Container for hot fill food packaging applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0058] The following example is provided as a further description of one embodiment of the invention, and is not intended to be limiting.
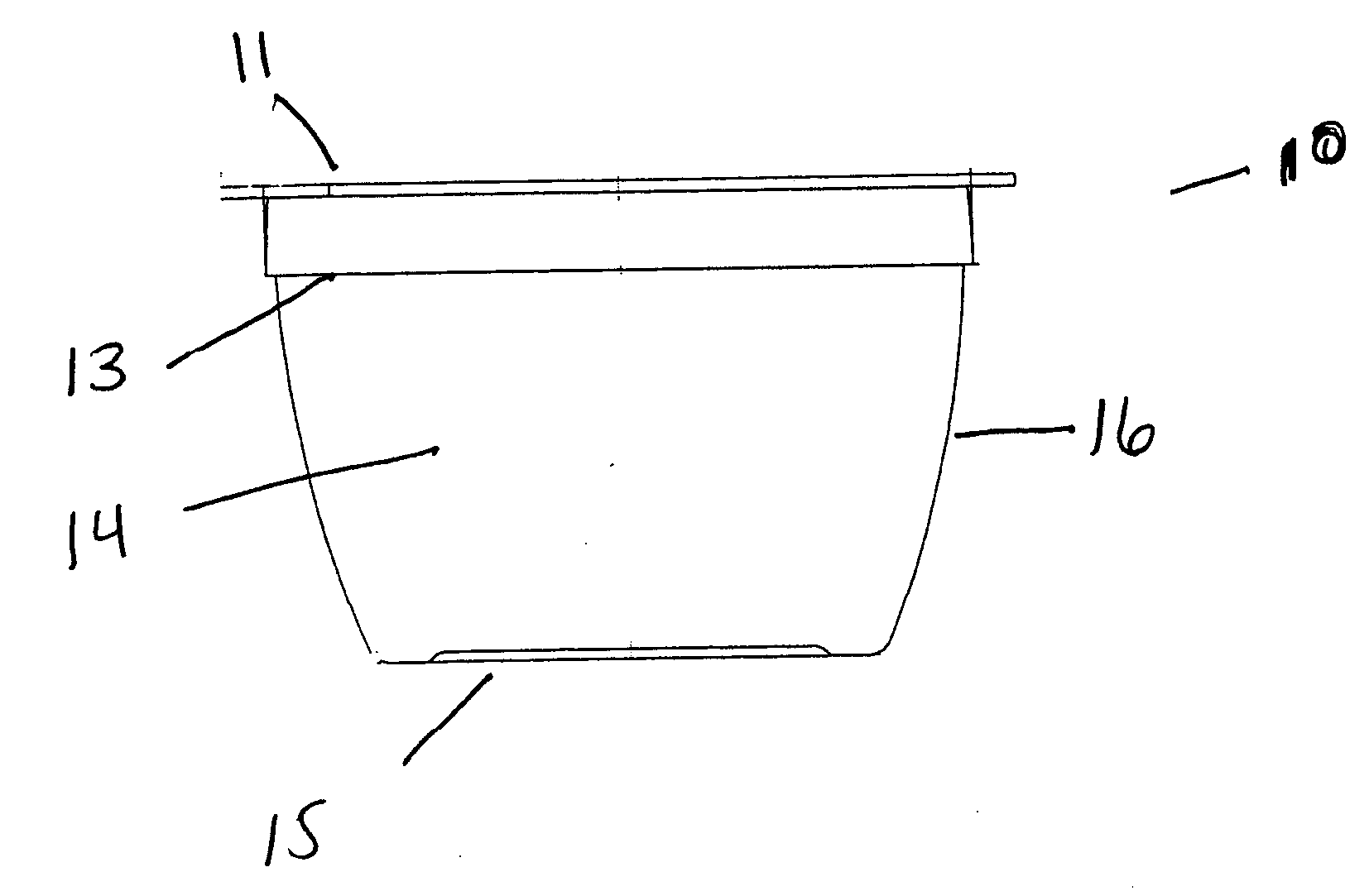
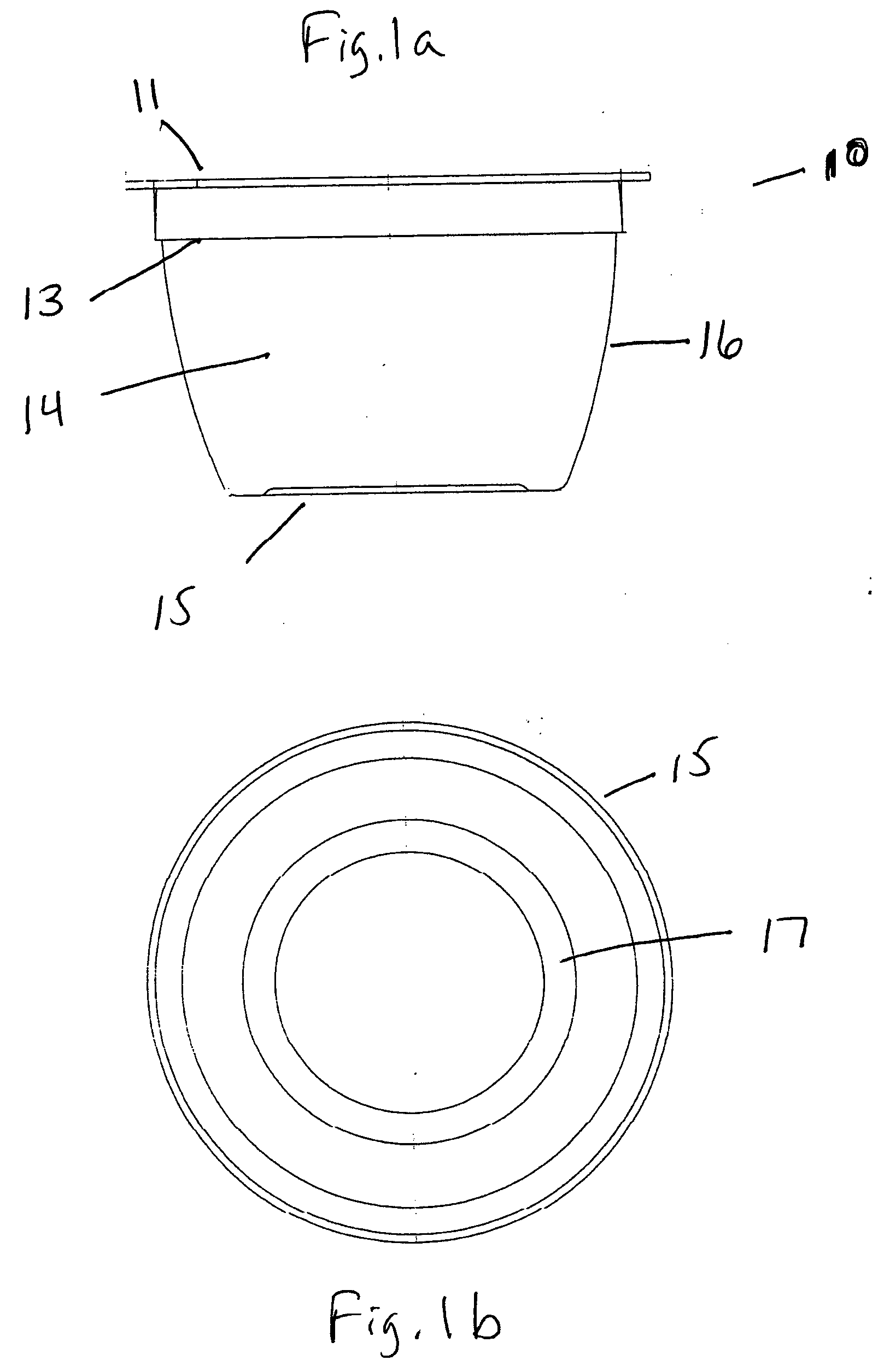
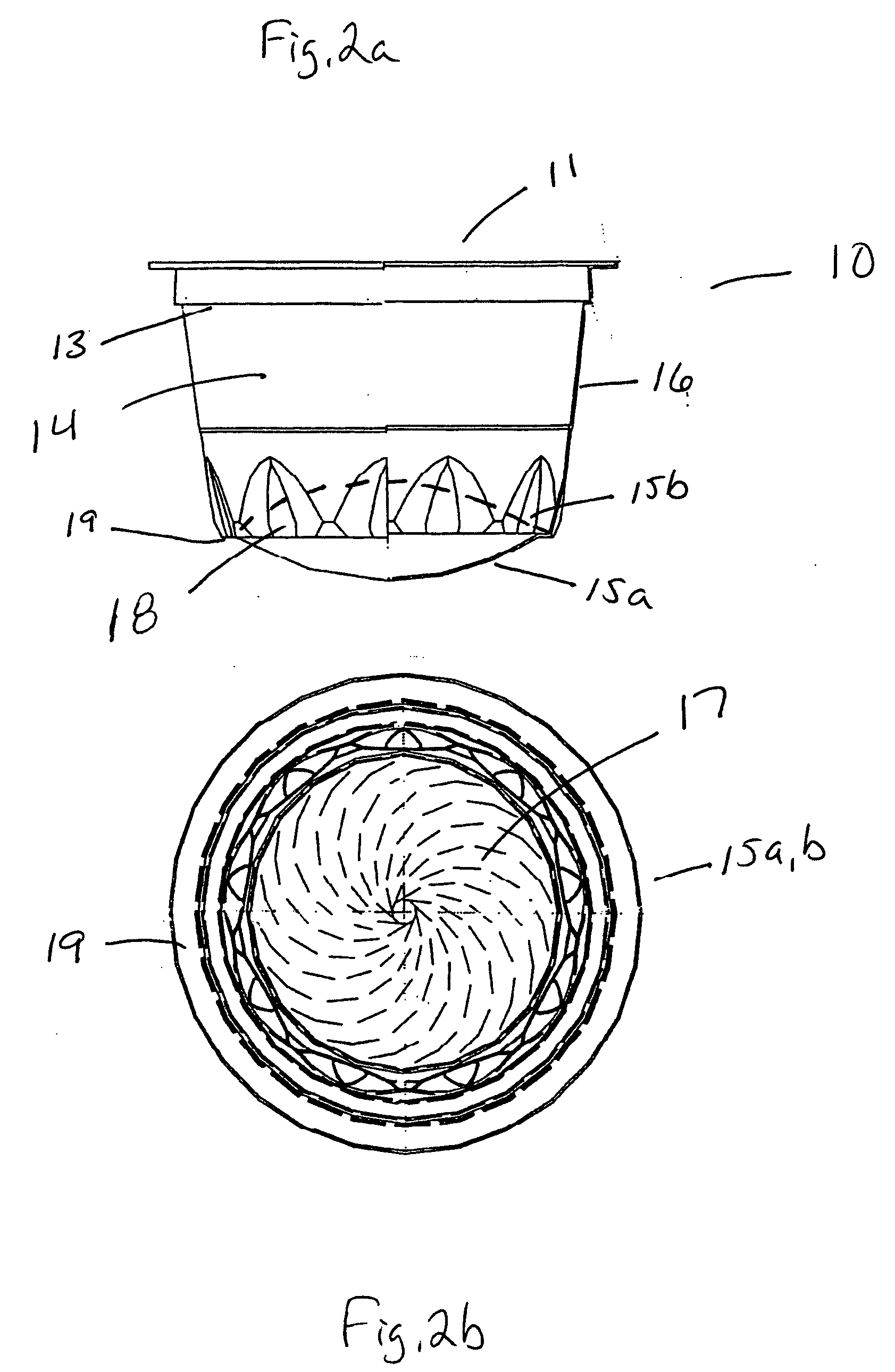
[0059] A four ounce cup was made according to the invention that corresponds to the cup depicted in FIG. 1 by the thermoforming process. The place of manufacture was Medellin, Colombia, having an altitude above sea level of about 6500 feet. Note that the forming conditions should be adjusted according to the ambient conditions of the location of the manufacturing facility.
[0060] A starting plastic multilayer sheet comprising about 70-80 volume % EVAL™ J102B resin, about 20-40 volume % PROPILCO™ 03H96 PP and about 15-20 volume % Comai 745-2AS™ adhesive, based on a total thickness of the multilayer sheet of about 1.02 mm, was formed by coextrusion. The approximately 49 mm wide sheet was continuously fed at a rate sufficient to mold four ounce cups, ten cups at a time, 14 cycles per minute. The plastic sheet was fed into an Illig 50K™ thermoforming ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com