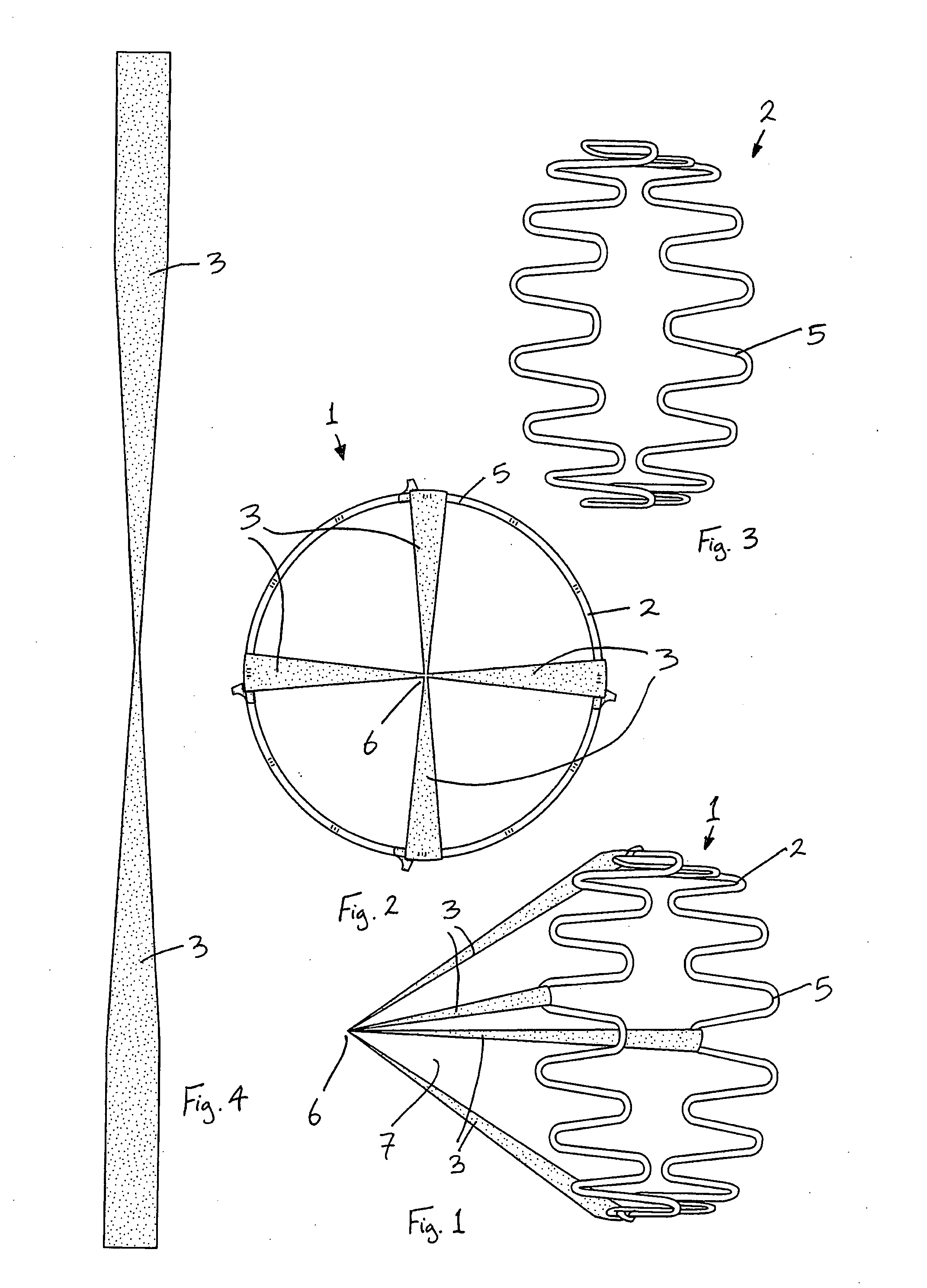
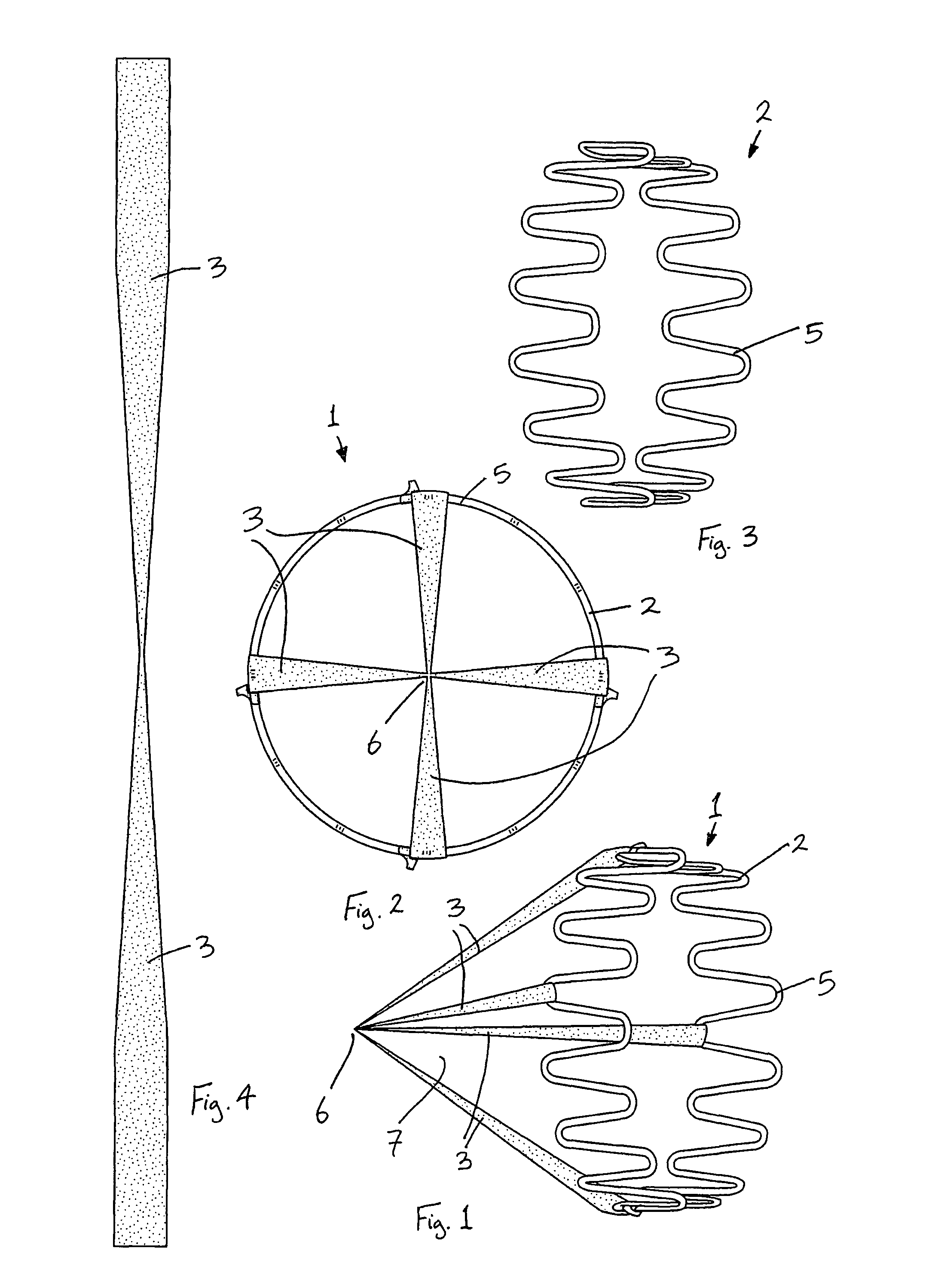
Vena cava filter with filament
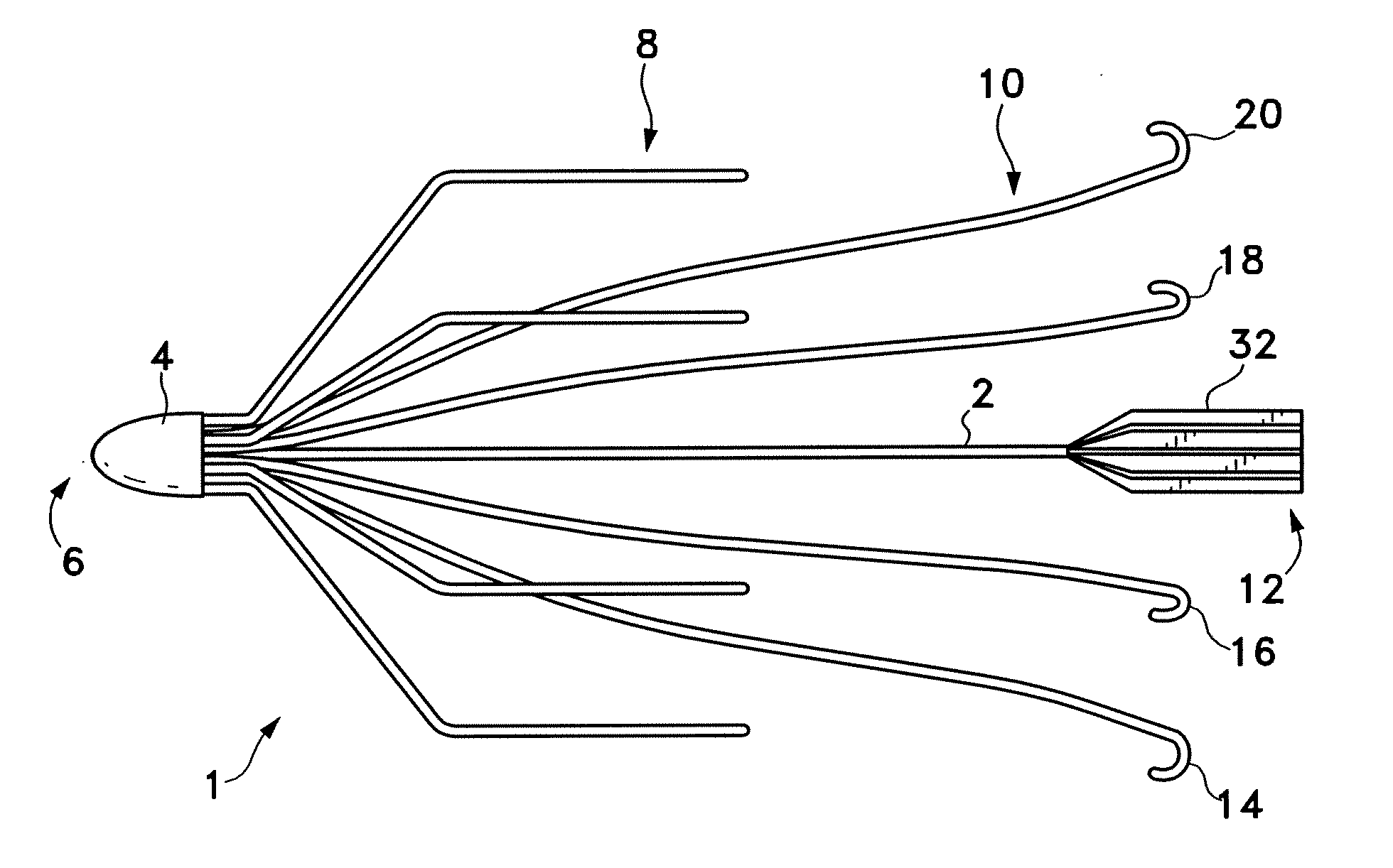
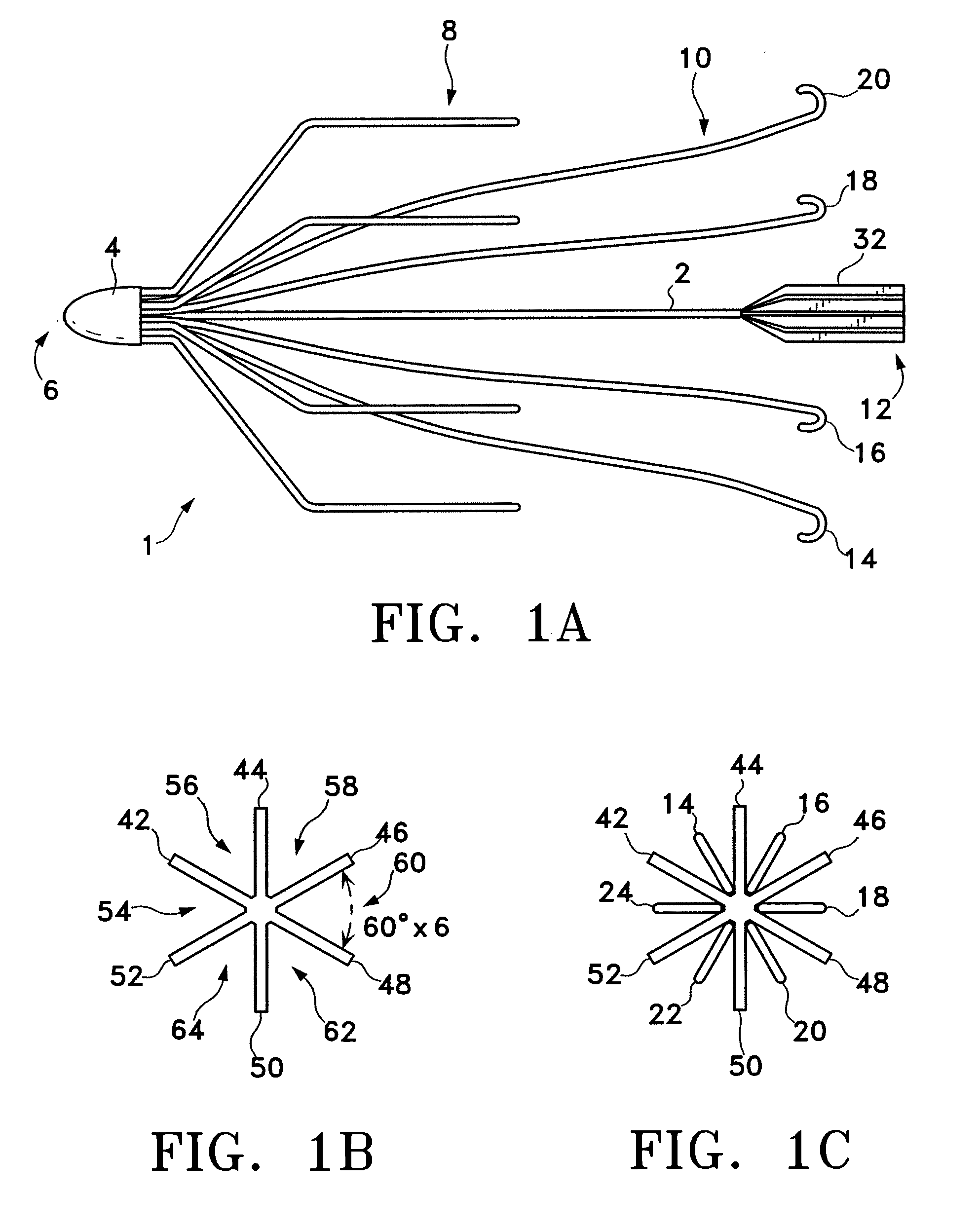
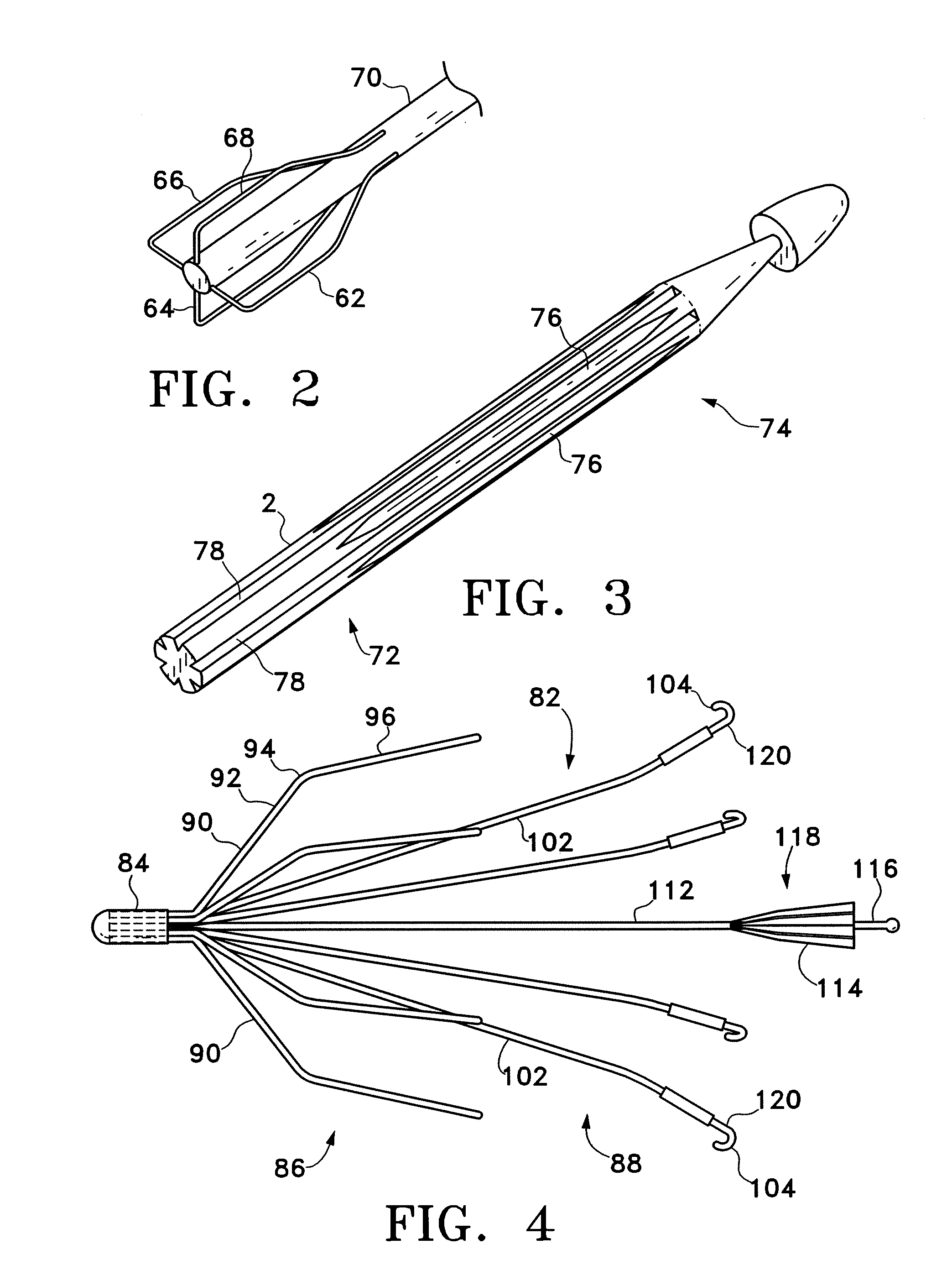
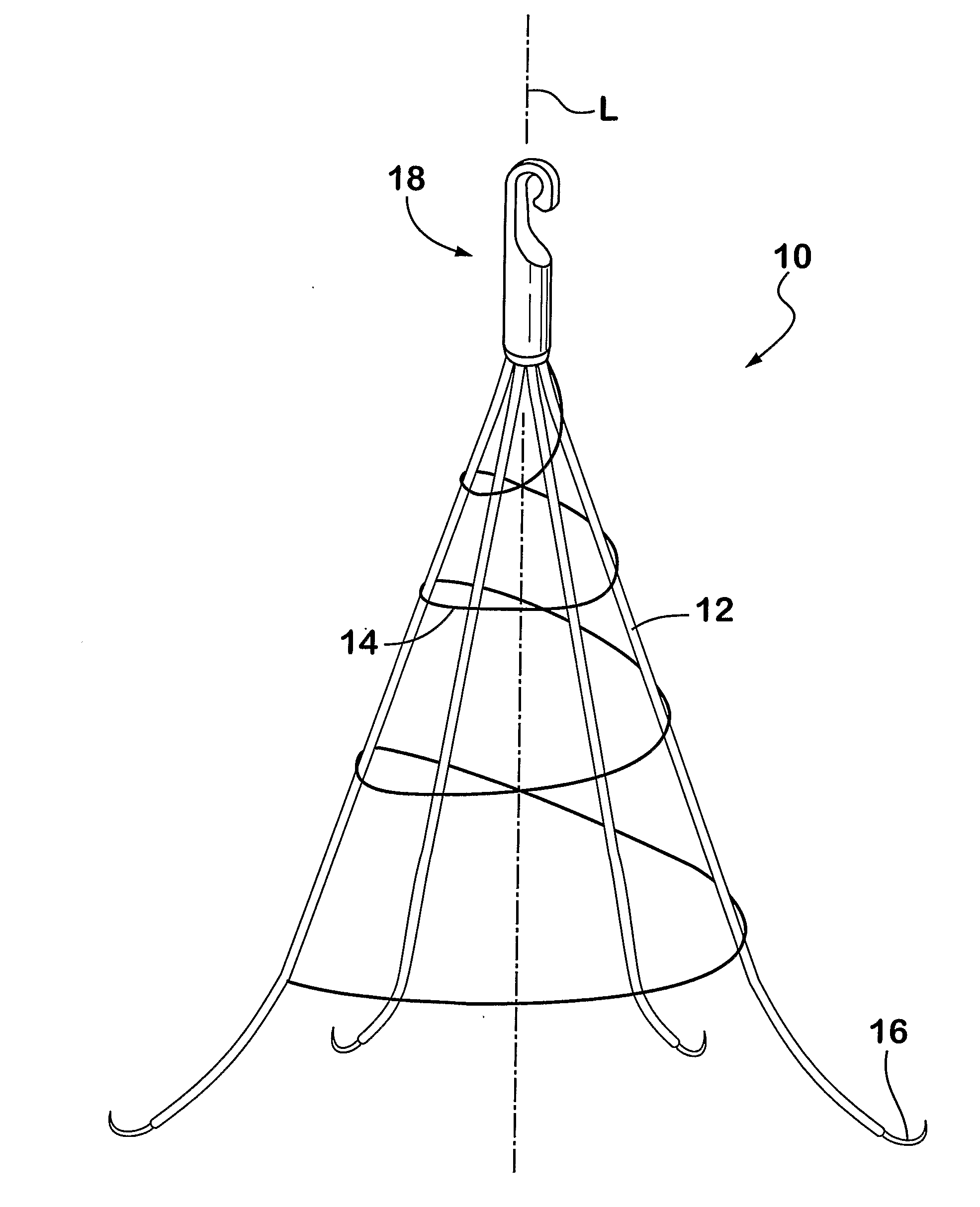
A vena cava filter is described, having one or more frame members or an elongated member arranged in helical fashion. A plurality of filaments connect frame members or portions of the elongated member. The filaments may be made of suture material. Hooks may be placed on a free end of the filaments, along the length thereof, or on one or more frame members to engage the blood vessel wall and anchor the filter. A retrieval member may be positioned on the filter to facilitate withdrawal of the filter from the blood vessel.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Inferior vena cava filter
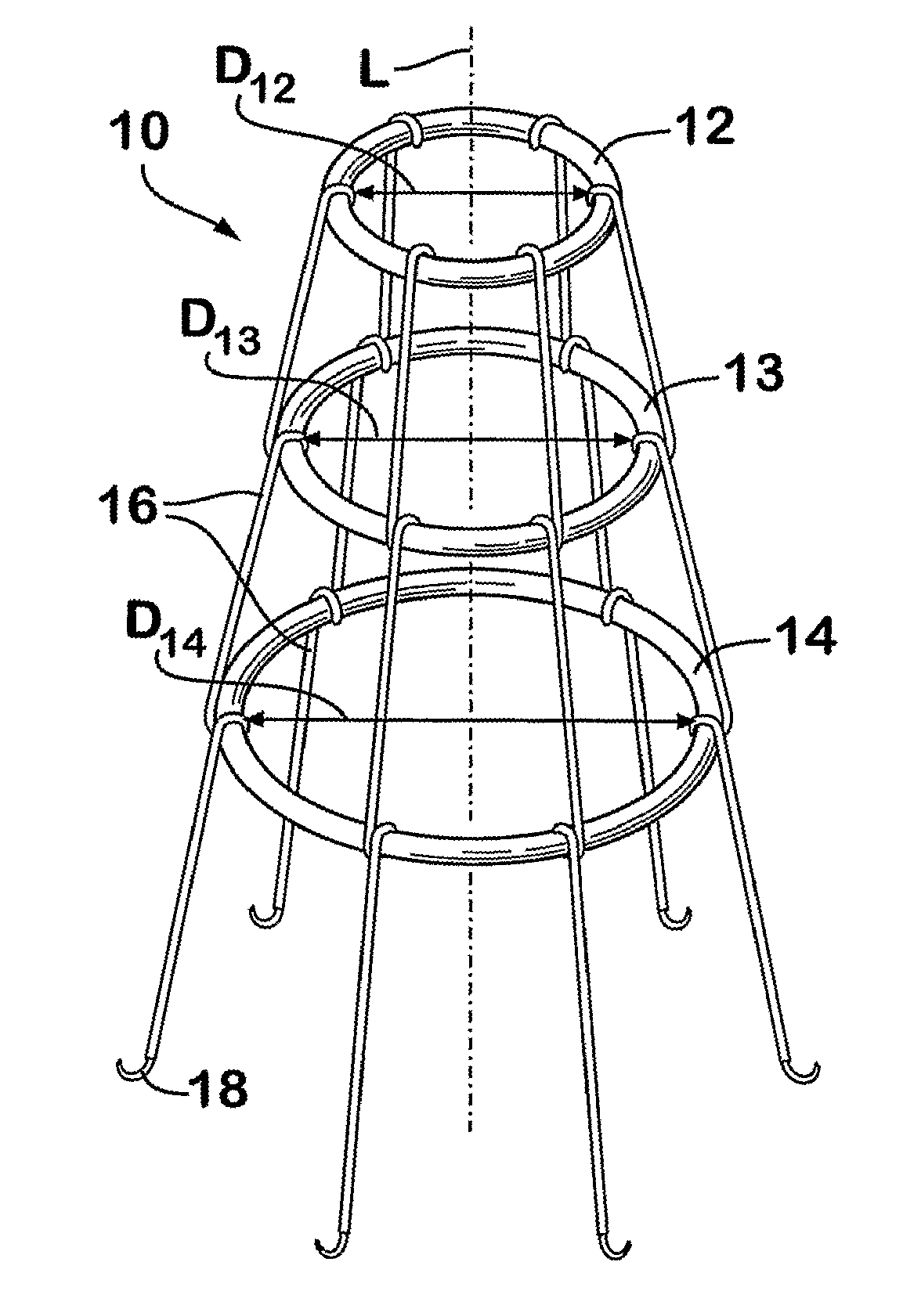
The present invention relates to a vascular filter including a coiled wire formed of a shape memory material for implantation into a vessel. The vascular filter captures particulates within the blood flow in the vessel, without substantially interfering with the normal blood flow. Prior to implantation, the coiled wire is generally elongated and thereafter it reverts to a predetermined shape that is suitable for filtering the blood flow. The predetermined shape of the vascular filter includes a plurality of loops coaxially disposed about a longitudinal axis and has a conical portion and a cylindrical portion.
Owner:JAYARAMAN SWAMINATHAN
Vascular filter
ActiveUS8162970B2Avoid passingPromote crashStentsSemi-permeable membranesVascular filterInferior vena cava filter
An inferior vena cava filter (340) for use in the inferior vena cava (4) to capture thrombus (8) passing through the inferior vena cava (4) towards the heart and lungs to prevent pulmonary embolism comprises a proximal support hoop (302), a distal support hoop (312) and a plurality of support struts (303) extending between the proximal support hoop (302) and the distal support hoop (312). The filter (340) also comprises a plurality of capture arms (121) which are movable from a capturing configuration to an open configuration. The capture arms (121) are biased towards the open configuration. A biodegradable suture holds the capture arms (121) in the capturing configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD +1
Non-entangling vena cava filter
ActiveUS20100174310A1Avoid entanglementReduce deliverySurgeryDilatorsBiomedical engineeringVena cava filters
Owner:CR BARD INC
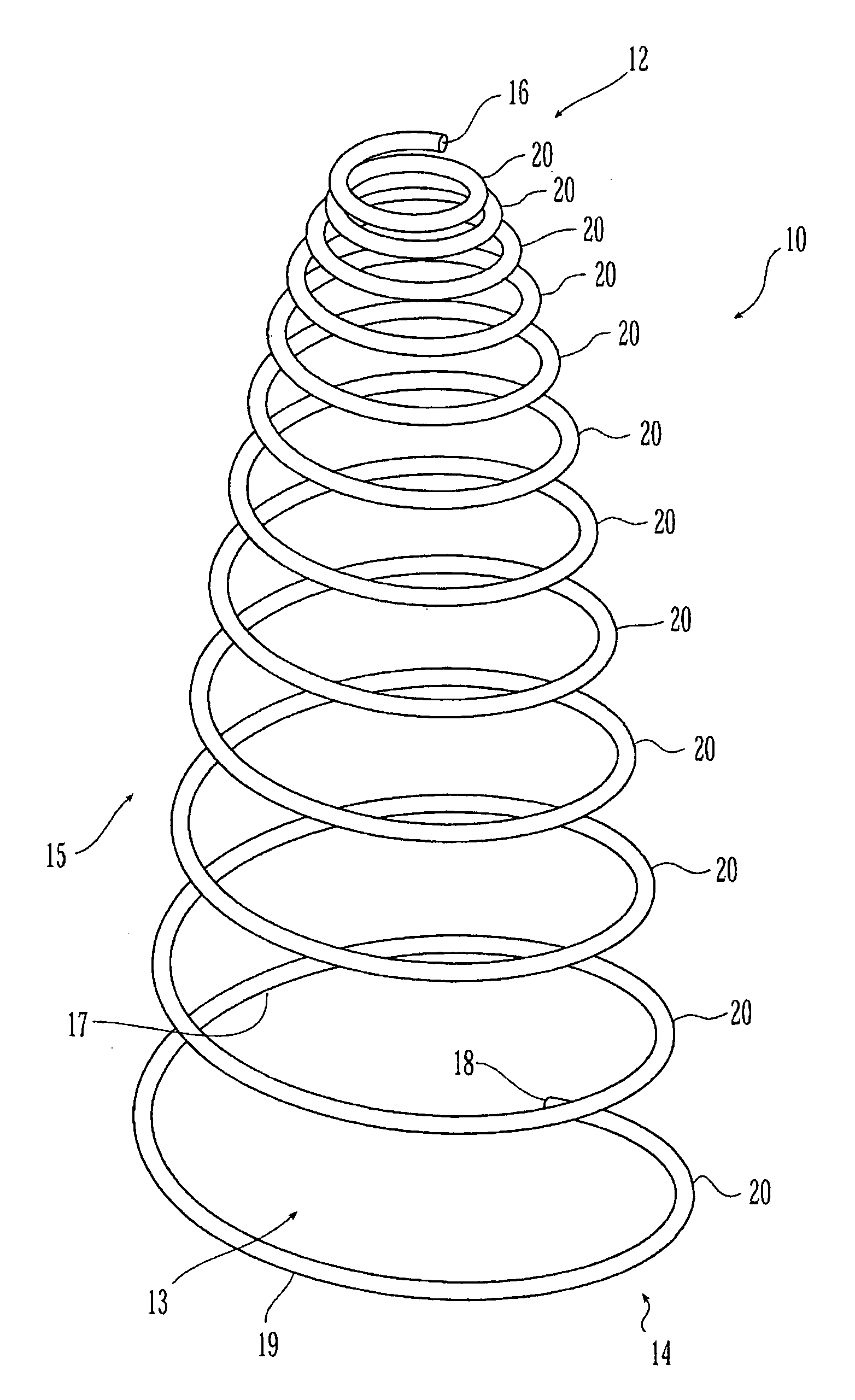
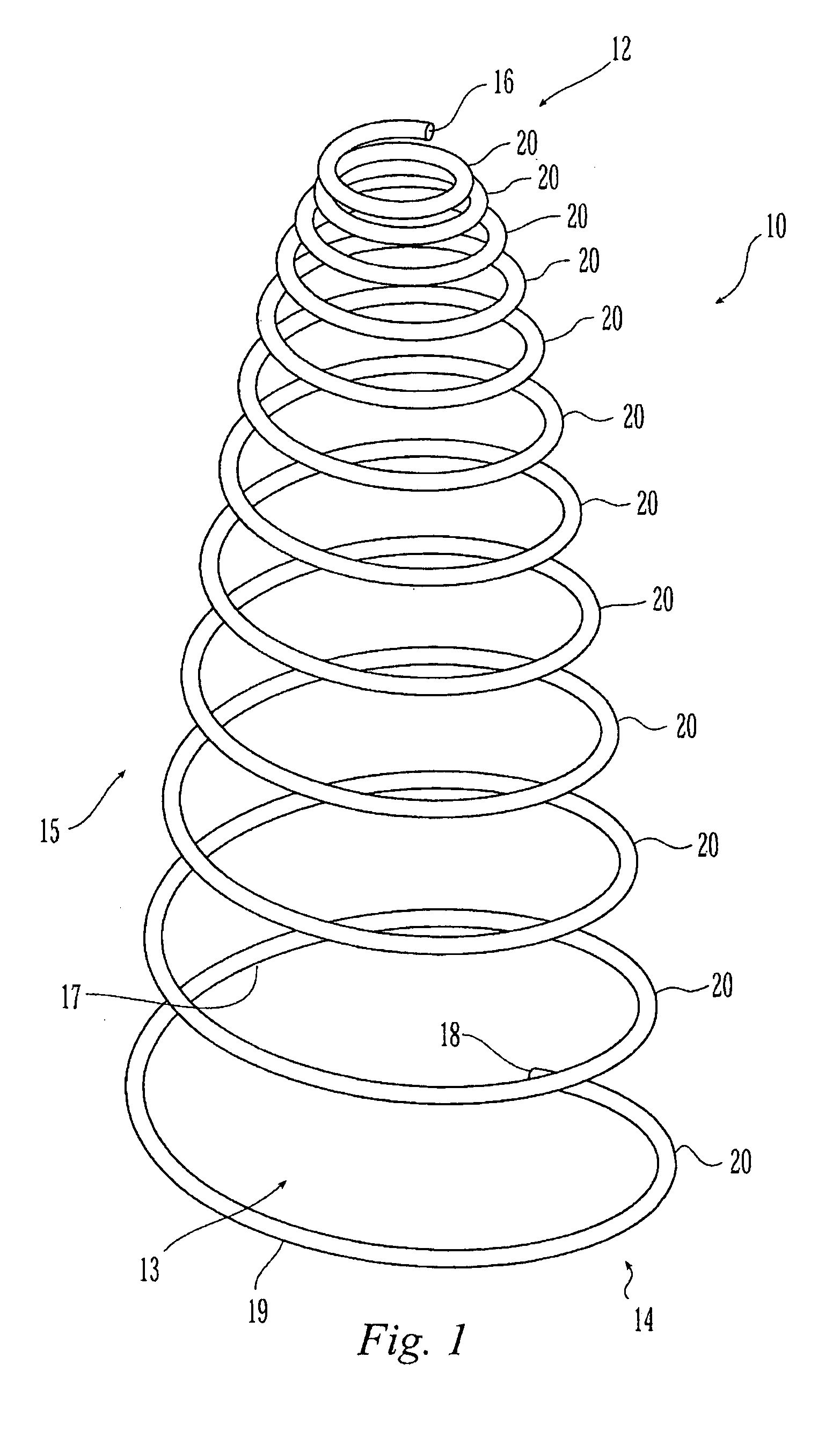
Helical Vena Cava Filter
A vena cava filter is described, having at least one member arranged helically along a longitudinal axis of the filter. The filter may include a plurality of legs around which is arranged one or more filaments traveling in a helical path, or an elongated wire member arranged to define a first and second helecal path. The filter may include hooks and / or a retreival member.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Vena cava filter formed from a sheet
A filter formed from a sheet is described herein. In one aspect of the invention, a filter is formed from a sheet of material and, following removal of portions of the sheet, the filter is folded into a shape for insertion into a blood vessel. In another aspect of the invention, features for a filter are formed from a sheet of material and incorporated into the filter.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Multi-lumen sheath central venous catheter with vena cava filter apparatus and method of using same
A combined multi-lumen sheath with a wire body and a filter. The filter may be removably coupled to the multi-lumen sheath within a filter capsule for temporary placement and retrieval.
Owner:BIO2MEDICAL
Retrievable ivc filter
Retrievable vena cava filters for filtering blood clots within a vessel are disclosed. A retrievable vena cava filter in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention may include a plurality of elongated filter legs each having a hook portion configured to engage the vessel wall, and an expandable member releasably connected to the filter. In certain embodiments, the expandable member may comprise a bendable member and several tubular members, or a coiled wire.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
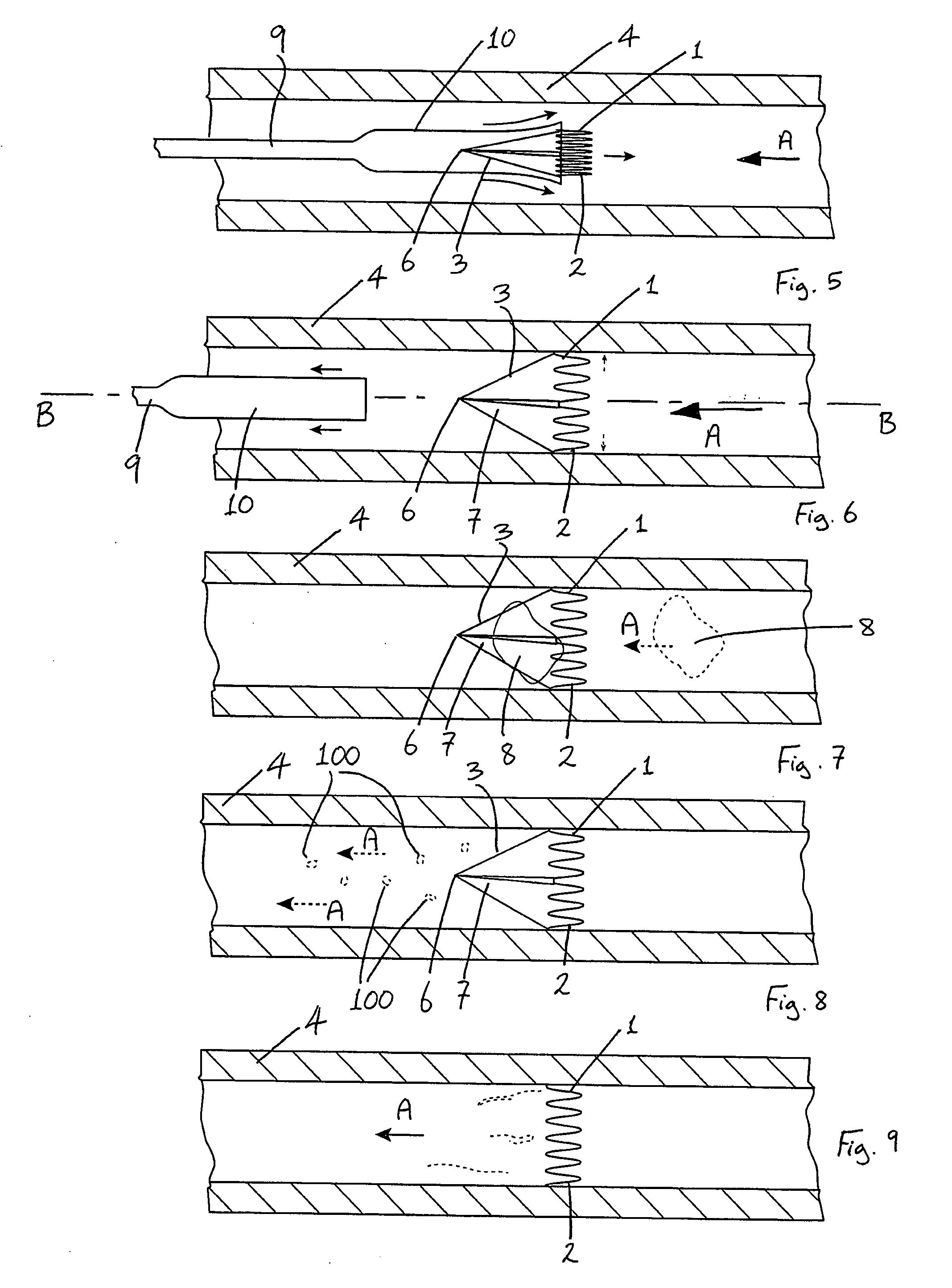
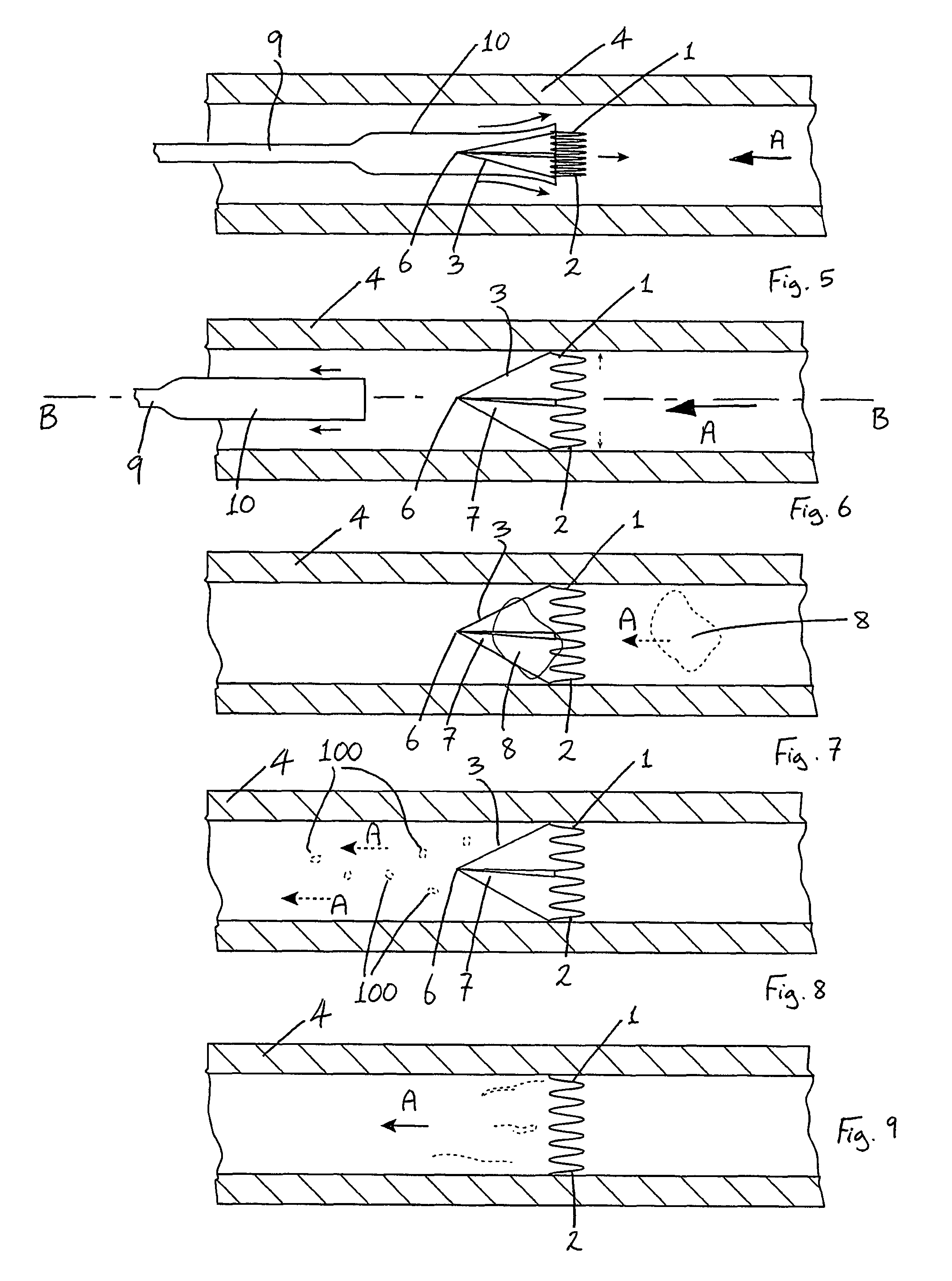
Puncture and abrasion resistant sheath
InactiveUS20080119867A1Excellent abrasion resistanceImprove puncture resistanceGuide needlesEar treatmentDistal portionPolyether ether ketone
A delivery apparatus for introducing an implant, such as a vena cava filter, for capturing emboli in a body vessel. The apparatus includes an outer sheath having a tubular wall defining a lumen formed therethrough and having a proximal end extending to a distal end. The tubular wall includes an inner surface and may also include optional reinforcing members. A radiopaque marker band is disposed about the inner surface adjacent the distal end, and a tubular liner is disposed along the inner surface. The tubular liner comprises at least one of polyimide, PEEK, and PVDF. An inner catheter is slidably disposed within the lumen of the outer sheath and has a distal portion configured to engage and deliver the implant through the distal end of the outer sheath in the body vessel.
Owner:COOK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com