Patents
Literature
86results about How to "Promote crash" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
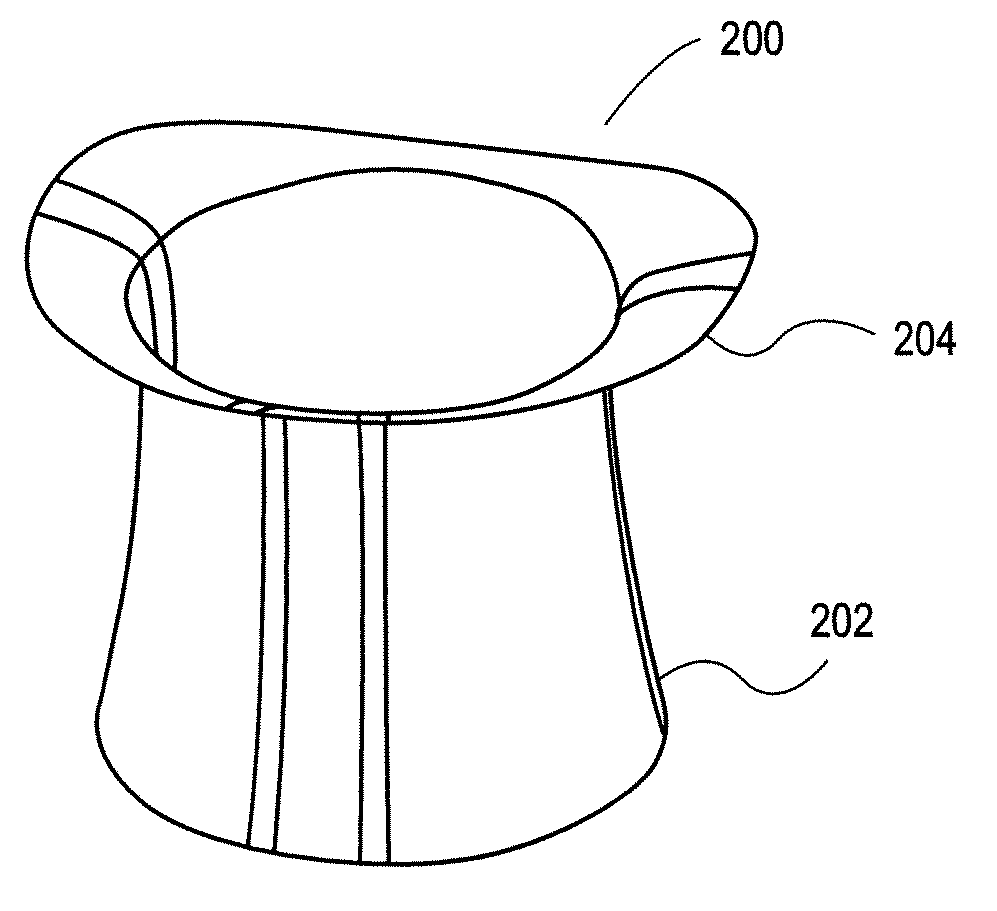
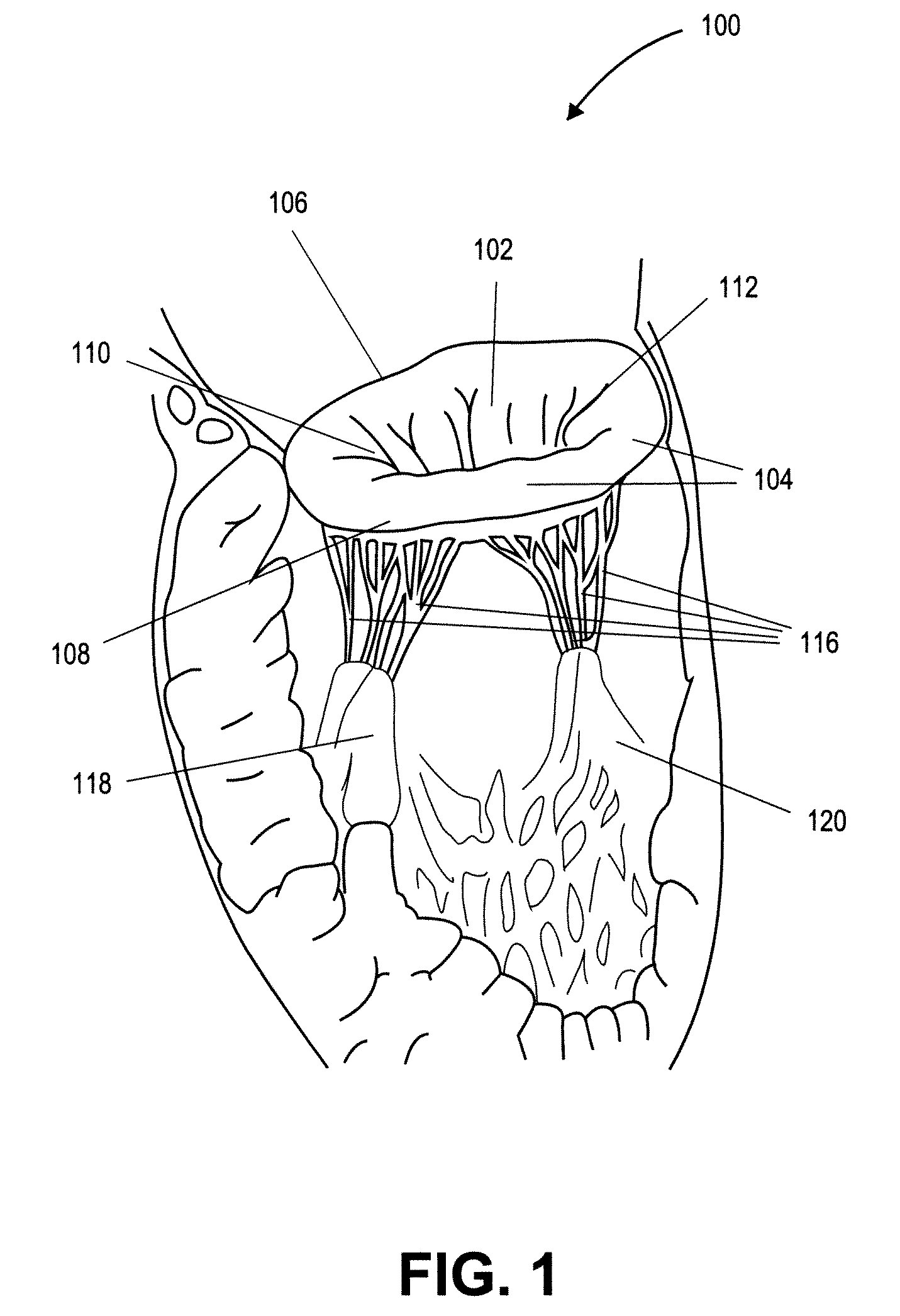
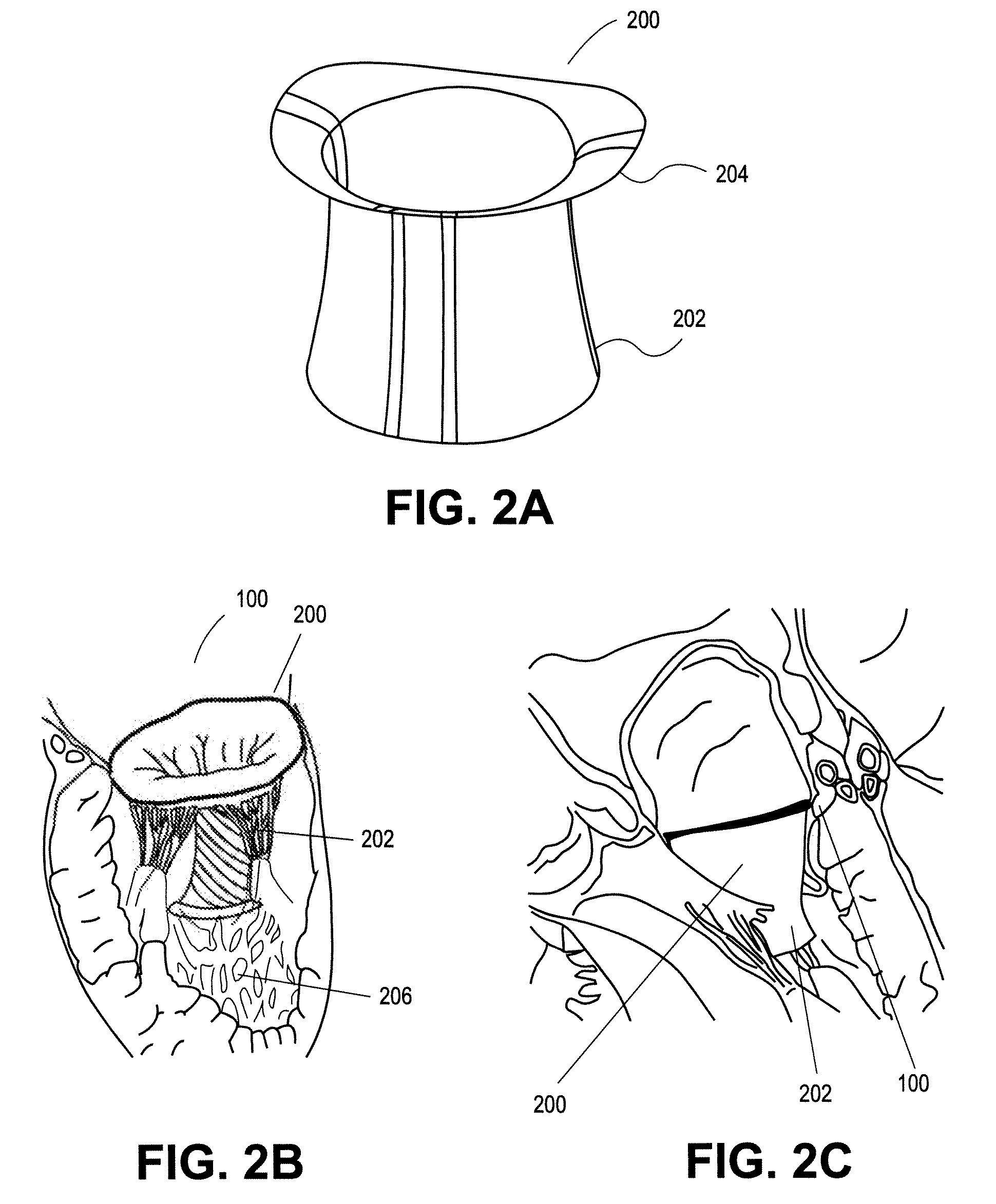
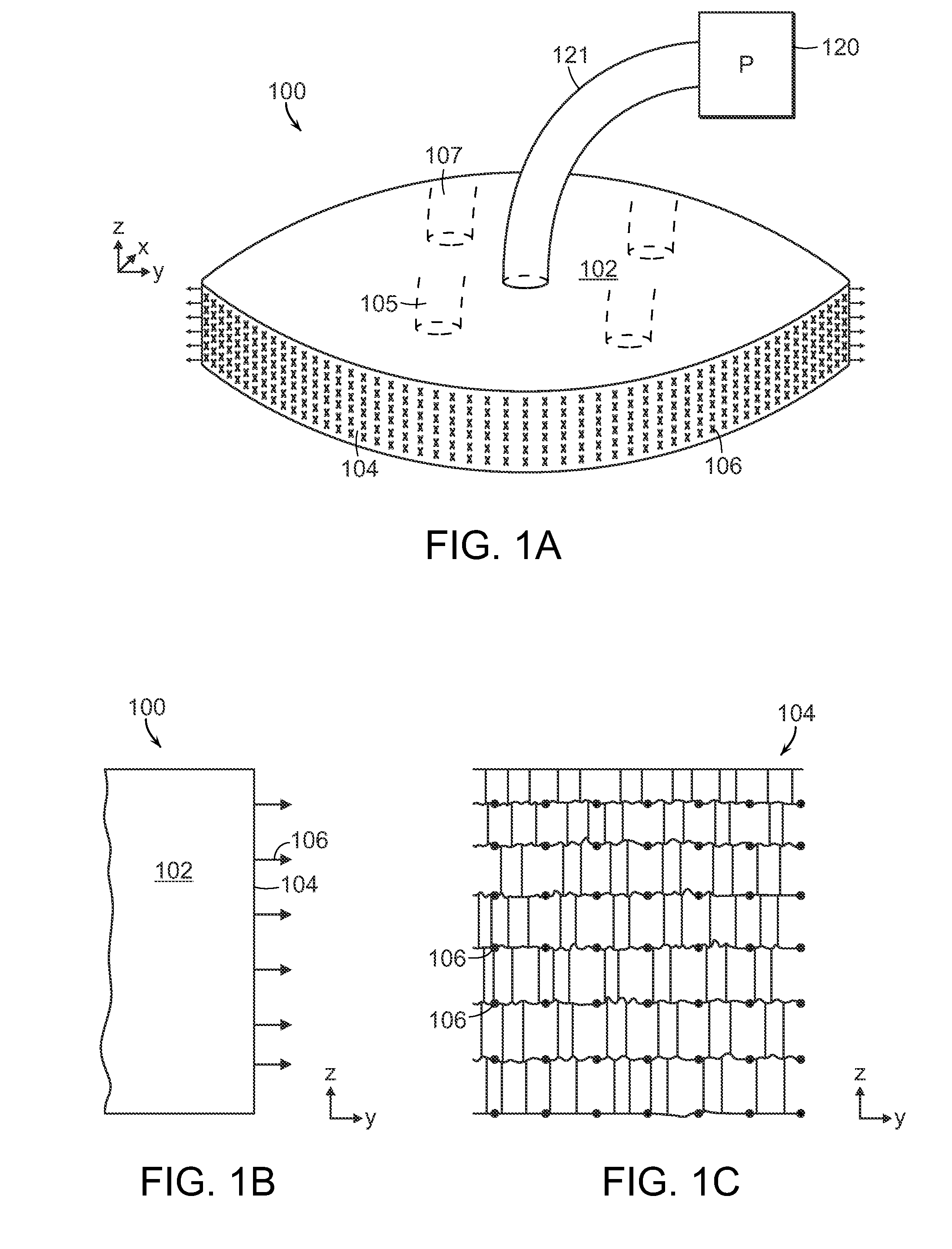
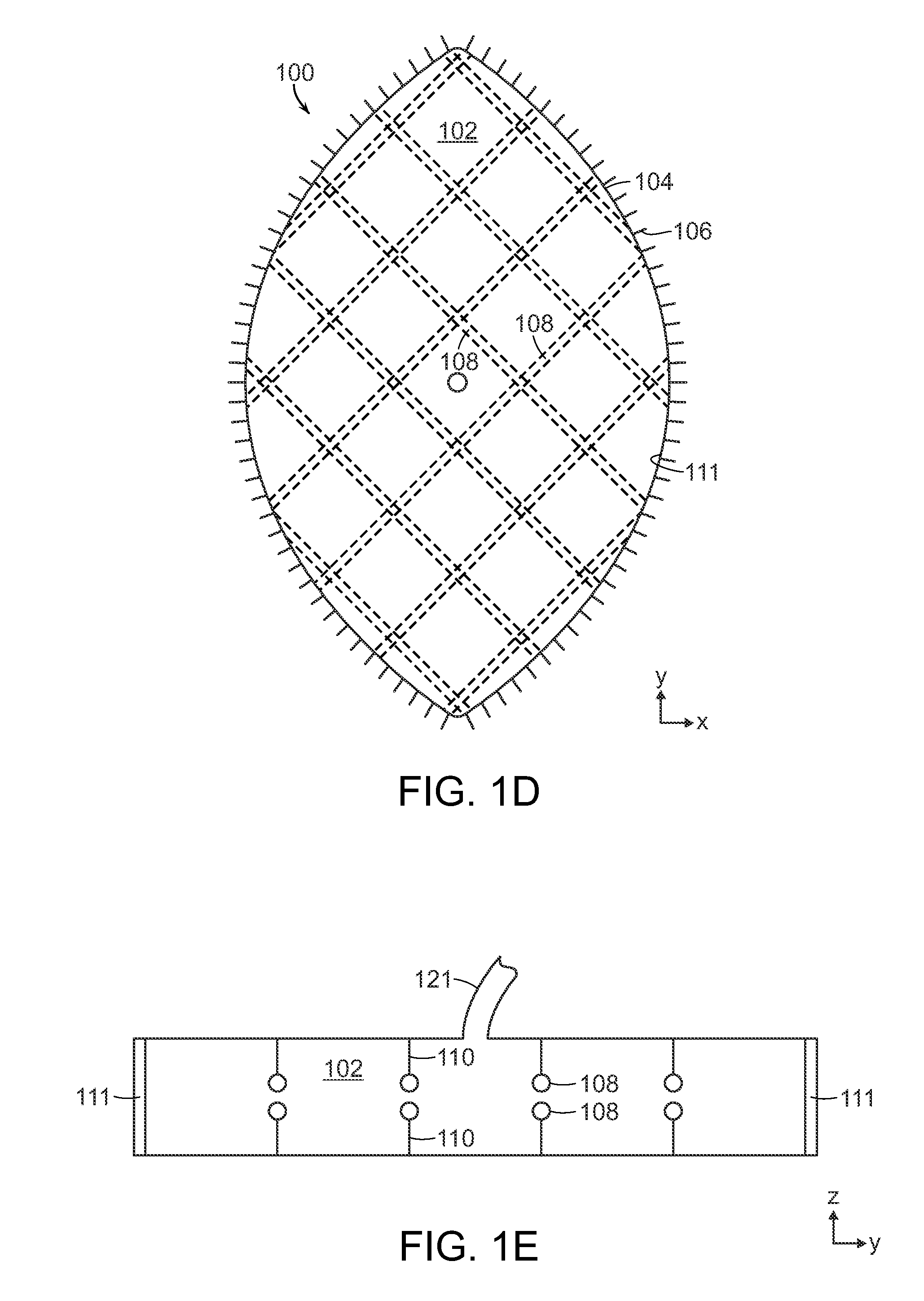
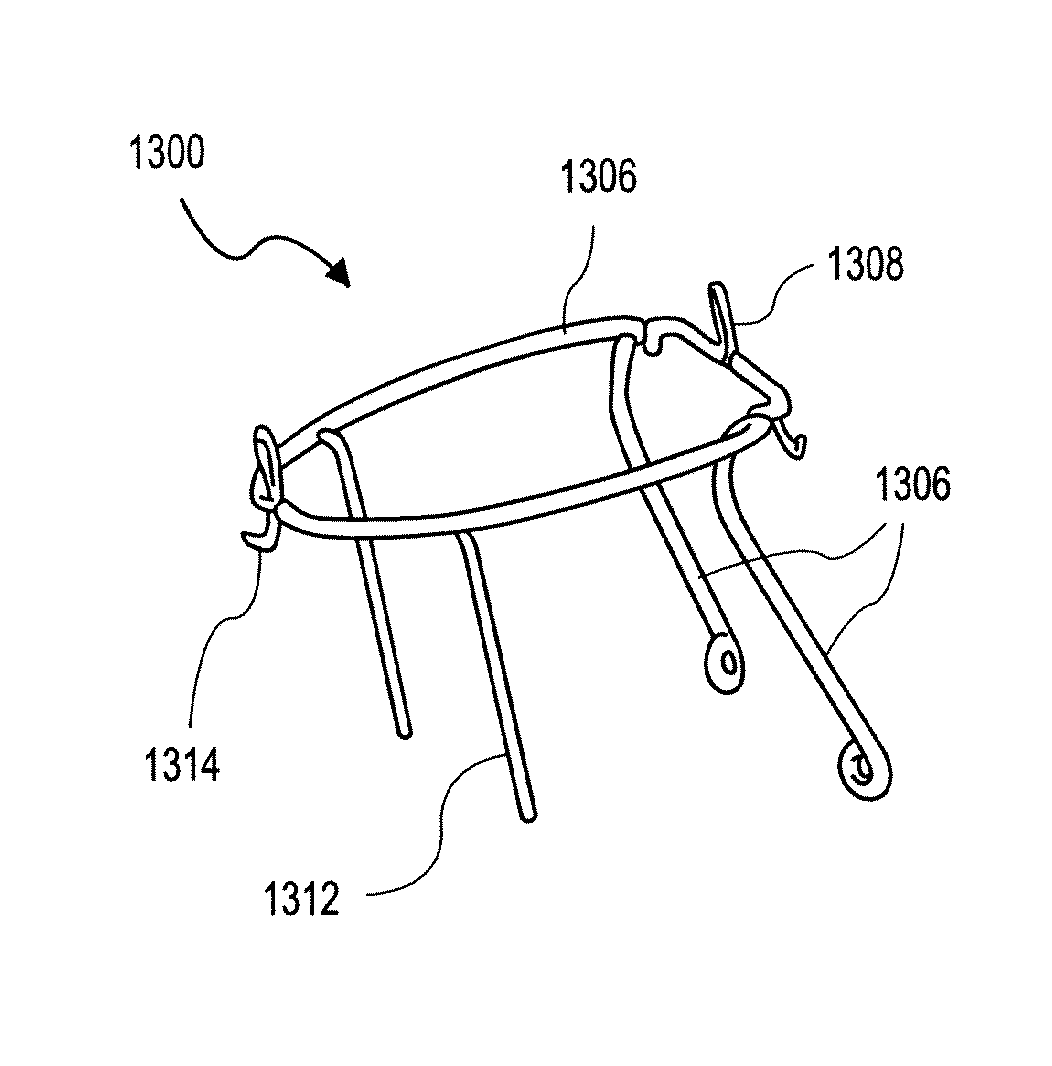
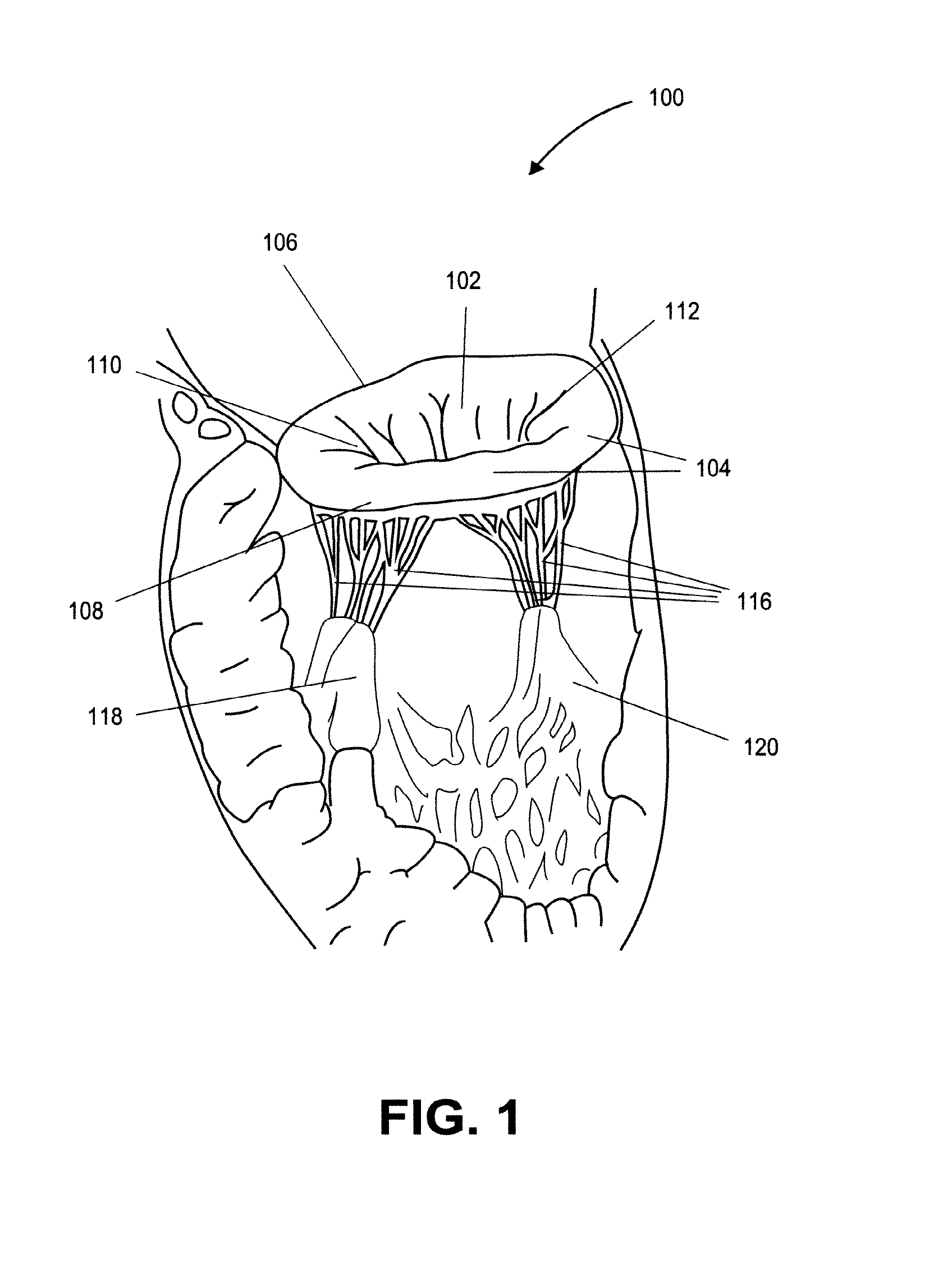
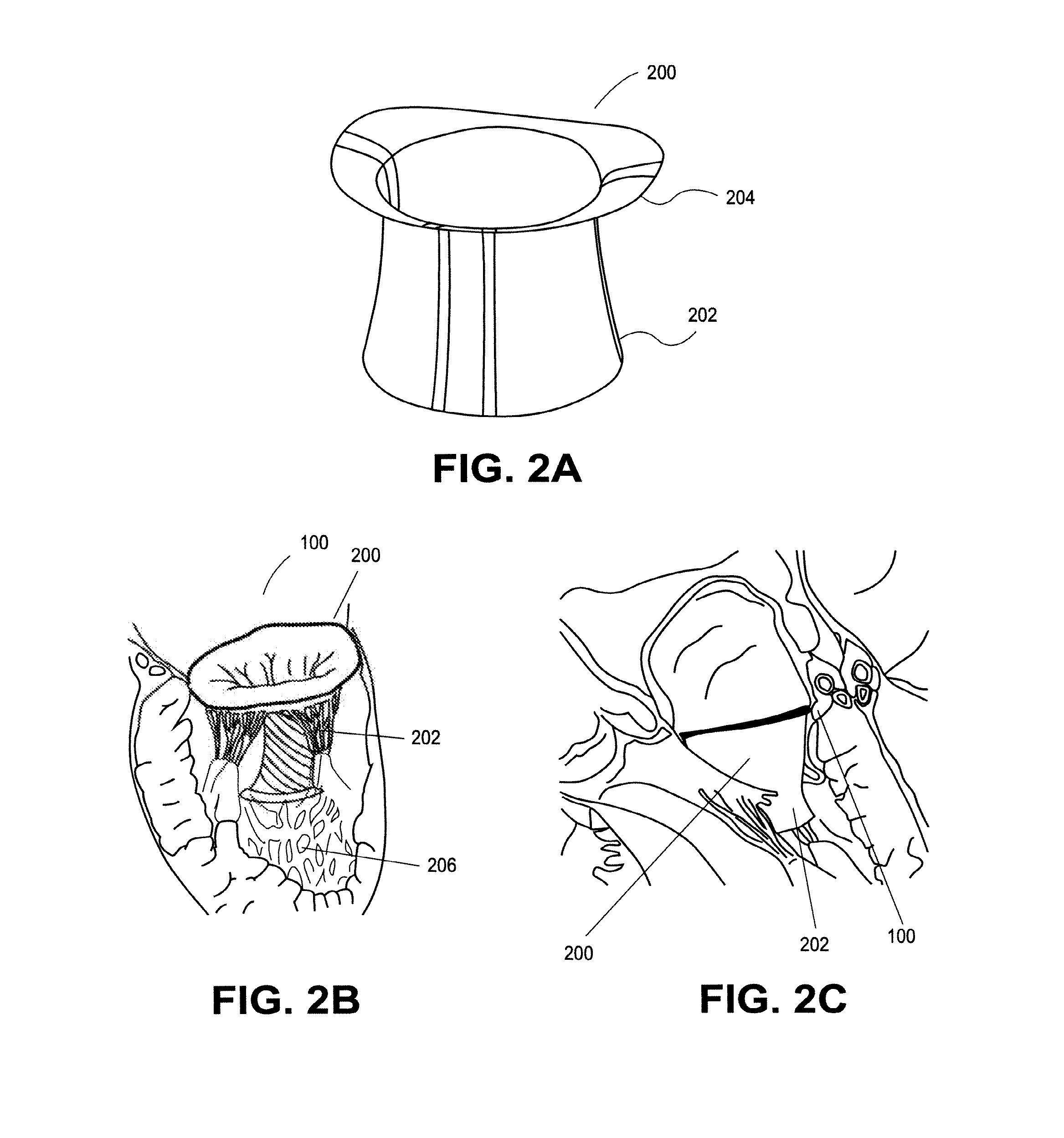
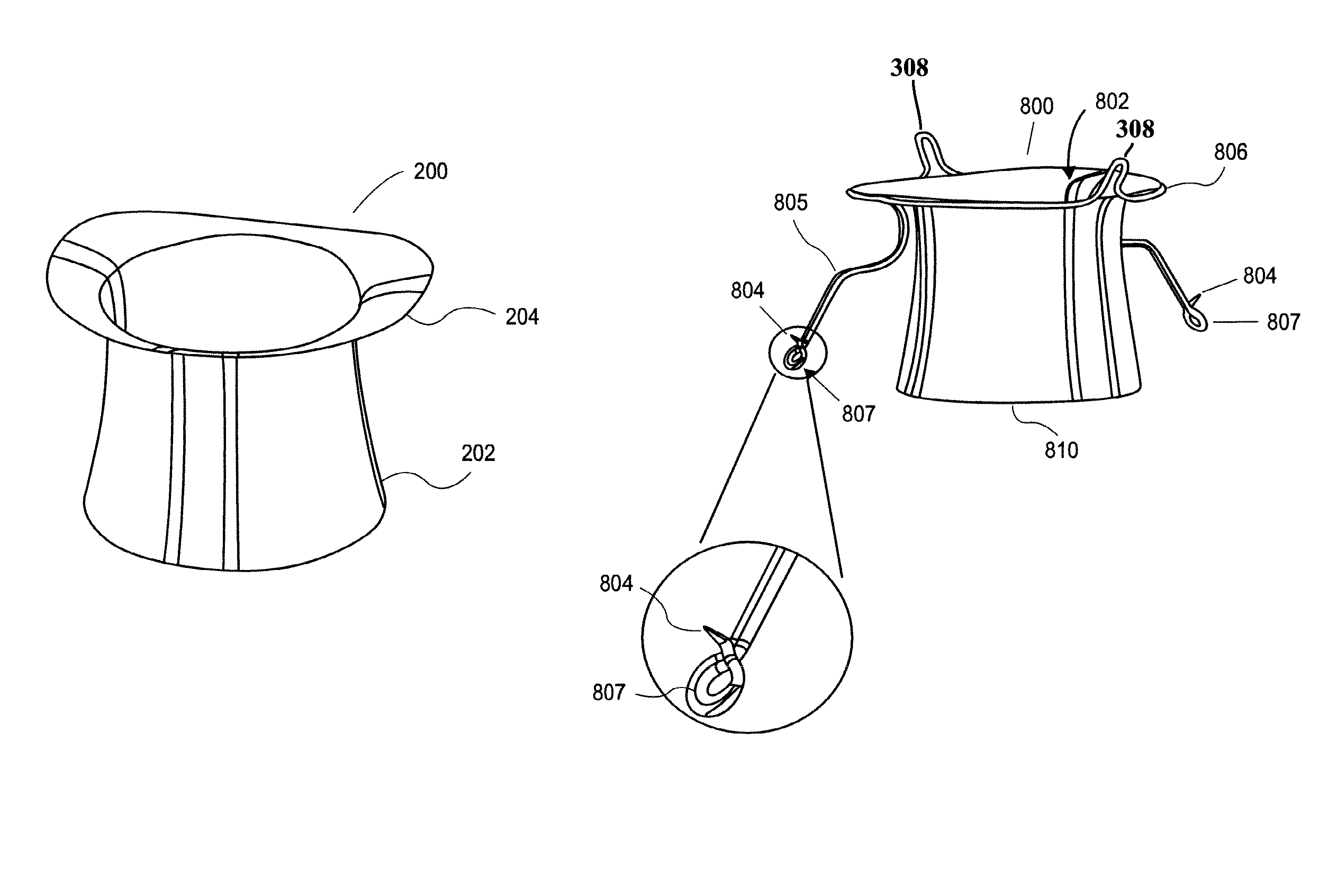
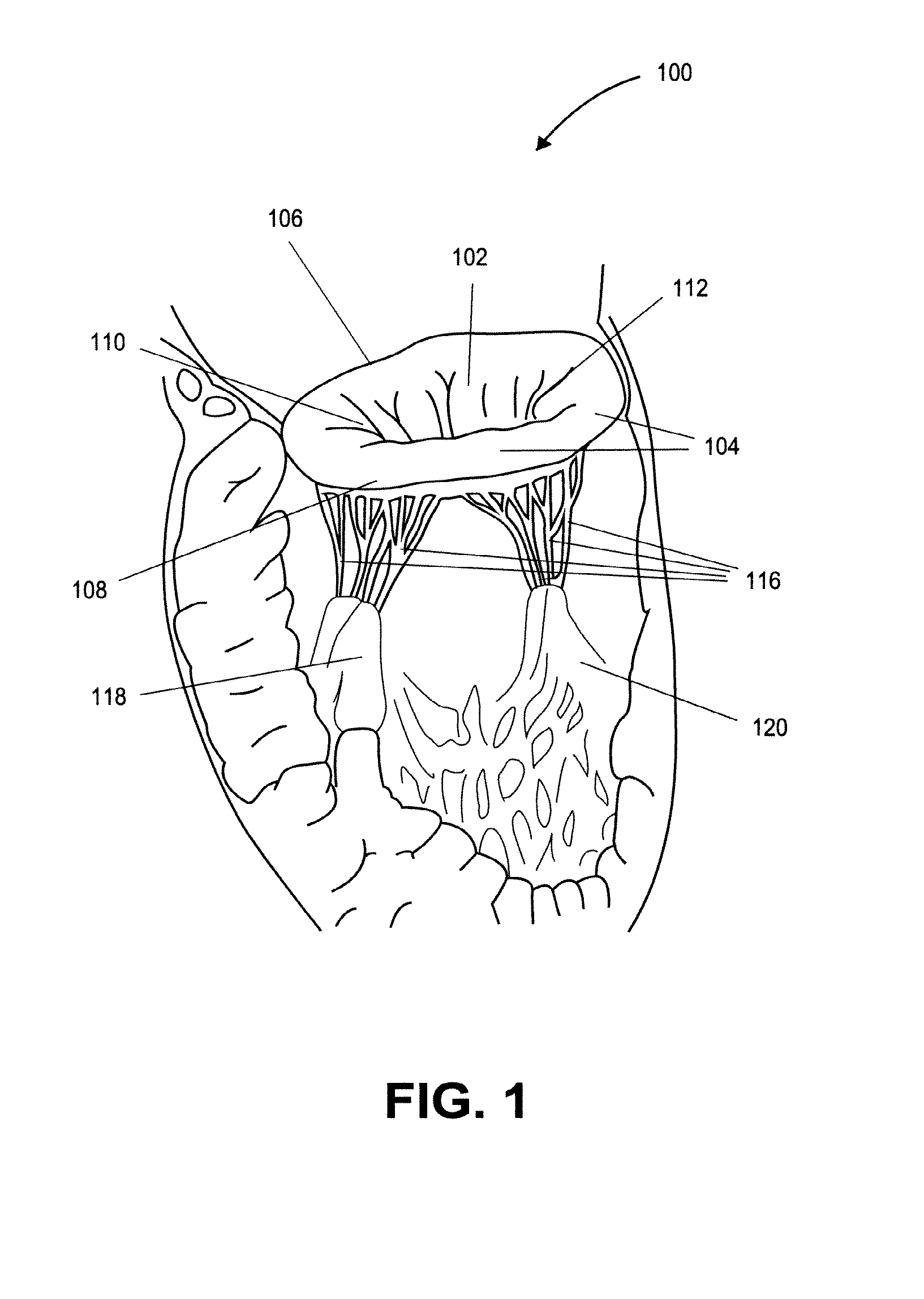
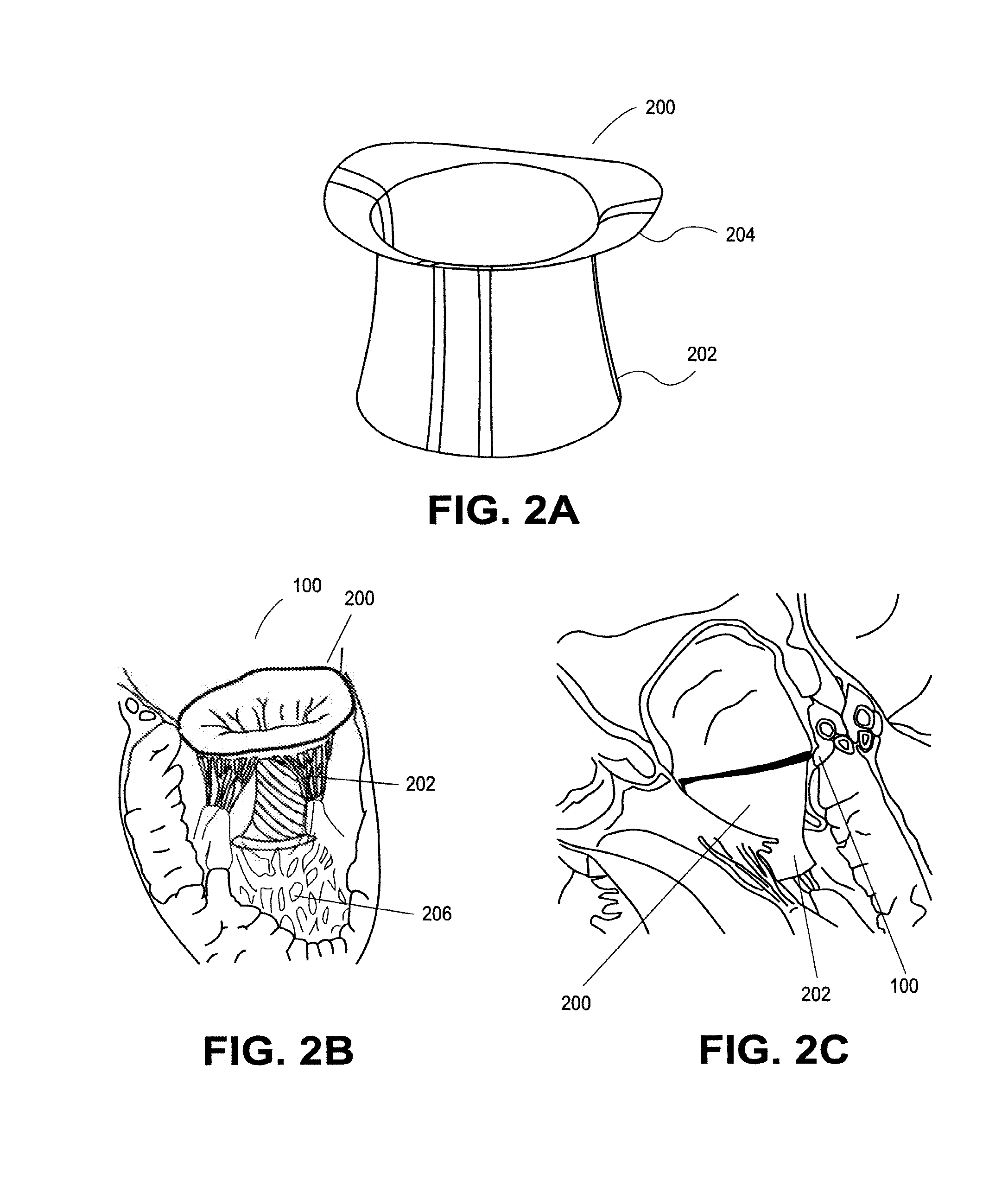
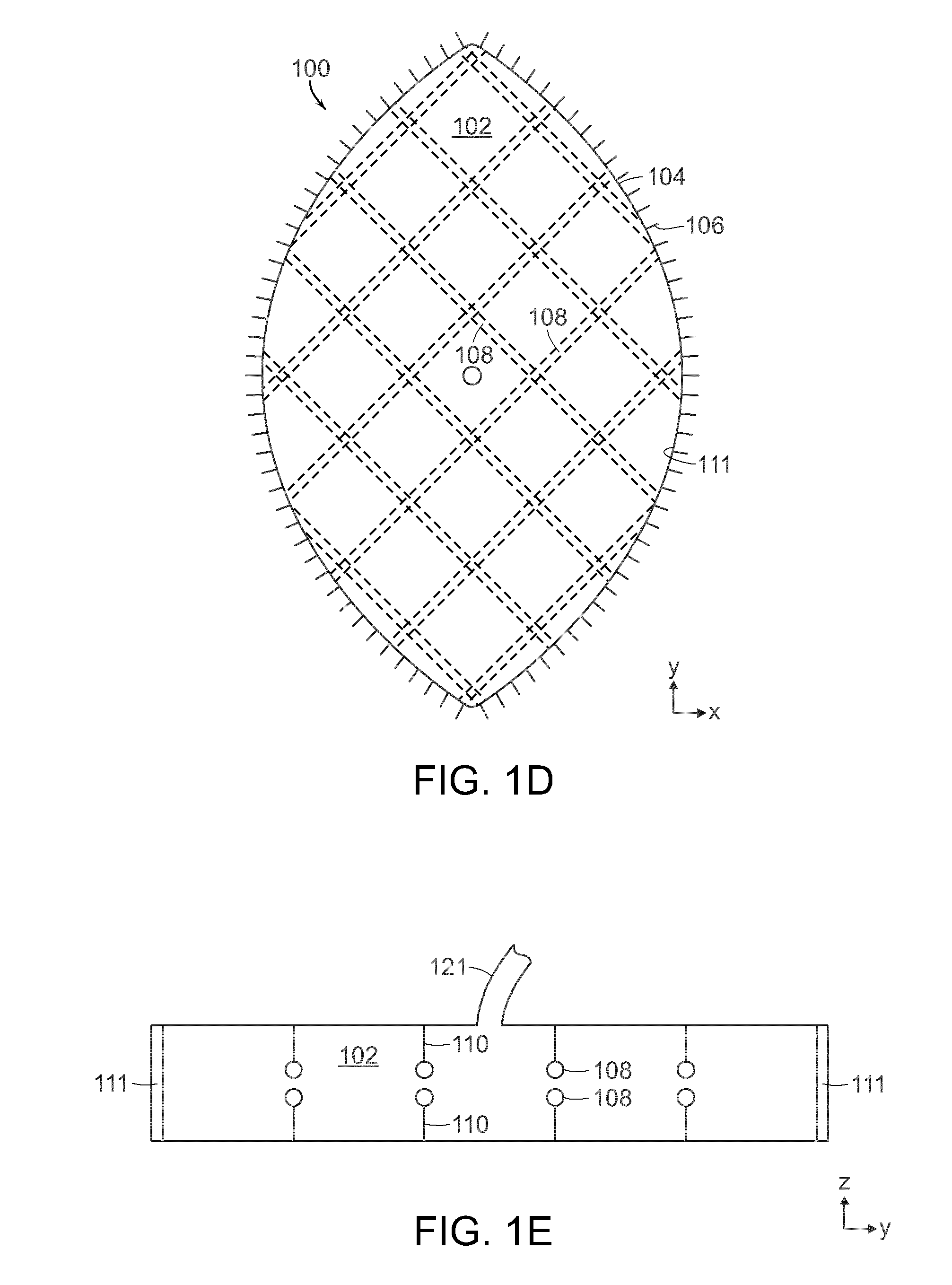
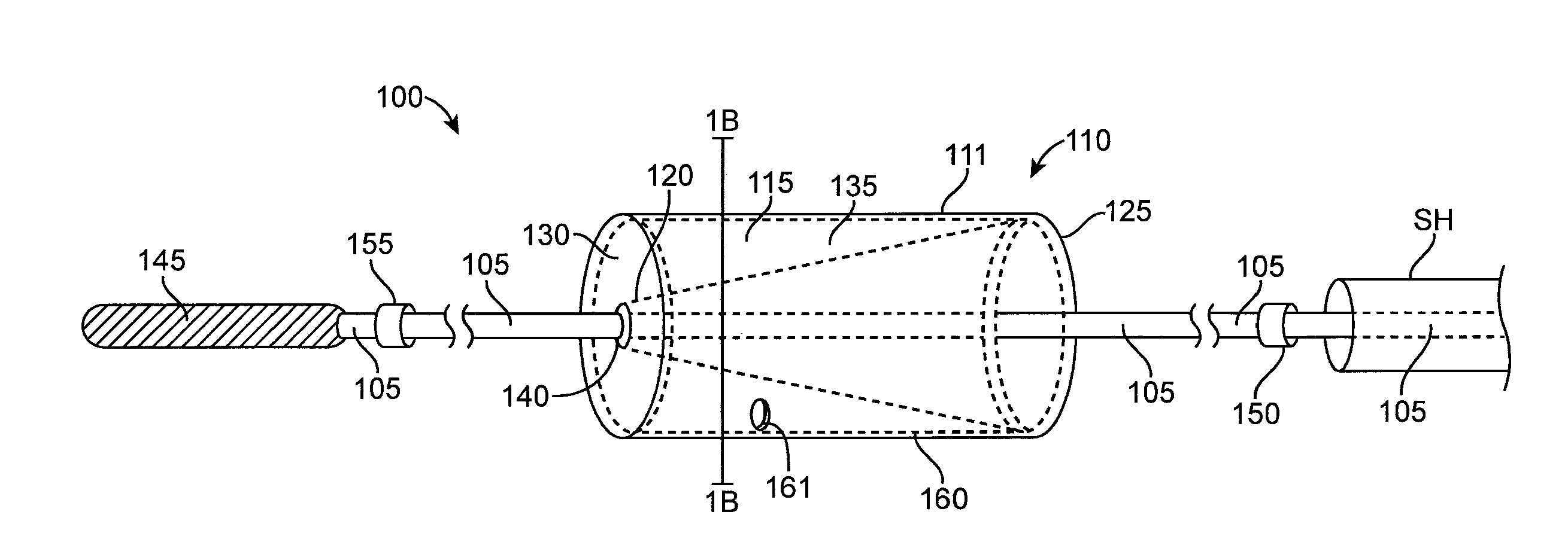
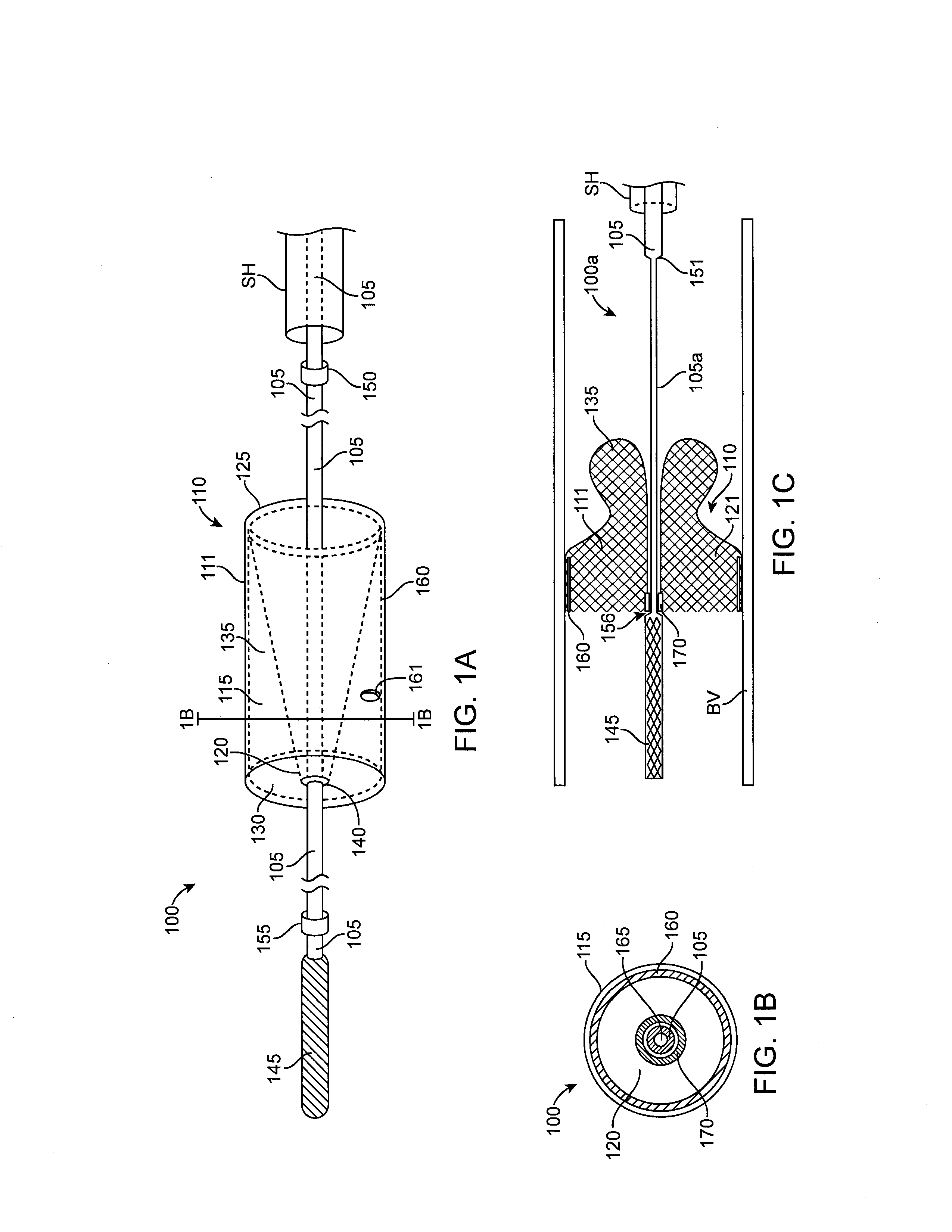
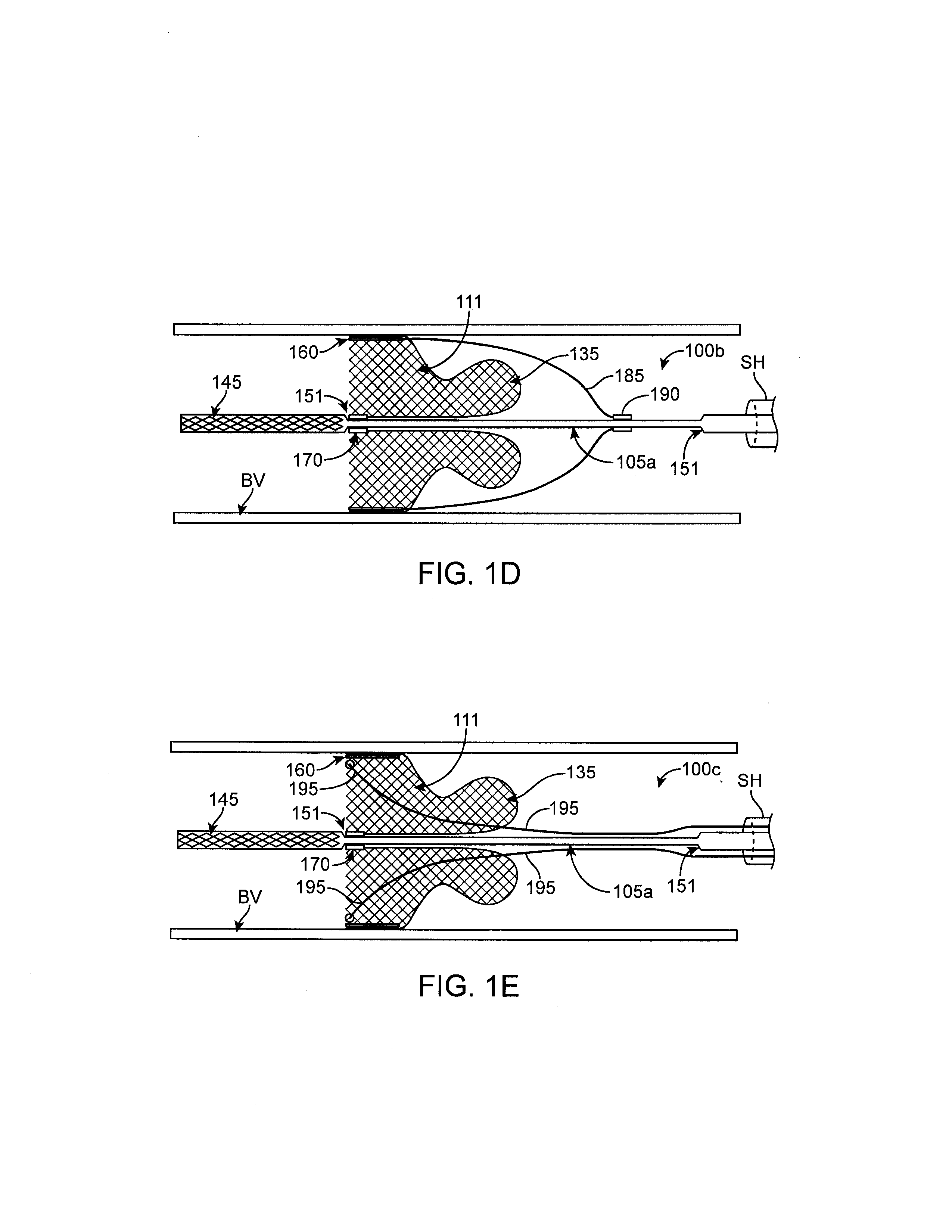
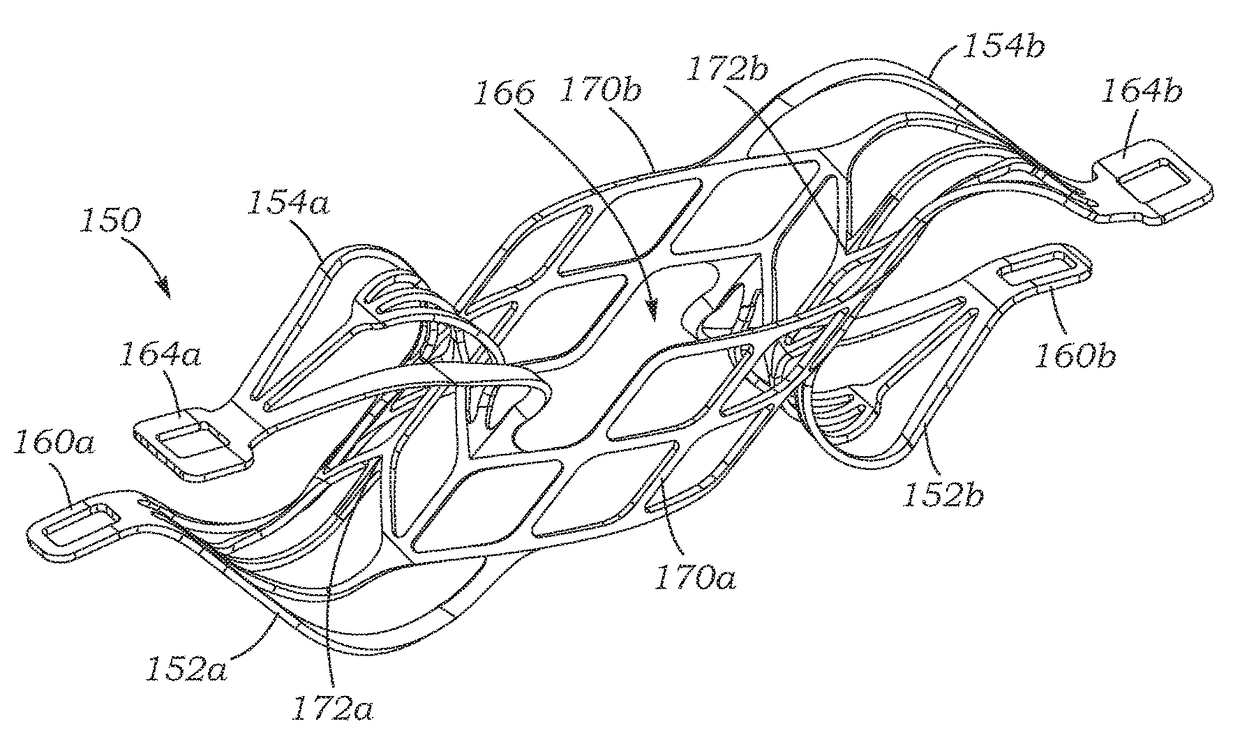
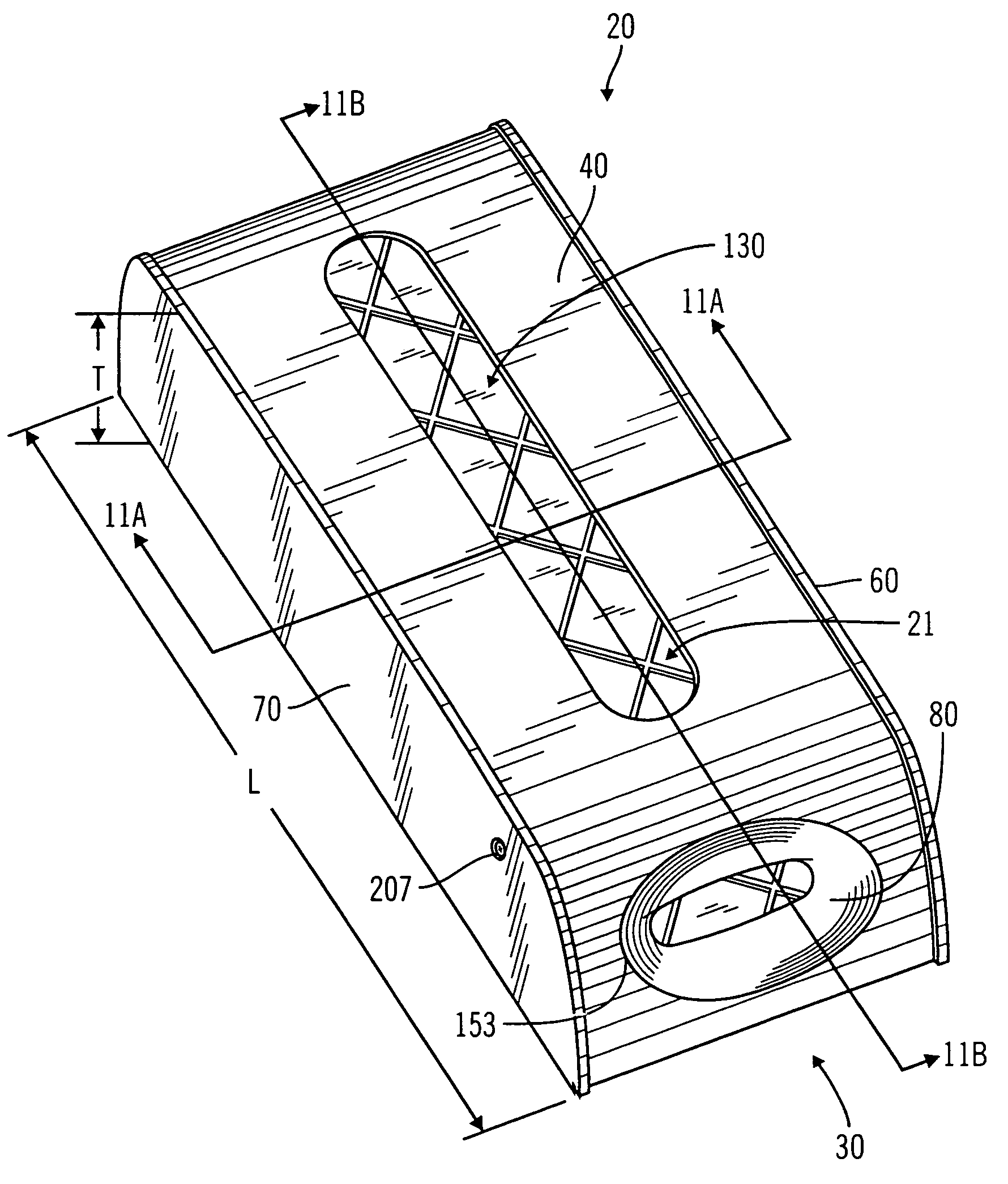
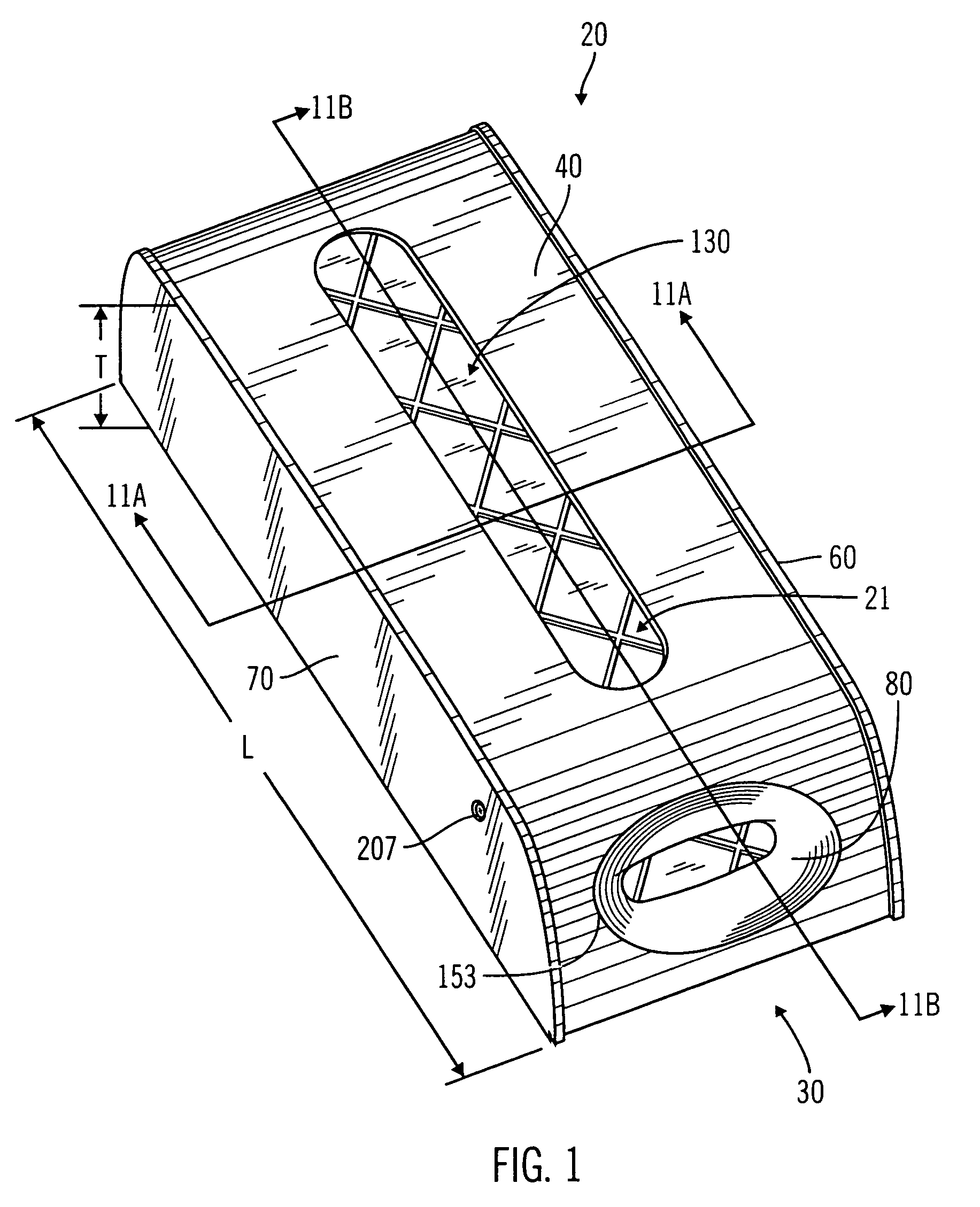
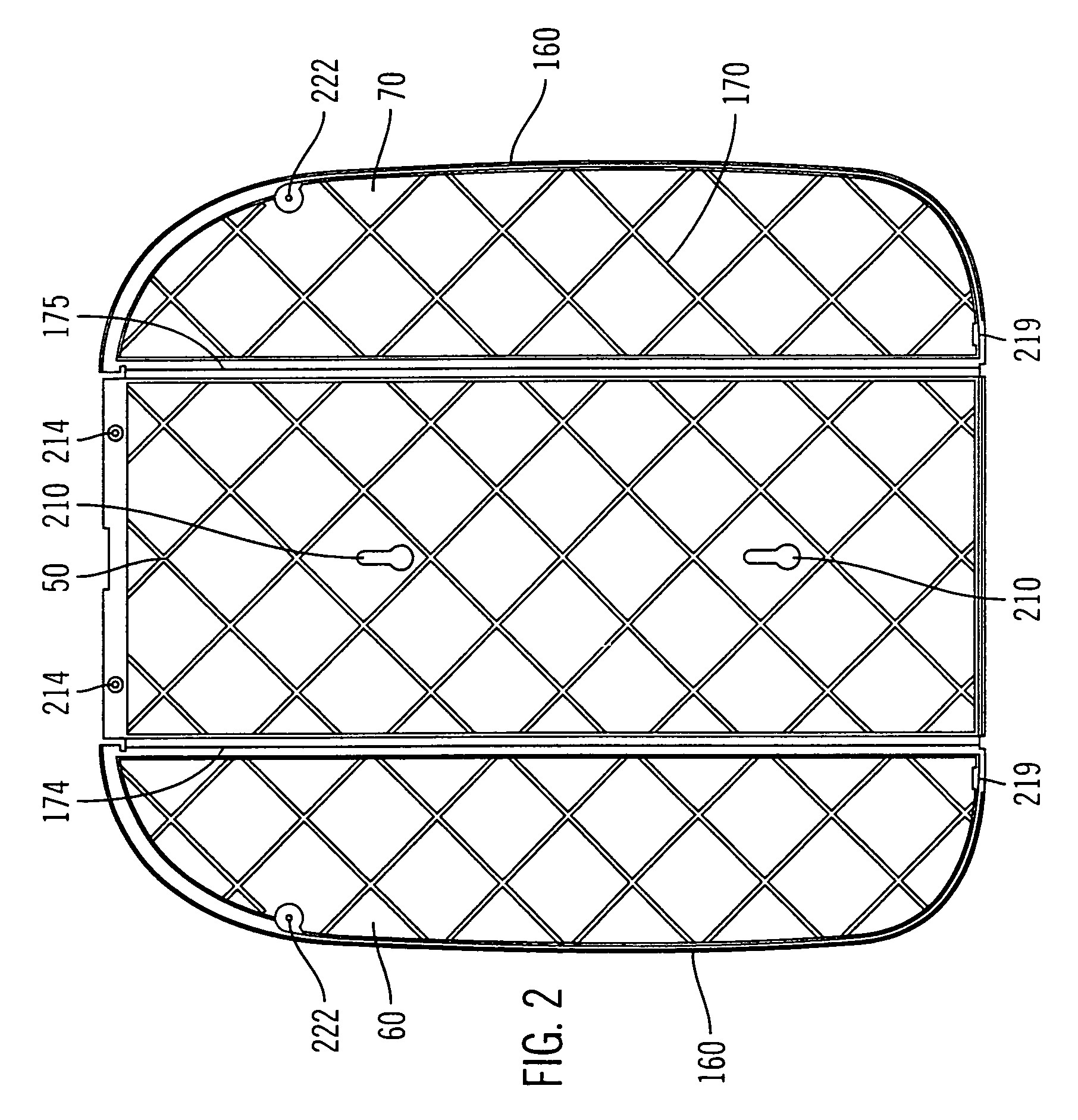
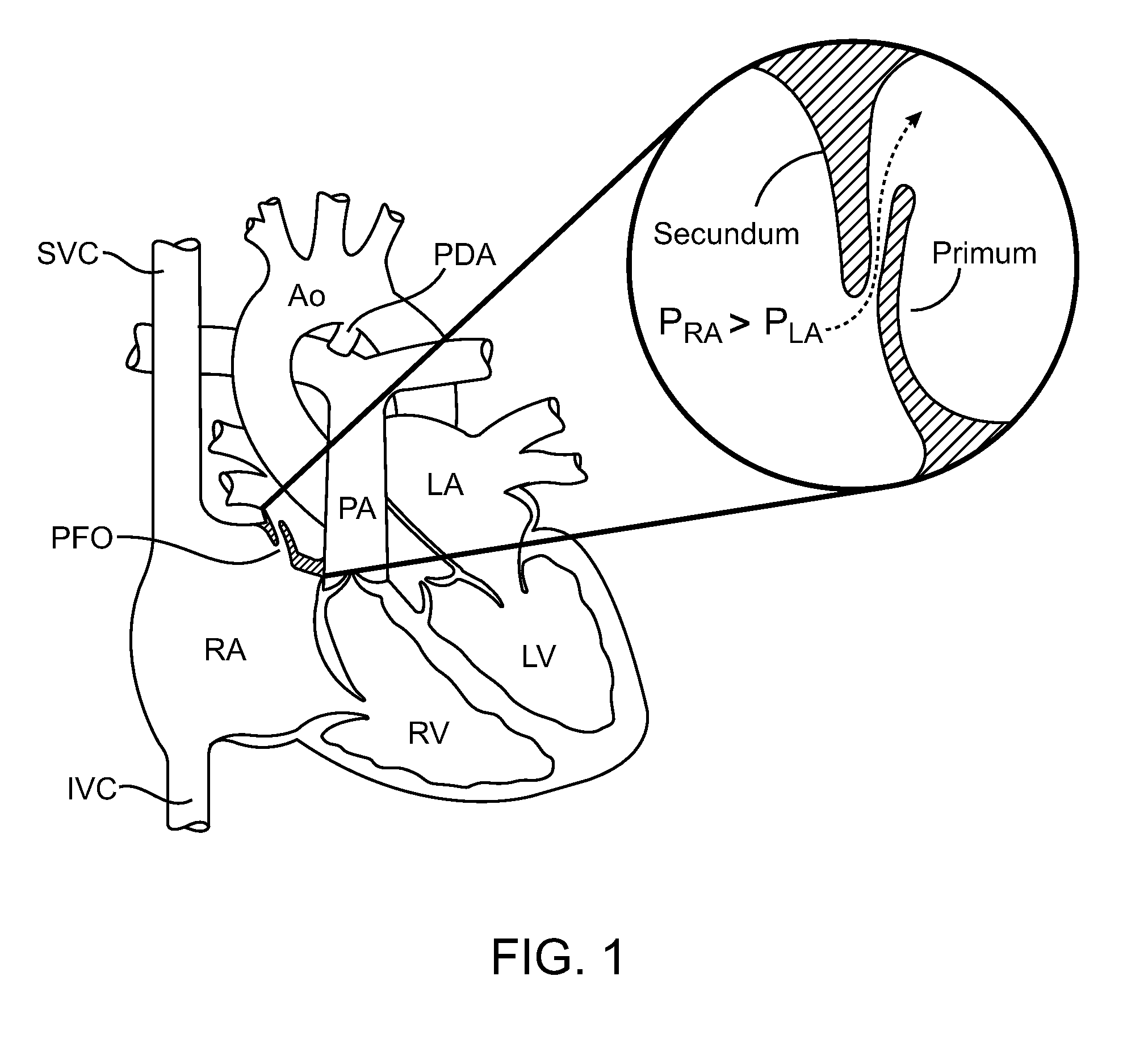
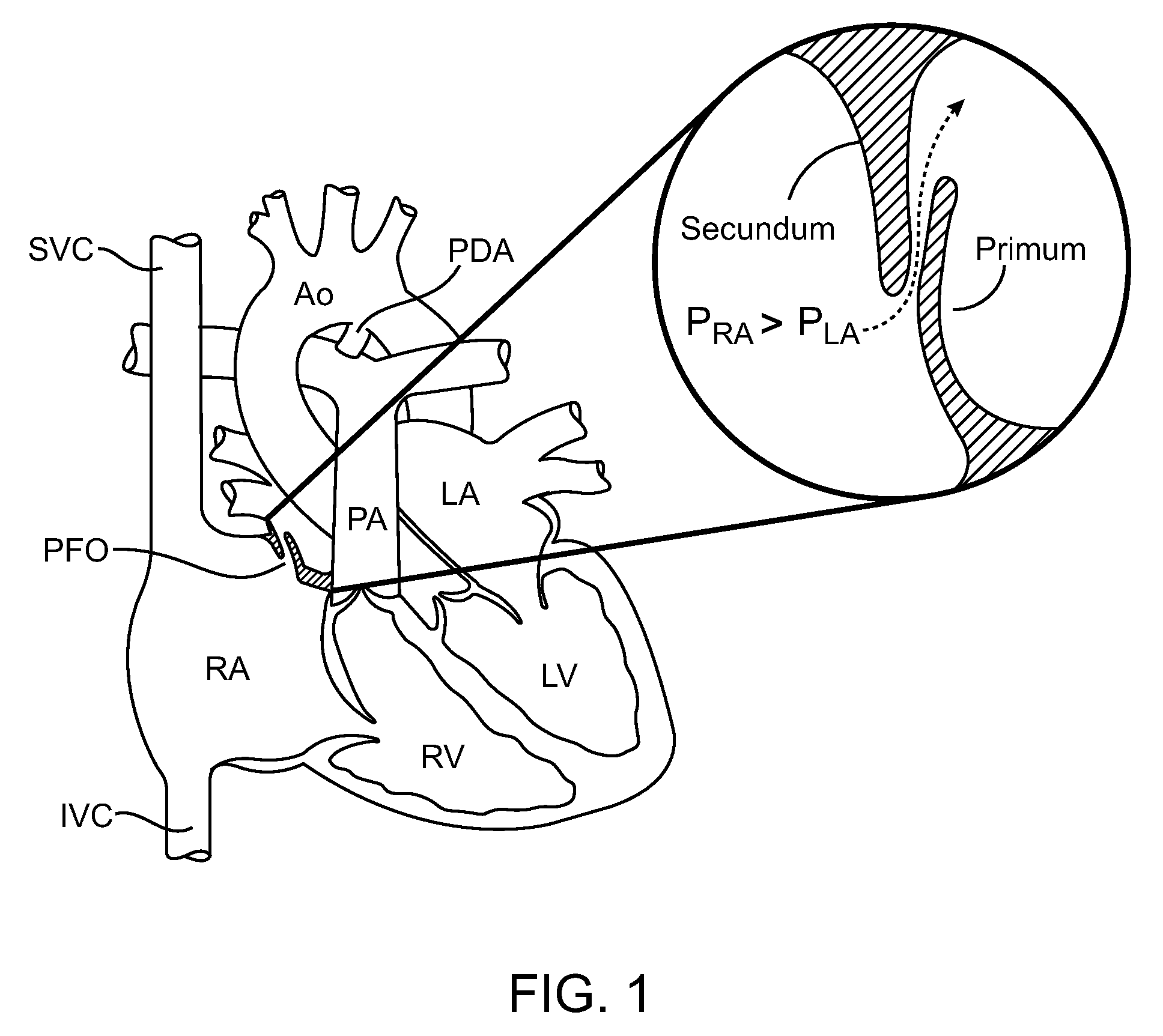
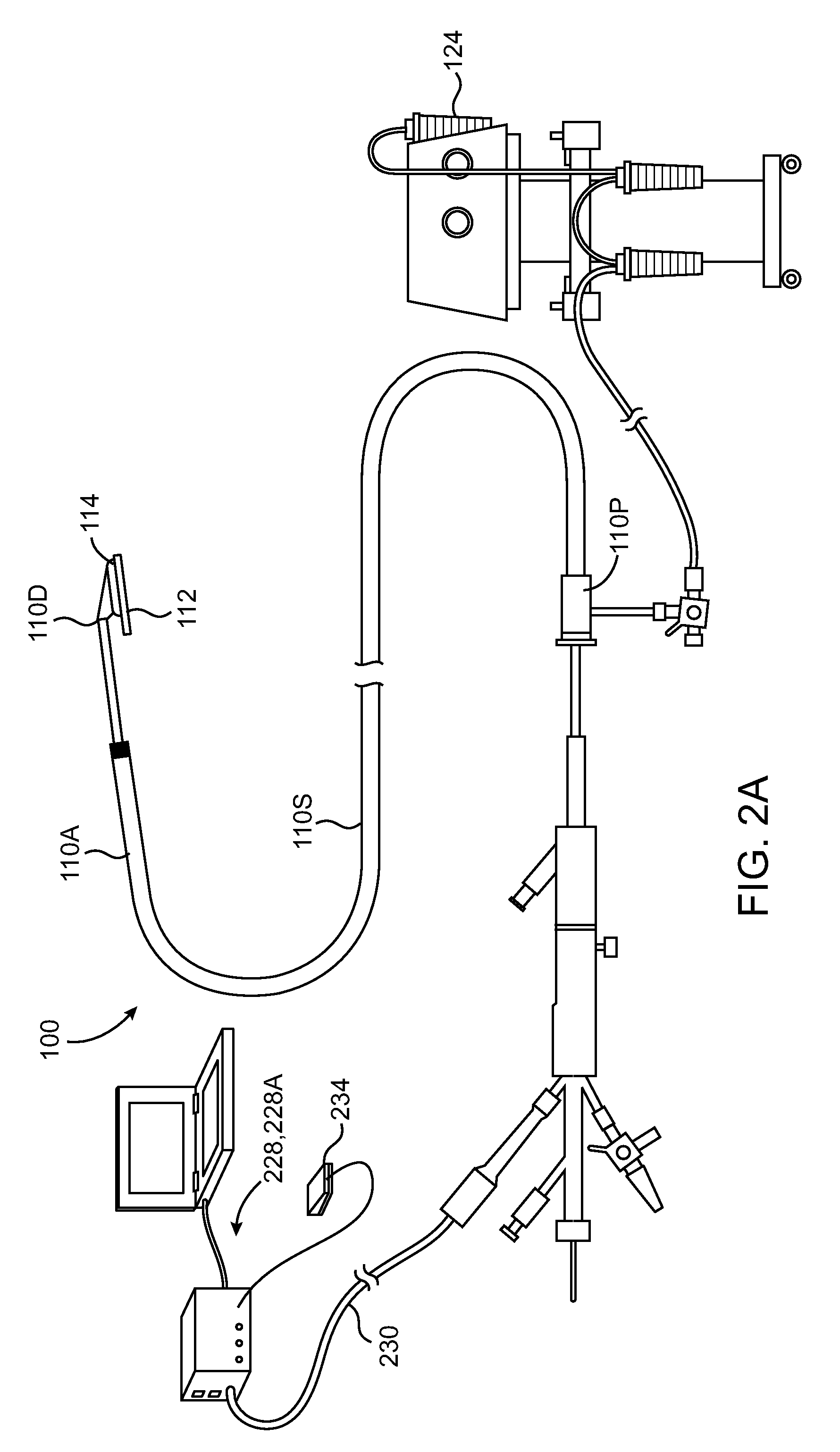
Heart valve prosthesis with collapsible valve and method of delivery thereof
ActiveUS20100280606A1Promote crashReduce the effective areaAnnuloplasty ringsPlasma viscosityCardiac valve prosthesis
A valve prosthesis is adapted to operate in conjunction with native heart valve leaflets. The prosthesis includes an annulus and a skirt extending from the annulus. The skirt may be configured to be positioned through a native heart valve annulus, and the skirt may be movable between an open configuration permitting blood flow through the skirt and a closed configuration blocking blood flow through the skirt in cooperation with opening and closing of the native heart valve leaflets.
Owner:MITRASSIST MEDICAL
Negative pressure wound closure device
ActiveUS20120209227A1Low costEasy to closePlastersCupping glassesBiomedical engineeringNegative-pressure wound therapy
The present invention relates to a negative pressure wound closure system and methods for using such a system. Preferred embodiments of the invention facilitate closure of the wound by preferentially contracting to provide for movement of the tissue. Preferred embodiments can utilize tissue grasping elements to apply a wound closing force to the tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
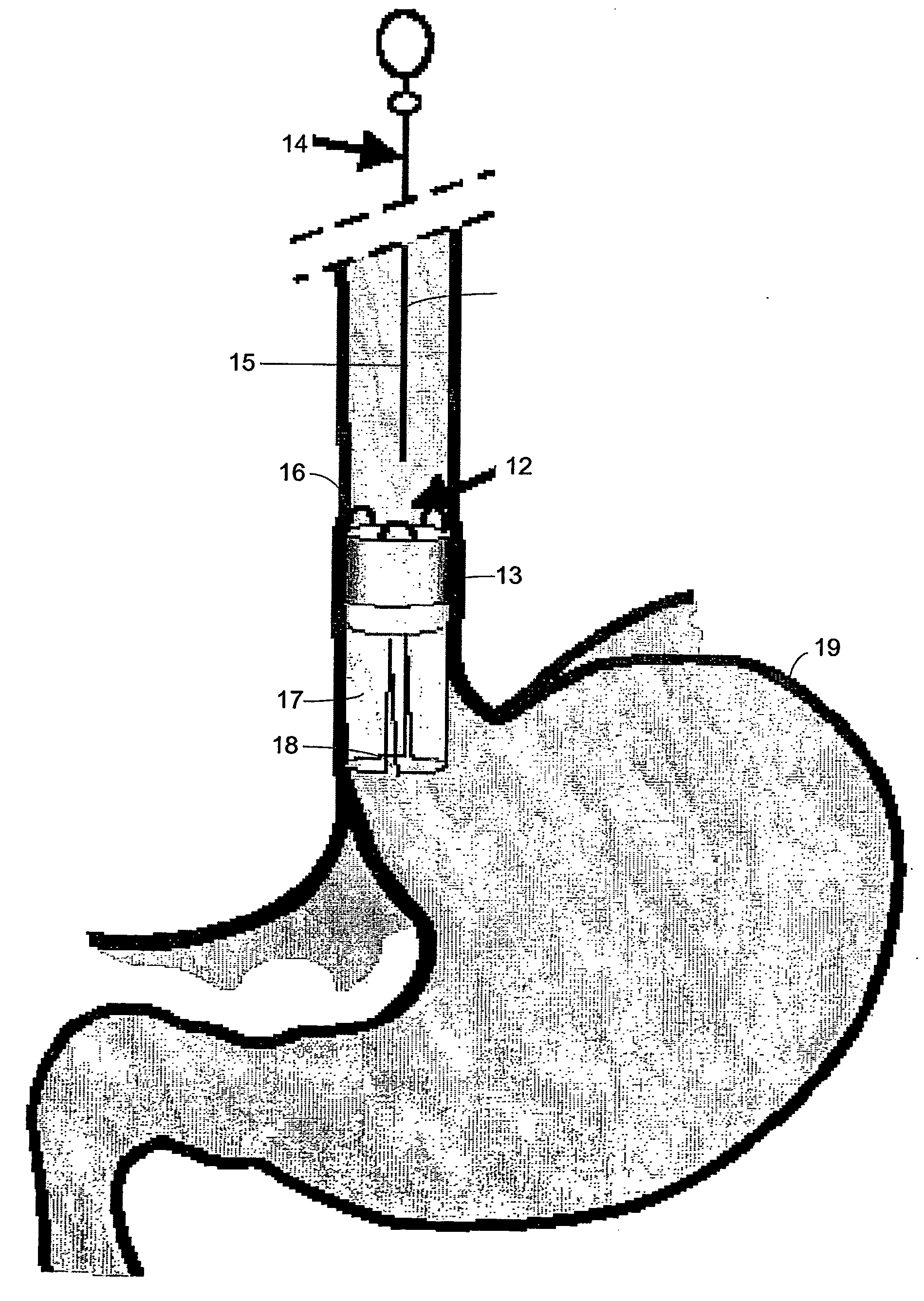
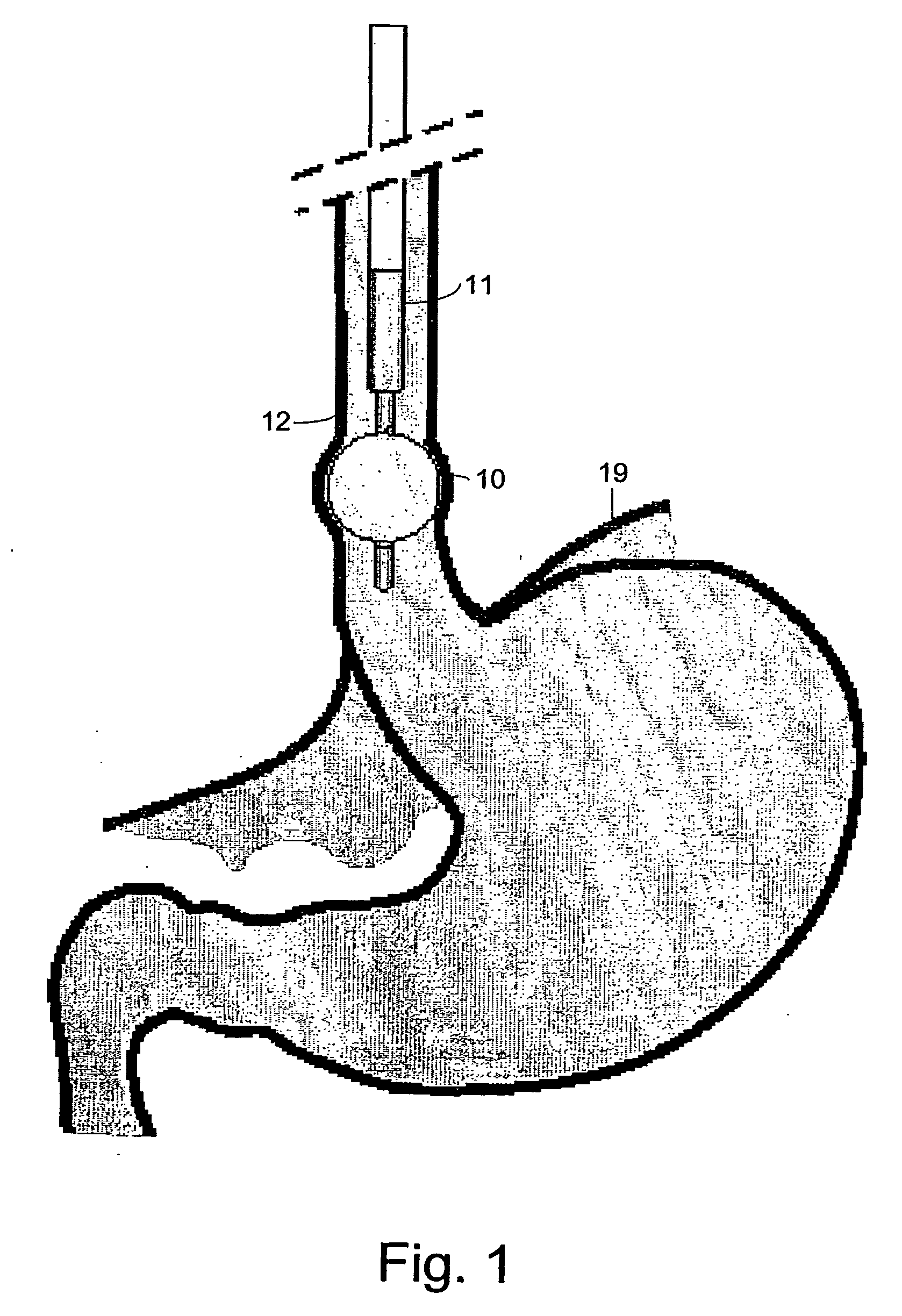
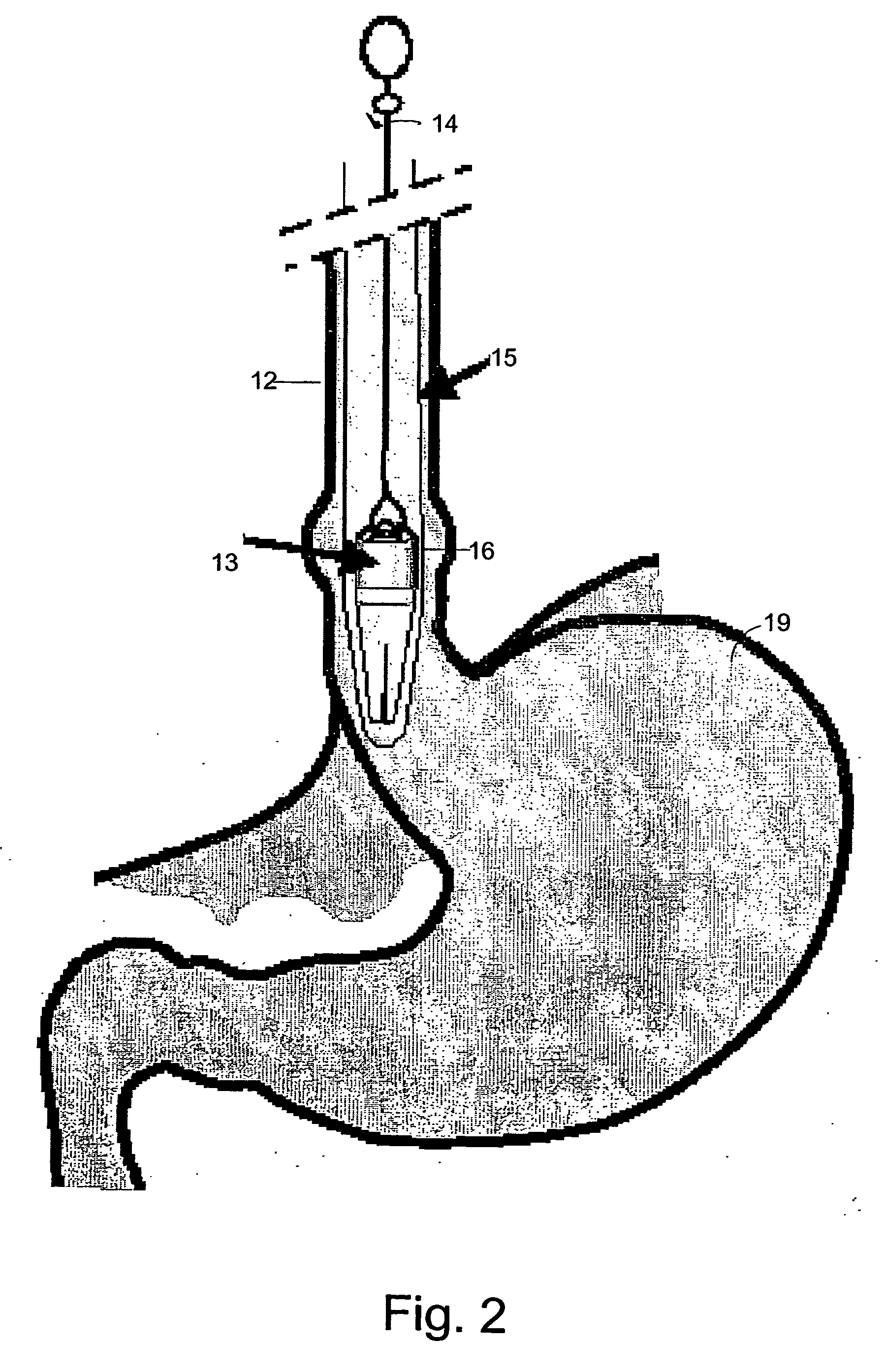
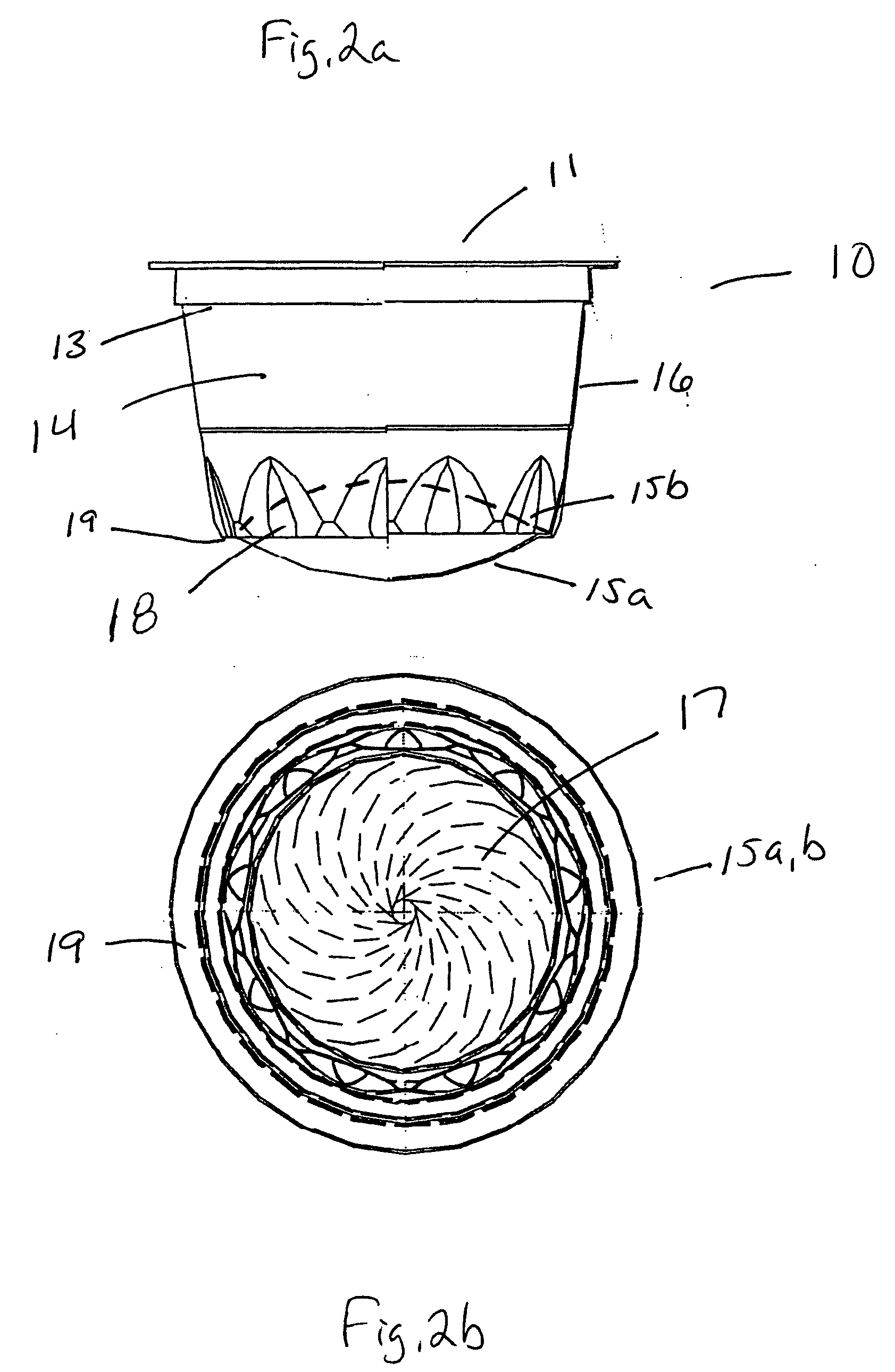
Gastrointestinal anti-reflux prosthesis apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070027549A1Prevent gastric refluxFacilitating inversionHeart valvesOesophagiGastric refluxProsthesis
A prosthesis (13) for implanting in an upper stomach to prevent gastric reflux in an esophagus comprising a tube (17) made of a biocompatible polymer that is resistant to gastric acid, the tube having an upper end and a lower end, a length, and a generally constant diameter along the entire length thereof, the upper end having means (16) for securing to the upper stomach, the lower end having at least one slit (18) to facilitate inversion of the tube during vomiting but to facilitate collapsing of the tube under pressure generated by gastric reflux.
Owner:GODIN NORMAN
Blood pump with expandable cannula
ActiveUS8535211B2Improve performanceMinimizing potential poolingBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesImpellerDrive shaft
A blood pump includes an impeller having a plurality of foldable blades and a cannula having a proximal portion with a fixed diameter, and a distal portion with an expandable diameter. The impeller can reside in the expandable portion of the cannula. The cannula has a collapsed condition for percutaneous delivery to a desired location within the body, and an expanded condition in which the impeller can rotate to pump blood. A flexible drive shaft can extend through the cannula for rotationally driving the impeller within the patient's body.
Owner:TC1 LLC +1
Heart valve prosthesis with collapsible valve and method of delivery thereof
ActiveUS20140214160A1Avoid flowPromote crashBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsCardiac valve prosthesisValve leaflet
A valve prosthesis is adapted to operate in conjunction with native heart valve leaflets. The prosthesis includes an annulus and a skirt extending from the annulus. The skirt may be configured to be positioned through a native heart valve annulus, and the skirt may be movable between an open configuration permitting blood flow through the skirt and a closed configuration blocking blood flow through the skirt in cooperation with opening and closing of the native heart valve leaflets.
Owner:MITRASSIST MEDICAL
Heart valve prosthesis with collapsible valve and method of delivery thereof
A valve prosthesis is adapted to operate in conjunction with native heart valve leaflets. The prosthesis includes an annulus and a skirt extending from the annulus. The skirt may be configured to be positioned through a native heart valve annulus, and the skirt may be movable between an open configuration permitting blood flow through the skirt and a closed configuration blocking blood flow through the skirt in cooperation with opening and closing of the native heart valve leaflets.
Owner:MITRASSIST MEDICAL
Negative pressure wound closure device
ActiveUS20140180225A1Easy to closeReduce needPlastersMedical devicesBiomedical engineeringNegative-pressure wound therapy
The present invention relates to a negative pressure wound closure system and methods for using such a system. Preferred embodiments of the invention facilitate closure of the wound by preferentially contracting to provide for movement of the tissue. Preferred embodiments can utilize tissue grasping elements to apply a wound closing force to the tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
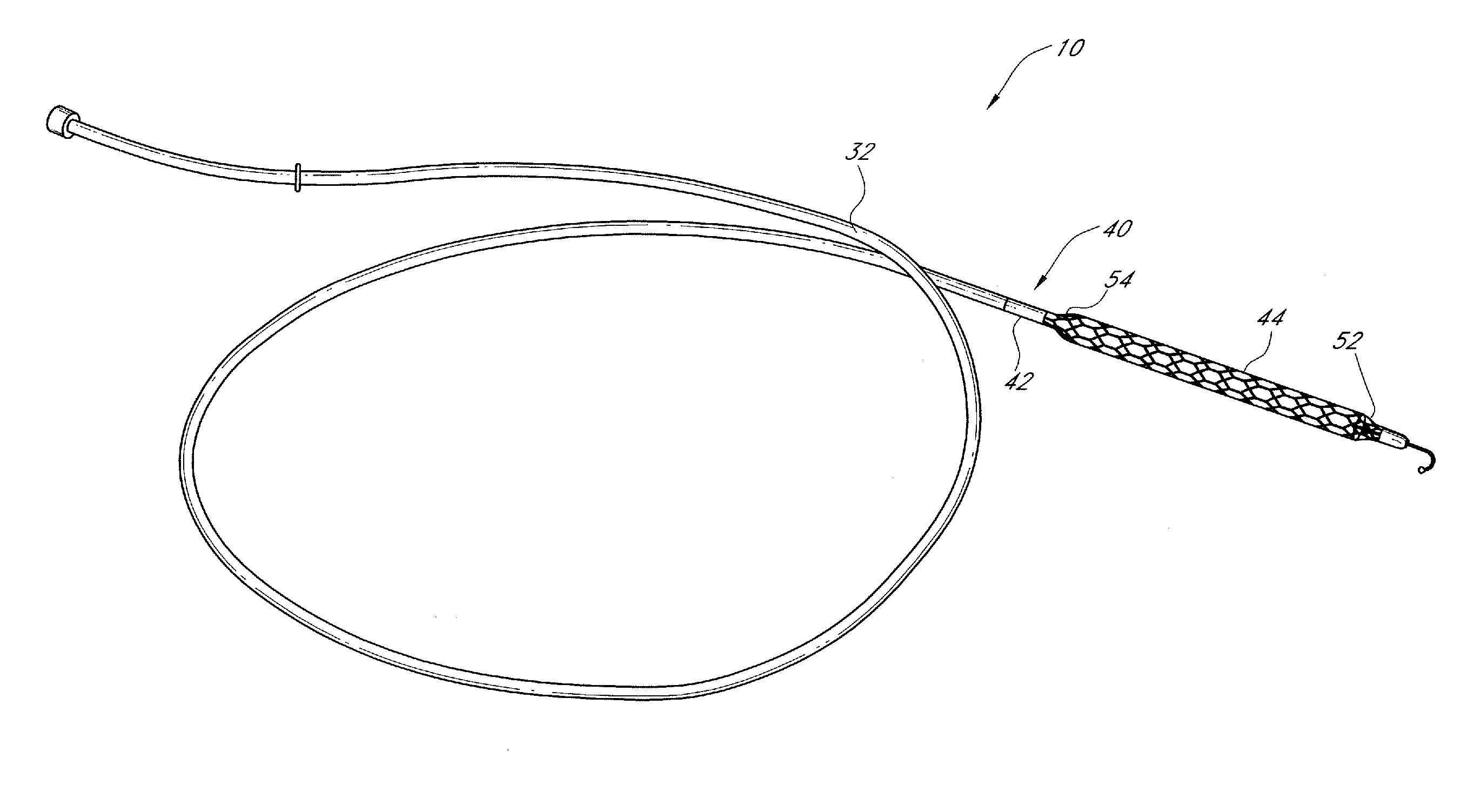
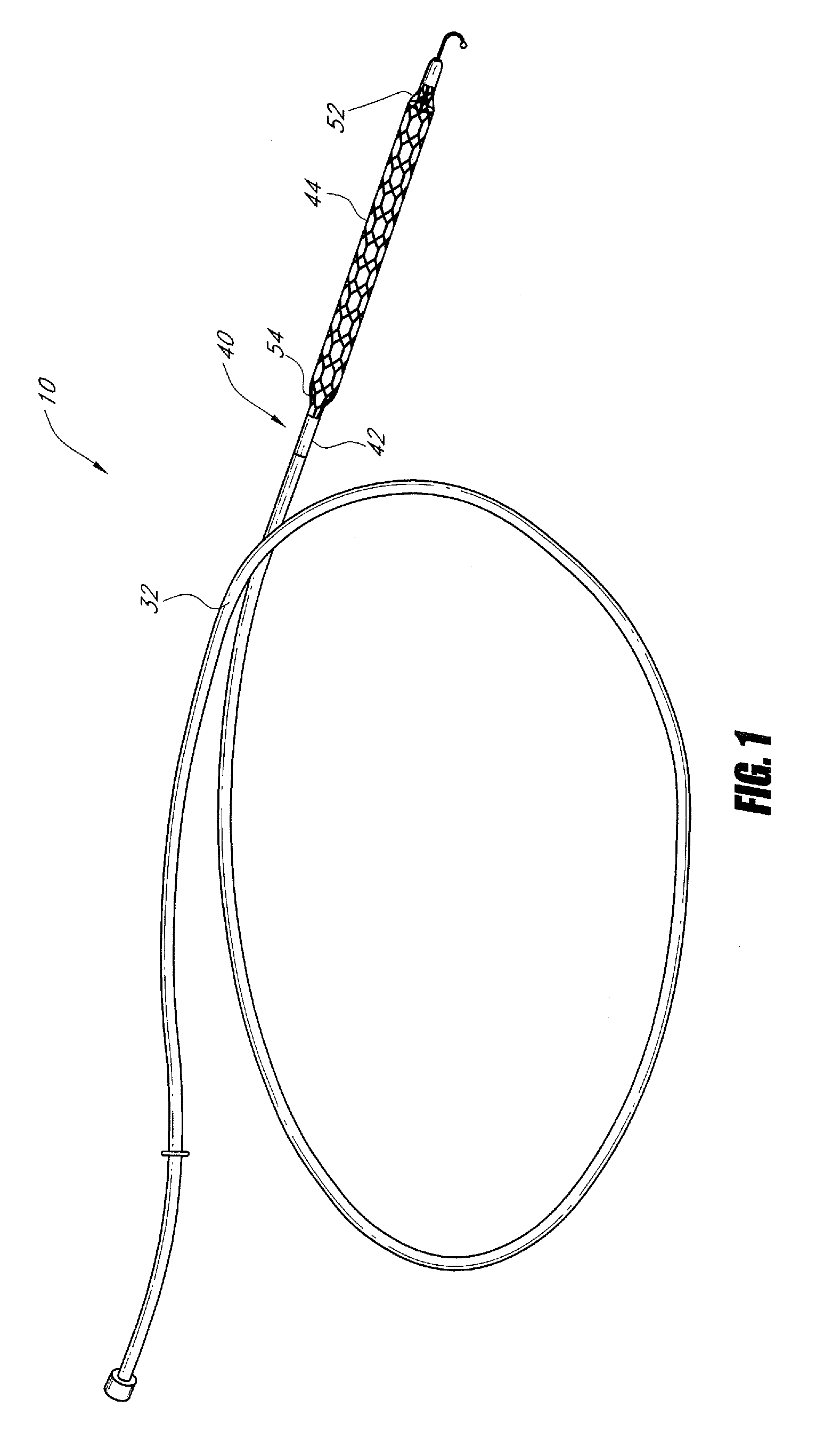
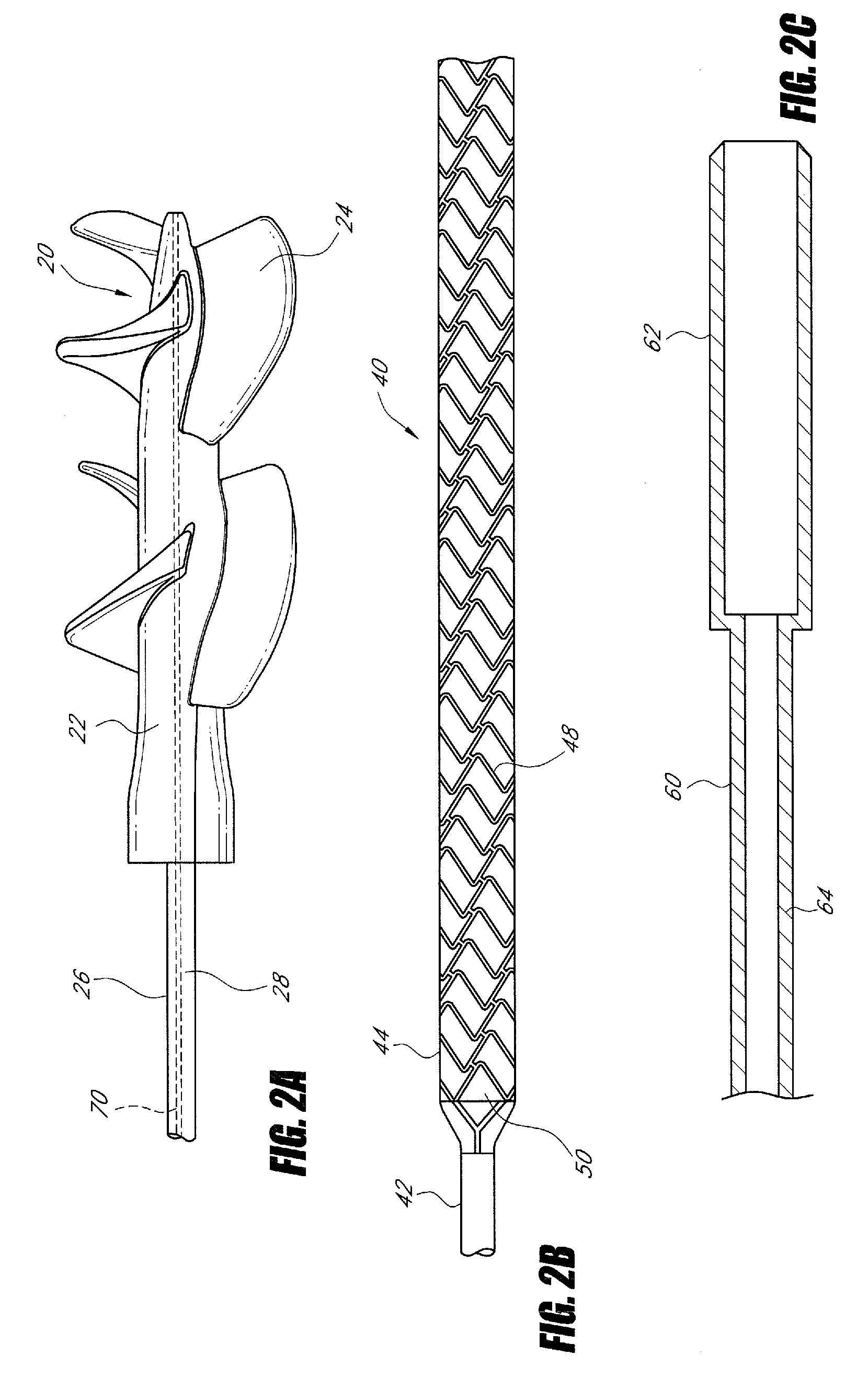
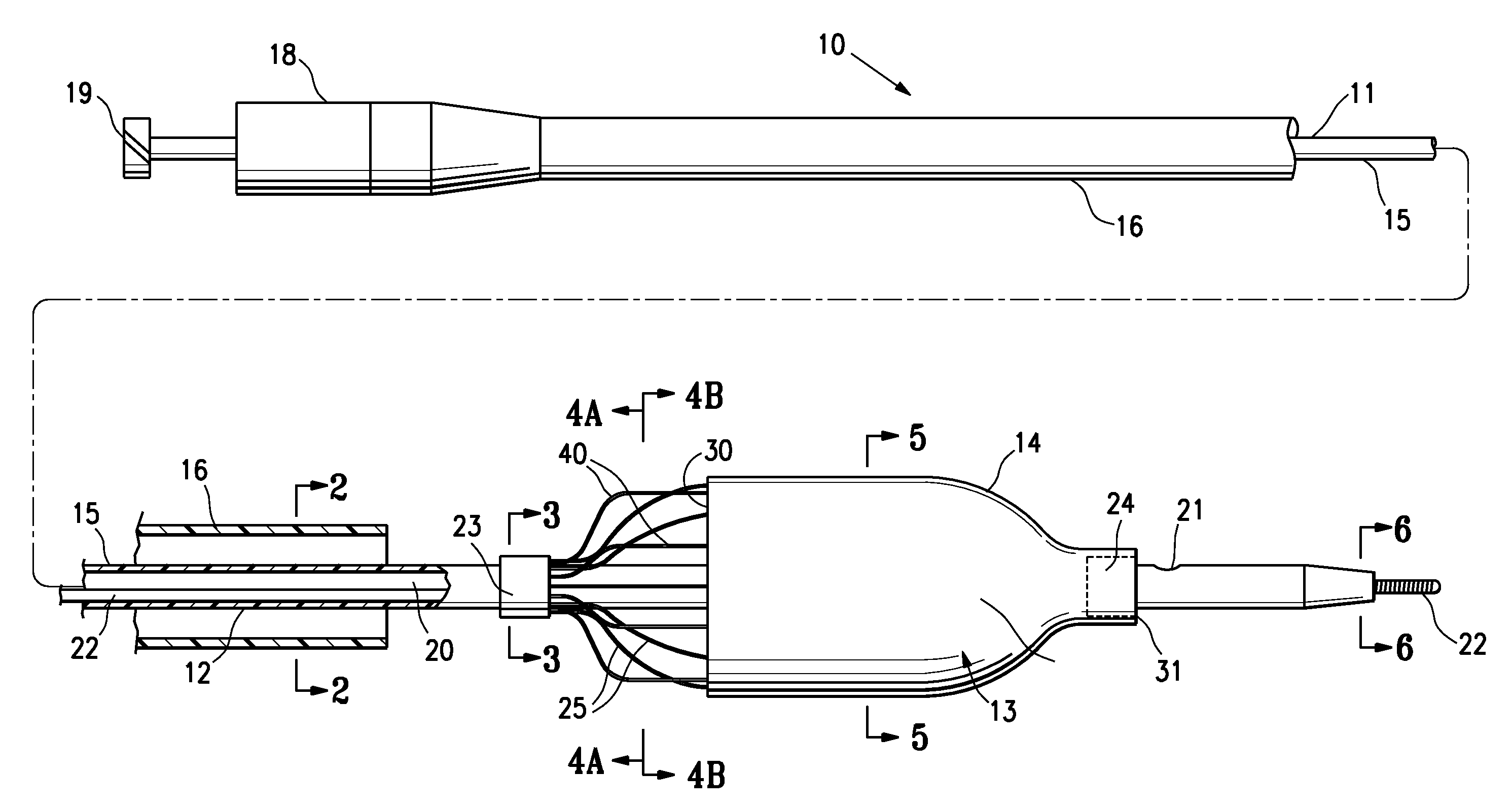
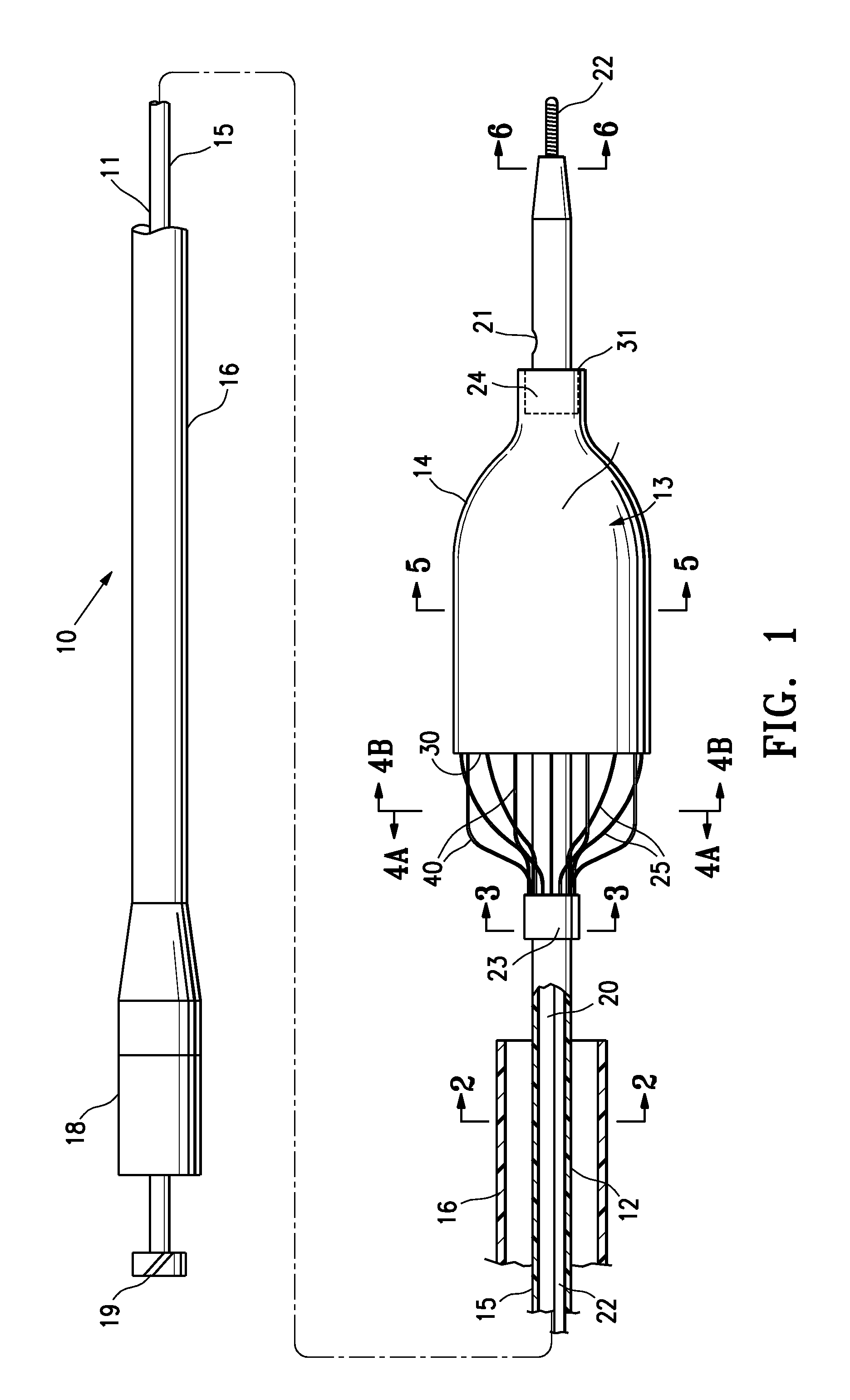
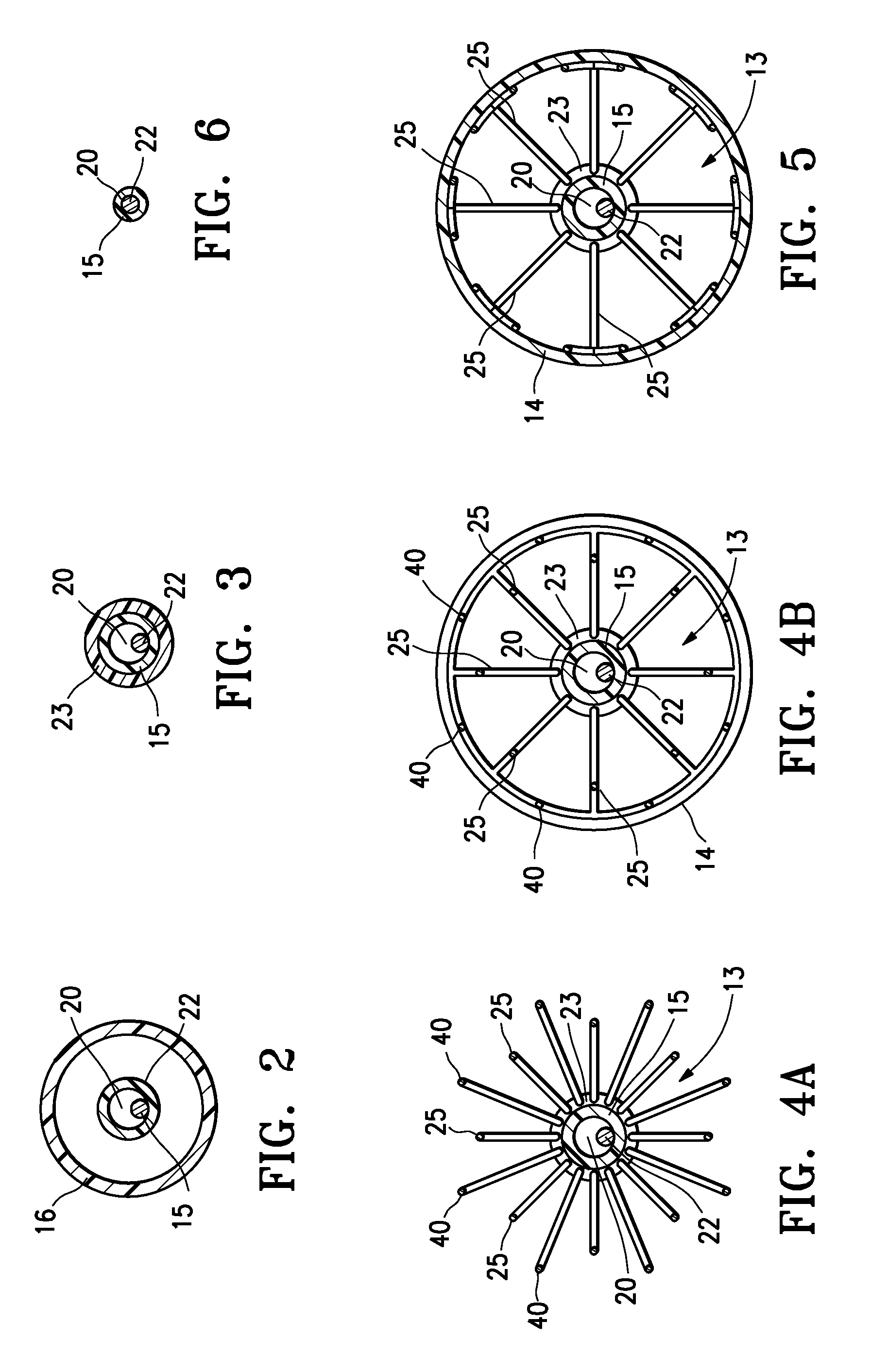
Integrated embolic protection devices
ActiveUS20130178891A1Promote resultsMinimization requirementsHeart valvesSurgeryDistal portionEmbolic Protection Devices
Embolic protection elements are integrated with a catheter or access sheath for any catheter. A catheter with an integrated embolic protection element comprises a catheter shaft, an embolic filter slidably mounted on a distal portion of the shaft, a proximal stop for limiting the proximal movement of the embolic filter, and a distal stop for limiting the distal movement of the embolic filter. The filter comprises a porous mesh material defining a collection chamber for captured emboli and has a collapsed and a deployed configuration. The filter may be collapsed by an access sheath used with the catheter. An access sheath may comprise a tubular main body and an embolic filter mounted on the distal portion of the tubular main body. The embolic filter may evert into the central lumen of the sheath or may be constrained on the exterior of the sheath with a larger diameter outer tube.
Owner:EMBOLINE
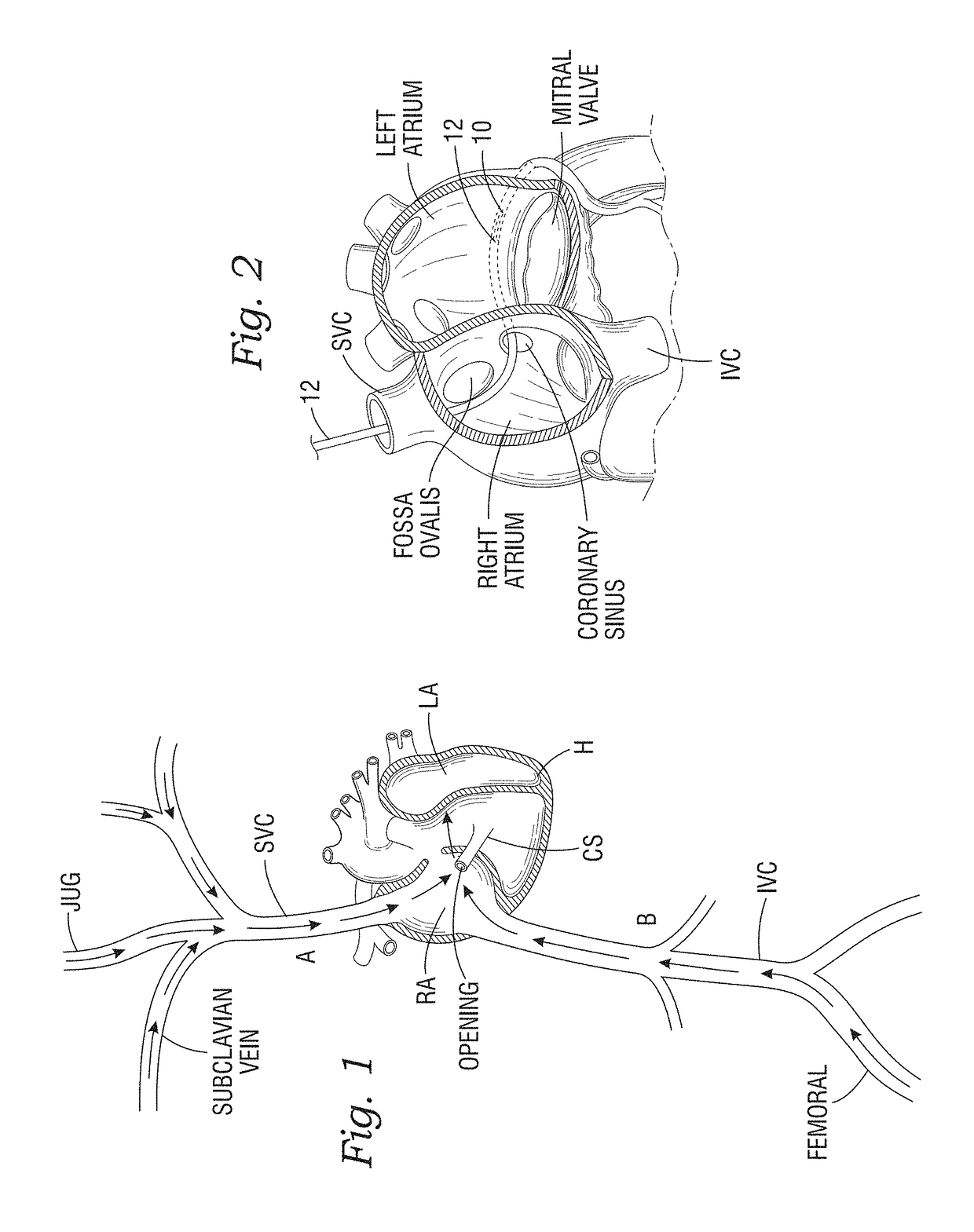
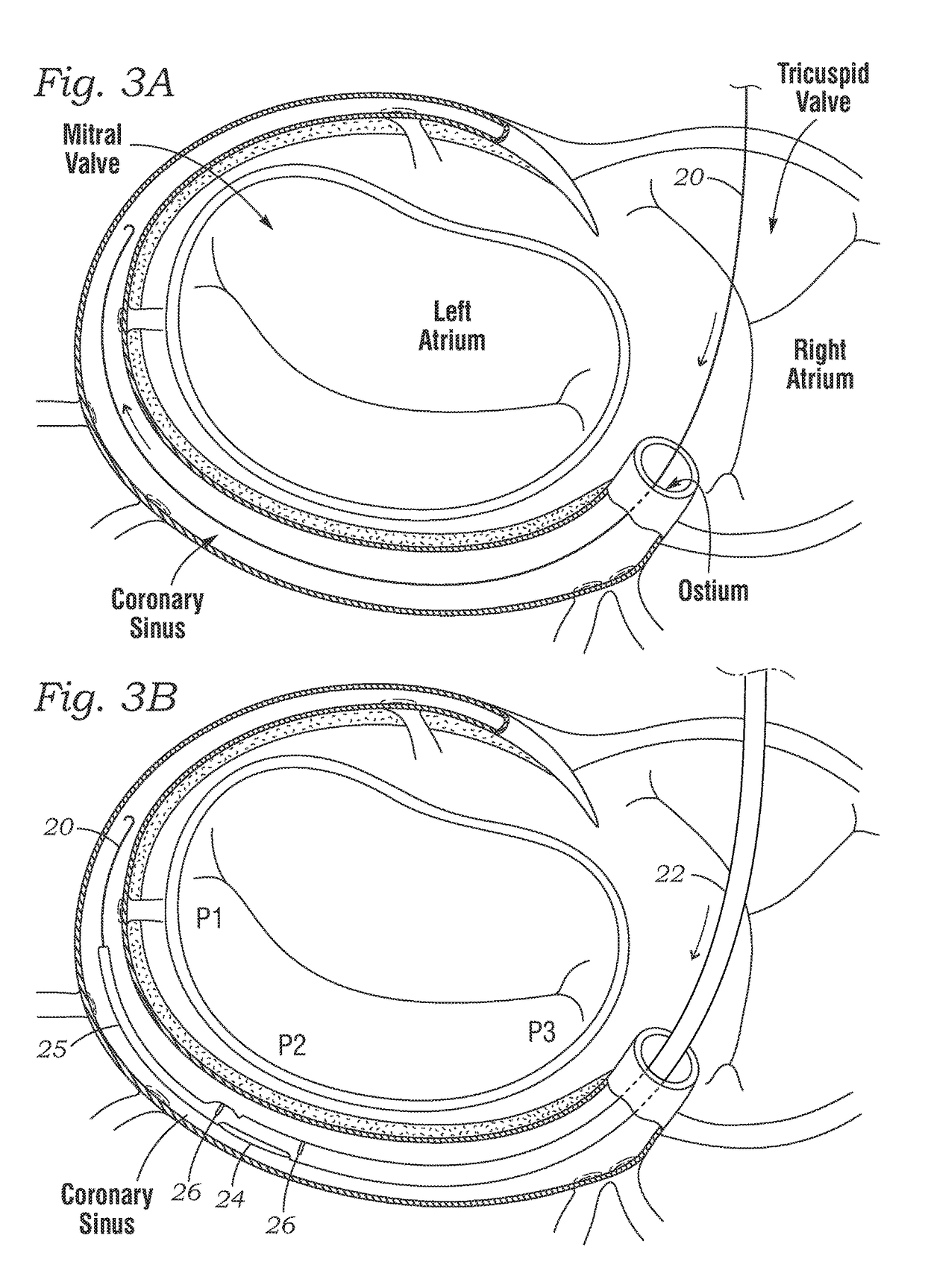
Expandable cardiac shunt
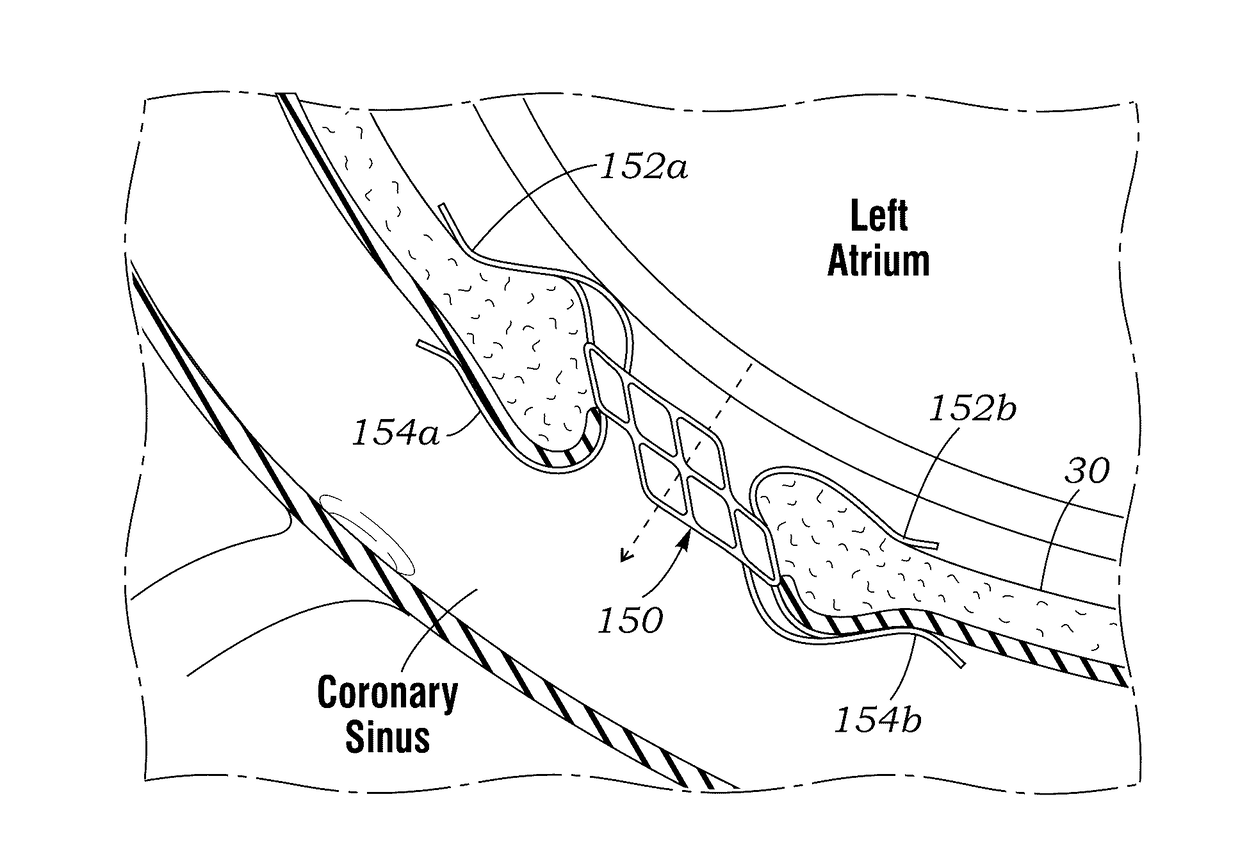
Disclosed are cardiac shunts and method of delivery, and in particular, to a shunt to reduce elevated left atrial pressure (LAP). The methods include forming a puncture hole between the left atrium and the coronary sinus, widening the puncture hole, and placing an expandable shunt within the widened puncture hole. A first catheter having a side-extending needle may be used to form a puncture into the left atrium. A second catheter extends along a guidewire and an expandable shunt with distal and proximal flanges is expelled therefrom into the puncture. The shunt defines a blood flow passage therethrough that permits shunting of blood from the left atrium to the coronary sinus when the LAP is elevated. The shunt is desirable formed of a super-elastic material and manipulated with control rods. The shunt defines a tilted flow tube that facilitates collapse into the catheter.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
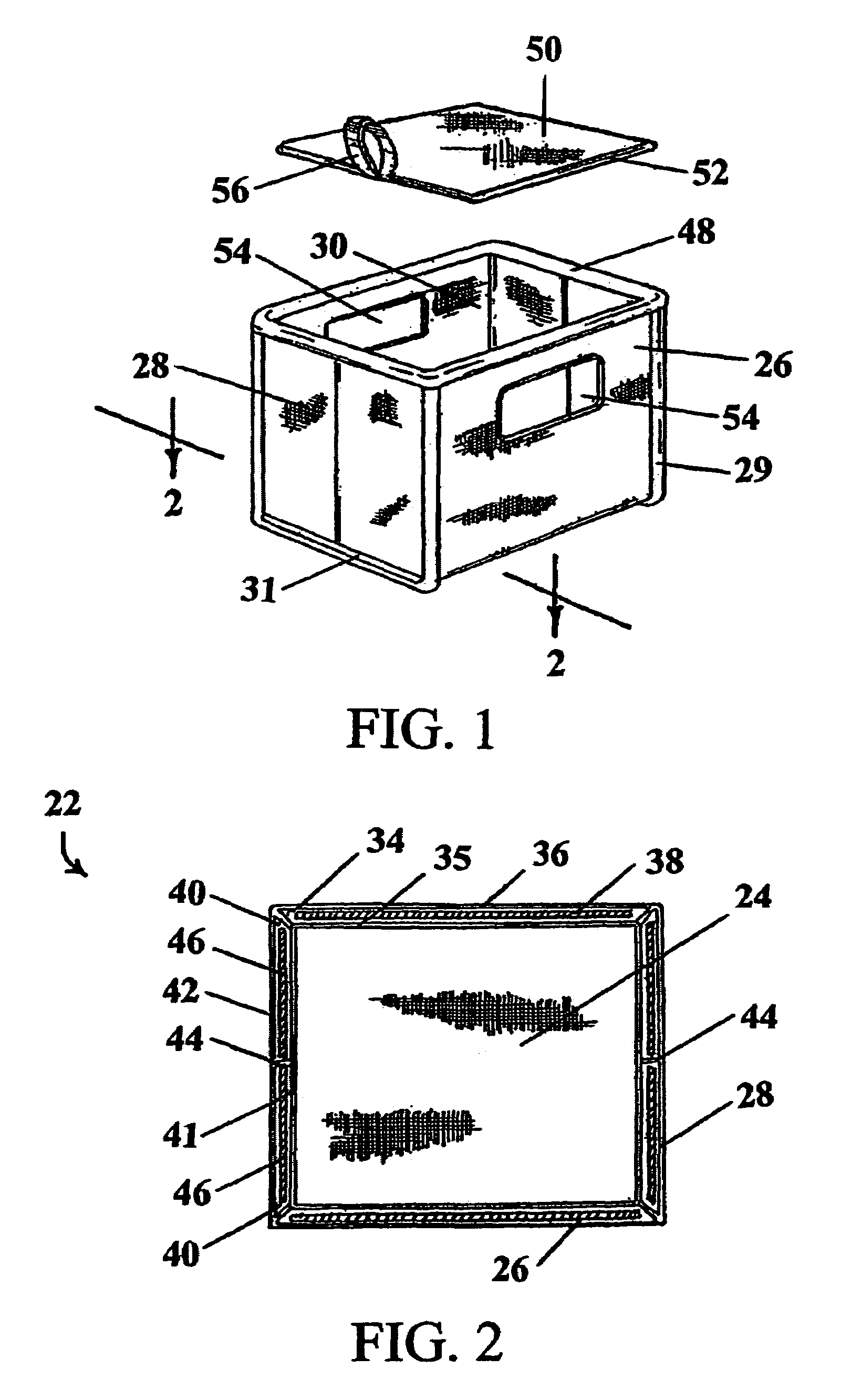
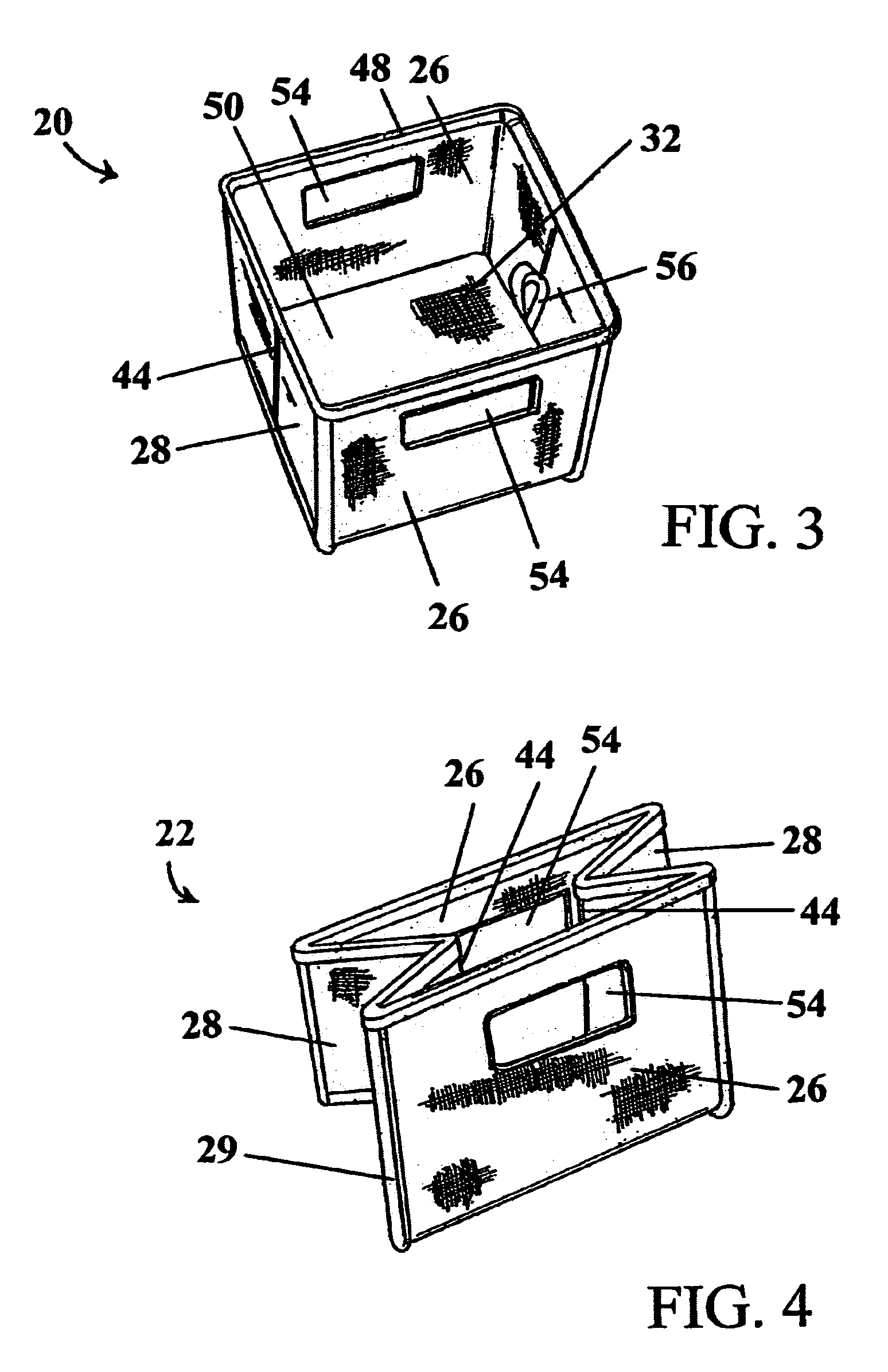
Tamper resistant seals for transparent or other egg cartons
InactiveUS20060060493A1Promote crashHigh mechanical strengthPackaging eggsContainers to prevent mechanical damageCartonEngineering
A tamper proof seal for egg cartons that is particularly suitable for transparent egg cartons is described The seal is typically located on the side rims of the tray and lid. The seal is comprised of first contact area on the tray rim and a second contact area on the lid rim. The first and second contact areas are mechanically engaged or bonded together to form a sealed area between the lid and the tray that prevents the lid from being opened from the tray. A tear-away section on the tray and lid rim surrounds the sealed area. The tear-away section allows the sealed area to be easily removed from the egg carton by tearing-away the sealed area from the rim thereby allowing the egg carton to be opened.
Owner:AARDEMA MARVIN RICHARD AARDEMA & JOHN CAMPHOUSE
Container for hot fill food packaging applications
A plastic container suitable for hot-fill food packaging applications is disclosed which is characterized by walls of proportionately decreasing thickness from the mouth of the container to a predetermined collapsible point. The wall thickness is designed such that the container walls will collapse, or deform, only at the collapsible point during cooling after hot-filling of food product or during transportation of the container between locations of varying altitudes and pressures. The container preferably collapses in the base area such that the collapse is not visible to the consumer and also the collapse does not affect stability of the container while in use or during loading and storage. The container of the invention is advantageous in that it requires less plastic material to form than other known hot-fill containers, and also can be formed out of any suitable food-grade plastic material or by any process.
Owner:PHOENIX CAPITAL
Intravascular medical device having a readily collapsible covered frame
InactiveUS20090105644A1Reduce deliveryExtended staySurgeryDilatorsMedical deviceIntravascular device
An elongated intravascular device having a frame configured for reversibly expanding in a patient's body lumen, which has a sleeve secured to the frame, and at least one sleeve-folding strut configured to fold the sleeve inwardly as the frame radially collapses in the patient's body lumen. Additional aspects of the invention are directed to methods of recovering such expanded frame type devices, and a recovery catheter configured for collapsing an expanded frame. The devices and methods of the invention facilitate the collapse of expanded frame devices, for repositioning or removal from the patient's body lumen.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
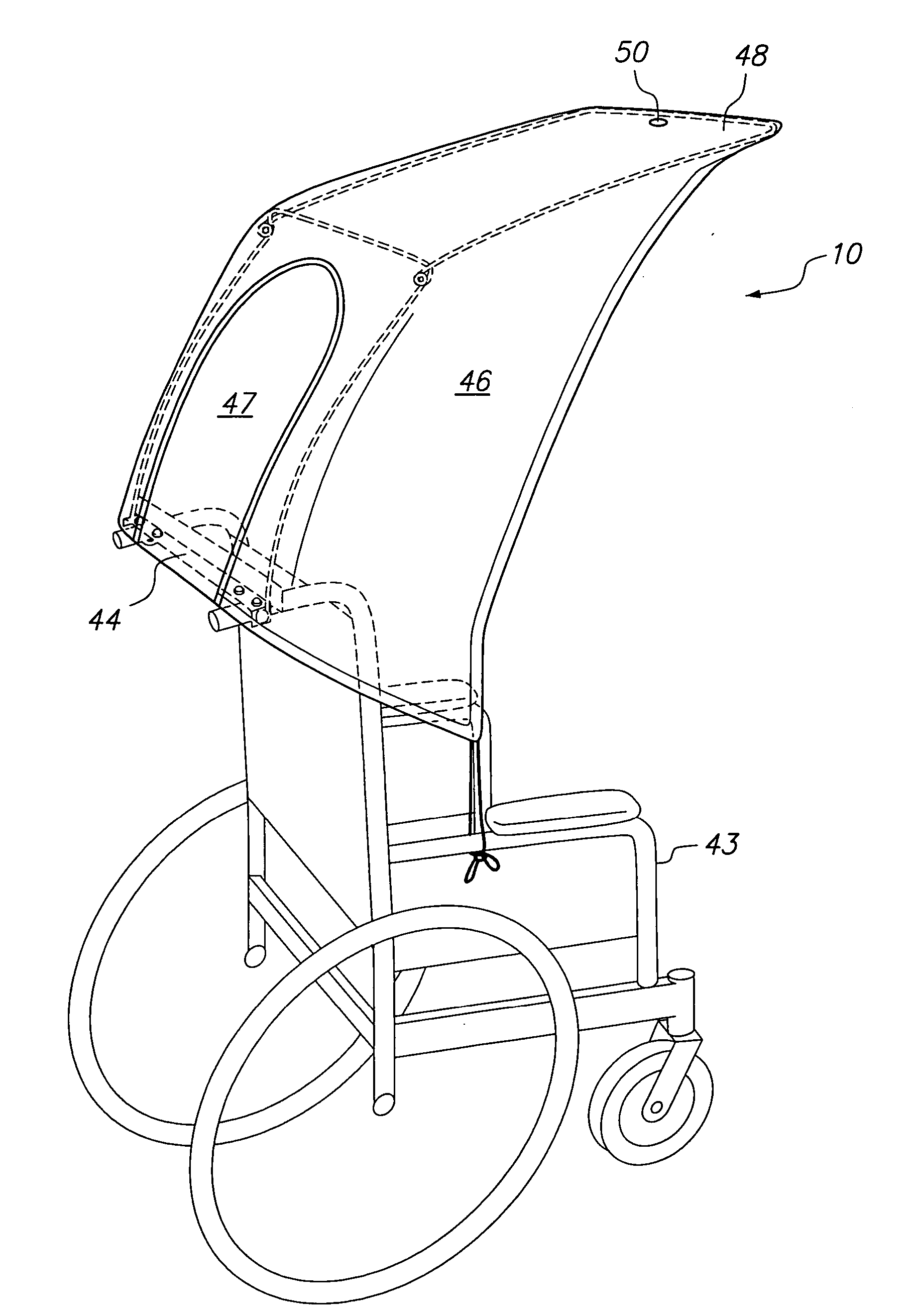
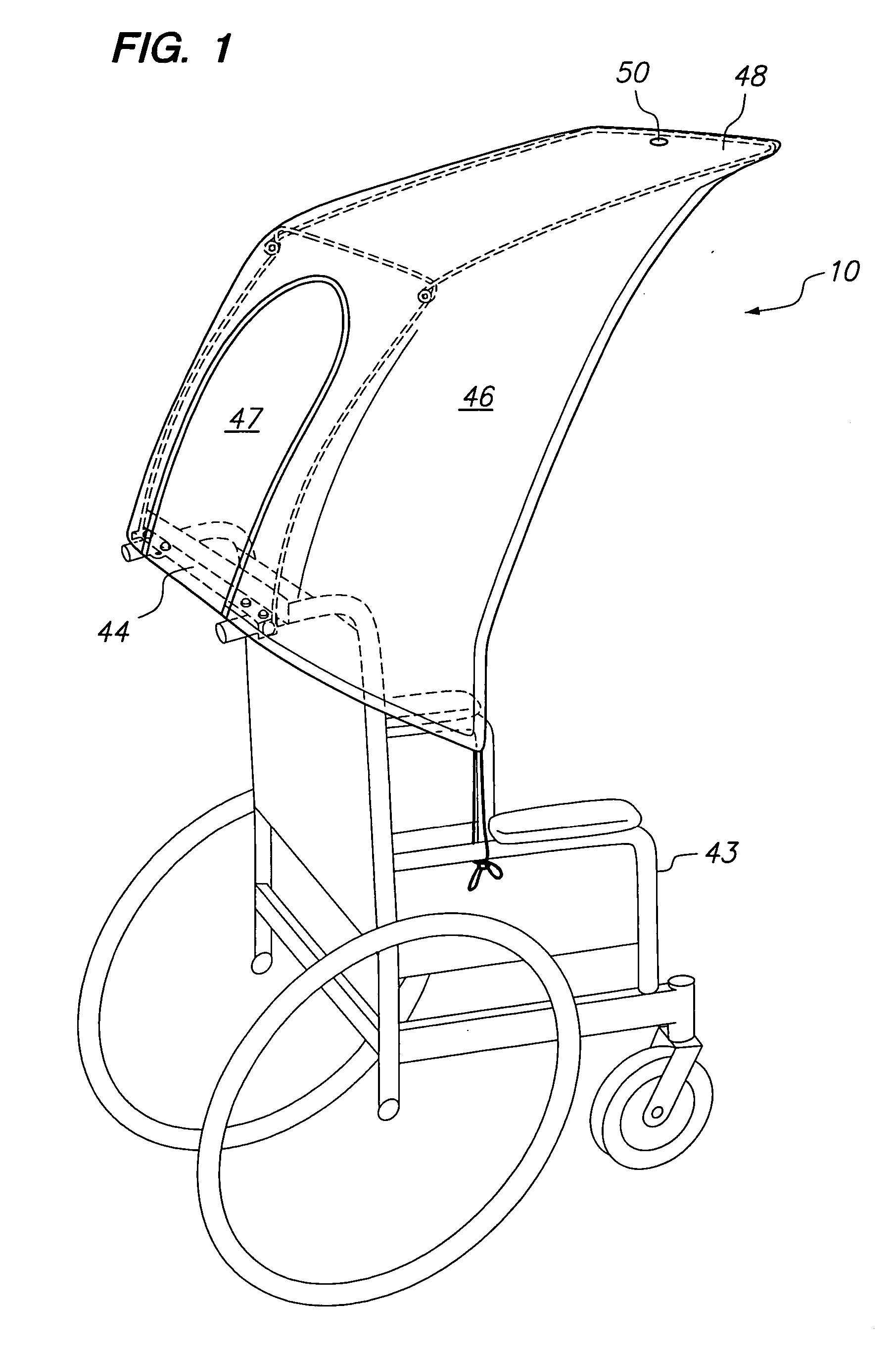
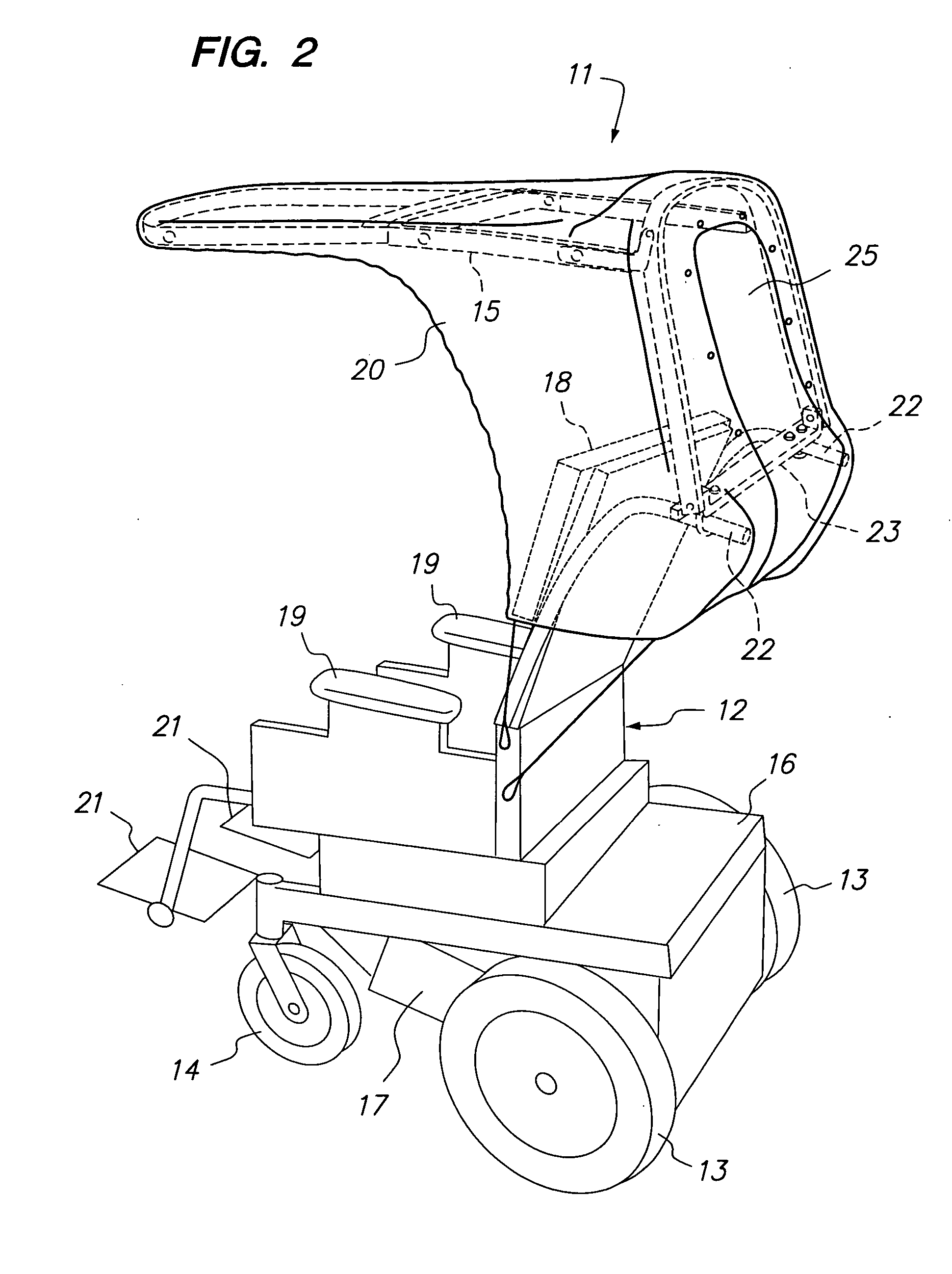
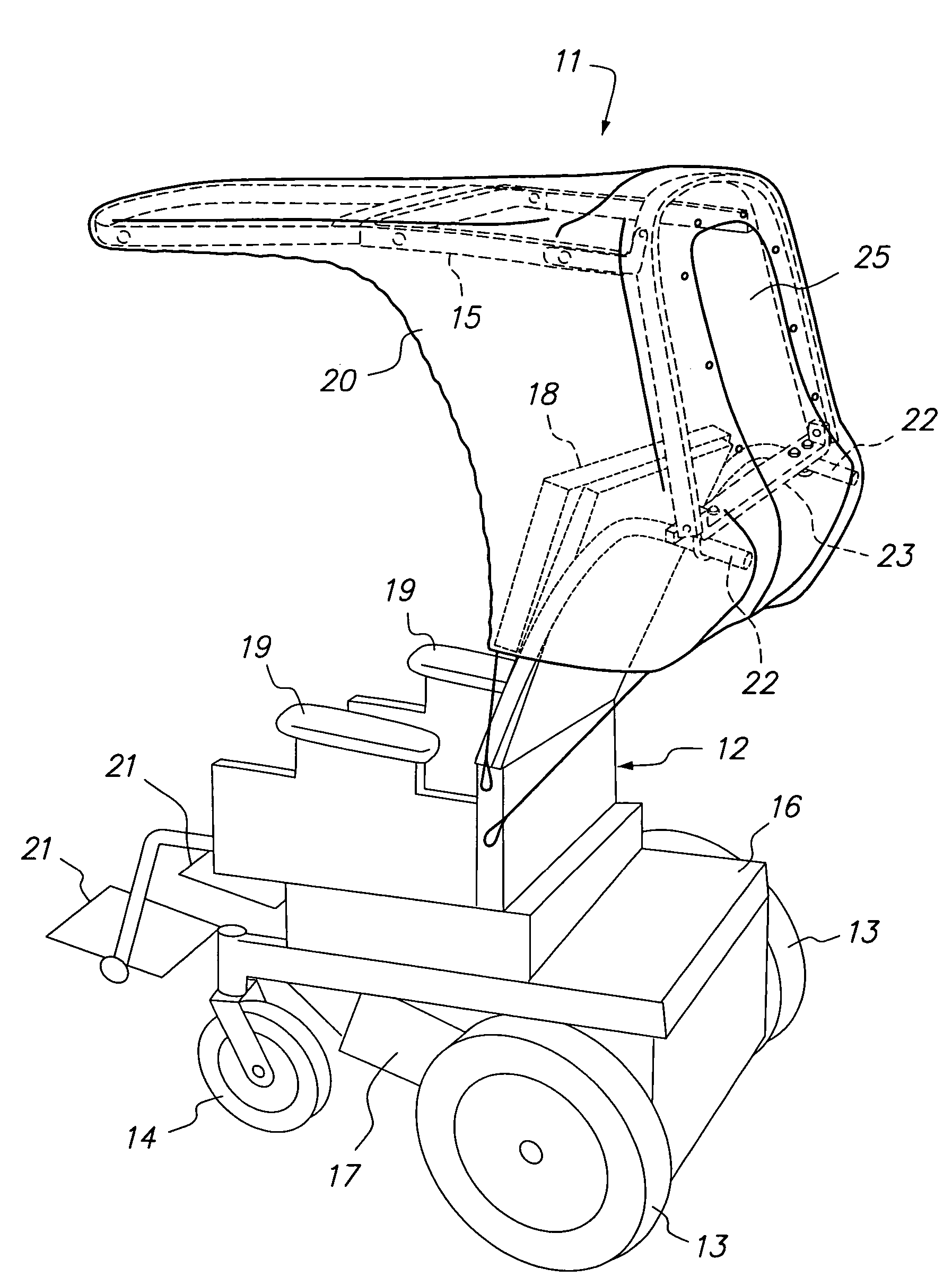
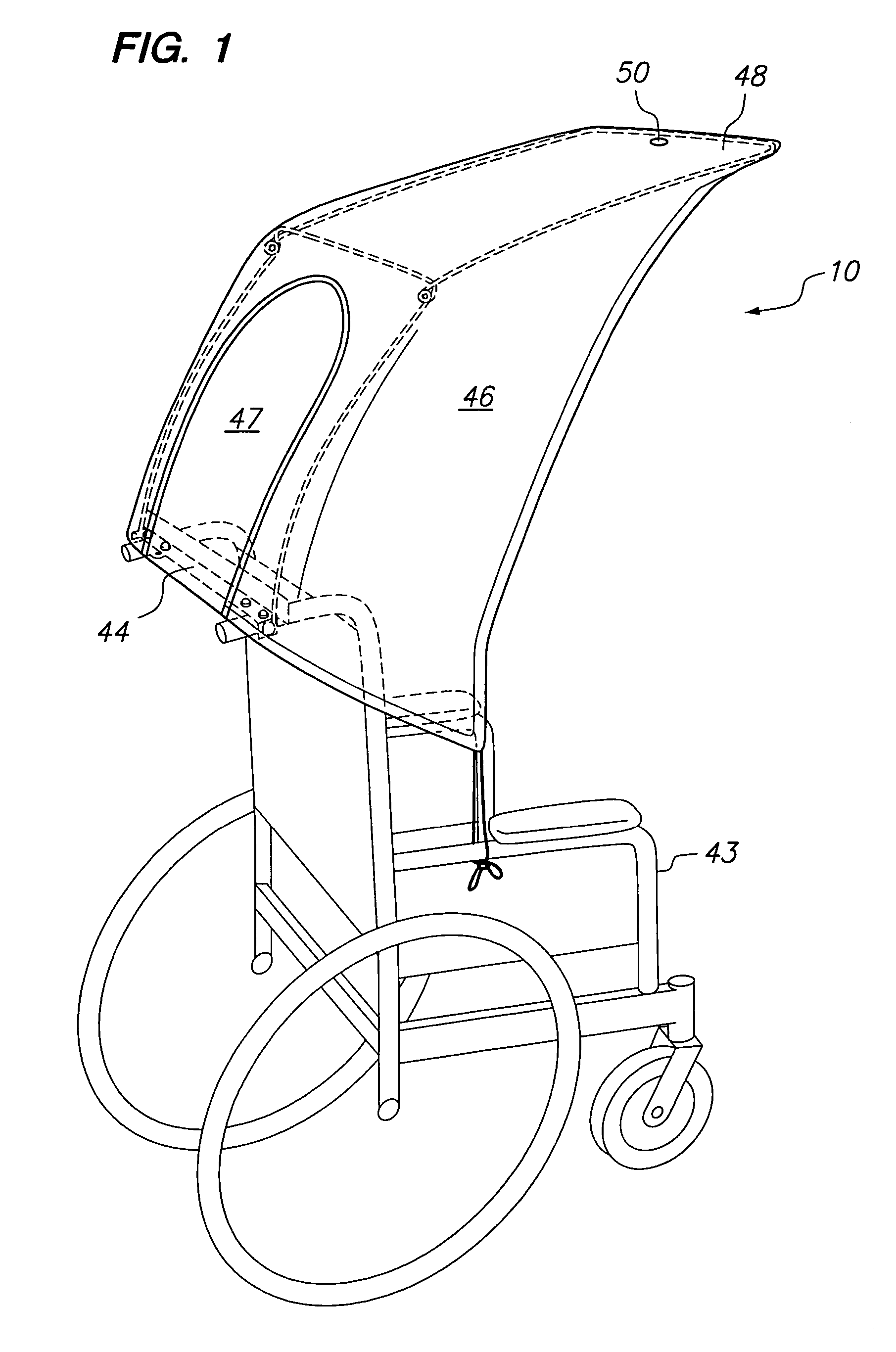
Foldable cover for the overhead protection of an occupant of a wheelchair or other wheeled vehicle
Two embodiments of a foldable cover for protecting the occupant of a wheelchair or other wheeled vehicle is described. The foldable cover includes a frame having two sections, a back section and a top section cantileverable from the back section over the normal space provided for an occupant. A mounting bar for rigidly mounting the back section and, hence, the remainder of the foldable cover is provided with both embodiments. The back section is pivotally connected to the mounting bar for pivoting movement between a stowed position in which such cover is out of the way of the occupant in a protected position in which it and the cantilevered top section cooperate to cover the occupant.
Owner:AYERS RONALD LEE +1
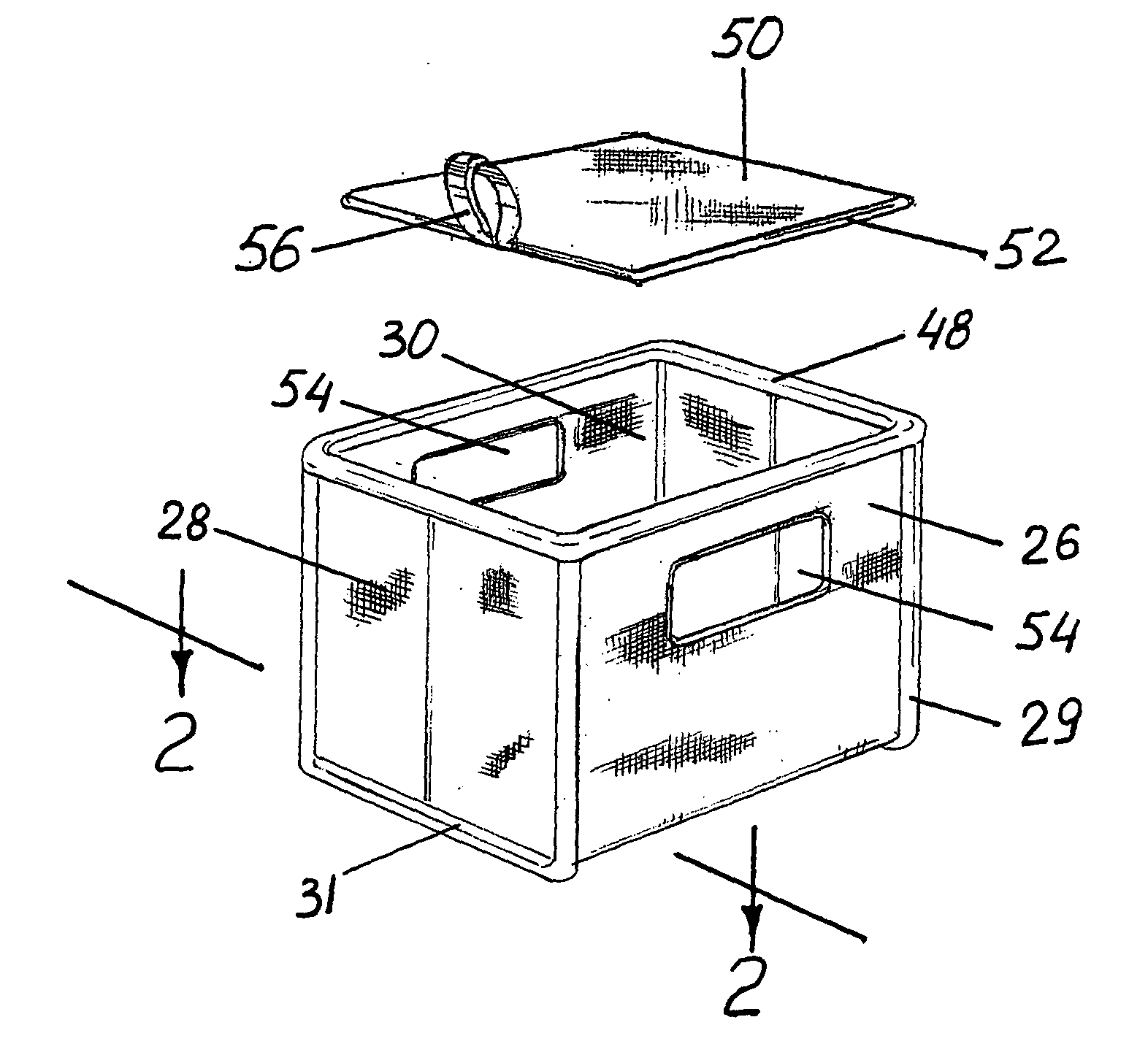
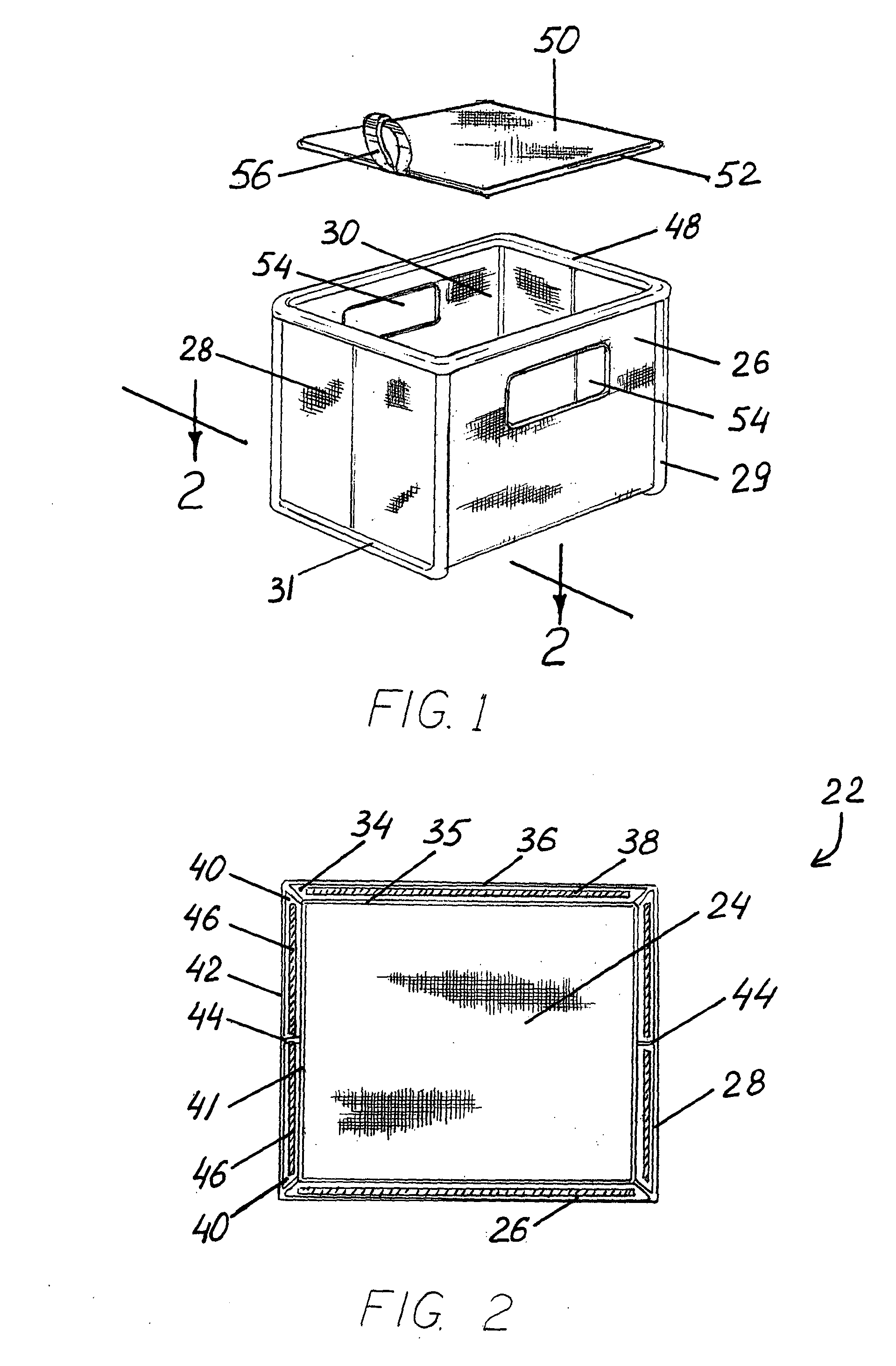
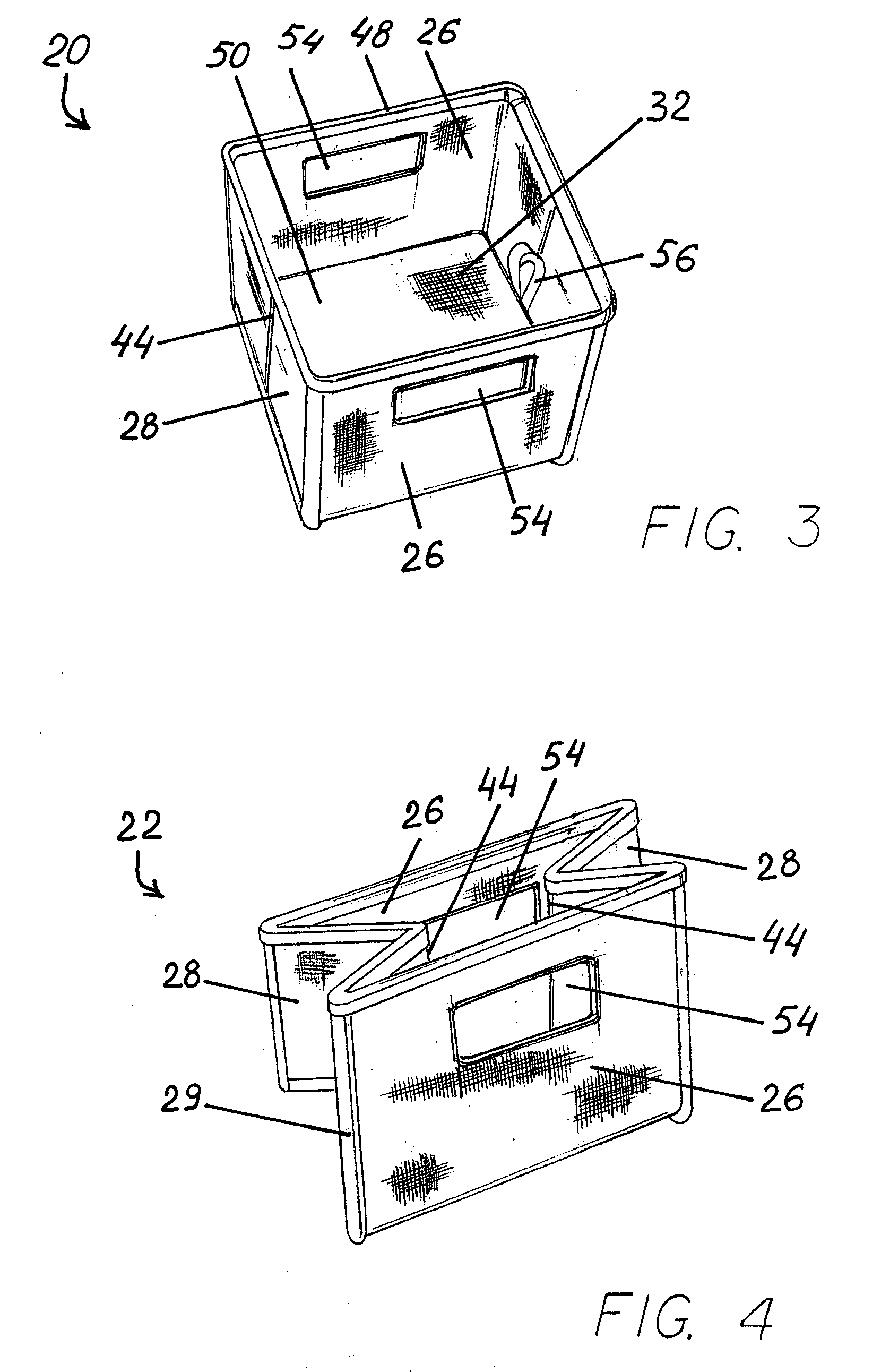
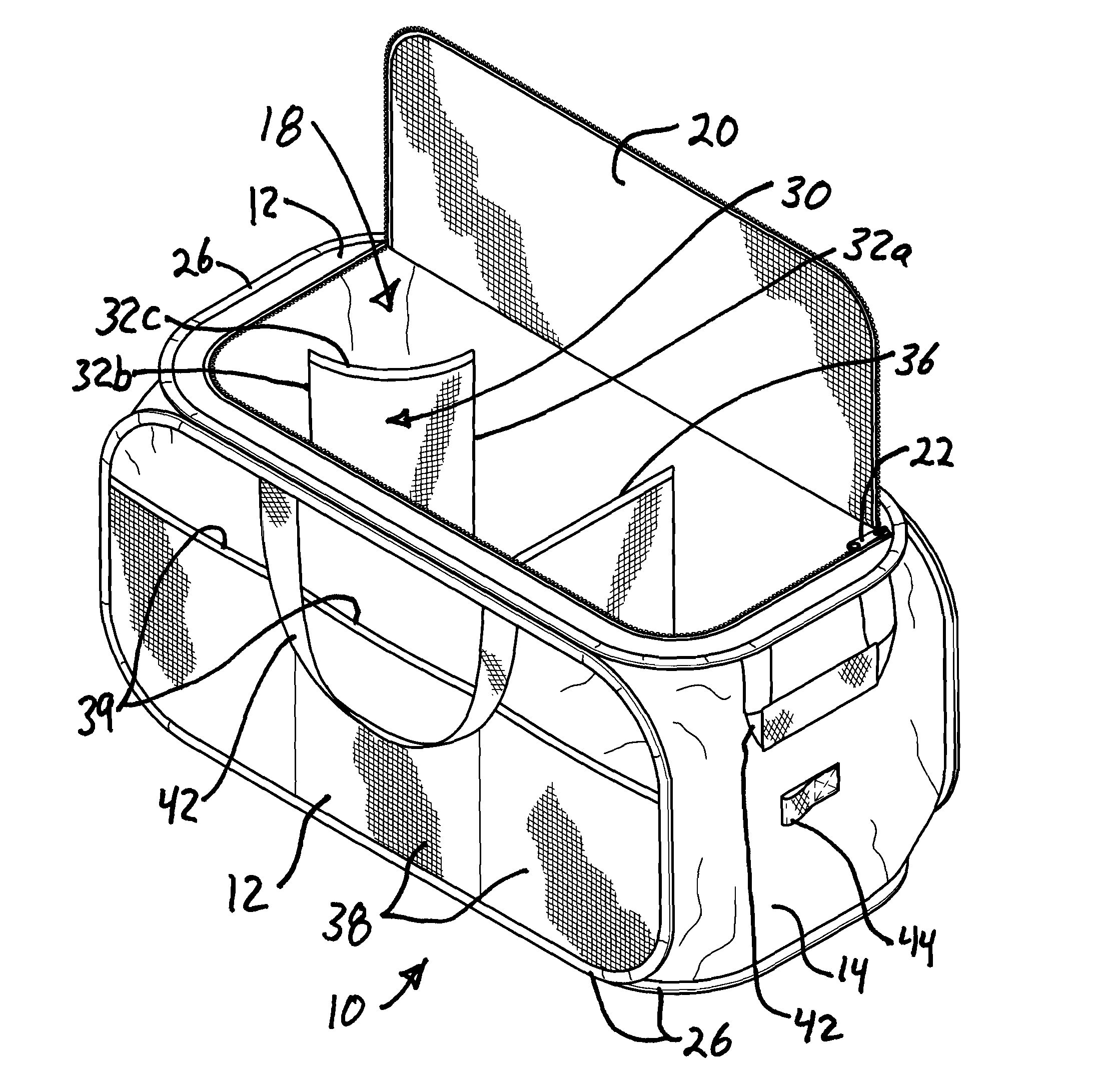
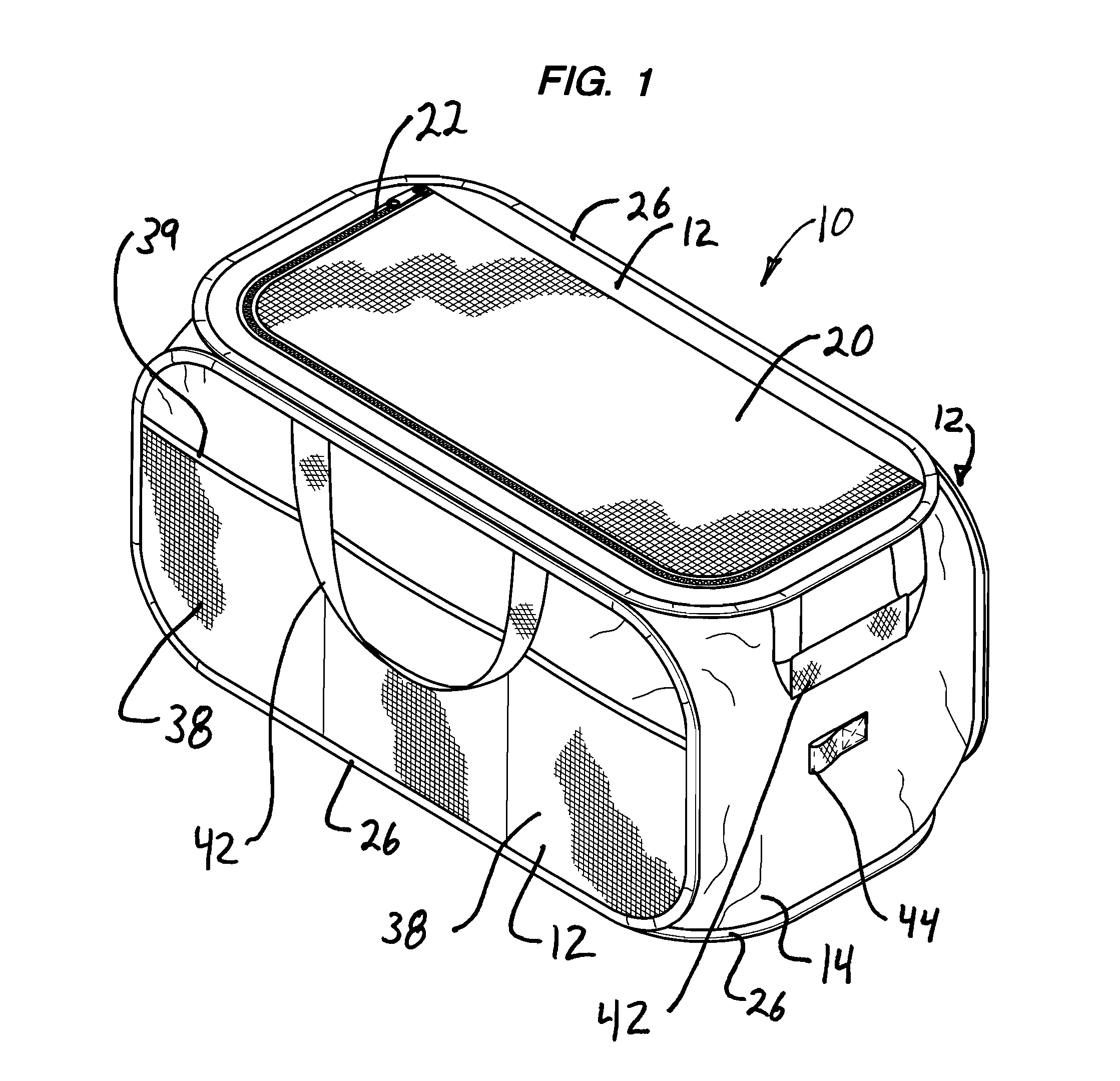
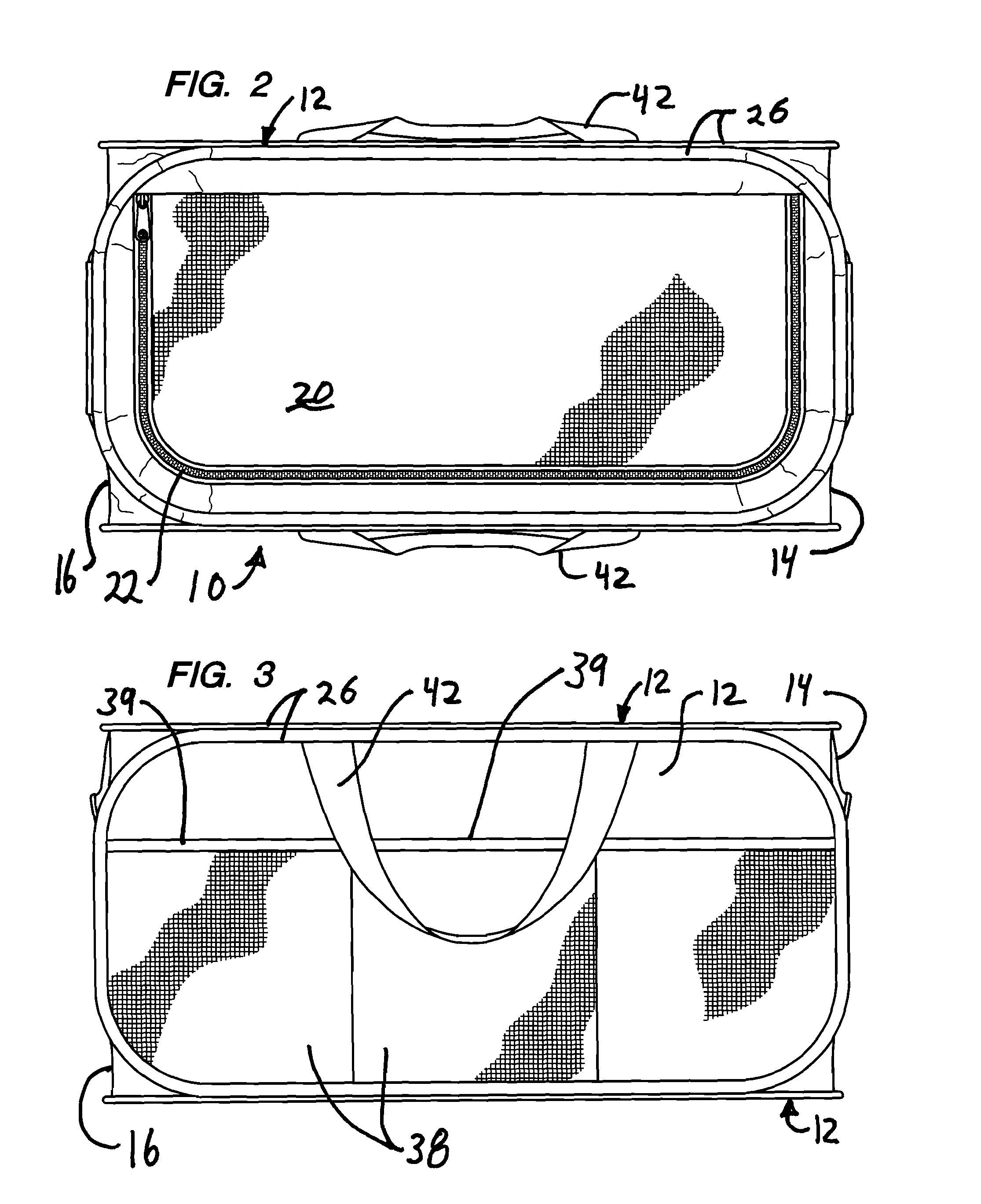
Soft storage bin
Owner:SOURCING SOLUTIONS
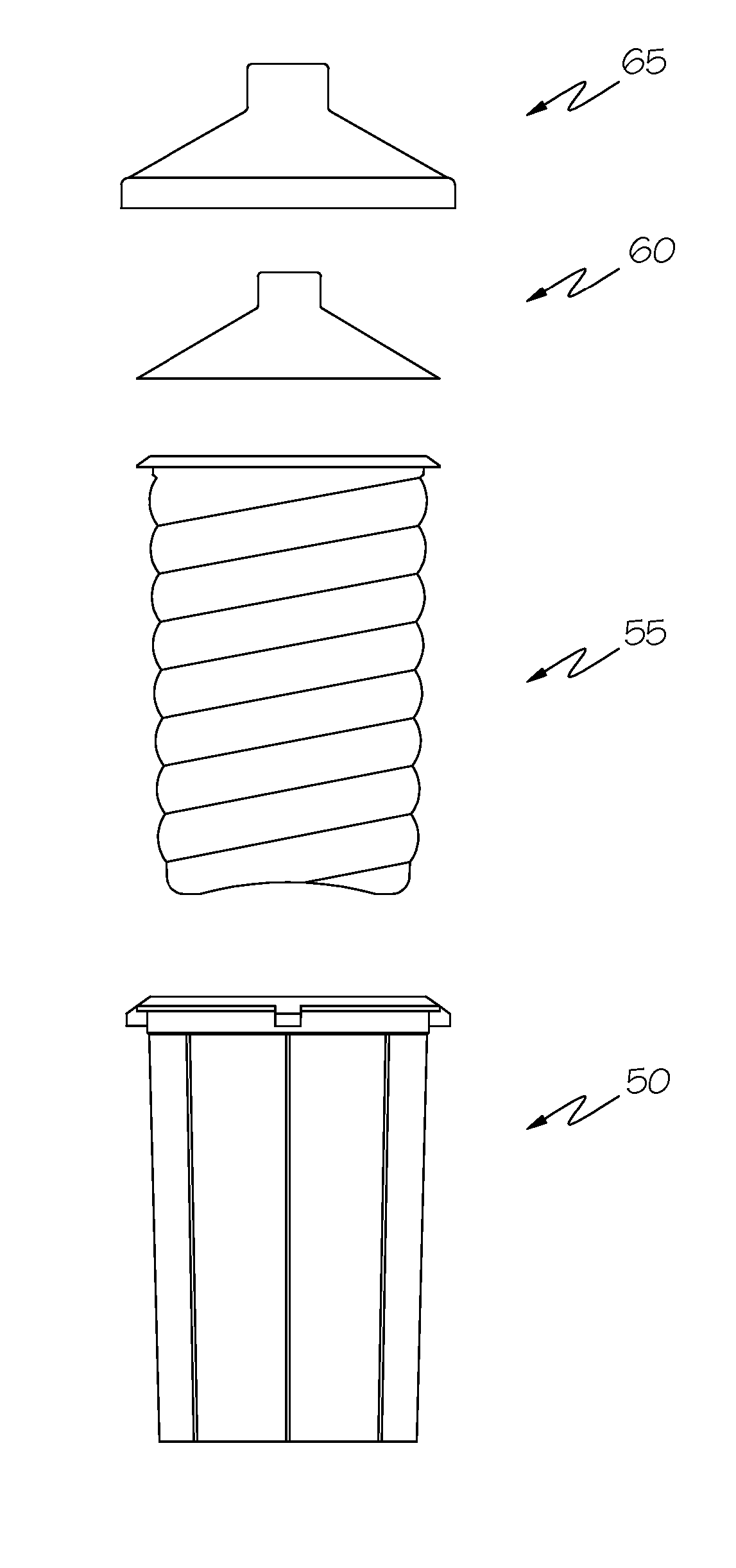
Fluid supply assembly
InactiveUS7380680B2Promote crashLarge containersSingle-unit apparatusDisposable cupBiomedical engineering
A fluid supply assembly. The fluid supply assembly includes a disposable cup and lid, and a reusable shell and outer lid. A flexible, disposable cup, a reusable shell, and a method of preparing a fluid supply assembly for use with a fluid supply applicator are also described.
Owner:CARLISLE FLUID TECH INC
Negative pressure wound closure device
ActiveUS9421132B2Easy to closeReduce needPlastersMedical devicesBiomedical engineeringNegative-pressure wound therapy
The present invention relates to a negative pressure wound closure system and methods for using such a system. Preferred embodiments of the invention facilitate closure of the wound by preferentially contracting to provide for movement of the tissue. Preferred embodiments can utilize tissue grasping elements to apply a wound closing force to the tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
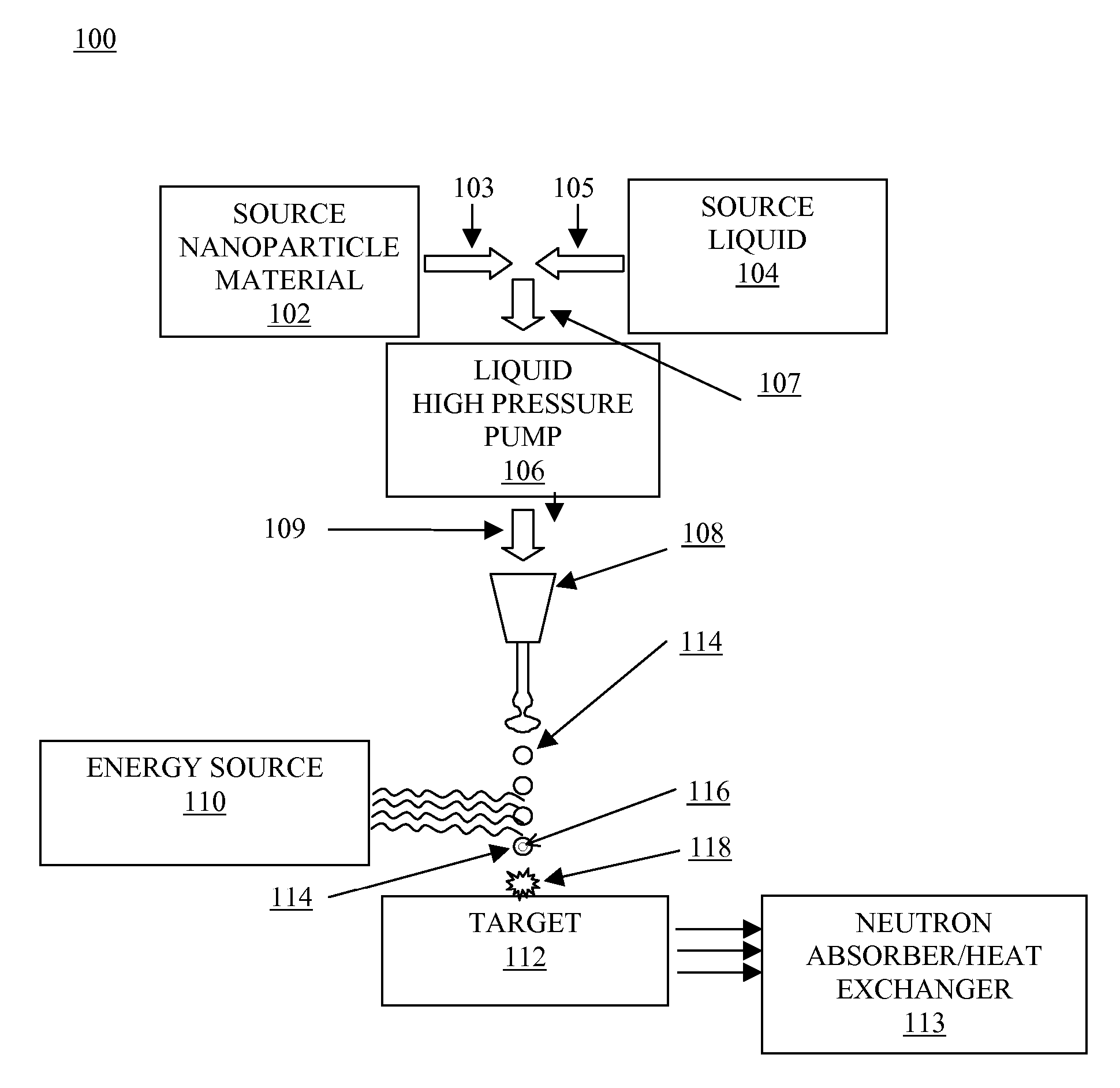
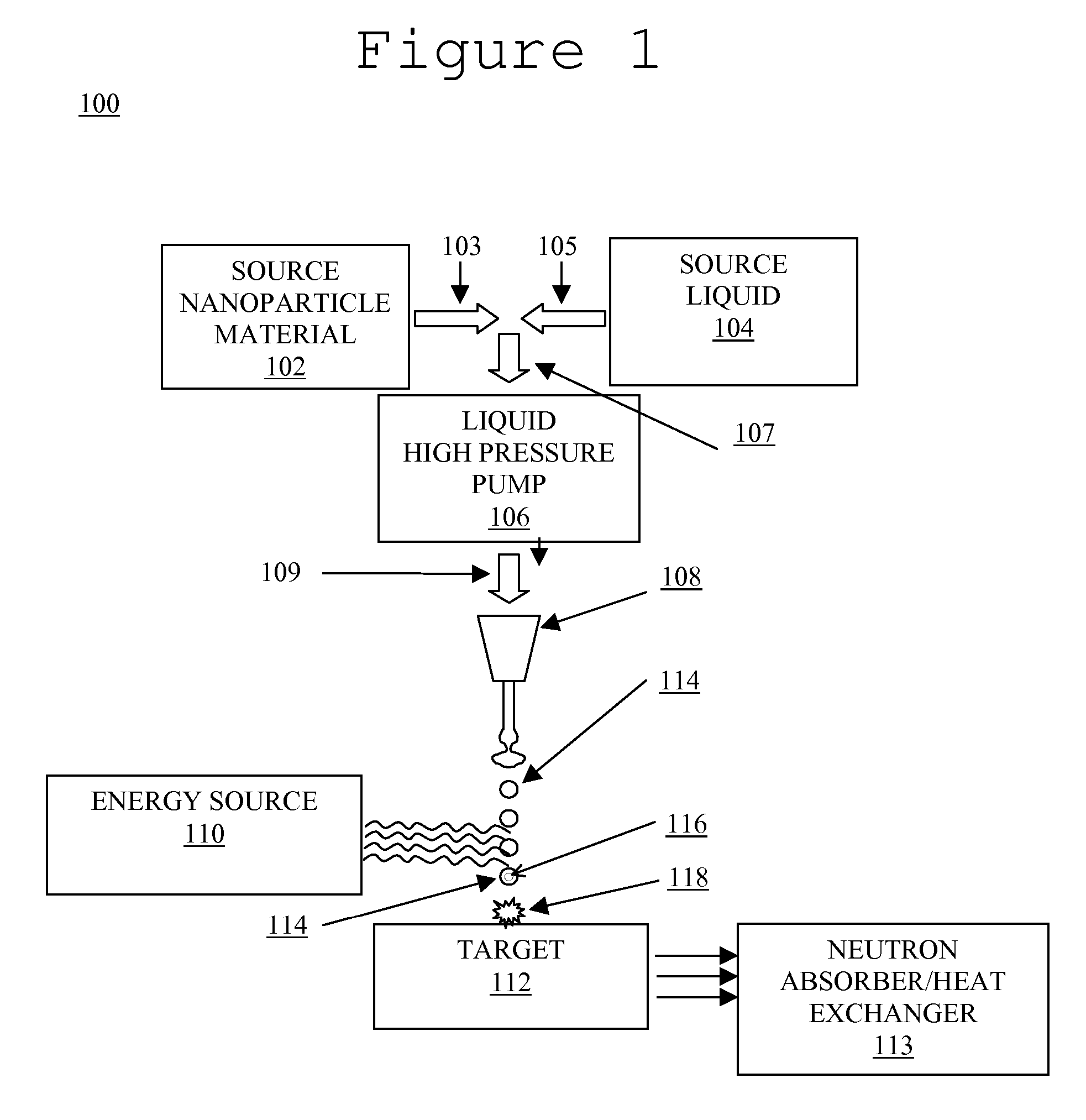
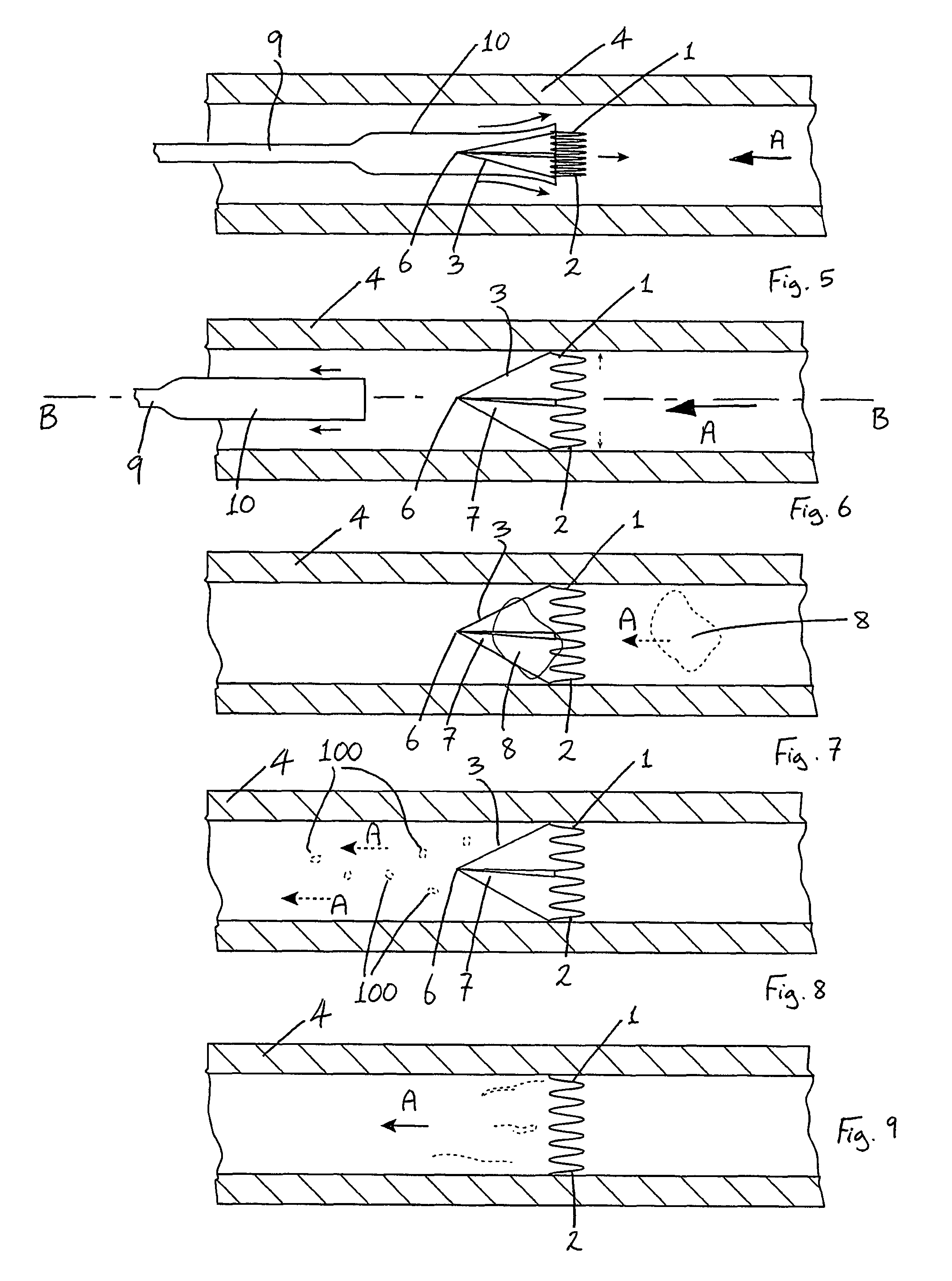
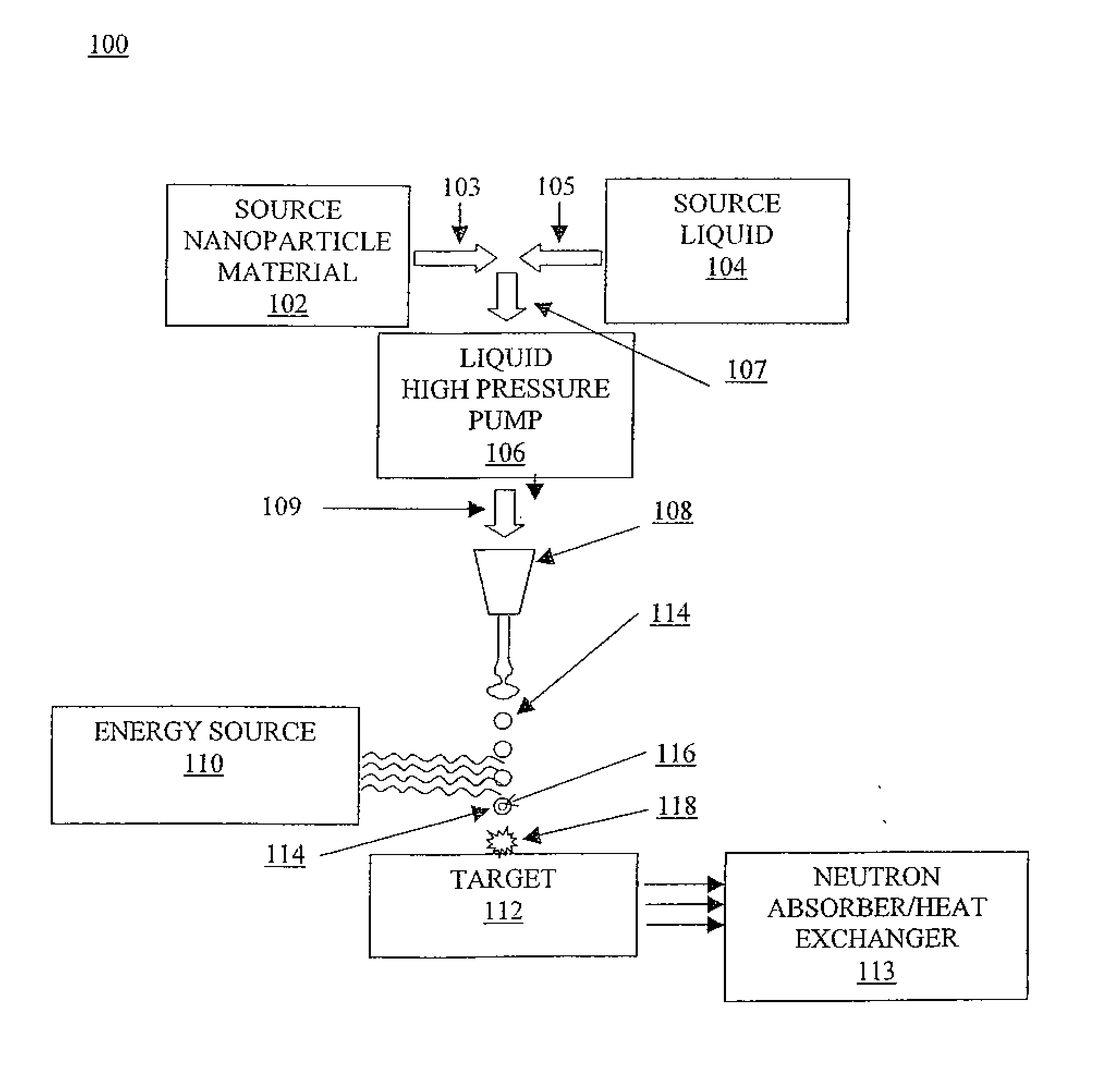
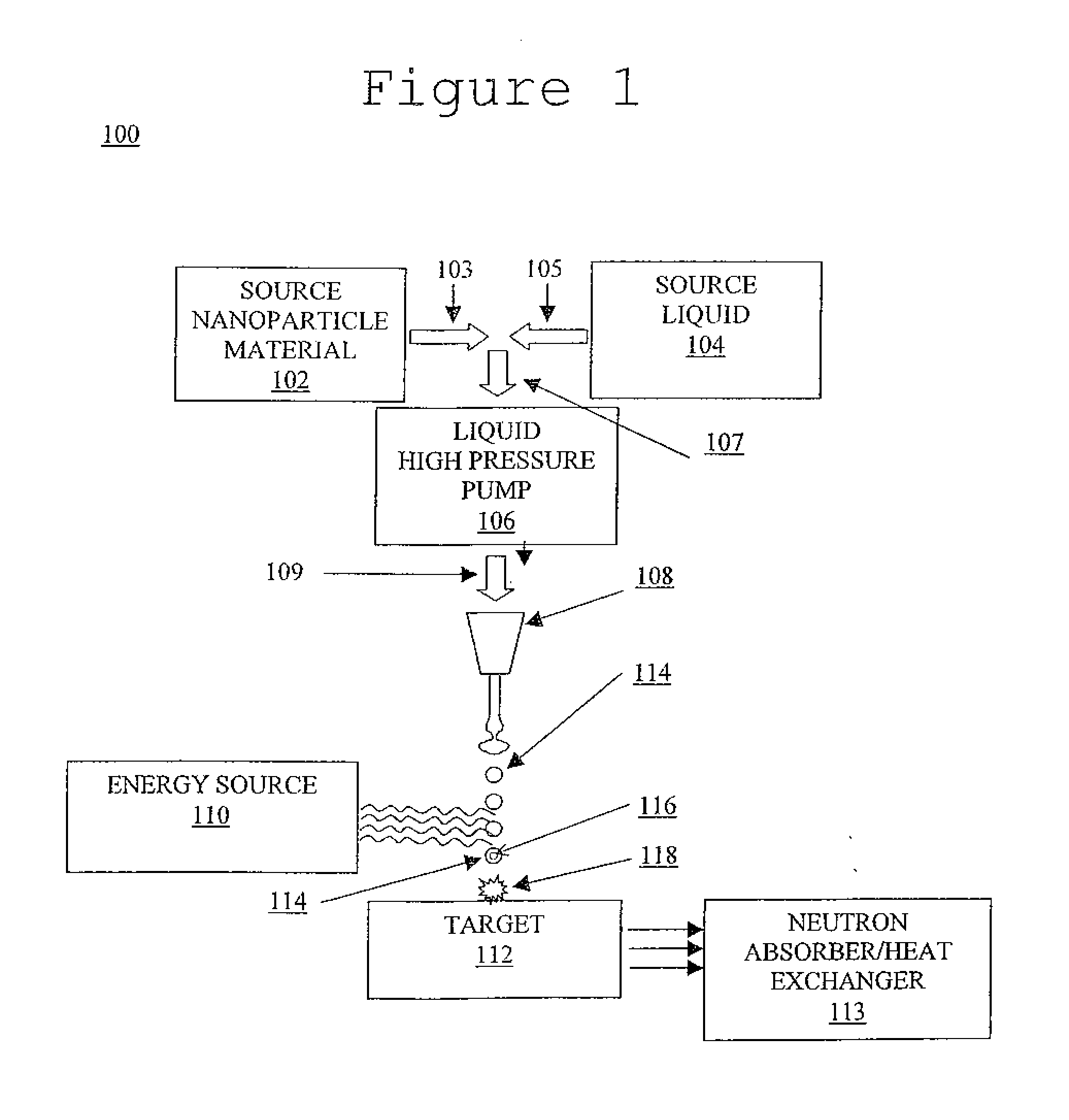
System and method for creating liquid droplet impact forced collapse of laser nanoparticle nucleated cavities for controlled nuclear reactions
InactiveUS7445319B2Promote crashHigh energyMaterial nanotechnologyNuclear energy generationNanoparticleBreakup
Owner:SYNERGY INNOVATIONS INC
Soft storage bin
Owner:SOURCING SOLUTIONS
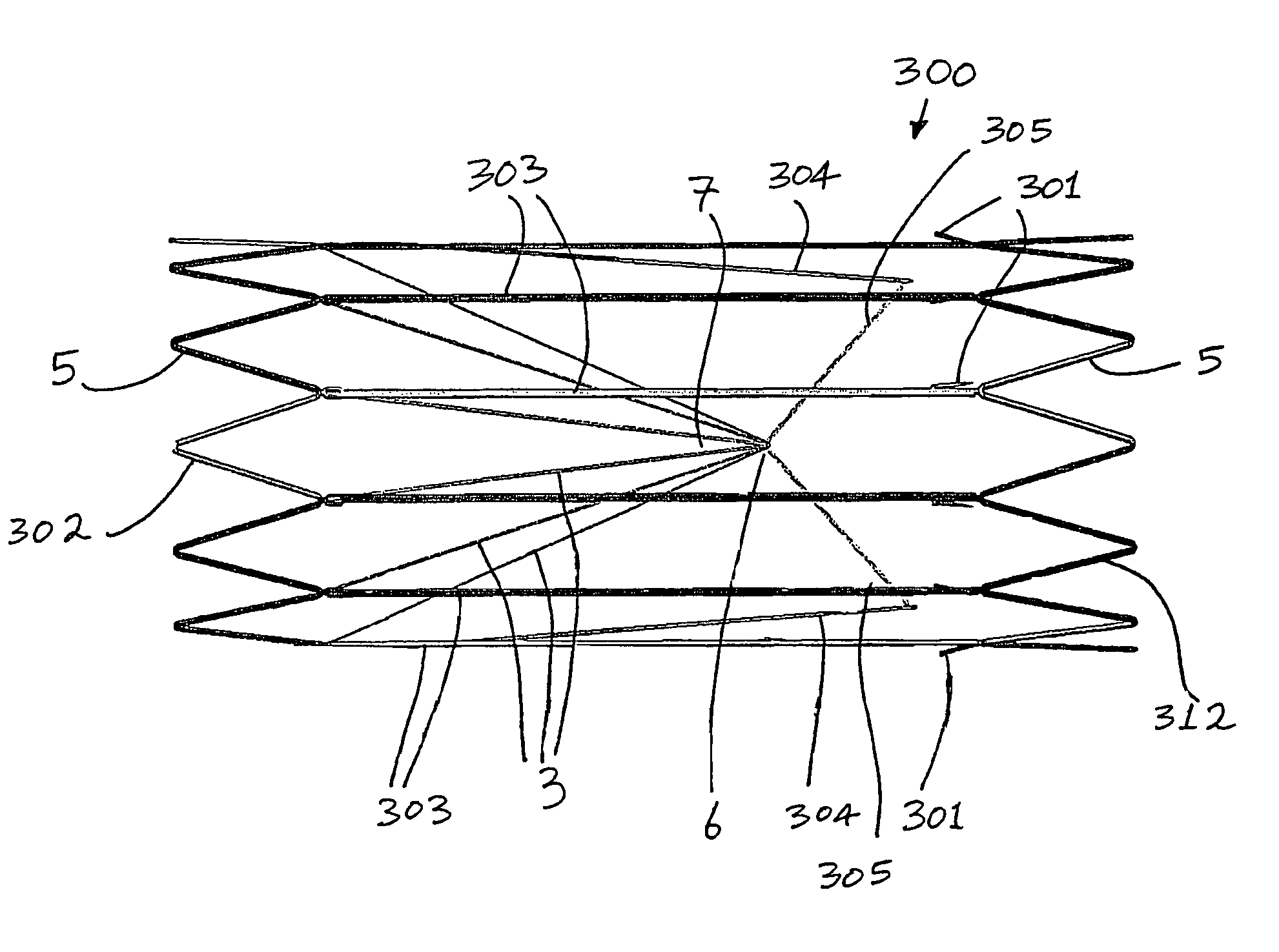
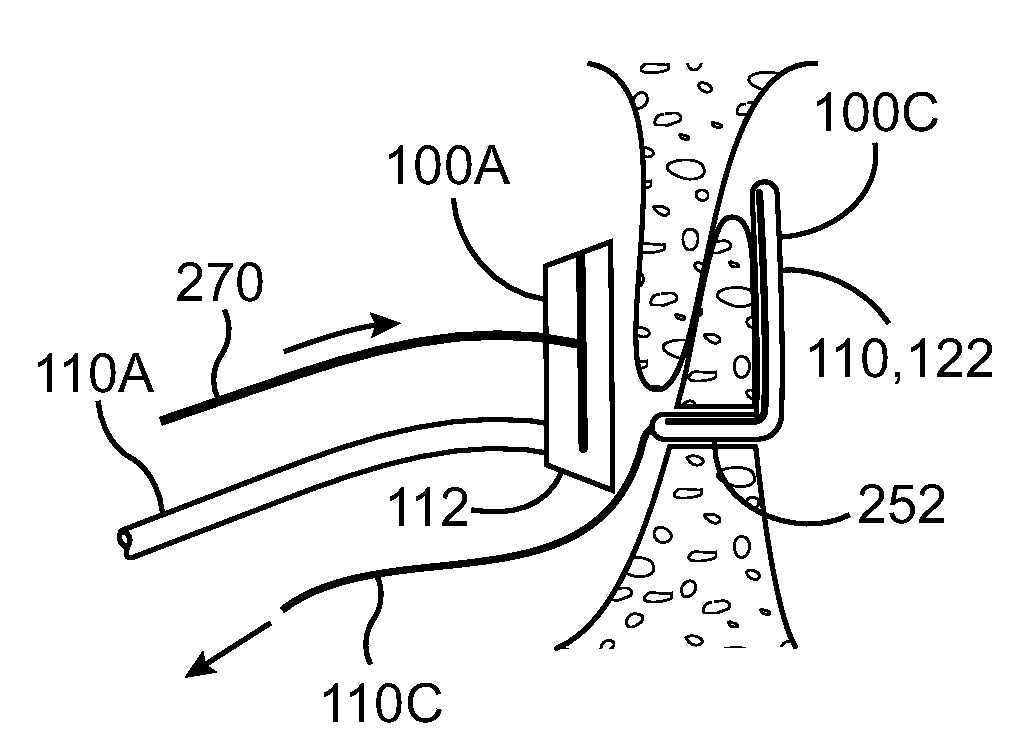
Vascular filter
ActiveUS8162970B2Avoid passingPromote crashStentsSemi-permeable membranesVascular filterInferior vena cava filter
An inferior vena cava filter (340) for use in the inferior vena cava (4) to capture thrombus (8) passing through the inferior vena cava (4) towards the heart and lungs to prevent pulmonary embolism comprises a proximal support hoop (302), a distal support hoop (312) and a plurality of support struts (303) extending between the proximal support hoop (302) and the distal support hoop (312). The filter (340) also comprises a plurality of capture arms (121) which are movable from a capturing configuration to an open configuration. The capture arms (121) are biased towards the open configuration. A biodegradable suture holds the capture arms (121) in the capturing configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD +1
System and method for creating liquid droplet impact forced collapse of laser nanoparticle nucleated cavities
InactiveUS20110228890A1Promote crashEnhance implosion energyNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsNanoparticleBreakup
A device, method and system for causing a controlled collapse of cavities formed within liquid droplets wherein a pressurized jet comprising a liquid and nanoparticle material produces droplets from the breakup of the jet stream. The liquid droplets may be irradiated with energy to produce and expand cavities formed within the droplets by irradiation of the nanoparticles contained within the droplets or alternatively, a volatile fluid with or without a metal nanoparticle may form the cavity. The droplets are collided with a target to collapse the cavities within the droplets. The irradiating (if provided) and colliding are timed to enhance implosion energy resulting from the cavities' collapse. The implosion energy and the fuel in the cavity may be used to activate and sustain a fusion reaction or from any other purposes.
Owner:SYNERGY INNOVATIONS INC
Upright container for storing and dispensing bags
InactiveUS7172092B2Easy to storeMinimizes entanglementContainer/bottle contructionLike countersFront panelFunnel shape
A container for storing and dispensing plastic bags and process for manufacturing the same. The container includes a front panel extending from the top of the container to the bottom of the container and having a substantially smooth surface with no sharp bents. The container includes a funnel-shaped aperture for facilitating insertion of the plastic bags into the container in a compact and collapsed form. One embodiment of the container has a flat profile that allows the container to be mounted to a vertical surface in a space-saving manner and that helps minimize entanglement as more bags are inserted into the container. The container also includes an access opening for dispensing the plastic bags. Another embodiment of the container is a free-standing structure having a base that can be rested on a horizontal surface.
Owner:SIMPLEHUMAN
Foldable cover for the overhead protection of an occupant of a wheelchair or other wheeled vehicle
Two embodiments of a foldable cover for protecting the occupant of a wheelchair or other wheeled vehicle is described. The foldable cover includes a frame having two sections, a back section and a top section cantileverable from the back section over the normal space provided for an occupant. A mounting bar for rigidly mounting the back section and, hence, the remainder of the foldable cover is provided with both embodiments. The back section is pivotally connected to the mounting bar for pivoting movement between a stowed position in which such cover is out of the way of the occupant in a protected position in which it and the cantilevered top section cooperate to cover the occupant.
Owner:AYERS RONALD LEE +1
Fluid supply assembly
InactiveUS20070158348A1Promote crashSingle-unit apparatusLiquid spraying apparatusBiomedical engineeringDisposable cup
A fluid supply assembly. The fluid supply assembly includes a disposable cup and lid, and a reusable shell and outer lid. A flexible, disposable cup, a reusable shell, and a method of preparing a fluid supply assembly for use with a fluid supply applicator are also described.
Owner:CARLISLE FLUID TECH INC
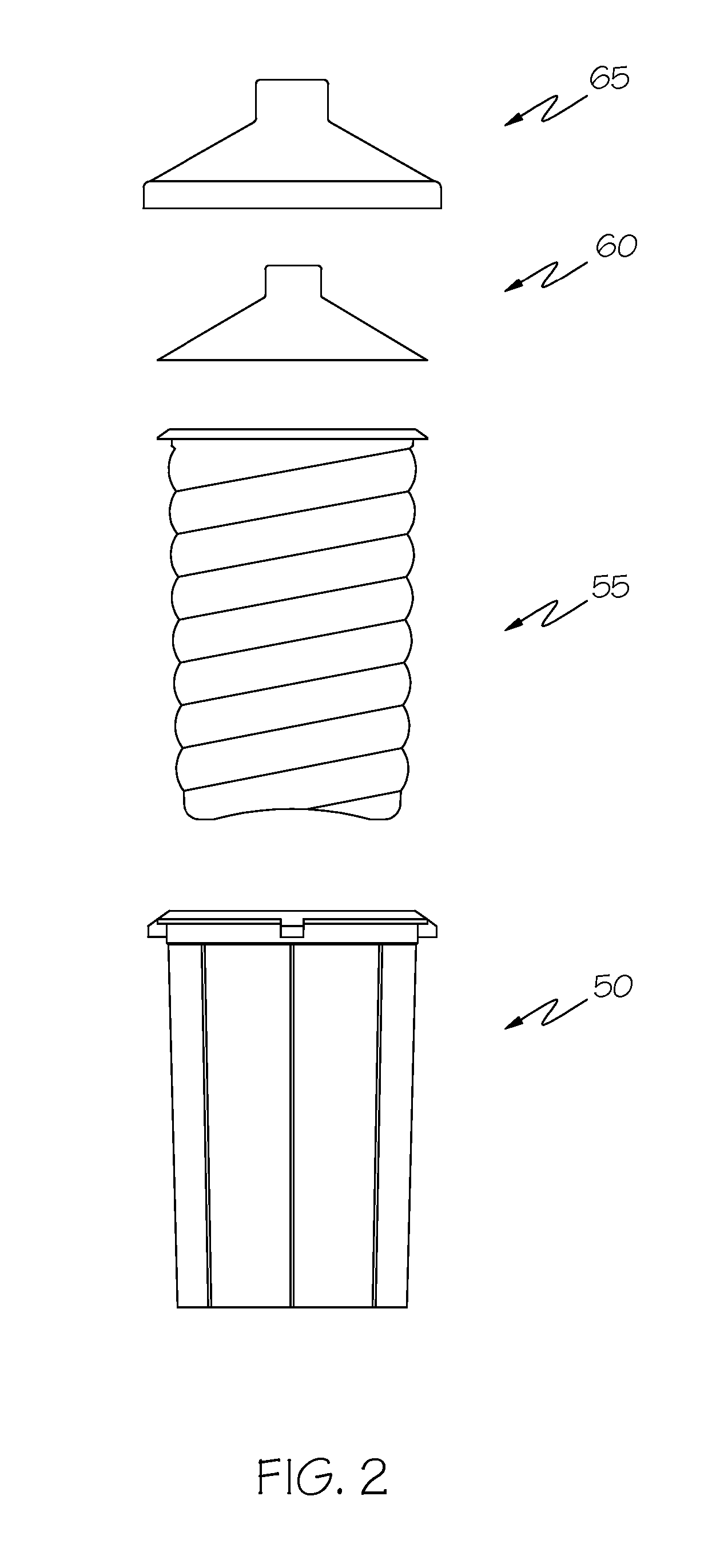
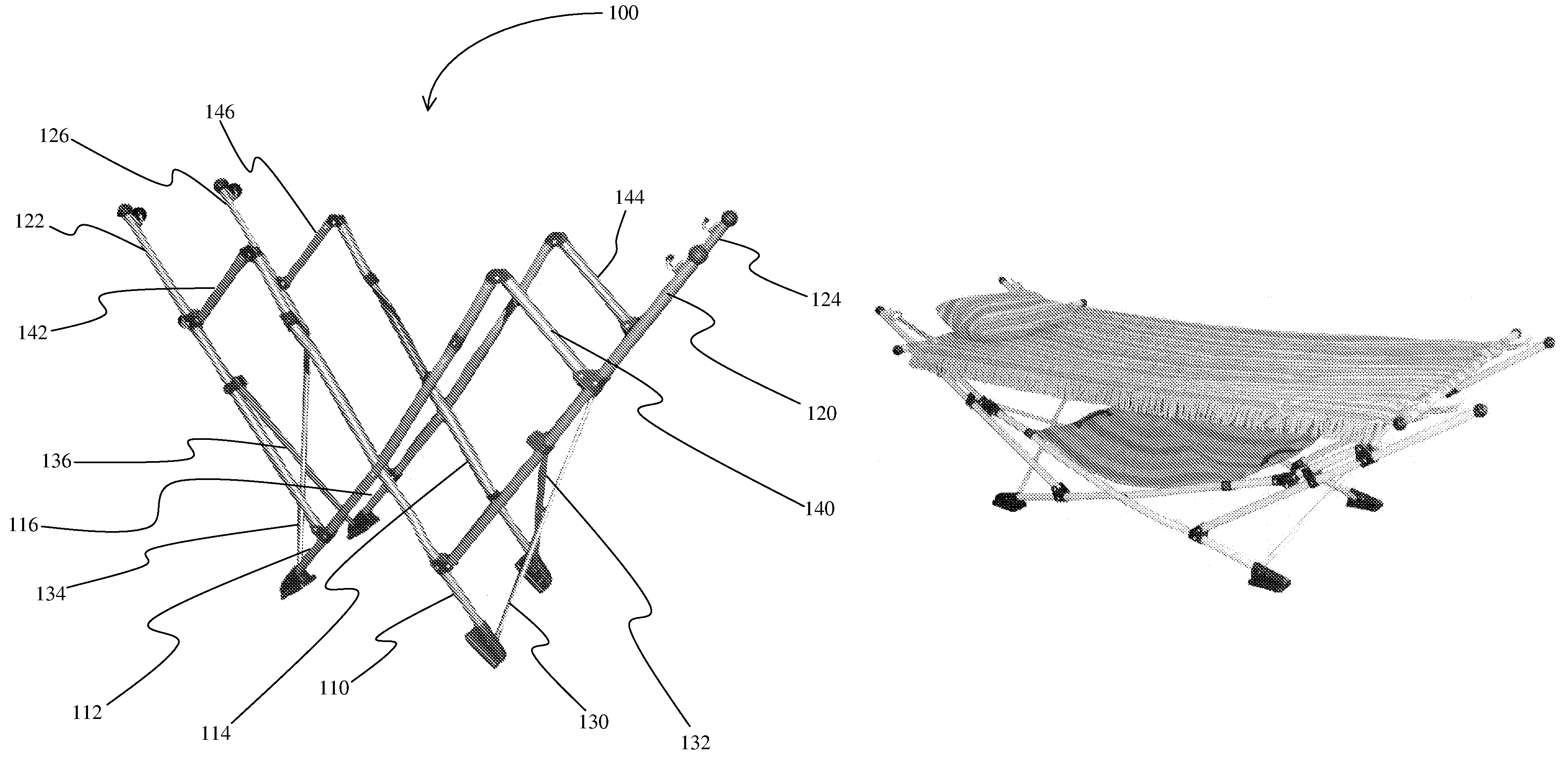
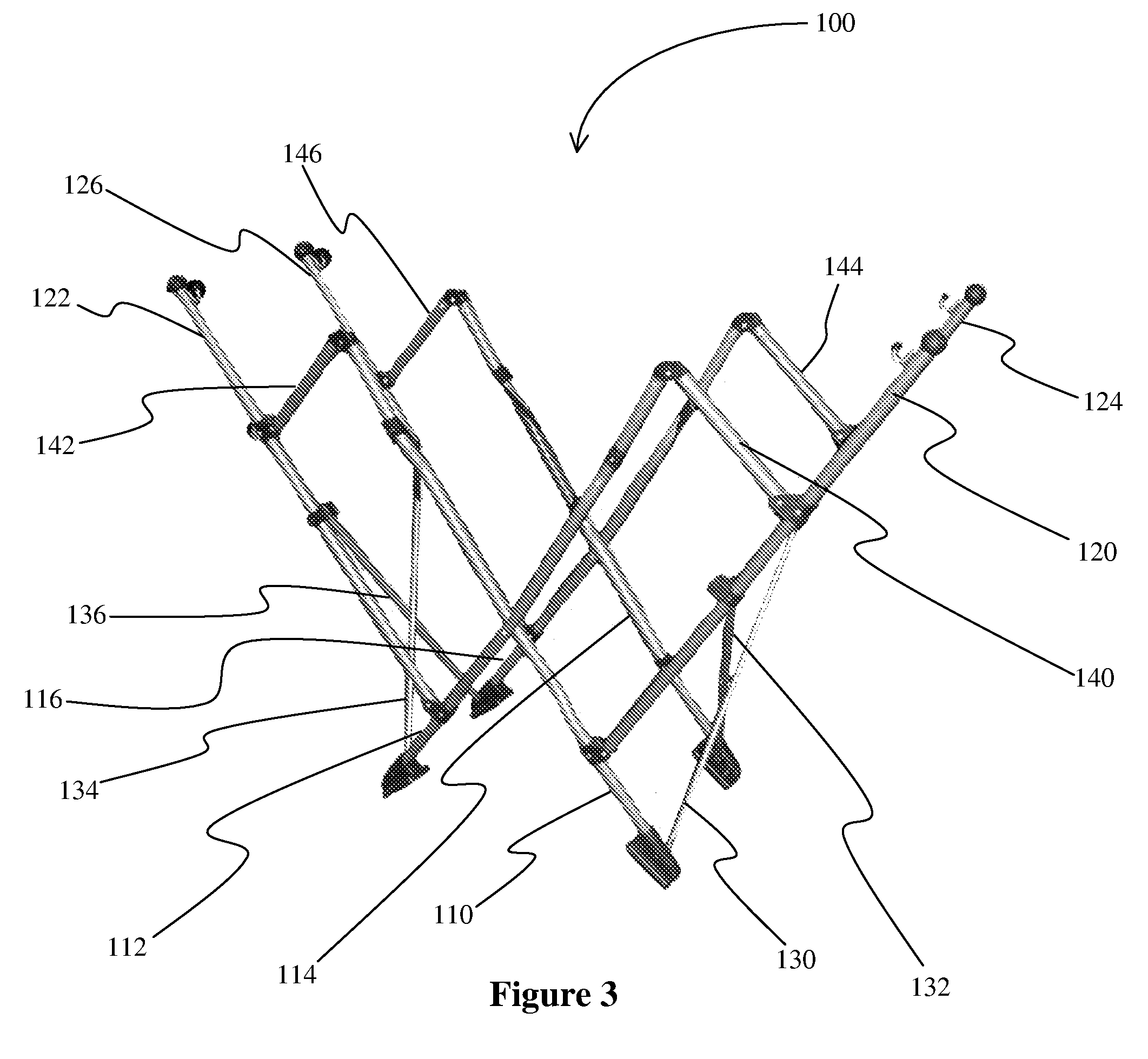
Collapsible hammock stand
Owner:IP POWER HLDG
Collapsible container with pockets
A collapsible container having four tension-loop panels covered by flexible material with each panel joined to two other panels to form an enclosure with opposing top and bottom panels and two opposing side panels, the container having two flexible ends each located on opposing ends of the frames and attached to a plurality of the frames, the container comprises an opening in the one of the panels and at least one interior pocket having two opposing sides with each side fastened to a flexible side panel or flexible end, the interior pocket having an open top.
Owner:PRO MART IND
Multi-electrode apparatus for tissue welding and ablation
InactiveUS20080140070A1Promote crashSurgical instruments using microwavesTissue weldingBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for delivering energy to tissue, comprising: an elongate flexible shaft having a proximal end and a distal end; a sheath disposed over at least a portion of the flexible shaft; a housing provided on the distal end of the flexible shaft; a plurality of electrodes mounted on the housing, the electrodes having a tissue apposition surface having a non-coplanar shape that conforms to the anatomy of a patient.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Debris-Capturing Apparatus for Cleaner
InactiveUS20140042063A1Relieve resistancePromote crashWater/sewage treatmentGymnasiumEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:HAYWARD IND INC
Collapsible truck bed cover
A collapsible truck bed cover comprising a frame and an outer covering, wherein the frame comprises four primary support bars, four secondary support bars, and four cross bars. The primary support bars are pivotally connected to each other at a swinging pivot point. The secondary support bars are pivotally connected to the primary support bars. The two rear primary support bars are pivotally connected to the truck bed rails at two stationary pivot points. When the cover is fully collapsed, it fits underneath an existing tonneau cover.
Owner:BISMARCK CANVAS
Expandable cardiac shunt
ActiveUS20170106176A1Facilitate collapsePromote crashGuide needlesBalloon catheterCardiac shuntingFlow diverter
Disclosed are cardiac shunts and method of delivery, and in particular, to a shunt to reduce elevated left atrial pressure (LAP). The methods include forming a puncture hole between the left atrium and the coronary sinus, widening the puncture hole, and placing an expandable shunt within the widened puncture hole. A first catheter having a side-extending needle may be used to form a puncture into the left atrium. A second catheter extends along a guidewire and an expandable shunt with distal and proximal flanges is expelled therefrom into the puncture. The shunt defines a blood flow passage therethrough that permits shunting of blood from the left atrium to the coronary sinus when the LAP is elevated. The shunt is desirable formed of a super-elastic material and manipulated with control rods. The shunt defines a tilted flow tube that facilitates collapse into the catheter.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Electrode apparatus having deformable distal housing
InactiveUS20080140170A1Promote crashElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for delivering energy to tissue, comprising an elongate flexible shaft having a proximal end and a distal end; a sheath disposed over at least a portion of the flexible shaft; a resilient housing near the distal end of the flexible shaft, the housing adapted to deflect so as to appose the tissue; and at least one electrode mounted to the distal housing; an elongated pusher coupled with one of the housing and the at least one electrode and adapted to deflect the at least one electrode into apposition with the tissue.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com